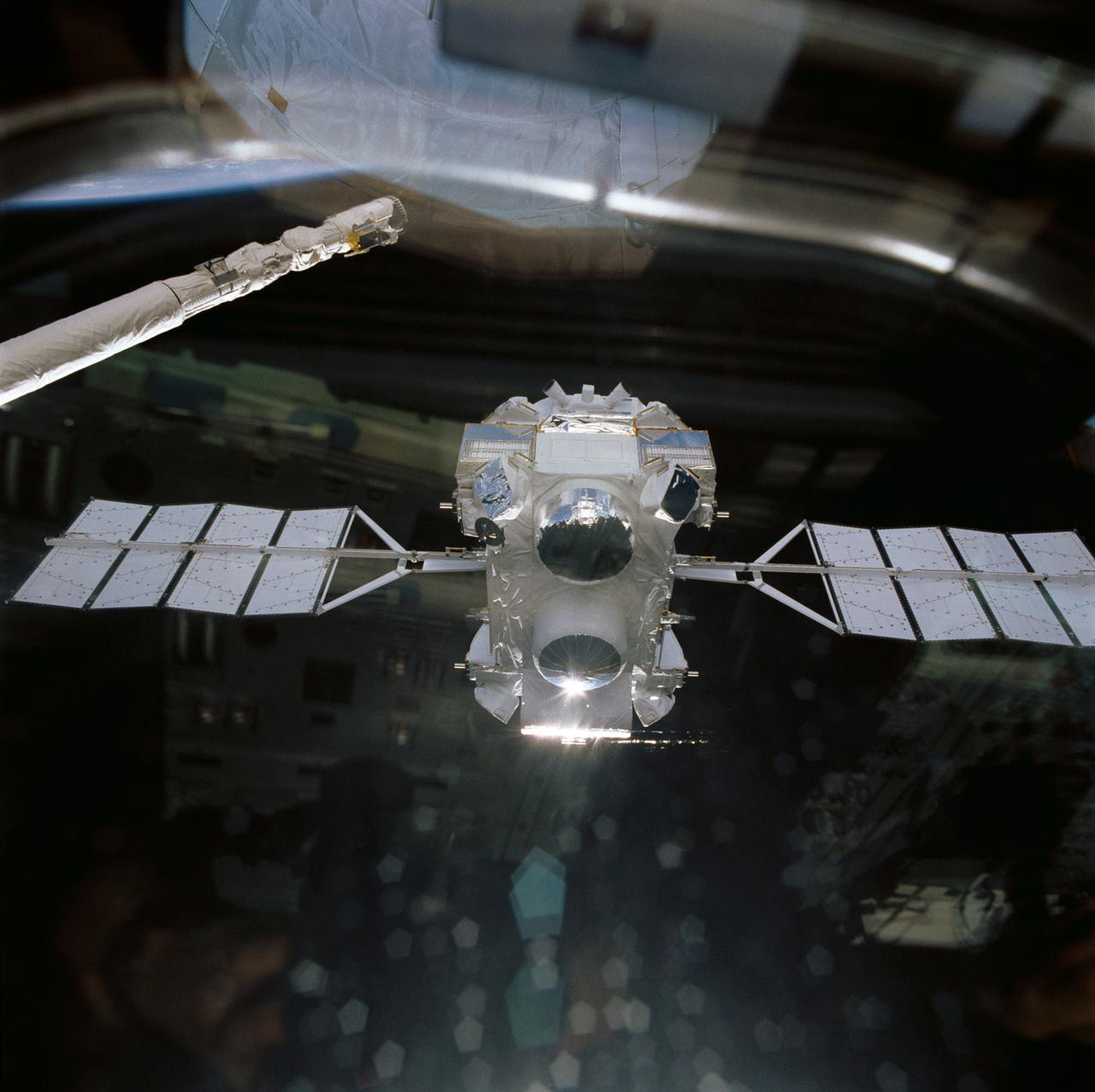

Atlantis', Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104's, remote manipulator system (RMS) releases Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) during STS-37 deployment. Visible on the GRO as it drifts away from the RMS end effector are the four complement instruments: the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment (bottom); Imaging Compton Telescope (COMPTEL) (center); Oriented Scintillation Spectrometer Experiment (OSSE) (top); and Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE) (at four corners). GRO's solar array (SA) panels are extended and are in orbit configuration. View was taken through aft flight deck window which reflects some of the crew compartment interior.

STS037-99-098 (7 April 1991) --- Backdropped against clouds over water, the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) is still in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Atlantis' Remote Manipulator System (RMS) in this 70mm scene. A special Extravehicular Activity (EVA) was required by astronauts Jerry L. Ross and Jerome (Jay) Apt to manually extend the high-gain antenna on GRO. The five-member crew capped off a busy Flight Day 3 by releasing the heavy payload.
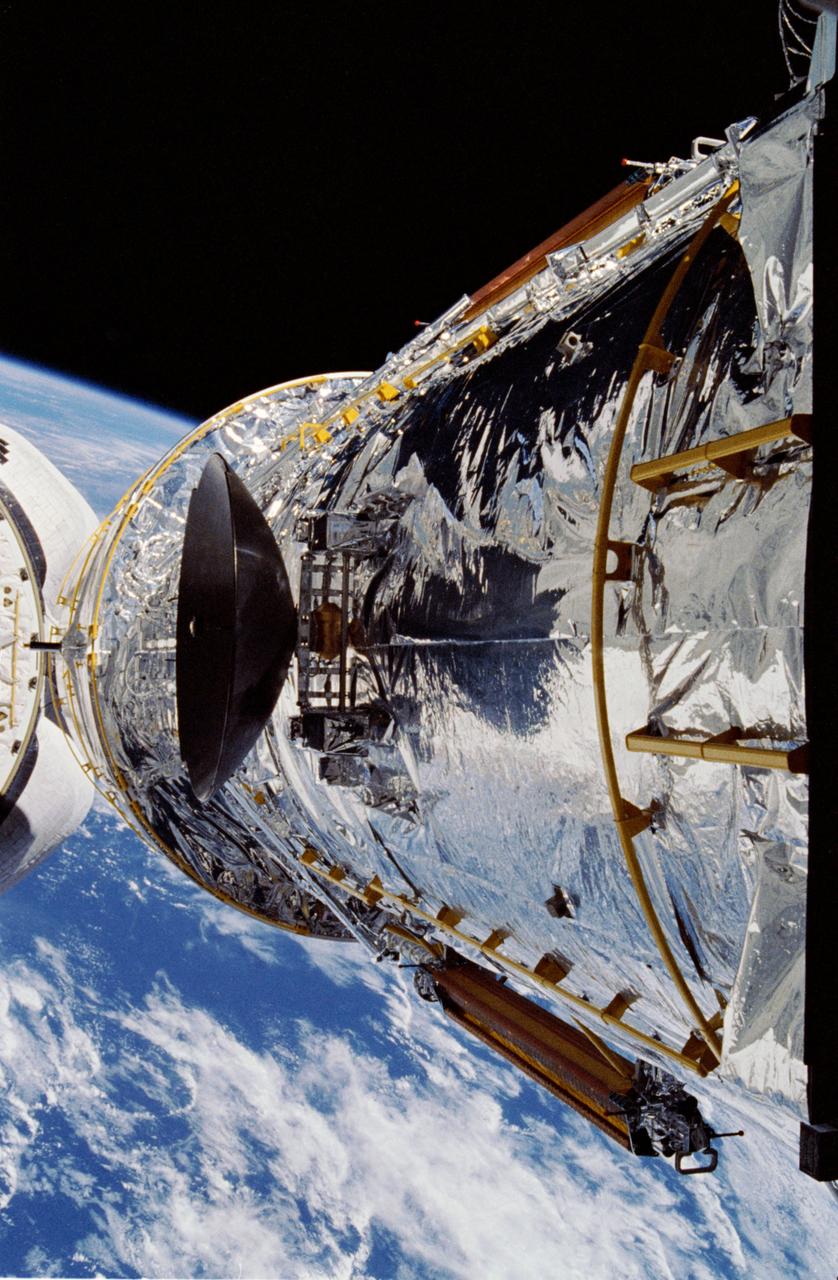
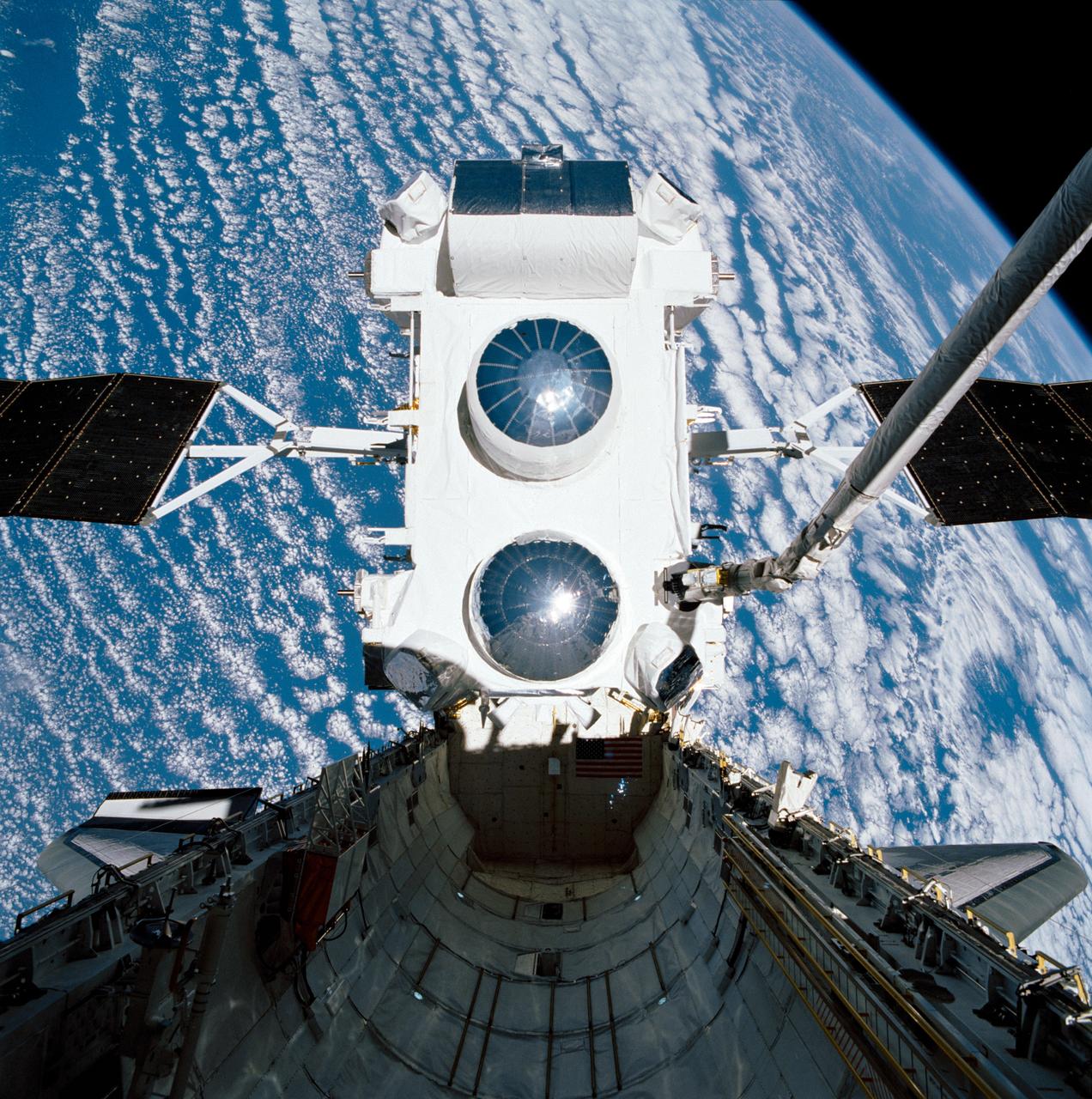
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is raised above the payload bay (PLB) in low hover position during STS-31 checkout and pre-deployment procedures aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Stowed along the HST Support System Module (SSM) are the high gain antenna (HGA) (center) and the two solar arrays (one either side). In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's surface.

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), is held in a pre-deployment position. During STS-31 checkout procedures, the solar array (SA) panels and the high gain antennae (HGA) will be deployed. The starboard SA (center) and the two HGA are stowed along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The sun highlights HST against the blackness of space.
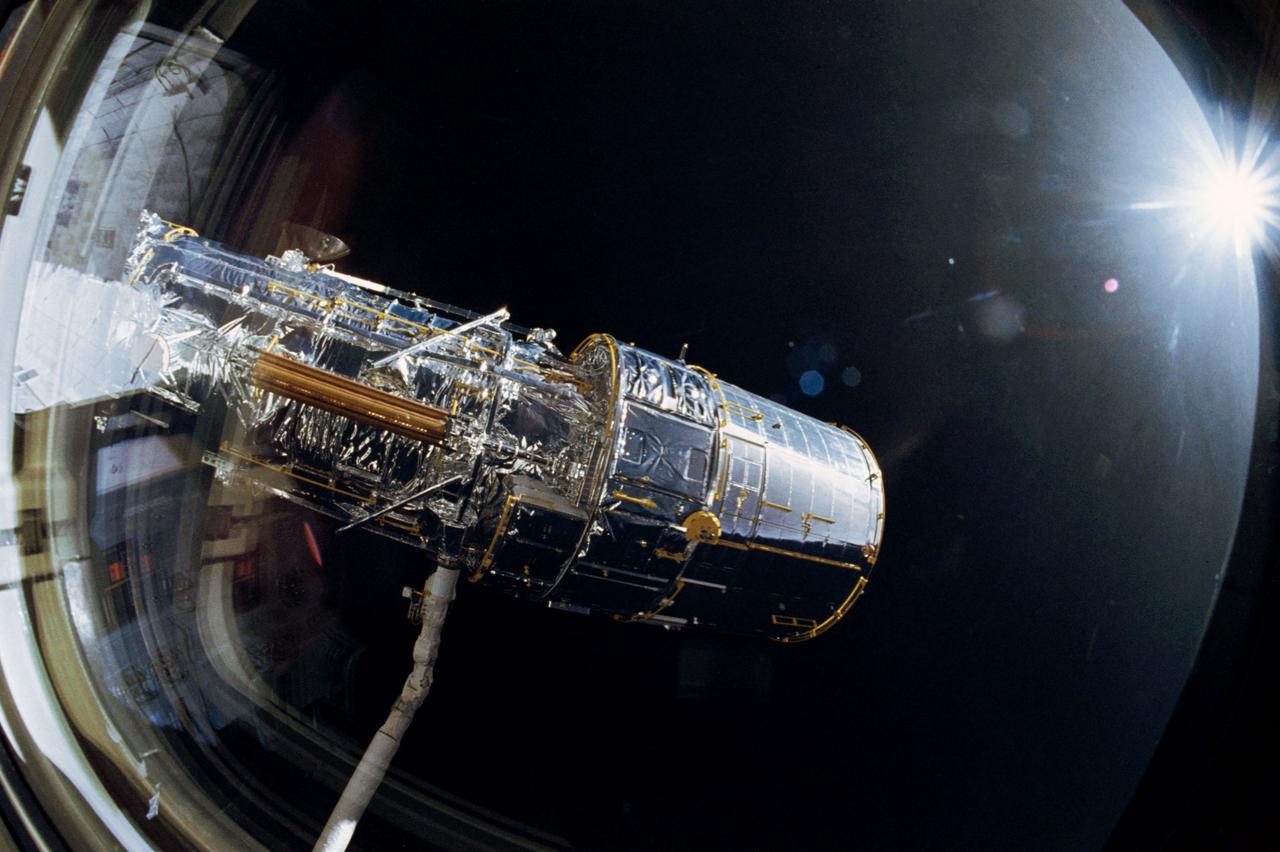
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), is oriented in a 90 degree pitch position during STS-31 pre-deployment checkout procedures. The solar array (SA) panel (center) and high gain antennae (HGA) (on either side) are stowed along the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell prior to deployment. The sun highlights HST against the blackness of space.
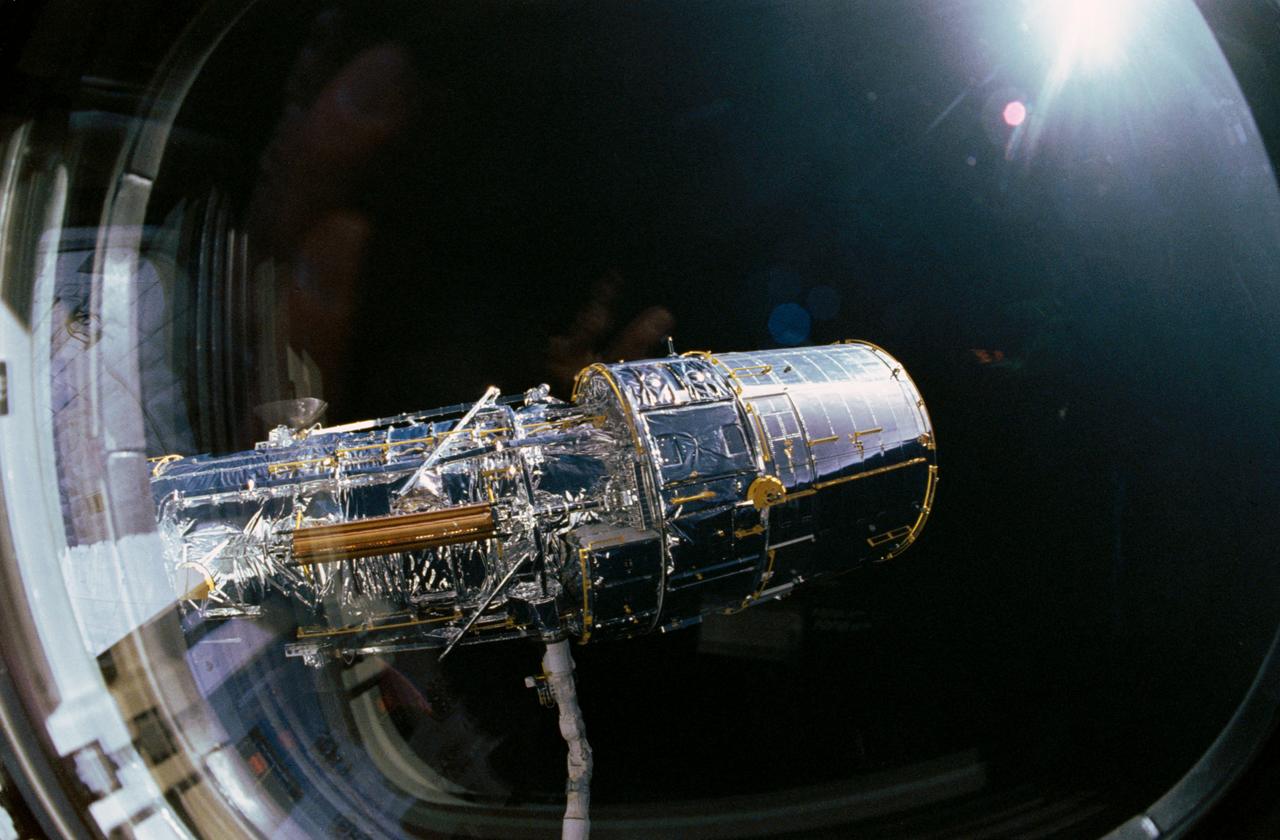
View taken through overhead window W7 aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) and held in a 90 degree pitch position against the blackness of space. The solar array (SA) panel (center) and the high gain antennae (HGA) (on either side) are visible along the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell prior to deployment during STS-31.
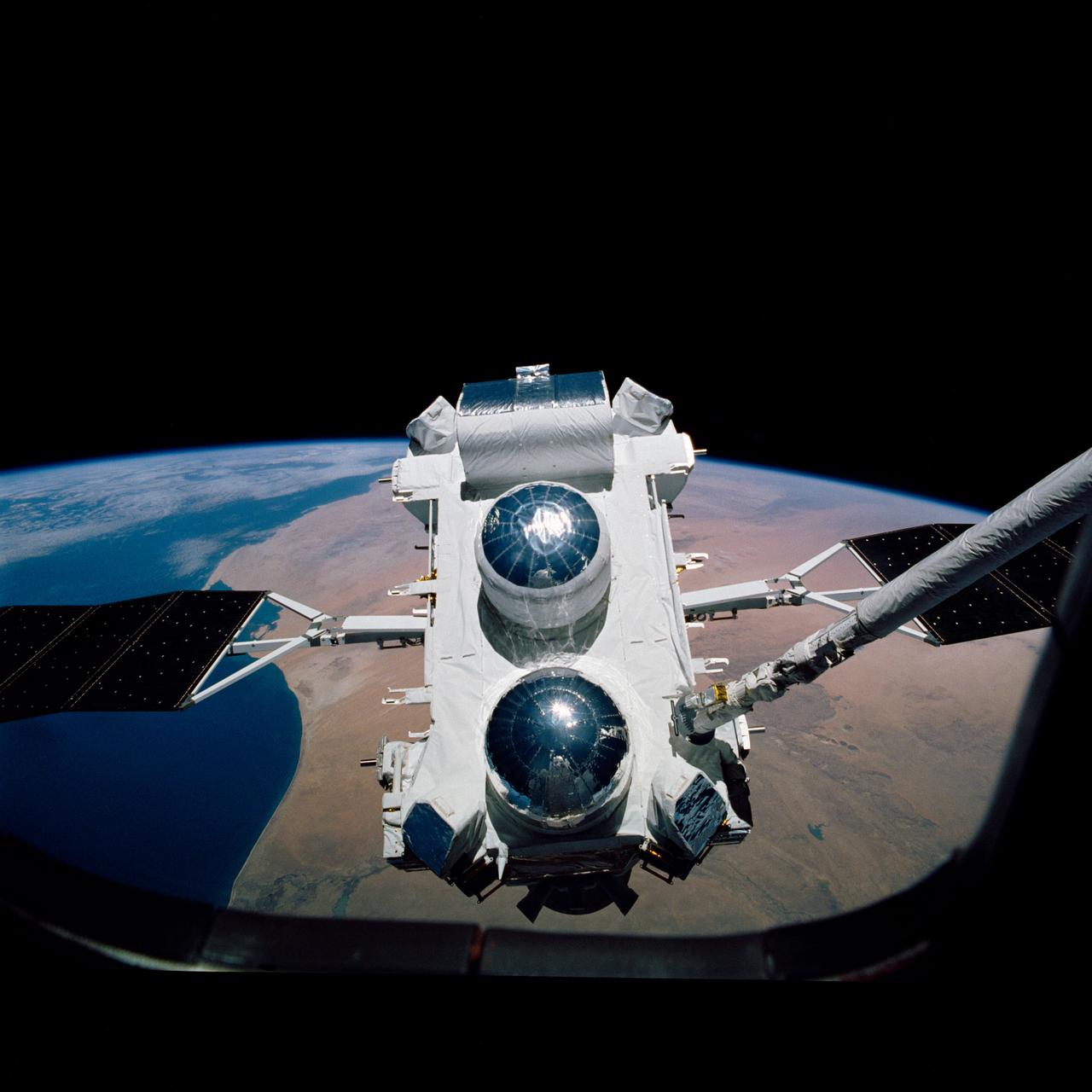

Backdropped against the Earth's surface, the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) with its solar array (SA) panels deployed is grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) during STS-37 systems checkout. GRO's four complement instruments are visible: the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET) (at the bottom); the Imaging Compton Telescope (COMPTEL) (center); the Oriented Scintillation Spectrometer Experiment (OSSE) (top); and Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE) (on four corners). The view was taken by STS-37 crew through an aft flight deck overhead window.
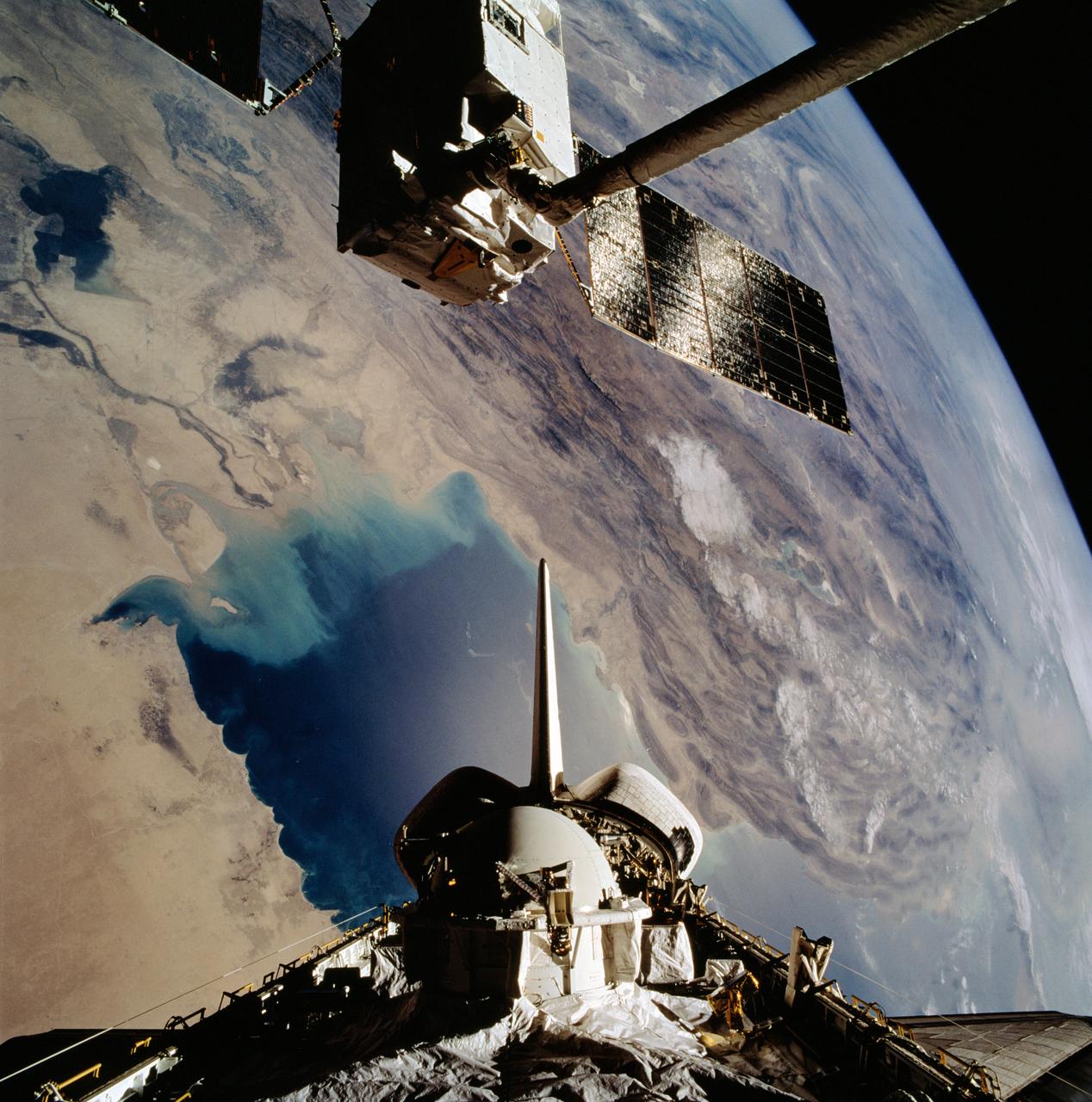

STS046-102-021 (1 Aug 1992) --- The European Space Agency's (ESA) EURECA satellite remains in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Atlantis' Remote Manipulator System (RMS) as the Space Shuttle passes over the Persian Gulf. Most of the theater of the recent war is visible in the frame. Parts of Kuwait, Iraq, Iran and Saudi Arabia can be delineated. The Tethered Satellite System (TSS) remains stowed in the aft cargo bay of Atlantis.
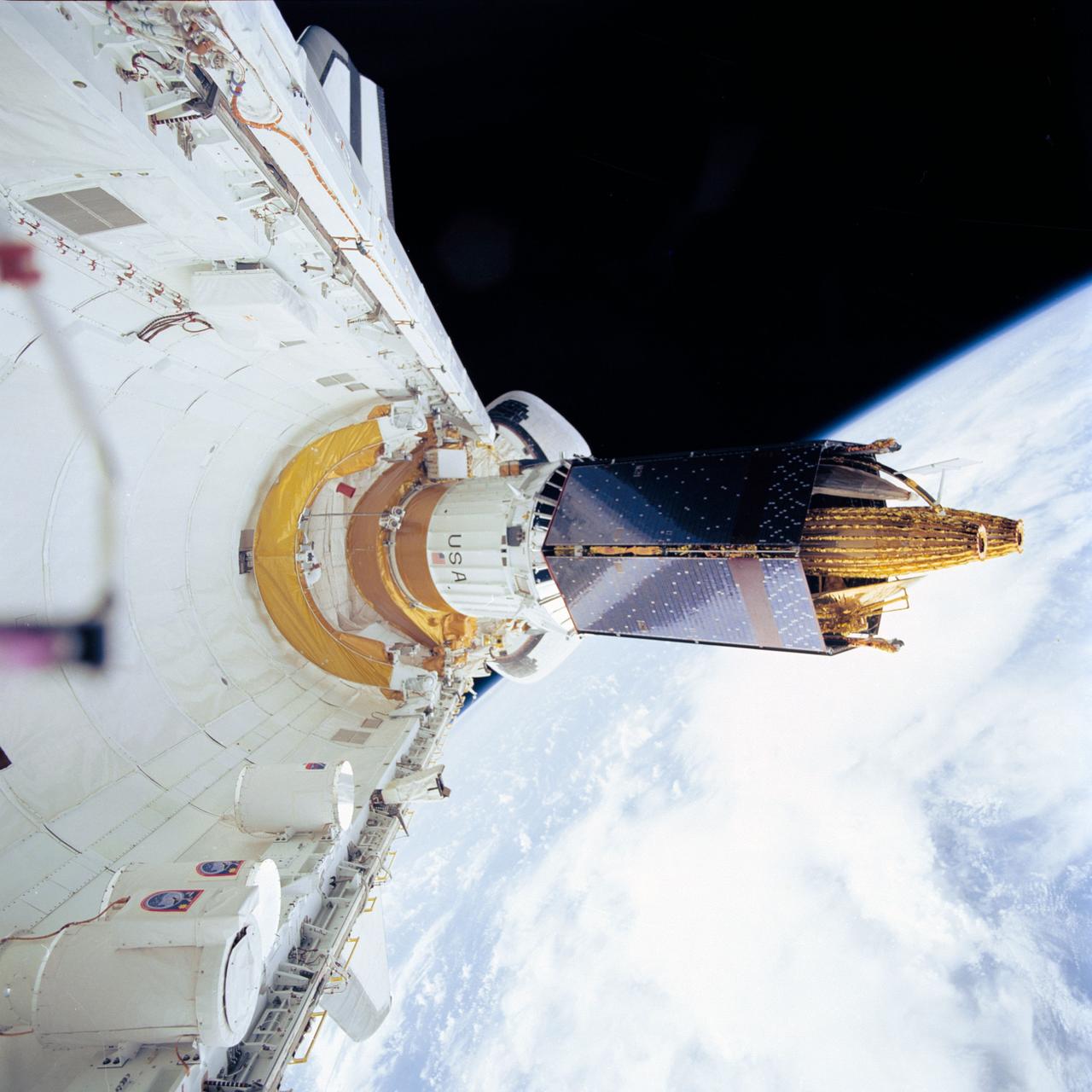

STS043-72-002 (2 Aug 1991) --- The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-E), leaves the payload bay of the earth-orbiting Atlantis a mere six hours after the Space Shuttle was launched from Pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. TDRS, built by TRW, will be placed in a geosynchronous orbit and after on-orbit testing, which requires several weeks, will be designated TDRS-5. The communications satellite will replace TDRS-3 at 174 degrees West longitude. The backbone of NASA's space-to-ground communications, the Tracking and Data Relay satellites have increased NASA's ability to send and receive data to spacecraft in low-earth orbit to more than 85 percent of the time. The five astronauts of the STS 43 mission are John E. Blaha, mission commander, Michael A. Baker, pilot, and Shannon W. Lucid, G. David Low, and James C. Adamson, all mission specialists.
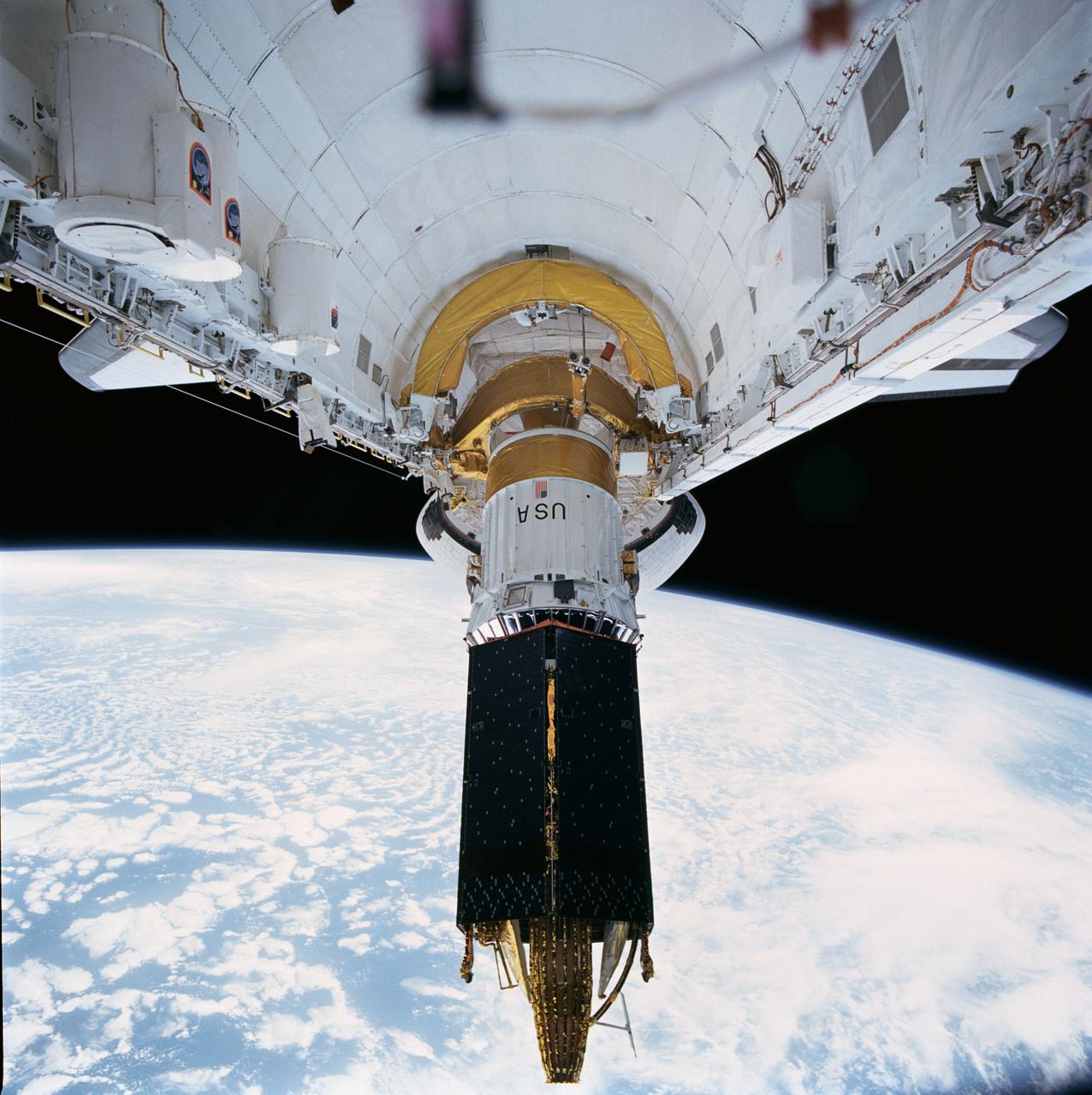

STS043-72-020 (2 Aug 1991) --- The Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS-E), is loosened from its restraint device and begins to leave the payload bay of the earth-orbiting Atlantis. The deployment came a mere six hours after the Space Shuttle was launched from Pad 39A at Kennedy Space Center, Florida. TDRS, built by TRW, will be placed in a geosynchronous orbit and after on-orbit testing, which requires several weeks, will be designated TDRS-5. The communications satellite will replace TDRS-3 at 174 degrees West longitude. The backbone of NASA's space-to-ground communications, the Tracking and Data Relay satellites have increased NASA's ability to send and receive data to spacecraft in low-earth orbit to more than 85 percent of the time. The five astronauts of the STS 43 mission are John E. Blaha, mission commander, Michael A. Baker, pilot, and Shannon W. Lucid, G. David Low, and James C. Adamson, all mission specialists.
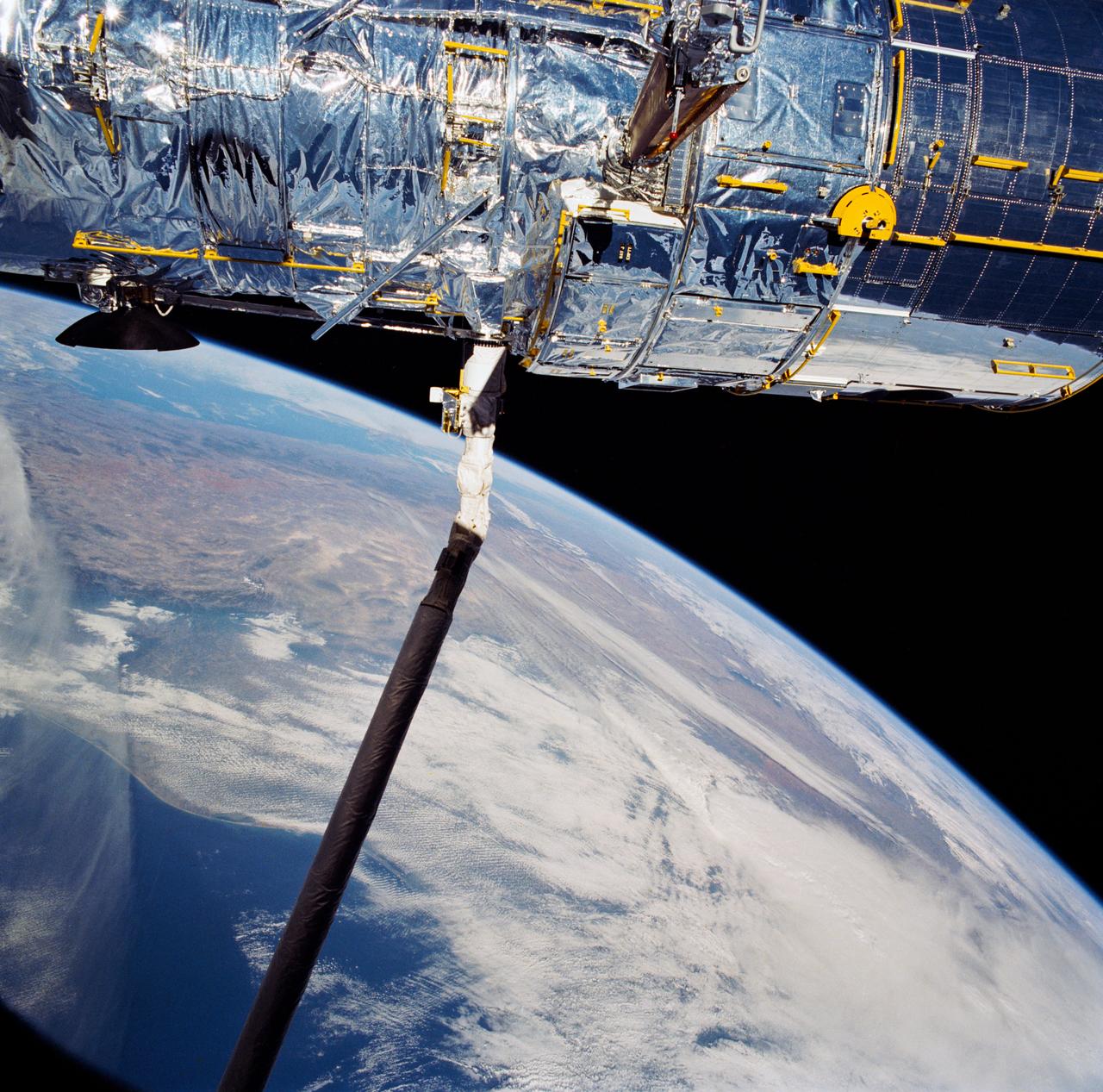

During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is held in appendage deploy position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS) above the payload bay (PLB) and crew compartment cabin. While in this position the solar array (SA) wing bistem cassette (HST center) is deployed from its stowed location along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. A high gain antenna (HGA) remains stowed along the SSM. The Earth's surface and the Earth limb creates a dramatic backdrop.
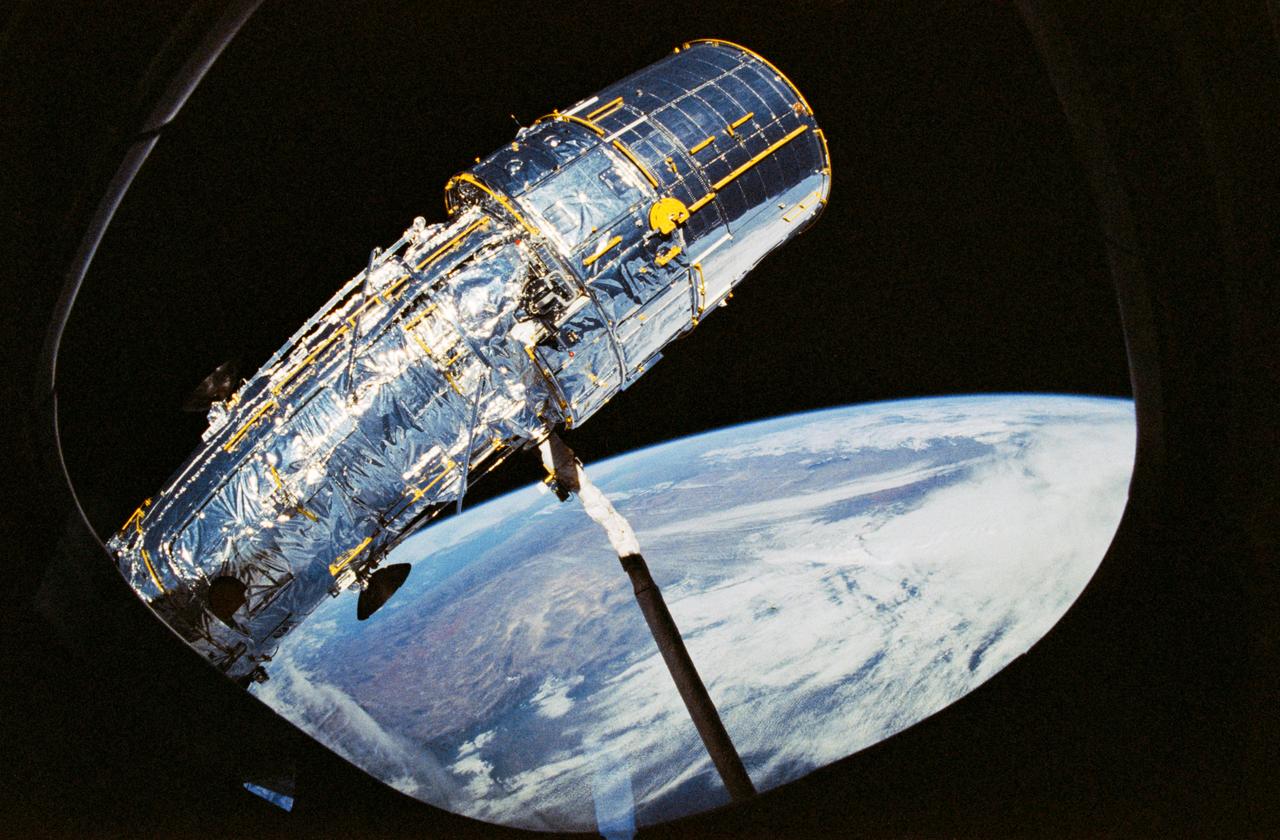

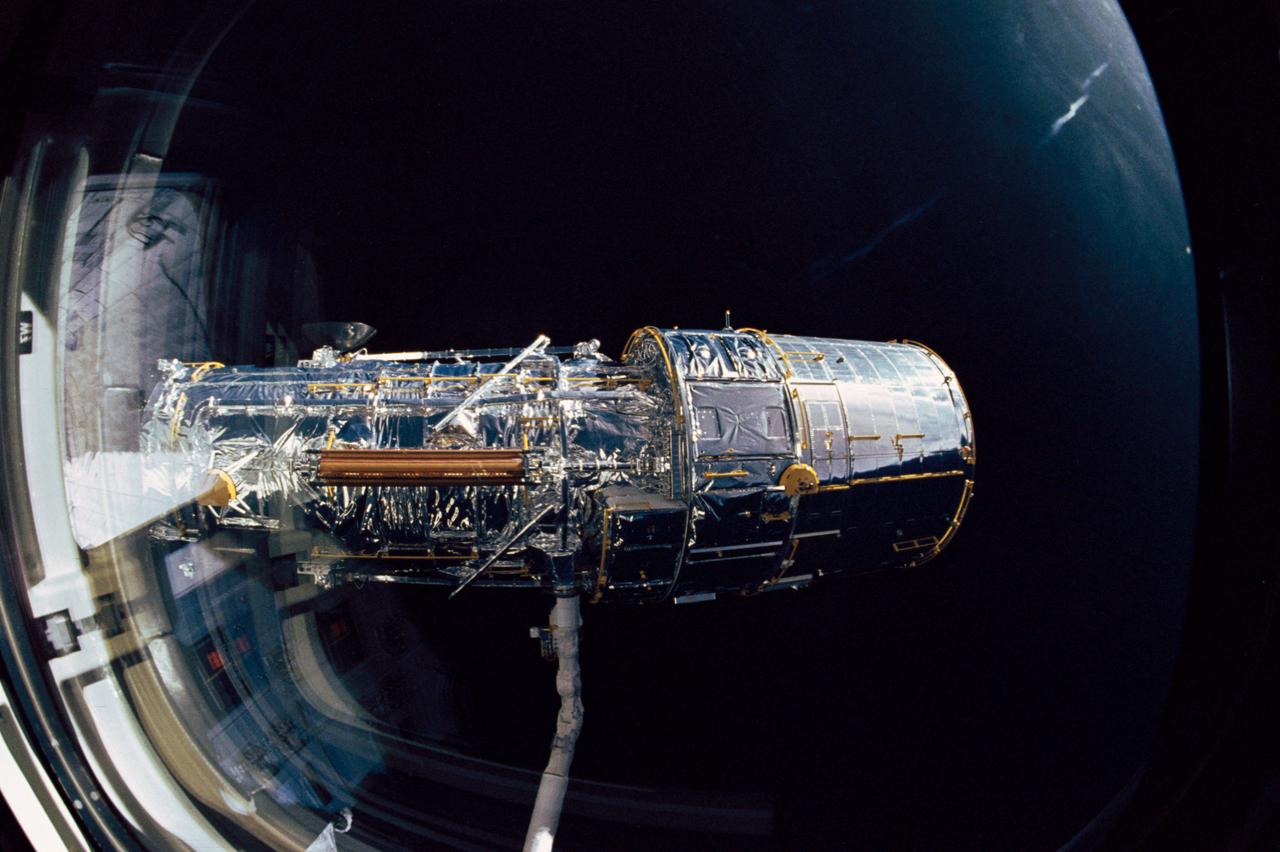
STS031-10-023 (25 April 1990) --- View of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on the end of Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm prior to deployment of its antennae and solar array panels.
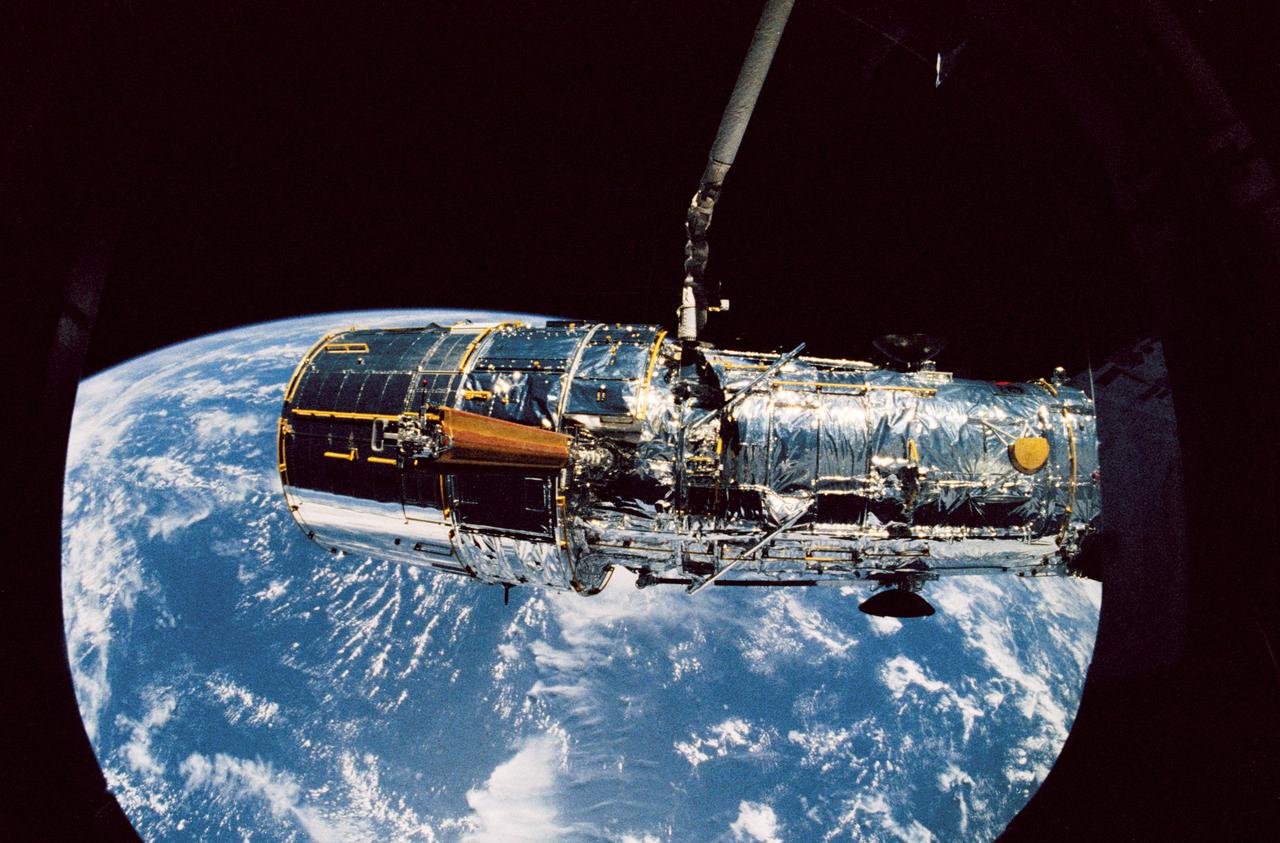

Held in appendage deploy position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) starboard solar array (SA) bistem cassette is released from its stowed position on the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The spreader bar & bistem begin to unfurl the SA wing. View was taken by an STS-31 crewmember through an overhead window & is backdropped against the surface of the Earth.