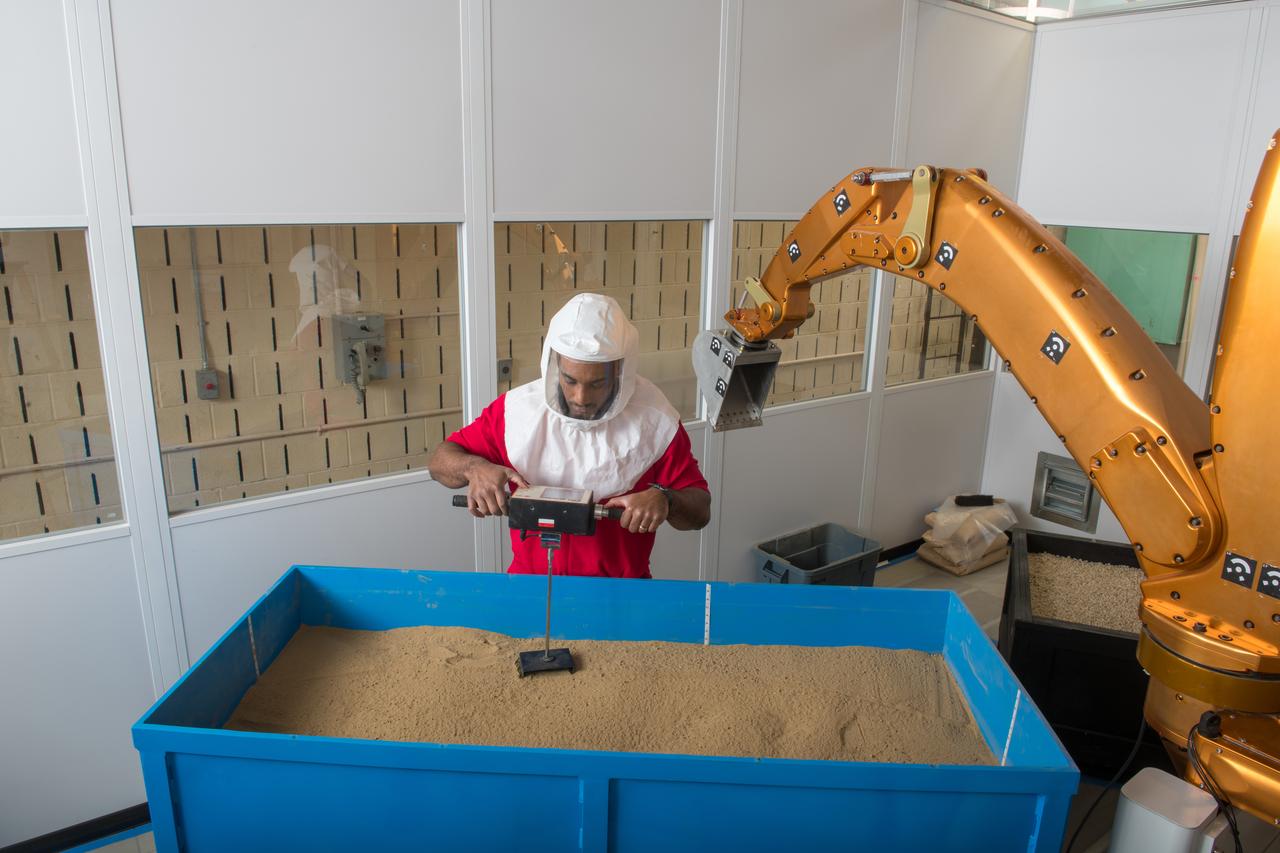
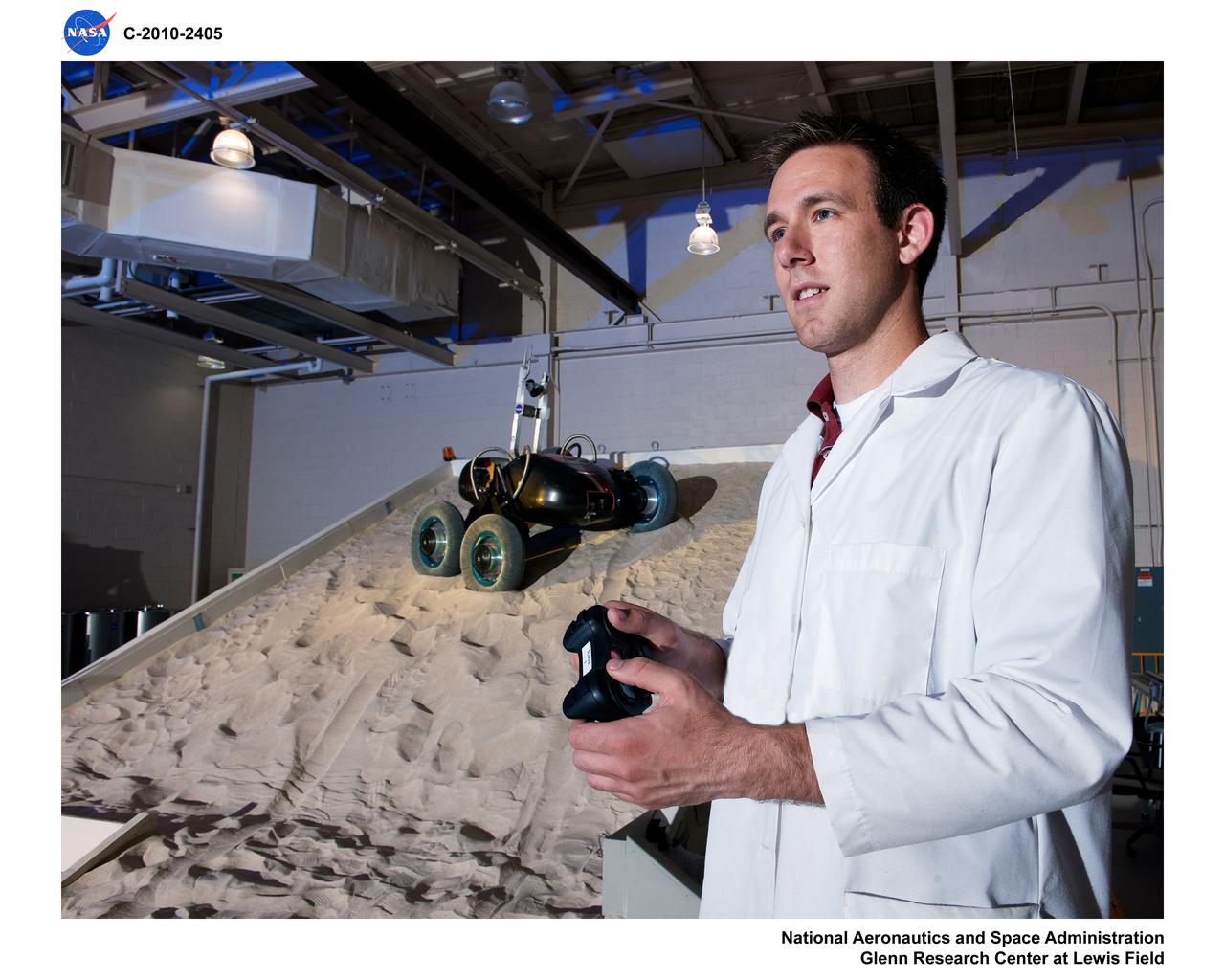
SLOPE Excavation Laboratory
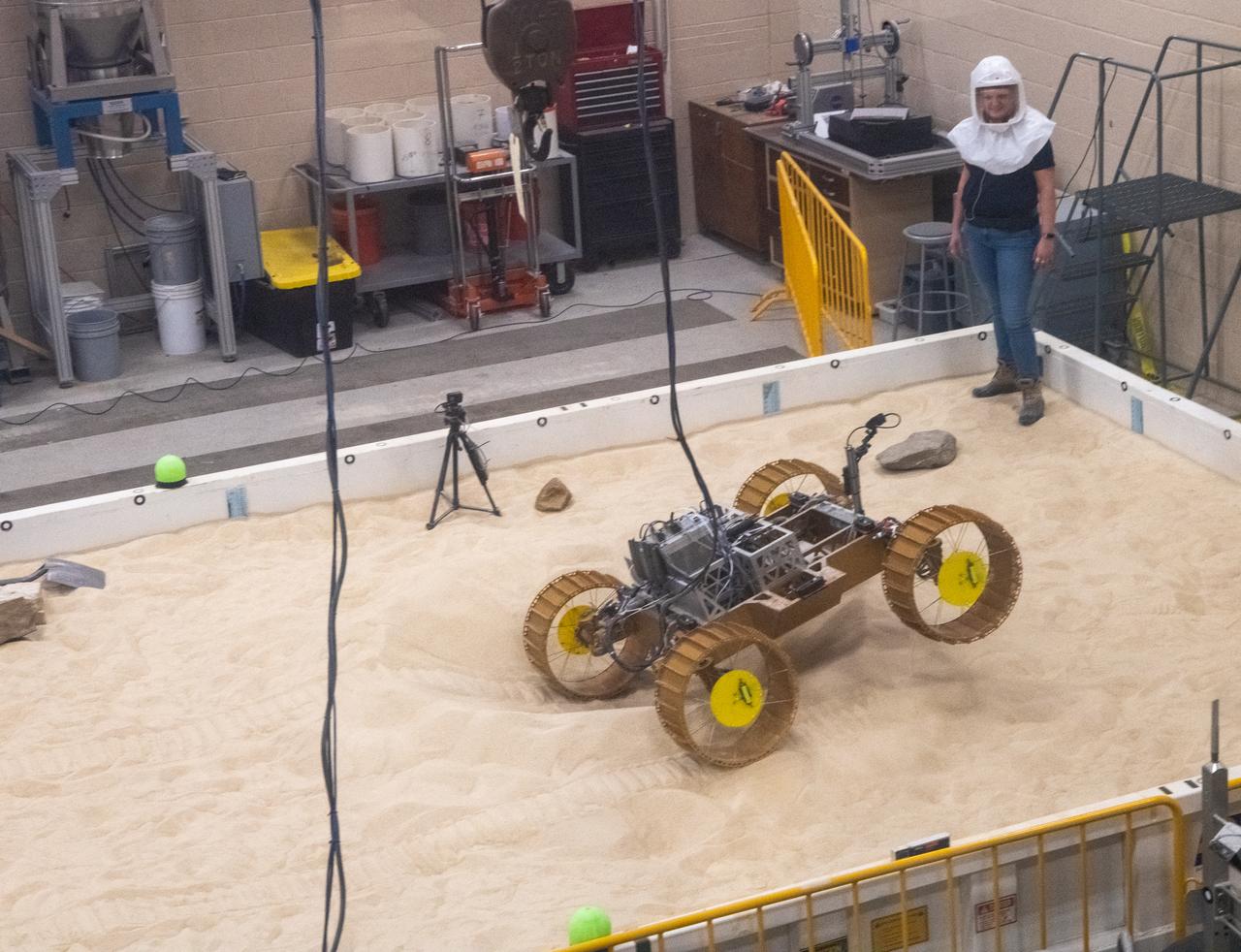

Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER Testing in the Simulated Lunar Operations Lab, SLOPE Laboratory

This image taken at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory shows a rover test drive up a manmade slope.
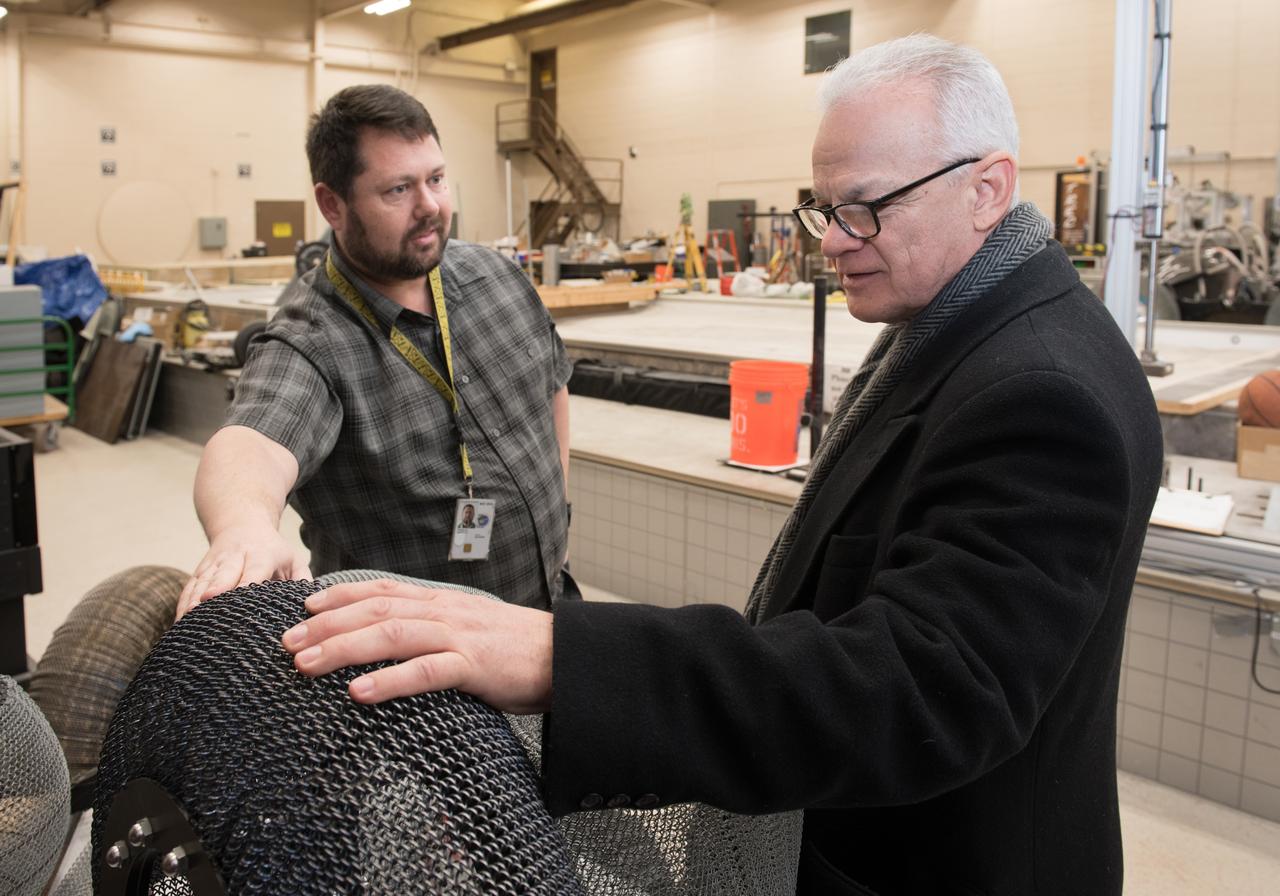

A Co-inventor of the Shape Memory Alloy, Spring Tire, shows the NASA Chief Technologist the first SMA Spring Tire Prototype during a tour of the Glenn Research Center, Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory (SLOPE).

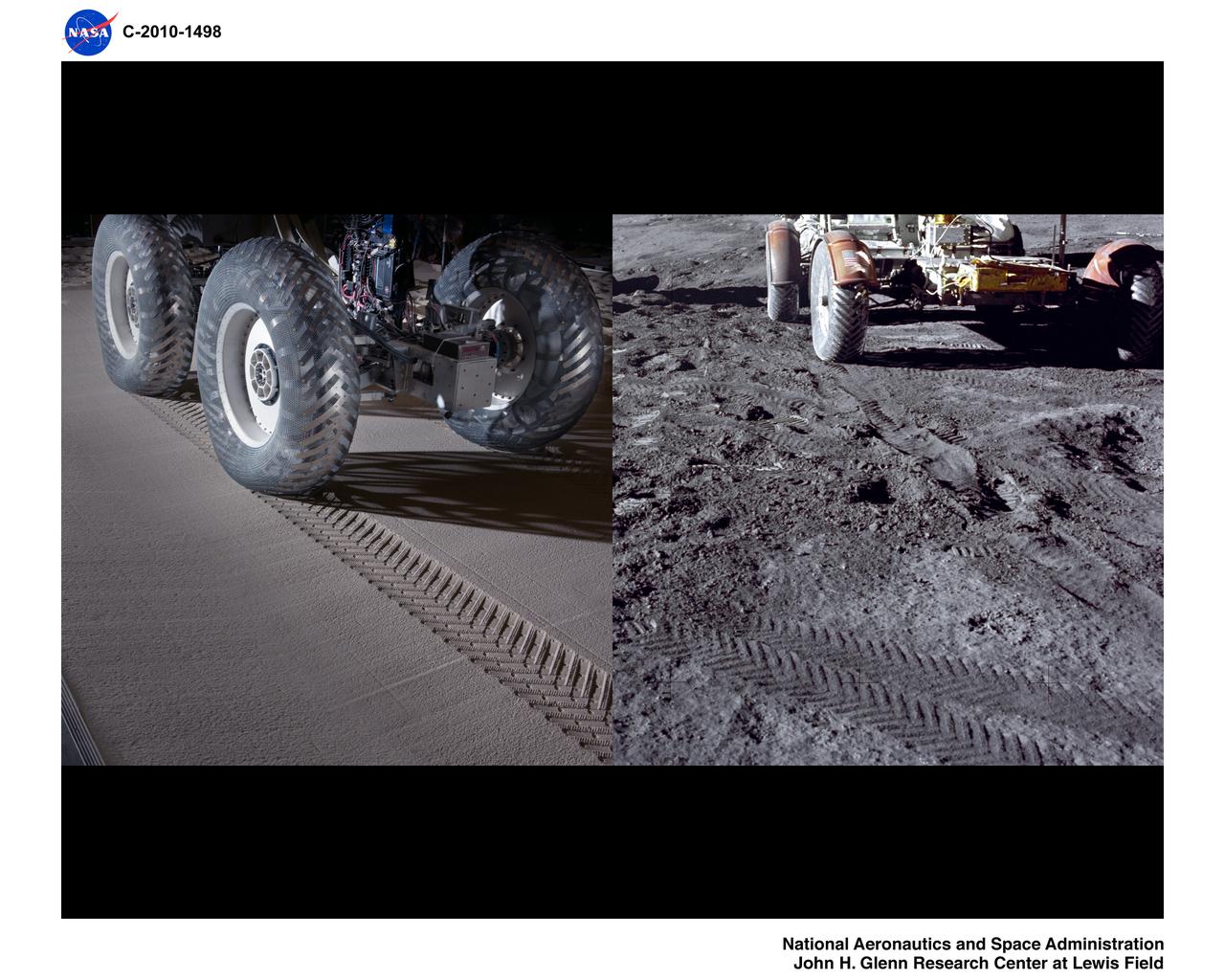
Airless Spring Wheel Prototype in the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory, SLOPE Lab
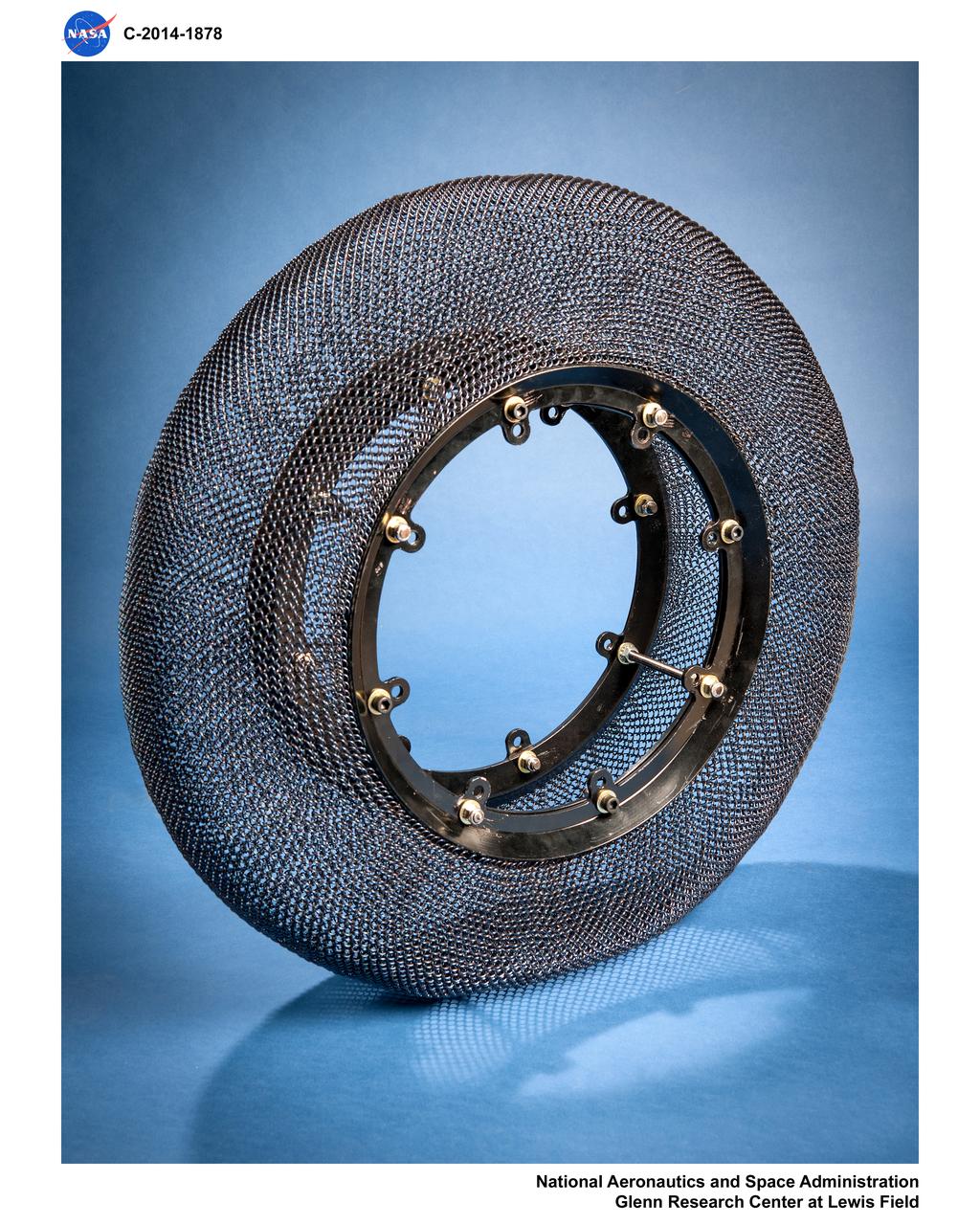

Airless Spring Wheel Prototype in the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory, SLOPE Lab
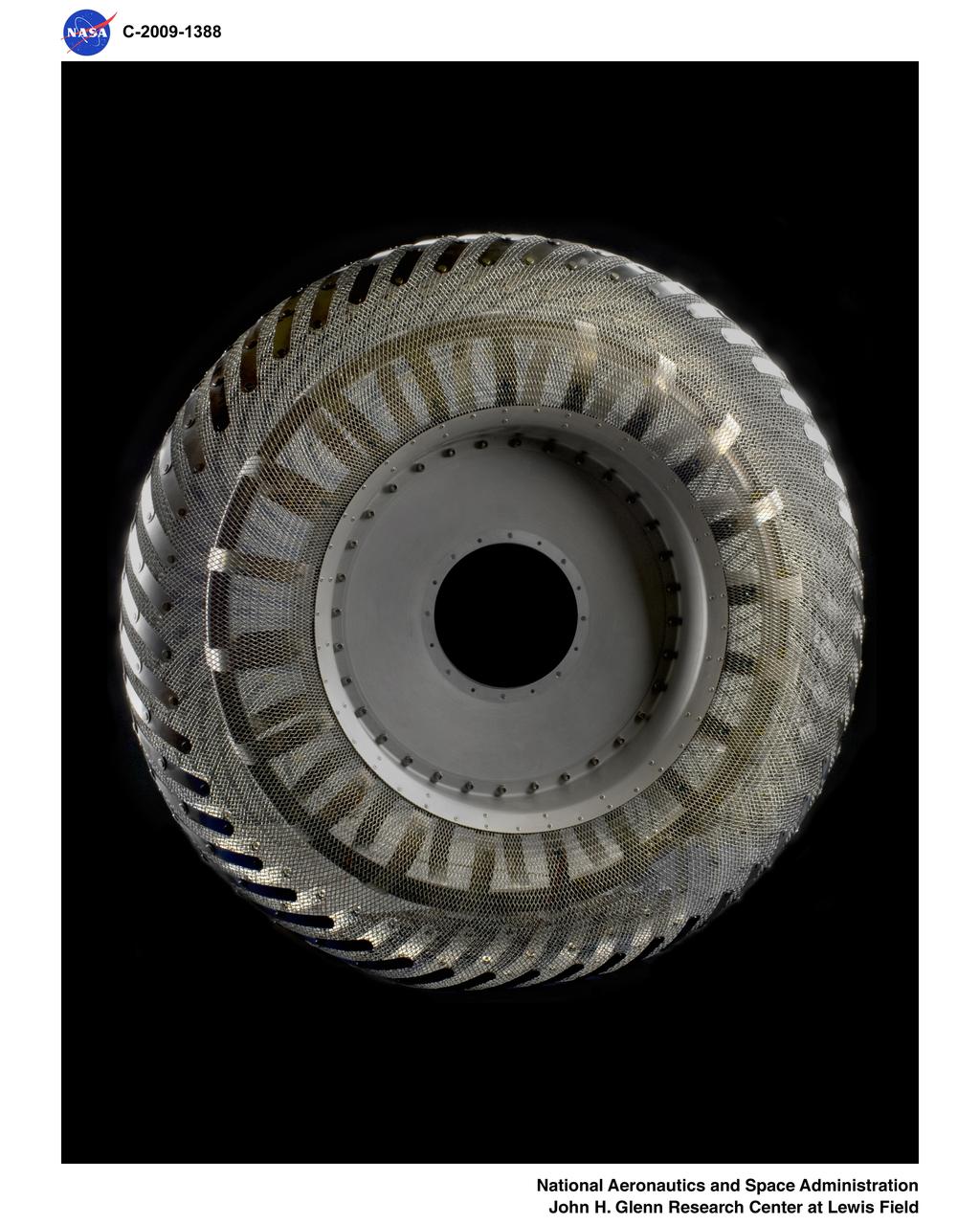

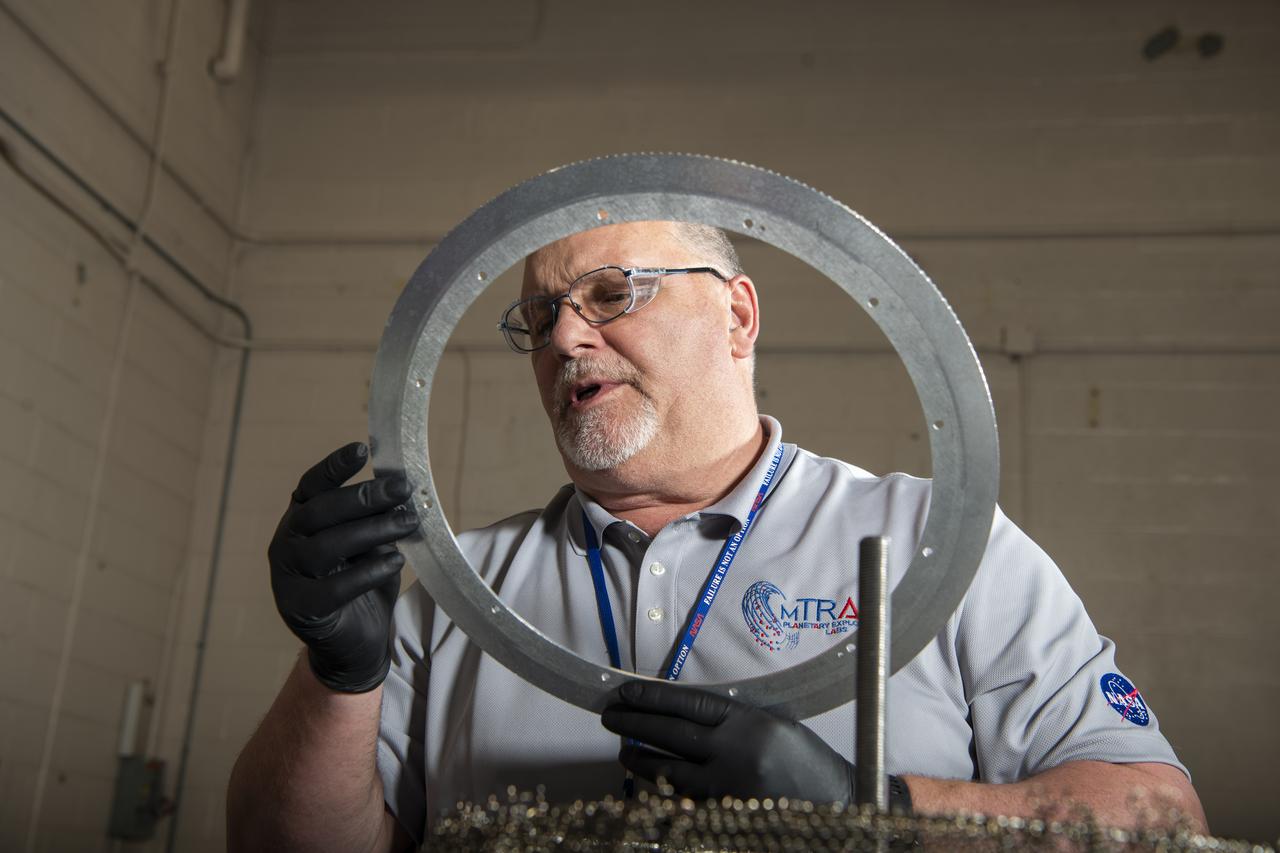
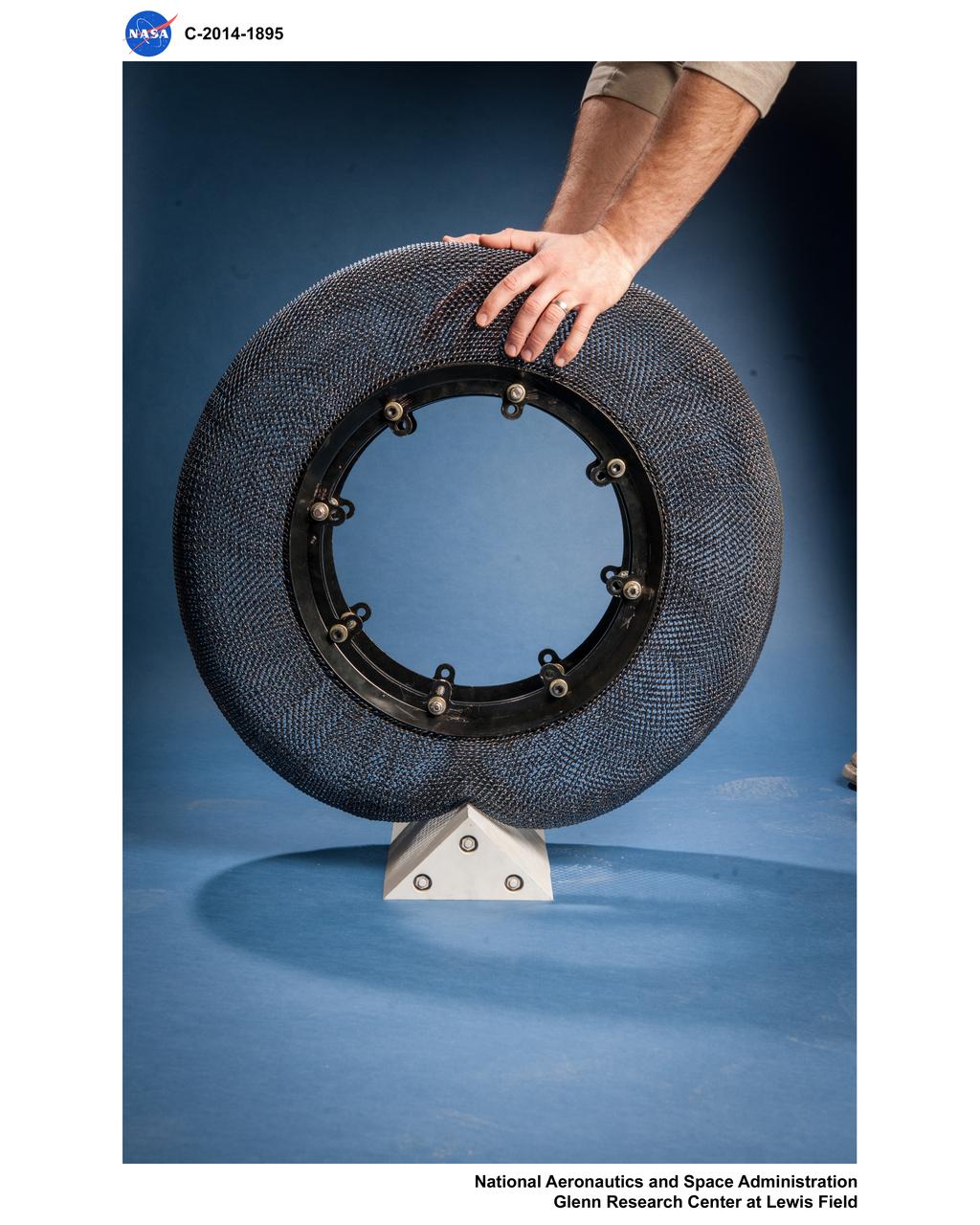
Wire Mesh Tire from the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory (SLOPE Lab)
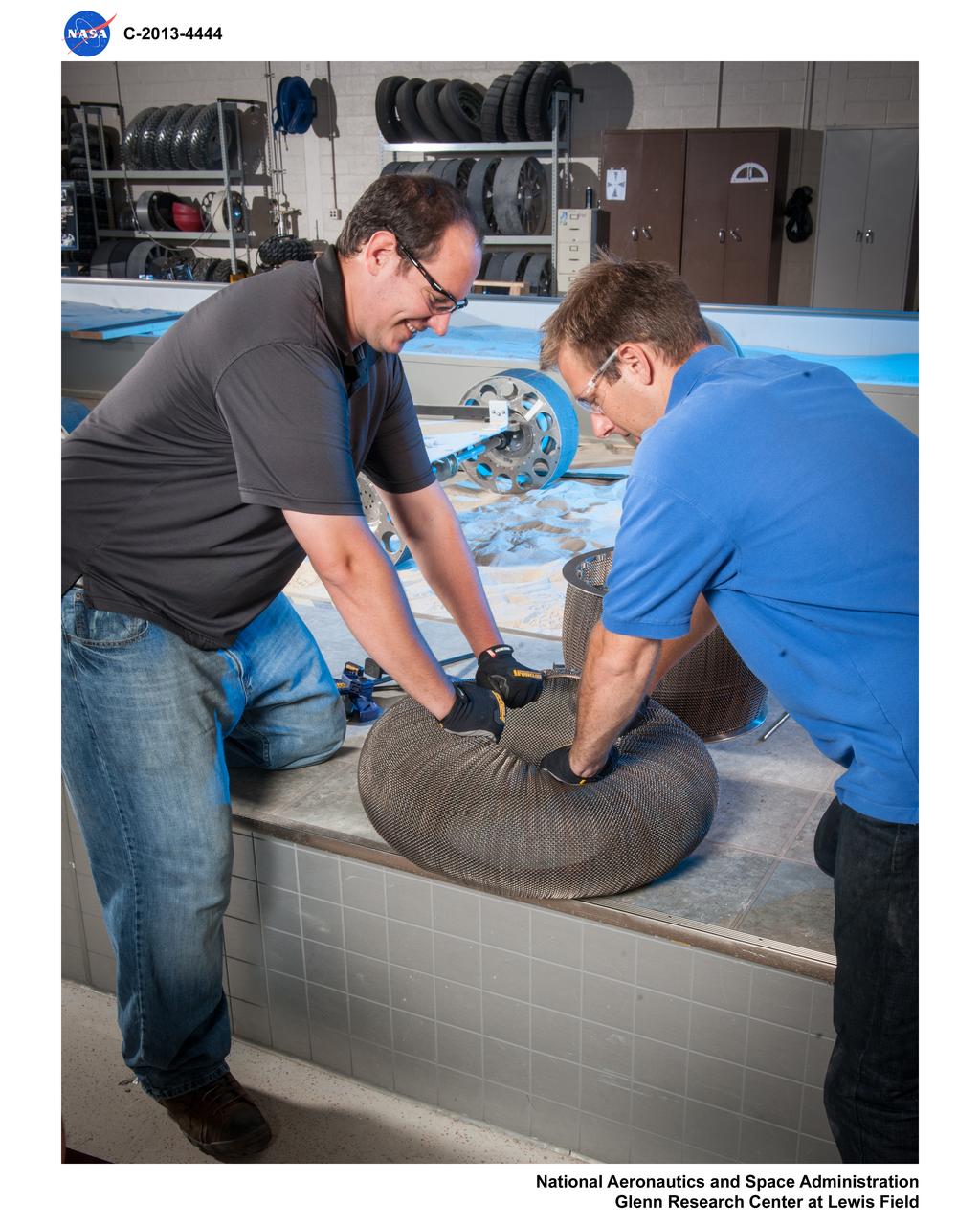

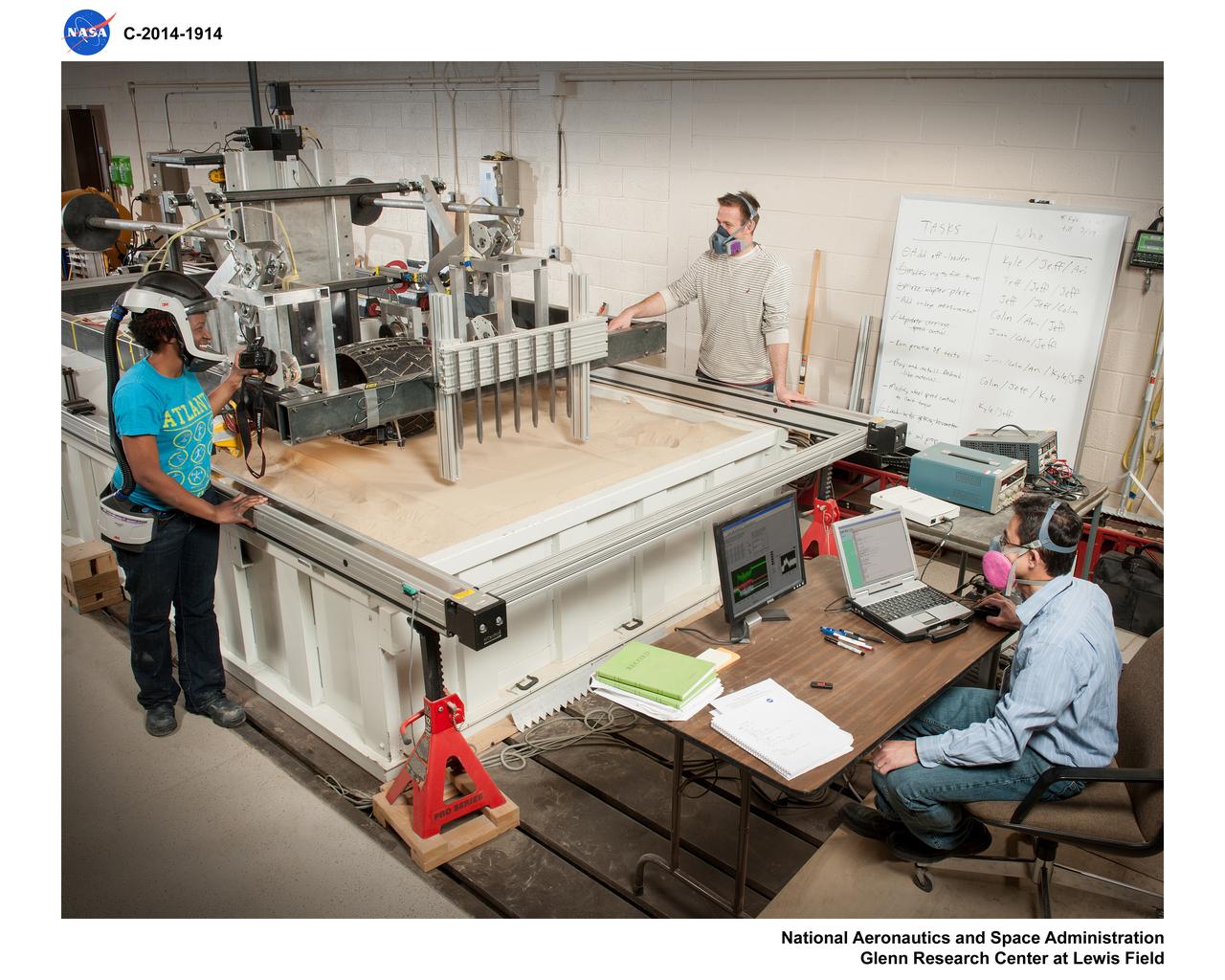
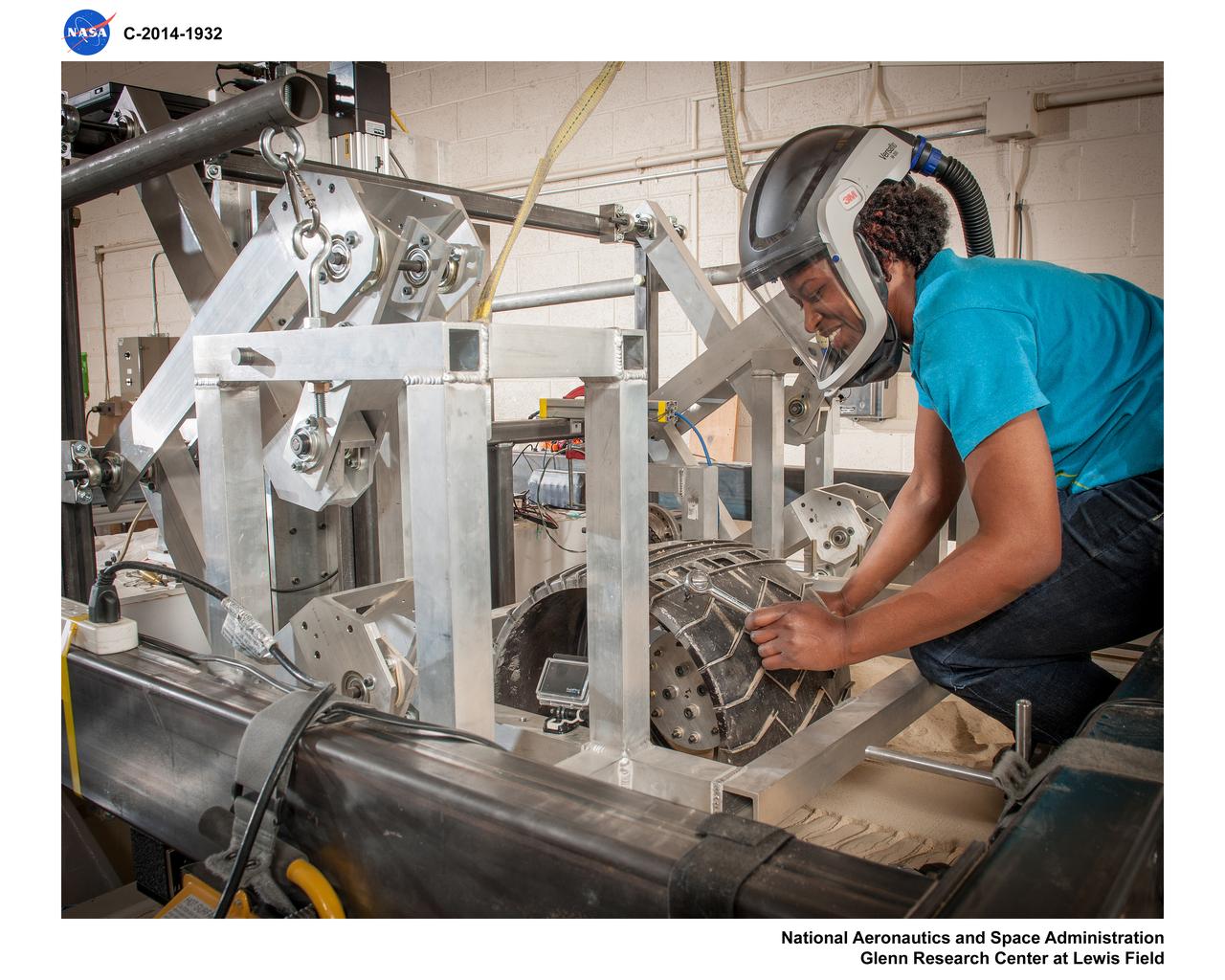
Fabrication of rover spring tires in the Simulated Lunar Operations, SLOPe Lab, Laboratory

Airless Spring Wheel Prototype in the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory, SLOPE Lab

Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory (SLOPE), Surface Mobility Research

Airless Spring Wheel Prototype in the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory, SLOPE Lab

Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory (SLOPE) Lab; Scarab Lunar Rover
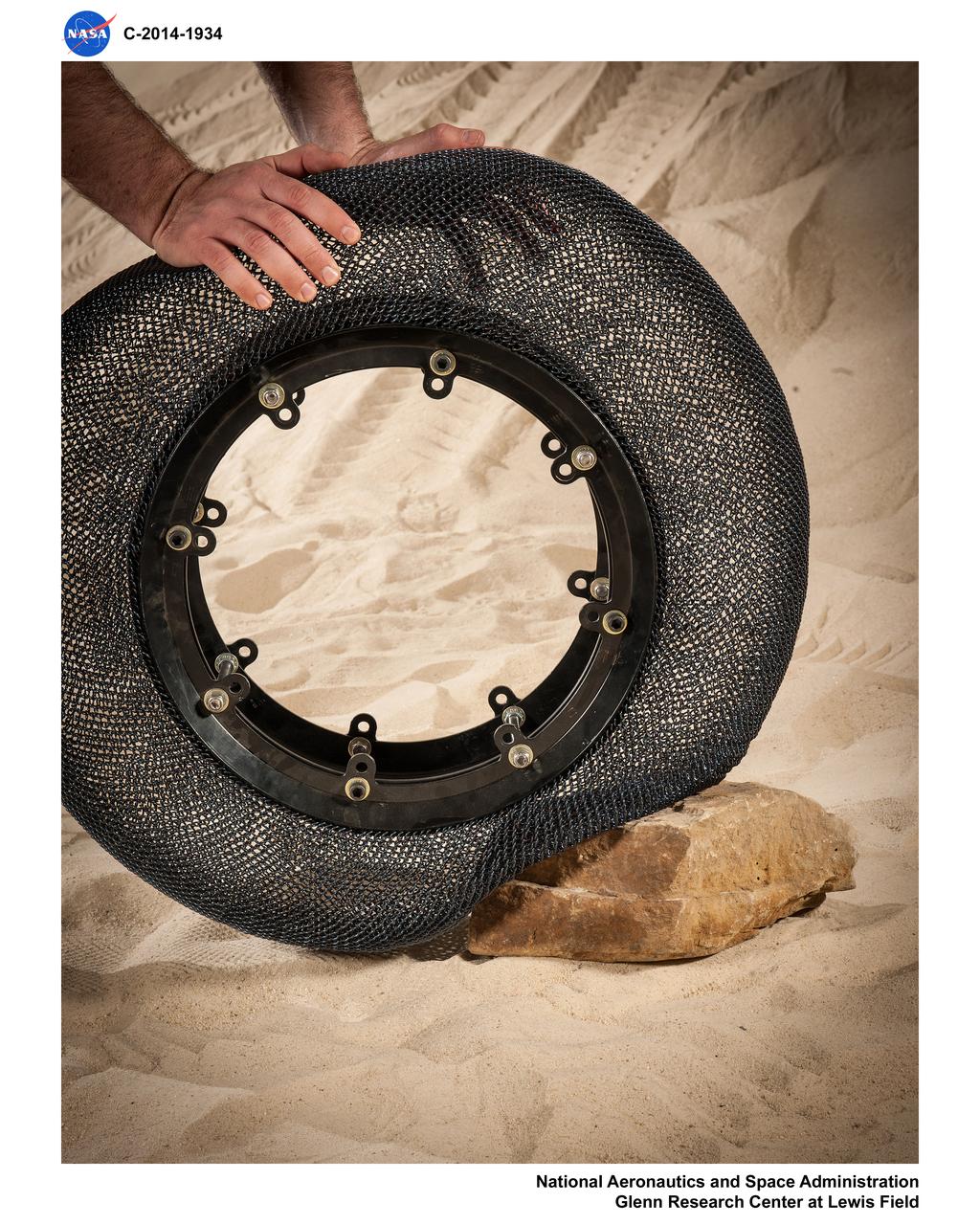

Airless Spring Wheel Prototype in the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory, SLOPE Lab
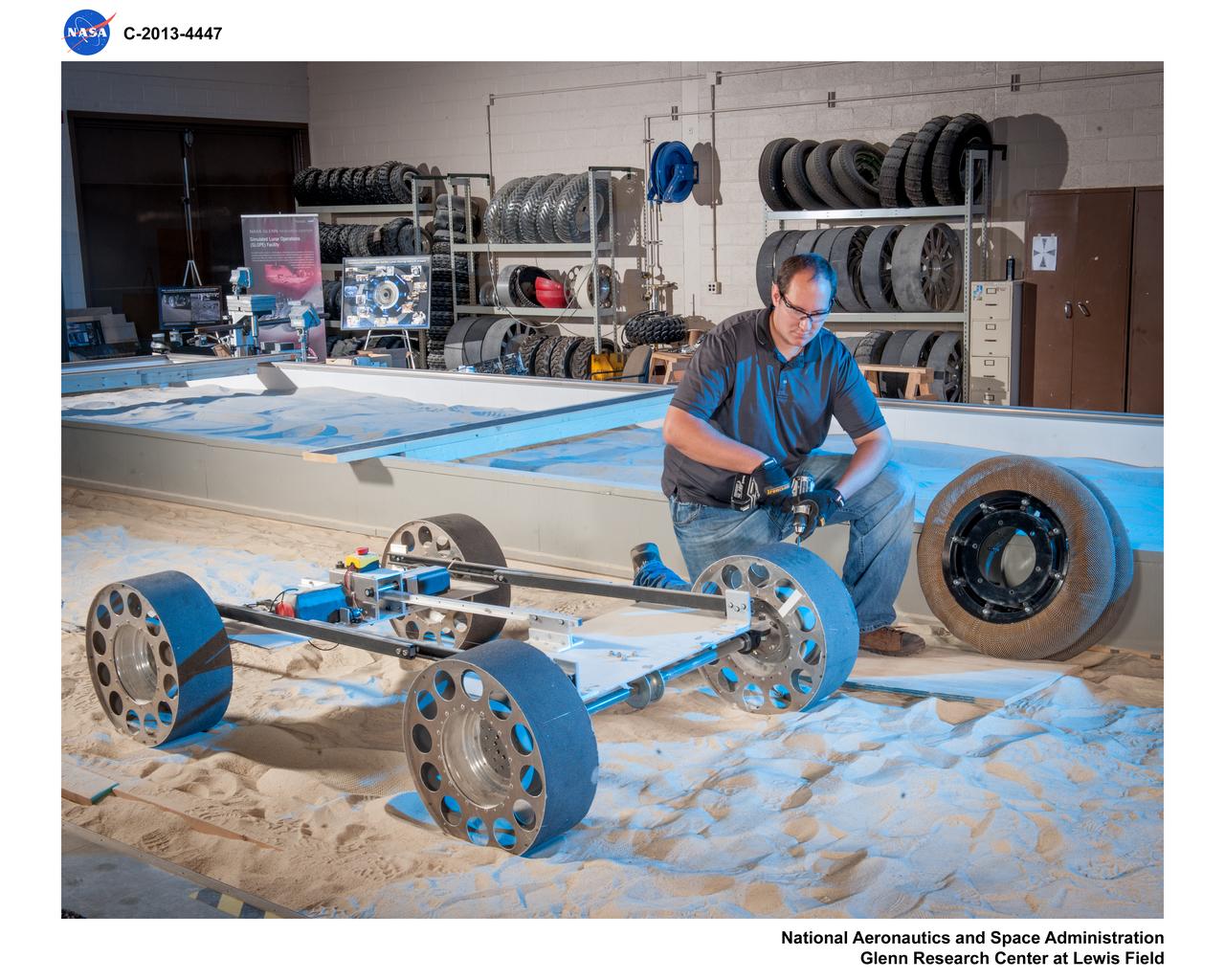

Fabrication of rover spring tires in the Simulated Lunar Operations, SLOPe Lab, Laboratory

Fabrication of rover spring tires in the Simulated Lunar Operations, SLOPe Lab, Laboratory
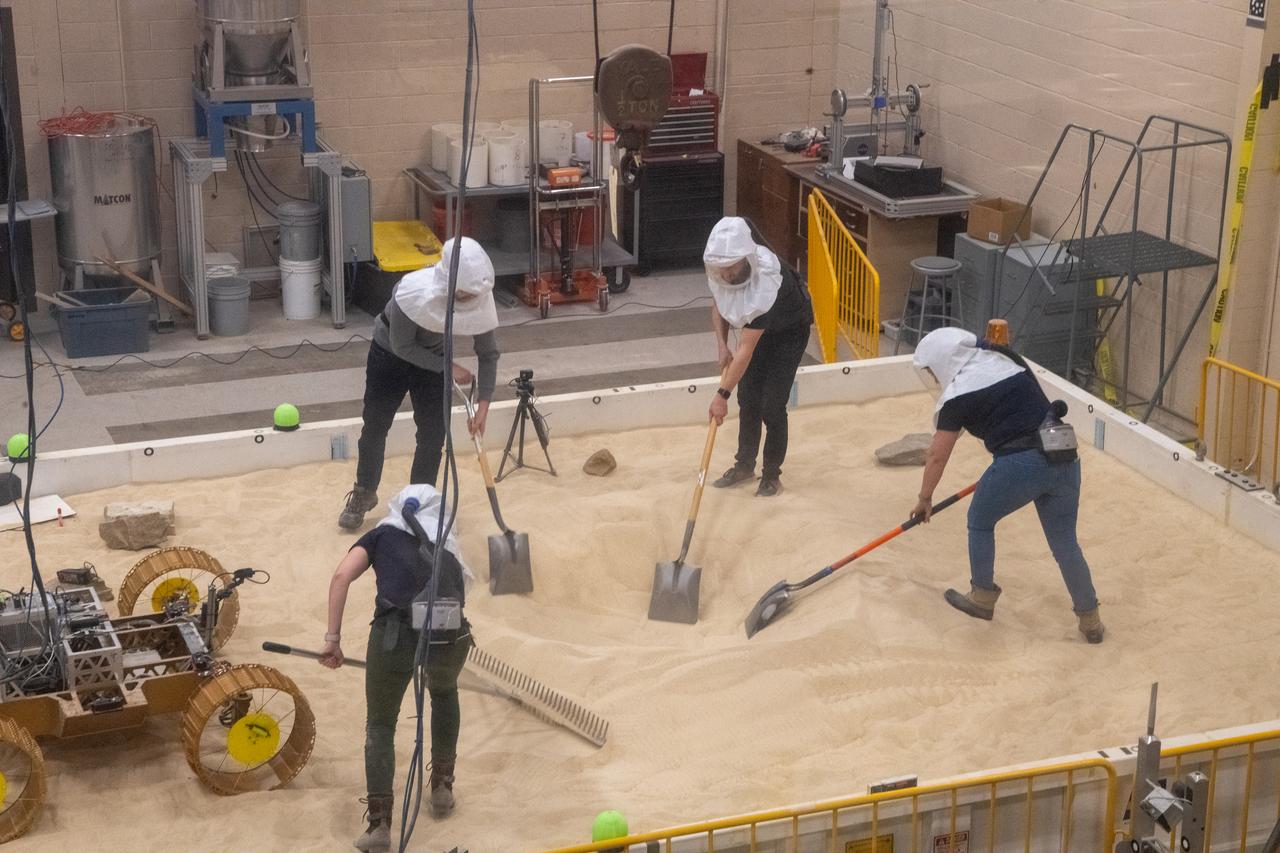

Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER Testing in the Simulated Lunar Operations Lab, SLOPE Laboratory
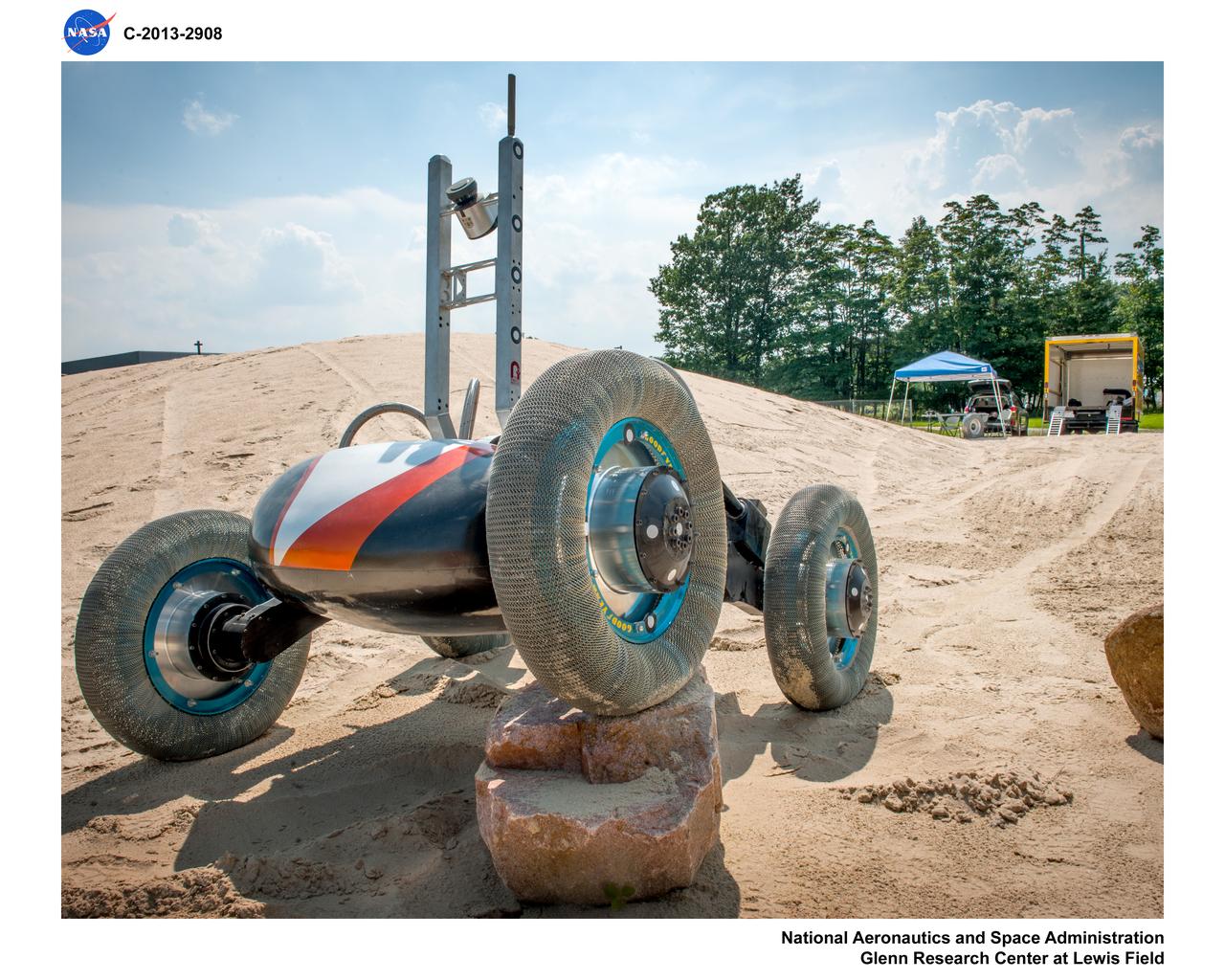

Photos of test hardware, Scarab Lunar Exploration Rover at the DUNE, outdoor Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory, SLOPE
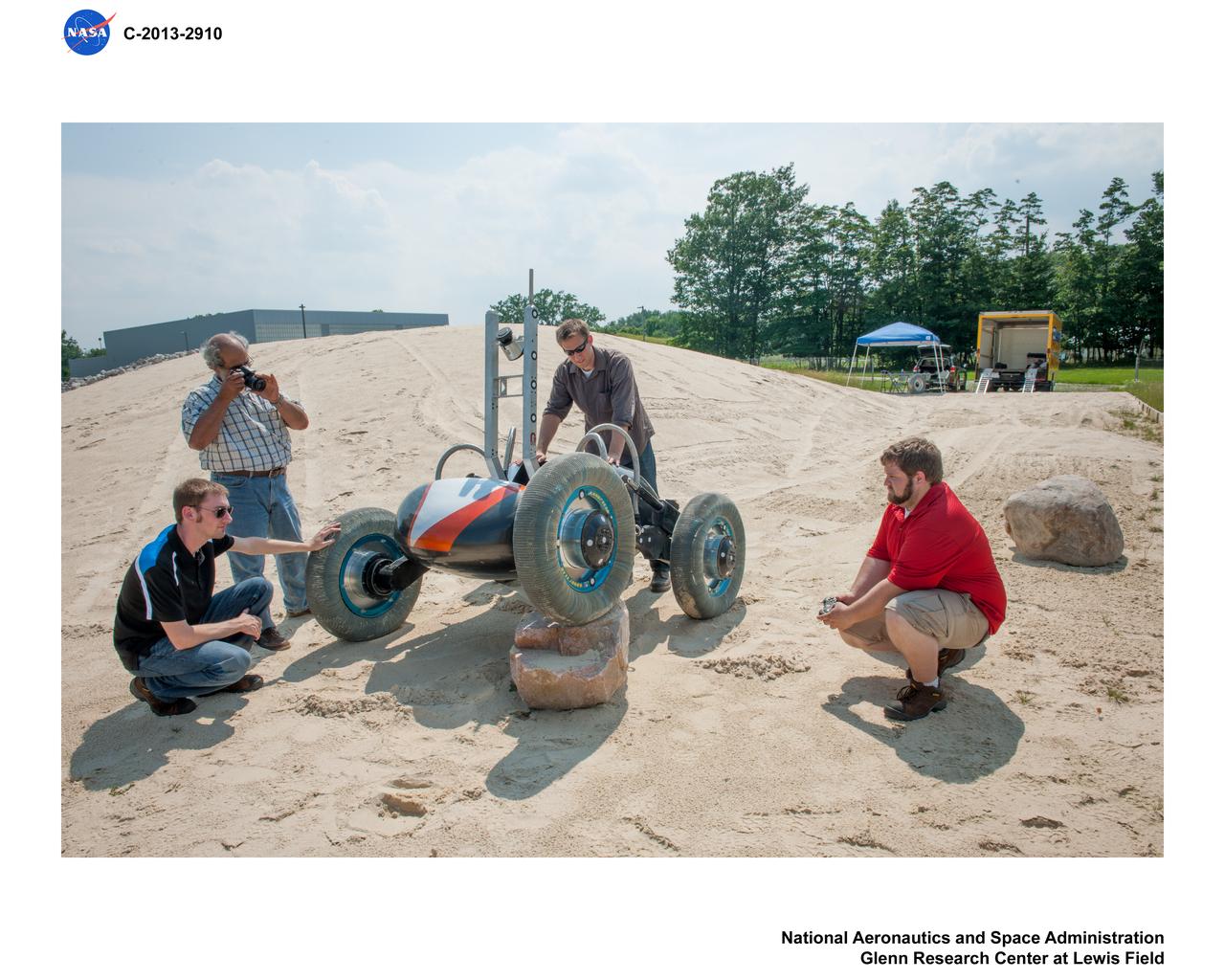

Photos of test hardware, Scarab Lunar Exploration Rover at the DUNE, outdoor Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory, SLOPE
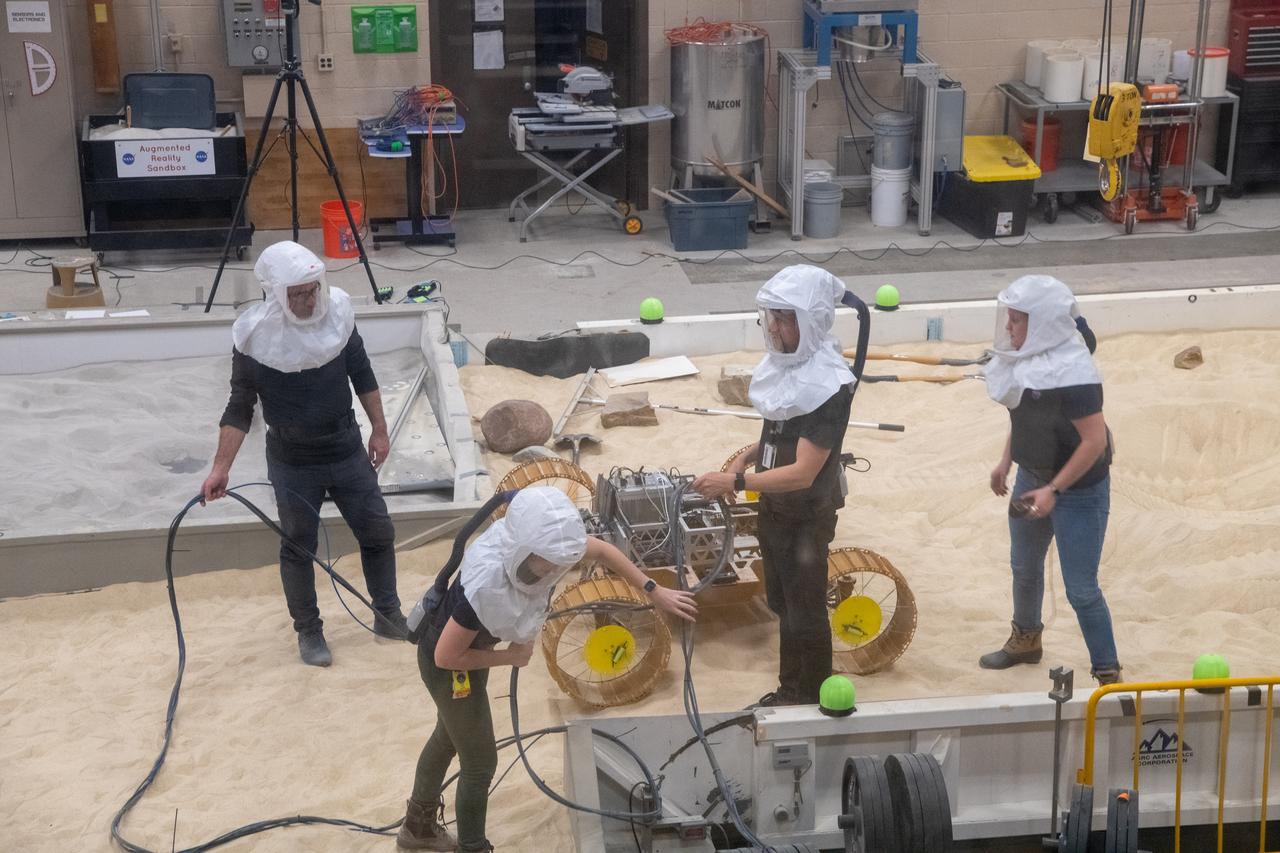

Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER Testing in the Simulated Lunar Operations Lab, SLOPE Laboratory
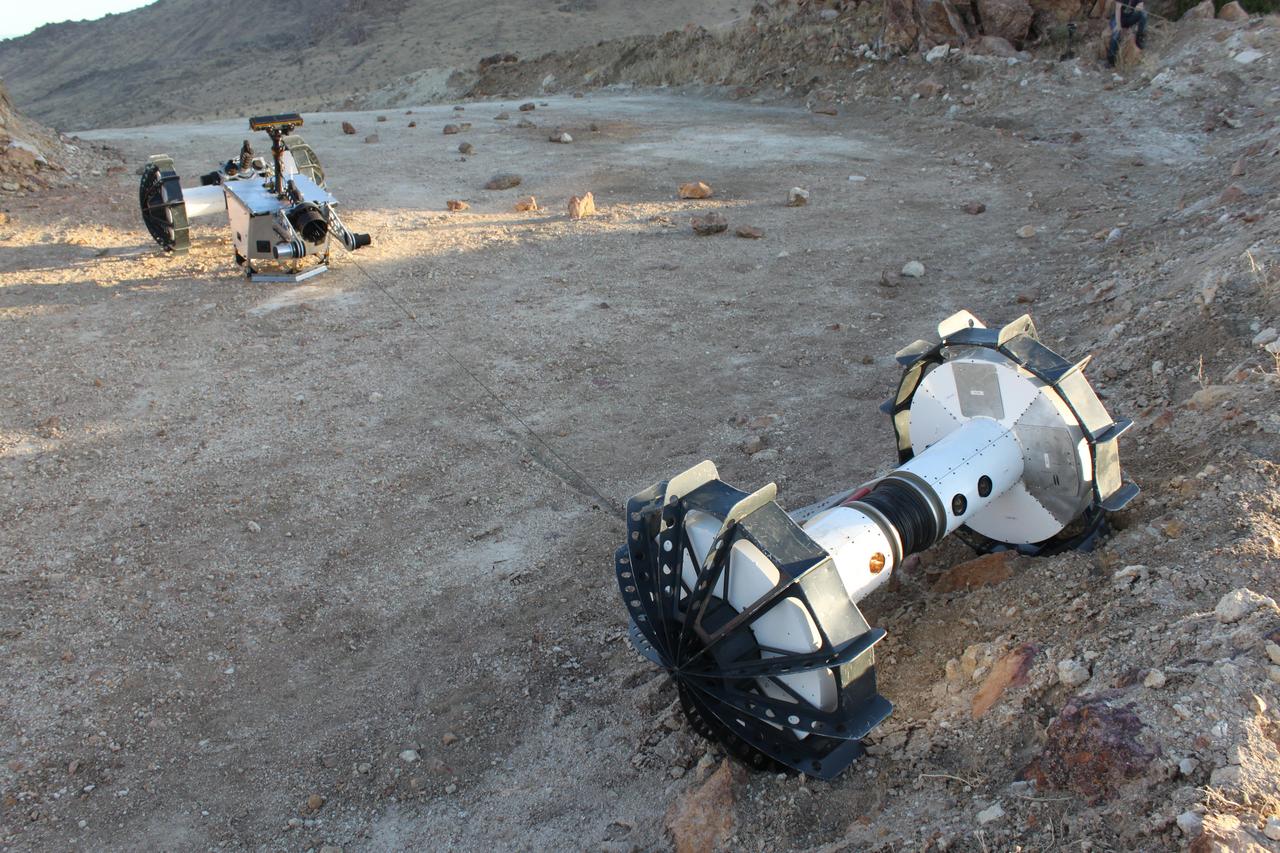

During a field test in the Mojave Desert, the DuAxel robot separates into two single-axled robots so that one can rappel down a slope too steep for conventional rovers. The tether connecting both Axels not only allows the one robot to descend the slope while the other remains anchored in place, it also provides power and a means of communication with the anchoring robot above. The DuAxel project is a technology demonstration being developed by roboticists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to see how this unconventional rover might fill a niche in the exploration the Moon, Mars, and beyond. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24109
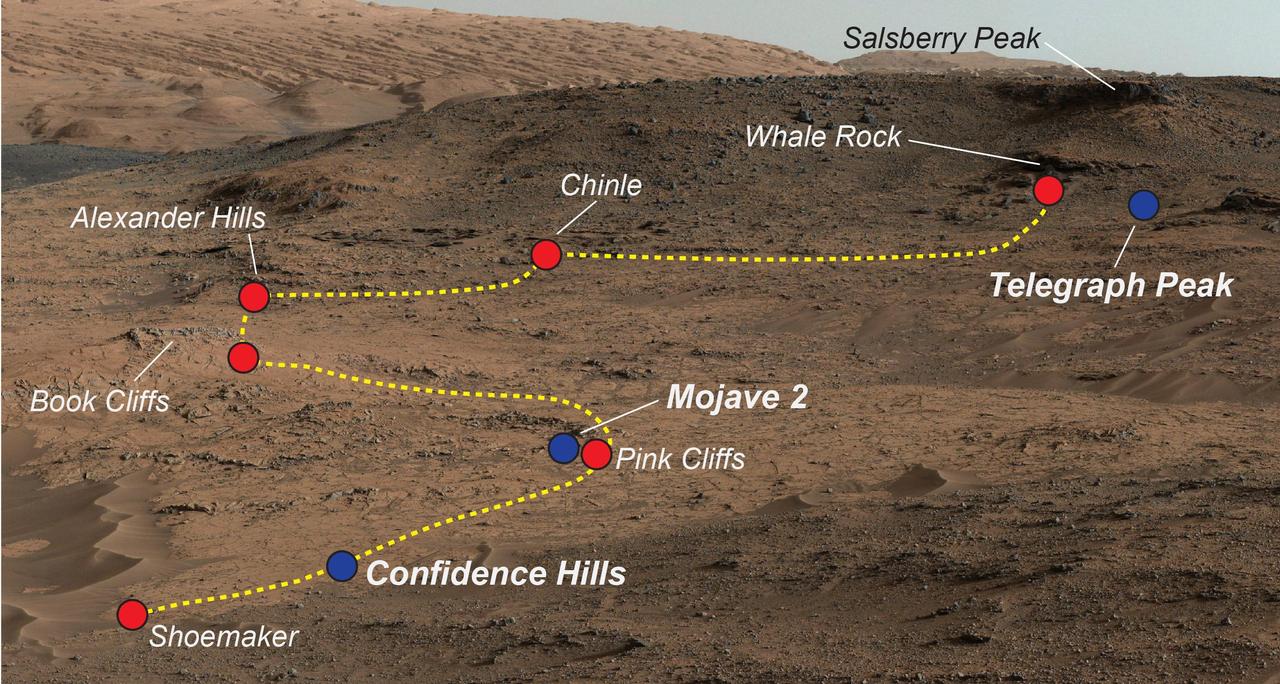
NASA's Curiosity Mars rover examined a mudstone outcrop area called "Pahrump Hills" on lower Mount Sharp, in 2014 and 2015. This view shows locations of some targets the rover studied there. The blue dots indicate where drilled samples of powdered rock were collected for analysis. The rover drilled a sample of rock powder at "Confidence Hills" in September 2014 and analyzed it with internal laboratory instruments. Then the mission conducted a walkabout survey up the slope, along the route indicated in yellow, stopping for close inspection at the red-dot locations. Observations from the walkabout were used to choose where to take additional drilled samples for analysis during a second pass up the slope. The "Mojave 2" sample was collected in January 2015 and the "Telegraph Peak" one in February 2015. This view of the outcrop and other portions of Mount Sharp beyond is a mosaic of images taken by the rover's Mast Camera (Mastcam) in September 2014. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21709
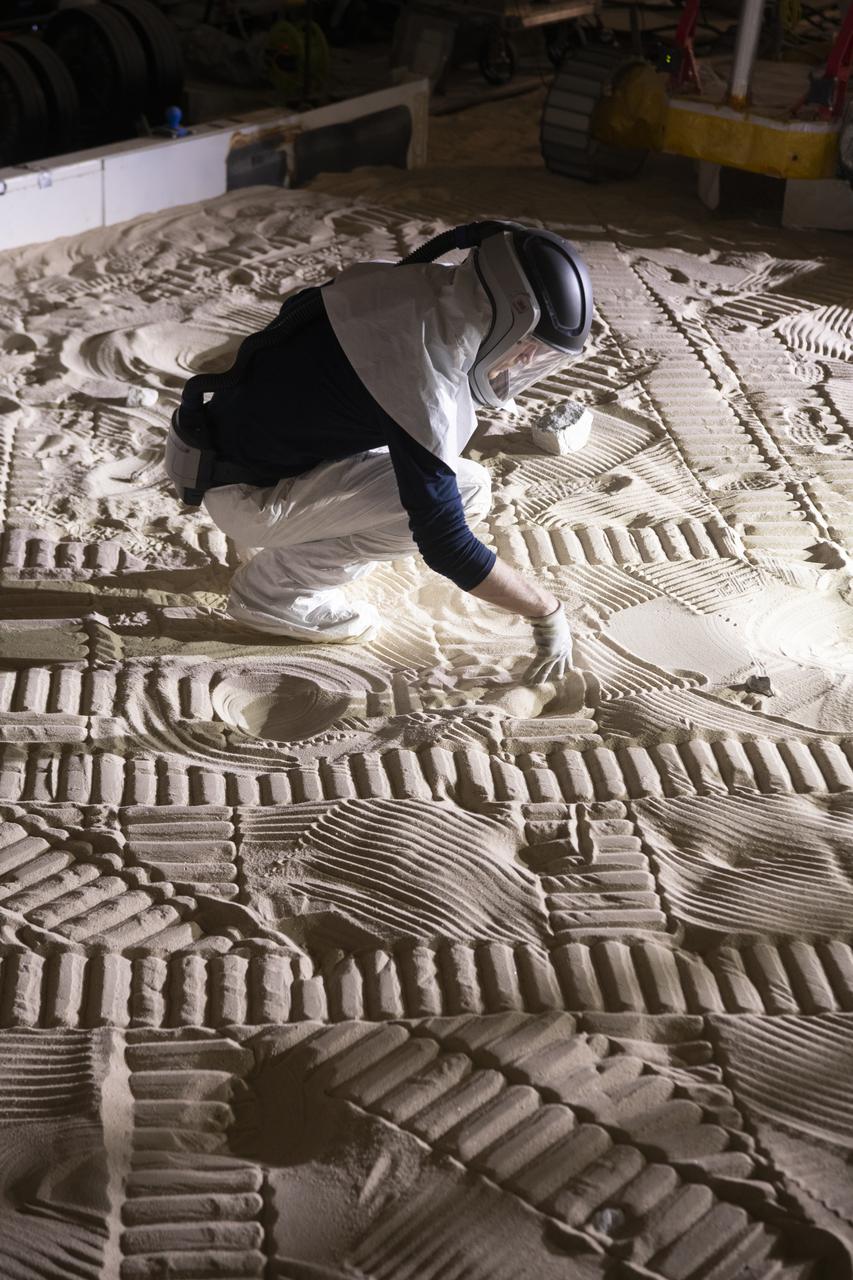

An Engineer maps out the position of rocks during VIPER testing at The NASA Glenn Research Center. A test version of the VIPER rover continues to show how well it moves through a simulated lunar surface in our SLOPE lab. This is a critical step toward ensuring the rover is ready for its 2023 mission to find water ice at the Moon’s South pole.
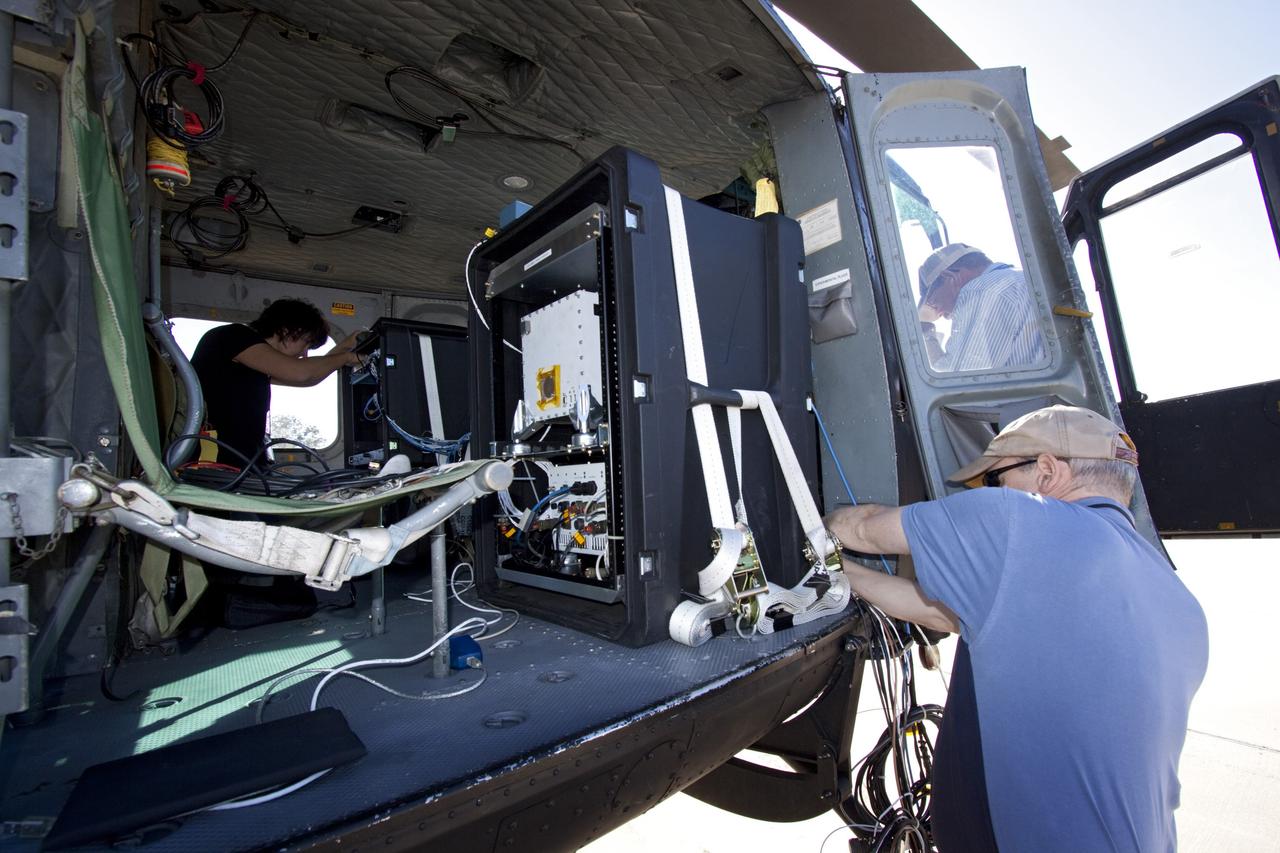

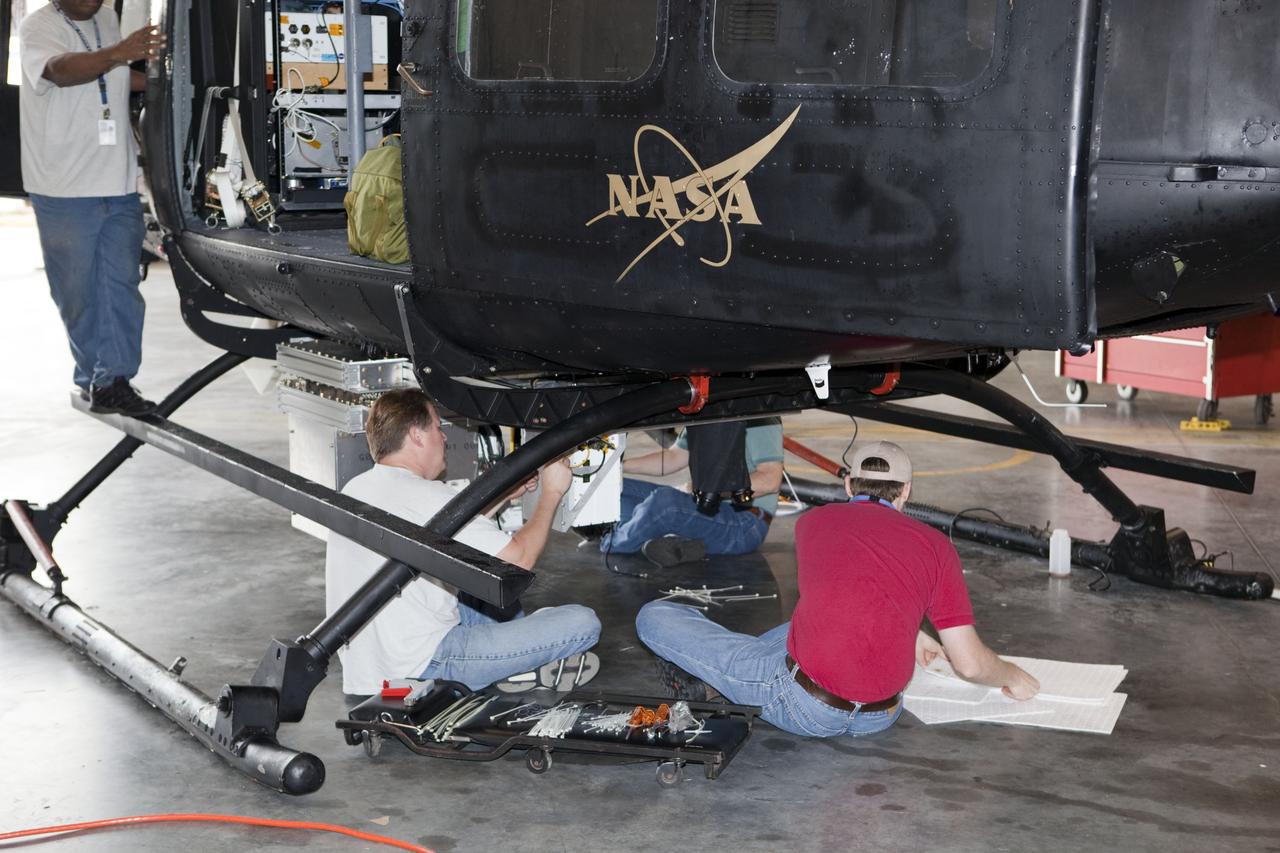
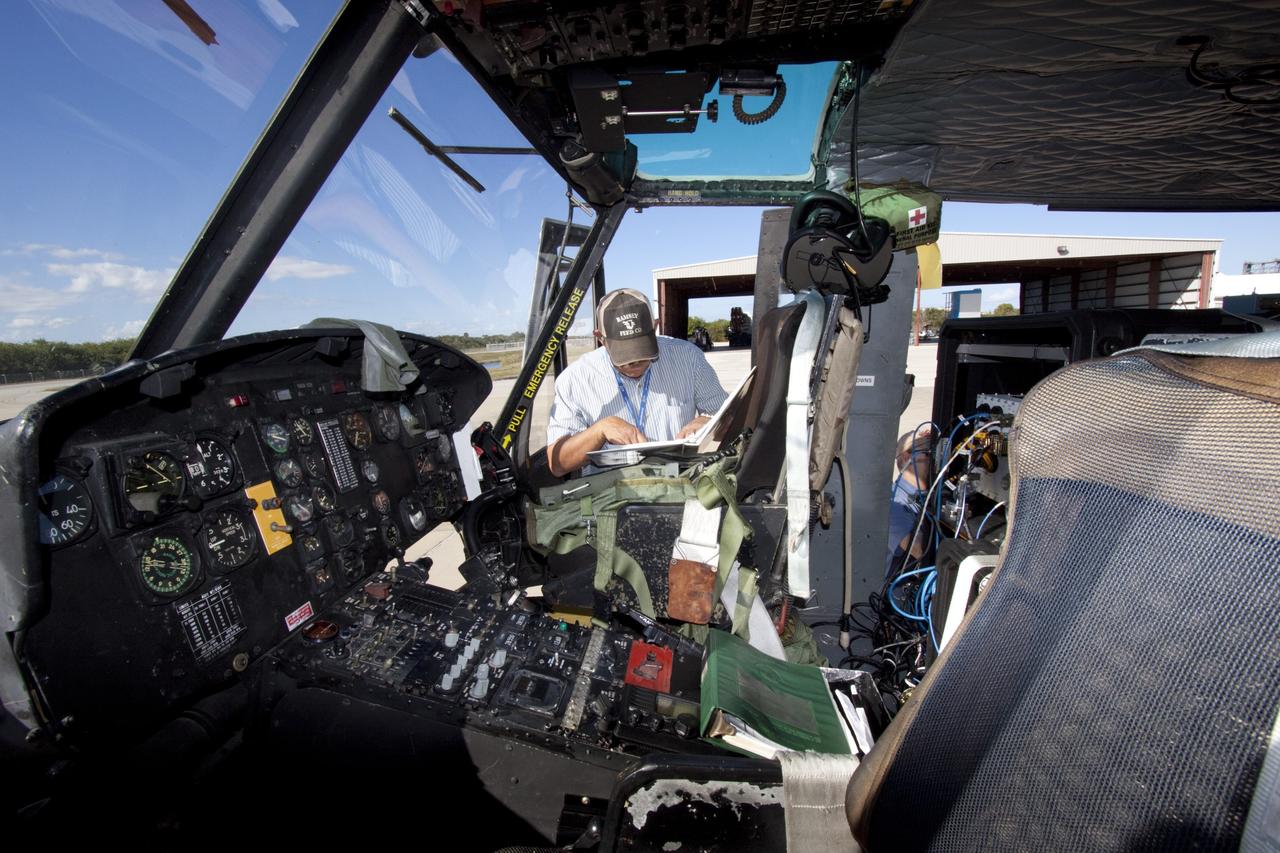
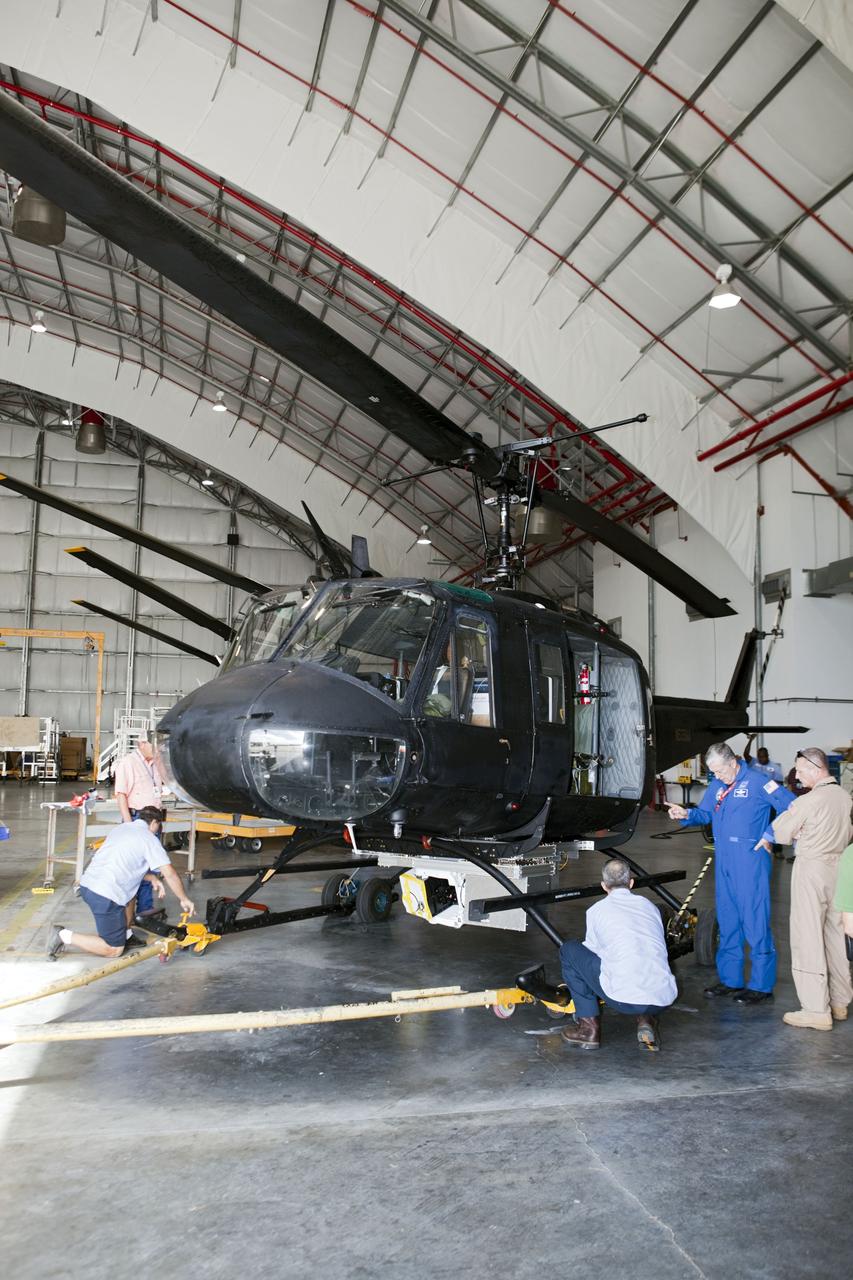
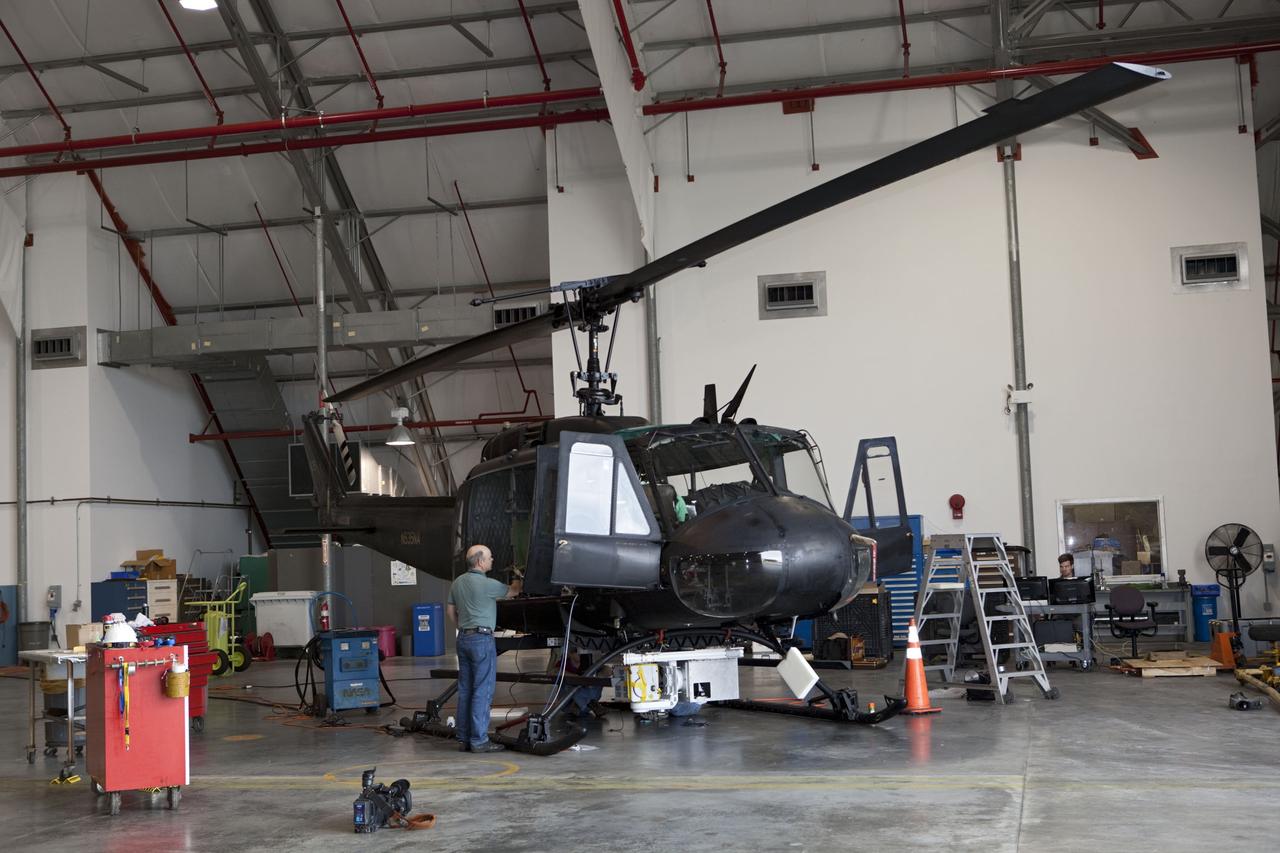
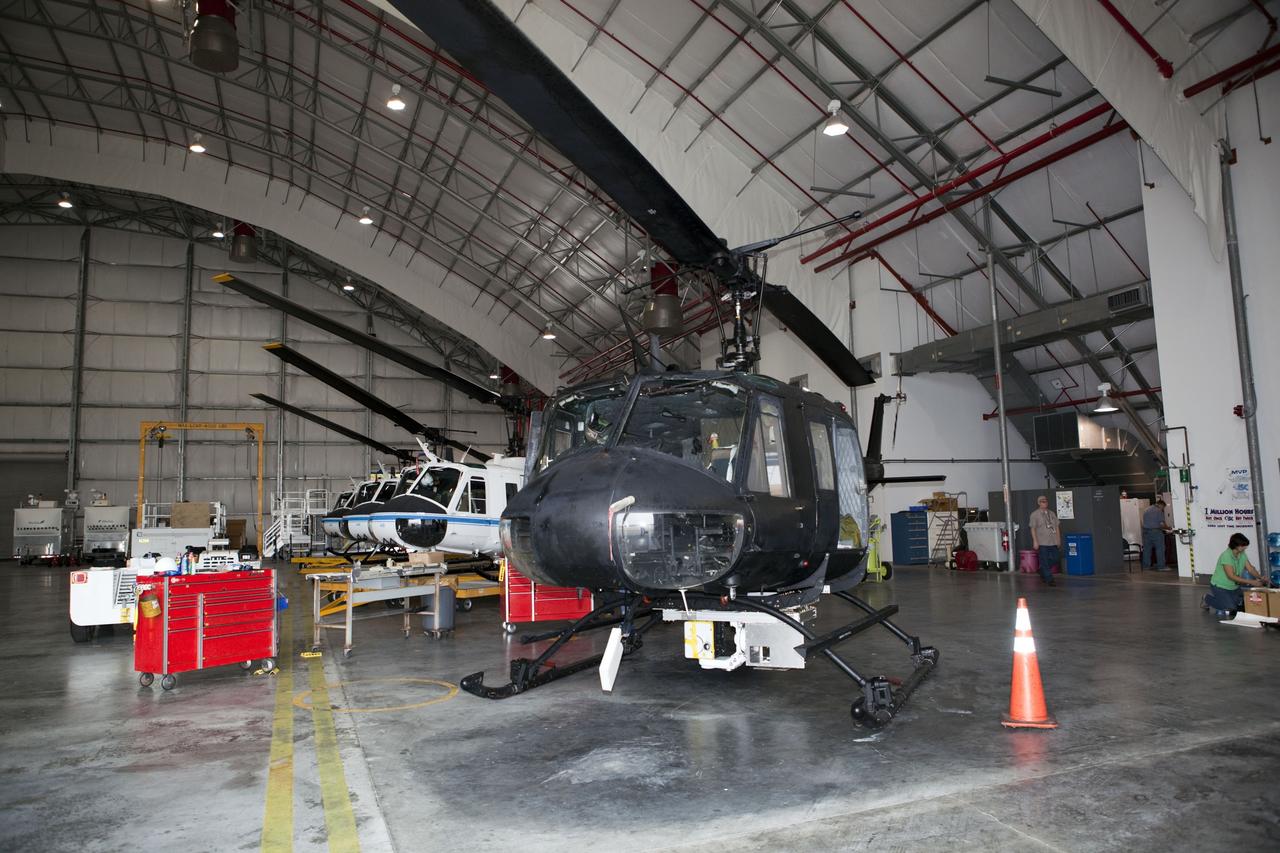
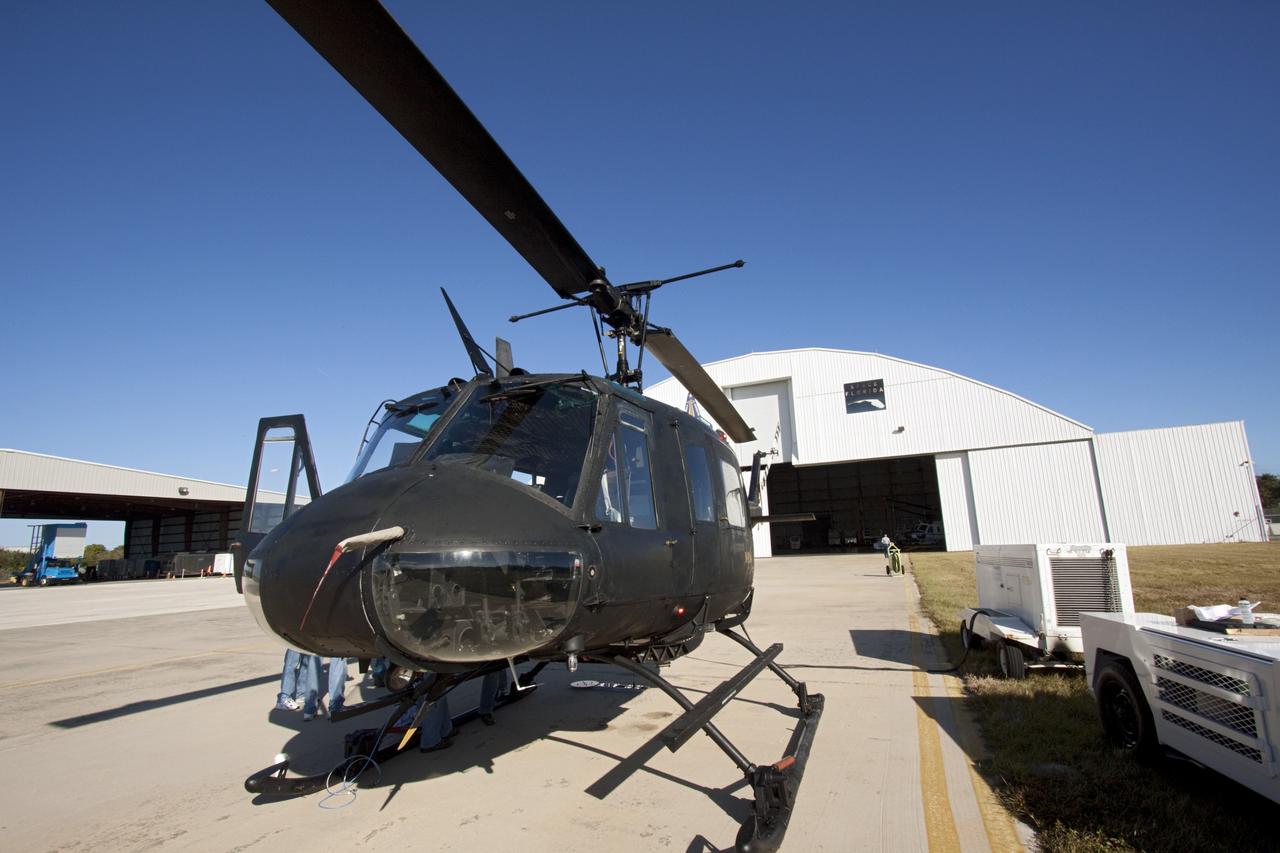
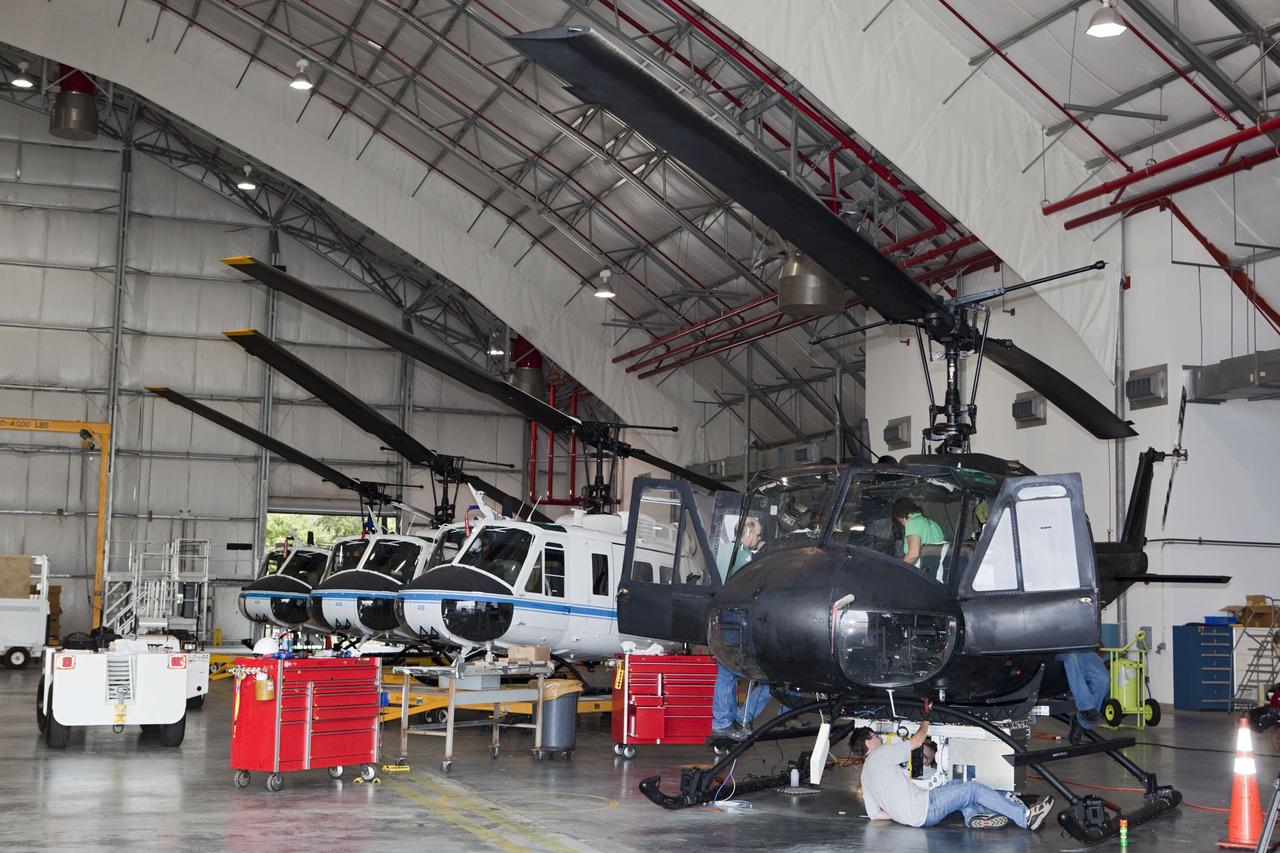
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician installs hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
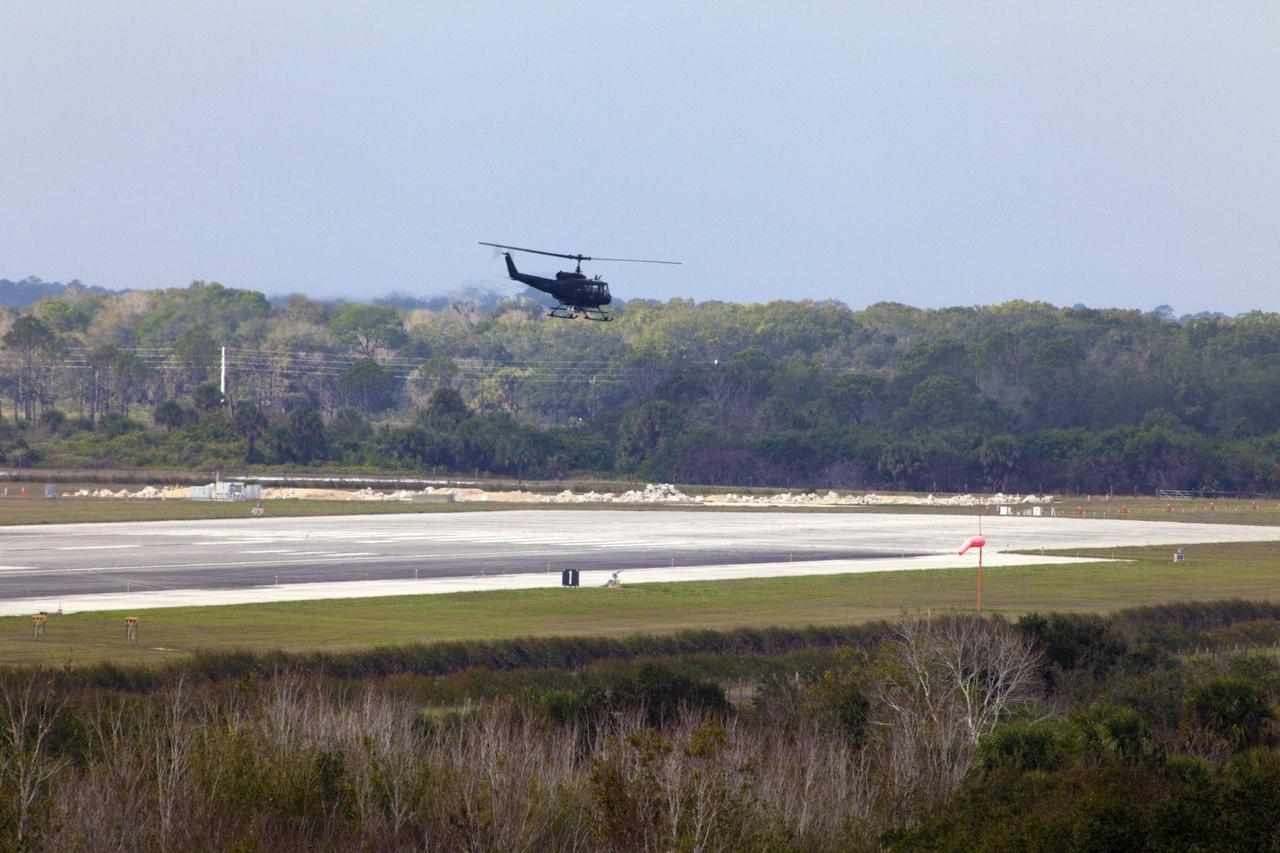

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A Huey helicopter tests hazard avoidance instrumentation at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks using the instrument. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
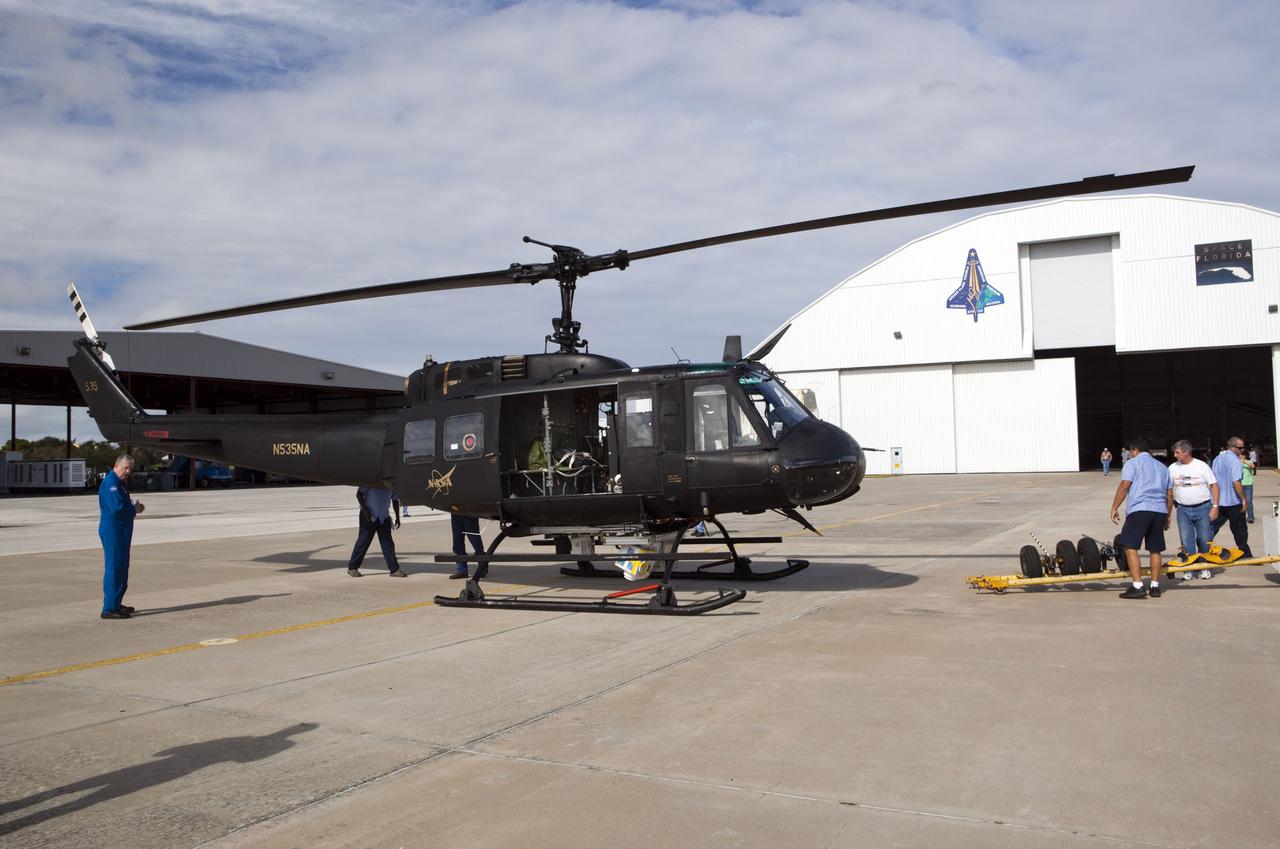

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA_Dmitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
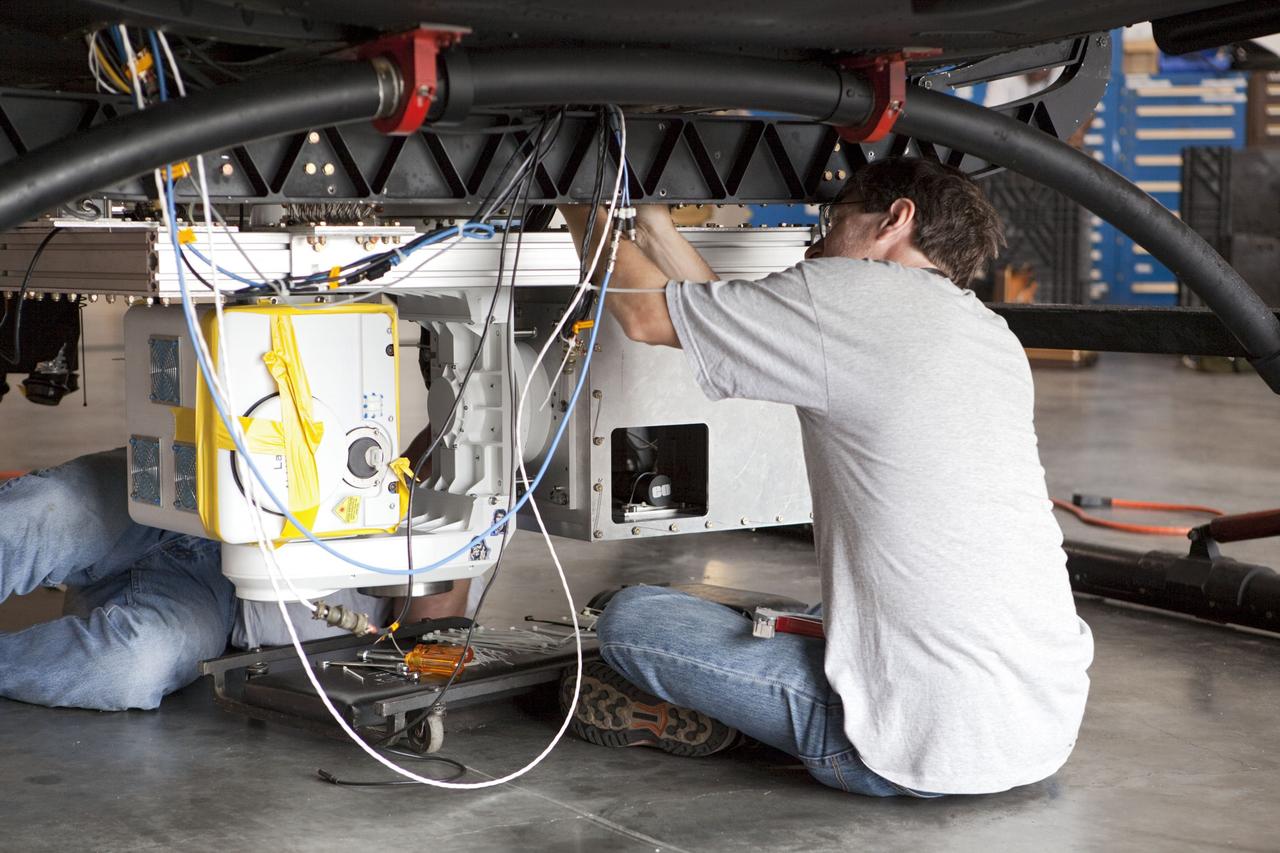

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
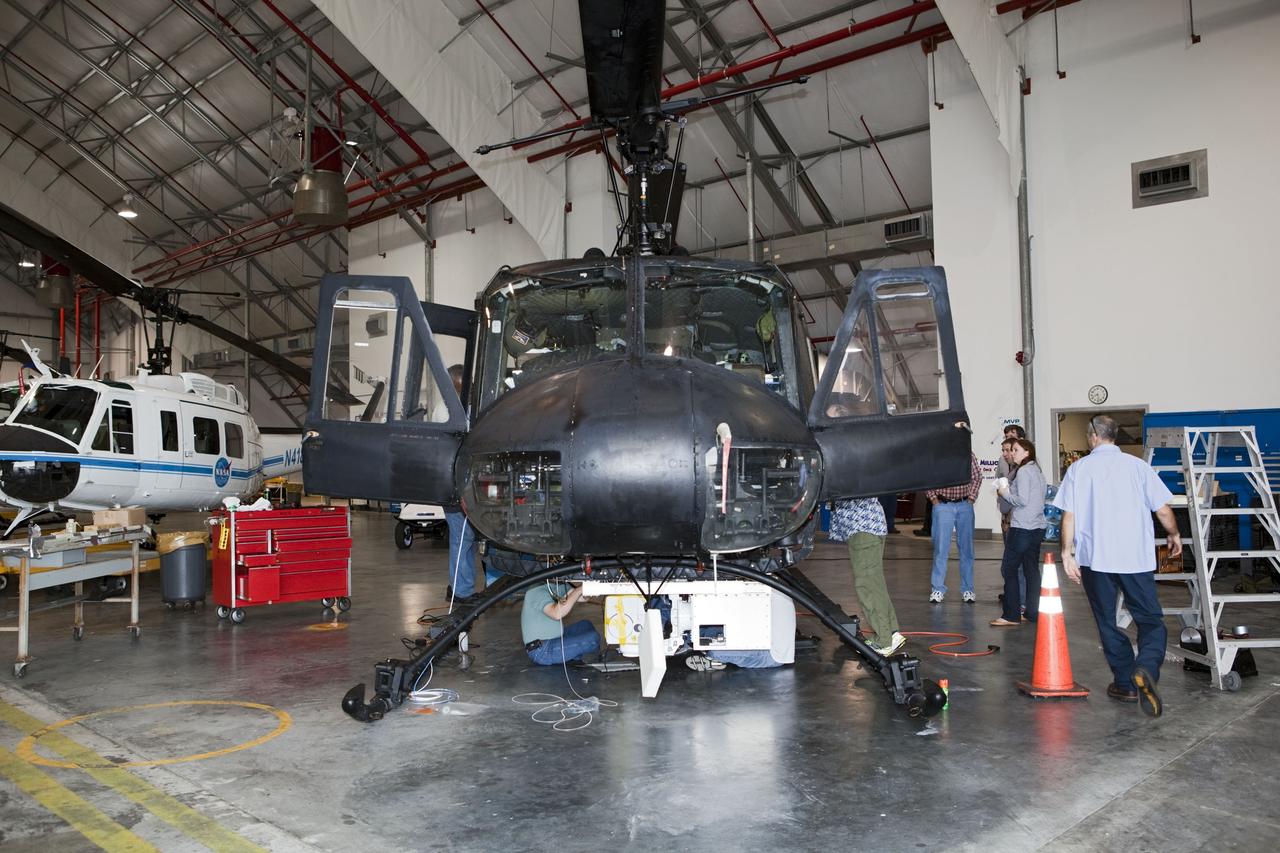

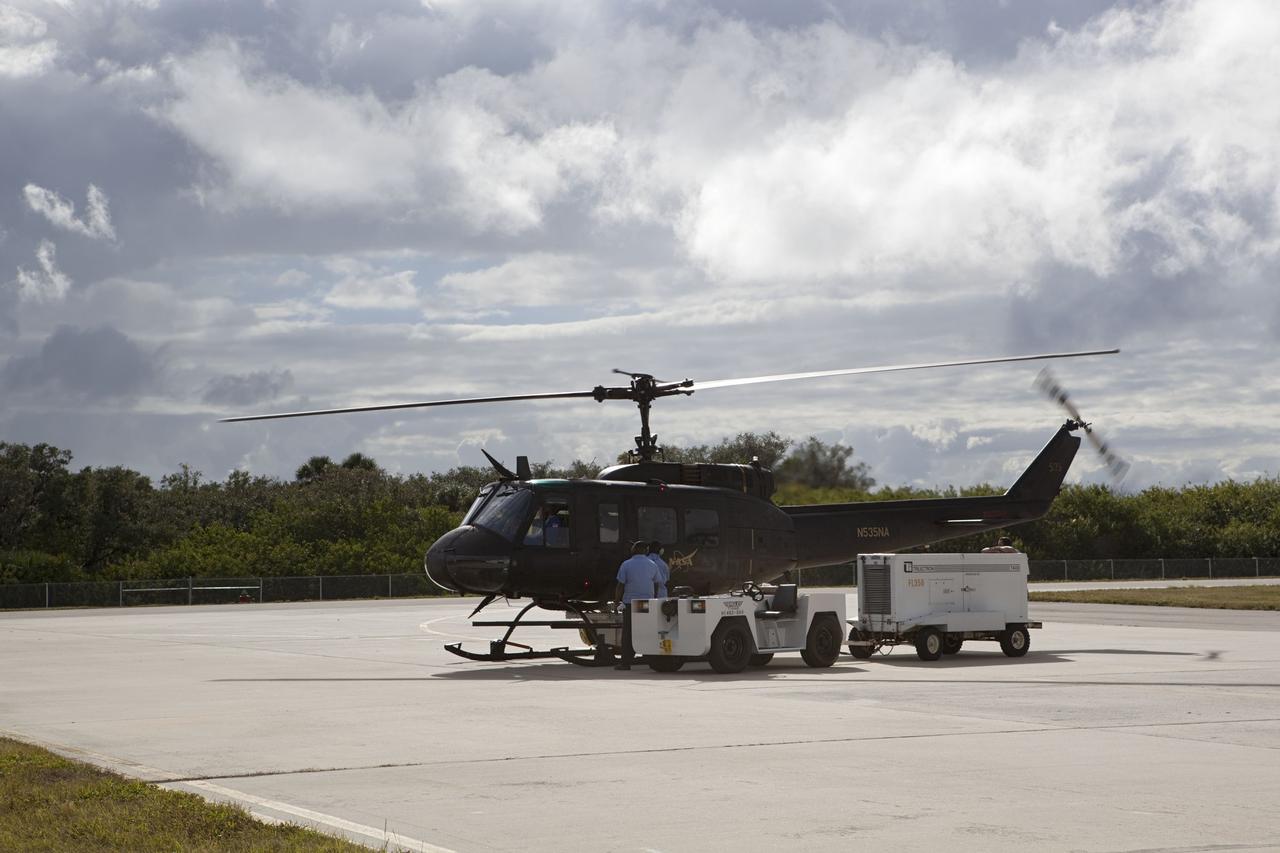
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
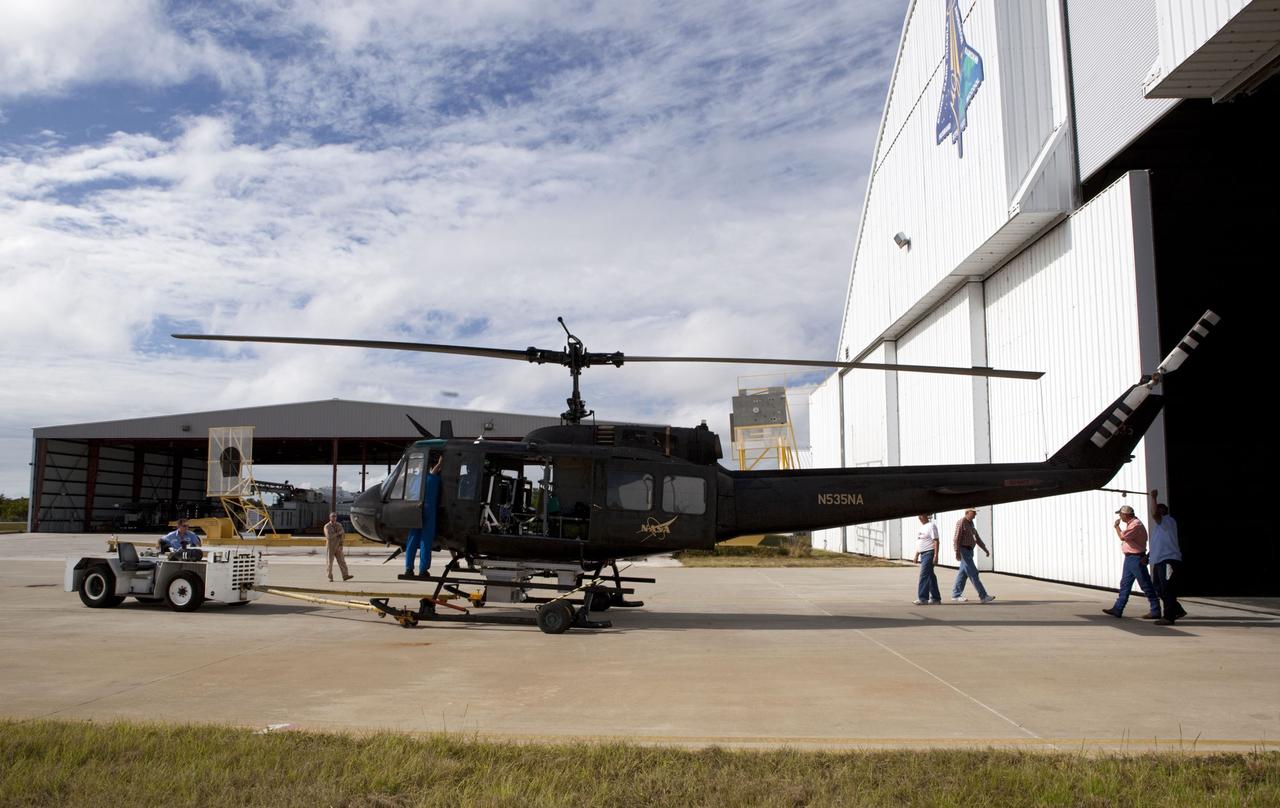

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
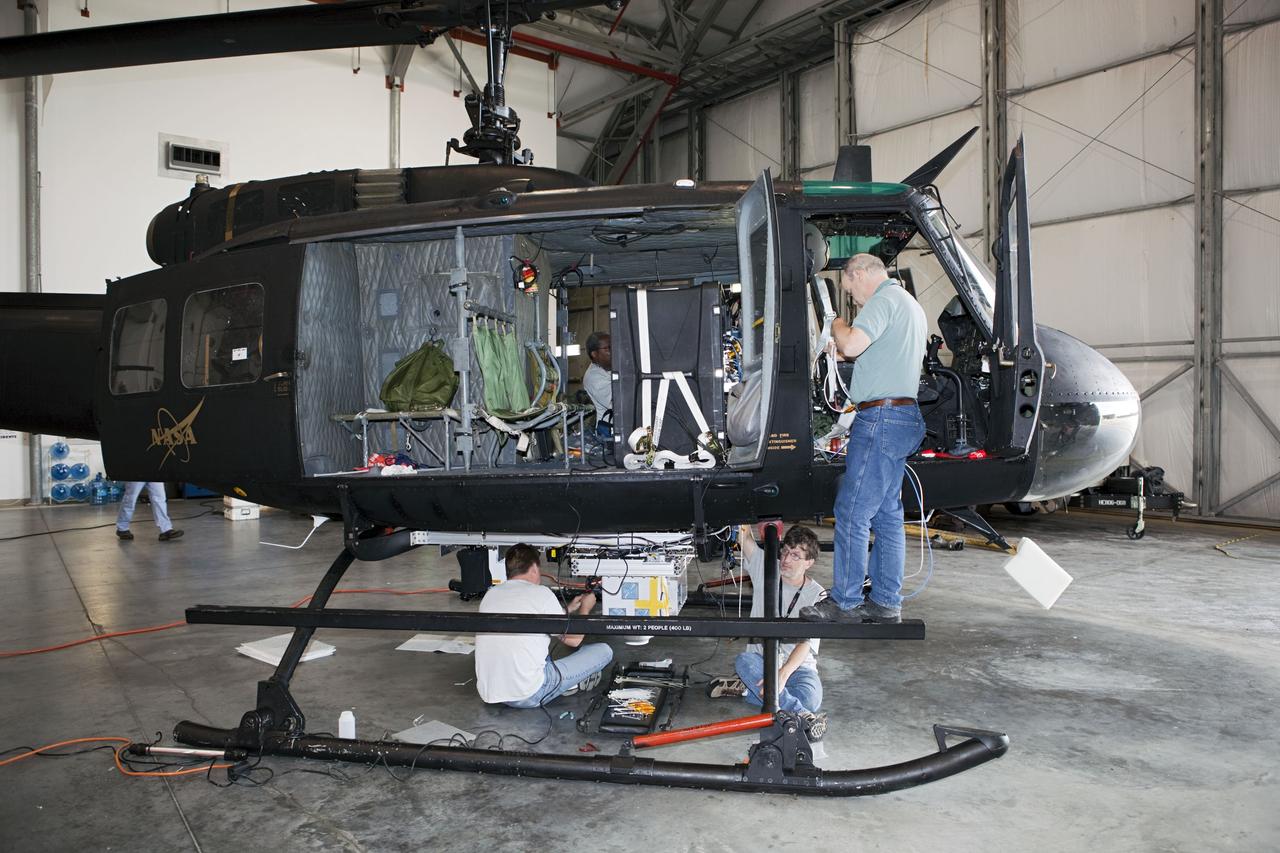

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
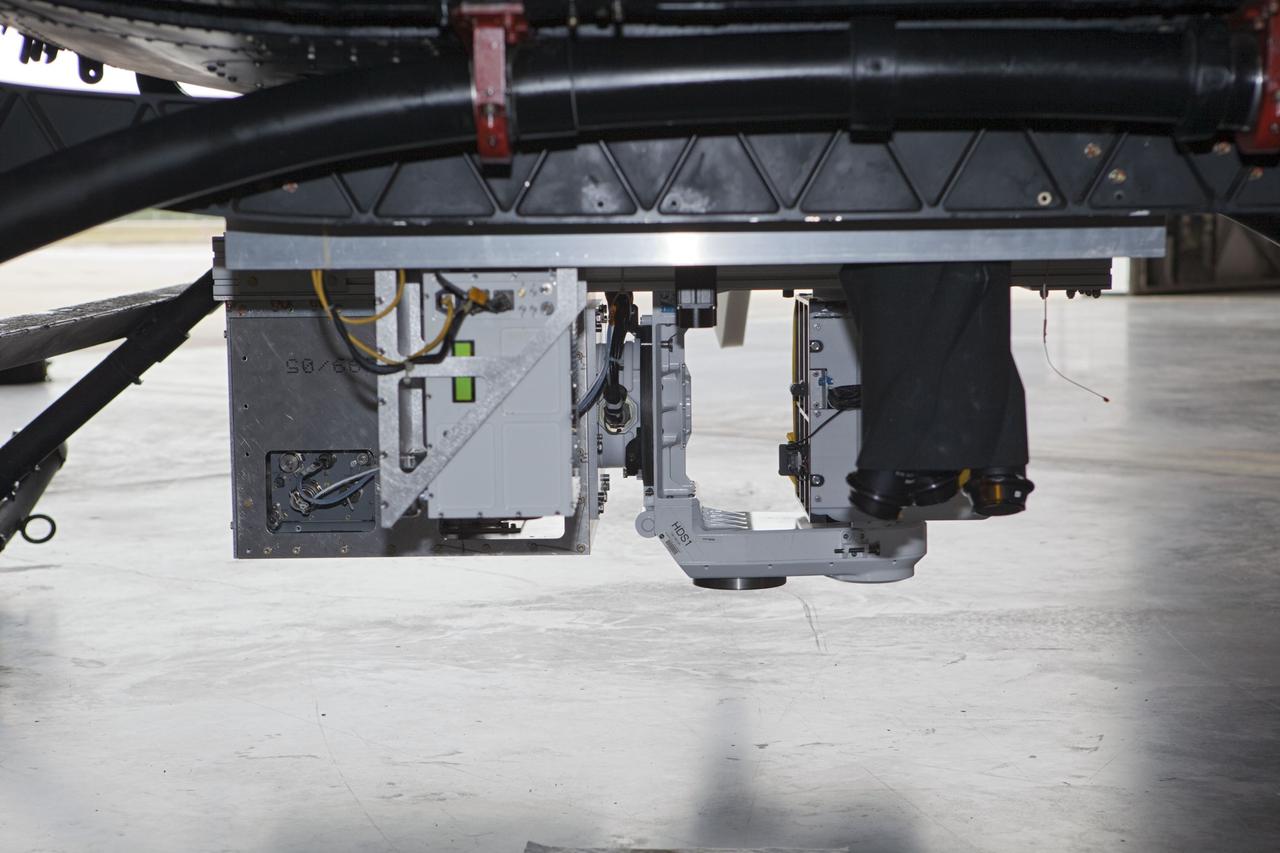
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
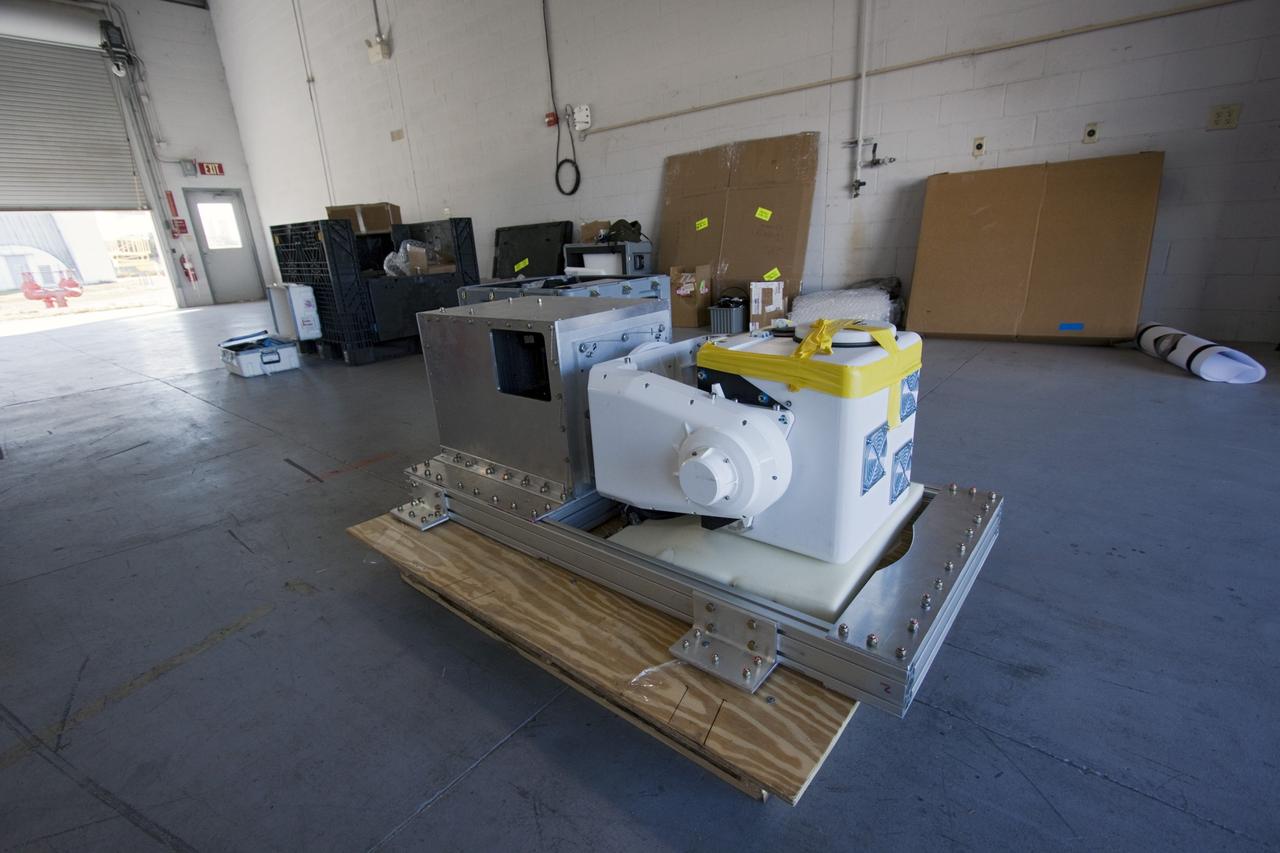

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, hazard avoidance instrumentation it being prepared for installation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
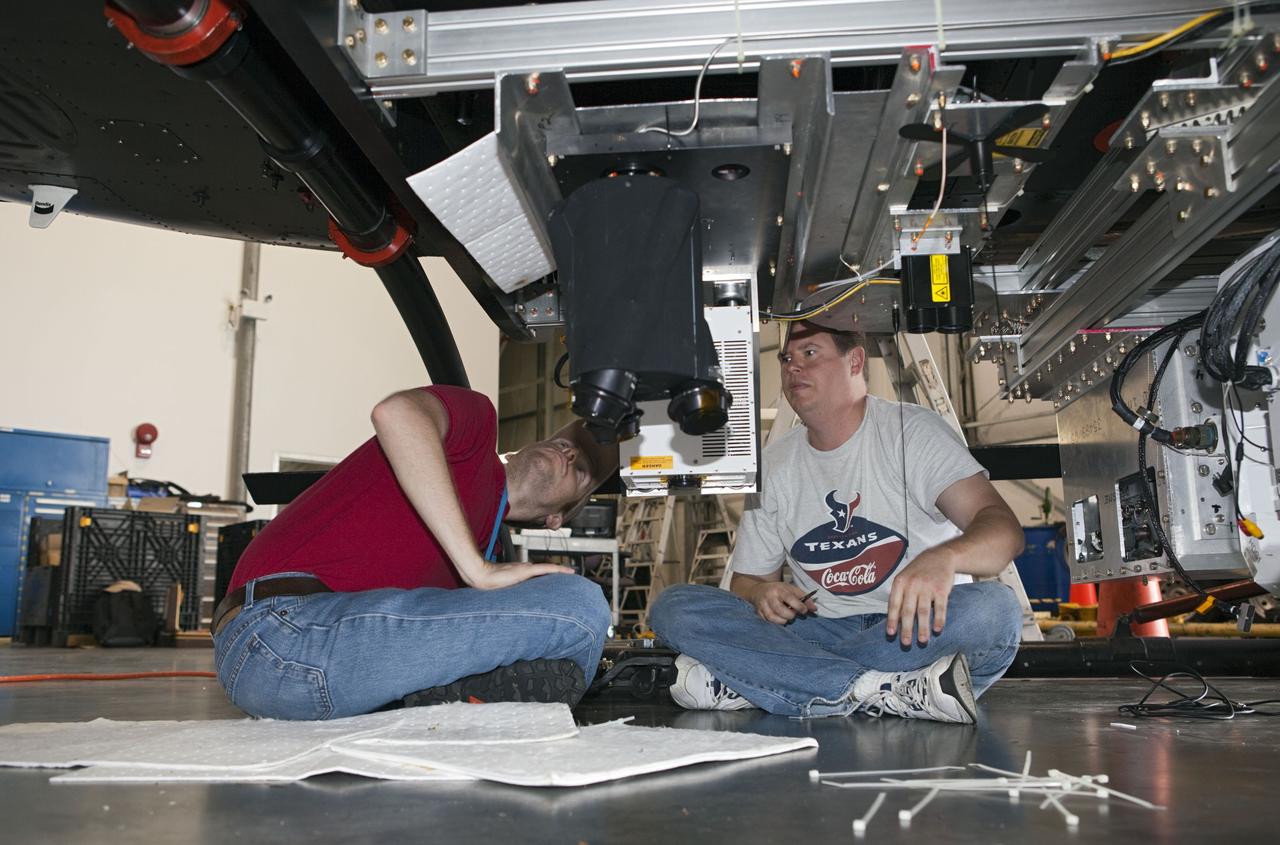

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
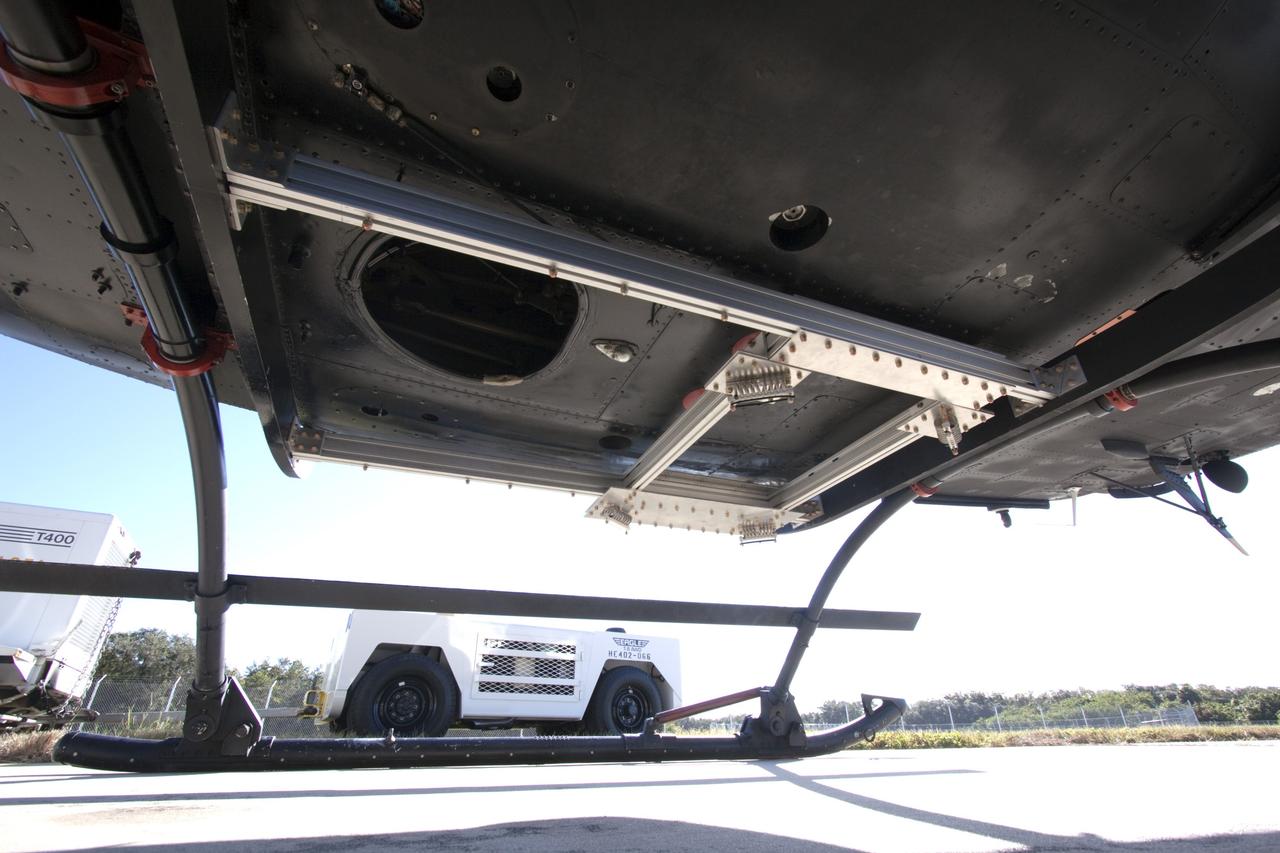

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
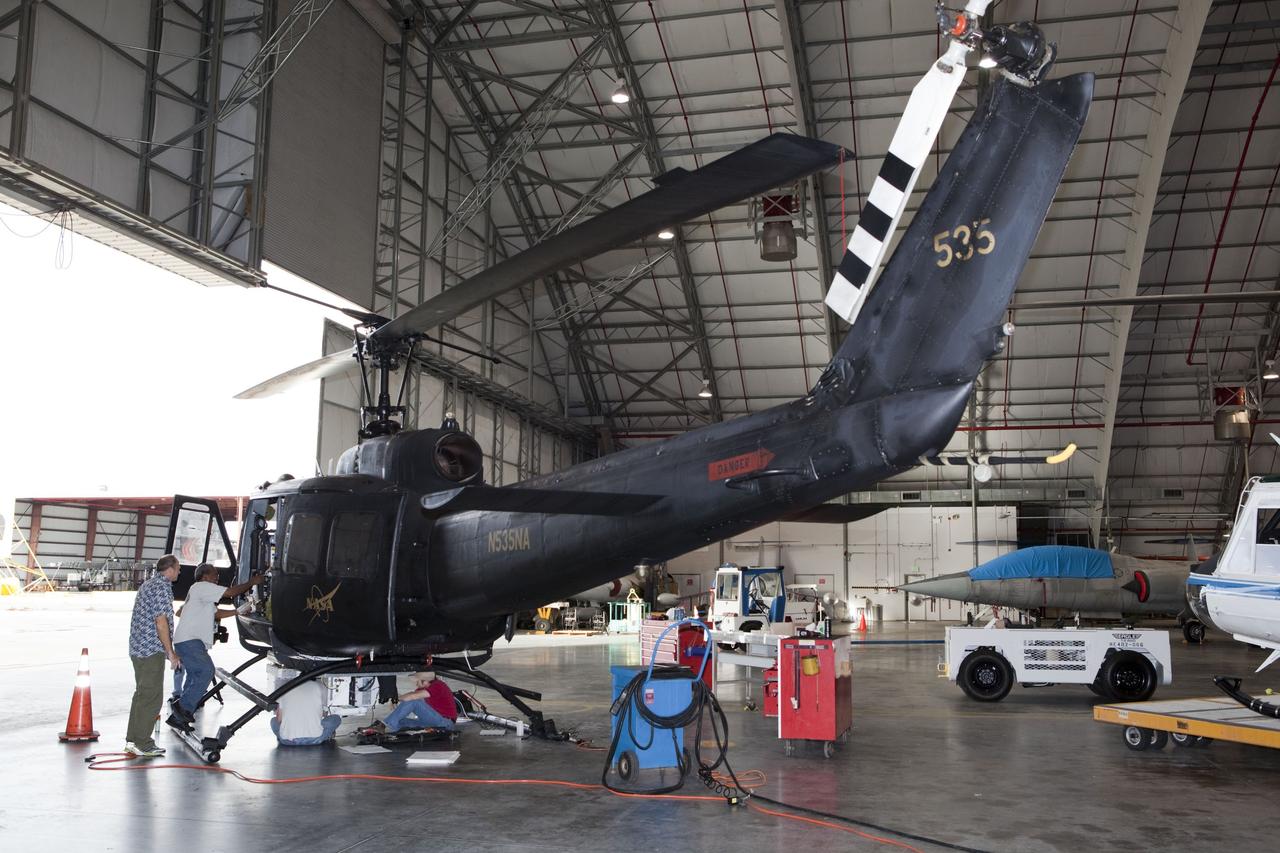

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician tests hazard avoidance instrumentation recently installed on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
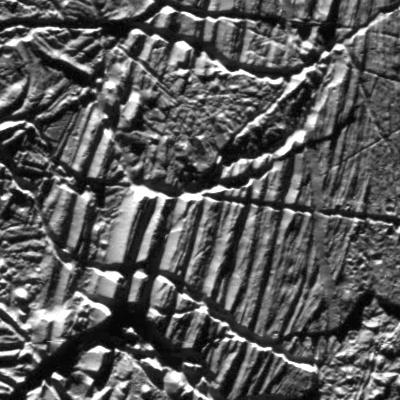
This mosaic shows a portion of one of the highest-resolution images captured of Jupiter's moon Europa in the 1990s by NASA's Galileo spacecraft. This picture is cropped from a larger image. These are the kind of features studied by scientists who recently modeled how moonquakes may trigger landslides on icy moons circling Jupiter and Saturn. Visible here are possible fault scarps (like those found on Earth when tectonic activity breaks the crust) with smooth slopes and nearby rubble that may have been produced by small landslides triggered by the faulting activity. These images were obtained on Nov. 6, 1997, when Galileo was approximately 1,983 miles (3,250 kilometers) from Europa. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California managed the mission for the agency. JPL is a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25498
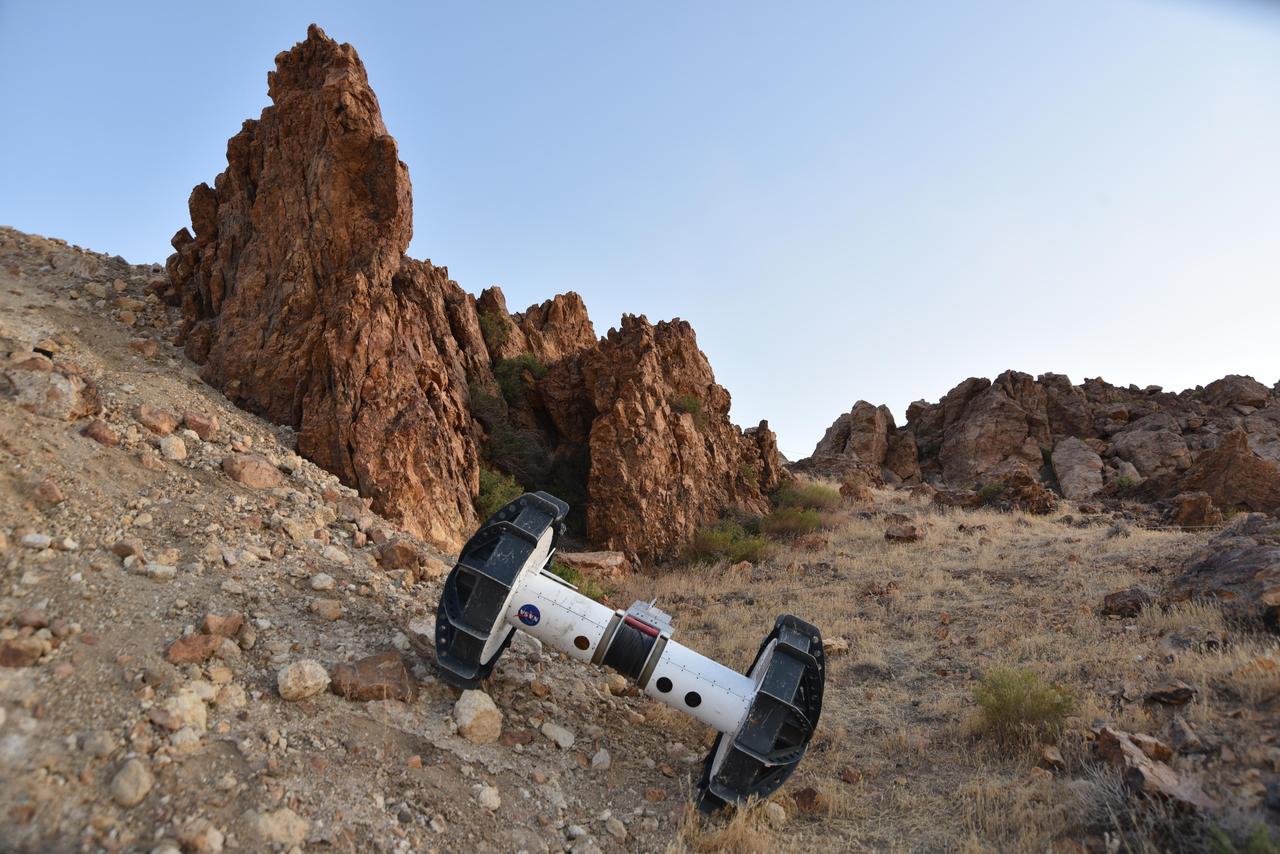

In this photograph, a tethered Axel robot — part of the four-wheeled DuAxel rover — navigates a steep slope during a field test in the Mojave Desert. The tether, which connects to the rover's other half, serves as a climbing rope of sorts while also providing power and a means of communication. This flexibility was built with crater walls, pits, scarps, vents, and other extreme terrain in mind. That's because on Earth, some of the best locations to study geology can be found in rocky outcrops and cliff faces, where many layers of the past are neatly exposed. They're hard enough to reach here, let alone on the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies. The DuAxel project is a technology demonstration being developed by roboticists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to see how this unconventional rover might fill a niche in planetary exploration. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24110
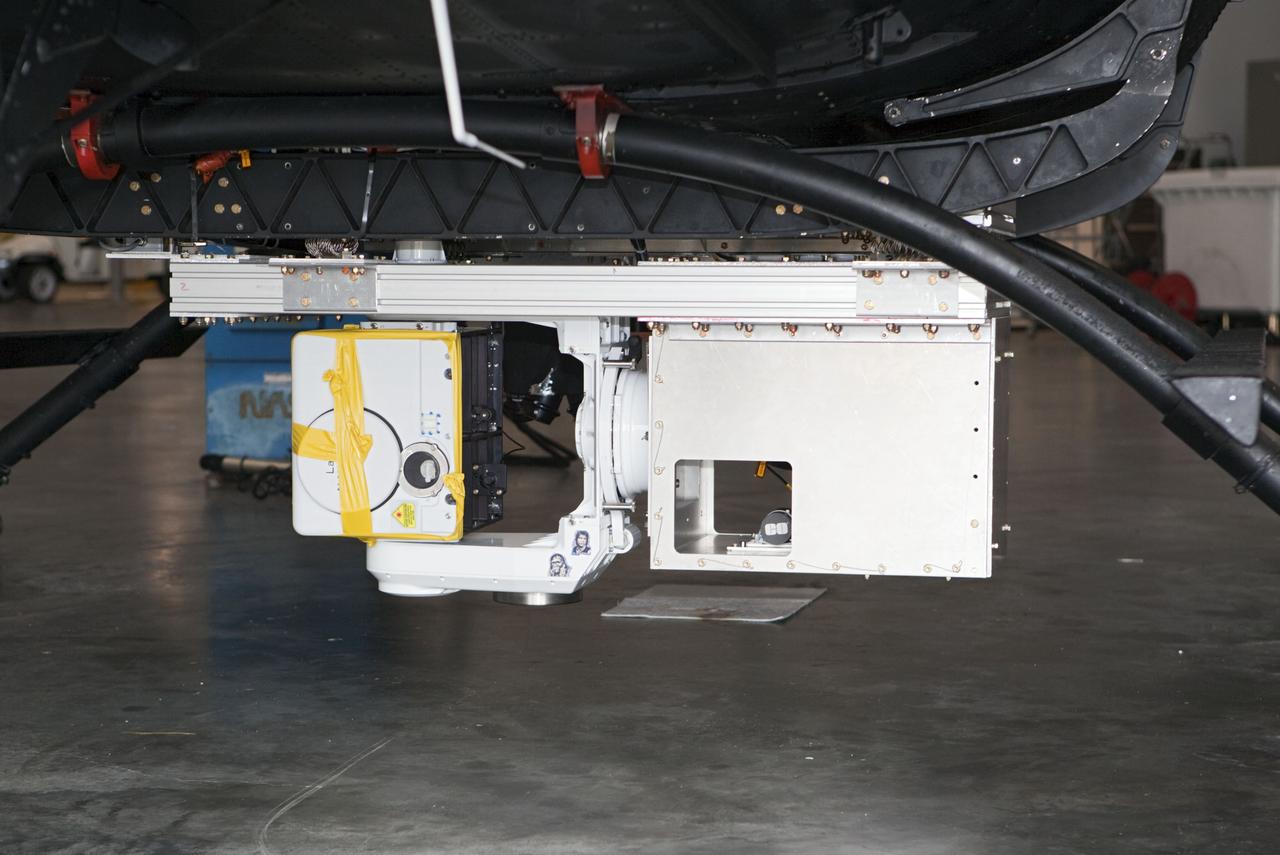

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Dmitri Gerondidakis
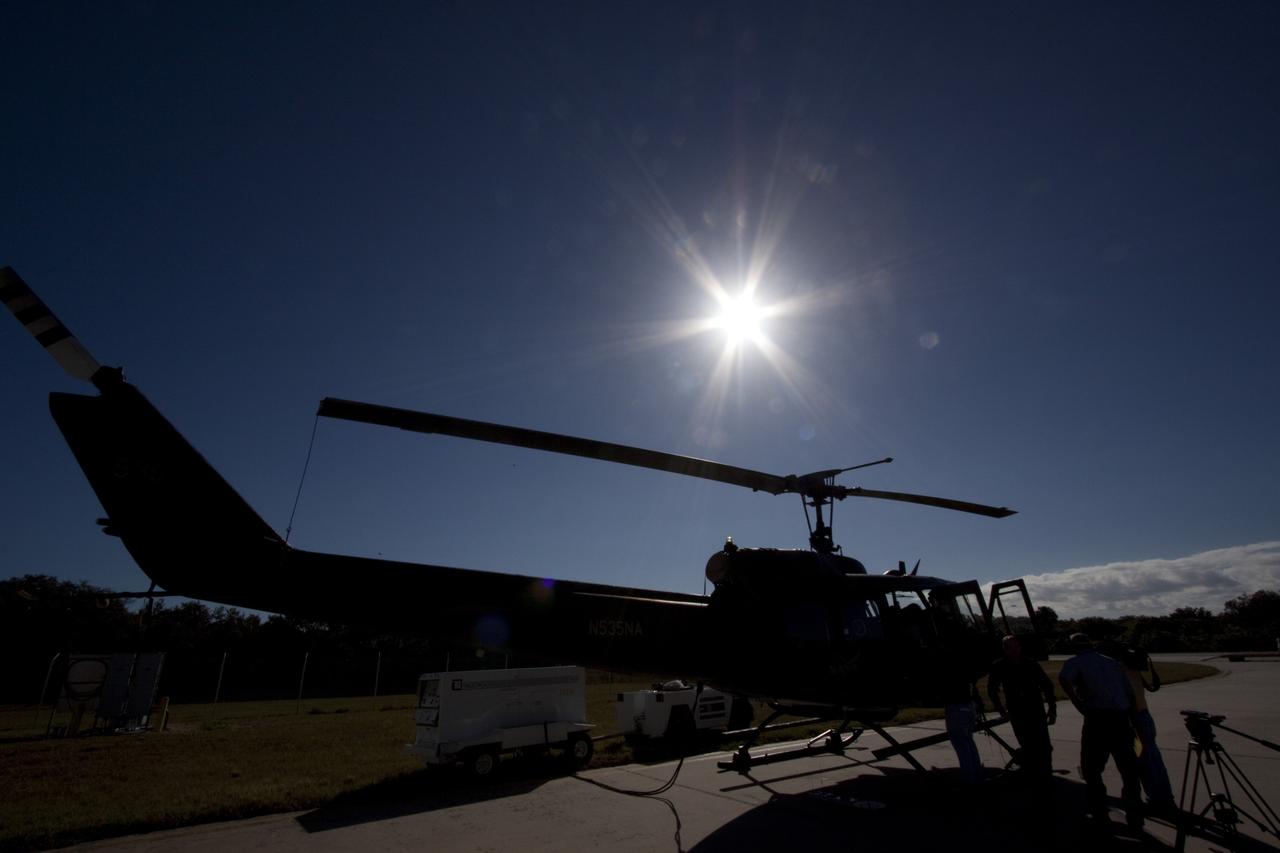

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Near the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a space agency team installed and tested hazard avoidance instrumentation on a Huey helicopter. Led by the Johnson Space Center and supported by Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Langley Research Center, the Autonomous Landing Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, laser system provides a planetary lander the ability to precisely land safely on a surface while detecting any dangerous obstacles such as rocks, holes and slopes. Just north of Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility runway, a rock- and crater-filled planetary scape has been built so engineers can test the ability to negotiate away from risks. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
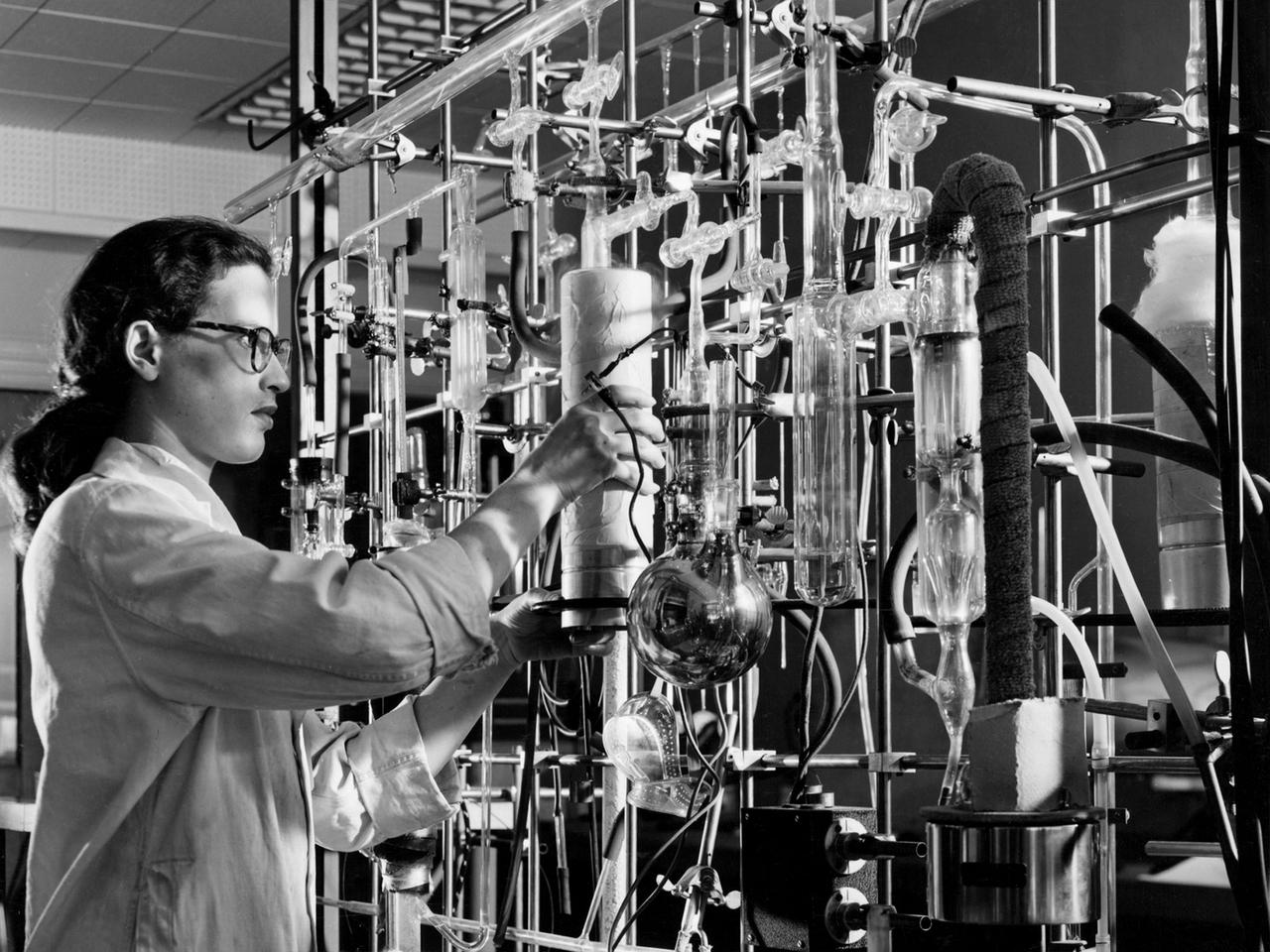

A materials researcher at the NACA’s Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory examines a surface crack detection apparatus in the Materials and Stresses Building during December 1952. Materials research was an important aspect of propulsion technology. Advanced engine systems relied upon alloys, and later composites, that were strong, lightweight, and impervious to high temperatures. Jet engines which became increasingly popular in the late 1940s, produced much higher temperatures than piston engines. These higher temperatures stressed engine components, particularly turbines. Although Lewis materials research began during World War II, the Materials and Thermodynamics Division was not created until 1949. Its primary laboratories were located in the Materials and Stresses Building. The group sought to create new, improved materials and to improve engine design through increased understanding of materials. The Lewis materials researchers of the 1950s made contributions to nickel-aluminum alloys, cermet blades, metal matrix composites, oxide dispersion strengthened superalloys, and universal slopes.
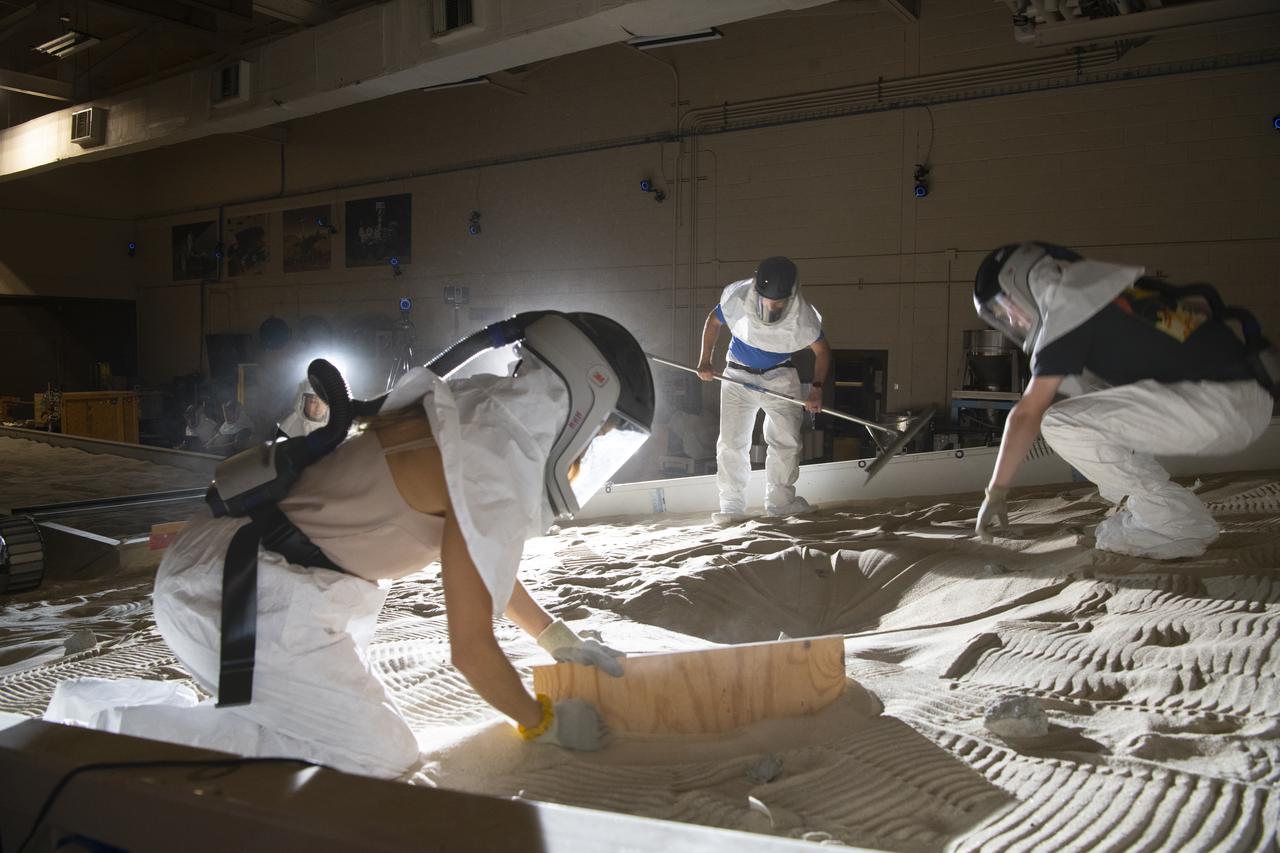

The Simulated Lunar Operations Lab at NASA Glenn Research Center serve to test planetary roving vehicle systems and components in simulated planetary and lunar conditions such as the VIPER Rover.
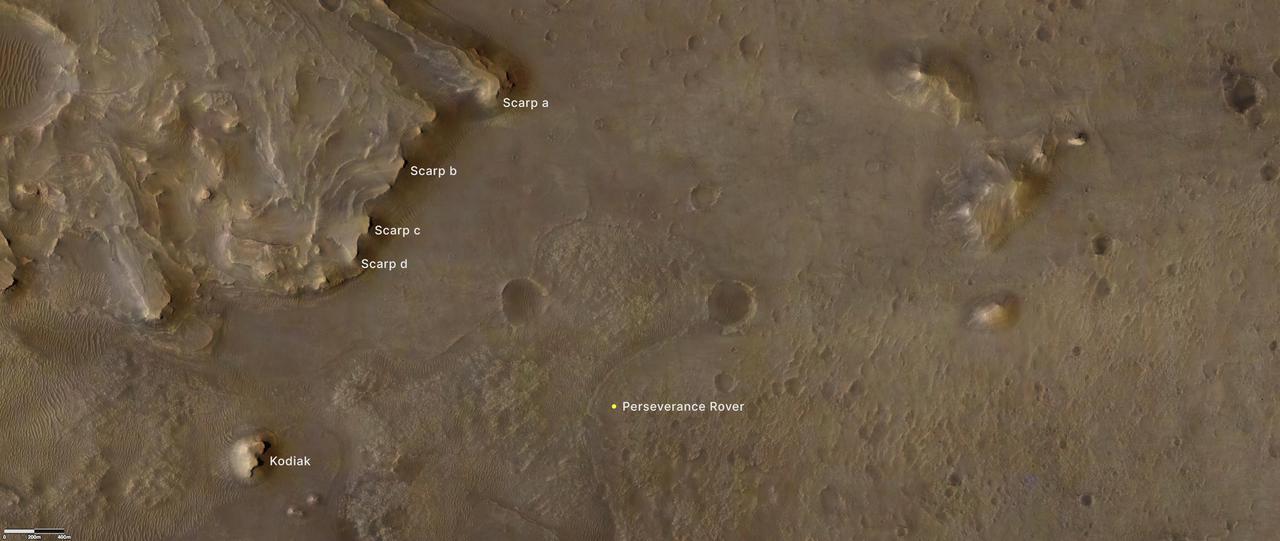

Provided by the High Resolution Imaging Experiment (HiRISE) aboard NASA's Mars Reconnaissance orbiter, this overhead image captures a portion of Mars' Jezero Crater. The yellow dot on lower right indicates the location of NASA's Perseverance rover. The remnant of Jezero Crater's rover delta the science team refers to as "Kodiak" is to the lower left. Long, steep slopes, called scarps, along the delta are on the upper left, labeled A through D. The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24814

Large-scale crossbedding in the sandstone of this ridge on a lower slope of Mars' Mount Sharp is common in petrified sand dunes. The scene combines multiple images taken with both cameras of the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on Curiosity on Aug. 27, 2015, during the 1,087th Martian day, or sol of the rover's work on Mars. It spans from east, at left, to south-southwest. Figure 1 includes a scale bar of 200 centimeters (about 6.6 feet). Sets of bedding laminations lie at angles to each other. Such crossbedding is common in wind-deposited sandstone of the U.S. Southwest. An example from Utah is pictured at http://3dparks.wr.usgs.gov/zion/html2/3d153.html. The sandstone in the image from Mars is part of the Stimson unit on Mount Sharp. The color of the Mastcam mosaic has been approximately white-balanced to resemble how the scene would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. The component images in the center and upper portion of the mosaic are from Mastcam's right-eye camera, which is equipped with a 100-millimeter-focal-length telephoto lens. Images used in the foreground and at far left and right were taken with Mastcam's left-eye camera, using a wider-angle, 34-millimeter lens. Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego, built and operates Curiosity's Mastcam. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, built the rover and manages the project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. For more information about Curiosity, visit http://www.nasa.gov/msl and http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl . http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19818
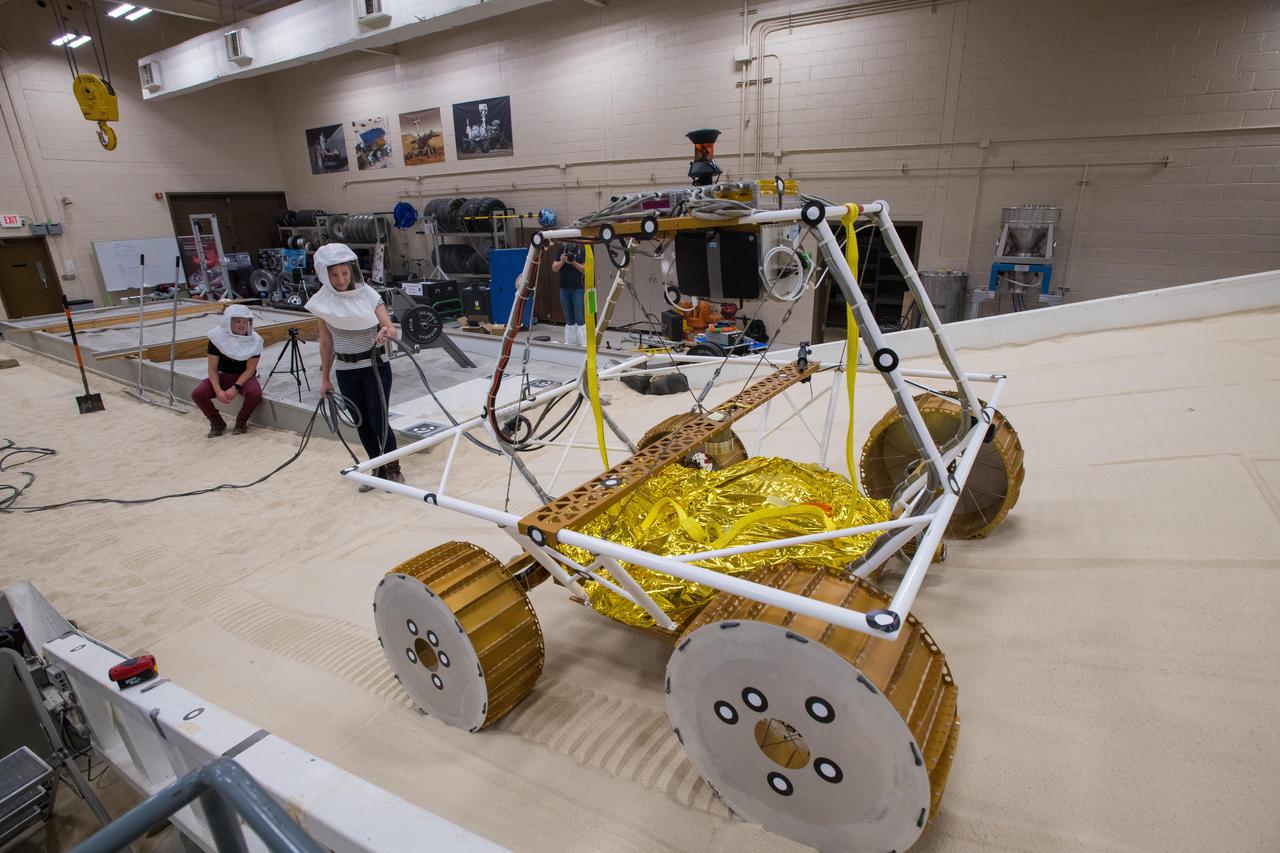
Virtual Intelligent Planetary Exploration Rover, VIPER Mobility Platform Testing An engineering model of the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER, is tested in the Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. About the size of a golf cart, VIPER is a mobile robot that will roam around the Moon’s South Pole looking for water ice in the region and for the first time ever, actually sample the water ice at the same pole where the first woman and next man will land in 2024 under the Artemis program. The large, adjustable soil bin contains lunar simulant and allows engineers to mimic the Moon’s terrain. Engineers from NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, where the rover was designed and built, joined the Glenn team to complete the tests. Test data will be used to evaluate the traction of the vehicle and wheels, determine the power requirements for a variety of maneuvers and compare methods of traversing steep slopes. Respirators are worn by researchers to protect against the airborne silica that is present during testing. VIPER is a collaboration within and beyond the agency. NASA's Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley is managing the project, leading the mission’s science, systems engineering, real-time rover surface operations and software. The rover’s instruments are provided by Ames, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida and commercial partner, Honeybee Robotics in California. The spacecraft, lander and launch vehicle that will deliver VIPER to the surface of the Moon will be provided through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services program, delivering science and technology payloads to and near the Moon.
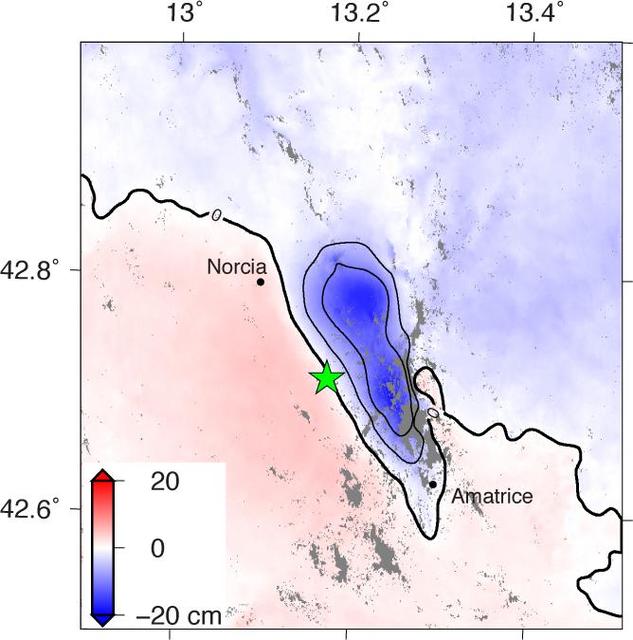
Amatrice earthquake in central Italy, which caused widespread building damage to several towns throughout the region. This earthquake was the strongest in that area since the 2009 earthquake that destroyed the city of L'Aquila. The Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis (ARIA) data system, a collaborative project between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, and the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, automatically generated interferometric synthetic aperture radar images from the Copernicus Sentinel 1A satellite operated by the European Space Agency (ESA) for the European Commission to calculate a map of the deformation of Earth's surface caused by the quake. This false-color map shows the amount of permanent surface movement, as viewed by the satellite, during a 12-day interval between two Sentinel 1 images acquired on Aug. 15, 2016, and Aug. 27, 2016. The movement was caused almost entirely by the earthquake. In this map, the colors of the surface displacements are proportional to the surface motion. The red and pink tones show the areas where the land moved toward the satellite by up to 2 inches (5 centimeters). The area with various shades of blue moved away from the satellite, mostly downward, by as much as 8 inches (20 centimeters). Contours on the surface motion are 2 inches (5 centimeters) The green star shows the epicenter where the earthquake started as located by the U.S. Geological Survey National Earthquake Information Center. Black dots show town locations. Scientists use these maps to build detailed models of the fault slip at depth and associated land movements to better understand the impact on future earthquake activity. The map shows the fault or faults that moved in the earthquake is about 14 miles (22 kilometers) long between Amatrice and Norcia and slopes to the west beneath the area that moved downward. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20896
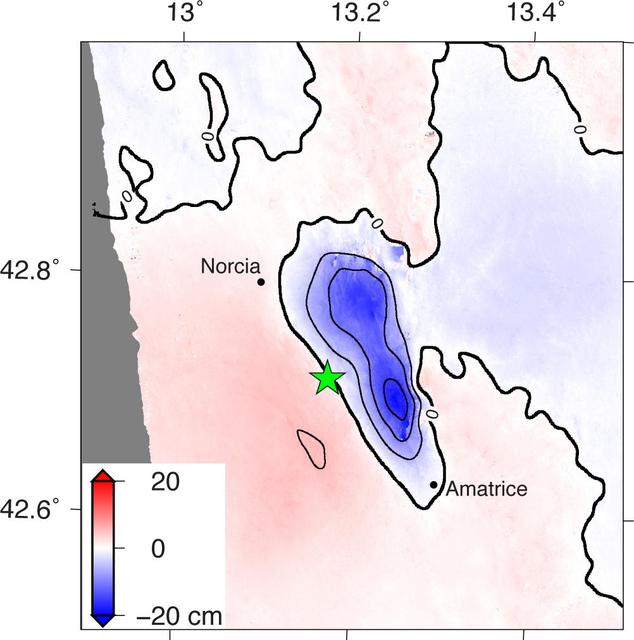
NASA and its partners are contributing observations and expertise to the ongoing response to the Aug. 23, 2016, magnitude 6.2 Amatrice earthquake in central Italy caused widespread building damage to several towns throughout the region. This earthquake was the strongest in that area since the 2009 earthquake that destroyed the city of L'Aquila. Scientists with the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis project (ARIA), a collaboration between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, and the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, analyzed interferometric synthetic aperture radar images from the PALSAR-2 instrument on the ALOS-2 satellite operated by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to calculate a map of the deformation of Earth's surface caused by the quake. This false-color map shows the amount of permanent surface movement, as viewed by the satellite, during a seven-month interval between two ALOS-2 images acquired on Sept. 9, 2015 and Aug. 24, 2016. The movement was caused almost entirely by the earthquake. In this map, the colors of the surface displacements are proportional to the surface motion. The red and pink tones show the areas where the land moved toward the satellite by up to 2 inches (5 centimeters). The area with various shades of blue moved away from the satellite, mostly downward, by as much as 8 inches (20 centimeters). Contours on the surface motion are 2 inches (5 centimeters) The green star shows the epicenter where the earthquake started as located by the U.S. Geological Survey National Earthquake Information Center. Black dots show town locations. Scientists use these maps to build detailed models of the fault slip at depth and associated land movements to better understand the impact on future earthquake activity. The map shows the fault or faults that moved in the earthquake is about 14 miles (22 kilometers) long between Amatrice and Norcia and slopes to the west beneath the area that moved downward. The PALSAR-2 data were provided by JAXA through a science project. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20893

STS059-S-072 (13 April 1994) --- This image is a false-color composite of Oetztal, Austria located in the Central Alps, centered at 46.8 degrees north latitude, and 10.70 degrees east longitude, at the border between Switzerland (top), Italy (left) and Austria (right and bottom). The area shown is 50 kilometers (30 miles) south of Innsbruck, Austria. This image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on its 14th orbit. Oetztal is a SIR-C/X-SAR hydrology supersite. Approximately one quarter of this image is covered by glaciers, the largest of which, Gepatschferner, is visible as a triangular yellow patch in the center of the scene. The summits of the main peaks reach elevations between 3,500 and 3,768 meters (11,500 and 12,362 feet) above sea level. The tongues of the glaciers are descending from elevated plateaus down into narrow valleys which were formed during the last ice age. This color image was produced in C-Band using multi-polarization information (Red=CHV, Green=CVV, Blue=CVV/CHV). The blue areas are lakes (Gepatsch Dam at center right; Lake Muta at top right) and glacier ice. The yellow areas are slopes facing the radar and areas of dry snow. Purple corresponds to slopes facing away from the radar. Yellow in the valley bottom corresponds to tree covered areas. There is 30 to 50 centimeters (12 to 20 inches) of dry, fresh snow on the glaciers, and about 10 centimeters (4 inches) in the valley at the city of Vent, Austria (center). At these data were taken, the weather was cold, with snow and thick fog. The entire area would appear white to an optical sensor because it is all covered under a winter snowpack. Researchers are interested in Oetztal because knowing how glaciers shrink and grow over time is an important indication of climatic change. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43890
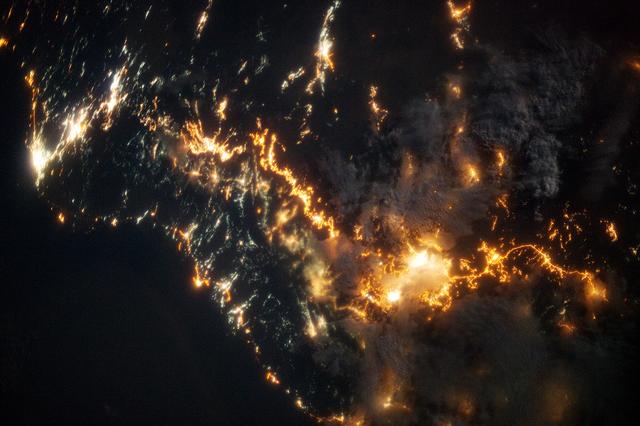

This striking image of the coastline of southwestern Saudi Arabia was taken by astronauts on the International Space Station. Patchy cloud cover partially obscures and blurs the city lights, especially in the vicinity of Khamis Mushait and Abha. While much of the country is lightly populated desert—and relatively dark at night due to lack of city and roadway lights—the southwestern coastal region has a more moderate climate and several large cities. Three brightly lit urban centers are visible at image top left: Jeddah, Mecca, and Taif. Jeddah is the gateway city for Islamic pilgrims going to nearby Mecca, a religious journey known as the Hajj. Taif is located on the slopes of the Sarawat Mountains and provides a summer retreat for the Saudi government from the desert heat of the capital, Riyadh. Bright yellow-orange lighting marks highways that parallel the trend of the Asir Mountains (image center), connecting Mecca to the resort cities of Al Bahah and Abha. Smaller roadways, lit with blue lights, extend to the west to small cities along the Red Sea coastline. The bright yellow-orange glow of the city of Abha is matched by that of Khamis Mushait (or Khamis Mushayt) to the northeast. The brightly lit ribbon of highway continues towards other large cities to the south (Jazan, not shown) and southeast (Najran, not shown). Astronaut photograph ISS036-E-25802 was acquired on July 26, 2013, with a Nikon D3S digital camera using a 50 millimeter lens, and is provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations experiment and Image Science & Analysis Laboratory, Johnson Space Center. The image was taken by the Expedition 36 crew. It has been cropped and enhanced to improve contrast, and lens artifacts have been removed. The International Space Station Program supports the laboratory as part of the ISS National Lab to help astronauts take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth. Caption by William L. Stefanov, Jacobs/JETS at NASA-JSC. Instrument: ISS - Digital Camera More info: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/13TqPcr" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/13TqPcr</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
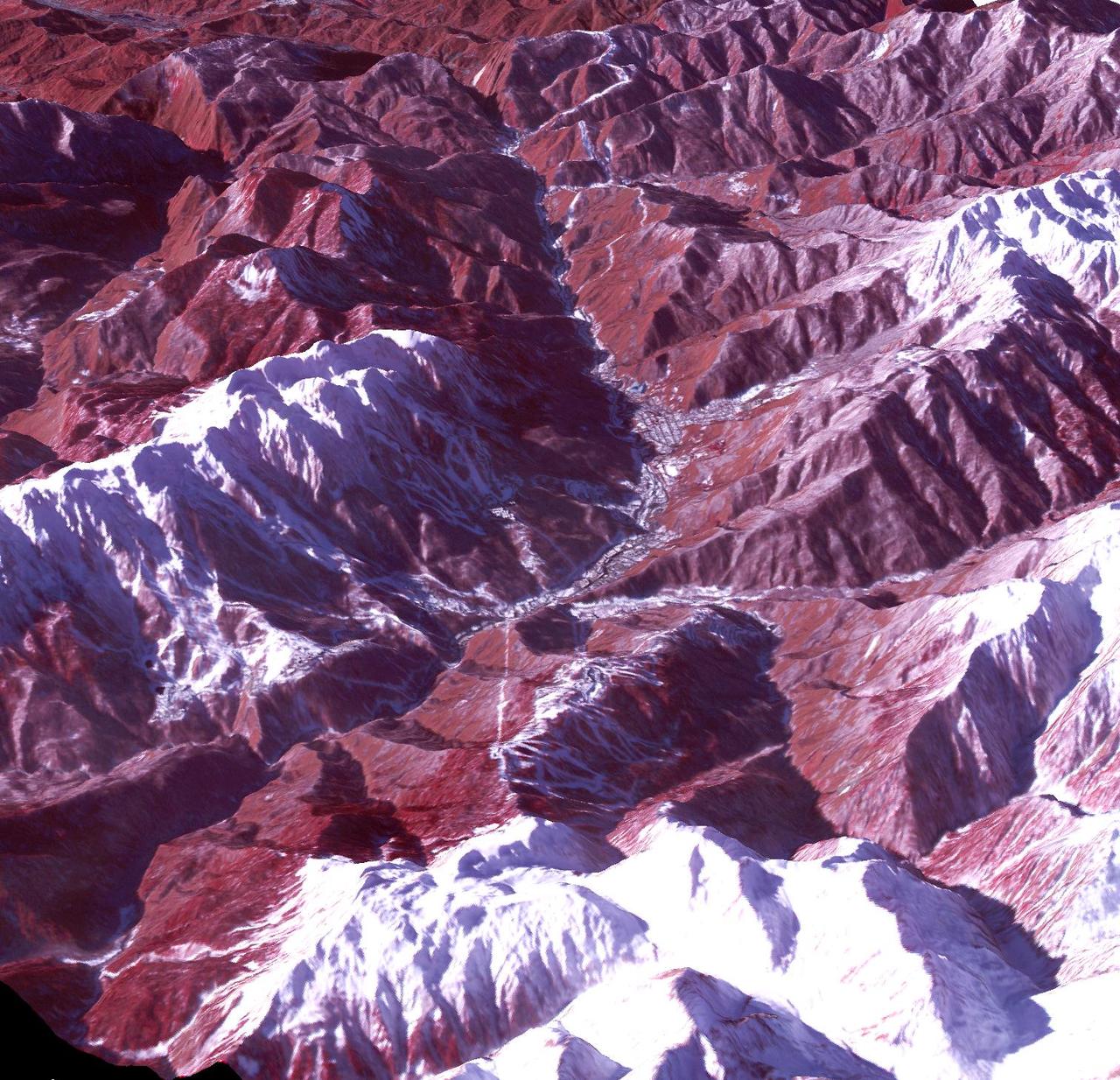

Sochi, Russia Winter Olympic Sites (Mountain Cluster) The 2014 Winter Olympic ski runs may be rated double black diamond, but they're not quite as steep as they appear in this image of the skiing and snowboarding sites for the Sochi Winter Olympic Games, acquired on Jan. 4, 2014, by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft. Rosa Khutar ski resort near Sochi, Russia, is in the valley at center, and the runs are visible on the shadowed slopes on the left-hand side of the valley. Height has been exaggerated 1.5 times to bring out topographic details. The games, which begin on Feb. 7 and continue for 17 days, feature six new skiing and boarding events plus the return of the legendary Jamaican bobsled team to the winter games for the first time since 2002. In this southwest-looking image, red indicates vegetation, white is snow, and the resort site appears in gray. The area imaged is about 11 miles (18 kilometers) across in the foreground and 20 miles (32 kilometers) from front to back. The image was created from the ASTER visible and near-infrared bands, draped over ASTER-derived digital elevation data. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched Dec. 18, 1999, on Terra. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and data products. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER provides scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping and monitoring of dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are: monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. The U.S. science team is located at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. The Terra mission is part of NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. More information about ASTER is available at <a href="http://asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">asterweb.jpl.nasa.gov/</a>. credit:NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
