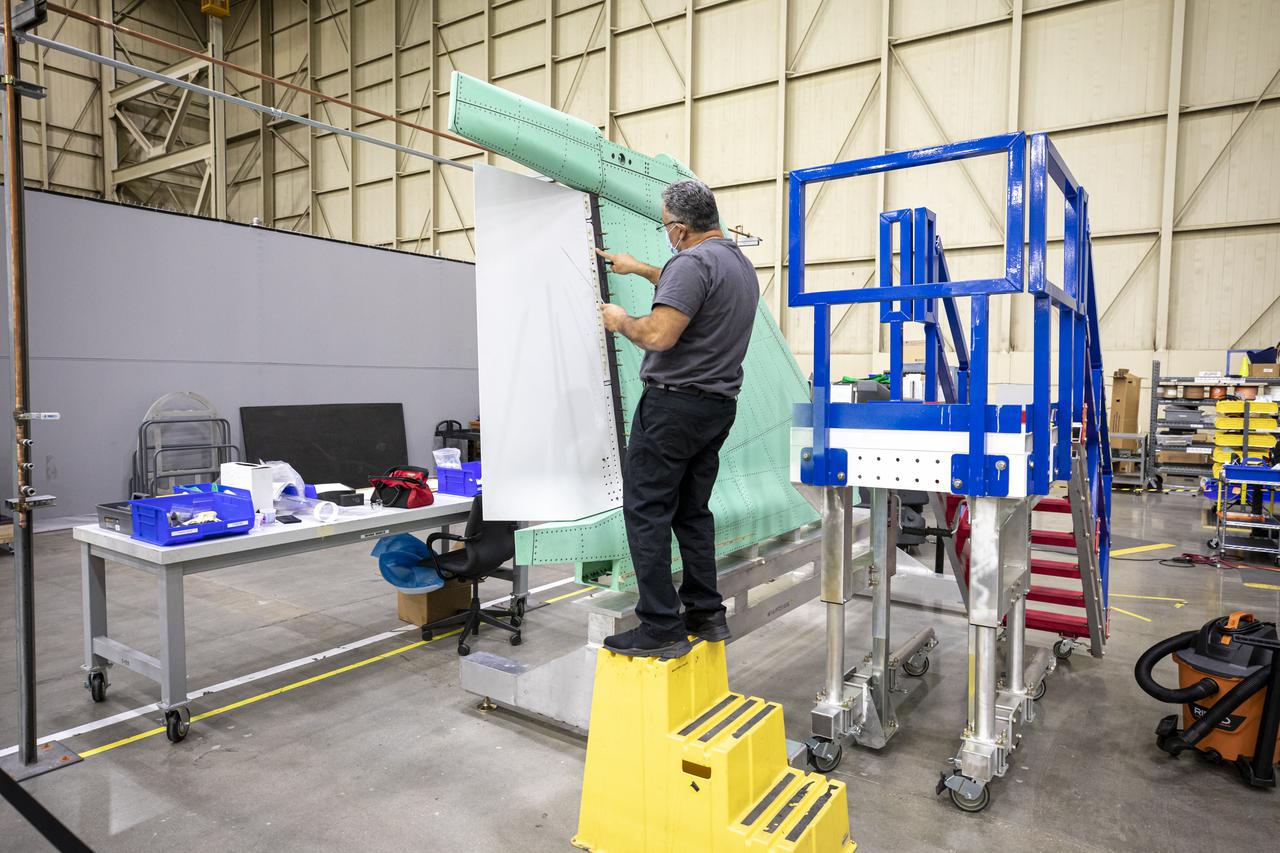

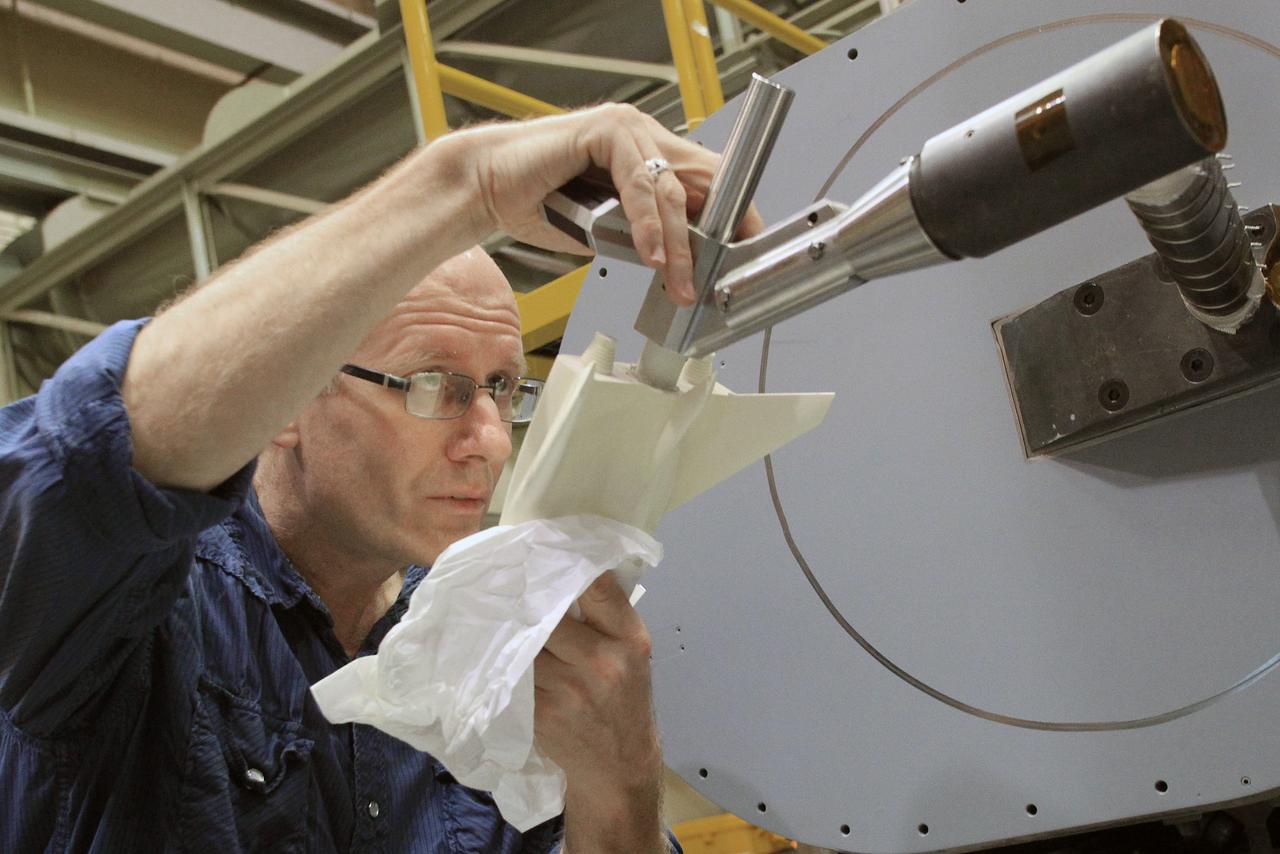
A technician is shown working on the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft’s vertical tail prior to installation. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 530 Vertical Tail - Rudder Installed Date: 5/12/2021
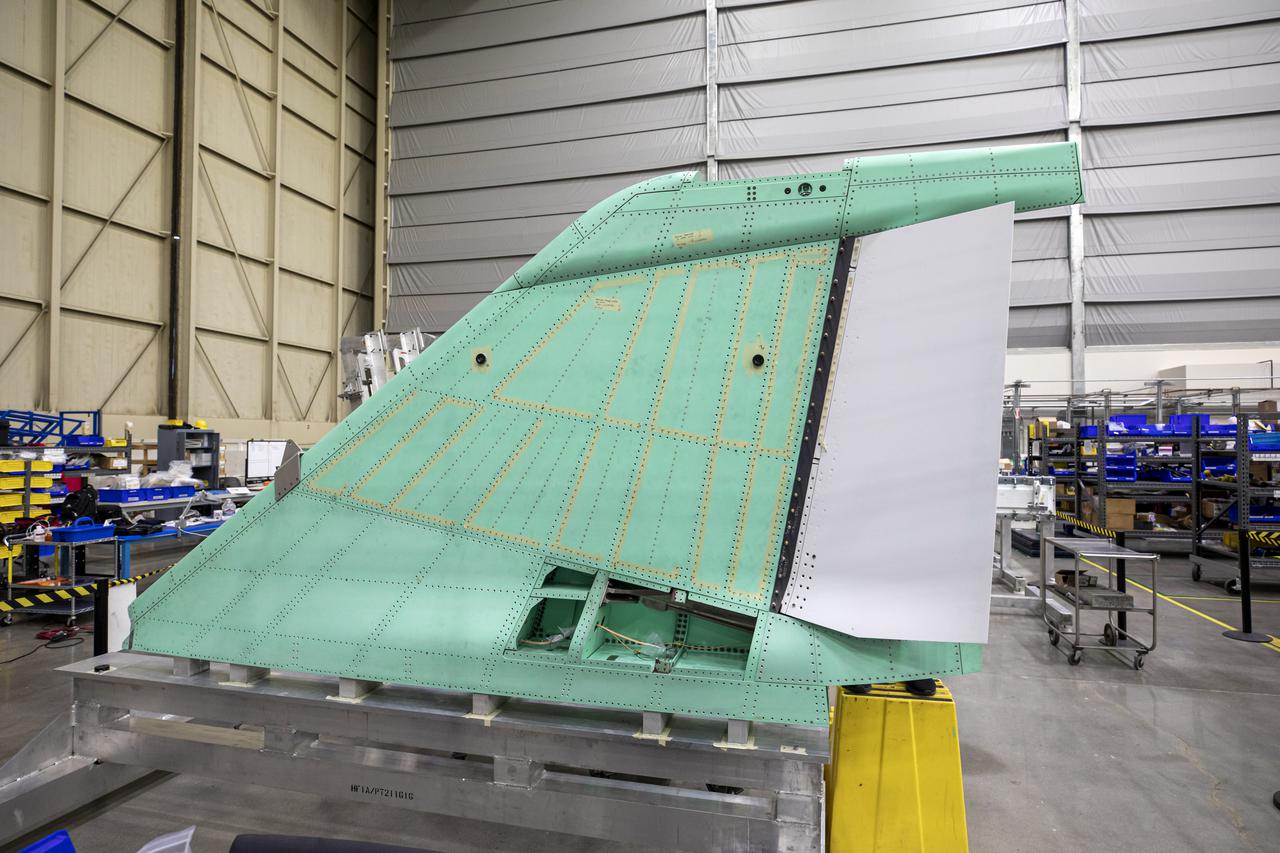

Pictured here is a close up view of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft’s vertical tail prior to installation. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 530 Vertical Tail - Rudder Installed Date: 5/12/2021
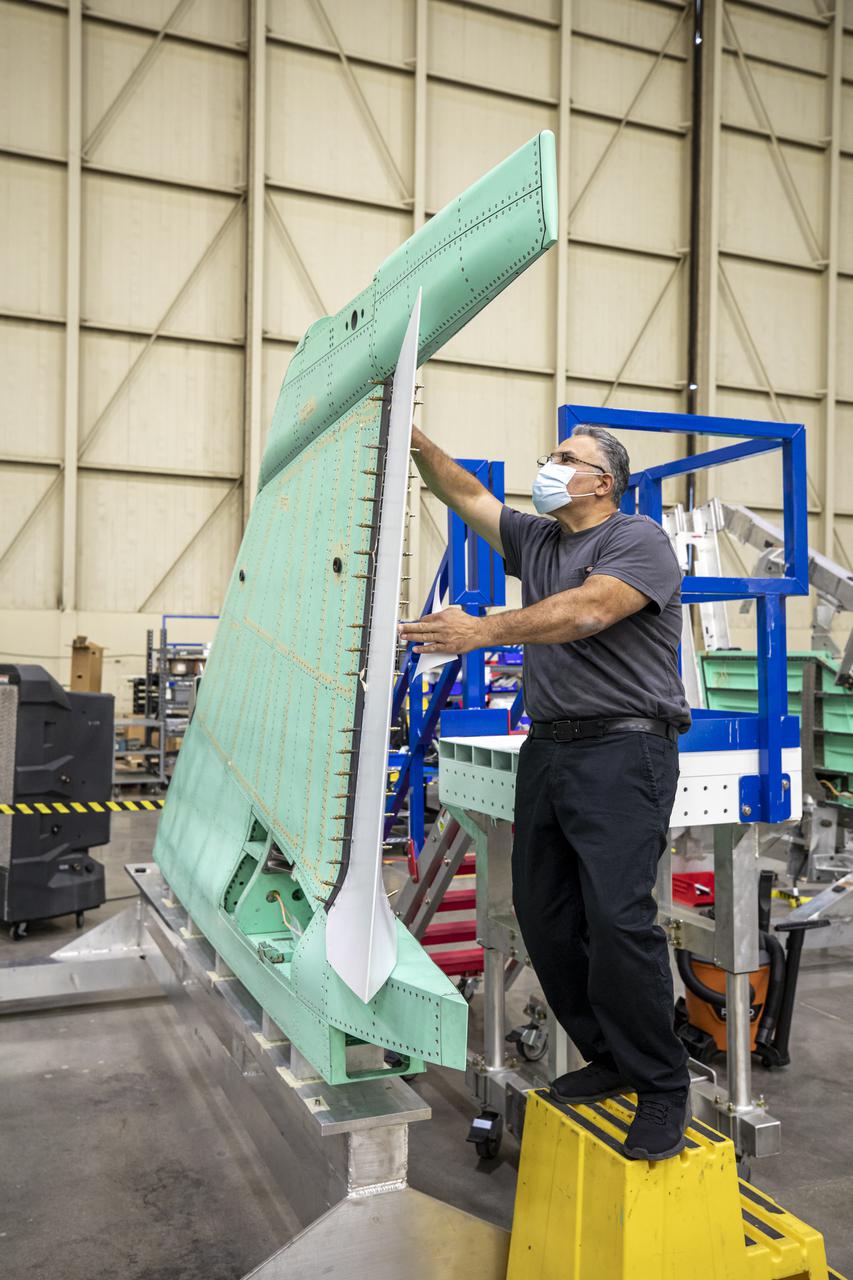

A technician is shown working on the X-59 vertical tail prior to installation. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 530 Vertical Tail - Rudder Installed Date: 5/12/2021
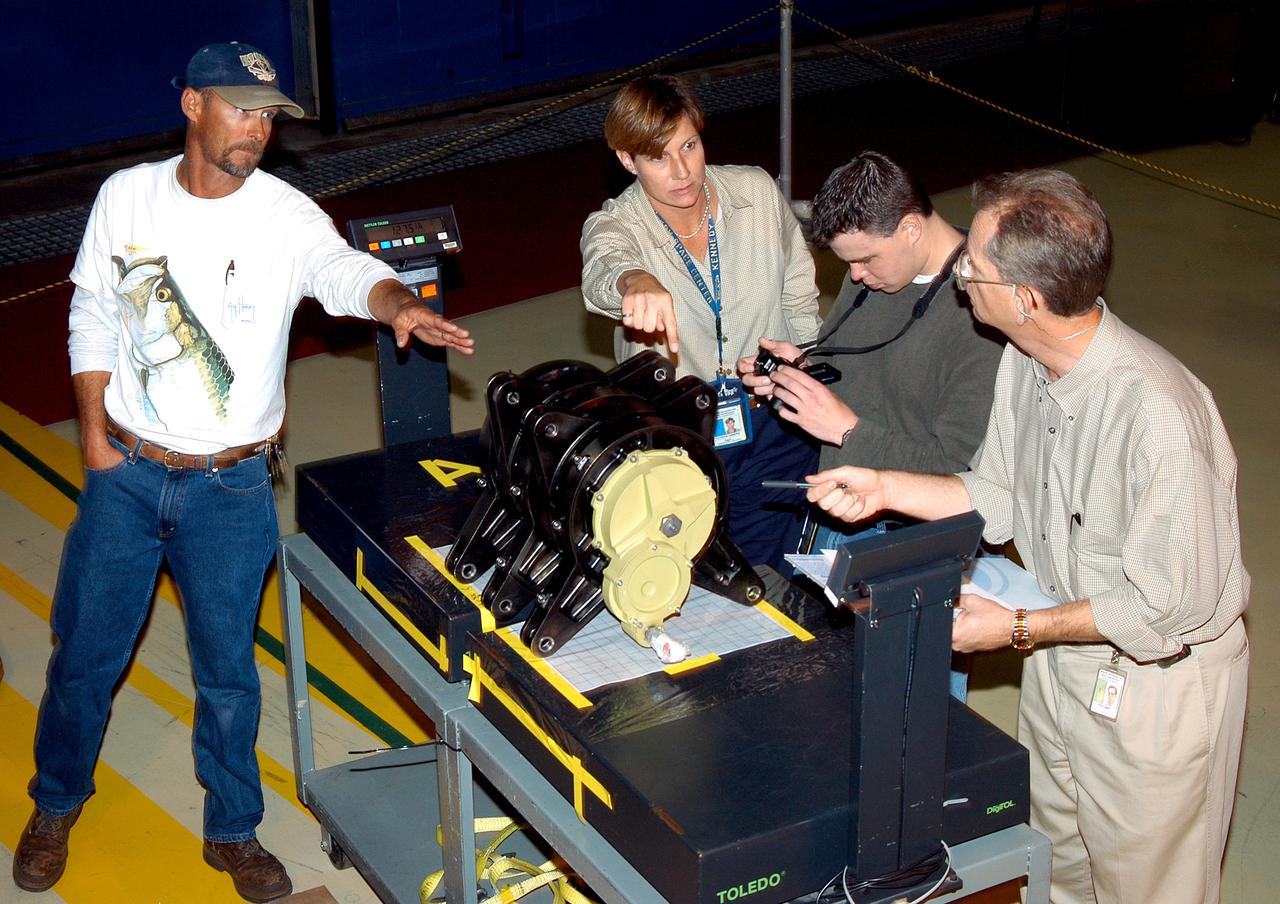

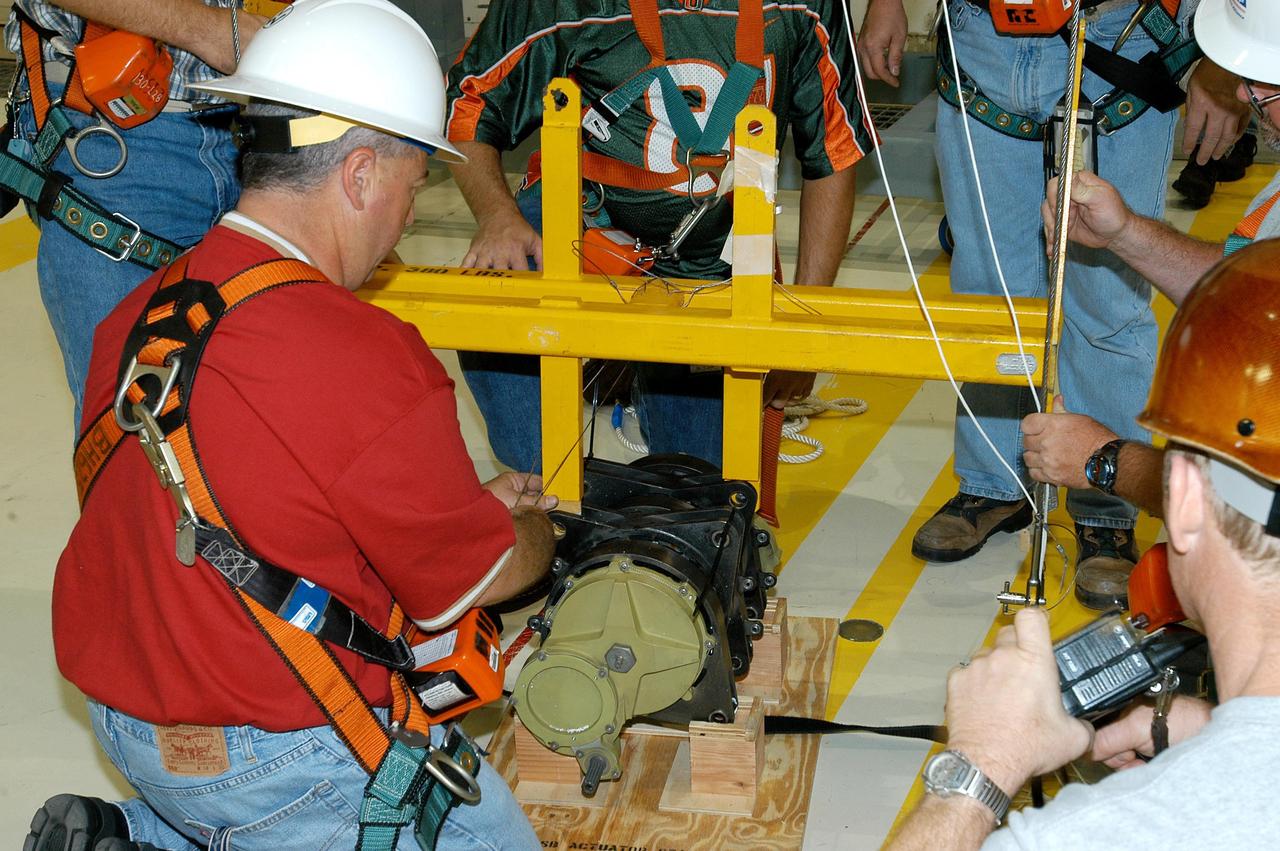
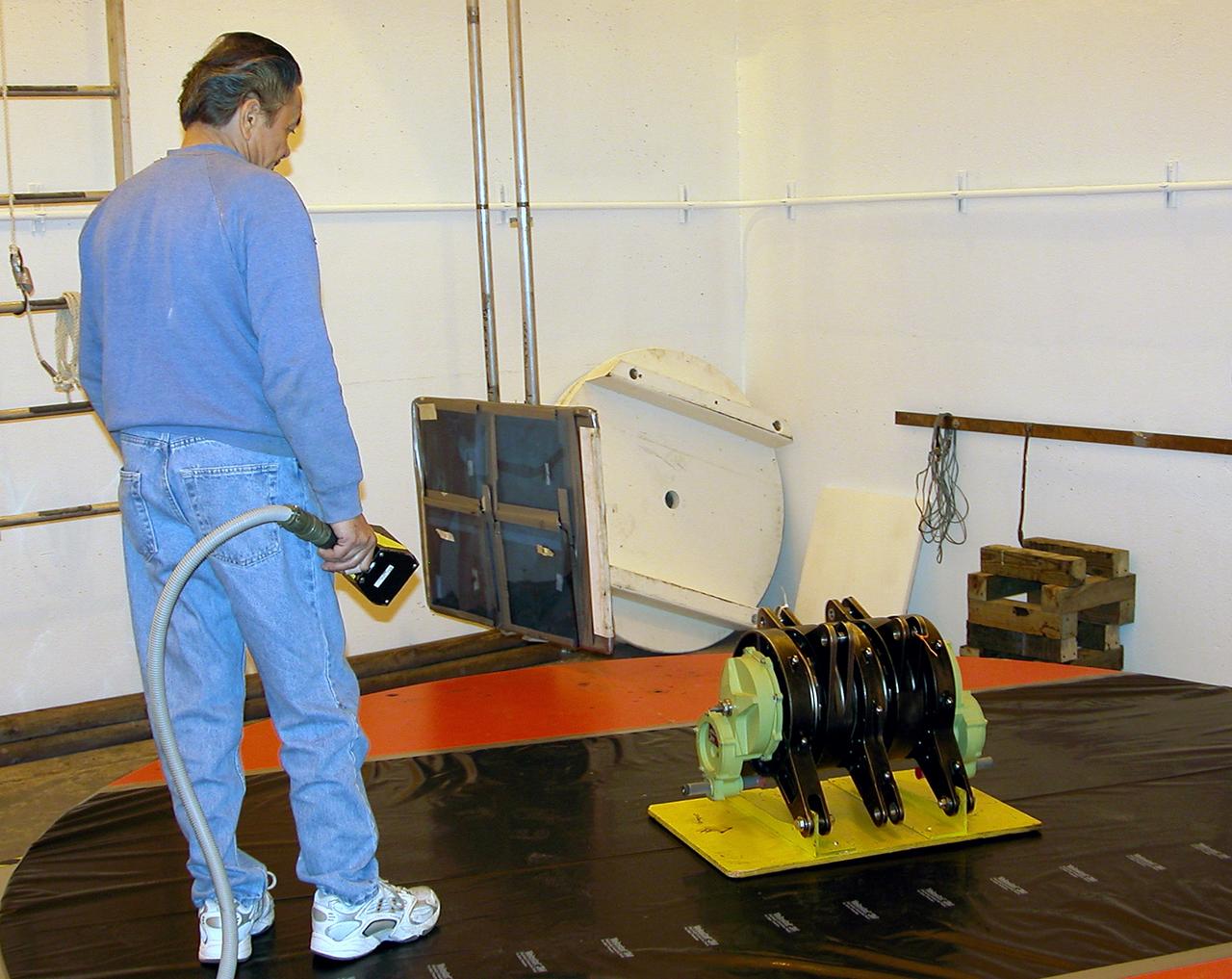
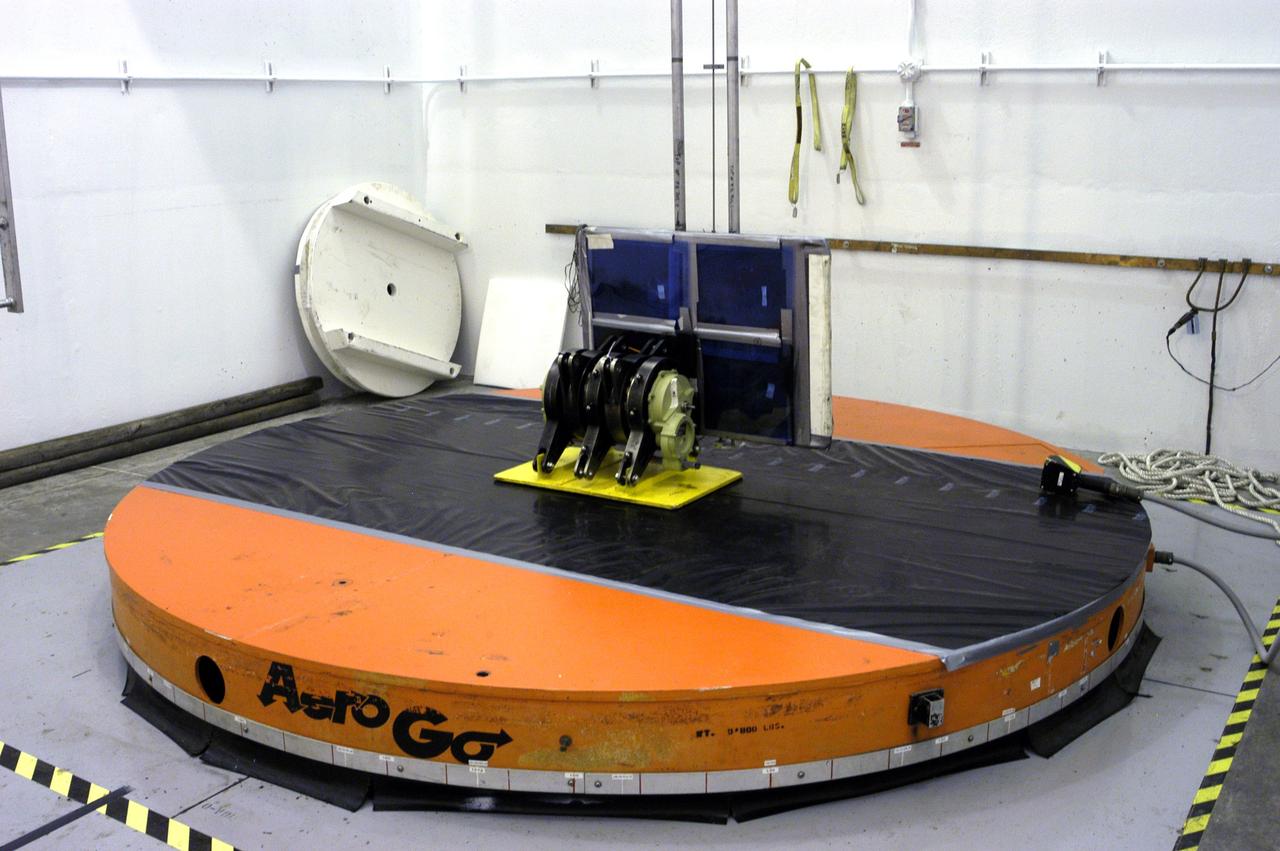
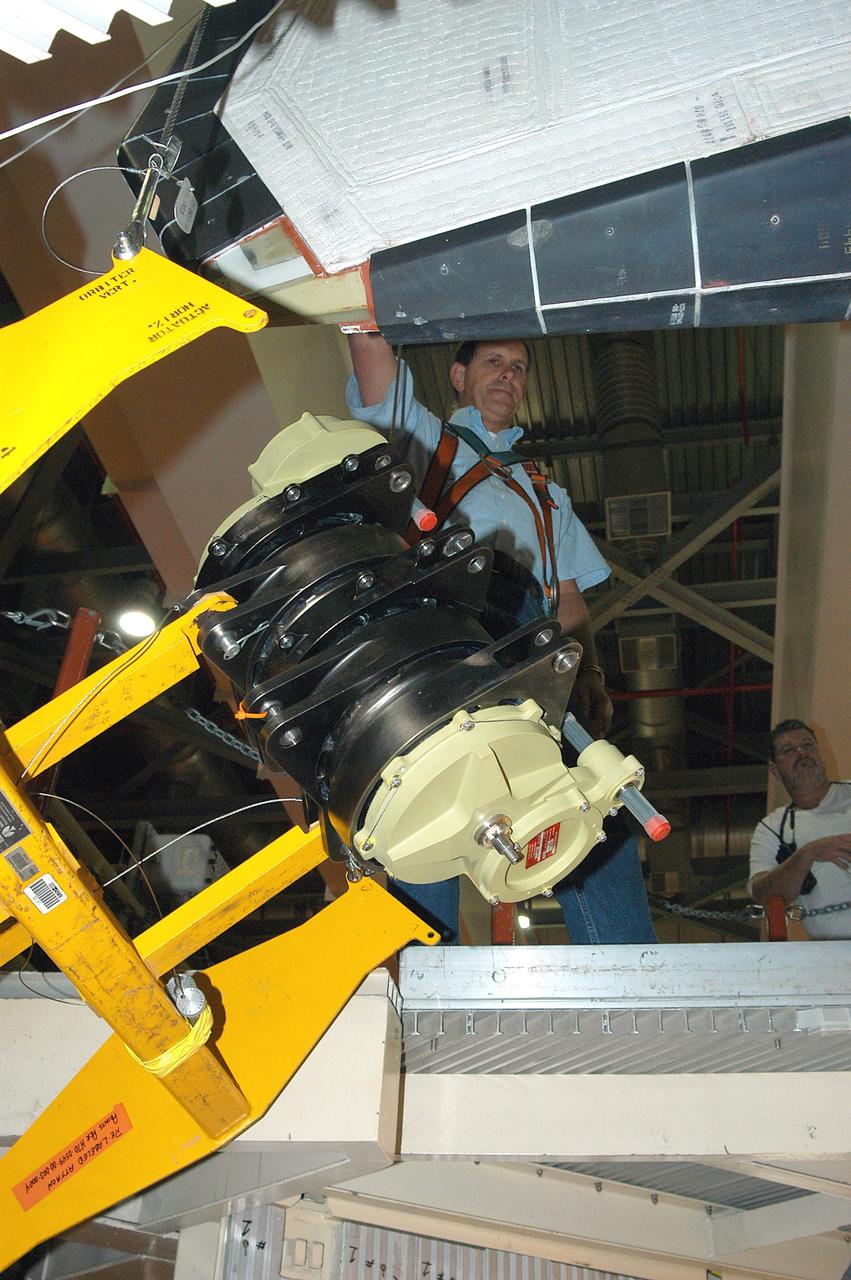
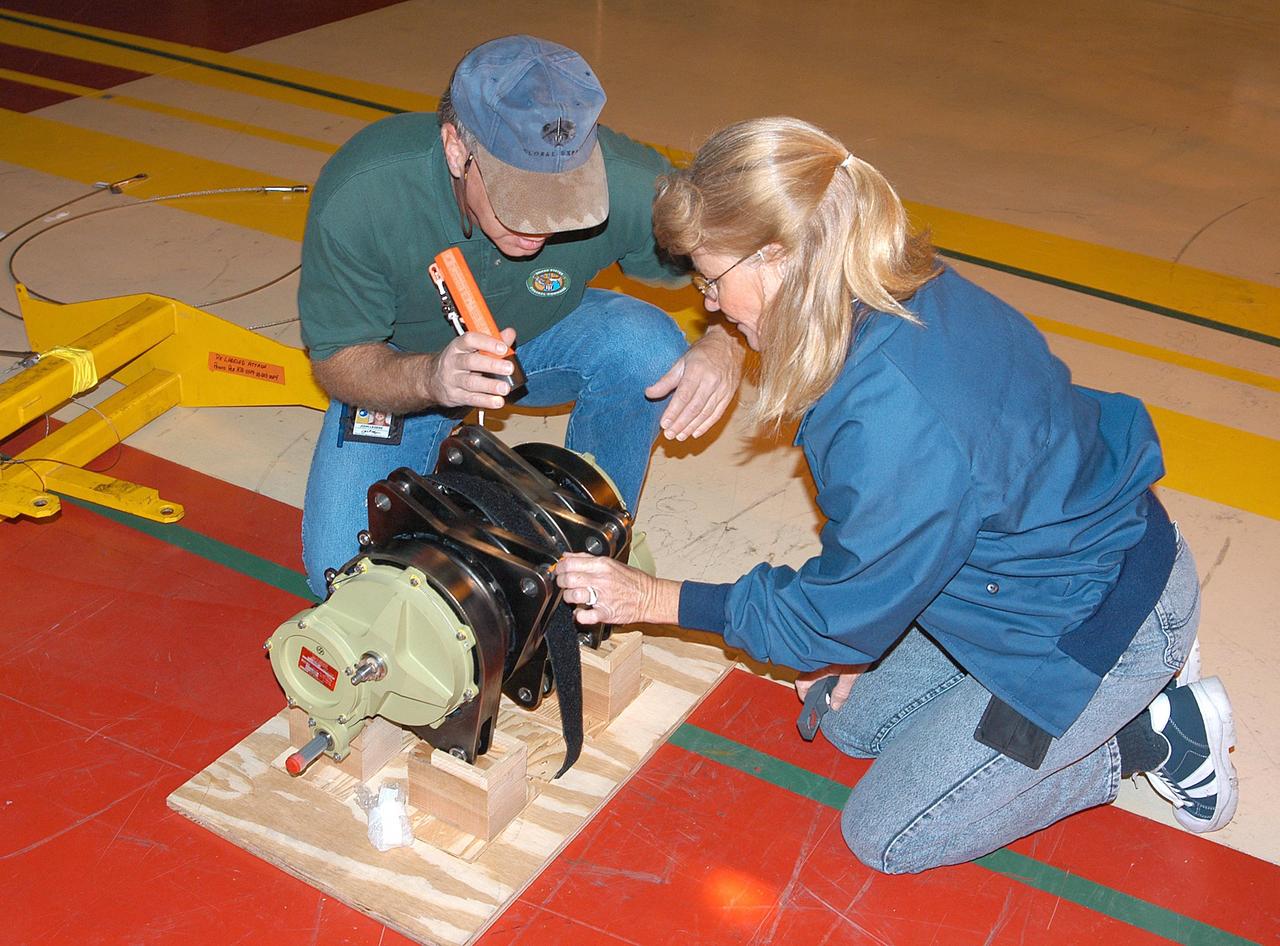
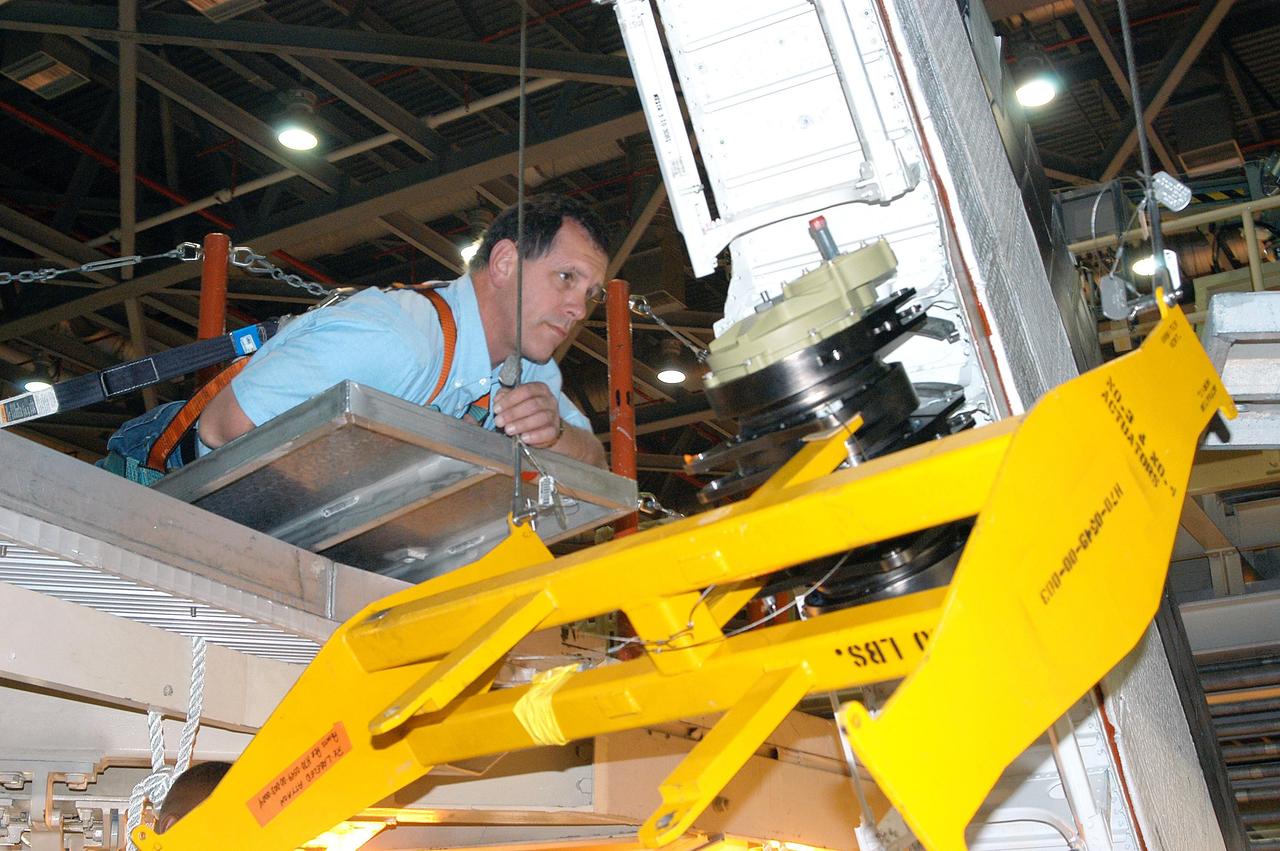
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility measure the alignment of bearings on a rudder speed brake actuator. Actuators move an orbiter’s rudder, speed brake, elevons and main engines during flight.
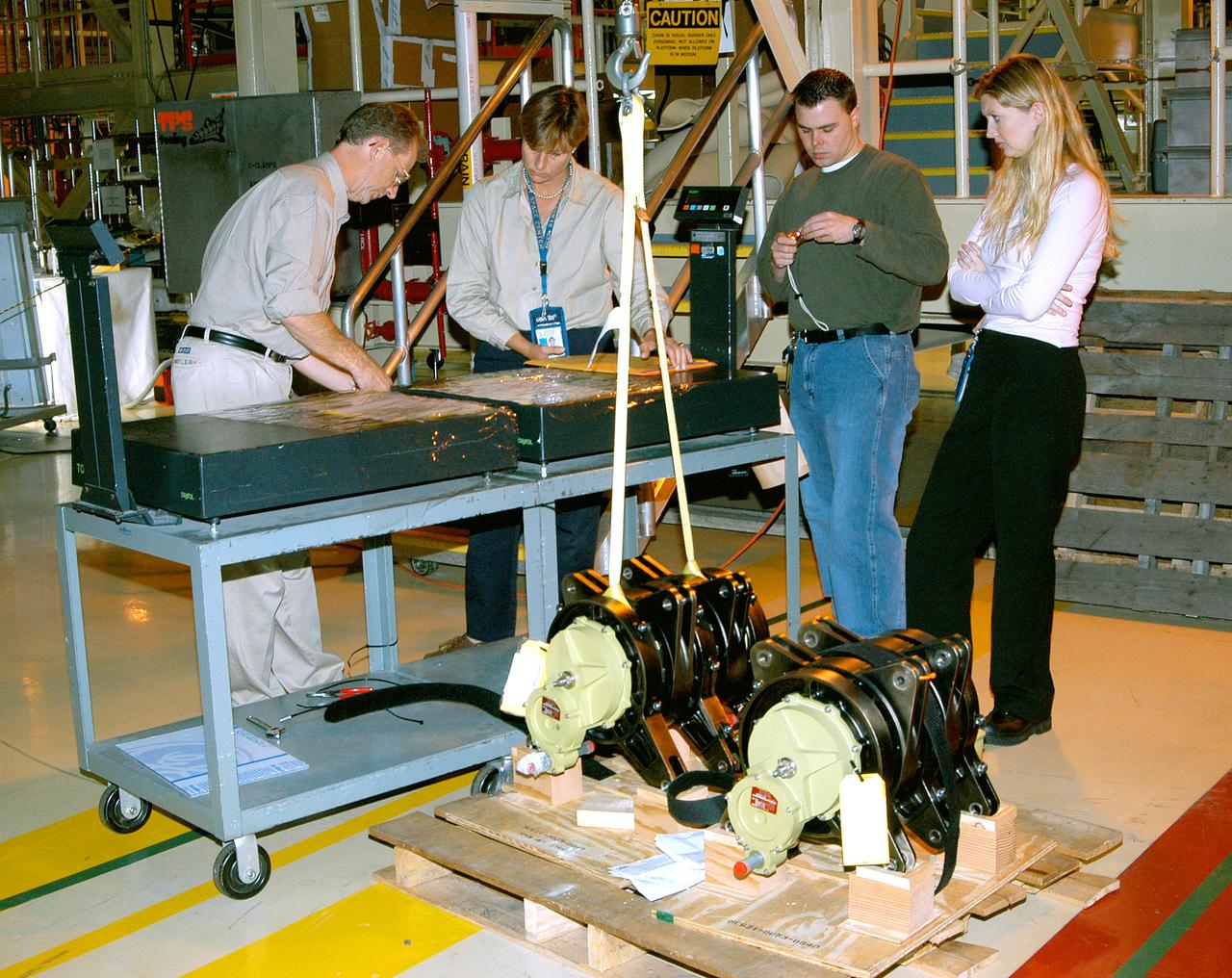

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility get ready to measure the alignment of the bearings on the rudder speed brake actuators sitting on the floor in the foreground. The actuators move an orbiter’s rudder, speed brake, elevons and main engines during flight.
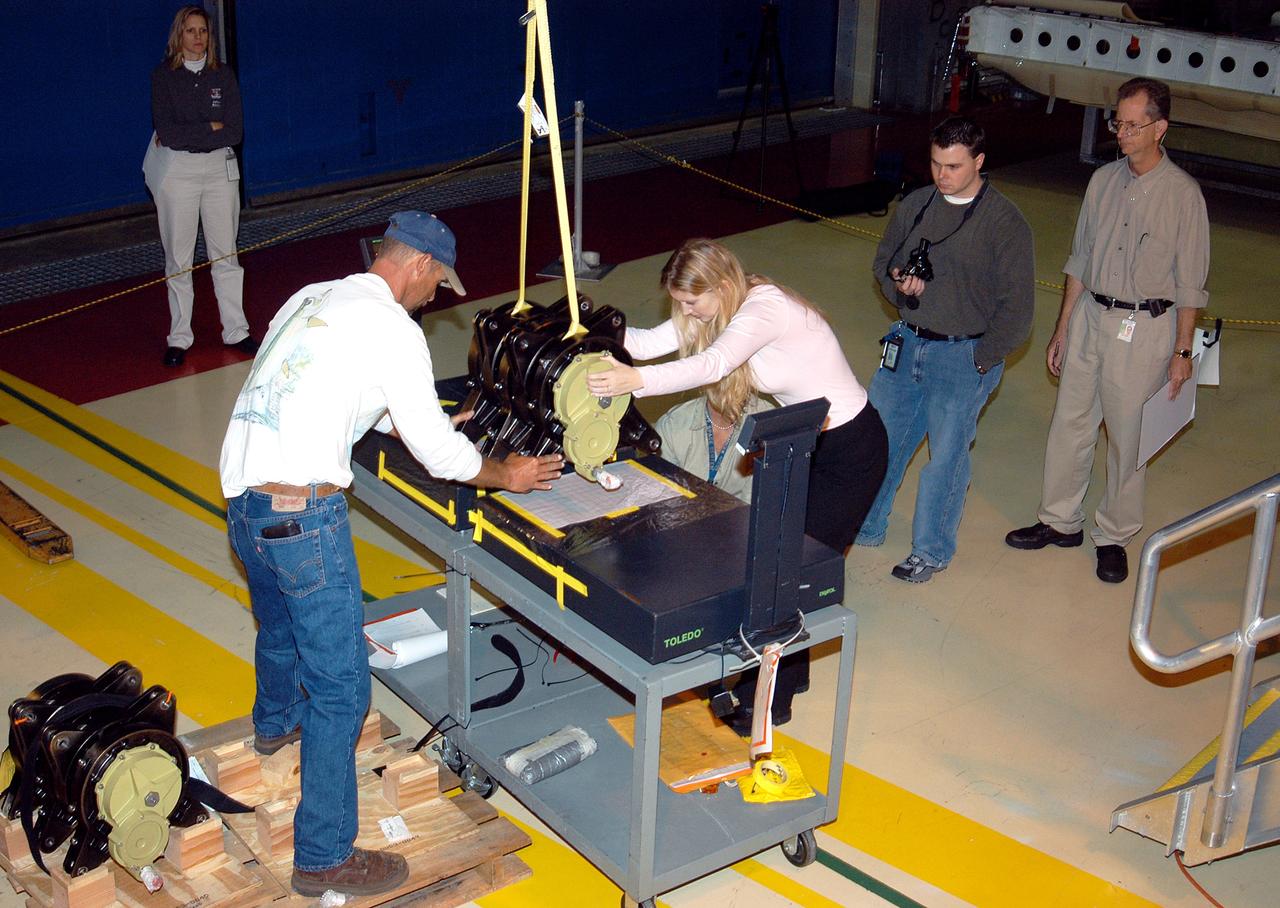

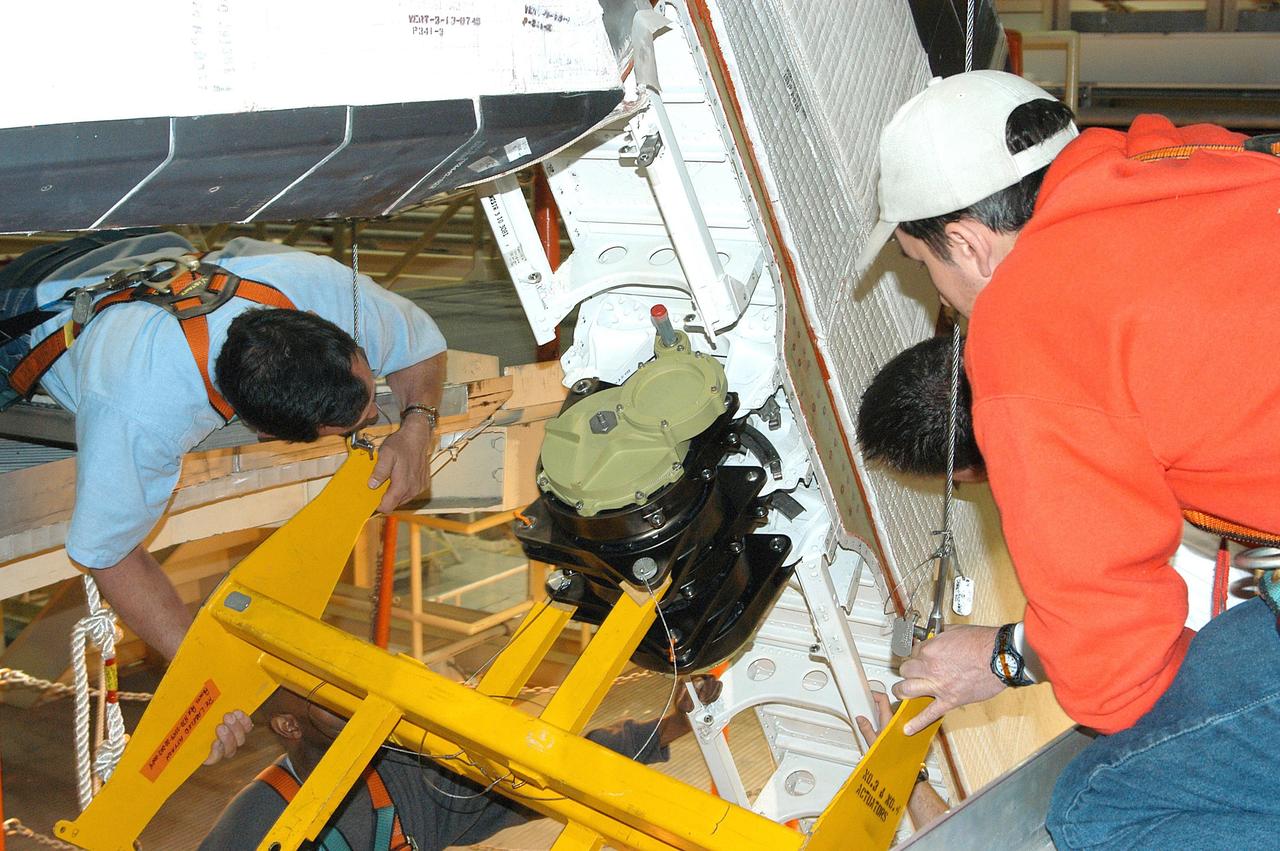
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility settle into place one of two rudder speed brake actuators onto a table to measure the alignment of its bearings. The actuators move an orbiter’s rudder, speed brake, elevons and main engines during flight.
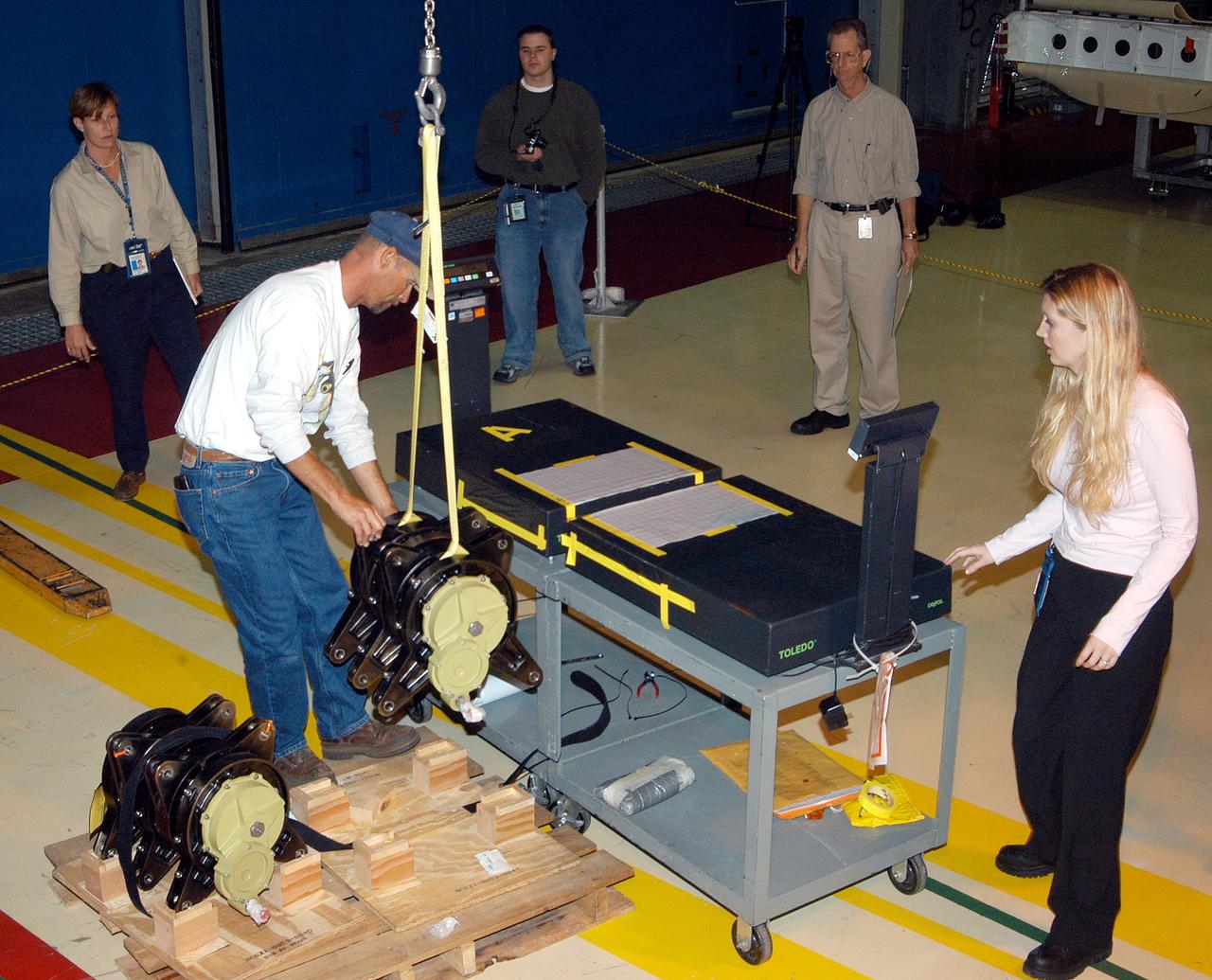

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility stand by while another guides the lifting of one of two rudder speed brake actuators onto a table to measure the alignment of its bearings. The actuators move an orbiter’s rudder, speed brake, elevons and main engines during flight.
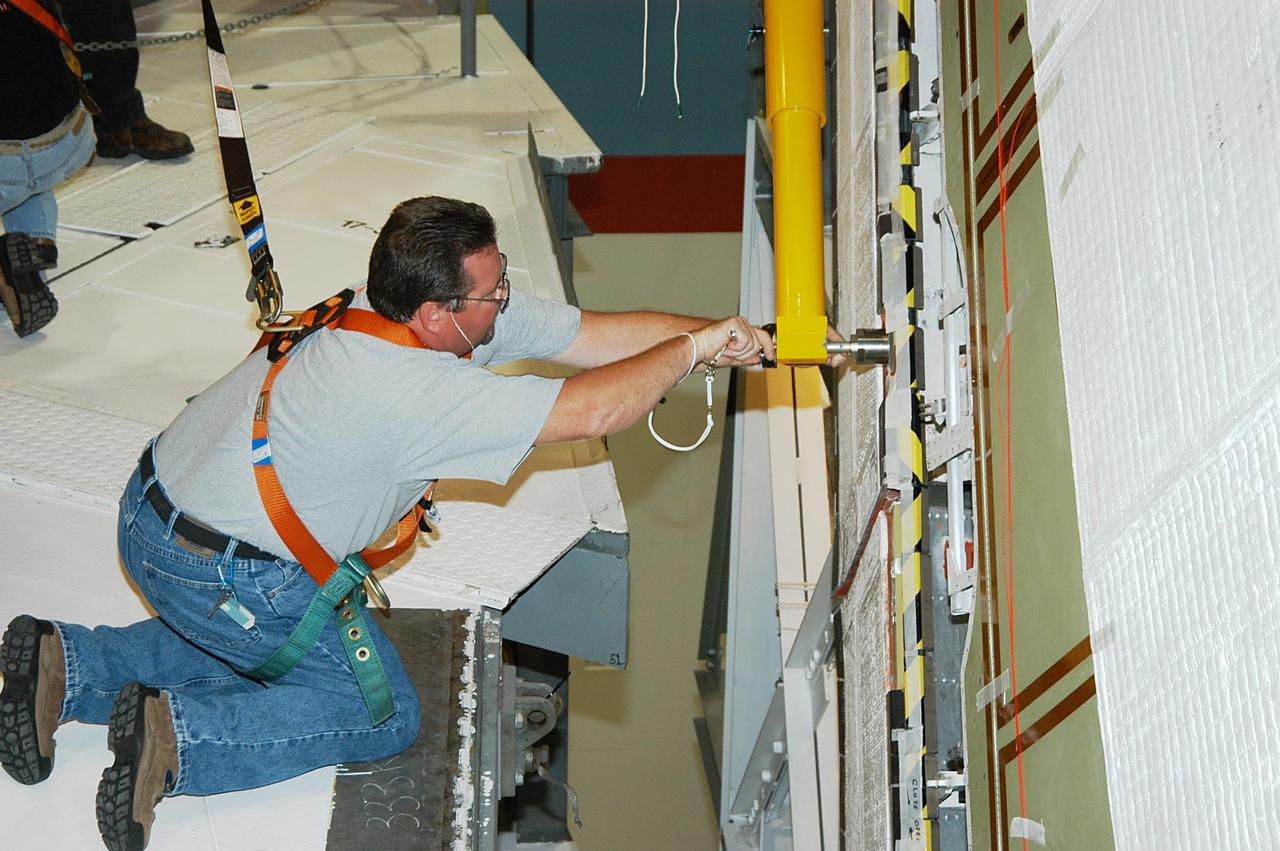

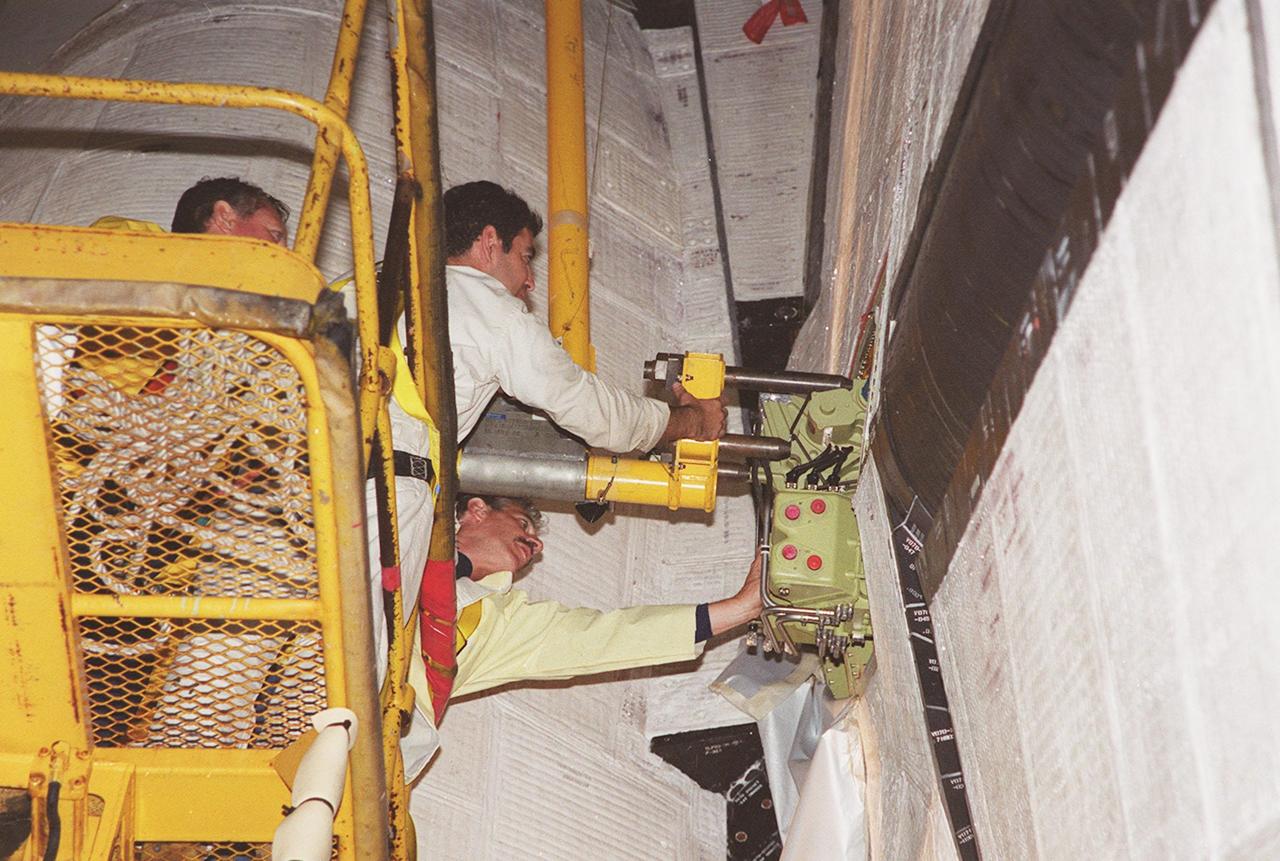
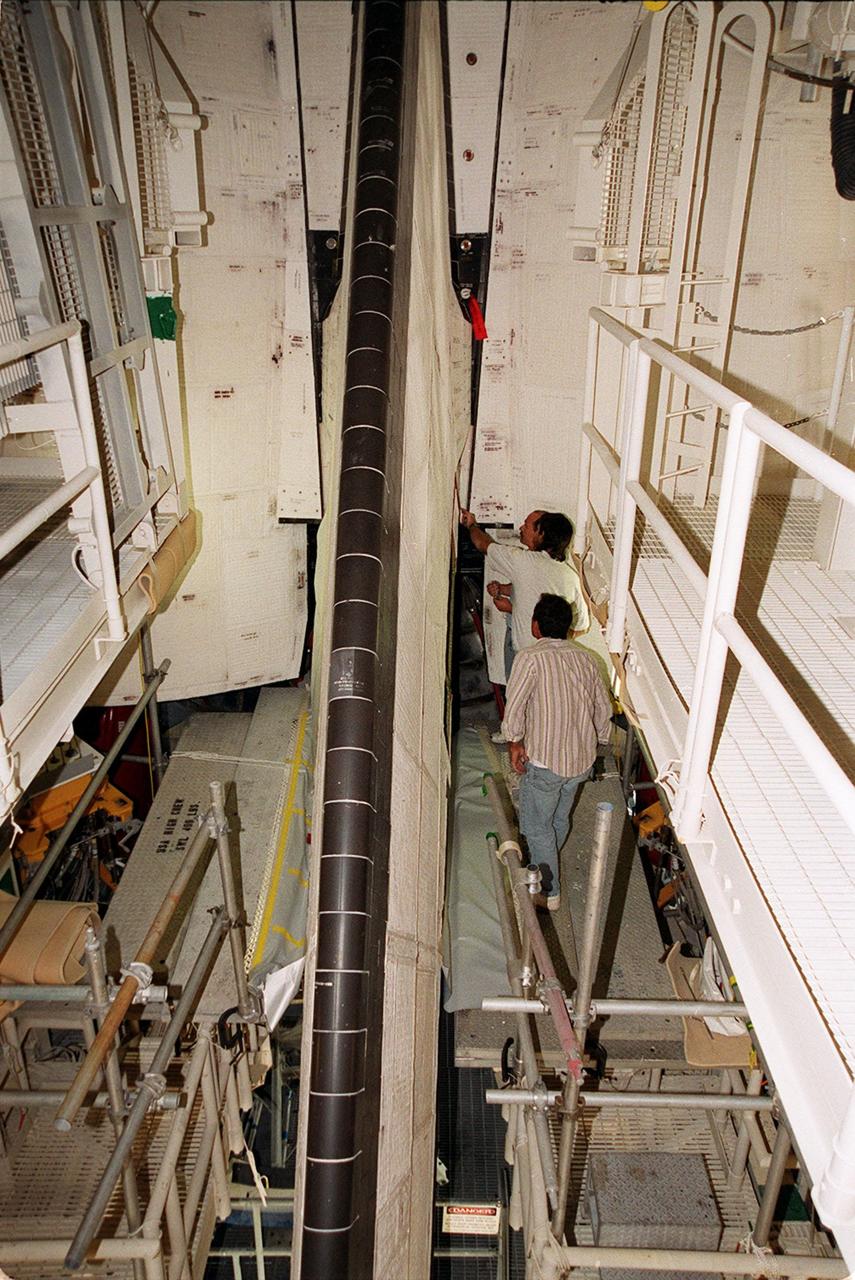
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a worker tightens a fitting on the device being used to remove the Rudder Speed Brake panel on the vertical tail of the orbiter Atlantis. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
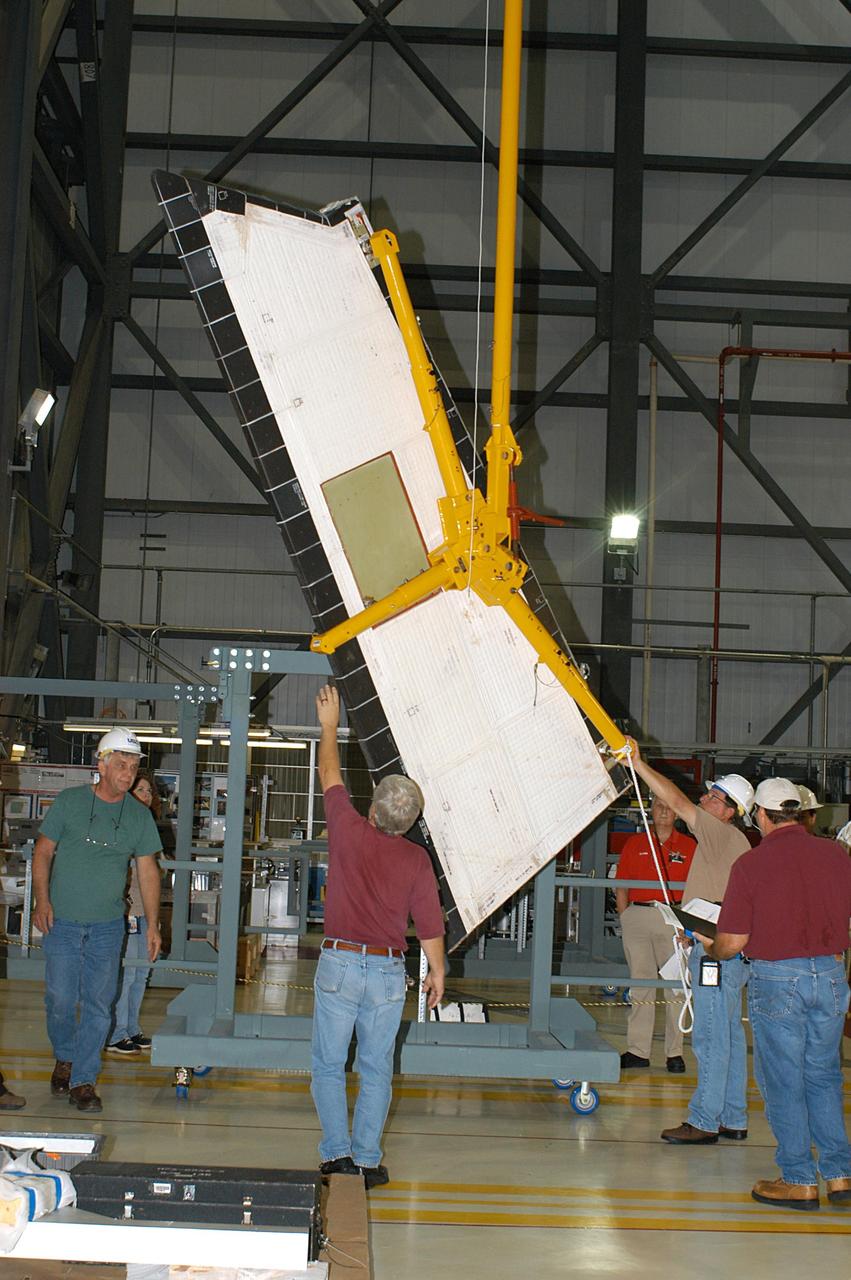

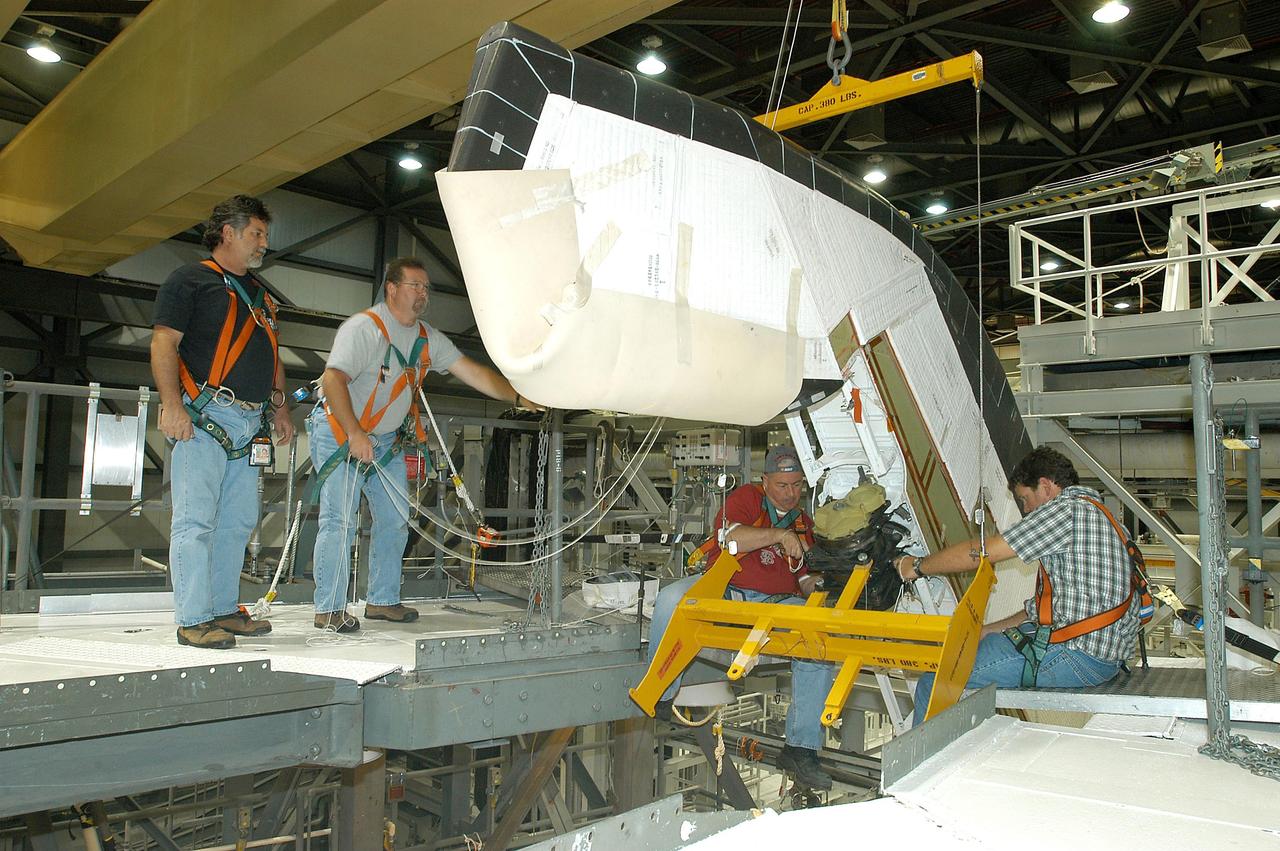
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers lower Atlantis’ Rudder Speed Brake panel toward the floor after removing the panel from the vertical tail. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers attach Atlantis’ Rudder Speed Brake panel to a stand after removing the panel from the vertical tail. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
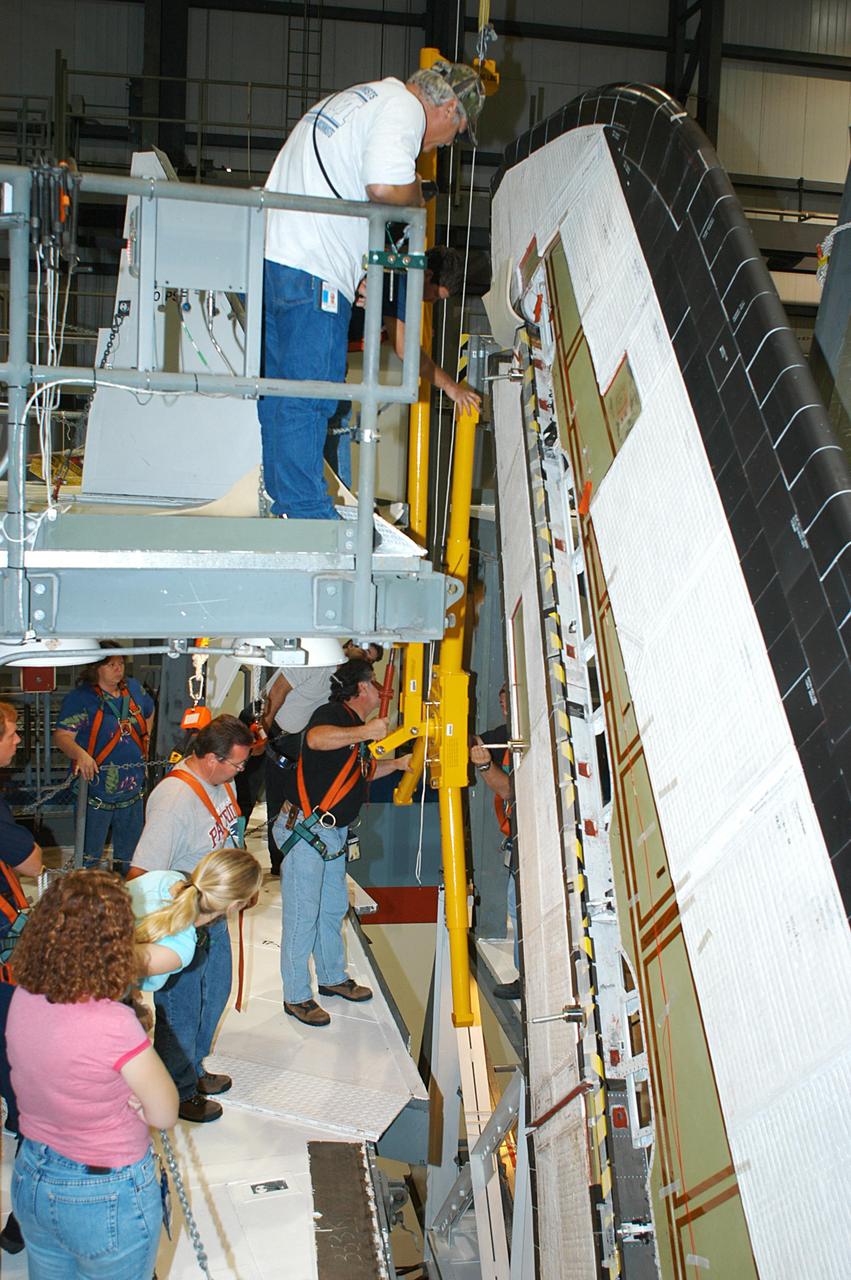

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a worker (below the upper framework) begins connecting a device to remove the Rudder Speed Brake panel on the vertical tail of orbiter Atlantis. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
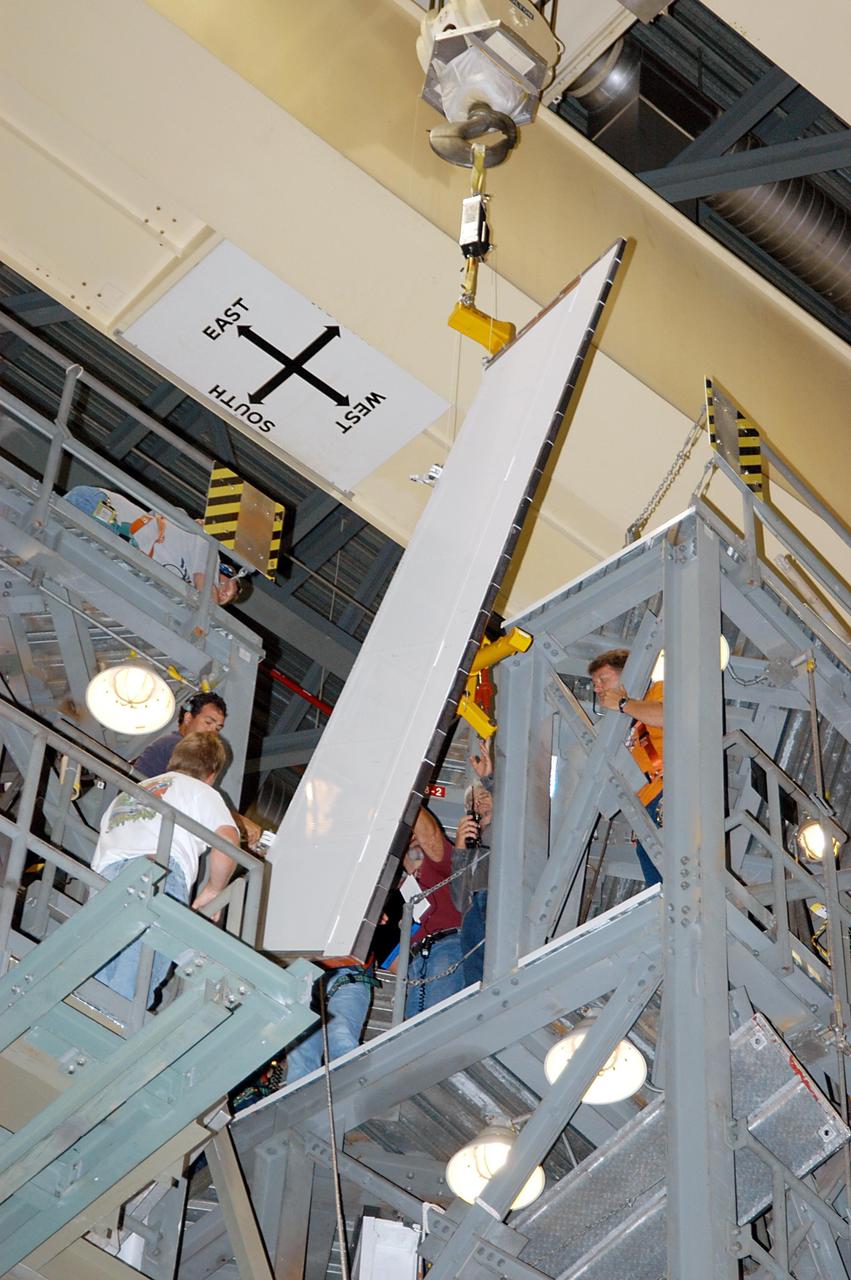

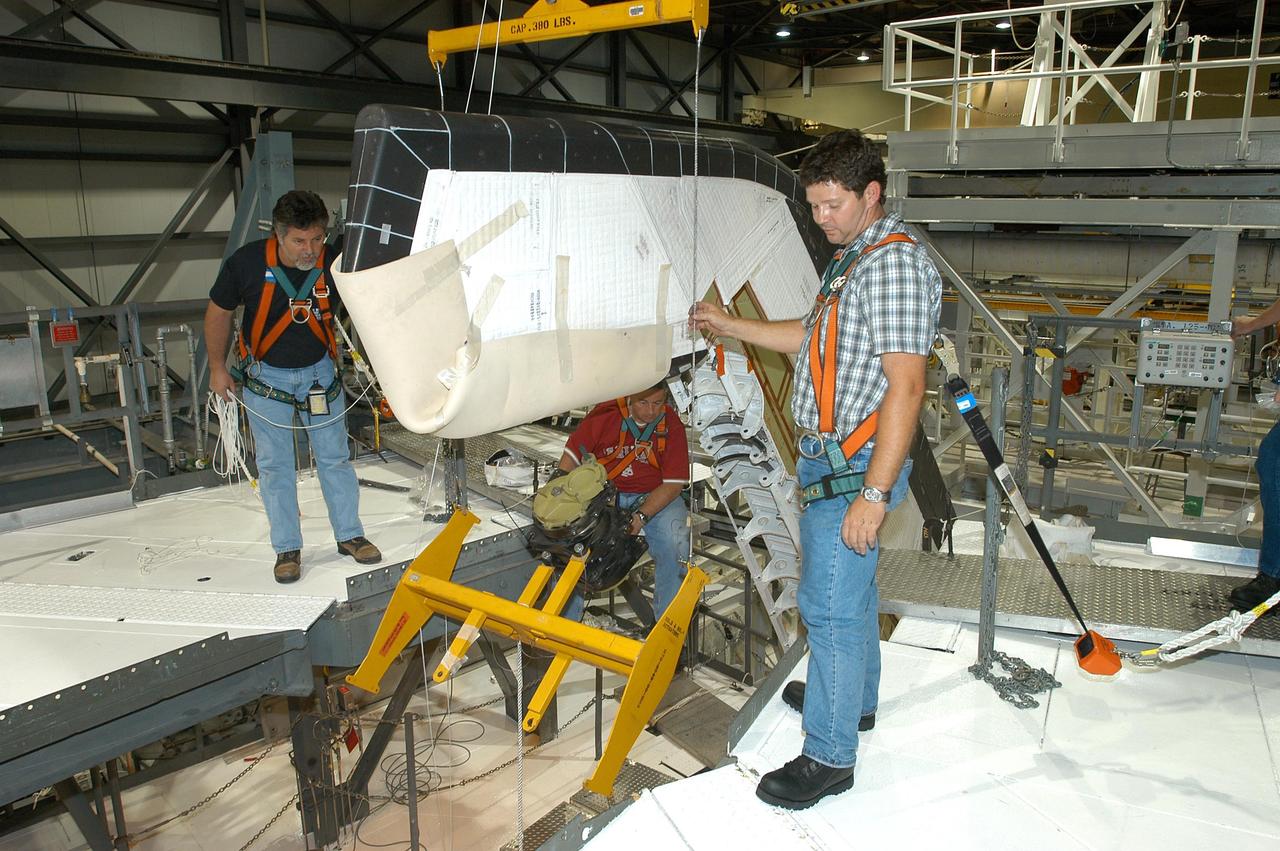
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Rudder Speed Brake panel from orbiter Atlantis is lifted clear after being removed. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
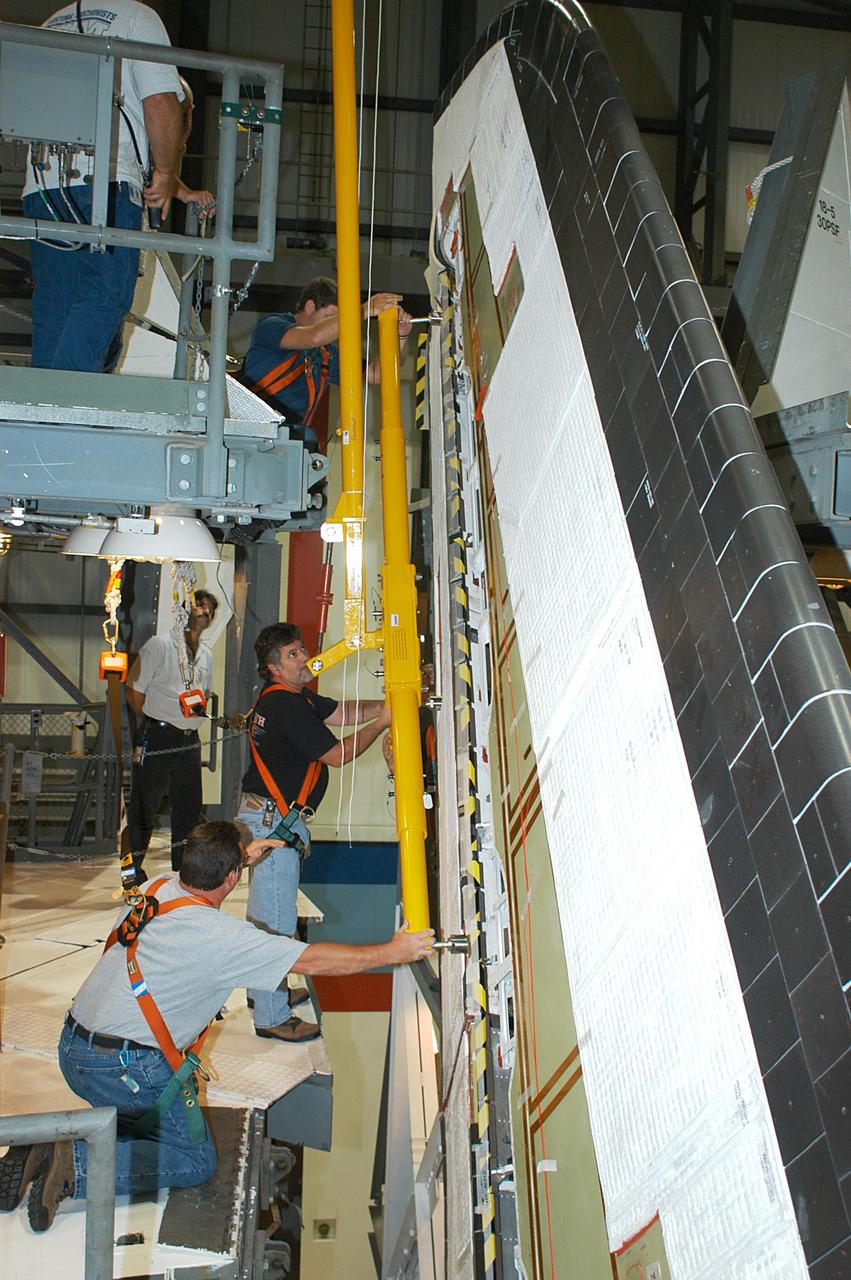

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers connect a device onto the vertical tail of the orbiter Atlantis to remove the Rudder Speed Brake panel. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
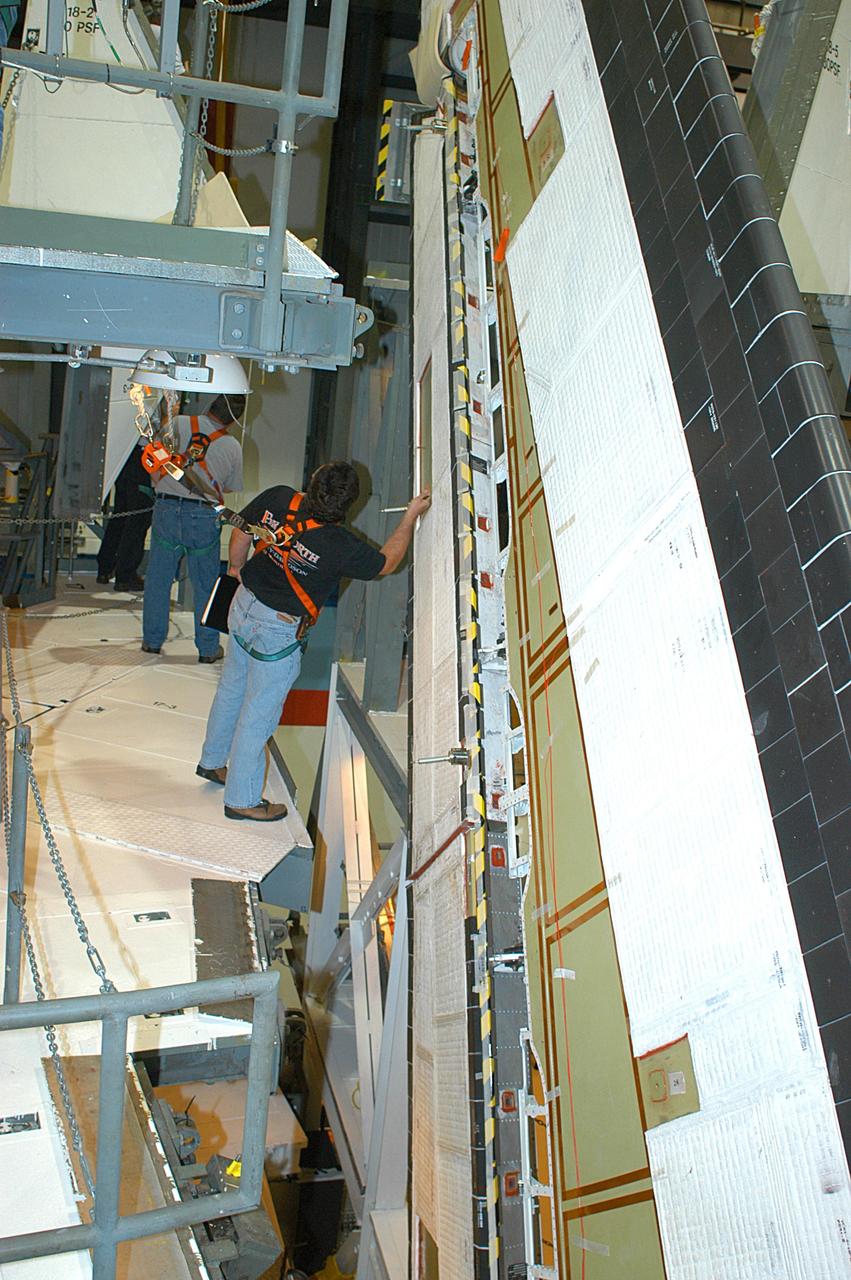

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a technician looks at the Rudder Speed Brake panel on the vertical tail of orbiter Atlantis. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
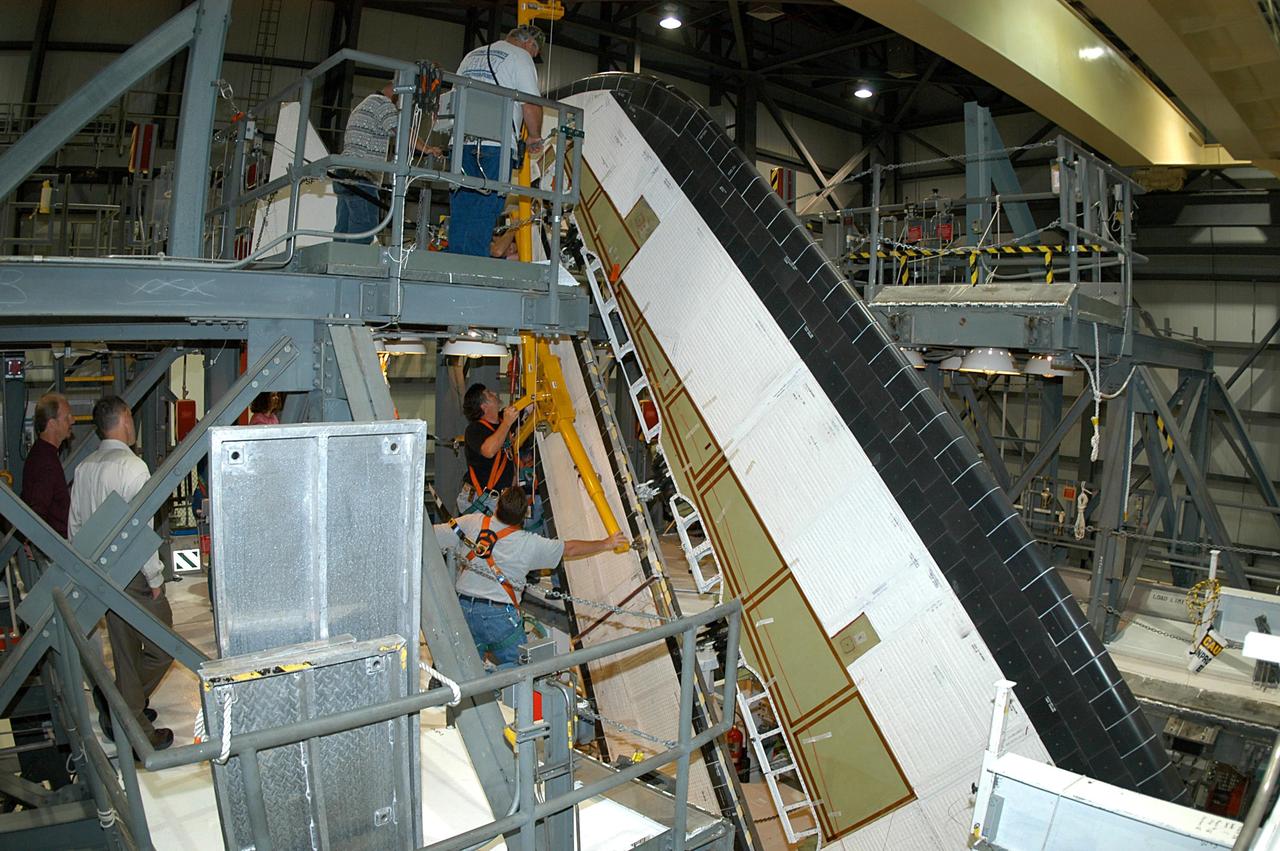

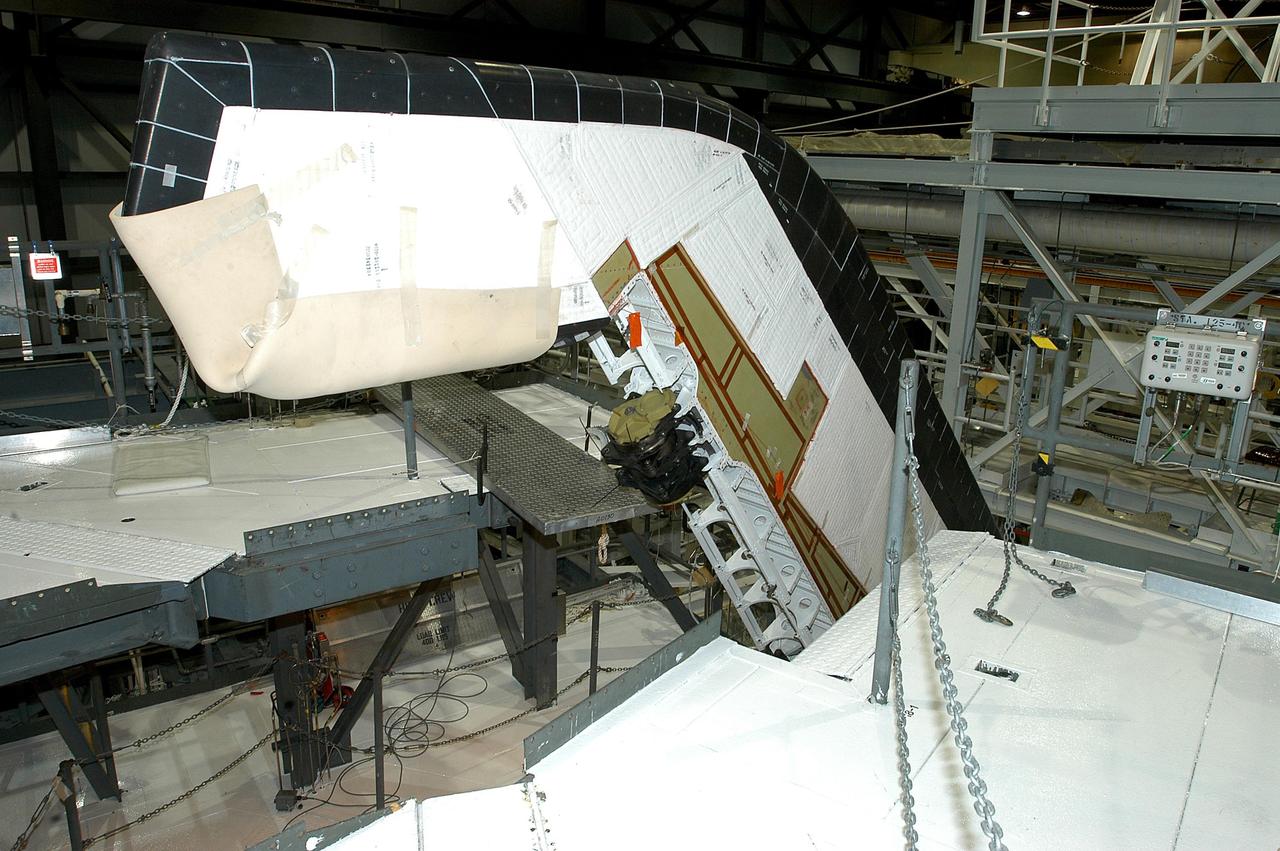
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers begin removing the Rudder Speed Brake panel on the vertical tail of the orbiter Atlantis. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
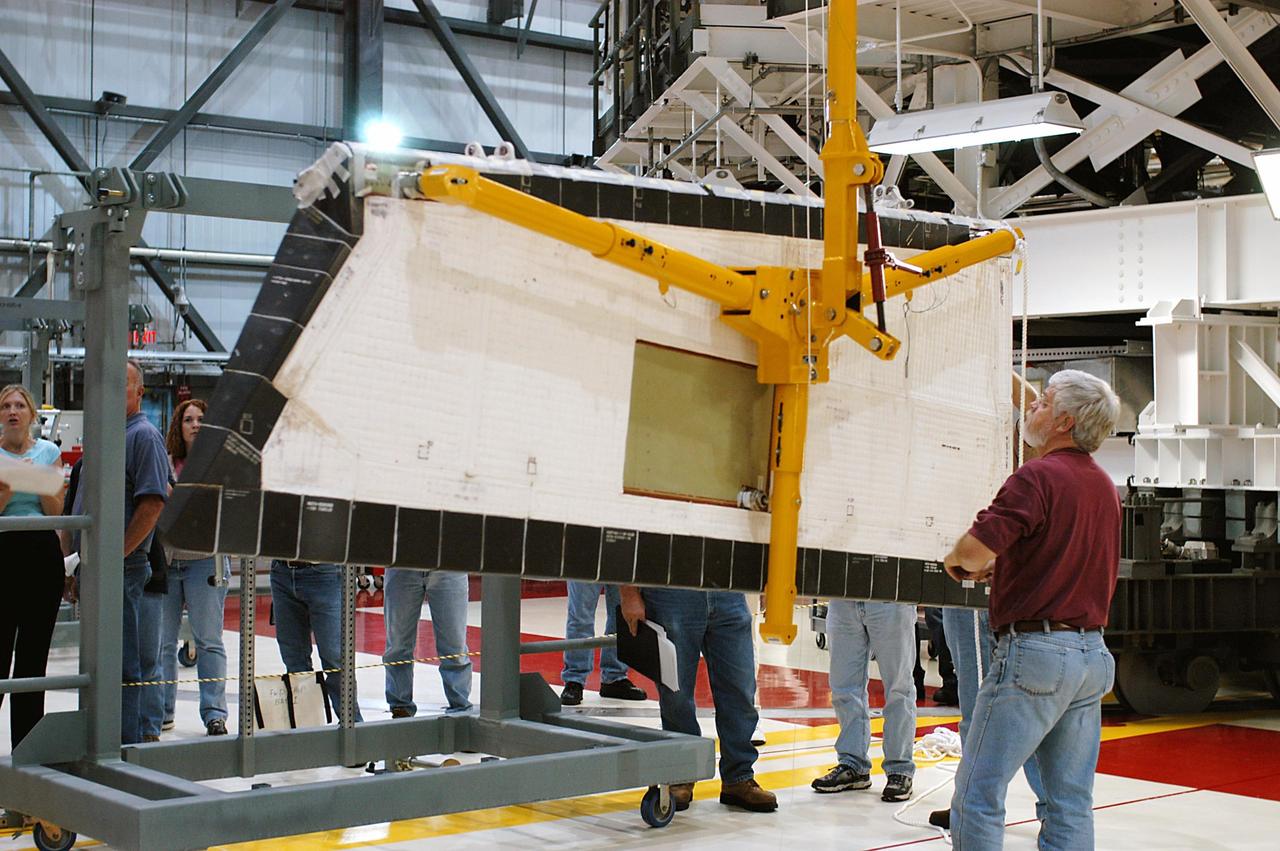

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers lower Atlantis’ Rudder Speed Brake panel onto a stand after removing the panel from the vertical tail. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
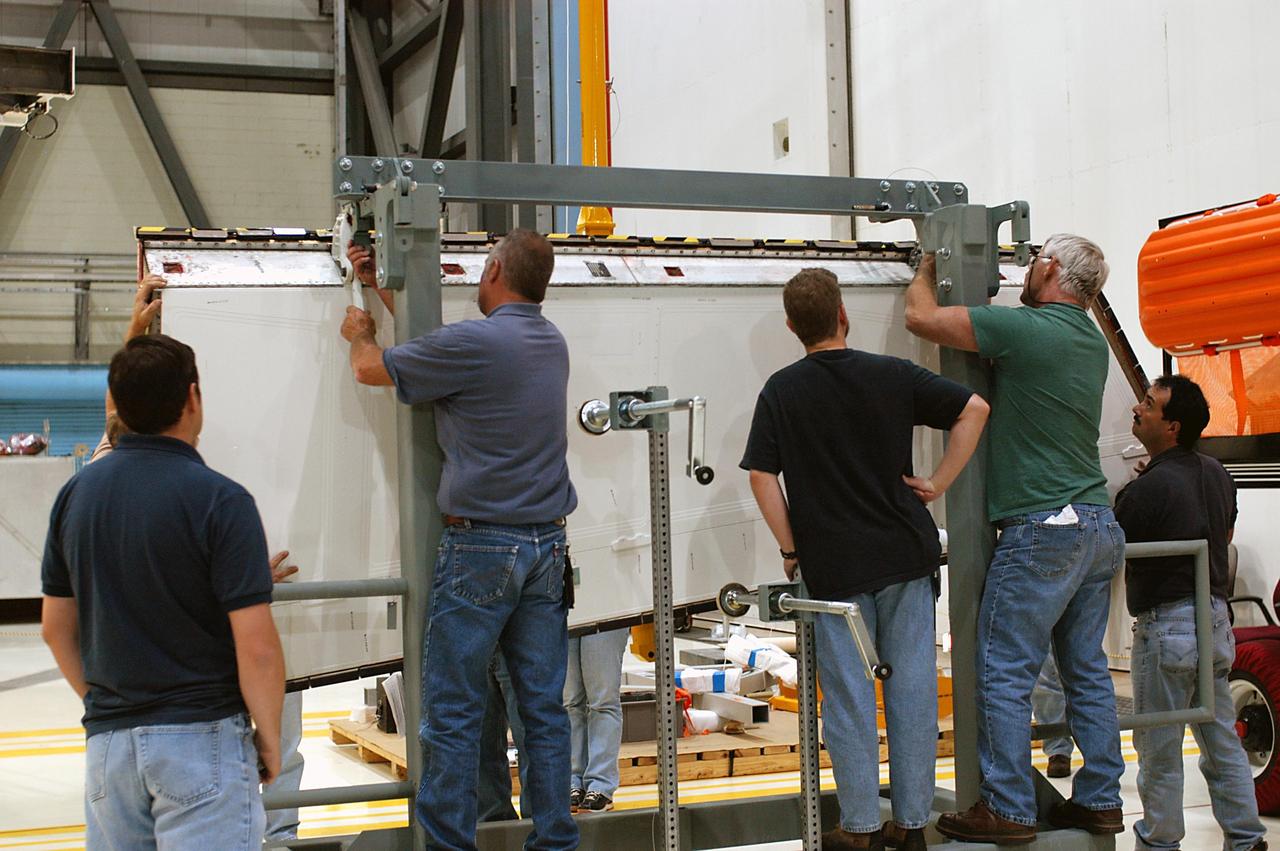

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers attach Atlantis’ Rudder Speed Brake panel to a stand after removing the panel from the vertical tail. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
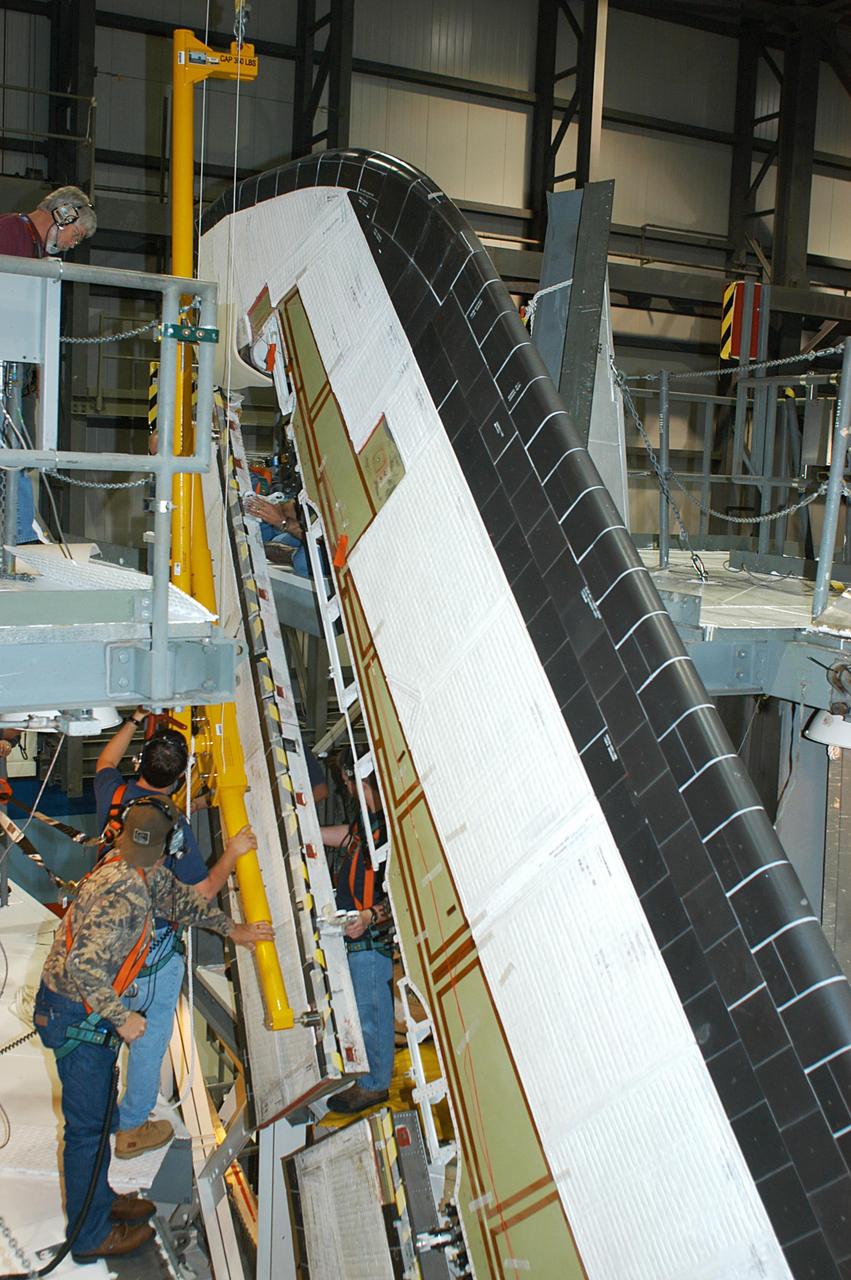

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers remove the Rudder Speed Brake panel on the vertical tail of the orbiter Atlantis. The Rudder Speed Brake is being removed for inspection and maintenance prior to Return to Flight. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. The Rudder Speed Brake is used to guide and slow the Shuttle as it comes in for a landing.
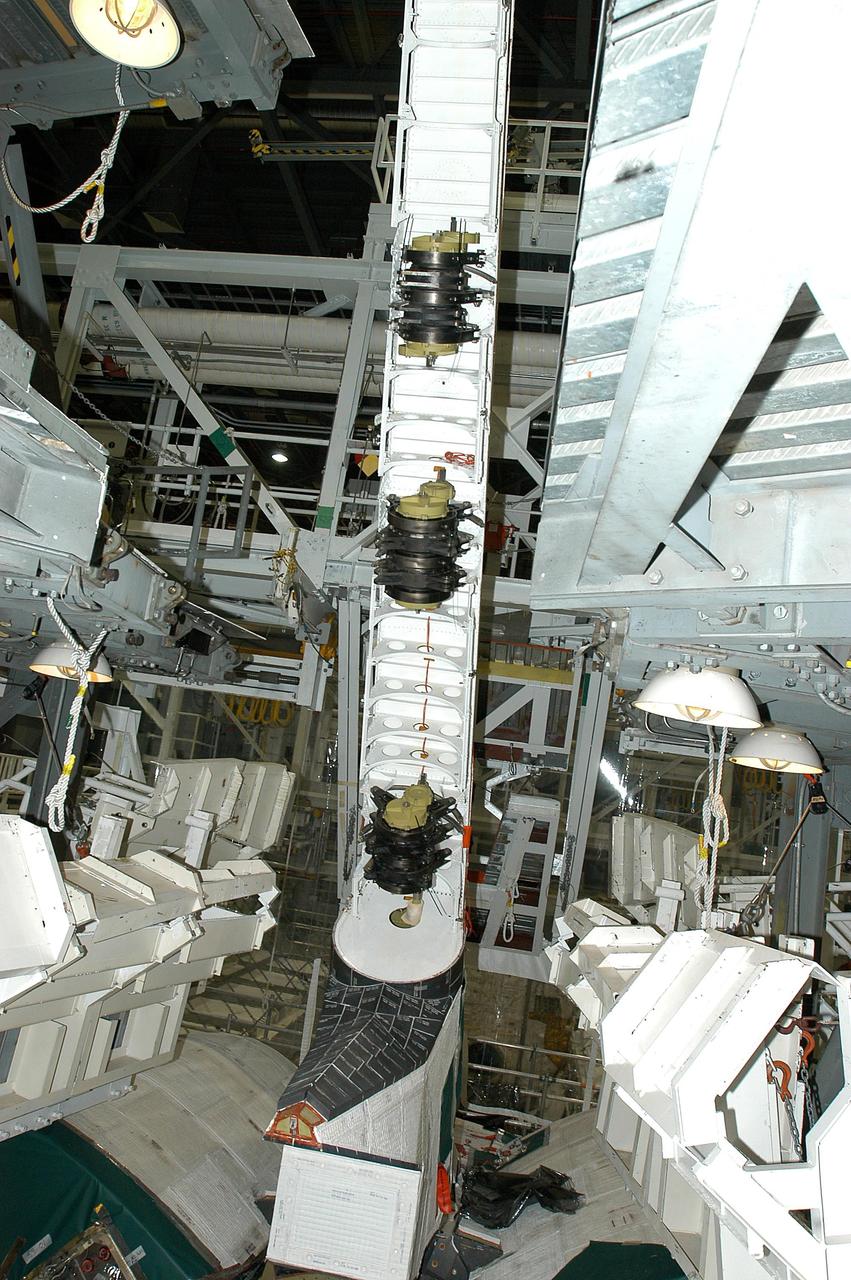

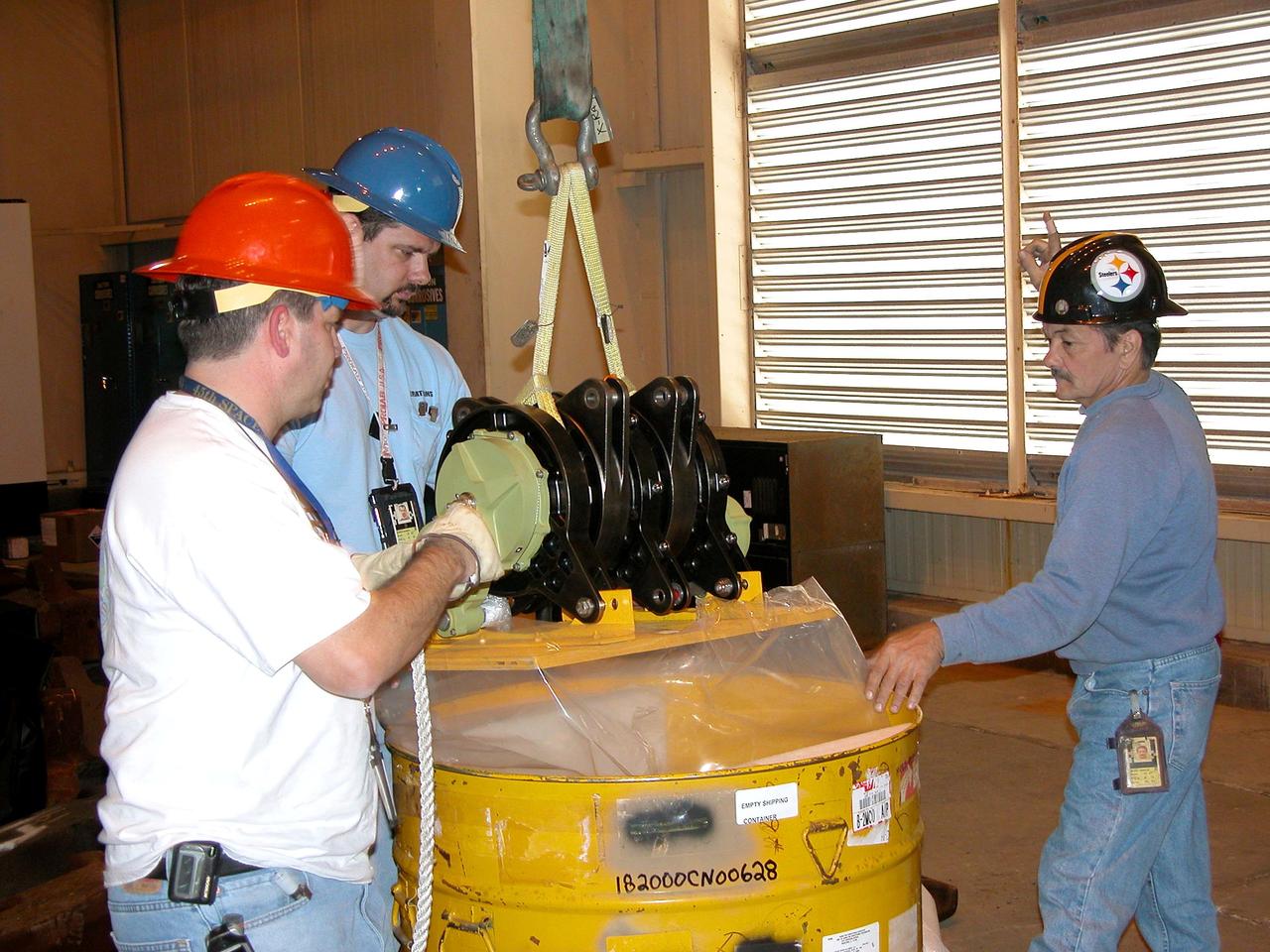
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A Rudder Speed Brake Actuator is being removed from the orbiter Atlantis for shipment to the vendor for inspection. An actuator is a motor that moves the tail rudder back and forth to help steer it during landing and brake its speed. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. Atlantis is undergoing maintenance and inspection in the Orbiter Processing Facility for a future mission.
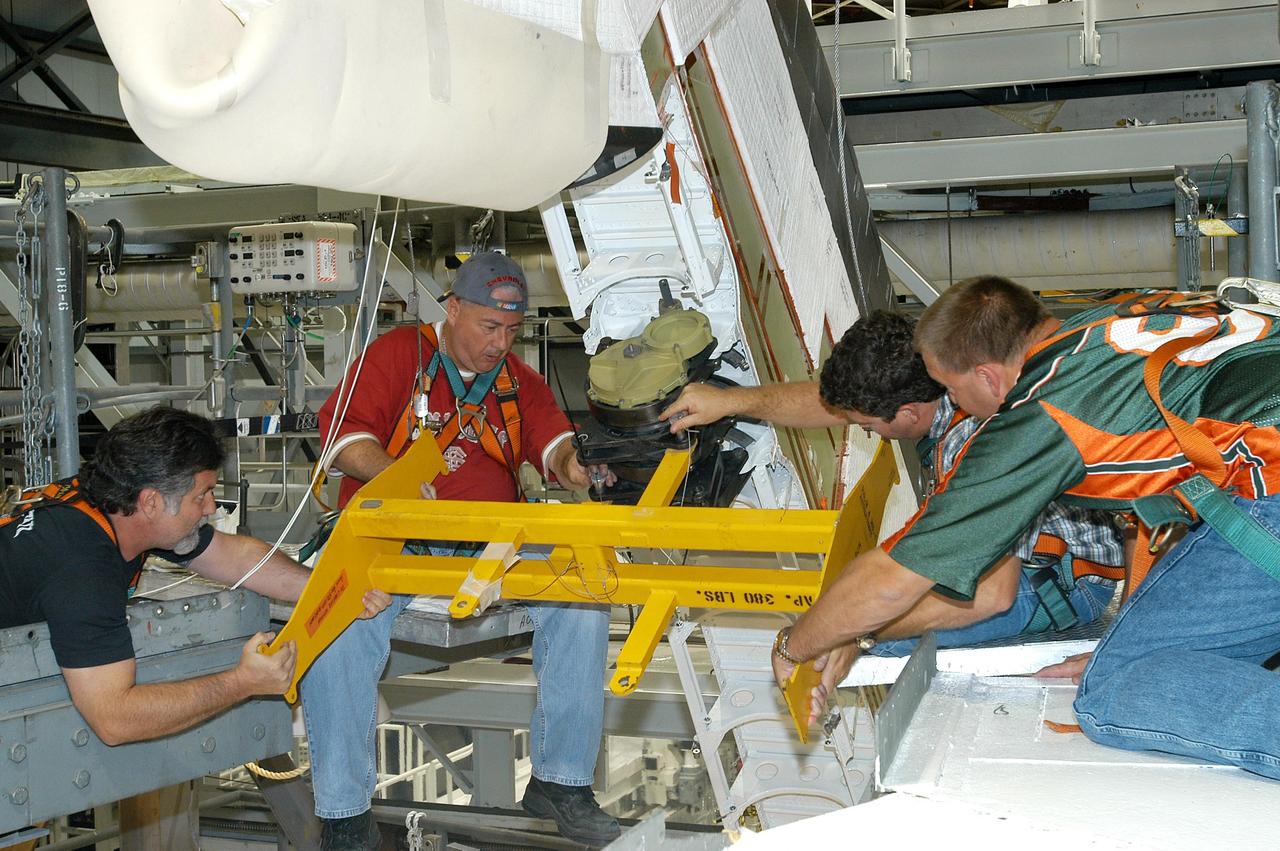

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers attach a crane to one of the Rudder Speed Brake Actuators that are being removed from the orbiter Atlantis for shipment to the vendor for inspection. An actuator is a motor that moves the tail rudder back and forth to help steer it during landing and brake its speed. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. Atlantis is undergoing maintenance and inspection in the Orbiter Processing Facility for a future mission.
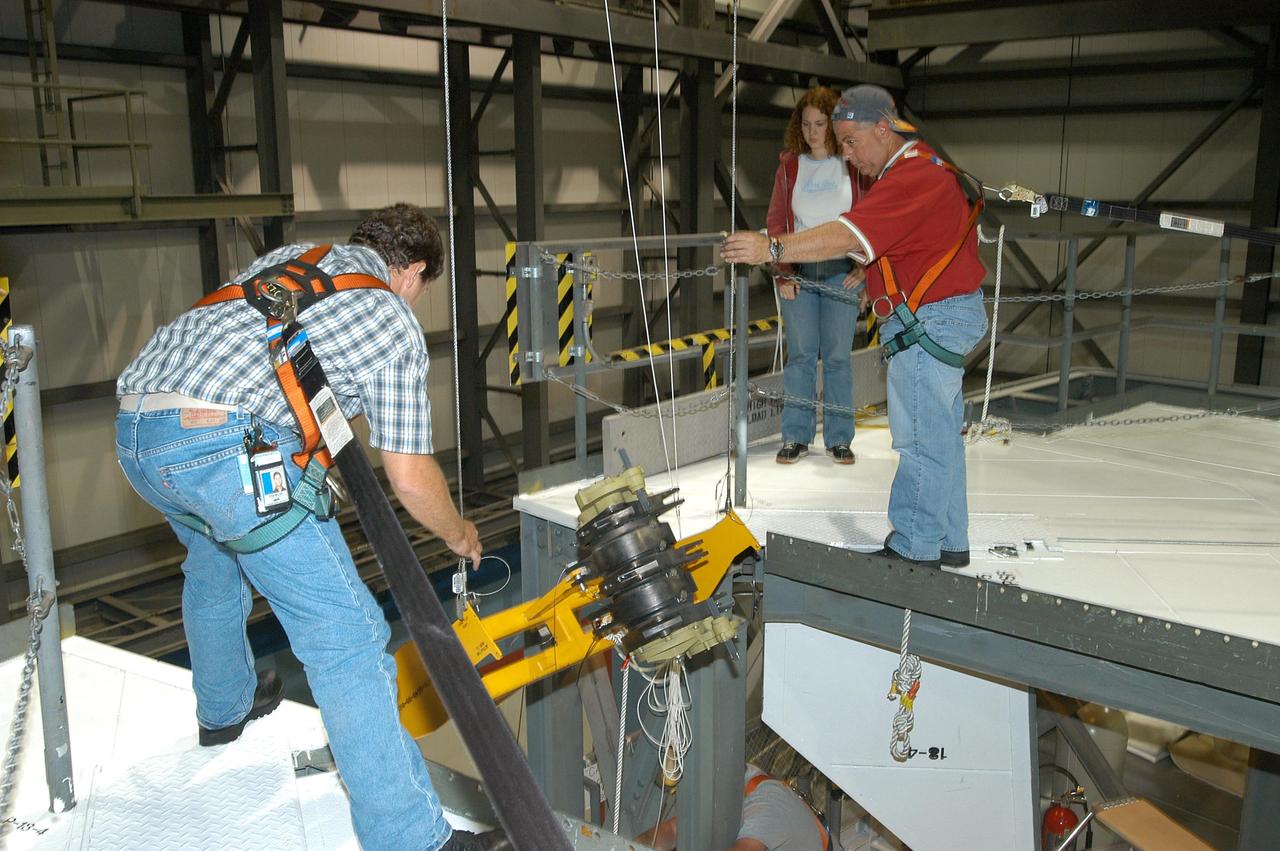

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers ensure the safe removal of a Rudder Speed Brake Actuator from the orbiter Atlantis. This and three other actuators are being shipped to the vendor for inspection. An actuator is a motor that moves the tail rudder back and forth to help steer it during landing and brake its speed. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. Atlantis is undergoing maintenance and inspection in the Orbiter Processing Facility for a future mission.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A Rudder Speed Brake Actuator is being removed from the orbiter Atlantis for shipment to the vendor for inspection. An actuator is a motor that moves the tail rudder back and forth to help steer it during landing and brake its speed. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. Atlantis is undergoing maintenance and inspection in the Orbiter Processing Facility for a future mission.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers ensure the safe removal of a Rudder Speed Brake Actuator from the orbiter Atlantis. This and three other actuators are being shipped to the vendor for inspection. An actuator is a motor that moves the tail rudder back and forth to help steer it during landing and brake its speed. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. Atlantis is undergoing maintenance and inspection in the Orbiter Processing Facility for a future mission.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A Rudder Speed Brake Actuator from the orbiter Atlantis is set on a stand on the floor of the Orbiter Processing Facility. This and three other actuators are being shipped to the vendor for inspection. An actuator is a motor that moves the tail rudder back and forth to help steer it during landing and brake its speed. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. Atlantis is undergoing maintenance and inspection for a future mission.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers attach a crane to one of the Rudder Speed Brake Actuators that are being removed from the orbiter Atlantis for shipment to the vendor for inspection. An actuator is a motor that moves the tail rudder back and forth to help steer it during landing and brake its speed. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. Atlantis is undergoing maintenance and inspection in the Orbiter Processing Facility for a future mission.
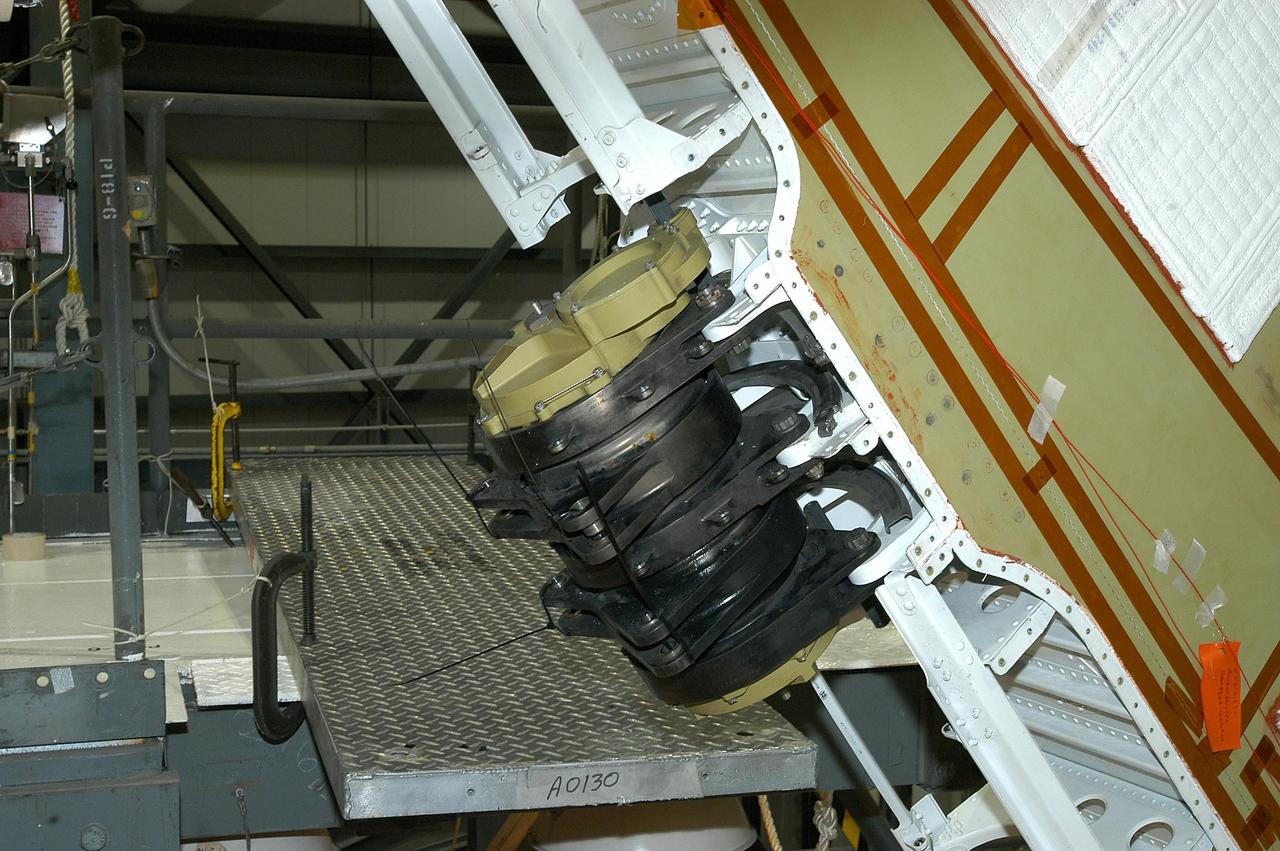

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- This is a closeup of one of the Rudder Speed Brake Actuators that are being removed from the orbiter Atlantis for shipment to the vendor for inspection. An actuator is a motor that moves the tail rudder back and forth to help steer it during landing and brake its speed. The vertical tail consists of a structural fin surface made of aluminum, the Rudder Speed Brake surface, a tip and a lower trailing edge. The rudder splits into two halves to serve as a speed brake. The vertical tail and Rudder Speed Brake are covered with a reusable thermal protection system. Atlantis is undergoing maintenance and inspection in the Orbiter Processing Facility for a future mission.
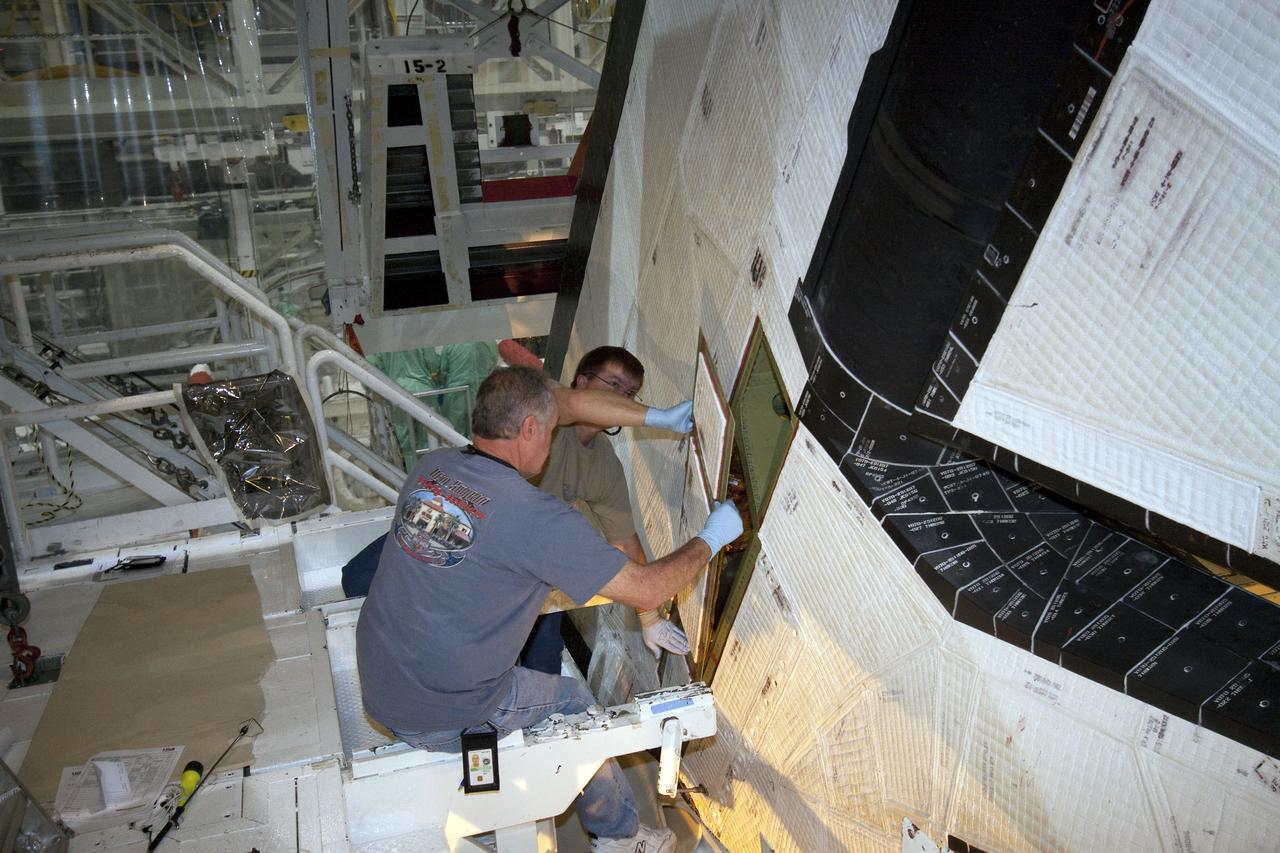

STS-132 ATLANTIS RUDDER SPEED BRAKE CLOSEOUT
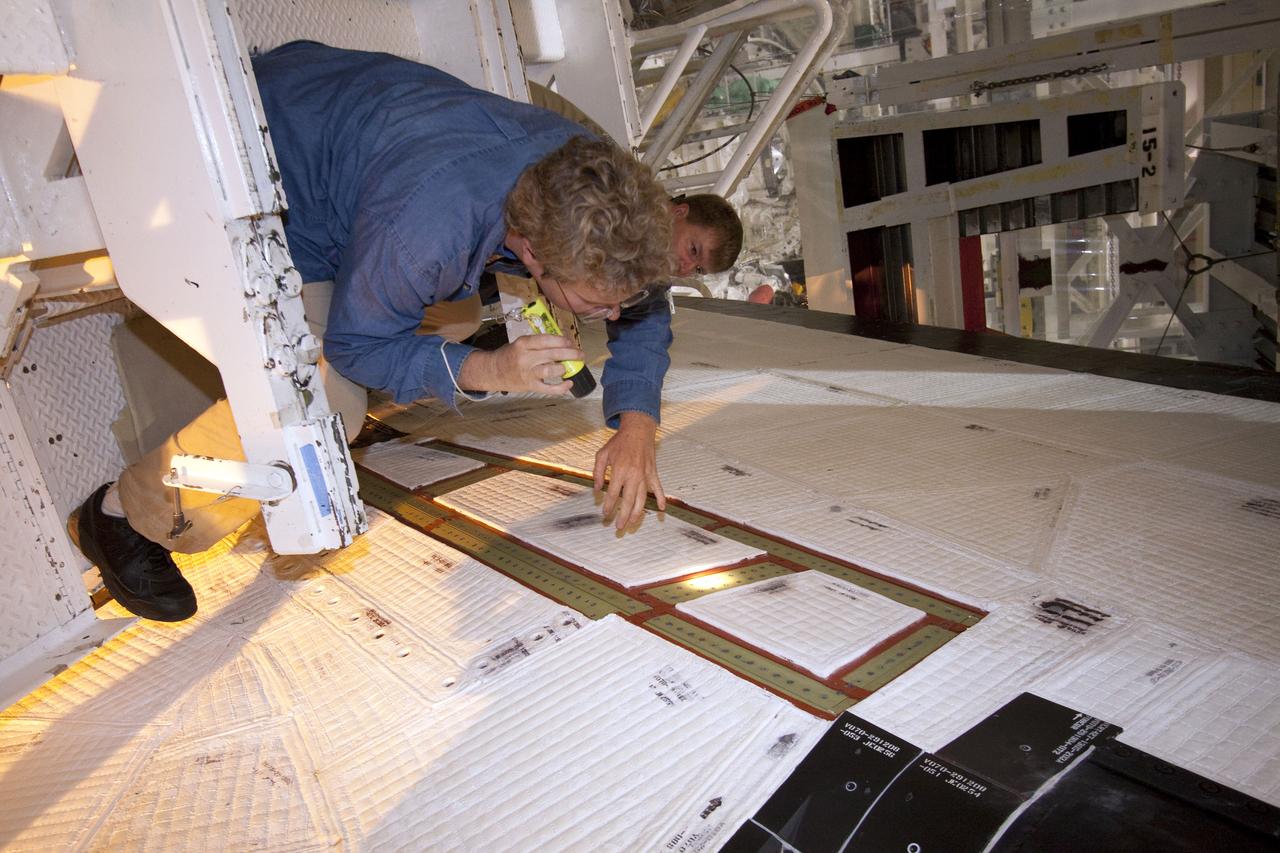

STS-132 ATLANTIS RUDDER SPEED BRAKE CLOSEOUT
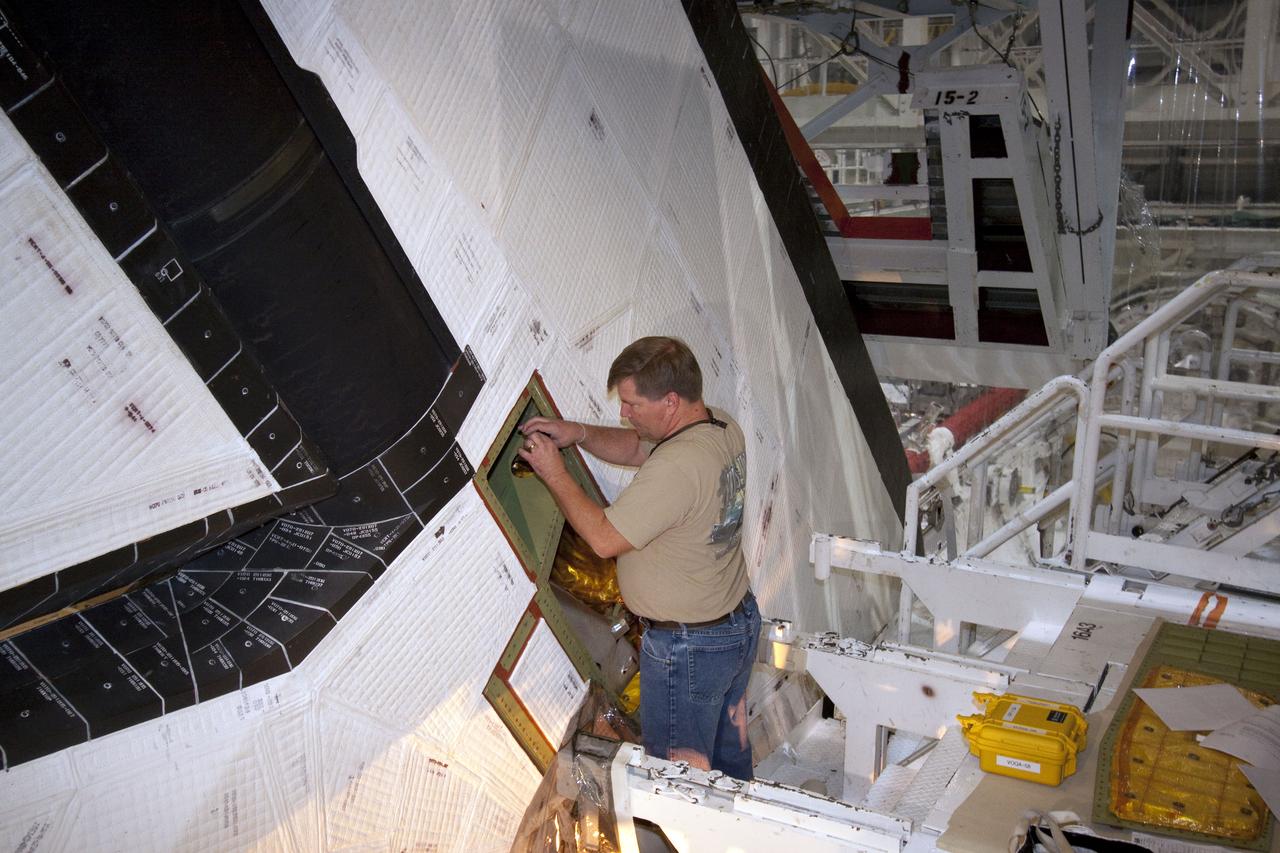

STS-132 ATLANTIS RUDDER SPEED BRAKE CLOSEOUT
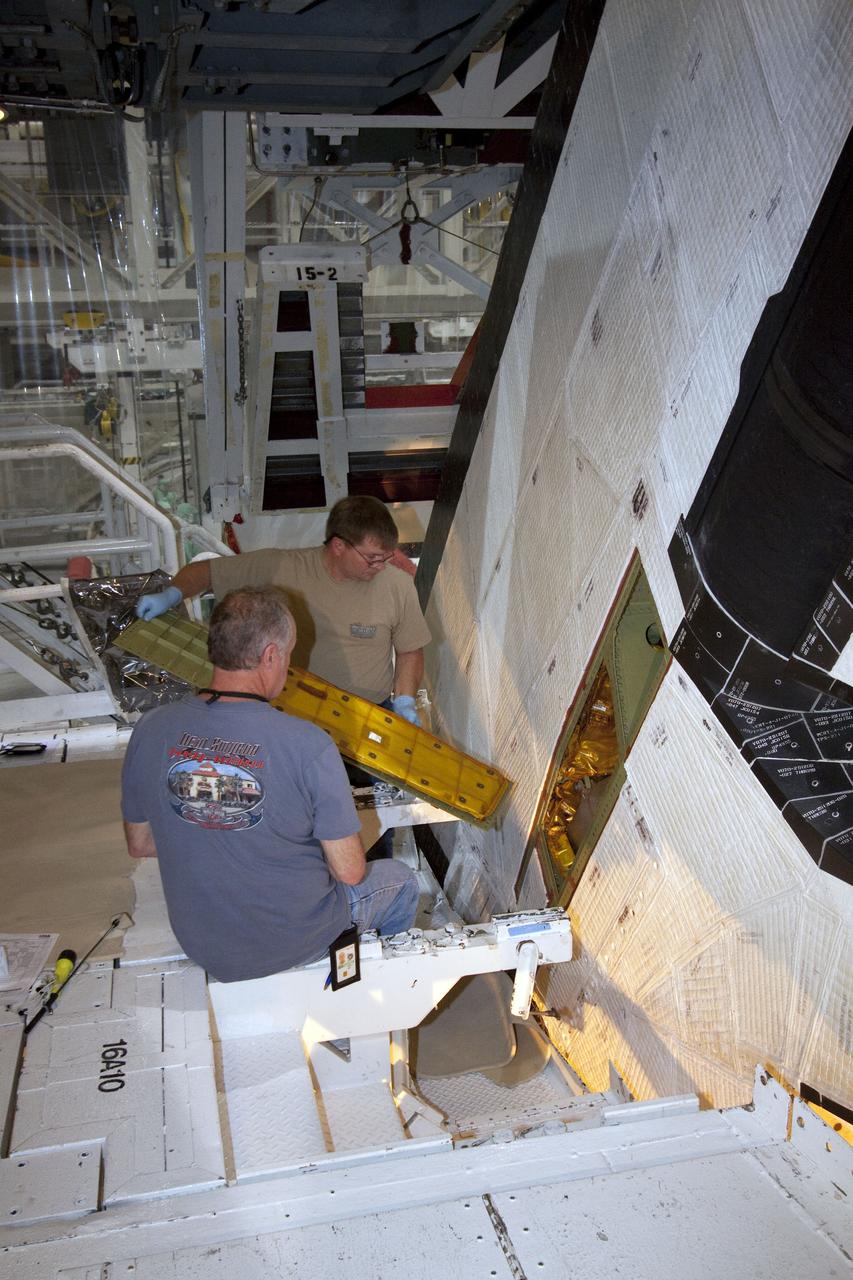

STS-132 ATLANTIS RUDDER SPEED BRAKE CLOSEOUT

Close up documentation of the Left Side Rudder Leading Edge becoming delaminated on T-38A, NASA 962, on Dec. 6, 1983.
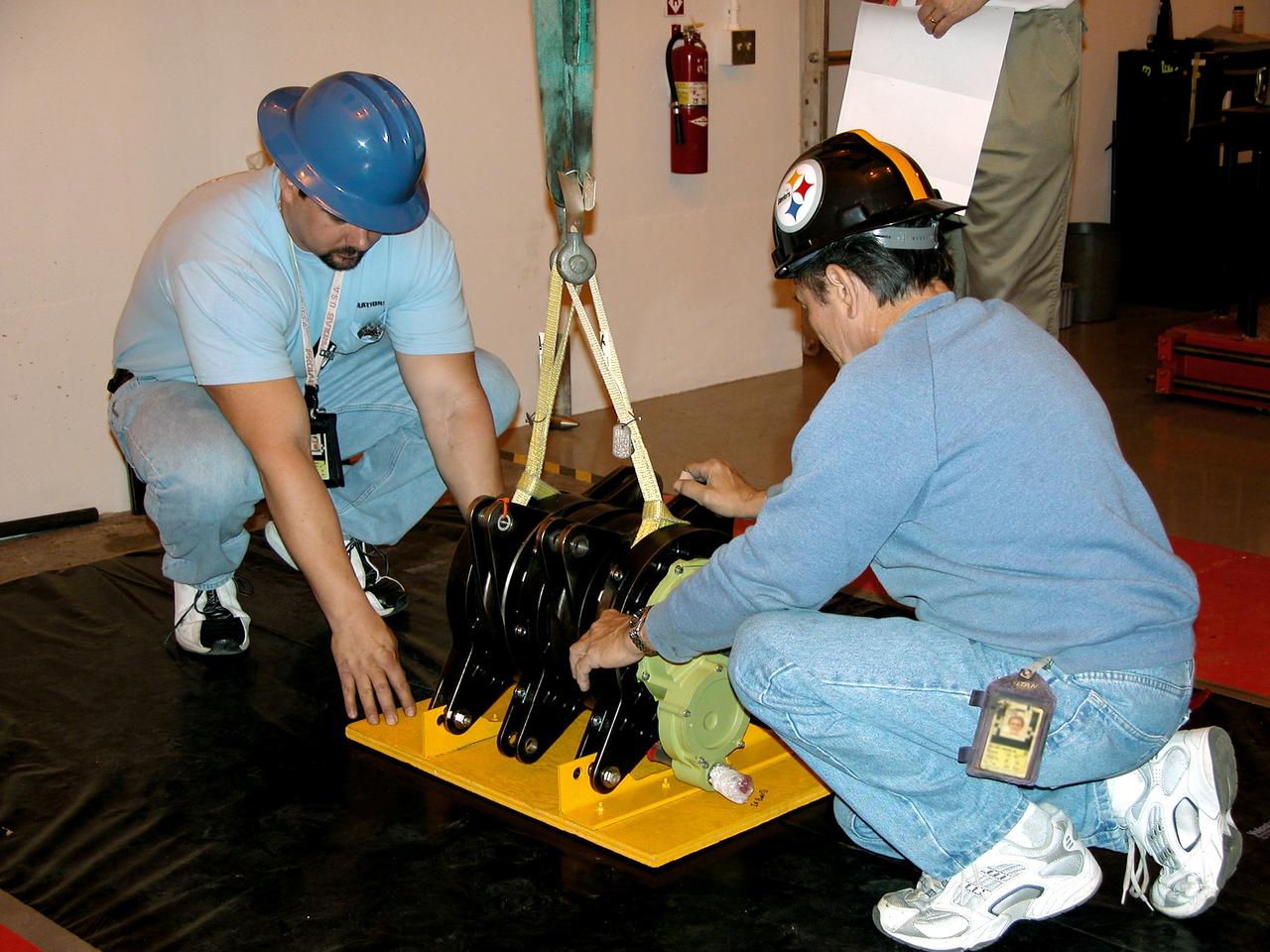

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station place one of four rudder speed brake actuators onto a pallet for X-ray. The actuators, to be installed on the orbiter Discovery, are being X-rayed at the Radiographic High-Energy X-ray Facility to determine if the gears were installed correctly. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.
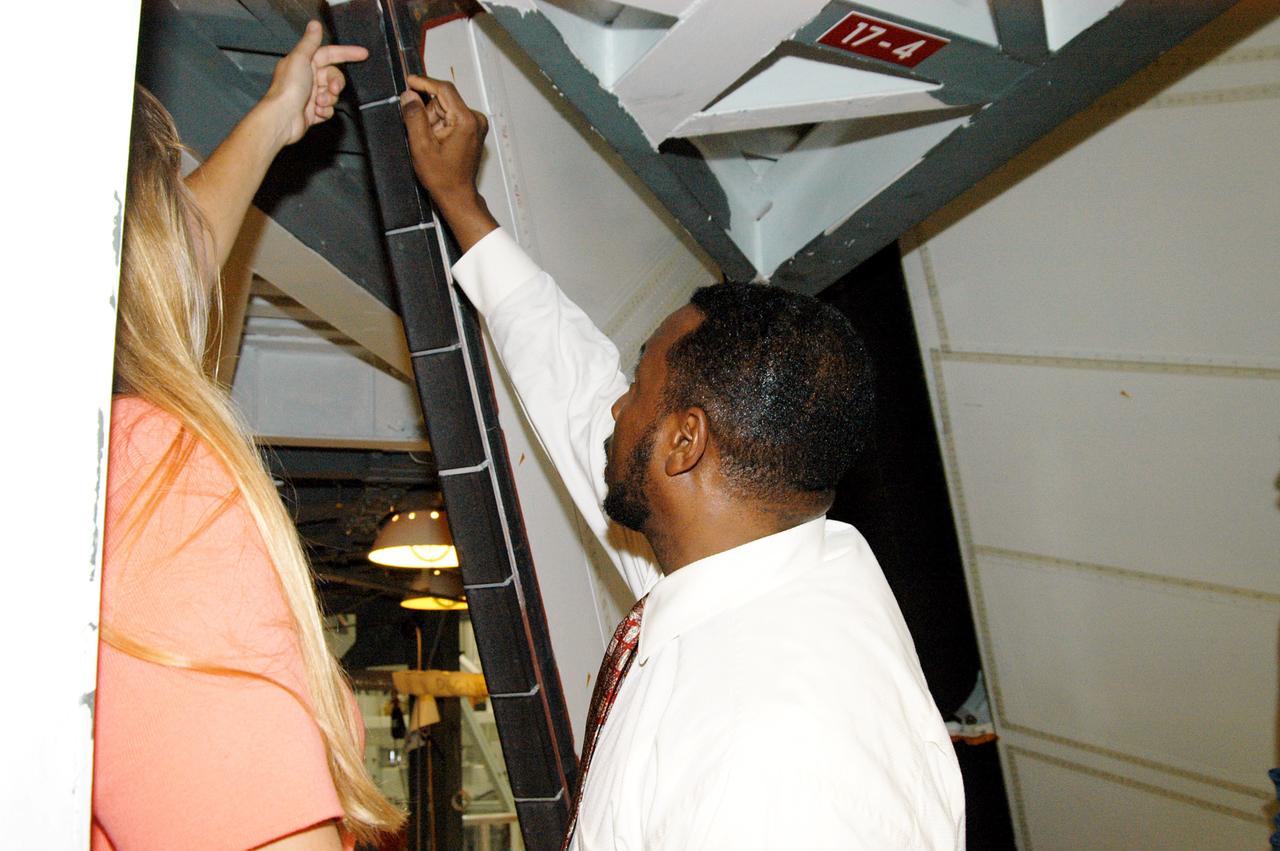

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On a tour of the Orbiter Processing Facility, Kathy Laufenberg (left) directs the attention of Deputy Director Woodrow Whitlow Jr. to an area on a rudder speed brake panel on Endeavour. The Center Director, Jim Kennedy, and Whitlow are on a tour of the Orbiter Processing Facility. Endeavour is in its Orbiter Major Modification period, which began in December 2003.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A rudder speed brake actuator sits on an air-bearing pallet to undergo X-raying. Four actuators to be installed on the orbiter Discovery are being X-rayed at the Radiographic High-Energy X-ray Facility to determine if the gears were installed correctly. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - One of four rudder speed brake actuators arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The actuators, to be installed on the orbiter Discovery, are being X-rayed at the Radiographic High-Energy X-ray Facility to determine if the gears were installed correctly. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.
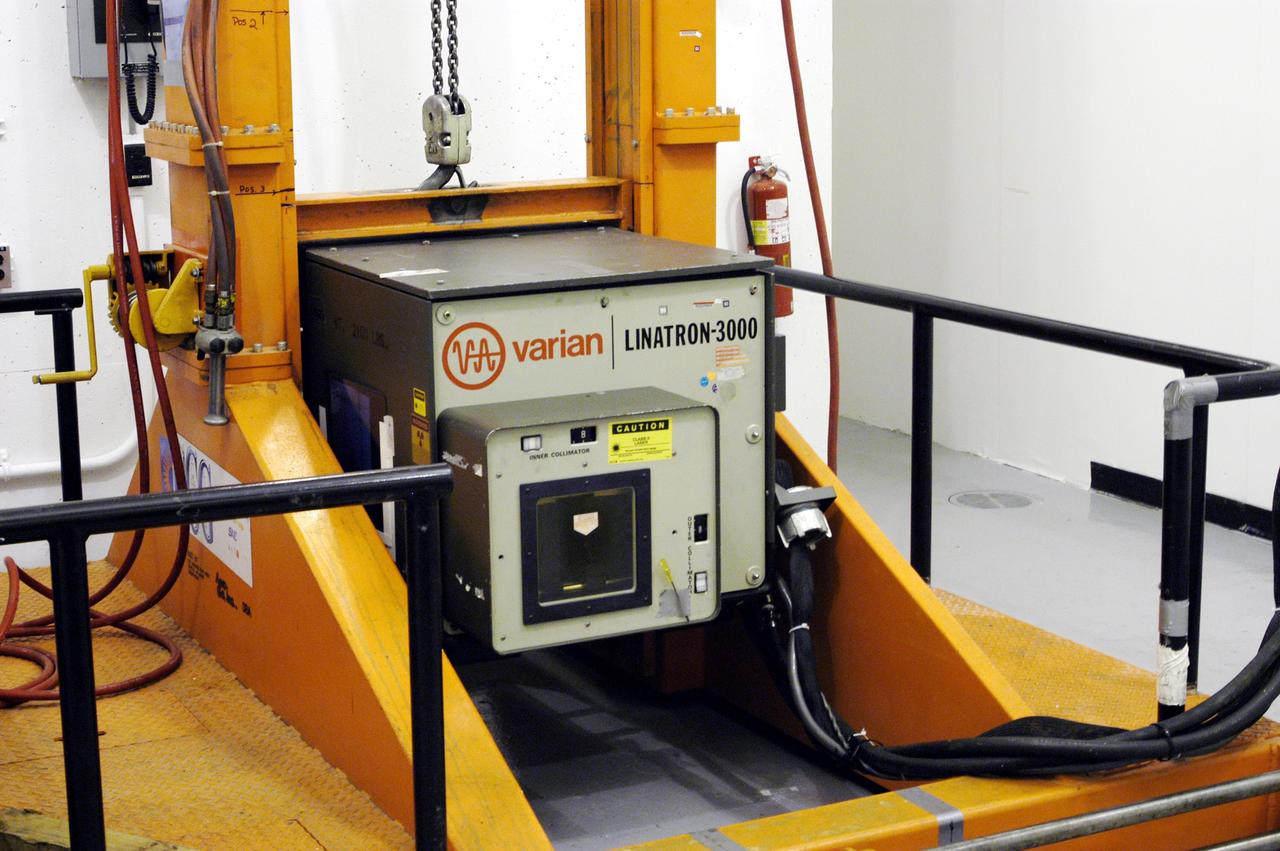

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An X-ray machine is in place to take images of four rudder speed brake actuators to be installed on the orbiter Discovery. The actuators are being X-rayed at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Radiographic High-Energy X-ray Facility to determine if the gears were installed correctly. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A rudder speed brake actuator sits on an air-bearing pallet to undergo X-raying. Four actuators to be installed on the orbiter Discovery are being X-rayed at the Radiographic High-Energy X-ray Facility to determine if the gears were installed correctly. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.
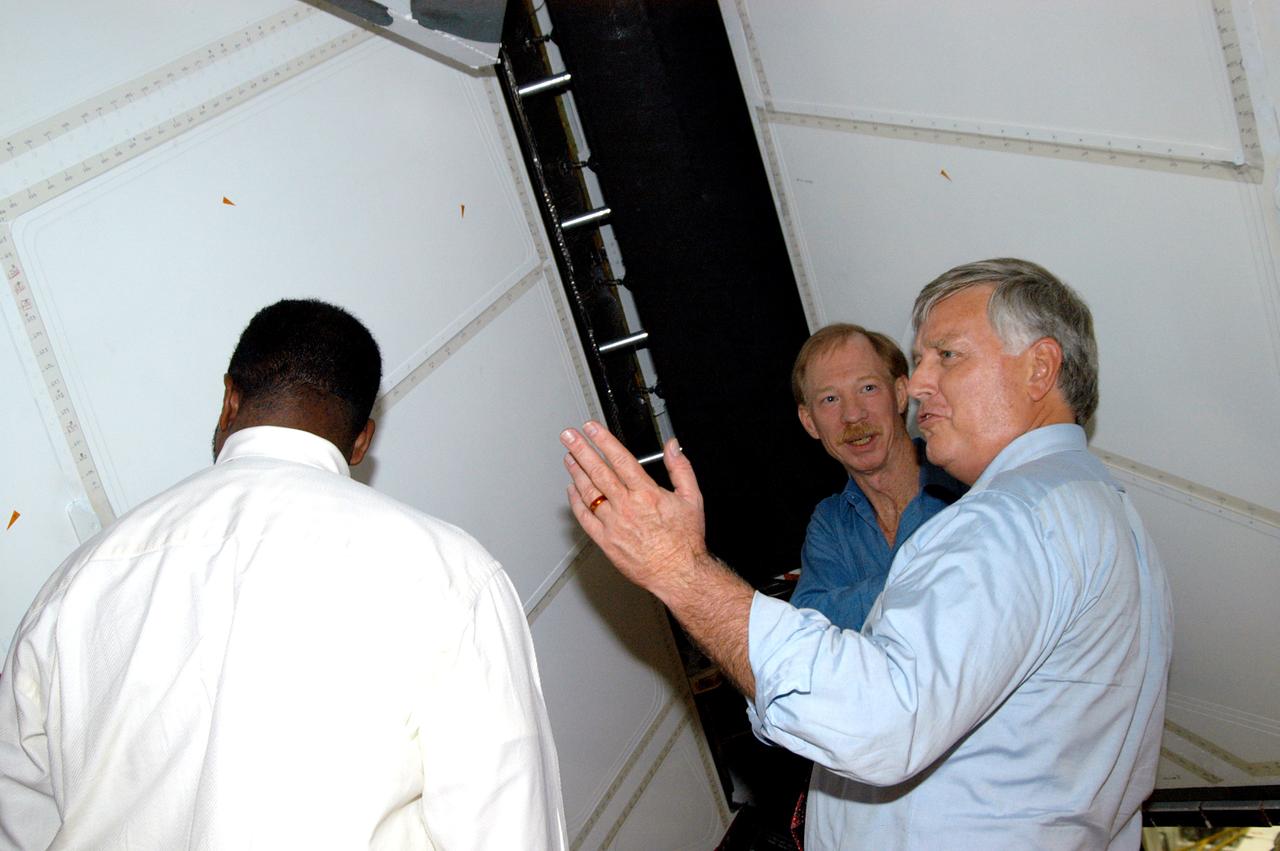

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On a tour of the Orbiter Processing Facility, Center Director Jim Kennedy (right) and Deputy Director Woodrow Whitlow Jr. (center) look at the rudder speed brake panels on the orbiter Endeavour. In the background is Tom Roberts, who is with United Space Alliance. Endeavour is in its Orbiter Major Modification period, which began in December 2003.
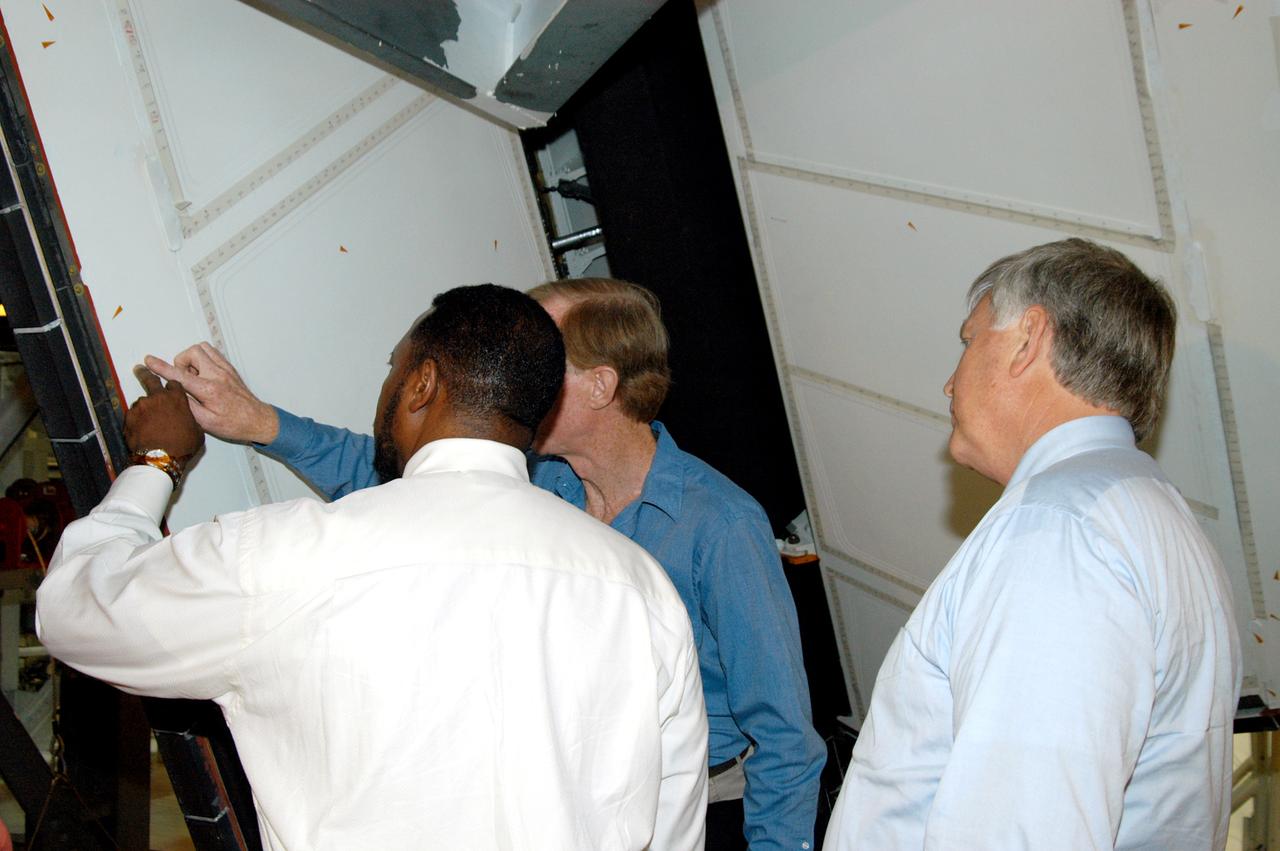

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On a tour of the Orbiter Processing Facility, Deputy Director Woodrow Whitlow Jr. points to an area on a rudder speed brake panel on Endeavour that Tom Roberts, who is with United Space Alliance, is showing him. At right is Center Director Jim Kennedy. Endeavour is in its Orbiter Major Modification period, which began in December 2003.
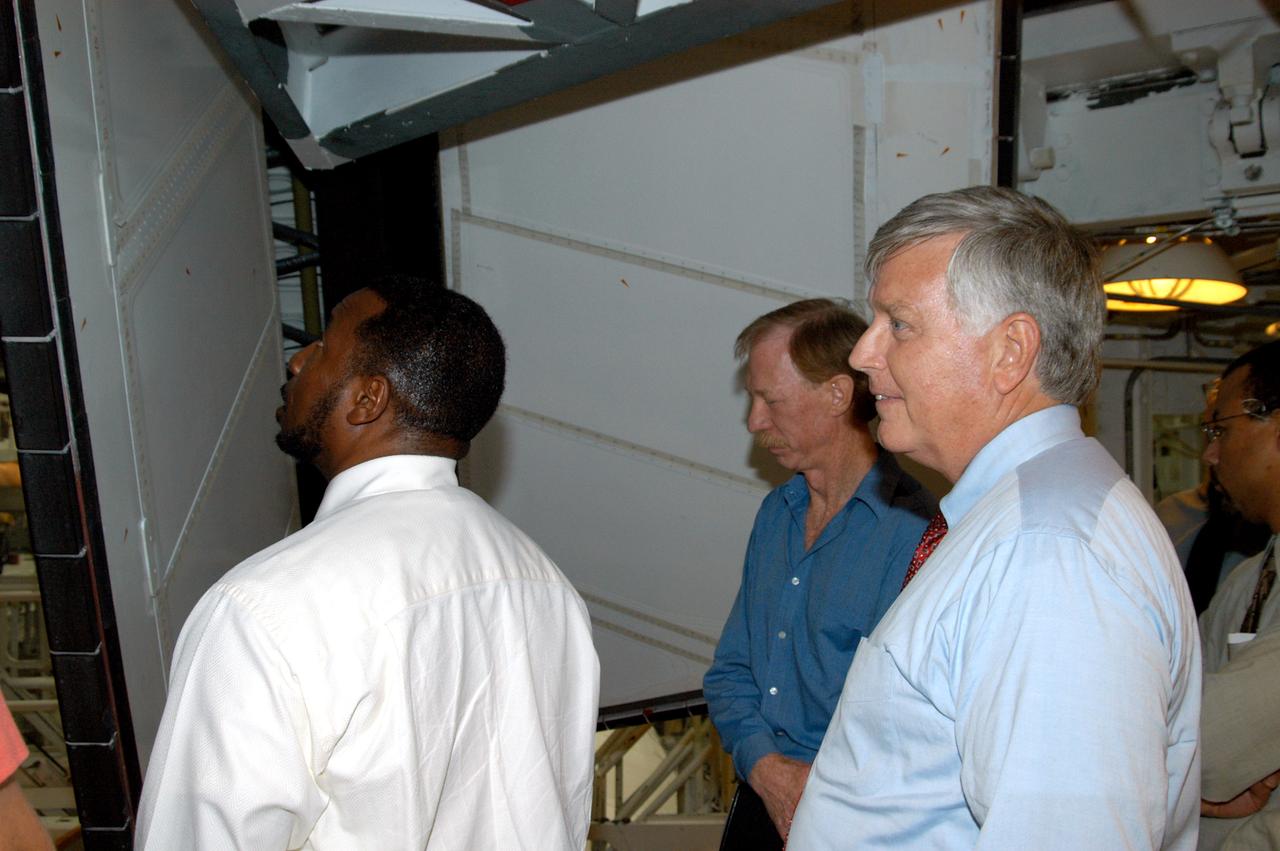

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On a tour of the Orbiter Processing Facility, Center Director Jim Kennedy (right) and Deputy Director Woodrow Whitlow Jr. (left) look at rudder speed brake panels on Endeavour In the background is Tom Roberts, who is with United Space Alliance. Endeavour is in its Orbiter Major Modification period, which began in December 2003.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A NASA quality inspector checks the placement of Rudder Speed Brake actuator No. 4 as work to install it on Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery nears completion in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance technicians start the lift of Rudder Speed Brake actuator No. 4 to Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.
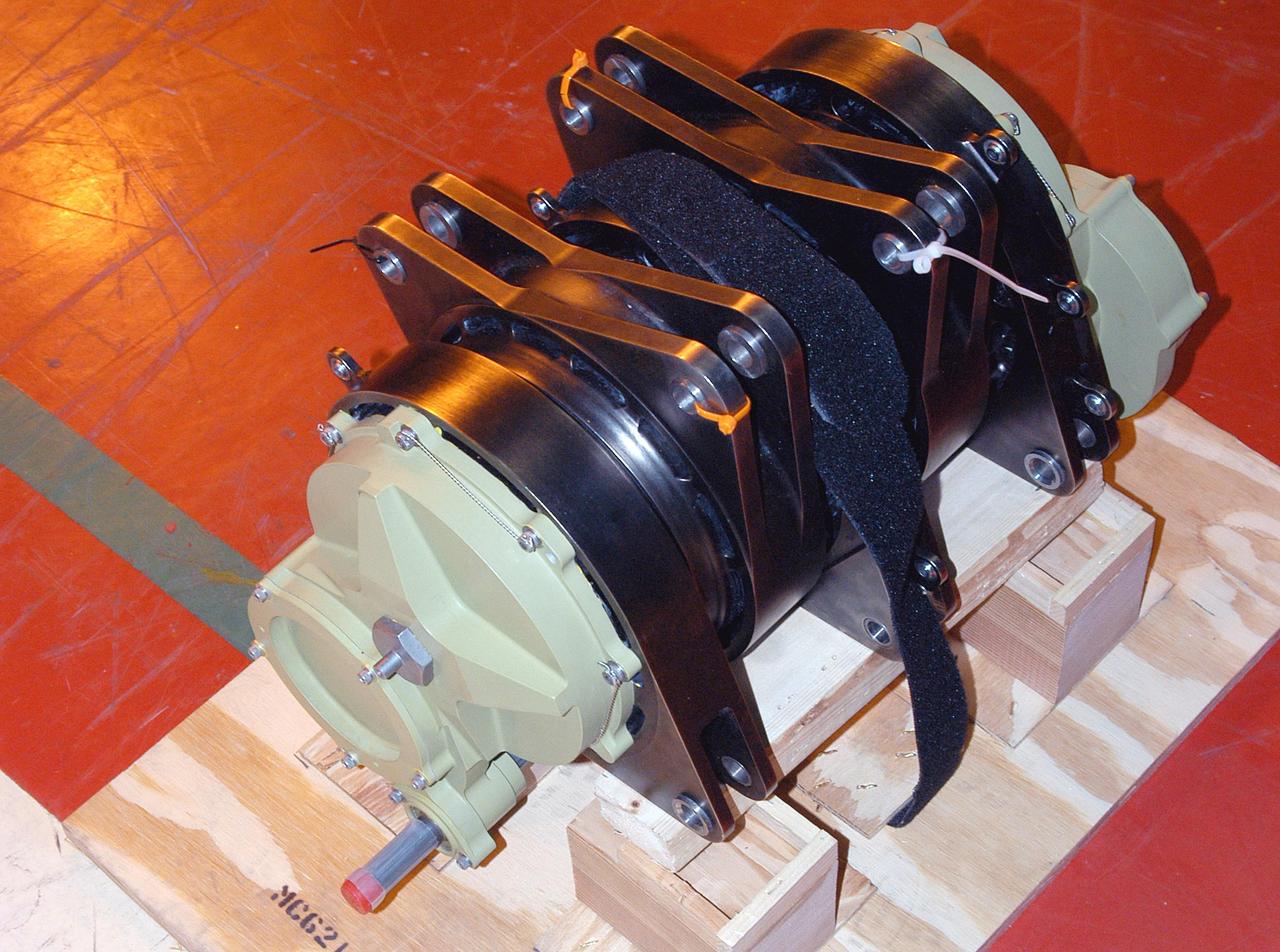

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Rudder Speed Brake actuator No. 4 is ready for installation on Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance technicians verify the alignment of Rudder Speed Brake actuator No.4 as it is attached to Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A United Space Alliance technician monitors Rudder Speed Brake actuator No. 4 as it is moved into position for installation on Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - United Space Alliance technicians check out Rudder Speed Brake actuator No. 4 before installing it on Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A United Space Alliance technician monitors the placement of Rudder Speed Brake actuator No.4 as work proceeds to install it on Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.
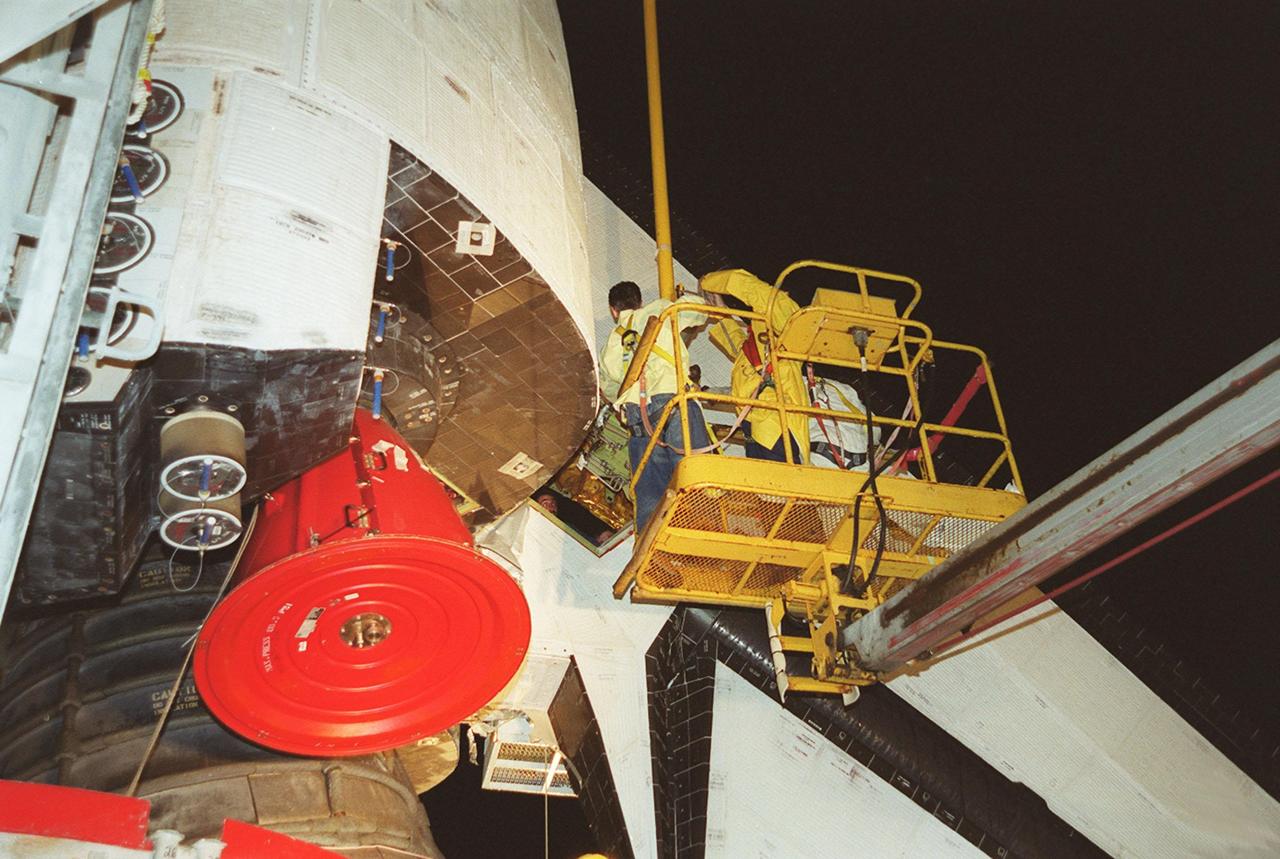

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers help guide the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis into place. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
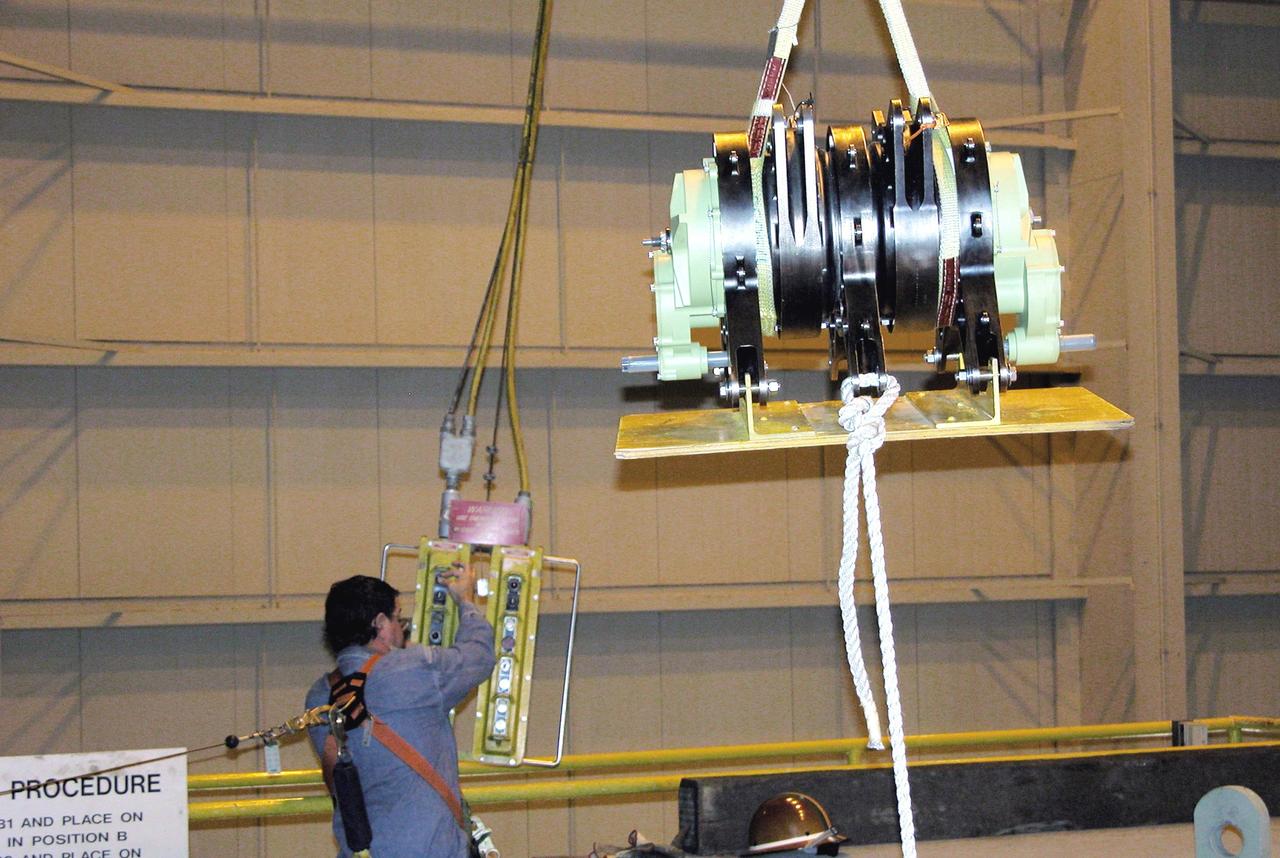
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - One of four rudder speed brake actuators is lifted for transfer to a pallet where it will be X-rayed. The actuators, to be installed on the orbiter Discovery, are being X-rayed at the Radiographic High-Energy X-ray Facility at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station to determine if the gears were installed correctly. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.
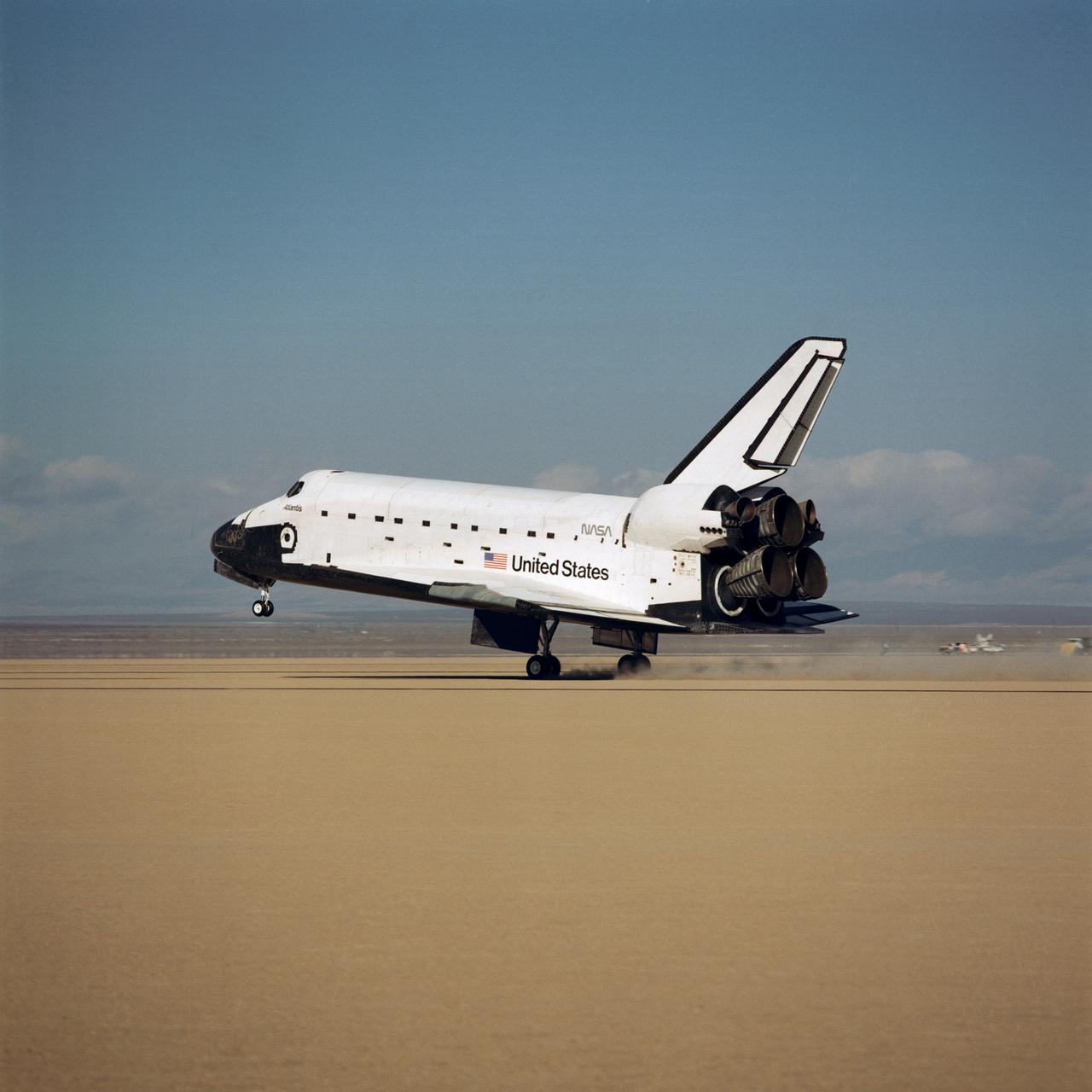

STS-34 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, main landing gear (MLG) touches down on Runway 23 dry lake bed at Edwards Air Force Base (EAFB), California. The nose landing gear rides above runway before touchdown as the MLG wheels produce a cloud of dust. OV-104's port side profile is captured as it glides by at a speed of approximately 195 knots (224 miles per hour). The tail section with deployed speedbrake/rudder and space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) are visible.
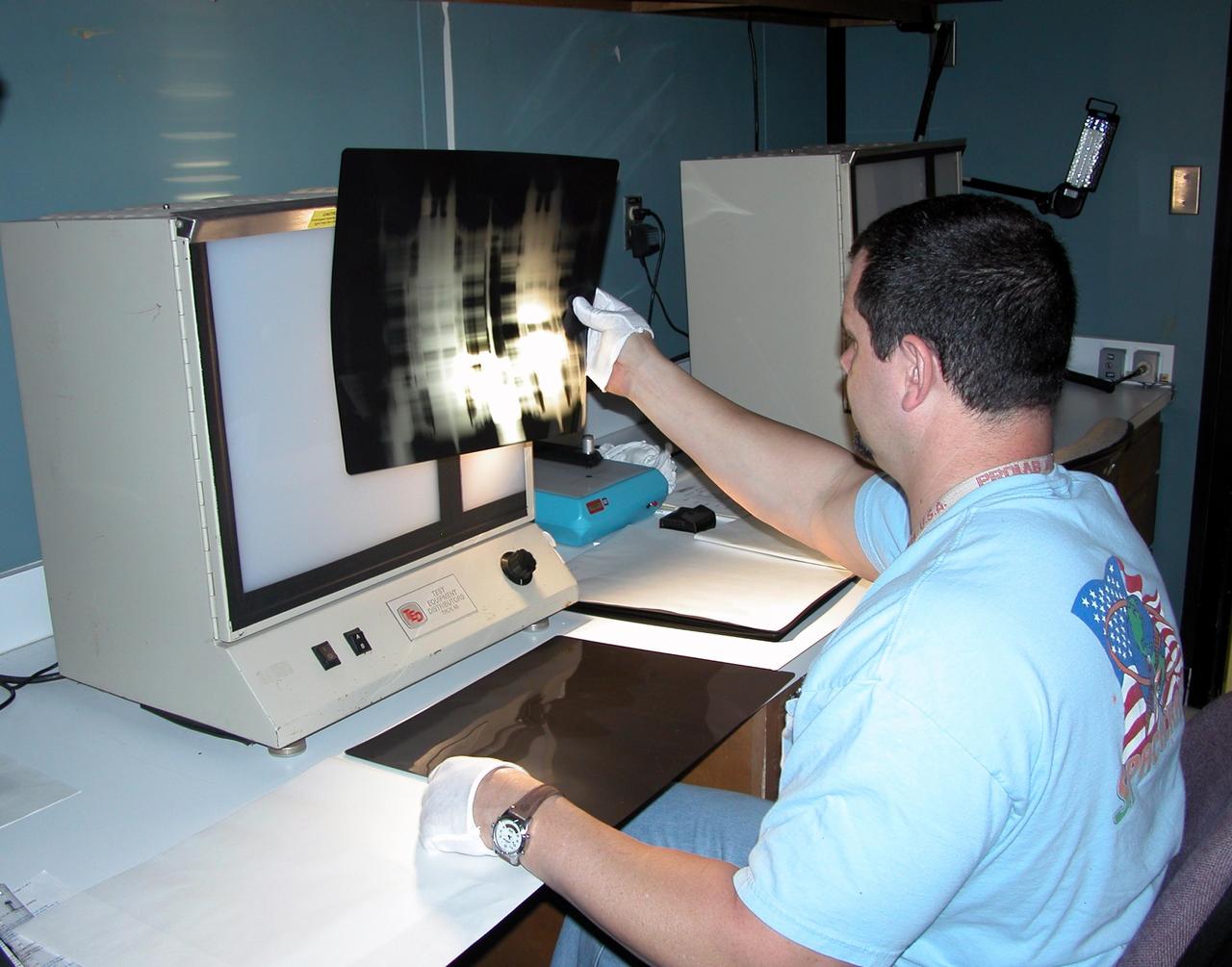

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A technician at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Radiographic High-Energy X-ray Facility looks at an X-ray of one of the four rudder speed brake actuators to be installed on the orbiter Discovery. The actuators are being X-rayed to determine if the gears were installed correctly. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.
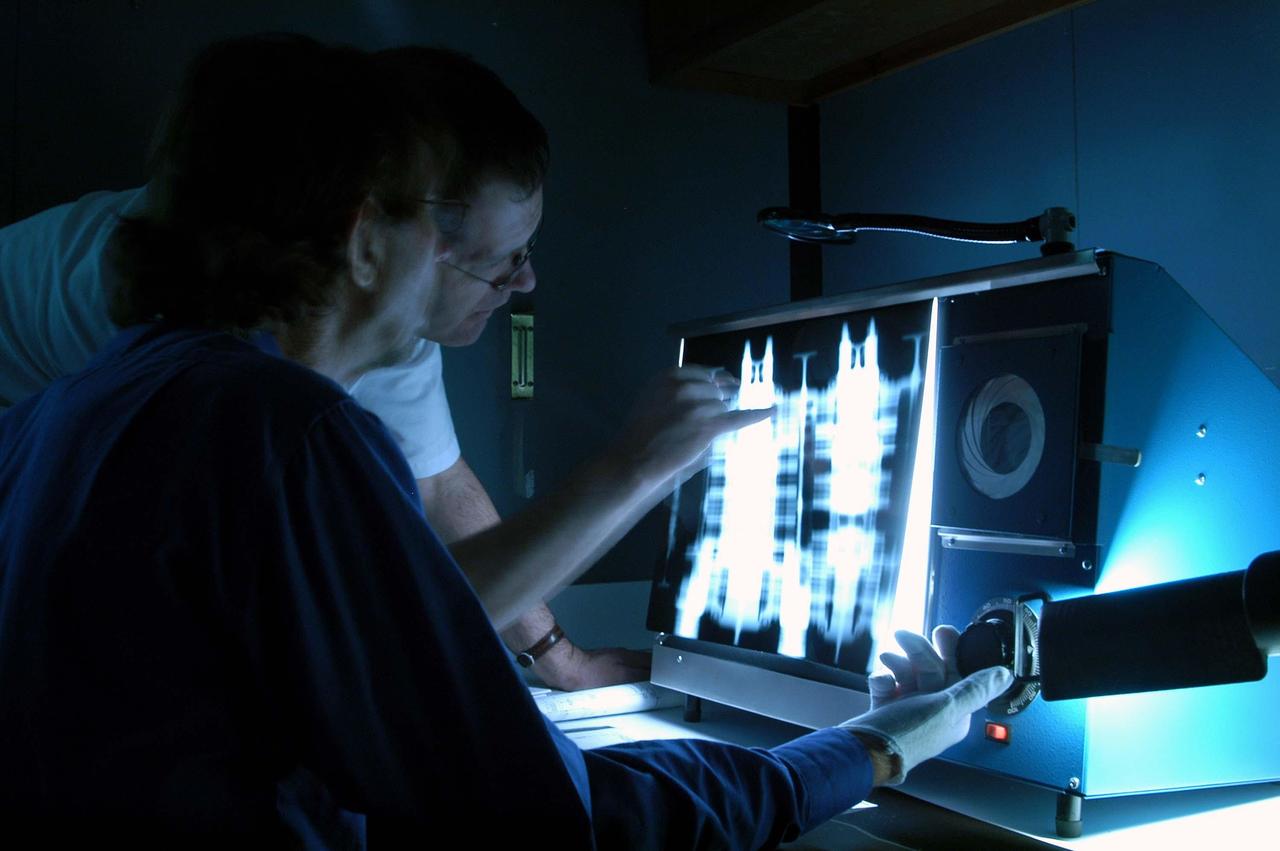

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - While adjusting the image, technicians at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Radiographic High-Energy X-ray Facility look at X-rays taken of one of the rudder speed brake actuators to be installed on the orbiter Discovery. The four actuators are being X-rayed to determine if the gears were installed correctly. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers move the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) into the body of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
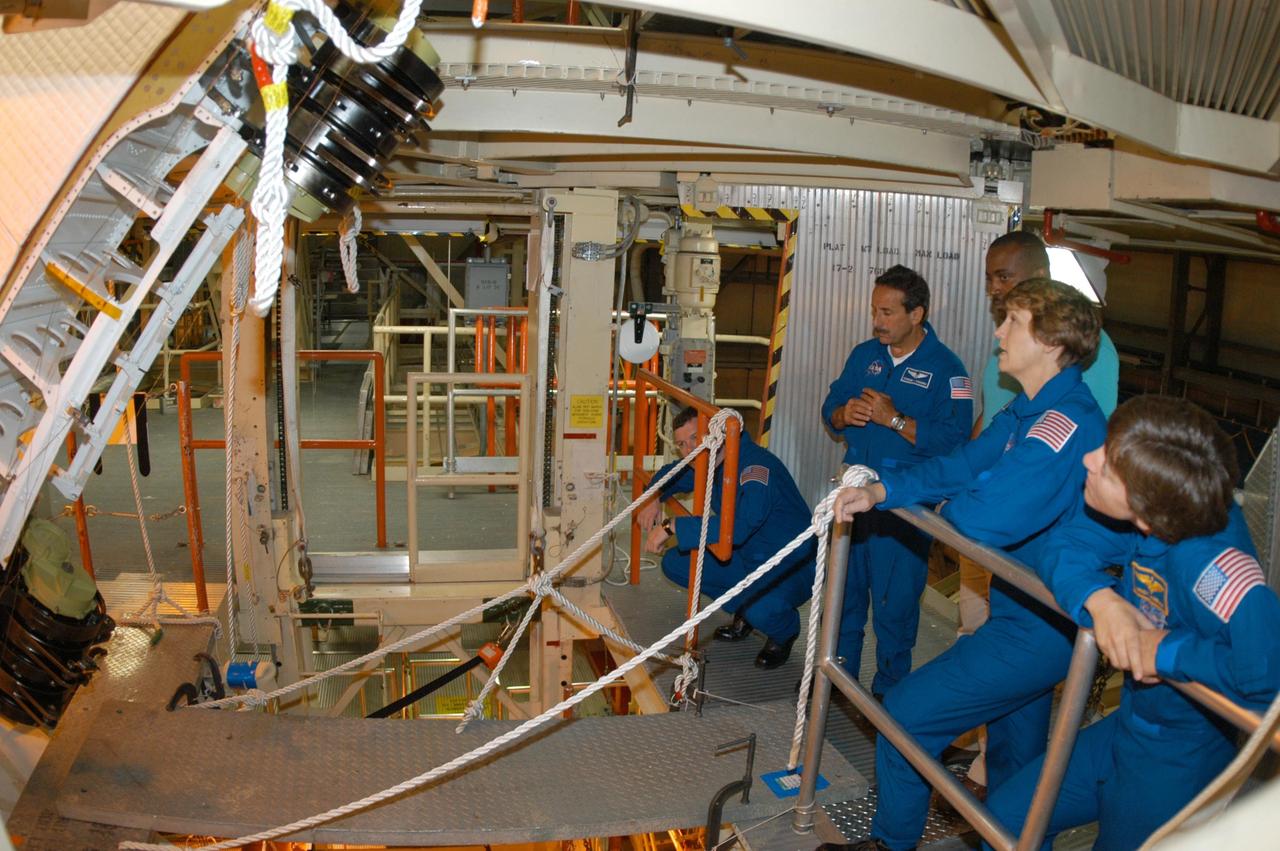

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, STS-114 crew members look at one of the Rudder Speed Brake actuators. Seen at right are Mission Specialist Charles Camarda, Mission Commander Eileen Collins and Mission Specialist Wendy Lawrence. Crew members are touring several areas on Center. The STS-114 mission is Logistics Flight 1, which is scheduled to deliver supplies and equipment plus the external stowage platform to the International Space Station.
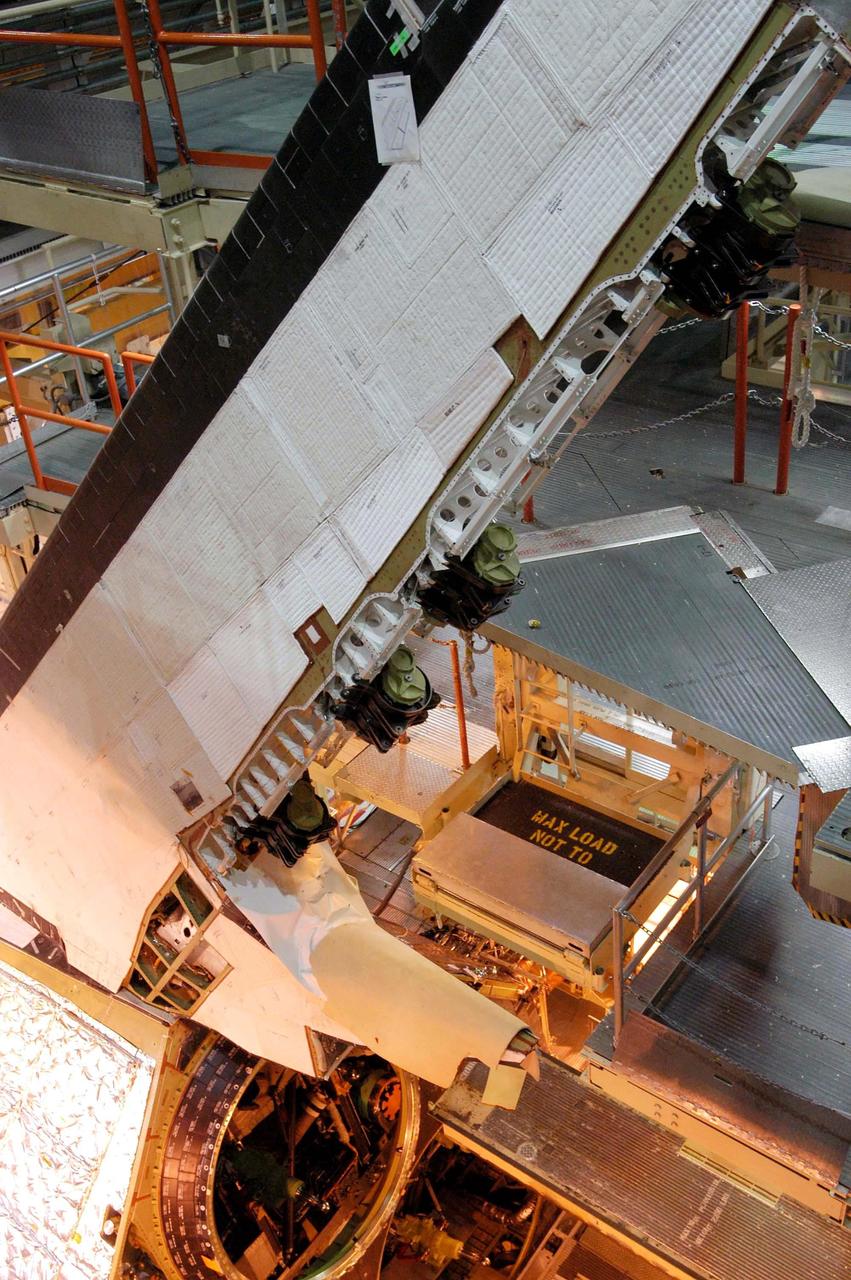

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, seen here is the vertical stabilizer on the orbiter Discovery. On the edge of the stabilizer are the four Rudder Speed Brake Actuators recently installed. Below is the engine number 1 interface. Discovery has been assigned to the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, a logistics flight to the International Space Station.
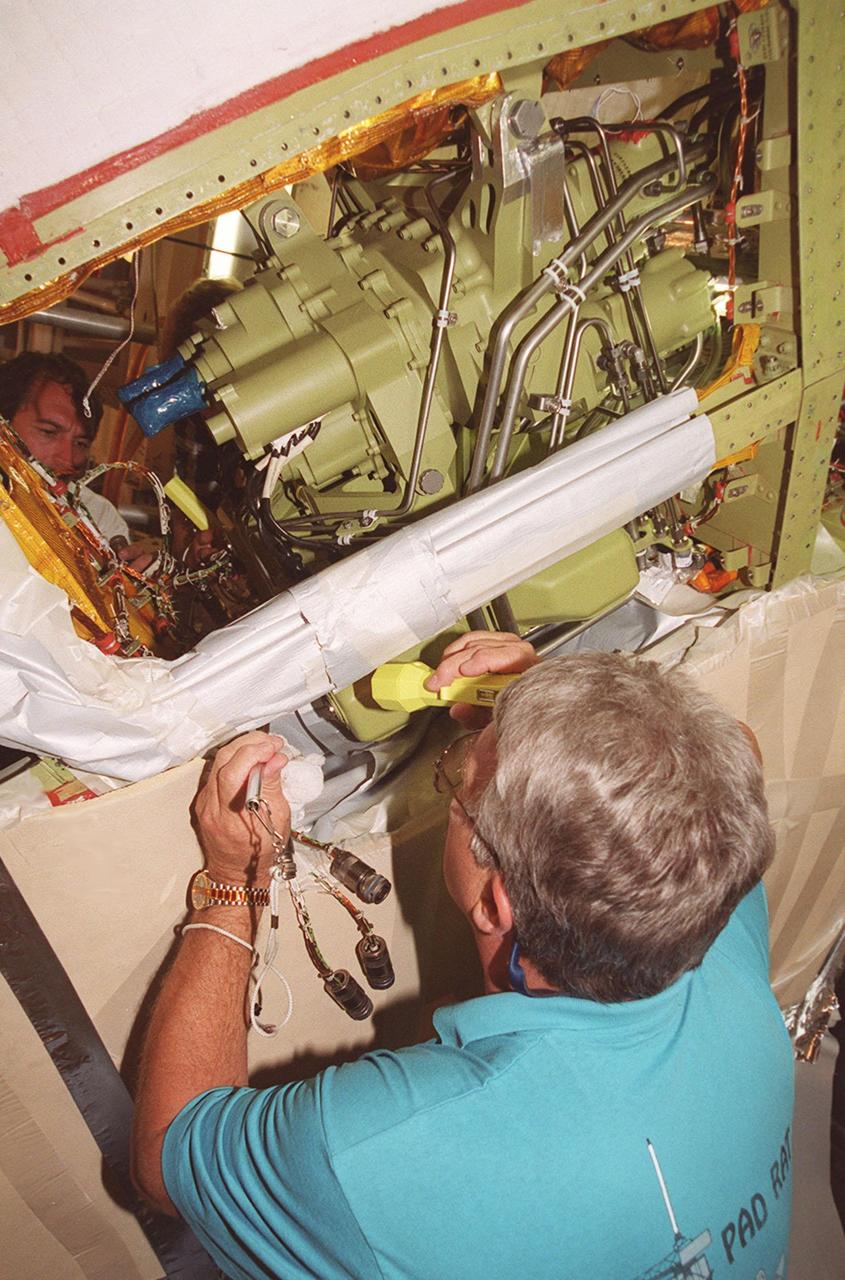

At Launch Pad 39A, Greg Lohning, who is with NASA, inspects the wiring on the newly installed Power Drive Unit (PDU) in Space Shuttle Atlantis. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
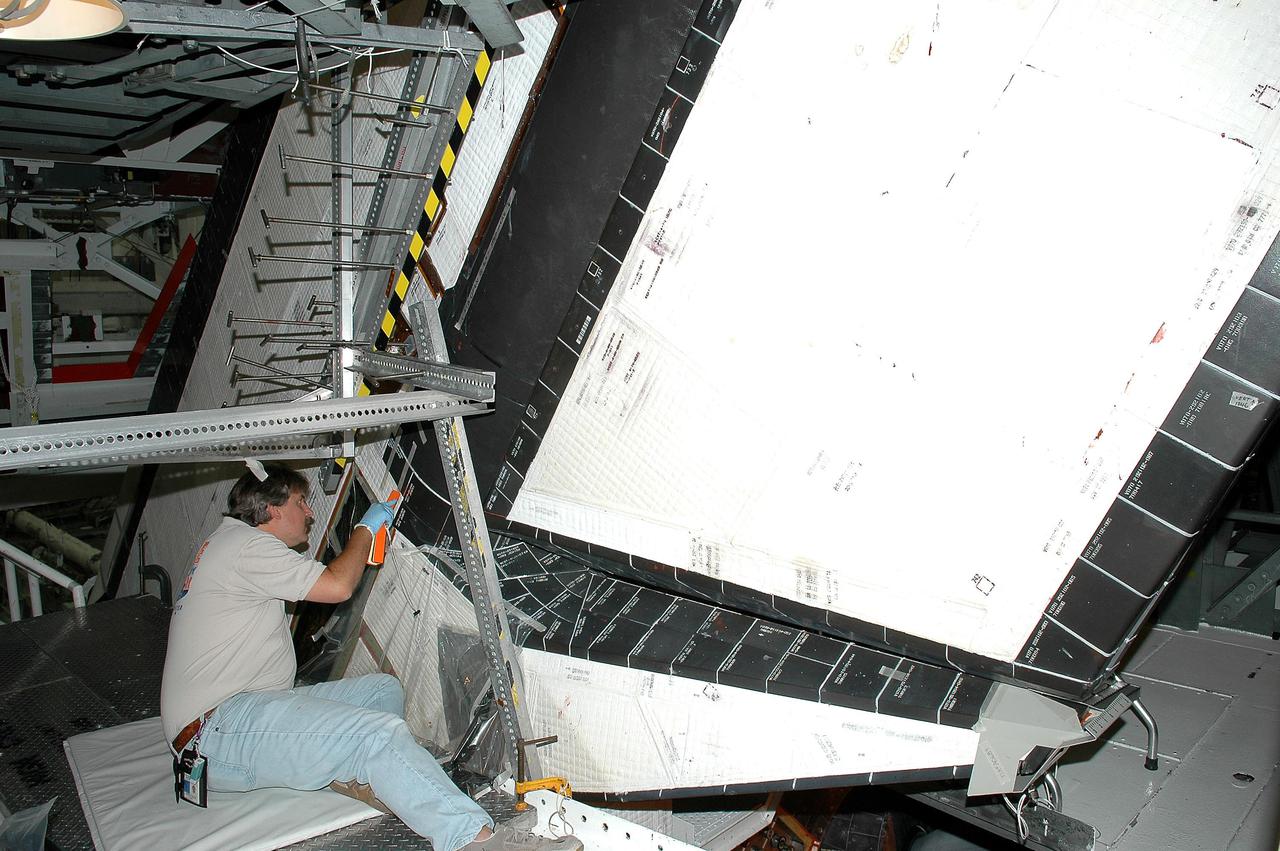

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, United Space Alliance tile technician Tim Marks places Thermal Protection System tiles on Atlantis’ rudder speed brake. Atlantis is being processed for launch on the second Return to Flight mission, STS-121, which is scheduled to fly in July.
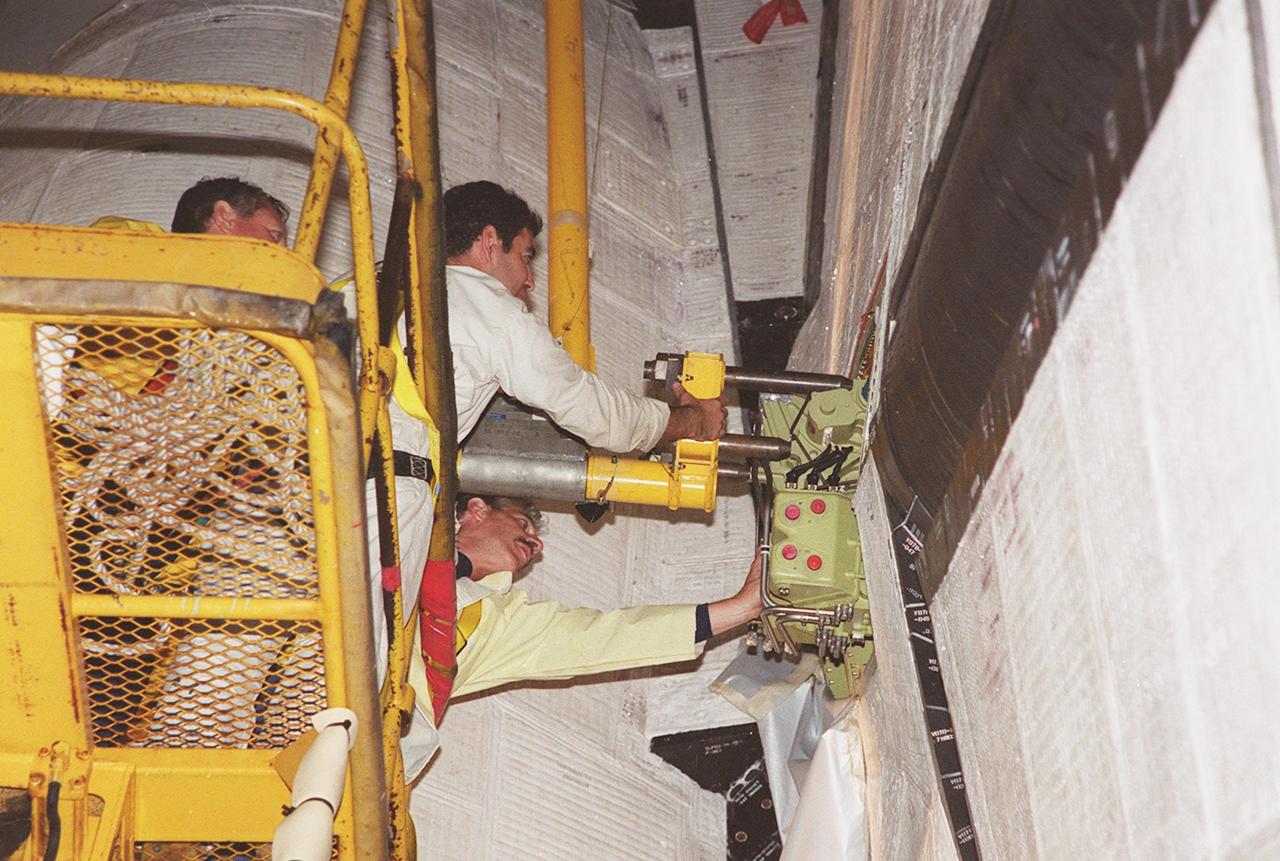

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers move the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) into the body of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
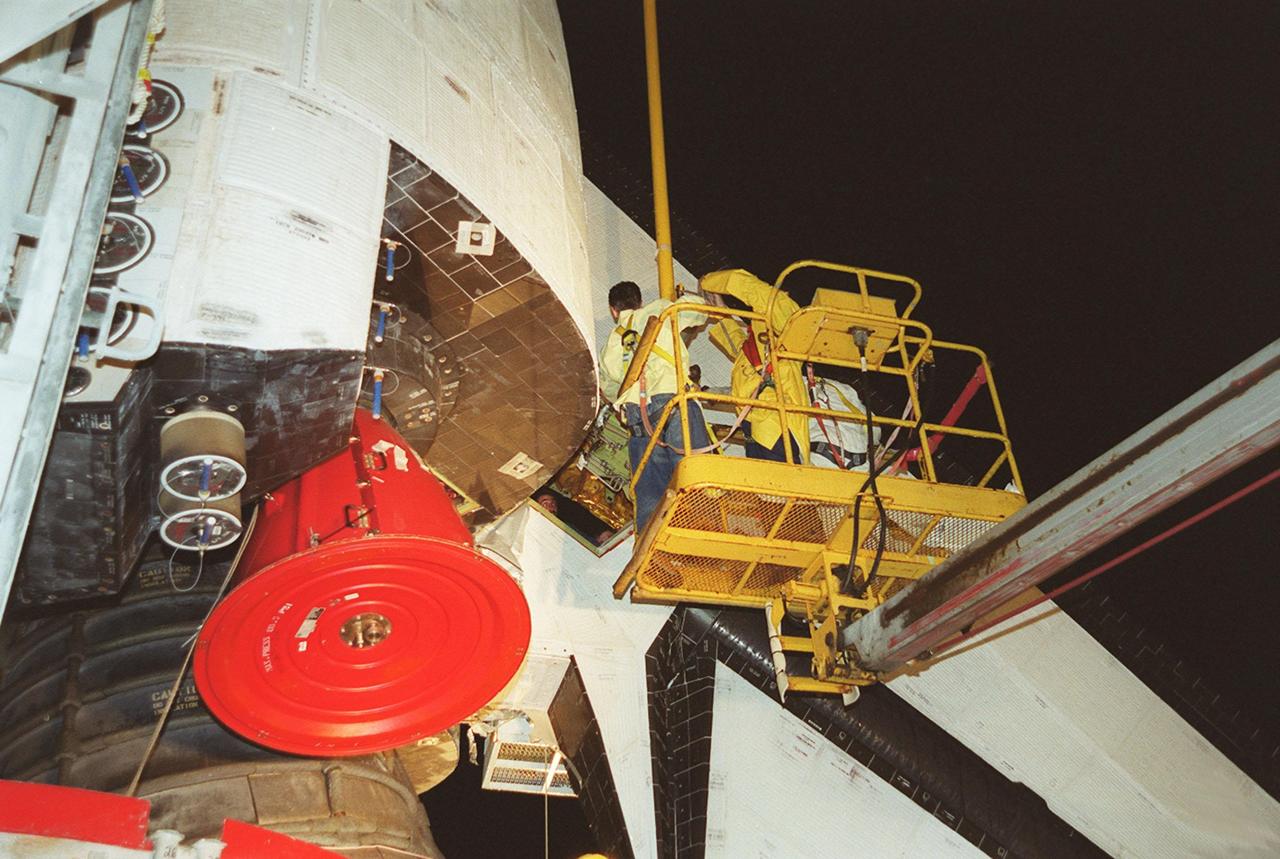

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers help guide the replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis into place. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
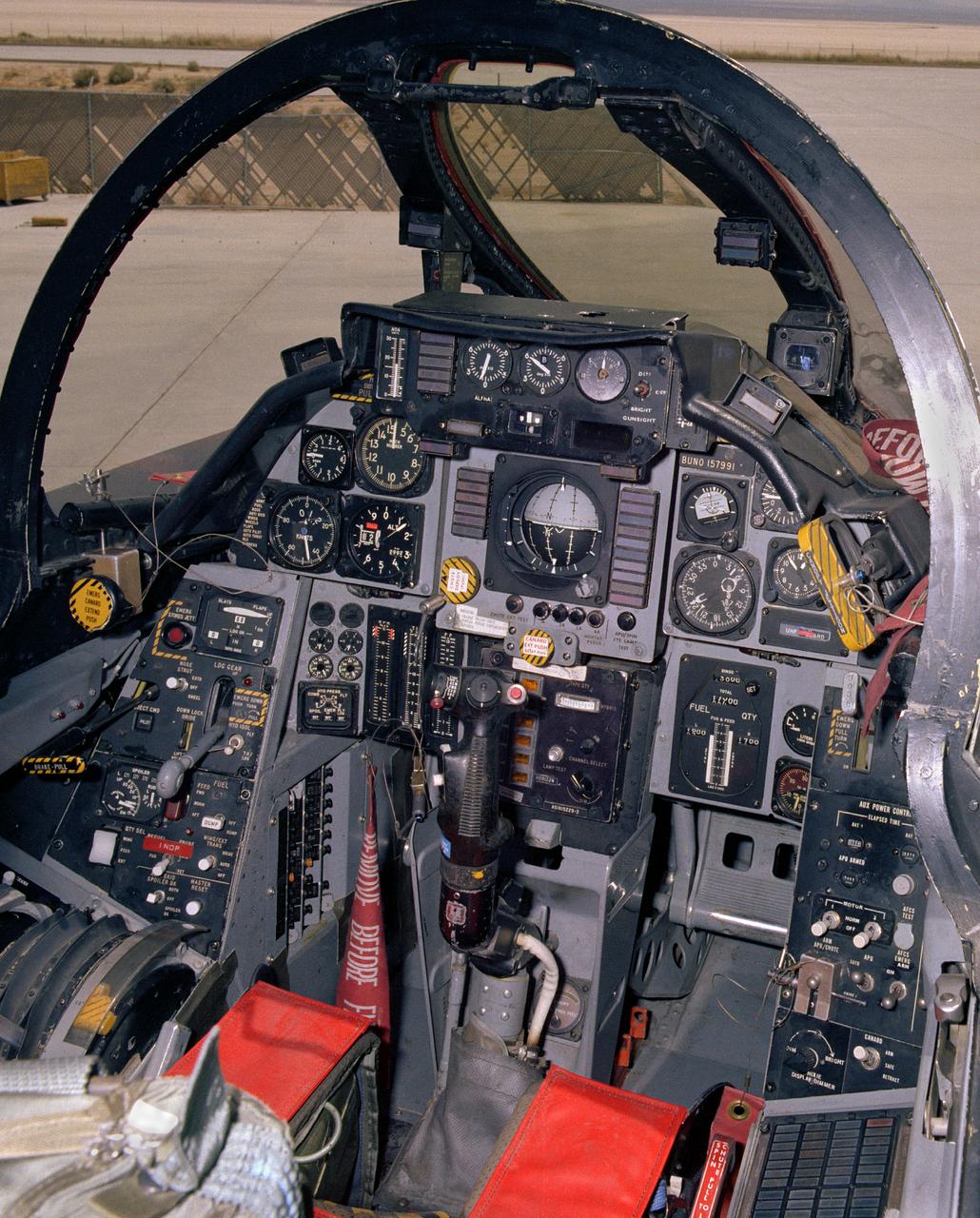

View of the cockpit of NASA's F-14, tail number 991. This aircraft was the first of a series of post-Vietnam fighters, followed by the F-15, F-16, and F-18. They were designed for maneuverability in air-to-air combat. The F-14s had a spin problem that posed problems for its ability to engage successfully in a dogfight, since it tended to depart from controlled flight at the high angles of attack that frequently occur in close-in engagements.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, a worker reaches toward the plastic-covered replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis as it is lifted by crane toward the tail. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, a worker watches as the plastic-covered replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis is lifted by crane toward the tail. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
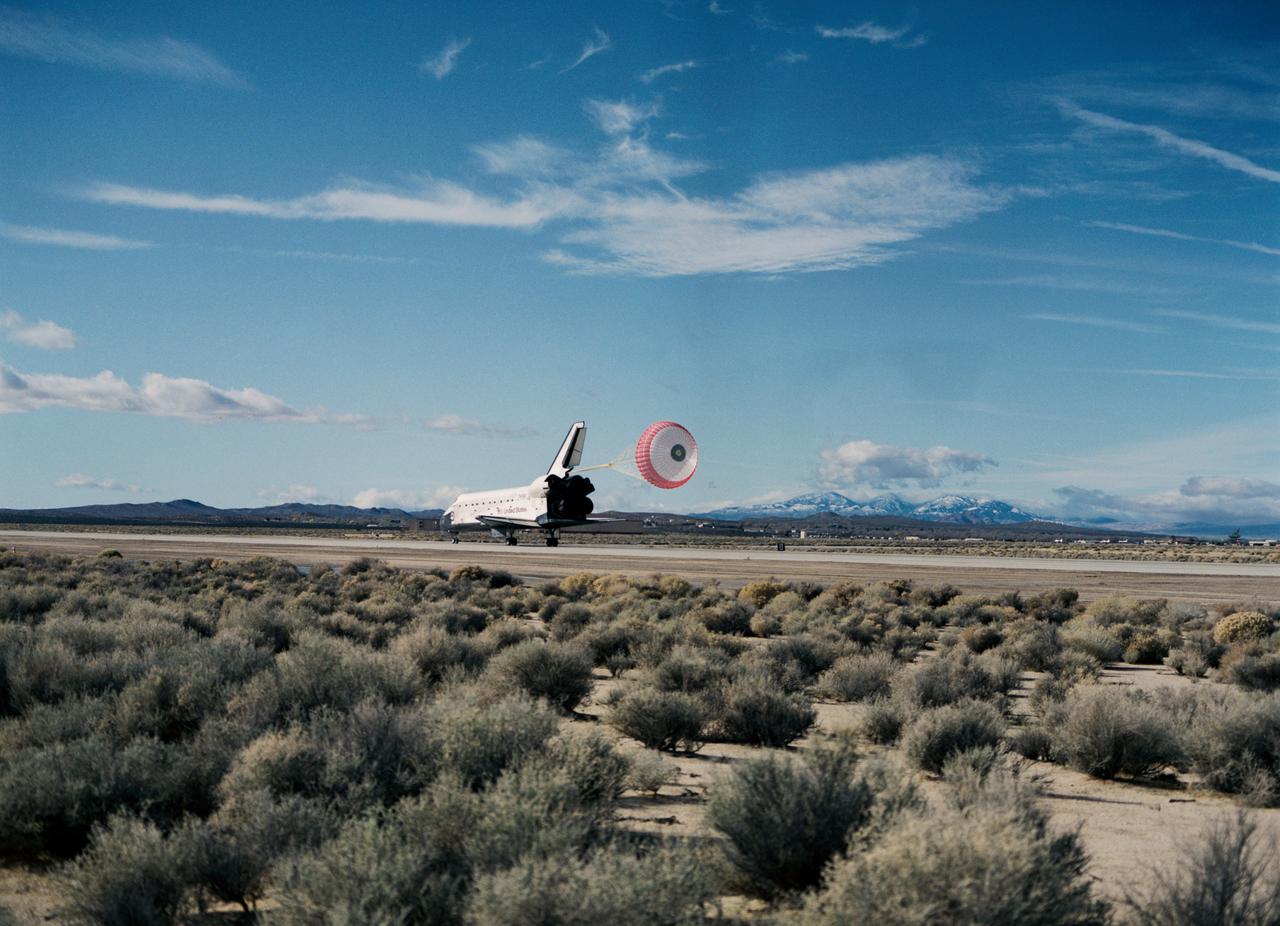

STS-53 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is slowed by a red, white, and blue drag chute during its landing on concrete runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base (EAFB), California. Main landing gear (MLG) touchdown occurred at 12:43:17 pm (Pacific Standard Time (PST)). This aft view of OV-103 shows the drag chute deployed from its compartment at the base of the vertical tail, the speedbrake/rudder flaps open, and the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs). Both MLG and nose landing gear (NLG) ride along the runway surface. Desert scrub brush appears in the foreground and mountains are seen in the background.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers wait to begin replace Shuttle Atlantis' Power Drive Unit (PDU), which is attached to the crane (center). The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
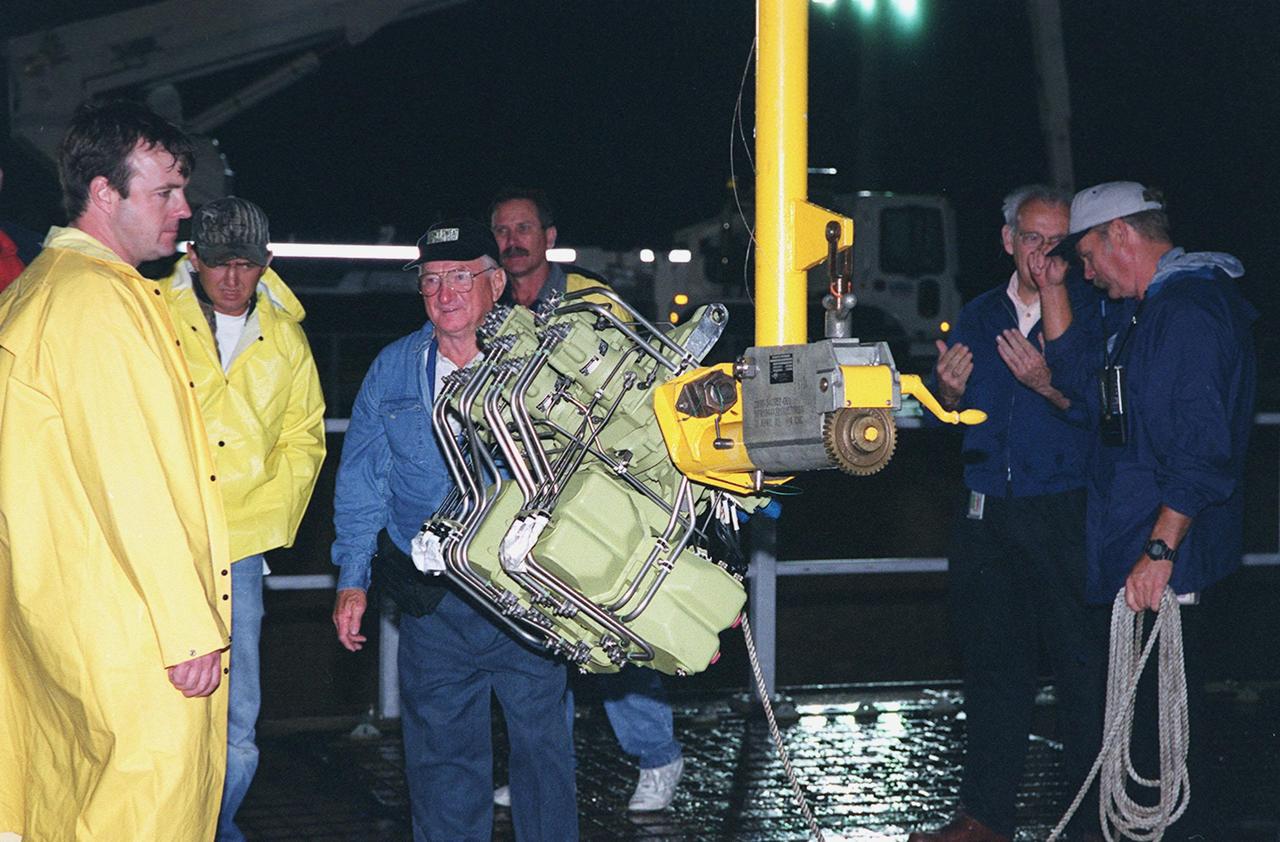

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers wait to begin replace Shuttle Atlantis' Power Drive Unit (PDU), which is attached to the crane (center). The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
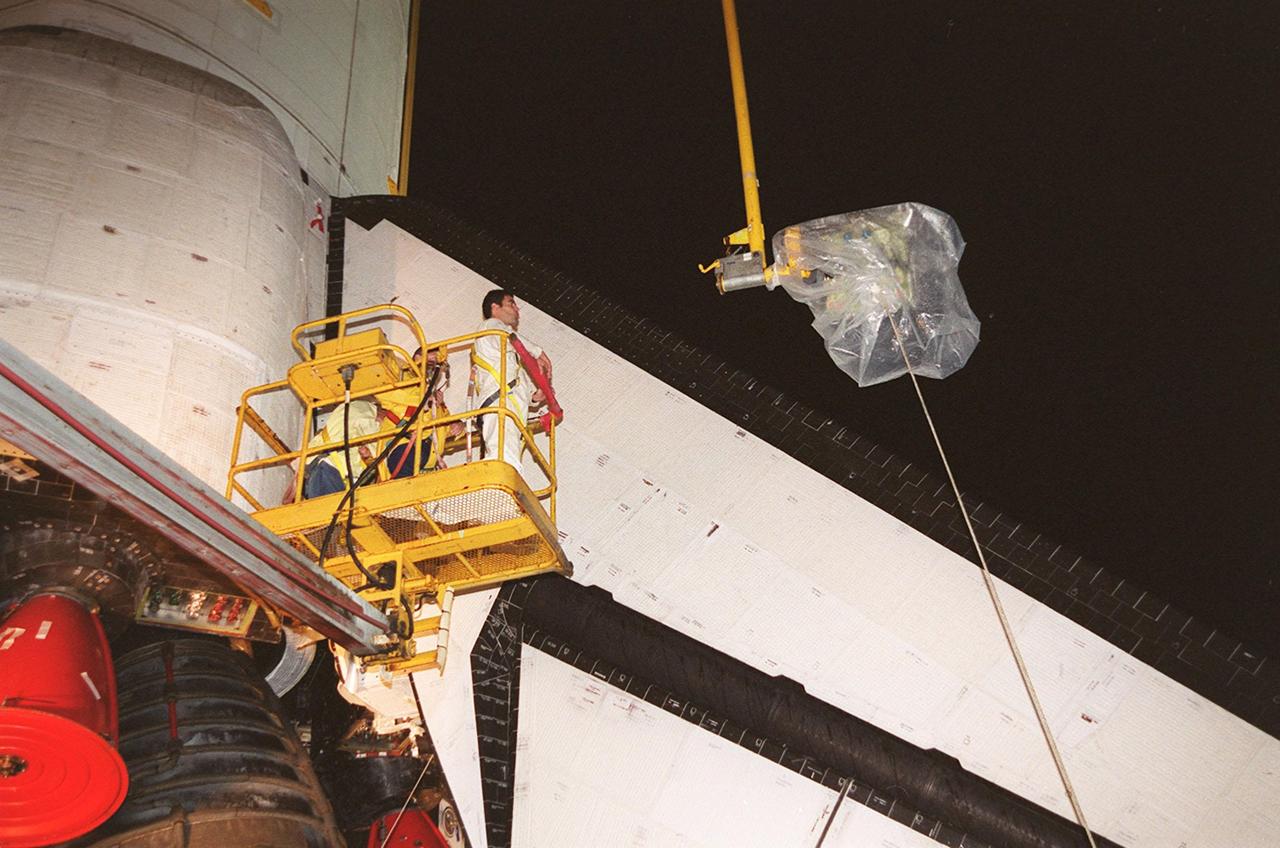

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, a worker watches as the plastic-covered replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis is lifted by crane toward the tail. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
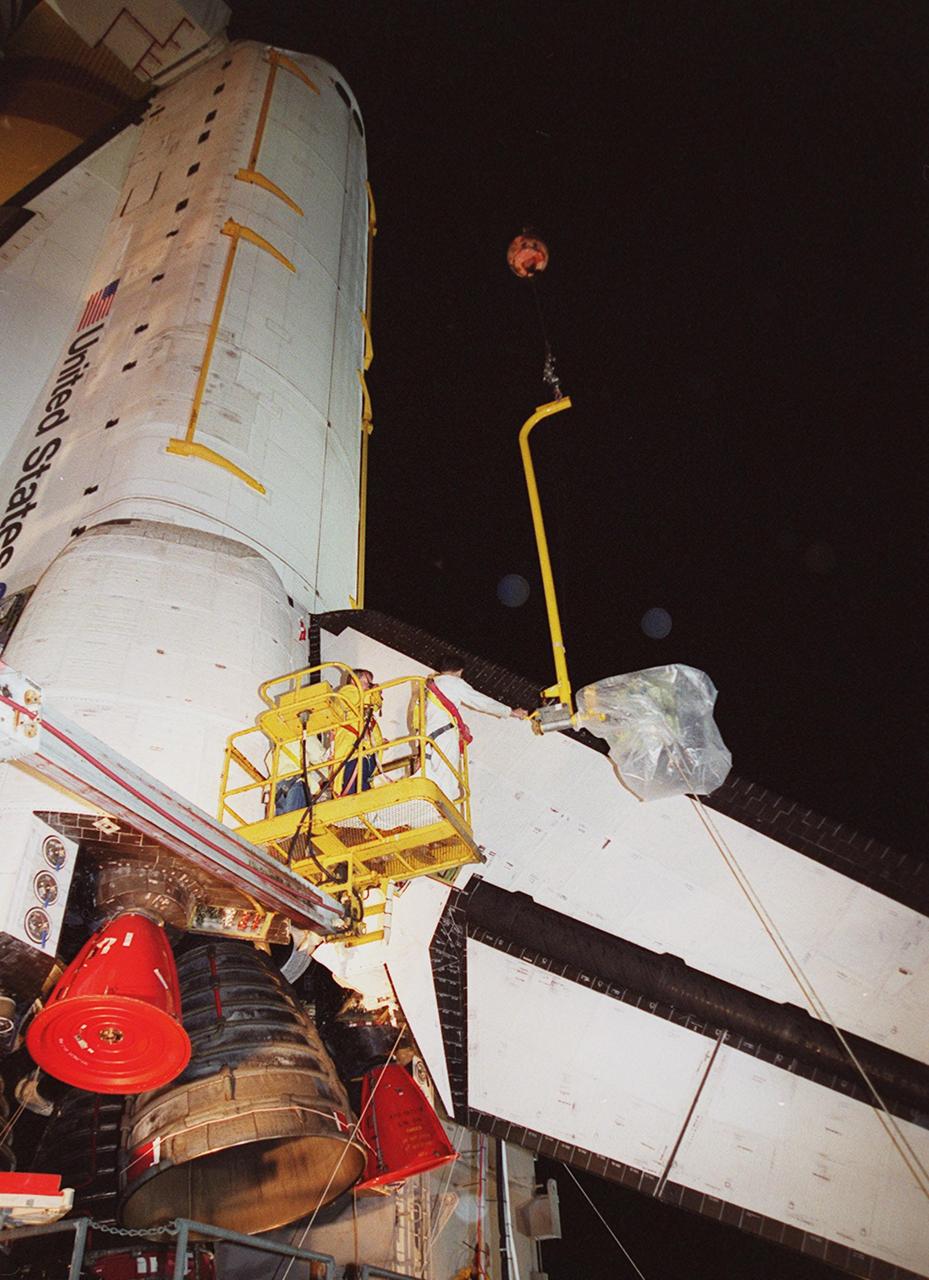

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, a worker reaches toward the plastic-covered replacement Power Drive Unit (PDU) for Space Shuttle Atlantis as it is lifted by crane toward the tail. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Atlantis is scheduled to lift off April 24 at 4:15 p.m. EDT on mission STS-101, the third flight to the International Space Station. The primary mission is to carry logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000
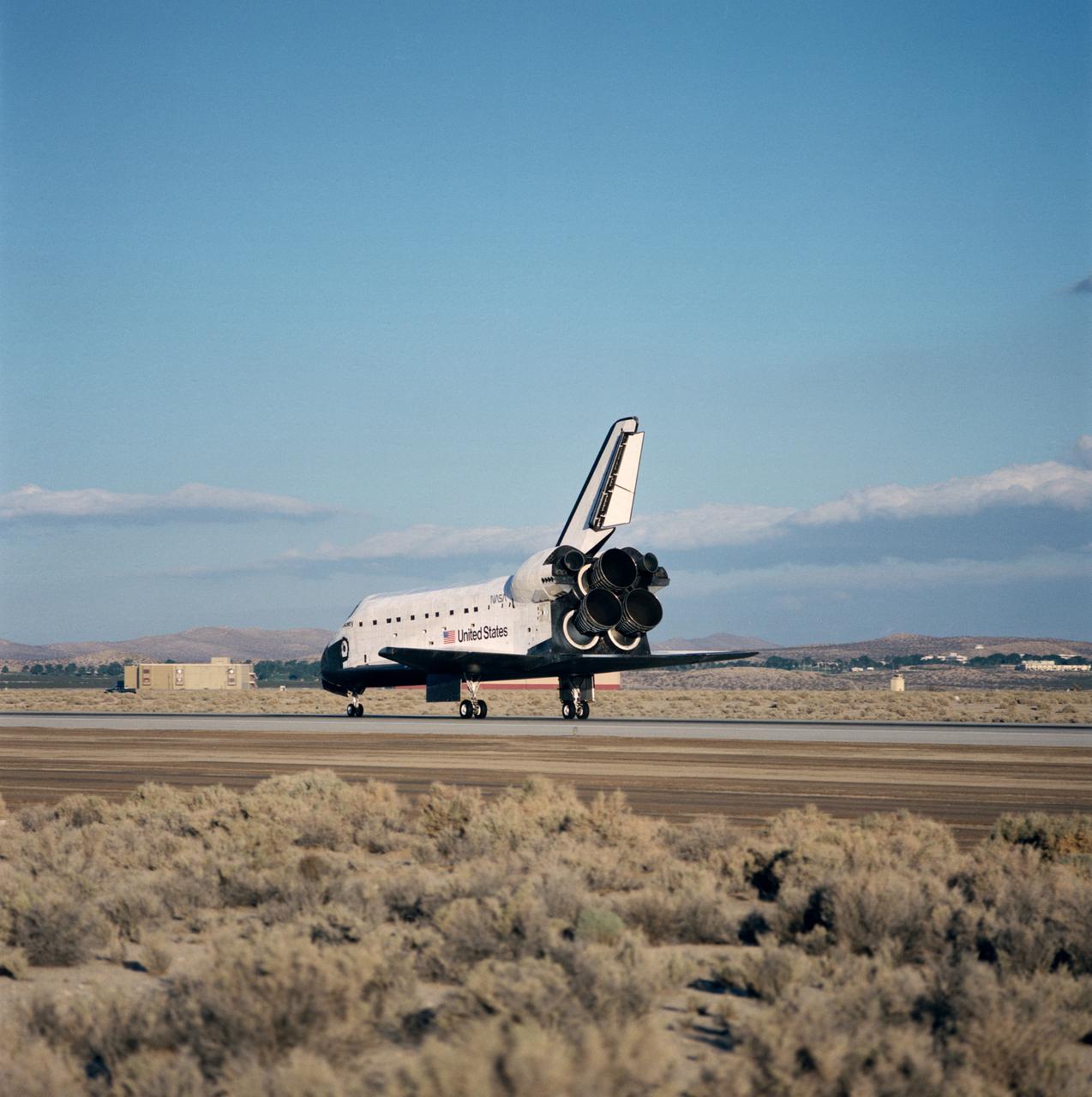

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, rolls along concrete runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base (EAFB), California, after nose landing gear (NLG) and main landing gear (MLG) touchdown. This view looks down OV-103's port side from the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) to the nose section. The SSMEs are gimbaled to their descent position and the rudder/speedbrake is deployed on the vertical stabilizer. Wheel stop occurred at 6:51 am (Pacific Daylight Time (PDT)). In the distance EAFB facilities are visible.
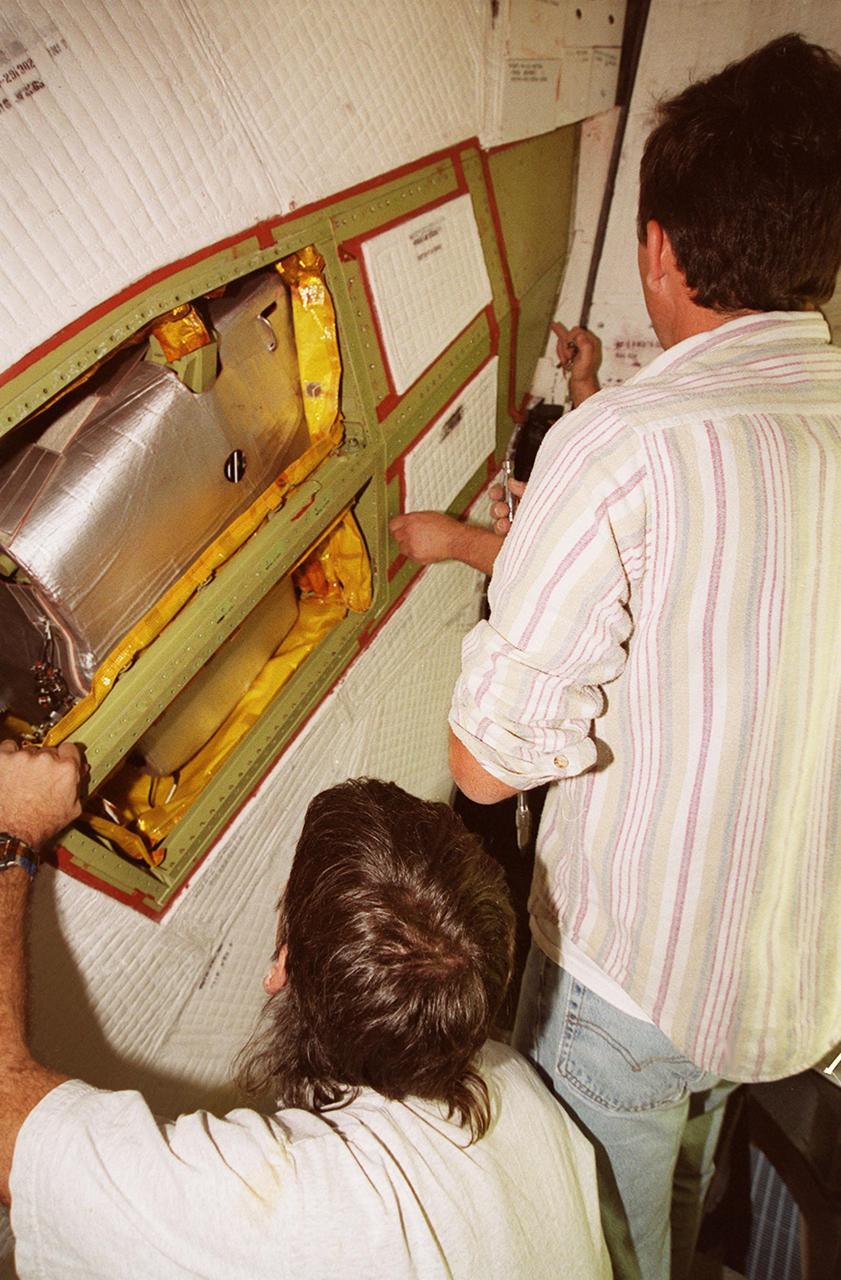

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technicians (left to right) Tod Biddle, Bob Wright and Mark Noel (hidden) remove the coverings from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis to reveal the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
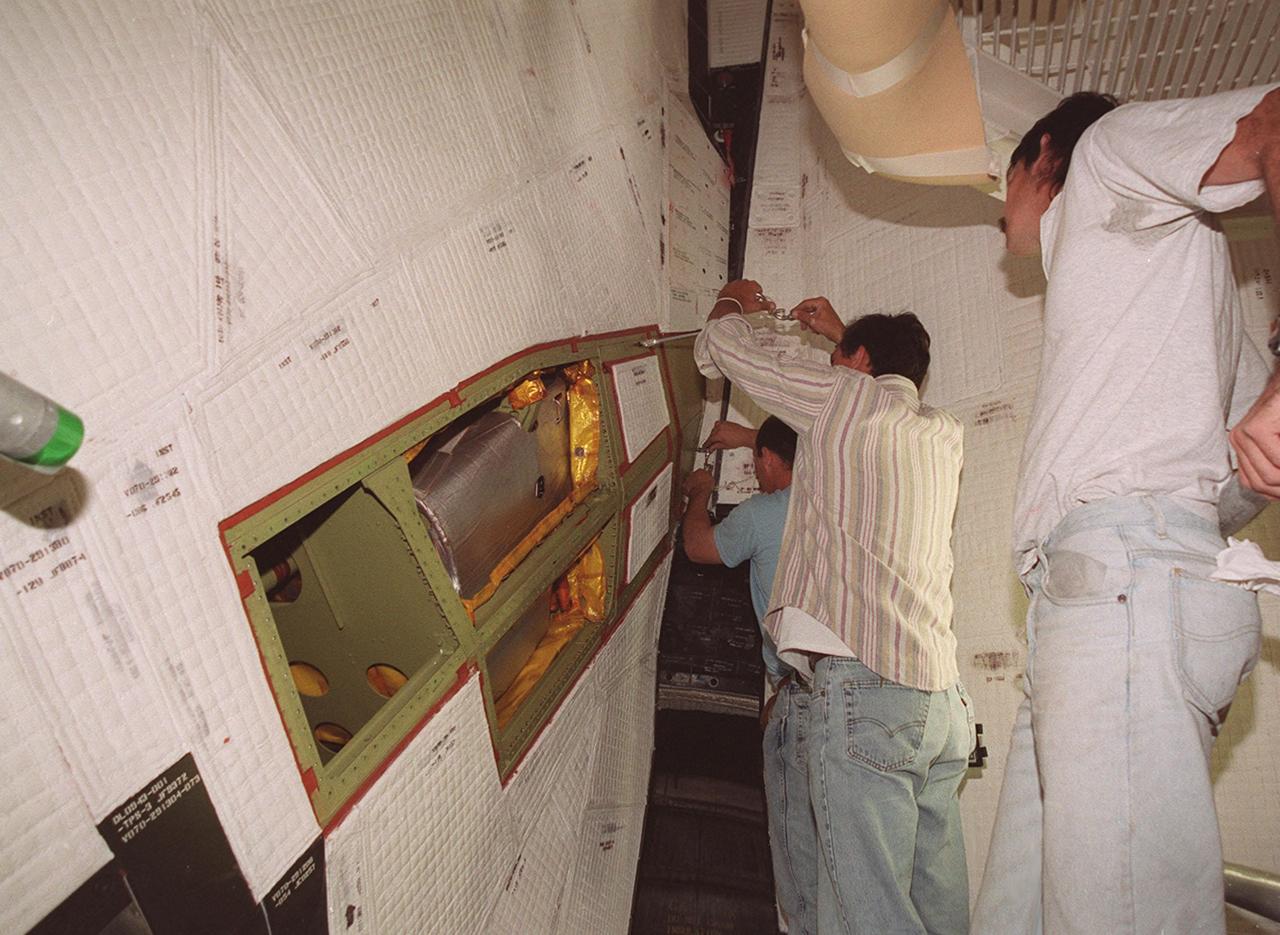

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians at Launch Pad 39A begin removing thermal blankets and panels from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis in order to reach the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. From left to right are Mark Noel, Bob Wright and Tod Biddle, with United Space Alliance. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
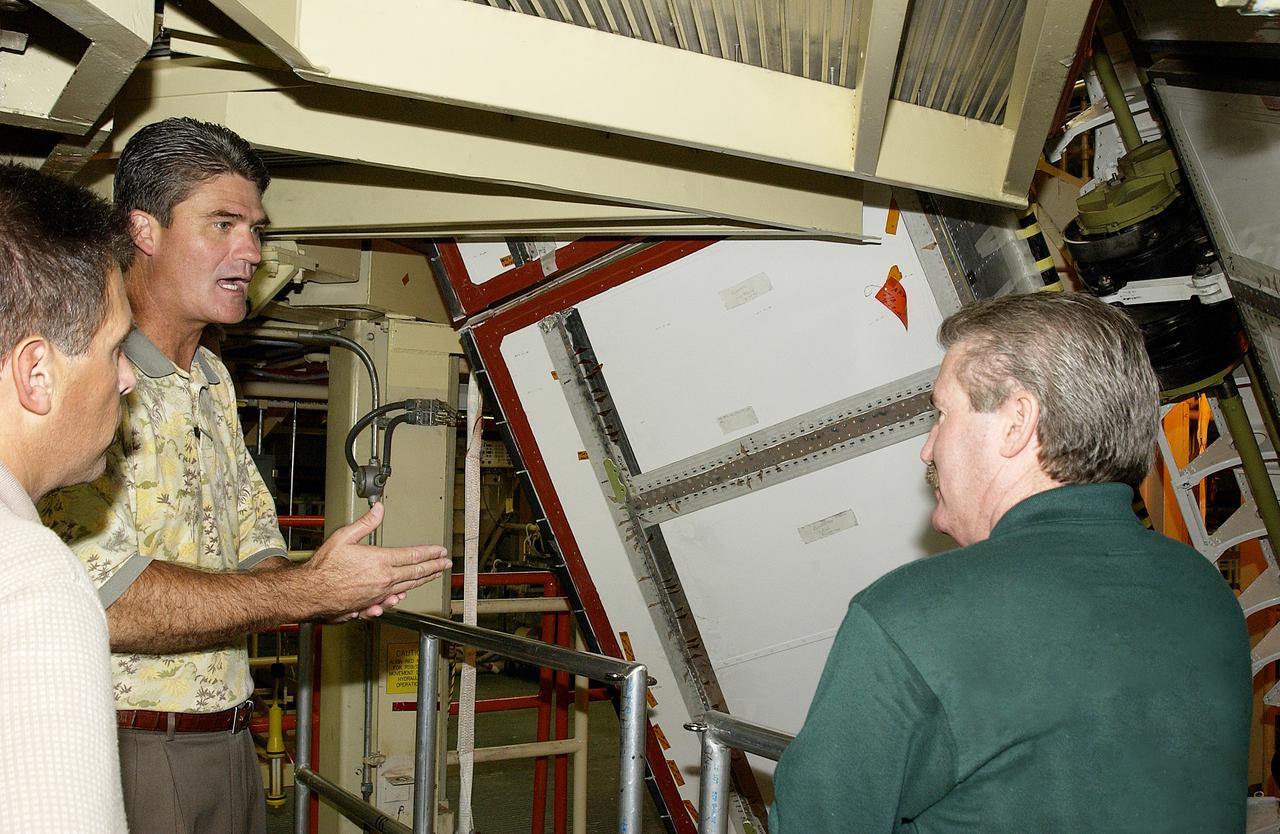

Mark McGee (right) shows the bead blasting completed on the rudder speed brake on orbiter Discovery to Shuttle Program Manager Bill Parsons (center). McGee is manager, Orbiter Processing Facility, with United Space Alliance. At left is Mark Nappi, deputy associate program manager, ground operations, USA. The work was part of Orbiter Major Modifications (OMM) that were recently completed on Discovery. The OMM work ranged from wiring, control panels and black boxes to gaseous and fluid systems tubing and components. These systems were deserviced, disassembled, inspected, modified, reassembled, checked out and reserviced, as were most other systems onboard. The work included the installation of the Multifunction Electronic Display Subsystem (MEDS) - a state-of-the-art “glass cockpit.”
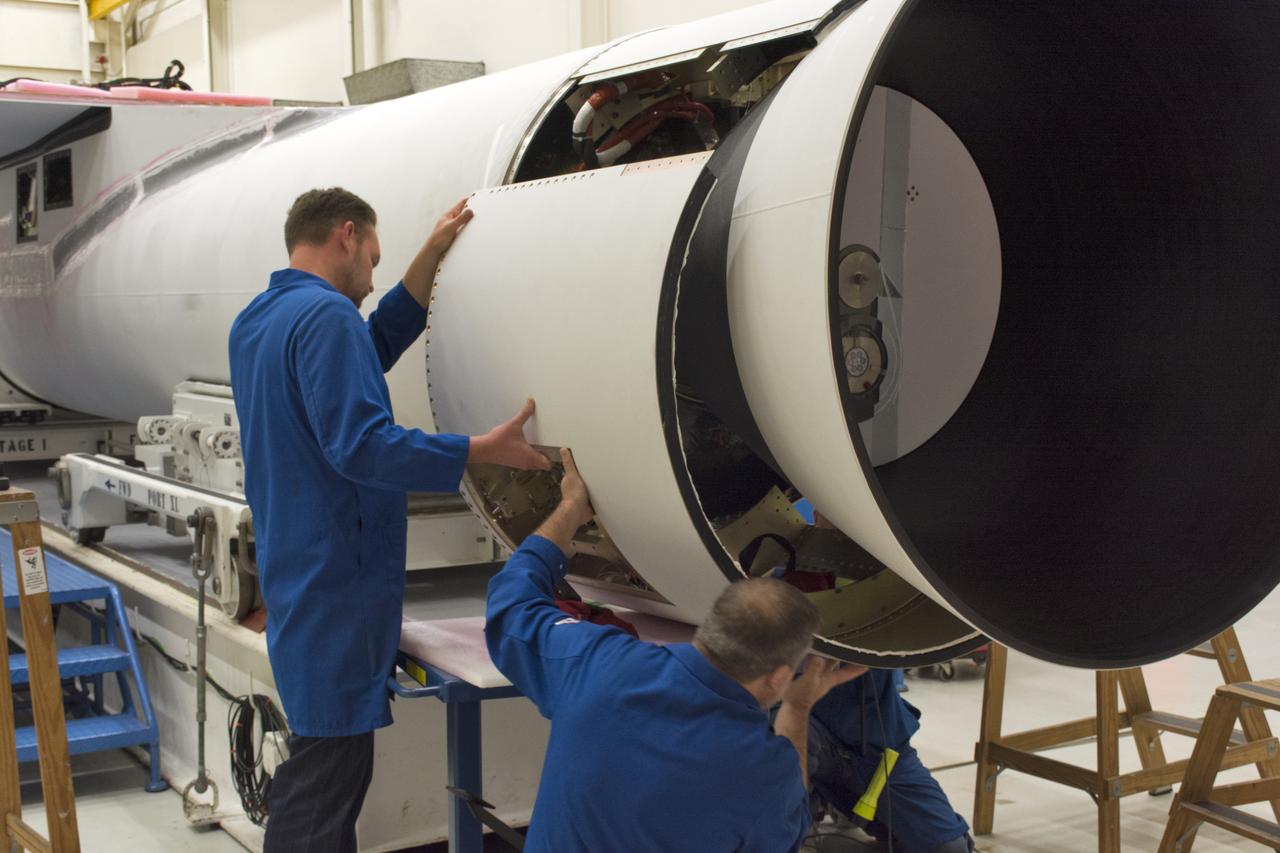

Technicians install the aft skirt on the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket July 8, 2017, inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. When the aft skirt is installed, the rudder and fins can be installed. The Pegasus rocket is being prepared for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer, or ICON, mission. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATKS's Pegasus XL, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
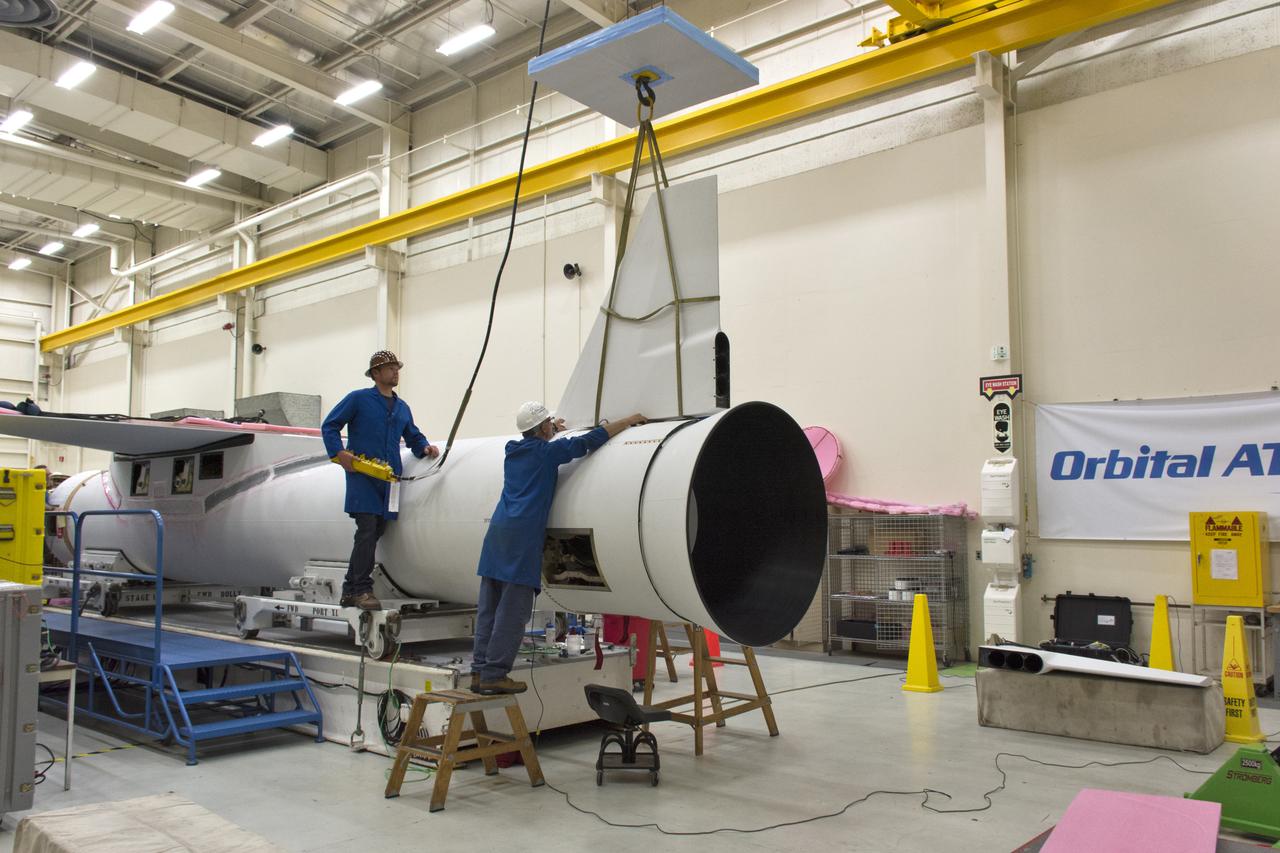

Technicians install the rudder on the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket July 8, 2017, inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Pegasus rocket is being prepared for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer, or ICON, mission. ICON will launch on June 15 from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATK's Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
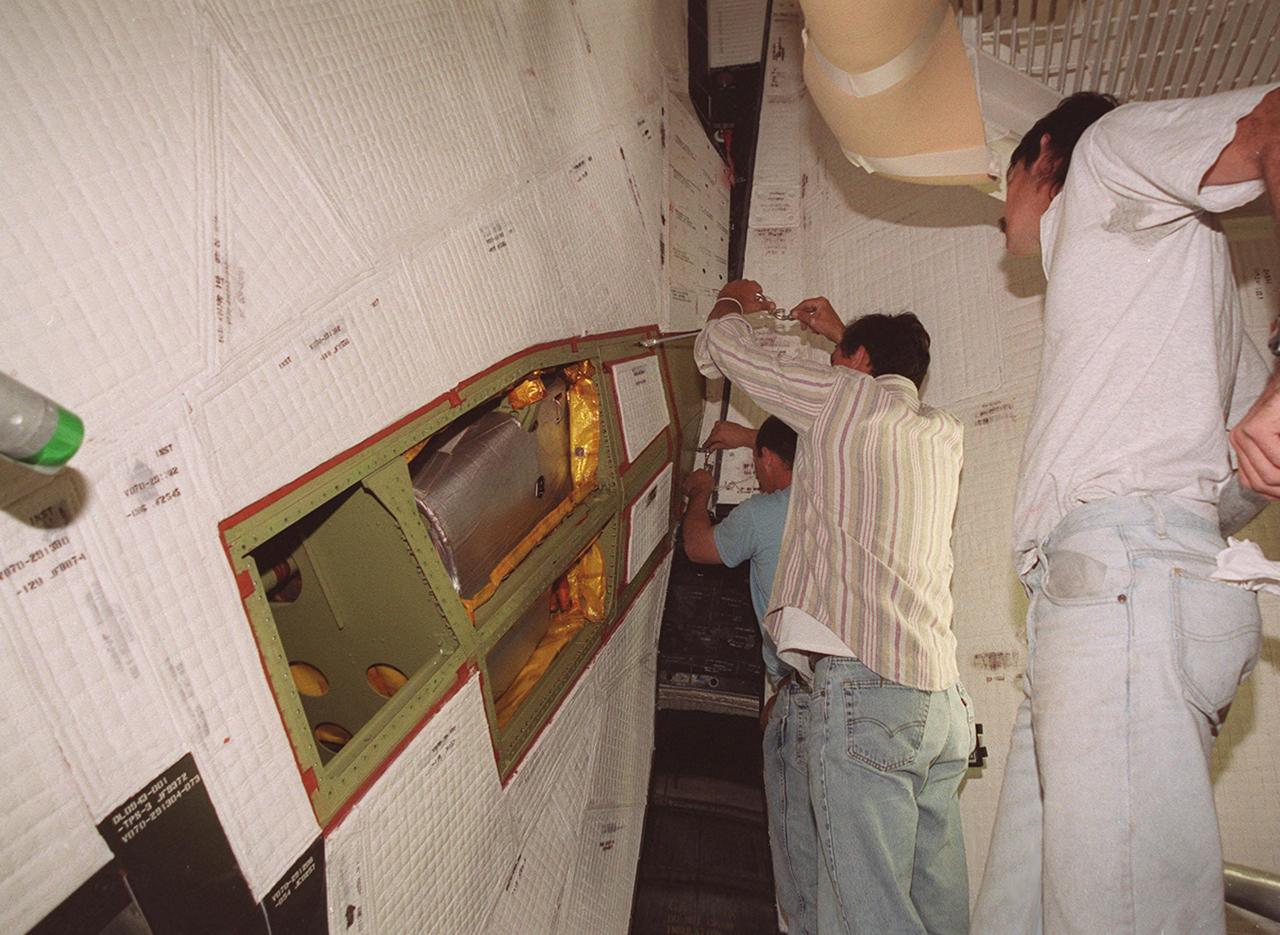

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians at Launch Pad 39A begin removing thermal blankets and panels from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis in order to reach the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. From left to right are Mark Noel, Bob Wright and Tod Biddle, with United Space Alliance. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station

HAMPTON, Va. –A 10-inch long ceramic model of the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser spacecraft is prepared for high-speed wind tunnel tests at NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va. The tests measure how much heat the winged vehicle would experience during ascent and re-entry through the atmosphere, including the spacecraft's lower- and upper-body flaps, elevons and a rudder. They're also helping the company obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the spacecraft's thermal protection system. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/David Bowman
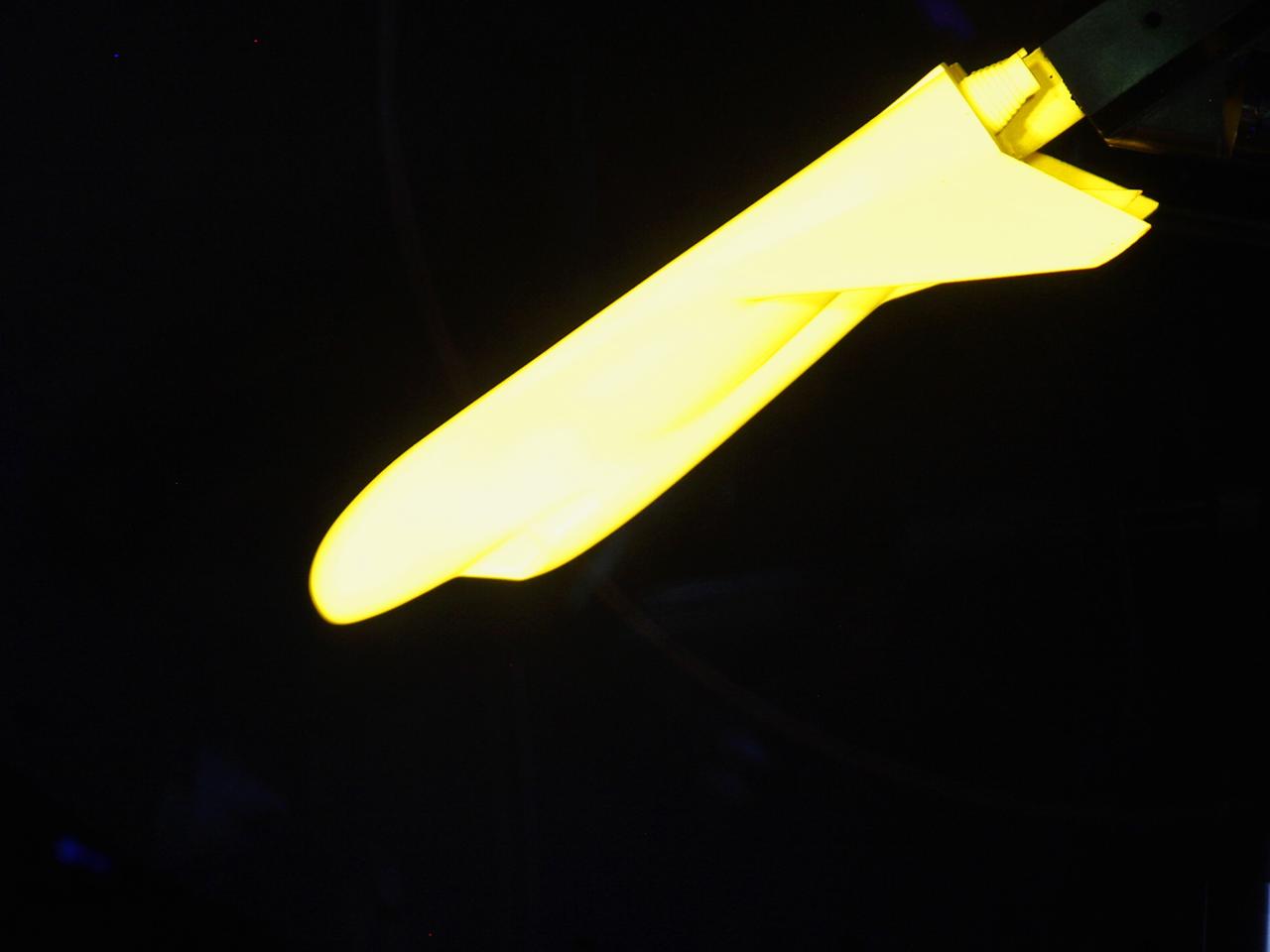

HAMPTON, Va. –A 10-inch long ceramic model of the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser spacecraft undergoes high-speed wind tunnel tests at NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va. The tests measure how much heat the winged vehicle would experience during ascent and re-entry through the atmosphere, including the spacecraft's lower- and upper-body flaps, elevons and a rudder. They're also helping the company obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the spacecraft's thermal protection system. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/David Bowman

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technicians at Launch Pad 39A look at the site of the power drive unit (PDU) for the rudder/speed brake on Shuttle Atlantis. From left are Mark Noel, Tod Biddle and Bob Wright. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
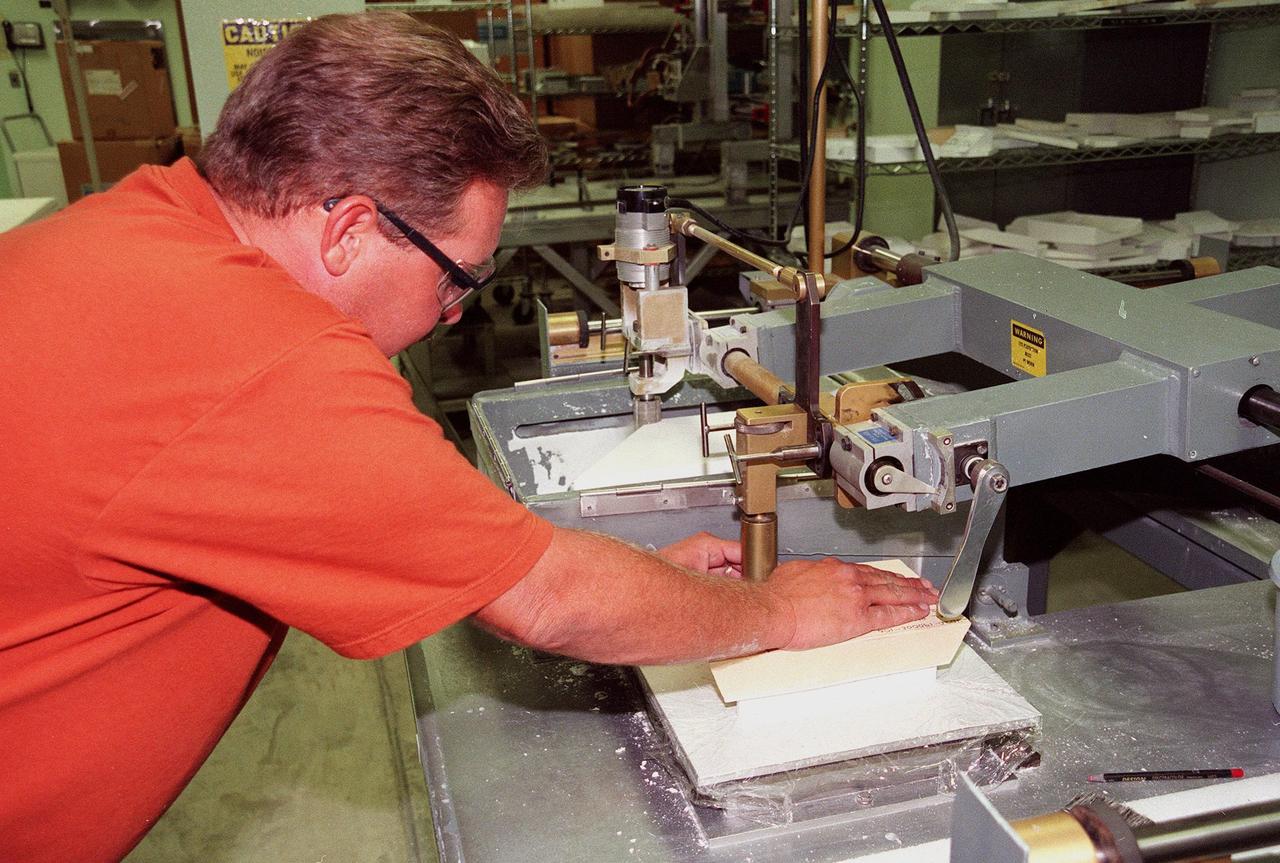

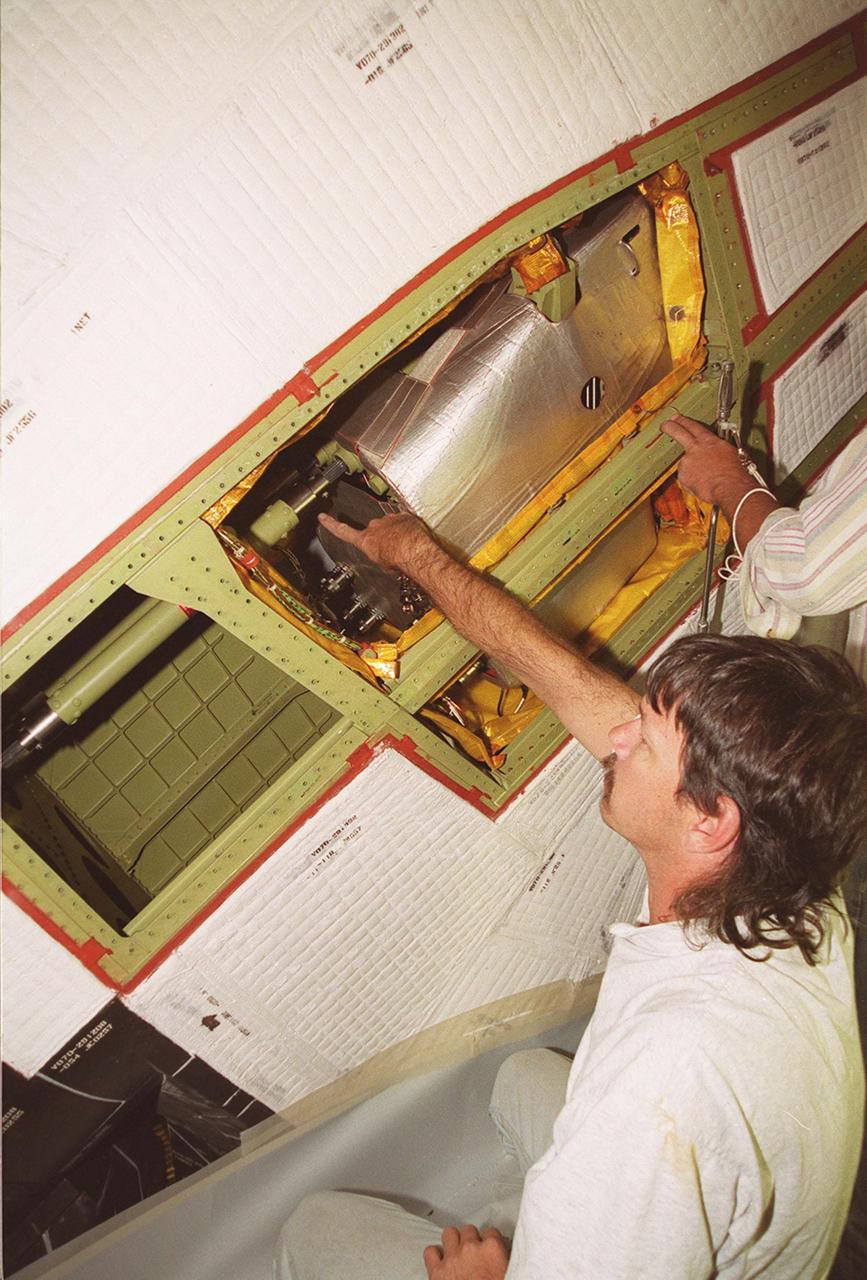
In the Tile Fabrication Shop, Tony Rollins, with United Space Alliance, cuts a High-Temperature Reusable Surface Insulation (HRSI) tile on a gun stock contour milling machine. About 70 percent of a Space Shuttle orbiter’s external surface is shielded from heat by a network of more than 24,000 tiles formed from a silica fiber compound. HRSI tiles cover the lower surface of the orbiter, areas around the forward windows, upper body flap, the base heat shield, the "eyeballs" on the front of the Orbital Maneuvering System (OMS) pods, and the leading and trailing edges of the vertical stabilizer and the rudder speed brake. They are generally 6 inches square, but may also be as large as 12 inches square in some areas, and 1 to 5 inches thick. More advanced materials such as Flexible Insulation Blankets have replaced tiles on some upper surfaces of the orbiter
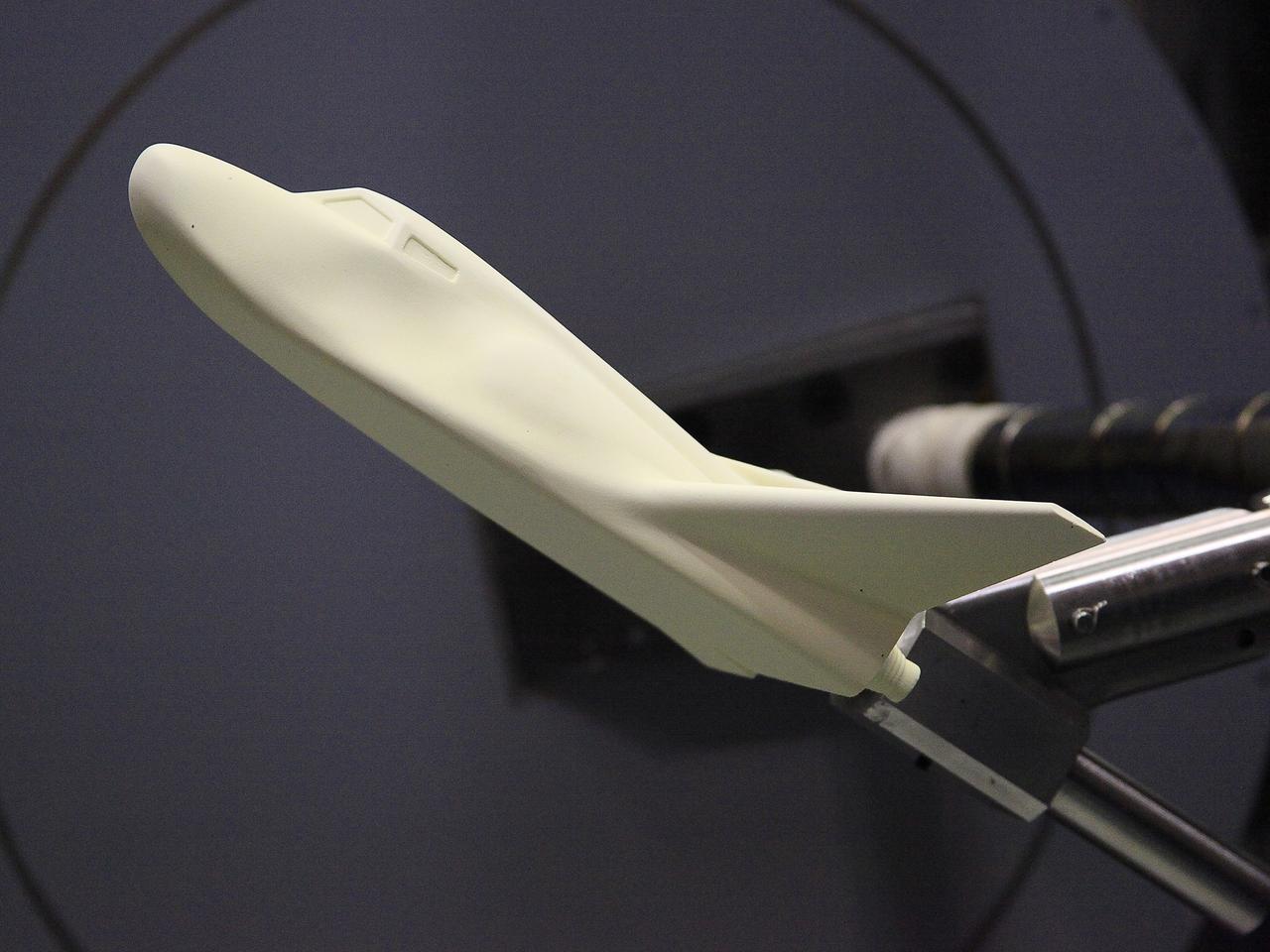
HAMPTON, Va. –A 10-inch long ceramic model of the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser spacecraft is prepared for high-speed wind tunnel tests at NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va. The tests measure how much heat the winged vehicle would experience during ascent and re-entry through the atmosphere, including the spacecraft's lower- and upper-body flaps, elevons and a rudder. They're also helping the company obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the spacecraft's thermal protection system. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/David Bowman

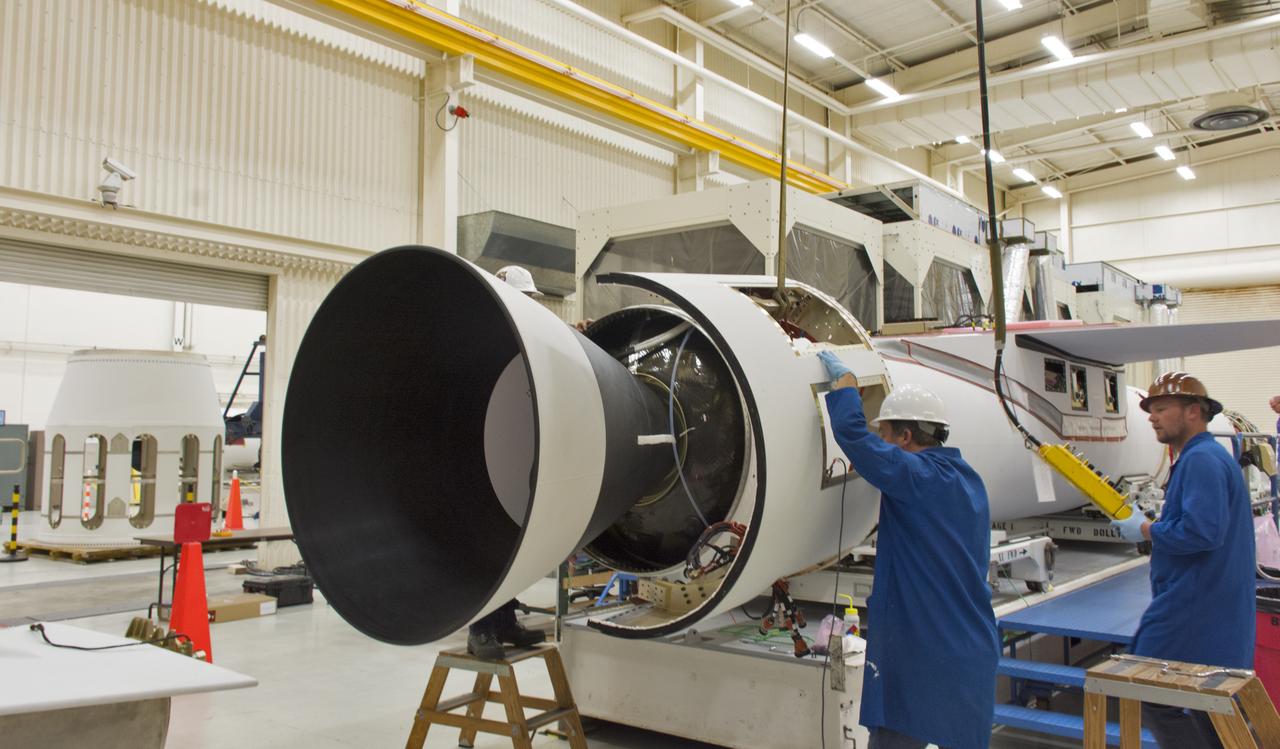
Technicians prepare the rudder for installation on the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket July 8, 2017, inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Pegasus rocket is being prepared for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer, or ICON, mission. ICON will launch on June 15 from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATK's Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

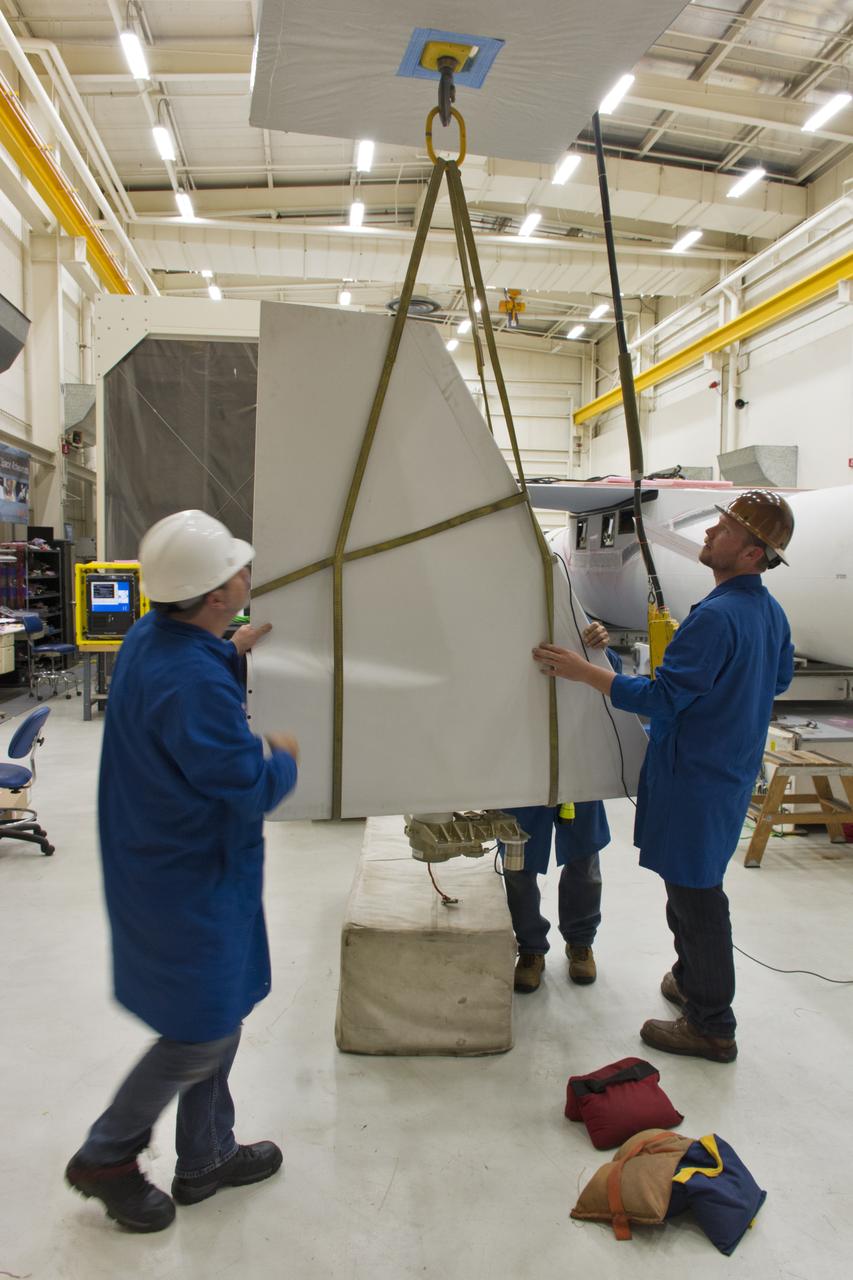
A technician installs the aft skirt on the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket July 8, 2017, inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. When the aft skirt is installed, the rudder and fins can be installed. The Pegasus rocket is being prepared for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer, or ICON, mission. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATKS's Pegasus XL, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

Outlined with gold stripes are the hinged nose strakes, modifications made to NASA's F-18 HARV (High Alpha Research Vehicle) at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. Actuated Nose Strakes for Enhanced Rolling (ANSER) were installed to fly the third and final phase in the HARV flight test project. Normally folded flush, the units -- four feet long and six inches wide -- can be opened independently to interact with the nose vortices to produce large side forces for control. Early wind tunnel tests indicated that the strakes would be as effective in yaw control at high angles of attack as rudders are at lower angles. Testing involved evaluation of the strakes by themselves as well as combined with the aircraft's Thrust Vectoring System. The strakes were designed by NASA's Langley Research Center, then installed and flight tested at Dryden.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With coverings removed from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis, Tod Biddle, a United Space Alliance (USA) technician, points to the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. The hands at right belong to Bob Wright, also a USA technician. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
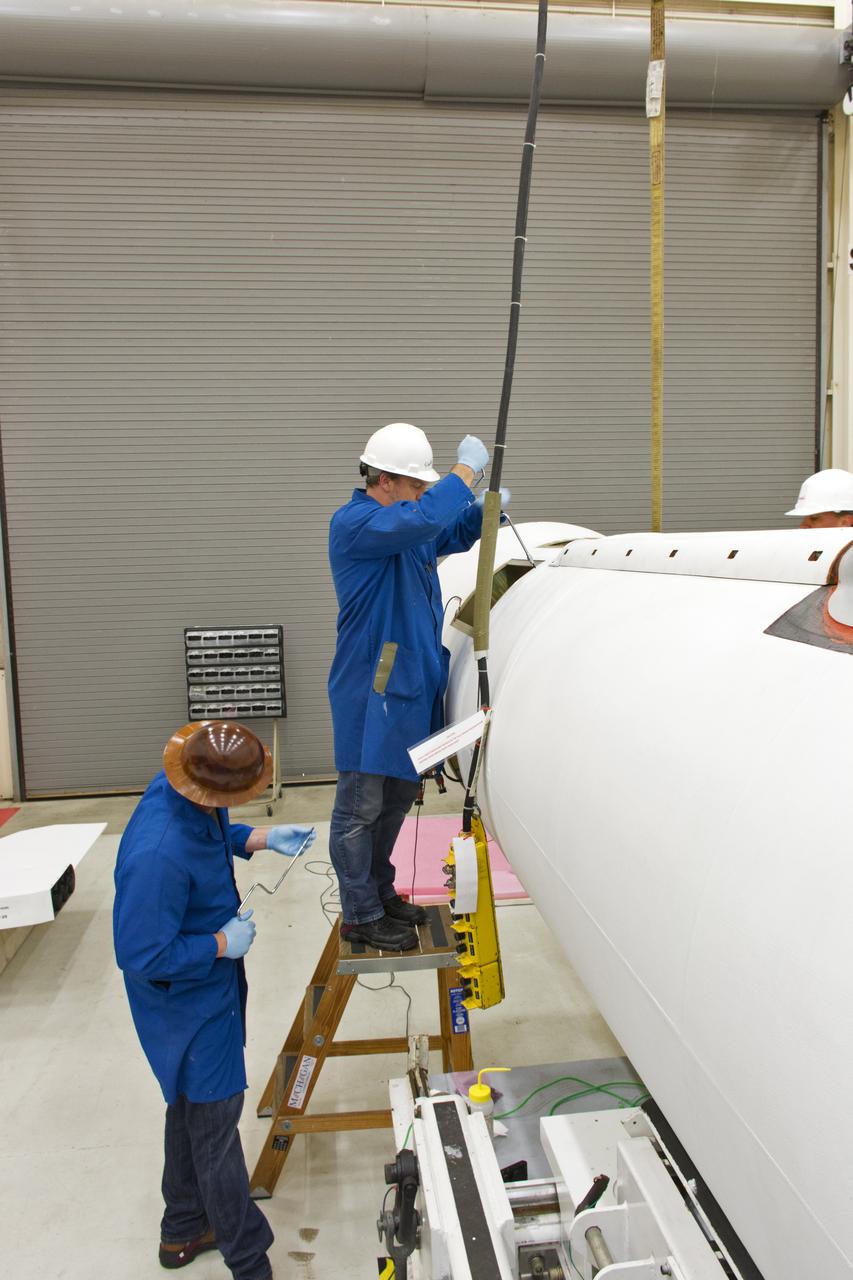

Technician install the aft skirt on the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket July 8, 2017, inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. When the aft skirt is installed, the rudder and fins can be installed. The Pegasus rocket is being prepared for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer, or ICON, mission. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on Orbital ATKS's Pegasus XL, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
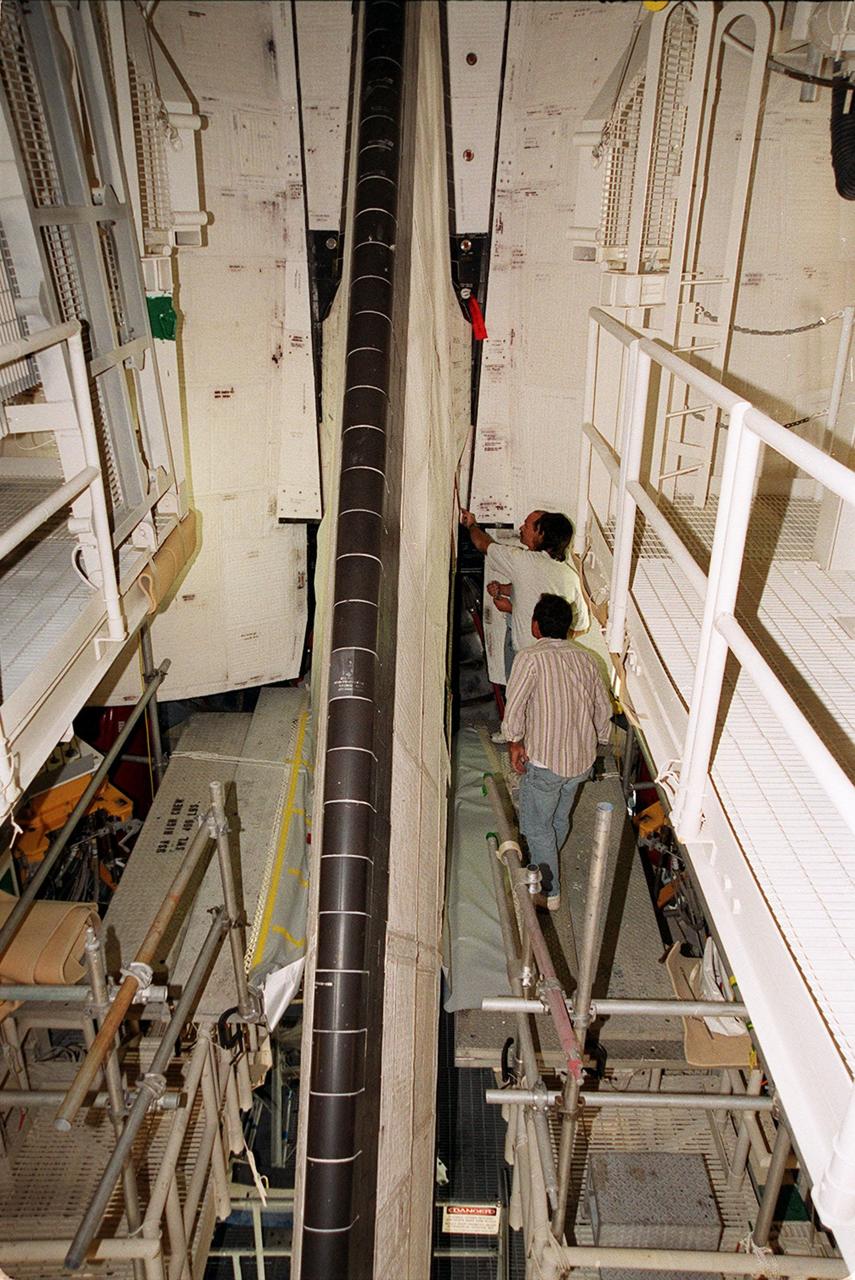

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technicians at Launch Pad 39A look at the site of the power drive unit (PDU) for the rudder/speed brake on Shuttle Atlantis. From left are Mark Noel, Tod Biddle and Bob Wright. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
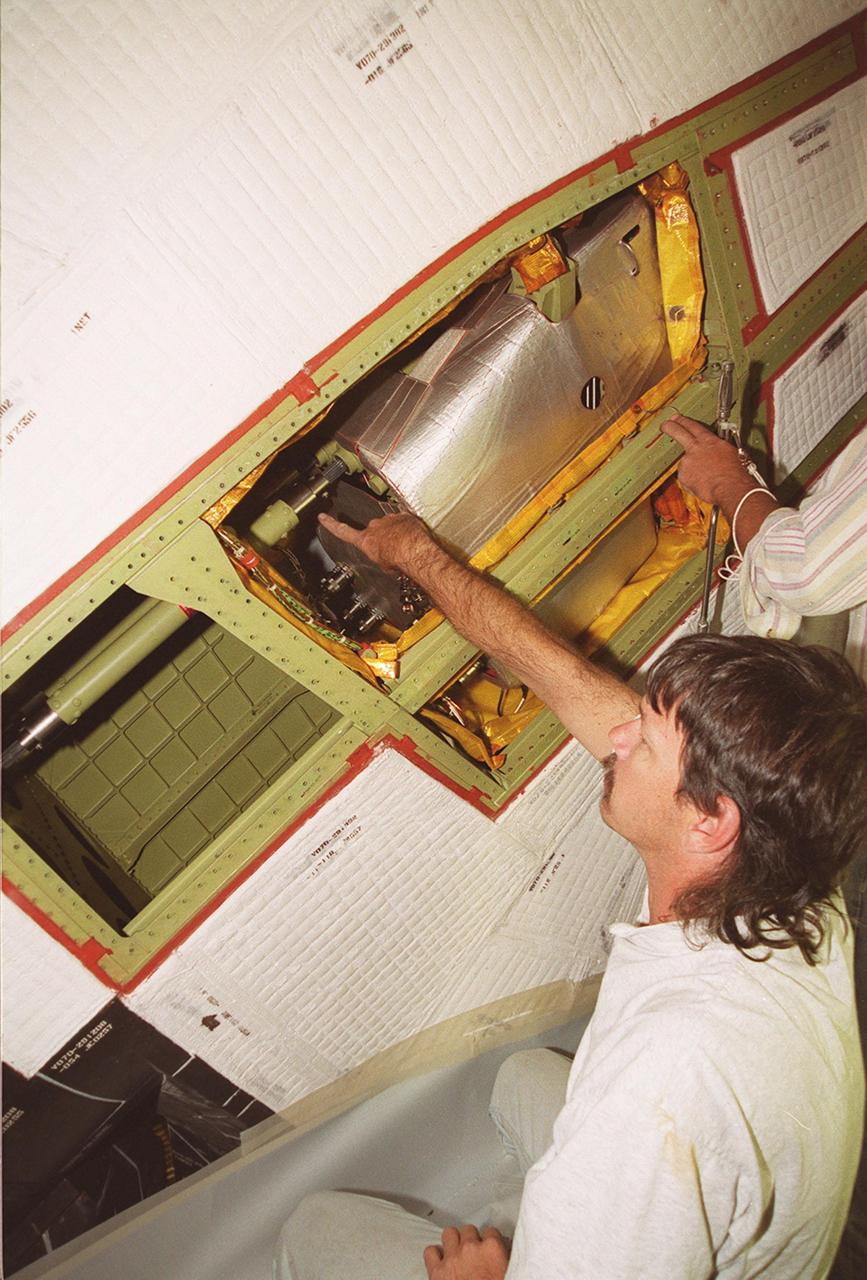

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With coverings removed from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis, Tod Biddle, a United Space Alliance (USA) technician, points to the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. The hands at right belong to Bob Wright, also a USA technician. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
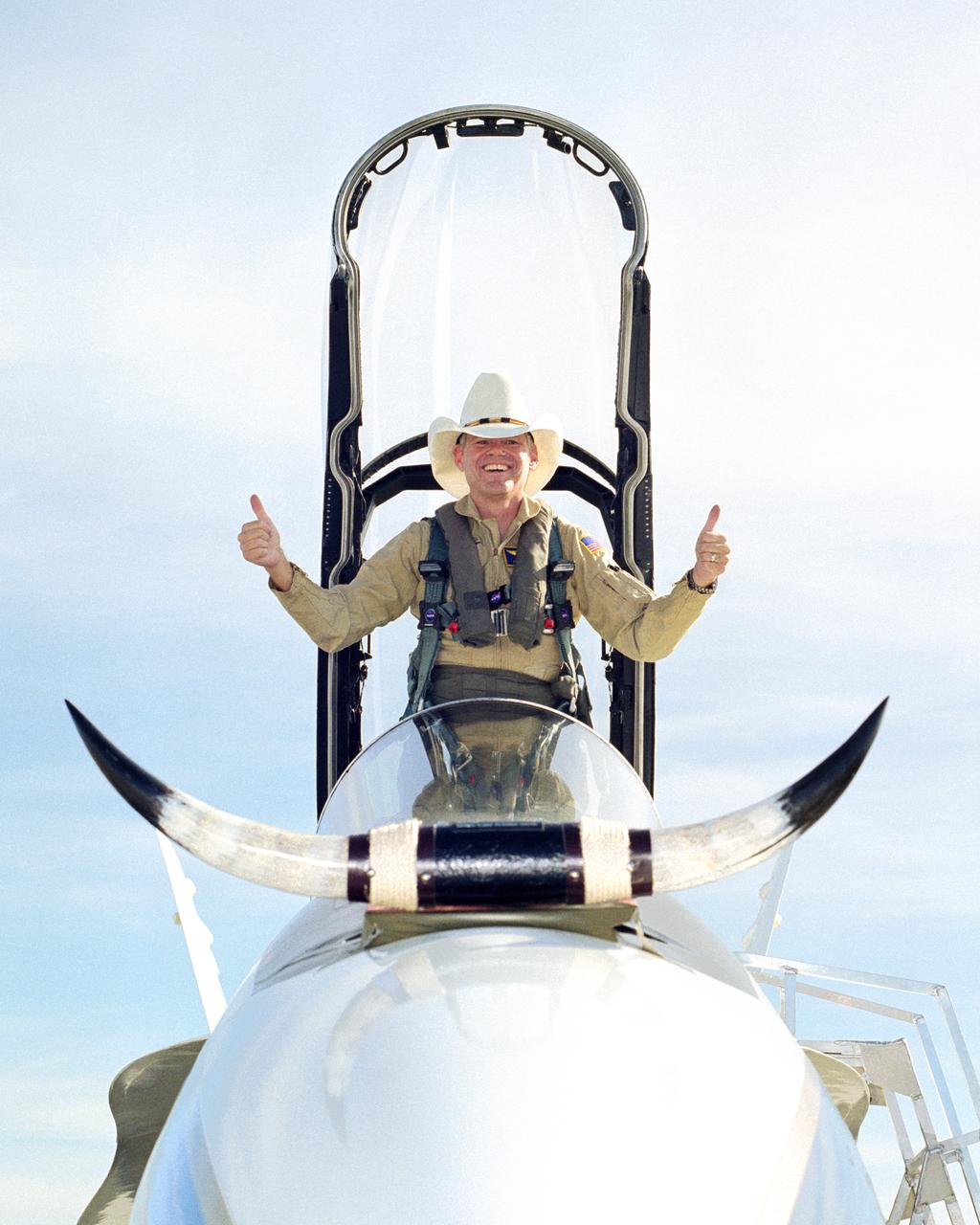

In a lighter mood, Ed Schneider gives a "thumbs-up" after his last flight at the Dryden Flight Research Center on September 19, 2000. Schneider arrived at the NASA Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility on July 5, 1982, as a Navy Liaison Officer, becoming a NASA research pilot one year later. He has been project pilot for the F-18 High Angle-of-Attack program (HARV), the F-15 aeronautical research aircraft, the NASA B-52 launch aircraft, and the SR-71 "Blackbird" aircraft. He also participated in such programs as the F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire, the FAA/NASA 720 Controlled Impact Demonstration, the F-14 Automatic Rudder Interconnect and Laminar Flow, and the F-104 Aeronautical Research and Microgravity projects.
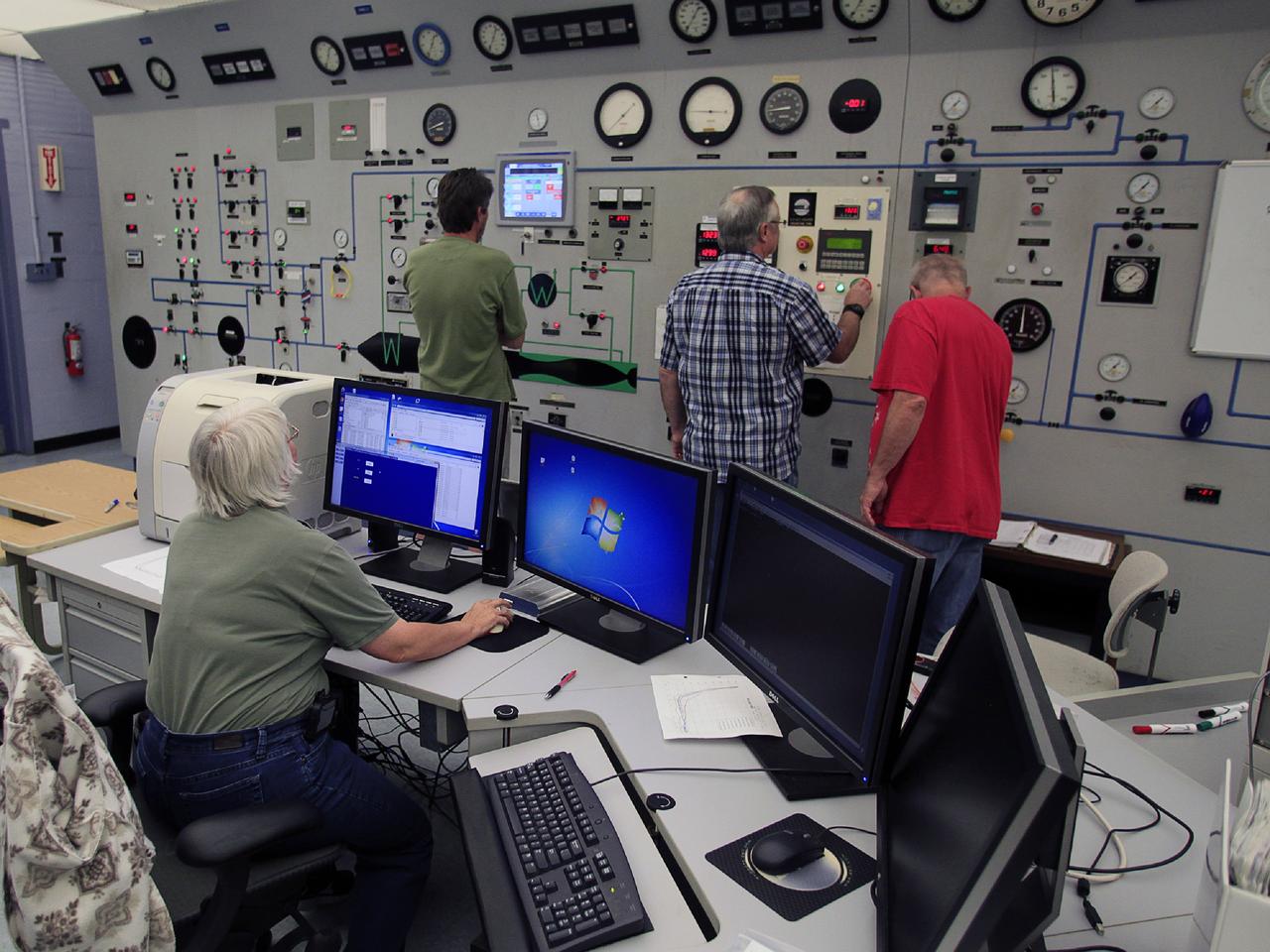

HAMPTON, Va. –Engineers monitor high-speed wind tunnel testing of a 10-inch long ceramic model of the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser spacecraft at NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va. The tests measure how much heat the winged vehicle would experience during ascent and re-entry through the atmosphere, including the spacecraft's lower- and upper-body flaps, elevons and a rudder. They're also helping the company obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the spacecraft's thermal protection system. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/David Bowman
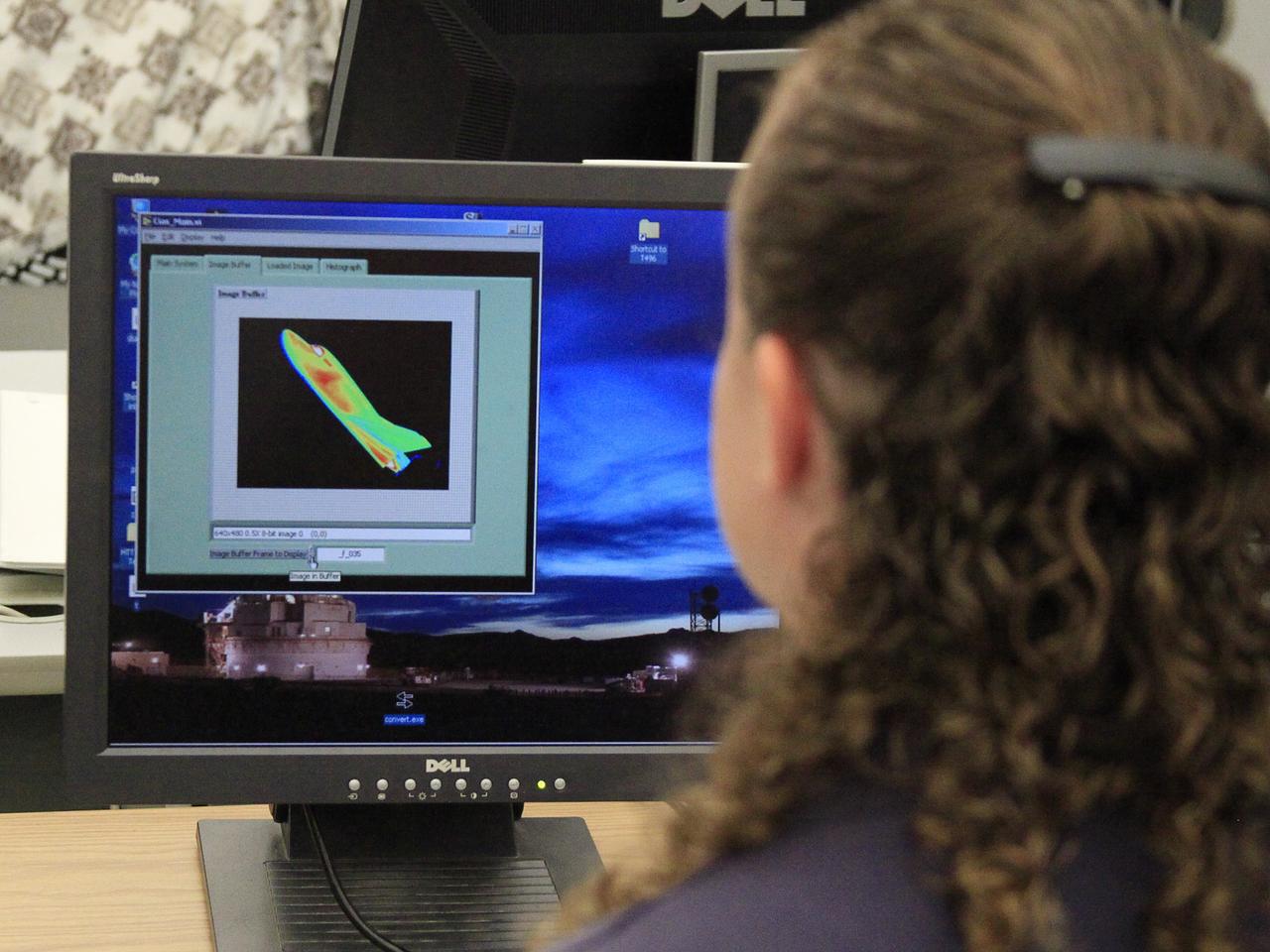

HAMPTON, Va. –An engineer monitors high-speed wind tunnel testing of a 10-inch long ceramic model of the Sierra Nevada Corporation, or SNC, Dream Chaser spacecraft at NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va. The tests measure how much heat the winged vehicle would experience during ascent and re-entry through the atmosphere, including the spacecraft's lower- and upper-body flaps, elevons and a rudder. They're also helping the company obtain necessary data for the material selection and design of the spacecraft's thermal protection system. SNC is continuing the development of its Dream Chaser spacecraft under the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP and its industry partners, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: NASA/David Bowman
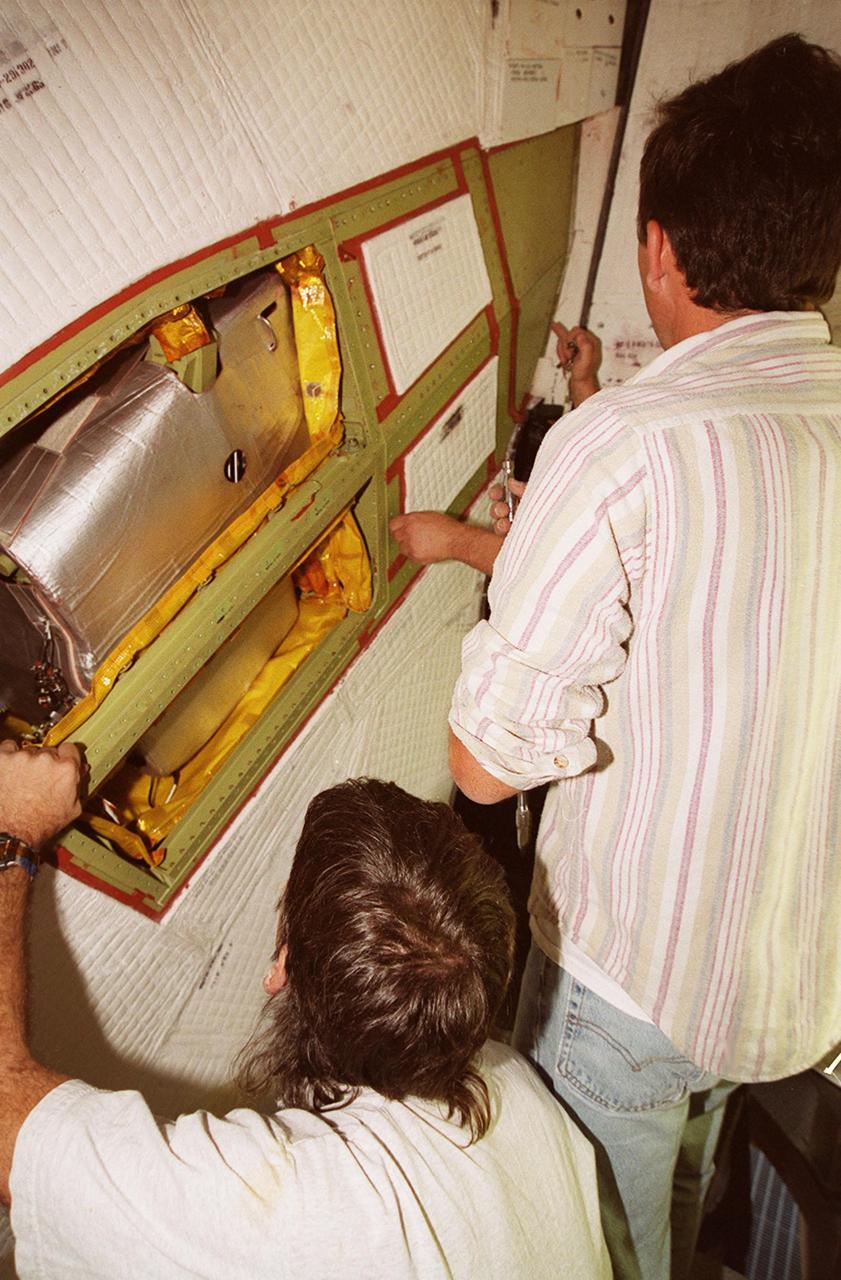

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technicians (left to right) Tod Biddle, Bob Wright and Mark Noel (hidden) remove the coverings from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis to reveal the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
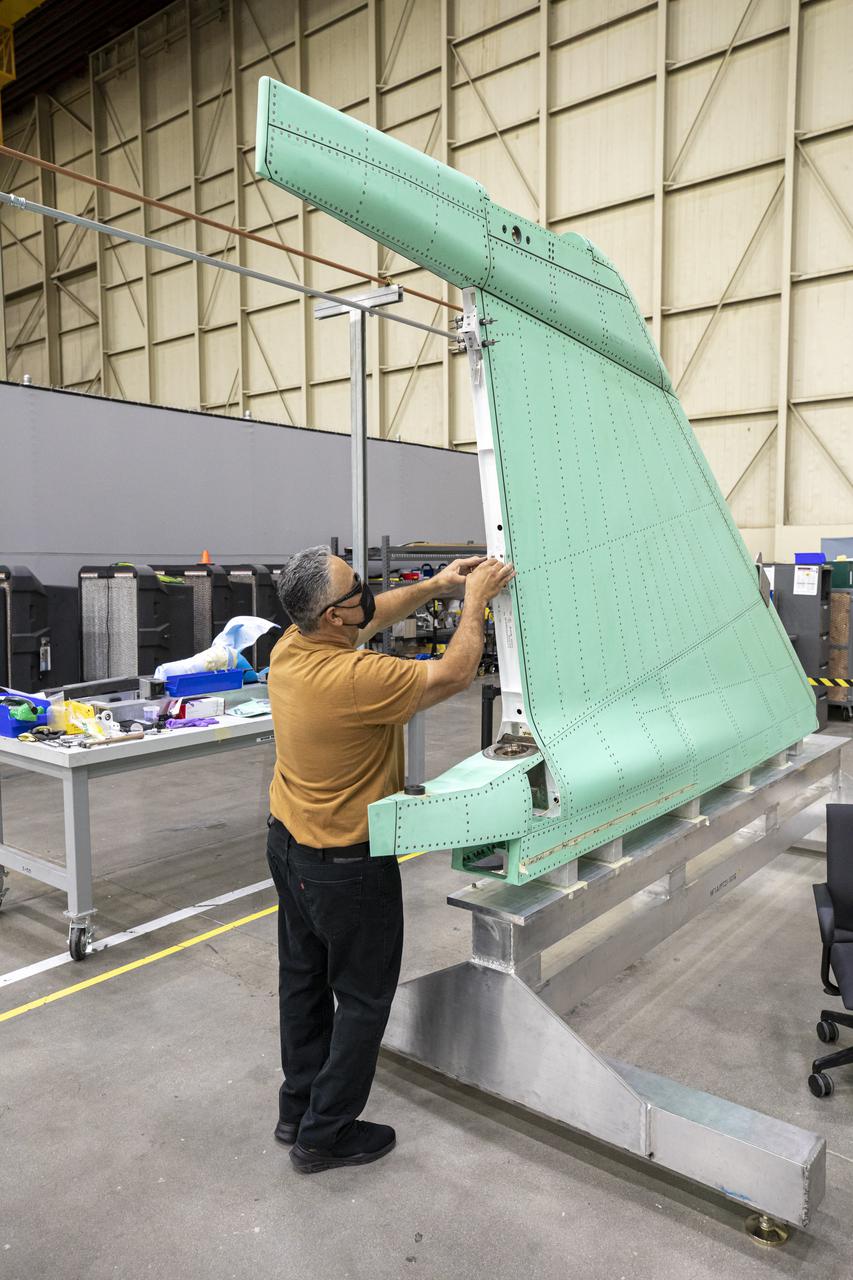

A technician is shown working on the X-59 vertical tail prior to installation at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The aircraft will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 530 Vertical Tail, Landing Gear Bay Doors Date: 4/28/2021