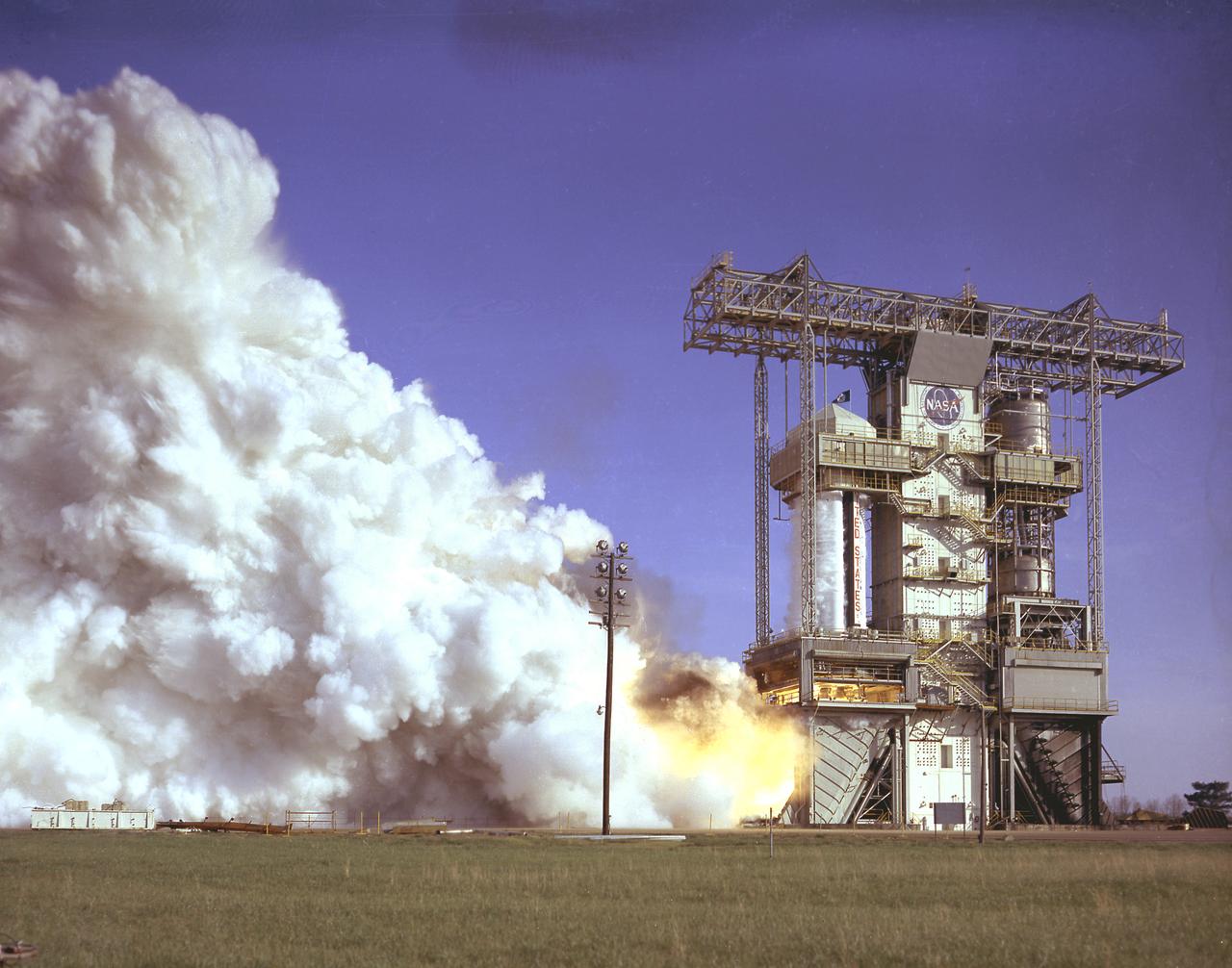

S-IB-1, the first flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB stage), undergoes a full-duration static firing in Saturn IB static test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) on April 13, 1965. Developed by the MSFC and built by the Chrysler Corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) in New Orleans, Louisiana, the 90,000-pound booster utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds. Between April 1965 and July 1968, MSFC performed thirty-two static tests on twelve different S-IB stages.
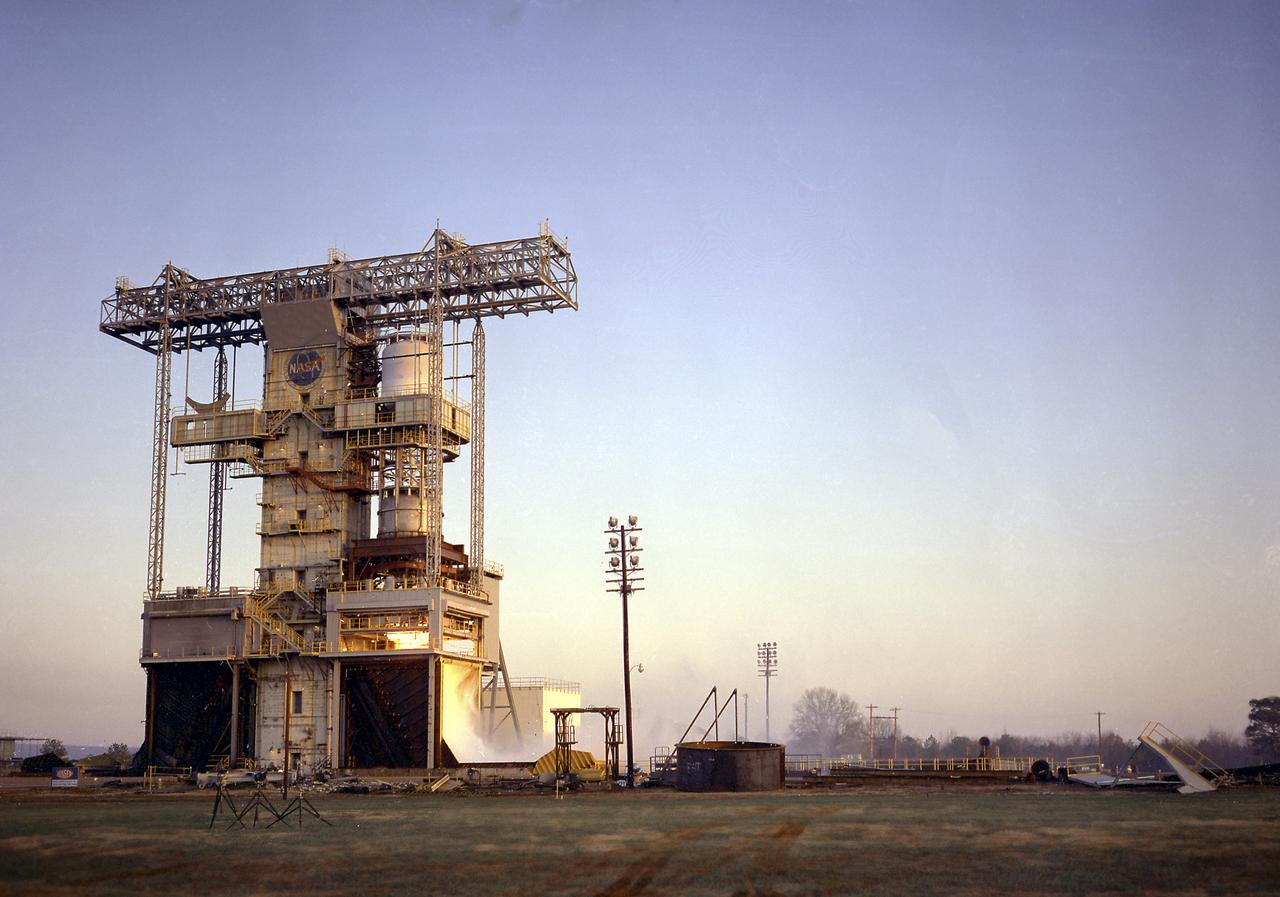

The test laboratory of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) tested the F-1 engine, the most powerful rocket engine ever fired at MSFC. The engine was tested on the newly modified Saturn IB static test stand that had been used for three years to test the Saturn I eight-engine booster, S-I (first) stage. In 1961, the test stand was modified to permit static firing of the S-I/S-IB stage and the name of the stand was then changed to the S-IB Static Test Stand. Producing a combined thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, five F-1 engines powered the S-IC (first) stage of the Saturn V vehicle for the marned lunar mission.
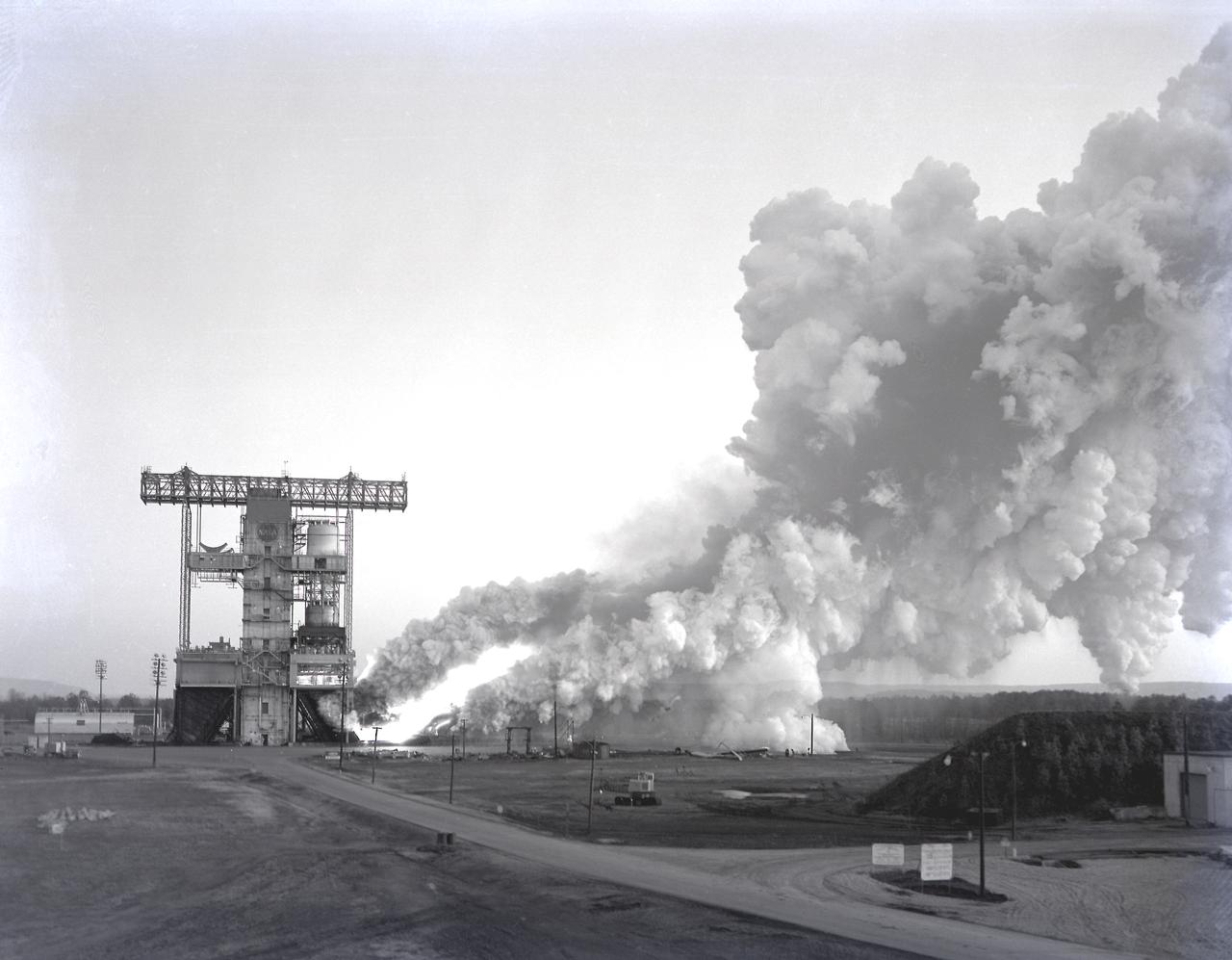

The test laboratory of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) tested the F-1 engine, the most powerful rocket engine ever fired at MSFC. The engine was tested on the newly modified Saturn IB Static Test Stand which had been used for three years to test the Saturn I eight-engine booster, S-I (first) stage. In 1961 the test stand was modified to permit static firing of the S-I/S-IB stage and the name of the stand was then changed to the S-IB Static Test Stand. Producing a combined thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, five F-1 engines powered the S-IC (first) stage of the Saturn V vehicle for the marned lunar mission.
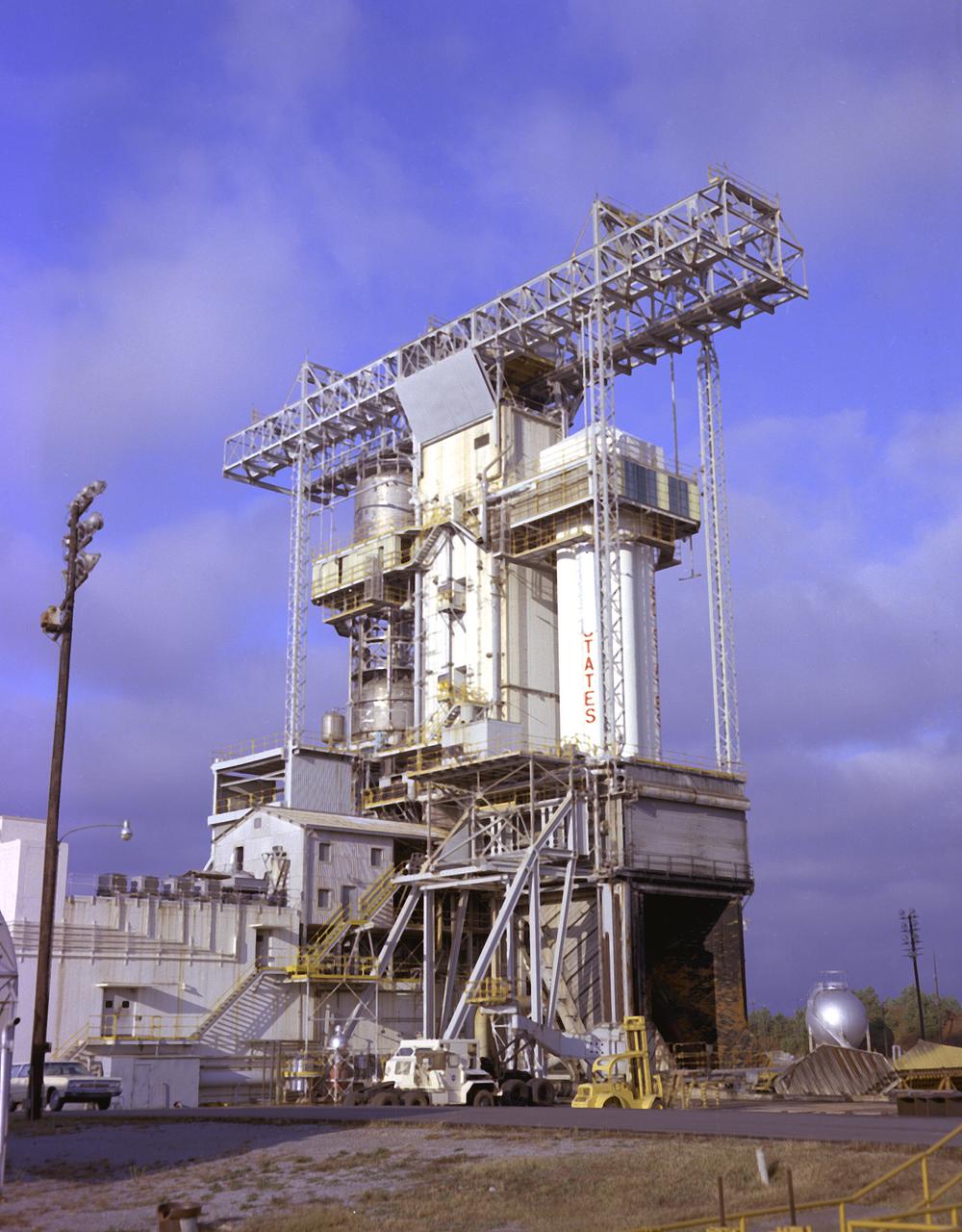

S-IB-211, the flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's (S-IVB) first stage, after installation at the Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) S-IB static test stand. Between December 1967 and April 1968, the stage would undergo seven static test firings. The S-IB, developed by the MSFC and built by the Chrysler Corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana, utilized eight H-1 engines and each produced 200,000 pounds of thrust.
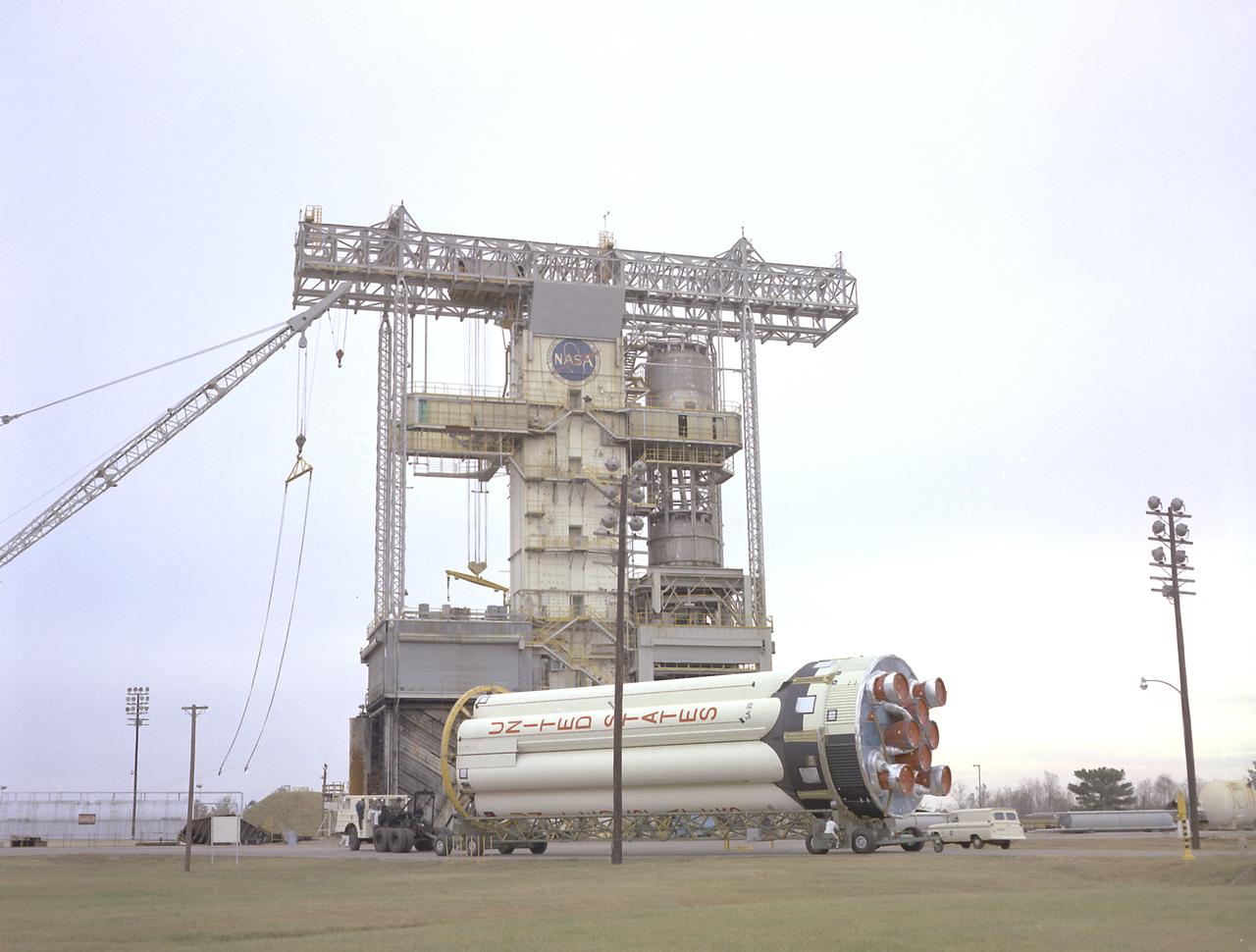

S-IB-211, the flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first (S-IVB) stage, arrives at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) S-IB static test stand. Between December 1967 and April 1968, the stage would undergo seven static test firings. The S-IB, developed by the MSFC and built by the Chrysler Corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans, Louisiana, utilized eight H-1 engines and each produced 200,000 pounds of thrust.
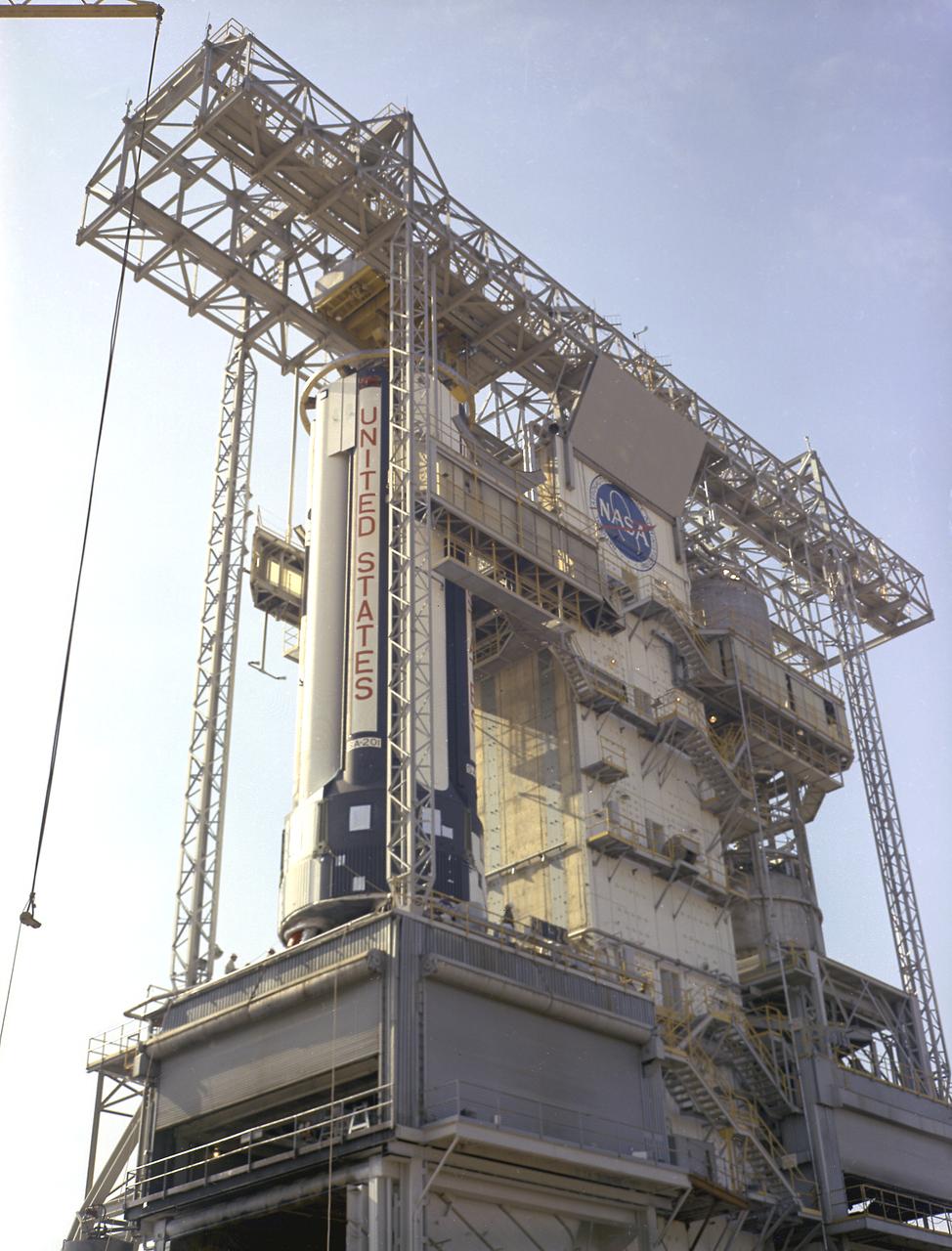

S-IB-1, the first flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB stage), sat in the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Saturn IB static test stand on March 15, 1965. Developed by the MSFC and built by the Chrysler Corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) in New Orleans, Louisiana, the 90,000-pound booster utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.
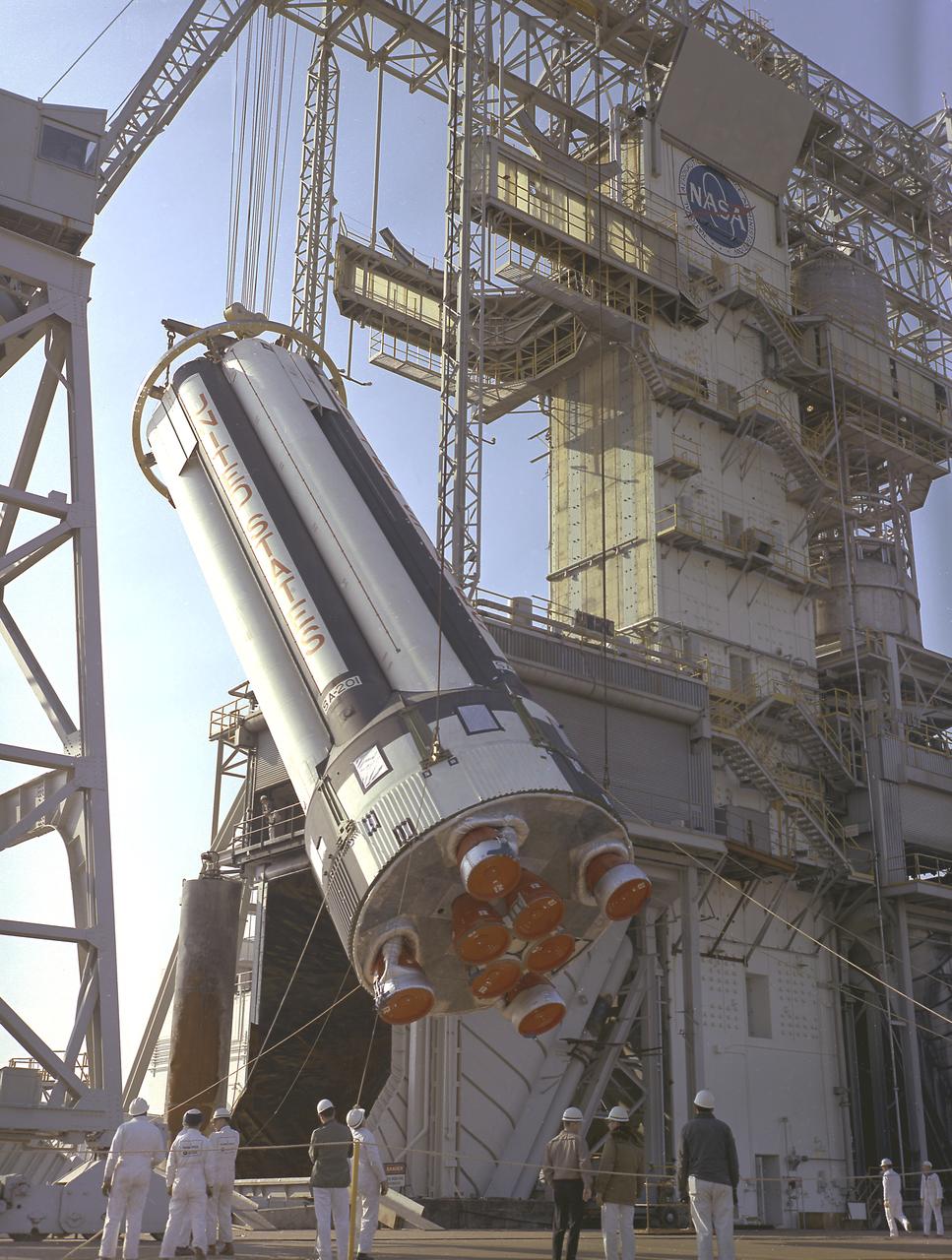

Workers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) hoist S-IB-1, the first flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB stage), into the Saturn IB static test stand on March 15, 1965. Developed by the MSFC and built by the Chrysler Corporation at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF) in New Orleans, Louisiana, the 90,000-pound booster utilized eight H-1 engines to produce a combined thrust of 1,600,000 pounds.
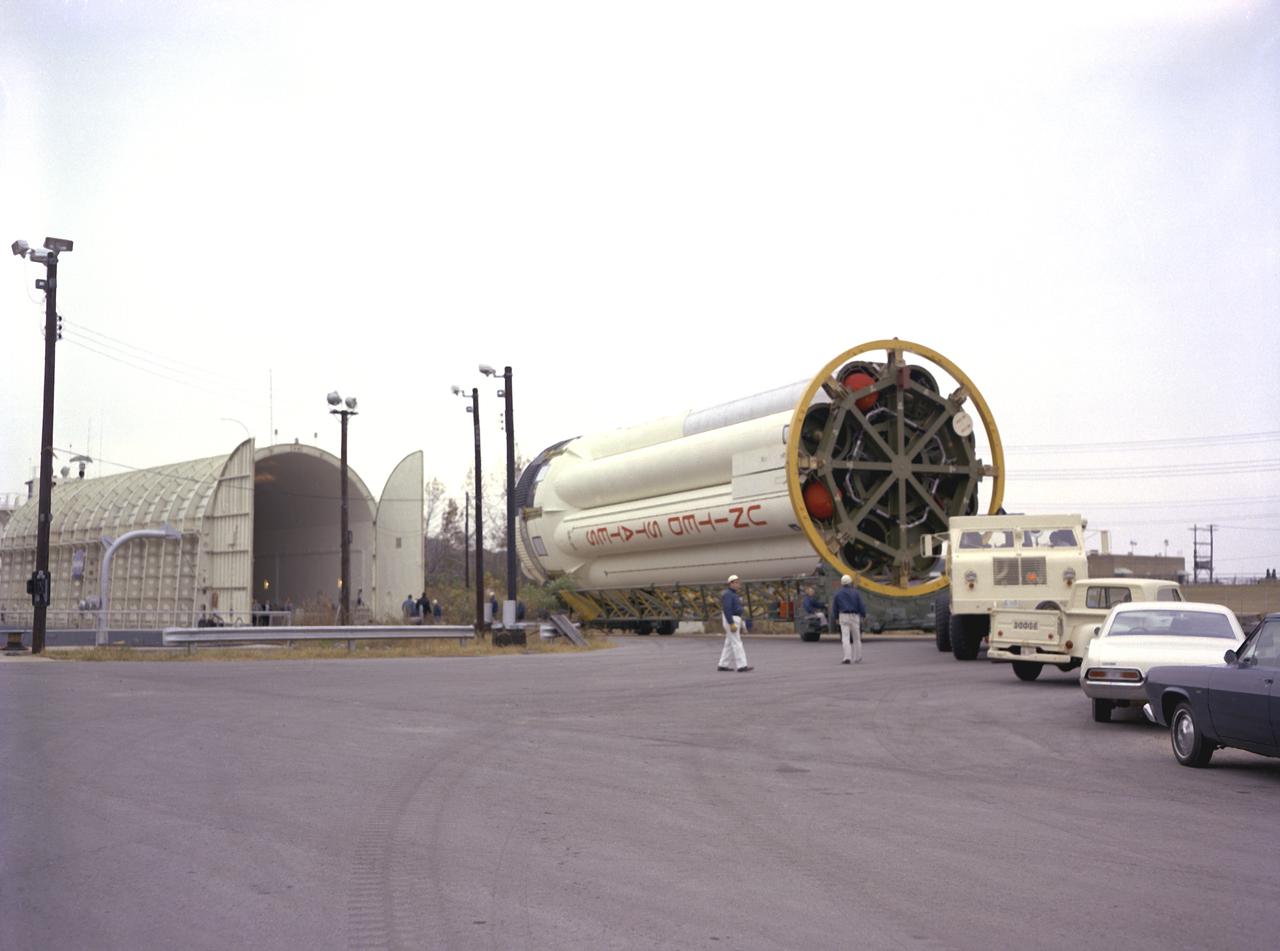

Workmen at the Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) dock on the Ternessee River unload S-IB-211, the flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage, from the NASA barge Palaemon. Between December 1967 and April 1968, the stage would undergo seven static test firings in Marshall's S-IB static test stand.
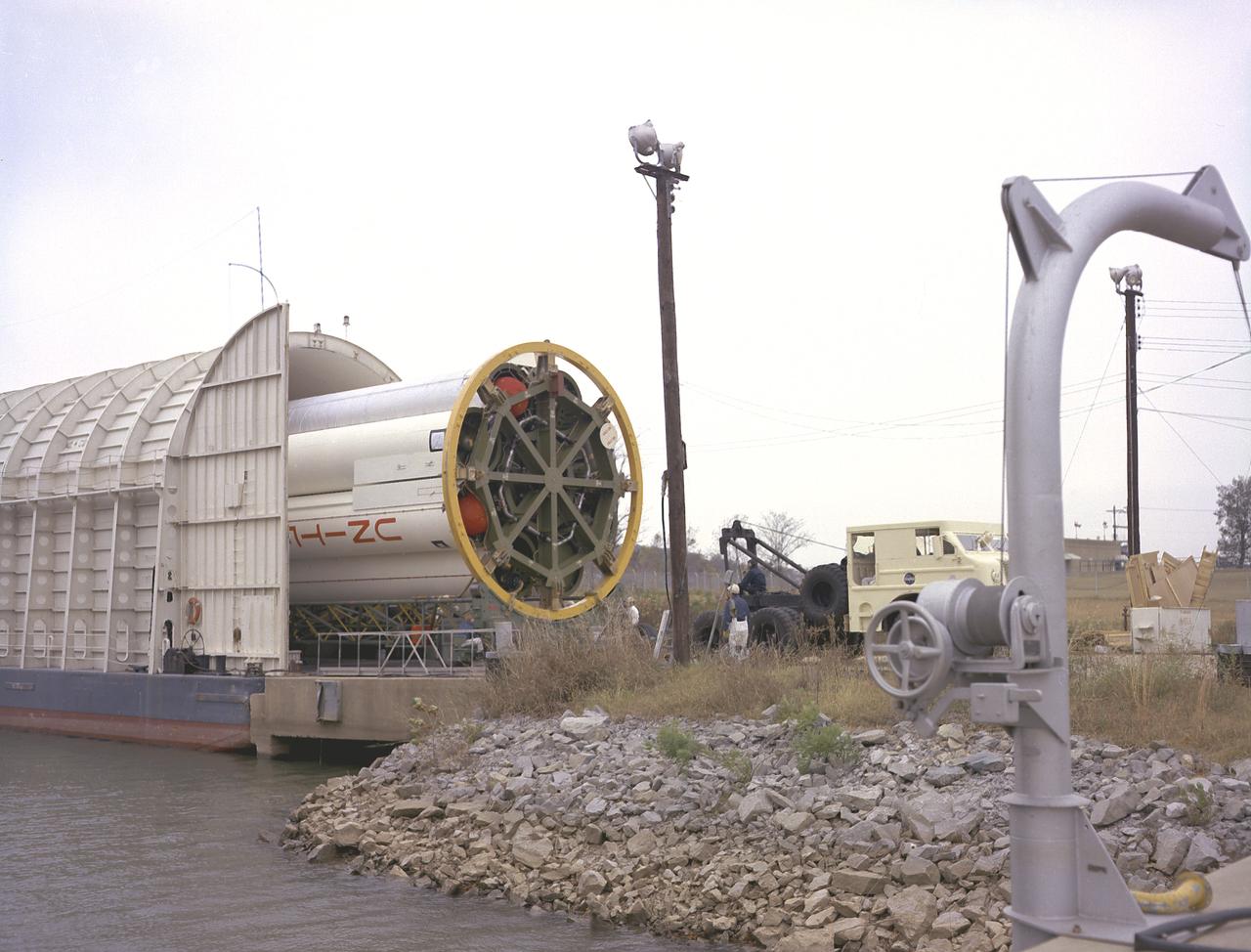

Workmen at the Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) dock on the Ternessee River unload S-IB-211, the flight version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage, from the NASA barge Palaemon. Between December 1967 and April 1968, the stage would undergo seven static test firings in MSFC's S-IB static test stand.
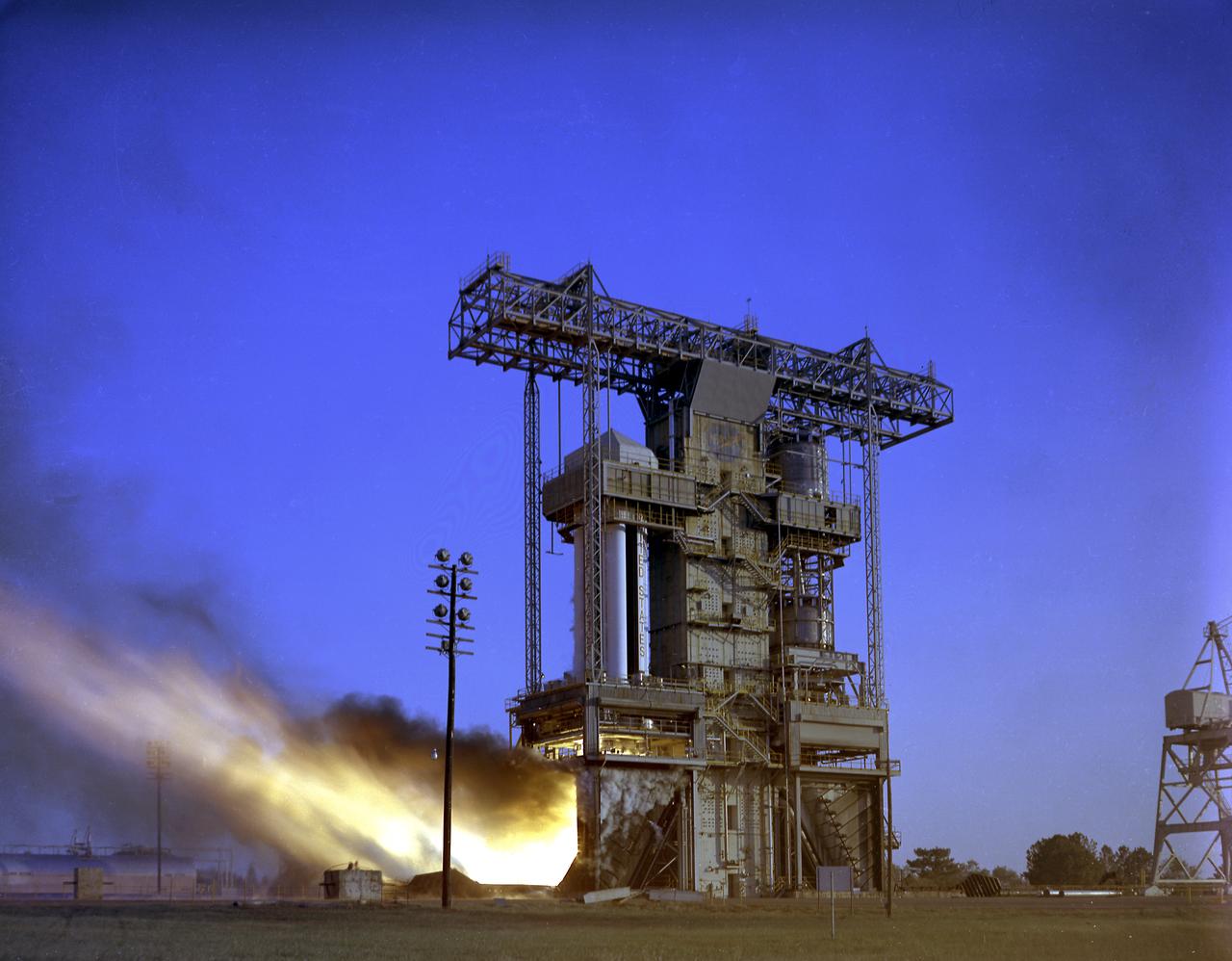

Test firing of the Saturn I S-I Stage (S-1-10) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. This test stand was originally constructed in 1951 and sometimes called the Redstone or T tower. In l961, the test stand was modified to permit static firing of the S-I/S-IB stages, which produced a total thrust of 1,600,000 pounds. The name of the stand was then changed to the S-IB Static Test Stand.
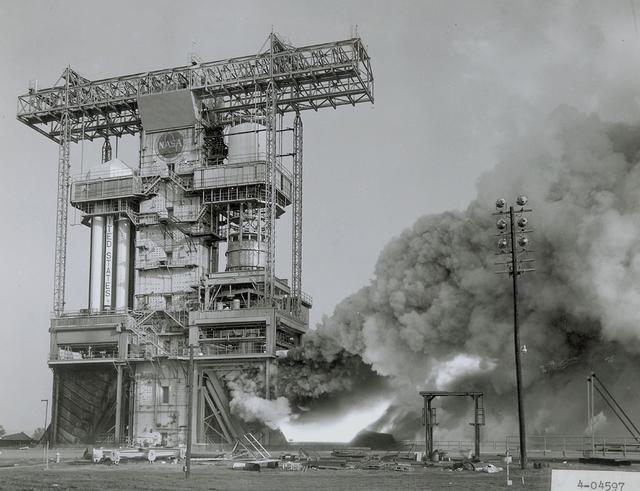
The flame and exhaust from the test firing of an F-1 engine blast out from the Saturn S-IB Static Test Stand in the east test area of the Marshall Space Flight Center. A Cluster of five F-1 engines, located in the S-IC (first) stage of the Saturn V vehicle, provided over 7,500,000 pounds of thrust to launch the giant rocket. The towering 363-foot Saturn V was a multistage, multiengine launch vehicle standing taller than the Statue of Liberty. Altogether, the Saturn V engines produced as much power as 85 Hoover Dams.