
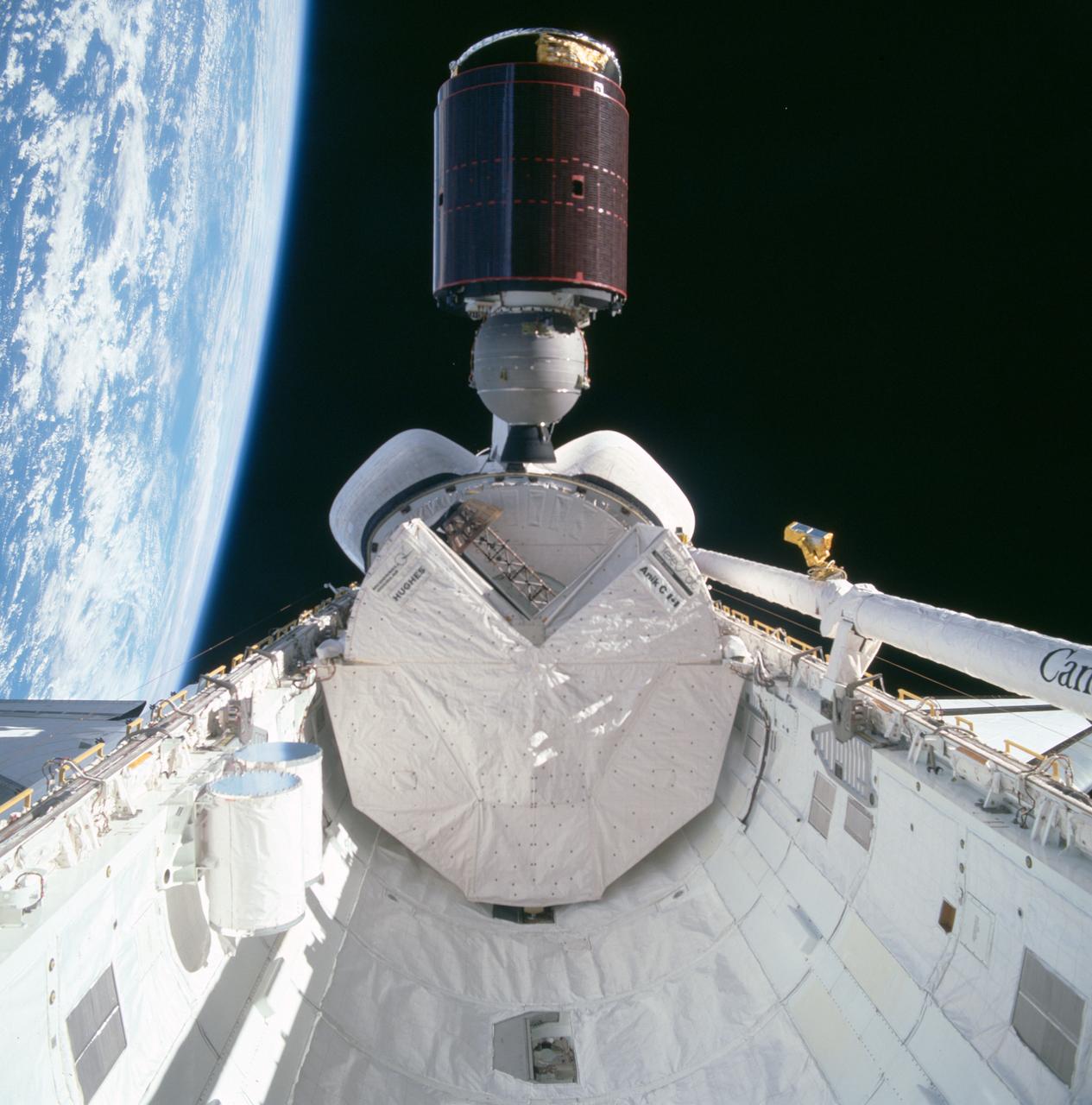
S83-35764 (19 June 1983) --- The Indonesian Palapa B communications satellite is just about to clear the vertical stabilizer of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger to begin its way toward its Earth-orbital destination. Also visible in this 70mm exposure, photographed through the flight deck?s aft windows, are the Shuttle pallet satellite, the experiment package for NASA?s office of space and terrestrial applications (OSTA-2), the now vacated protective cradles for Palapa and Telesat Canada?s Anik C2 satellites, some getaway special (GAS) canisters and the Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS) arm.

Arabsat communications satellite deploying from Discovery's payload bay. Cloudy Earth's surface can be seen to the left of the frame.

Telstar 3-D communications satellite deploying from Discovery's payload bay. Cloudy Earth's surface can be seen to the left of the frame.

61B-38-36W (28 Nov 1985) --- The 4,144-pound RCA Satcom K-2 communications satellite is photographed as it spins from the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Atlantis. A TV camera at right records the deployment for a later playback to Earth. This frame was photographed with a handheld Hasselblad camera inside the spacecraft.
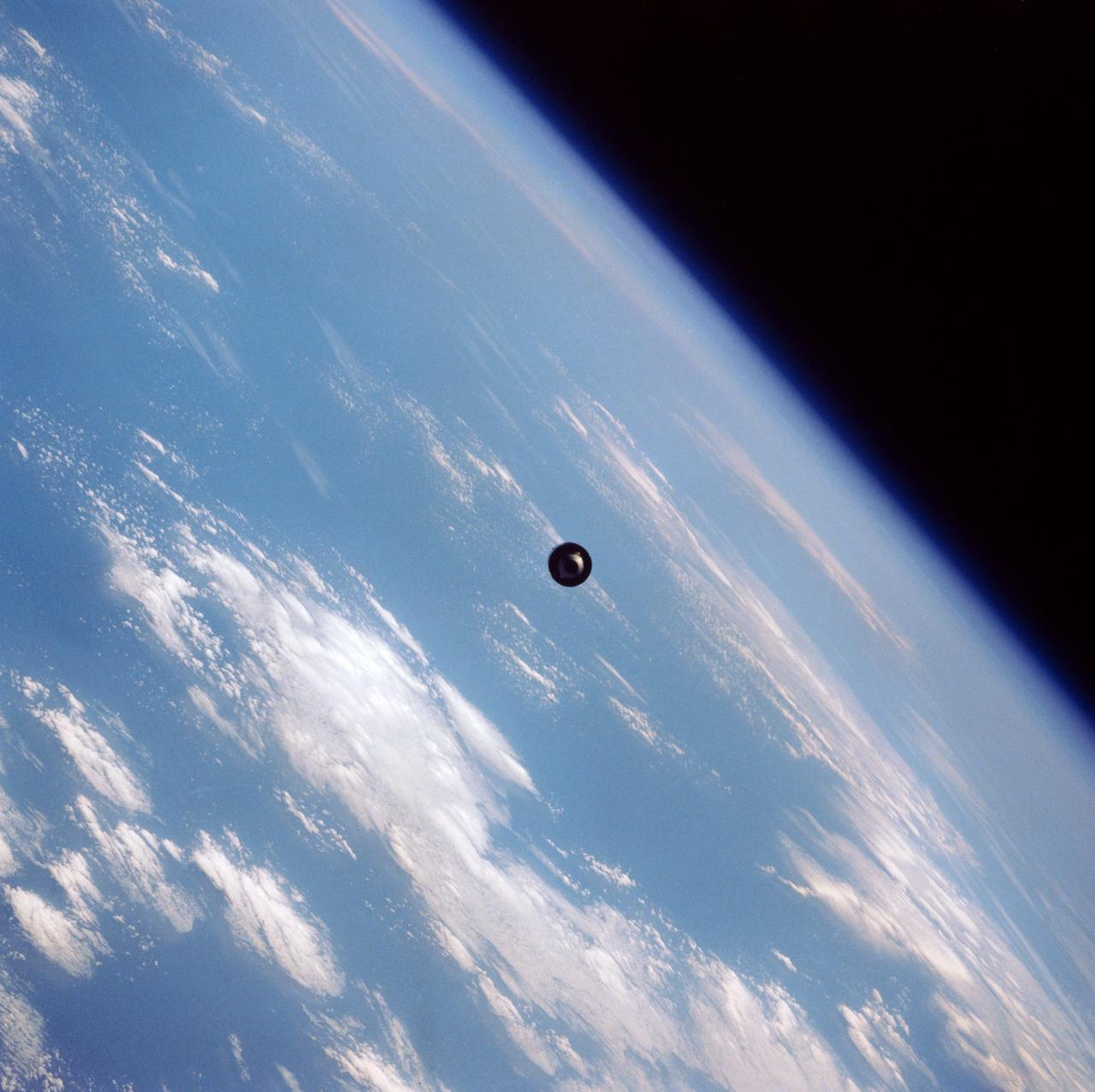

41D-39-068 (1 Sept 1984) --- Quickly moving away from the Space Shuttle Discovery is the Telstar 3 communications satellite, deployed September 1, 1984. The 41-D crew successfully completed three satellite placements, of which this was the last. Telstar was the second 41-D deployed satellite to be equipped with a payload assist module (PAM-D). The frame was exposed with a 70mm camera.
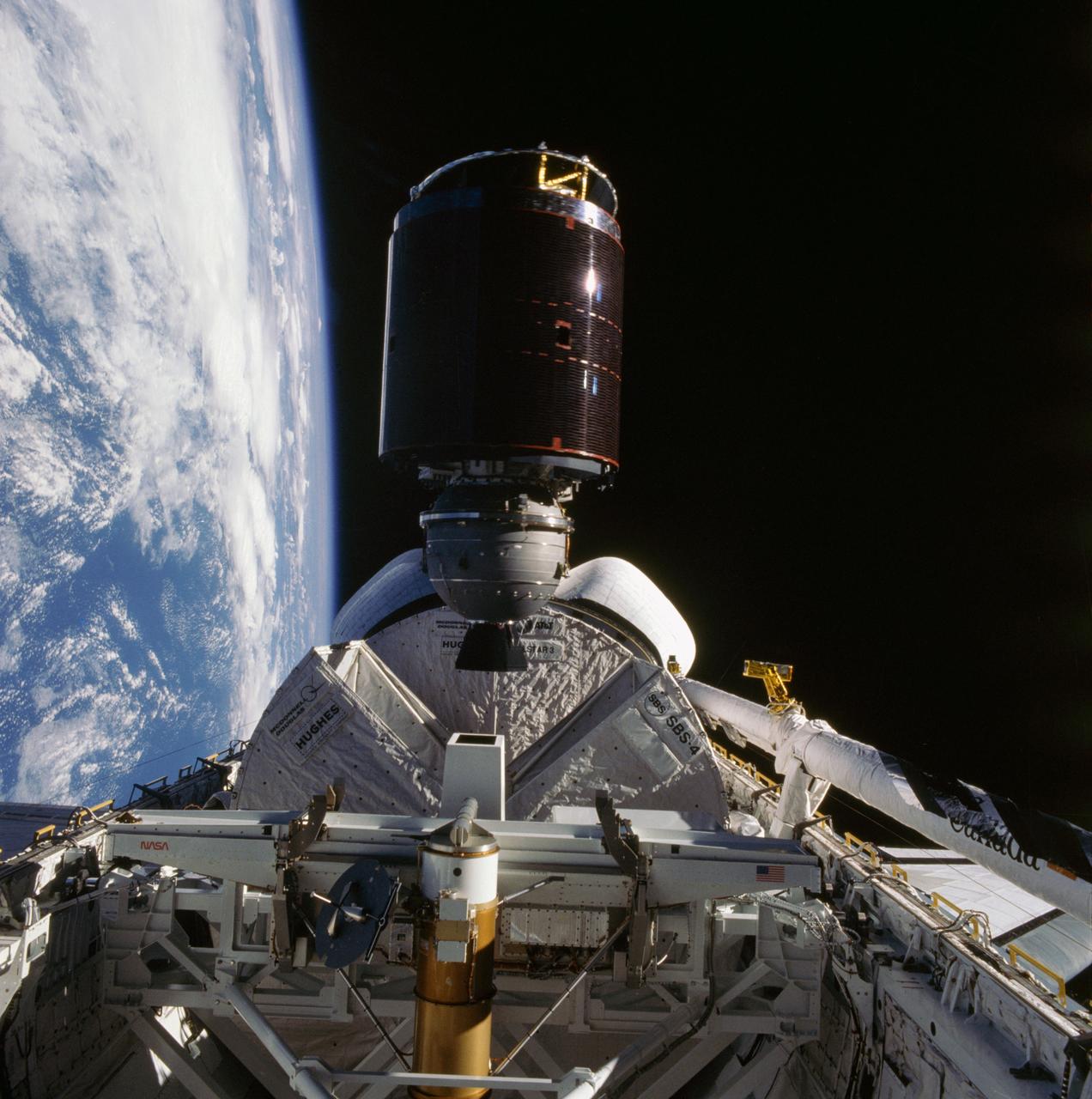

41D-36-034 (30 Aug 1984) --- Less than nine hours after the first launch of the Discovery, its astronaut crewmembers photographed deployment of the SBS-4 communications satellite. The cylindrical spacecraft spins and rises from its cradle-like protective shield to begin life in space. A number of maneuvers will place it in its desired orbit. A 70mm camera, aimed through the spacecraft’s aft flight deck windows, was used to expose the frame.
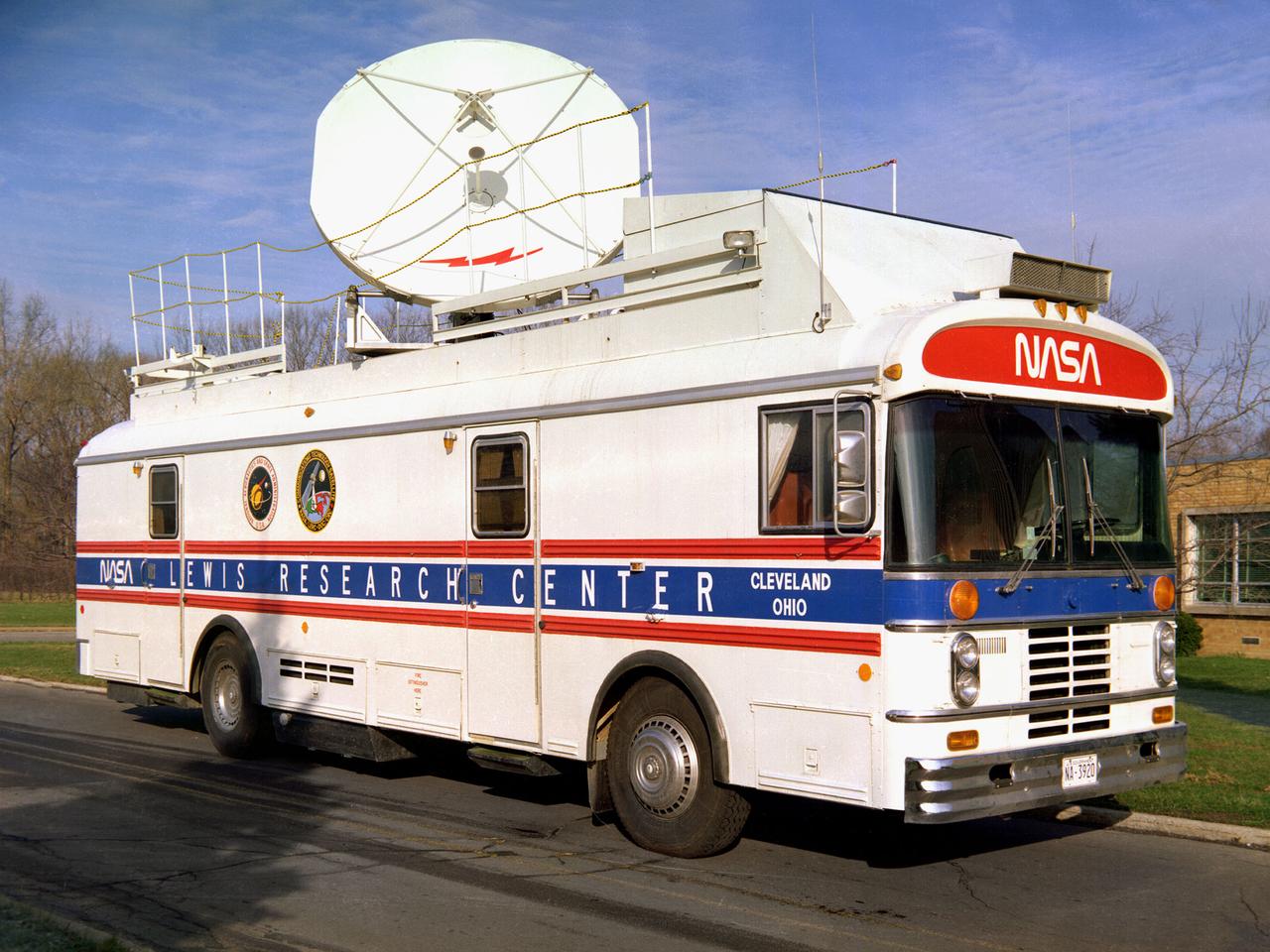

This vehicle served as a mobile terminal for the Communications Technology Satellite. The Communications Technology Satellite was an experimental communications satellite launched in January 1976 by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Canadian Department of Communications. The satellite operated in a new frequency band reserved for broadcast satellites with transmitting power levels that were 10 to 20 times higher than those of contemporary satellites. Throughout 1977 and 1978 NASA allowed qualified groups to utilize the satellite from one of the three ground-based transmission centers. NASA’s Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio was NASA’s lead center on the project. Lewis was responsible for the control and coordination of all US experiments on the satellite. The center housed the satellite’s main control center which included eight parabolic reflector antennae ranging from 2 to 15 feet in diameter. Many of the satellite’s components had been tested in simulated space conditions at Lewis. The Lewis-designed vehicle seen here served as a field unit for transmitting and receiving wideband signals and narrowband voice. The vehicle permitted live television interviews, recording equipment, and cameras. An 8-foot diameter parabolic reflector was mounted on the roof. The interior of the vehicle had workstations, monitors, transmitting equipment, and a lounge area.

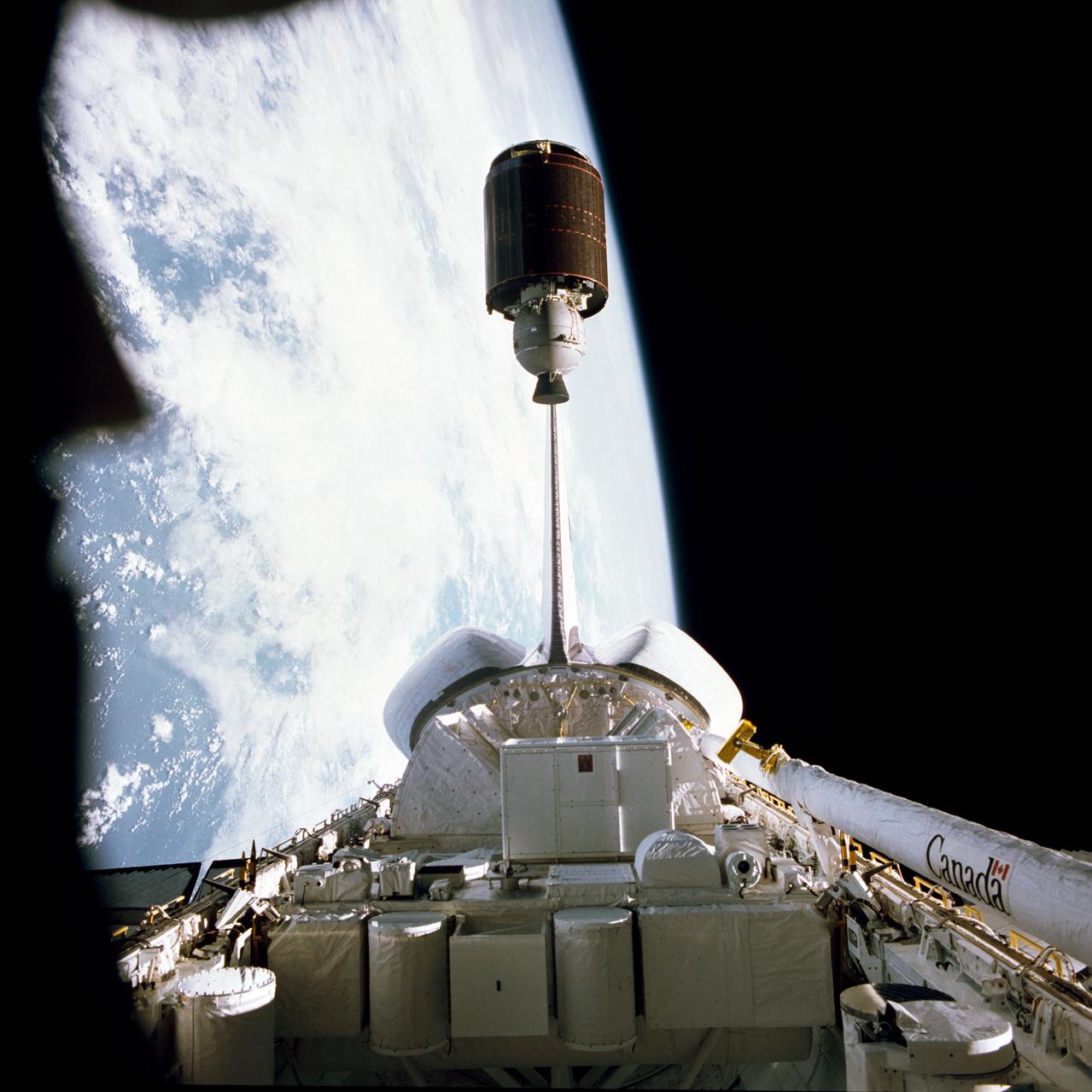
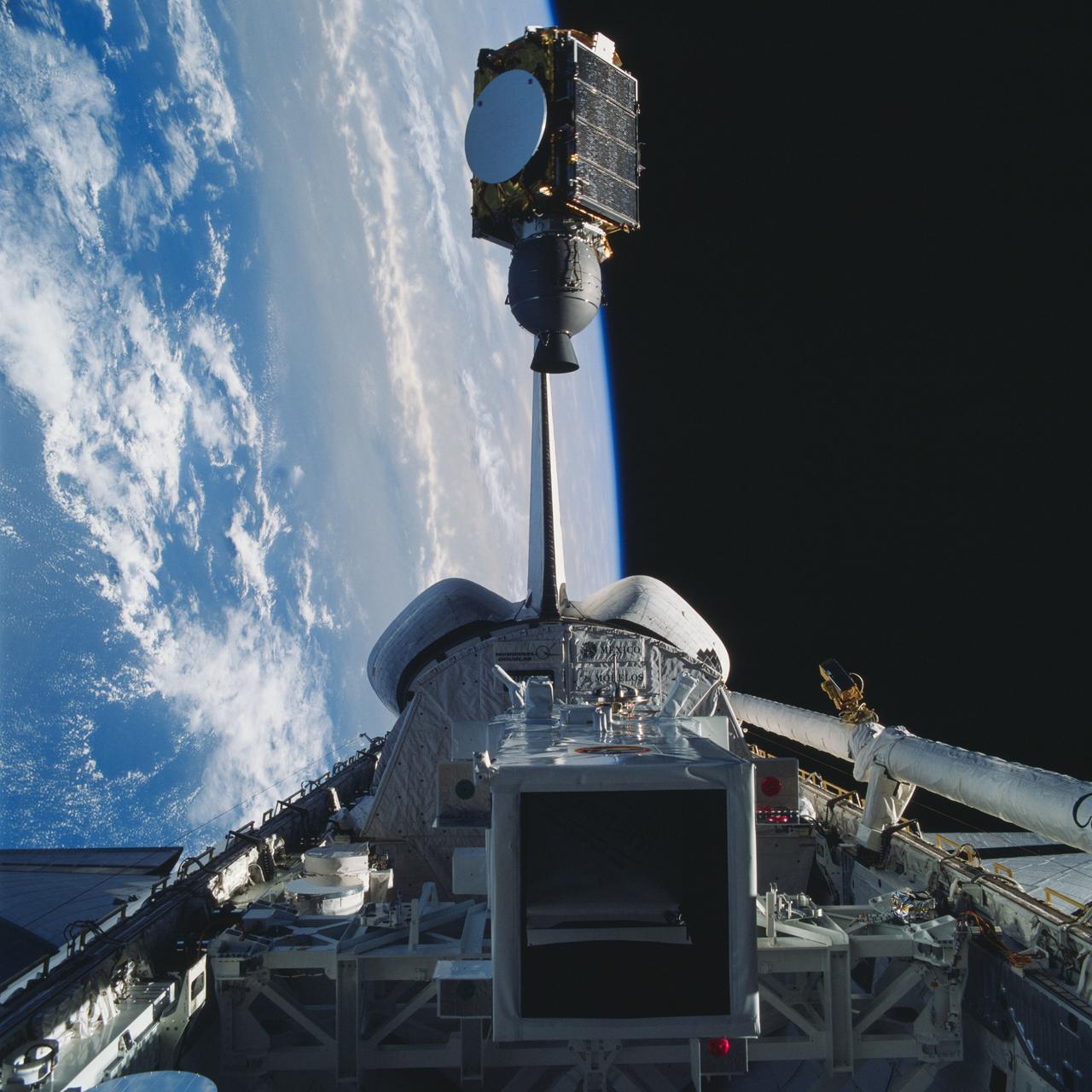
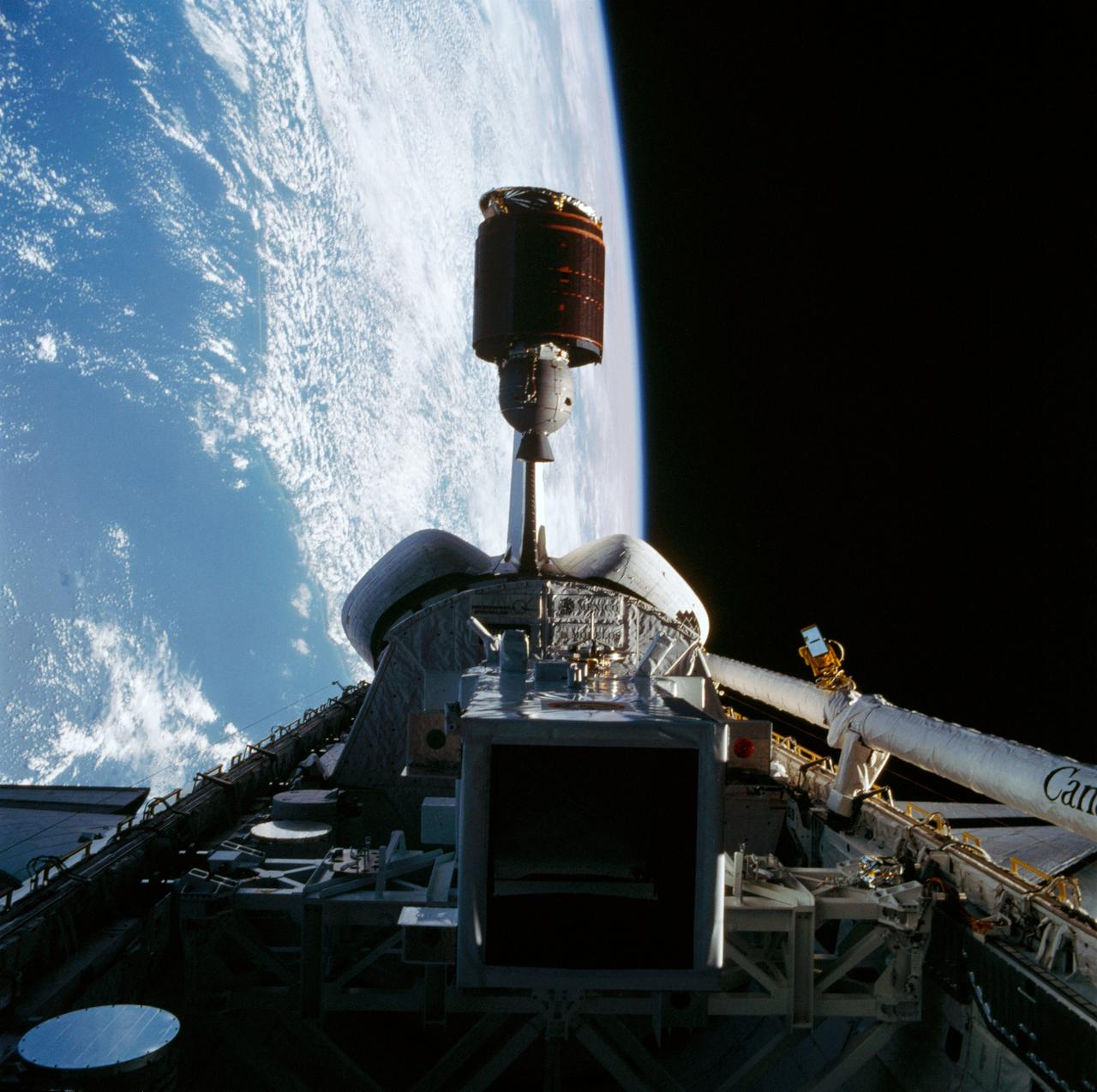
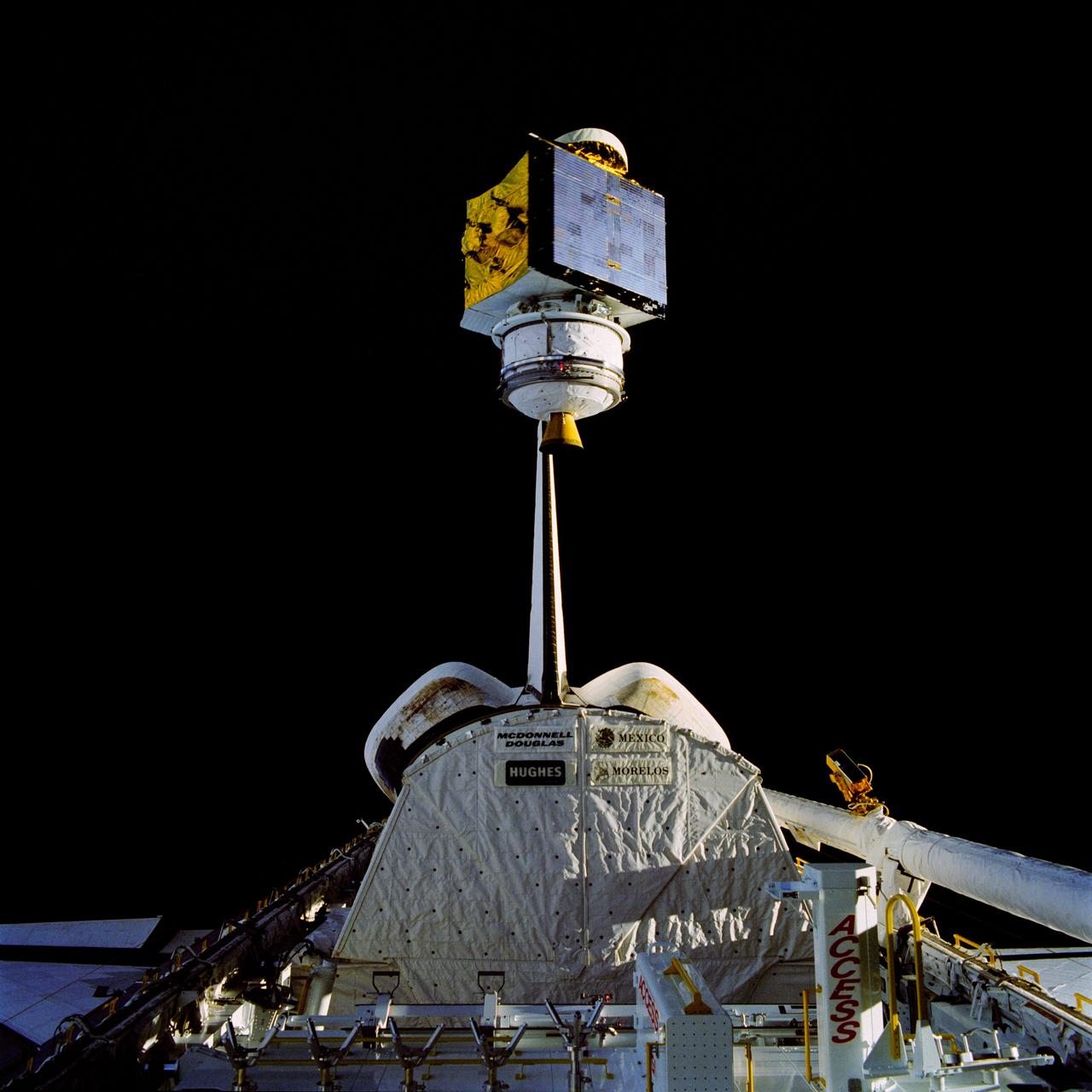
61B-39-031 (27 Nov 1985) --- Deployment of Morelos-B satellite, the second in a series of communications satellites for Mexico, was initiated by Sherwood C. Spring, mission specialist, on November 27, 1985, and recorded on film by a fellow crew member using a 70mm camera.
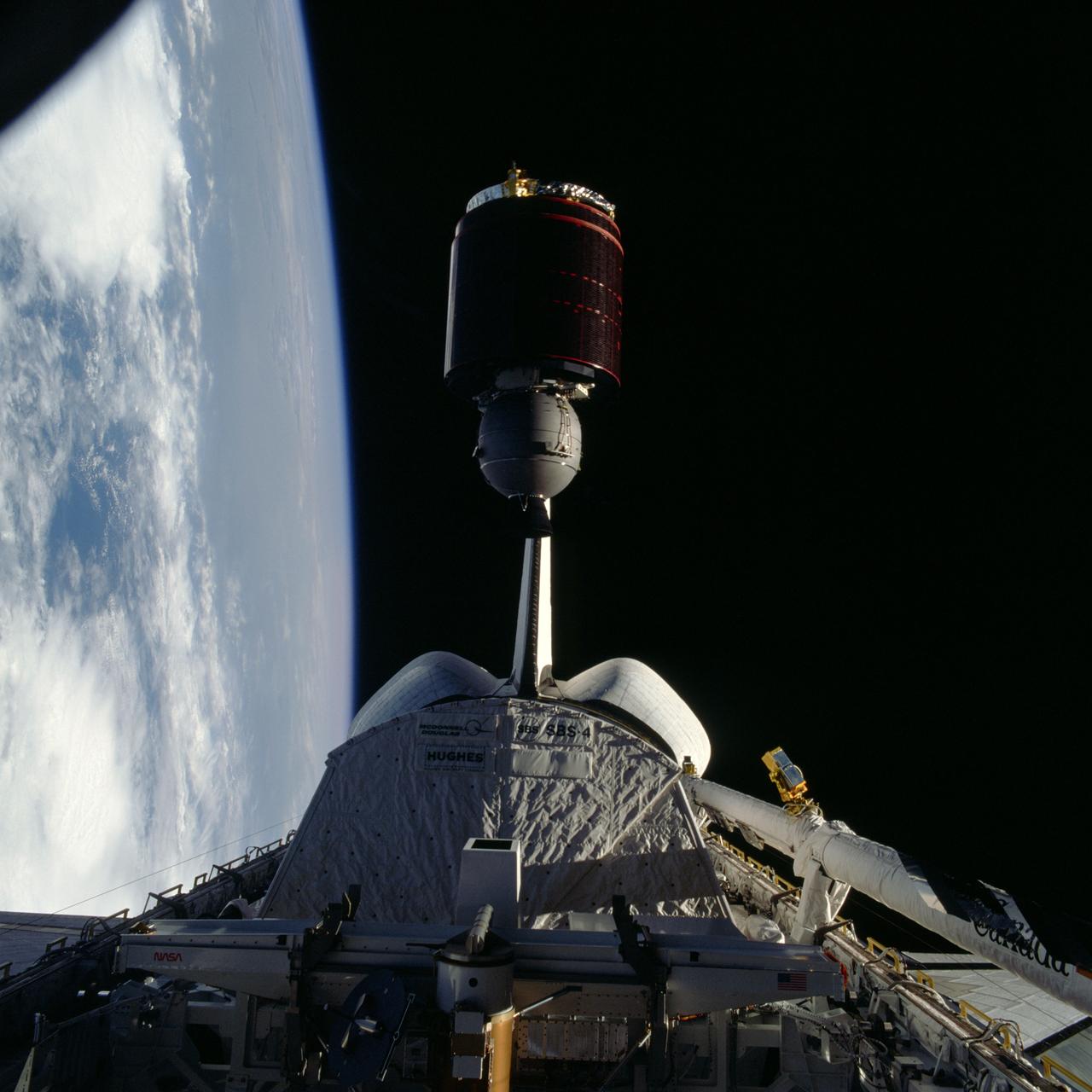

41D-37-050 (1 Sept 1984) --- Telstar, the third of three satellites to be placed into space via the Earth-orbiting Discovery, departs from the cargo bay of the manned vehicle during 41-D's third day in space. The scene was photographed at 9:35 a.m. (CDT), Sept. 1, 1984, with a 70mm handheld hasselblad camera aimed through the windows on the flight deck. Heavy clouds cover much of the water and land mass of Earth in the background.
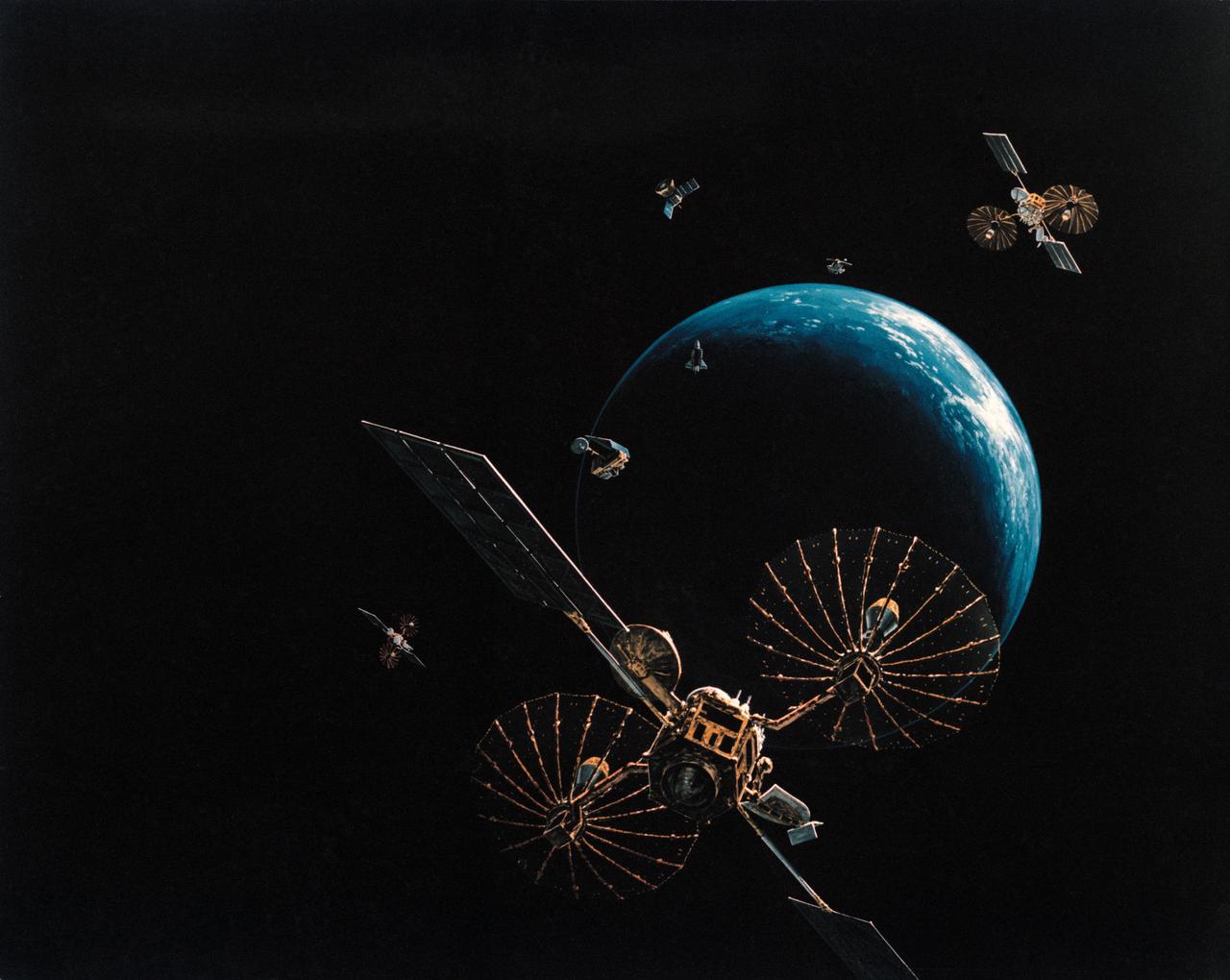

Artist concept shows the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite E (TDRS-E) augmenting a sophisticated TDRS system (TDRSS) communications network after deployment during STS-43 from Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104. TDRS, built by TRW, will be placed in a geosynchronous orbit and after onorbit testing, which requires several weeks, will be designated TDRS-5. The communications satellite will replace TDRS-3 at 174 degrees West longitude. The backbone of NASA's space-to-ground communications, the TDRSs have increased NASA's ability to send and receive data to spacecraft in low-earth orbit to more than 85 percent of the time. Before TDRS, NASA relied solely on a system of ground stations that permitted communications only 15 percent of the time. Increased coverage has allowed onorbit repairs, live television broadcast from space and continuous dialogues between astronaut crews and ground control during critical periods such as Space Shuttle landings.

51I-32-059 (27 August 1985) --- The American Satellite Company (ASC) communications satellite rises from the cargo bay at 6:54 a.m. August 27, 1985.
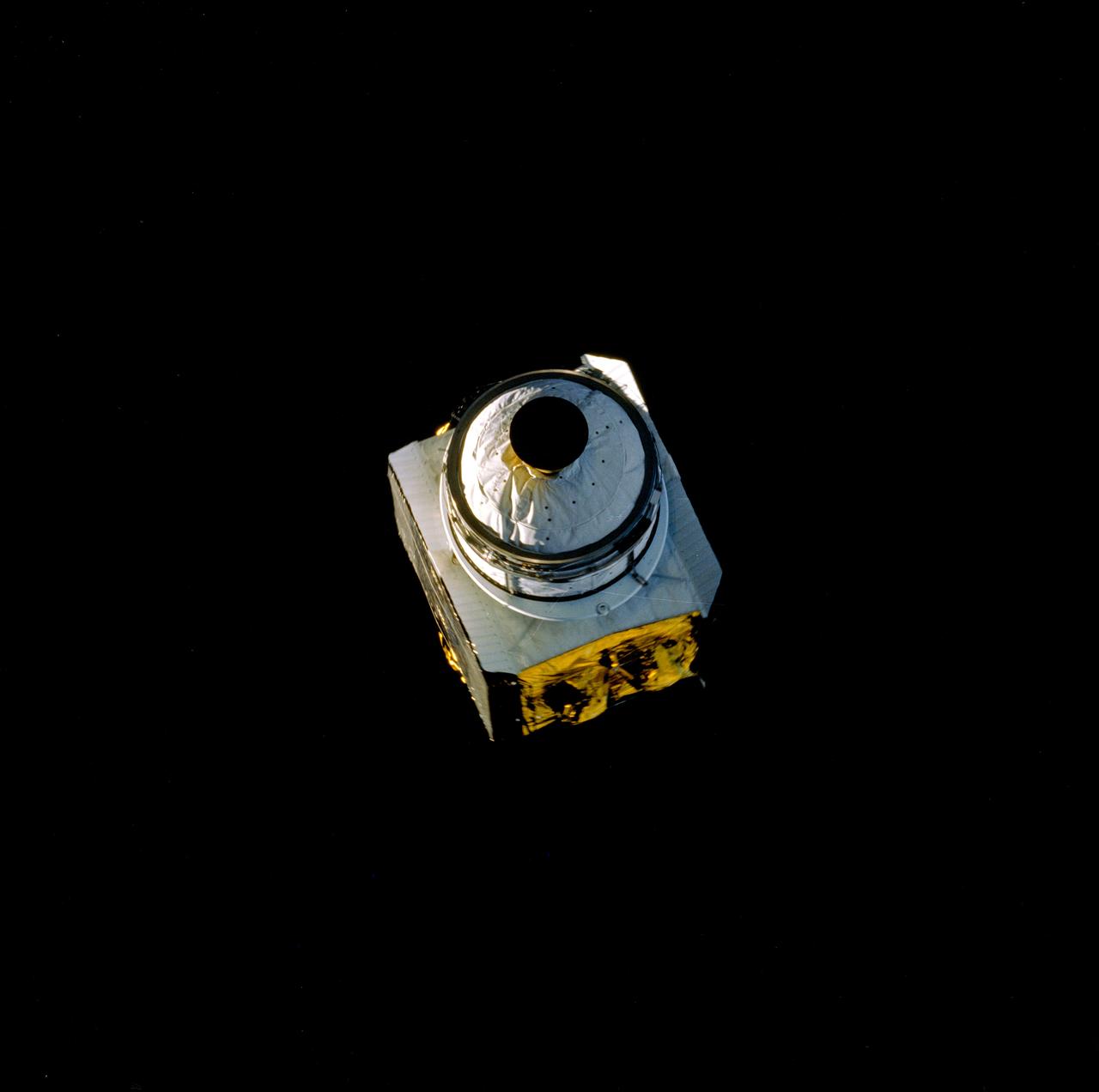

61B-44-054E (28 Nov 1985) --- The 4,1444 pound RCA Satcom K-2 communications satellite is photographed with a 70mm Hasselblad as it moves quickly away from the Atlantis.
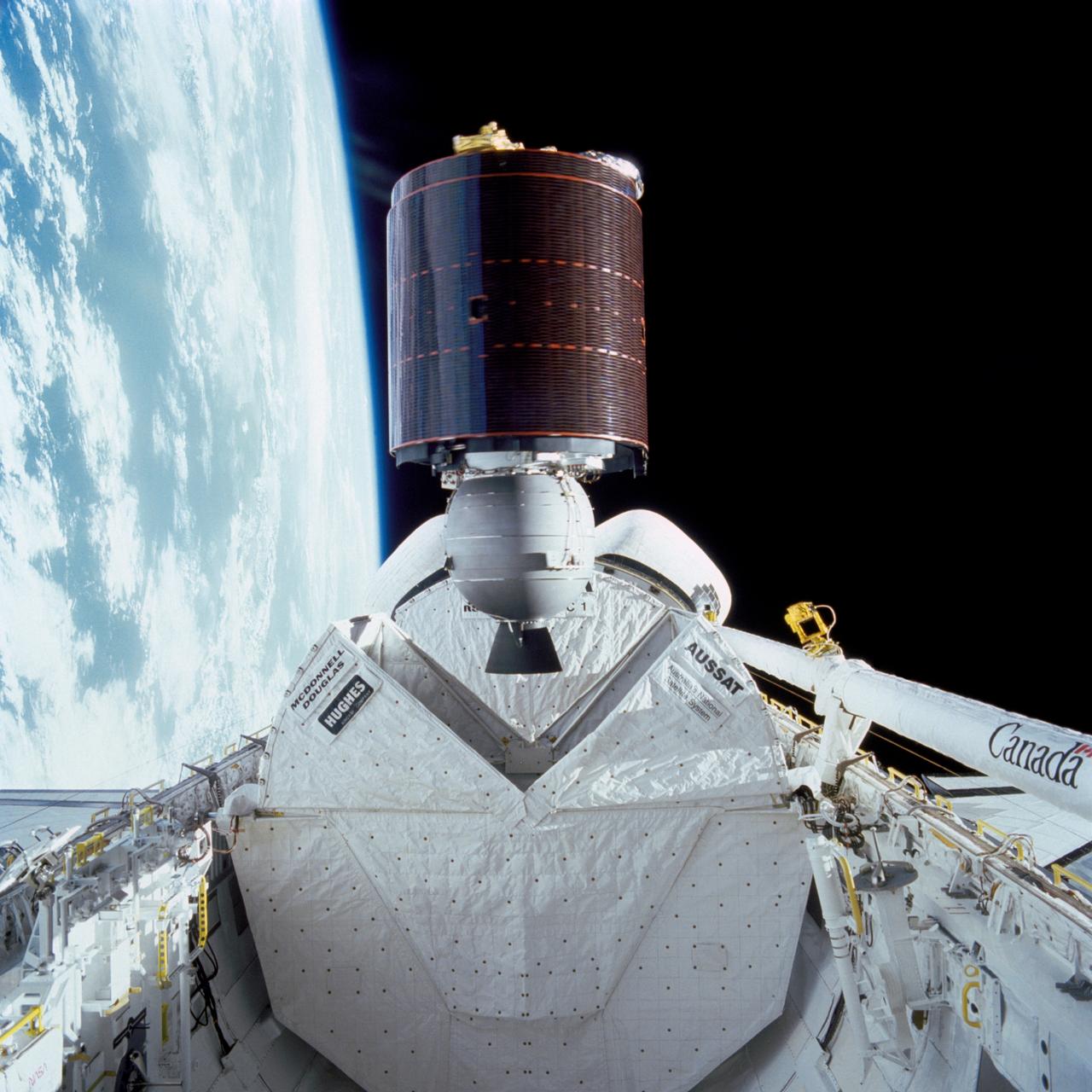

51I-32-023 (27 Aug. 1985) --- Australia's AUSSAT communications satellite is deployed from the payload bay of the space shuttle Discovery on flight day one. A portion of the cloudy surface of Earth can be seen to the left of the frame. Photo credit: NASA
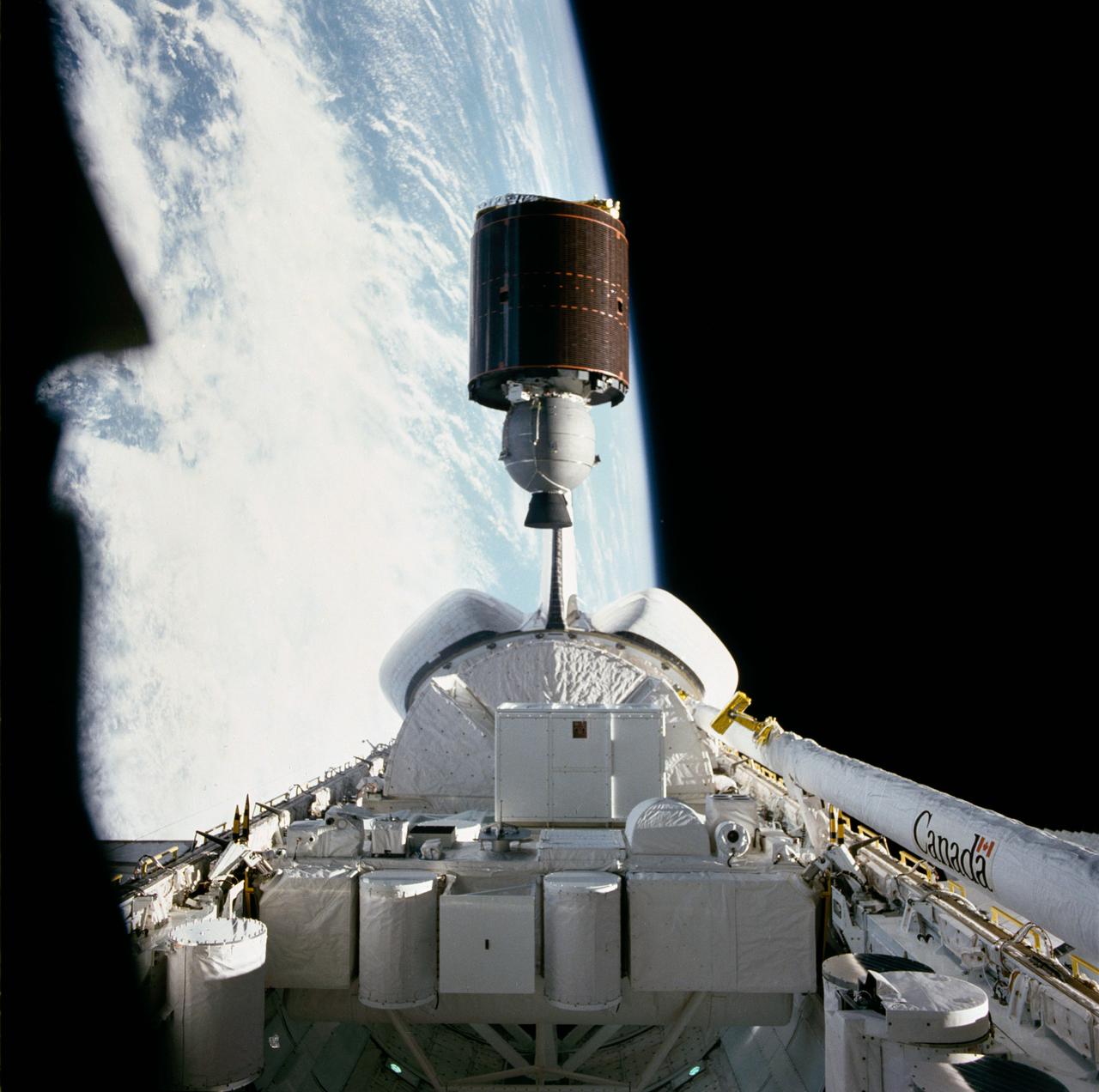

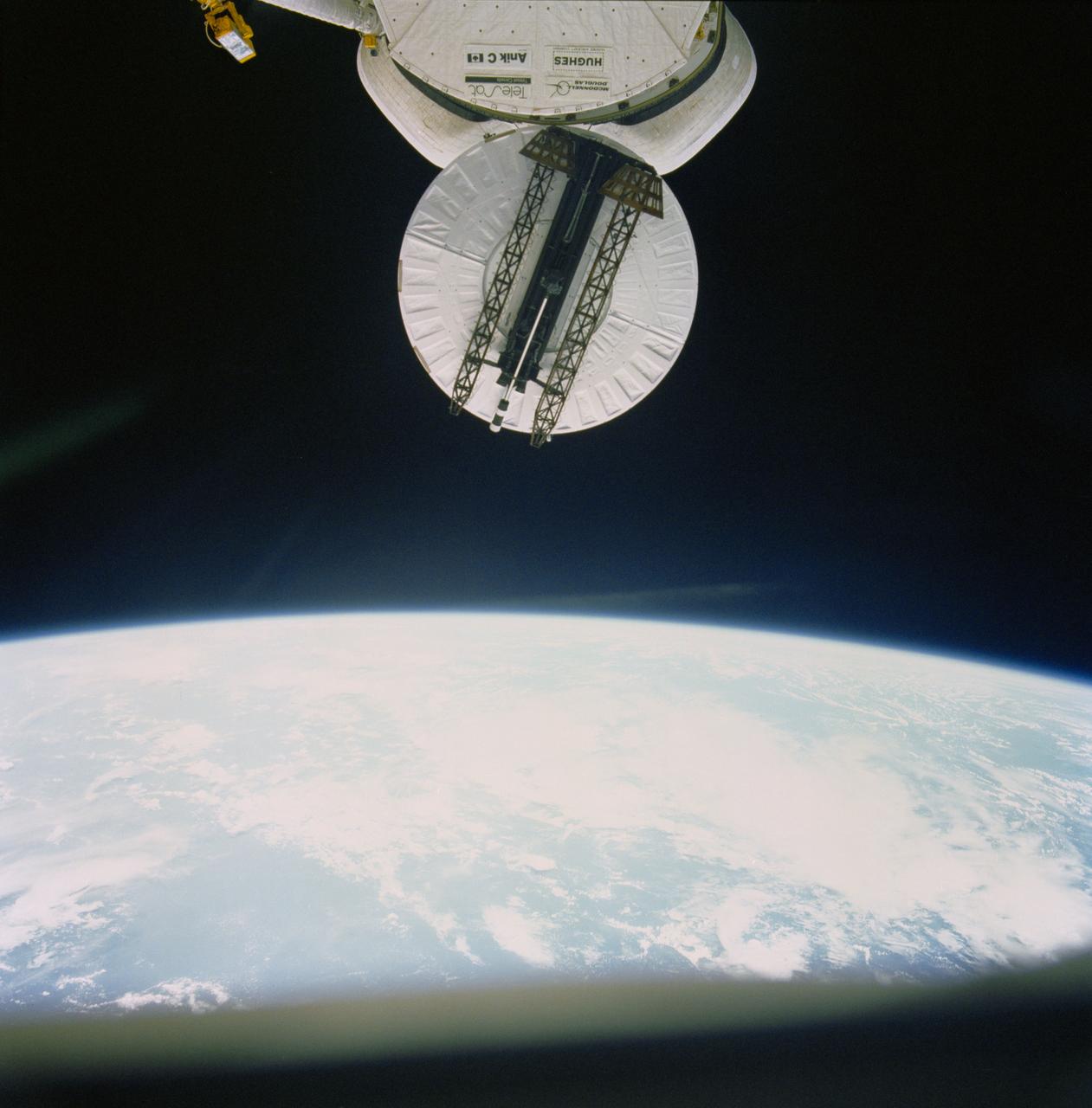
STS007-18-770 (18-24 June 1983) --- Telesat-F communications satellite is just about to clear the vertical stabilizer of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger to begin its way toward its Earth-orbital destination.
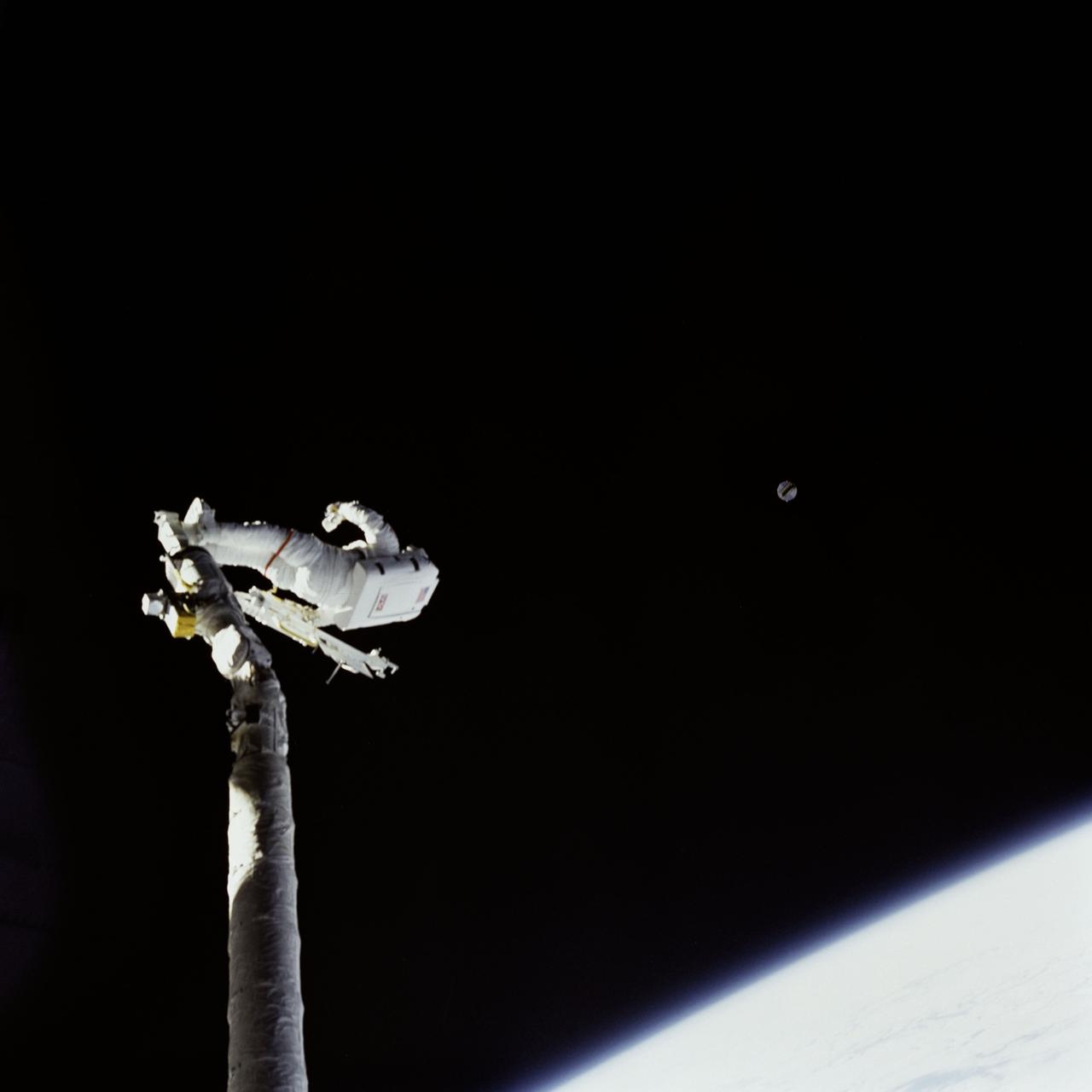

51I-44-081 (1 Sept 1985) --- Astronaut James D. van Hoften on the Discovery's remote manipulator system (RMS) arm visually tracks the distant Syncom IV-3 communications satellite after its second release, on Sept. 1, 1985.
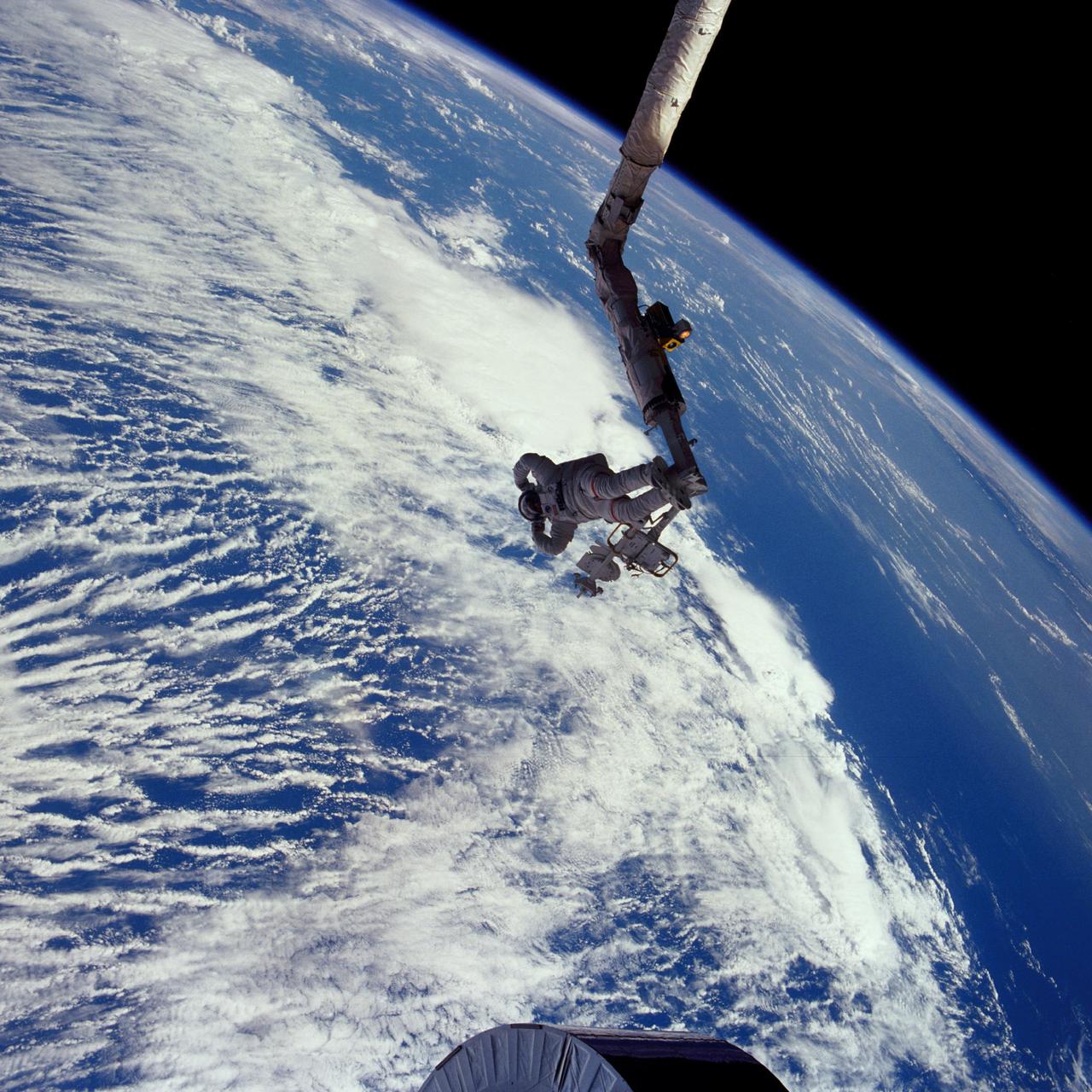

51I-41-086 (1 September 1985) --- Astronaut James D. van Hoften, mission specialist, flexes his muscles in celebration of a triumphant extravehicular task. Clouds over the ocean form the backdrop for this 70mm scene, toward the end of a two-day effort to capture, repair and release the previously errant Syncom IV-3 communications satellite. Van Hoften, anchored to a special foot restraint device on the end of Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS), had just performed the final "shove" that started the relative separation of the Shuttle and the Syncom, which is not far out of frame. He had been joined by astronaut William F. Fisher for the busy two days of EVA.
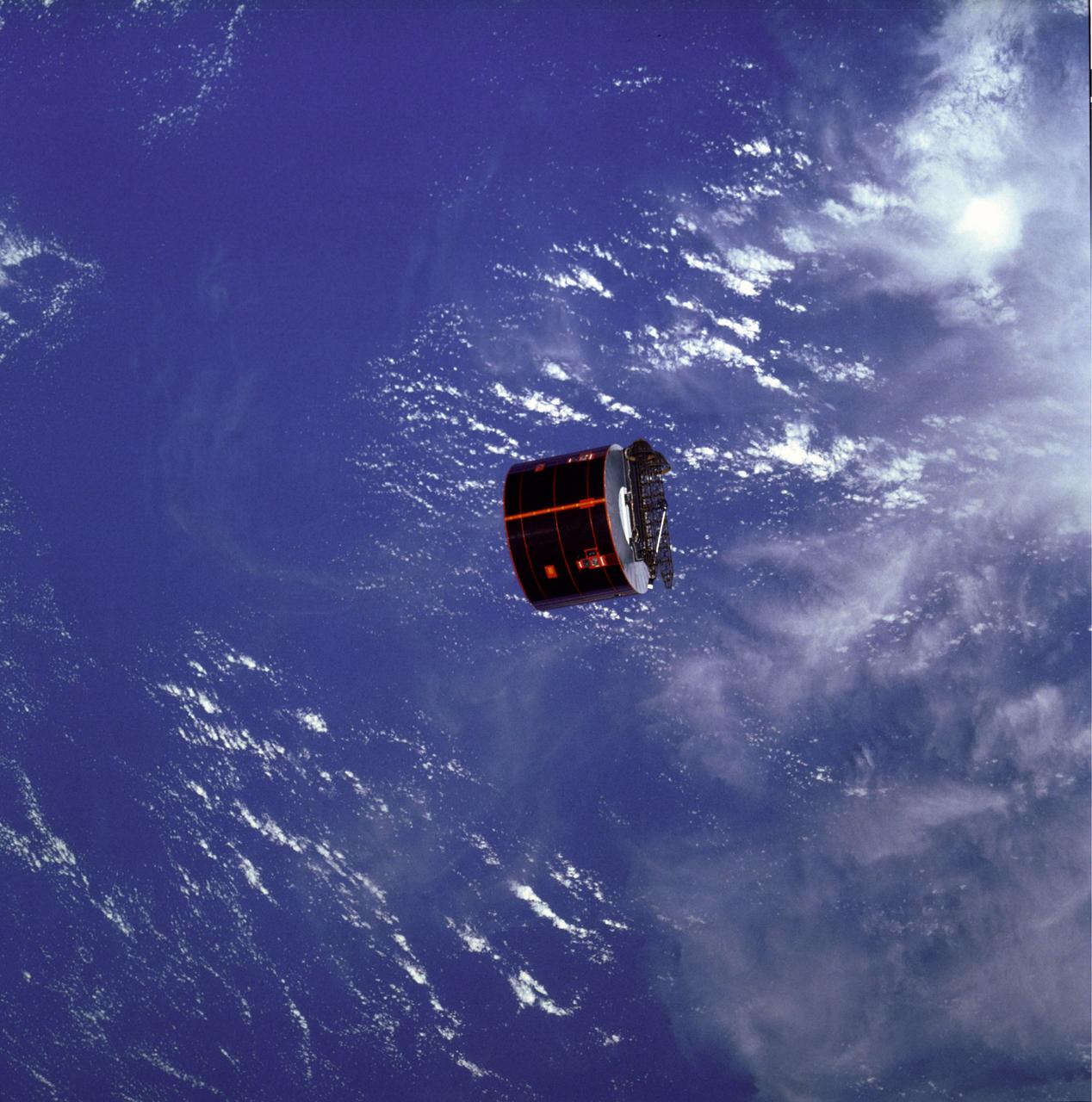

In this photograph the SYNCOM IV-3, also known as LEASAT 3, satellite moves away from the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery. SYNCOM (Hughes Geosynchronous Communication Satellite) provides communication services from geosynchronous orbit, principally to the U.S. Government. The satellite was launched on April 12, 1985, aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery.

Communications Satellite Station with Hoarfrost on Trees

ADVANCED COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY SATELLITE - ACTS - VISITOR CENTER
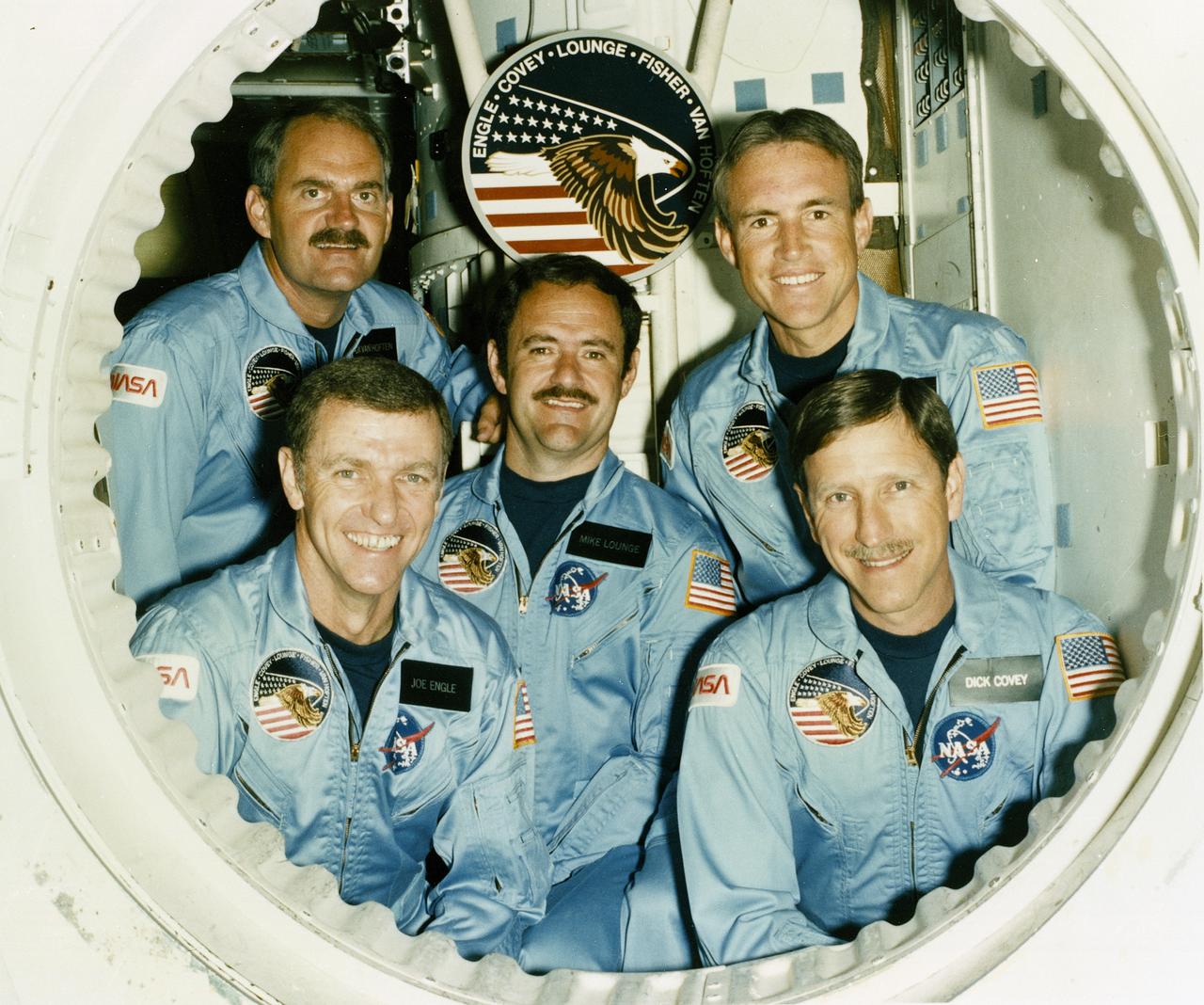

The crew assigned to the STS-51I mission included (front row left to right) Joe H. Engle, commander; and Richard O. Covey, pilot. In the center is John M. (Mike) Lounge, mission specialist. On the back row, from left to right, are mission specialists James D. van Hoften, and William F. Fisher. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on August 27, 1985 at 6:58:01 am (EDT), the STS-51I mission’s primary payloads were three communication satellites: the ASC-1 for the American Satellite Company; the AUSSAT-1, an Australian communications satellite; and the SYNCOM-IV-4, the synchronous communications satellite.
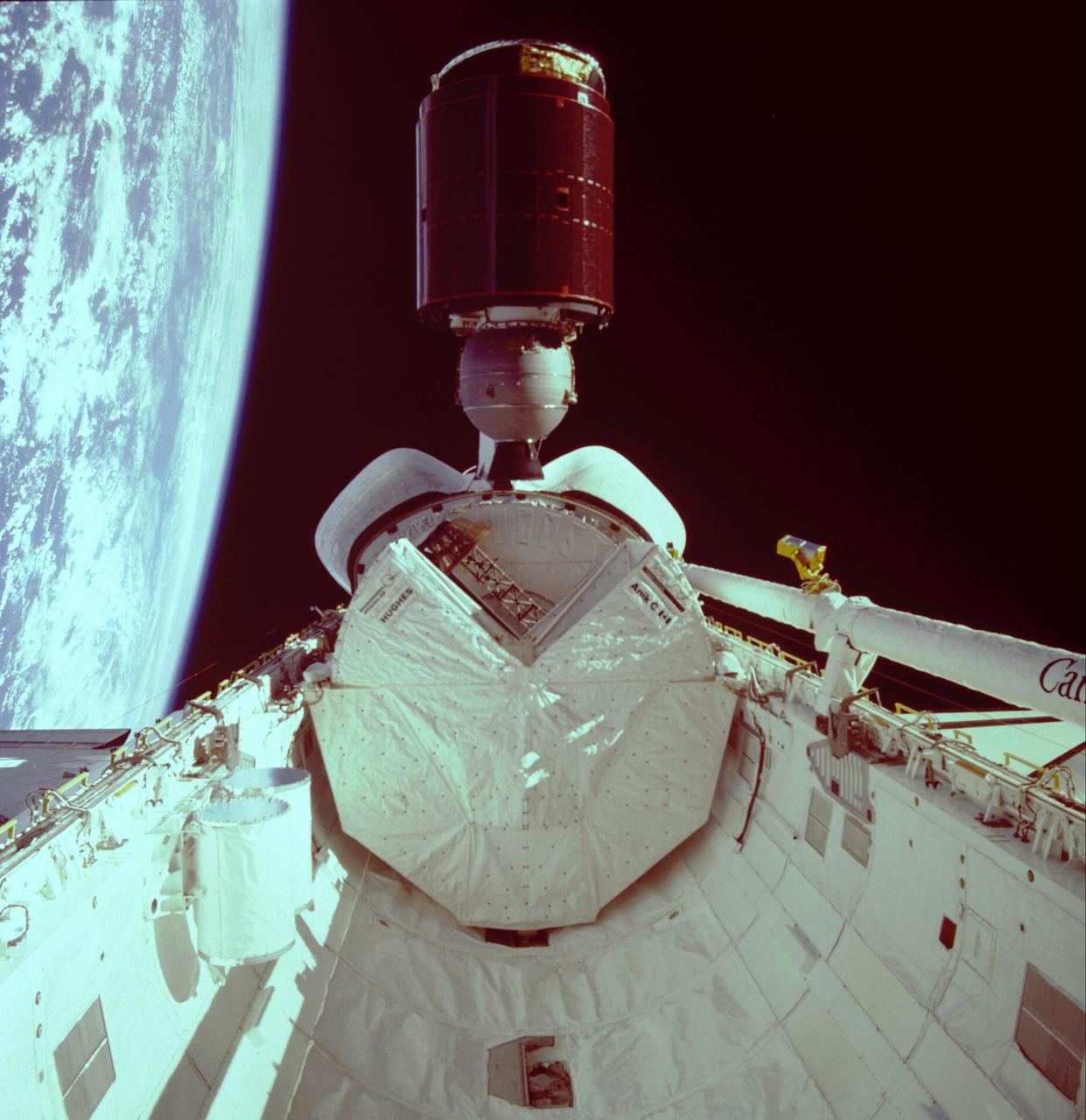

The TELESAT-1, also known as ANIK C-1, satellite is being released from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery during STS-51D, the 16th Shuttle mission. TELESAT-1 is a communication satellite built for Telesat Canada to provide voice and TV coverage of the Earth stations to trans-Canada network. Also shows in this photograph is an anterna for SYNCOM IV-3, also known as LEASAT-3, folded in a stowage. The SYNCOM is the Hughes Geosynchronous Communication Satellite and provides communication services from geosynchronous orbits principally to the U.S. Government. Both satellites were launched on April 12, 1985, aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery.

Astronat Dale A. Gardner achieves a hard dock with the previously spinning Westar VI satellite. Gardner uses a "stinger" device to stabilize the communications satellite.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The TDRS-J satellite arrives at the gantry on Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to be launched Dec. 4 aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

Technicians inspect the twin GRACE Follow-On satellites and their multi-satellite dispenser at the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The satellites were subsequently stacked atop another satellite dispenser containing the five Iridium NEXT communications satellites they will share a ride to orbit with. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22452

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the TDRS-J satellite clears the tower as it launches aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle at the beginning of the launch window at 9:42 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites and 10th overall, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
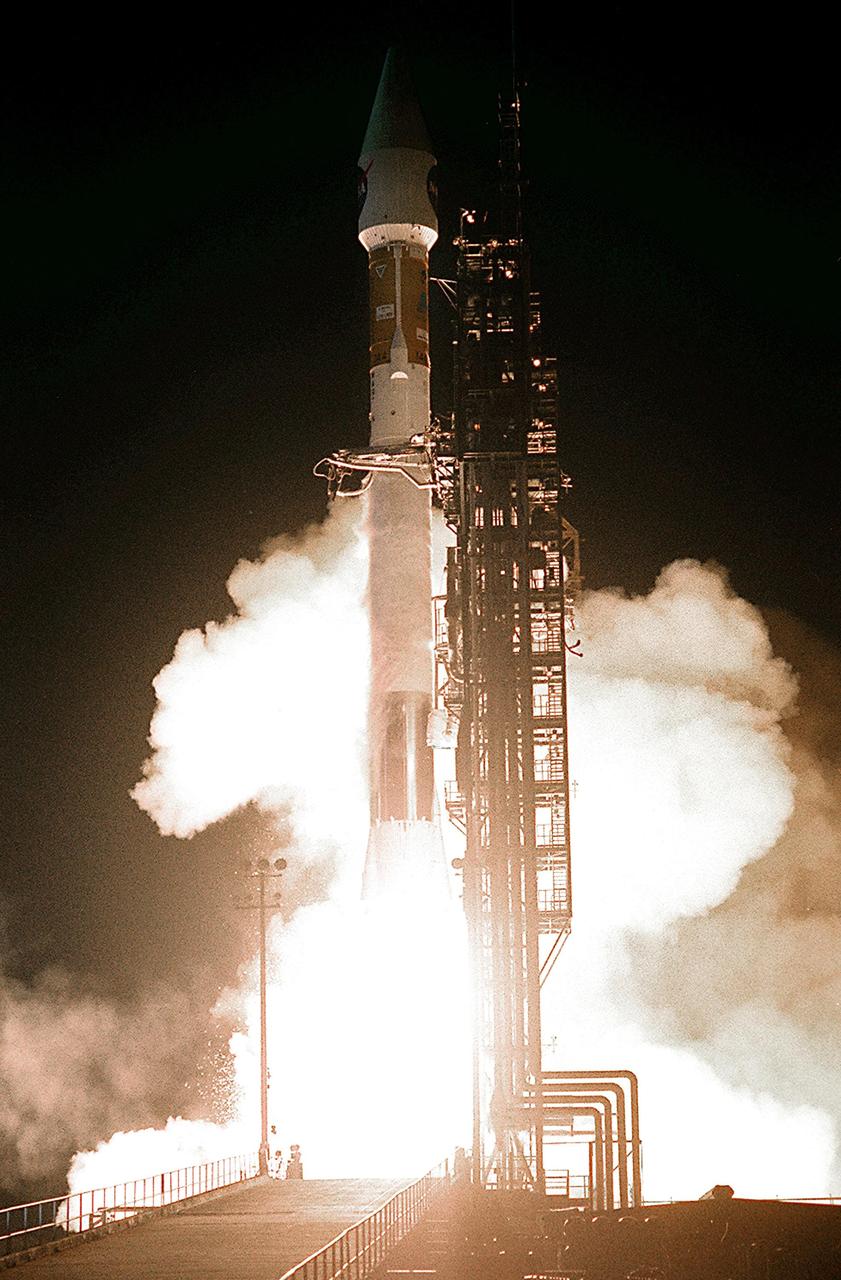

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the TDRS-J satellite launches aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle at the beginning of the launch window at 9:42 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
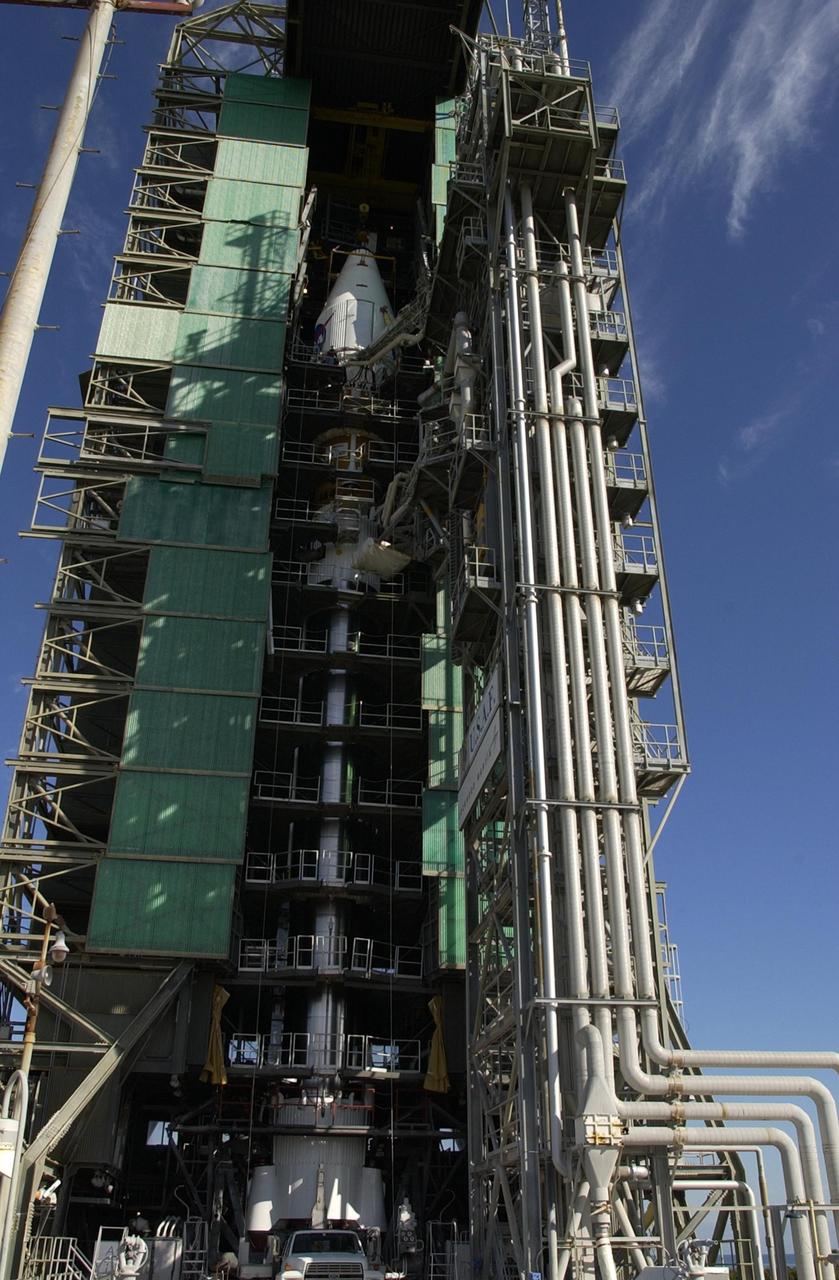

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Atlas IIA launch vehicle with the TDRS-J satellite aboard is ready for launch Dec. 4. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
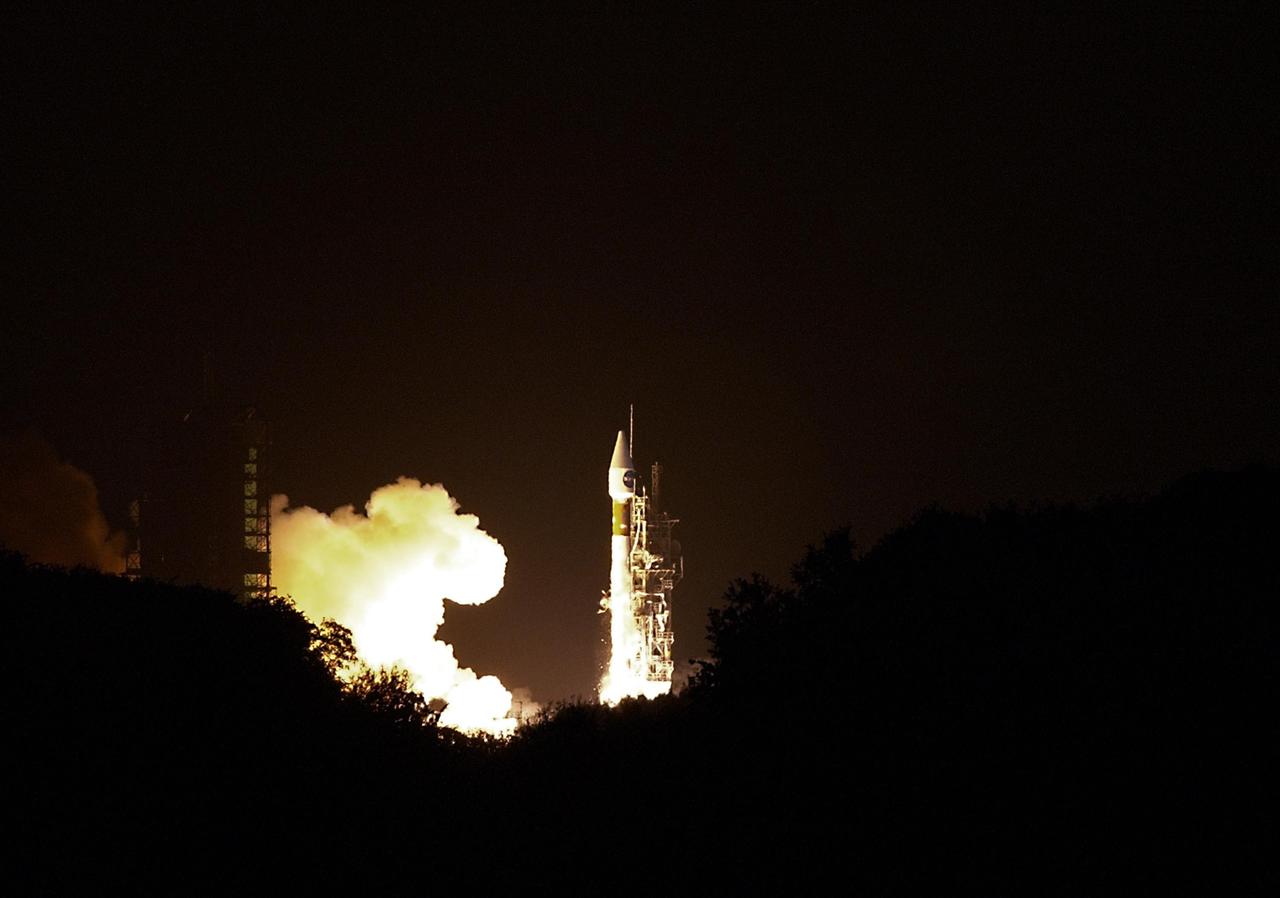

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the TDRS-J satellite launches aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle on Dec. 4 at the beginning of the launch window at 9:42 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
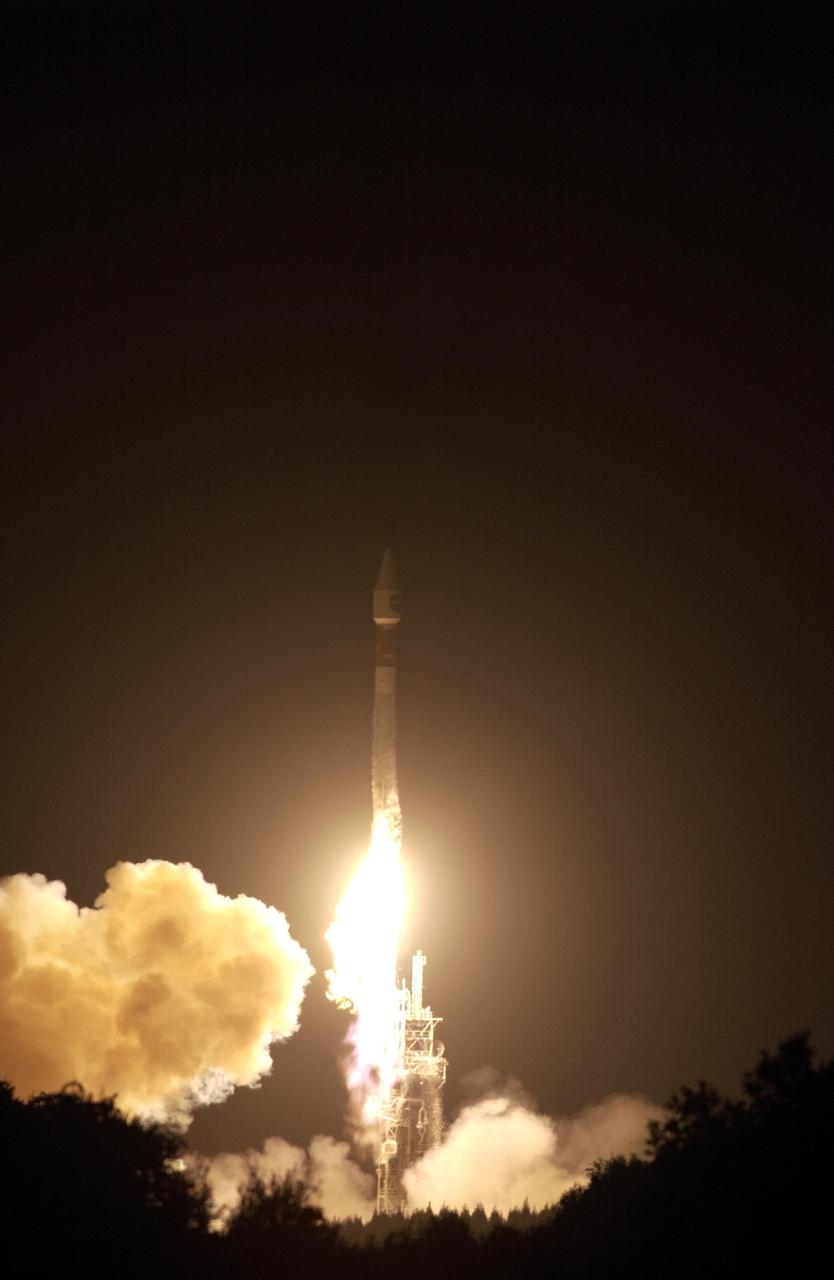

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the TDRS-J satellite launches aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle on Dec. 4 at the beginning of the launch window at 9:42 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
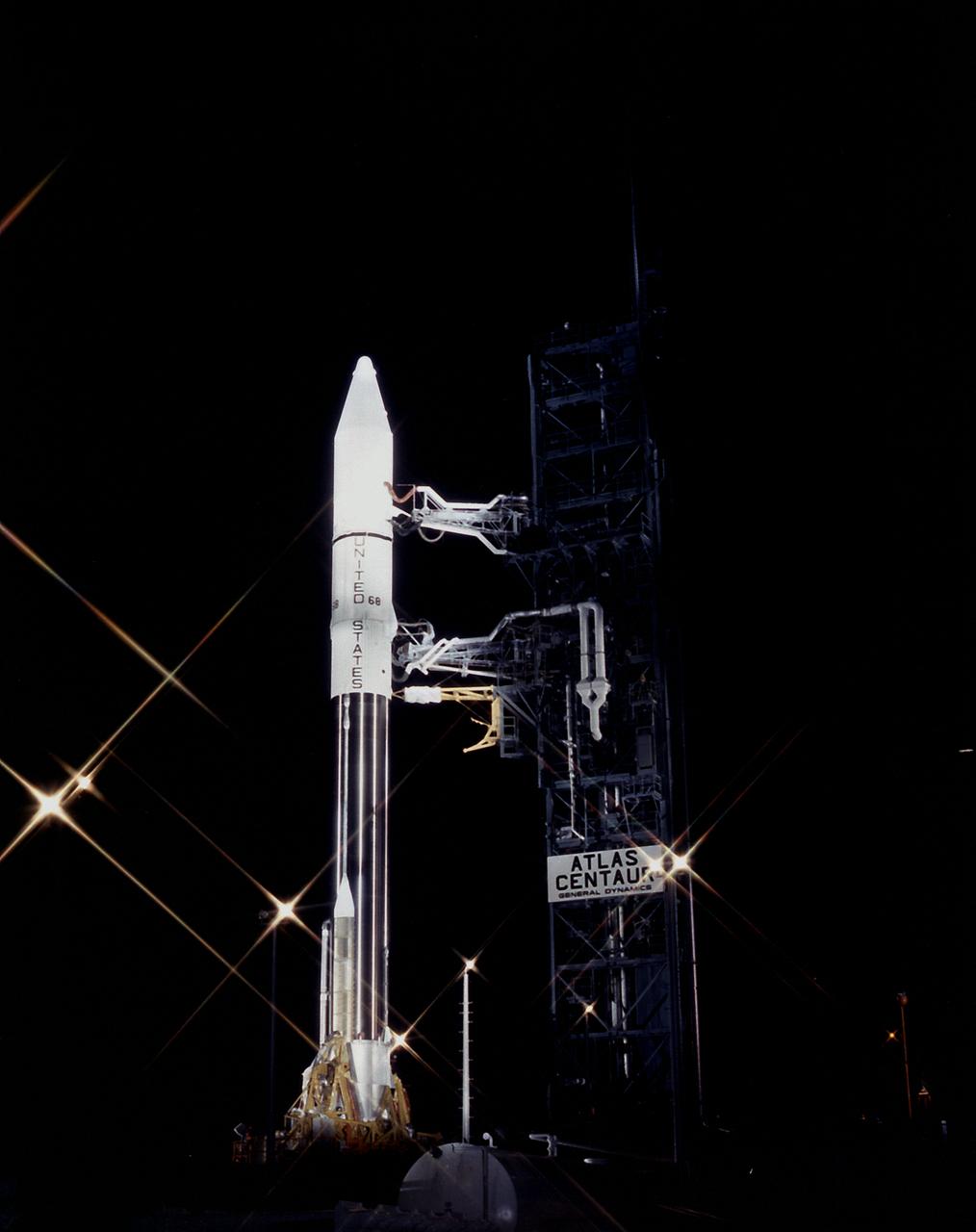

The Atlas-Centaur, AC-68 vehicle, with the FLTSATCOM (F-8 Communication Satellite) aboard, on the Complex 36 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The FLTSATCOM will provide communications for ships and submarines at sea, planes in the air and military ground units throughout the world. It will also provide instant communications between the President and the Commanding Officers.
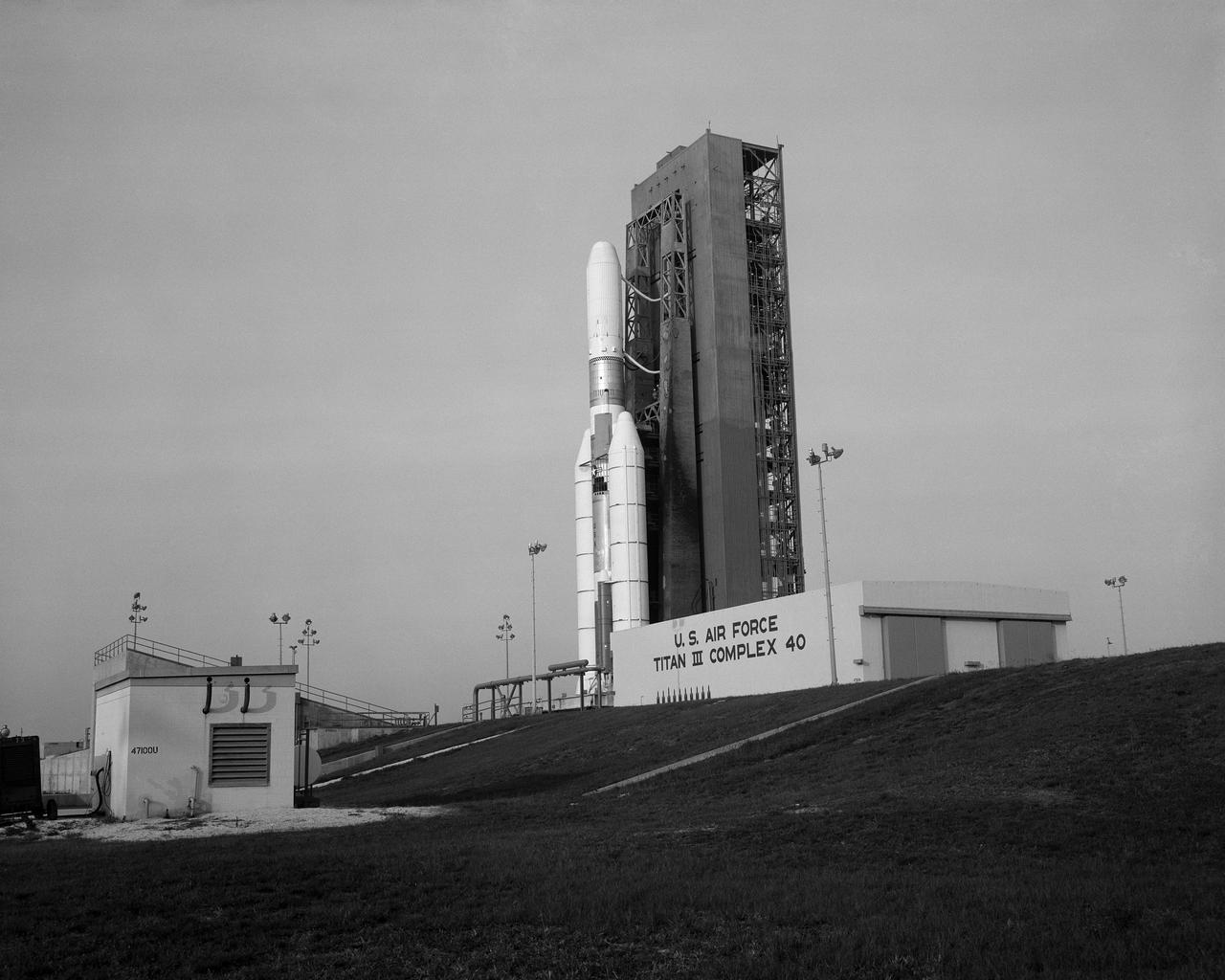

A Titan III-C stands poised on Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for the launch of Application Technology Satellite-F, first in a new generation of NASA communications satellites. (1.3-2)
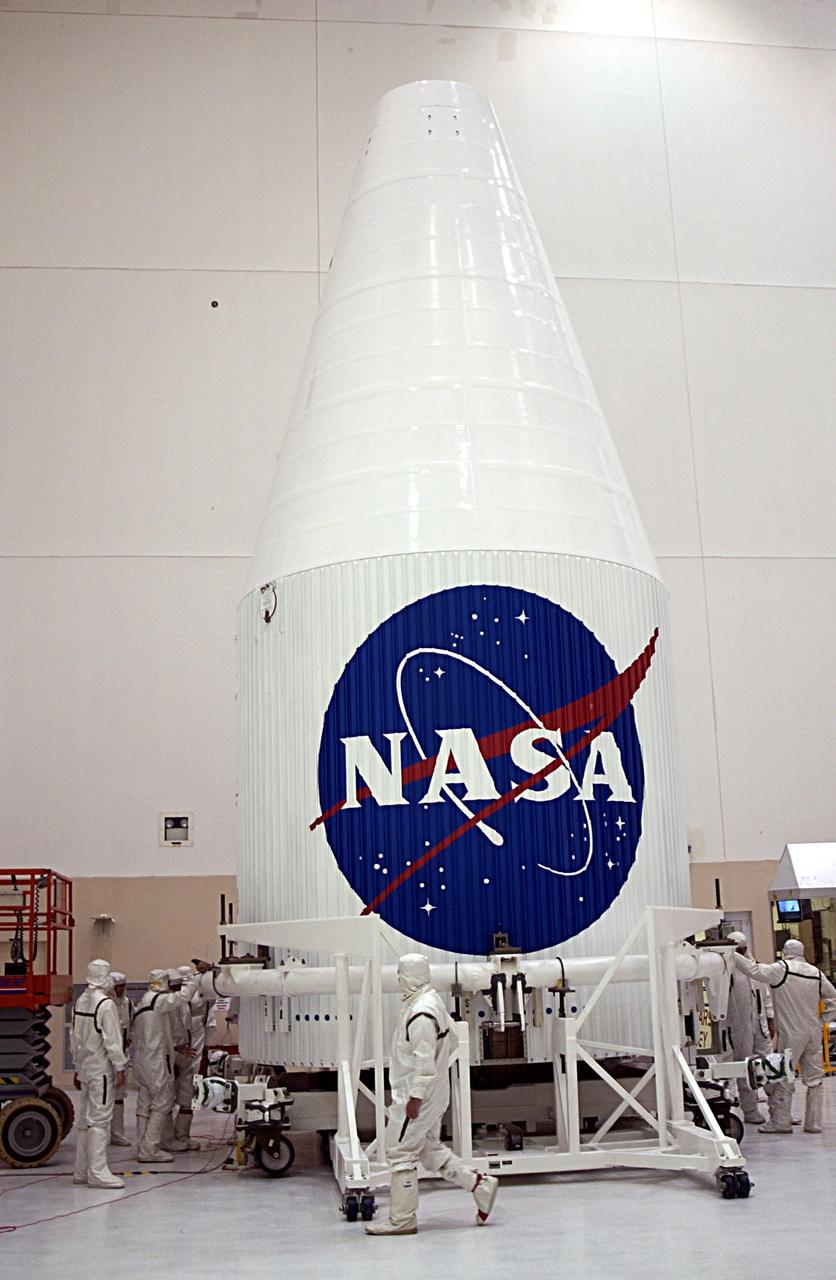

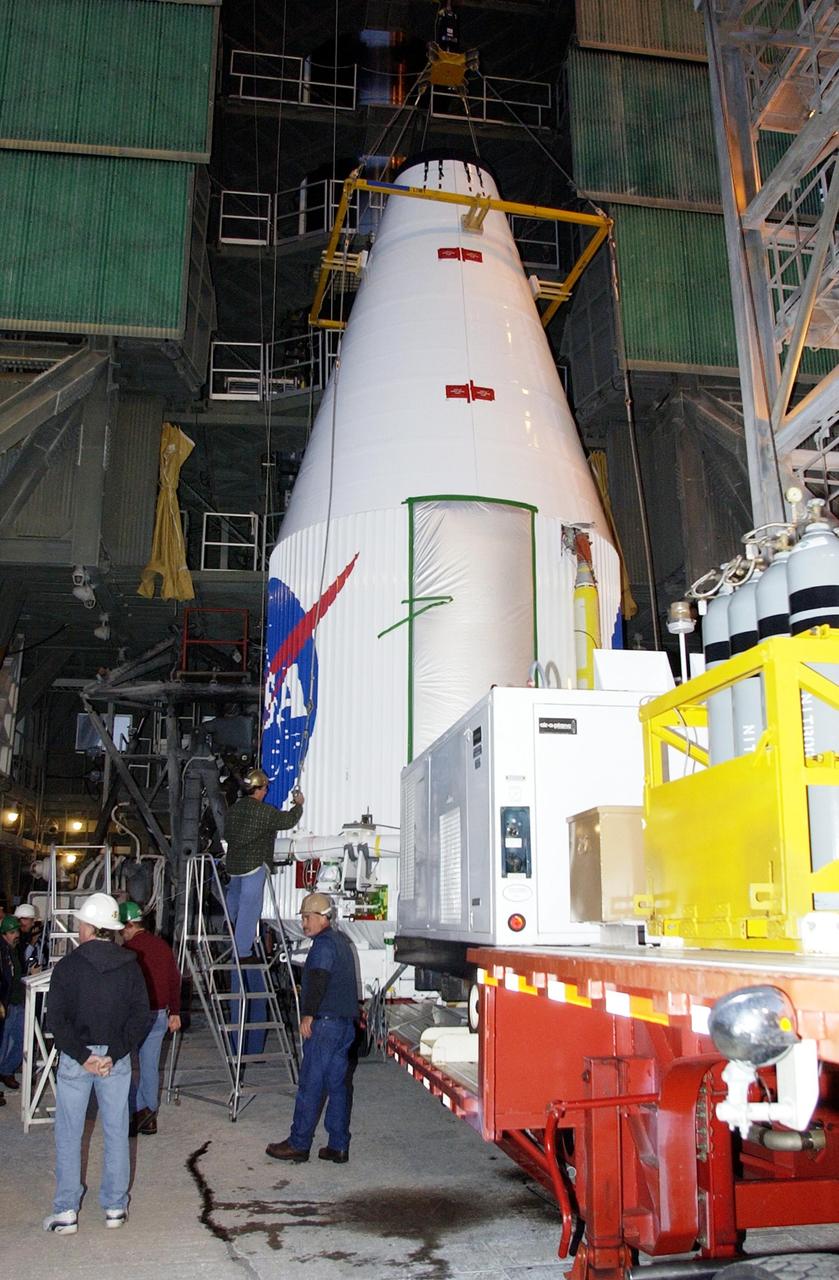
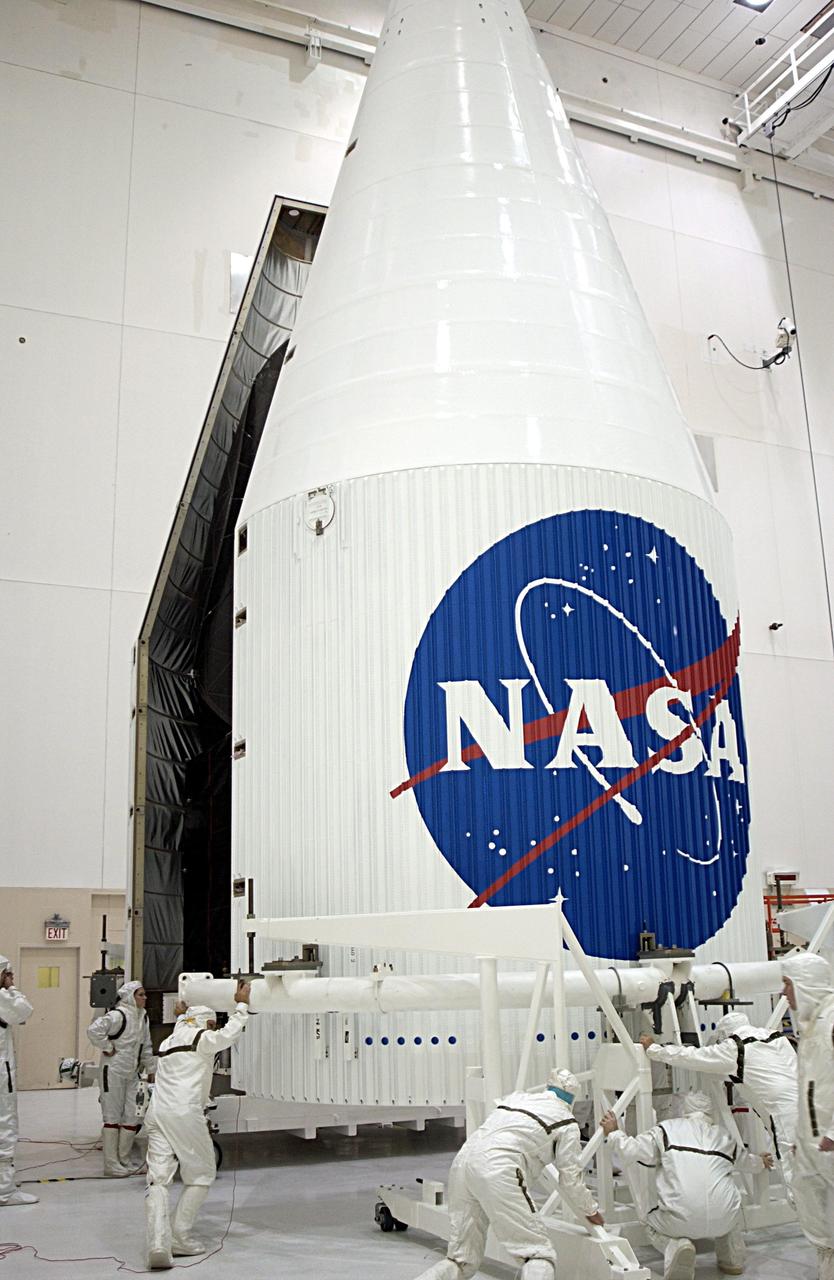
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J satellite is fully encapsulated and ready for transport to Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. There it will be mated with the Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket for launch on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
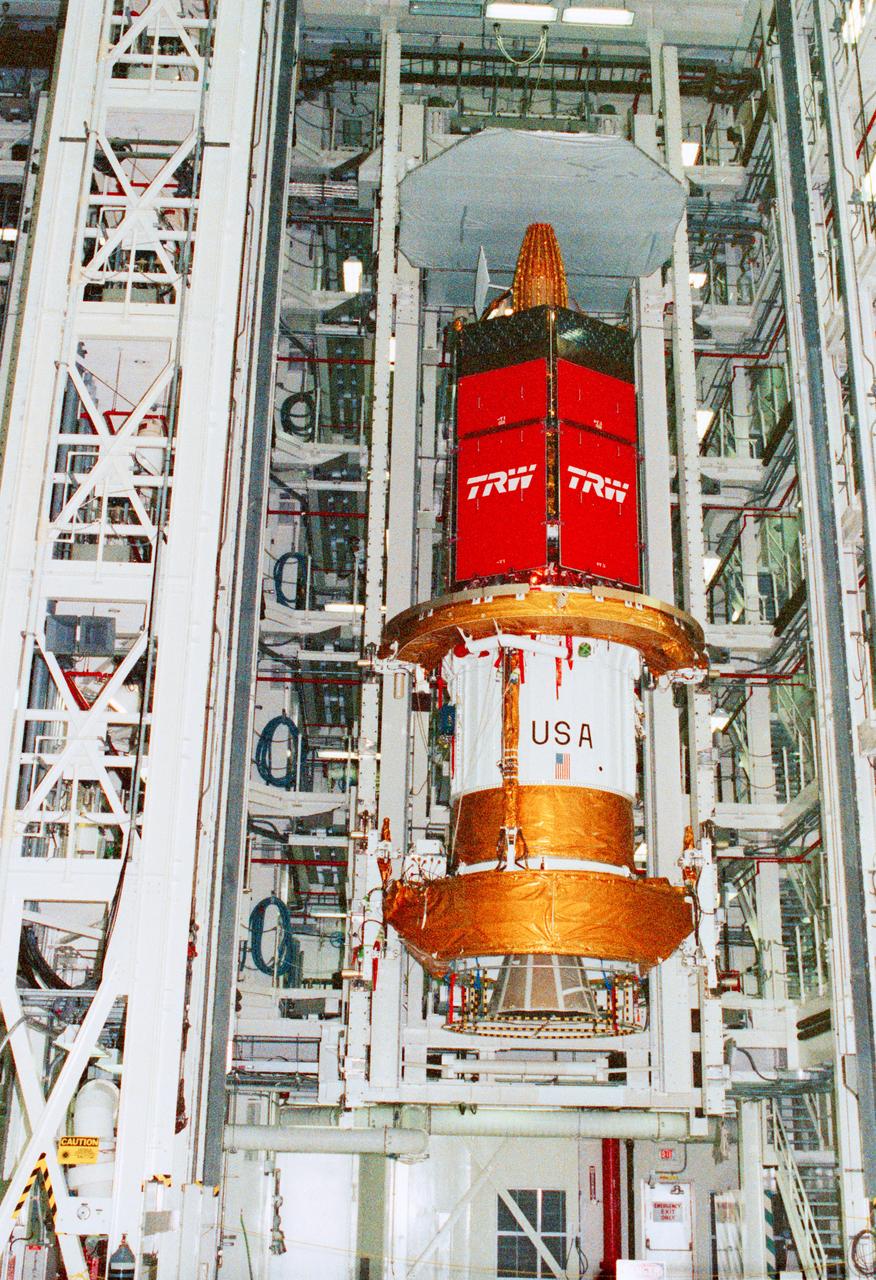
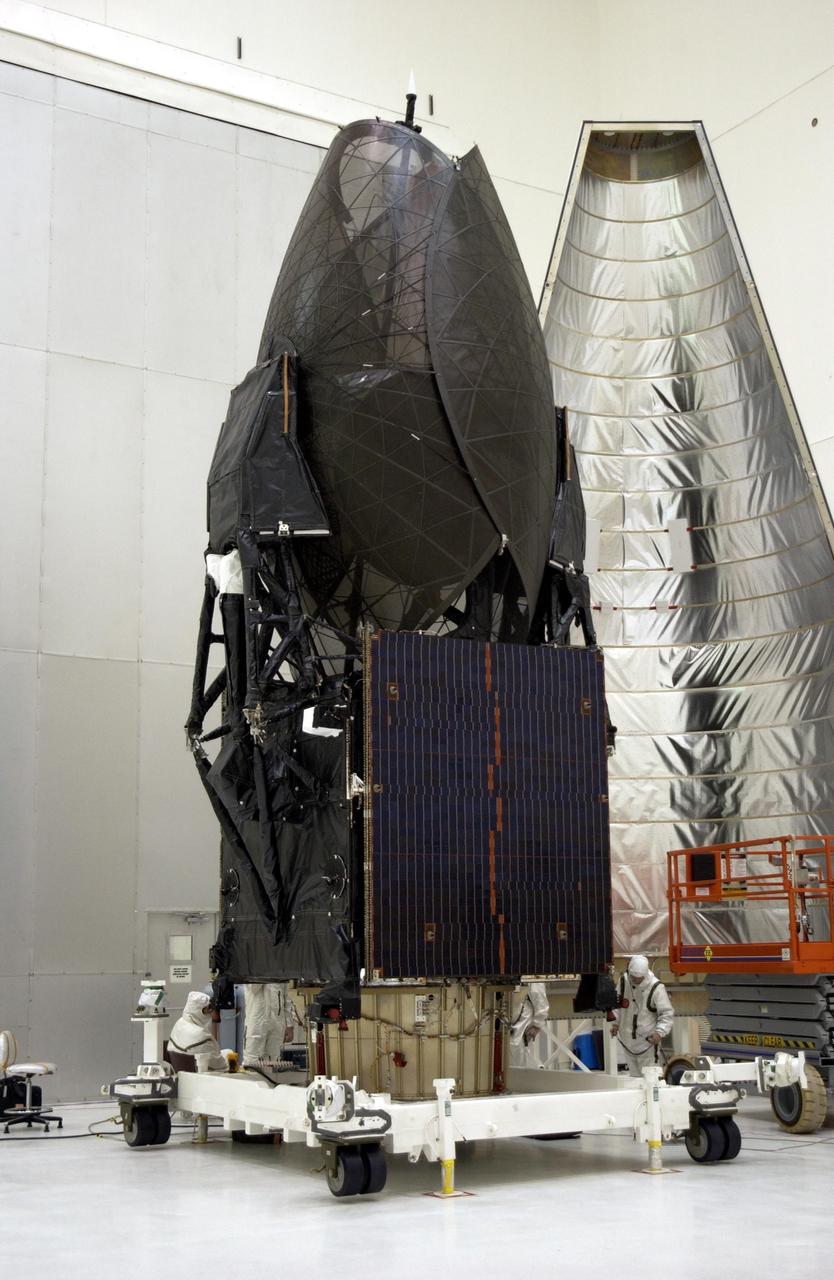
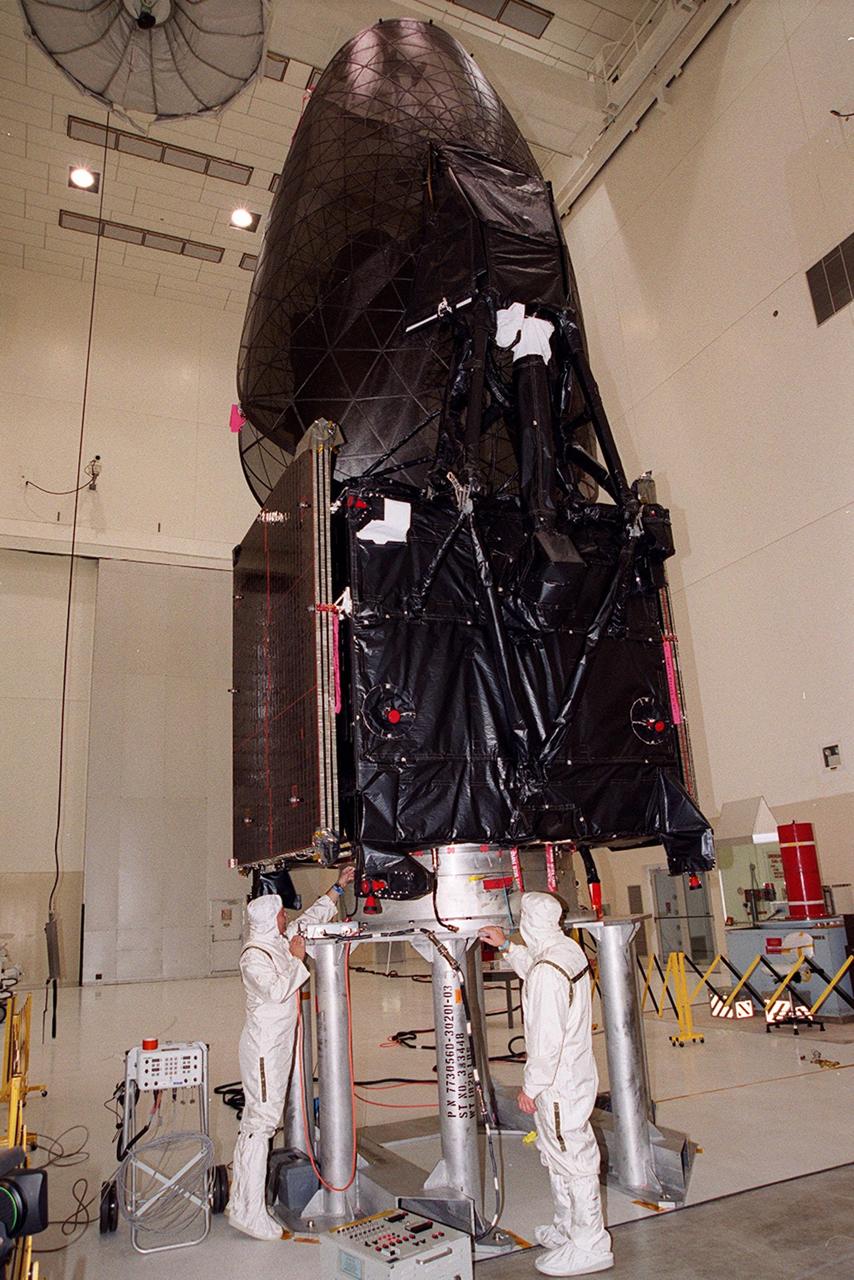
STS-43 Tracking and Data Relay Satellite E (TDRS-E) undergoes preflight processing in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC's) Vertical Processing Facility (VPF) before being loaded into a payload canister for transfer to the launch pad and eventually into Atlantis', Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104's, payload bay (PLB). This side of the TDRS-E will rest at the bottom of the PLB therefore the airborne support equipment (ASE) forward frame keel pin (at center of spacecraft) and the umbilical boom running between the two ASE frames are visible. The solar array panels are covered with protective TRW shields. Above the shields the stowed antenna and solar sail are visible. The inertial upper stage (IUS) booster is the white portion of the spacecraft and rests in the ASE forward frame and ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) frame (at the bottom of the IUS). The IUS booster nozzle extends beyond the AFTA frame. View provided by KSC with alternate number KSC-91PC-1079.

View of the Syncom-IV (LEASAT) satellite from the flight deck window taken by Astronaut S. David Griggs.
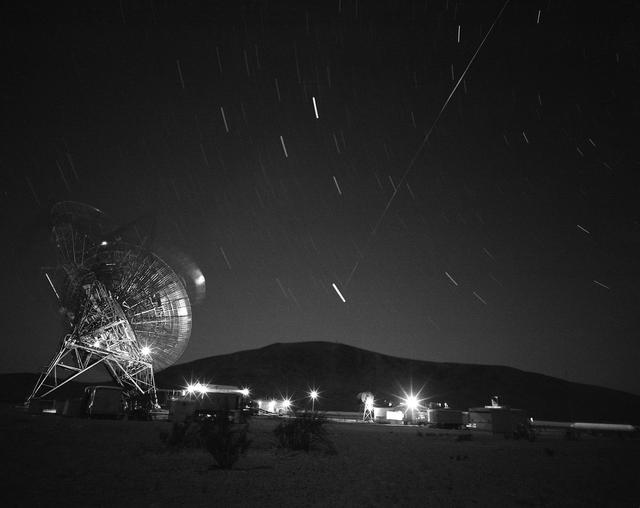

This archival image was released as part of a gallery comparing JPL’s past and present, commemorating the 80th anniversary of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on Oct. 31, 2016. This photograph shows the first pass of Echo 1, NASA's first communications satellite, over the Goldstone Tracking Station managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, California, in the early morning of Aug. 12, 1960. The movement of the antenna, star trails (shorter streaks), and Echo 1 (the long streak in the middle) are visible in this image. Project Echo bounced radio signals off a 10-story-high, aluminum-coated balloon orbiting the Earth. This form of "passive" satellite communication -- which mission managers dubbed a "satelloon" -- was an idea conceived by an engineer from NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, and was a project managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. JPL's role involved sending and receiving signals through two of its 85-foot-diameter (26-meter-diameter) antennas at the Goldstone Tracking Station in California's Mojave Desert. The Goldstone station later became part of NASA's Deep Space Network. JPL, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Deep Space Network for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21114
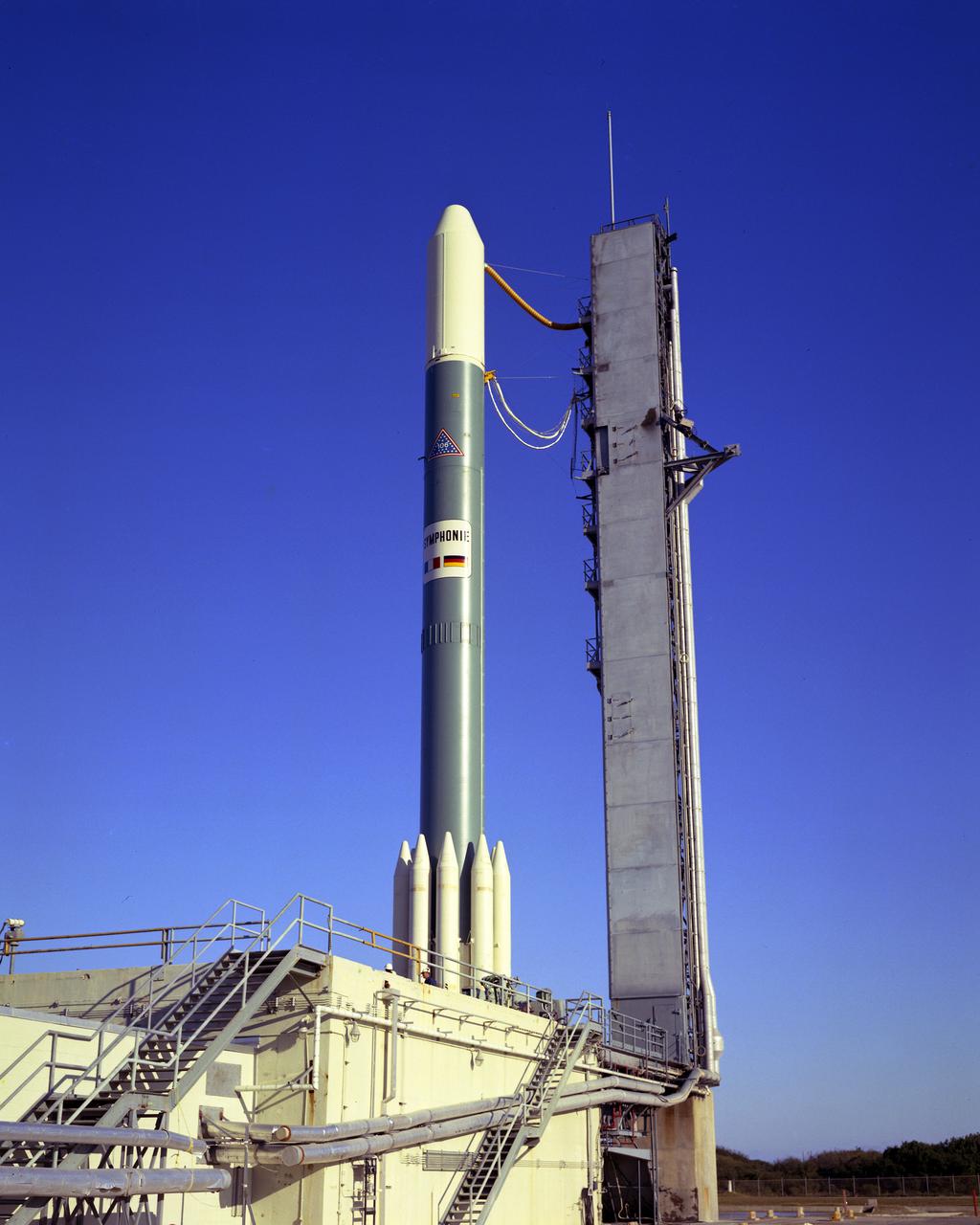

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Prelaunch of Symphonie-A on Complex 17-B, a communications satellite for Franco-German industrial consortium. Photo credit: NASA
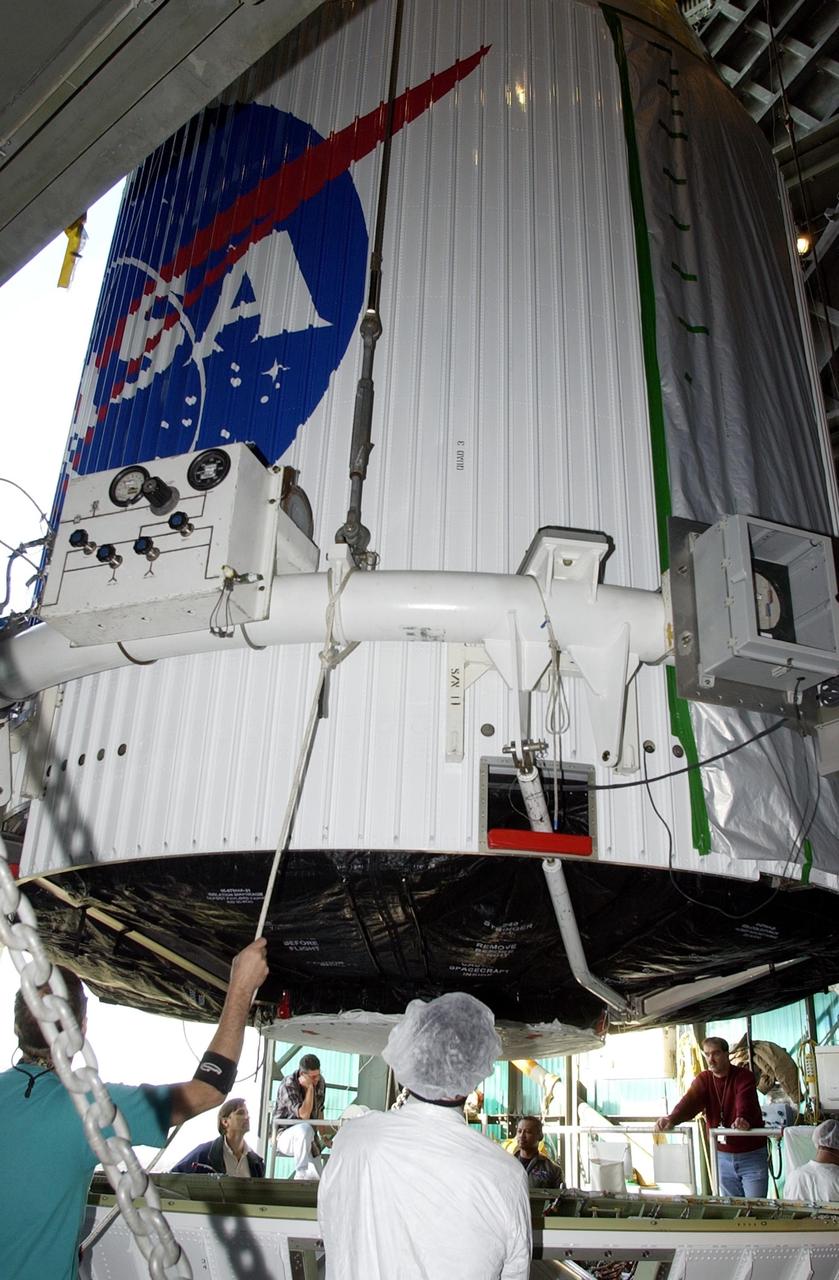

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The encapsulated TDRS-J satellite is lowered toward the Atlas IIA launch vehicle on Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to be launched Dec. 4 aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017..
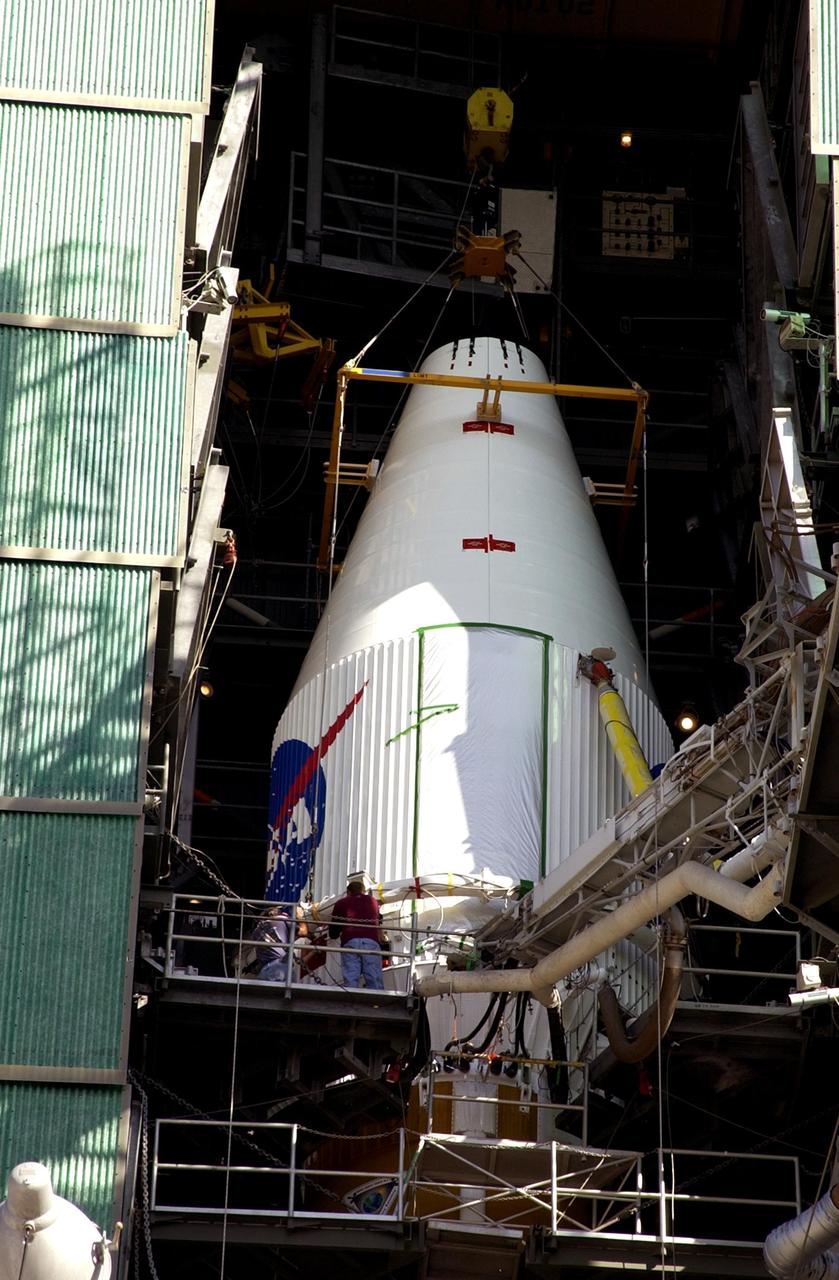

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The encapsulated TDRS-J satellite is mated with the Atlas IIA launch vehicle on Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to be launched Dec. 4 aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
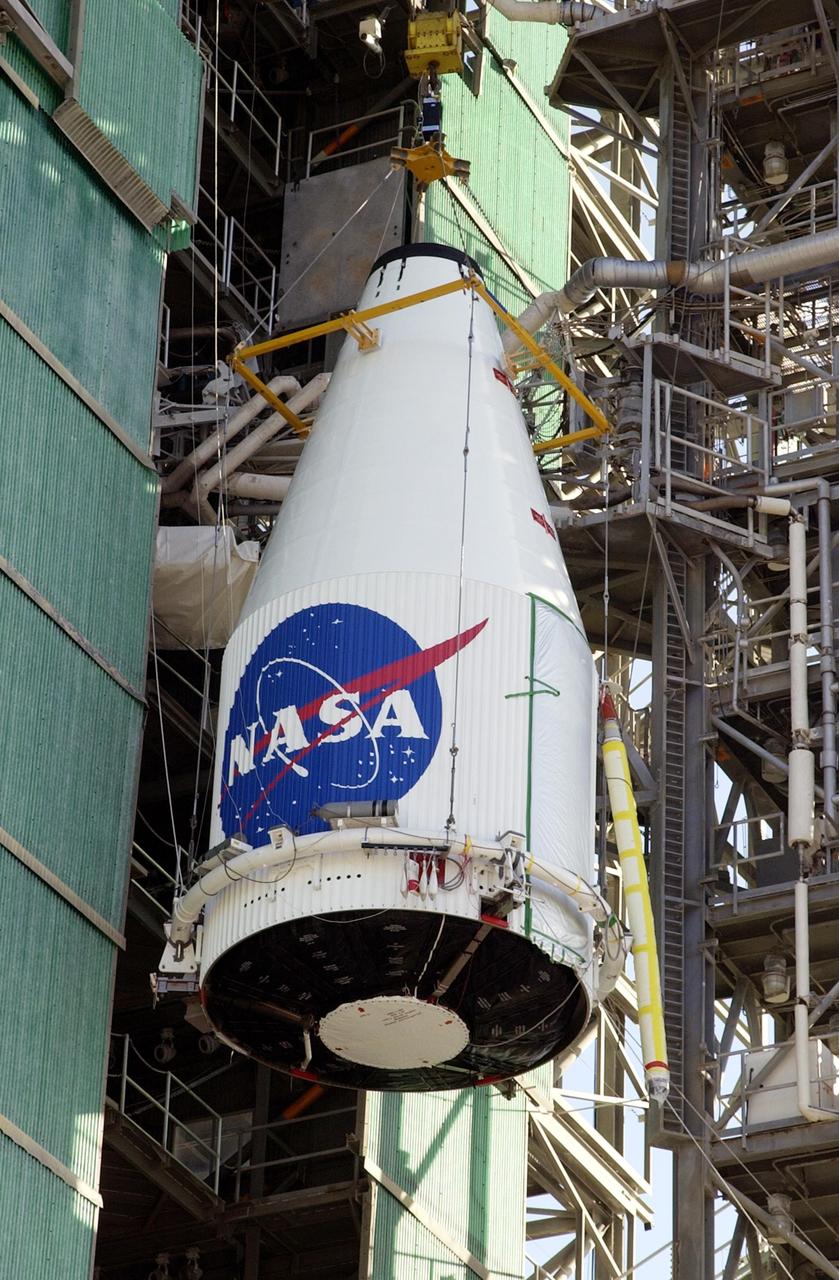

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J satellite is lifted up the gantry on Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to be launched Dec. 4 aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
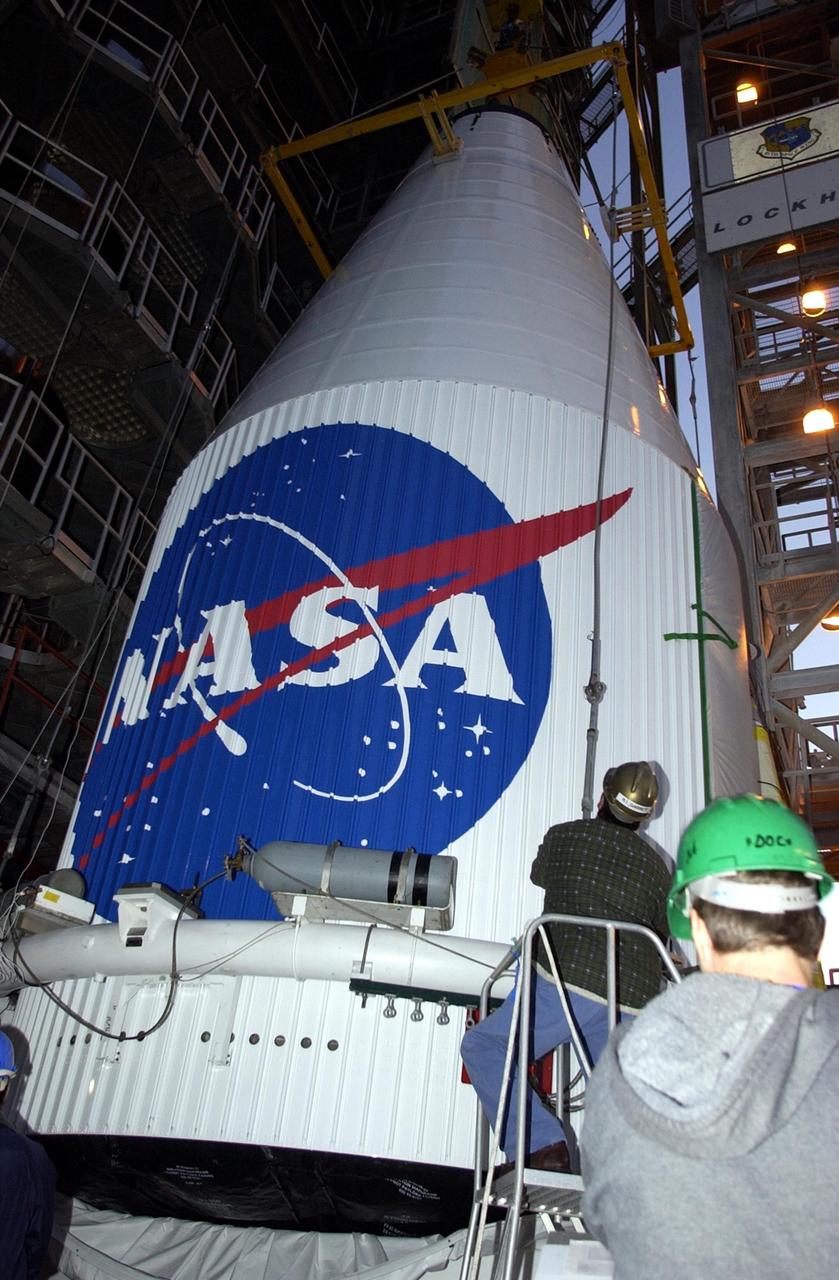

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J satellite is prepared for lifting up the gantry on Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to be launched Dec. 4 aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
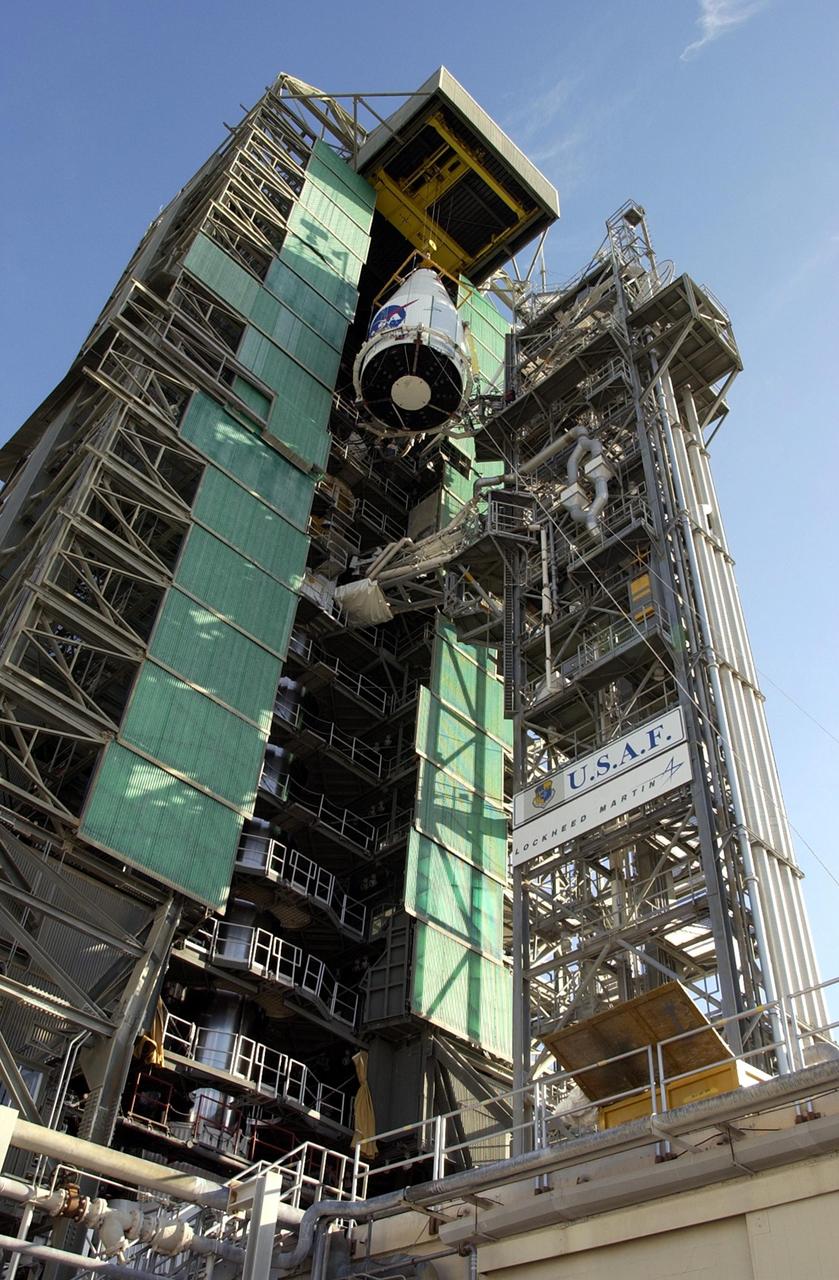

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J satellite nears the top of the gantry on Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to be launched Dec. 4 aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
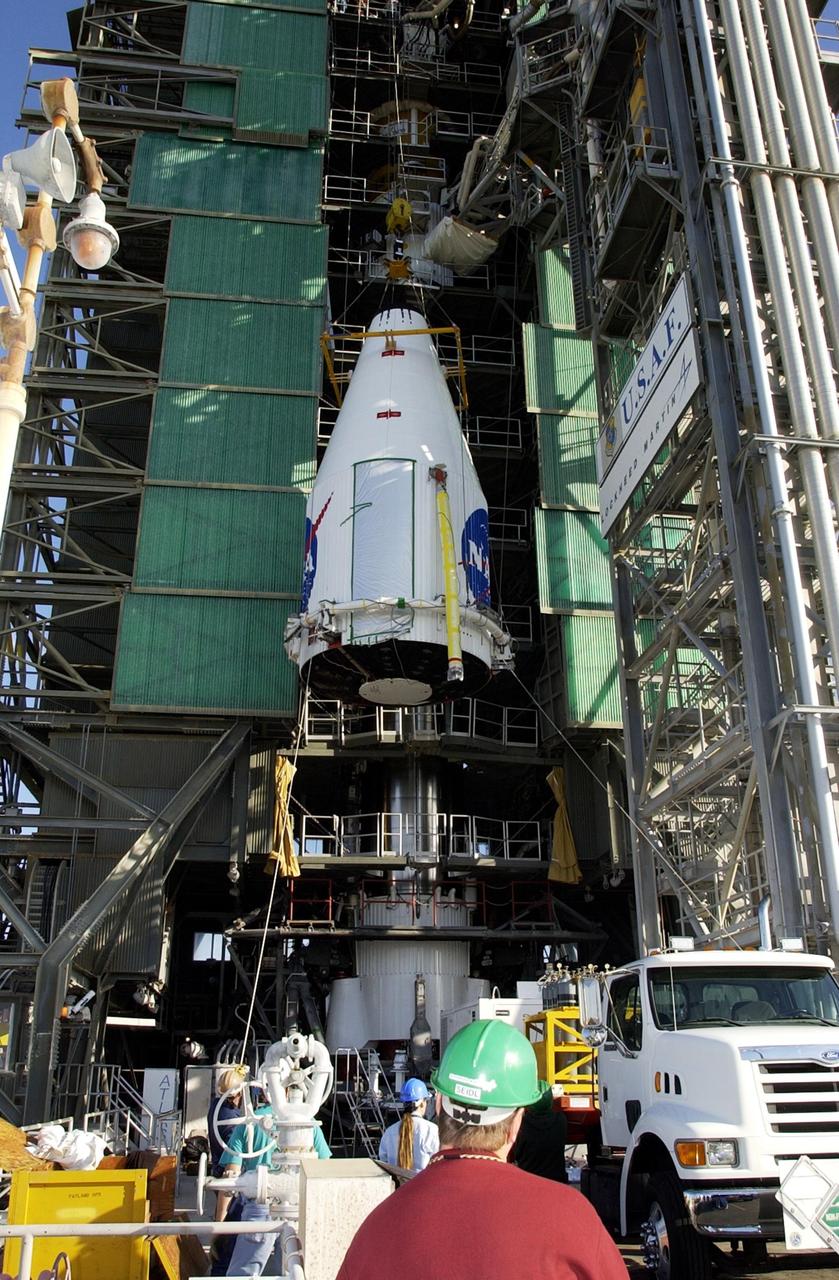

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The TDRS-J satellite is lifted up the gantry on Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to be launched Dec. 4 aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
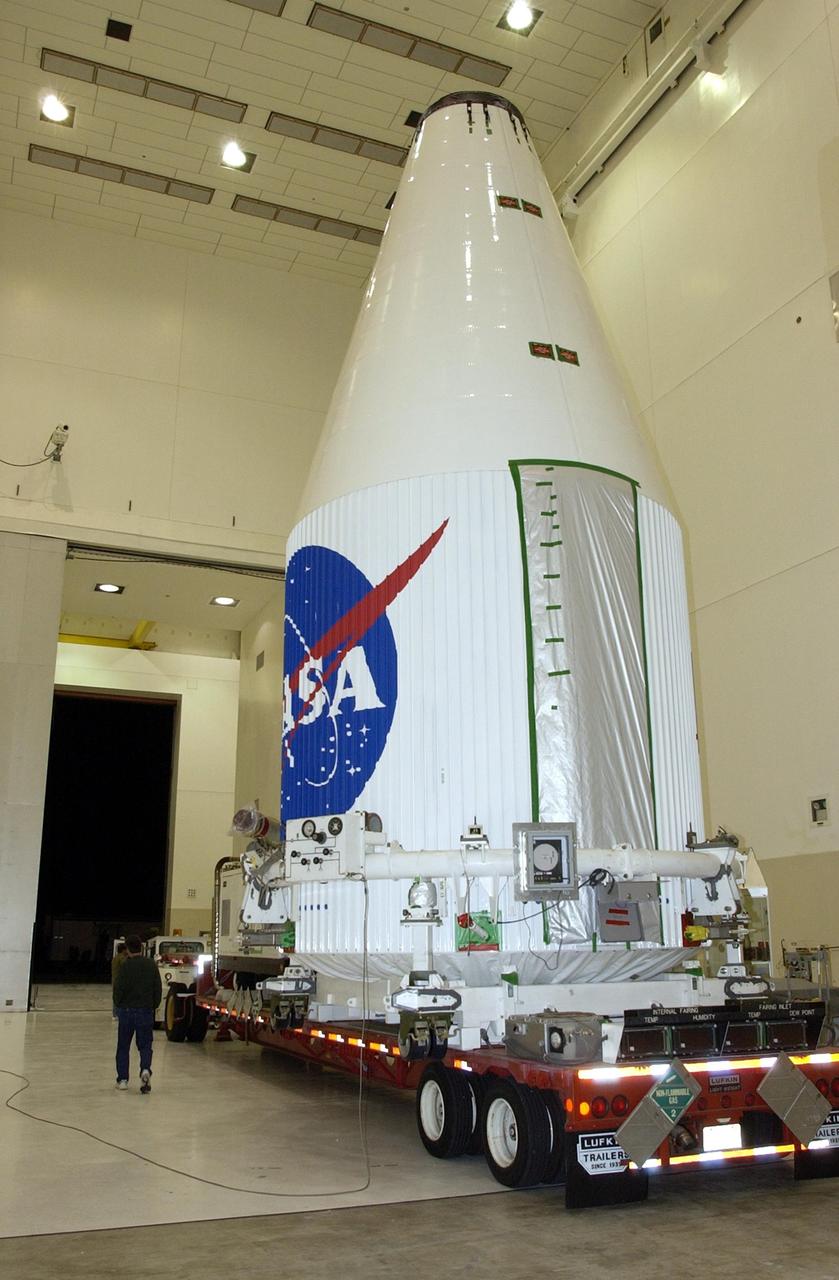

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A transporter carrying the encapsulated TDRS-J satellite makes its way to the exit. The satellite is being taken to Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for a launch aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle Dec. 4. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
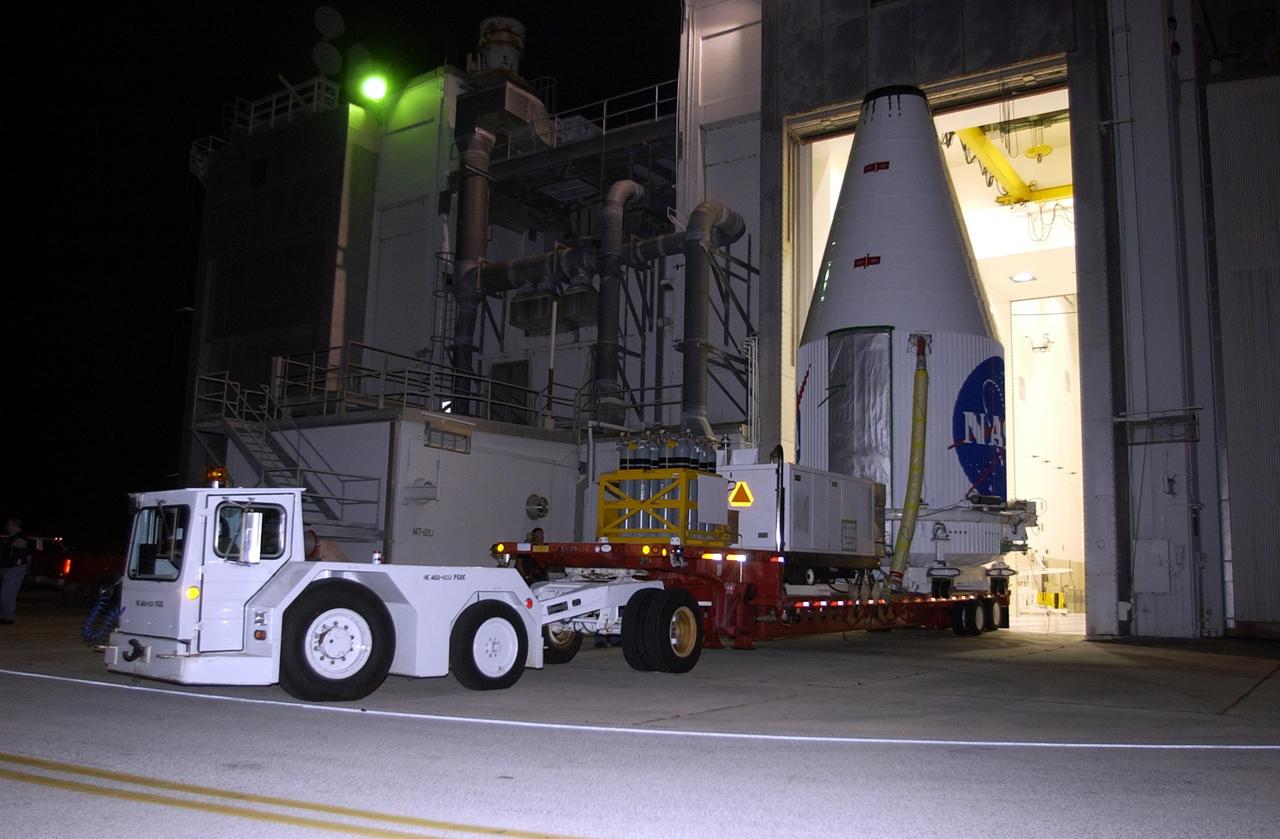

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A transporter carrying the encapsulated TDRS-J satellite exits the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility -2. The satellite is being taken to Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for a launch aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle Dec. 4. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
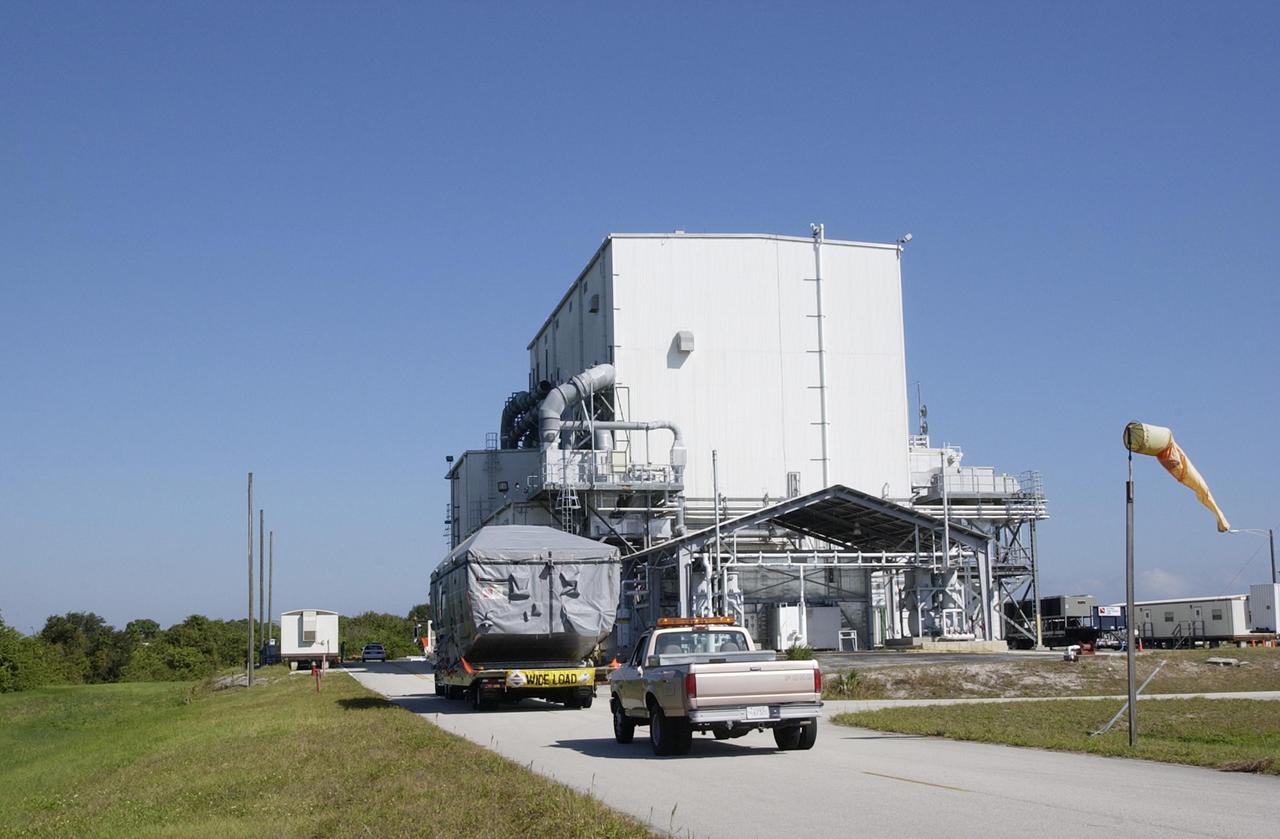

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The TDRS-J spacecraft, enclosed in a container, arrives at the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) for processing. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
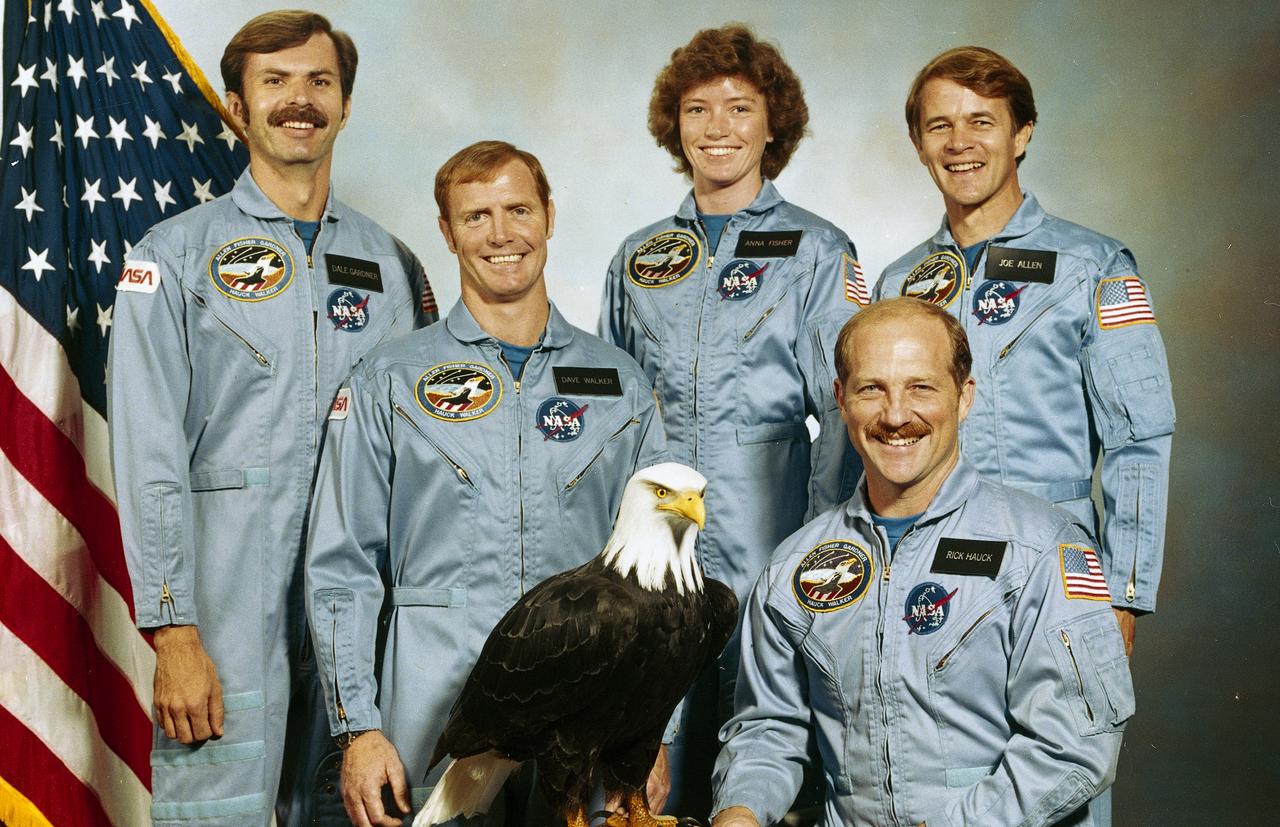

The crew assigned to the STS-51A mission included Frederick H. Hauck, commander,who is seated to the right. Standing, left to right, are Dale A. Gardner, mission specialist; David M. Walker, pilot; and mission specialists Anna L. Fisher, and Joseph P. Allen. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on November 8, 1984 at 7:15:00 am (EST), the STS-51A mission deployed the Canadian communications satellite TELLESAT-H (ANIK), and the defense communications satellite SYCOM IV-1 (also known as LEASAT-1). In addition, 2 malfunctioning satellites were retrieved: the PALAPA-B2 and the WESTAR-VI.
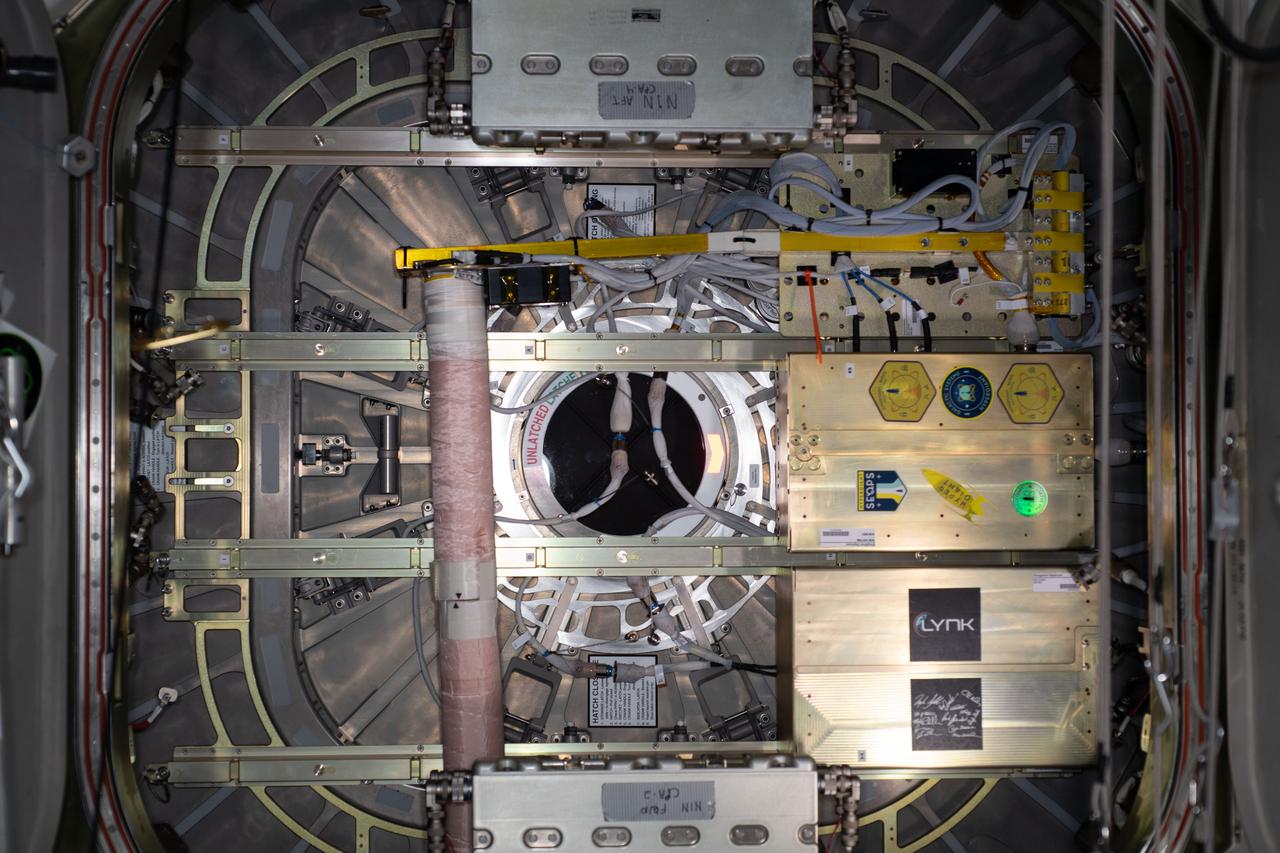
iss063e010534 (5/10/2020) --- A view from the Unity module aboard the International Space Station (ISS) of the Northrop Grumman NG-13 hatch. Attached to the hatch is the SlingShot small satellite deployer loaded with two CubeSats that will be deployed into Earth orbit after Cygnus departs the orbiting lab on May 11, 2020. The SEOPS-UbiquitiLink investigation furthers demonstrates the premise that small satellites/nano satellites can perform vital communications missions and provide valuable communications services. The SEOPS-WIDAR investigation demonstrates technologies that increase the utility of low-cost microsatellites, contributing to the increased commercialization of the International Space Station and low-Earth orbit.
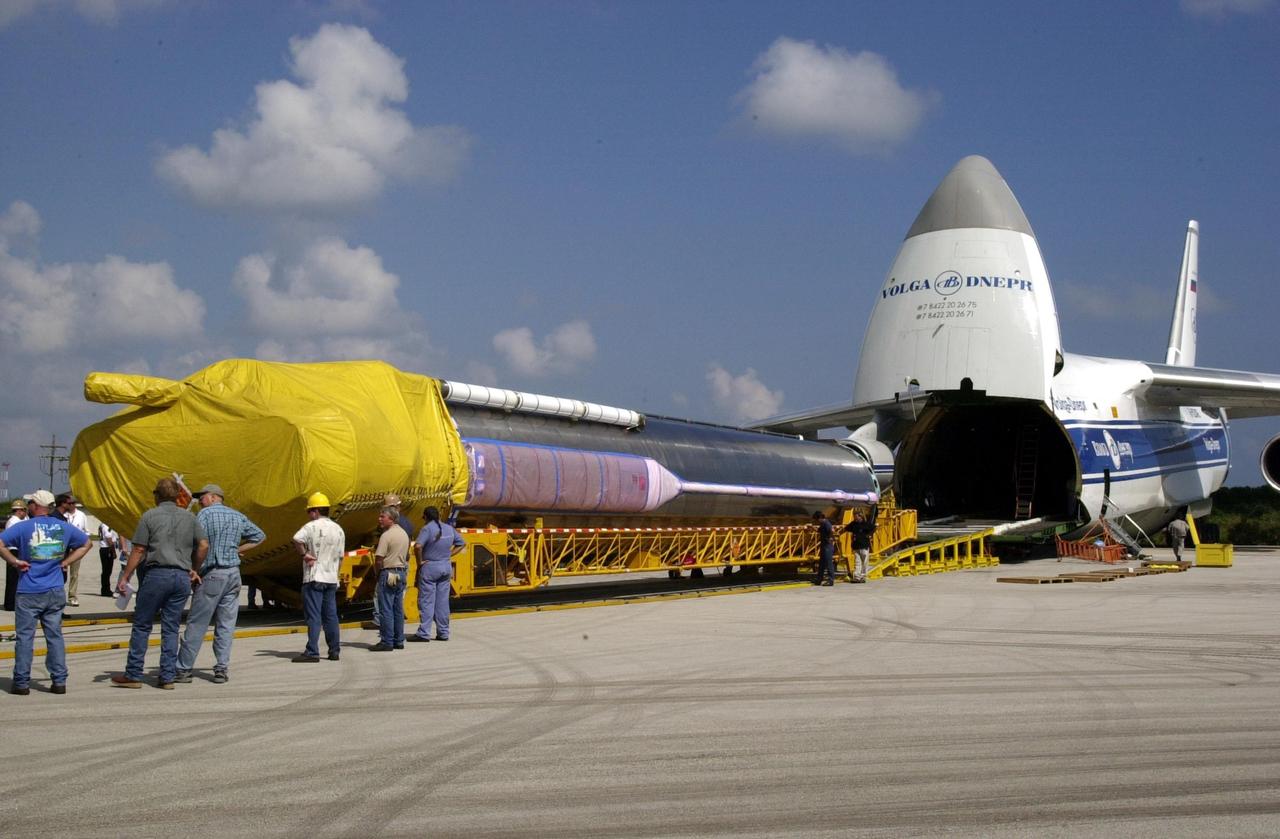

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Following its arrival at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, an Atlas/Centaur booster is ready for its move to Launch Pad 36A in preparation for the launch of TDRS-J. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
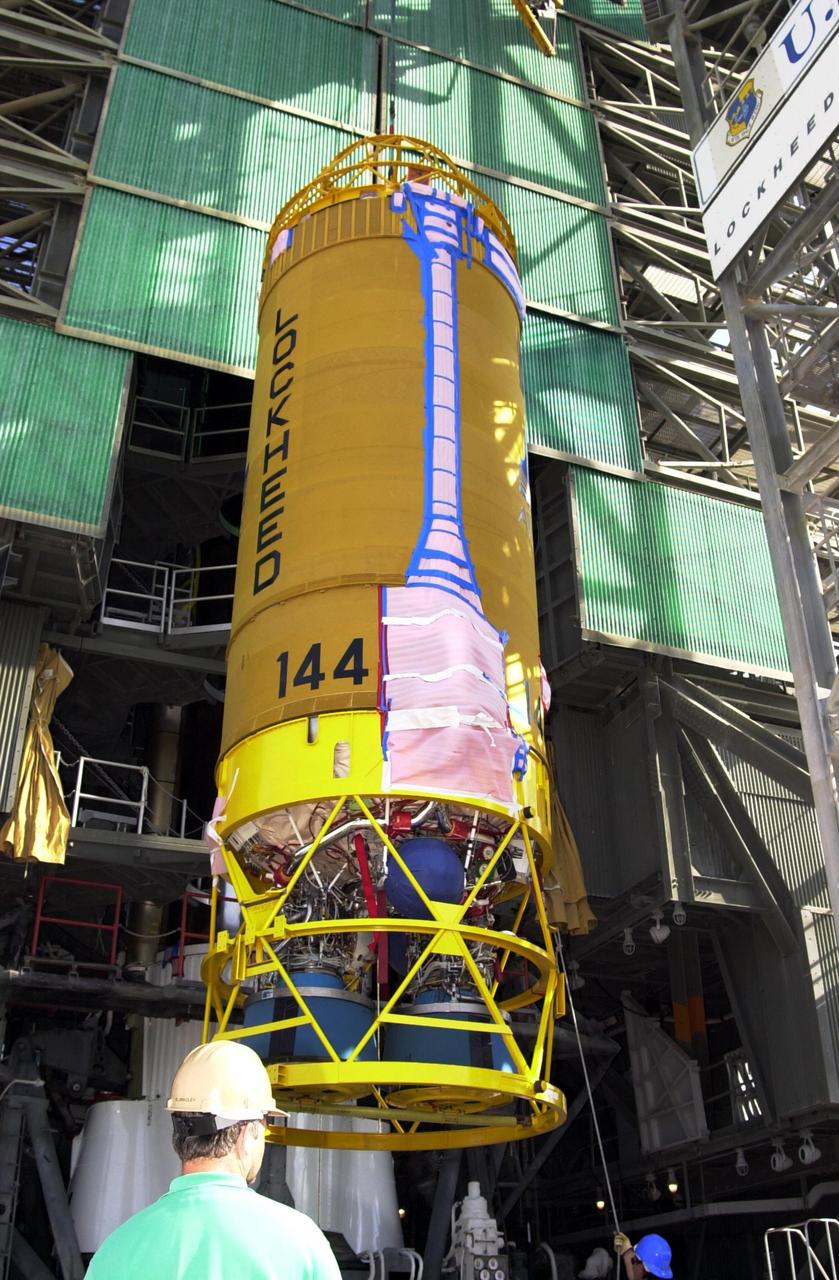

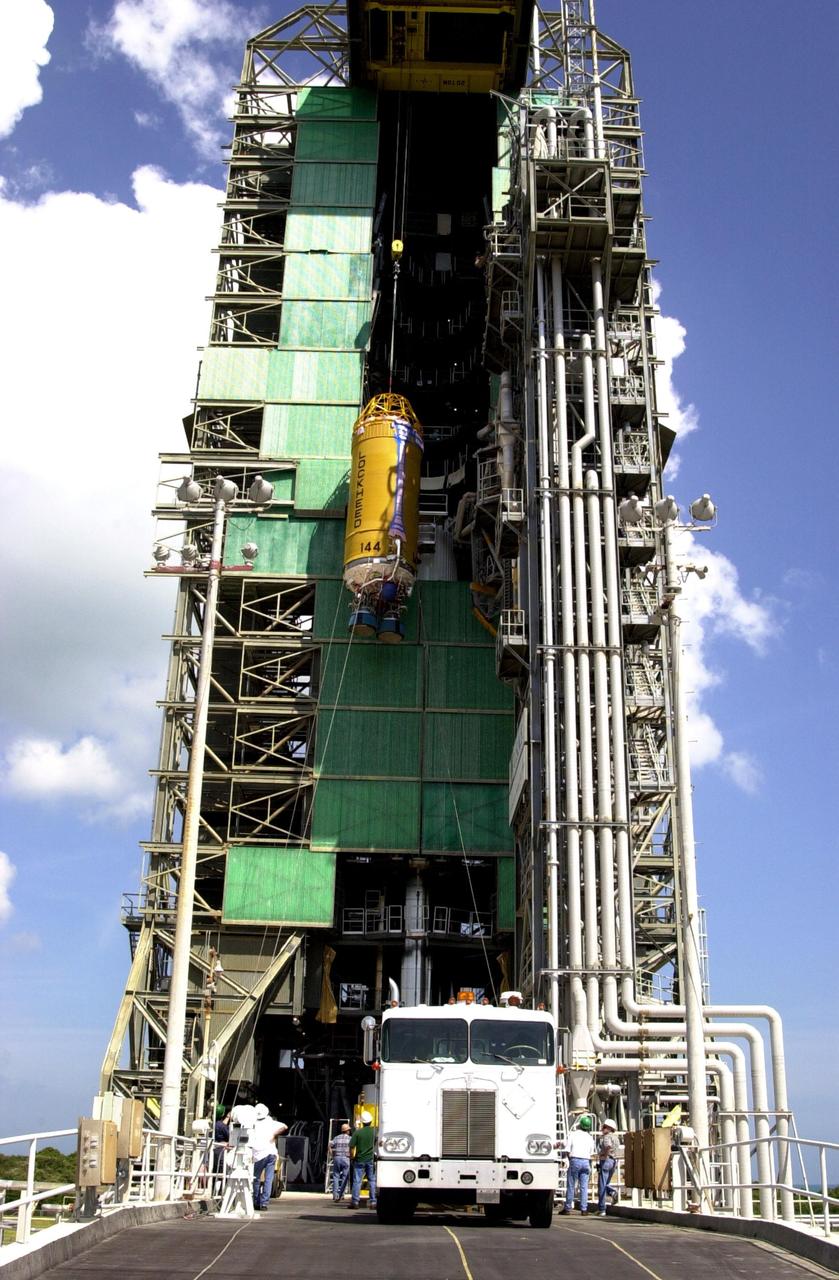
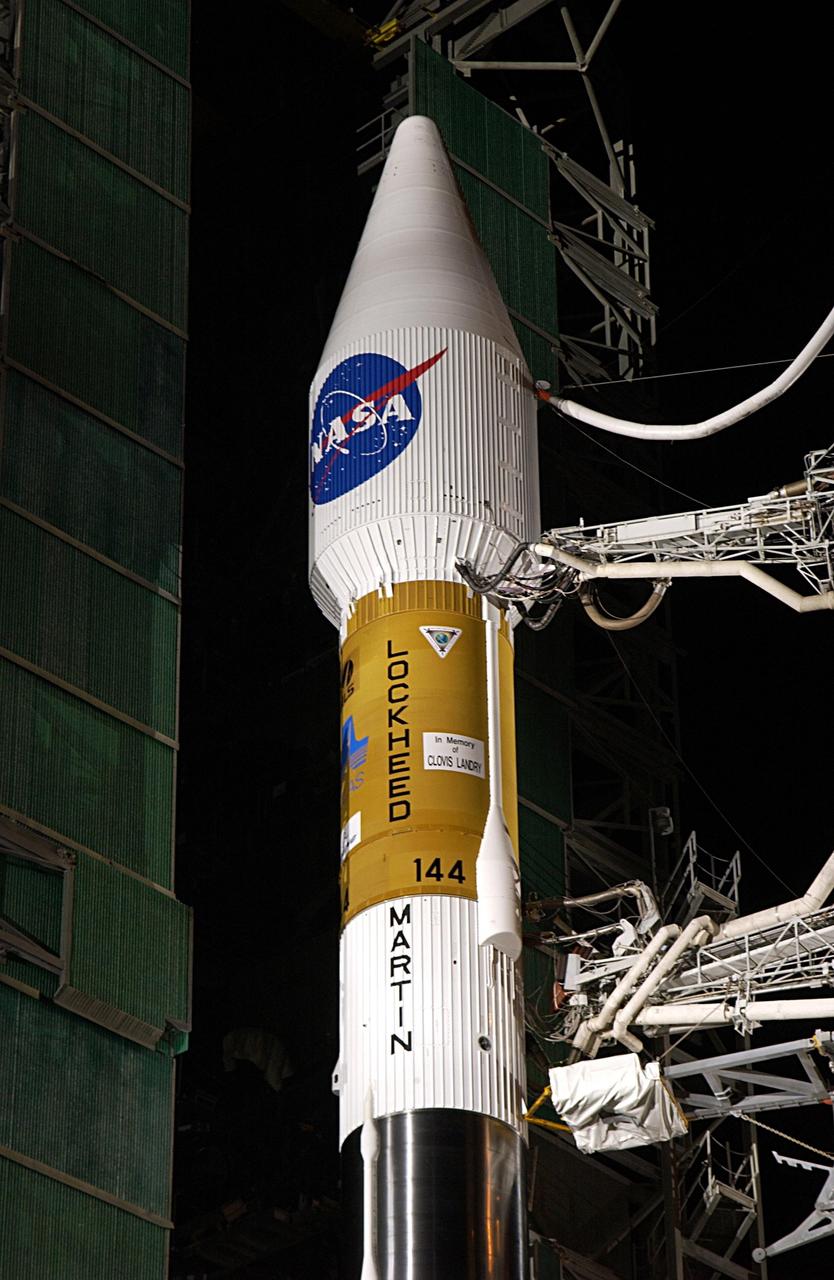
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Lockheed Martin Atlas Centaur IIA (AC-144) rocket is lifted up the launch tower. The rocket will be used in the launch of TDRS-J, scheduled for Nov. 20. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
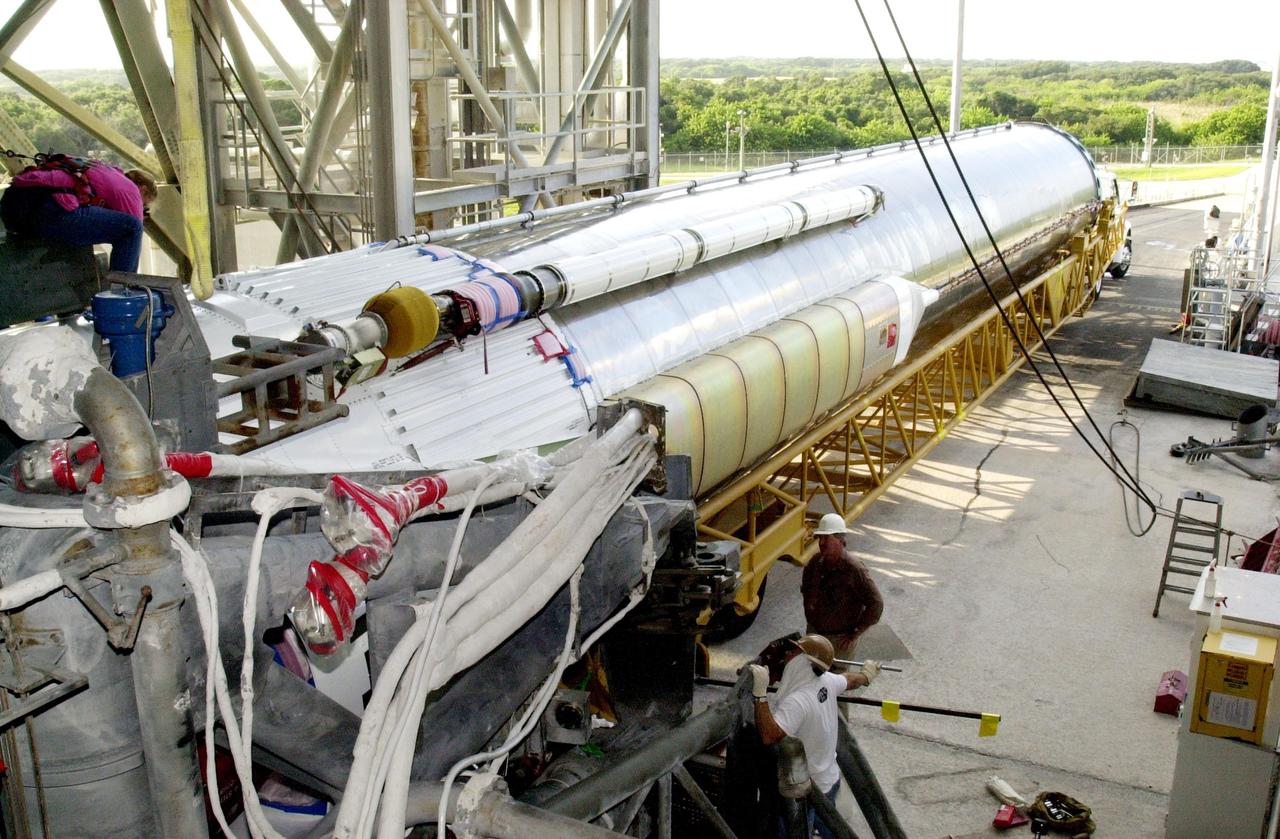

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The first stage of an Atlas/Centaur booster (AC-144) is delivered to Launch Complex 36A at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for the launch of TDRS-J. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
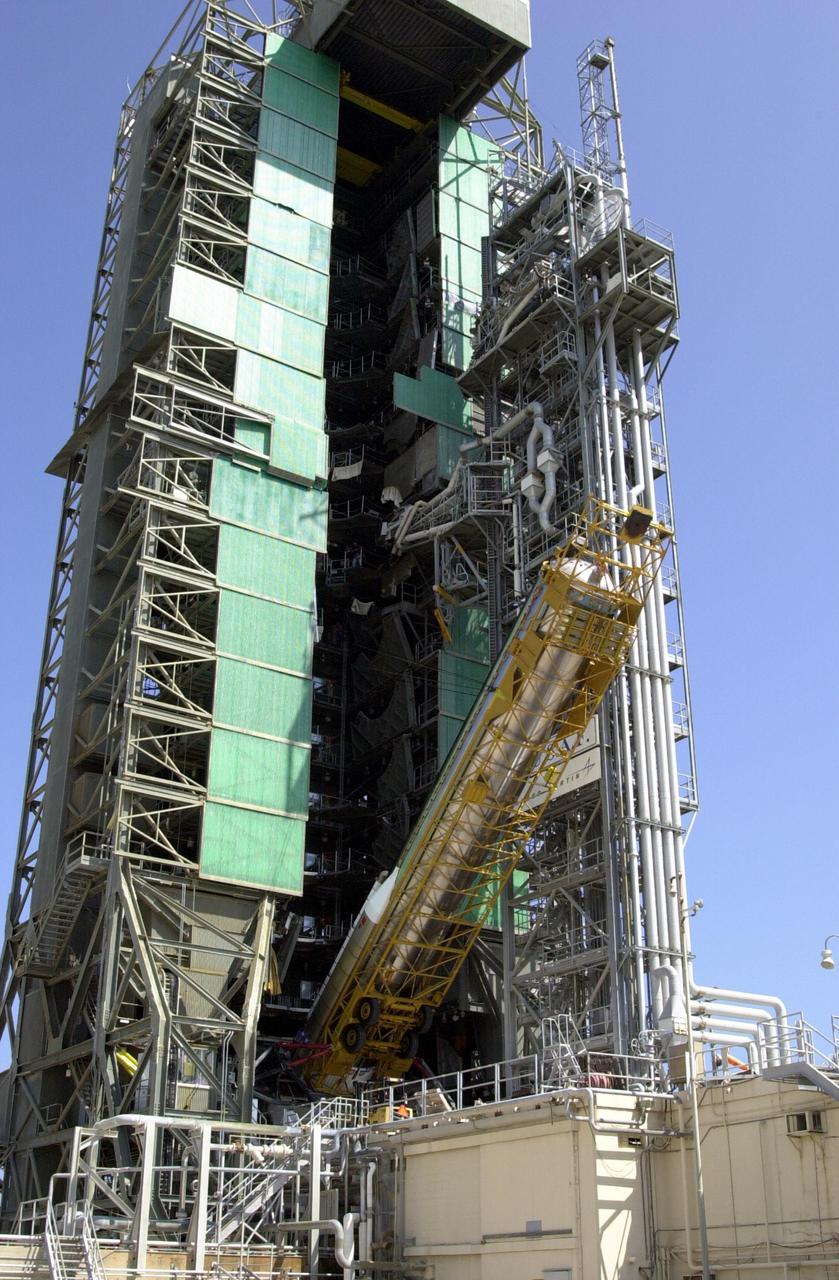

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The first stage of an Atlas/Centaur booster (AC-144) is lifted into an upright position at Launch Complex 36A at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for the launch of TDRS-J. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
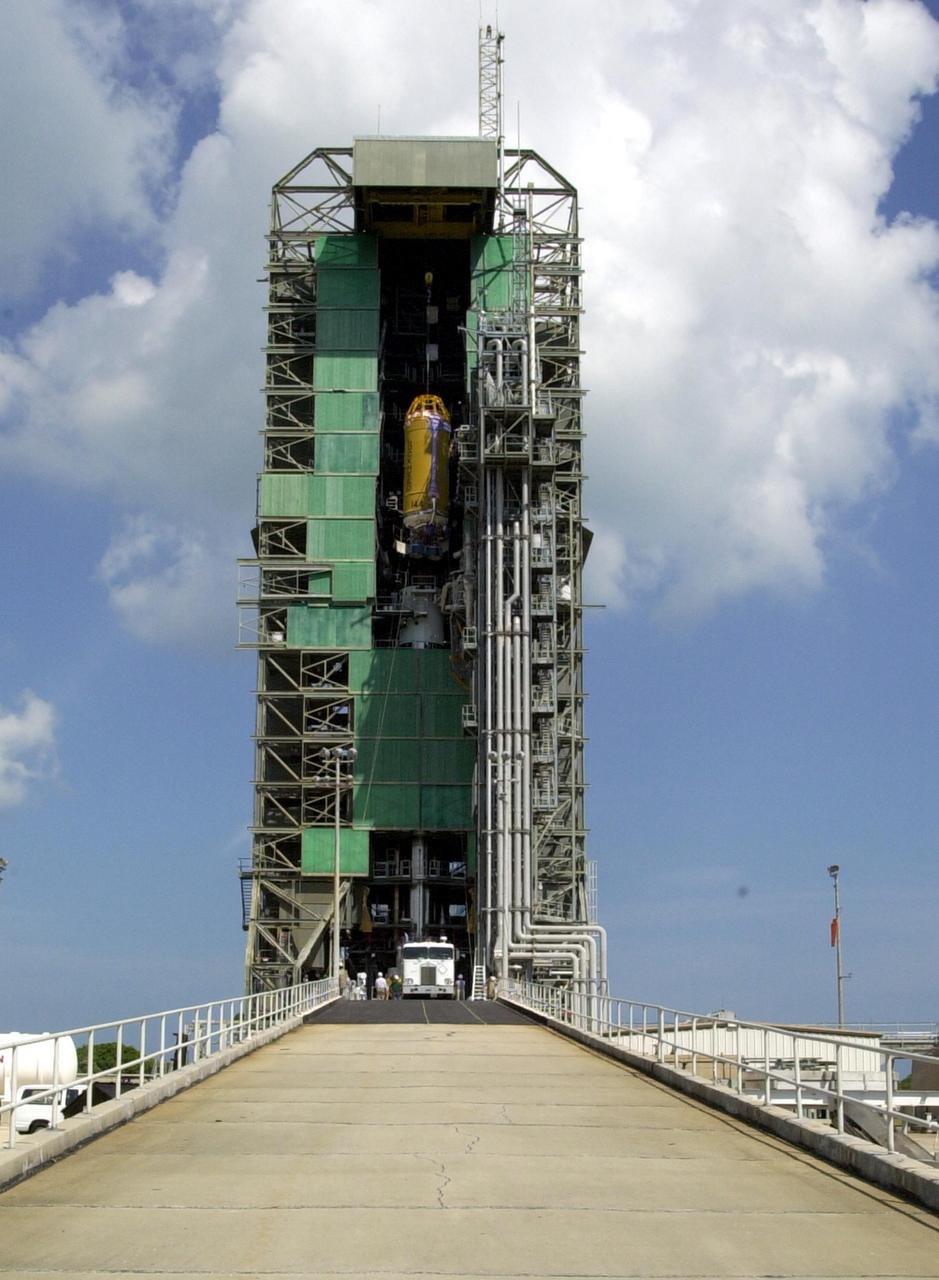

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Lockheed Martin Atlas Centaur IIA (AC-144) rocket nears the top of the launch tower. The rocket will be used in the launch of TDRS-J, scheduled for Nov. 20. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
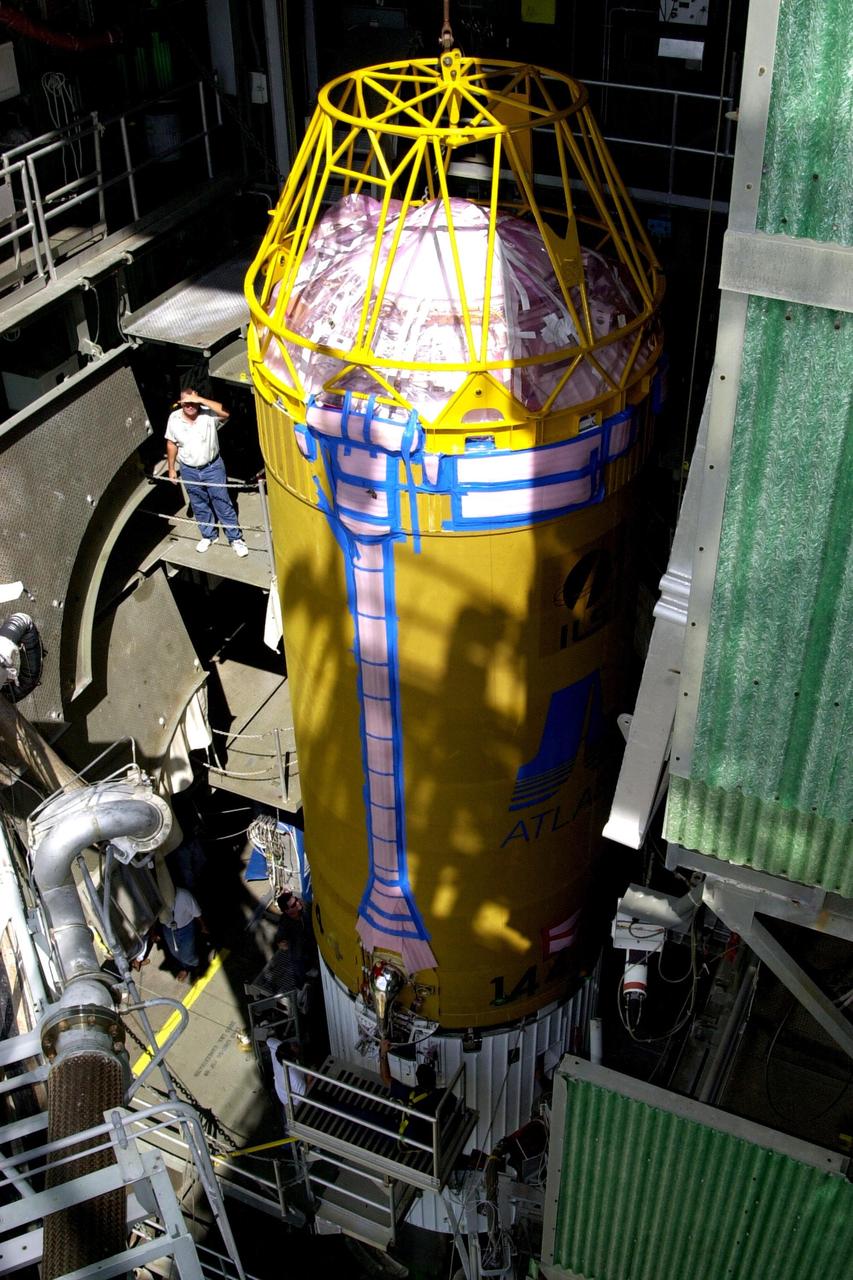

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Lockheed Martin Atlas Centaur IIA (AC-144) rocket arrives at the top of the launch tower. The rocket will be used in the launch of TDRS-J, scheduled for Nov. 20. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
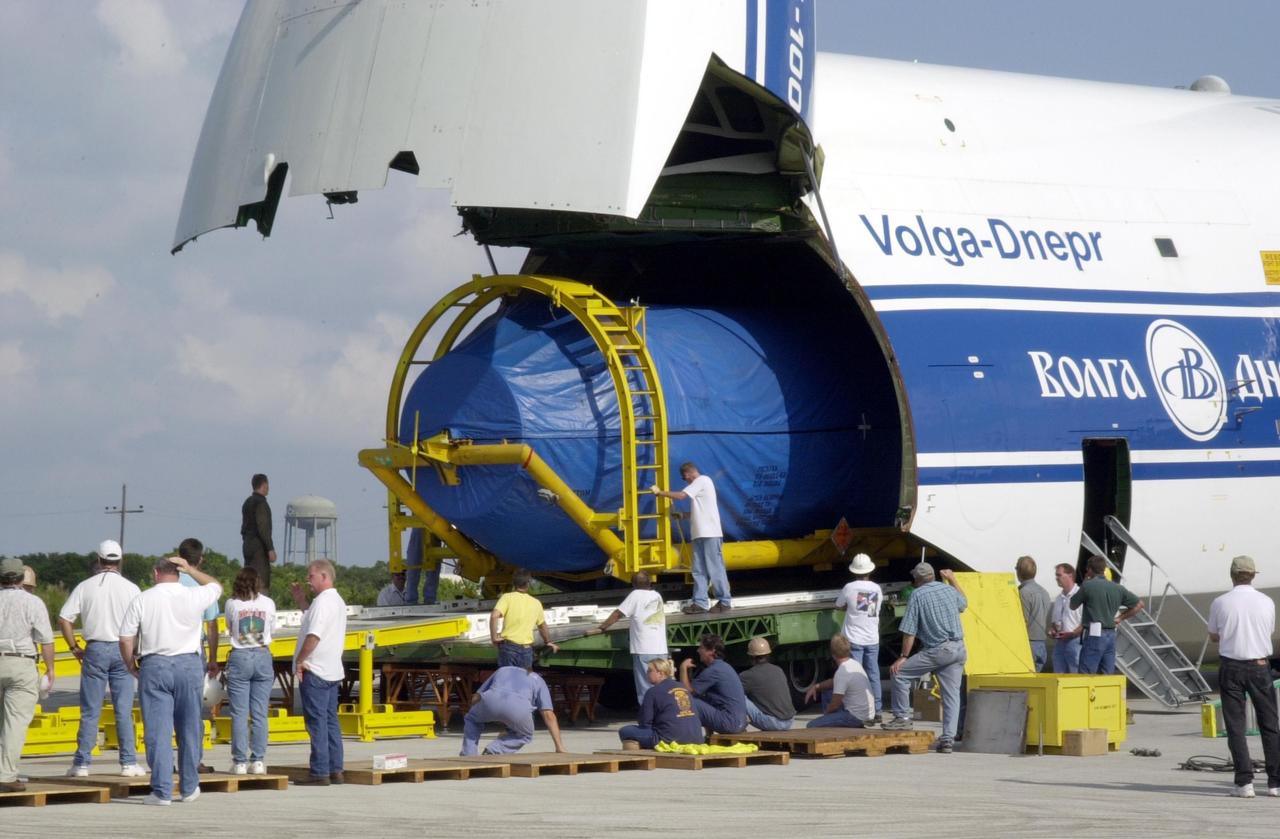

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An Atlas/Centaur booster arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for the launch of TDRS-J. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
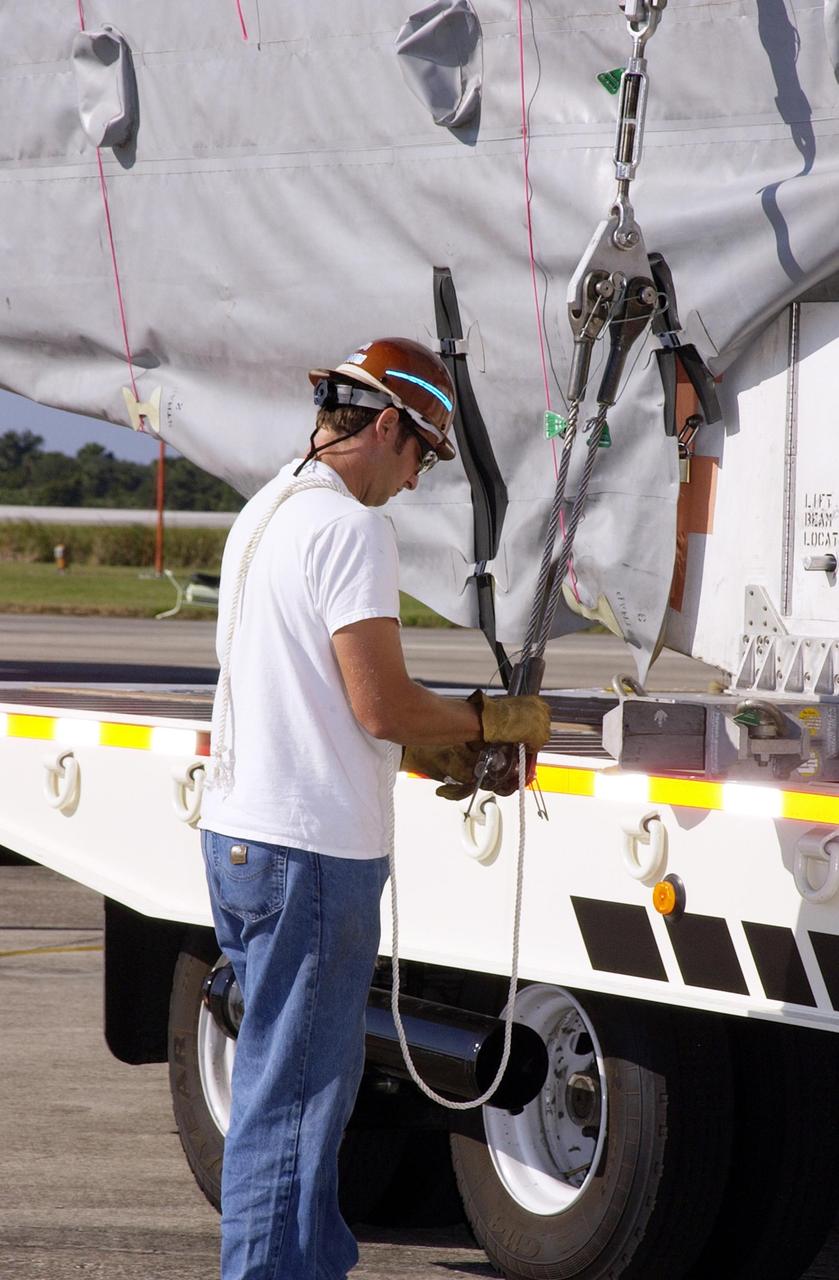

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A worker ties down the container with the TDRS-J spacecraft onto a transport vehicle. TDRS-J is the third in the current series of three Tracking and Data Relay Satellites designed to replenish the existing on-orbit fleet of six spacecraft, the first of which was launched in 1983. The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope, and launch support for some expendable vehicles. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until approximately 2017.
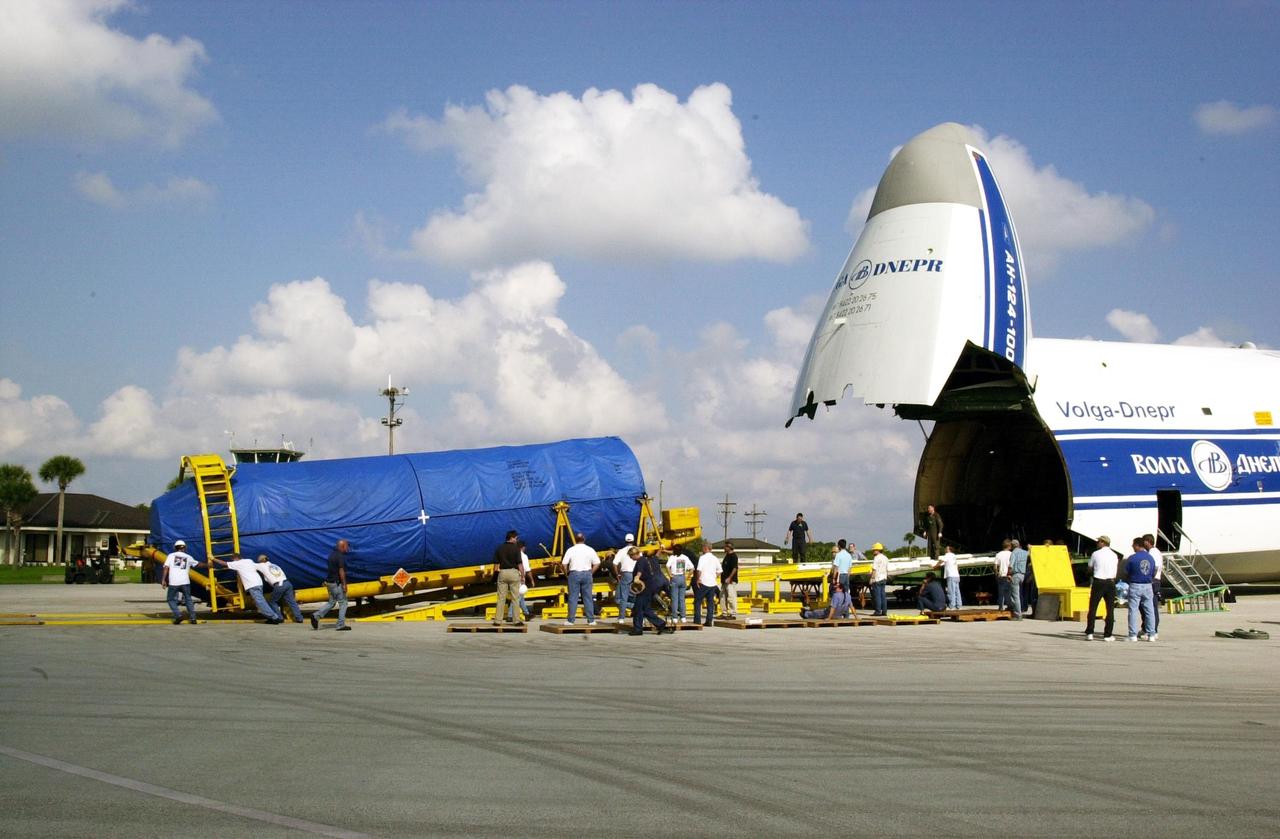

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Following its arrival at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, an Atlas/Centaur booster is offloaded and readied for its move to Launch Pad 36A in preparation for the launch of TDRS-J. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The first stage of an Atlas/Centaur booster (AC-144) is lifted into an upright position at Launch Complex 36A at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in preparation for the launch of TDRS-J. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit, such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

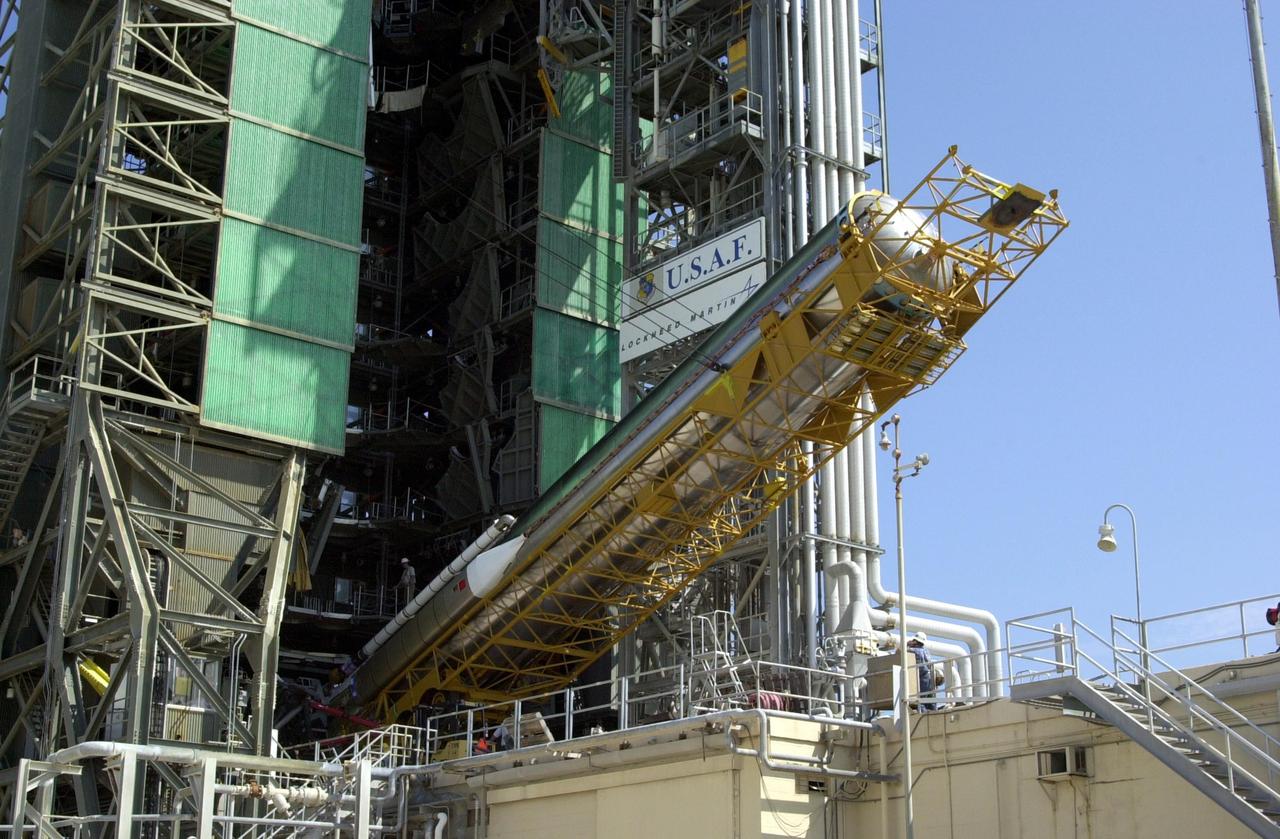
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Lockheed Martin Atlas Centaur IIA (AC-144) rocket is halfway up the launch tower . The rocket will be used in the launch of TDRS-J, scheduled for Nov. 20. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Following its arrival at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, an Atlas/Centaur booster emerges from the nose of its transport aircraft. The booster is being offloaded and readied to move to Launch Pad 36A in preparation for the launch of TDRS-J. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers move the second half of the fairing around the TDRS-J satellite to complete encapsulation. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The fairing (left) is moved toward the TDRS-J satellite (right) for encapsulation. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers make adjustments on the first part of the fairing around the TDRS-J satellite before encapsulation continues. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the mobile service tower is rolled back to reveal the encapsulated TDRS-J satellite aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle awaiting launch on Dec. 4. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J satellite rests inside the first half of the fairing during encapsulation. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The second half of the fairing (right) is prepared for mating with the first half and encapsulating the TDRS-J satellite for launch. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

Workers in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) conduct electrical testing on the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) above them. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
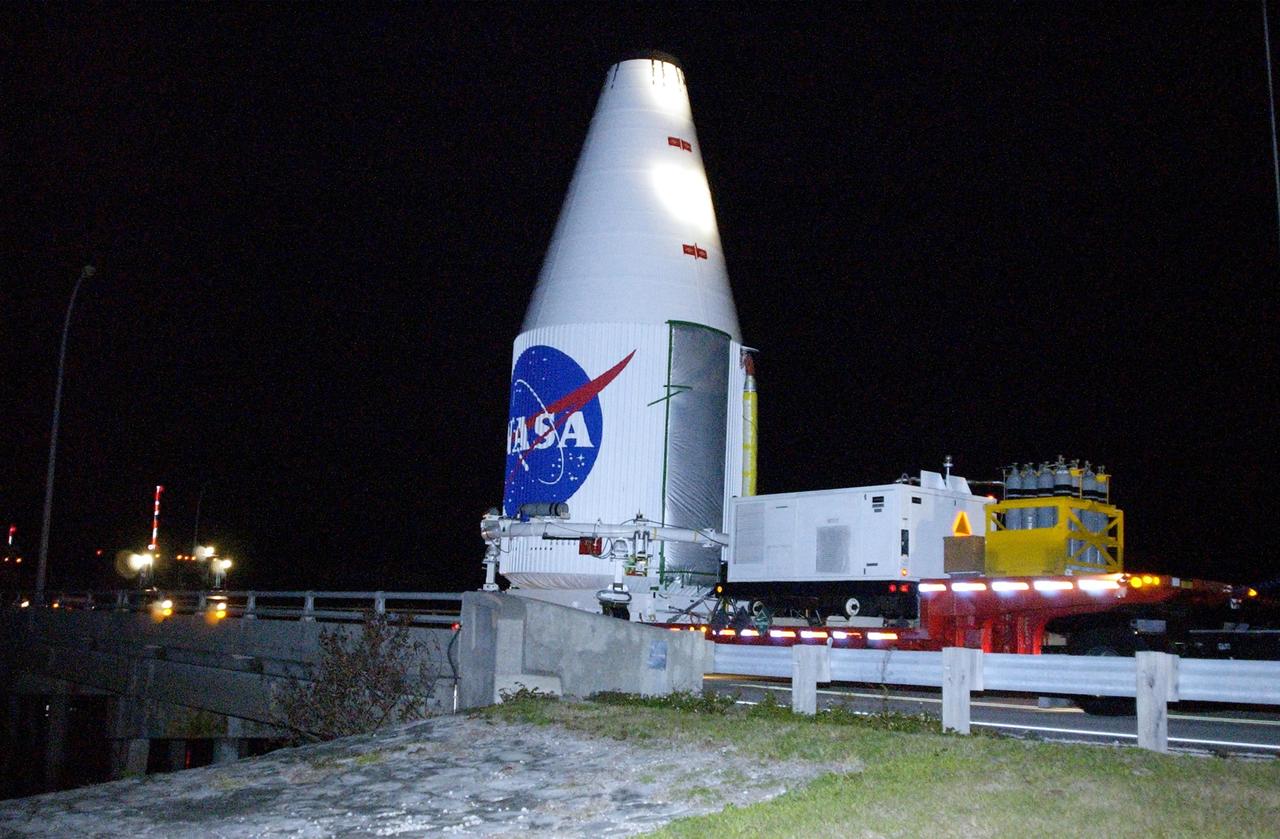

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A transporter carrying the encapsulated TDRS-J satellite crosses a bridge heading to Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, for a launch Dec. 4 aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
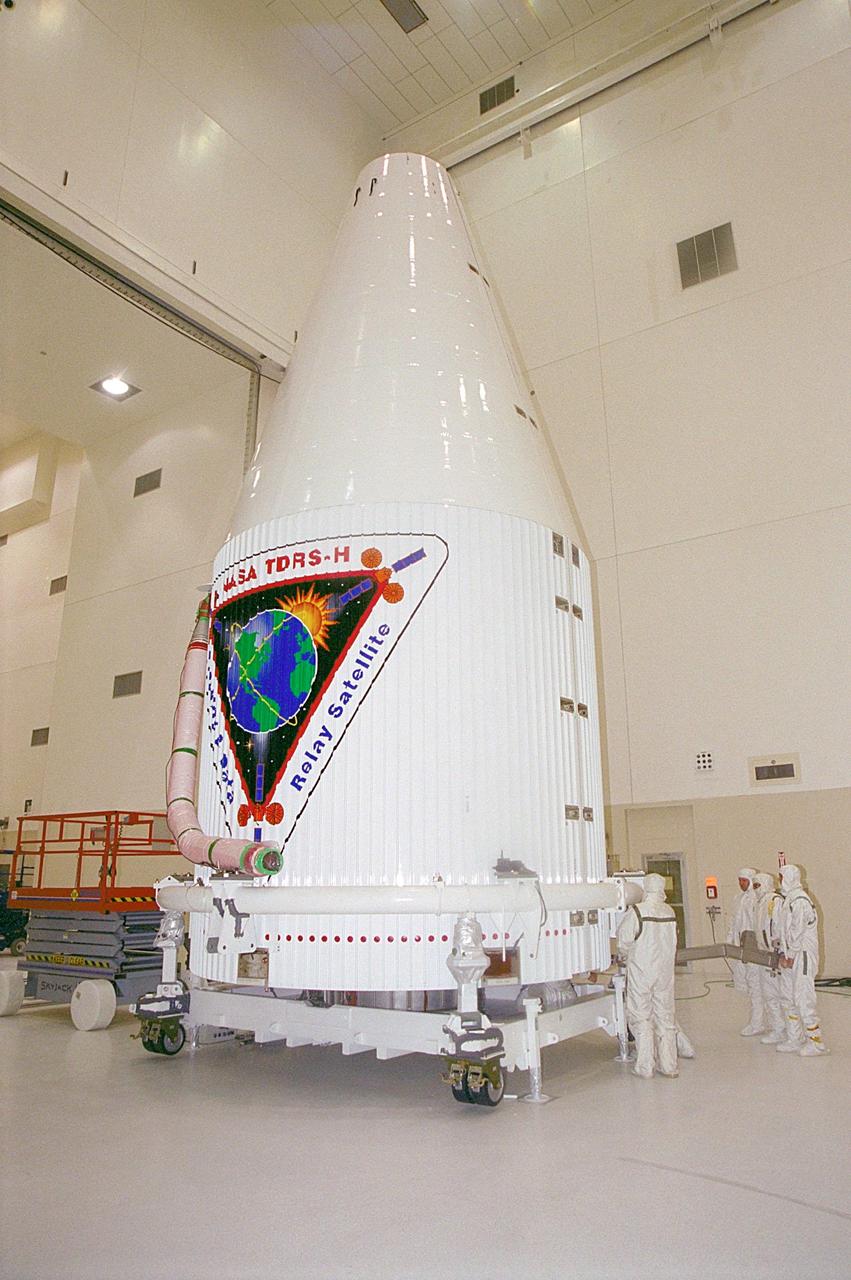

The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) sits fully encapsulated inside the fairing. Next, it will be transported to Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for launch scheduled June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
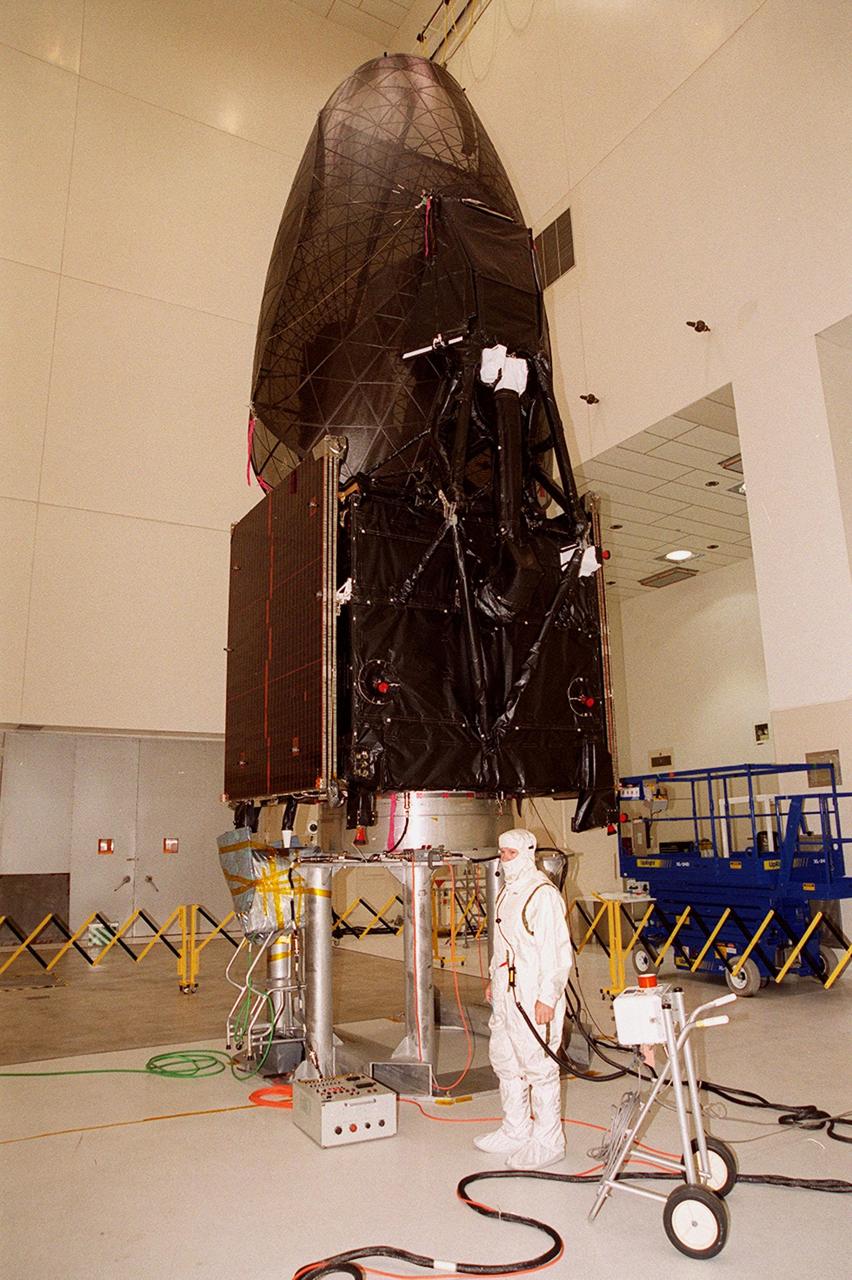

The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) sits on a workstand in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) in order to undergo electrical testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
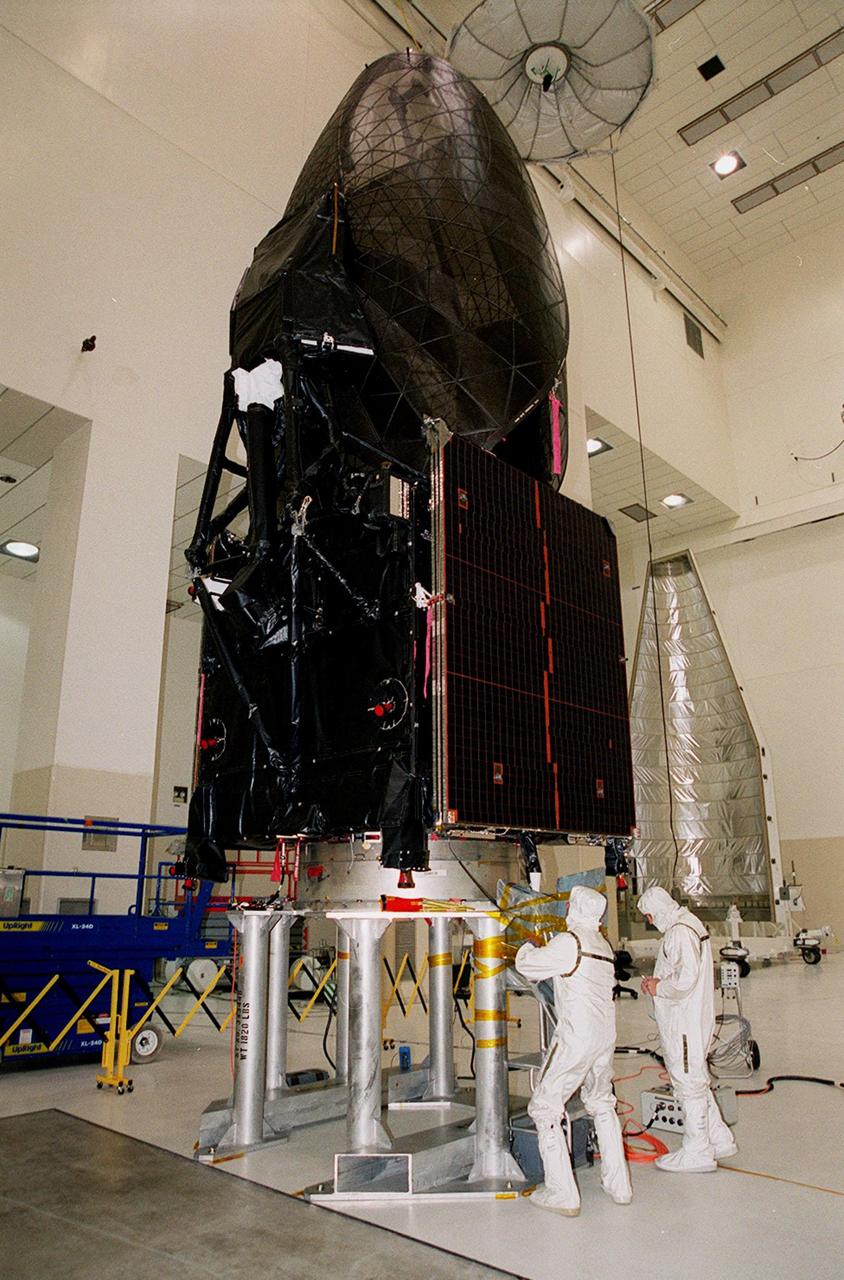

Workers in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) prepare the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) above them for electrical testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
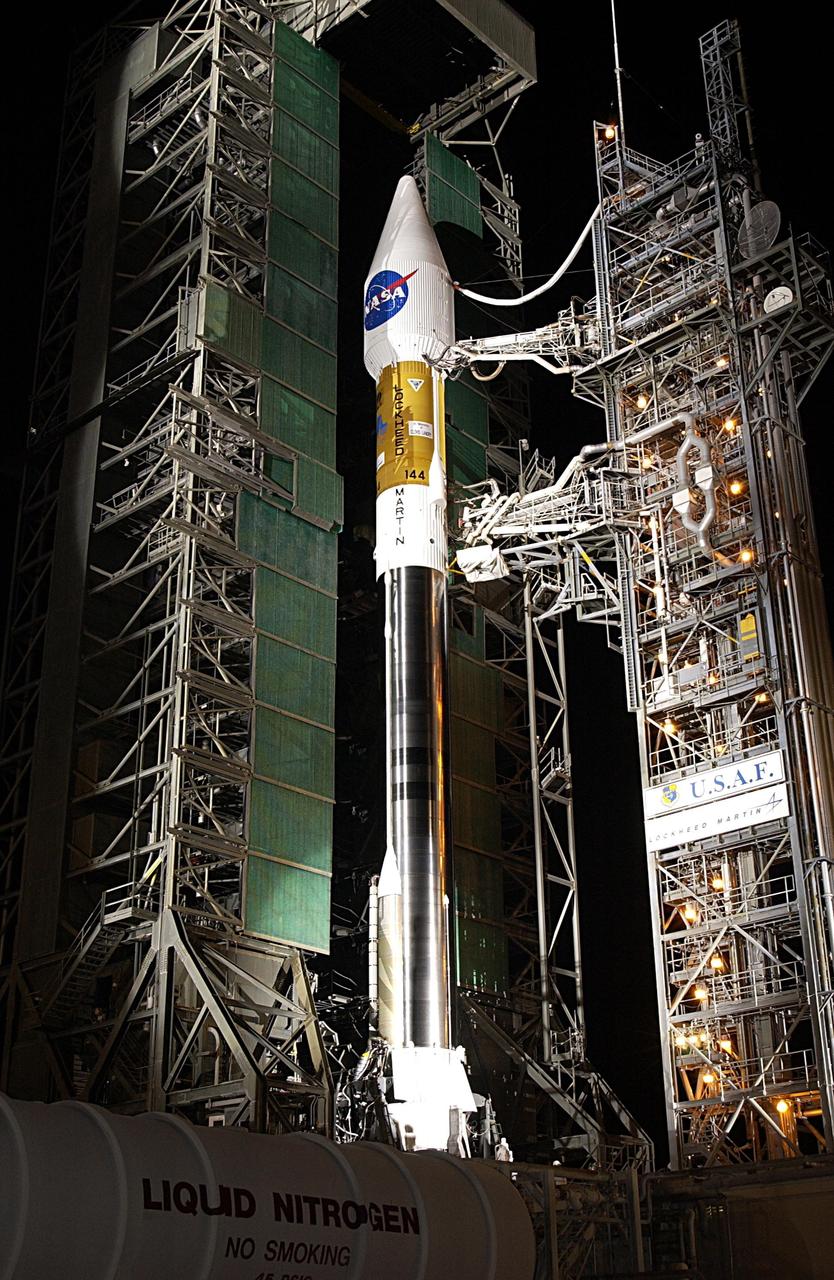

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the mobile service tower is rolled back to reveal the encapsulated TDRS-J satellite aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle awaiting launch on Dec. 4. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
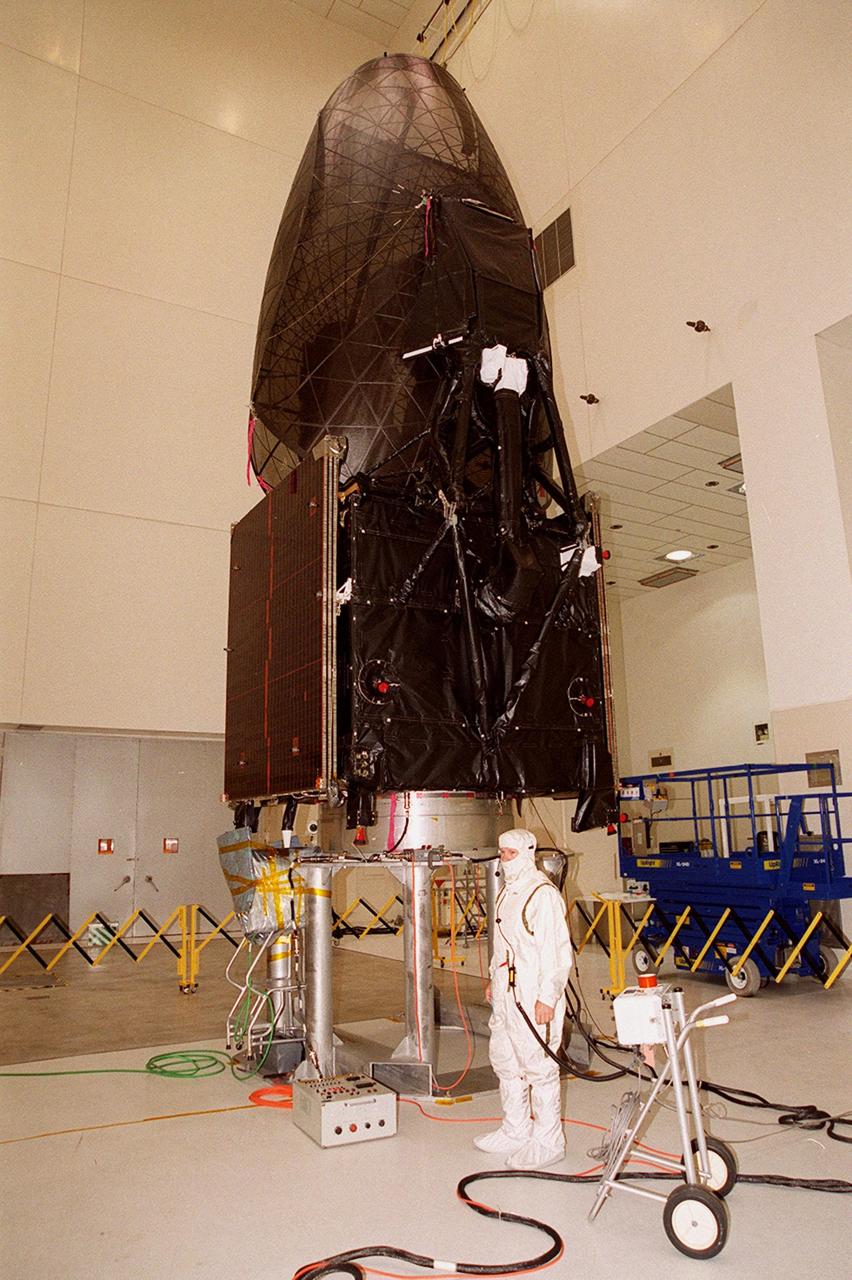

The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) sits on a workstand in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) in order to undergo electrical testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit

Workers in KSC’s Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility (SAEF-2) prepare the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) above them for electrical testing. The TDRS is scheduled to be launched from CCAFS June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
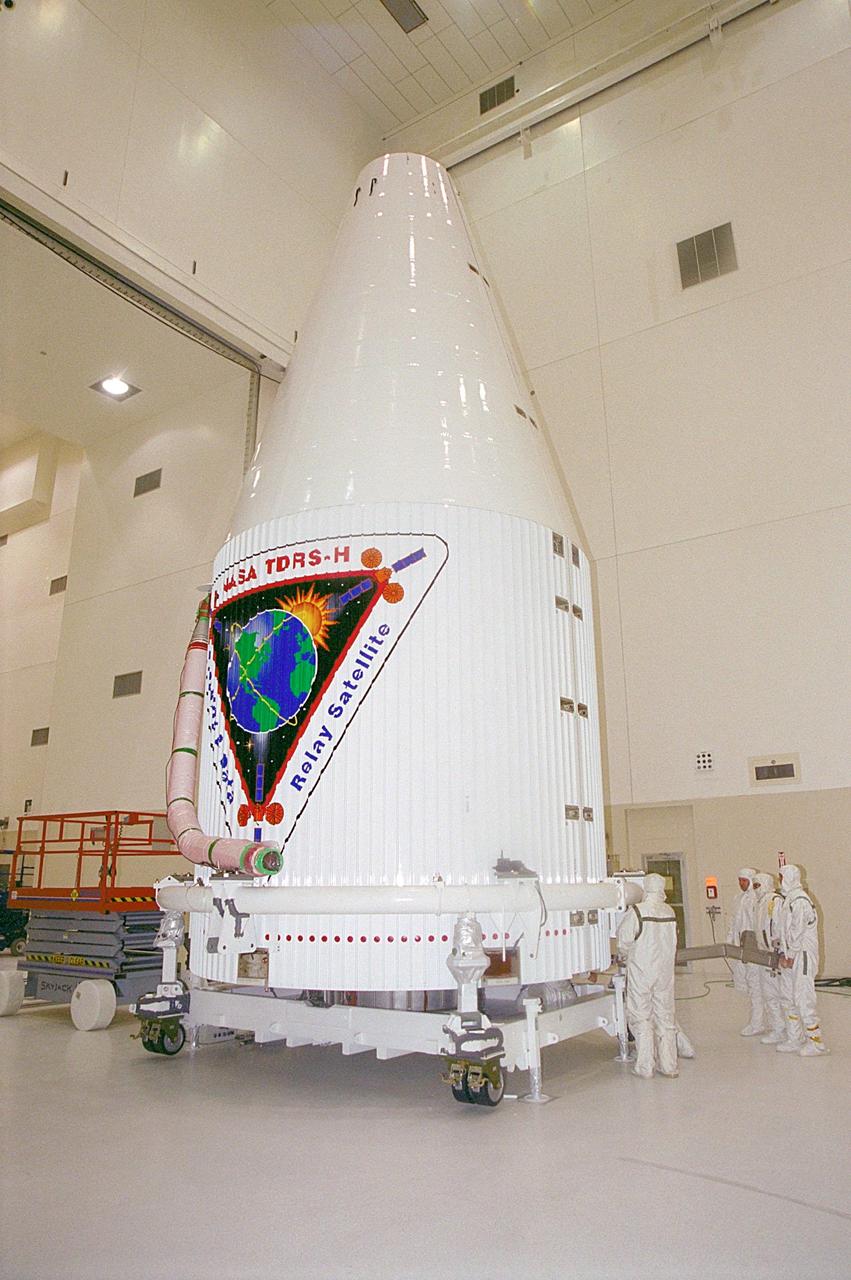

The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) sits fully encapsulated inside the fairing. Next, it will be transported to Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for launch scheduled June 29 aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif., the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
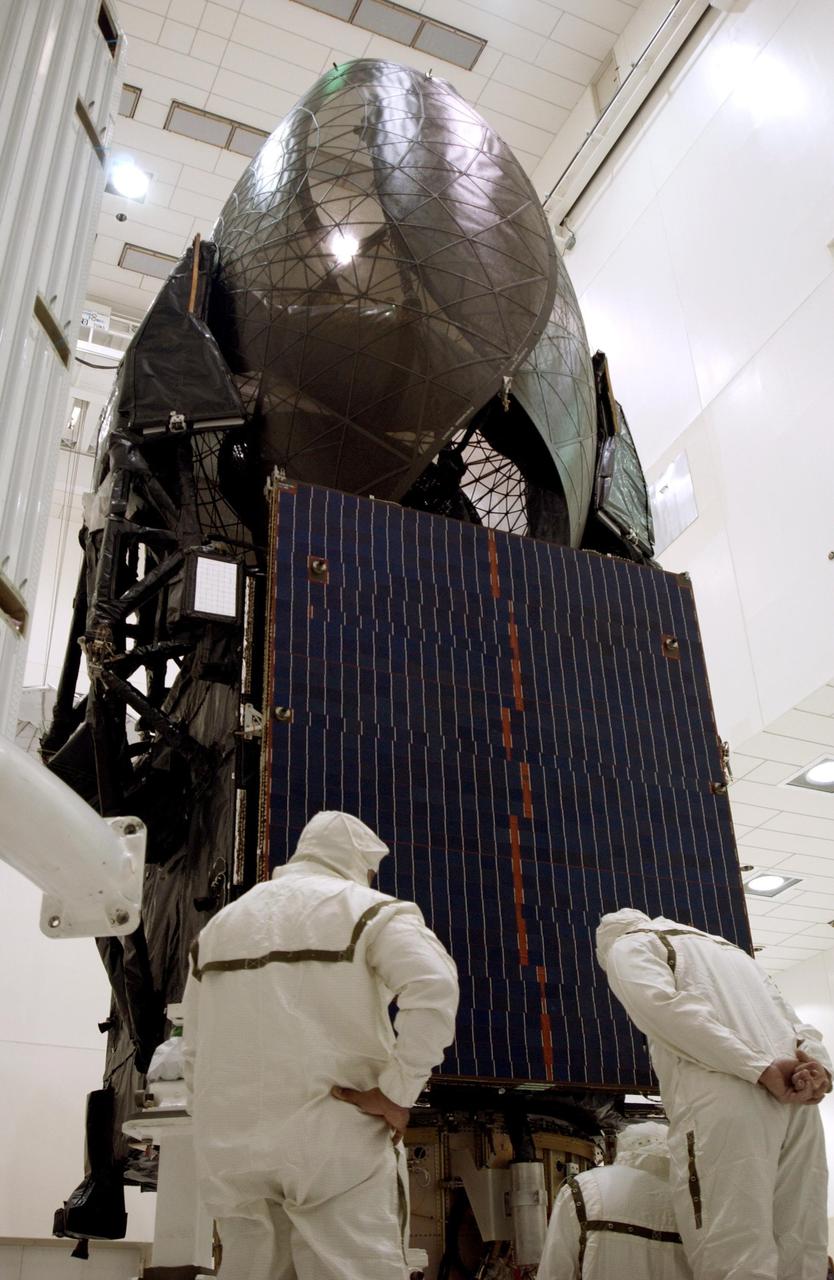

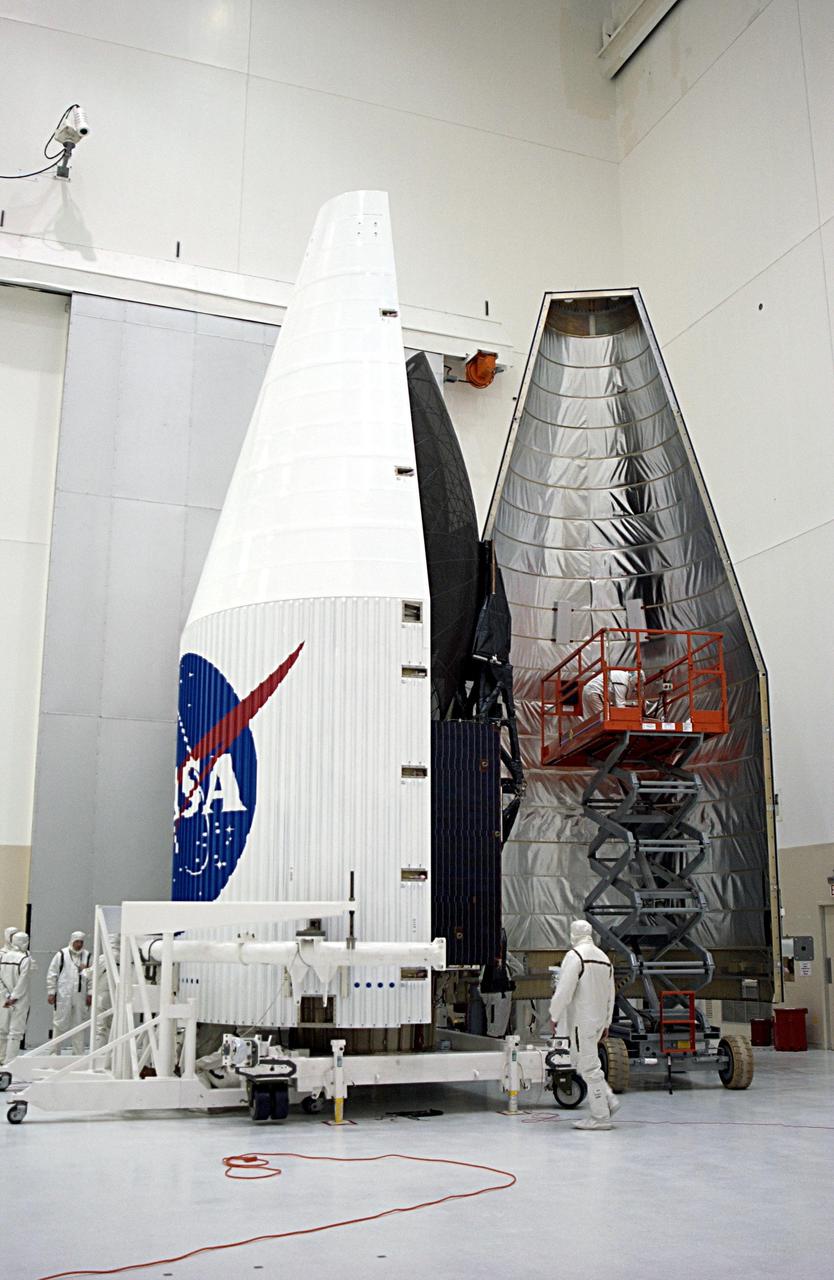
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers keep check on the TDRS-J satellite (foreground) as the fairing (background) moves toward it for encapsulation. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
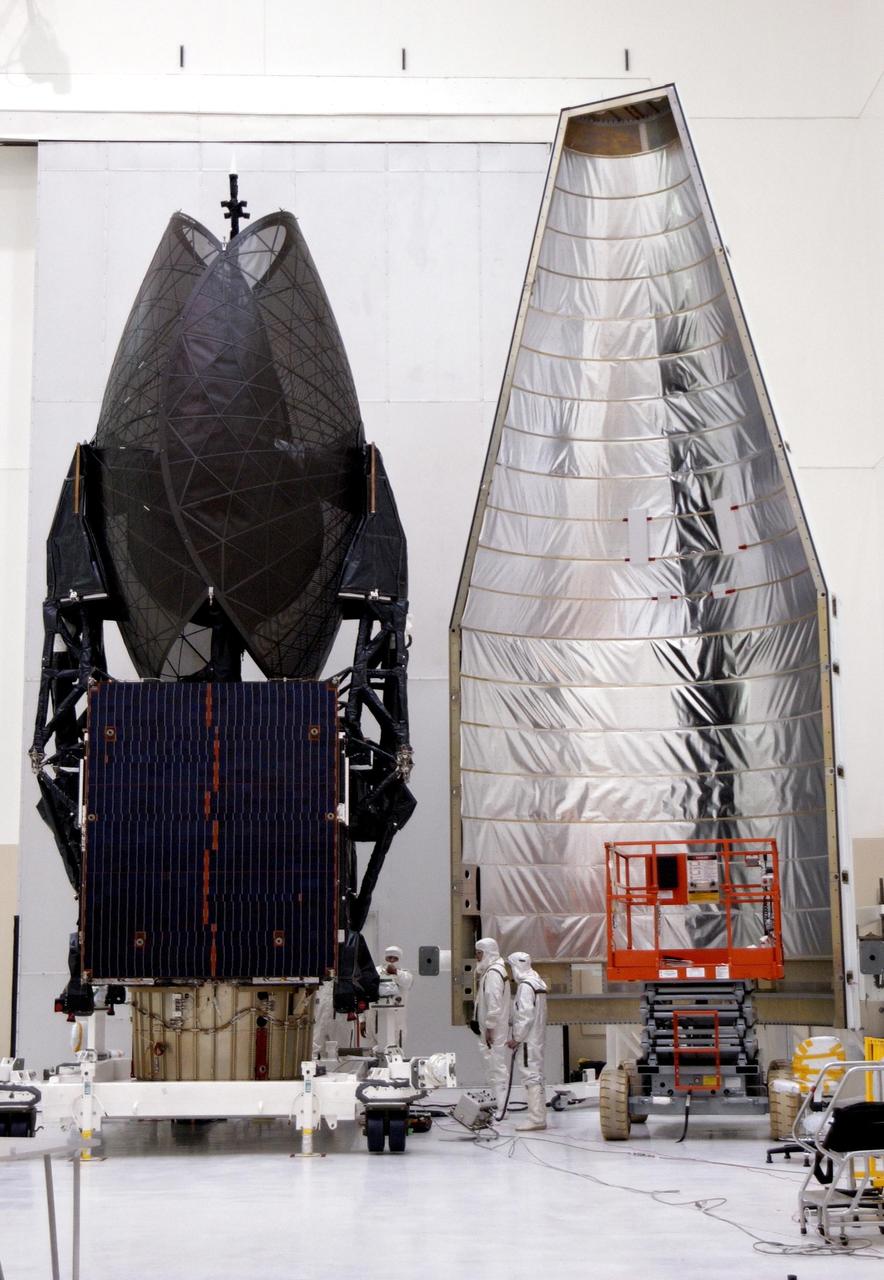

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- TheTDRS-J satellite (left) and part of the fairing (right) are on display for the media before encapsulation. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
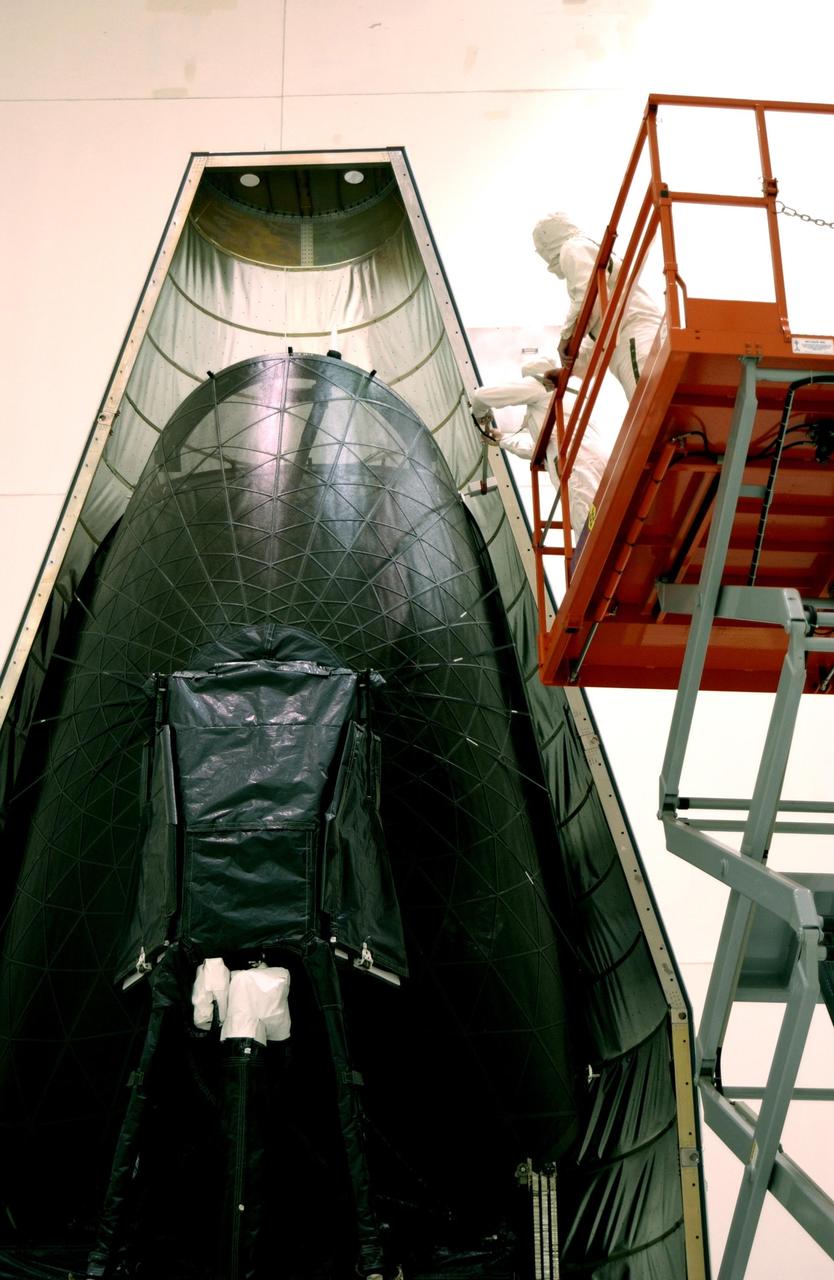

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J satellite rests inside the first half of the fairing during encapsulation. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.
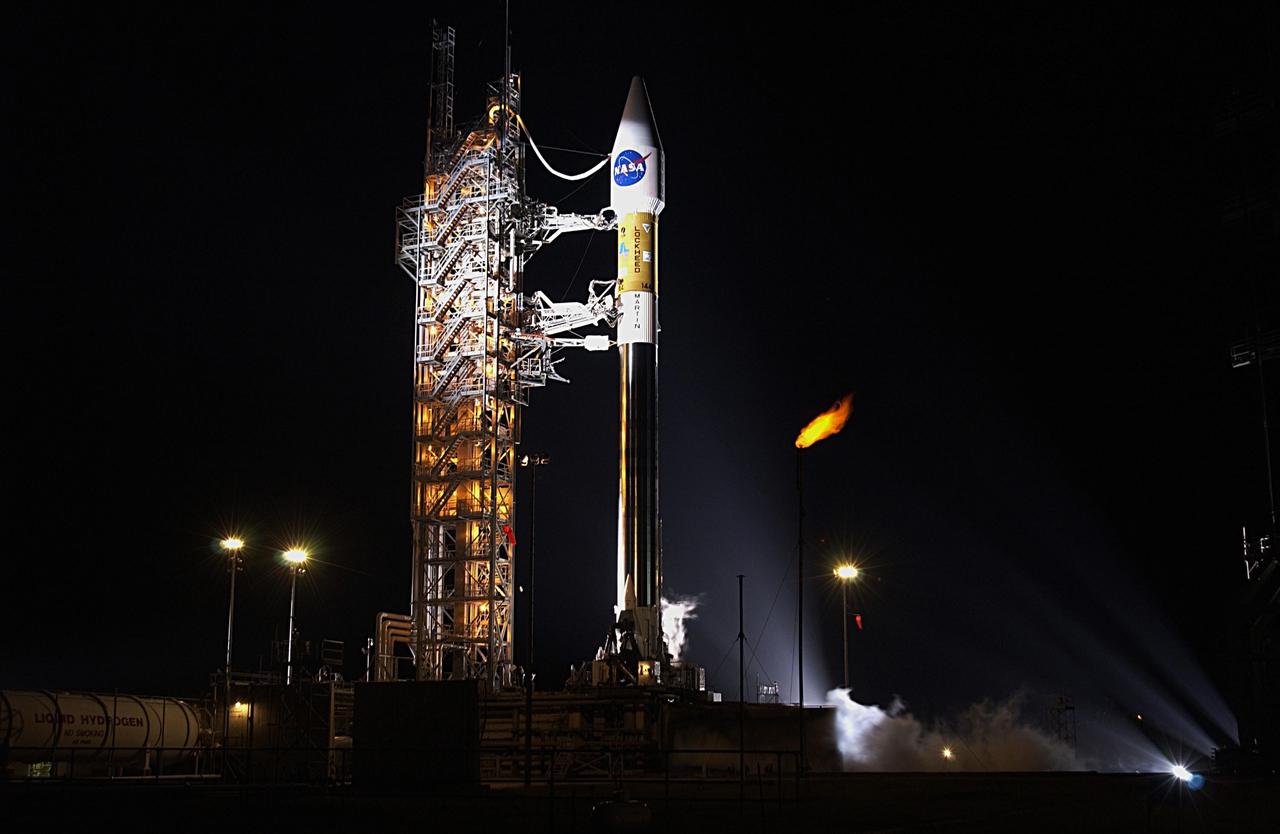

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the mobile service tower is rolled back to reveal the encapsulated TDRS-J satellite aboard an Atlas IIA vehicle awaiting launch on Dec. 4. The launch window is 9:42 to 10:22 p.m. EST. TDRS-J, the third in a series of telemetry satellites, will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites that are the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. The satellites also provide communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

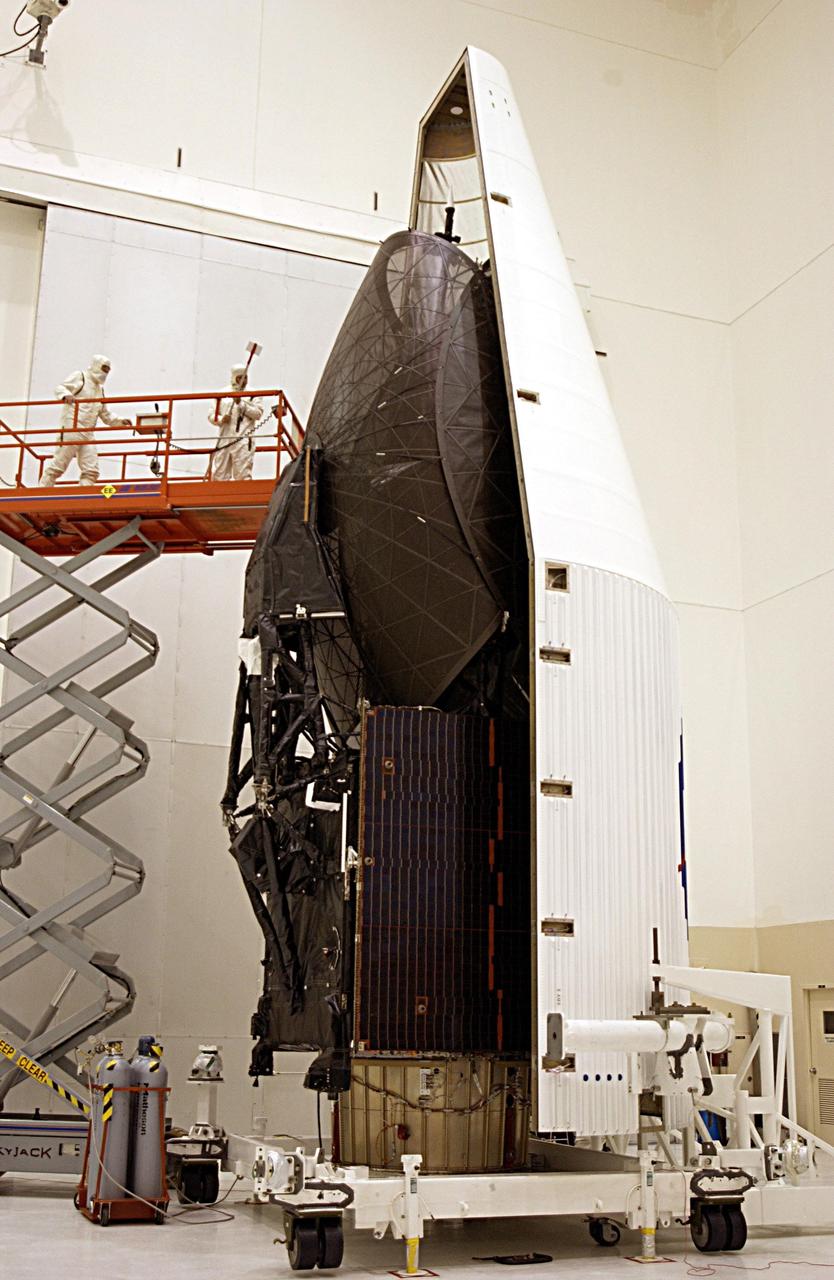
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The TDRS-J satellite sits between the two halves of the fairing before encapsulation for launch. The satellite is scheduled to be launched aboard a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIA-Centaur rocket from Launch Complex 36-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., on Dec. 4. The third in a series of telemetry satellites, TDRS-J will help replenish the current constellation of geosynchronous TDRS satellites. The TDRS System is the primary source of space-to-ground voice, data and telemetry for the Space Shuttle. It also provides communications with the International Space Station and scientific spacecraft in low-Earth orbit such as the Hubble Space Telescope. This new advanced series of satellites will extend the availability of TDRS communications services until about 2017.

An Air Force Titan III-C lifted off from Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 9:00 A.M. EDT today to launch Application Technology Satellite 6, first in a new generation of NASA Communications satellites. (1.3-13)(Test 7670)
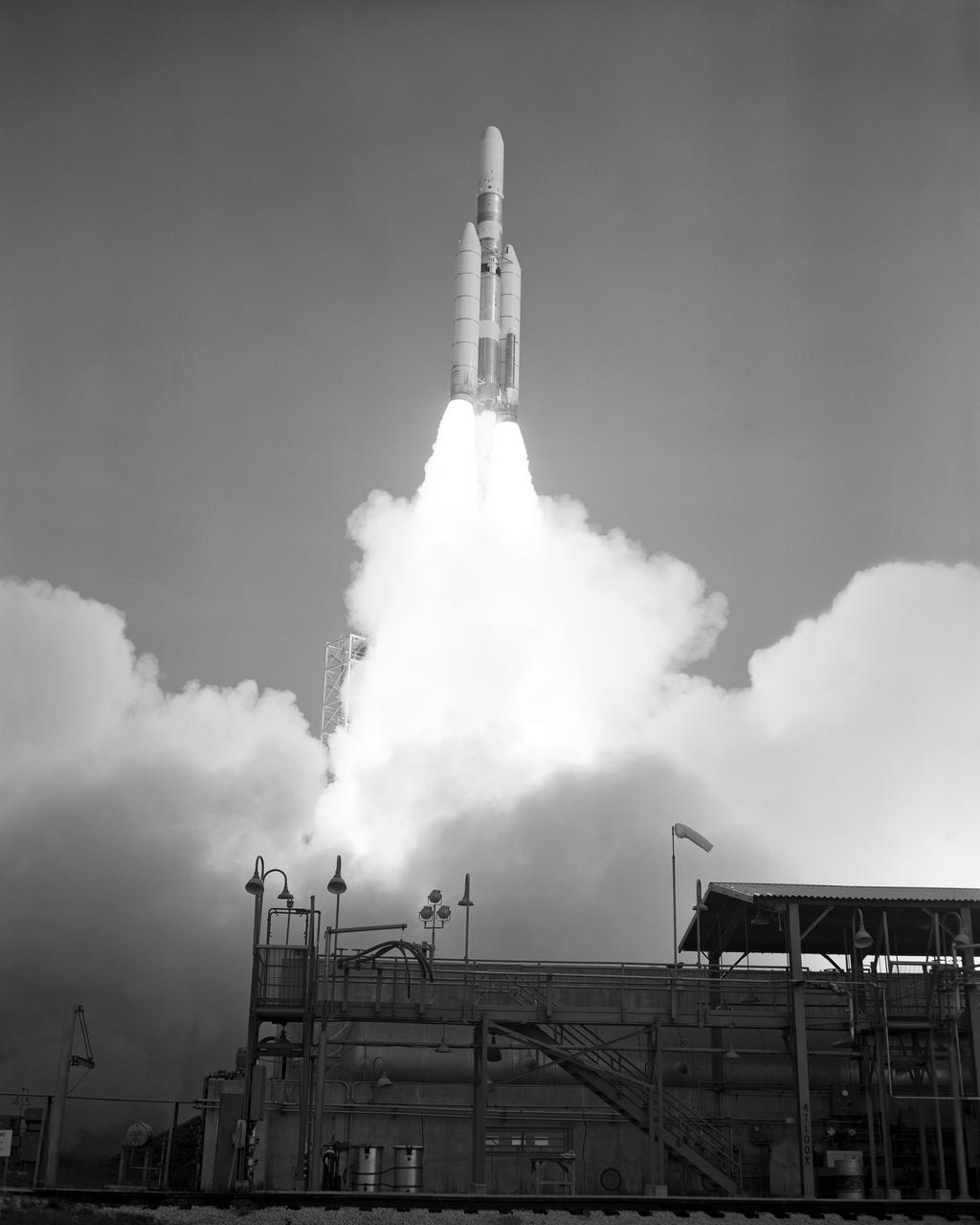

An Air Force Titan III-C lifted off from Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station at 9:00 A.M. EDT today to launch Application Technology Satellite 6, first in a new generation of NASA Communications satellites. (1.3-22)
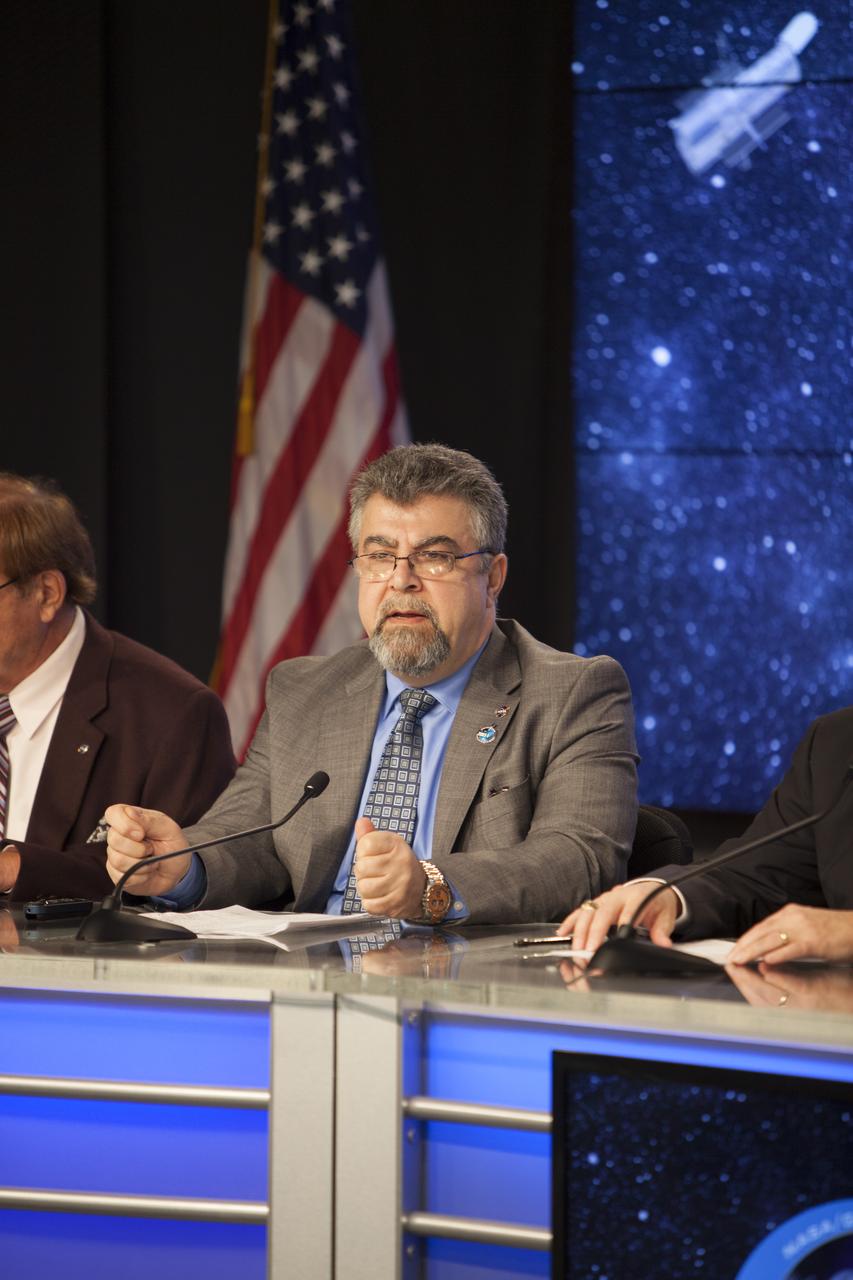

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, agency and contractor officials discussed preparations for the launch of NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft. Participants included Badri Younes, deputy associate administrator, Space Communications and Navigation SCaN NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C. The TDRS-L spacecraft is the second of three new satellites designed to ensure vital operational continuity for NASA by expanding the lifespan of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System TDRSS fleet, which consists of eight satellites in geosynchronous orbit. The spacecraft provide tracking, telemetry, command and high bandwidth data return services for numerous science and human exploration missions orbiting Earth. These include NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the International Space Station. TDRS-L has a high-performance solar panel designed for more spacecraft power to meet the growing S-band communications requirements. TDRSS is one of NASA Space Communication and Navigation’s SCaN three networks providing space communications to NASA’s missions. For more information more about TDRS-L, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/tdrs To learn more about SCaN, visit: www.nasa.gov/scan Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
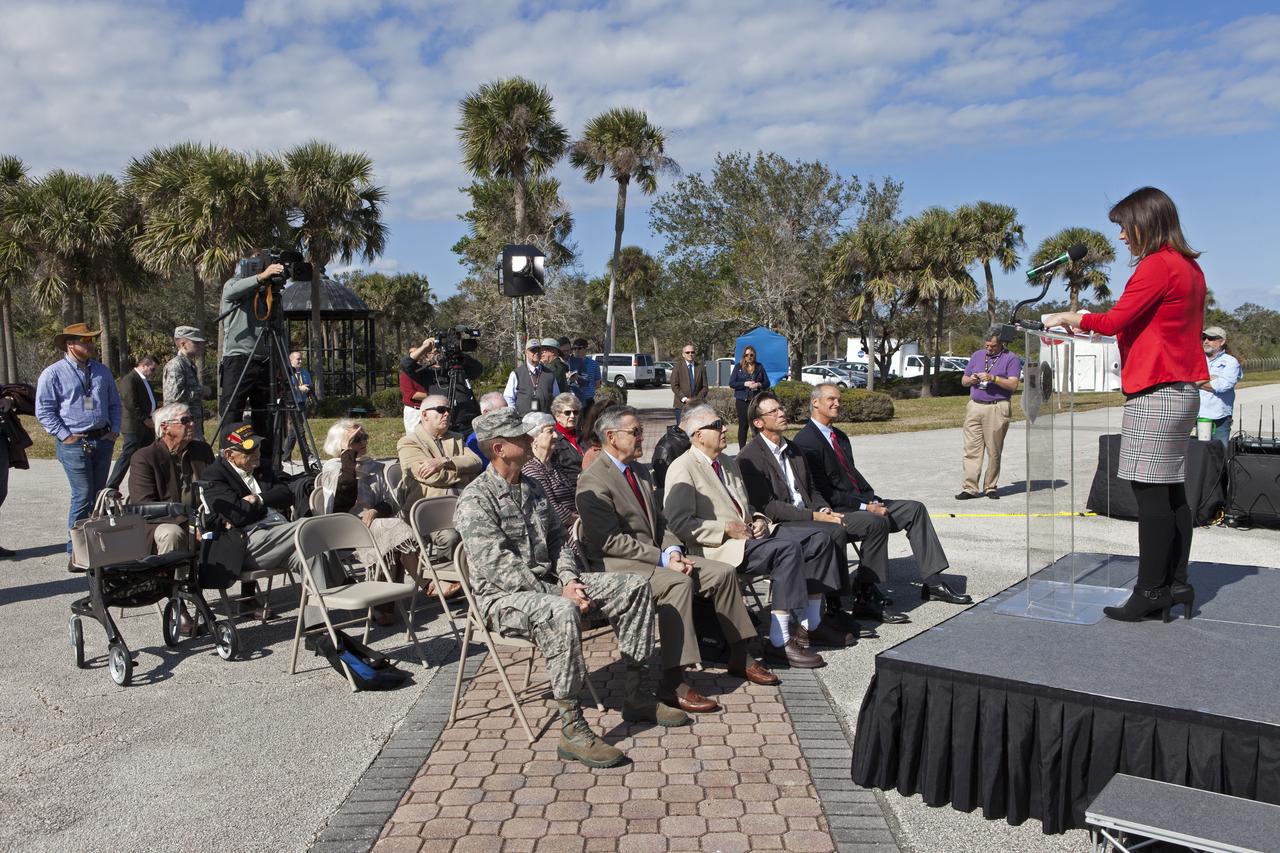

Tori McLendon of NASA Communications, speaks to guests at an event celebrating the 60th anniversary of America's first satellite. The ceremony took place in front of the Space Launch Complex 26 blockhouse at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station where the Explorer 1 satellite was launched atop a Jupiter C rocket on Jan. 31, 1958. During operation, the satellite's cosmic ray detector discovered radiation belts around Earth which were named for Dr. James Van Allen, principal investigator for the satellite.
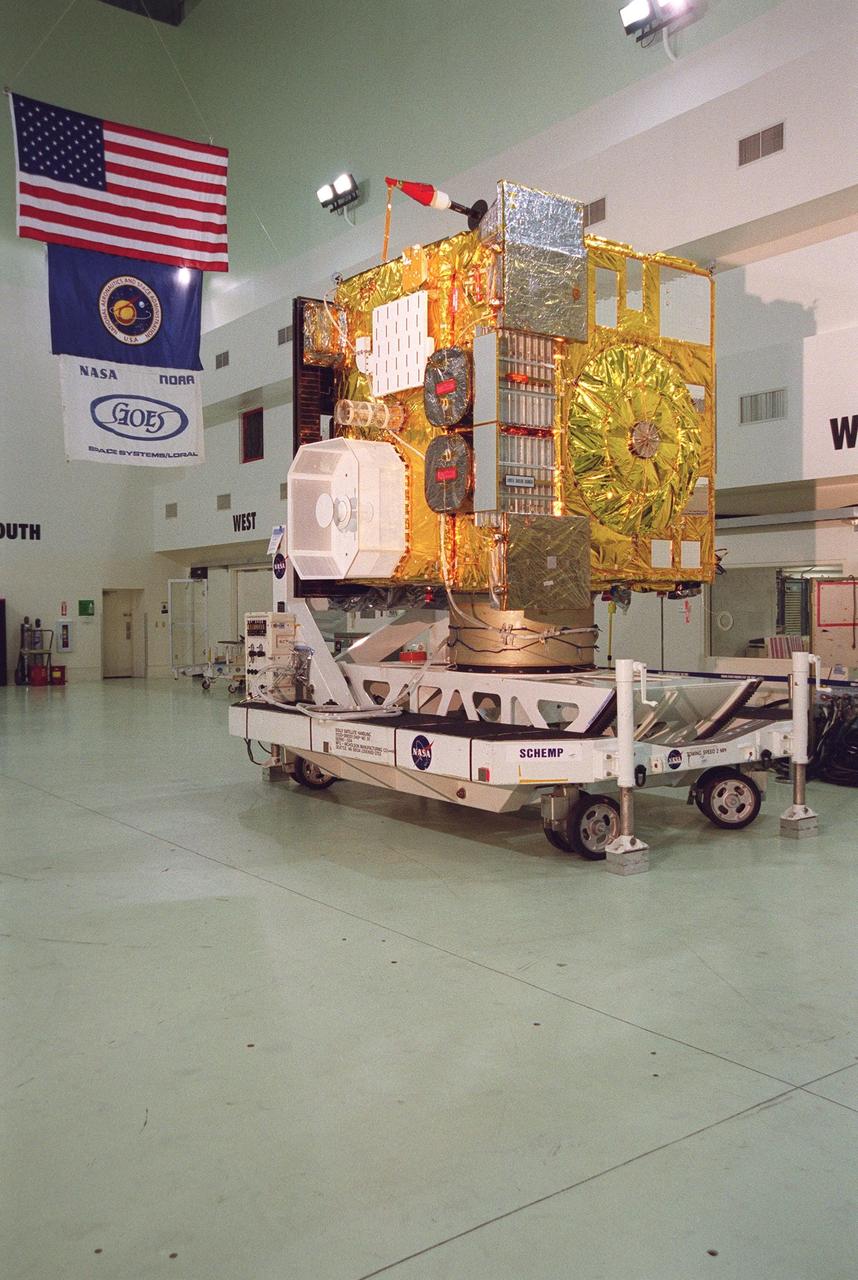

The newest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-M (GOES-M) satellite is in the spotlight at Astrotech, in Titusville, for the media to see the last in the current series of advanced geostationary weather satellites in service. GOES-M has a new instrument not on earlier spacecraft, a Solar X-ray Imager that can be used in forecasting space weather, the effects of solar storms that create electromagnetic disturbances on earth that affect other satellites, communications and power grids. GOES is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on an Atlas II rocket in July
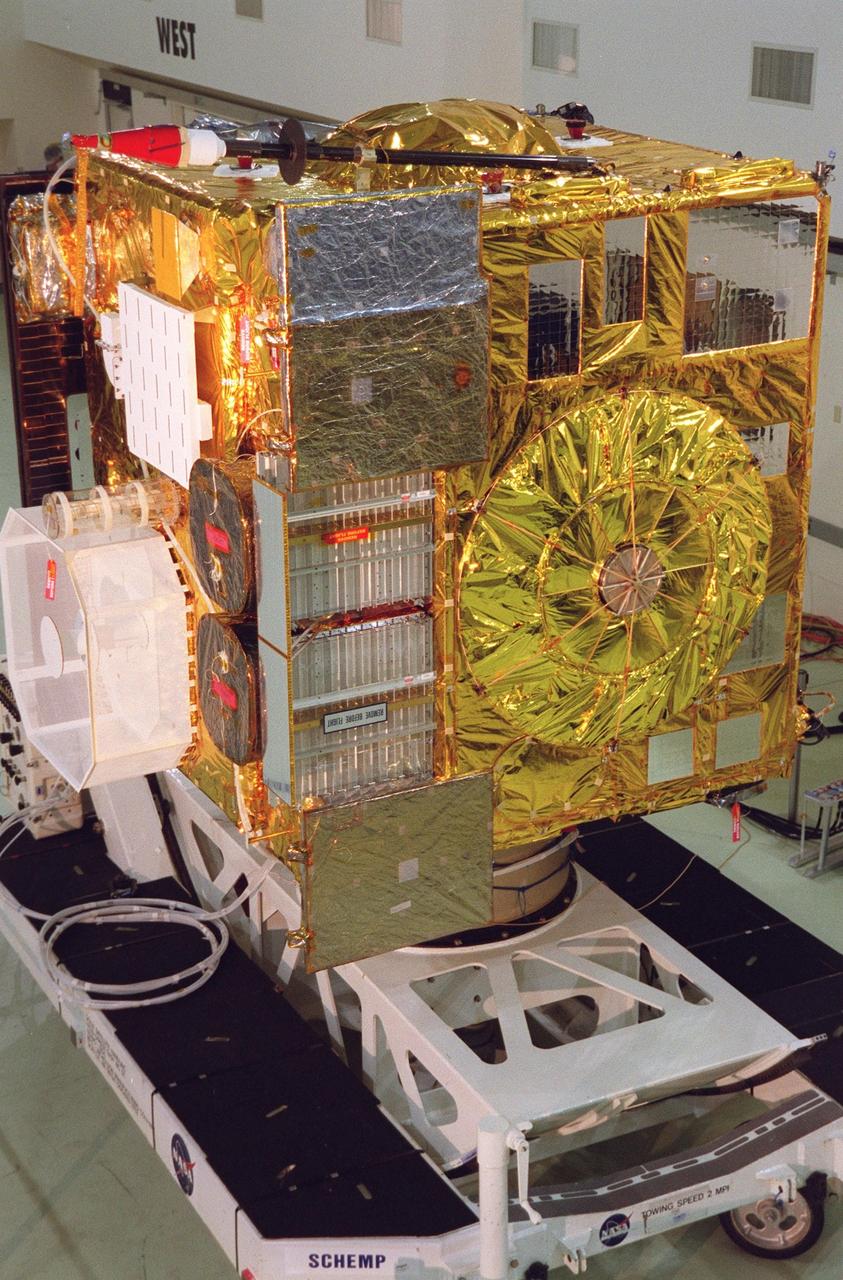

The newest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-M (GOES-M) satellite is ready at Astrotech, in Titusville for the media to see the last in the current series of advanced geostationary weather satellites in service. GOES-M has a new instrument not on earlier spacecraft, a Solar X-ray Imager that can be used in forecasting space weather, the effects of solar storms that create electromagnetic disturbances on earth that affect other satellites, communications and power grids. GOES is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on an Atlas II rocket in July
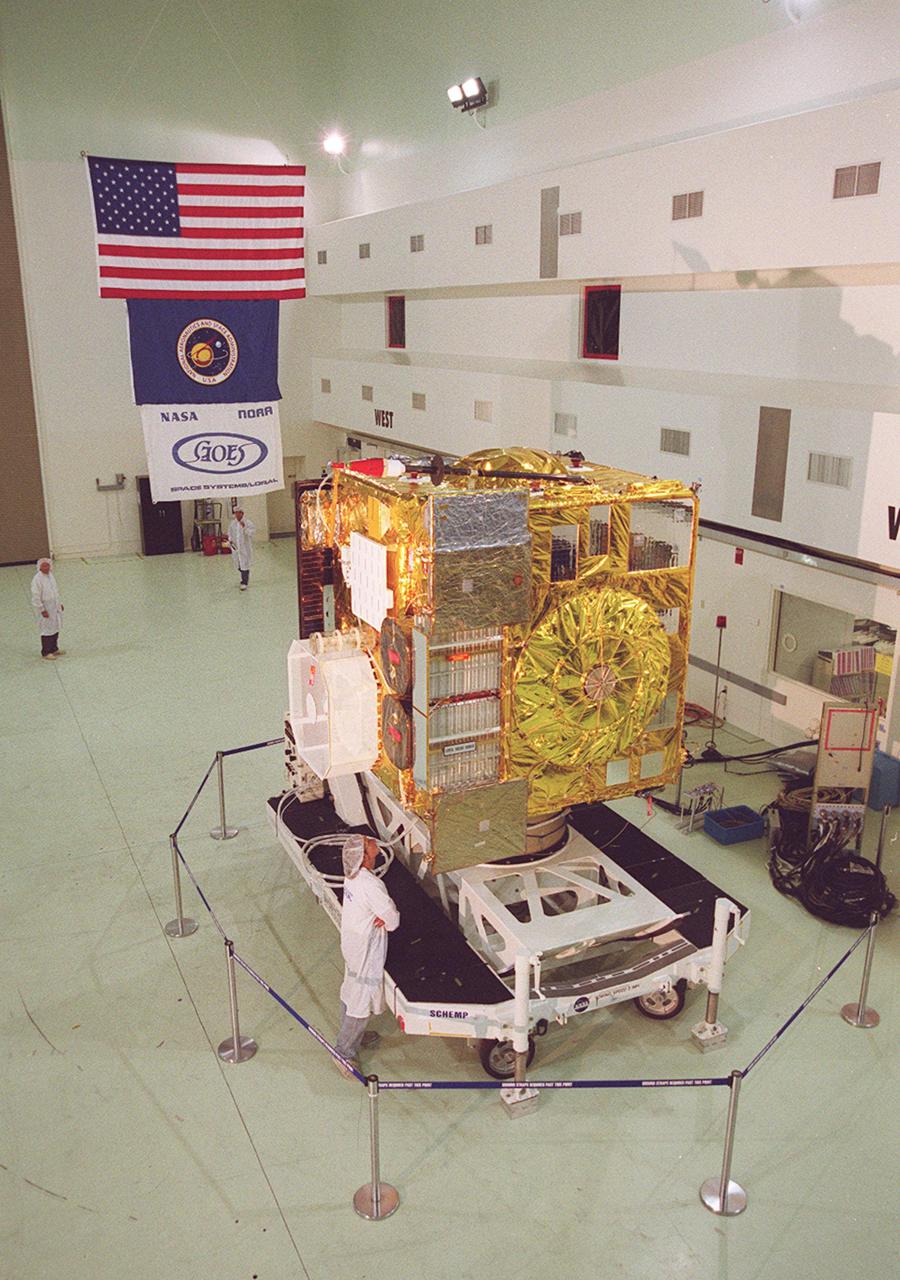

The newest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-M (GOES-M) satellite is ready at Astrotech, in Titusville for the media to see the last in the current series of advanced geostationary weather satellites in service. GOES-M has a new instrument not on earlier spacecraft, a Solar X-ray Imager that can be used in forecasting space weather, the effects of solar storms that create electromagnetic disturbances on earth that affect other satellites, communications and power grids. GOES is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on an Atlas II rocket in July
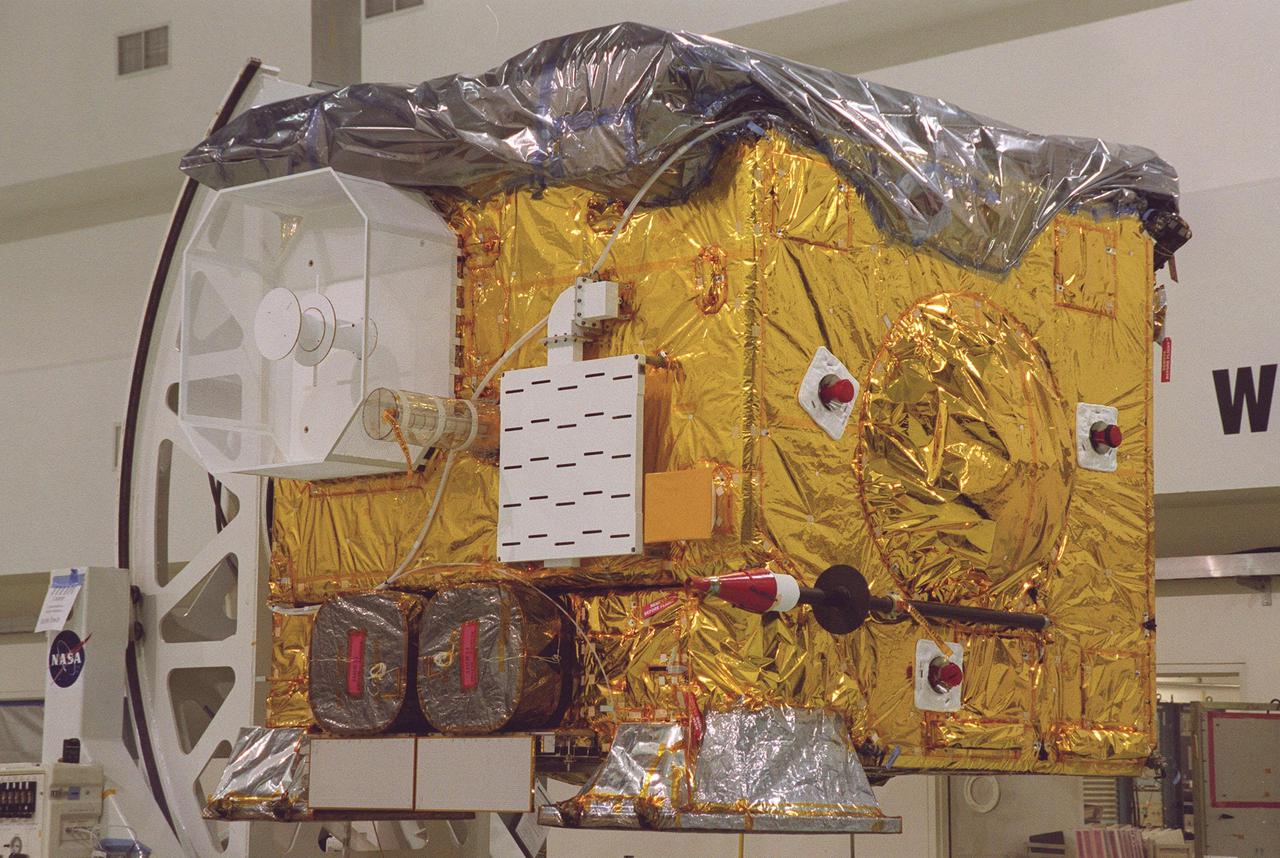

The newest Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-M (GOES-M) satellite is in the spotlight at Astrotech, in Titusville, for the media to see the last in the current series of advanced geostationary weather satellites in service. GOES-M has a new instrument not on earlier spacecraft, a Solar X-ray Imager that can be used in forecasting space weather, the effects of solar storms that create electromagnetic disturbances on earth that affect other satellites, communications and power grids. GOES is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on an Atlas II rocket in July
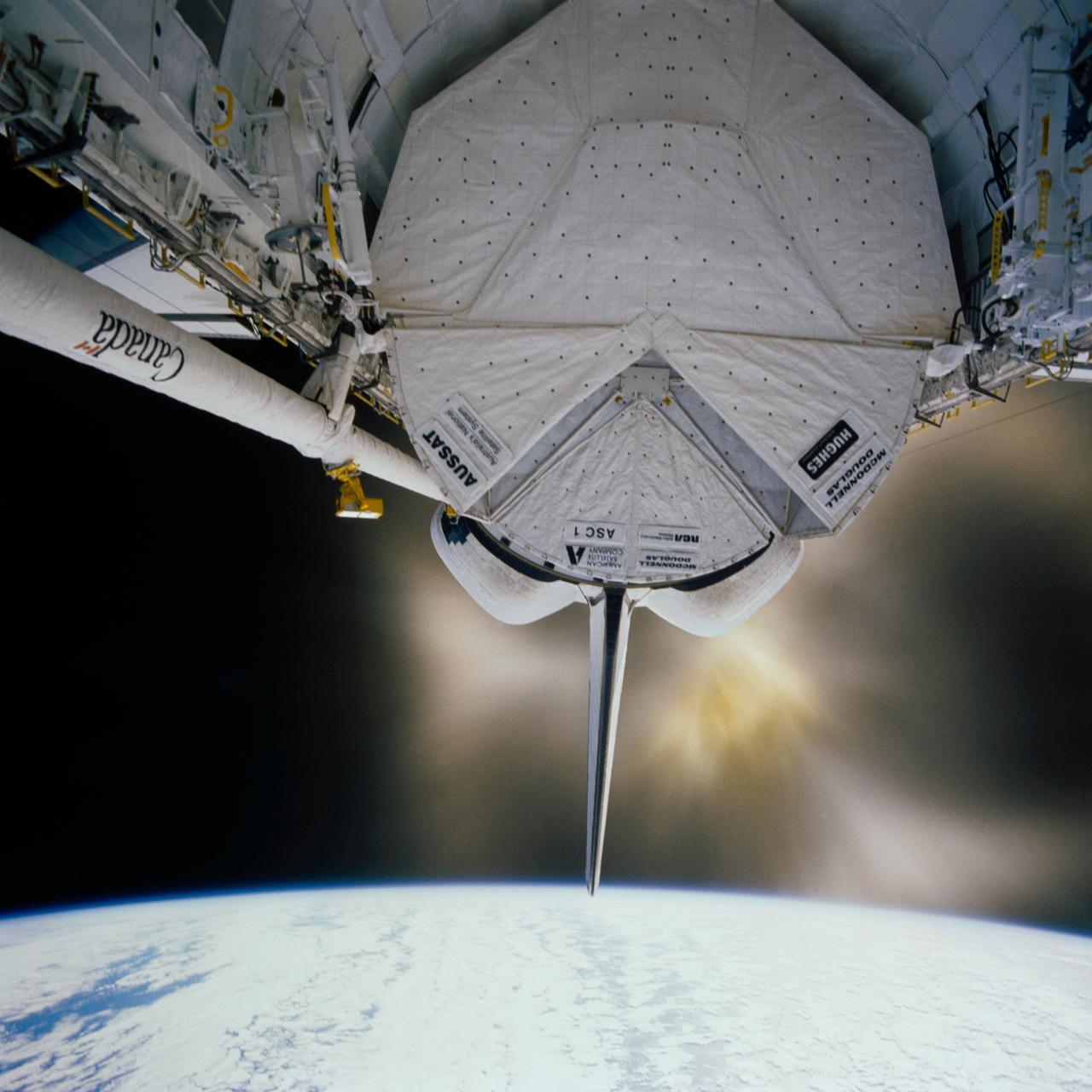

View of a single engine orbital maneuvering system (OMS) firing on the Discovery. The payload bay is open and the protective canisters for the AUSSAT communications satellite (open) and the ASC-1 are visible. A cloudy Earth's horizon can be seen above the orbiter.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians check out the Symphonie-B spacecraft during launch preparations at KSC. Symphonie is a synchronous-orbit communications satellite, jointly owned and managed by West Germany and France. Photo credit: NASA
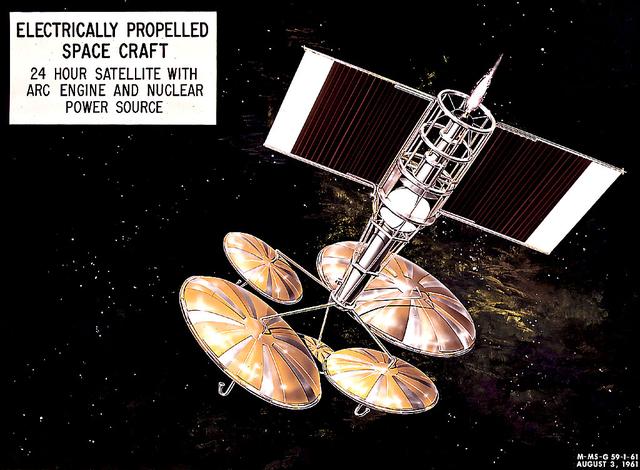
This 1960 artist's concept shows a 24-hour communication satellite design incorporating an arc engine with a nuclear power source. The concept was one of many missions proposed by the Marshall Space Flight Center for electrically-propelled spacecraft.
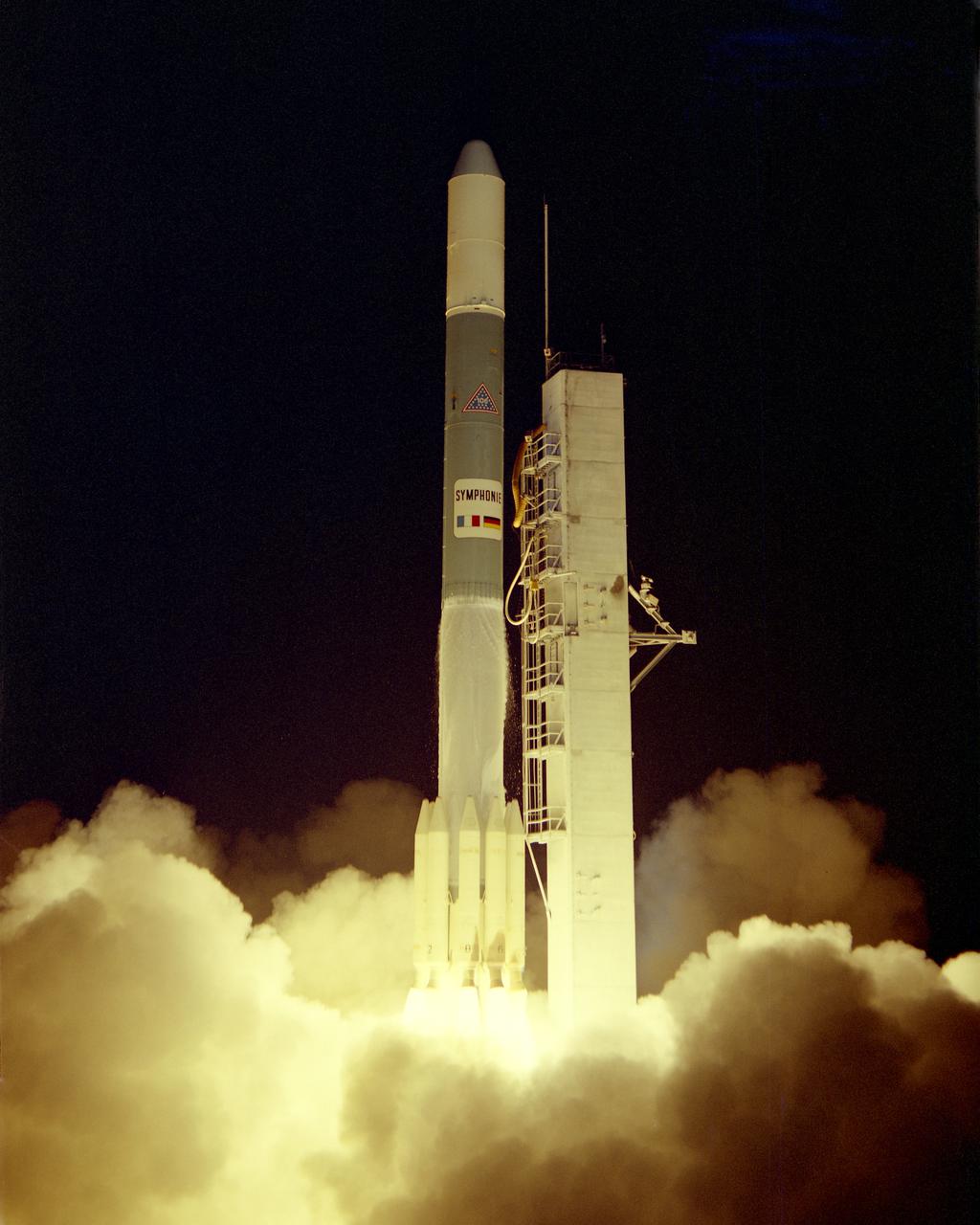

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Launch of Symphonie-A on Complex 17-B at 9:39 p.m. EST. Symphonie-A is a communications satellite for a Franco-German industrial consortium. Photo credit: NASA

51D-31-050 (12 April 1985) --- Among 51-D's first day activities was the deployment of the Telesat-I (Anik C-1) communications satellite. Earth and blackness of space share the background in the 70mm frame.

51D-31-081 (13 April 1985) --- 70mm view of the Syncom IV (LEASAT) communications satellite as it spins, frisbee fashion, from the cargo bay of the Earth orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery.
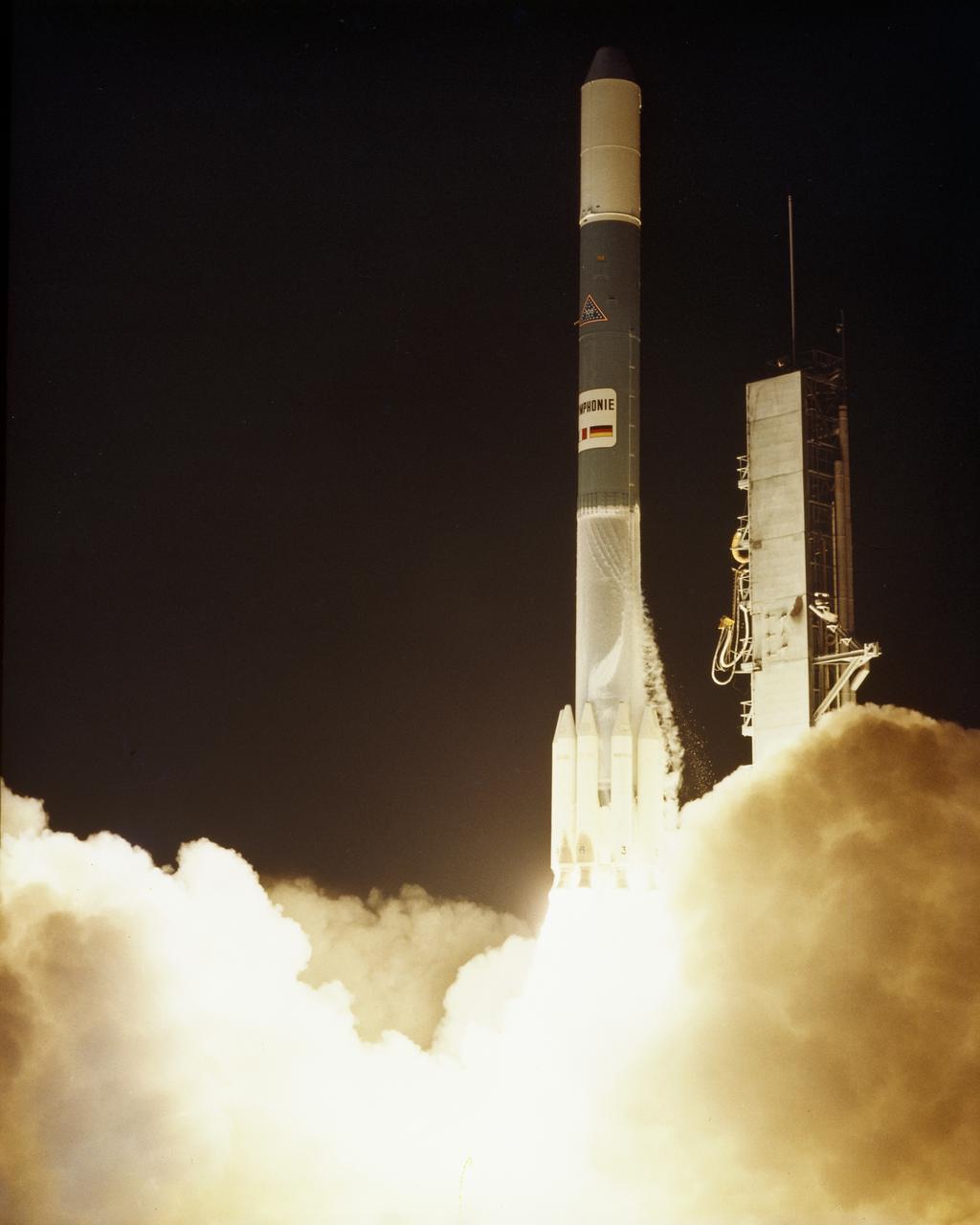

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Launch of Symphonie-A on Complex 17-B at 9:39 p.m. EST. Symphonie-A is a communications satellite for a Franco-German industrial consortium. Photo credit: NASA
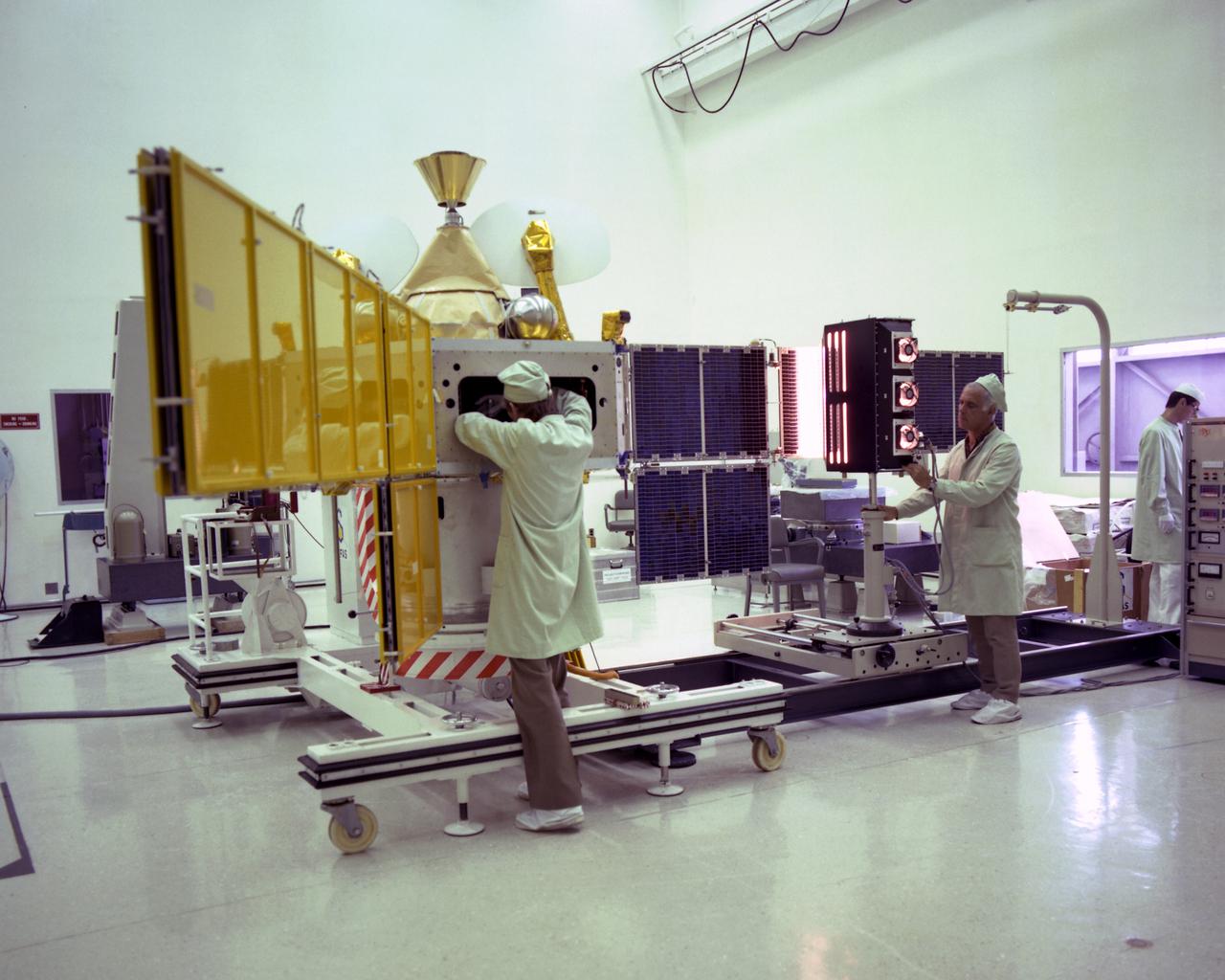

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians check out the Symphonie-B spacecraft during launch preparations at KSC. Symphonie is a synchronous-orbit communications satellite, jointly owned and managed by West Germany and France. Photo credit: NASA
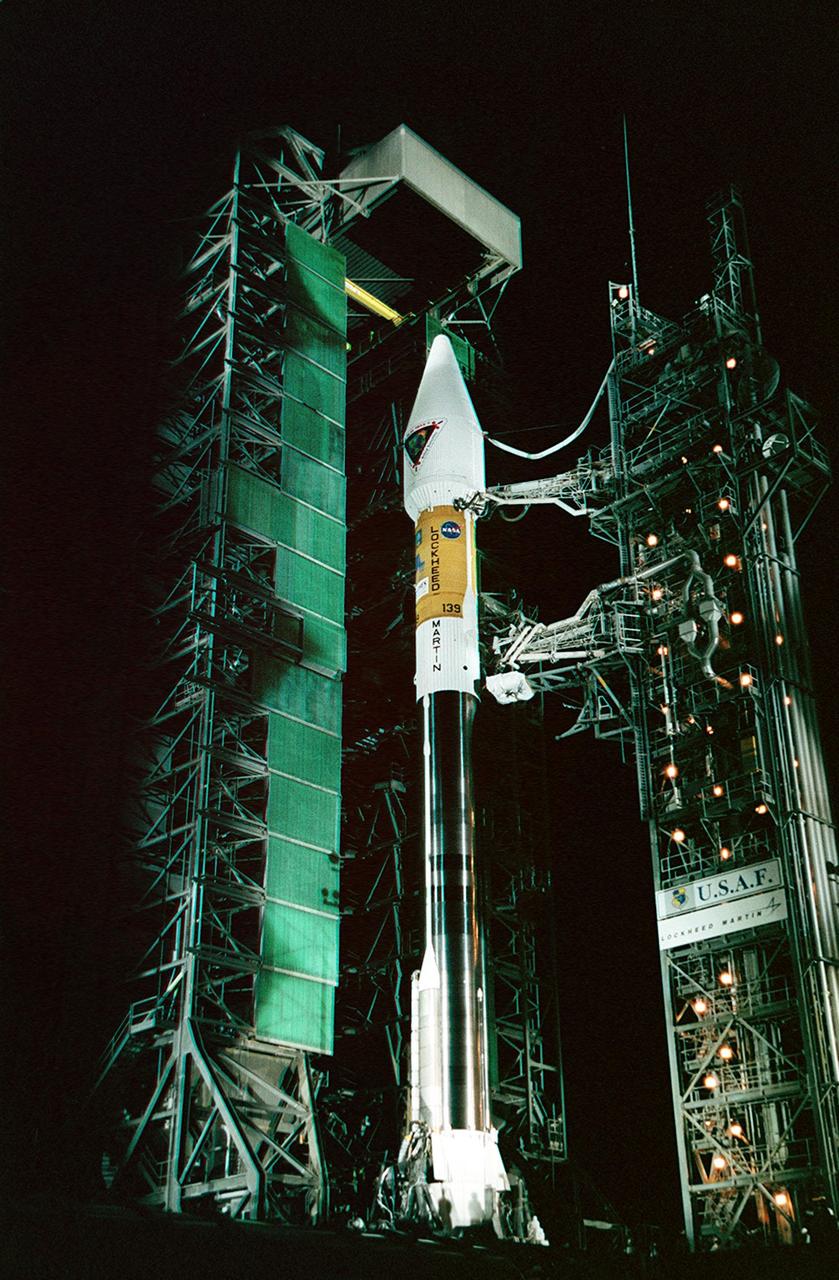
In the early morning hours on Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the tower rolls back from NASA’s Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) before liftoff atop an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built by the Hughes Space and Communications Company, the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the Space Shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
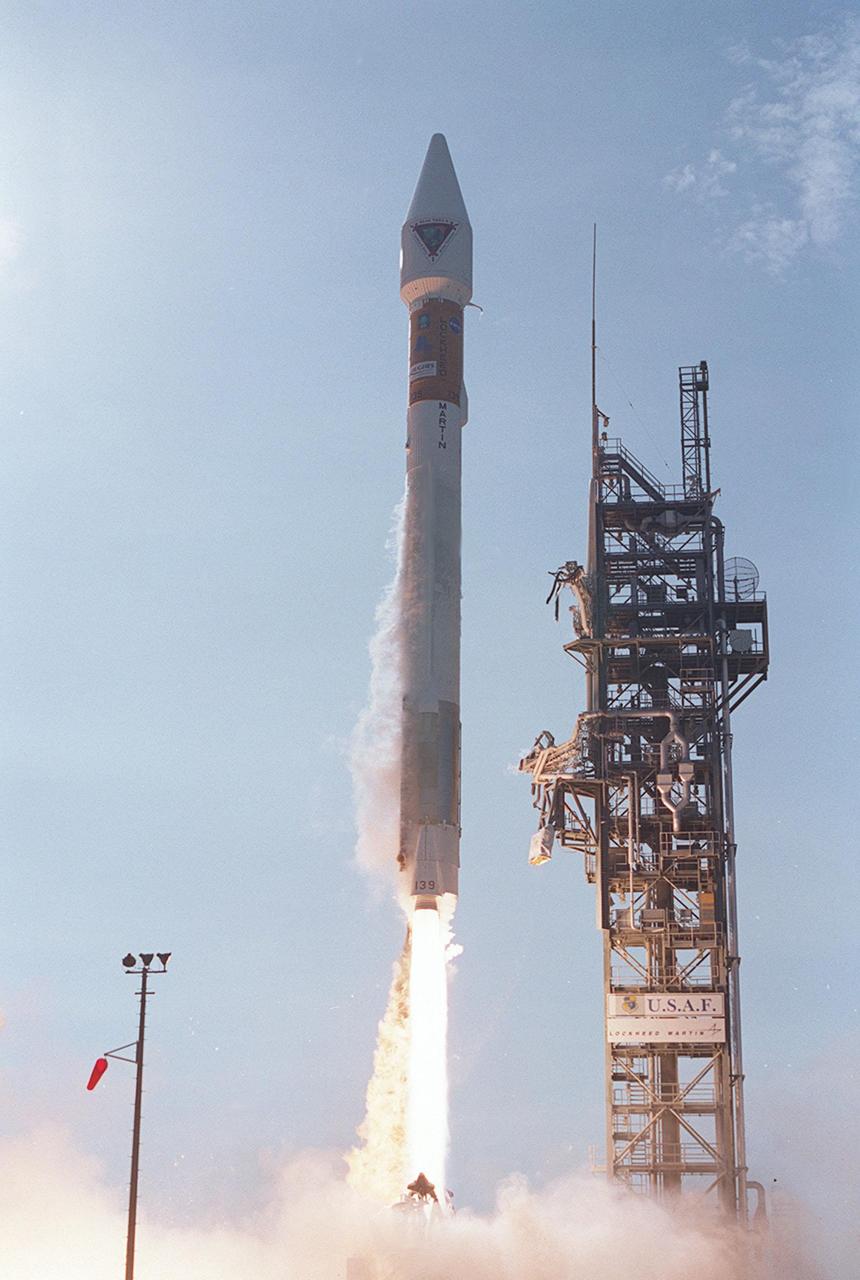

Looking like a Roman candle, NASA’s Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) shoots into the blue sky aboard an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket from Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Liftoff occurred at 8:56 a.m. EDT. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built by the Hughes Space and Communications Company, the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
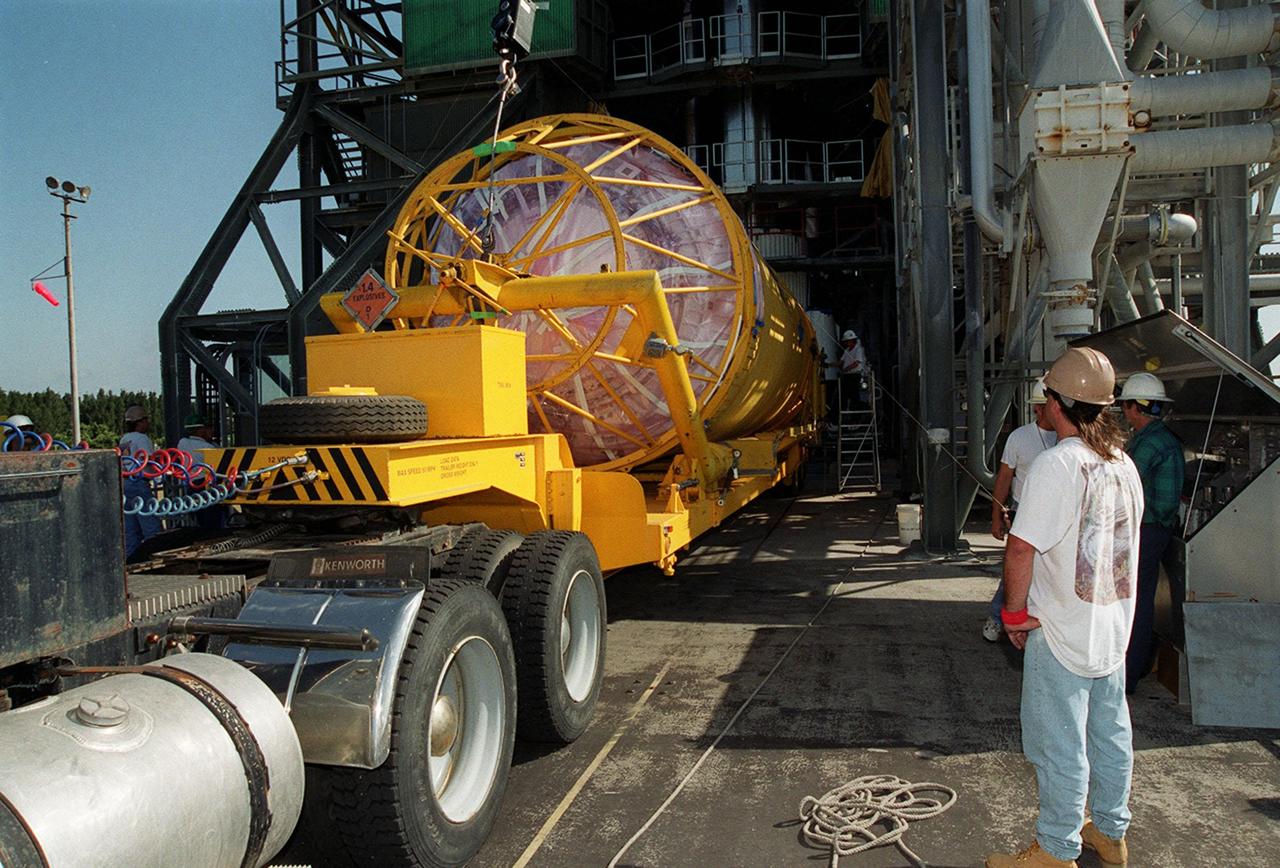

At Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a Centaur rocket arrives for mating with the Atlas IIA rocket already in the tower. The Centaur upper stage is 10.0 m (33-ft) long and 3.05 m (10 ft) in diameter. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
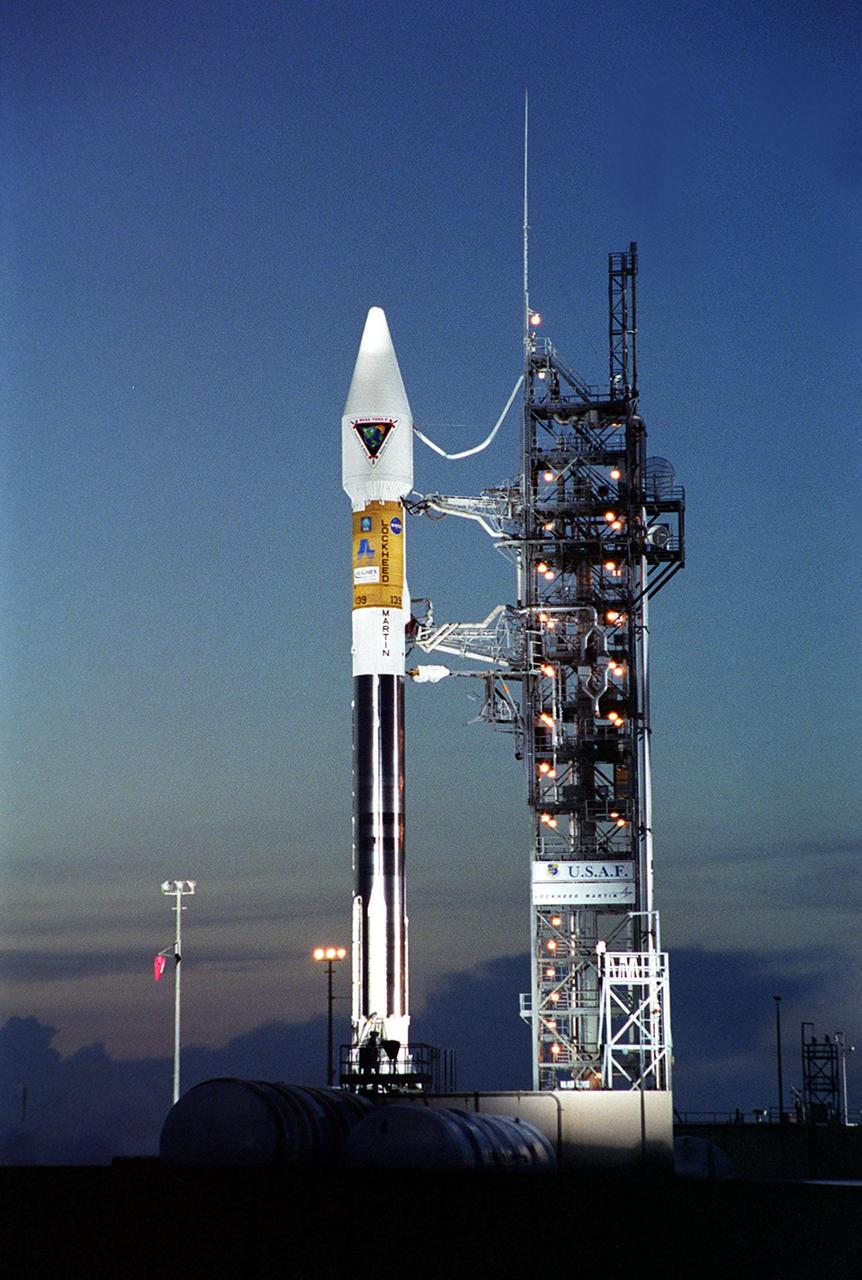

After tower rollback just before dawn on Launch Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, NASA’s Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-H) sits bathed in spotlights before liftoff atop an Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket. One of three satellites (labeled H, I and J) being built by the Hughes Space and Communications Company, the latest TDRS uses an innovative springback antenna design. A pair of 15-foot-diameter, flexible mesh antenna reflectors fold up for launch, then spring back into their original cupped circular shape on orbit. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the Space Shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit
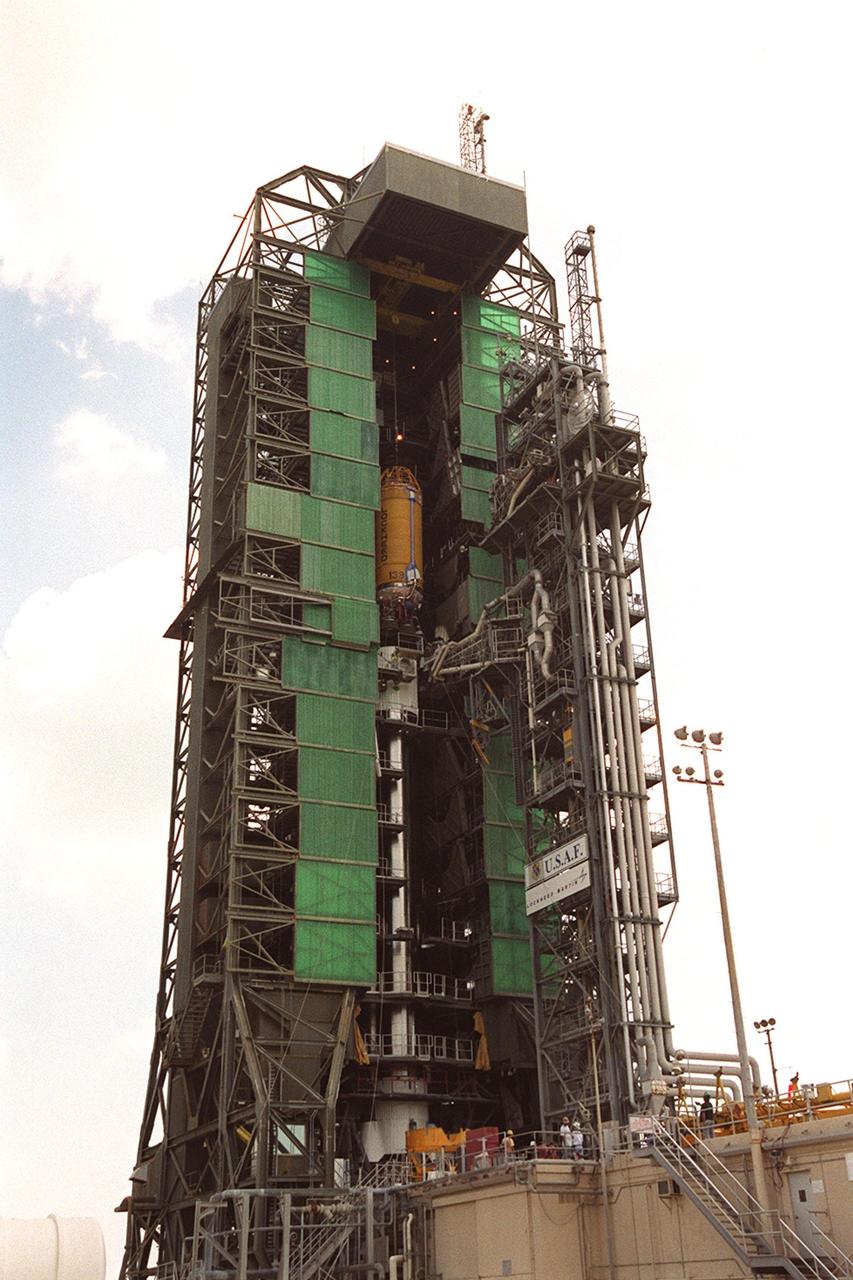

In this long view of the launch tower at Pad 36A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the upper stage Centaur rocket can be seen as it rises up the tower to be mated to the lower stage Atlas IIA rocket already there. The Lockheed-built Atlas IIA/Centaur rocket will launch the latest Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) June 29 from CCAFS. The TDRS is one of three (labeled H, I and J) being built in the Hughes Space and Communications Company Integrated Satellite Factory in El Segundo, Calif. The new satellites will augment the TDRS system’s existing Sand Ku-band frequencies by adding Ka-band capability. TDRS will serve as the sole means of continuous, high-data-rate communication with the space shuttle, with the International Space Station upon its completion, and with dozens of unmanned scientific satellites in low earth orbit