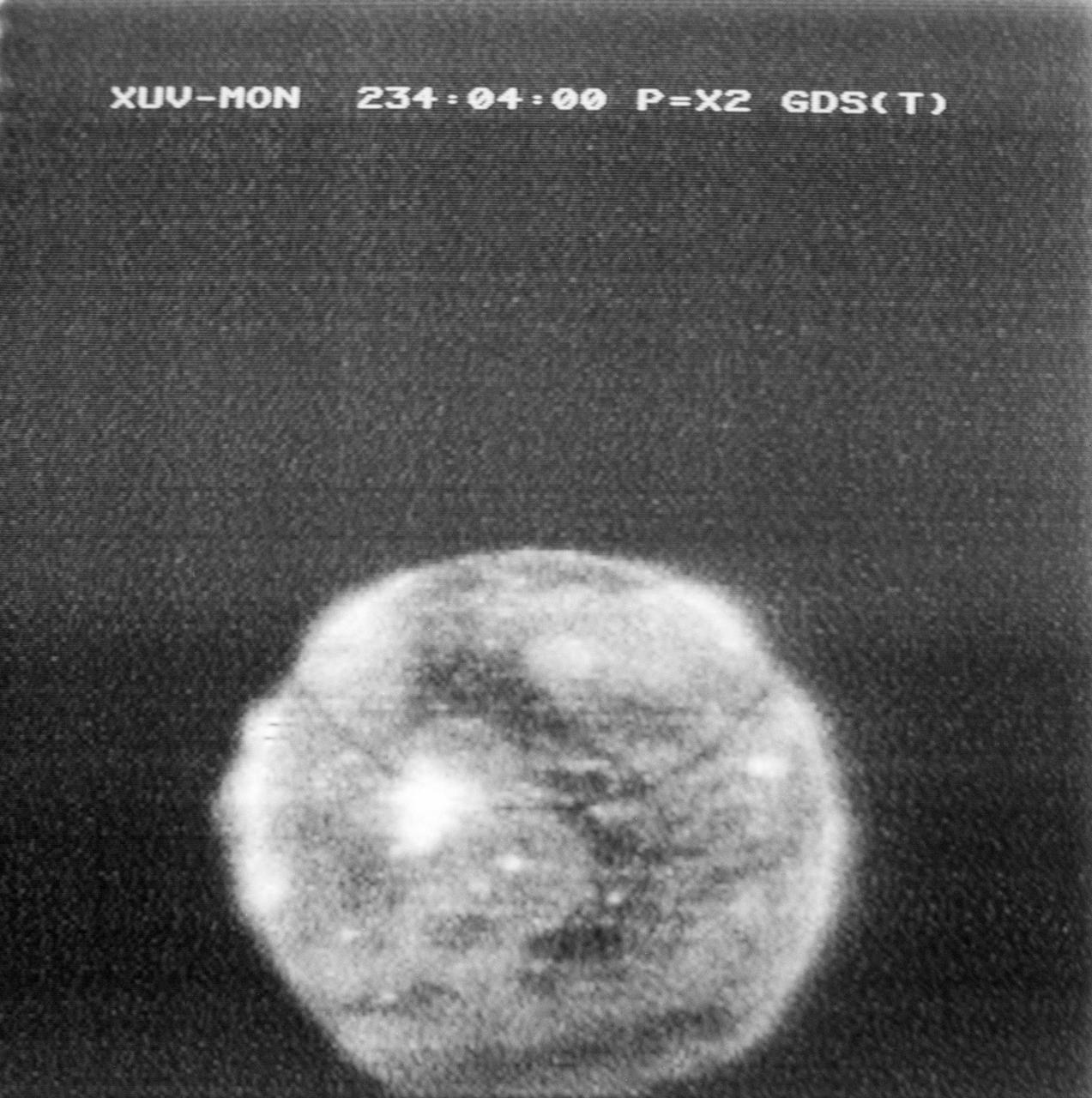
S73-32867 (21 Aug. 1973) --- The solar sphere viewed through the Skylab solar physics experiment (S082) Extreme Ultraviolet Spectroheliographis seen in this photographic reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The solar chromosphere and lower corona are much hotter than the surface of the sun characterized by the white light emissions. This image was recorded during the huge solar prominence which occurred on Aug. 21, 1973. Photo credit: NASA
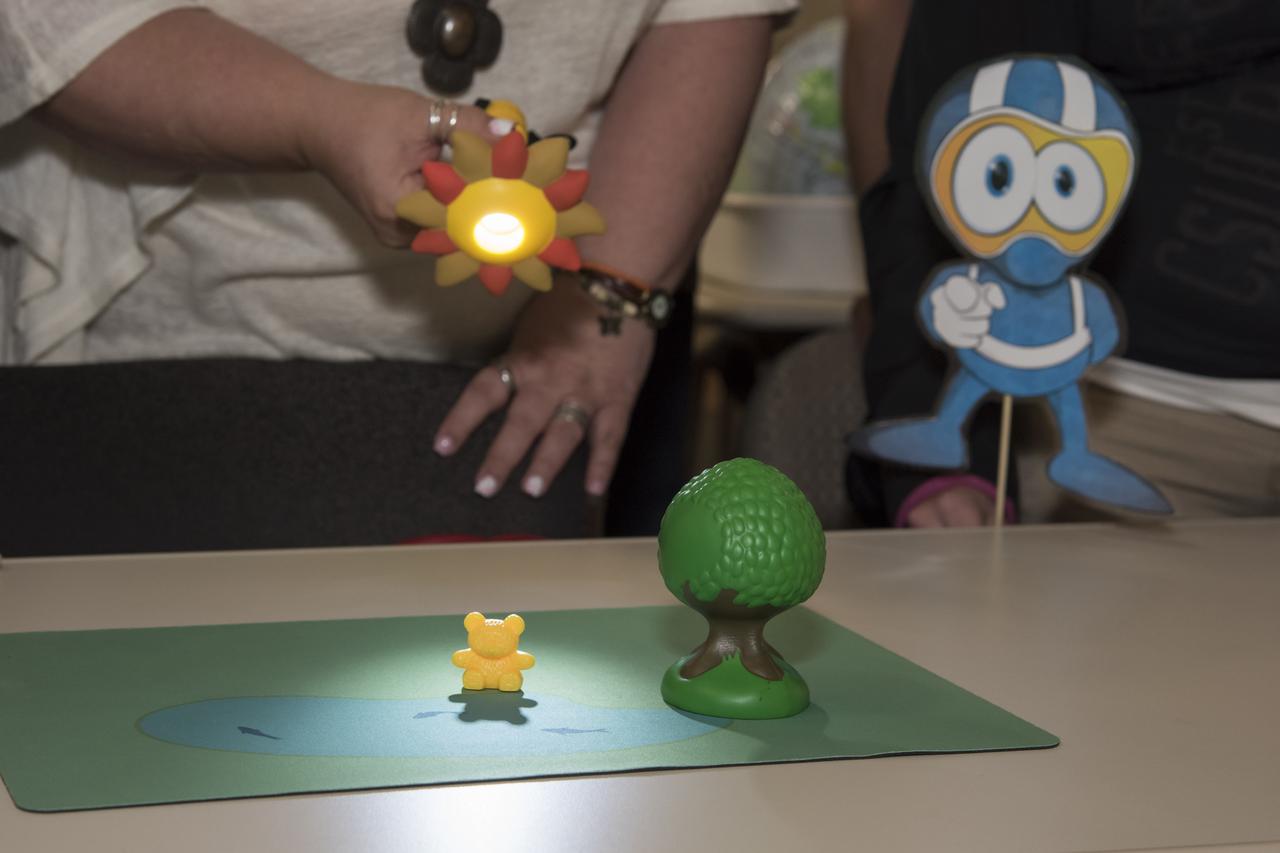

Educators shine a flashlight onto a toy bear to simulate the physics behind solar eclipses.
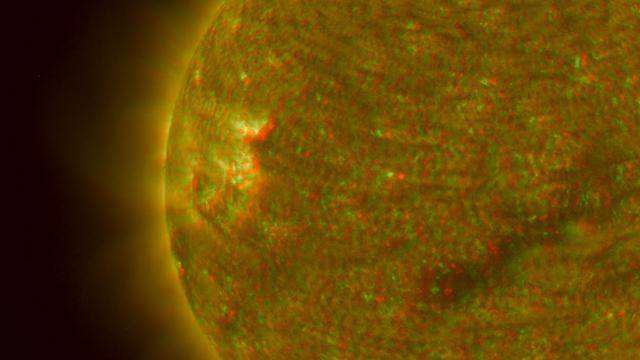
NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting. 3D glasses are necessary.

NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting. 3D glasses are necessary.

NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting. 3D glasses are necessary.
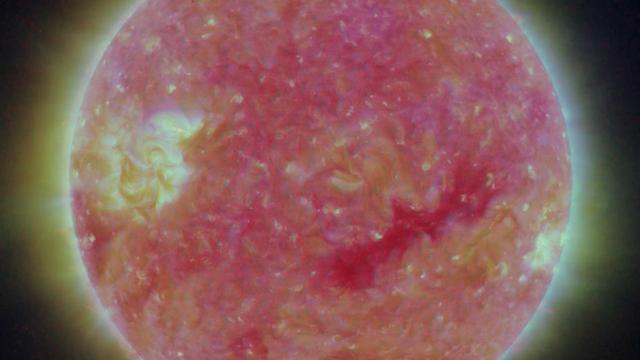
NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting.
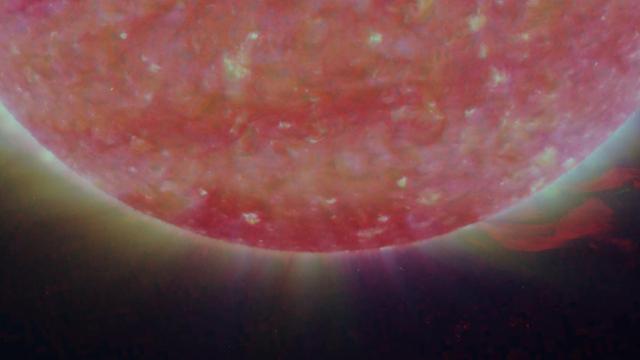
NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting. .

NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting.
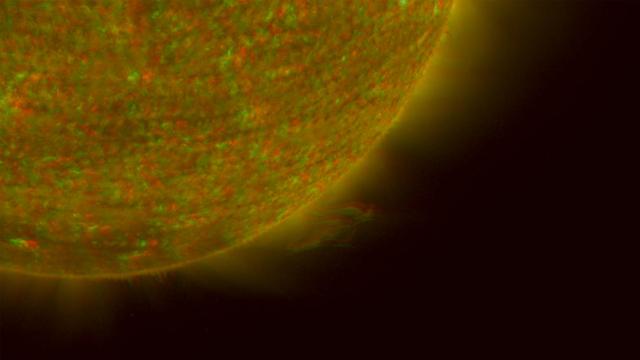
NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting. 3D glasses are necessary.
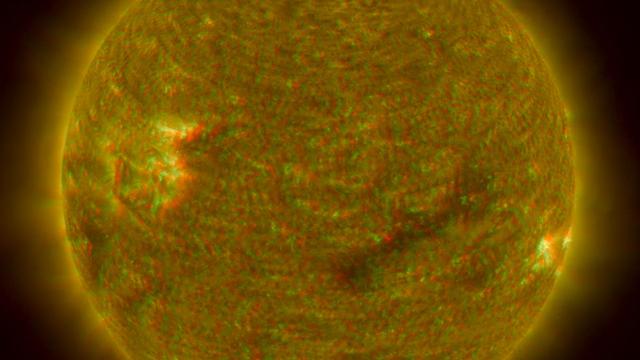
NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting. 3D glasses are necessary.
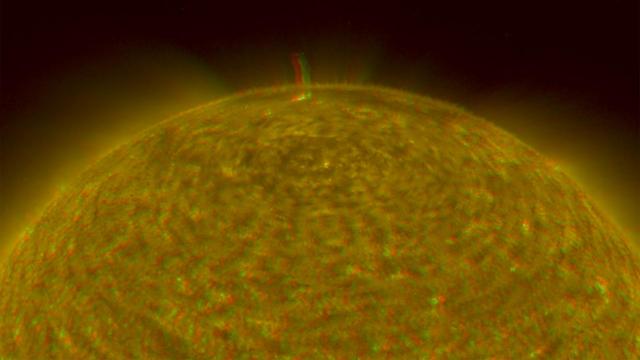
NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting. 3D glasses are necessary.

NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting.

NASA Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory satellites have provided the first 3-dimensional images of the Sun. This view will aid scientists ability to understand solar physics to improve space weather forecasting.

Detailed measurements of the physical properties of the seven rocky TRAPPIST-1 planets and the four terrestrial planets in our solar system help scientists find similarities and differences between the two planet families. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24373

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Moderating the science briefing are Karen Fox, far left, Goddard Space Flight Center; and Dwaye Brown, far right, NASA Communications. Briefers are Andy Driesman, Parker Solar Probe project manager, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory; Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory; and Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Speaking to the media is Andy Driesman, Parker Solar Proble project manager, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Speaking to the media is Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist, Johnson Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
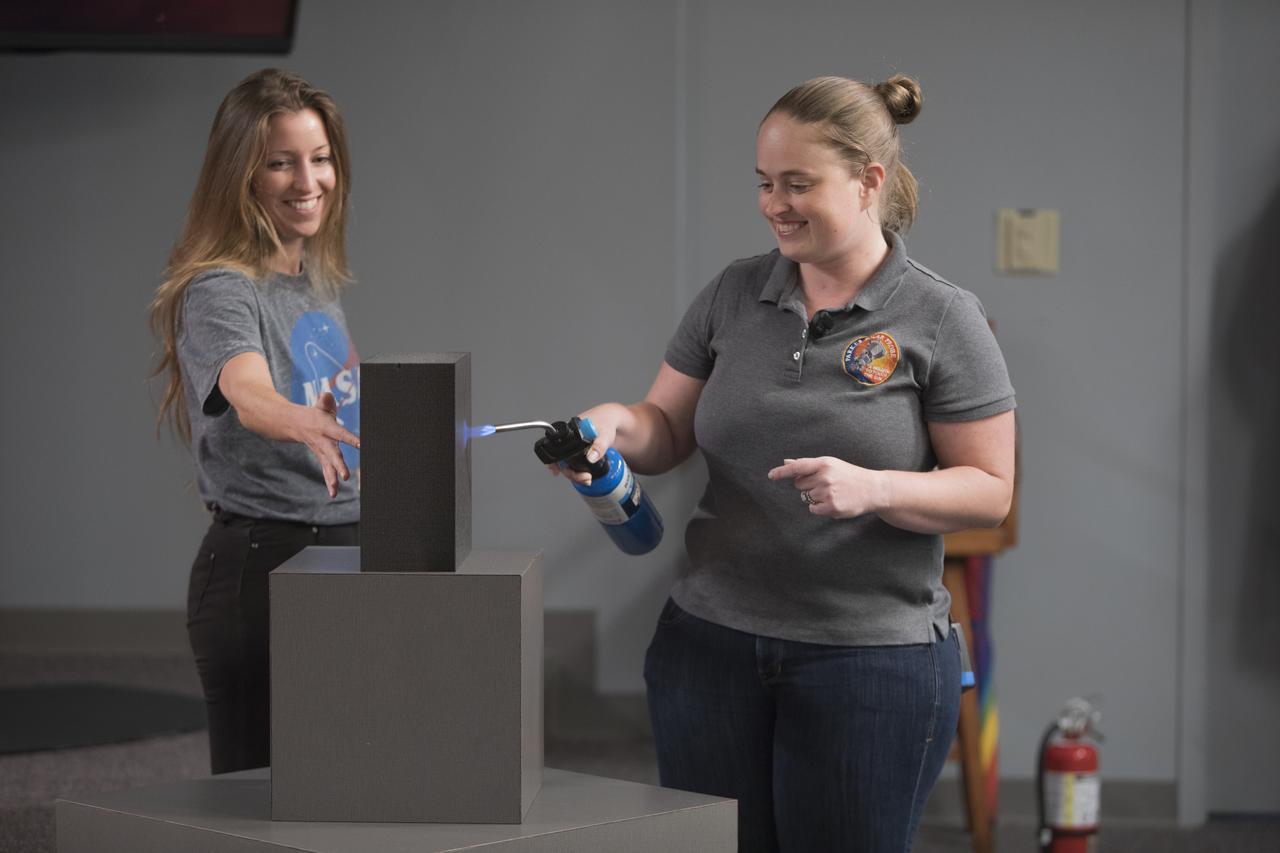

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, on Friday, July 20, 2018, Betsy Congdon, Thermal Protection System engineer with the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, right, demonstrates the ability of the Parker Solar Probe's heat shield to protect the spacecraft. The presentation for the media took place during a prelaunch mission briefing for the Parker Solar Probe mission. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel in Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
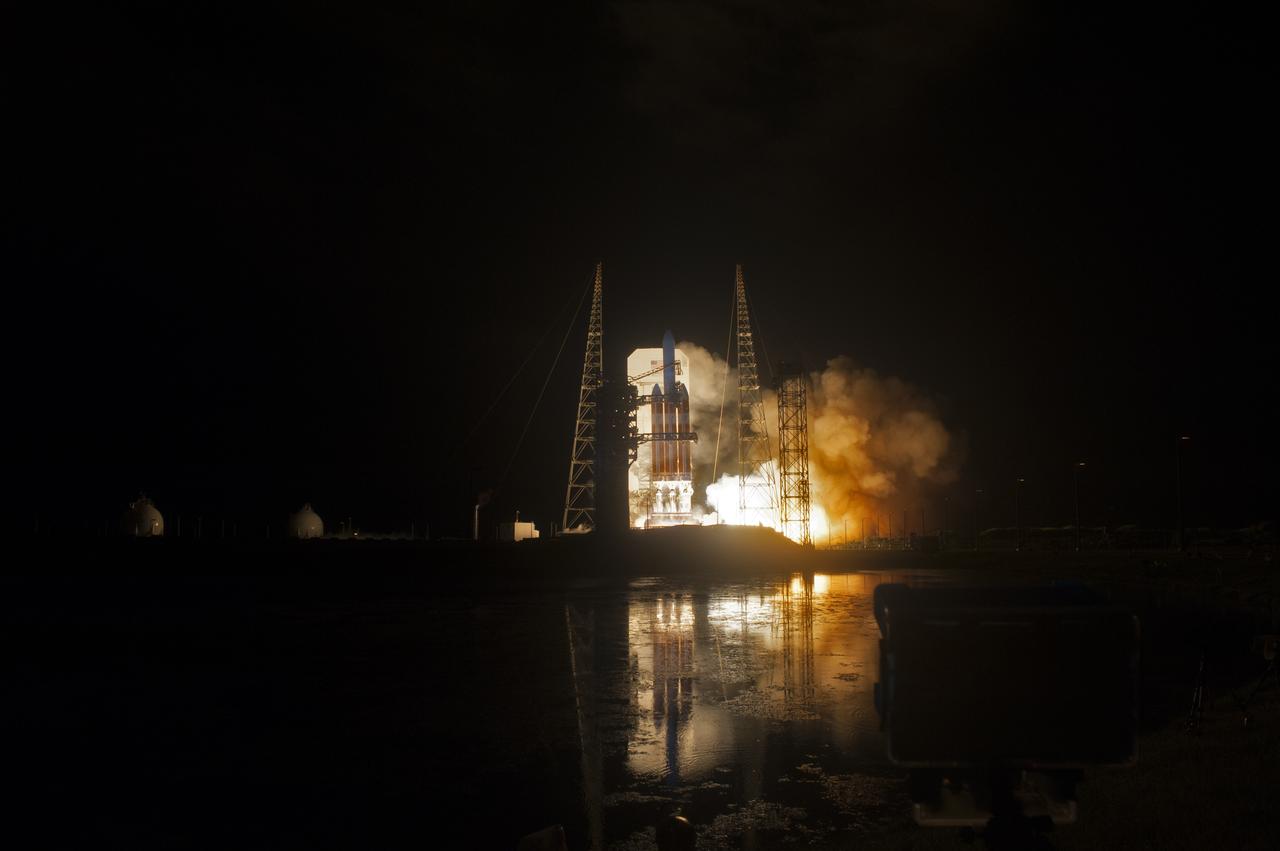

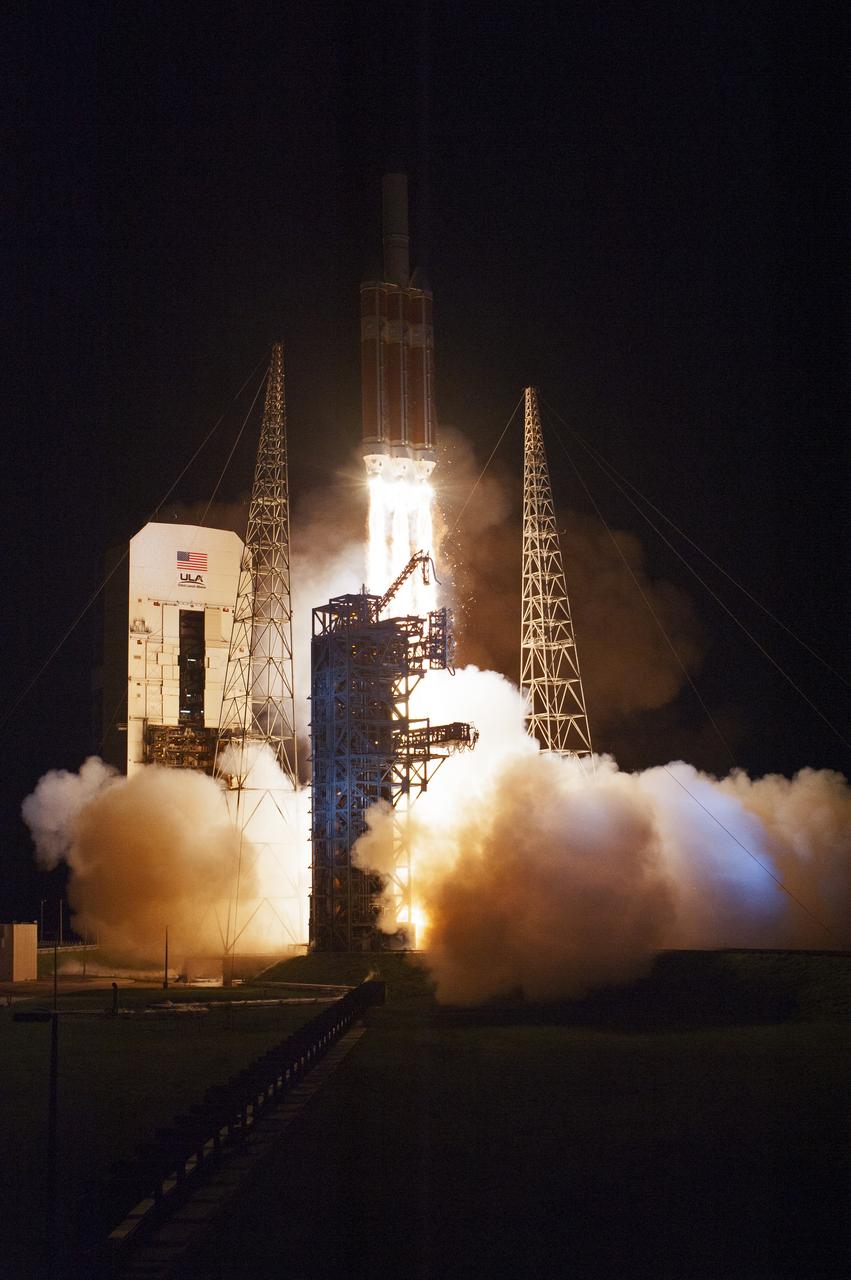
At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
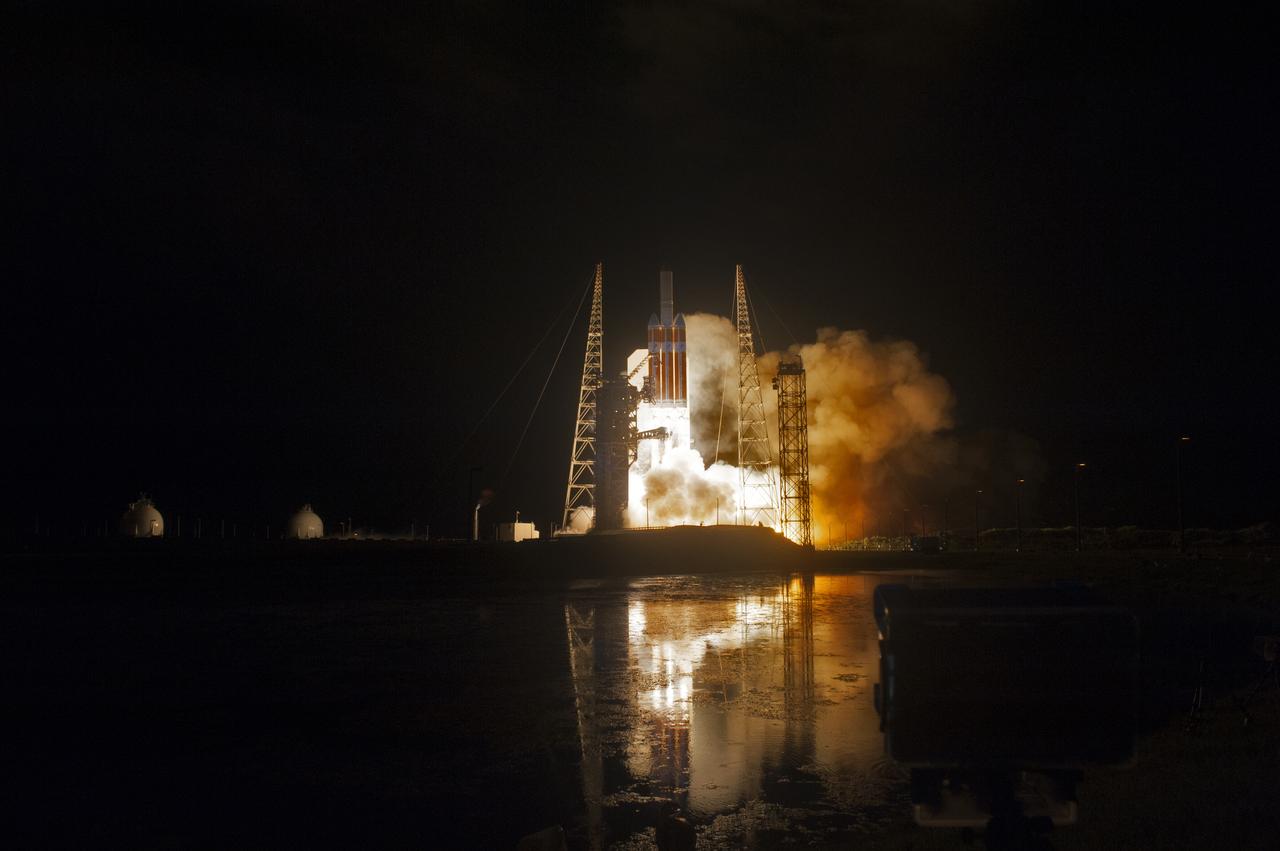

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
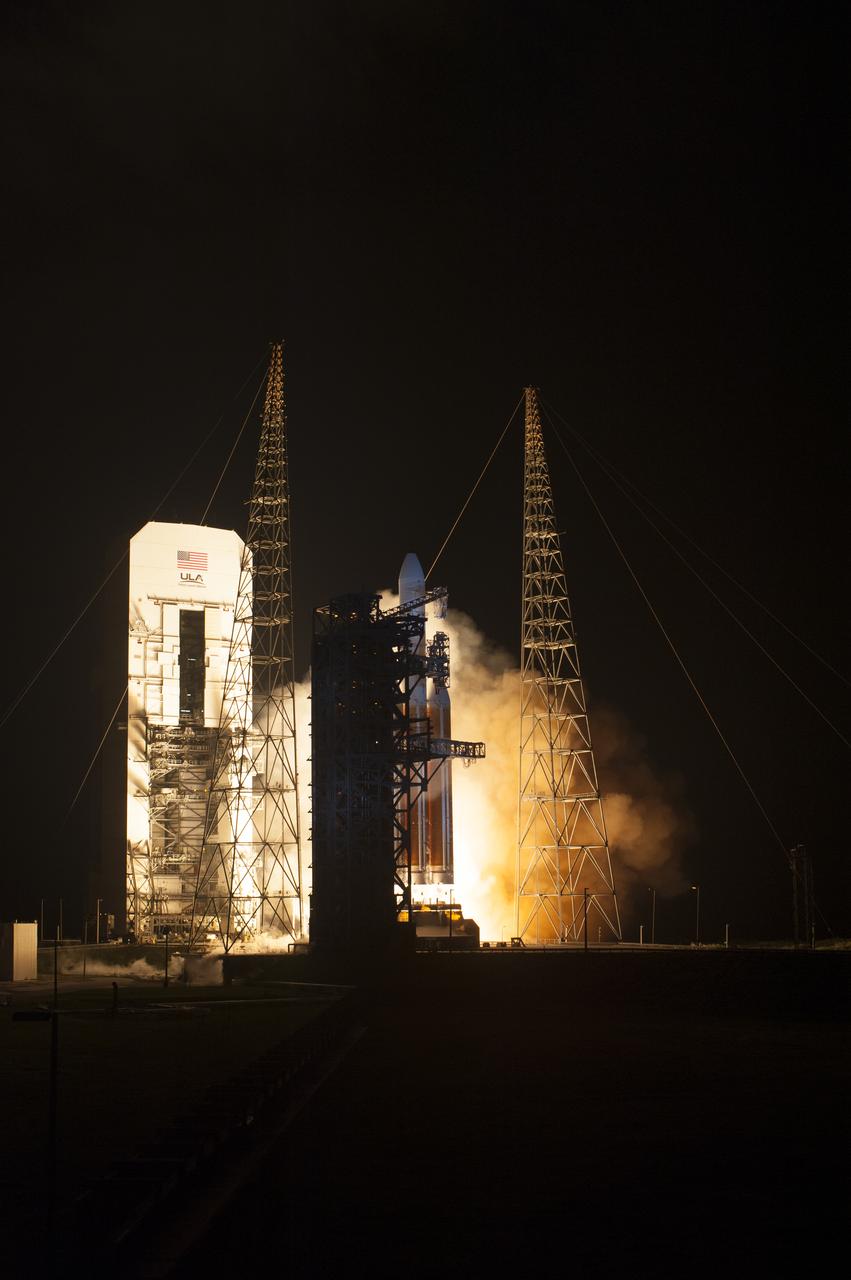

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
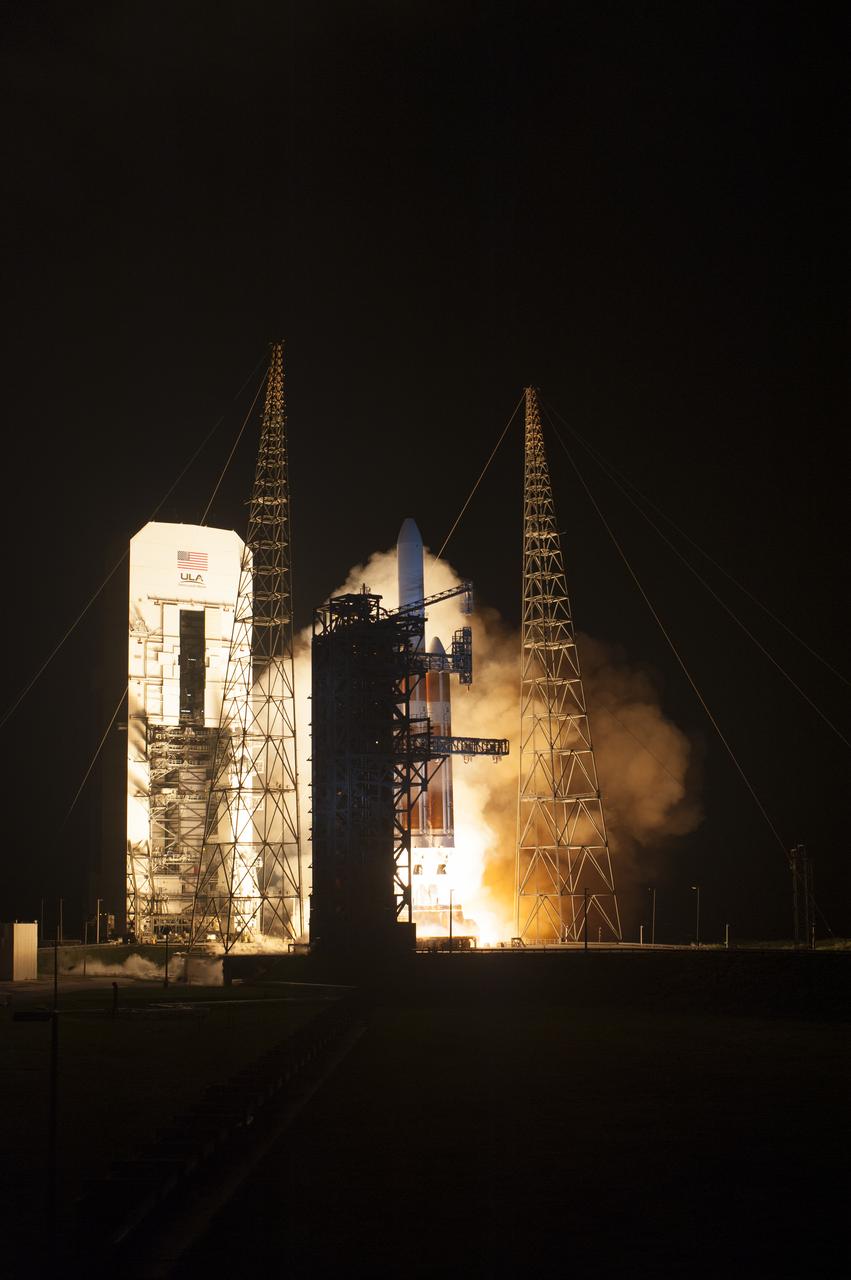

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
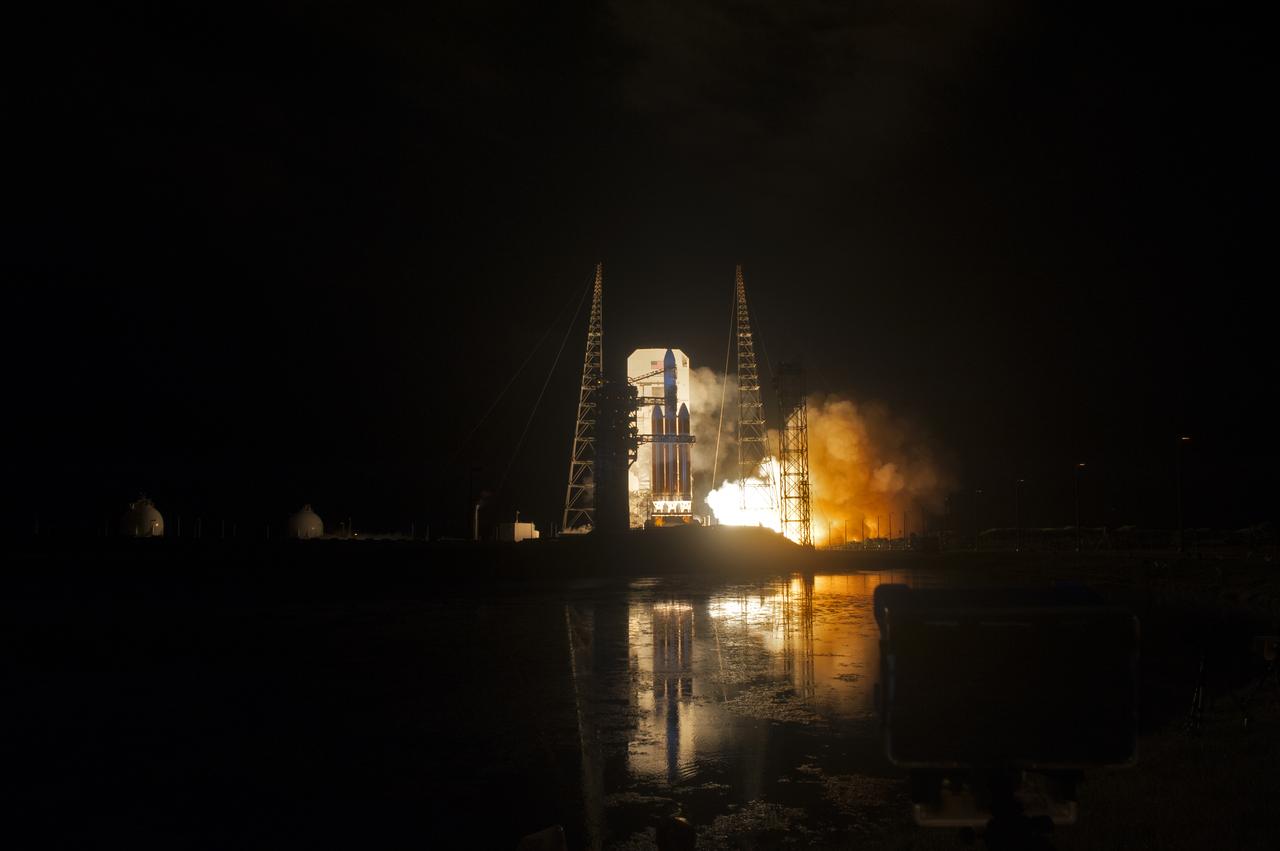

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
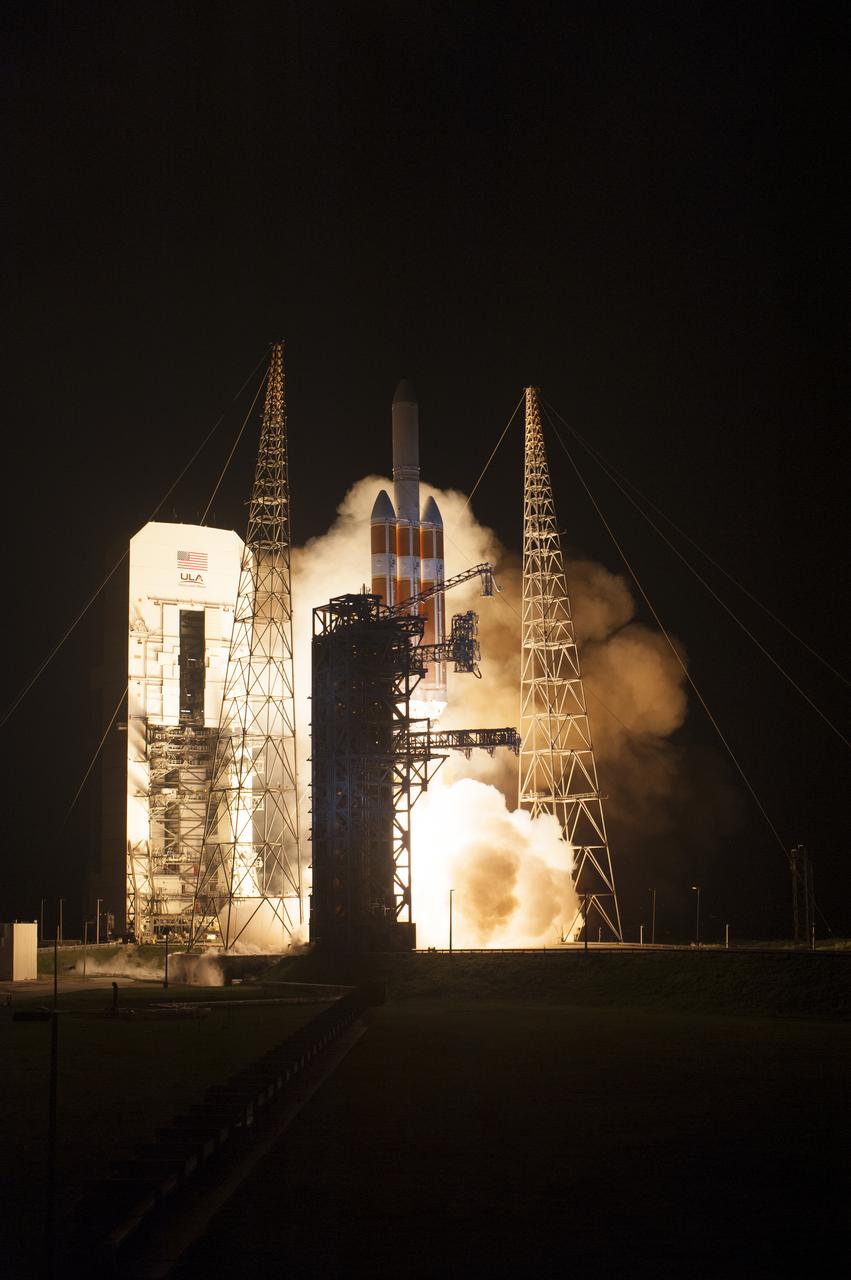

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
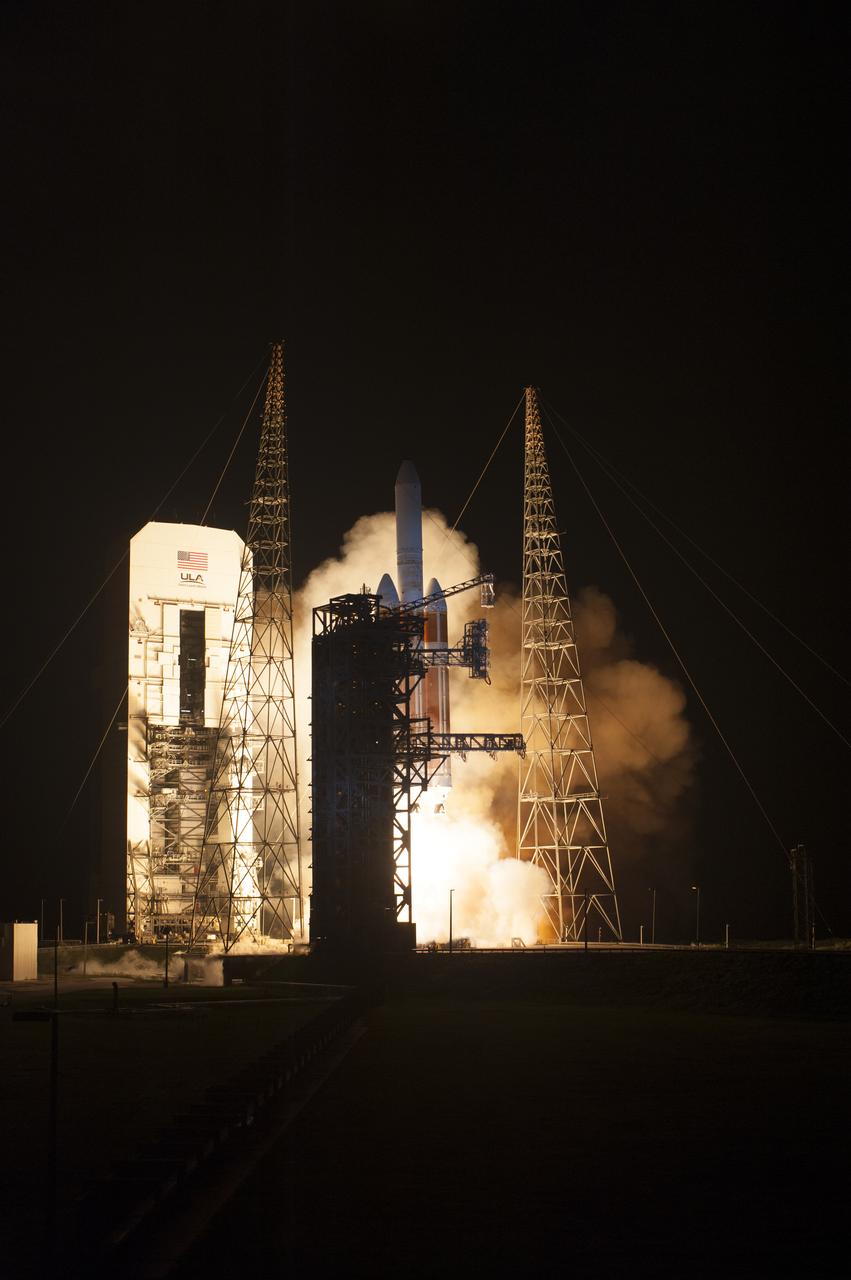

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
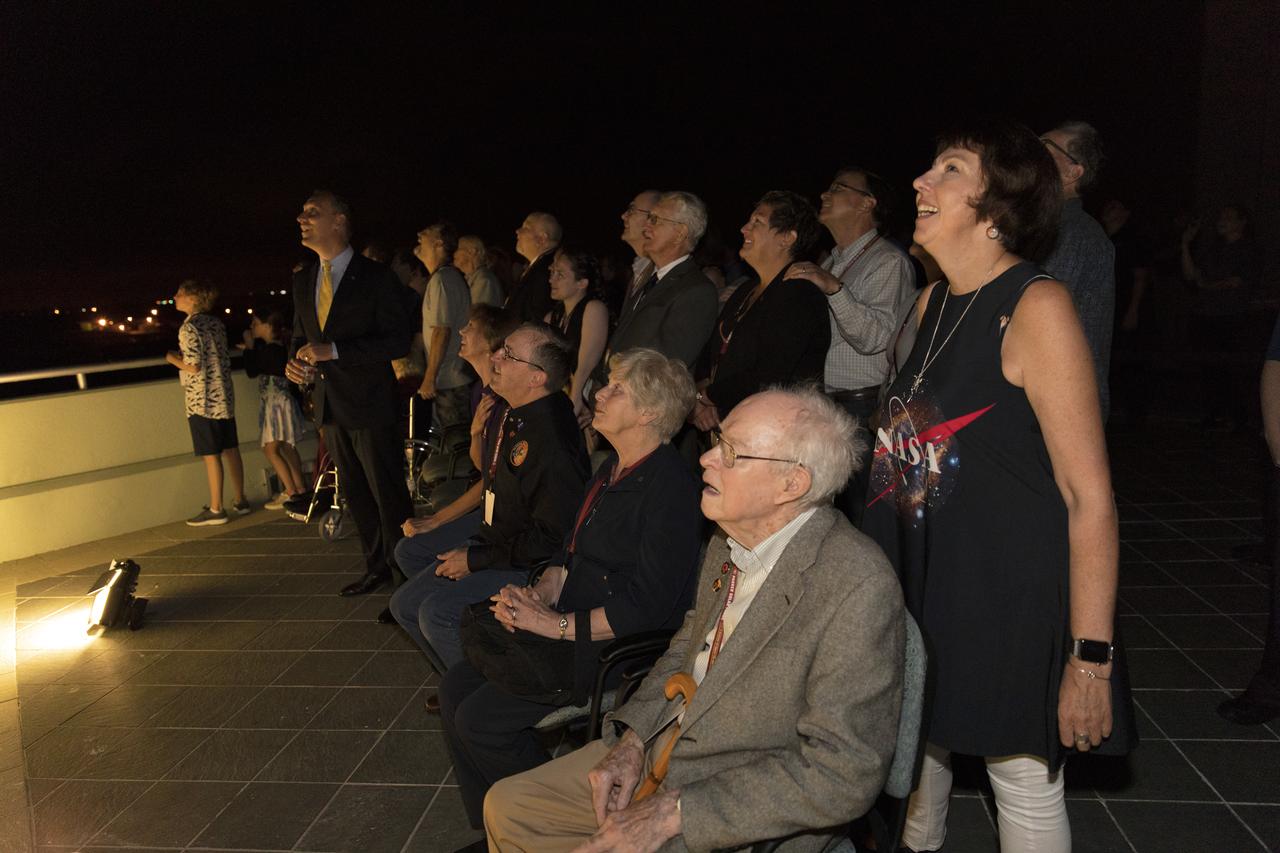

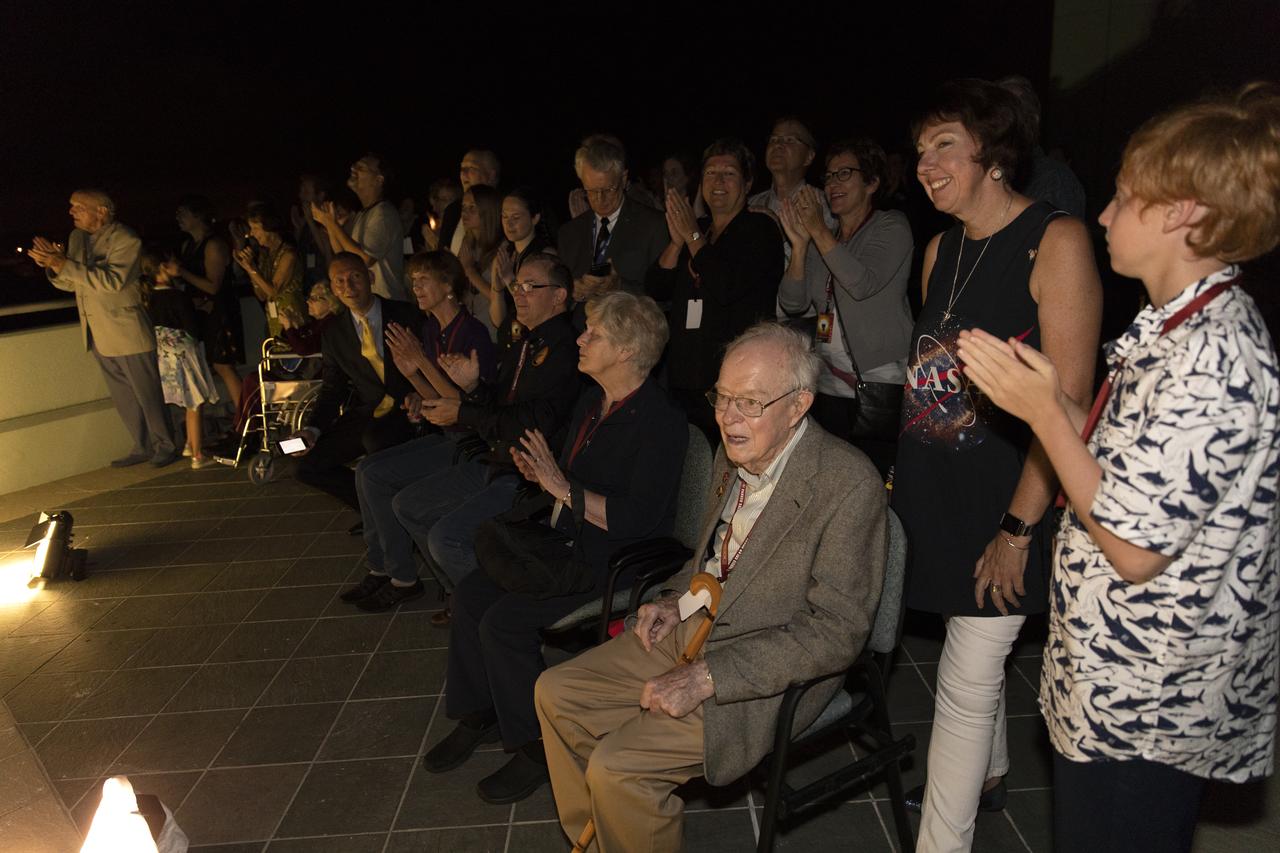
Dr. Eugene Parker (seated in the foreground), a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, watches the launch of NASA's Parker Solar Probe. This is the first agency mission named for a living person. Standing behind Parker is Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. The liftoff took place at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
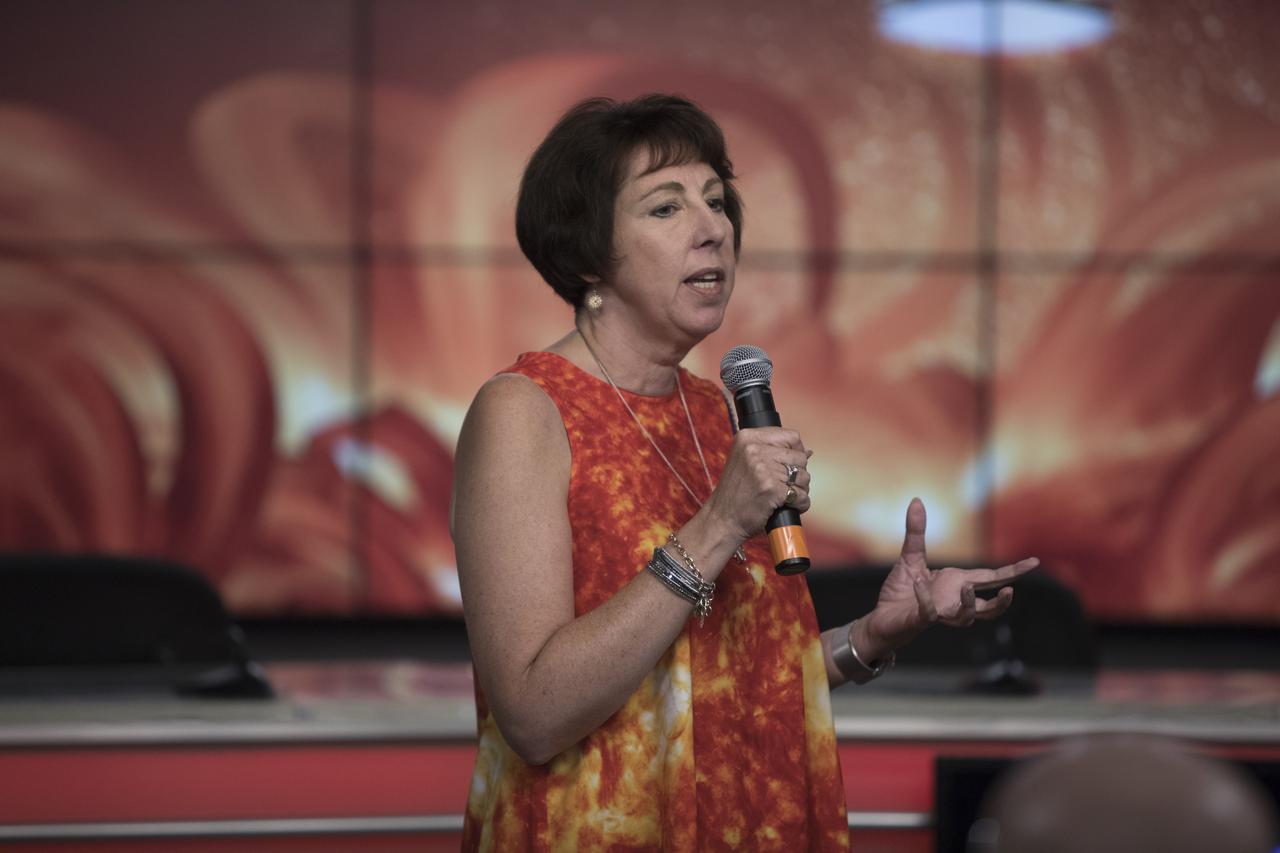

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, on Friday, July 20, 2018, Nicky Fox, project scientist with the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, speaks to members of the media during a prelaunch mission briefing for the Parker Solar Probe mission. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel in Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
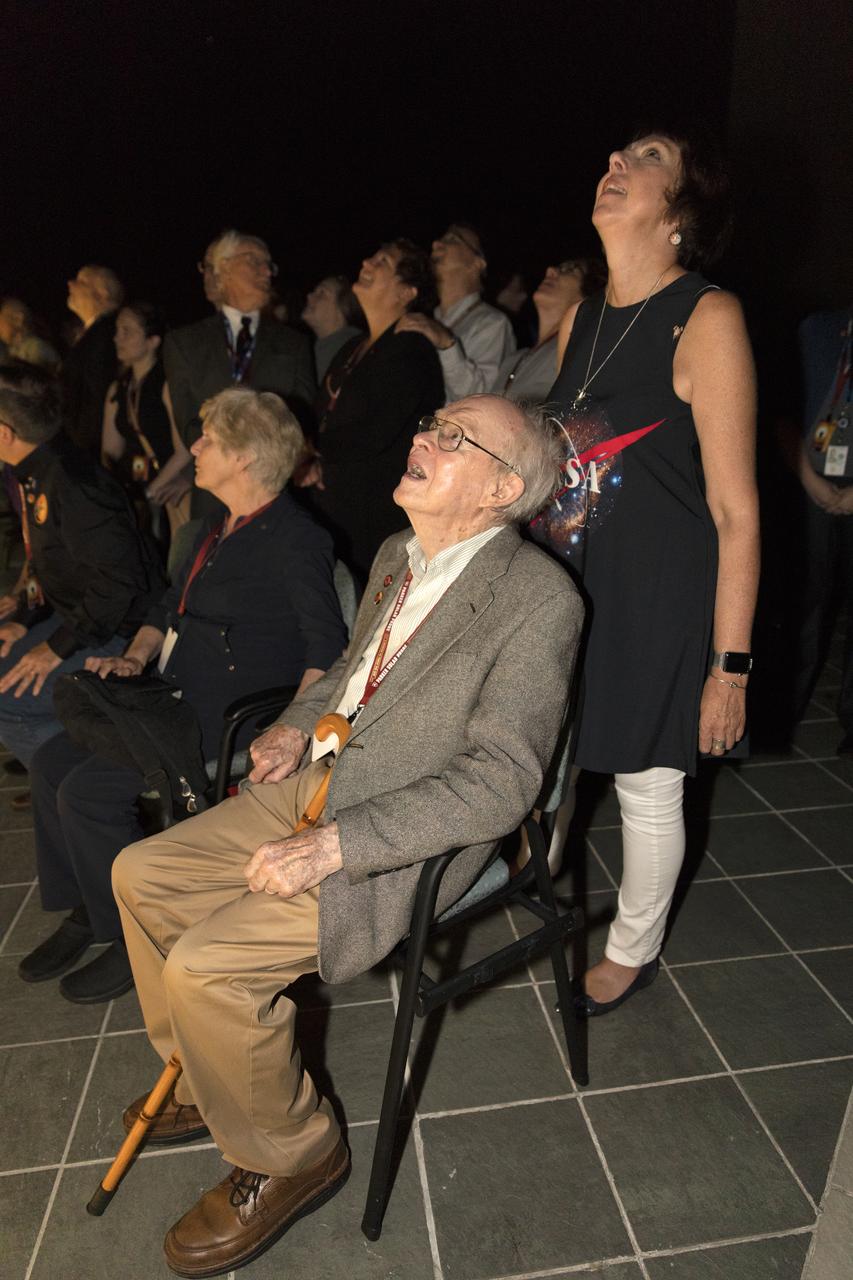

Dr. Eugene Parker (seated in the foreground), a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, watches the launch of NASA's Parker Solar Probe. This is the first agency mission named for a living person. Standing behind Parker is Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. The liftoff took place at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

Dr. Eugene Parker (seated in the foreground), a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, watches the launch of NASA's Parker Solar Probe. This is the first agency mission named for a living person. Standing behind Parker is Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. The liftoff took place at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
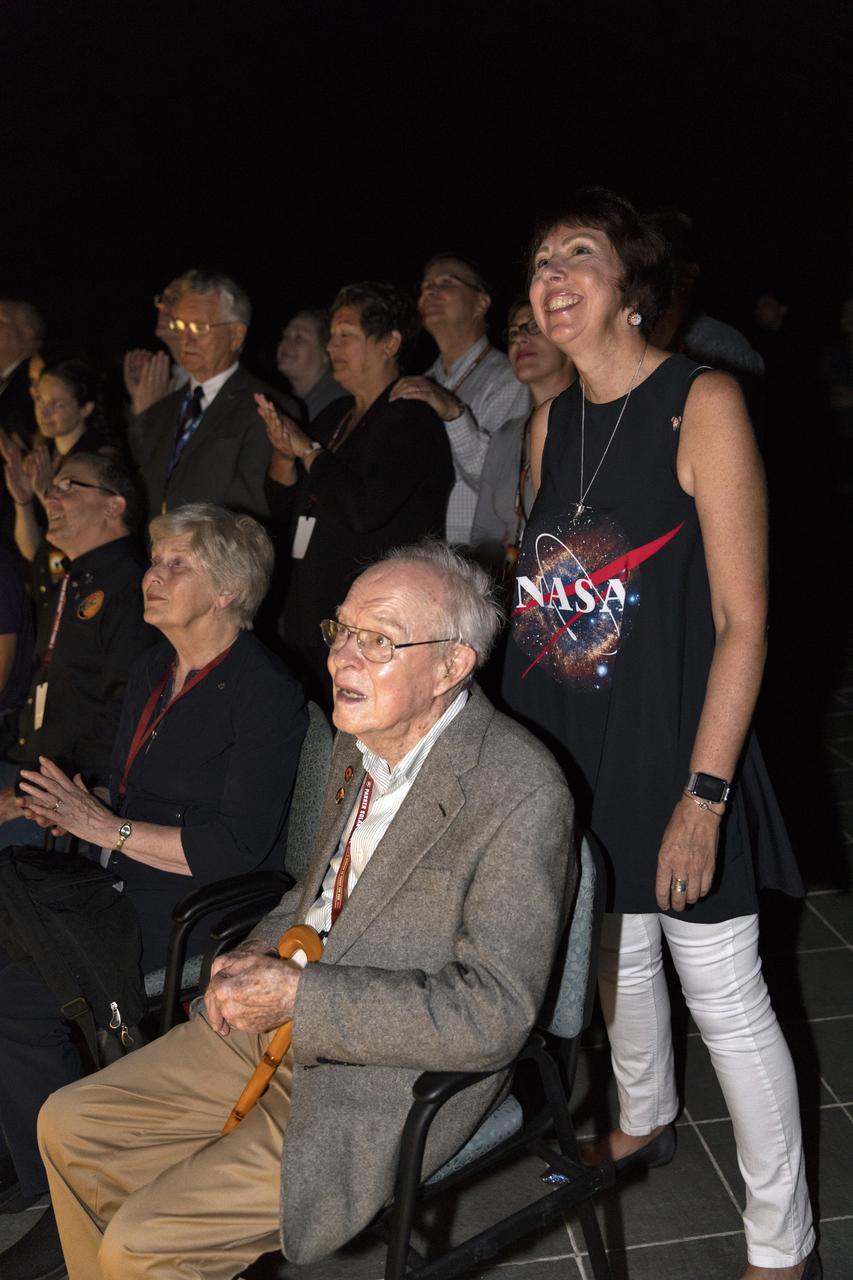

Dr. Eugene Parker (seated in the foreground), a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, watches the launch of NASA's Parker Solar Probe. This is the first agency mission named for a living person. Standing behind Parker is Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. The liftoff took place at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, on Friday, July 20, 2018, agency and mission leaders speak to members of the media during a prelaunch briefing for the Parker Solar Probe mission. From left are: Betsy Congdon, Thermal Protection System engineer with Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Alex Young, solar scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Nicky Fox, project scientist with the Johns Hopkins University APL, and Karen Fox of NASA Communications. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel in Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the news and social media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing participants from left are: Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. This is the first NASA mission named for a living person. The Parker Solar Probe is designed to provide key observations on his groundbreaking theories about the Sun. Lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket will take place from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
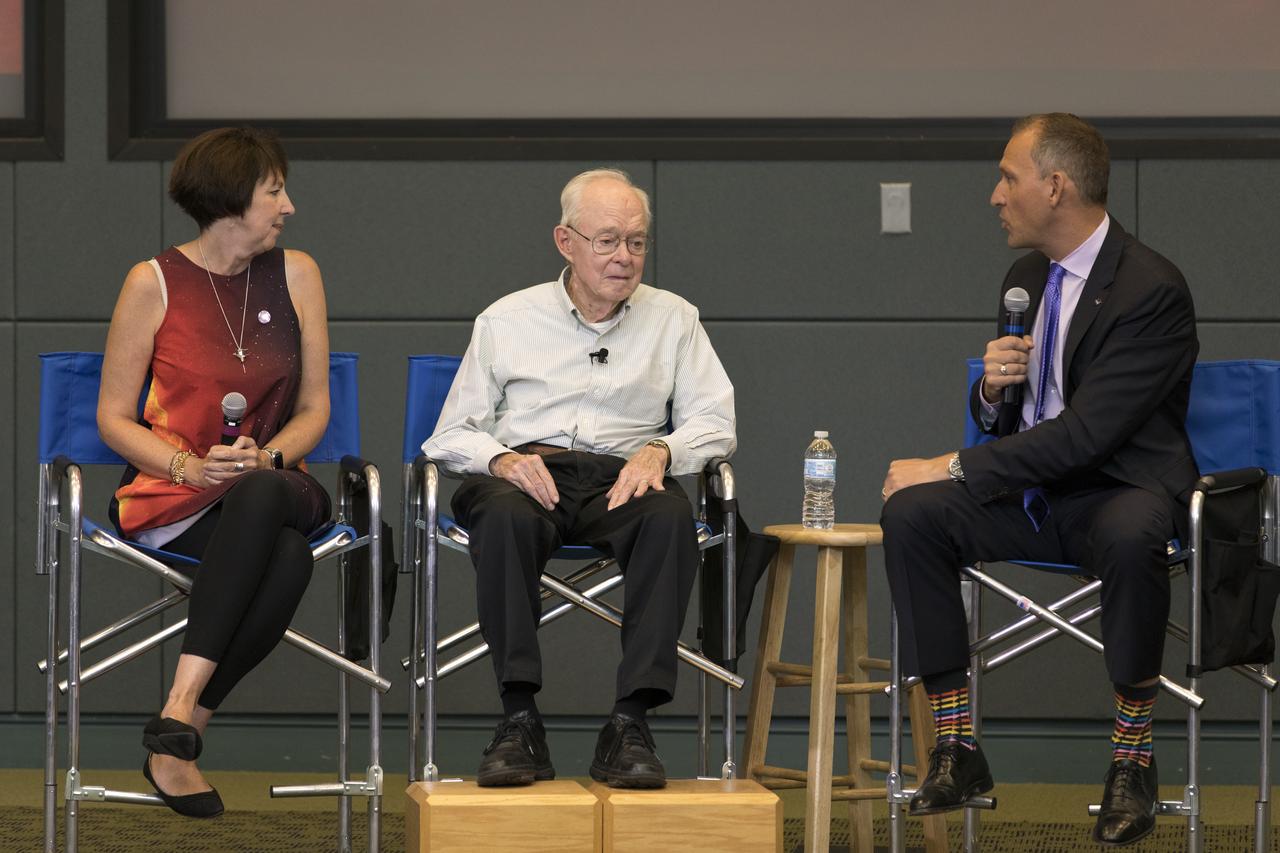

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the news and social media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing participants from left are: Nicky Fox, Parker Solar Probe project scientist at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. This is the first NASA mission named for a living person. The Parker Solar Probe is designed to provide key observations on his groundbreaking theories about the Sun. Lift off atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket will take place from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, on Friday, July 20, 2018, Karen Fox of NASA Communications, speaks to members of the media during a prelaunch mission briefing for the Parker Solar Probe mission. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel in Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
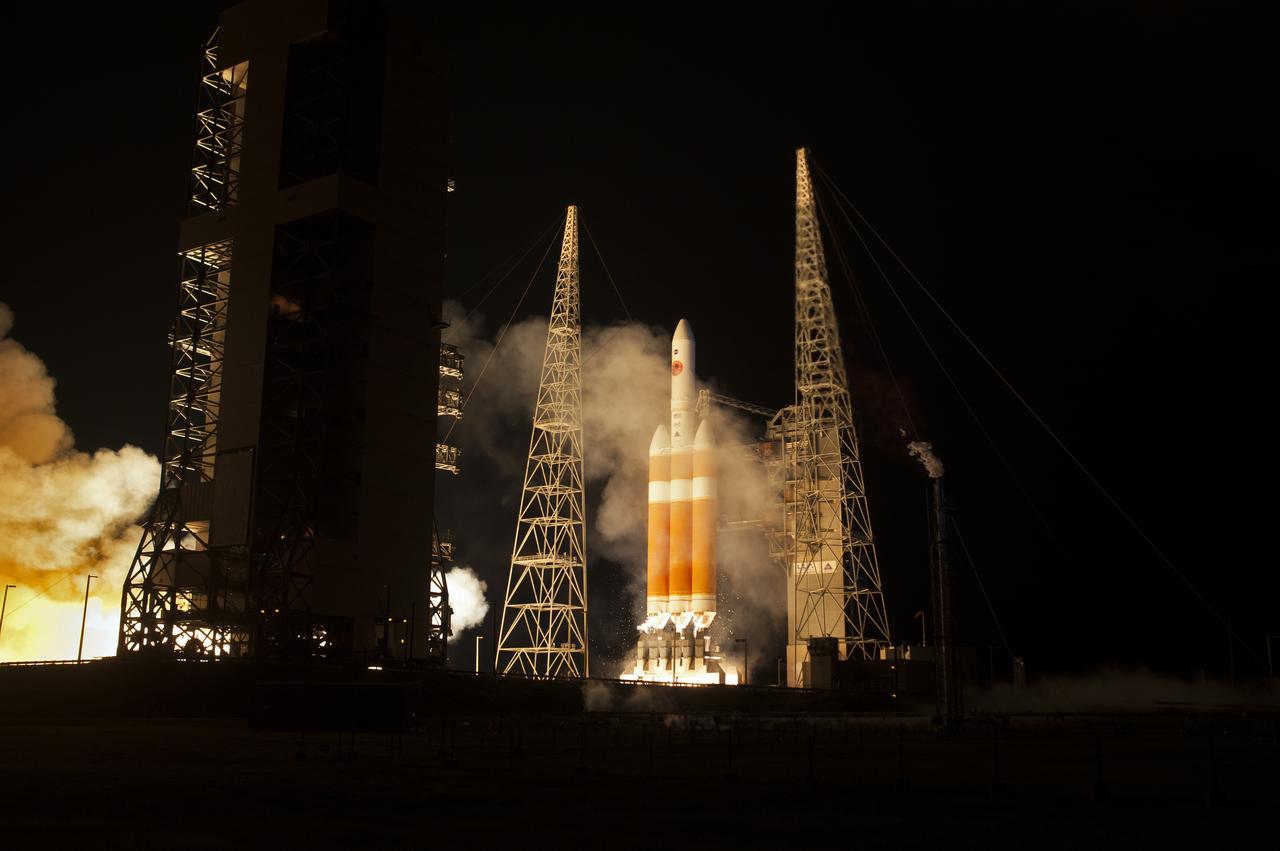

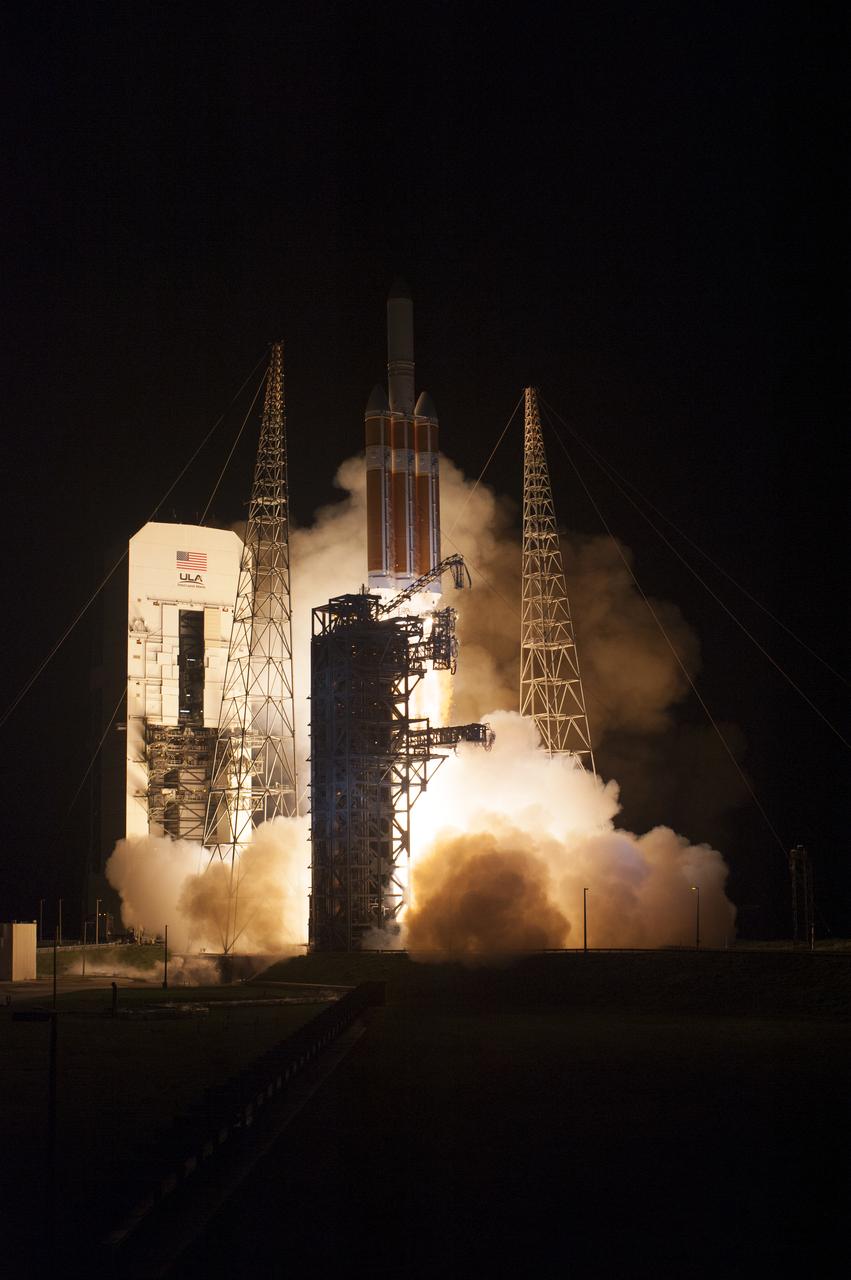
At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
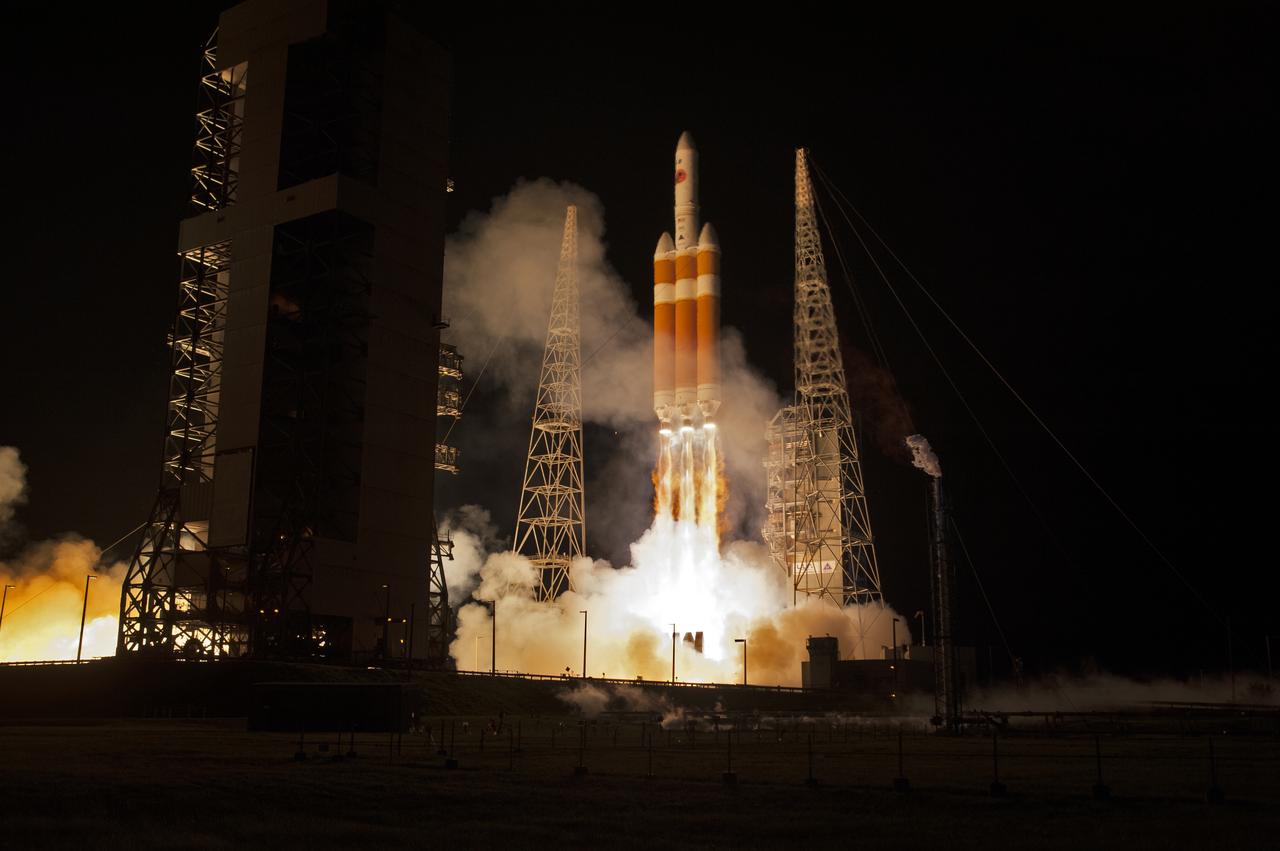

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
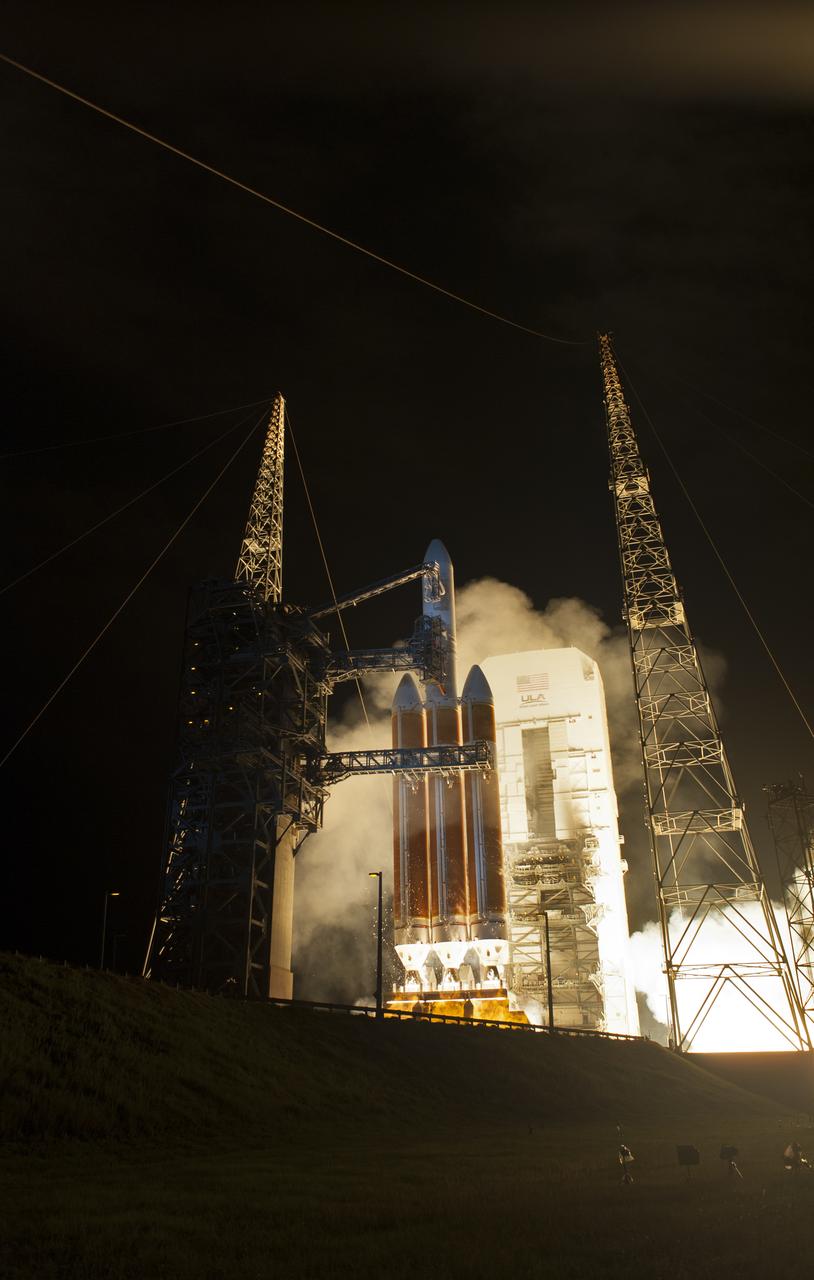

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
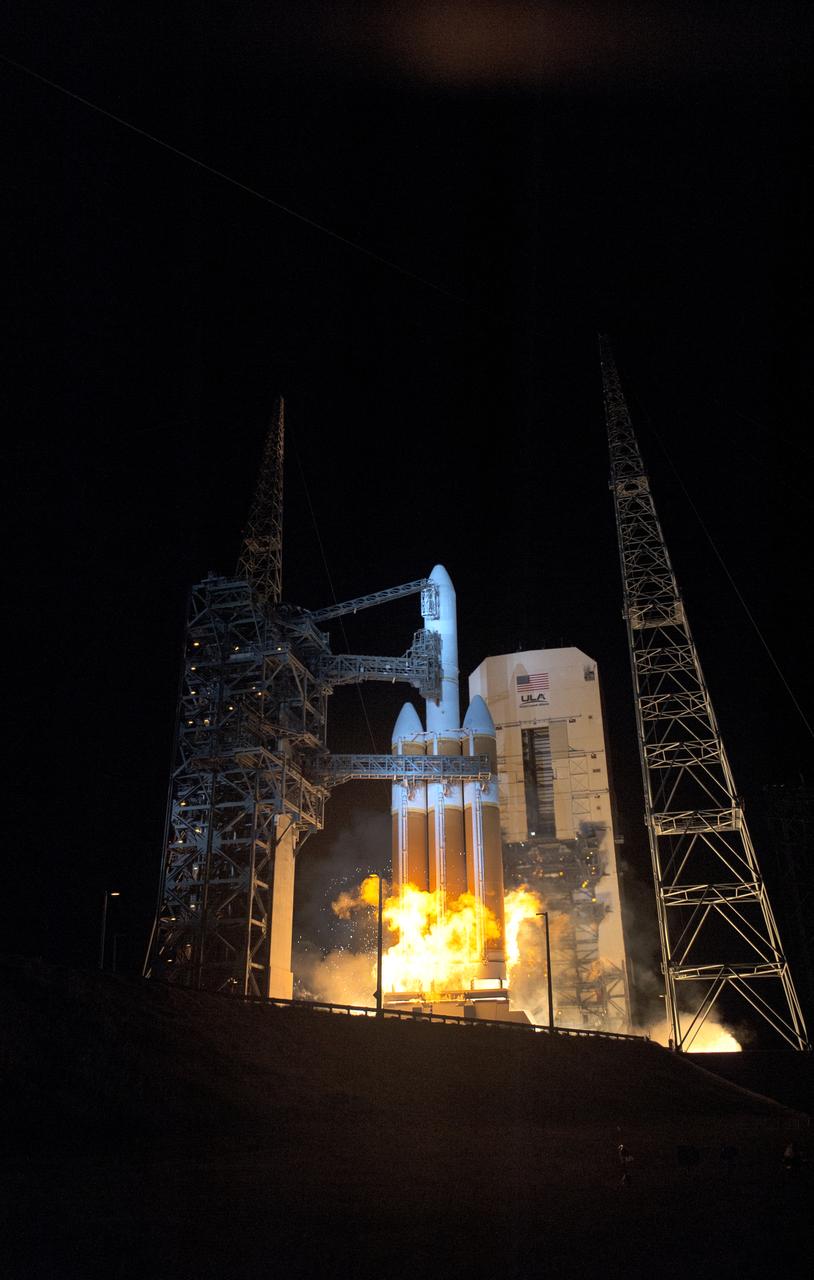

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
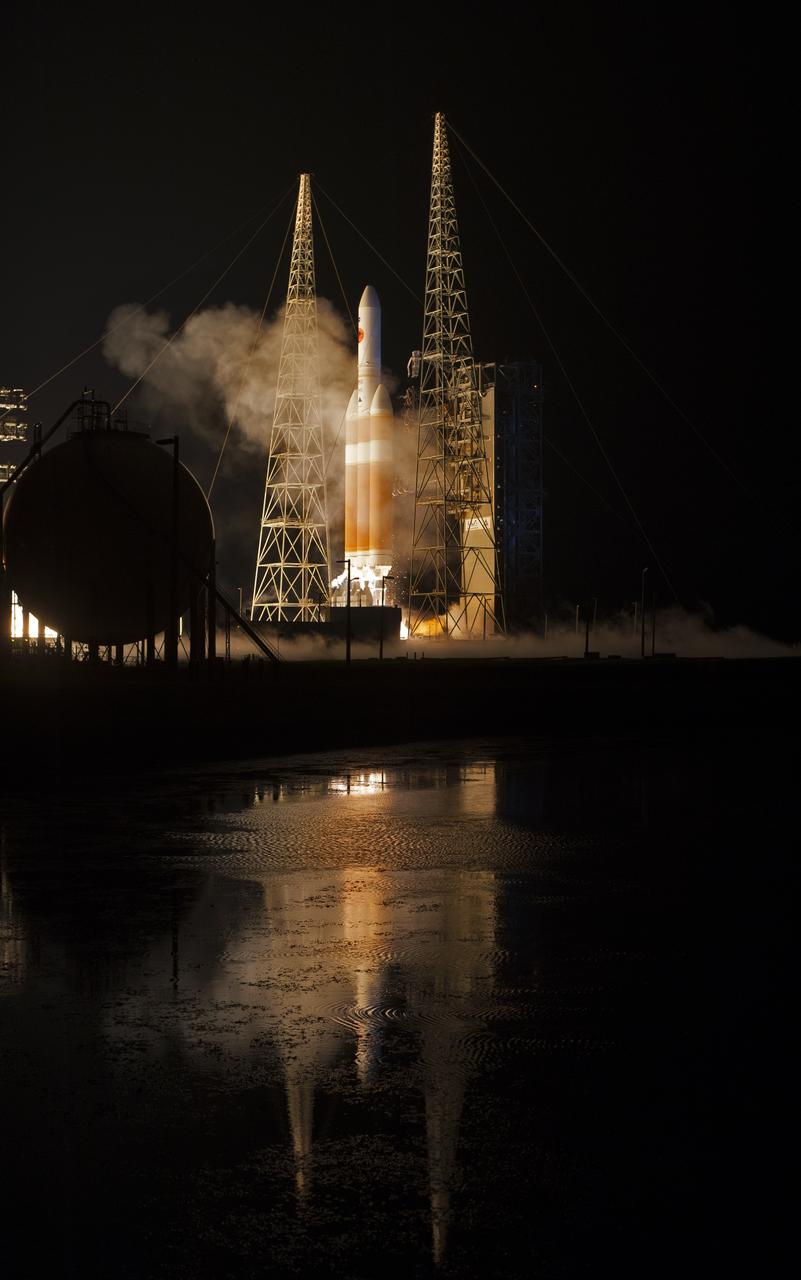

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
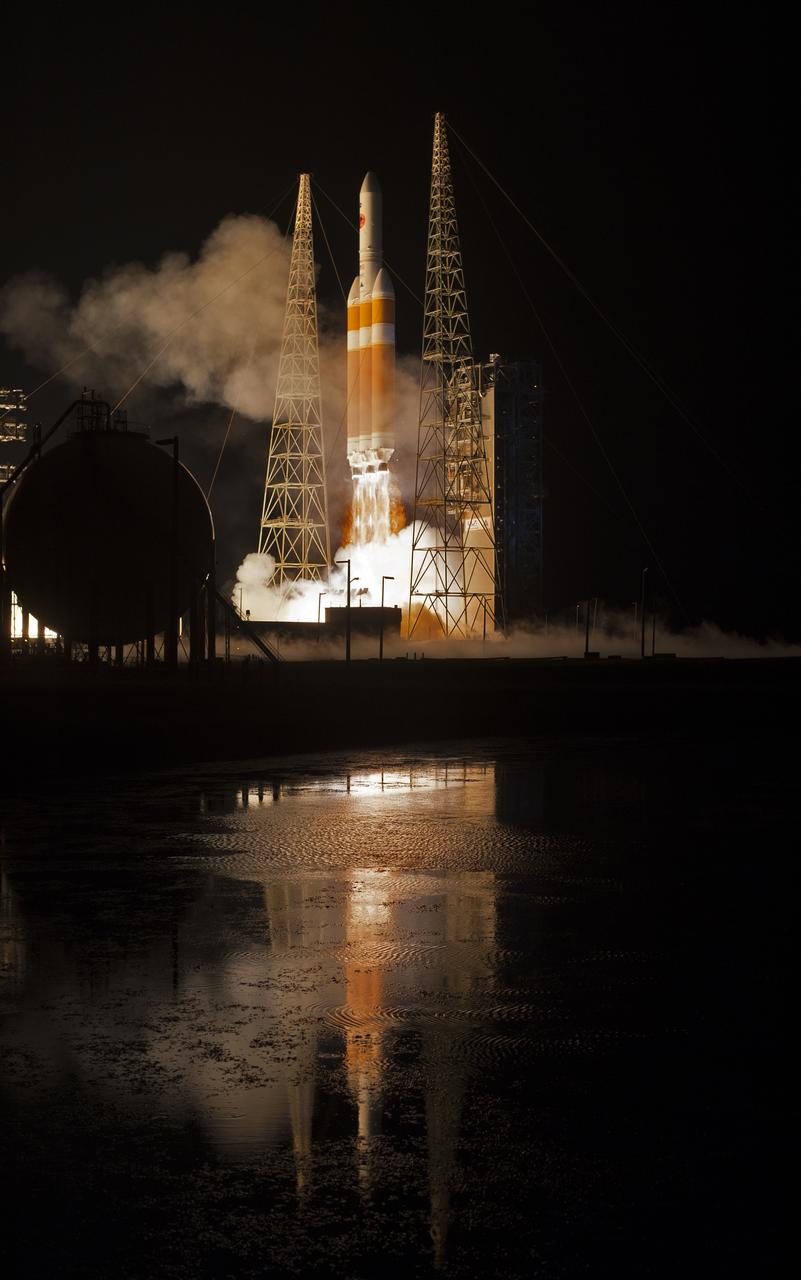

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
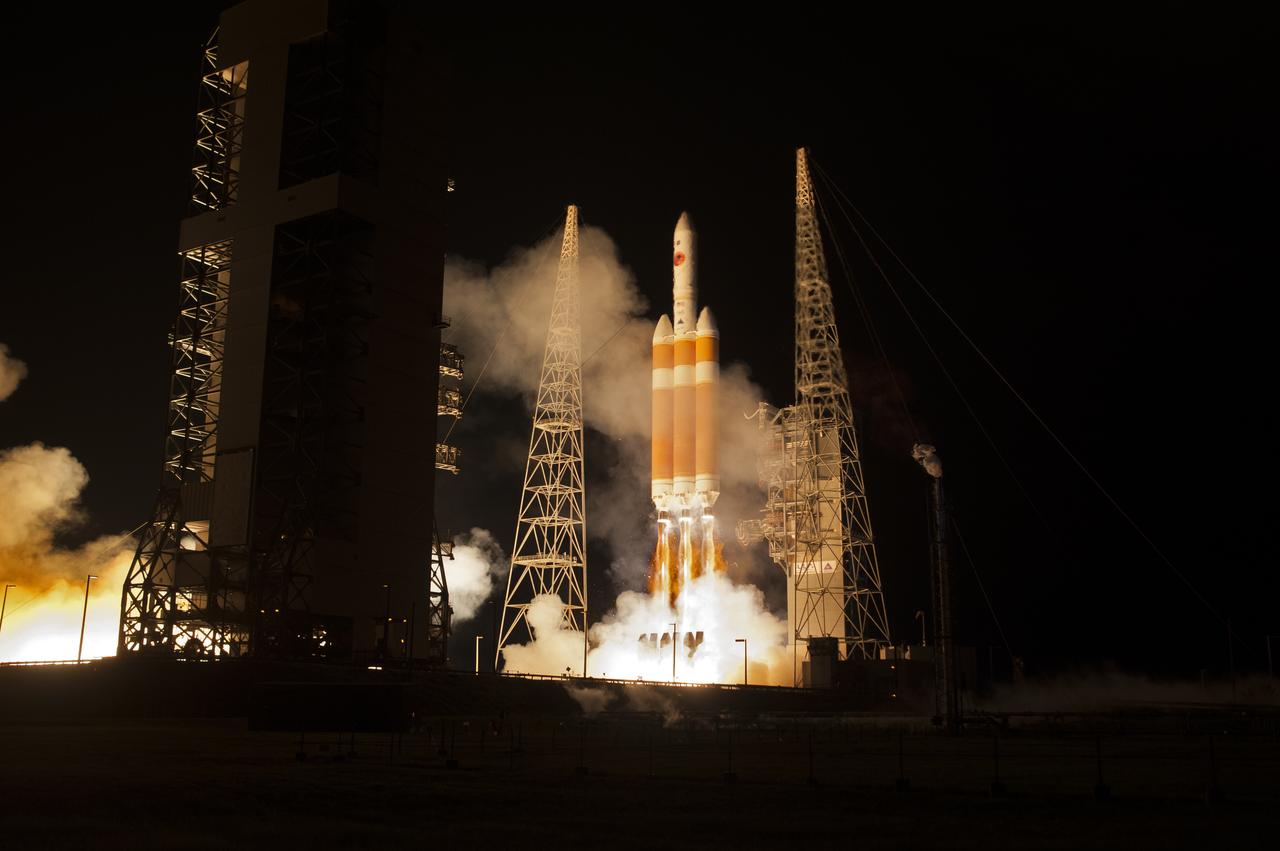

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
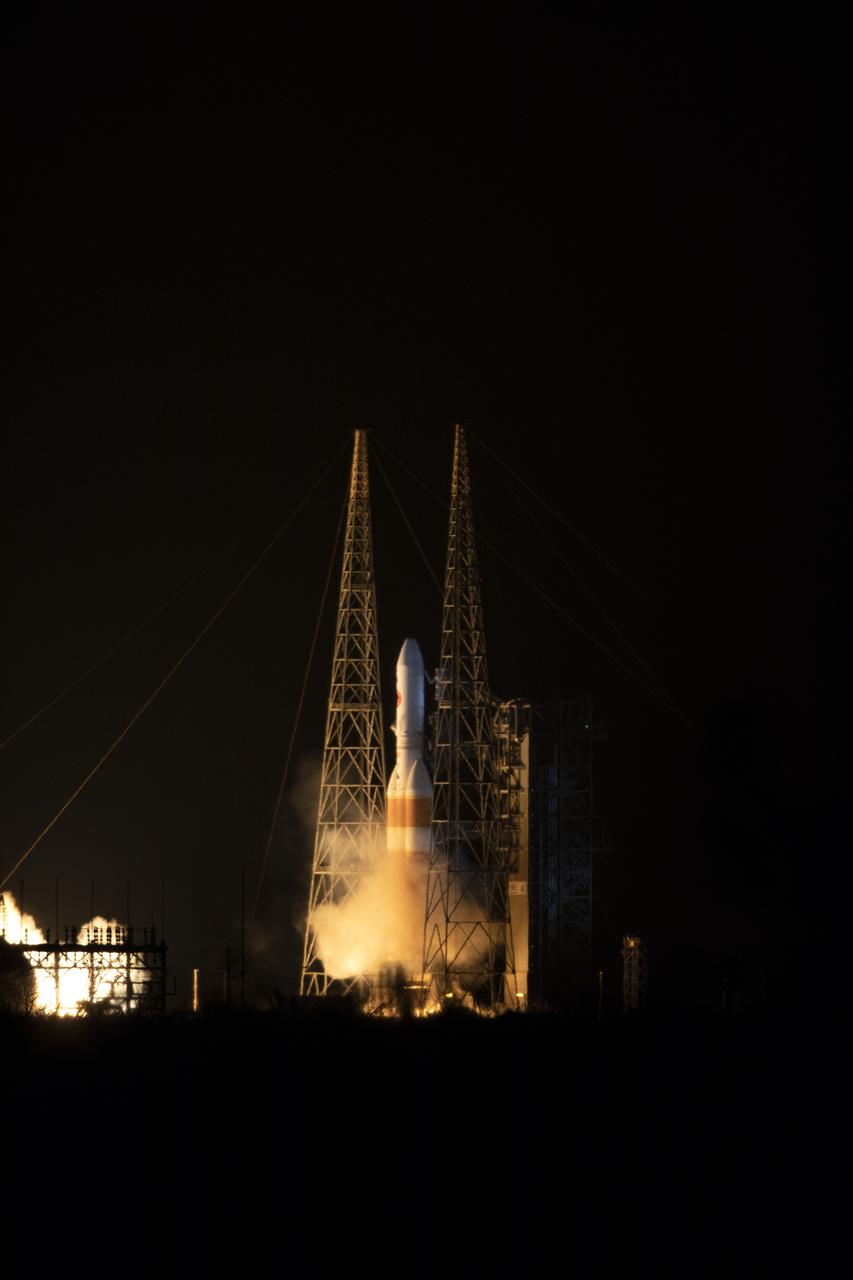

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
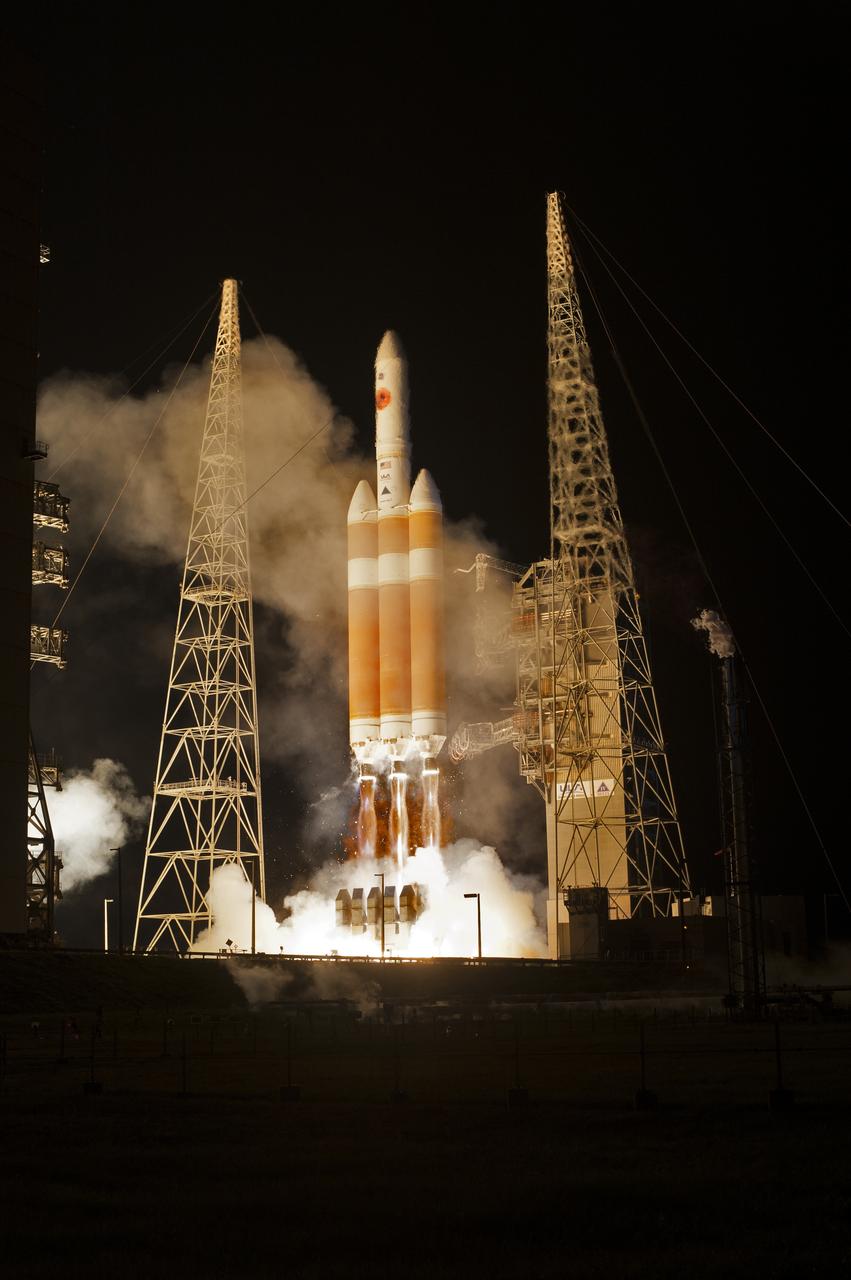

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
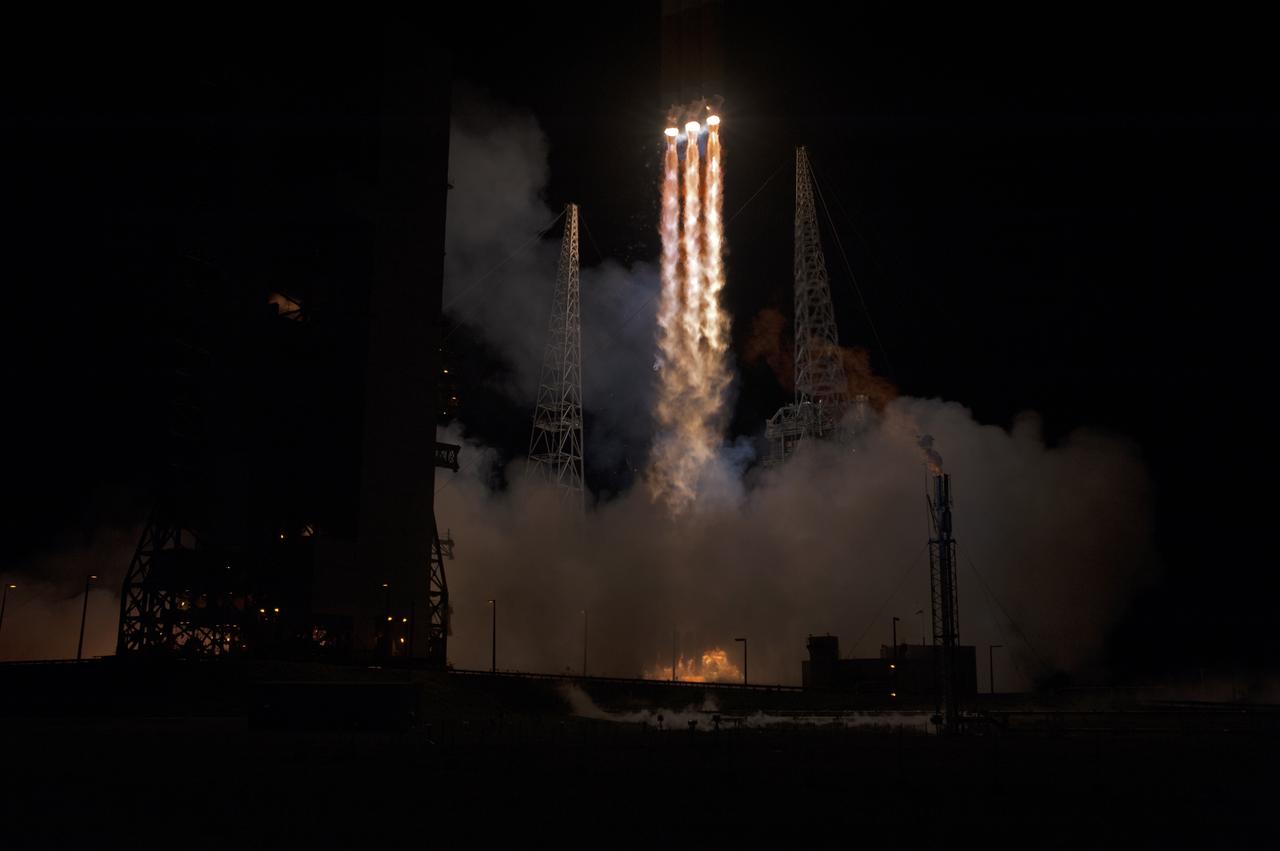

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
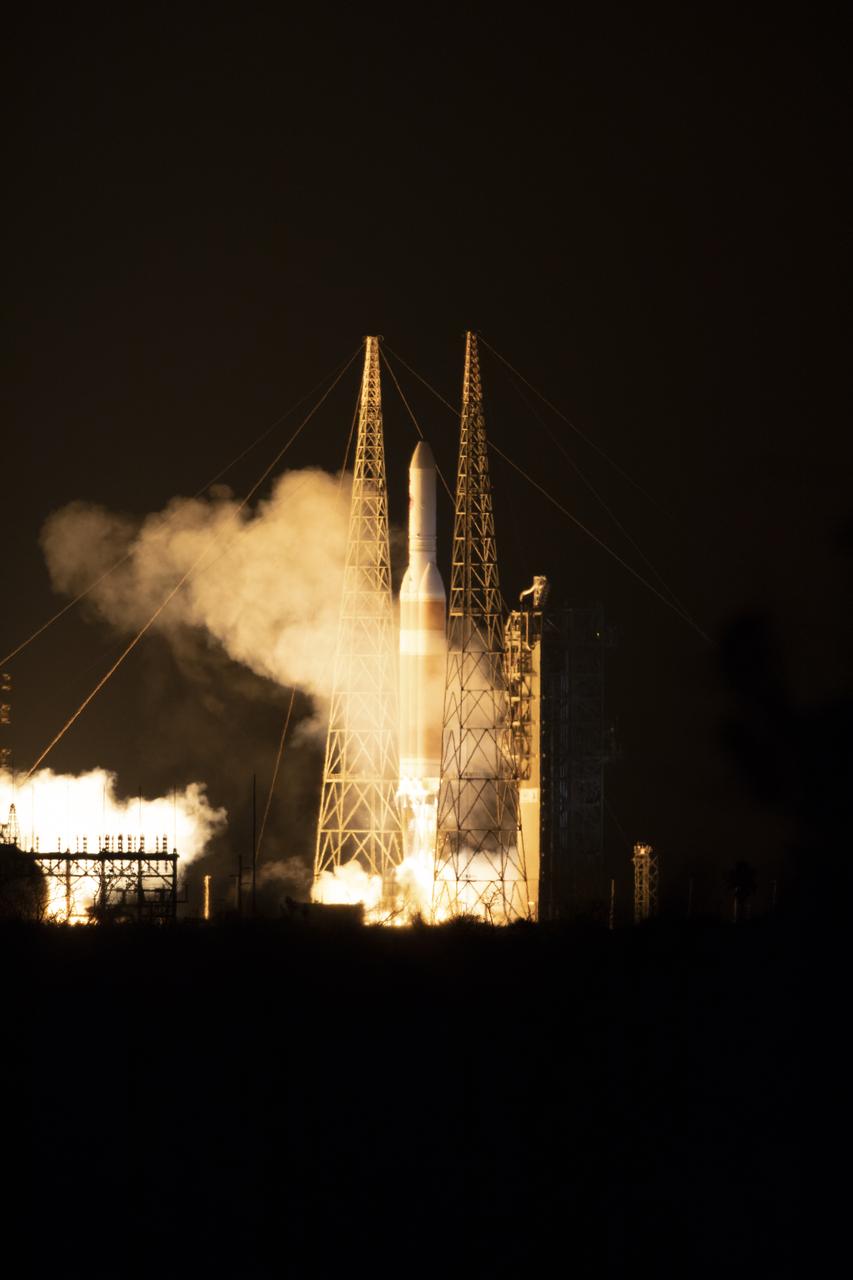

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
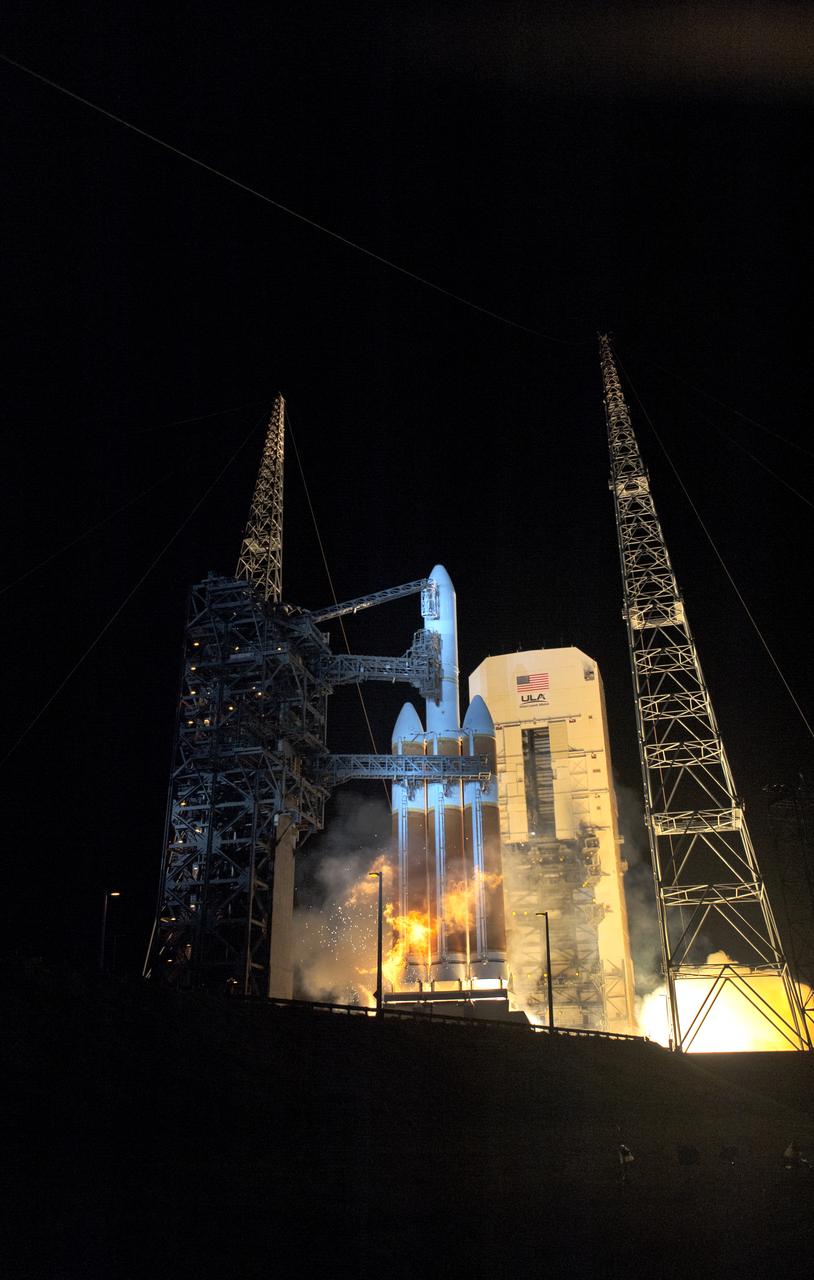

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
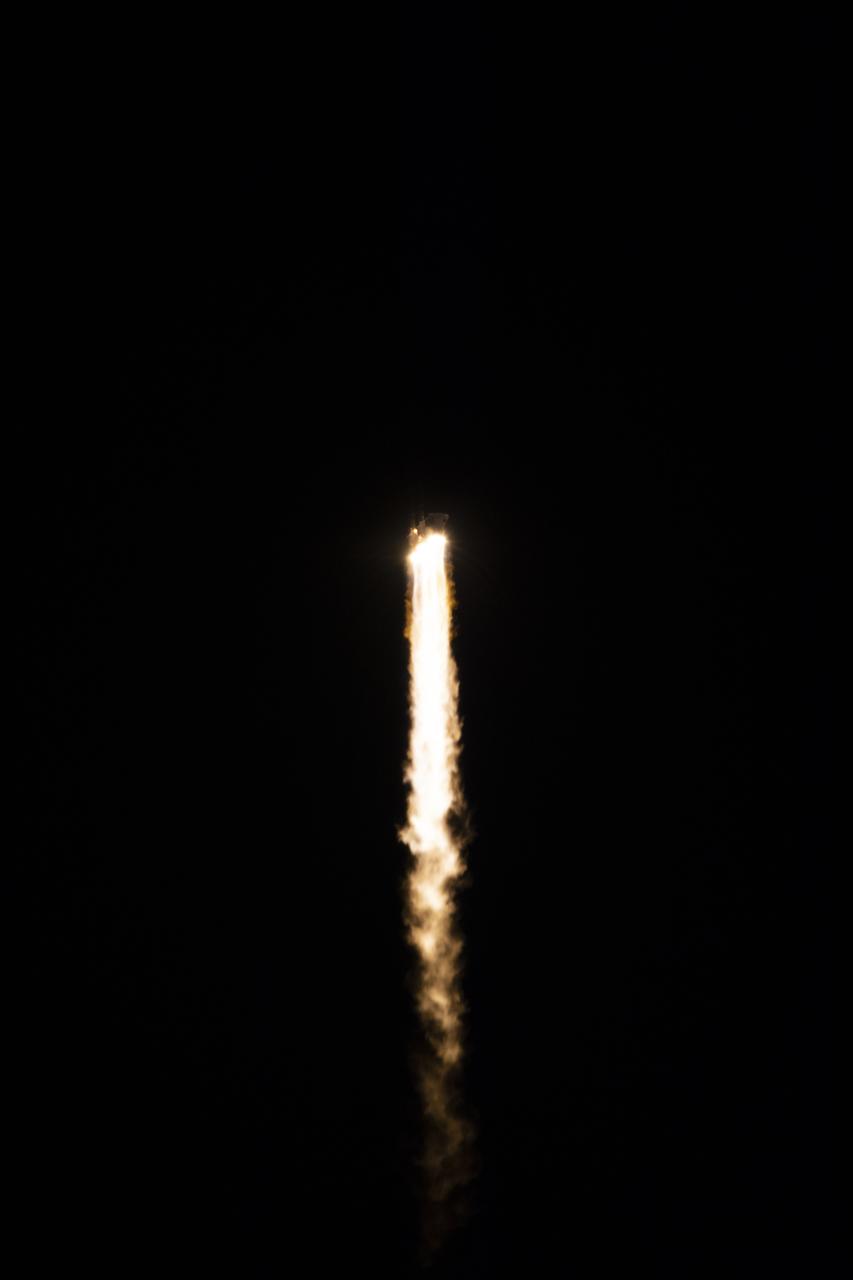

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
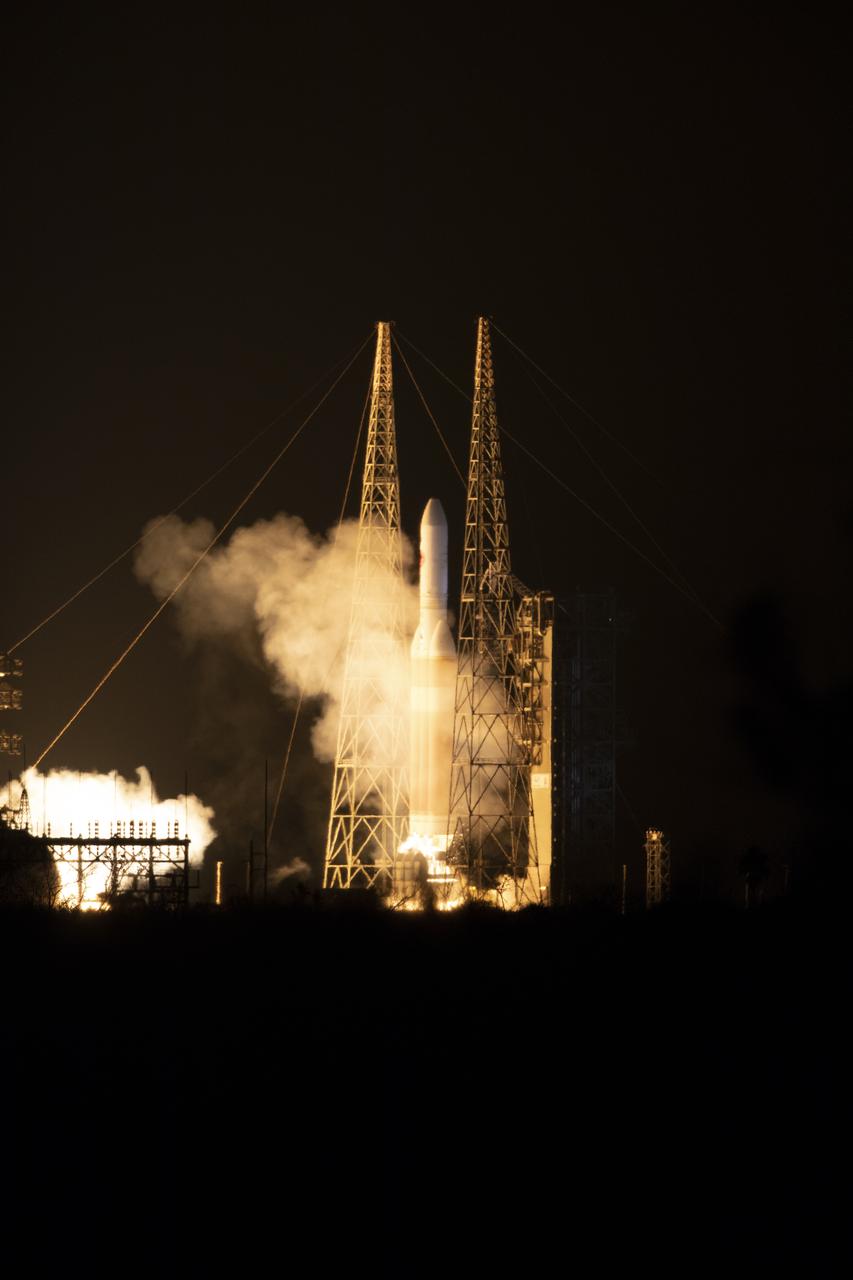

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
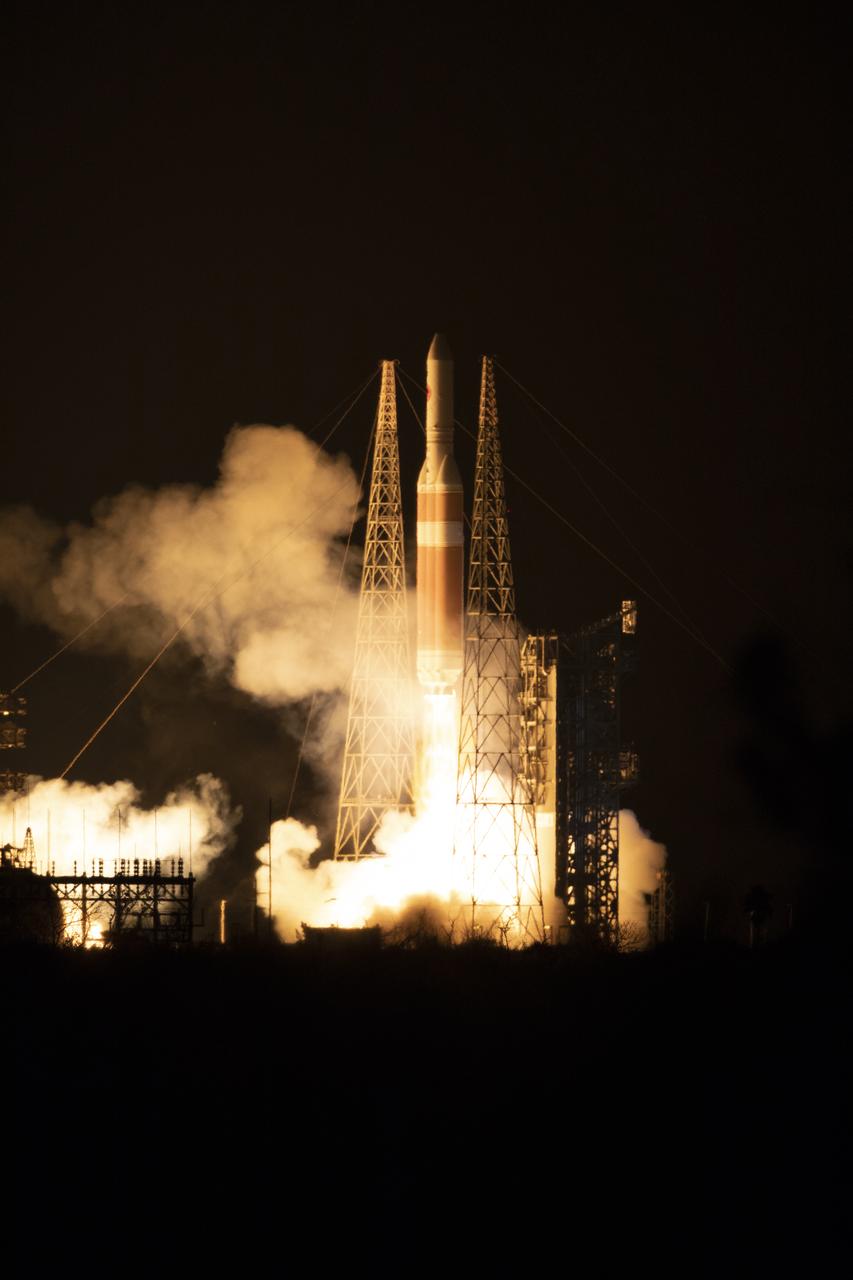

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
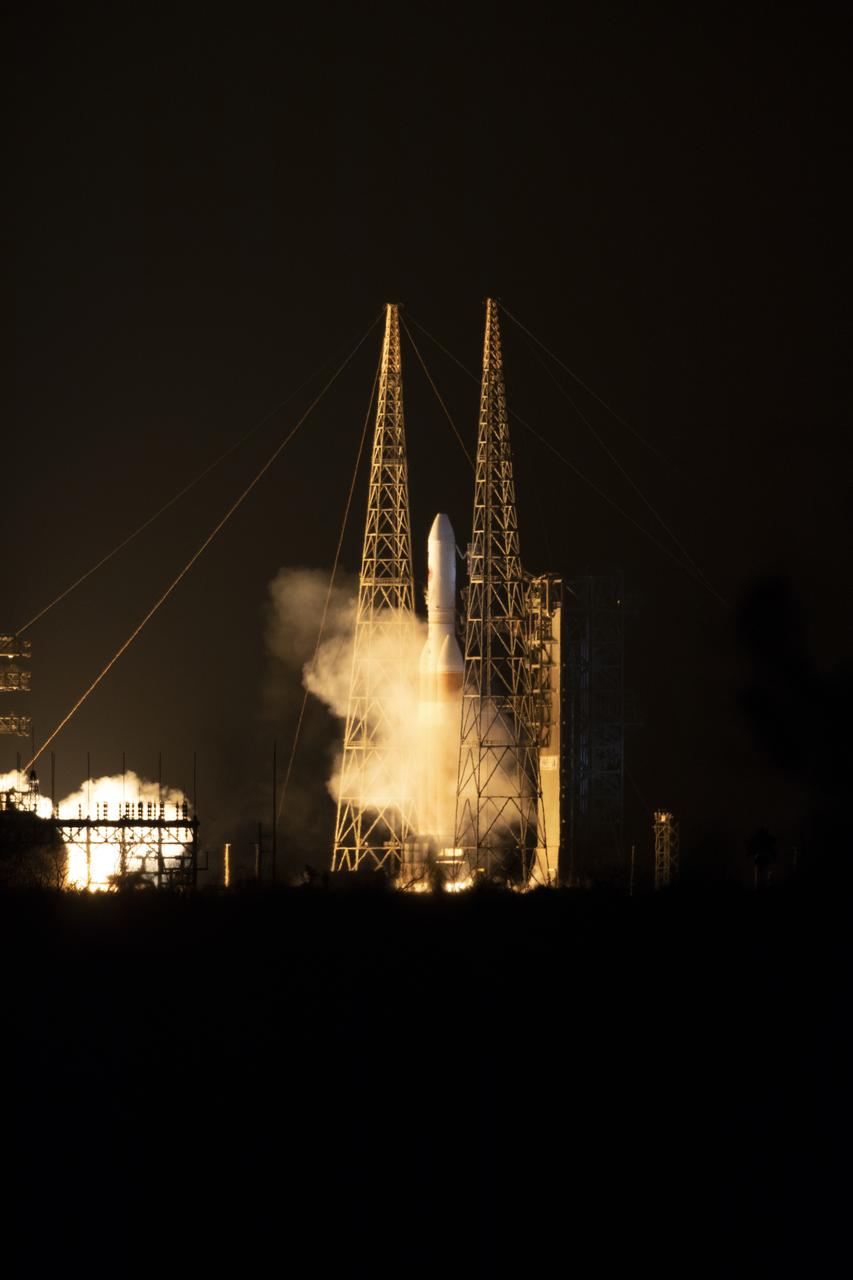

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
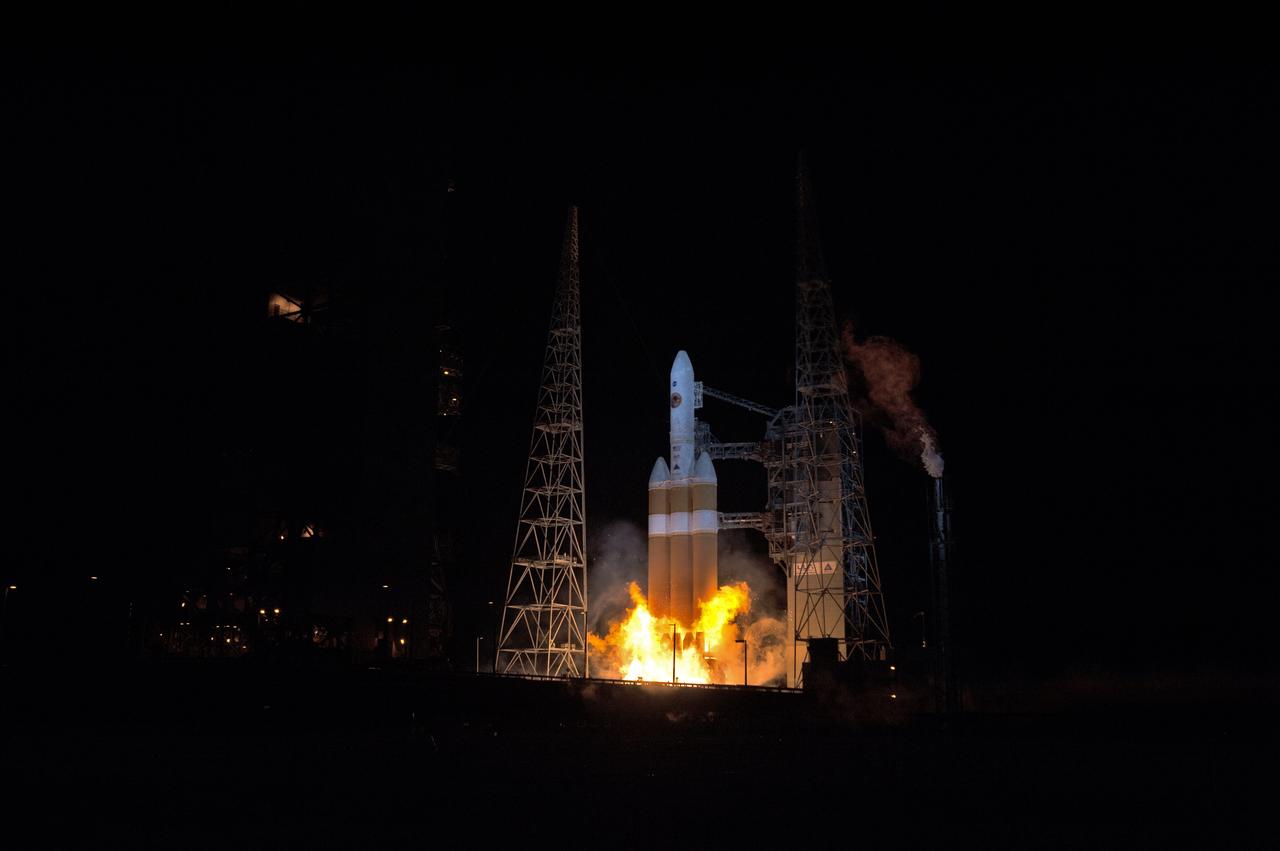

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
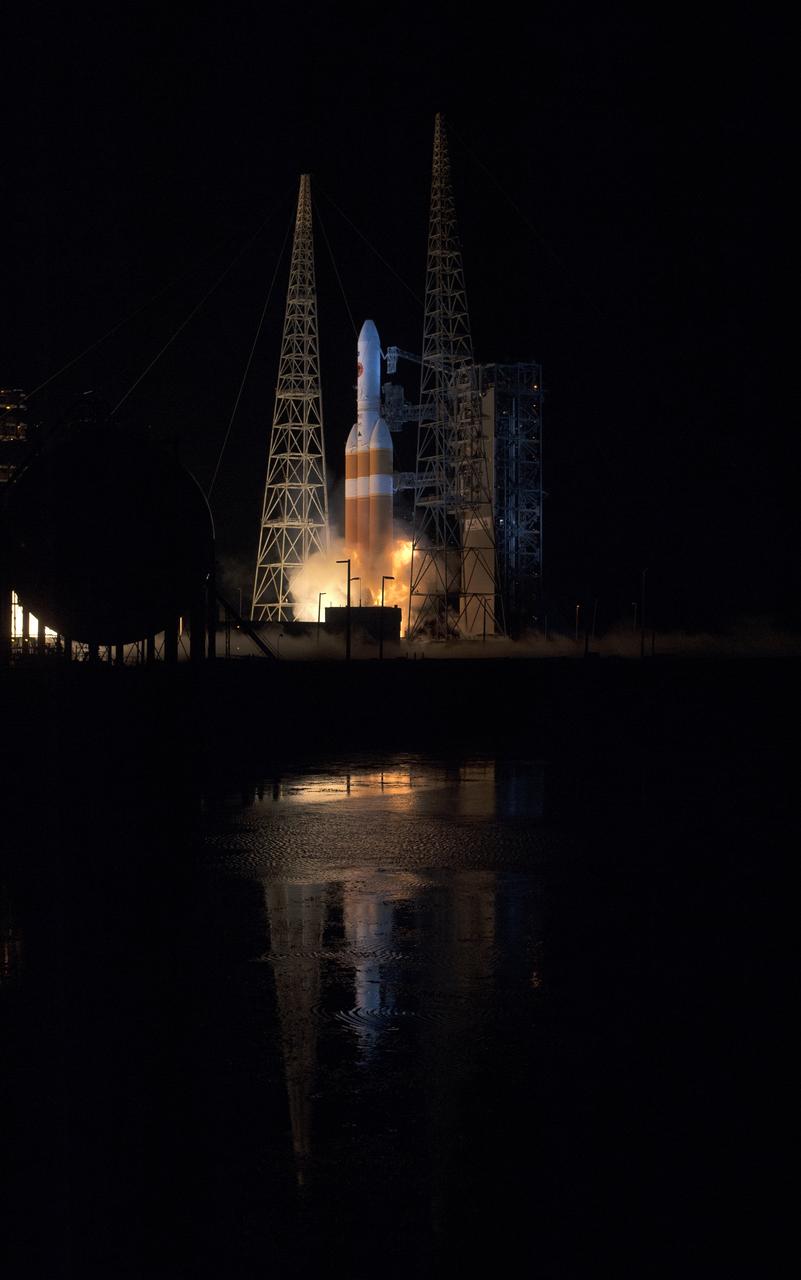

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
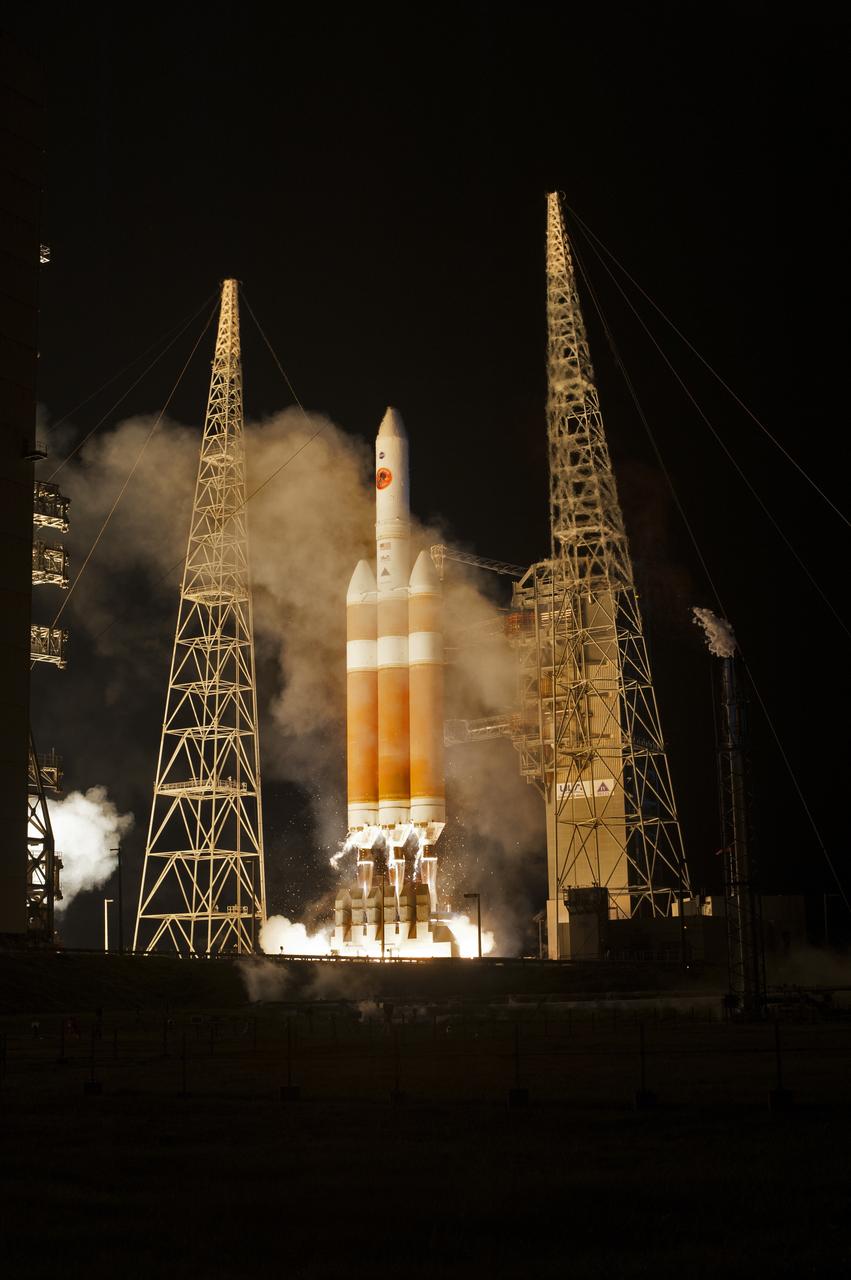

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
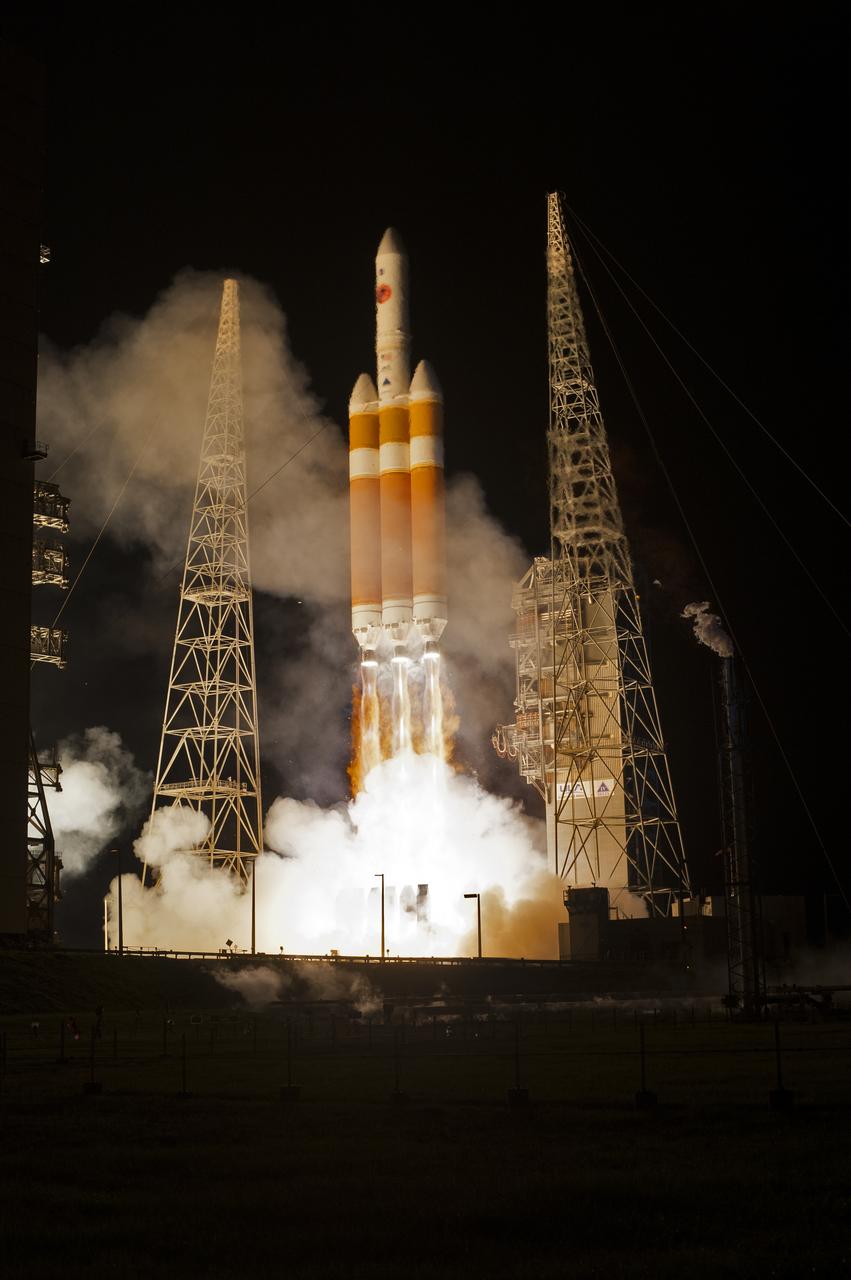

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
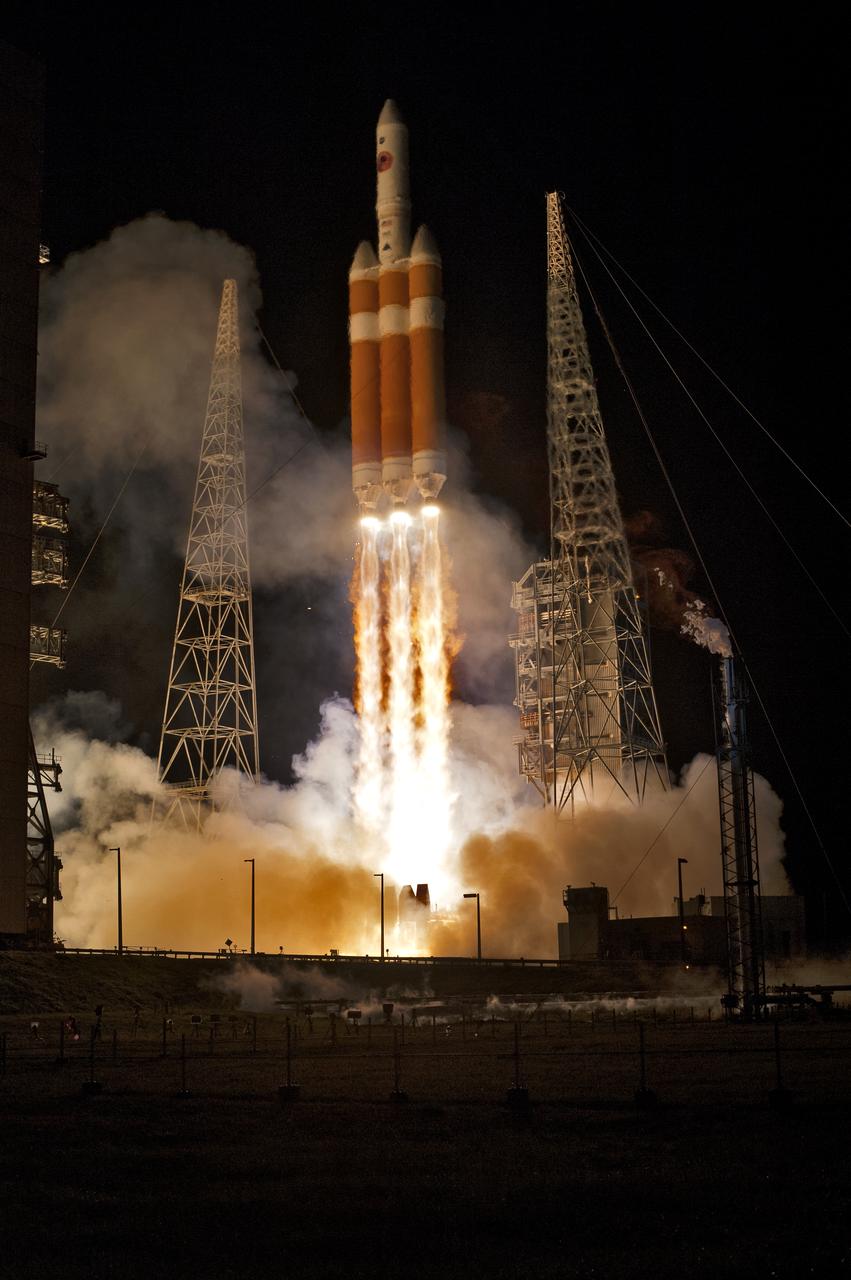

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
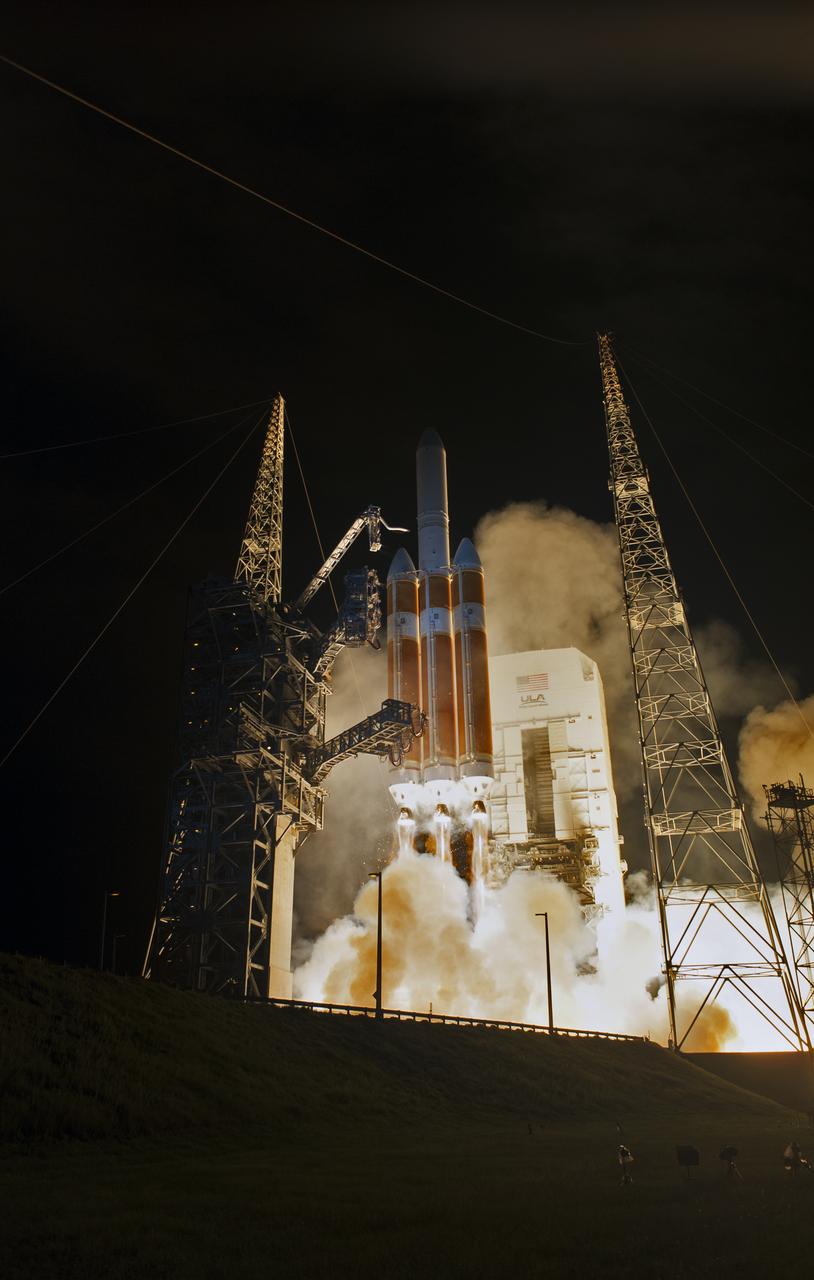

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
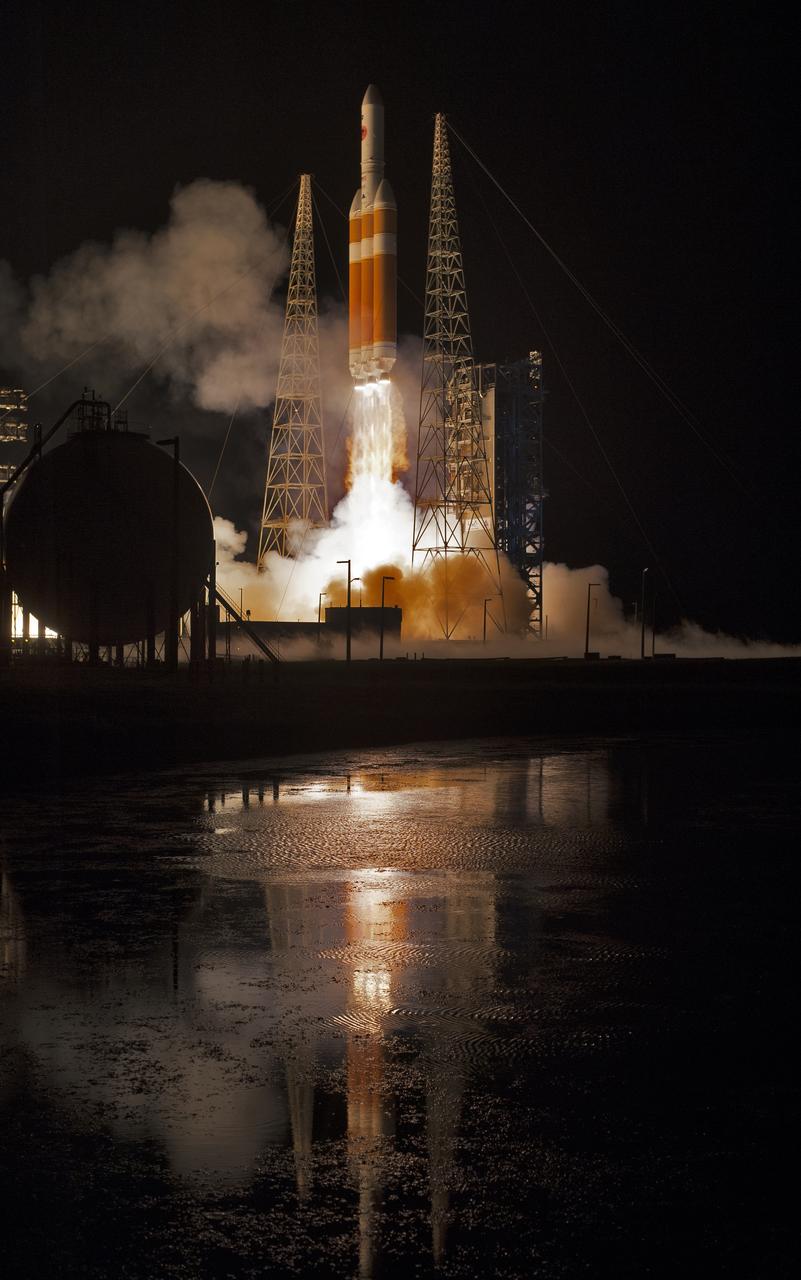

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
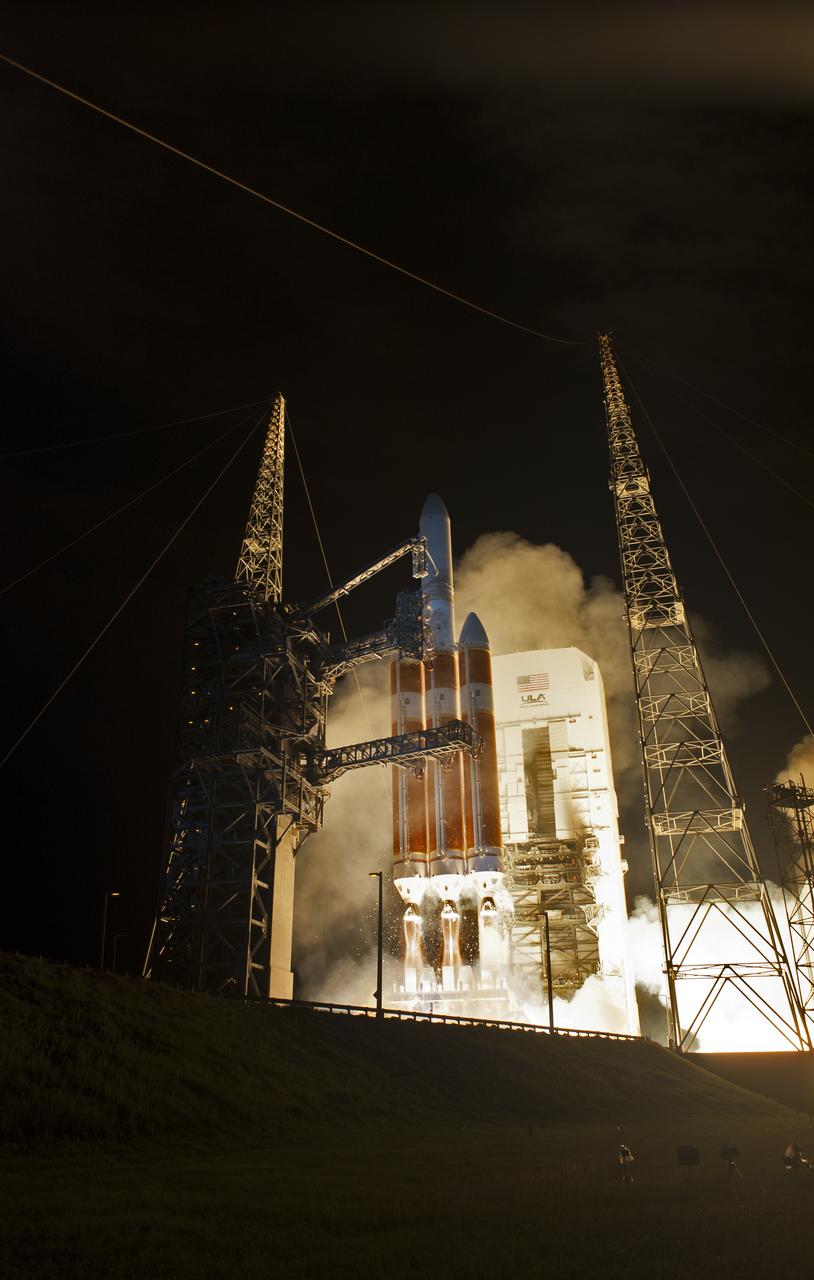

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
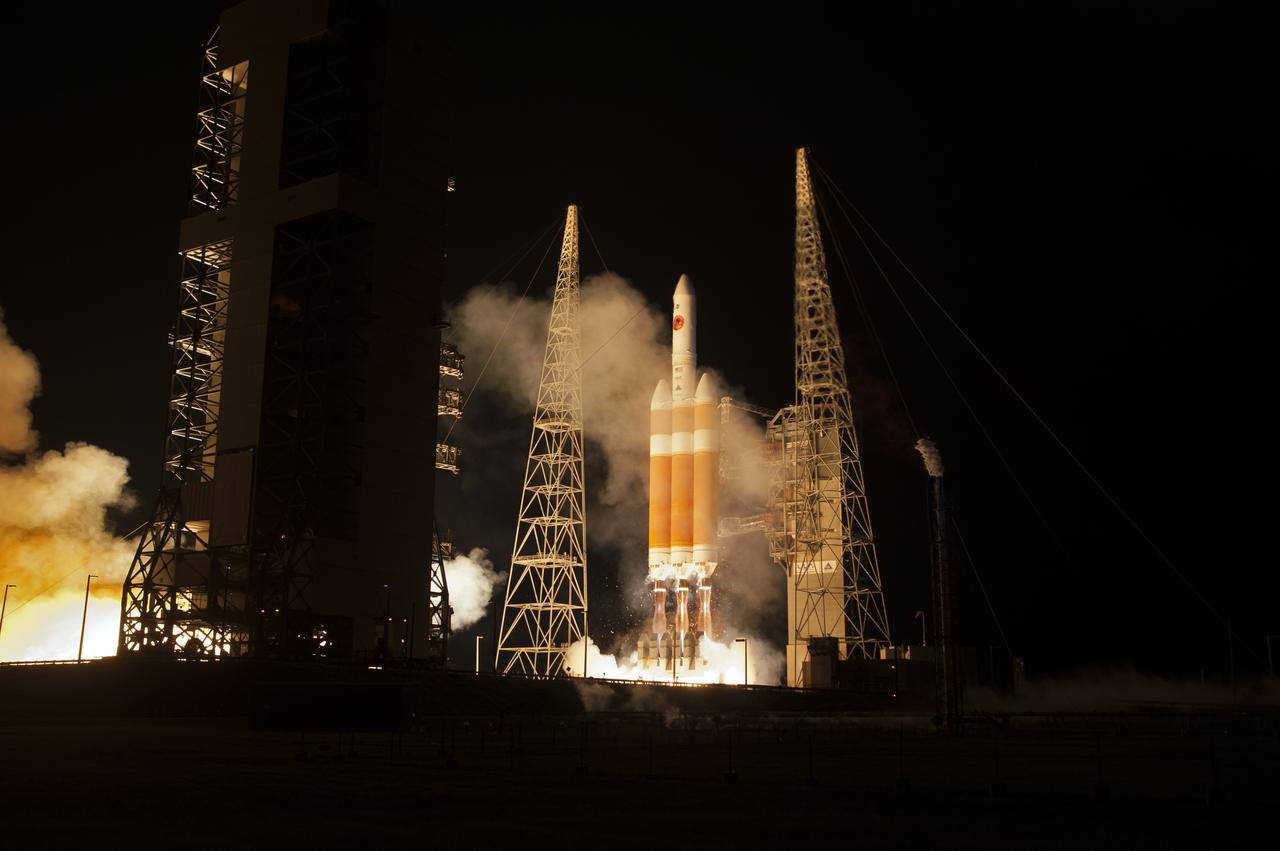

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
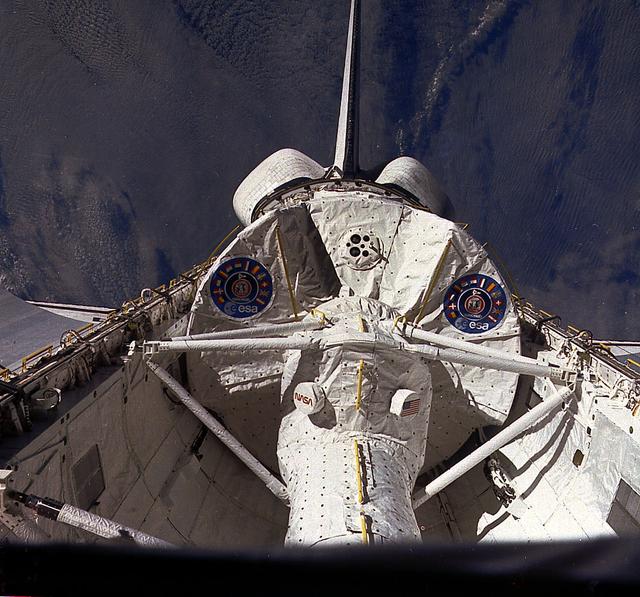

A Space Shuttle mission STS-9 onboard view show's Spacelab-1 (SL-1) module in orbiter Columbia's payload bay. Spacelab-1 was a cooperative venture of NASA and the European Space Agency. Scientists from eleven European nations plus Canada, Japan and the U.S. provided instruments and experimental procedures for over 70 different investigations in five research areas of disciplines: astronomy and solar physics, space plasma physics, atmospheric physics and Earth observations, life sciences and materials science.
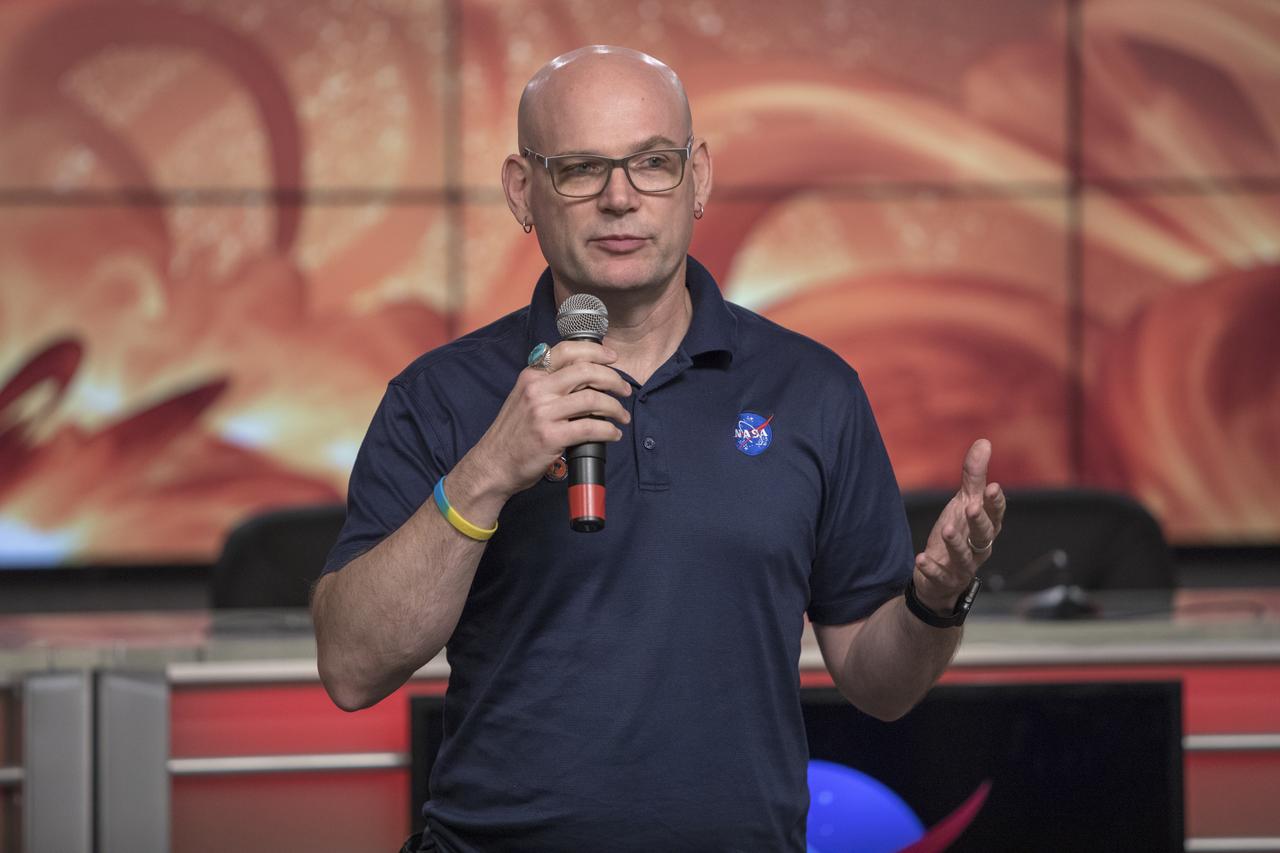

In the Kennedy Space Center’s Press Site auditorium, on Friday, July 20, 2018, Alex Young, solar scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, speaks to members of the media during a prelaunch mission briefing for the Parker Solar Probe mission. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel in Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
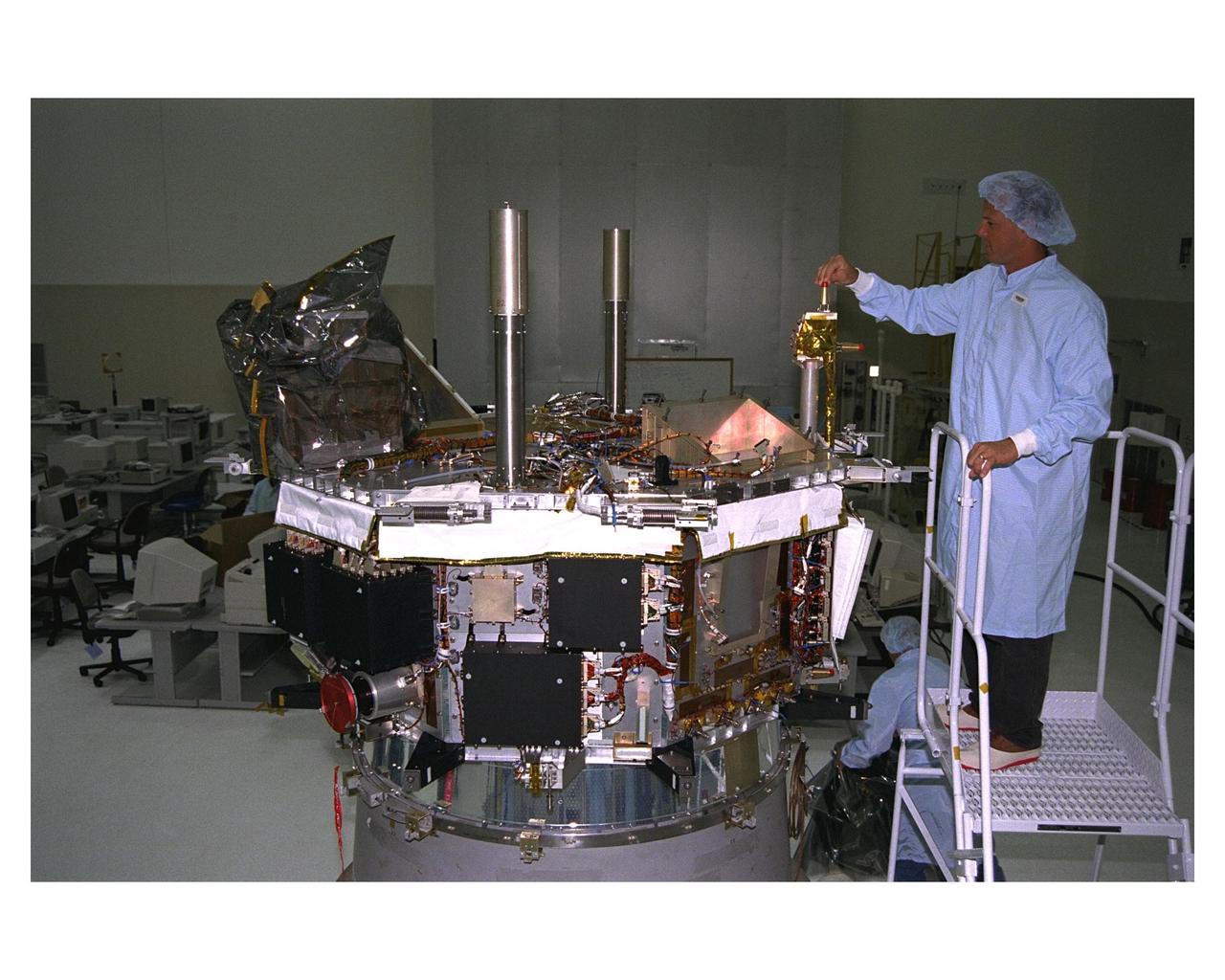
Workers in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2) begin prelaunch processing of the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) which will investigate the origin and evolution of solar phenomenon, the formation of the solar corona, solar flares and the acceleration of the solar wind. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. The spacecraft is scheduled to be launched Aug. 21 aboard a two-stage Delta II 7920-8 rocket from Space Launch Complex 17, Pad A
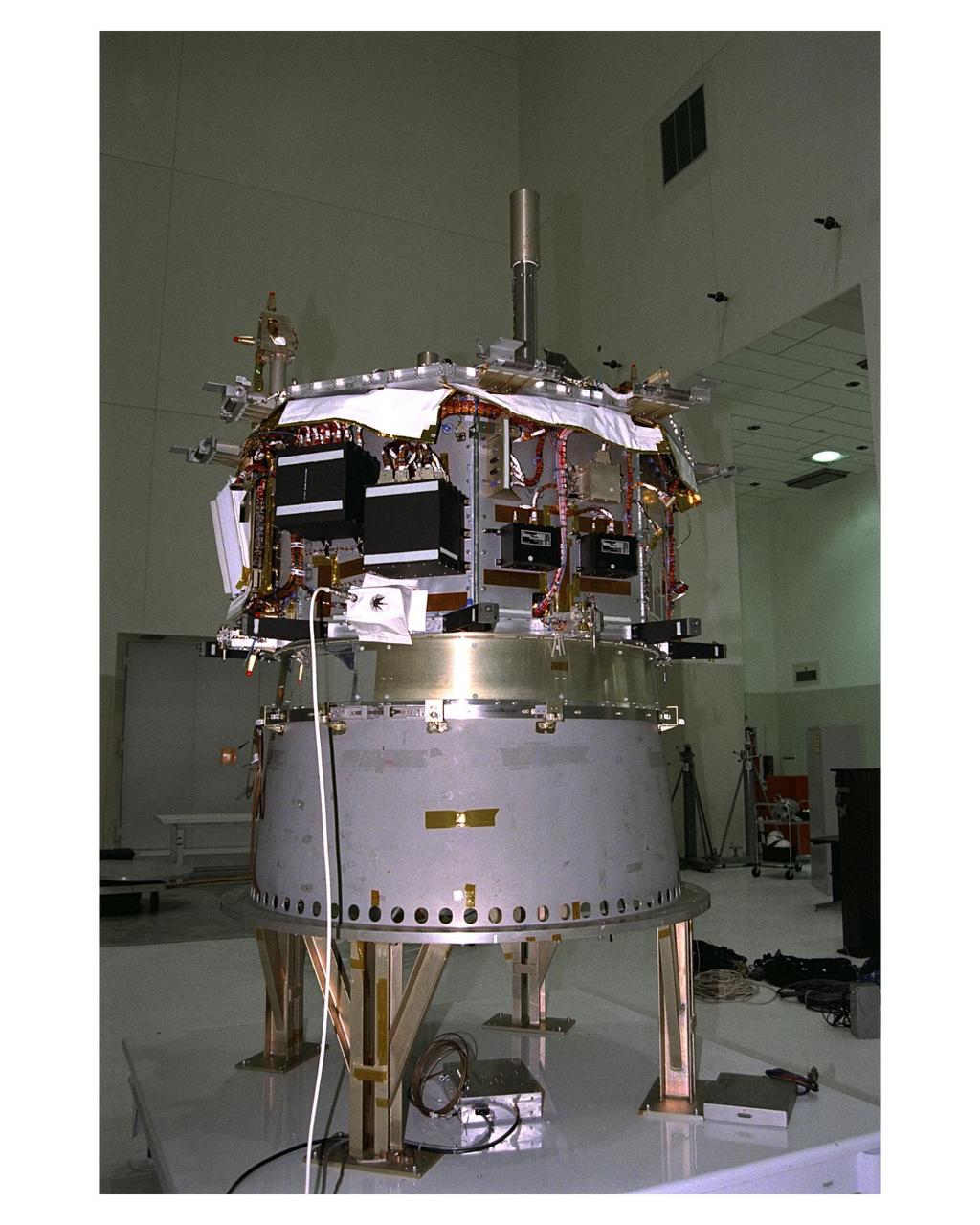

Prelaunch processing begins on the Advanced Composition Explorer (ACE) spacecraft in the Spacecraft Assembly and Encapsulation Facility-2 (SAEF-2). ACE will investigate the origin and evolution of solar phenomenon, the formation of the solar corona, solar flares and the acceleration of the solar wind. ACE was built for NASA by the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory. The spacecraft is scheduled to be launched Aug. 21 aboard a two-stage Delta II 7920-8 rocket from Space Launch Complex 17, Pad A
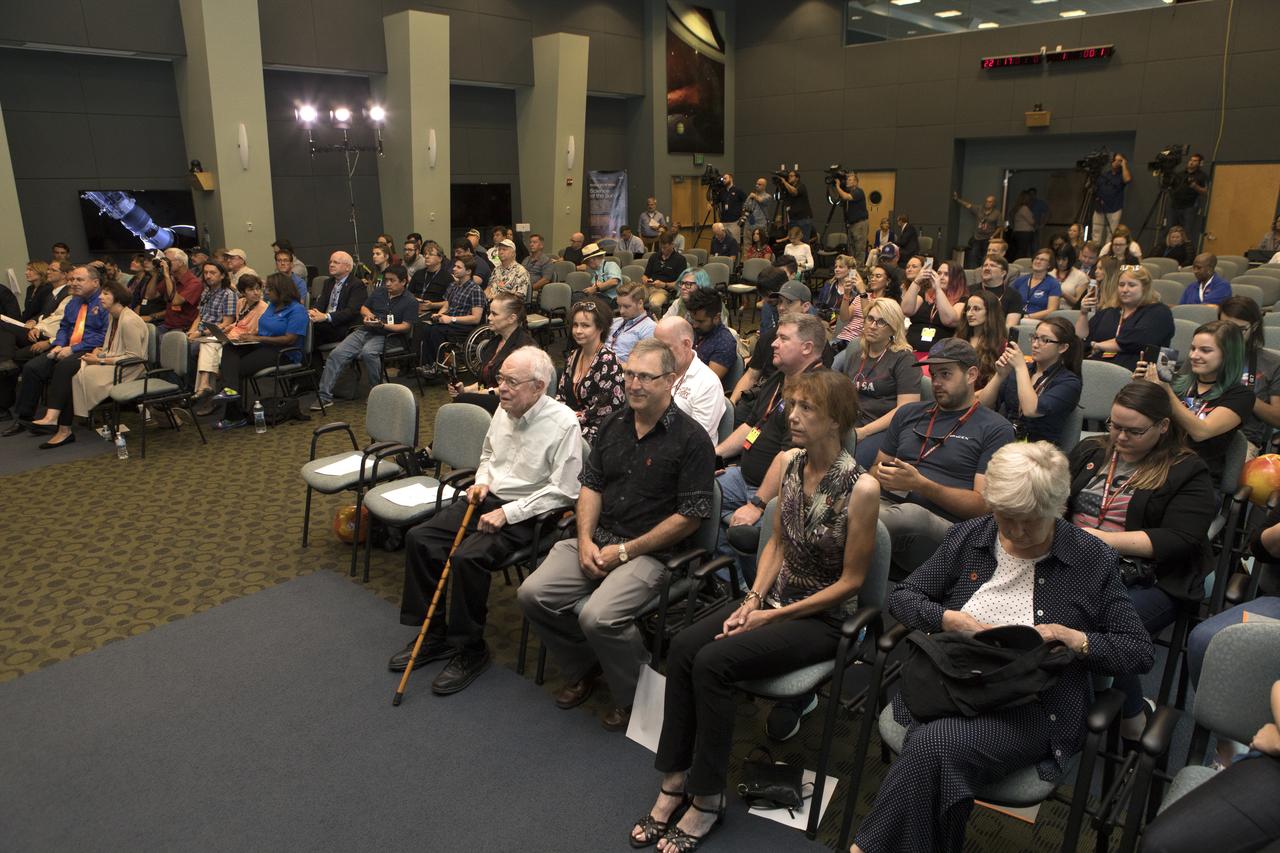

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Listening to the presentation is Eugene Parker, front row, far left, the S. Chandrasekhar Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus, Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago. This is the first NASA mission that has been named for a living individual. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing moderators from left, are Karen Fox, Goddard Space Flight Center, and Dwayne Brown, NASA Communications. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
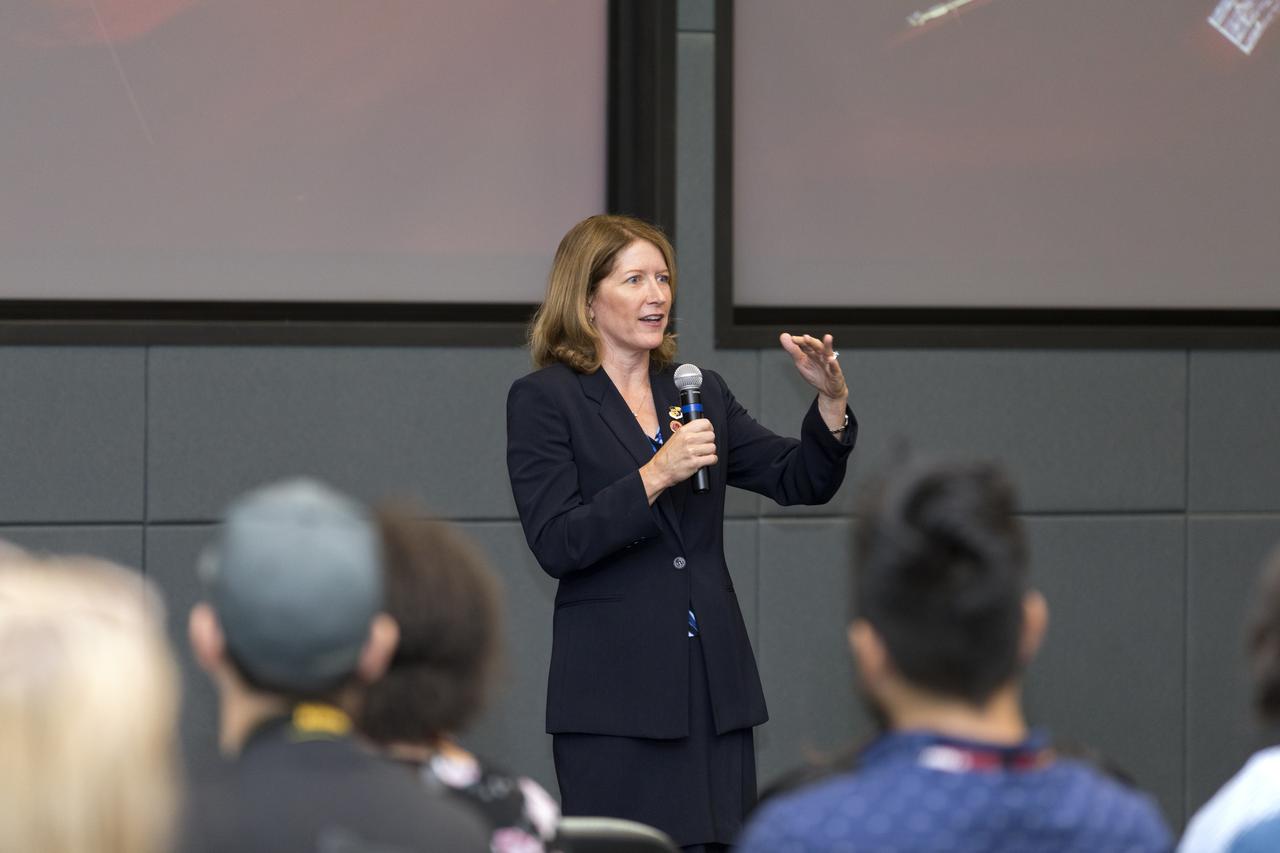

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Speaking to the media is Kathy Rice, launch weather officer, 45th Weather Squadron, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
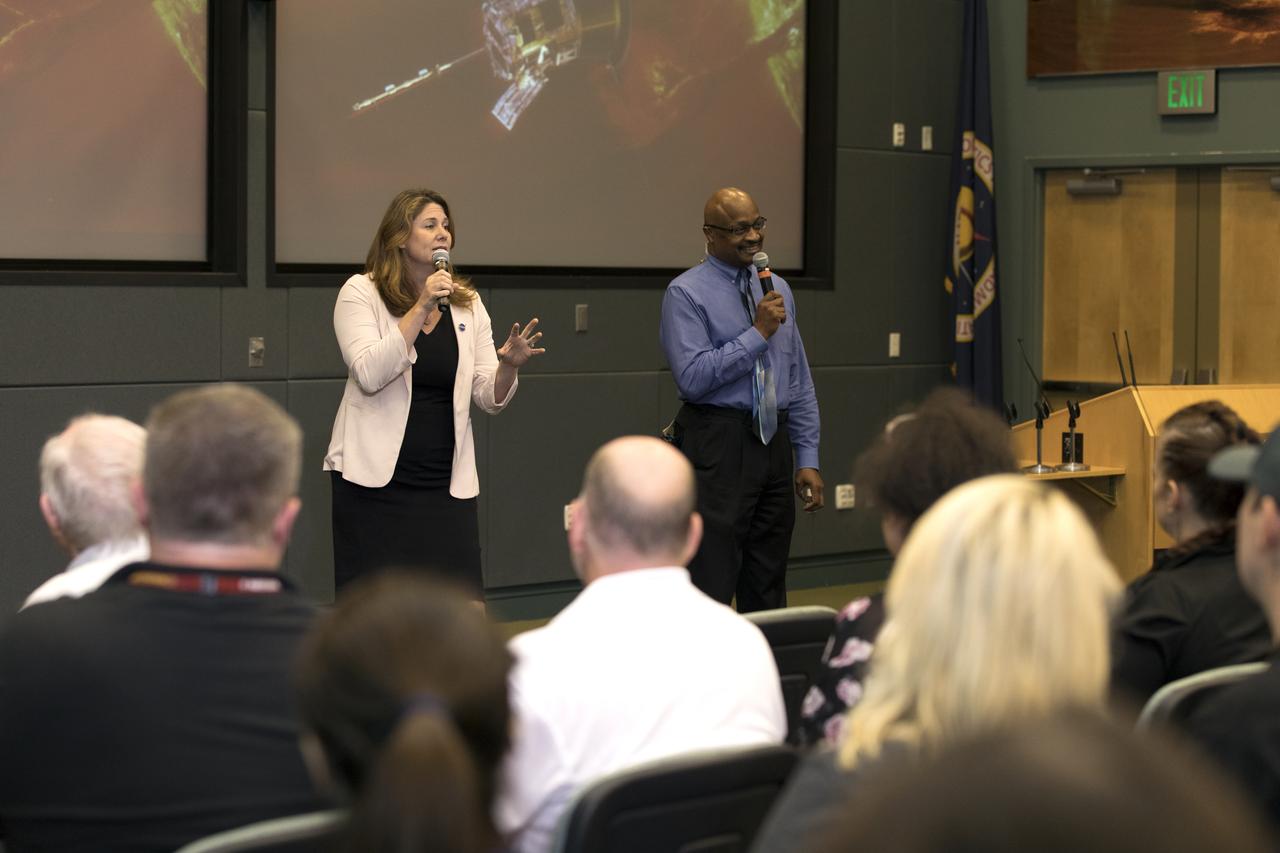

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Briefing moderators from left, are Karen Fox, Goddard Space Flight Center, and Dwayne Brown, NASA Communications. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
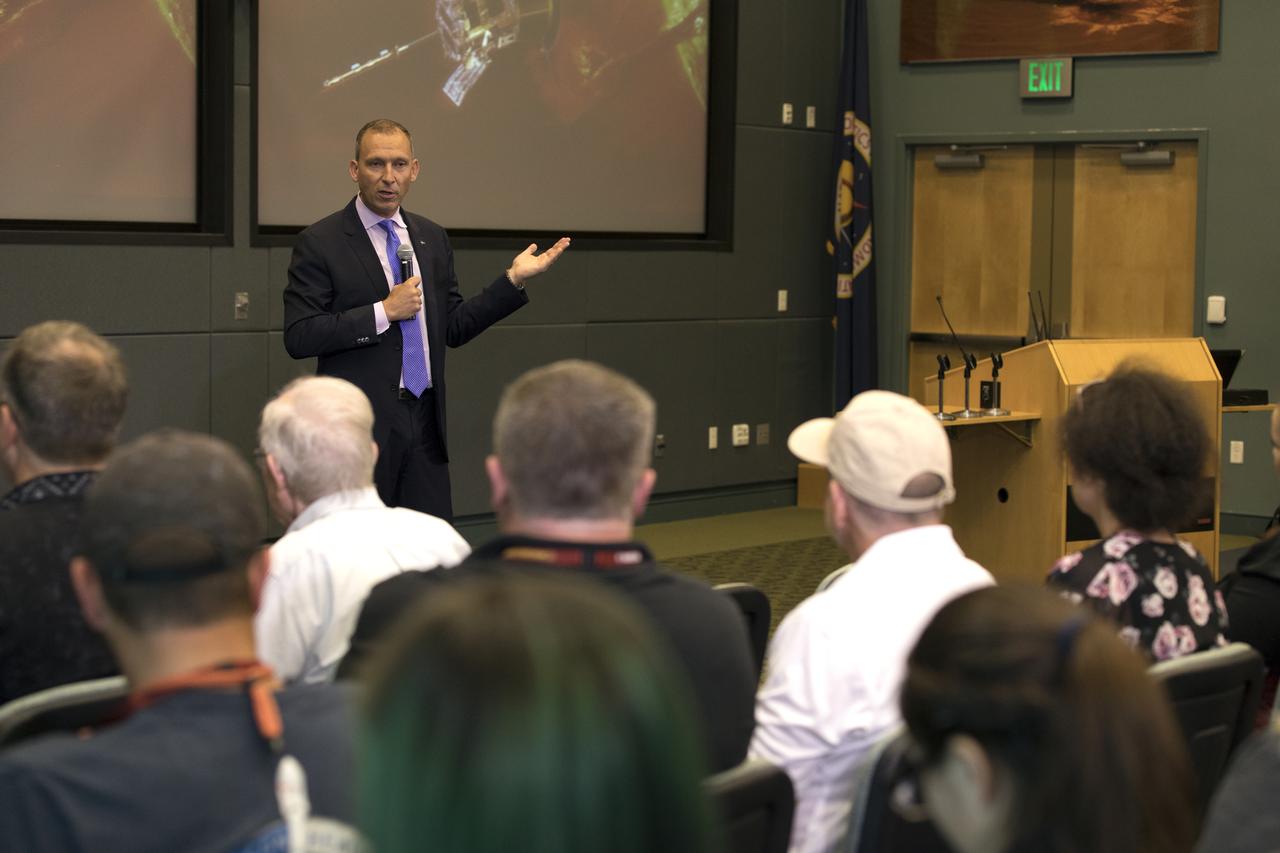

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Speaking to the media is Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directore in Washington. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
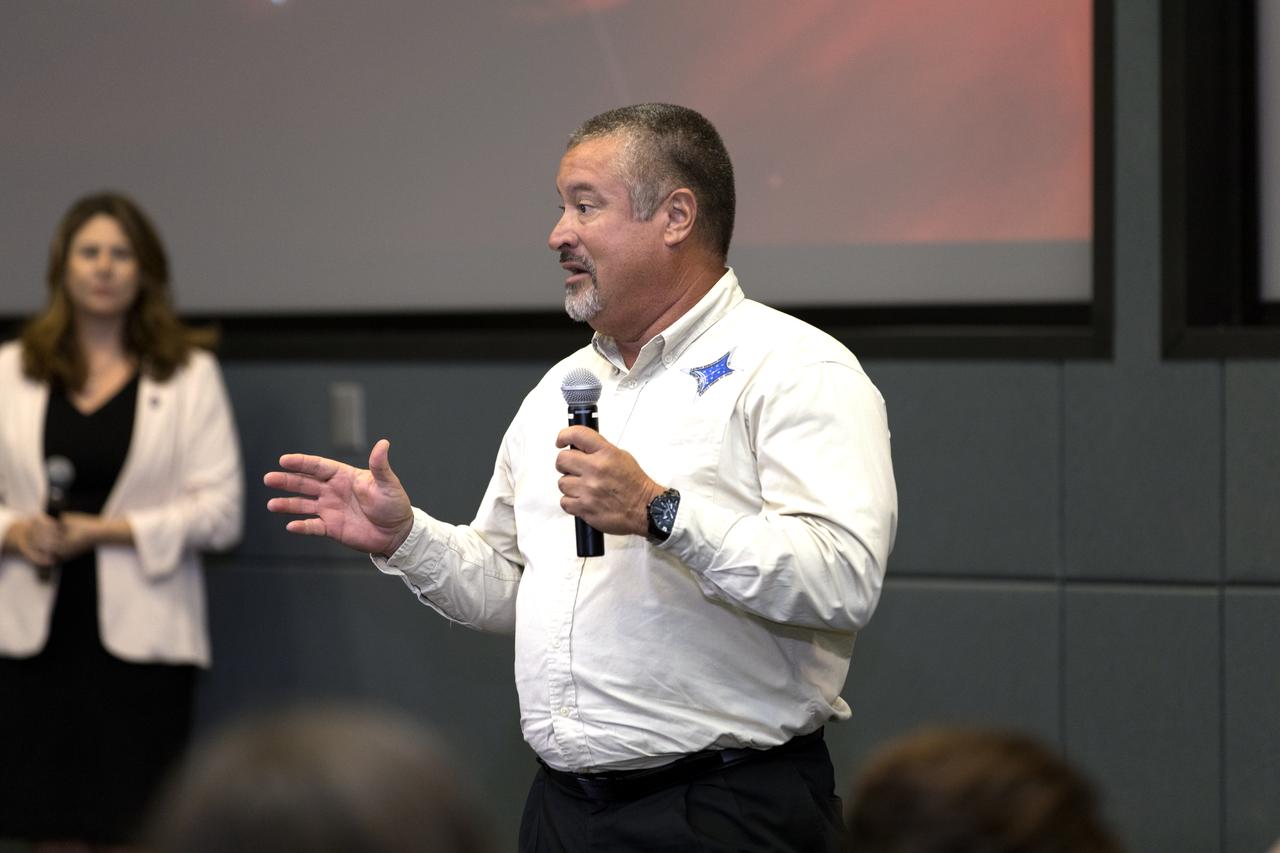

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Speaking to the media is Omar Baez, launch director, NASA Kennedy Space Center. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
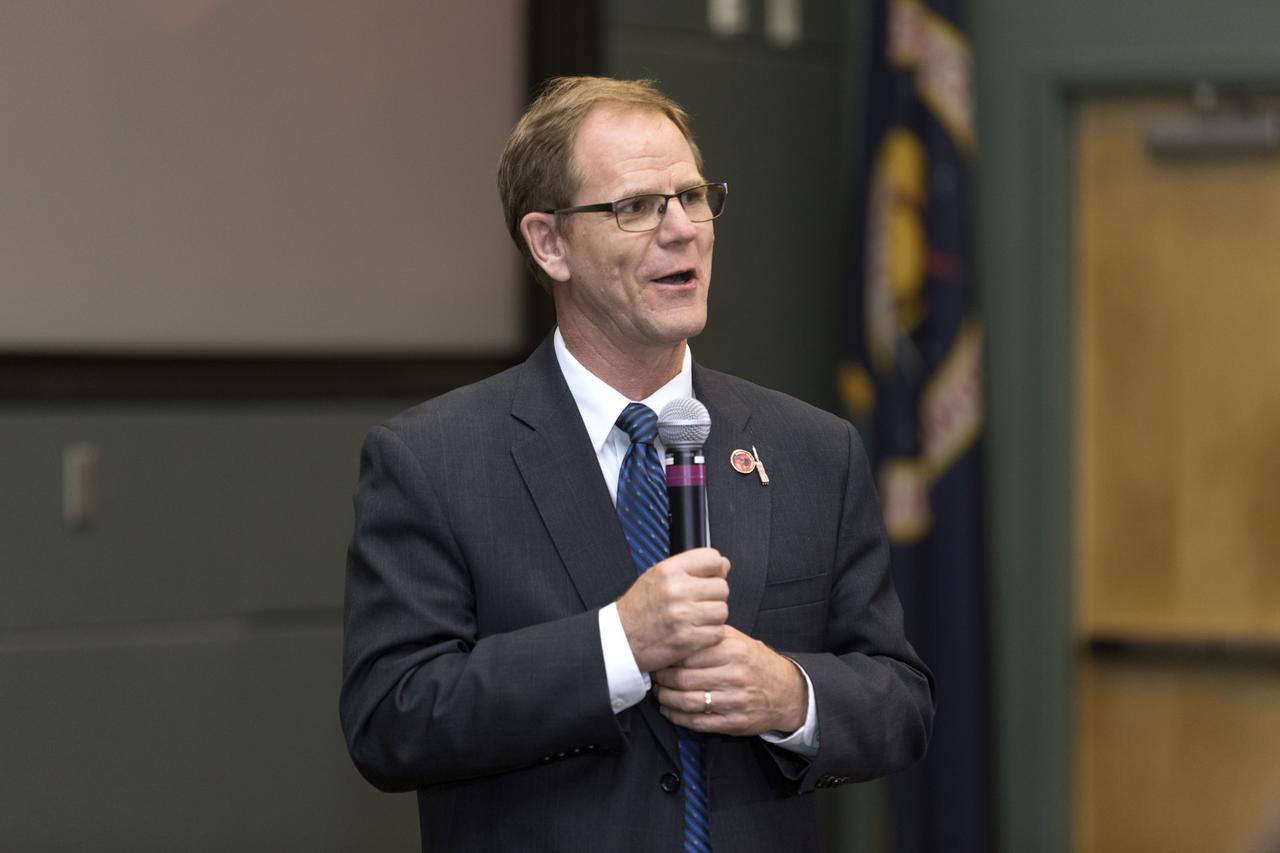

In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Speaking to the media is Scott Messer, program manager, NASA Programs, United Launch Alliance. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
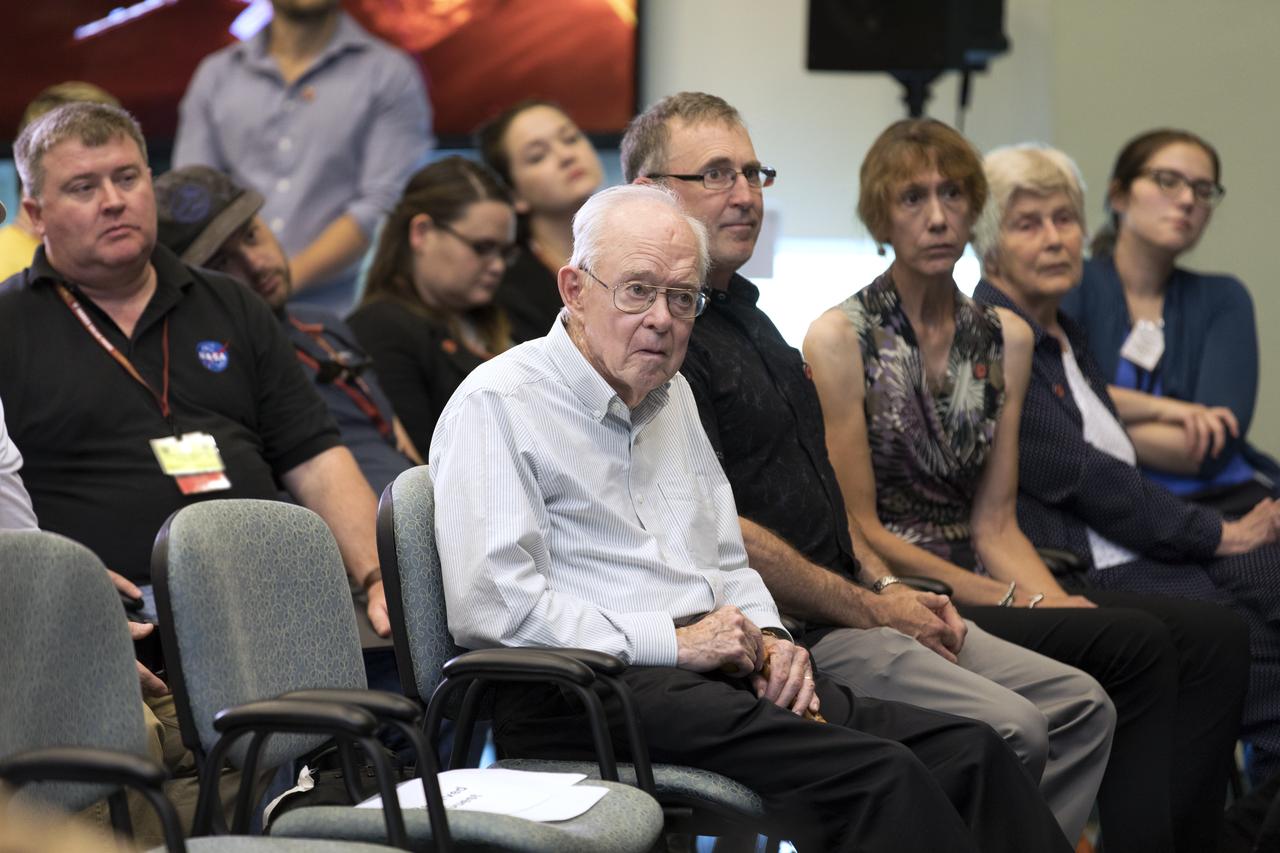
In the Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Support Building II, Thursday, Aug. 9, 2018, members of the media participate in a prelaunch mission briefing on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Listening to the presentation is Eugene Parker, front row, far left, the S. Chandrasekhar Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus, Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago. This is the first NASA mission that has been named for a living individual. The Parker Solar Probe will lift off on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

iss014e14541 (2/22/2007) --- A view of the BTN-ME experiment, also called BTN-Neutron experiment, attached to the Zvezda Service module as seen by the Expedition 14 crew during Russian EVA 17A. The BTN-ME experiment builds a physical model for generation of charged and neutral particles during solar flares. It also develops a physical model of neutron albedo of the earth atmosphere with regard to helio- and geophysical environment, measurement point longitude and altitude effects, time of the day and lighting conditions, atmosphere conditions. Also it develops a physical model of neutron background in the vicinity of the ISS in different flight conditions, as well as recording space gamma bursts.

Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, watches the launch of NASA's Parker Solar Probe. This is the first agency mission named for a living person. The liftoff took place at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

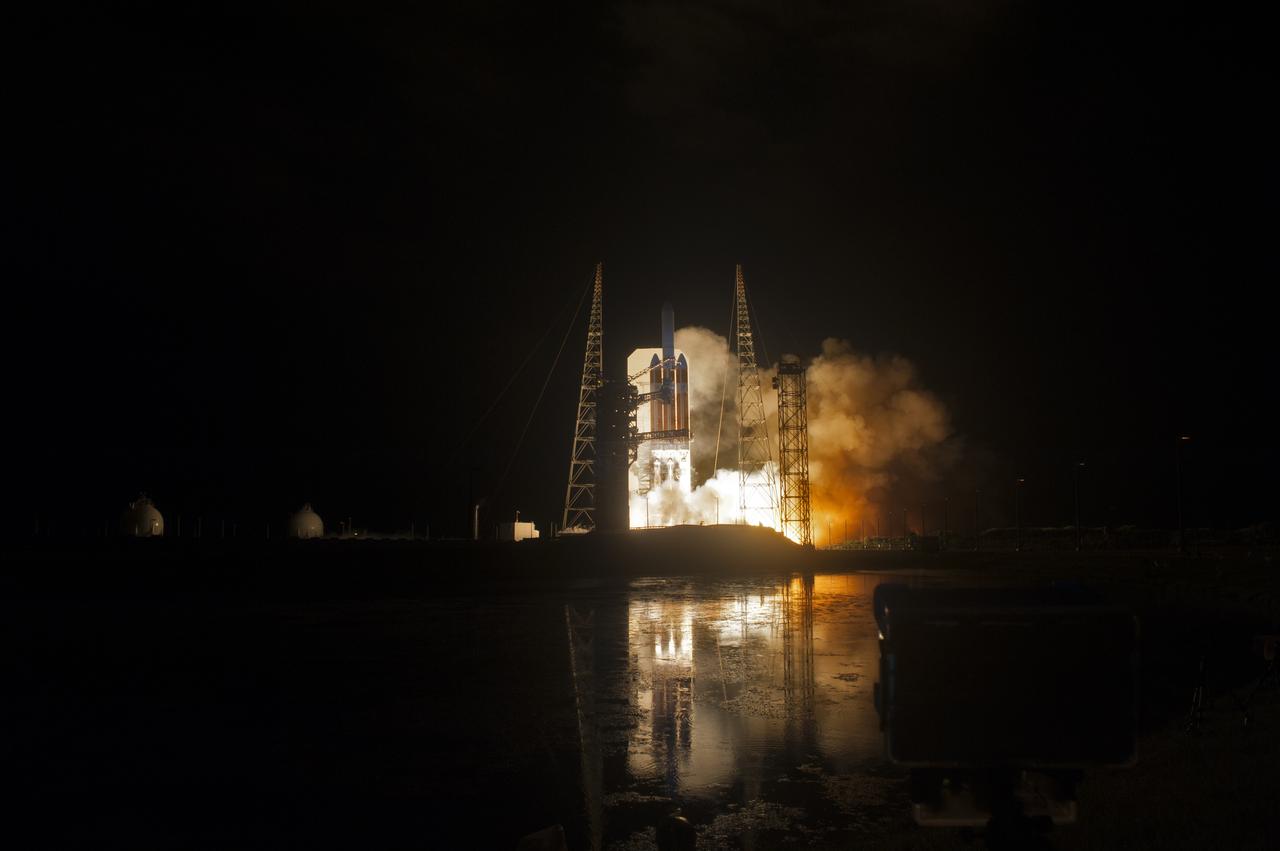
Lighting up the night sky at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
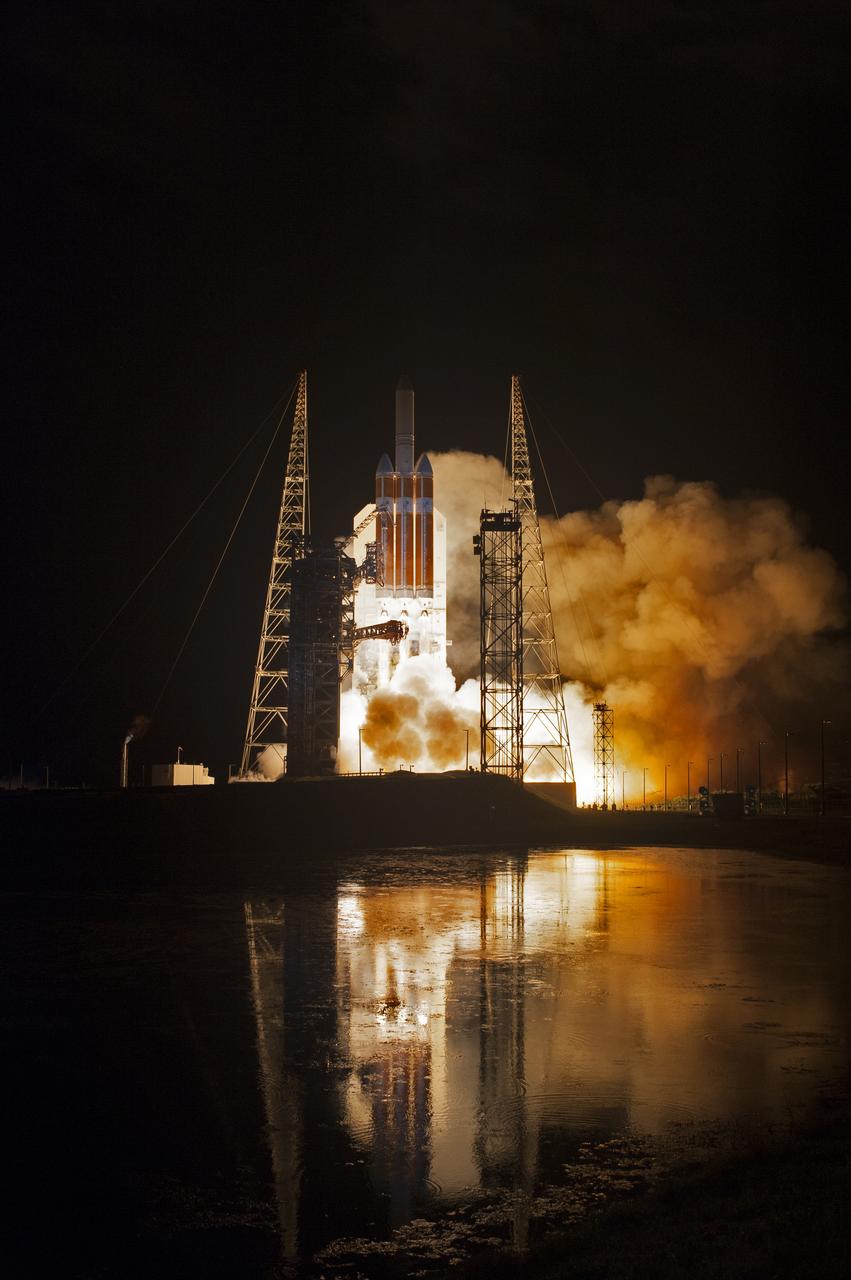

Lighting up the night sky at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
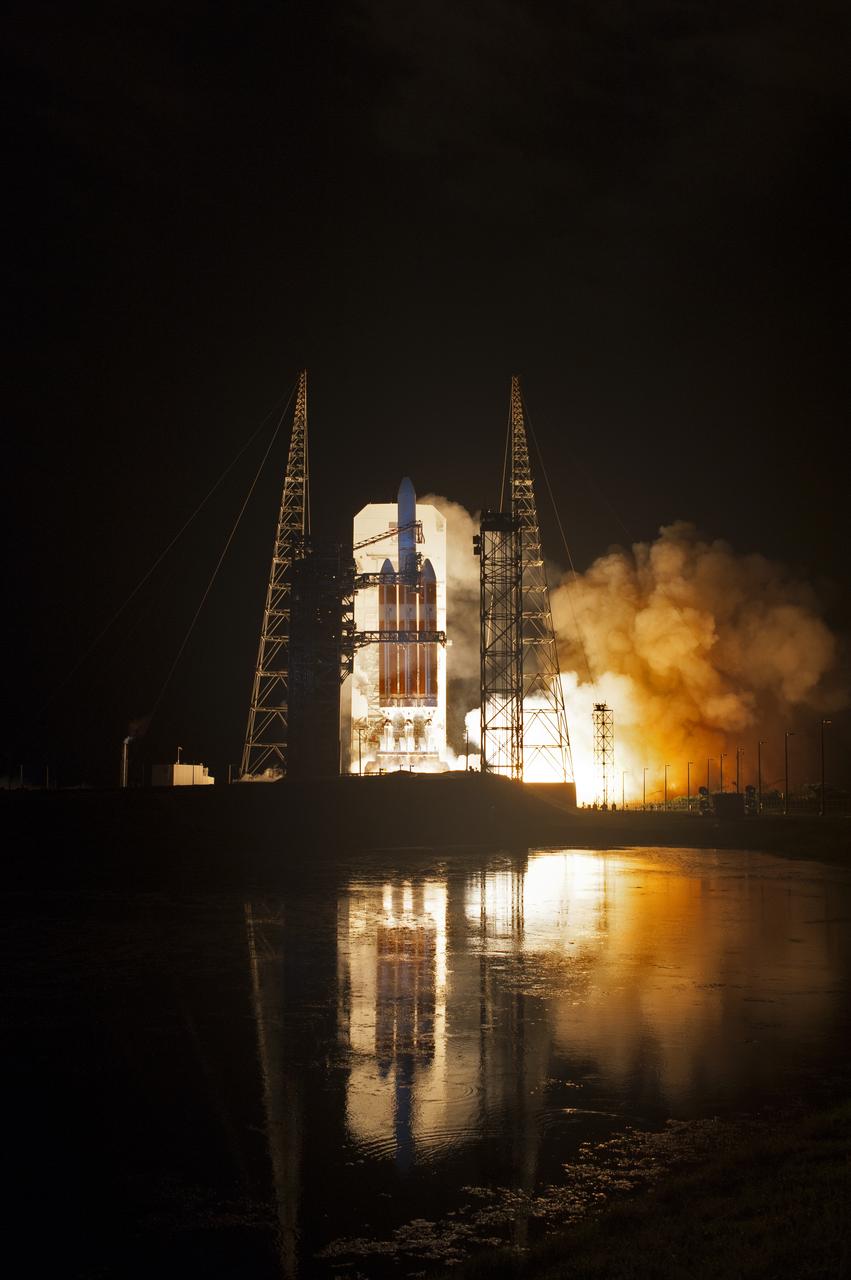

Lighting up the night sky at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
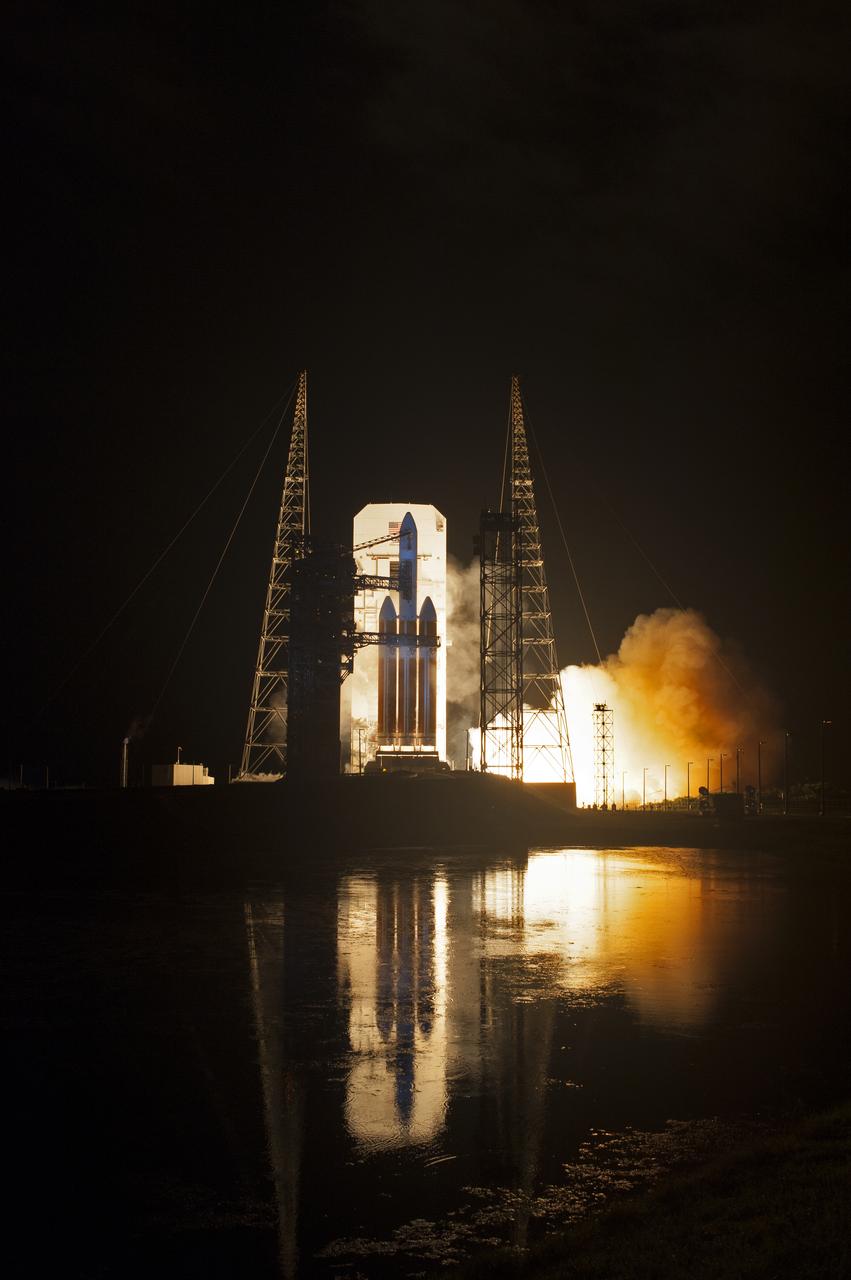

Lighting up the night sky at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
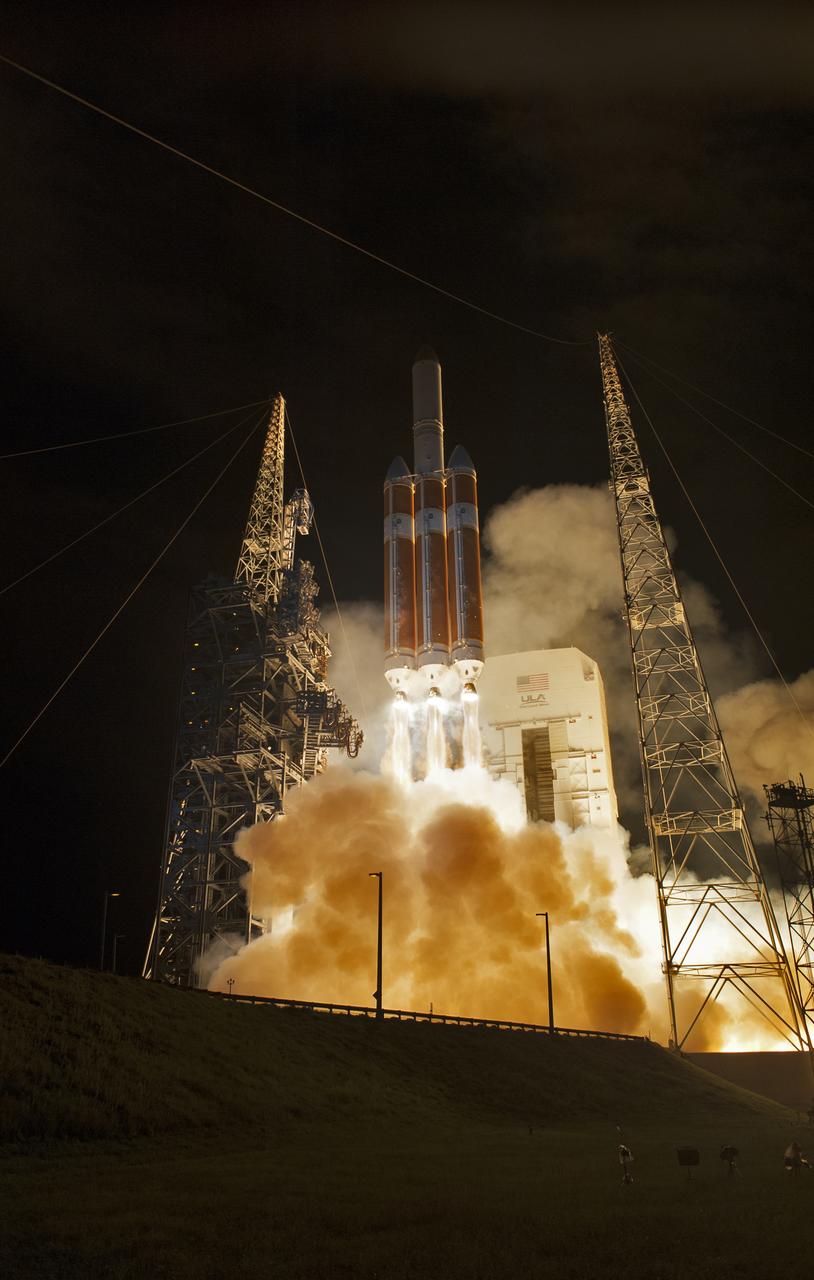

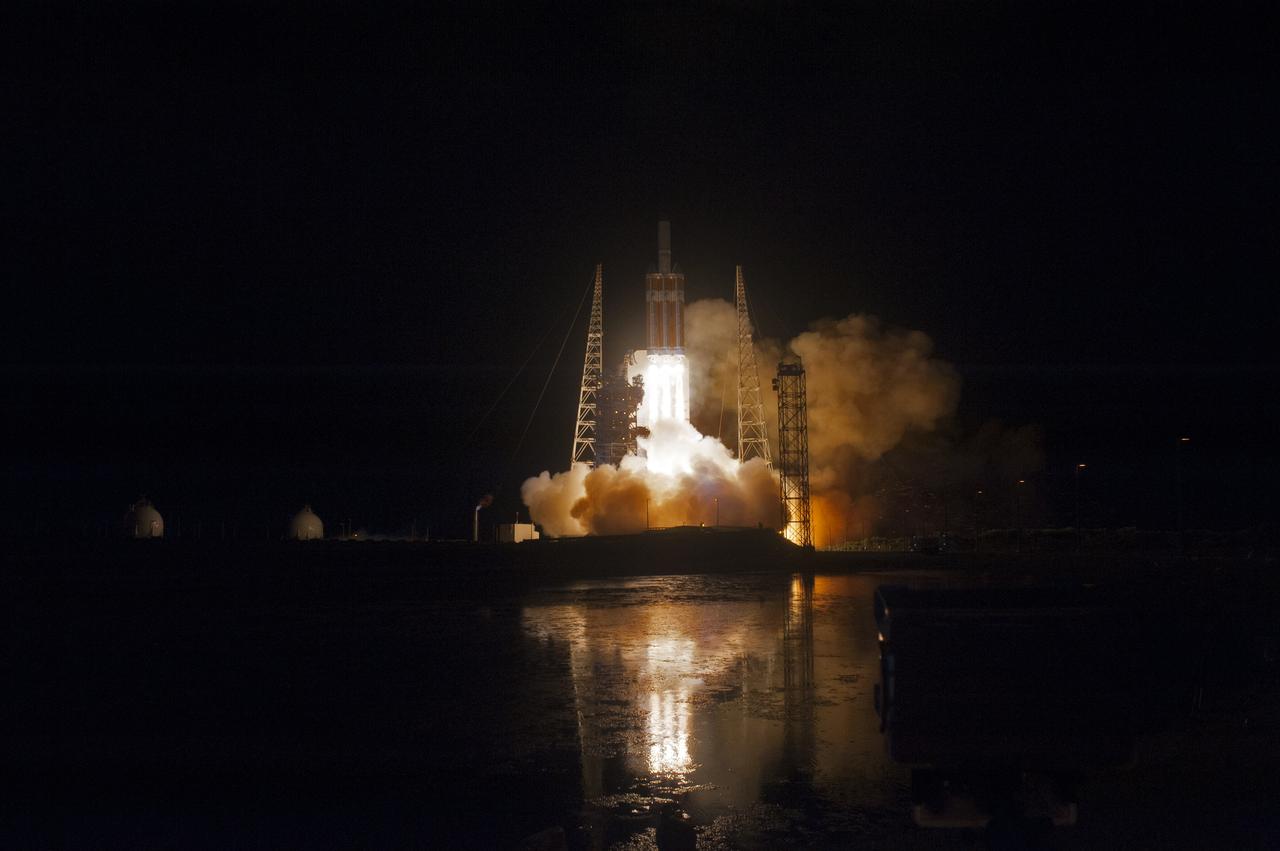
At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lights up the night sky as it lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
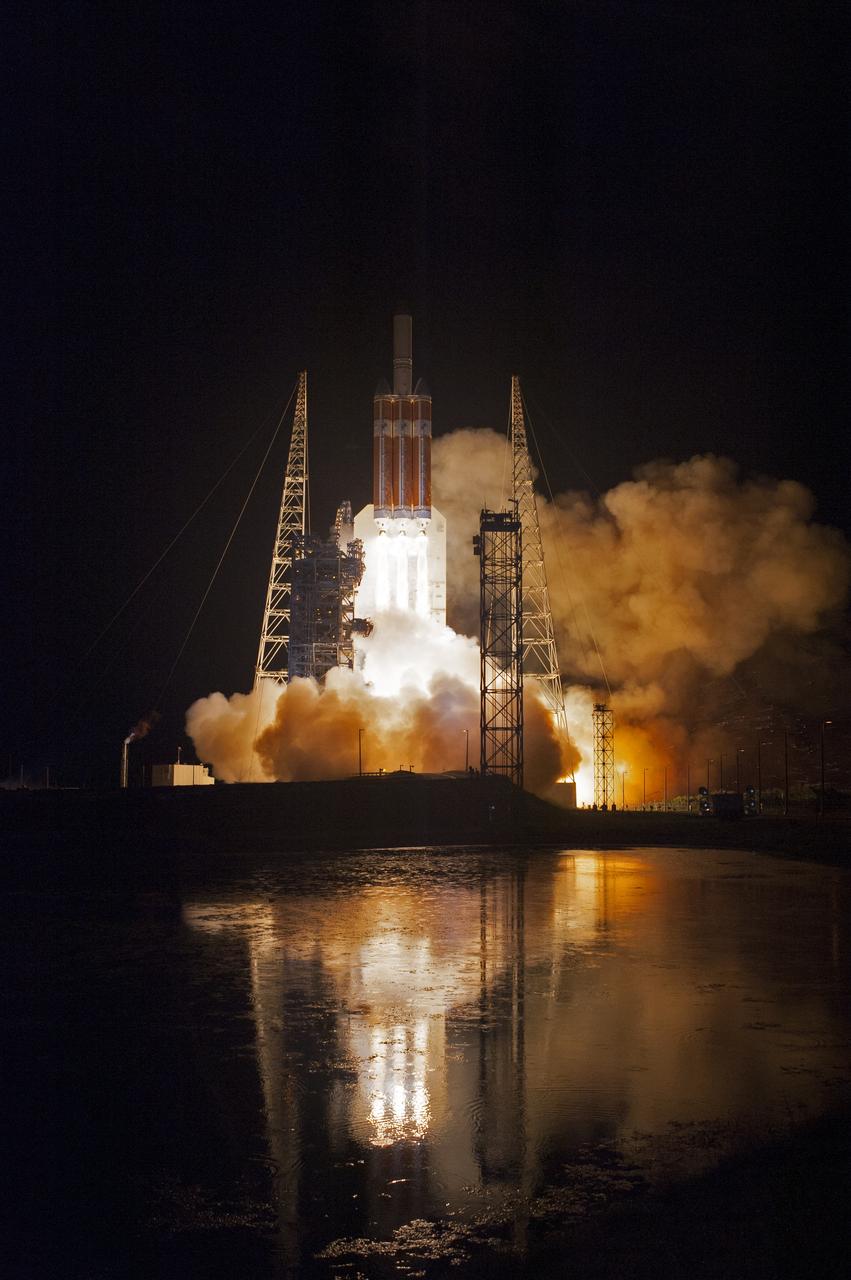

Lighting up the night sky at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
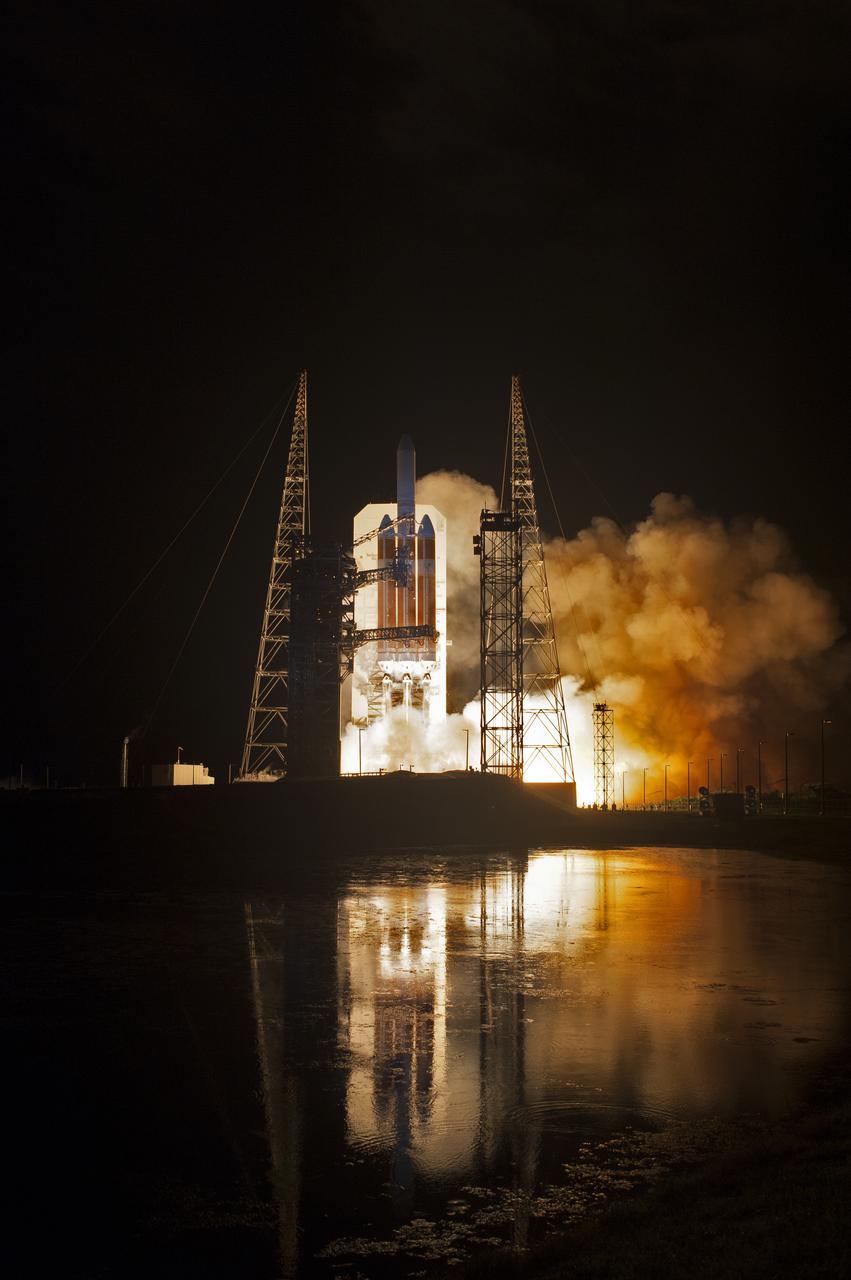

Lighting up the night sky at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Space Launch Complex 37, the United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket with NASA's Parker Solar Probe, lifts off at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by Applied Physics Laboratory of Johns Hopkins University in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
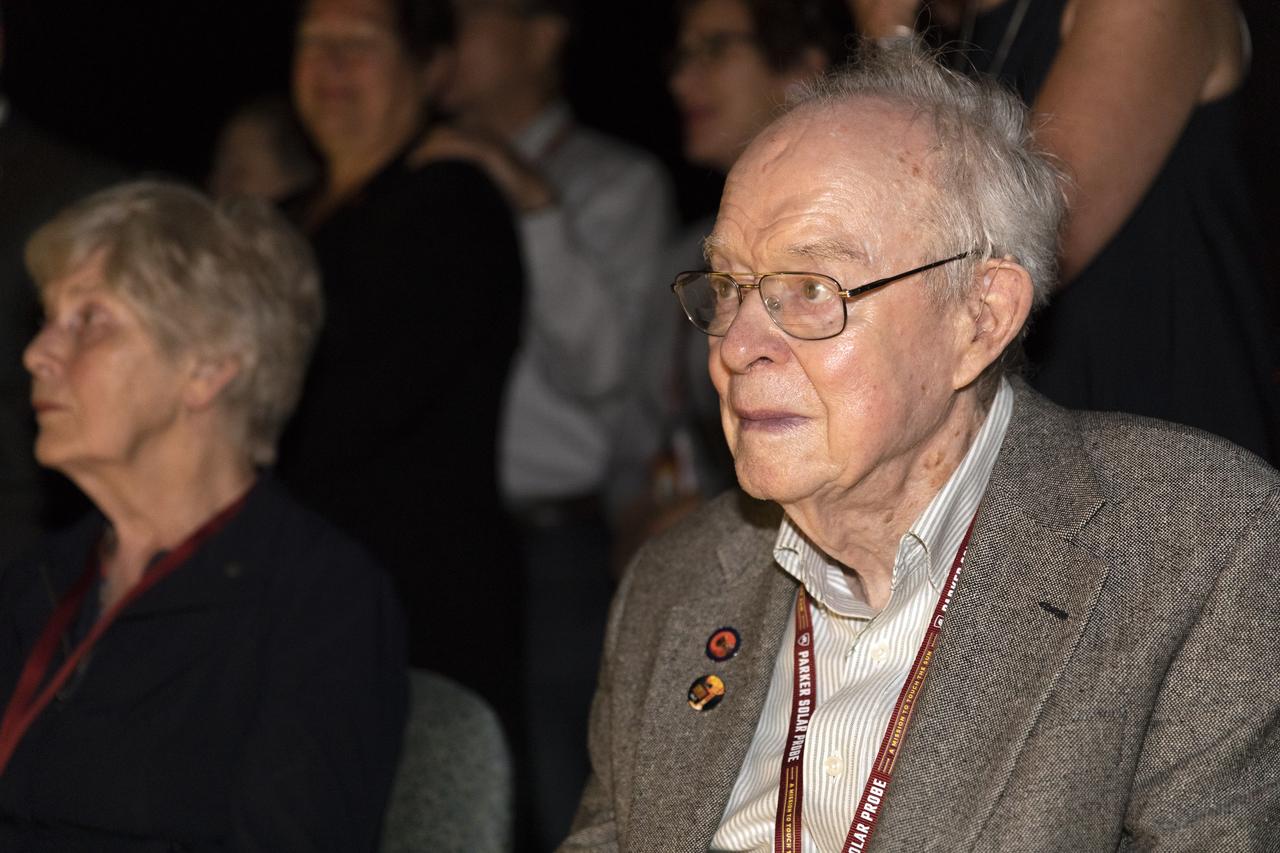

Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, watches the launch of NASA's Parker Solar Probe. This is the first agency mission named for a living person. The liftoff took place at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

Dr. Eugene Parker, a pioneer in heliophysics and S. Chandrasekhar distinguished service professor emeritus for the Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics at the University of Chicago, watches the launch of NASA's Parker Solar Probe. This is the first agency mission named for a living person. The liftoff took place at 3:31 a.m. EDT on Sunday, Aug. 12, 2018. The spacecraft was built by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
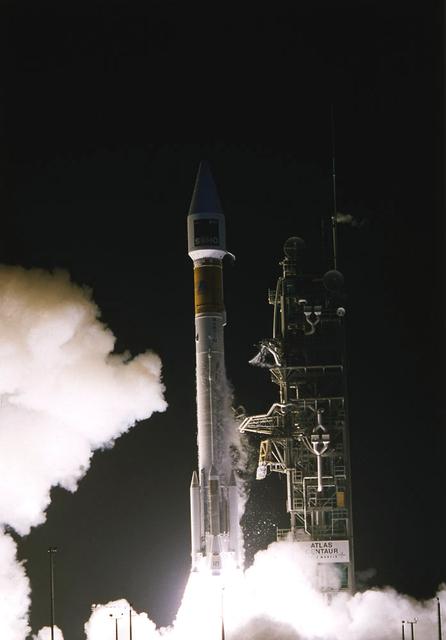

The Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) is launched atop an ATLAS-IIAS expendable launch vehicle. Liftoff from launch complex 36B at Cape Canaveral Air Station marked the 10th Atlas launch from the Eastern range for 1995. SOHO is a cooperative effort involving NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) within the framework of the International Solar-Terrestrial Physics Program. During its 2-year mission, the SOHO spacecraft gathered data on the internal structure of the Sun, its extensive outer atmosphere and the origin of the solar wind.
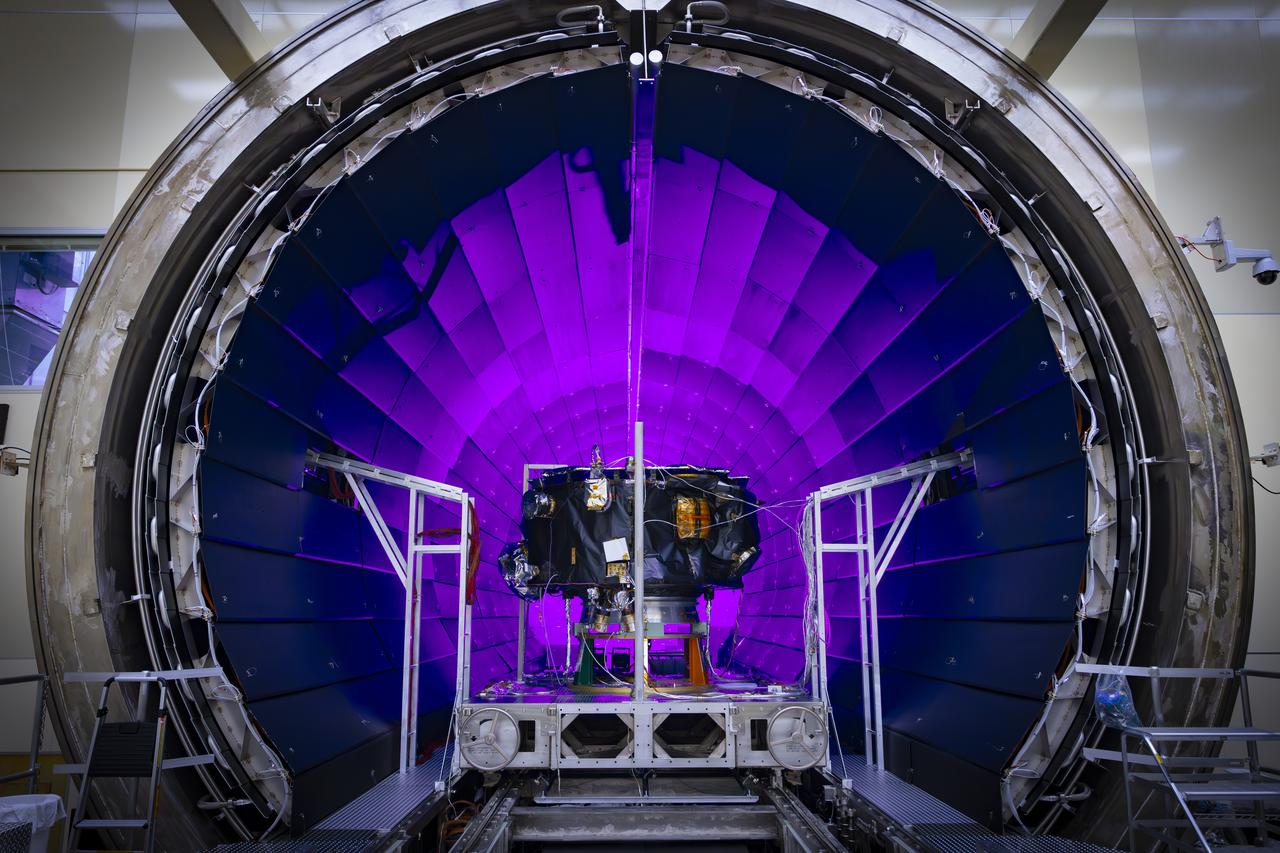

These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
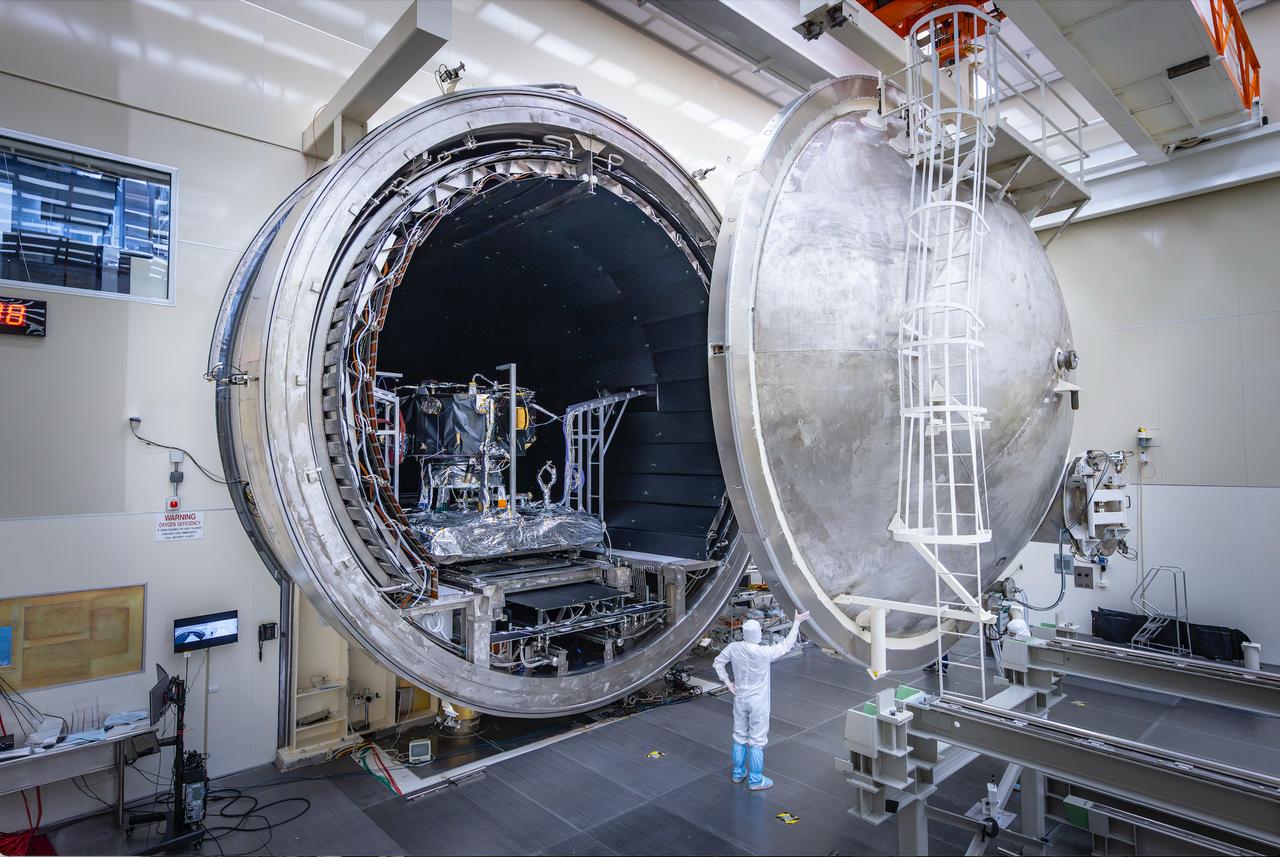
These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
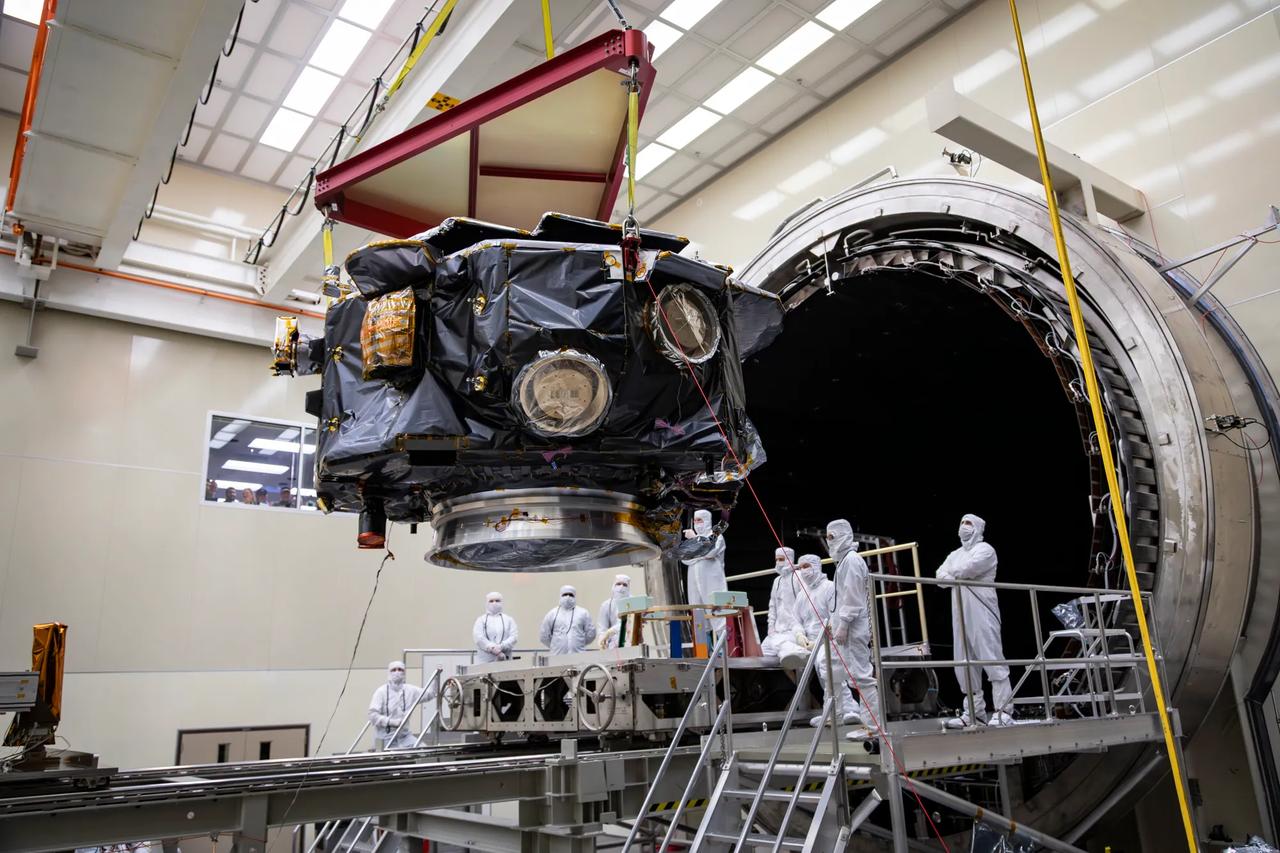

These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
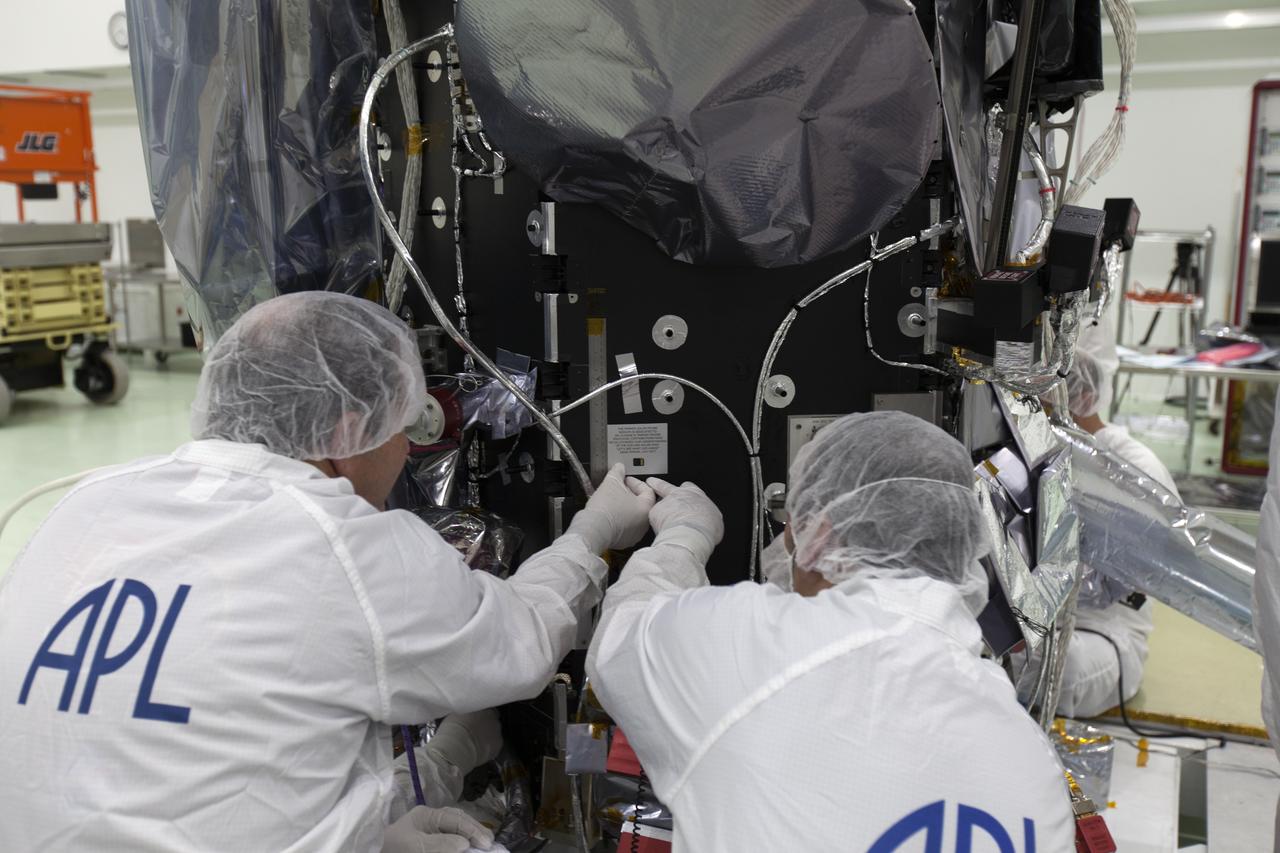

On Friday, May 18, 2018, at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, scientists and engineers from the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University install a computer chip on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Throughout its seven-year mission, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe will swoop through the Sun’s atmosphere, carrying more than scientific instruments on this historic journey — it will also hold more than 1.1 million names submitted by the public to go to the Sun. The submitted names were loaded into a memory card and mounted on a plaque bearing a dedication to the mission’s namesake, heliophysicist Dr. Eugene Parker. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

On Friday, May 18, 2018, at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, scientists and engineers from the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University install a computer chip on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Throughout its seven-year mission, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe will swoop through the Sun’s atmosphere, carrying more than scientific instruments on this historic journey — it will also hold more than 1.1 million names submitted by the public to go to the Sun. The submitted names were loaded into a memory card and mounted on a plaque bearing a dedication to the mission’s namesake, heliophysicist Dr. Eugene Parker. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
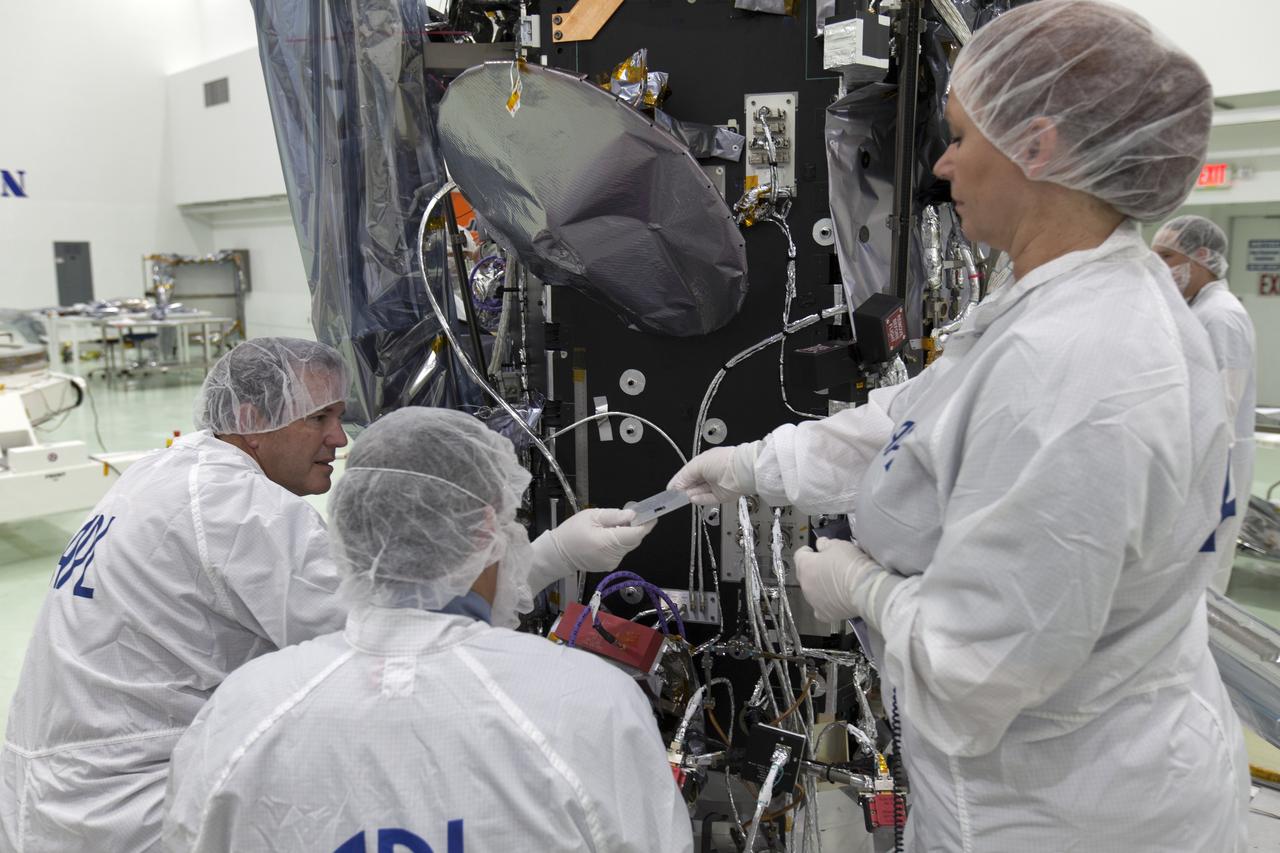

On Friday, May 18, 2018, at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, scientists and engineers from the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University install a computer chip on NASA's Parker Solar Probe. Throughout its seven-year mission, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe will swoop through the Sun’s atmosphere, carrying more than scientific instruments on this historic journey — it will also hold more than 1.1 million names submitted by the public to go to the Sun. The submitted names were loaded into a memory card and mounted on a plaque bearing a dedication to the mission’s namesake, heliophysicist Dr. Eugene Parker. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida no earlier than Aug. 4, 2018. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
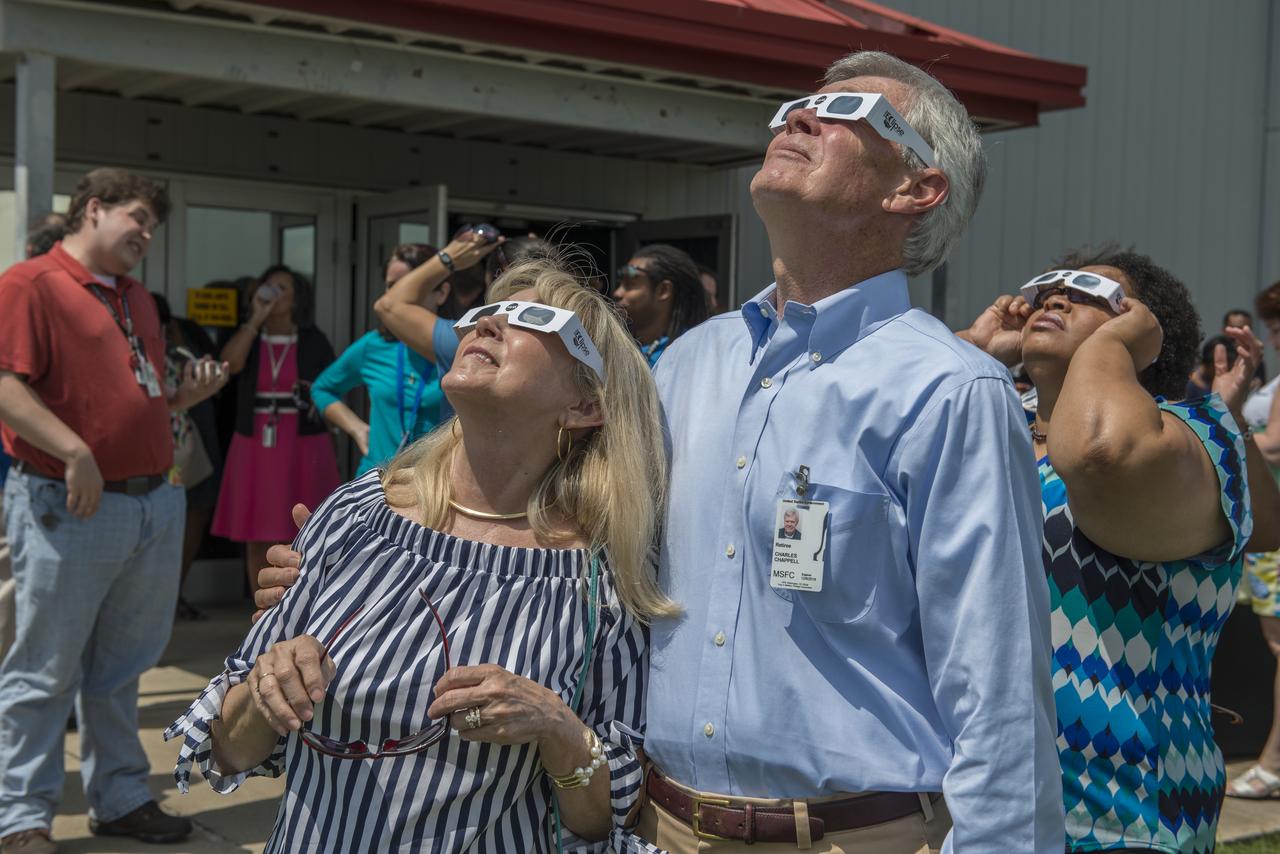

Former Spacelab 1 Mission scientist Rick Chappell views the August 21, 2017 solar eclipse with his wife. Chappell, a former associate director for science at Marshall and now a physics professor at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, joined a throng of Marshall personnel to marvel at the eclipse.

Scientist-Astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot of the Skylab 3 mission, is stationed at the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) console in the Multiple Docking Adapter of the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. From this console the astronauts actively control the ATM solar physics telescope.
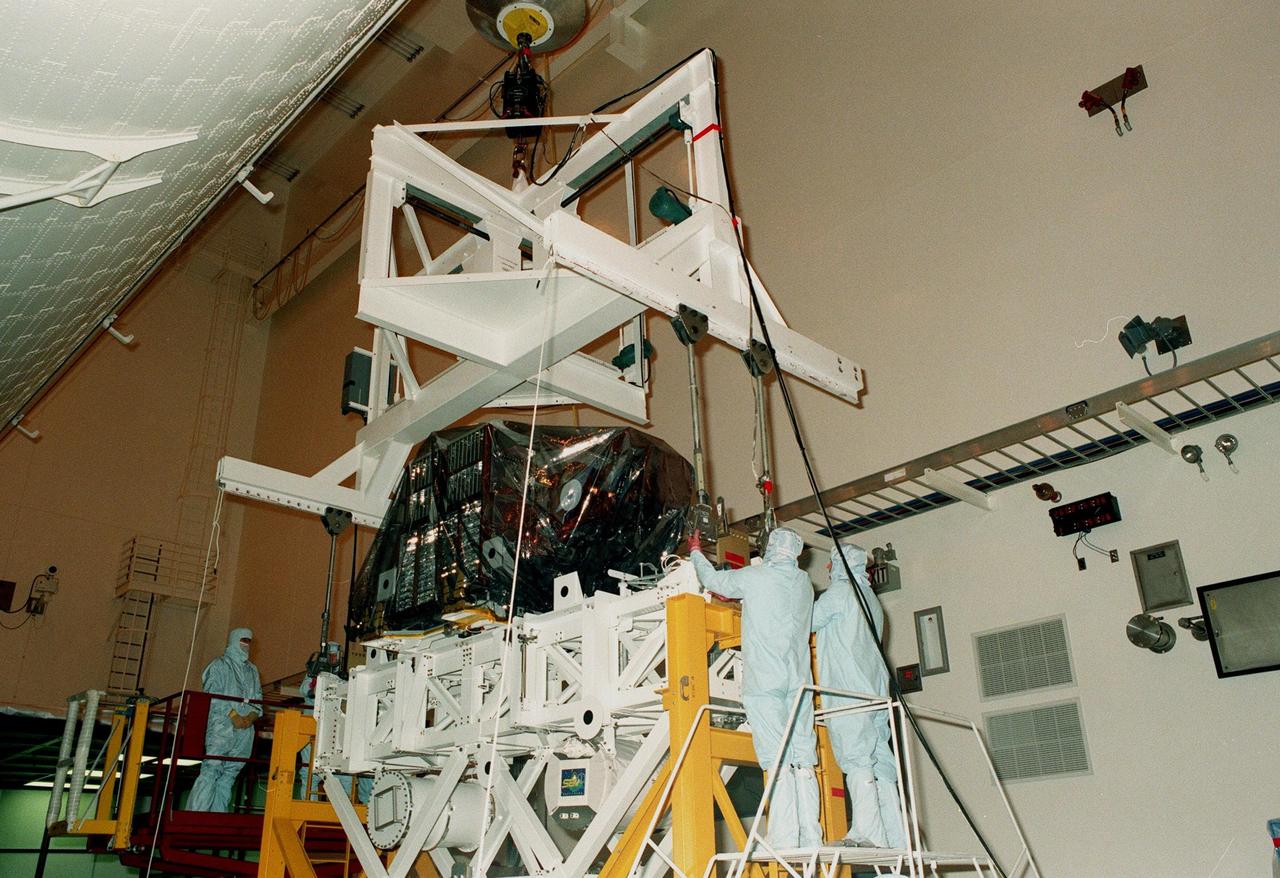

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Spartan solar-observing deployable spacecraft is lifted from its work stand to move it to a payload canister in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at KSC. Spartan is one of the payloads for the STS-95 mission, scheduled to launch Oct. 29. Spartan is a solar physics spacecraft designed to perform remote sensing of the hot outer layers of the sun's atmosphere or corona. The objective of the observations is to investigate the mechanisms causing the heating of the solar corona and the acceleration of the solar wind which originates in the corona. Other research payloads include the Hubble Space Telescope Orbital Systems Test Platform, the International Extreme Ultraviolet Hitchhiker, and the SPACEHAB single module with experiments on space flight and the aging process
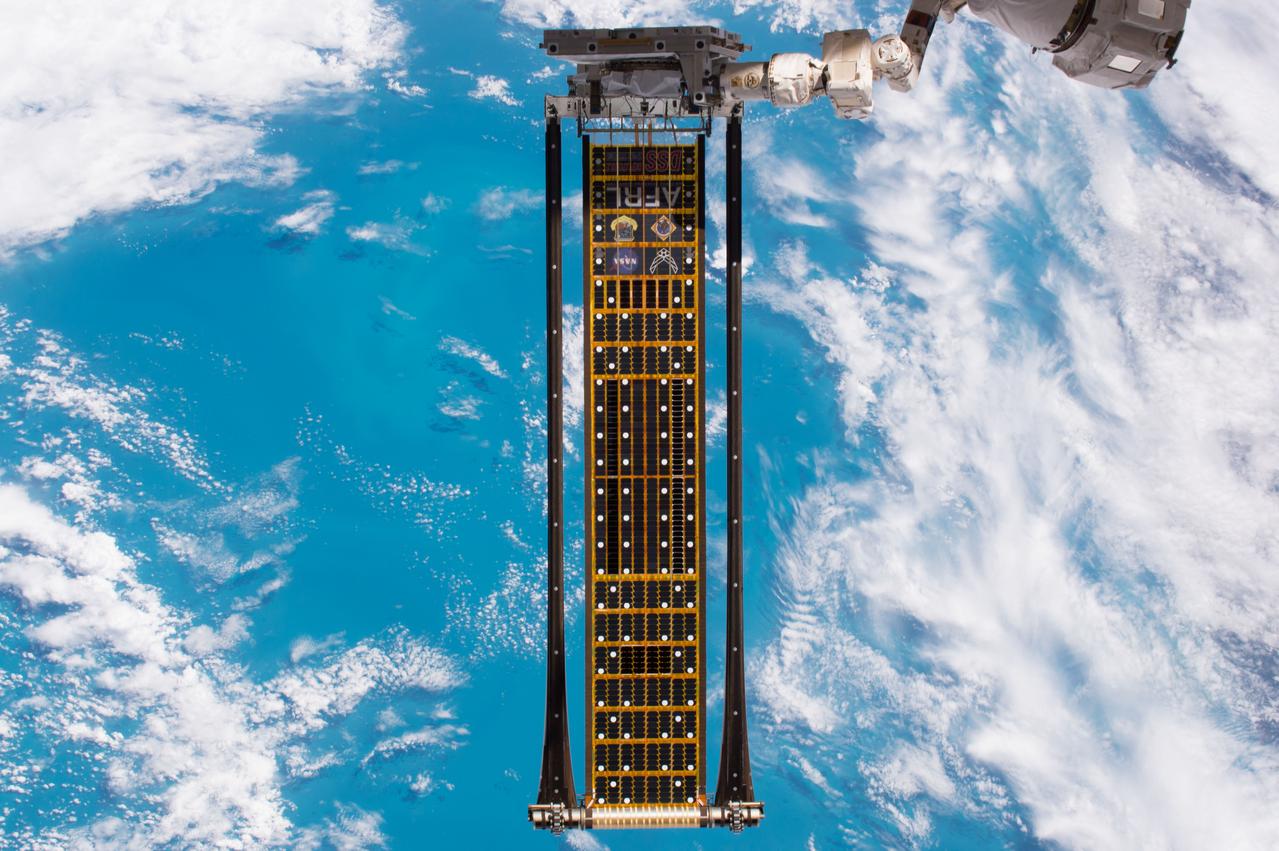

iss052e002871 (6/18/2017) --- The Roll-Out Solar Array (ROSA) is a new type of solar panel that rolls open in space like a party favor and is more compact than current rigid panel designs. The ROSA investigation tests deployment and retraction, shape changes when the Earth blocks the sun, and other physical challenges to determine the array’s strength and durability. ROSA has the potential to replace solar arrays on future satellites, making them more compact and lighter weight. Satellite radio and television, weather forecasting, GPS and other services used on Earth would all benefit from high-performance solar arrays.