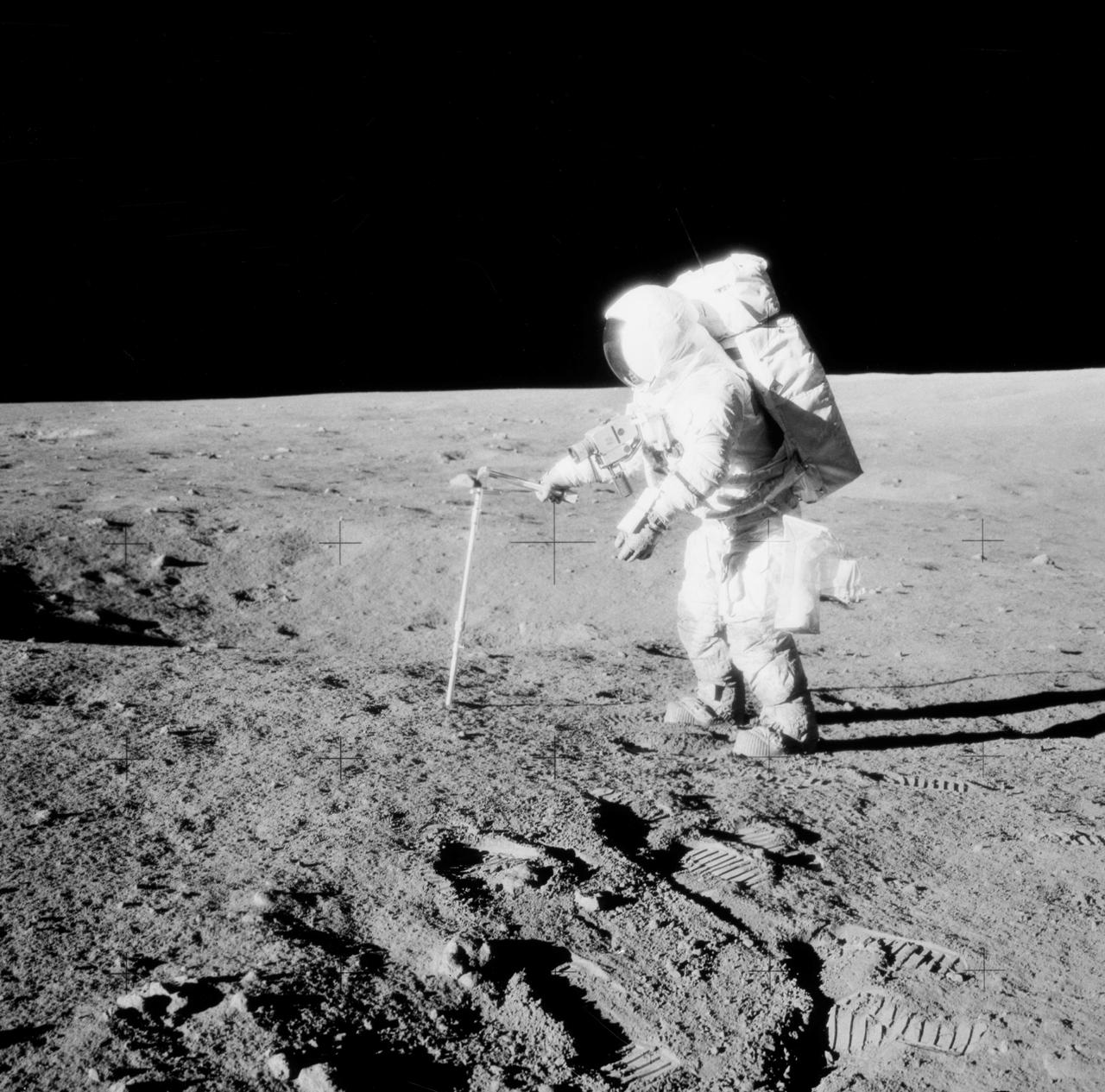

AS12-49-7286 (20 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, drives a core sample tube into the lunar surface during the Apollo 12 extravehicular activity. Good view of lunar soil.
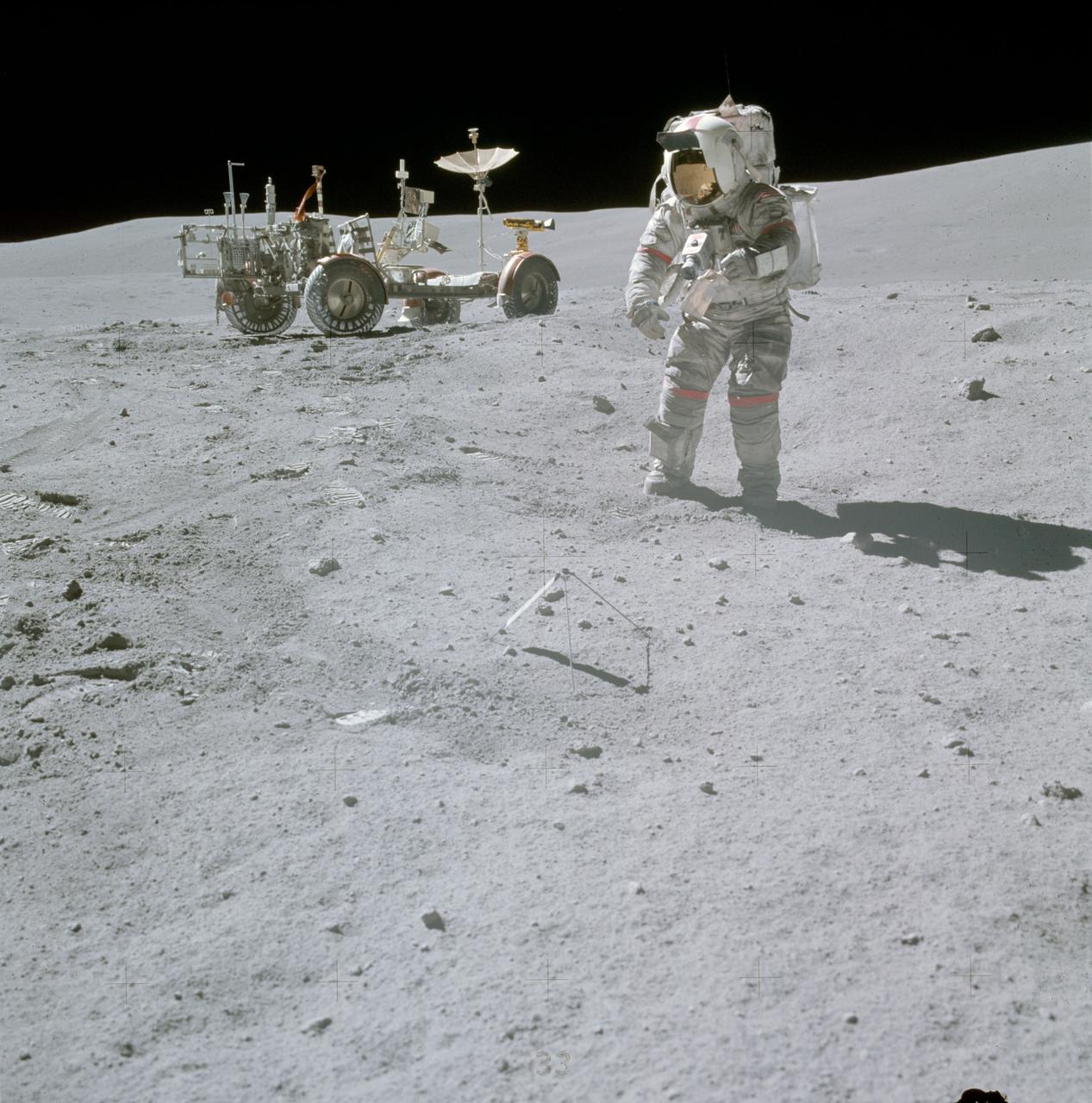

AS16-117-18825 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, Apollo 16 commander, with a sample bag in his left hand, moves toward the bottom part of the gnomon (center) while collecting samples at the North Ray Crater geological site. Note how soiled Young's Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) is during this the third and final Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked at upper left.
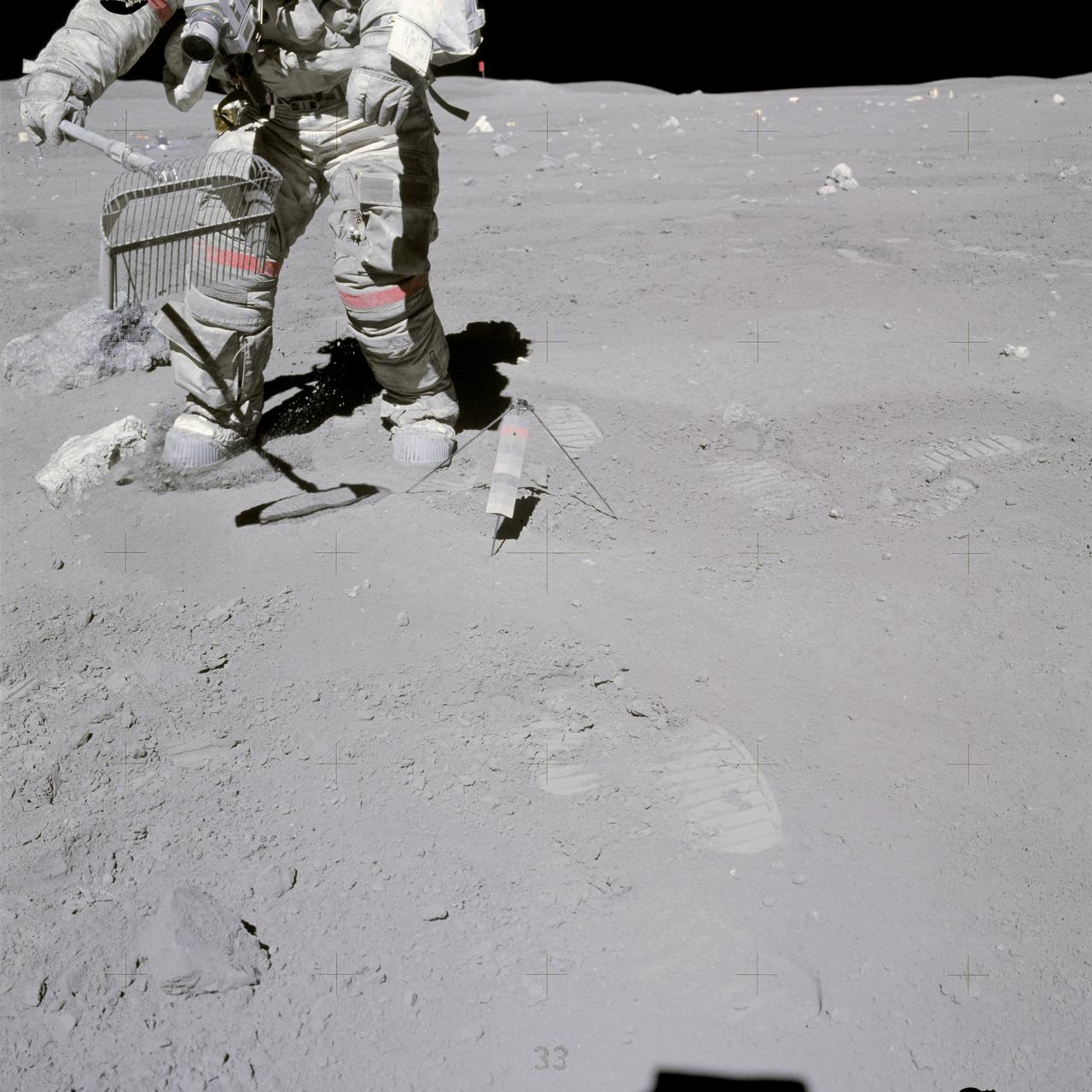

AS16-117-18826 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young collects samples at the North Ray Crater geological site during the mission's third and final Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). He has a rake in his hand, and the gnomon is near his foot. Note how soiled Young's Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) is. While astronauts Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

AS12-47-6932 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Close-up view of a set of tongs, an Apollo Lunar Hand Tool, being used by astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, to pick up lunar samples during the Apollo 12 extravehicular activity. This photograph shows Conrad's legs and a good view of the lunar soil.
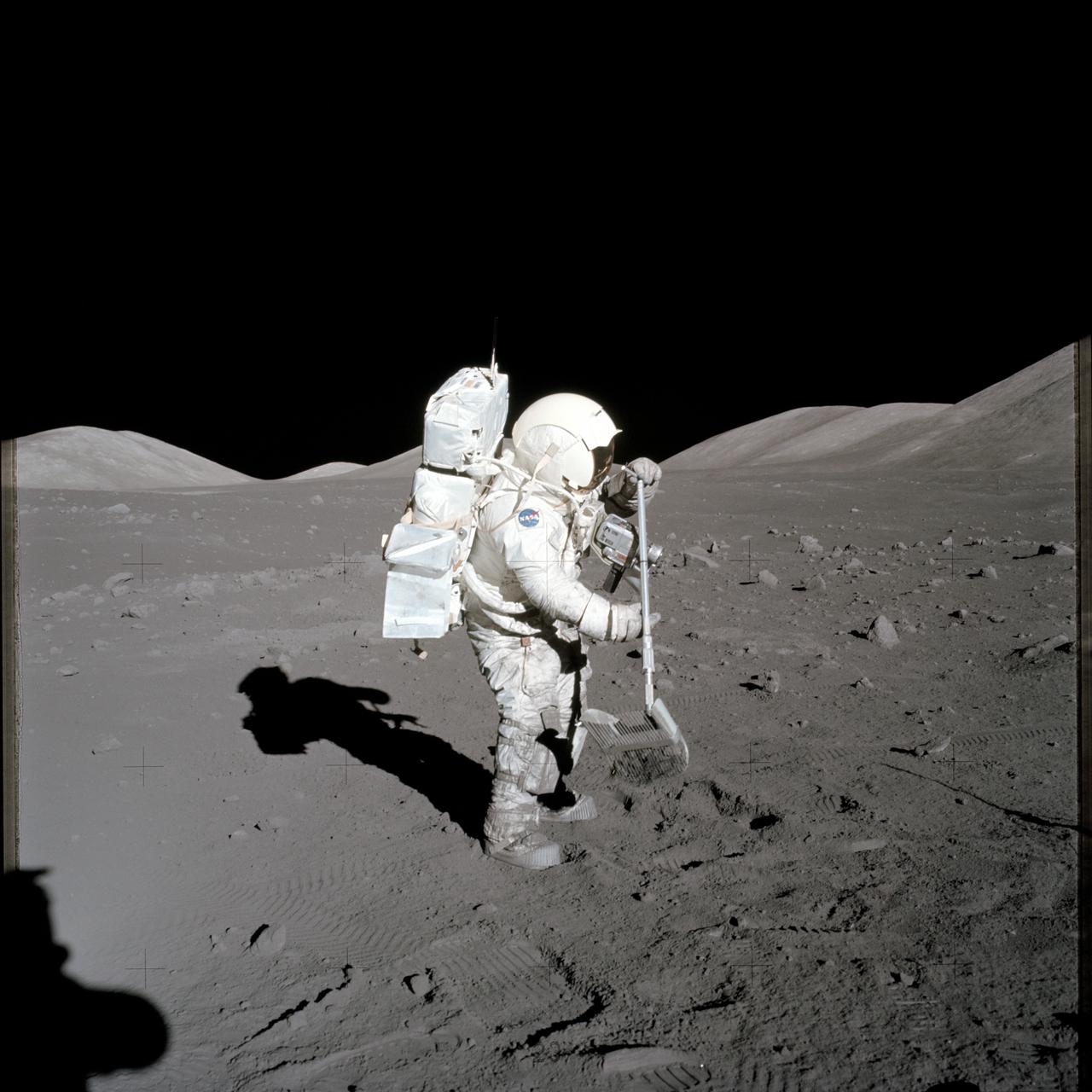

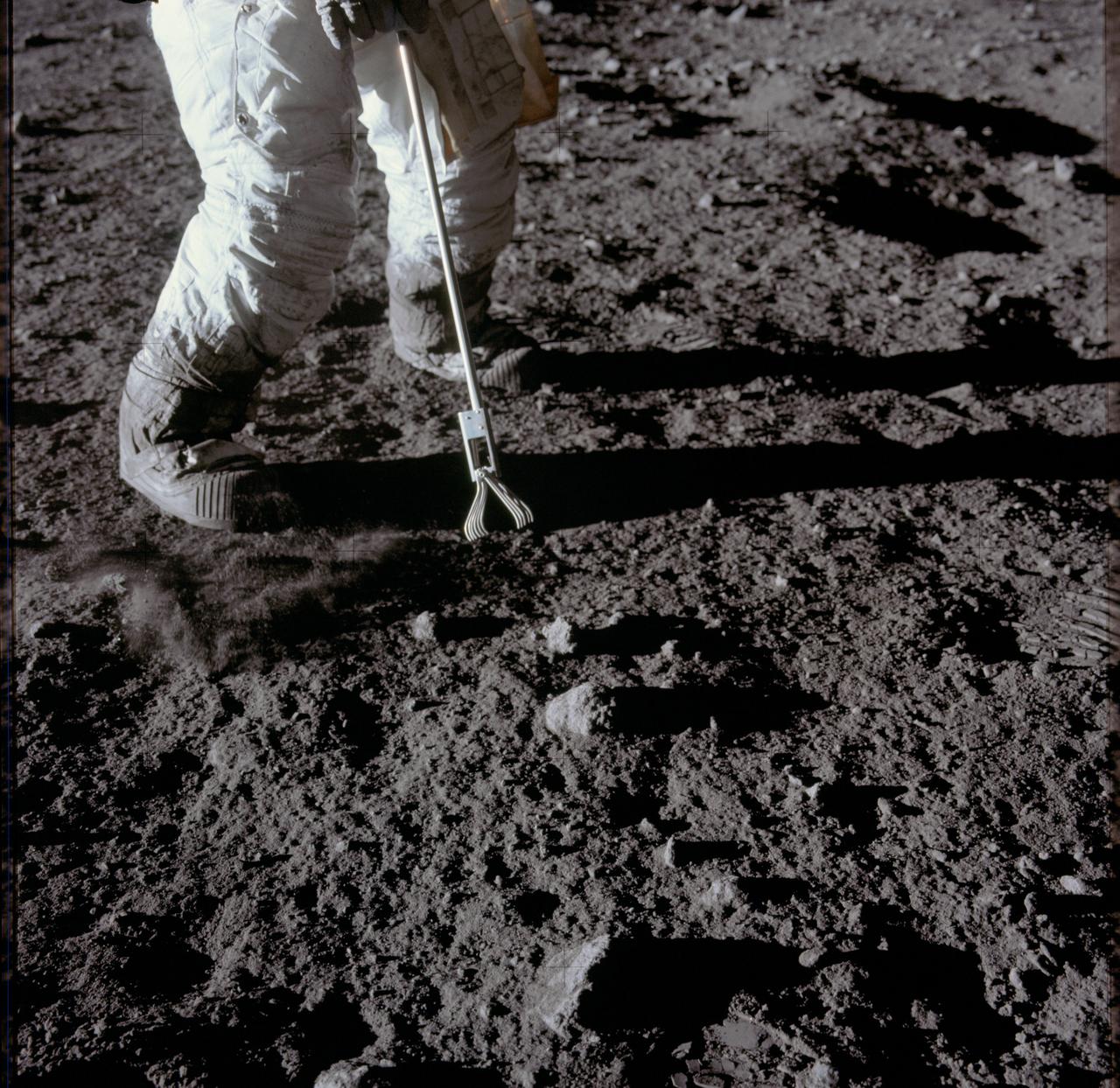
AS17-134-20425 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, collects lunar rake samples at Station 1 during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene Cernan, commander. The lunar rake, an Apollo lunar geology hand tool, is used to collect discrete samples of rocks and rock chips ranging in size from one-half inch (1.3 centimeter) to one inch (2.5 centimeter).
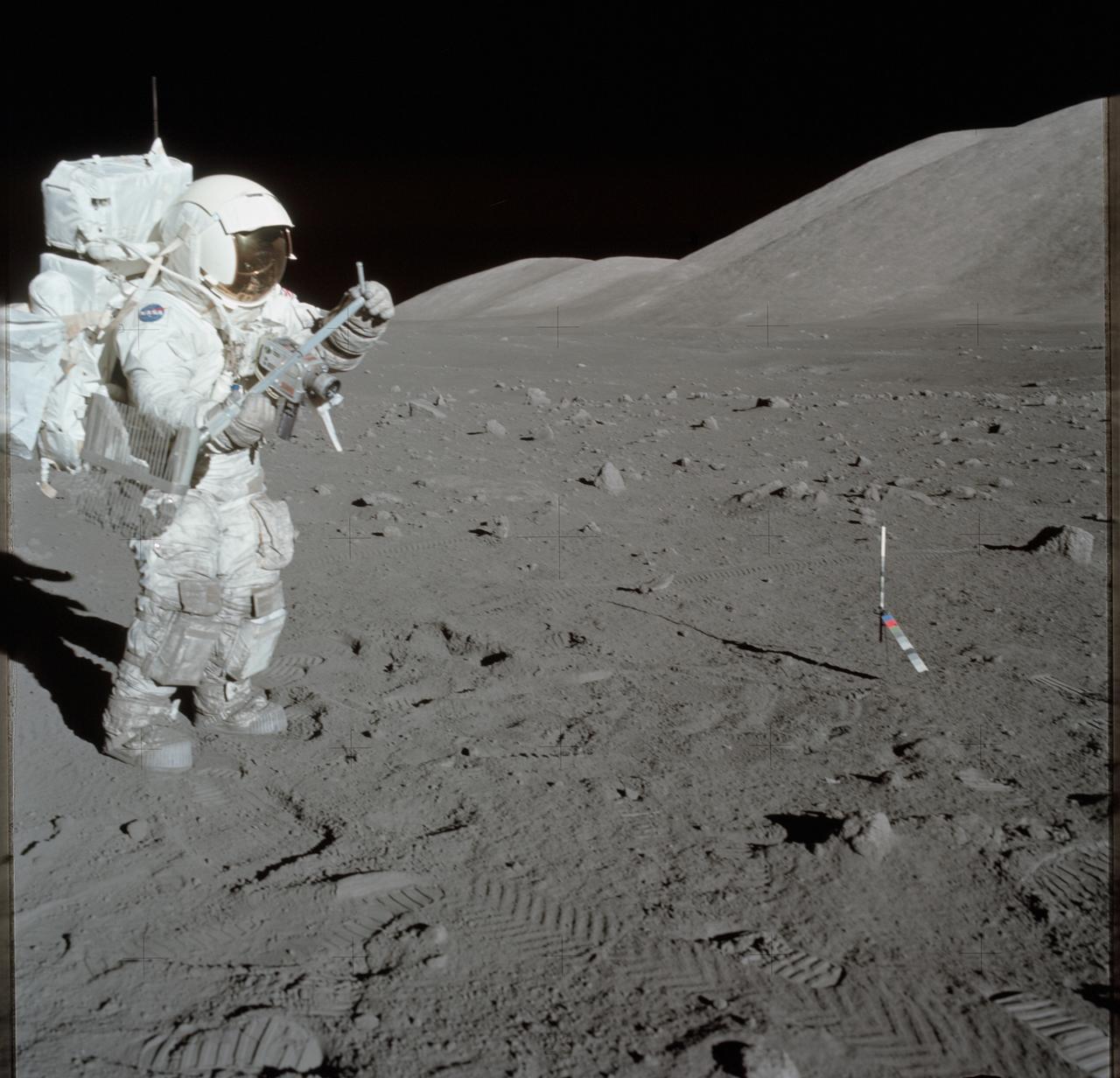

AS17-134-20426 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt collects lunar rake samples at Station 1 during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot. The Lunar Rake, an Apollo Lunar Geology Hand Tool, is used to collect discrete samples of rocks and rock chips ranging in size from one-half inch (1.3 cm) to one inch (2.5 cm).
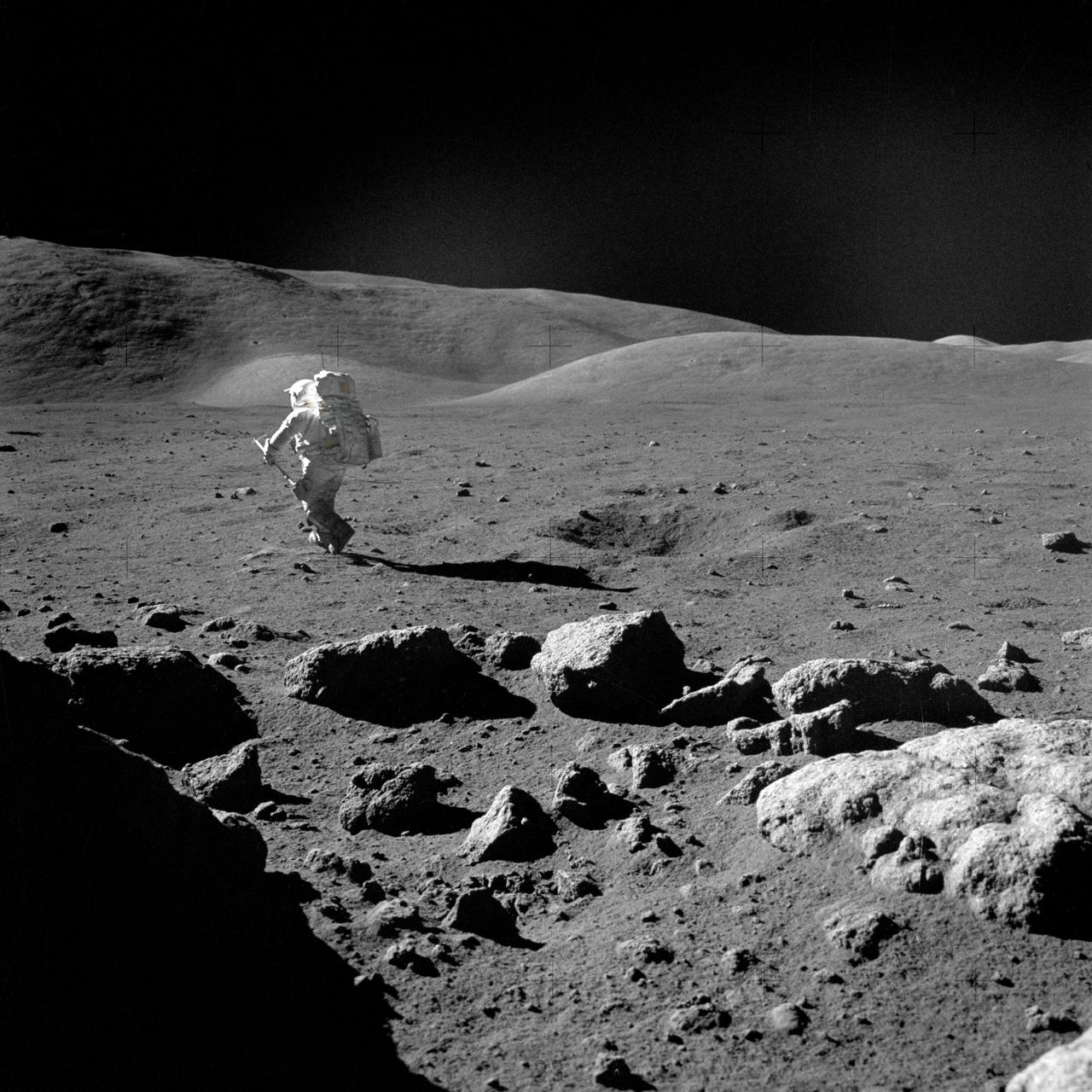

AS17-145-22165 (12 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, with his adjustable sampling scoop, heads for a selected rock on the lunar surface to retrieve the sample for study. The action was photographed by Apollo 17 crew commander, astronaut Eugene A. Cernan on the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA), at Station 5 at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. Cernan used a 70mm Hasselblad camera equipped with a 60mm lens and type SO-368 color film for this photograph. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.

AS17-145-22157 (12 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison Schmitt, Apollo 17 lunar module pilot, uses an adjustable sampling scoop to retrieve lunar samples during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA), at Station 5 at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. A gnomon is atop the large rock in the foreground. The gnomon is a stadia rod mounted on a tripod, and serves as an indicator of the gravitational vector and provides accurate vertical reference and calibrated length for determining size and position of objects in near-field photographs. The color scale of blue, orange and green is used to accurately determine color for photography. The rod of it is 18 inches long. The scoop Dr. Schmitt is using is 11 3/4 inches long and is attached to a tool extension which adds a potential 30 inches of length to the scoop. The pan portion, obscured in this view, has a flat bottom, flanged on both sides with a partial cover on the top. It is used to retrieve sand, dust and lunar samples too small for the tongs, another geological tool used by the astronauts. The pan and the adjusting mechanism are made of stainless steel and the handle is made of aluminum. Within the foreground of this scene, three lunar samples were taken--numbers 75060, 75075 and 75080. Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, crew commander, was using a 60mm lens on the 70mm Hasselblad camera and type SO-368 film to take this photograph.
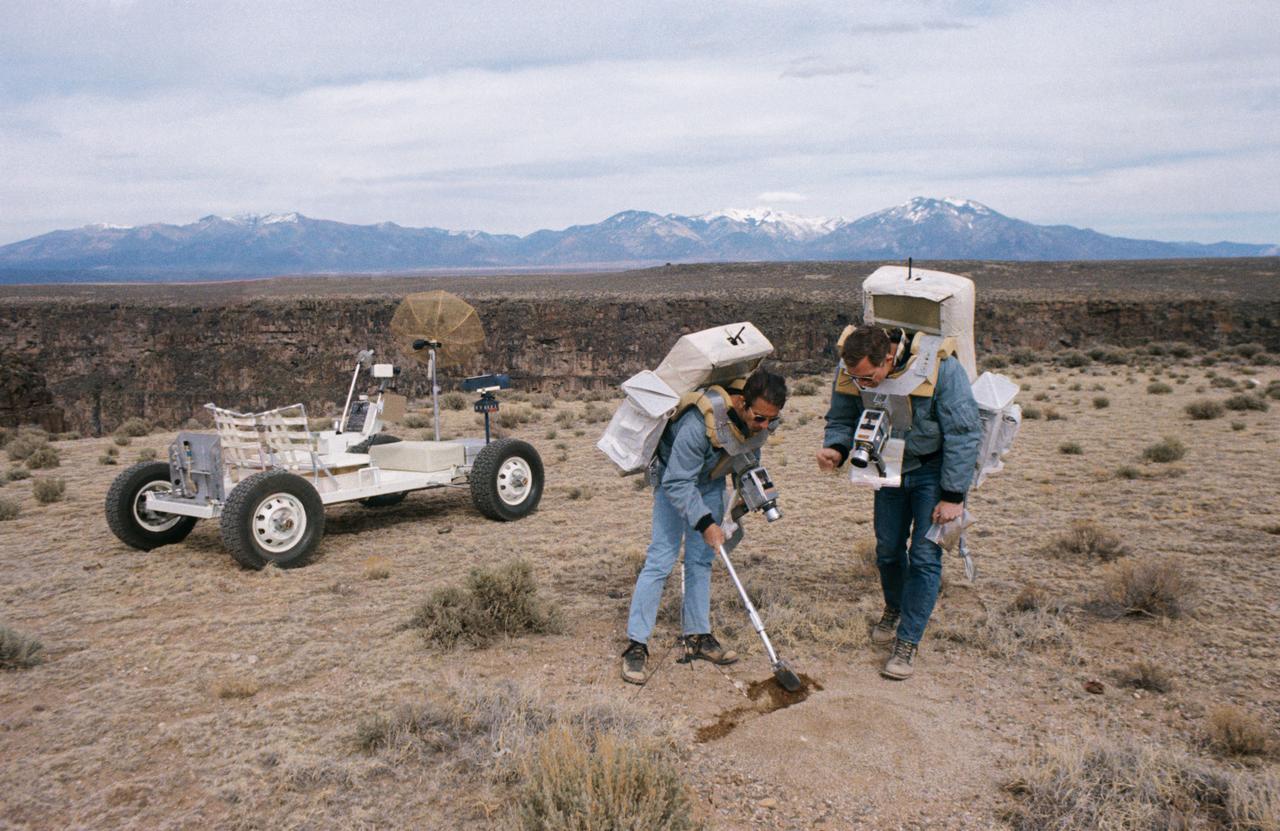

S71-23772 (11-12 March 1971) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission collect soil samples during a simulation of lunar surface extravehicular activity in the Taos, New Mexico area. Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, is using a scoop. Astronaut David R. Scoot (right), commander, is holding a sample bag. On the left is a Lunar Roving Vehicle trainer.
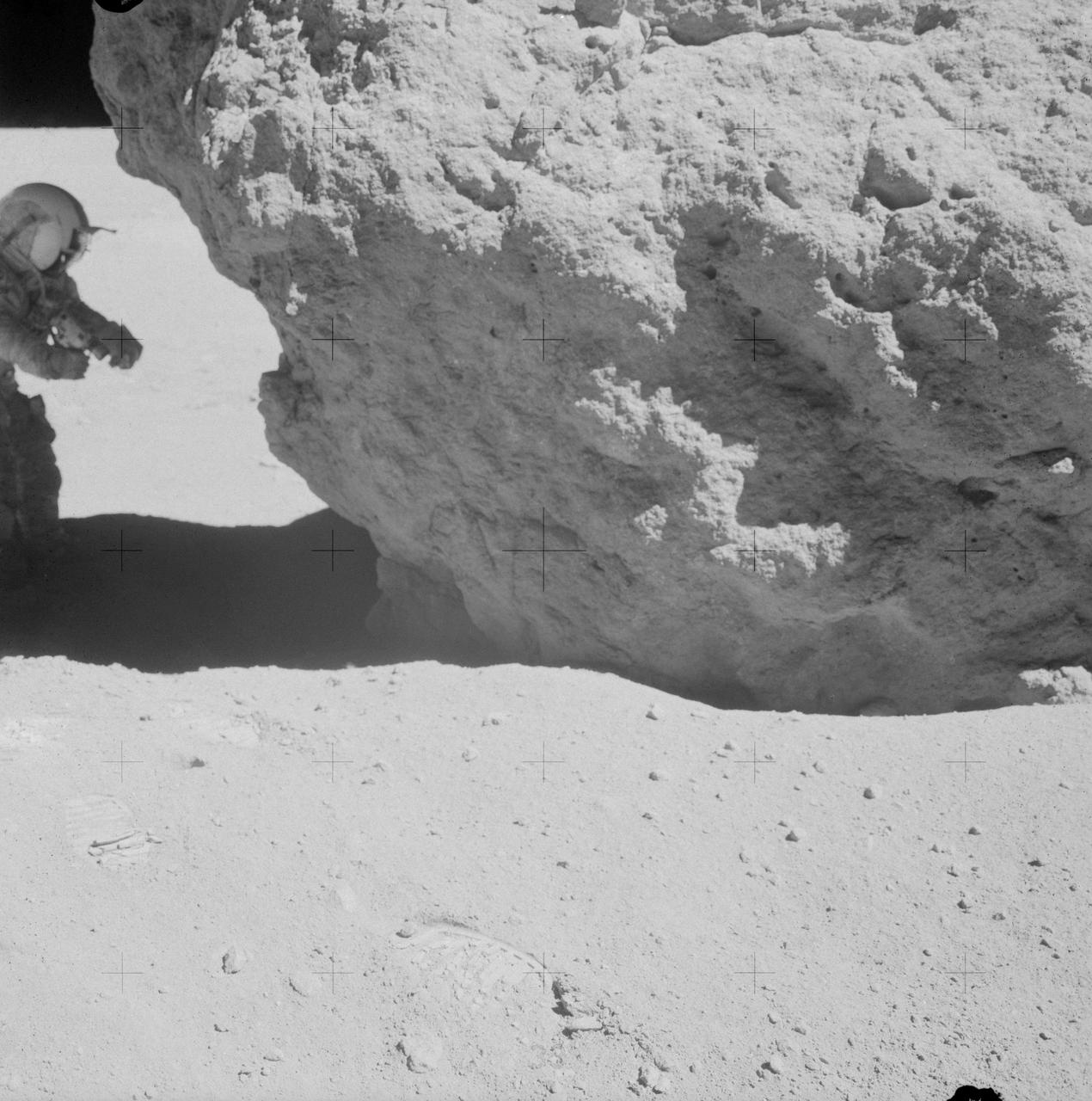

AS16-106-17413 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, looks over a large boulder at Station No.13 during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This was the site of the permanently shadowed soil sample which was taken from a hole extending under overhanging rock. Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this photograph. Concerning Young's reaching under the big rock, Duke remarked: "You do that in west Texas and you get a rattlesnake!"
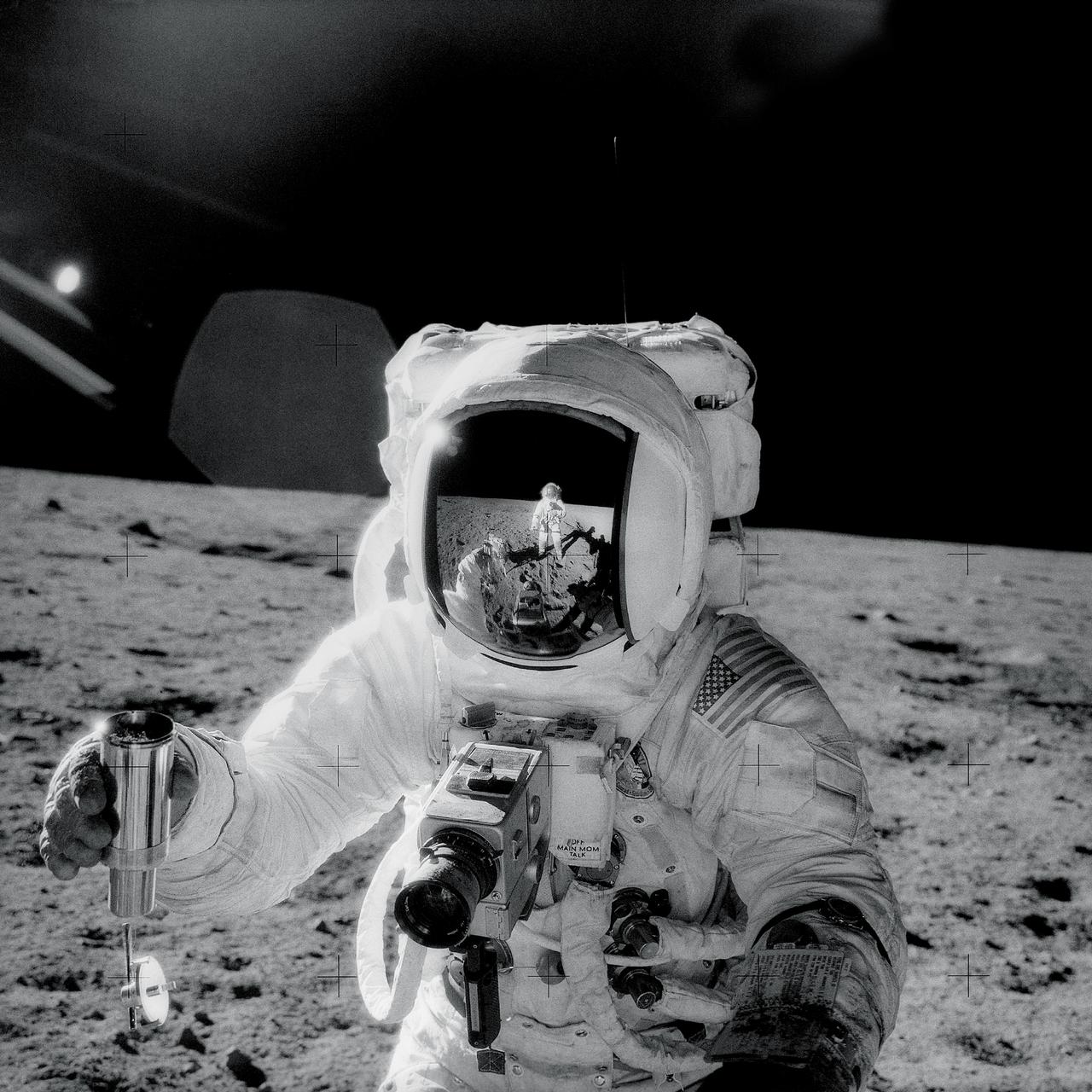

AS12-49-7278 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean holds a Special Environmental Sample Container filled with lunar soil collected during the extravehicular activity (EVA) in which astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Bean, lunar module pilot, participated. Conrad, who took this picture, is reflected in Bean's helmet visor. Conrad and Bean descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) to explore the lunar surface while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
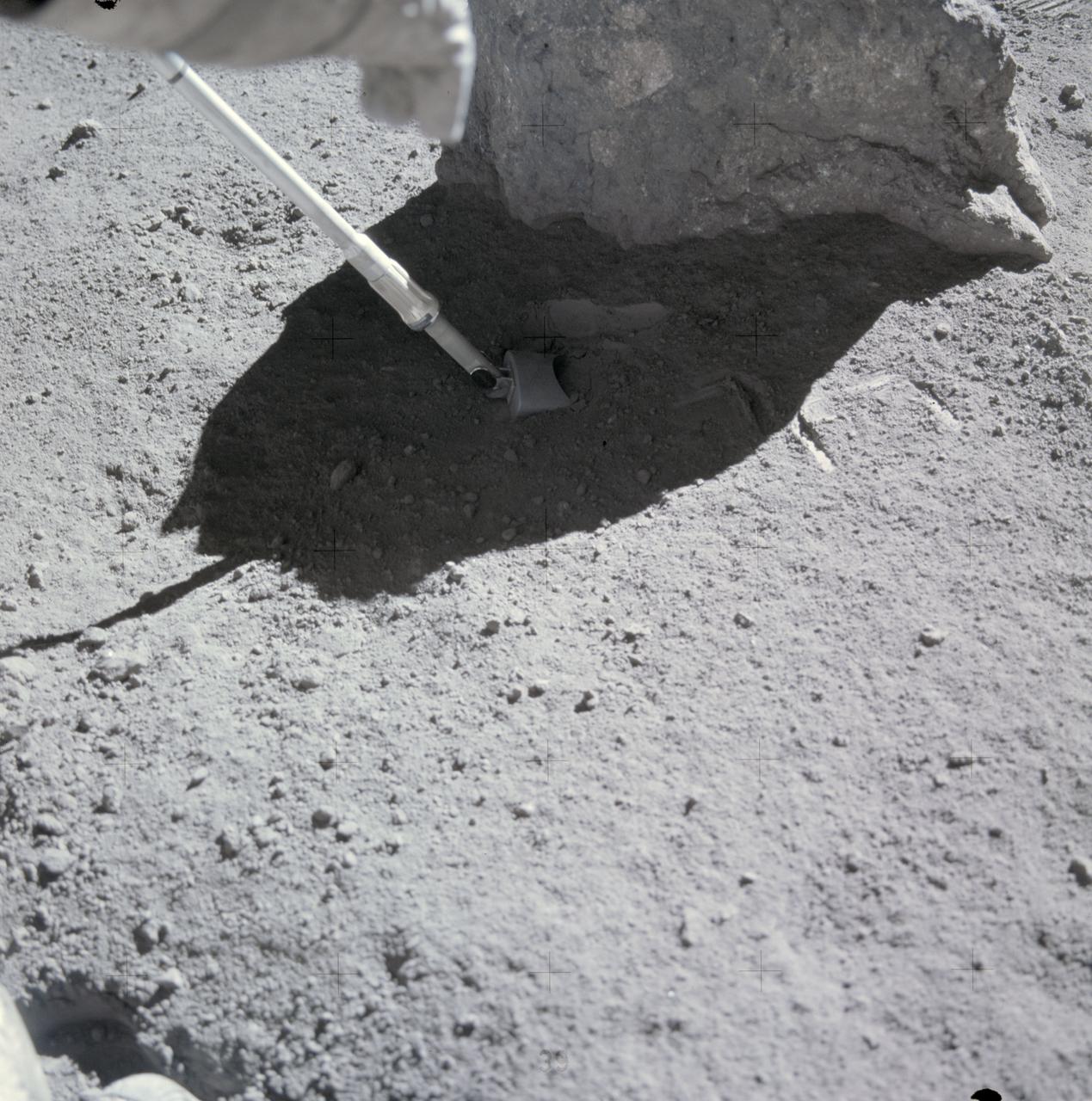

AS16-107-17561 (16-27 April 1972) --- One of the Apollo 16 astronauts scoops up lunar soil at the base of a small boulder at Station No. 9 during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Depressions to the right of the scoop were made when a surface sample was taken. This photograph was taken just before the boulder was rolled over. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
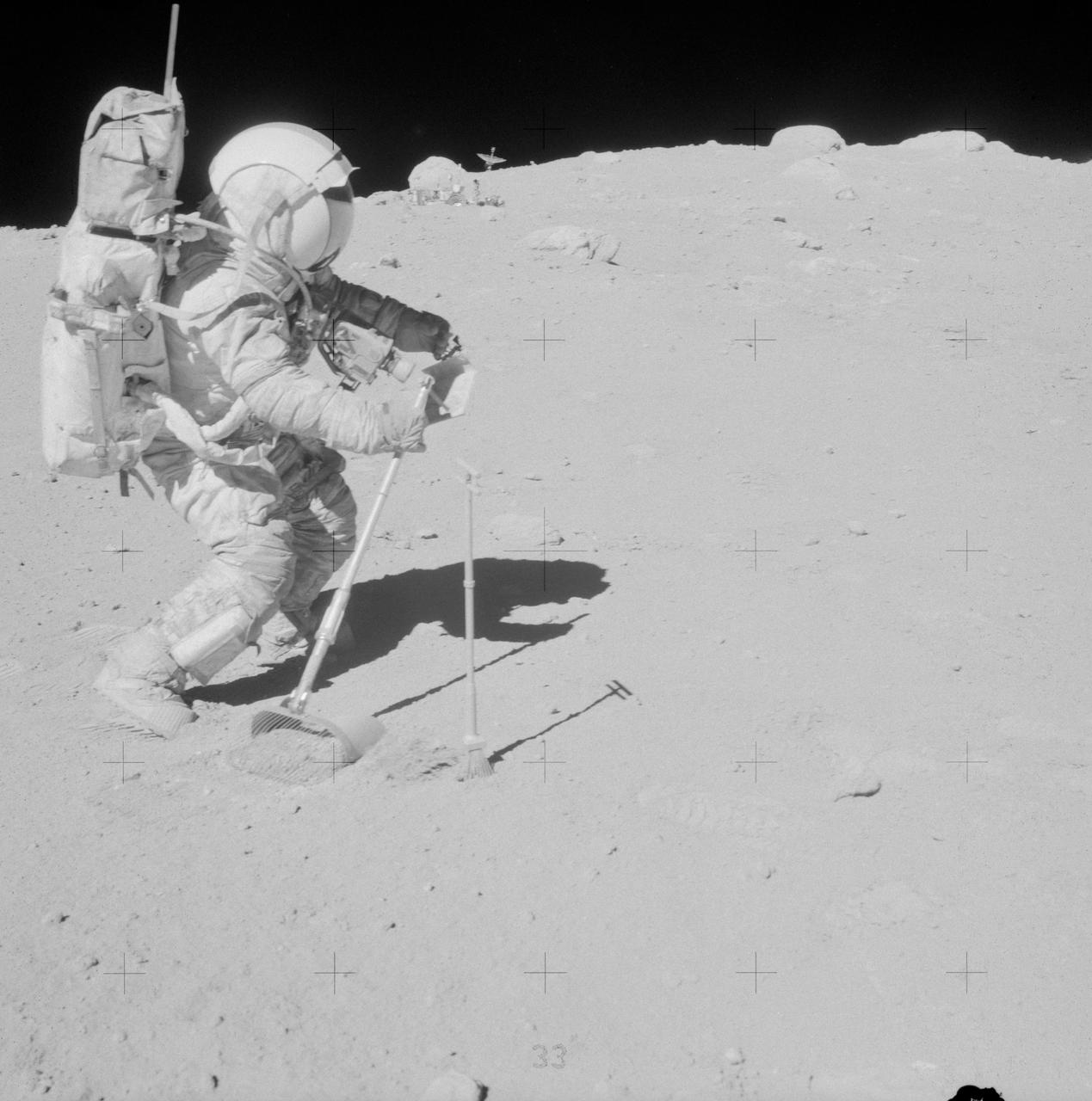

AS16-106-17340 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, is photographed collecting lunar samples near North Ray Crater during the third Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. This picture was taken by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot. Young is using the lunar surface rake and a set of tongs. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked in the field of large boulders in the background. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS16-114-18423 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed collecting lunar samples at Station No. 1, during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA), at the Descartes landing site. This picture, looking eastward, was taken by astronaut John W. Young, commander. Duke is standing at the rim of Plum Crater. The parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) can be seen in the left background. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands region of the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
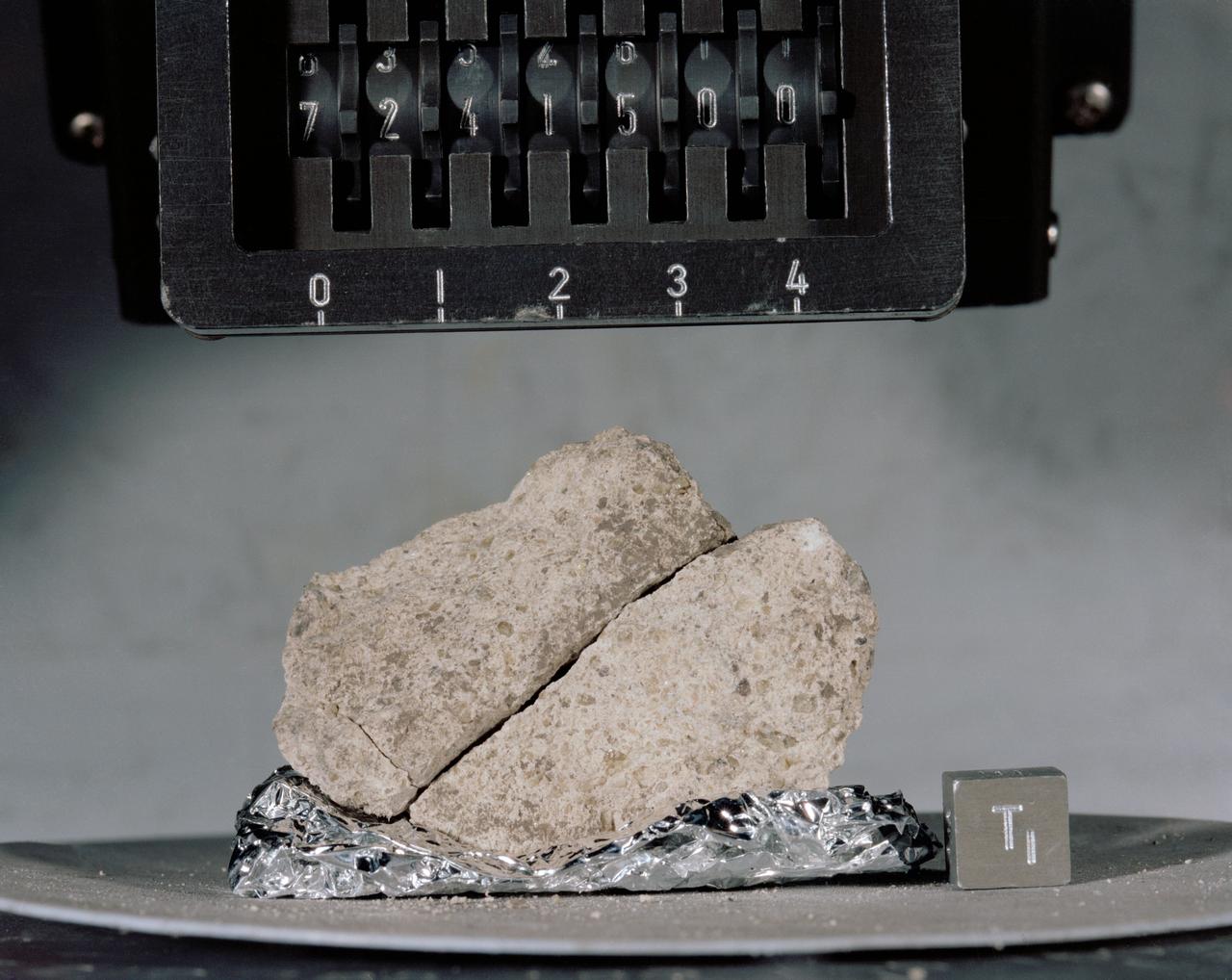

S73-16199 (December 1972) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar sample number 72415,0 which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. This sample is a brecciated dunite clast weighing a little over 32 grams (about 1.14 ounces). This sample was collected at station 2 (South Massif) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA). IMPORTANT NOTE FOR CREDIT: The view was photographed by Karl Mills, Scientific Photo Arts, Berkeley, California.
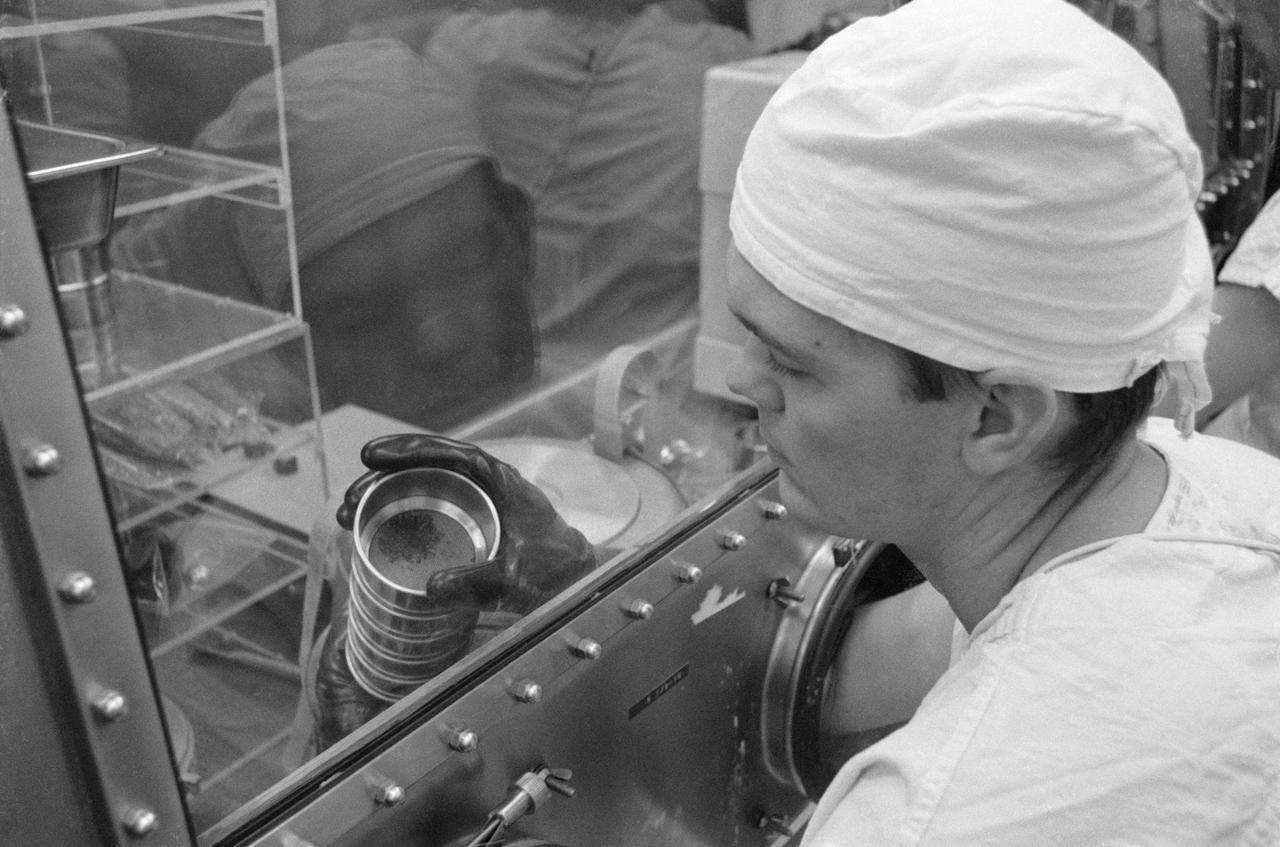

S69-40749 (July 1969) --- Dr. Grant Heikan, MSC and a Lunar Sample Preliminary Examination Team member, examines lunar material in a sieve from the bulk sample container which was opened in the Biopreparation Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory. The samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.
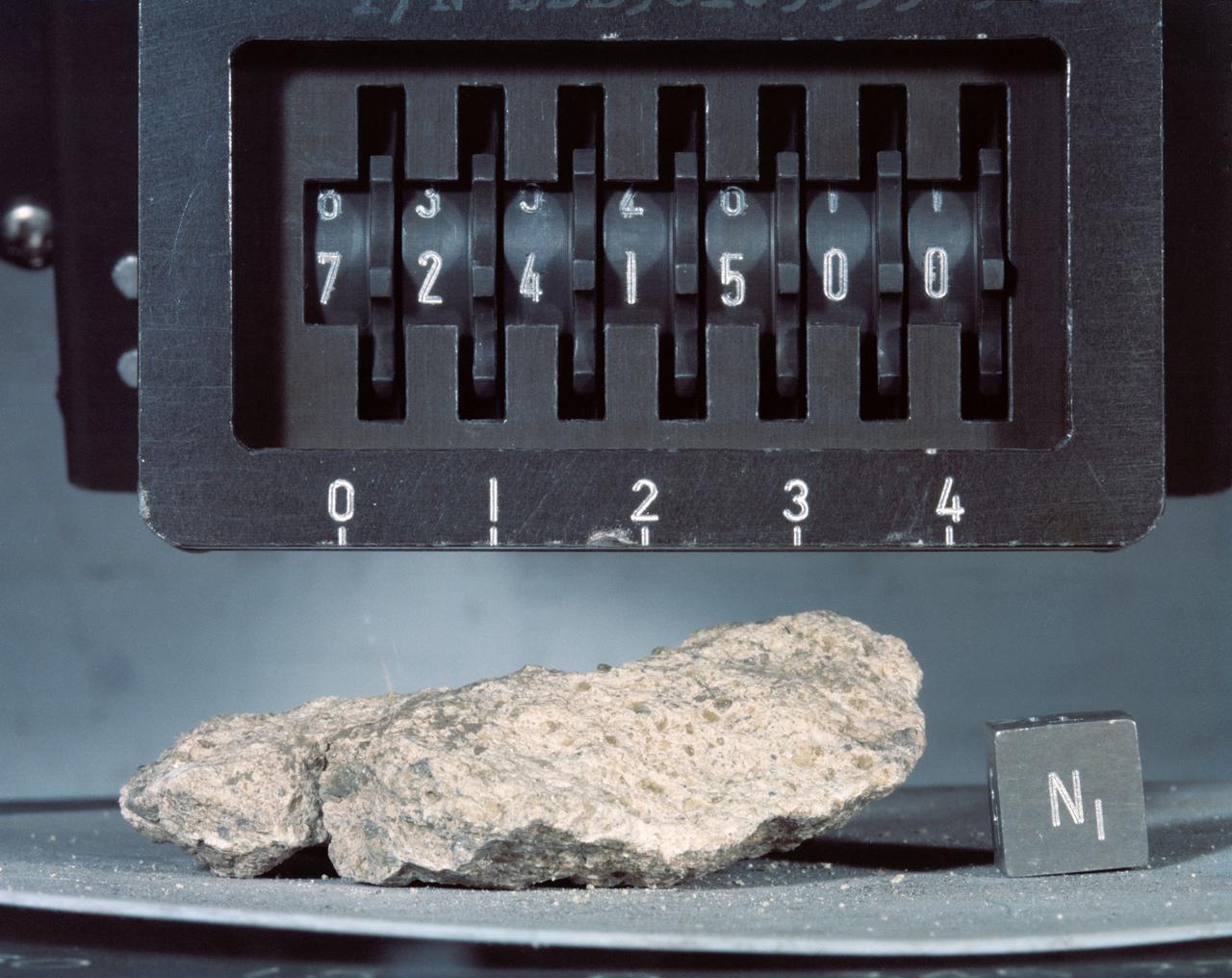

S73-16198 (December 1972) --- A close-up view of Apollo 17 lunar sample number 72415,0 which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. This sample is a brecciated dunite clast weighing a little over 32 grams (about 1.14 ounces). This sample was collected at station 2 (South Massif) during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA).
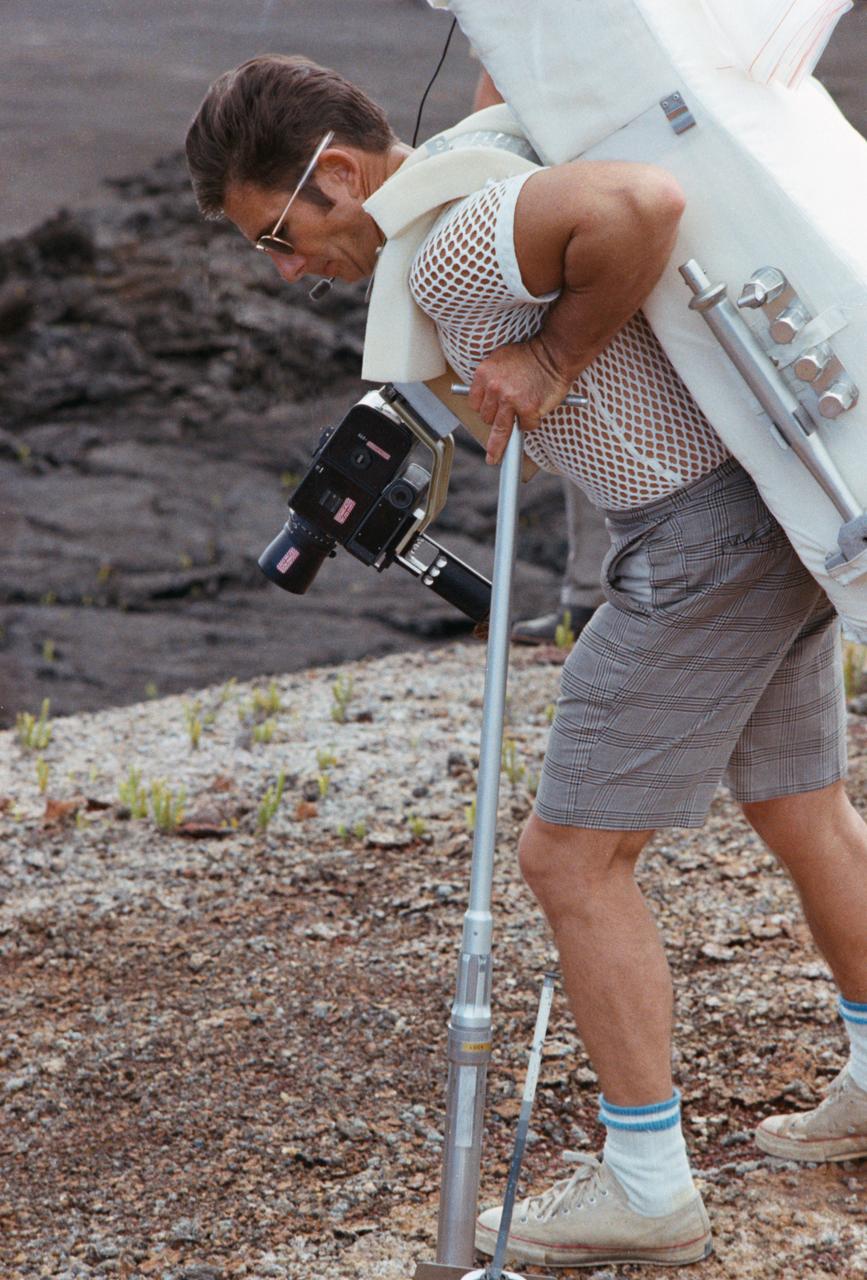

S70-56433 (December 1970) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission, participates in lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) training during a visit to Hawaii. He is simulating using lunar surface geological tools to collect a core sample.
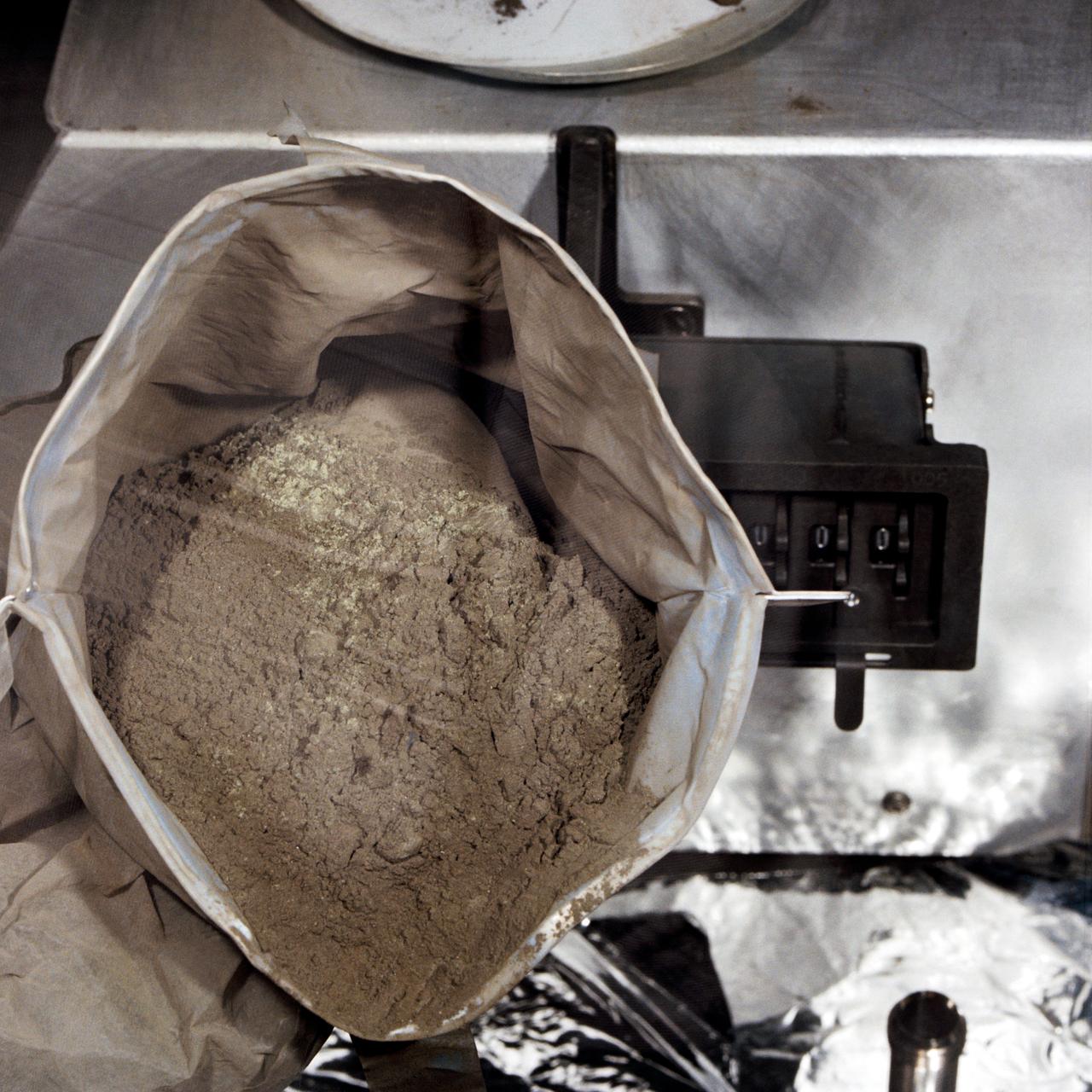

S71-43052 (August 1971) --- A close-up view of a container full of green-colored lunar soil in the Non-Sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). This sample, broken down into six separate samples after this photo was made, was made up of comprehensive fines from near Spur Crater on the Apennine Front. The numbers assigned to the sample include numbers 15300 through 15305. Astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin took the sample during their second extravehicular activity (EVA) at a ground elapsed time (GET) of 146:05 to 146:06.
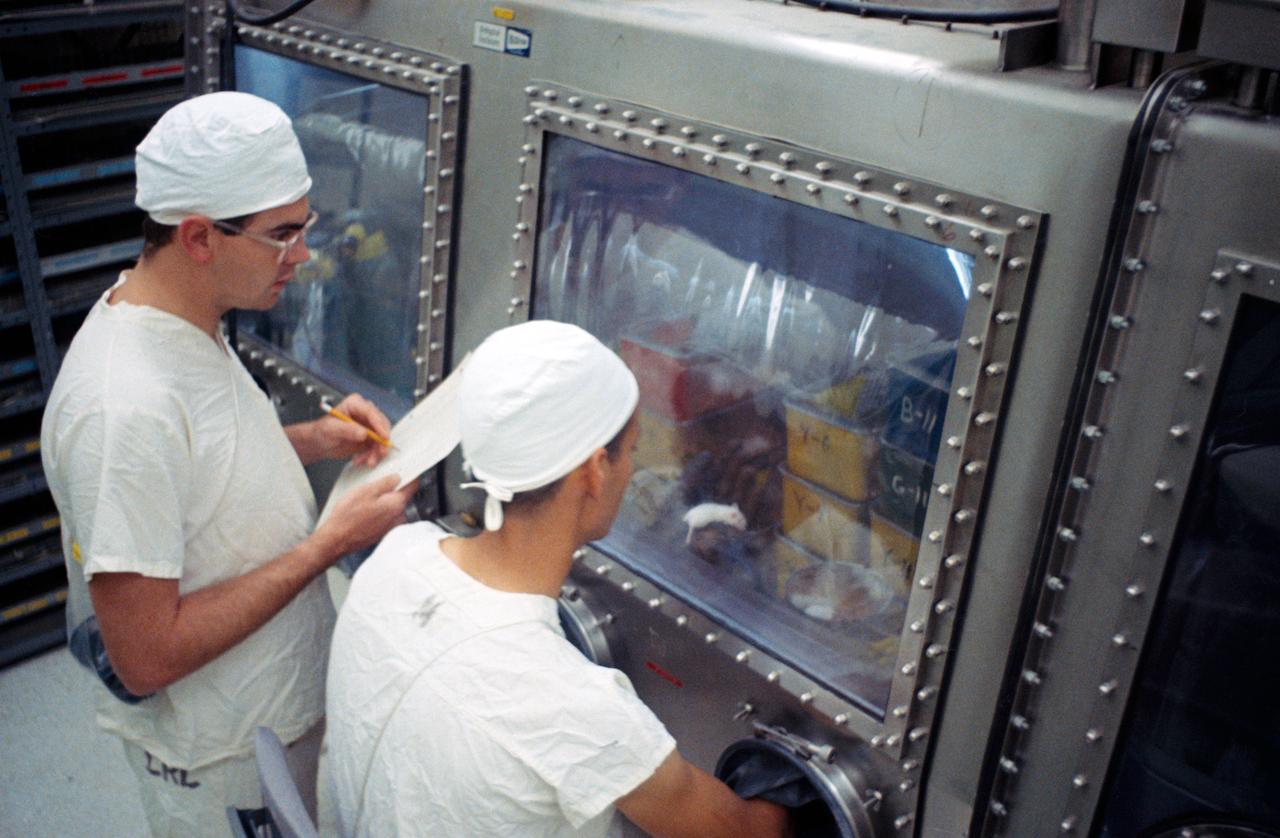

S69-40940 (August 1969) --- Landrum Young (seated), Brown and Root - Northrop, and Russell Stullken, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), examine mice in the Animal Laboratory which have been inoculated with lunar sample material. The sample material was collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.
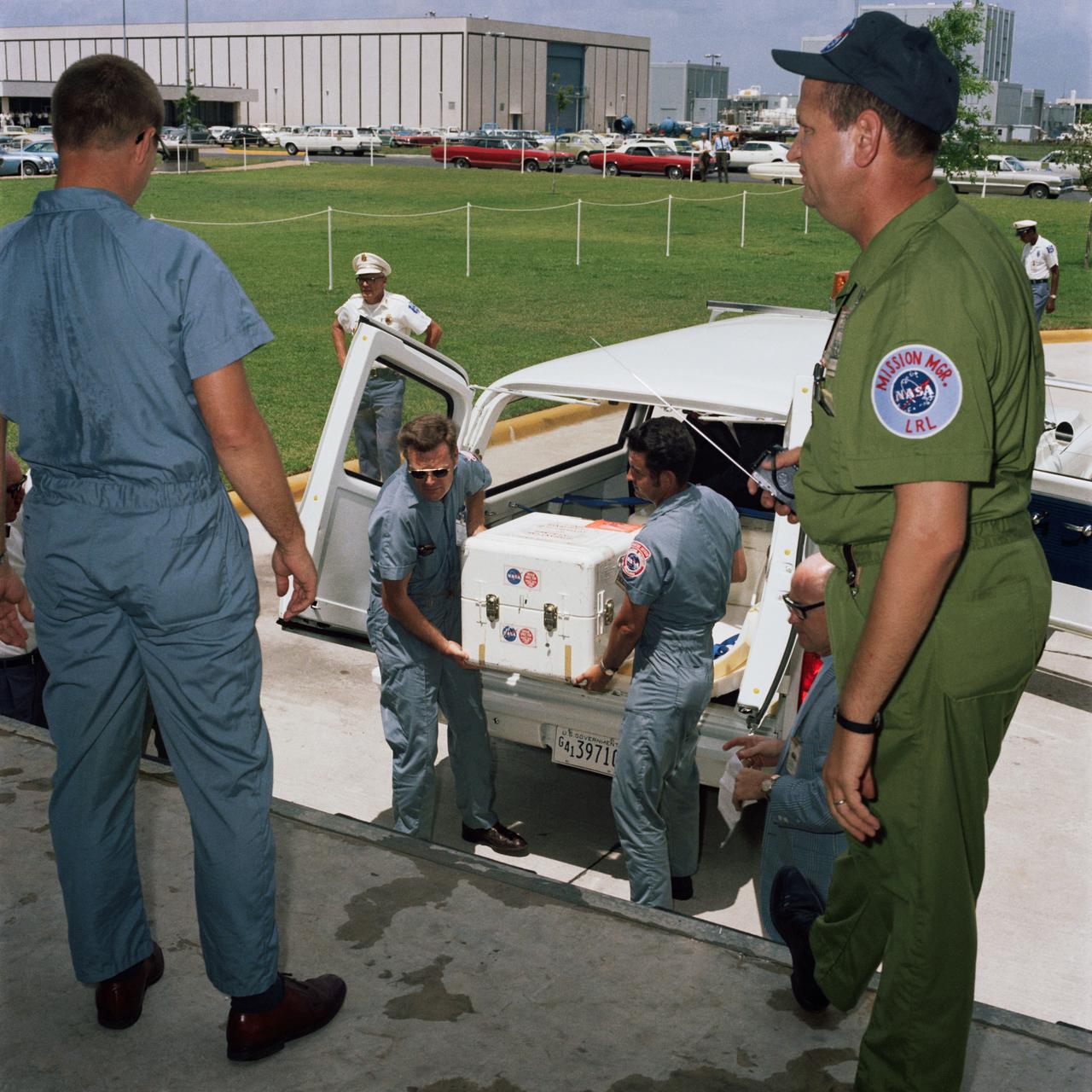

S69-39996 (25 July 1969) --- The first Apollo 11 sample return container, with lunar surface material inside, is unloaded at the Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The rock box had arrived only minutes earlier at Ellington Air Force Base by air from the Pacific recovery area. The lunar samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity.

S69-40939 (August 1969) --- Landrum Young, Brown and Root - Northrop technician, examines mice in the Animal Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) which have been inoculated with lunar sample material. The sample material was collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.
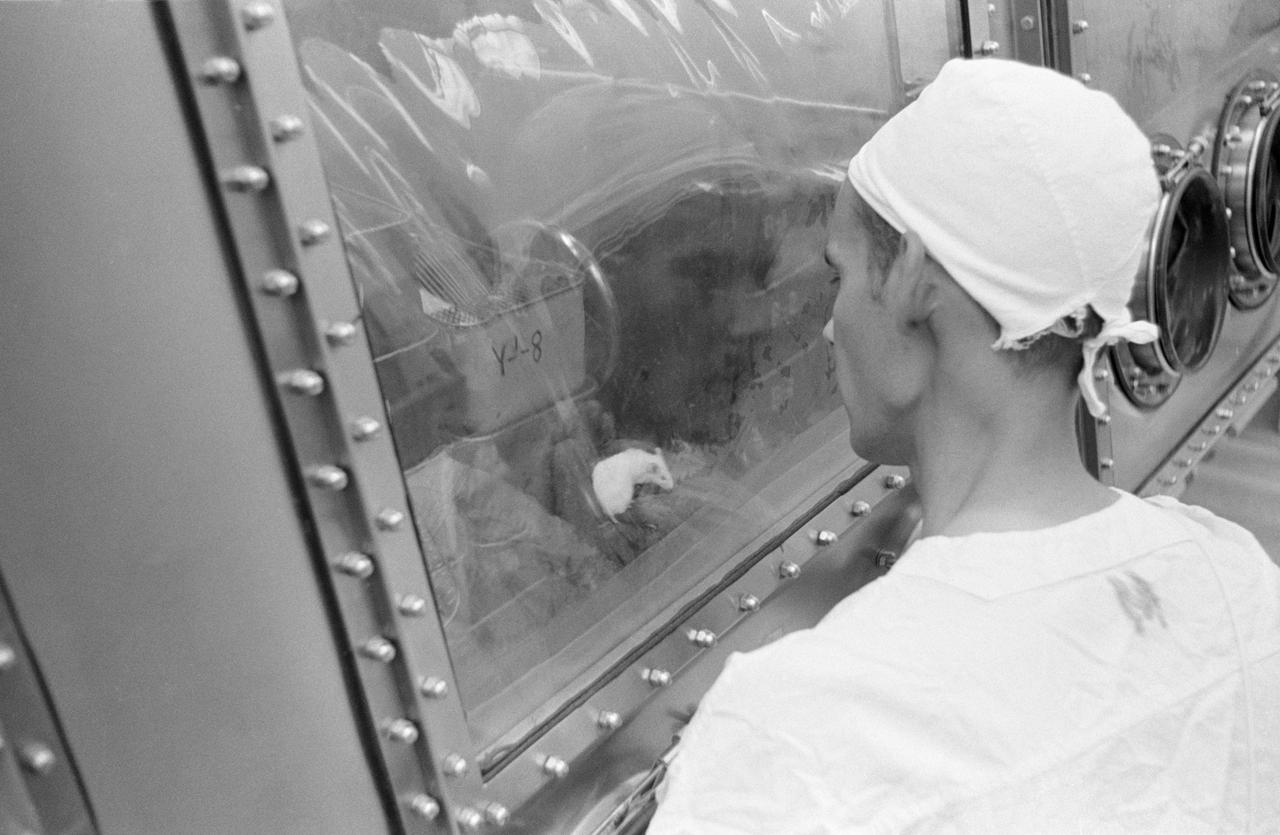

S69-40752 (August 1969) --- Landrum Young, Brown and Root - Northrop technician examines mice in the Animal Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) which have been inoculated with lunar sample material. The sample material was collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.
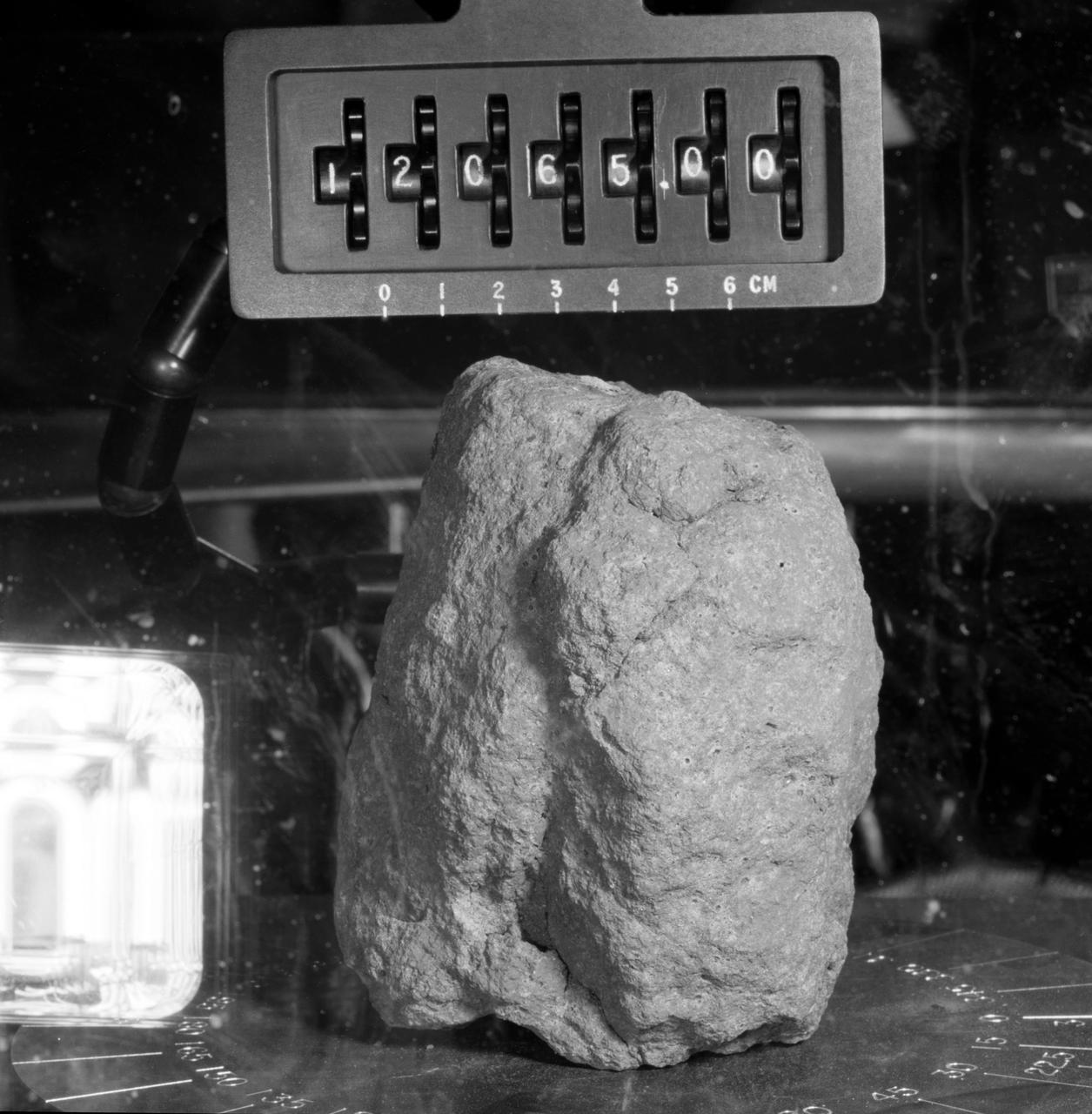

S69-60580 (November 1969) --- Close-up view of Apollo 12 sample 12,065 under observation in the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). This sample, collected during the second Apollo 12 extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean, is a fine-grained rock. Note the glass-lined pits. Viewer can gain an idea of the size of the rock by reference to the gauge on the bottom portion of the number meter.
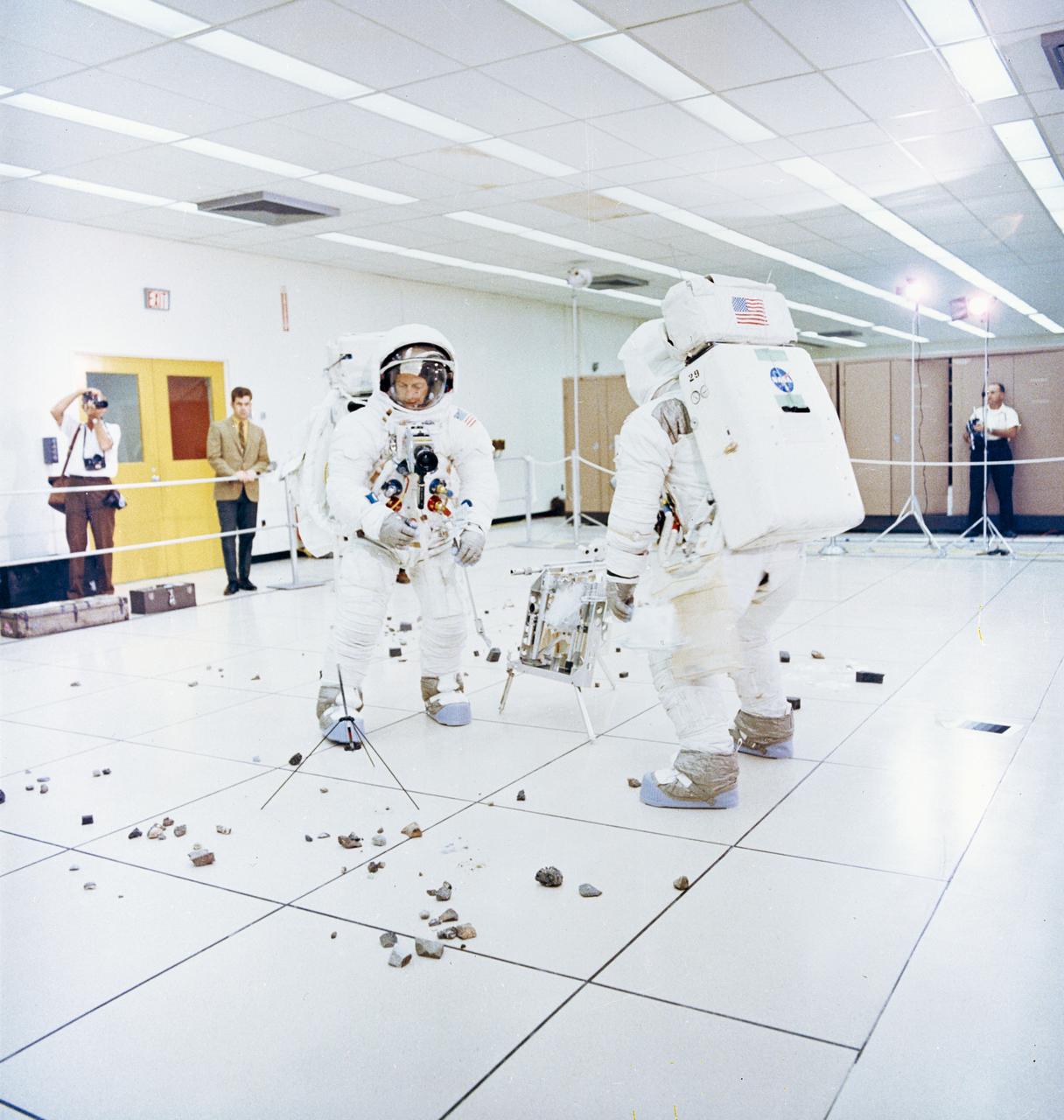

S69-55368 (6 Oct. 1969) --- Two members of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission participate in lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) simulations in the Flight Crew Training Building at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander (facing camera), simulates picking up samples. Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, simulates photographic lunar rock sample documentation.
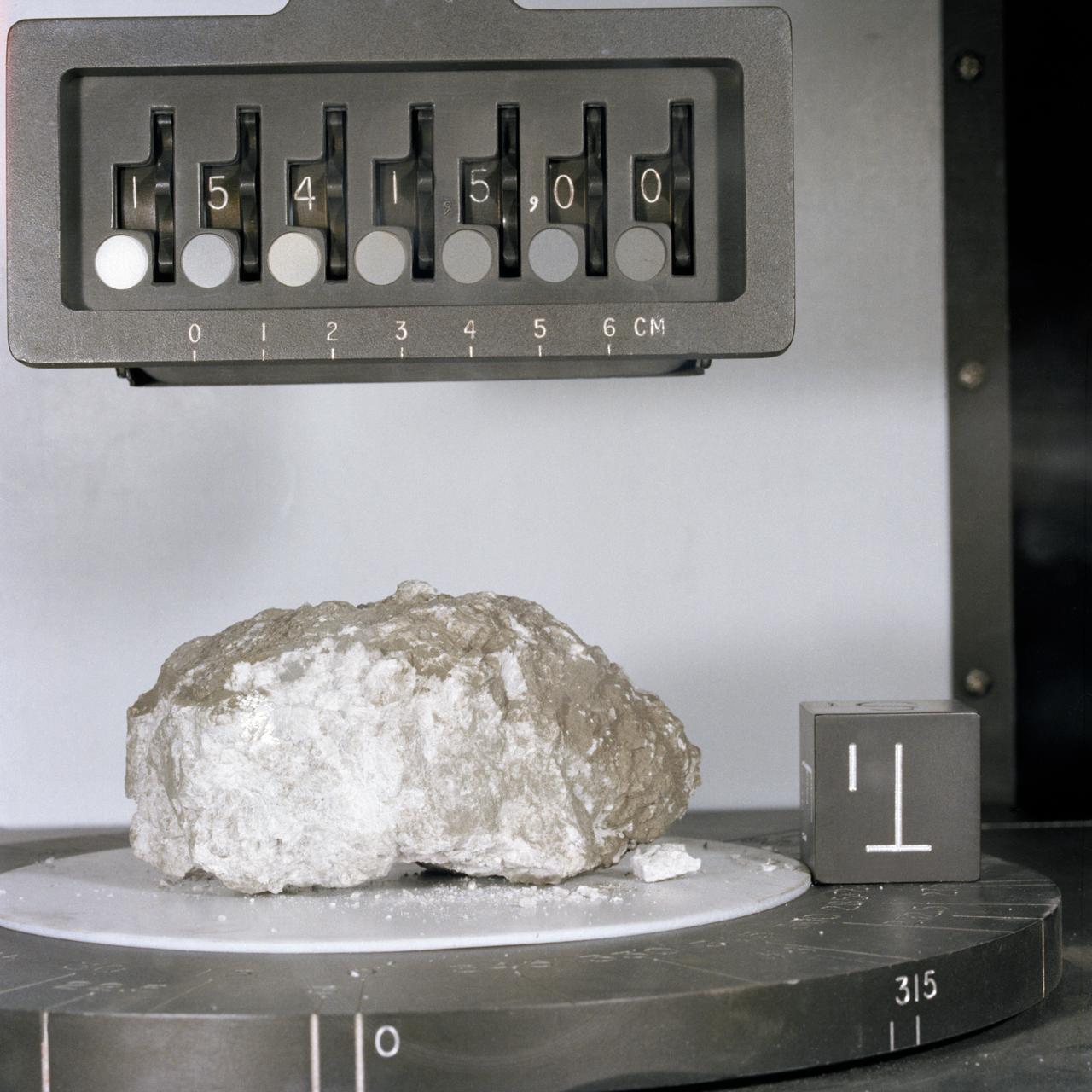

S71-42955 (August 1971) --- A close-up view of Apollo 15 lunar sample no. 15415 in the Non-Sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). This sample is the white anorthositic rock (Genesis Rock) collected by astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin in container no. 196 at Site no. 7 at a Ground Elapsed Time of 145 hours and 42 minutes, on the mission's second extravehicular activity (EVA).
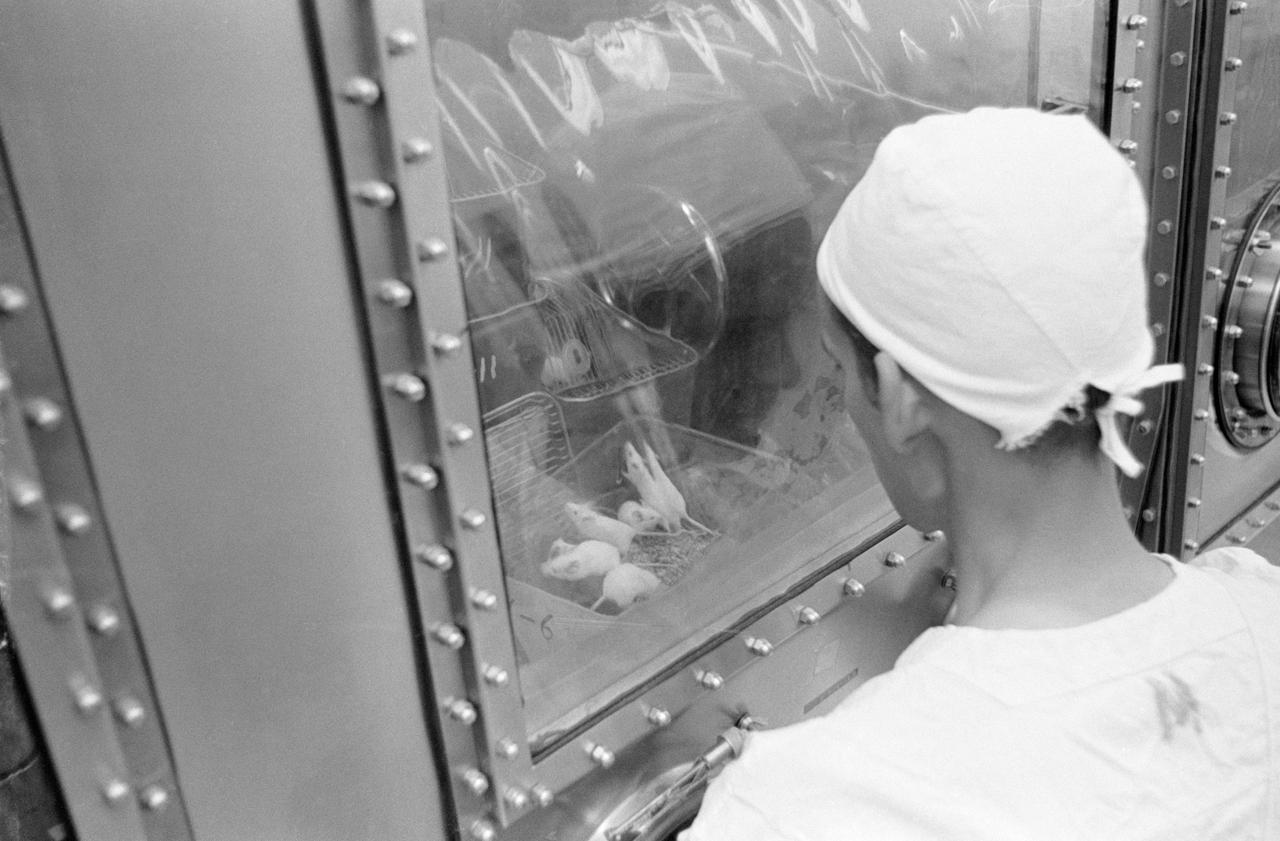

S69-40751 (August 1969) --- Landrum Young, Brown and Root - Northrop technician, examines mice in the Animal Laboratory of the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) which have been inoculated with lunar sample material. The sample material was collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.
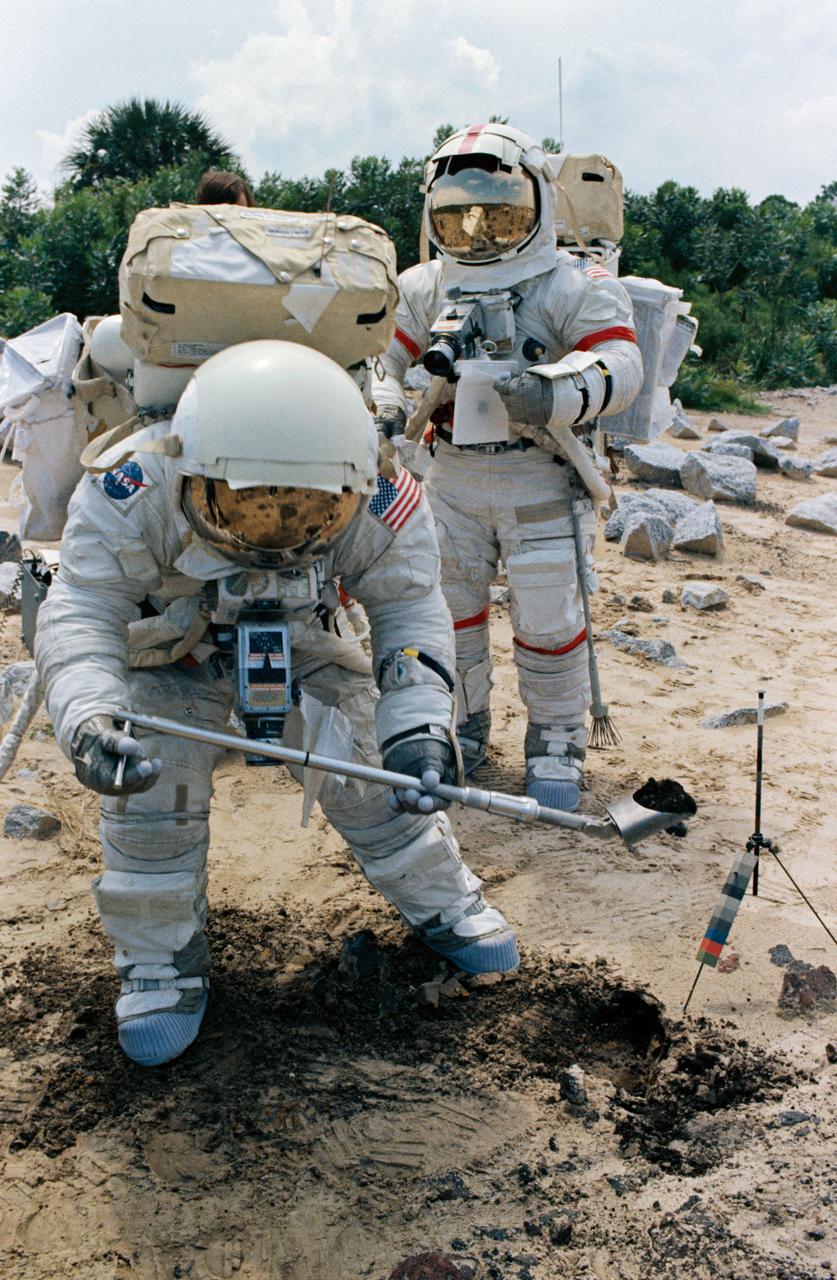

S72-48891 (September 1972) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission participate in lunar surface extravehicular activity simulation training at the Kennedy Space Center, Florida. Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt (foreground), lunar module pilot, simulates scooping up lunar sample material. Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (background), commander, holds a sample bag.
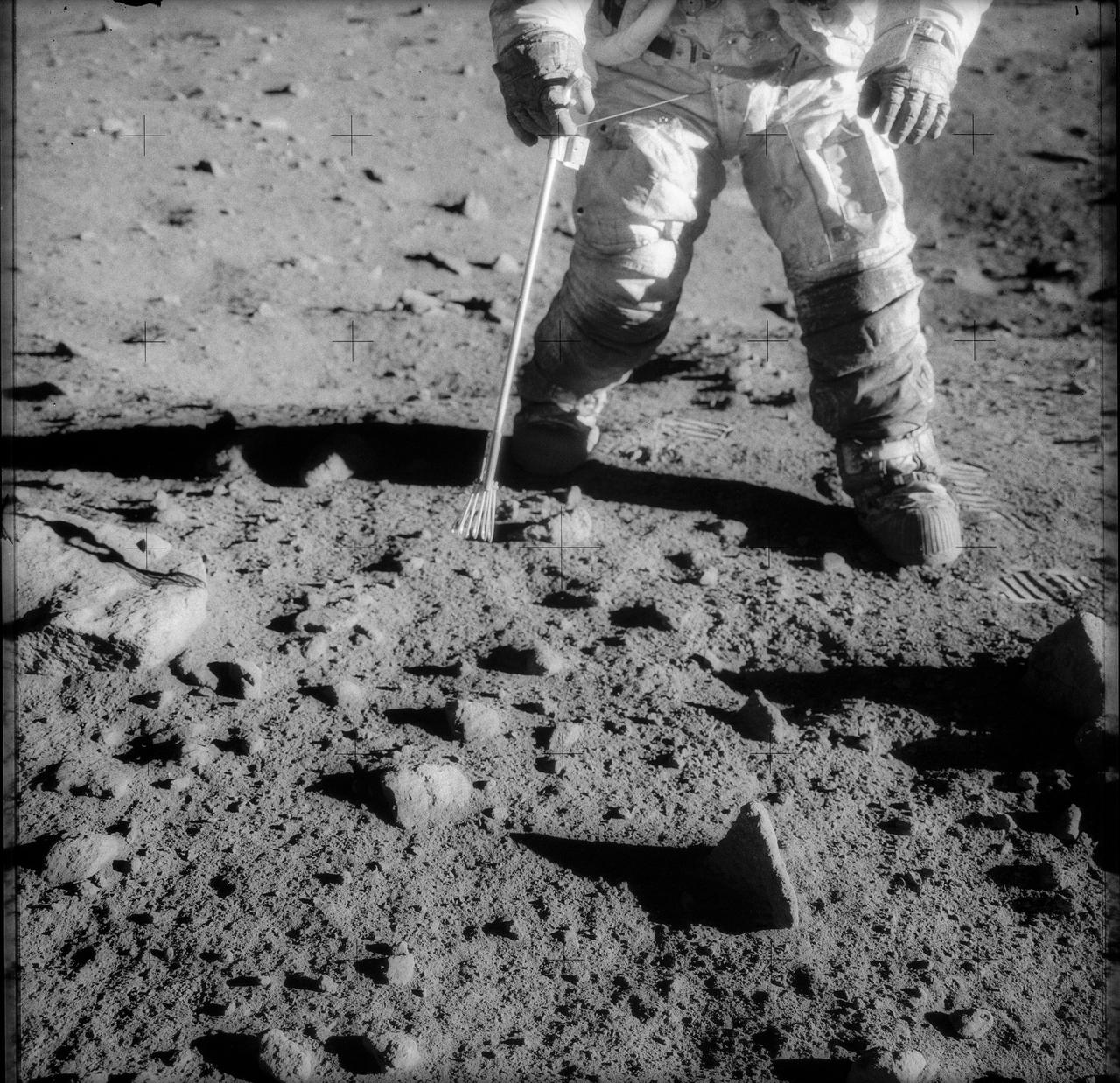

AS12-48-7149 (20 Nov. 1969) --- A close-up view of astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, photographed during the extravehicular activity (EVA) on the surface of the moon. An EVA checklist is on Conrad's left wrist. A set of tongs, an Apollo Lunar Hand Tool (ALHT), is held in his right hand. Several footprints can be seen. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit while astronauts Conrad and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon. Note lunar soil on the suit of Conrad, especially around the knees and below.
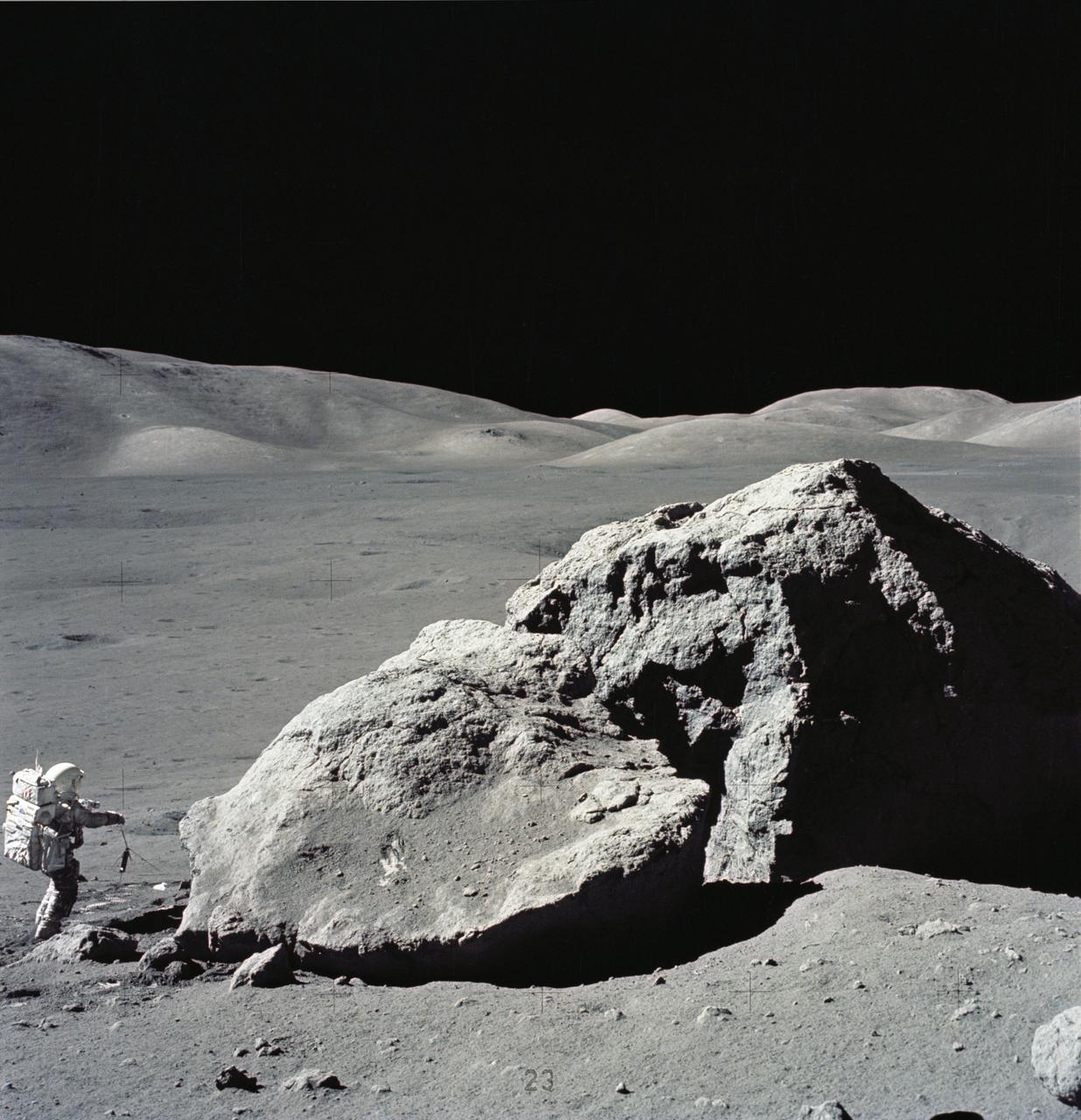

AS17-140-21496 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt is photographed standing next to a huge, split boulder during the third Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site on the moon. Schmitt is the Apollo 17 lunar module pilot. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander. While Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

S69-45009 (27 July 1969) --- This is the first lunar sample that was photographed in detail in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The photograph shows a granular, fine-grained, mafic (iron magnesium rich) rock. At this early stage of the examination, this rock appears similar to several igneous rock types found on Earth. The scale is printed backwards due to the photographic configuration in the Vacuum Chamber. The sample number is 10003. This rock was among the samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969.
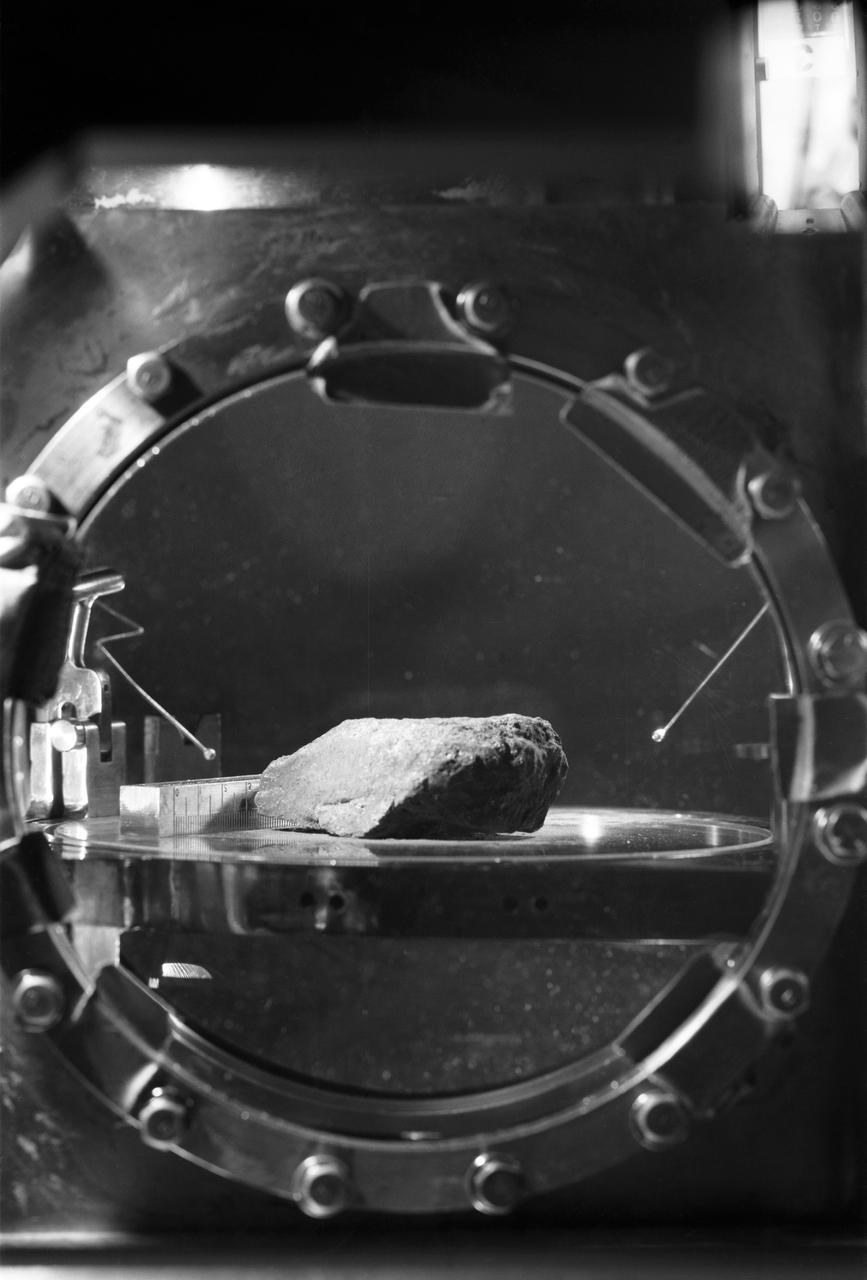

S69-45025 (27 July 1969) --- This is the first lunar sample that was photographed in detail in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. The photograph shows a granular, fine-grained, mafic (iron magnesium rich) rock. At this early stage of the examination, this rock appears similar to several igneous rock types found on Earth. The scale is printed backwards due to the photographic configuration in the Vacuum Chamber. The sample number is 10003. This rock was among the samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.
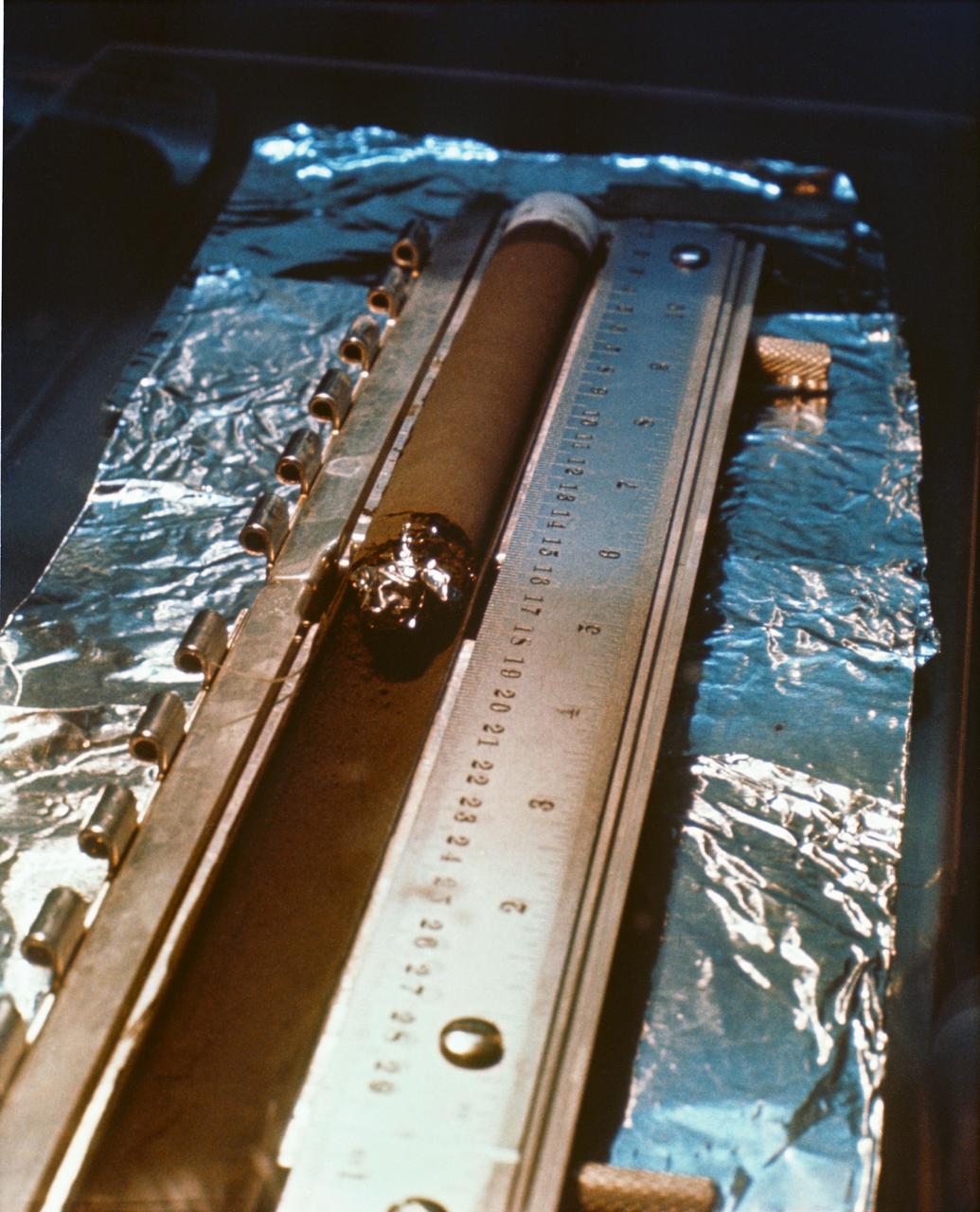
S69-40945 (August 1969) --- This is a core tube sample under study and examination in the Manned Spacecraft Center?s (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). The sample was among lunar soil and rock samples collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their extravehicular activity (EVA) on July 20, 1969. While astronauts Armstrong, commander; and Aldrin, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility landing site on the moon. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
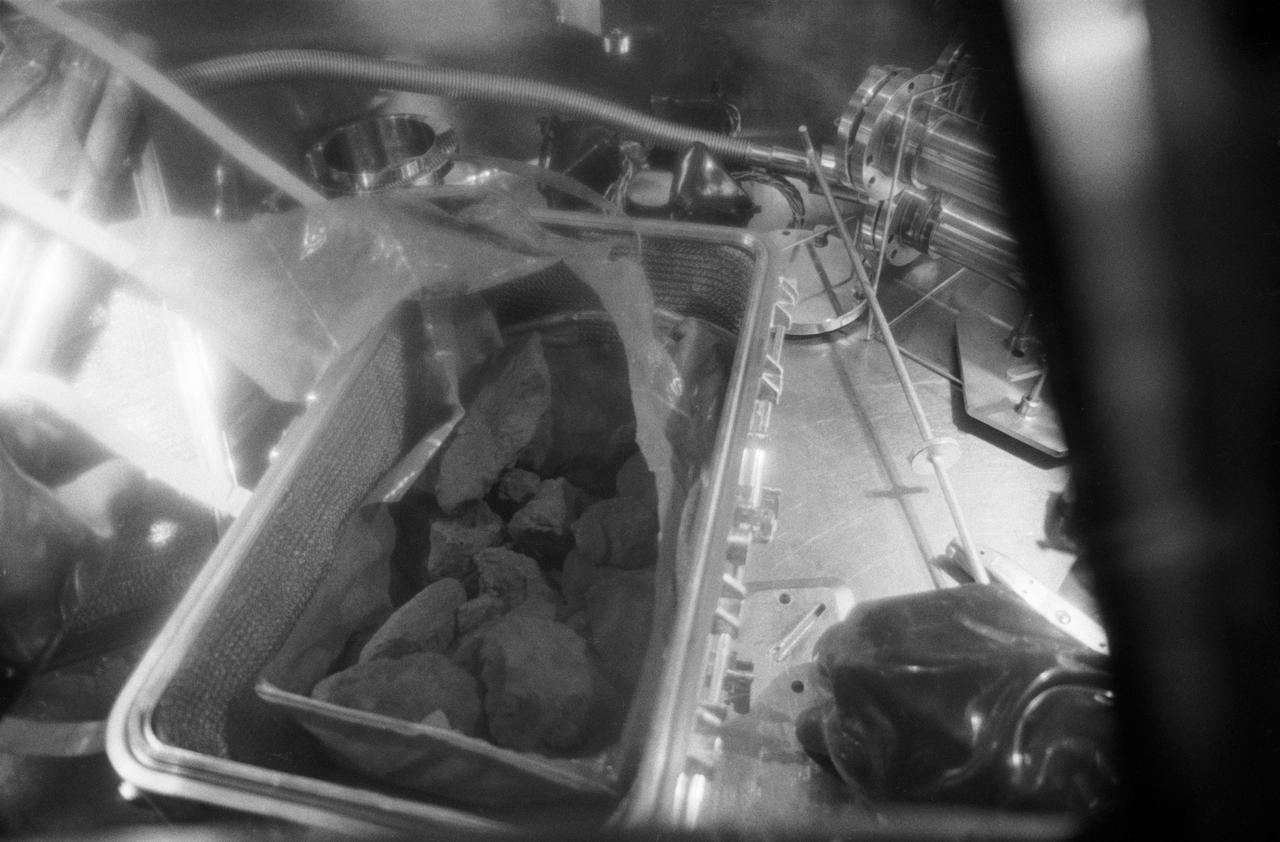

S69-45002 (26 July 1969) --- A close-up view of the lunar rocks contained in the first Apollo 11 sample return container. The rock box was opened for the first time in the Vacuum Laboratory of the Manned Spacecraft Center’s Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37, at 3:55 p.m. (CDT), Saturday, July 26, 1969. The gloved hand gives an indication of size. This box also contained the Solar Wind Composition experiment (not shown) and two core tubes for subsurface samples (not shown). These lunar samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.
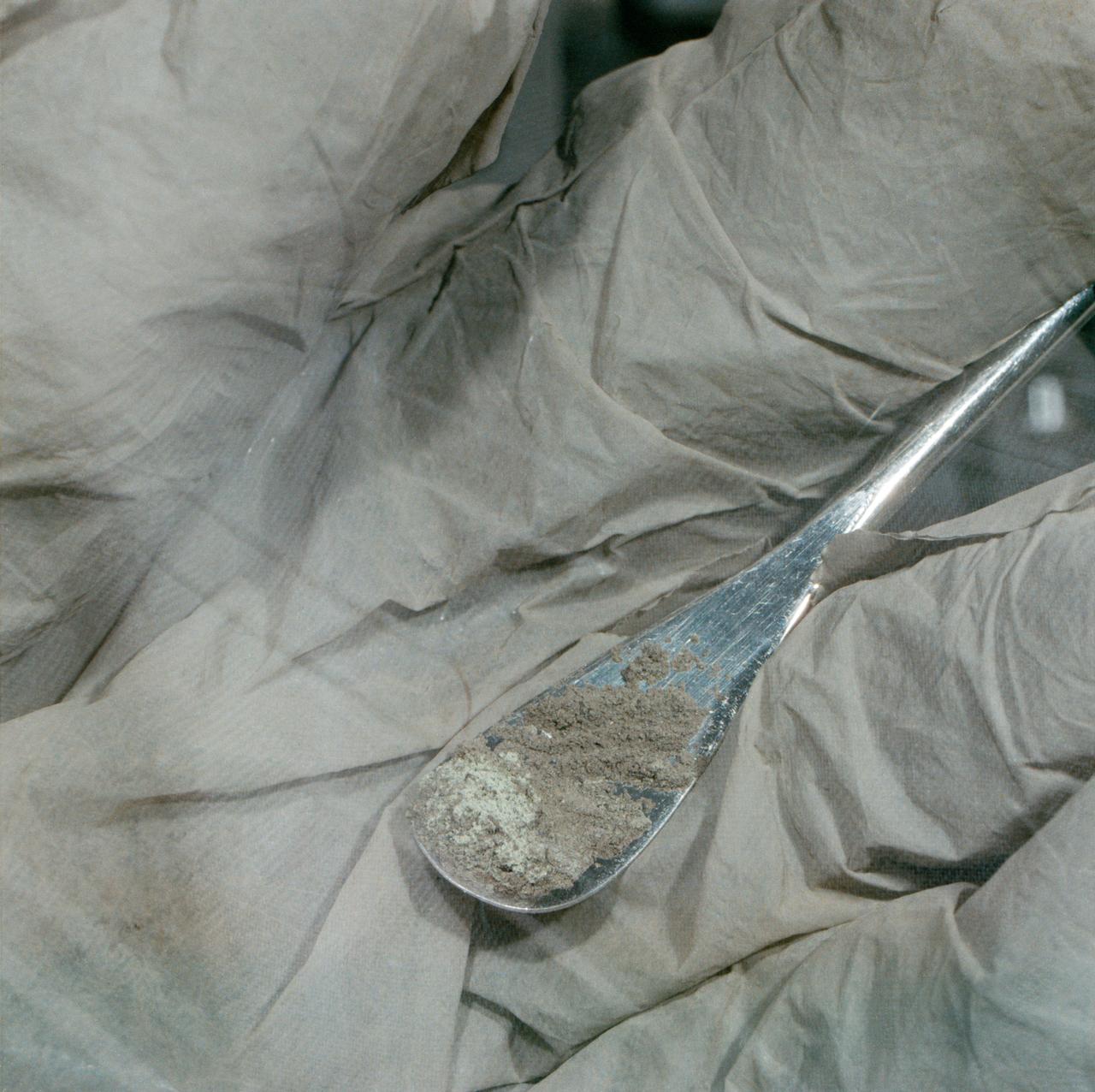

S71-43050 (August 1971) --- A close-up view of Apollo 15 lunar sample No. 15305 in the Non-sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). This sample, pictured on a small spatula in a lab technician's glove, is green and is one of six recently taken from container No. 173, made up of comprehensive fines from the Apennine Front, Site No. 7. Astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, took the sample during their second extravehicular activity (EVA), at a ground elapsed time (GET) of 146:05 to 146:06.

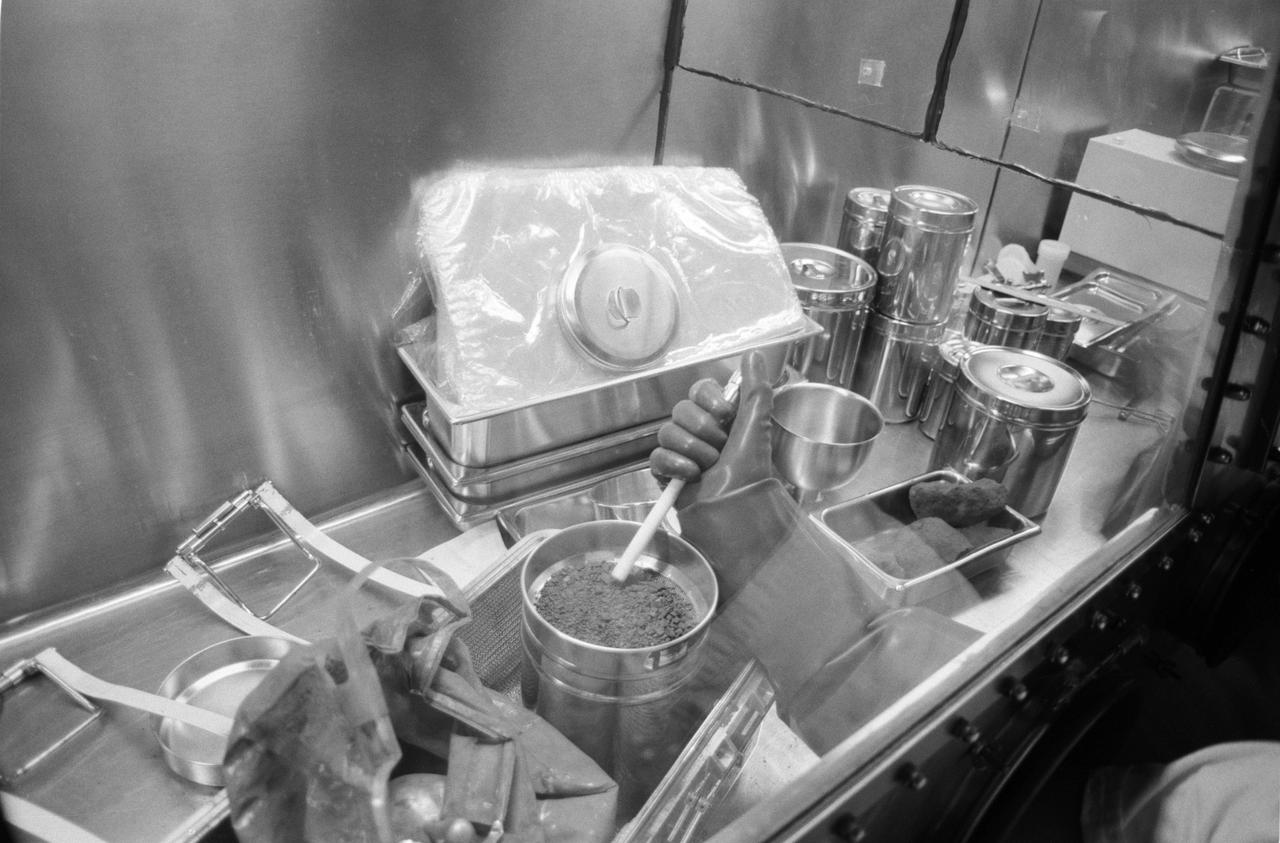
S69-40110 (25 July 1969) --- The first Apollo 11 sample return container, containing lunar surface material, is photographed just after it arrives at the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL), Building 37, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). The box arrived by air at Ellington Air Force Base just before noon on Friday, July 25, 1969, from the Pacific recovery area. It was taken immediately to the Manned Spacecraft Center. The lunar samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA).

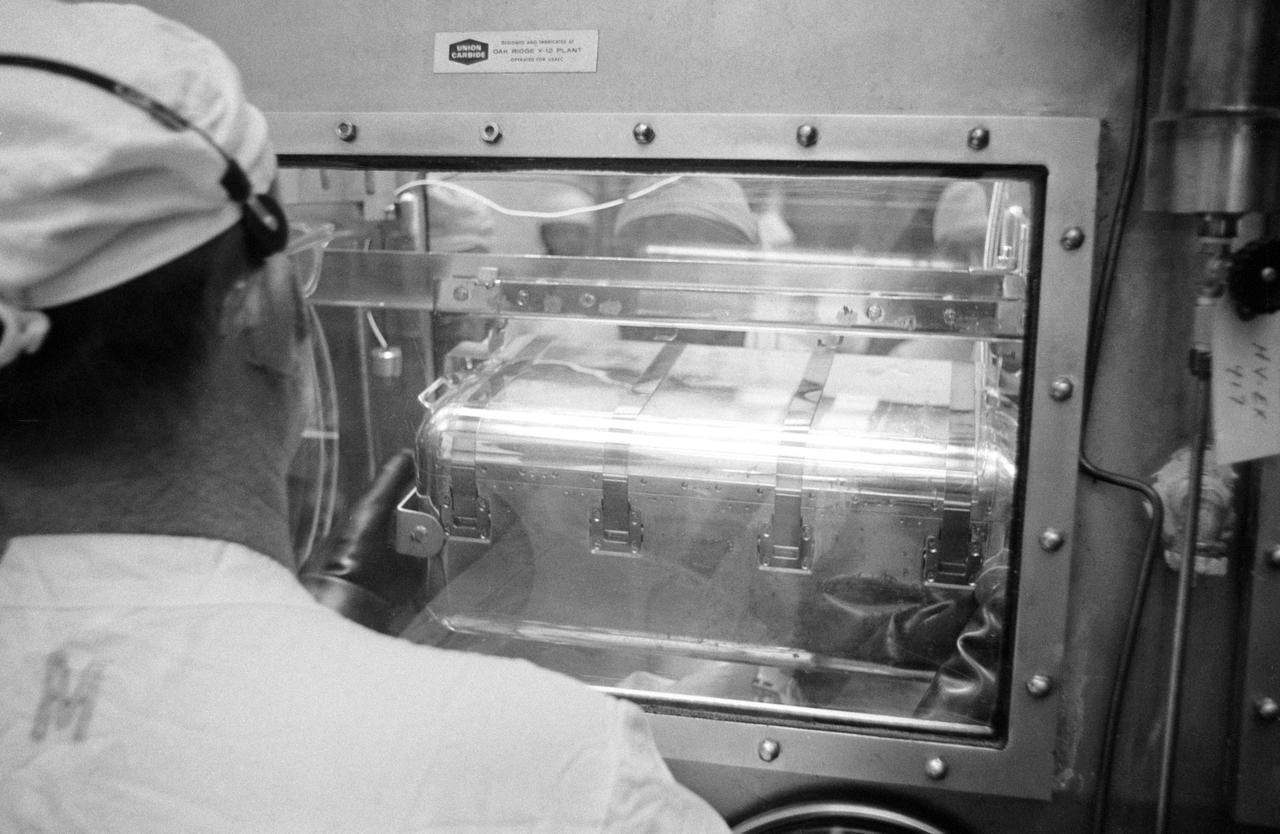
S69-45507 (4 Aug. 1969) --- A close-up of the second Apollo 11 sample return container in the Vacuum Laboratory of the Manned Spacecraft Center’s Lunar Receiving Laboratory, Building 37. This rock box was opened for the first time at 1 p.m. (CDT), Aug. 4, 1969. Some of the material has already been removed from the ALSRC in this view. The stainless steel can contains some course lunar surface material. The lunar samples were collected by astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. during their lunar surface extravehicular activity on July 20, 1969.
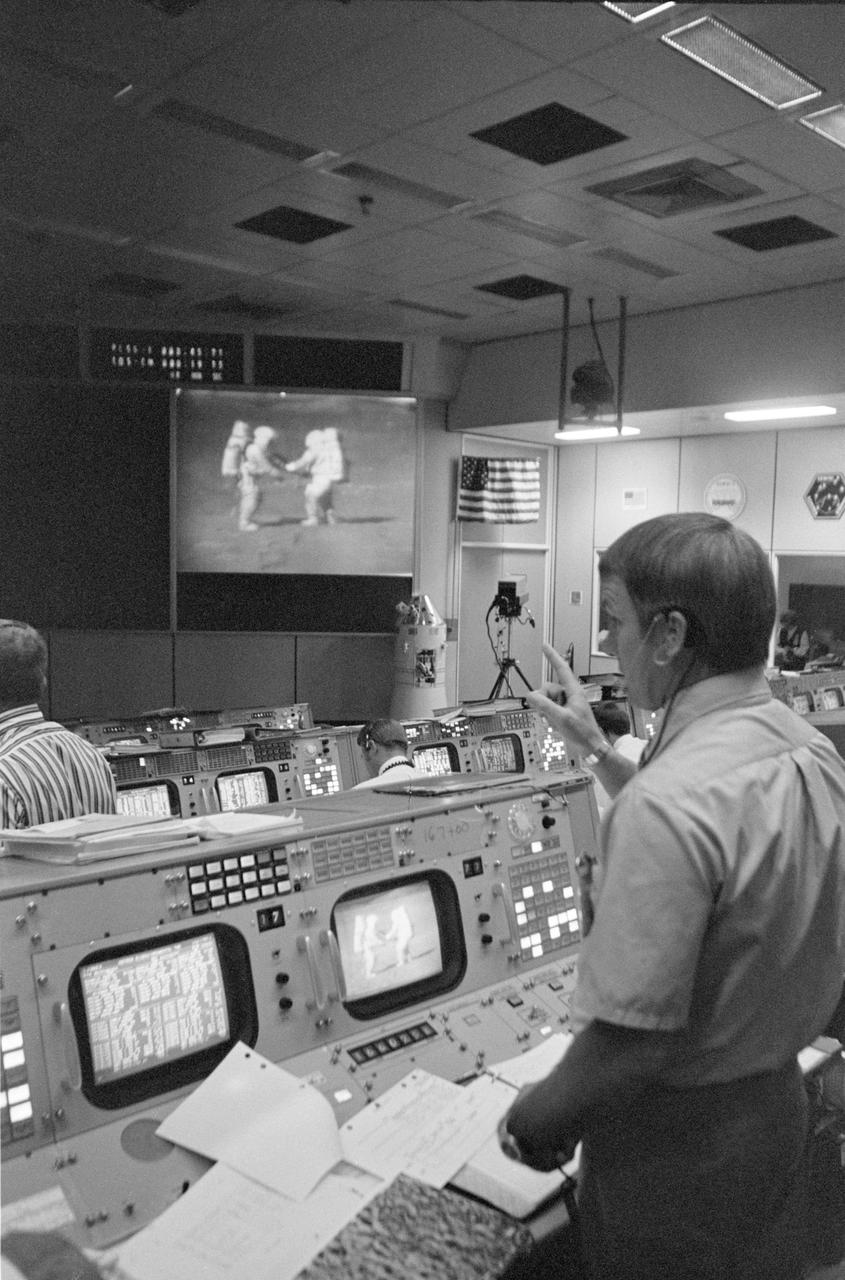

S71-41852 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Gerald D. Griffin, foreground, stands near his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) during Apollo 15's third extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. Griffin is Gold Team (Shift 1) flight director for the Apollo 15 mission. Astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin can be seen on the large screen at the front of the MOCR as they participate in sample-gathering on the lunar surface.
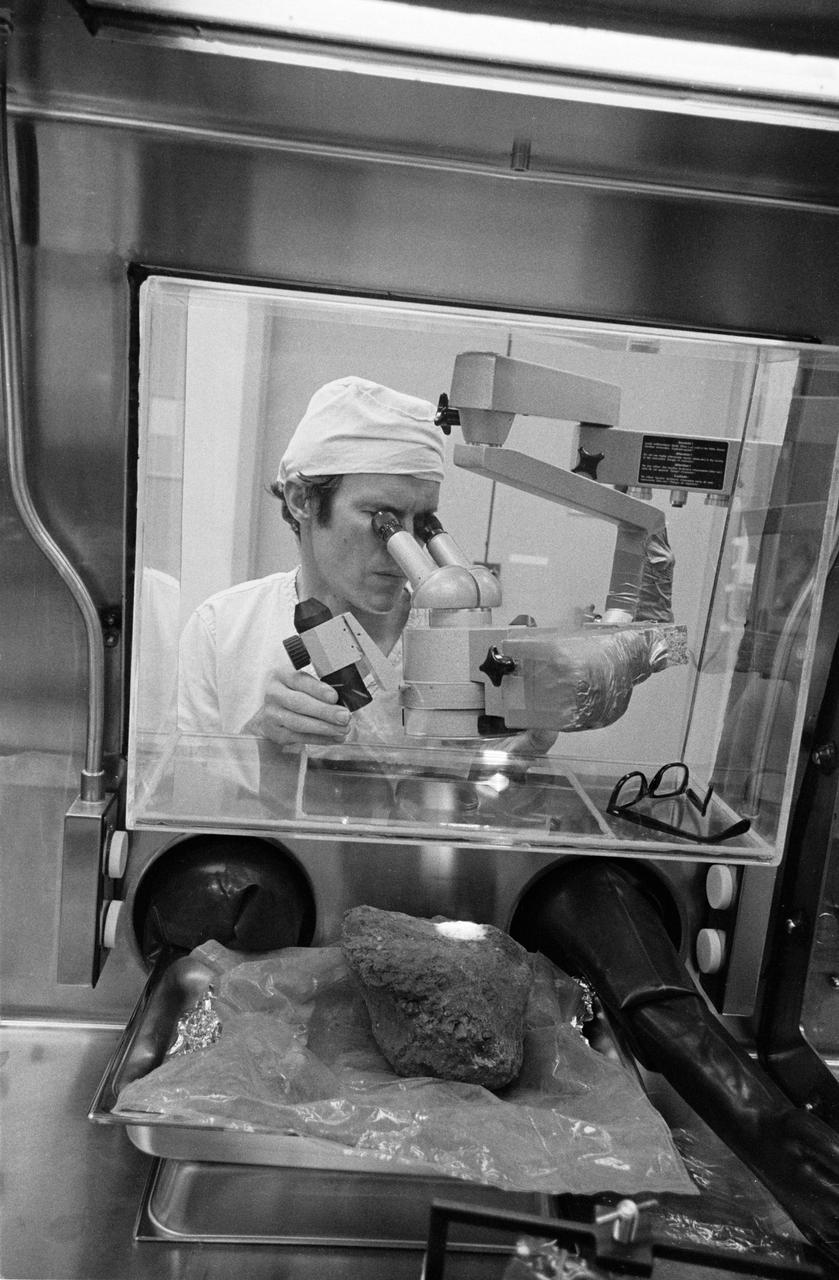

S71-21245 (24 Feb. 1971) --- Dr. Daniel H. Anderson, an aerospace technologist and test director in the Nonsterile Nitrogen Processing Laboratory in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) looks at much-discussed Apollo 14 basketball-size rock through a microscope. The two moon-exploring crew men of Apollo 14 brought back 90-odd pounds of lunar sample material from their two periods of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface in the Fra Mauro area.
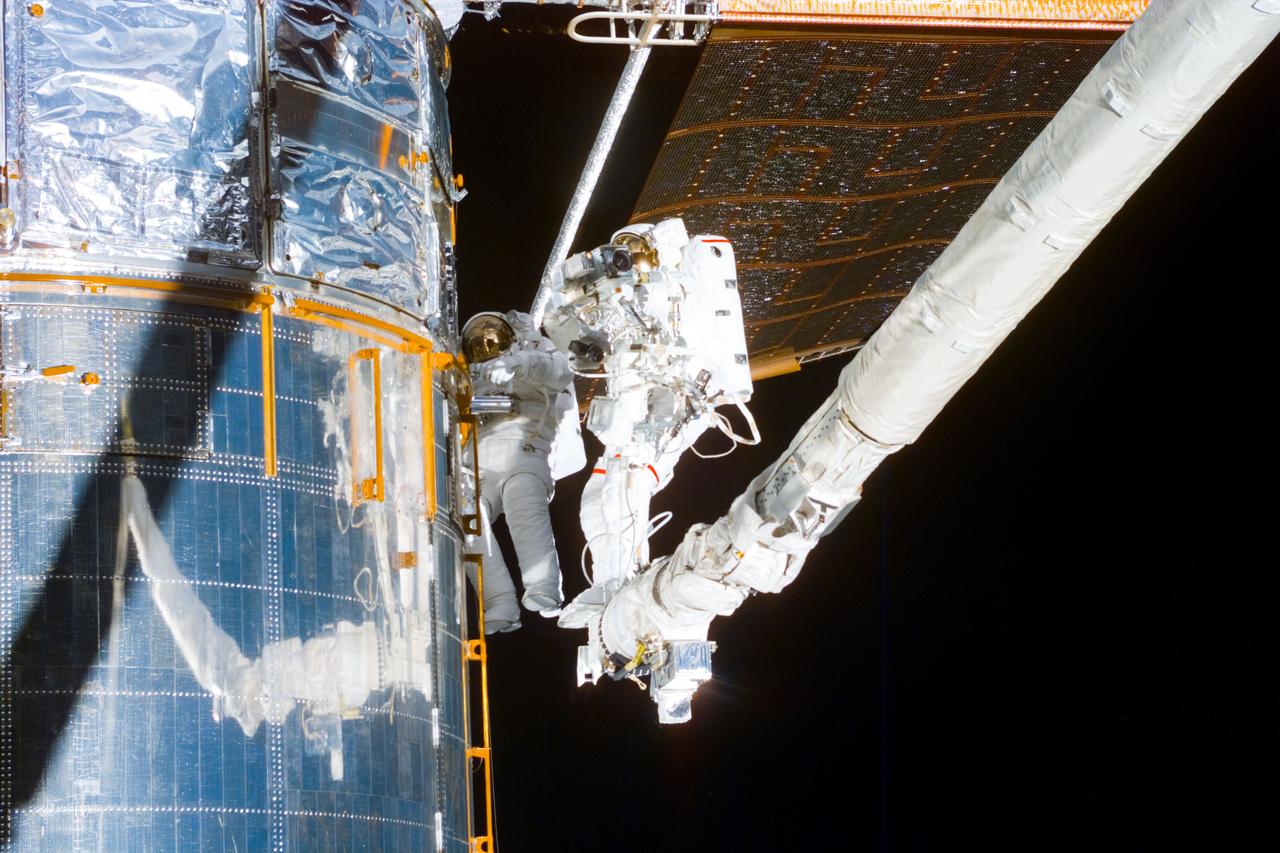

S82-E-5718 (18 Feb. 1997) --- Making use of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) astronauts Mark C. Lee (left), STS-82 payload commander, and Steven L. Smith, mission specialist, perform the final phases of Extravehicular Activity (EVA) duty. Lee holds a patch piece for Bay #10, out of view, toward which the two were headed. A sample of the patch work can be seen on Bay #9 in the upper left quadrant of the picture. This view was taken with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC).
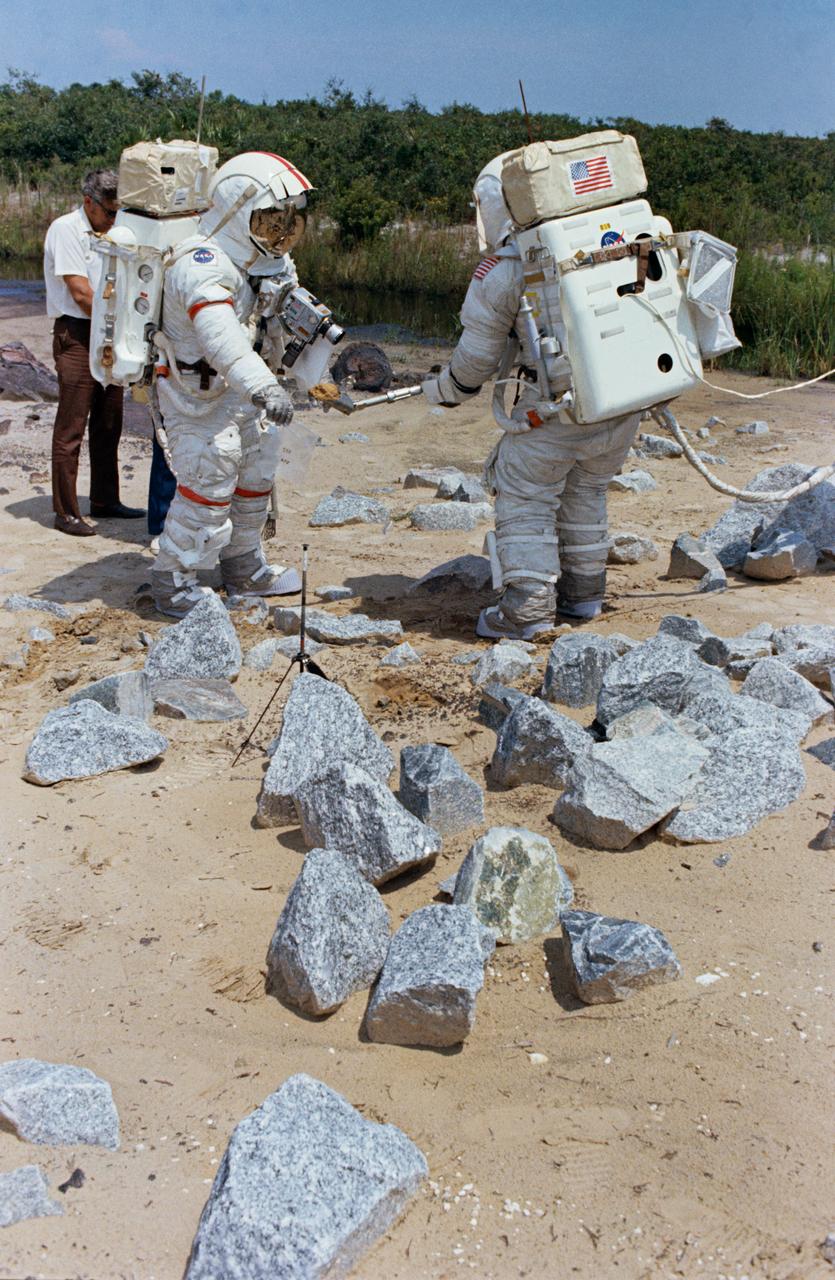

S72-48888 (September 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (left), commander, and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, simulate collecting lunar samples during extravehicular activity training at the Kennedy Space Center, Florida. Astronauts Cernan, Schmitt, and Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, are the prime crewmen of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission.
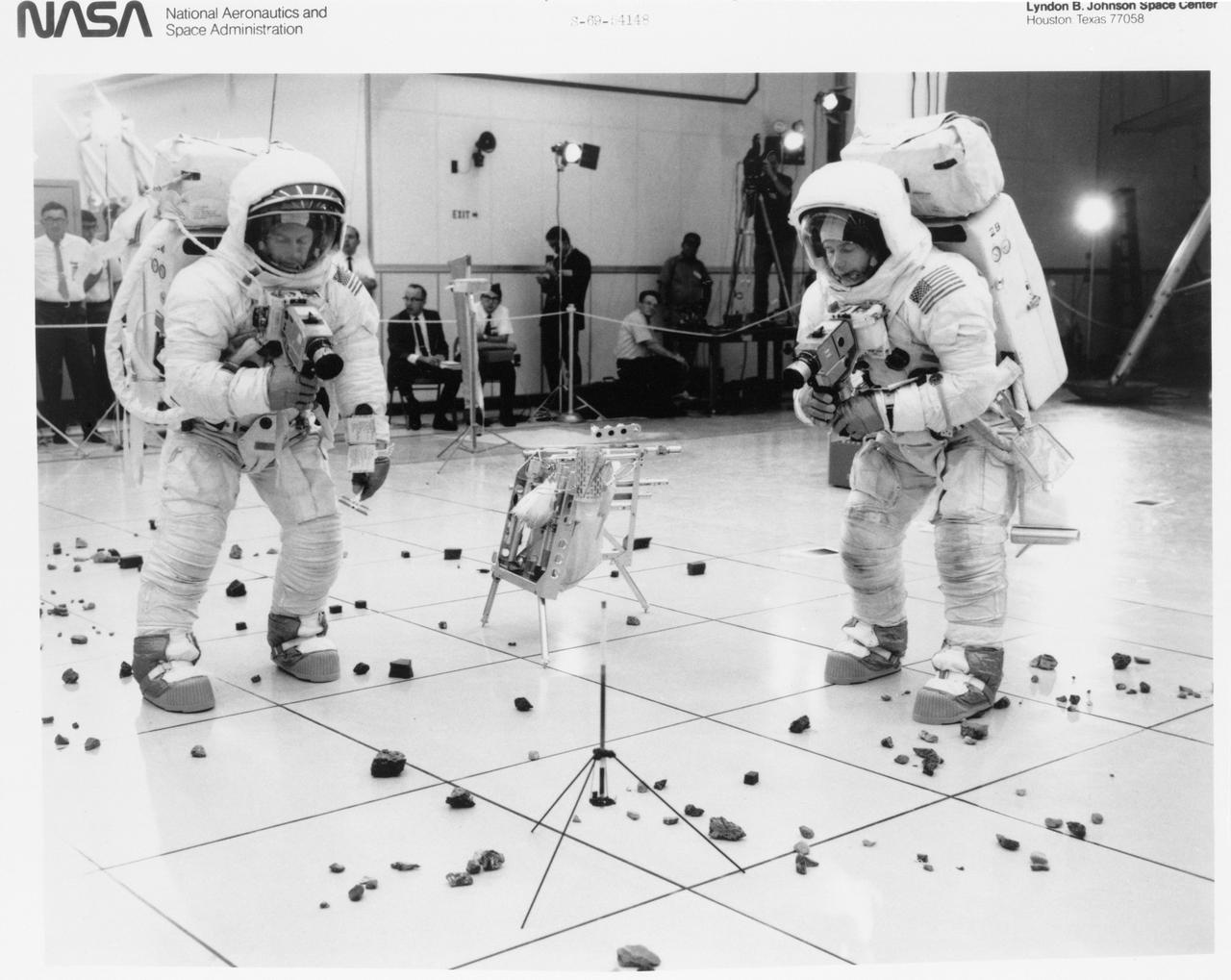

S69-54148 (October 1969) --- Two members of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission participates in lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) simulations in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Flight Crew Training Building. Here, astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. (on left), commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, simulate the photographic documentation of lunar rock samples. The simulations were part of a run-through of the Apollo 12 lunar surface "timeline".
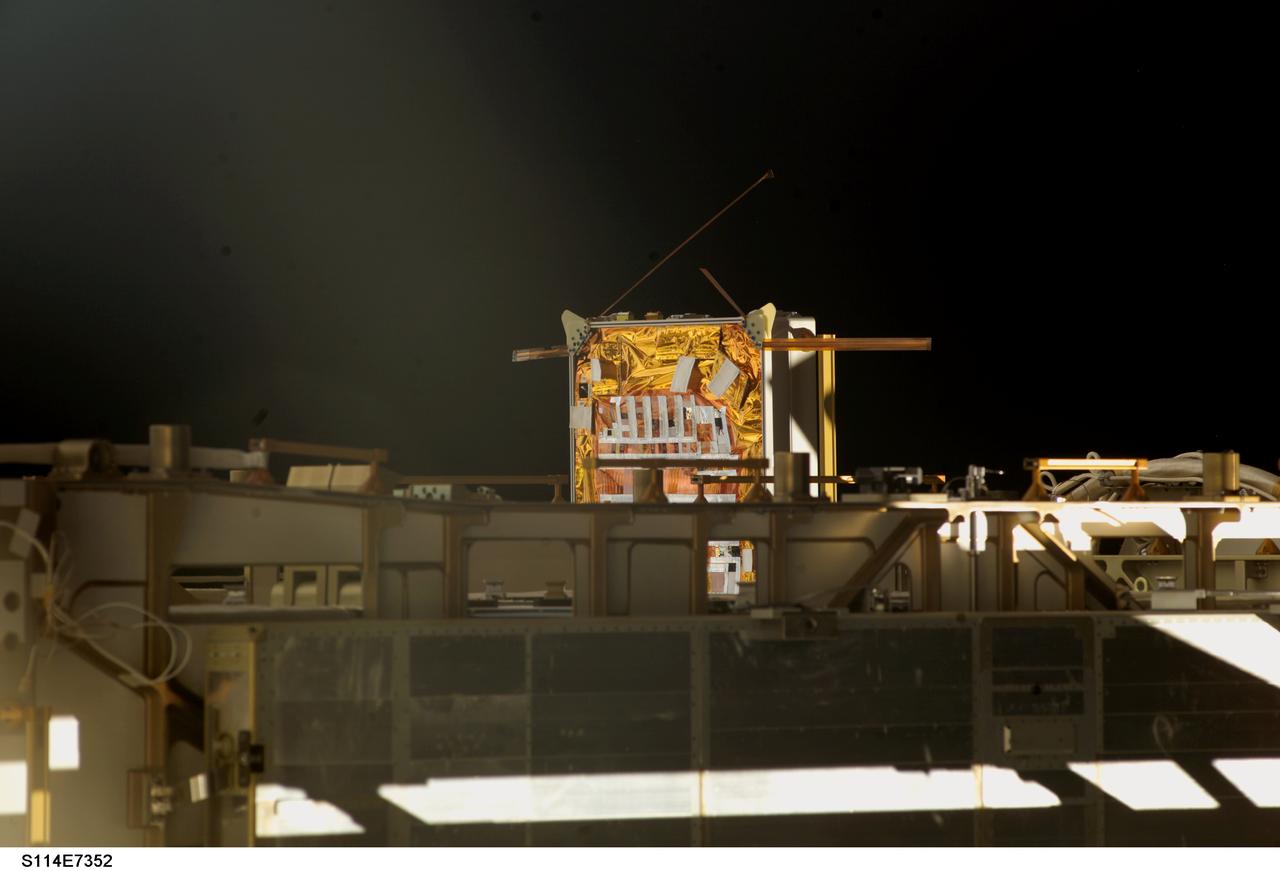

s114e7352 (8/6/2005) --- A view of the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) 5 Passive Experiment Containter (PEC) mounted on the P6 Truss during one of the STS-114 missions Extravehicular Activities (EVAs). The Materials International Space Station Experiment-5 (MISSE-5) was an external payload that flew on-board the ISS from August 2005 until September 2006. MISSE-5 provided an opportunity for researchers to test a wide range of samples in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) environment.
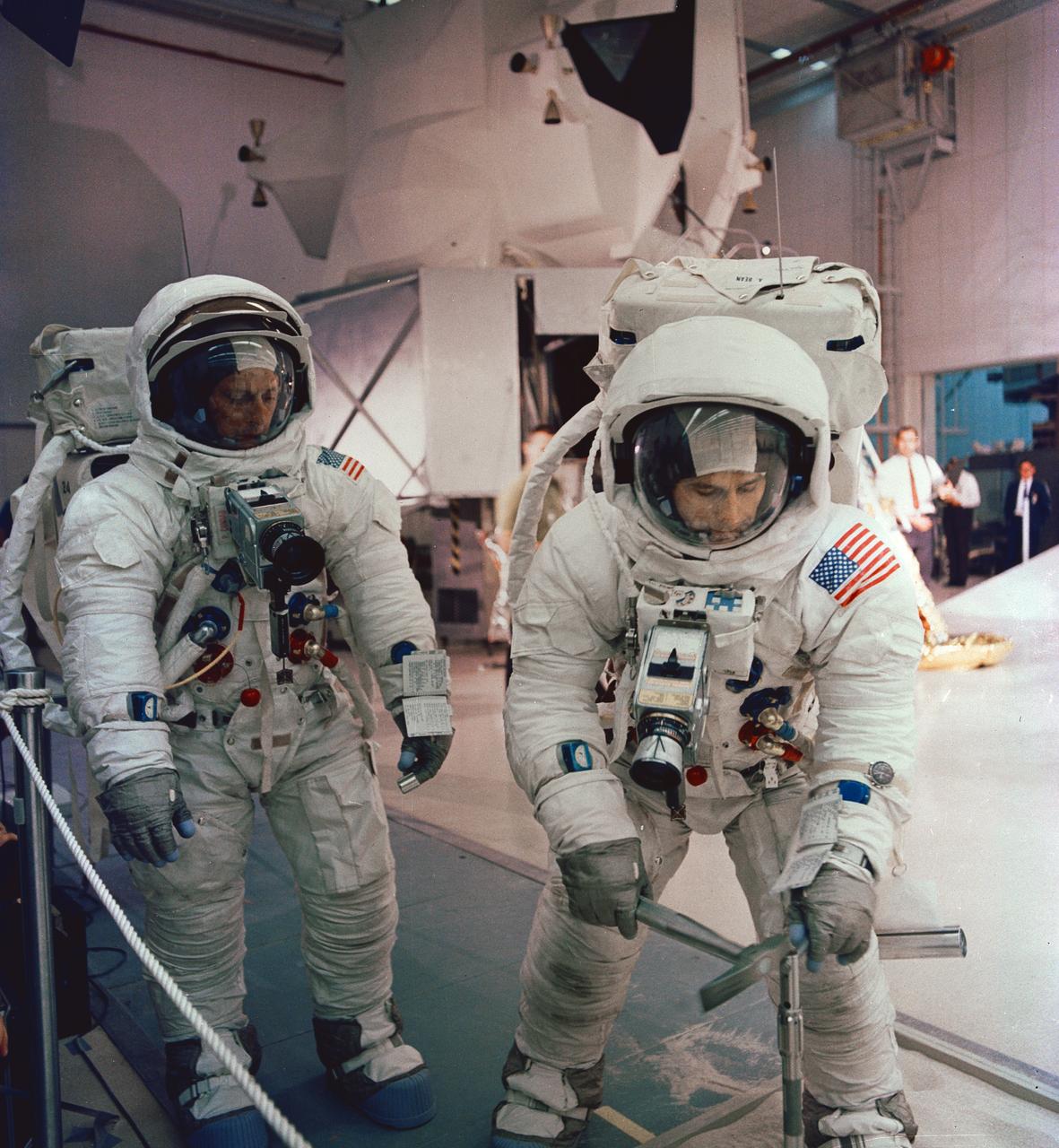

S69-55362 (6 Oct. 1969) --- The two assigned moon-walking crew members for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission participate in lunar surface extravehicular activity simulations in the Kennedy Space Center's Flight Crew Training Building. Here, astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, simulates driving core tube into lunar surface to obtain a sample. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, looks on. A Lunar Module mock-up is in the center background. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
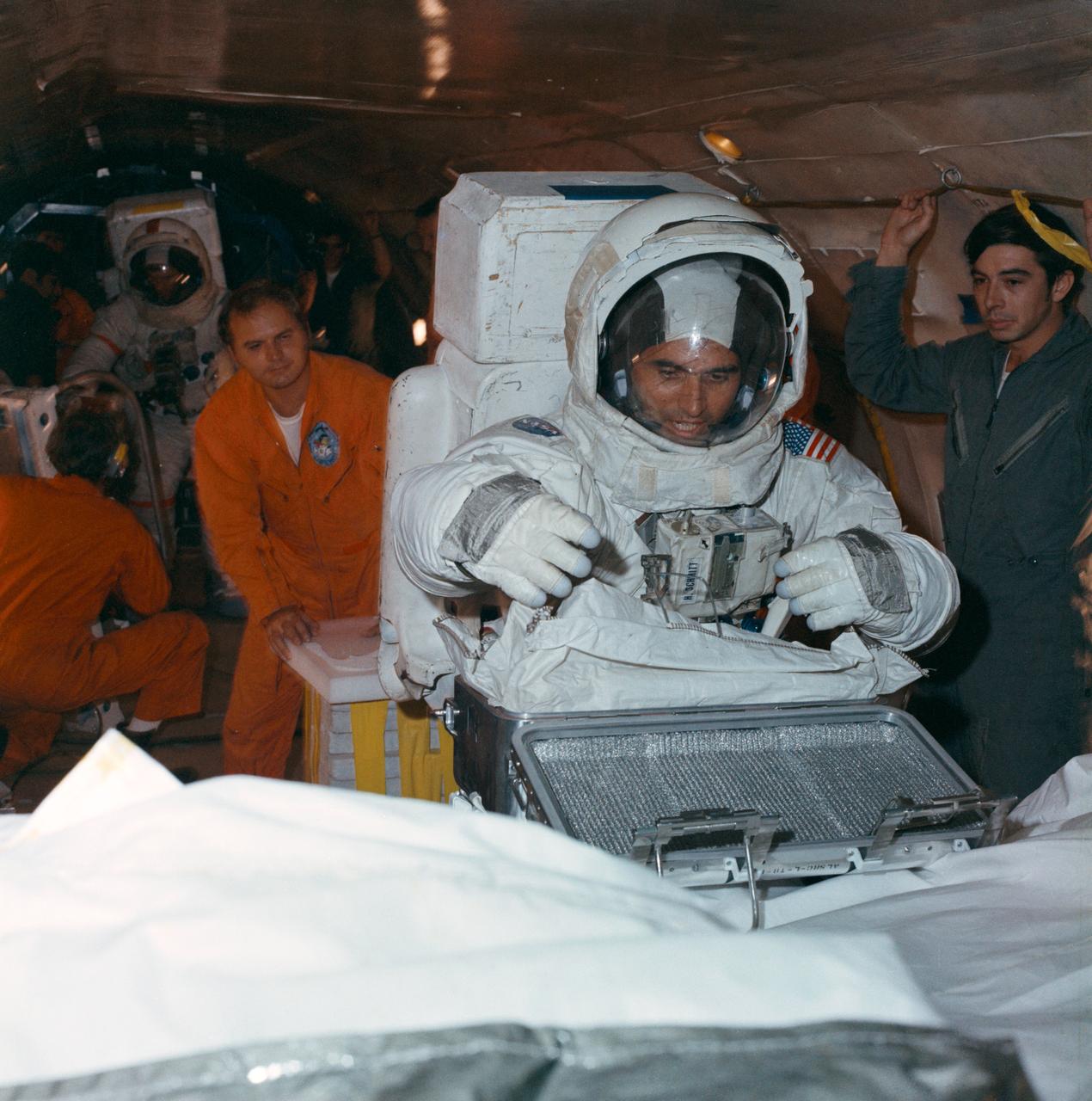

S72-50269 (September 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission, seals an Apollo lunar sample return container during lunar surface extravehicular activity simulation training under one-sixth gravity conditions aboard a U.S. Air Force KC-135 aircraft. Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, can be seen in the left background.
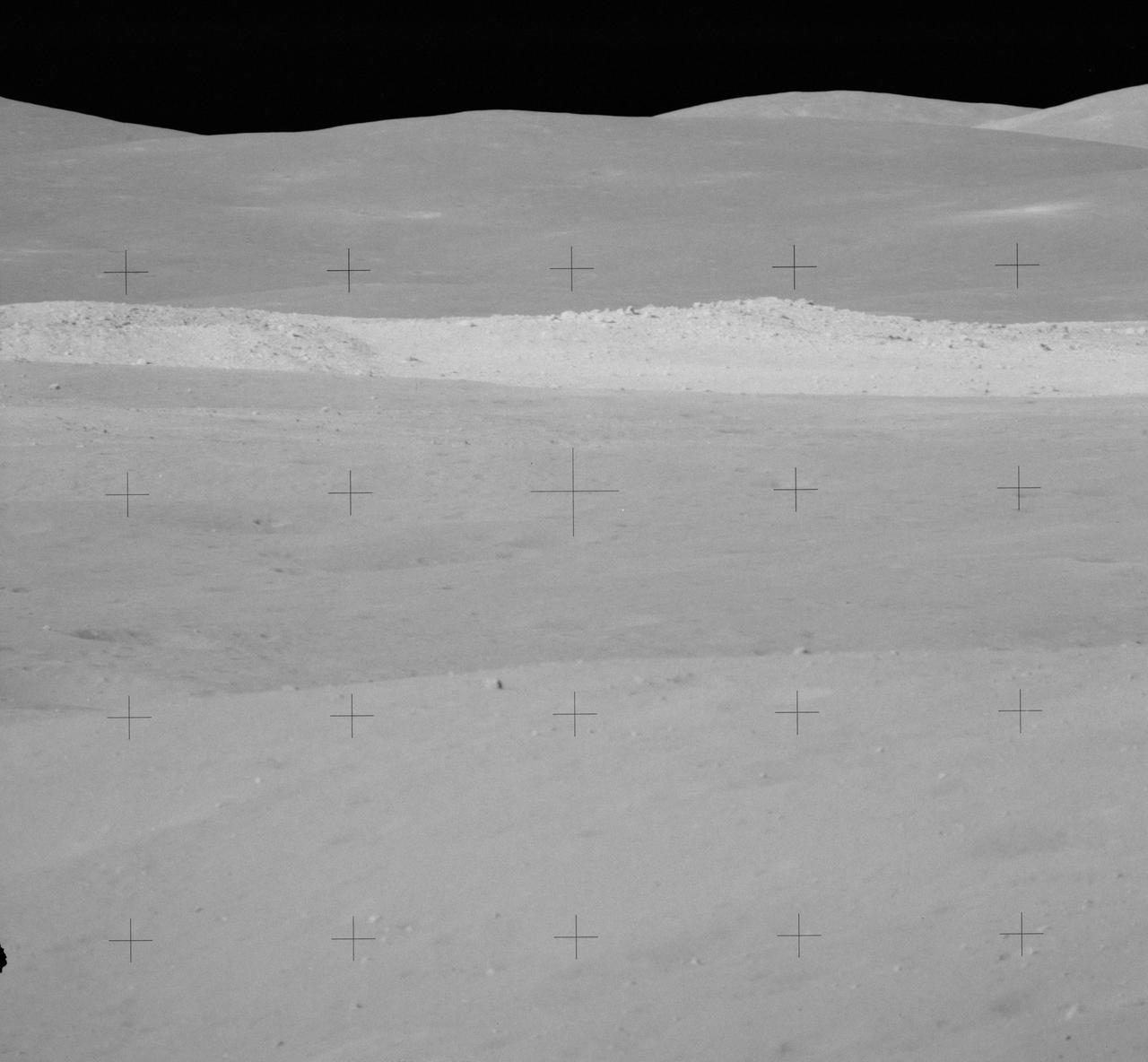

AS16-112-18234 (22 April 1972) --- This view of South Ray Crater was taken during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) from Station No. 4 -- highest point on the traverse up Stone Mountain -- using a 500mm lens. South Ray Crater is a "fresh" source of angular ejecta in the LM-ALSEP area and samples at Station No. 8.
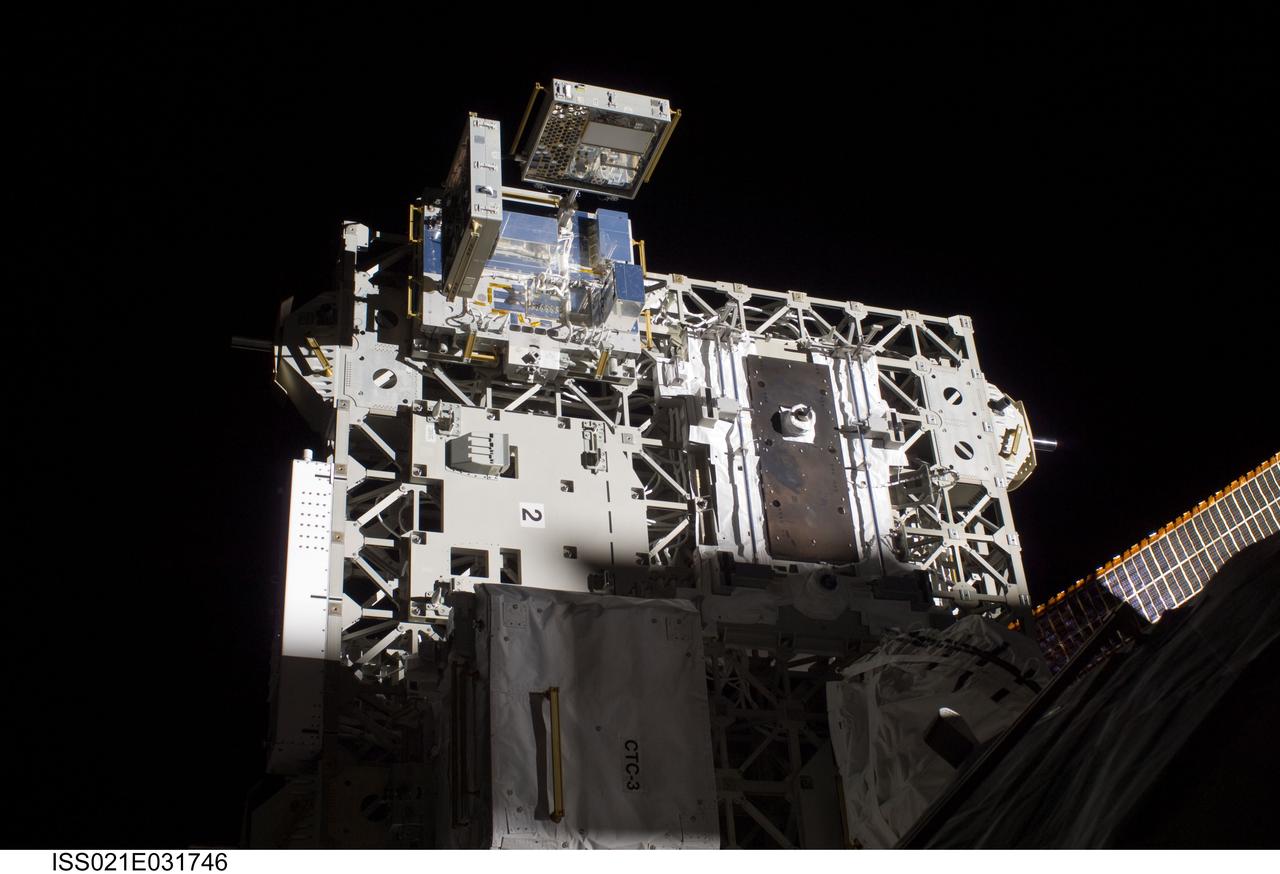

ISS021-E-031746 (23 Nov. 2009) --- The MISSE 7 experiment on the Express Logistics Carrier 2 of the International Space Station was photographed by a space-walking STS-129 astronaut during the mission's third and final session of extravehicular activity (EVA). This is the latest in a series of experiments that expose materials and composite samples to space for several months before they are returned for experts to analyze. This MISSE experiment actually is plugged into the space station’s power supply.
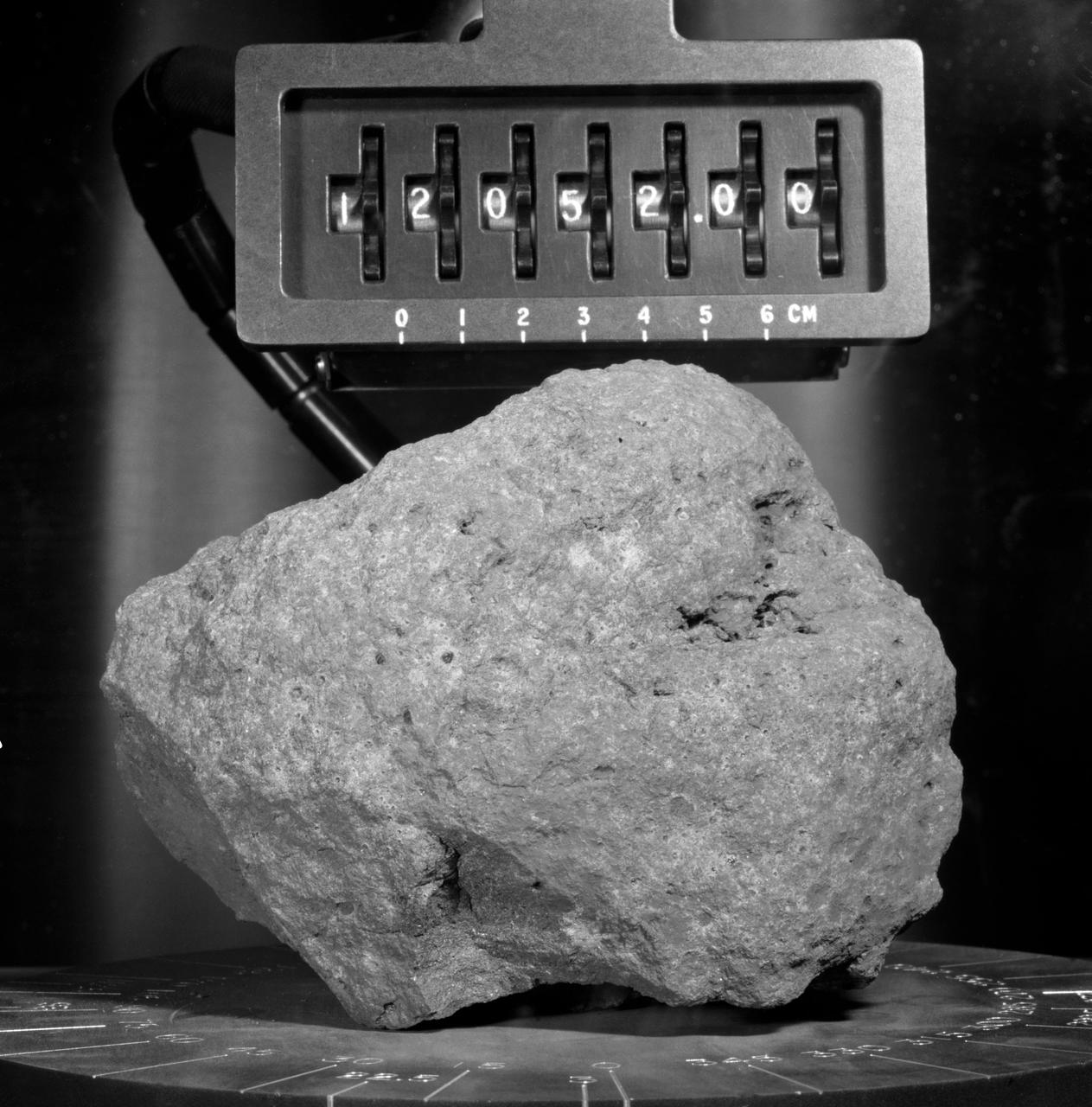

S69-60909 (November 1969) --- A close-up view of lunar sample 12,052 under observation in the Manned Spacecraft Center's Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., and Alan L. Bean collected several rocks and samples of finer lunar matter during their Apollo 12 lunar landing mission extravehicular activity (EVA). This particular sample was picked up during the second space walk (EVA) on Nov. 20, 1969. It is a typically fine-grained crystalline rock with a concentration of holes on the left part of the exposed side. These holes are called vesicles and have been identified as gas bubbles formed during the crystallization of the rock. Several glass-lined pits can be seen on the surface of the rock.
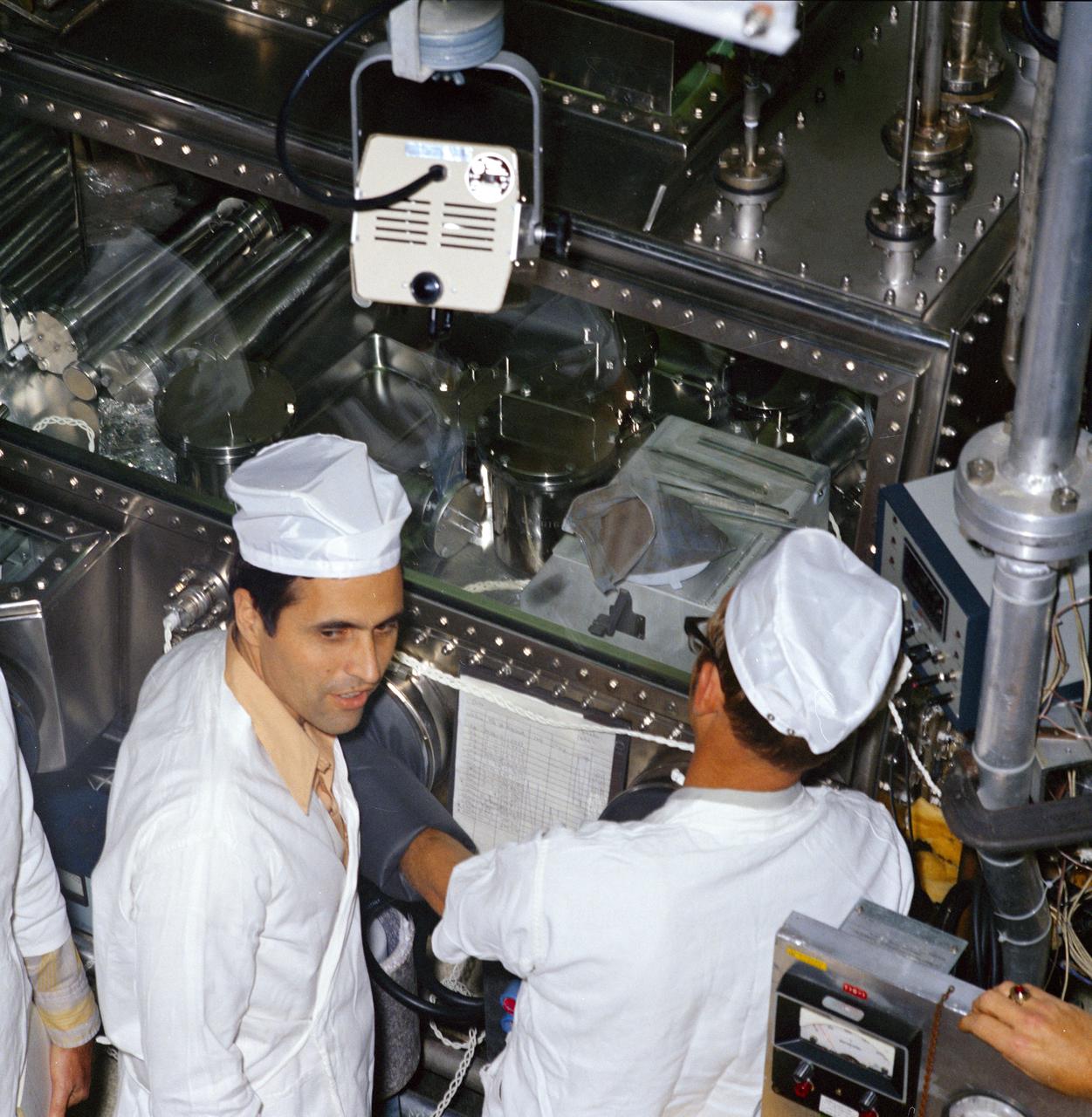

S72-56362 (27 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt (facing camera), Apollo 17 lunar module pilot, was one of the first to look at the sample of "orange" soil which was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. Schmitt discovered the material at Shorty Crater during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA). The "orange" sample, which was opened Wednesday, Dec. 27, 1972, is in the bag on a weighing platform in the sealed nitrogen cabinet in the upstairs processing line in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. Just before, the sample was removed from one of the bolt-top cans visible to the left in the cabinet. The first reaction of Schmitt was "It doesn't look the same." Most of the geologists and staff viewing the sample agreed that it was more tan and brown than orange. Closer comparison with color charts showed that the sample had a definite orange cast, according the MSC geology branch Chief William Phinney. After closer investigation and sieving, it was discovered that the orange color was caused by very fine spheres and fragments of orange glass in the midst of darker colored, larger grain material. Earlier in the day the "orange" soil was taken from the Apollo Lunar Sample Return Container No. 2 and placed in the bolt-top can (as was all the material in the ALSRC "rock box").
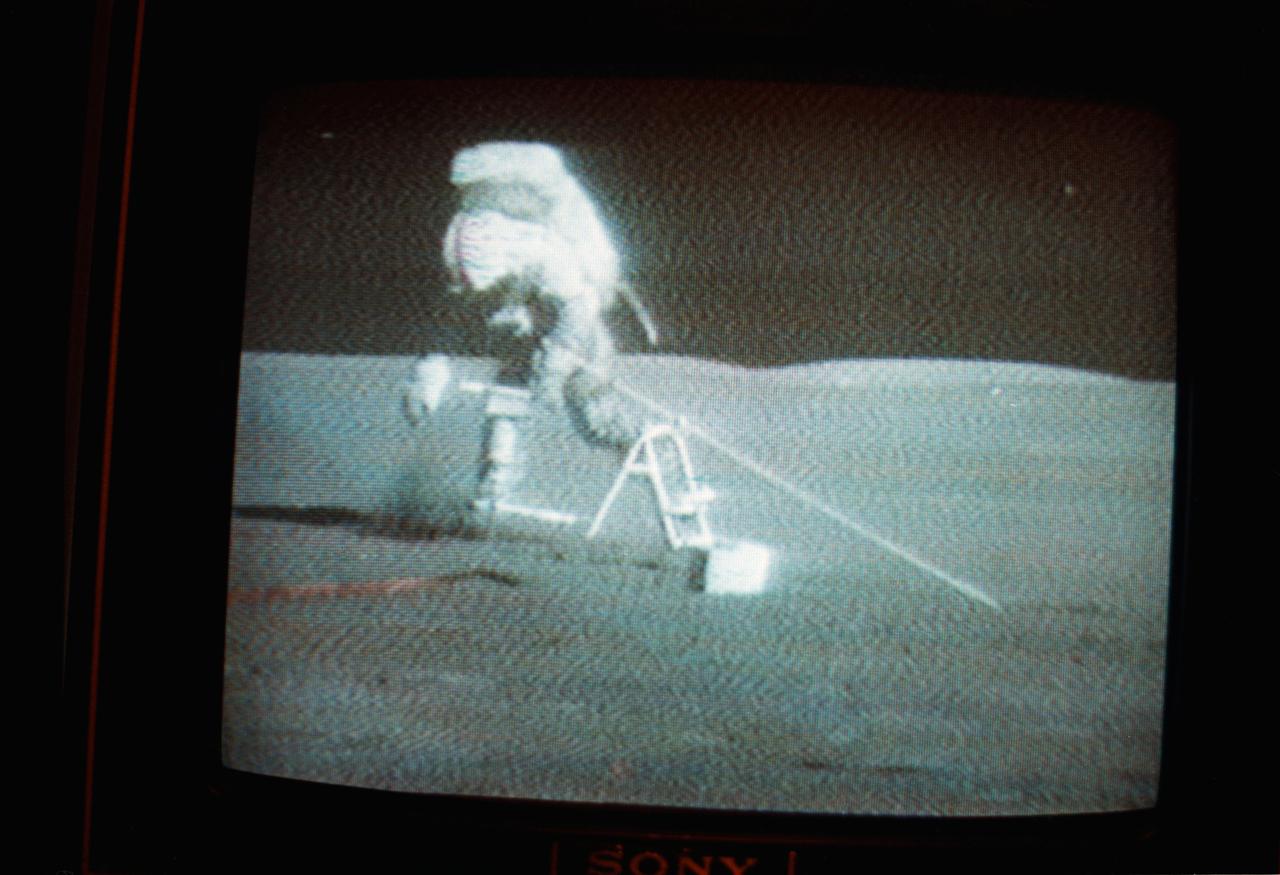

S71-41501 (1 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut David R. Scott, Apollo 15 commander, is seen carrying the Apollo Lunar Surface Drill (ALSD) during the second lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) in this black and white reproduction taken from a color transmission made by the RCA color television camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This transmission was the fourth made during the mission.
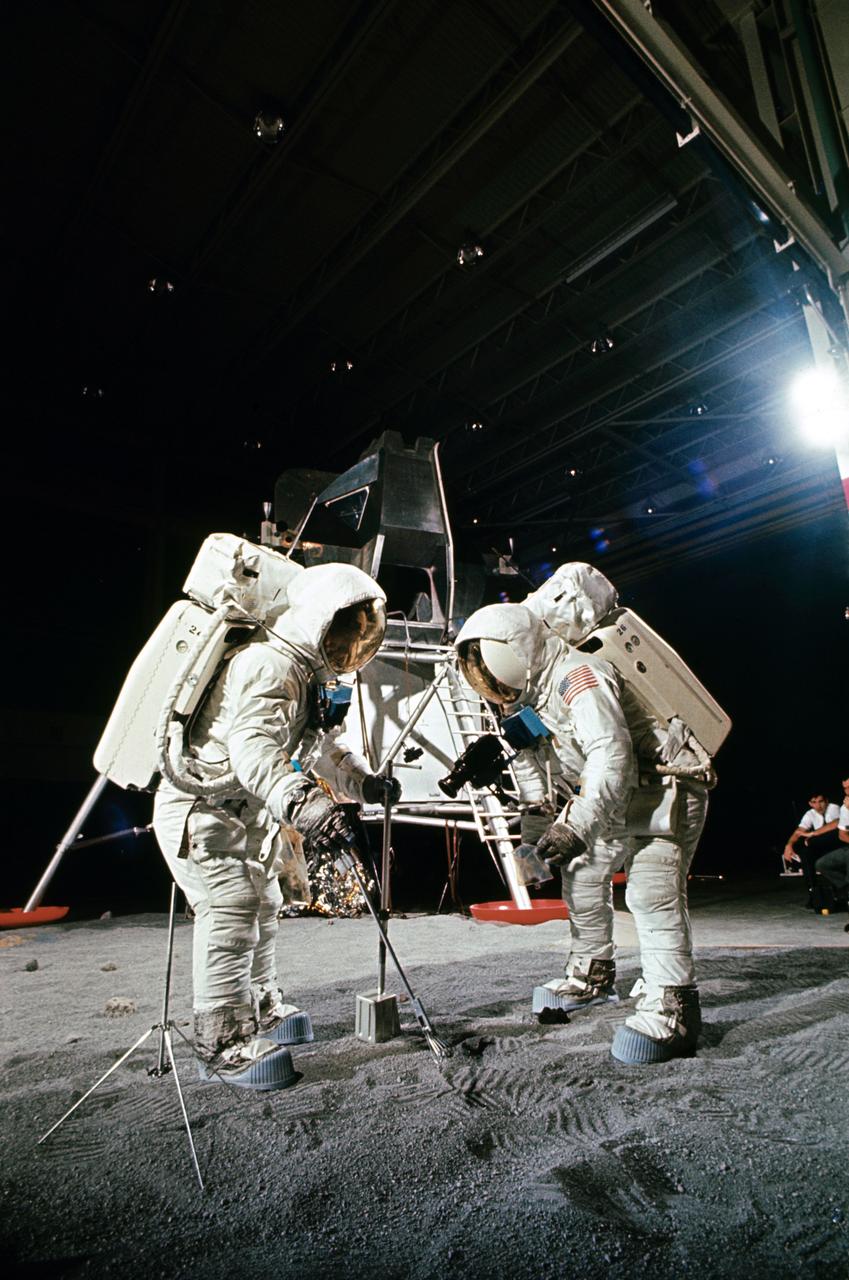

Two members of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission participate in a simulation of deploying and using lunar tools on the surface of the moon during a training exercise in bldg 9 on April 22, 1969. Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. (on left), lunar module pilot, uses scoop and tongs to pick up sample. Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, holds bag to receive sample. In the background is a Lunar Module mockup. Both men are wearing Extravehicular Mobility Units (EMU).
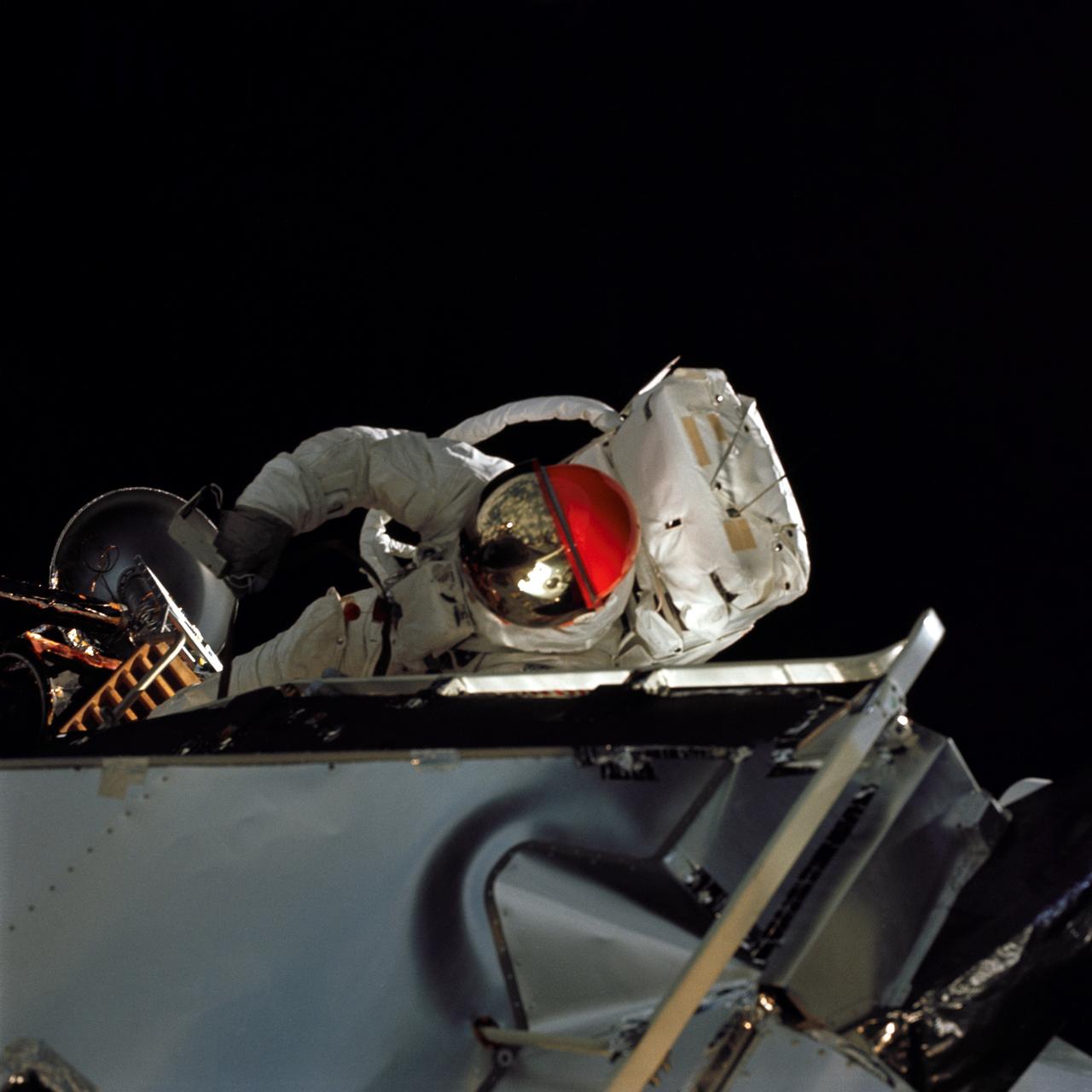

AS09-19-2994 (6 March 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, is photographed from the Command Module (CM) "Gumdrop" during his extravehicular activity (EVA) on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. He holds, in his right hand, a thermal sample which he is retrieving from the Lunar Module (LM) exterior. The Command and Service Modules (CSM) and LM "Spider" are docked. Schweickart, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is standing in "golden slippers" on the LM porch. Visible on his back are the Portable Life Support System (PLSS) and Oxygen Purge System (OPS). Astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, was inside the "Spider". Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the CM "Gumdrop".
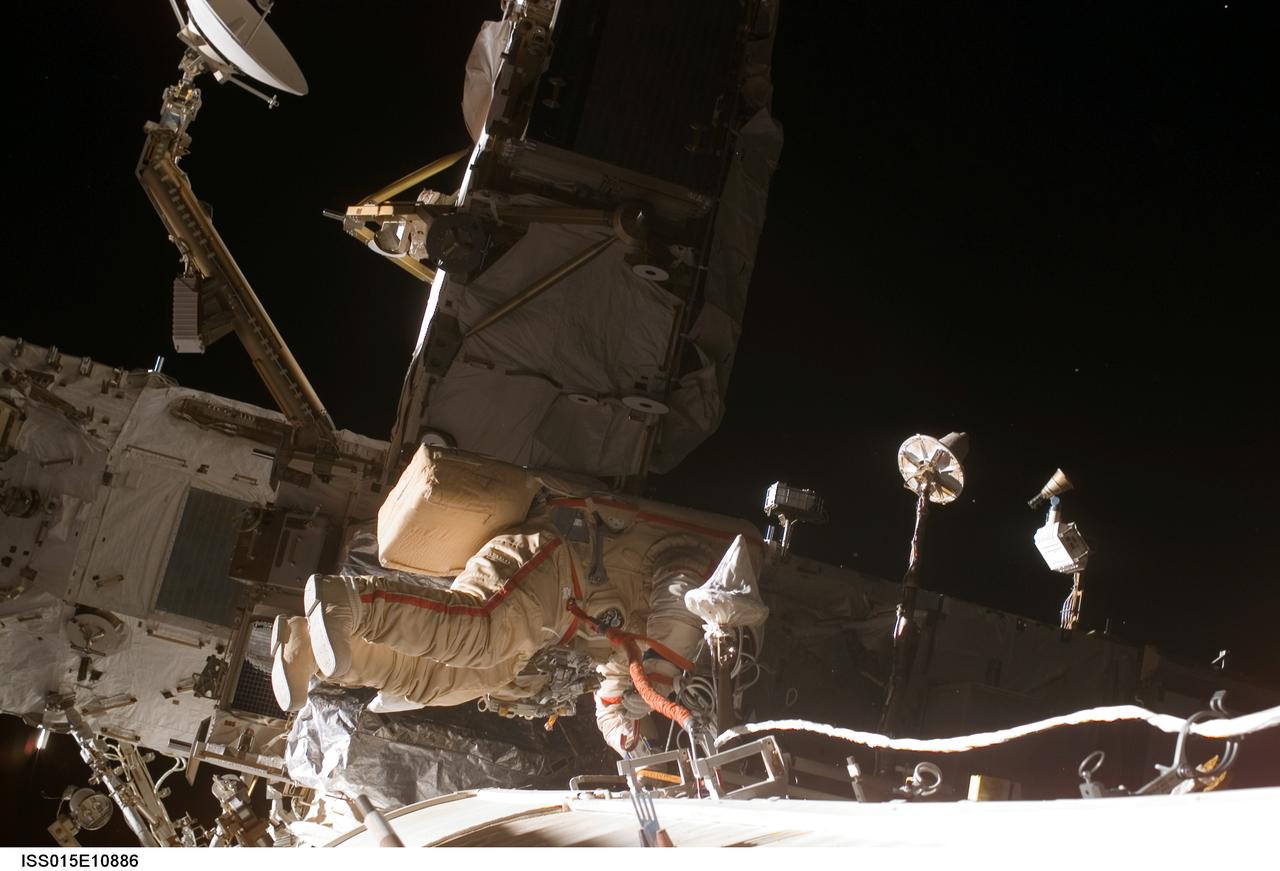

ISS015-E-10886 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). Among other tasks, Yurchikhin and cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov (out of frame), flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
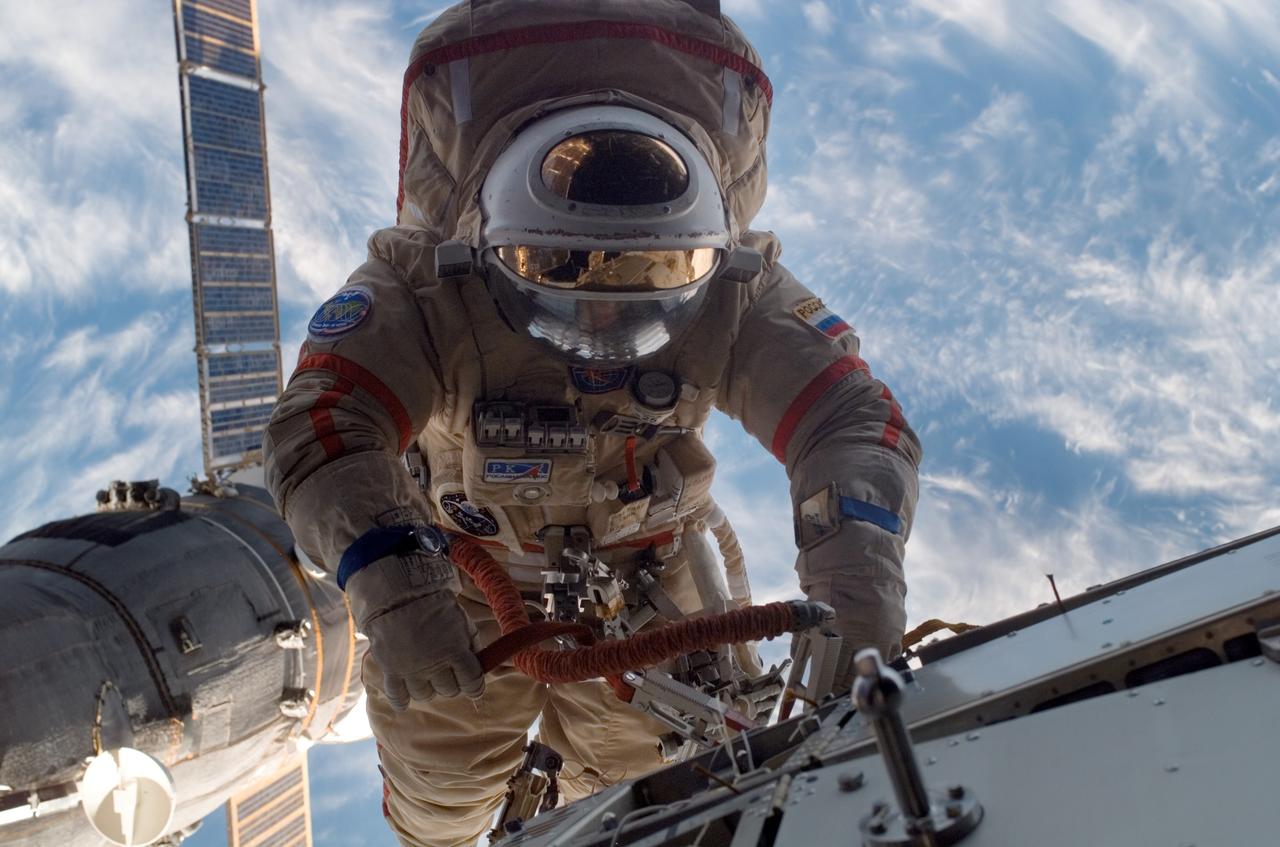

ISS015-E-11009 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). Among other tasks, Yurchikhin and cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov (out of frame), flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
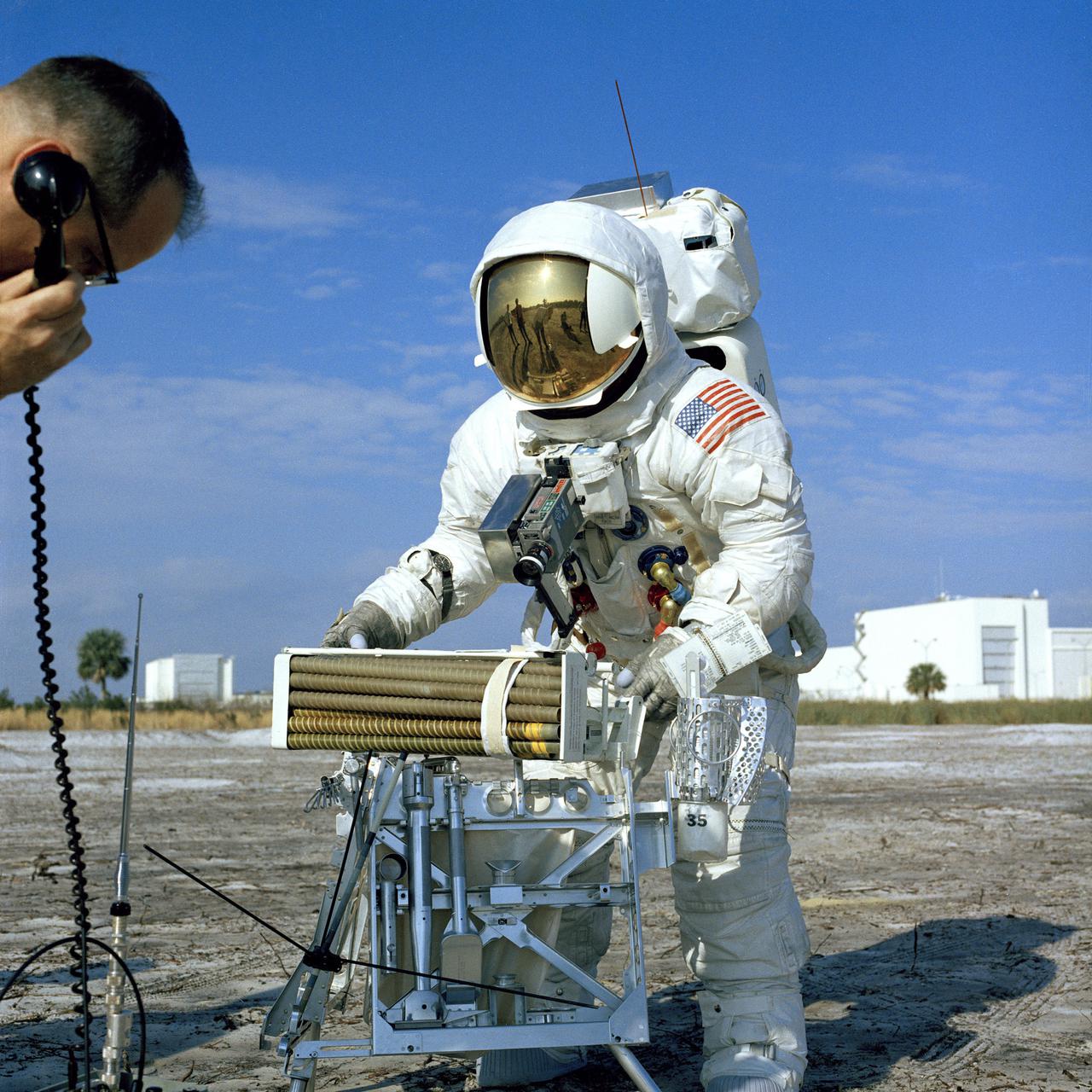

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, participated in a walk-through of the extravehicular activity timeline near the Flight Crew Training Building here today. In the foreground is the lunar surface tool carrier topped by auger-like pipes to be used with a motorized device to obtain soil sample cores in the moon's rugged Fra Mauro region. Apollo 13 is scheduled for launch from Complex 39A no earlier than April 11. The other crew members are James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot. Photo credit: NASA
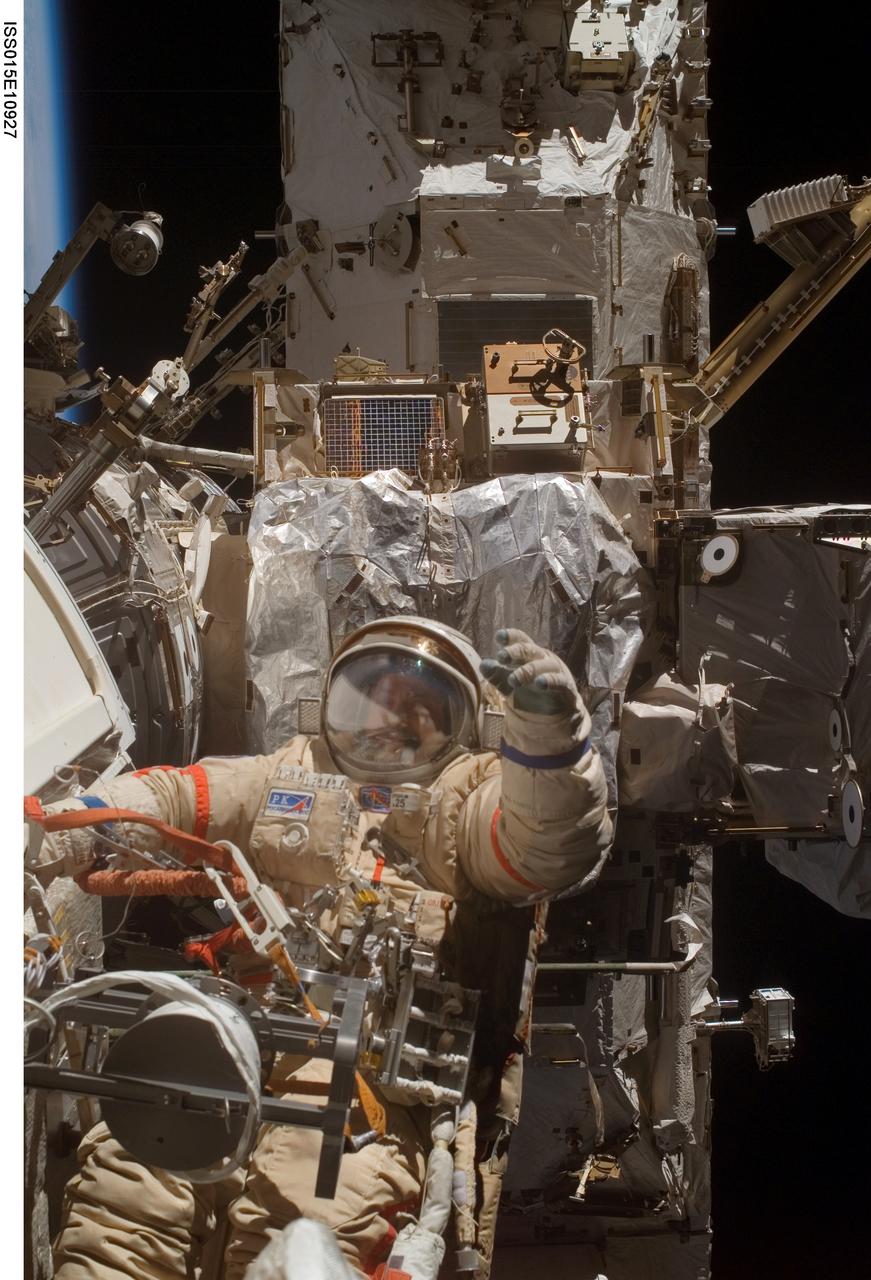

ISS015-E-10927 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). Among other tasks, Yurchikhin and cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov (out of frame), flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
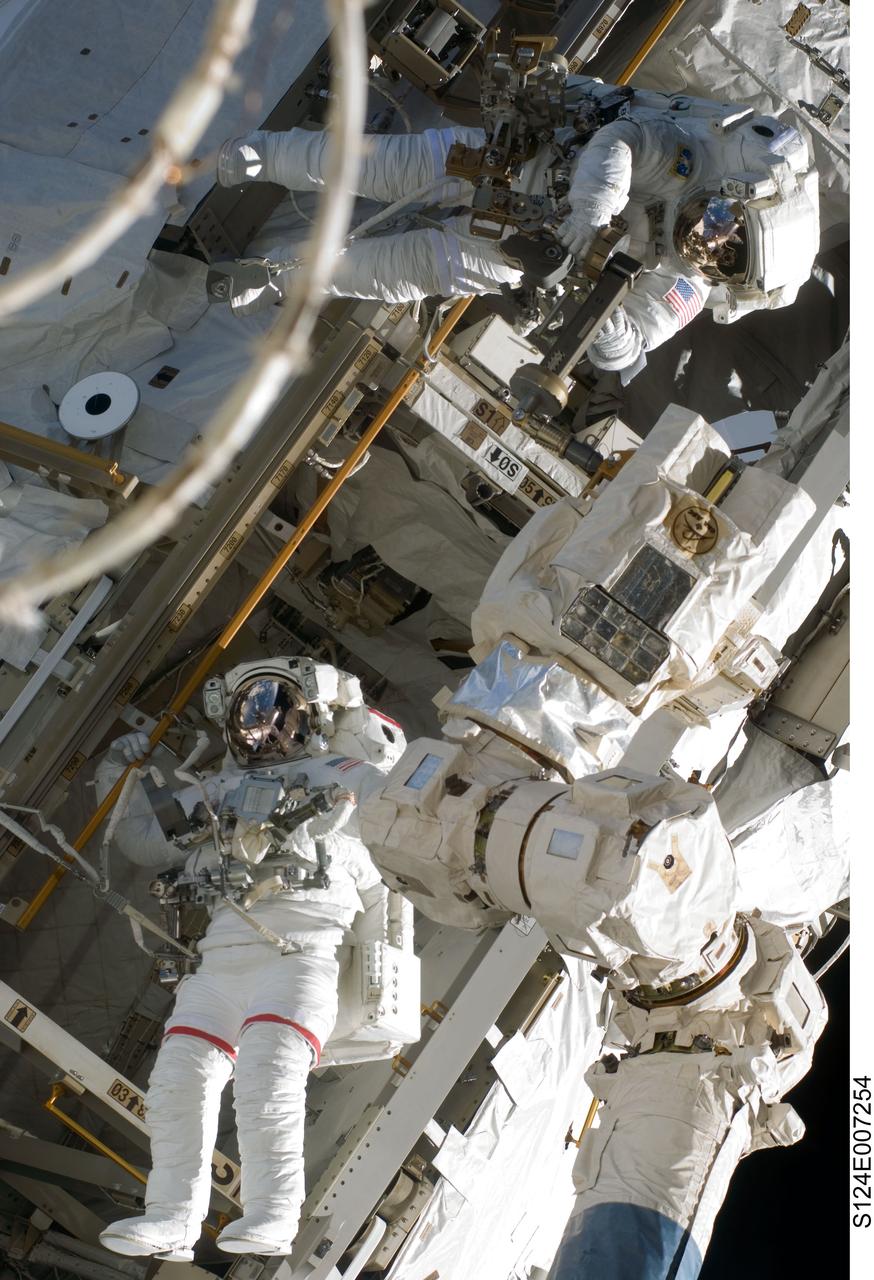

S124-E-007254 (8 June 2008) --- Astronauts Mike Fossum (bottom) and Ron Garan, both STS-124 mission specialists, participate in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Fossum and Garan exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground.
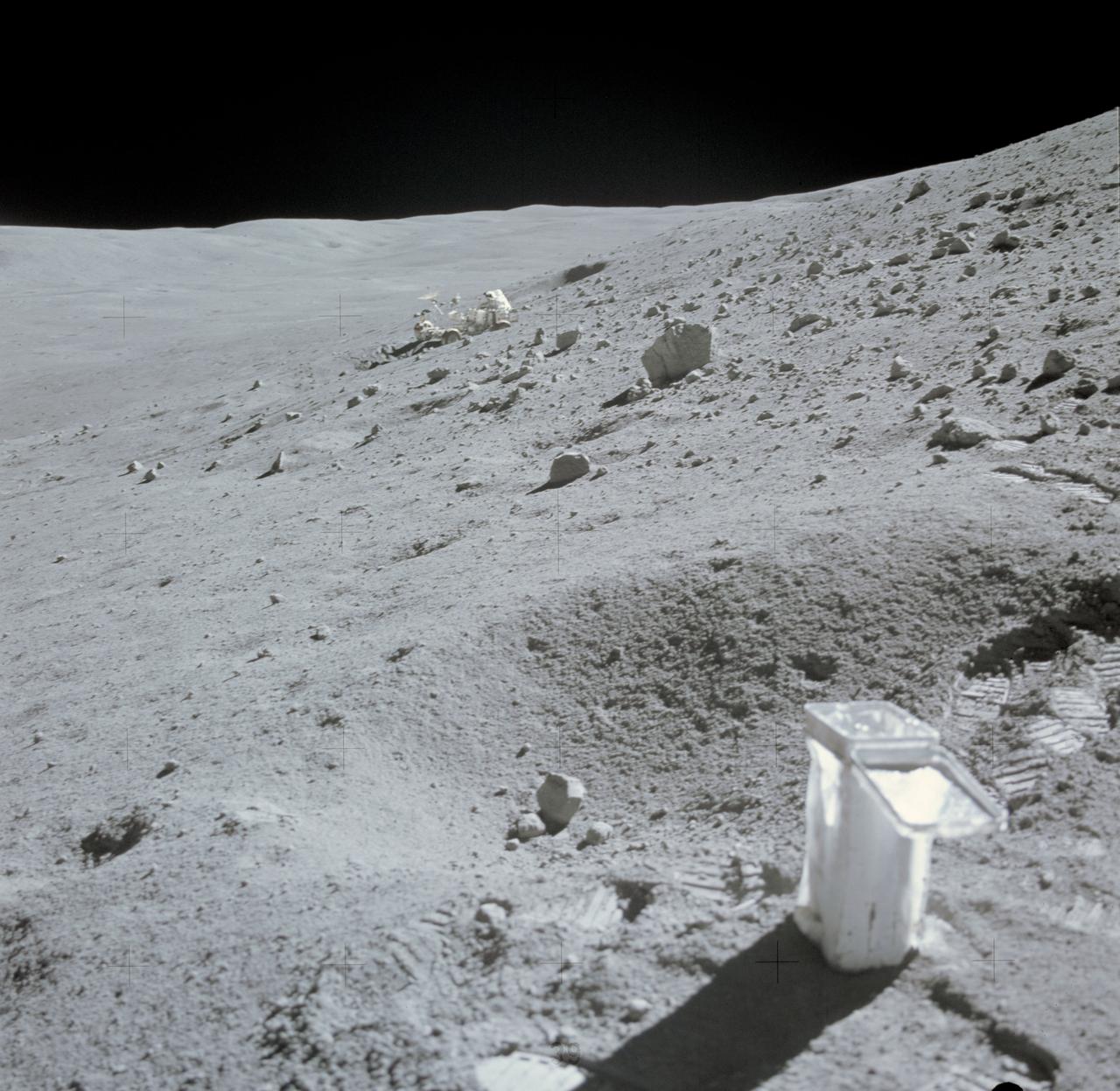

AS16-107-17473 (22 April 1972) --- The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) appears to be parked in a deep lunar depression, on the slope of Stone Mountain. This photograph of the lunar scene at Station No. 4 was taken during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. A sample collection bag is in the right foreground. Note field of small boulders at upper right. While astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
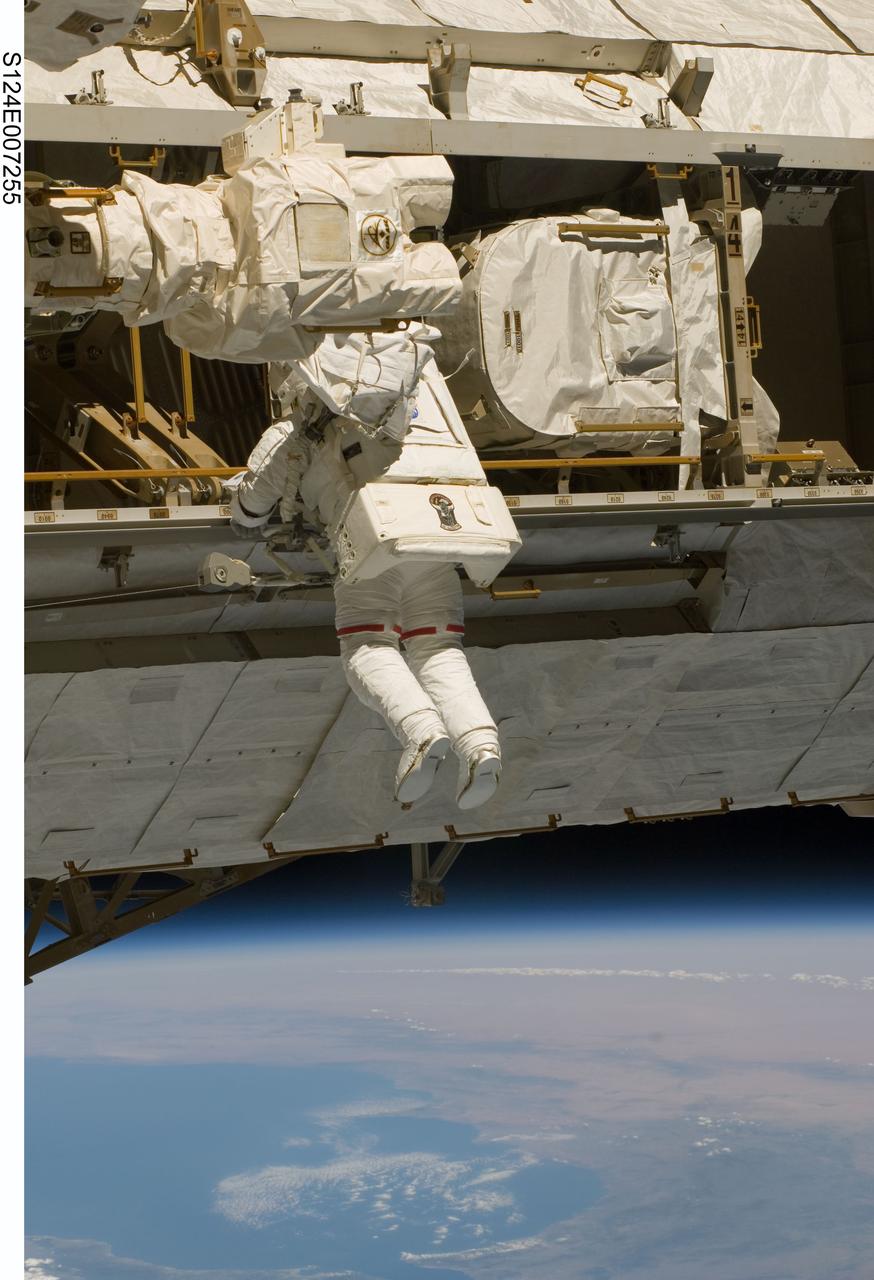

S124-E-007255 (8 June 2008) --- Astronaut Mike Fossum, STS-124 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Fossum and astronaut Ron Garan (out of frame), mission specialist, exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground.
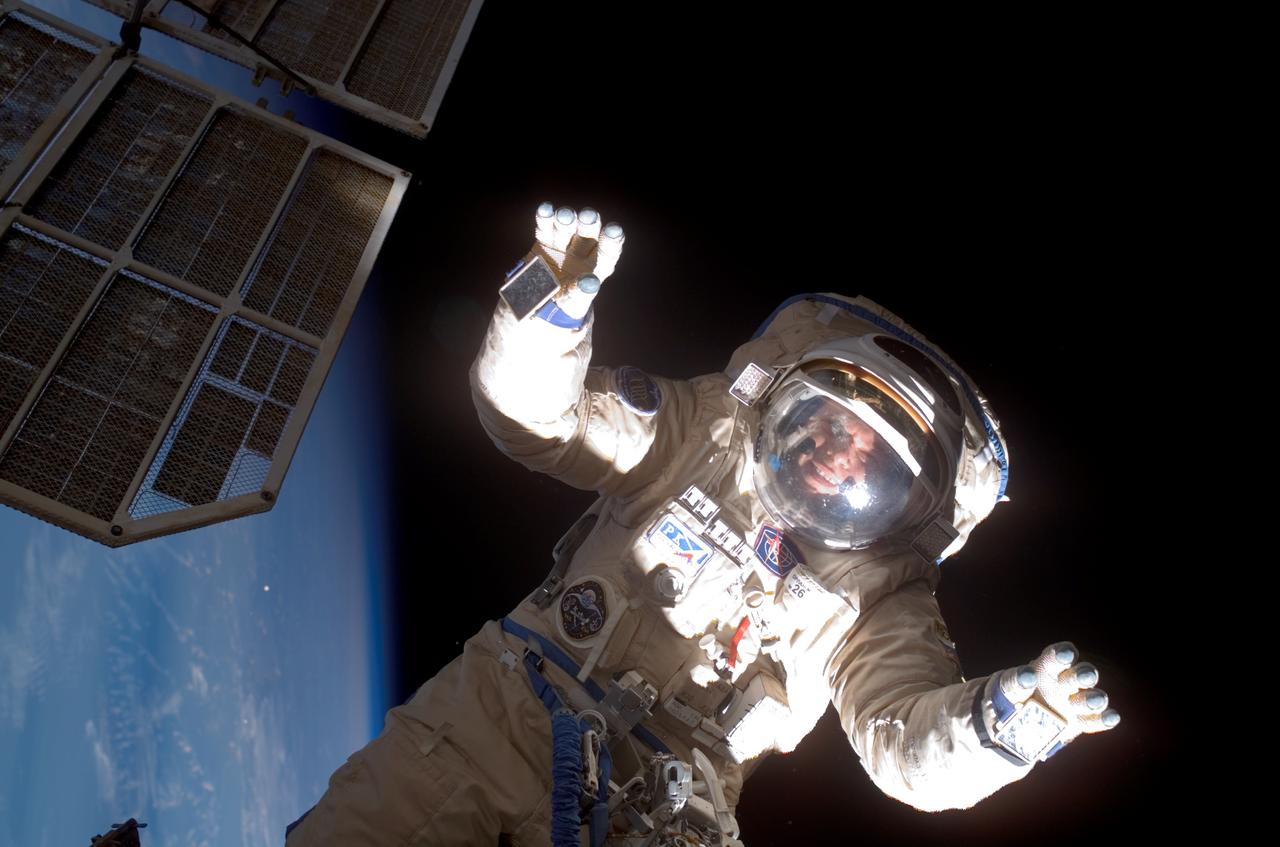

ISS015-E-11026 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov, Expedition 15 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). Among other tasks, Kotov and cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin (out of frame), commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
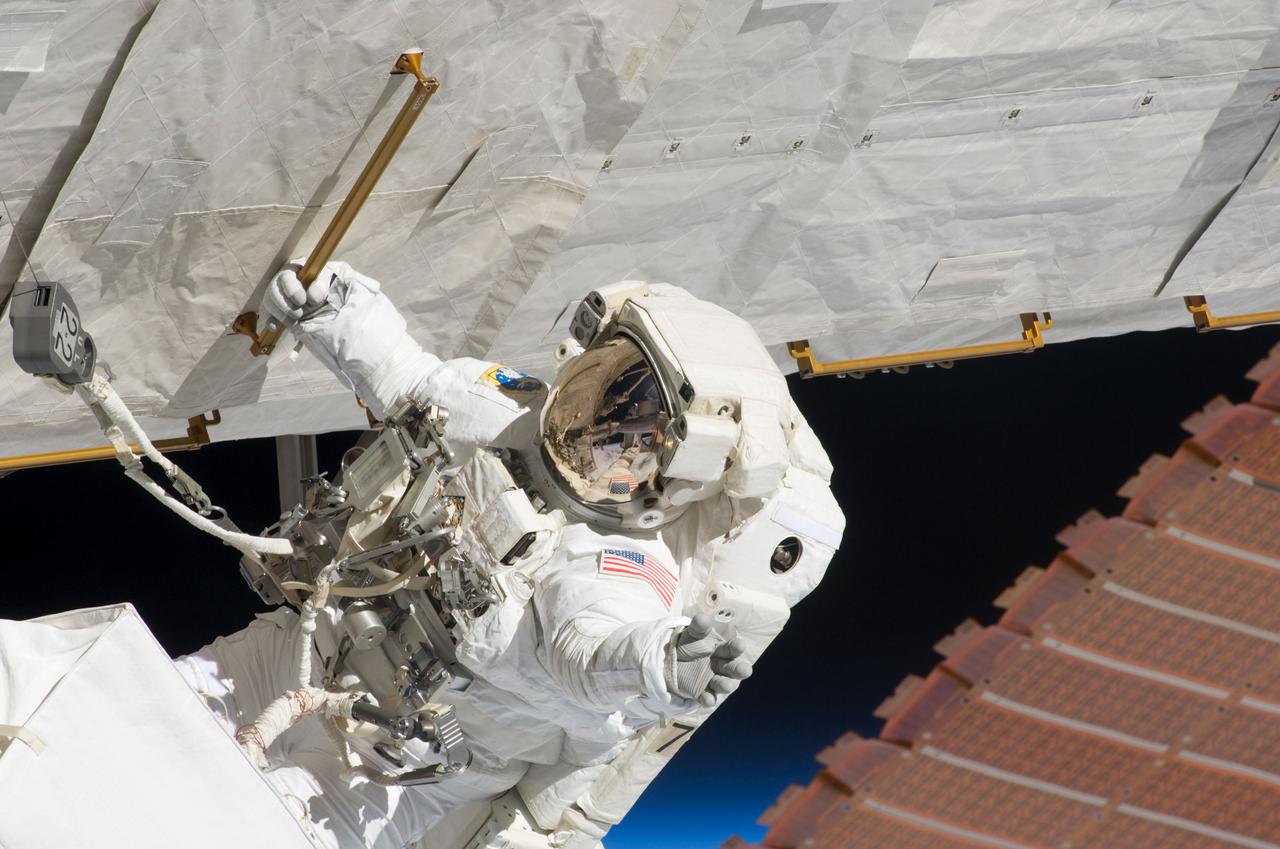

S124-E-007400 (8 June 2008) --- Astronaut Ron Garan, STS-124 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Garan and astronaut Mike Fossum (out of frame), mission specialist, exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground.
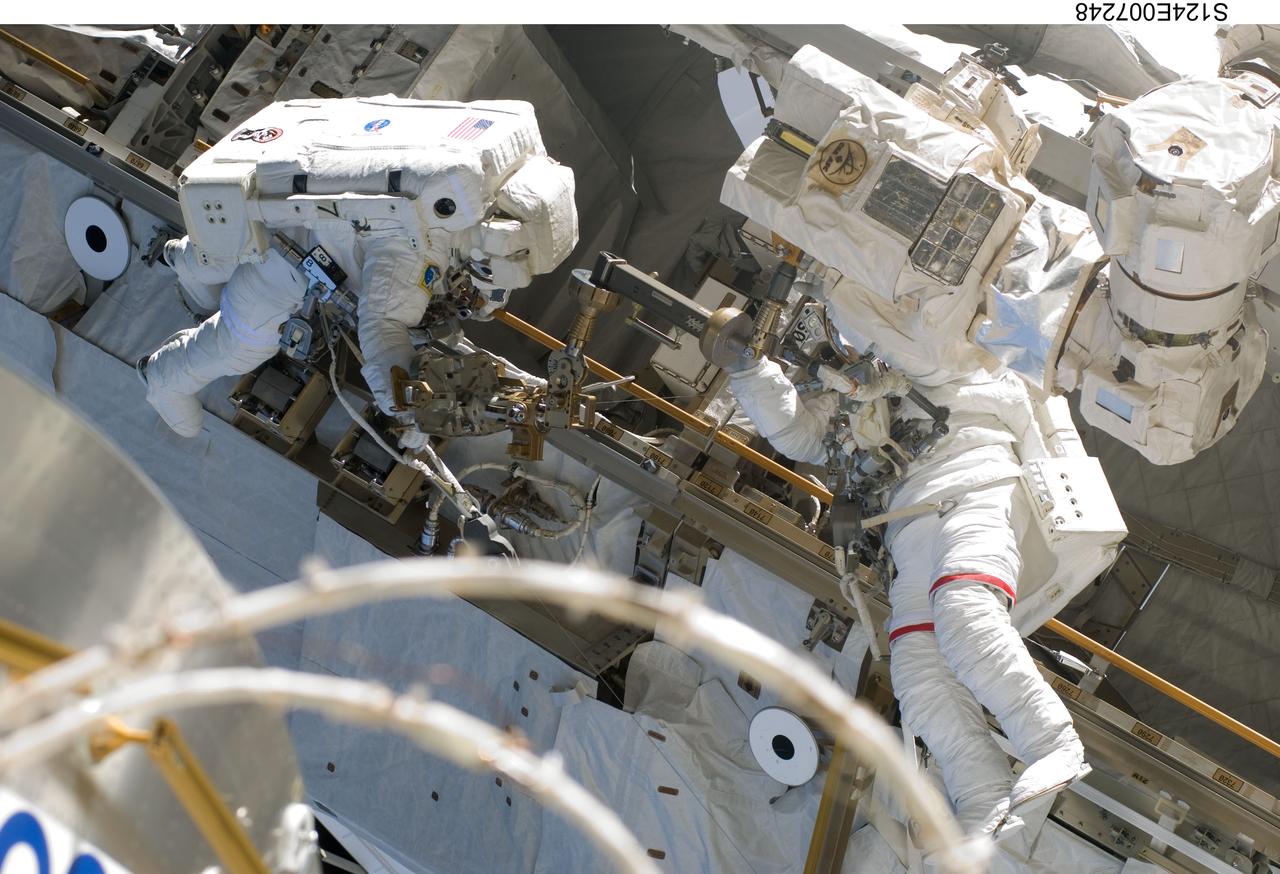

S124-E-007248 (8 June 2008) --- Astronauts Mike Fossum (right) and Ron Garan, both STS-124 mission specialists, participate in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Fossum and Garan exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground.
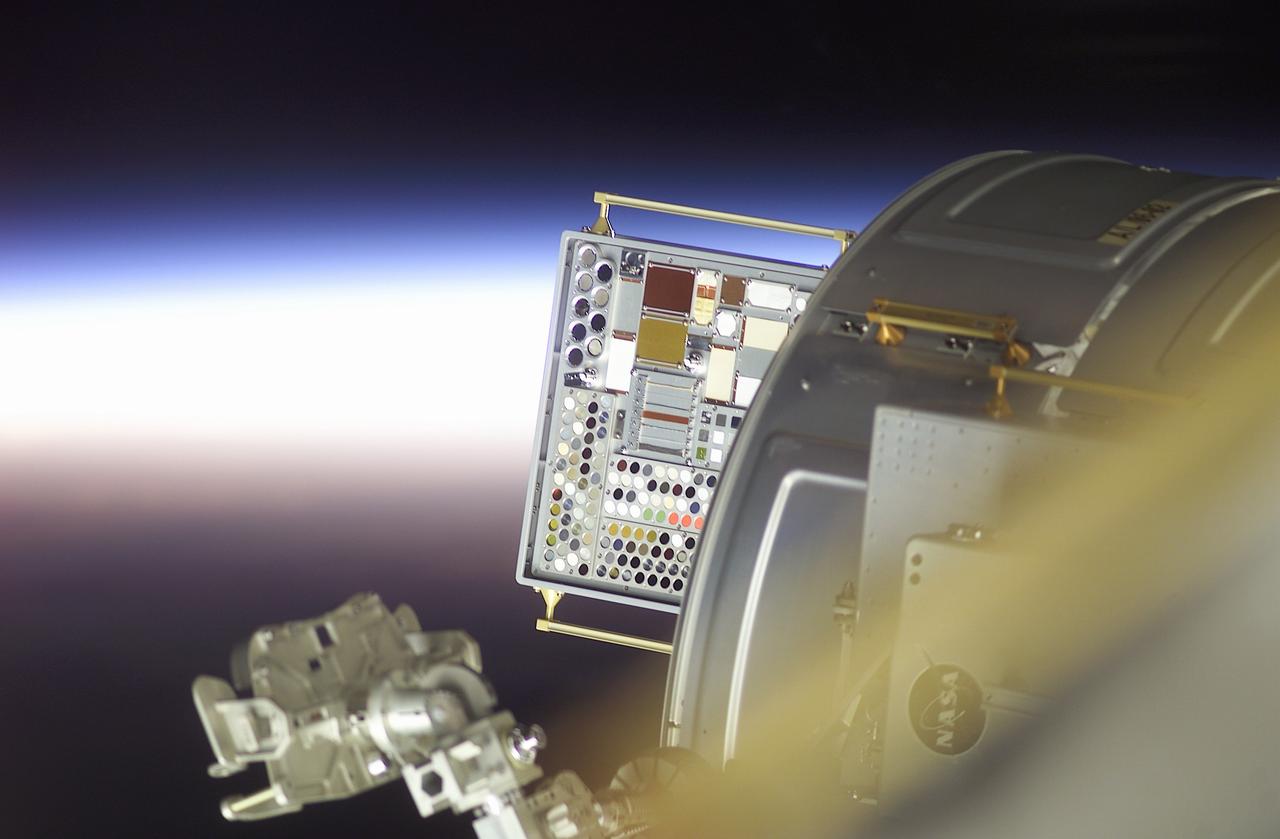
Backdropped by a sunrise, the newly installed Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) is visible on this image. MISSE would expose 750 material samples for about 18 months and collect information on how different materials weather the space environment. The objective of MISSE is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components plarned for use on future spacecraft. The experiment was the first externally mounted experiment conducted on the International Space Station (ISS) and was installed on the outside of the ISS Quest Airlock during extravehicular activity (EVA) of the STS-105 mission. MISSE was launched on August 10, 2001 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery.

S72-55066 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt chips samples from a large boulder during the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while astronauts Schmitt and Eugene A. Cernan, commander, descended in the Lunar Module to explore the moon.
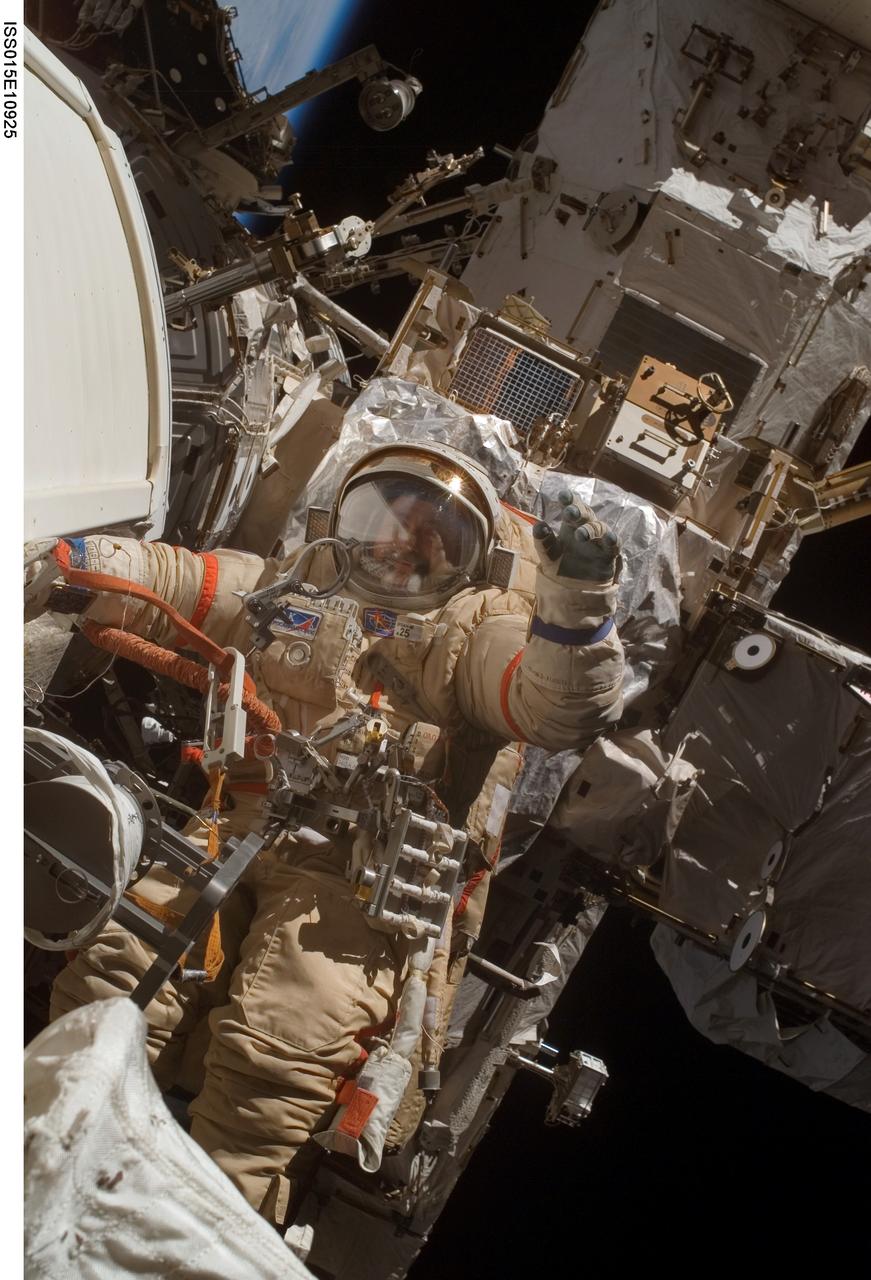

ISS015-E-10925 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). Among other tasks, Yurchikhin and cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov (out of frame), flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.

ISS015-E-10870 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). Among other tasks, Yurchikhin and cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov (out of frame), flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
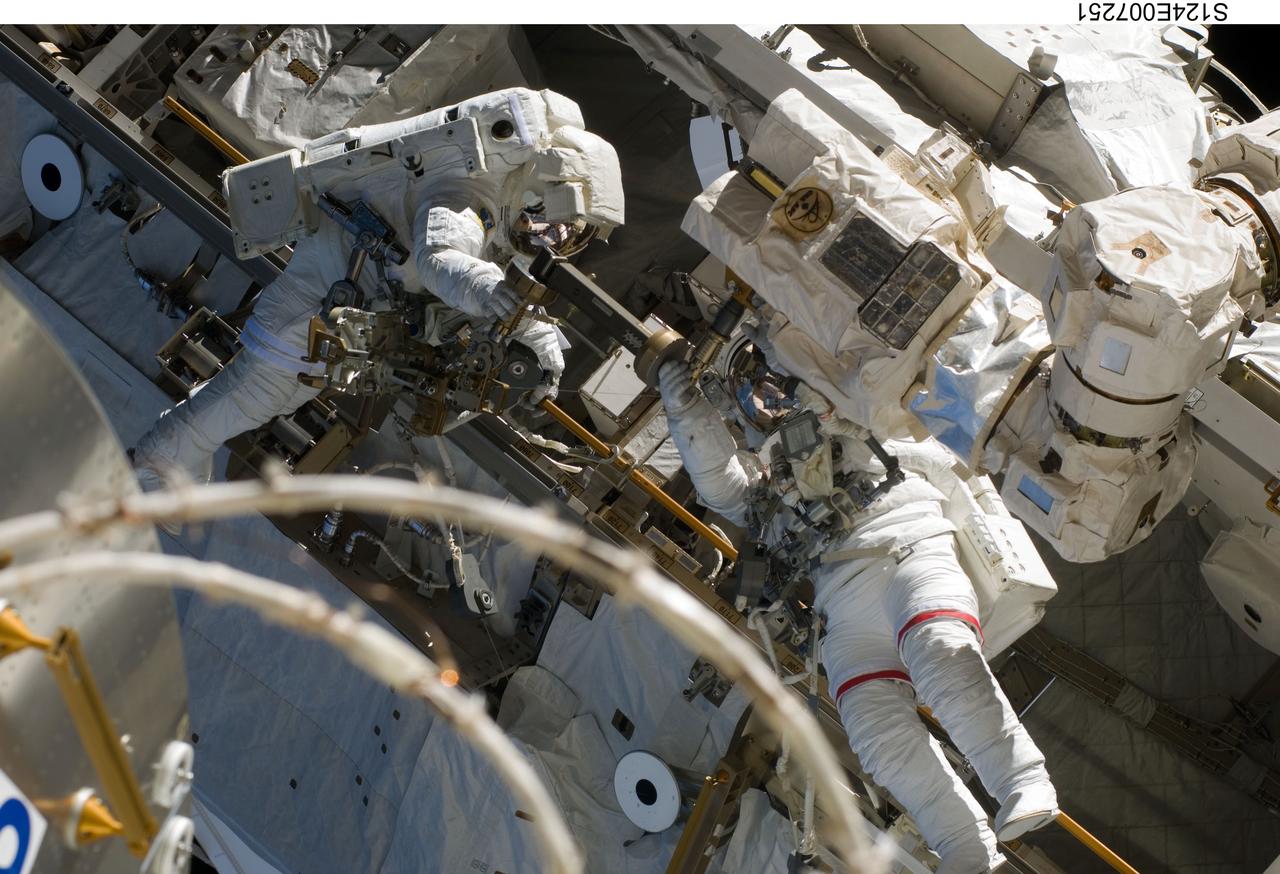

S124-E-007251 (8 June 2008) --- Astronauts Mike Fossum (right) and Ron Garan, both STS-124 mission specialists, participate in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Fossum and Garan exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground.
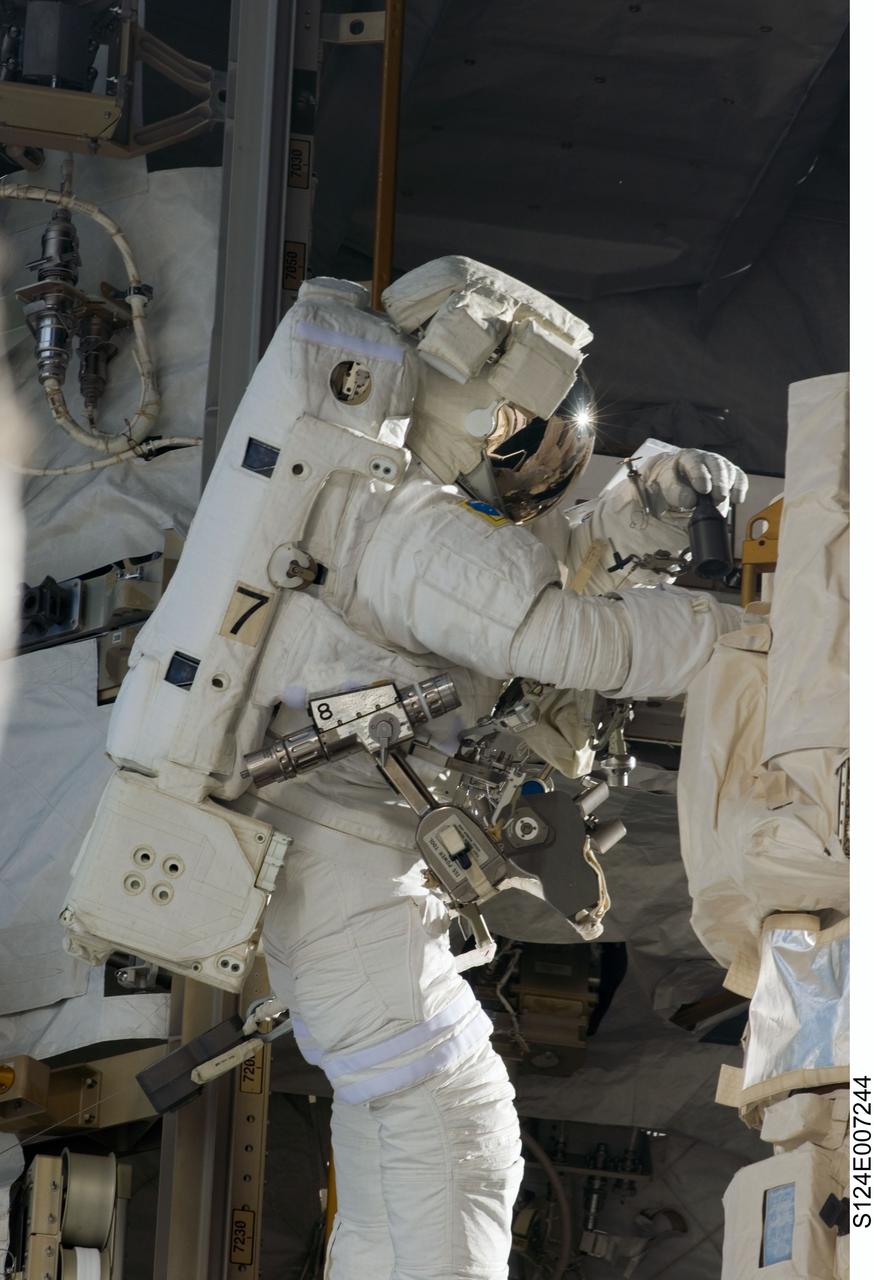

S124-E-007244 (8 June 2008) --- Astronaut Ron Garan, STS-124 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Garan and astronaut Mike Fossum (out of frame), mission specialist, exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground.
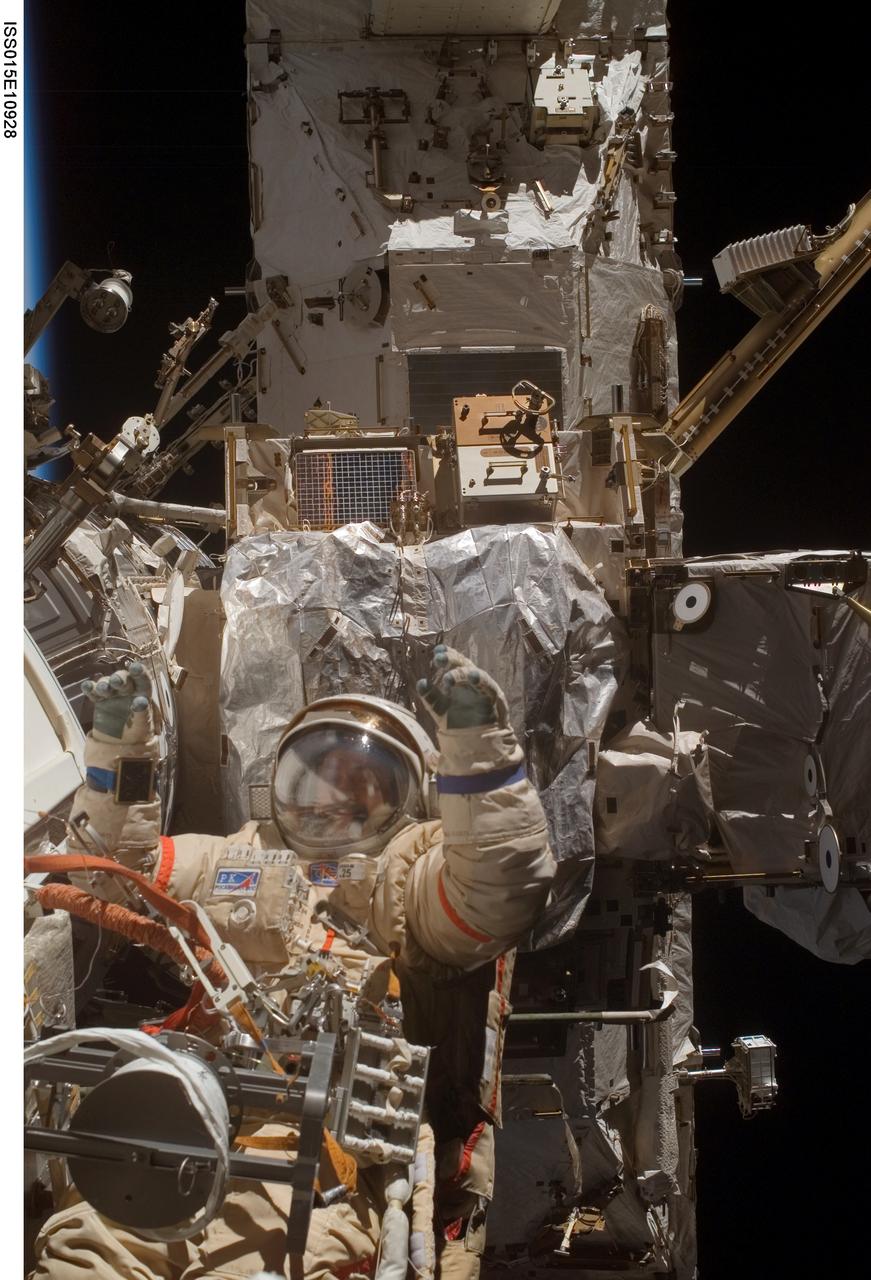

ISS015-E-10928 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). Among other tasks, Yurchikhin and cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov (out of frame), flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
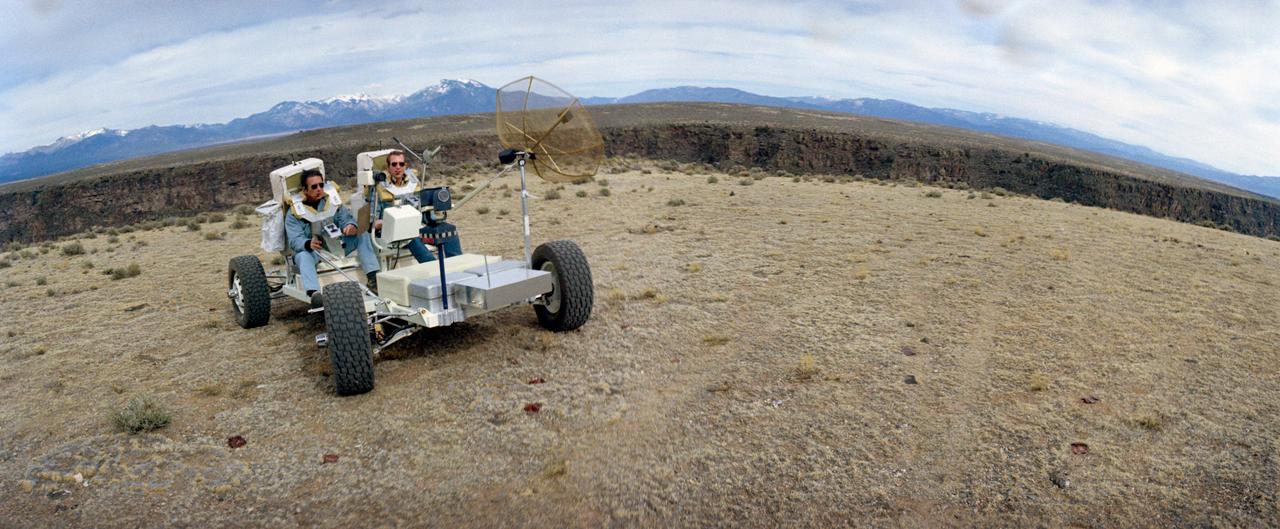

S71-23774 (11-12 March 1971) --- A wide-angle view showing two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission riding in a Lunar Roving Vehicle trainer called "Grover" during a simulation of lunar surface extravehicular activity in the Taos, New Mexico area. They are astronauts David R. Scott (riding in left side seat), commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. Apollo 15 will be the first mission to the moon to carry a Lunar Roving Vehicle, which will permit the astronauts to cover a larger area for exploration and sample collecting than on previous missions.
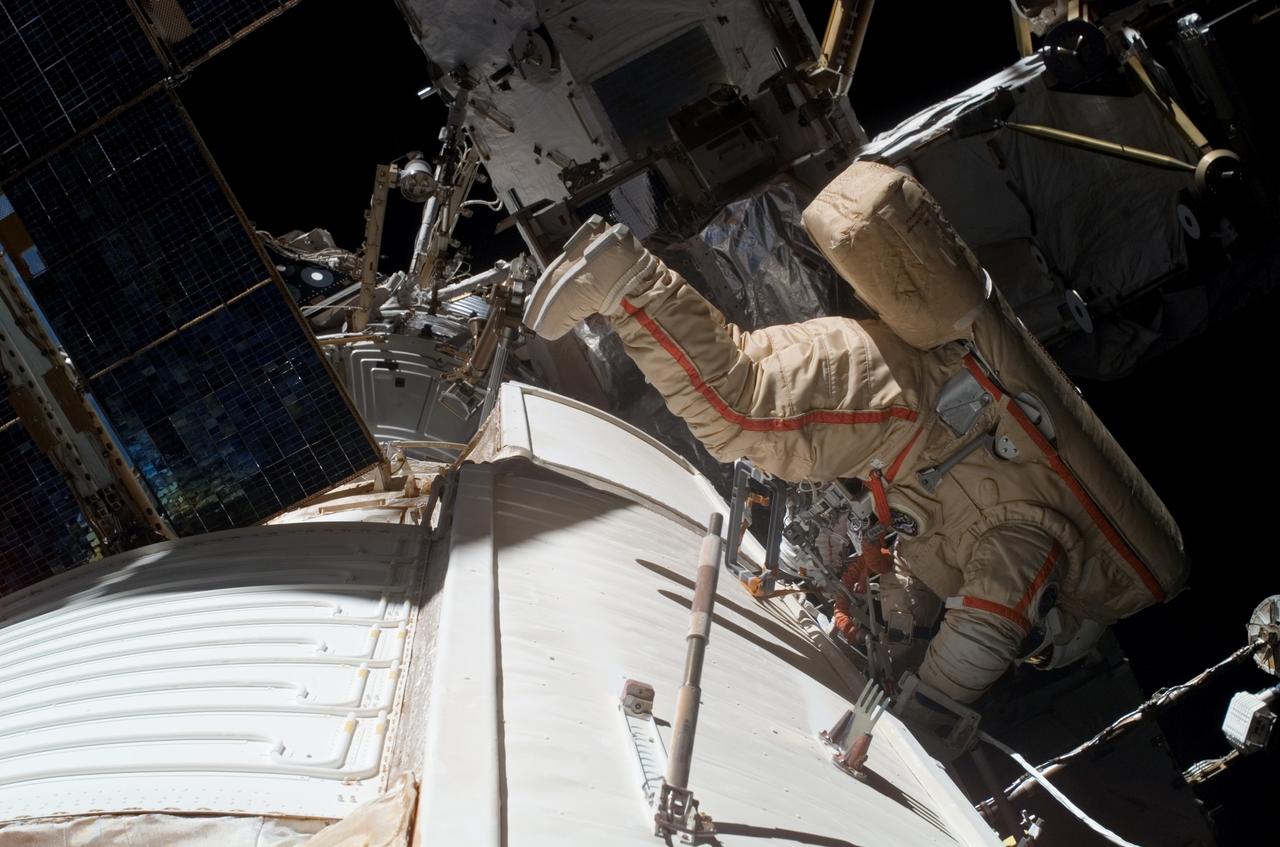

ISS015-E-10901 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin, Expedition 15 commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). Among other tasks, Yurchikhin and cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov (out of frame), flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
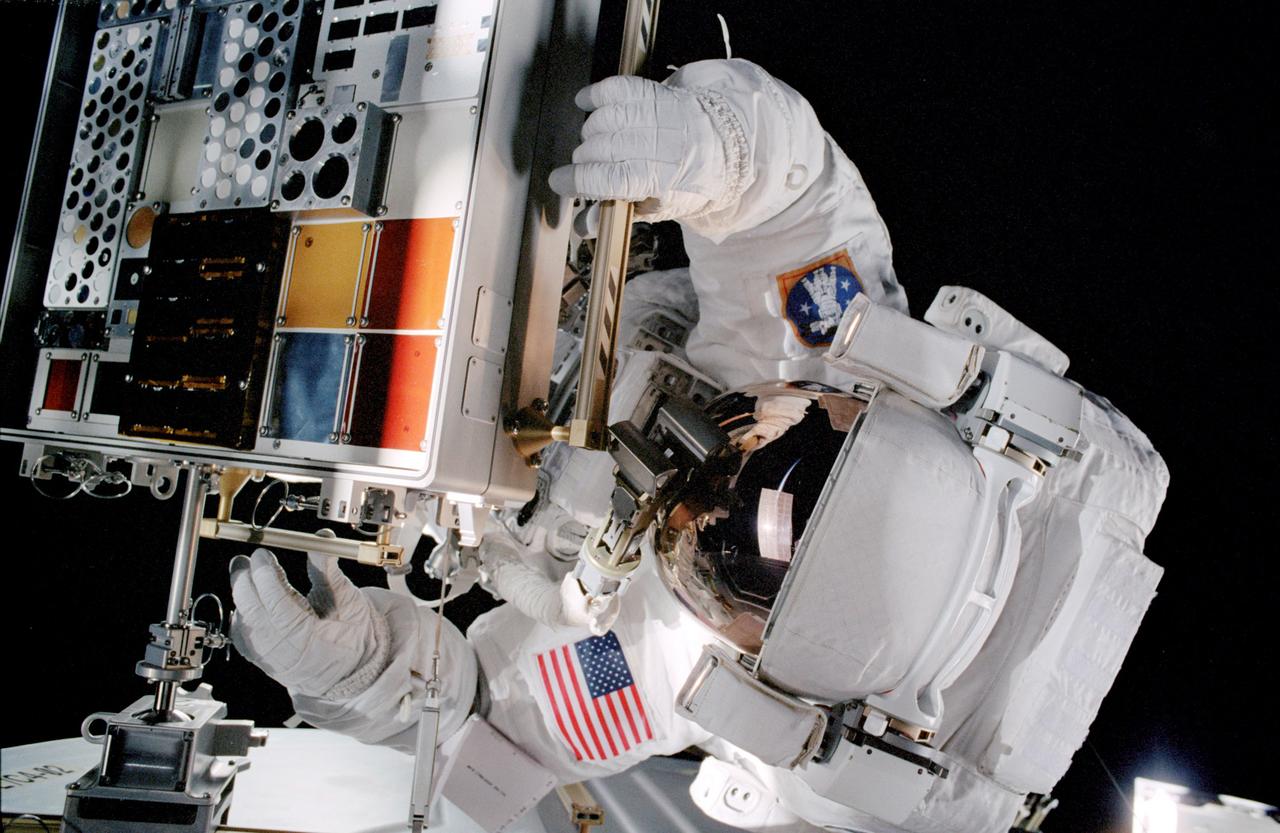

Astronaut Patrick G. Forrester works with the the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) during extravehicular activity (EVA). MISSE would expose 750 material samples for about 18 months and collect information on how different materials weather the space environment The objective of MISSE is to develop early, low-cost, non-intrusive opportunities to conduct critical space exposure tests of space materials and components plarned for use on future spacecraft. The experiment was the first externally mounted experiment conducted on the International Space Station (ISS) and was installed on the outside of the ISS Quest Airlock. MISSE was launched on August 10, 2001 aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery.
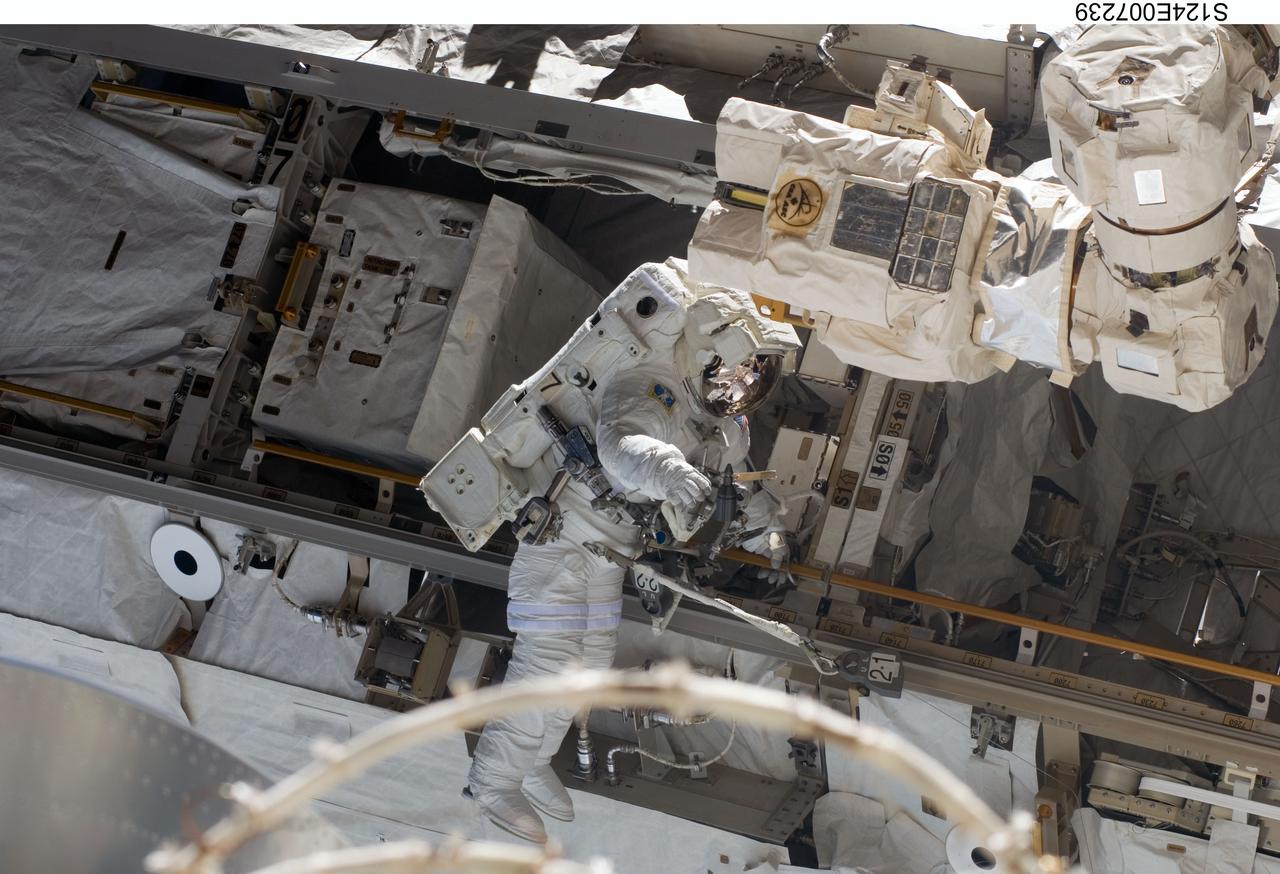

S124-E-007239 (8 June 2008) --- Astronaut Ron Garan, STS-124 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Garan and astronaut Mike Fossum (out of frame), mission specialist, exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground.
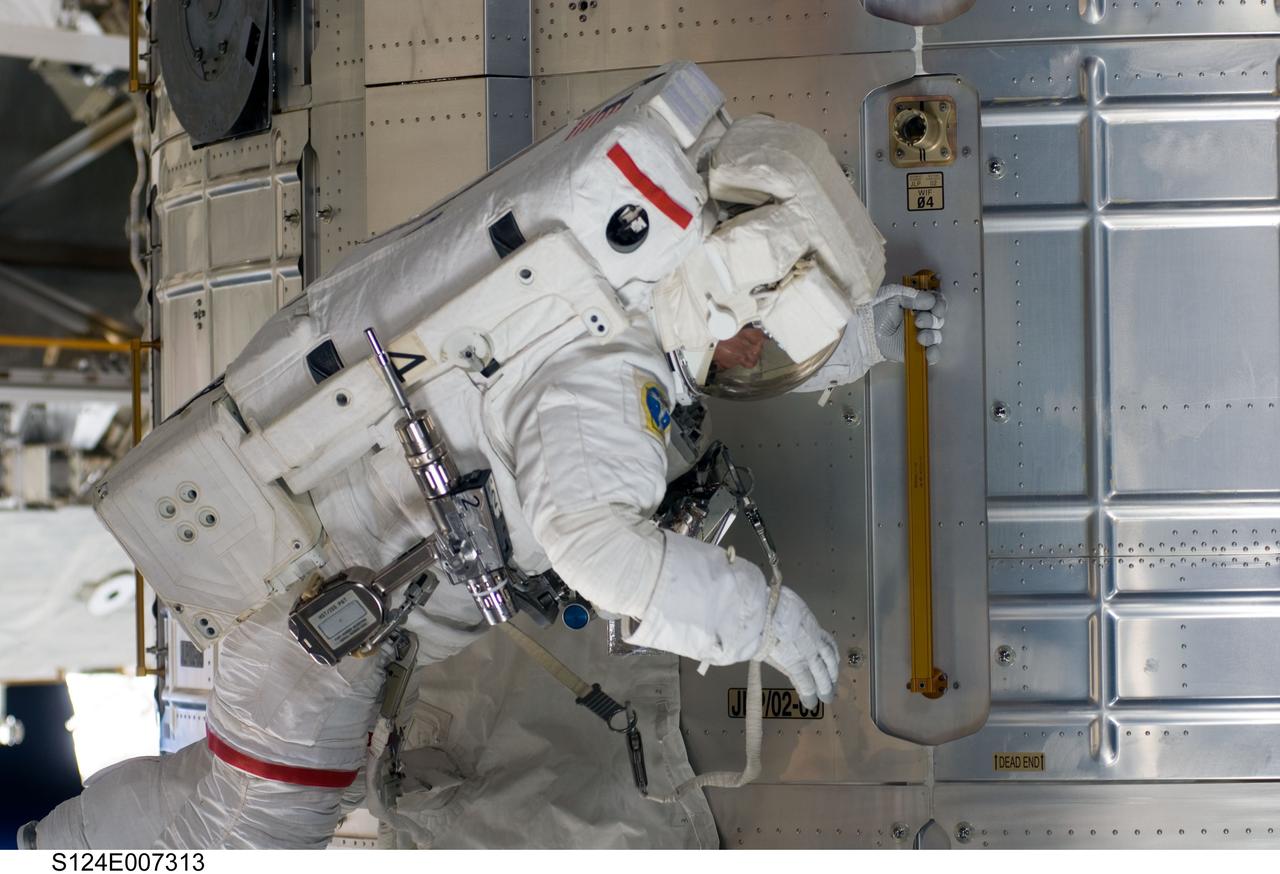

S124-E-007313 (8 June 2008) --- Astronaut Mike Fossum, STS-124 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Fossum and astronaut Ron Garan (out of frame), mission specialist, exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground.
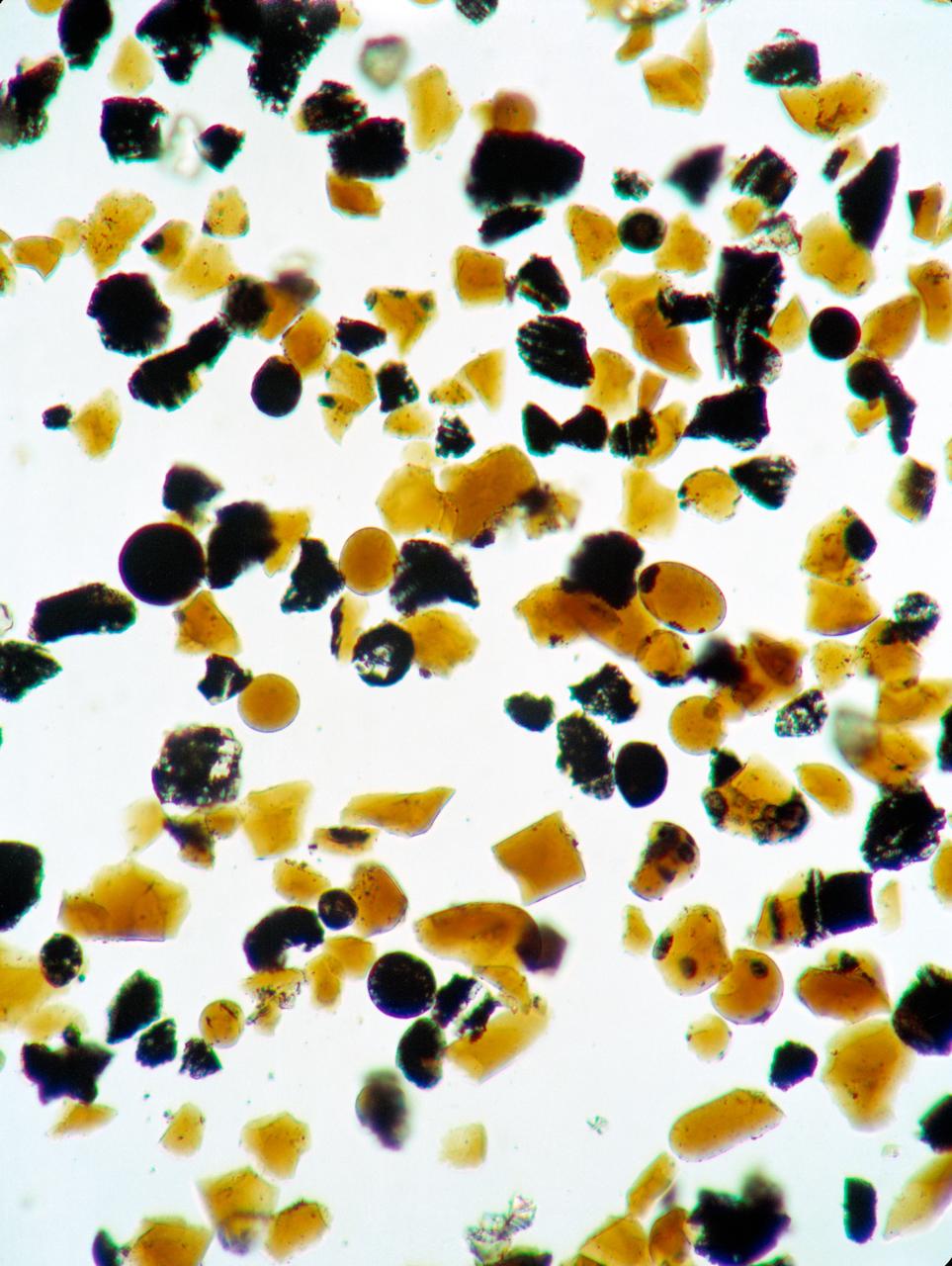
S73-15171 (4 Jan. 1973) --- These orange glass spheres and fragments are the finest particles ever brought back from the moon. Ranging in size from 20 to 45 microns (about 1/1000 of an inch) the particles are magnified 160 times in this photomicrograph made in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. The orange soil was brought back from the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. "Jack" Schmitt discovered the orange soil at Shorty Crater during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA). This lunar material is being studied and analyzed by scientists in the LRL. The orange particles in this photomicrograph, which are intermixed with black and black-speckled grains, are about the same size as the particles that compose silt on Earth. Chemical analysis of the orange soil material has shown the sample to be similar to some of the samples brought back from the Apollo 11 (Sea of Tranquility) site several hundred miles to the southwest. Like those samples, it is rich in titanium (8%) and iron oxide (22%). But unlike the Apollo 11 samples, the orange soil is unexplainably rich in zinc ? an anomaly that has scientists in a quandary. This Apollo 17 sample is not high in volatile elements, nor do the minerals contain substantial amounts of water. These would have provided strong evidence of volcanic activity. On the other hand, the lack of agglutinates (rocks made up of a variety of minerals cemented together) indicates that the orange glass is probably not the product of meteorite impact -- strengthening the argument that the glass was produced by volcanic activity.
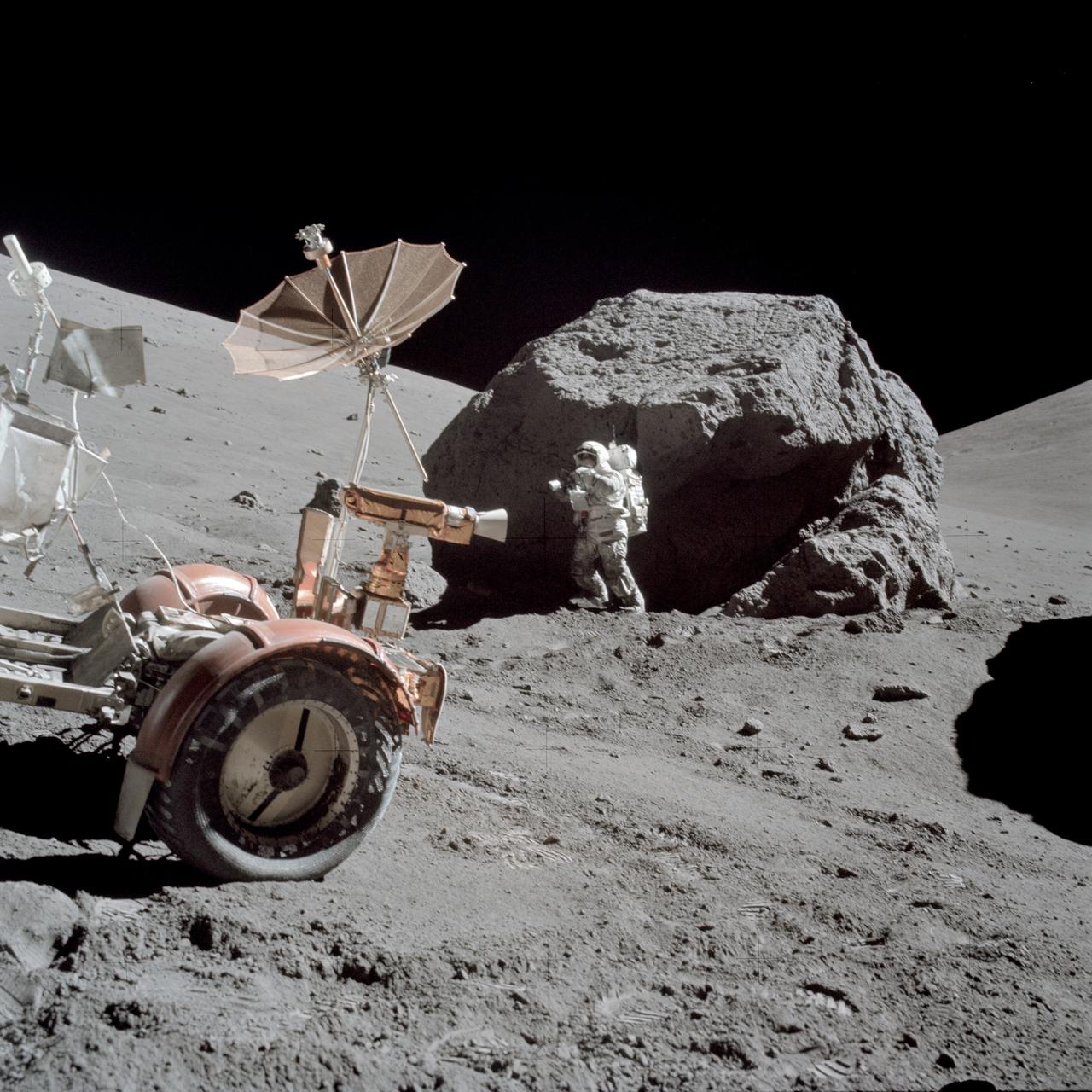

AS17-146-22294 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt is photographed working beside a huge boulder at Station 6 (base of North Massif) during the third Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. The front portion of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is visible on the left. This picture was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander. Schmitt is the lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
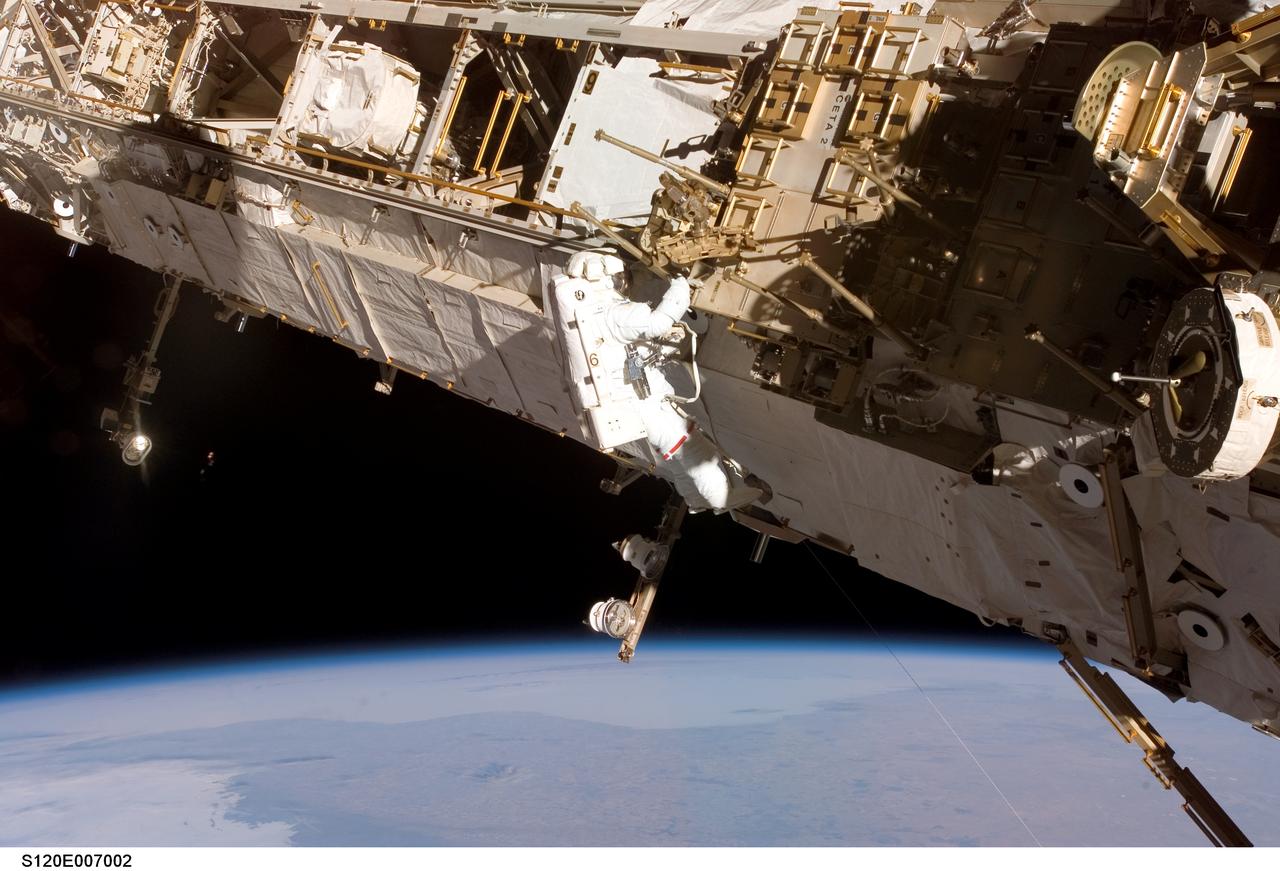

S120-E-007002 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.

S124-E-007263 (8 June 2008) --- Astronaut Ron Garan, STS-124 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Garan and astronaut Mike Fossum (out of frame), mission specialist, exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground. The Columbus laboratory is visible in the foreground. The blackness of space and Earth's horizon provide the backdrop for the scene.
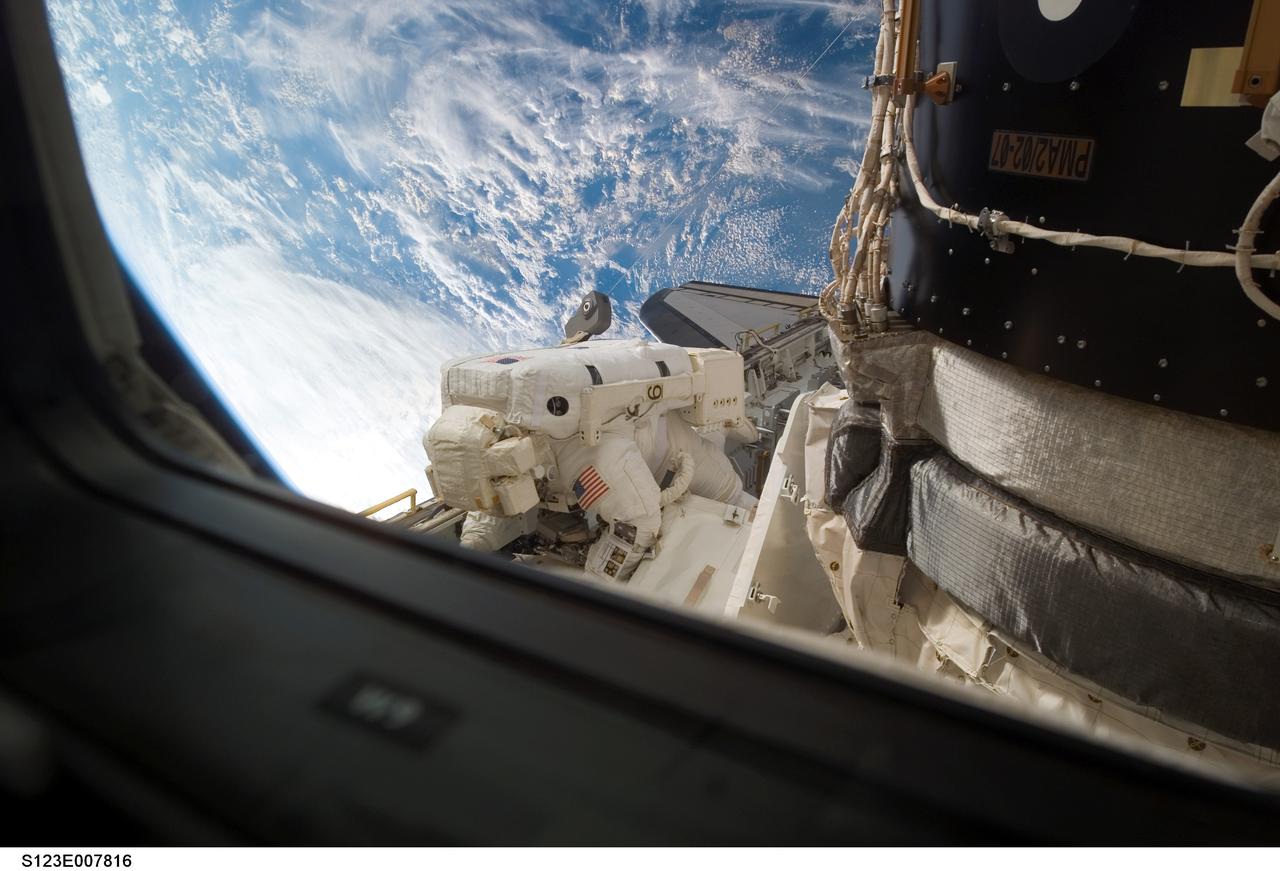

S123-E-007816 (21 March 2008) --- Astronaut Robert L. Behnken, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's fourth scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 24-minute spacewalk, Behnken and astronaut Mike Foreman (out of frame), mission specialist, replaced a failed Remote Power Control Module -- essentially a circuit breaker -- on the station's truss. The spacewalkers also tested a repair method for damaged heat resistant tiles on the space shuttle. This technique used a caulk-gun-like tool named the Tile Repair Ablator Dispenser to dispense a material called Shuttle Tile Ablator-54 into purposely damaged heat shield tiles. The sample tiles will be returned to Earth to undergo extensive testing on the ground.
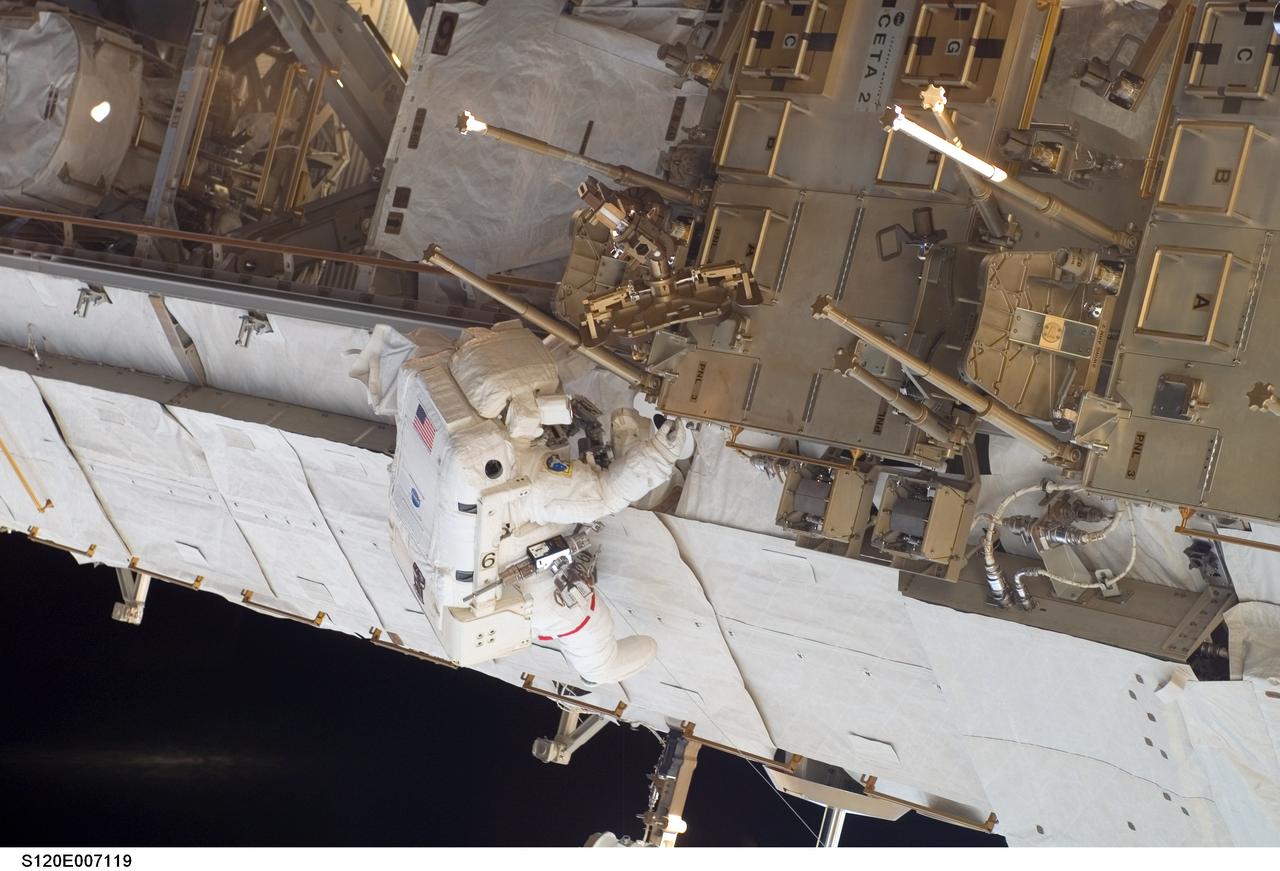

S120-E-007119 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
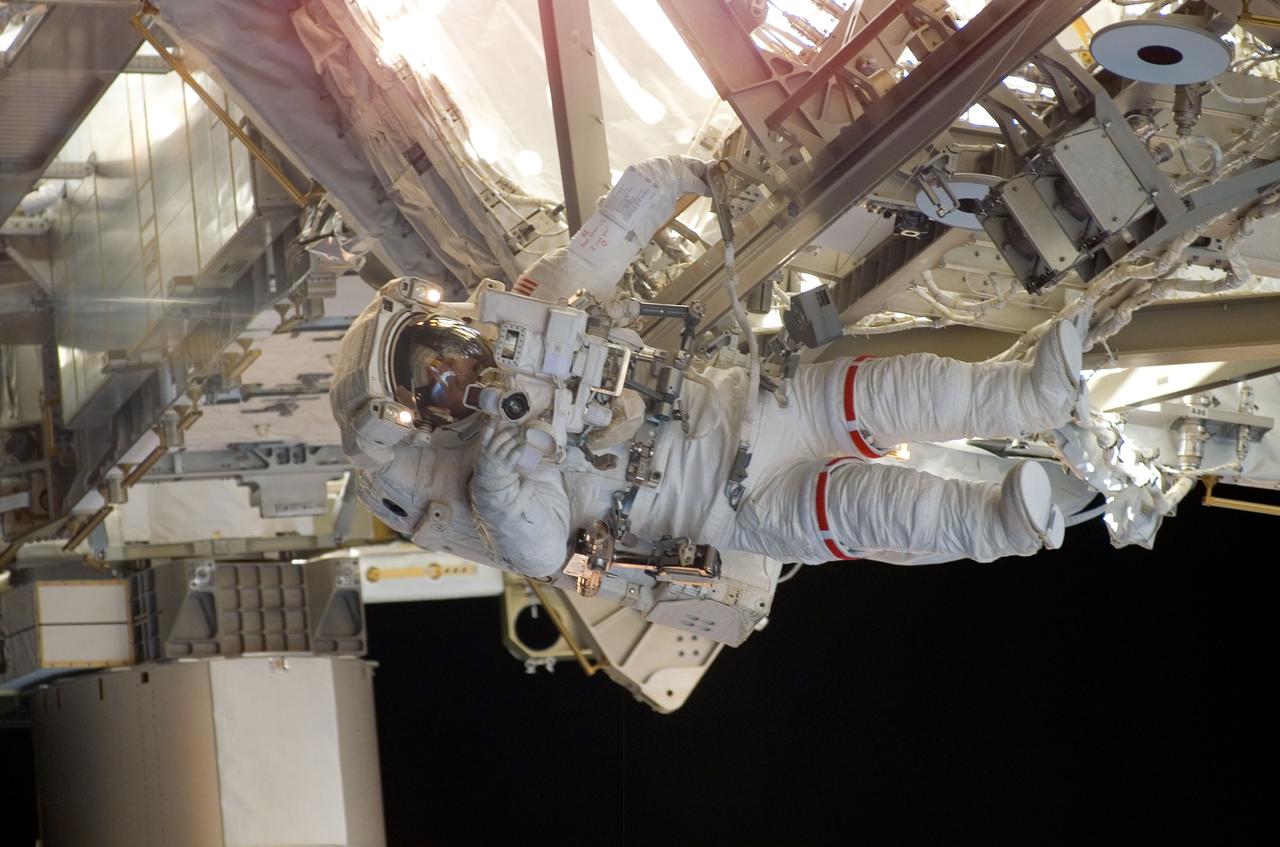

S120-E-007100 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
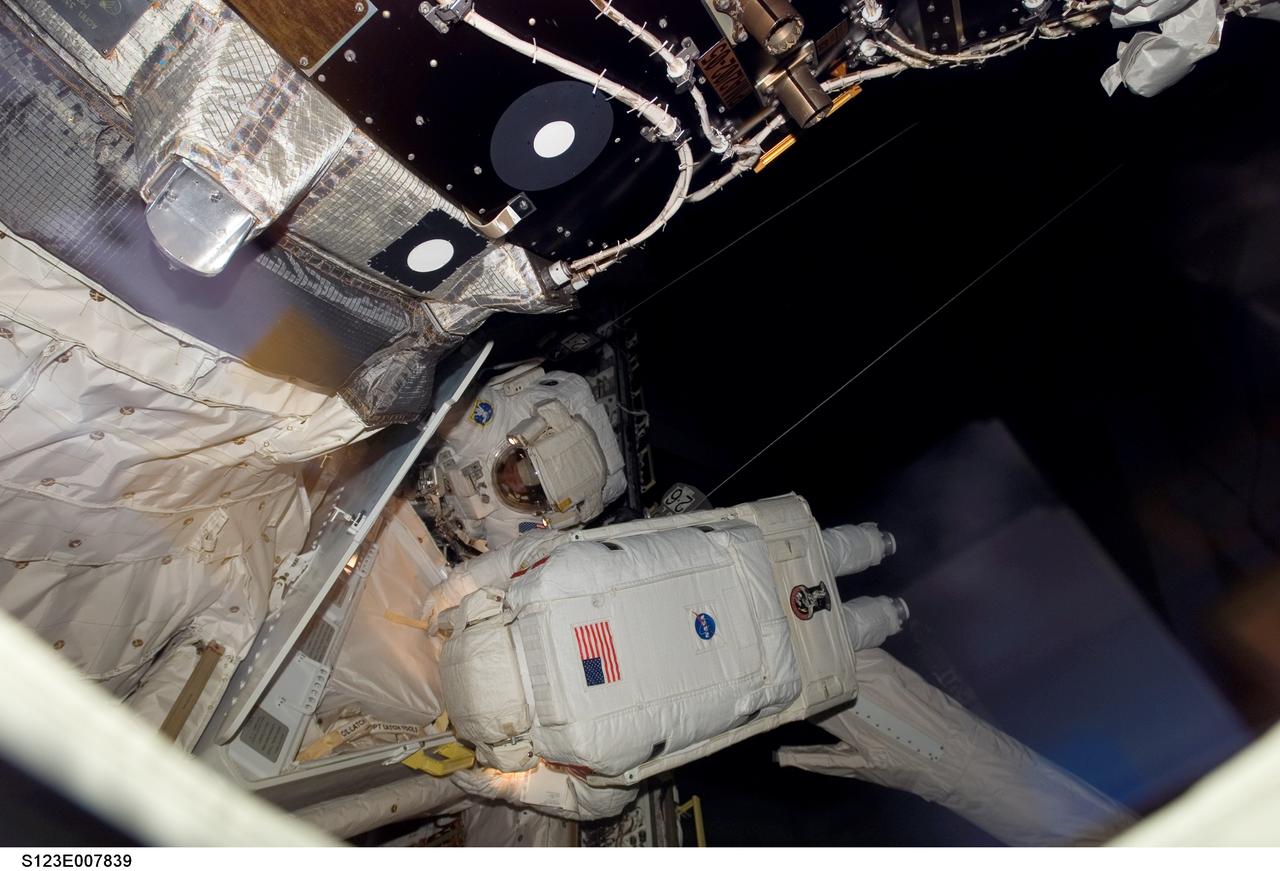

S123-E-007839 (21 March 2008) --- Astronauts Mike Foreman (foreground) and Robert L. Behnken, both STS-123 mission specialists, participate in the mission's fourth scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 24-minute spacewalk, Foreman and Behnken replaced a failed Remote Power Control Module -- essentially a circuit breaker -- on the station's truss. The spacewalkers also tested a repair method for damaged heat resistant tiles on the space shuttle. This technique used a caulk-gun-like tool named the Tile Repair Ablator Dispenser to dispense a material called Shuttle Tile Ablator-54 into purposely damaged heat shield tiles. The sample tiles will be returned to Earth to undergo extensive testing on the ground.
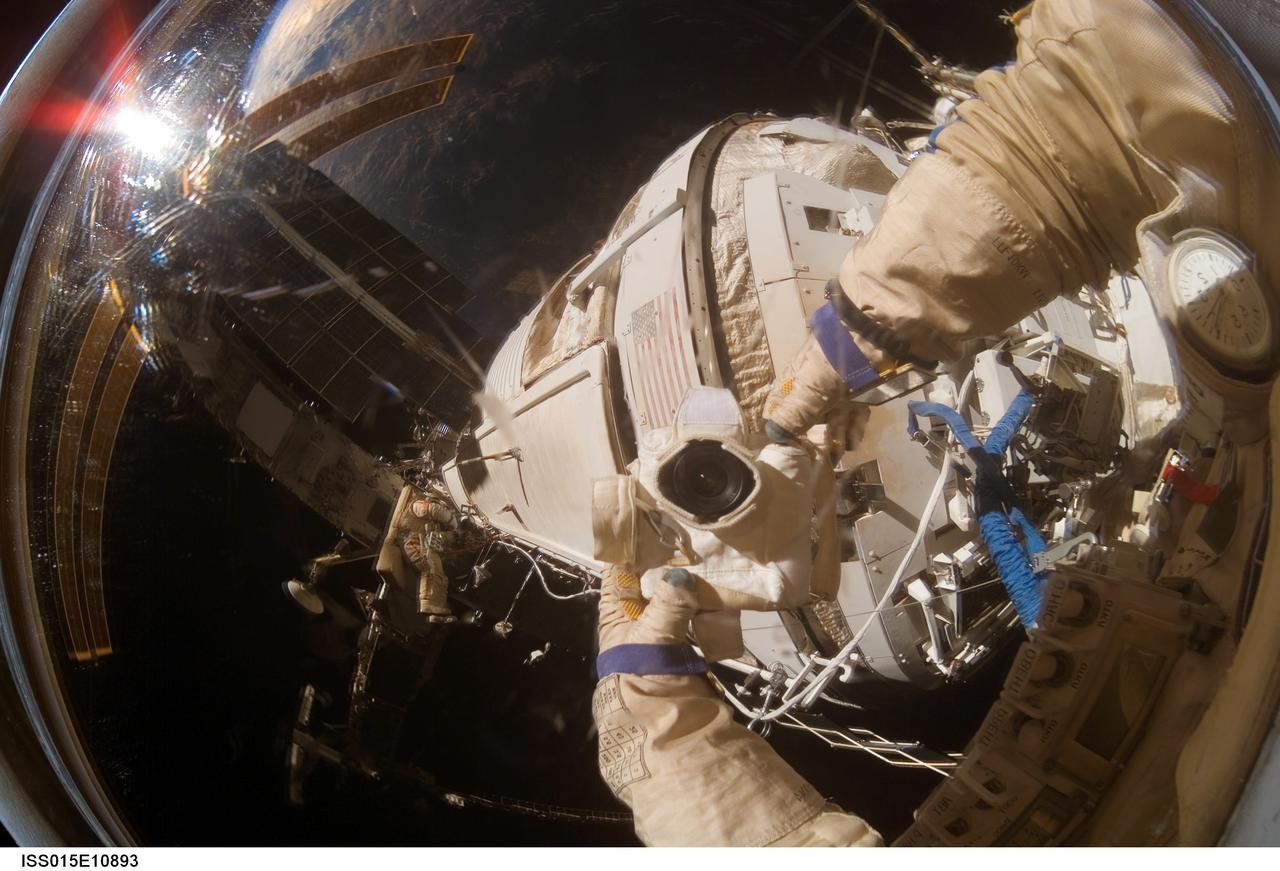

ISS015-E-10893 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov, Expedition 15 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, uses a digital still camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). A portion of the International Space Station is also visible in the reflections. Among other tasks, Kotov and cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin (out of frame), commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
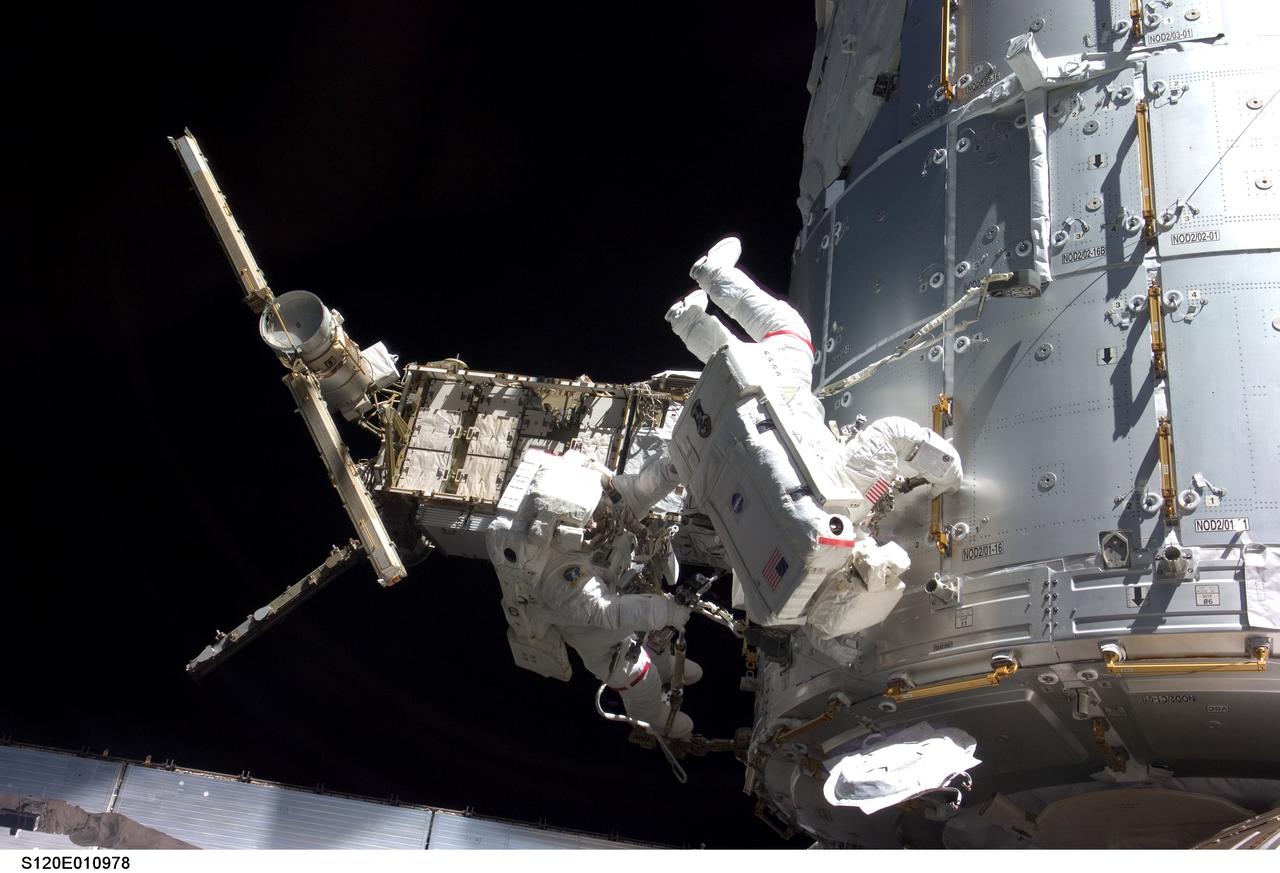

S120-E-010978 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
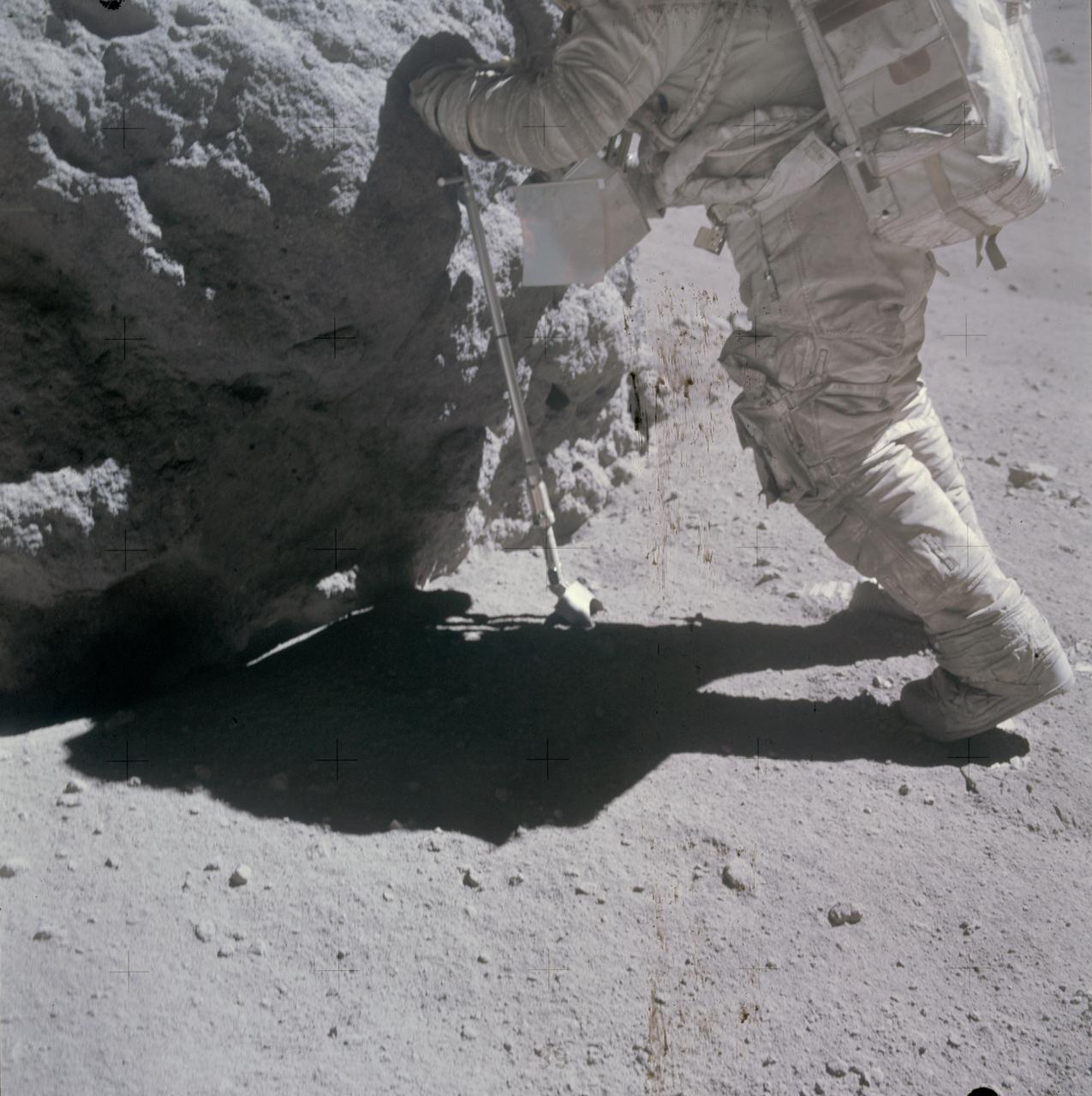

AS16-116-18671 (23 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, works at the "Shadow Rock", discovered during the missions third extravehicular activity (EVA) in the area of North Ray Crater (Station 13), April 23, 1972. The scoop, a geological hand tool, leans against the rock. This view was exposed by astronaut John W. Young, commander. The two moon-exploring crew men sampled this rock, which got its name because of a permanently shadowed area it protected. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
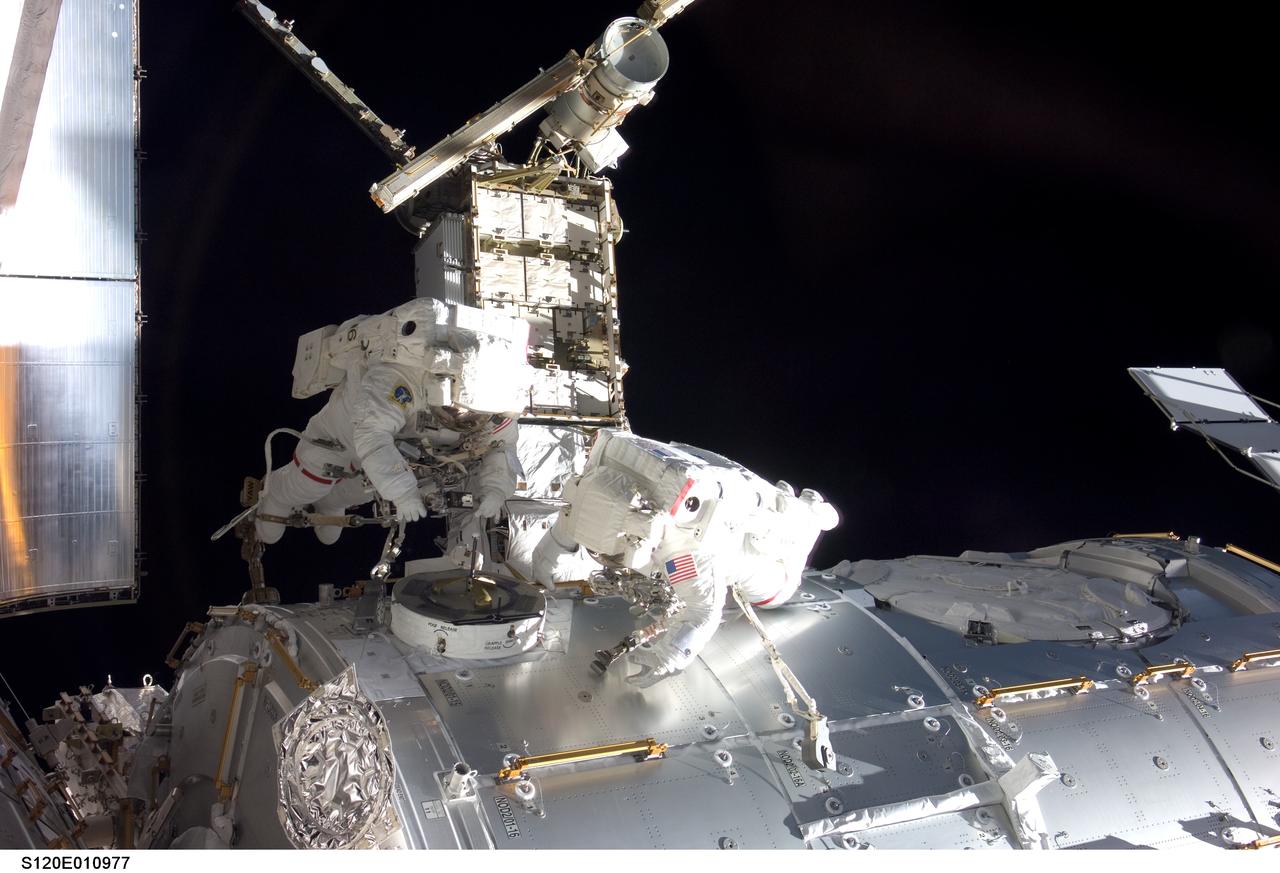
S120-E-010977 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
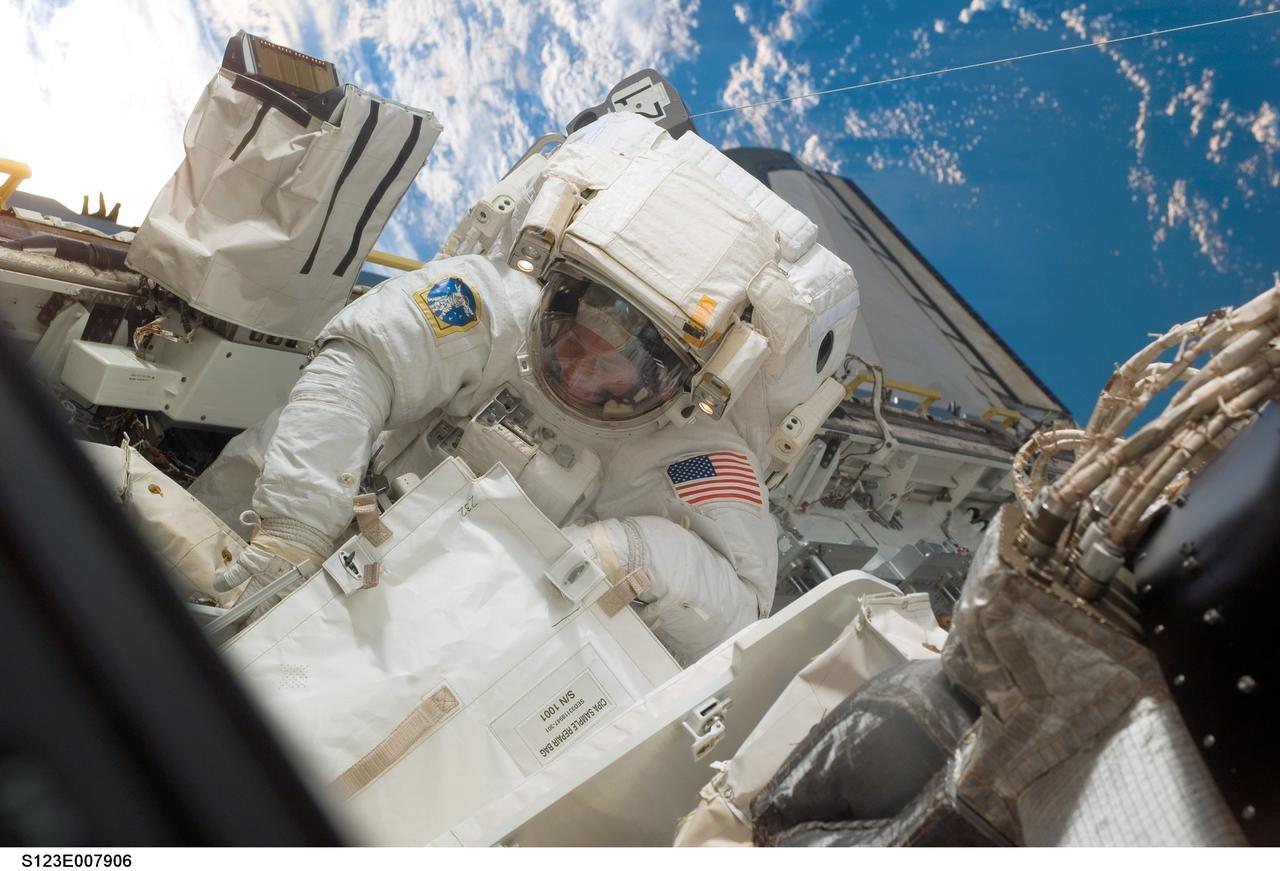

S123-E-007906 (21 March 2008) --- Astronaut Robert L. Behnken, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's fourth scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 24-minute spacewalk, Behnken and astronaut Mike Foreman (out of frame), mission specialist, replaced a failed Remote Power Control Module -- essentially a circuit breaker -- on the station's truss. The spacewalkers also tested a repair method for damaged heat resistant tiles on the space shuttle. This technique used a caulk-gun-like tool named the Tile Repair Ablator Dispenser to dispense a material called Shuttle Tile Ablator-54 into purposely damaged heat shield tiles. The sample tiles will be returned to Earth to undergo extensive testing on the ground.
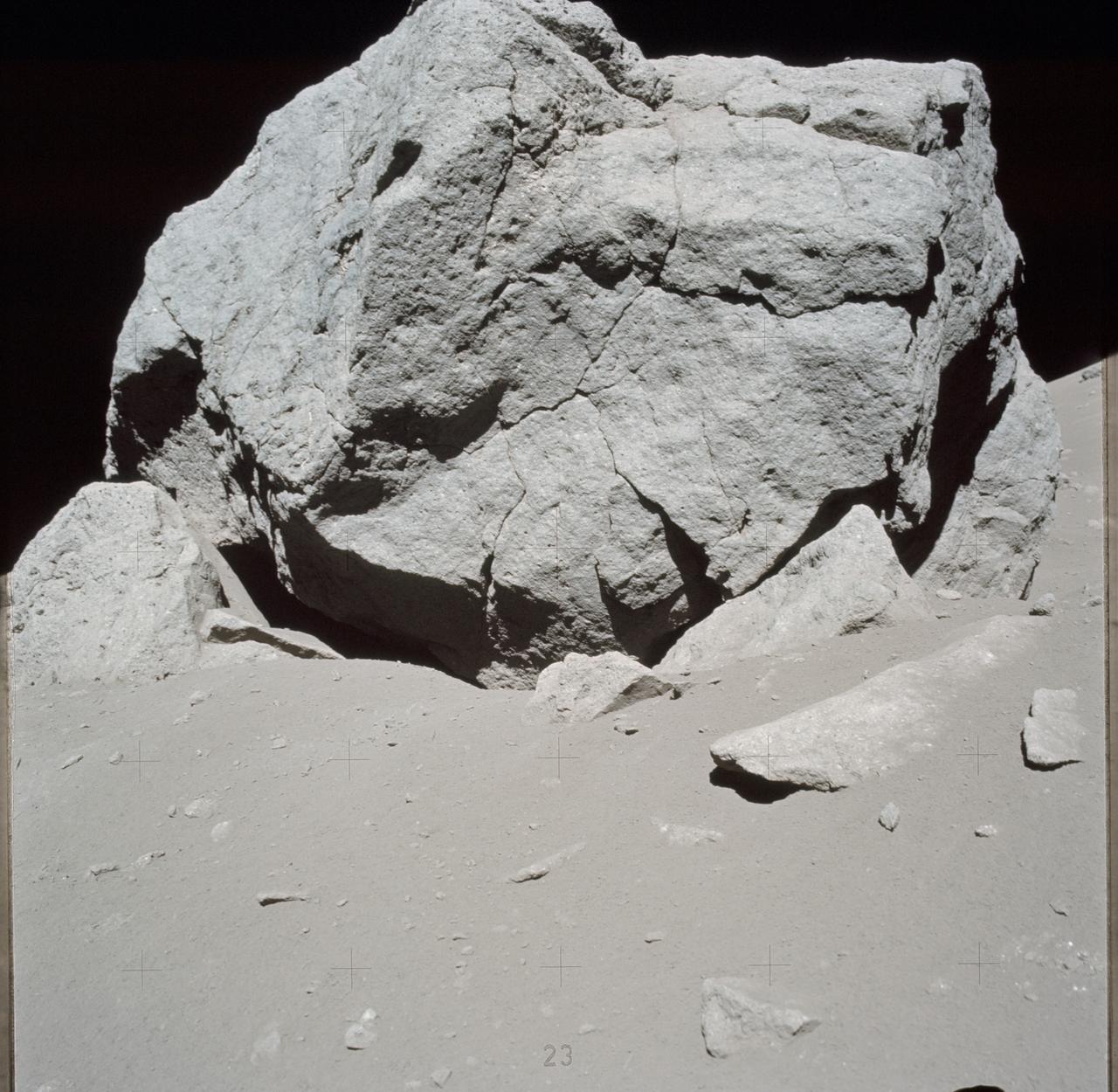

AS17-140-21438 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This 70mm frame features a close-up view of a large multi-cracked boulder discovered by astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. (Jack) Schmitt, lunar module pilot, during their visit to extravehicular activity (EVA) Station 6. This boulder, referred to as number two, provided several samples for the crew members' record-setting volume of rock collections. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit. Cernan and Schmitt were the last crew members to explore the moon in the Apollo Program.
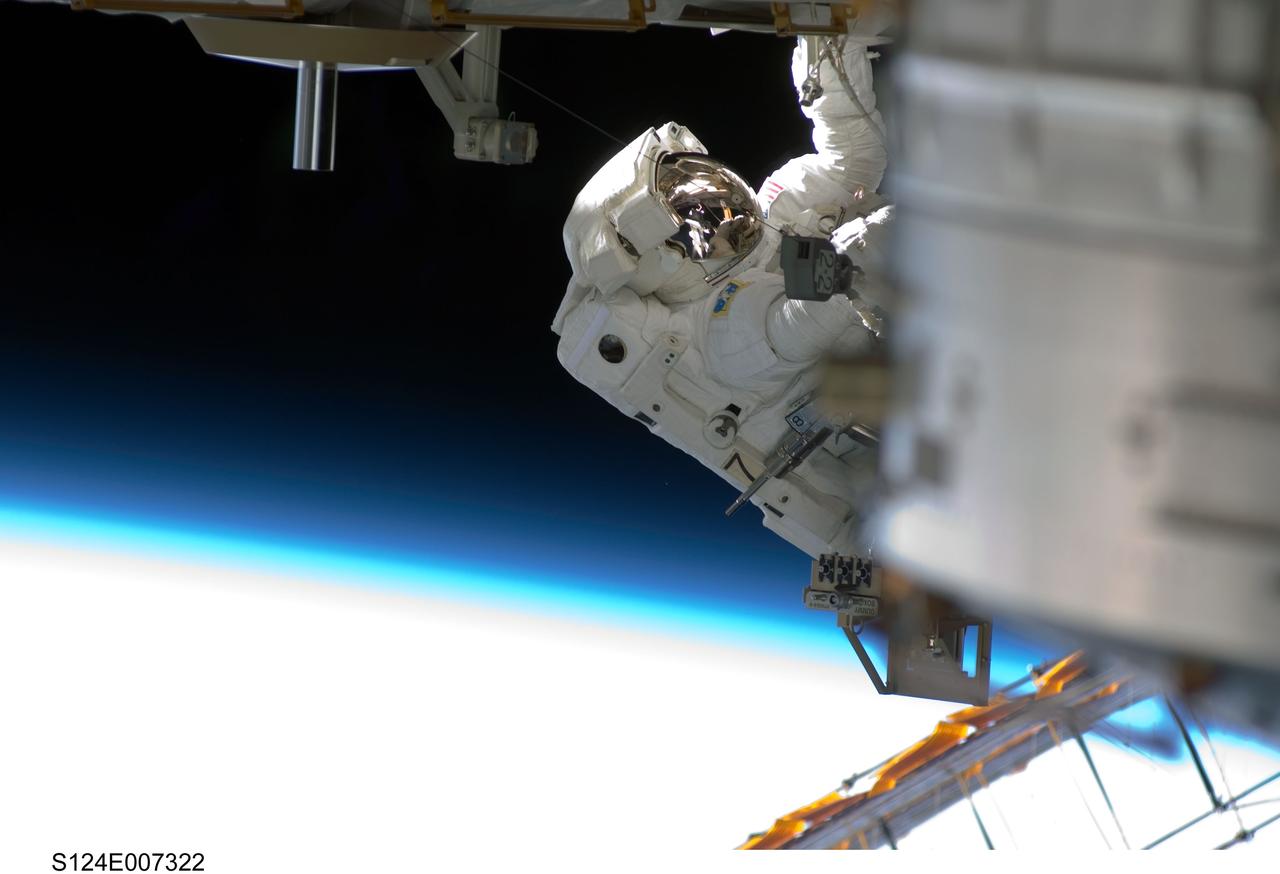

S124-E-007322 (8 June 2008) --- Astronaut Ron Garan, STS-124 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 33-minute spacewalk, Garan and astronaut Mike Fossum (out of frame), mission specialist, exchanged a depleted Nitrogen Tank Assembly for a new one, removed thermal covers and launch locks from the Kibo laboratory, reinstalled a repaired television camera onto the space station's left P1 truss, and retrieved samples of a dust-like substance from the left Solar Alpha Rotary Joint for analysis by experts on the ground. The blackness of space and Earth's atmosphere provide the backdrop for the scene.
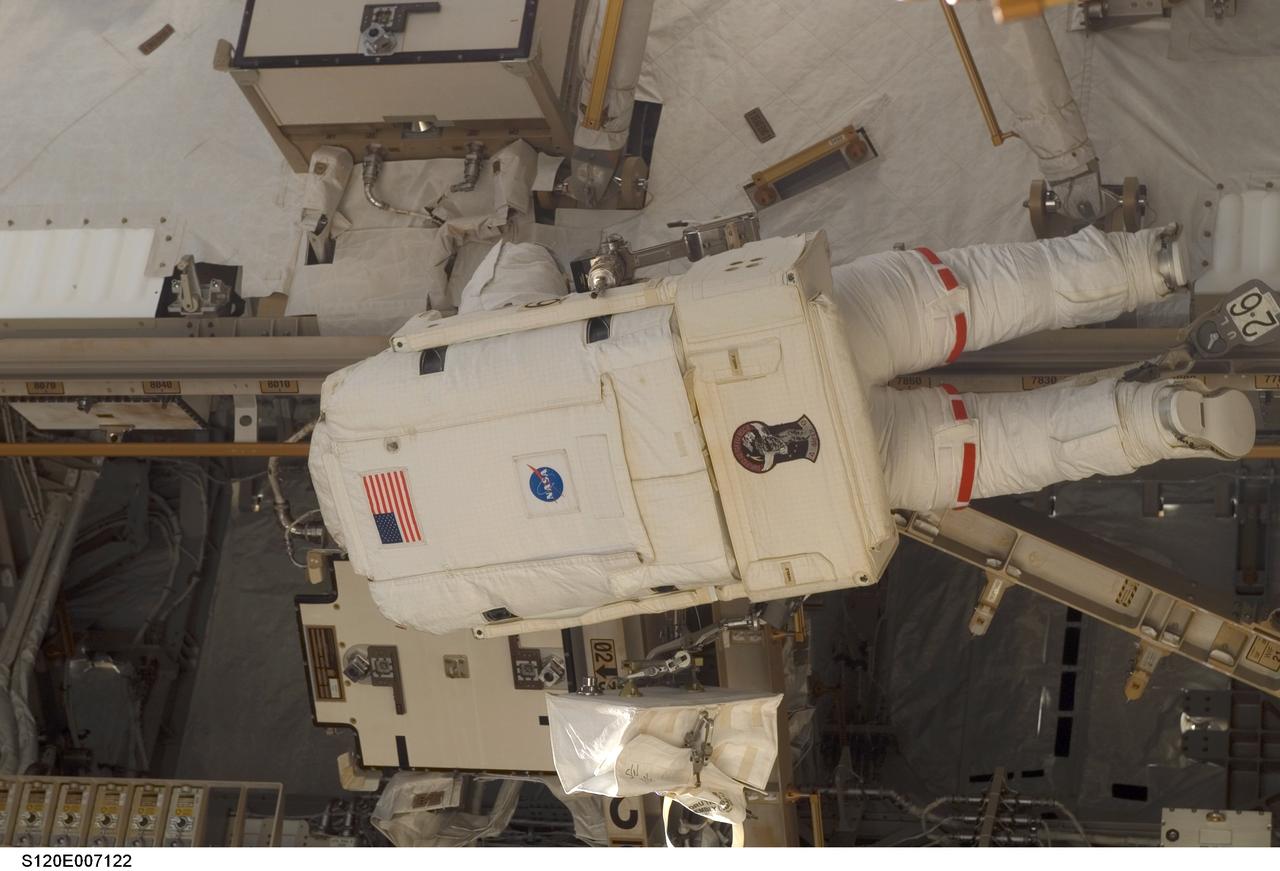

S120-E-007122 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
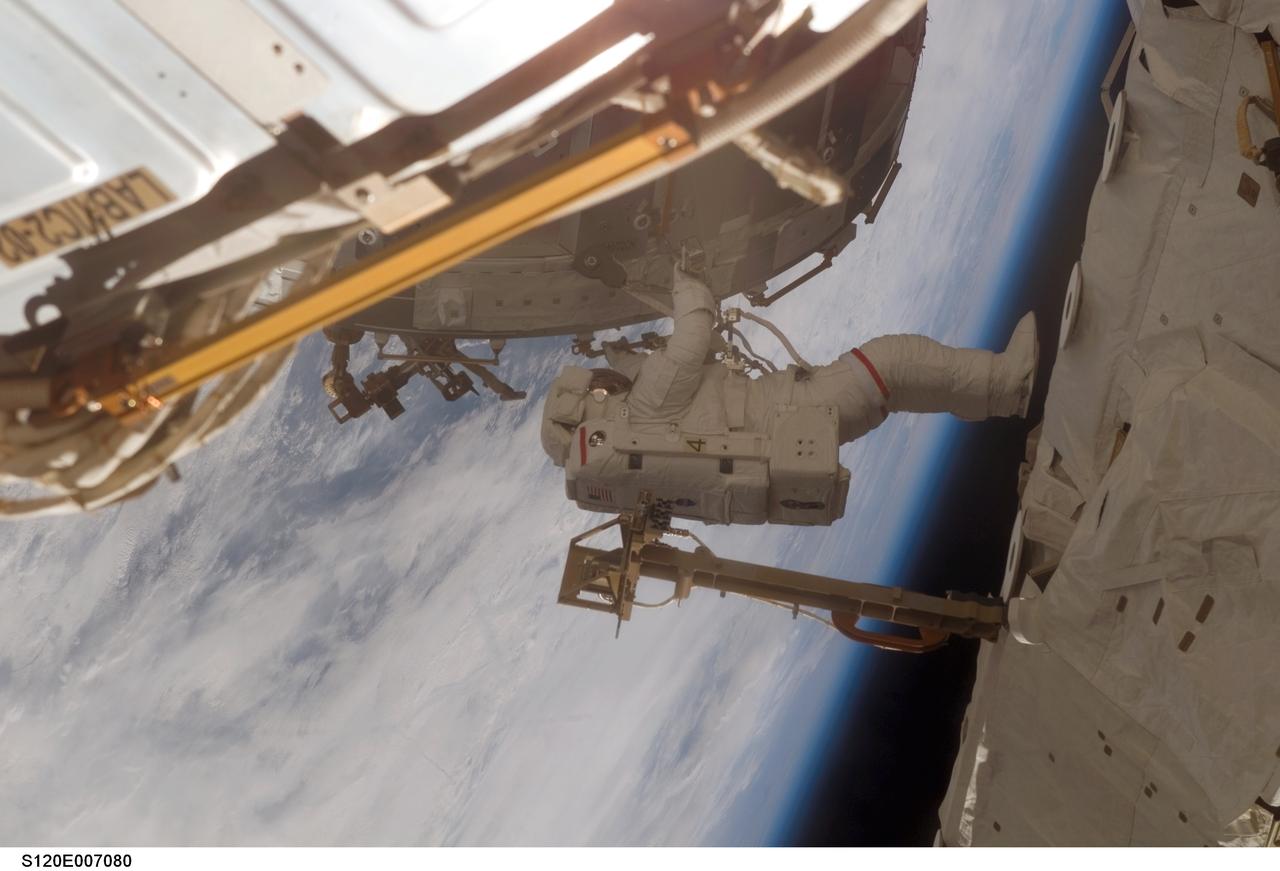

S120-E-007080 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Parazynski and astronaut Daniel Tani (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
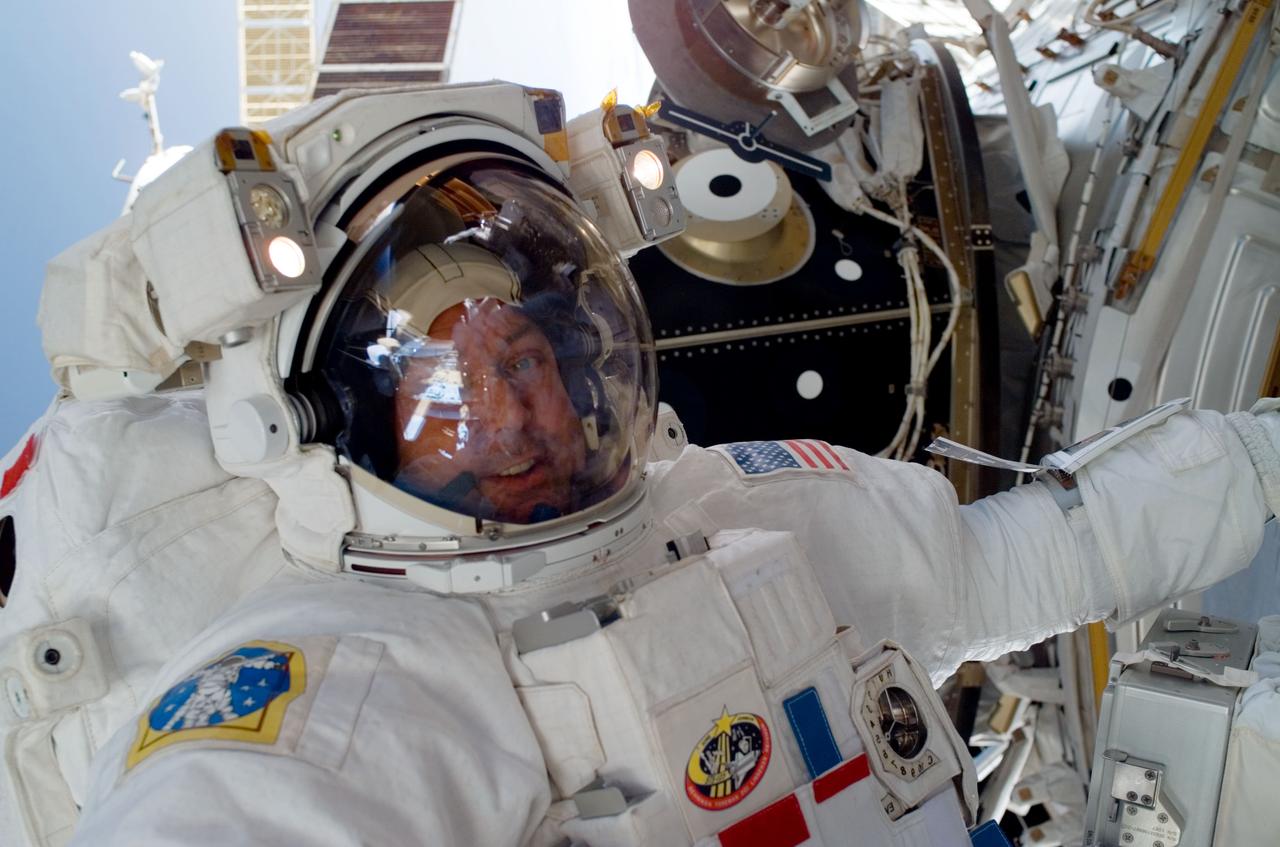

ISS016-E-033394 (21 March 2008) --- Astronaut Mike Foreman, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's fourth scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 24-minute spacewalk, Foreman and astronaut Robert L. Behnken (out of frame), mission specialist, replaced a failed Remote Power Control Module -- essentially a circuit breaker -- on the station's truss. The spacewalkers also tested a repair method for damaged heat resistant tiles on the space shuttle. This technique used a caulk-gun-like tool named the Tile Repair Ablator Dispenser to dispense a material called Shuttle Tile Ablator-54 into purposely damaged heat shield tiles. The sample tiles will be returned to Earth to undergo extensive testing on the ground.
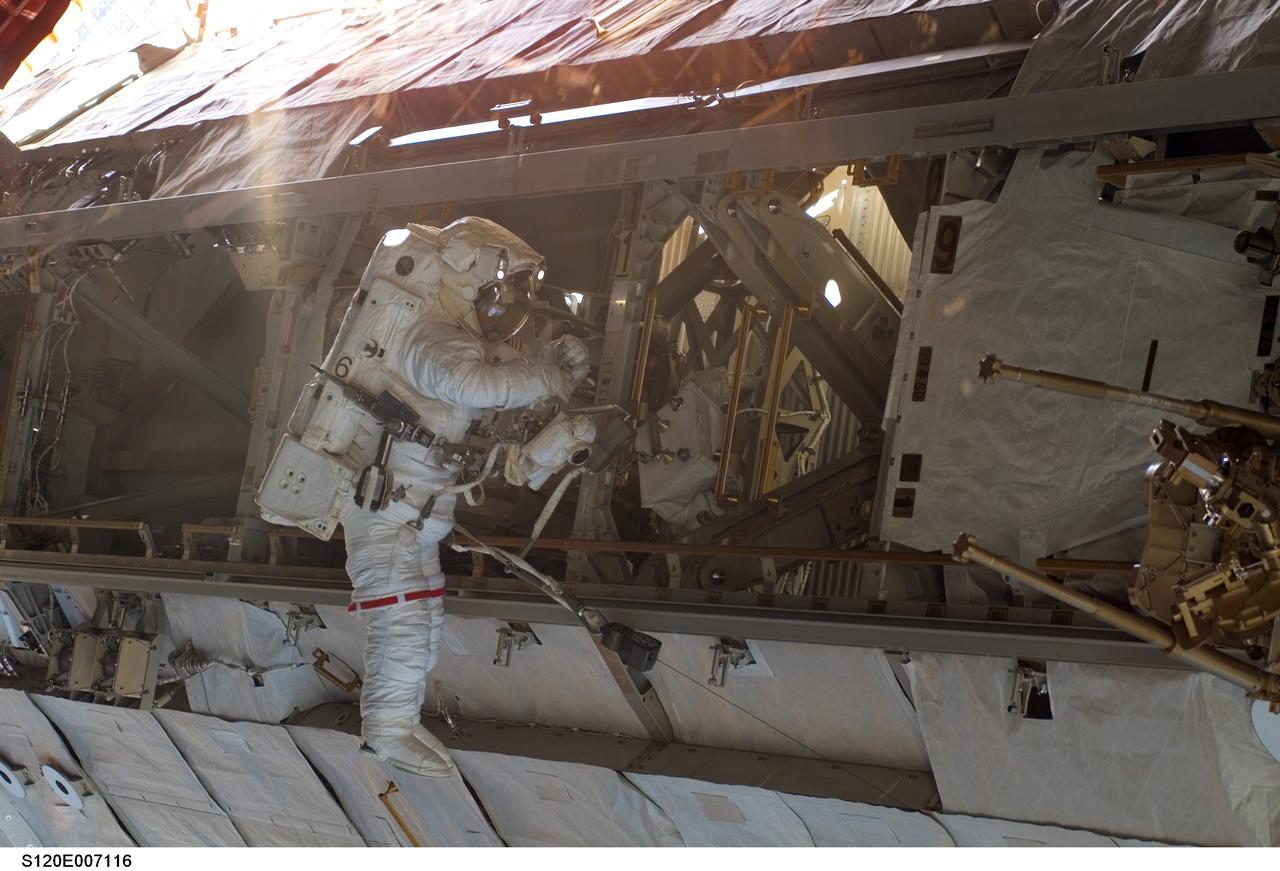

S120-E-007116 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.

S123-E-007838 (21 March 2008) --- Astronauts Robert L. Behnken (top) and Mike Foreman, both STS-123 mission specialists, participate in the mission's fourth scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 24-minute spacewalk, Behnken and Foreman replaced a failed Remote Power Control Module -- essentially a circuit breaker -- on the station's truss. The spacewalkers also tested a repair method for damaged heat resistant tiles on the space shuttle. This technique used a caulk-gun-like tool named the Tile Repair Ablator Dispenser to dispense a material called Shuttle Tile Ablator-54 into purposely damaged heat shield tiles. The sample tiles will be returned to Earth to undergo extensive testing on the ground.
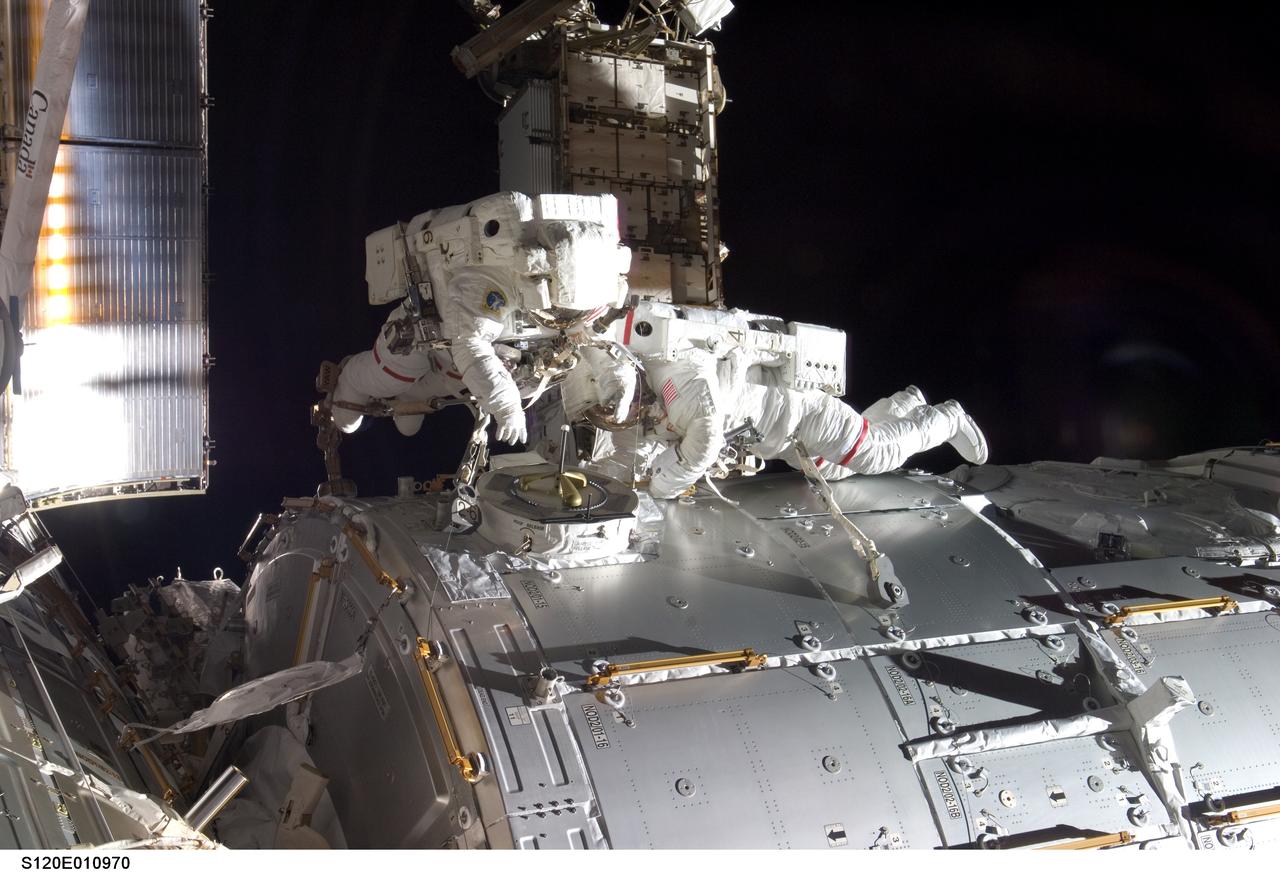

S120-E-010970 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
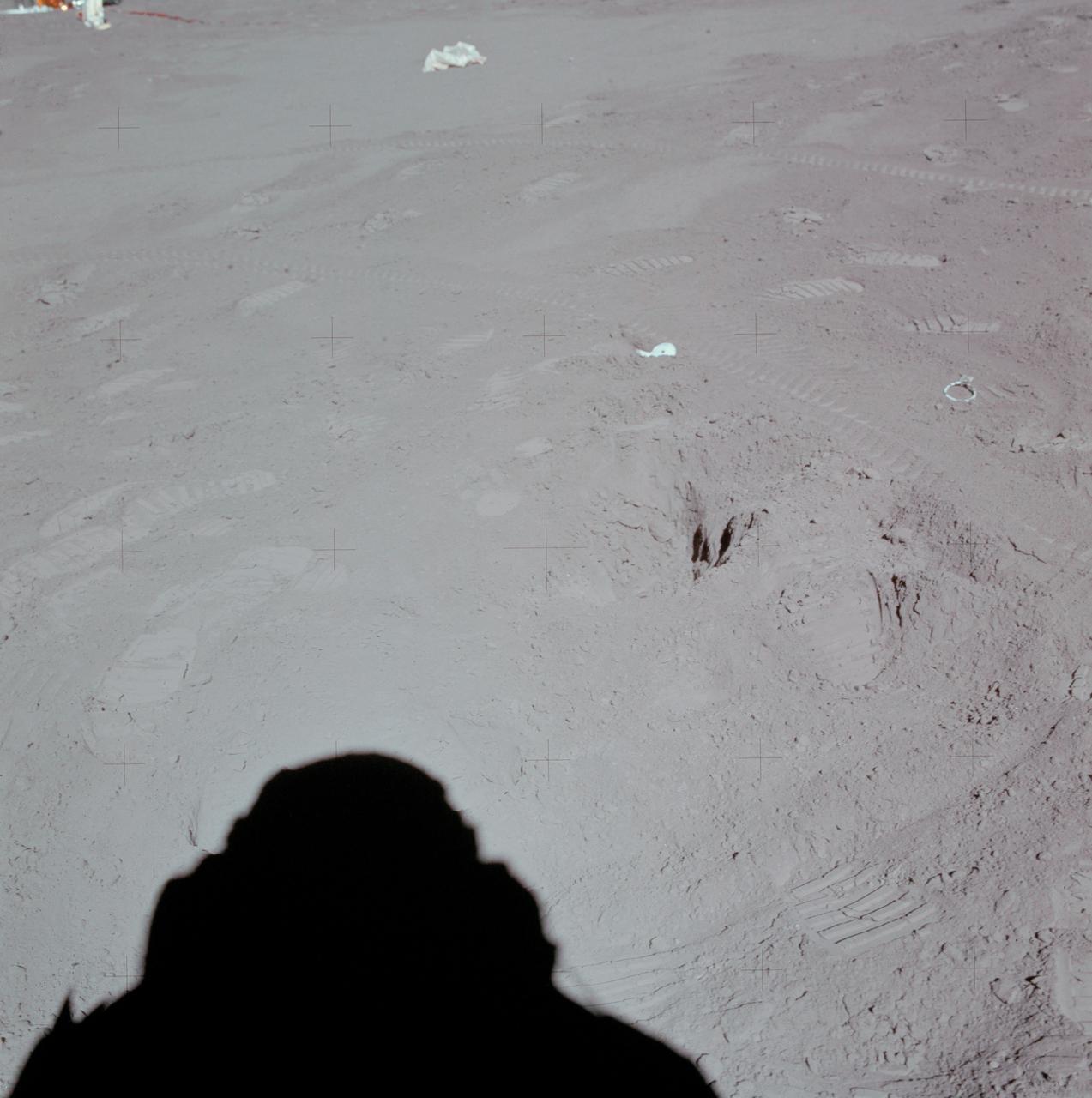

AS15-88-11872 (31 July 1971) --- This north-looking view at Station 8 near the Hadley-Apennine landing site was photographed by one of the missions two moon explorer's (see shadow, foreground) during the third Apollo 15 extravehicular activity (EVA). Prints from the boots of astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, as well as tire tracks from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) are scattered throughout the view. A small part of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) is in the upper left corner. Lunar samples 15252 and 15253 were removed from this area and returned to Earth for analysis by scientists. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
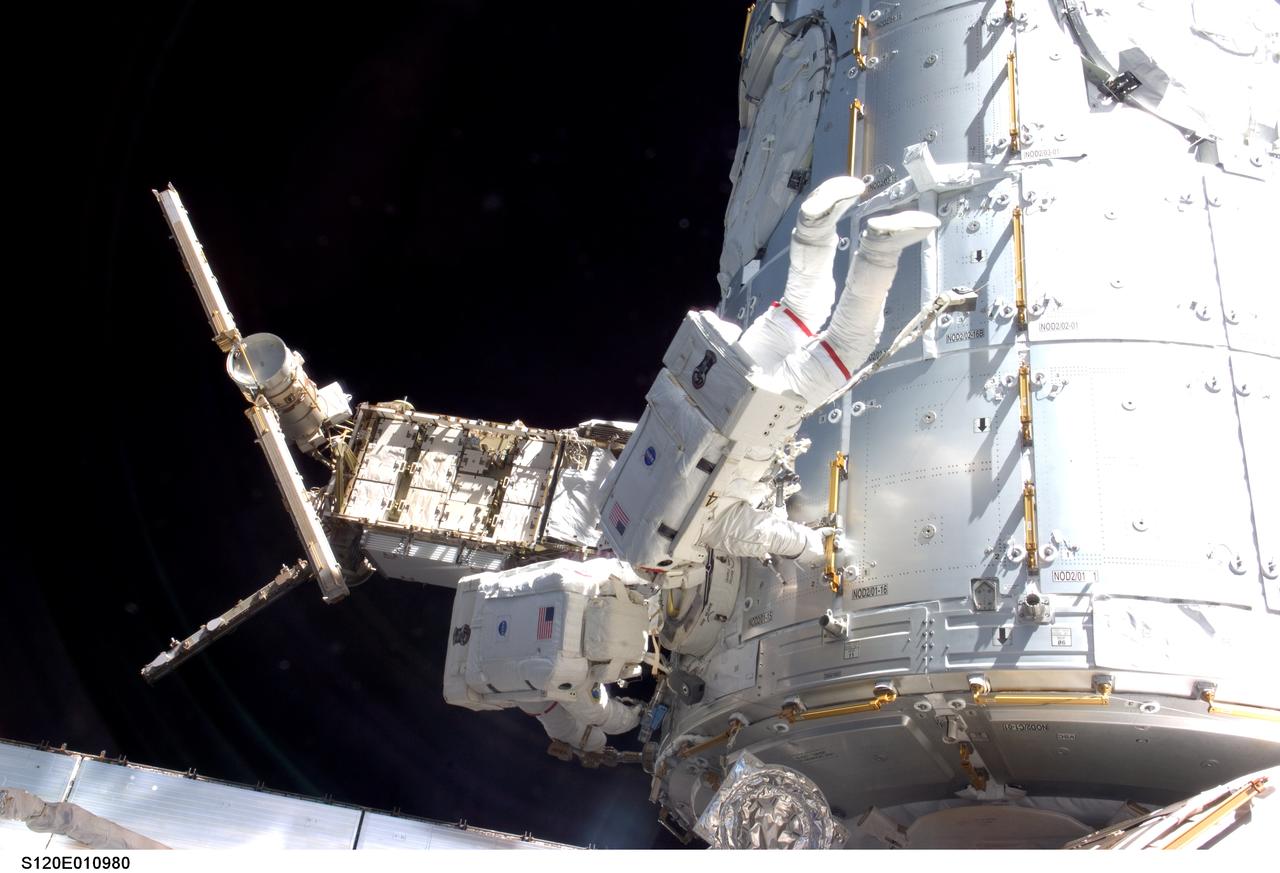

S120-E-010980 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronauts Daniel Tani (left), Expedition 16 flight engineer, and Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participate in the second scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and Parazynski outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. Also the spacewalkers worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers.
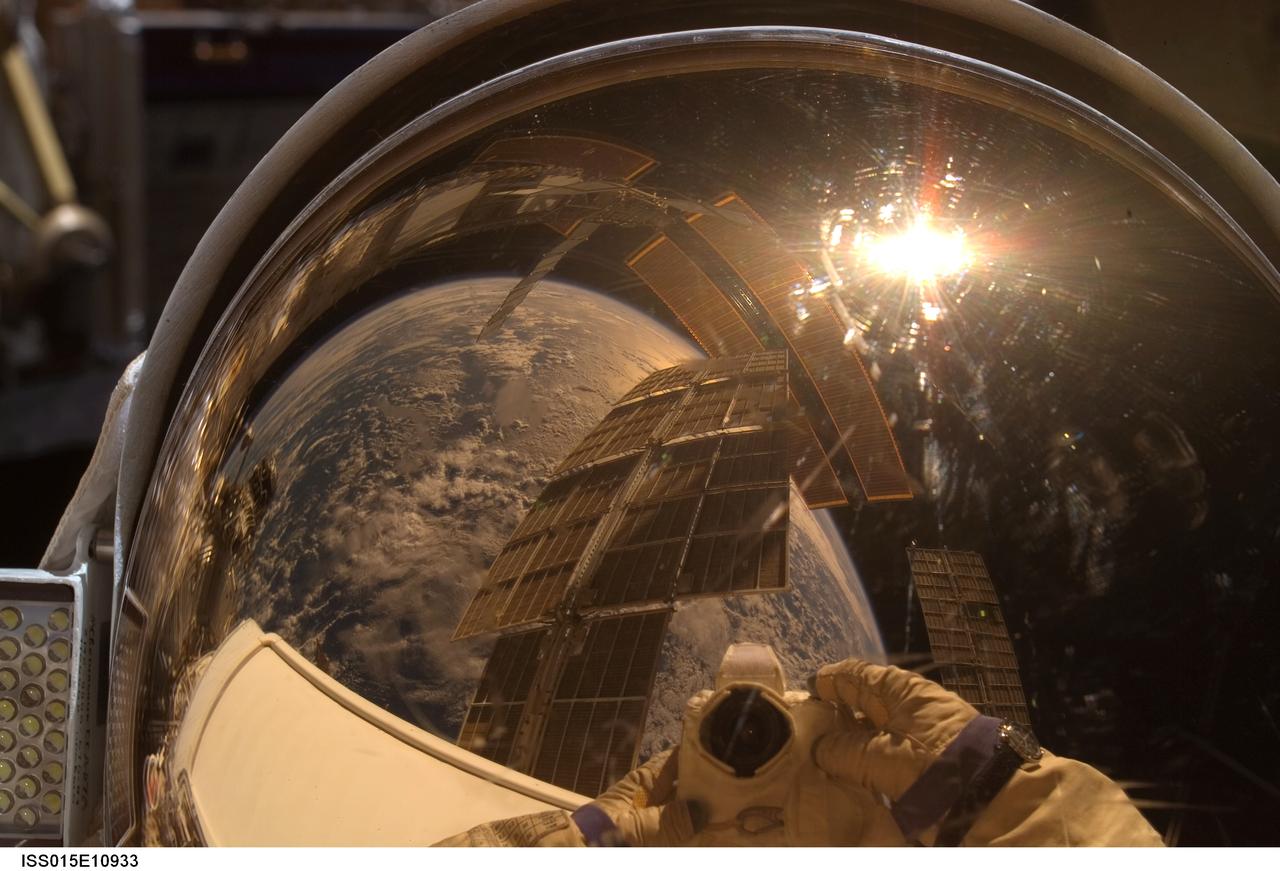

ISS015-E-10933 (6 June 2007) --- Cosmonaut Oleg V. Kotov, Expedition 15 flight engineer representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, wearing a Russian Orlan spacesuit, uses a digital still camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA). With the Earth in the background, International Space Station solar array panels are also visible in the reflections. Among other tasks, Kotov and cosmonaut Fyodor N. Yurchikhin (out of frame), commander representing Russia's Federal Space Agency, completed the installation of 12 more Zvezda Service Module debris panels and installed sample containers on the Pirs Docking Compartment for a Russian experiment, called Biorisk, which looks at the effect of space on microorganisms.
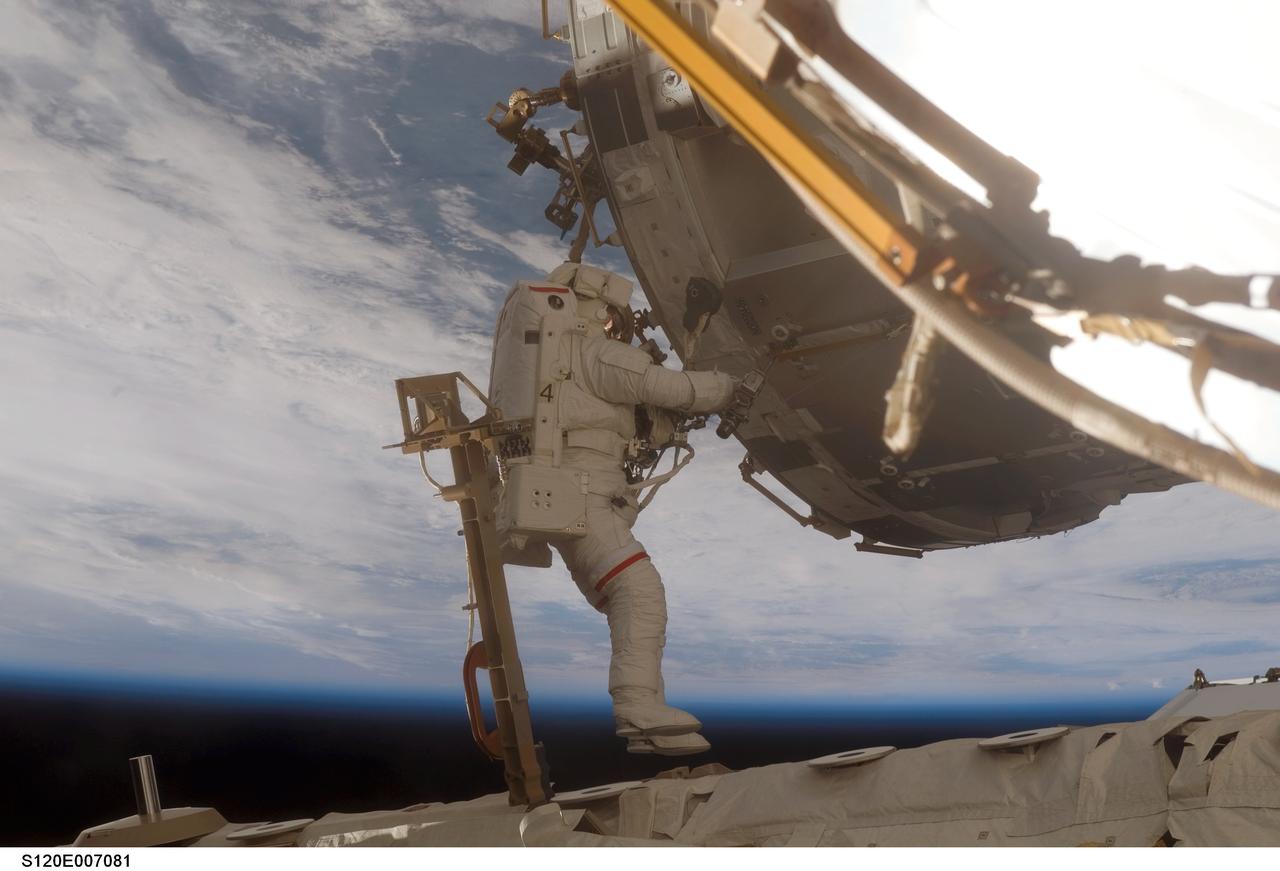

S120-E-007081 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Parazynski and astronaut Daniel Tani (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
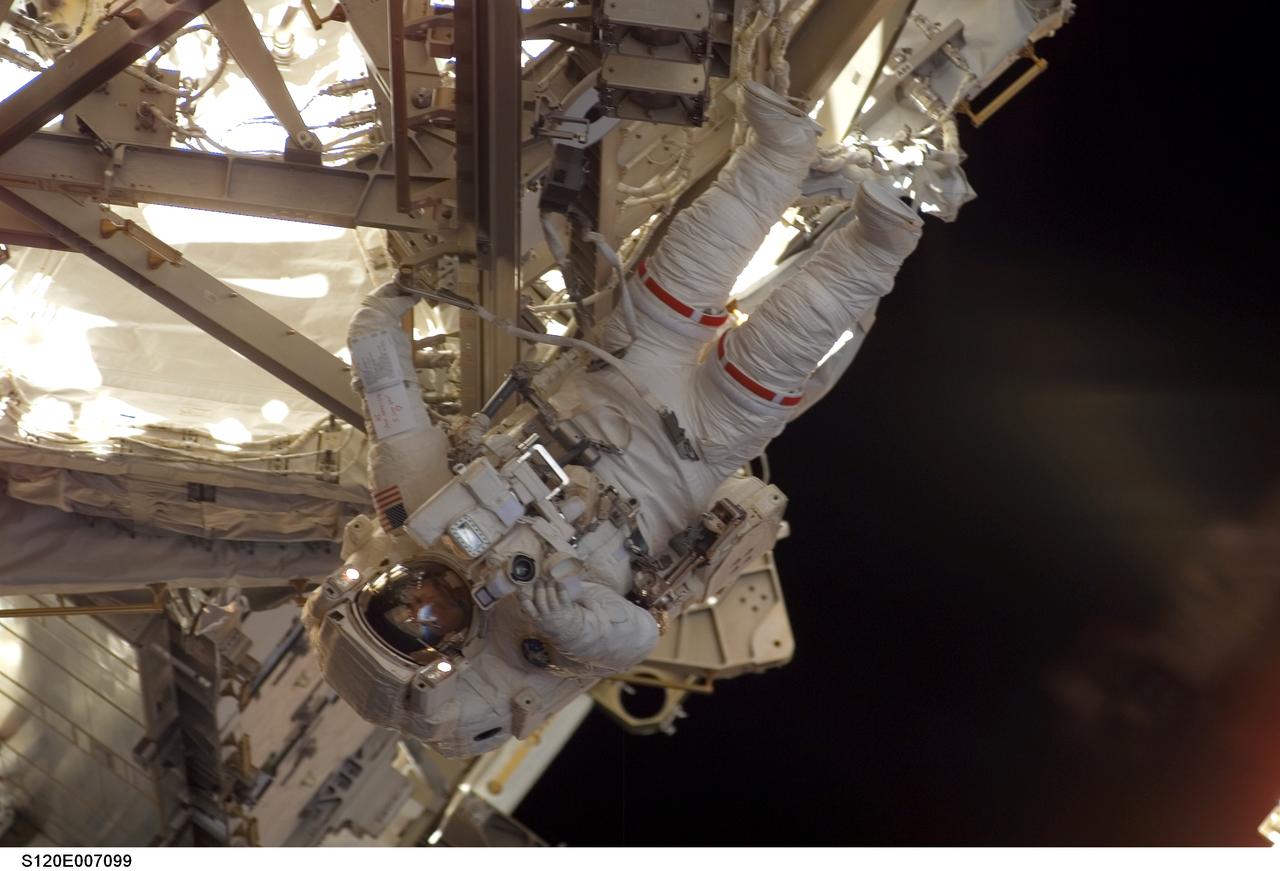

S120-E-007099 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.