
Rotating for Even Sharper Images

Hubble Captures A Full Rotation Of Mars
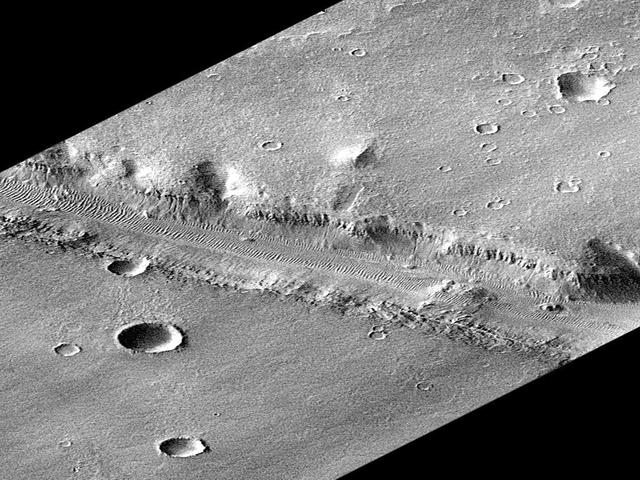

Rotated Perspective View of Nirgal Vallis
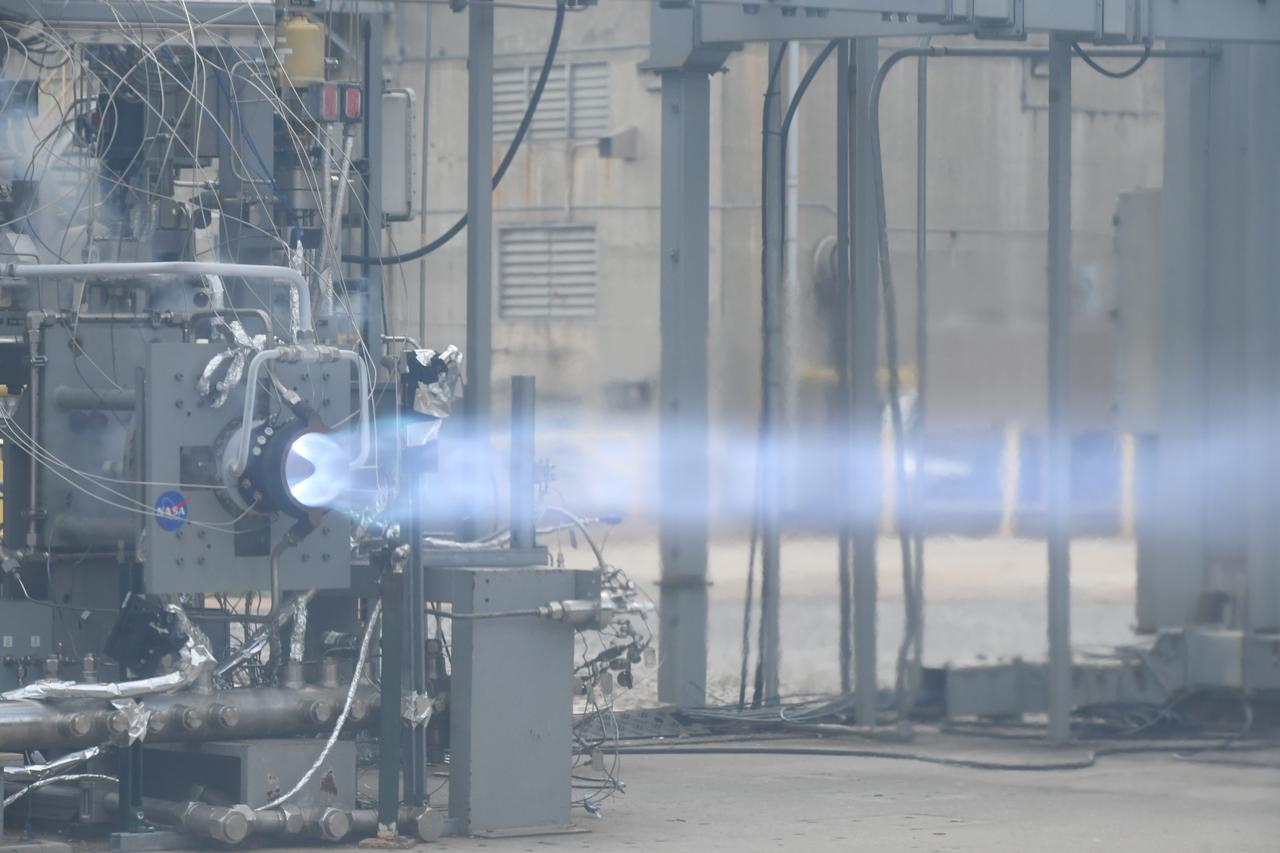
Engineers at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, conduct a successful, 251-second hot fire test of a full-scale Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine combustor in fall 2023, achieving more than 5,800 pounds of thrust.
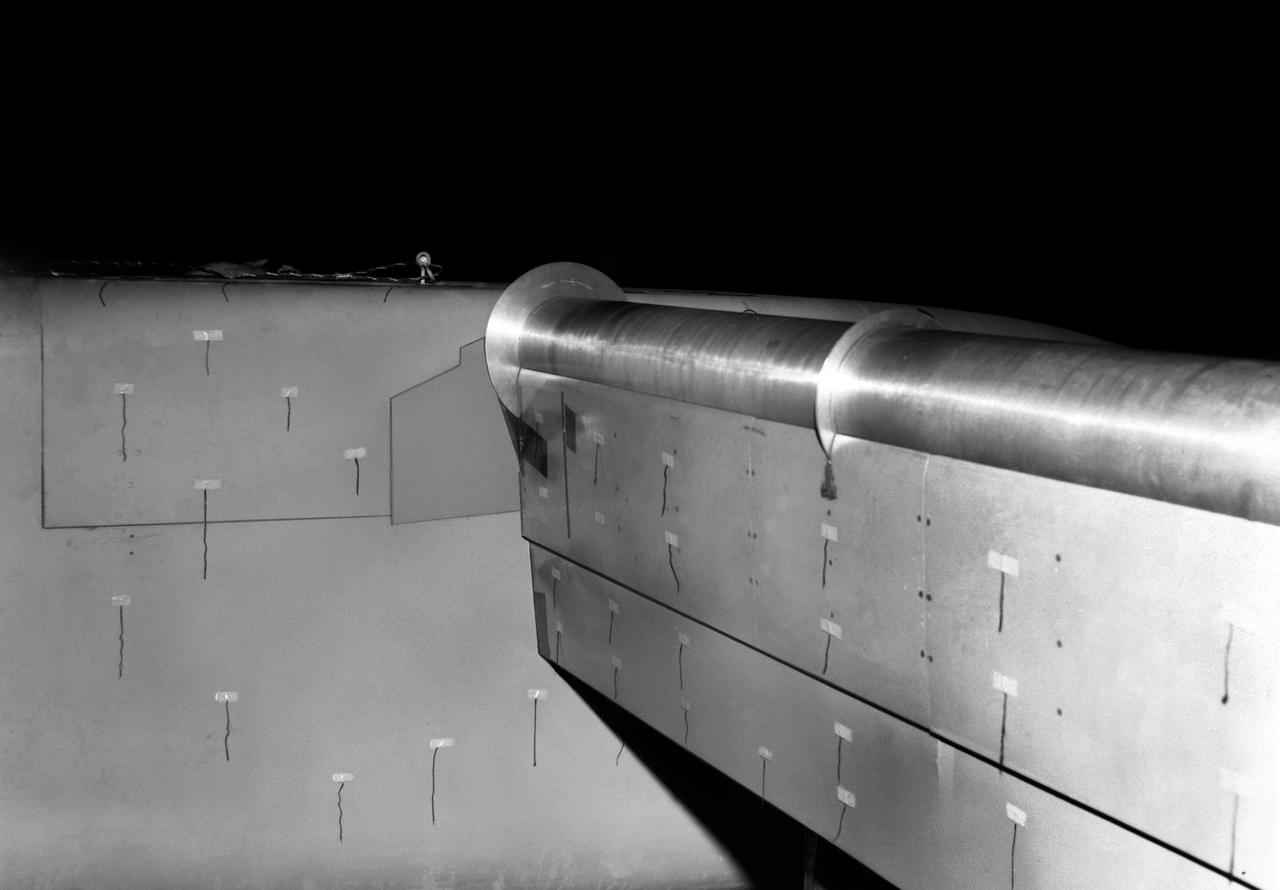

Detail view of 4 propeller model rotating cylinder flap at 90 degrees with yarn tufts attached.
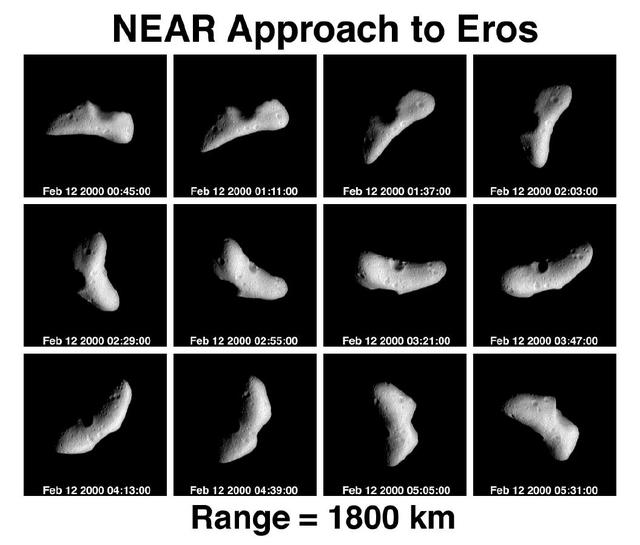
NEAR Approach to Eros - 12 Panel Rotation Sequence
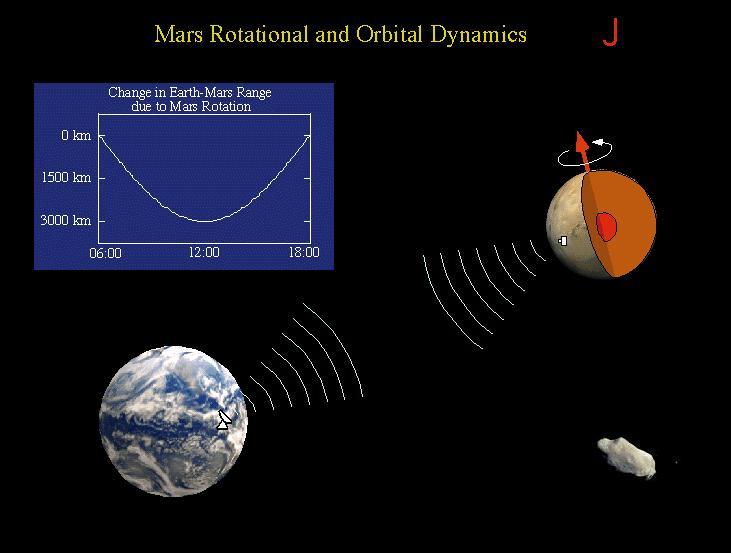
The Rotation and Orbit Dynamics experiment is based on measuring the Doppler range to Pathfinder using the radio link. Mars rotation about it's pole causes a signature in the data with a daily minimum when the lander is closest to the Earth. Changes in the daily signature reveal information about the planetary interior, through its effect on Mars' precession and nutation. The signature also is sensitive to variations in Mars' rotation rate as the mass of the atmosphere increases and decreases as the polar caps are formed in winter and evaporate in spring. Long term signatures in the range to the lander are caused by asteroids perturbing Mars' orbit. Analysis of these perturbations allows the determination of the masses of asteroids. Sojourner spent 83 days of a planned seven-day mission exploring the Martian terrain, acquiring images, and taking chemical, atmospheric and other measurements. The final data transmission received from Pathfinder was at 10:23 UTC on September 27, 1997. Although mission managers tried to restore full communications during the following five months, the successful mission was terminated on March 10, 1998. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00975
Counter Rotating Propeller Model in the NASA Glenn 8x6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel
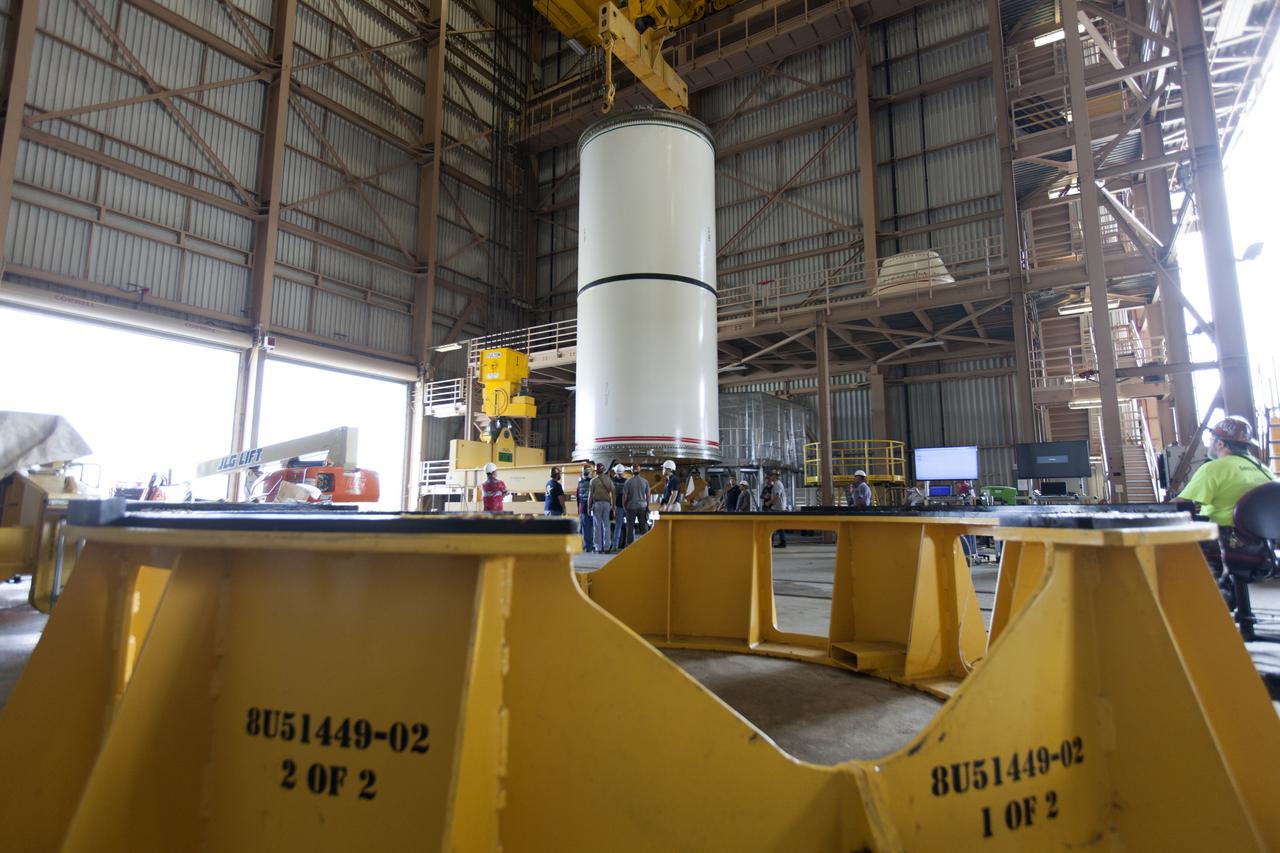

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
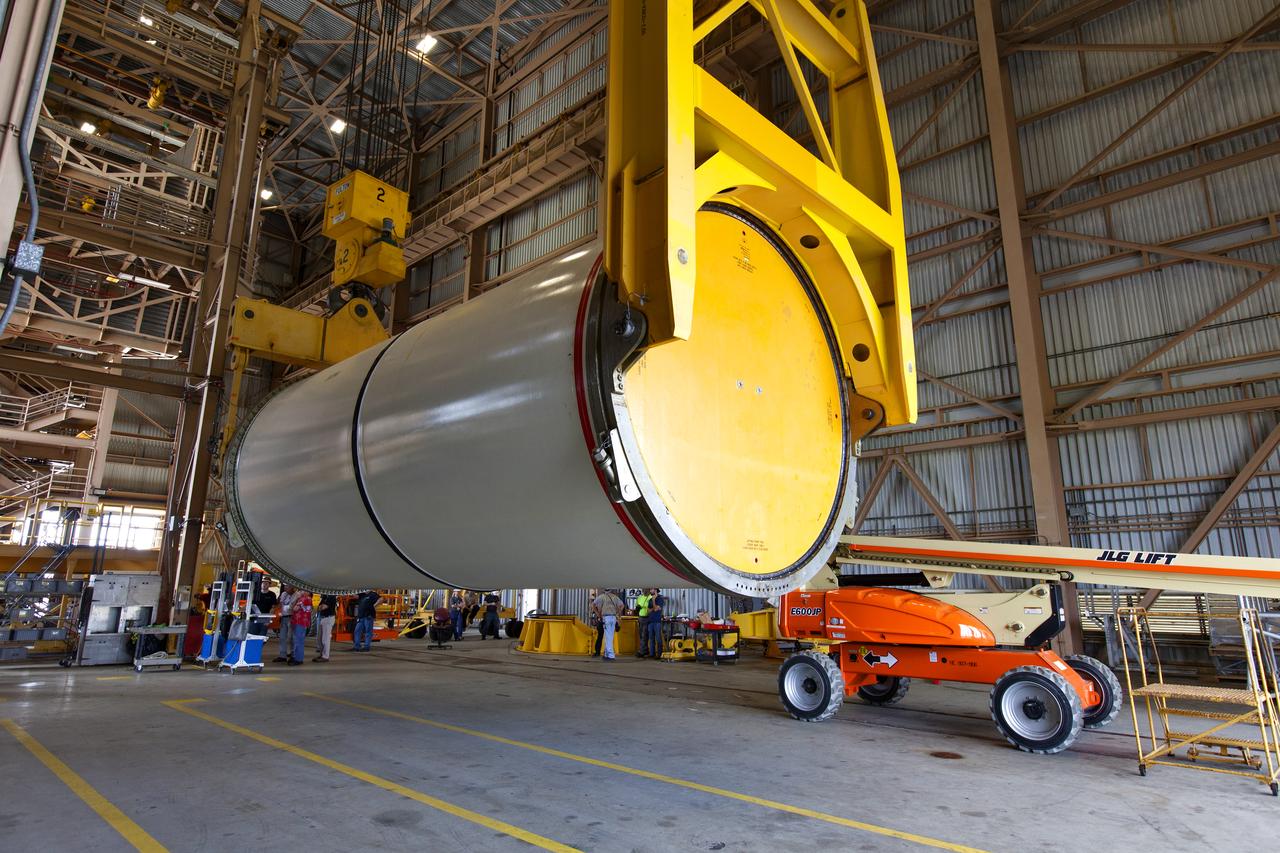

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes were used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
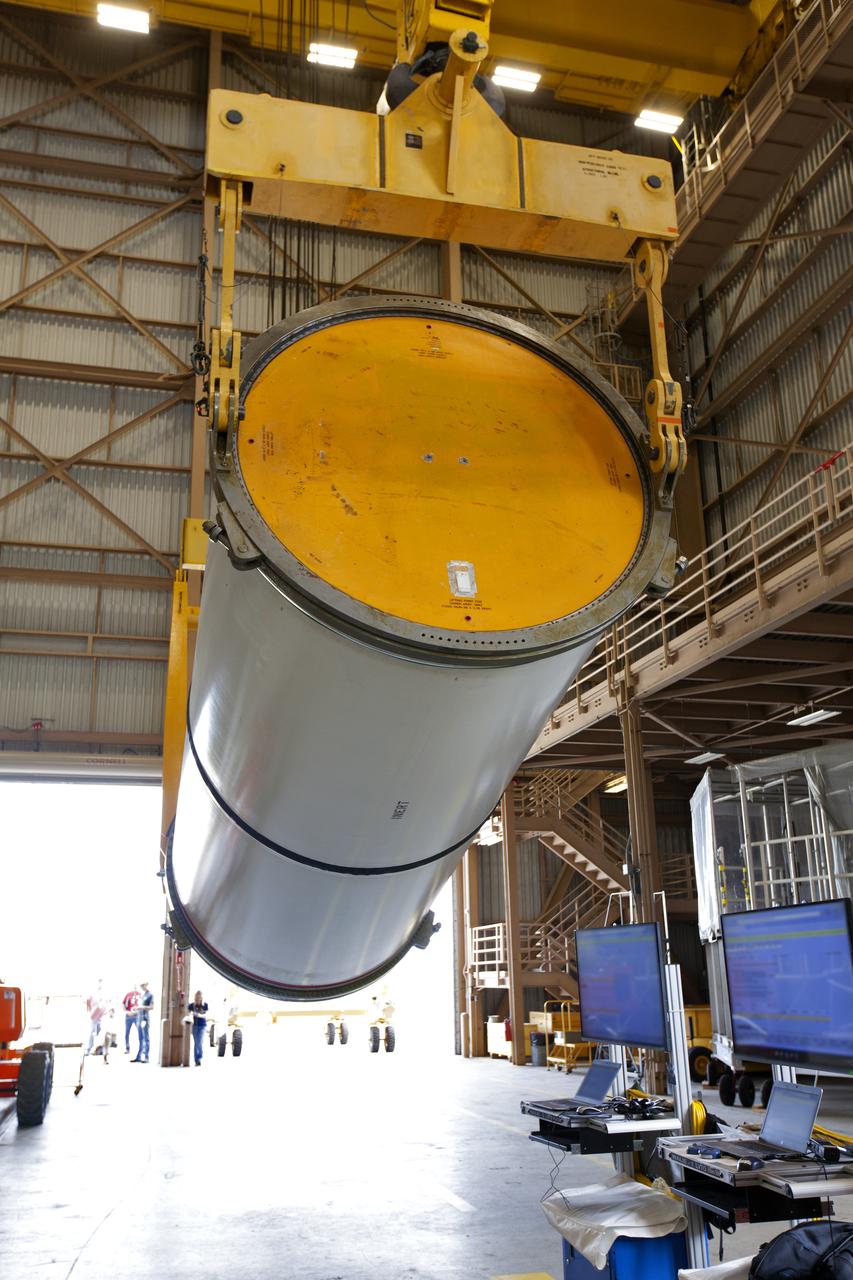

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
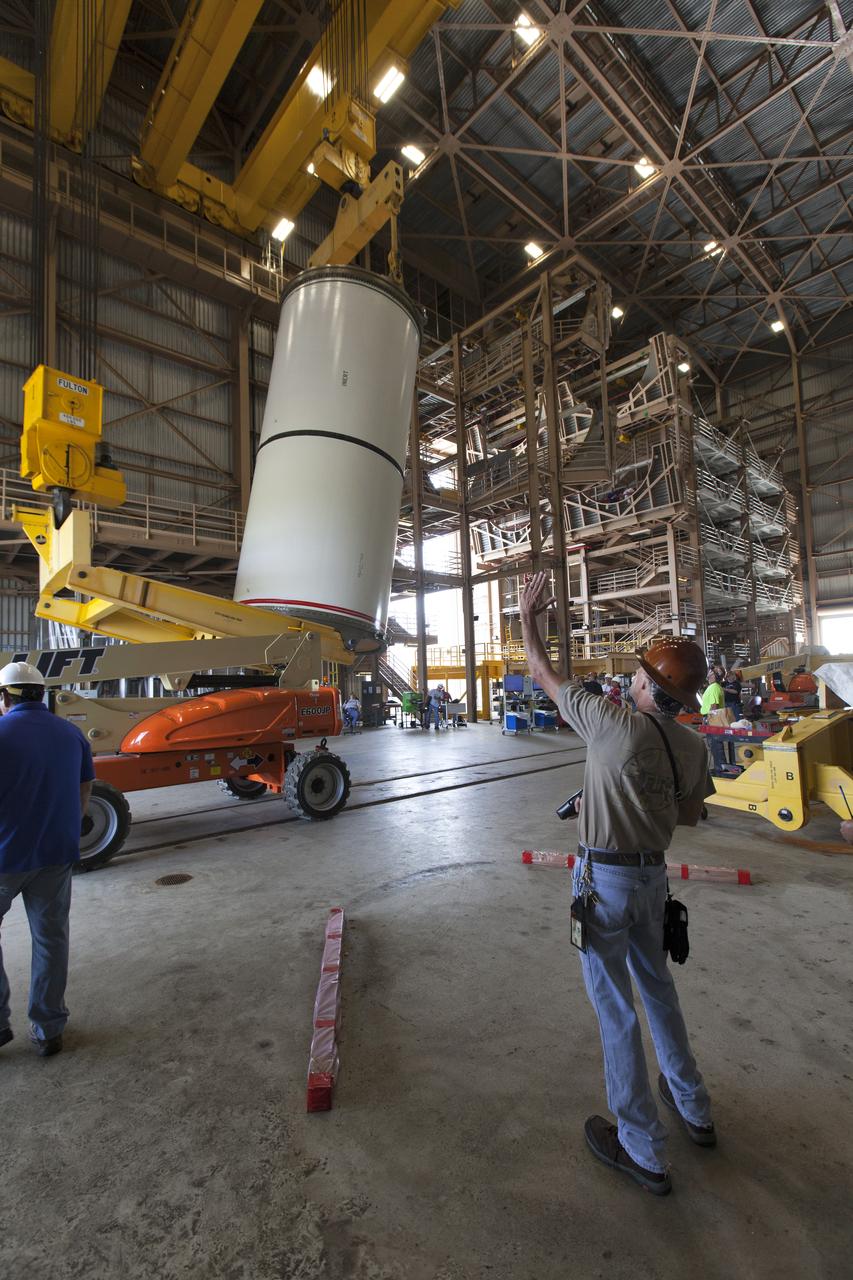

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
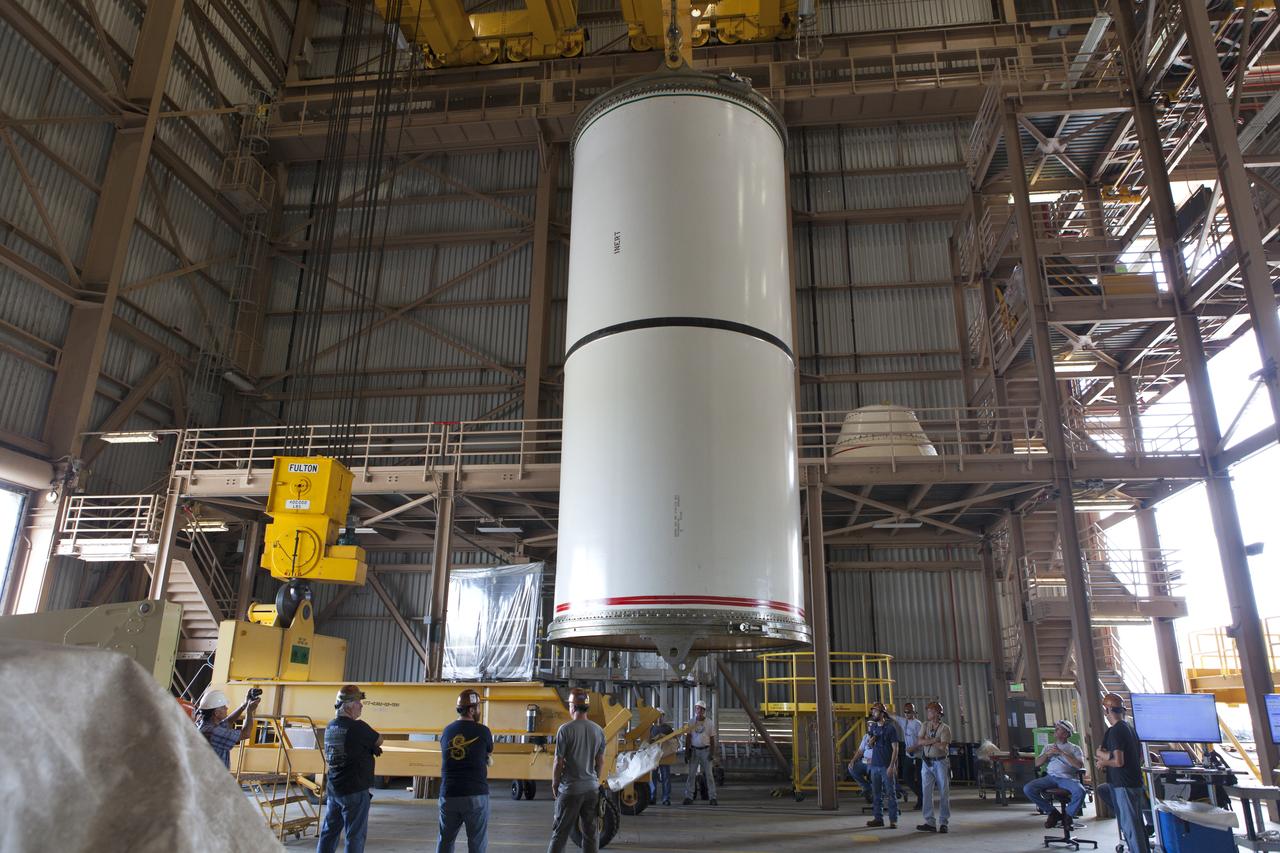

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
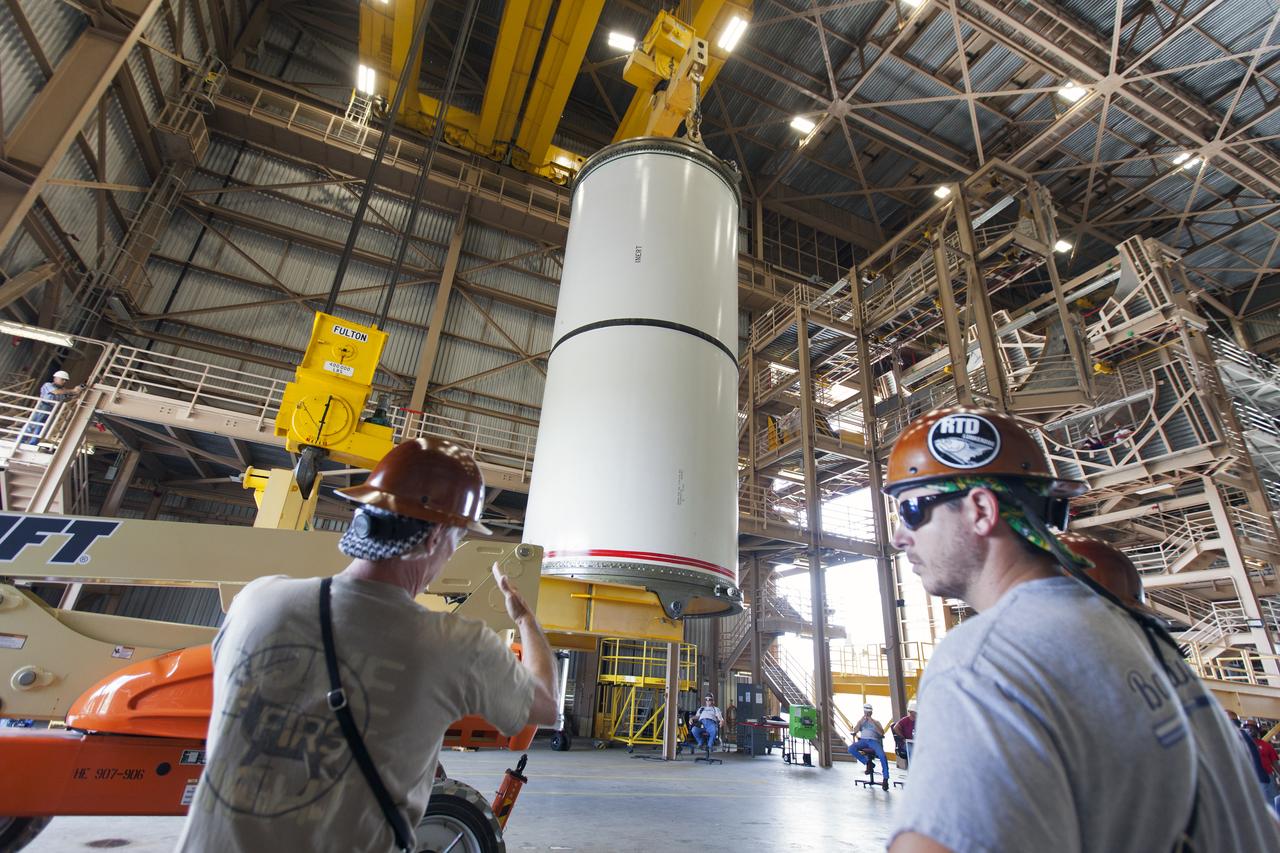

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
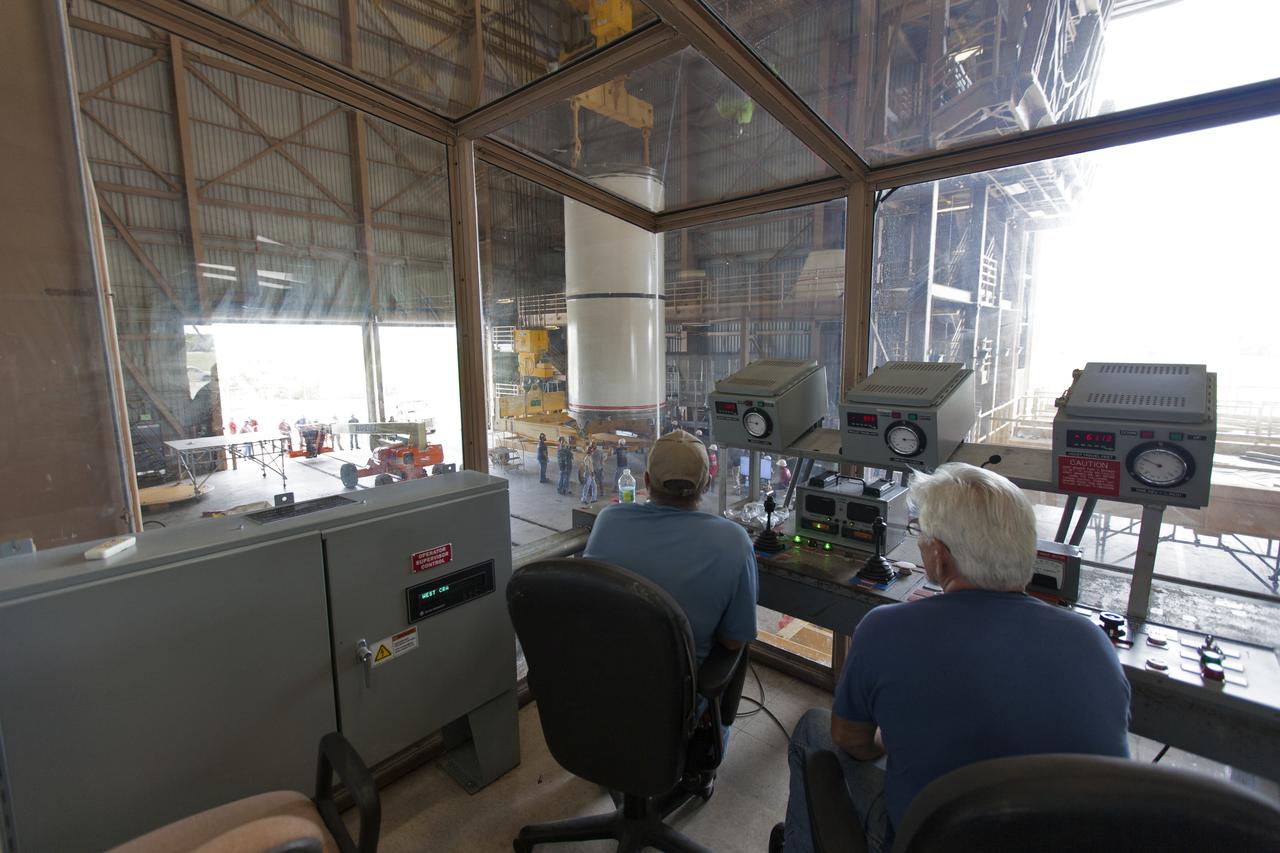

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
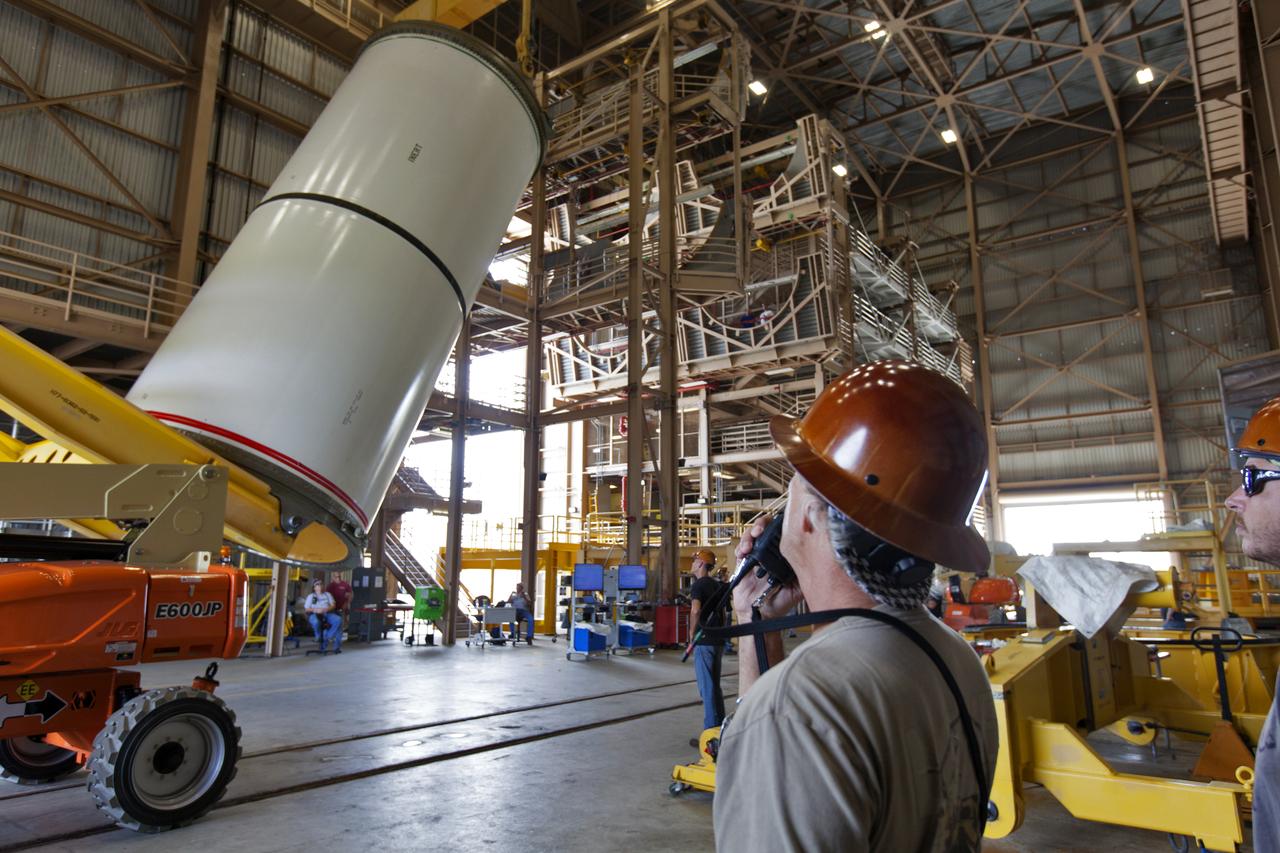

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
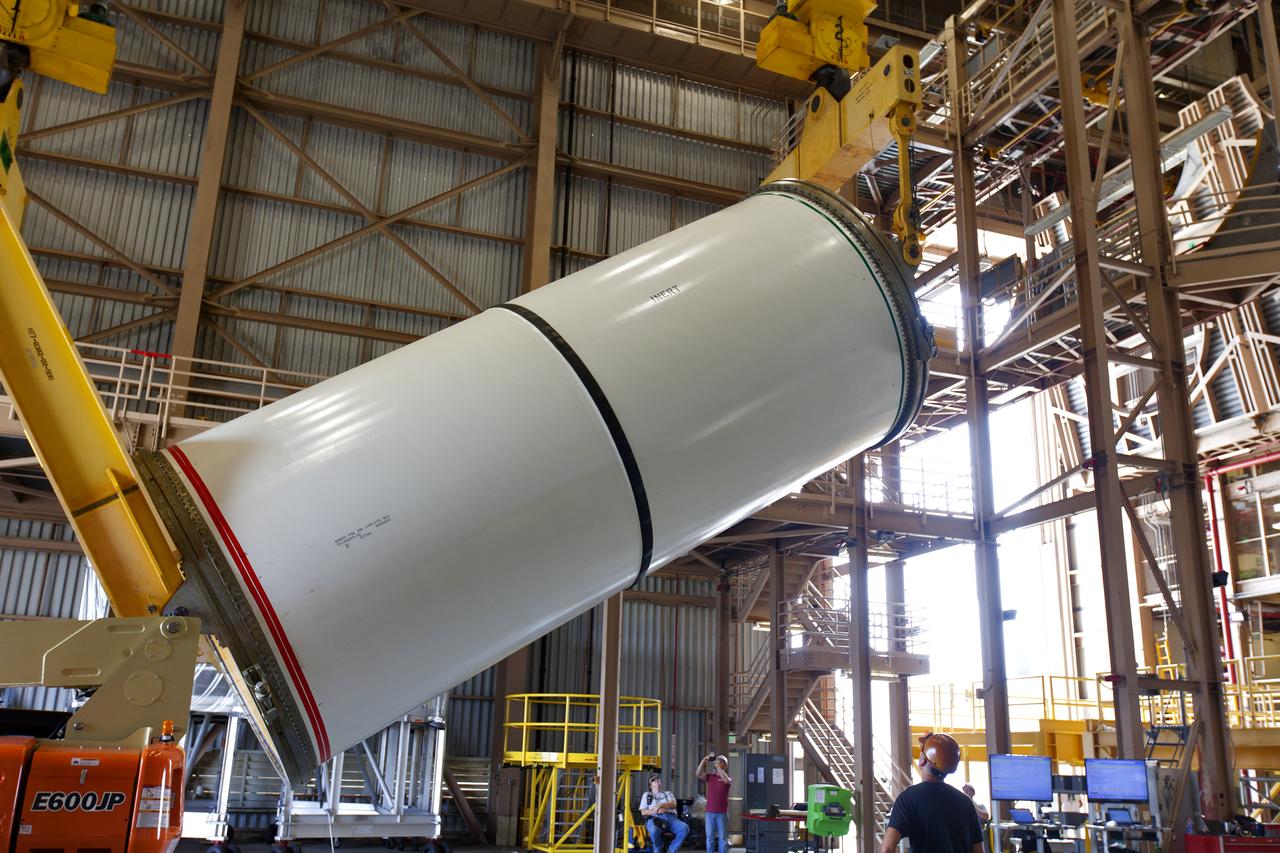

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
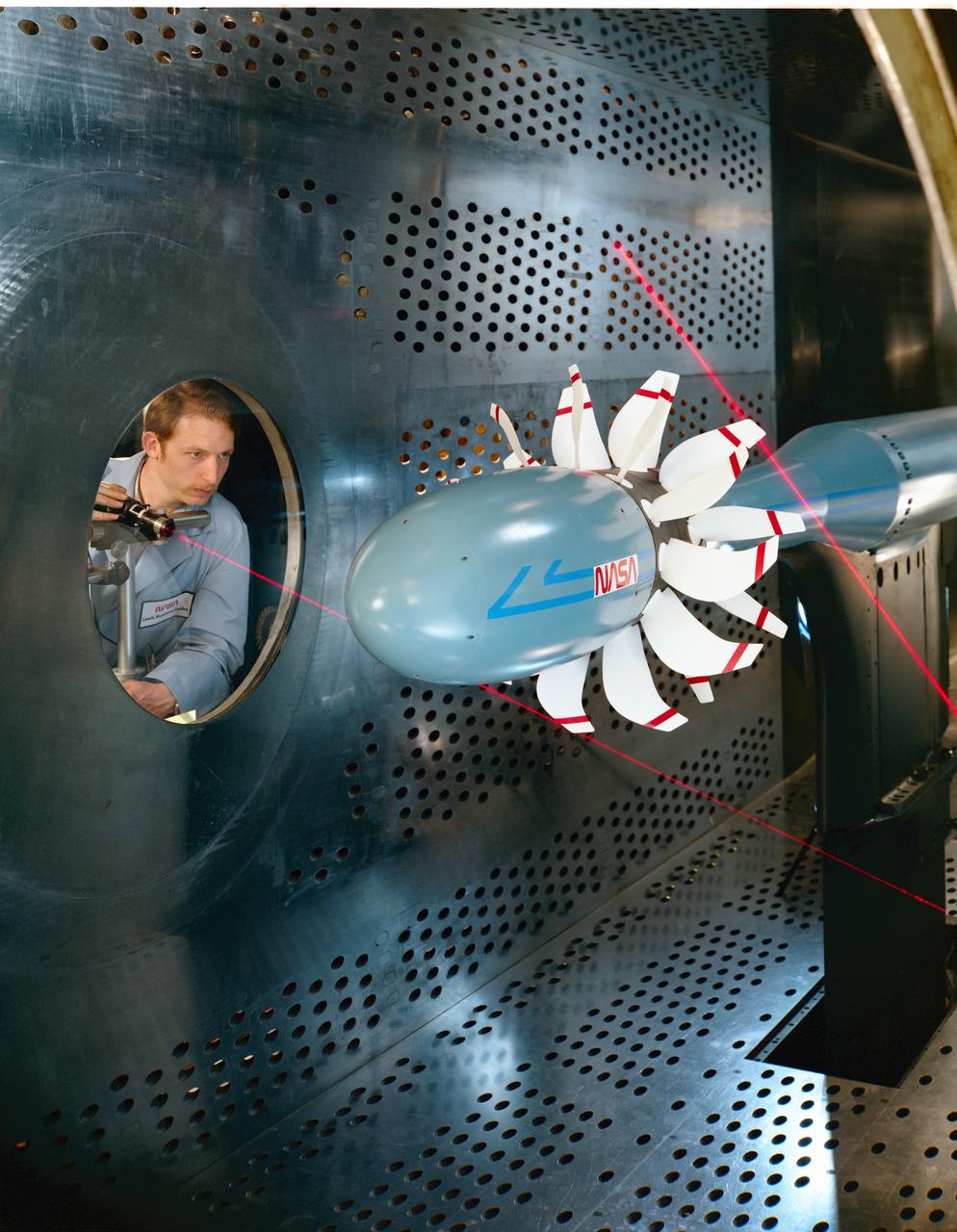
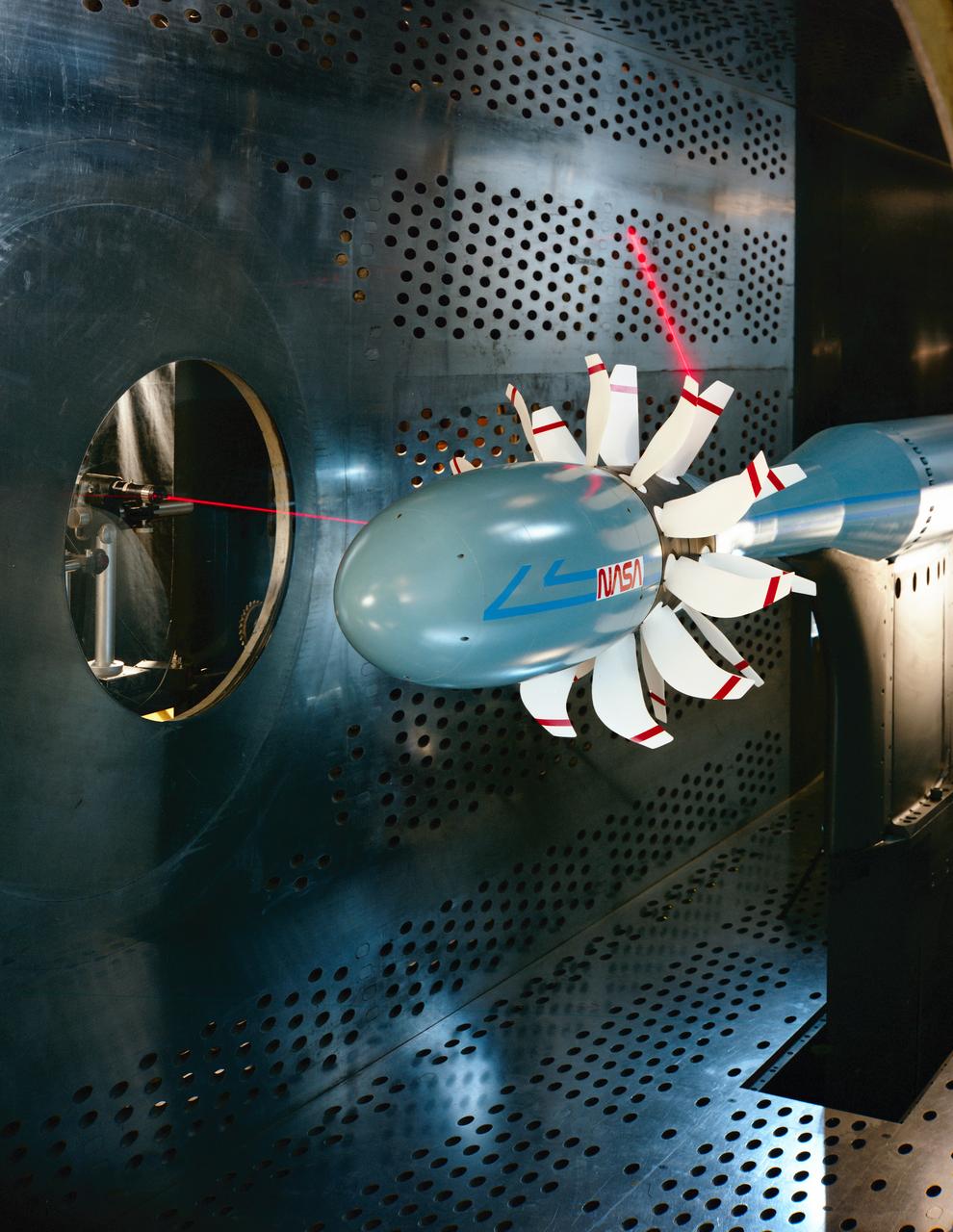
Laser based blade deflection measurement system on Counter Rotation Pusher Propeller model in 8x6 SWT (Supersonic Wind Tunnel)
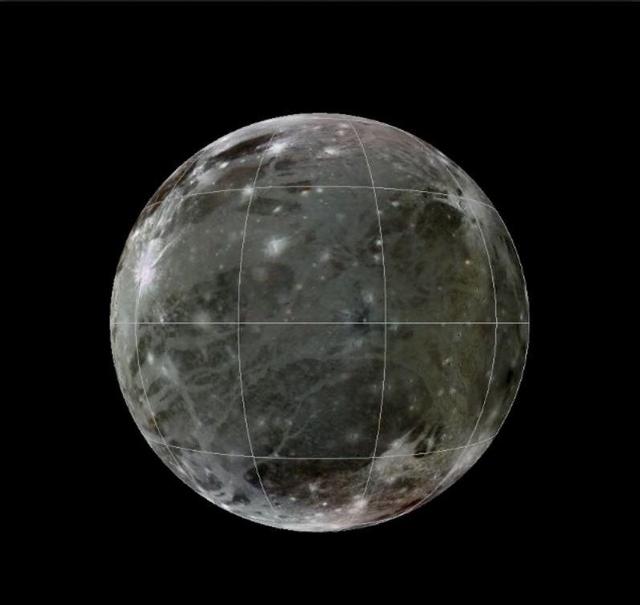

This is a frame from an animation of a rotating globe of Jupiter moon Ganymede, with a geologic map superimposed over a global color mosaic, incorporating the best available imagery from NASA Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft, and Galileo spacecraft.

This image is one from a series of images provided by the framing camera on NASA Dawn spacecraft; the series shows a full rotation of Vesta, which occurs over the course of roughly five hours.
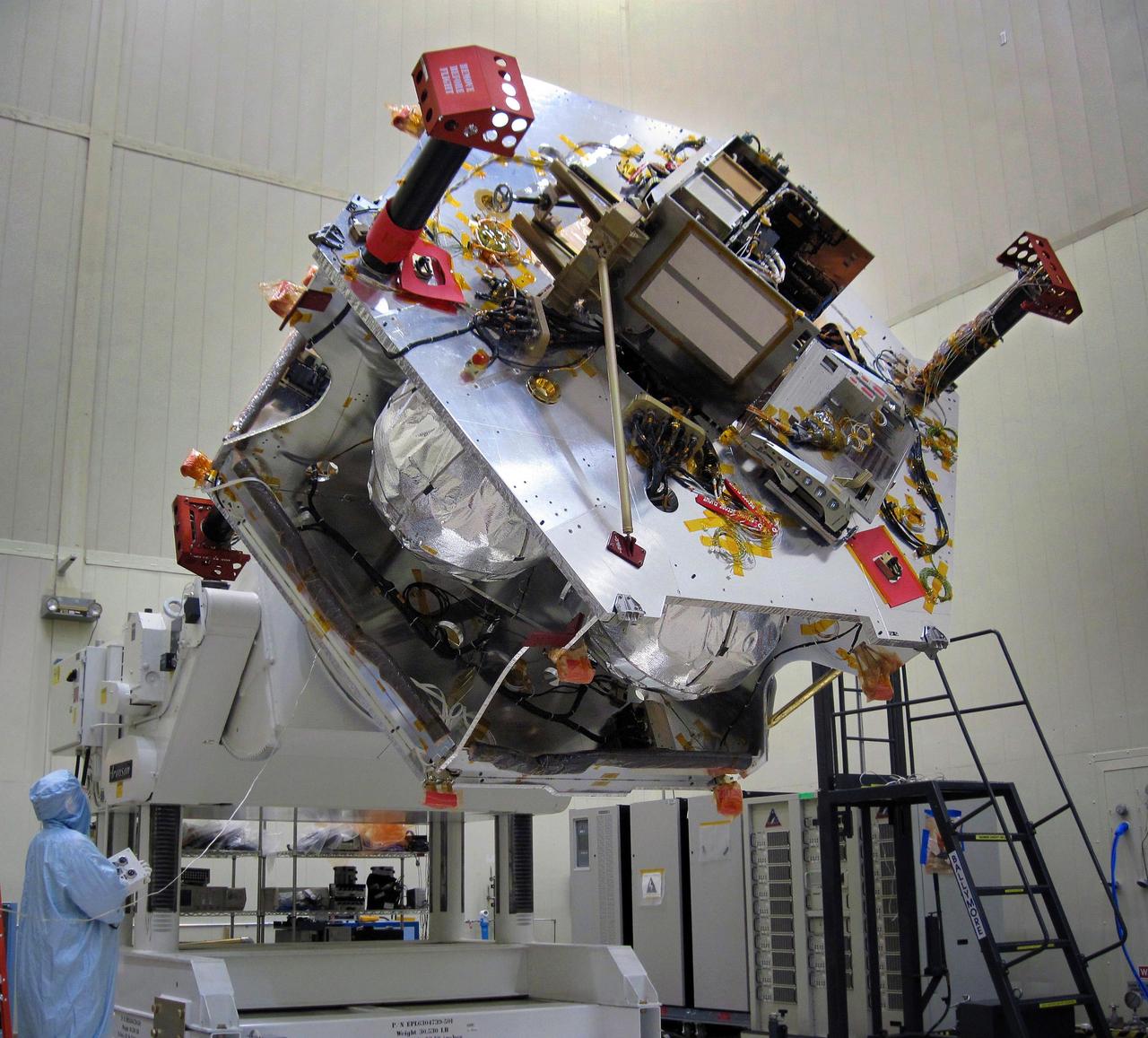

Once the radiation vault was installed on top of the propulsion module, NASA Juno spacecraft was lifted onto a large rotation fixture. The fixture allows the spacecraft to be turned for convenient access for integrating and testing instruments.
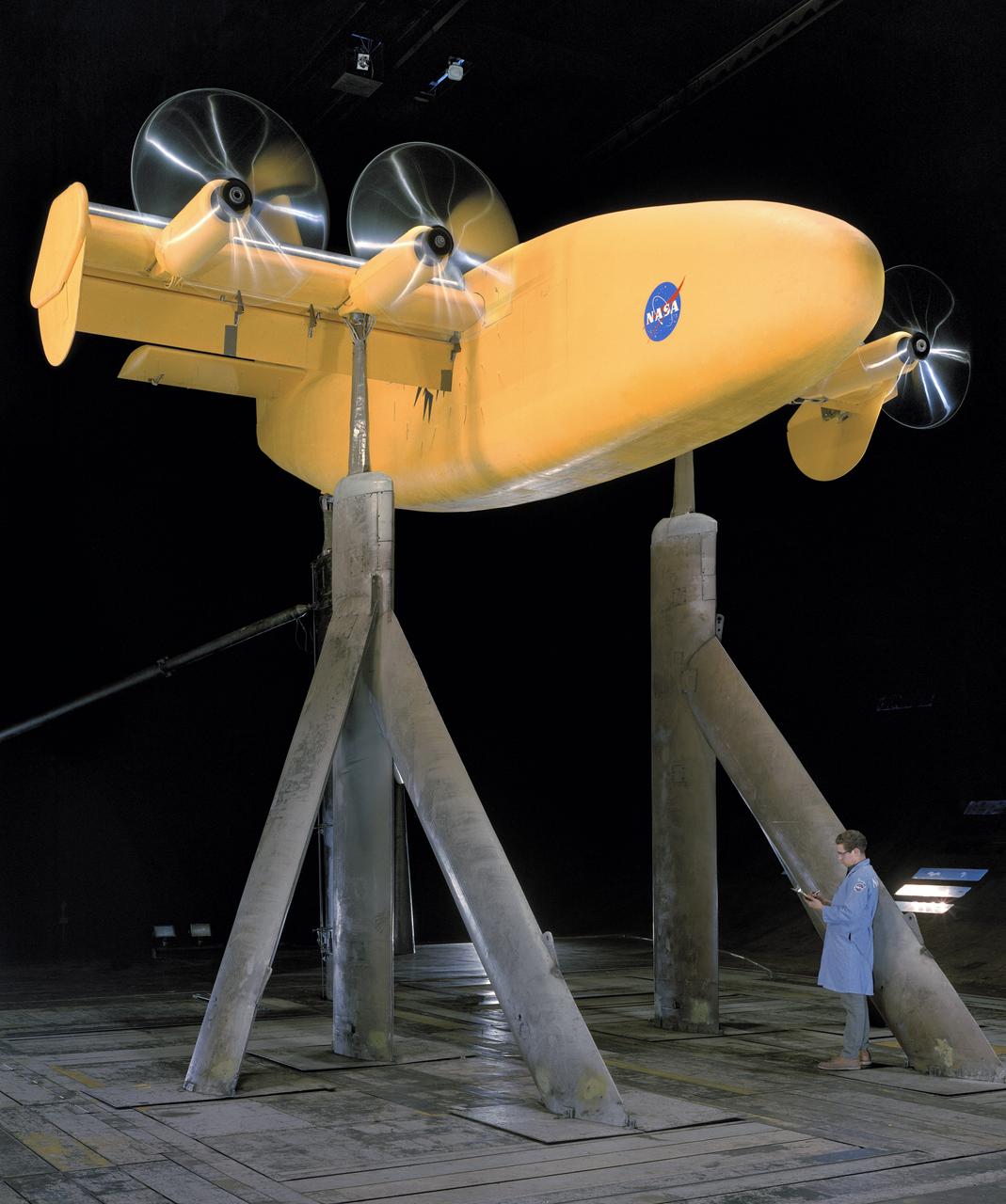

4 propeller model with rotating cylinder flap. Propellers running. 3/4 front view. DAVE JONES (PROPS TURNING)
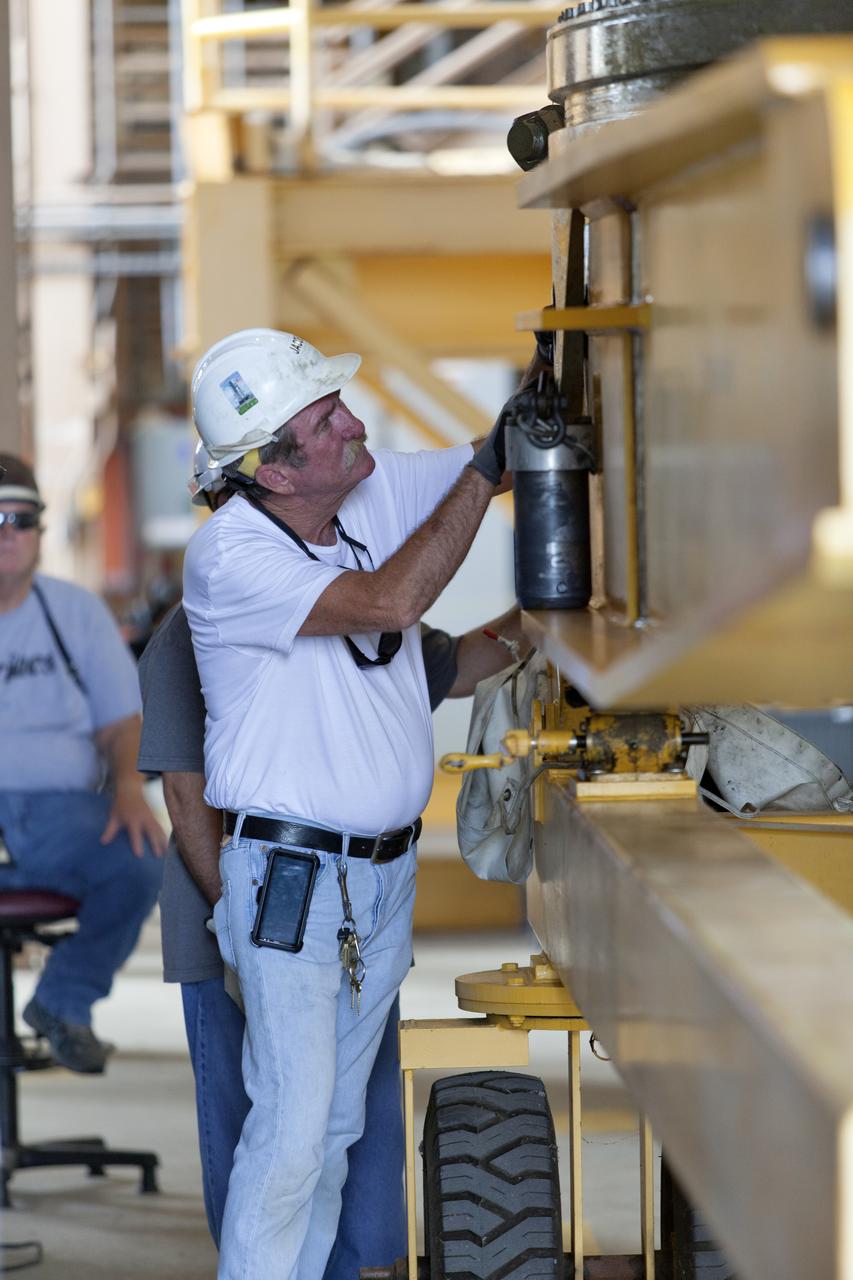

A Jacobs technician, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, checks bolt fittings during practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes will be used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
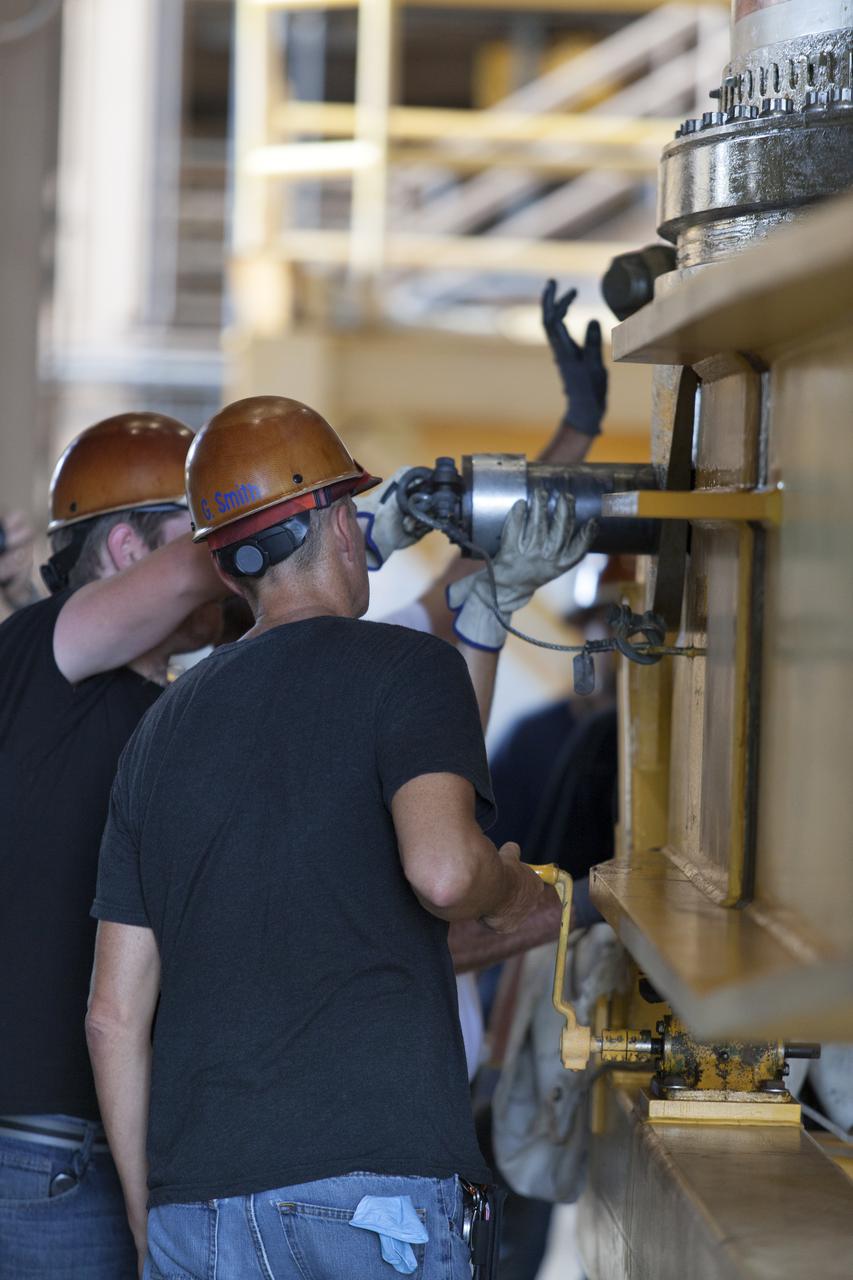

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, check bolt fittings as they practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
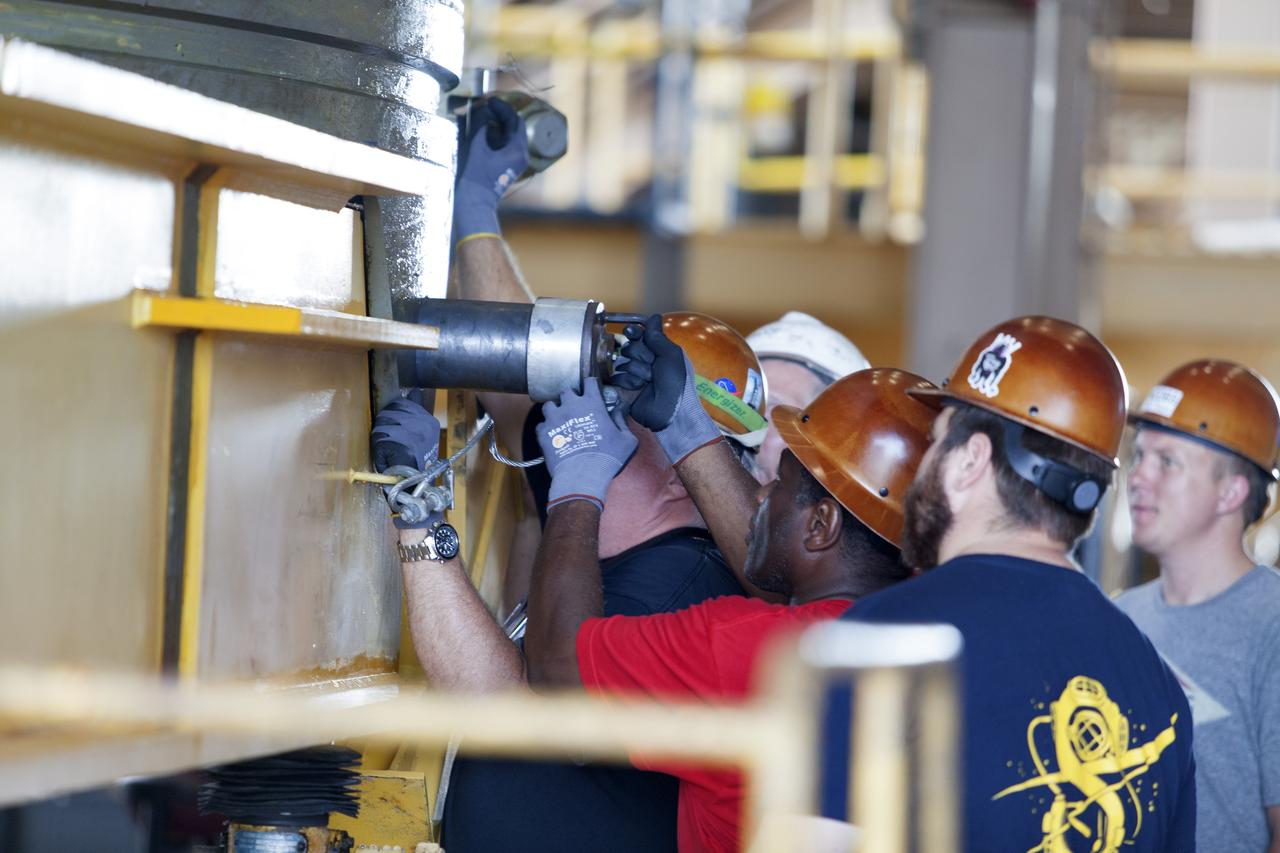

Jacobs technicians, on the Test and Operations Support Contract, check bolt fittings as they practice crane operations with an inert booster rocket segment in the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on June 22, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Dual cranes are being used to move the segment from vertical to horizontal, a maneuver known as a "breakover rotation." As part of routine processing operations for the agency's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, the RPSF team will receive all of the solid rocket fuel segments for inspection and preparation prior to transporting them to the Vehicle Assembly Building for stacking on the mobile launcher. Many pathfinding operations are being done to prepare for launch of the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

Team members assist as the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is raised and prepared for lifting to the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November

Team members assist as the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is raised and prepared for lifting to the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.

Team members check the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) after it was lifted to the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.

Team members monitor the progress as the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is lifted to the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.

The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is lifted to the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
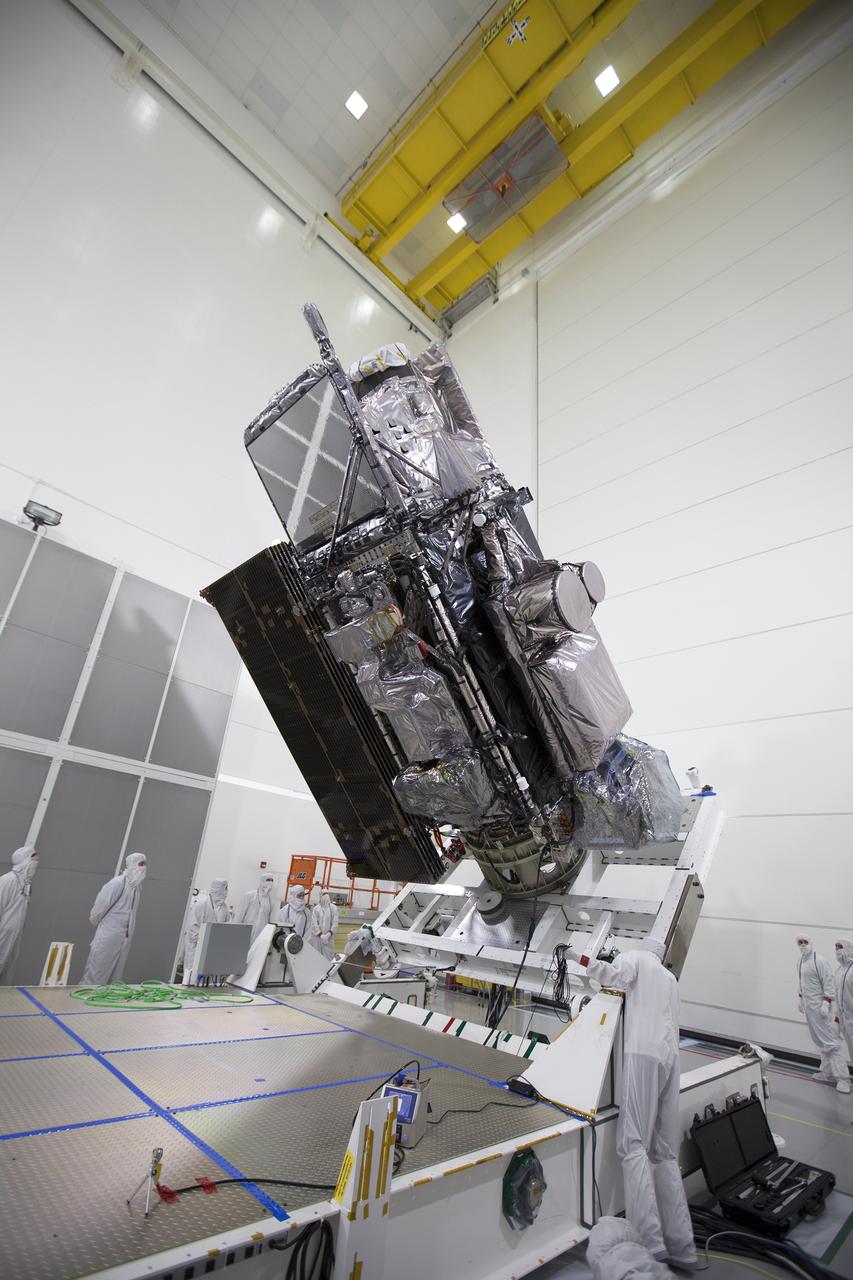

The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is raised to the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.

The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) has been secured in the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
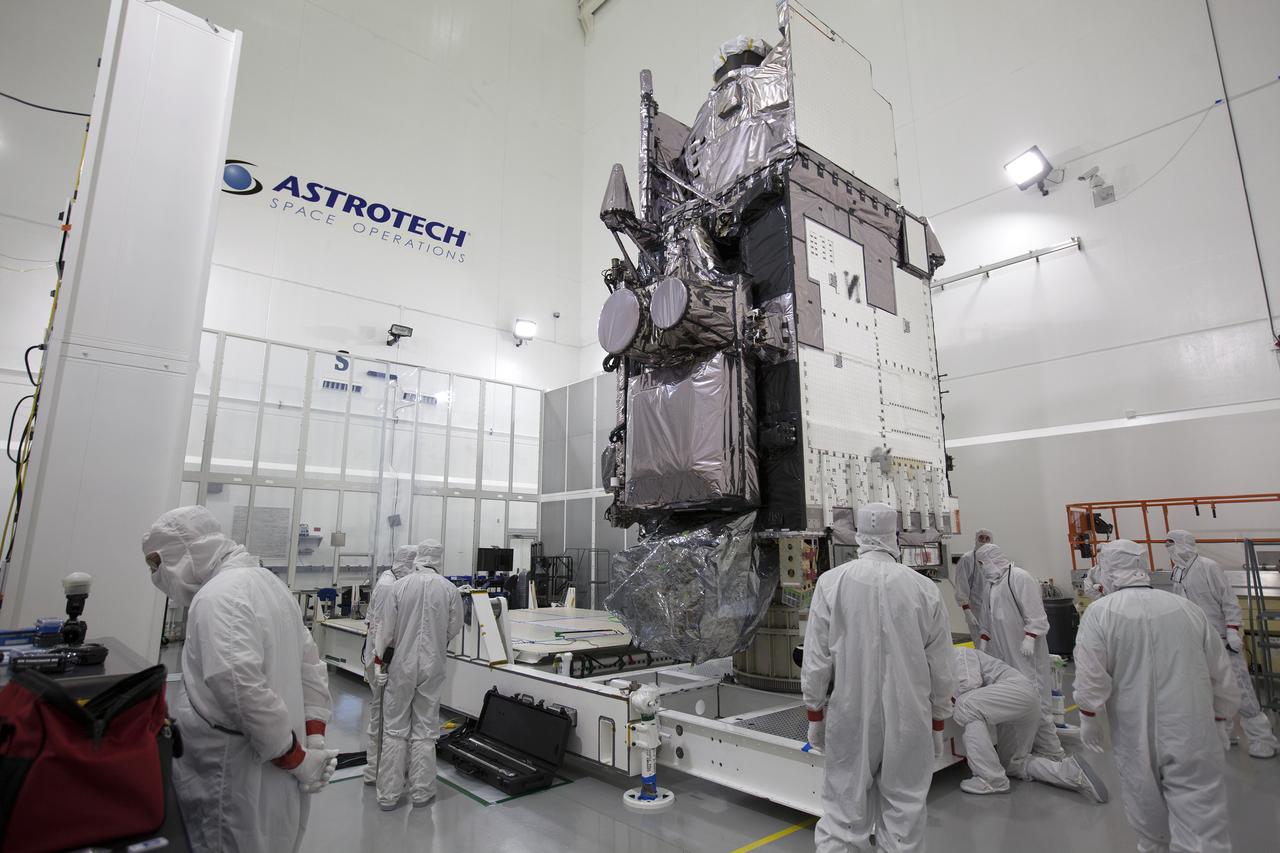

Team members are securing the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) in the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
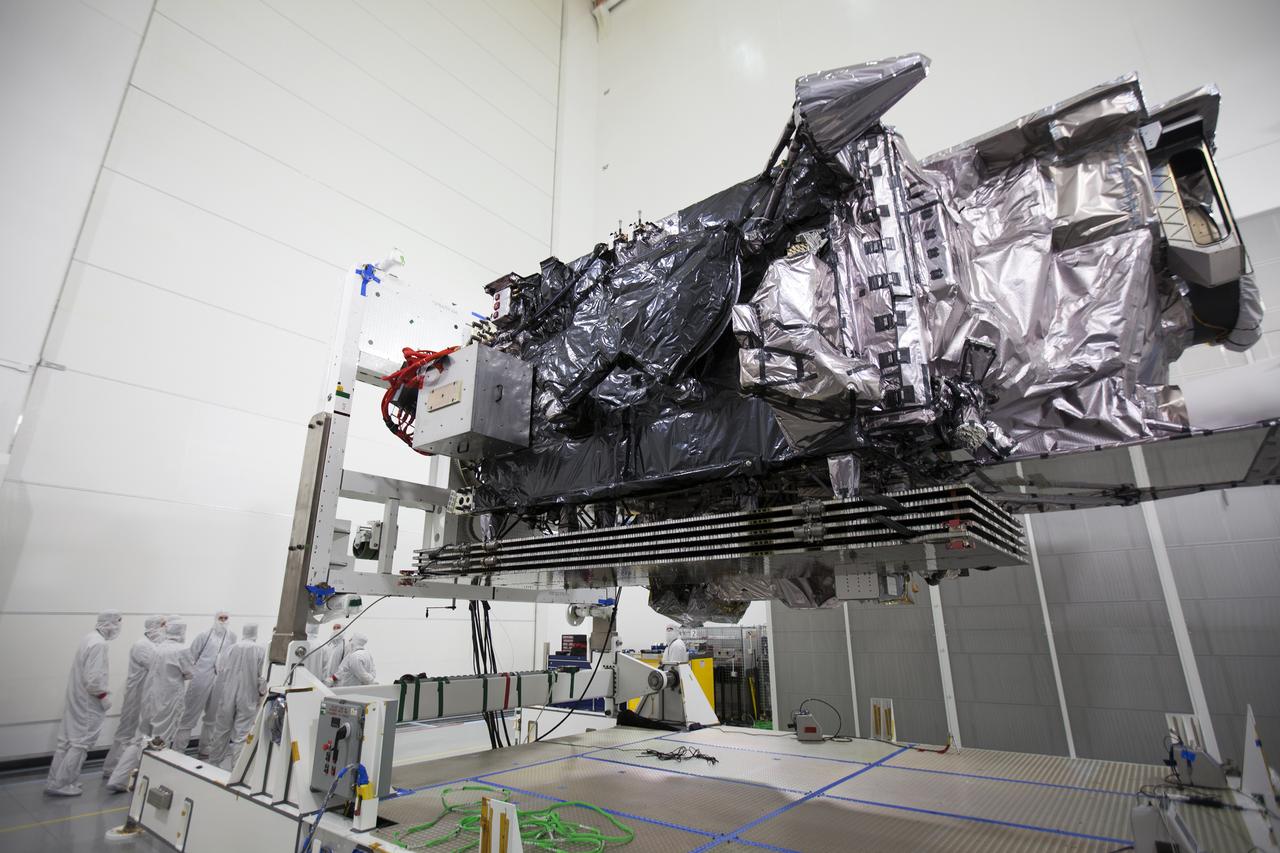

Team members assist as the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES-R) is prepared for lifting to the vertical position on an “up-ender” inside the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. GOES-R will be the first satellite in a series of next-generation NOAA GOES Satellites. The spacecraft is to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket in November.
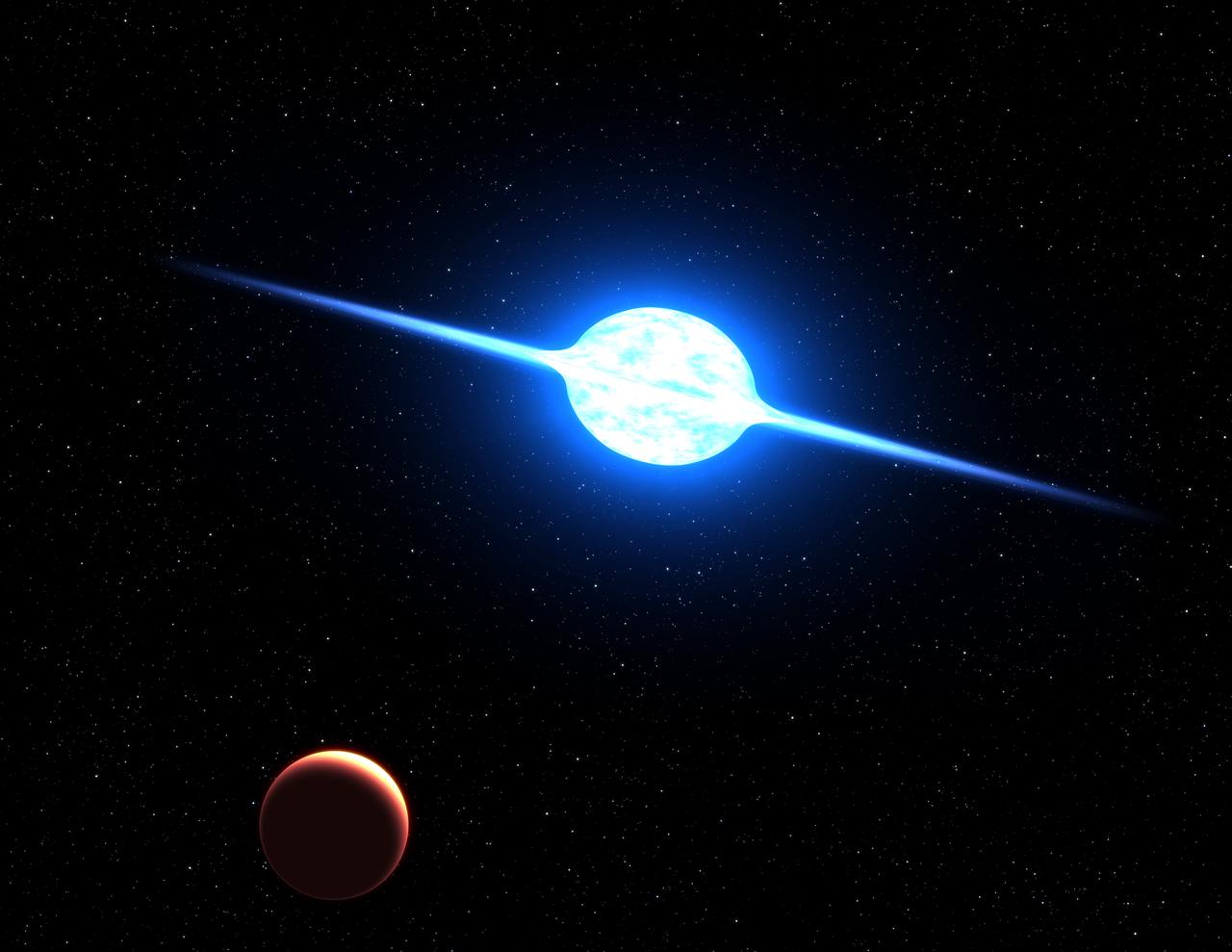

NASA image release December 5, 2011 This is an artist's concept of the fastest rotating star found to date. The massive, bright young star, called VFTS 102, rotates at a million miles per hour, or 100 times faster than our Sun does. Centrifugal forces from this dizzying spin rate have flattened the star into an oblate shape and spun off a disk of hot plasma, seen edge on in this view from a hypothetical planet. The star may have "spun up" by accreting material from a binary companion star. The rapidly evolving companion later exploded as a supernova. The whirling star lies 160,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy of our Milky Way. The team will use NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to make precise measurements of the star's proper motion across space. To read more go to: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2011/39/full/" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2011/39/full/</a> Image Type: Artwork Credit: NASA, ESA, and G. Bacon (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
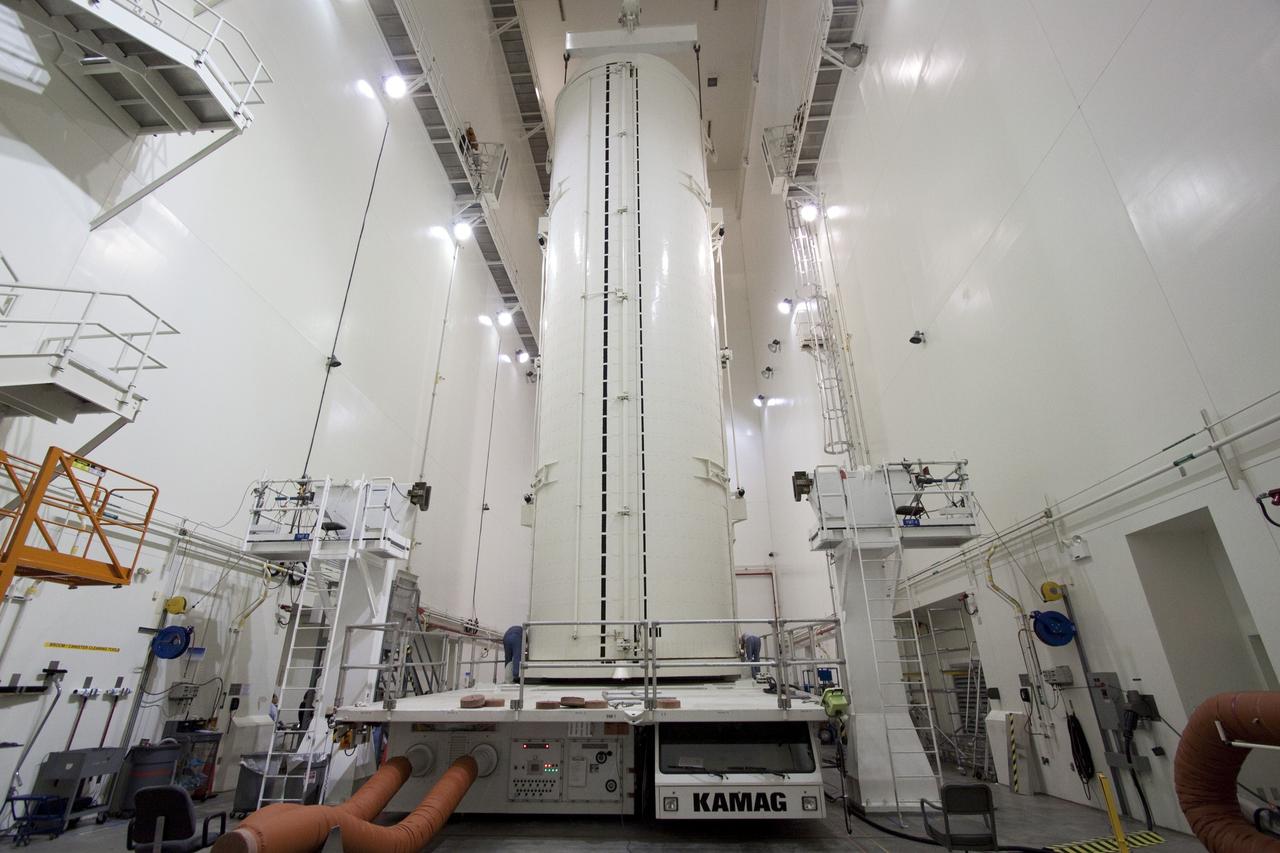

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the payload canister rests on a transport vehicle after being rotated into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

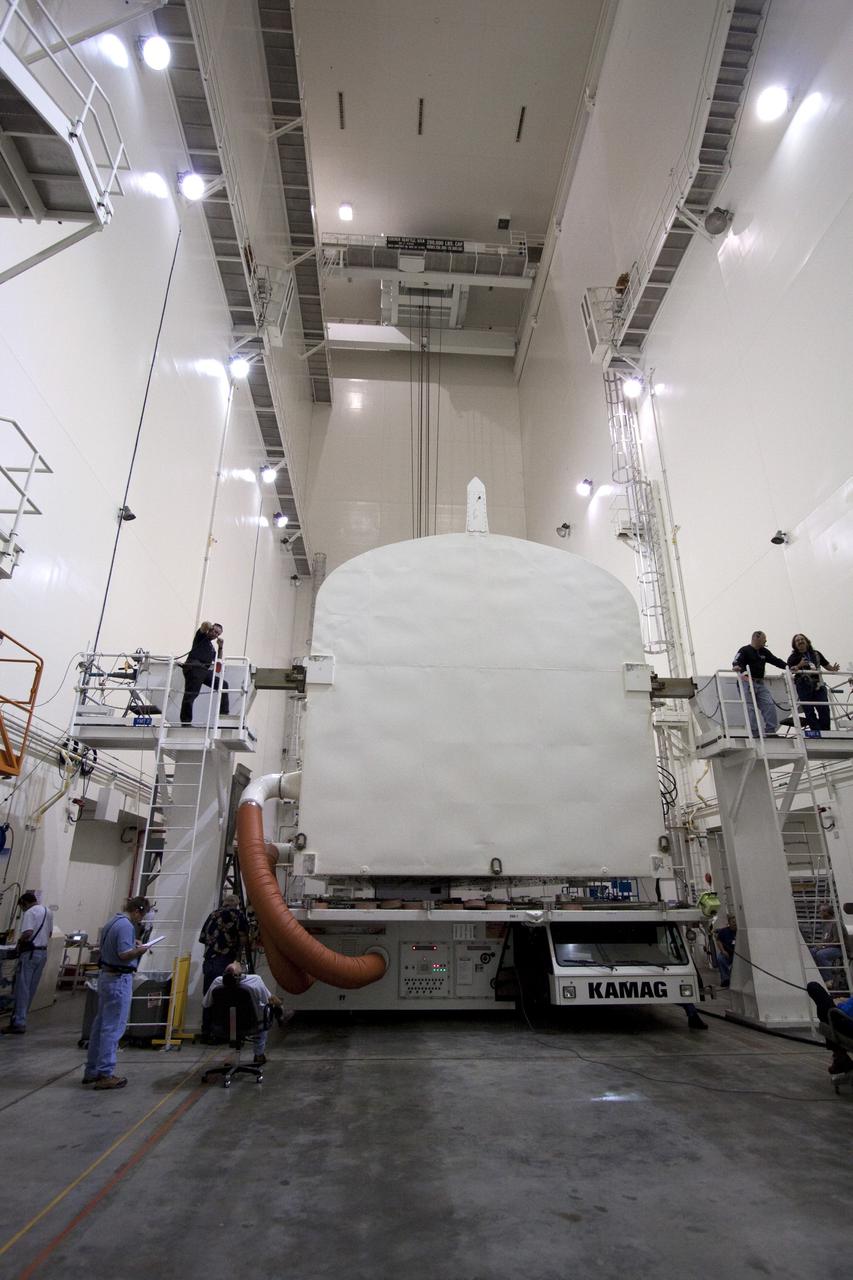
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers monitor the progress of the payload canister as an overhead crane rotates it into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

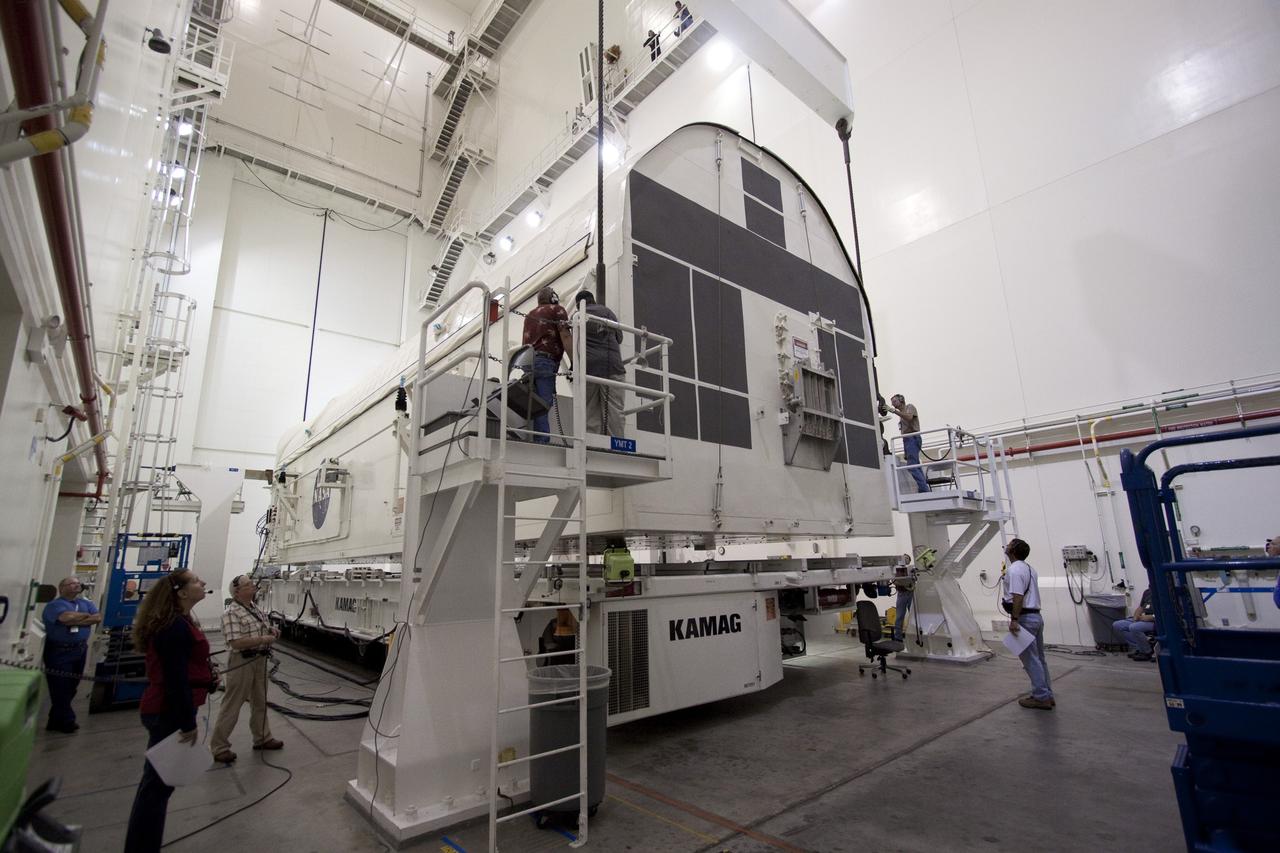
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are preparing the payload canister for its rotation into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

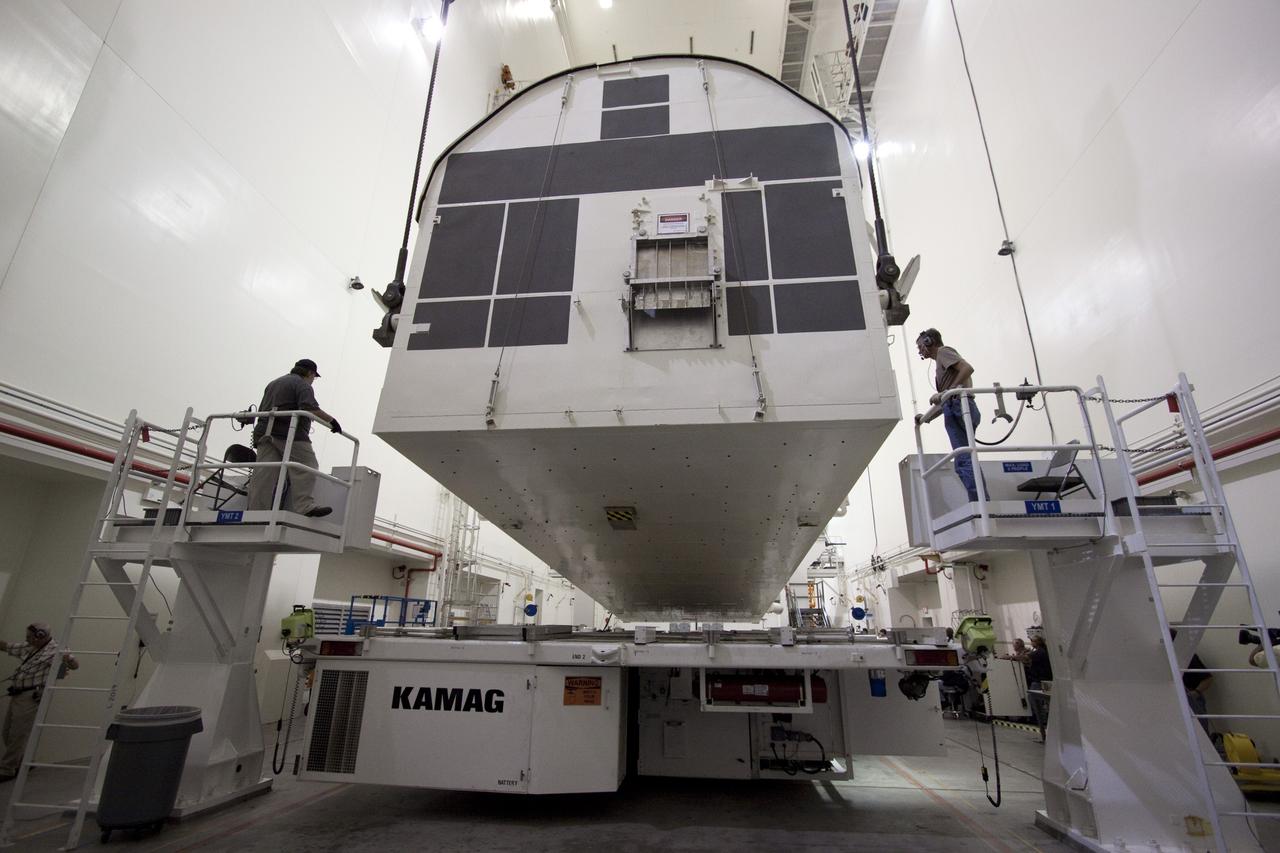
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers connect an overhead crane to the payload canister for its rotation into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers monitor the progress of the payload canister as an overhead crane rotates it into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers monitor the progress of the payload canister as an overhead crane rotates it into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
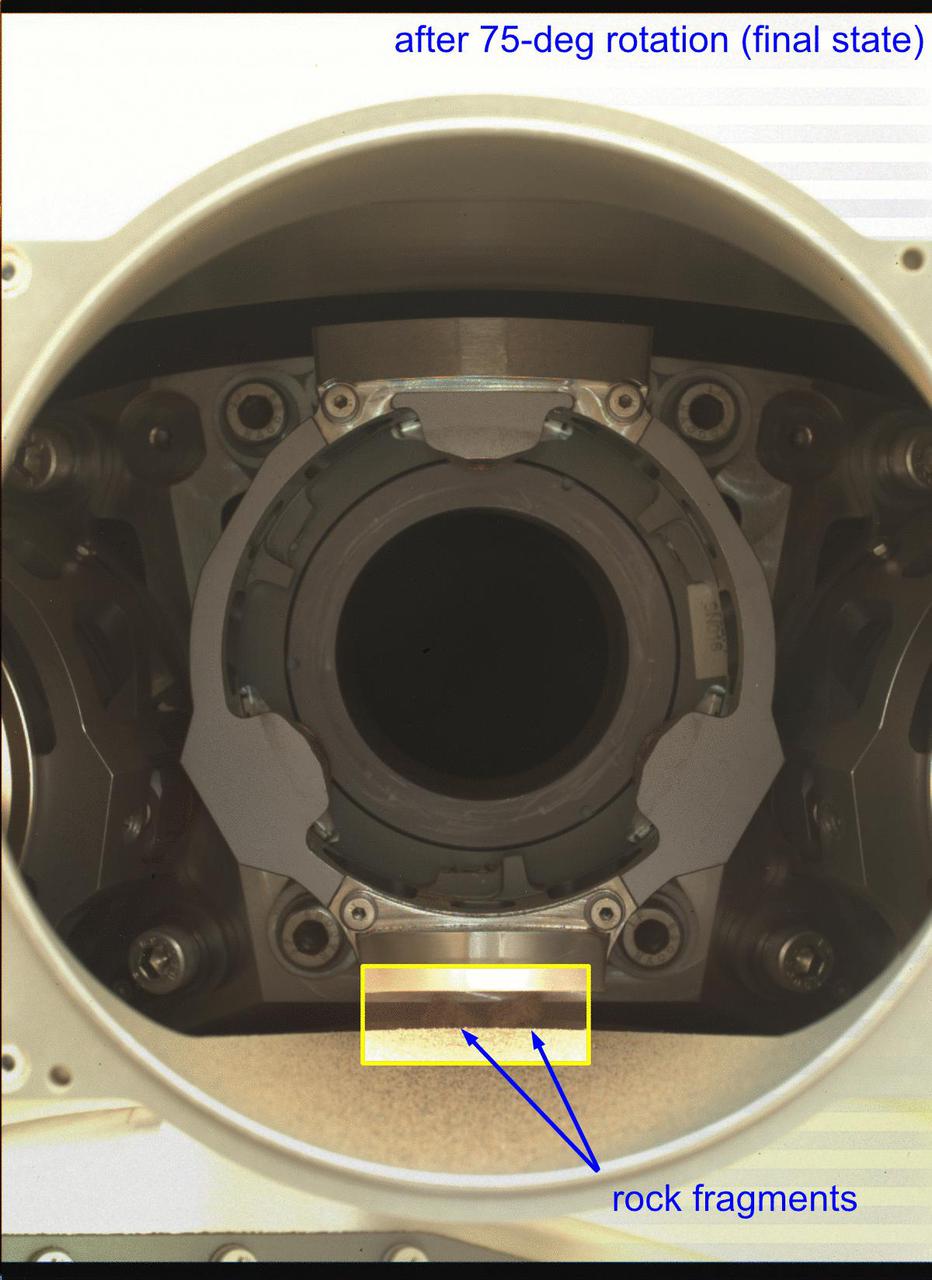
In this annotated animated GIF, the bit carousel on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover can be seen rotating during a test of the component on Jan. 17, 2022, the 325th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The carousel was rotated about 75 degrees during the test, then was returned back to its original position. The five images that compose this animated GIF were captured to determine the status – after the test – of four fragments of the cored rock that fell out of the sample tube during Perseverance sampling activity on Dec. 29, 2021. After completion of the test, the upper two rock fragments (seen in the first image) have disappeared, having been ejected during the rotation. However, the lower two rock fragments, located below the bit carousel housing, remain. The five images that make up the GIF were obtained by the WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) camera. Located in the turret at the end of the rover's robotic arm, WATSON can document the structure and texture within a drilled or abraded target, and its data can be used to derive depth measurements. The camera is a subsystem of the SHERLOC (Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics & Chemicals) instrument. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and manages operations of Perseverance and Ingenuity for the agency. Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA. WATSON was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) in San Diego and is operated jointly by MSSS and JPL. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25071

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a workers watches the progress of an overhead crane as it lowers the payload canister onto a transport vehicle. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lifts the payload canister into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
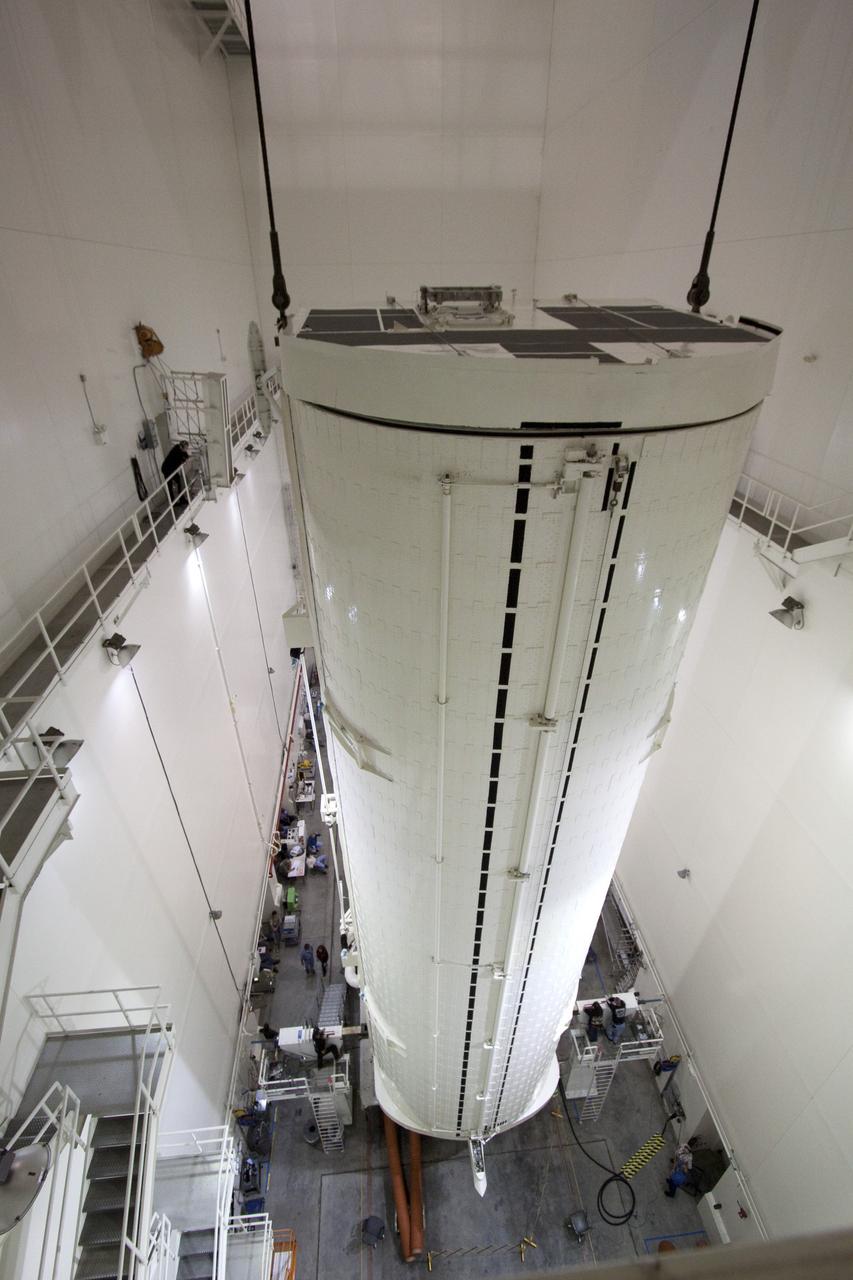

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lifts the payload canister into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

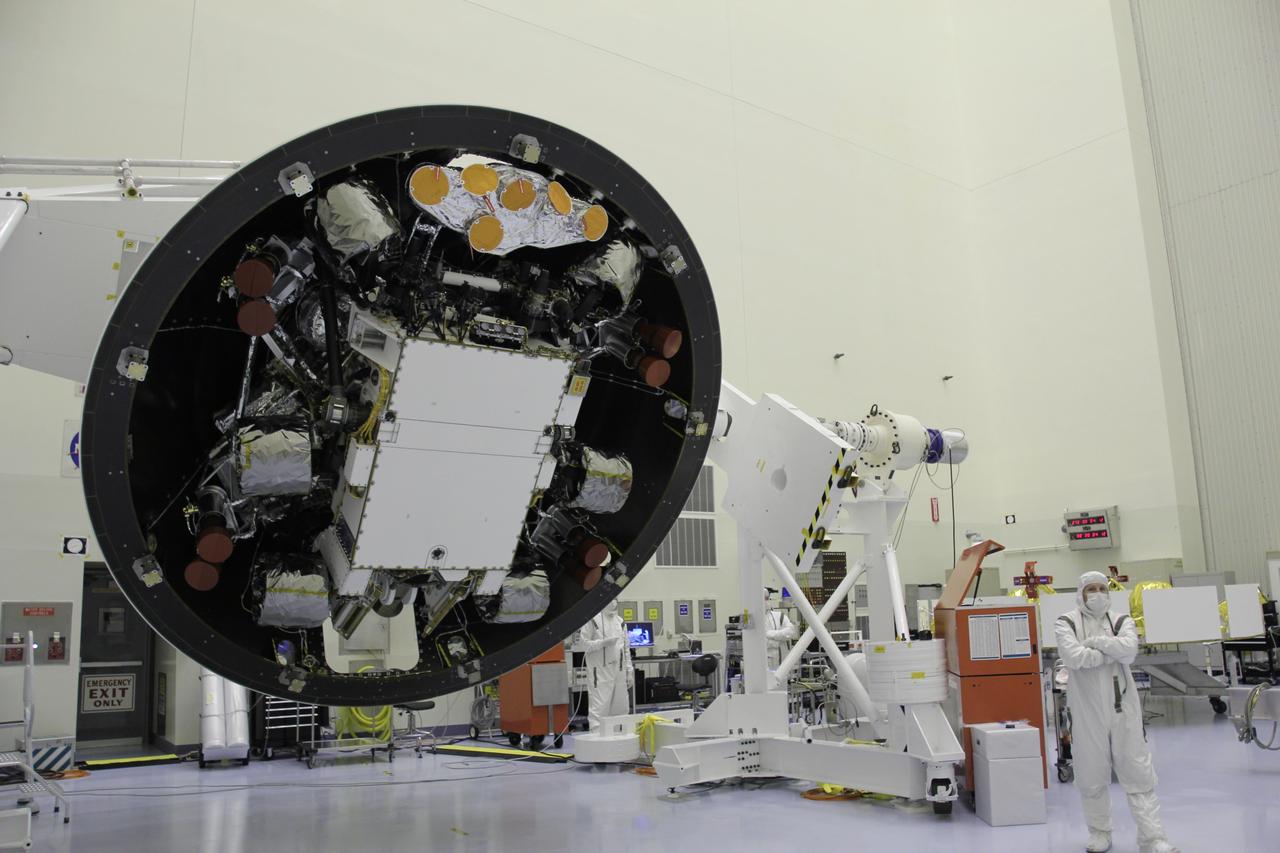
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers monitor the progress of the payload canister as an overhead crane lifts it into a vertical position. The canister will then be delivered to Launch Pad 39A, lifted into the rotating service structure where the module will be moved into the clean room before it is installed into space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery and its STS-133 crew will deliver the PMM, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 4:40 p.m. EDT, Nov. 1. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
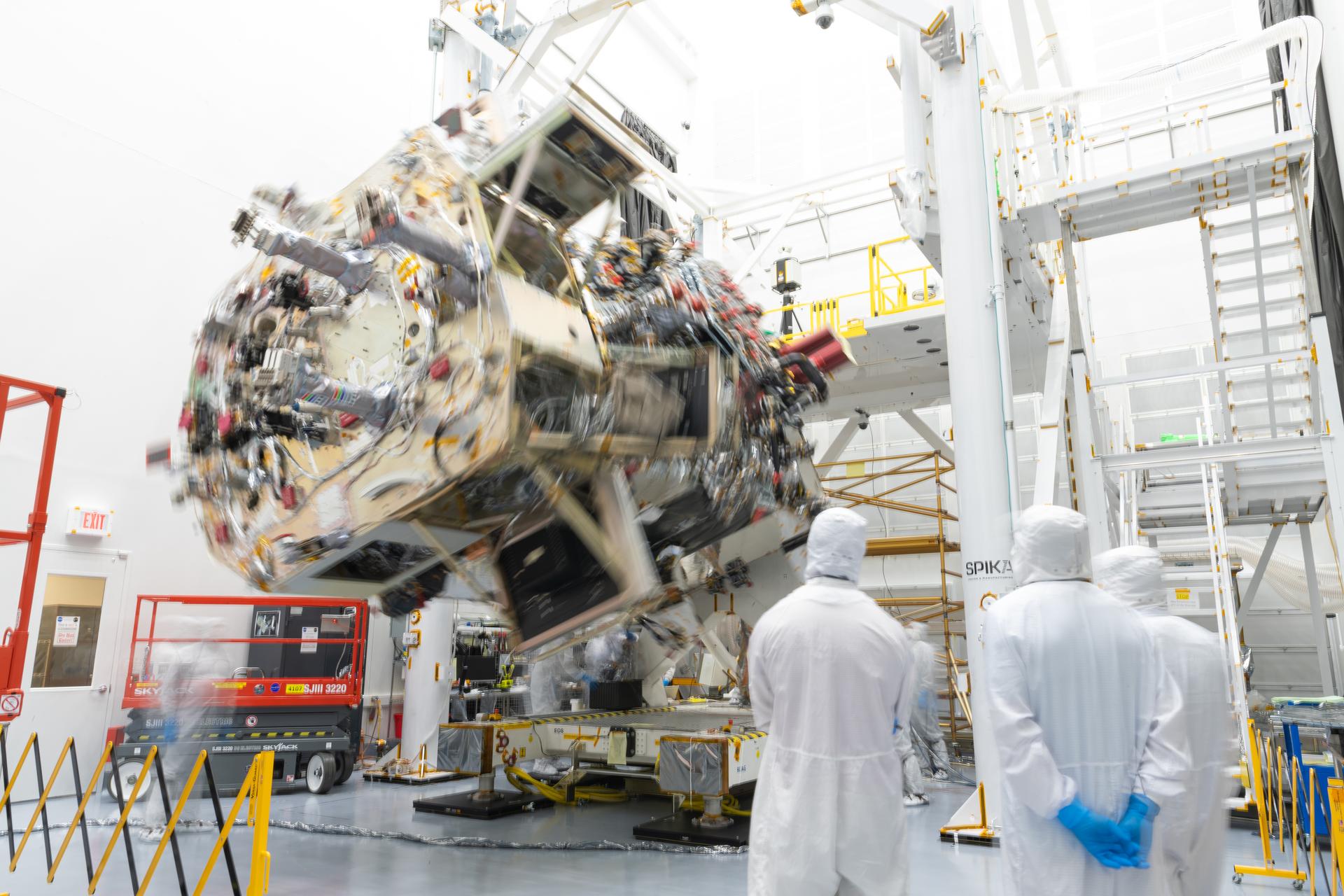

The OSAM-1 Spacecraft is rotated while in the horizontal position inside the cleanroom at Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt Md., July 29, 2024. This photo has been reviewed by the Export Control Office, project Management, and Maxar release authority and is released for public view. NASA/Mike Guinto
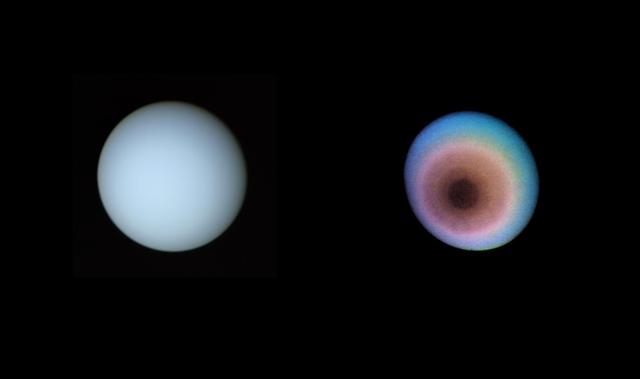
These two pictures of Uranus were compiled from images recorded by NASA Voyager 2 on Jan. 1O, 1986. This view is toward the planet pole of rotation, which lies just left of center. The image on the right is a false-color image.

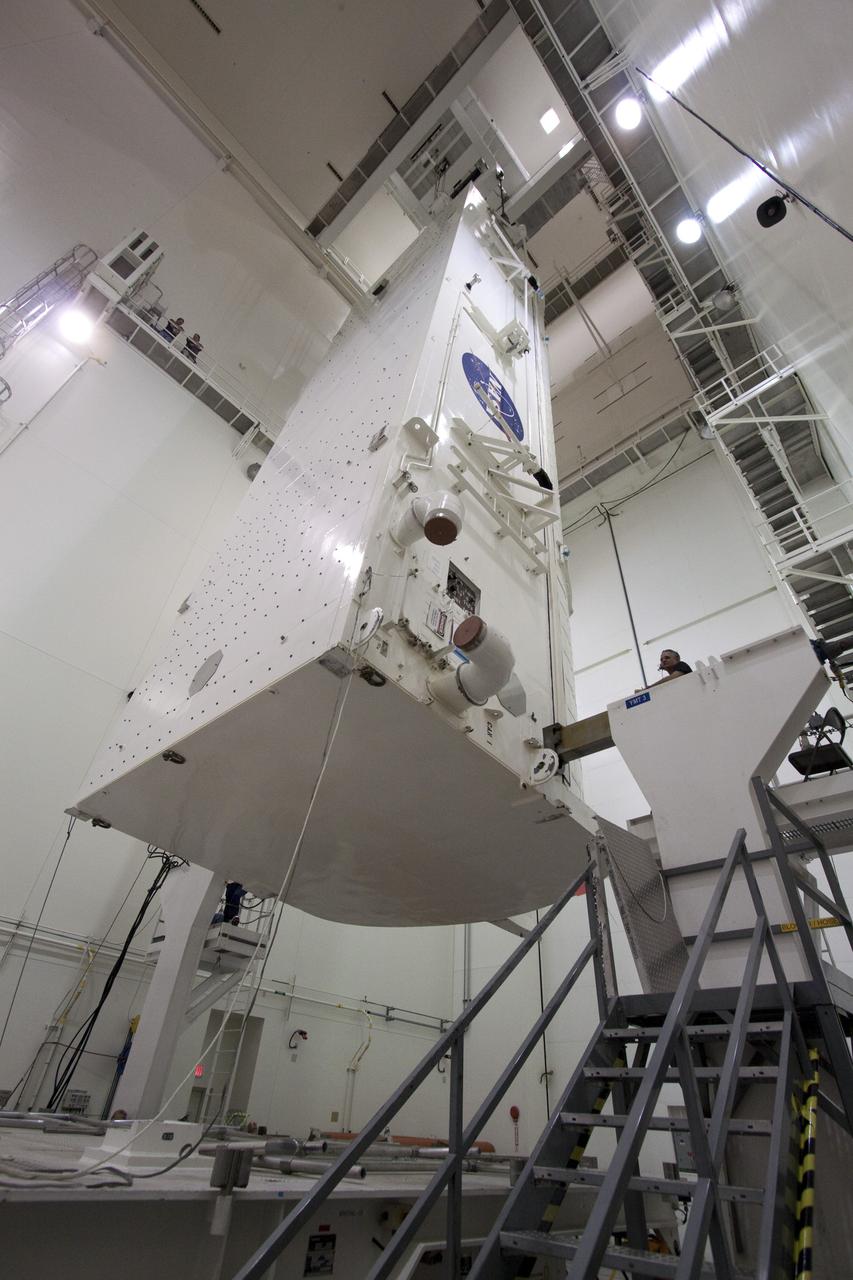
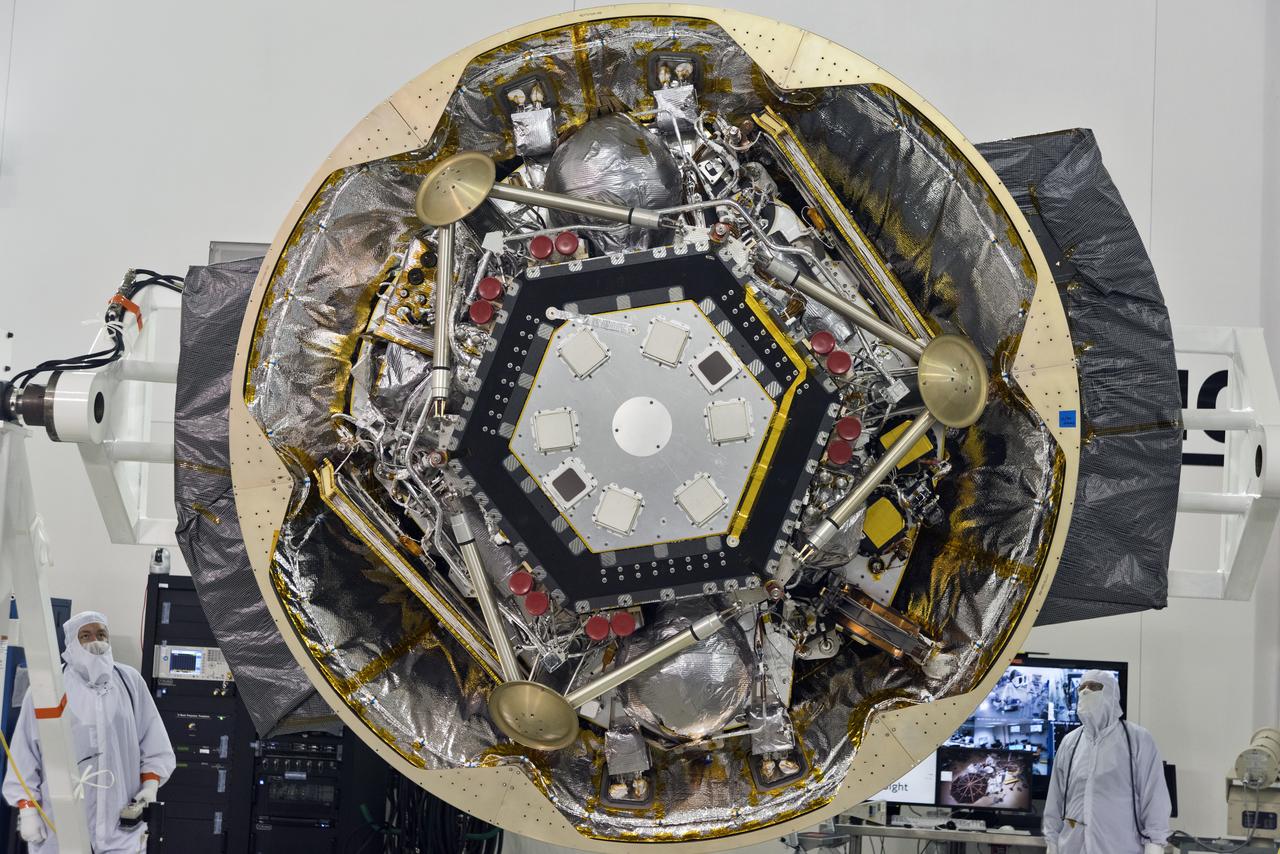
At the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the back shell powered descent vehicle configuration of NASA Mars Science Laboratory is being rotated for final closeout actions.
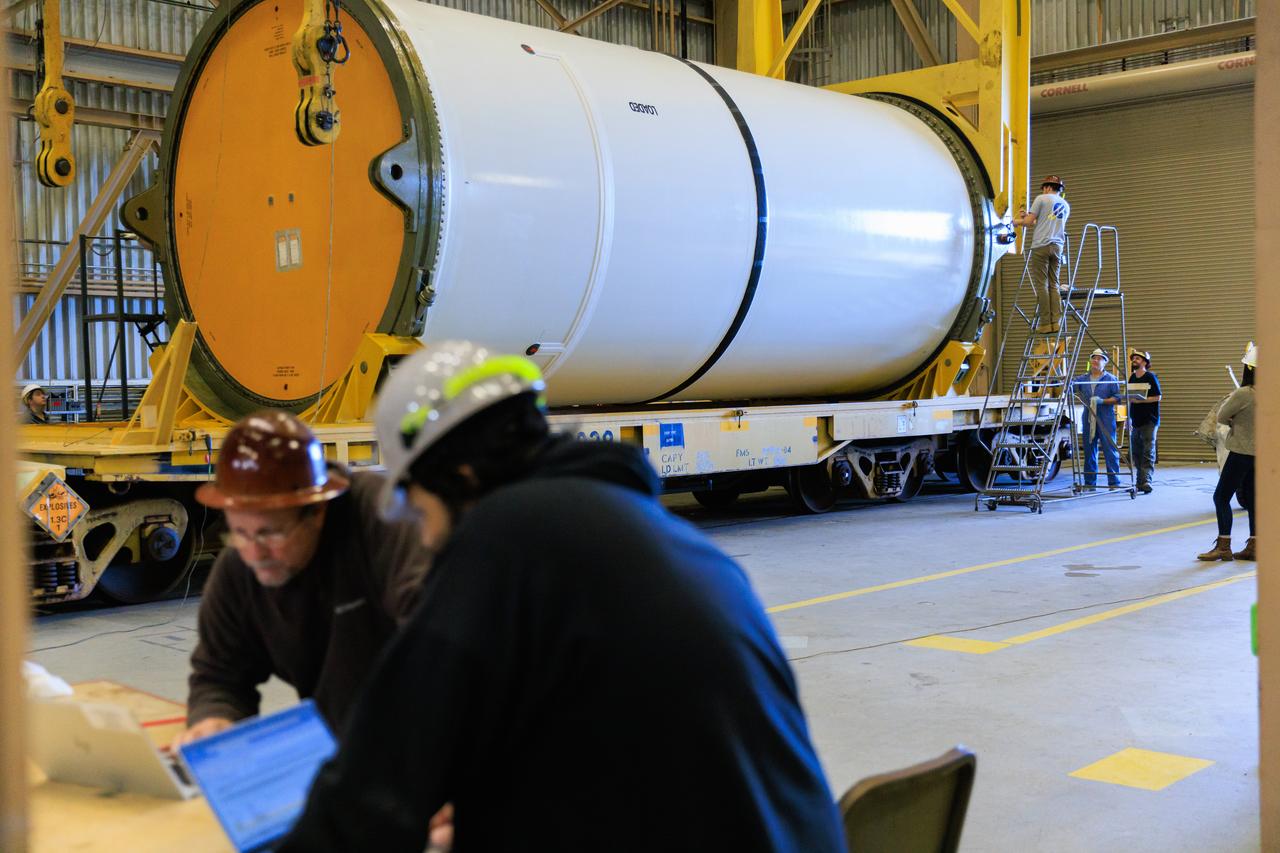

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
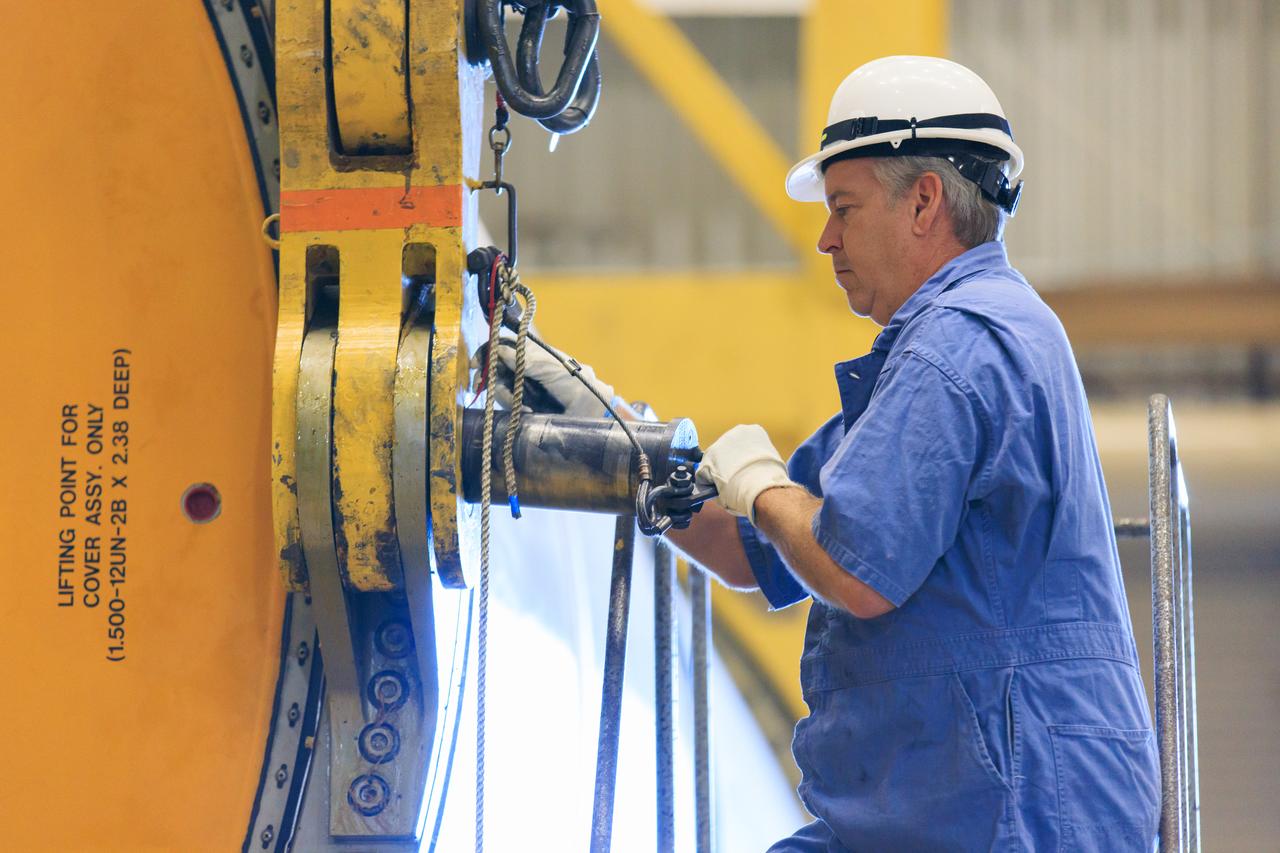

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
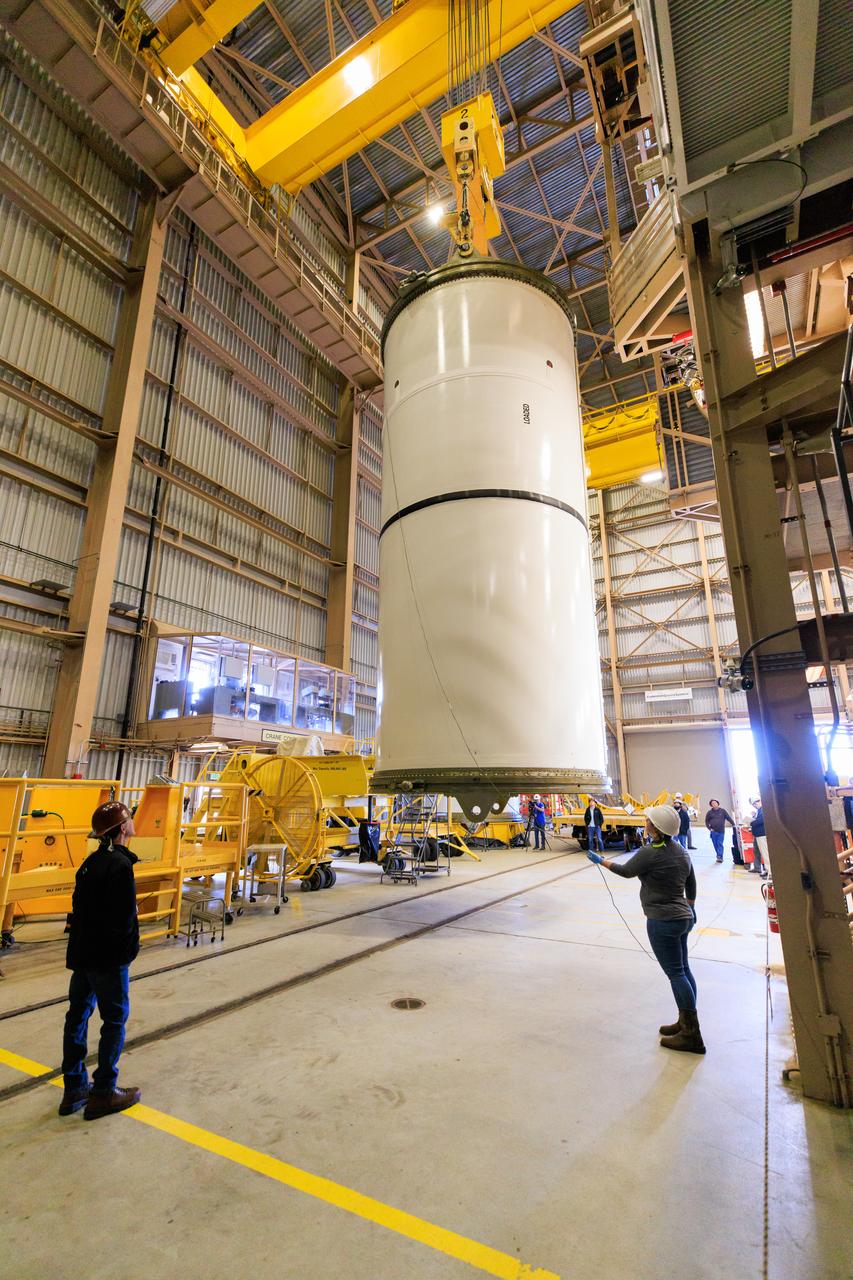

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
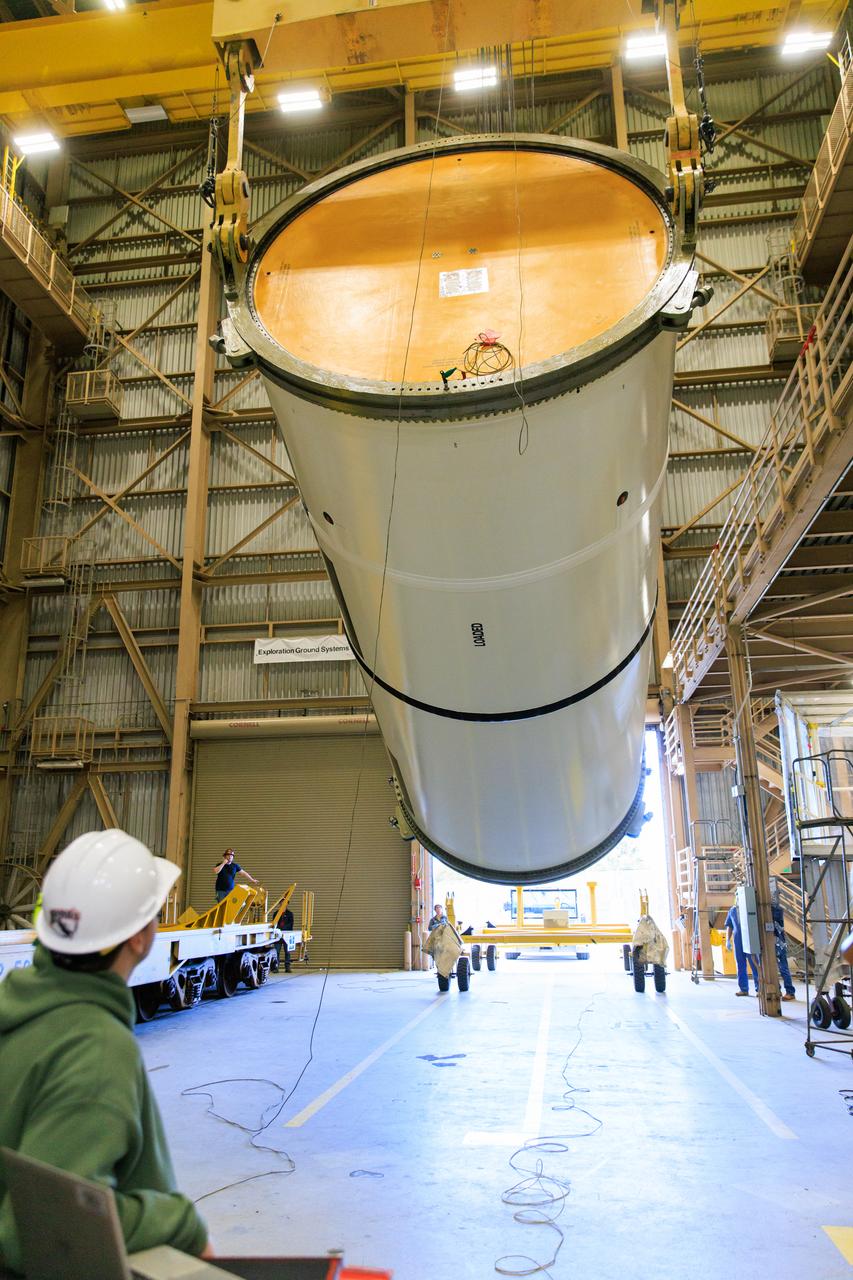

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
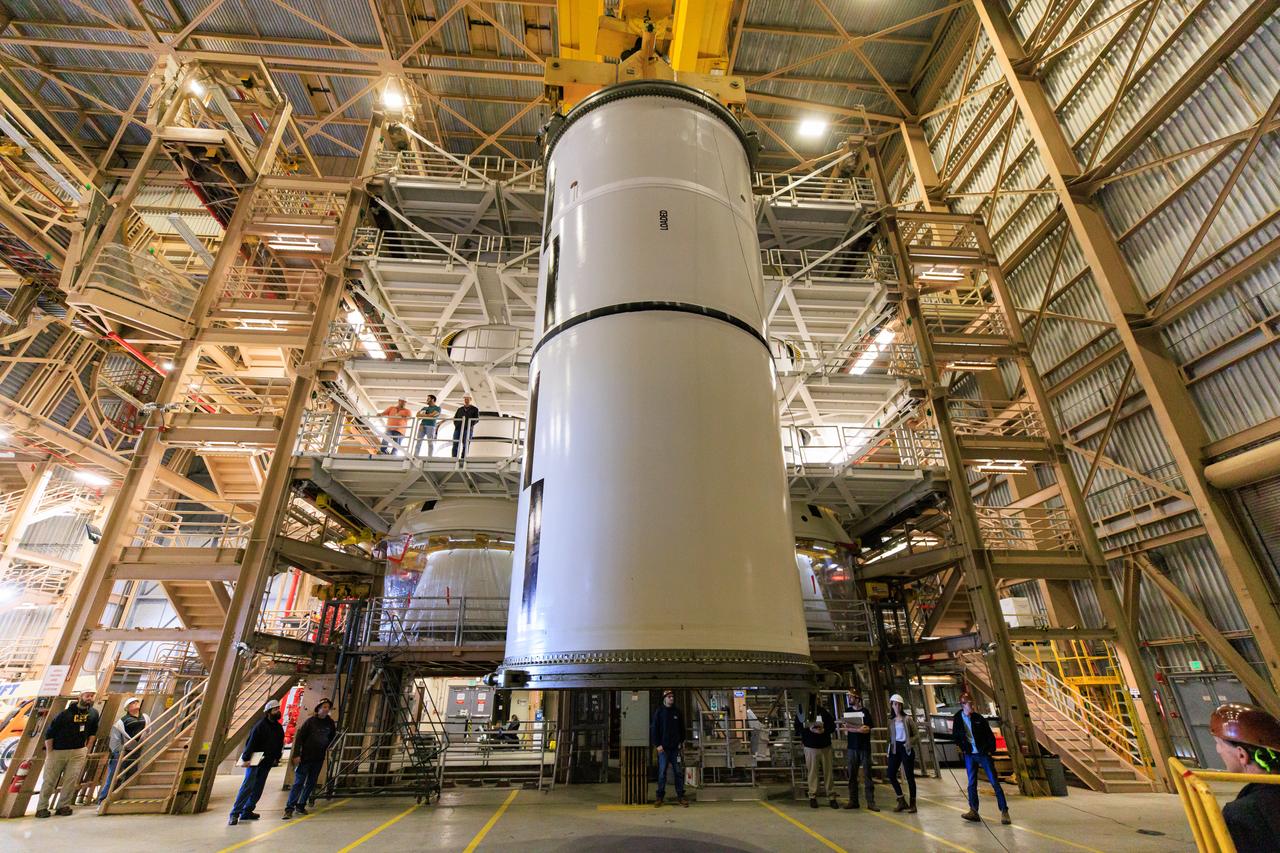

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
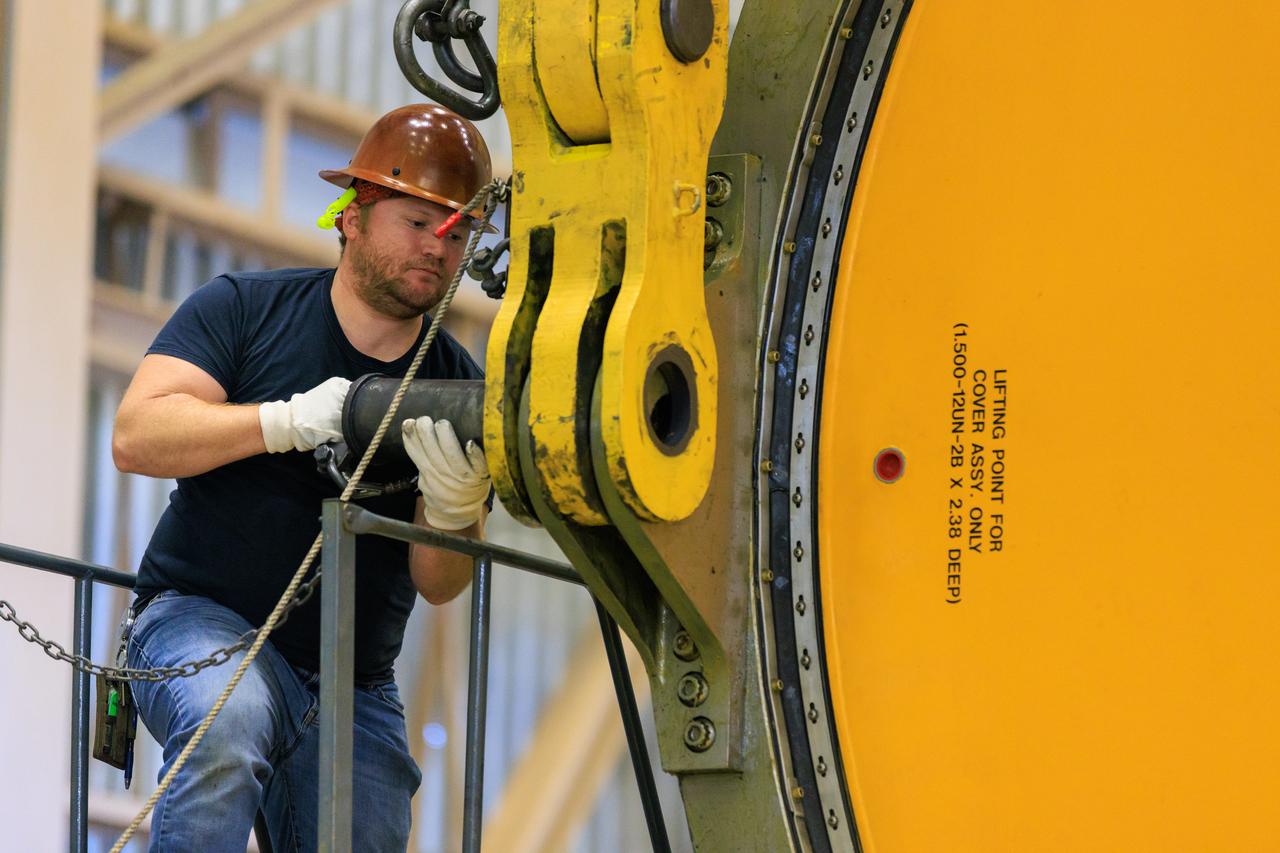

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
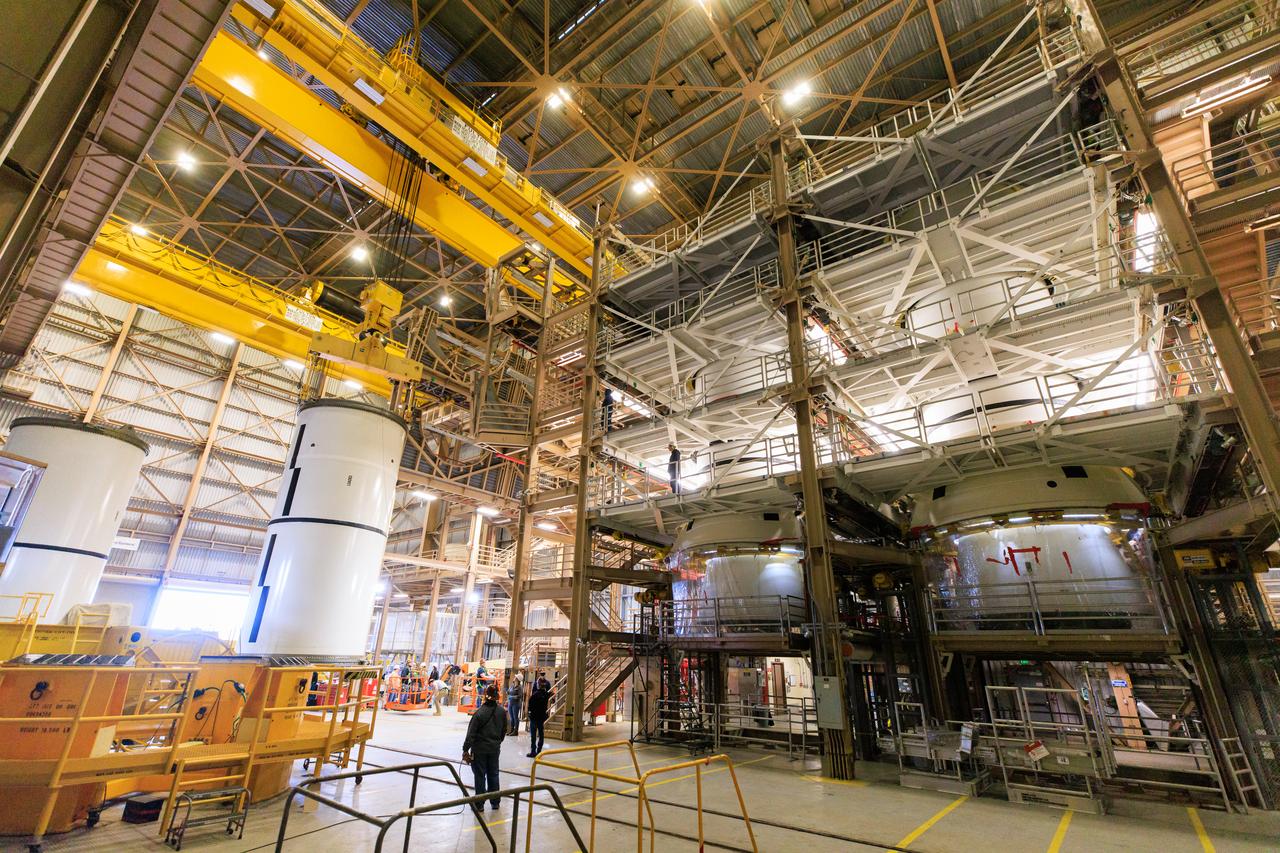

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
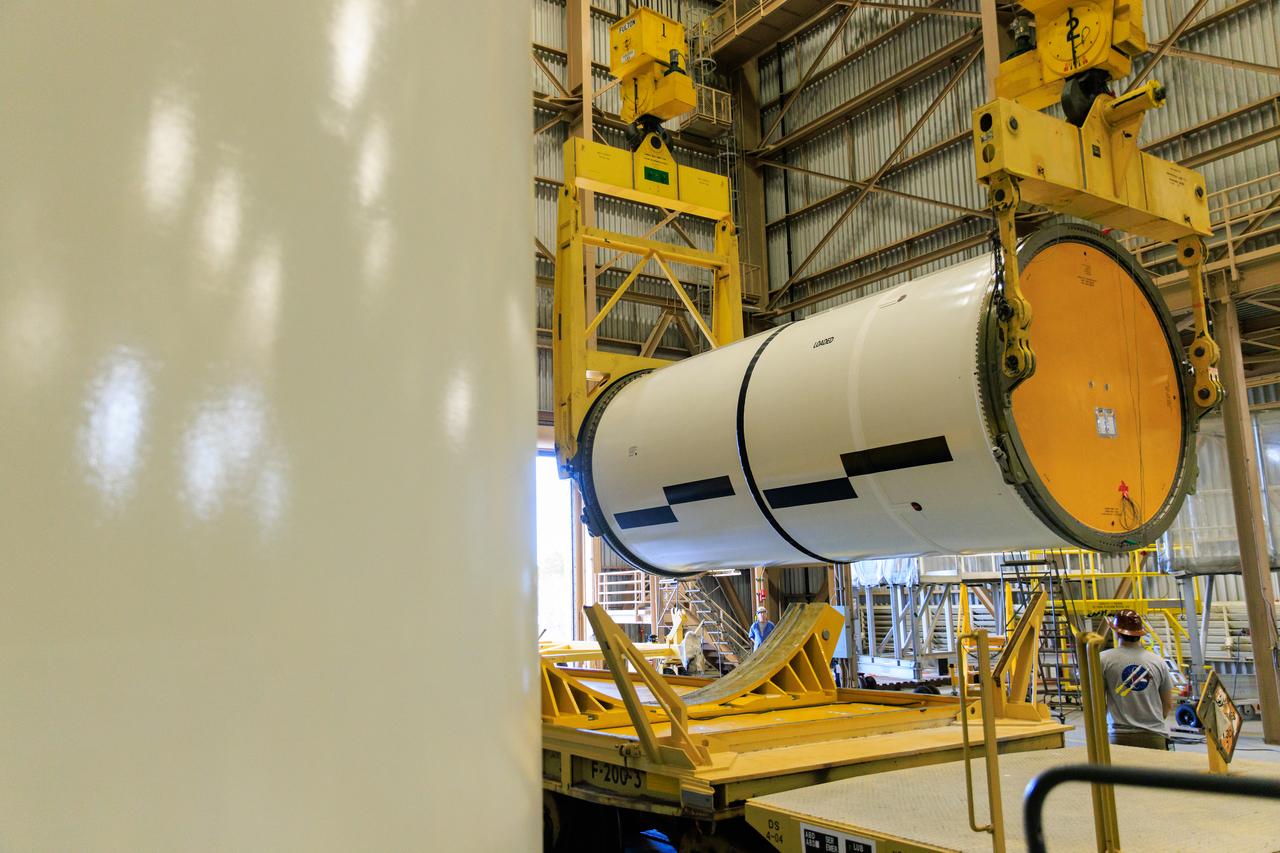

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
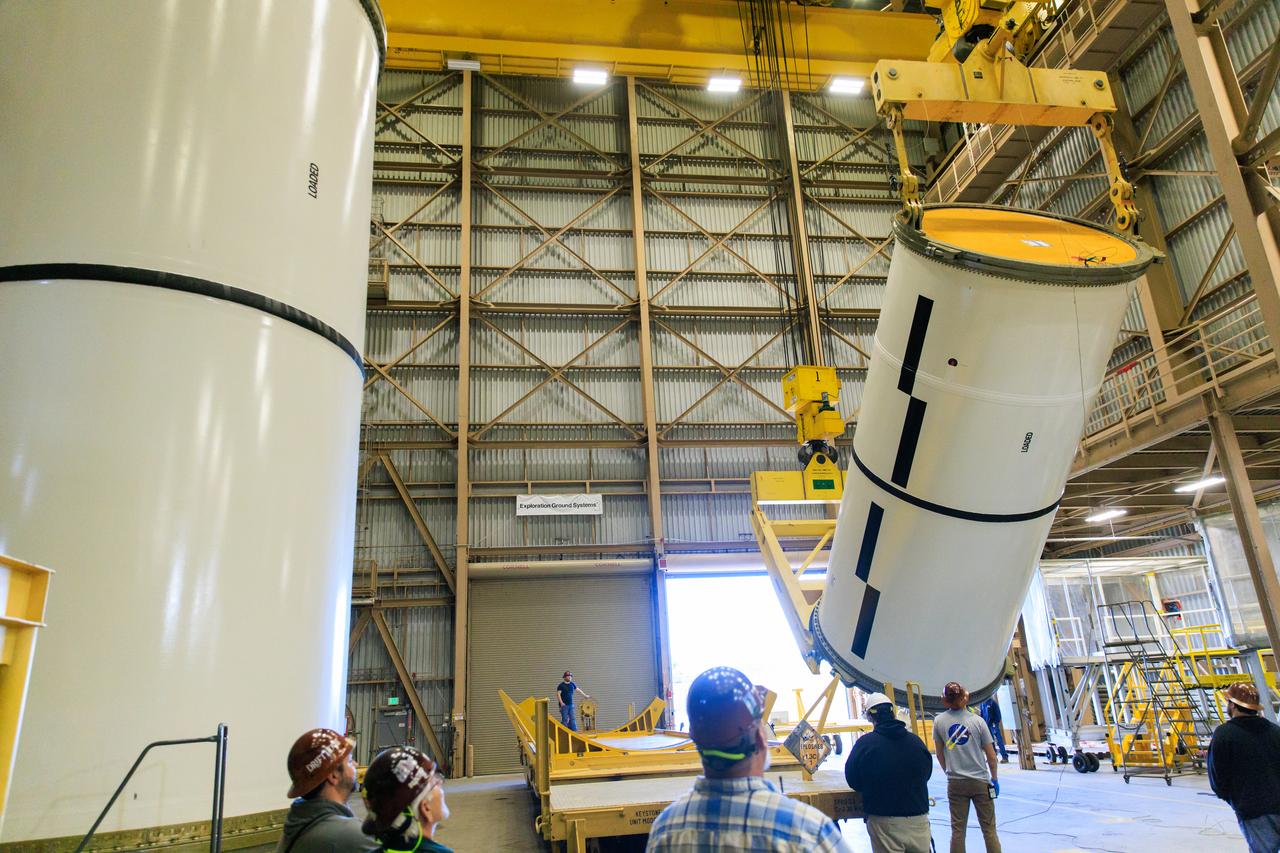

Following the successful propellant grain inspection of two segments of the solid rocket boosters for NASA’s Space Launch System inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, crews on Thursday, Dec. 21, 2023, rotate and lift the segments from horizontal into a vertical position in preparation for the agency’s Artemis II launch campaign. The Artemis II mission will send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
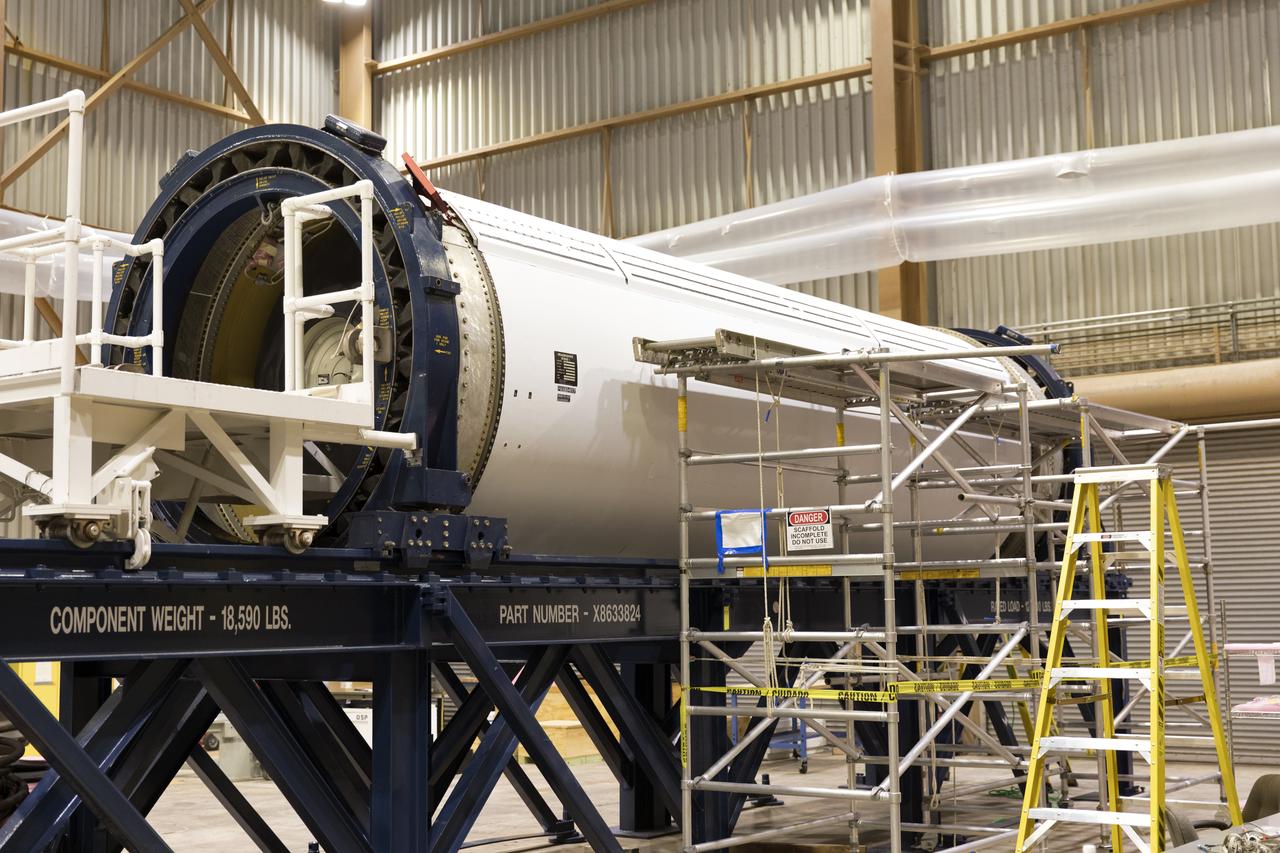

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
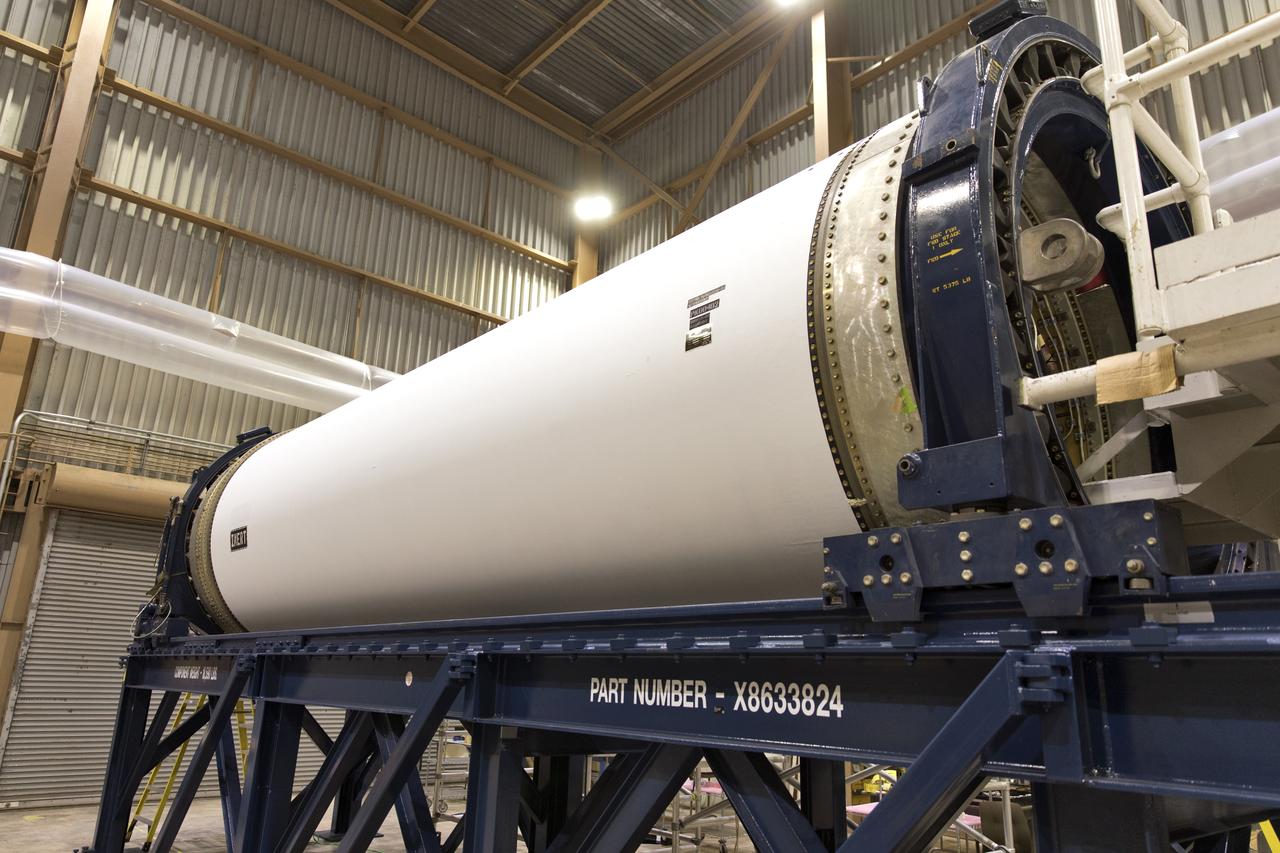

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
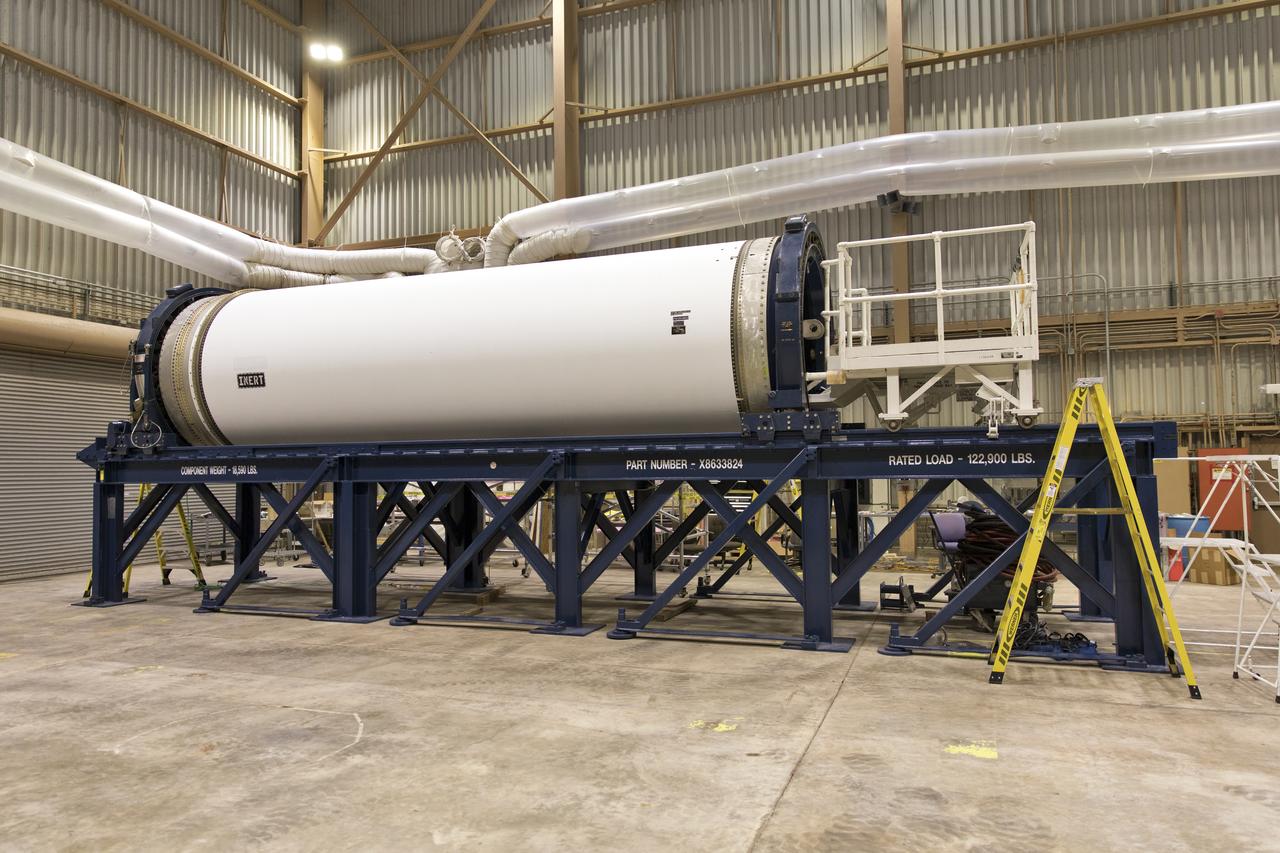

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
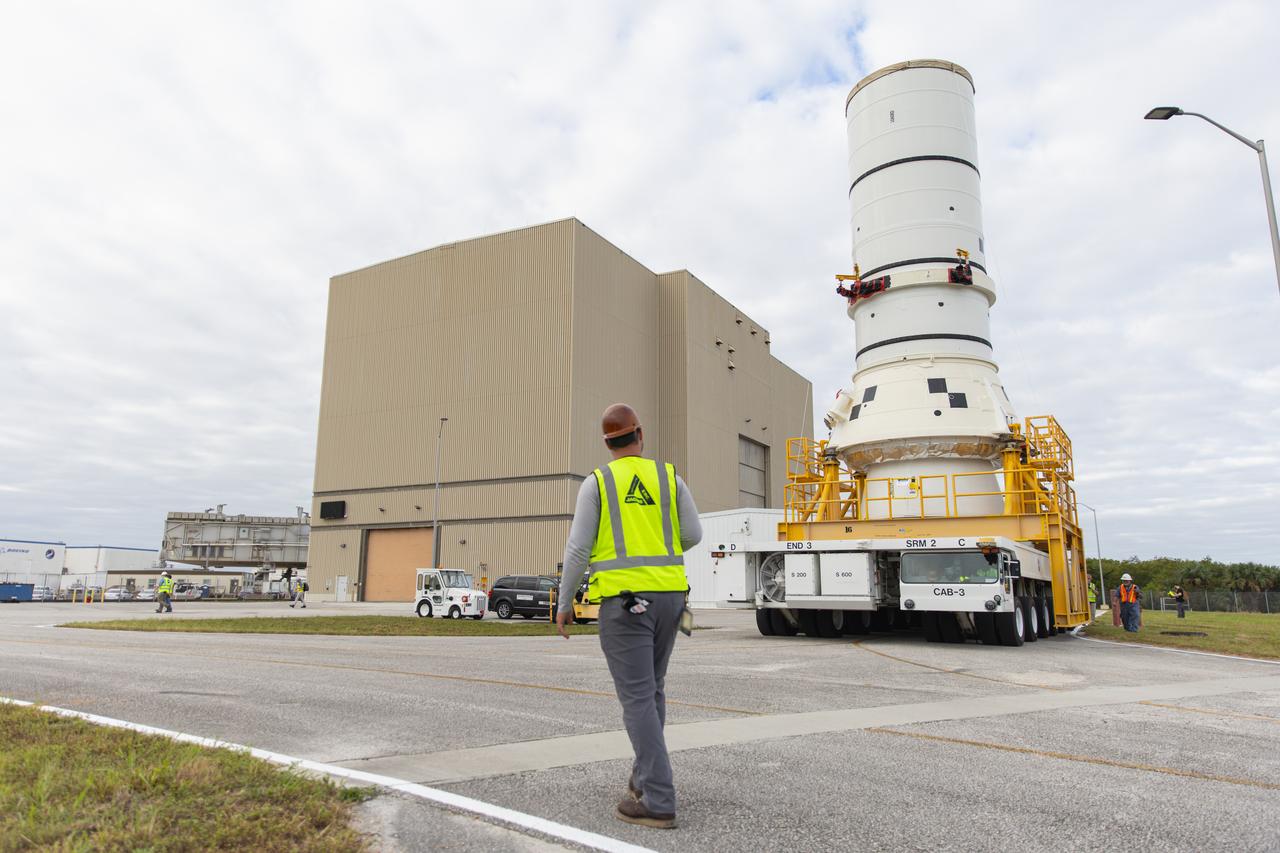

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
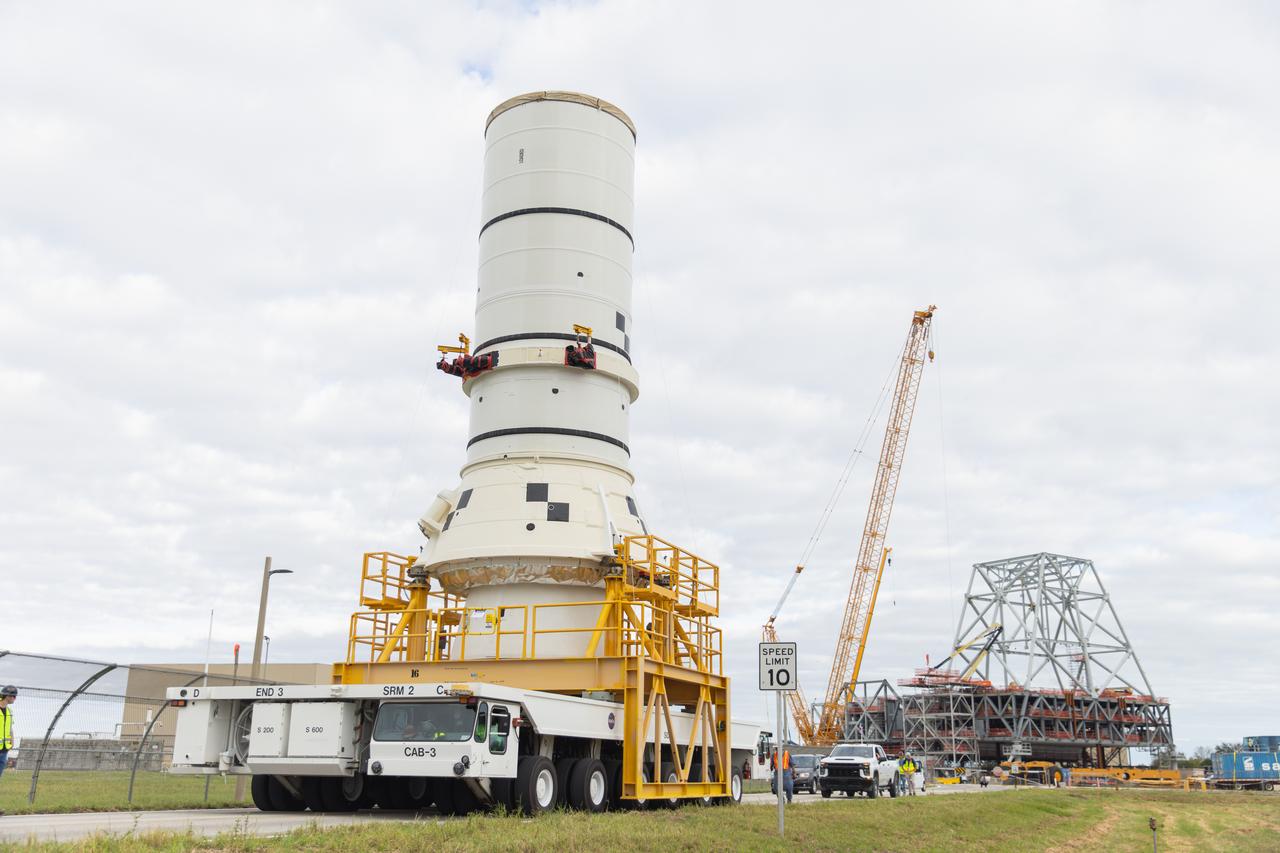

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
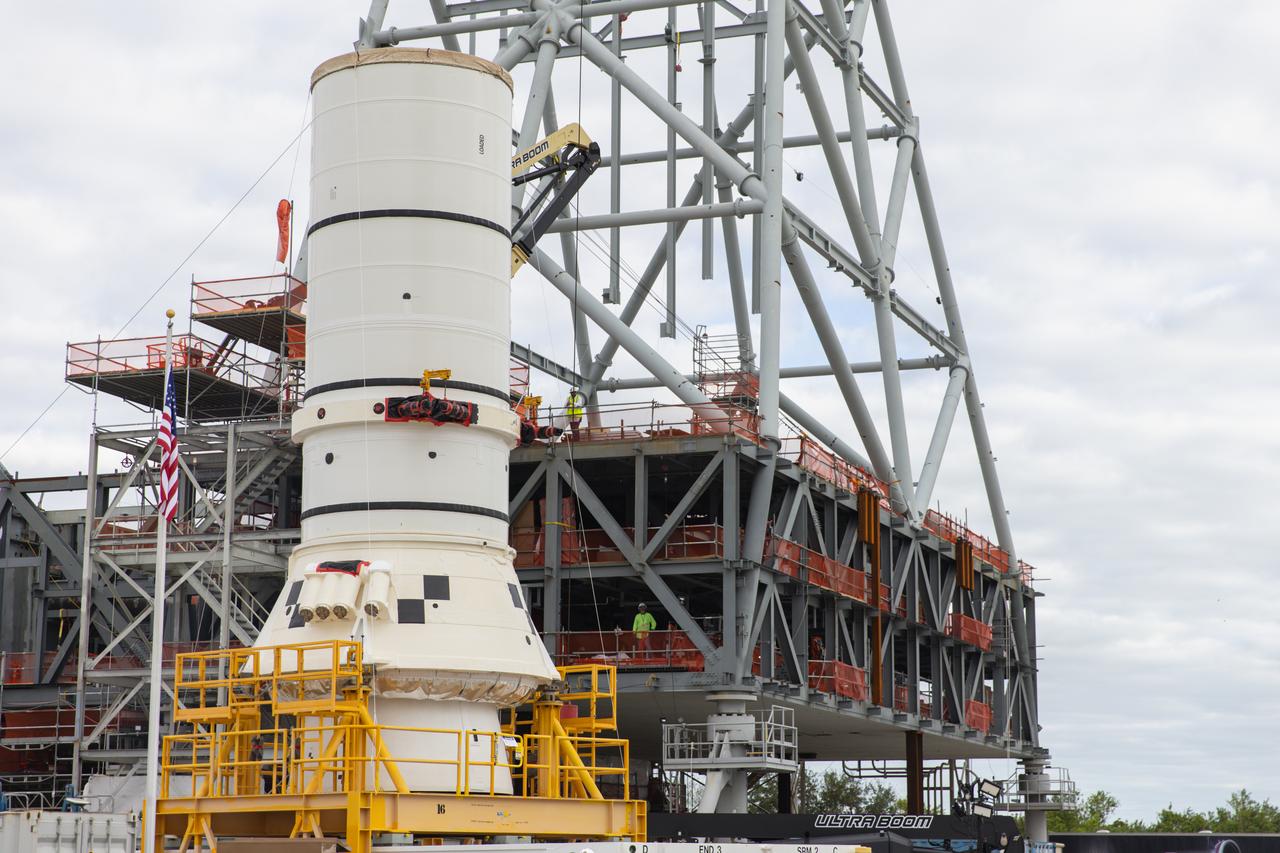

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
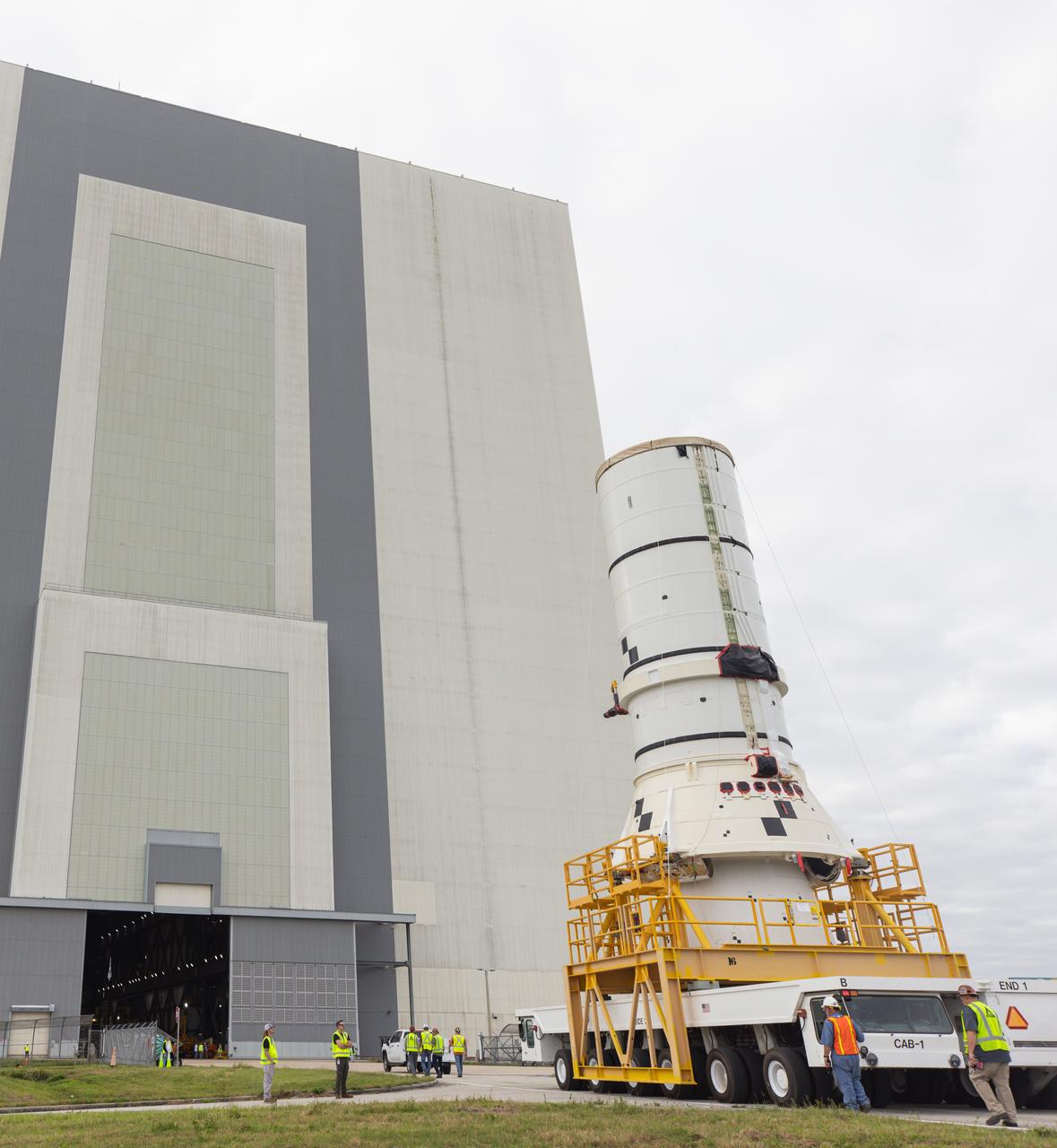

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
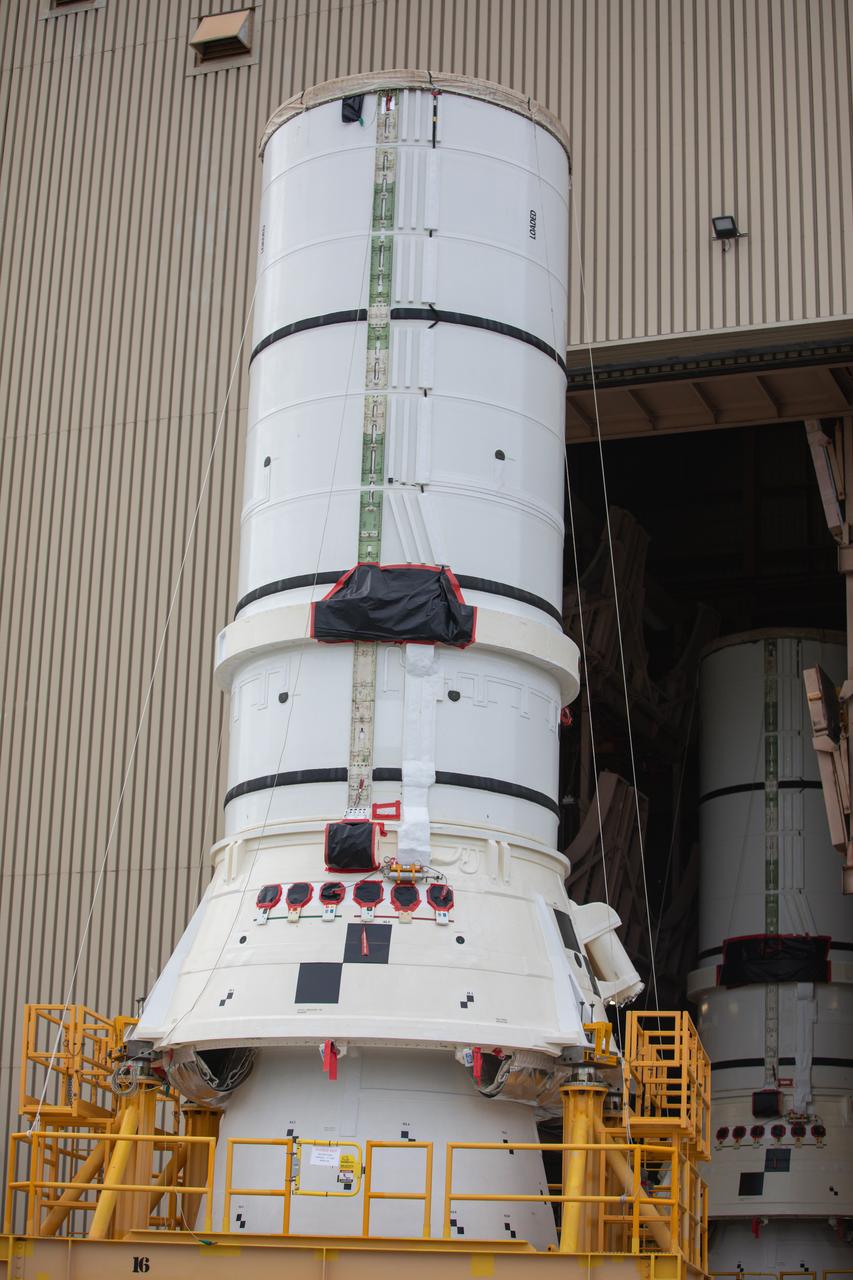

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
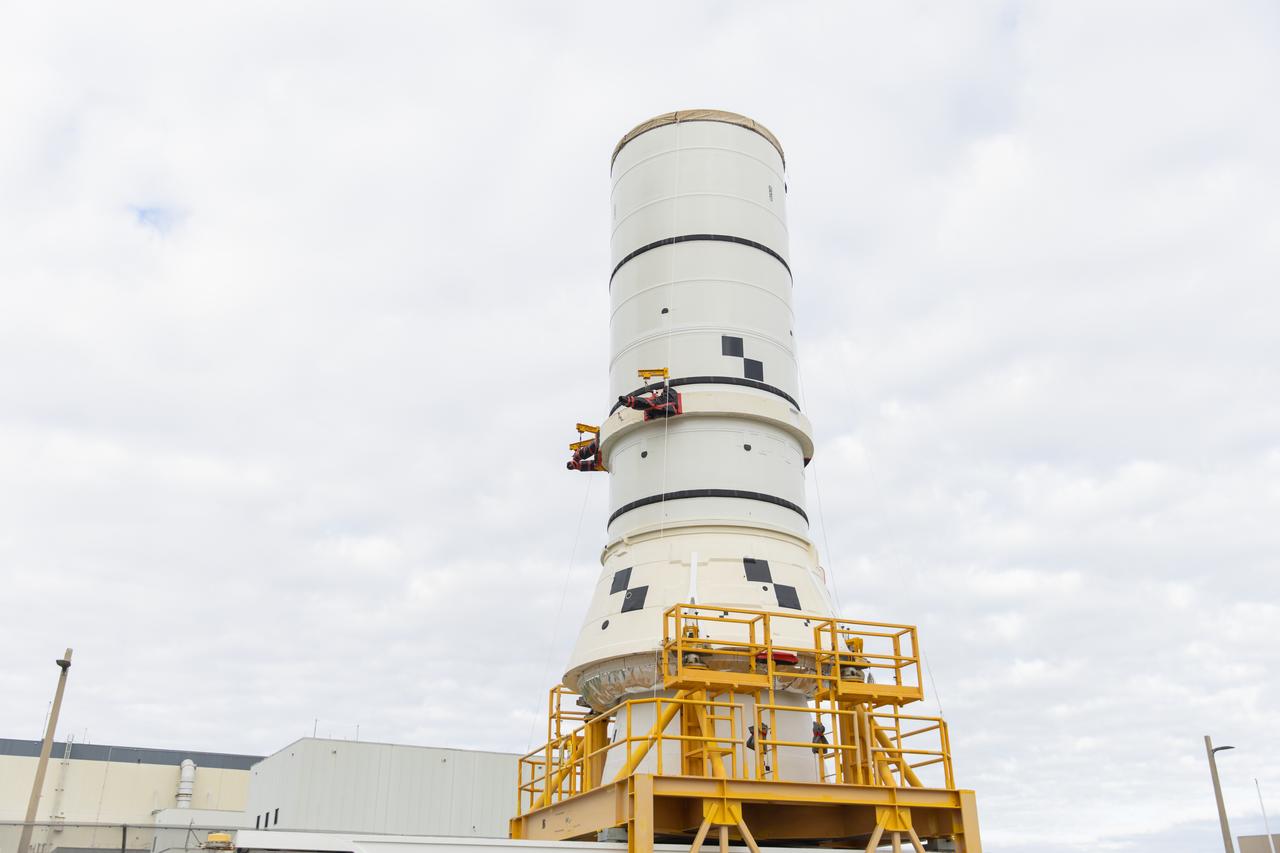

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
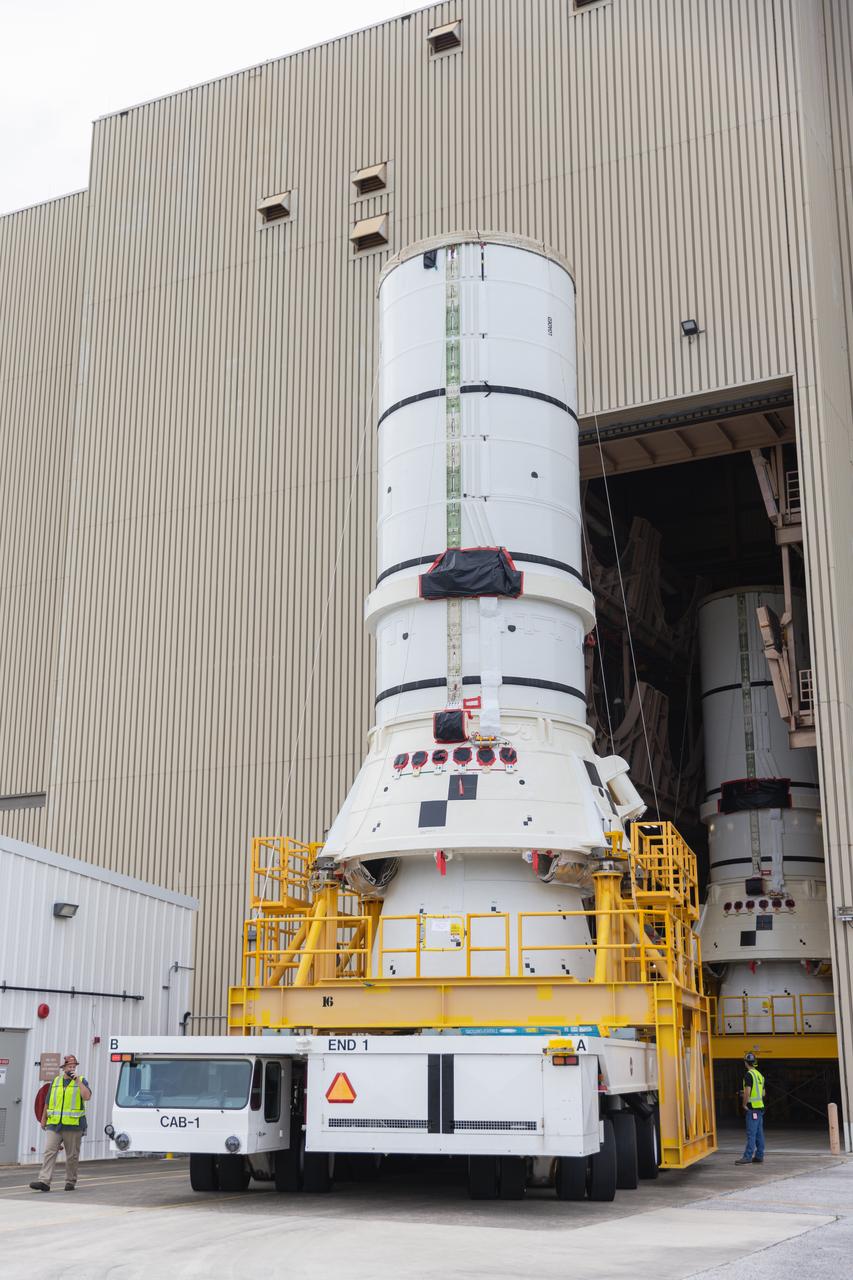

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.

The left aft assembly of the SLS (Space Launch System) solid rocket boosters for the Artemis II mission is moved from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Nov. 18, 2024. The aft assembly will be lifted atop the mobile launcher, followed by the right aft assembly and remaining booster segments.
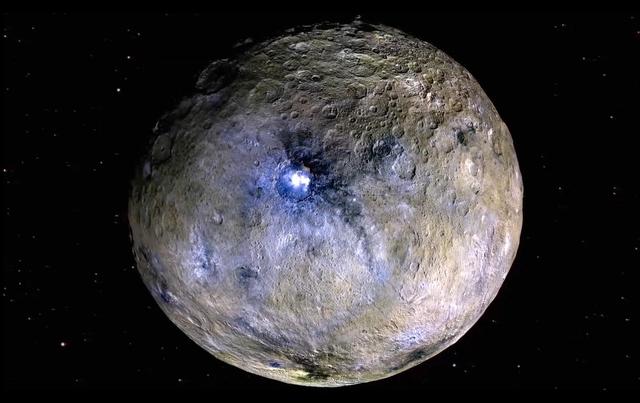

This frame from a video from NASA's Dawn mission shows dwarf planet Ceres in false-color renderings, which highlight differences in surface materials. Images were used to create a movie of Ceres rotating, followed by a flyover view of Occator Crater, home of Ceres' brightest area. A video is available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20182
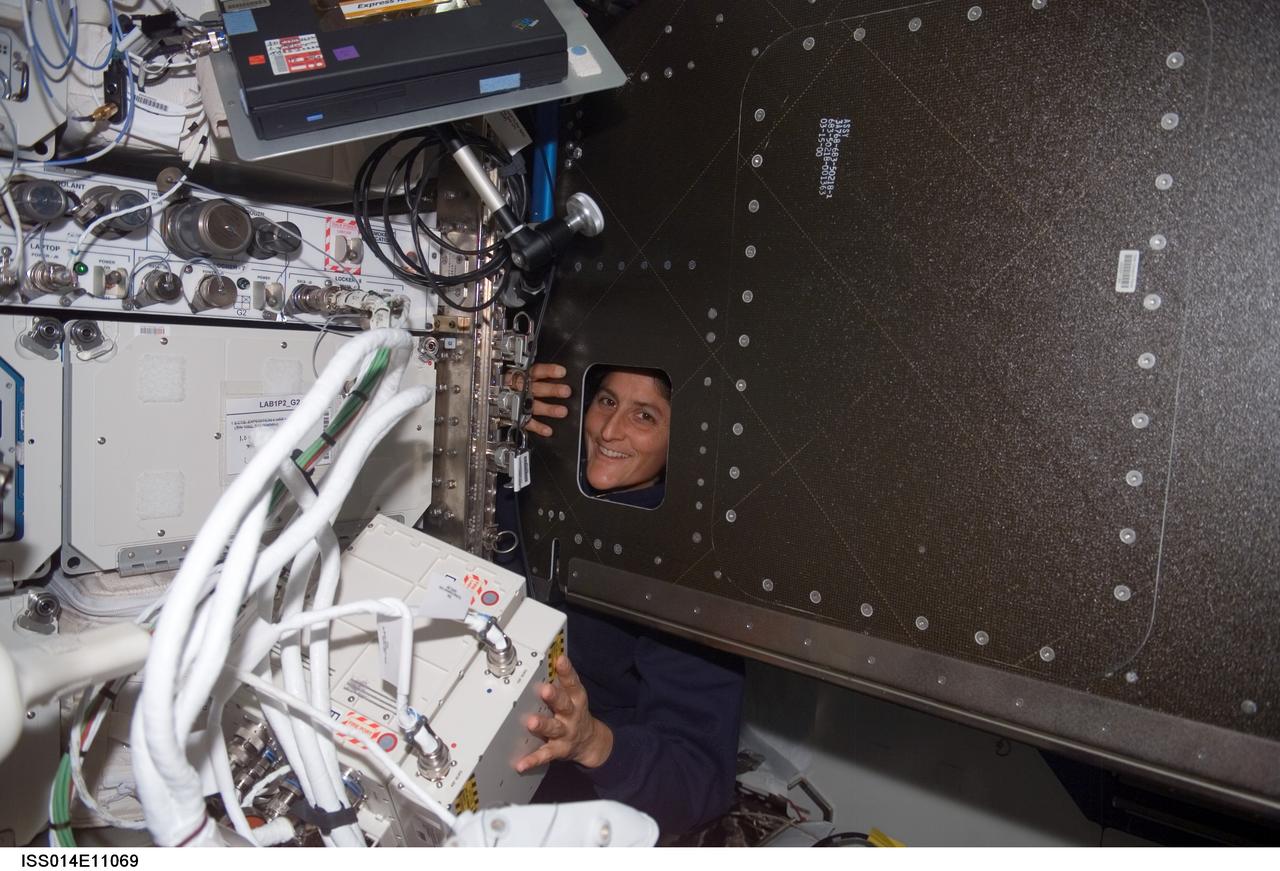

ISS014-E-11069 (3 Jan. 2007) --- Astronaut Sunita L. Williams, Expedition 14 flight engineer, looks through an opening during the Oxygen Generator System (OGS) rack rotation in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
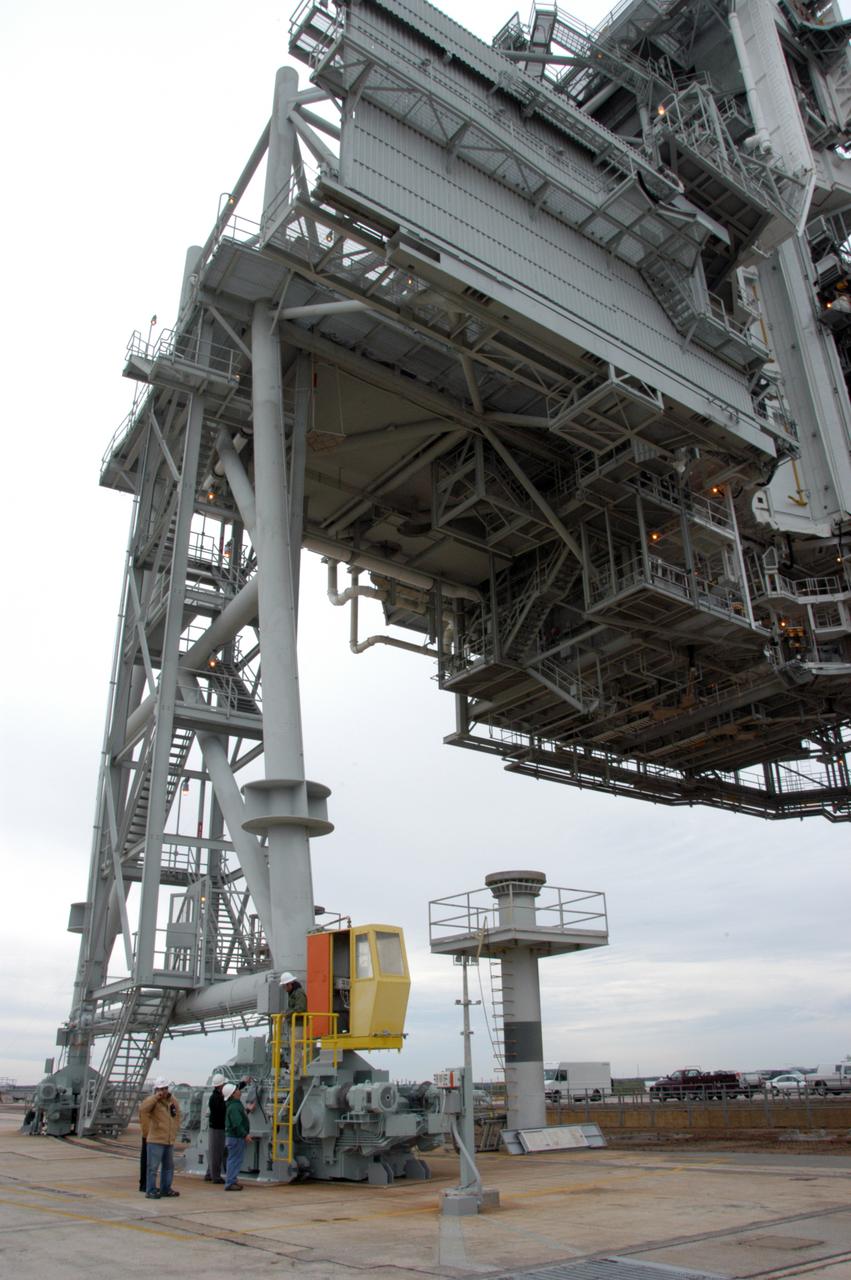

Workers on Launch Pad 39A get ready to begin the movement of the rotating service structure above them. The RSS has not been rotated for more than a year during the maintenance and upgrades on the pad. Some of the work included sandblasting the structure to remove rust and repainting. In addition, the RSS was jacked up and a new upper-bearing race assembly installed where the RSS pivots against the fixed service structure and a half-inch steel plate added. Pad 39A is being made ready for its first launch in four years, the upcoming STS-117 on March 15.
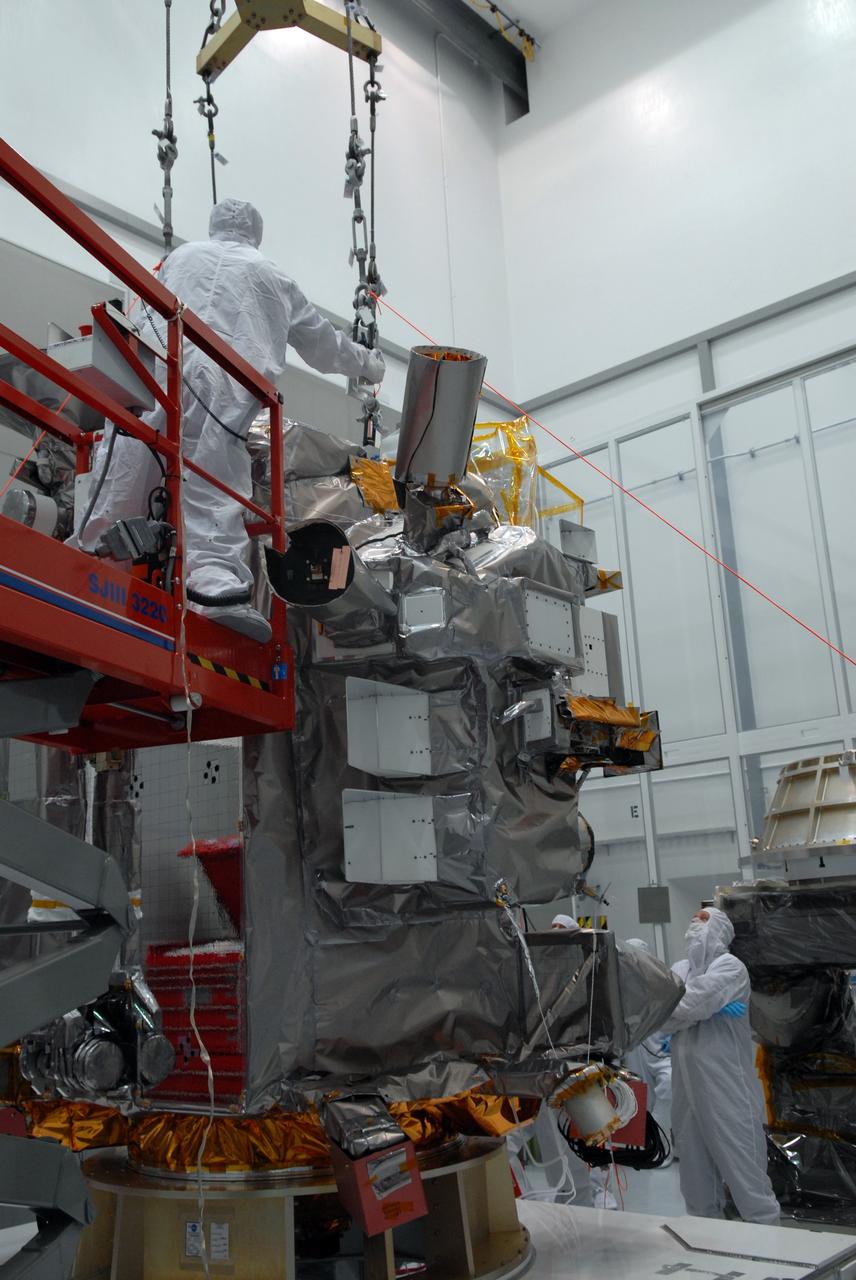

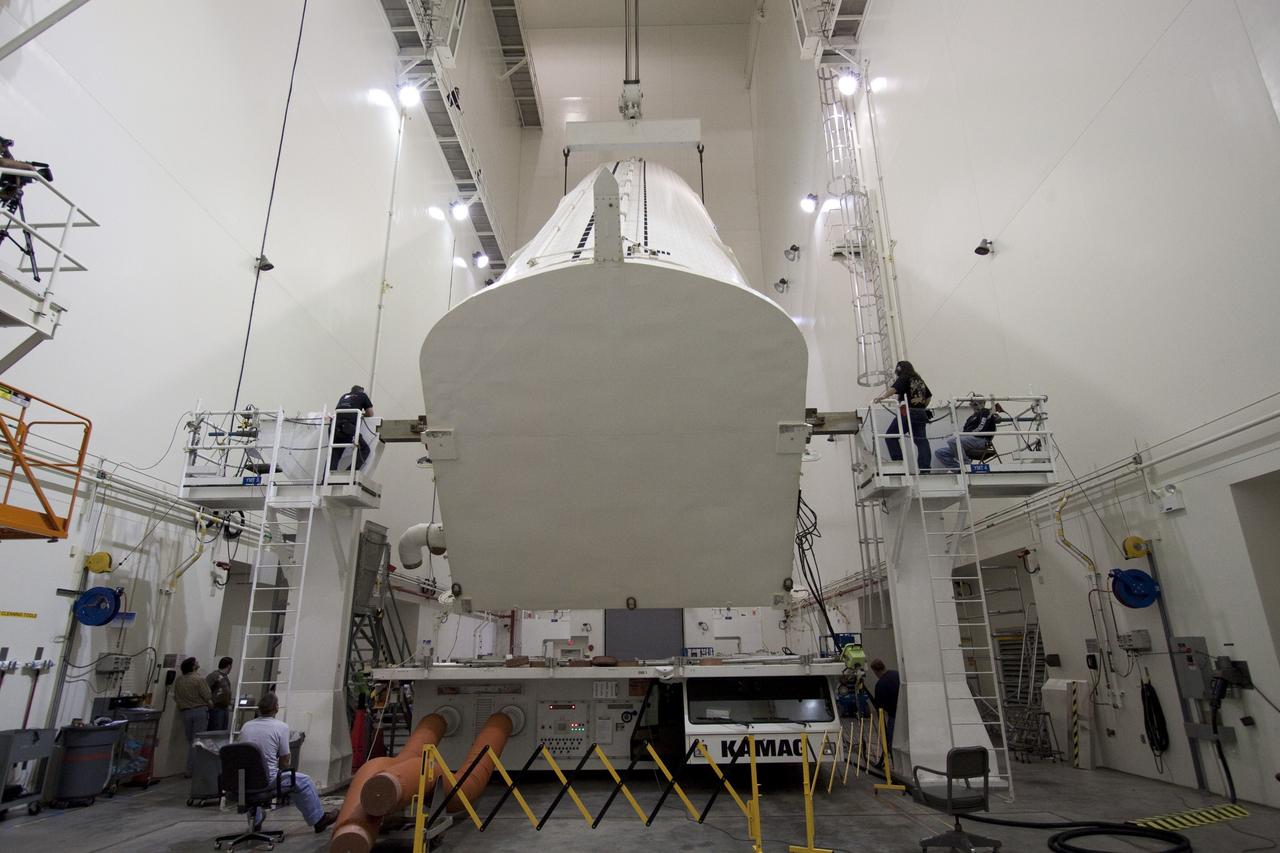
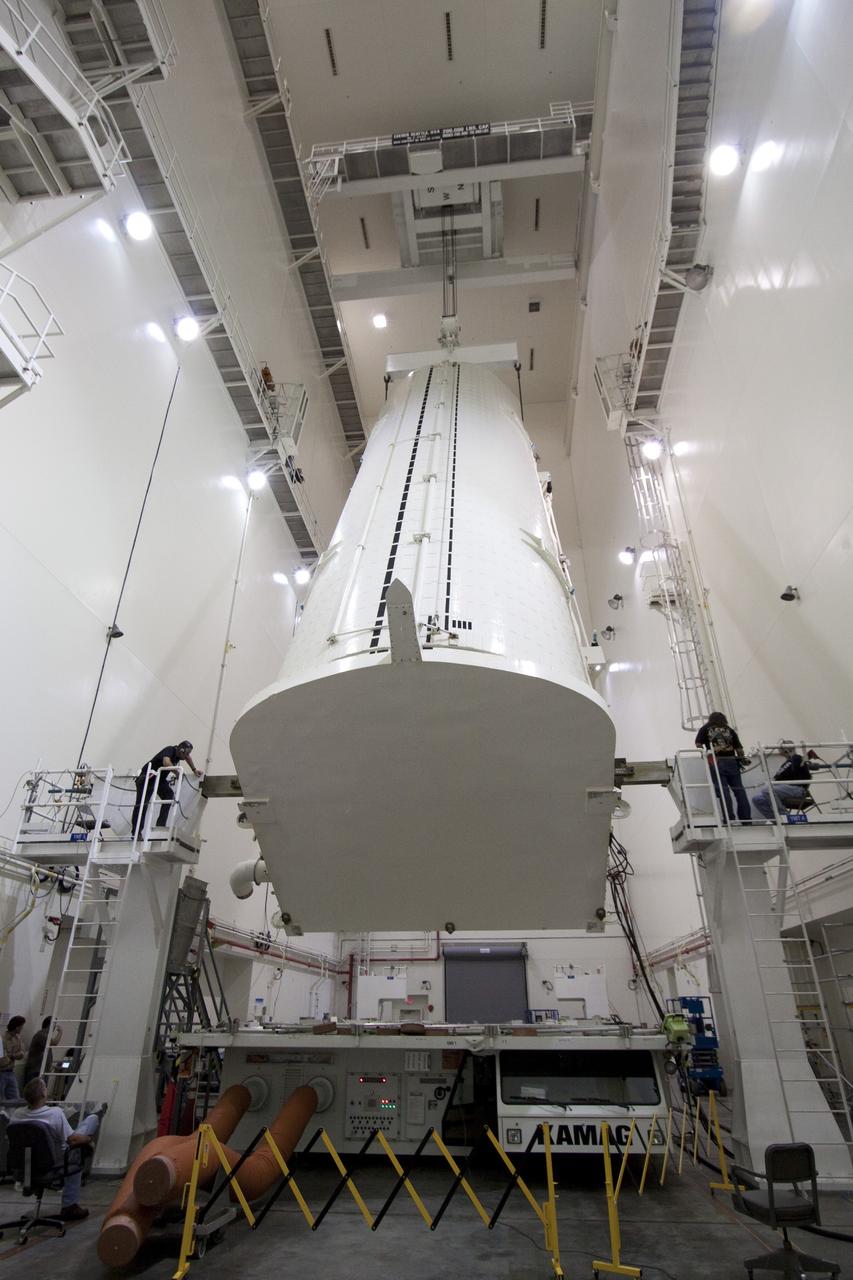
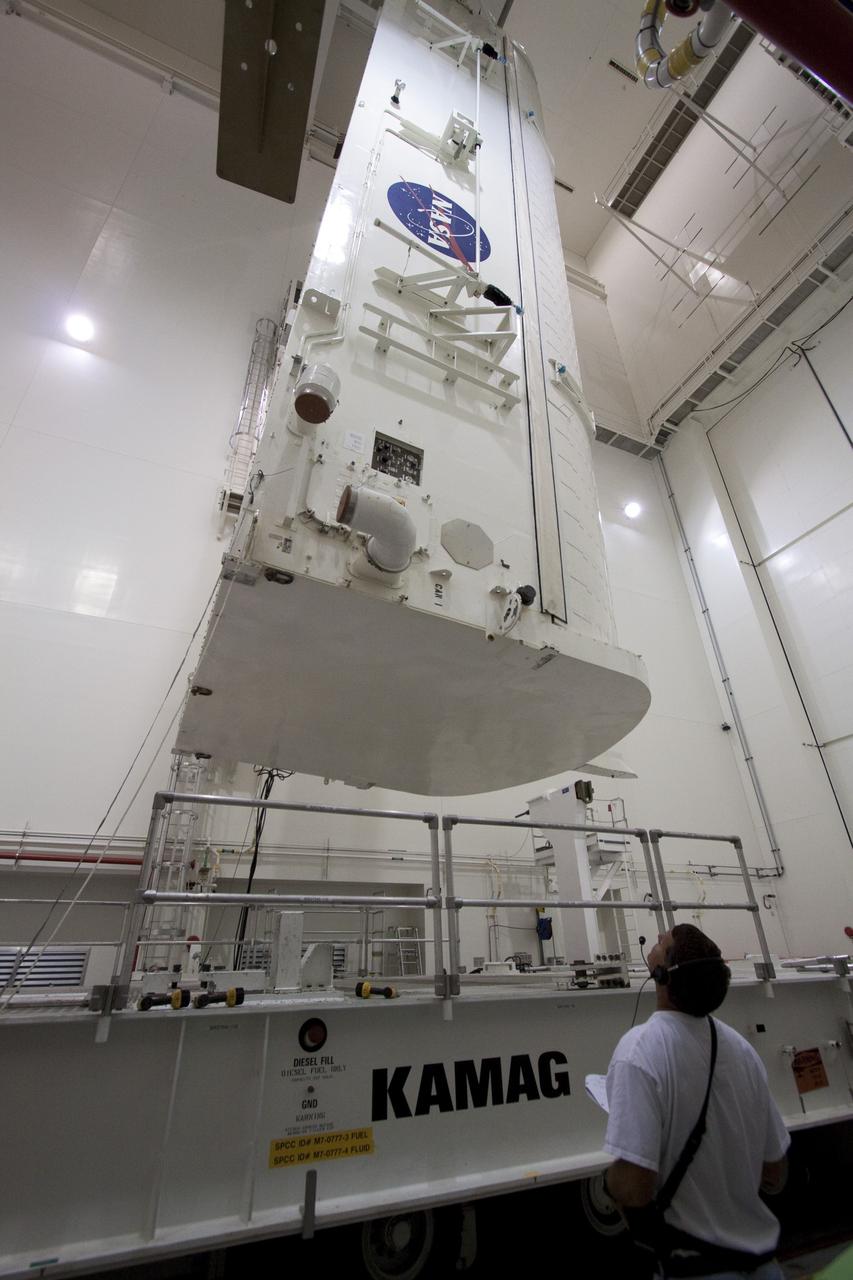
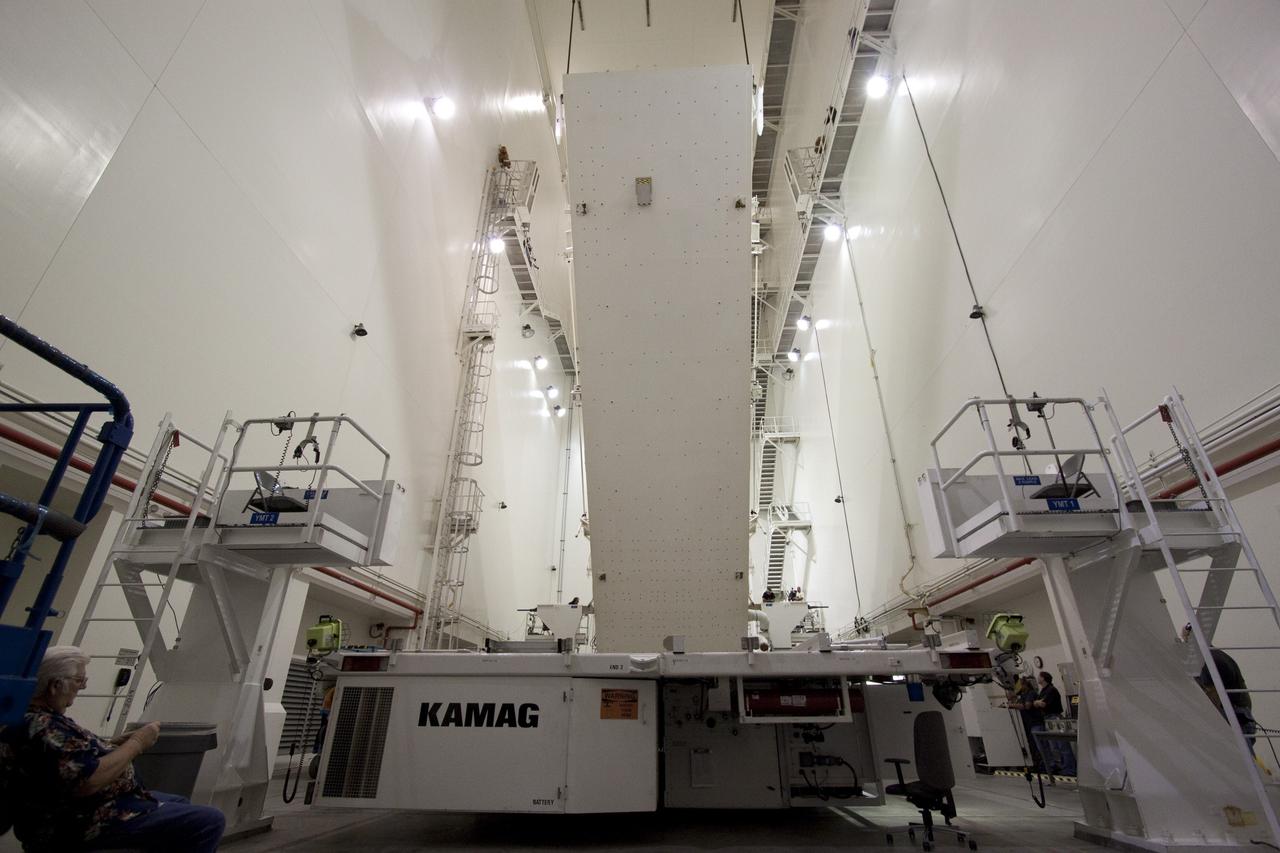
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians get ready to lift NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. It will be moved to an Aronson table for rotation to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
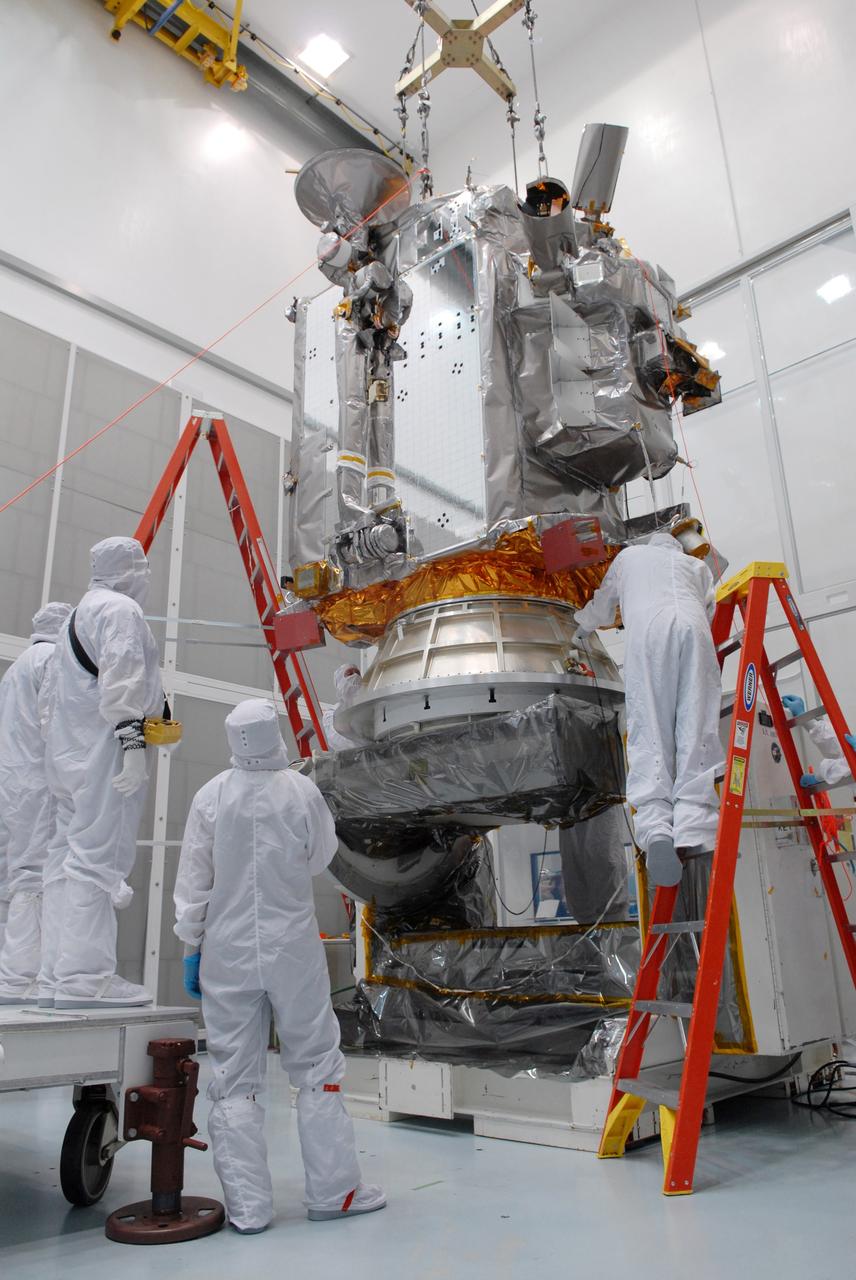

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., an overhead crane lowers NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, onto the Aronson table. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
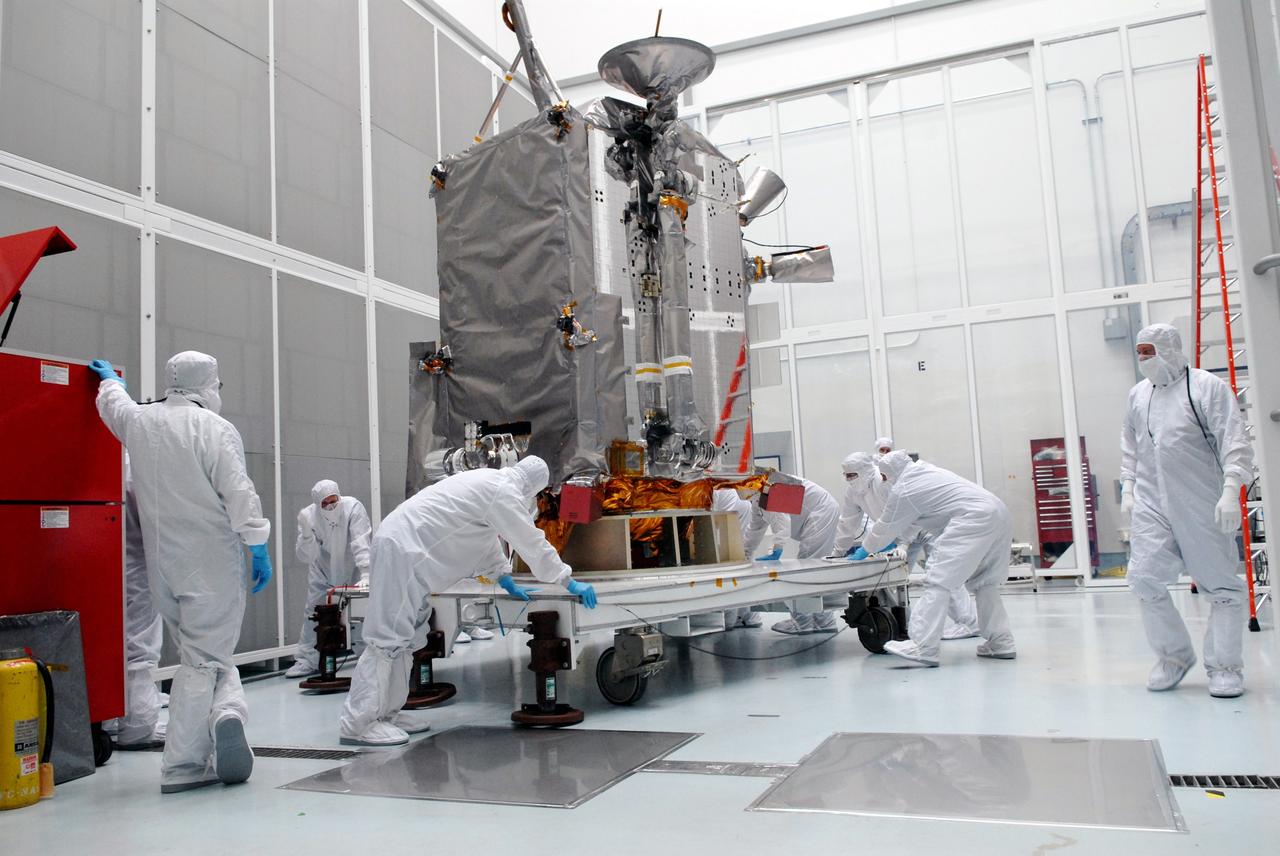

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians moved the stand with NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
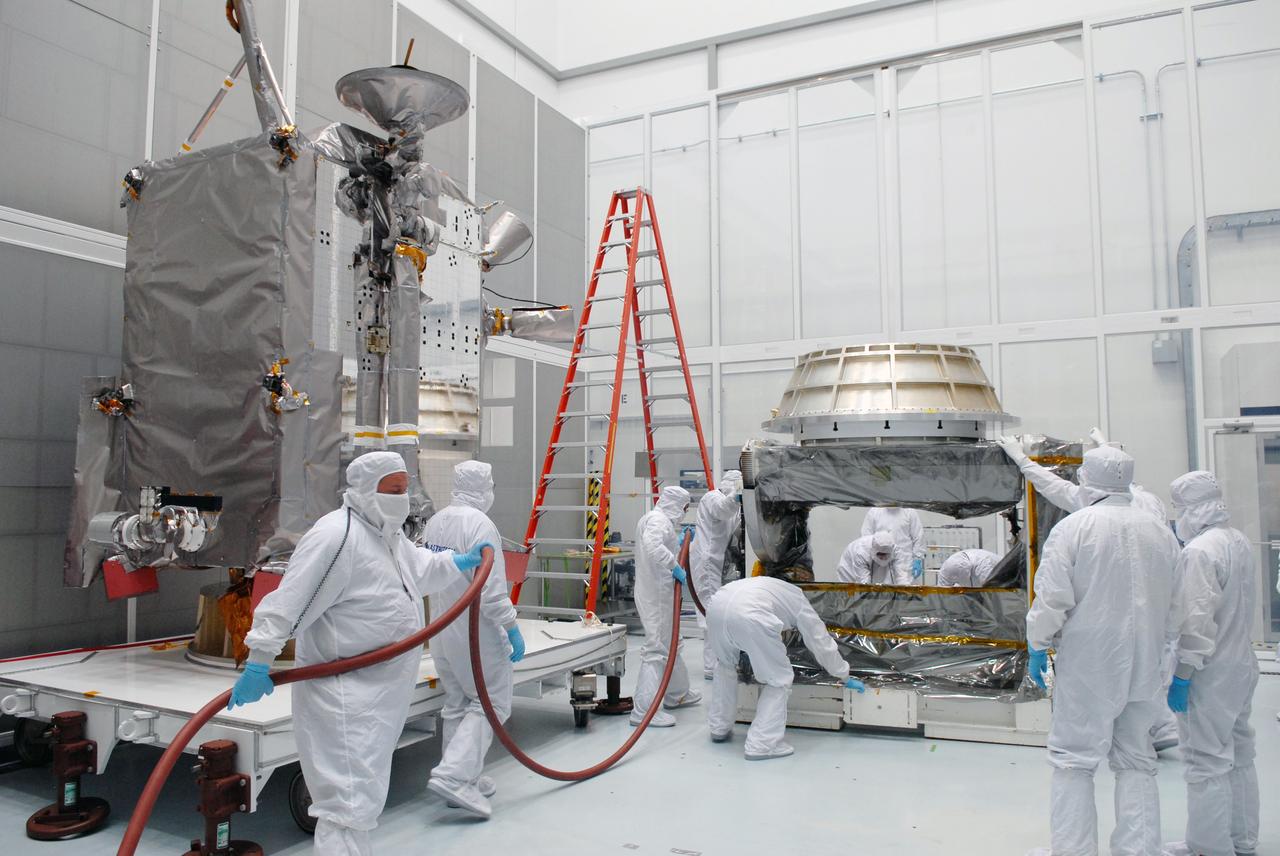

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare an Aronson table to receive NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, at left. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
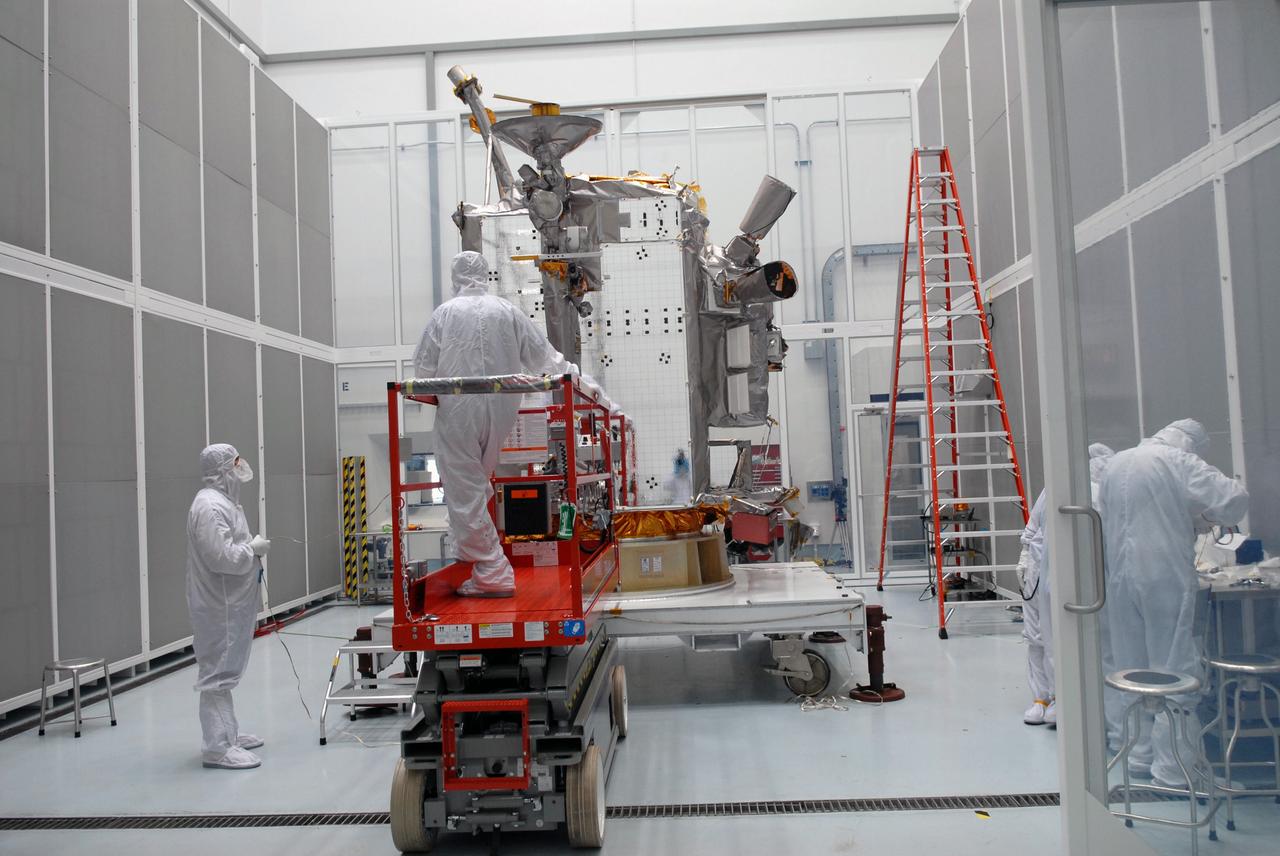

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, spacecraft is being prepared for lifting to an Aronson table. The LRO will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
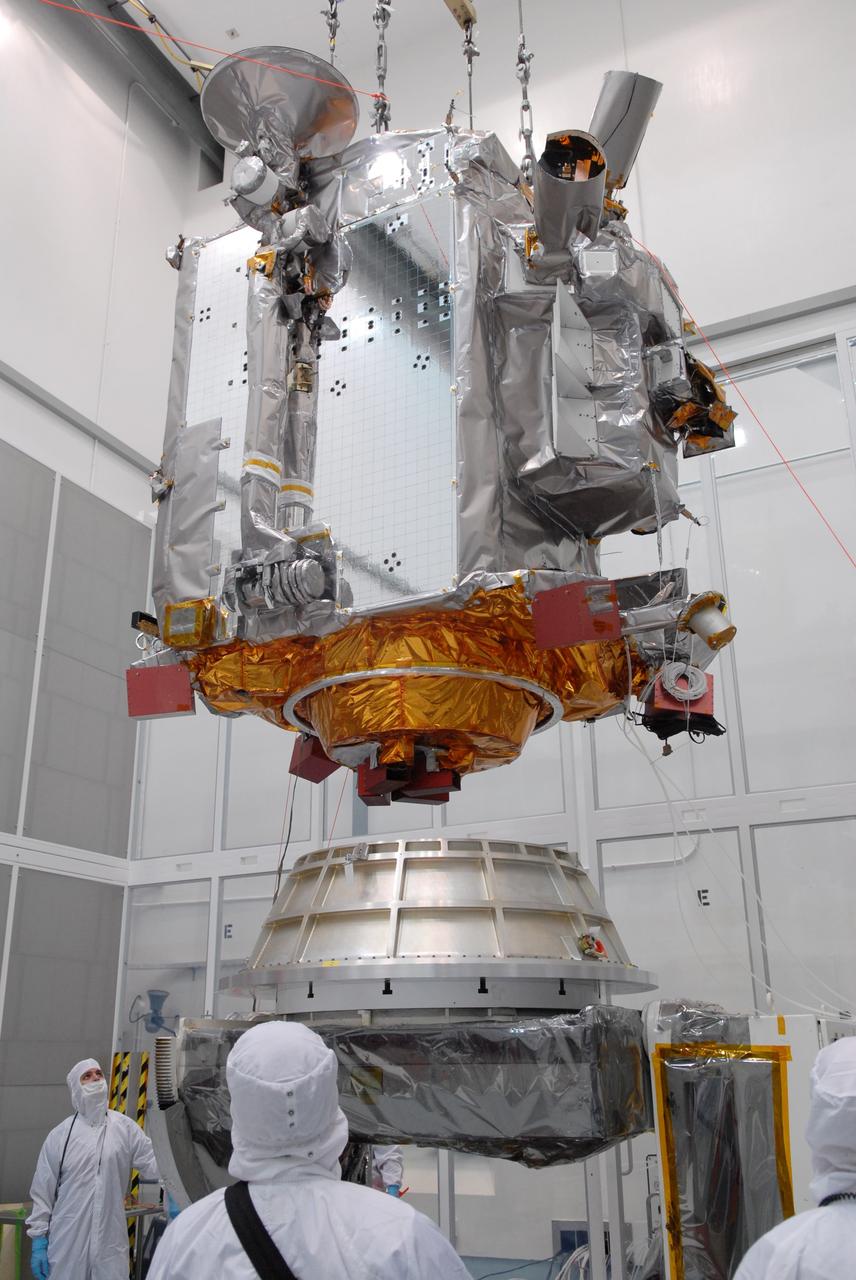

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., an overhead crane lowers NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, toward the Aronson table. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
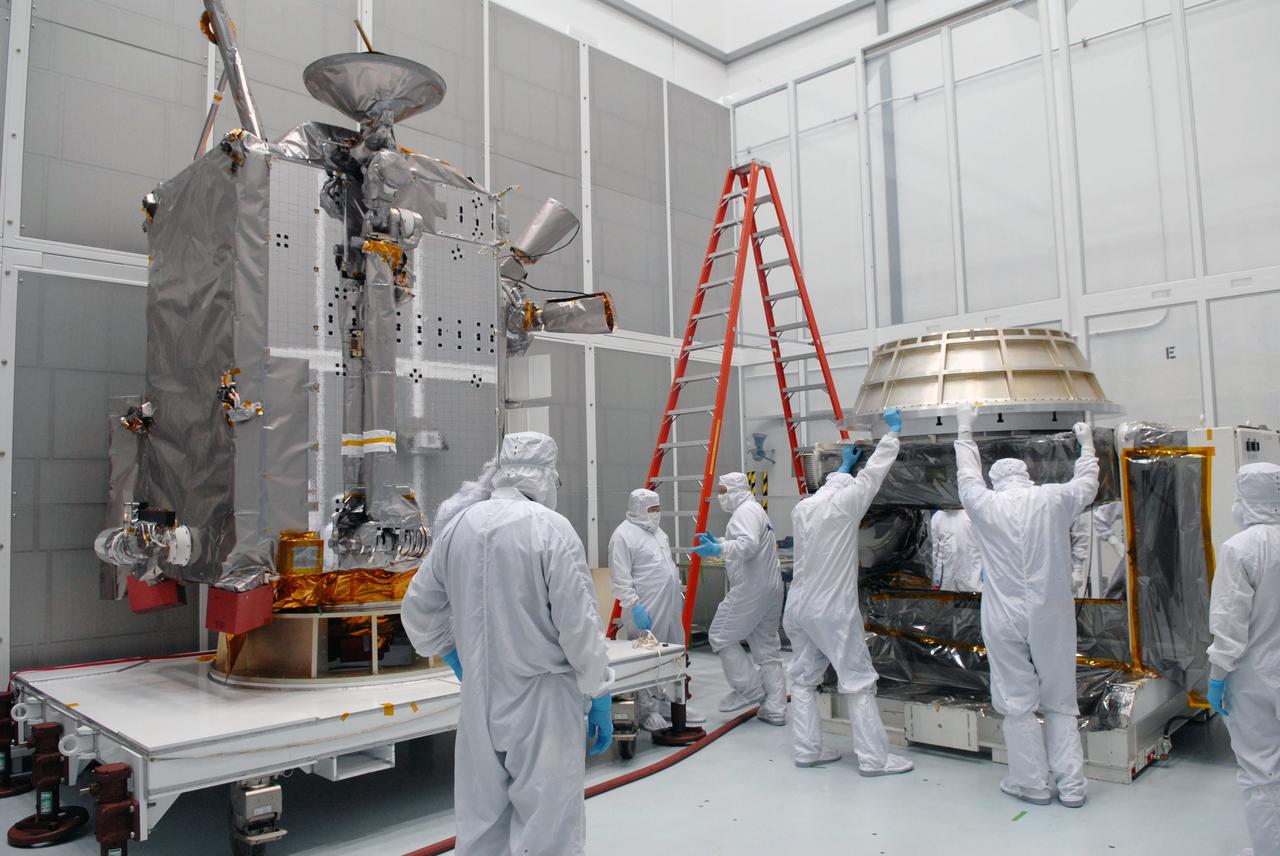

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., technicians prepare an Aronson table to receive NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, at left. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
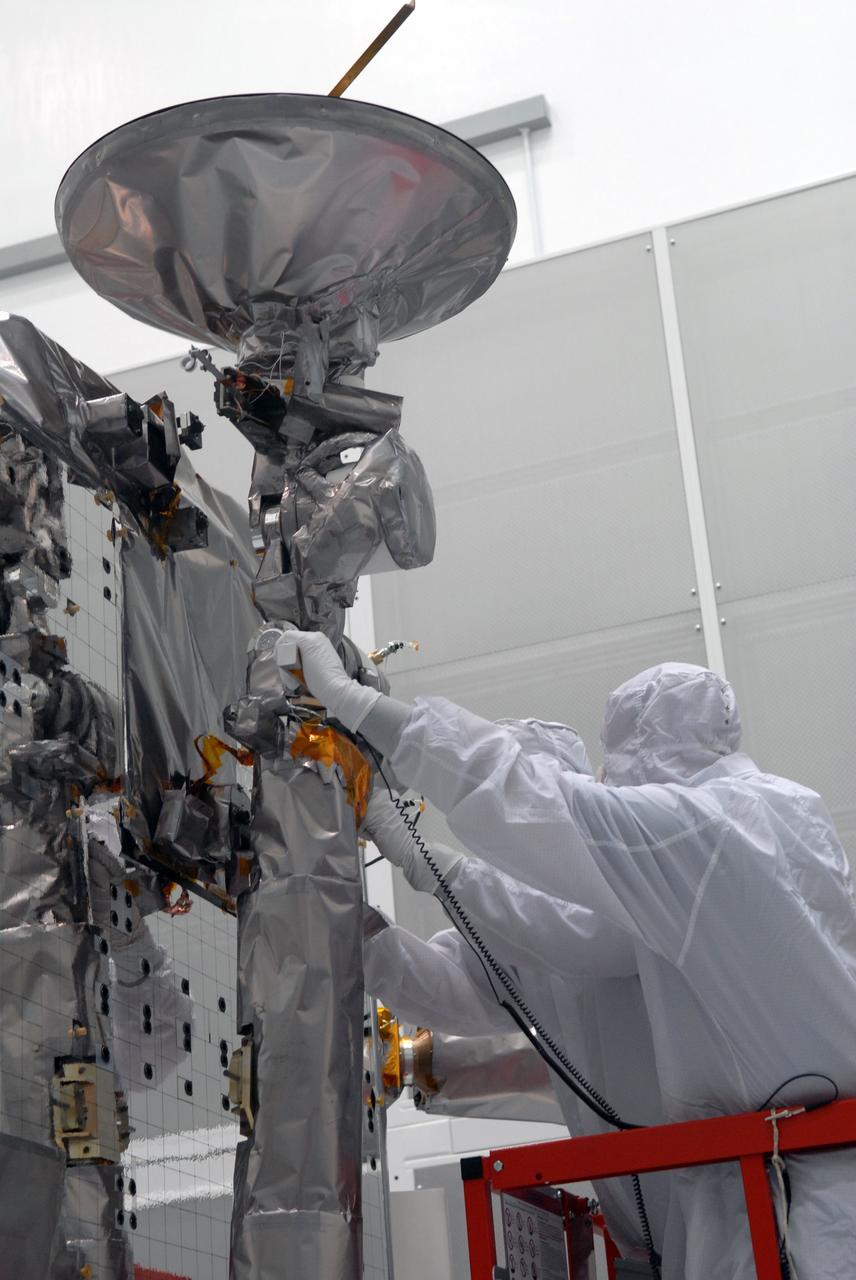

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., a technician attaches cables to NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO. The orbiter will be rotated on the table to provide proper access for processing. The orbiter will carry seven instruments to provide scientists with detailed maps of the lunar surface and enhance our understanding of the moon's topography, lighting conditions, mineralogical composition and natural resources. Information gleaned from LRO will be used to select safe landing sites, determine locations for future lunar outposts and help mitigate radiation dangers to astronauts. The polar regions of the moon are the main focus of the mission because continuous access to sunlight may be possible and water ice may exist in permanently shadowed areas of the poles. Accompanying LRO on its journey to the moon will be the Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, a mission that will impact the lunar surface in its search for water ice. Launch of LRO is targeted for May 20. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
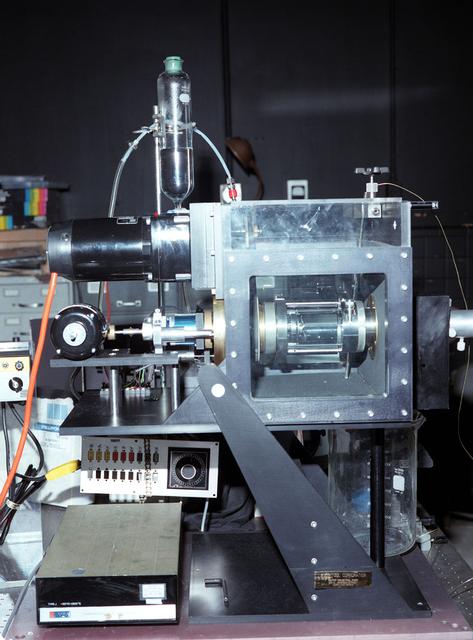
The NASA Bioreactor provides a low turbulence culture environment which promotes the formation of large, three-dimensional cell clusters. Due to their high level of cellular organization and specialization, samples constructed in the bioreactor more closely resemble the original tumor or tissue found in the body. NASA-sponsored bioreactor research has been instrumental in helping scientists to better understand normal and cancerous tissue development. In cooperation with the medical community, the bioreactor design is being used to prepare better models of human colon, prostate, breast and ovarian tumors. Cartilage, bone marrow, heart muscle, skeletal muscle, pancreatic islet cells, liver and kidney are just a few of the normal tissues currently being cultured in rotating bioreactors by investigators.
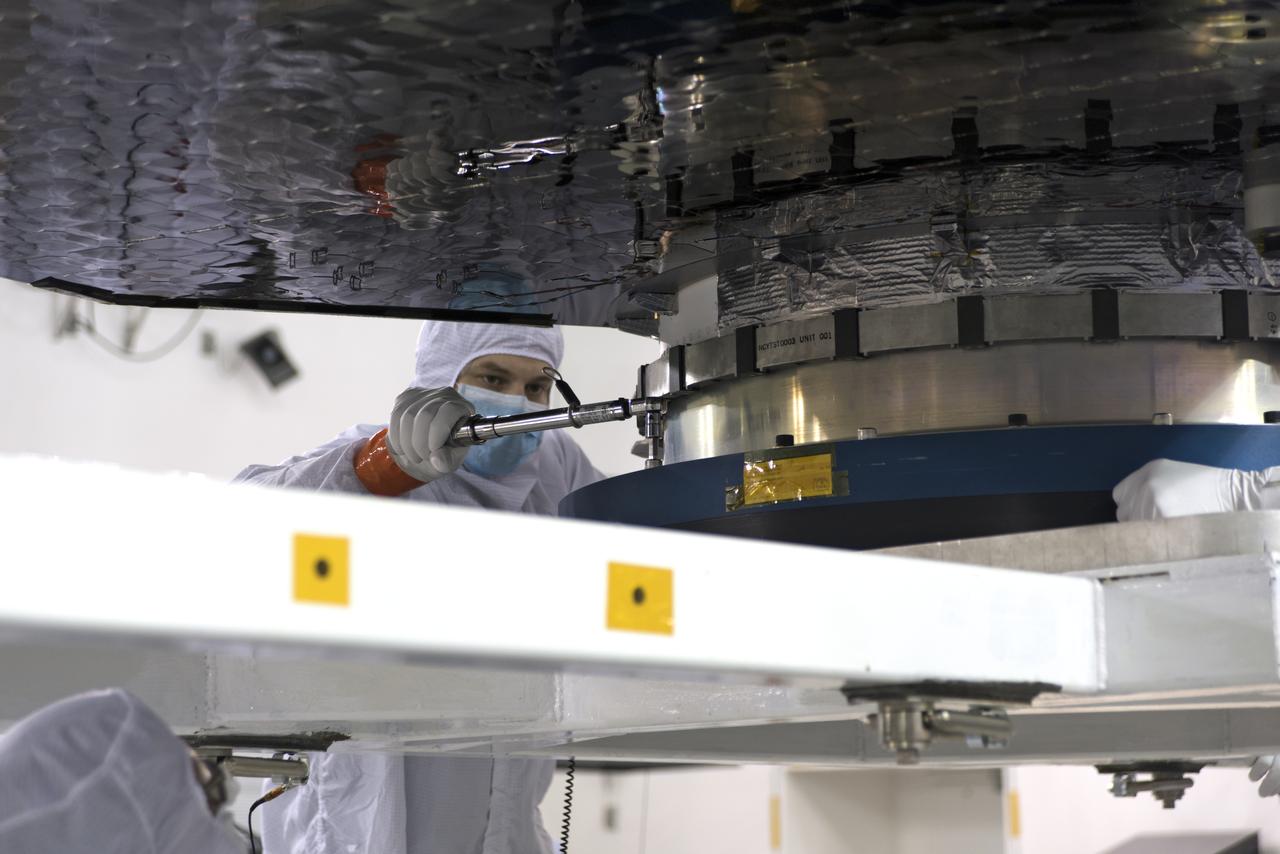

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft has been mounted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
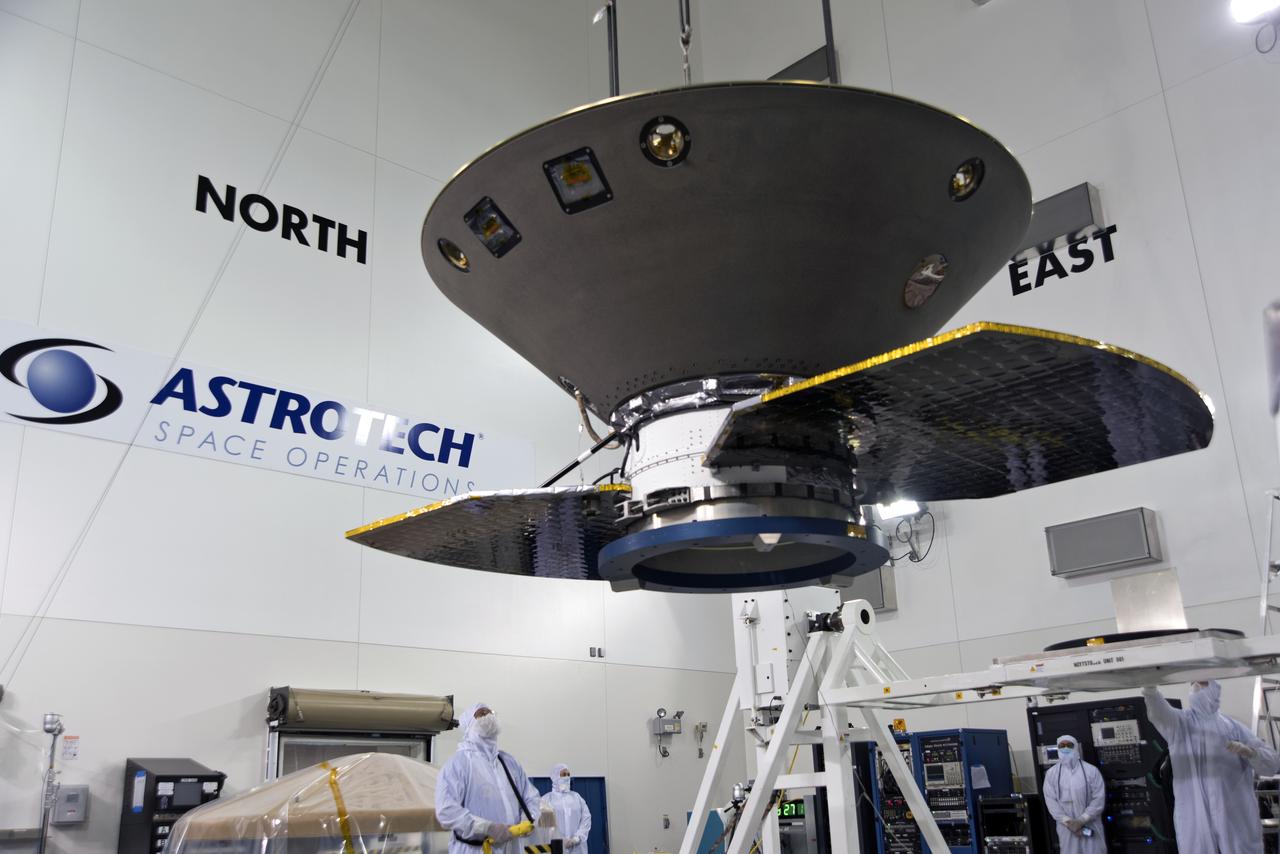

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is lifted for mounting on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
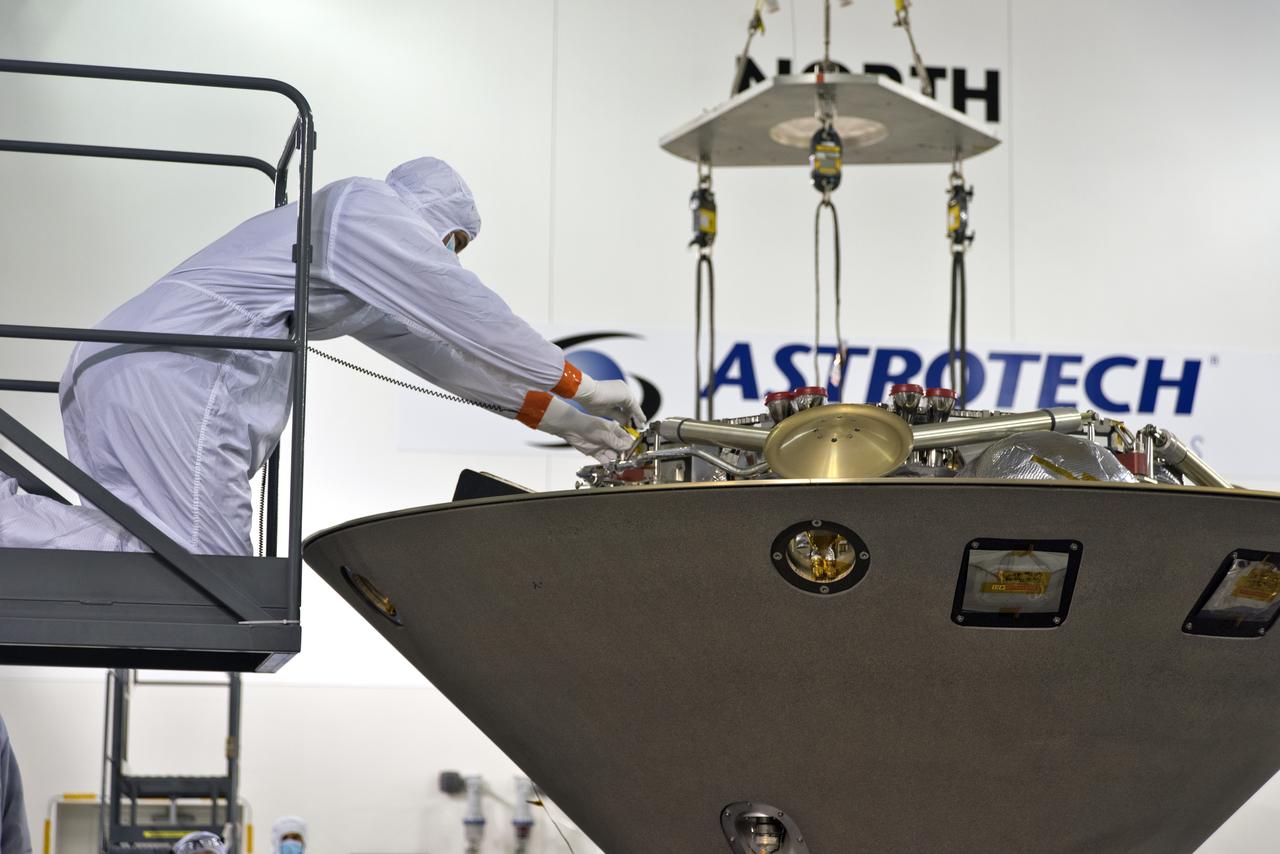

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is prepared to be lifted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
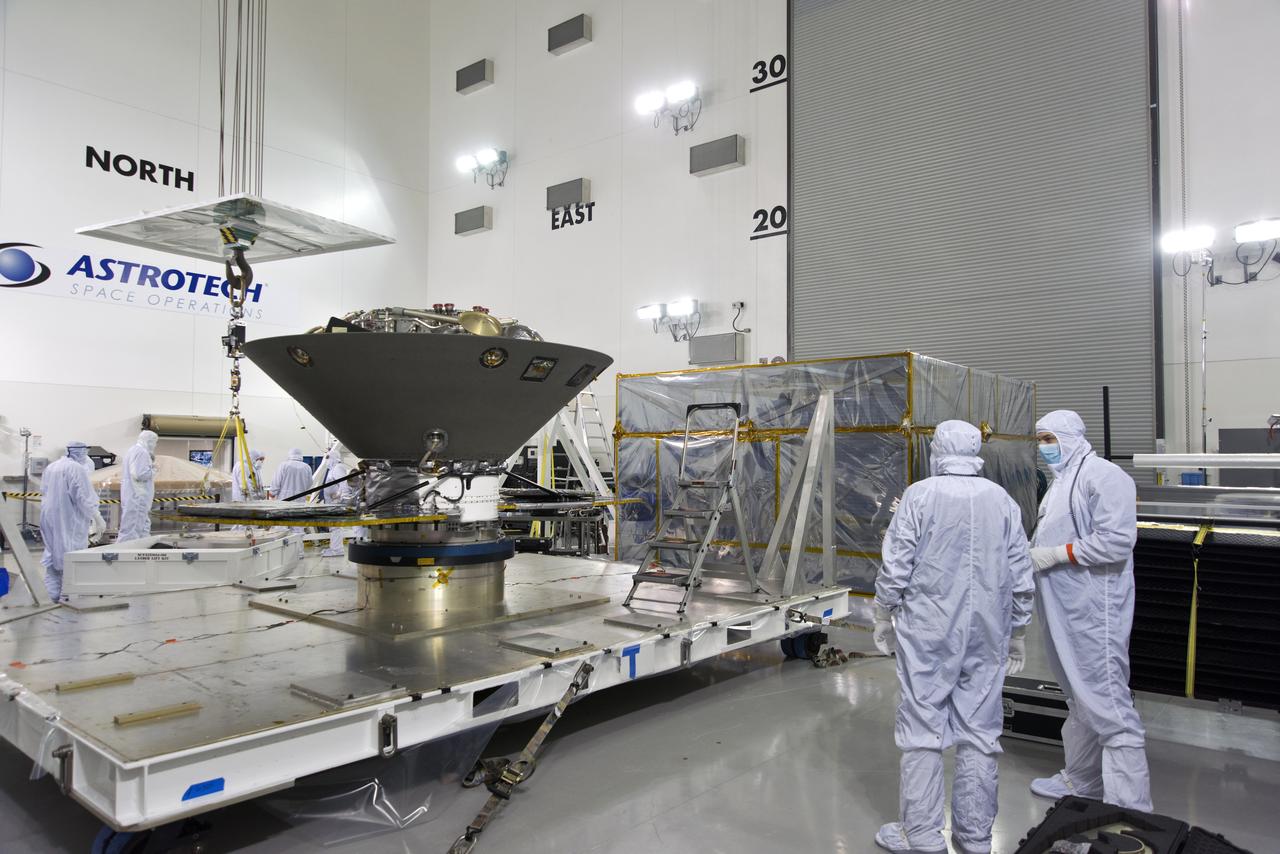

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is prepared to be lifted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
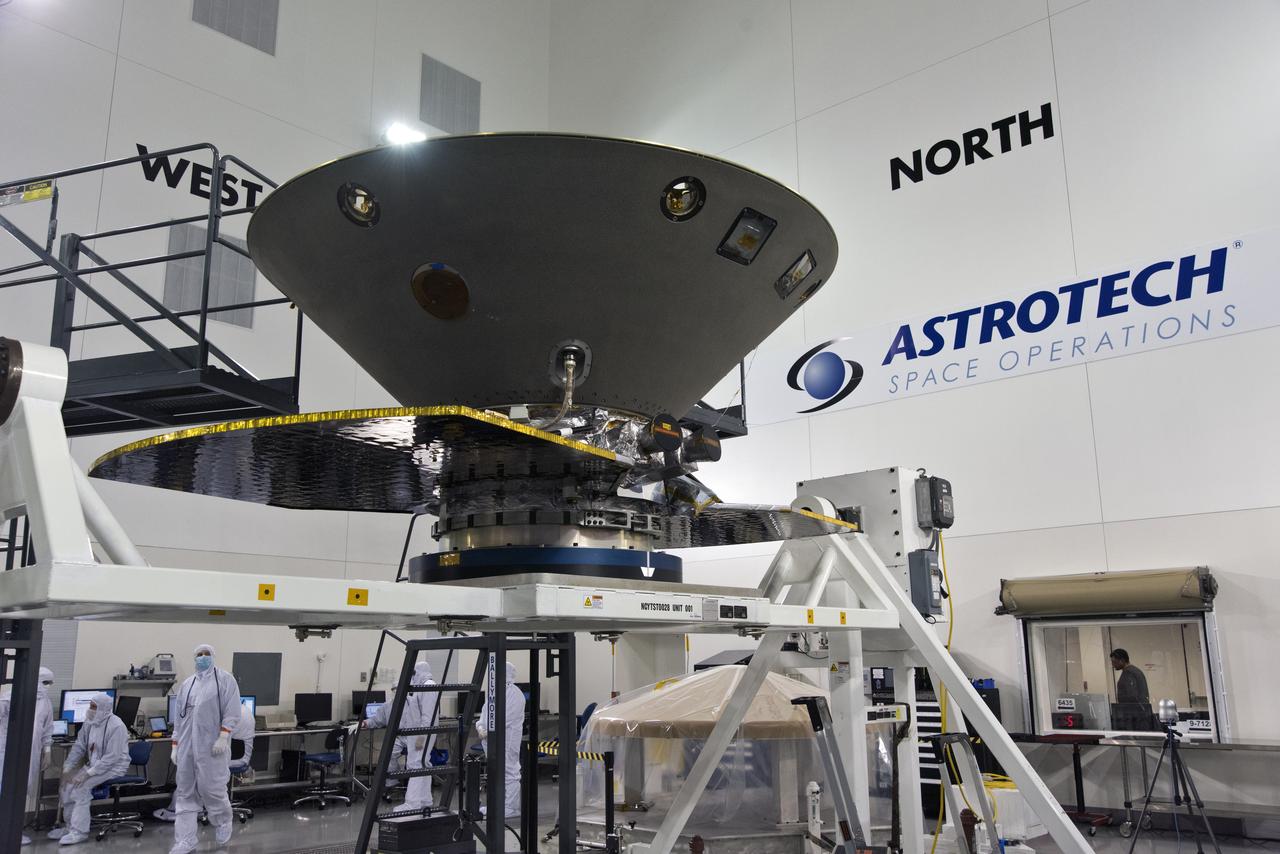

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft has been mounted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
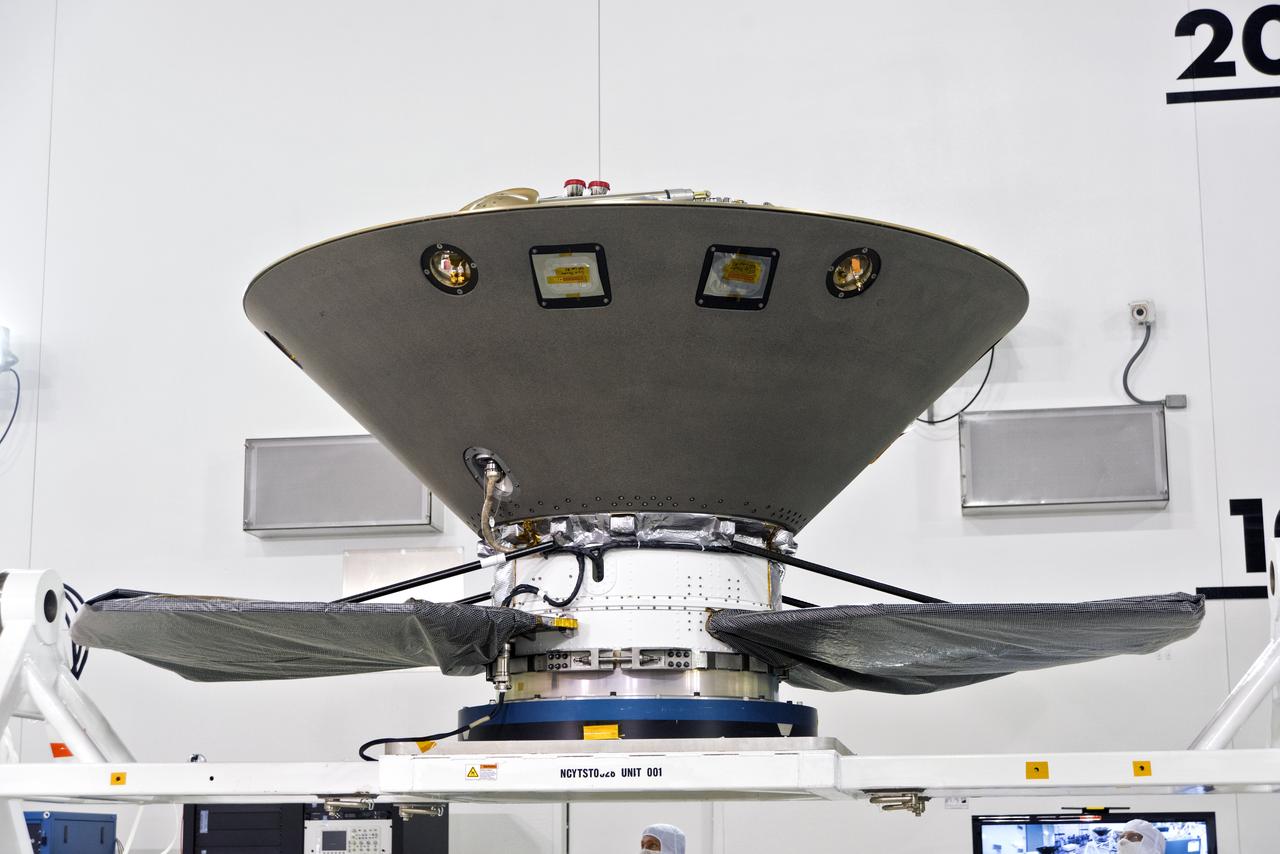

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft has been mounted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.

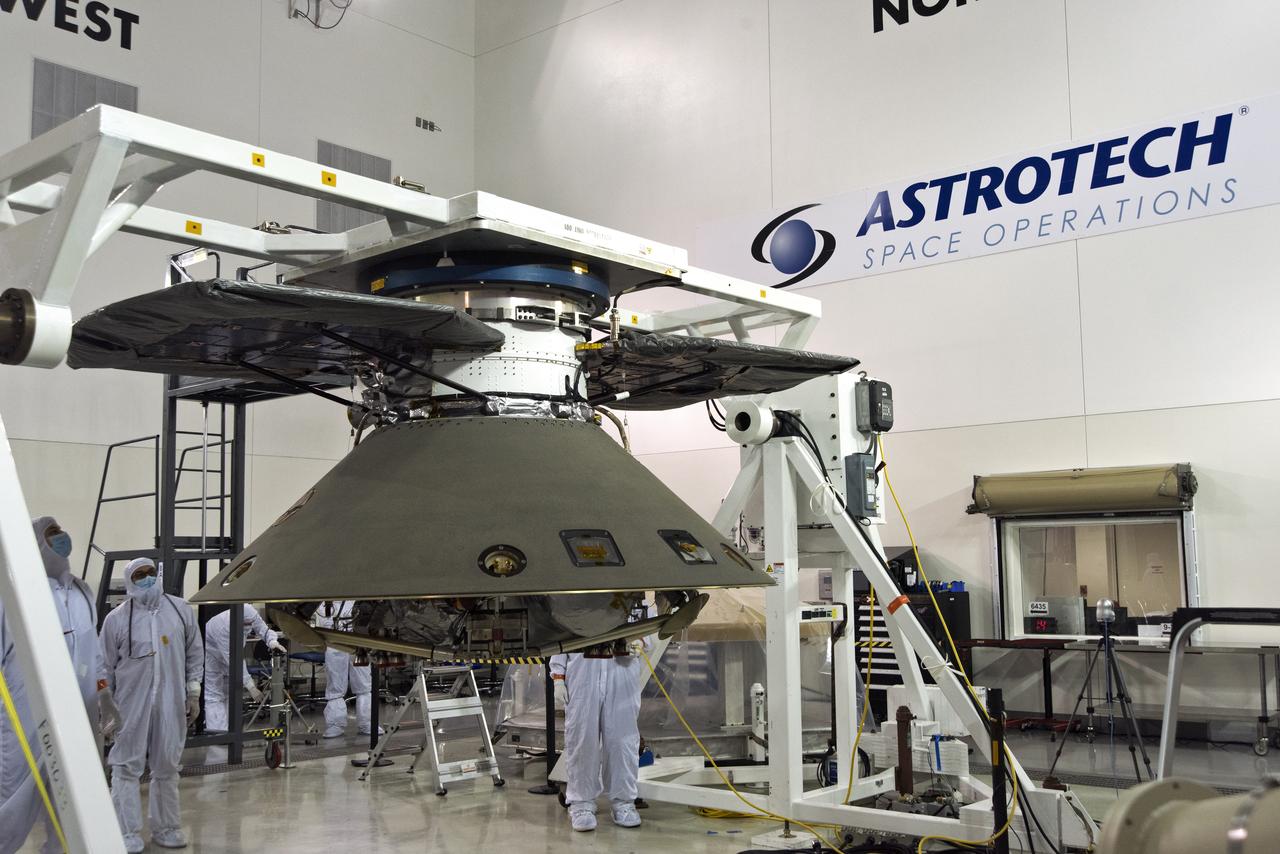
Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is prepared to be lifted on to a rotation fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft is rotated on a fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.

Inside the Astrotech processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft has been rotated on a fixture for further testing. InSight was developed and built by Lockheed-Martin Space Systems in Denver, Colorado, and is scheduled for liftoff is May 5, 2018. InSight is the first mission to land on Mars and explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth.
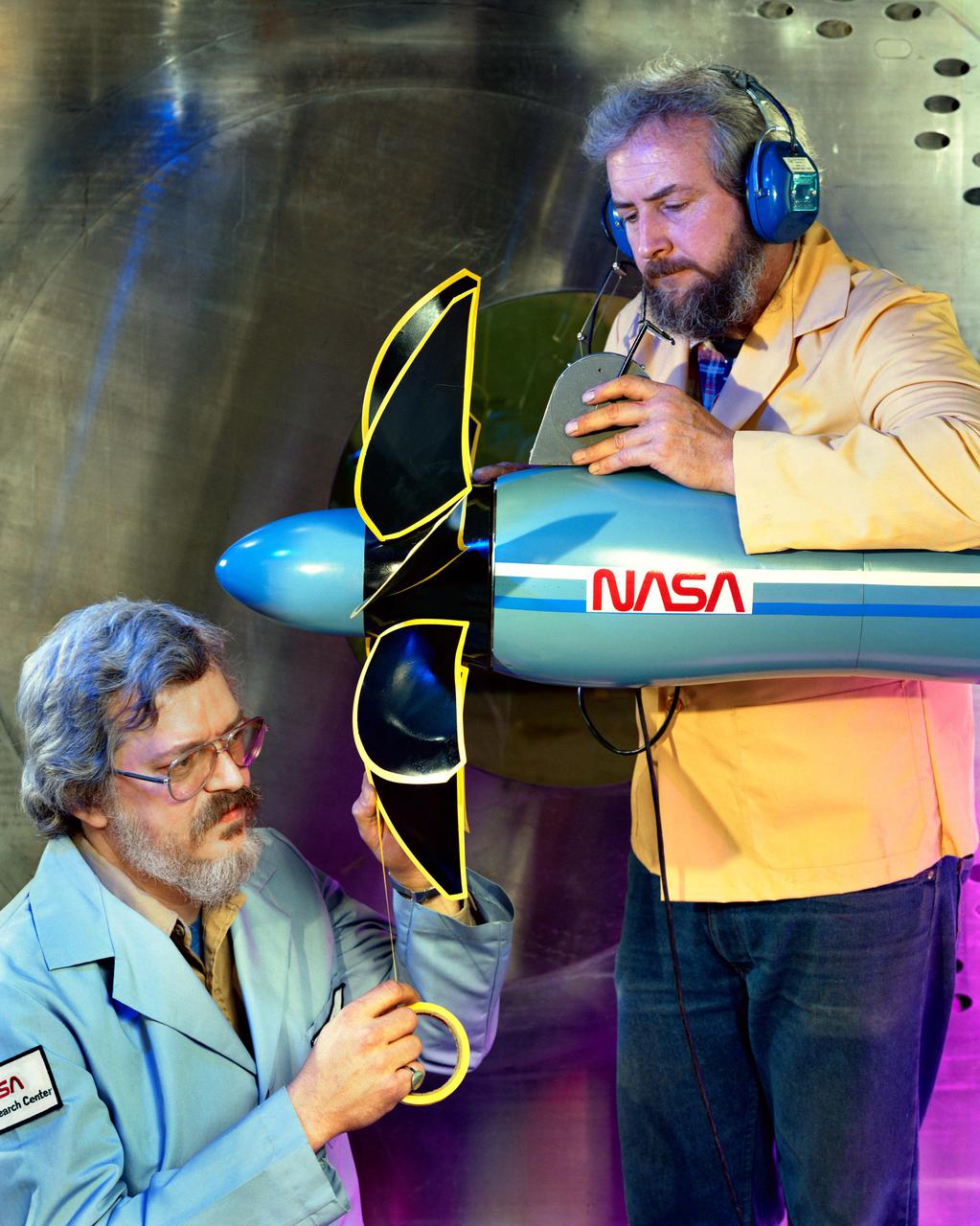

Technicians ready a single rotating propeller model in the 8x6 Supersonic Wind Tunnel
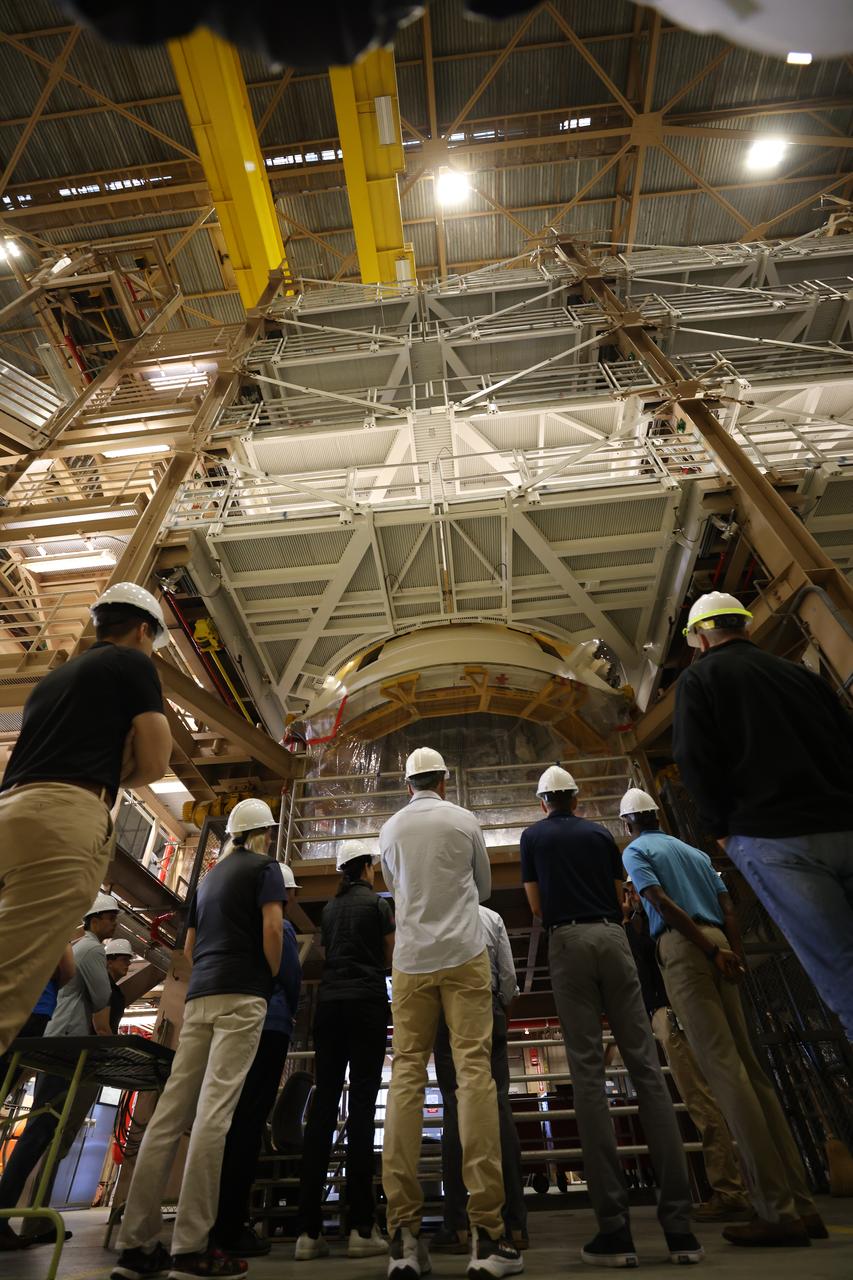

NASA’s 2021 class of astronaut candidates view a booster segment for Artemis II inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility during a familiarization tour of facilities on Tuesday, Oct. 17, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
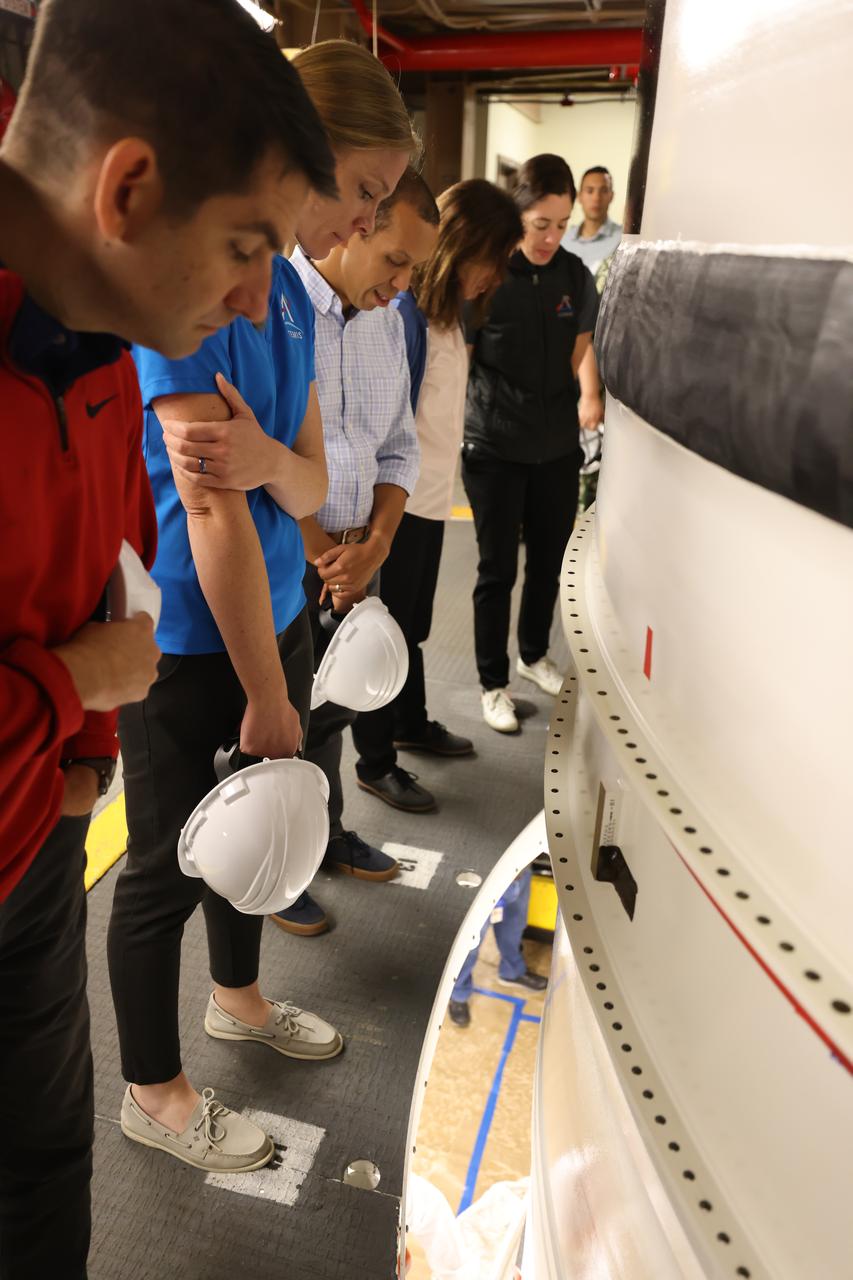

NASA’s 2021 class of astronaut candidates view a booster segment for Artemis II inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility during a familiarization tour of facilities on Tuesday, Oct. 17, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
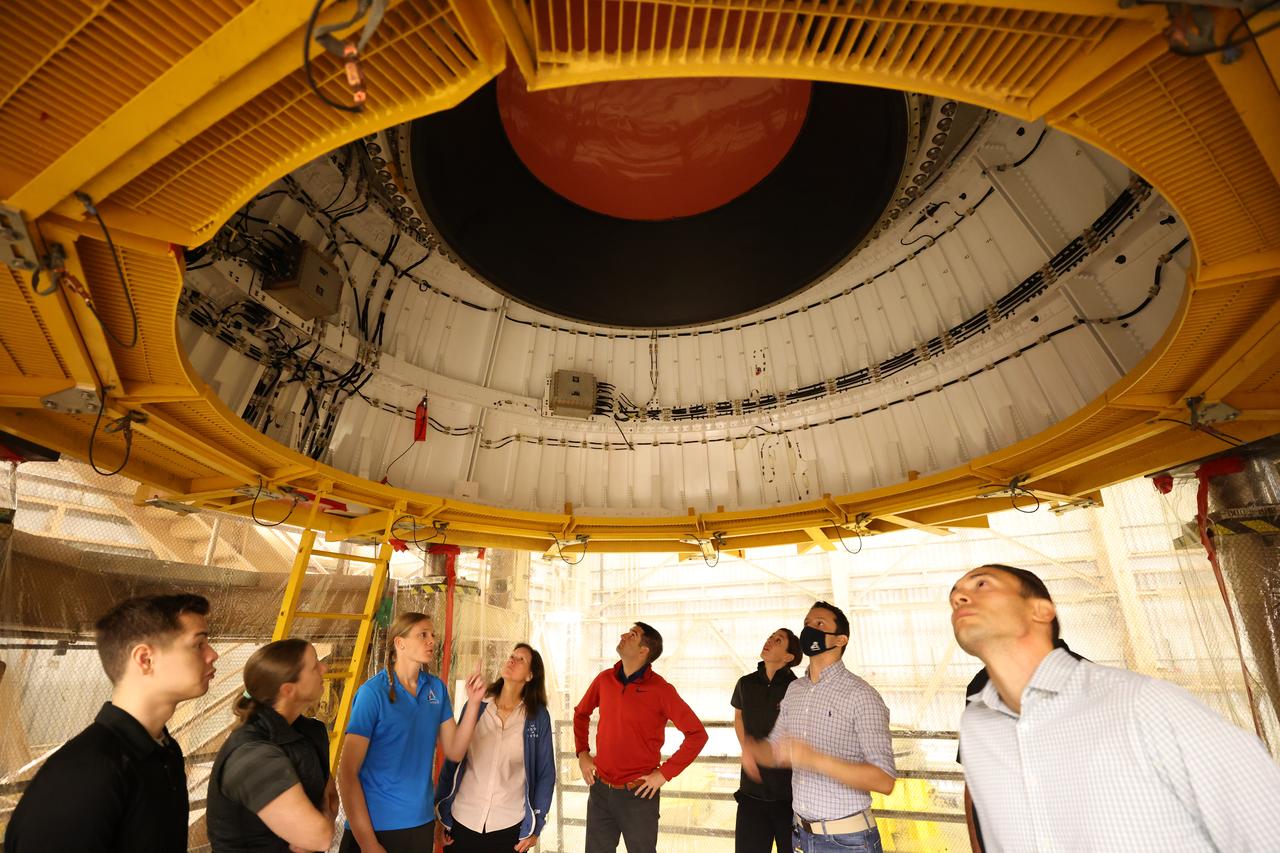

NASA’s 2021 class of astronaut candidates view a booster segment for Artemis II inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility during a familiarization tour of facilities on Tuesday, Oct. 17, 2023, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
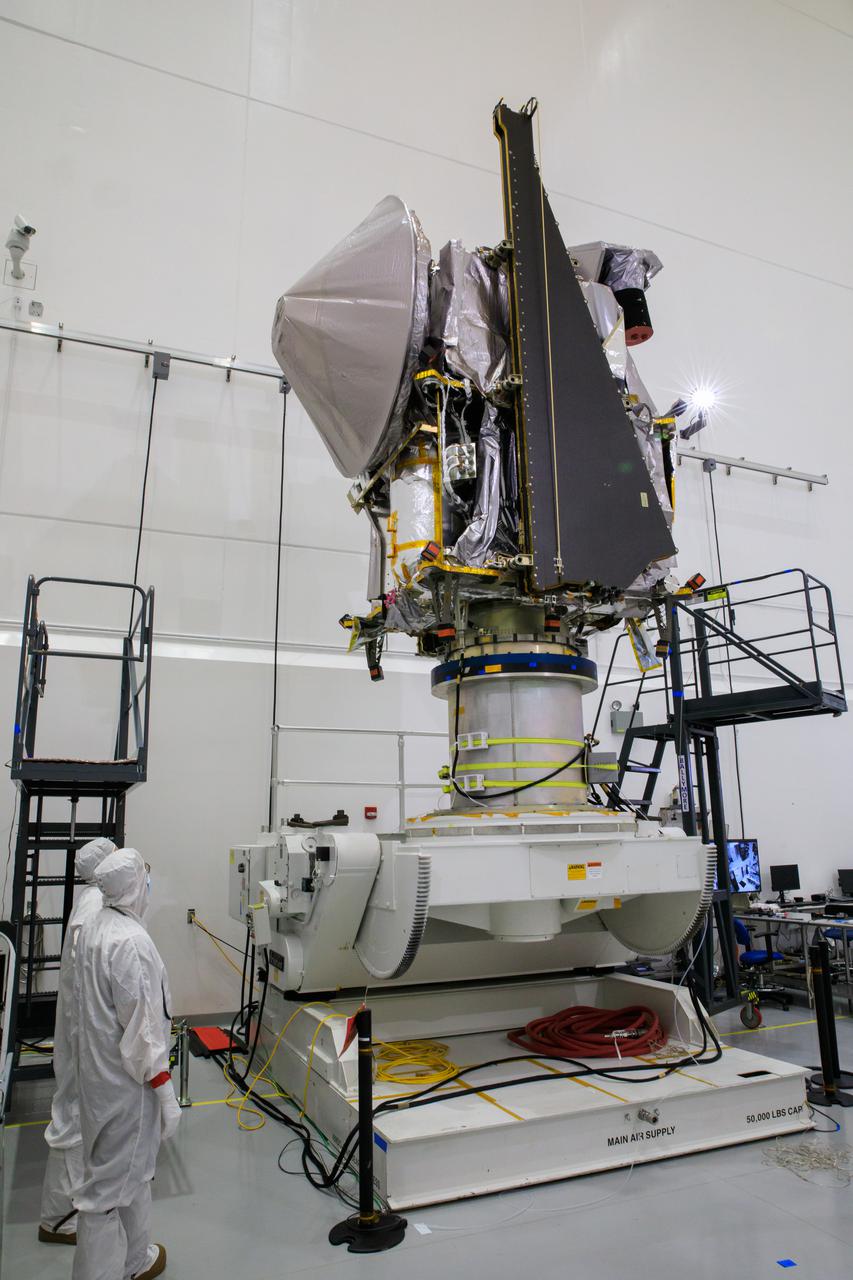

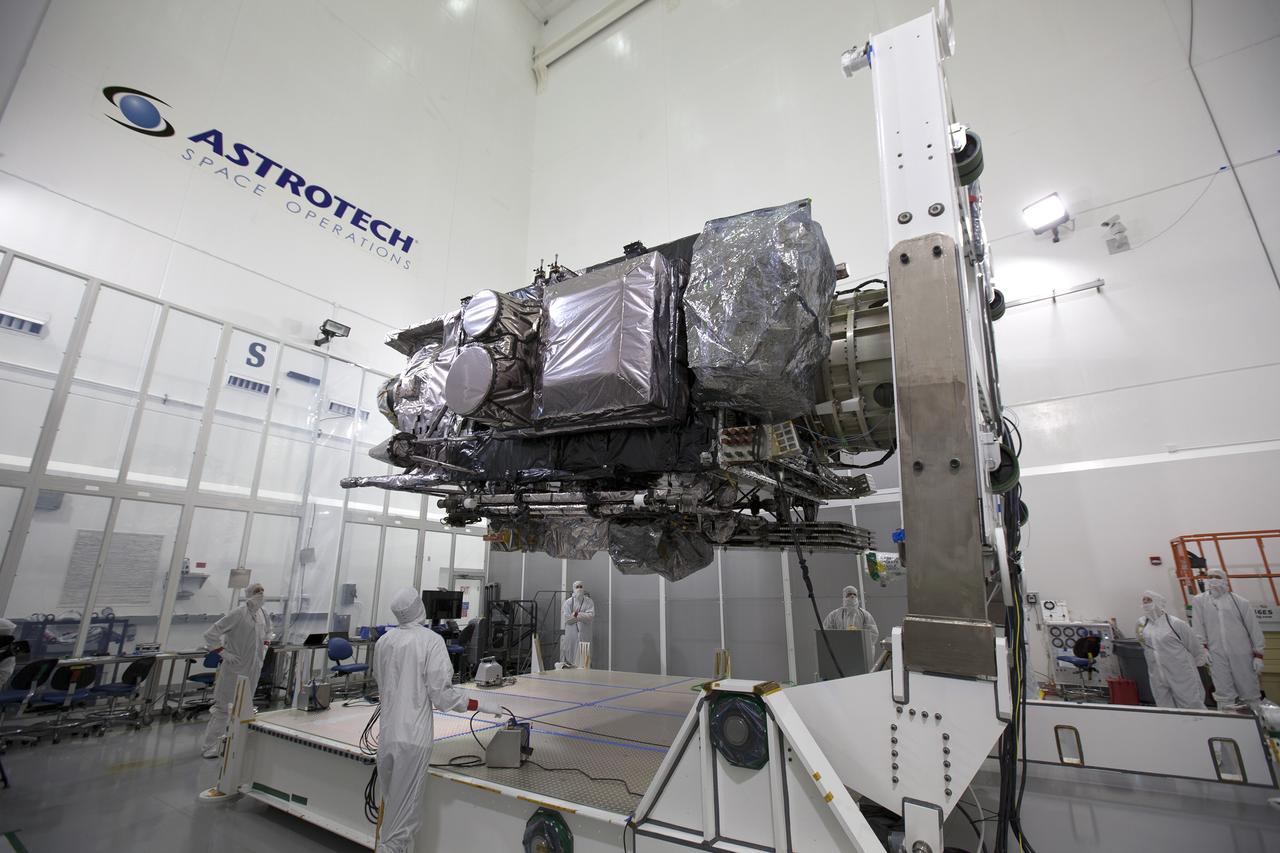
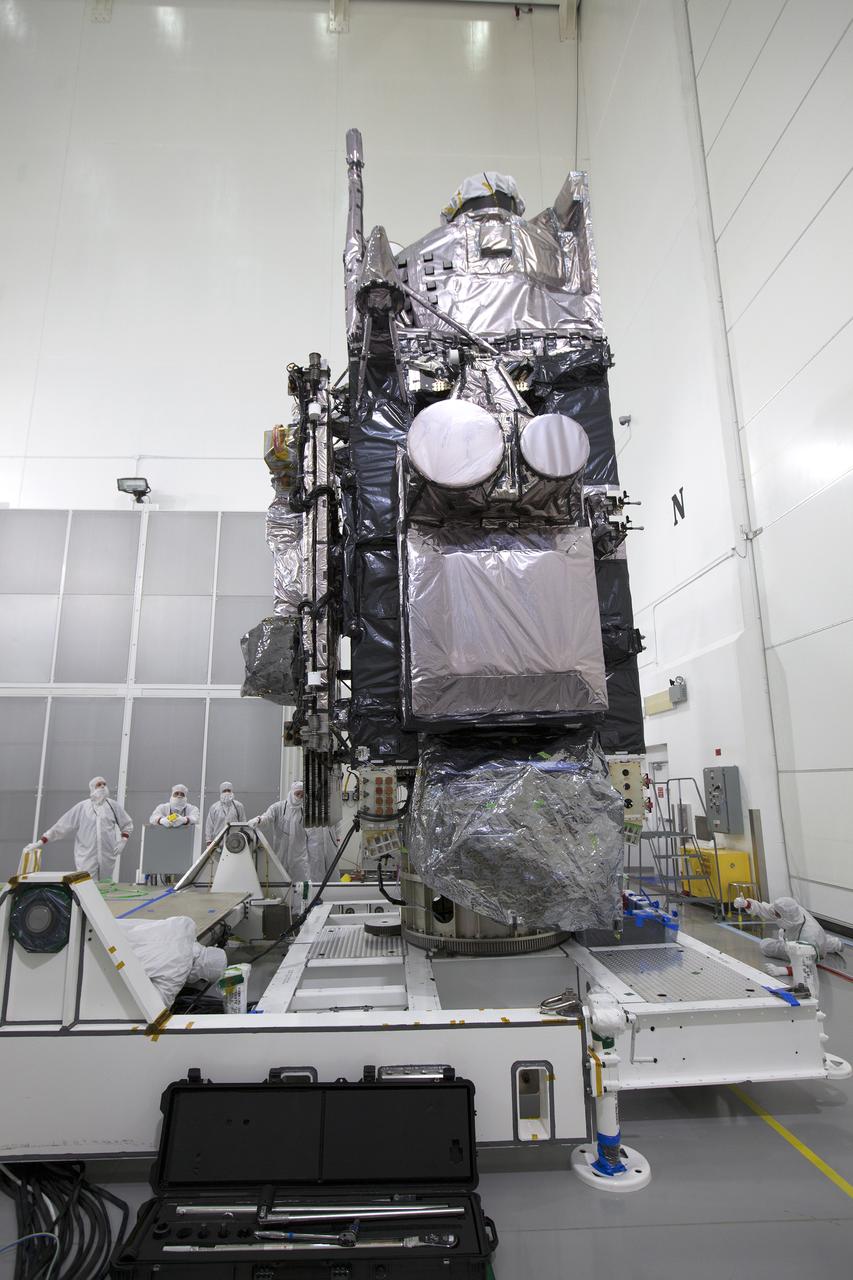
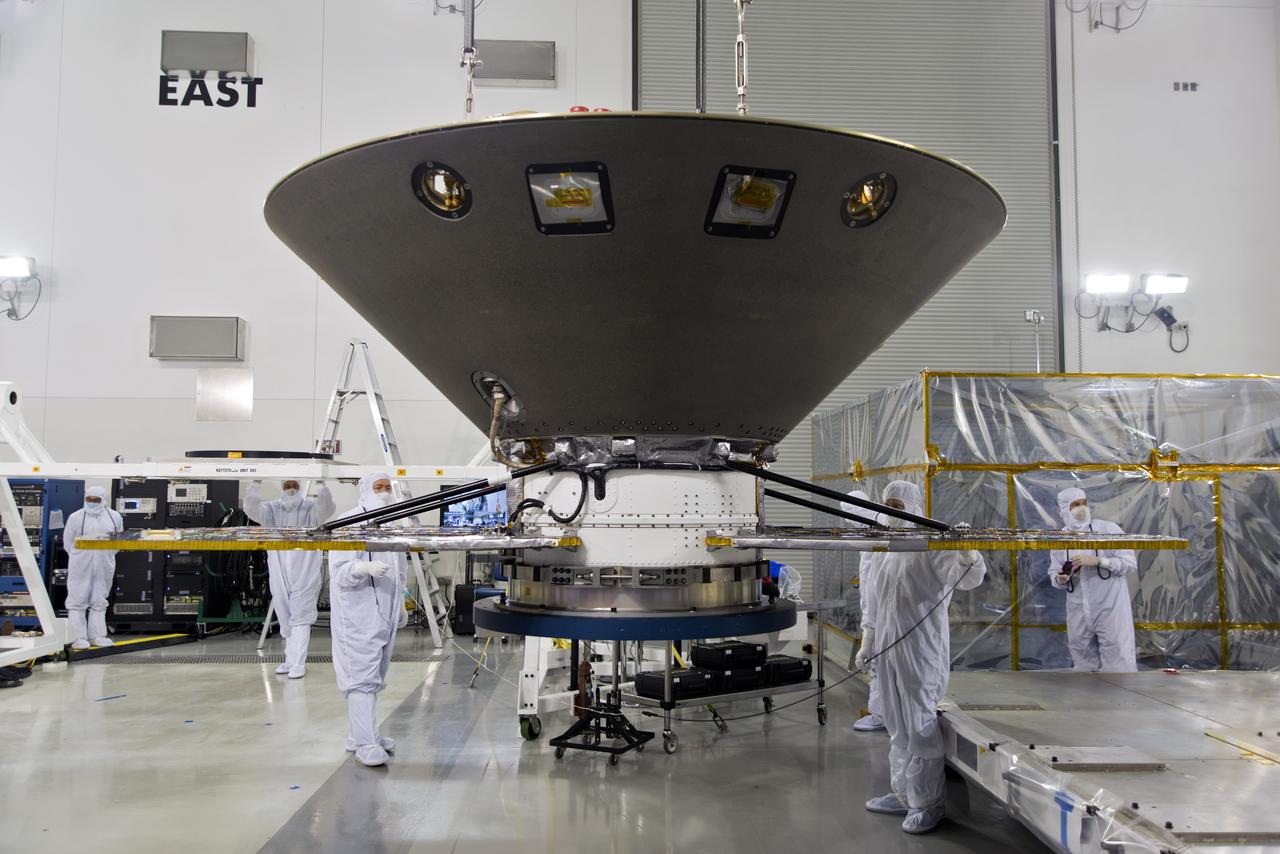
NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is moved to the vertical position on a rotation stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 1, 2021. In view, the high gain antenna and solar arrays have been installed on the Lucy spacecraft. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
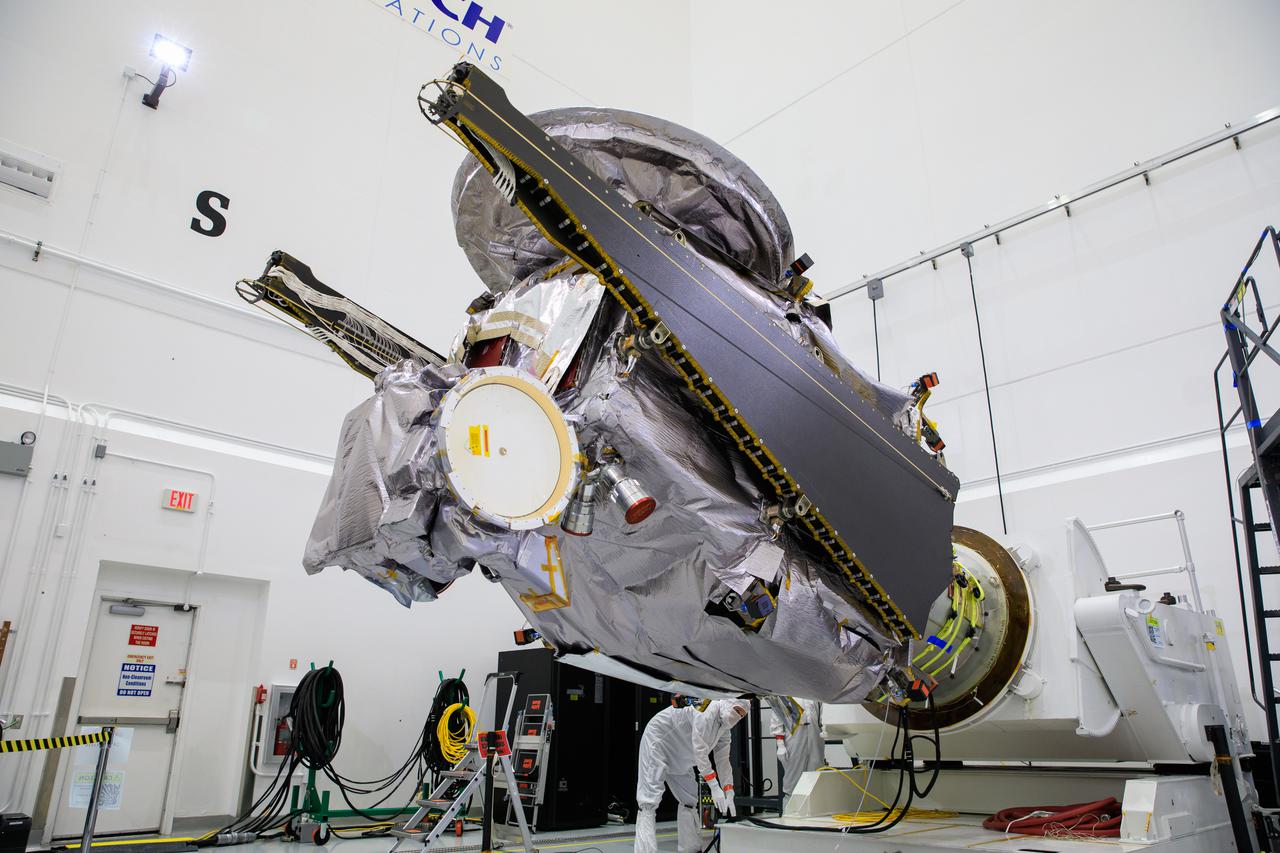

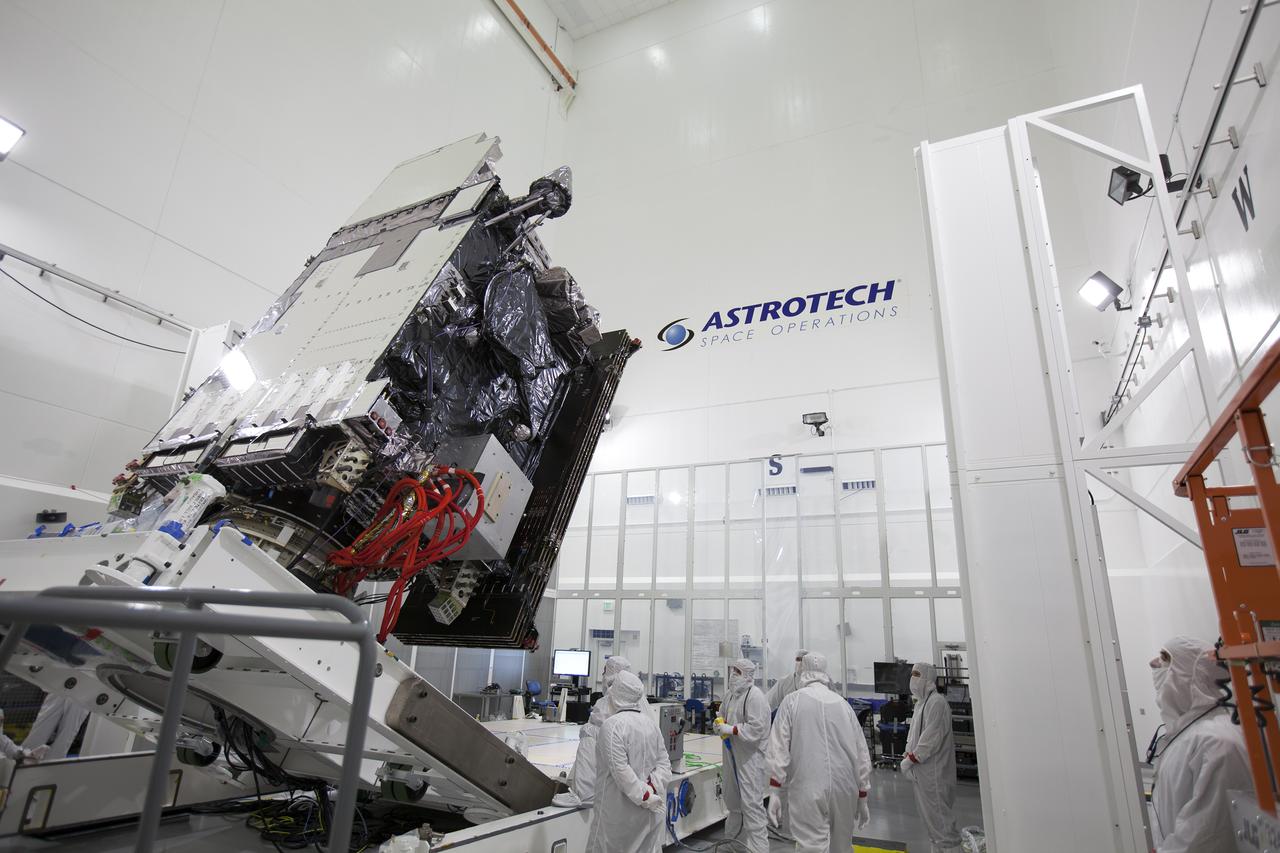
NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is moved to the horizontal position on a rotation stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 1, 2021. In view, the high gain antenna and solar arrays have been installed on the Lucy spacecraft. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
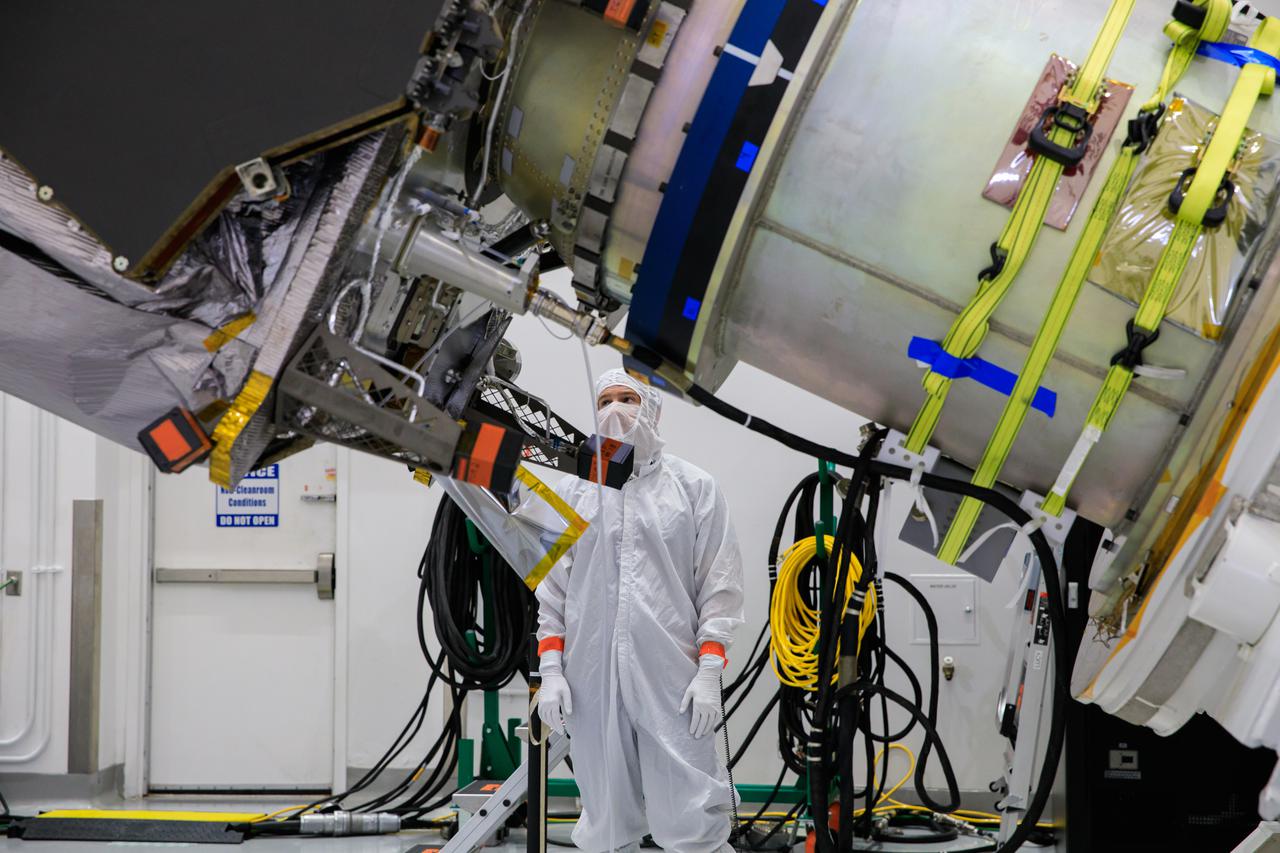

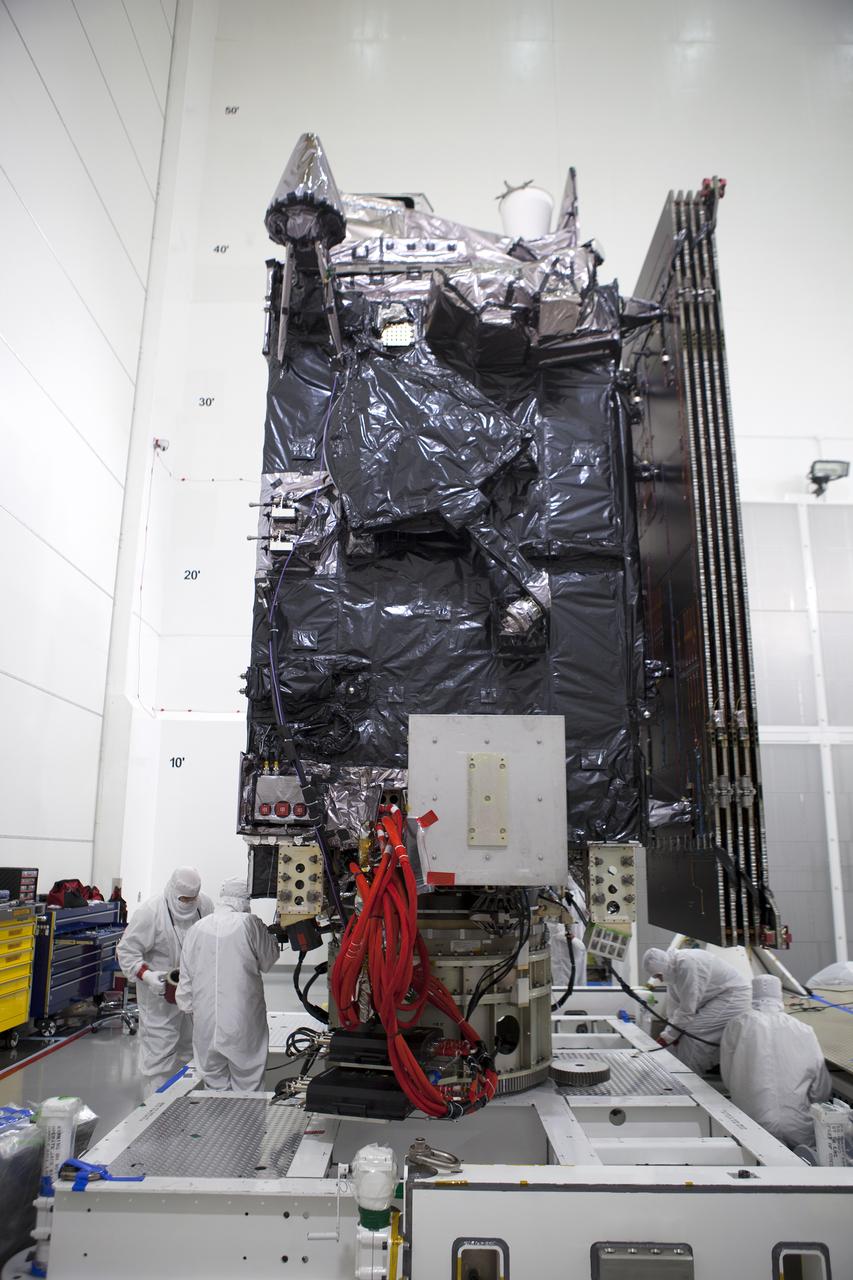
A close-up view of NASA’s Lucy spacecraft secured on a rotation stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 1, 2021. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
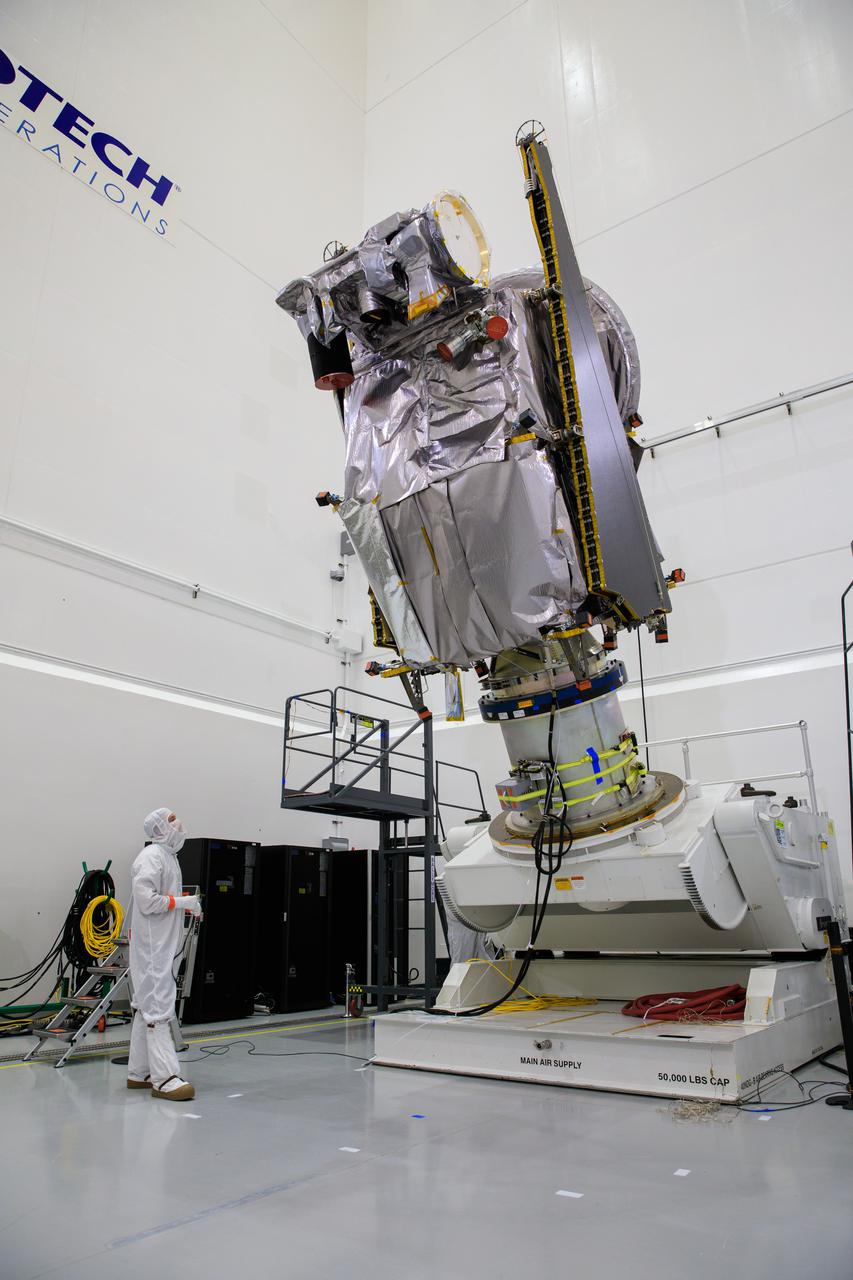

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is moved to the vertical position on a rotation stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 1, 2021. In view, the high gain antenna and solar arrays have been installed on the Lucy spacecraft. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
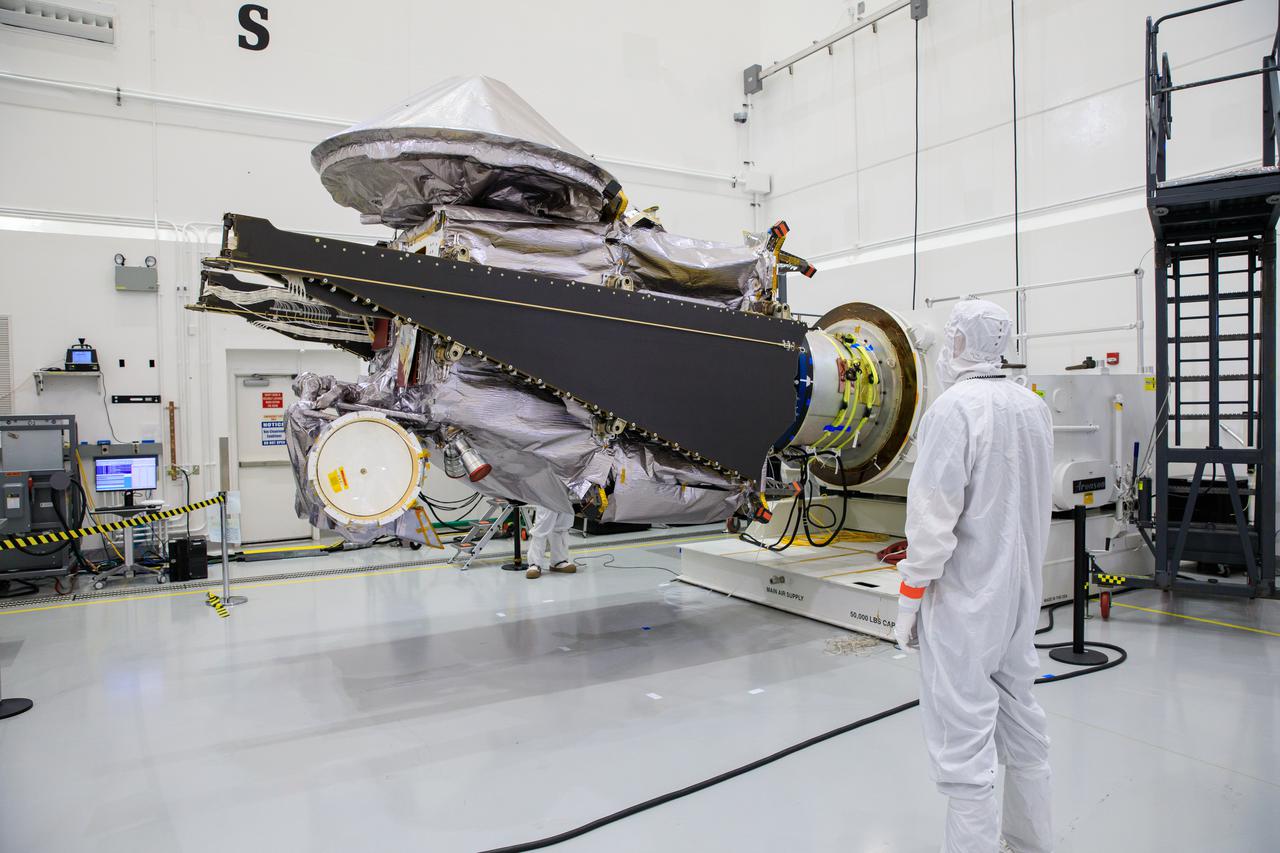

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is moved to the horizontal position on a rotation stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 1, 2021. In view, the high gain antenna and solar arrays have been installed on the Lucy spacecraft. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
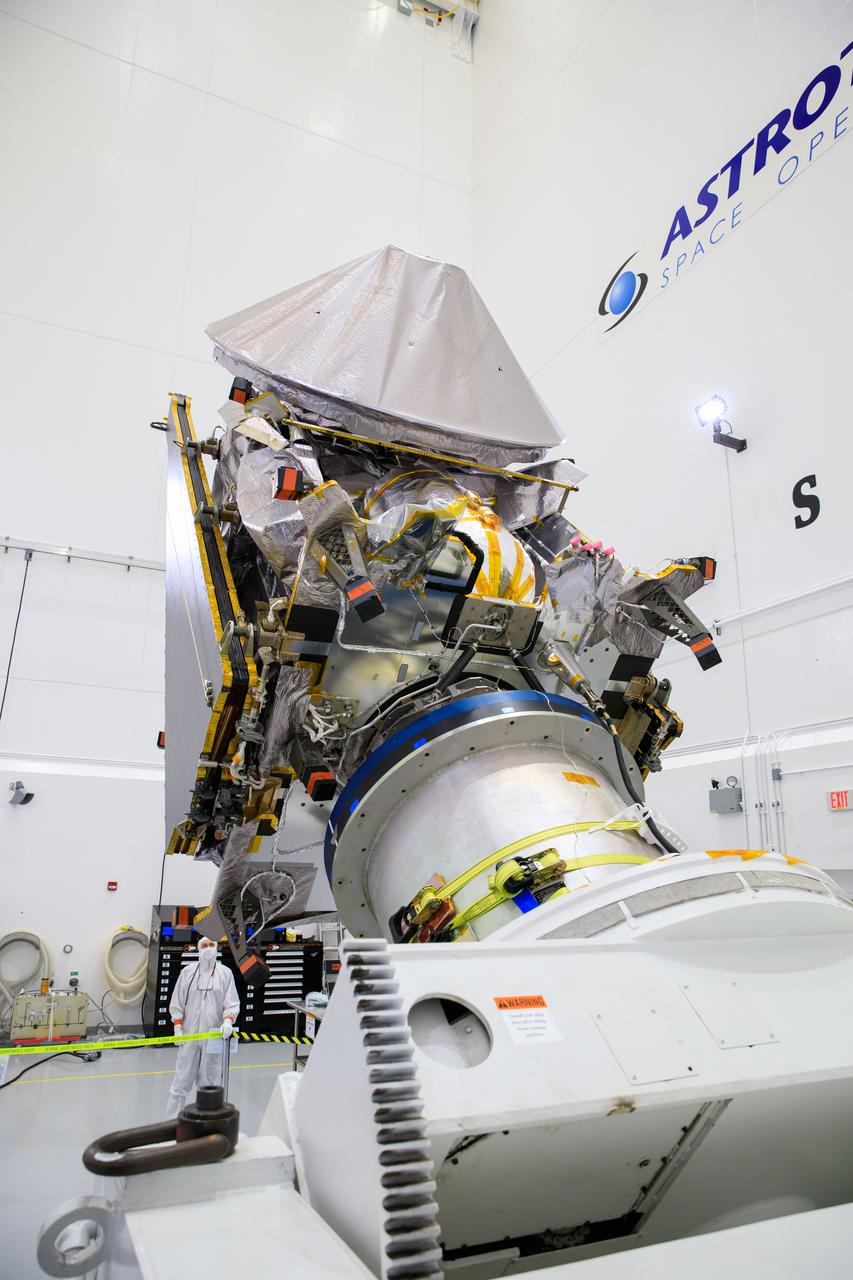

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is moved to the horizontal position on a rotation stand inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 1, 2021. In view, the high gain antenna and solar arrays have been installed on the Lucy spacecraft. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V 401 rocket from Launch Pad 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.