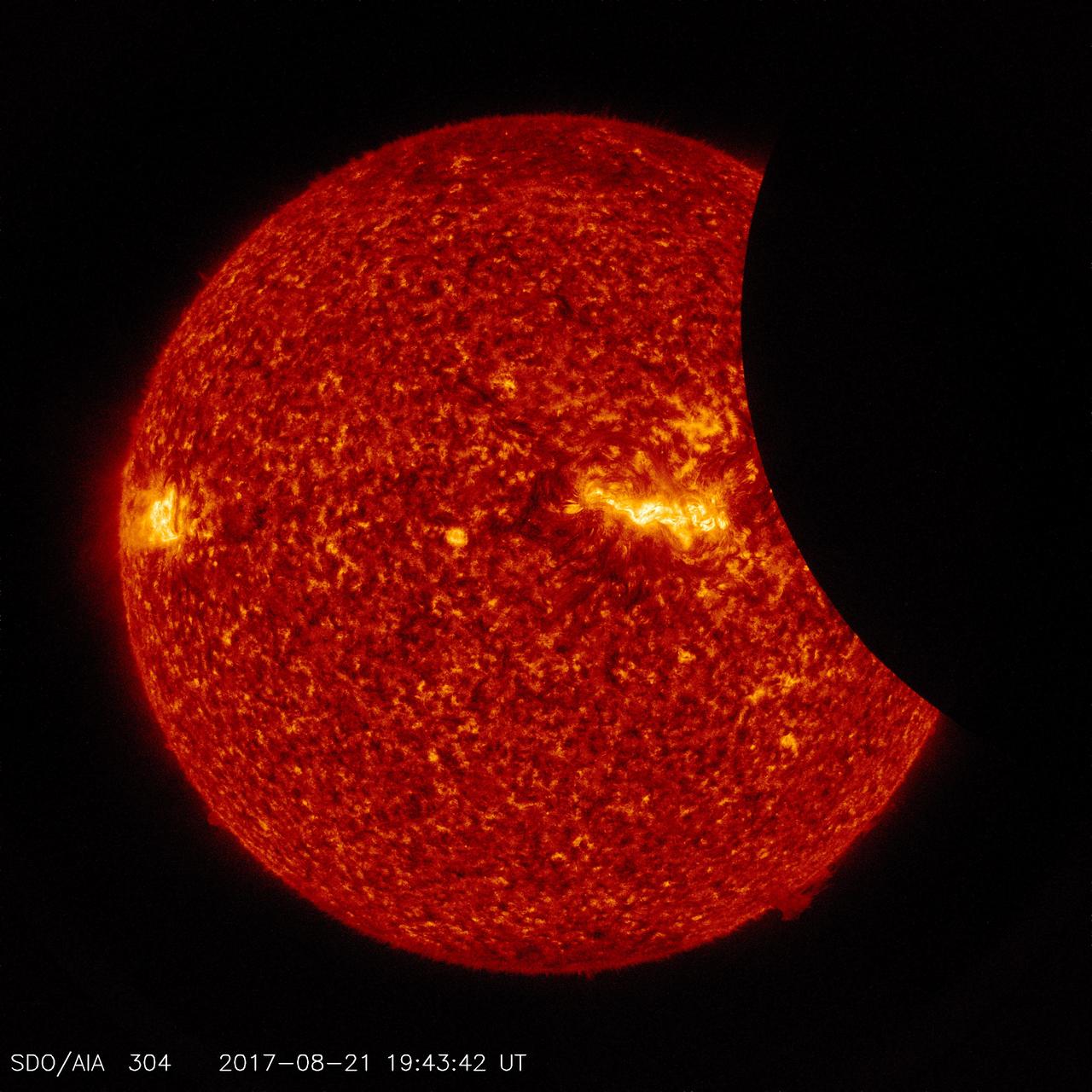

Image of the Moon transiting across the Sun, taken by SDO in 304 angstrom extreme ultraviolet light on August 21, 2017. Credit: NASA/SDO
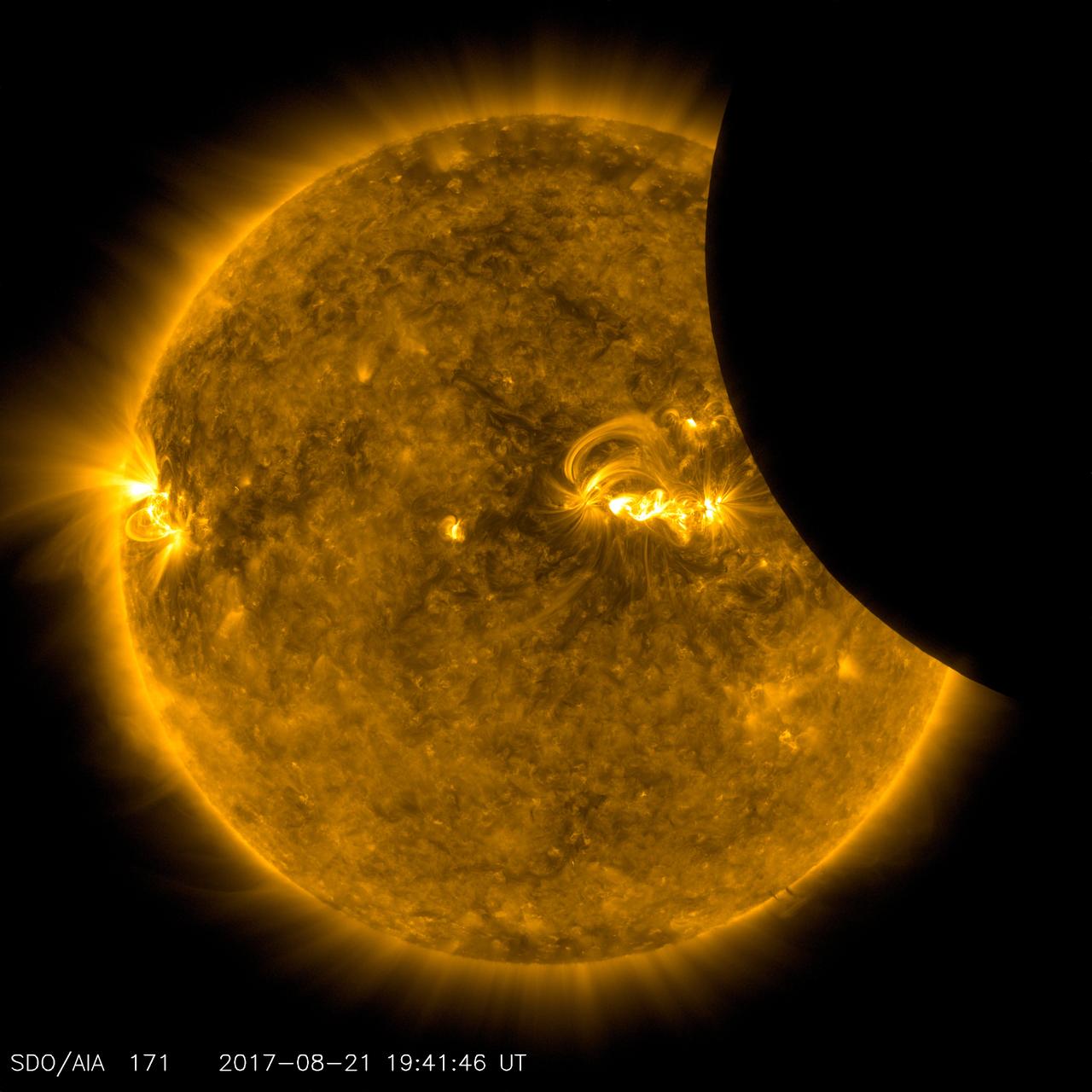
Image of the Moon transiting across the Sun, taken by SDO in 171 angstrom extreme ultraviolet light on August 21, 2017. Credit: NASA/SDO

Millions of excited people in the U.S. traveled many miles see a total eclipse, and what a show it was. The SDO spacecraft was not so fortunate: its orbit only allowed it to observe a partial eclipse that at its peak covered only about 14 per cent of the sun (Aug. 21, 2017). Most of the people in the U.S. (weather permitting) observed at least 60 per cent coverage of the sun by the Moon. The good news for SDO is that it gets to see partial and solar eclipses several times a year. So, it all kind of balances out, in a way. An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21929
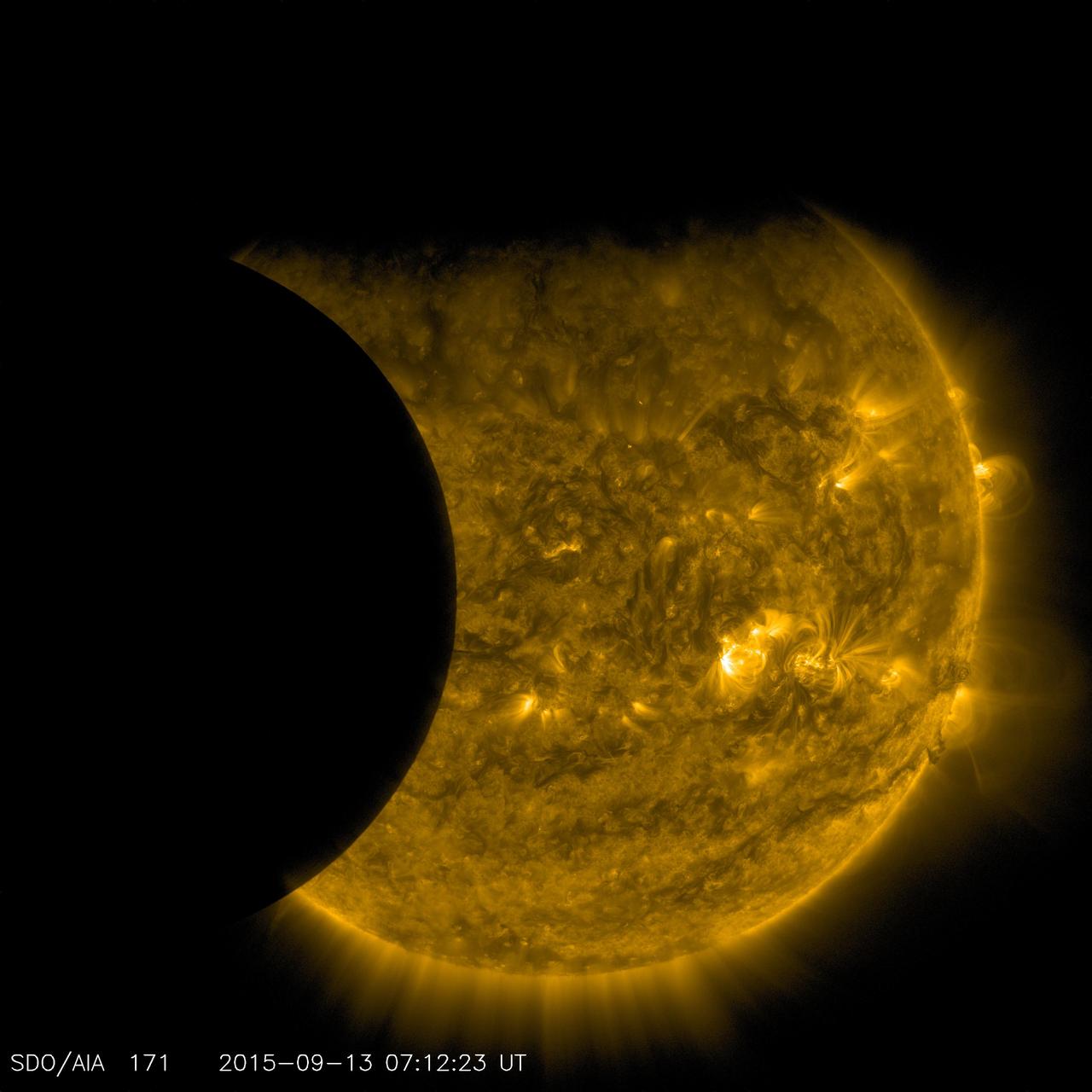
On Sept. 13, 2015, as NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, kept up its constant watch on the sun, its view was photobombed not once, but twice. Just as the moon came into SDO's field of view on a path to cross the sun, Earth entered the picture, blocking SDO's view completely. When SDO's orbit finally emerged from behind Earth, the moon was just completing its journey across the sun's face. Though SDO sees dozens of Earth eclipses and several lunar transits each year, this is the first time ever that the two have coincided. SDO's orbit usually gives us unobstructed views of the sun, but Earth's revolution around the sun means that SDO's orbit passes behind Earth twice each year, for two to three weeks at a time. During these phases, Earth blocks SDO's view of the sun for anywhere from a few minutes to over an hour once each day. Earth's outline looks fuzzy, while the moon's is crystal-clear. This is because-while the planet itself completely blocks the sun's light-Earth's atmosphere is an incomplete barrier, blocking different amounts of light at different altitudes. However, the moon has no atmosphere, so during the transit we can see the crisp edges of the moon's horizon. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19949

On Sept. 13, 2015, as NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, kept up its constant watch on the sun, its view was photobombed not once, but twice. Just as the moon came into SDO’s field of view on a path to cross the sun, Earth entered the picture, blocking SDO’s view completely. When SDO's view of the sun emerged from Earth’s shadow, the moon was just completing its journey across the sun’s face. Though SDO sees dozens of Earth eclipses and several lunar transits each year, this is the first time ever that the two have coincided. This alignment of the sun, moon and Earth also resulted in a partial solar eclipse on Sept. 13, visible only from parts of Africa and Antarctica. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasas-sdo-catches-a-double-photobomb" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasas-sdo-catches-a-double-p...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
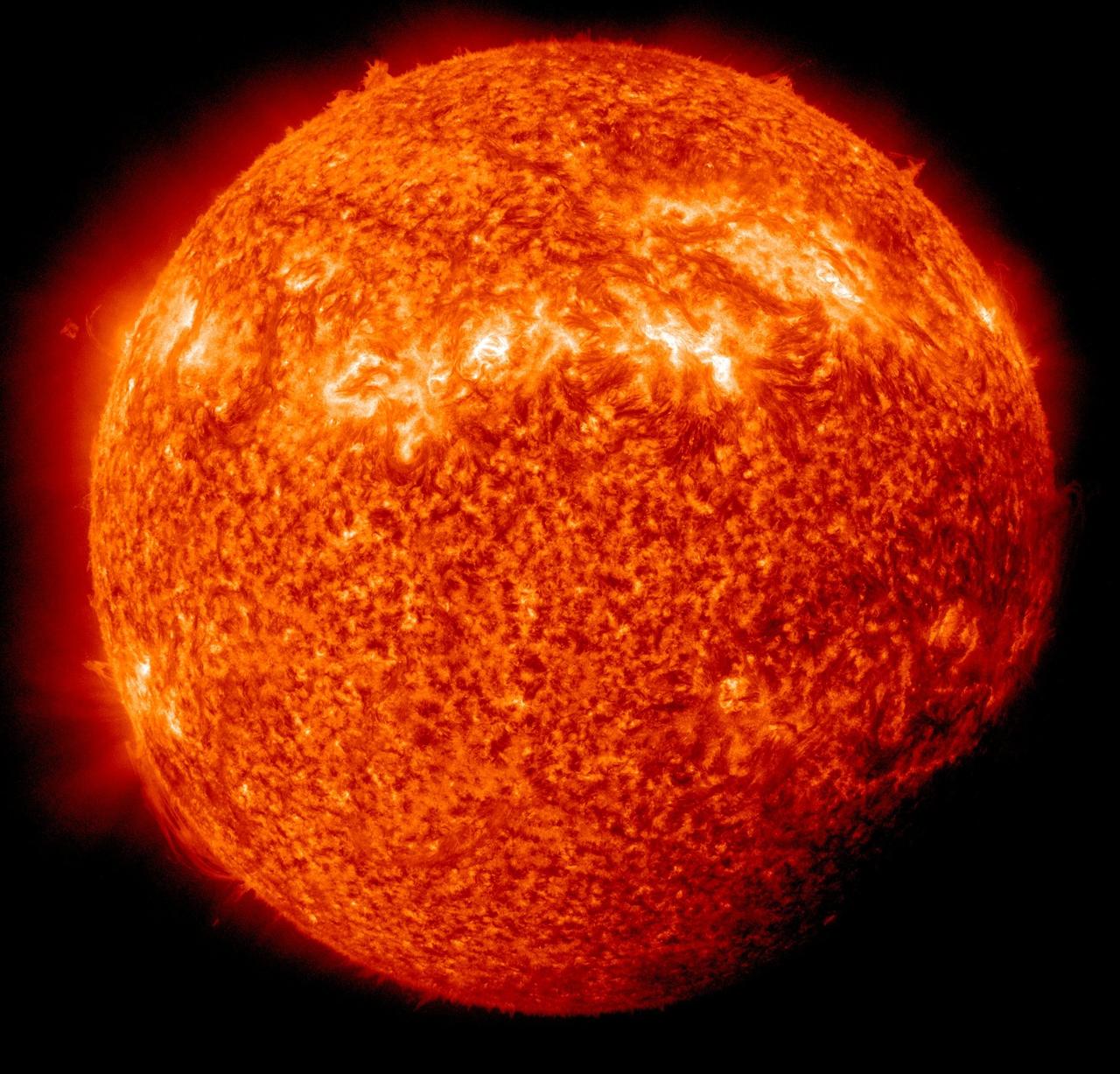
NASA image captured April 3, 2011 Twice a year, SDO enters an eclipse season where the spacecraft slips behind Earth for up to 72 minutes a day. Unlike the crisp shadow one sees on the sun during a lunar eclipse, Earth's shadow has a variegated edge due to its atmosphere, which blocks the sun light to different degrees depending on its density. Also, light from brighter spots on the sun may make it through, which is why some solar features extend low into Earth's shadow. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
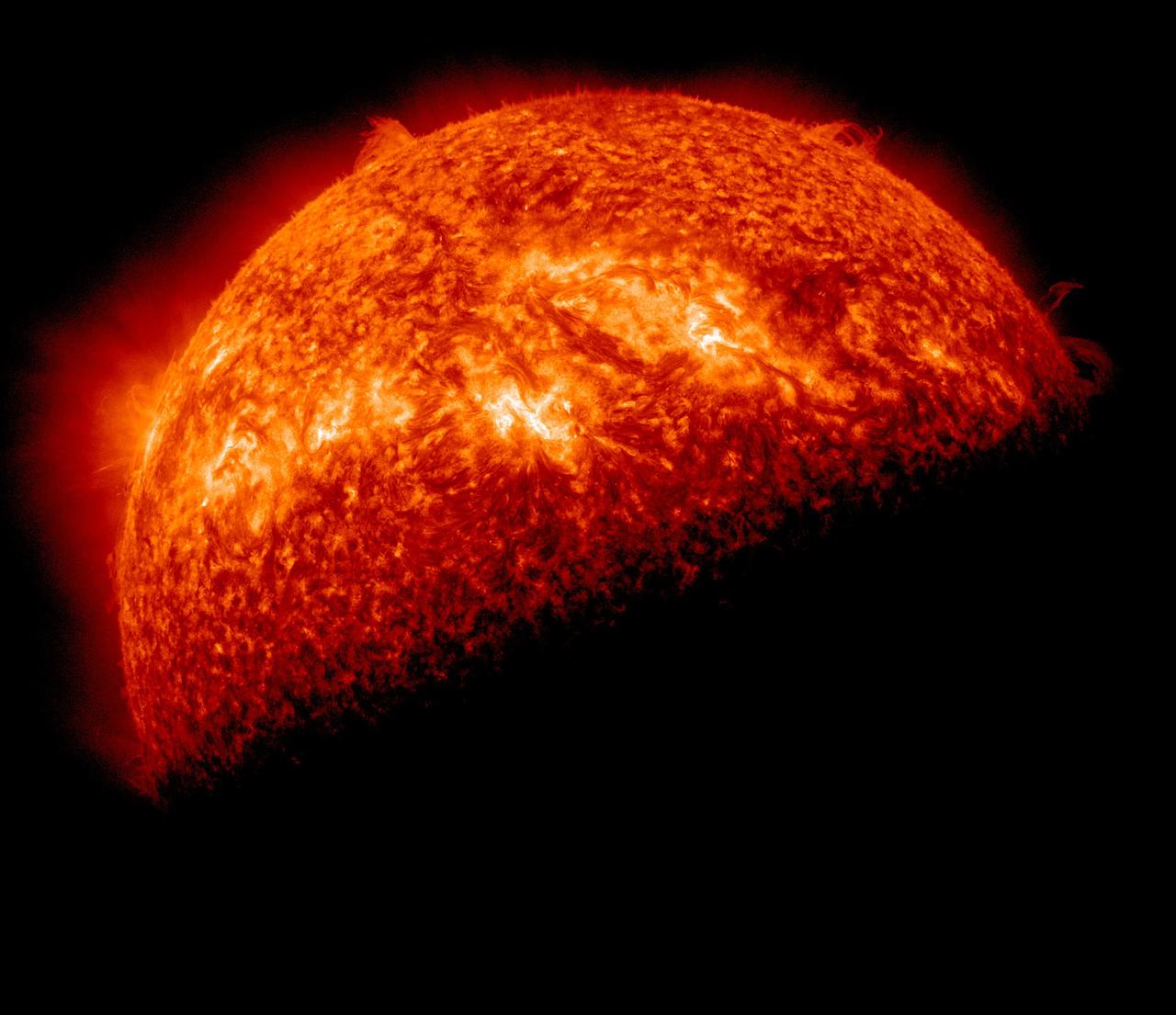

NASA image captured April 1, 2011 Twice a year, SDO enters an eclipse season where the spacecraft slips behind Earth for up to 72 minutes a day. Unlike the crisp shadow one sees on the sun during a lunar eclipse, Earth's shadow has a variegated edge due to its atmosphere, which blocks the sun light to different degrees depending on its density. Also, light from brighter spots on the sun may make it through, which is why some solar features extend low into Earth's shadow. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

NASA image captured April 2, 2011 Twice a year, SDO enters an eclipse season where the spacecraft slips behind Earth for up to 72 minutes a day. Unlike the crisp shadow one sees on the sun during a lunar eclipse, Earth's shadow has a variegated edge due to its atmosphere, which blocks the sun light to different degrees depending on its density. Also, light from brighter spots on the sun may make it through, which is why some solar features extend low into Earth's shadow. Credit: NASA/GSFC/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
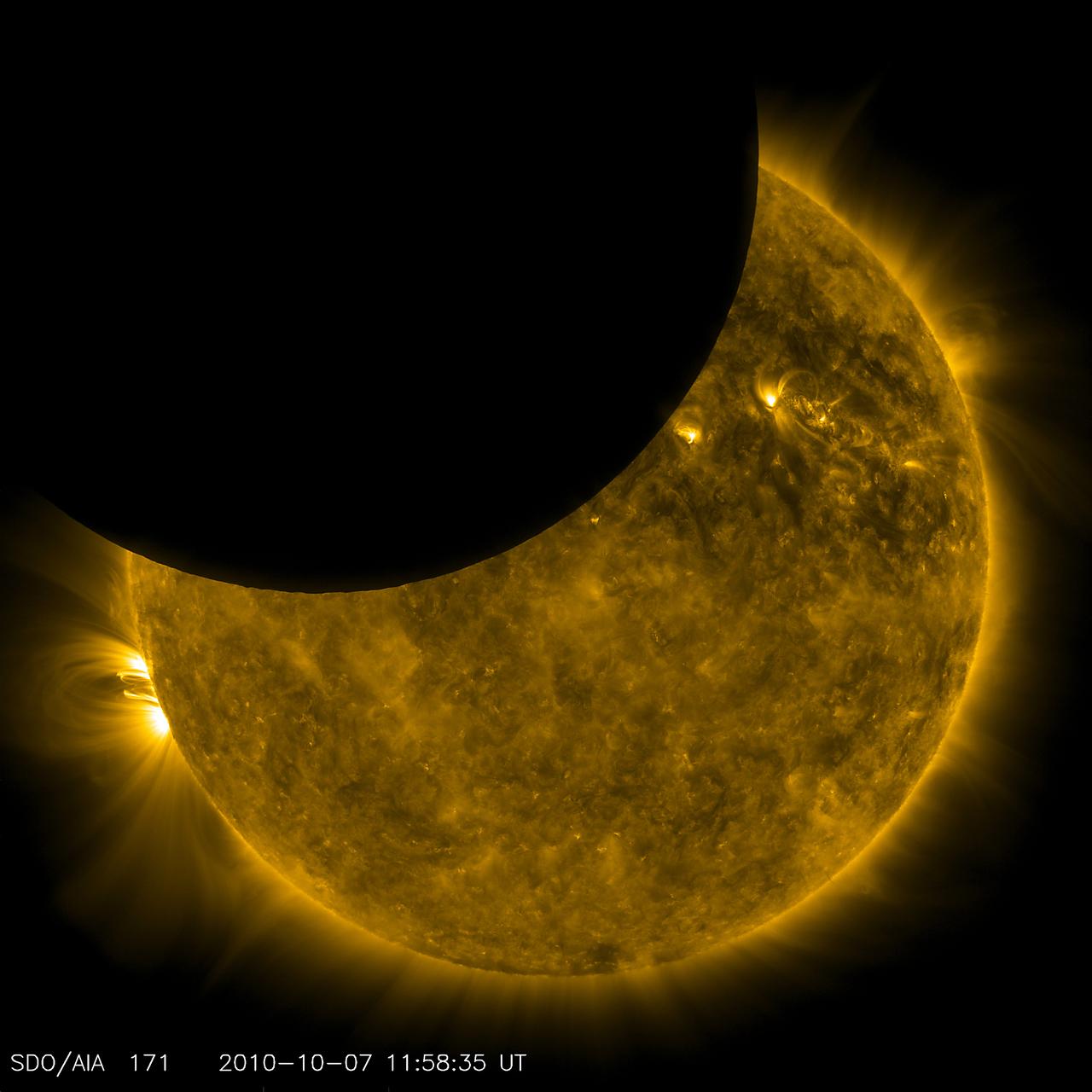

NASA image captured October 7, 2010 View a video of this event here: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5099028189">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5099028189</a> This was a first for SDO and it was visually engaging too. On October 7, 2010, SDO observed its first lunar transit when the new Moon passed directly between the spacecraft (in its geosynchronous orbit) and the Sun. With SDO watching the Sun in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light, the dark Moon created a partial eclipse of the Sun. These images, while unusual and cool to see, have practical value to the SDO science team. Karel Schrijver of Lockheed-Martin's Solar and Astrophysics Lab explains: "The very sharp edge of the lunar limb allows us to measure the in-orbit characteristics of the telescope e.g., light diffraction on optics and filter support grids. Once these are characterized, we can use that information to correct our data for instrumental effects and sharpen up the images to even more detail." To learn more about SDO go to: <a href="http://sdo.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">sdo.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> Credit: NASA/SDO <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>