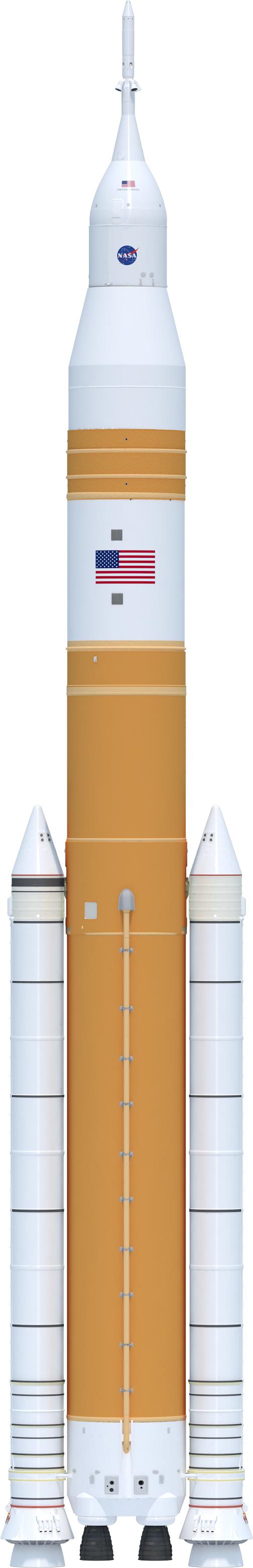

Illustration of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant outer mold line. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
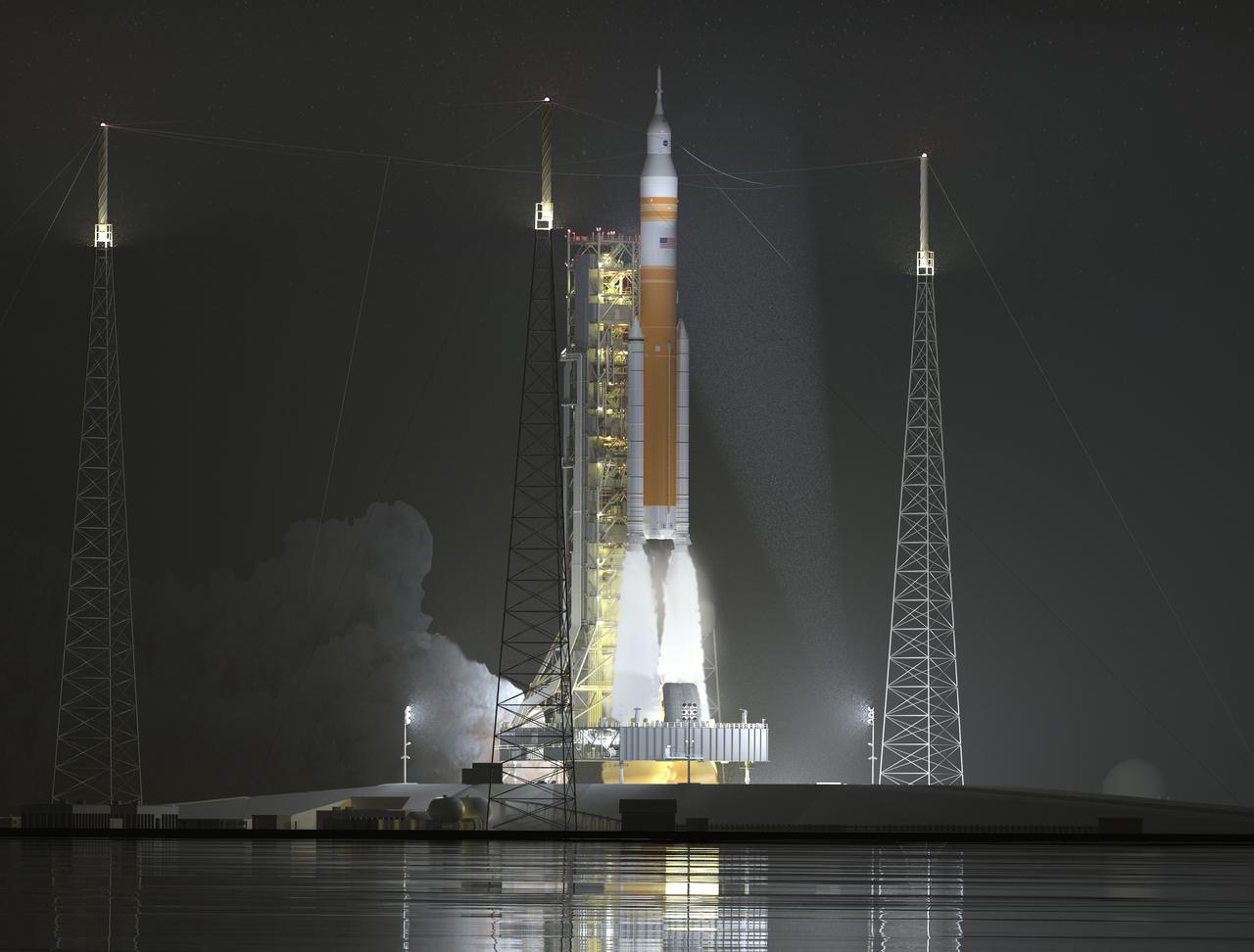

Illustration of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant night launch. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA) In album: B1B_Crew_SLS
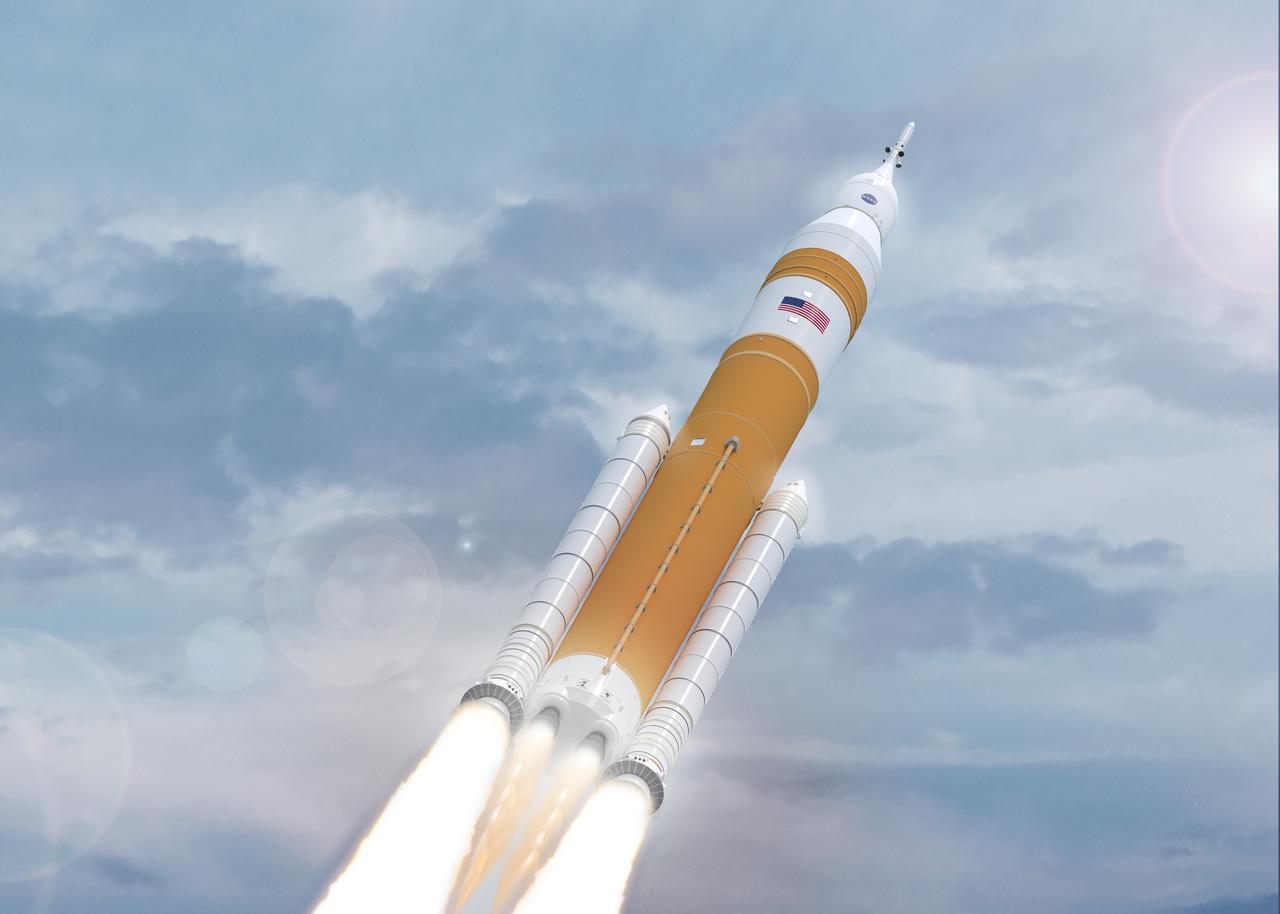

Illustration of evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant in flight. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
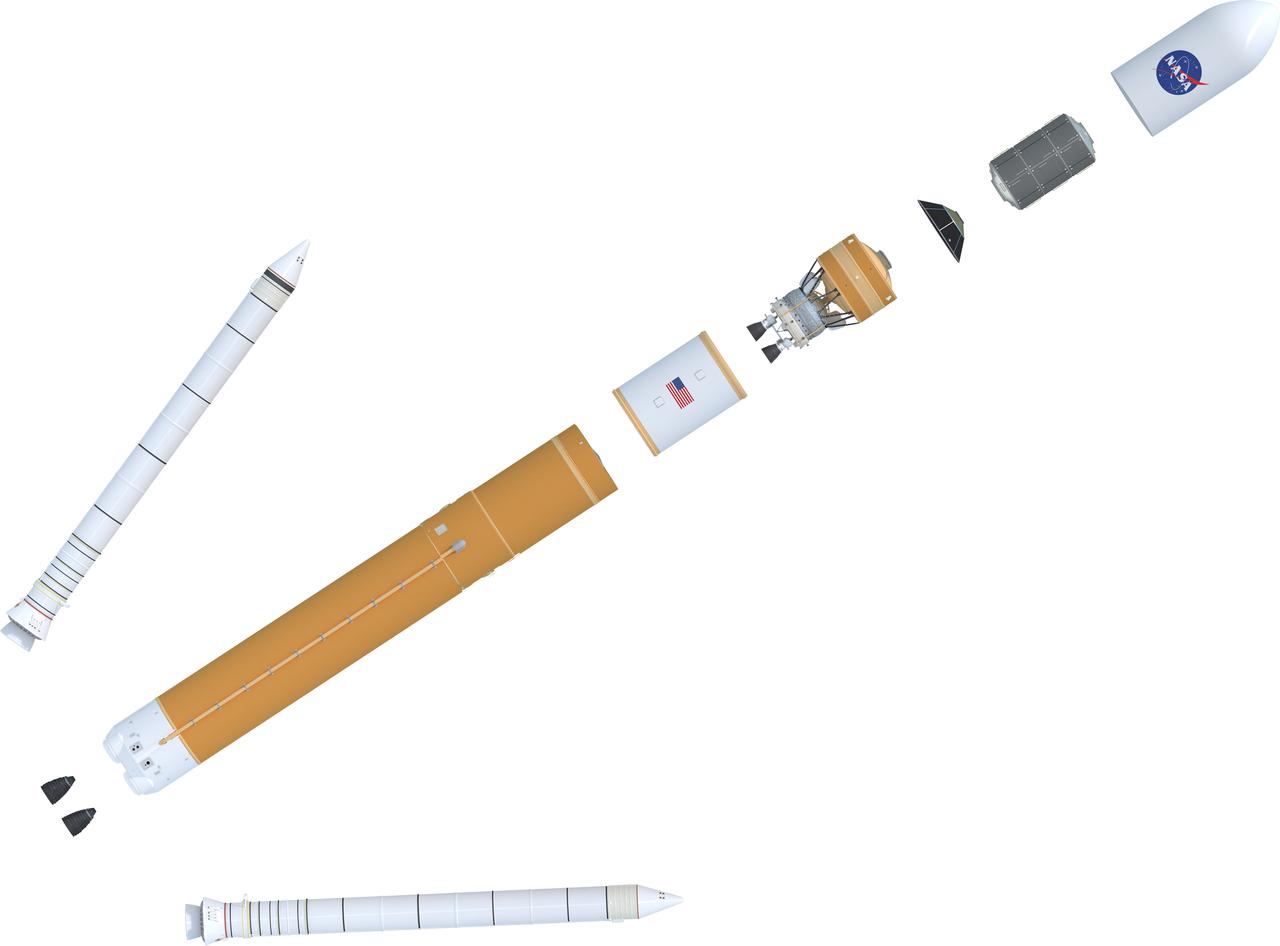
Expanded view illustration of elements of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
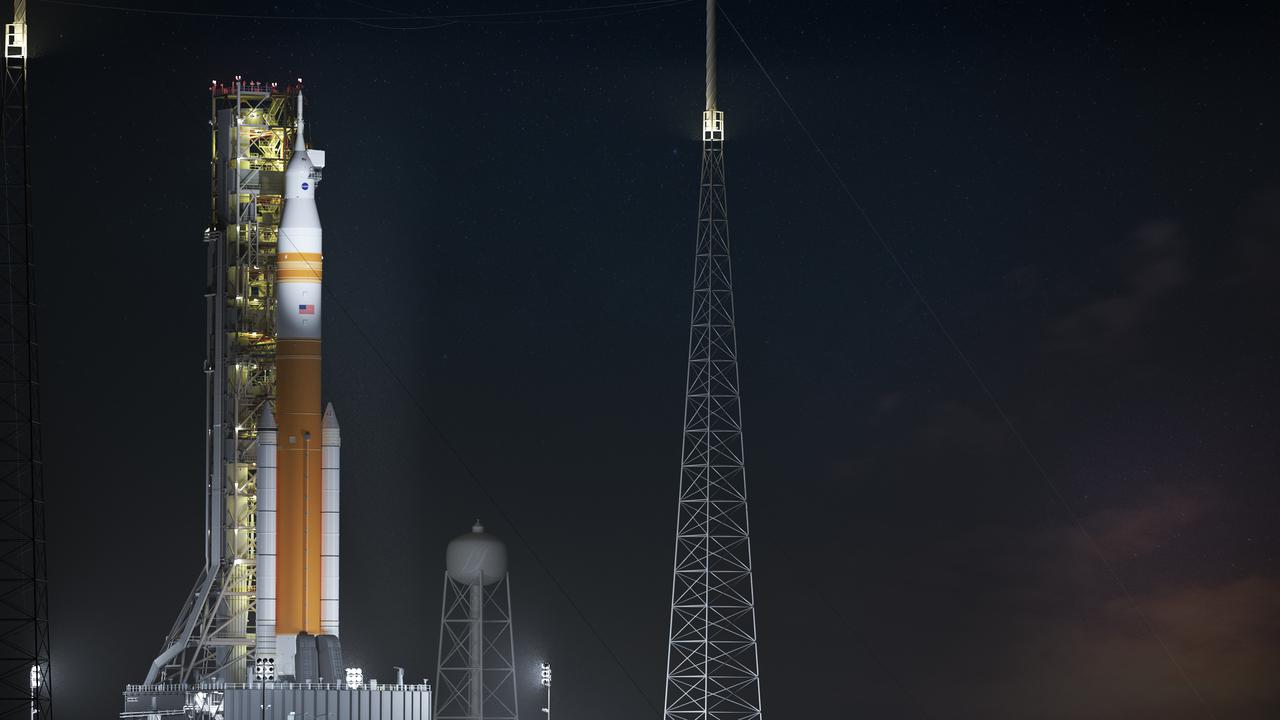

Illustration of nighttime scene of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant on Pad 39B.. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

Seen here, is a nighttime rendering of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant positioned on the mobile launcher. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
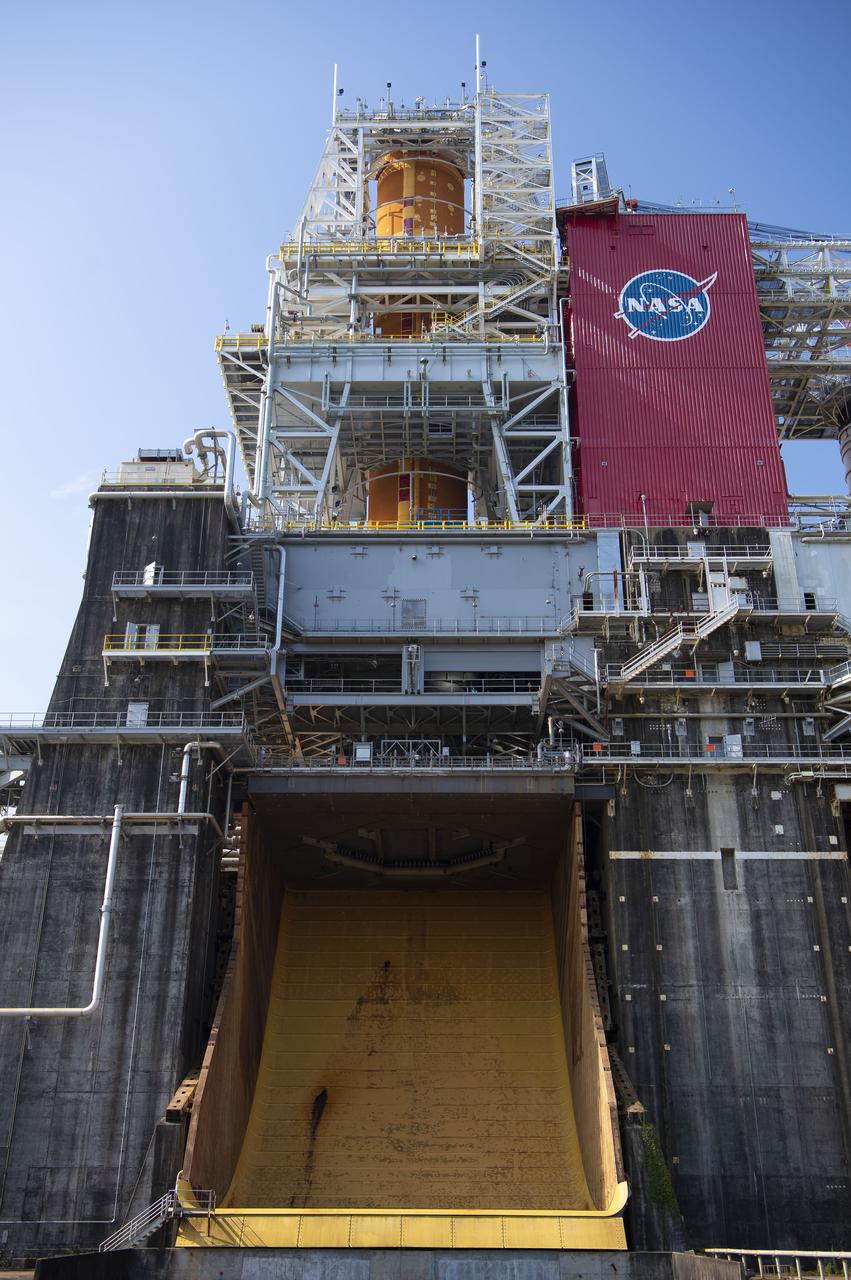

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
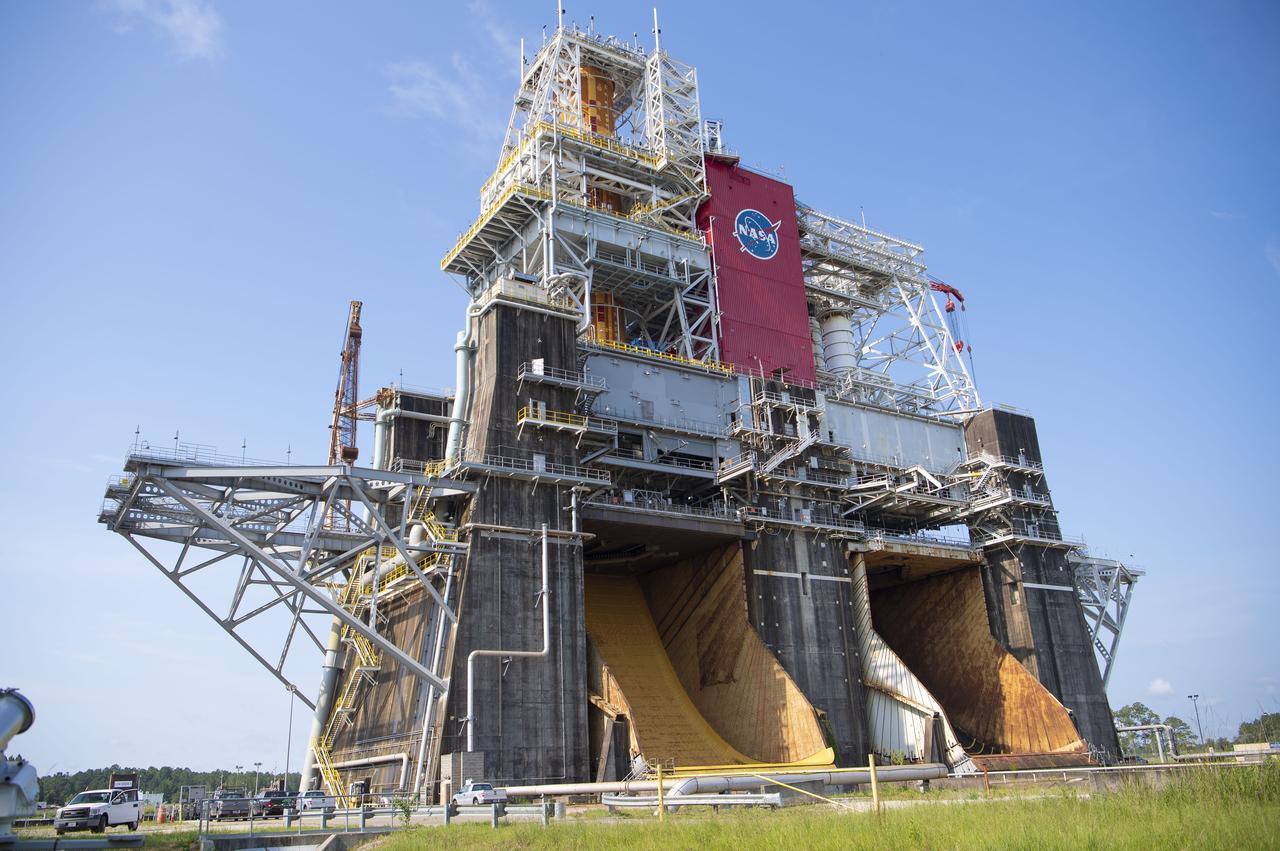

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
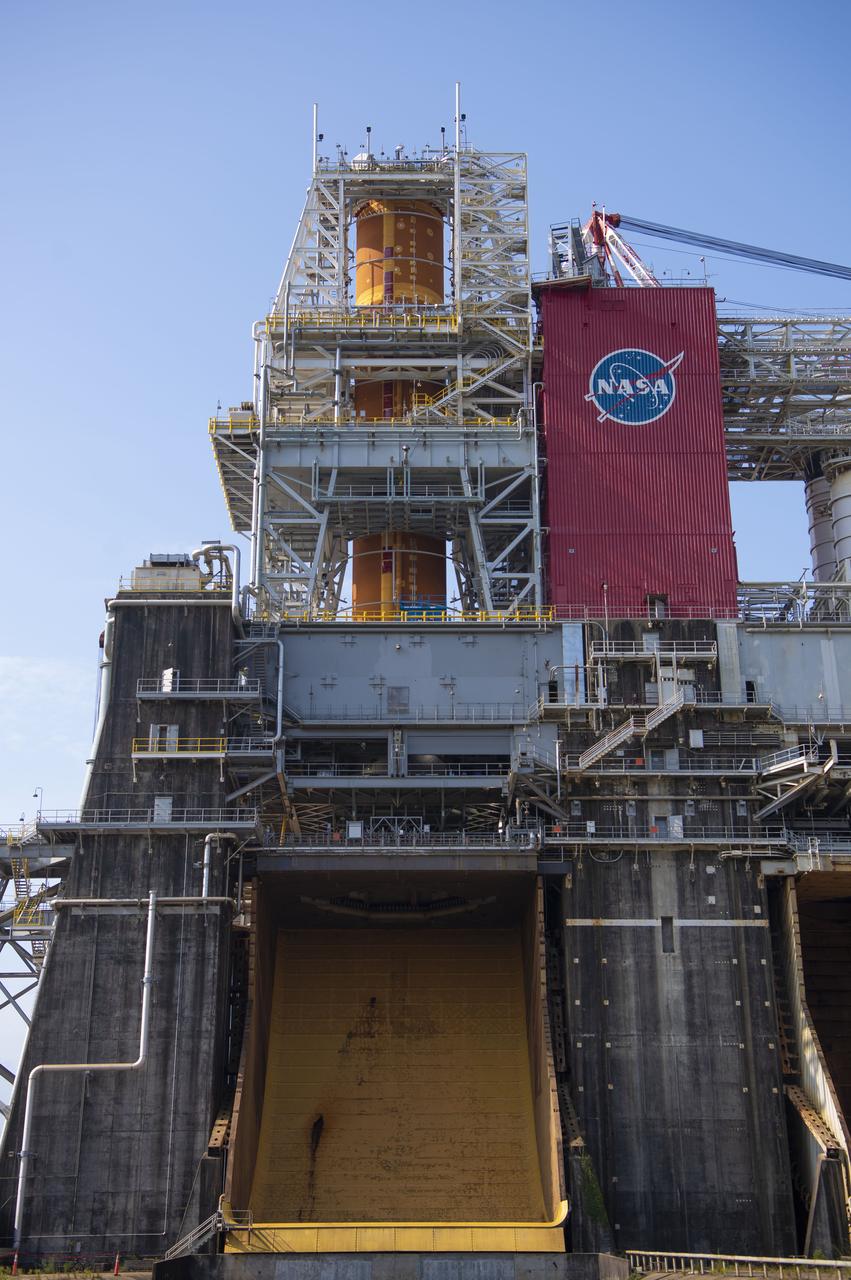

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
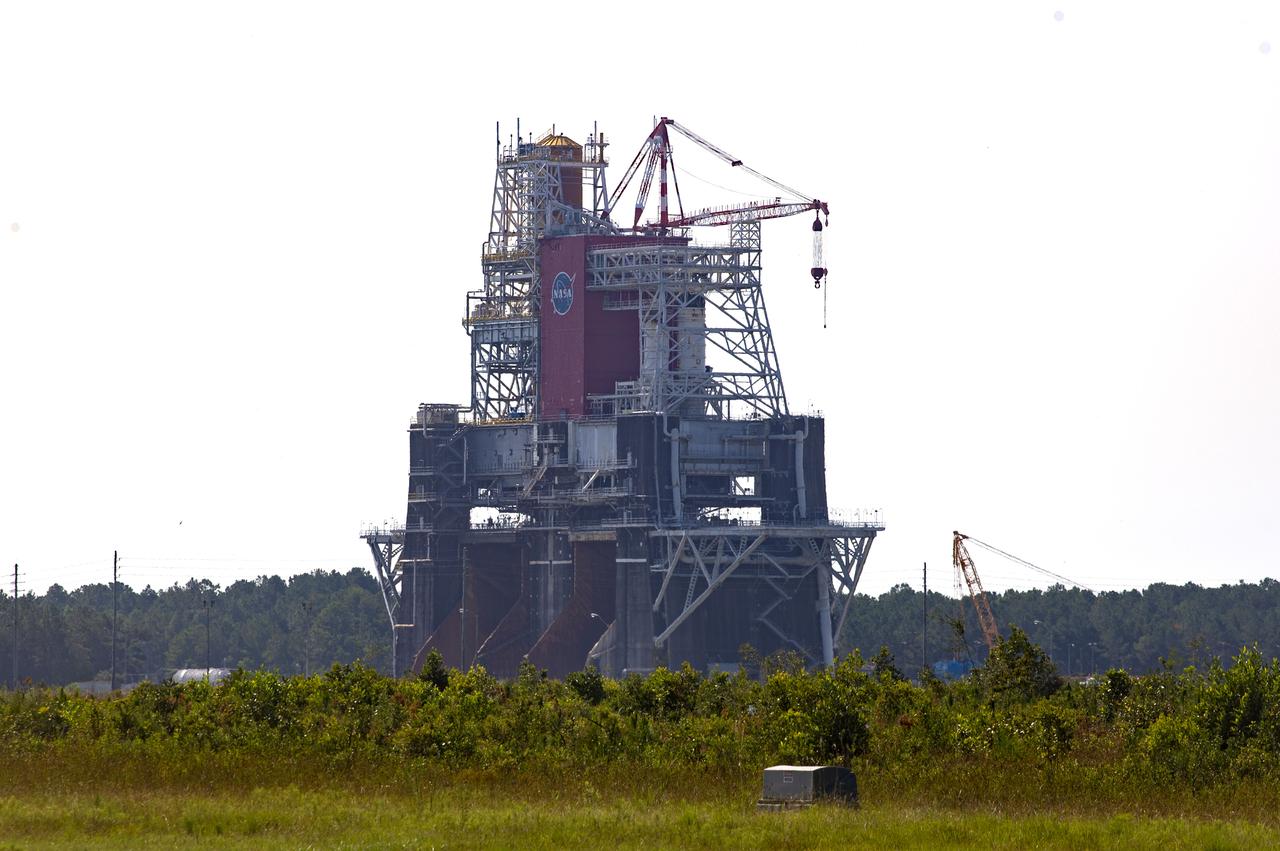

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
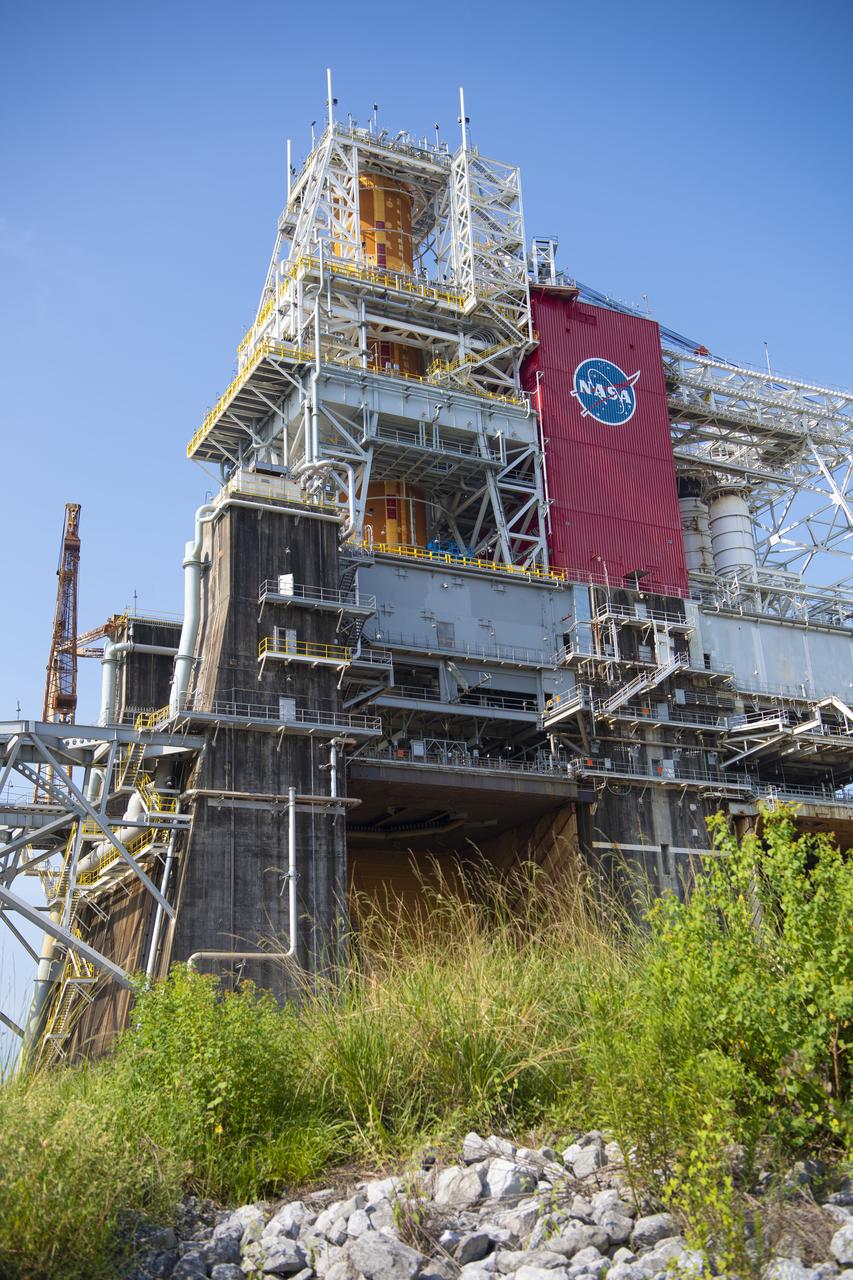

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
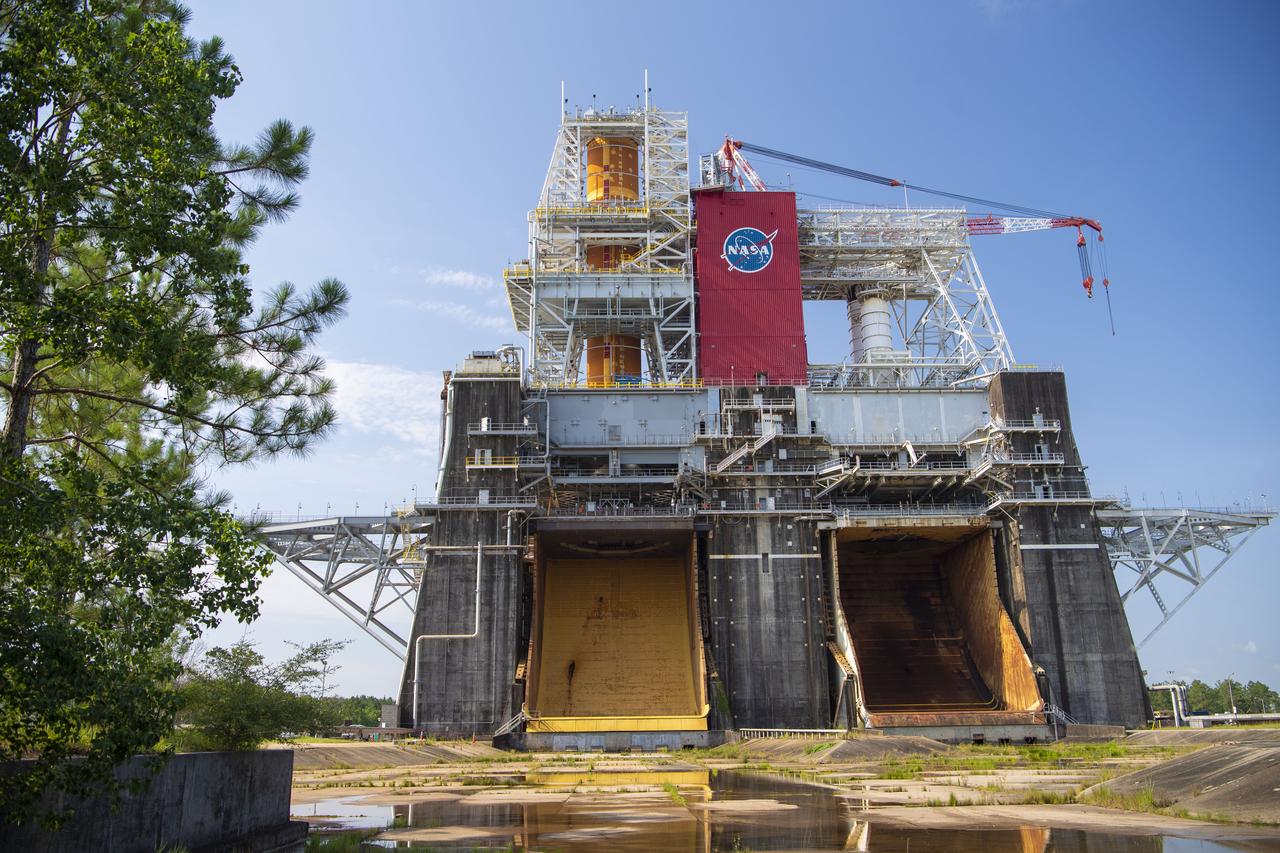

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
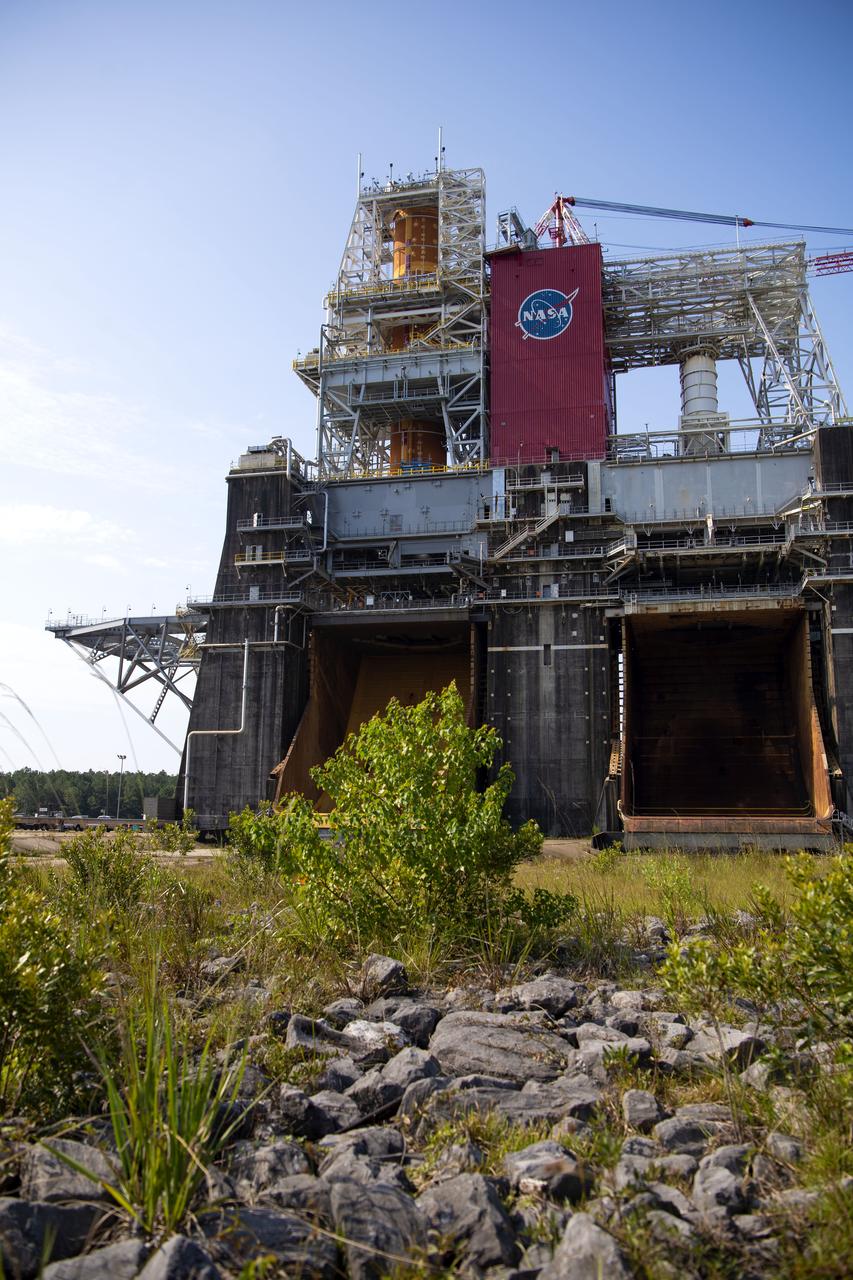

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
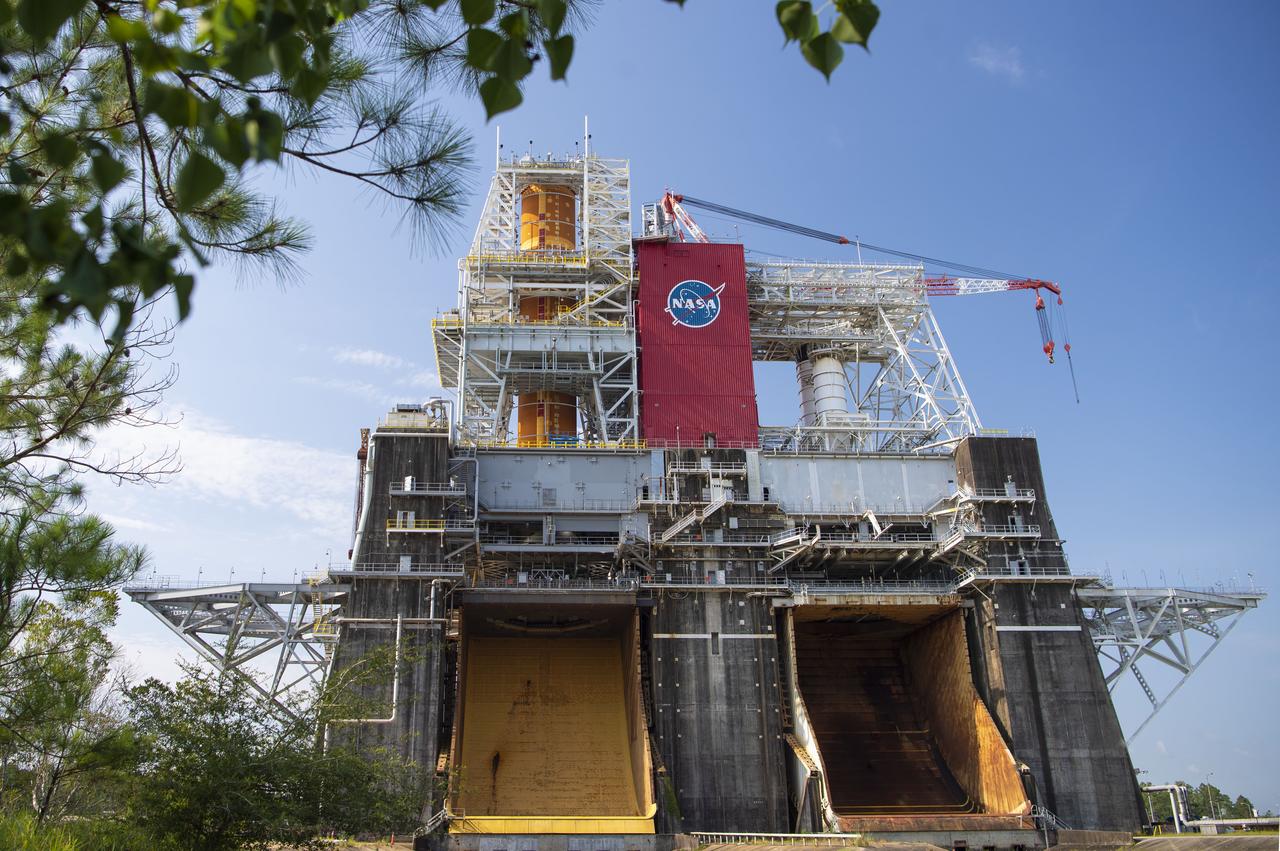

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
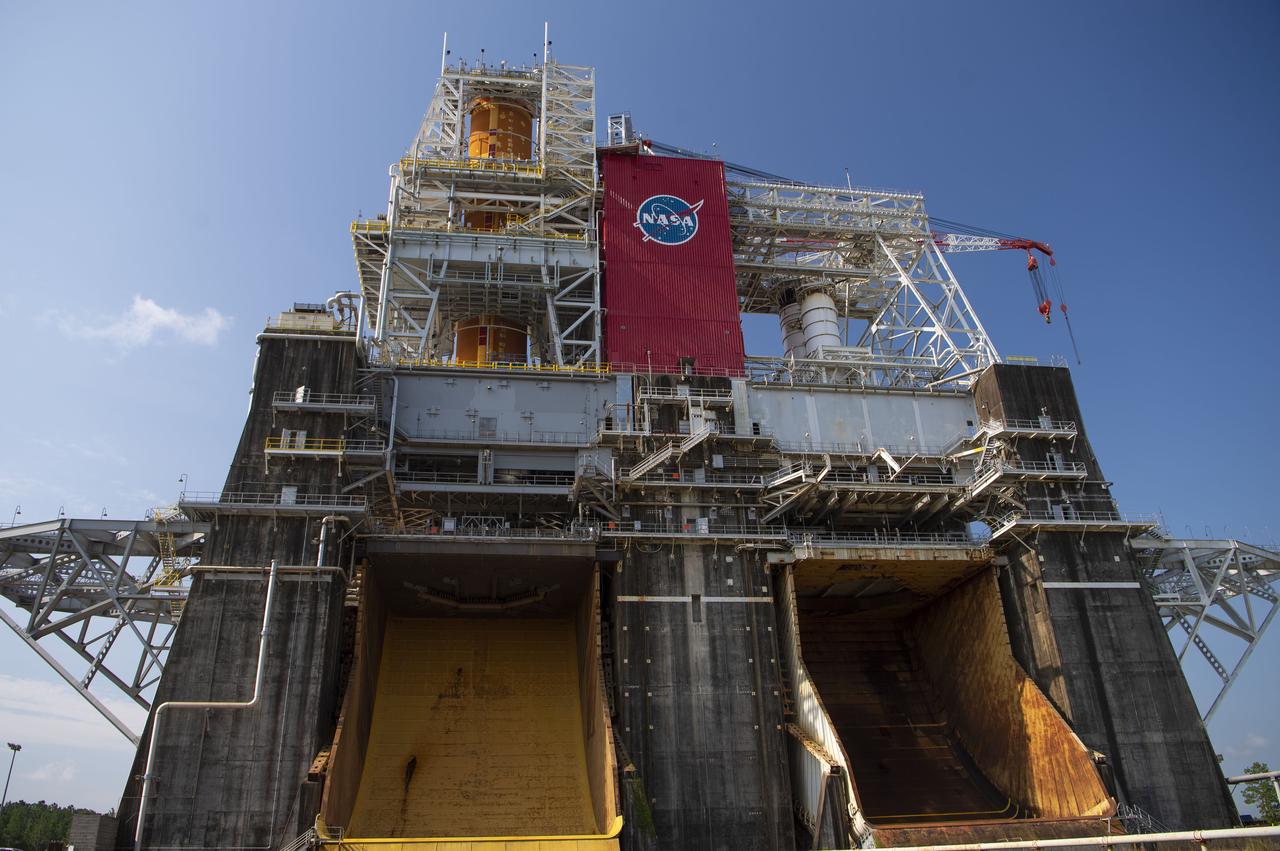

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
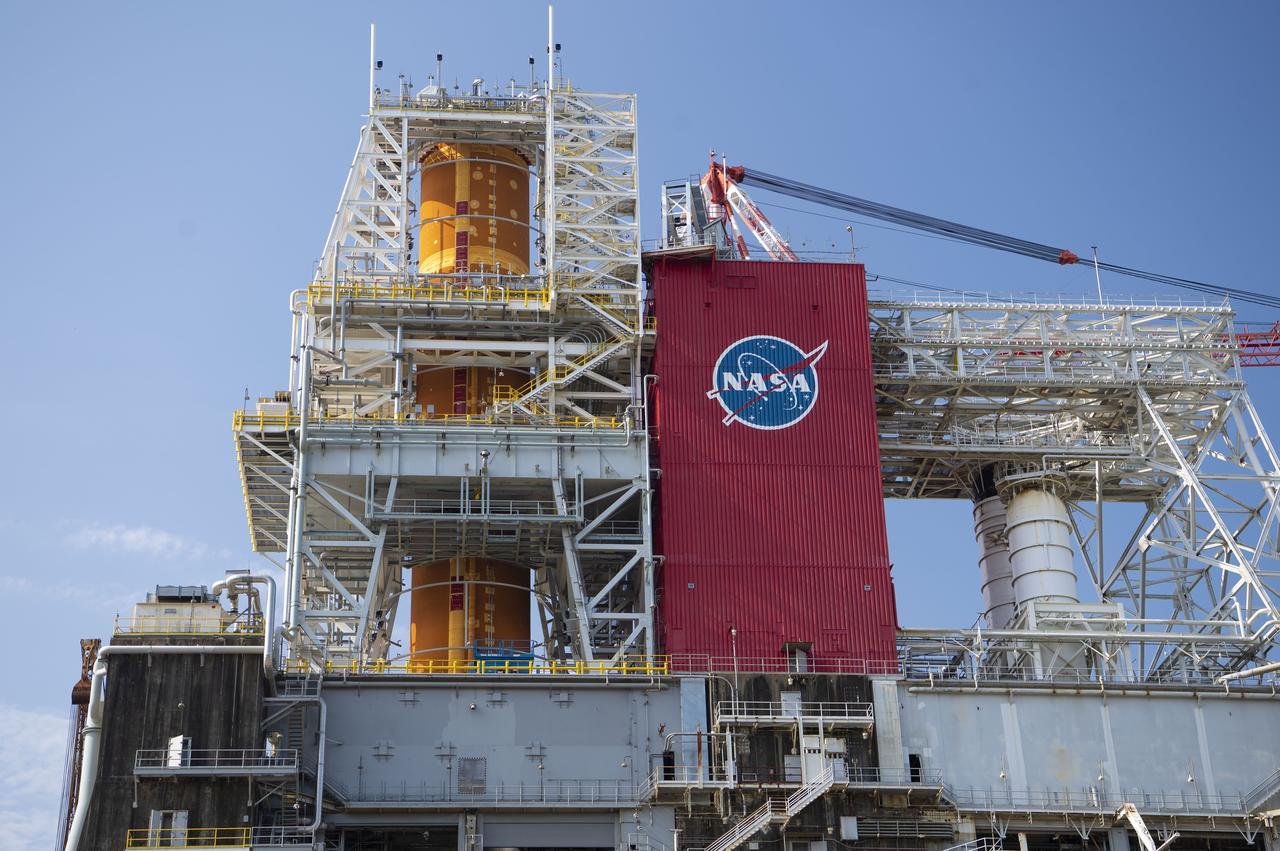

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.

A photo from the north (flame trench) side of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center shows the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) rocket installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage was transported to Stennis in January to begin Green Run testing prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. At Stennis, the SLS core stage will undergo a series of tests on its integrated systems, culminating with a hot fire of its four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.

Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft rollout at Kennedy Space Center

Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft rollout at Kennedy Space Center

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
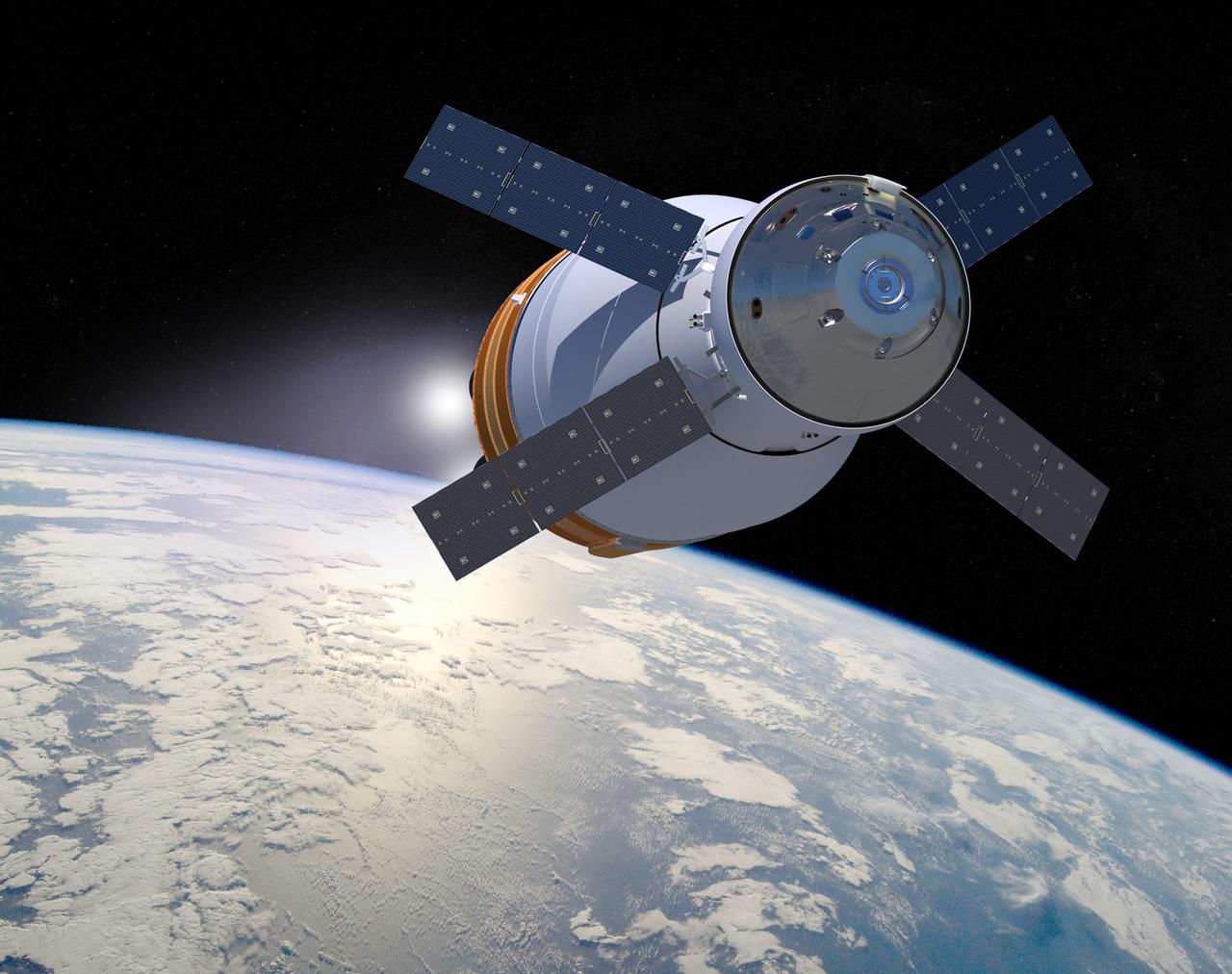

Seen here is an image of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage with the Orion Space craft on its way to a deep space mission. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

MIKE BOLGER ADDRESSES AUDIENCE AT SLS ALL HANDS

MARK GEYER ADDRESSES AUDIENCE AT SLS ALL HANDS

MIKE BOLGER ADDRESSES AUDIENCE AT SLS ALL HANDS

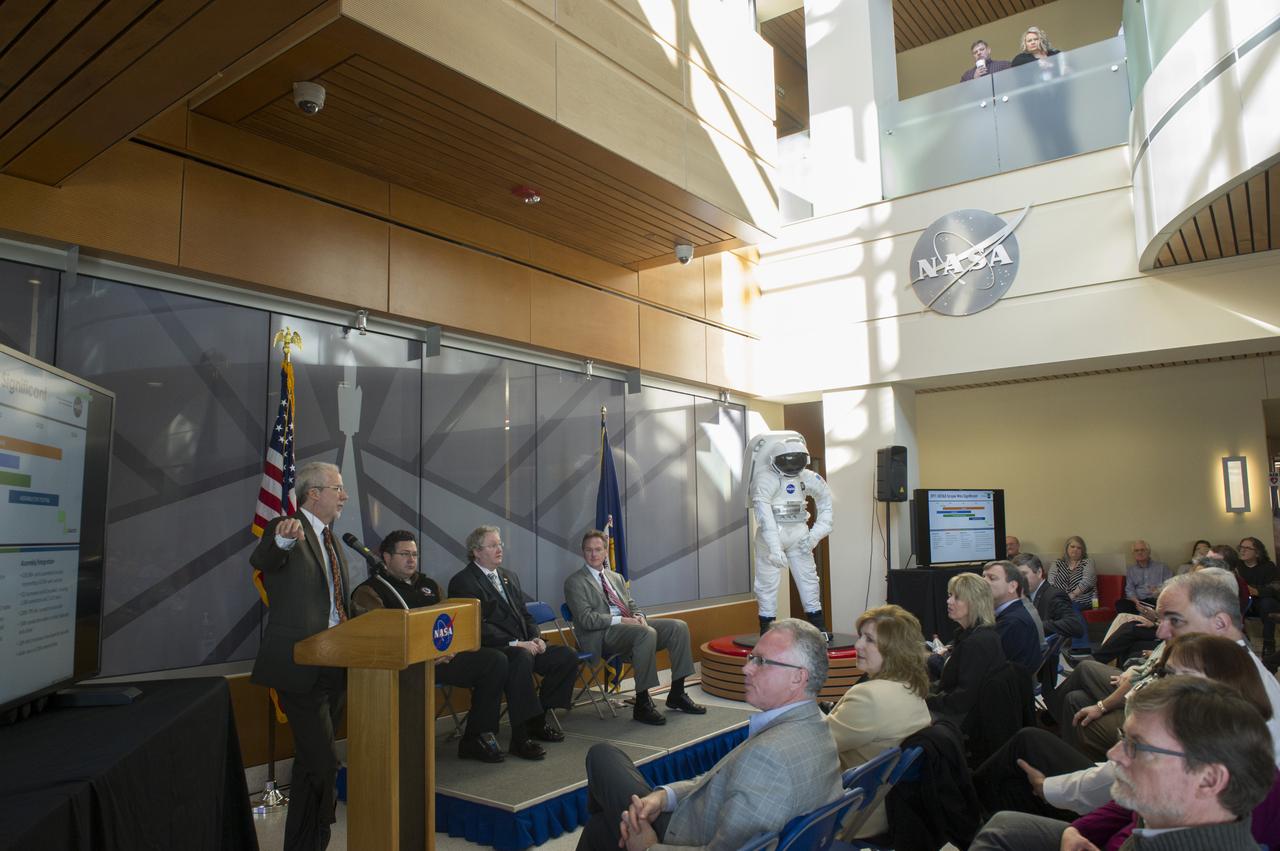
BILL HILL ADDRESSES AUDIENCE AT SLS ALL HANDS

TODD MAYADDRESSES AUDIENCE AT SLS ALL HANDS
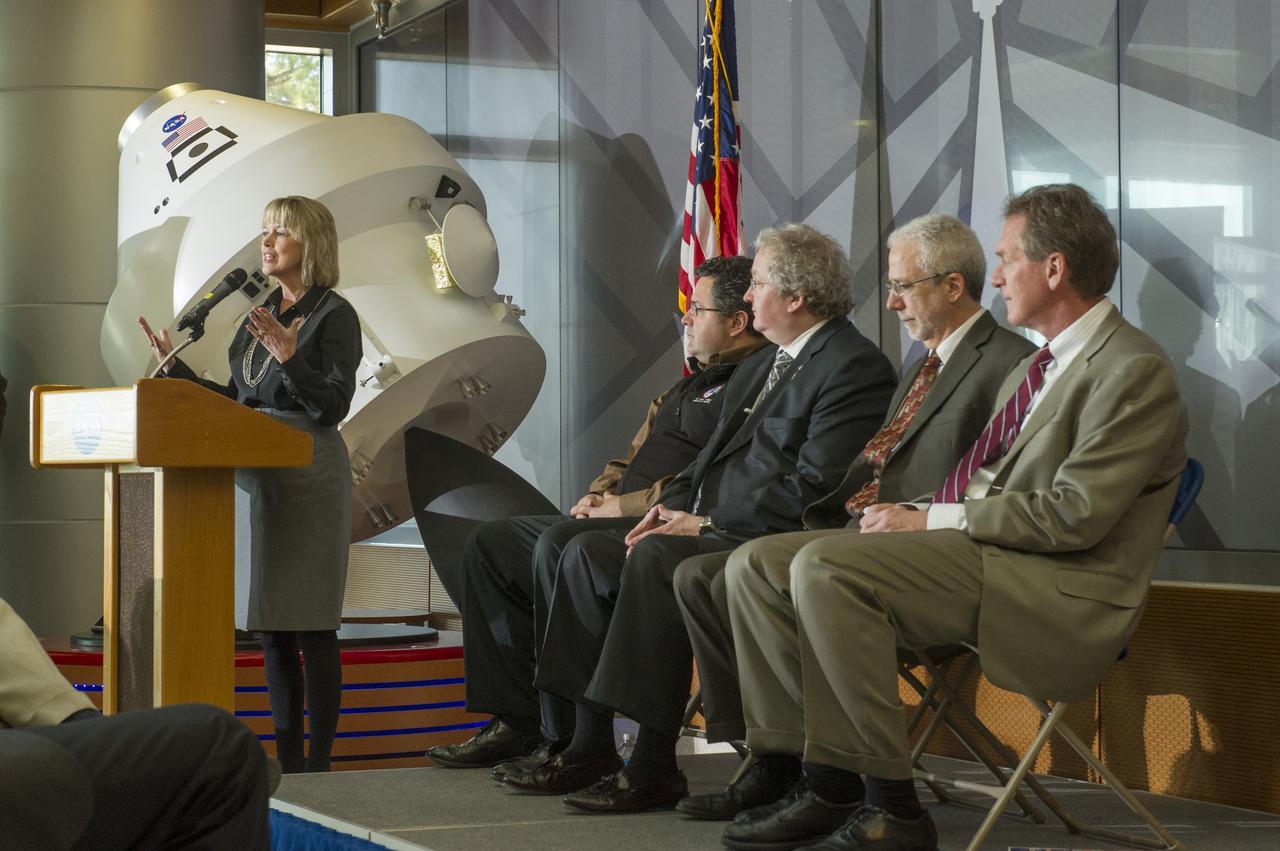

TERESA VANHOOSER ADDRESSES AUDIENCE AT SLS ALL HANDS

BILL HILL ADDRESSES AUDIENCE AT SLS ALL HANDS

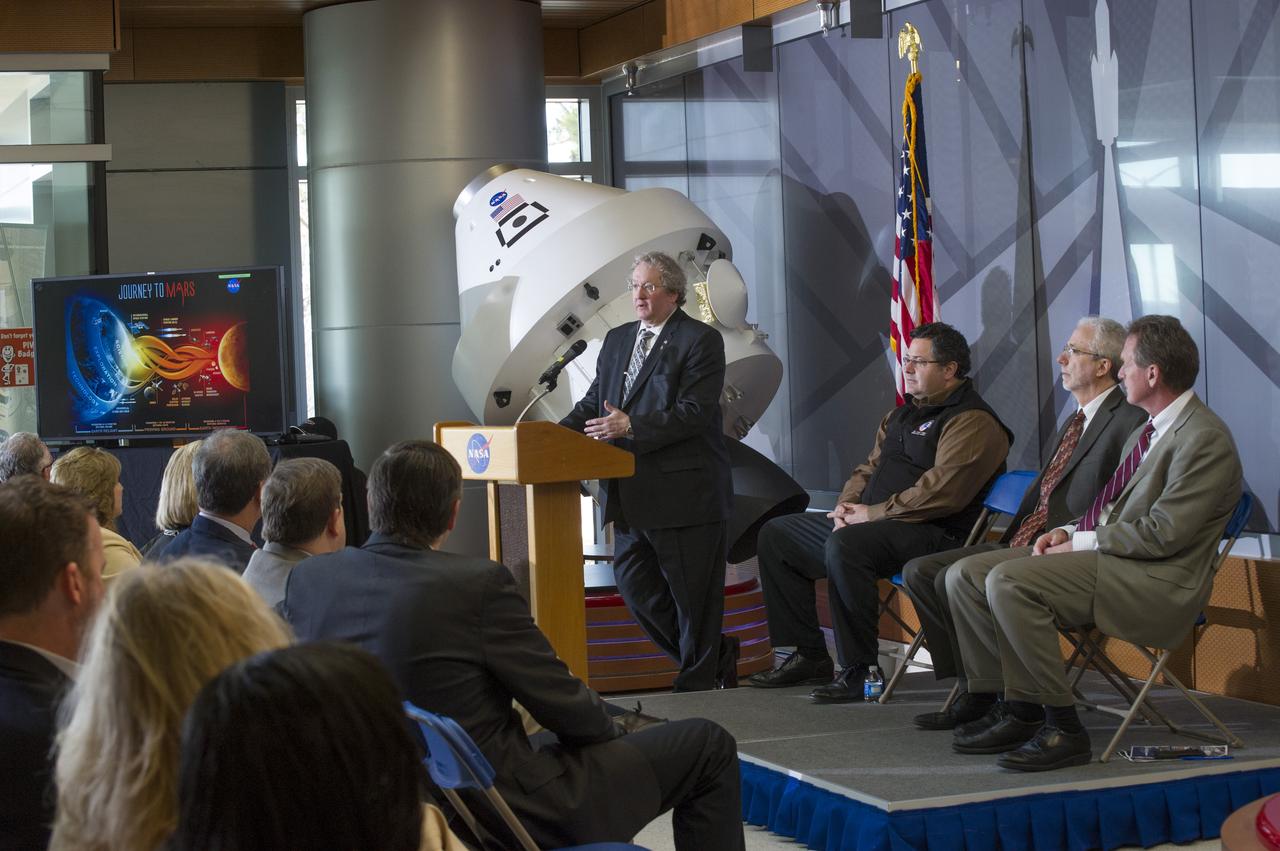
MARK GEYER ADDRESSES AUDIENCE AT SLS ALL HANDS
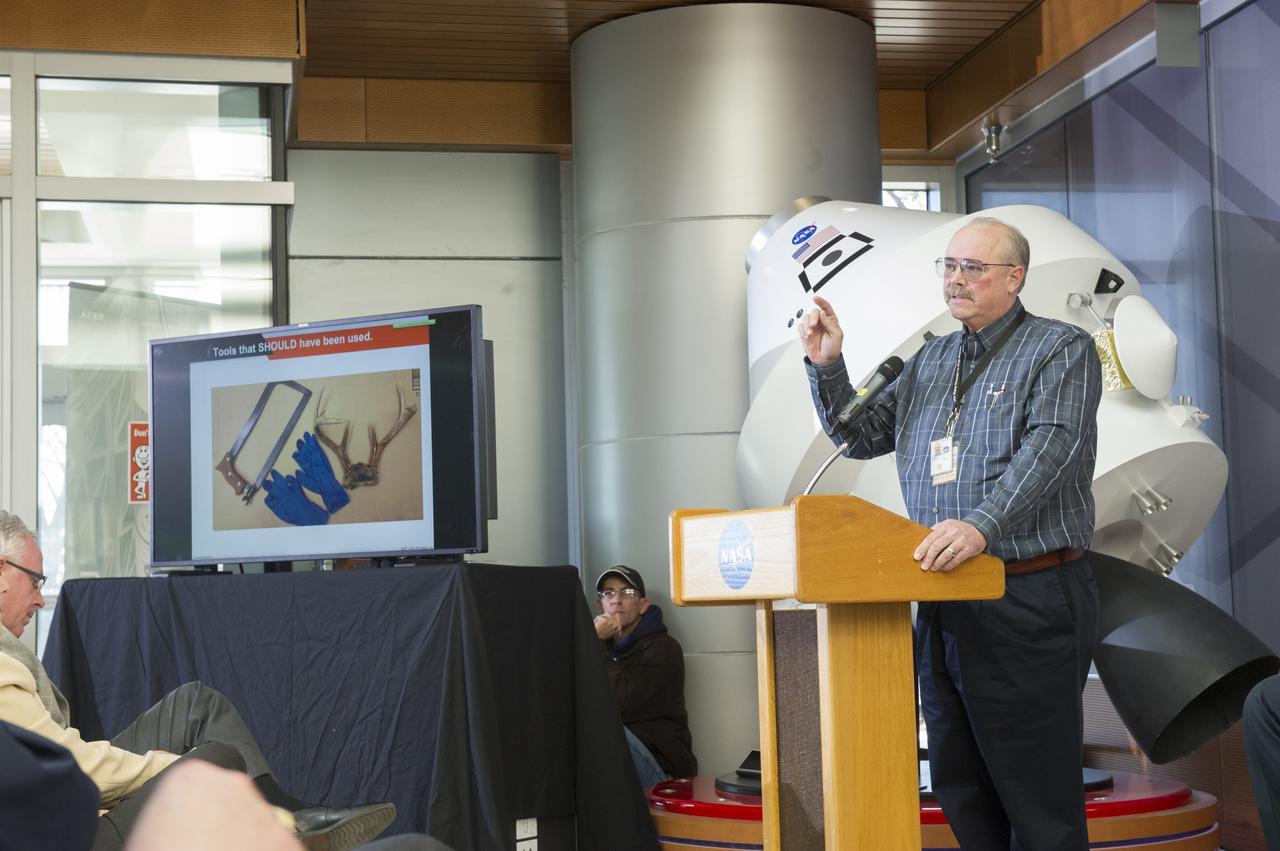

RICK BURT PRESENTS SAFETY MOMENT AT SLS ALL HANDS
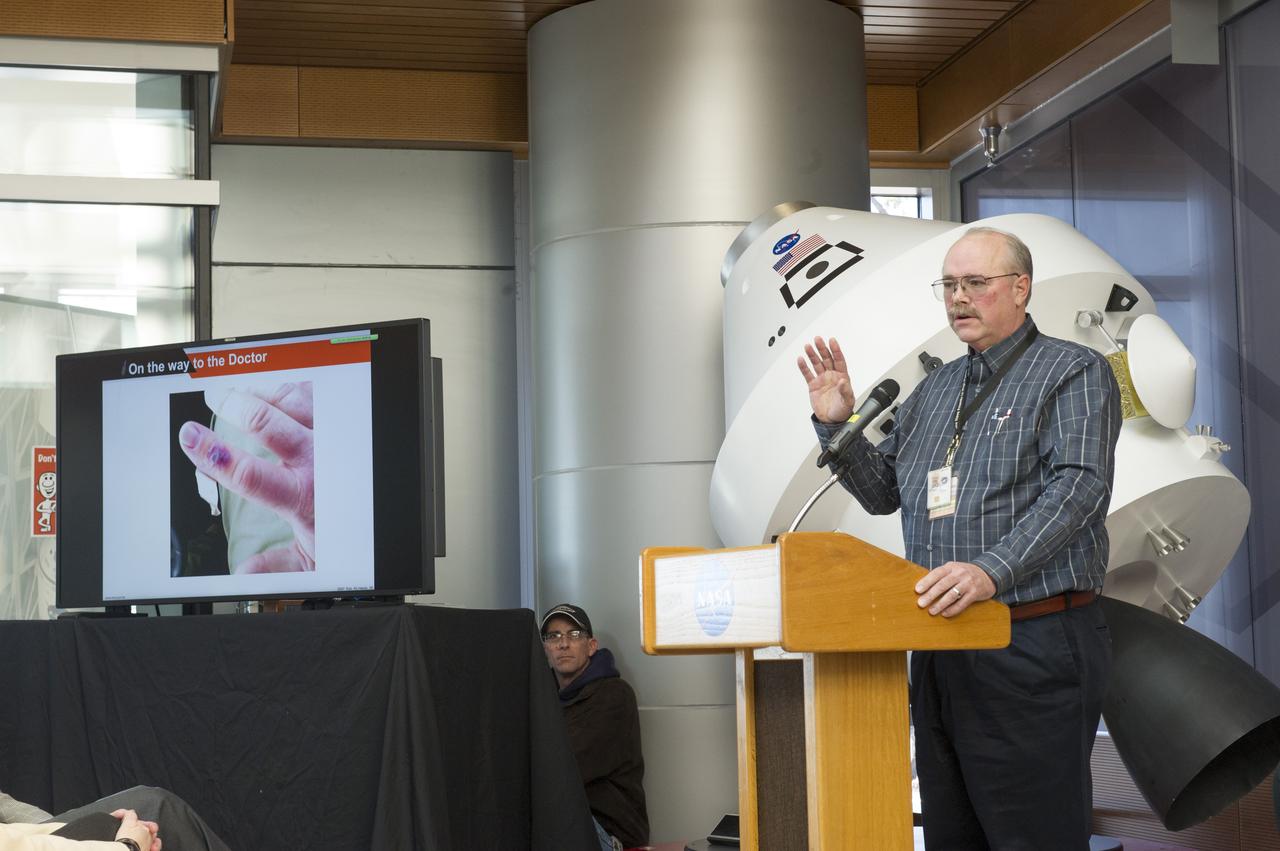

RICK BURT PRESENTS SAFETY MOMENT AT SLS ALL HANDS
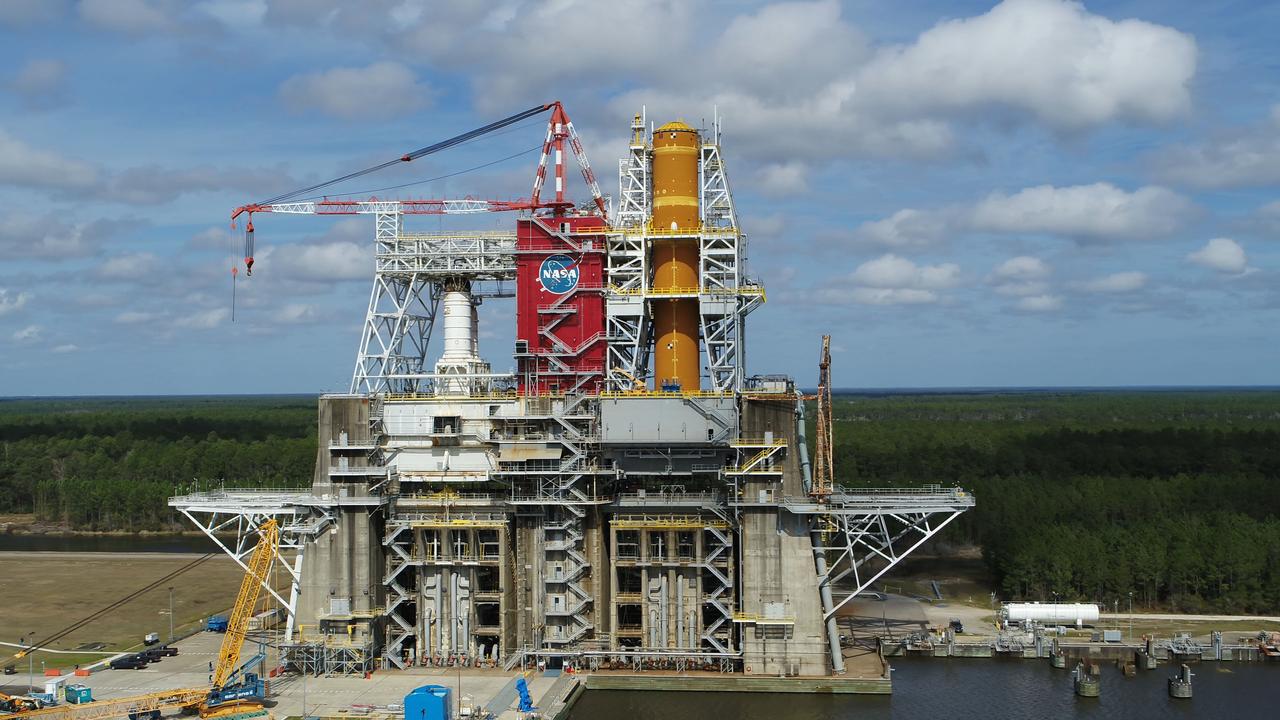
A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
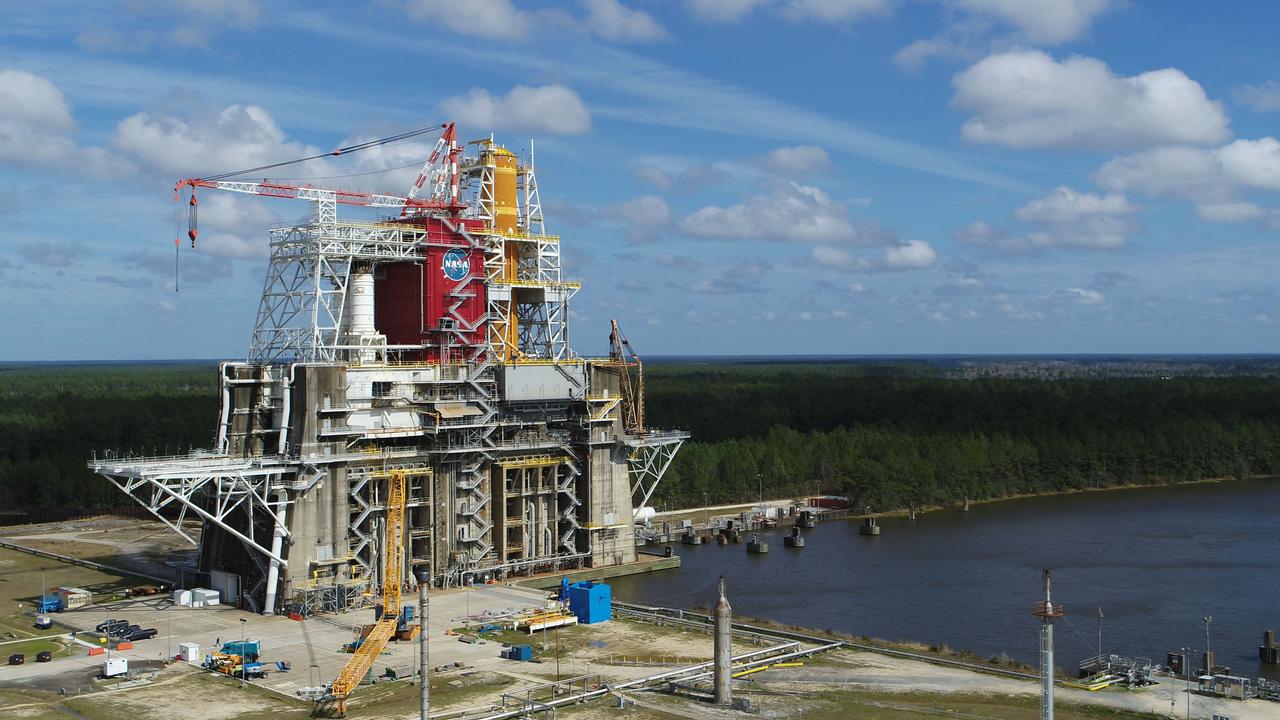

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
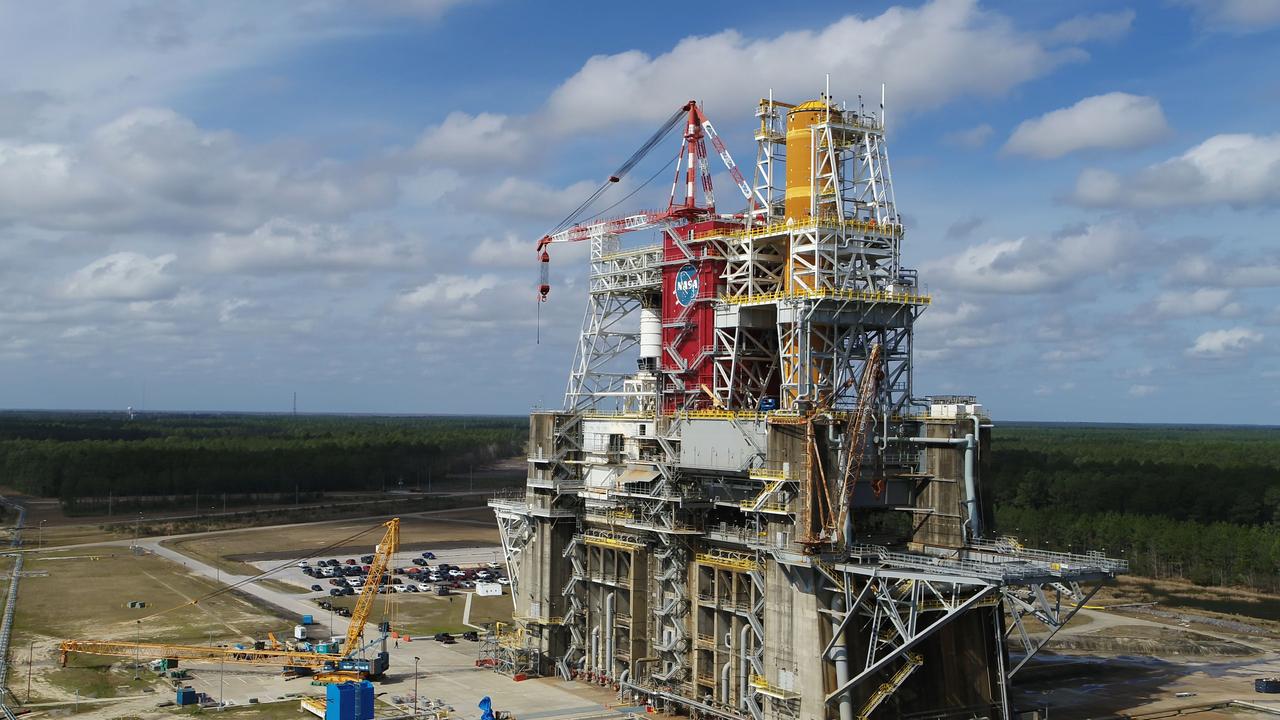

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.
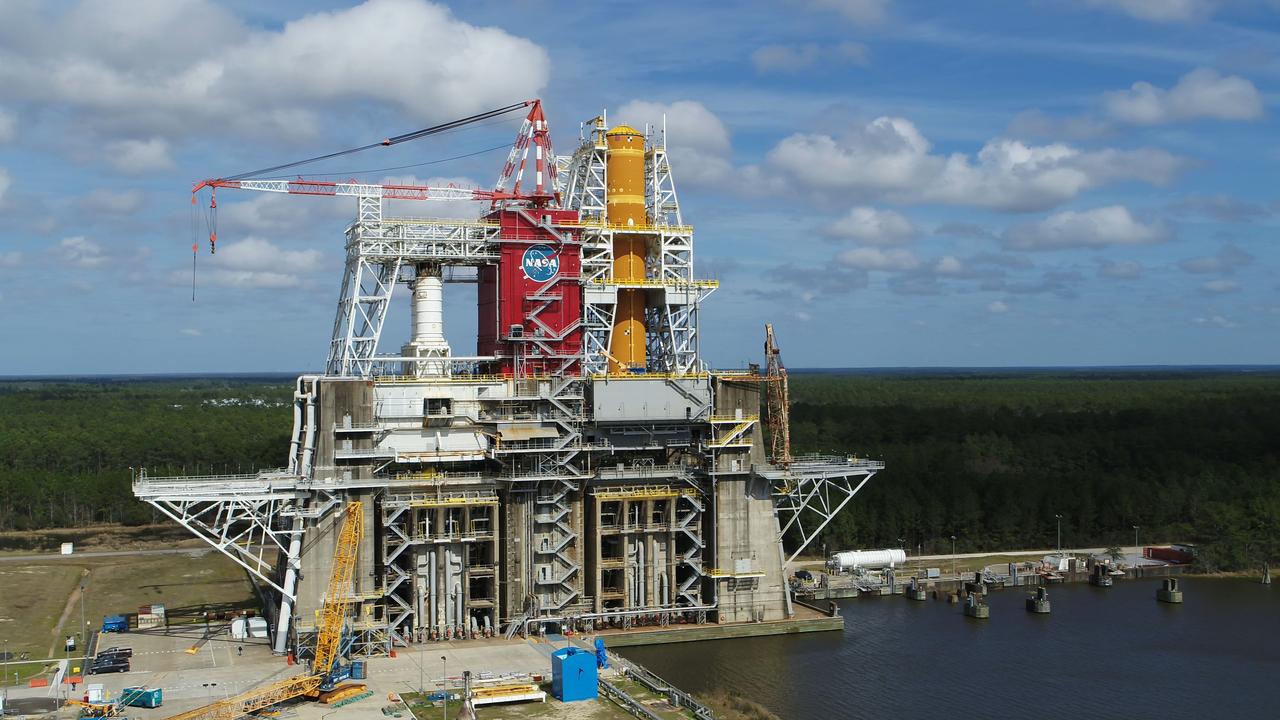

A NASA drone photo offers a bird’s-eye view of the B-2 Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center with the first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System (SLS) installed for Green Run testing. The SLS core stage is undergoing a series of tests on its integrated systems prior to its use on the Artemis I mission. NASA is building SLS to return humans, including the first woman, to the Moon as part of the Artemis program and to prepare for eventual missions to Mars. The Green Run series at Stennis culminates with a hot fire of the core stage’s four RS-25 engines, just as during an actual launch.

TODD MAY (SEATED) AND MEMBERS OF THE SLS CDR BOARD.

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND WITH CONSTRUCTION CREW

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND WITH CONSTRUCTION CREW
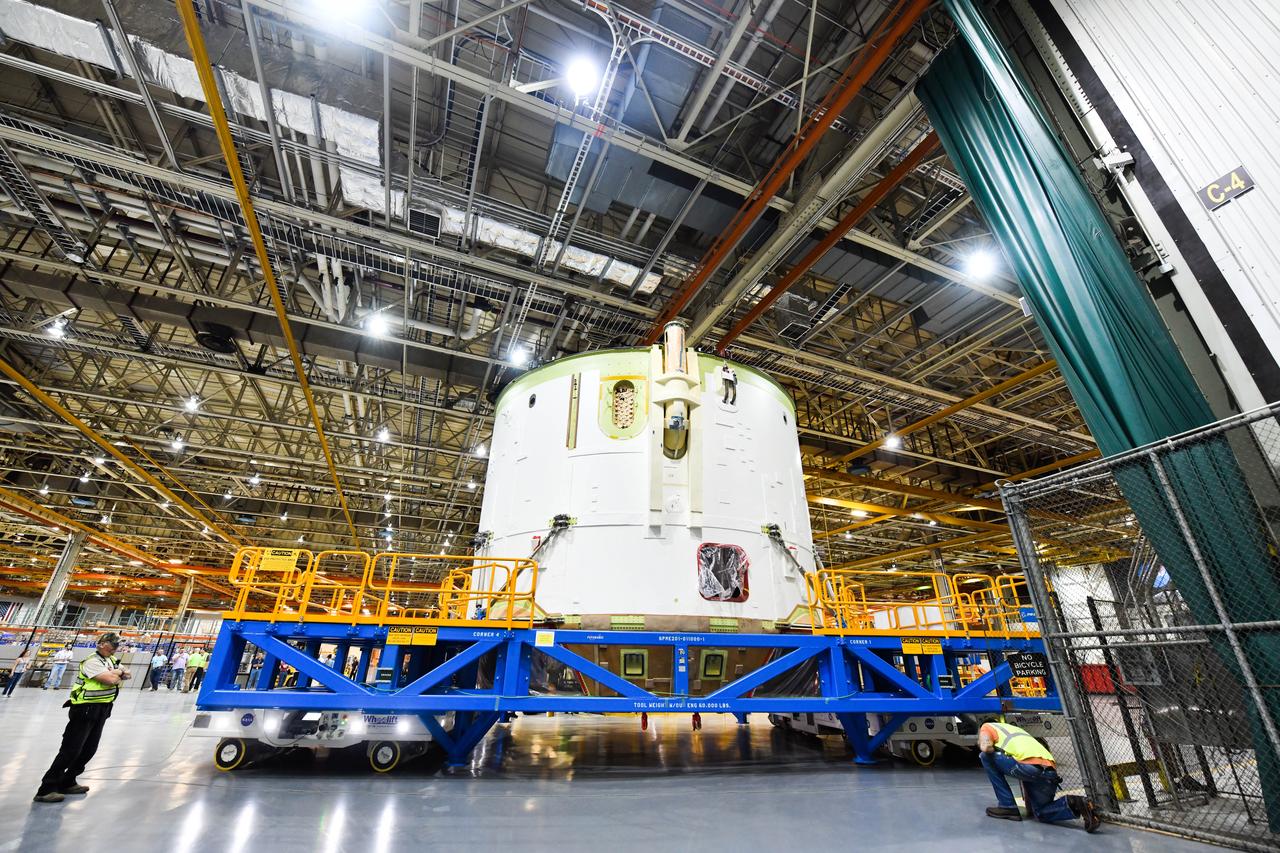

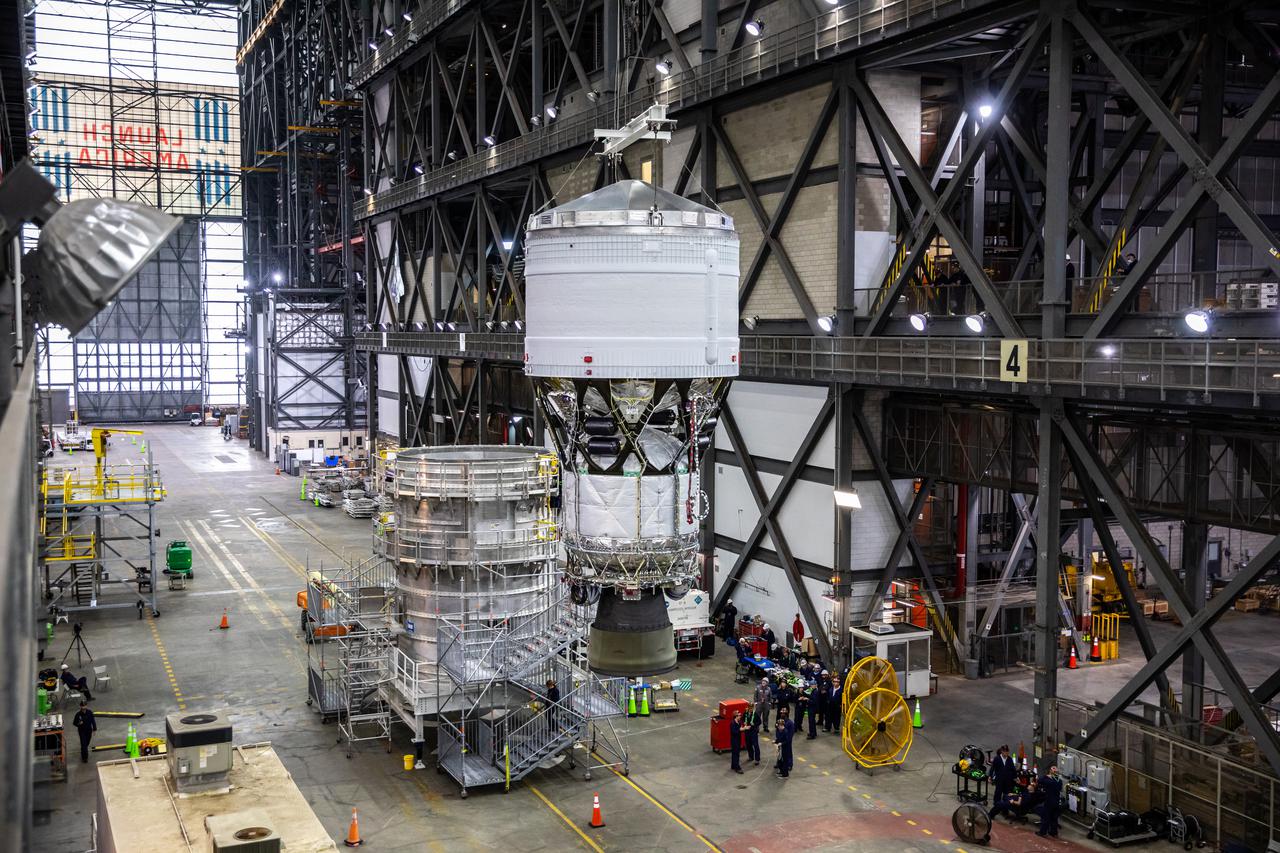
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
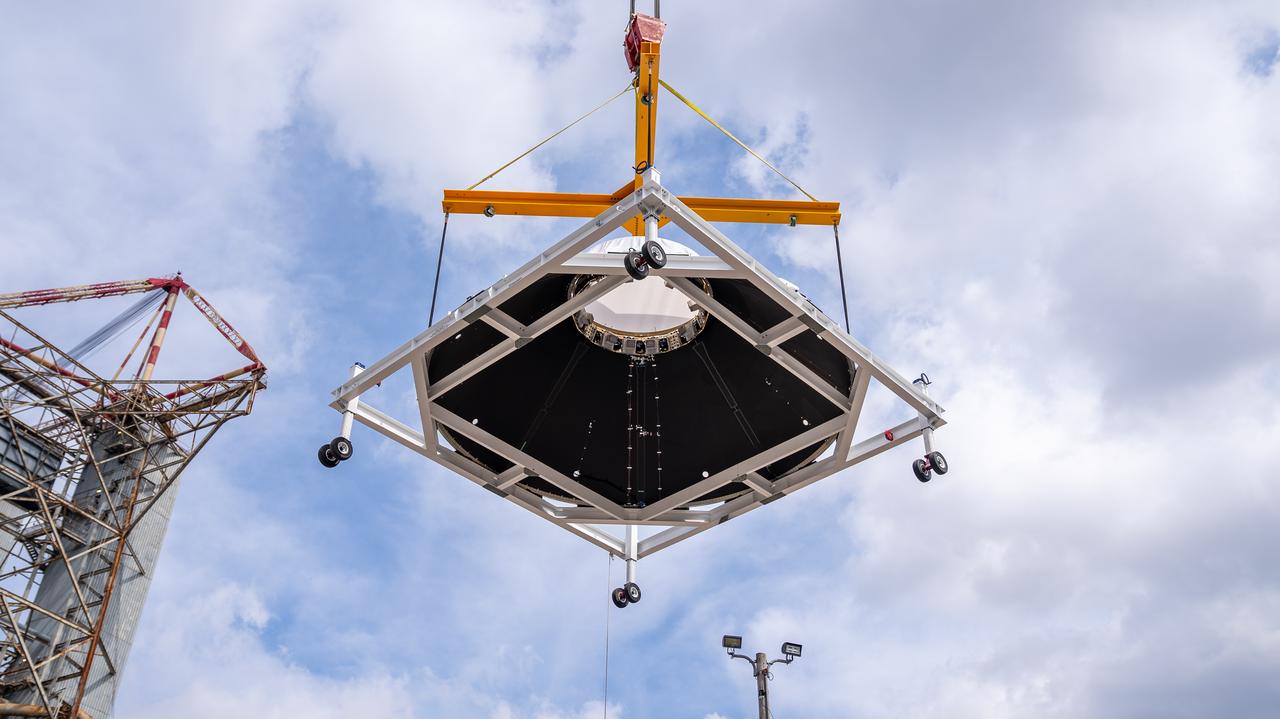

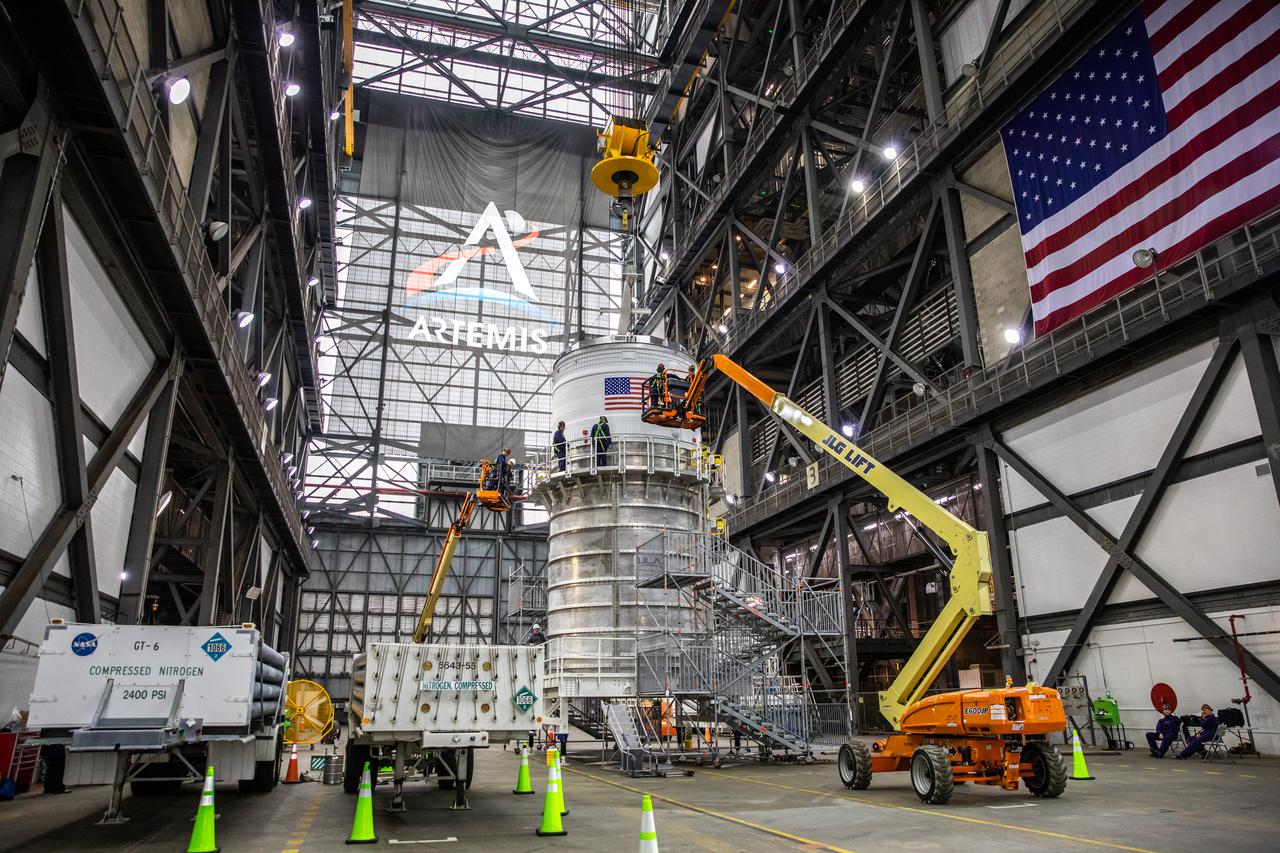
Crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13.
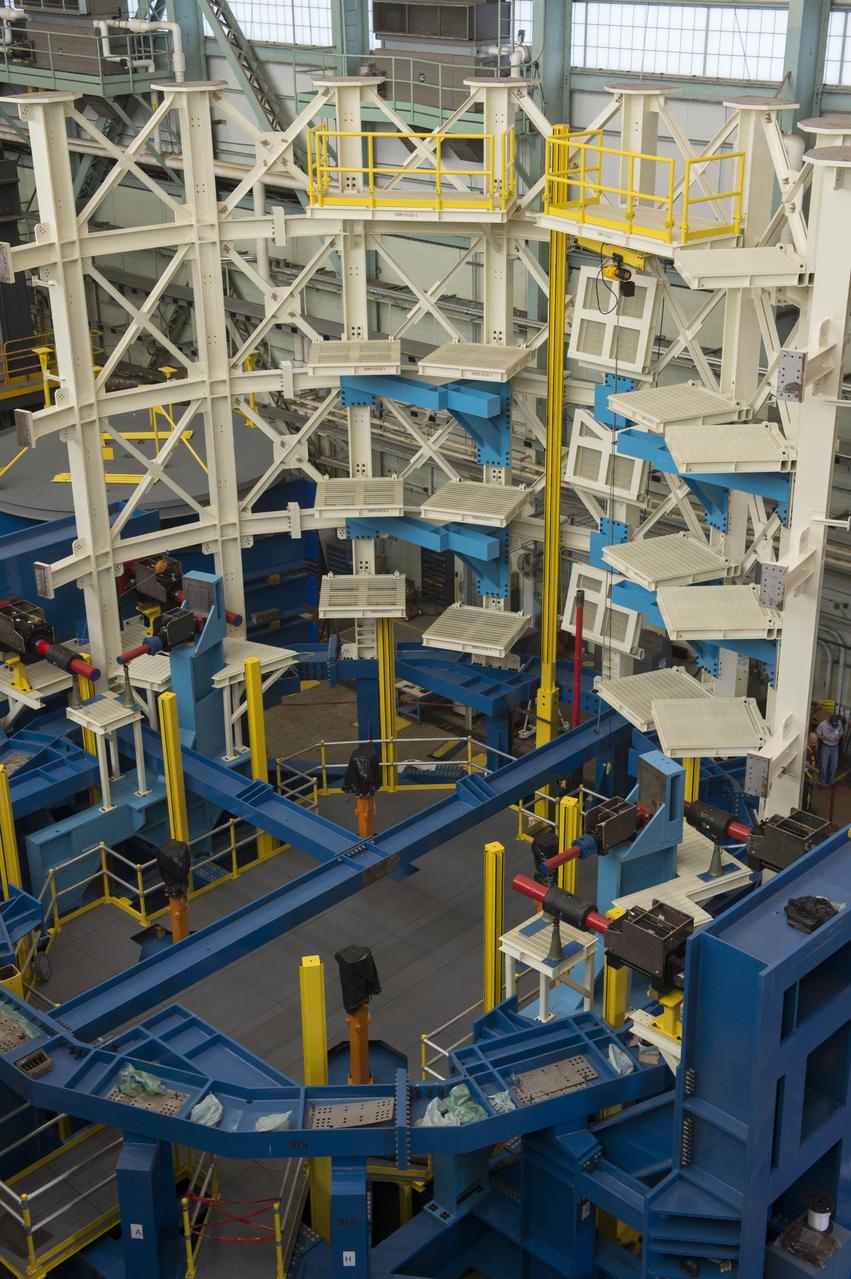

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND READY FOR STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE
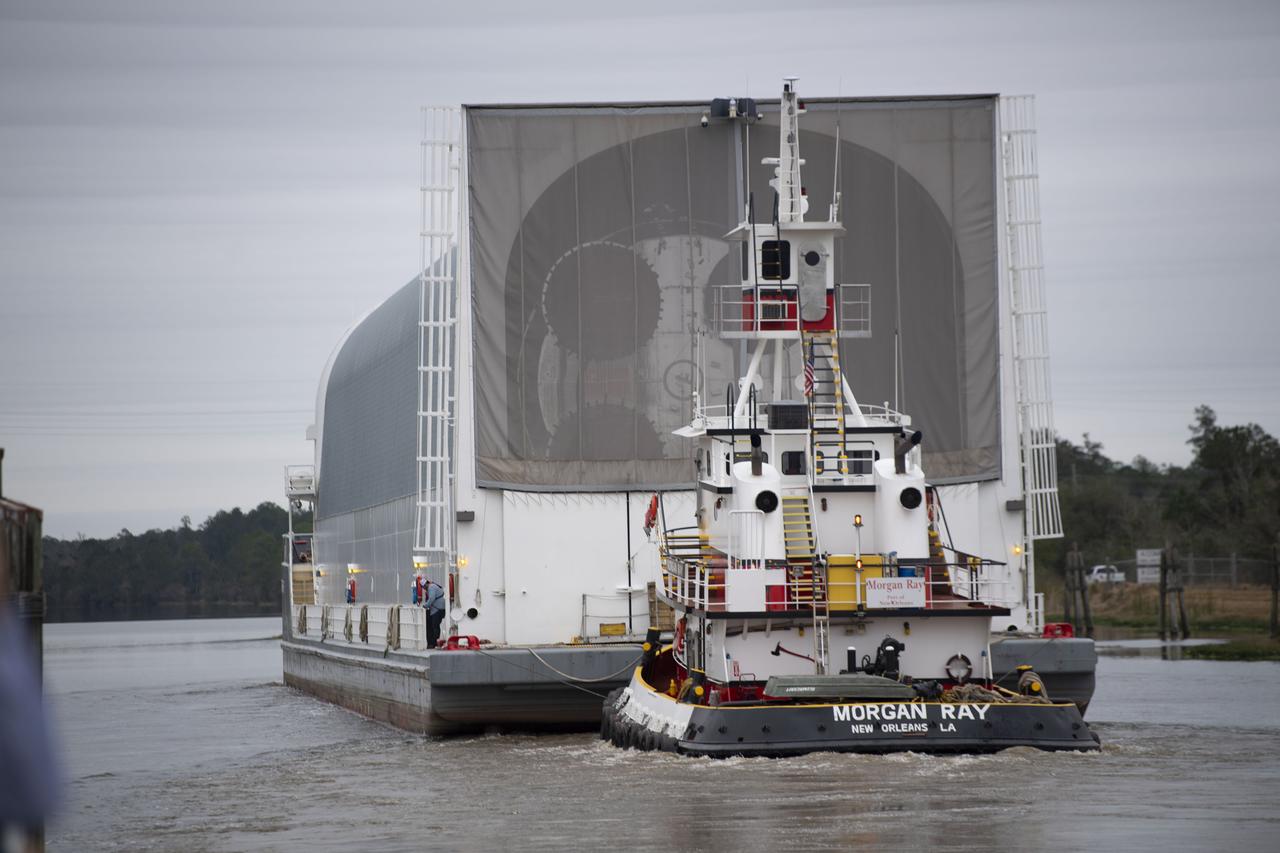

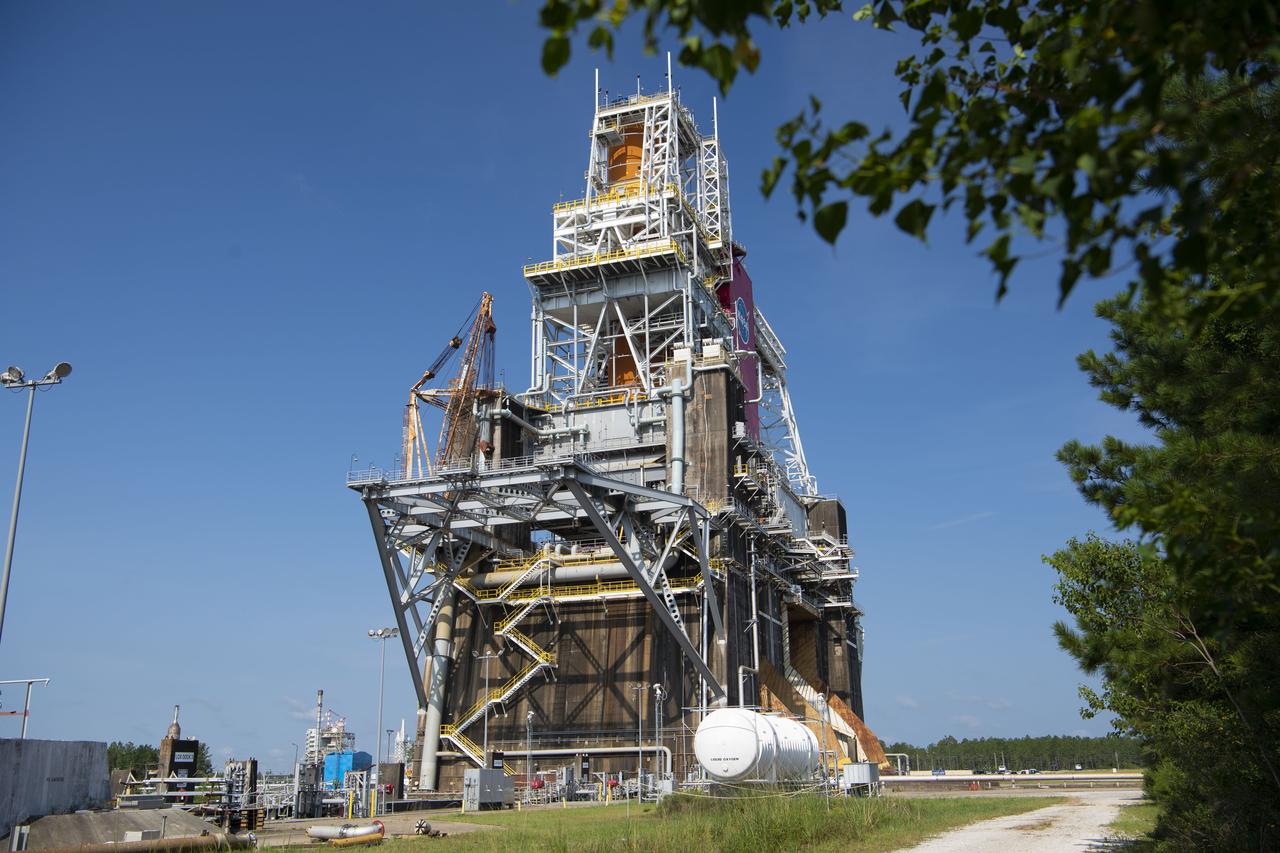
The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.
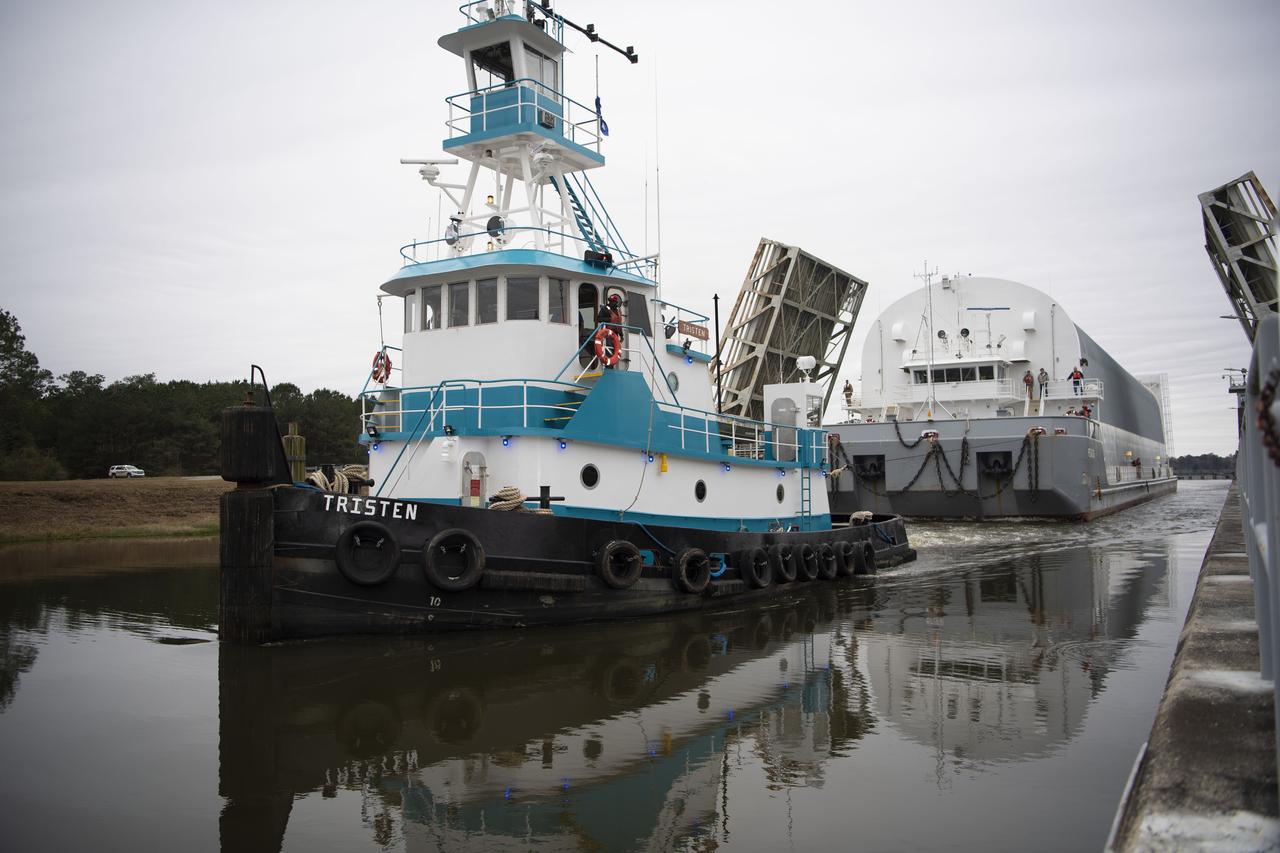

The first flight core stage for NASA’s new Space Launch System rocket arrived at Stennis Space Center on Jan. 12 for a series of tests prior to its maiden Artemis I flight. The core stage was transported from Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to the B-2 Test Stand dock at Stennis aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Soon after arrival, the stage was rolled off of Pegasus onto the B-2 Test Stand tarmac. After the stage is lifted and installed on the B-2 stand, it will undergo a series of “Green Run” systems test that represent the first integrated testing of its sophisticated systems.
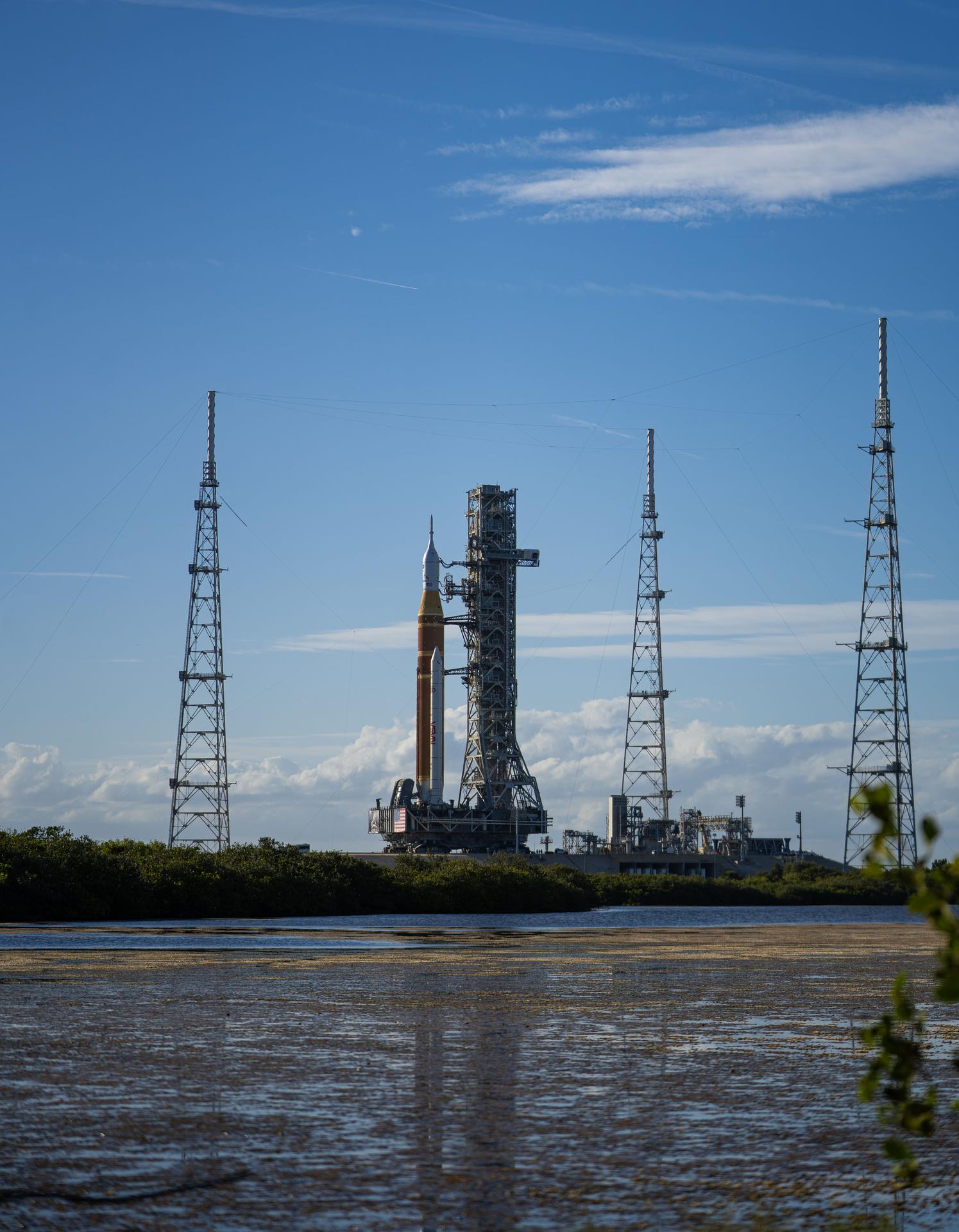

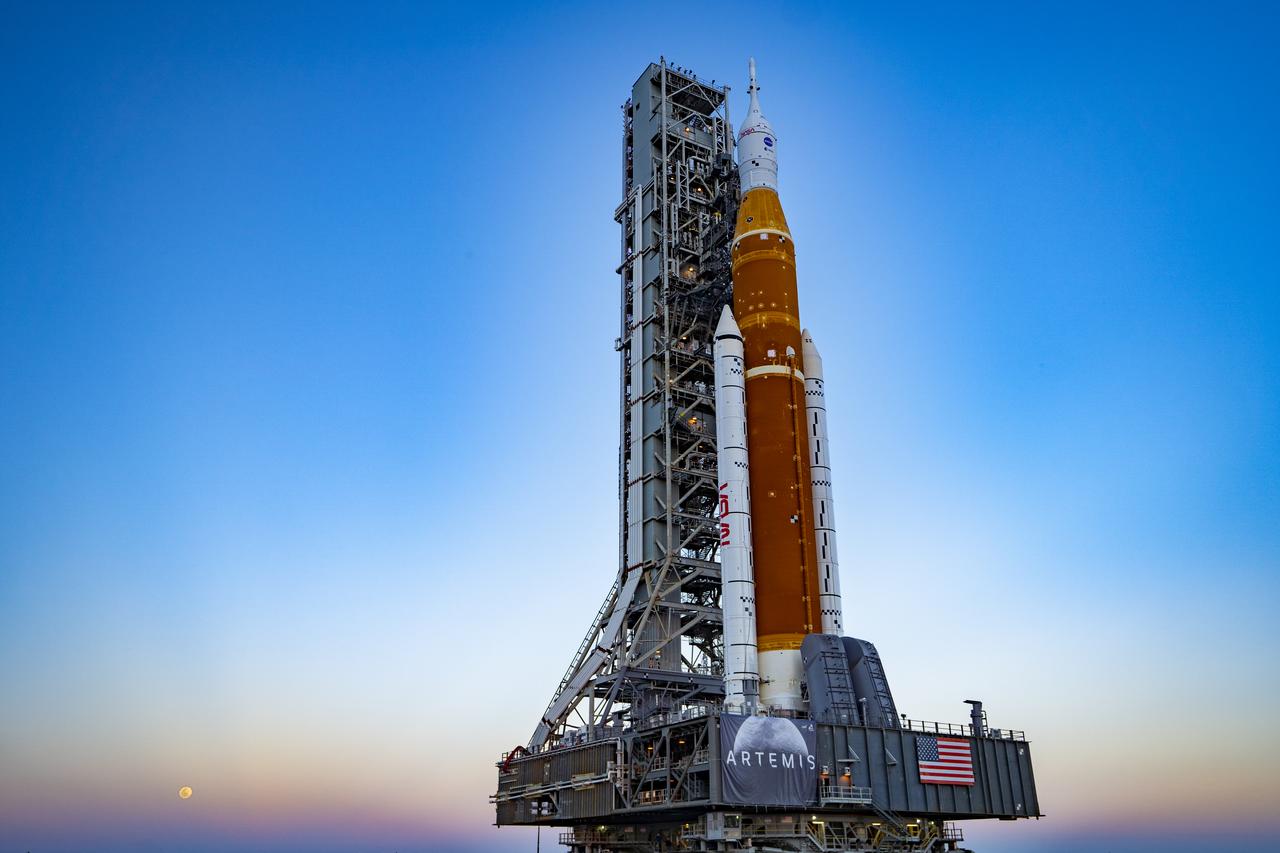
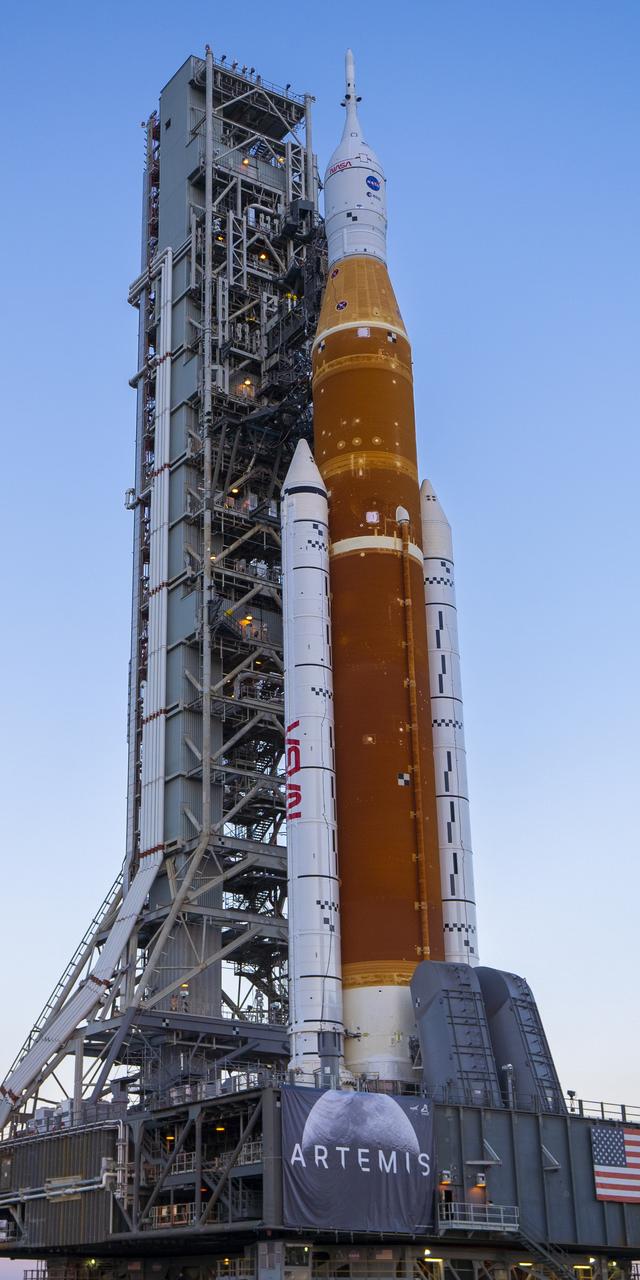
This image shows NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
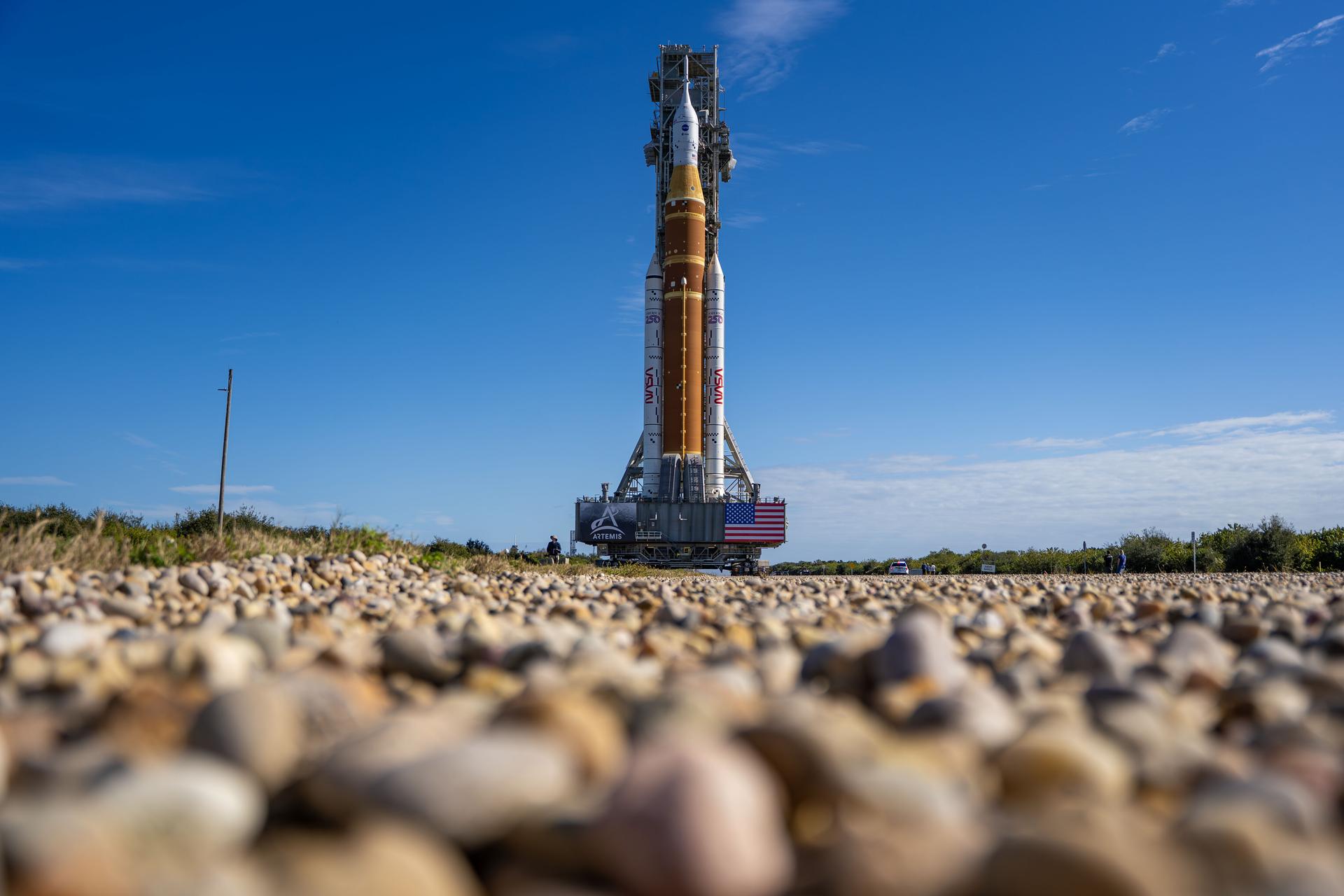

These images and video show NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) and Orion spacecraft rolling out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. NASA's massive Crawler-Transporter, upgraded for the Artemis program, carries the powerful SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on the Mobile Launcher from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

JONATHAN LOOSER, SLS CORE STAGE PROPULSION LEAD AT NASA’S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA

Photo shows how the Space Launch Sysetm (SLS) rocket liquid oxygen tank failed during a structural qualification test at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The photos show both the water flowing from the tank as it ruptured and the resultant tear left in the tank when it buckled during the test. Engineers pushed the liquid oxygen structural test article to the limits on purpose. The tank is a test article that is identical to tanks that are part of the SLS core stage that will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket on the Artemis missions to the Moon. During the test, hydraulic cylinders were then calibrated and positioned along the tank to apply millions of pounds of crippling force from all sides while engineers measured and recorded the effects of the launch and flight forces. For the test, water used to simulate the liquid oxygen flows out of the tank after it ruptures. The structural test campaign was conducted on the rocket to ensure the SLS rocket’s structure can endure the rigors of launch and safely send astronauts to the Moon on the Artemis missions. For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/nasa-completes-artemis-sls-structural-testing-campaign.html

Photo shows how the Space Launch Sysetm (SLS) rocket liquid oxygen tank failed during a structural qualification test at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The photos show both the water flowing from the tank as it ruptured and the resultant tear left in the tank when it buckled during the test. Engineers pushed the liquid oxygen structural test article to the limits on purpose. The tank is a test article that is identical to tanks that are part of the SLS core stage that will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket on the Artemis missions to the Moon. During the test, hydraulic cylinders were then calibrated and positioned along the tank to apply millions of pounds of crippling force from all sides while engineers measured and recorded the effects of the launch and flight forces. For the test, water used to simulate the liquid oxygen flows out of the tank after it ruptures. The structural test campaign was conducted on the rocket to ensure the SLS rocket’s structure can endure the rigors of launch and safely send astronauts to the Moon on the Artemis missions. For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/nasa-completes-artemis-sls-structural-testing-campaign.html

Photo shows how the Space Launch Sysetm (SLS) rocket liquid oxygen tank failed during a structural qualification test at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The photos show both the water flowing from the tank as it ruptured and the resultant tear left in the tank when it buckled during the test. Engineers pushed the liquid oxygen structural test article to the limits on purpose. The tank is a test article that is identical to tanks that are part of the SLS core stage that will produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket on the Artemis missions to the Moon. During the test, hydraulic cylinders were then calibrated and positioned along the tank to apply millions of pounds of crippling force from all sides while engineers measured and recorded the effects of the launch and flight forces. For the test, water used to simulate the liquid oxygen flows out of the tank after it ruptures. The structural test campaign was conducted on the rocket to ensure the SLS rocket’s structure can endure the rigors of launch and safely send astronauts to the Moon on the Artemis missions. For more information: https://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls/nasa-completes-artemis-sls-structural-testing-campaign.html
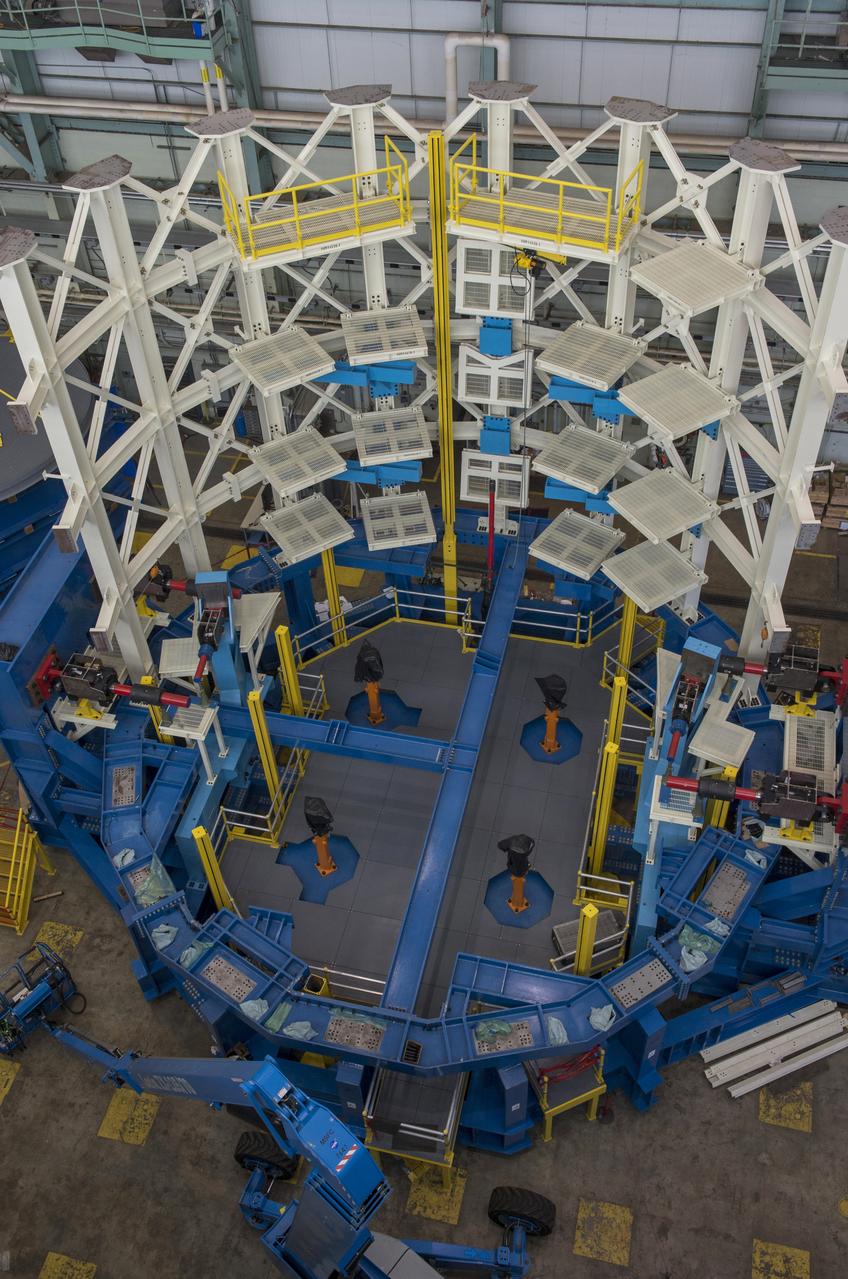

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND READY FOR STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE
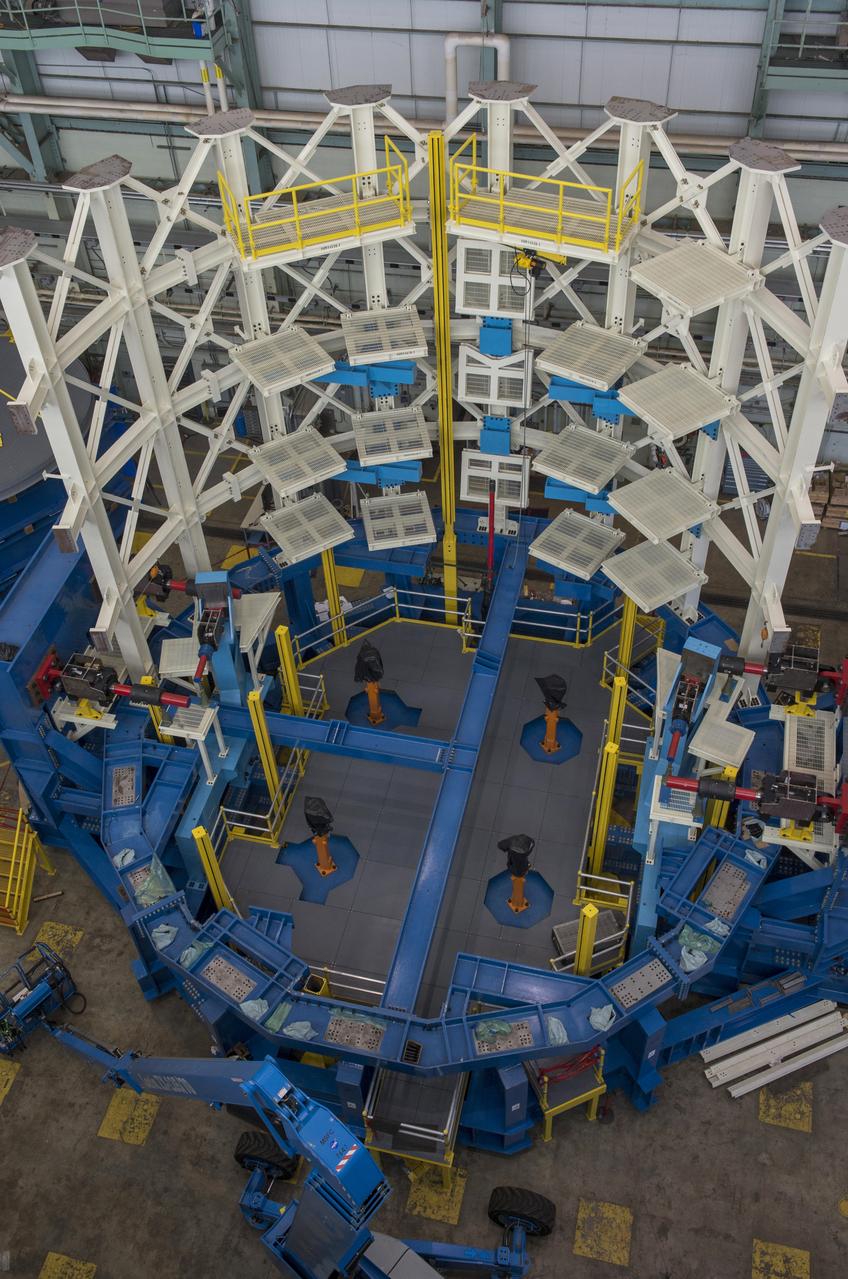

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND READY FOR STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE
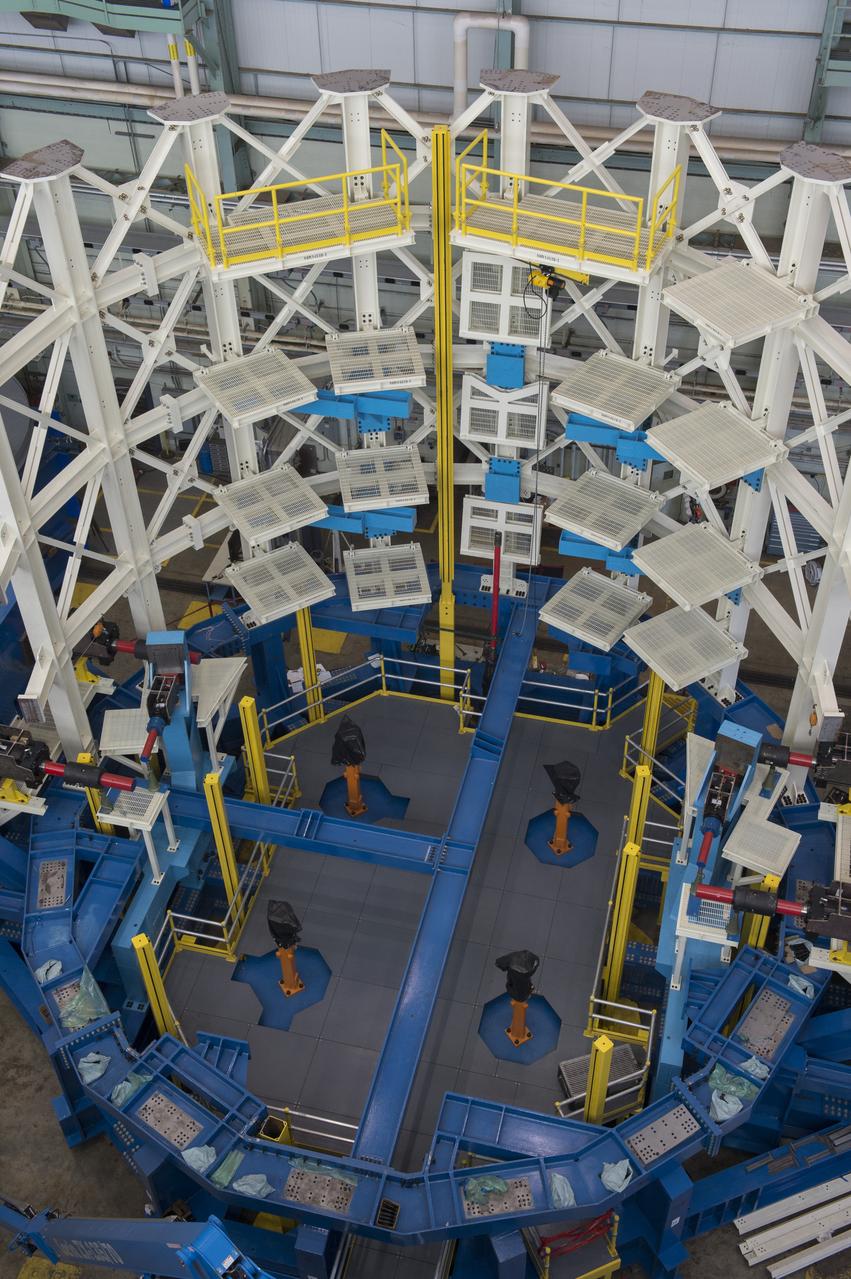

SLS ENGINE SECTION TEST STAND READY FOR STRUCTURAL TEST ARTICLE

NASA ADMINISTRATOR BOLDEN GETS SLS HARDWARE UPDATE FROM ANDY SCHORR
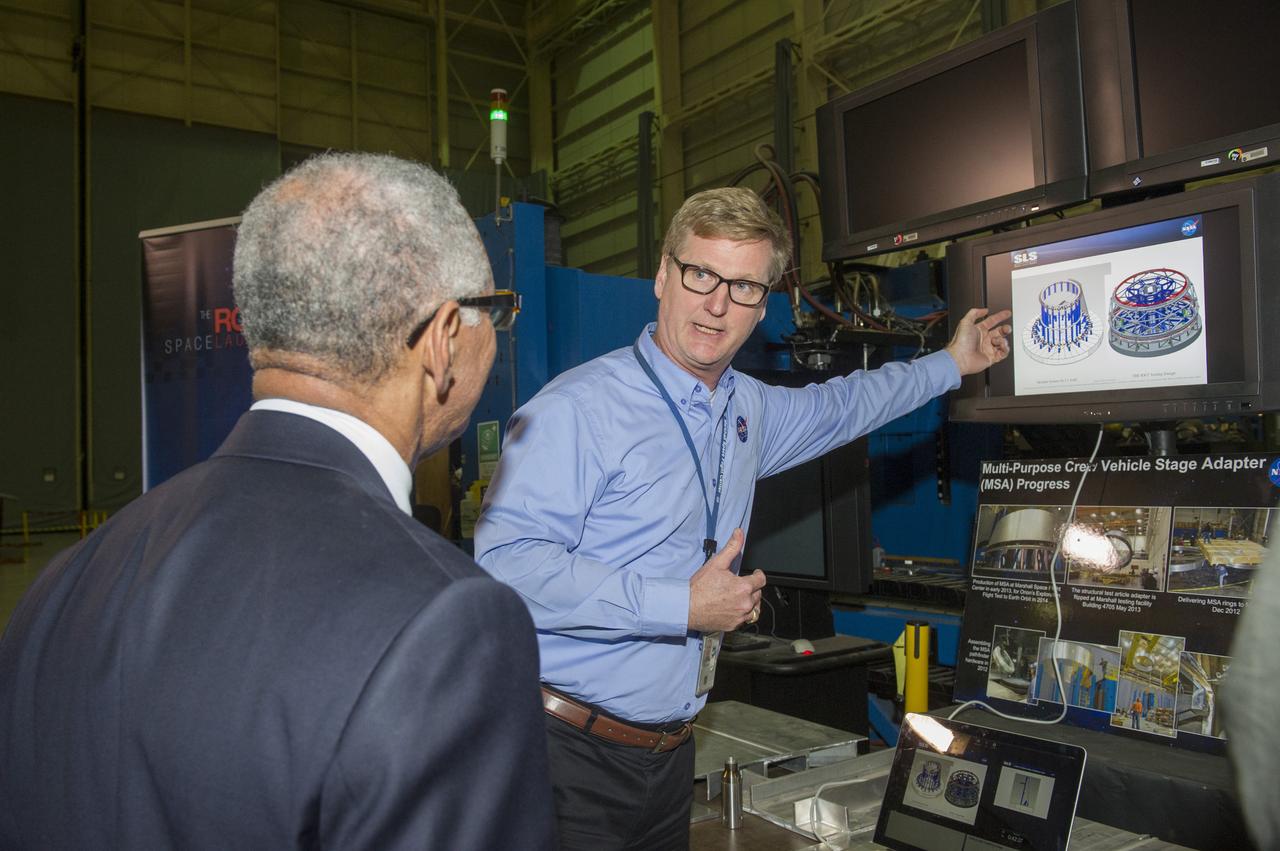

NASA ADMINISTRATOR BOLDEN GETS SLS HARDWARE UPDATE FROM JOHN STREET
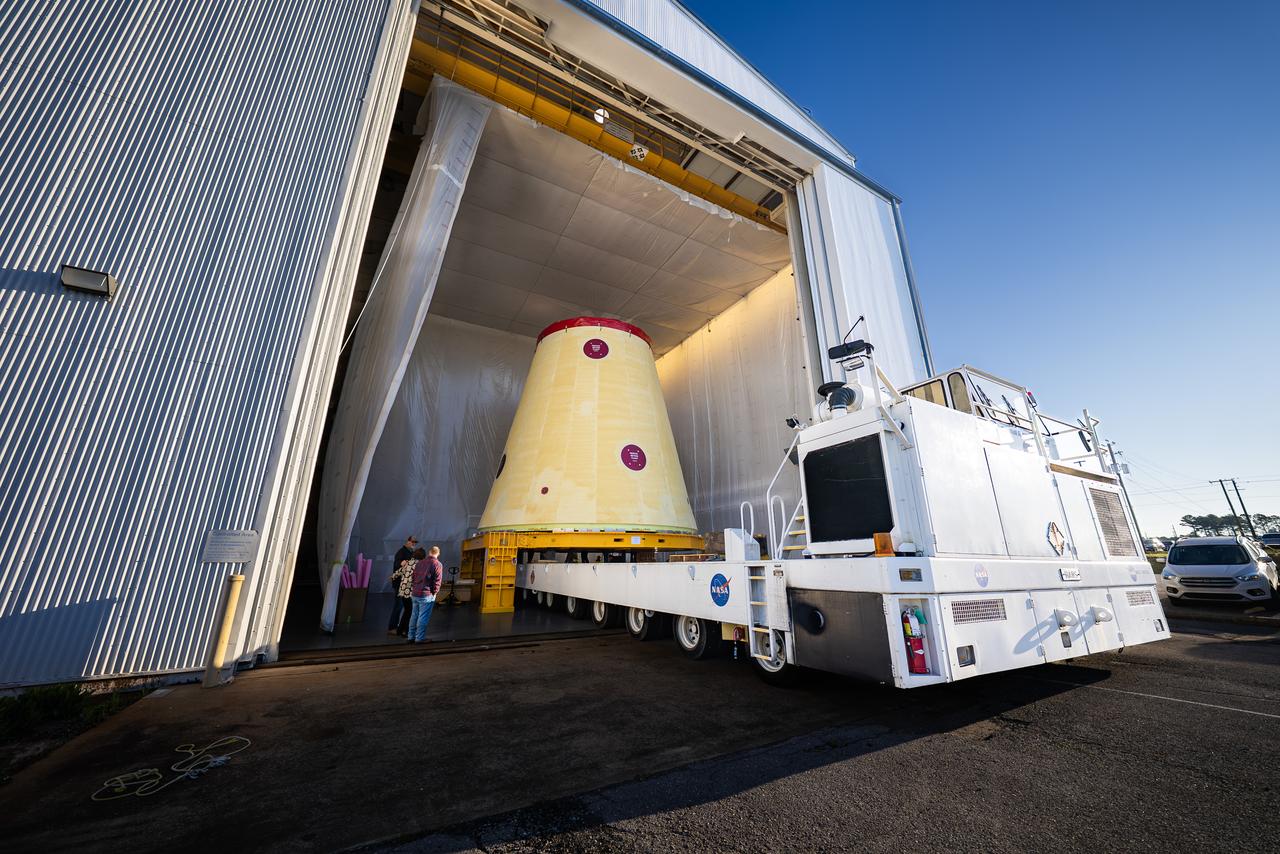

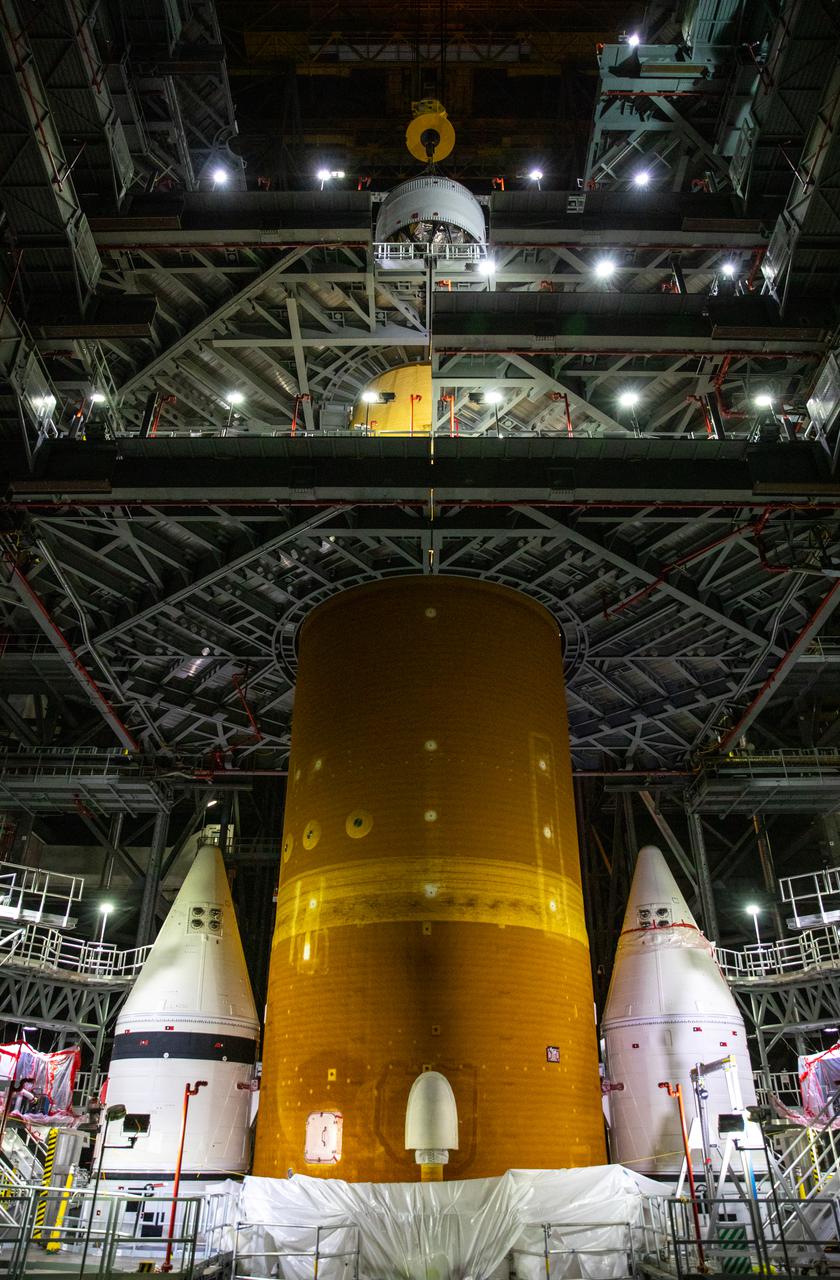
These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
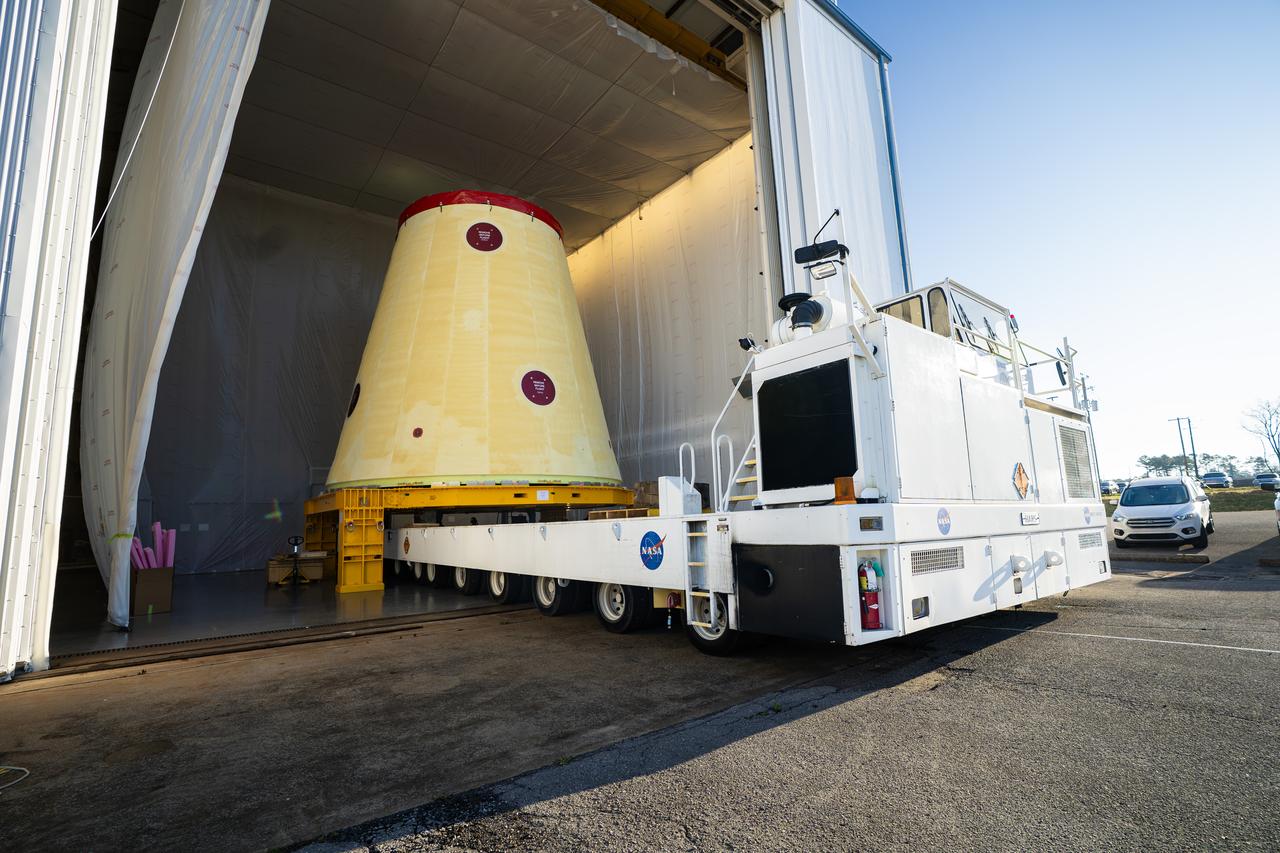

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
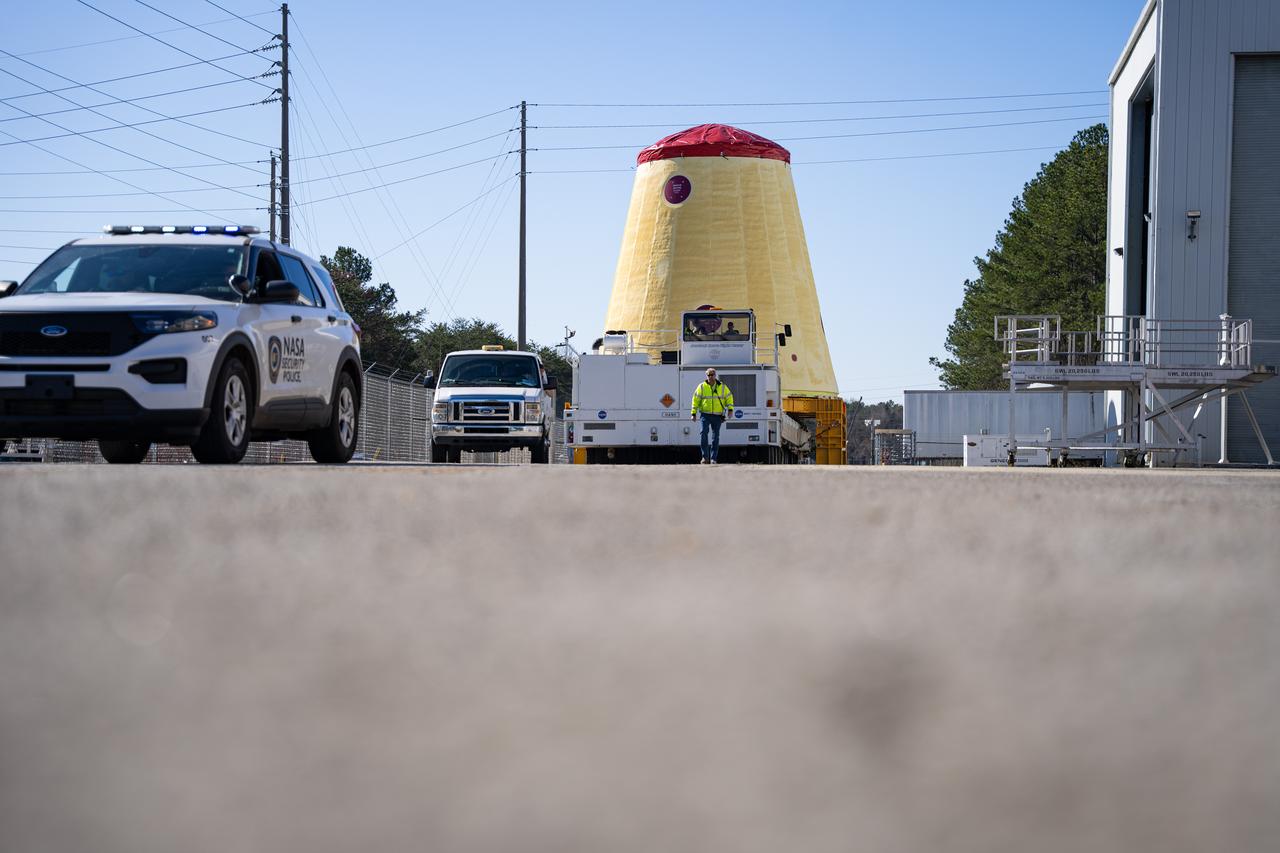

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708, where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
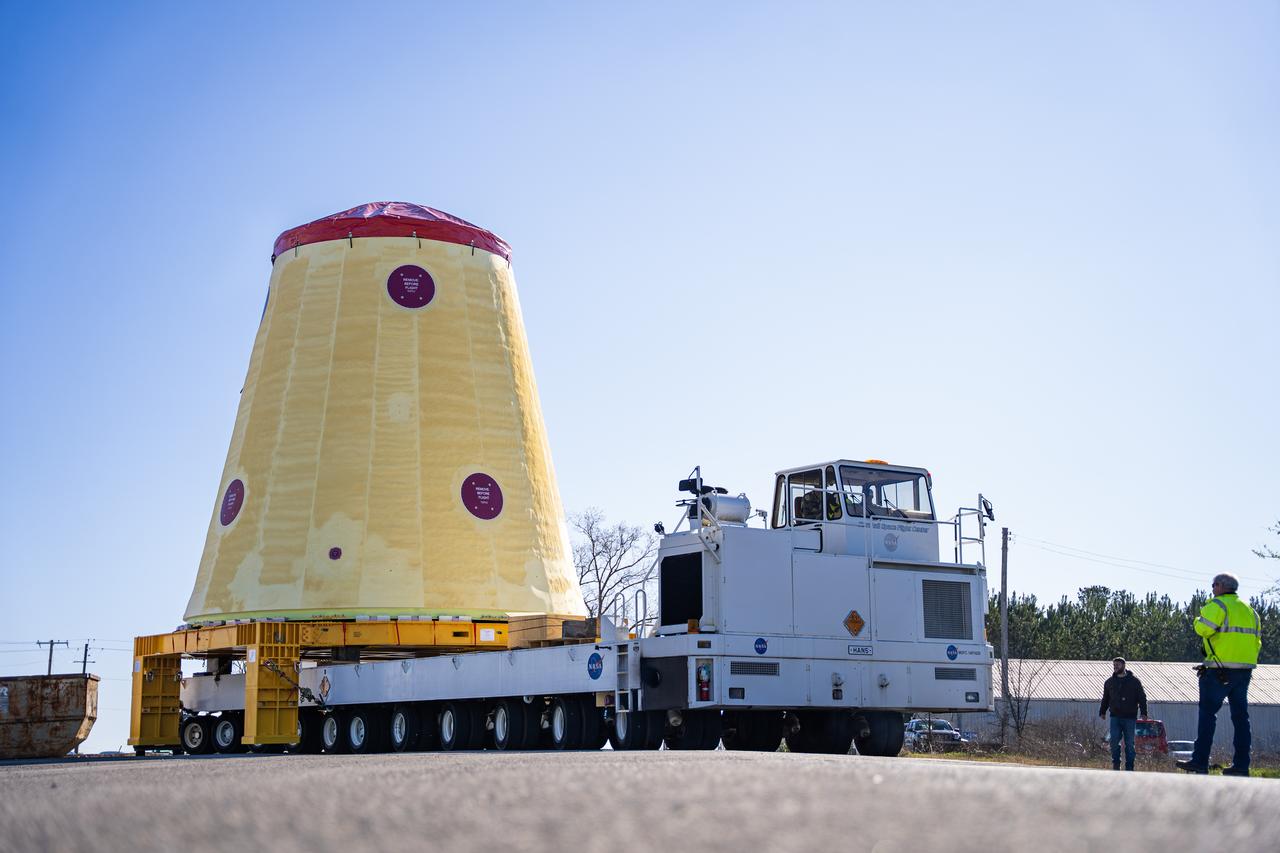

These images and videos show technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, March 17, 2025, moving the completed launch vehicle stage adapter for Artemis III from Building 4649 to Building 4708 where it will remain until it is time to ship the hardware to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cone-shaped hardware connects the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to the upper stage, the interim cryogenic propulsion stage, and protects the rocket’s flight computers, avionics, and electrical devices during launch and ascent during the Artemis missions.
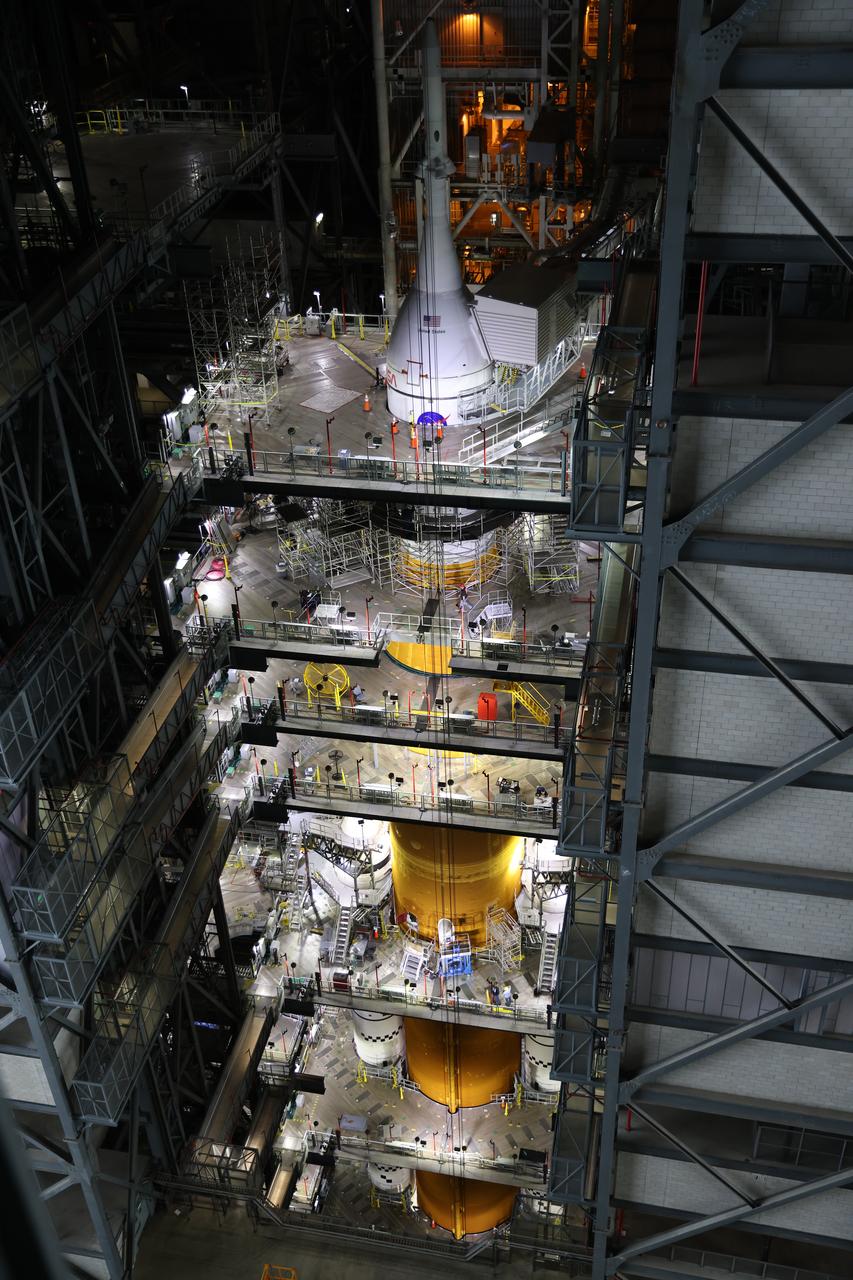

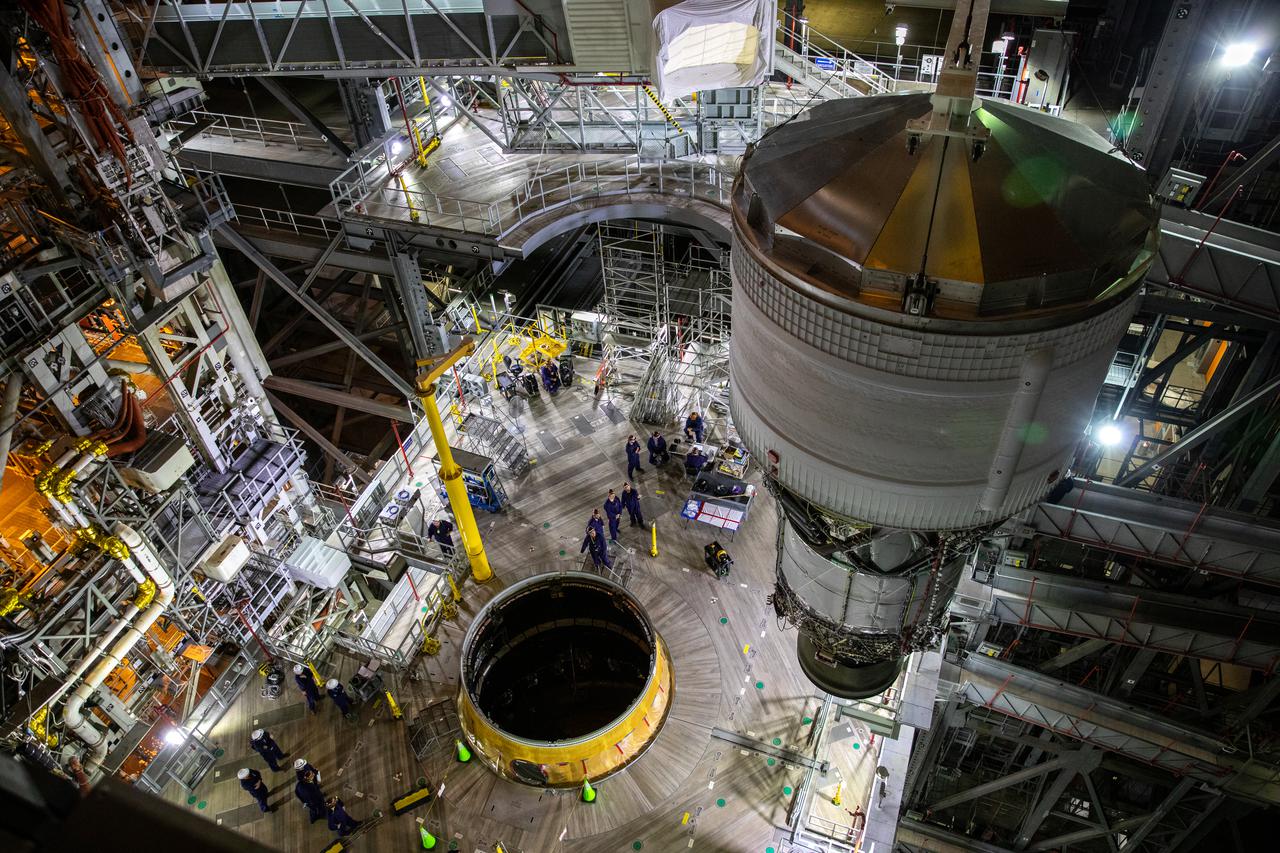
In a view from above, NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Artemis I are in High Bay 3 inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 3, 2022. Work platforms surround the SLS and Orion stack. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
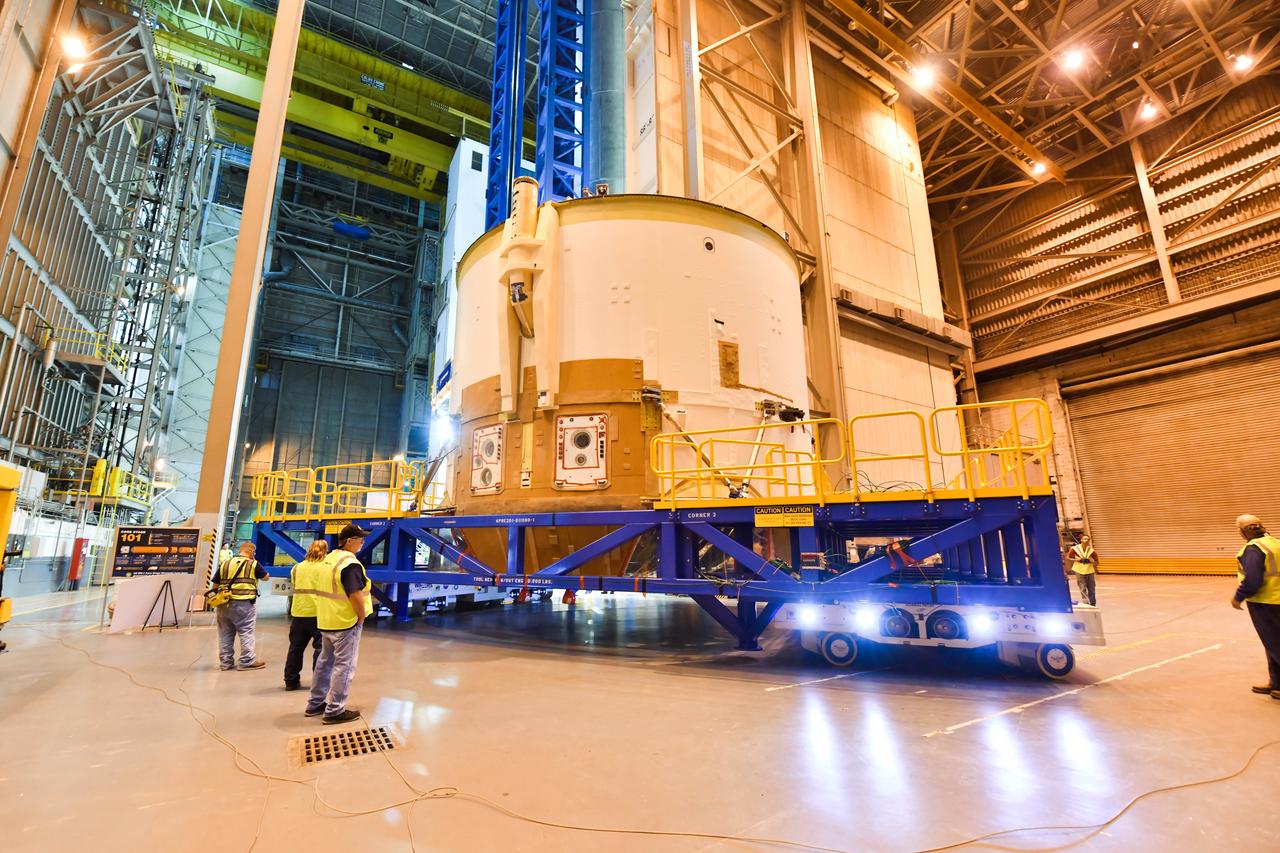

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
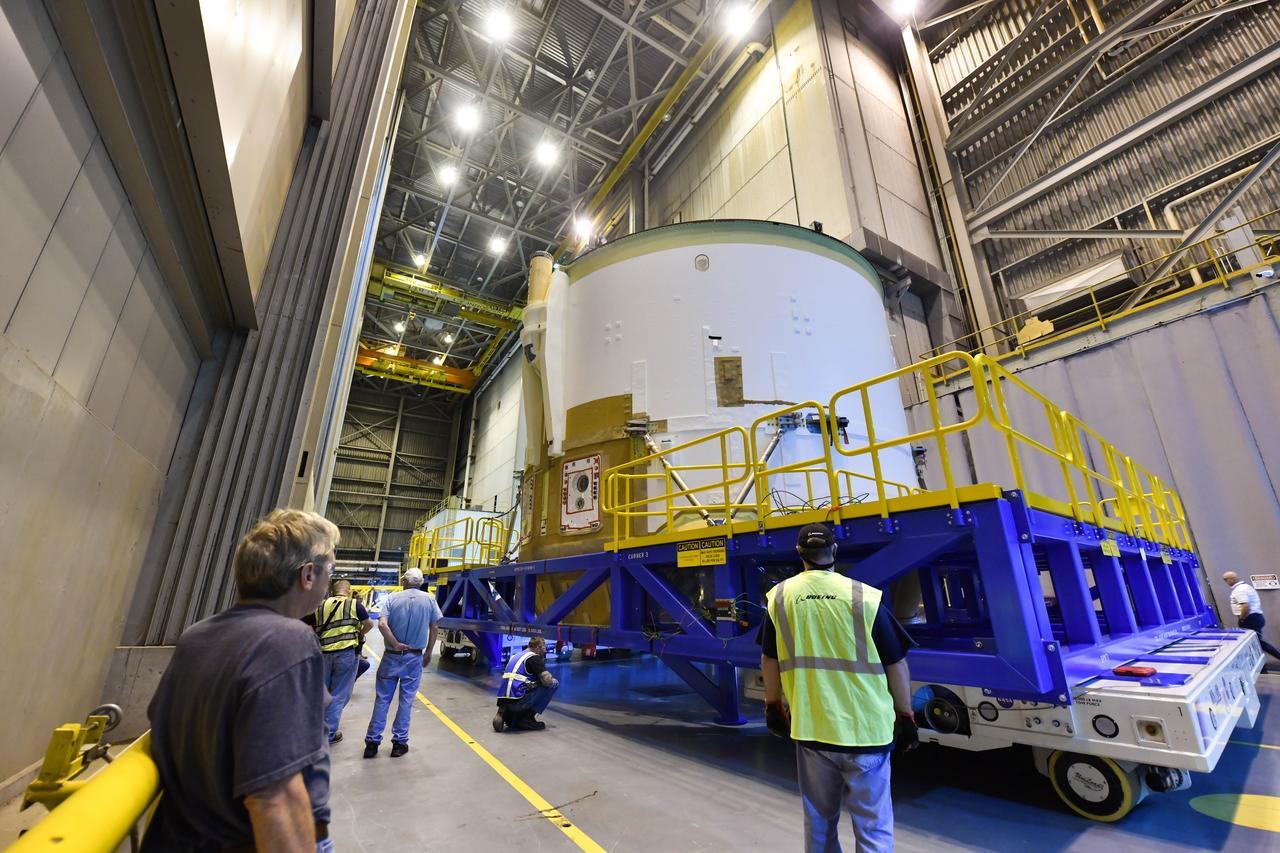

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
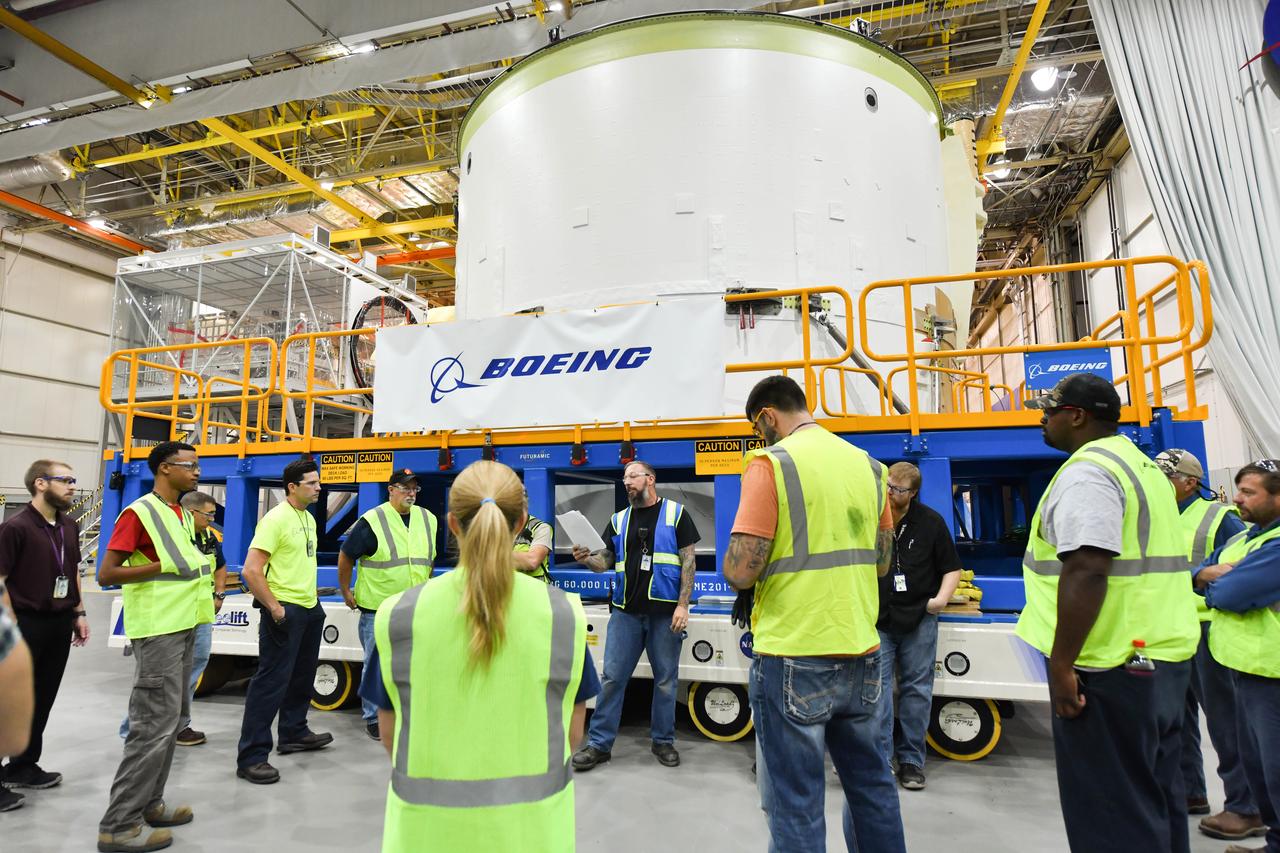

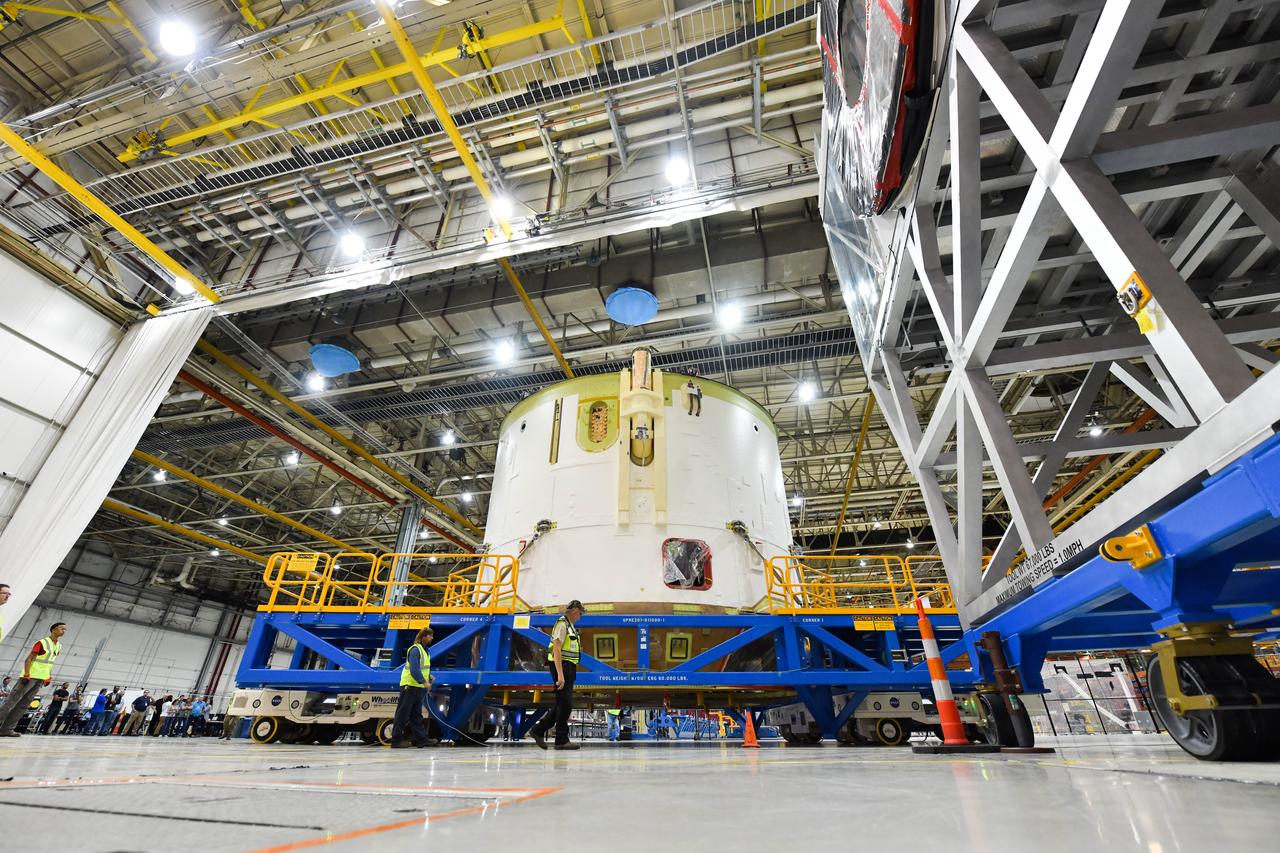
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
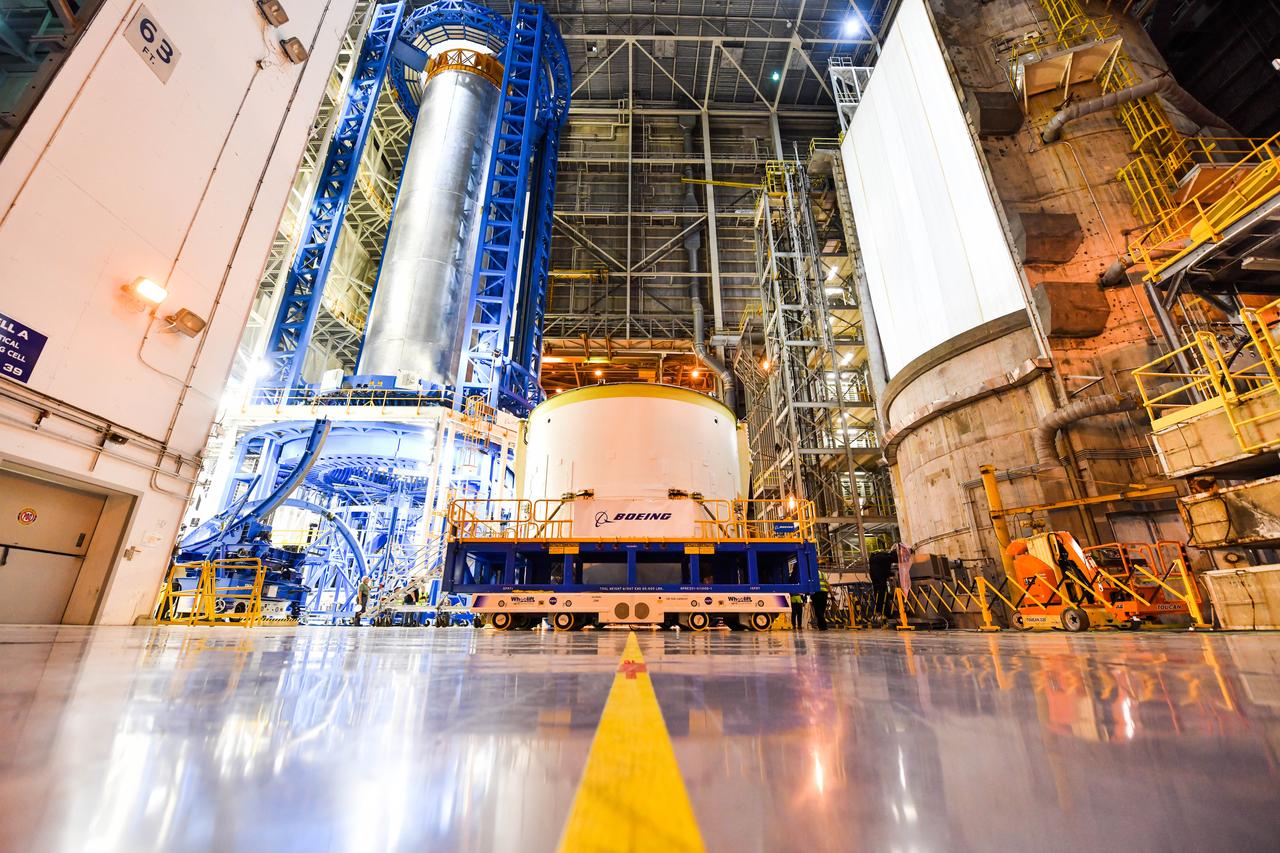

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
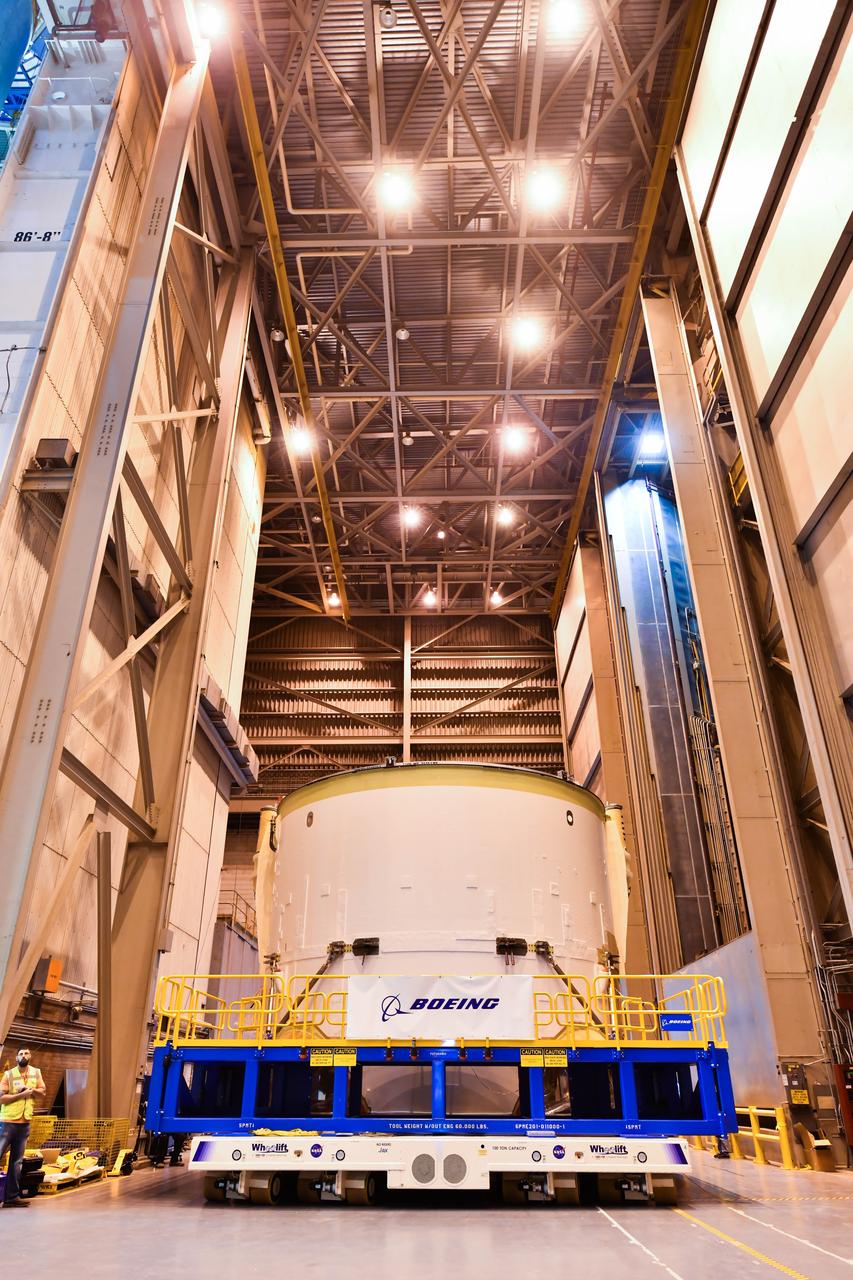

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
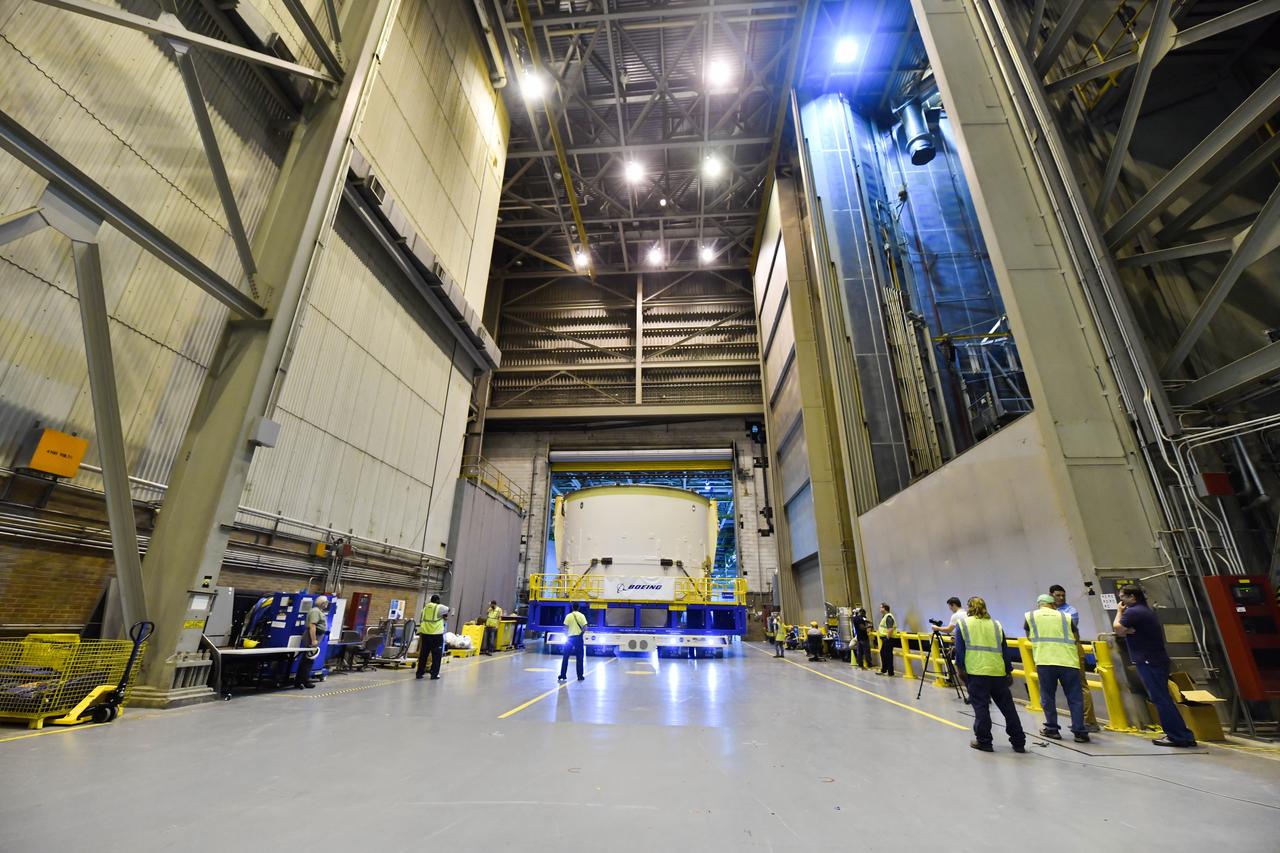

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
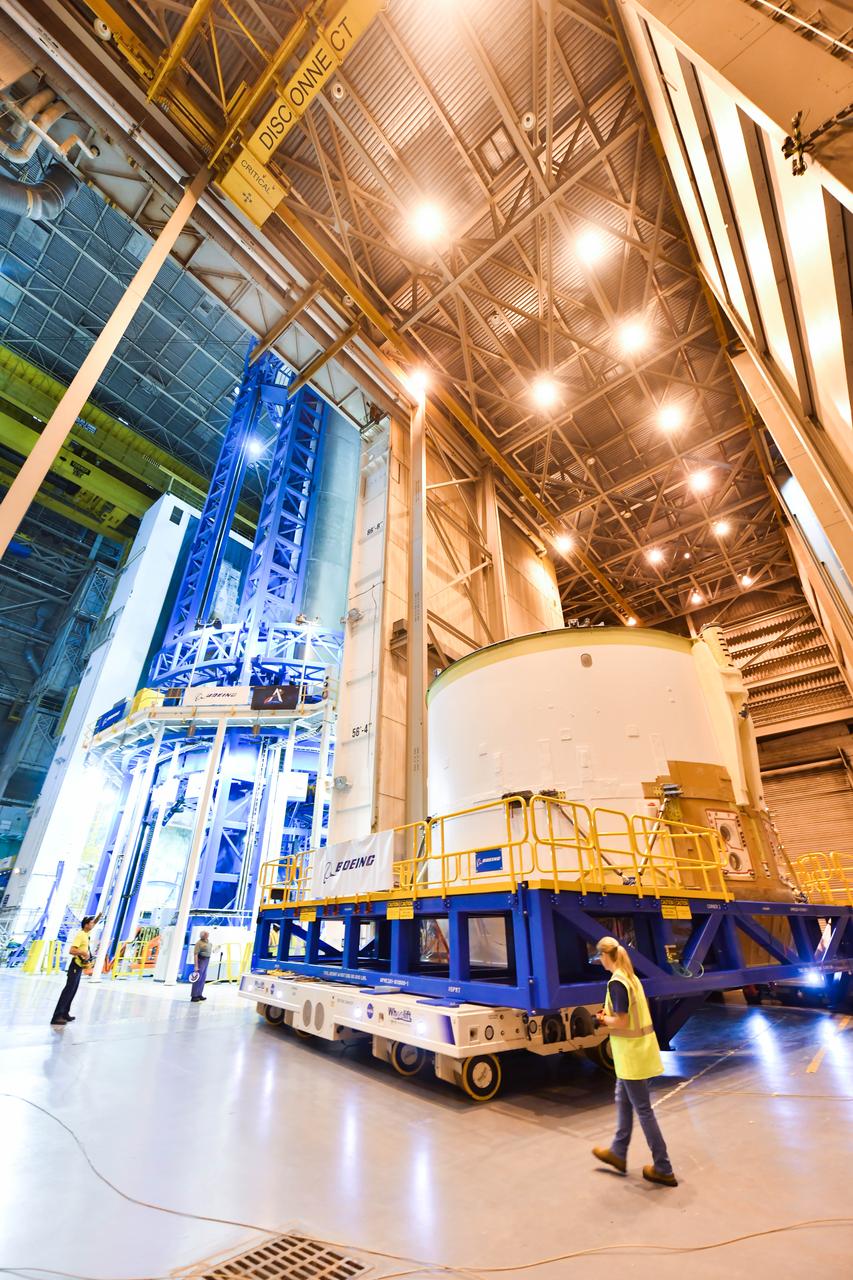

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
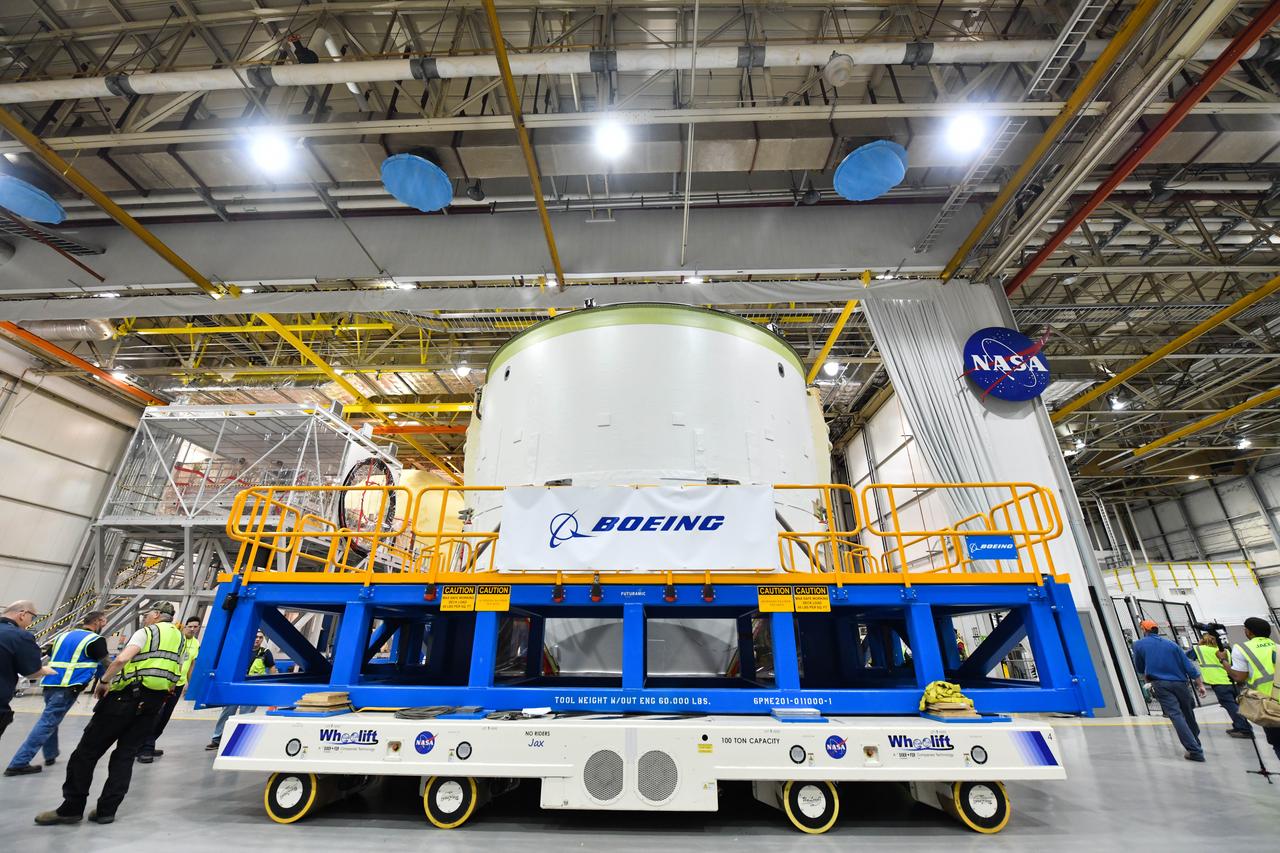

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
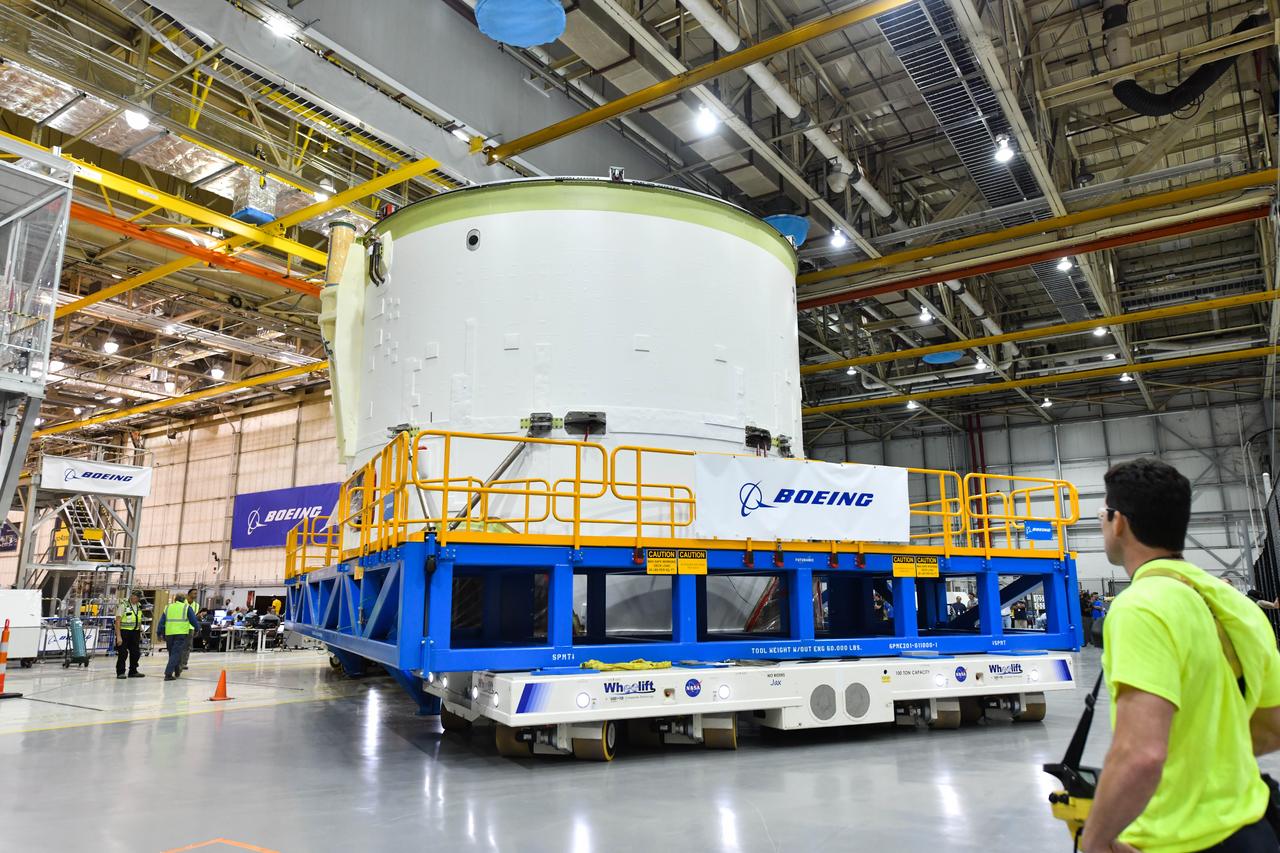

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
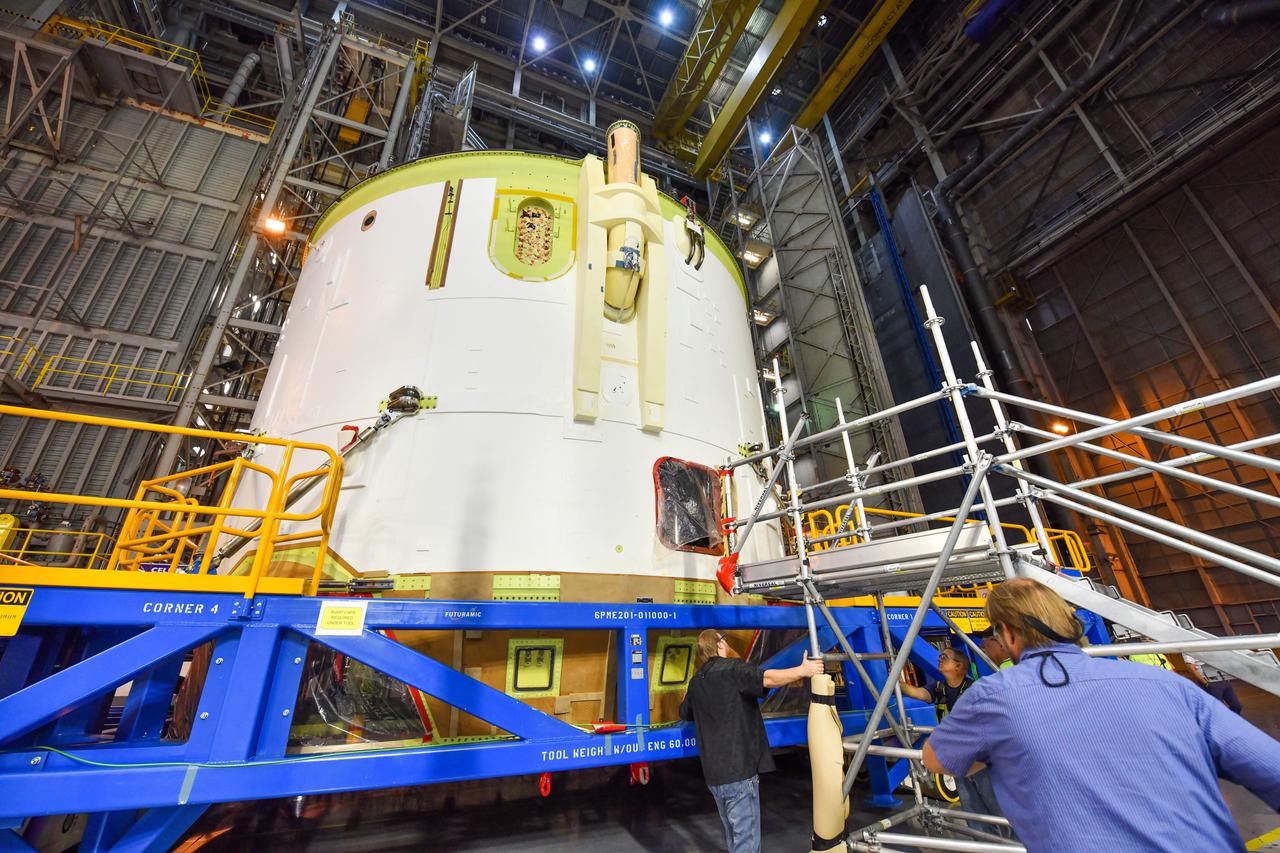

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
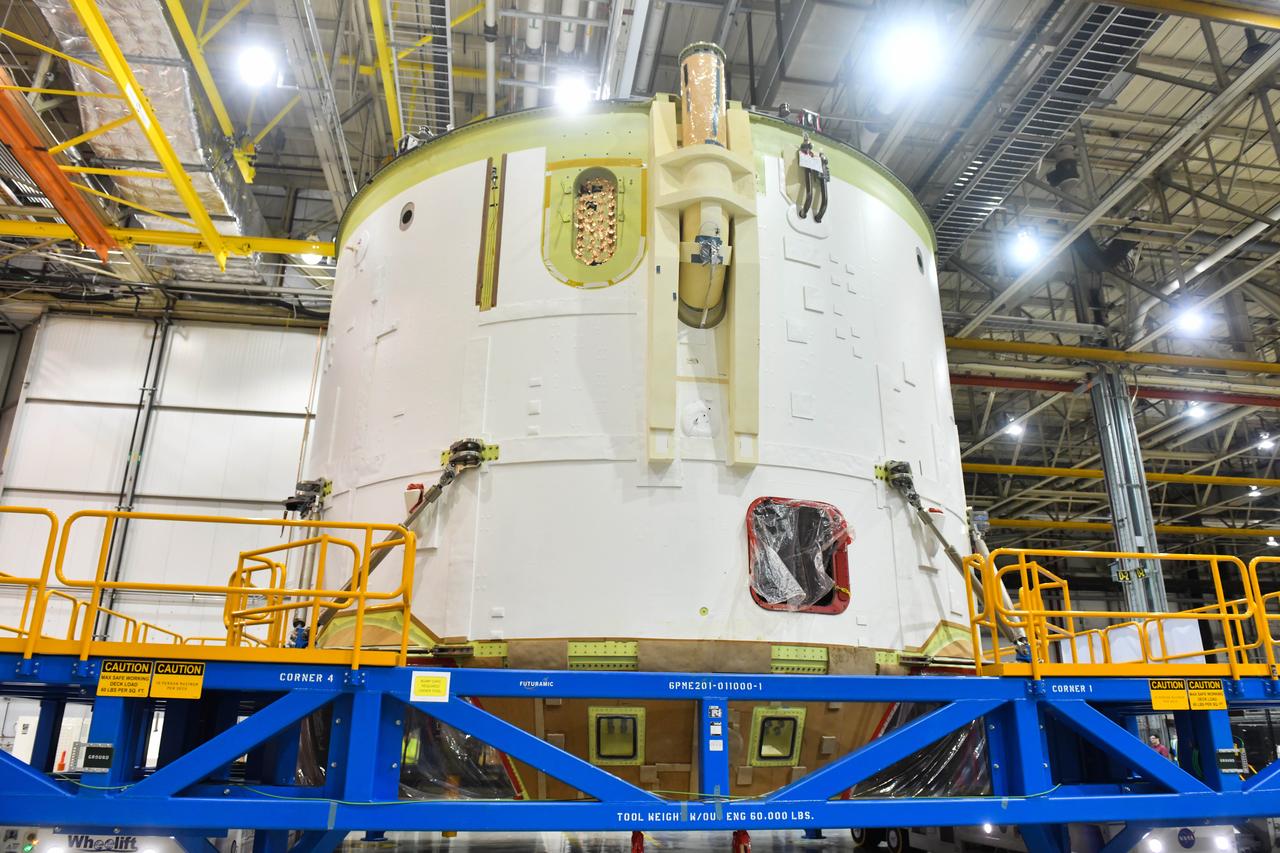

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
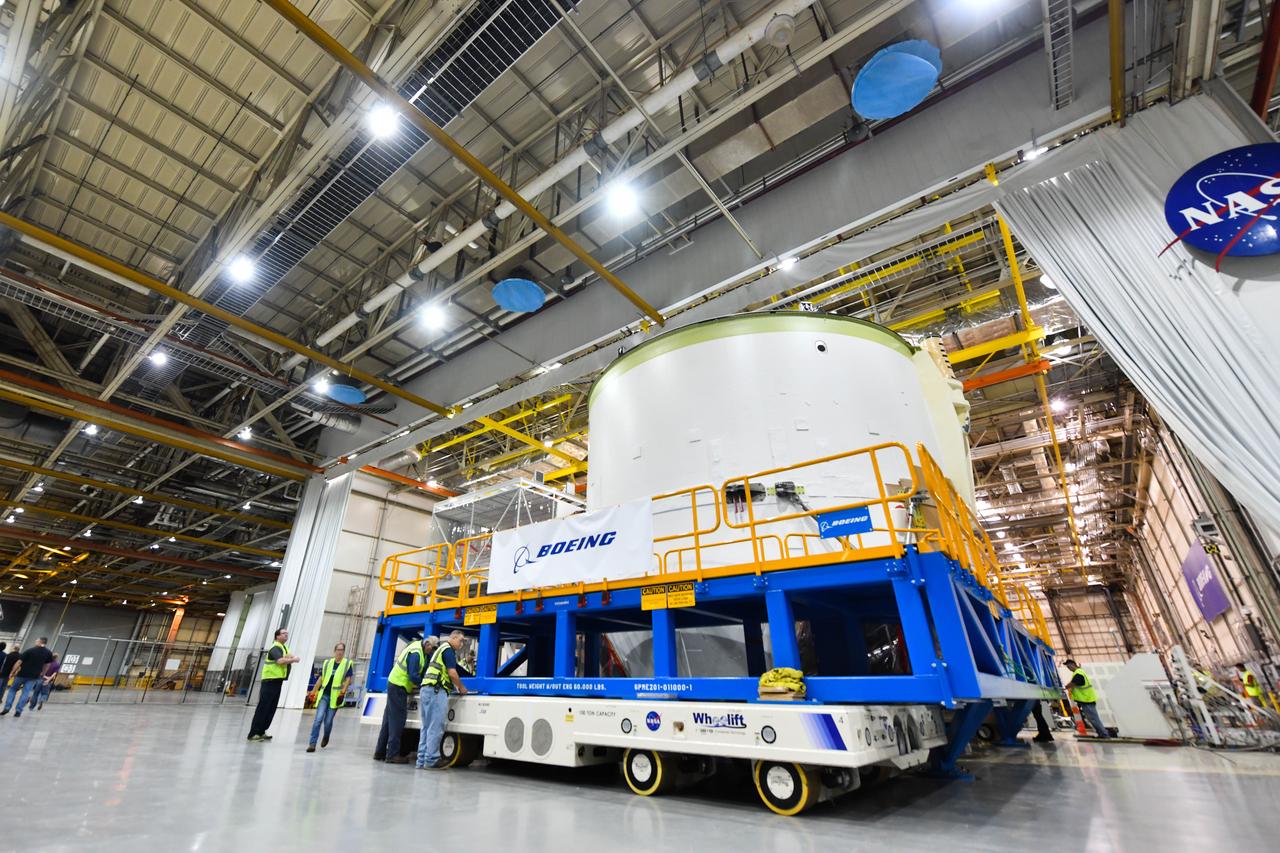

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
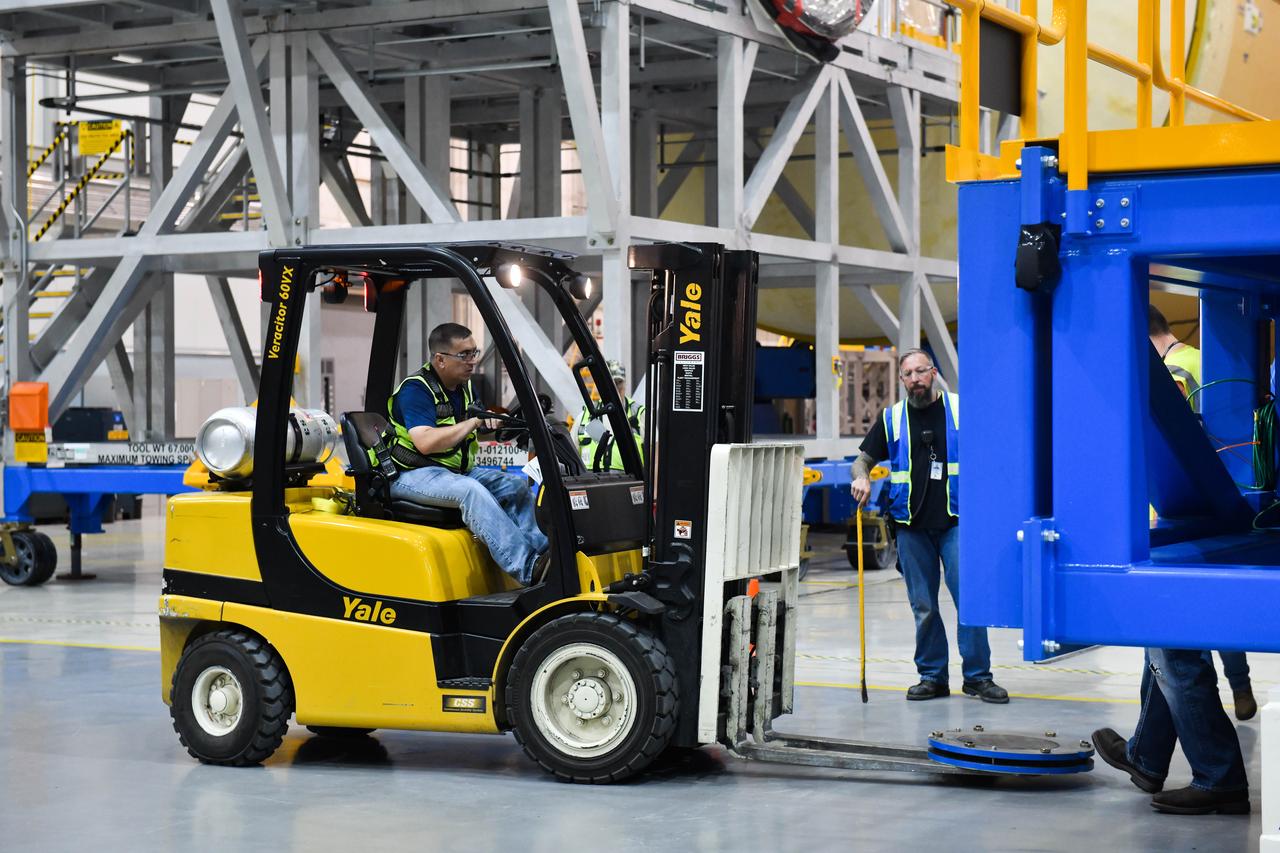

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
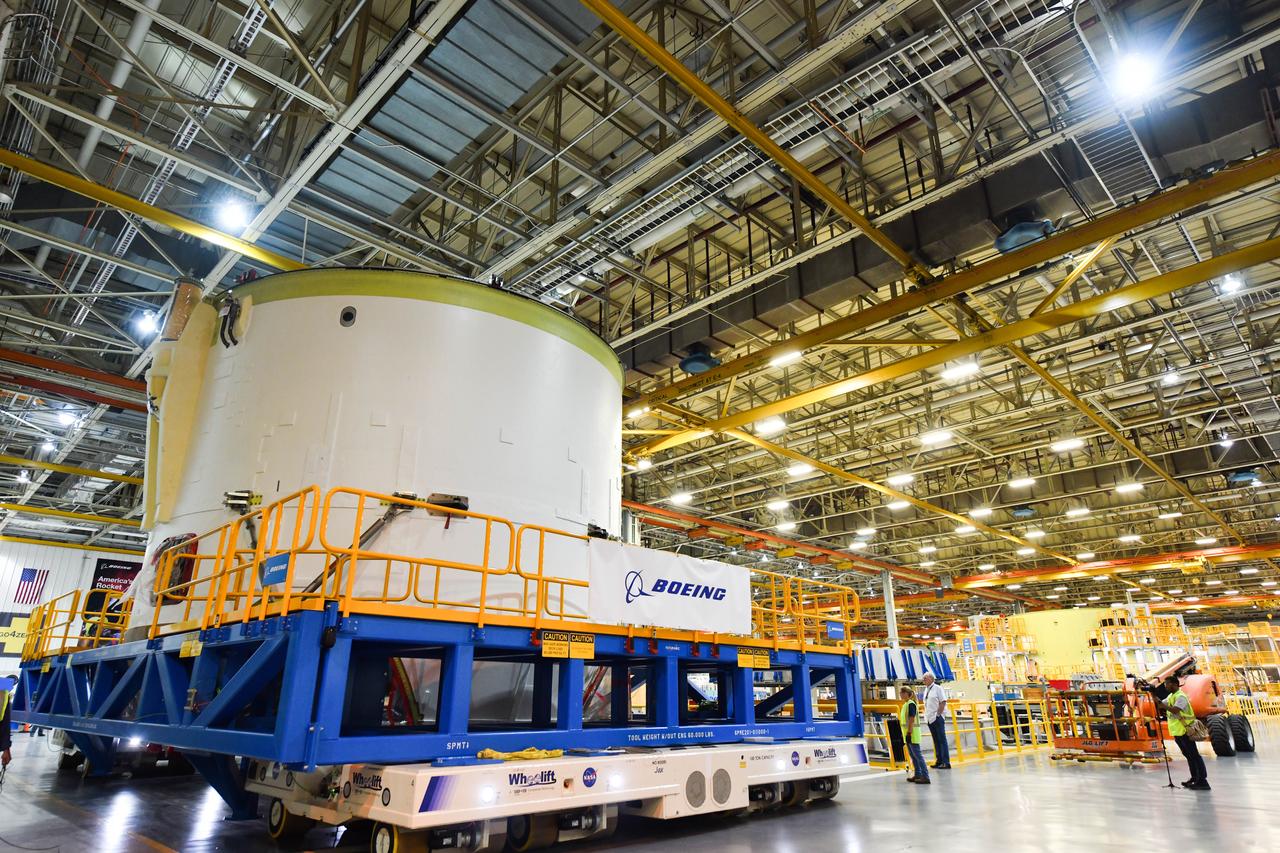

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
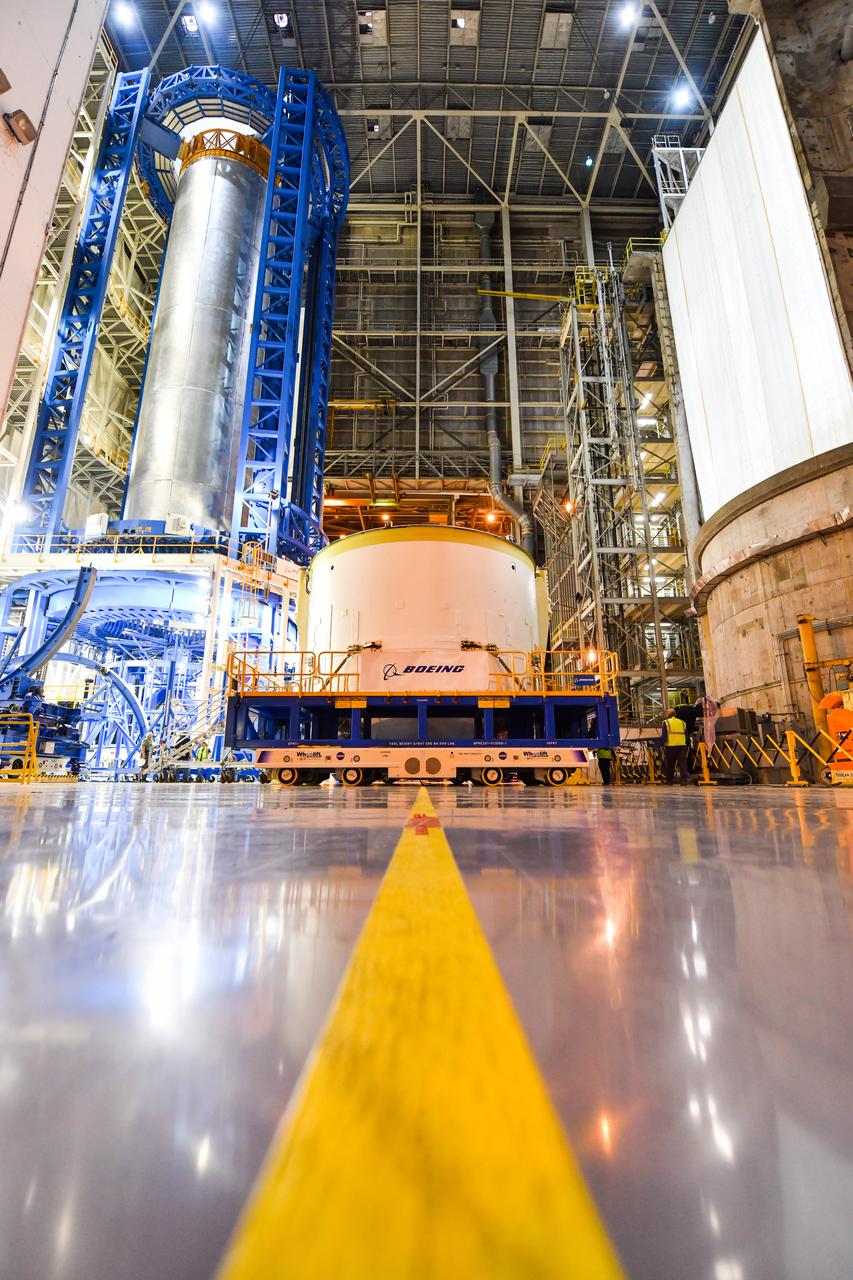

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
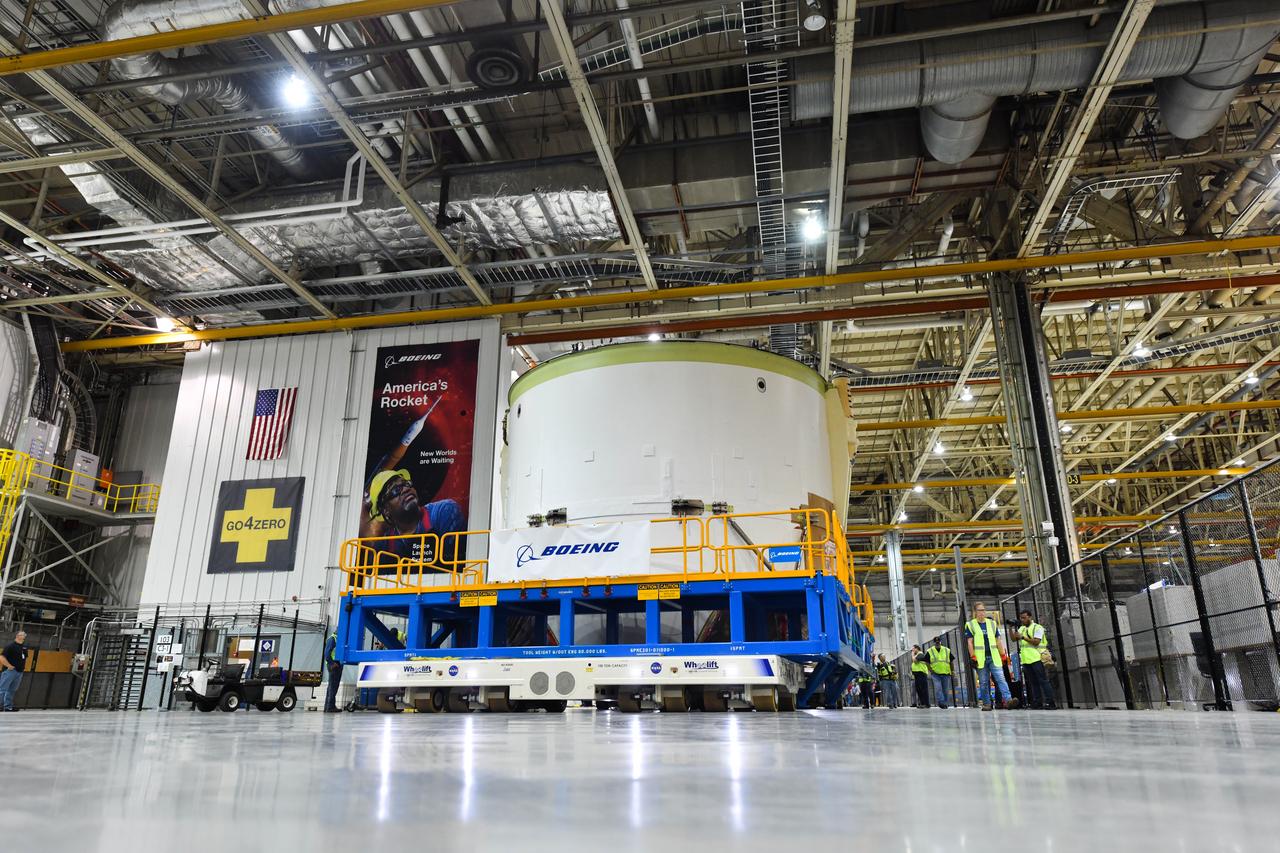

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
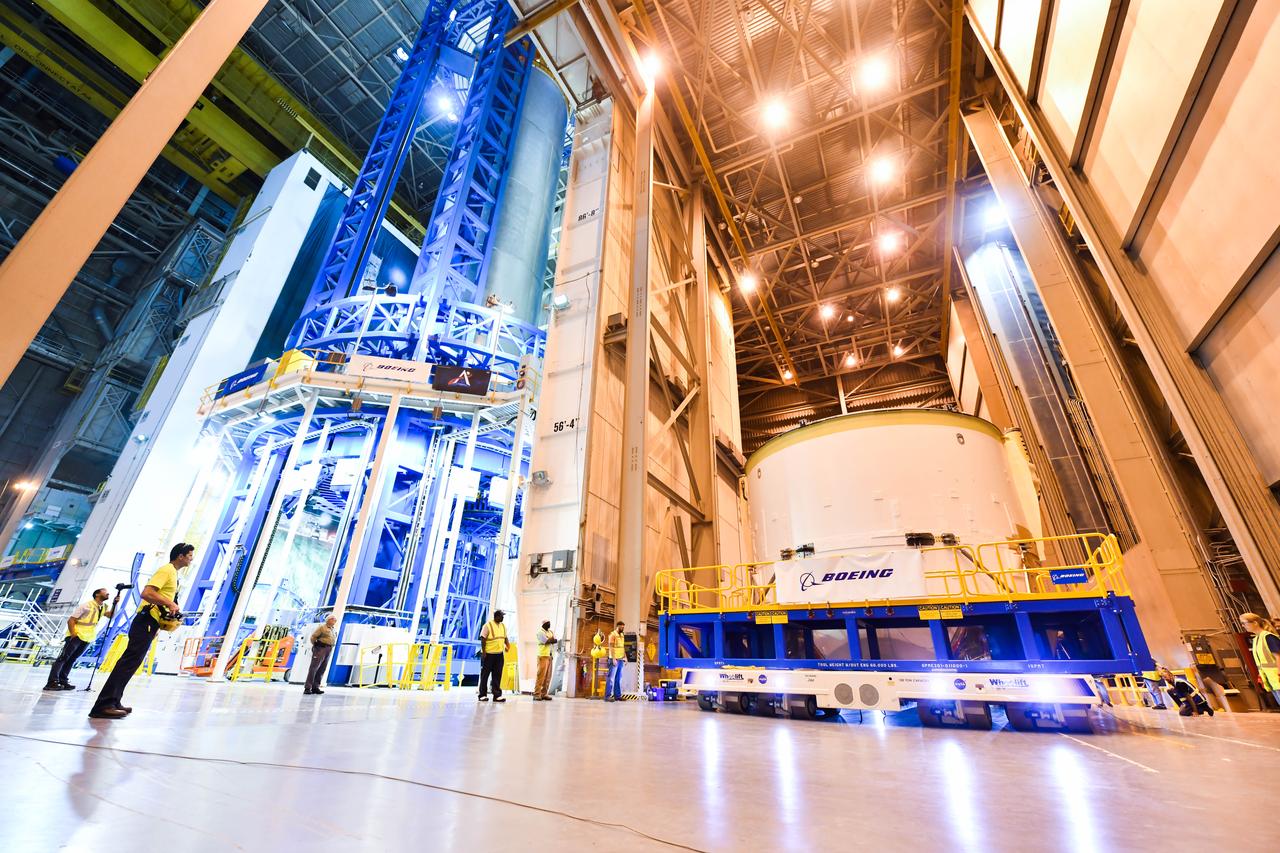

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
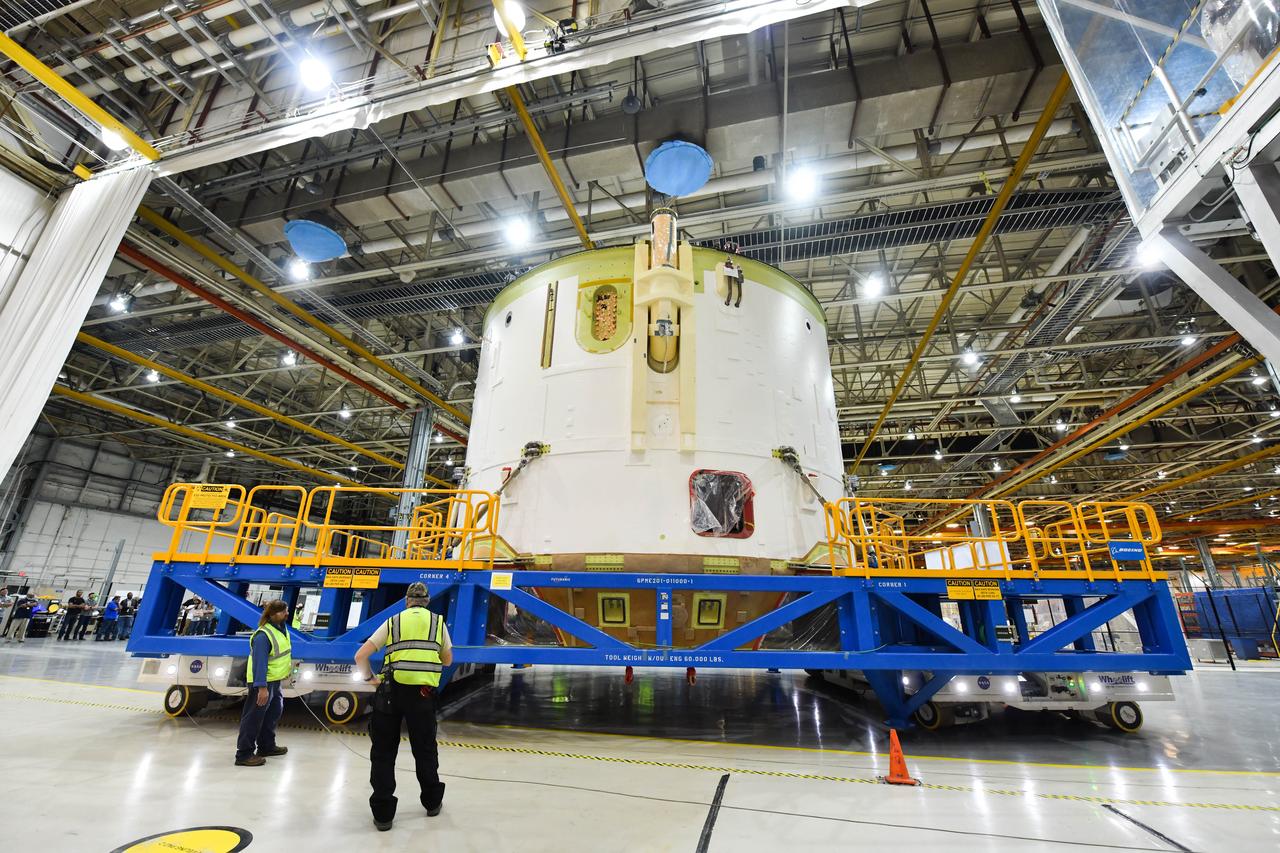

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
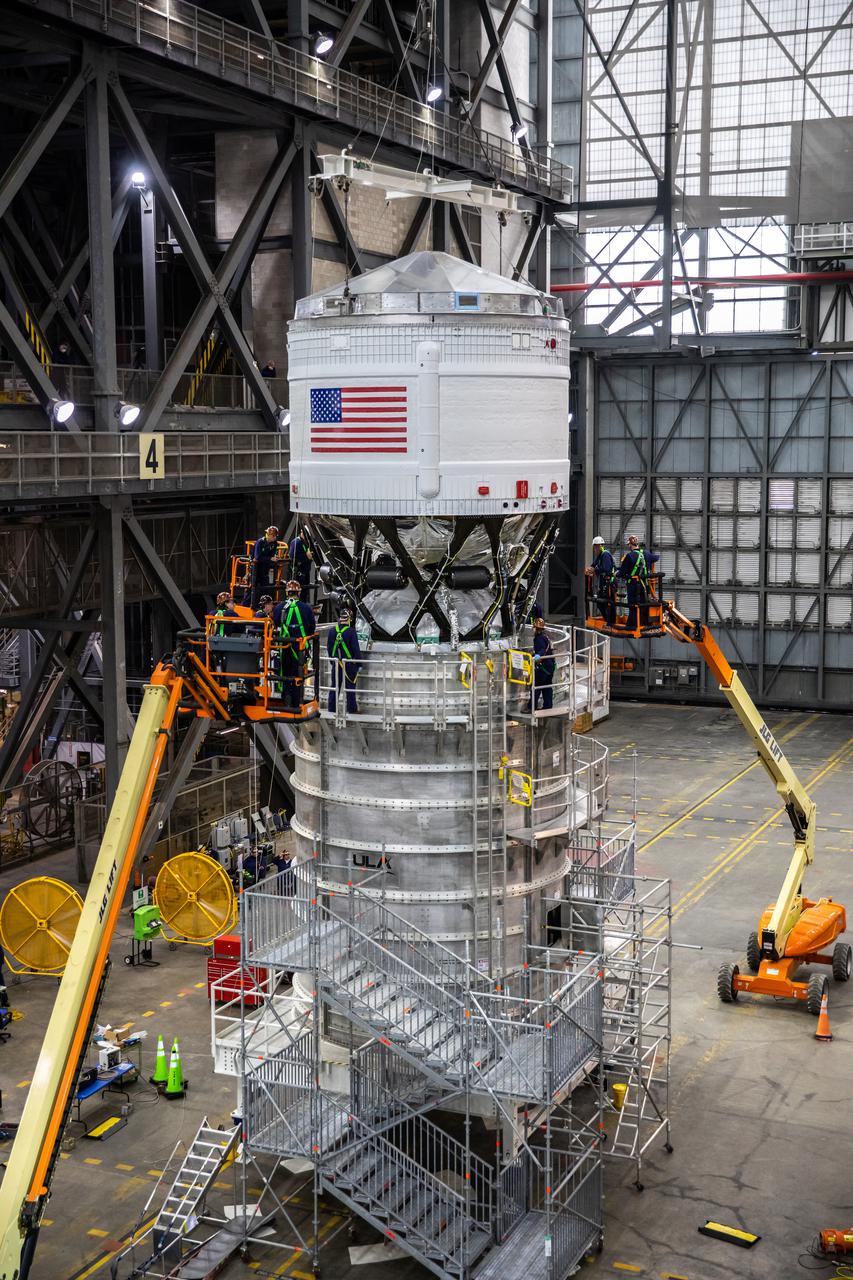

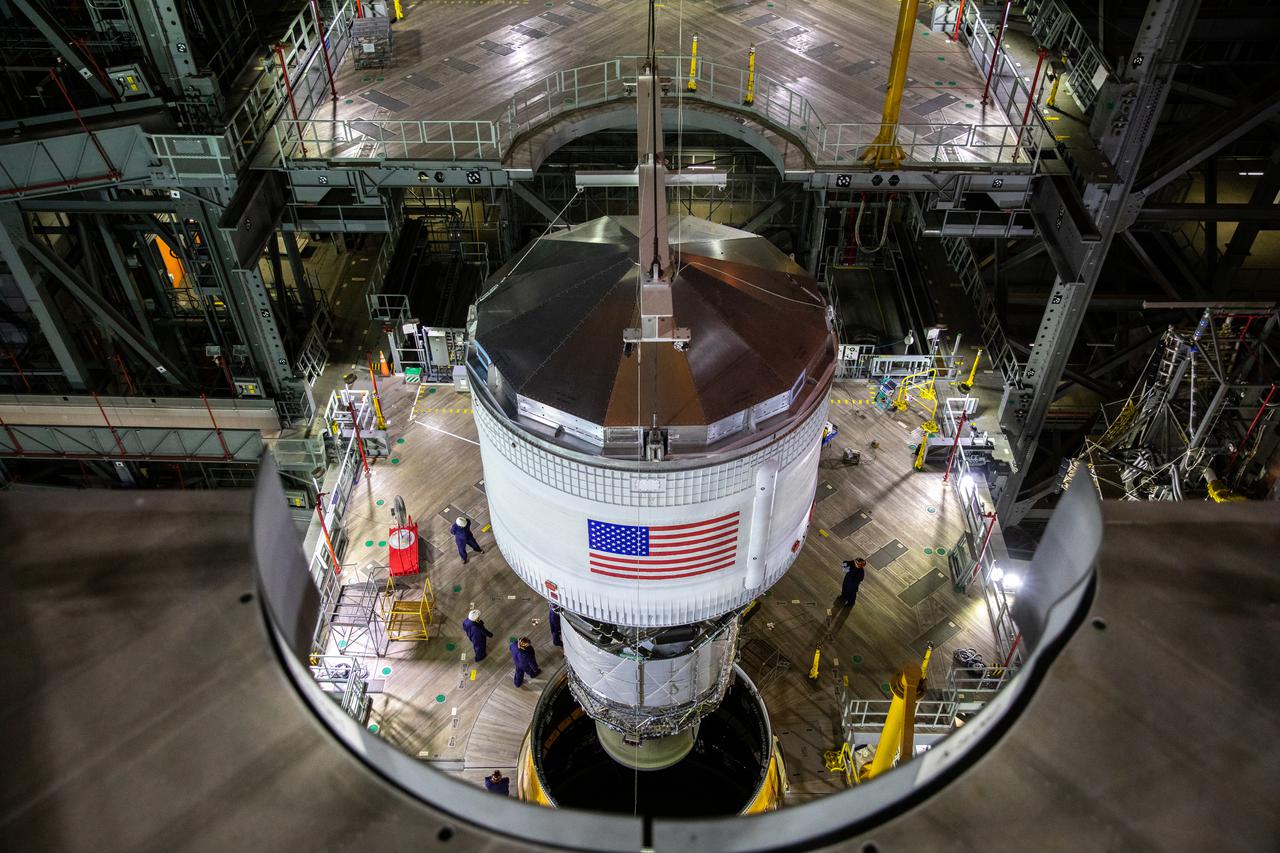
Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
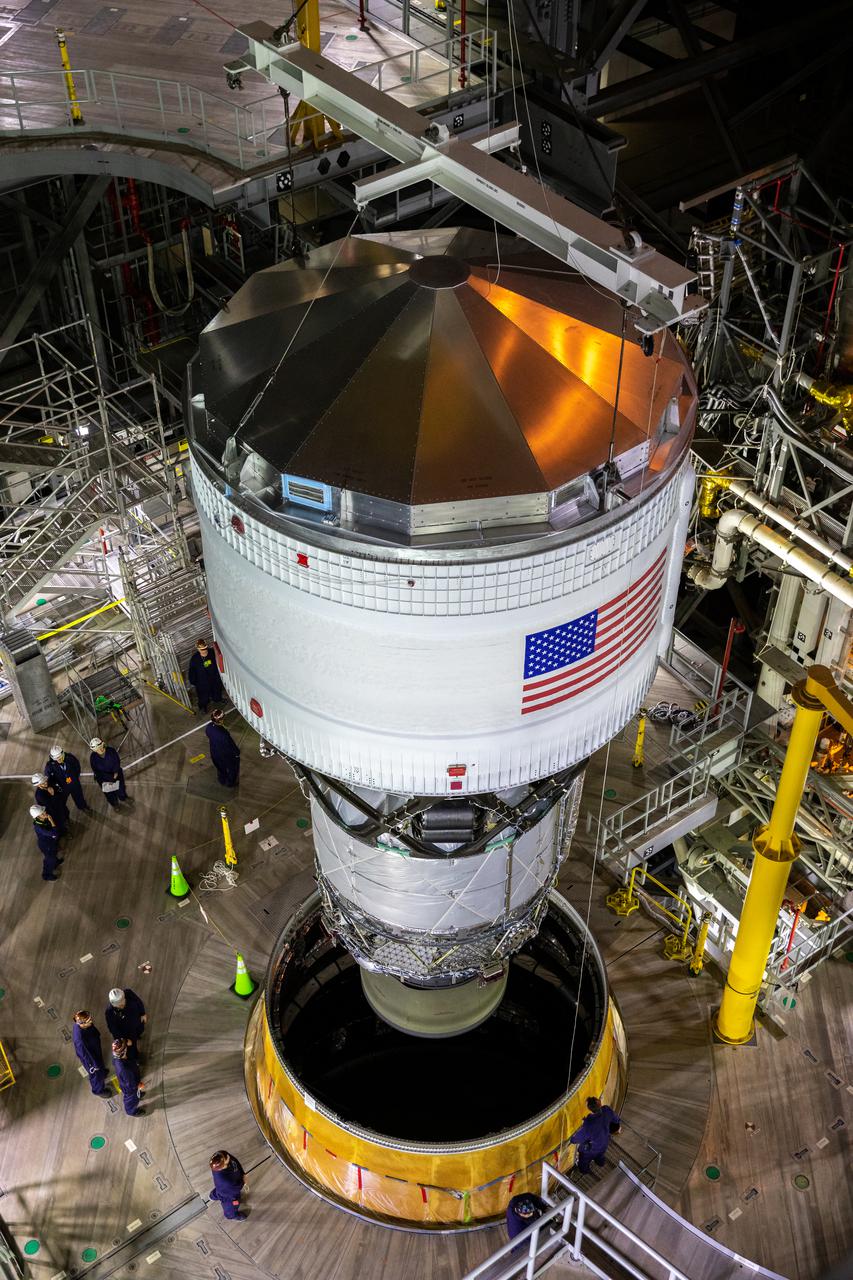

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
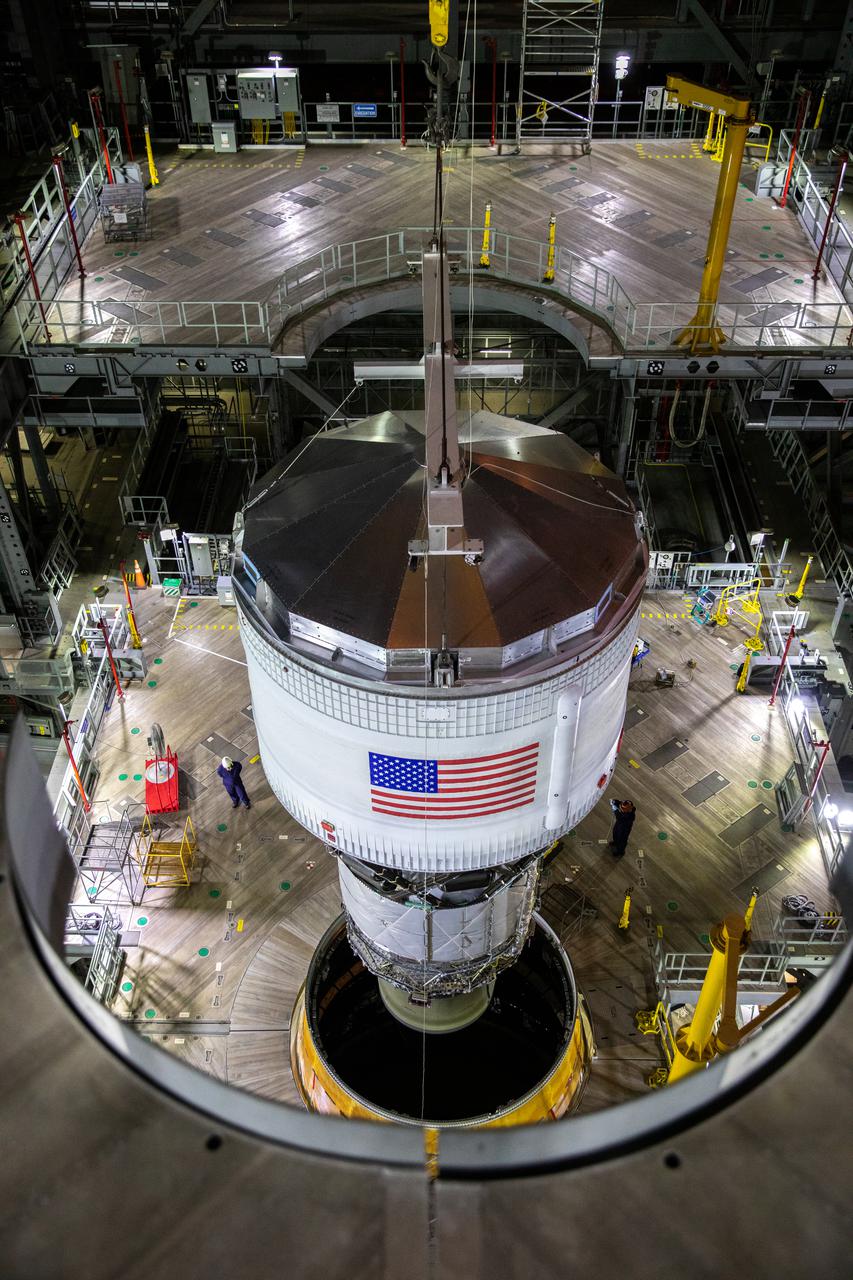

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
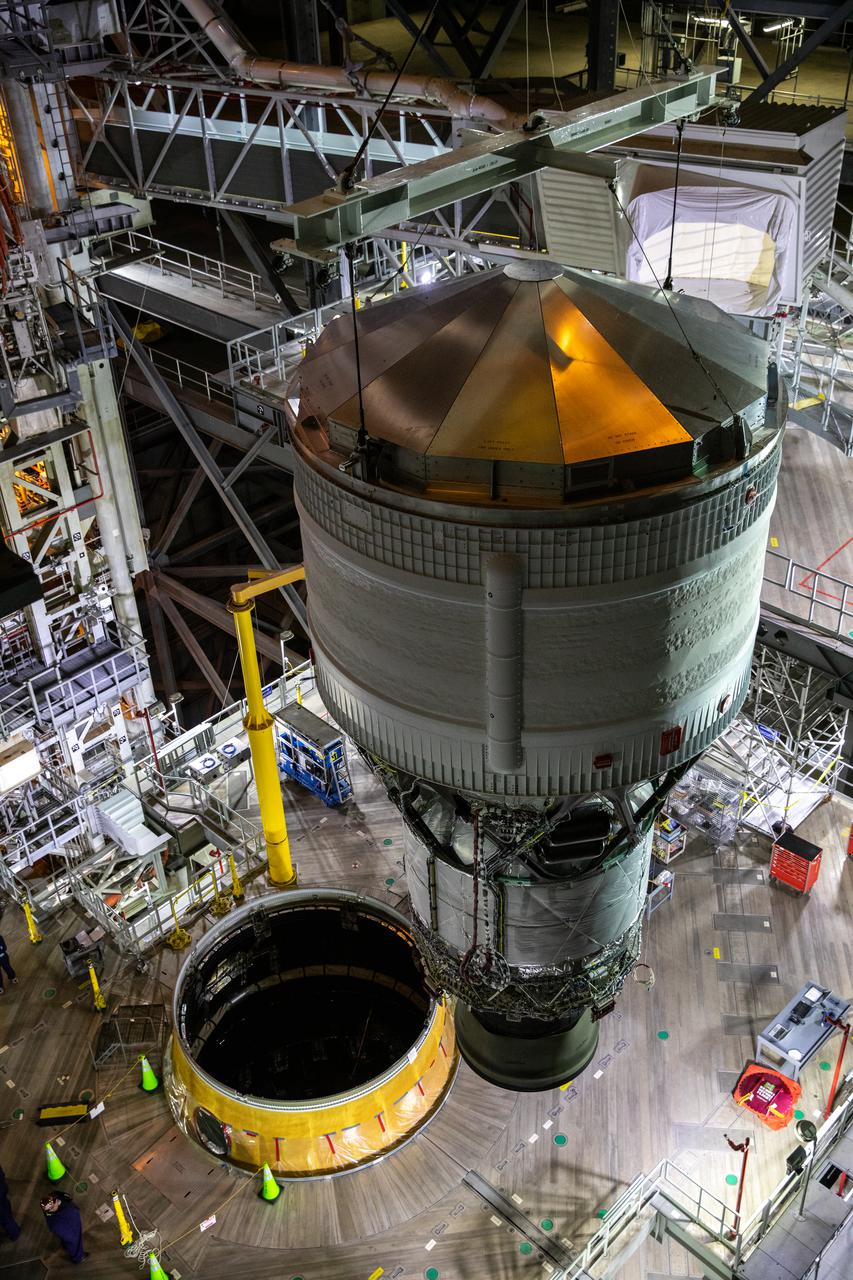

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
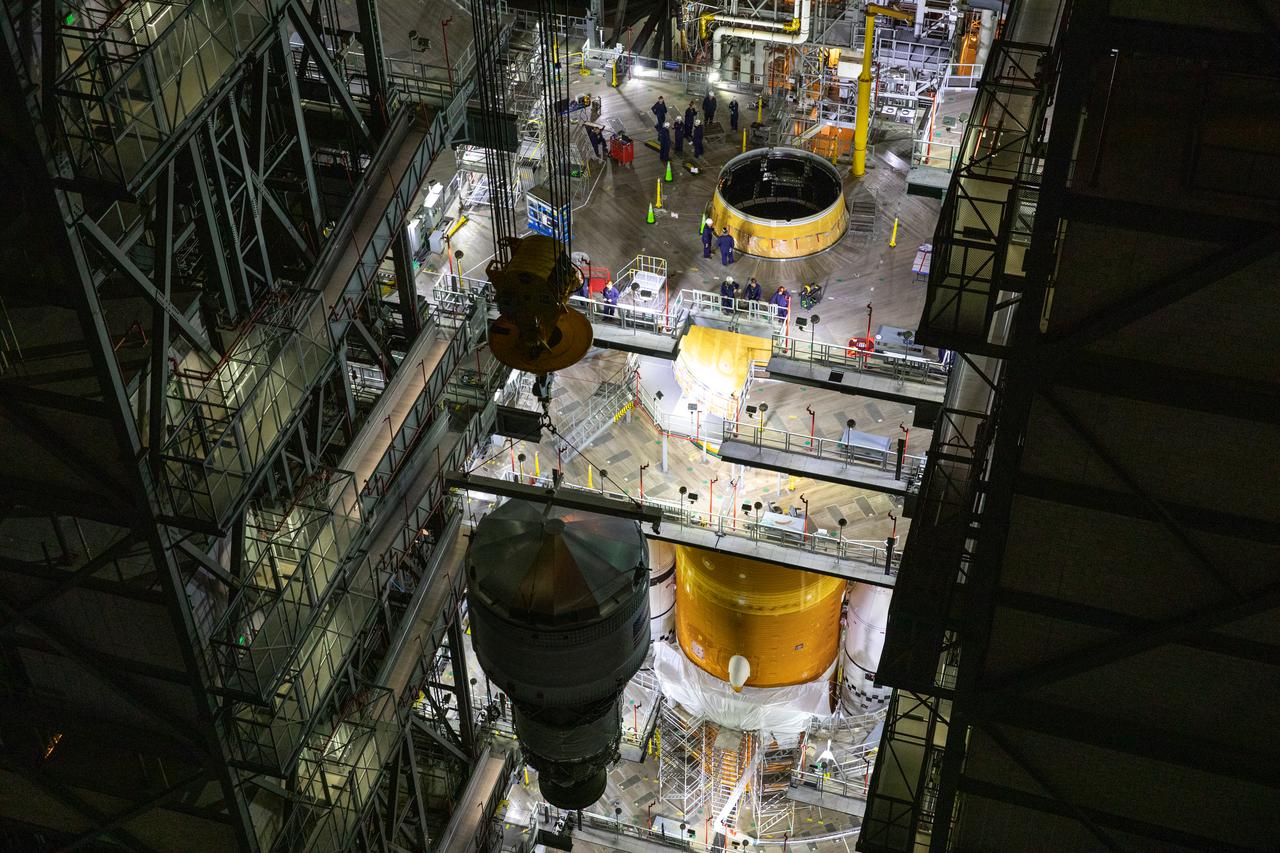

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.
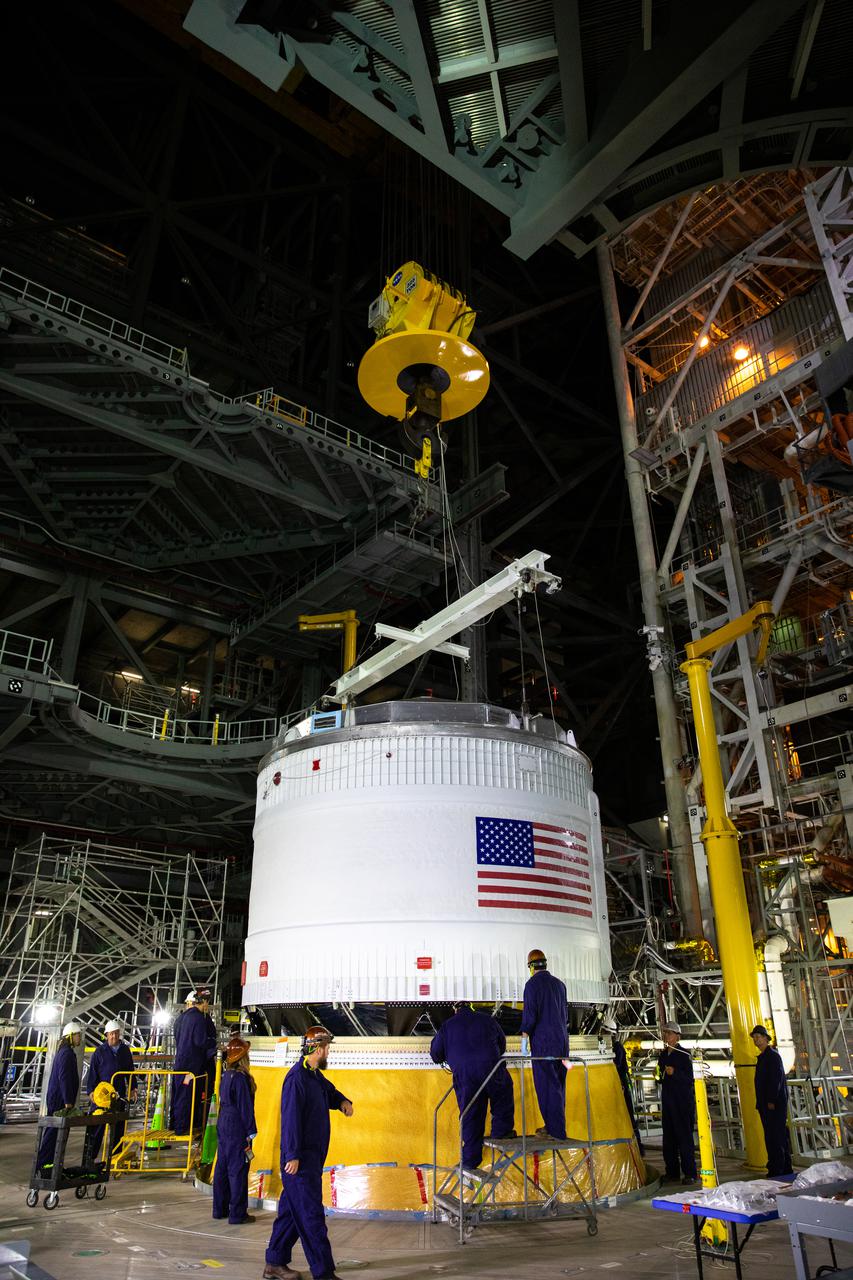

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and contractor Jacobs integrate the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS) for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) atop the massive SLS core stage in the agency’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 5, 2021. The ICPS is a liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen-based system that will fire its RL 10 engine to give the Orion spacecraft the big in-space push needed to fly tens of thousands of miles beyond the Moon. The next component to be stacked on top of ICPS will be the Orion stage adapter, which will connect the ICPS with the spacecraft. Through Artemis, NASA will send the first woman and the first person of color to the lunar surface, as well as establish a sustainable presence on and around the Moon. As the first in an increasingly complex set of missions, Artemis I will test SLS and Orion as an integrated system prior to crewed flights to the Moon.

John Honeycutt and Mark White compare model of SLS test stand with actual test stand
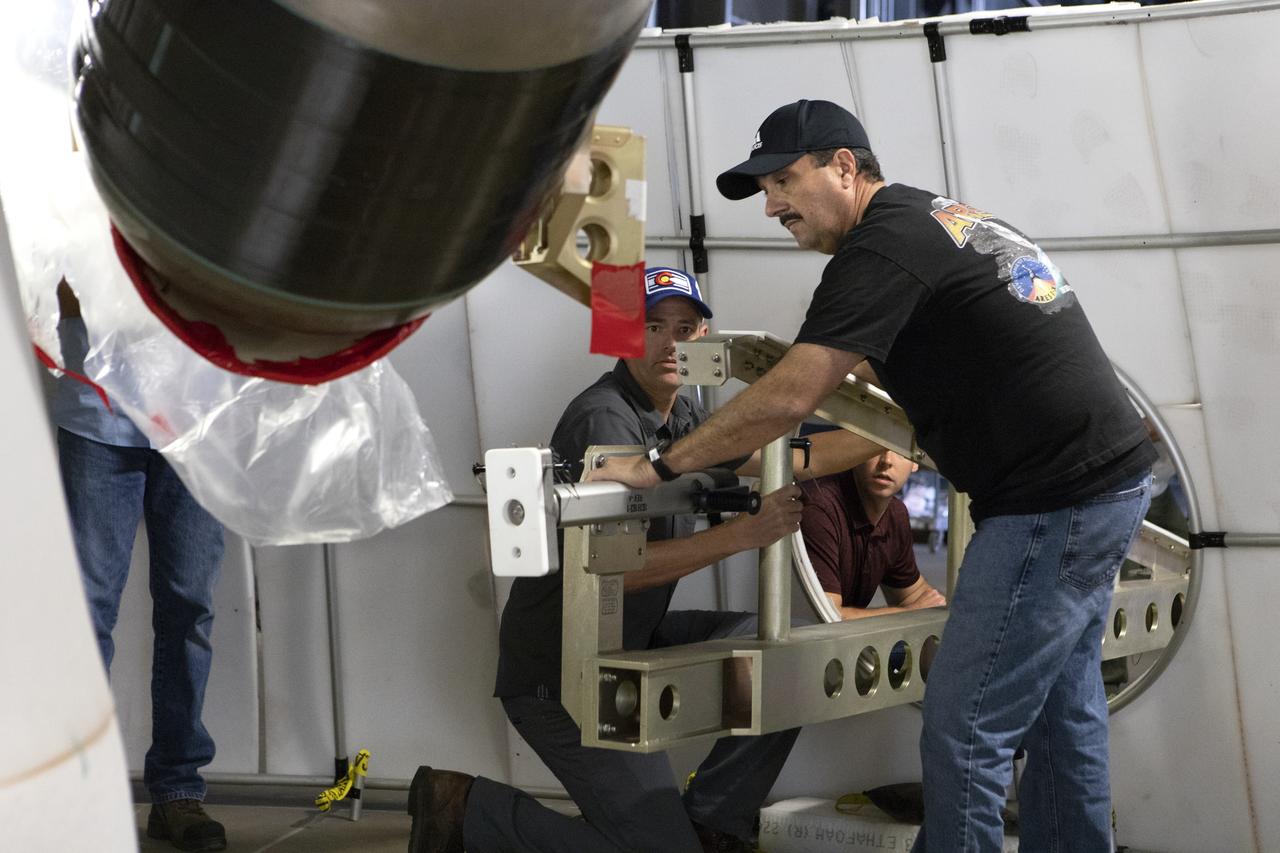

A Space Launch System (SLS) avionics handling tool demonstration takes place inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on April 4, 2019. The demonstration showed that avionics boxes could be successfully and safely mounted into the SLS rocket’s upper stage — called the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, or ICPS — with low risk of damaging a closely located hydrazine tank. Avionics boxes include the Inertial Navigation and Control Assembly and flight batteries. The actual installation will take place just weeks before NASA’s SLS rocket and uncrewed Orion spacecraft lift off on Exploration Mission-1 from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy.
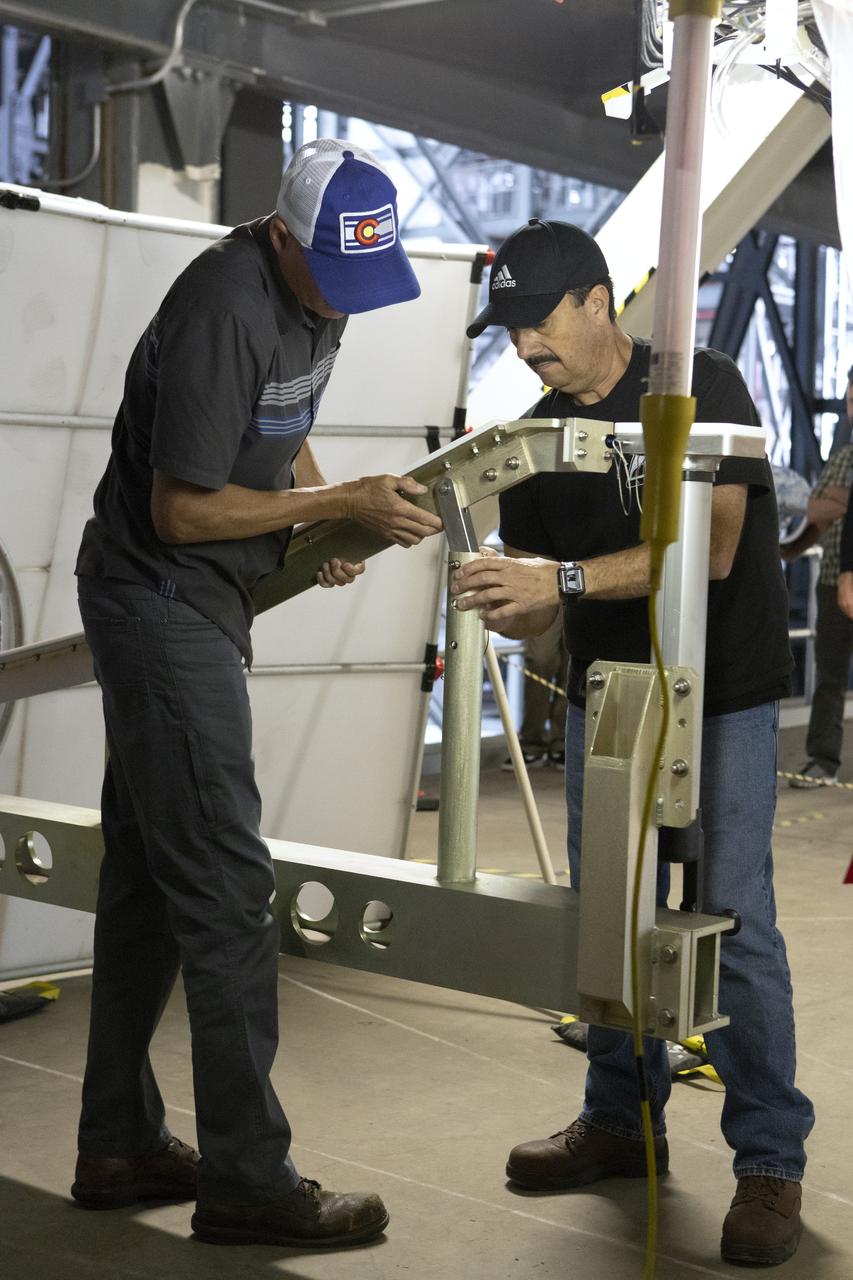

A Space Launch System (SLS) avionics handling tool demonstration takes place inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on April 4, 2019. The demonstration showed that avionics boxes could be successfully and safely mounted into the SLS rocket’s upper stage — called the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, or ICPS — with low risk of damaging a closely located hydrazine tank. Avionics boxes include the Inertial Navigation and Control Assembly and flight batteries. The actual installation will take place just weeks before NASA’s SLS rocket and uncrewed Orion spacecraft lift off on Exploration Mission-1 from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy.
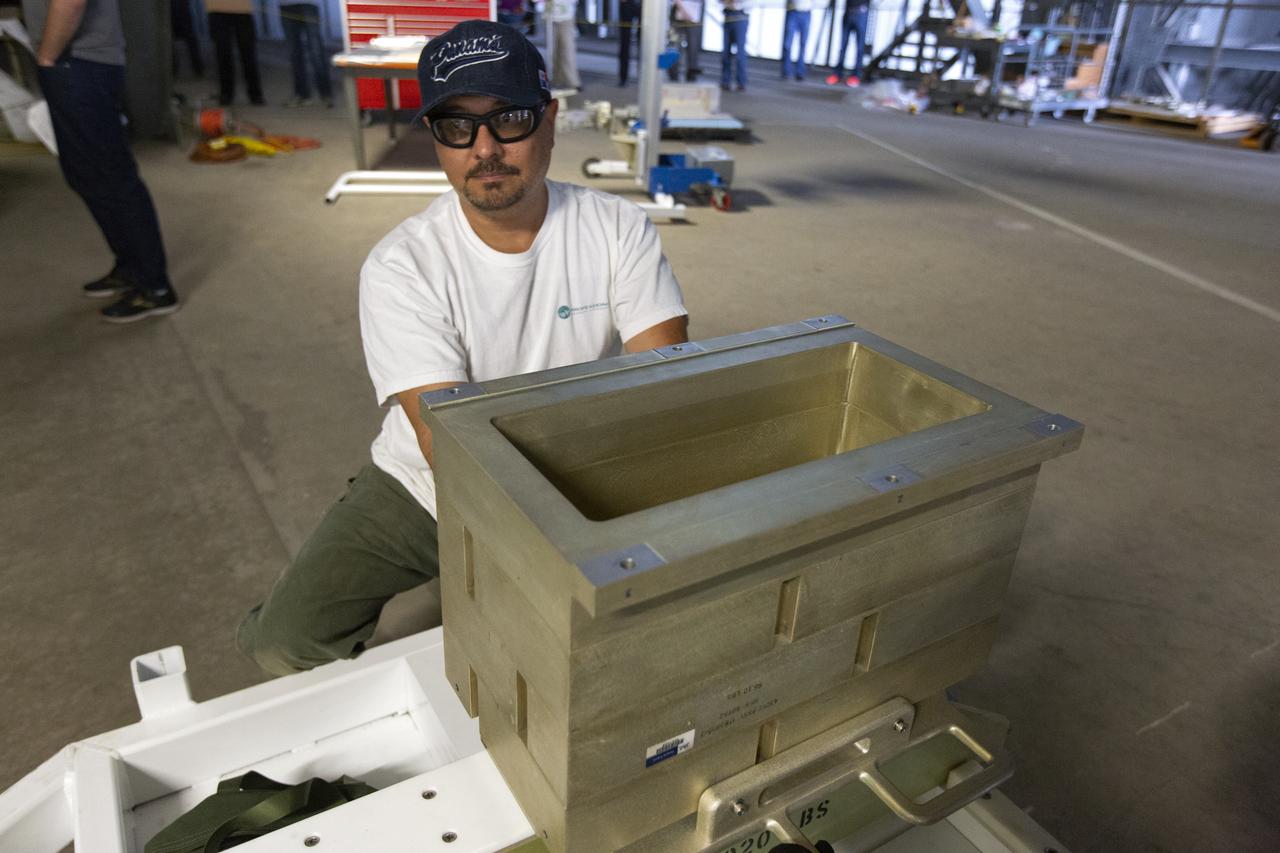

A Space Launch System (SLS) avionics handling tool demonstration takes place inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on April 4, 2019. The demonstration showed that avionics boxes could be successfully and safely mounted into the SLS rocket’s upper stage — called the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, or ICPS — with low risk of damaging a closely located hydrazine tank. Avionics boxes include the Inertial Navigation and Control Assembly and flight batteries. The actual installation will take place just weeks before NASA’s SLS rocket and uncrewed Orion spacecraft lift off on Exploration Mission-1 from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy.
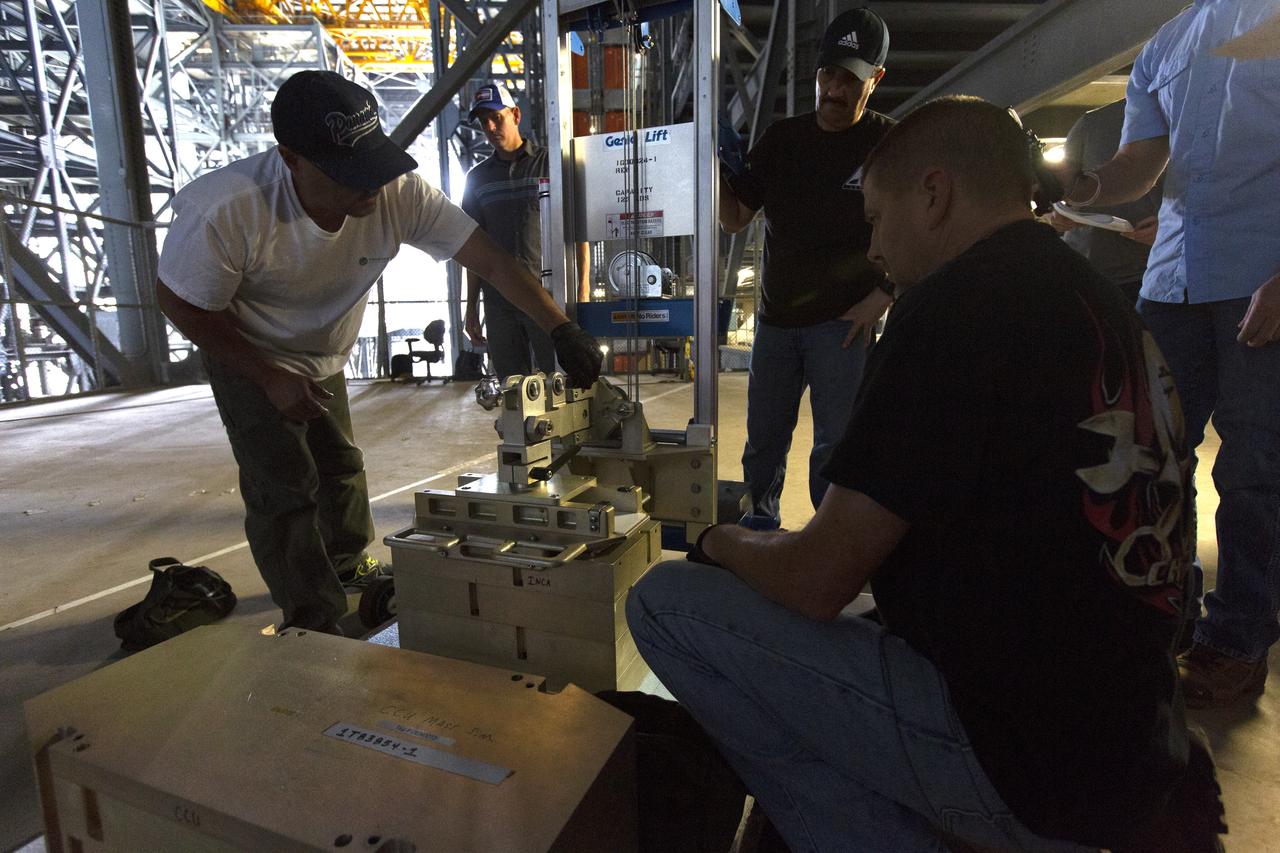

A Space Launch System (SLS) avionics handling tool demonstration takes place inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on April 4, 2019. The demonstration showed that avionics boxes could be successfully and safely mounted into the SLS rocket’s upper stage — called the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, or ICPS — with low risk of damaging a closely located hydrazine tank. Avionics boxes include the Inertial Navigation and Control Assembly and flight batteries. The actual installation will take place just weeks before NASA’s SLS rocket and uncrewed Orion spacecraft lift off on Exploration Mission-1 from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy.
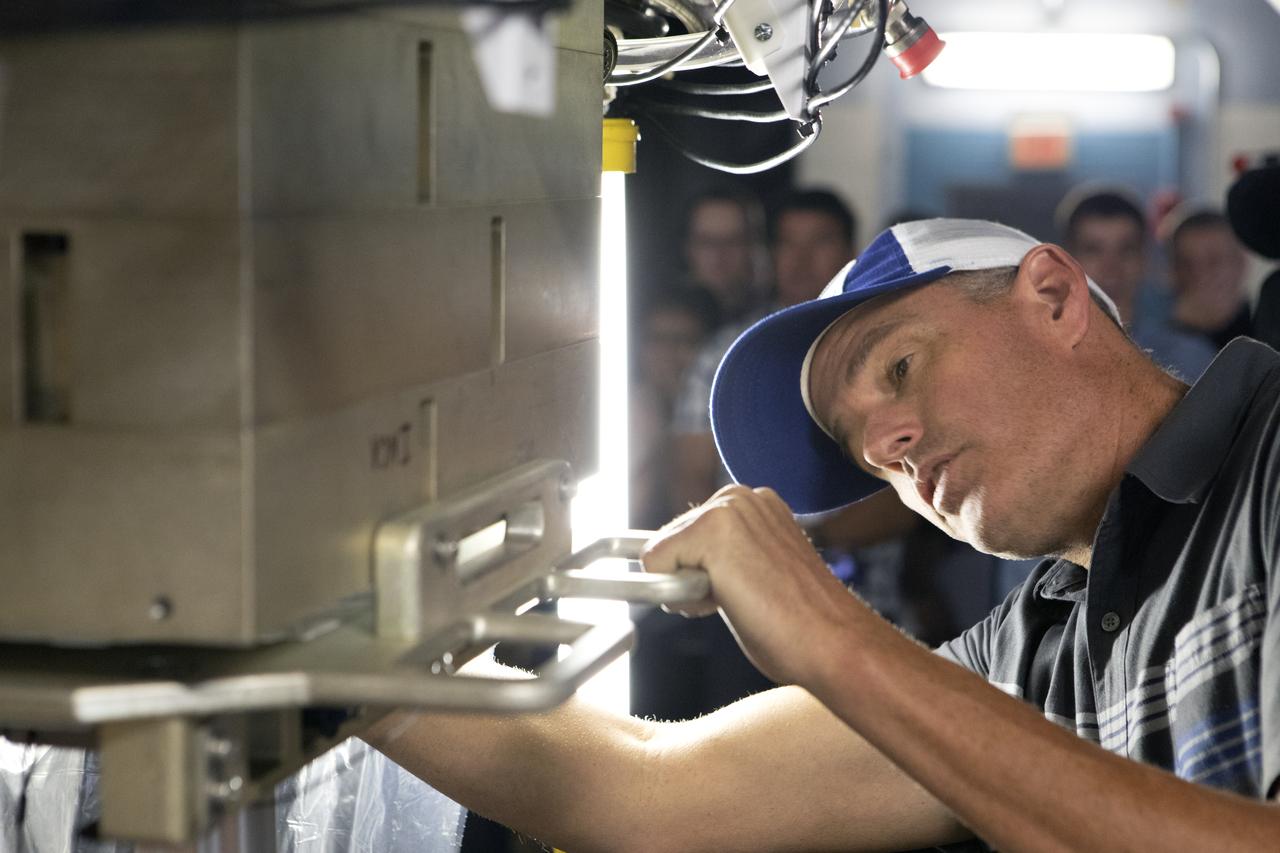

A Space Launch System (SLS) avionics handling tool demonstration takes place inside Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building on April 4, 2019. The demonstration showed that avionics boxes could be successfully and safely mounted into the SLS rocket’s upper stage — called the Interim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage, or ICPS — with low risk of damaging a closely located hydrazine tank. Avionics boxes include the Inertial Navigation and Control Assembly and flight batteries. The actual installation will take place just weeks before NASA’s SLS rocket and uncrewed Orion spacecraft lift off on Exploration Mission-1 from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy.
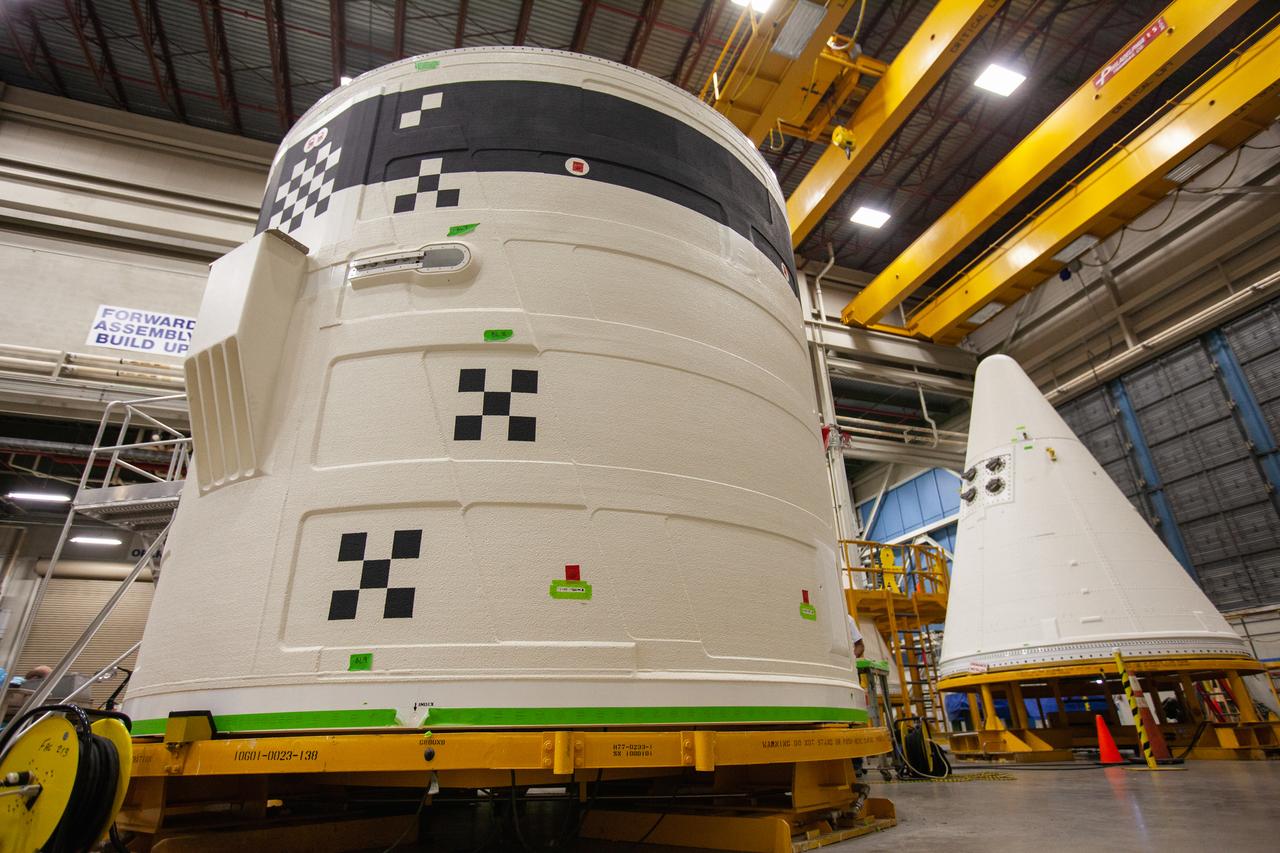

The forward skirt for one of the Space Launch System’s (SLS) two solid boosters is inside the Booster Fabrication Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 16, 2019. Segments of the boosters are being inspected and prepared for Artemis I, the agency’s first uncrewed flight of Orion atop the SLS. The forward skirt houses booster avionics that communicate with the SLS avionics to monitor booster conditions and steer the booster exhaust nozzle.