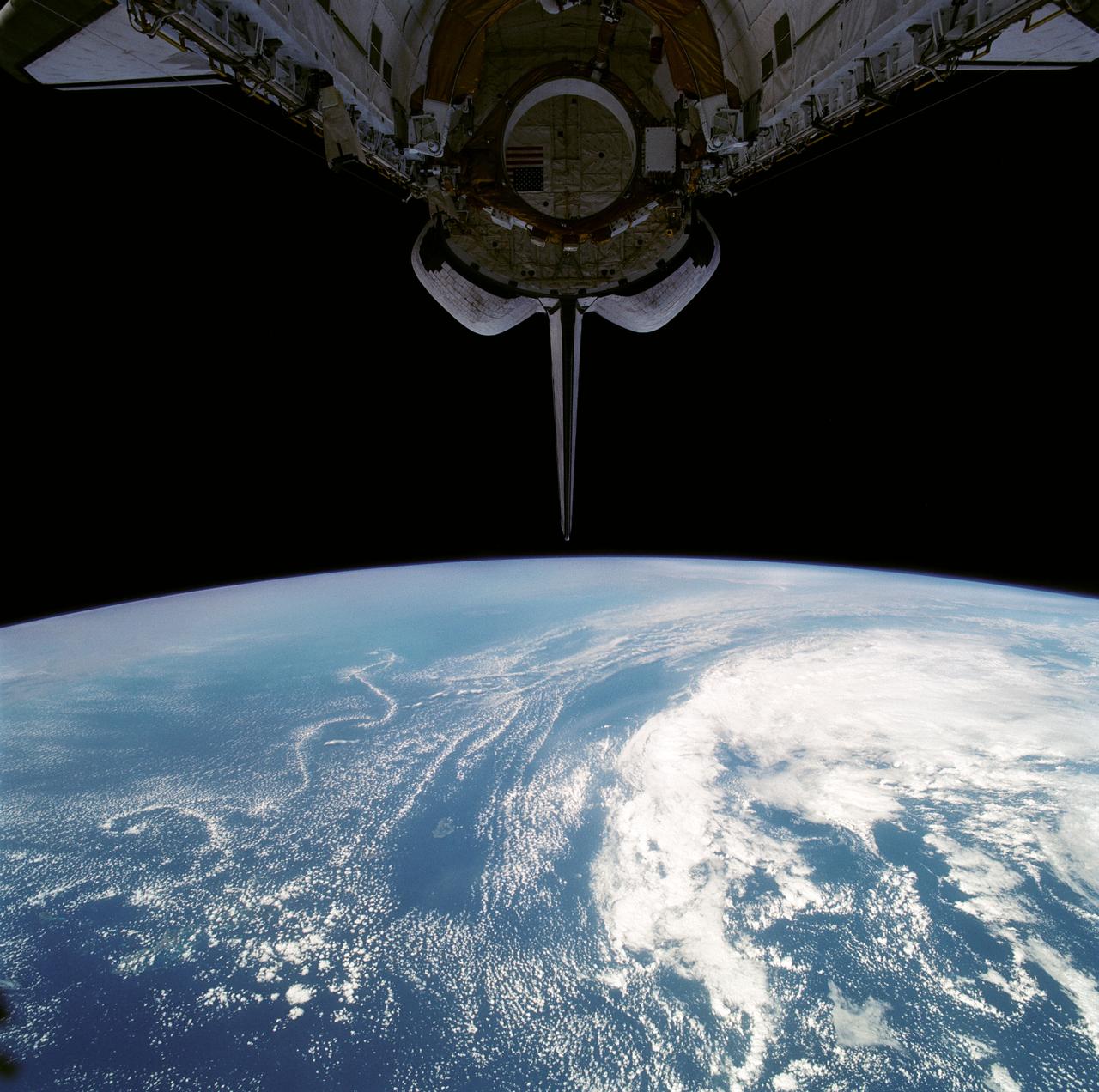

Stable, south flowing air over the western Pacific Ocean (26.0N, 131.0E) is disturbed by islands south of Korea, resulting in sinuous clouds known as von Karman vortices. The smoke plume from Japan's Mount Unzen Volcano on Kyushu, is visible just west of the large cloud mass and extending southward. A very large, purple tinged dust pall, originating in Mongolia, can be seen on the Earth's Limb, covering eastern China and extending into the East China Sea.
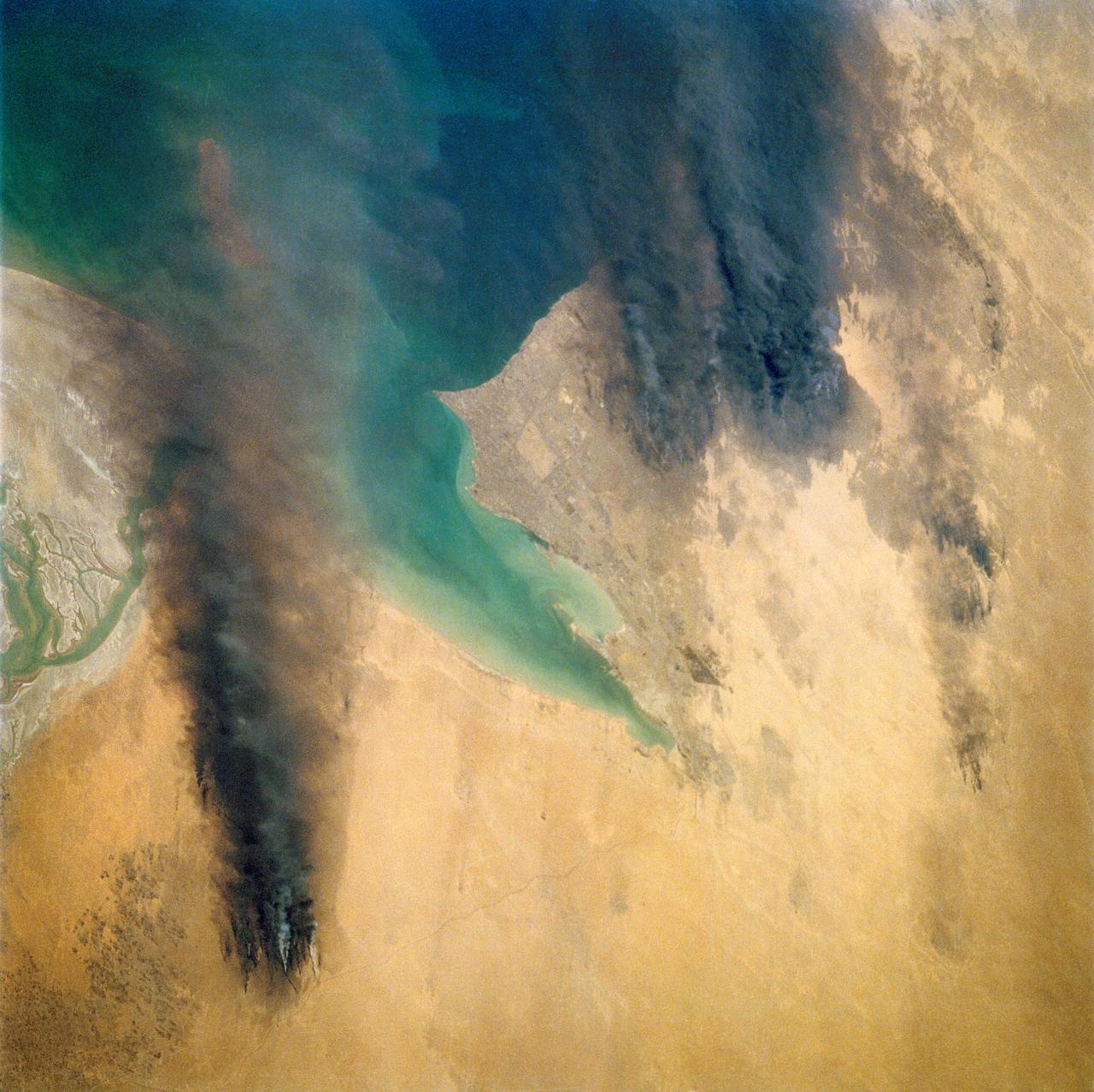

STS039-72-060 (28 April-6 May 1991) --- This view from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery shows the smoke from burning oil well fires, aftermath of Iraqi occupation. Oil wells to the north of the Bay of Kuwait and just south of Kuwait City, on the south shore, can be seen burning out of control. Compared with pictures of the same area shot during STS-37 (April 1991), this frame shows a complete shift of winds, with much of the smoke blowing eastward over the Gulf. The STS-37 scenes showed lengthy southward-blowing sheets of smoke toward Saudi Arabia. In this view, the Gulf island Faylakah Awhah is barely visible through the smoke.
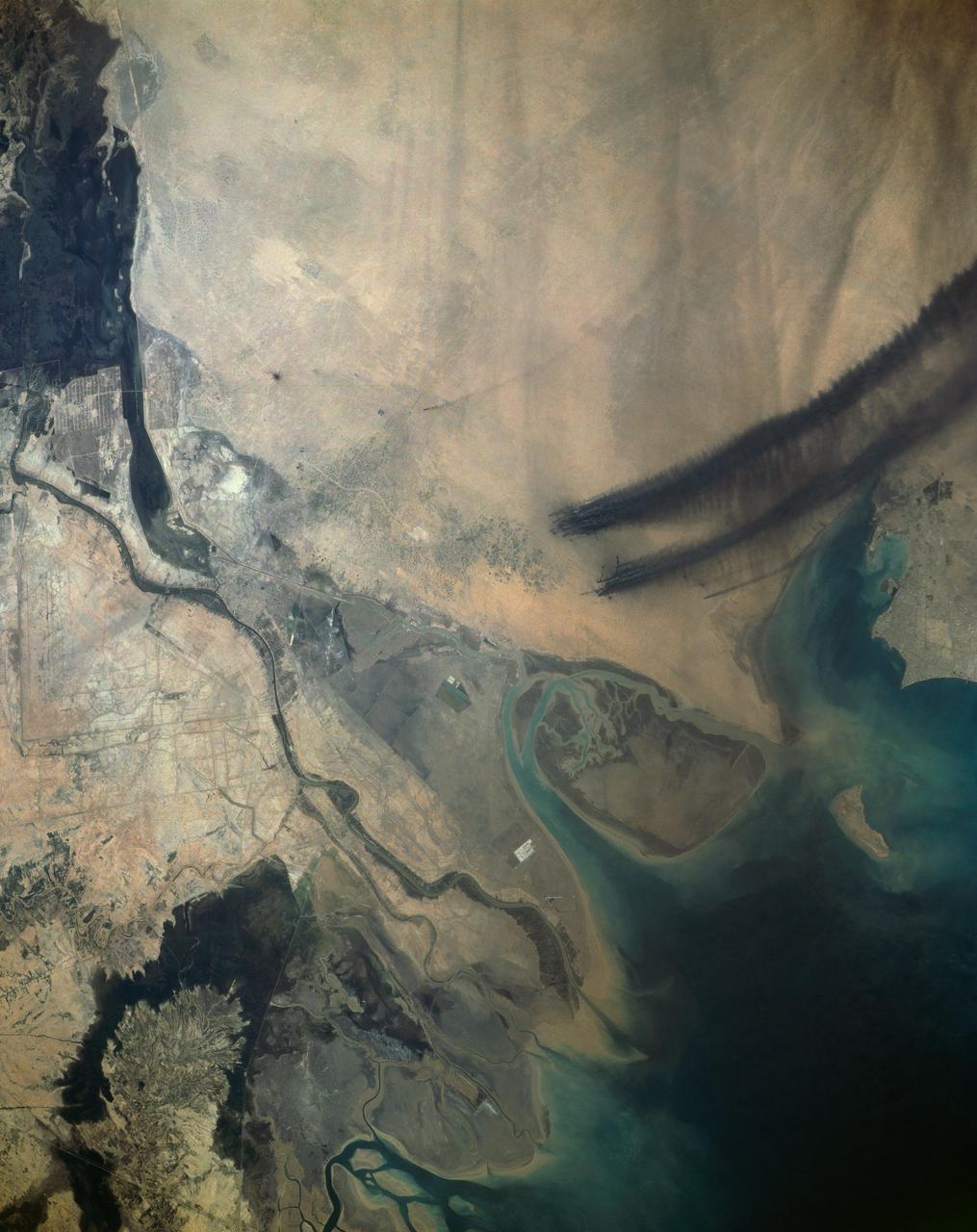

Smoke from the burning oil fields to the north of Kuwait City, seen on the south shore of Kuwayt Bay, almost totally obscures the view of the tiny, but oil rich, nation of Kuwait (30.0N, 48.0E). During the brief war between Iraq and the Allied forces, many of the oil wells in Kuwait were destroyed and set afire. For several months, those fires burned out of control, spewing wind borne smoke and ash for hundreds of miles.
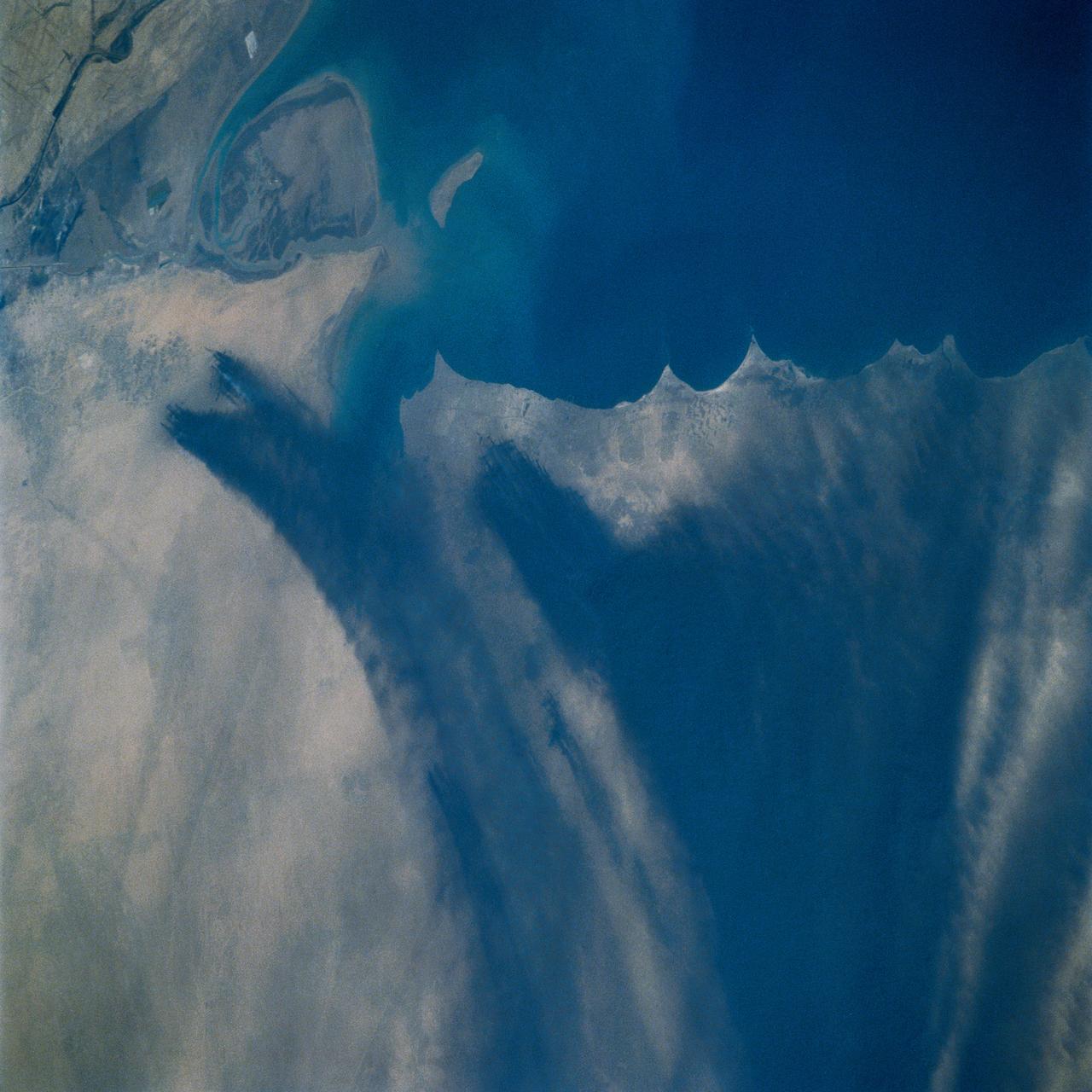

Smoke from the burning oil fields to the north and south of Kuwait City, seen on the south shore of Kuwayt Bay almost totally obscures the view of the tiny, but oil rich, nation of Kuwait (29.0N, 48.0E). During the brief war between Iraq and the Allied forces, many of the oil wells in Kuwait were destroyed and set afire. For several months, those fires burned out of control, spewing wind borne smoke and ash for hundreds of miles.
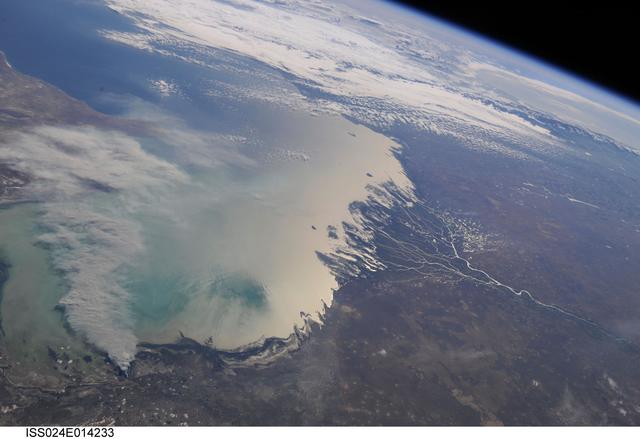

ISS024-E-014233 (11 Sept. 2010) --- A smoke plume near the northern Caspian Sea, Kazakhstan is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member on the International Space Station. This broad view of the north coast of the Caspian Sea shows a smoke plume (left) and two river deltas (bottom and lower right). The larger delta is that of the Volga River which appears prominently here in sunglint (light reflected off a water surface back towards the observer), and the smaller less prominent delta is that of the Ural River. Wide angle, oblique views ? taken looking outward at an angle, rather than straight down towards Earth ? such as this give an excellent impression of how crew members onboard the space station view Earth. For a sense of scale, the Caucasus Mts. (across the Caspian, top right) are approximately 1,100 kilometers to the southwest of the International Space Station?s nadir point location ? the point on Earth directly underneath the spacecraft ? at the time this image was taken. The smoke plume appears to be sourced in the dark-toned coastal marsh vegetation along the outer fringe of the Ural River delta, rather than in a city or at some oil storage facility. Although even small fires produce plumes that are long and bright and thus easily visible from space, the density of the smoke in this plume, and its 350-kilometer length across the entire north lobe of the Caspian Sea, suggest it was a significant fire. The smoke was thick enough nearer the source to cast shadows on the sea surface below. Lines mark three separate pulses of smoke, the most recent, nearest the source, extending directly south away from the coastline (lower left). With time, plumes become progressively more diffuse. The oldest pulse appears to be the thinnest, casting no obvious shadows (center left).
![ISS007-E-18078 (26 October 2003) --- The fires in the San Bernardino Mountains, fueled by Santa Ana winds, burned out of control on the morning of Oct. 26, 2003, when these images were taken from the International Space Station at roughly 11 a.m. (PST). Thick yellow smoke blows south, blanketing the valley below. This image and ISS007-E-18082, looking southeast, capture the smoke pall as the ISS approached and passed over the region. Image numbers 18078 and 18082 were taken roughly a minute apart. A small break in the smoke marks Cajon pass. Content was provided by JSC’s Earth Observation Lab. The International Space Station Program {link to http://spaceflight.nasa.gov} supports the laboratory to help crew members take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth [link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/].](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss007e18078/iss007e18078~medium.jpg)
ISS007-E-18078 (26 October 2003) --- The fires in the San Bernardino Mountains, fueled by Santa Ana winds, burned out of control on the morning of Oct. 26, 2003, when these images were taken from the International Space Station at roughly 11 a.m. (PST). Thick yellow smoke blows south, blanketing the valley below. This image and ISS007-E-18082, looking southeast, capture the smoke pall as the ISS approached and passed over the region. Image numbers 18078 and 18082 were taken roughly a minute apart. A small break in the smoke marks Cajon pass. Content was provided by JSC’s Earth Observation Lab. The International Space Station Program {link to http://spaceflight.nasa.gov} supports the laboratory to help crew members take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth [link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/].
![ISS007-E-18082 (26 October 2003) --- The fires in the San Bernardino Mountains, fueled by Santa Ana winds, burned out of control on the morning of Oct. 26, 2003, when these images were taken from the International Space Station at roughly 11 a.m. (PST). Thick yellow smoke blows south, blanketing the valley below. This image and ISS007-E-18078, looking southeast, capture the smoke pall as the ISS approached and passed over the region. Image numbers 18078 and 18082 were taken roughly a minute apart. A small break in the smoke marks Cajon pass. Content was provided by JSC’s Earth Observation Lab. The International Space Station Program {link to http://spaceflight.nasa.gov} supports the laboratory to help crew members take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth [link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/].](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss007e18082/iss007e18082~medium.jpg)
ISS007-E-18082 (26 October 2003) --- The fires in the San Bernardino Mountains, fueled by Santa Ana winds, burned out of control on the morning of Oct. 26, 2003, when these images were taken from the International Space Station at roughly 11 a.m. (PST). Thick yellow smoke blows south, blanketing the valley below. This image and ISS007-E-18078, looking southeast, capture the smoke pall as the ISS approached and passed over the region. Image numbers 18078 and 18082 were taken roughly a minute apart. A small break in the smoke marks Cajon pass. Content was provided by JSC’s Earth Observation Lab. The International Space Station Program {link to http://spaceflight.nasa.gov} supports the laboratory to help crew members take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth [link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/].
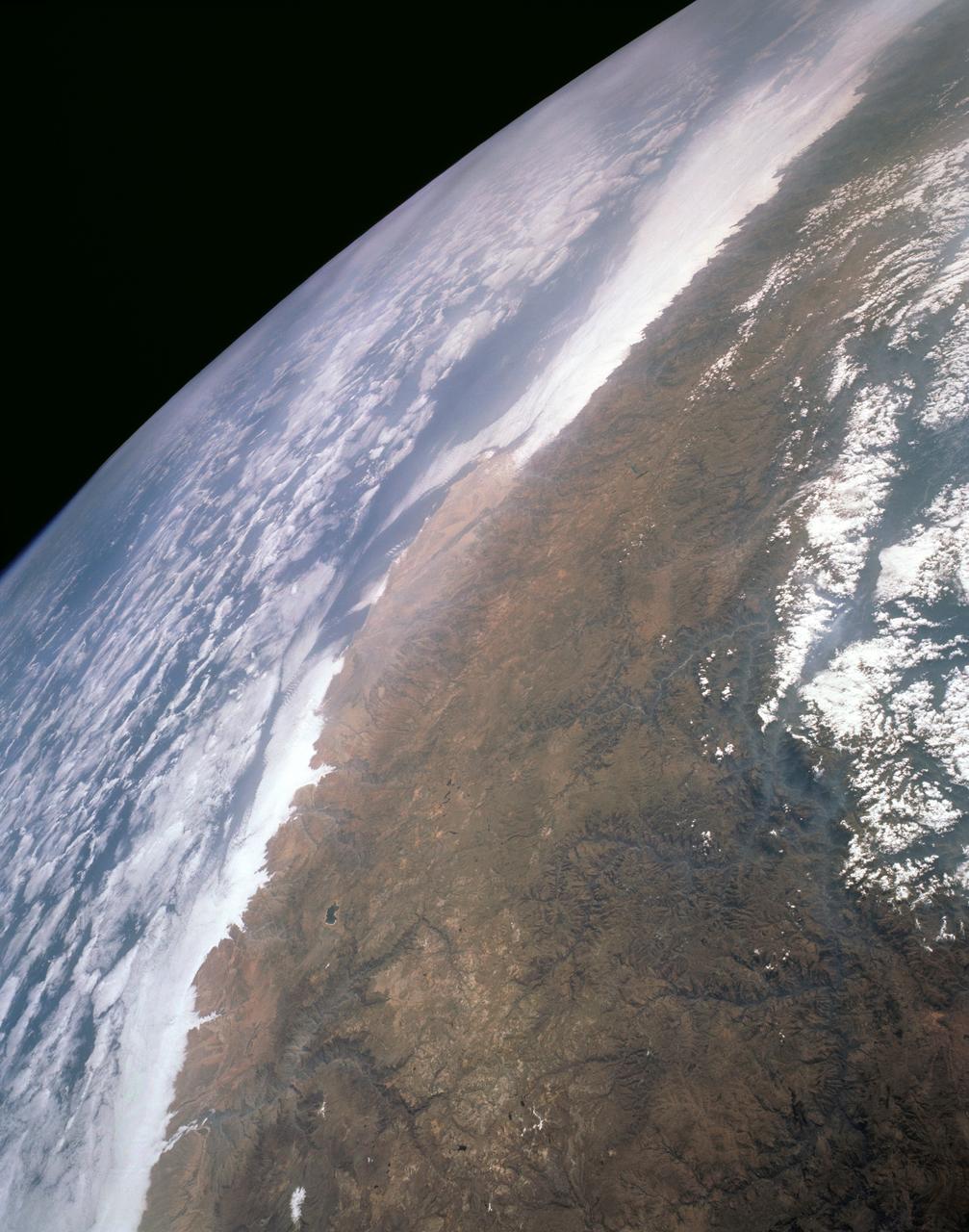

STS043-151-159 (2-11 August 1991) --- This photograph looks westward over the high plateau of the southern Peruvian Andes west and north of Lake Titicaca (not in field of view). Lima, Peru lies under the clouds just north of the clear coastal area. Because the high Andes have been uplifted 10,000 to 13,000 feet during the past 20 million years, the rivers which cut down to the Pacific Ocean have gorges almost that deep, such as the Rio Ocona at the bottom of the photograph. The eastern slopes of the Andes are heavily forested, forming the headwaters of the Amazon system. Smoke from burning in the Amazon basin fills river valleys on the right side of the photograph. A Linhof camera was used to take this view.
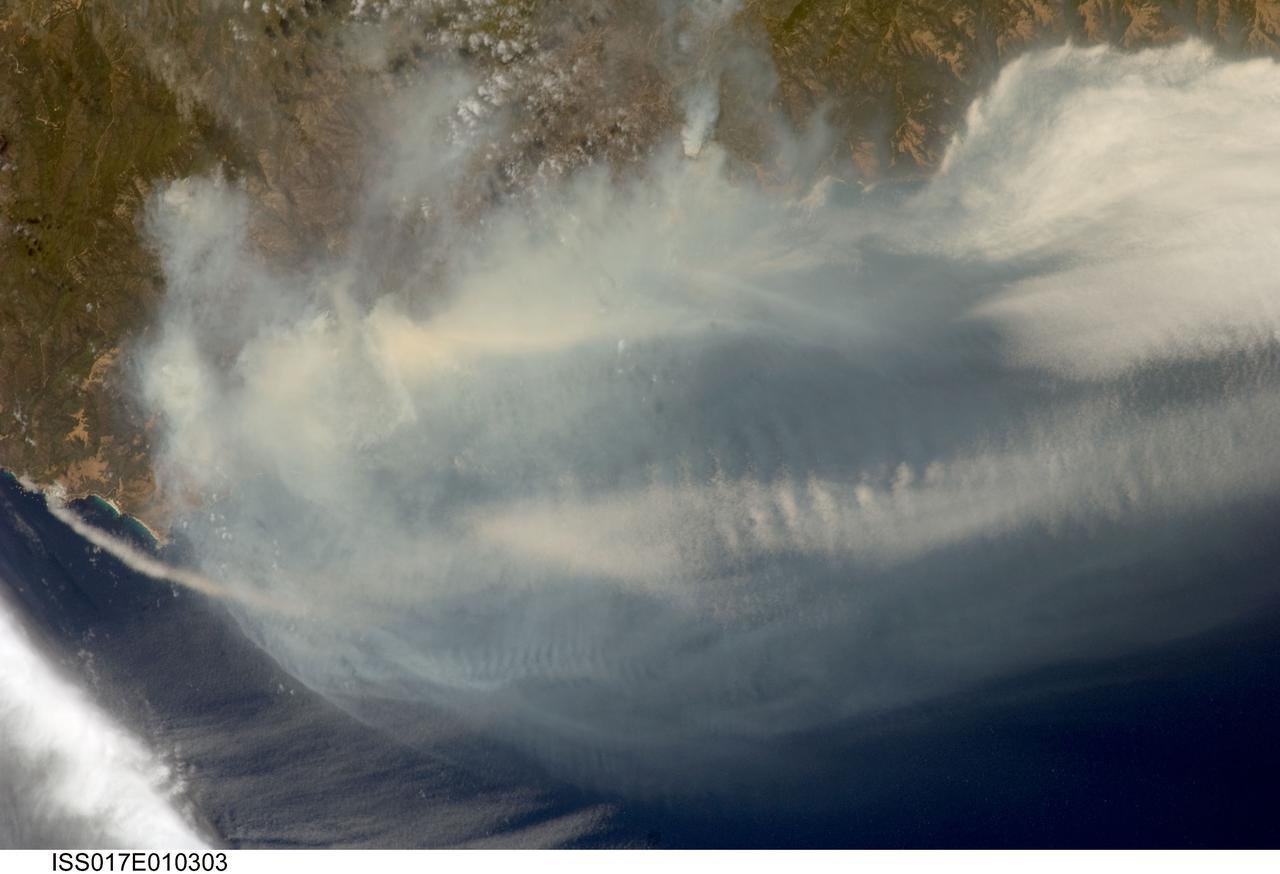

ISS017-E-010303 (4 July 2008) --- The Basin fire in central California is featured in this image photographed by astronaut Greg Chamitoff, Expedition 17 flight engineer, on the International Space Station. One of the largest and most destructive fires raging across California over the July 4 weekend was the Basin fire, threatening Big Sur, and covering the coast in a thick blanket of smoke. Chamitoff, observing the fires from approximately 344 kilometers above Earth (215 miles), was able to capture the regional view of the smoke pall. At the time this image was taken, more than 300 fires were burning in California alone. This Basin fire was triggered by a thunderstorm, has burned 77,000 acres, and is still only partially contained.
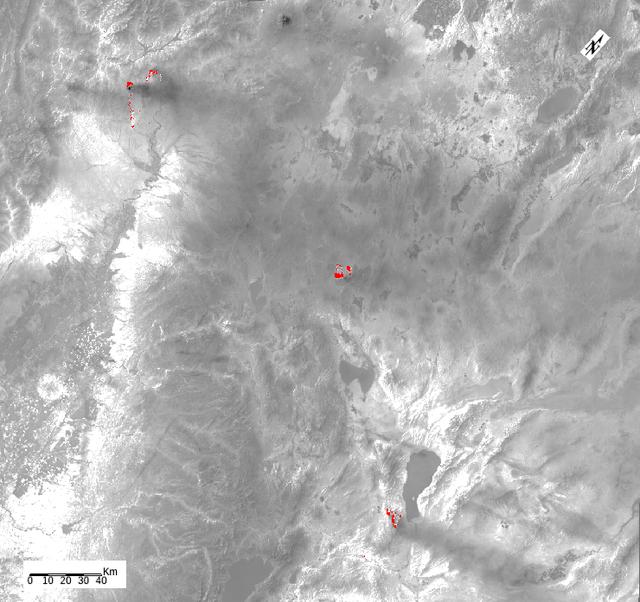
ECOSTRESS, NASA's new Earth-observing mission aboard the International Space Station, detected three wildfires burning in the western US on July 28, 2018 -- the Carr and Whaleback fires in California, and the Perry Fire in Nevada. The fires can be seen in red in Figures 1 and 2. Zooming in on the two larger fires shows the heat data in more detail and also reveals the fires' thick smoke plumes. ECOSTRESS launched on June 29 as part of a SpaceX commercial resupply mission to the space station. Its primary mission is to measure surface temperatures to detect plant health; however, it can also detect other heat-related phenomenon like heat waves, volcanoes and wildfires. This is the first image of wildfires acquired from ECOSTRESS. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22490
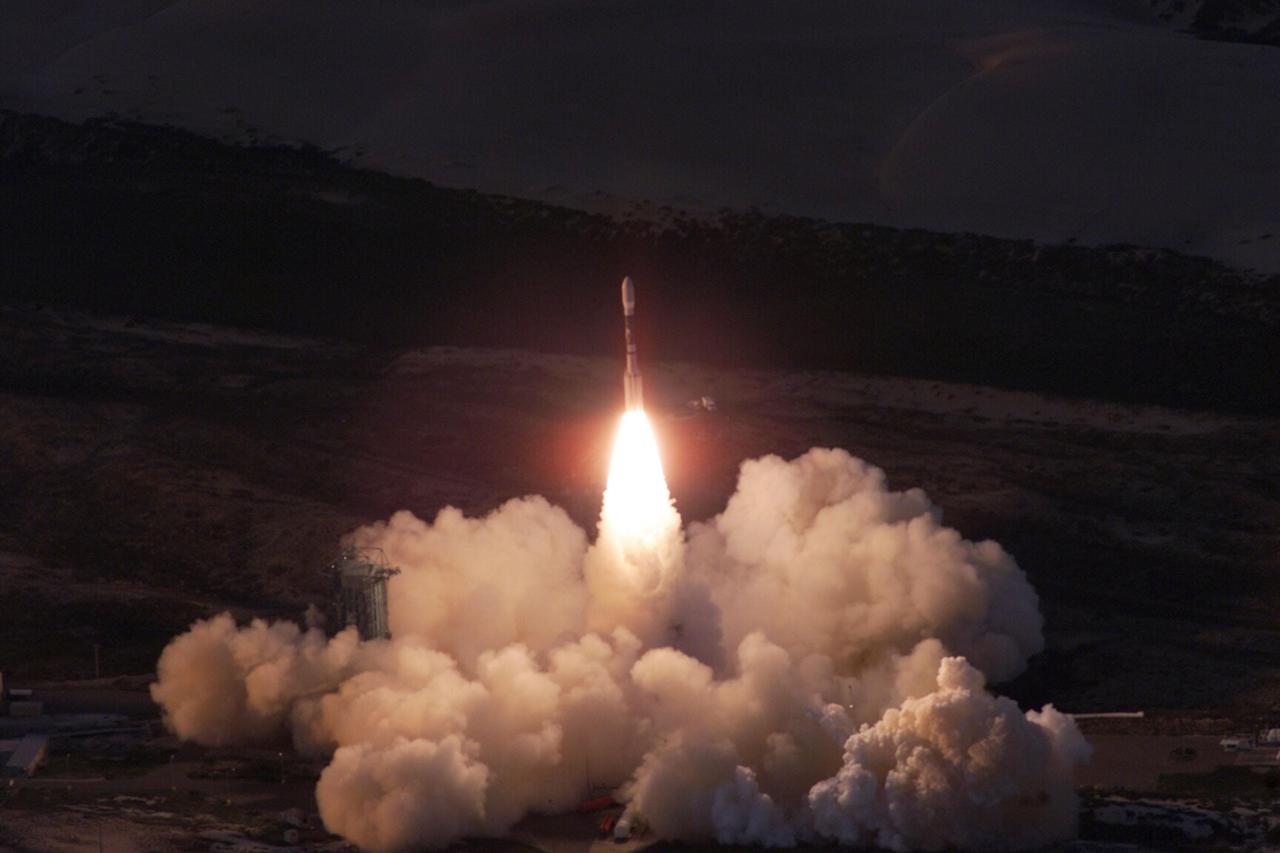

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A Delta II rocket appears to erupt from the undulating clouds of smoke below as it launches with the joint NASA/French Space Agency oceanography satellite Jason 1 and Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite aboard. Liftoff from Launch Complex 2W occurred at 7:07 a.m. PST (10:07 a.m. EST or 15:07 GMT). Jason 1 joins the orbiting Topex/Poseidon satellite to continue observations of the global climate interaction occurring between the sea and the atmosphere as a result of stored solar energy. Instruments on Jason 1 will map variations in ocean surface topography to monitor world ocean circulation, study interactions of the oceans and atmosphere, improve climate predictions and observe events like El Nino. The mission is expected to last three years. The TIMED satellite will study a little-known region above the atmosphere, some 40 to 110 miles from the Earth's surface. Studying this region has been nearly impossible until now because conventional airplanes and balloons cannot reach this high altitude, and it is too low for direct satellite measurements
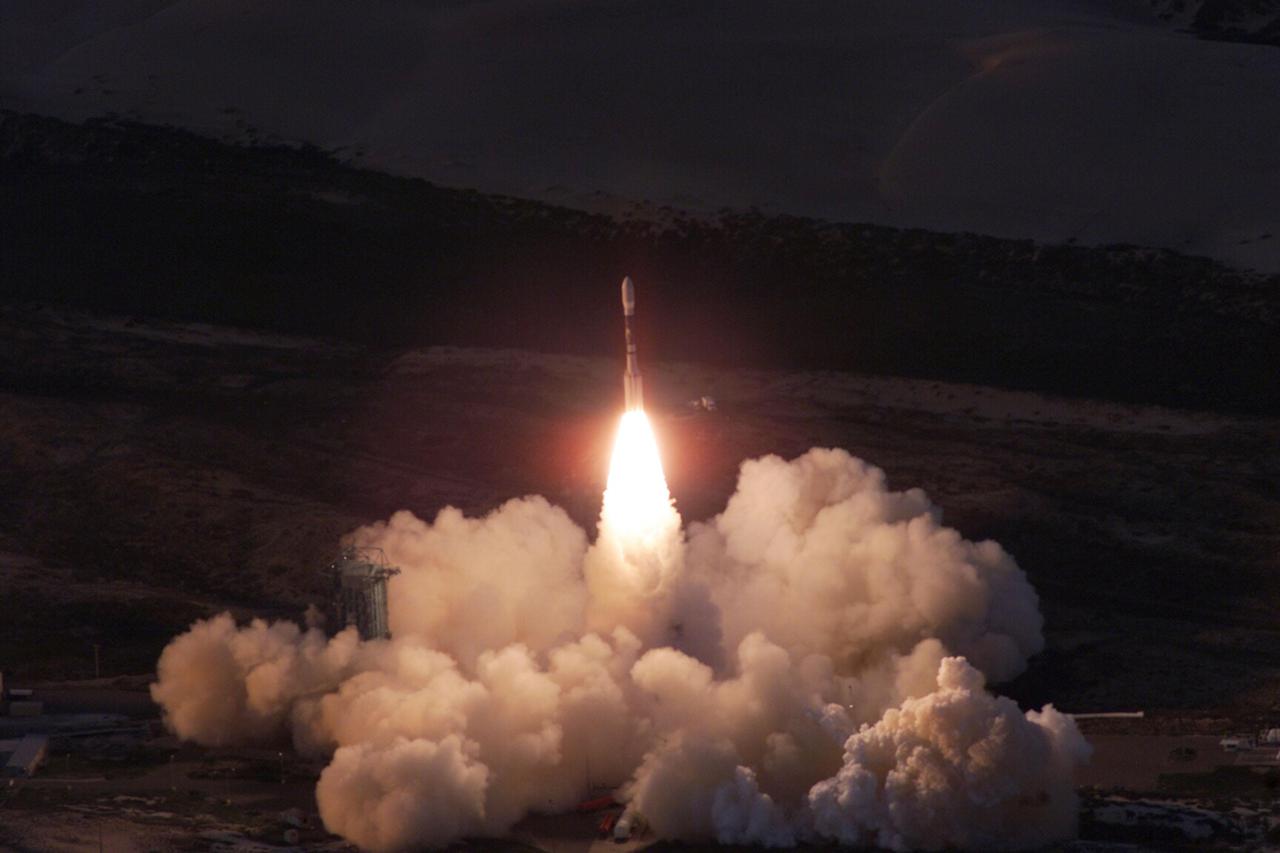

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- A Delta II rocket appears to erupt from the undulating clouds of smoke below as it launches with the joint NASA_French Space Agency oceanography satellite Jason 1 and Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics satellite aboard. Liftoff from Launch Complex 2W occurred at 7:07 a.m. PST (10:07 a.m. EST or 15:07 GMT). Jason 1 joins the orbiting Topex_Poseidon satellite to continue observations of the global climate interaction occurring between the sea and the atmosphere as a result of stored solar energy. Instruments on Jason 1 will map variations in ocean surface topography to monitor world ocean circulation, study interactions of the oceans and atmosphere, improve climate predictions and observe events like El Nino. The mission is expected to last three years. The TIMED satellite will study a little-known region above the atmosphere, some 40 to 110 miles from the Earth's surface. Studying this region has been nearly impossible until now because conventional airplanes and balloons cannot reach this high altitude, and it is too low for direct satellite measurements
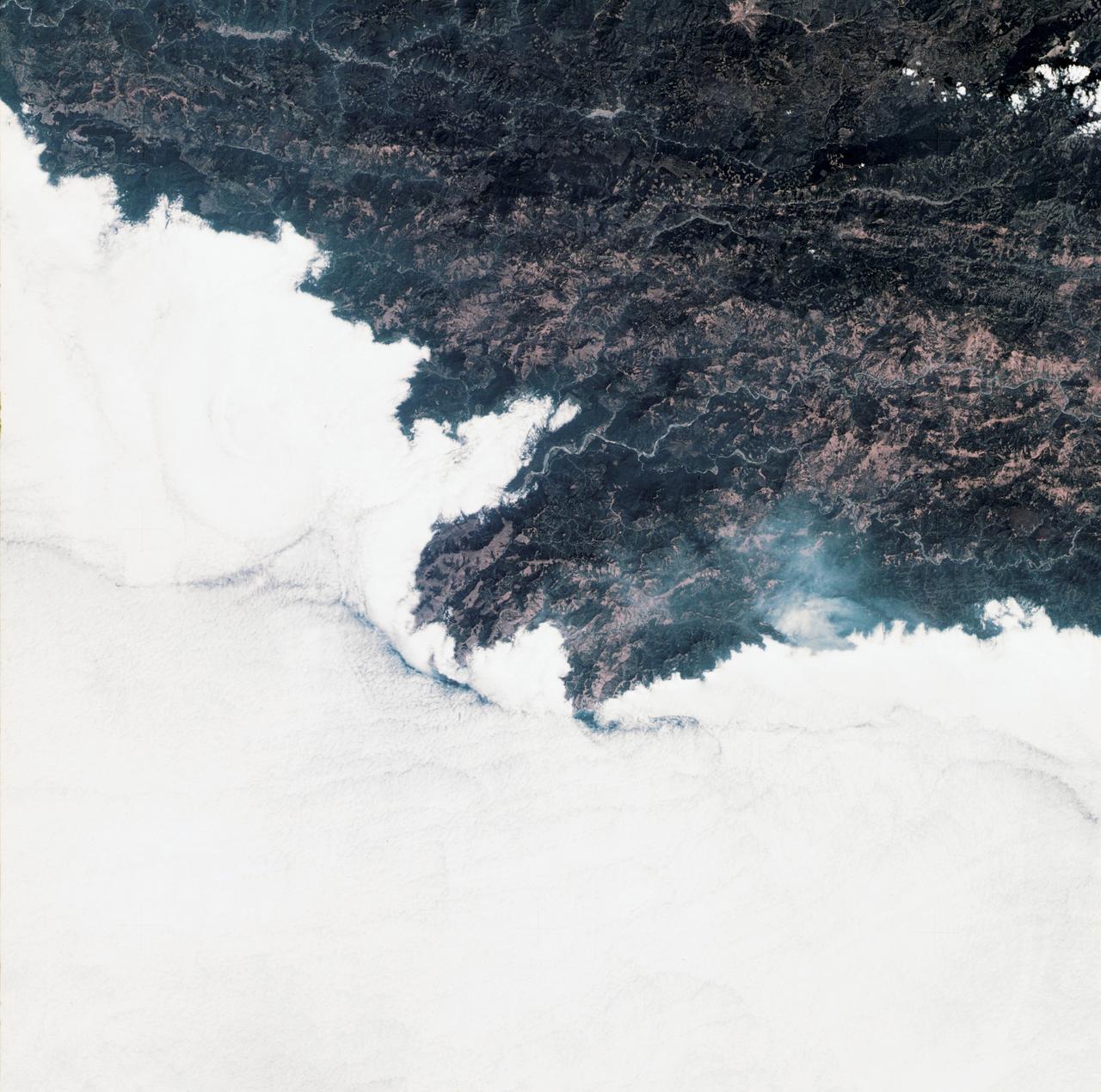

SL3-34-336 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of a portion of northern California near the Pacific coast as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment in the Multiple Docking Adapter of the Skylab space station. A cloud deck covers the Pacific Ocean. Most of Cape Mendocino is clear of clouds and extends into the Pacific as the westernmost part of California. The sinuous pattern of the Bel River (in center) flows northward into the ocean and is characteristic of the rivers that drain the coastal ranges. This area is immediately southeast of Eureka. During Skylab 3 extensive forest fires occurred near Briceland and the smoke rising from the fires is clearly visible next to the cloud bank. Redwood and fir forests are sources of lumber in this region; and a variety of clear cut (timbering) patterns appear as light against the dark forest. The patterns appear to be related to the topography. Analysis of this photograph will aid Dr. P.G. Langley, Earth Satellite Corporation, in developing methods for forest inventory using space photography. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
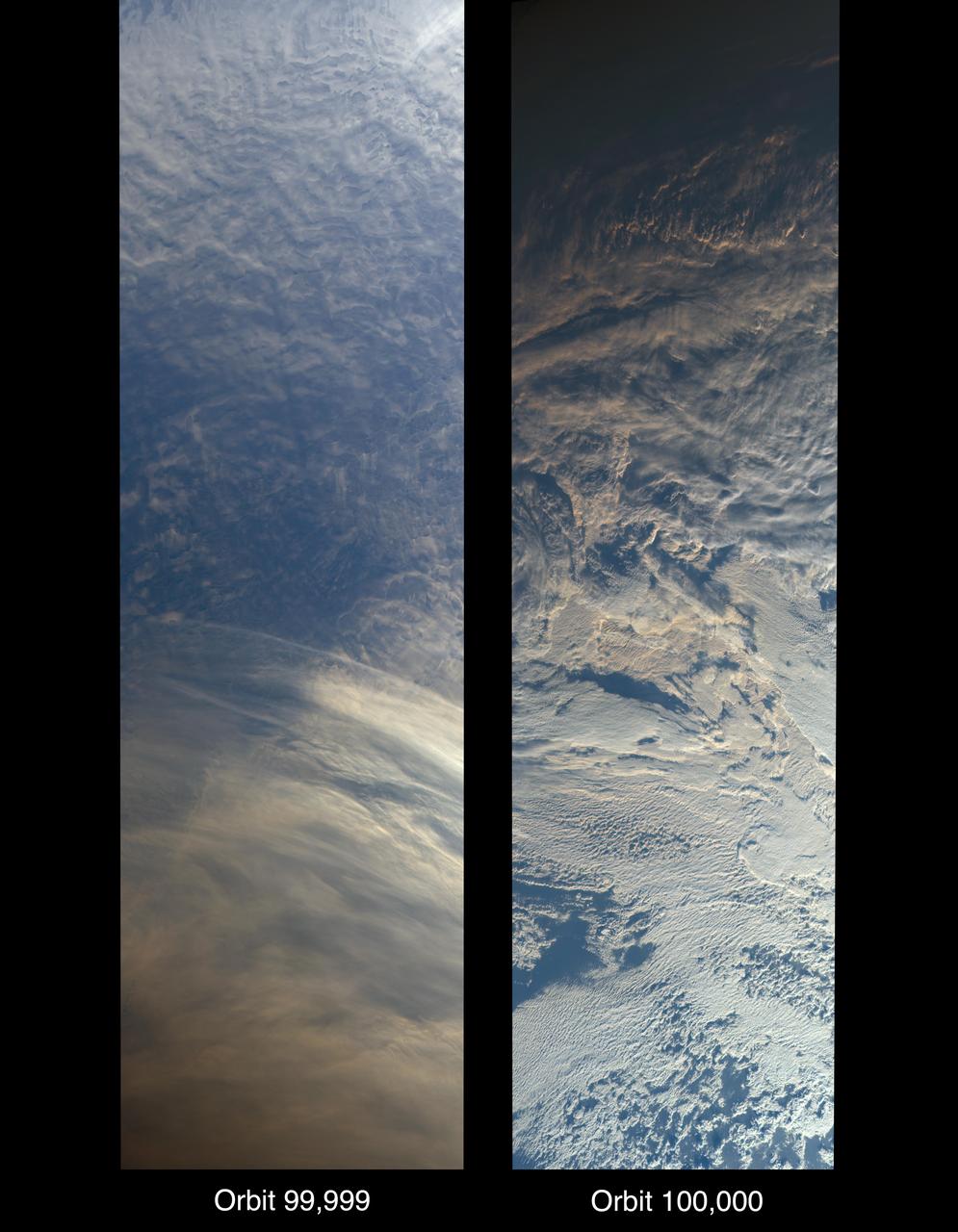
On Oct. 6, 2018, NASA's Terra satellite became one of a handful of NASA satellite ever to complete 100,000 orbits. Launched in 1999, Terra and its five scientific instruments were originally slated to last six years. More than 18 years later, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR), built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, and other instruments on Terra are still collecting data and are expected to continue into the 2020s, limited only by the amount of fuel in the spacecraft. MISR carries nine cameras that view the sunlit Earth simultaneously at widely spaced angles, providing global coverage with high spatial detail. The left image shows dusk falling over snowy Queen Maud Land, Antarctica, at the end of orbit 99,999, as captured by MISR's 70-degree backward-looking camera. On the right is MISR's first view from orbit 100,000, taken by its 70-degree forward-looking camera as sunrise illuminated clouds over the Kara Sea, north of Siberia. Over the years, researchers have used MISR's observations to construct a variety of global data sets that have advanced our understanding of Earth. These include the heights of clouds and wildfire smoke, the amounts of dangerous pollutants in the atmosphere, the movements of global wind systems, and the health of vegetation. The instrument remains as healthy as it was in 1999. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22836
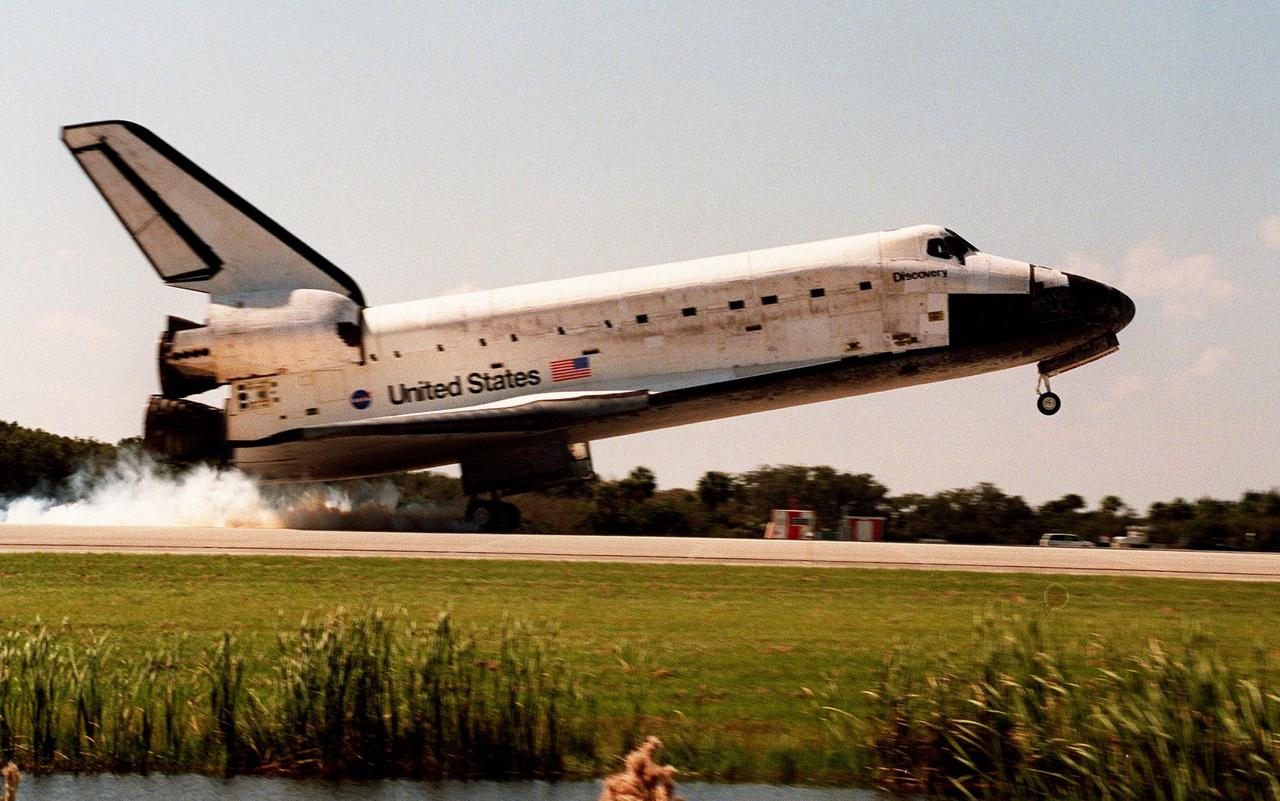

Orbiter Discovery smokes its tires as it touches down on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The crew consists of Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai,M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
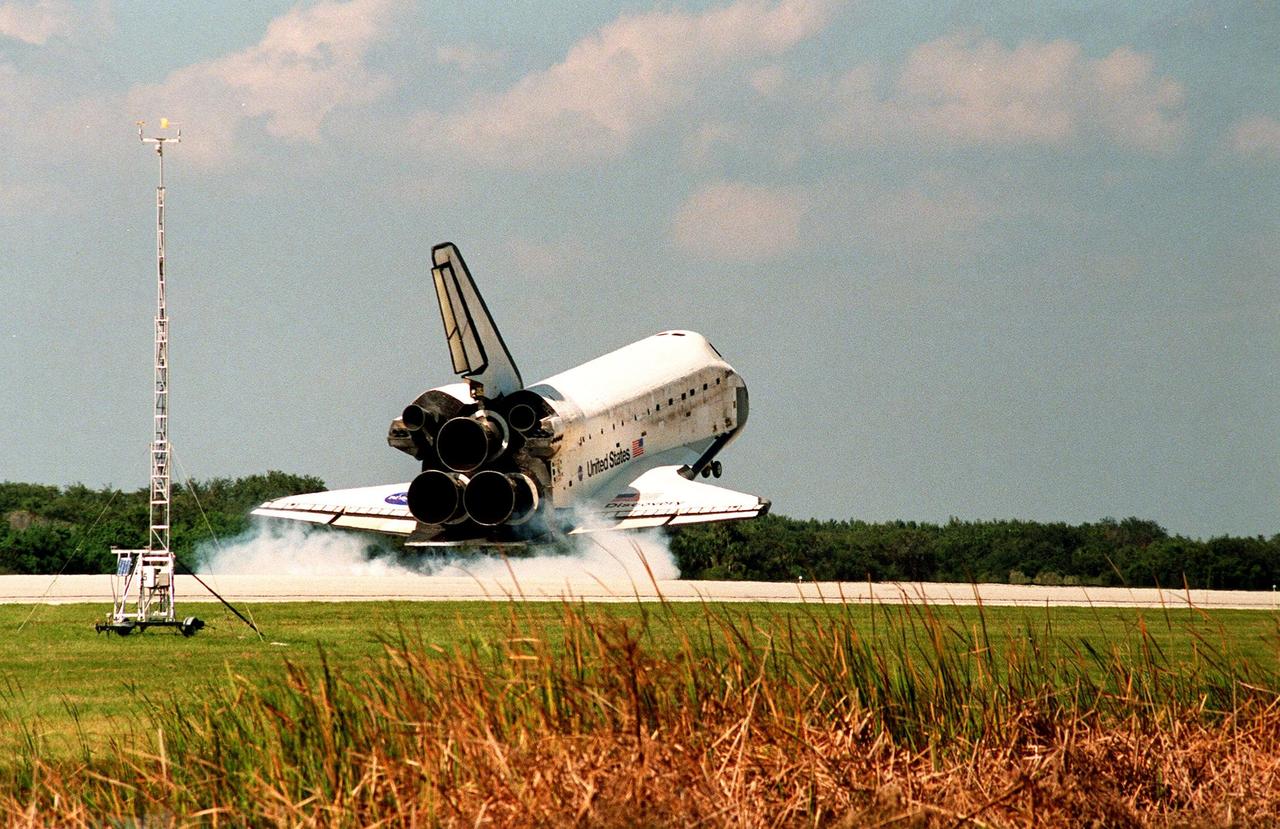

Orbiter Discovery touches down in a cloud of smoke on runway 33 at the Shuttle Landing Facility. Main gear touchdown was at 12:04 p.m. EST, landing on orbit 135. Discovery returns to Earth with its crew of seven after successfully completing mission STS-95, lasting nearly nine days and 3.6 million miles. The crew members are Mission Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr.; Pilot Steven W. Lindsey; Mission Specialist Scott E. Parazynski; Mission Specialist Stephen K. Robinson; Payload Specialist John H. Glenn Jr., a senator from Ohio; Mission Specialist Pedro Duque of Spain, with the European Space Agency (ESA); and Payload Specialist Chiaki Mukai, M.D., with the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). The mission included research payloads such as the Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft, the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, as well as the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
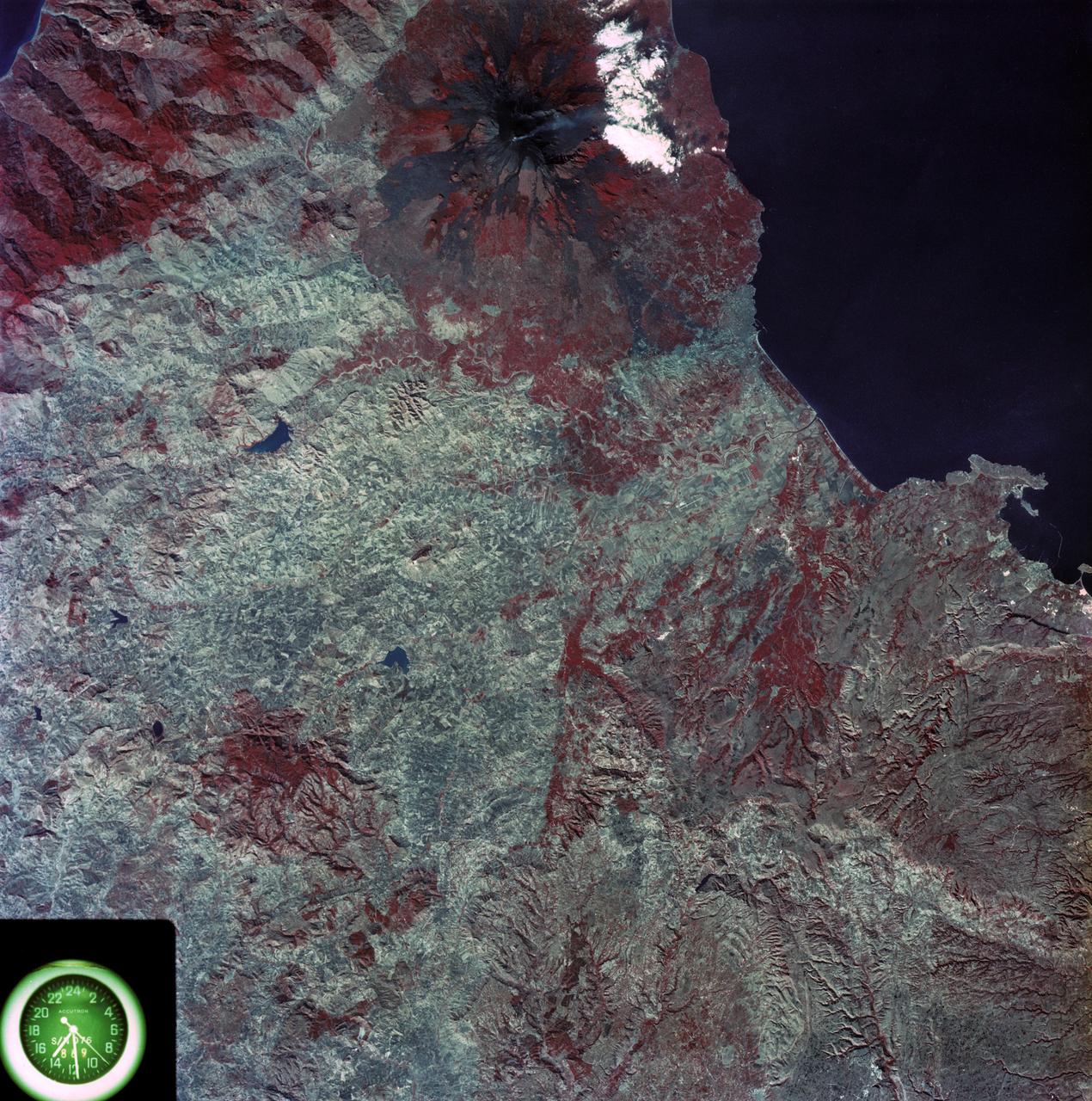
SL3-87-355 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the eastern coast of Sicily area is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch earth terrain camera) infrared photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Mount Etna, the highest volcano in Europe (10,958 feet), is still active as evidenced by the thin plume of smoke emanating from its crest. (The altitude is approximate because the height of the volcano changes with each eruption). On the flanks of Etna recent lava flows appear black in contrast to the older flows and volcanic debris that are red. Numerous small, circular cinder cones on the flanks represent sites of previous eruptions. Catania, on the Mediterranean coast south of Etna, is the largest of several cities and villages which appear as light-gray patches on the lower slopes of the volcano. Plano de Catania, south of the city of Catania, is outlined by polygonal light and dark agricultural tracts. Several lakes, the largest of which is Lake Pozzillo, show up as dark blue in the photograph. The unusual colors in the picture are due to the use of color infrared film in which vegetation appears red. This is very evident on the slopes of Etna, in the Monti Nebrodi area at upper let, and in the local areas in the lower part of the picture. Studies of Mount Etna and related volcanic features will be undertaken by Professor Roberto Cassinis of Servizio Geologio d?Italia, Rome. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observation Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
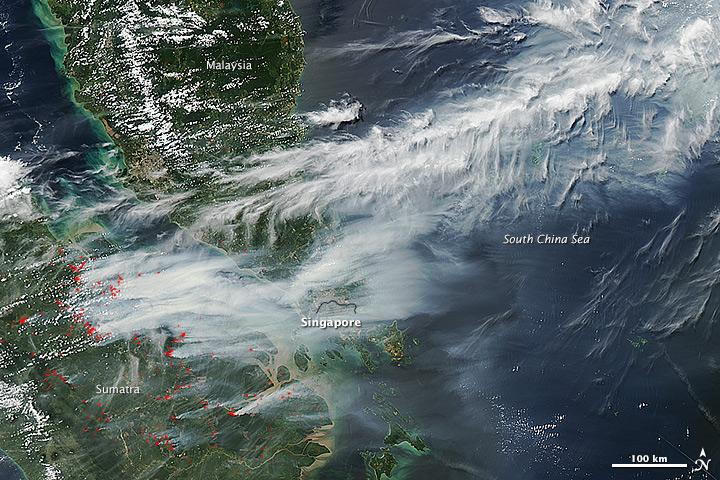

On June 19, 2013, NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a striking image of smoke billowing from illegal wildfires on the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The smoke blew east toward southern Malaysia and Singapore, and news media reported that thick clouds of haze had descended on Singapore, pushing pollution levels to record levels. Singapore’s primary measure of pollution, the Pollutant Standards Index (PSI)—a uniform measure of key pollutants similar to the Air Quality Index (AQI) used by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency—spiked to 371 on the afternoon of June 20, 2013, the highest level ever recorded. The previous record occurred in 1997, when the index hit 226. Health experts consider any level above 300 to be “hazardous” to human health. Levels above 200 are considered “very unhealthy.” The image above was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), an instrument that observes the entire surface of Earth’s every 1 to 2 days. The image was captured during the afternoon at 6:30 UTC (2:30 p.m. local time). Though local laws prohibit it, farmers in Sumatra often burn forests during the dry season to prepare soil for new crops. The BBC reported that Singapore’s Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong warned that the haze could “easily last for several weeks and quite possibly longer until the dry season ends in Sumatra.” NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE/EOSDIS Rapid Response. Caption by Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> Instrument: Aqua - MODIS <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
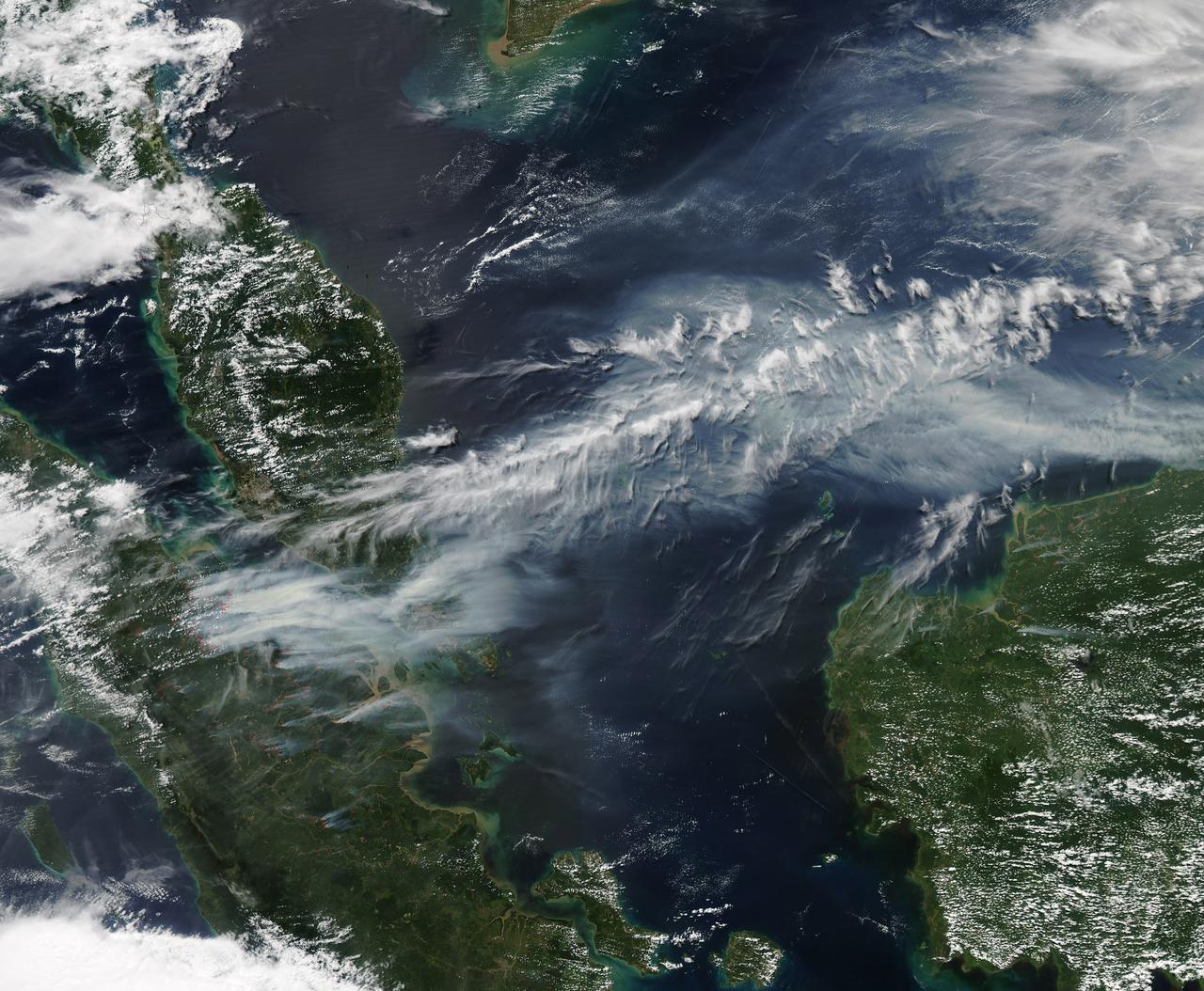
On June 19, 2013, NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a striking image of smoke billowing from illegal wildfires on the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The smoke blew east toward southern Malaysia and Singapore, and news media reported that thick clouds of haze had descended on Singapore, pushing pollution levels to record levels. Singapore’s primary measure of pollution, the Pollutant Standards Index (PSI)—a uniform measure of key pollutants similar to the Air Quality Index (AQI) used by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency—spiked to 371 on the afternoon of June 20, 2013, the highest level ever recorded. The previous record occurred in 1997, when the index hit 226. Health experts consider any level above 300 to be “hazardous” to human health. Levels above 200 are considered “very unhealthy.” The image above was captured by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS), an instrument that observes the entire surface of Earth’s every 1 to 2 days. The image was captured during the afternoon at 6:30 UTC (2:30 p.m. local time). Though local laws prohibit it, farmers in Sumatra often burn forests during the dry season to prepare soil for new crops. The BBC reported that Singapore’s Prime Minister Lee Hsien Loong warned that the haze could “easily last for several weeks and quite possibly longer until the dry season ends in Sumatra.” NASA image by Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE/EOSDIS Rapid Response. Caption by Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> Instrument: Aqua - MODIS <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

ISS012-E-21250 (2 March 2006) --- Dust and smog in northeast China are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 12 crewmember on the International Space Station. Much of the land surface is obscured in this oblique image of the North China Plain and parts of Inner Mongolia. In the center of the view a mass of gray smog—mainly industrial pollution and smoke from domestic burning—obscures Beijing and surrounding cities. Numerous plumes with their source points appear within the mass. Beijing suffers some of the worst air pollution in the world from these chronic sources, and the characteristic colors and textures of the smog can be easily seen through windows of the International Space Station. The coastline of Bo Hai Bay, 300 kilometers east of Beijing, is visible at left. The light brown material in Bo Hai Bay is sediment from the Yellow and other rivers. Separated from the smog mass by a band of puffy, white cumulus clouds is a light brown plume of dust. The line of white cloud has developed along the escarpment that separates the heavily populated North China Plain – location of the largest population agglomeration on Earth – and the sparsely populated semi-desert plains of Inner Mongolia. Observers saw a number of dust events in most Northern Hemisphere deserts in the spring of 2006, and the Gobi and the Takla Makan deserts of western China were no exception. Dust plumes originating in these deserts typically extend eastward hundreds of kilometers, regularly depositing dust on Beijing, the Korean peninsula and Japan. Some plumes even extend over the Pacific Ocean. In extreme cases, visible masses of Gobi-derived dust have reached North America.
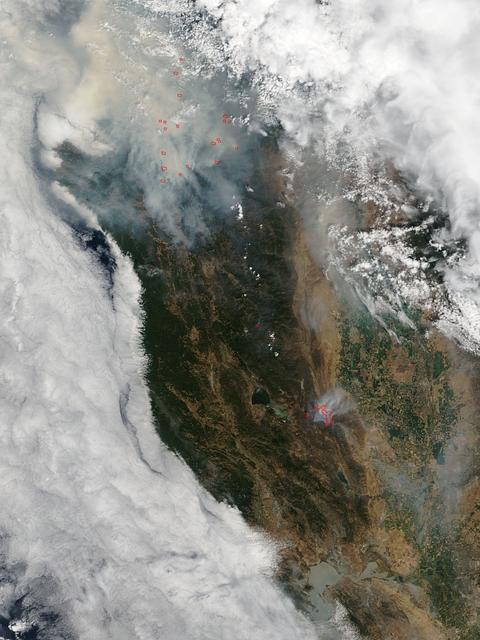

This satellite image shows smoke from several fires in Oregon and California on Aug. 2, 2015. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of smoke from these fires Aug. 2 at 21:05 UTC (5:05 p.m. EDT). The multiple red pixels are heat signatures detected by MODIS. The smoke appears to be a light brown color. InciWeb is an interagency all-risk incident information management system that coordinates with federal, state and local agencies to manage wildfires. In Oregon smoke from the Cable Crossing Fire, the Stouts Fire and the Potter Mountain Complex Fire commingle. The Cable Crossing Fire was reported burning on forestlands protected by the Douglas Forest Protective Association (DFPA) at approximately 3:25 p.m. on Tuesday, July 28, 2015, near Oregon Highway 138 East, near Mile Post 23, east of Glide. South of the Cable Crossing Fire is the Stouts Fire also in forestlands of the DFPA. This fire was reported on Thursday, July 30, 2015, burning approximately 11 miles east of Canyonville near the community of Milo. East of the other fires is the Potter Mountain Complex Fire. These fires are located in the Deschutes Forest consists of eight fires. According to Inciweb they were started by dry lightning on Saturday, Aug. 2, at approximately 5:30 p.m. about five miles north of Toketee Lake. In northern California, smoke from the River Complex Fire, the Fork Complex Fire and the Shf July Lightning Fire was visible in the MODIS image. The River Complex currently consists of seven reported and observed fires on the Six Rivers and Shasta Trinity National Forests. Originally identified as 18 fires, some have burned together. Inciweb noted that in the Six Rivers National Forest there are fires in the Trinity Alps Wilderness. Those fires include the Groves Fire and the Elk Fire. In the Shasta-Trinity National Forest the fires include the Happy Fire at 2,256 acres, Daily Fire at 16 acres, the Look Fire at 7 acres, Onion Fire at 136 acres and Smokey Fire at 1 acre. In the same forest, south of the River Complex is the Fork Complex fire. Inciweb reported that the Fork Complex consists of (at current count) over 40 fires, all of which were ignited by lightning between July 29 and 31, 2015. To the southwest of this complex is the Mad River Complex. This is a series of seven lightning fires that started on July 30, 2015 after a lightning storm moved through Northern California. To the east of this and the other fires, burns another near Redding, California, called the Shf July Lightning Fire. This is also under the Shasta-Trinity National Forest management. At 8 p.m. PDT on Aug. 2, Inciweb reported that approximately 15 lightning strikes occurred within 24 hours throughout the Shasta Trinity National Forest and resulted in two new fires. The Caves fire, east of Mt. Shasta, is approximately one-tenth of an acre. The Bluejay fire, east of Shasta Lake, is approximately four acres. Image credit: NASA Goddard's MODIS Rapid Response Team, Jeff Schmaltz <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release July 3, 2012 Caption: Resembling a Fourth of July skyrocket, Herbig-Haro 110 is a geyser of hot gas from a newborn star that splashes up against and ricochets off the dense core of a cloud of molecular hydrogen. Although the plumes of gas look like whiffs of smoke, they are actually billions of times less dense than the smoke from a July 4 firework. This Hubble Space Telescope photo shows the integrated light from plumes, which are light-years across. -- Herbig-Haro (HH) objects come in a wide array of shapes, but the basic configuration stays the same. Twin jets of heated gas, ejected in opposite directions away from a forming star, stream through interstellar space. Astronomers suspect that these outflows are fueled by gas accreting onto a young star surrounded by a disk of dust and gas. The disk is the "fuel tank," the star is the gravitational engine, and the jets are the exhaust. When these energetic jets slam into colder gas, the collision plays out like a traffic jam on the interstate. Gas within the shock front slows to a crawl, but more gas continues to pile up as the jet keeps slamming into the shock from behind. Temperatures climb sharply, and this curving, flared region starts to glow. These "bow shocks" are so named because they resemble the waves that form at the front of a boat. In the case of the single HH 110 jet, astronomers observe a spectacular and unusual permutation on this basic model. Careful study has repeatedly failed to find the source star driving HH 110, and there may be good reason for this: perhaps the HH 110 outflow is itself generated by another jet. Astronomers now believe that the nearby HH 270 jet grazes an immovable obstacle - a much denser, colder cloud core - and gets diverted off at about a 60-degree angle. The jet goes dark and then reemerges, having reinvented itself as HH 110. The jet shows that these energetic flows are like the erratic outbursts from a Roman candle. As fast-moving blobs of gas catch up and collide with slower blobs, new shocks arise along the jet's interior. The light emitted from excited gas in these hot blue ridges marks the boundaries of these interior collisions. By measuring the current velocity and positions of different blobs and hot ridges along the chain within the jet, astronomers can effectively "rewind" the outflow, extrapolating the blobs back to the moment when they were emitted. This technique can be used to gain insight into the source star's history of mass accretion. This image is a composite of data taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys in 2004 and 2005 and the Wide Field Camera 3 in April 2011. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
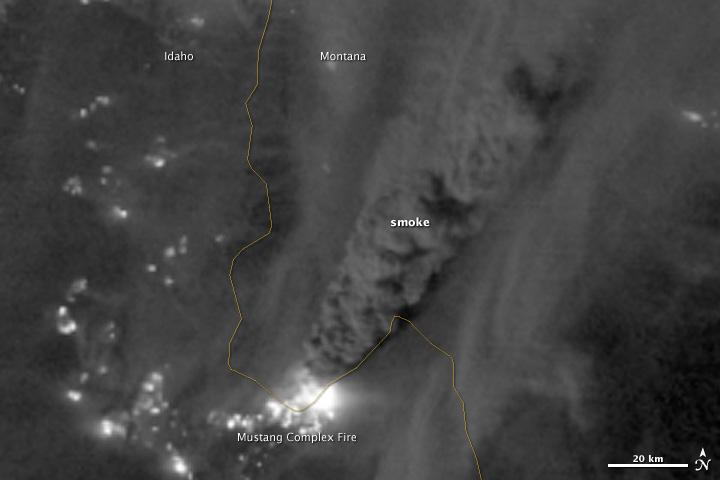

On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
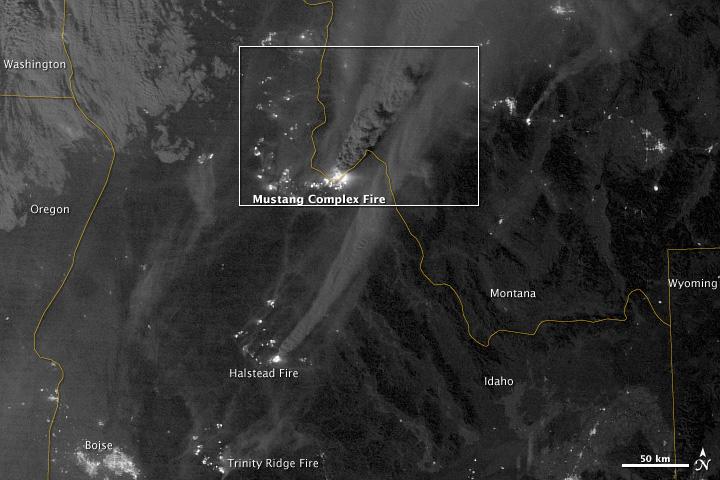
On August 29, 2012, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured this nighttime view of wildfires burning in Idaho and Montana. The image was captured by the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. When the image was acquired, the moon was in its waxing gibbous phase, meaning it was more than half-lit, but less than full. Numerous hot spots from the Mustang Complex Fire are visible in northern Idaho. A plume of thick, billowing smoke streams west from the brightest fires near the Idaho-Montana border. The Halstead and Trinity Ridge fires are visible to the south. In addition to the fires, city lights from Boise and other smaller cities appear throughout the image. A bank of clouds is located west of the Mustang Complex, over southeastern Washington and northeastern Oregon. The Operational Line System (OLS)—an earlier generation of night-viewing sensors on the U.S. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) satellites—was also capable of detecting fires at night. But the VIIRS “day-night band” is far better than OLS at resolving them. Each pixel of an VIIRS image shows roughly 740 meters (0.46 miles), compared to the 3-kilometer footprint (1.86 miles) on the OLS system. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS Day-Night Band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Adam Voiland. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79754" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>