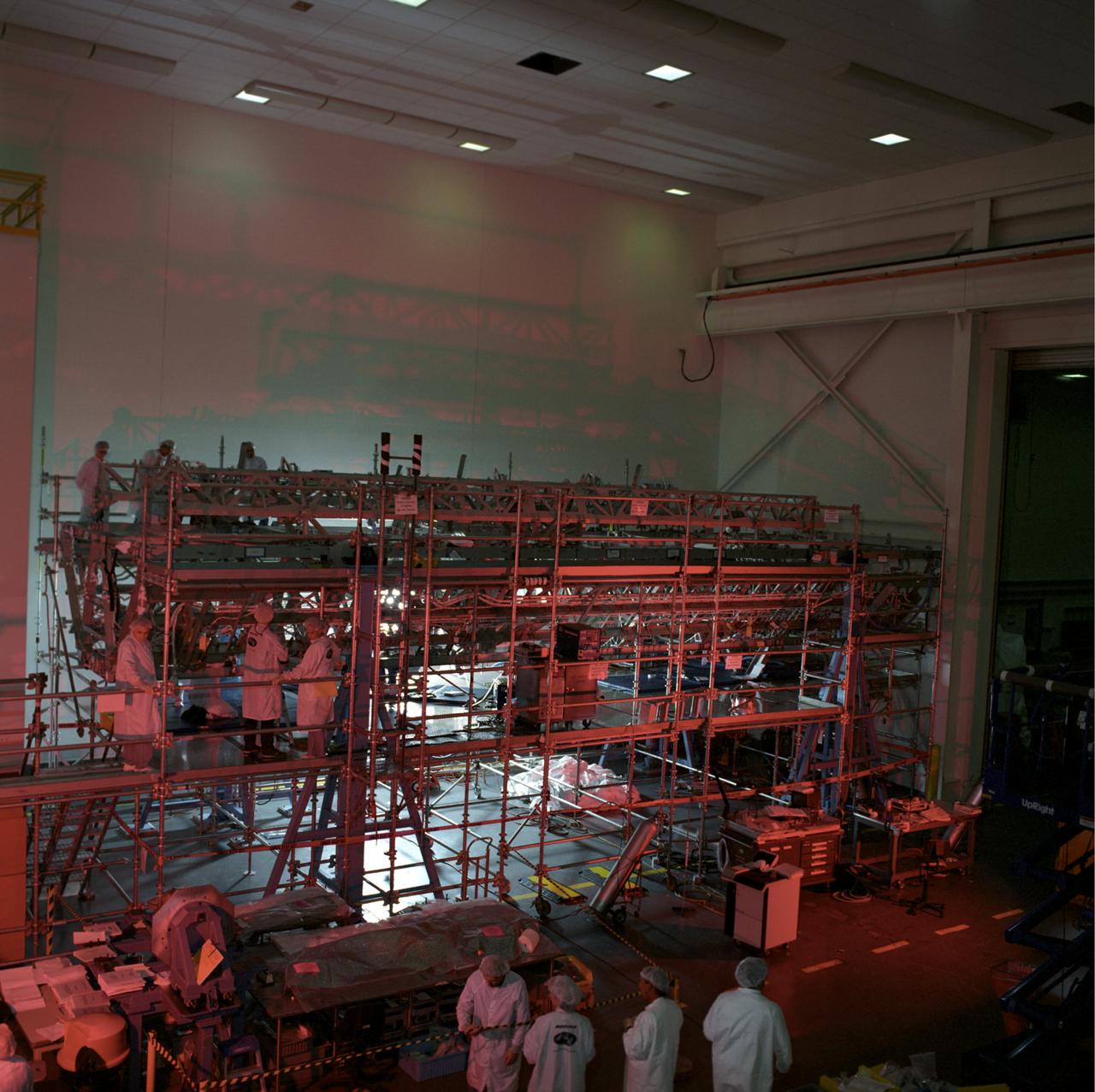

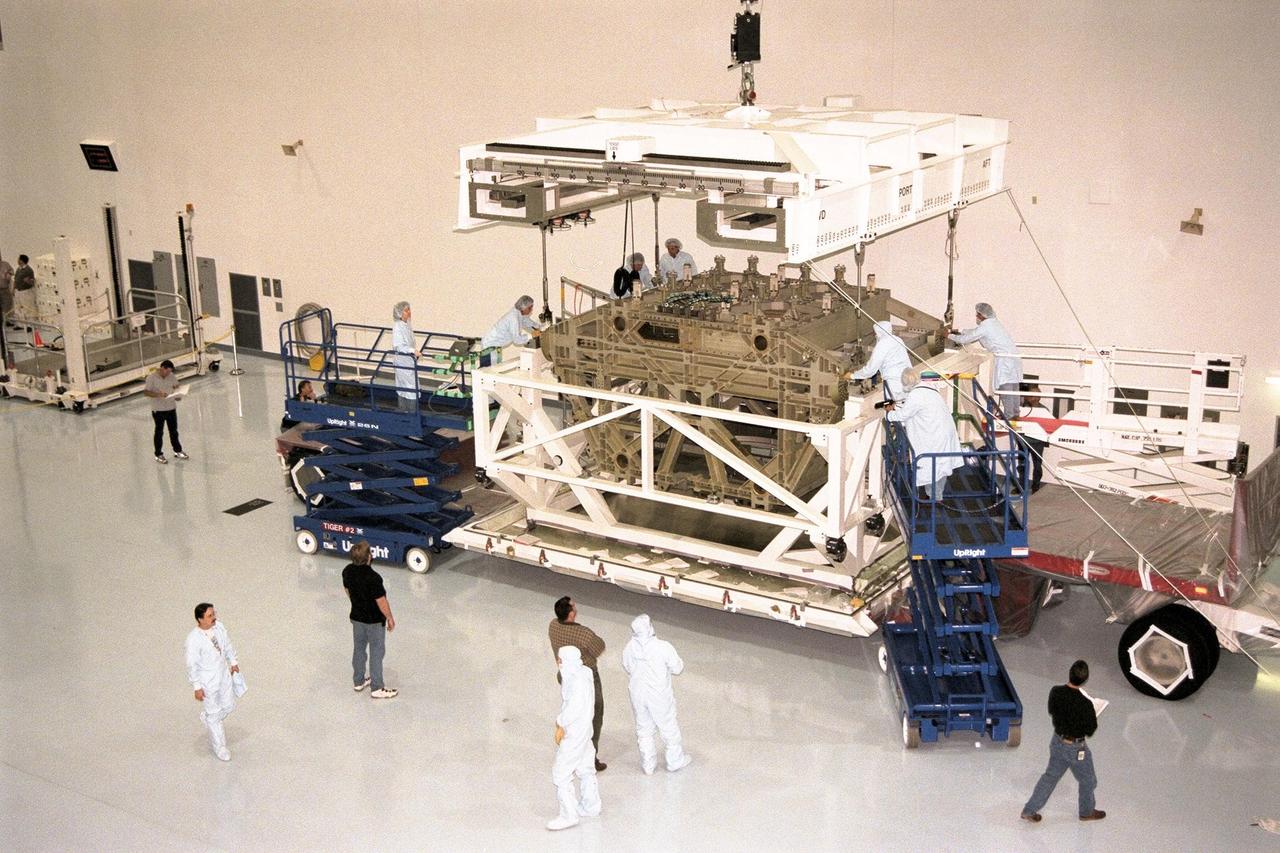
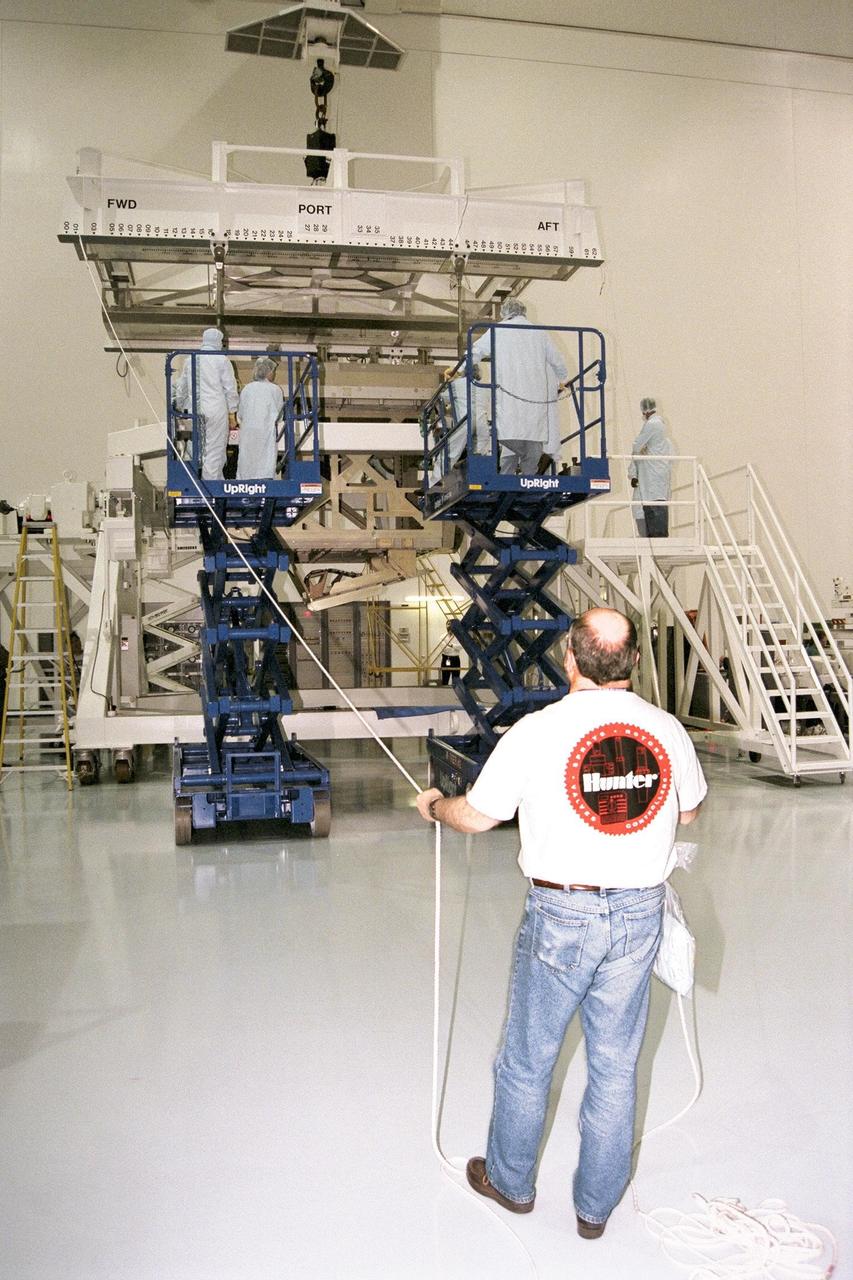
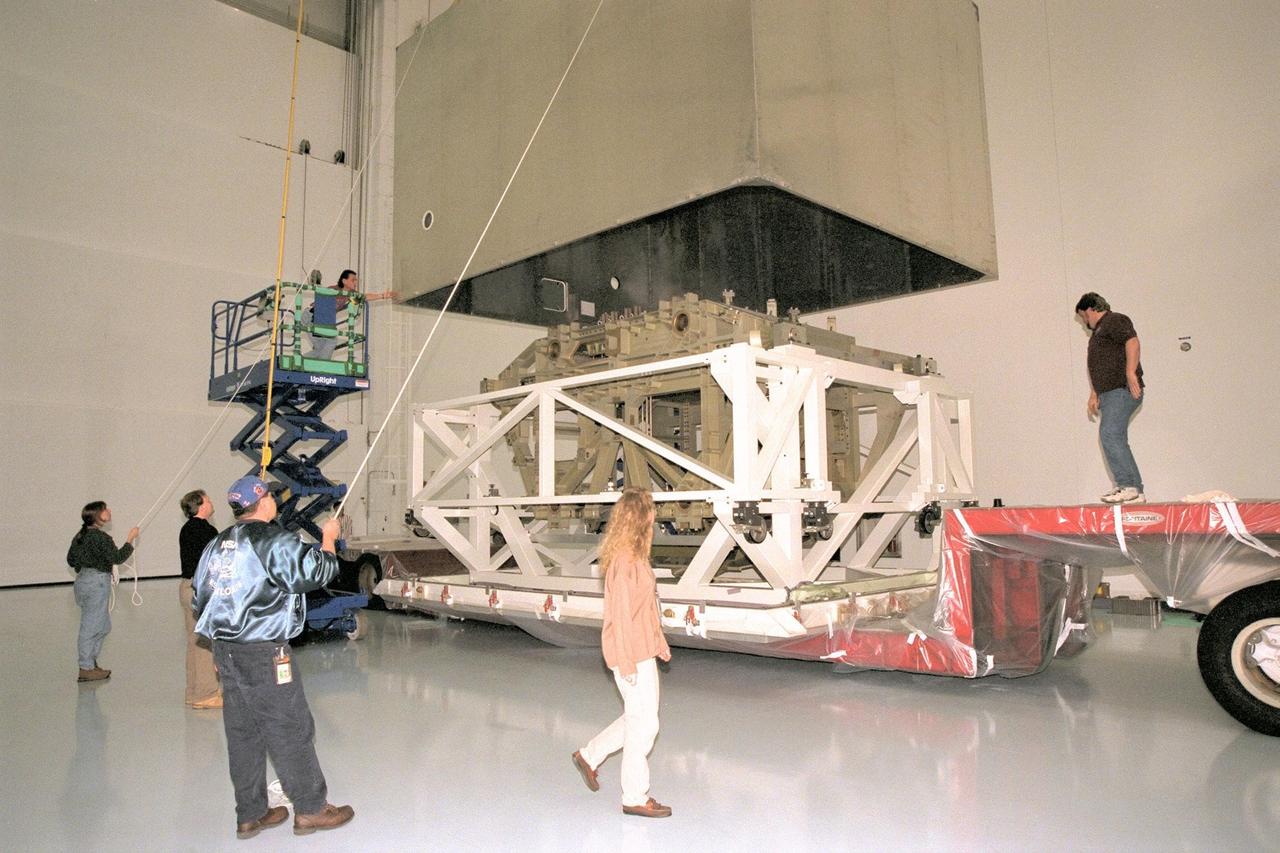
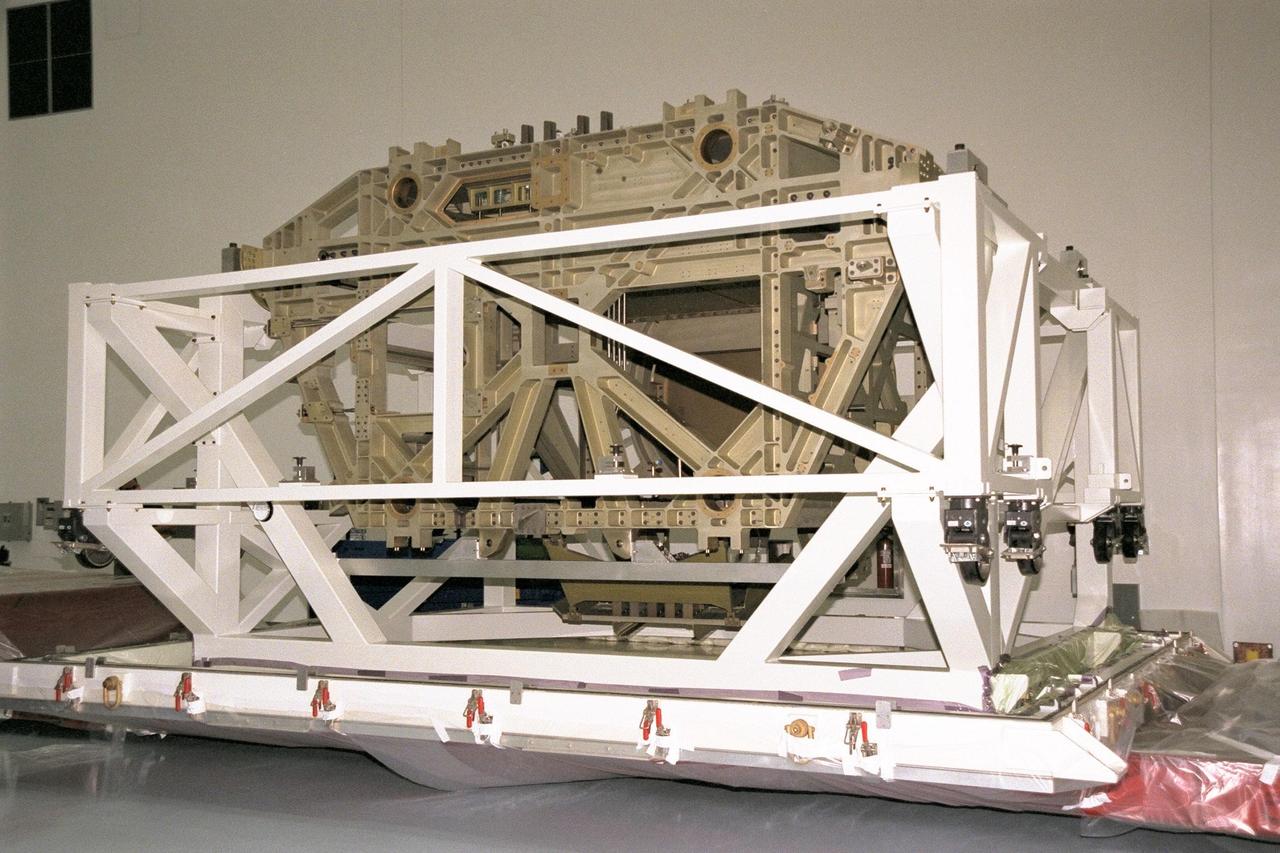
This image shows the Integrated Truss Assembly S-1 (S-One), the Starboard Side Thermal Radiator Truss, for the International Space Station (ISS) undergoing final construction in the Space Station manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The S1 truss provides structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels, which use ammonia to cool the Station's complex power system. Delivered and installed by the STS-112 mission, the S1 truss, attached to the S0 (S Zero) truss installed by the previous STS-110 mission, flows 637 pounds of anhydrous ammonia through three heat rejection radiators. The truss is 45-feet long, 15-feet wide, 10-feet tall, and weighs approximately 32,000 pounds. Manufactured by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, California, the truss primary structure was transferred to the Marshall Space Flight Center in February 1999 for hardware installations and manufacturing acceptance testing.
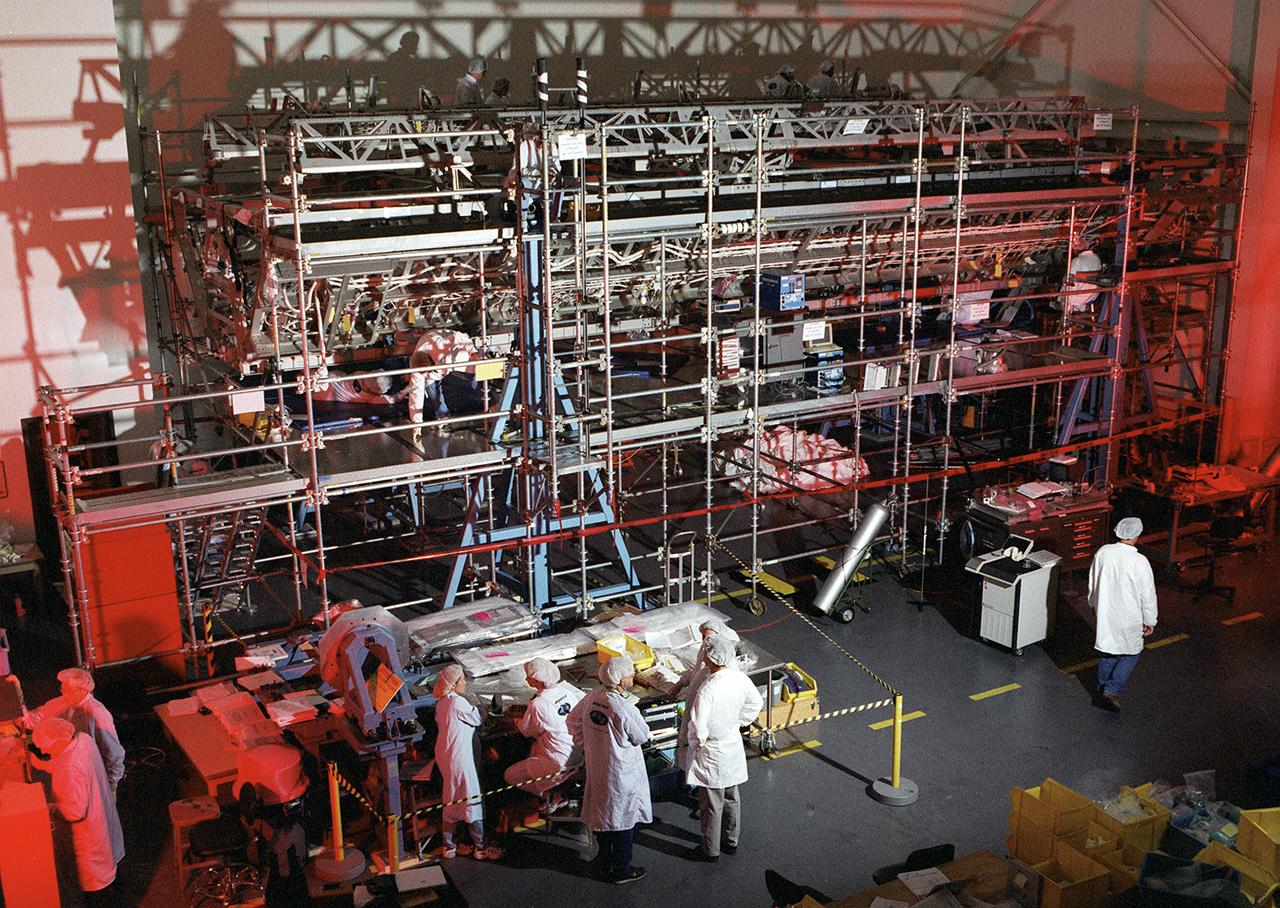

Boeing Company technicians assemble the S-1 truss (starboard side truss) for the International Space Station at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
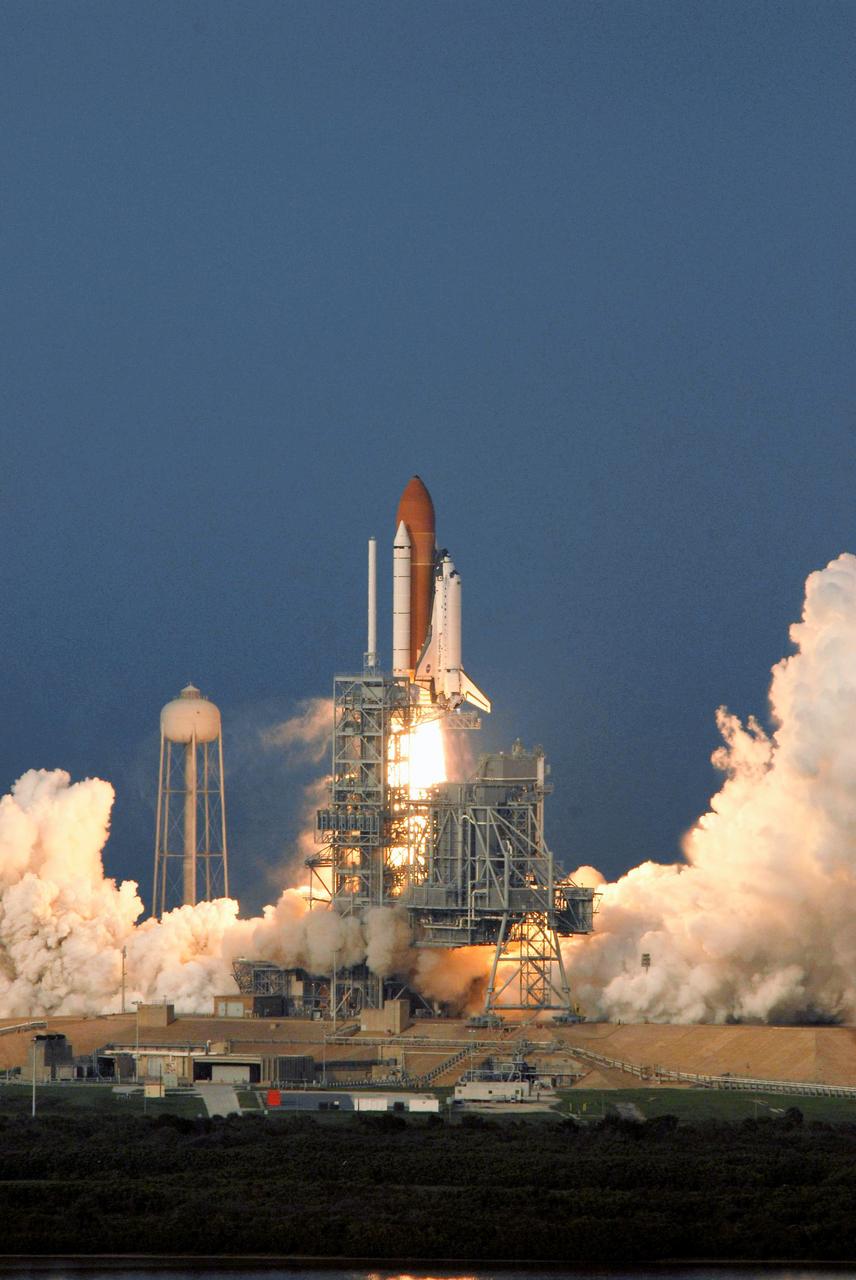

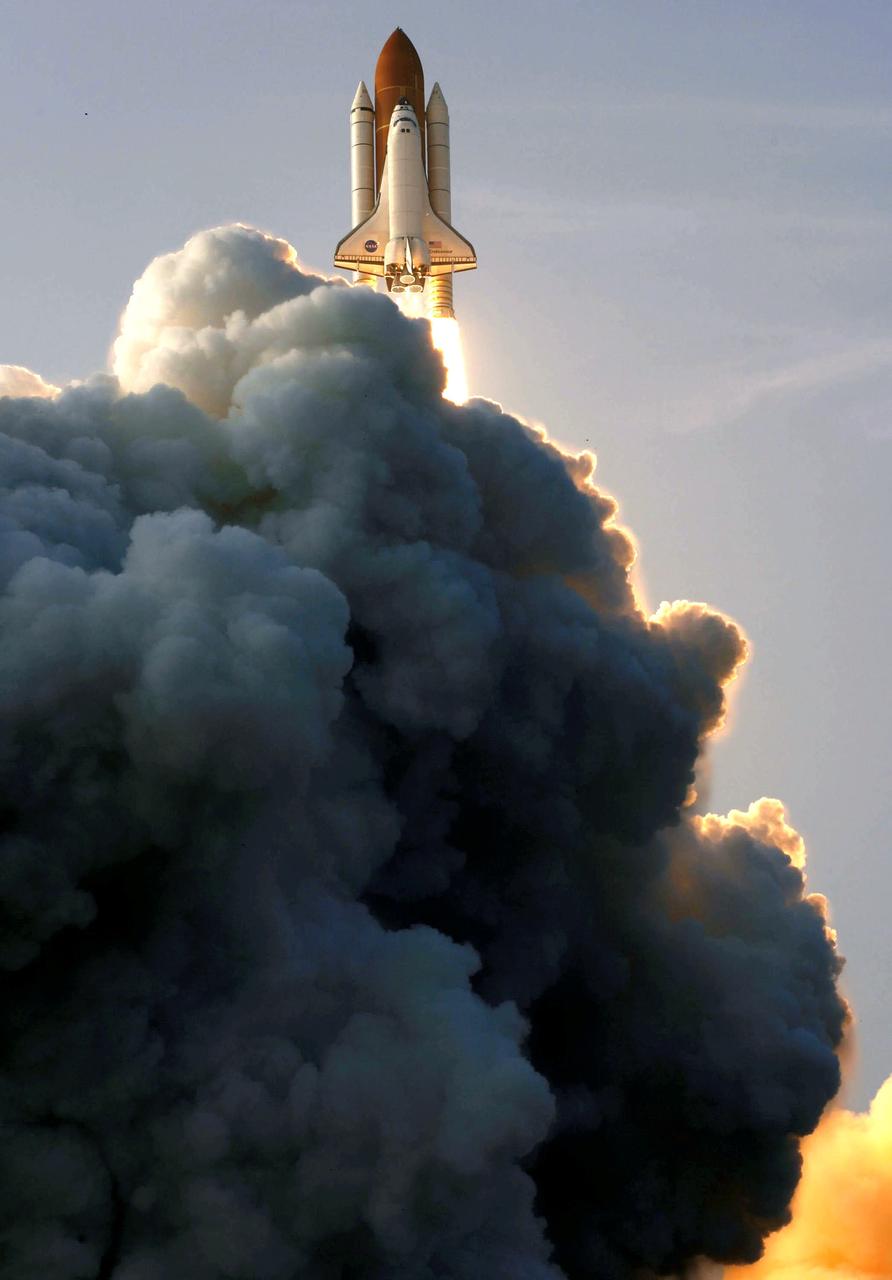
Enroute to the International Space Station (ISS), Space Shuttle Endeavor and its seven member STS-118 crew, blasted off from the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center on August 8, 2007. Construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the third Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.
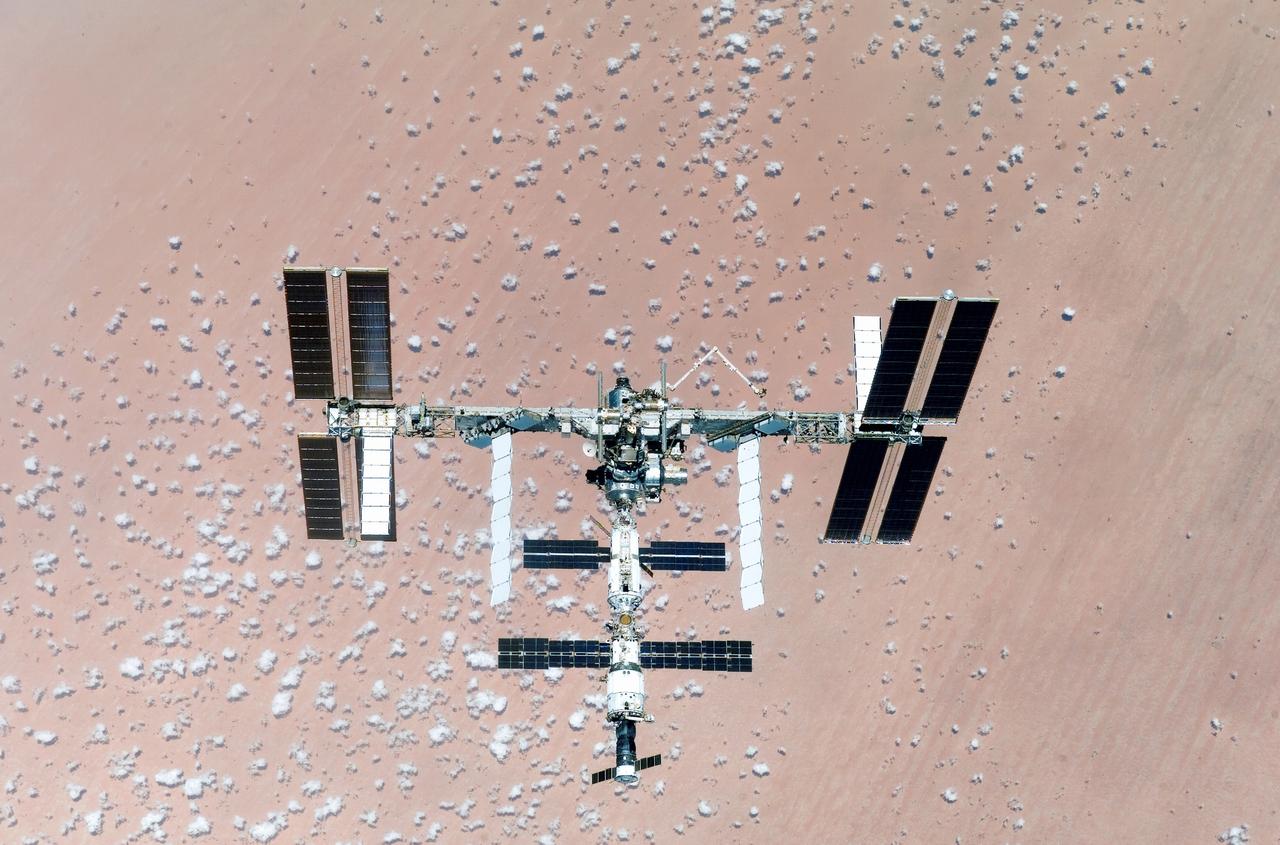

Back dropped by the colorful Earth, the International Space Station (ISS) boasts its newest configuration upon the departure of Space Shuttle Endeavor and STS-118 mission. Days earlier, construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of supplies.
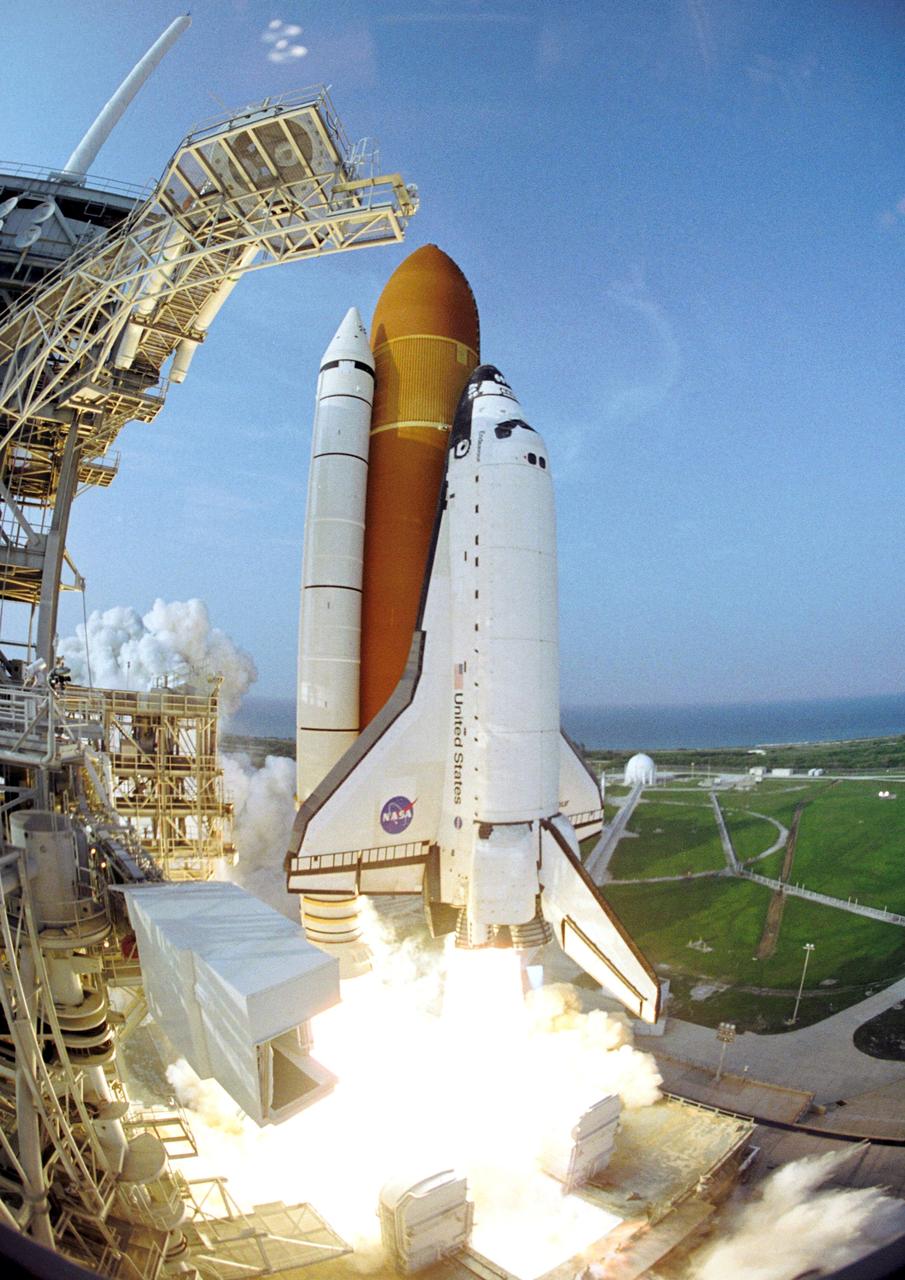

Enroute to the International Space Station (ISS), Space Shuttle Endeavor and its seven member STS-118 crew, blasted off from the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center on August 8, 2007. Construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the third Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.
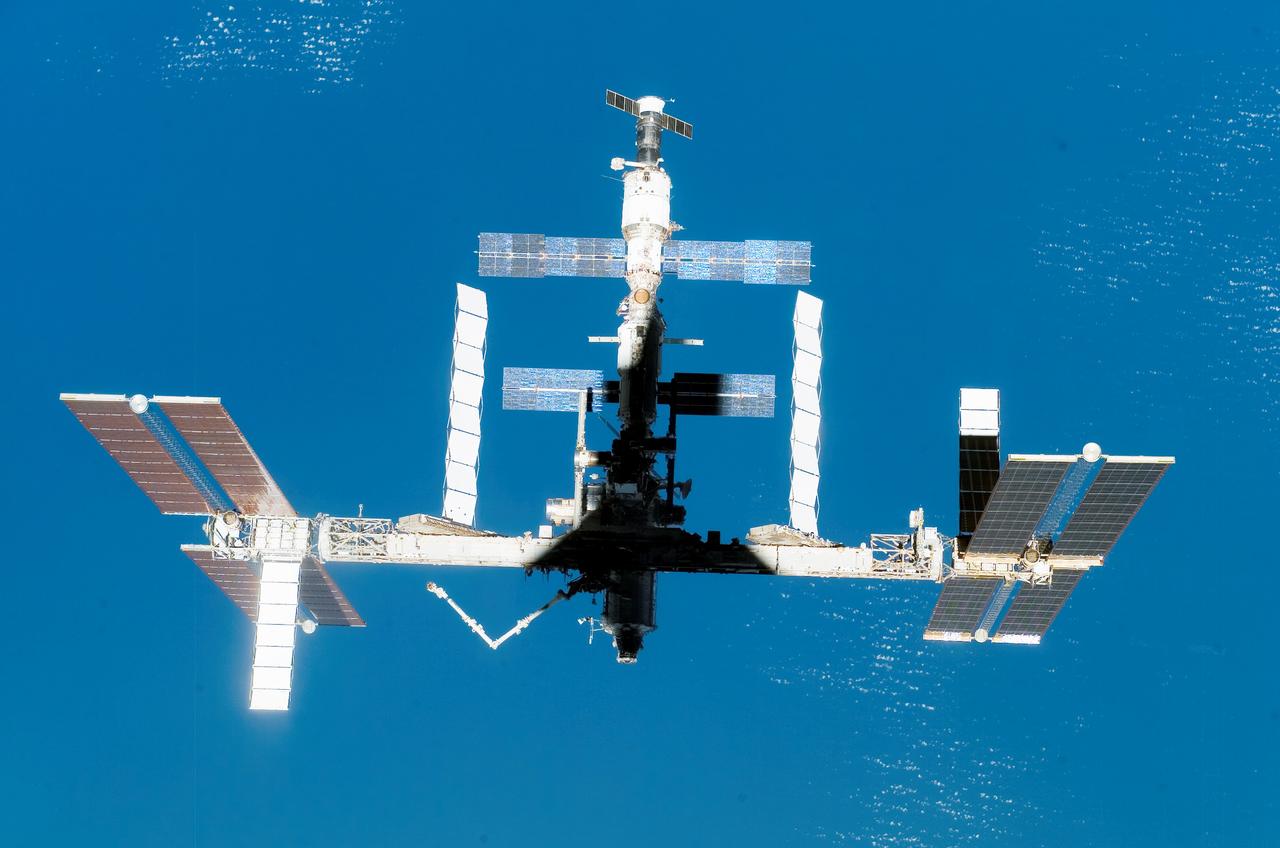

Back dropped by the blue Earth, the International Space Station (ISS) boasts its newest configuration upon the departure of Space Shuttle Endeavor and STS-118 mission. Days earlier, construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.

Enroute to the International Space Station (ISS), Space Shuttle Endeavor and its seven member STS-118 crew, blasted off from the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center on August 8, 2007. Construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the third Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.
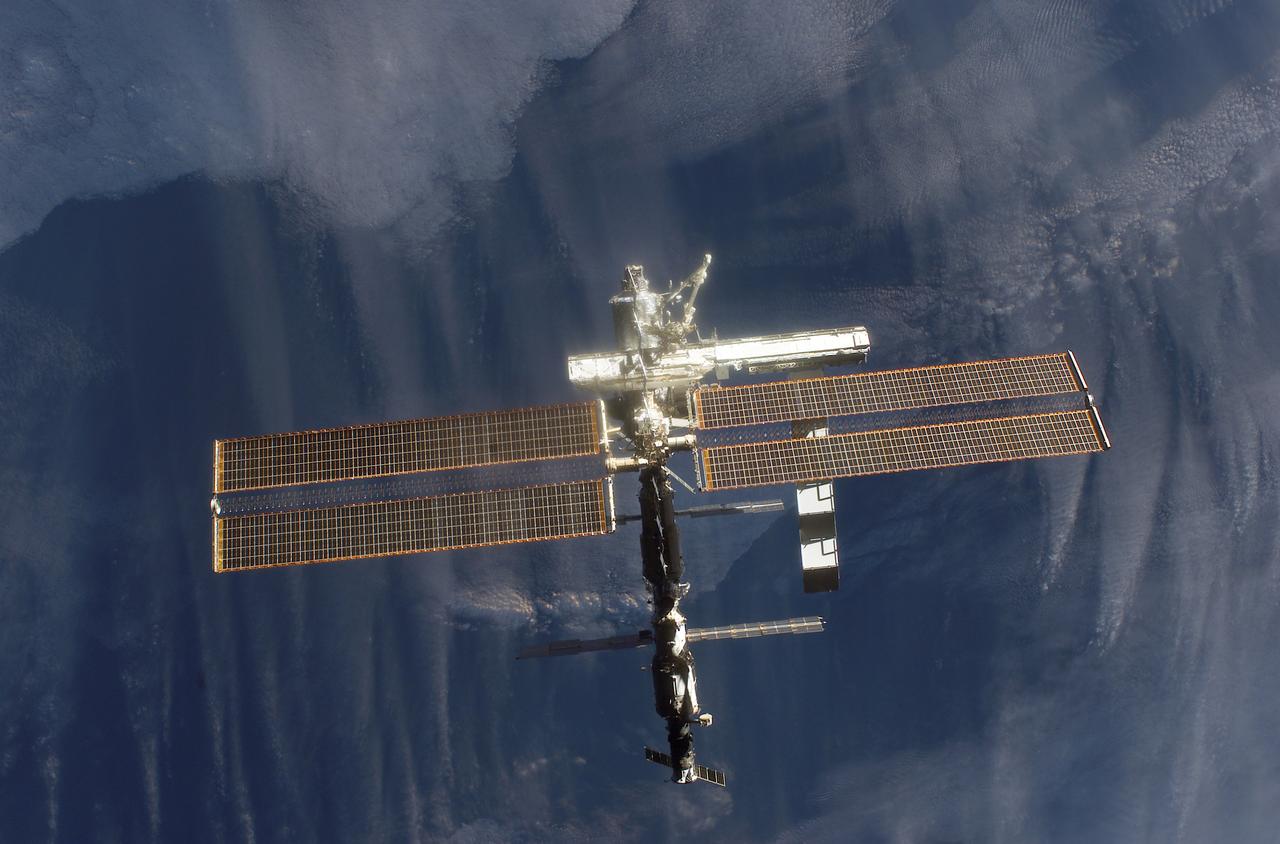

This image of the International Space Station (ISS) was photographed by one of the crewmembers of the STS-112 mission following separation from the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis as the orbiter pulled away from the ISS. The newly added S1 truss is visible in the center frame. The primary payloads of this mission, International Space Station Assembly Mission 9A, were the Integrated Truss Assembly S-1 (S-One), the Starboard Side Thermal Radiator Truss,and the Crew Equipment Translation Aid (CETA) cart to the ISS. The S1 truss provides structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels, which use ammonia to cool the Station's complex power system. The S1 truss was attached to the S0 (S Zero) truss, which was launched on April 8, 2002 aboard the STS-110, and flows 637 pounds of anhydrous ammonia through three heat rejection radiators. The truss is 45-feet long, 15-feet wide, 10-feet tall, and weighs approximately 32,000 pounds. The CETA cart was attached to the Mobil Transporter and will be used by assembly crews on later missions. Manufactured by the Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, California, the truss primary structure was transferred to the Marshall Space Flight Center in February 1999 for hardware installations and manufacturing acceptance testing. The launch of the STS-112 mission occurred on October 7, 2002, and its 11-day mission ended on October 18, 2002.
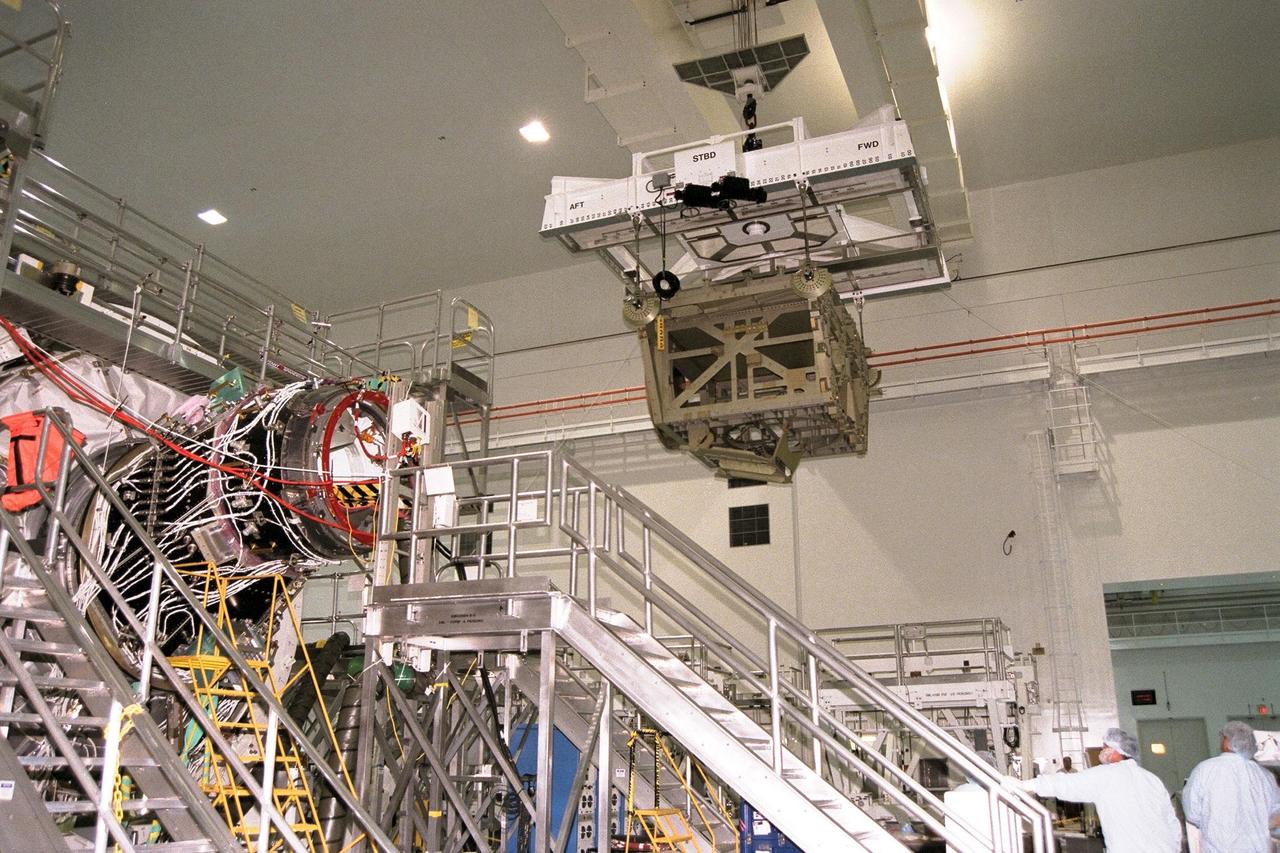
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Z1 Integrated Truss Segment (ITS), a major element of the STS-92 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis in January 1999, is lowered into its workstand for processing in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Z-1 truss supports the staged buildup of International Space Station (ISS) on this third scheduled flight for ISS. The Z1 truss allows the temporary installation of the U.S. power module to Node 1. Early in the assembly sequence, the purpose of Z1 is to provide a mounting location for Ku-band and S-band telemetry and extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment. It also provides common berthing mechanism hardcover stowage. In addition, it will assist with the execution of nonpropulsive attitude control. The truss arrived at KSC on Feb. 17 for preflight processing in the SSPF

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Z1 Integrated Truss Segment (ITS), a major element of the STS-92 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis in January 1999, is lowered into its workstand for processing in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Z-1 truss supports the staged buildup of International Space Station (ISS) on this third scheduled flight for ISS. The Z1 truss allows the temporary installation of the U.S. power module to Node 1. Early in the assembly sequence, the purpose of Z1 is to provide a mounting location for Ku-band and S-band telemetry and extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment. It also provides common berthing mechanism hardcover stowage. In addition, it will assist with the execution of nonpropulsive attitude control. The truss arrived at KSC on Feb. 17 for preflight processing in the SSPF

Workers in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF) assist in removing the protective casing from the Z1 Integrated Truss Segment (ITS), a major element of the STS-92 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis in January 1999. The Z-1 truss supports the staged buildup of International Space Station (ISS) on this third scheduled flight for ISS. The Z1 truss allows the temporary installation of the U.S. power module to Node 1. Early in the assembly sequence, the purpose of Z1 is to provide a mounting location for Ku-band and S-band telemetry and extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment. It also provides common berthing mechanism hardcover stowage. In addition, it will assist with the execution of nonpropulsive attitude control. The truss arrived at KSC on Feb. 17 for preflight processing in the SSPF

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Z1 Integrated Truss Segment (ITS), a major element of the STS-92 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis in January 1999, is lowered into its workstand for processing in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Z-1 truss supports the staged buildup of International Space Station (ISS) on this third scheduled flight for ISS. The Z1 truss allows the temporary installation of the U.S. power module to Node 1. Early in the assembly sequence, the purpose of Z1 is to provide a mounting location for Ku-band and S-band telemetry and extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment. It also provides common berthing mechanism hardcover stowage. In addition, it will assist with the execution of nonpropulsive attitude control. The truss arrived at KSC on Feb. 17 for preflight processing in the SSPF

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Z1 Integrated Truss Segment (ITS), a major element of the STS-92 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis in January 1999, is moved to its workstand for processing in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Z-1 truss supports the staged buildup of International Space Station (ISS) on this third scheduled flight for ISS. The Z1 truss allows the temporary installation of the U.S. power module to Node 1. Early in the assembly sequence, the purpose of Z1 is to provide a mounting location for Ku-band and S-band telemetry and extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment. It also provides common berthing mechanism hardcover stowage. In addition, it will assist with the execution of nonpropulsive attitude control. The truss arrived at KSC on Feb. 17 for preflight processing in the SSPF
The Z1 Integrated Truss Segment (ITS), a major element of the STS-92 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis in January 1999, awaits processing in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Z-1 truss supports the staged buildup of International Space Station (ISS) on this third scheduled flight for ISS. The Z1 truss allows the temporary installation of the U.S. power module to Node 1. Early in the assembly sequence, the purpose of Z1 is to provide a mounting location for Ku-band and S-band telemetry and extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment. It also provides common berthing mechanism hardcover stowage. In addition, it will assist with the execution of nonpropulsive attitude control. The truss arrived at KSC on Feb. 17 for preflight processing in the SSPF

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Z1 Integrated Truss Segment (ITS), a major element of the STS-92 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis in January 1999, is moved toward its workstand for processing in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Z-1 truss supports the staged buildup of International Space Station (ISS) on this third scheduled flight for ISS. The Z1 truss allows the temporary installation of the U.S. power module to Node 1. Early in the assembly sequence, the purpose of Z1 is to provide a mounting location for Ku-band and S-band telemetry and extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment. It also provides common berthing mechanism hardcover stowage. In addition, it will assist with the execution of nonpropulsive attitude control. The truss arrived at KSC on Feb. 17 for preflight processing in the SSPF
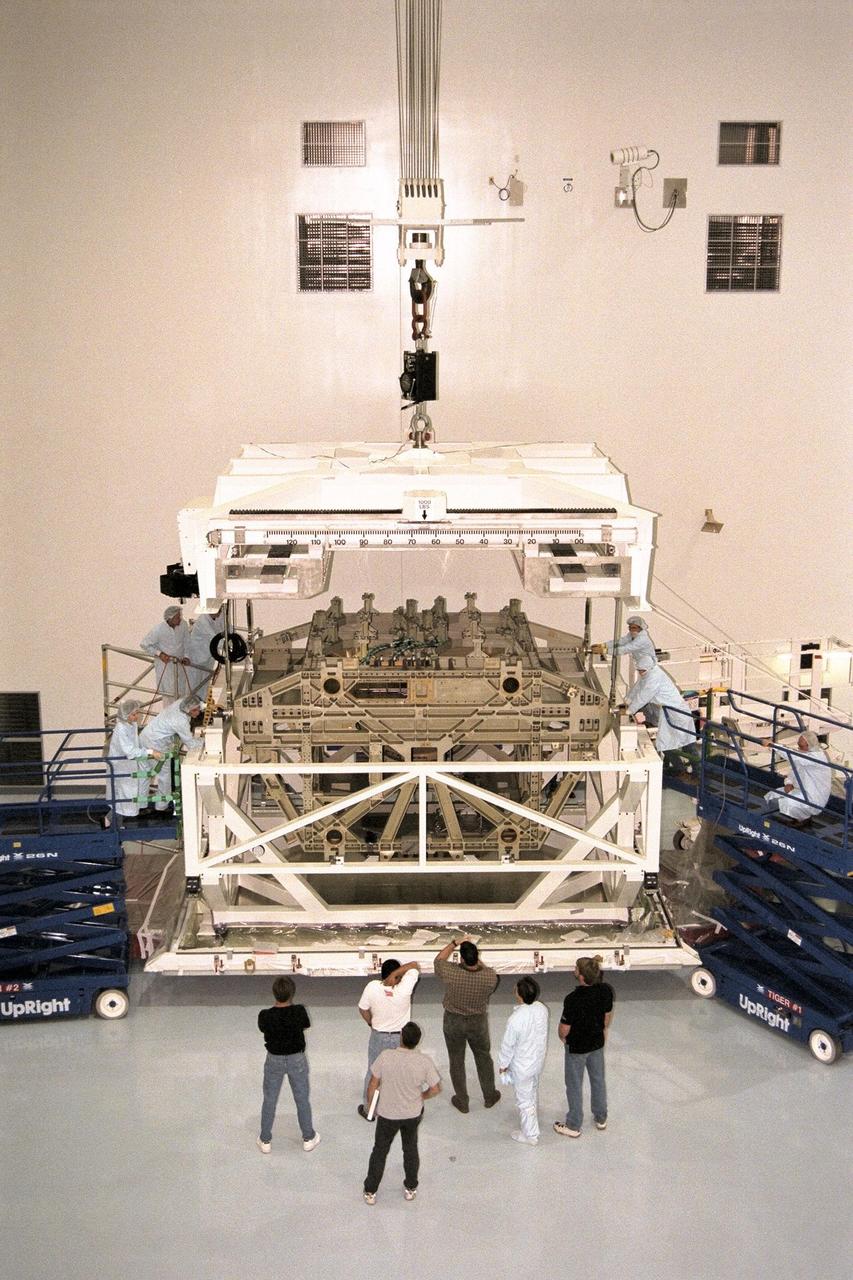

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Z1 Integrated Truss Segment (ITS), a major element of the STS-92 mission scheduled for launch aboard Space Shuttle Atlantis in January 1999, is lowered into its workstand for processing in KSC's Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). The Z-1 truss supports the staged buildup of International Space Station (ISS) on this third scheduled flight for ISS. The Z1 truss allows the temporary installation of the U.S. power module to Node 1. Early in the assembly sequence, the purpose of Z1 is to provide a mounting location for Ku-band and S-band telemetry and extravehicular activity (EVA) equipment. It also provides common berthing mechanism hardcover stowage. In addition, it will assist with the execution of nonpropulsive attitude control. The truss arrived at KSC on Feb. 17 for preflight processing in the SSPF
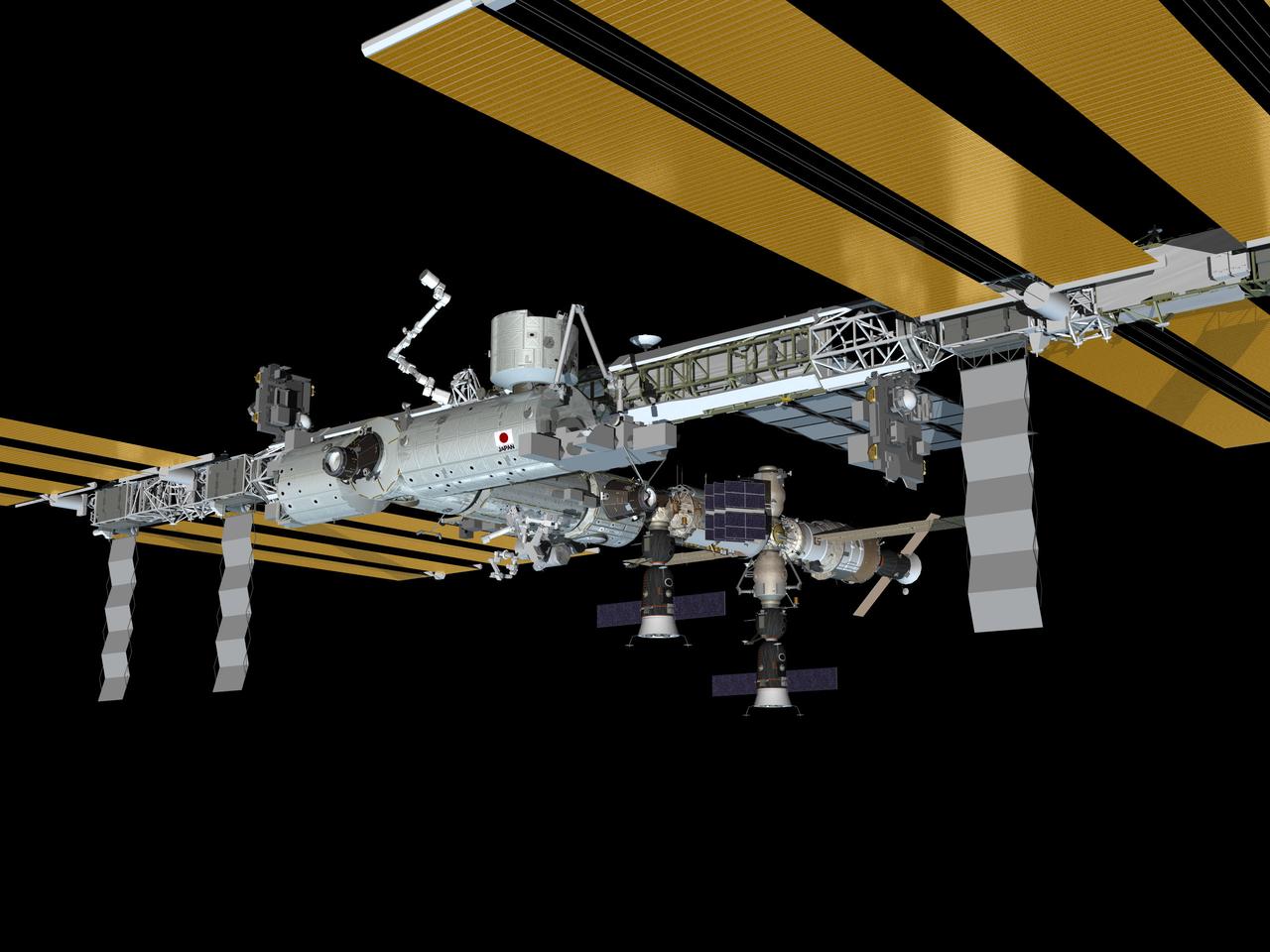

JSC2009-E-224040 (November 2009) --- Computer-generated artist?s rendering of the International Space Station as of November 2009, after the STS-129/ULF3 installation of the ExPRESS Logistic Carrier 1 (port nadir) and ExPRESS Logistic Carrier 2 (starboard zenith) on the central truss. The Russian Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) docks to the Zvezda Service Module?s zenith port as of Nov. 12.
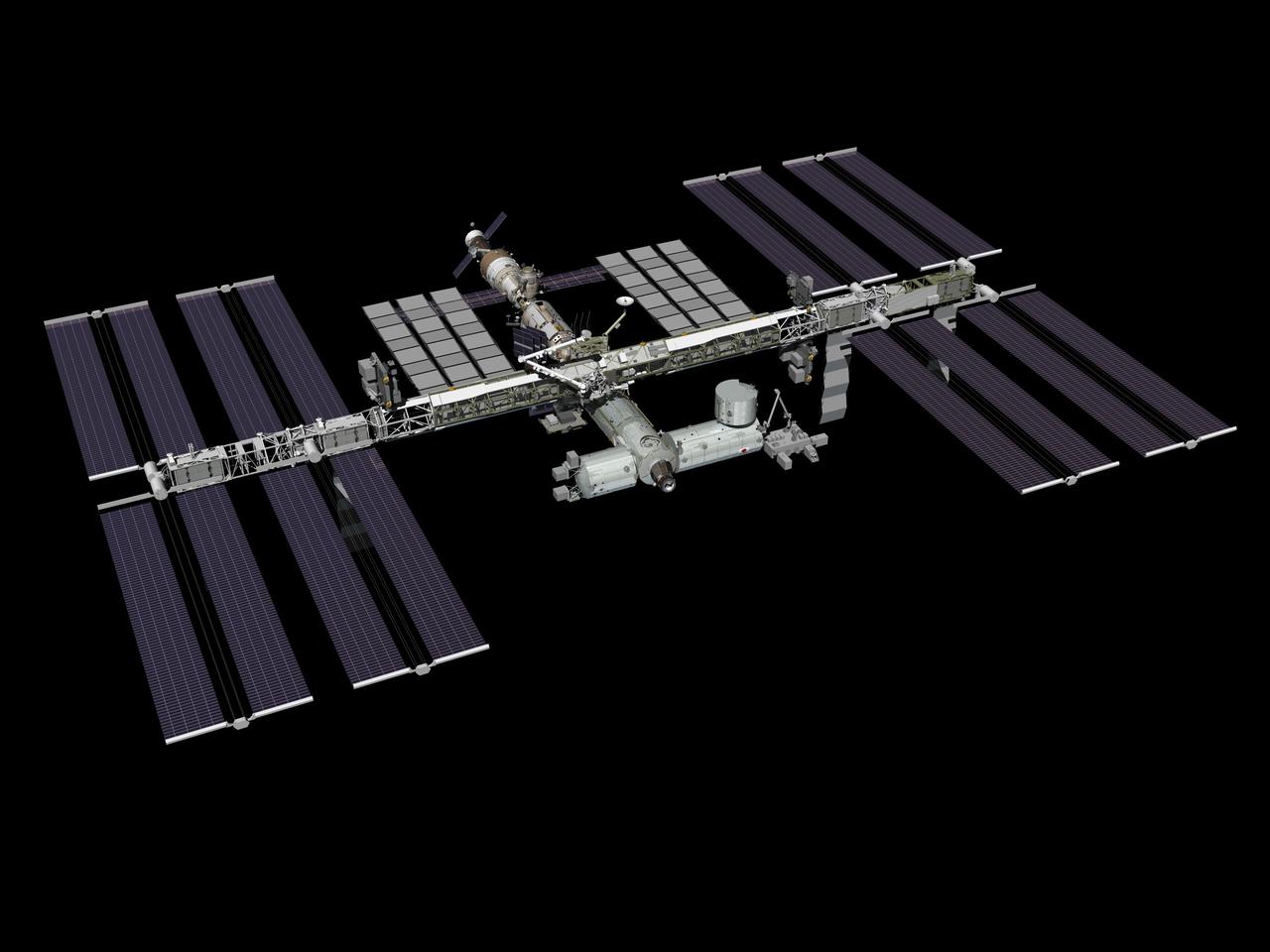
JSC2009-E-224041 (November 2009) --- Computer-generated artist?s rendering of the International Space Station as of November 2009, after the STS-129/ULF3 installation of the ExPRESS Logistic Carrier 1 (port nadir) and ExPRESS Logistic Carrier 2 (starboard zenith) on the central truss. The Russian Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2) docks to the Zvezda Service Module?s zenith port as of Nov. 12.

STS111-E-5132 (9 June 2002) --- Astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, STS-111 mission specialist, anchored to the foot restraint at the end of the International Space Station’s (ISS) Canadarm2, participates in the first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) for the STS-111 mission. During the spacewalk, Chang-Diaz and Perrin attached a Power and Data Grapple Fixture onto the International Space Station’s (ISS) P6 Truss, setting the stage for the future relocation of the P6. The next major task was to remove Service Module Debris Panels from Space Shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay and attach them to their temporary location on Pressurized Mating Adapter 1 (PMA-1). The spacewalkers also removed thermal blankets to prepare the Mobile Base System (MBS) for installation onto the station’s Mobile Transporter (MT).
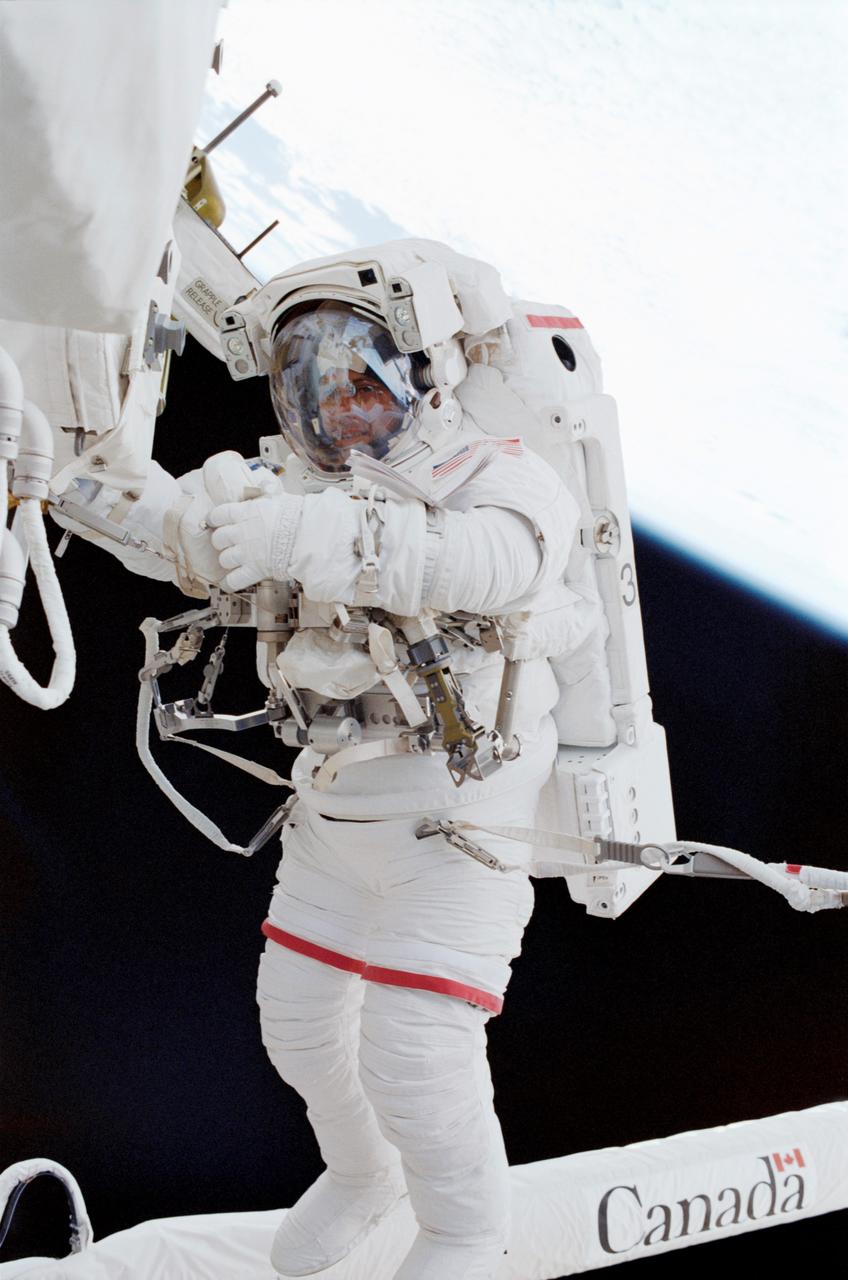

STS111-306-023 (9 June 2002) --- Astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, STS-111 mission specialist, participates in the first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) for the STS-111 mission. During the spacewalk, Chang-Diaz and Perrin attached a Power and Data Grapple Fixture onto the International Space Station’s (ISS) P6 Truss, setting the stage for the future relocation of the P6. The next major task was to remove Service Module Debris Panels from Space Shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay and attach them to their temporary location on Pressurized Mating Adapter 1 (PMA-1). The spacewalkers also removed thermal blankets to prepare the Mobile Base System (MBS) for installation onto the station’s Mobile Transporter (MT).
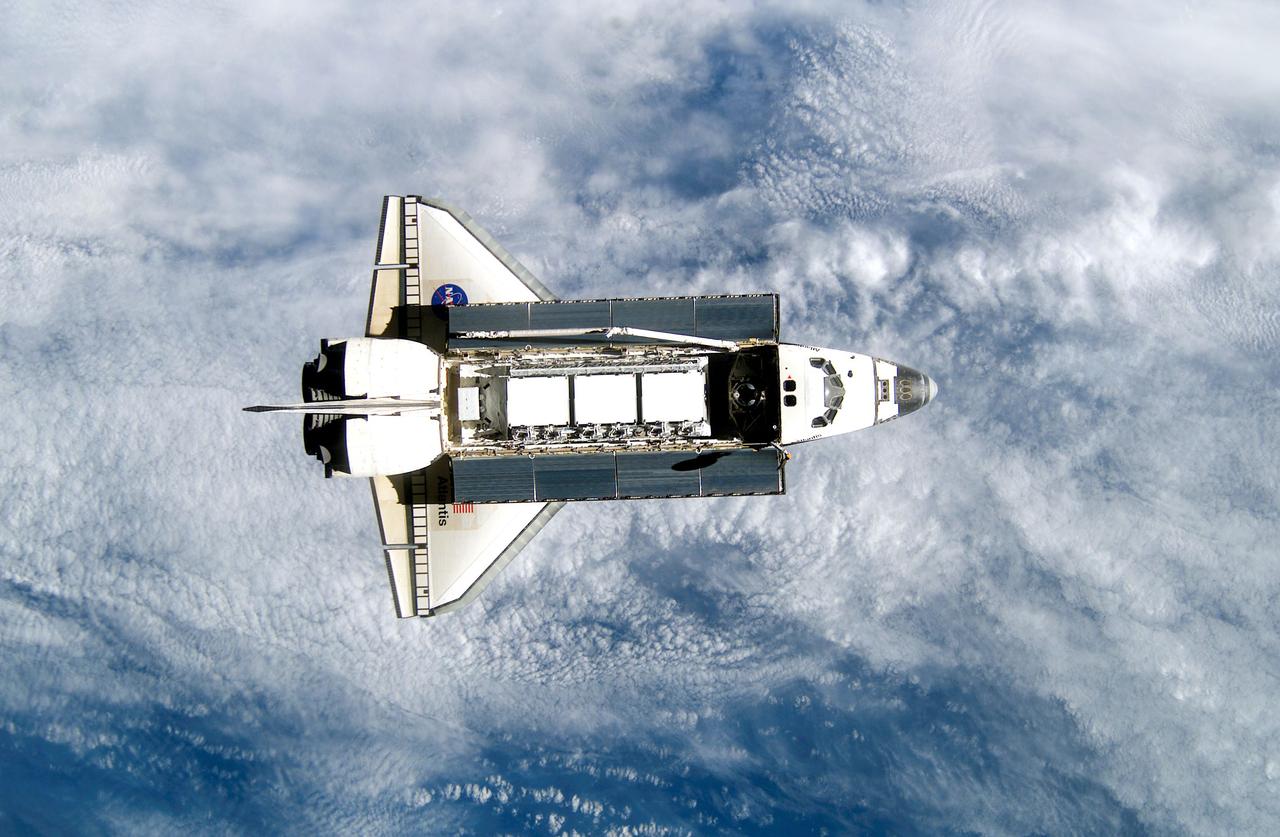

Back dropped against a blue and white Earth, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis was photographed by an Expedition 5 crew member onboard the International Space Station (ISS) during rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 10:17 am on October 9, 2002. The Starboard 1 (S1) Integrated Truss Structure, the primary payload of the STS-112 mission, can be seen in Atlantis' cargo bay. Installed and outfitted within 3 sessions of Extravehicular Activity (EVA) during the 11 day mission, the S1 truss provides structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels, which use ammonia to cool the Station's complex power system. The S1 truss, attached to the S0 (S Zero) truss installed by the previous STS-110 mission, flows 637 pounds of anhydrous ammonia through three heat rejection radiators.

Back dropped against a blue and white Earth, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis was photographed by an Expedition 5 crew member onboard the International Space Station (ISS) during rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 10:17 am on October 9, 2002. The Starboard 1 (S1) Integrated Truss Structure, the primary payload of the STS-112 mission, can be seen in Atlantis' cargo bay. Installed and outfitted within 3 sessions of Extravehicular Activity (EVA) during the 11 day mission, the S1 truss provides structural support for the orbiting research facility's radiator panels, which use ammonia to cool the Station's complex power system. The S1 truss, attached to the S0 (S Zero) truss installed by the previous STS-110 mission, flows 637 pounds of anhydrous ammonia through three heat rejection radiators.

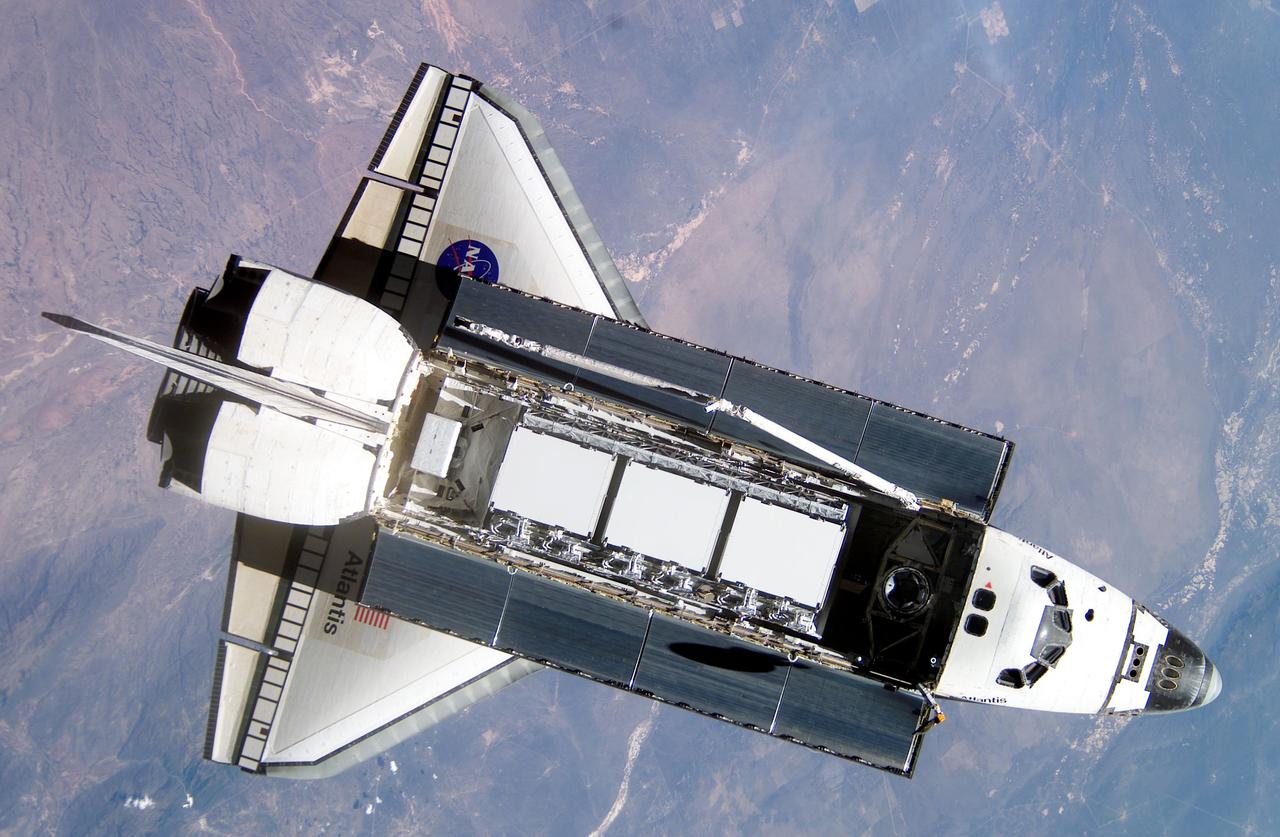
STS110-E-6006 (17 April 2002) --- The International Space Station (ISS), newly equipped with the 27,000 pound S0 (S-zero) truss, was photographed with a digital still camera by one of the astronauts on board the Space Shuttle Atlantis. Seen just above center frame, S0 is the first segment of a truss structure which will ultimately expand the station to the length of a football field. Atlantis pulled away from the complex at 1:31 p.m. (CDT) as two spacecraft flew some 247 statute miles above Earth. After more than a week of joint operations between the shuttle and station crews, astronaut Stephen N. Frick, pilot, backed Atlantis away to a distance of about 400 feet in front of the station, where he began a 1 1/4 lap flyaround of the ISS.
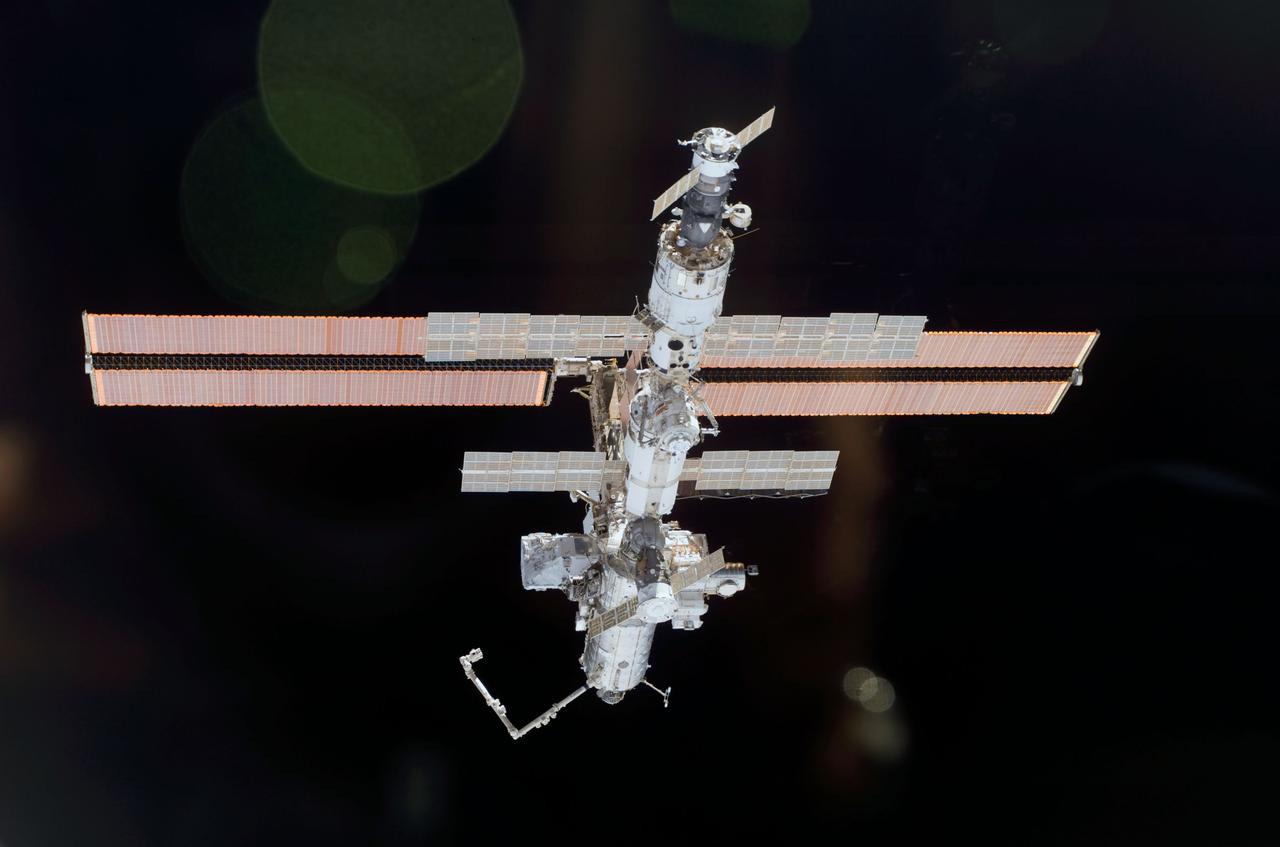
STS110-E-5912 (17 April 2002) --- This is one a series of digital still images of the International Space Station (ISS) recorded by the STS-110 crew members on board the Space Shuttle Atlantis following the undocking of the two spacecraft some 247 statute miles above the North Atlantic. Atlantis pulled away from the complex at 1:31 p.m. (CDT). After more than a week of joint operations between the shuttle and station crews, astronaut Stephen N. Frick, pilot, backed Atlantis away to a distance of about 400 feet in front of the station, where he began a 1 1/4 lap flyaround of the ISS, newly equipped with the 27,000 pound S0 (S-zero) truss, visible in this series of images. S0 is the first segment of a truss structure which will ultimately expand the station to the length of a football field.
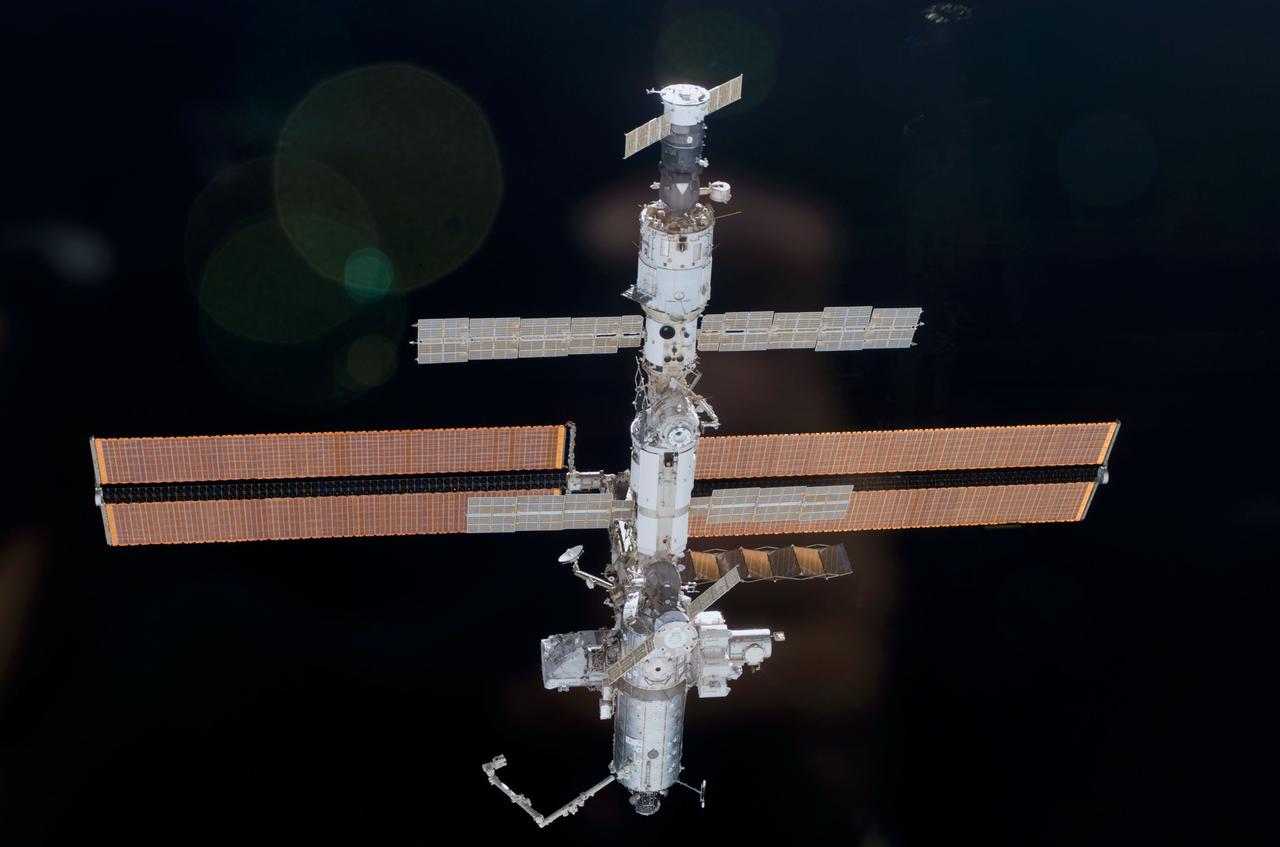

STS110-E-5918 (17 April 2002) --- This is one a series of digital still images of the International Space Station (ISS) recorded by the STS-110 crew members on board the Space Shuttle Atlantis following the undocking of the two spacecraft some 247 statute miles above the North Atlantic. Atlantis pulled away from the complex at 1:31 p.m. (CDT). After more than a week of joint operations between the shuttle and station crews, astronaut Stephen N. Frick, pilot, backed Atlantis away to a distance of about 400 feet in front of the station, where he began a 1 1/4 lap flyaround of the ISS, newly equipped with the 27,000 pound S0 (S-zero) truss, visible in this series of images. S0 is the first segment of a truss structure which will ultimately expand the station to the length of a football field.
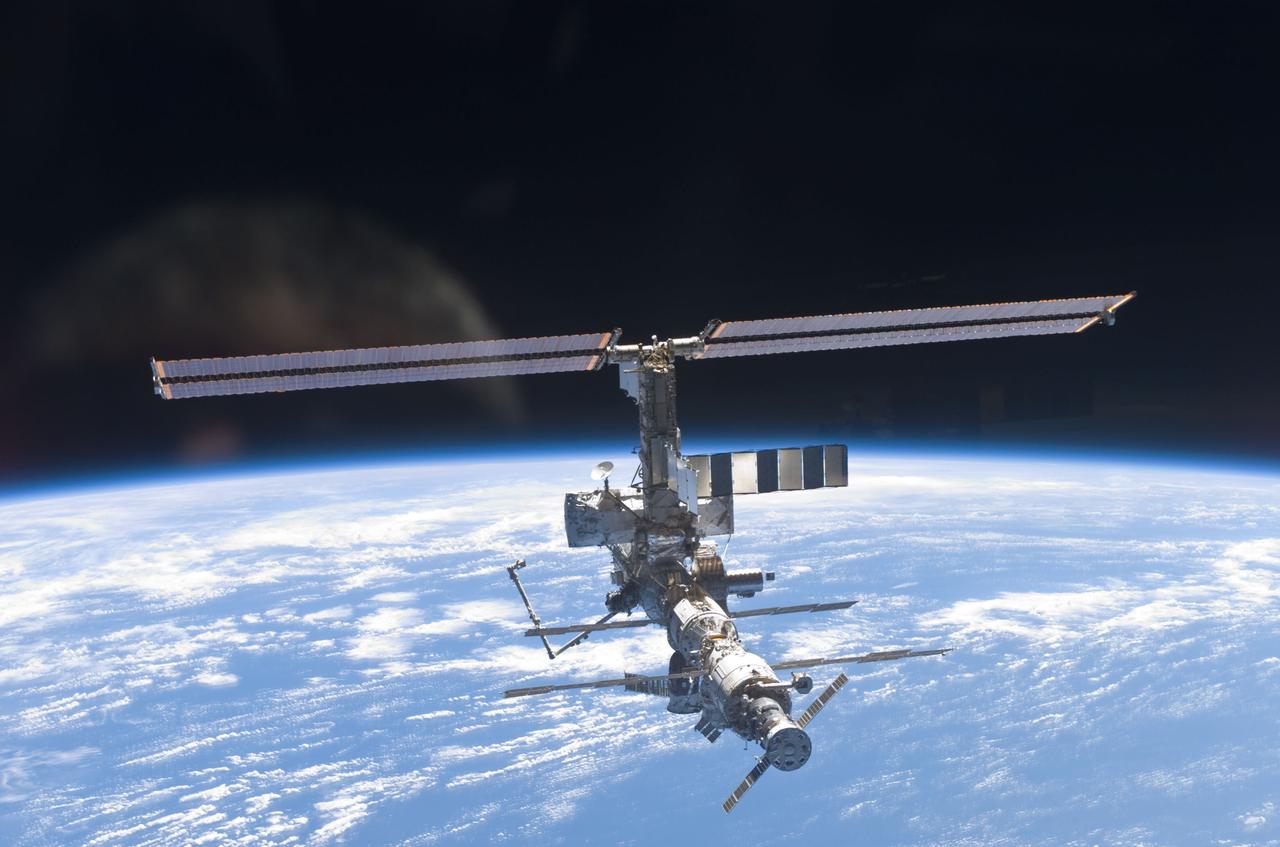

STS110-E-6058 (17 April 2002) --- This is one a series of digital still images of the International Space Station (ISS) recorded by the STS-110 crew members on board the Space Shuttle Atlantis following the undocking of the two spacecraft some 247 statute miles above the North Atlantic. Atlantis pulled away from the complex at 1:31 p.m. (CDT). After more than a week of joint operations between the shuttle and station crews, astronaut Stephen N. Frick, pilot, backed Atlantis away to a distance of about 400 feet in front of the station, where he began a 1 1/4 lap flyaround of the ISS, newly equipped with the 27,000 pound S0 (S-zero) truss, visible in this series of images. S0 is the first segment of a truss structure which will ultimately expand the station to the length of a football field.
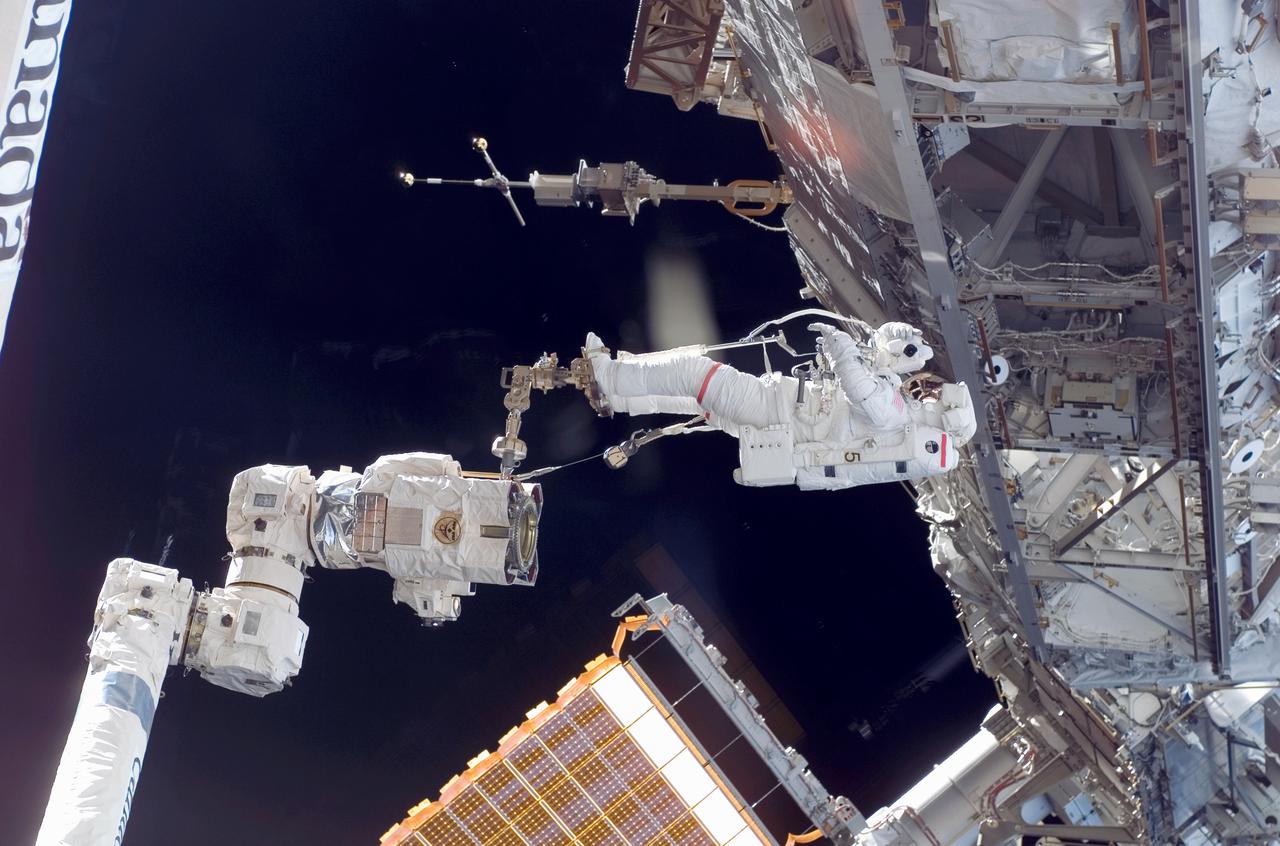

As the construction continued on the International Space Station (ISS), STS-118 astronaut and mission specialist Rick Mastracchio was anchored on the foot restraint of the Canadarm2 as he participated in the third session of Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) for the mission. Assisting Mastracchio was Expedition 15 flight engineer Clay Anderson (out of frame). During the 5 hour, 28 minute space walk, the two relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) truss to the Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
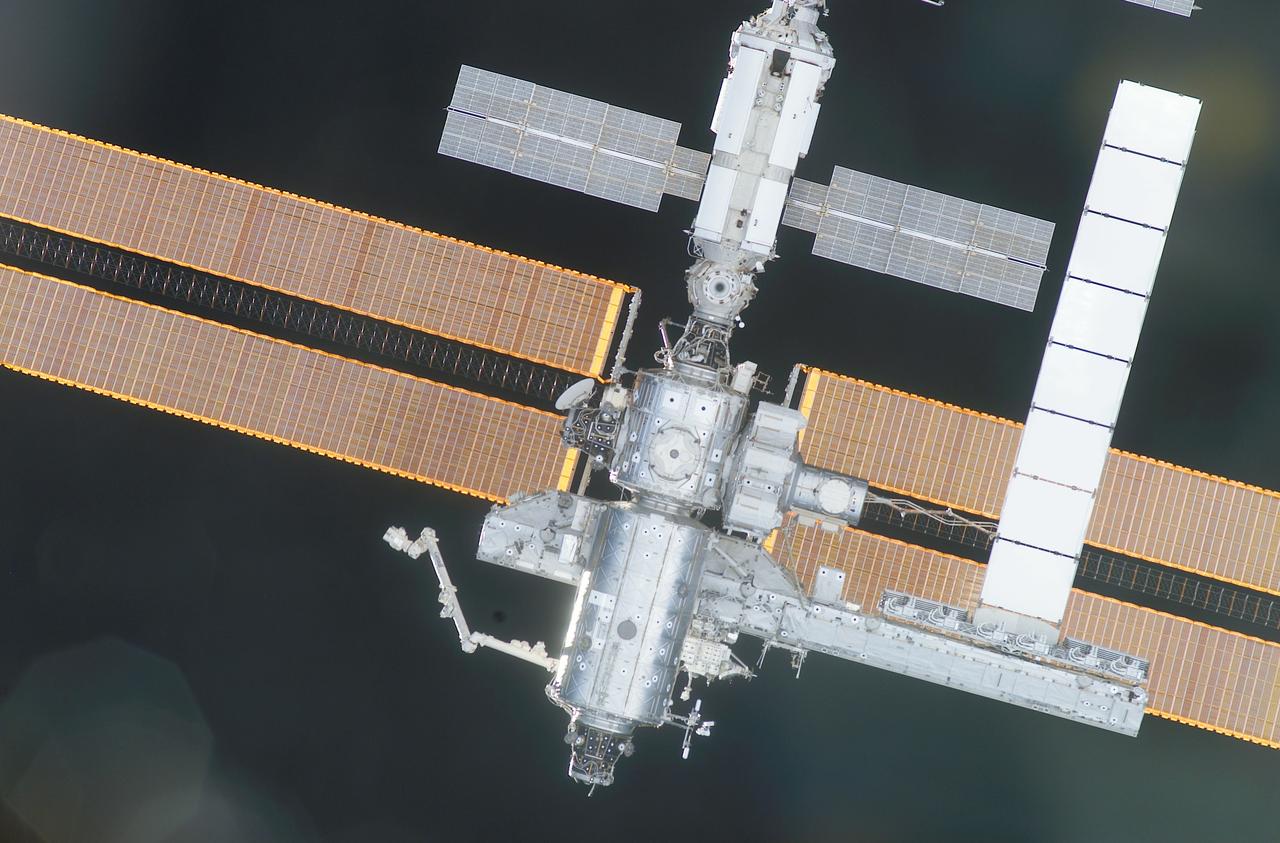
Back dropped against the blackness of space, the International Space Station (ISS) sporting its new S-1 Truss (lower right) and cooling radiator (white portion to the right of frame) is captured on film by the STS-113 crew as the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor approaches the International Space Station (ISS). STS-112 mission installed the S1 truss in October 2000. It is one of nine similar truss segments that, combined, will serve as the Station's main backbone, measuring 356 feet from end to end upon completion. The Space Station's labs, living modules, solar arrays, heat radiators, and other main components will be attached to the truss. The 16th American assembly flight and 112th overall American flight to the ISS launched on November 23, 2002 from Kennedy's launch pad 39A aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor STS-113. The main mission objective was to install and activate the Port 1 Integrated Truss Assembly (P1) to the left side of the station.
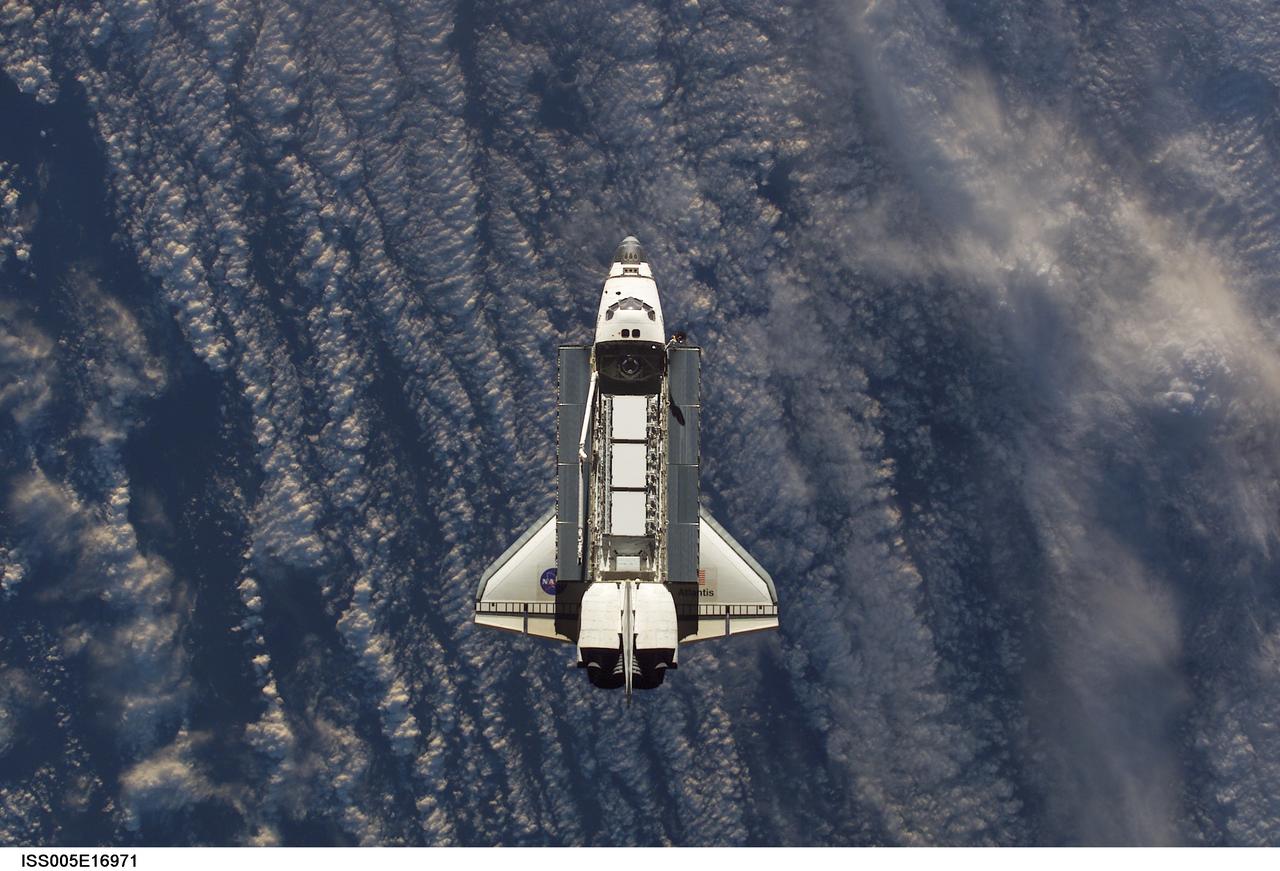

ISS005-E-16971 (9 October 2002) --- Backdropped against a blue and white Earth, this view of the Space Shuttle Atlantis was photographed by an Expedition Five crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS) during rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 10:17 a.m. (CDT) on October 9, 2002. The Starboard One (S-1) Truss, which was later attached to the station and outfitted during three spacewalks, can be seen in Atlantis’ cargo bay.
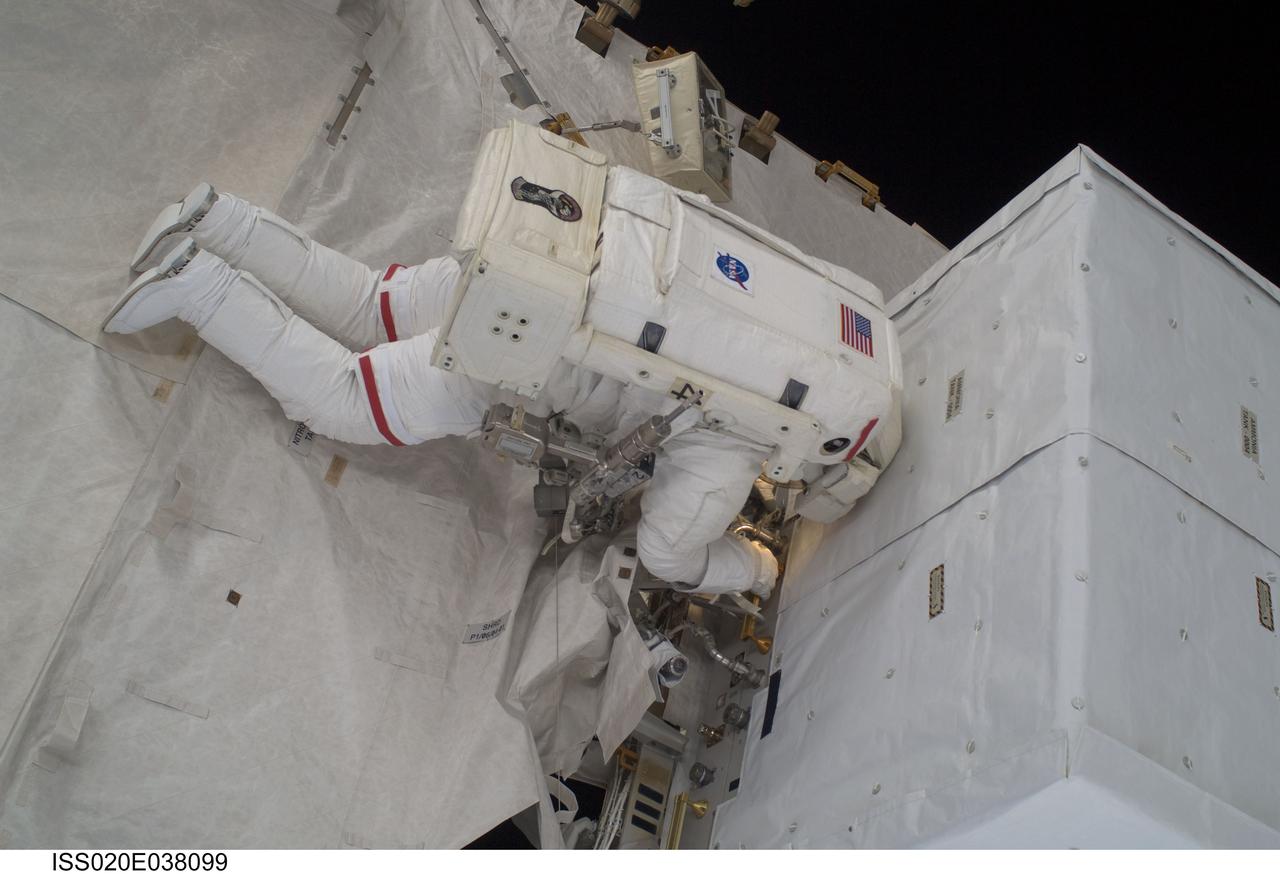

ISS020-E-038099 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
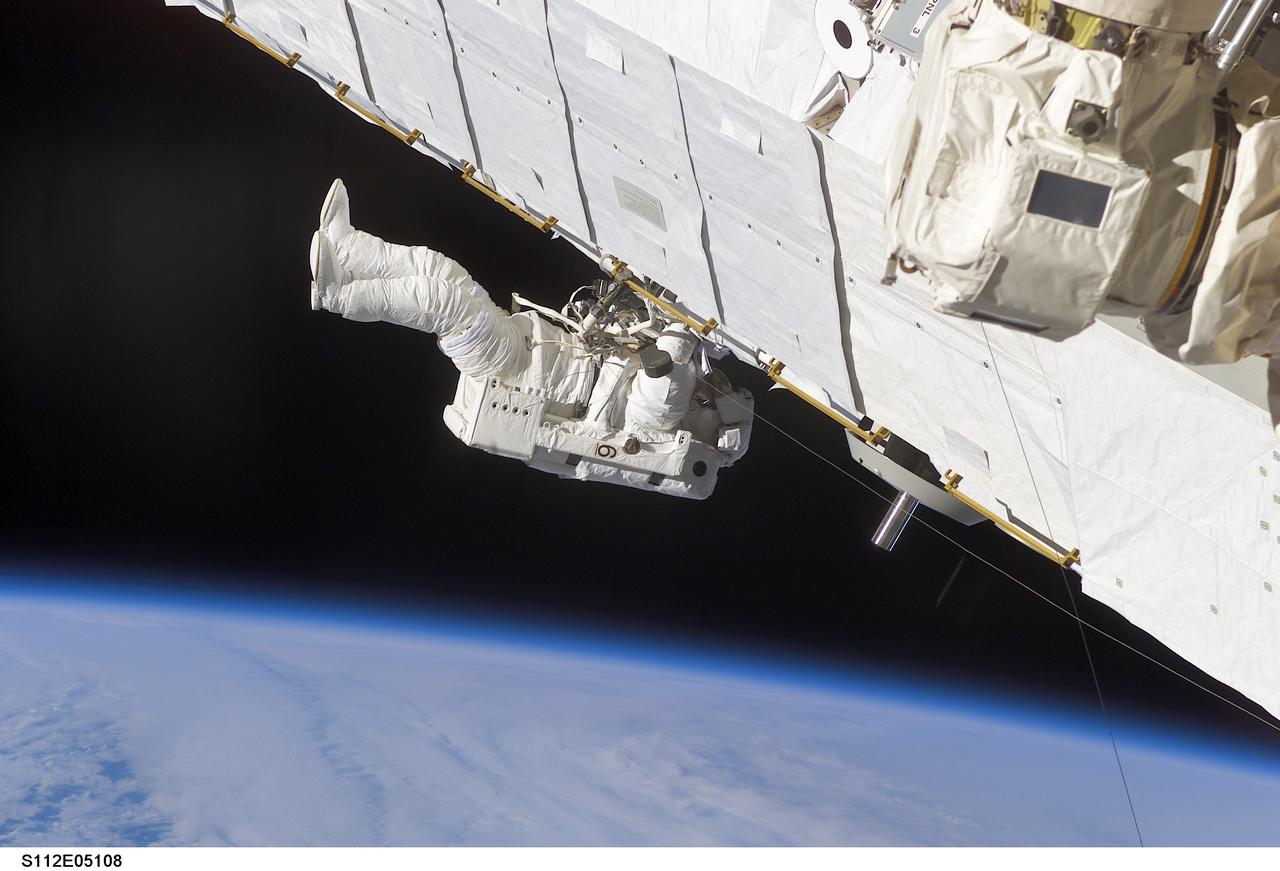

STS112-E-05108 (10 October 2002) --- Astronaut Piers J. Sellers, STS-112 mission specialist, works on the Starboard One (S1) Truss, newly installed on the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut David A. Wolf (out of frame), mission specialist, worked in tandem with Sellers during the spacewalk. STS-112’s first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) lasted 7 hours and 1 minute.
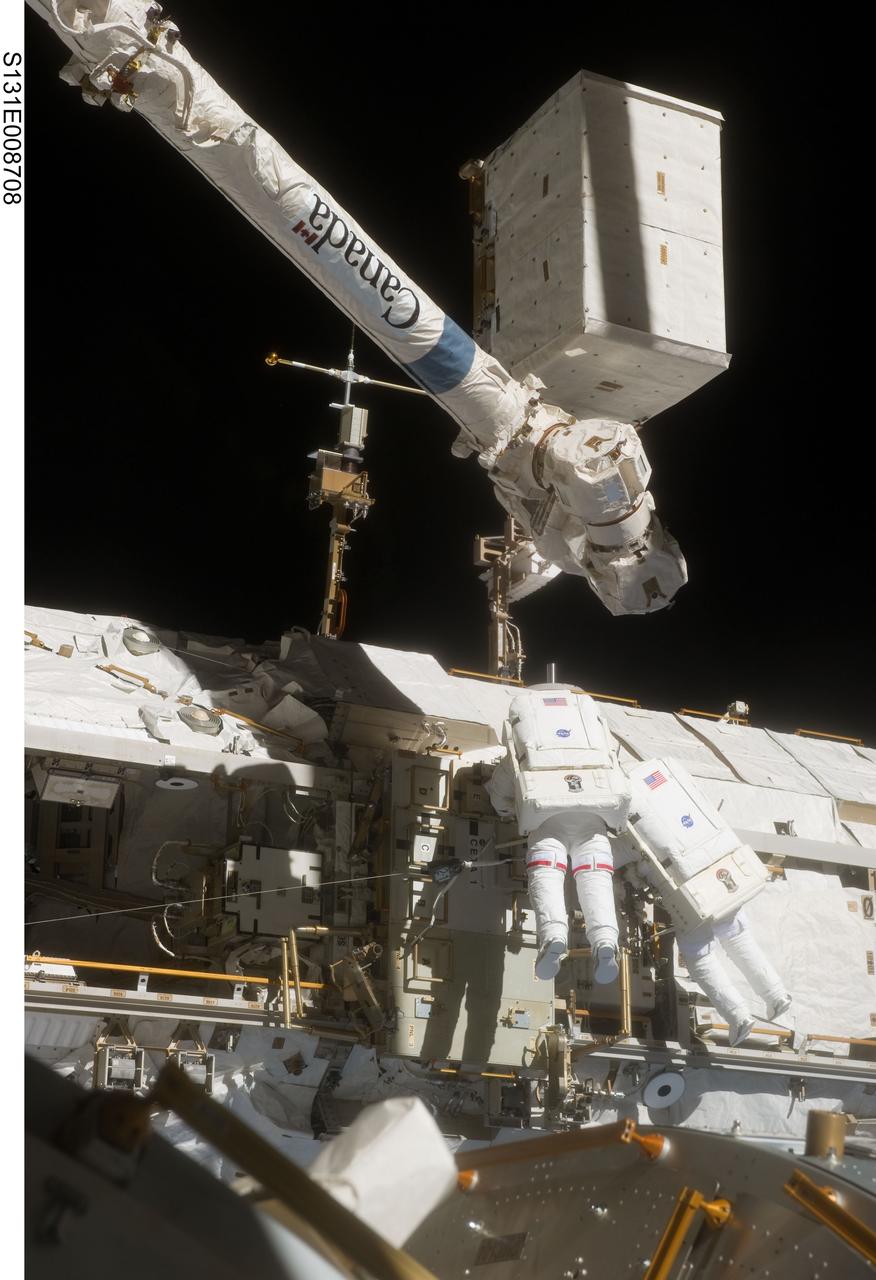

S131-E-008708 (11 April 2010) --- NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio (left) and Clayton Anderson, both STS-131 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour, 26-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson unhooked and removed the depleted ammonia tank and installed a 1,700-pound ammonia tank on the station?s Starboard 1 truss, completing the second of a three-spacewalk coolant tank replacement process.
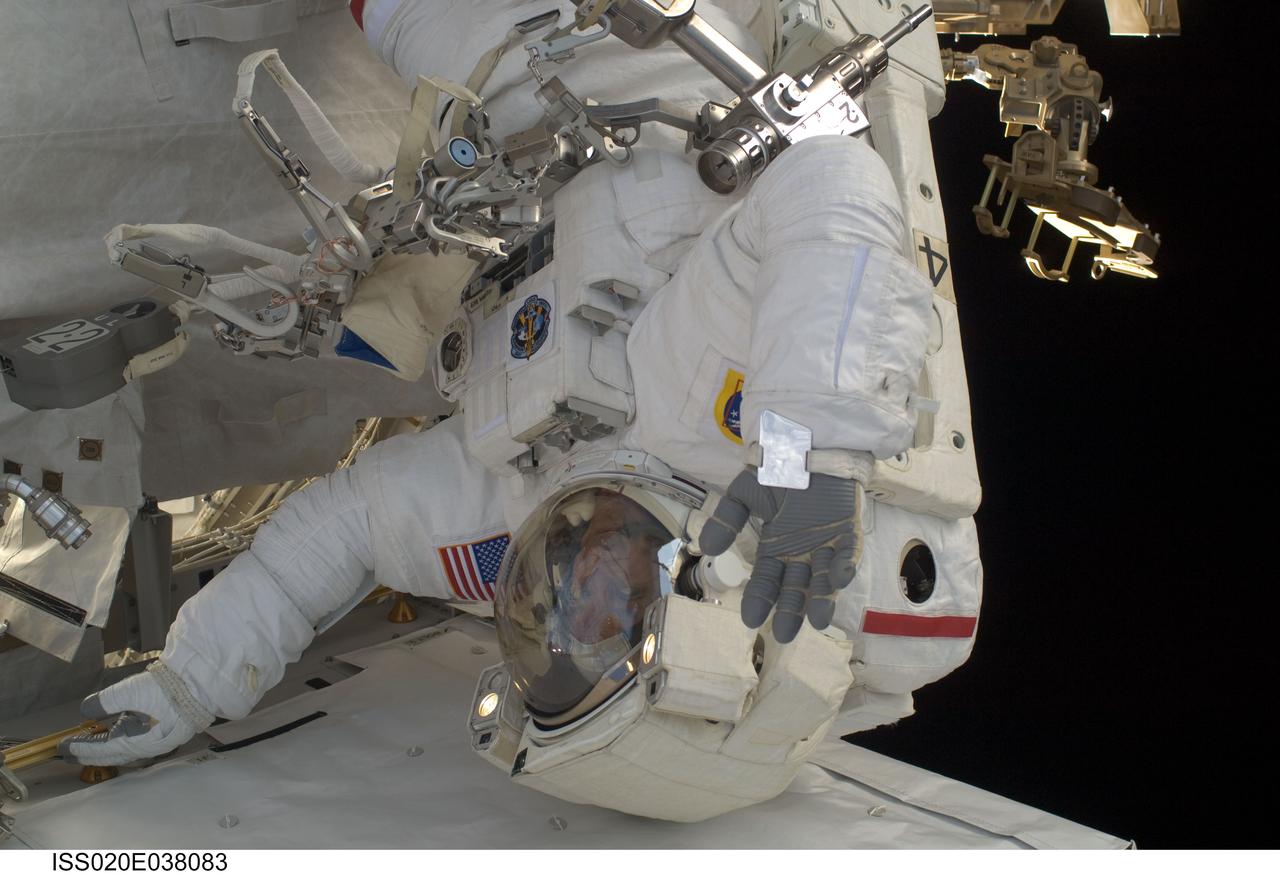

ISS020-E-038083 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
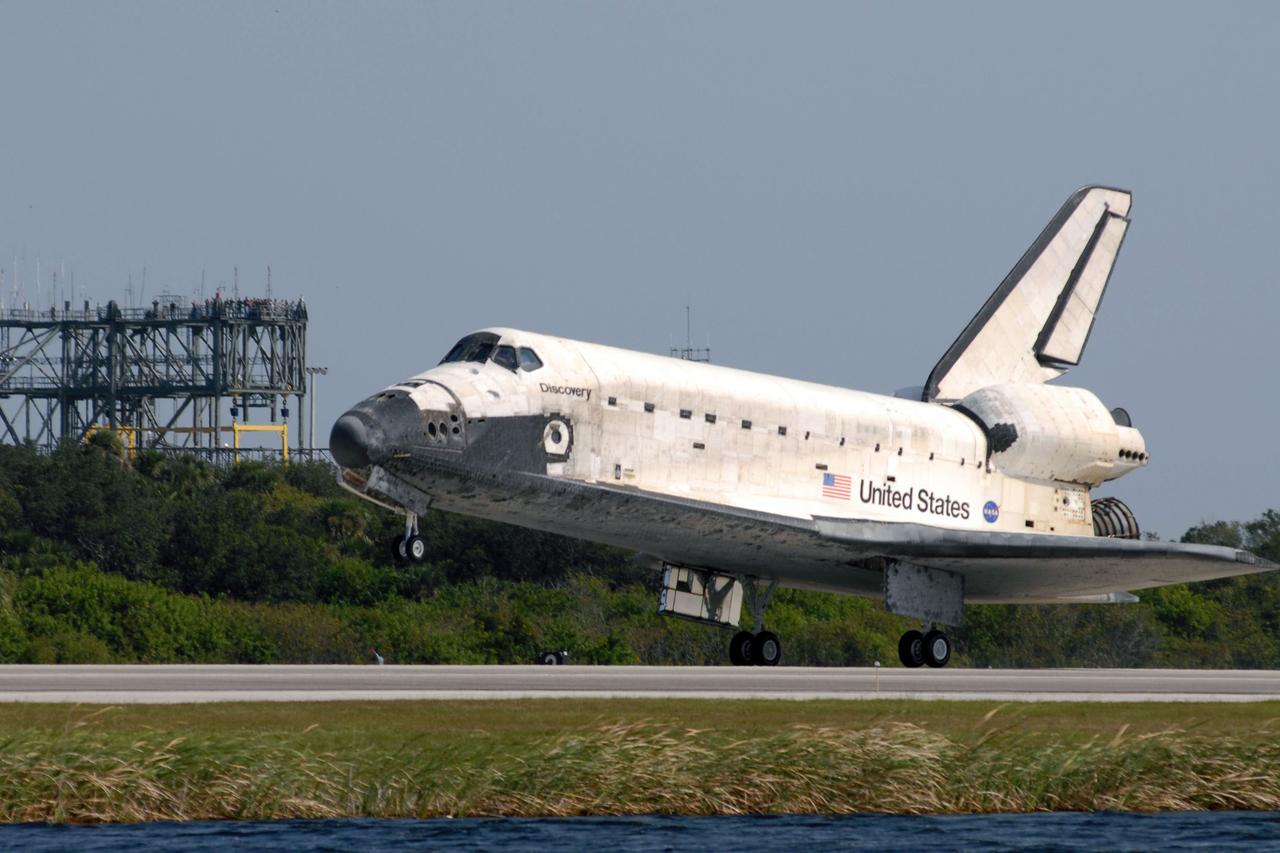

STS120-S-082 (7 Nov. 2007) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery lands at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, completing the 15-day STS-120 mission to the International Space Station. Discovery landed at 1:01 p.m. (EST) Nov. 7 after a mission that included on-orbit construction of the station with the installation of the Harmony Node 2 module and the relocation of the P6 truss.
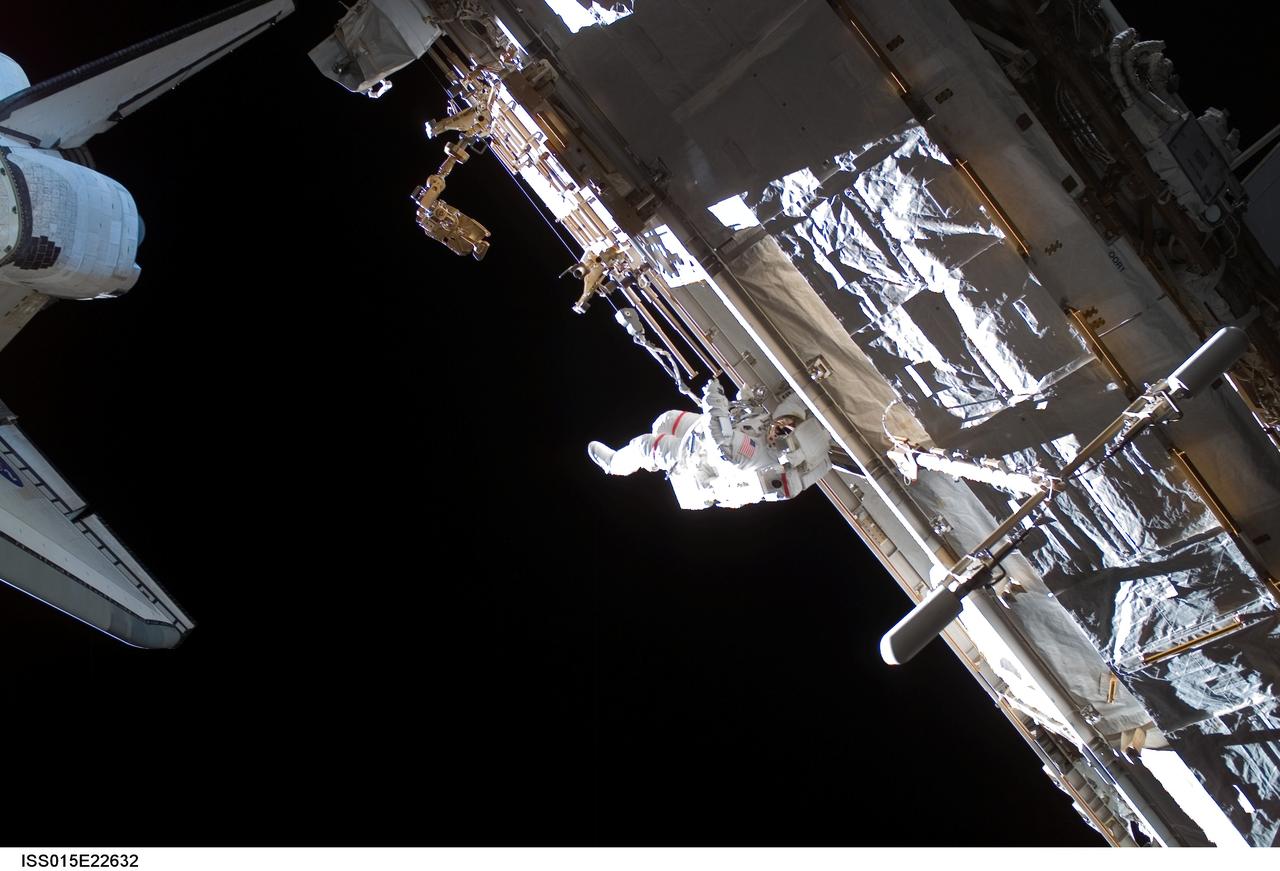

ISS015-E-22632 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
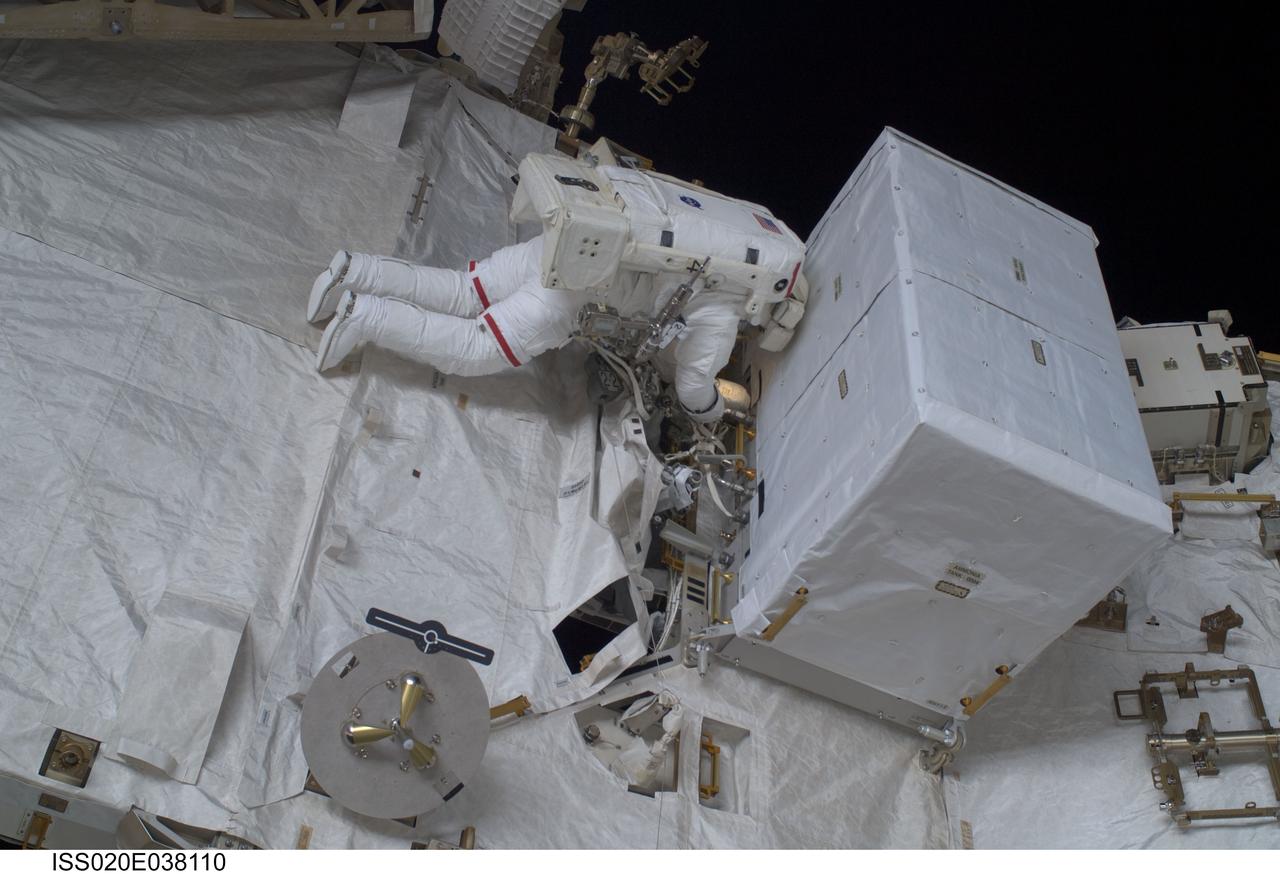

ISS020-E-038110 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
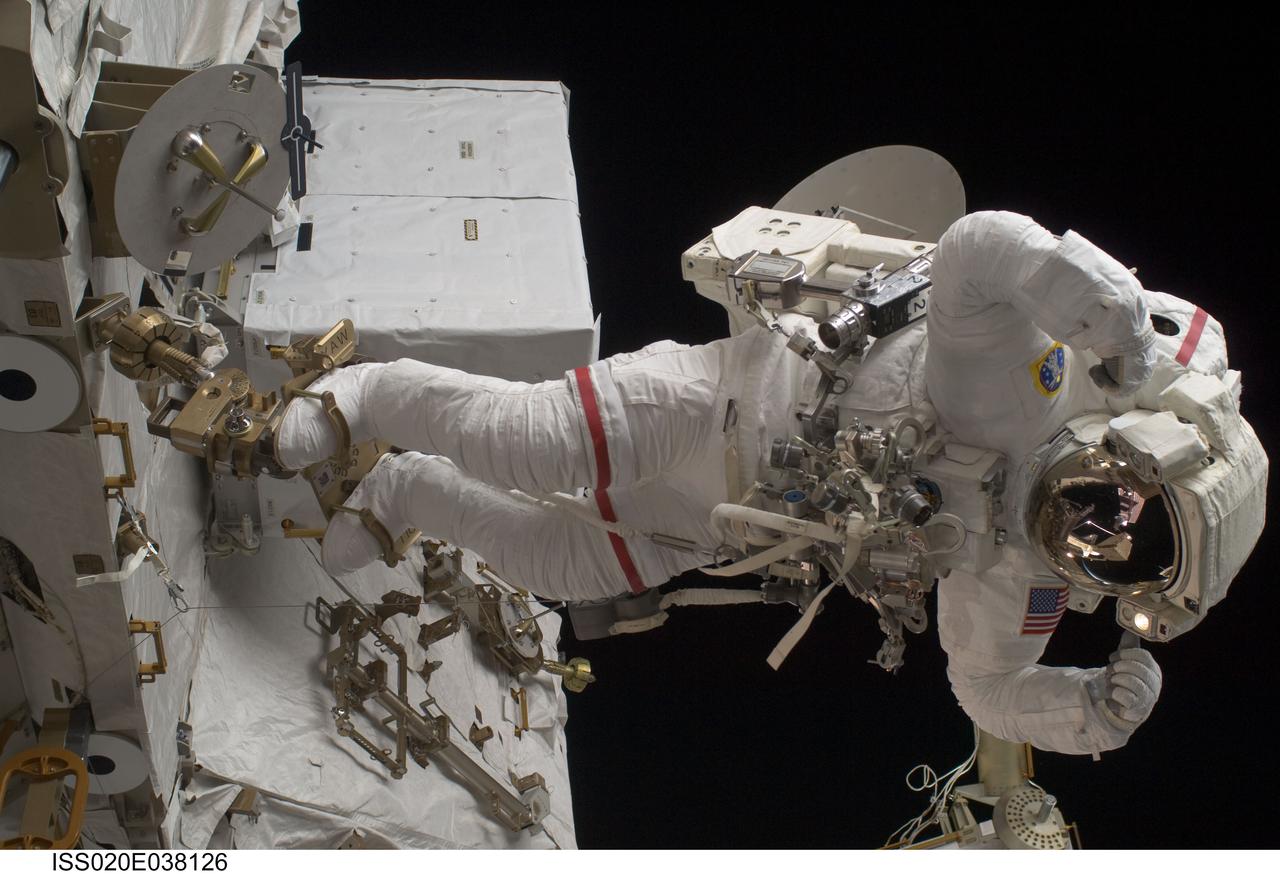

ISS020-E-038126 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
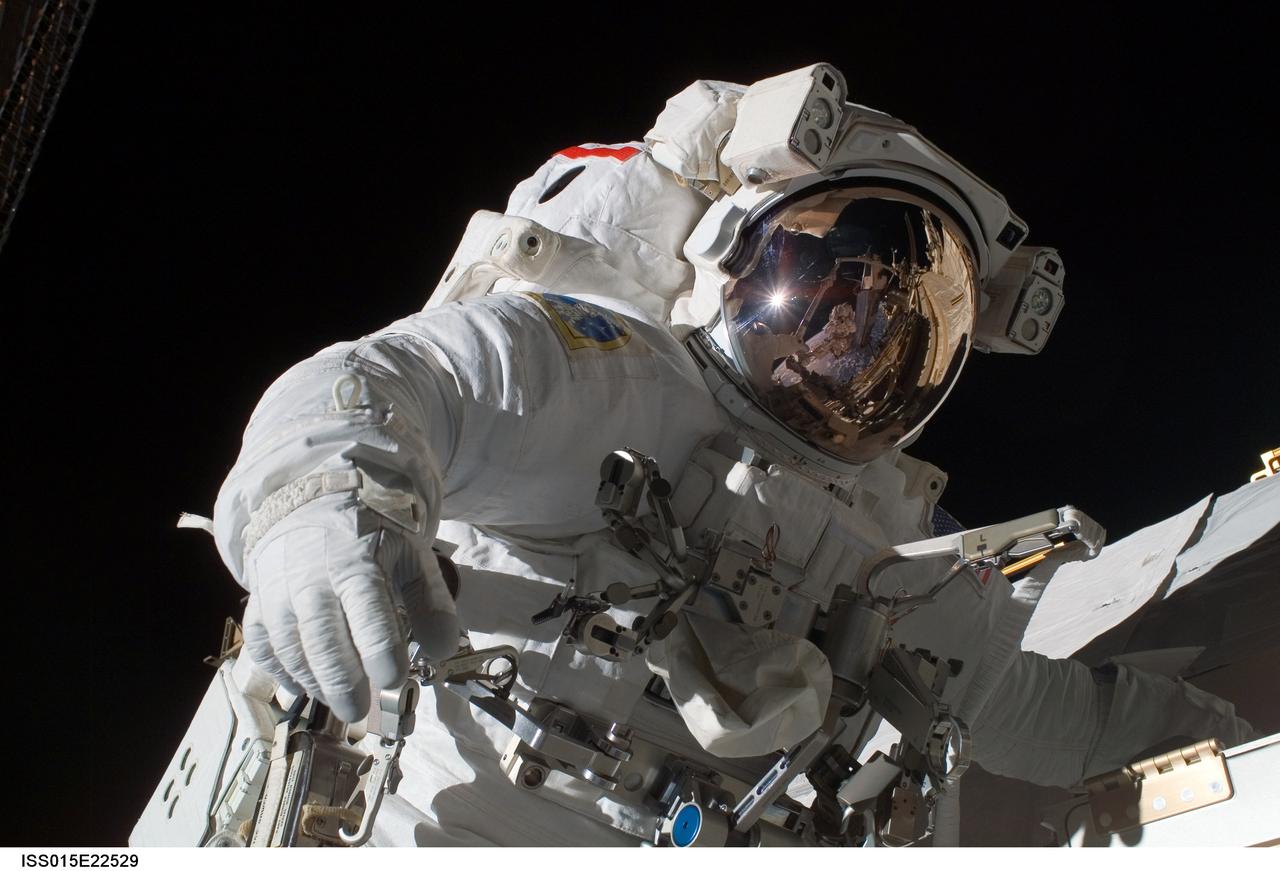

ISS015-E-22529 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
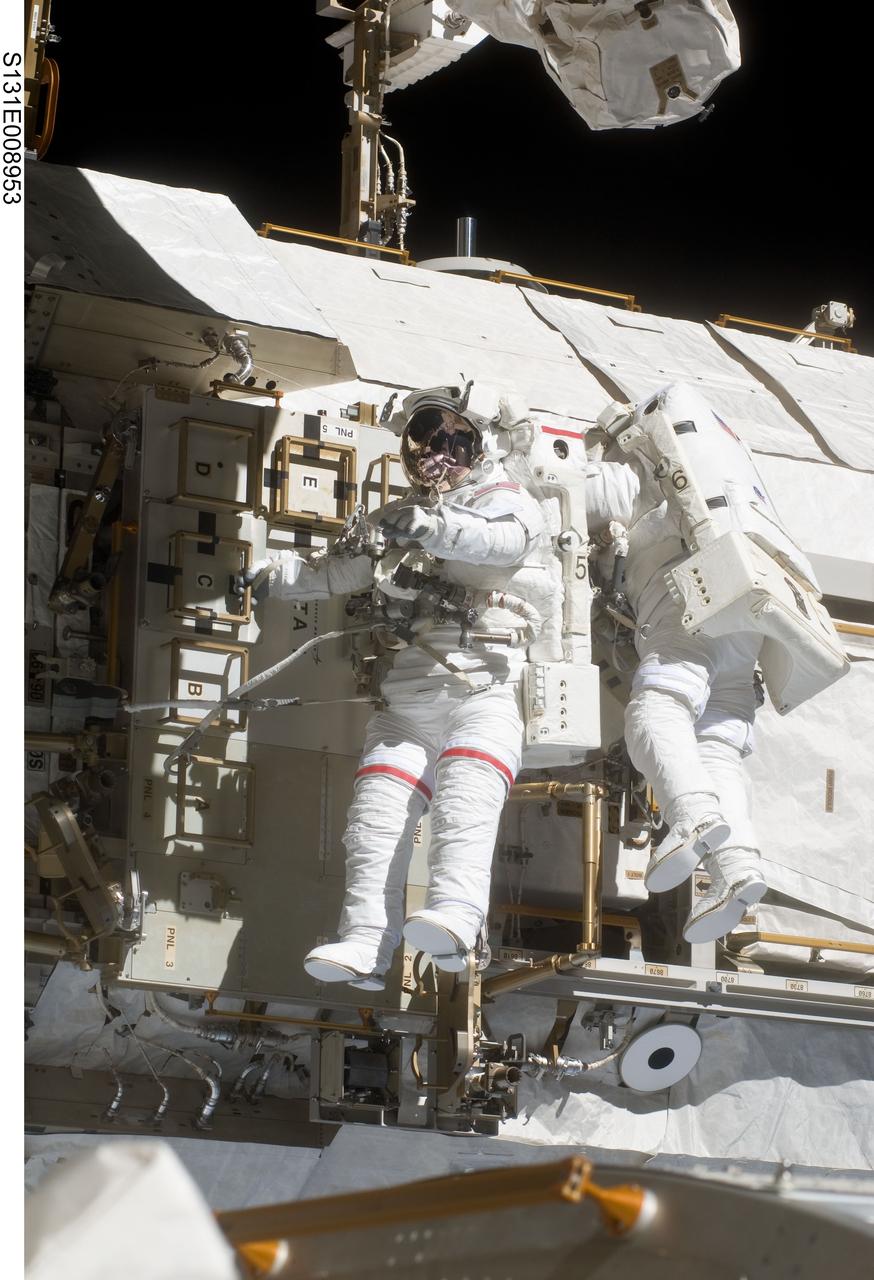

S131-E-008953 (11 April 2010) --- NASA astronauts Rick Mastracchio (left) and Clayton Anderson, both STS-131 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour, 26-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson unhooked and removed the depleted ammonia tank and installed a 1,700-pound ammonia tank on the station?s Starboard 1 truss, completing the second of a three-spacewalk coolant tank replacement process.
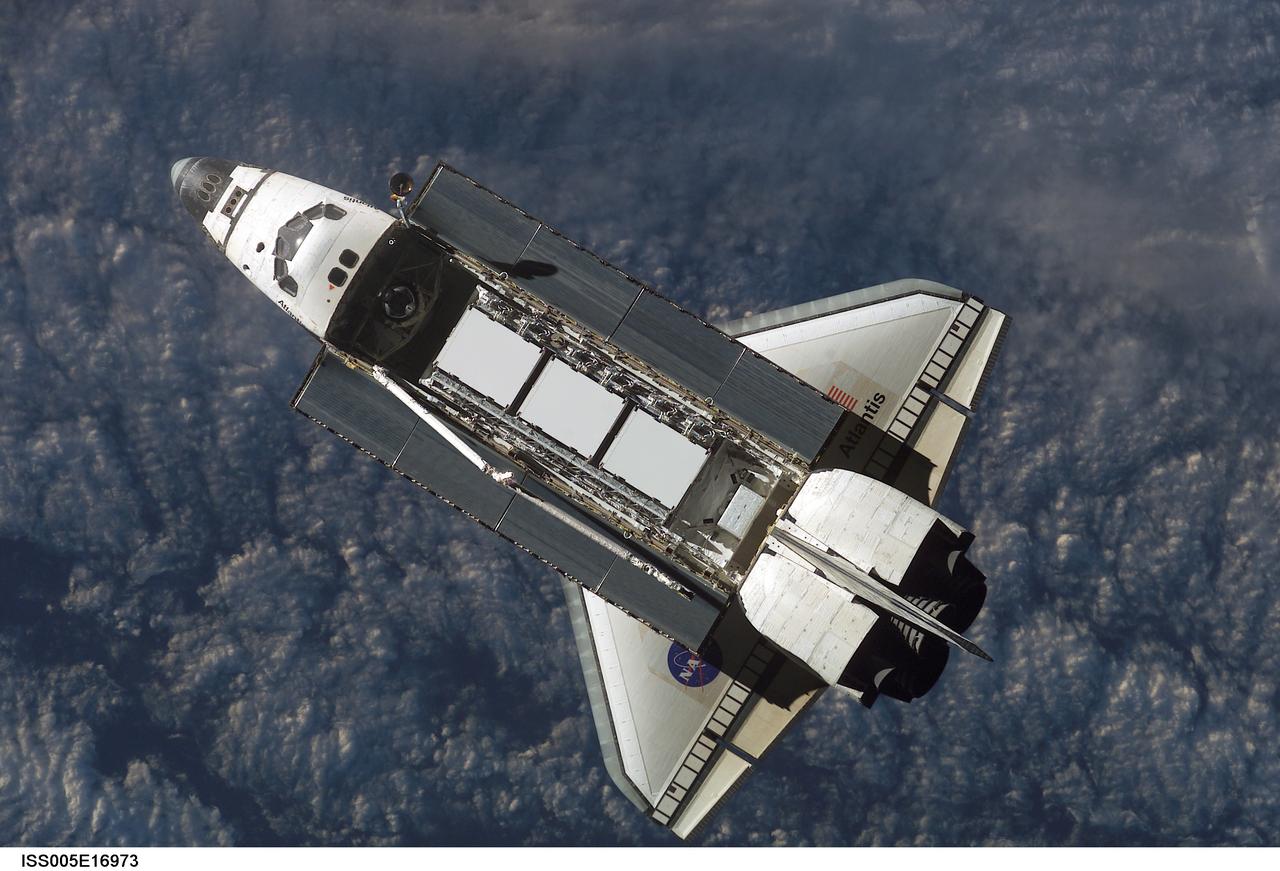

ISS005-E-16973 (9 October 2002) --- Backdropped against a blue and white Earth, this view of the Space Shuttle Atlantis was photographed by an Expedition Five crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS) during rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 10:17 a.m. (CDT) on October 9, 2002. The Starboard One (S-1) Truss, which was later attached to the station and outfitted during three spacewalks, can be seen in Atlantis’ cargo bay.
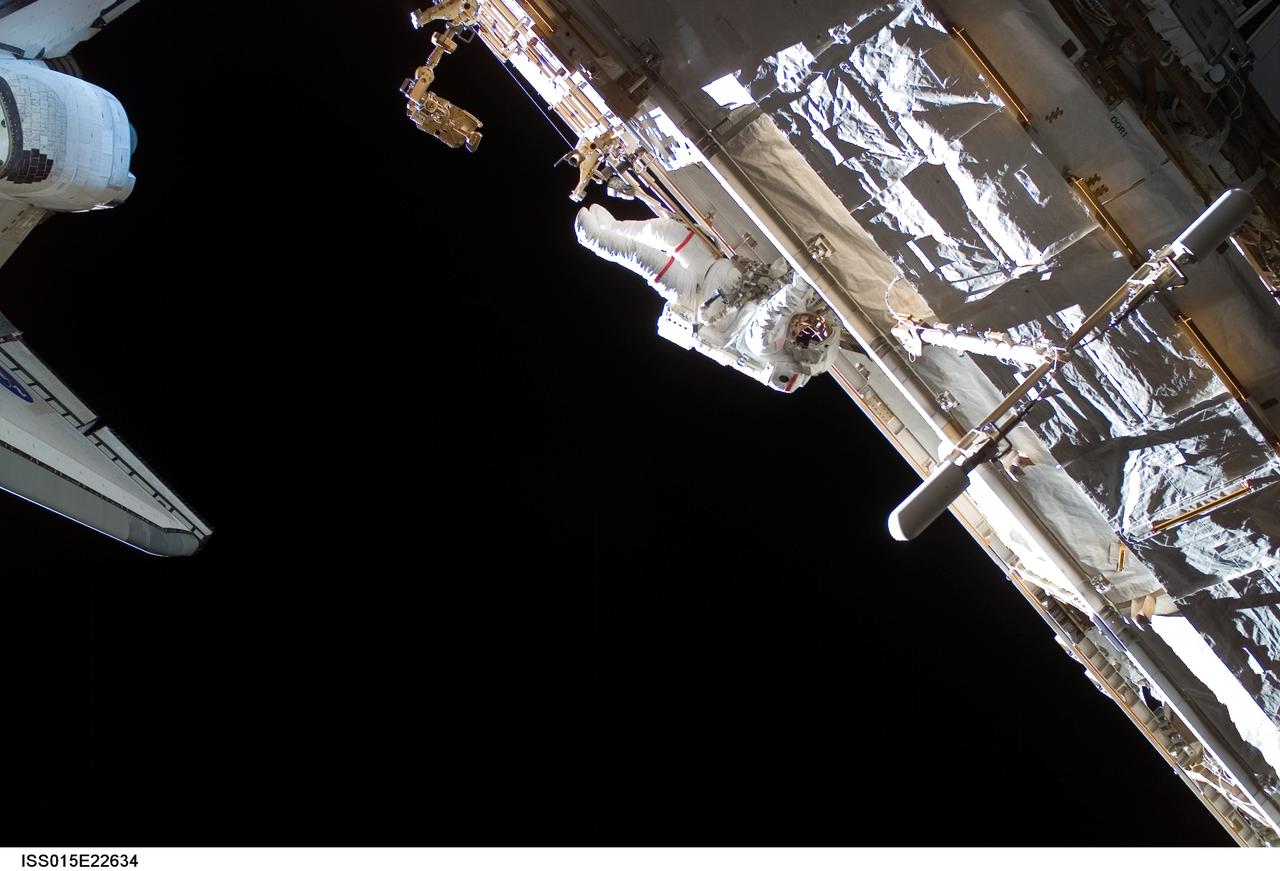

ISS015-E-22634 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
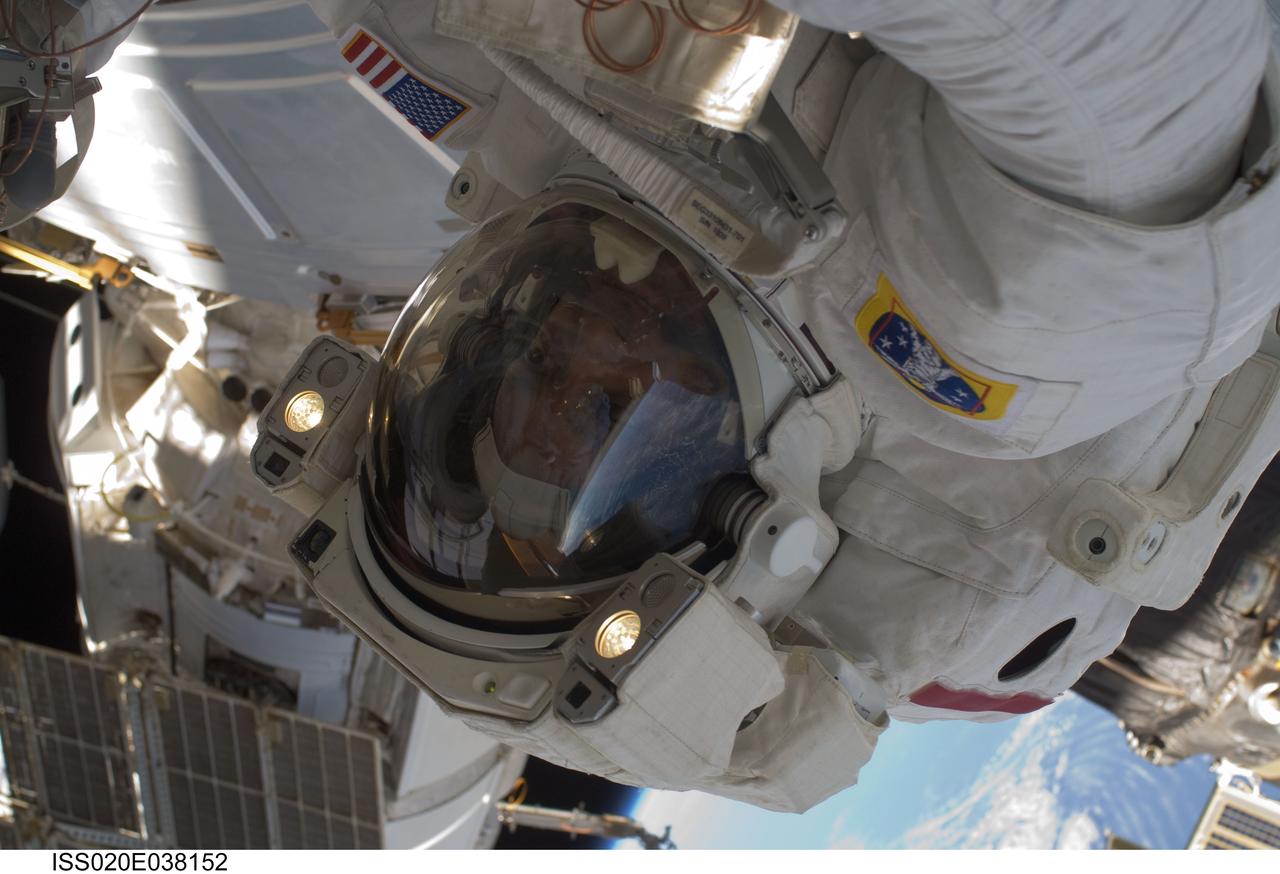

ISS020-E-038152 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
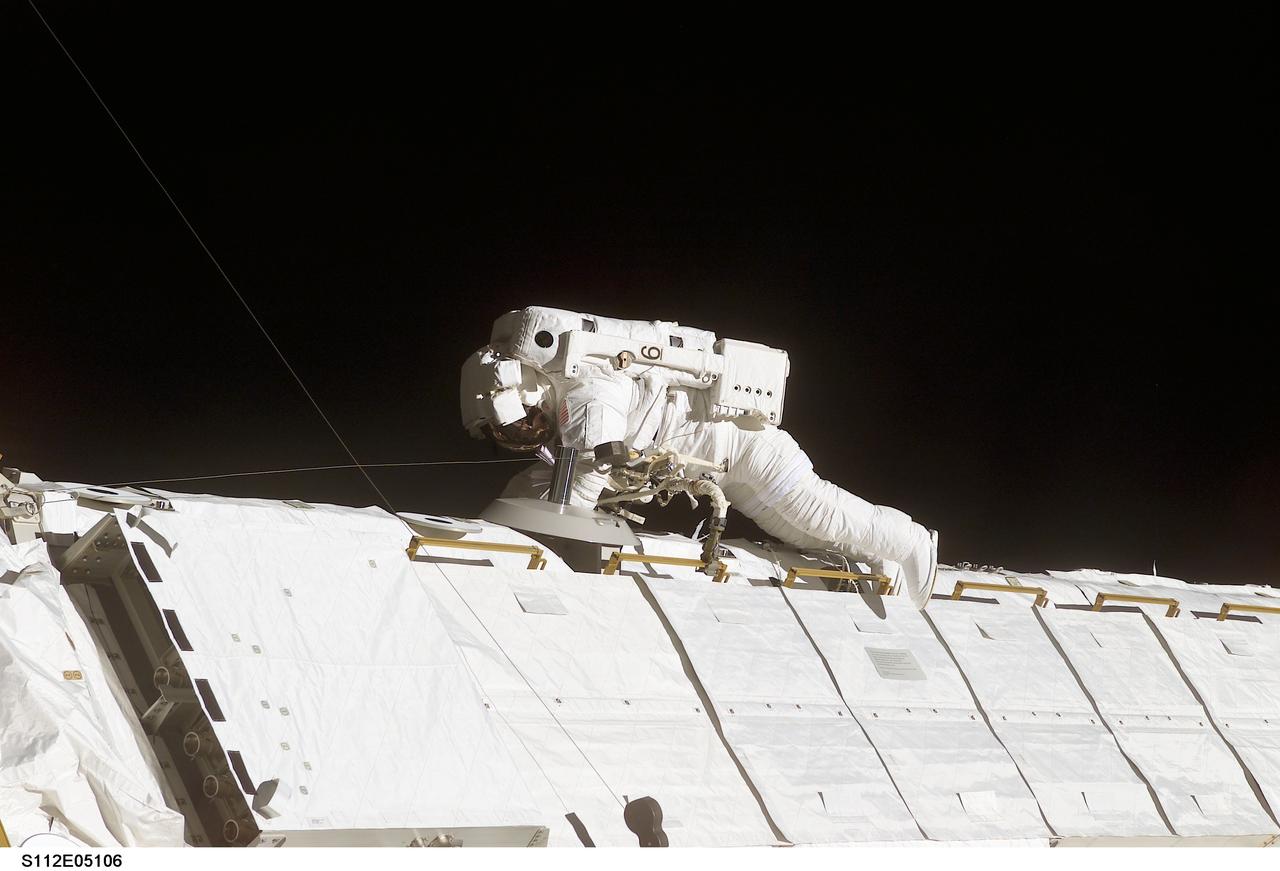

STS112-E-05106 (10 October 2002) --- Astronaut Piers J. Sellers, STS-112 mission specialist, works on the Starboard One (S1) Truss, newly installed on the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut David A. Wolf (out of frame), mission specialist, worked in tandem with Sellers during the spacewalk. STS-112’s first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) lasted 7 hours and 1 minute.
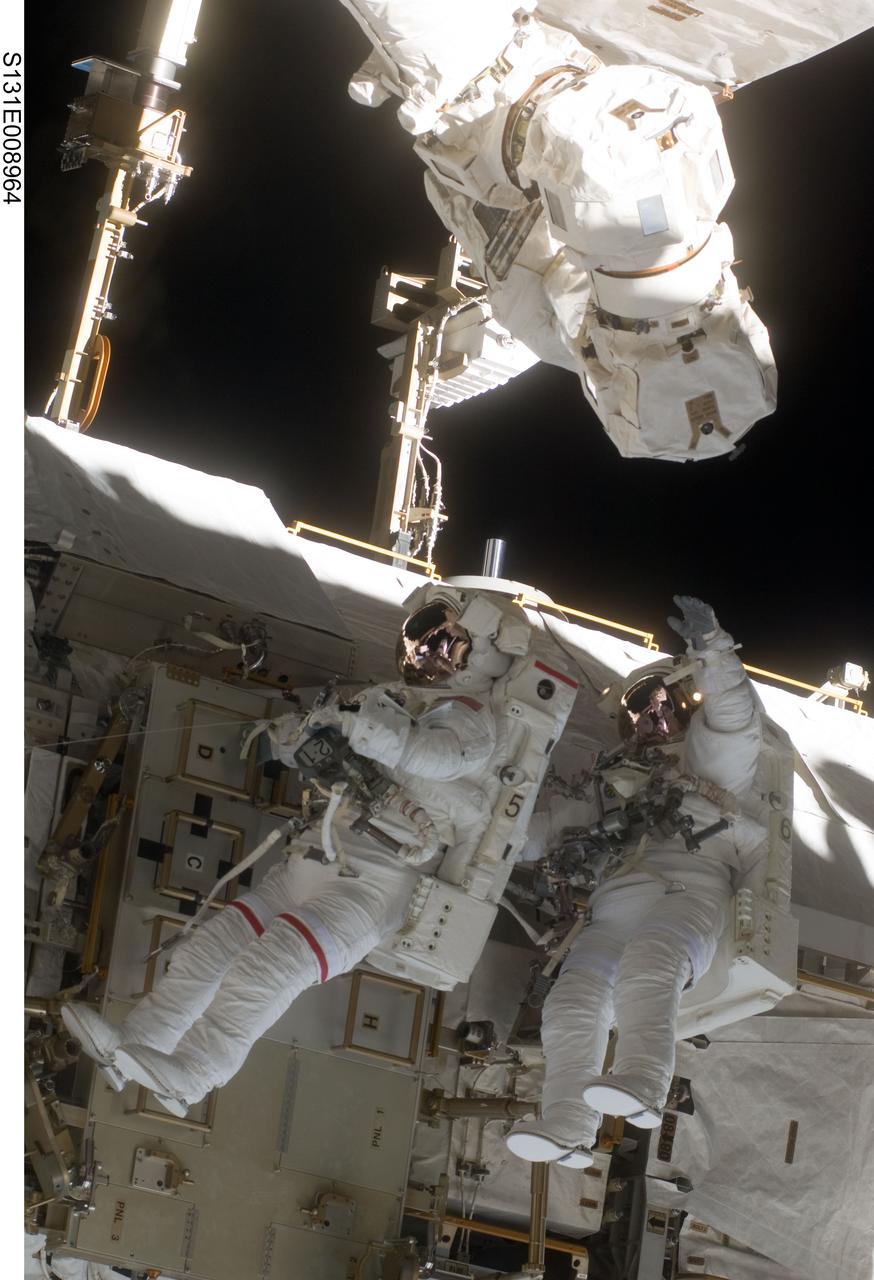

S131-E-008964 (11 April 2010) --- NASA astronauts Rick Mastracchio (left) and Clayton Anderson, both STS-131 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour, 26-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson unhooked and removed the depleted ammonia tank and installed a 1,700-pound ammonia tank on the station?s Starboard 1 truss, completing the second of a three-spacewalk coolant tank replacement process.
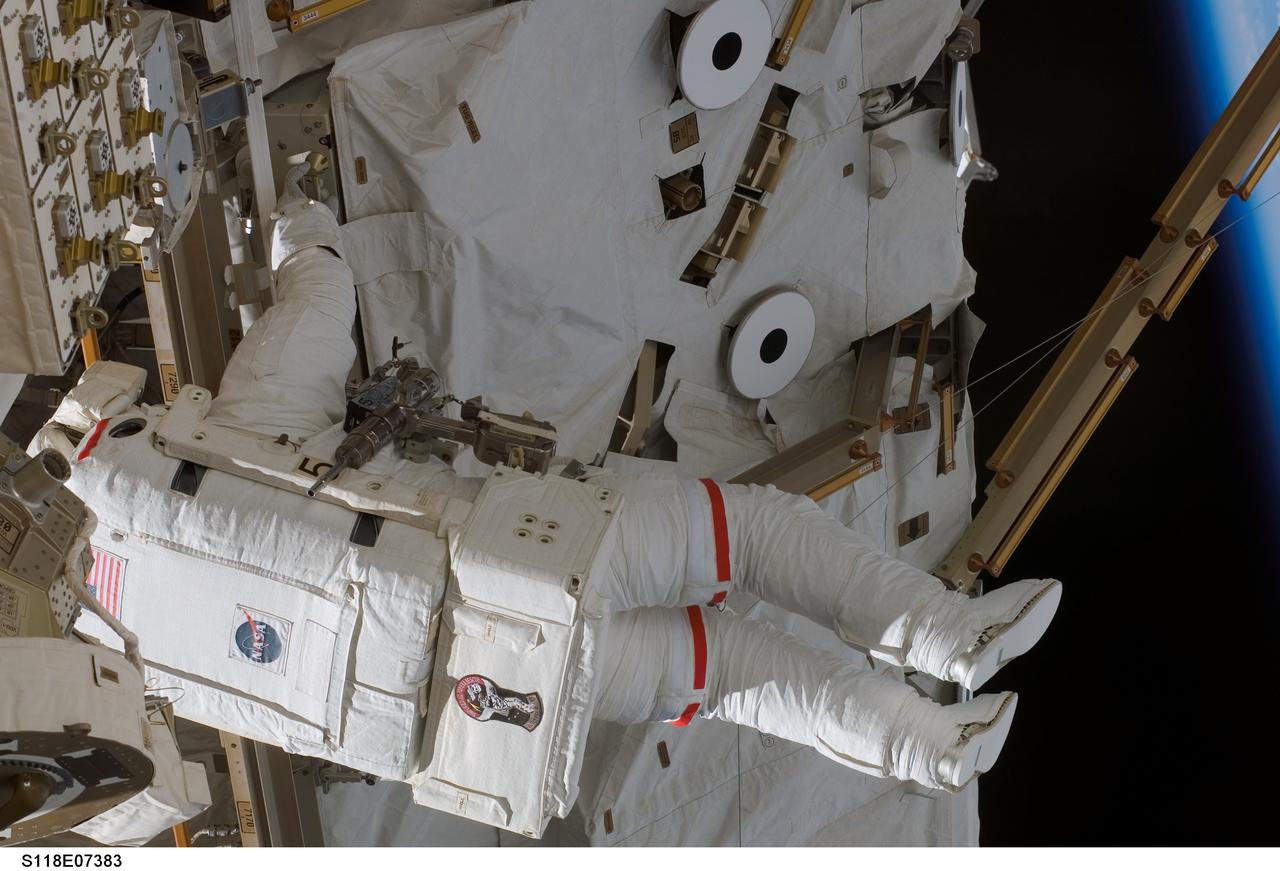

S118-E-07383 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
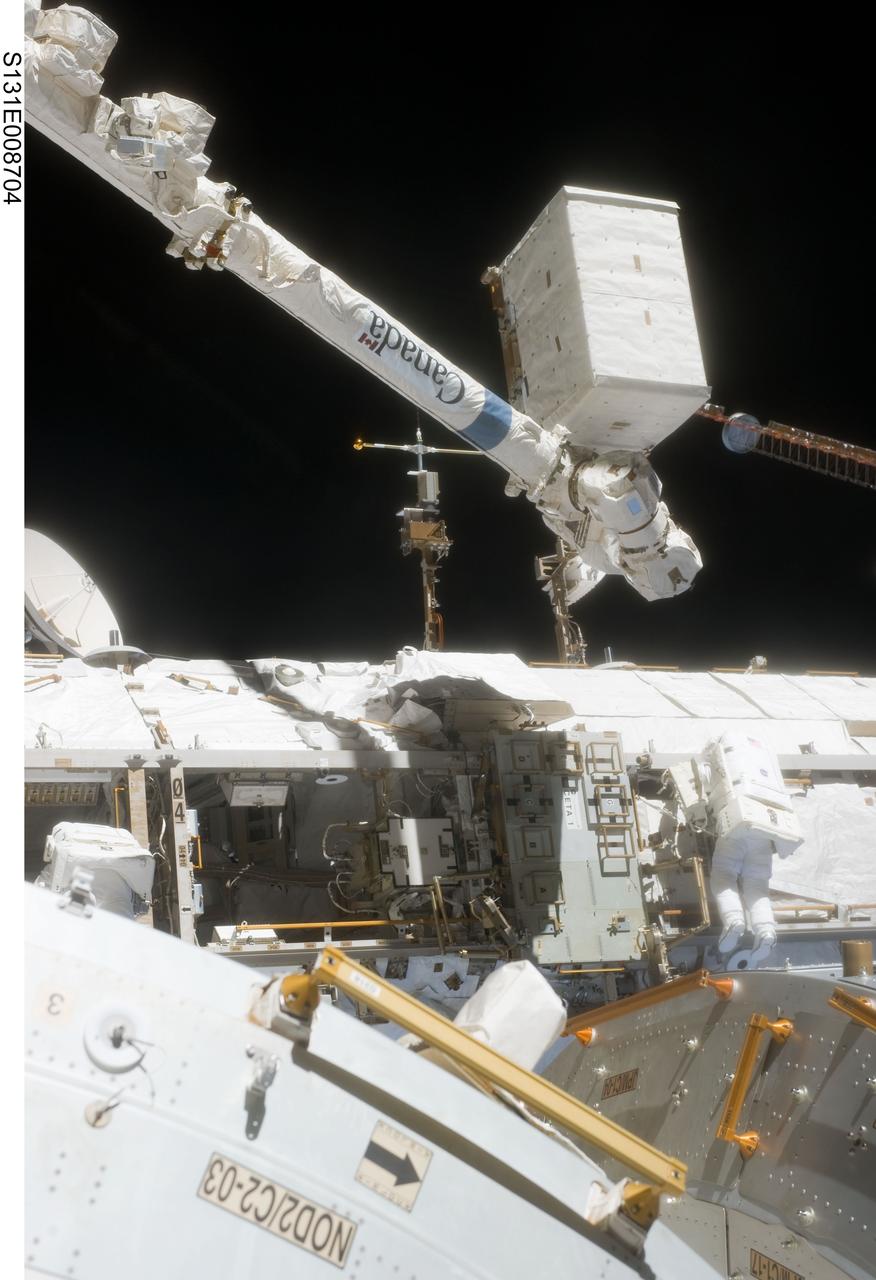

S131-E-008704 (11 April 2010) --- NASA astronaut Clayton Anderson, STS-131 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour, 26-minute spacewalk, Anderson and Rick Mastracchio (out of frame), mission specialist, unhooked and removed the depleted ammonia tank and installed a 1,700-pound ammonia tank on the station?s Starboard 1 truss, completing the second of a three-spacewalk coolant tank replacement process.
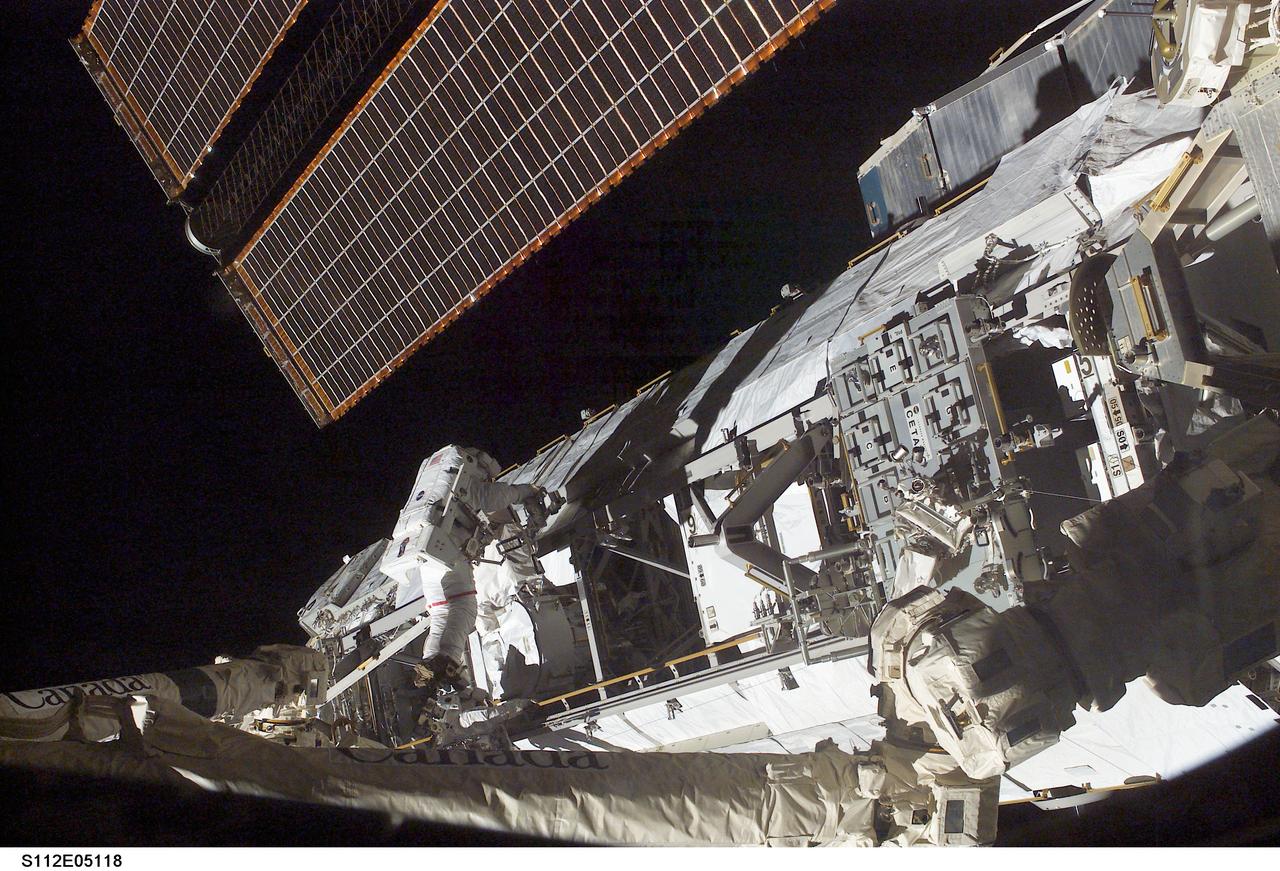

STS112-E-05118 (10 October 2002) --- Astronaut David A. Wolf, STS-112 mission specialist, works on the Starboard One (S1) Truss, newly installed on the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut Piers J. Sellers (out of frame), mission specialist, worked in tandem with Wolf during the spacewalk. STS-112’s first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) lasted 7 hours and 1 minute.
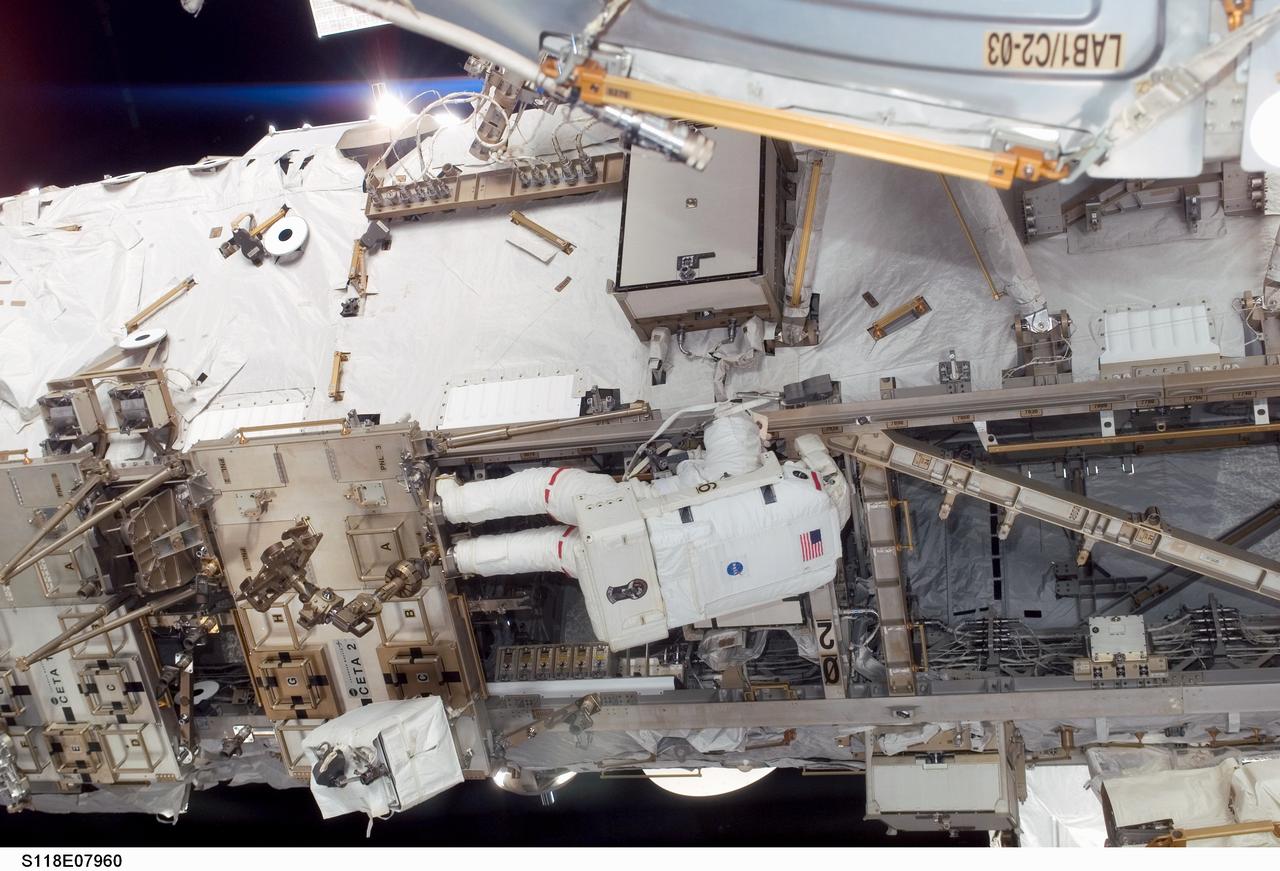

S118-E-07960 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Anderson and astronaut Rick Mastracchio (out of frame), STS-118 mission specialist, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
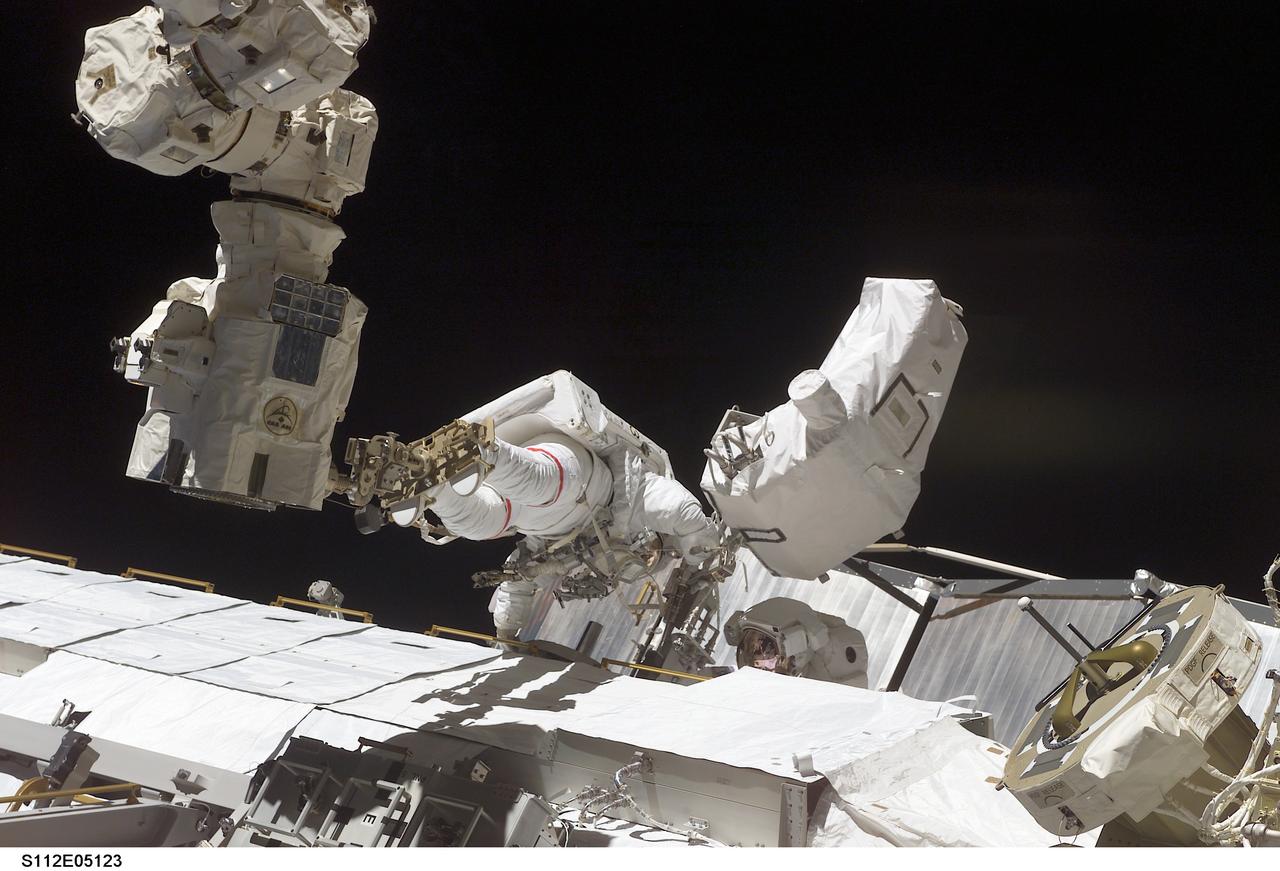

STS112-E-05123 (10 October 2002) --- Astronaut David A. Wolf, STS-112 mission specialist, anchored to the end of the Canadarm2, works on the Starboard One (S1) Truss, newly installed on the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut Piers J. Sellers (partially obscured), mission specialist, worked in tandem with Wolf during the spacewalk. STS-112’s first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) lasted 7 hours and 1 minute.
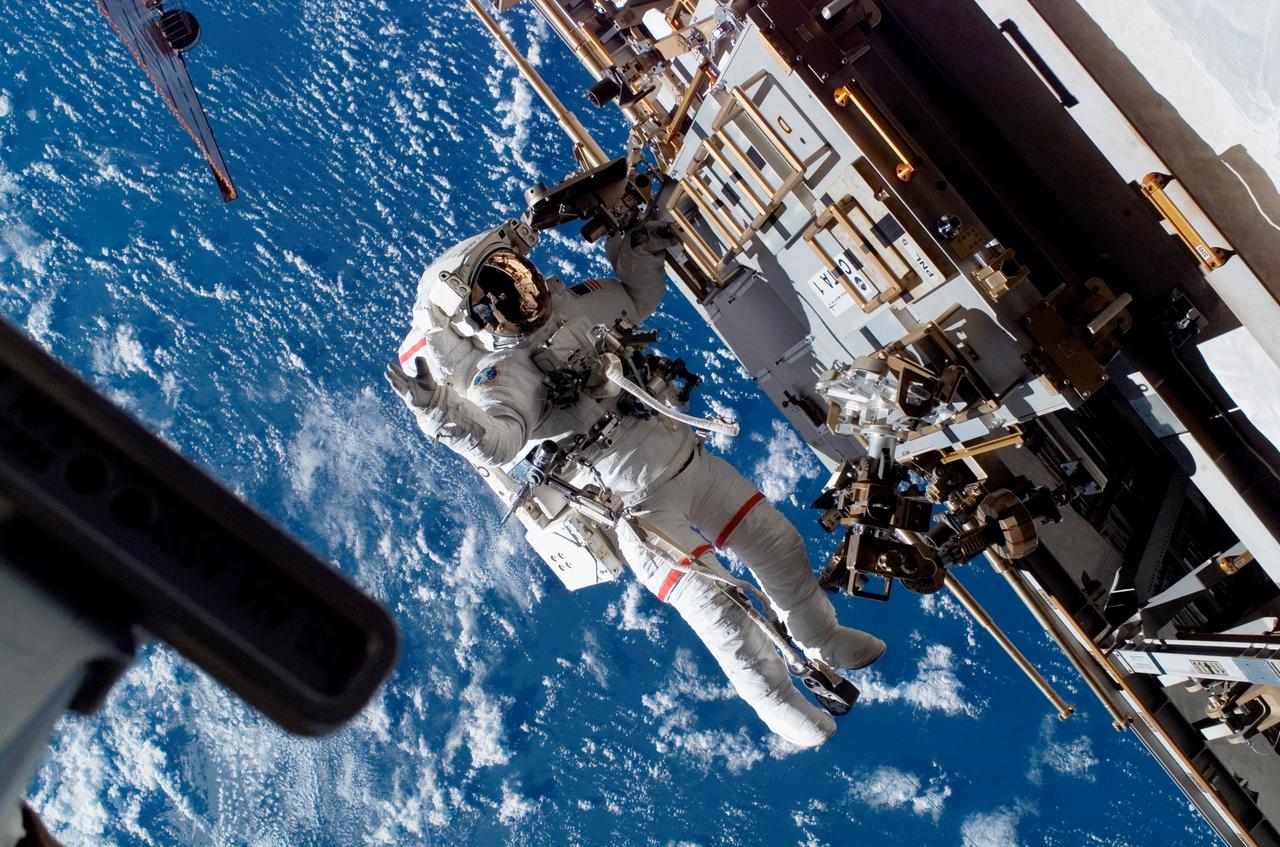

ISS015-E-22539 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
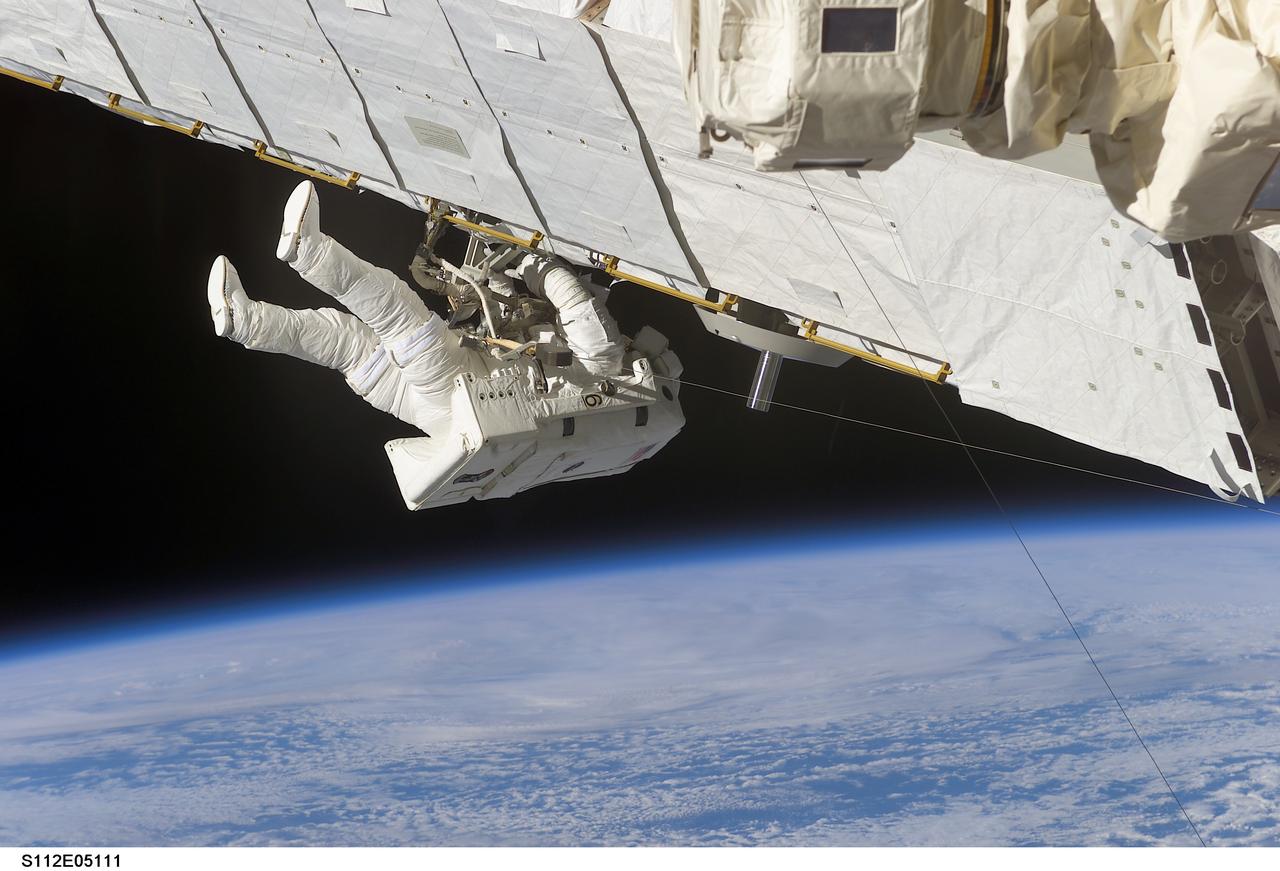

STS112-E-05111 (10 October 2002) --- Astronaut Piers J. Sellers, STS-112 mission specialist, works on the Starboard One (S1) Truss, newly installed on the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut David A. Wolf (out of frame), mission specialist, worked in tandem with Sellers during the spacewalk. STS-112’s first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) lasted 7 hours and 1 minute.
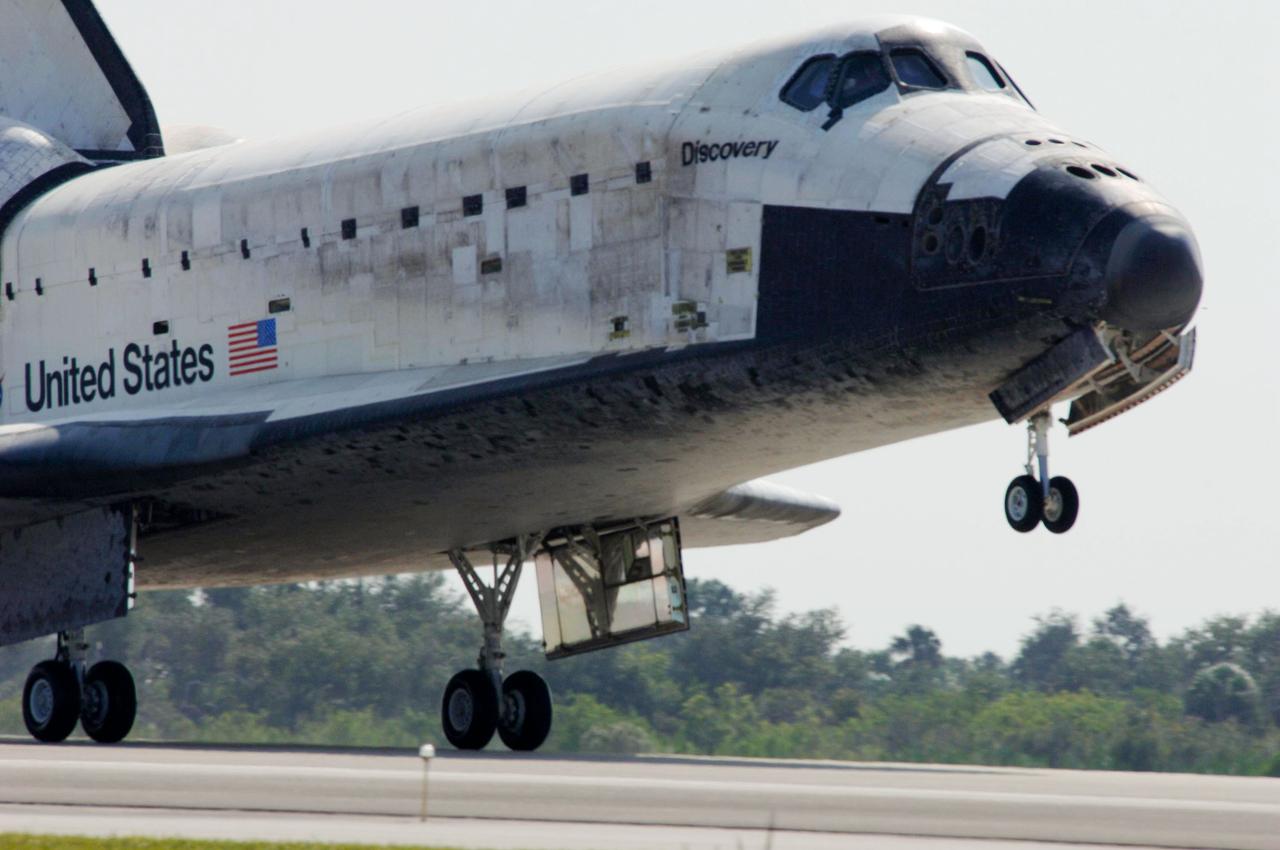

STS120-S-083 (7 Nov. 2007) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery lands at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, completing the 15-day STS-120 mission to the International Space Station. Discovery landed at 1:01 p.m. (EST) Nov. 7 after a mission that included on-orbit construction of the station with the installation of the Harmony Node 2 module and the relocation of the P6 truss.
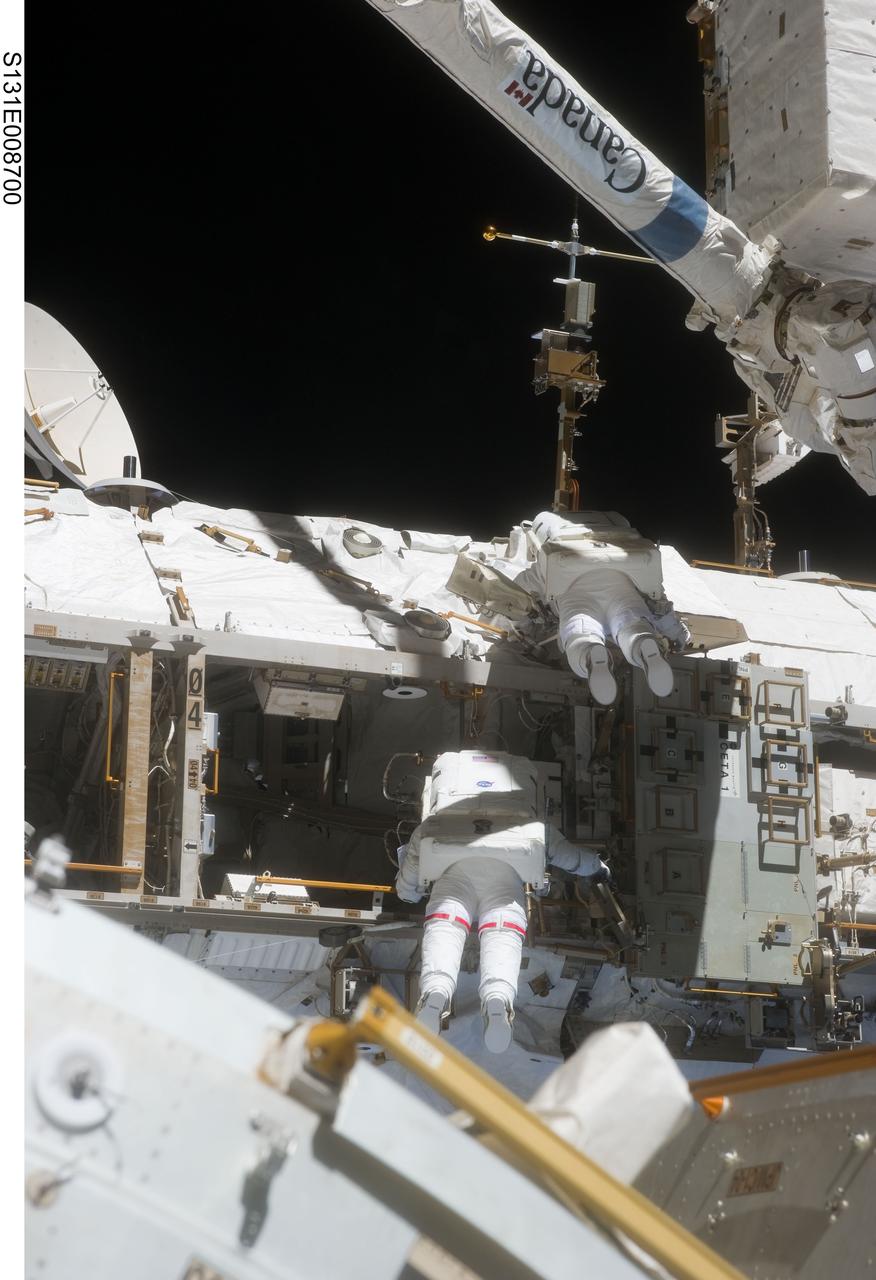

S131-E-008700 (11 April 2010) --- NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio (bottom) and Clayton Anderson, both STS-131 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour, 26-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson unhooked and removed the depleted ammonia tank and installed a 1,700-pound ammonia tank on the station?s Starboard 1 truss, completing the second of a three-spacewalk coolant tank replacement process.

ISS005-E-16977 (9 October 2002) --- Backdropped against a blue and white Earth, this view of the Space Shuttle Atlantis was photographed by an Expedition Five crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS) during rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 10:17 a.m. (CDT) on October 9, 2002. The Starboard One (S-1) Truss, which was later attached to the station and outfitted during three spacewalks, can be seen in Atlantis’ cargo bay.
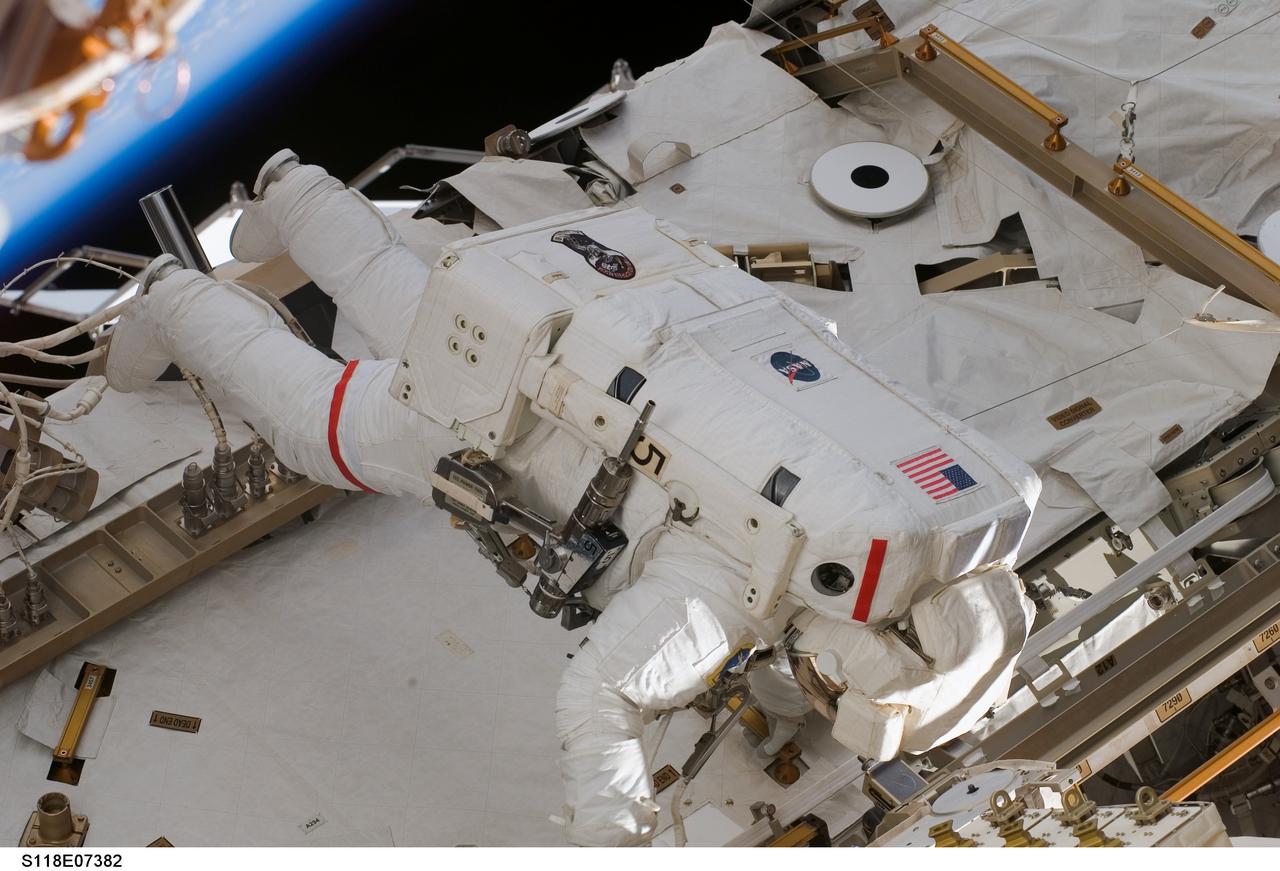

S118-E-07382 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
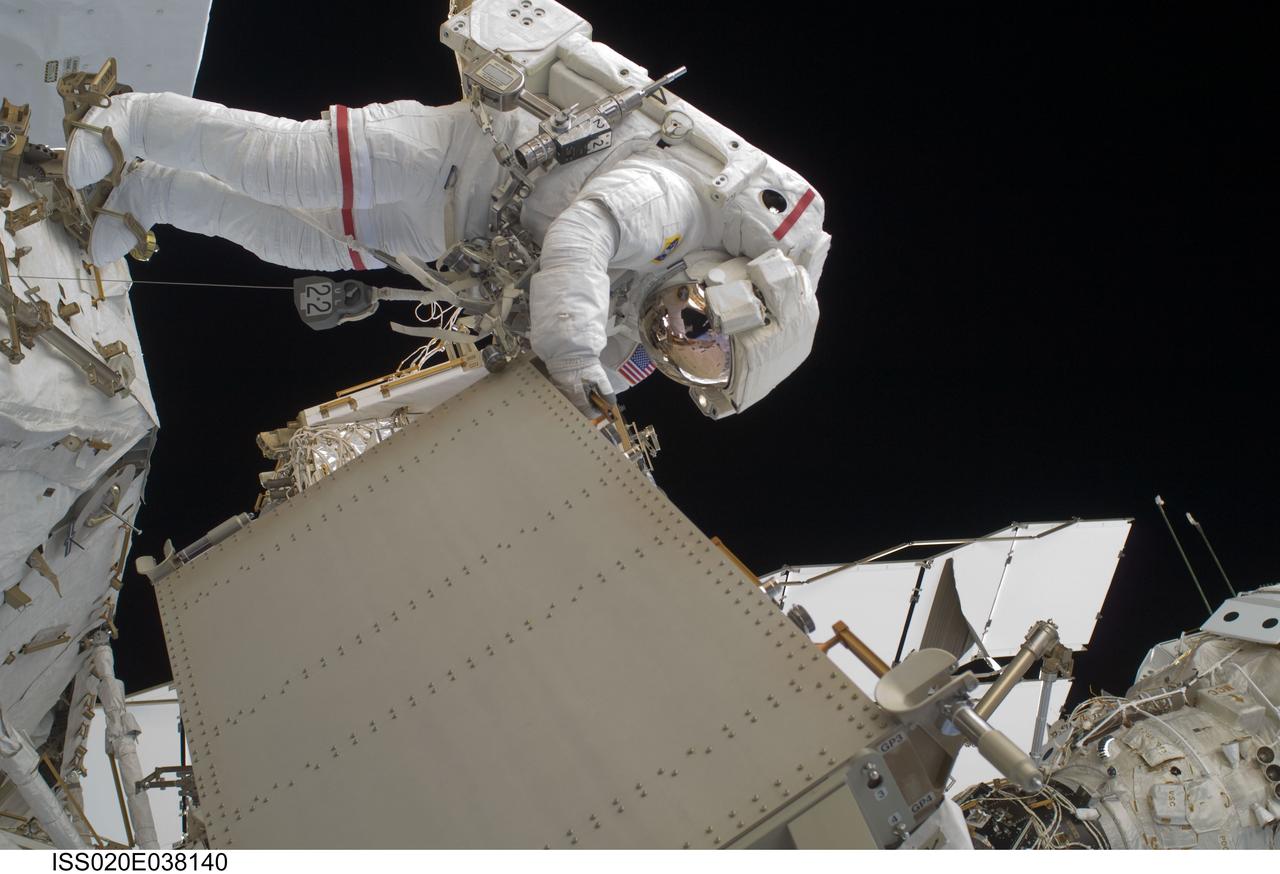

ISS020-E-038140 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
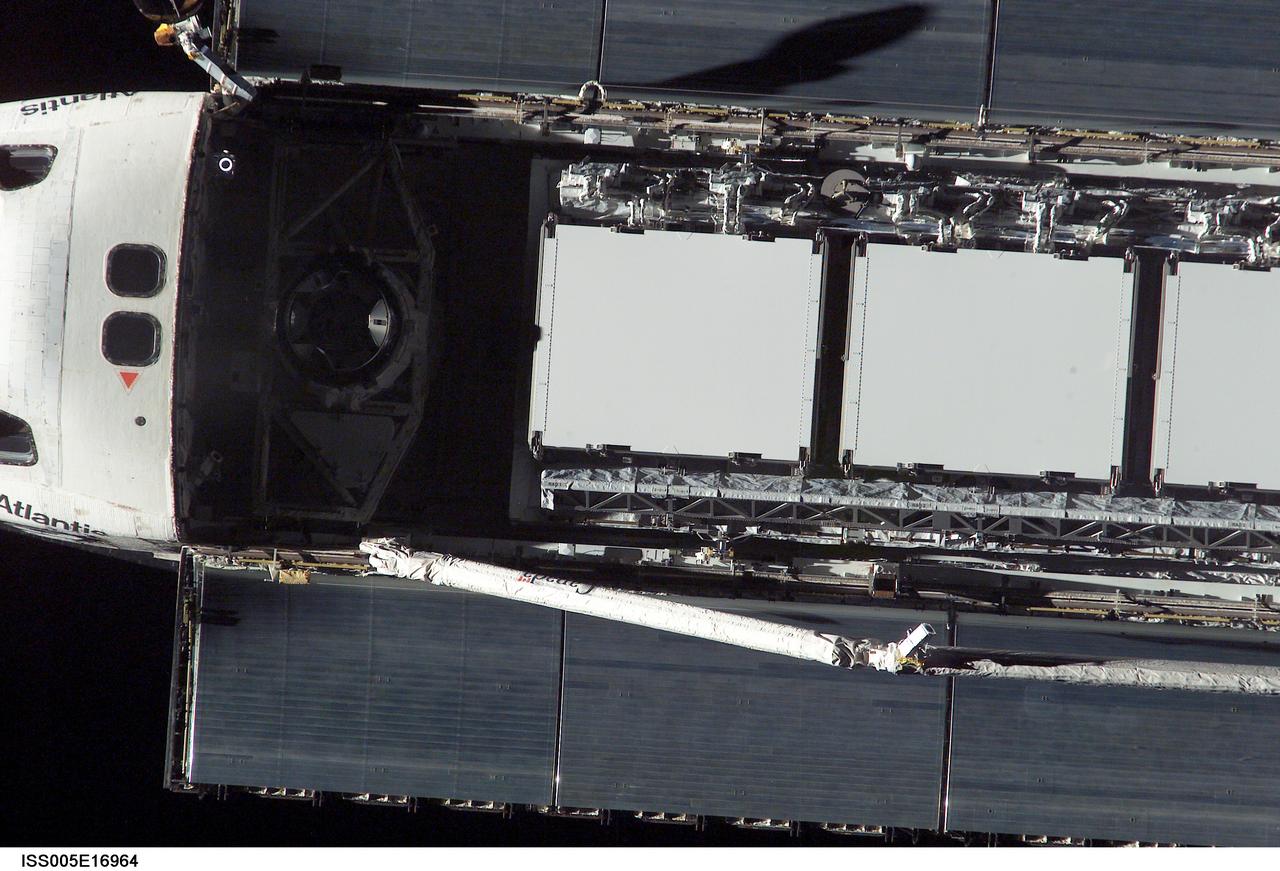

ISS005-E-16964 (9 October 2002) --- This close-up view of the Space Shuttle Atlantis was photographed by an Expedition Five crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS) during rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 10:17 a.m. (CDT) on October 9, 2002. The Starboard One (S-1) Truss, which was later attached to the station and outfitted during three spacewalks, can be seen in Atlantis’ cargo bay.
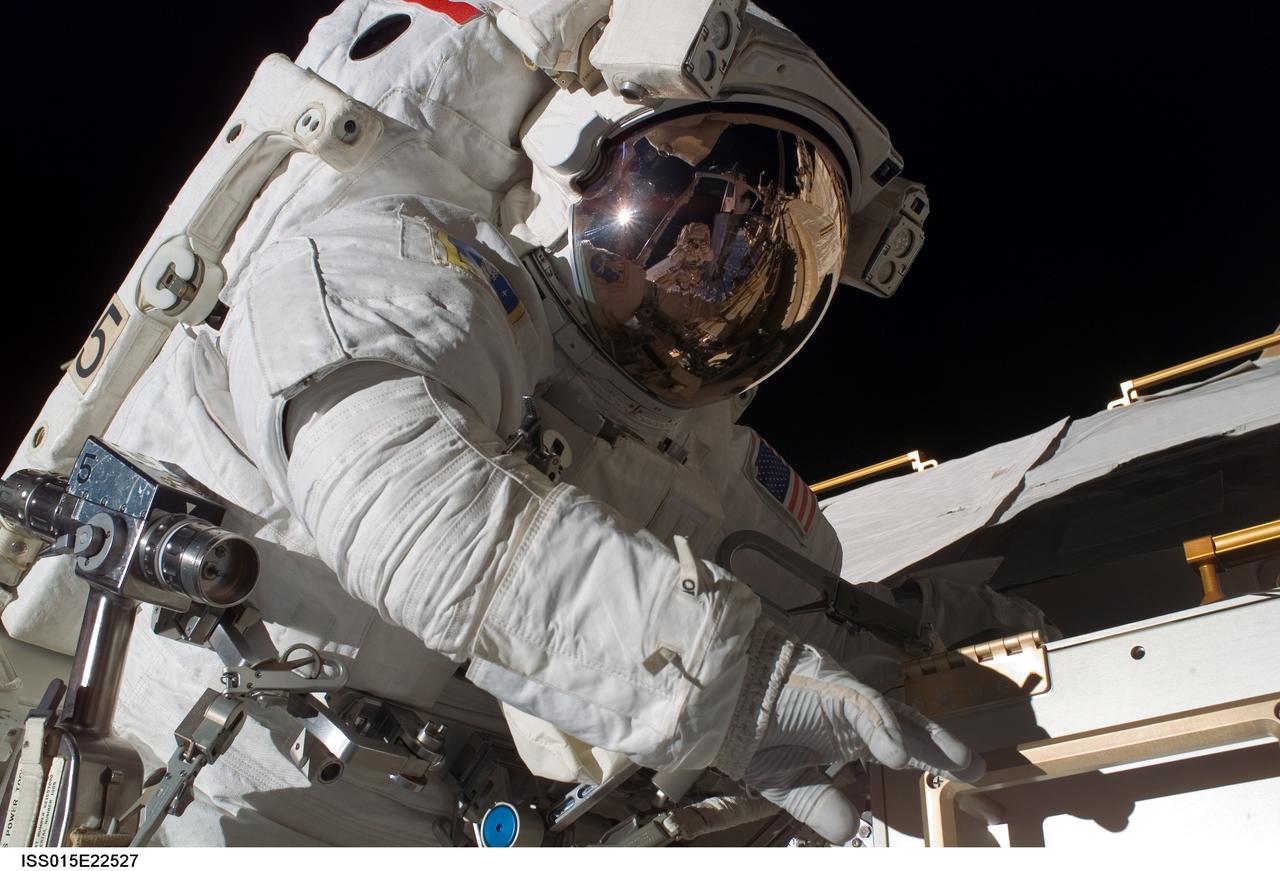

ISS015-E-22527 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
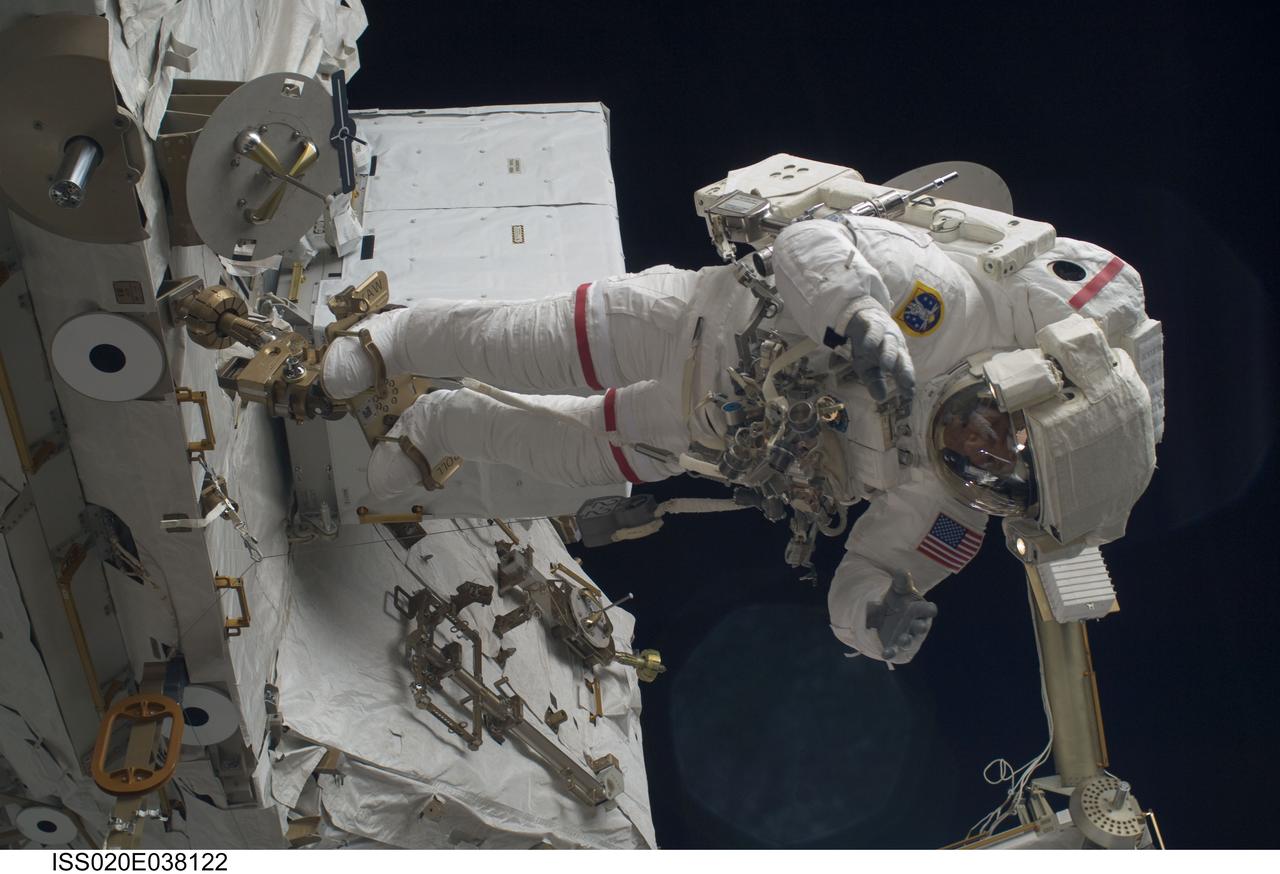

ISS020-E-038122 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
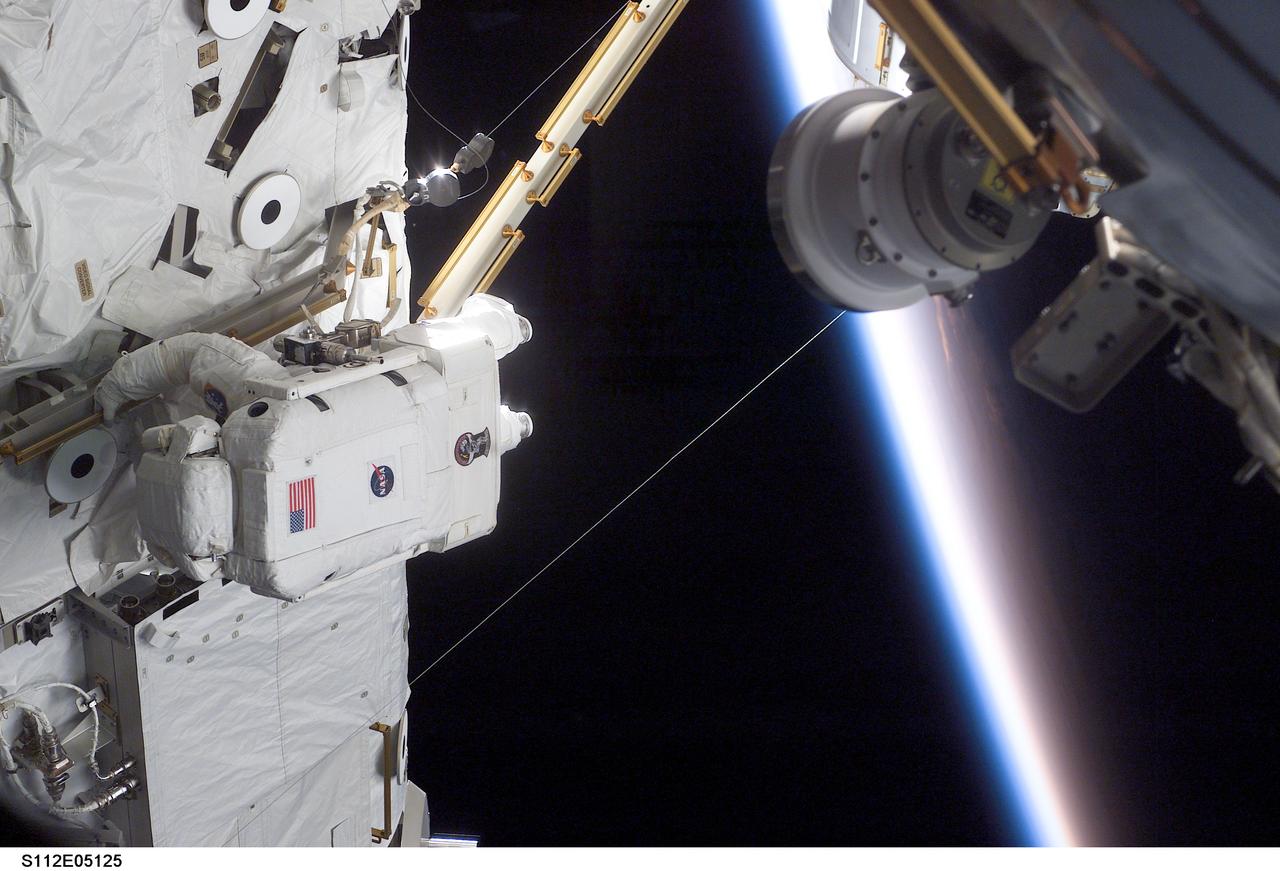

STS112-E-05125 (10 October 2002) --- Astronaut Piers J. Sellers, STS-112 mission specialist, works on the Starboard One (S1) Truss, newly installed on the International Space Station (ISS). Astronaut David A. Wolf (out of frame), mission specialist, worked in tandem with Sellers during the spacewalk. STS-112’s first session of extravehicular activity (EVA) lasted 7 hours and 1 minute.
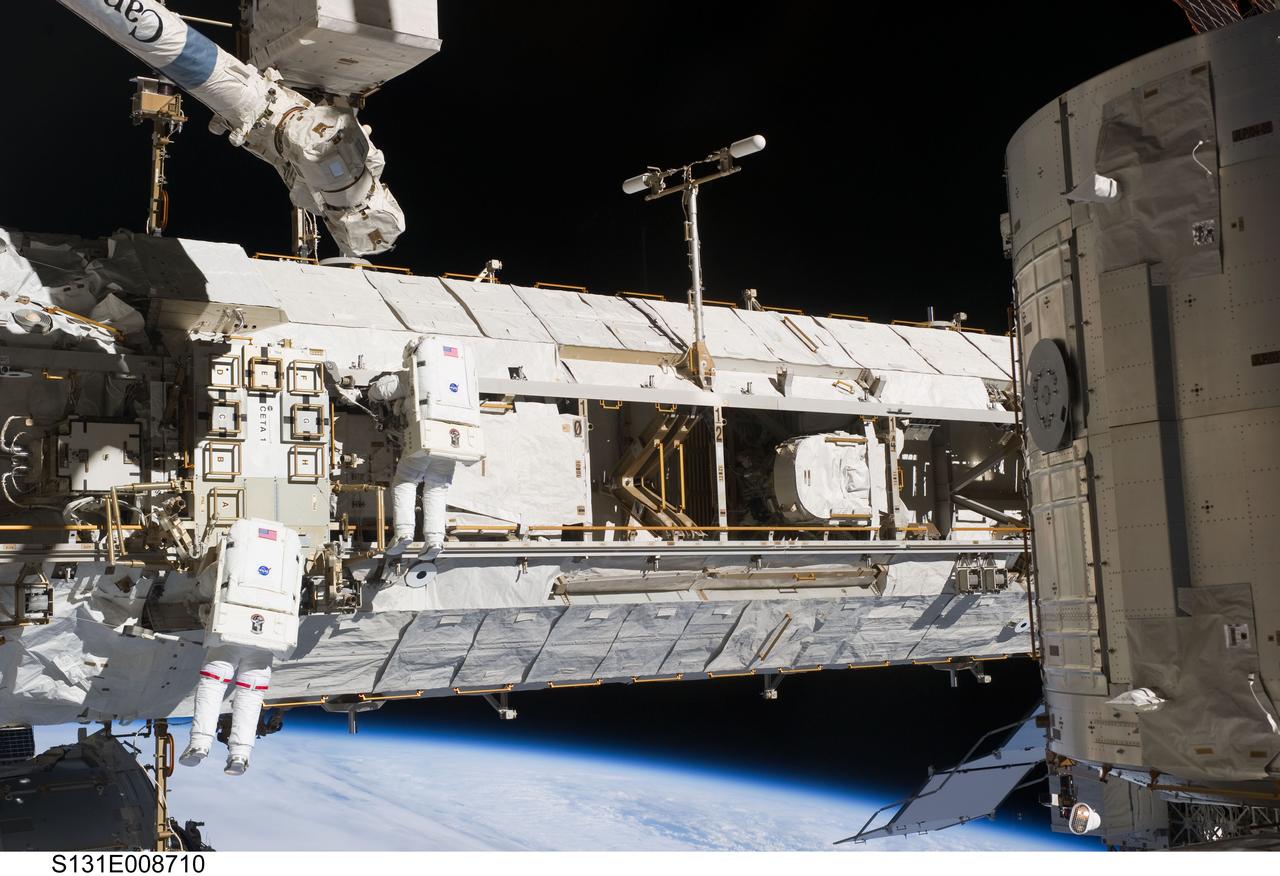

S131-E-008710 (11 April 2010) --- NASA astronauts Rick Mastracchio (left) and Clayton Anderson, both STS-131 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour, 26-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson unhooked and removed the depleted ammonia tank and installed a 1,700-pound ammonia tank on the station?s Starboard 1 truss, completing the second of a three-spacewalk coolant tank replacement process.

STS-92 Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. is fully suited up before the second launch attempt. He and the rest of the crew will be leaving soon for the ride to Launch Pad 39A on the Astrovan. During the 11-day mission to the International Space Station, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or spacewalks, are planned for construction. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. The Z-1 truss is the first of 10 that will become the backbone of the Space Station, eventually stretching the length of a football field. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight.; Launch is scheduled for 7:17 p.m. EDT. Landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT

STS-92 Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. signals thumbs up for launch, scheduled for 8:05 p.m. EDT. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the ISS. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or spacewalks, are planned. The Z-1 truss is the first of 10 that will become the backbone of the International Space Station, eventually stretching the length of a football field. PMA-3 will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. This launch is the third for McArthur. Landing is expected Oct. 21 at 3:55 p.m. EDT
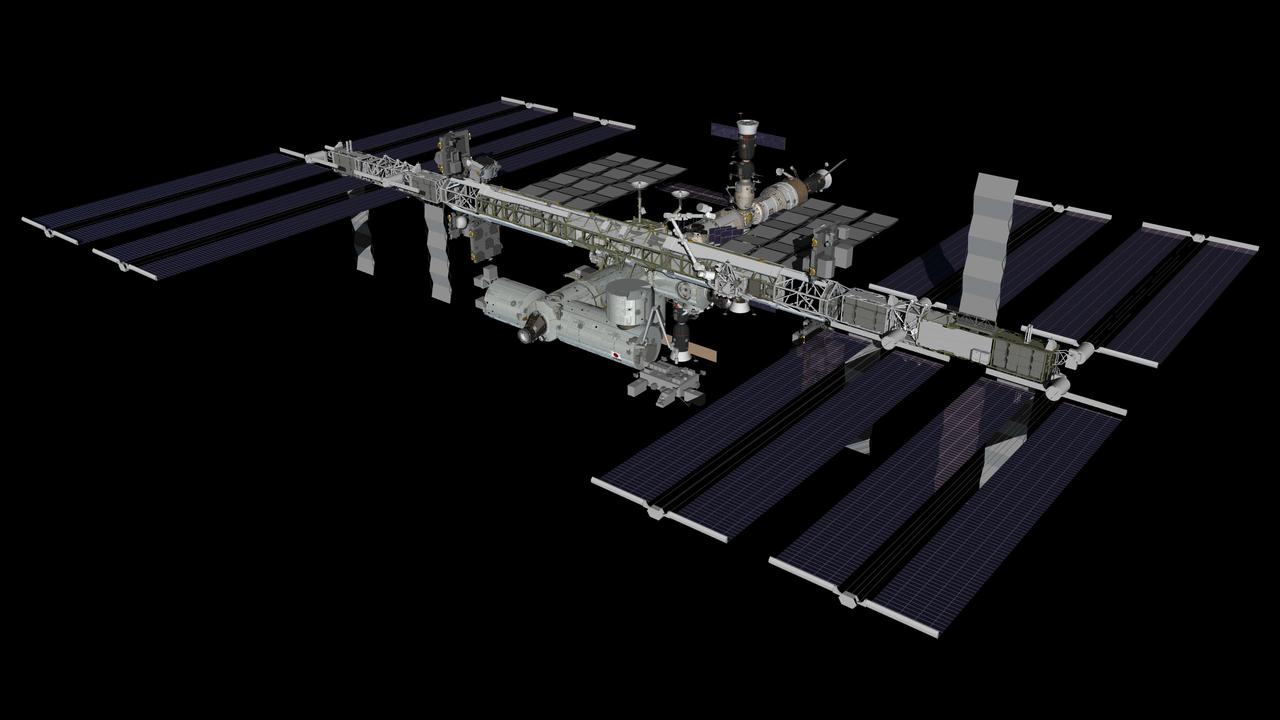
JSC2012-E-231604 (November 2012) --- Computer-generated artist?s rendering of the International Space Station as of Nov. 1, 2012. A Photovoltaic Radiator (PVR) is deployed on the ISS P6 truss during U.S. spacewalk 20. Progress 49 resupply vehicle is docked to the Zvezda Service Module aft port. Soyuz 32 (TMA-06M) is linked to the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2). Progress 48 is docked to the Pirs Docking Compartment and Soyuz 31 (TMA-05M) is attached to the Rassvet Mini-Research Module 1 (MRM1). Photo credit: NASA

STS-110 mission specialist Lee M.E. Morin carries an affixed 35 mm camera to record work which is being performed on the International Space Station (ISS). Working with astronaut Jerry L. Ross (out of frame), the duo completed the structural attachment of the S0 (s-zero) truss, mating two large tripod legs of the 13 1/2 ton structure to the station's main laboratory during a 7-hour, 30-minute space walk. The STS-110 mission prepared the Station for future space walks by installing and outfitting the 43-foot-long S0 truss and preparing the Mobile Transporter. The S0 Truss was the first of 9 segments that will make up the Station's external framework that will eventually stretch 356 feet (109 meters), or approximately the length of a football field. This central truss segment also includes a flatcar called the Mobile Transporter and rails that will become the first "space railroad," which will allow the Station's robotic arm to travel up and down the finished truss for future assembly and maintenance. The completed truss structure will hold solar arrays and radiators to provide power and cooling for additional international research laboratories from Japan and Europe that will be attached to the Station. Milestones of the S-110 mission included the first time the ISS robotic arm was used to maneuver space walkers around the Station and marked the first time all space walks were based out of the Station's Quest Airlock. It was also the first Shuttle to use three Block II Main Engines. The Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis, STS-110 mission, was launched April 8, 2002 and returned to Earth April 19, 2002.

STS-92 Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. undergoes final suit check in the White Room before entering Discovery. The White Room is an environmentally controlled area at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm that provides entry to the orbiter as well as emergency egress if needed. The arm remains in the extended position until 7 minutes 24 seconds before launch. McArthur and the rest of the crew are making the fifth flight to the International Space Station for construction. Discovery carries a payload that includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1, first of 10 trusses that will form the backbone of the Space Station, and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter that will provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth Station flight and Lab installation on the seventh Station flight. The mission includes four spacewalks for the construction activities. Discovery’s landing is expected Oct. 22 at 2:10 p.m. EDT

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, Houston -- STS118-S-001 -- The STS-118 patch represents Space Shuttle Endeavour on its mission to help complete the assembly of the International Space Station and symbolizes the pursuit of knowledge through space exploration. The flight will accomplish its ISS 13A.1 assembly tasks through a series of spacewalks, robotic operations, logistics transfers and the exchange of one of the three long-duration expedition crew members. On the patch, the top of the gold astronaut symbol overlays the starboard S-5 truss segment, highlighting its installation during the mission. The flame of knowledge represents the importance of education, and honors teachers and students everywhere. The seven white stars and the red maple leaf signify the American and Canadian crew members flying aboard Endeavour.
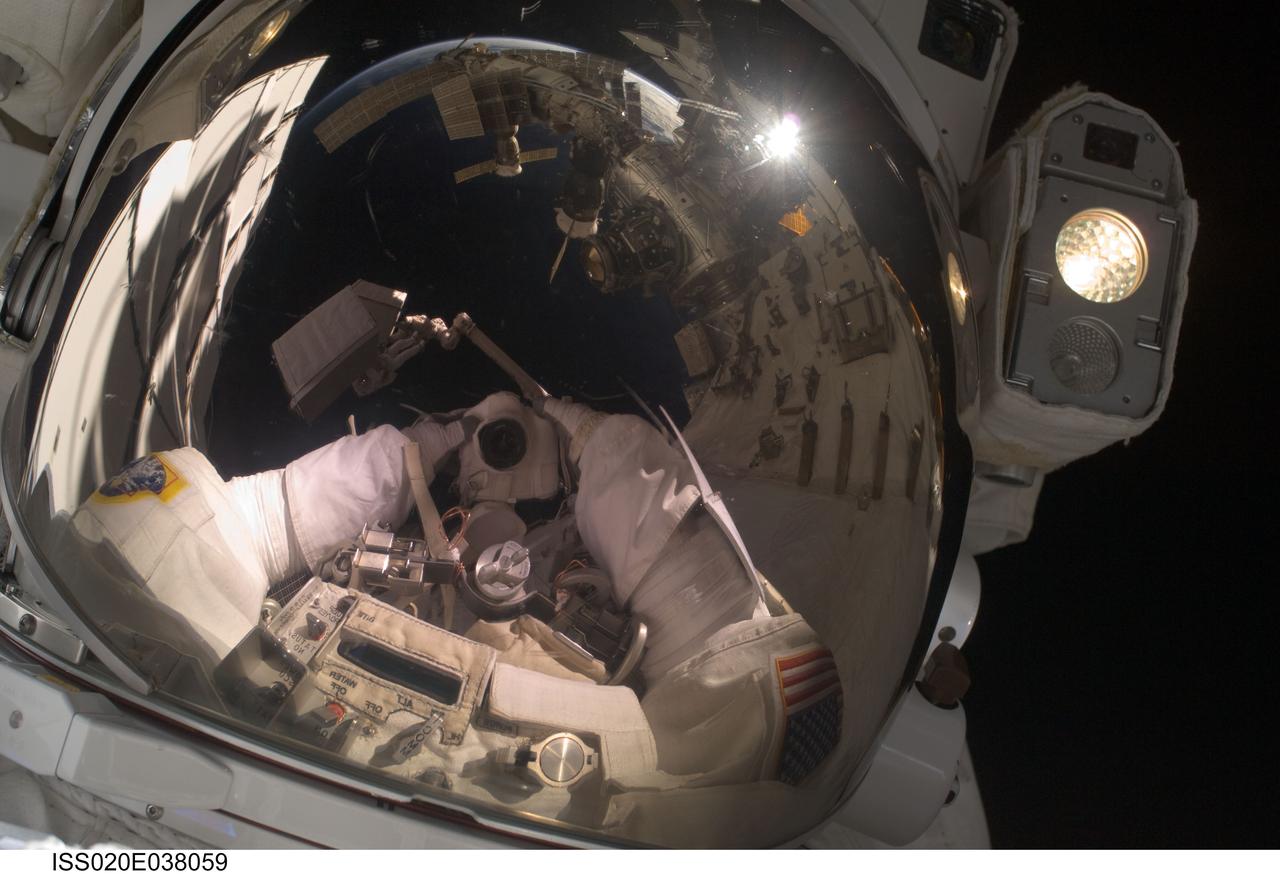

ISS020-E-038059 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, uses a digital still camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during the mission?s second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. Also visible in the reflections in the visor are various components of the station and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang, mission specialist, anchored to a Canadarm2 mobile foot restraint. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and Fuglesang installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
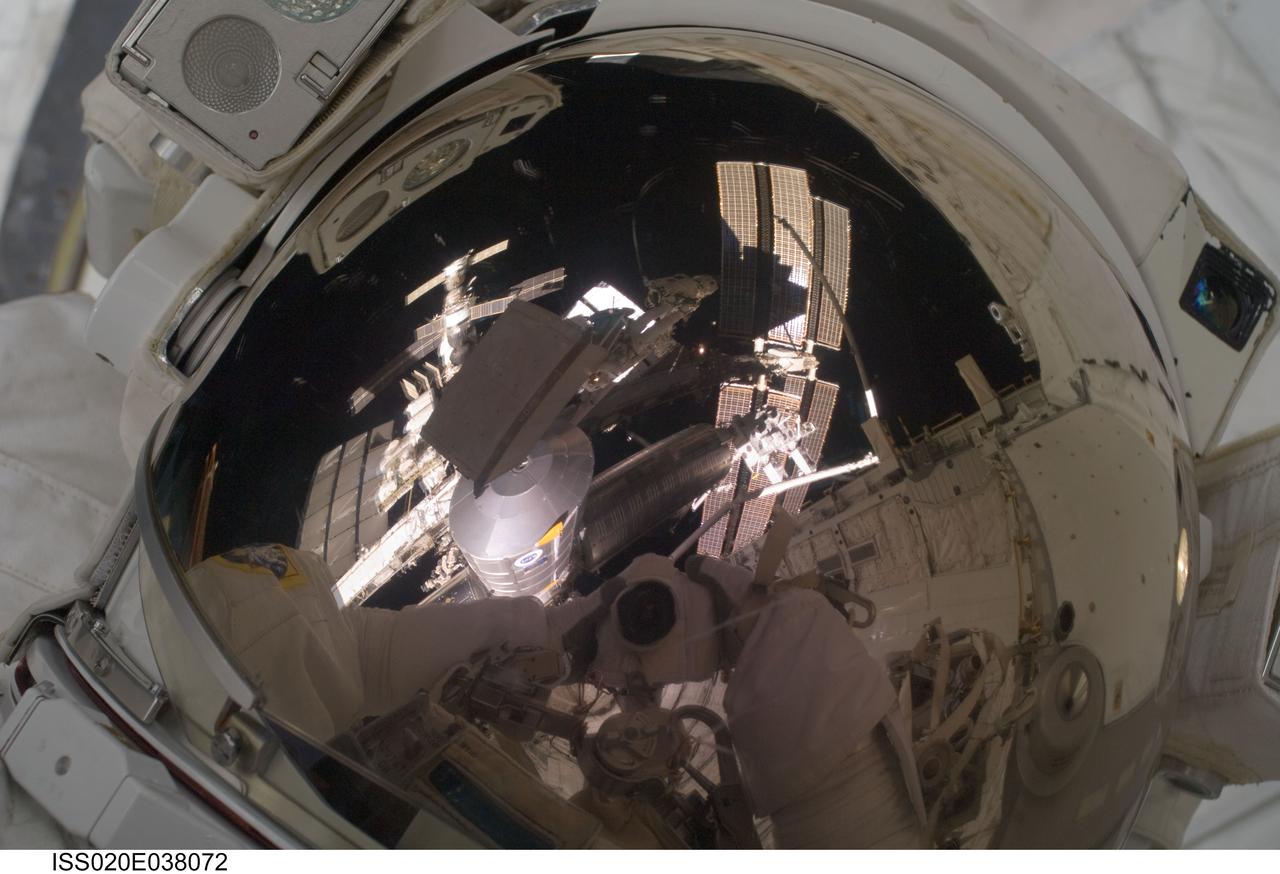

ISS020-E-038072 (3 Sept. 2009) --- NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas, STS-128 mission specialist, uses a digital still camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during the mission?s second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. Also visible in the reflections in the visor are various components of the station and European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang, mission specialist, anchored to a Canadarm2 mobile foot restraint. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Olivas and Fuglesang installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
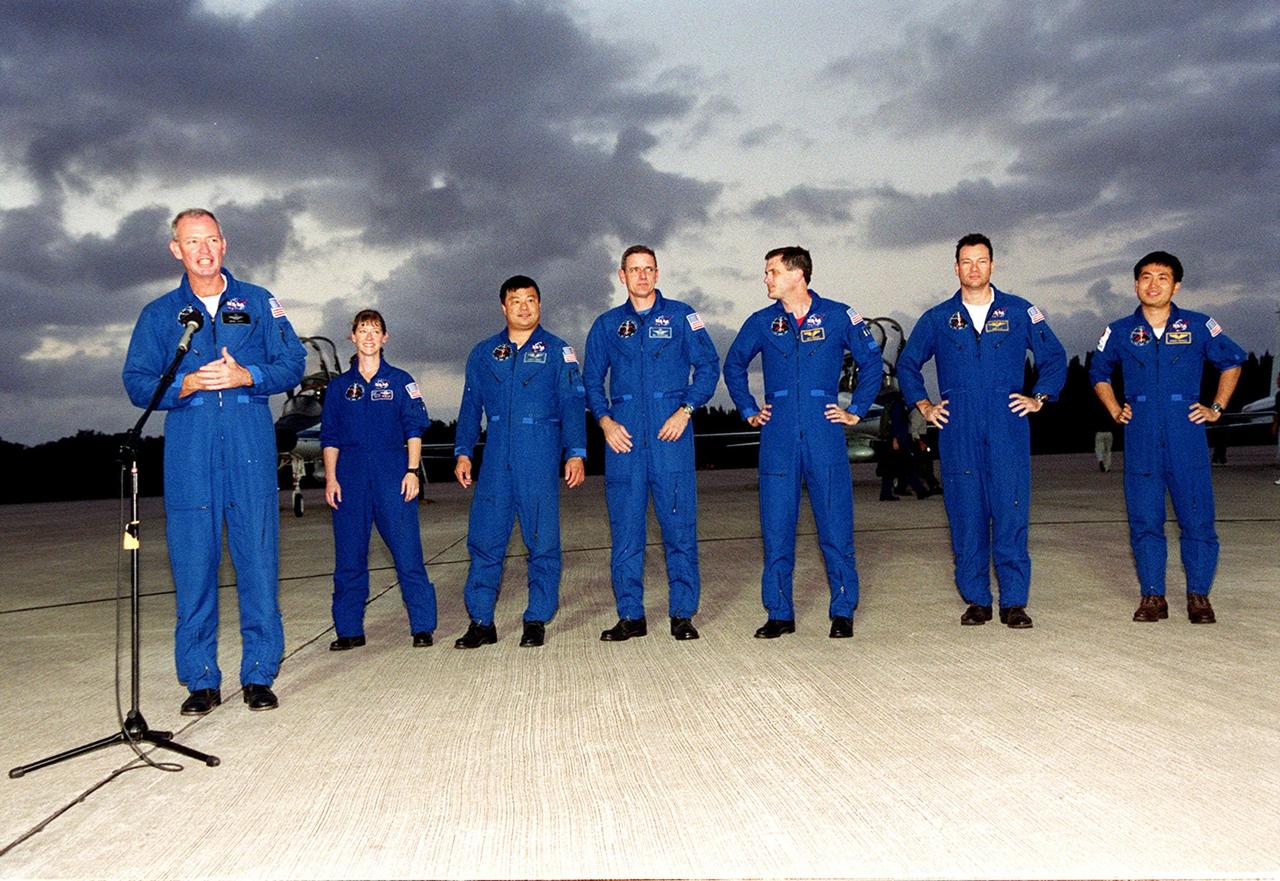

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After their arrival at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, the STS-92 crew paused to talk to the media, who were waiting nearby. At the microphone is Commander Brian Duffy. Standing behind him, left to right, are Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
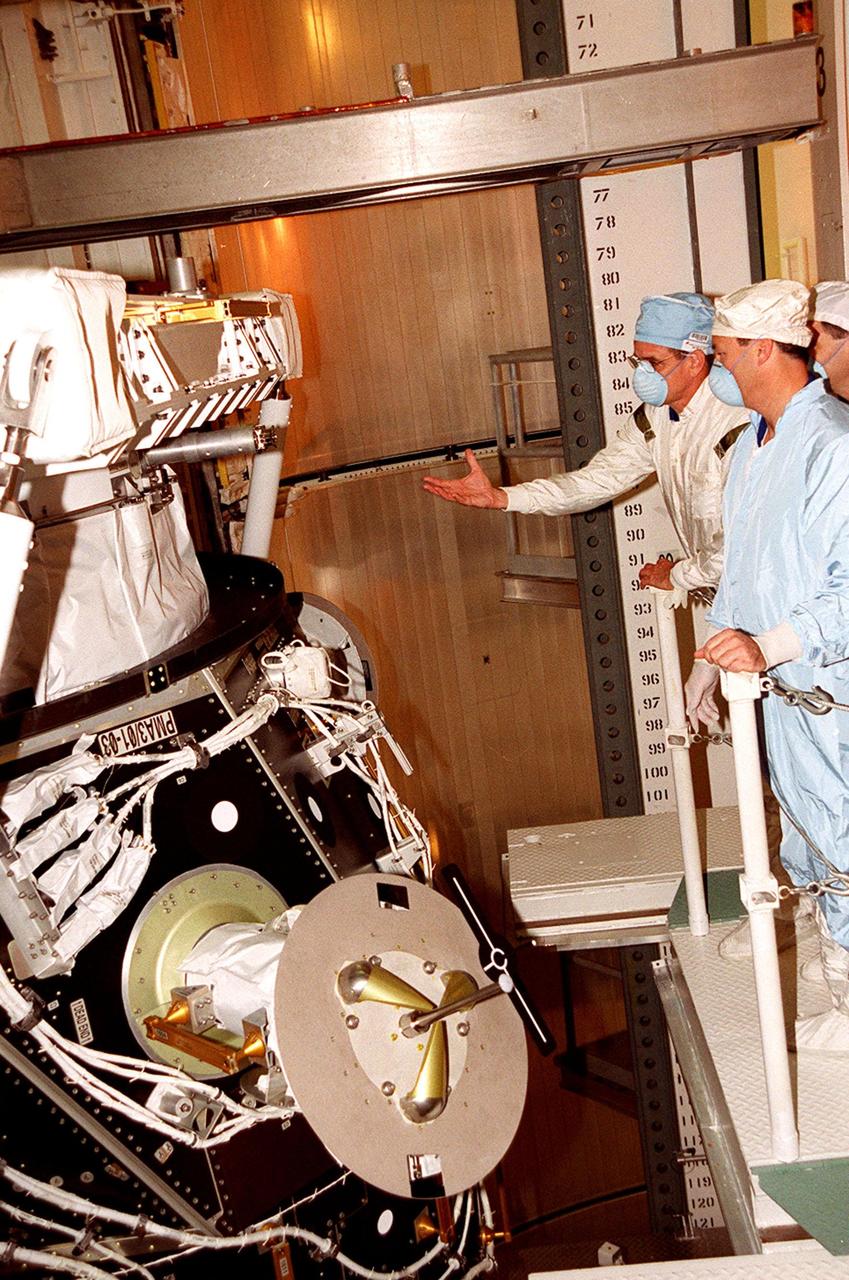

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay, STS-92 Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. explains something about the Pressurized Mating Adapter in front of him to other Mission Specialists Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Peter J.K. Wisoff. The STS-92 crew has been inspecting the payload in preparation for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
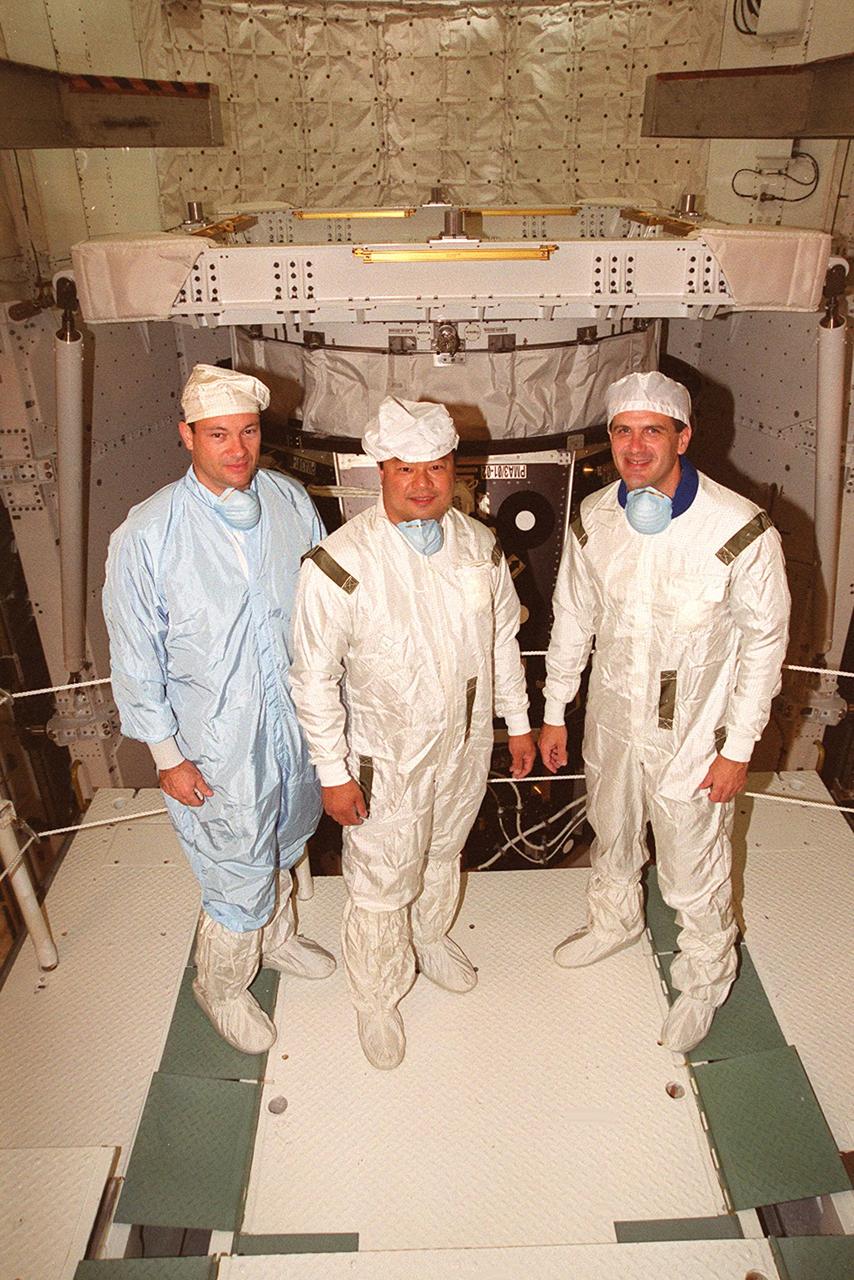

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During inspection of the payload in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay (background), STS-92 Mission Specialists Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, Leroy Chiao and Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff pause for a photo. They and other crew members Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan and William S. McArthur Jr. are preparing for launch on Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
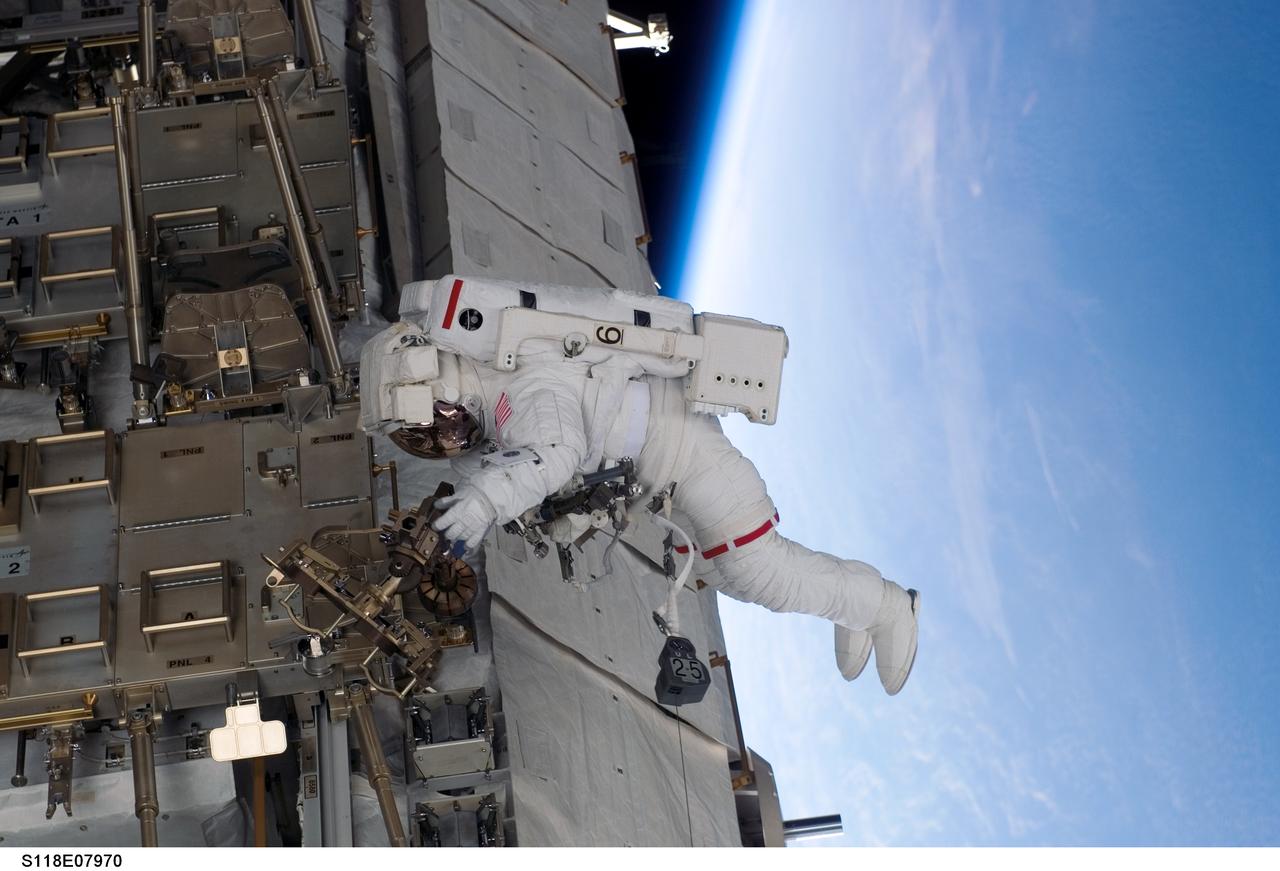

S118-E-07970 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Anderson and astronaut Rick Mastracchio (out of frame), STS-118 mission specialist, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.
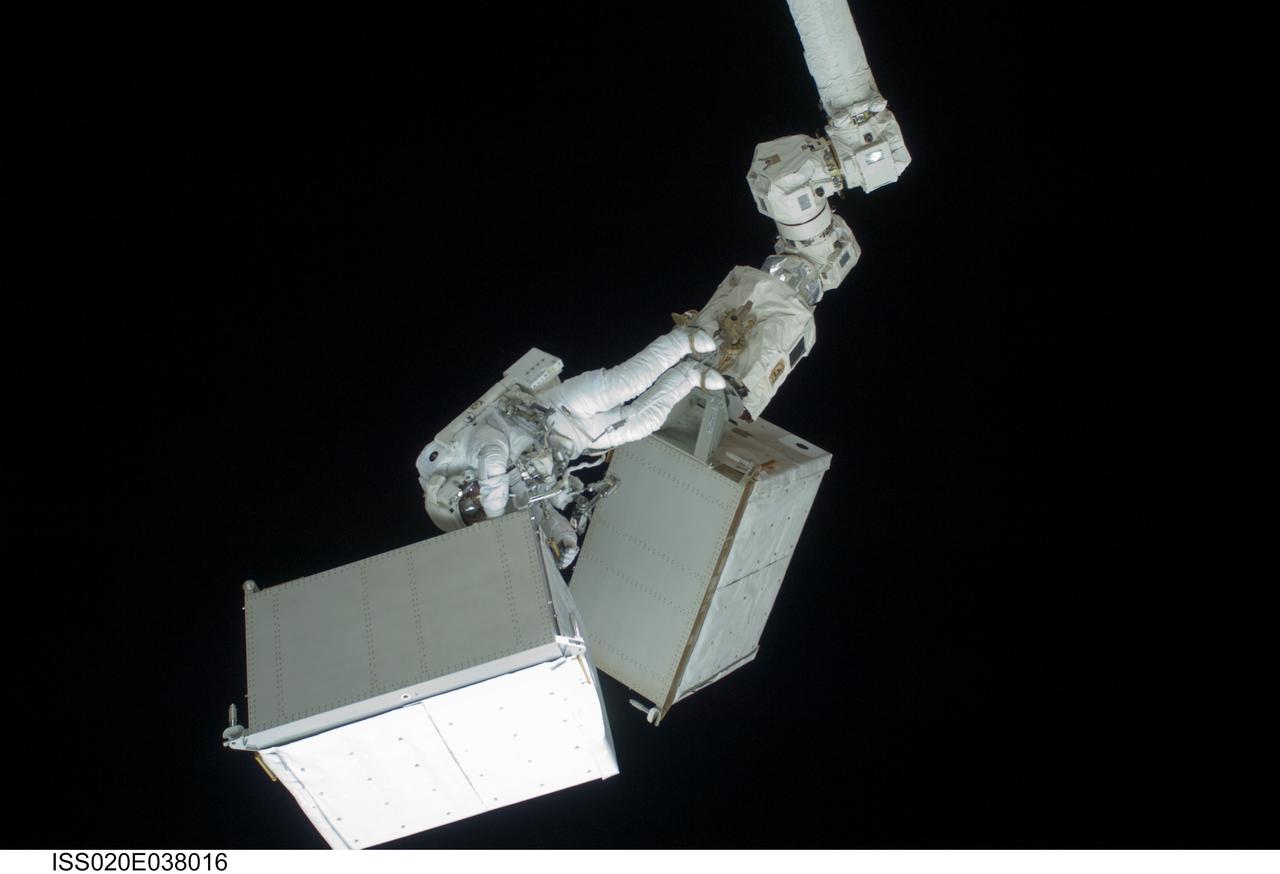

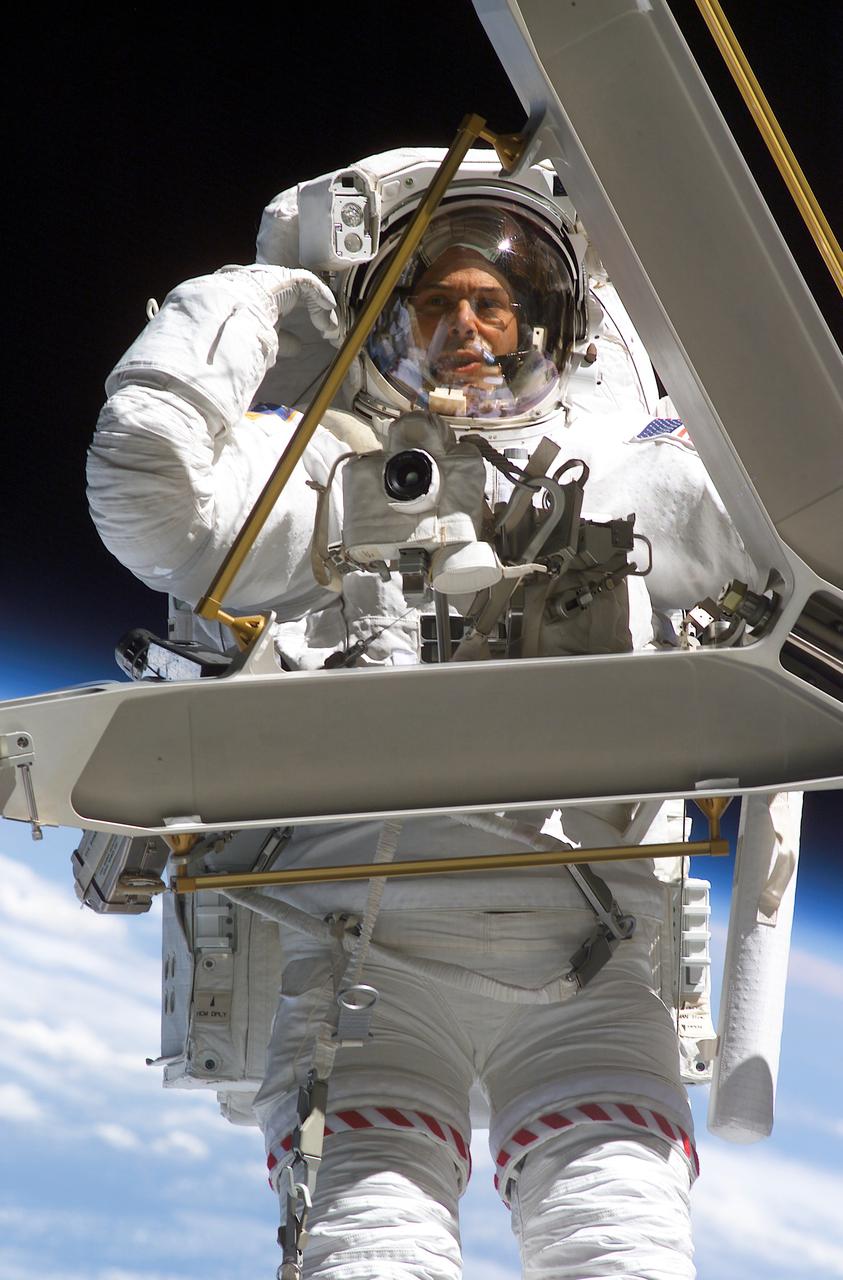
ISS020-E-038016 (3 Sept. 2009) --- Anchored to a Canadarm2 mobile foot restraint, European Space Agency astronaut Christer Fuglesang, STS-128 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 39-minute spacewalk, Fuglesang and NASA astronaut John ?Danny? Olivas (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the new Ammonia Tank Assembly on the Port 1 Truss and stowed the empty tank assembly into the Space Shuttle Discovery?s cargo bay.
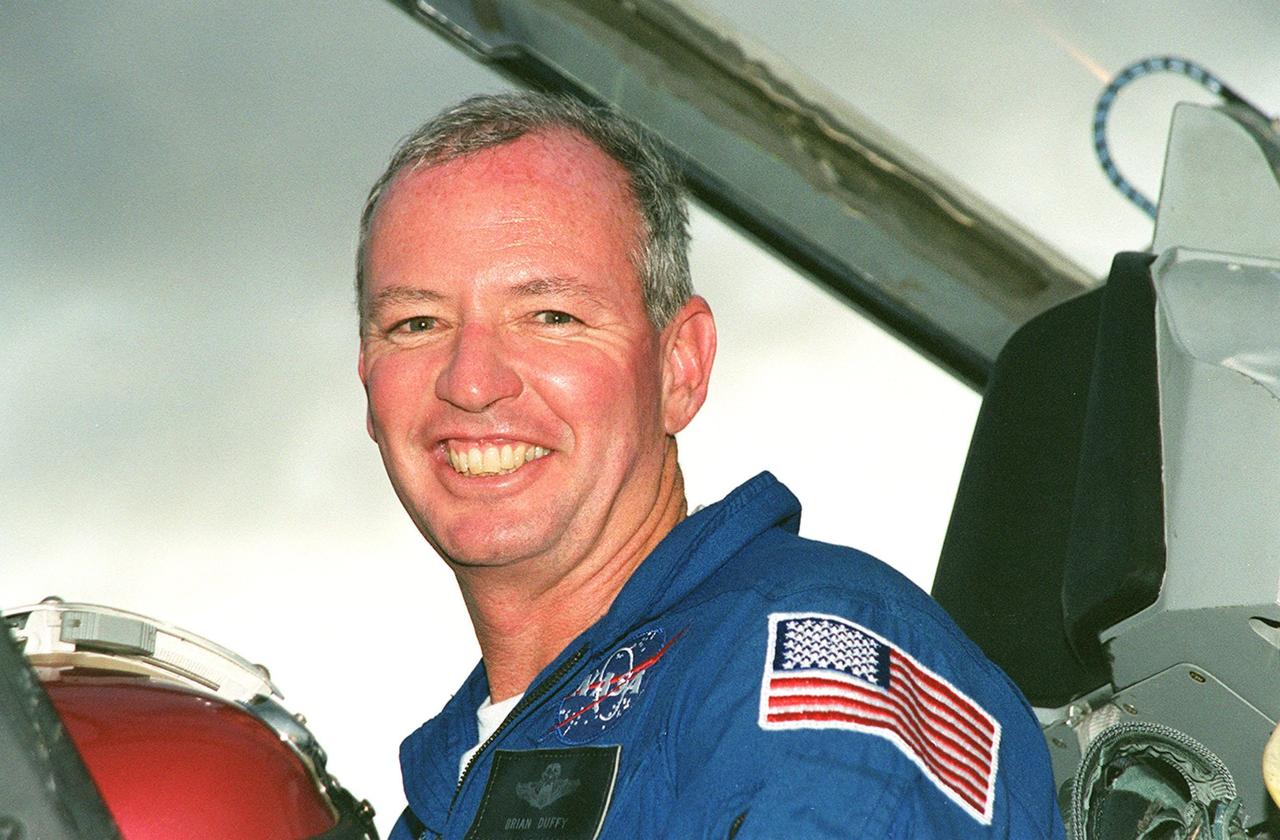

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy is happy to return to KSC for the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on Oct. 5. . He and other crew members Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and William S. McArthur Jr. expressed their eagerness to launch to a waiting group of media at the Shuttle Landing Facility. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned.
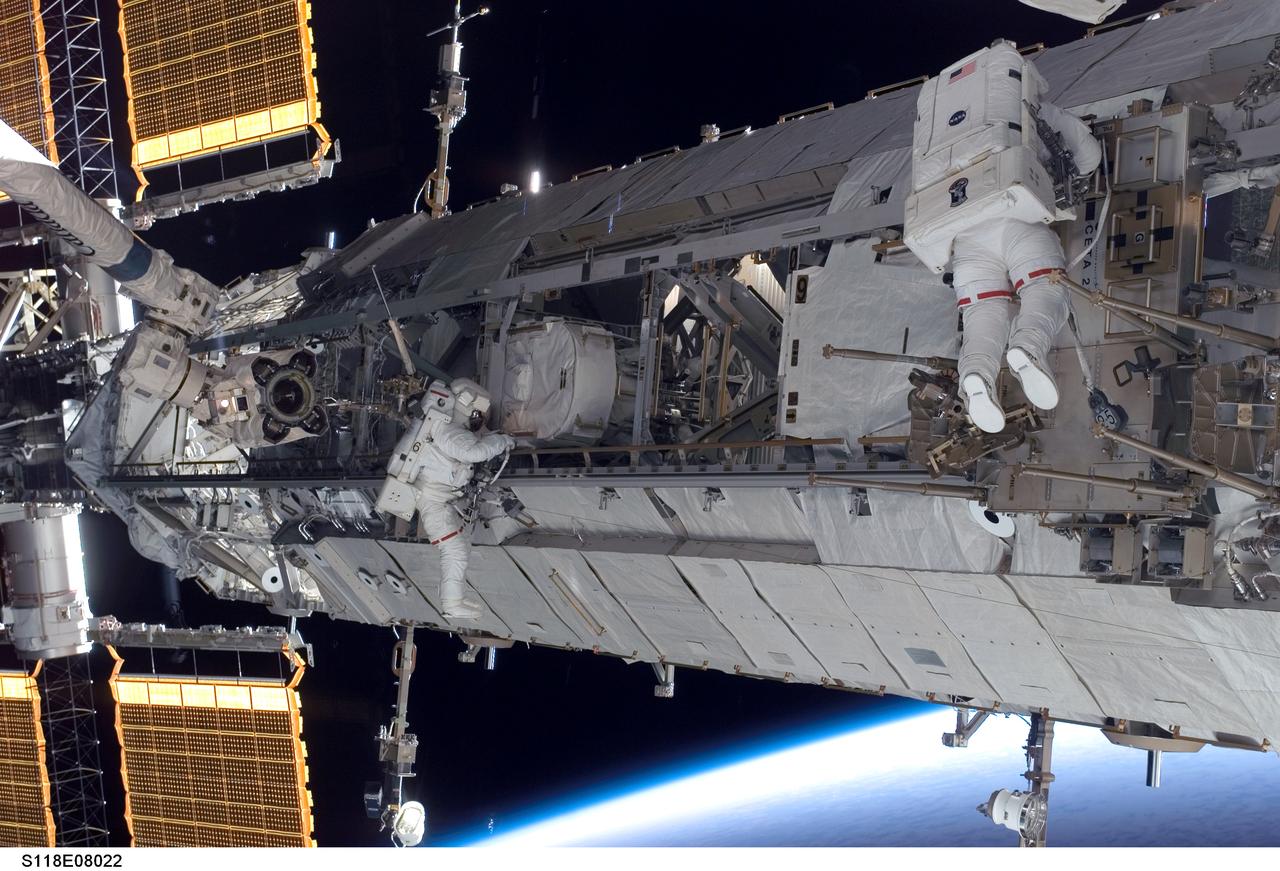

S118-E-08022 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronauts Clay Anderson (left), Expedition 15 flight engineer; and Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participate in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.

STS-92 Pamela Ann Melroy pauses during inspection of the payload (behind her) in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. She and other crew members Commander Brian Duffy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff. Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and William S. McArthur Jr. are preparing for launch on Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
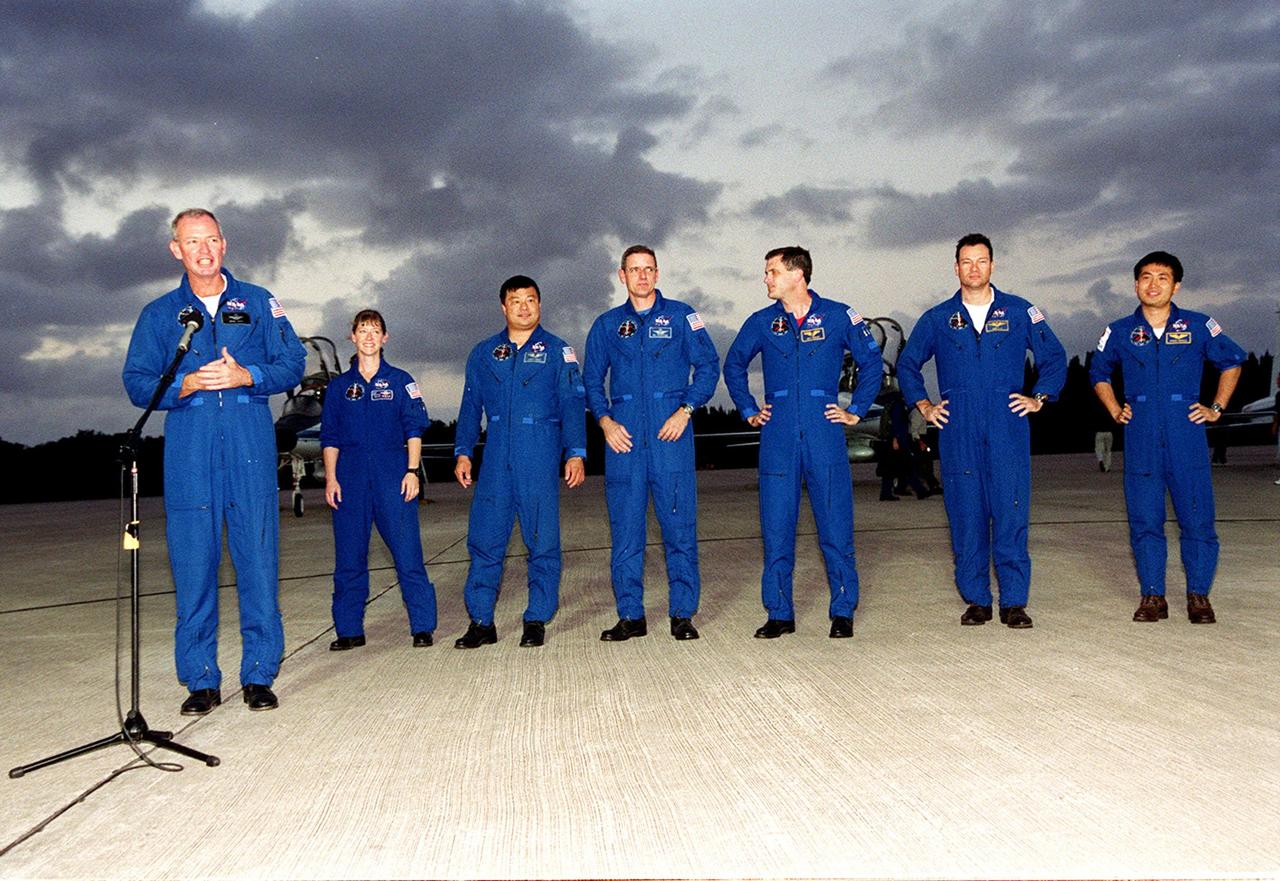

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After their arrival at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility, the STS-92 crew paused to talk to the media, who were waiting nearby. At the microphone is Commander Brian Duffy. Standing behind him, left to right, are Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, William S. McArthur Jr., Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Koichi Wakata of Japan. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
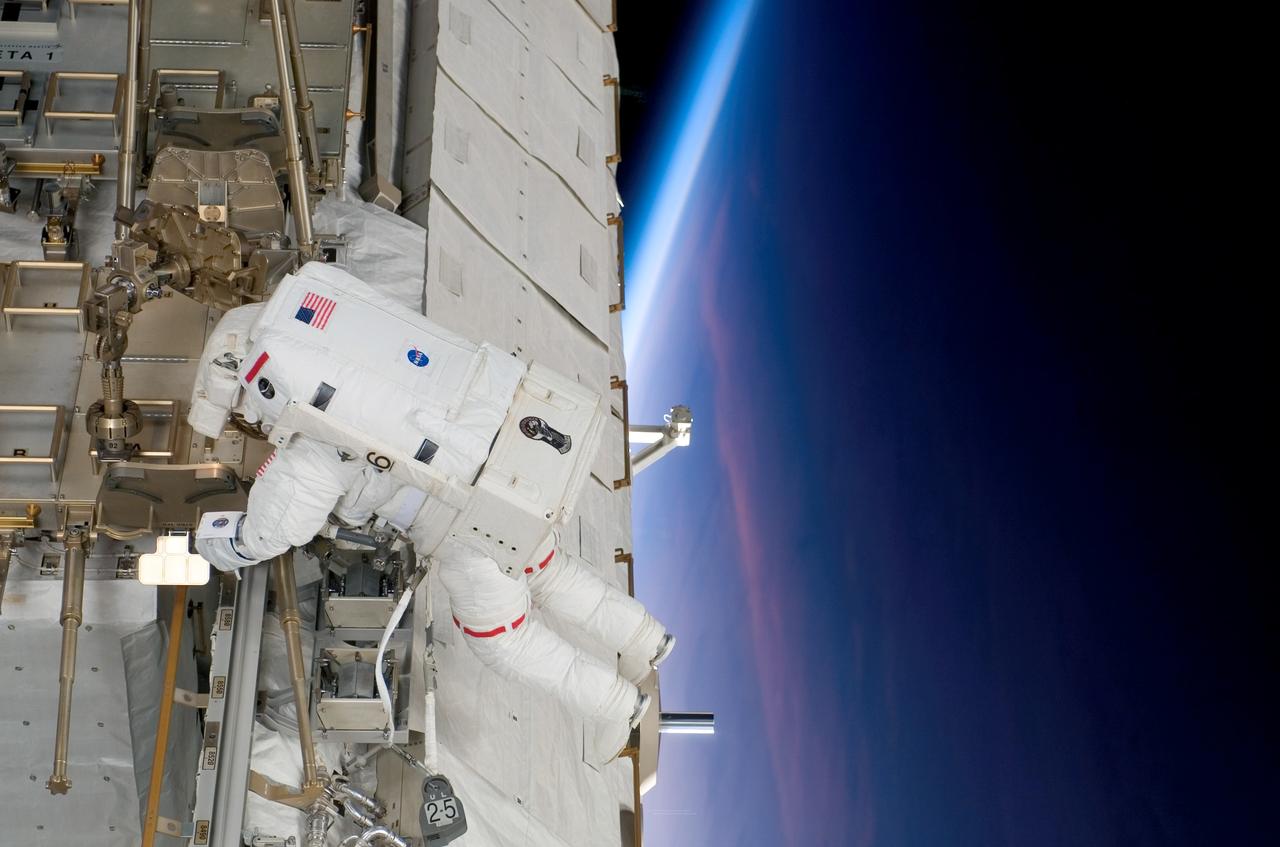

S118-E-07966 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Anderson and astronaut Rick Mastracchio (out of frame), STS-118 mission specialist, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.

ISS015-E-22561 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, uses a digital camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. Also visible in the reflections in the visor are various components of the station and a blue and white portion of Earth. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Anderson and astronaut Rick Mastracchio (out of frame), STS-118 mission specialist, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
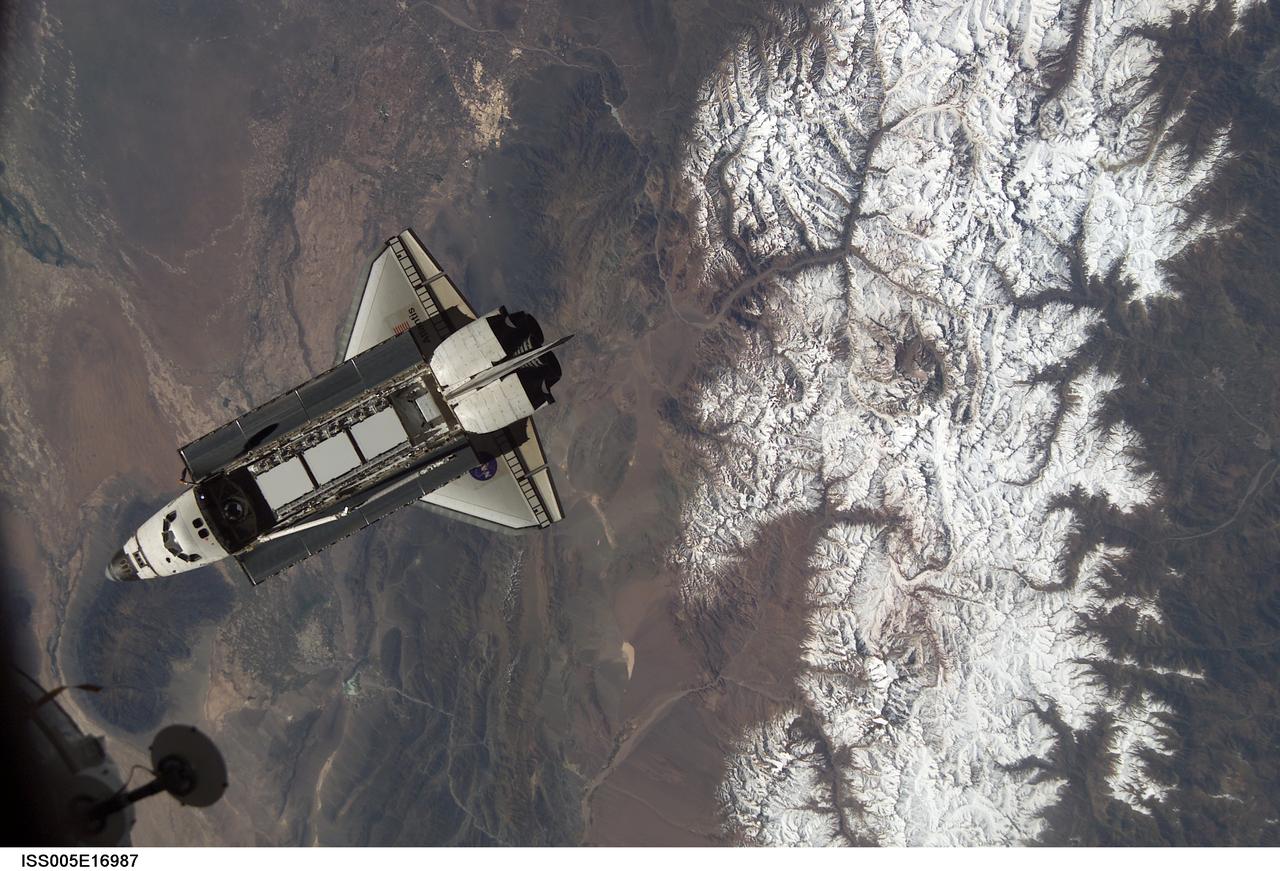

ISS005-E-16987 (9 October 2002) --- Backdropped against snowcapped Cordon del Plata of the Andes mountains, this view of the Space Shuttle Atlantis over Argentina was photographed by an Expedition Five crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS) during rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 10:17 a.m. (CDT) on October 9, 2002. The Starboard One (S-1) Truss, which was later attached to the station and outfitted during three spacewalks, can be seen in Atlantis’ cargo bay. Santiago, Chile is just out of frame in the upper right corner.
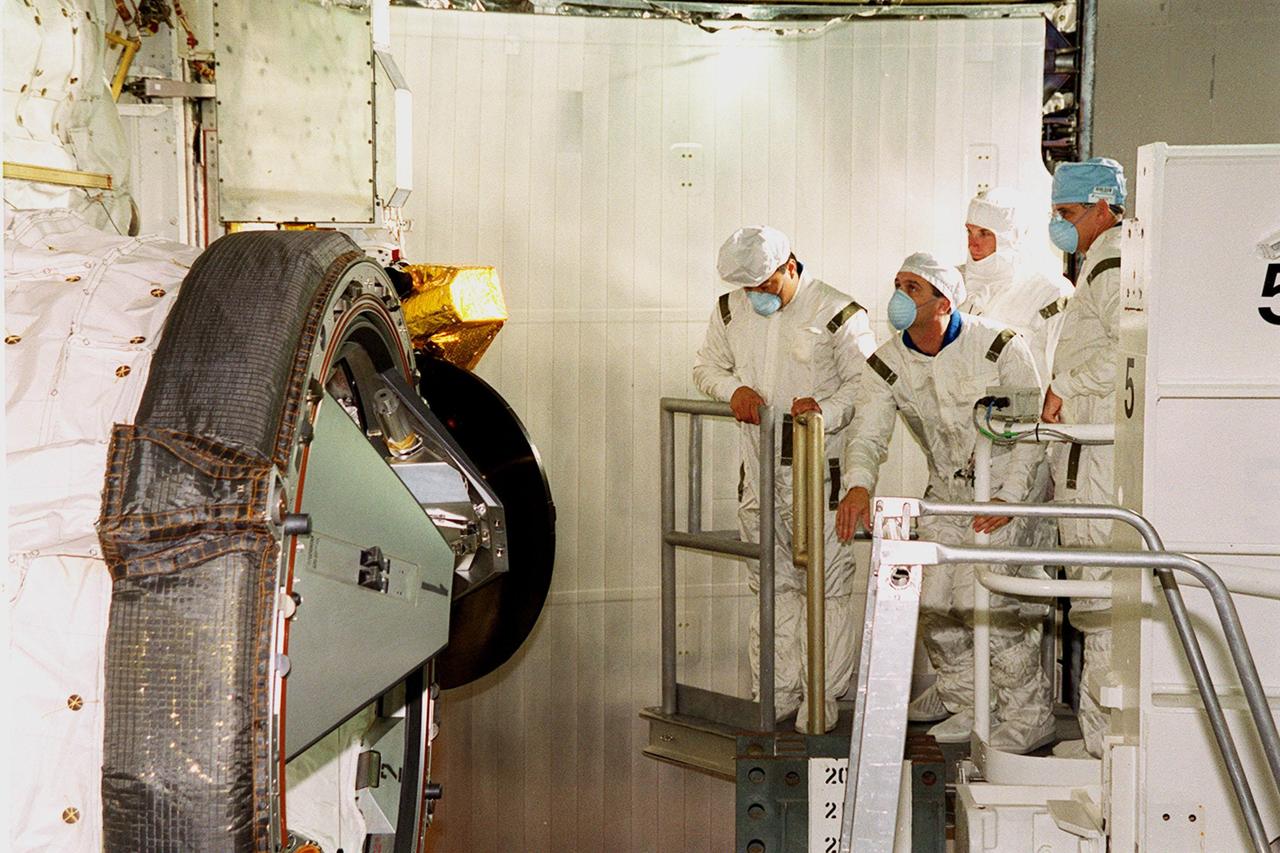

Members of the STS-92 crew look over the payload (left) in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. Left to right, in masks, are Mission Specialists Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff and William S. McArthur Jr. They and the other crew members Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan, and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria are preparing for launch on Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
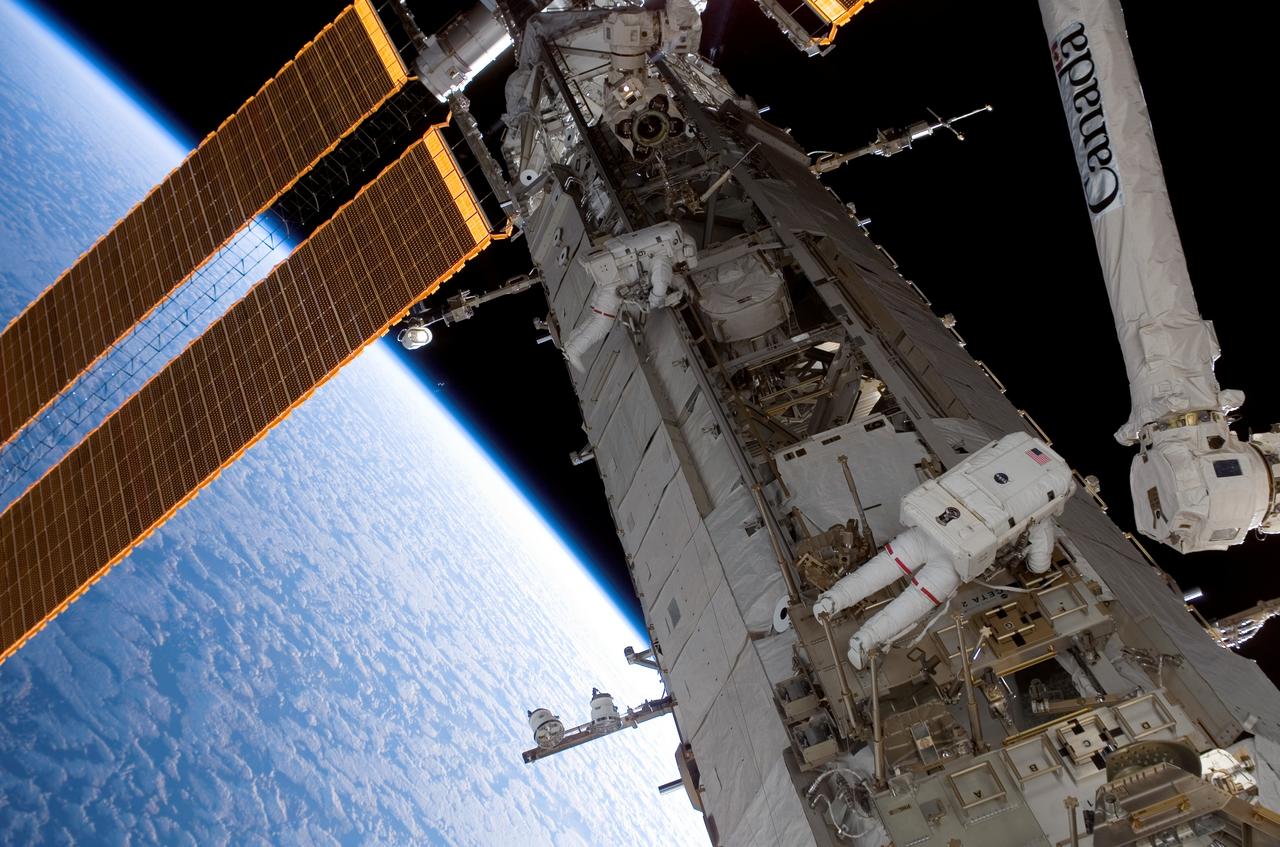

S118-E-08028 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronauts Clay Anderson (left), Expedition 15 flight engineer; and Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participate in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.
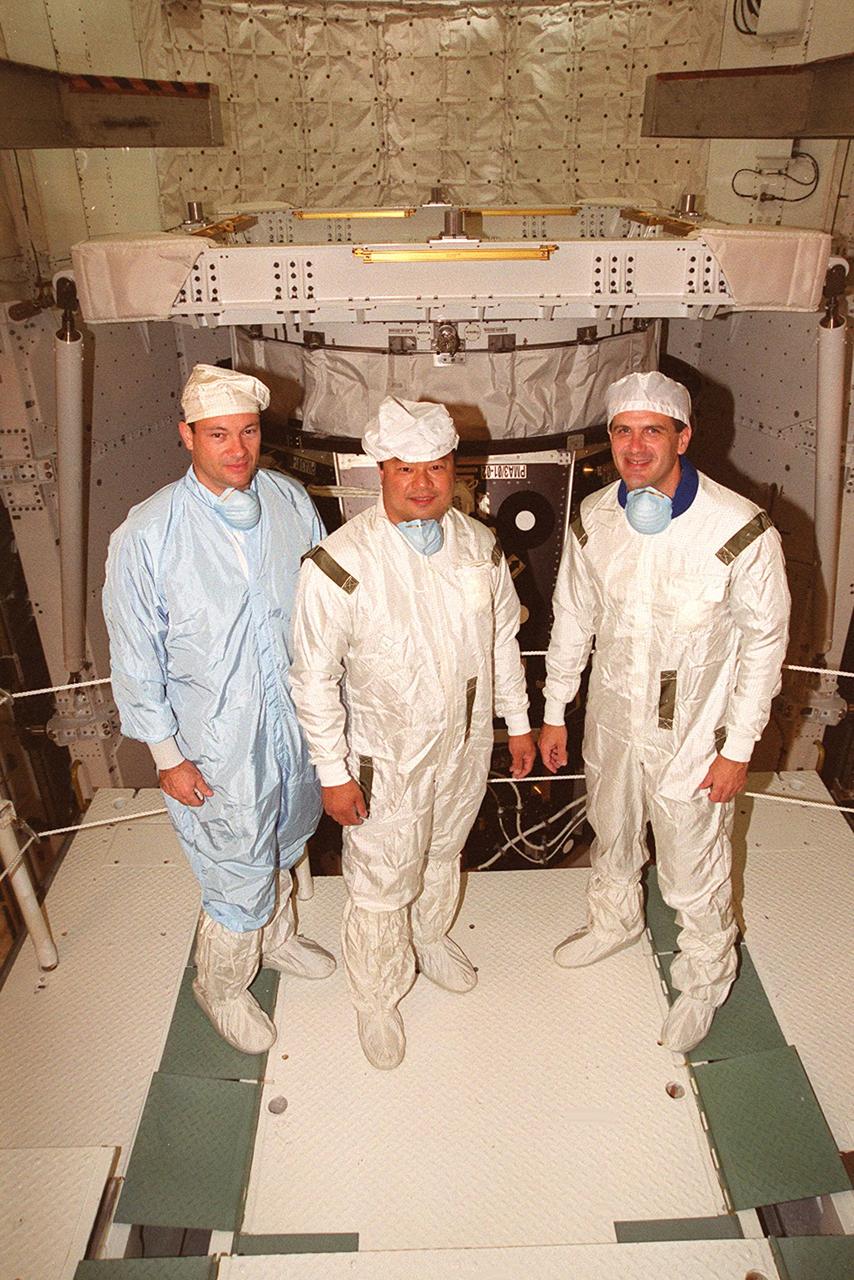

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During inspection of the payload in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay (background), STS-92 Mission Specialists Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, Leroy Chiao and Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff pause for a photo. They and other crew members Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan and William S. McArthur Jr. are preparing for launch on Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
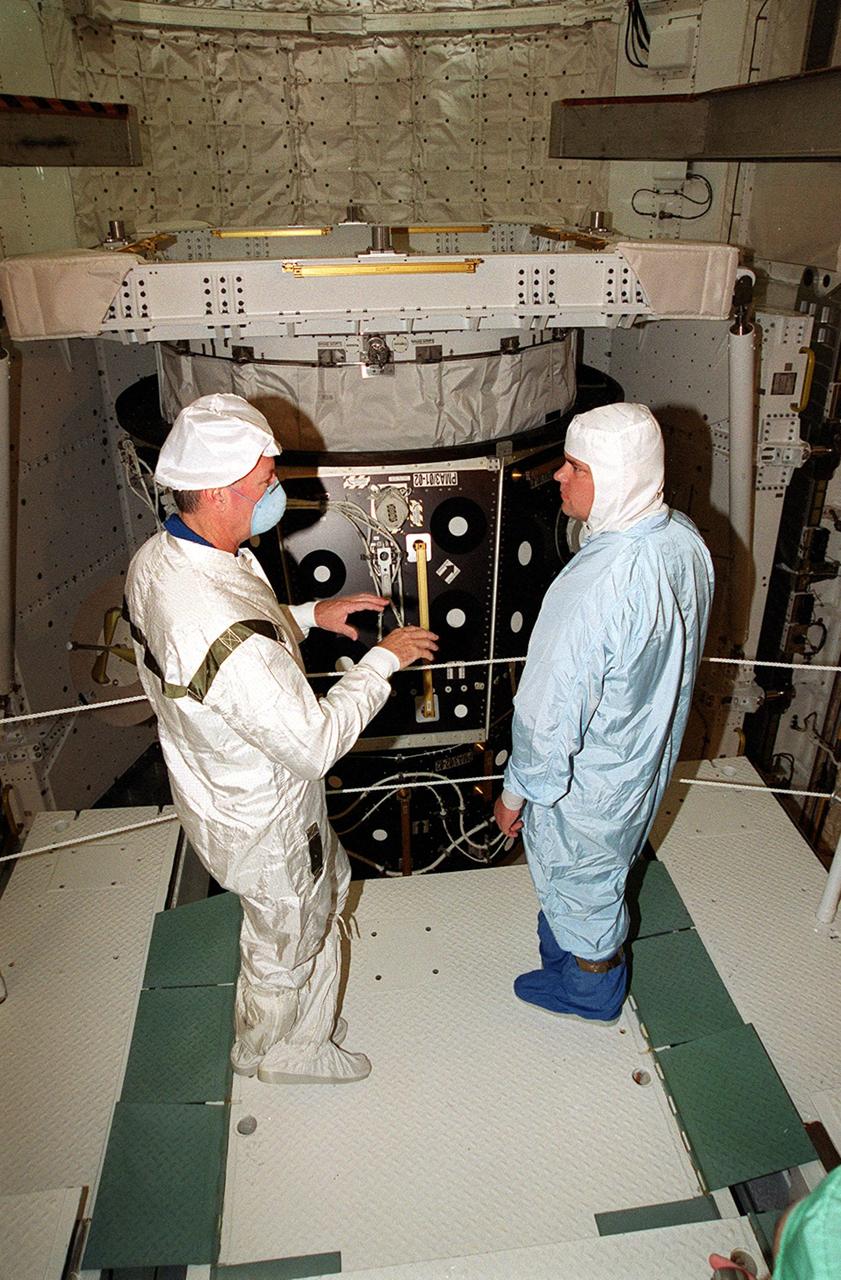

STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy (left) talks with a worker during inspection of the payload (behind them) in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. He and other crew members Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and William S. McArthur Jr. are preparing for launch on Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
STS-92 Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. smiles for the camera during inspection of the payload (left) in Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay. He and other crew members Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff and Michael E. Lopez-Alegria are preparing for launch on Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
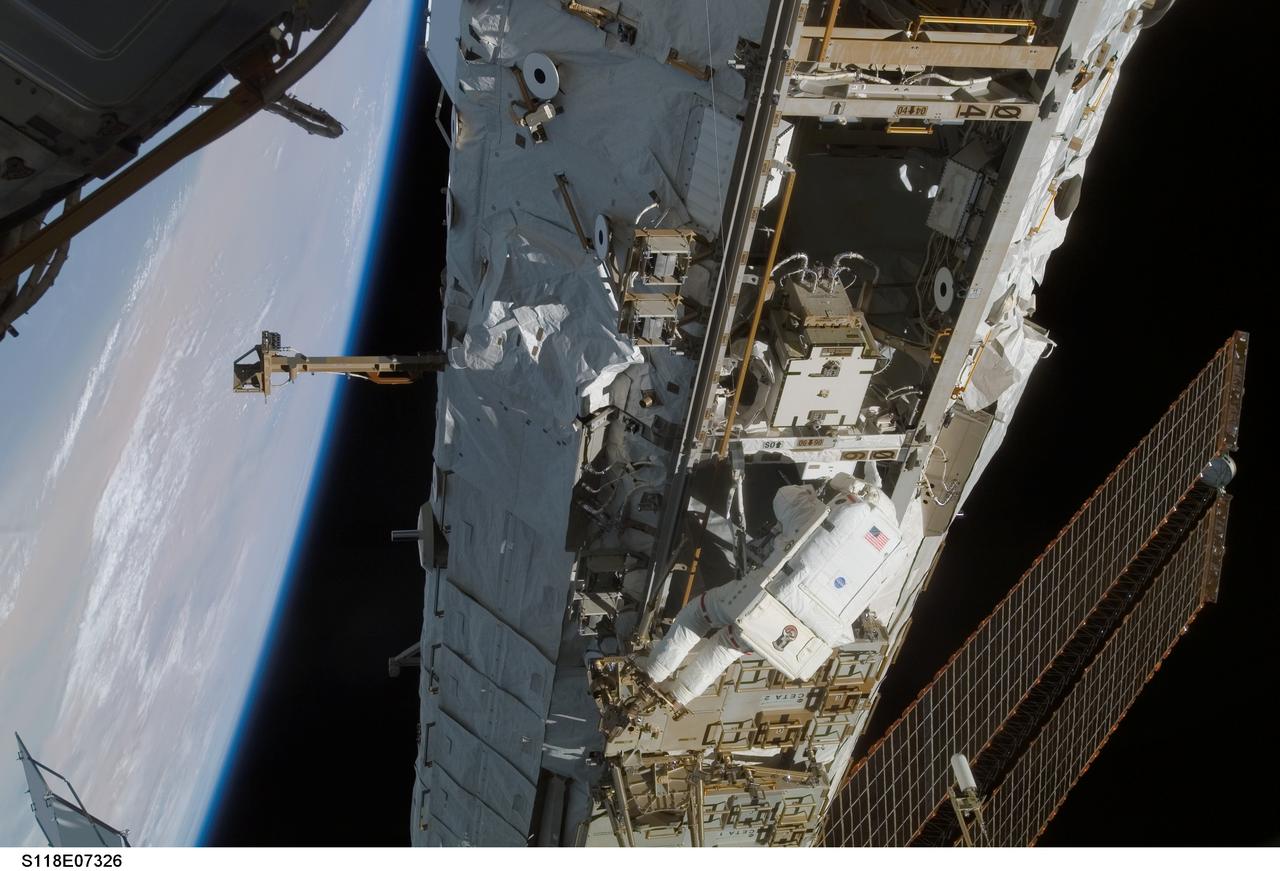

S118-E-07326 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Anderson and astronaut Rick Mastracchio (out of frame), STS-118 mission specialist, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-92 Commander Brian Duffy is happy to return to KSC for the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on Oct. 5. . He and other crew members Pilot Pamela Ann Melroy and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata of Japan, Leroy Chiao, Peter J.K. “Jeff” Wisoff, Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and William S. McArthur Jr. expressed their eagerness to launch to a waiting group of media at the Shuttle Landing Facility. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1 and the third Pressurized Mating Adapter. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned.
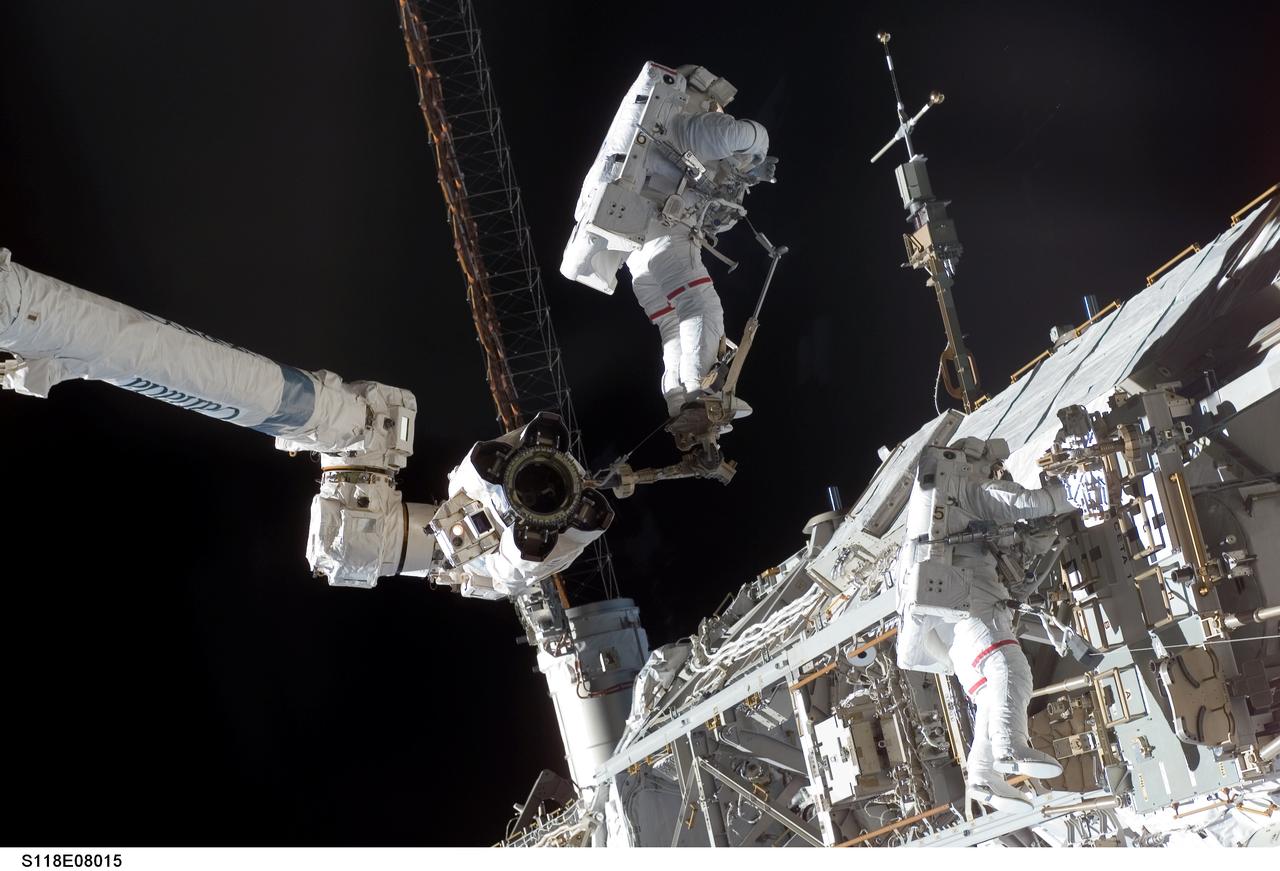

S118-E-08015 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronauts Rick Mastracchio (right), STS-118 mission specialist; and Clay Anderson (anchored to the foot restraint on the Canadarm2), Expedition 15 flight engineer, participate in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
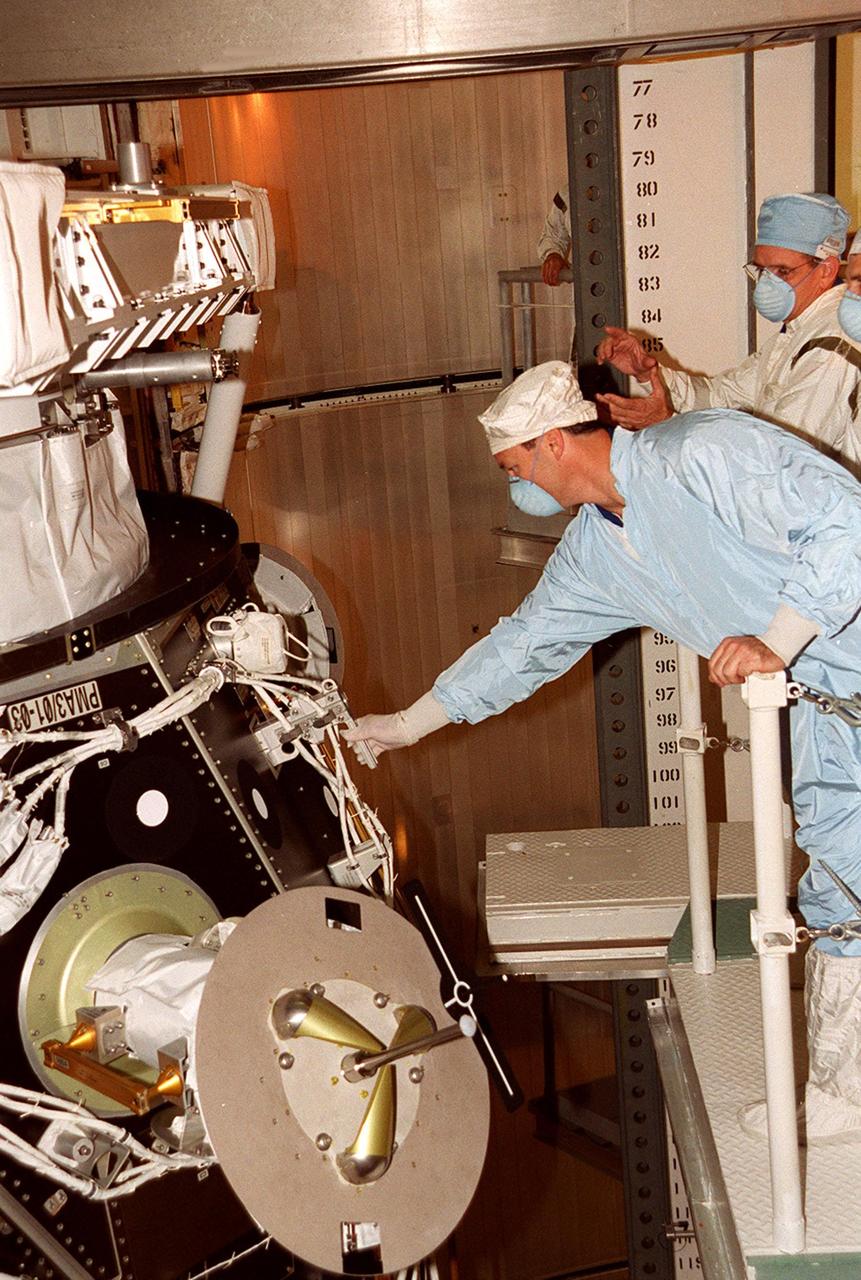

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay, STS-92 Mission Specialist Michael E. Lopez-Alegria takes hold of a lever on the Pressurized Mating Adapter, part of the payload on the mission. Behind him Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. describes a task while Mission Specialist Peter J.K. Wisoff looks on. The STS-92 crew has been inspecting the payload in preparation for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
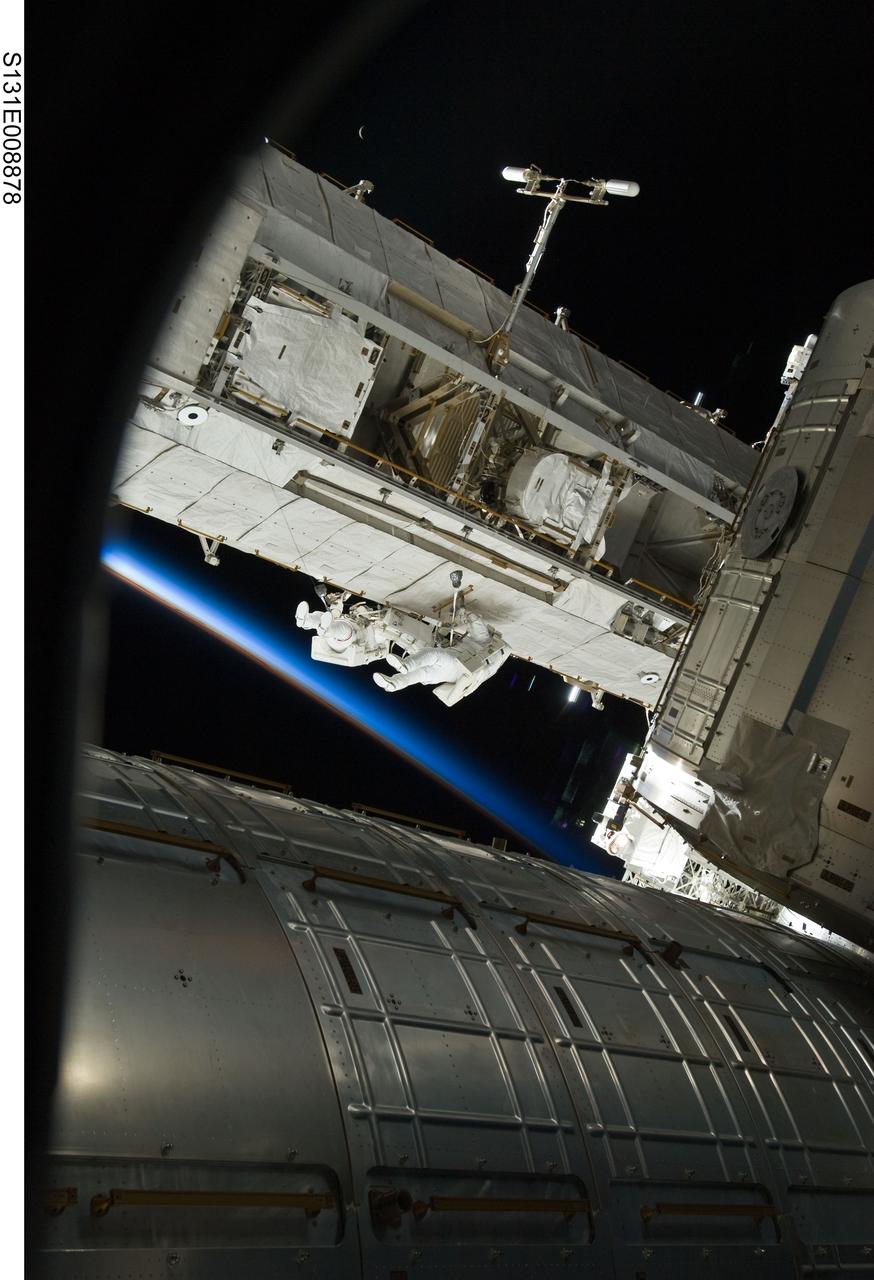
S131-E-008878 (11 April 2010) --- NASA astronauts Rick Mastracchio (left) and Clayton Anderson, both STS-131 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour, 26-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson unhooked and removed the depleted ammonia tank and installed a 1,700-pound ammonia tank on the station?s Starboard 1 truss, completing the second of a three-spacewalk coolant tank replacement process. The thin line of Earth's atmosphere appears in frame center.
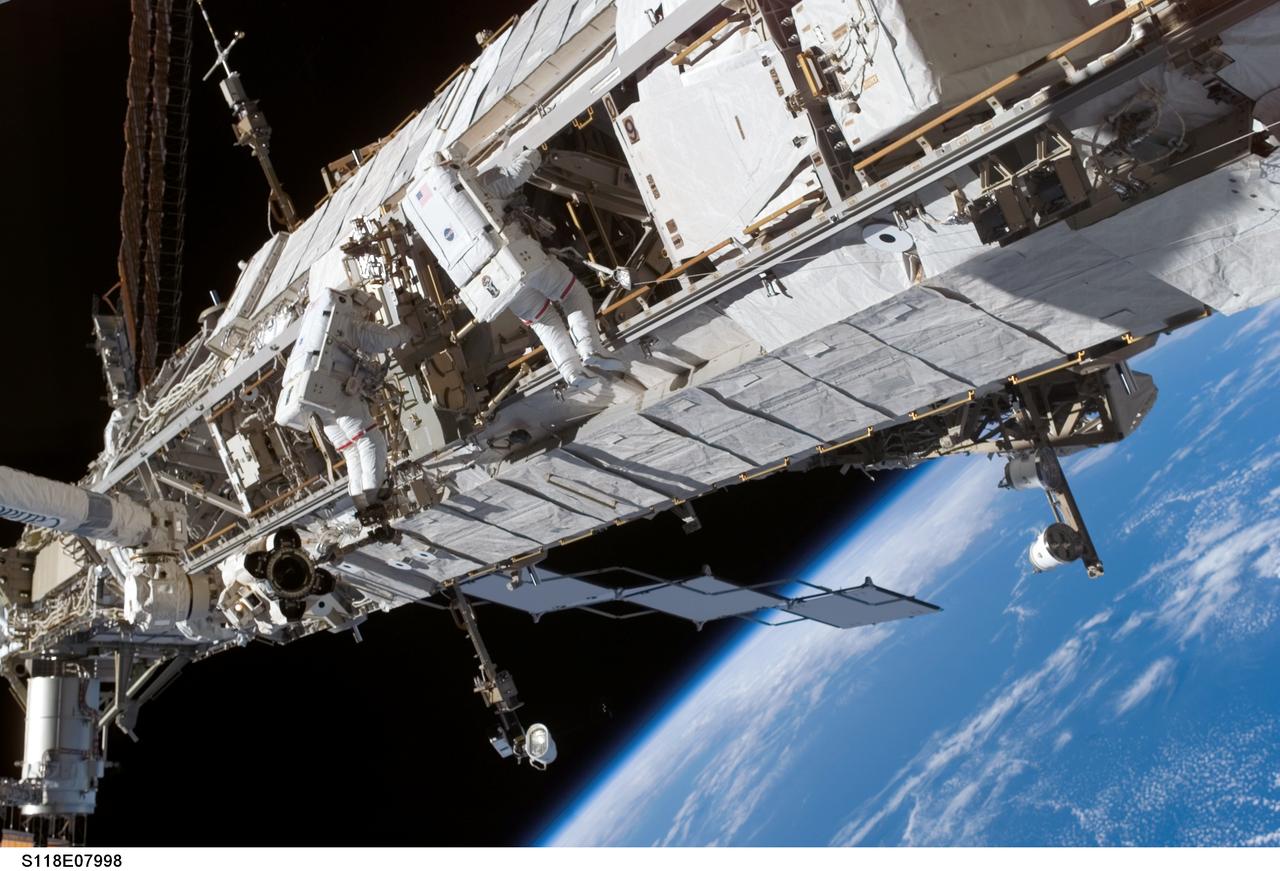

S118-E-07998 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronauts Rick Mastracchio (right), STS-118 mission specialist; and Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participate in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.
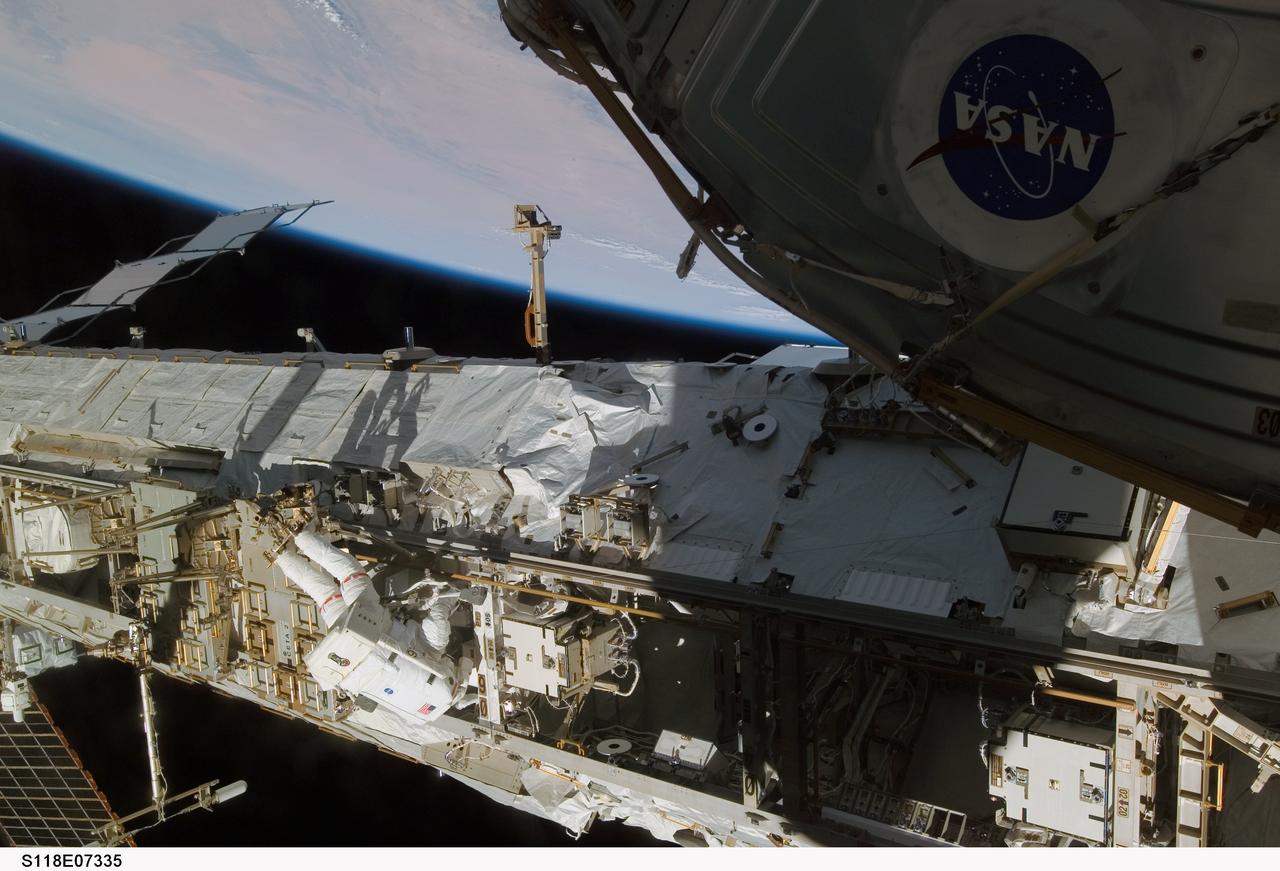

S118-E-07335 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Anderson and astronaut Rick Mastracchio (out of frame), STS-118 mission specialist, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay, STS-92 Mission Specialist Michael E. Lopez-Alegria takes hold of a lever on the Pressurized Mating Adapter, part of the payload on the mission. Behind him Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. describes a task while Mission Specialist Peter J.K. Wisoff looks on. The STS-92 crew has been inspecting the payload in preparation for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned
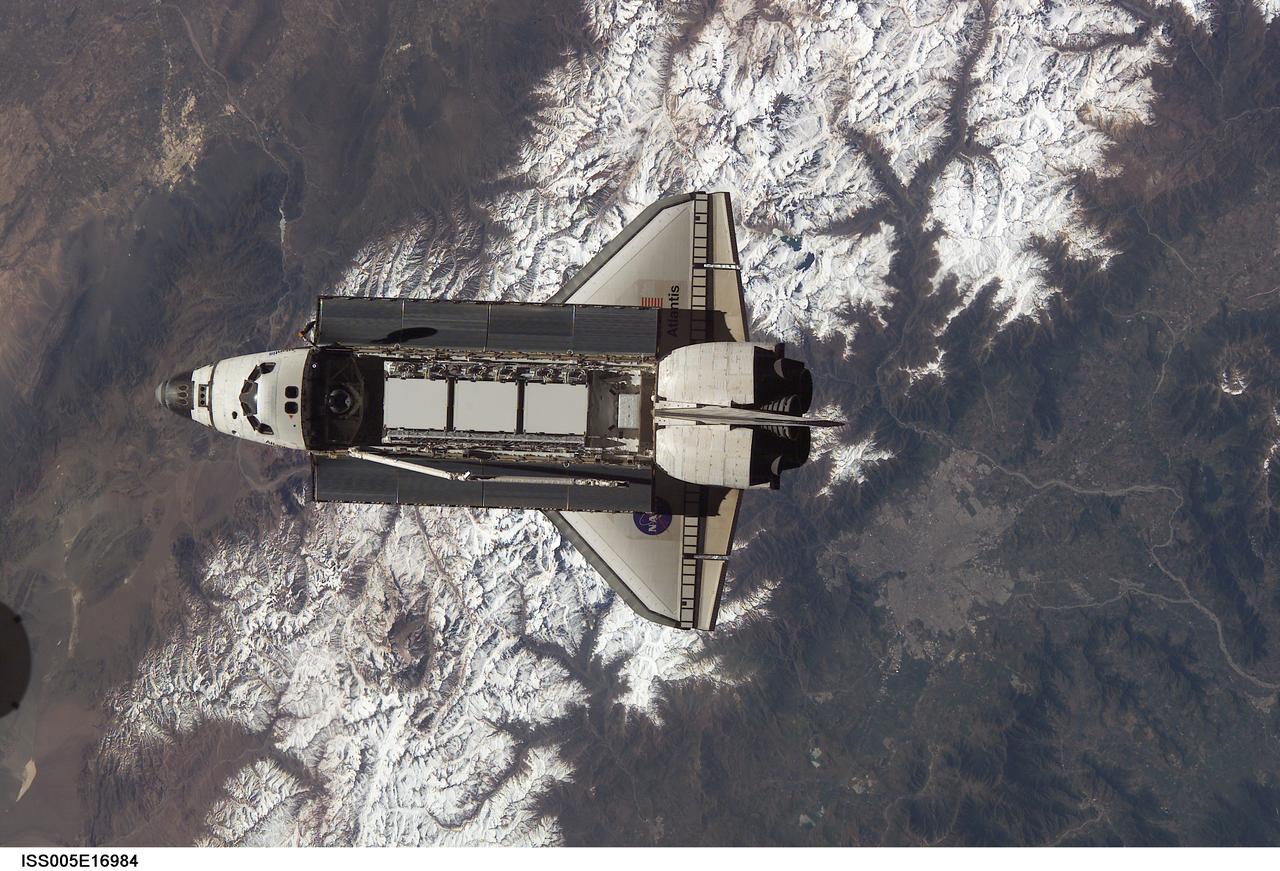

ISS005-E-16984 (9 October 2002) --- Backdropped against snowcapped Cordon del Plata of the Andes mountains, this view of the Space Shuttle Atlantis was photographed by an Expedition Five crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS) during rendezvous and docking operations. Docking occurred at 10:17 a.m. (CDT) on October 9, 2002. The Starboard One (S-1) Truss, which was later attached to the station and outfitted during three spacewalks, can be seen in Atlantis’ cargo bay. Argentina is visible in the upper left frame and Santiago, Chile is visible in the lower right frame.
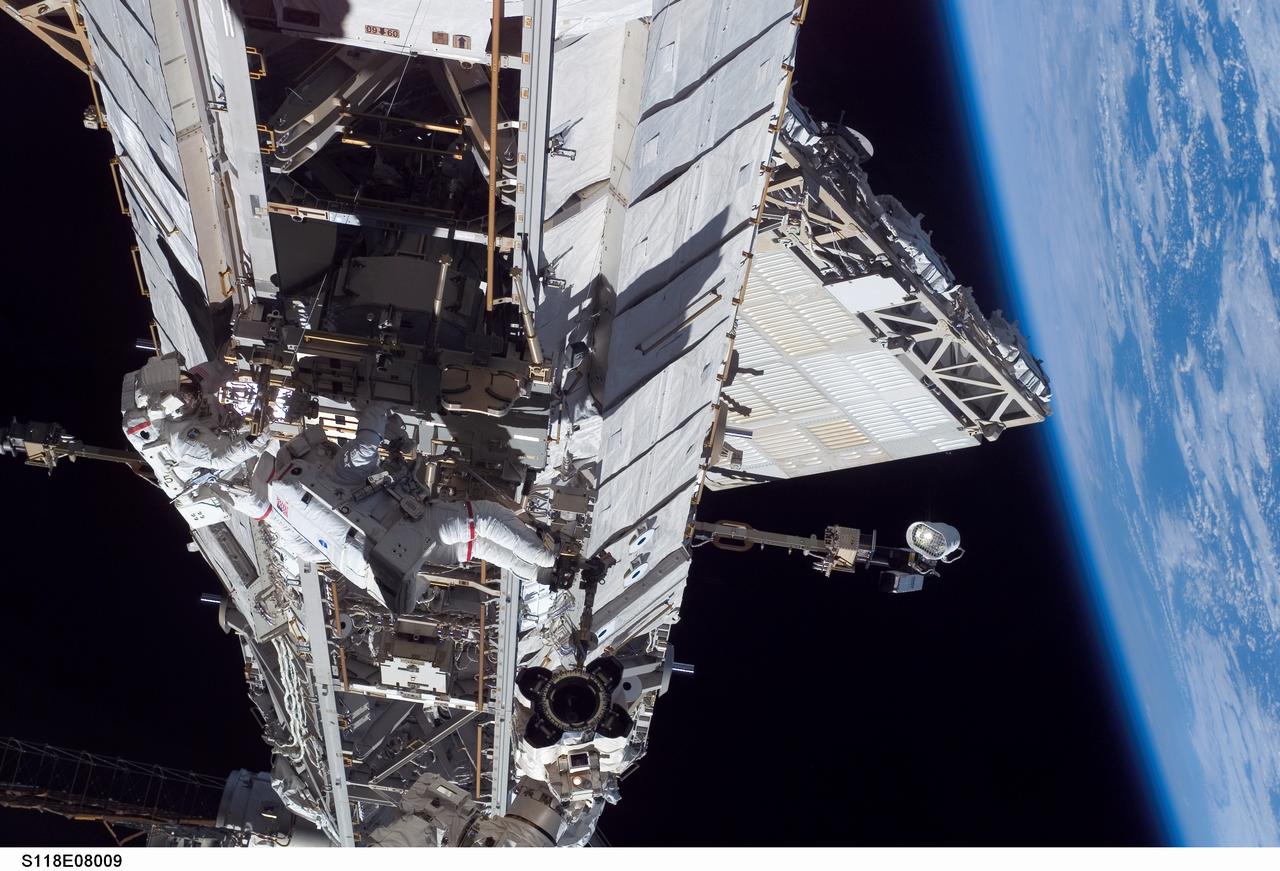

S118-E-08009 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronauts Rick Mastracchio (left), STS-118 mission specialist; and Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participate in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.
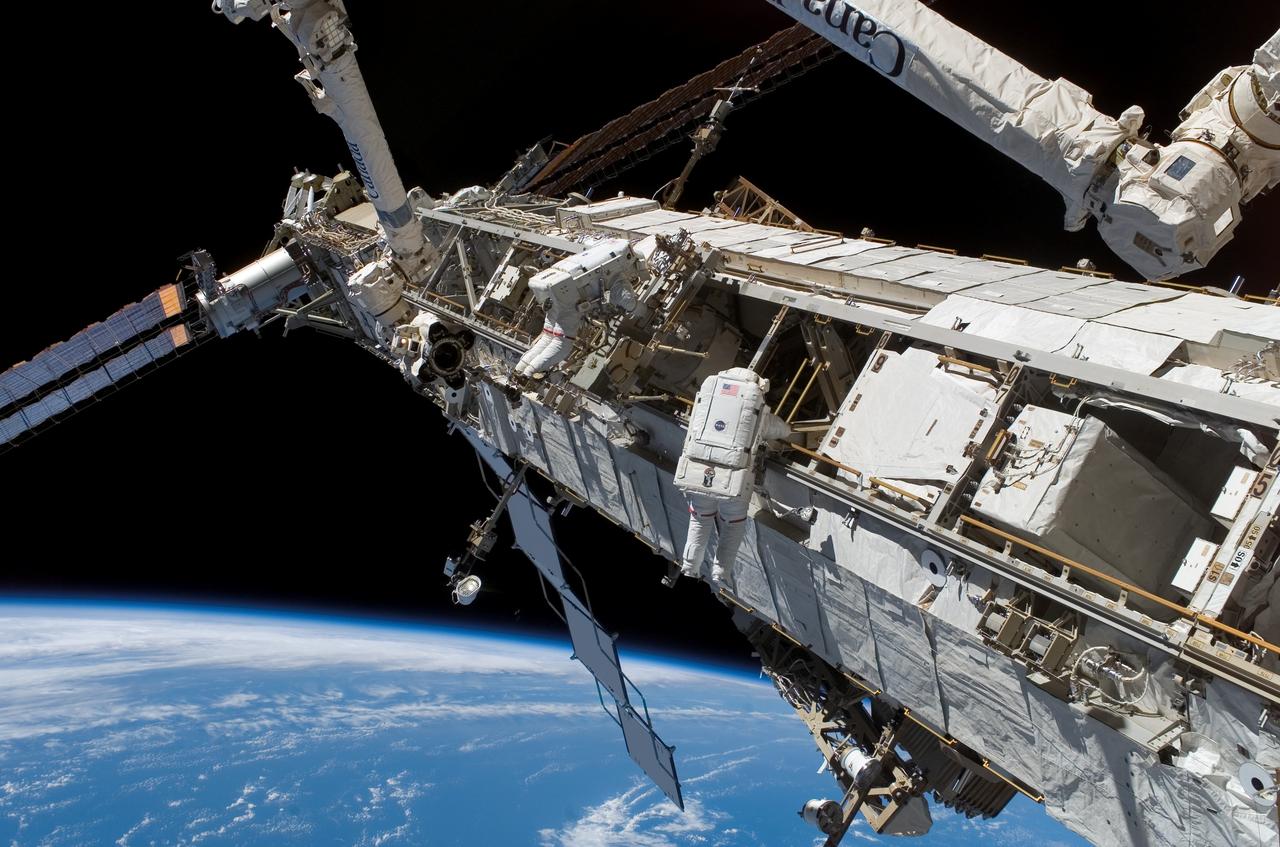

S118-E-07997 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronauts Rick Mastracchio (right), STS-118 mission specialist; and Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participate in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and Anderson relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.
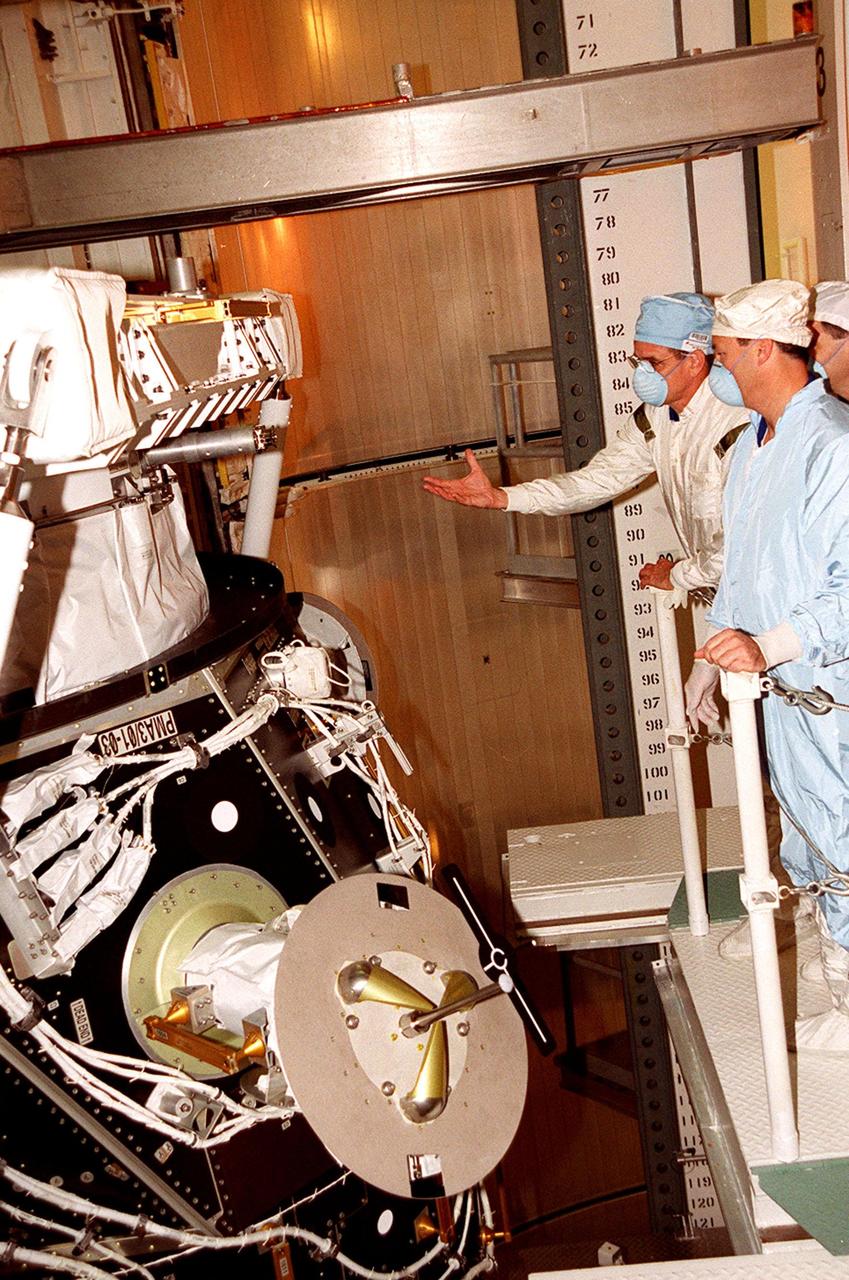

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Space Shuttle Discovery’s payload bay, STS-92 Mission Specialist William S. McArthur Jr. explains something about the Pressurized Mating Adapter in front of him to other Mission Specialists Michael E. Lopez-Alegria and Peter J.K. Wisoff. The STS-92 crew has been inspecting the payload in preparation for launch Oct. 5, 2000. The mission is the fifth flight for the construction of the International Space Station. The payload also includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z-1. During the 11-day mission, four extravehicular activities (EVAs), or space walks, are planned

S118-E-07973 (15 Aug. 2007) --- While anchored to the foot restraint on the Canadarm2, astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
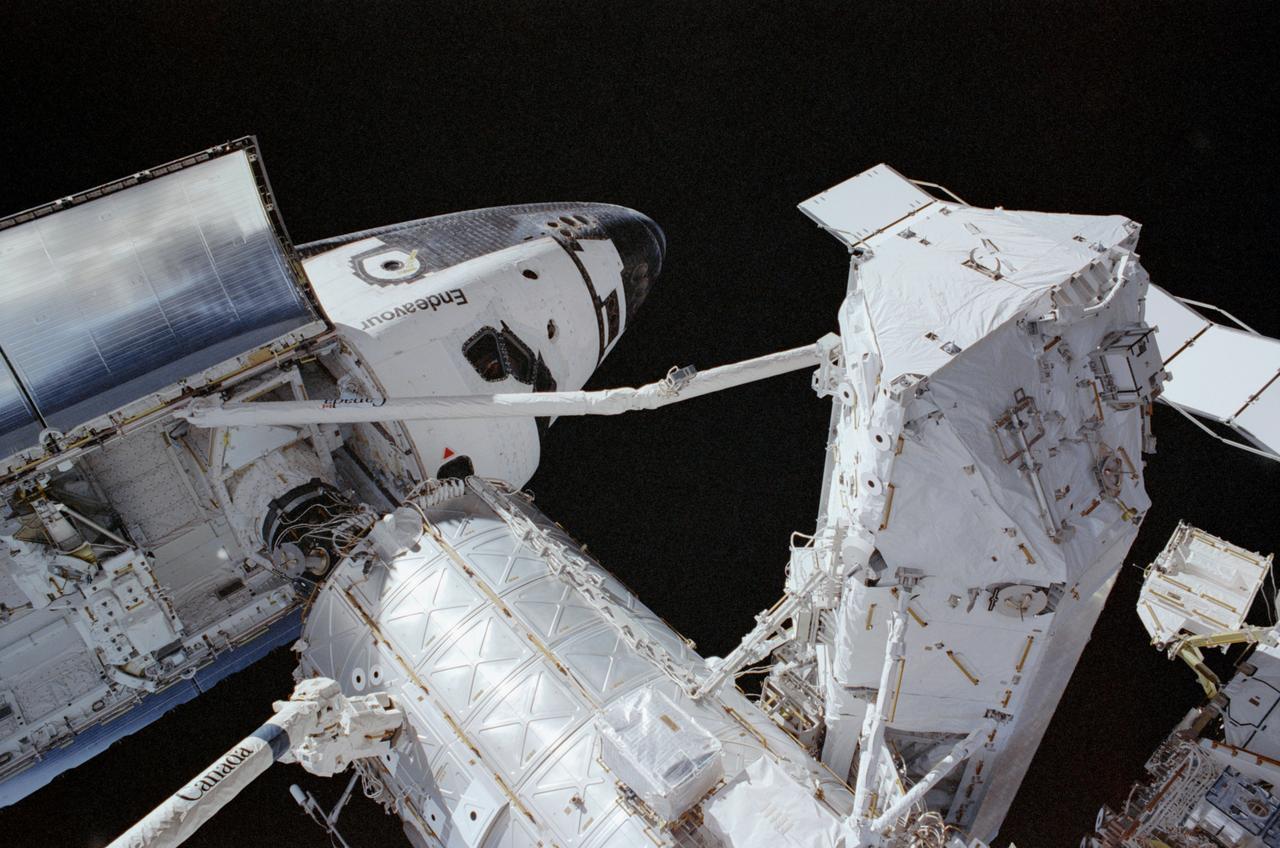
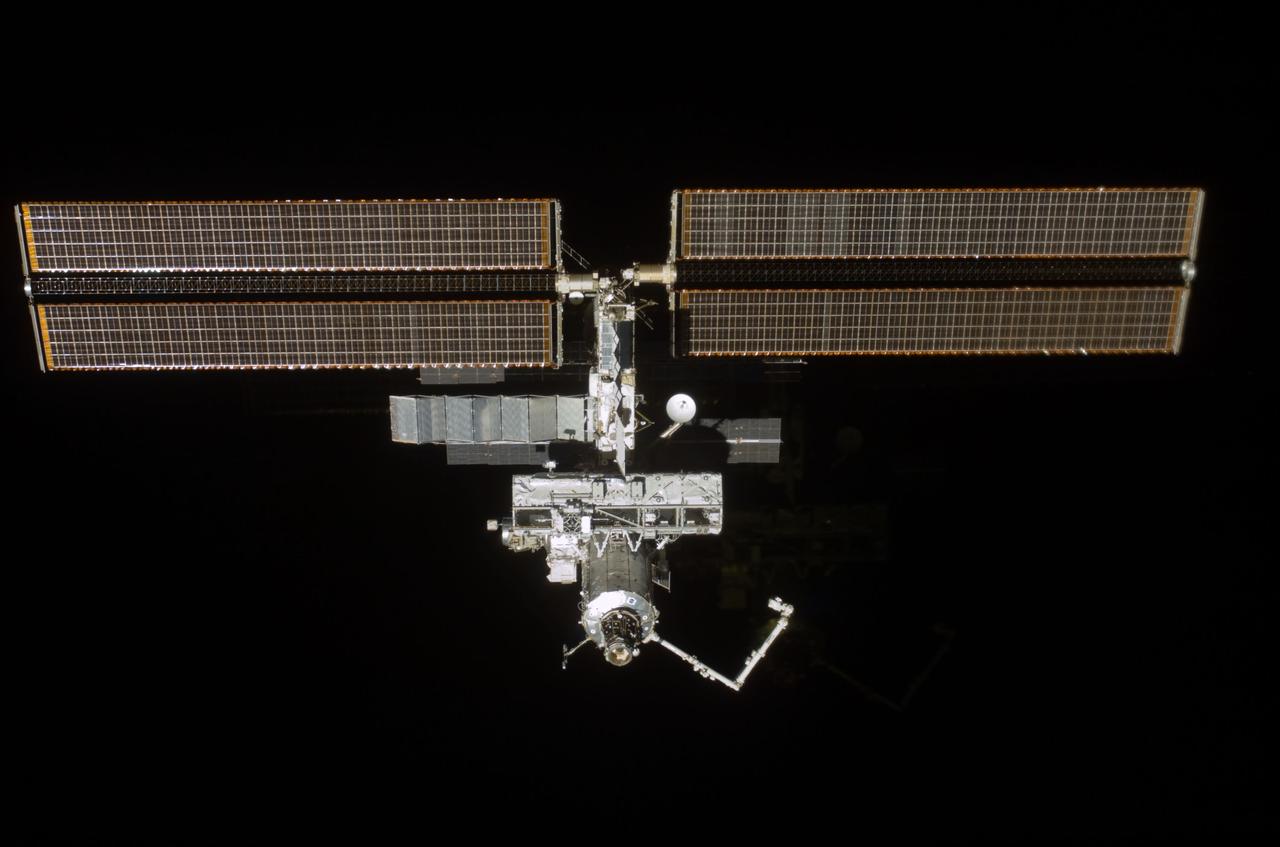
STS111-310-011 (9 June 2002) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space, the Space Shuttle Endeavour is pictured while docked to the Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-2) at the forward end of the Destiny laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS). A portion of the Canadarm2 is visible in the lower left corner and Endeavour’s robotic arm is in full view as it is stretched out with the S0 (S-zero) Truss at its end.