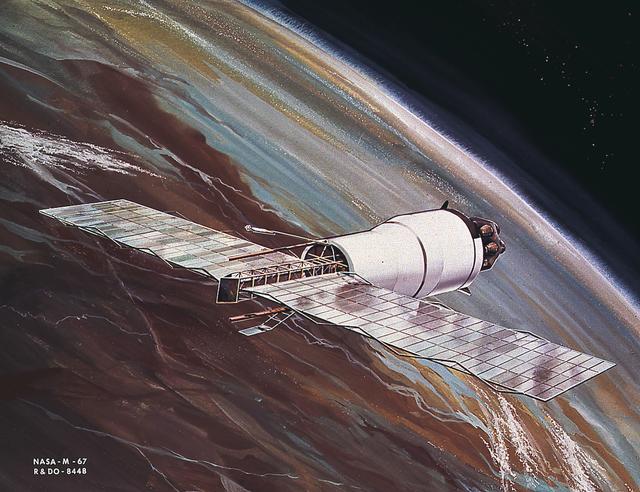

This image is an artist's conception of the Pegasus, meteoroid detection satellite, in orbit with meteoroid detector extended. The satellite, a payload for Saturn I SA-8, SA-9, and SA-10 missions, was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth.
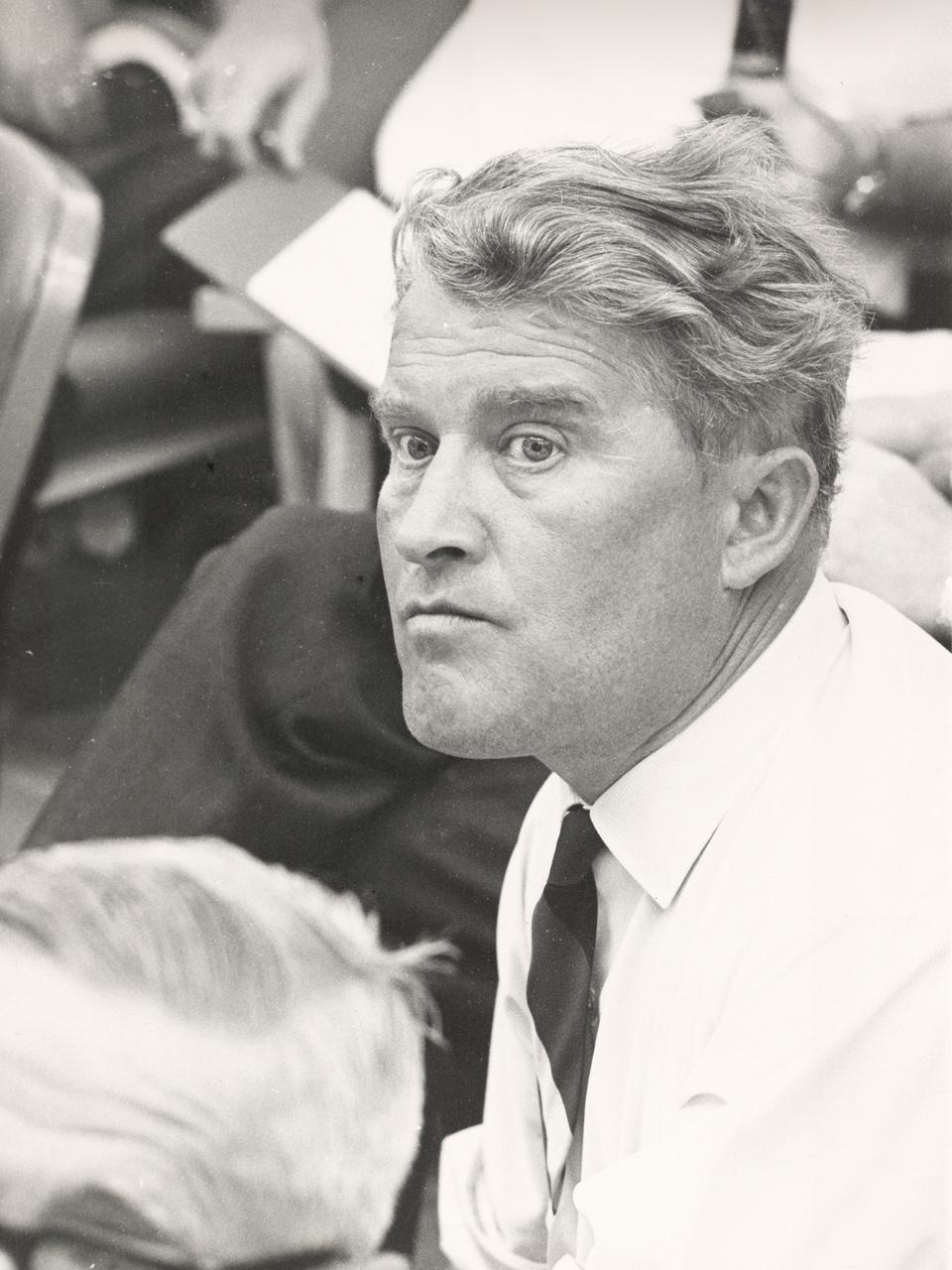

In this photo, Dr. von Braun anxiously awaits the launch of the Saturn I vehicle (SA-8) in the Launch Complex Control Center at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 1965. The SA-8 mission made the first night launch and deployed the Pegasus II micro meteoroid detection satellite.
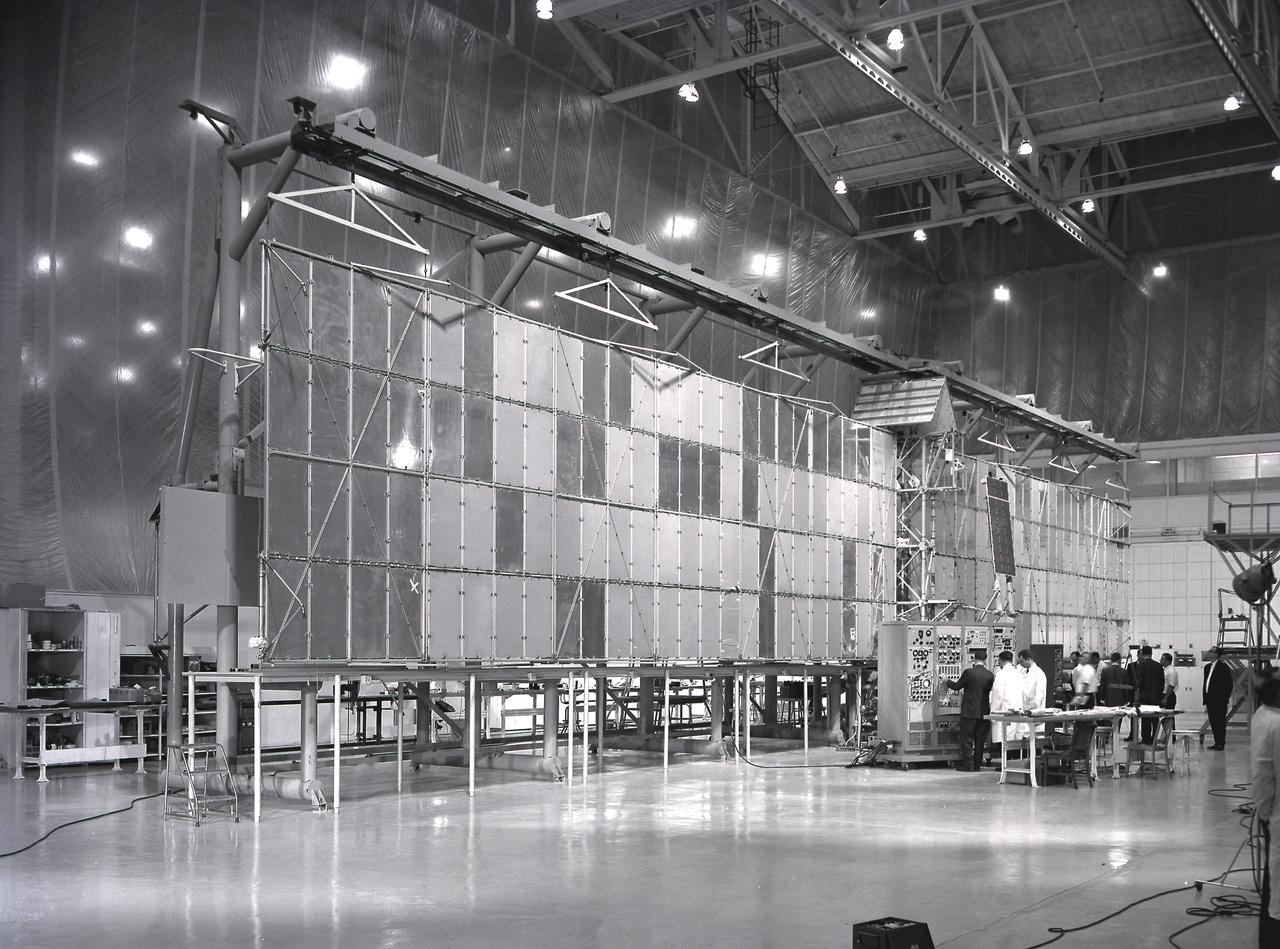

Fairchild technicians check out the extended Pegasus meteoroid detection surface. The Pegasus was developed by Fairchild Stratos Corporation, Hagerstown, Maryland, for NASA through the Marshall Space Flight Center. Three Pegasus satellites were flown aboard Saturn I SA-8, SA-9, and SA-10 missions. After being placed into orbit around the Earth, the satellite unfolded a series of giant panels to form a pair of wings measuring 96 feet across. The purpose of the satellite was to electronically record the size and frequency of particles in space, and compare the performance of protected and unprotected solar cells as important new preliminaries to a marned flight to the Moon.
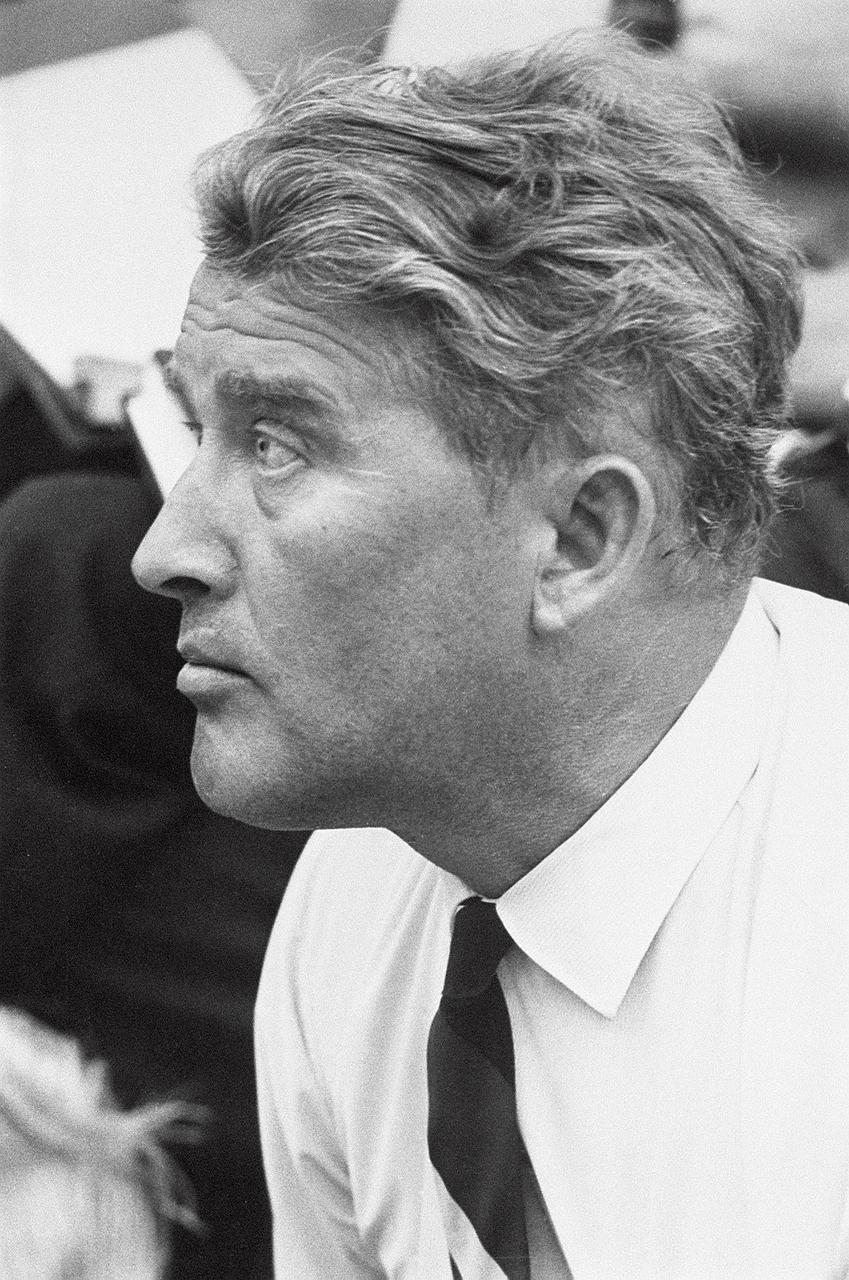

This profile of Dr. von Braun was taken in the Launch Complex Control Center at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the launch of Saturn I vehicle (SA-8) on May 25, 1965.
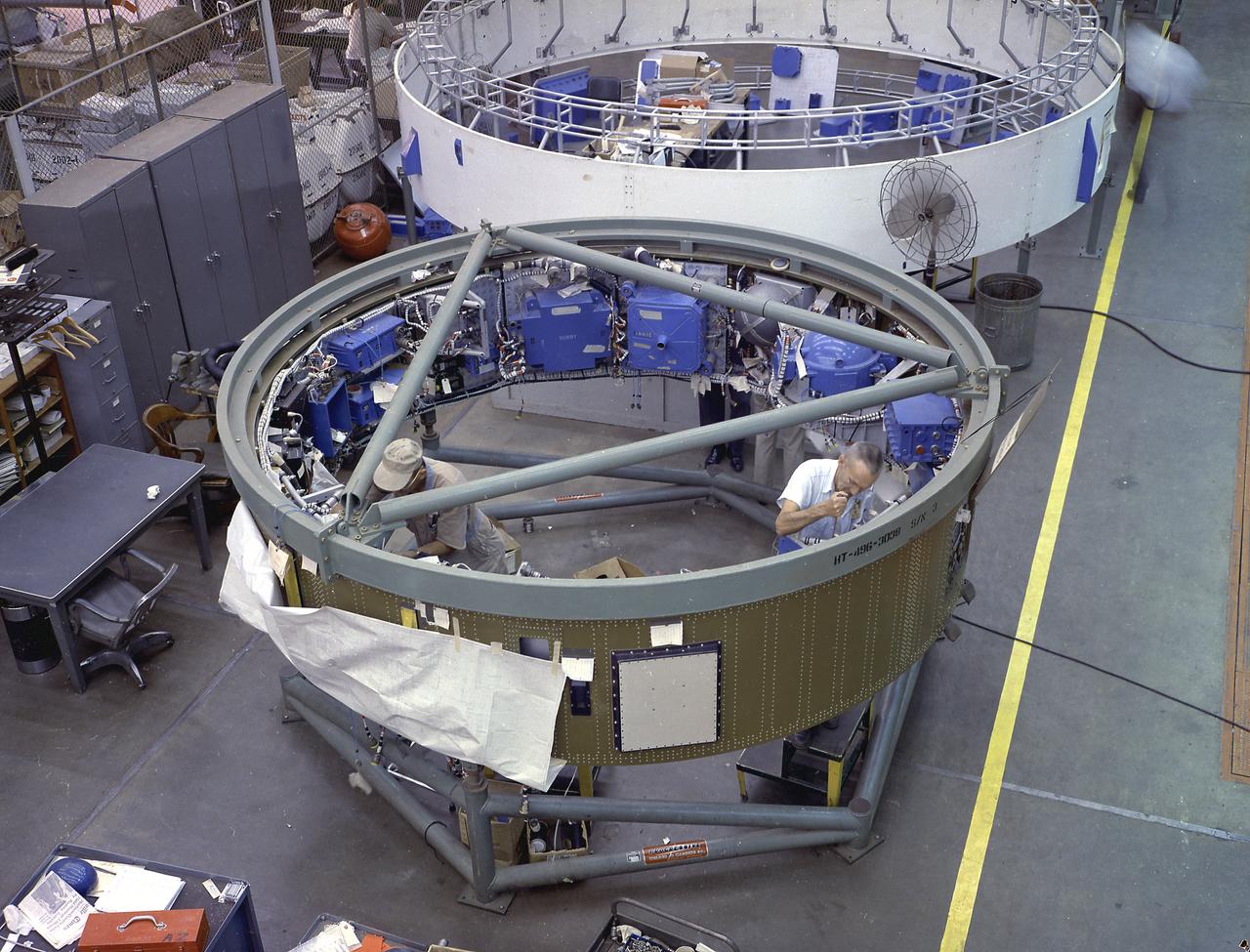
This image depicts a high angle view of technicians working on the instrument unit (IU) component assembly for the SA-8 mission in Marshall Space Flight Center's building 4705. A thin, circular structure, only 1-meter high and 7.6 meters in diameter, the IU was sandwiched between the S-IV and Apollo spacecraft. Packed inside were the computers, gyroscopes, and assorted black boxes necessary to keep the launch vehicle properly functioning and on its course.

This image depicts the tension in the Launch Control Center of the Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral, Florida, during the SA-8 on May 25, 1965. Pointing, center is Dr. Kurt Debus, Director, Launch Operations Directorate, MSFC. To the right is Dr. Hans Gruene, Deputy Director, Launch Operations Directorate, MSFC; Dr. von Braun, Director, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC); and leaning, Dr. Eberhard Rees, Director, Deputy Director for Research and Development, MSFC. The SA-8 mission, with a Saturn I launch vehicle, made the first night launch and deployed Pegasus II, micrometeoroid detection satellite.
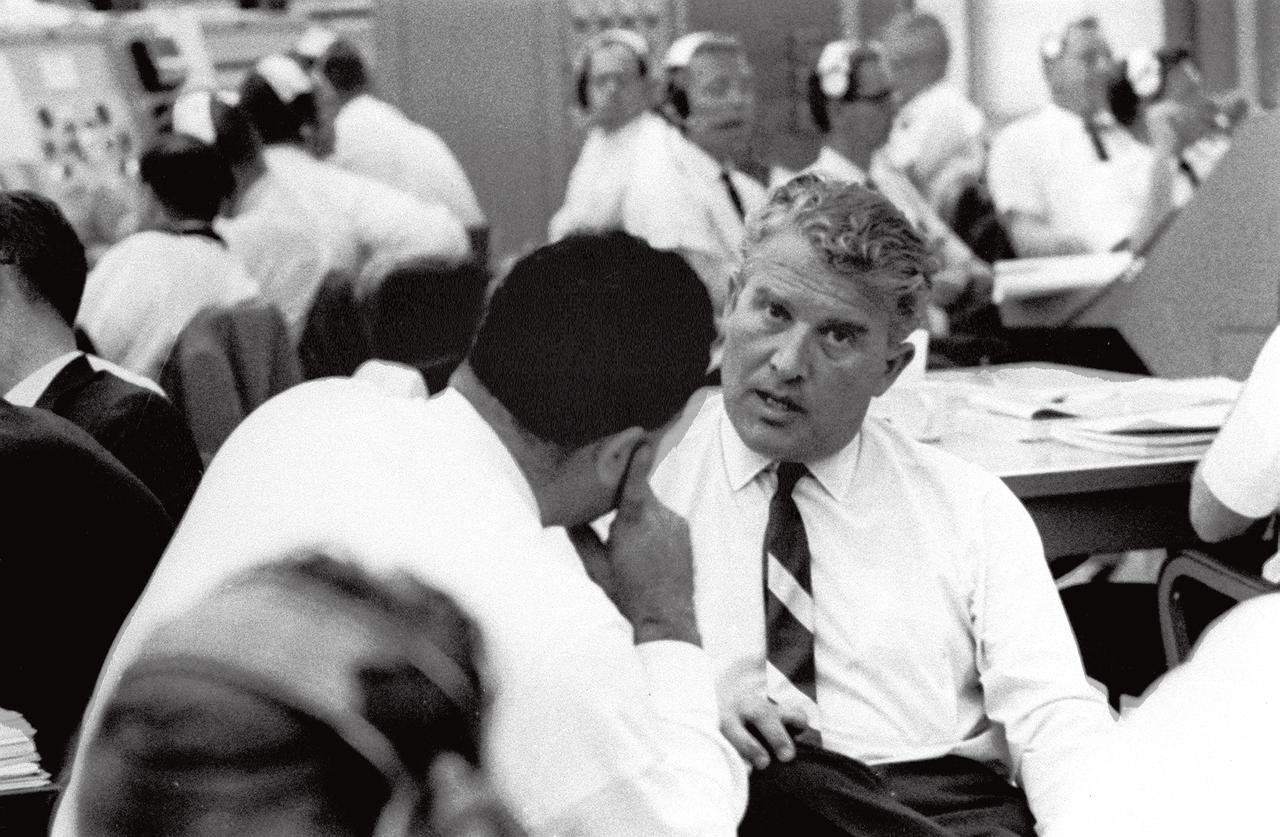

In this photograph at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Complex 37 Control Center, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director Wernher von Braun (right) talks with KSC's Rocco Petrone while awaiting the launch of SA-8 (Saturn I) on May 25, 1965. Petrone played key roles at KSC in the development of Saturn launch facilities before becoming the director of launch operations in 1966.
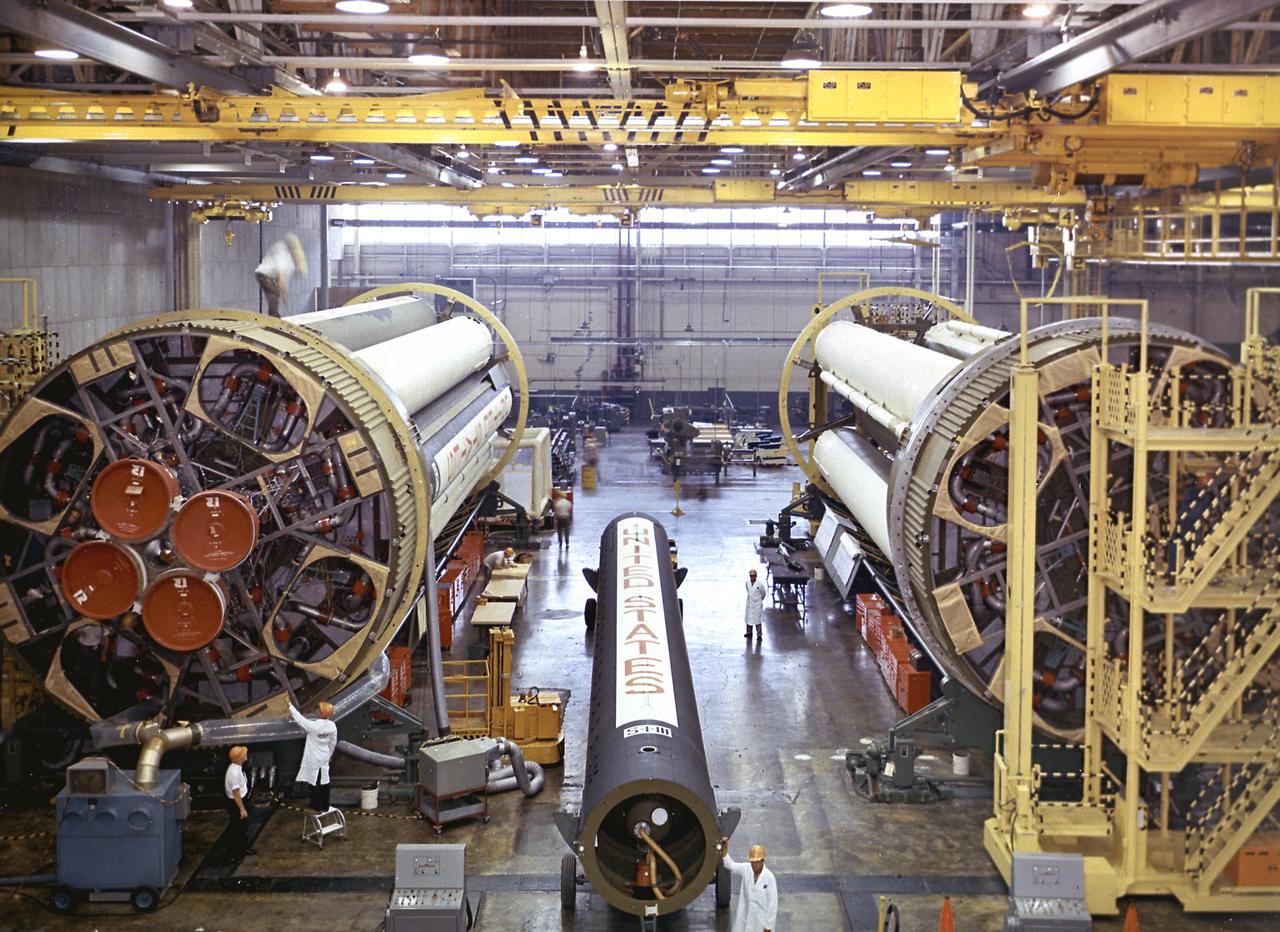

The Saturn I S-I stages for the SA-8 and SA-10 mission in final assembly phase in a manufacturing building at the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana. The SA-8 mission was launched on May 25, 1965 with the first industry-built booster, and deployed the Pegasus II Micrometeoroid Detection satellite. The SA-10 mission was the last Saturn I mission, launched on July 30, 1965, and carried the Pegasus III Meteoroid Detection satellite.

The third Saturn V launch vehicle (SA-503) for the Apollo 8 mission lifted off from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center on December 21, 1968. The first manned Saturn V vehicle with a crew of three astronauts, Frank Borman, James A. Lovell, Jr., and William Anders, escaped Earth's gravity, traveled to the lunar vicinity, and orbited the Moon.
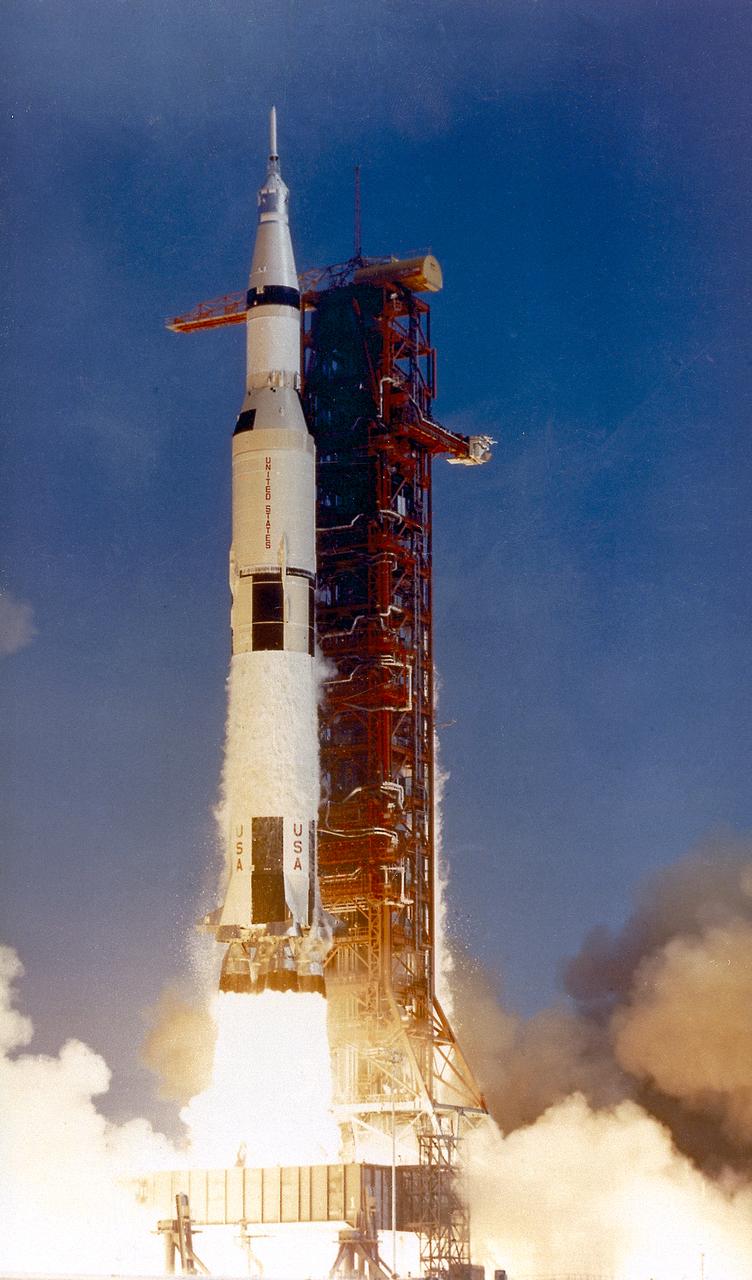
This photograph shows the Saturn V launch vehicle (SA-506) for the Apollo 11 mission liftoff at 8:32 am CDT, July 16, 1969, from launch complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center. Apollo 11 was the first manned lunar landing mission with a crew of three astronauts: Mission commander Neil A. Armstrong, Command Module pilot Michael Collins, and Lunar Module pilot Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr. It placed the first humans on the surface of the moon and returned them back to Earth. Astronaut Armstrong became the first man on the lunar surface, and astronaut Aldrin became the second. Astronaut Collins piloted the Command Module in a parking orbit around the Moon.
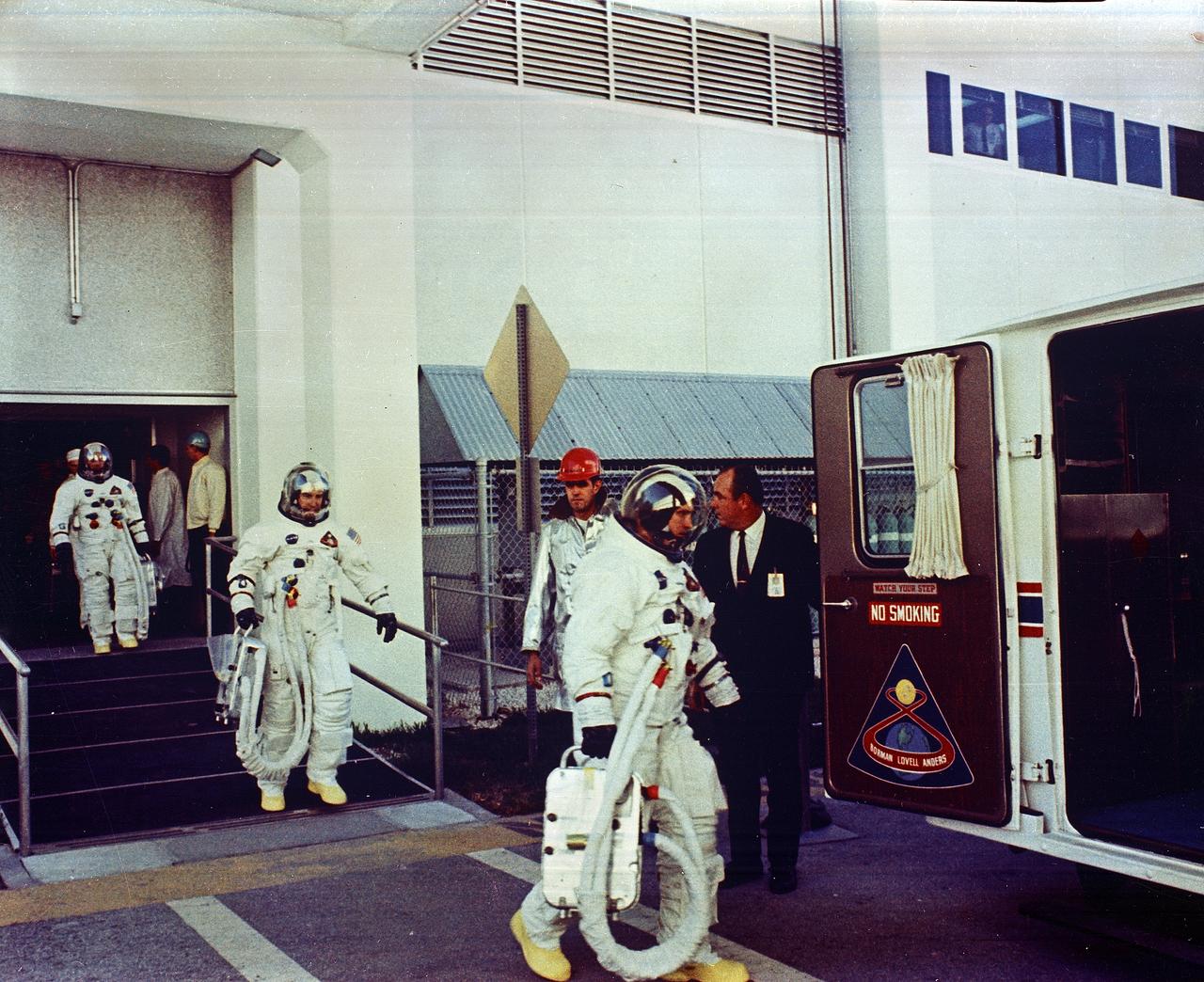

Apollo 8 Astronauts William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Frank Borman, commander, transfer to the astronaut van for the trip to the launch pad. The first manned Apollo mission launched aboard the Saturn V and first manned Apollo craft to enter lunar orbit, the SA-503, Apollo 8 mission liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
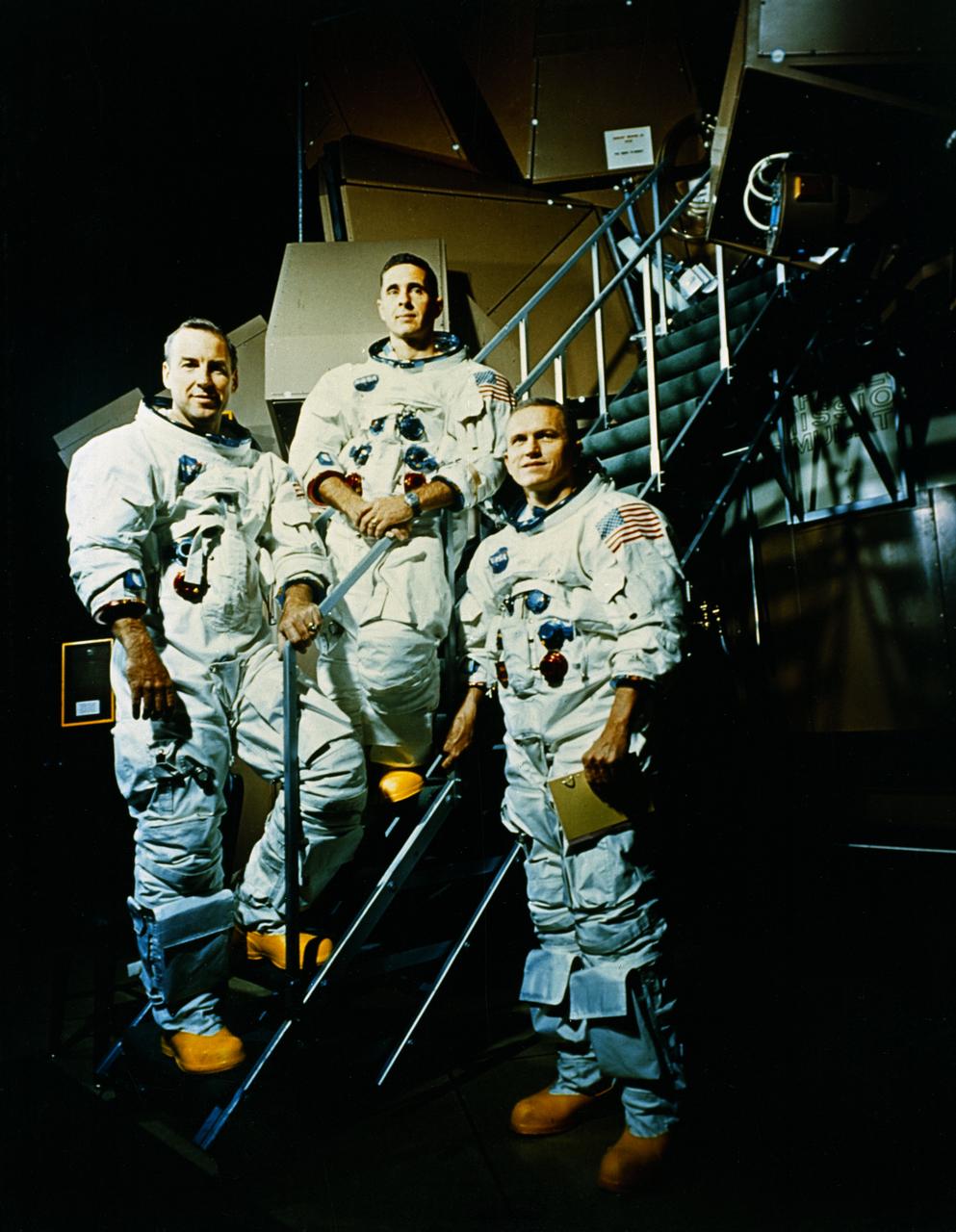

The Apollo 8 Crew included (L to R) James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; and Frank Borman, Commander. The first manned Apollo mission launched aboard the Saturn V and first manned Apollo craft to enter lunar orbit, the SA-503, Apollo 8 mission liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
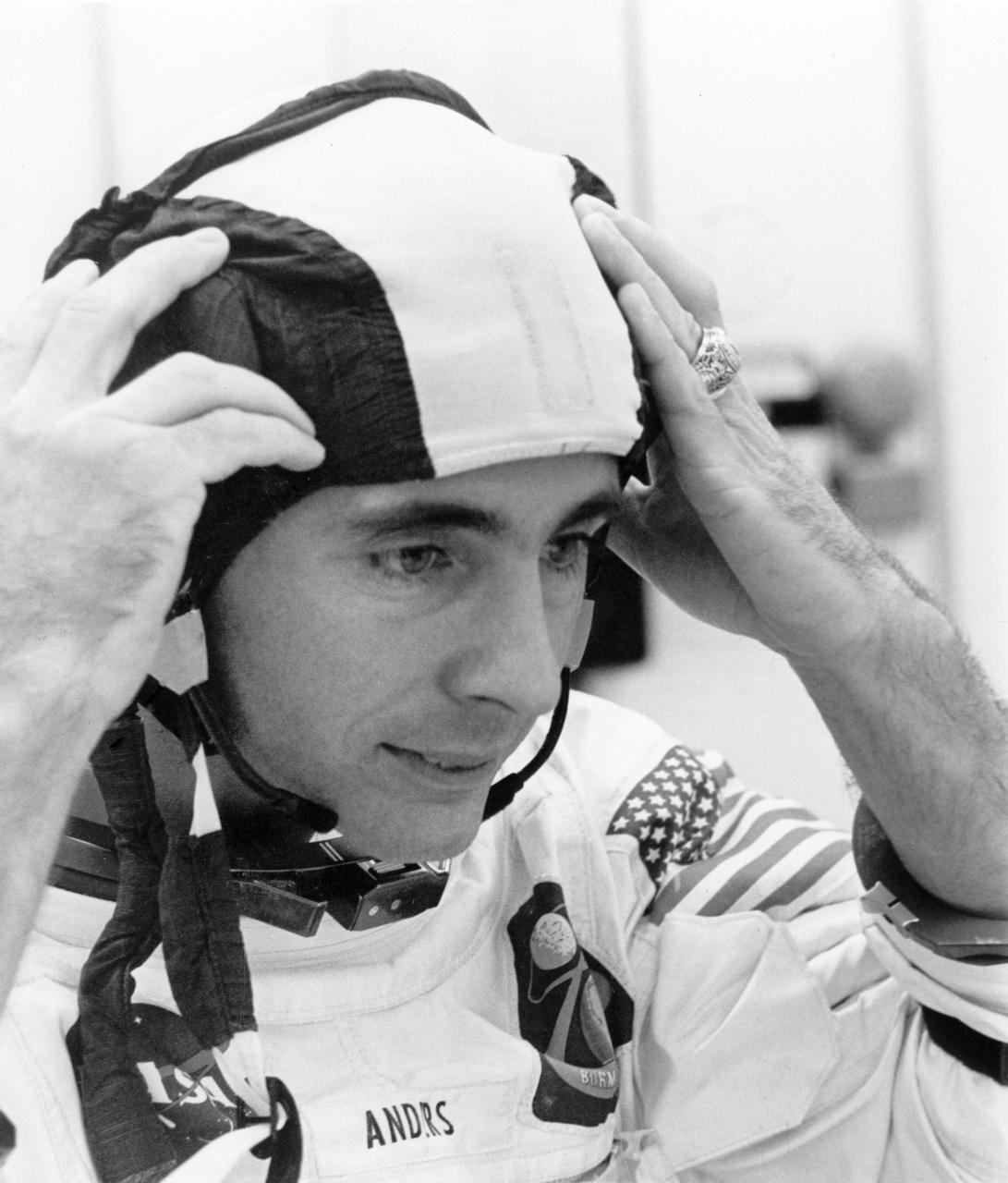

Apollo 8 Astronaut William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) pilot, adjusts his helmet as he suits up for the Apollo 8 mission. The first manned Apollo mission launched aboard the Saturn V and first manned Apollo craft to enter lunar orbit, the SA-503, Apollo 8 mission lift off occurred on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. Aboard were Anders and fellow astronauts James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Frank Borman, commander. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
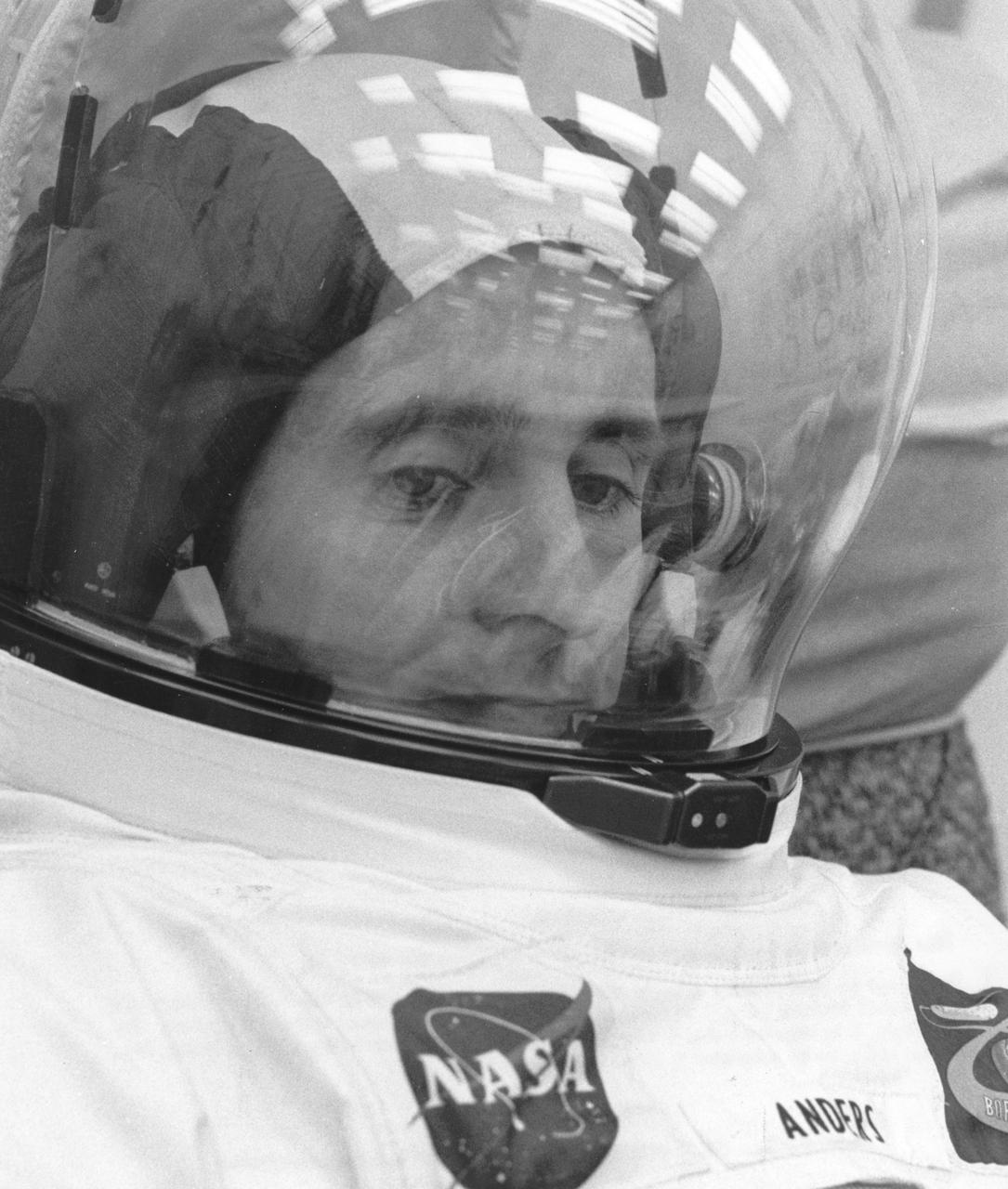

Apollo 8 astronaut William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) pilot, is suited up for the Apollo 8 mission countdown demonstration test. The first manned Apollo mission launched aboard the Saturn V and first manned Apollo craft to enter lunar orbit, the SA-503, Apollo 8 mission lift off occurred on December 21, 1968 and returned safely to Earth on December 27, 1968. Aboard were Anders and fellow astronauts James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Frank Borman, commander. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
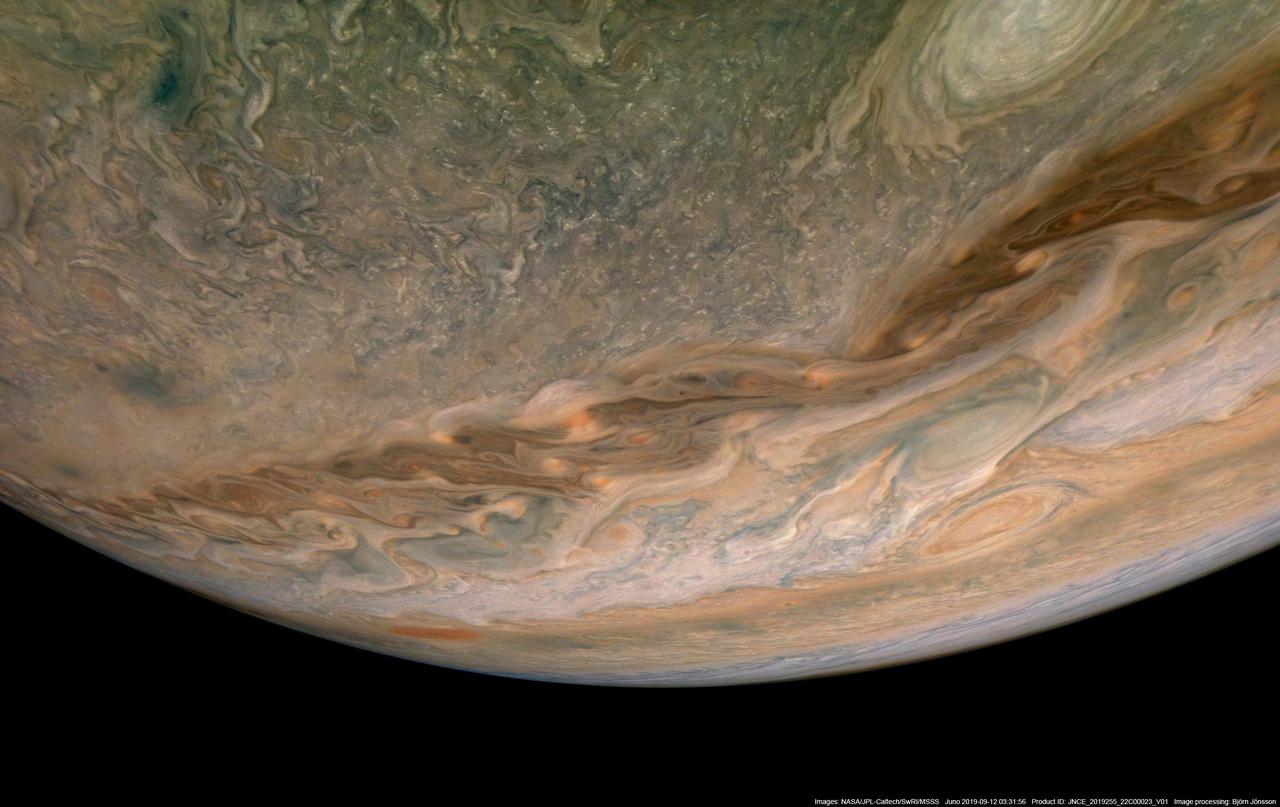

In this view of Jupiter, NASA's Juno spacecraft captures swirling clouds in the region of the giant planet's northern hemisphere known as "Jet N4." Jupiter spins once every 10 hours, and this fast rotation creates strong jet streams, separating its clouds into dark belts and bright zones that stretch across the face of the planet. More than a dozen prevailing winds sweep over Jupiter, some reaching more than 300 miles per hour (480 kilometers per hour) at the equator. The raw image was taken on Sept. 11, 2019 at 8:31 p.m. PDT (11:31 p.m. EDT), as Juno performed its 22nd close flyby of Jupiter. At the time the image was taken, the spacecraft was about 7,540 miles (12,140 kilometers) from the cloud tops at a latitude of 45 degrees. Enhanced image by Björn Jónsson (CC-NC-SA) based on images provided courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS.
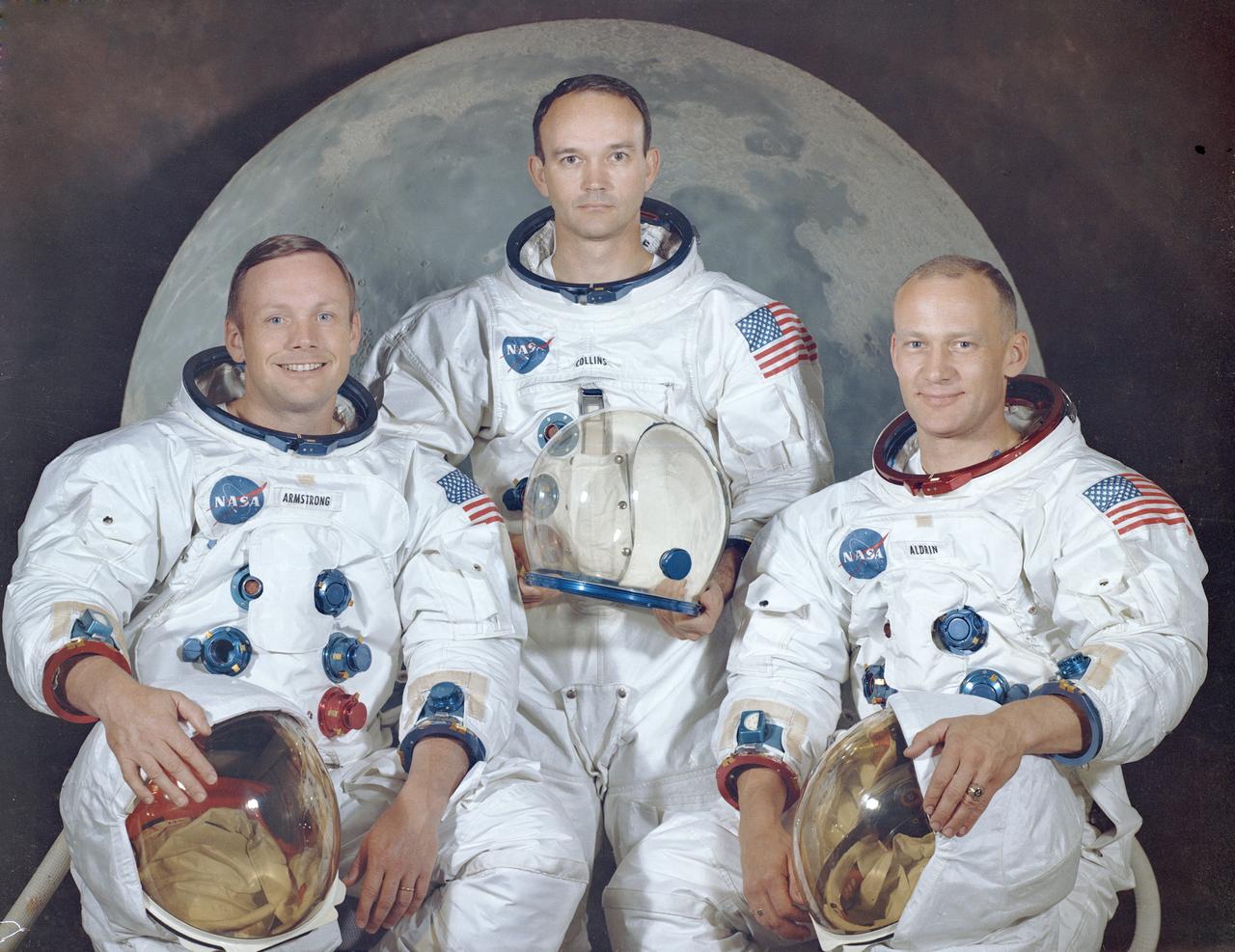

This is the official crew portrait of the Apollo 11 astronauts. Pictured from left to right are: Neil A. Armstrong, Commander; Michael Collins, Module Pilot; Edwin E. "Buzz" Aldrin, Lunar Module Pilot. Apollo 11 was the first marned lunar landing mission that placed the first humans on the surface of the moon and returned them back to Earth. Astronaut Armstrong became the first man on the lunar surface, and astronaut Aldrin became the second. Astronaut Collins piloted the Command Module in a parking orbit around the Moon. Launched aboard the Saturn V launch vehicle (SA-506), the three astronauts began their journey to the moon with liftoff from launch complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center at 8:32 am CDT, July 16, 1969.
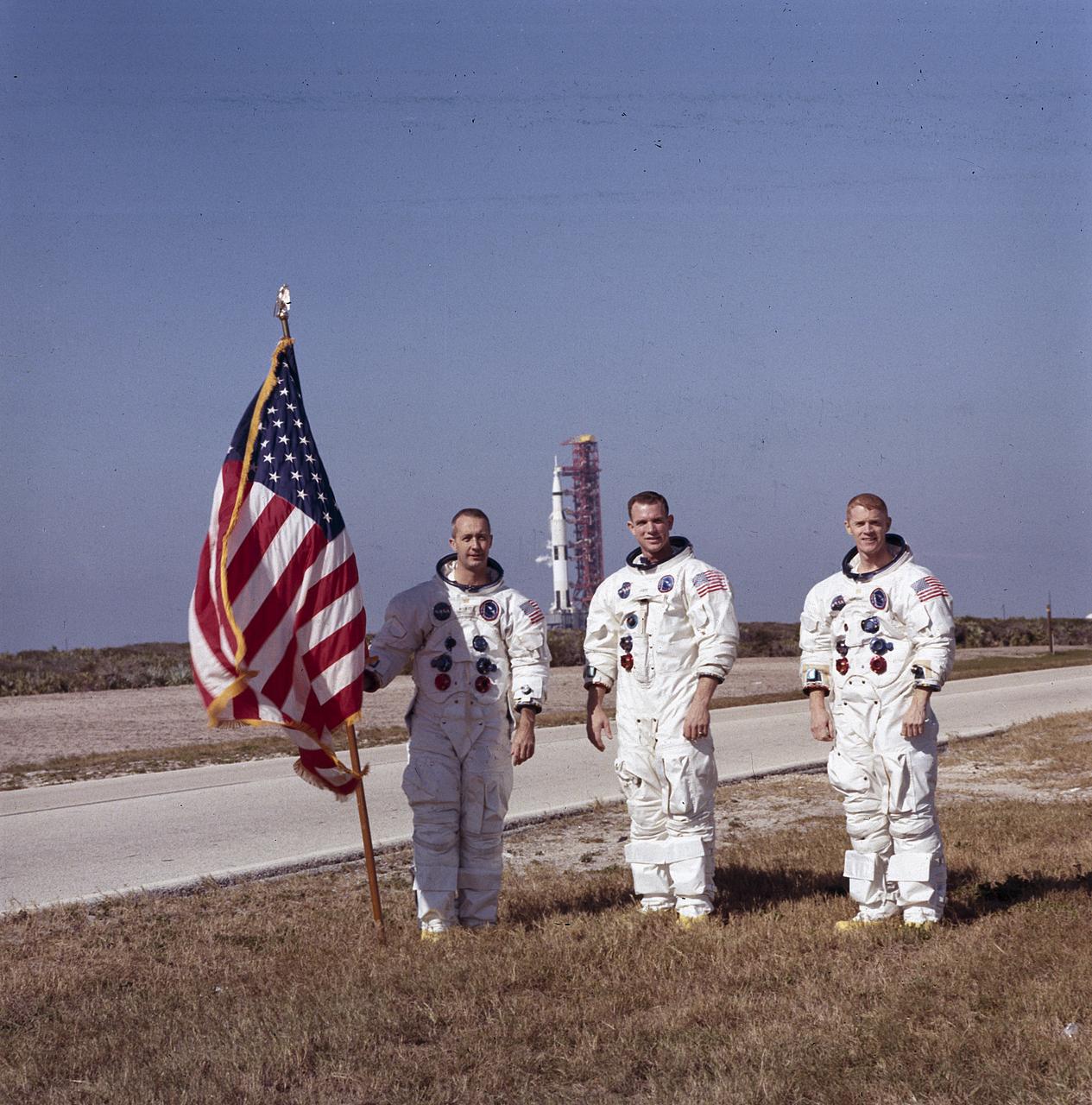

Pictured from left to right, the Apollo 9 astronauts, James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart, pause in front of the Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle that would launch the Apollo 8 crew. The launch of the Apollo 9 (Saturn V launch vehicle, SA-504) took place on March 3, 1968. The Apollo 9 spacecraft, in the lunar mission configuration, was tested in Earth orbit. The mission was designed to rehearse all the steps and reproduce all the events of the Apollo 11 mission with the exception of the lunar touchdown, stay, and liftoff. The command and service modules, and the lunar module were used in flight procedures identical to those that would later take similar vehicles to the Moon, and a landing. The flight mechanics, mission support systems, communications, and recording of data were tested in a final round of verification. Astronauts Scott and Schweickart conducted Extravehicular Activity during this mission.
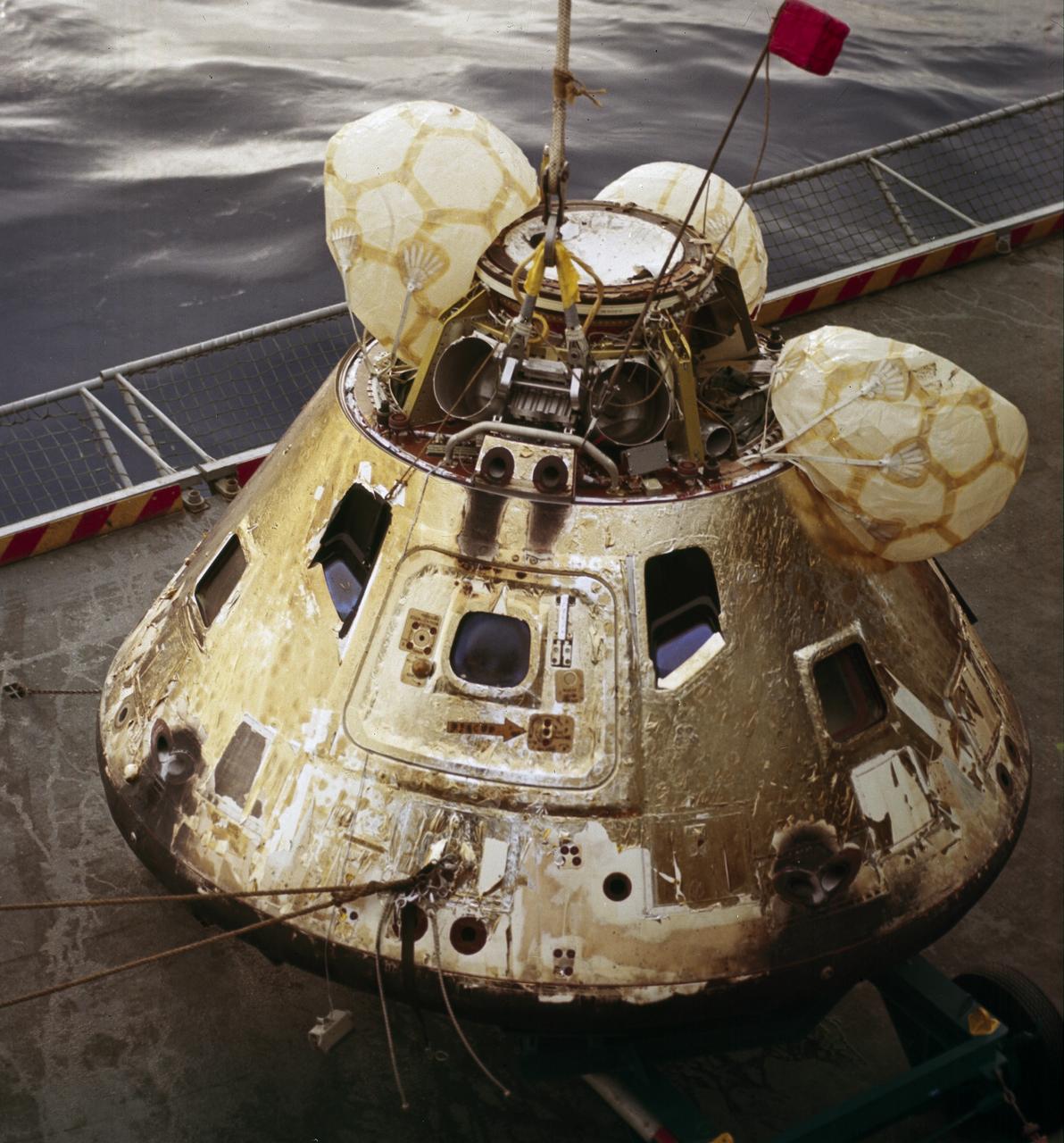

This is a photograph of the Apollo 8 Capsule being hoisted onto the recovery ship following splashdown on December 27, 1968. The first manned Apollo mission to escape Earth’s gravity and travel to the lunar vicinity, the Saturn V, SA-503, Apollo 8 mission liftoff occurred seven days prior, on December 21, 1968. Aboard were astronauts William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Frank Borman, commander. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.