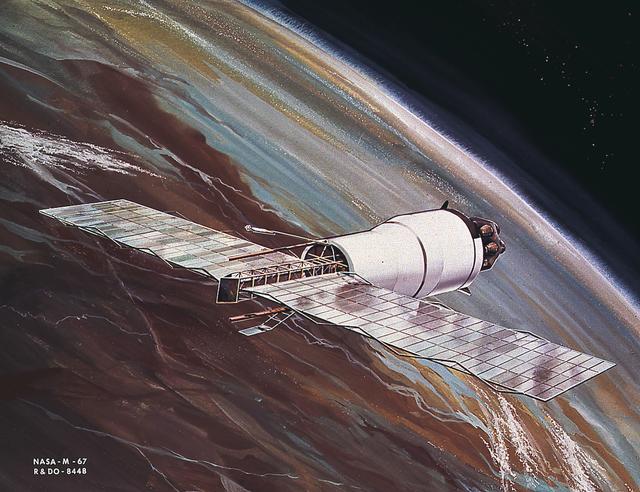

This image is an artist's conception of the Pegasus, meteoroid detection satellite, in orbit with meteoroid detector extended. The satellite, a payload for Saturn I SA-8, SA-9, and SA-10 missions, was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth.
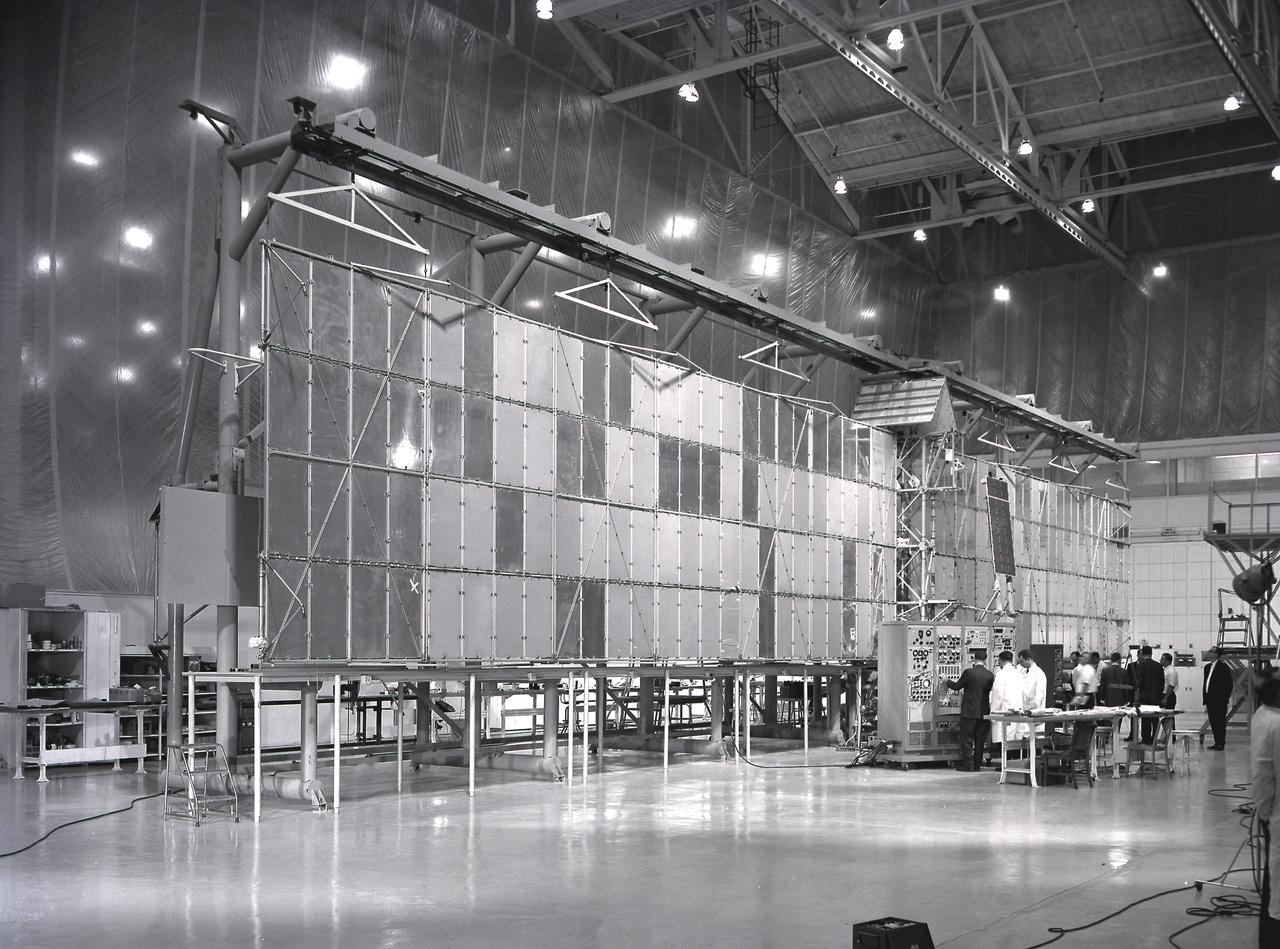

Fairchild technicians check out the extended Pegasus meteoroid detection surface. The Pegasus was developed by Fairchild Stratos Corporation, Hagerstown, Maryland, for NASA through the Marshall Space Flight Center. Three Pegasus satellites were flown aboard Saturn I SA-8, SA-9, and SA-10 missions. After being placed into orbit around the Earth, the satellite unfolded a series of giant panels to form a pair of wings measuring 96 feet across. The purpose of the satellite was to electronically record the size and frequency of particles in space, and compare the performance of protected and unprotected solar cells as important new preliminaries to a marned flight to the Moon.
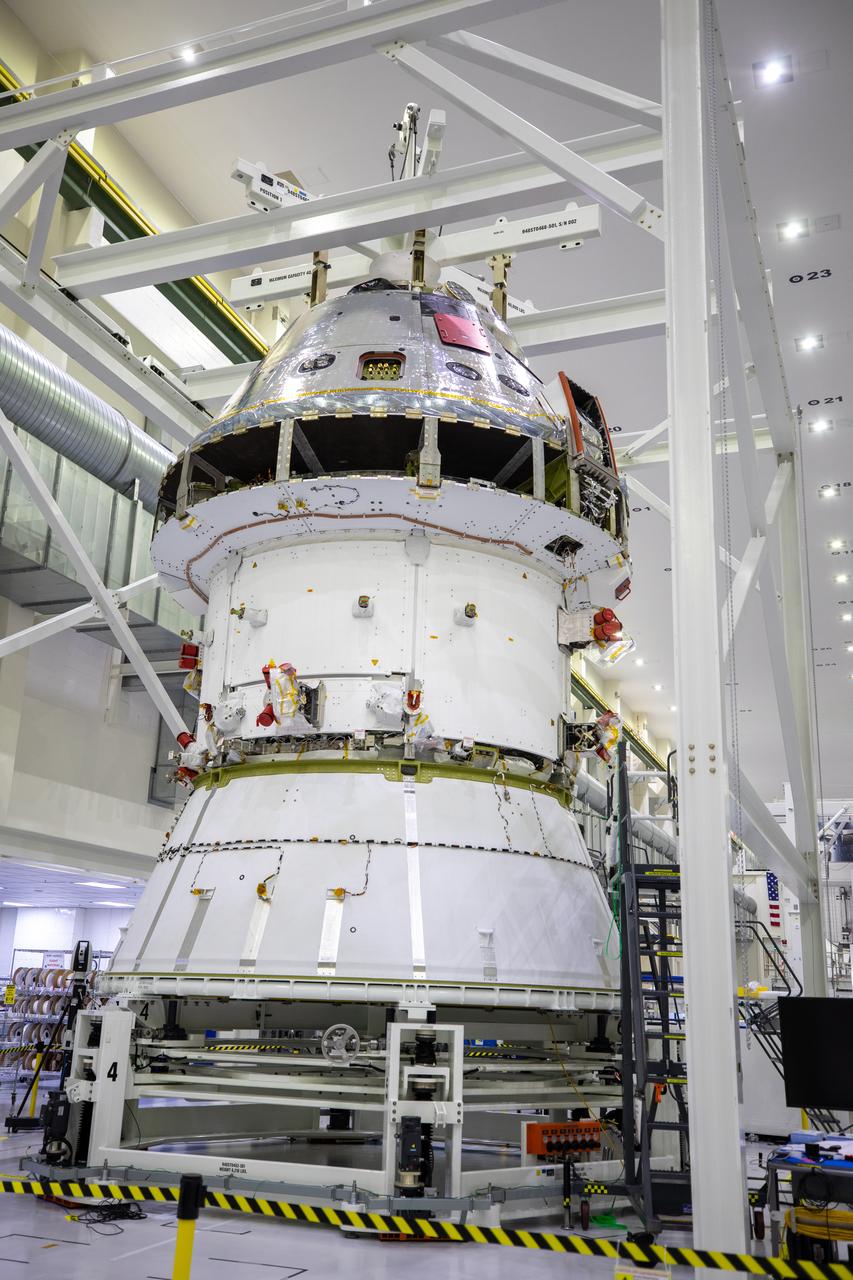

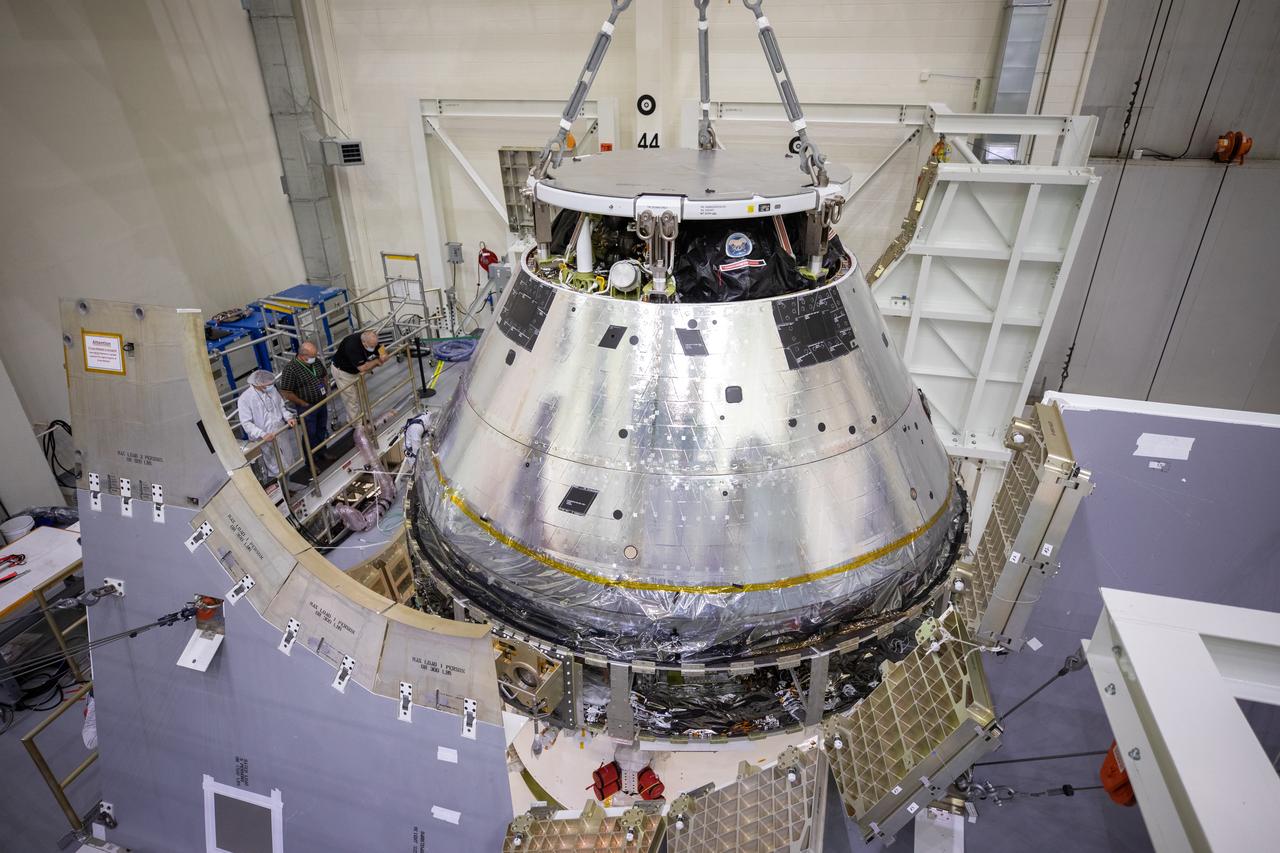
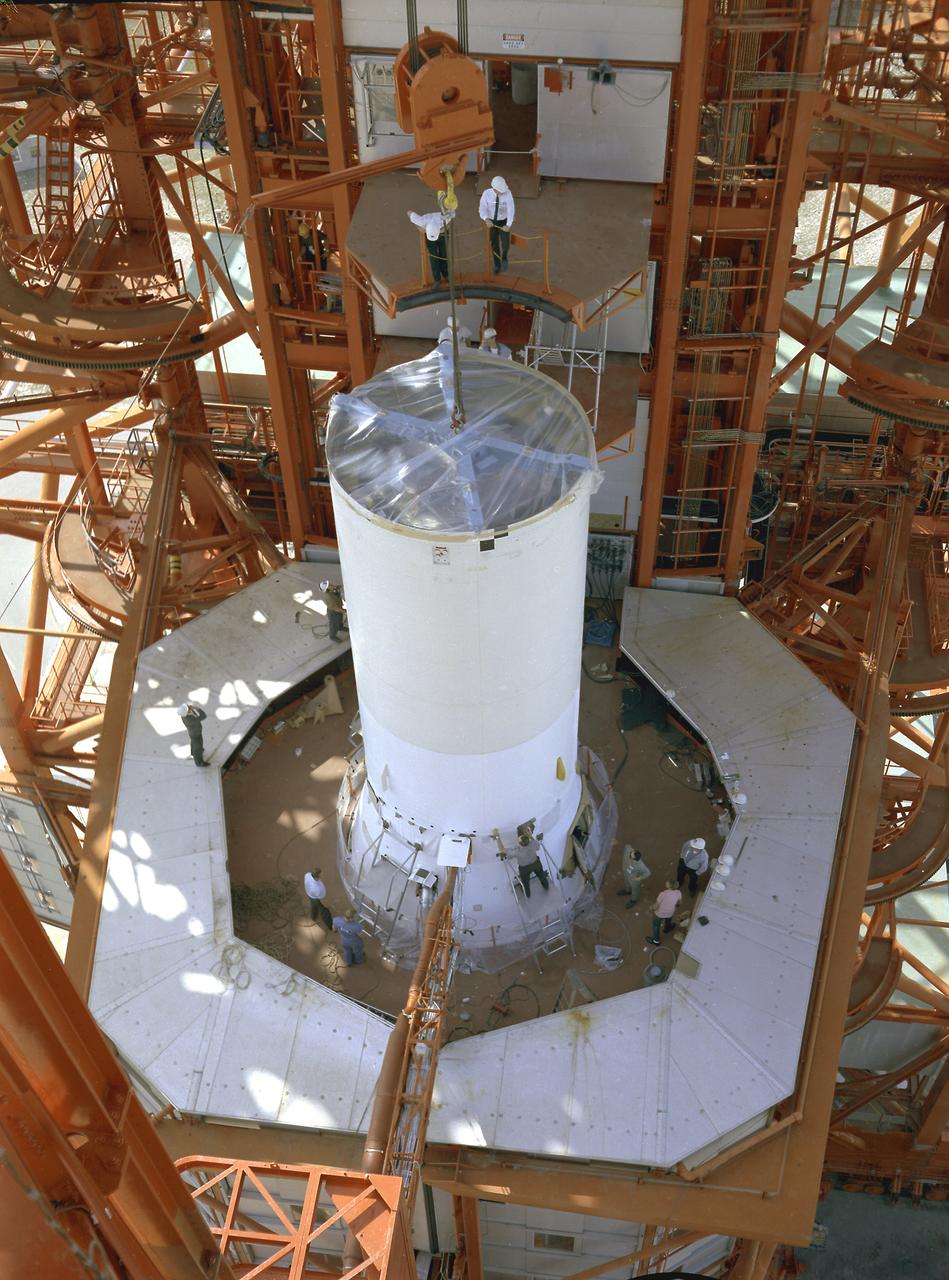
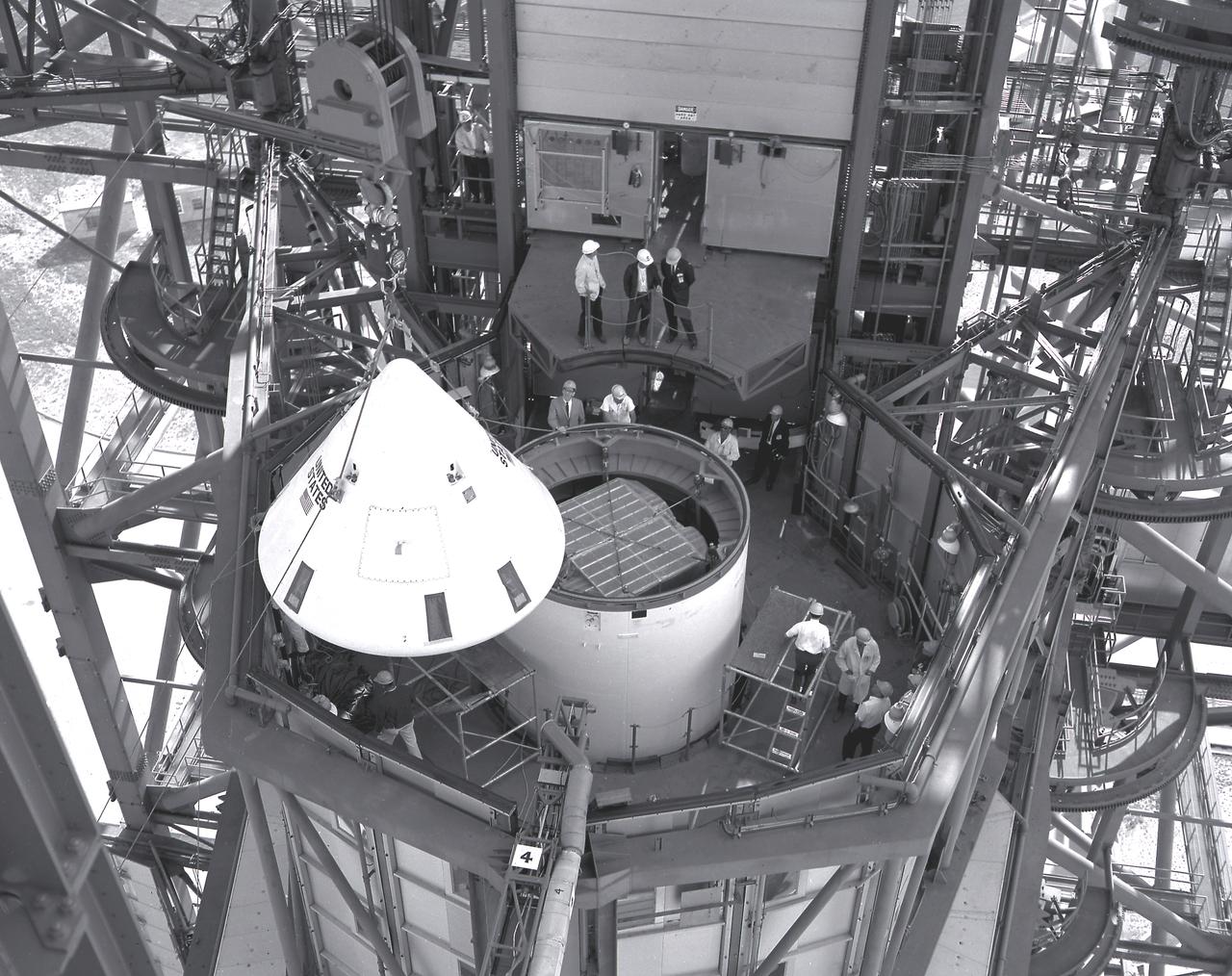
Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
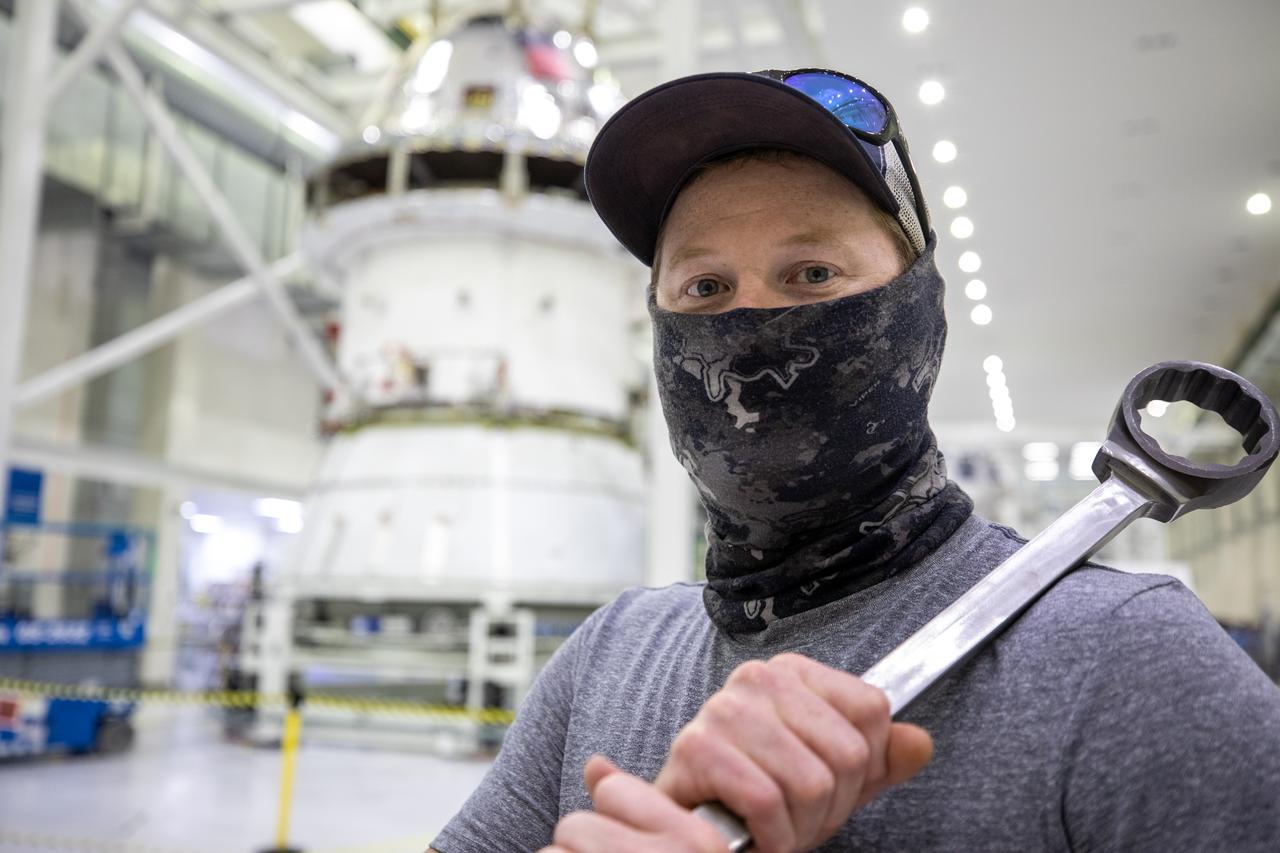

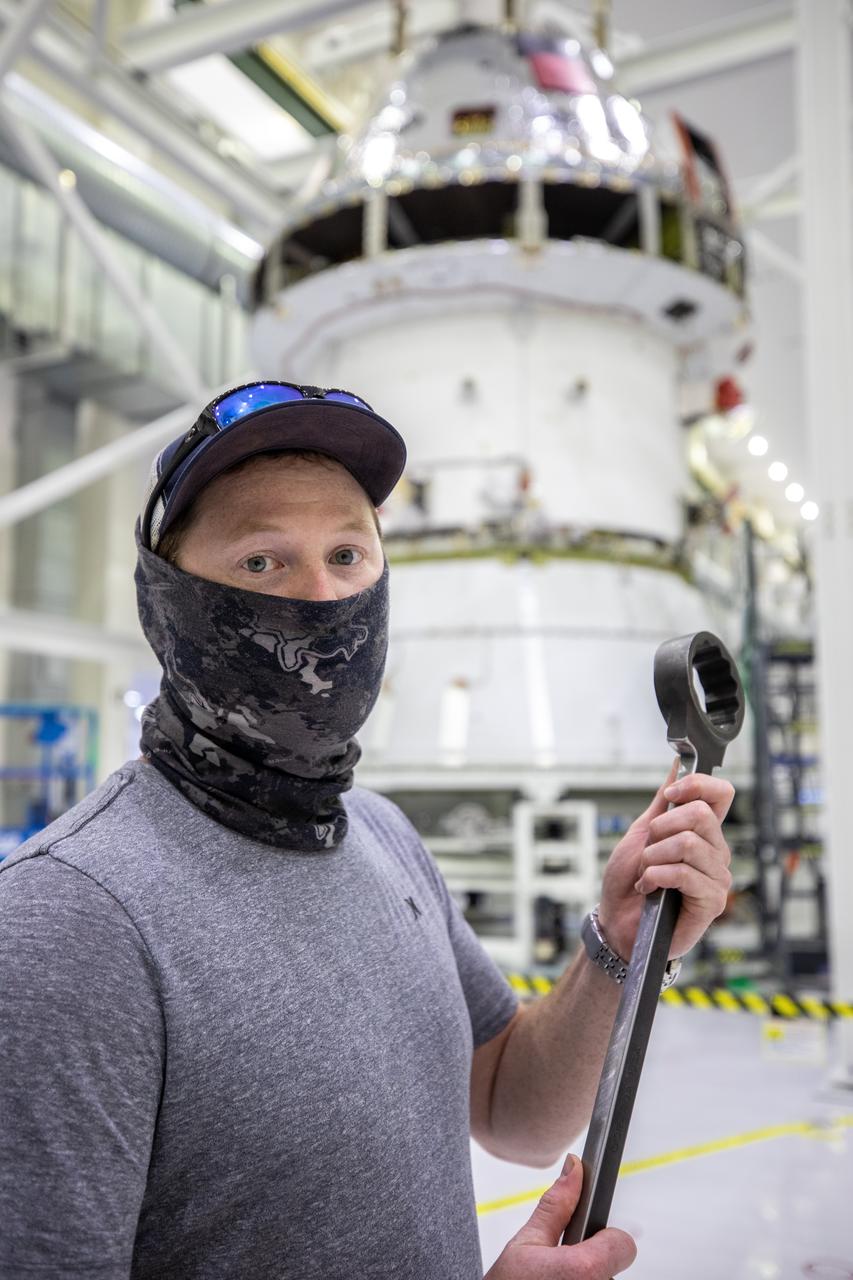
ASRC technician Chris Slack assists with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft is lowered by crane into the FAST cell after installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone was completed inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

ASRC technician Chris Slack assists with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
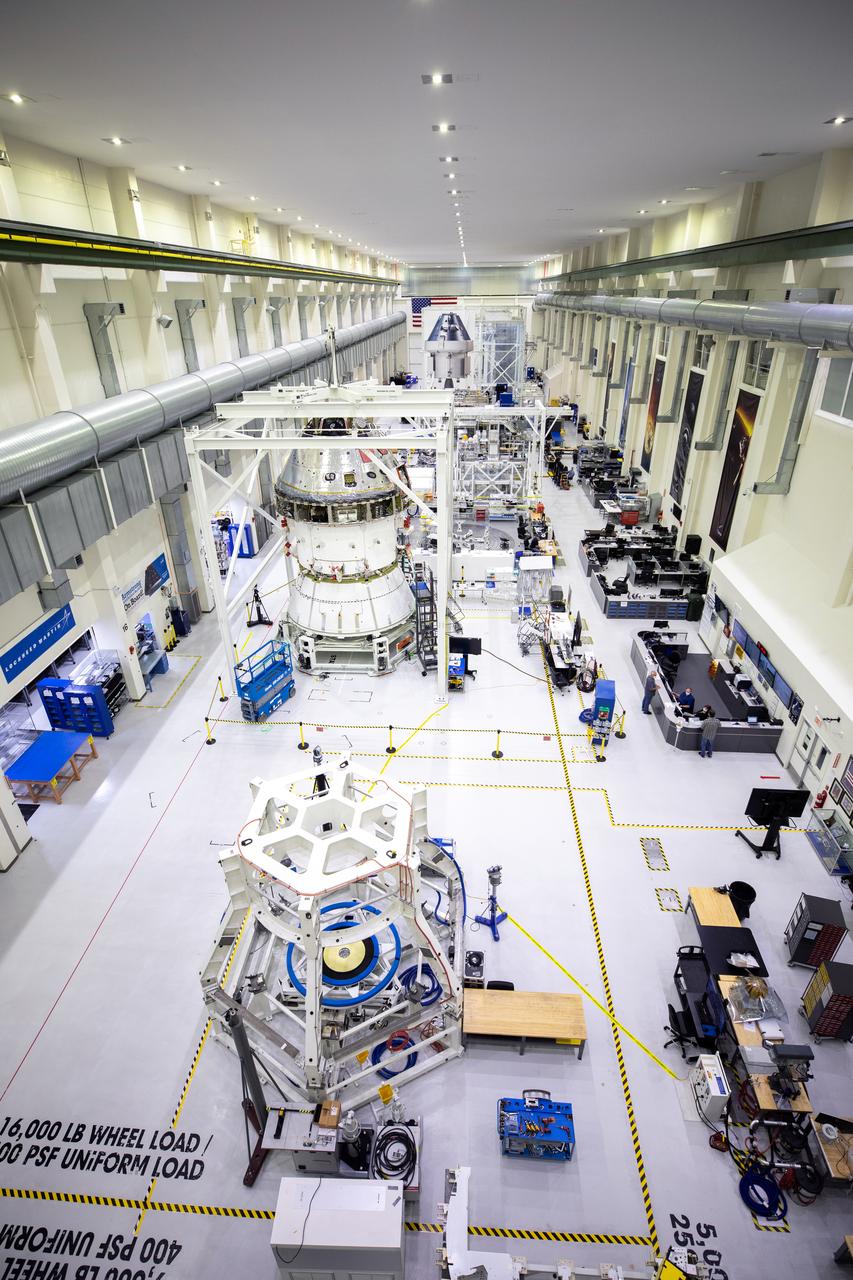
Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
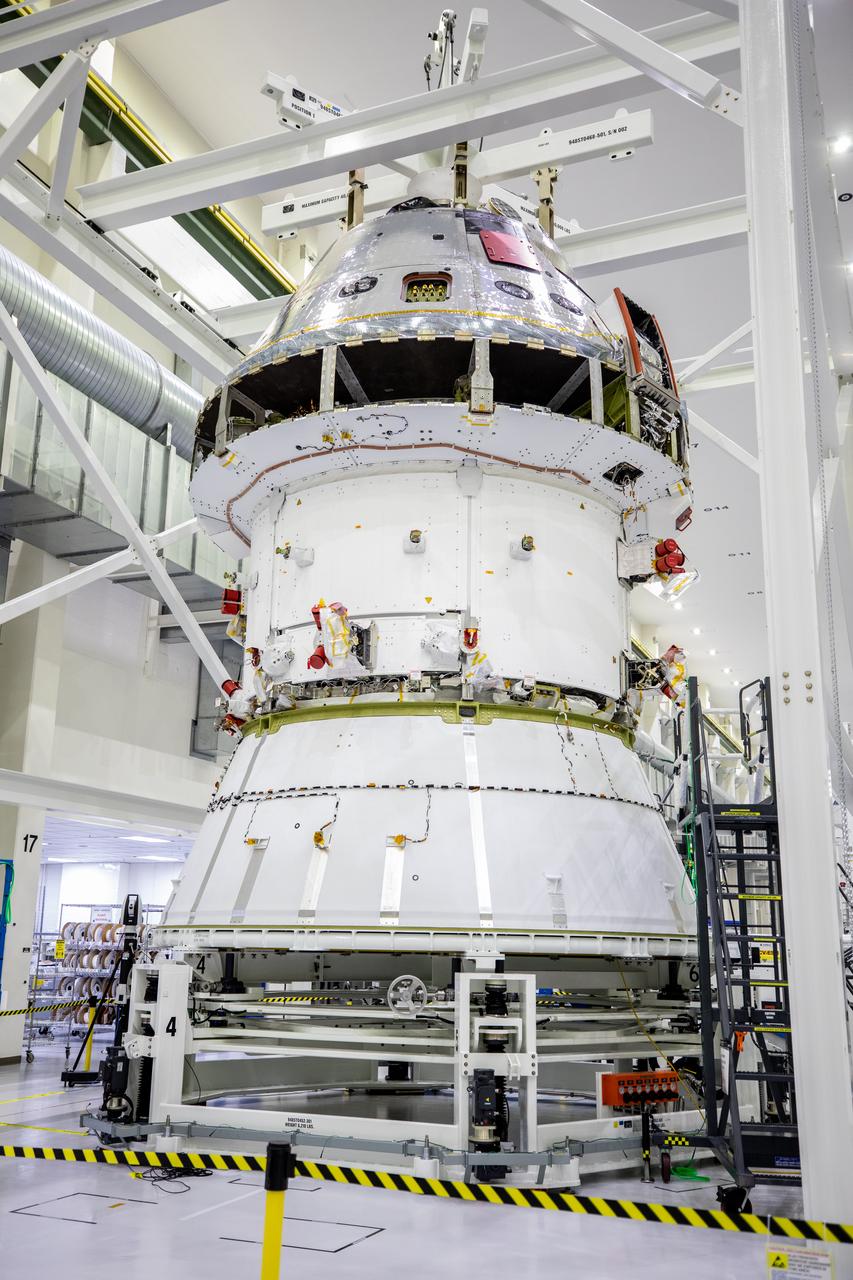
Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
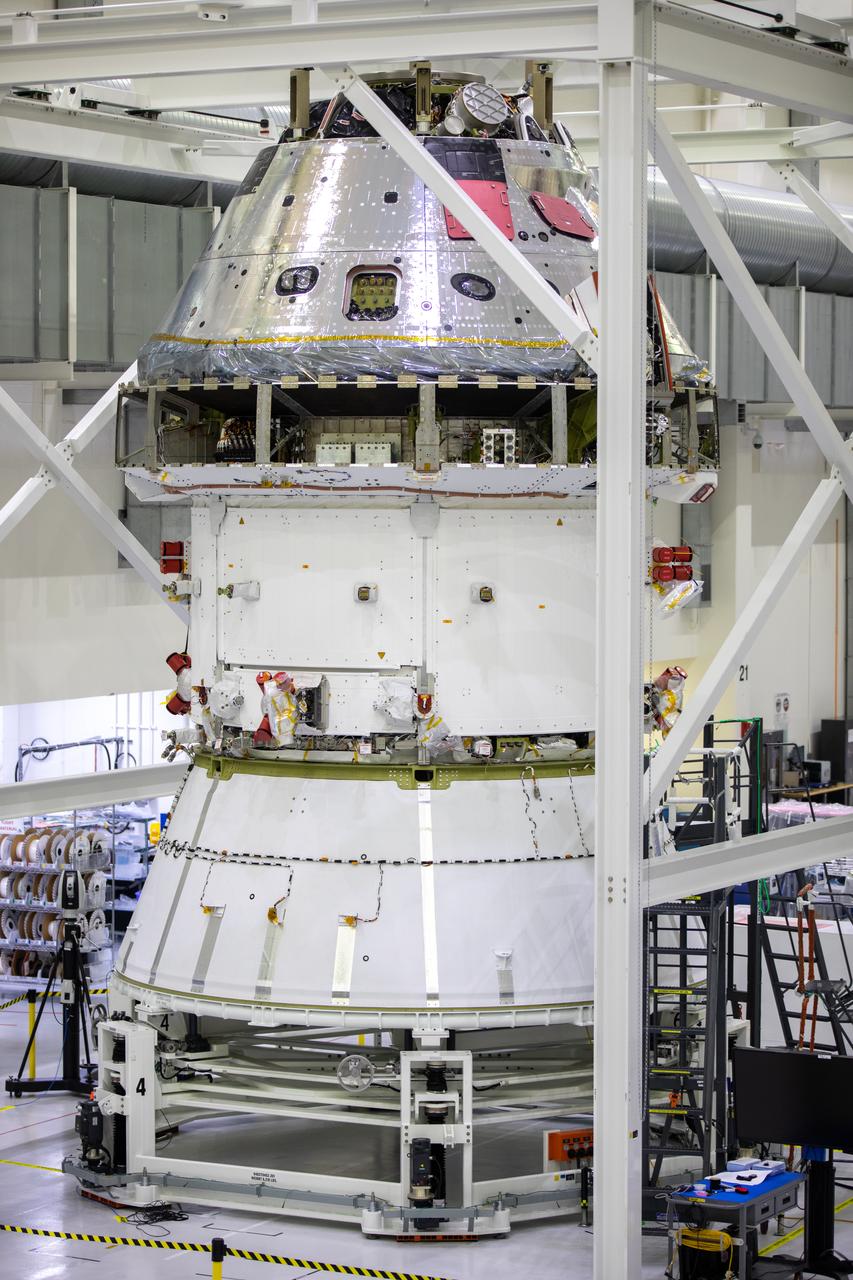

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
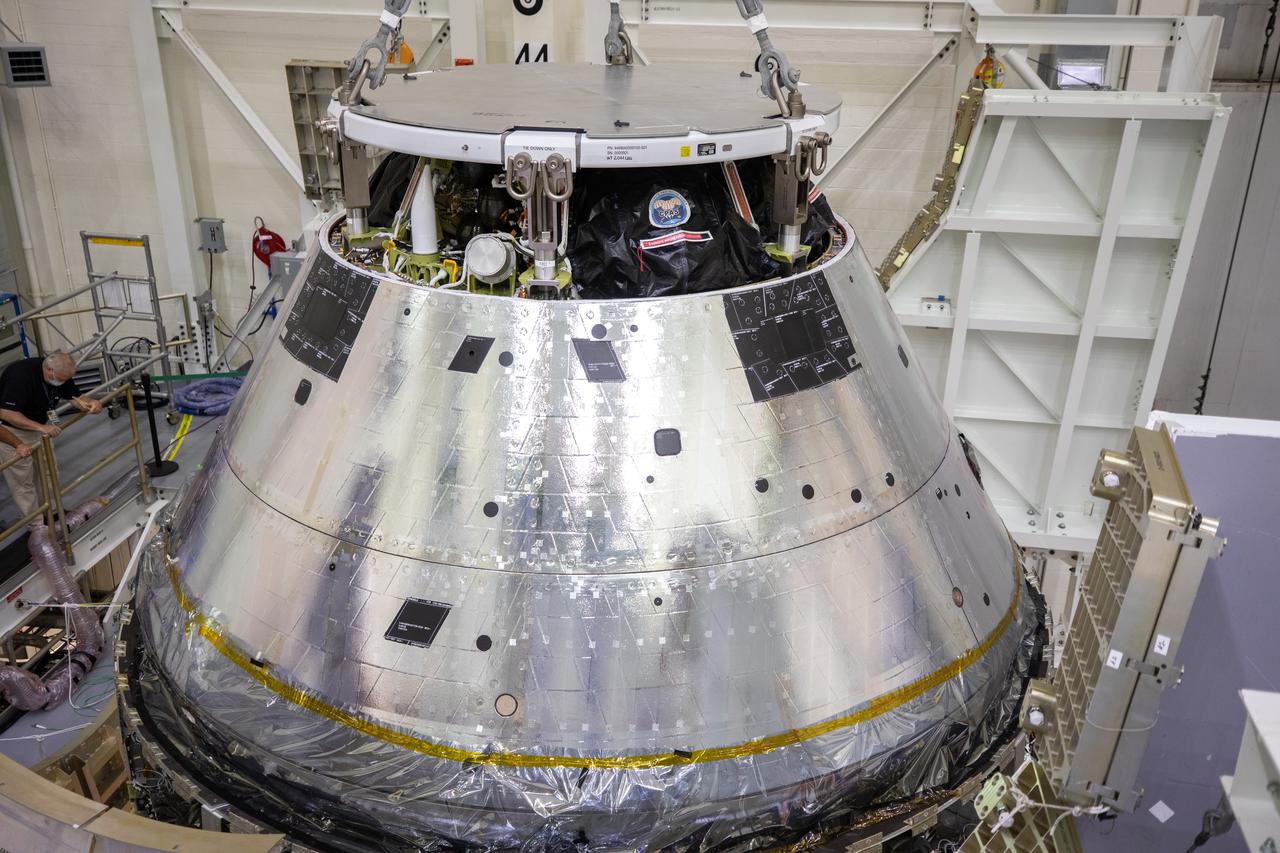

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft is lowered by crane into the FAST cell after installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone was completed inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
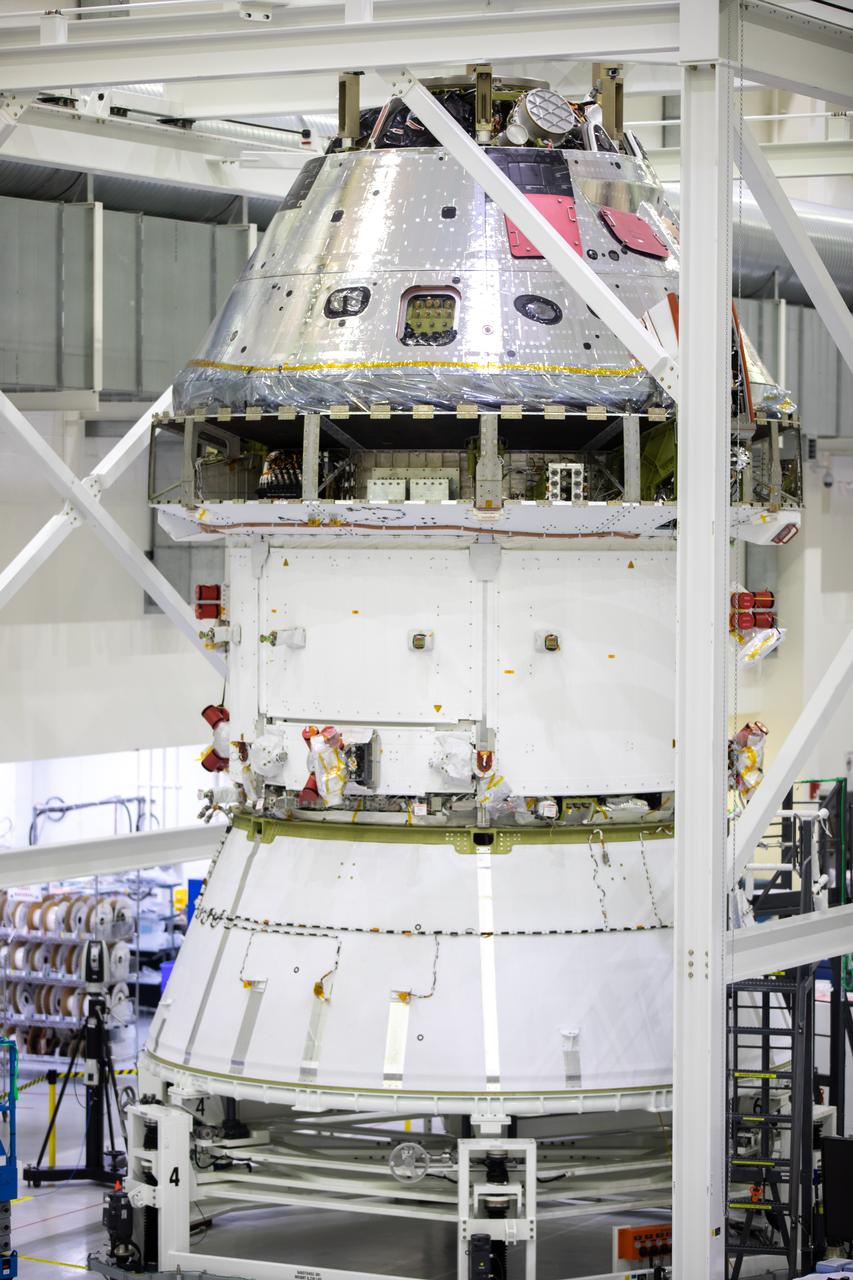

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
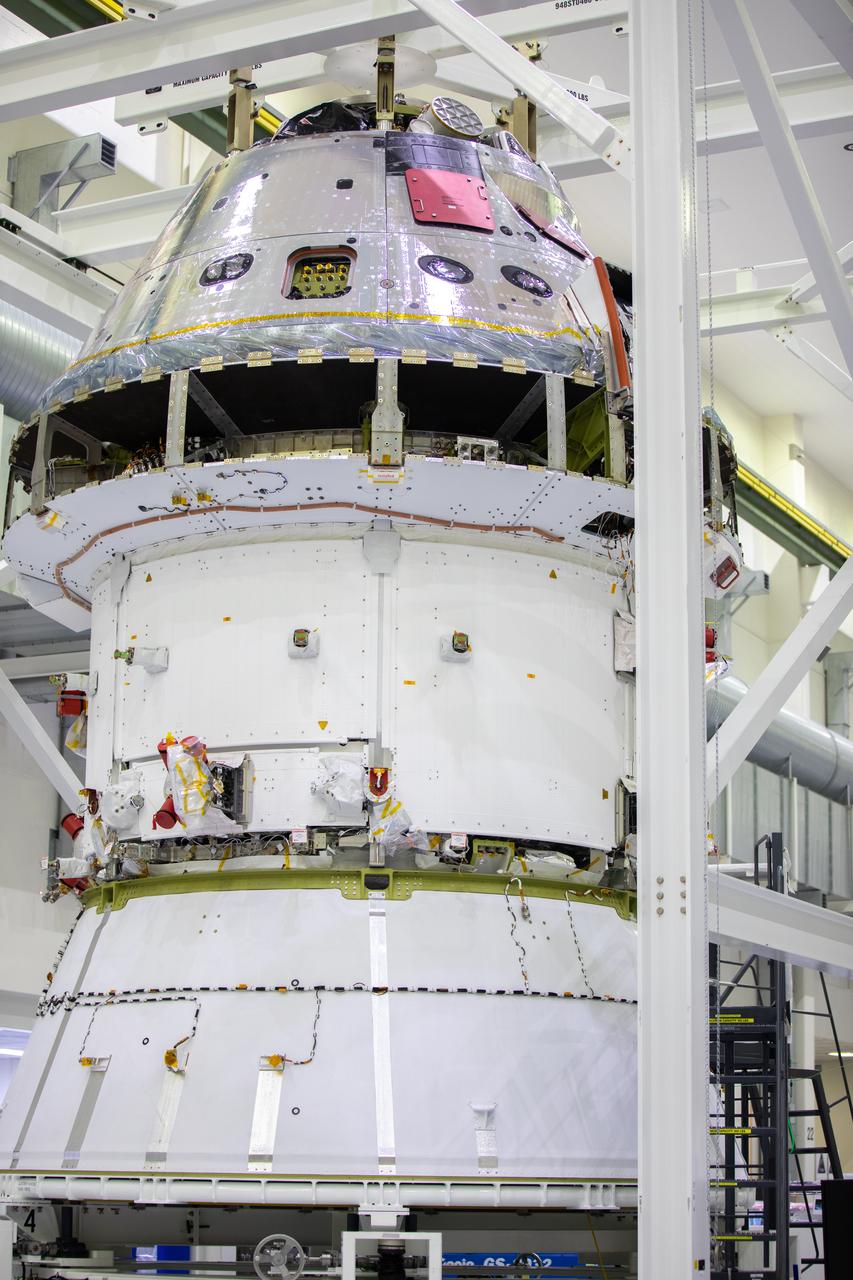

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
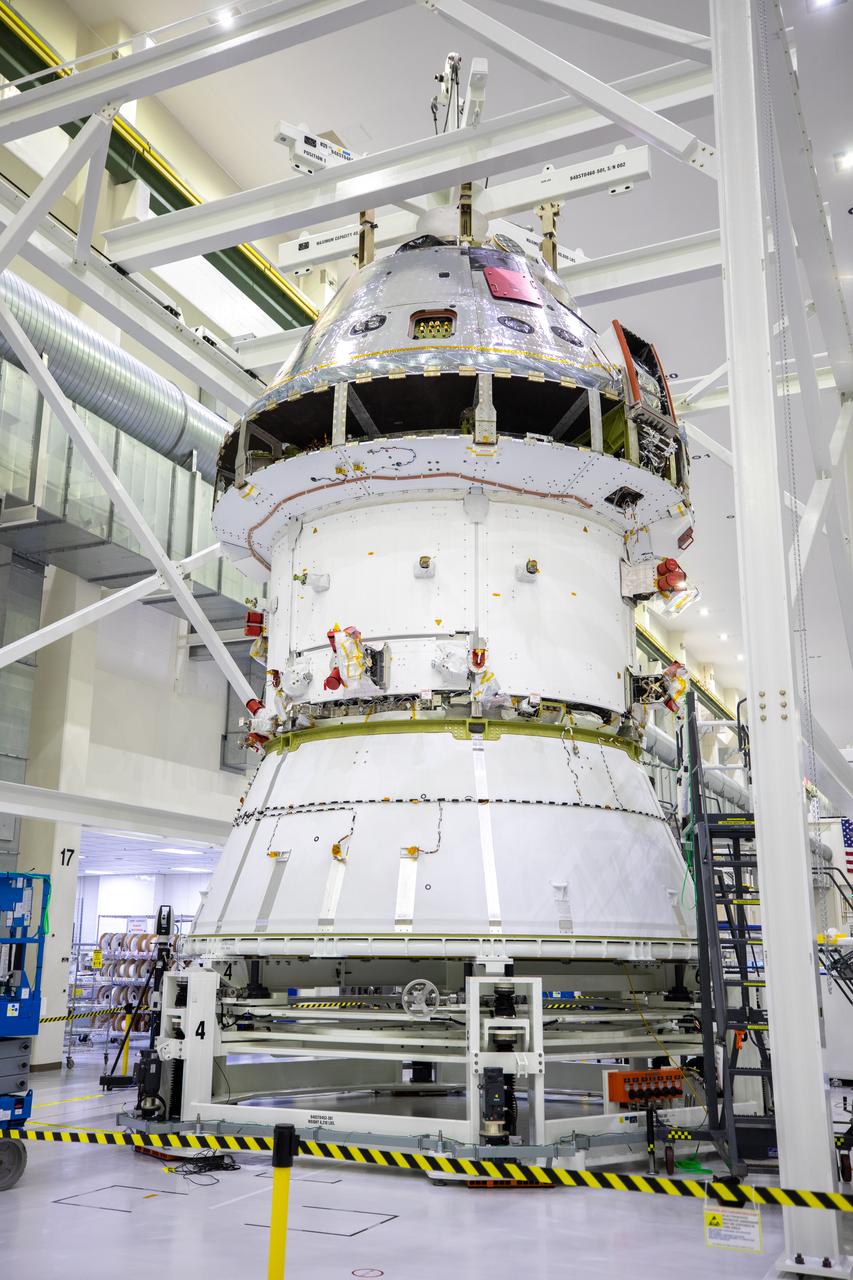

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
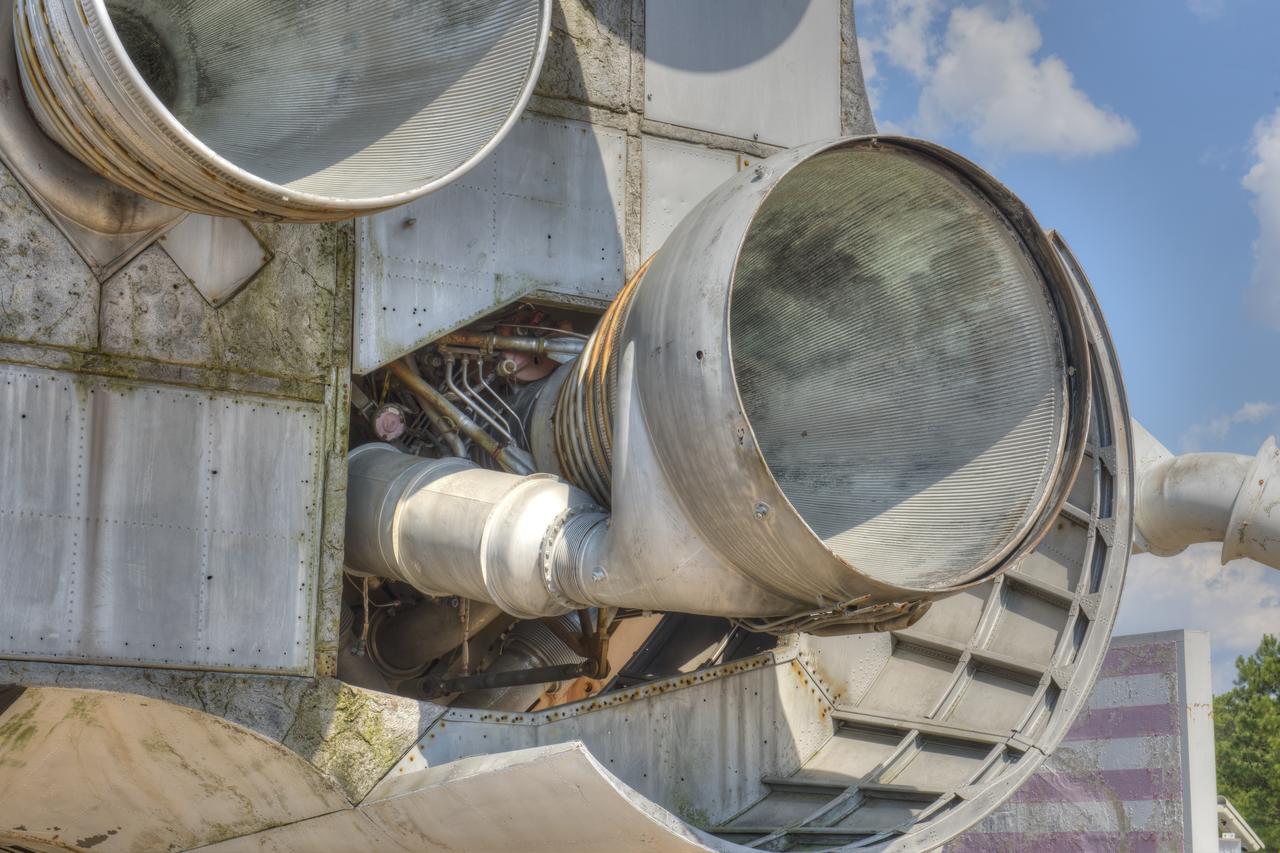

CLOSE-UP OF H-1 ENGINE INSTALLED ON SATURN S-1B STAGE (SA-T) NEAR PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER.
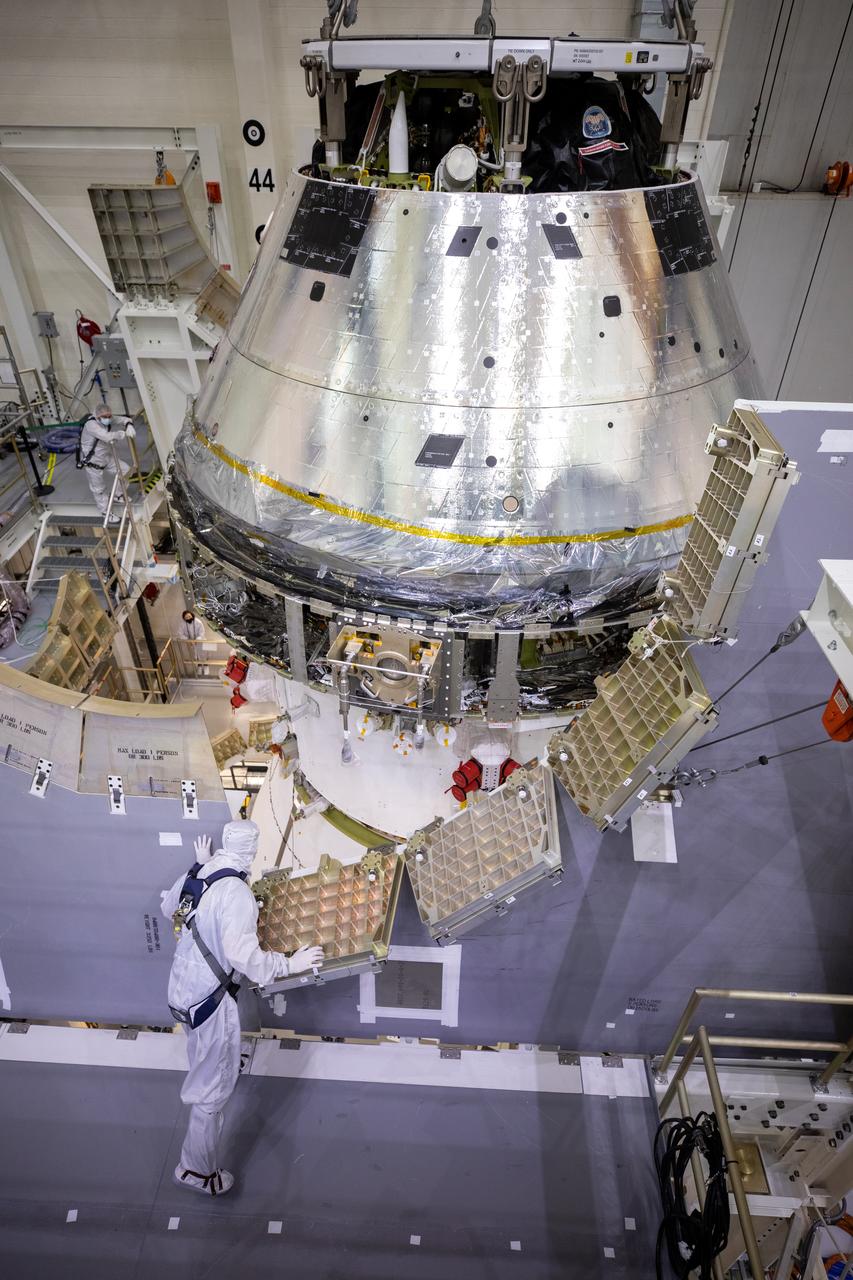

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely lower the Artemis I Orion spacecraft into the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
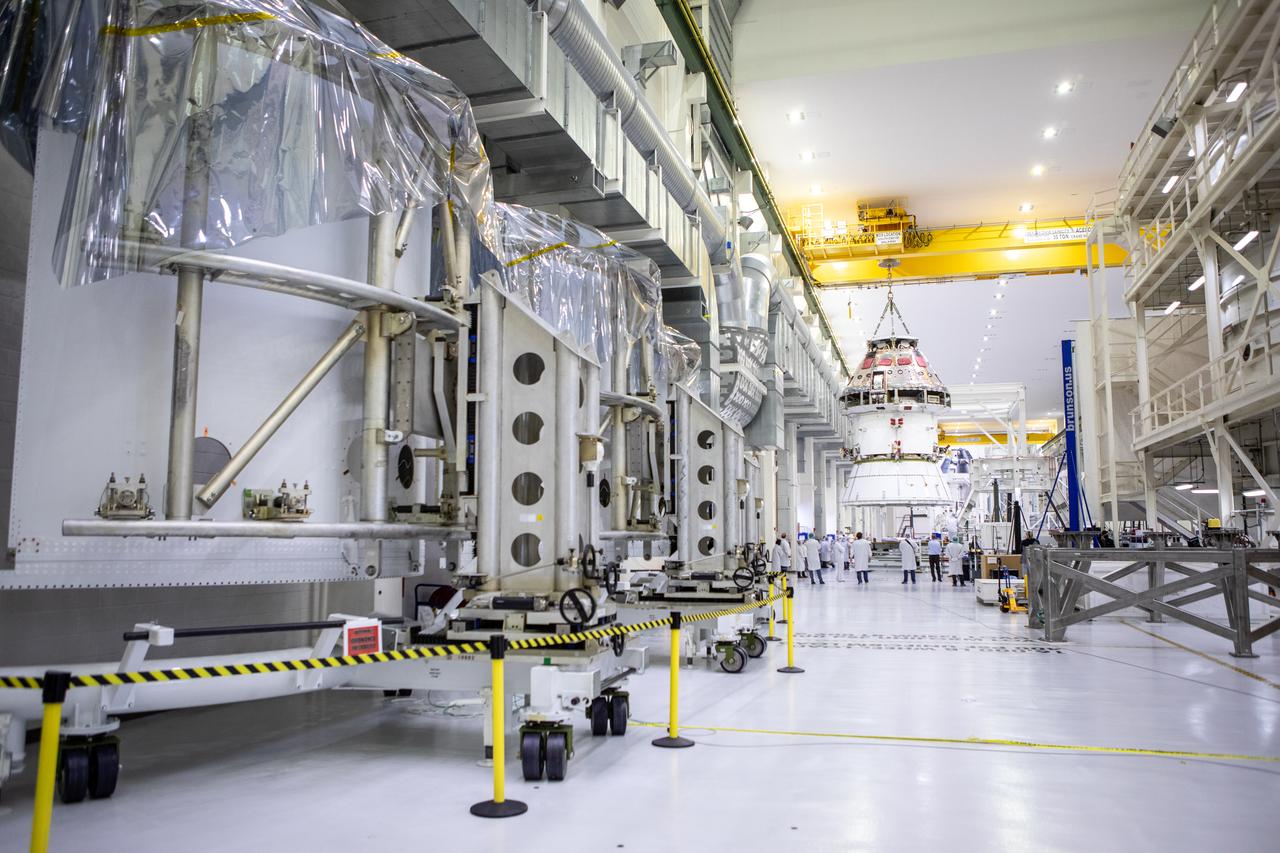

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). In view at left in the foreground are the Spacecraft Adapter Jettison Fairing panels that will protect Orion’s service module from the environment around it during the ascent. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
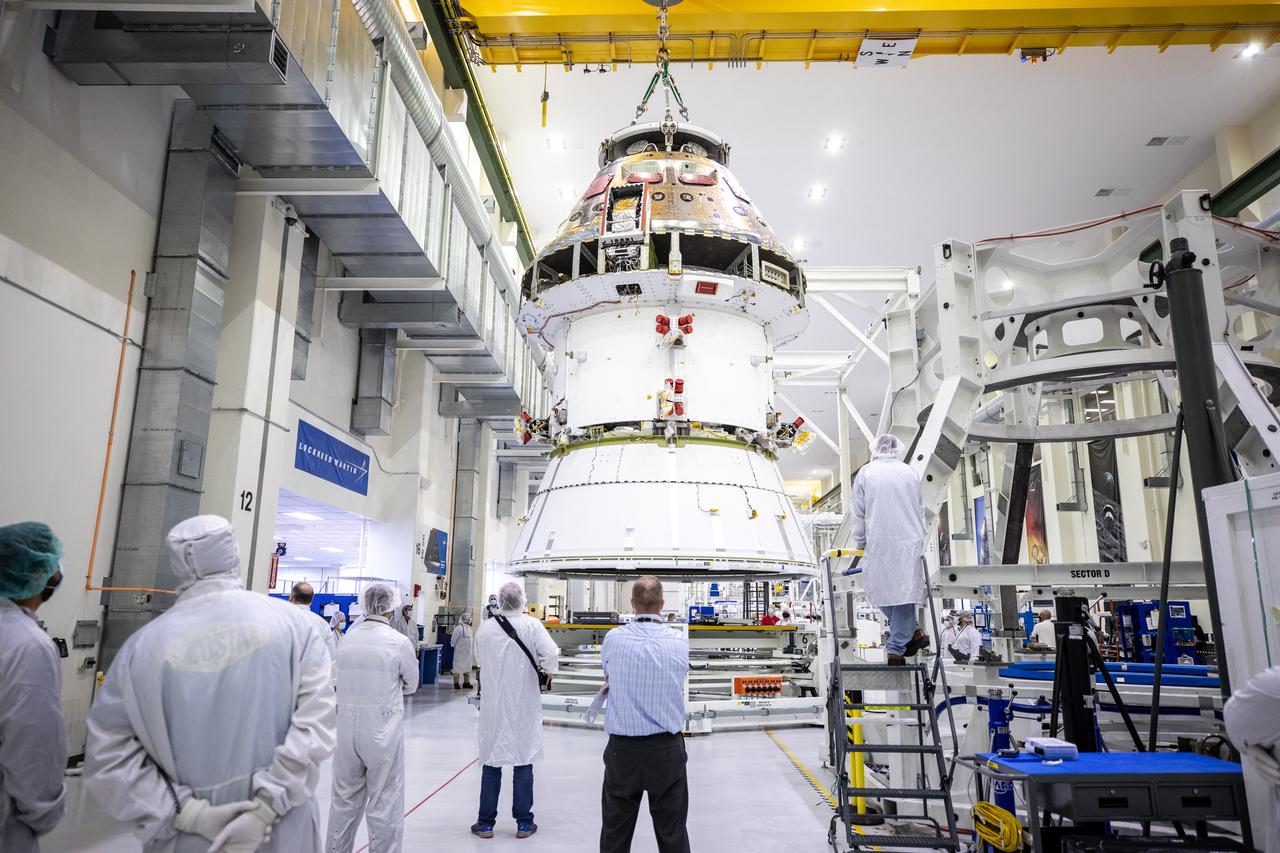

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
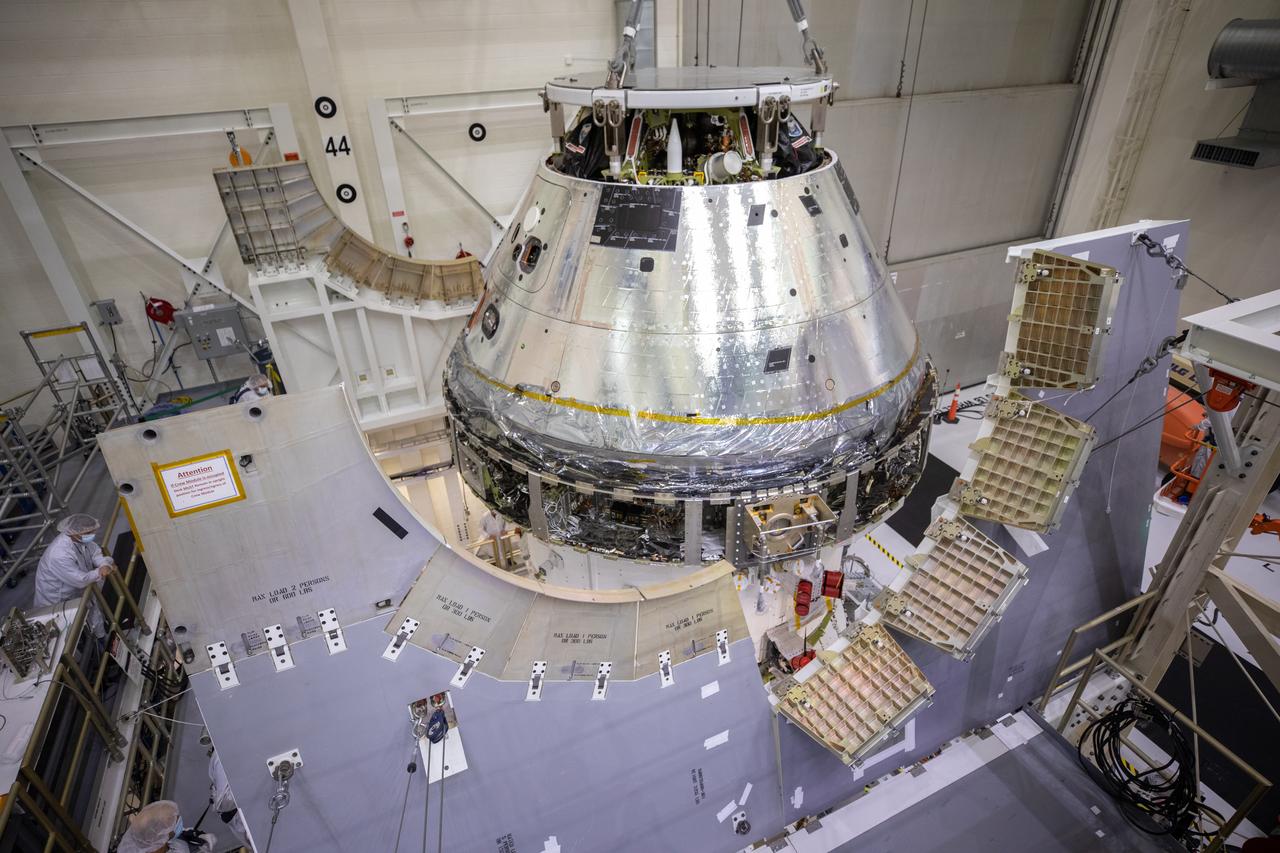

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely lower the Artemis I Orion spacecraft into the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
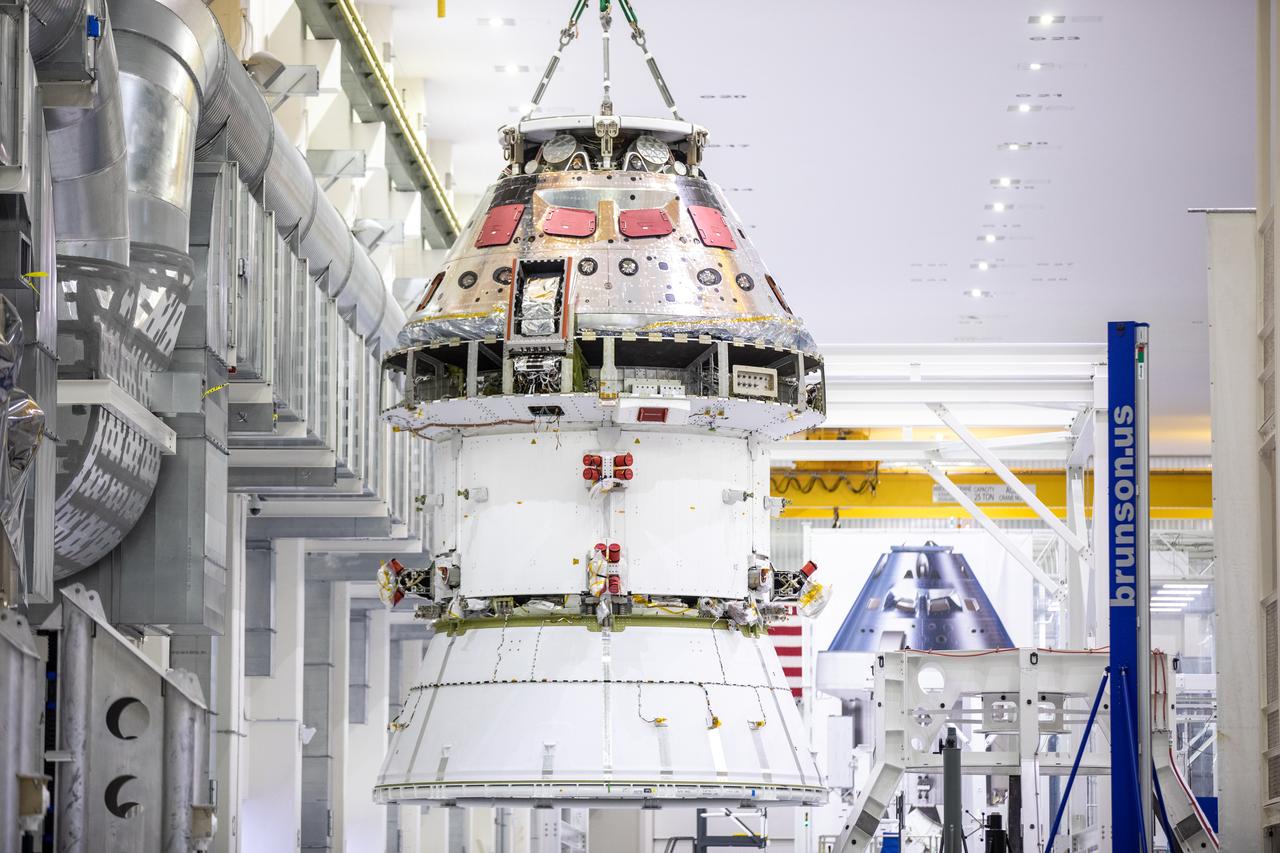

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
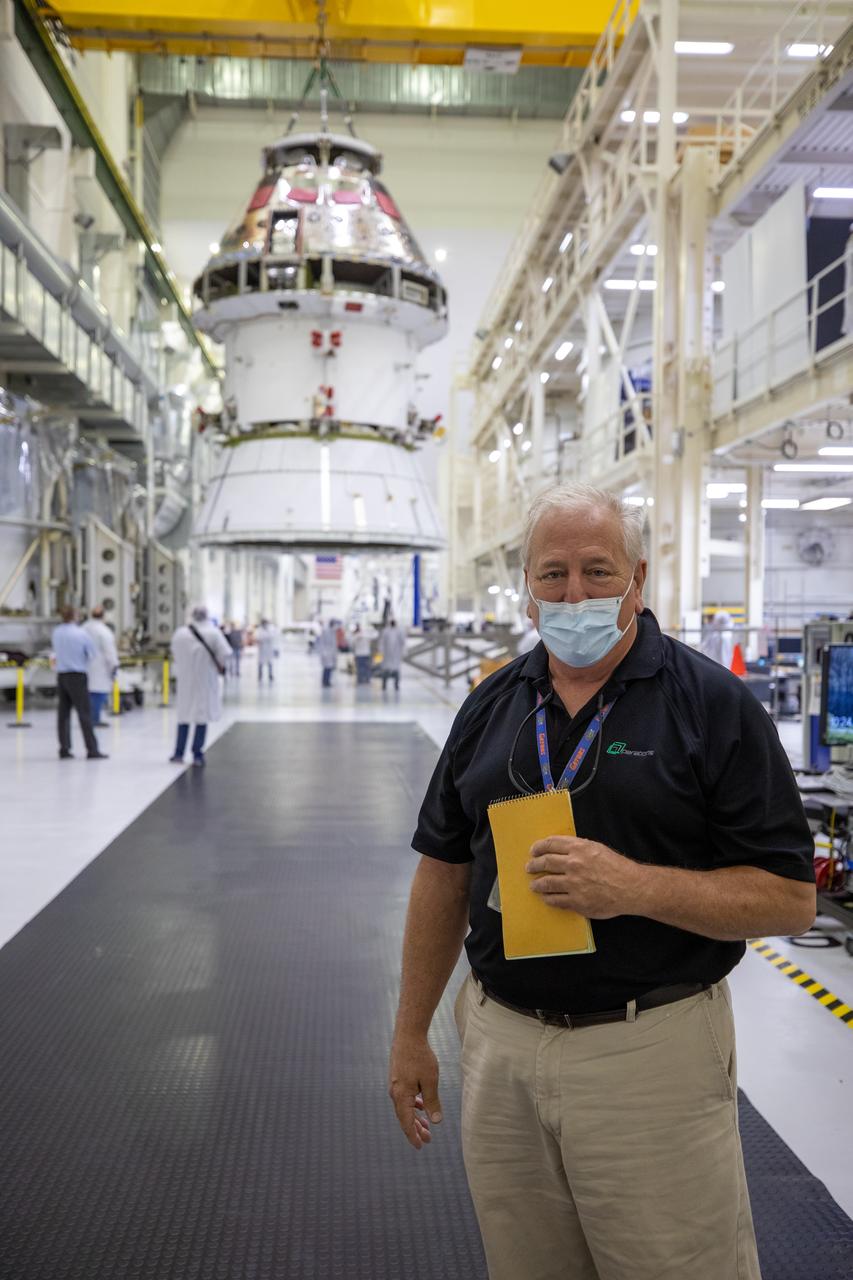

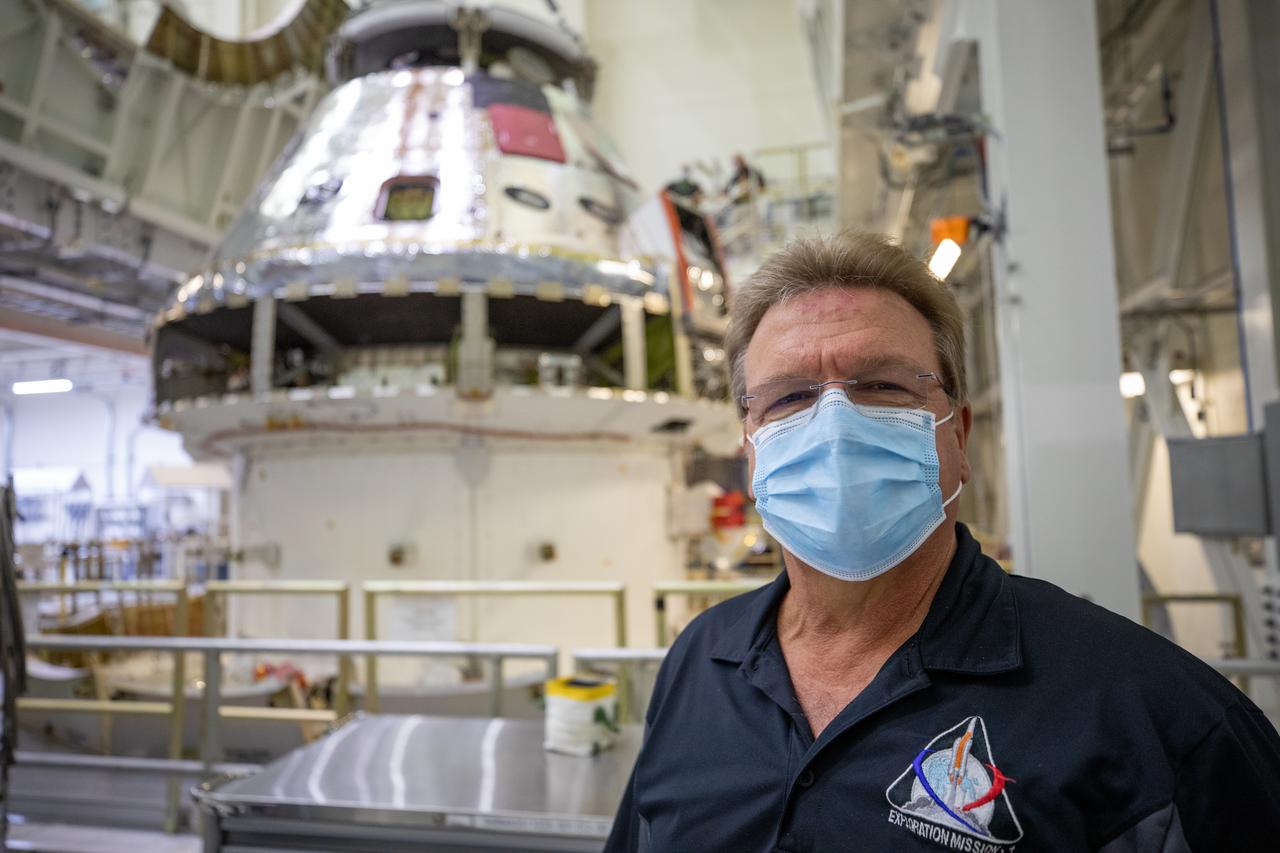
Bill Ruff, Lockheed Martin Safety manager, stands inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. Technicians are working to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the high bay. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
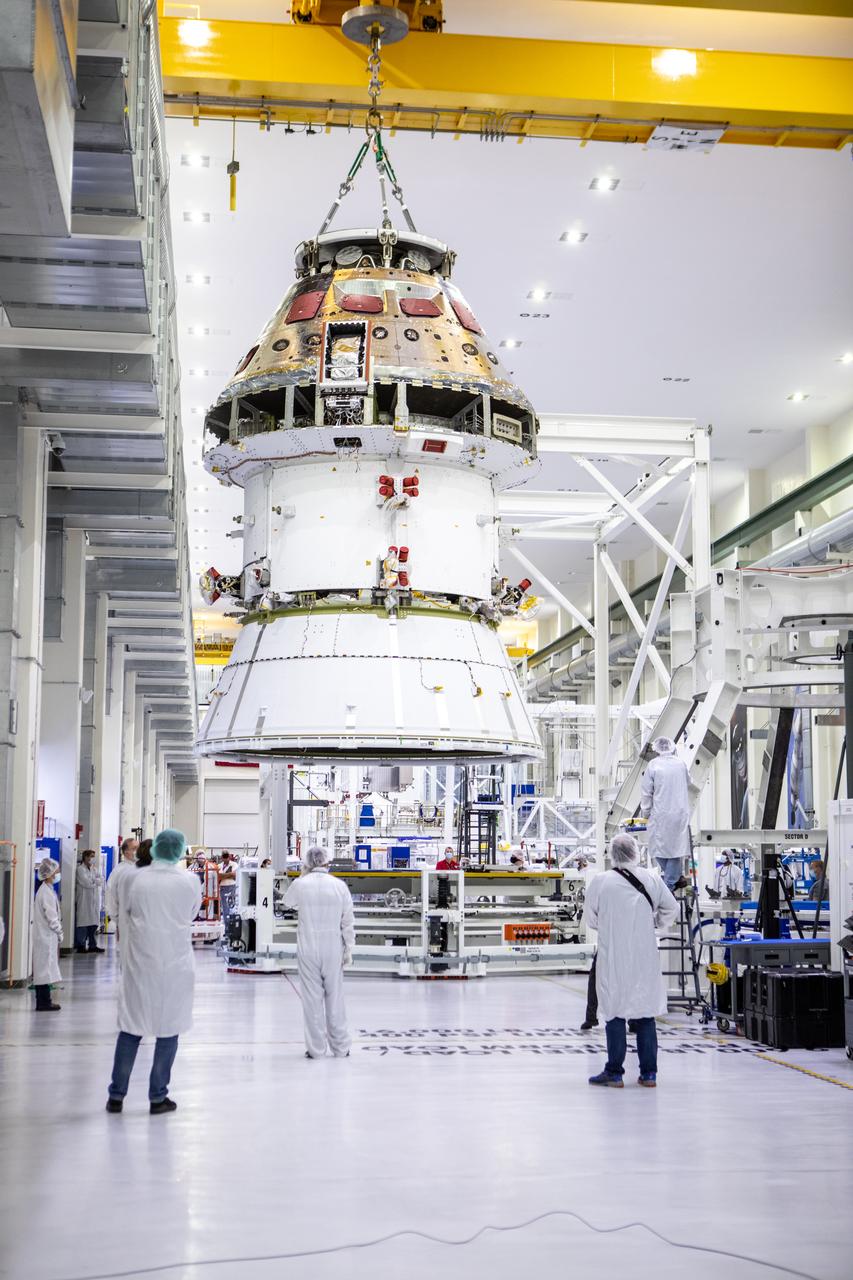

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Assembly, Test and Launch Operations director, is shown inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay in front of the FAST cell as the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is lowered by crane after installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone was completed on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
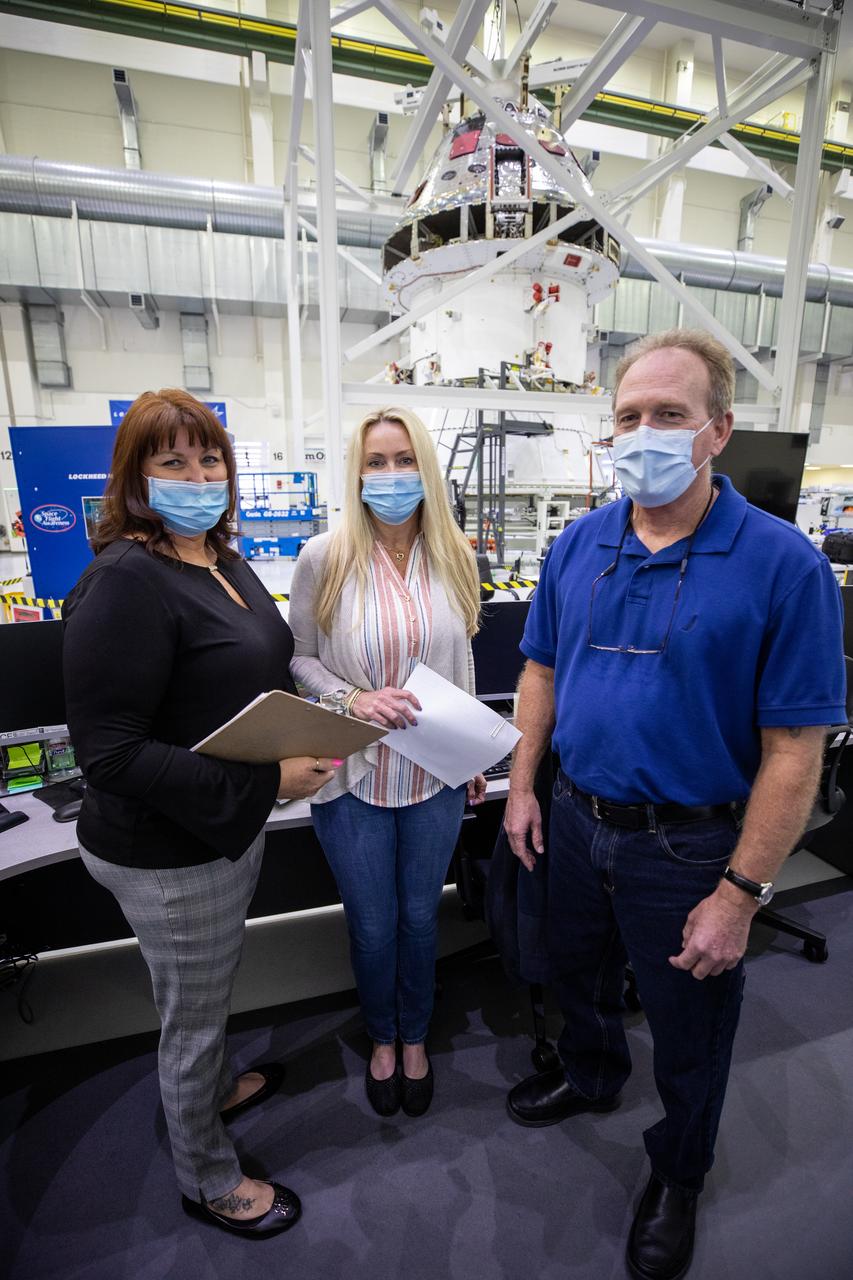

From left, Michelle Clontz and Sharon Prisco, with Lockheed Martin security operations, and Newt Allen, ASRC operations, assist with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
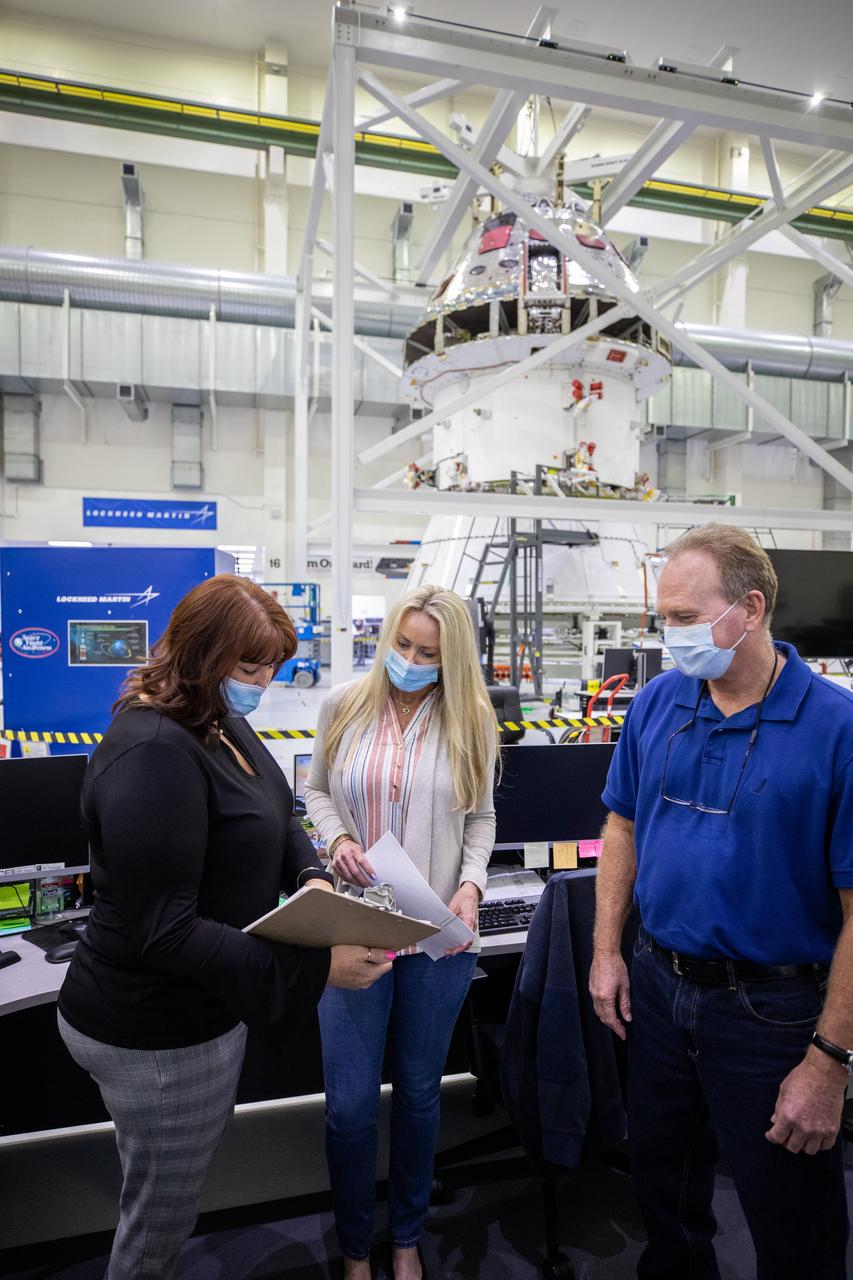

From left, Michelle Clontz and Sharon Prisco, with Lockheed Martin security operations, and Newt Allen, ASRC operations, assist with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
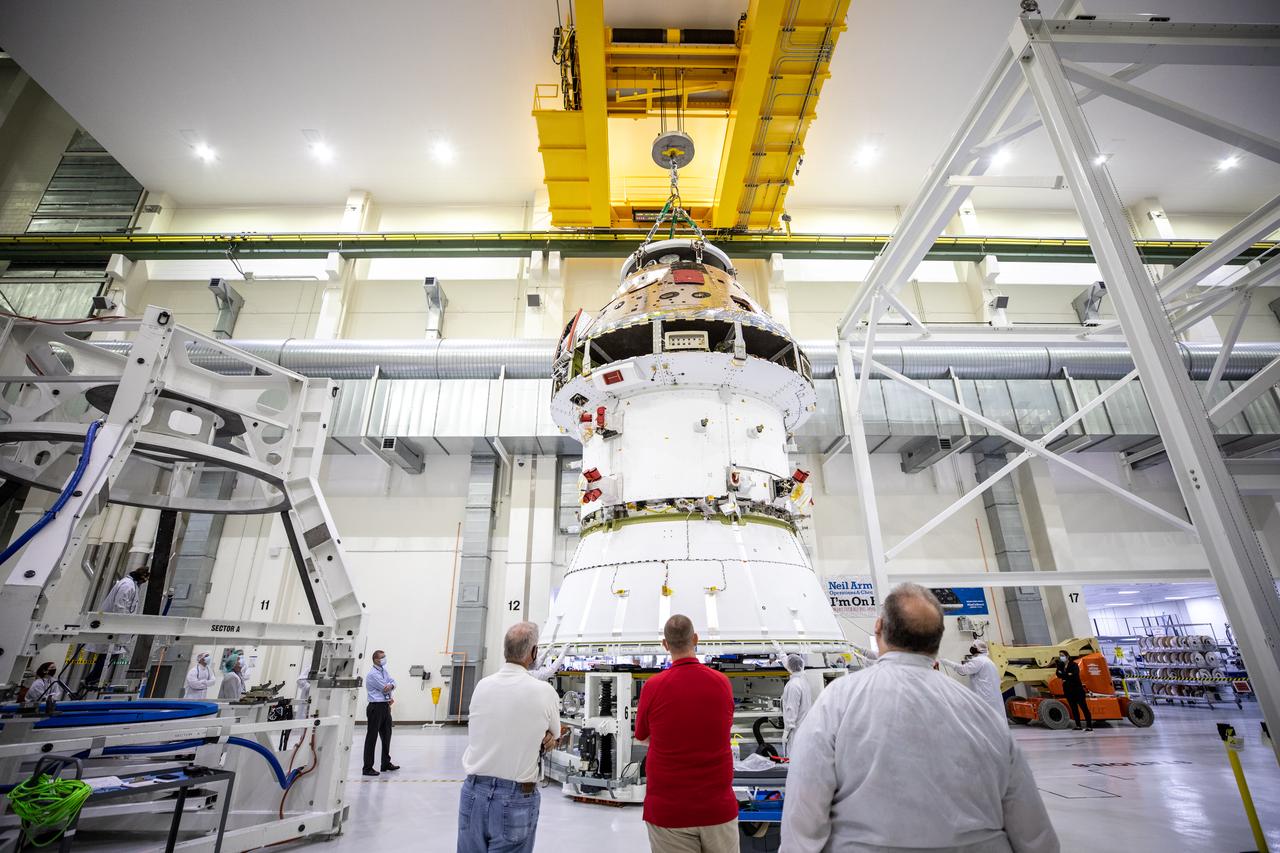

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
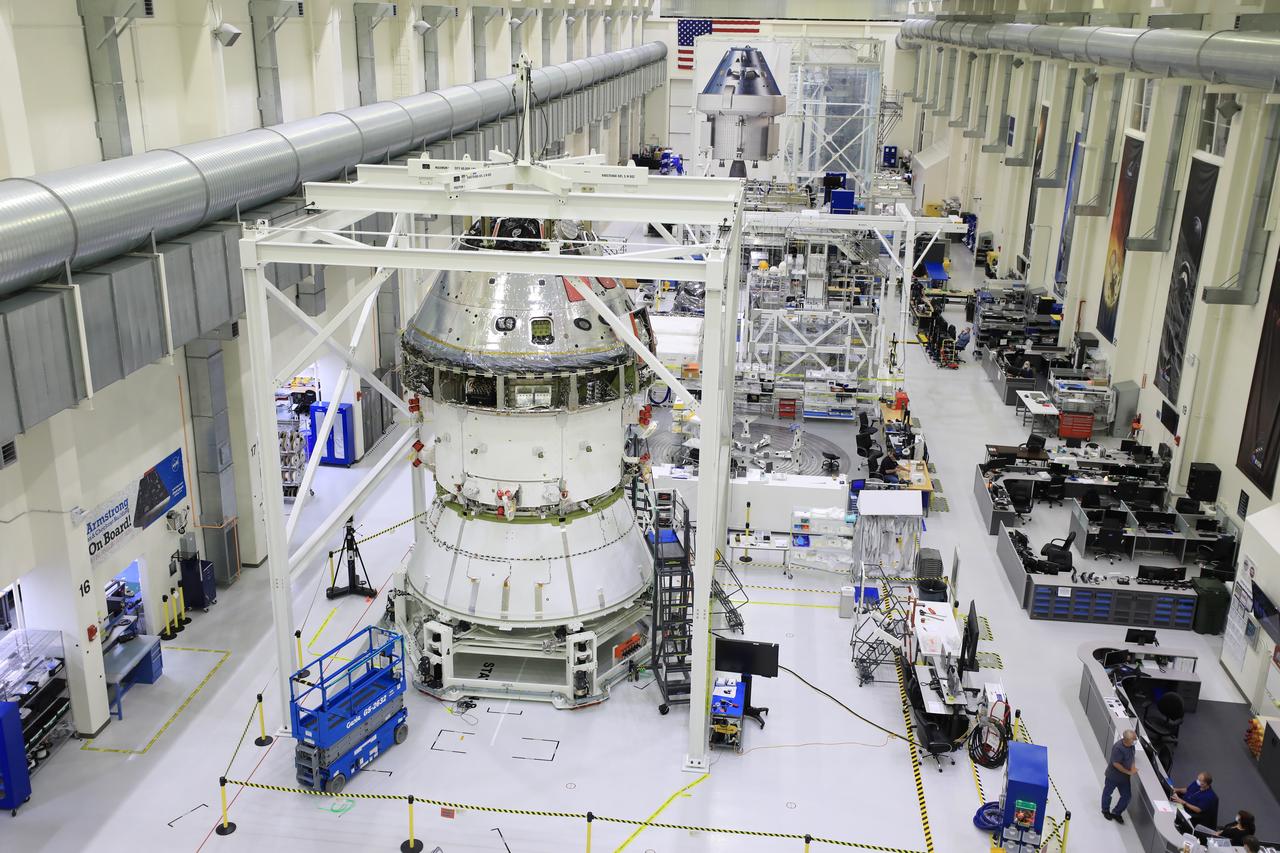
Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to install the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to install the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

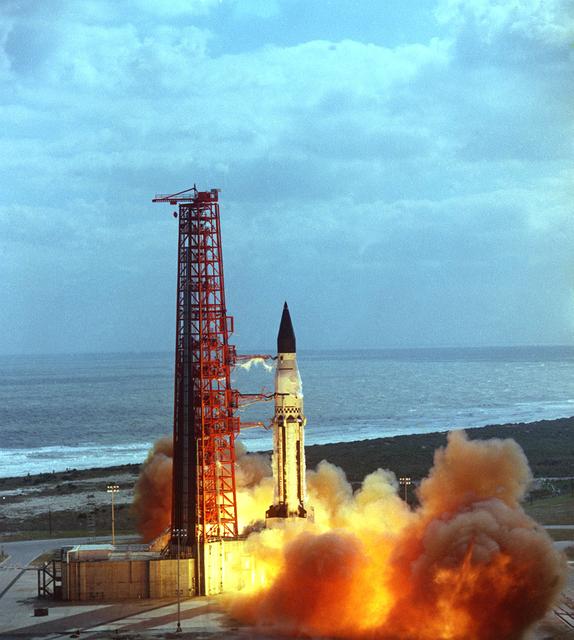
In this photo, Dr. von Braun anxiously awaits the launch of the Saturn I vehicle (SA-8) in the Launch Complex Control Center at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 1965. The SA-8 mission made the first night launch and deployed the Pegasus II micro meteoroid detection satellite.
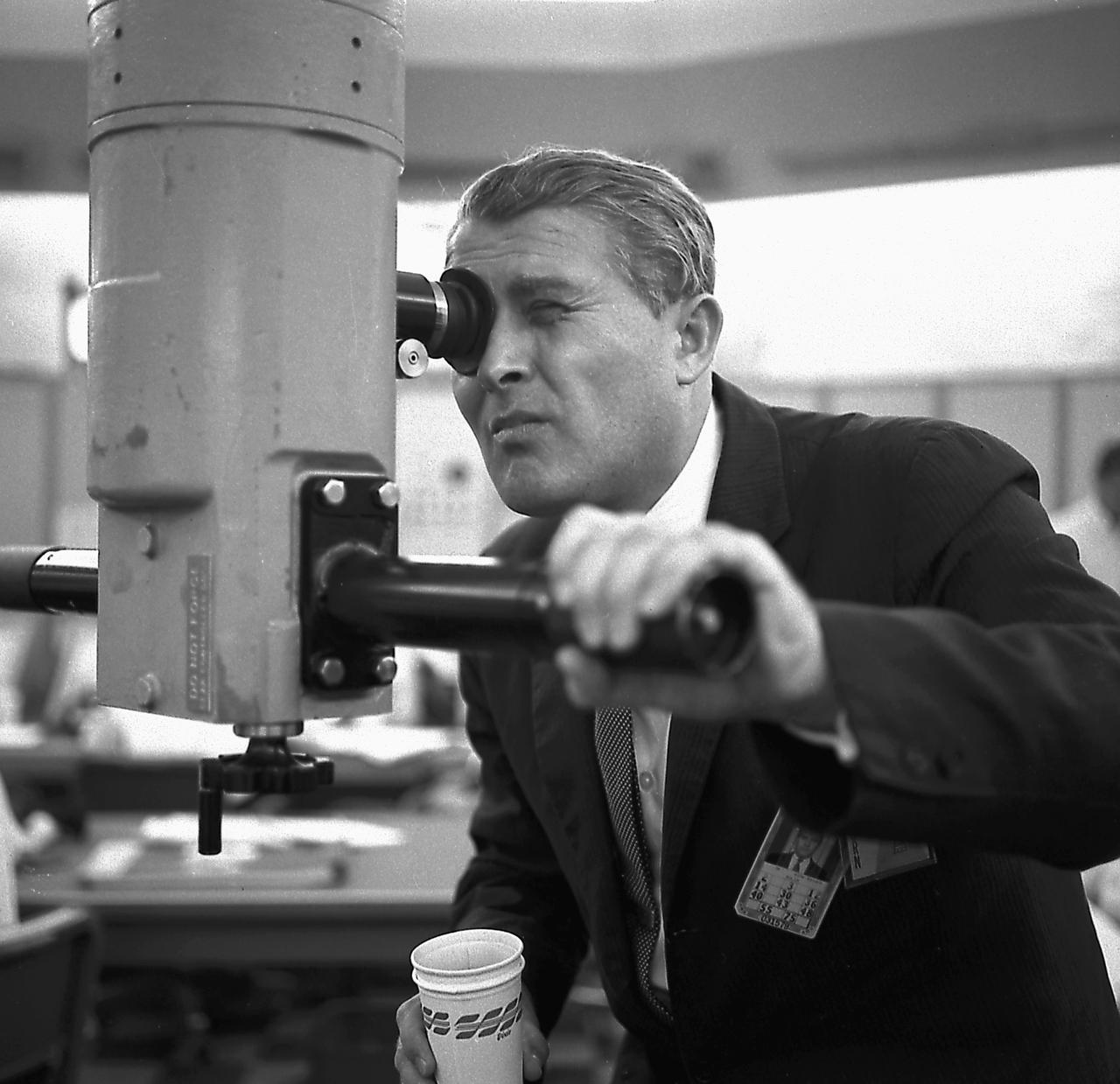

Dr. von Braun watches the Saturn 1 (SA-1) launch through a scope from the blockhouse 34 on October 27, 1961. The SA-1 was the first launch of Saturn launch vehicles developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. von Braun. The flight demonstrated the validity of the clustered engine concept and launched dummy upper stages.
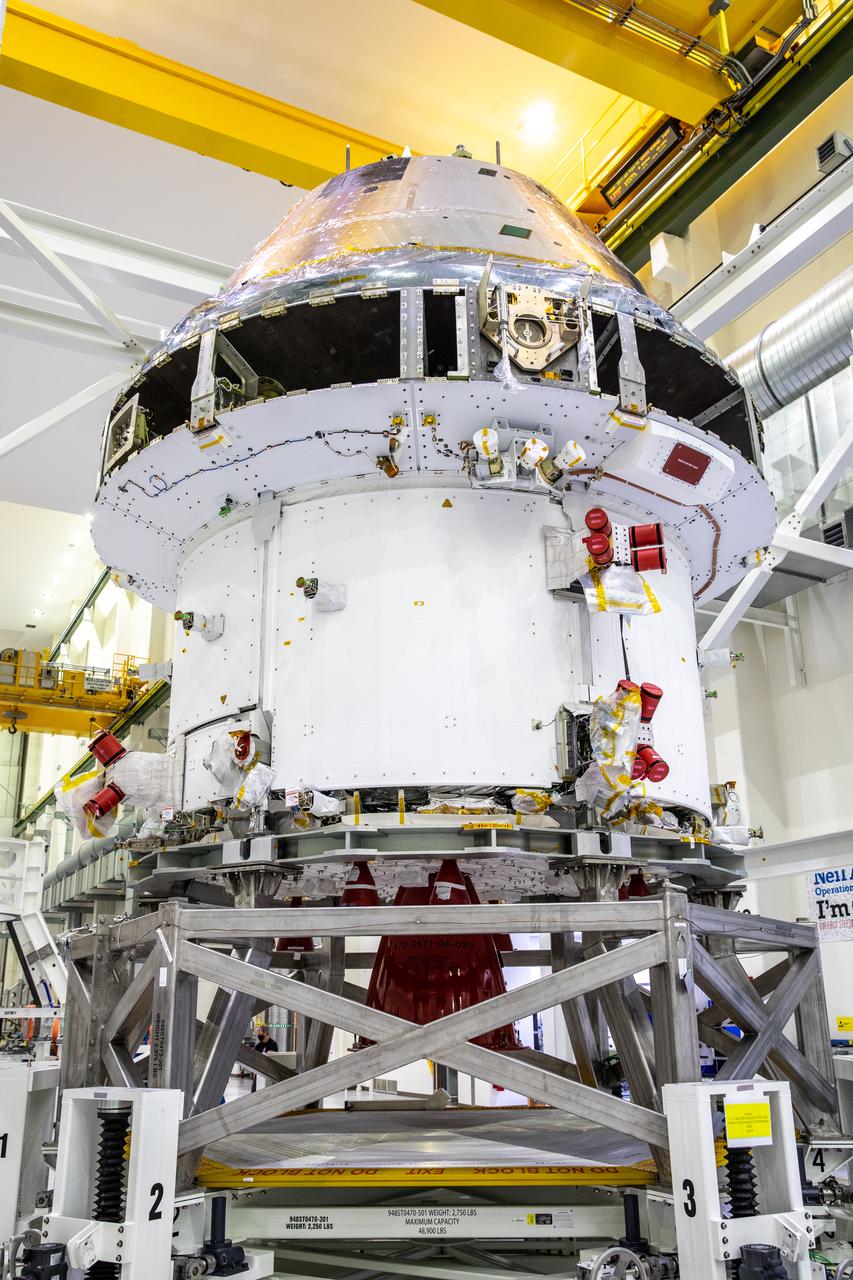

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
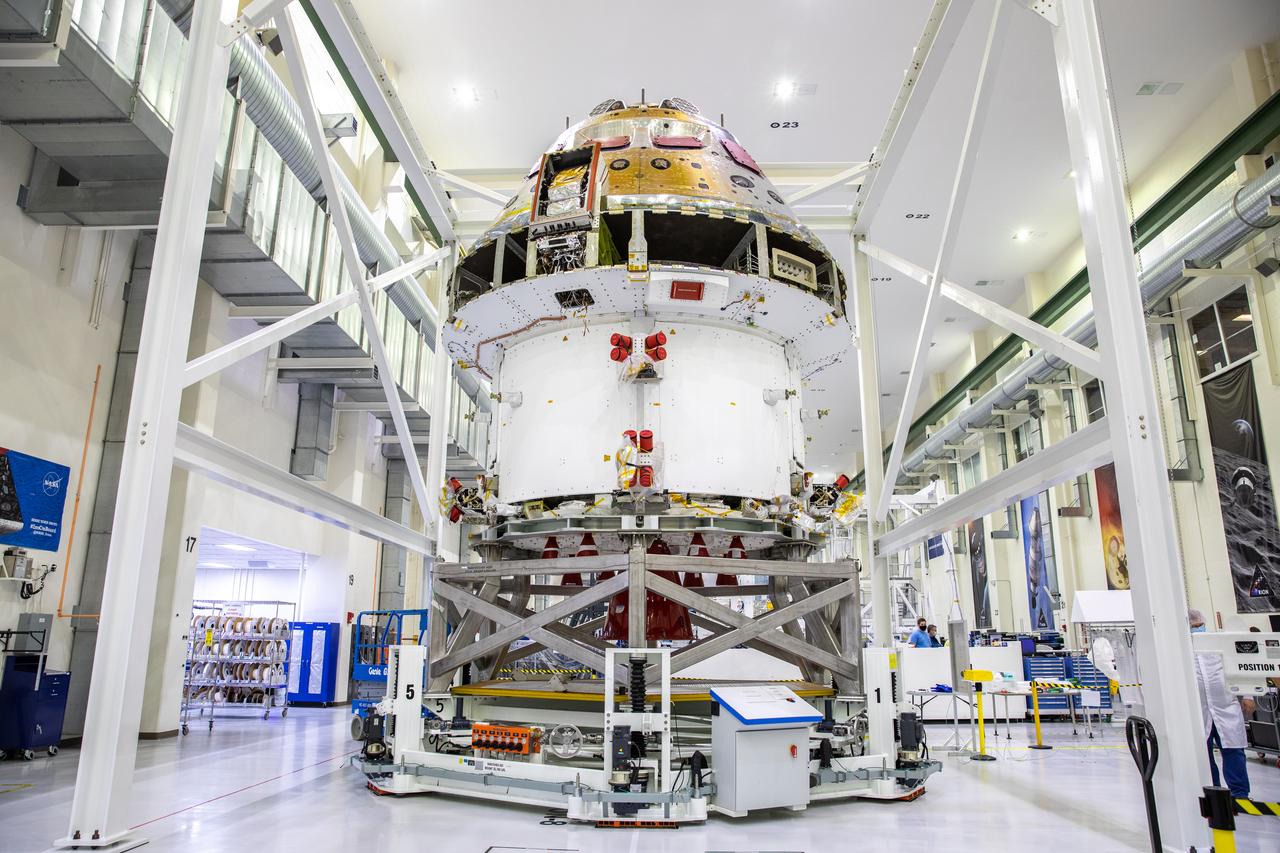

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
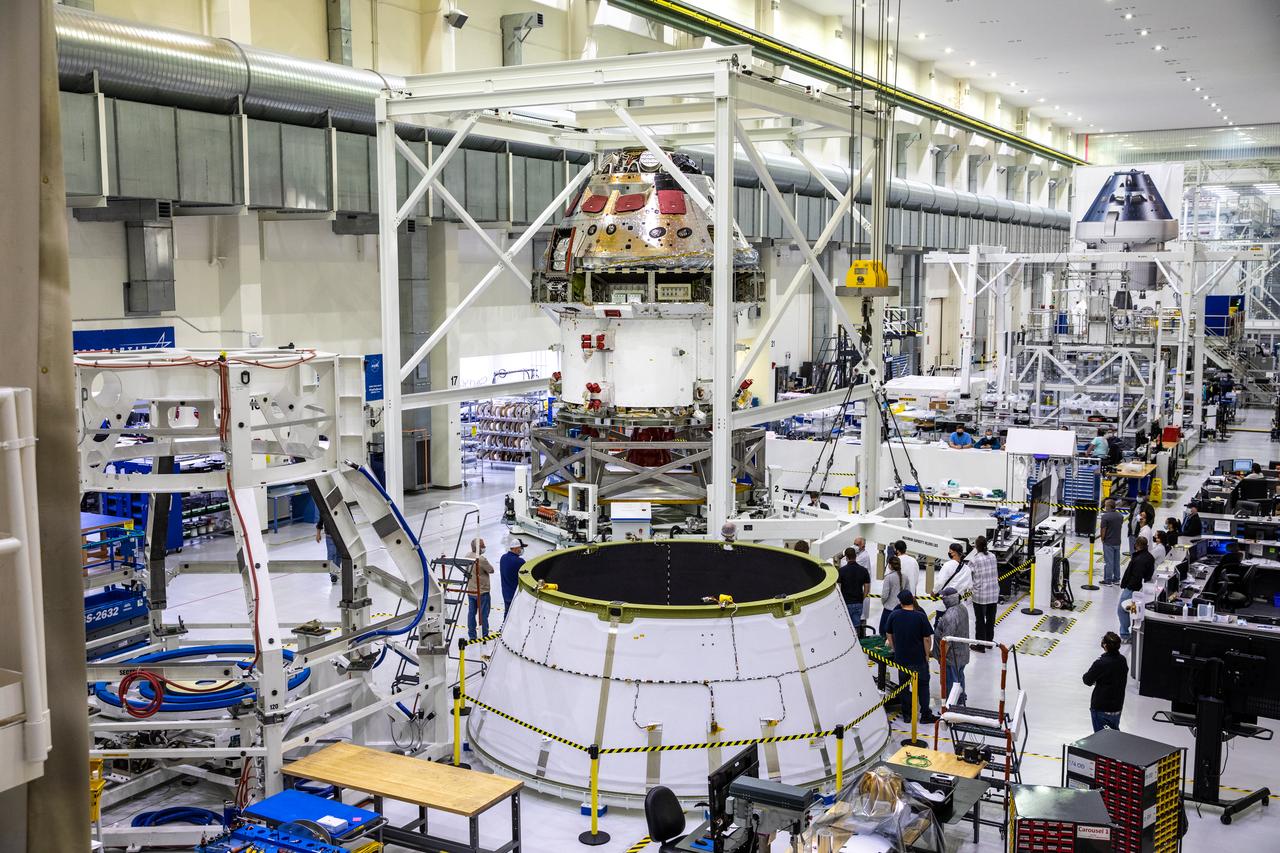

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
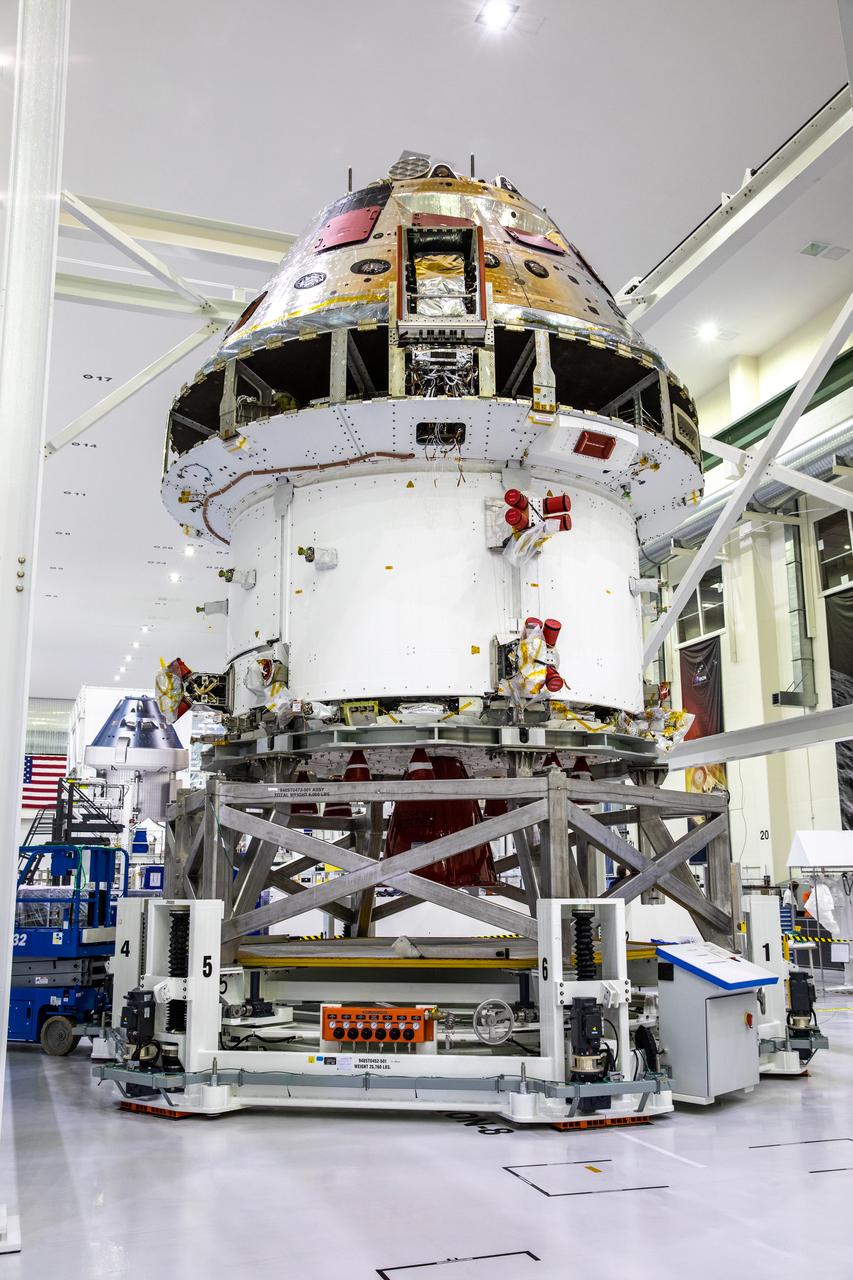

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

FORWARD END OF SATURN S-1B STAGE (SA-T) NEAR PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA
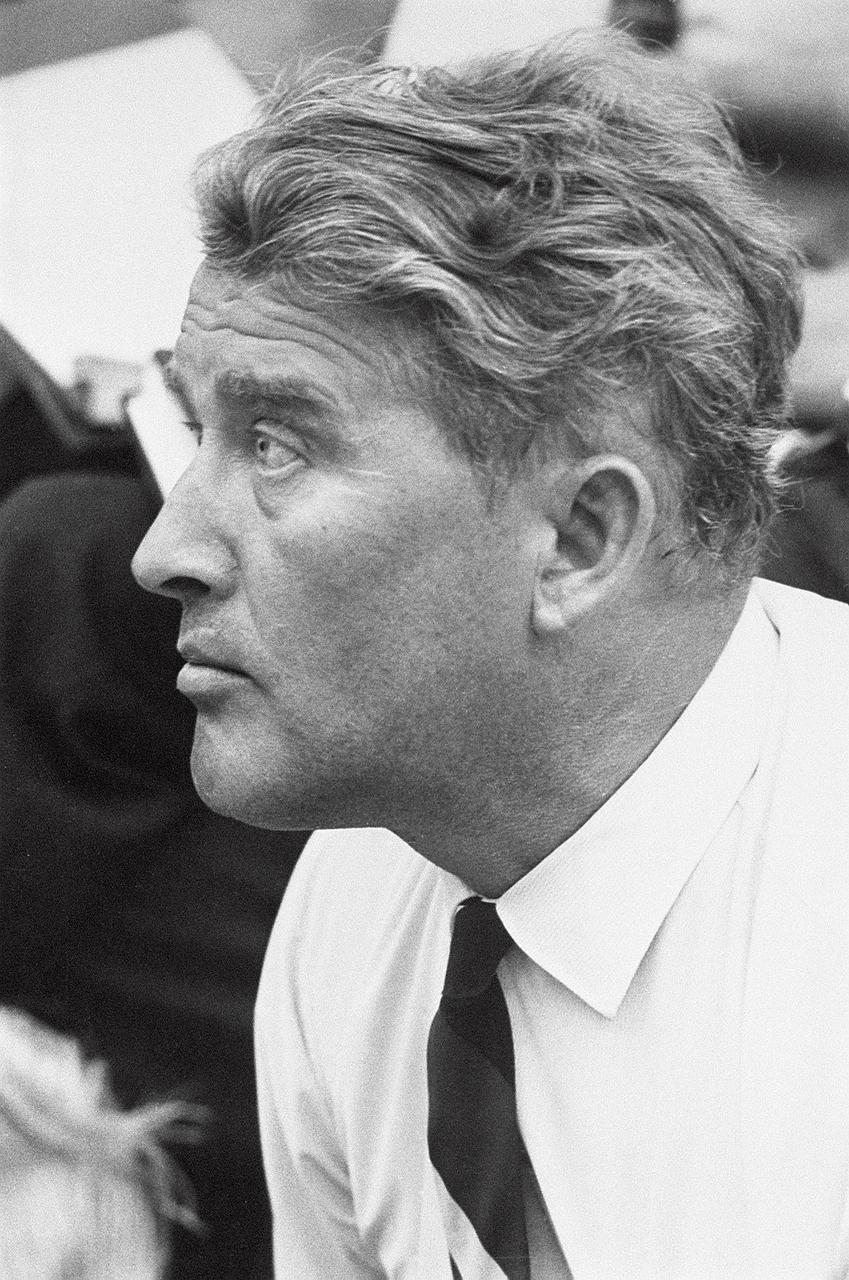

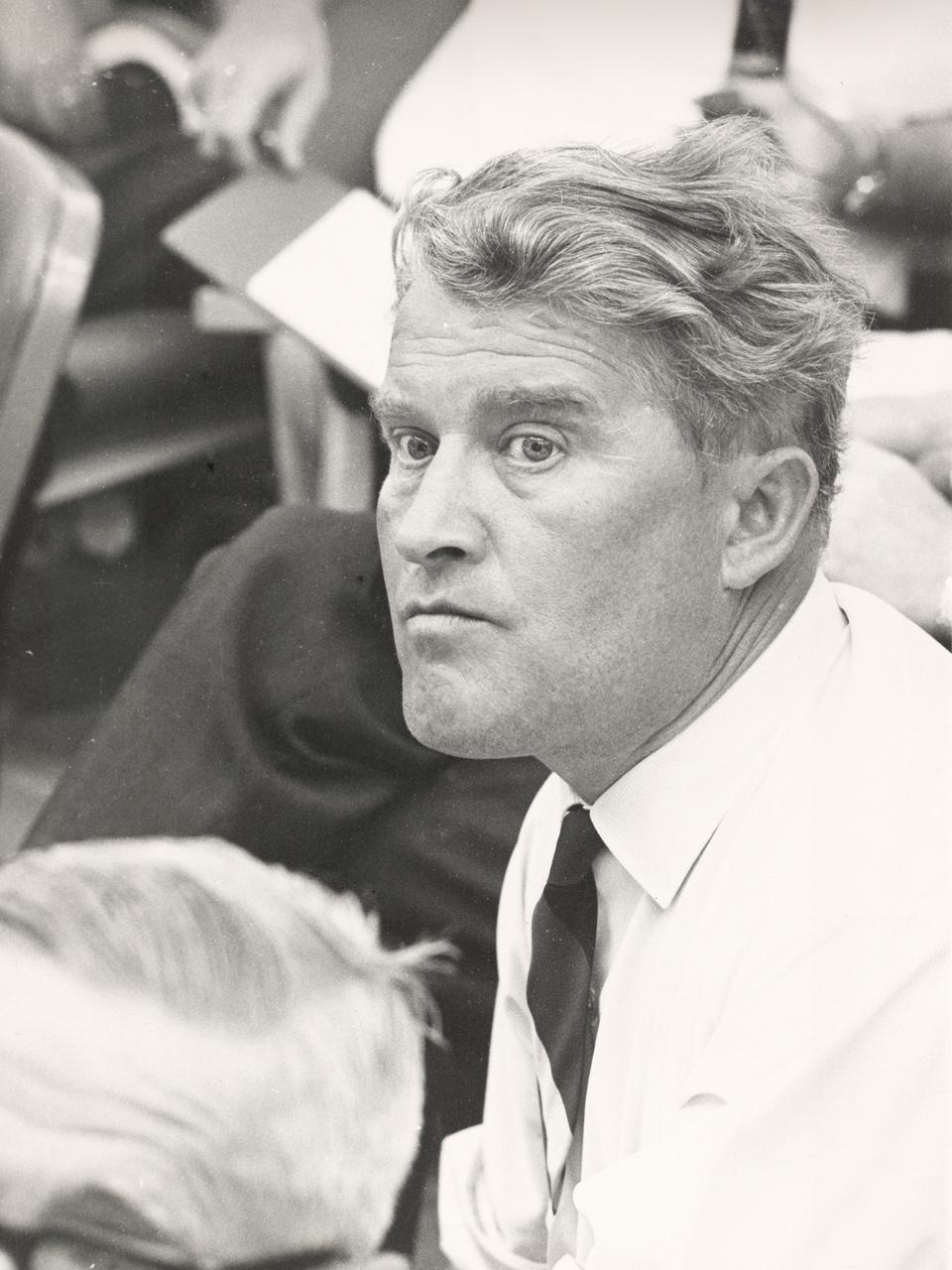
This profile of Dr. von Braun was taken in the Launch Complex Control Center at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the launch of Saturn I vehicle (SA-8) on May 25, 1965.
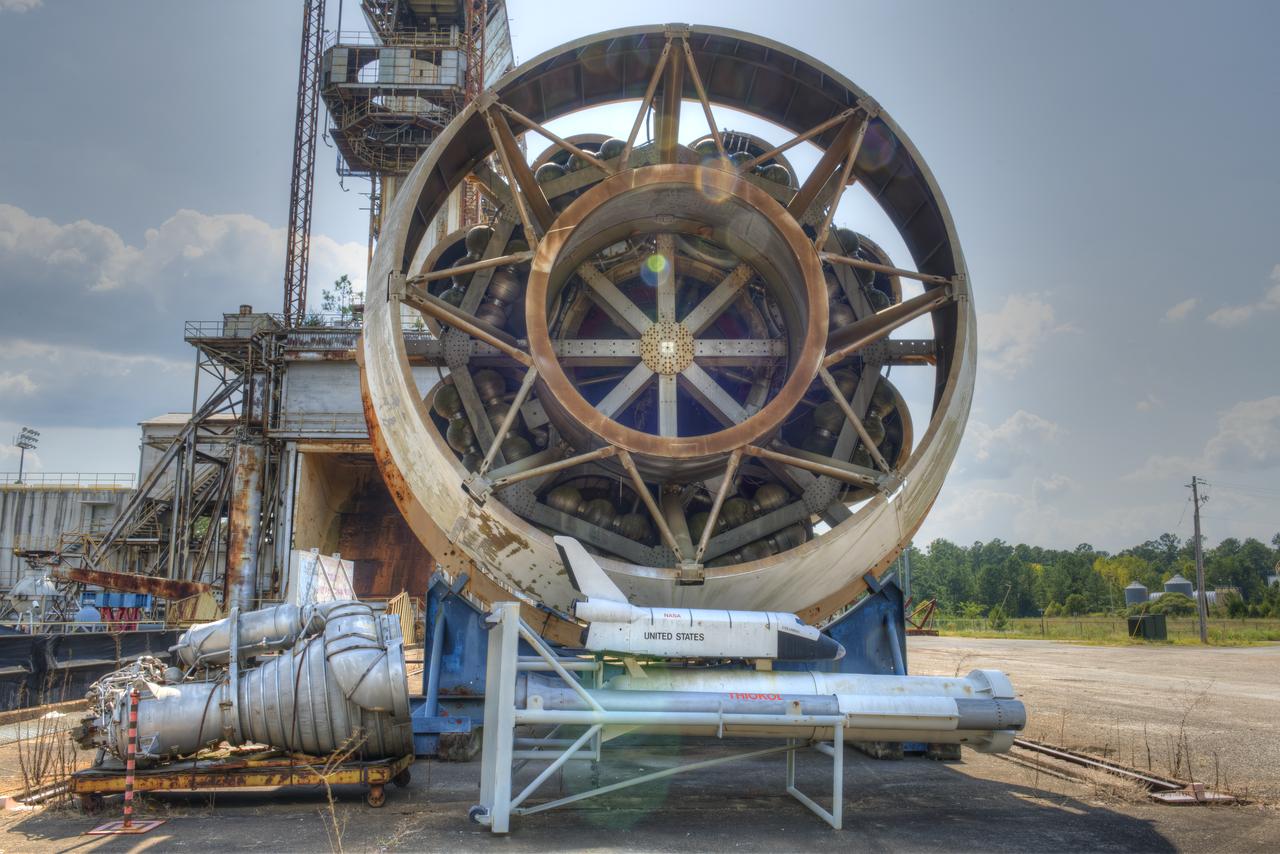

FORWARD END OF SATURN S-1B STAGE (SA-T) NEAR PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA

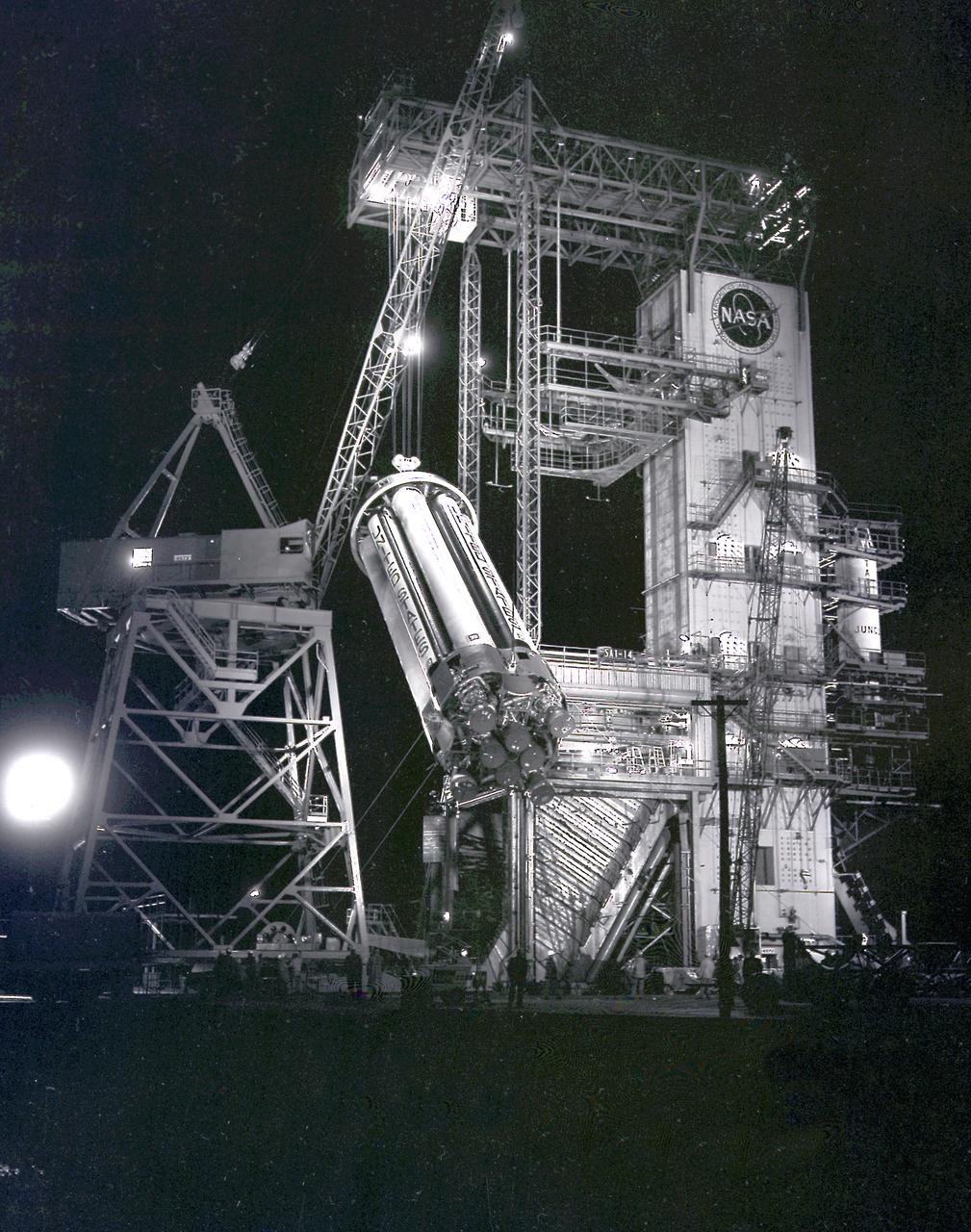
Pegasus-1, meteoroid detection satellite, installed on Saturn I (SA-9 mission) S-IV stage, January 13, 1965. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth. SA-9 was launched on February 16, 1965 and the Pegasus-1 satellite was the first operational payload for Saturn I.
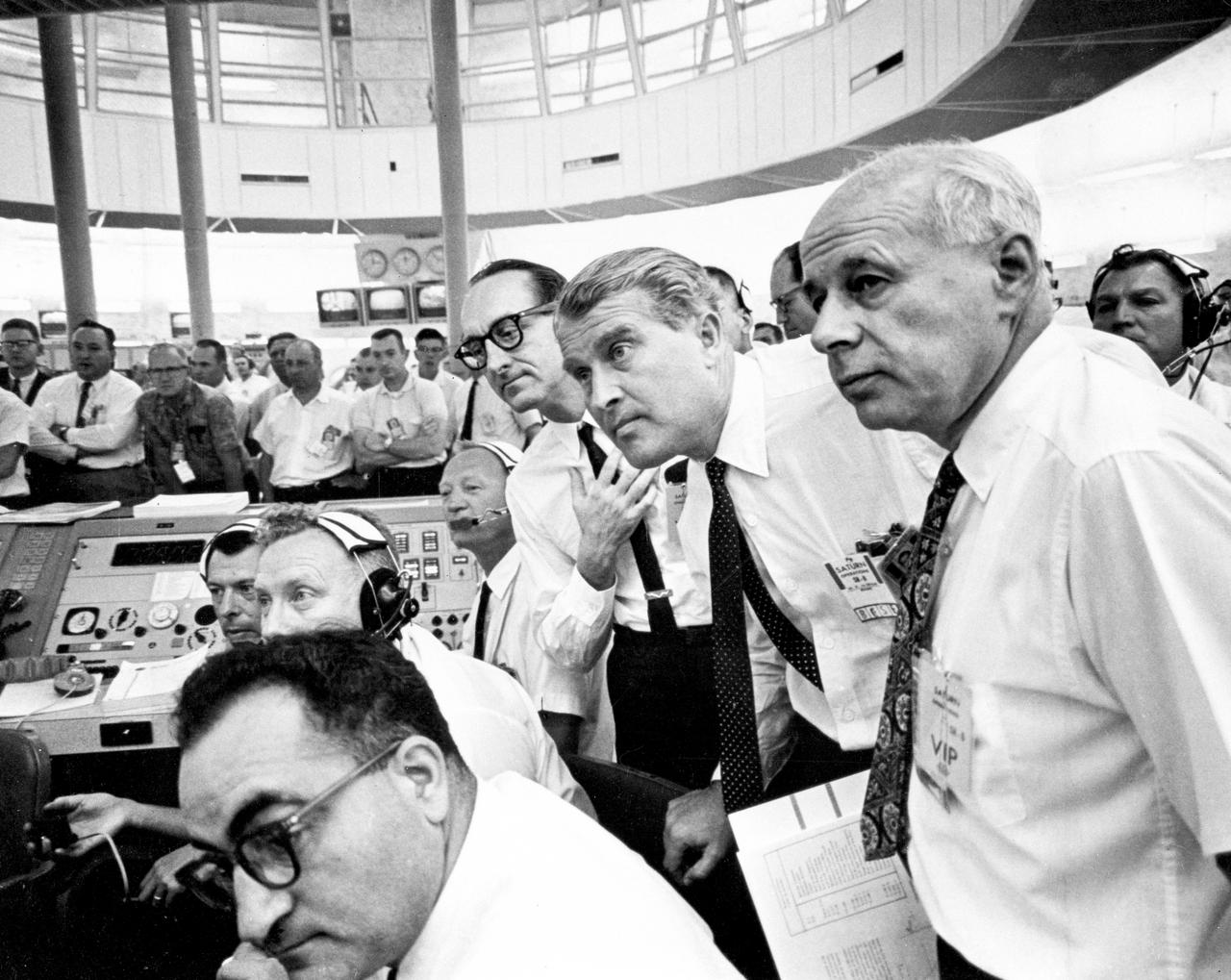

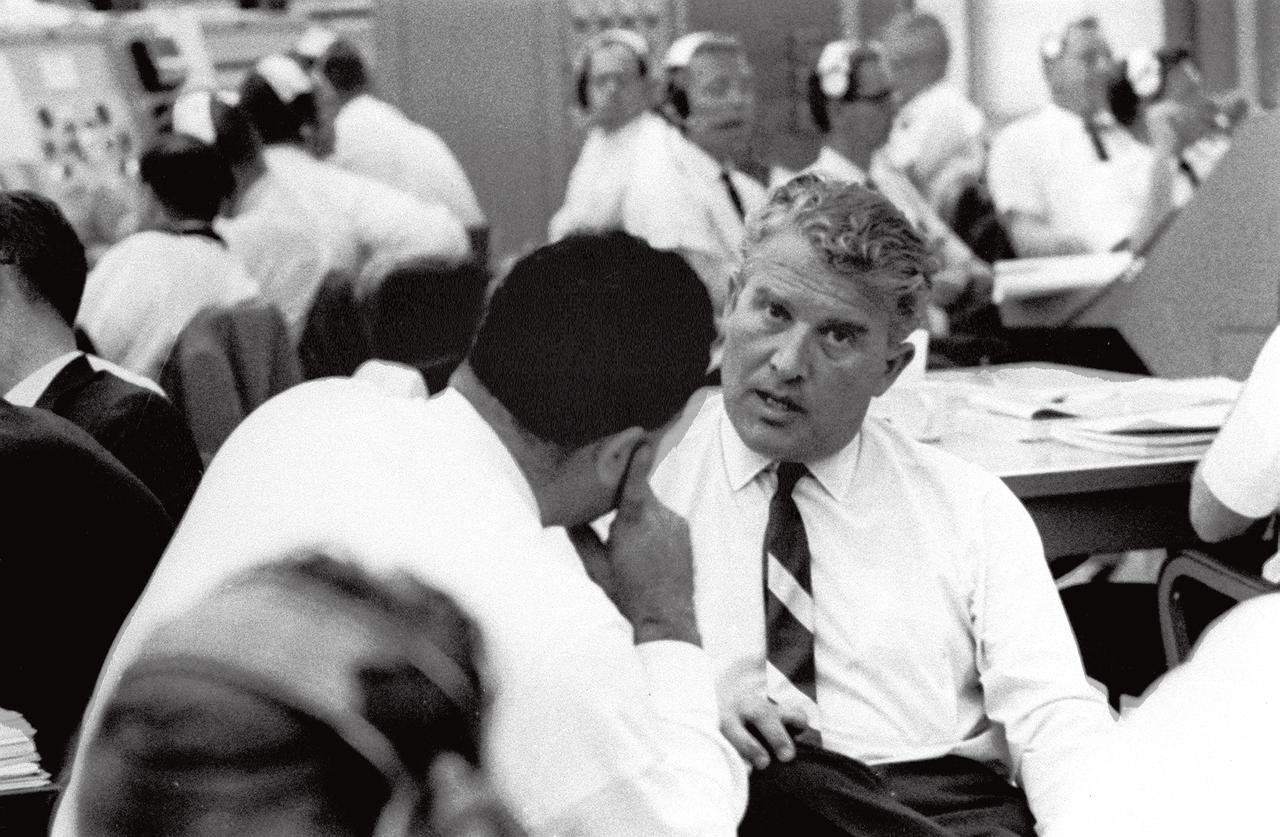
This photograph depicts an intense moment during the SA-6 launch at the Firing Room. Dr. von Braun, Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) is at center; to his left is Dr. George Mueller, Associate Director for Marned Space Flight; and far right is Dr. Eberhard Rees, Director for Research and Development, MSFC. The SA-6, the sixth flight of the Saturn 1 vehicle, launched a S-IV stage (a second stage) and an Apollo boilerplate spacecraft.
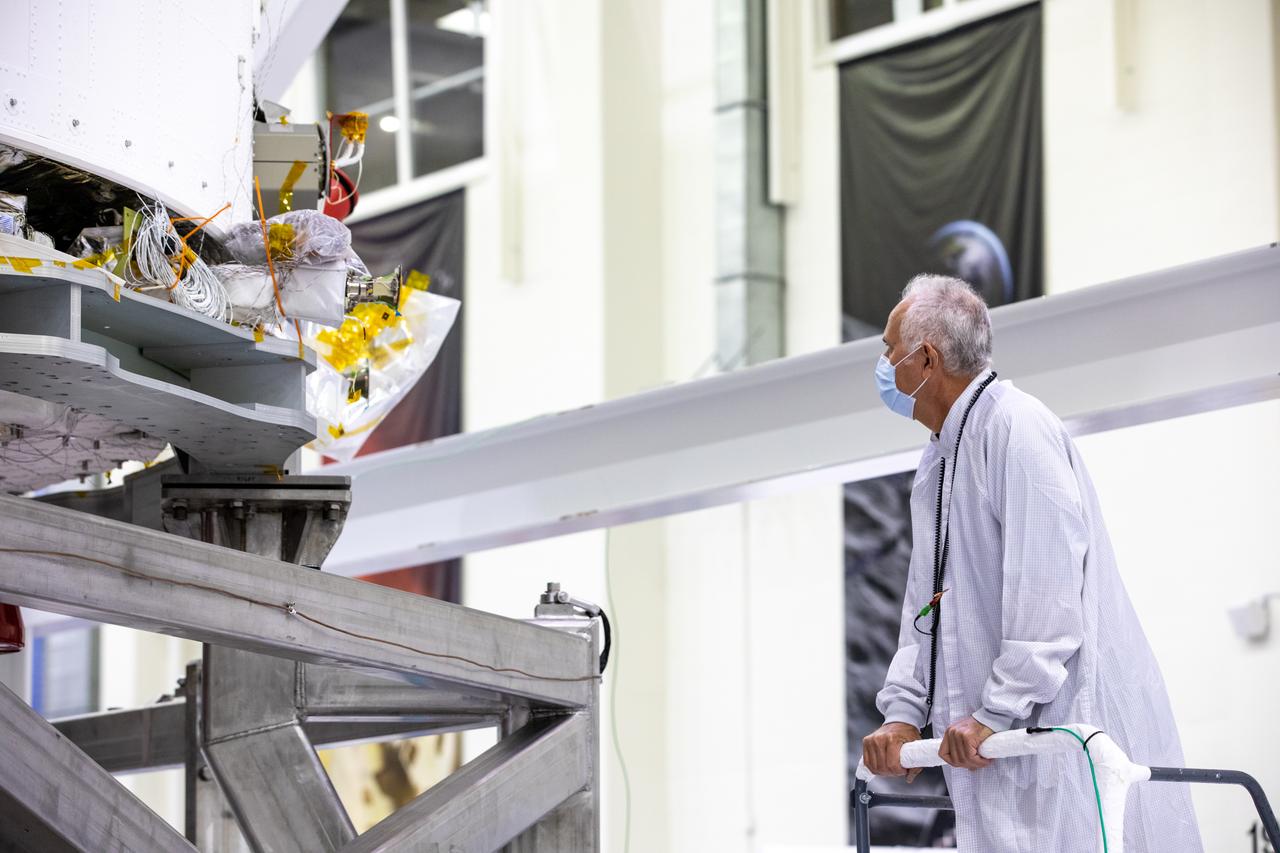

Vince Nichols, Lockheed Martin Floor Operations, inspects the Artemis I Orion spacecraft in preparation for installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
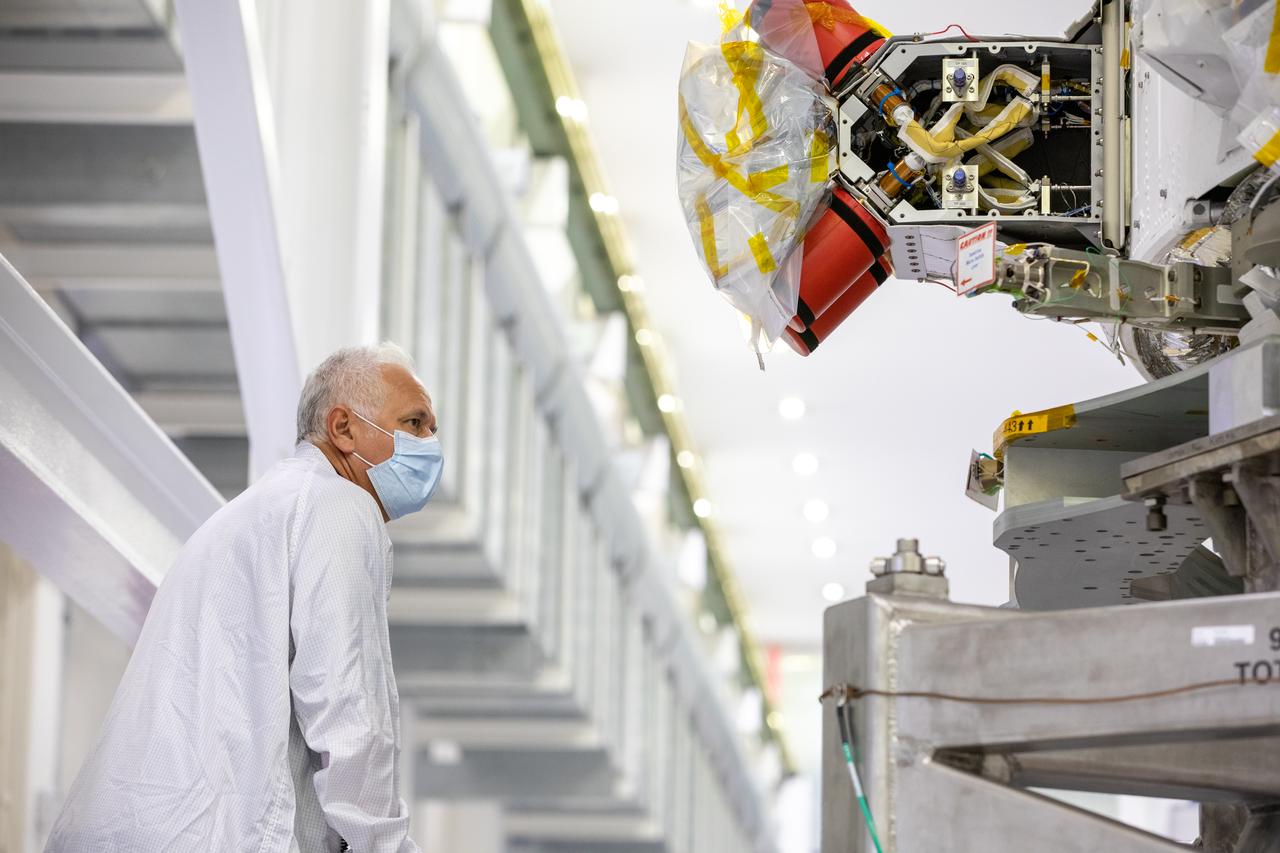

Vince Nichols, Lockheed Martin Floor Operations, inspects the Artemis I Orion spacecraft in preparation for installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
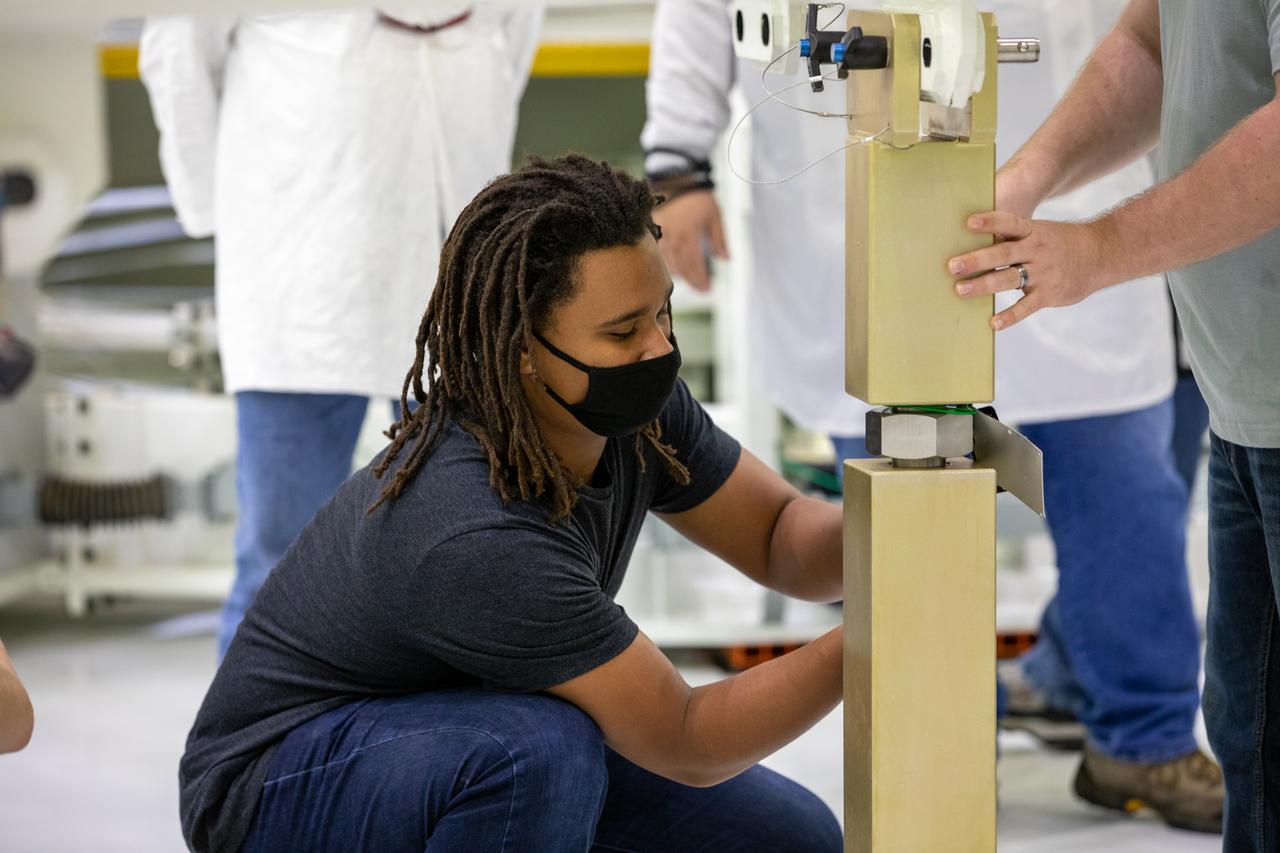

ASRC technician Nathaniel Bowman works to ready the Super Station fixture that will support the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
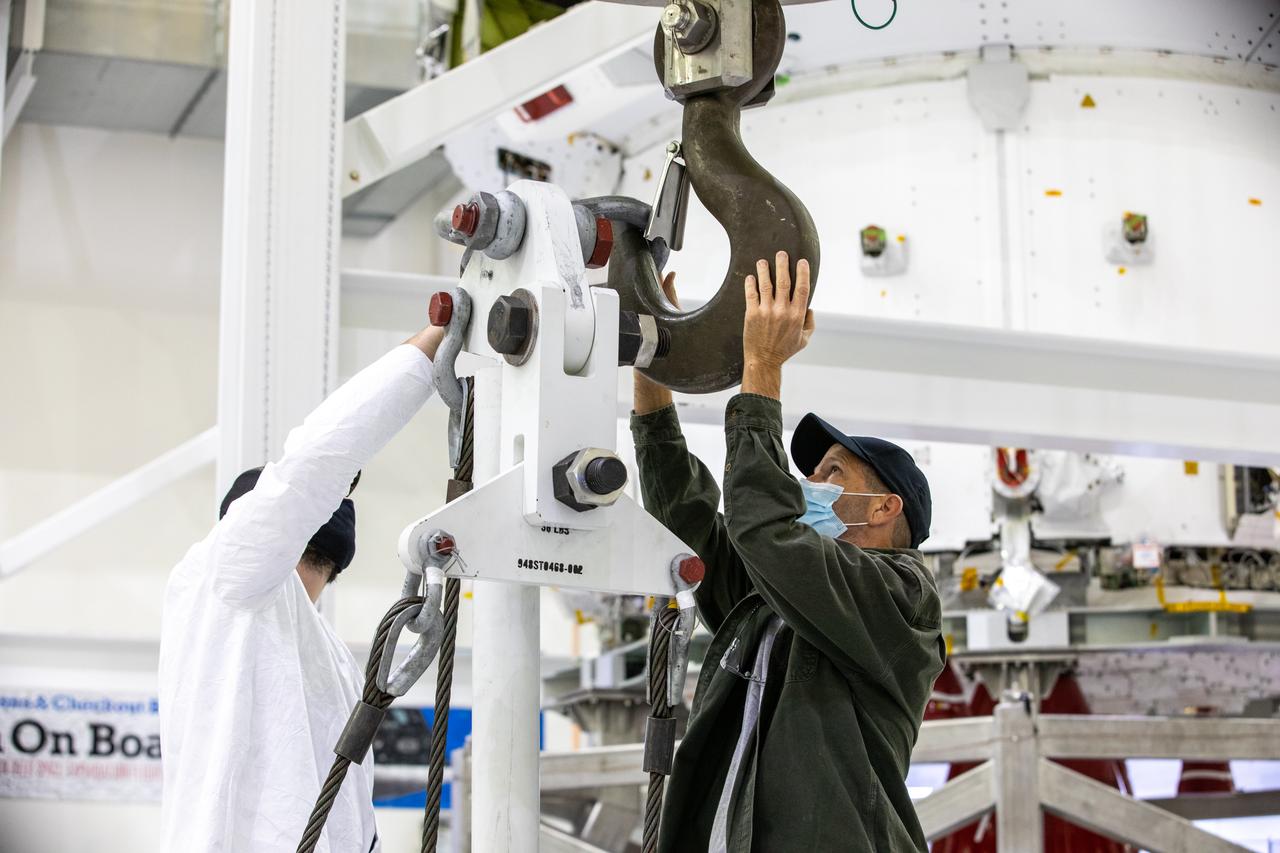

ASRC technicians Dustin Swickert, to the left. and John Nesbitt, to the right, work to attach the crane that lifts the Artemis I Orion spacecraft in preparation for installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
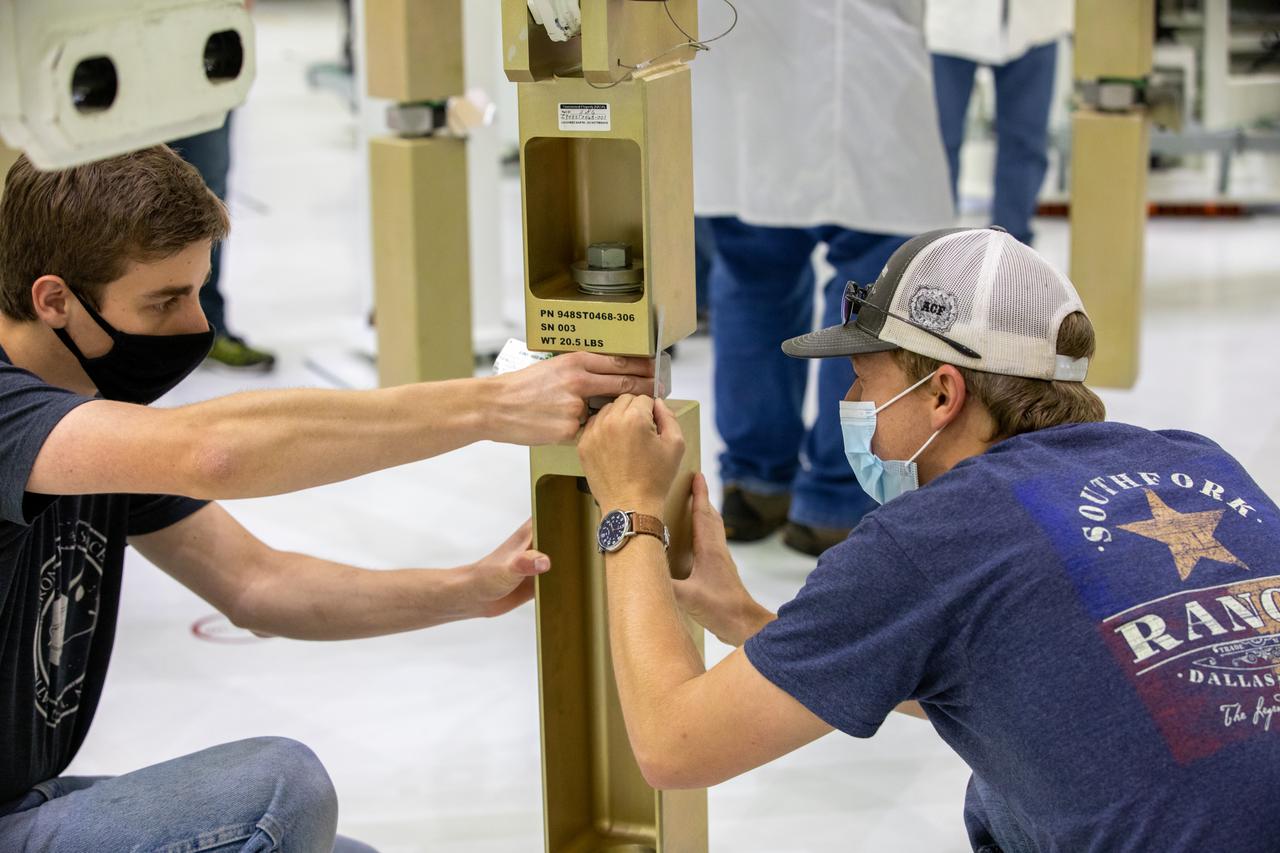

ASRC technicians William Coddington, to the left and Cameron Fitch, to the right, work to ready the Super Station fixture that will support the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
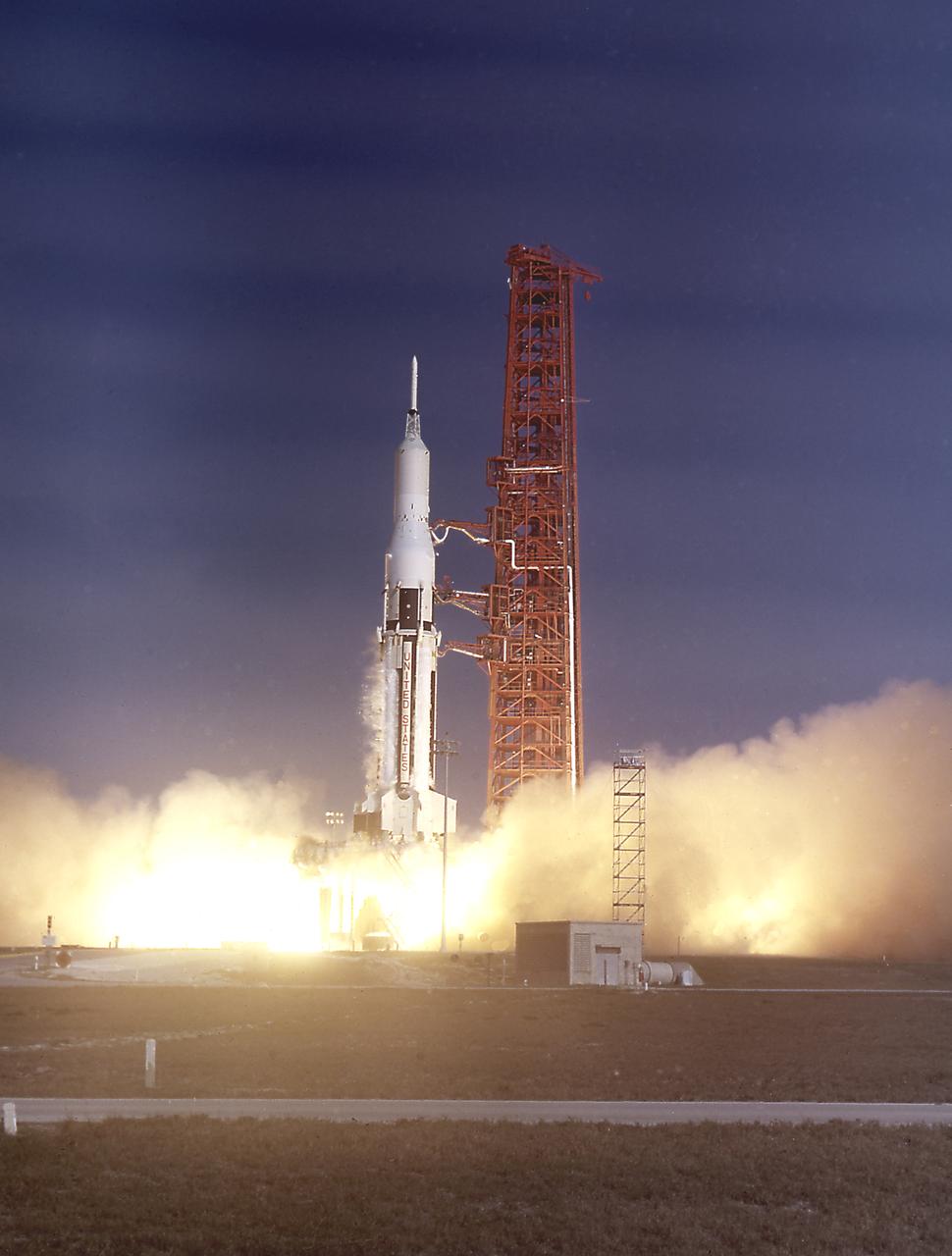

The SA-9 (Saturn I Block II), the eighth Saturn I flight, lifted off on February 16, 1965. This was the first Saturn with an operational payload, the Pegasus I meteoroid detection satellite. SA-9 successfully deployed the Pegasus I, NASA's largest unmarned instrumented satellite, into near Earth orbit.
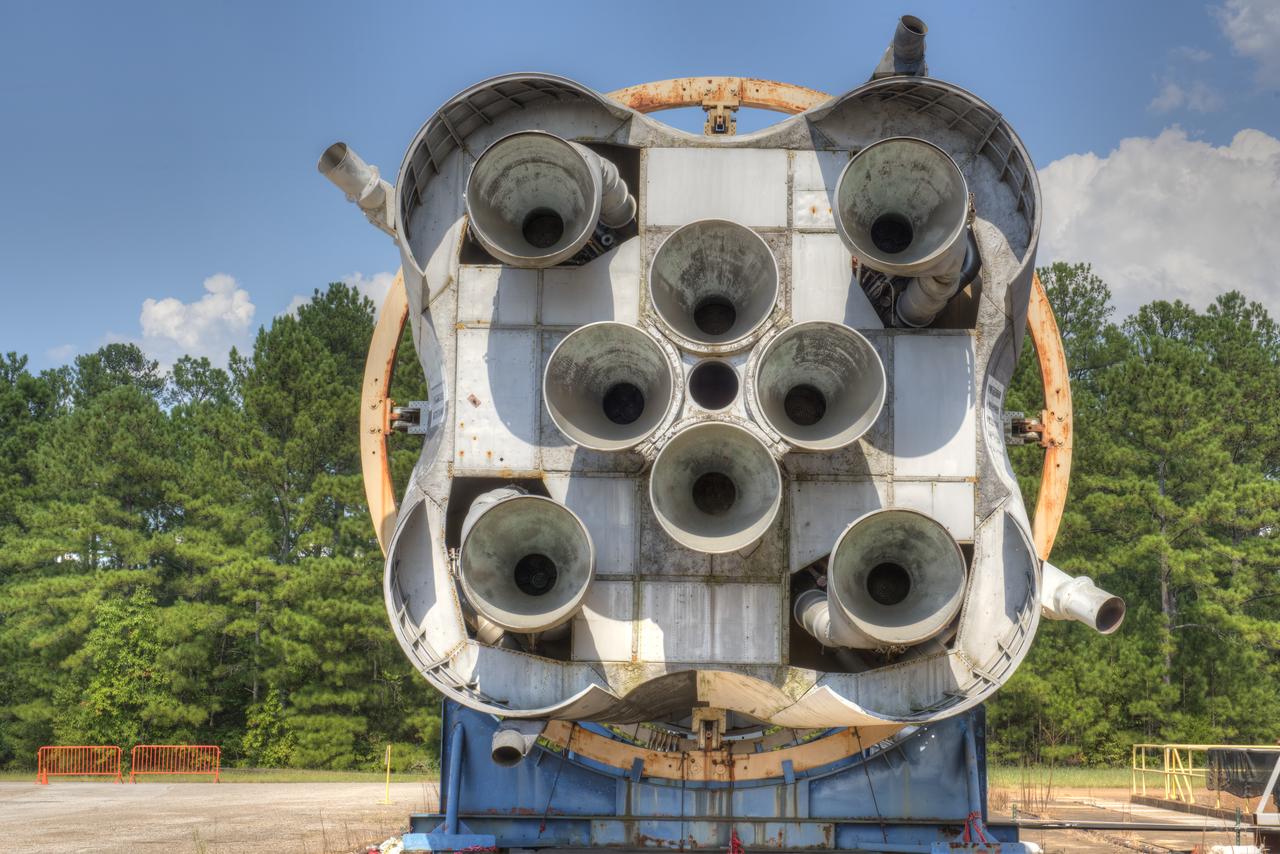

CLOSE-UP OF AFT END OF SATURN S-1B STAGE (SA-T) NEAR PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA.
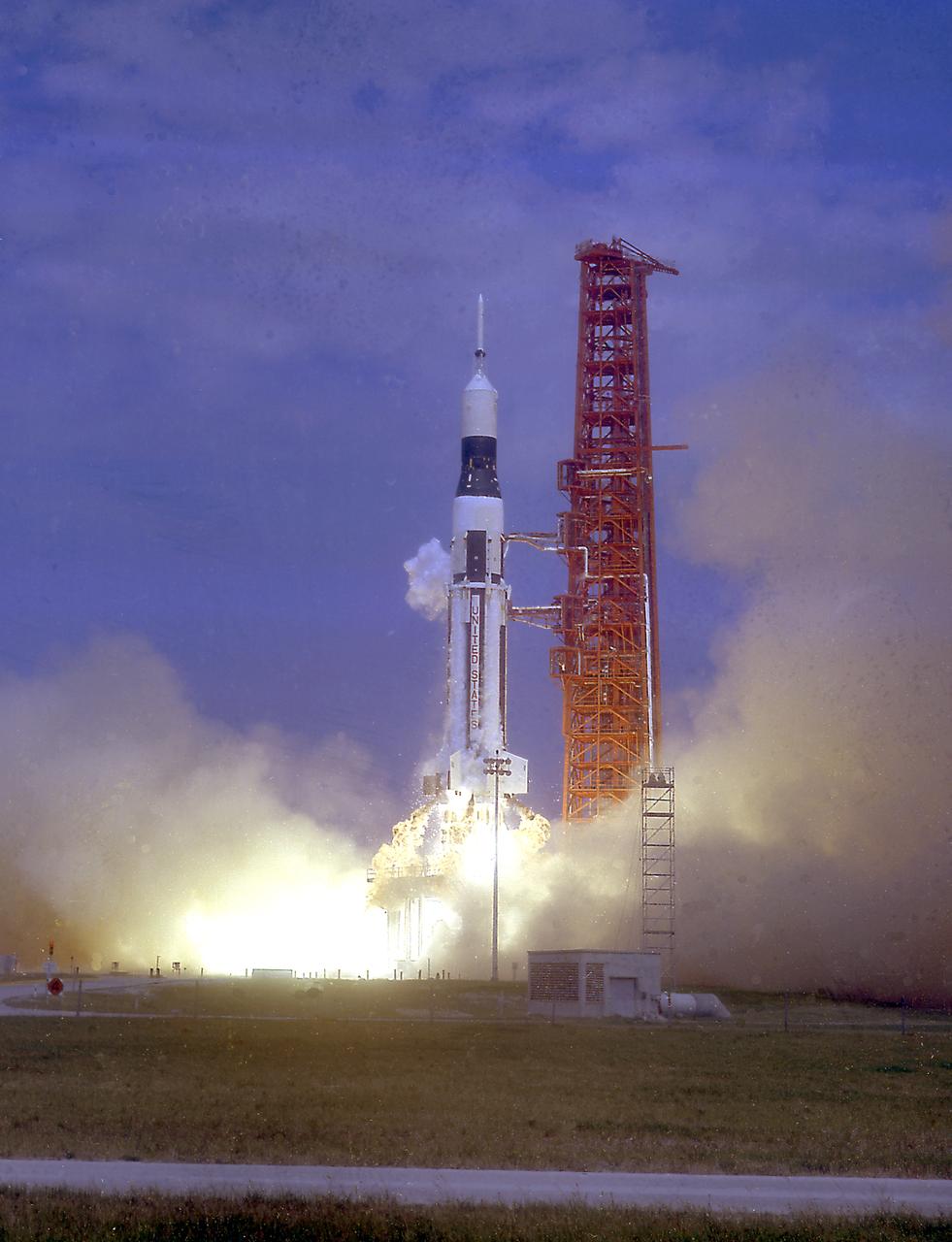

The launch of the SA-7 (Saturn I Block II) was on September 18, 1964. The SA-7 mission was the second orbital flight of the S-IV stage (second stage) with the payload consisting of the Apollo command and service module's instrument unit. The Saturn I Block II vehicle had two live stages, and were basically in the two-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. While the tank arrangement and the engine patterns were the same, there were marked changes between the Block I and II versions. The first stage (S-I stage) was an improved version of the Block I S-I stage. The Block II S-1 stage had eight fins added for greater aerodynamic stability in the lower atmosphere.
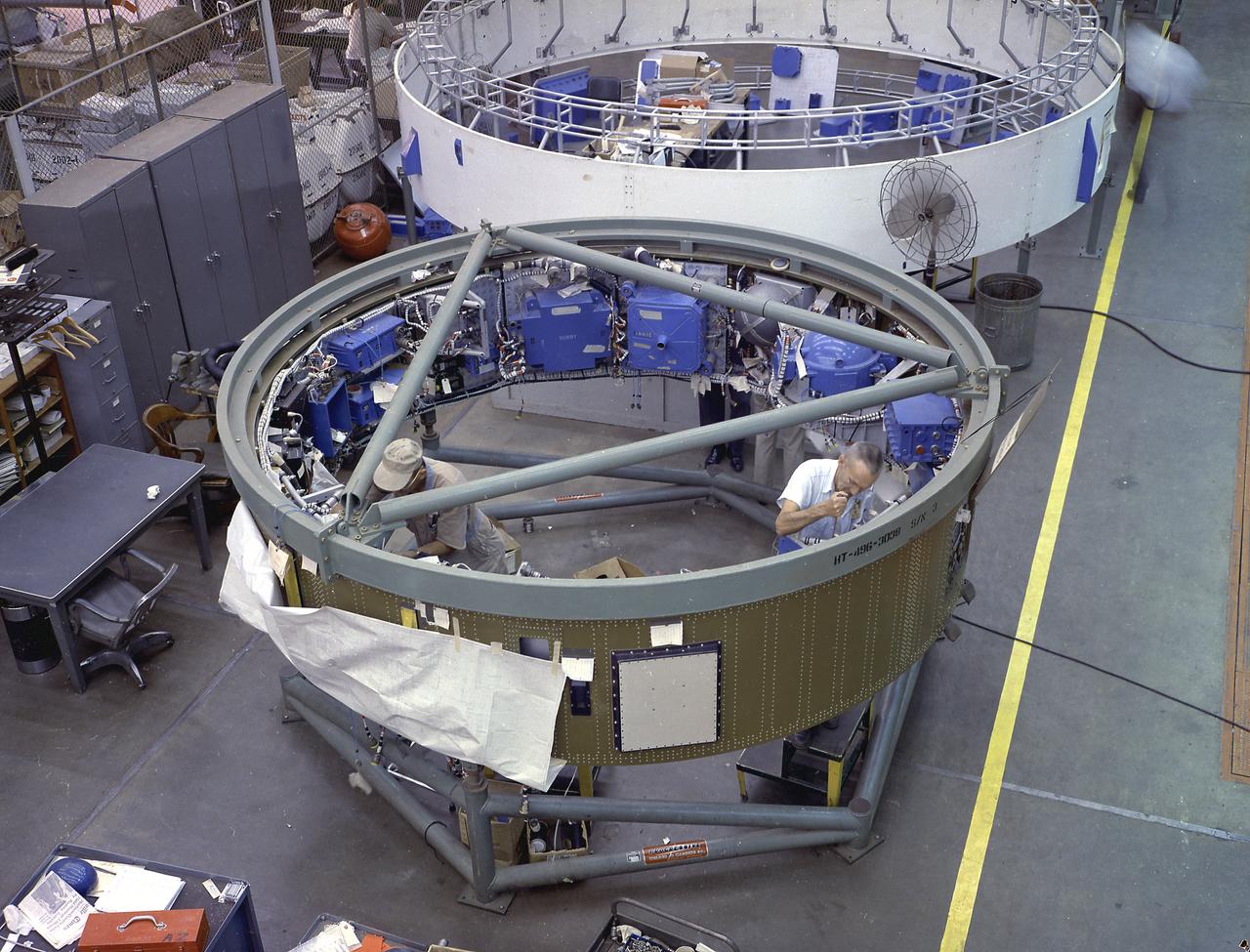
This image depicts a high angle view of technicians working on the instrument unit (IU) component assembly for the SA-8 mission in Marshall Space Flight Center's building 4705. A thin, circular structure, only 1-meter high and 7.6 meters in diameter, the IU was sandwiched between the S-IV and Apollo spacecraft. Packed inside were the computers, gyroscopes, and assorted black boxes necessary to keep the launch vehicle properly functioning and on its course.

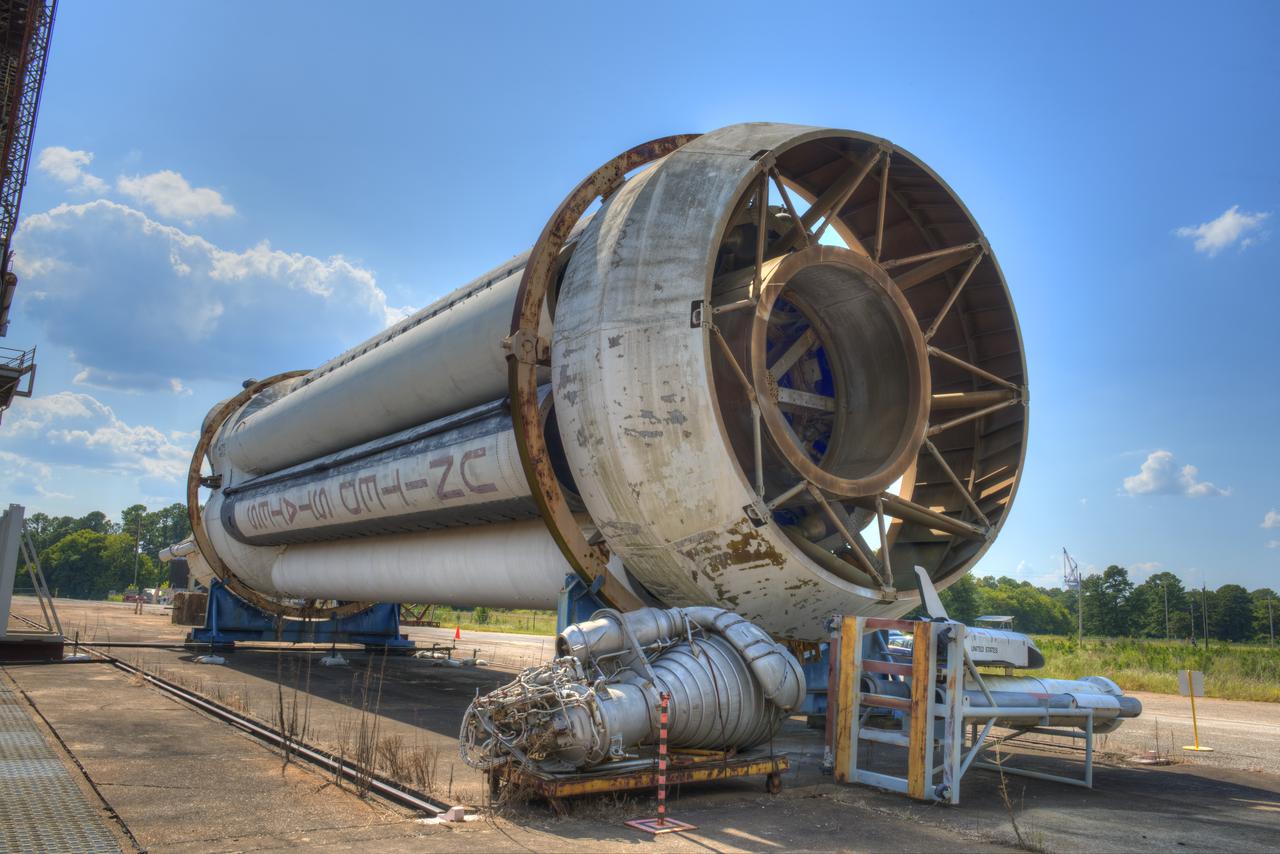
SATURN S-1B STAGE (SA-T) WITH PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) IN BACKGROUND
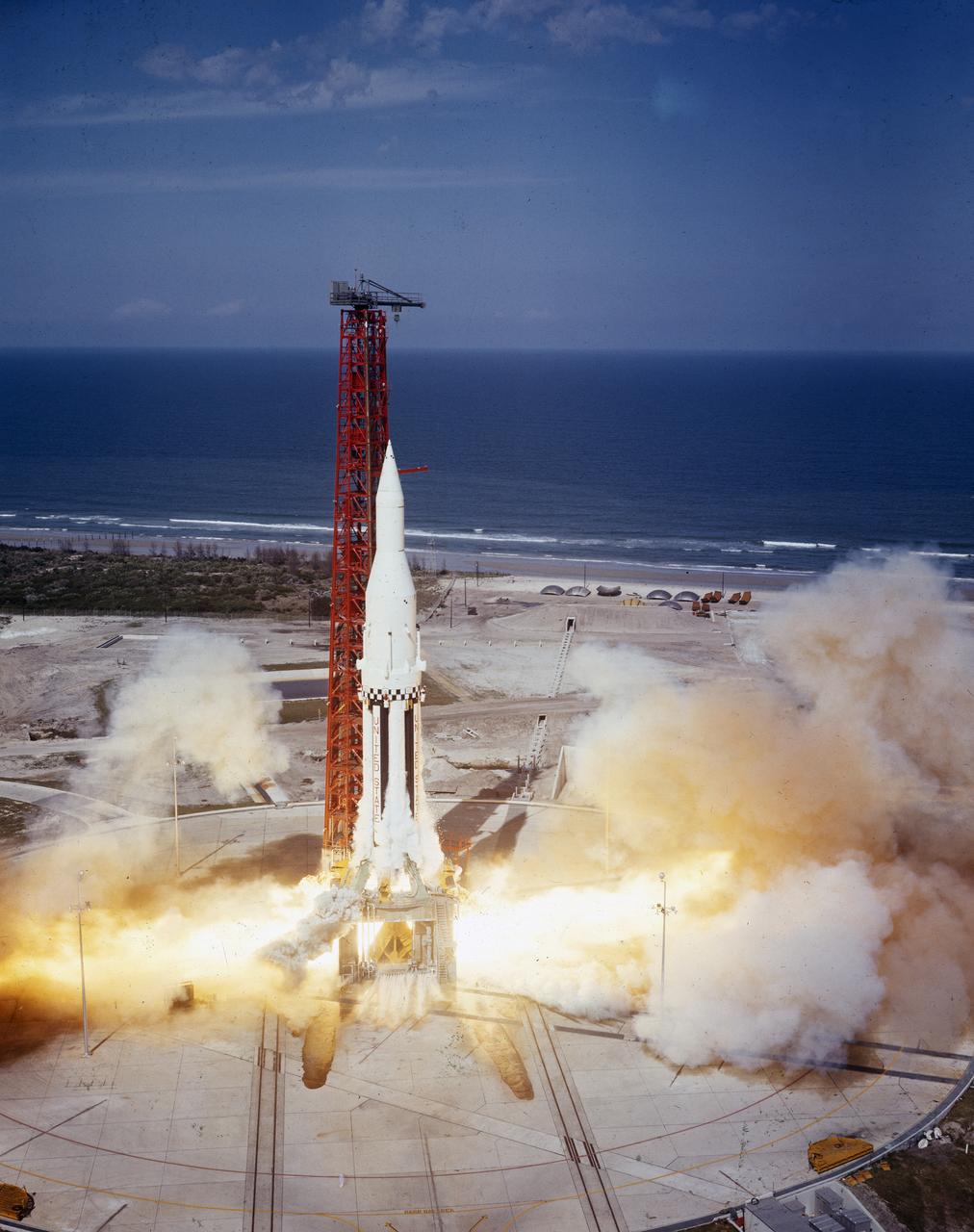

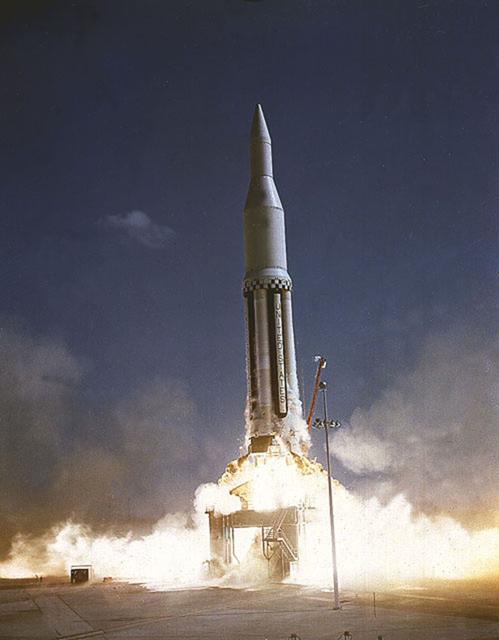
The Saturn I (SA-4) flight lifted off from Kennedy Space Center launch Complex 34, March 28, 1963. The fourth launch of Saturn launch vehicles developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, incorporated a Saturn I, Block I engine. The typical height of a Block I vehicle was approximately 163 feet and had only one live stage. It consisted of eight tanks, each 70 inches in diameter, clustered around a central tank, 105 inches in diameter. Four of the external tanks were fuel tanks for the RP-1 (kerosene) fuel. The other four, spaced alternately with the fuel tanks, were liquid oxygen tanks as was the large center tank. All fuel tanks and liquid oxygen tanks drained at the same rates respectively. The thrust for the stage came from eight H-1 engines, each producing a thrust of 165,000 pounds, for a total thrust of over 1,300,000 pounds. The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis and canted outward slightly, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern offset 40 degrees from the inner pattern. Unlike the inner engines, each outer engine was gimbaled. That is, each could be swung through an arc. They were gimbaled as a means of steering the rocket, by letting the instrumentation of the rocket correct any deviations of its powered trajectory. The block I required engine gimabling as the only method of guiding and stabilizing the rocket through the lower atmosphere. The upper stages of the Block I rocket reflected the three-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. Like SA-3, the SA-4 flight’s upper stage ejected 113,560 liters (30,000 gallons) of ballast water in the upper atmosphere for "Project Highwater" physics experiment. Release of this vast quantity of water in a near-space environment marked the second purely scientific large-scale experiment. The SA-4 was the last Block I rocket launch.
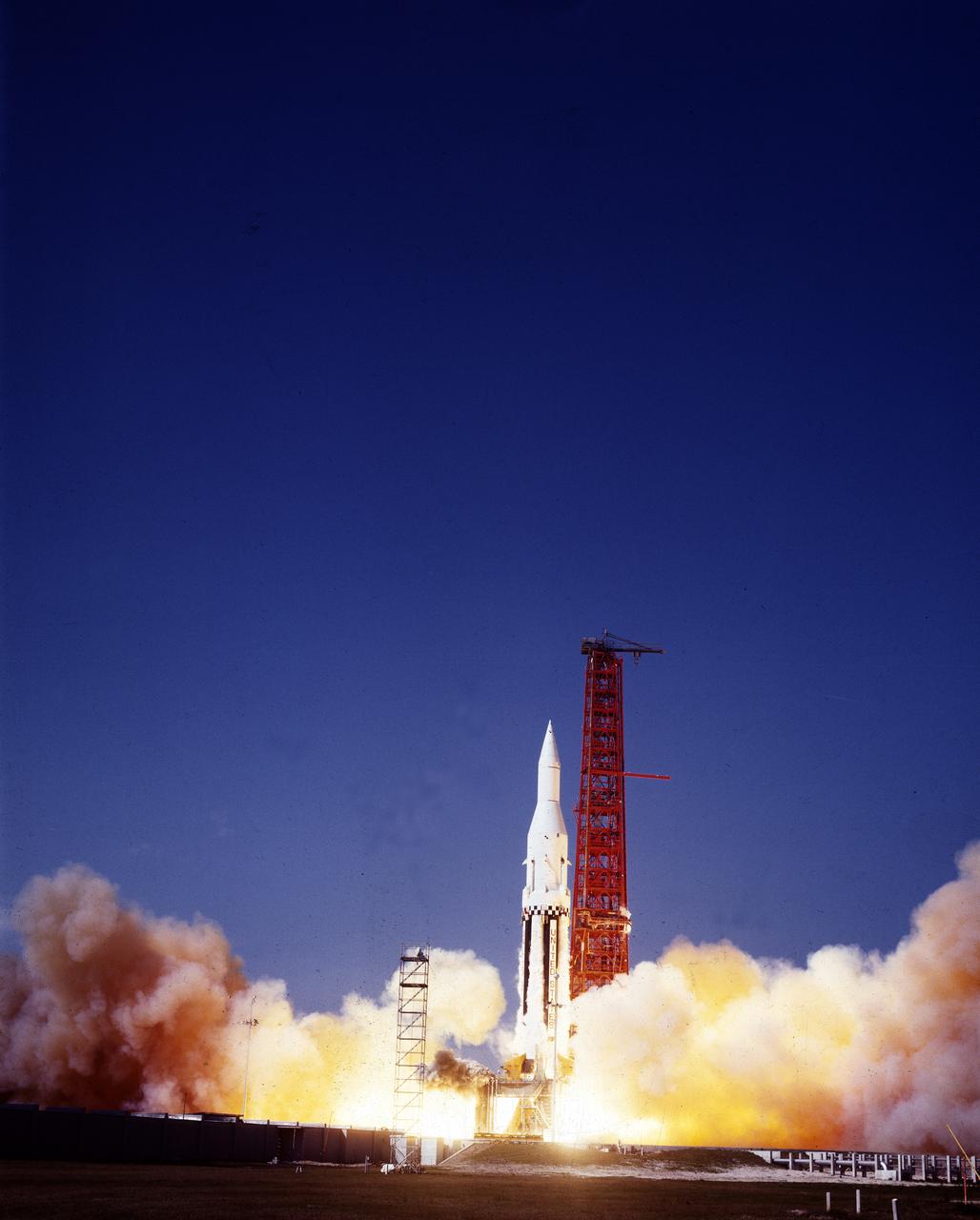

The Saturn I (SA-4) flight lifted off from Kennedy Space Center launch Complex 34, March 28, 1963. The fourth launch of Saturn launch vehicles, developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, incorporated a Saturn I, Block I engine. The typical height of a Block I vehicle was approximately 163 feet and had only one live stage. It consisted of eight tanks, each 70 inches in diameter, clustered around a central tank, 105 inches in diameter. Four of the external tanks were fuel tanks for the RP-1 (kerosene) fuel. The other four, spaced alternately with the fuel tanks, were liquid oxygen tanks as was the large center tank. All fuel tanks and liquid oxygen tanks drained at the same rates respectively. The thrust for the stage came from eight H-1 engines, each producing a thrust of 165,000 pounds, for a total thrust of over 1,300,000 pounds. The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis and canted outward slightly, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern offset 40 degrees from the inner pattern. Unlike the inner engines, each outer engine was gimbaled. That is, each could be swung through an arc. They were gimbaled as a means of steering the rocket, by letting the instrumentation of the rocket correct any deviations of its powered trajectory. The block I required engine gimabling as the only method of guiding and stabilizing the rocket through the lower atmosphere. The upper stages of the Block I rocket reflected the three-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. Like SA-3, the SA-4 flight’s upper stage ejected 113,560 liters (30,000 gallons) of ballast water in the upper atmosphere for "Project Highwater" physics experiment. Release of this vast quantity of water in a near-space environment marked the second purely scientific large-scale experiment. The SA-4 was the last Block I rocket launch.

This image depicts the tension in the Launch Control Center of the Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral, Florida, during the SA-8 on May 25, 1965. Pointing, center is Dr. Kurt Debus, Director, Launch Operations Directorate, MSFC. To the right is Dr. Hans Gruene, Deputy Director, Launch Operations Directorate, MSFC; Dr. von Braun, Director, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC); and leaning, Dr. Eberhard Rees, Director, Deputy Director for Research and Development, MSFC. The SA-8 mission, with a Saturn I launch vehicle, made the first night launch and deployed Pegasus II, micrometeoroid detection satellite.
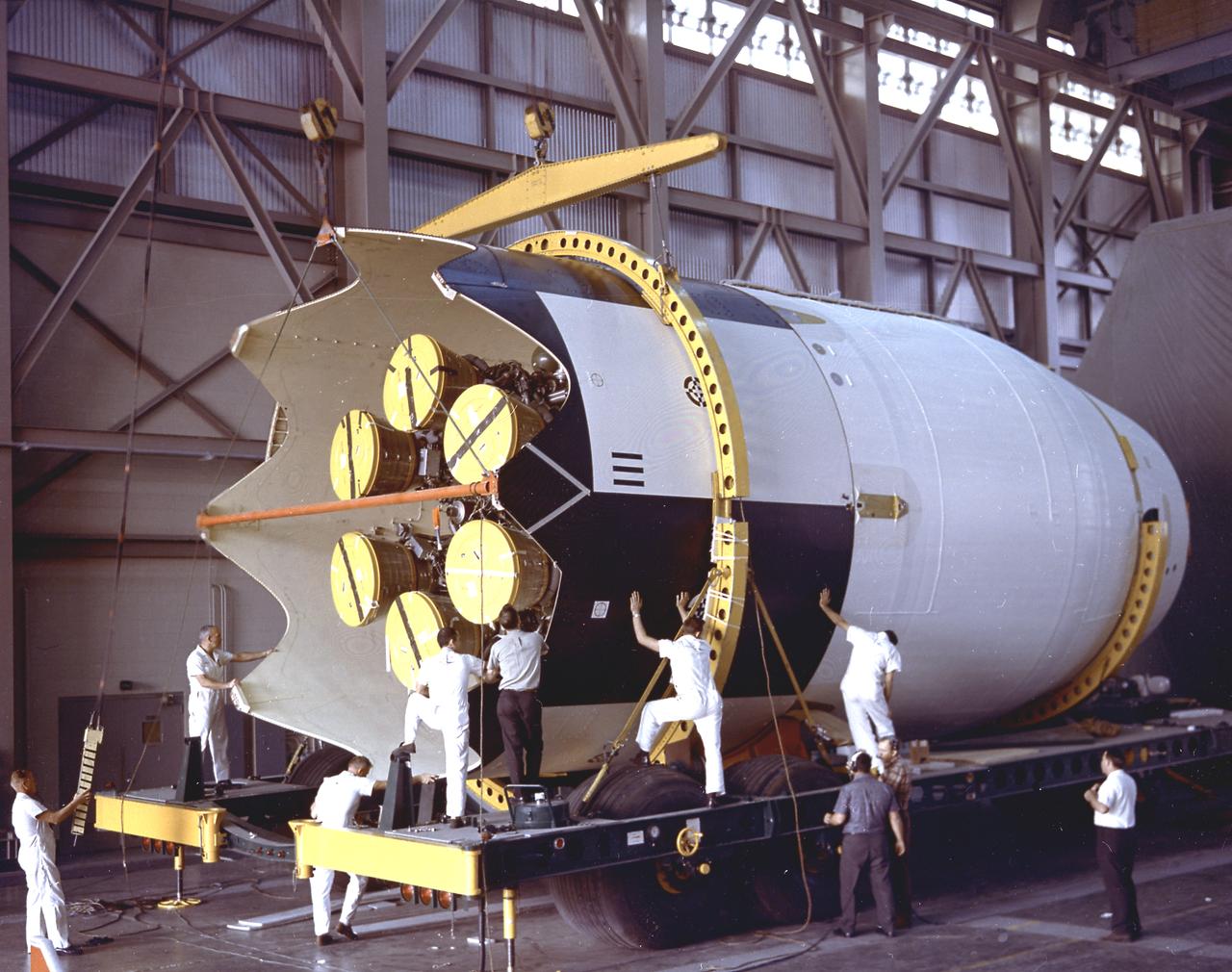
In this photograph, the Pegasus, meteoroid detection satellite is installed in its specially modified Apollo service module atop the S-IV stage (second stage) of a Saturn I vehicle for the SA-9 mission at Cape Kennedy. Personnel in the service structure moved the boilerplate Apollo command module into place to cap the vehicle. The command and service modules, visible here, were jettisoned into orbit to free the Pegasus for wing deployment. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth. The SA-9 was launched on February 16, 1965.
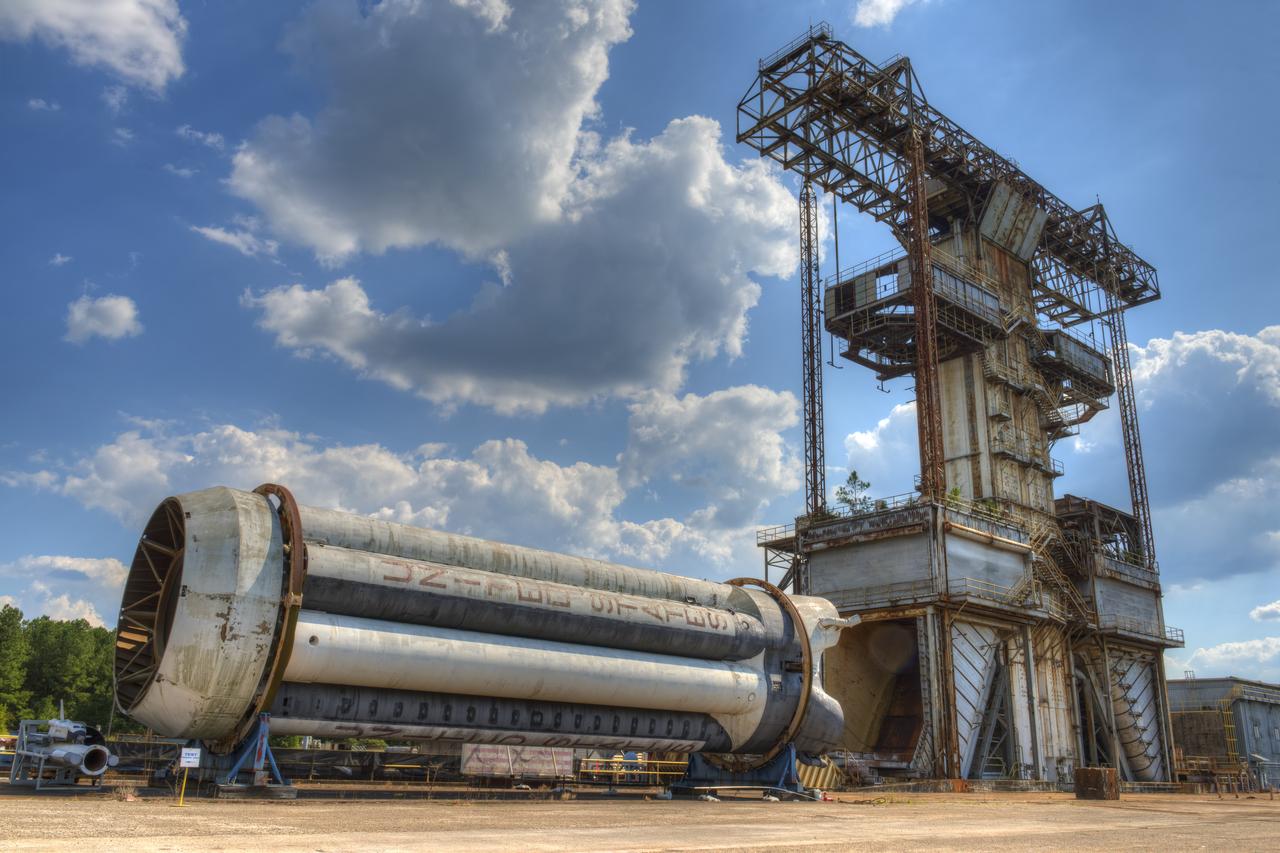

PROPULSION AND STRUCTURAL TEST FACILITY (BUILDING 4572) AT THE GEORGE C. MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA WITH THE SATURN S-1B STAGE (SA-) IN FOREGROUND
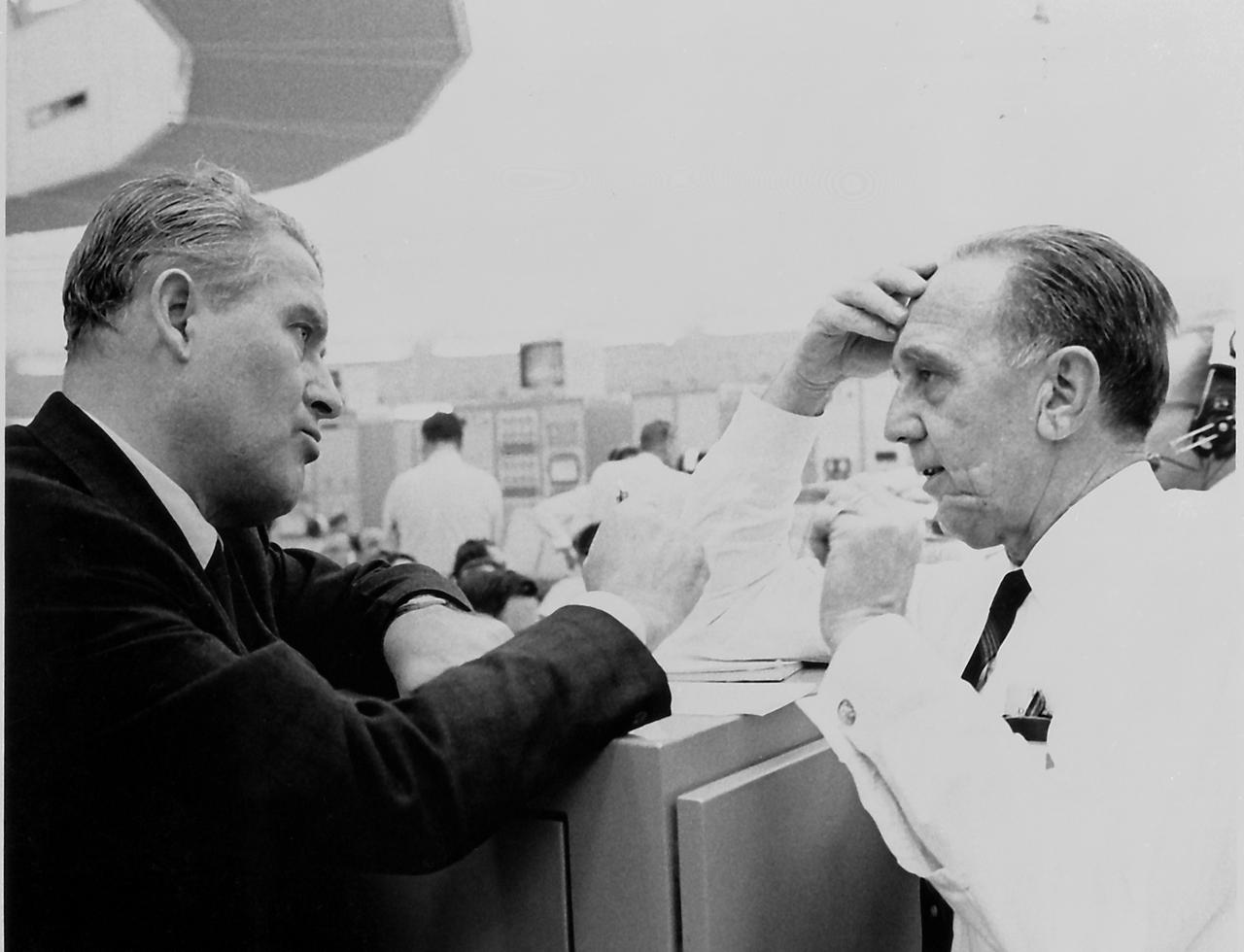

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun (left) confers with the Director of the MSFC Launch Operation Directorate, Dr. Debus, during the countdown for the Saturn/Pegasus (Saturn I, SA-9) launch. The successful launch of the Pegasus satellite marked the largest unmarned instrumented satellite in orbit up to 1965.

The Marshall Space Flight Center's first Saturn I vehicle, SA-1, lifts off from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on October 27, 1961. This early configuration, Saturn I Block I, 162 feet tall and weighing 460 tons, consisted of the eight H-1 engines S-I stage and the dummy second stage (S-IV stage).
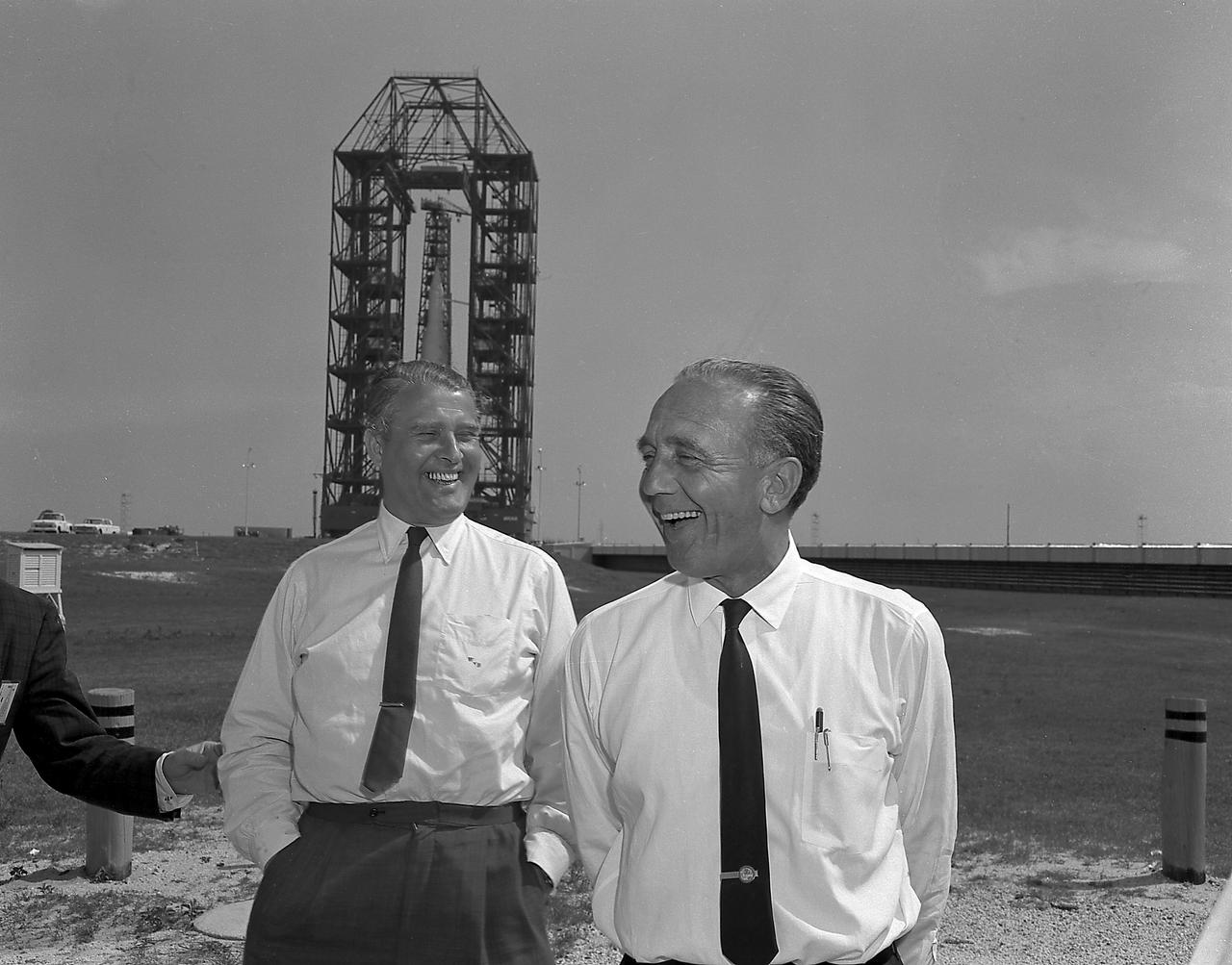

Dr. von Braun, Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), and Dr. Debus, Director of the Launch Operations Center, at Complex 34 prior to the Launch of the SA-4 (the fourth flight of Saturn I), March 28, 1963. The mission conducted the second "Project Highwater" experiment, which the upper stage ejected 30,000 gallons of ballast water in the upper atmosphere for a physics experiment.
The second flight of the Saturn I vehicle, the SA-2, was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida on April 15, 1962. This vehicle had a secondary mission. After the first stage shutoff, at a 65-mile altitude, the water-filled upper stage was exploded, dumping 95 tons of water in the upper atmosphere. The resulting massive ice cloud rose to a height of 90 miles. The experiment, called Project Highwater, was intended to investigate the effects on the ionosphere of the sudden release of such a great volume of water.
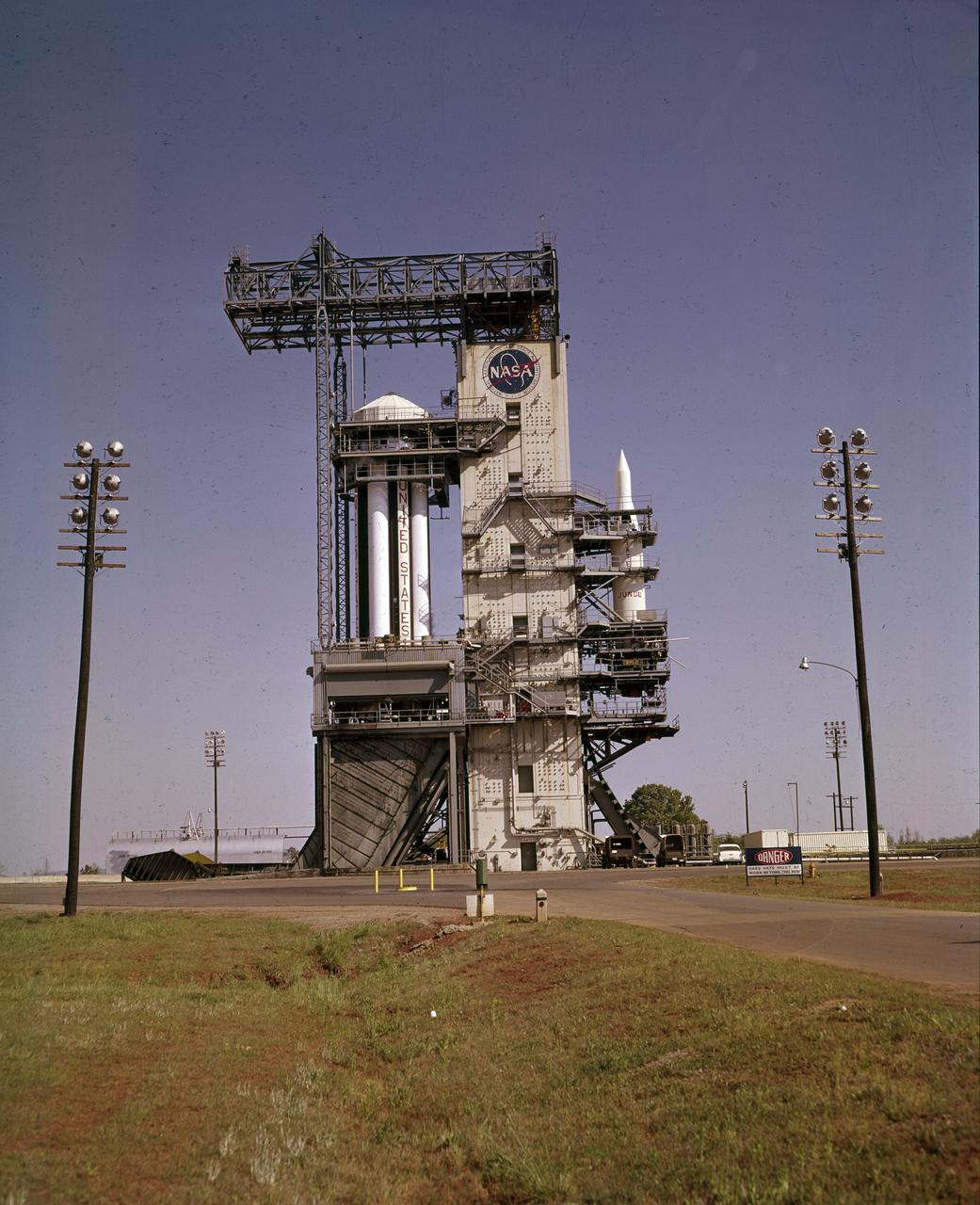

On October 27, 1961, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and the Nation marked a high point in the 3-year-old Saturn development program when the first Saturn vehicle flew a flawless 215-mile ballistic trajectory from Cape Canaveral, Florida. SA-1 is pictured here, five months before launch, in the MSFC test stand on May 16, 1961. Developed and tested at MSFC under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, SA-1 incorporated a Saturn I, Block I engine. The typical height of a Block I vehicle was approximately 163 feet. and had only one live stage. It consisted of eight tanks, each 70 inches in diameter, clustered around a central tank, 105 inches in diameter. Four of the external tanks were fuel tanks for the RP-1 (kerosene) fuel. The other four, spaced alternately with the fuel tanks, were liquid oxygen tanks, as was the large center tank. All fuel tanks and liquid oxygen tanks drained at the same rates respectively. The thrust for the stage came from eight H-1 engines, each producing a thrust of 165,000 pounds, for a total thrust of over 1,300,000 pounds. The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis and canted outward slightly, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern offset 40 degrees from the inner pattern. Unlike the inner engines, each outer engine was gimbaled. That is, each could be swung through an arc. They were gimbaled as a means of steering the rocket, by letting the instrumentation of the rocket correct any deviations of its powered trajectory. The block I required engine gimabling as the only method of guiding and stabilizing the rocket through the lower atmosphere. The upper stages of the Block I rocket reflected the three-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle.
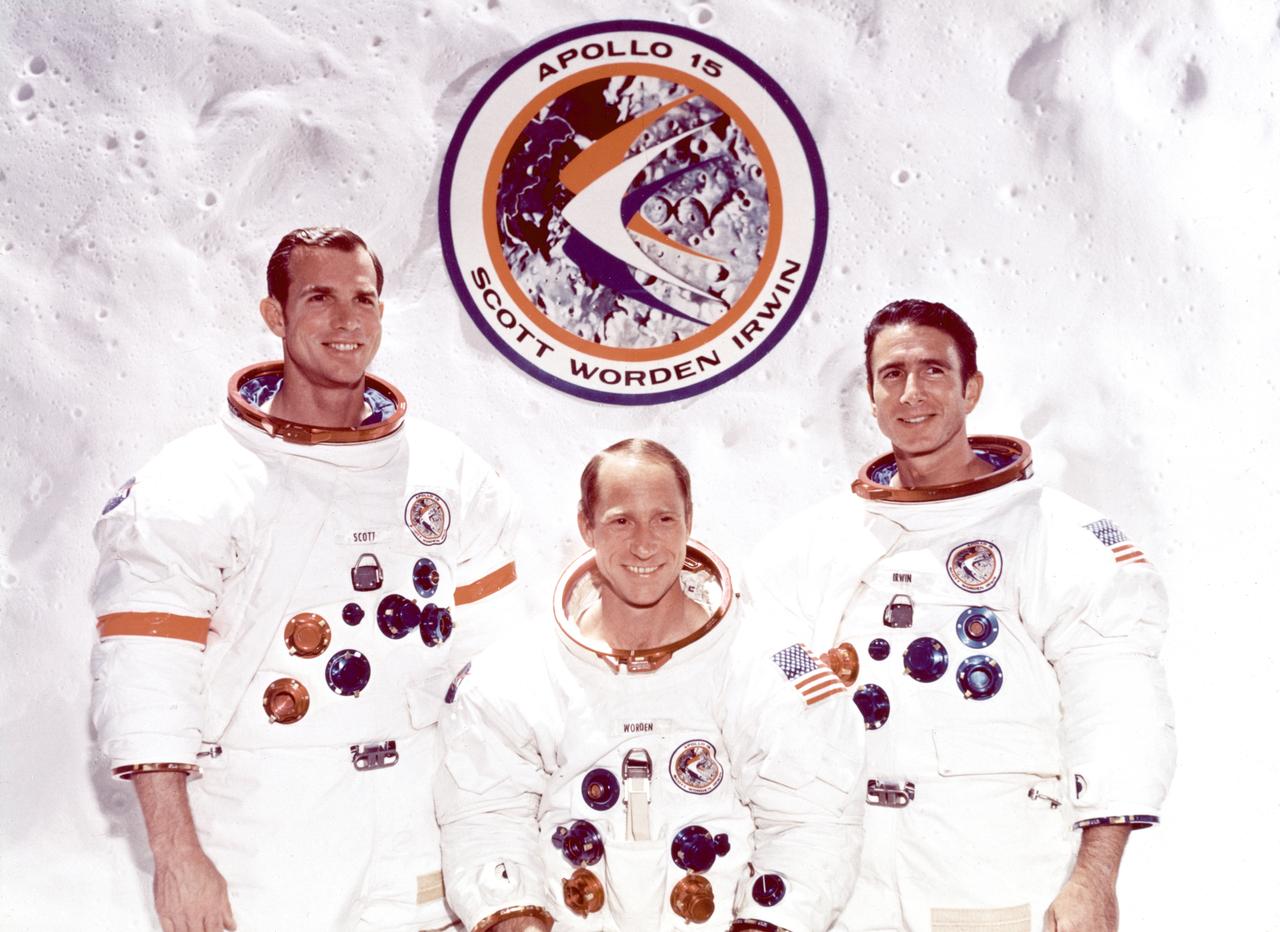

This is the official three-member crew portrait of the Apollo 15 (SA-510). Pictured from left to right are: David R. Scott, Mission Commander; Alfred M. Worden Jr., Command Module pilot; and James B. Irwin, Lunar Module pilot. The fifth marned lunar landing mission, Apollo 15 (SA-510), lifted off on July 26, 1971. Astronauts Scott and Irwin were the first to use a wheeled surface vehicle, the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), or the Rover, which was designed and developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center, and built by the Boeing Company. The astronauts spent 13 days, nearly 67 hours, on the Moon's surface to inspect a wide variety of its geological features.
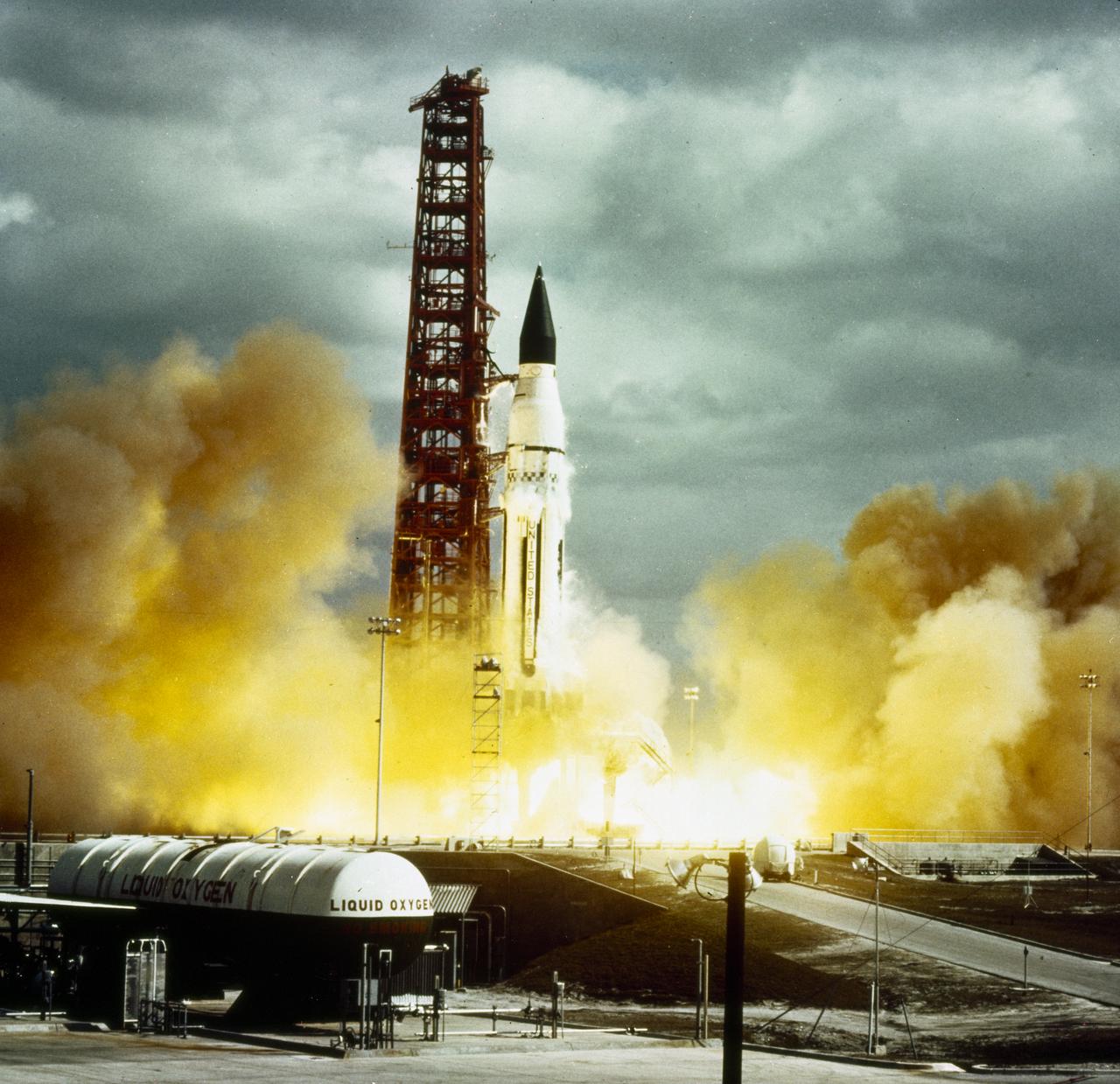

Developed at MSFC under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, the SA-5 incorporated a Saturn I, Block II engine. Launched on January 29, 1964, SA-5 was the first two stage (Block II) Saturn with orbital capability and performed the first test of Instrument Unit and successful stage separation. Block II vehicles had two live stages, and were basically in the two-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. There were marked changes between the Block I and II versions. The Block II S-I stage had eight fins added for greater aerodynamic stability in the lower atmosphere. All Block II H-1 engines had a thrust of 188,000 pounds each for a combined thrust over 1,500,000 pounds. The Block II second stage (S-IV) had six RL-10 hydrogen-oxygen engines, each producing a thrust of 15,000 pounds for a total combined thrust of 90,000 pounds. A motion picture camera capsule loated on stage I was successful recovered.
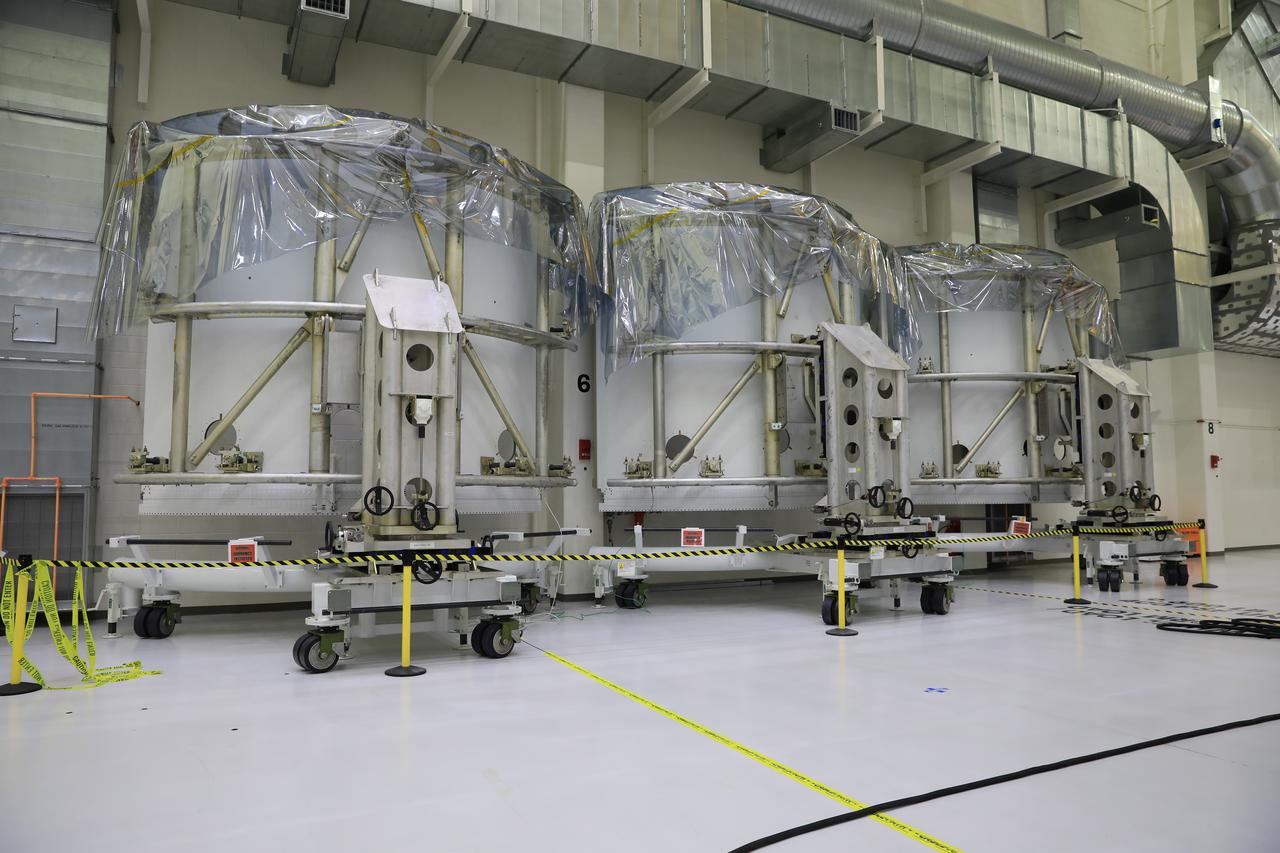

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
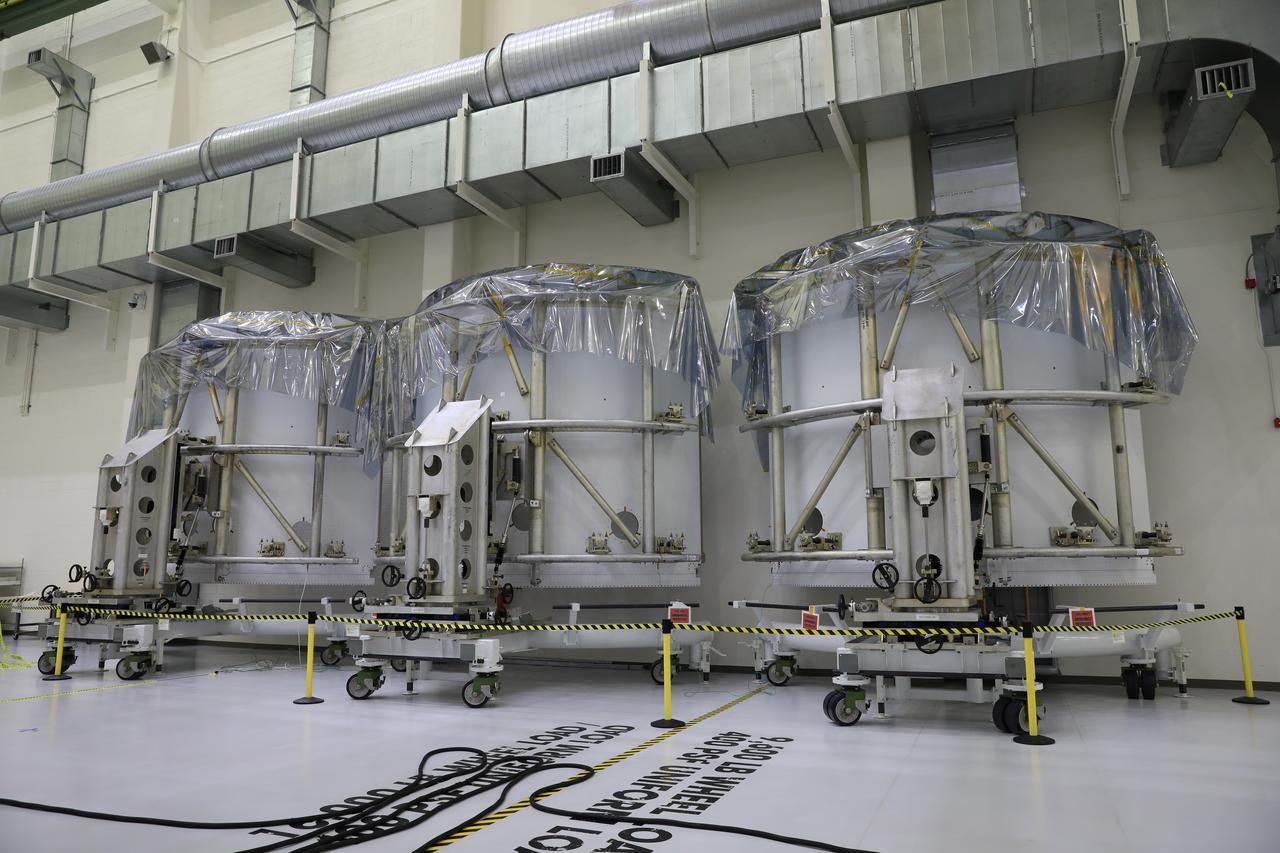

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
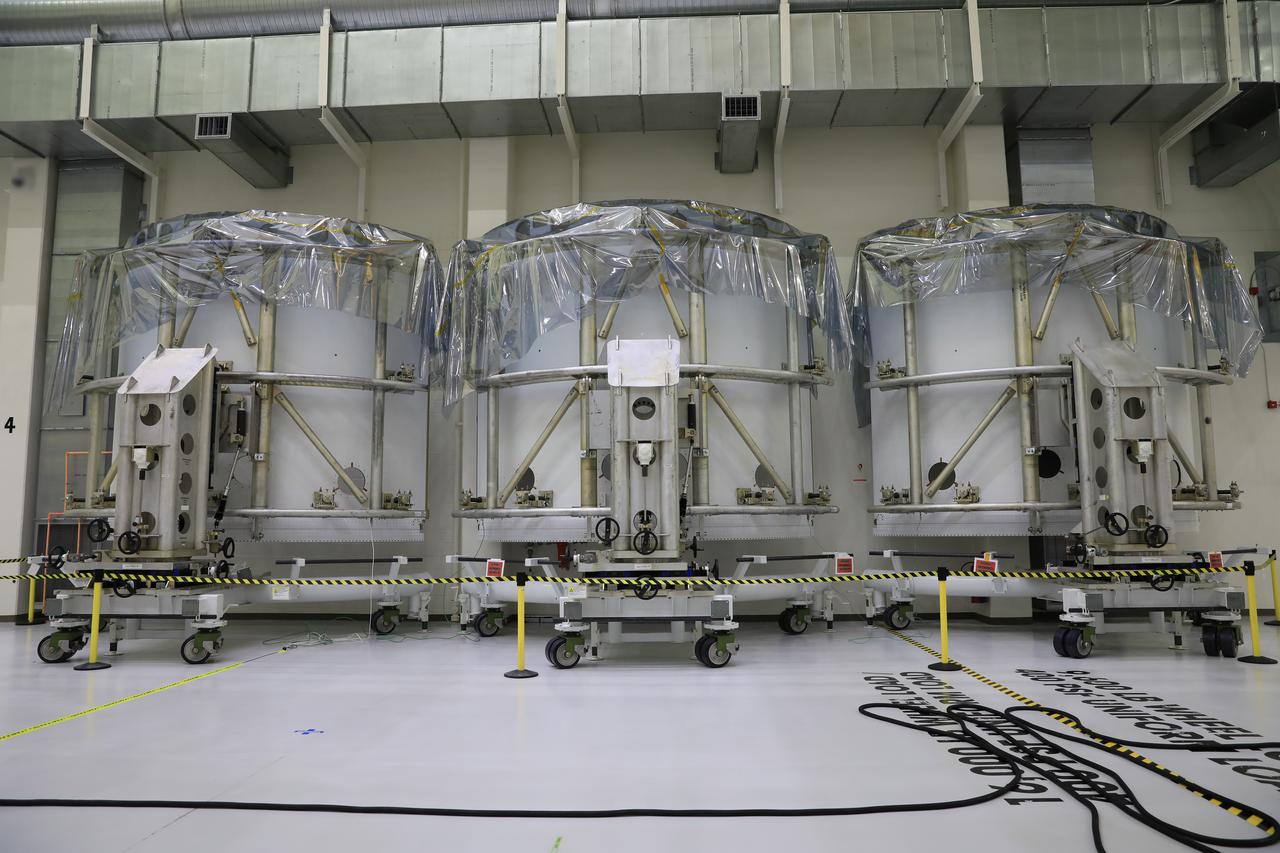

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
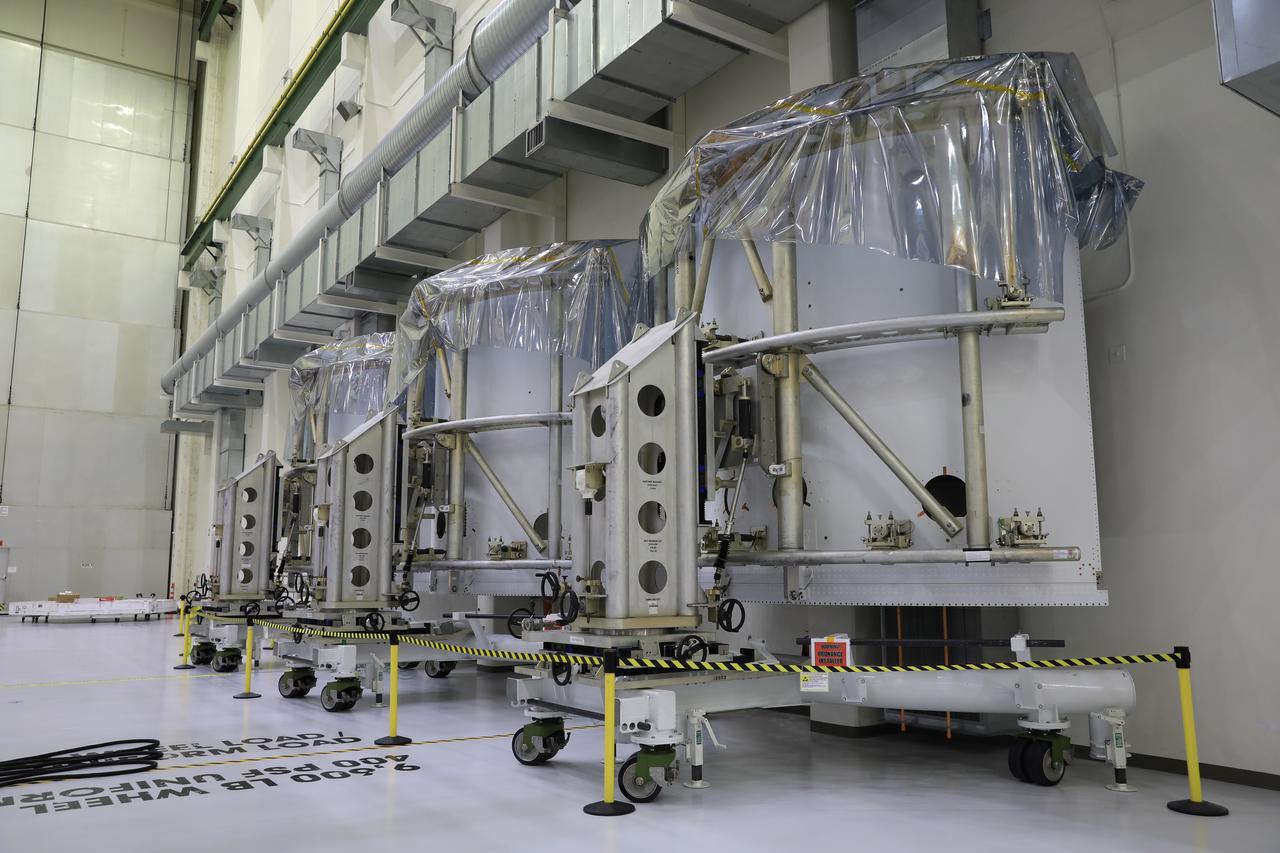

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
This night photograph depicts the SA-1 booster (Saturn I S-I stage) being removed from the test stand after the first flight qualification testing at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
![jsc2022e057892 (5/12/2022) --- The SpaceOMIX team traveling to Space Applications Services, Brussels, Belgium for sample integration [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2022e057892/jsc2022e057892~medium.jpg)
jsc2022e057892 (5/12/2022) --- The SpaceOMIX team traveling to Space Applications Services, Brussels, Belgium for sample integration [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]
![jsc2022e057886 (5/12/2022) --- ICE Cubes mission control centre at the Space Applications Services, Brussels, Belgium [credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2022e057886/jsc2022e057886~medium.jpg)
jsc2022e057886 (5/12/2022) --- ICE Cubes mission control centre at the Space Applications Services, Brussels, Belgium [credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]

The launch of the SA-5 on January 29, 1964 was the fifth Saturn I launch vehicle. The SA-5 marked a number of firsts in the Marshall Space Flight Center-managed Saturn development program, including the first flight of Saturn I Block II vehicle with eight aerodynamic fins at the bottom of the S-I stage (first stage) for enhanced stability in flight. This also was the first flight of a live S-IV (second or upper) stage with the cluster of six liquid hydrogen-fueled RL-10 engines. the first successful second stage separation, and the first use of the Launch Complex 37.

The Saturn I S-IV stage (second stage) assembly for the SA-9 mission underwent the weight and balance test in the hangar building at Cape Canaveral. The S-IV stage had six RL-10 engines which used liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as its propellants arranged in a circle. Each RL-10 engine produced a thrust of 15,000 pounds, a total combined thrust of 90,000 pounds. The SA-9 mission was the first Saturn with operational payload Pegasus I, meteoroid detection satellite, and launched on February 16, 1965.
![jsc2022e057891 (5/13/2022) --- A view of two samples from the onboard camera to the mission control centre and personal computer screen [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2022e057891/jsc2022e057891~medium.jpg)
jsc2022e057891 (5/13/2022) --- A view of two samples from the onboard camera to the mission control centre and personal computer screen [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]
![jsc2022e057894 (5/13/2022) --- Views of the Maltese Biocube based on the ICE Cubes platform by Belgian company Space Applications Services [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2022e057894/jsc2022e057894~medium.jpg)
jsc2022e057894 (5/13/2022) --- Views of the Maltese Biocube based on the ICE Cubes platform by Belgian company Space Applications Services [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]

In this photograph at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Complex 37 Control Center, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director Wernher von Braun (right) talks with KSC's Rocco Petrone while awaiting the launch of SA-8 (Saturn I) on May 25, 1965. Petrone played key roles at KSC in the development of Saturn launch facilities before becoming the director of launch operations in 1966.
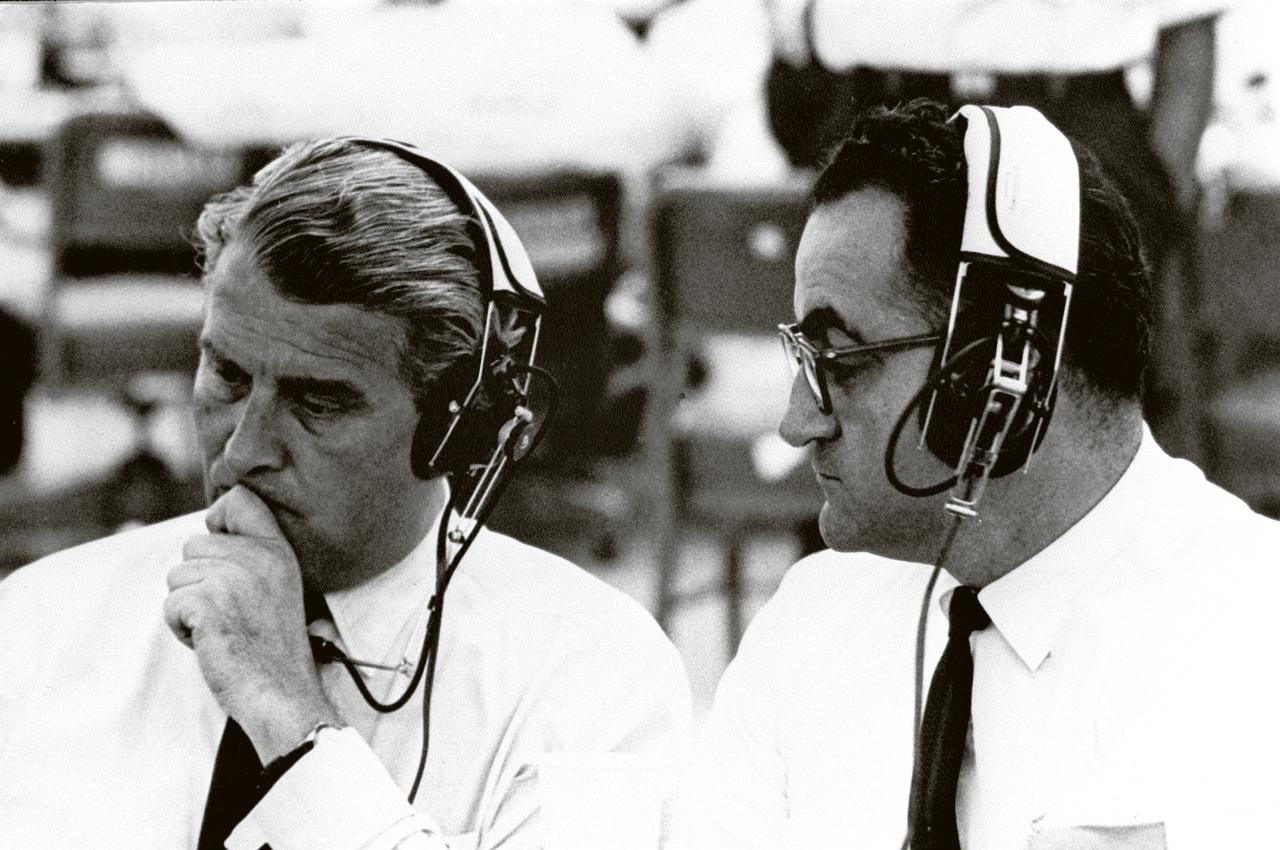

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director Dr. Wernher von Braun (left) with Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Rocco Petrone prior to the January 29, 1964 launch of SA-5, the first Block II configuration of the Saturn I launch vehicle. Petrone played key roles at KSC in the development of Saturn launch facilities before becoming director of launch operations in 1966.
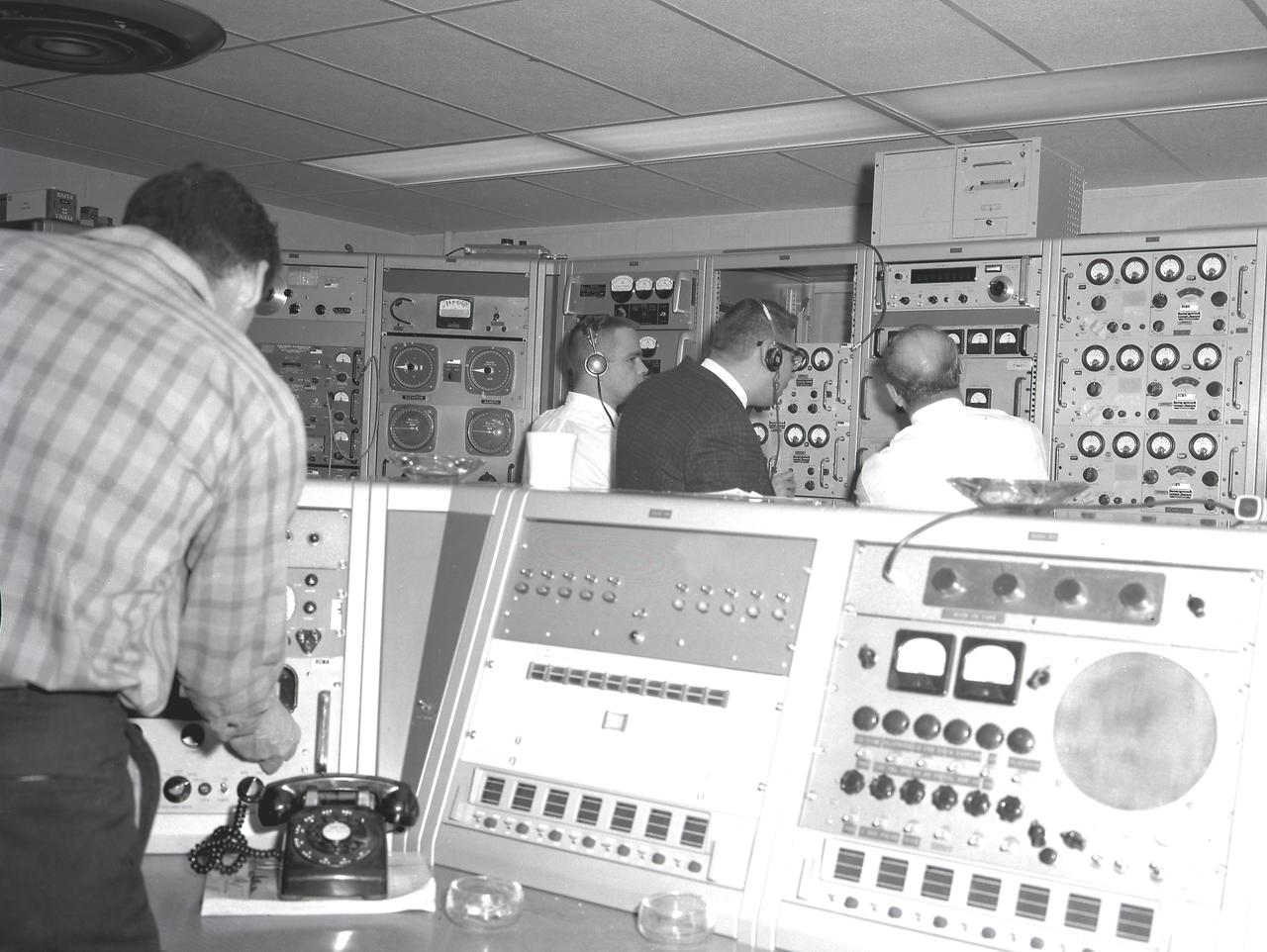

Activities at Green Mountain Tracking Station, Alabama, during lift-off of the Saturn I, SA-9 mission, showing the overall view of instrument panels used in tracking the Pegasus, meteoroid-detection satellite. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth.
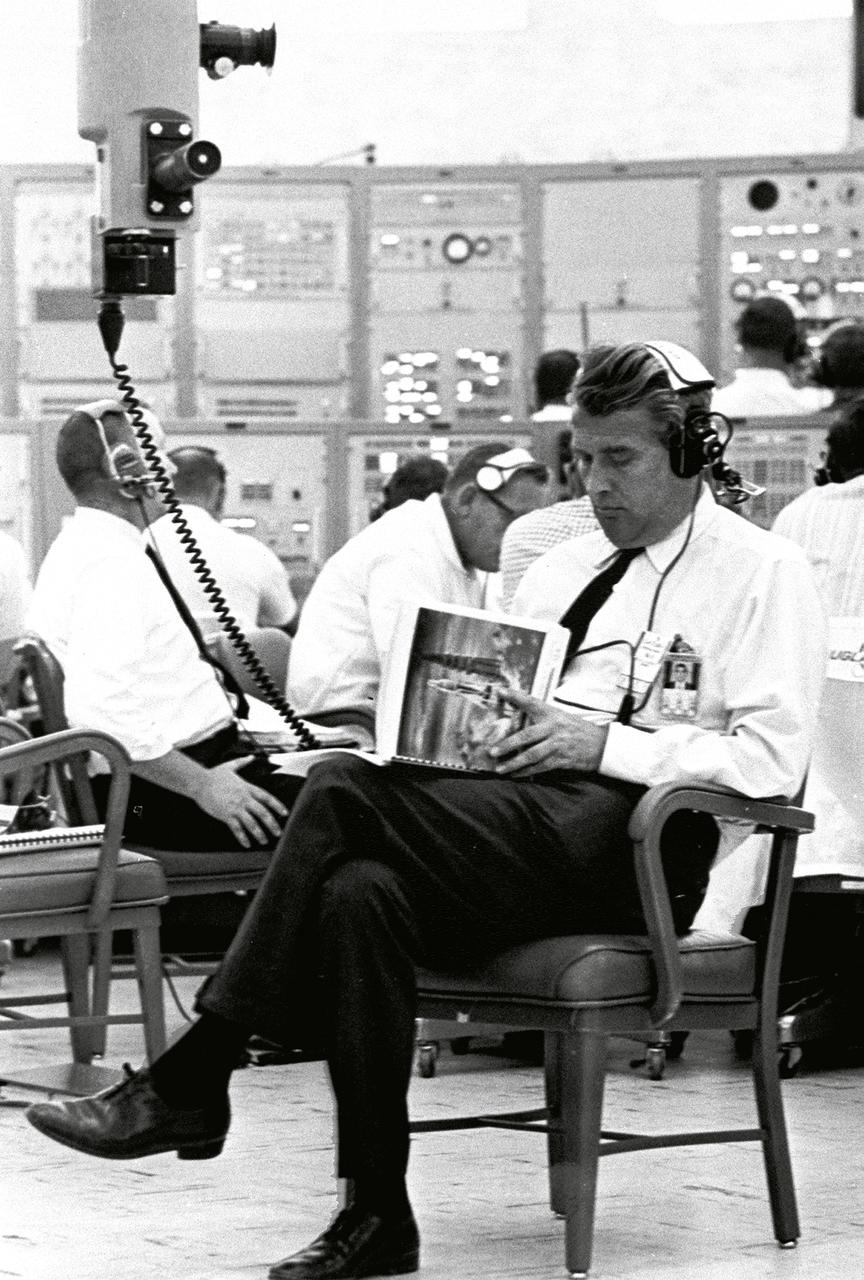

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director Wernher von Braun, seated near a periscope in Kennedy Space Center's Blockhouse 34, on May 28, 1964, looks over a flight manual while awaiting the launch of SA-6, the sixth Saturn I flight. Also known as Apollo Mission A-101, the launch marked the first flight of an Apollo spacecraft with a Saturn launch vehicle.
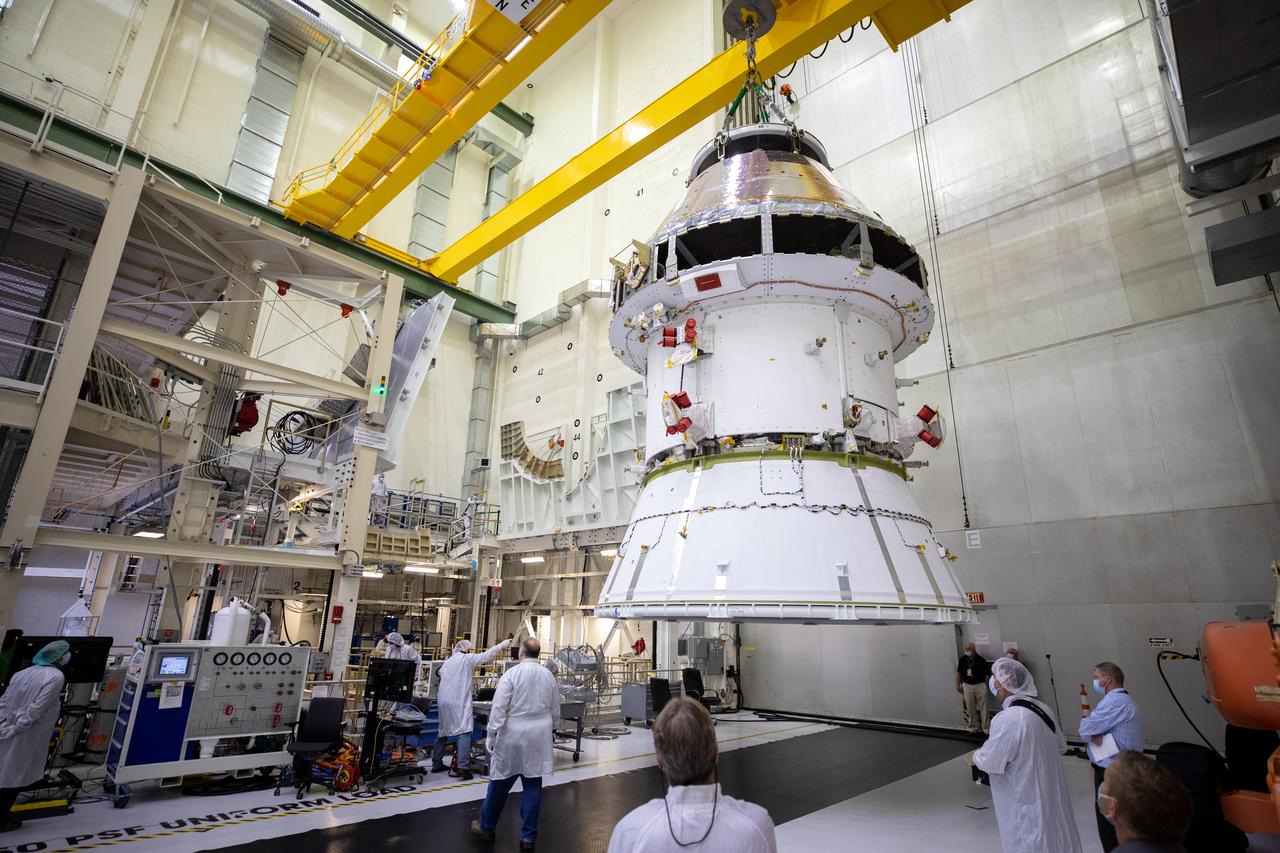

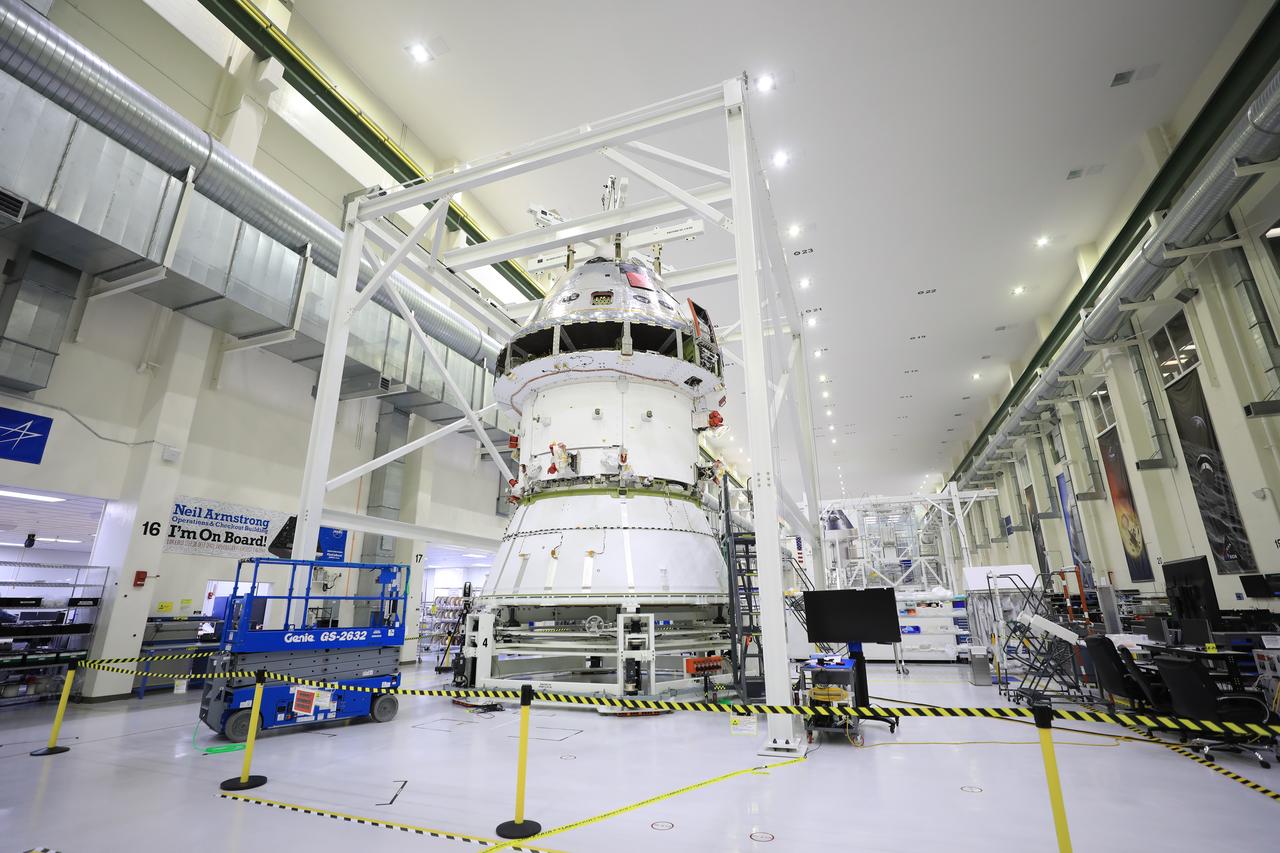
The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
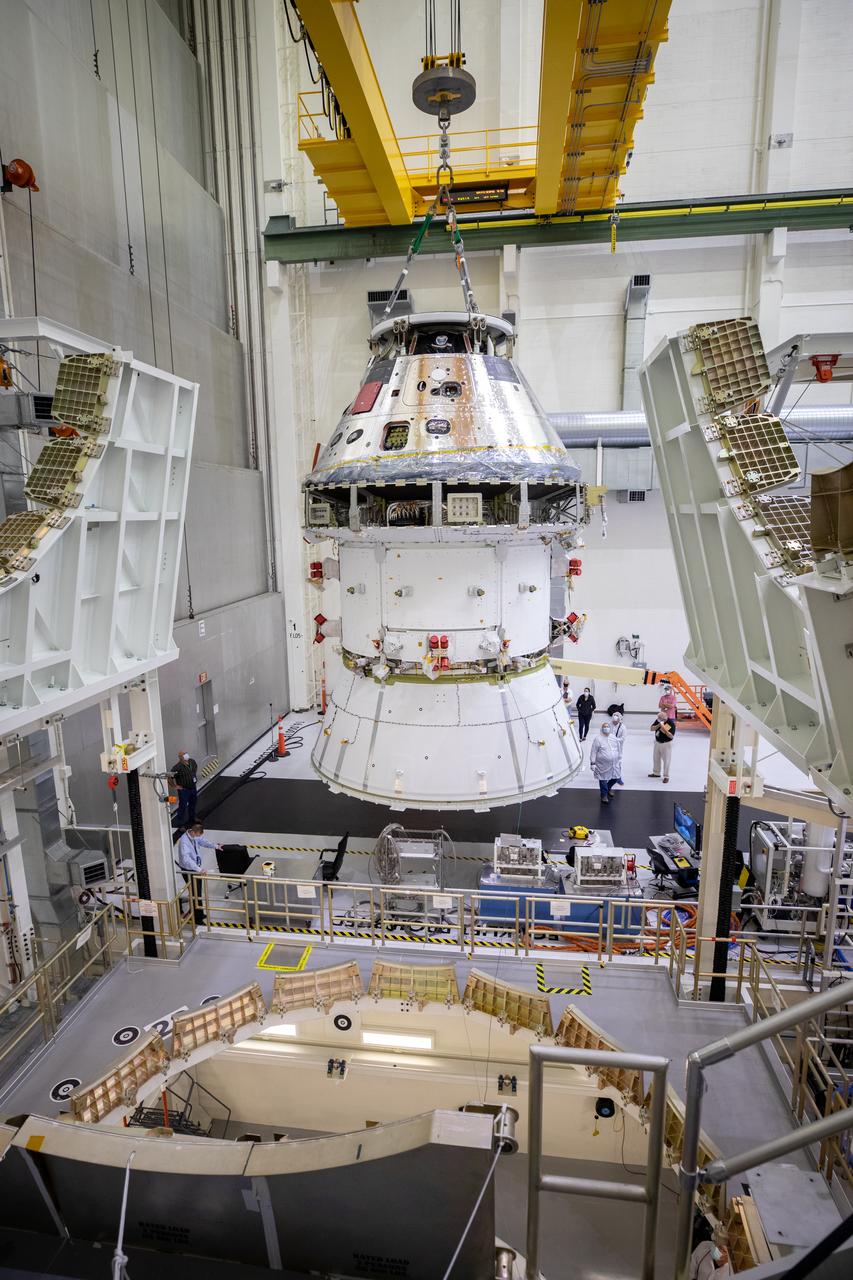

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane into the FAST cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
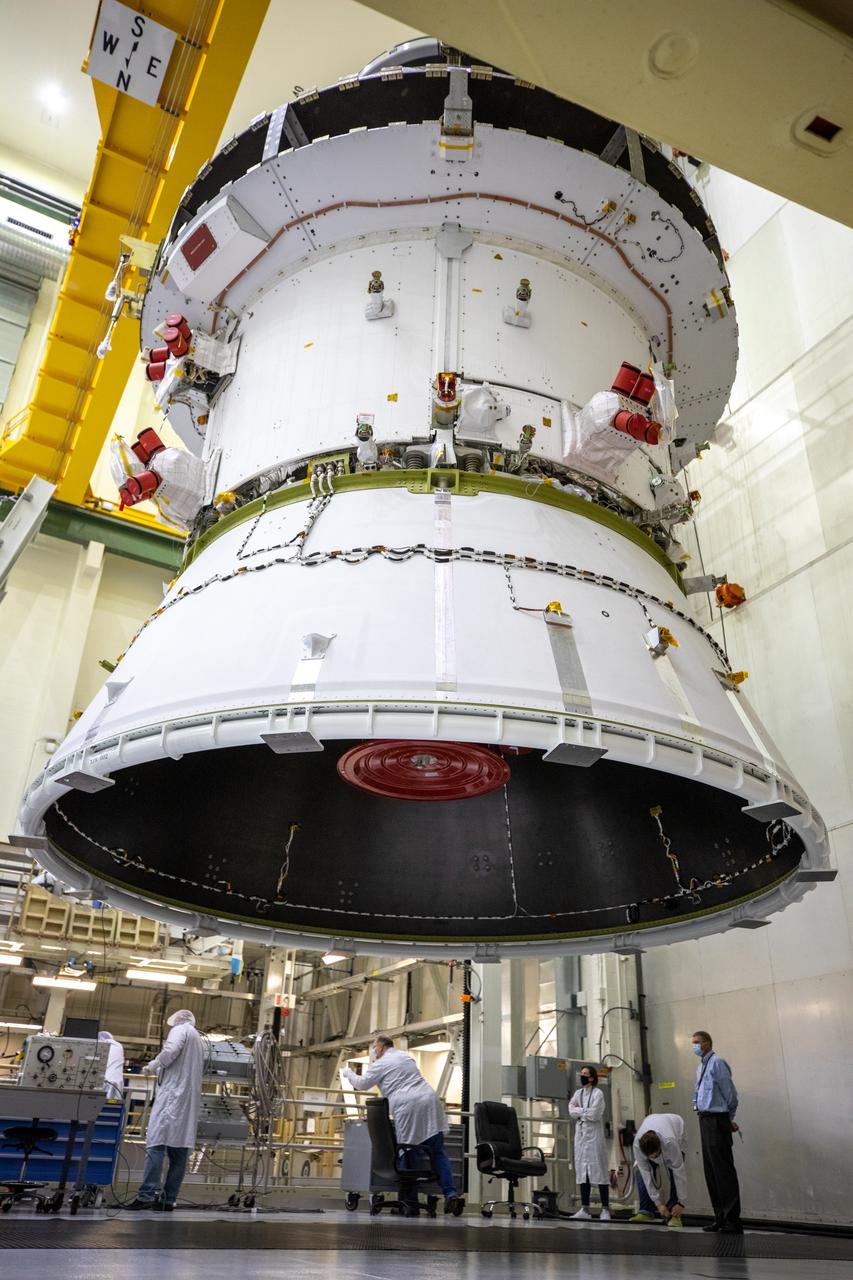

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
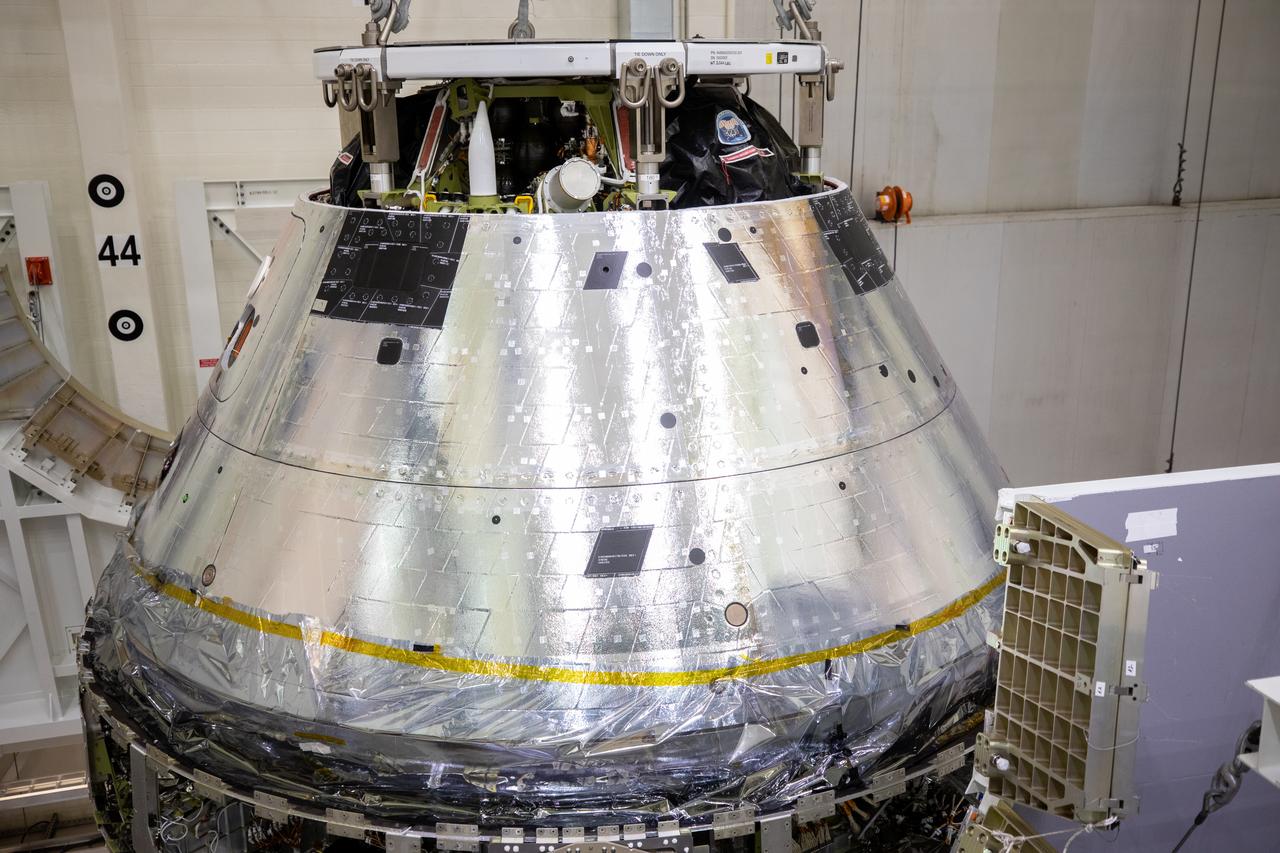

A close-up view of the Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is shown being lowered into the FAST cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
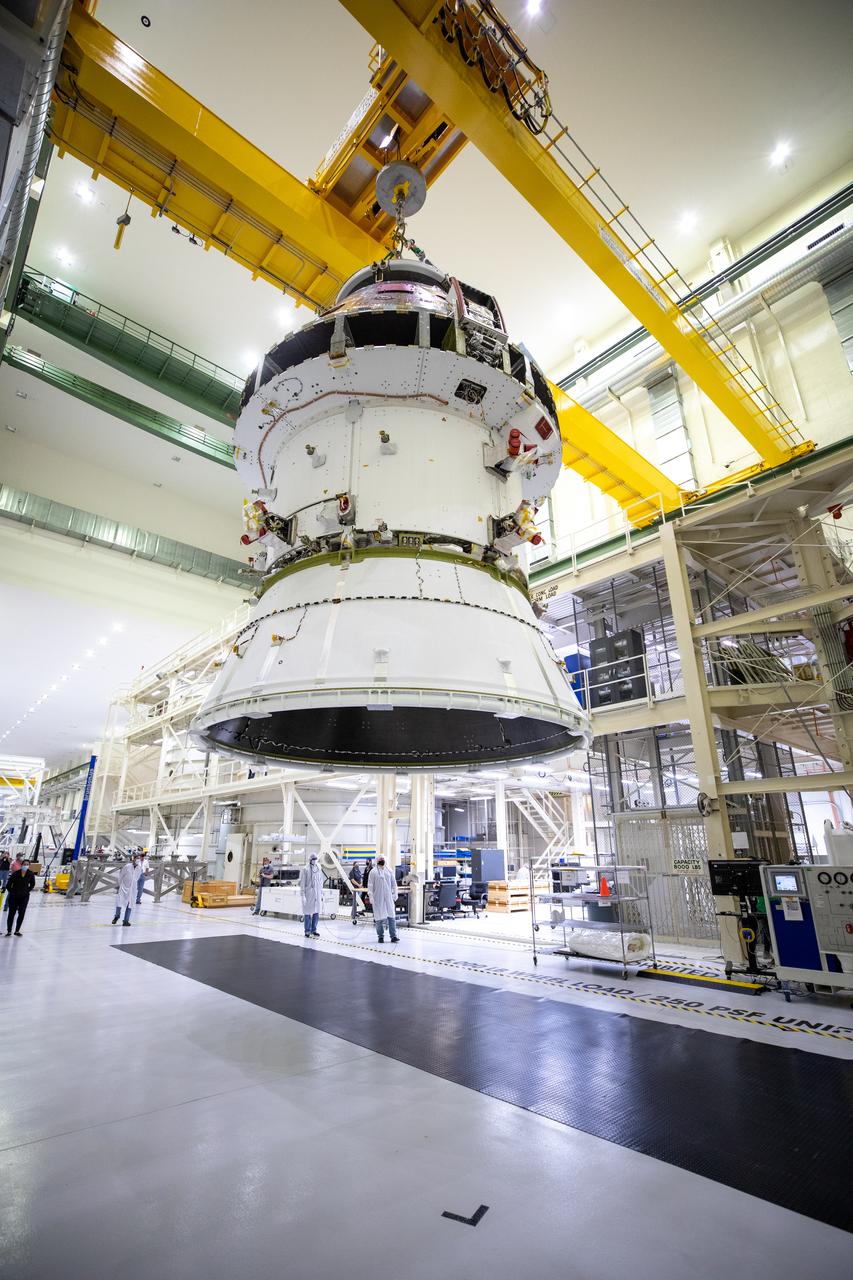

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
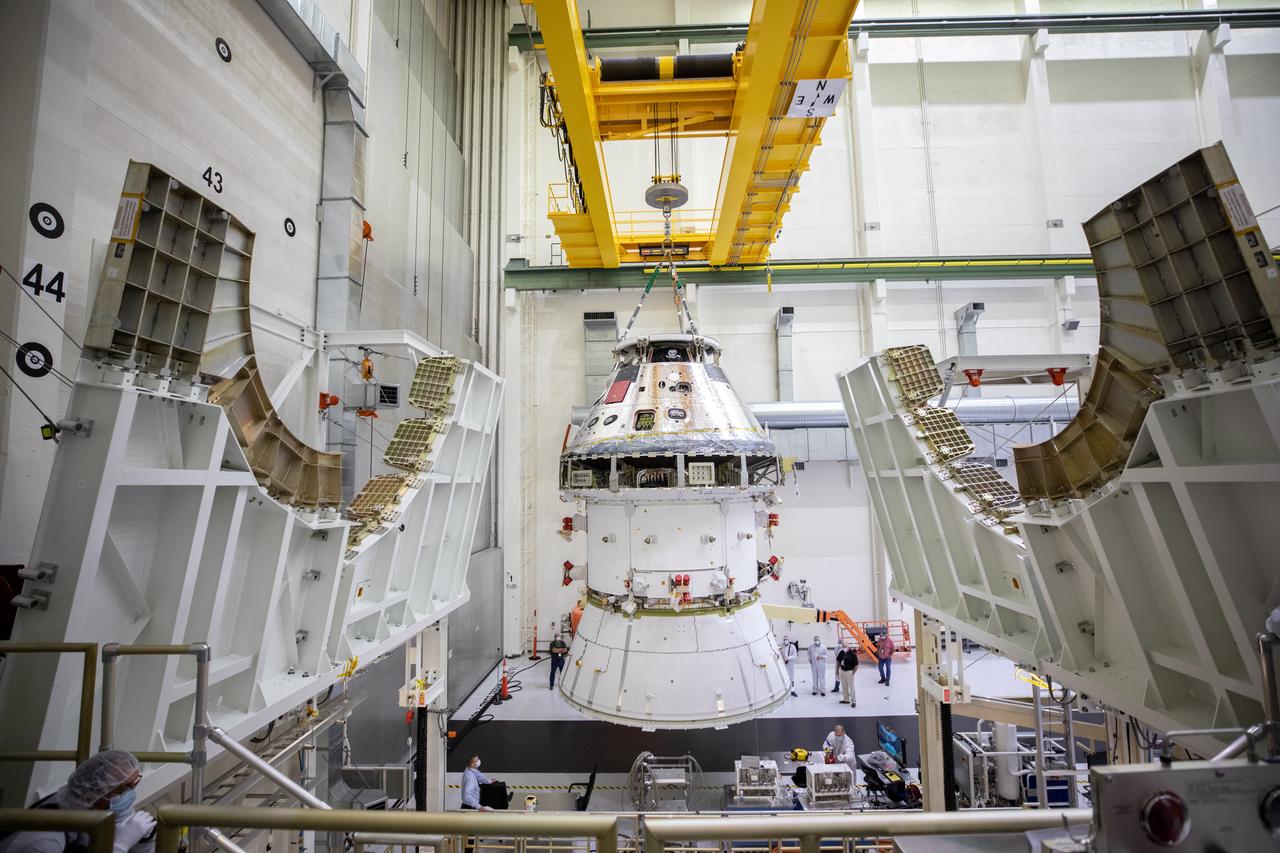

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane into the FAST cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
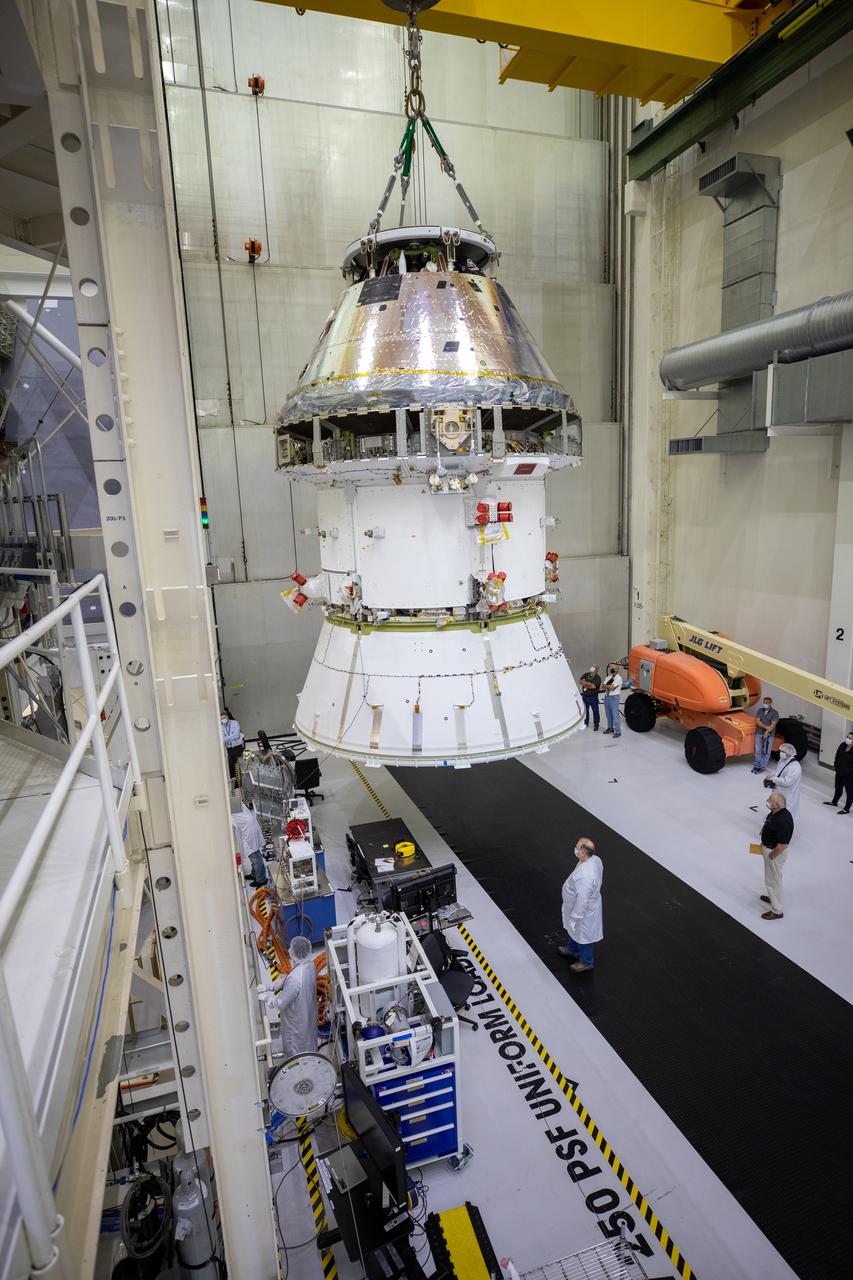

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
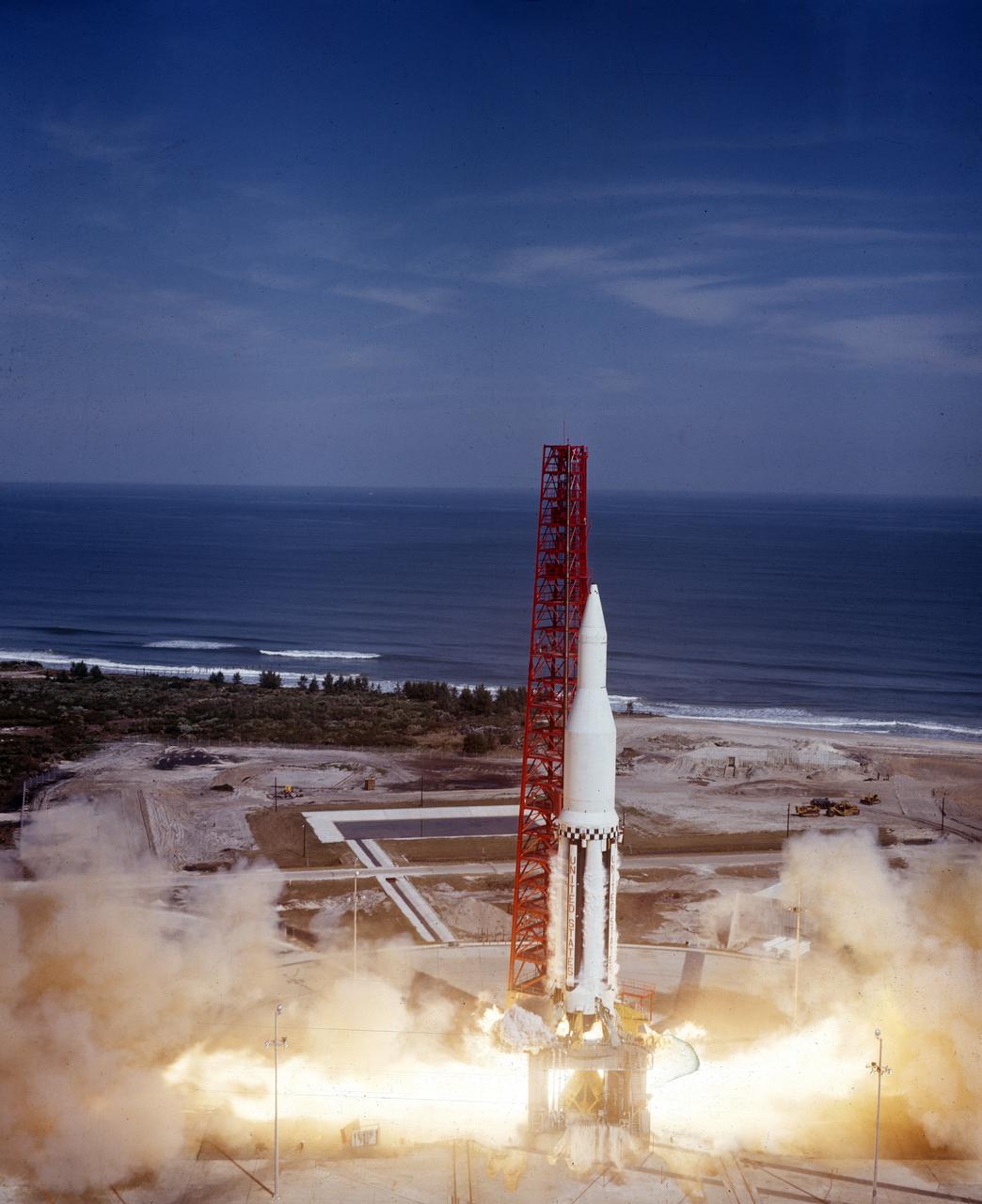

The Saturn I (SA-3) flight lifted off from Kennedy Space Center launch Complex 34, November 16, 1962. The third launch of Saturn launch vehicles, developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, incorporated a Saturn I, Block I engine. The typical height of a Block I vehicle was approximately 163 feet. and had only one live stage. It consisted of eight tanks, each 70 inches in diameter, clustered around a central tank, 105 inches in diameter. Four of the external tanks were fuel tanks for the RP-1 (kerosene) fuel. The other four, spaced alternately with the fuel tanks, were liquid oxygen tanks as was the large center tank. All fuel tanks and liquid oxygen tanks drained at the same rates respectively. The thrust for the stage came from eight H-1 engines, each producing a thrust of 165,000 pounds, for a total thrust of over 1,300,000 pounds. The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis and canted outward slightly, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern offset 40 degrees from the inner pattern. Unlike the inner engines, each outer engine was gimbaled. That is, each could be swung through an arc. They were gimbaled as a means of steering the rocket, by letting the instrumentation of the rocket correct any deviations of its powered trajectory. The block I required engine gimabling as the only method of guiding and stabilizing the rocket through the lower atmosphere. The upper stages of the Block I rocket reflected the three-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. During the SA-3 flight, the upper stage ejected 113,560 liters (30,000 gallons) of ballast water in the upper atmosphere for "Project Highwater" physics experiment. The water was released at an altitude of 65 miles, where within only 5 seconds, it expanded into a massive ice cloud 4.6 miles in diameter. Release of this vast quantity of water in a near-space environment marked the first purely scientific large-scale experiment.
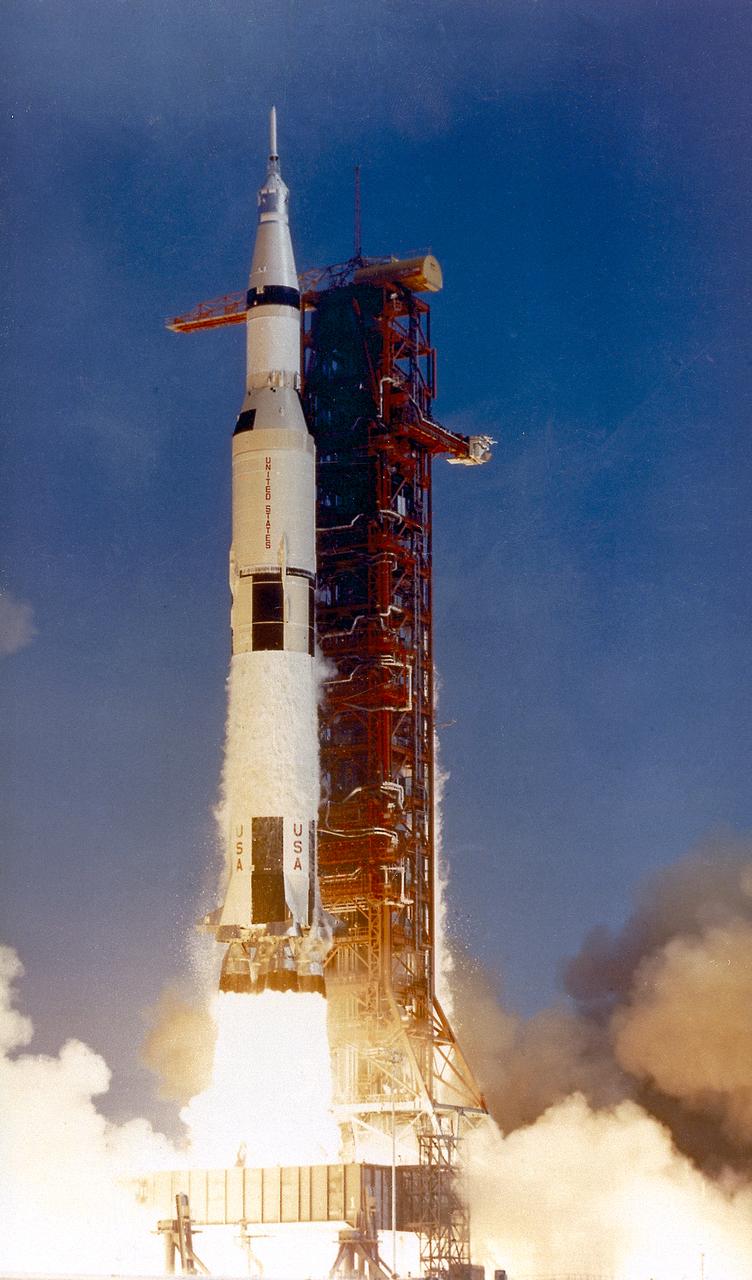
This photograph shows the Saturn V launch vehicle (SA-506) for the Apollo 11 mission liftoff at 8:32 am CDT, July 16, 1969, from launch complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. Apollo 11 was the first manned lunar landing mission with a crew of three astronauts: Mission commander Neil A. Armstrong, Command Module pilot Michael Collins, and Lunar Module pilot Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr. It placed the first humans on the surface of the moon and returned them back to Earth. Astronaut Armstrong became the first man on the lunar surface, and astronaut Aldrin became the second. Astronaut Collins piloted the Command Module in a parking orbit around the Moon.
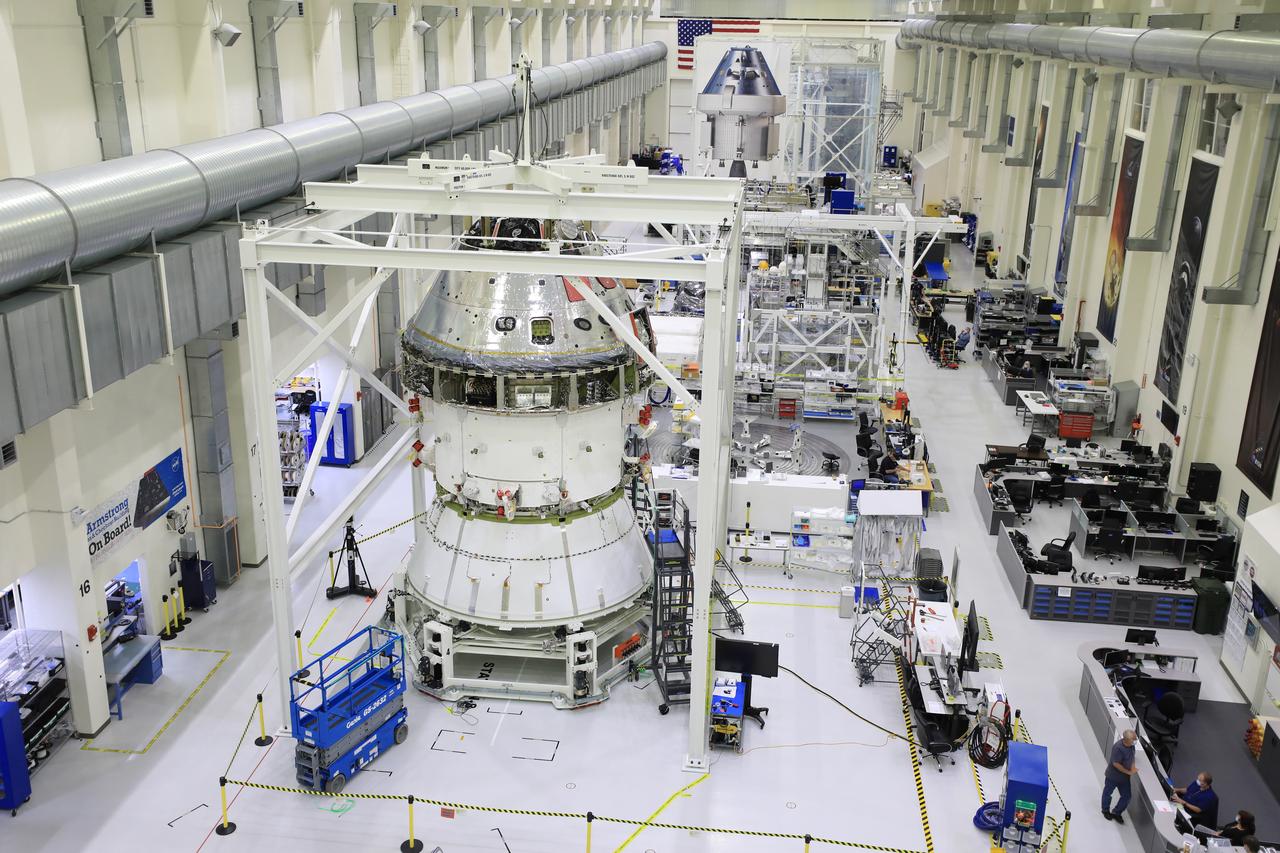
Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
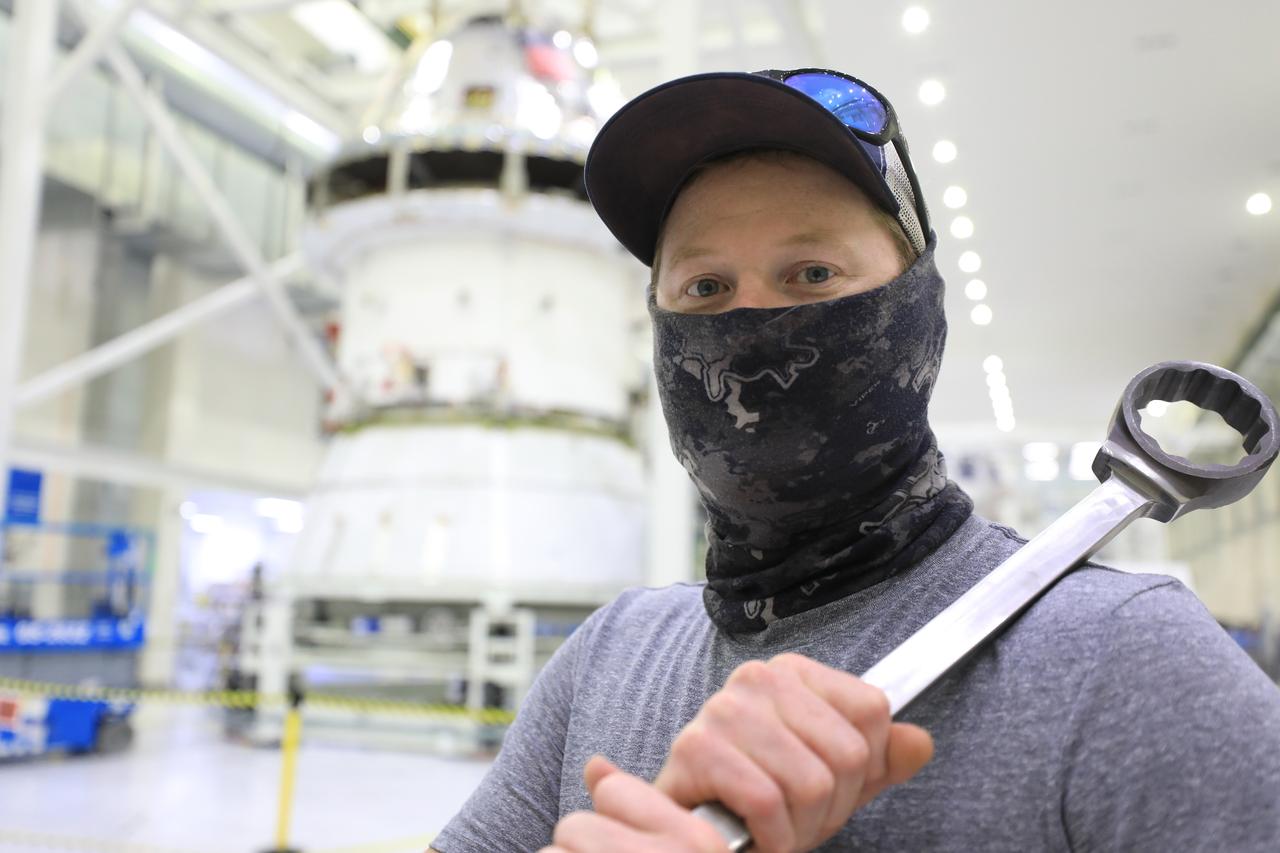

ASRC technician Chris Slack assists with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
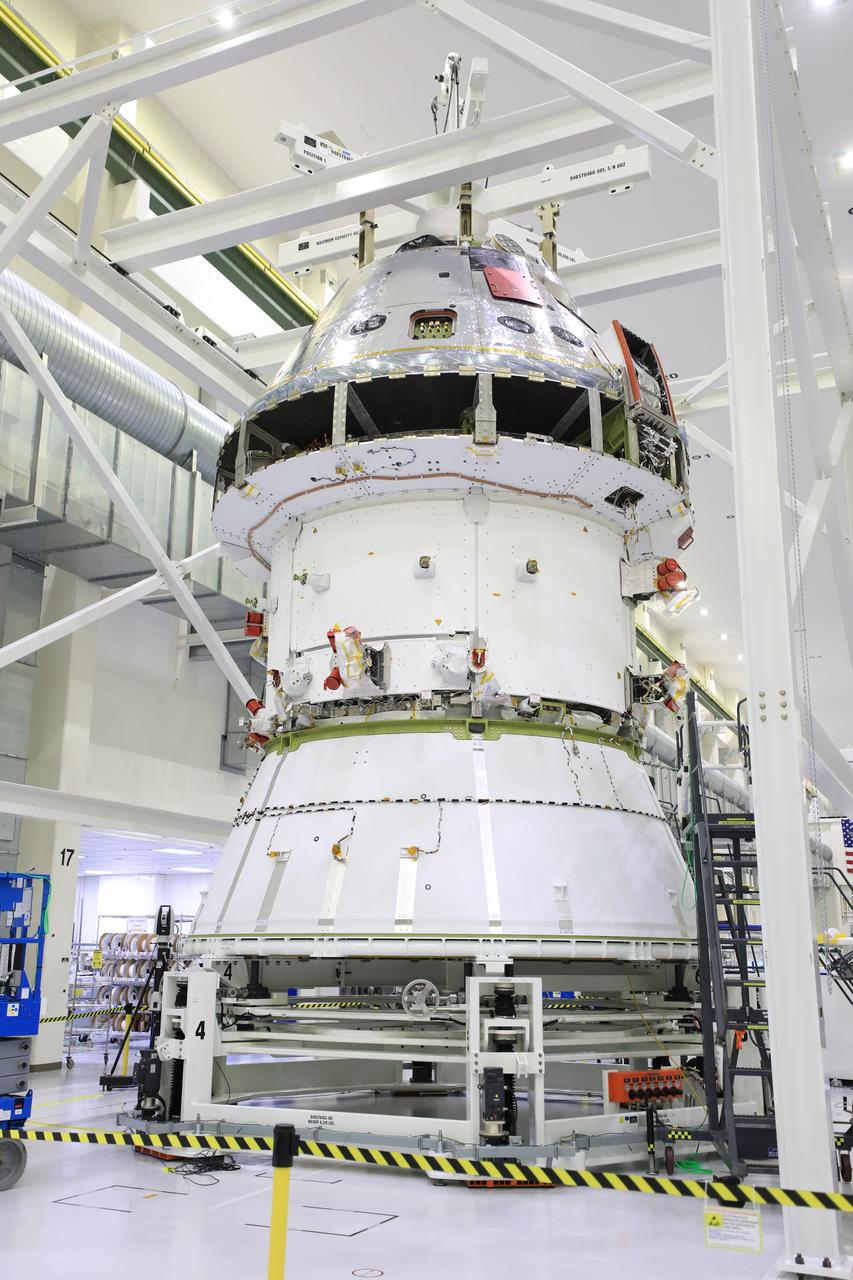

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
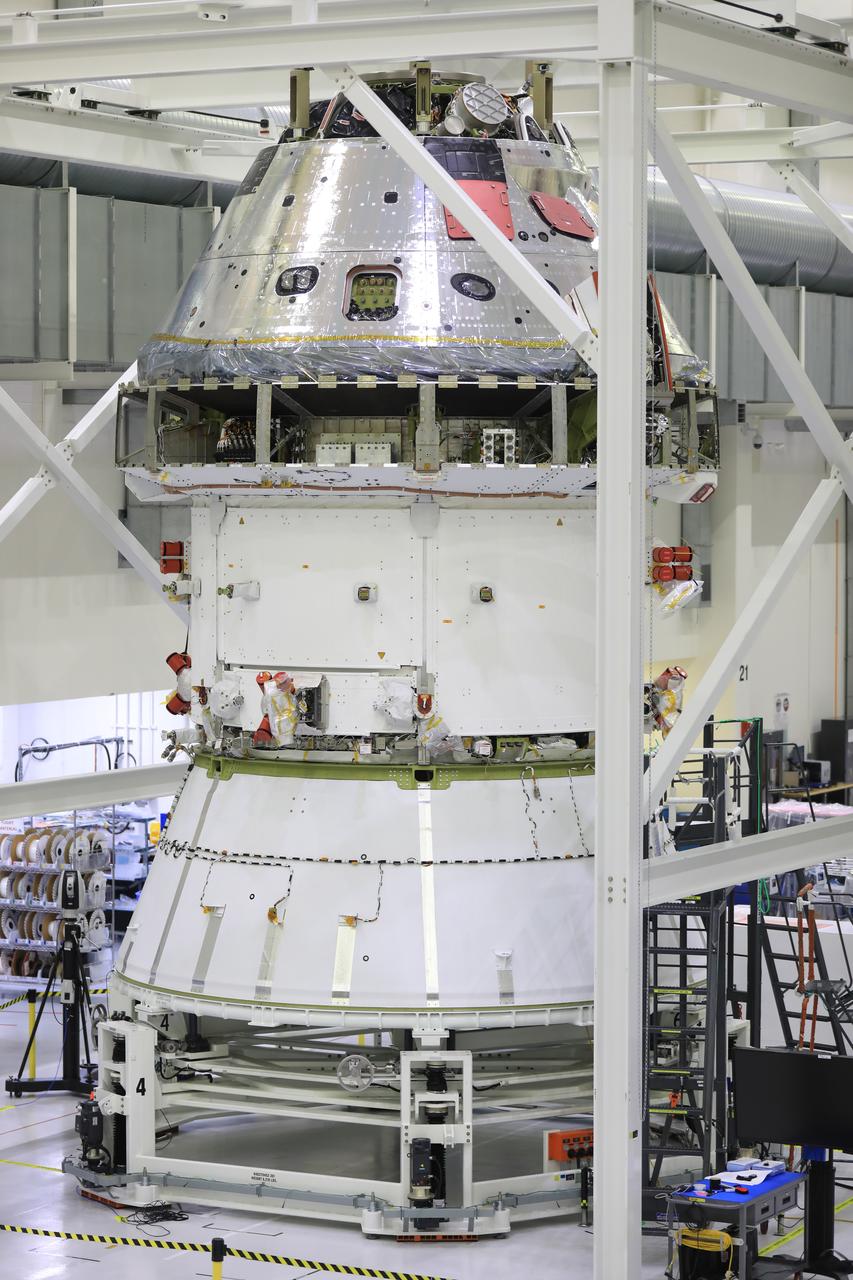

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
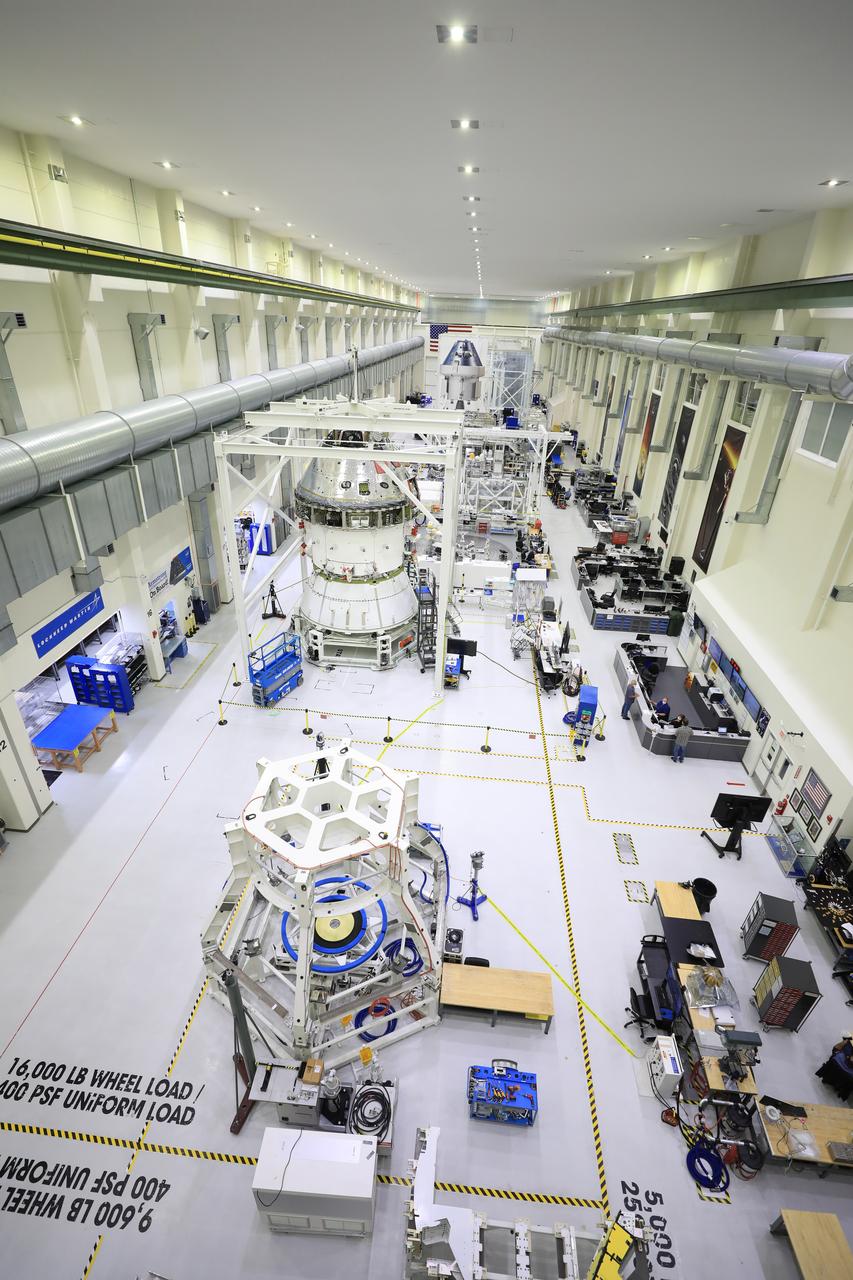

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
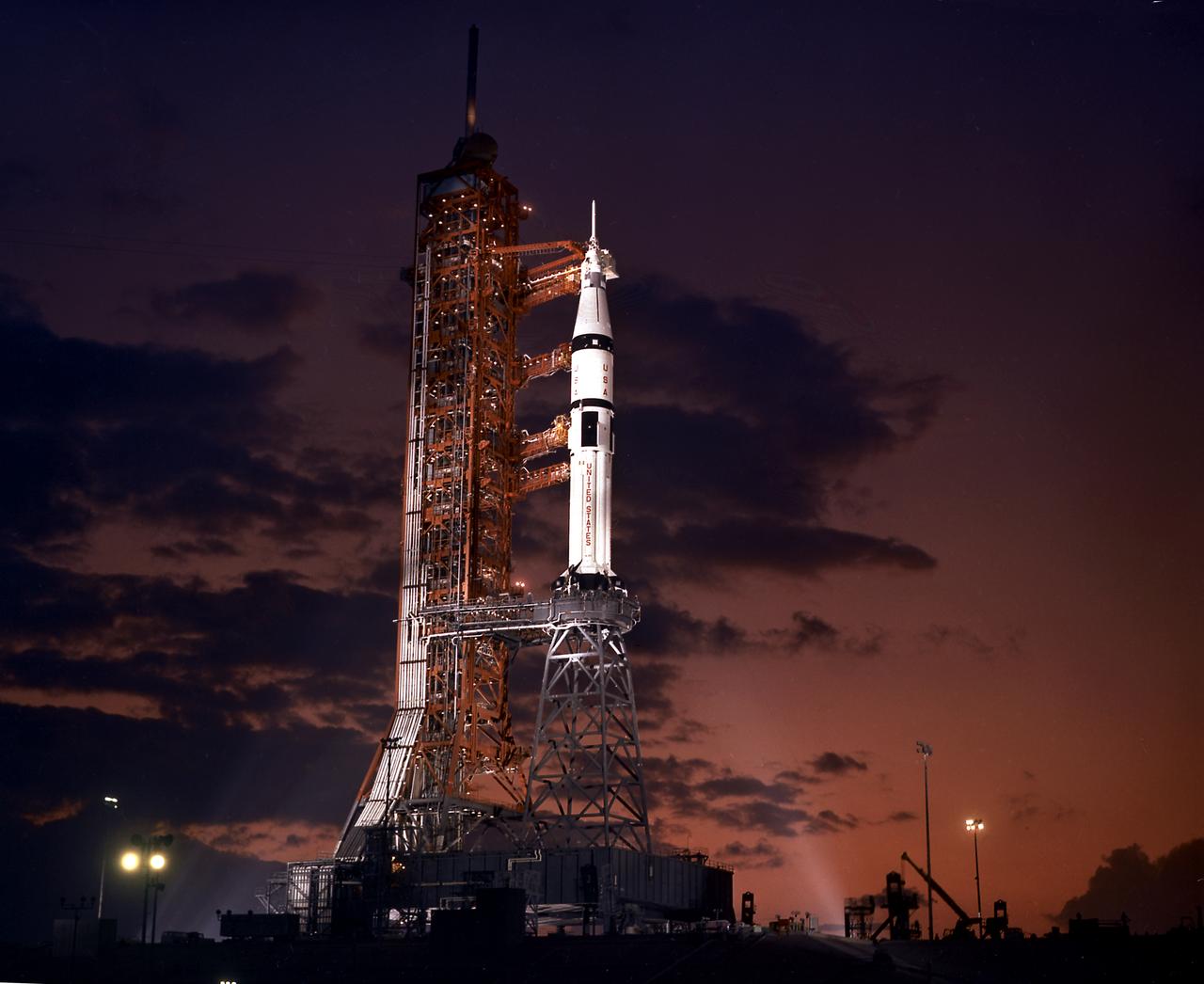

SA-210 Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) awaits the launch scheduled on July 15, 1975 on the launch pad at the Kennedy Space Center, the ASTP mission with astronauts Thomas Stafford, Vance Brand, and Donald "Deke" Slayton. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project .
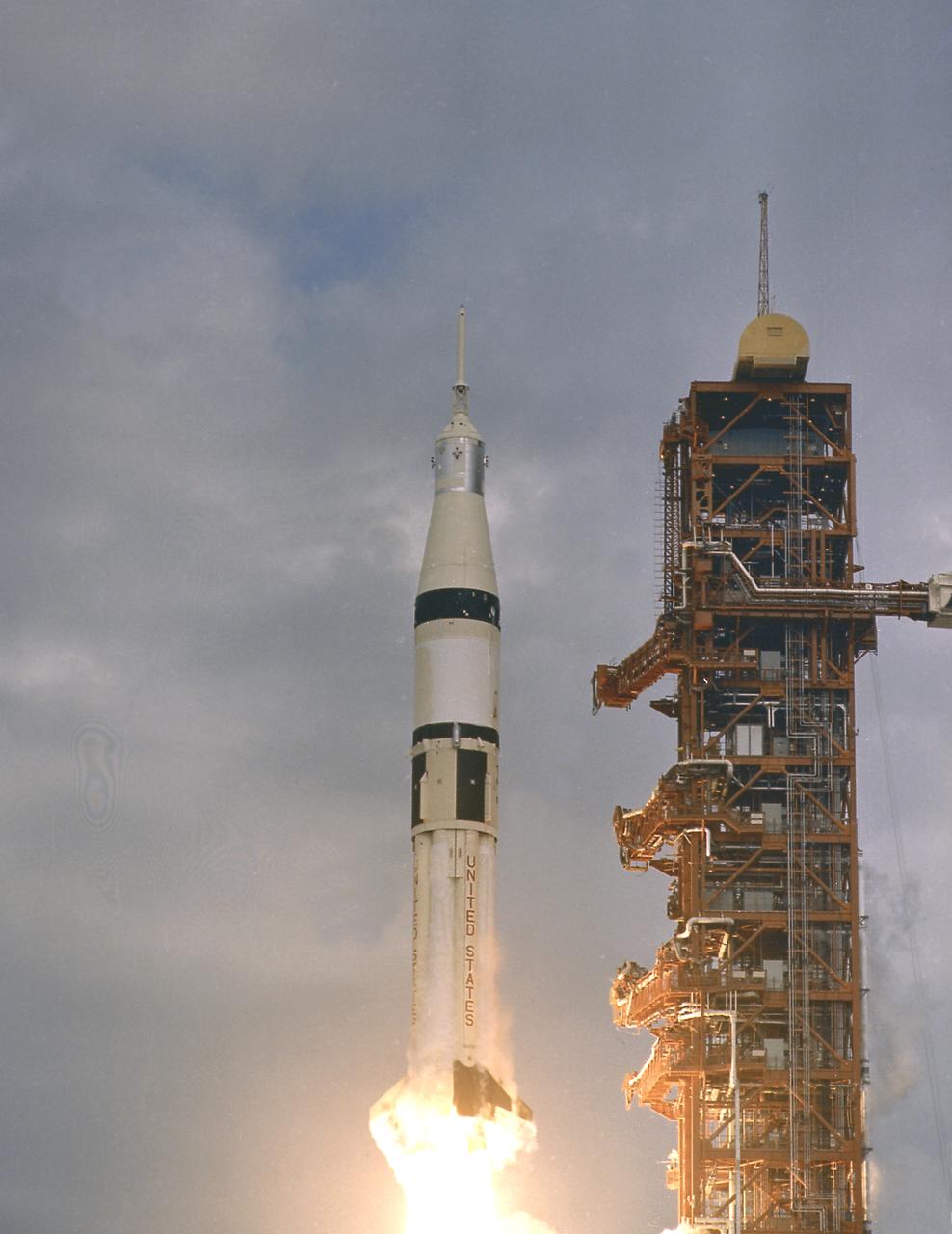
SA-206 lifts off from Kennedy Space Center's launch complex 39B, in Florida, on May 25, 1973, for the first manned Skylab mission (SL-2) with astronauts Pete Conrad, Joseph Kerwin, and Paul Weitz. The Saturn IB, developed under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), launched five manned Earth-orbital missions between 1968 and 1975: Apollo 7, Skylab 2, Skylab 3, Skylab 4, and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP).
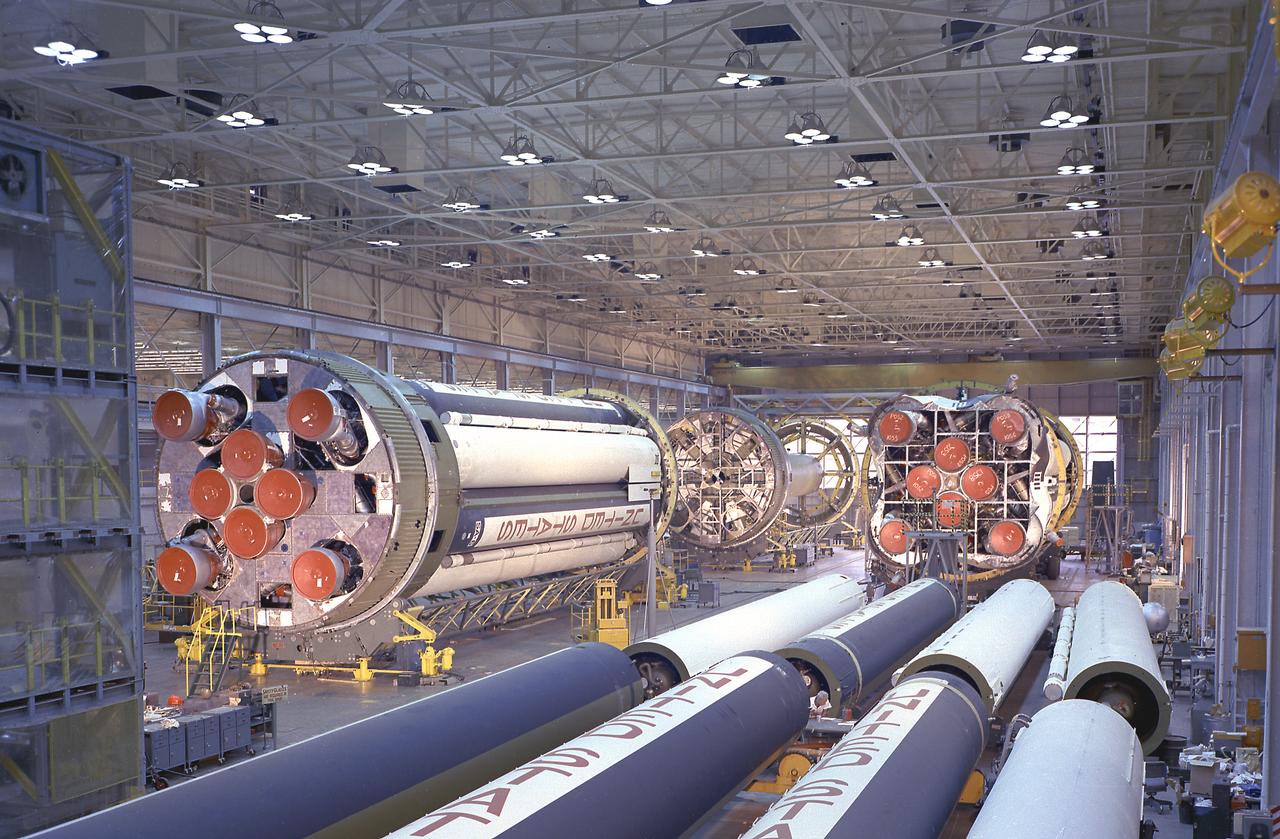

In this photograph, the Saturn I S-I stages for the SA-4, SA-6, and SA-7 missions were being assembled at the Fabrication and Assembly Engineering Division in the Marshall Space Flight Center building 4705, January 13, 1963.
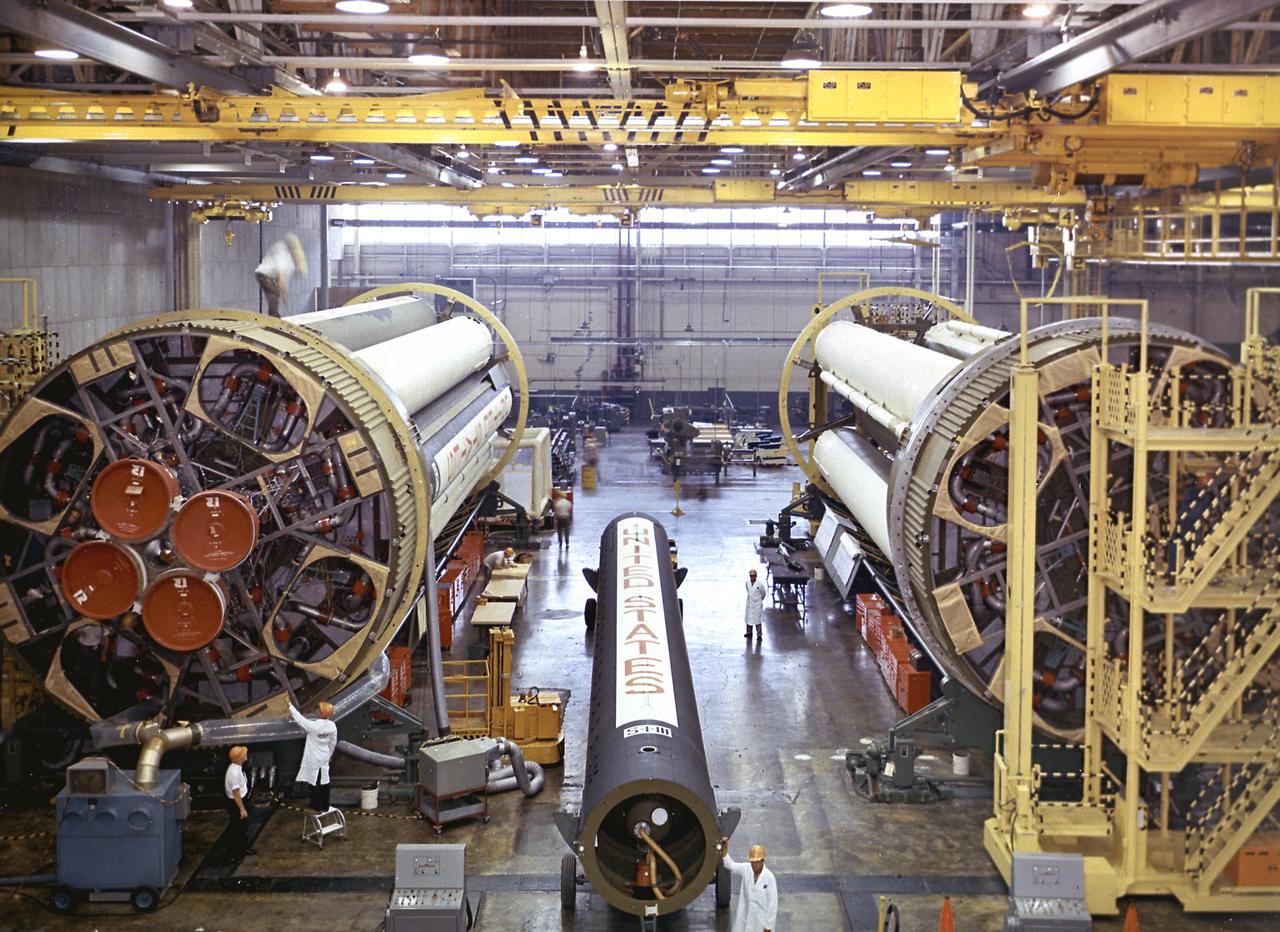

The Saturn I S-I stages for the SA-8 and SA-10 mission in final assembly phase in a manufacturing building at the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana. The SA-8 mission was launched on May 25, 1965 with the first industry-built booster, and deployed the Pegasus II Micrometeoroid Detection satellite. The SA-10 mission was the last Saturn I mission, launched on July 30, 1965, and carried the Pegasus III Meteoroid Detection satellite.
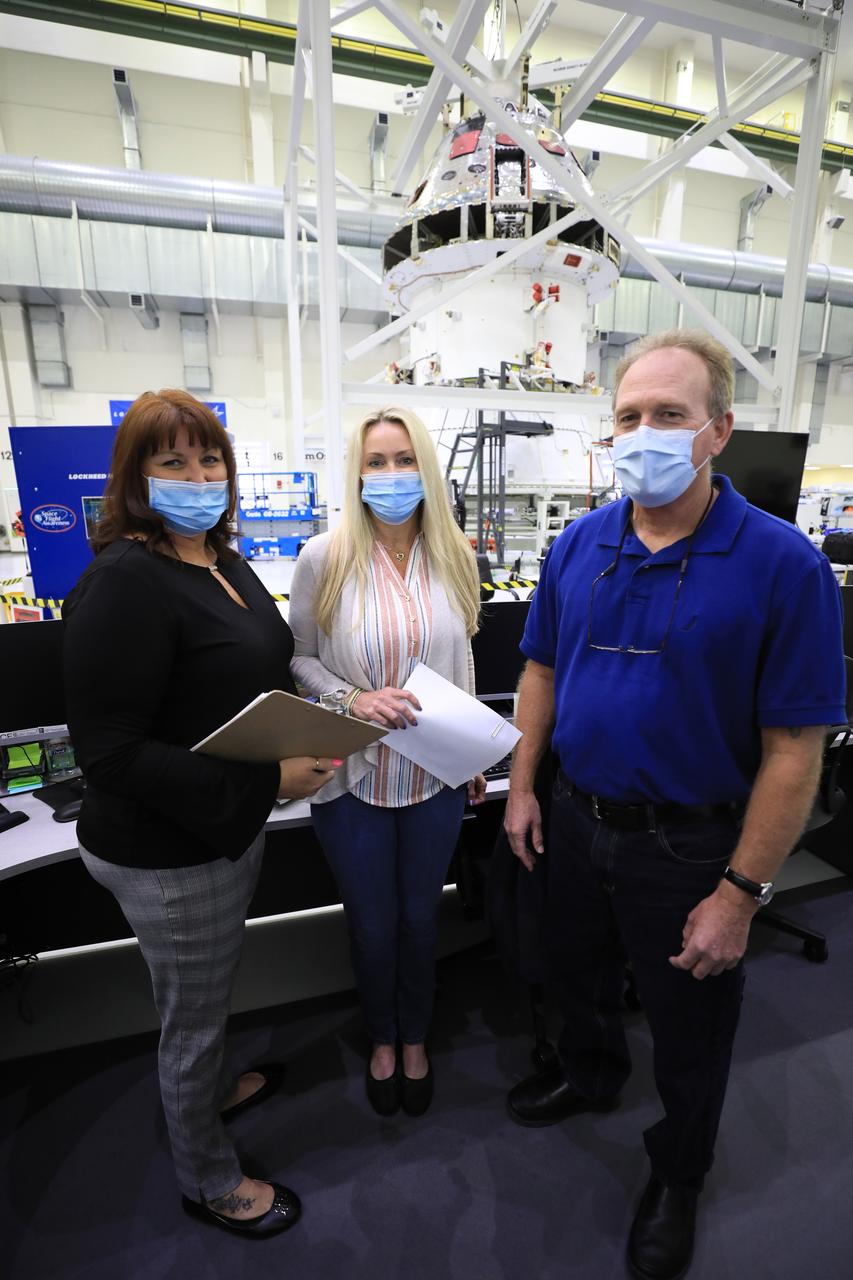

From left, Michelle Clontz and Sharon Prisco, with Lockheed Martin security operations, and Newt Allen, ASRC operations, assist with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
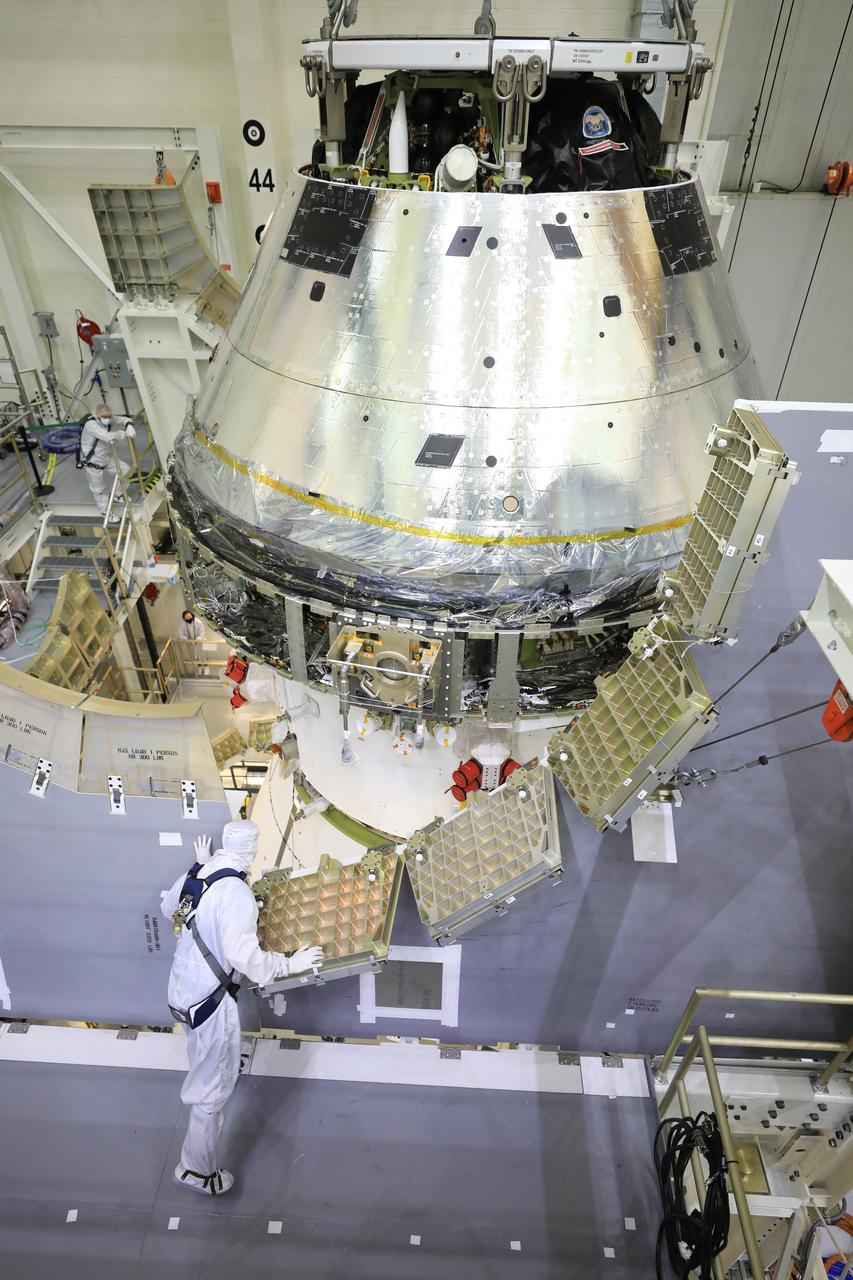

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely lower the Artemis I Orion spacecraft into the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
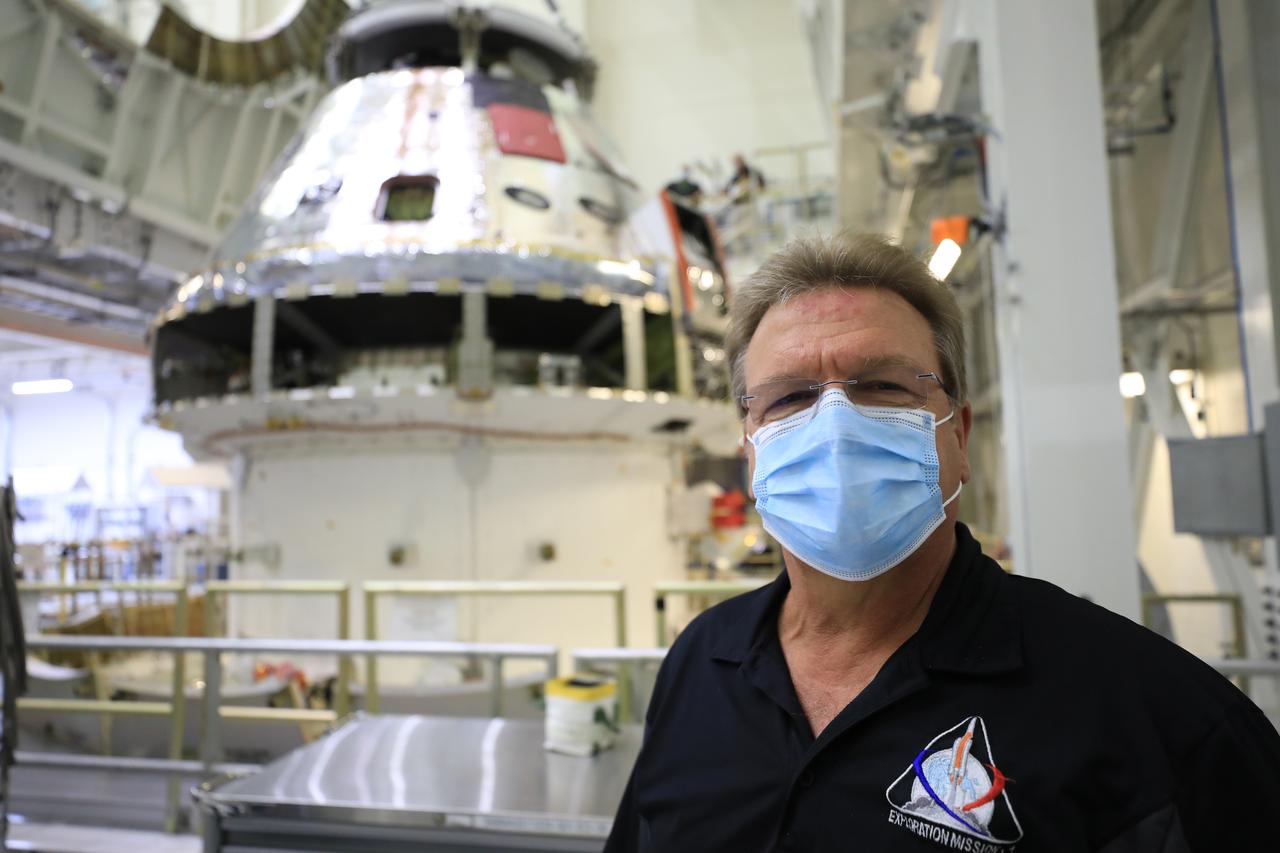

Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Assembly, Test and Launch Operations director, is shown inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay in front of the FAST cell as the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is lowered by crane after installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone was completed on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
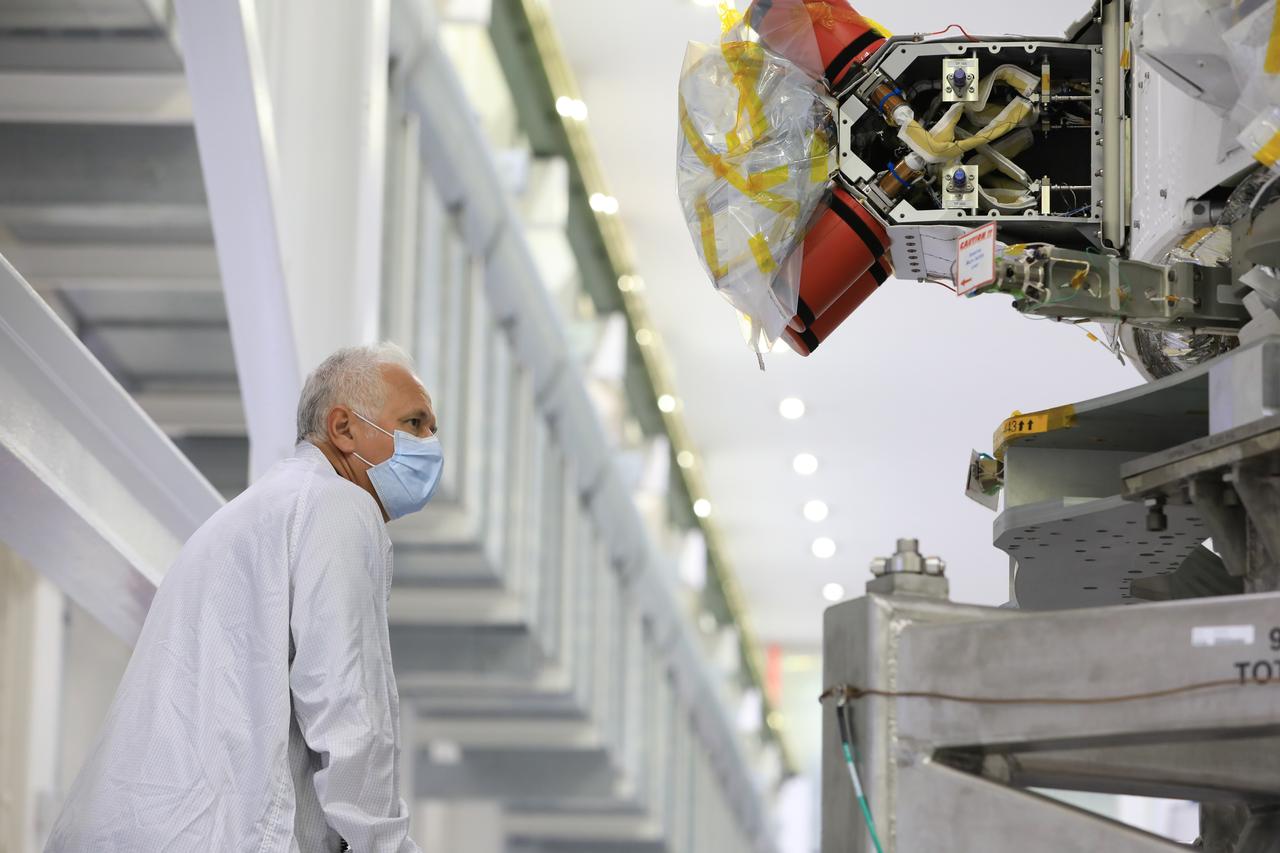

Vince Nichols, Lockheed Martin Floor Operations, inspects the Artemis I Orion spacecraft in preparation for installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
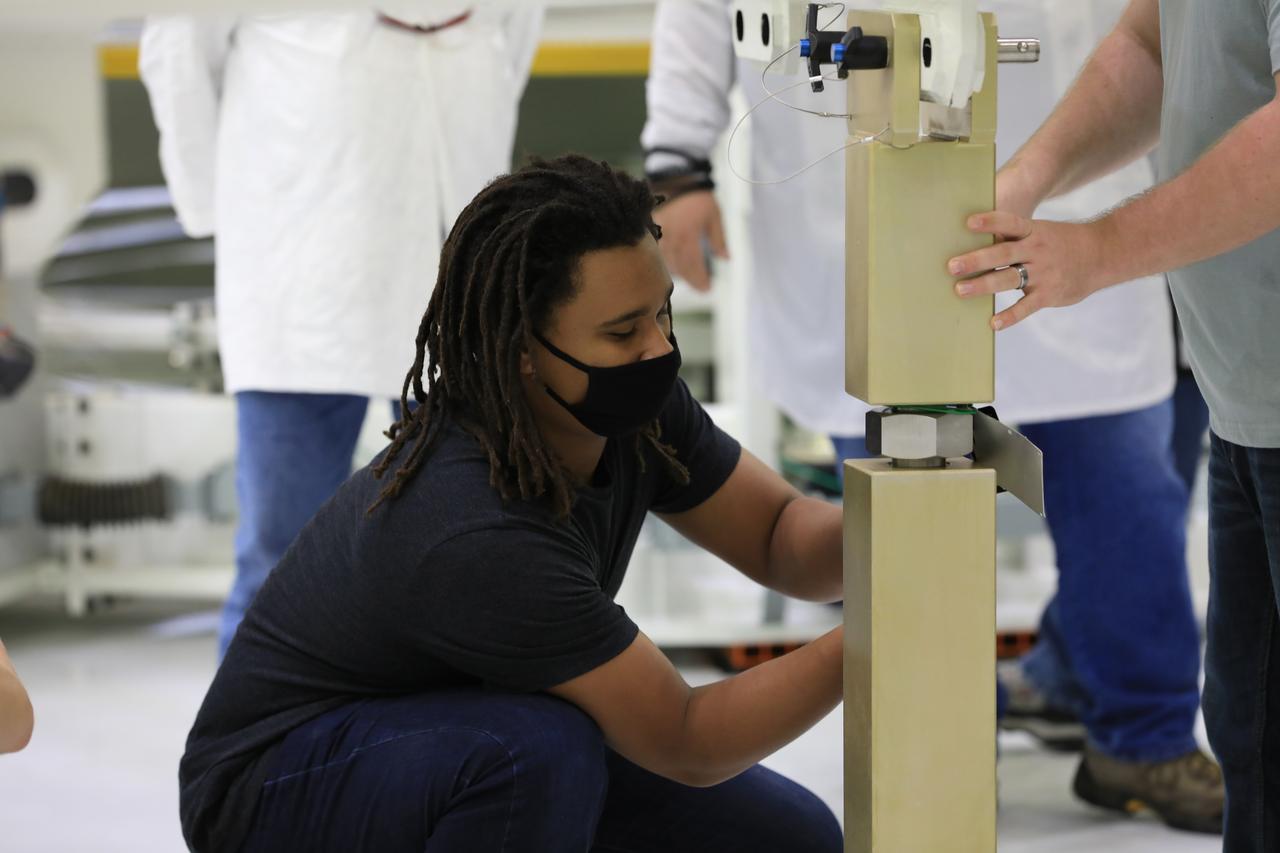

ASRC technician Nathaniel Bowman works to ready the Super Station fixture that will support the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.