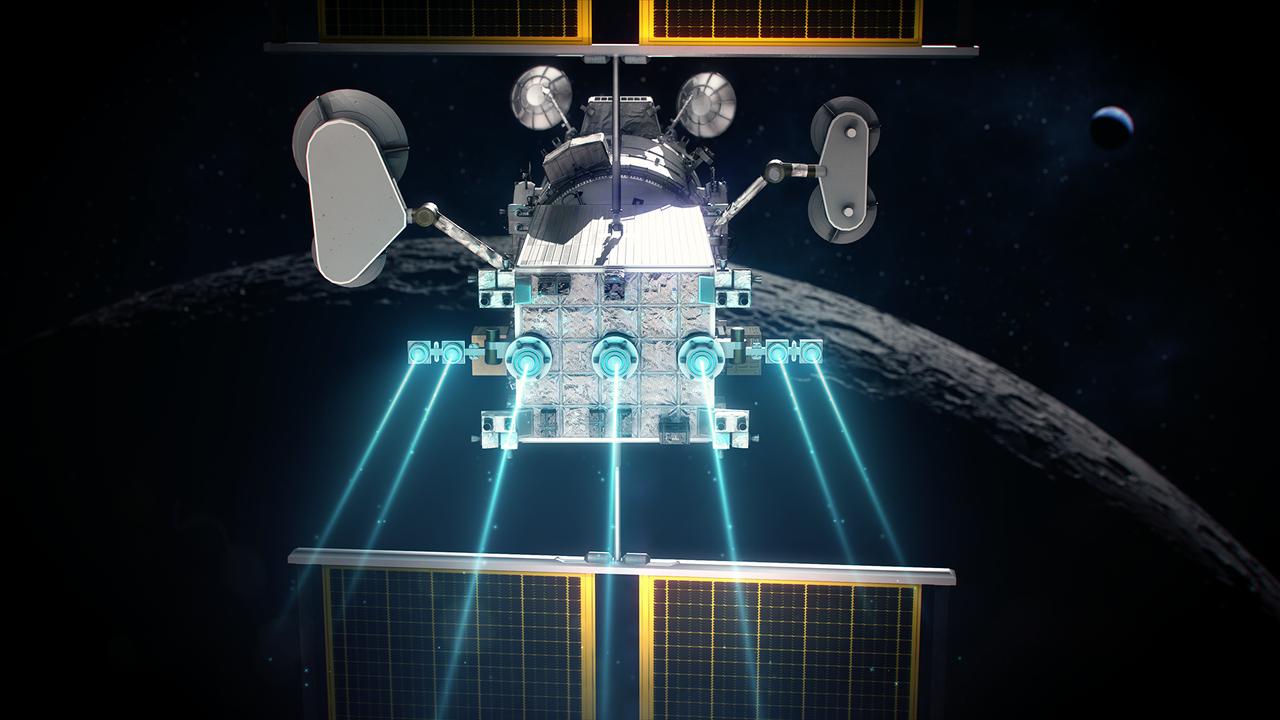
The Power and Propulsion Element's 12 kw thrusters will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
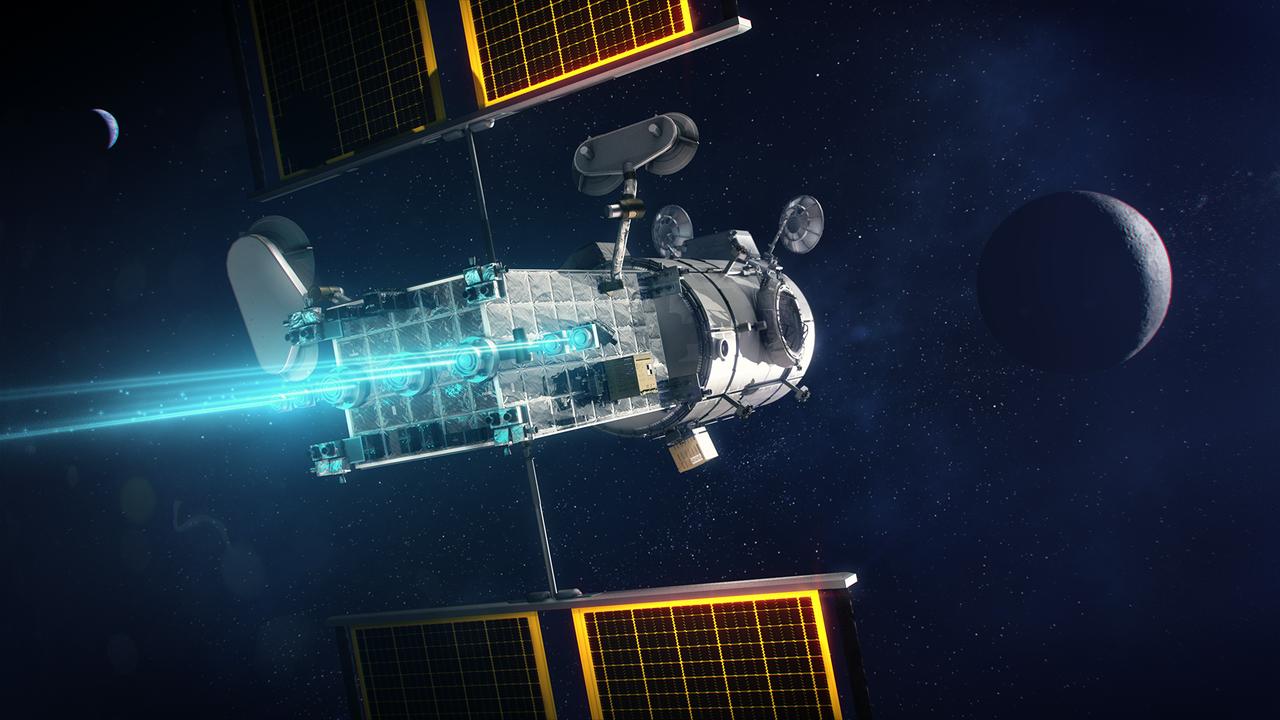

The Power and Propulsion Element's 12 kw thrusters will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
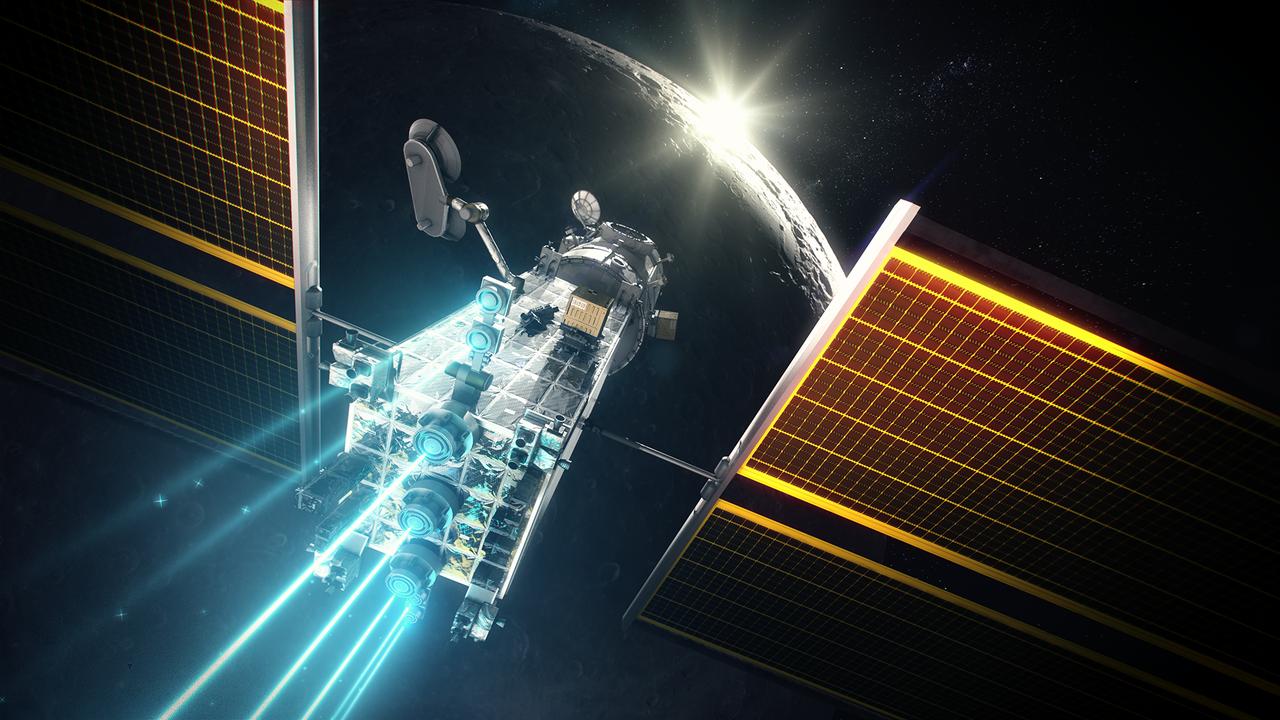

The Power and Propulsion Element's 12 kw thrusters will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
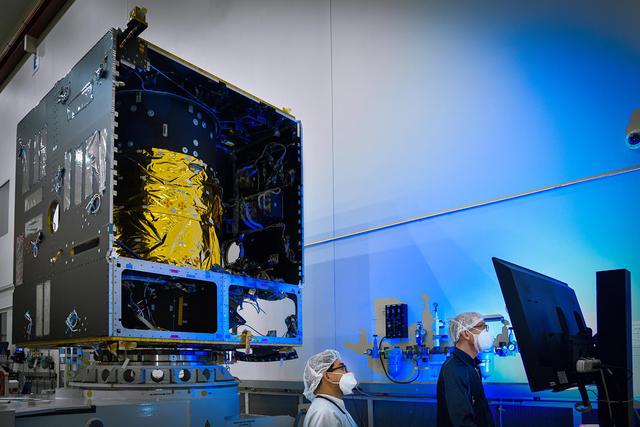

In this photo, taken in November 2020, technicians power on the main body of NASA's Psyche spacecraft — called the Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) Chassis — for the first time, in a clean room at Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California. Maxar will deliver the SEP Chassis to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in spring of 2021. Set to launch in August 2022, Psyche will investigate the composition of a metal-rich asteroid of the same name that lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The spacecraft will arrive in early 2026 and orbit the asteroid for nearly two years. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24326

The main body of NASA's Psyche spacecraft, called the Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) Chassis, is in a clean room at Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, where a technician prepares to integrate part of the electric propulsion system onto the chassis. Maxar will deliver the SEP Chassis to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in February 2021. Set to launch in August 2022, Psyche's will explore a metal-rich asteroid of the same name that lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The spacecraft will arrive in early 2026, and orbit the asteroid for nearly two years to investigate its composition. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23877

iss020e042647 (Sep. 26, 2009) --- Constrained Vapor Bubble (CVB) module with the science sample on the Fluids Integrated Rack (FIR). CVB aims to better understand the physics of evaporation and condensation to help create an efficient and highly reliable cooling equipment for space, where replacement parts are difficult or impossible.

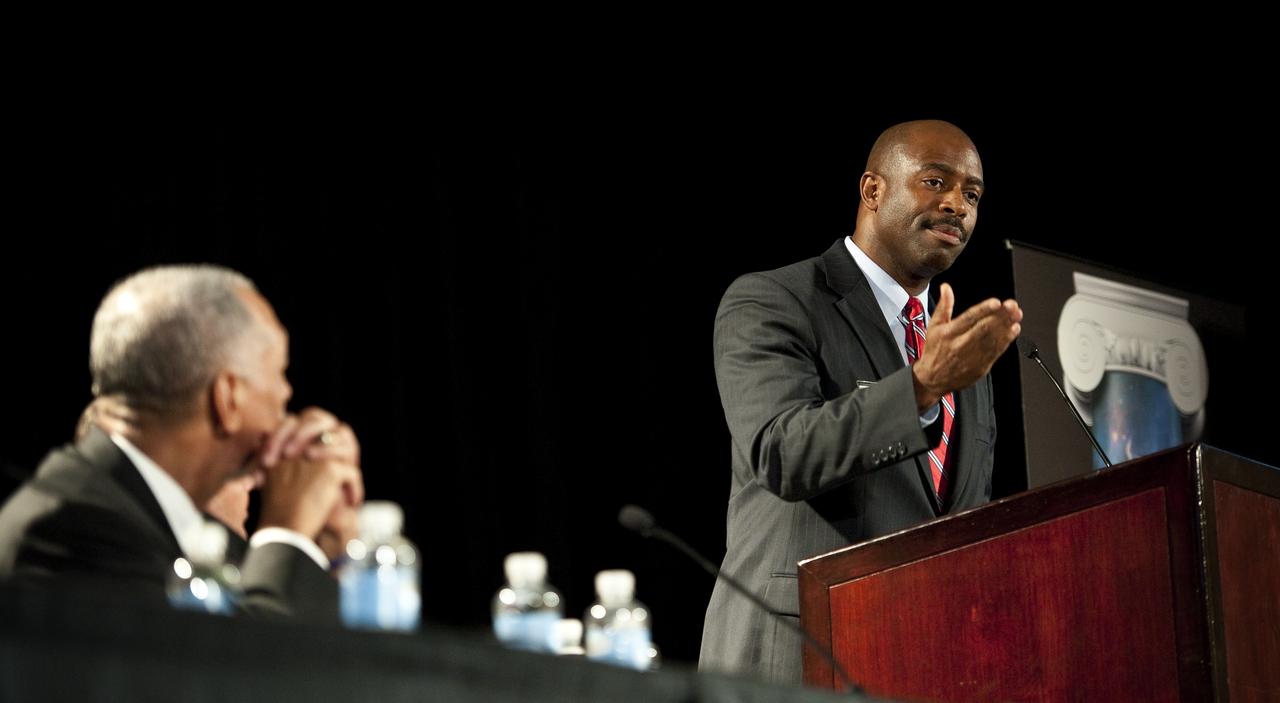
NASA Administrator Charles Bolden gives keynote remarks at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
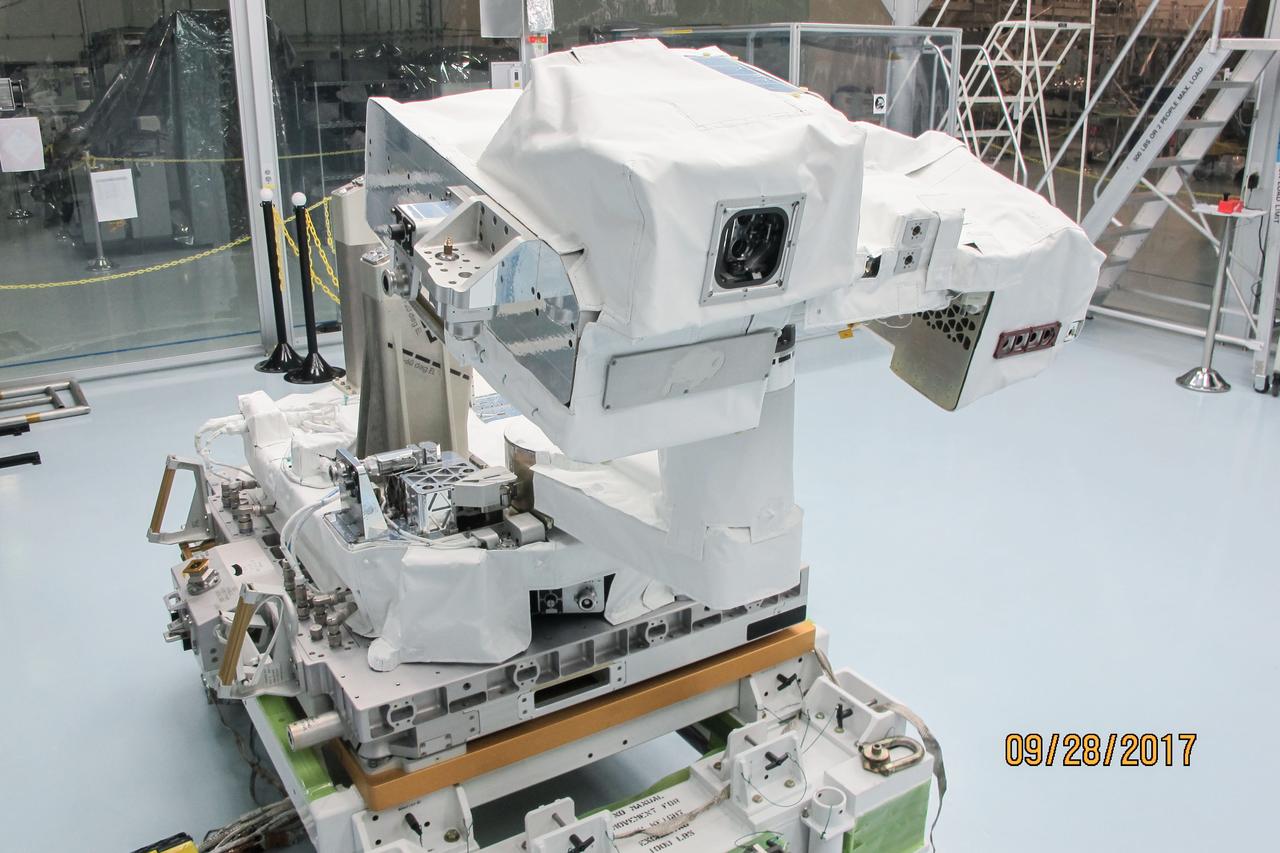

jsc2017e119290 (Sep. 28, 2017) --- Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor (TSIS) Thermal Pointing System (TPS) in its deployed configuration during spacewalk tool fit-checks and sharp edge inspection at NASA's Johnson Space Center. TSIS examines how Earth's atmosphere responds to solar ouput changes.

Cora B. Marrett, right, PhD, Acting Director, National Science Foundation gives keynote remarks at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
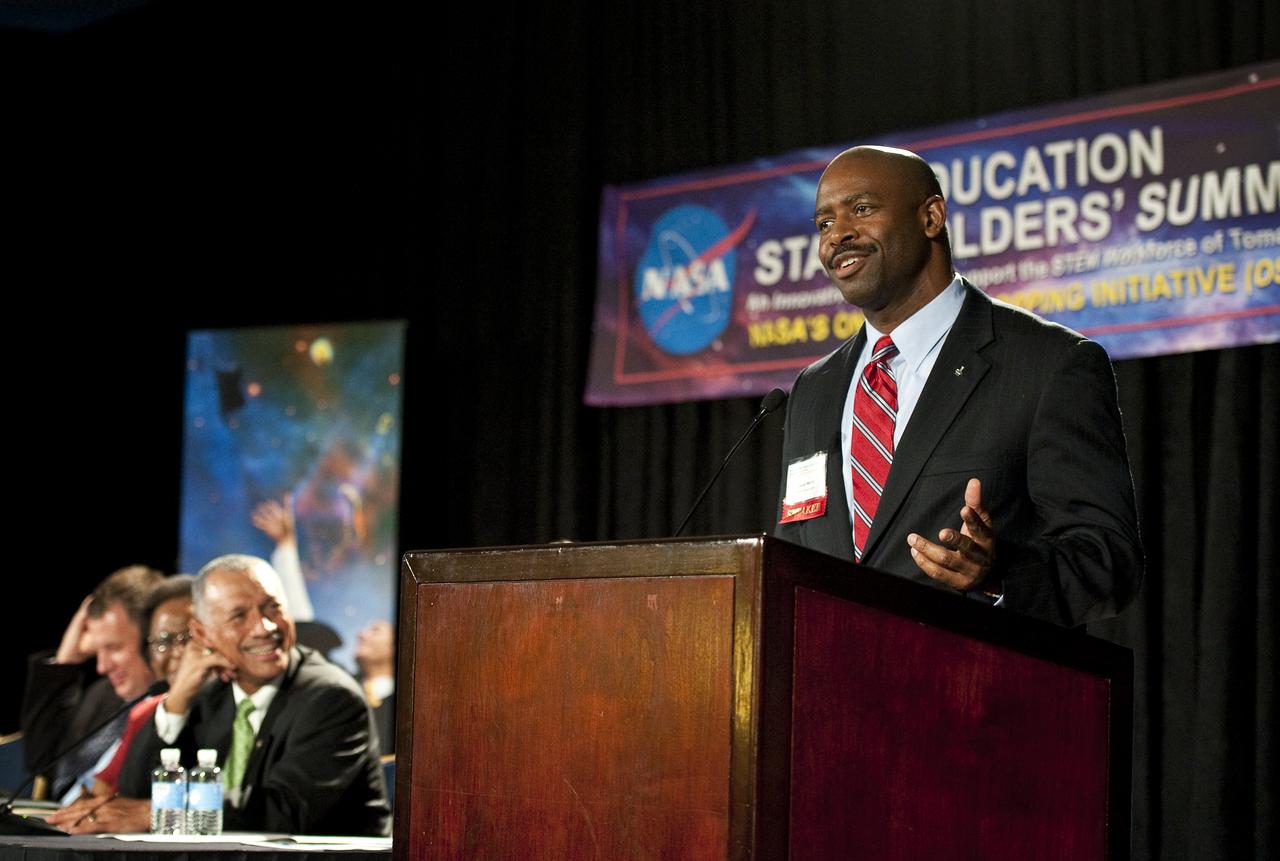

Leland Melvin, right, Education Design Team Co-Chair and NASA Astronaut, speaks at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Leland Melvin, right, Education Design Team Co-Chair and NASA Astronaut, speaks at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
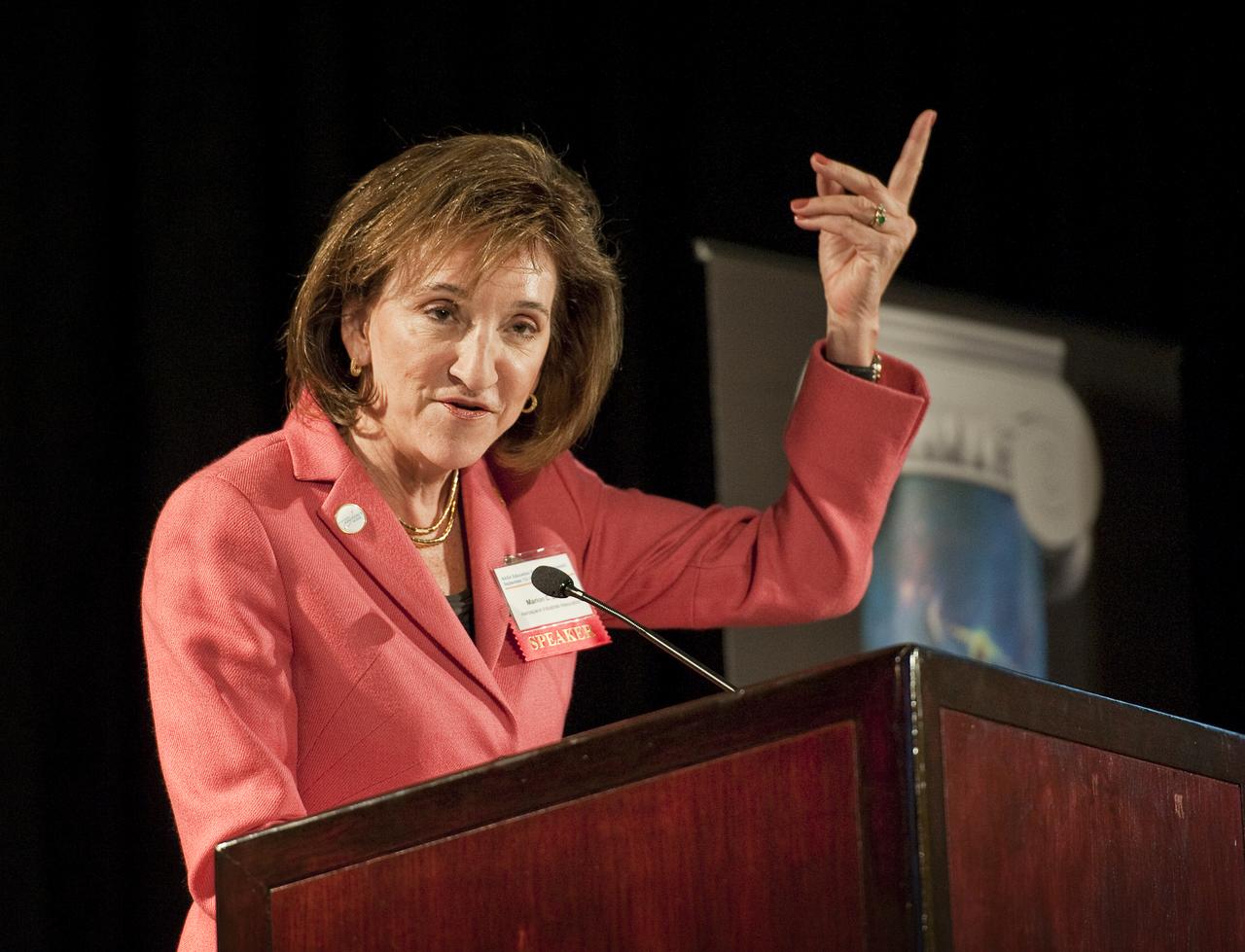

Marion C. Blakey, President and CEO, Aerospace Industries Association, addresses guests at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
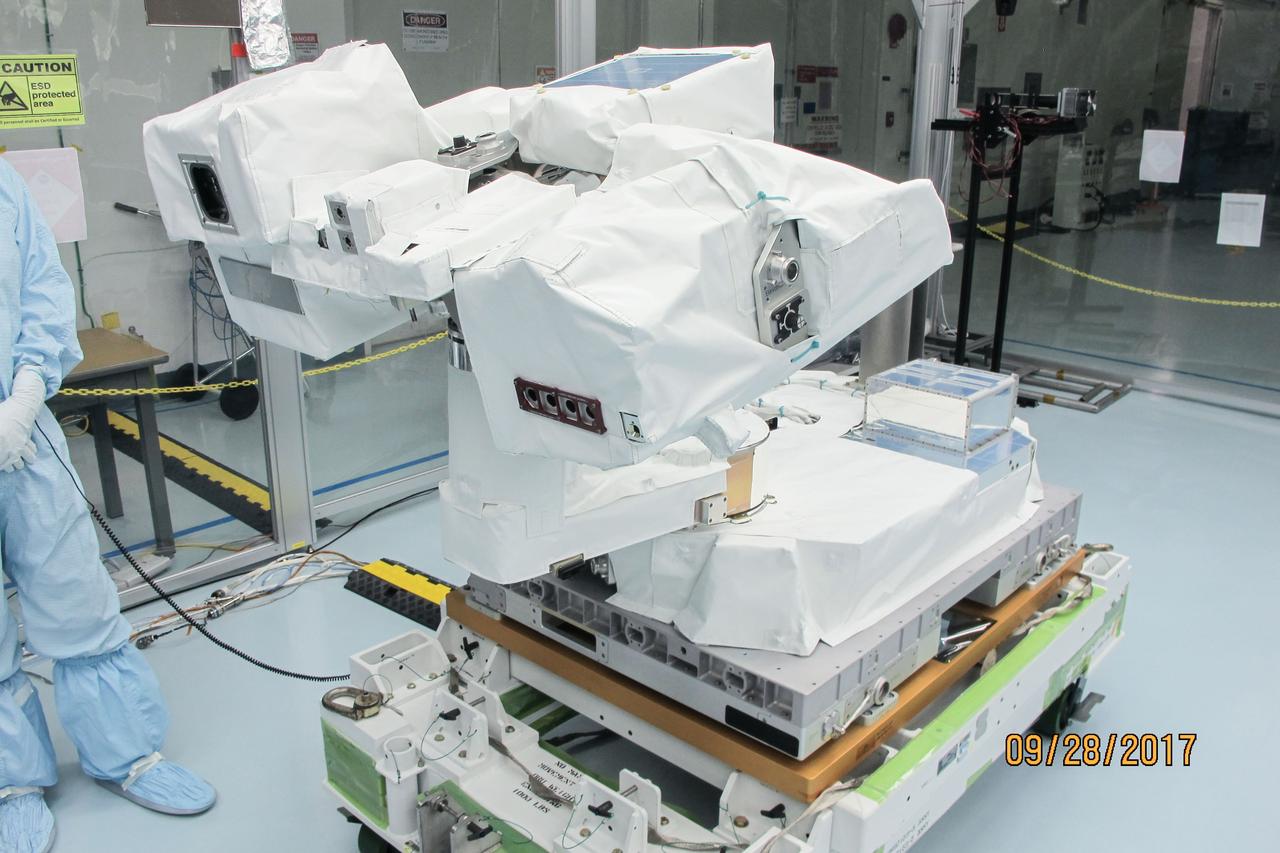

jsc2017e119287 (Sep. 28, 2017) --- Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor (TSIS) Thermal Pointing System (TPS) in its deployed configuration during spacewalk tool fit-checks and sharp edge inspection at NASA's Johnson Space Center. TSIS examines how Earth's atmosphere responds to solar ouput changes.

Cora B. Marrett, PhD, Acting Director, National Science Foundation gives keynote remarks at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
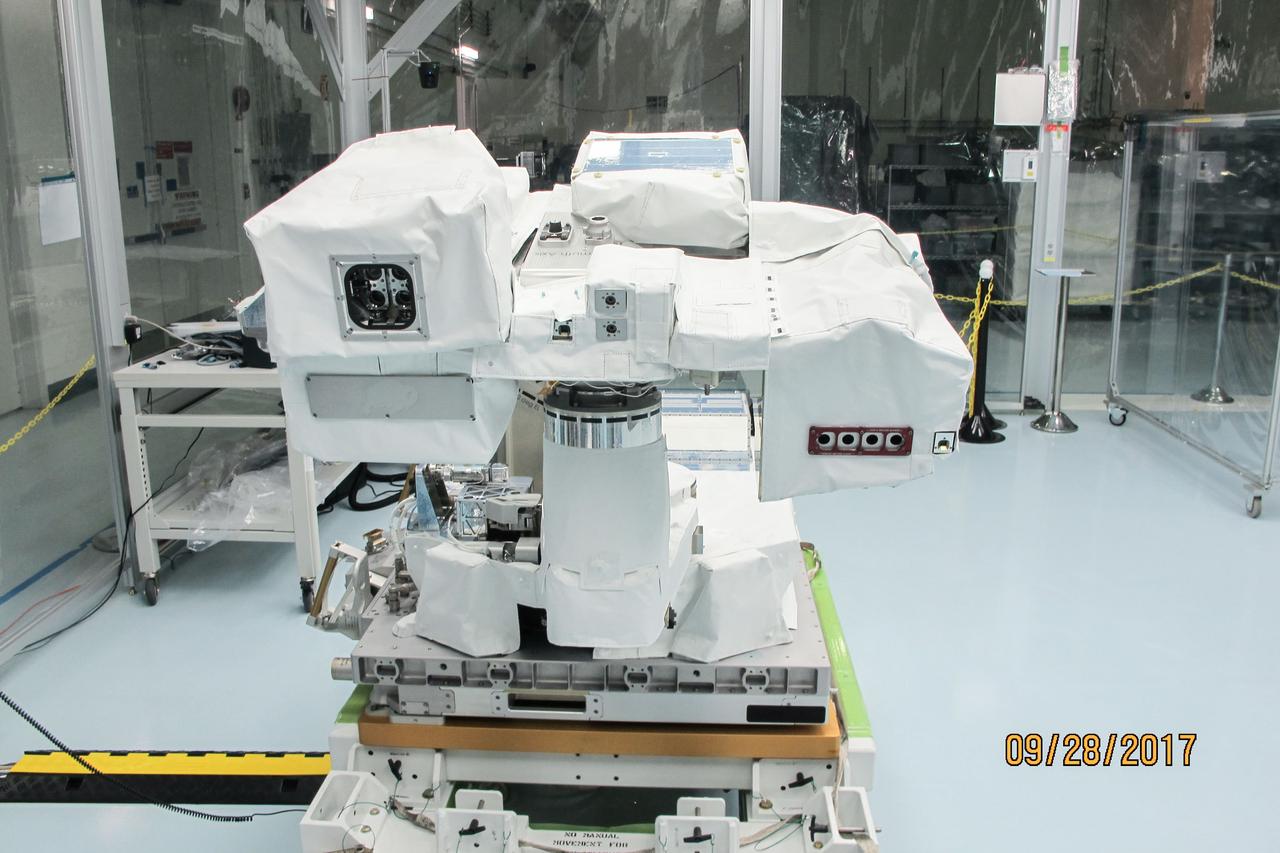

jsc2017e119288 (Sep. 28, 2017) --- Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor (TSIS) Thermal Pointing System (TPS) in its deployed configuration during spacewalk tool fit-checks and sharp edge inspection at NASA's Johnson Space Center. TSIS examines how Earth's atmosphere responds to solar ouput changes.

James Stofan, right, NASA Acting Associate Administrator for Education, introduces the keynote speakers at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)

A major component of NASA's Psyche spacecraft has been delivered to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, where the phase known as assembly, test, and launch operations (ATLO) is now underway. This photo, shot March 28, 2021 shows engineers and technicians preparing to move the Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) Chassis from its shipping container to a dolly in High Bay 1 of JPL's Spacecraft Assembly Facility. The photo was captured just after the chassis was delivered to JPL by Maxar Technologies. Maxar's team in Palo Alto, California, designed and built the SEP Chassis, which includes all the primary and secondary structure and the hardware components needed for the high-power electrical system, the propulsion system, the thermal system, guidance and navigation sensors and actuators, and the high-gain antenna. Over the next year, additional hardware will be added to the spacecraft including the command and data handling system, a power distribution assembly, the X-band telecommunications hardware suite, three science instruments (two imagers, two magnetometers, and a gamma ray neutron Spectrometer), and a deep space optical communications technology demonstrator. The spacecraft will finish assembly and then undergo rigorous checkout and testing before being shipped to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, for an August 2022 launch to the main asteroid belt. Psyche will arrive at the metal-rich asteroid of the same name in 2026, orbiting for 21 months to investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to Earth's core. Exploring the asteroid could give valuable insight into how our own planet and others formed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24475

iss049e006037 (Sep. 17, 2016) --- Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS) mounted on the Japanese Experiment Module's Exposed Facility (JEM-EF). The CATS investigation uses a light detection and ranging (LiDAR) system to measure the location, composition and distribution of pollution, dust, smoke, aerosols and other particulates in the atmosphere. CATS is used to study the atmospheric constituents that impact global climate. By gaining a better understanding of cloud and aerosol coverage, scientists can create a better model of the Earth's climate feedback processes.
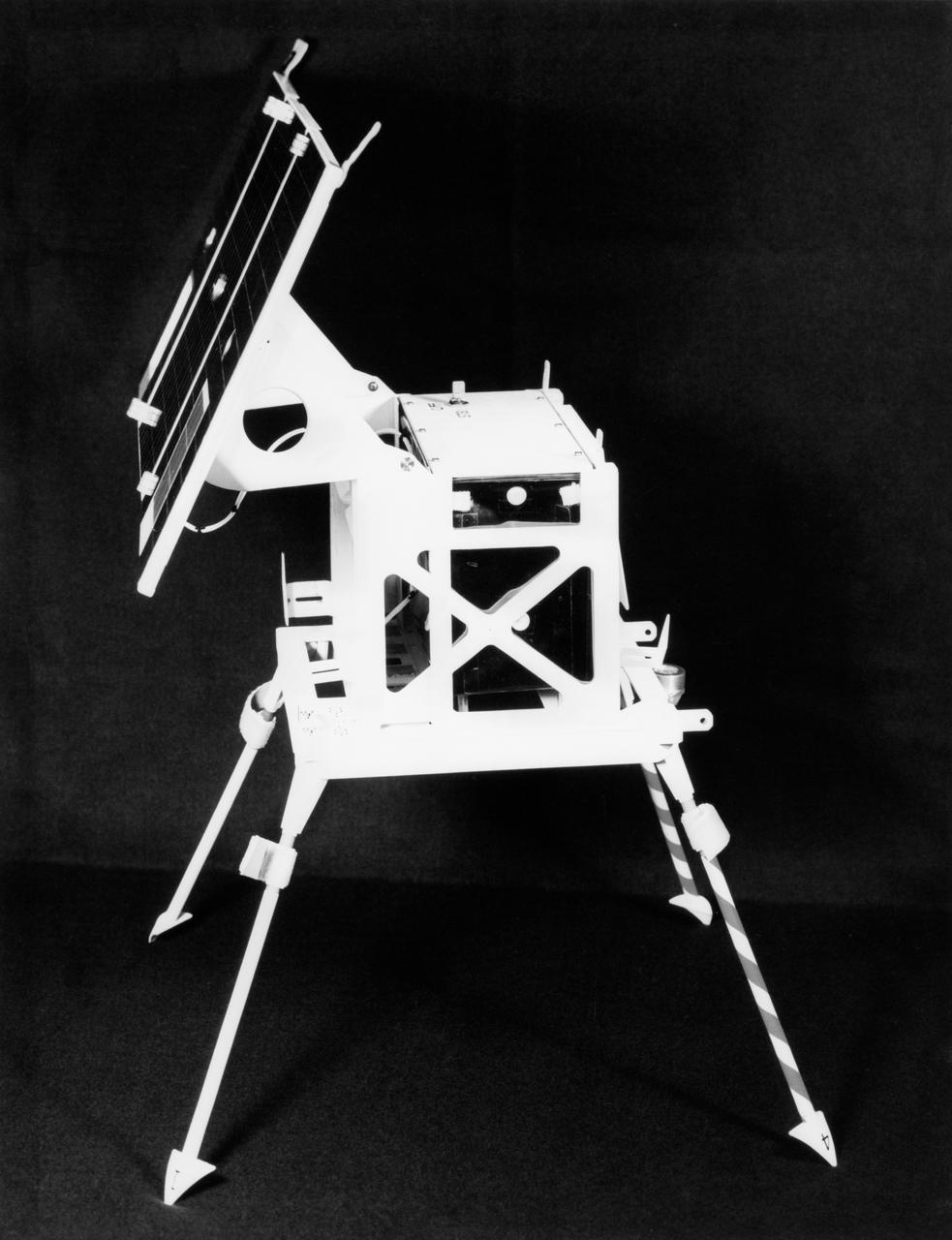
S72-53950 (November 1972) --- The transmitter of the Surface Electrical Properties Experiment (S-204) in a deployed configuration. This experiment will be deployed at the Taurus-Littrow landing site by the Apollo 17 crewmen. The purpose of the SEP experiment is to obtain data about the electromagnetic energy transmission, absorption and reflection characteristics of the lunar surface and subsurface for use in the development of a geological model of the upper layers of the moon. The experiment is designed to determine layering in the lunar surface, to search for the presence of water below the surface, and to measure electrical properties of the lunar material in situ.

William Kelly, PhD, PE, Manager, Public Affairs, American Society for Engineering Education speaks at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. Seated are NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and NASA Acting Associate Administrator for Education, James Stofan. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
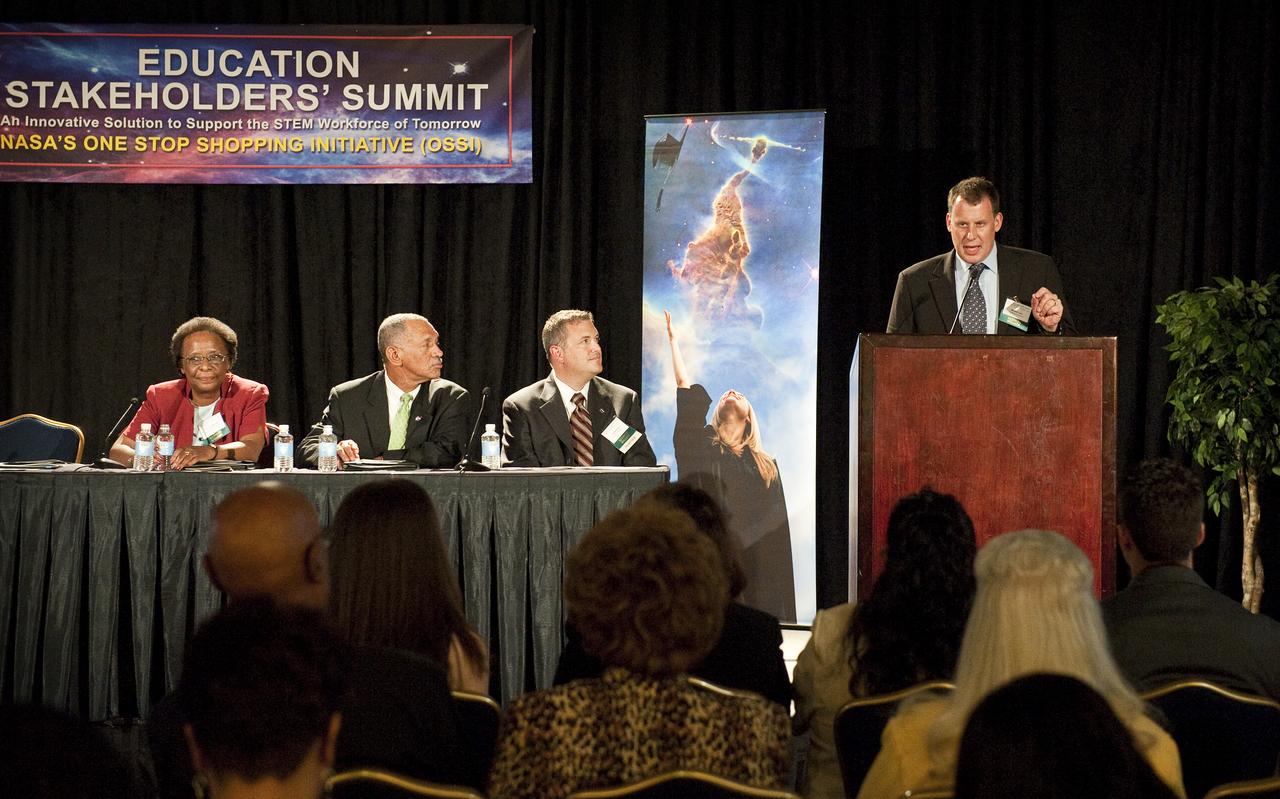

Special Assitant for STEM Education, U. S. Department of Education, Michael Lach, far right, addresses guests at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. Seated from right are James Stofan, NASA Acting Associate Administrator for Education; Charles Bolden, NASA Administrator; and Cora B. Marrett, Acting Director, National Science Foundation. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
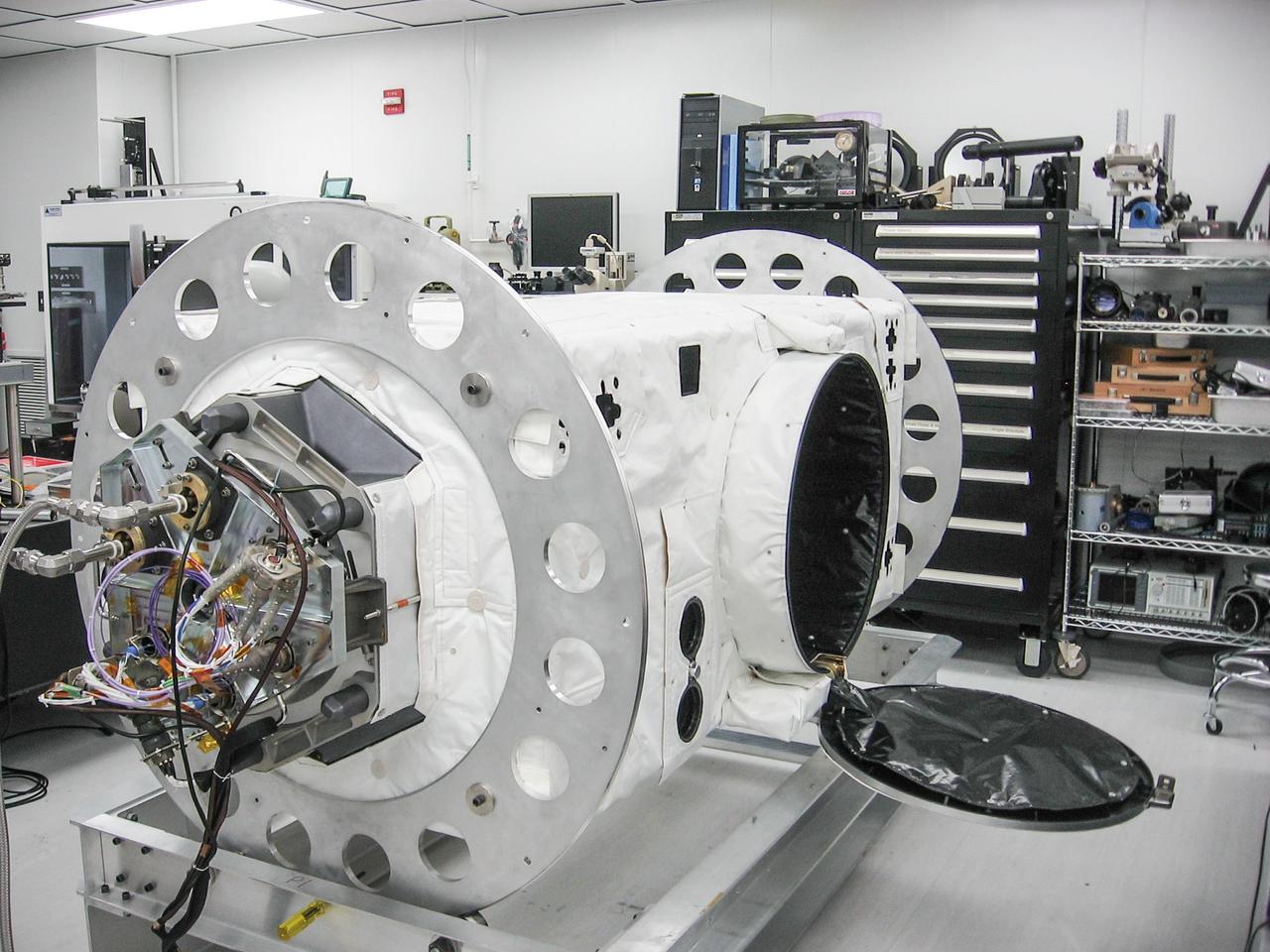
jsc2013e090265 (Sep. 26, 2013) --- Cloud Aerosol Transport System (CATS) at NASA's Johnson Space Center undergoing payload fit-check and Support Equipment Installation (SEI). The CATS investigation uses a light detection and ranging (LiDAR) system to measure the location, composition and distribution of pollution, dust, smoke, aerosols and other particulates in the atmosphere. CATS is used to study the atmospheric constituents that impact global climate. By gaining a better understanding of cloud and aerosol coverage, scientists can create a better model of the Earth's climate feedback processes.
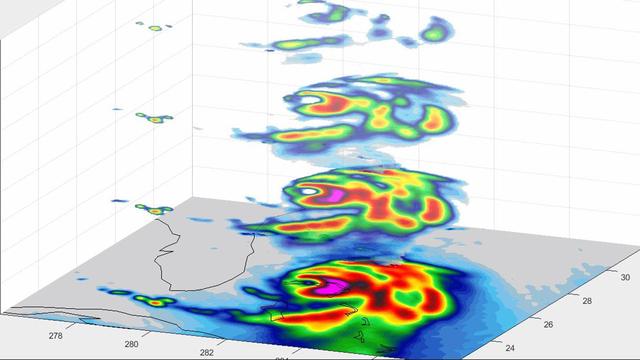
In this animation, TEMPEST-D — a weather-observing satellite the size of a cereal box — captured imagery of Hurricane Dorian off the coast of Florida at 2 a.m. EDT on Sep. 3, 2019 (11 p.m. PDT on Sept. 2, 2019). At a vantage point 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the storm, the CubeSat used its miniaturized radio-wave-based instrument to see through the clouds, revealing different depths of the hurricane with areas with heavy rainfall and moisture being pulled into the storm. The green colors indicate moisture spiraling into the storm's center, and the yellow, red and pink areas correspond to the most intense rainfall. TEMPEST-D — short for Temporal Experiment for Storms and Tropical Systems Demonstration — is an experiment in shrinking weather satellites to a size that makes them inexpensive enough to produce in multiples. The goal is eventual real-time storm coverage with many small satellites that can track storms around the world. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23431
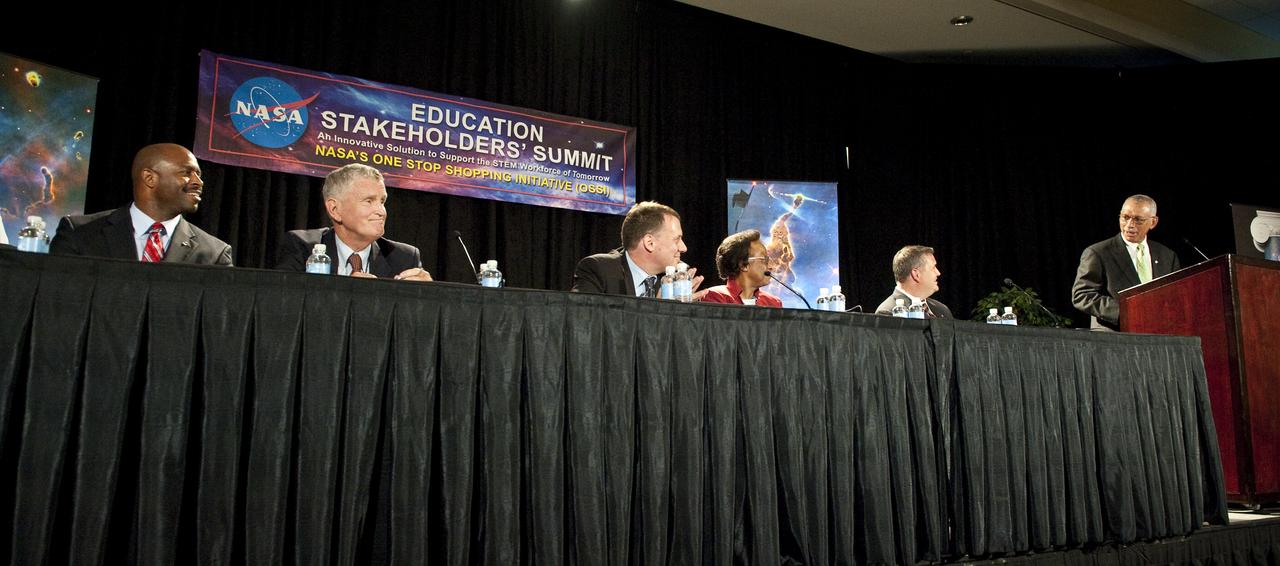

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, far right, gives keynote remarks at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. Administrator Bolden is joined on the panel from left to right by Leland Melvin, Education Design Team Co-Chair and NASA Astronaut; William Kelly, Manager, Public Affairs, American Society for Engineering Education; Michael Lach, Special Assistant for STEM Education, U.S. Department of Education; Cora Marrett, Acting Director, National Science Foundation; and James Stofan, NASA Acting Associate Administrator for Education. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, far right, gives keynote remarks at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. Administrator Bolden is joined on the panel from left to right by Leland Melvin, Education Design Team Co-Chair and NASA Astronaut; William Kelly, Manager, Public Affairs, American Society for Engineering Education; Michael Lach, Special Assistant for STEM Education, U.S. Department of Education; Cora Marrett, Acting Director, National Science Foundation; and James Stofan, NASA Acting Associate Administrator for Education. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
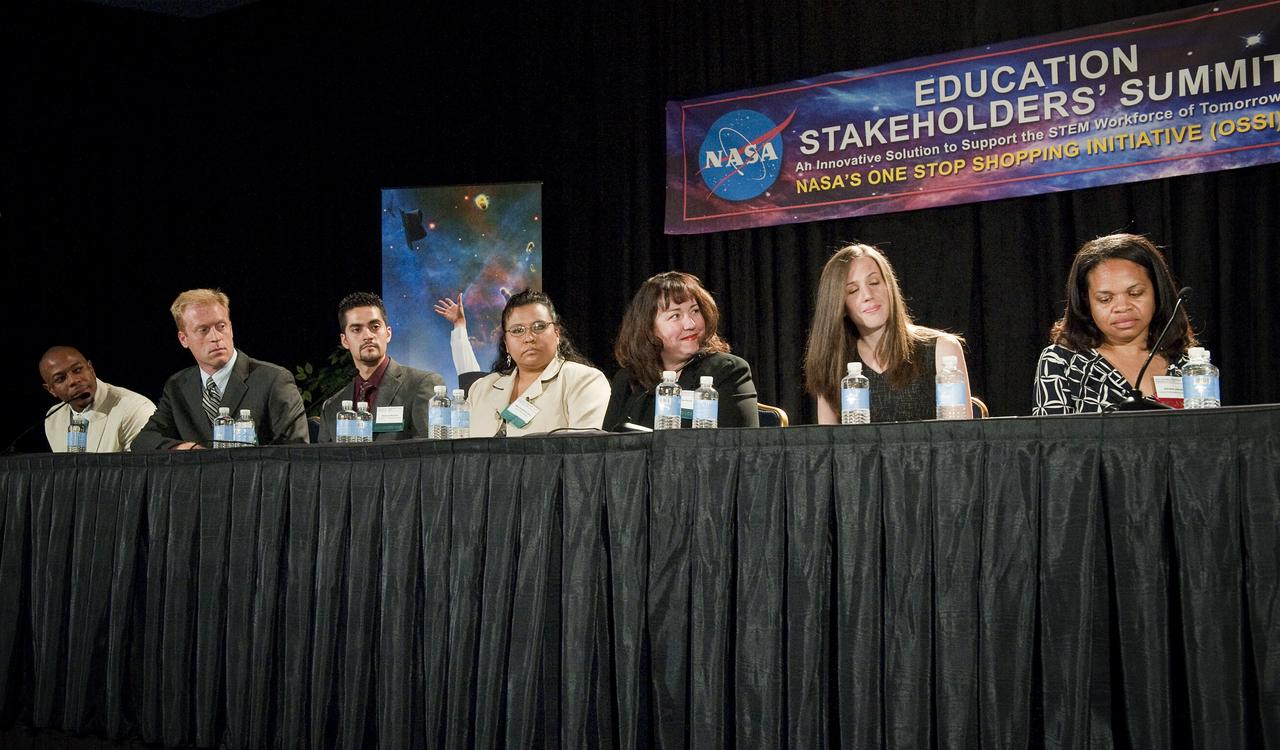

NASA Student Ambassadors and Facilitator are seen on a panel at the NASA Education Stakeholders’ Summit One Stop Shopping Initiative (OSSI), Monday, Sep. 13, 2010, at the Westfields Marriott Conference Center in Chantilly, VA. From left to right are: Quenton Bonds, University of South Florida; Geoffrey Wawrzyniak, Purdue University; Heriberto Reynoso, University of Texas at Brownsville; Marie Kingbird-Lowry, Leech Lake Tribal College; Kareen Borders, University of Washington; Katelyn Doran, University of North Carolina at Charlotte and Ashanti Johnson, PhD, Executive Director, Institute for Broadening Participation. (Photo Credit: NASA/Carla Cioffi)
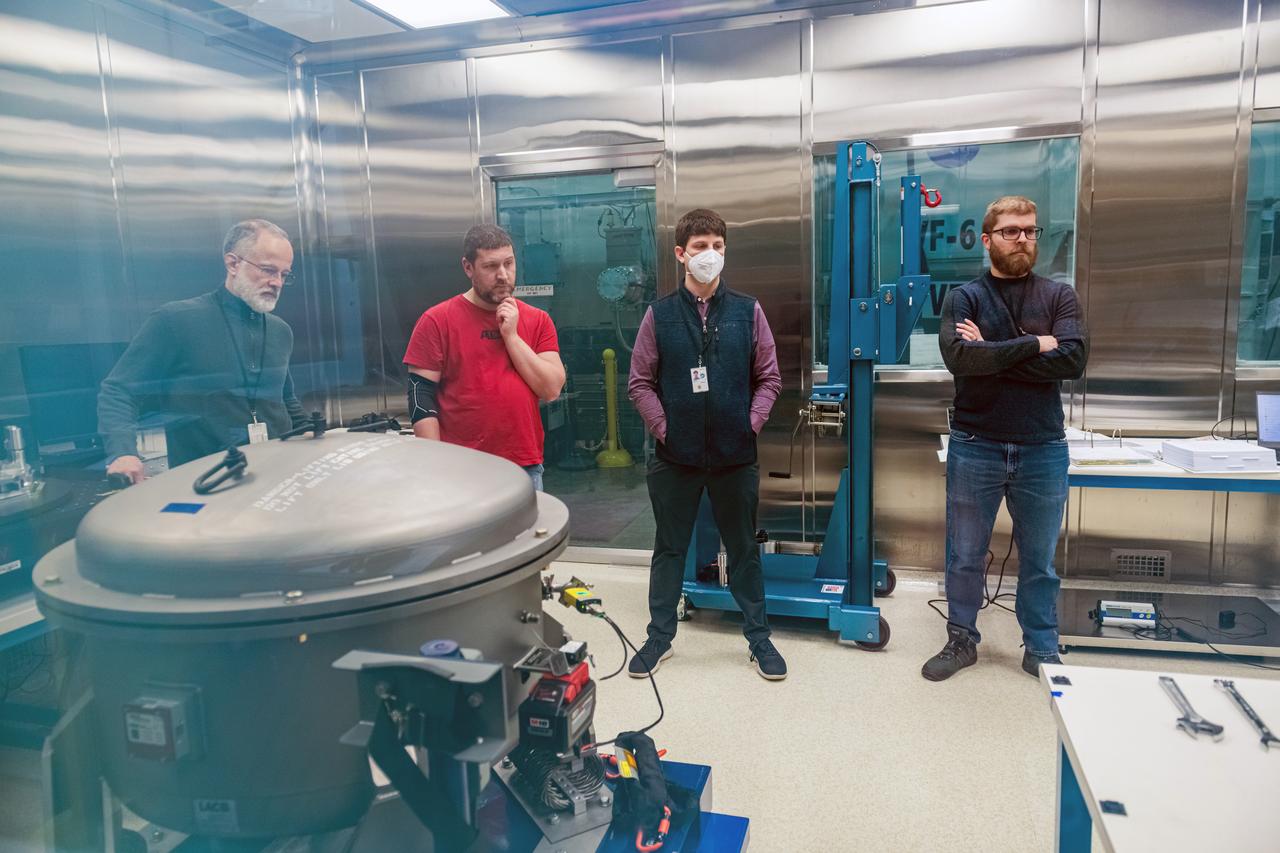

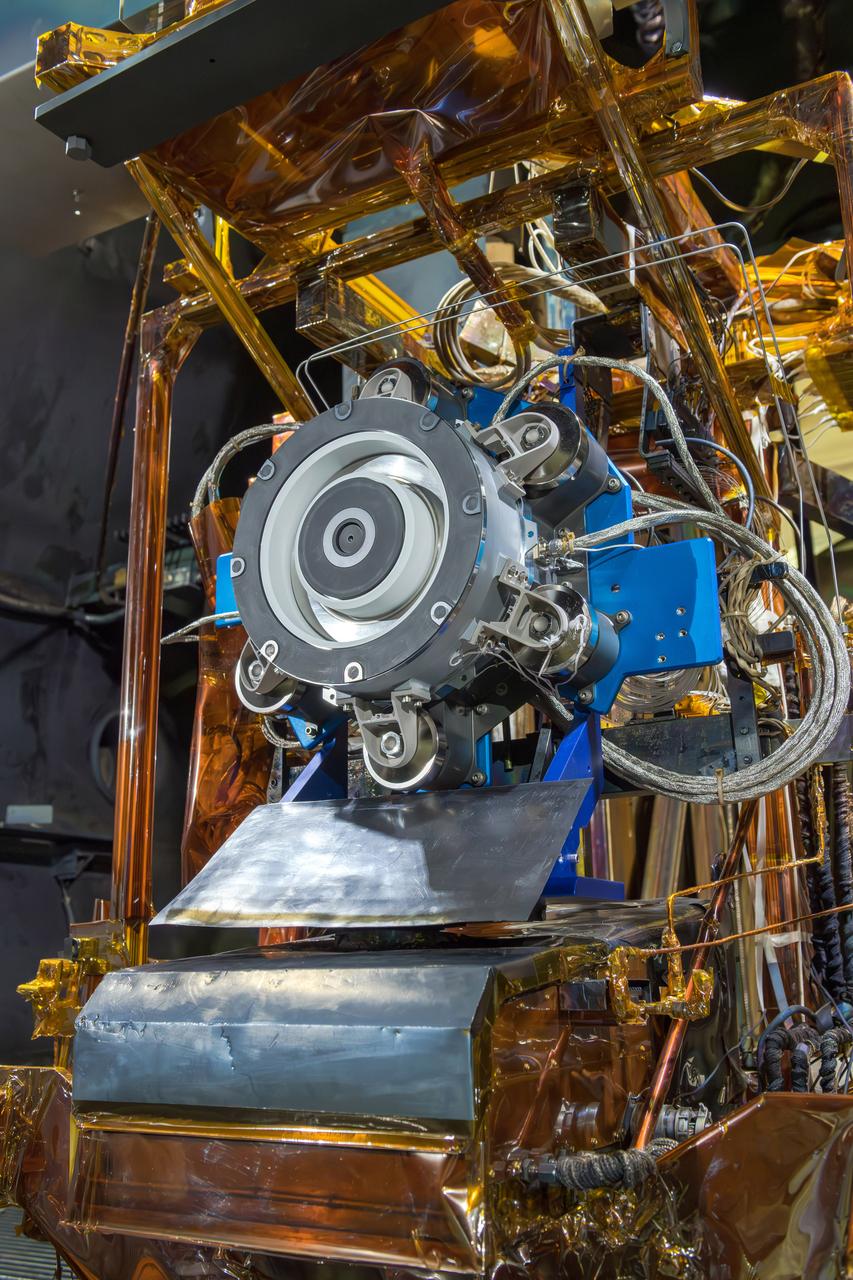
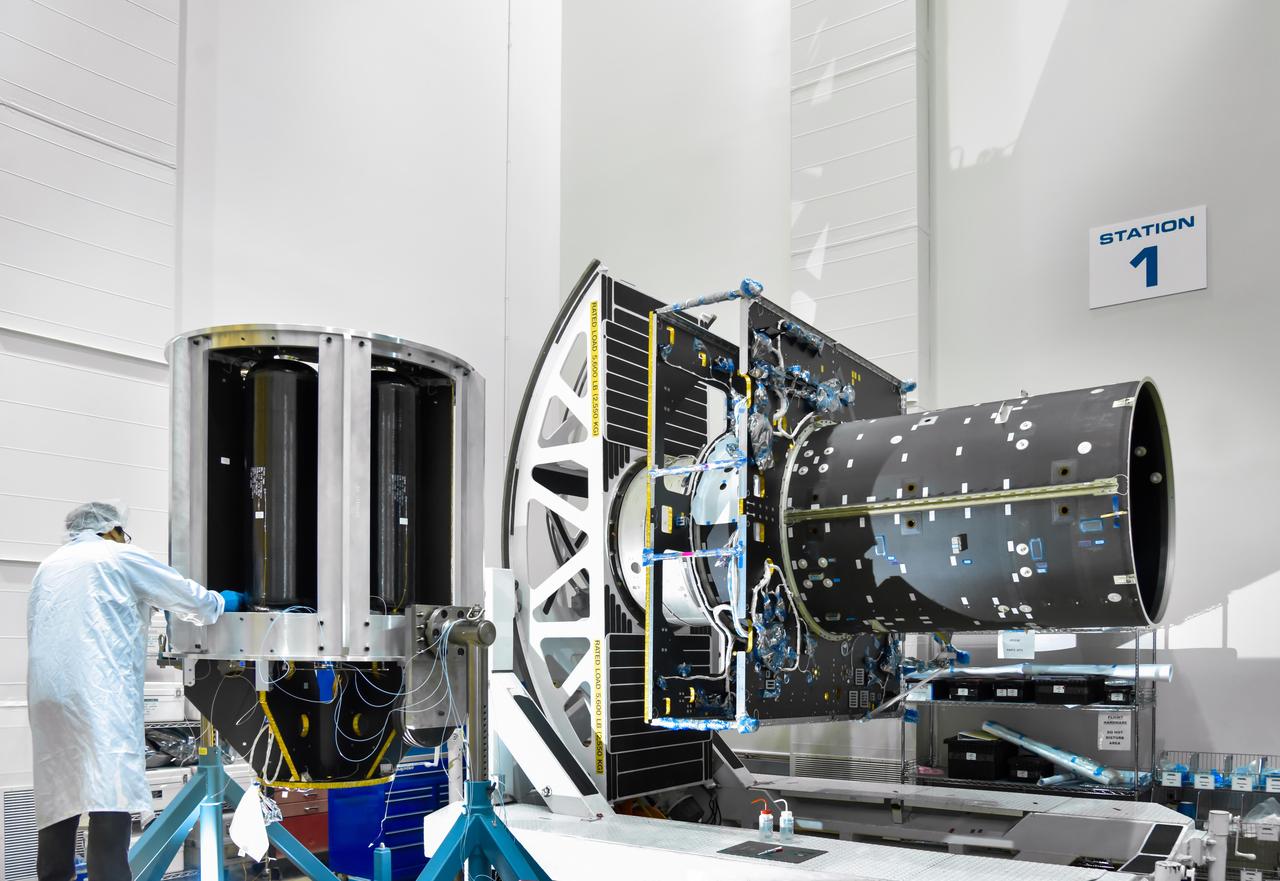
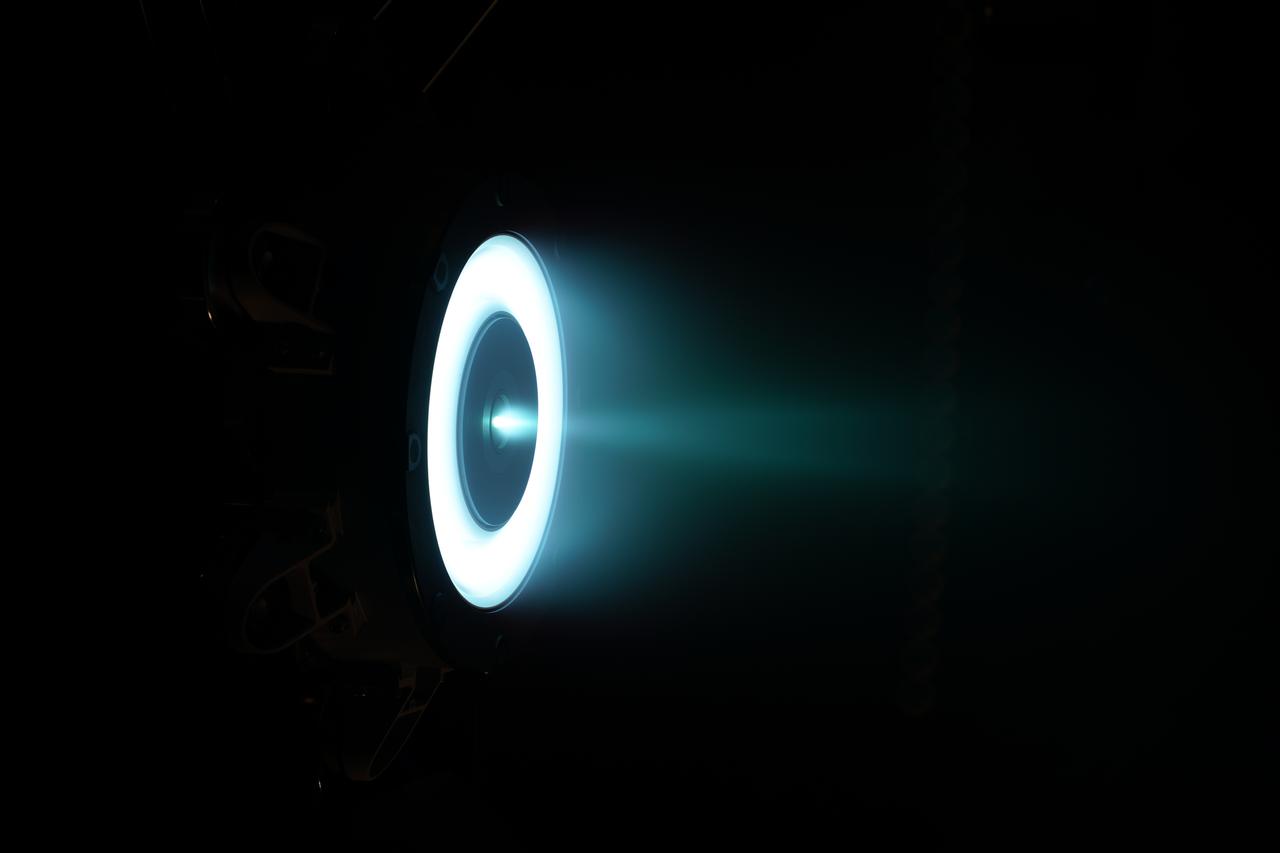
NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
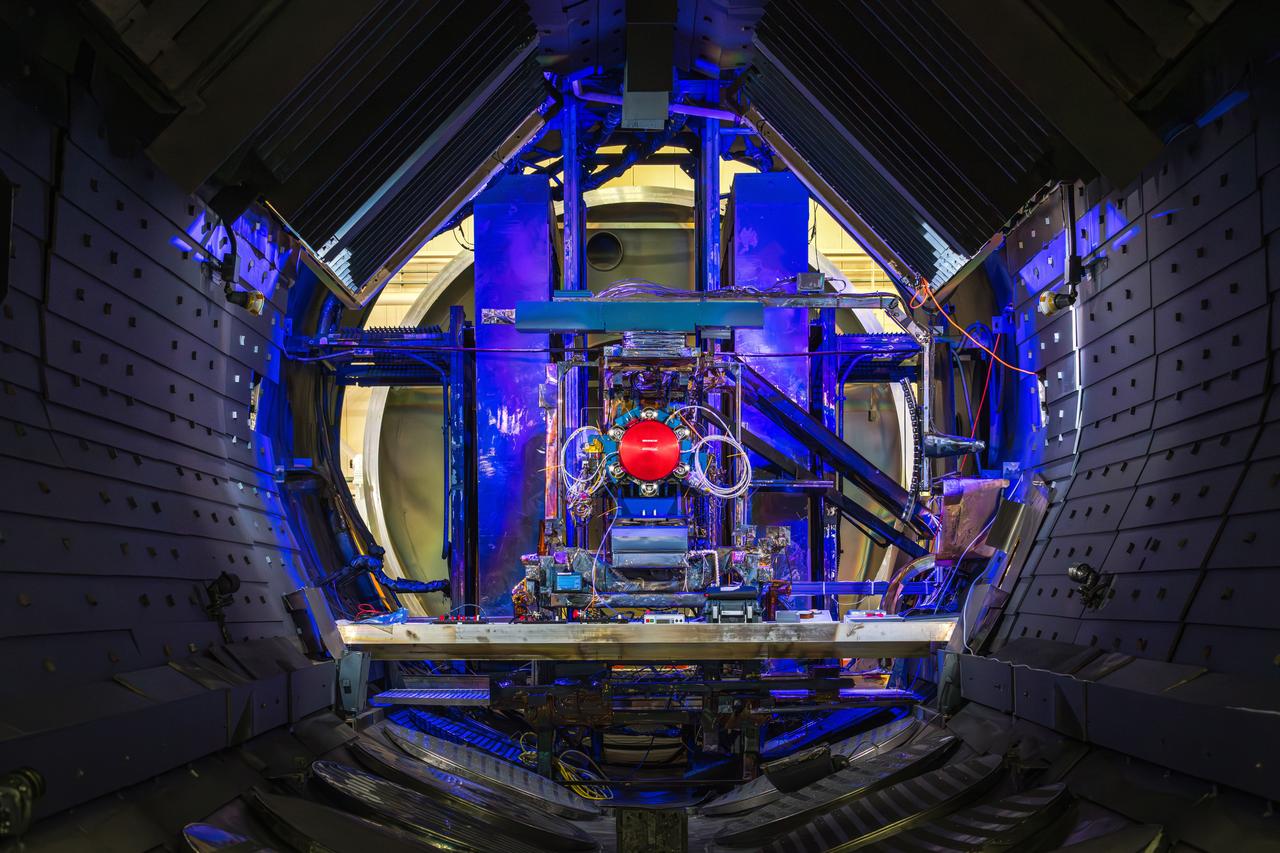
NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
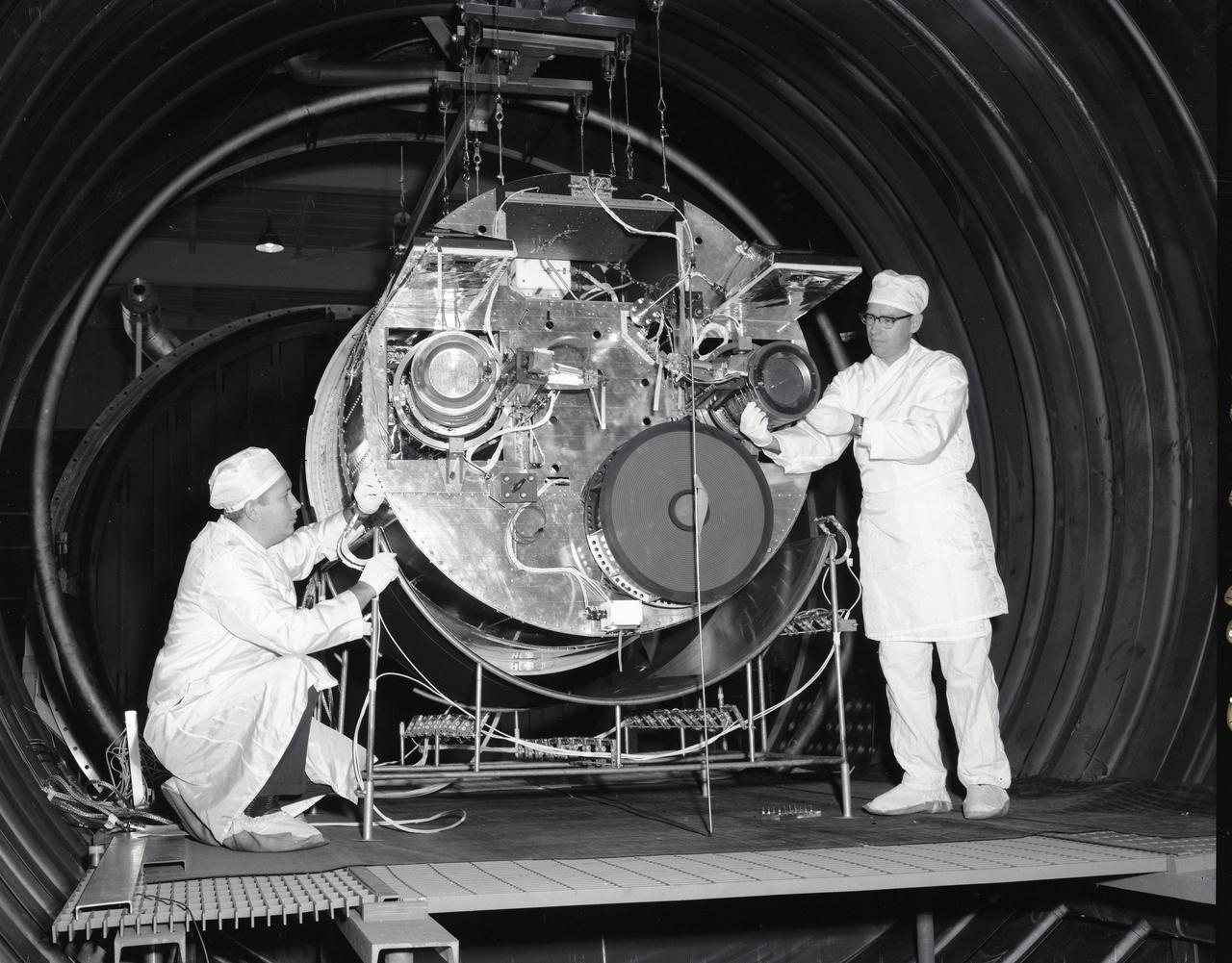

SPACE ELECTRIC ROCKET TEST, SERT II IN TANK 5
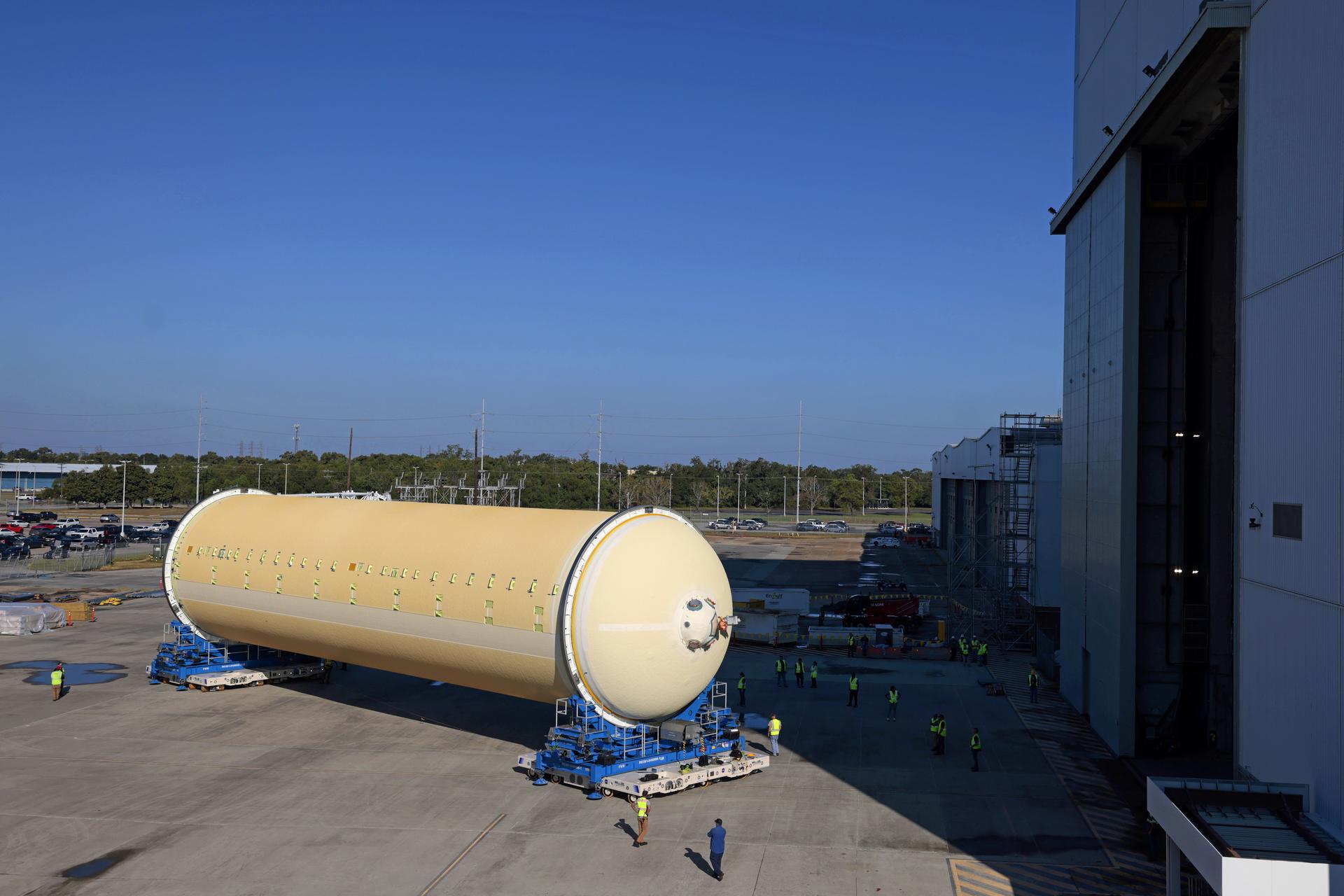

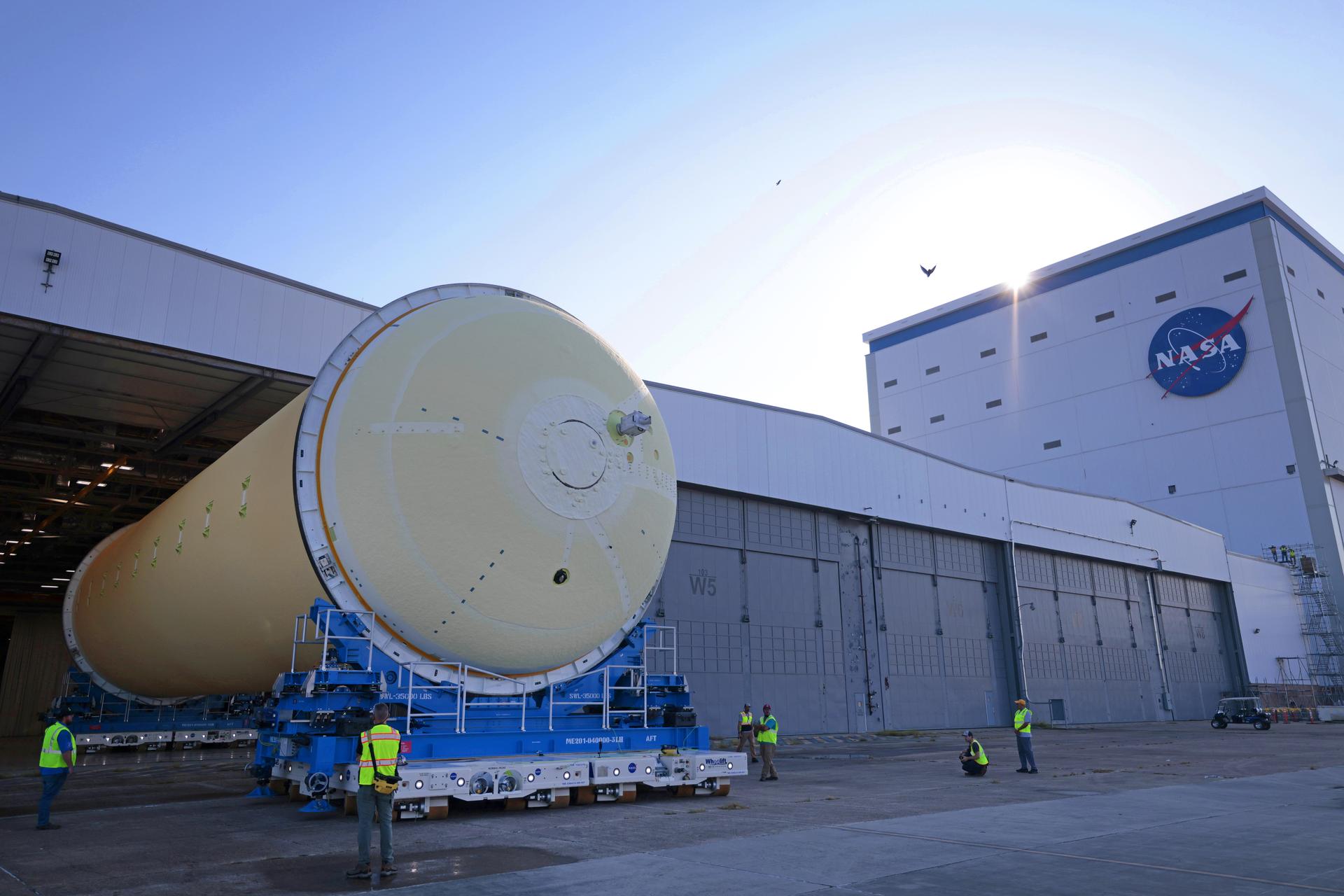
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
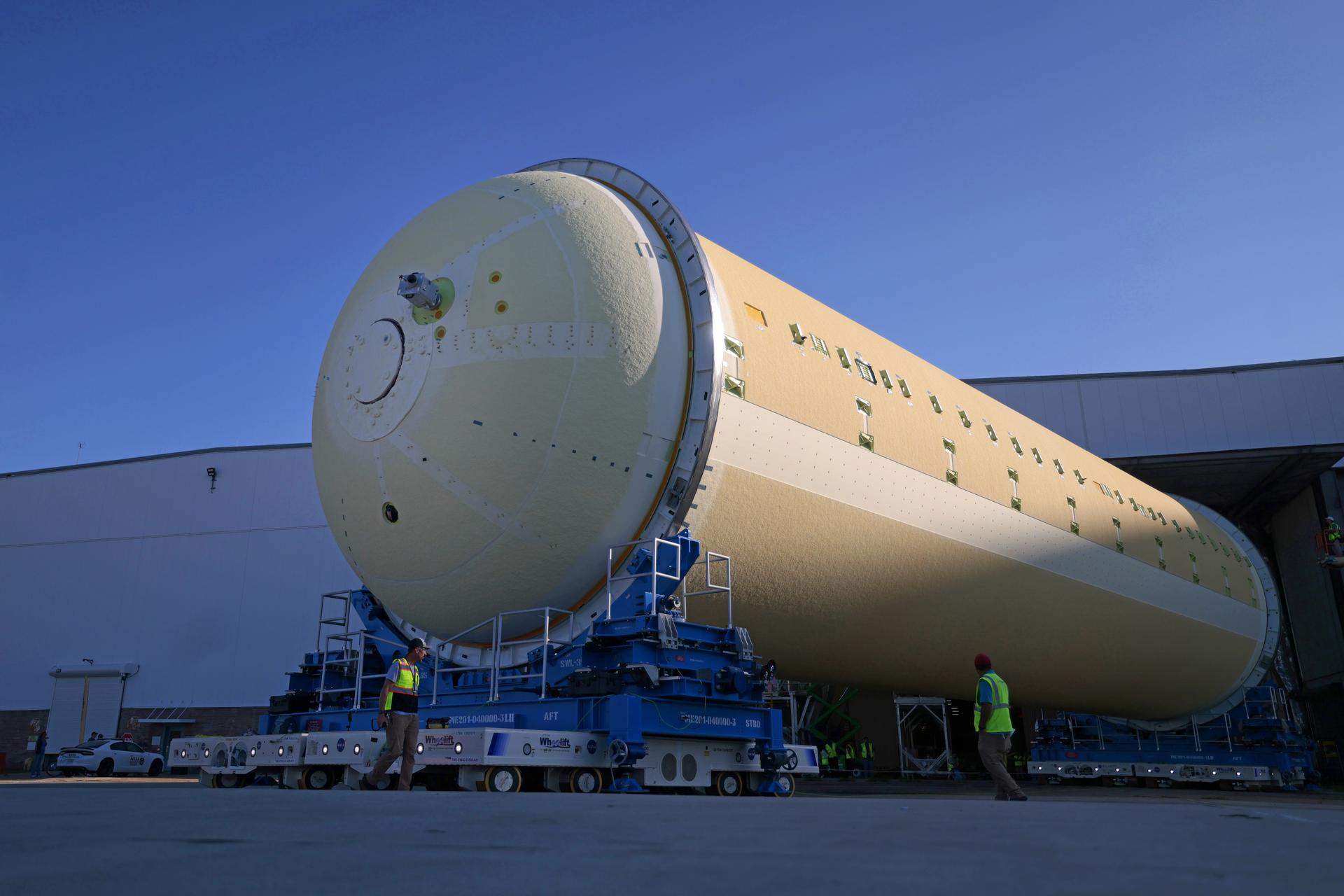

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
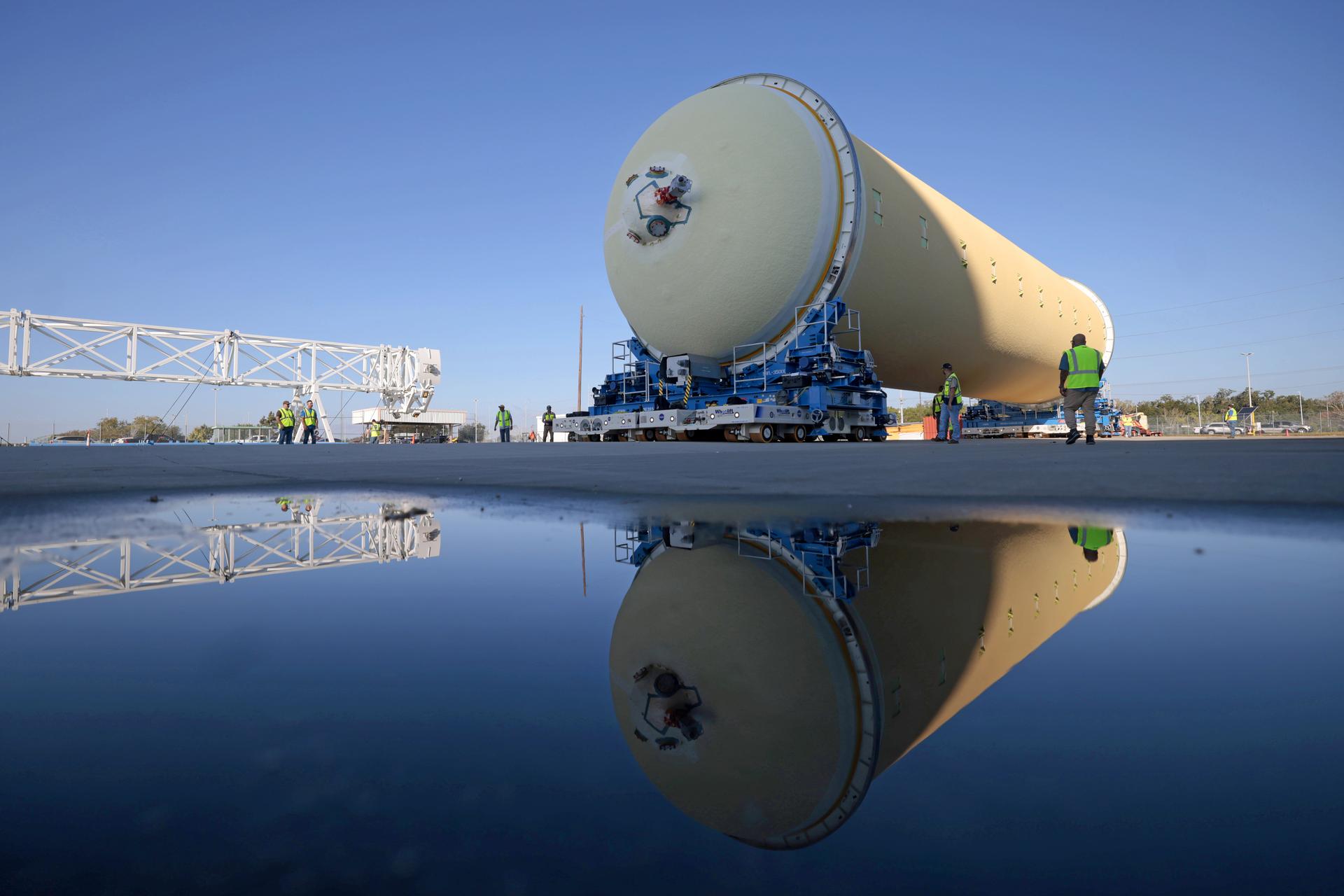

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
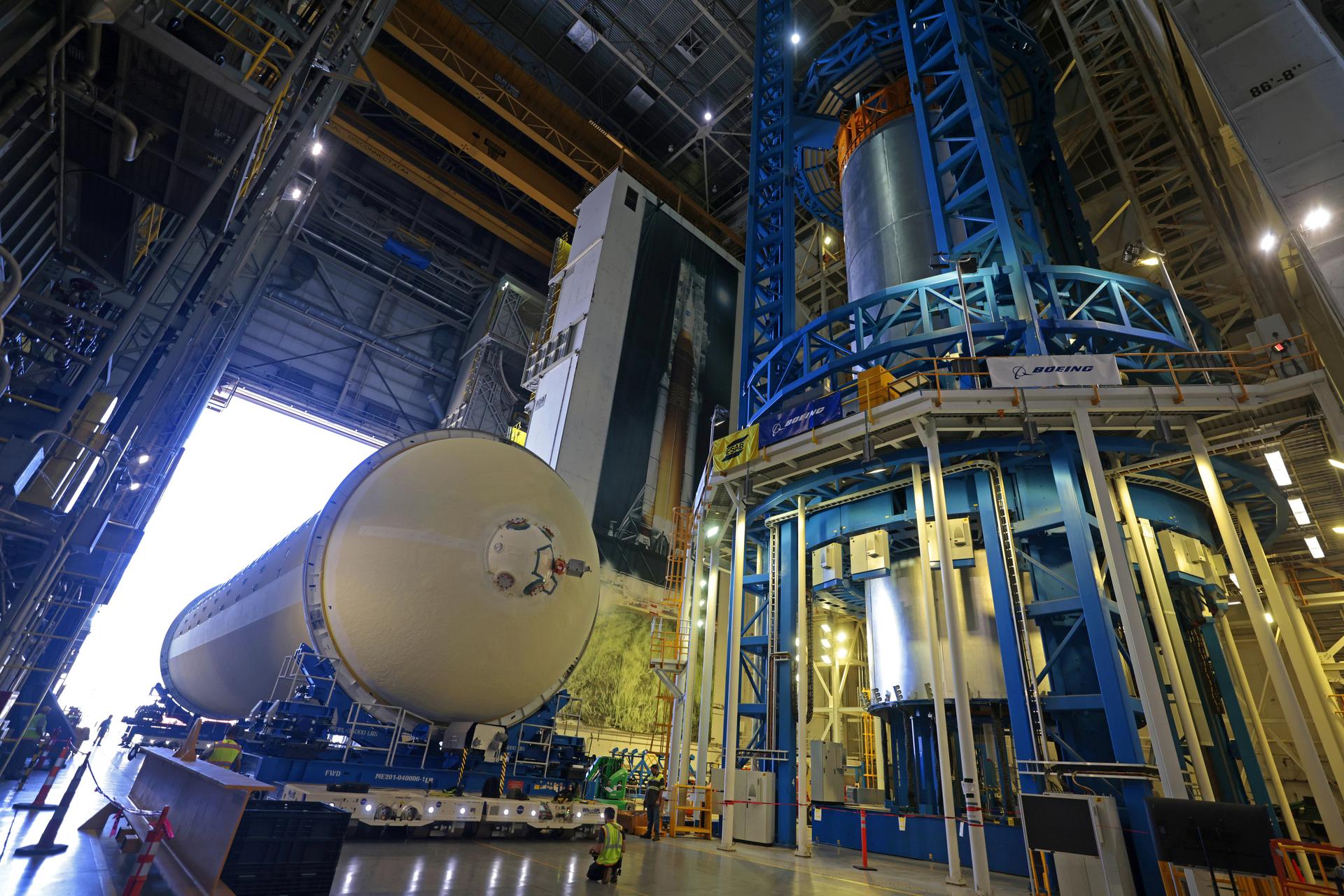

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket into the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 26, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
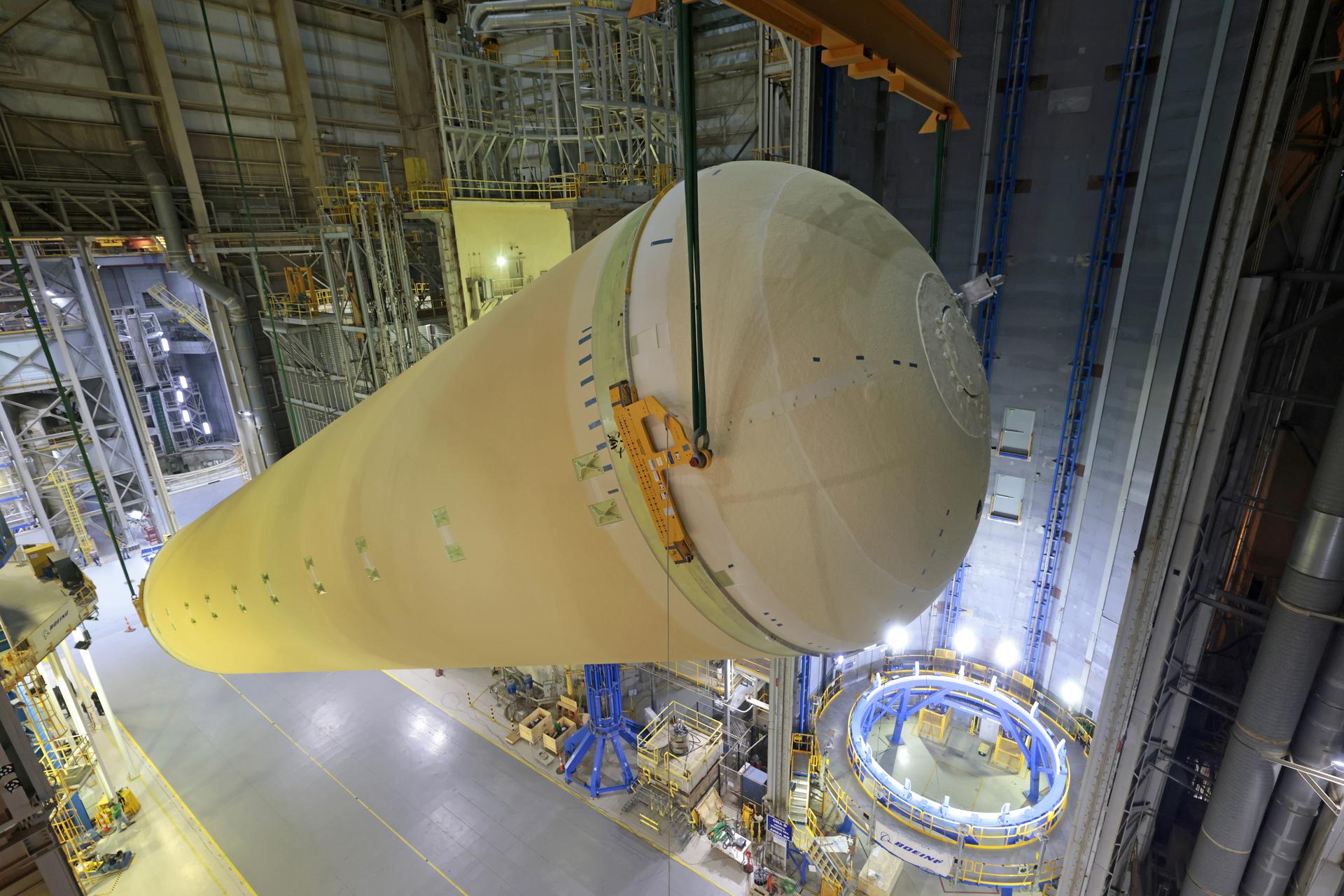

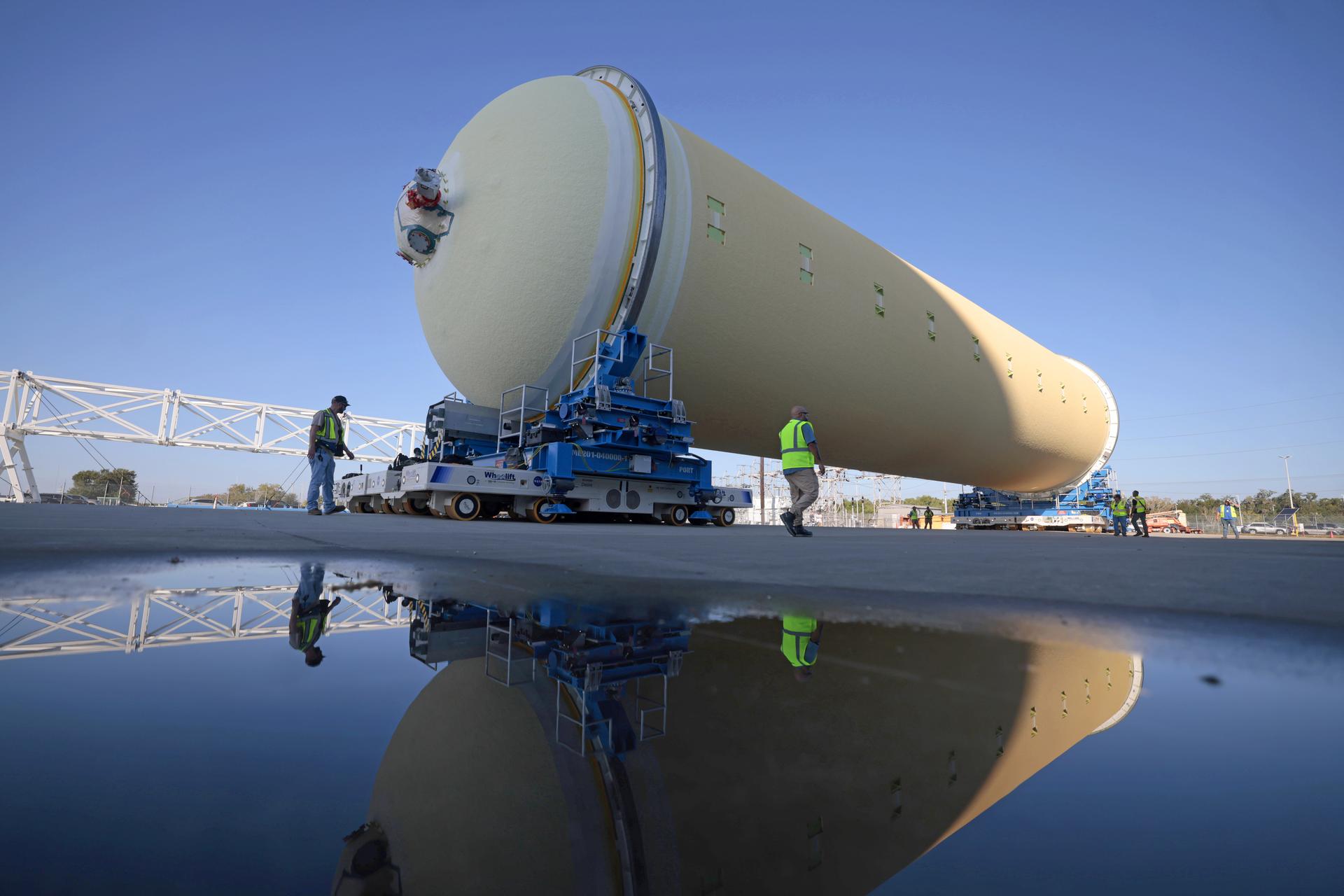
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 28, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is being lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
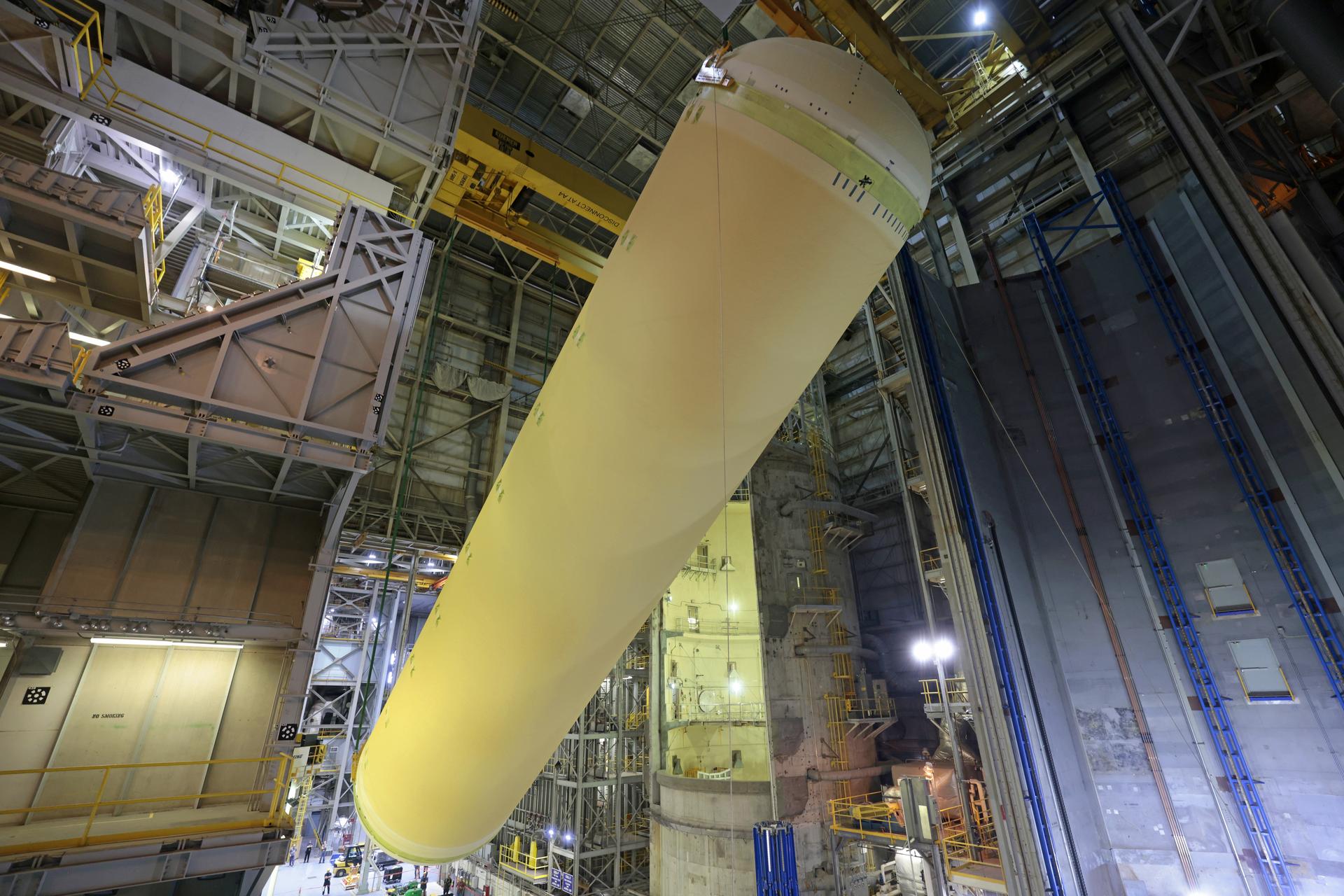

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 28, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is being lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
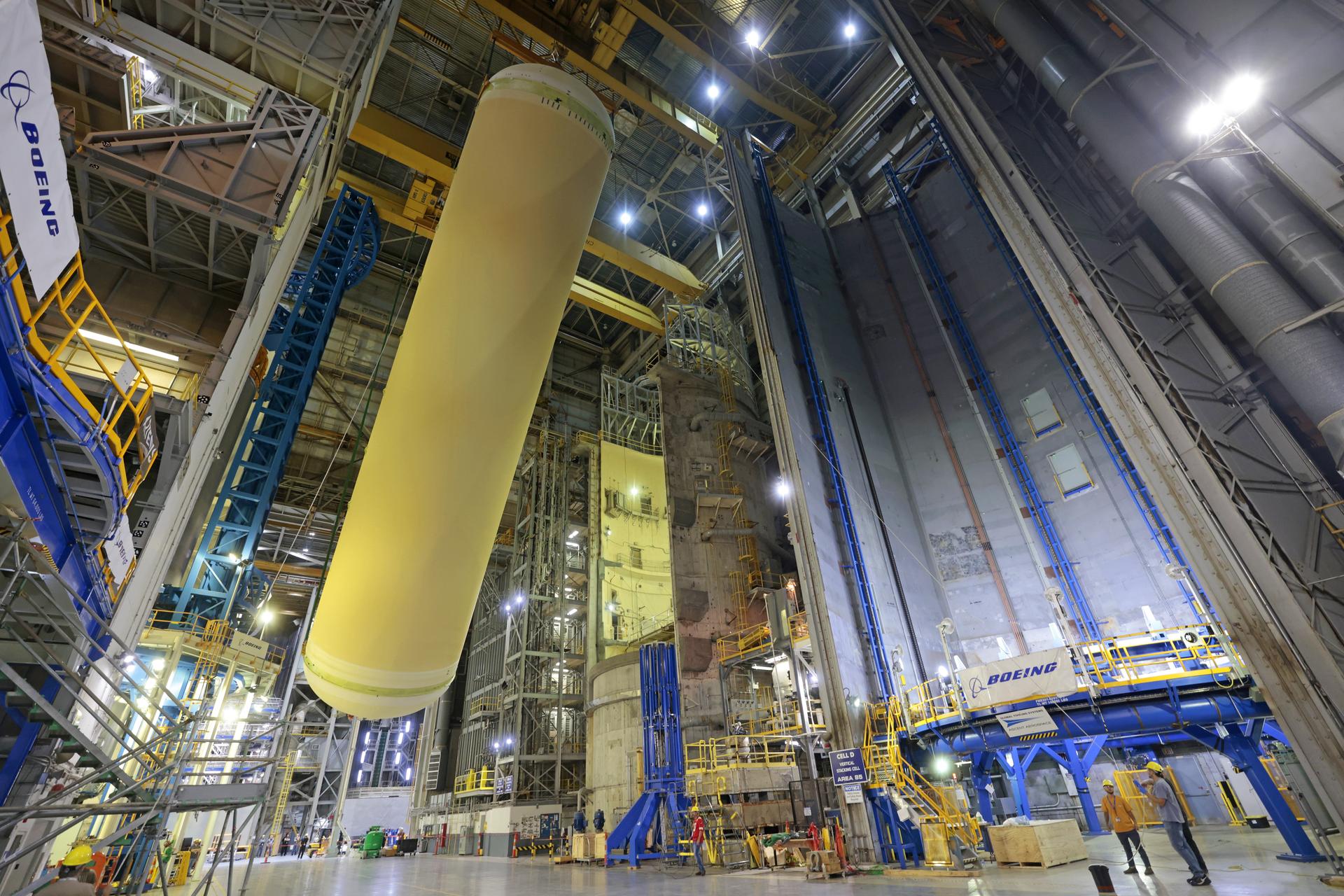

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 28, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is being lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
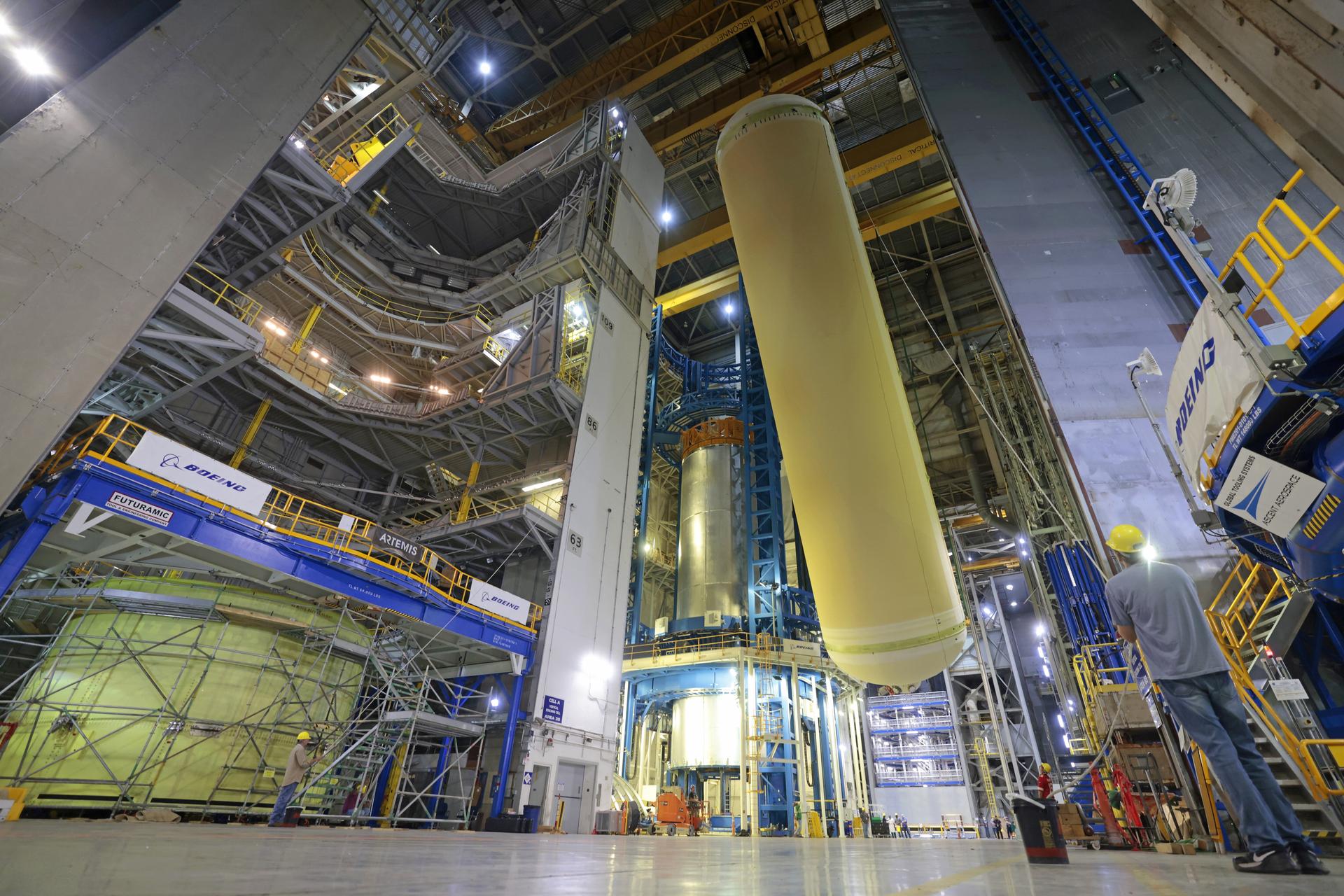

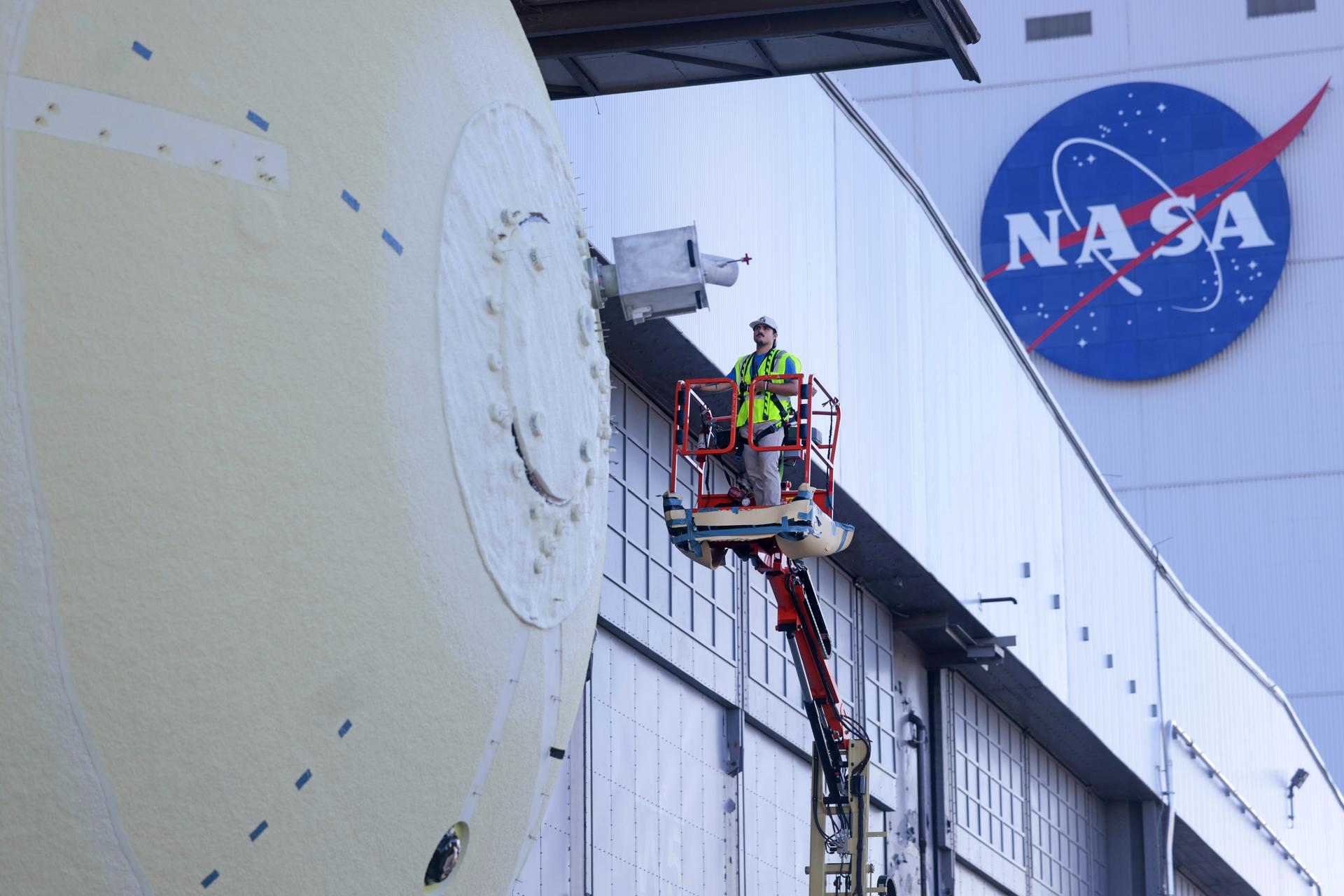
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 28, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is being lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
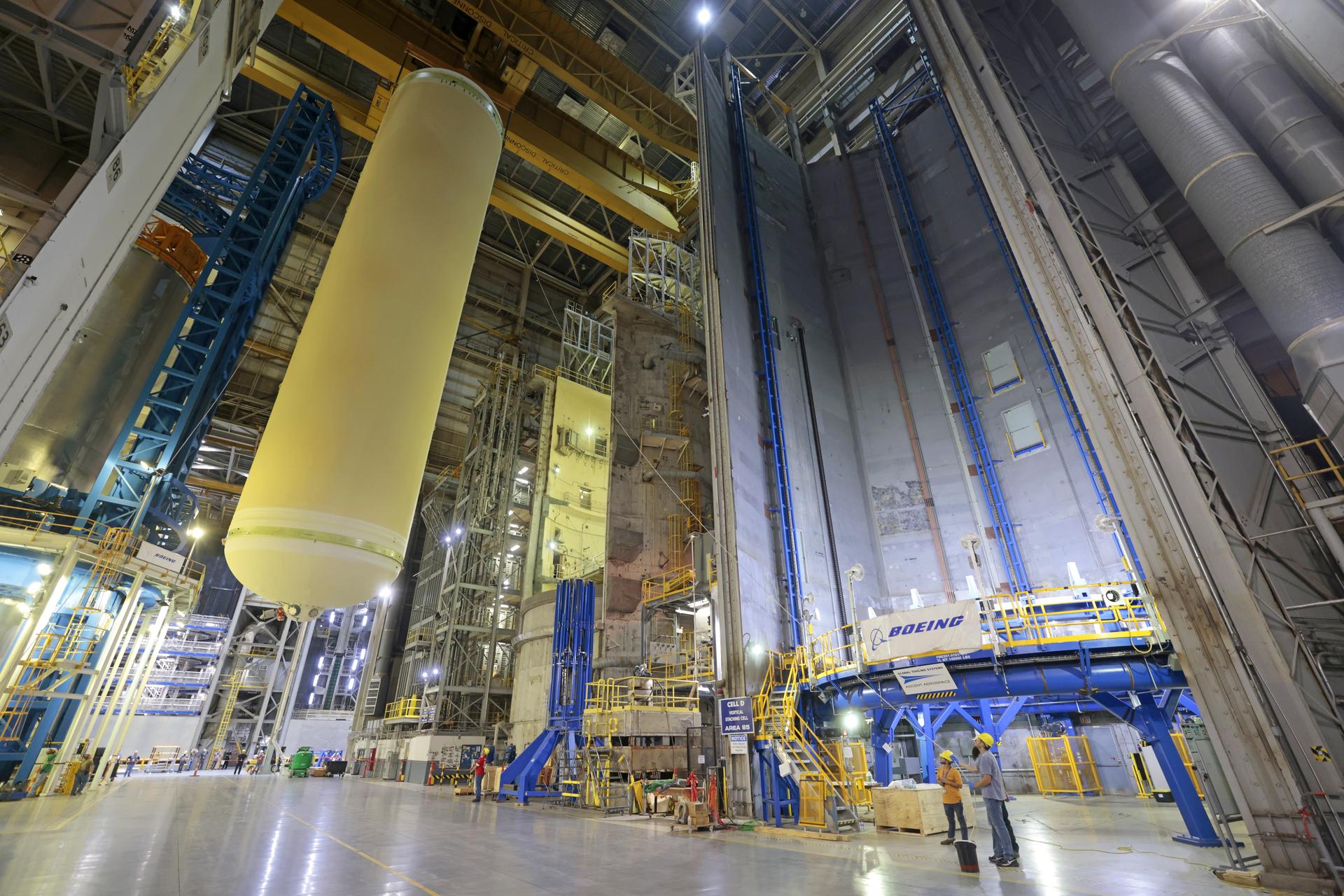

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans move a liquid hydrogen tank for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the factory’s vertical assembly building on Sep. 28, 2025. The tank, which is designated for the agency’s Artemis III mission, is being lifted and loaded into a production cell where it will be mated with the LH2 Transport Adapter Assembly for future transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. The engine section flight hardware structure was completed in 2022 and was shipped to Kennedy where teams continue to integrate vital systems. The propellant tank is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
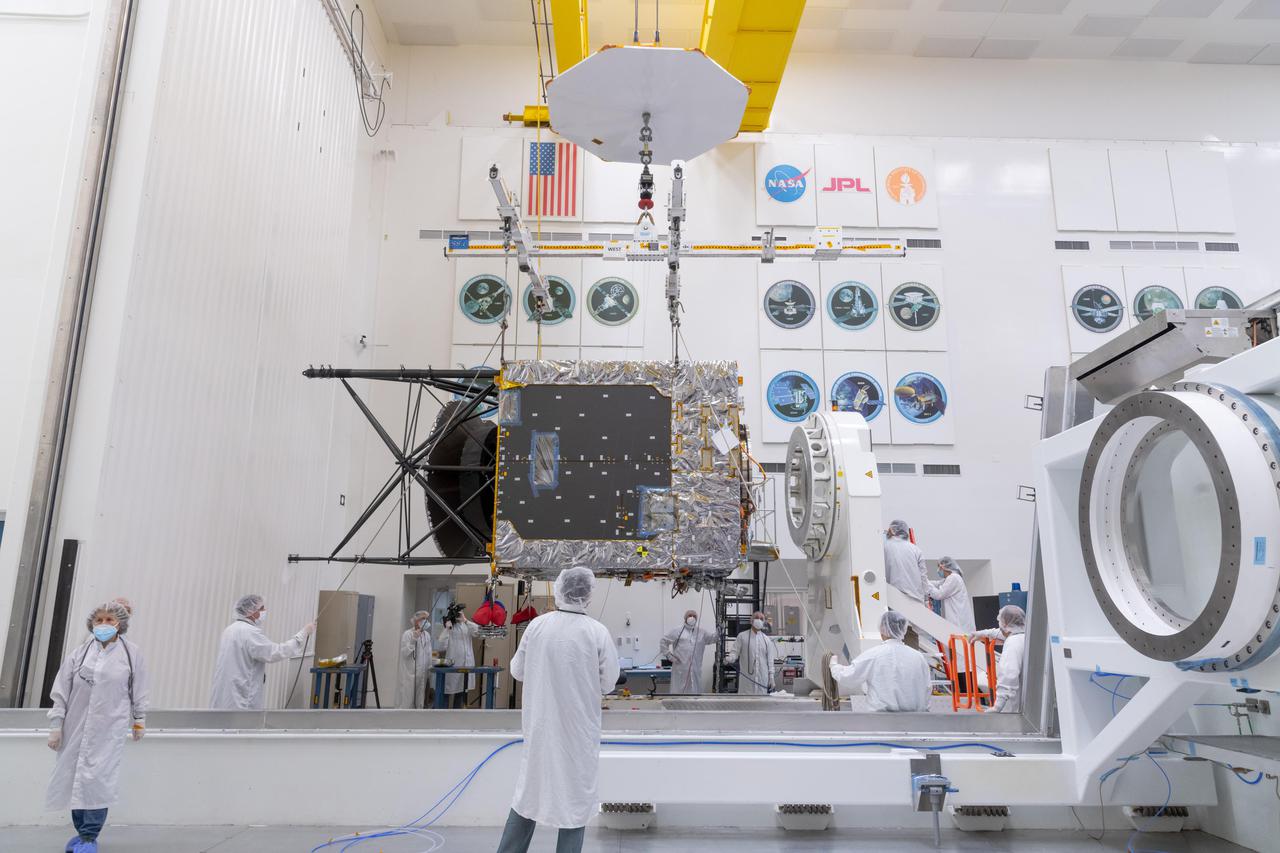

A major component of NASA's Psyche spacecraft has been delivered to the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, where the phase known as assembly, test, and launch operations (ATLO) is now underway. Taken on March 28, 2021, this photo shows the Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) Chassis just after it was delivered to JPL by Maxar Technologies. Here, the chassis is about to be attached to the dolly in High Bay 1 of JPL's Spacecraft Assembly Facility. Maxar's team in Palo Alto, California, designed and built the SEP Chassis, which includes all the primary and secondary structure and the hardware components needed for the high-power electrical system, the propulsion system, the thermal system, guidance and navigation sensors and actuators, and the high-gain antenna. Over the next year additional hardware will be added to the spacecraft, including the command and data handling system, a power distribution assembly, the X-band telecommunications hardware suite, three science instruments (two imagers, two magnetometers, and a Gamma Ray Neutron Spectrometer), and a deep space optical communications technology demonstrator. The spacecraft will finish assembly and then undergo rigorous checkout and testing before being shipped to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, for an August 2022 launch to the main asteroid belt. Psyche will arrive at the metal-rich asteroid of the same name in 2026, orbiting for 21 months to investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to Earth's core. Exploring the asteroid could give valuable insight into how our own planet and others formed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24474
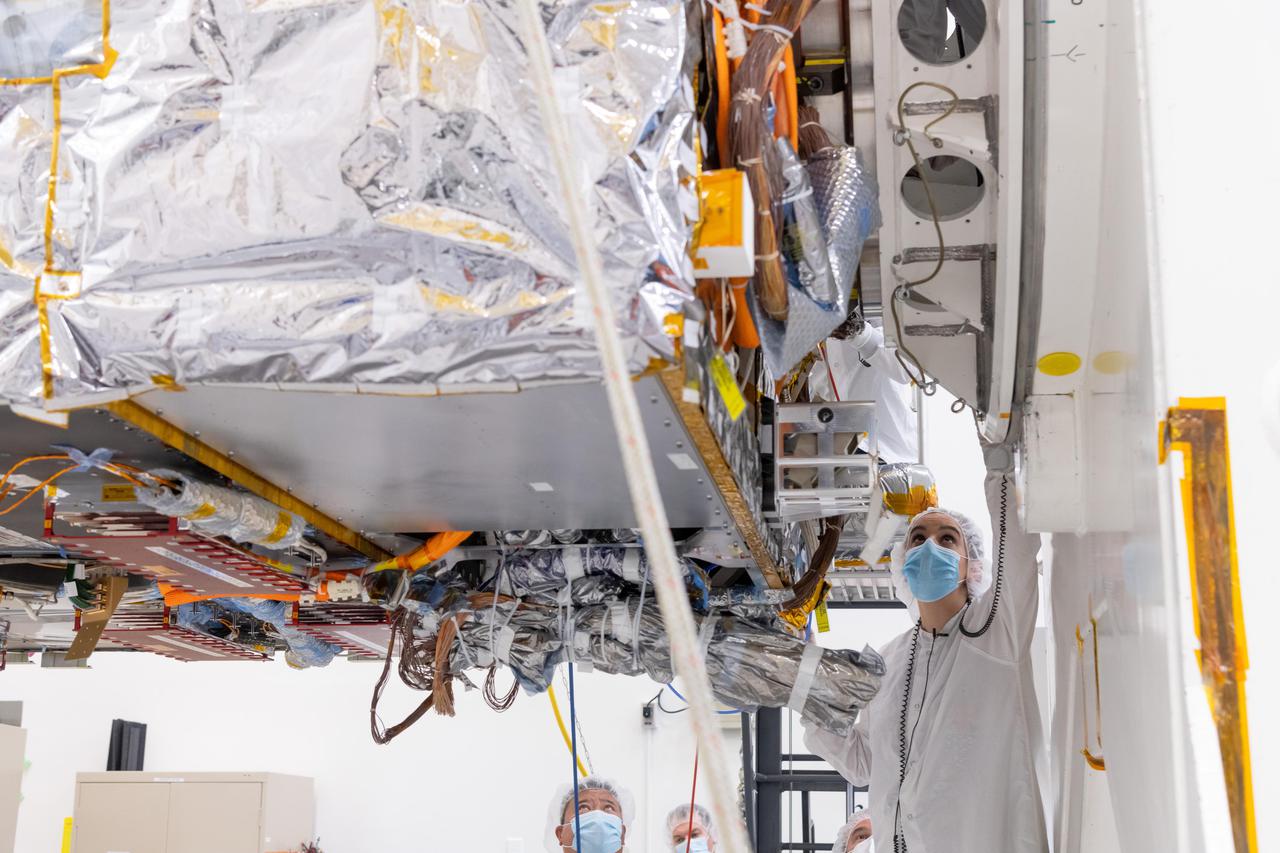

The Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) Chassis of NASA's Psyche spacecraft is mounted onto a rotation fixture in High Bay 1 of the Spacecraft Assembly Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. This photo was taken March 28, 2021, just after the chassis — a major component of the Psyche spacecraft — was delivered to JPL by Maxar Technologies. Maxar's team in Palo Alto, California, designed and built the chassis, which includes all the primary and secondary structure and the hardware components needed for the high-power electrical system, the propulsion system, the thermal system, guidance and navigation sensors and actuators, and the high-gain antenna. The phase known as assembly test, and launch operations (ATLO) for Psyche is now underway at JPL. In this photo, ATLO Mechanical Lead Michelle Colizzi of JPL oversees the docking of the chassis to the dolly. Over the next year additional hardware will be added to the spacecraft including the command and data handling system, a power distribution assembly, the X-band telecommunications hardware suite, three science instruments (two imagers, two magnetometers, and a Gamma Ray Neutron Spectrometer), and a deep space optical communications technology demonstrator. The spacecraft will finish assembly and then undergo rigorous checkout and testing, before it's shipped to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, for an August 2022 launch to the main asteroid belt. Psyche will arrive at the metal-rich asteroid of the same name in 2026, orbiting for 21 months to investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to Earth's core. Exploring the asteroid could give valuable insight into how our own planet and others formed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24476

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
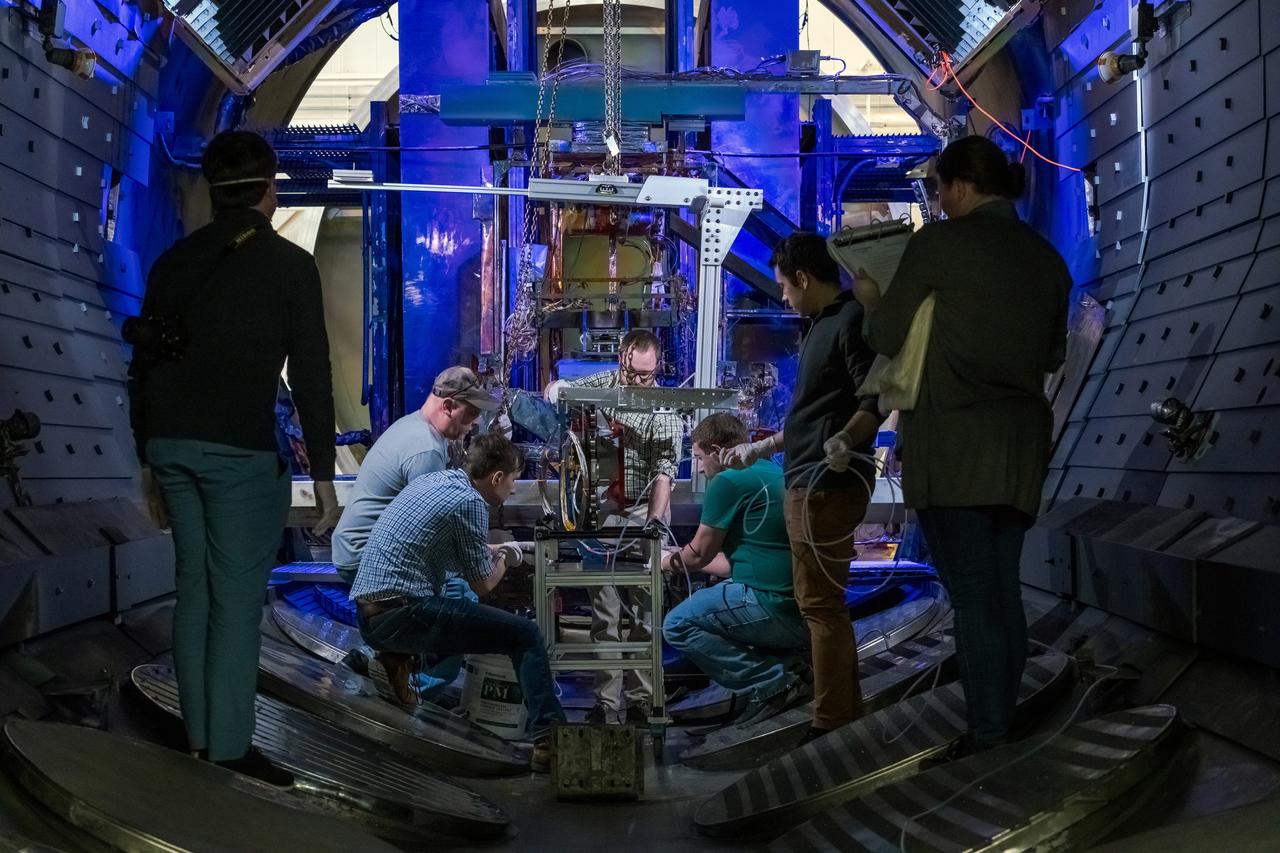

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
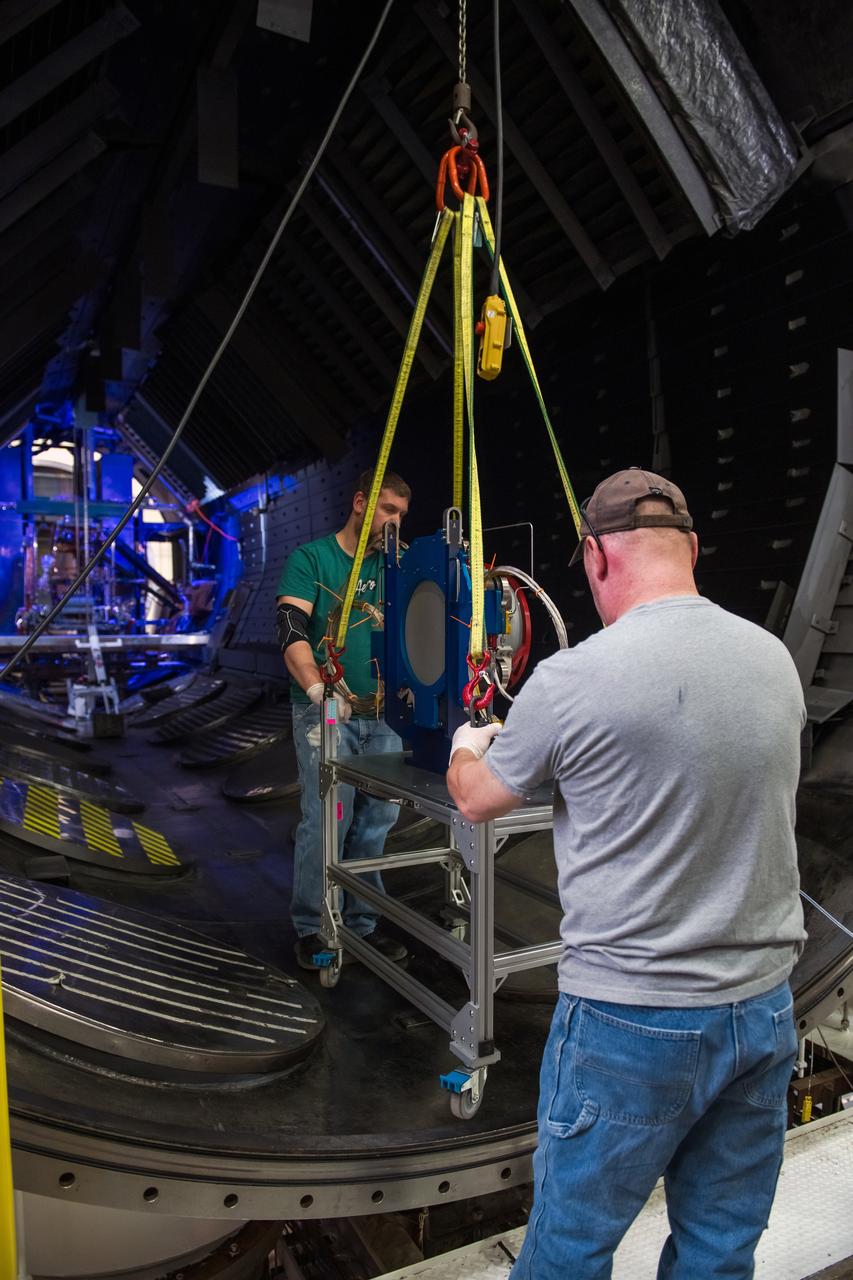

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
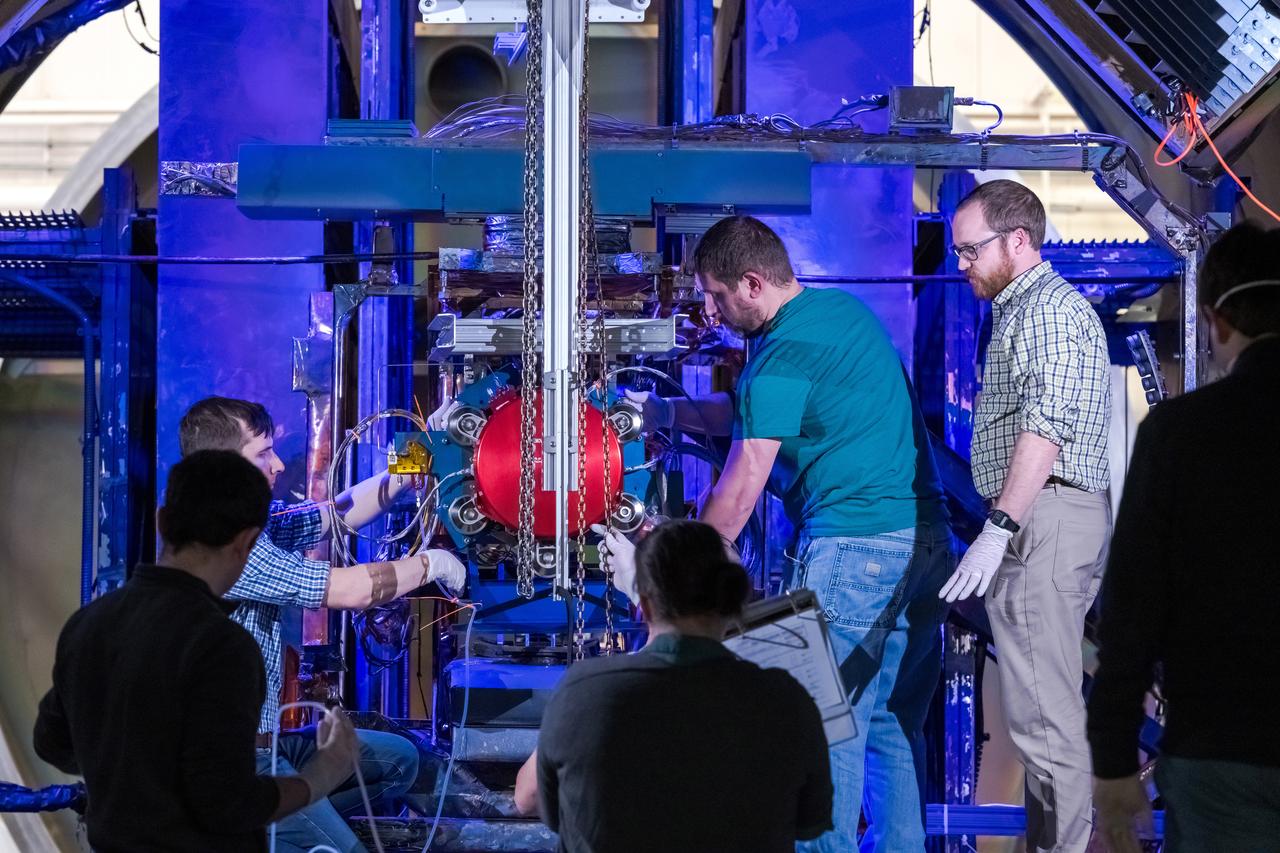
NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
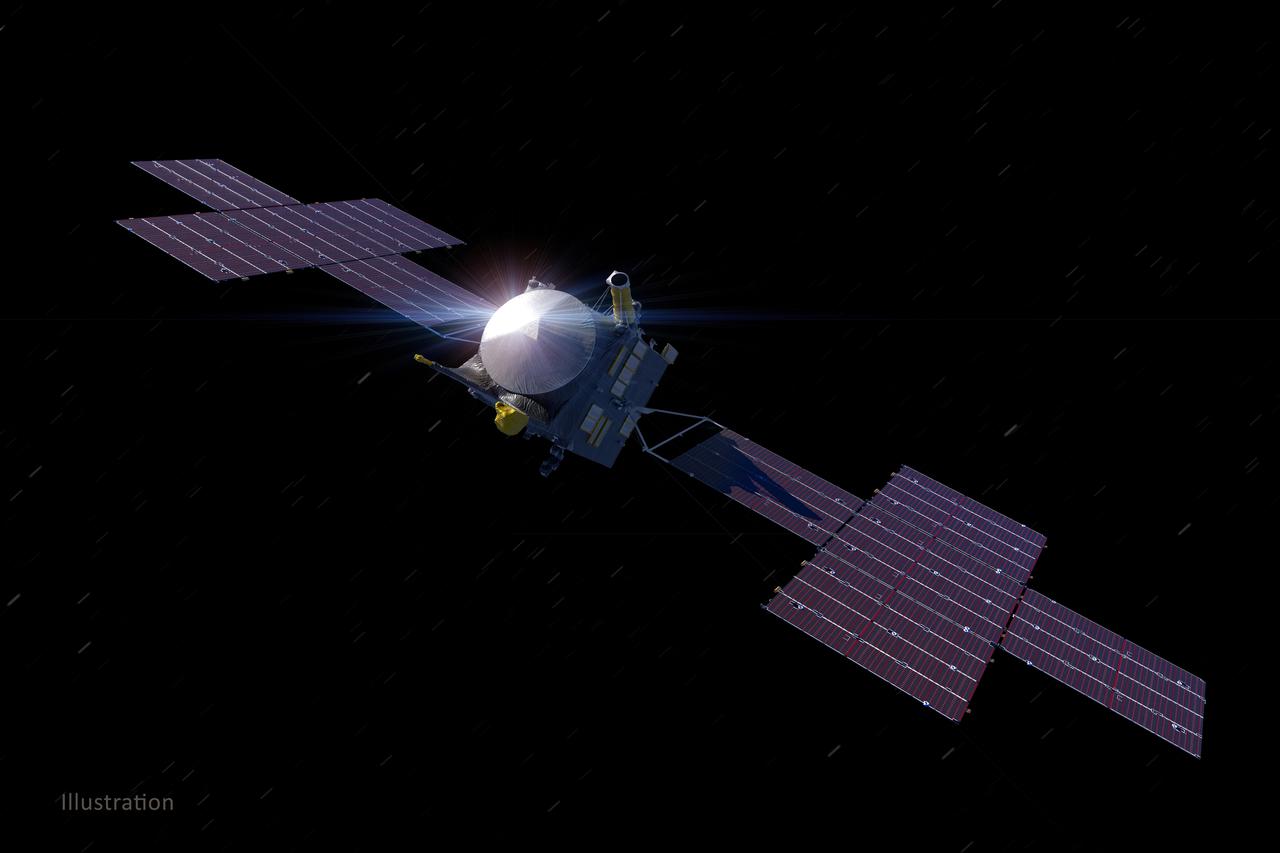

This illustration, updated as of March 2021, depicts NASA's Psyche spacecraft. Set to launch in August 2022, the Psyche mission will explore a metal-rich asteroid of the same name that lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. The spacecraft will arrive in early 2026 and orbit the asteroid for nearly two years to investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche, unlike most other asteroids that are rocky or icy bodies, is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to Earth's core. The Psyche team will use a magnetometer to measure the asteroid's magnetic field. A multispectral imager will capture images of the surface, as well as data about Psyche's composition and topography. Spectrometers will analyze the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the surface to reveal the elements that make up the asteroid. Maxar Technologies in Palo Alto, California, built the main body of the spacecraft, called the Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) Chassis. Maxar also will deliver the five-panel solar arrays, shown here, that will provide the power for the spacecraft systems. The image was created by Peter Rubin. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24473
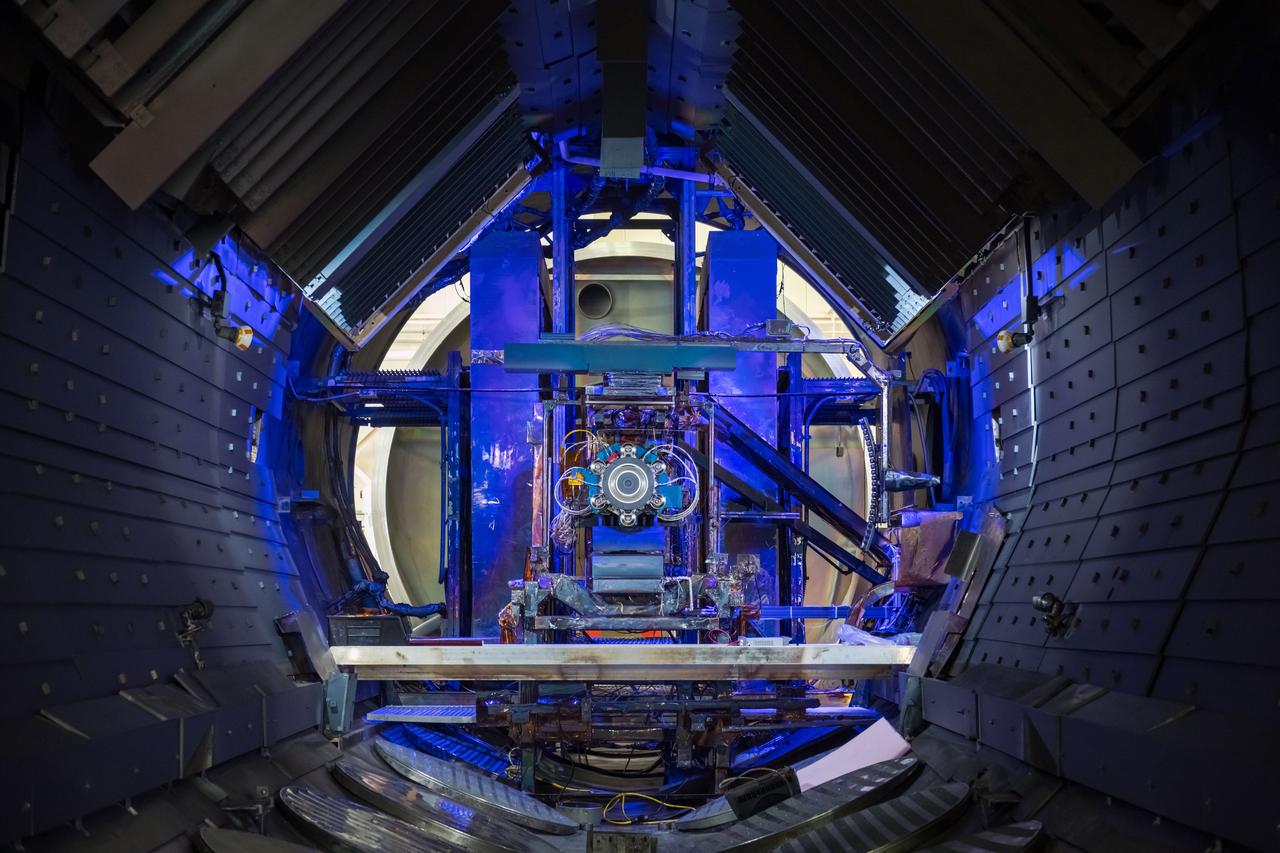

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.

Office of the Chief Technologist, OCT Innovation Workshop, and Facility Tours
![jsc2020e041336 (Sep 21, 2020) - “There are obvious highlights [about my job] and then there are some highlights that I didn’t really see coming. It’s such an honor to be just one person behind the scenes supporting the crewmembers while they’re up in space and focusing on their missions. It’s such an honor to be a part of them accomplishing their mission. The first time I got a call from space was a major highlight. Every call I’ve gotten from space since then has never gotten less exciting. The fact that I am continuously communicating with people who are living and working on the International Space Station — it’s just very surreal, it’s very mind-blowing still to this day even though I’ve been in this role for several years now. "But one of the highlights that I didn’t necessarily see coming is that a lot of the crewmembers have become mentors to me now. I look up to them for so many different reasons. And we have such a diverse corps that there’s really unlimited wisdom that I can take from listening to each crewmember’s story and from working with each crewmember. They show so much humility and perseverance. Hearing stories about their failures and their successes, watching them problem-solve and even problem-solving with them, has made me grow to be the kind of individual that I think I always wanted to become. I just never knew that I would have the opportunity to have these kinds of mentors to actually help me become that person.” — Stephanie Fernandez, Social Media and Outreach Specialist for the Astronaut Office, Johnson Space Center Image Credit: NASA / James Blair Interviewer: NASA / Thalia Patrinos](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2020e041336/jsc2020e041336~medium.jpg)
jsc2020e041336 (Sep 21, 2020) - “There are obvious highlights [about my job] and then there are some highlights that I didn’t really see coming. It’s such an honor to be just one person behind the scenes supporting the crewmembers while they’re up in space and focusing on their missions. It’s such an honor to be a part of them accomplishing their mission. The first time I got a call from space was a major highlight. Every call I’ve gotten from space since then has never gotten less exciting. The fact that I am continuously communicating with people who are living and working on the International Space Station — it’s just very surreal, it’s very mind-blowing still to this day even though I’ve been in this role for several years now. "But one of the highlights that I didn’t necessarily see coming is that a lot of the crewmembers have become mentors to me now. I look up to them for so many different reasons. And we have such a diverse corps that there’s really unlimited wisdom that I can take from listening to each crewmember’s story and from working with each crewmember. They show so much humility and perseverance. Hearing stories about their failures and their successes, watching them problem-solve and even problem-solving with them, has made me grow to be the kind of individual that I think I always wanted to become. I just never knew that I would have the opportunity to have these kinds of mentors to actually help me become that person.” — Stephanie Fernandez, Social Media and Outreach Specialist for the Astronaut Office, Johnson Space Center Image Credit: NASA / James Blair Interviewer: NASA / Thalia Patrinos
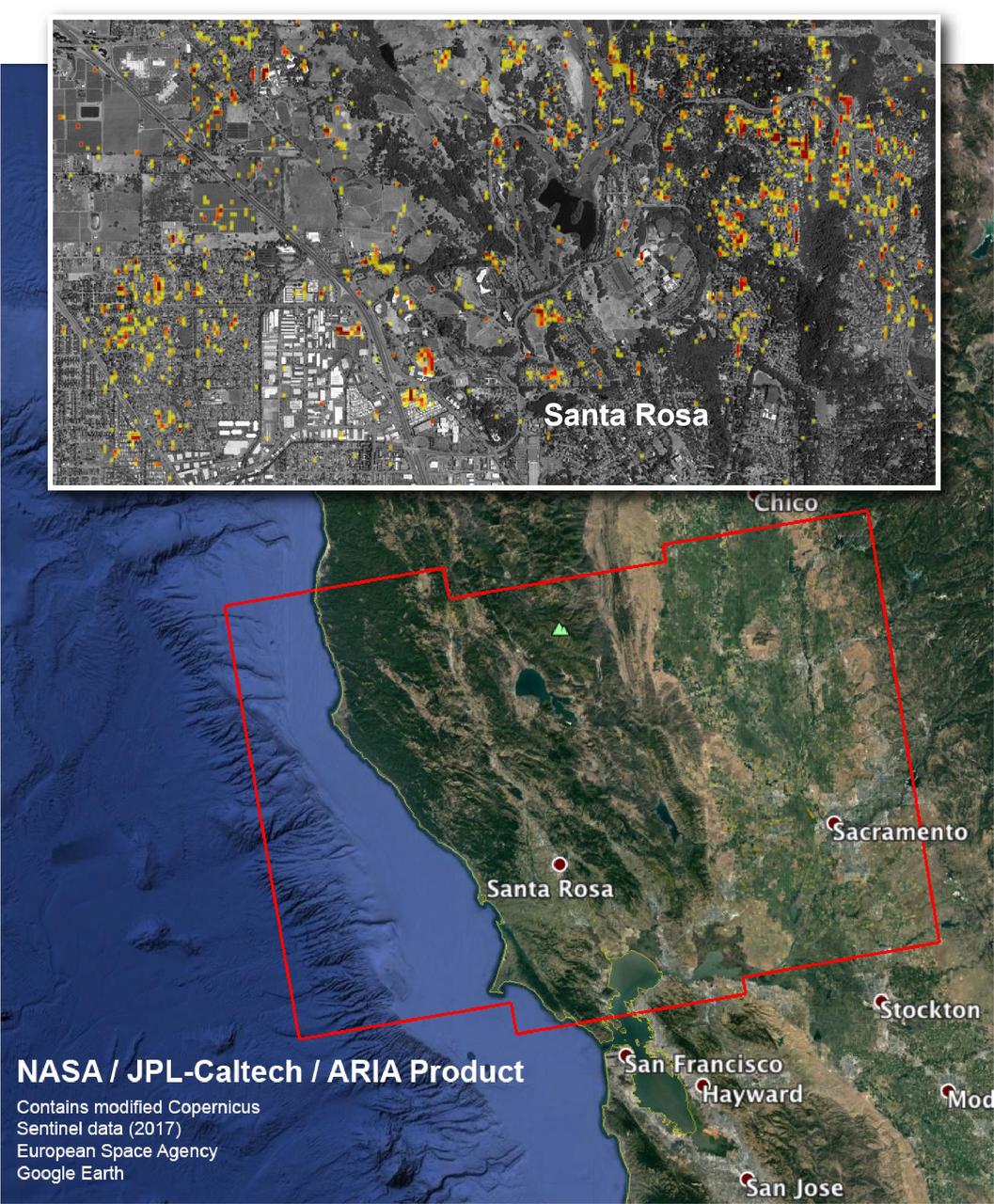
The Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis (ARIA) team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, and Caltech, also in Pasadena, created this Damage Proxy Map depicting areas in Northern California that are likely damaged (shown by red and yellow pixels) as a result of the region's current outbreak of wildfires. The map is derived from synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images from the Copernicus Sentinel-1 satellites, operated by the European Space Agency (ESA). The images were taken before (Sep. 27, 2017, 7 p.m. PDT) and after (Oct. 9, 2017, 7 p.m. PDT) the onset of the fires. The map has been provided to various agencies to aid in the wildfire response. The map covers the area within the large red polygon, and measures 155 by 106 miles (250 by 170 kilometers). The illustrative figure from the map depicted in the inset shows damage in the city of Santa Rosa. Each pixel in the Damage Proxy Map measures about 98 feet (30 meters) across. The color variation from yellow to red indicates increasingly more significant ground surface change. Preliminary validation was done by comparing to optical satellite imagery from DigitalGlobe. This Damage Proxy Map should be used as guidance to identify damaged areas, and may be less reliable over vegetated areas. Sentinel-1 data were accessed through the Copernicus Open Access Hub. The image contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2017), processed by ESA and analyzed by the NASA-JPL/Caltech ARIA team. This research was carried out at JPL under a contract with NASA. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22048
NASA and Aerojet