Pebble Puzzle Solved
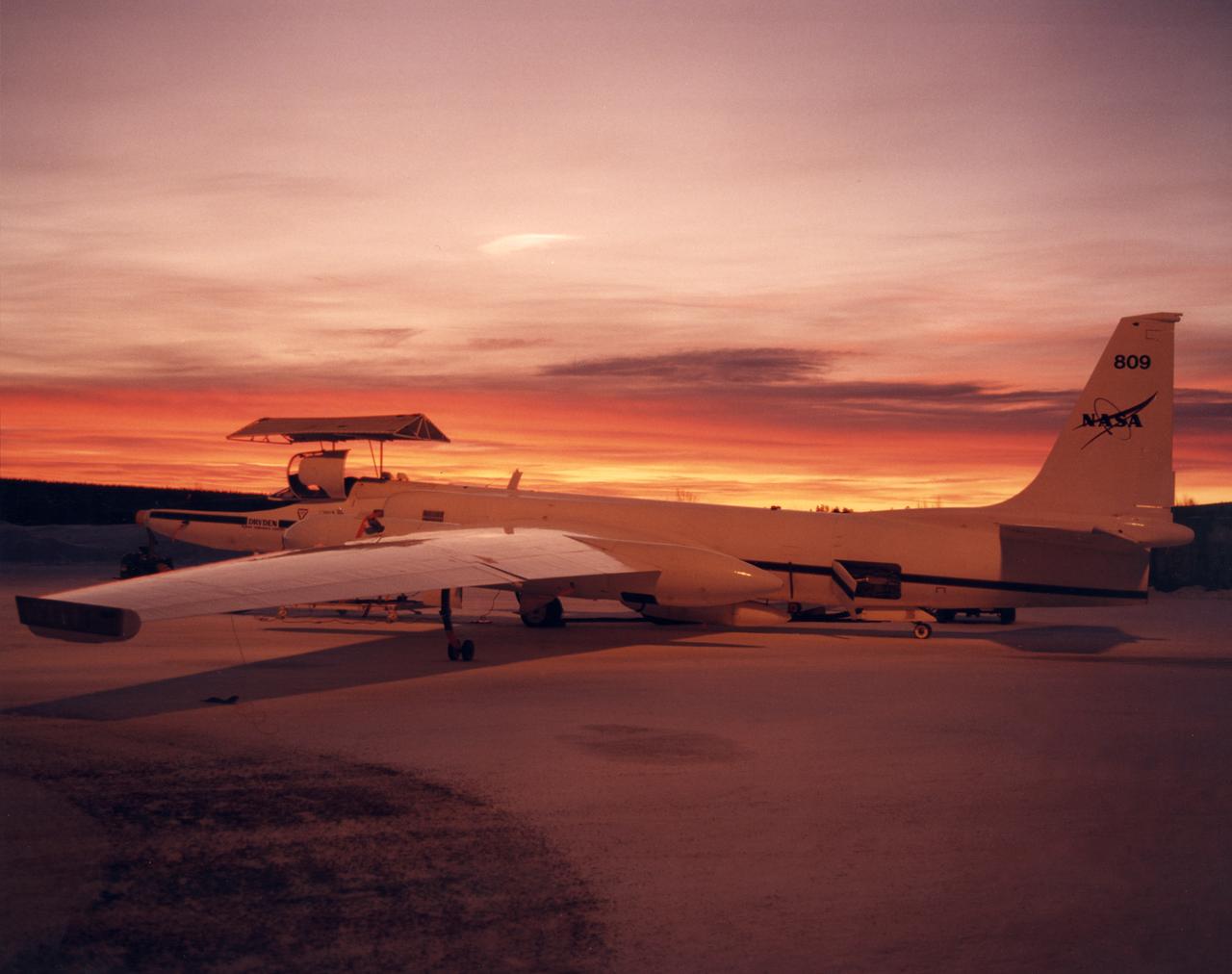

ER-2 #809 awaiting pilot entry for the third flight of the SAGE III Ozone Loss and Validation Experiment (SOLVE). The ER-2, a civilian variant of Lockheed's U-2, and another NASA flying laboratory, Dryden's DC-8, were based north of the Arctic Circle in Kiruna, Sweden during the winter of 2000 to study ozone depletion as part of SOLVE. A large hangar built especially for research, "Arena Arctica" housed the instrumented aircraft and the scientists. Scientists have observed unusually low levels of ozone over the Arctic during recent winters, raising concerns that ozone depletion there could become more widespread as in the Antarctic ozone hole. The NASA-sponsored international mission took place between November 1999 and March 2000 and was divided into three phases. The DC-8 was involved in all three phases returning to Dryden between each phase. The ER-2 flew sample collection flights between January and March, remaining in Sweden from Jan. 9 through March 16. "The collaborative campaign will provide an immense new body of information about the Arctic stratosphere," said program scientist Dr. Michael Kurylo, NASA Headquarters. "Our understanding of the Earth's ozone will be greatly enhanced by this research."
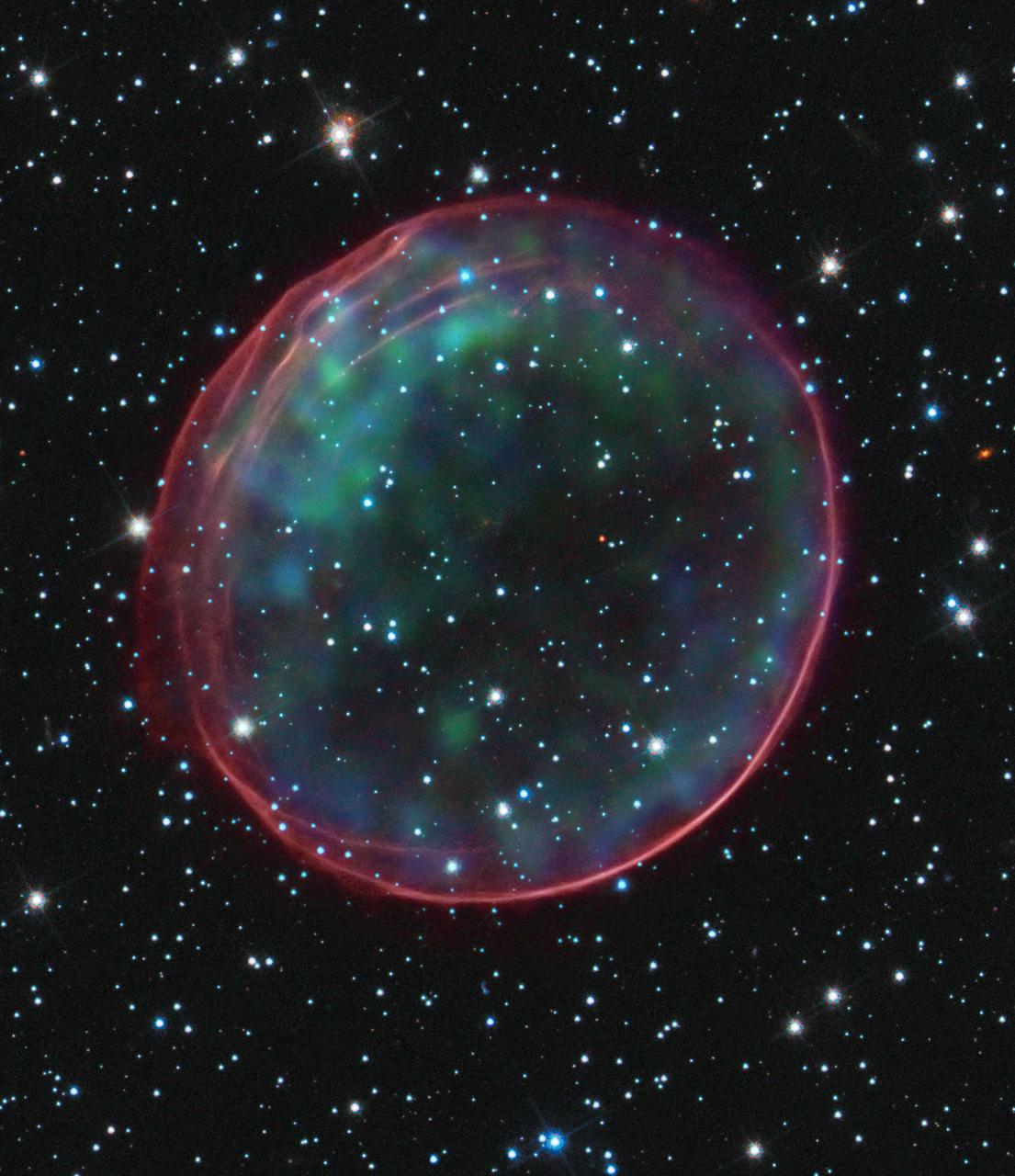

NASA image release January 11, 2012 Using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have solved a longstanding mystery on the type of star, or so-called progenitor, that caused a supernova in a nearby galaxy. The finding yields new observational data for pinpointing one of several scenarios that could trigger such outbursts. Based on previous observations from ground-based telescopes, astronomers knew that a kind of supernova called a Type Ia created a remnant named SNR 0509-67.5, which lies 170,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy. The type of system that leads to this kind of supernova explosion has long been a high importance problem with various proposed solutions but no decisive answer. All these solutions involve a white dwarf star that somehow increases in mass to the highest limit. Astronomers failed to find any companion star near the center of the remnant, and this rules out all but one solution, so the only remaining possibility is that this one Type Ia supernova came from a pair of white dwarfs in close orbit. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/supernova-source.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/hubble/science/supernova-sourc...</a> Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CXC, SAO, the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), and J. Hughes (Rutgers University) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
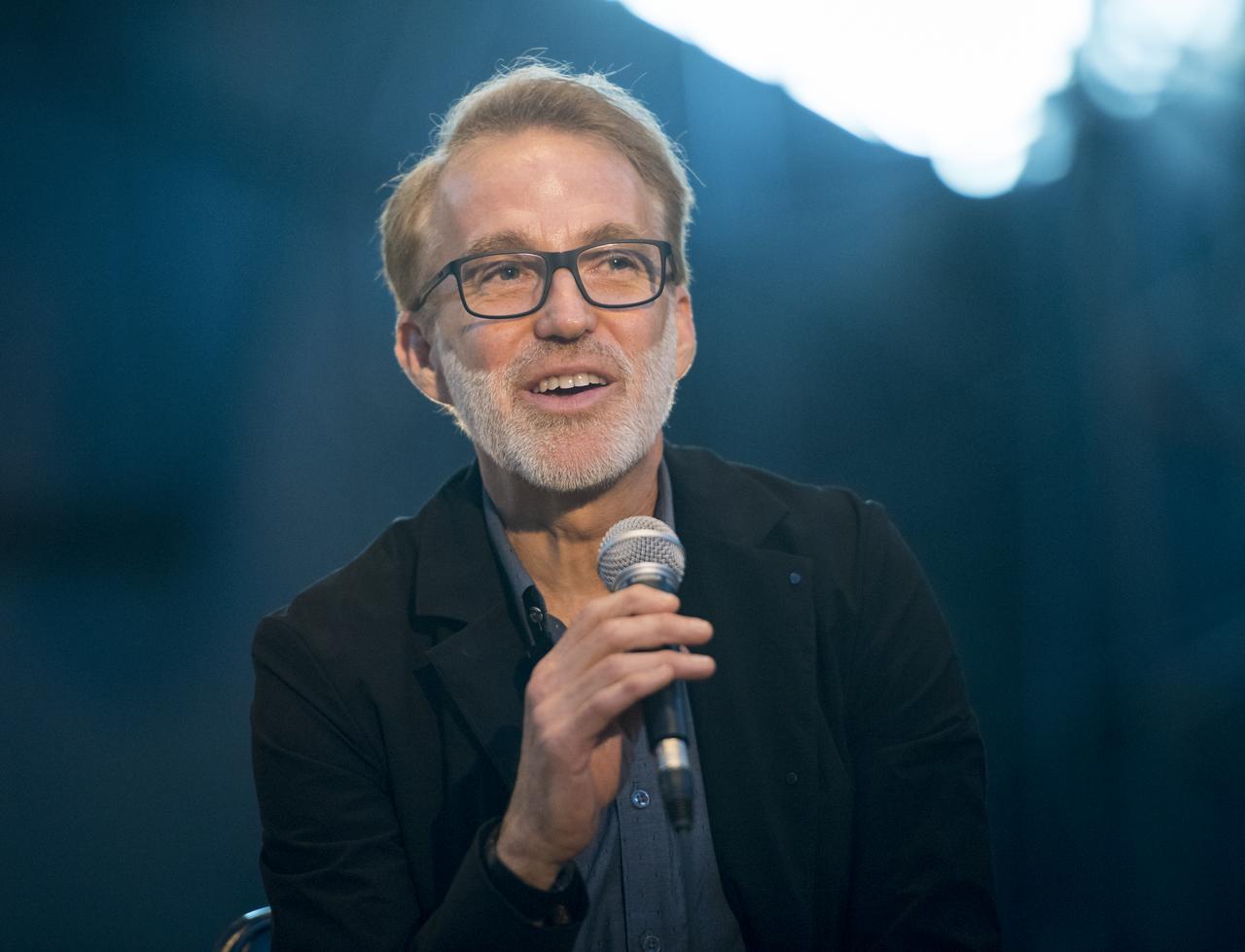

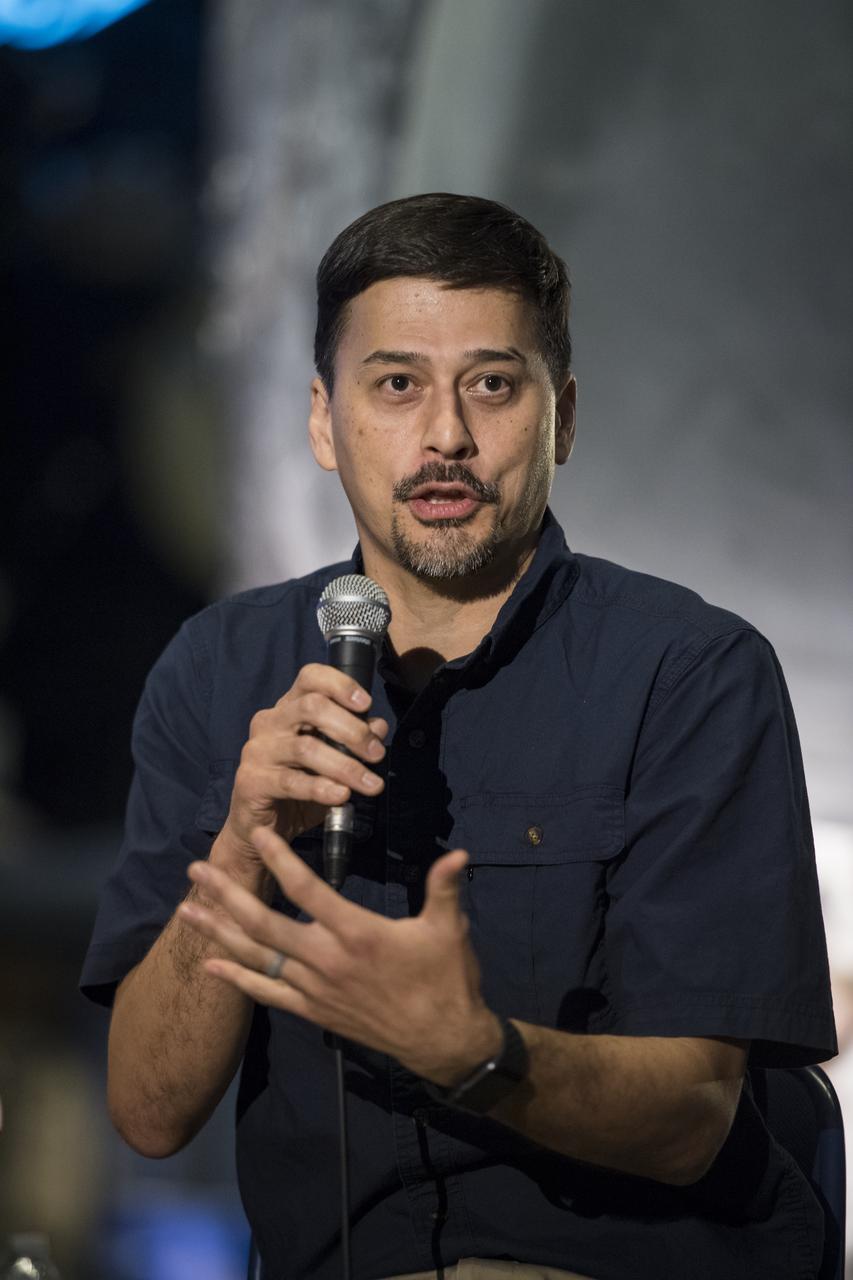
Michael Painter, senior program officer, Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, speaks on a panel on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
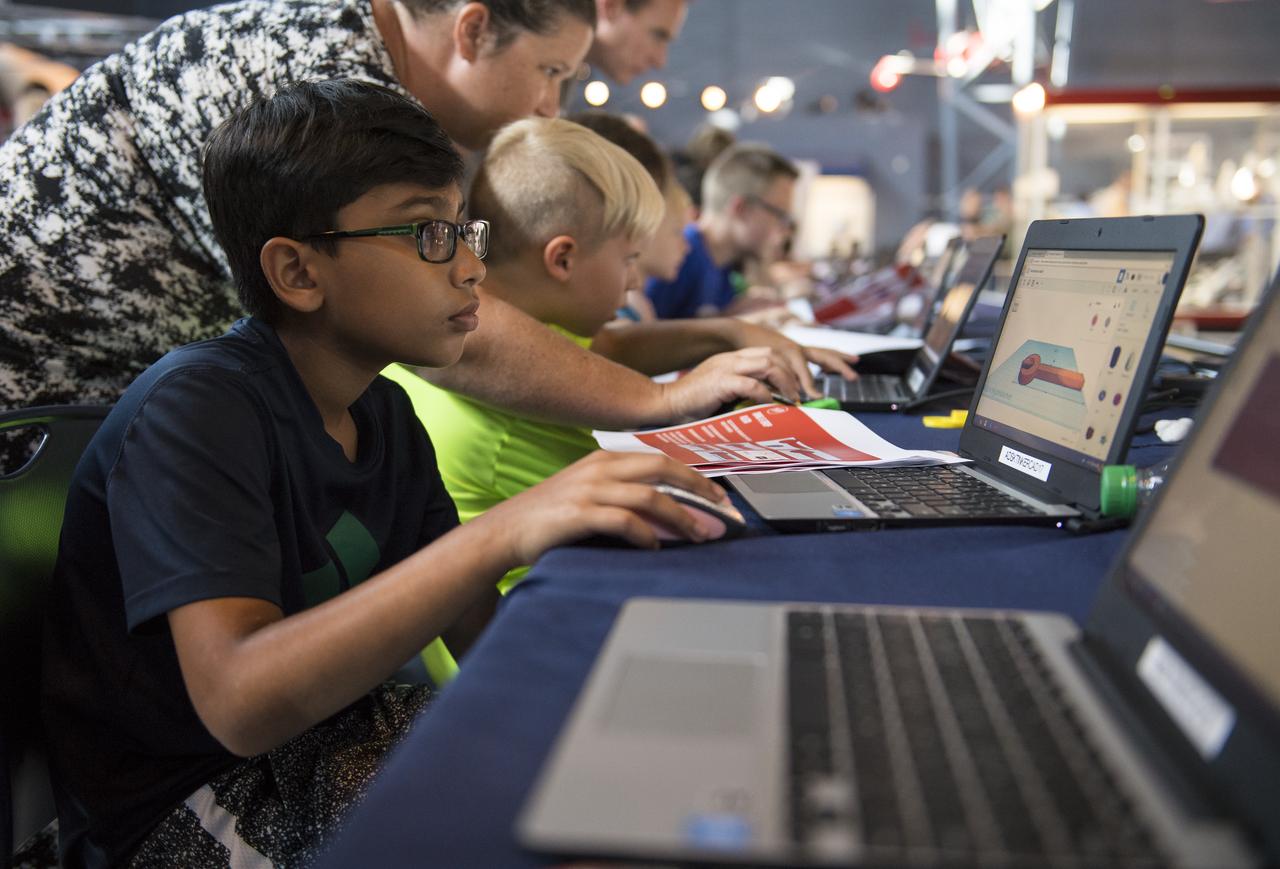

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Josh Ajima, instructional facilitator for technology, Loudoun County Public Schools and DesignMakeTeach.com blog, speaks on a panel on "igniting NOVA K-12 engineering and maker education", at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A visitor learns about 3D printing at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Paul Scott, interim executive director, The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), speaks on a panel on "igniting NOVA K-12 engineering and maker education", at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and ASME, at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
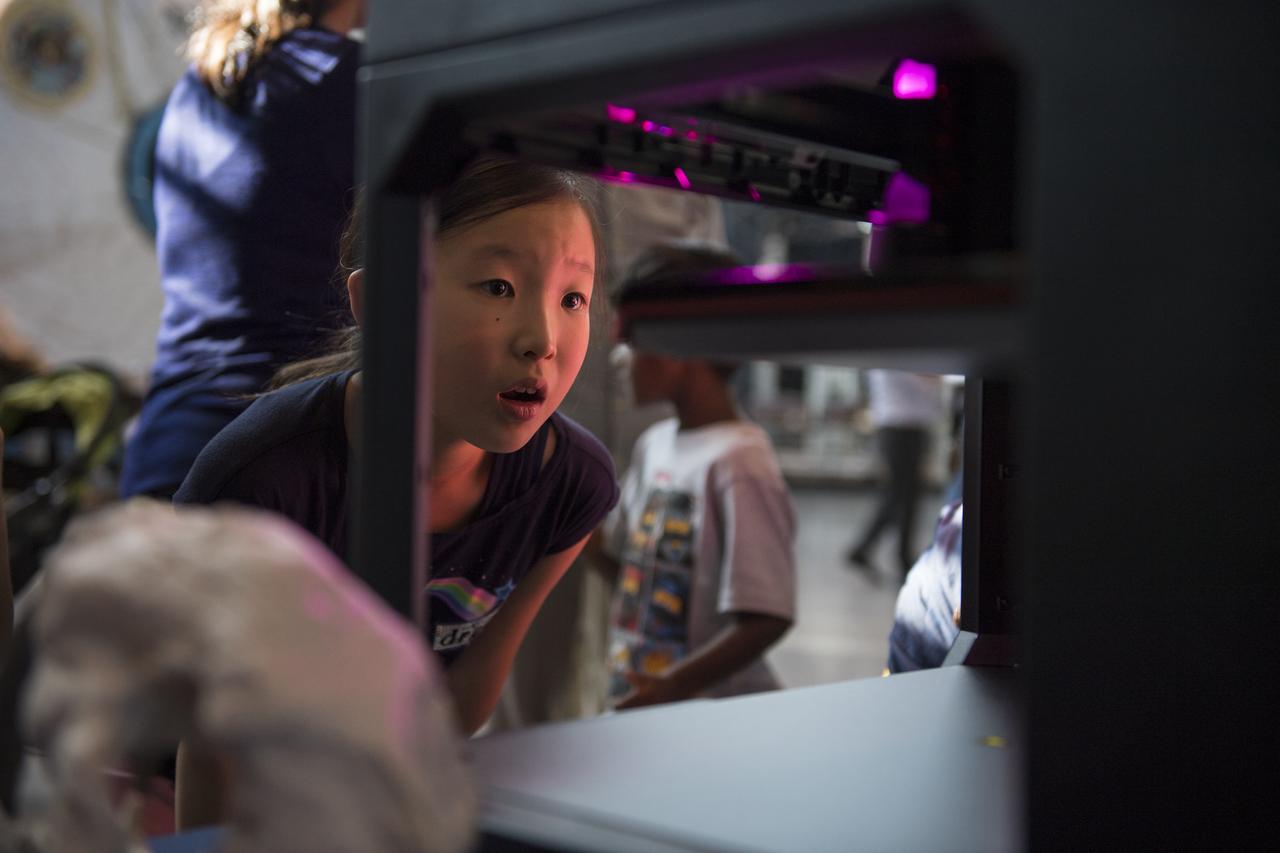

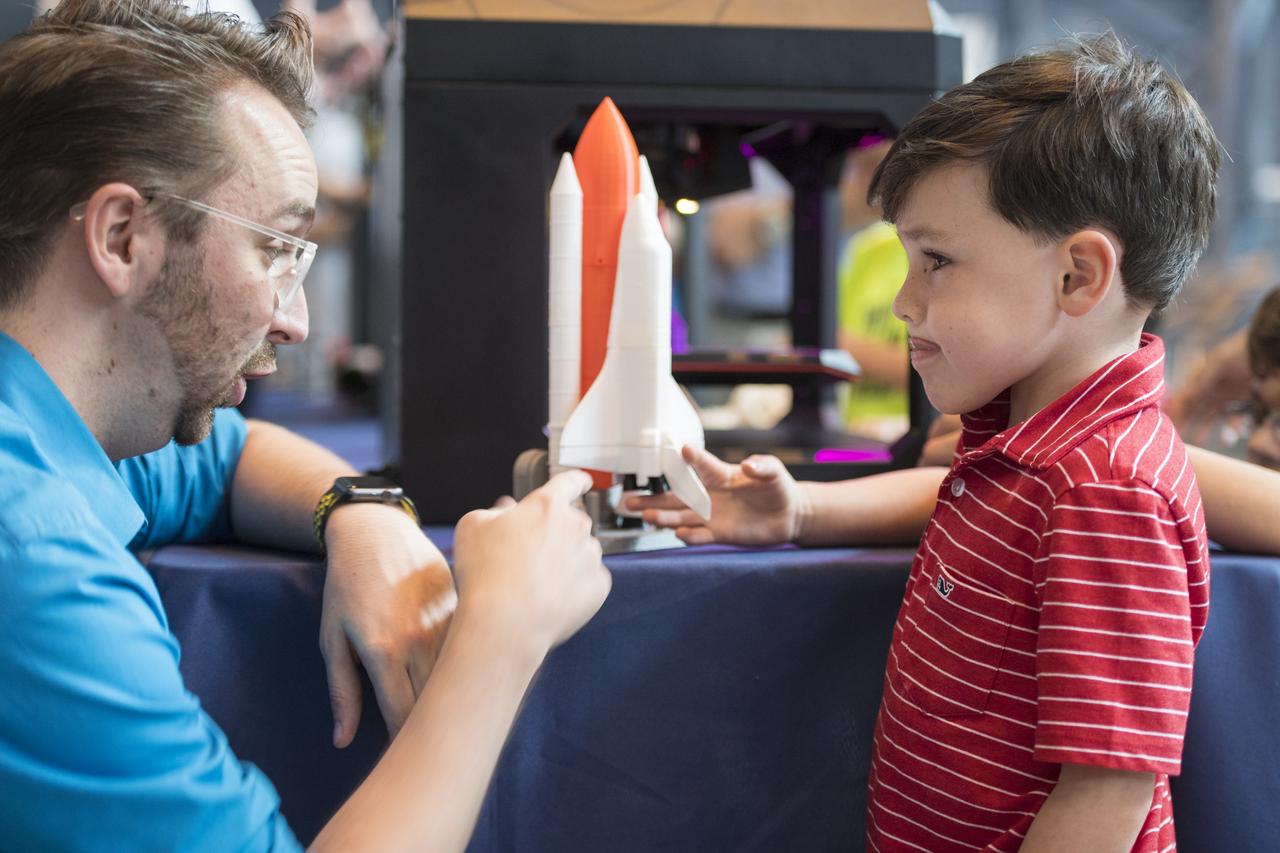
A visitor watches as a rocket is printed by a Makerbot 3D printer at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
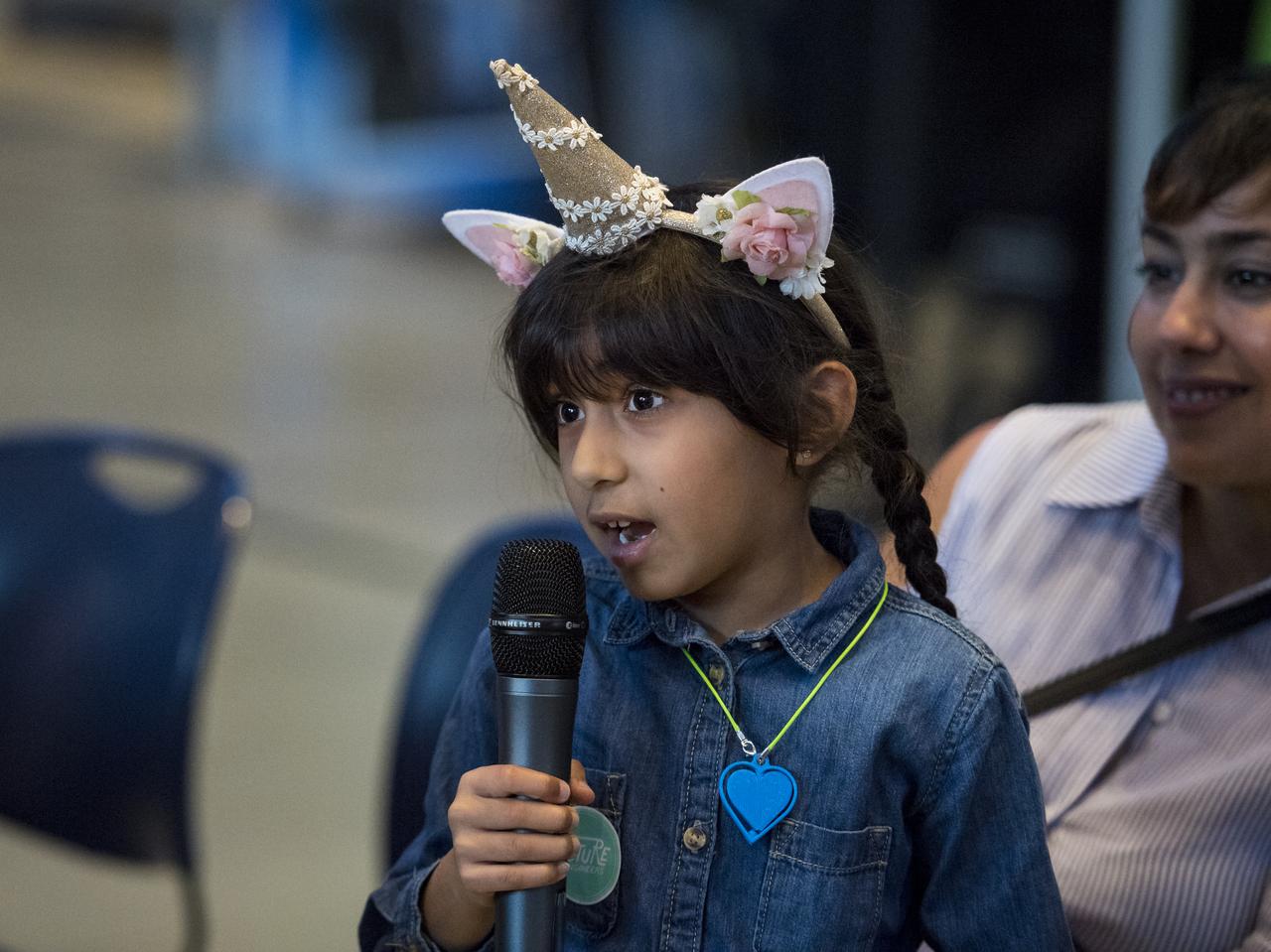

A young audience member asks the panel a question during a discussion on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

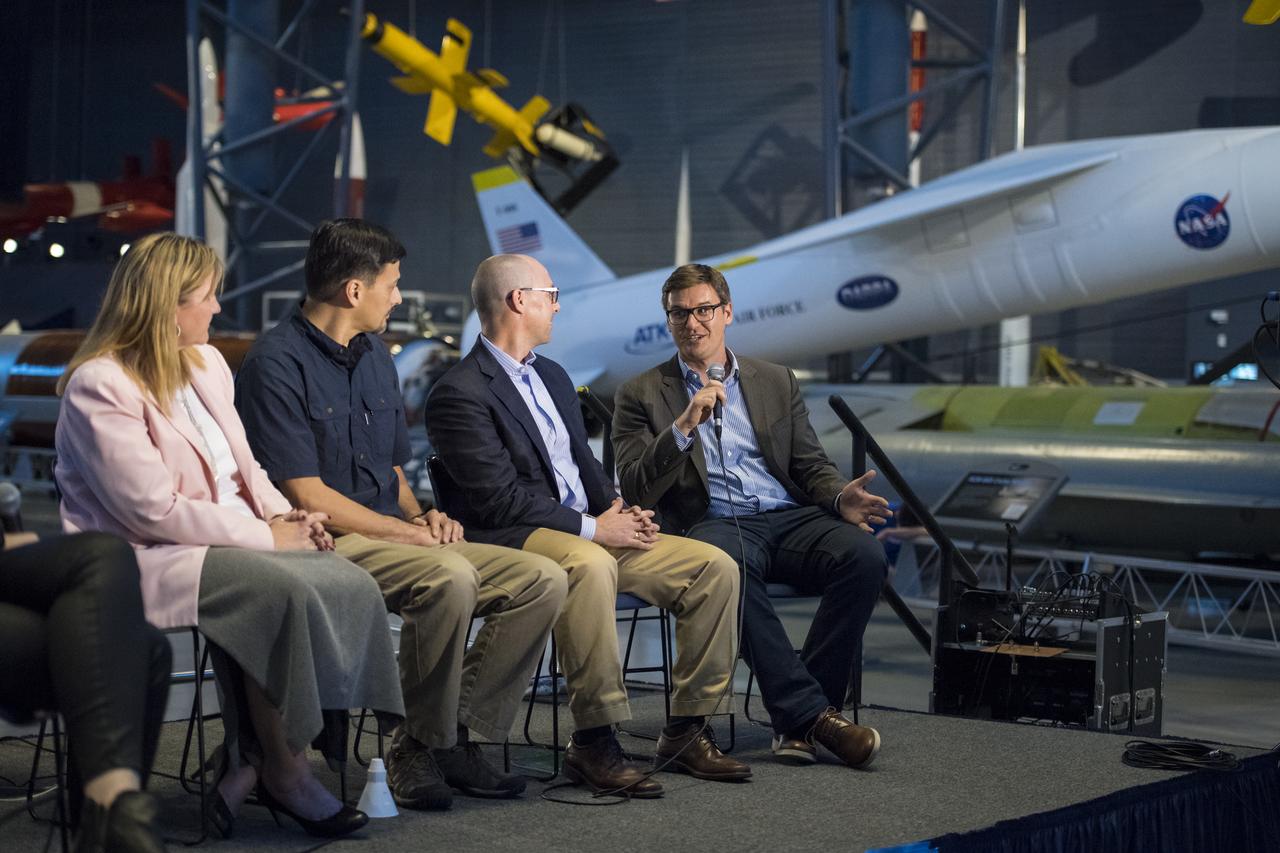
Ryan Heitz, co-founder and head of school, Ideaventions Academy, second from right, speaks on a panel on "igniting NOVA K-12 engineering and maker education", at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
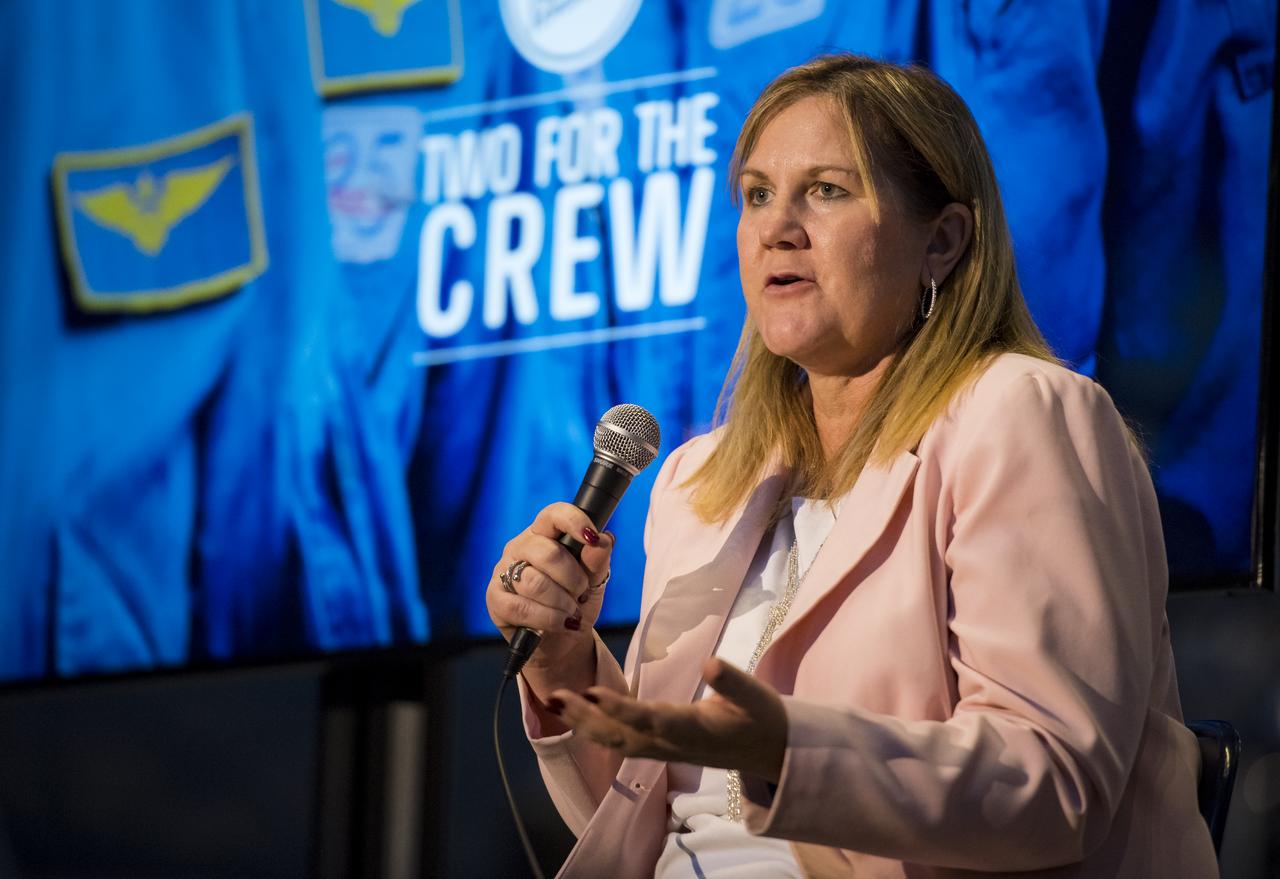

Barb Gruber, supervisor school programs, Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum, speaks on a panel on "igniting NOVA K-12 engineering and maker education", at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
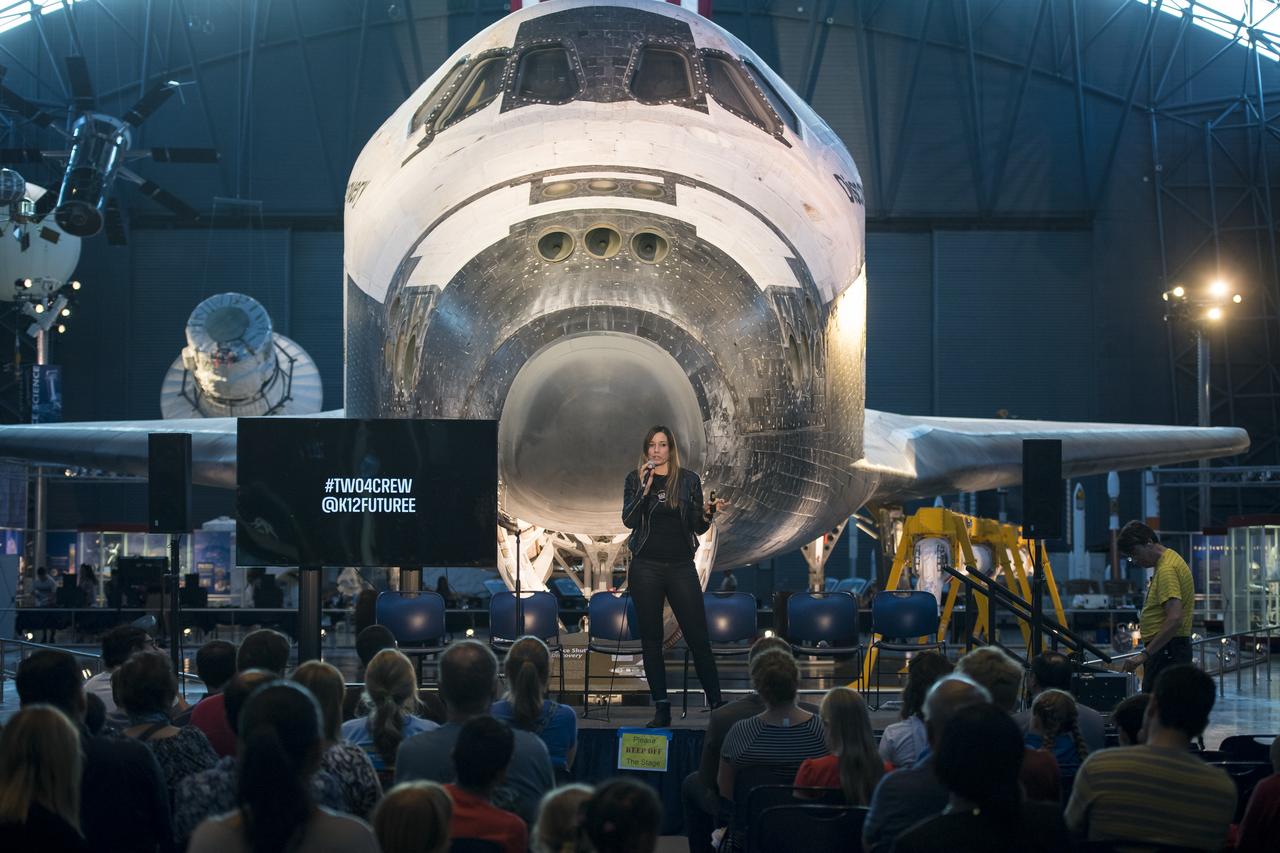

Founder and CEO of Future Engineers, Deanne Bell, speaks at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
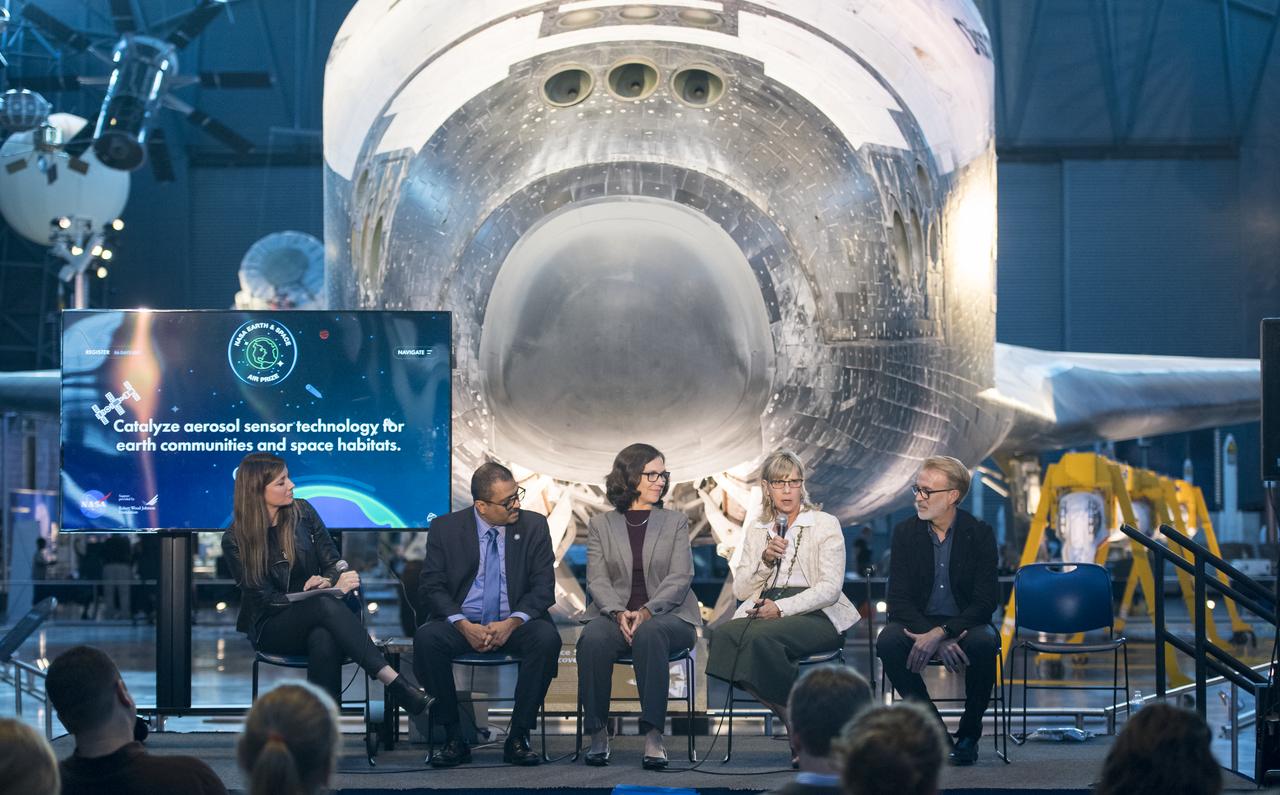

Lynn Buquo, manager, NASA Center of Excellence for Collaborative Innovation, speaks on a panel on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
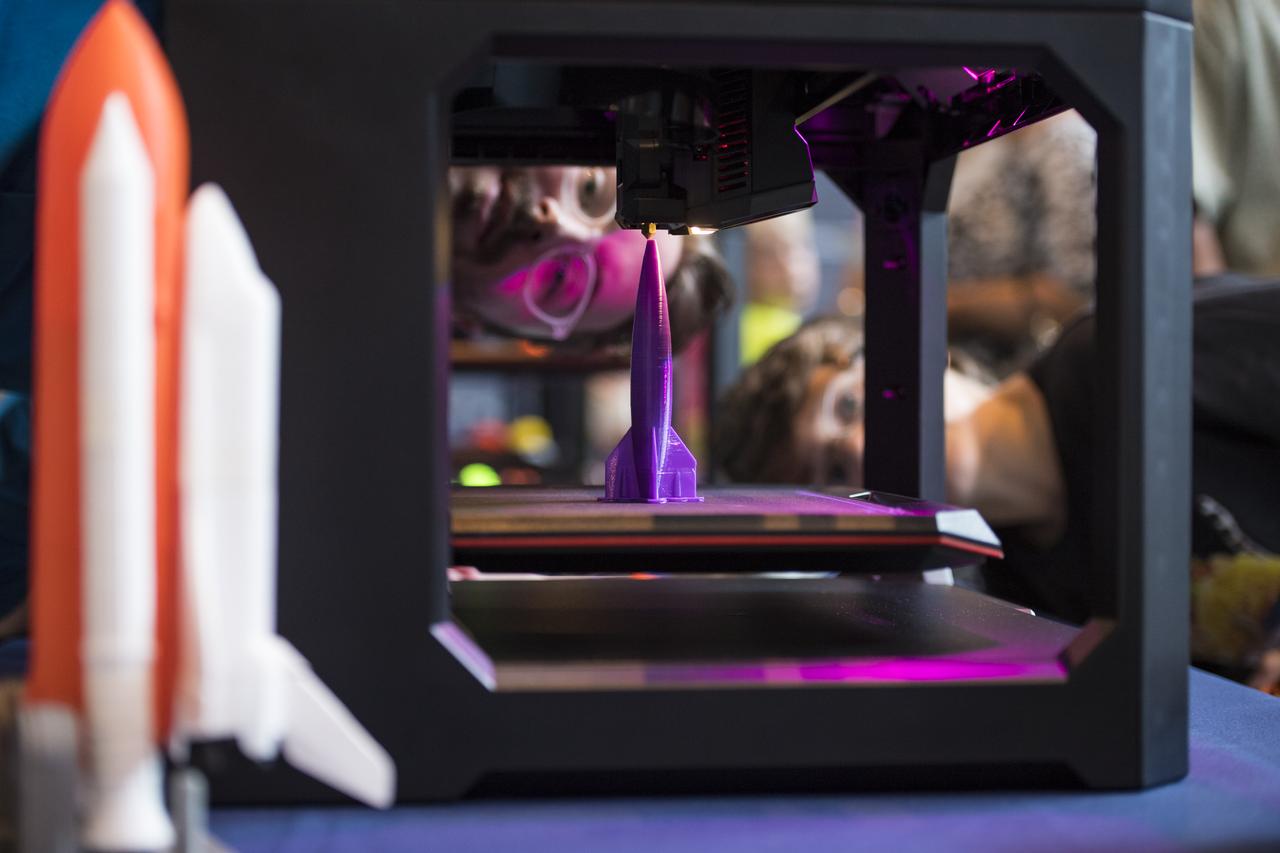

Visitors watch as a rocket is printed by a Makerbot 3D printer at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
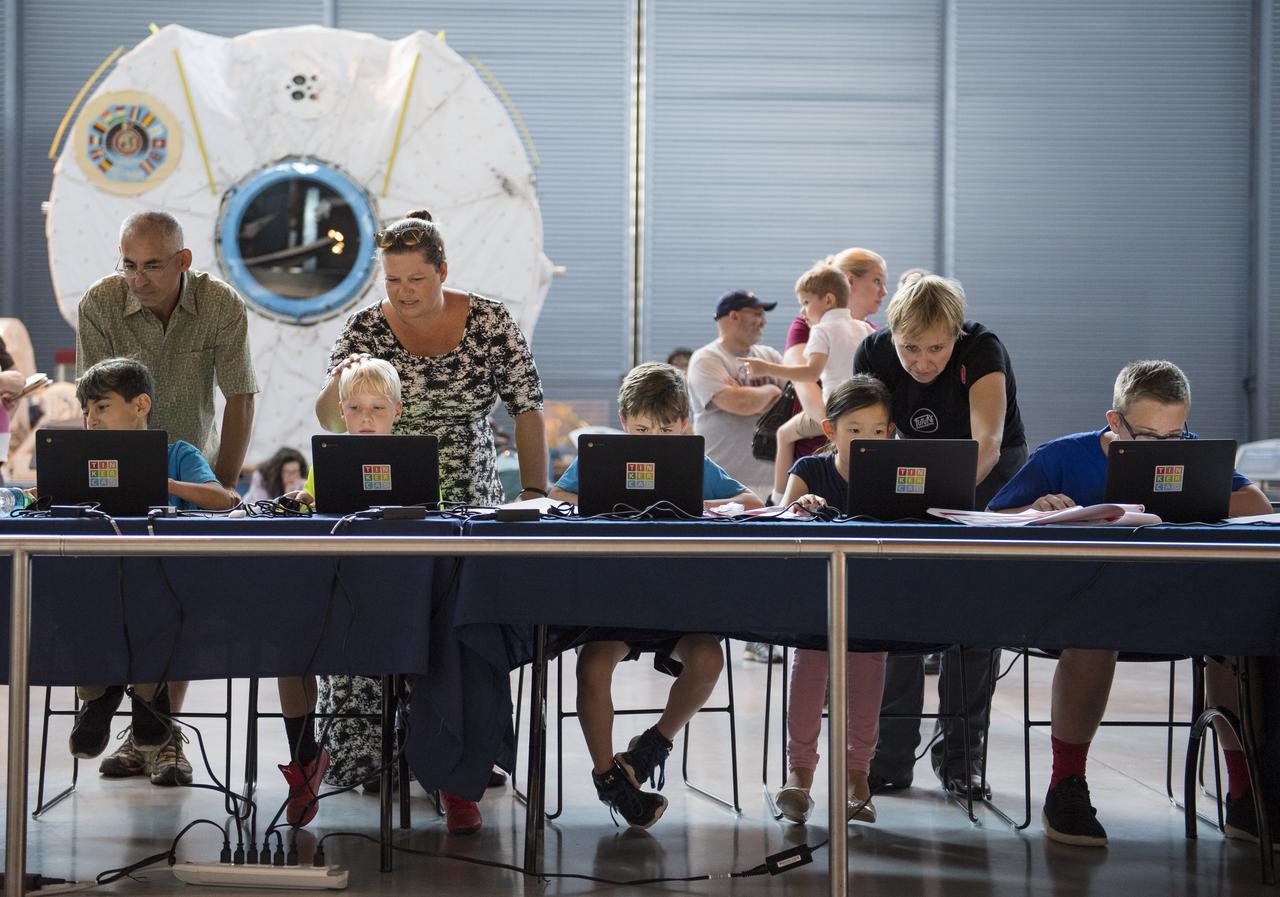

Participants create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. The winner of the Two for the Crew challenge will have their design printed on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
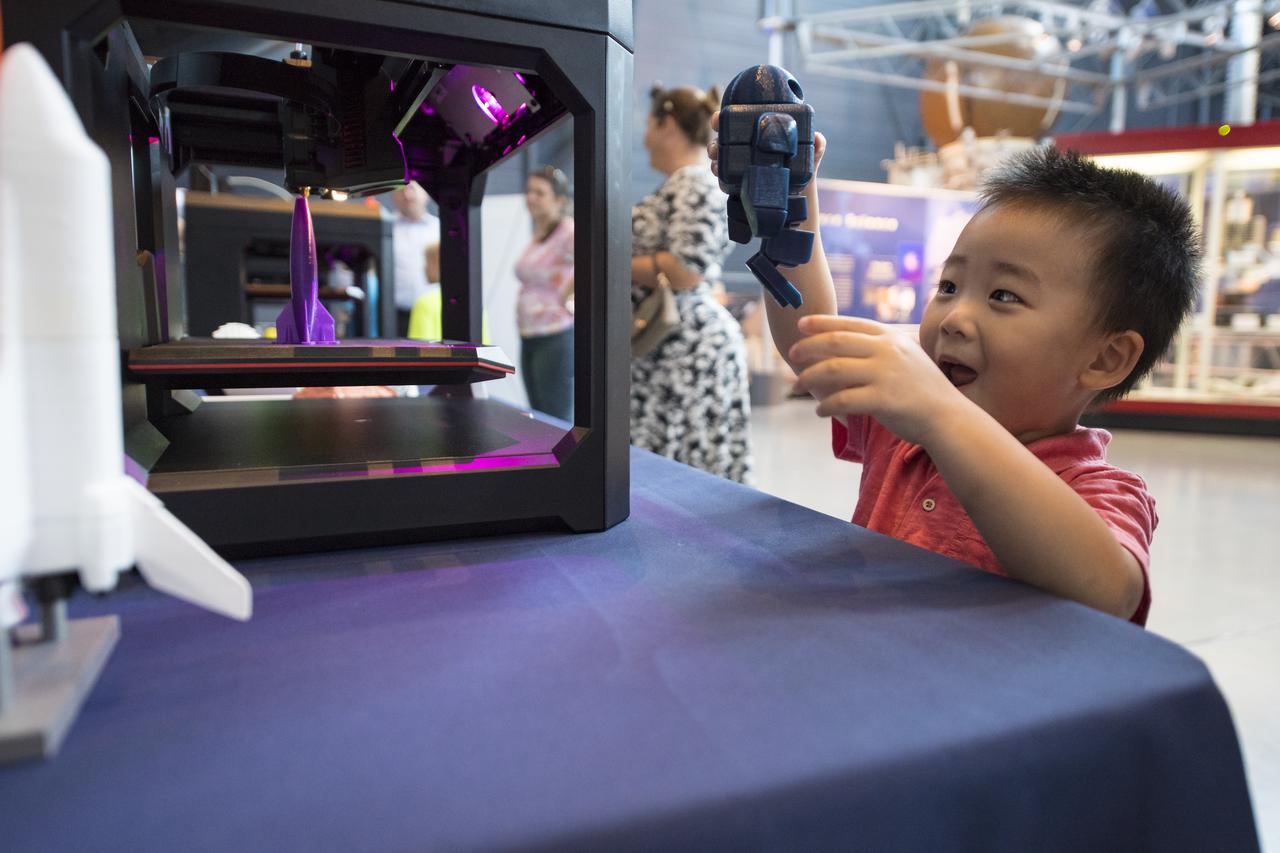

A visitor plays with a robot printed by a 3D printer at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
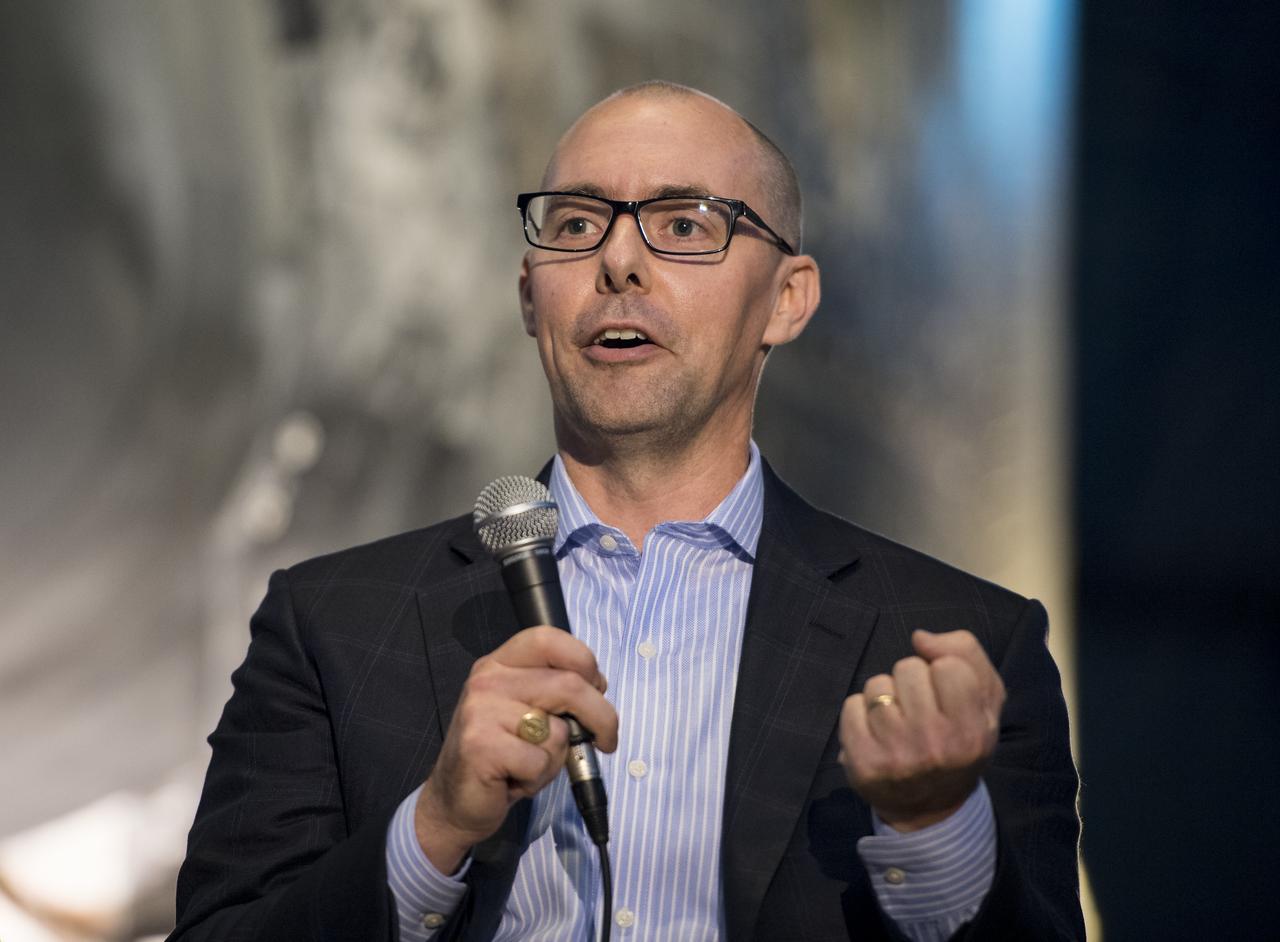

Ryan Heitz, co-founder and head of school, Ideaventions Academy, speaks on a panel on "igniting NOVA K-12 engineering and maker education", at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
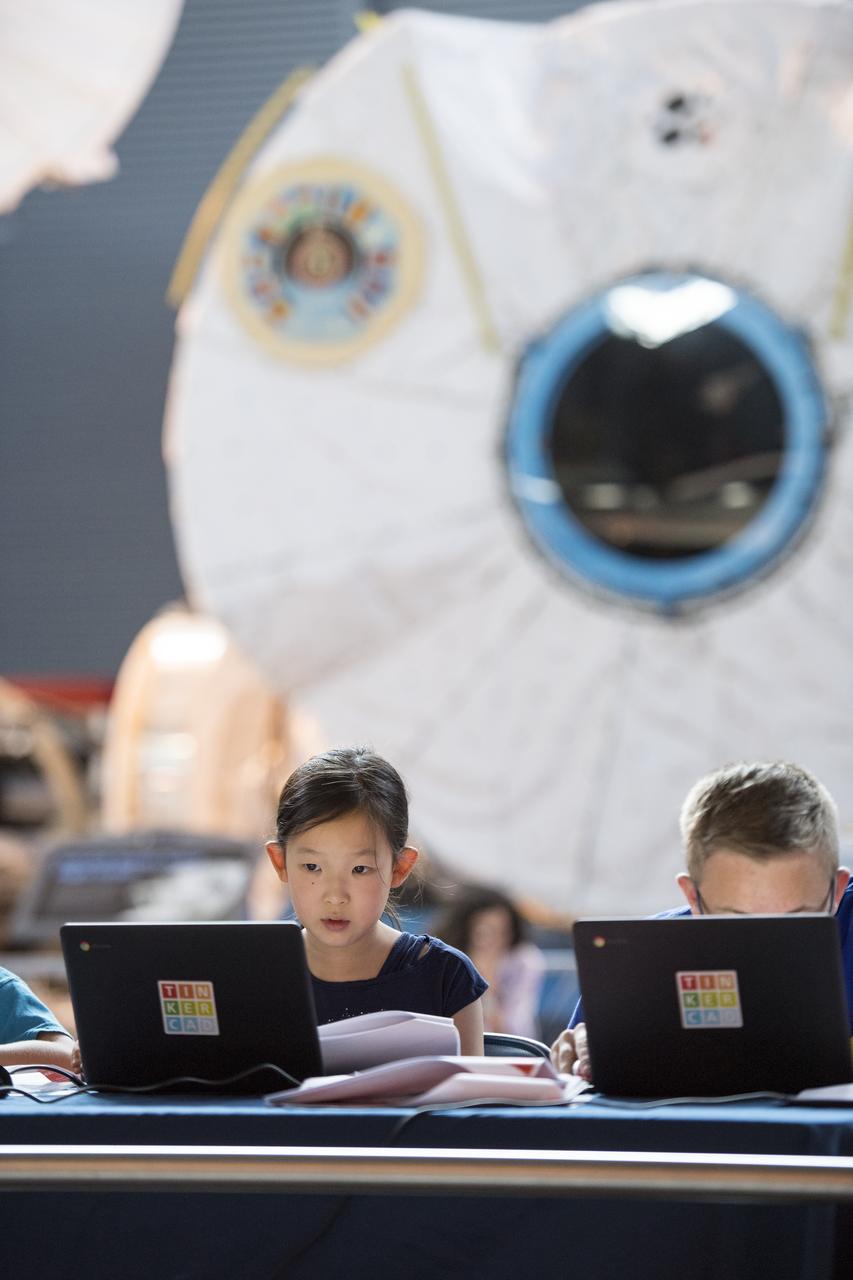

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
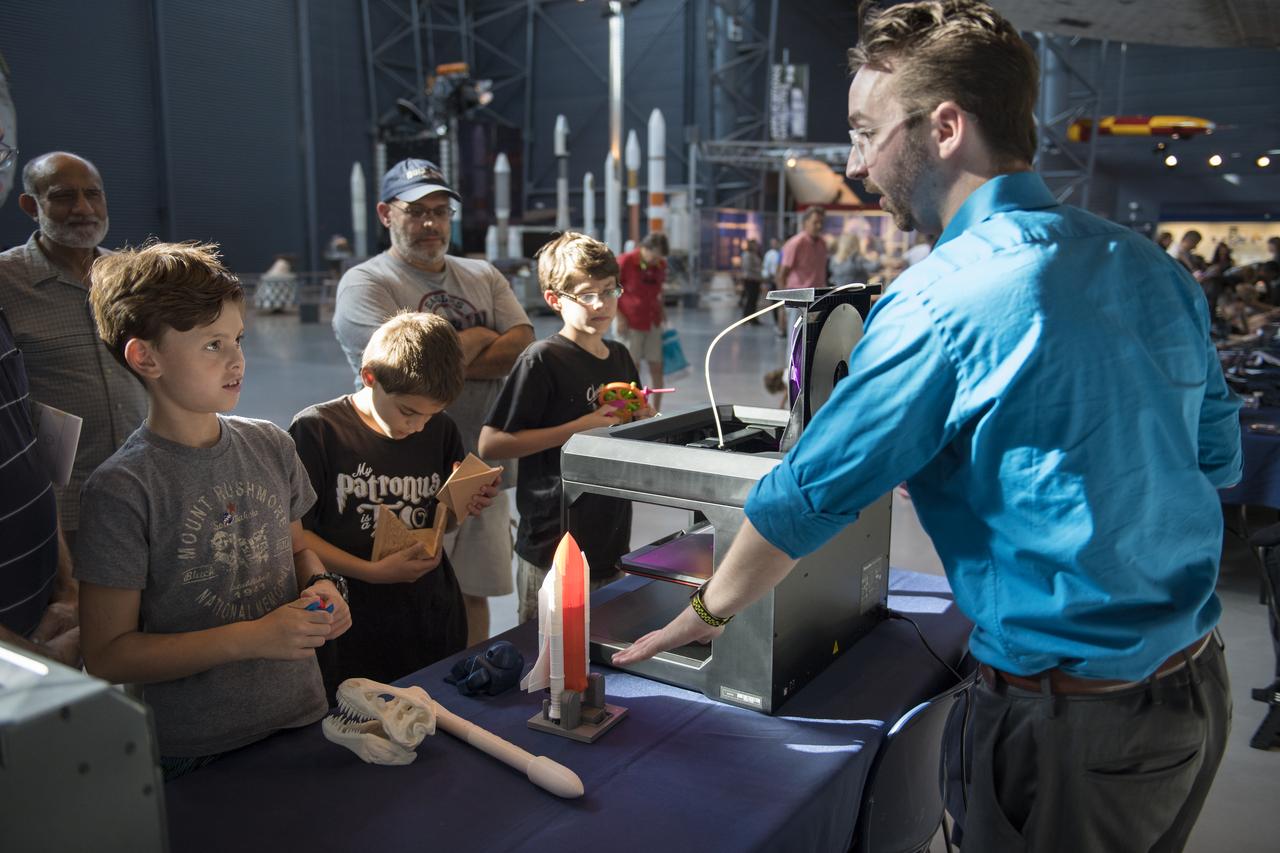

Visitors learn about 3D printing at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
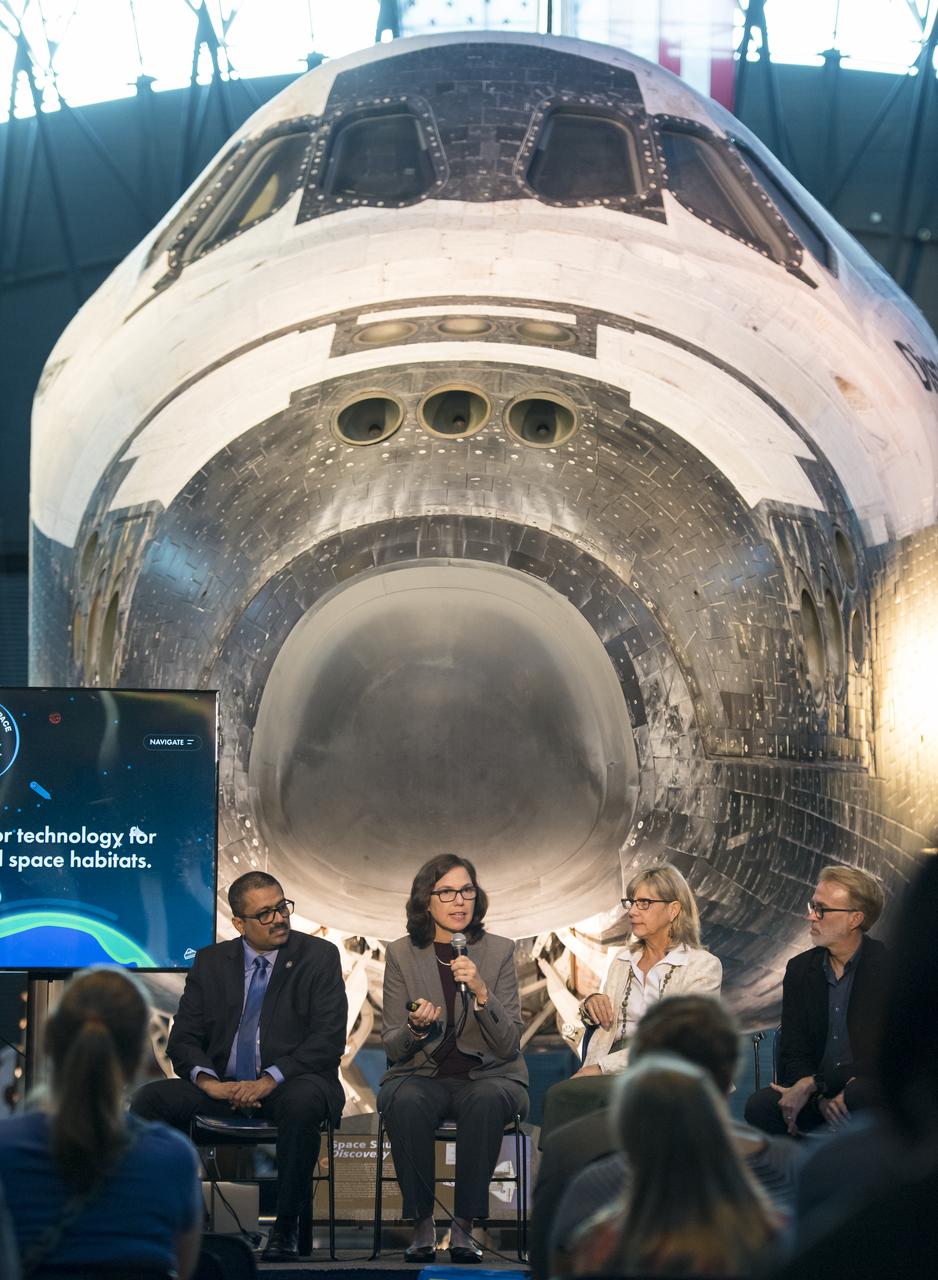

Marit Meyer, research aerospace engineer, Aerosol Science and Instrumentation, NASA, speaks on a panel on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
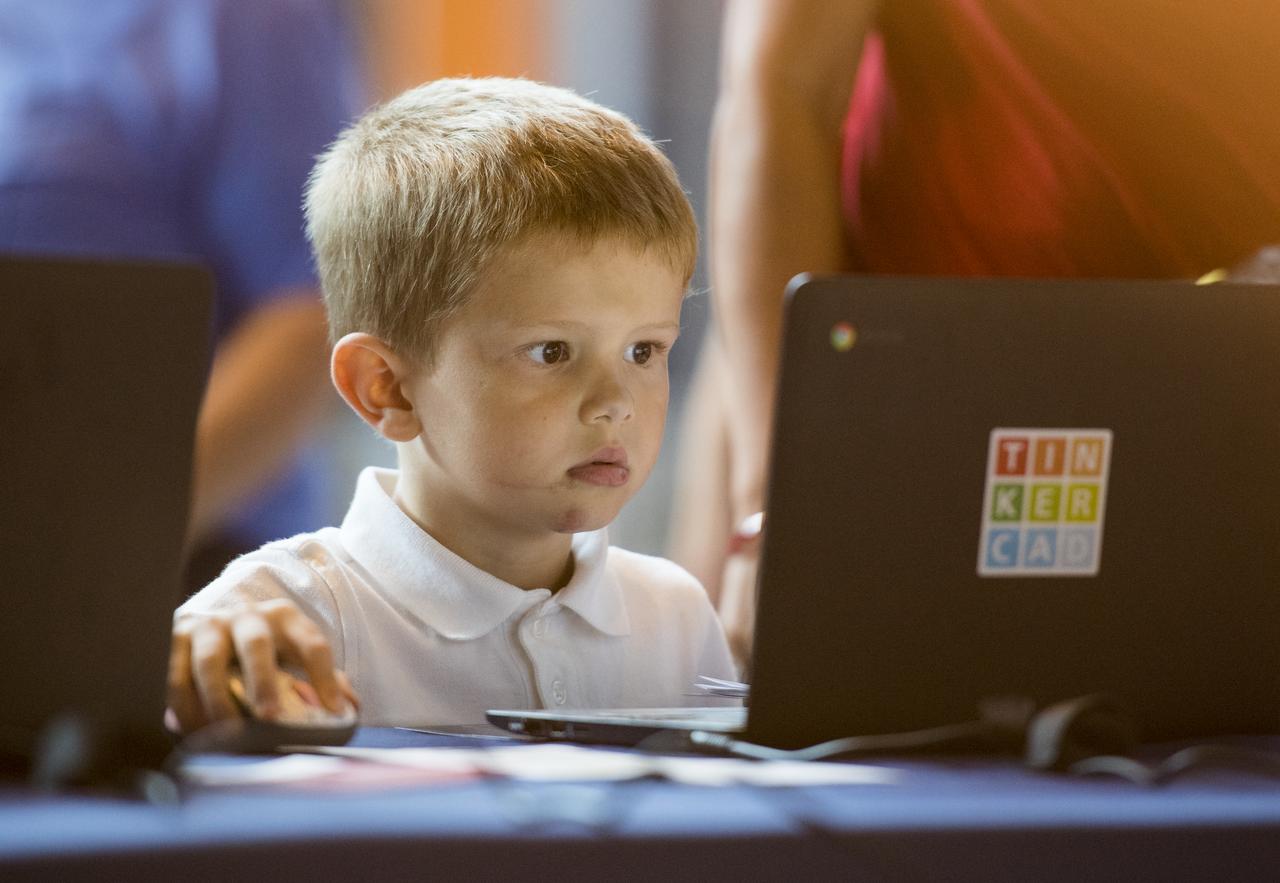

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
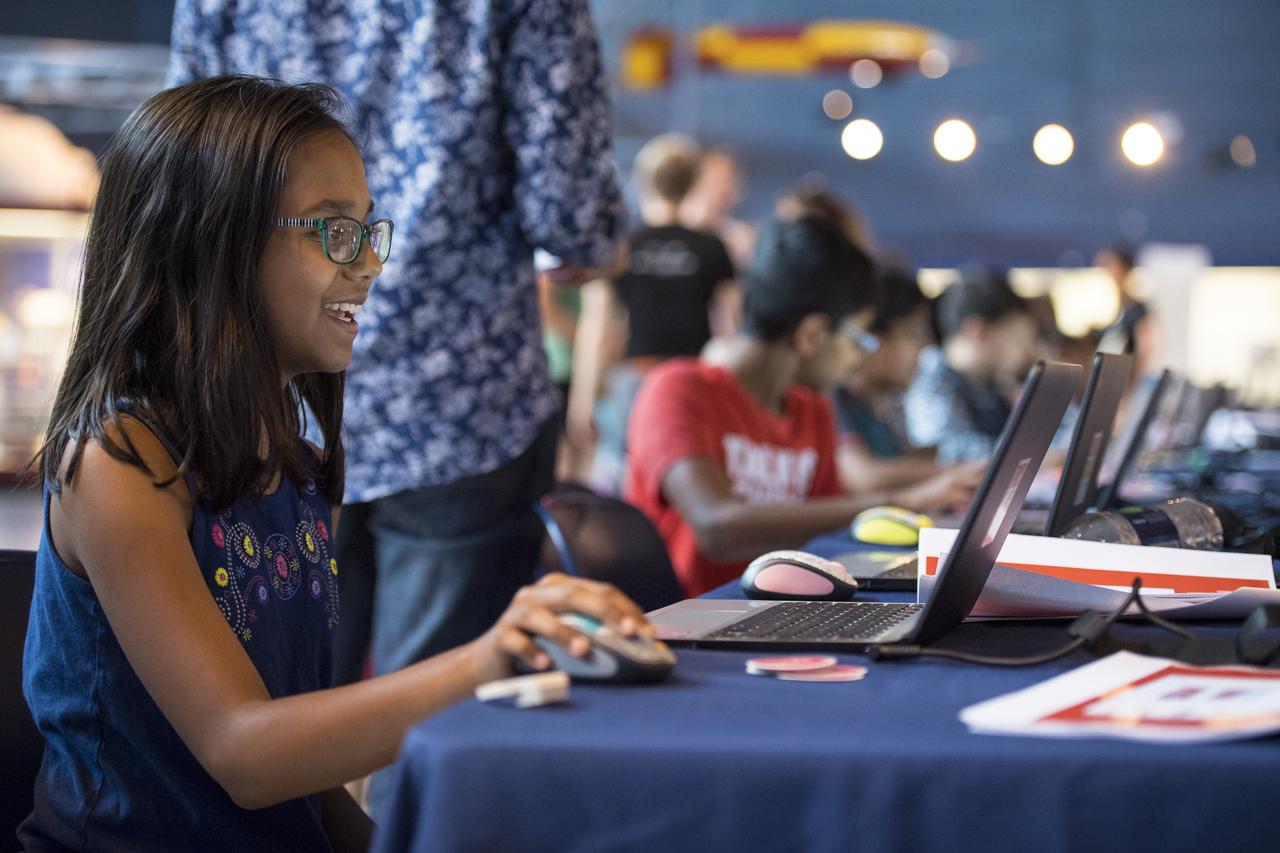

A participant creates digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad in the Two for the Crew Challenge at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers, with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants had the opportunity to create digital 3D models and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
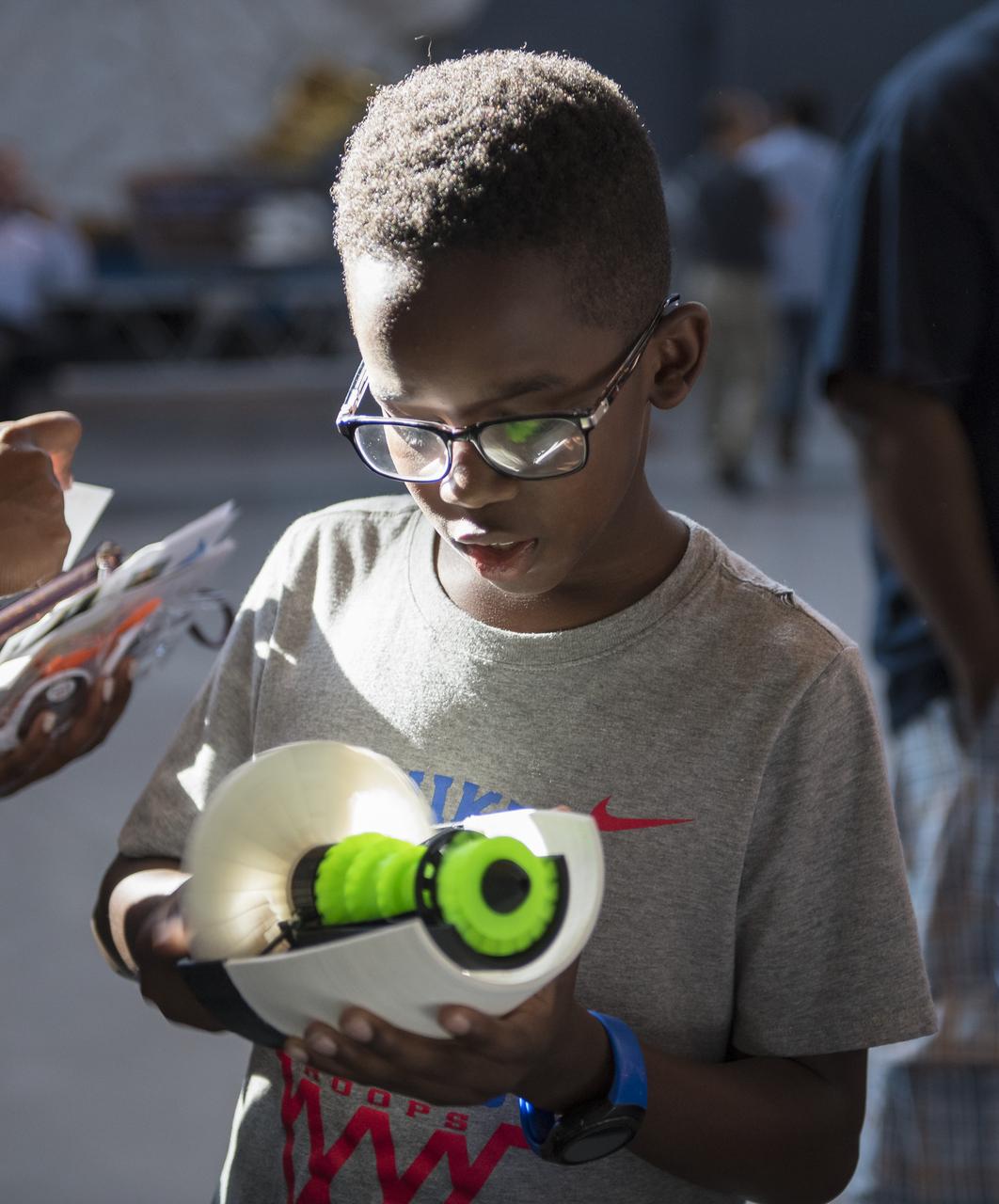

A participant examines a 3D printed object at a pop-up makerspace held by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants created digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watched objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
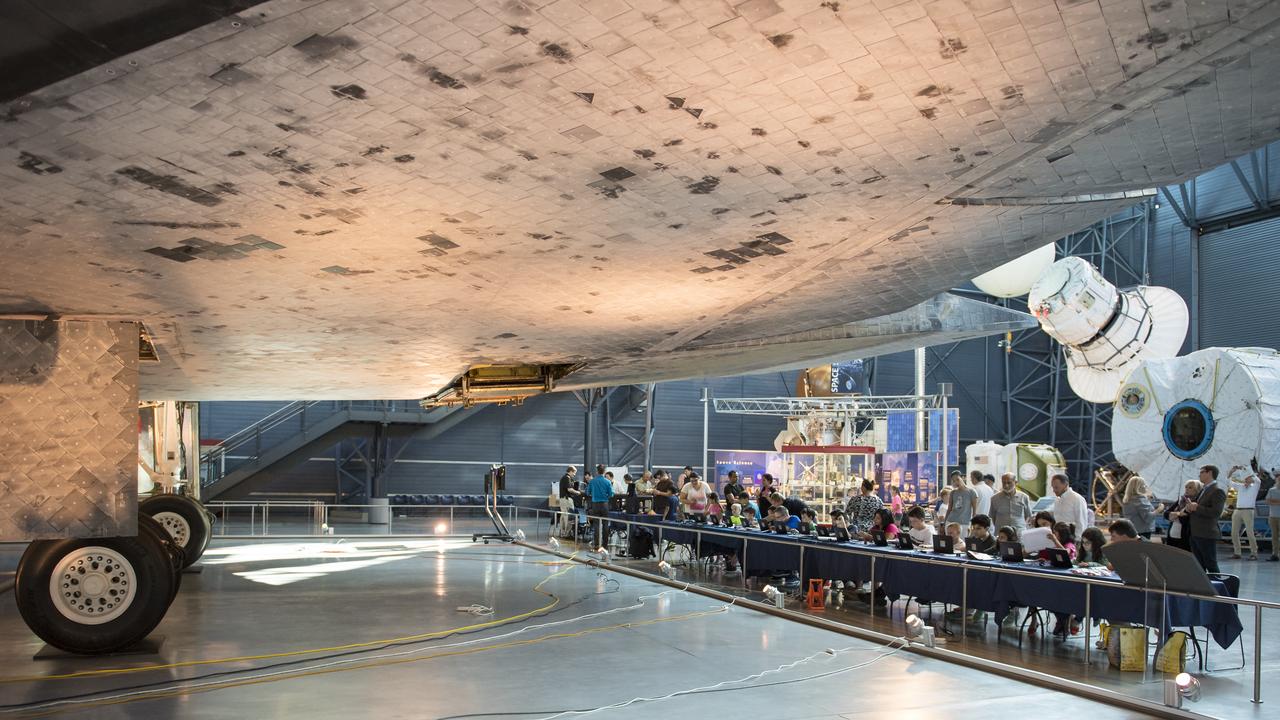

Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), hosted a future engineers pop-up makerspace where youth were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers, at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
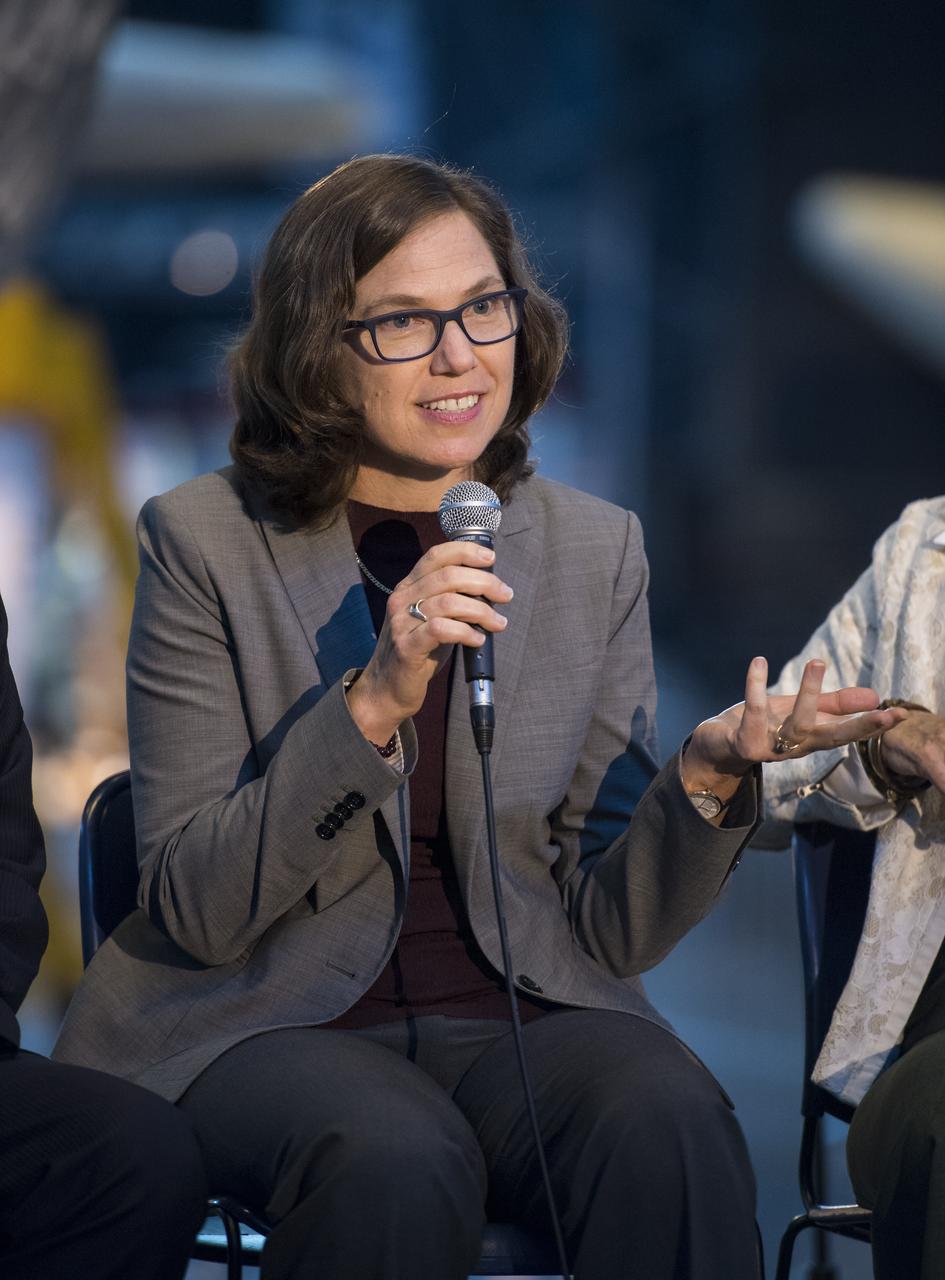

Marit Meyer, research aerospace engineer, Aerosol Science and Instrumentation, NASA, speaks on a panel on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
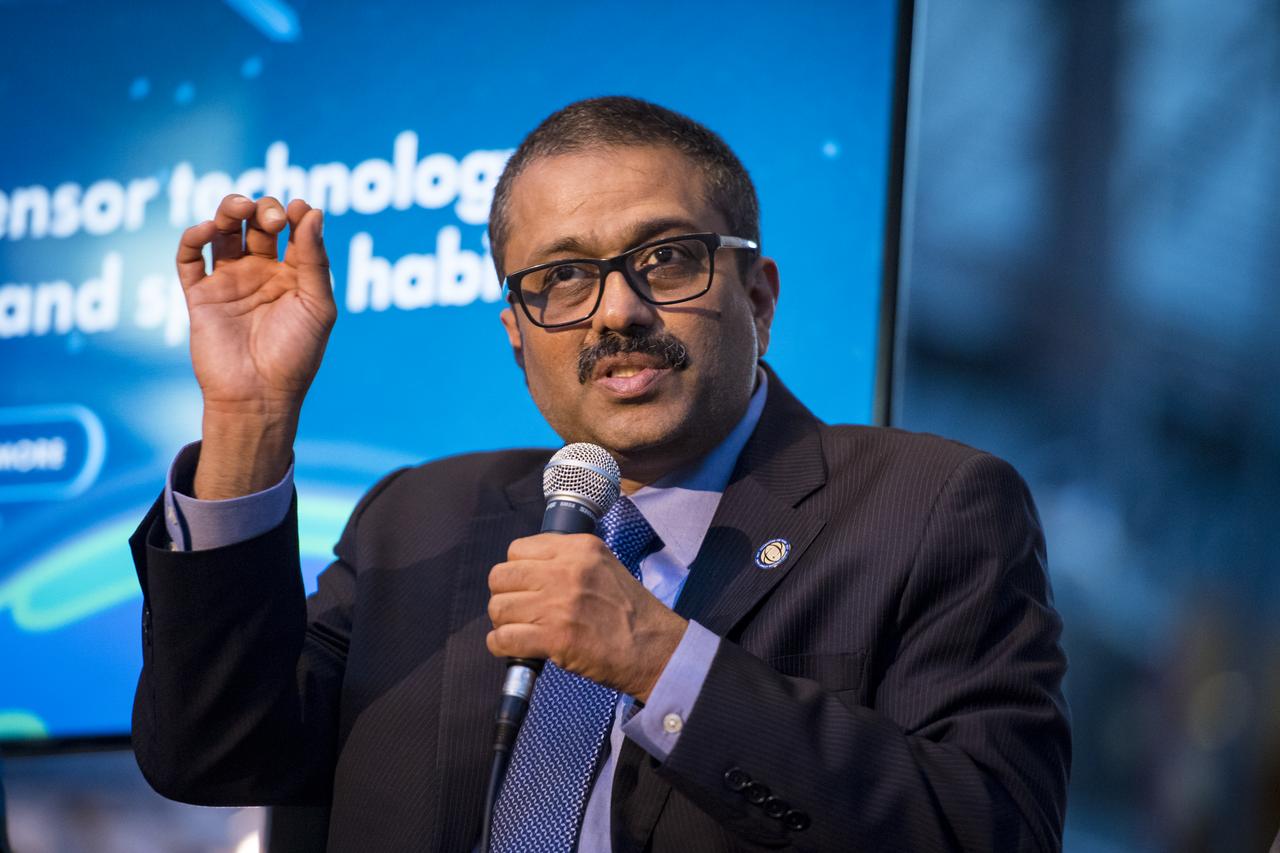

Jitendra Joshi, chief technology advisor, Advanced Exploration Systems, NASA, speaks on a panel on improving air quality for health in space and on Earth, at a pop-up makerspace hosted by Future Engineers with support from NASA and The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, September 21, 2017 in Chantilly, Virginia. Participants were able to create digital 3D models using Autodesk Tinkercad and watch objects being printed with Makerbot 3D printers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
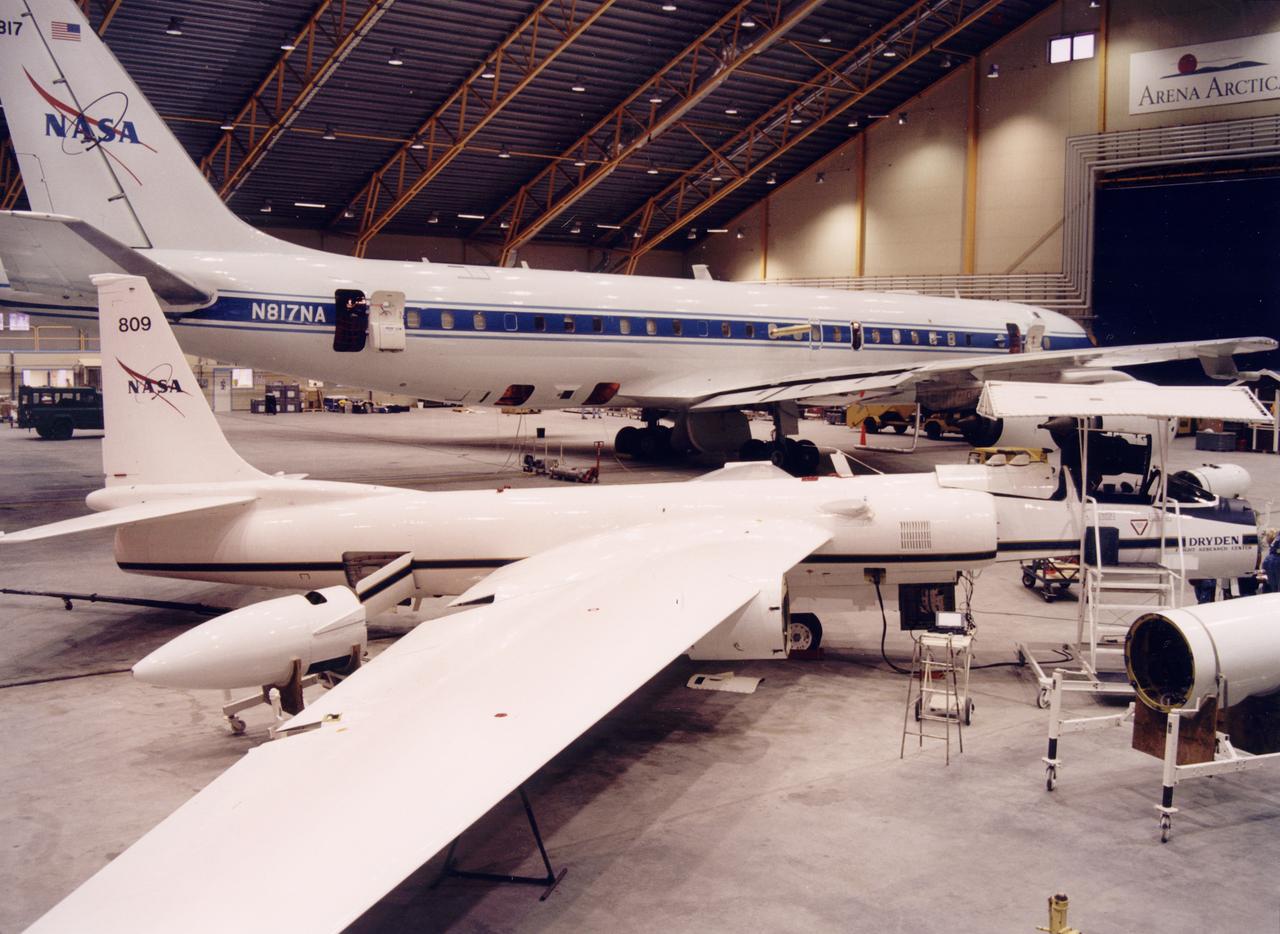

NASA ER-2 # 809 and its DC-8 shown in Arena Arctica before the SAGE III Ozone Loss and Validation Experiment (SOLVE). The two airborne science platforms were based north of the Arctic Circle in Kiruna, Sweden, during the winter of 2000 to study ozone depletion as part of SOLVE. A large hangar built especially for research, "Arena Arctica" housed the instrumented aircraft and the scientists. Scientists have observed unusually low levels of ozone over the Arctic during recent winters, raising concerns that ozone depletion there could become more widespread as in the Antarctic ozone hole. The NASA-sponsored international mission took place between November 1999 and March 2000 and was divided into three phases. The DC-8 was involved in all three phases returning to Dryden between each phase. The ER-2 flew sample collection flights between January and March, remaining in Sweden from Jan. 9 through March 16. "The collaborative campaign will provide an immense new body of information about the Arctic stratosphere," said program scientist Dr. Michael Kurylo, NASA Headquarters. "Our understanding of the Earth's ozone will be greatly enhanced by this research."

These postage-stamp images taken by NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer are helping to solve a mystery -- why do the littlest of galaxies produce the biggest of star explosions, or supernovae?
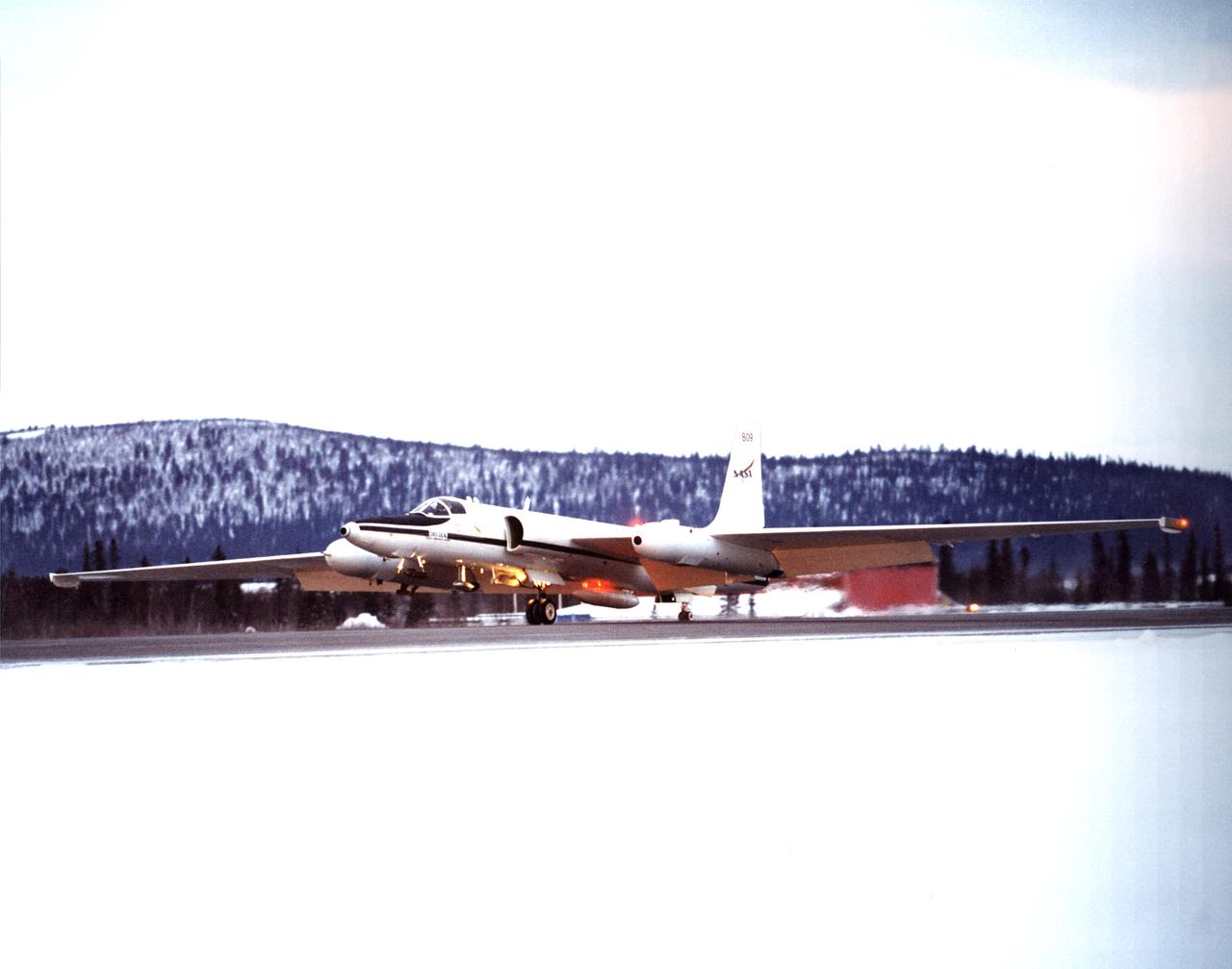

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
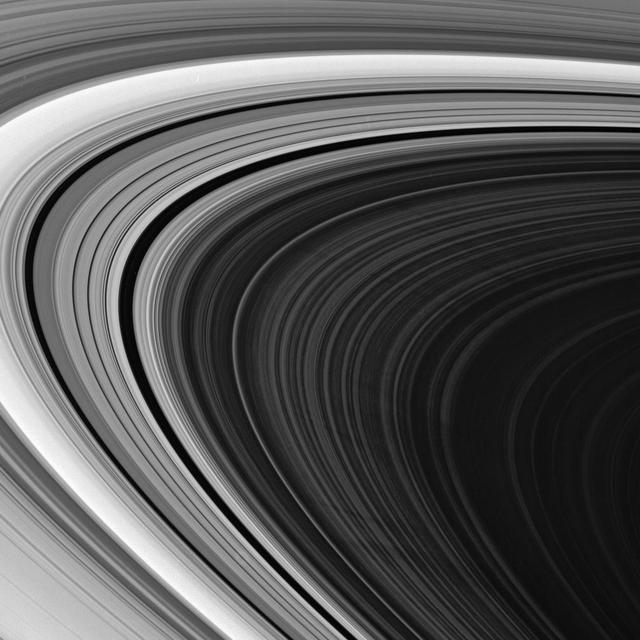

The Cassini spacecraft spies multiple spokes in Saturn outer B ring. The precise origin and evolution of these transient features continue to provide ring scientists with intriguing puzzles to solve
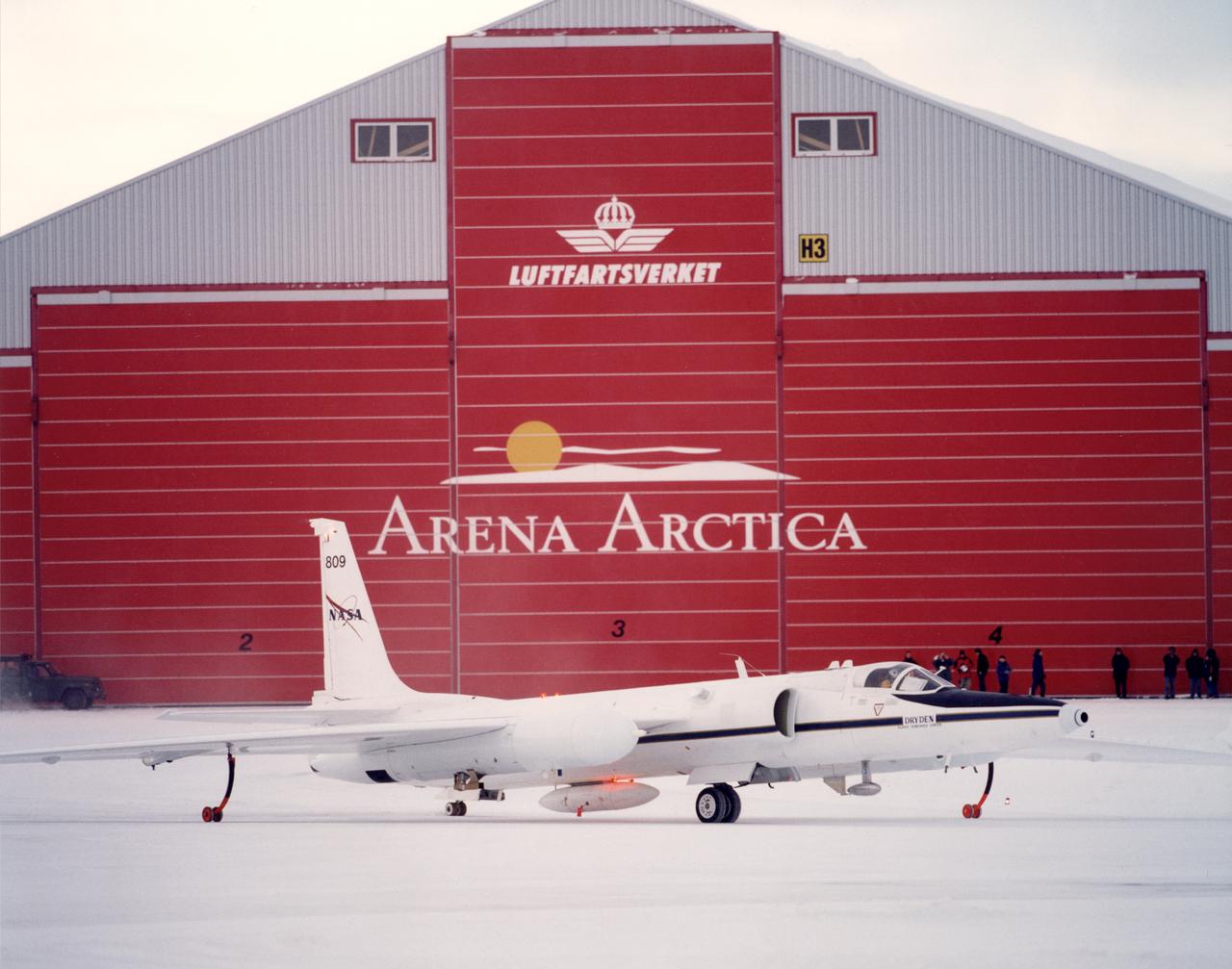

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
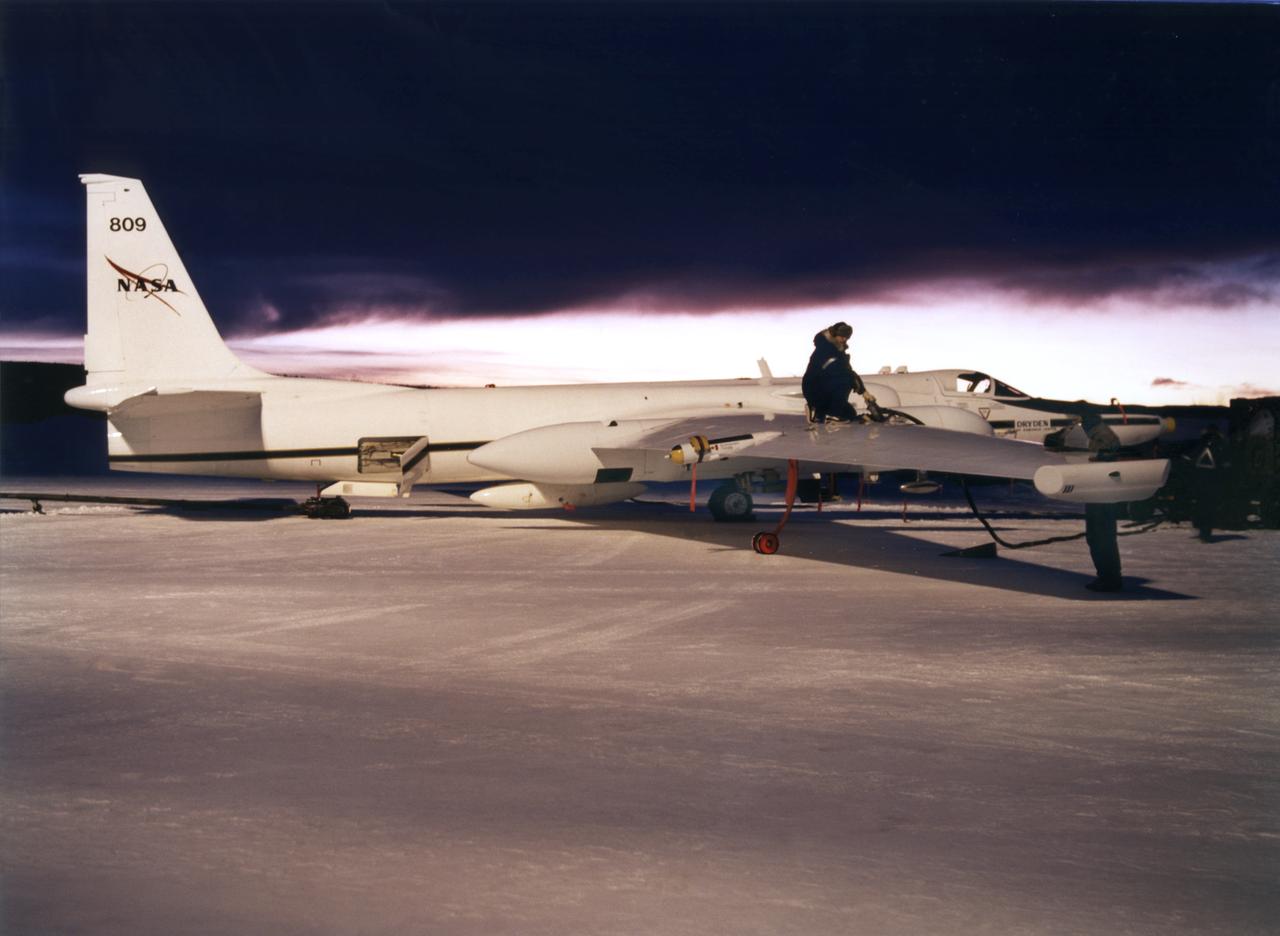

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
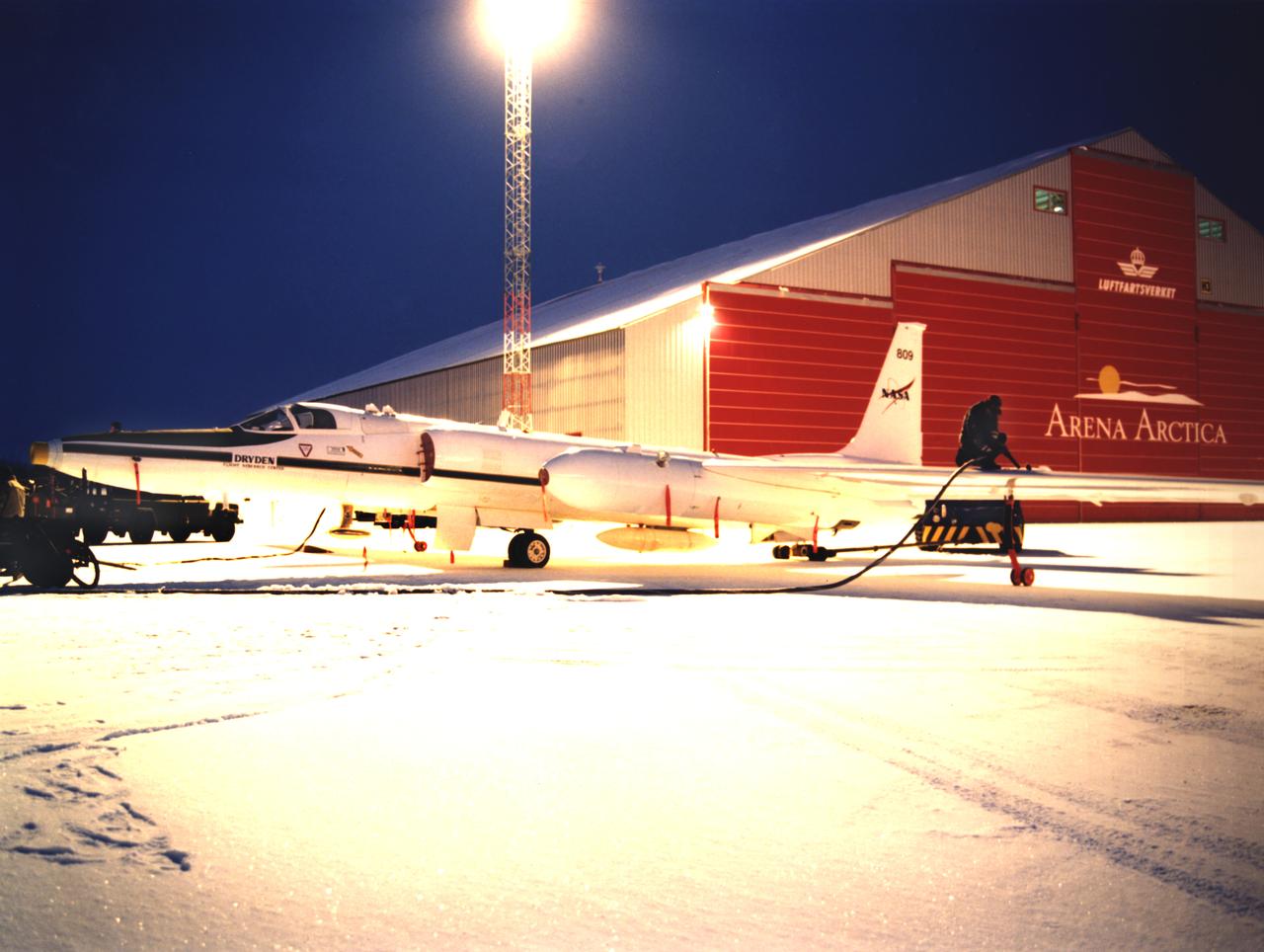

ER-2s bearing tail numbers 806 and 809 are used as airborne science platforms by NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The aircraft are platforms for a variety of high-altitude science missions flown over various parts of the world. They are also used for earth science and atmospheric sensor research and development, satellite calibration and data validation. The ER-2s are capable of carrying a maximum payload of 2,600 pounds of experiments in a nose bay, the main equipment bay behind the cockpit, two wing-mounted superpods and small underbody and trailing edges. Most ER-2 missions last about six hours with ranges of about 2,200 nautical miles. The aircraft typically fly at altitudes above 65,000 feet. On November 19, 1998, an ER-2 set a world record for medium weight aircraft reaching an altitude of 68,700 feet. The aircraft is 63 feet long, with a wingspan of 104 feet. The top of the vertical tail is 16 feet above ground when the aircraft is on the bicycle-type landing gear. Cruising speeds are 410 knots, or 467 miles per hour, at altitude. A single General Electric F-118 turbofan engine rated at 17,000 pounds thrust powers the ER-2.
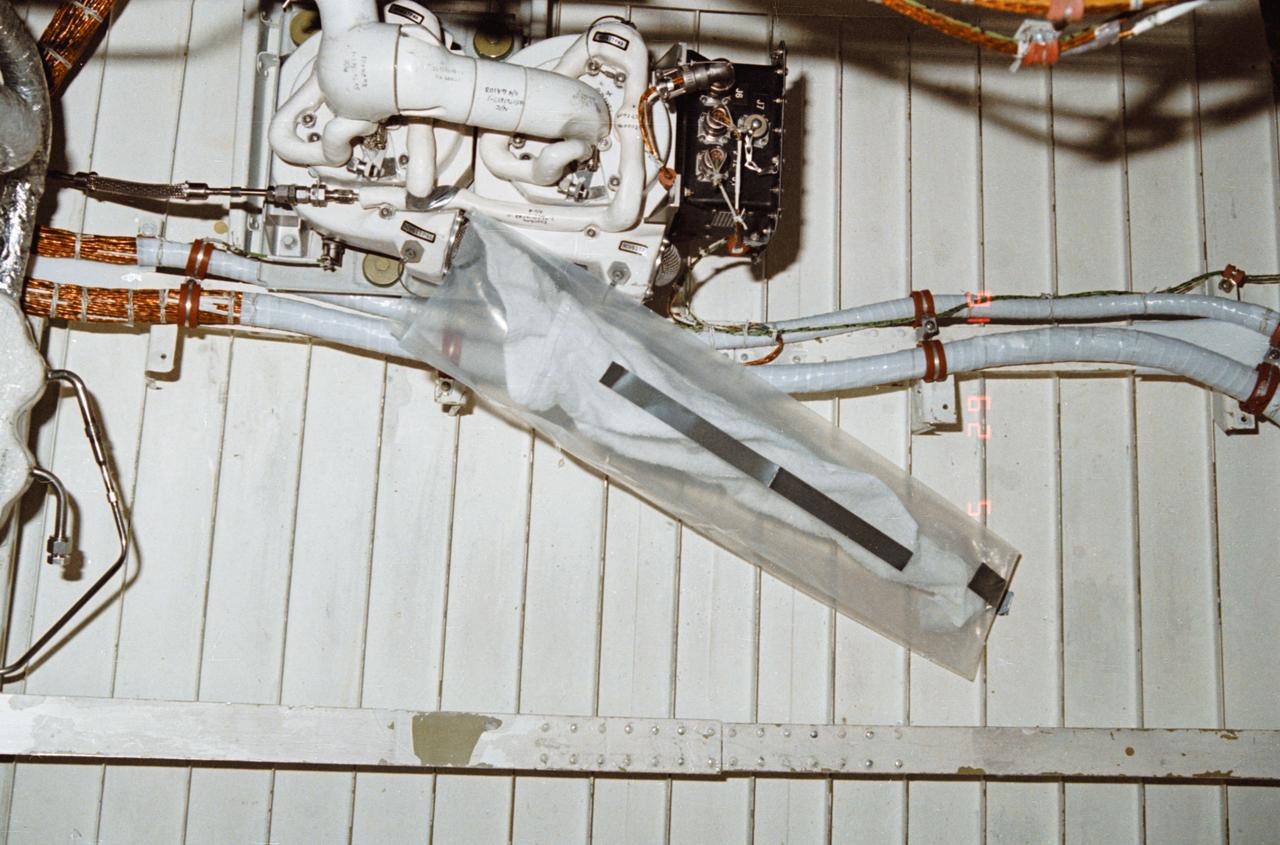
During STS-32, onboard Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, a leakage problem at environmental control and life support system (ECLSS) air revitalization system (ARS) humidity separator A below the middeck is solved with a plastic bag and a towel. The towel inserted inside a plastic bag absorbed the water that had collected at the separator inlet.
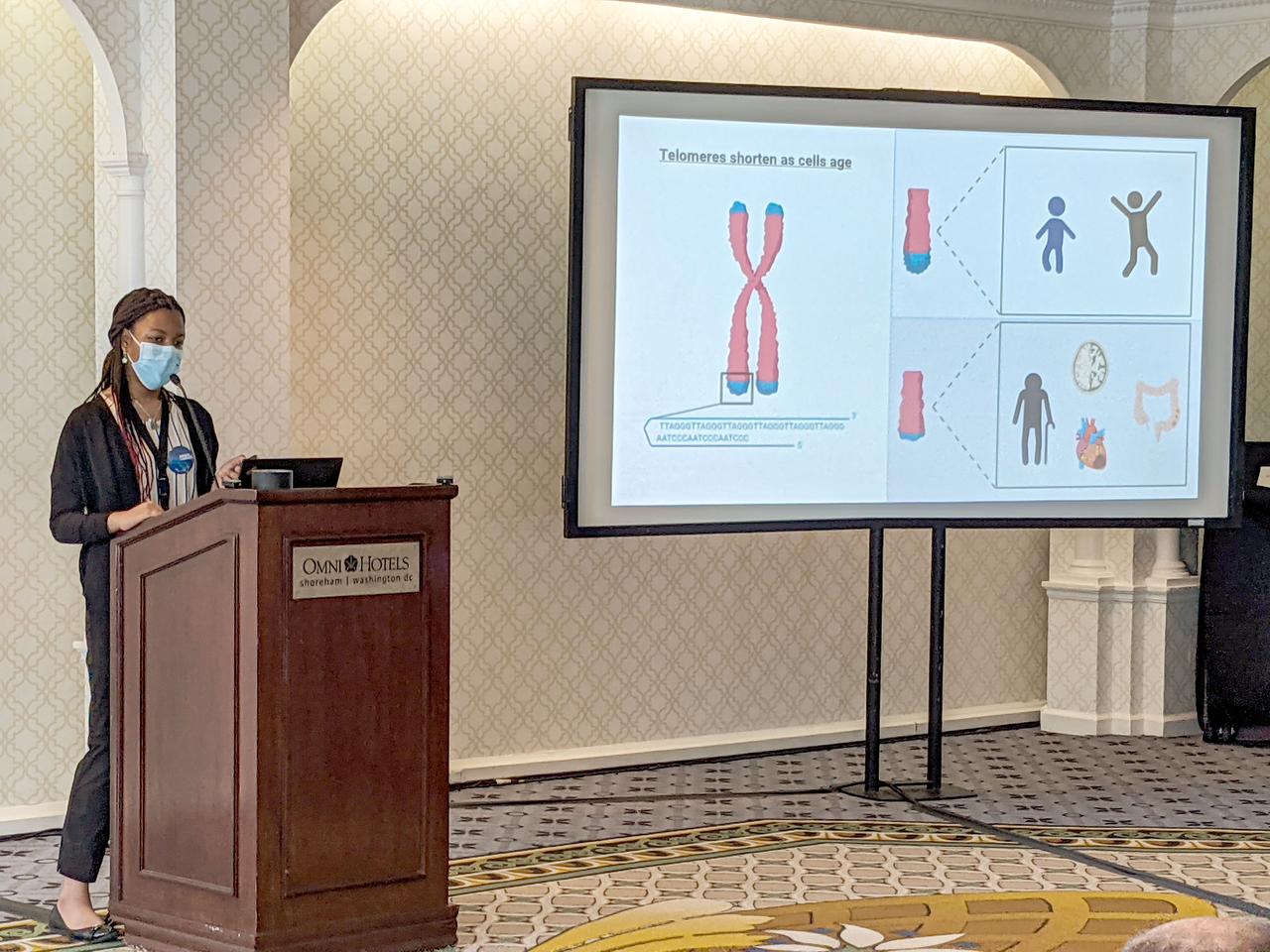

jsc2023e031078 (7/27/2022) --- Pristine Onuoha, Genes in Space-10 winner, presents her idea to contest judges. The Genes in Space program allows for 10 student projects to be selected for spaceflight analysis, which gives students a chance to attempt to solve real-world problems. Image courtesy of Genes in Space.

NASA Associate Administrator, Office of Communications, Bettina Inclán, introduces the cast of the film “Ad Astra” before a screening at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Tommy Lee Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine is interviewed by Entertainment Tonight after arriving on the red carpet for a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Pitt, Tommy Lee Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

From left to right, actor Brad Pitt, producer, co-writer, and director James Gray, and actor Tommy Lee Jones are seen on stage before a screening of their film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Pitt, Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NACA Laboratory Computers Help Compile Handbook: ''Monroe Methods for Algebra, " a new booklet describing short-cuts that can be used in solving frequently-used algebraic formulas with a calculating machine, is undergoing its first trial at the hands of Laboratory computers. Several Monro-matics were purchased recently by NACA. NACA Air Scoop August 17,1951 Page 4. People on the photos re W.H. Rankins, David M. Goldenbaum and Marian D. Holzbach
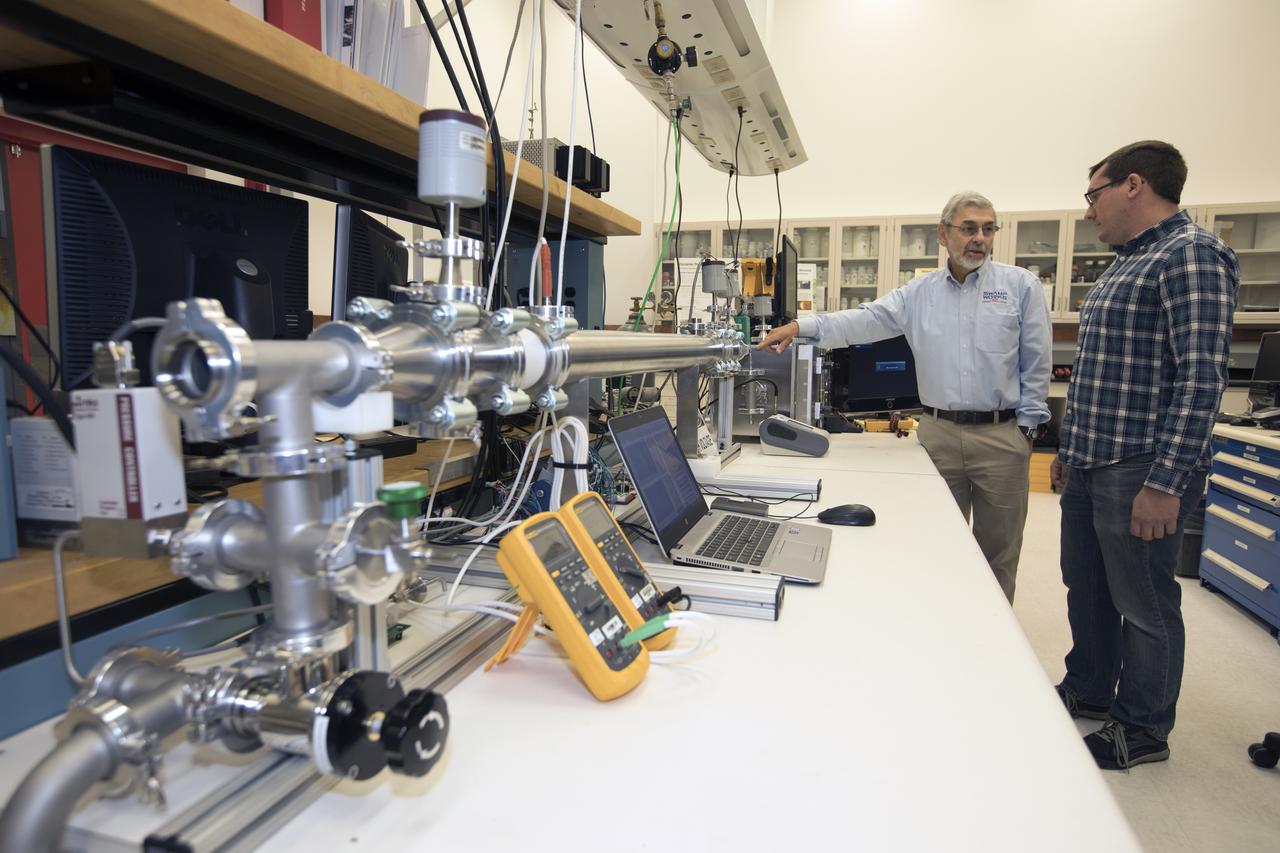
Dr. Carlos Calle, lead scientist in the Kennedy Space Center's Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory, left, and Jay Phillips, a research physicist, are modifying an electrostatic precipitator to help remove dust from a simulated Martian atmosphere. NASA's Journey to Mars requires cutting-edge technologies to solve the problems explorers will face on the Red Planet. Scientists are developing some of the needed solutions by adapting a device to remove the ever-present dust from valuable elements in the Martian atmosphere. Those commodities include oxygen, water and methane.
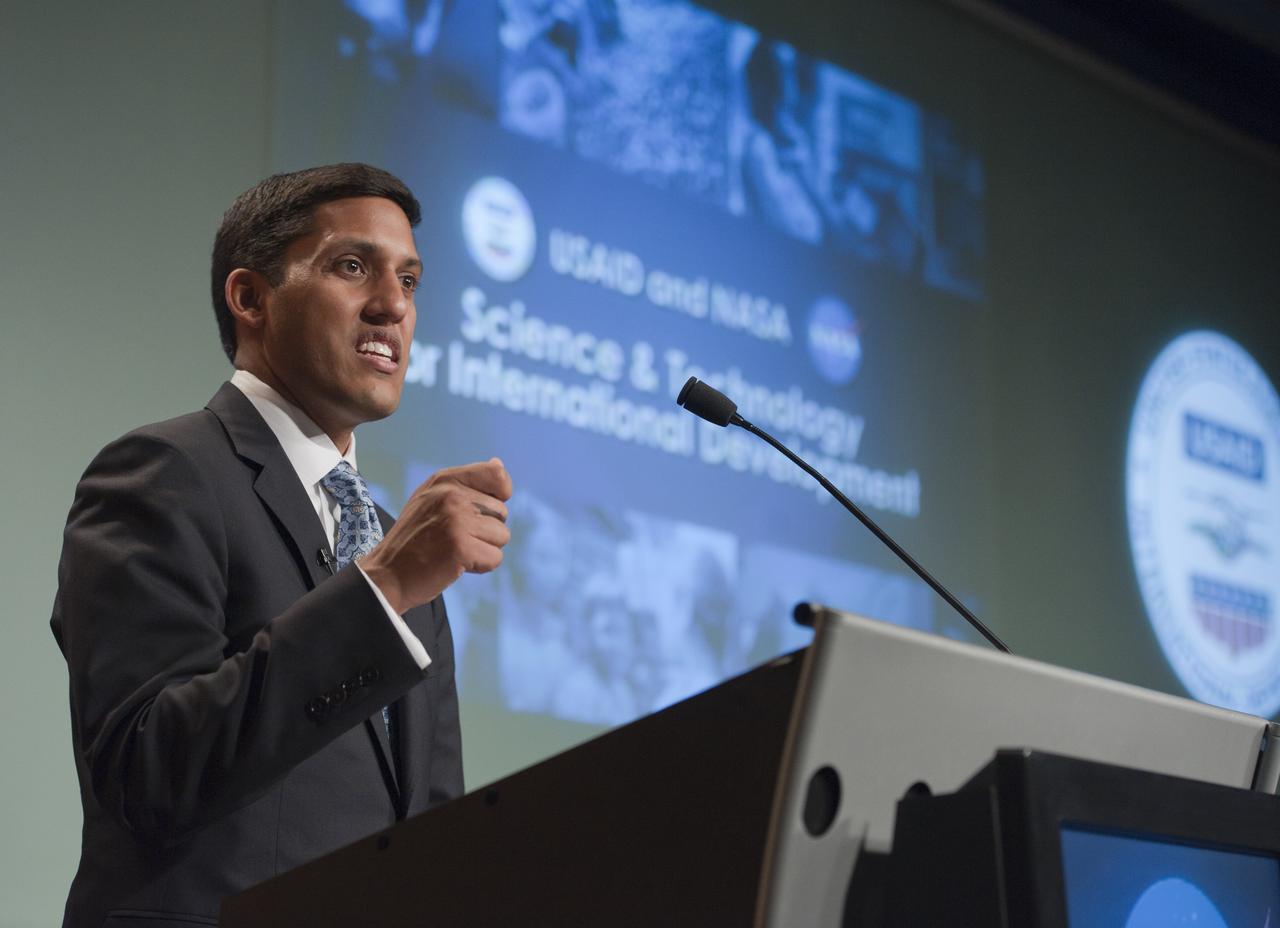

USAID Administrator Rajiv Shah speaks prior to signing a five-year memorandum of understanding with NASA, Monday, April 25, 2011, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agreement formalizes ongoing agency collaborations that use Earth science data to address developmental challenges, and to assist in disaster mitigation and humanitarian responses. The agreement also encourages NASA and USAID to apply geospatial technologies to solve development challenges affecting the United States and developing countries. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
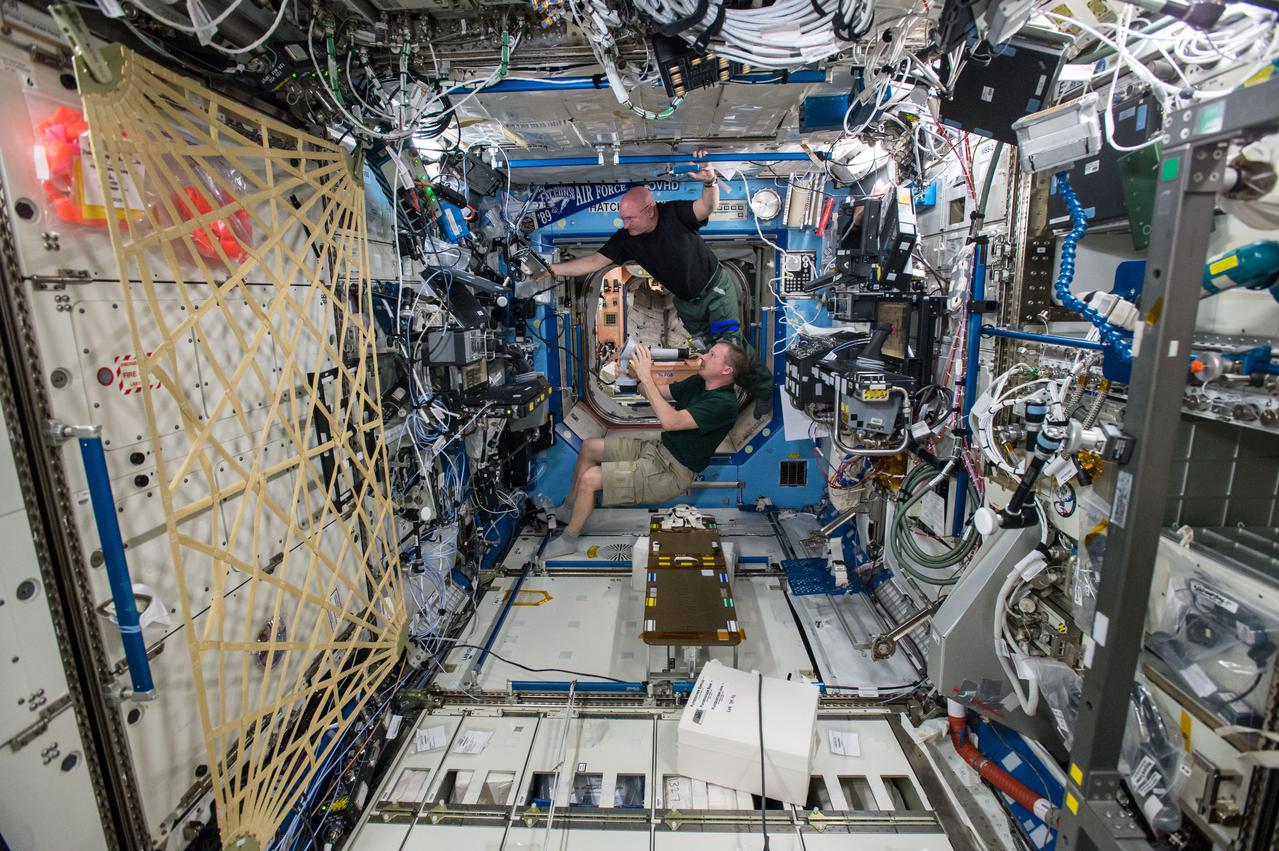

ISS043E099306 (04/09/2015) --- NASA astronauts Terry Virts (bottom) and Scott Kelly (top) are seen here inside the Destiny Laboratory performing eye exams as part of ongoing studies into crew vision health. Vision changes in astronauts spending long periods of time in microgravity is a critical health issue that scientists are looking to solve as humanity prepares to travel to destinations far outside our planet like an asteroid and Mars.
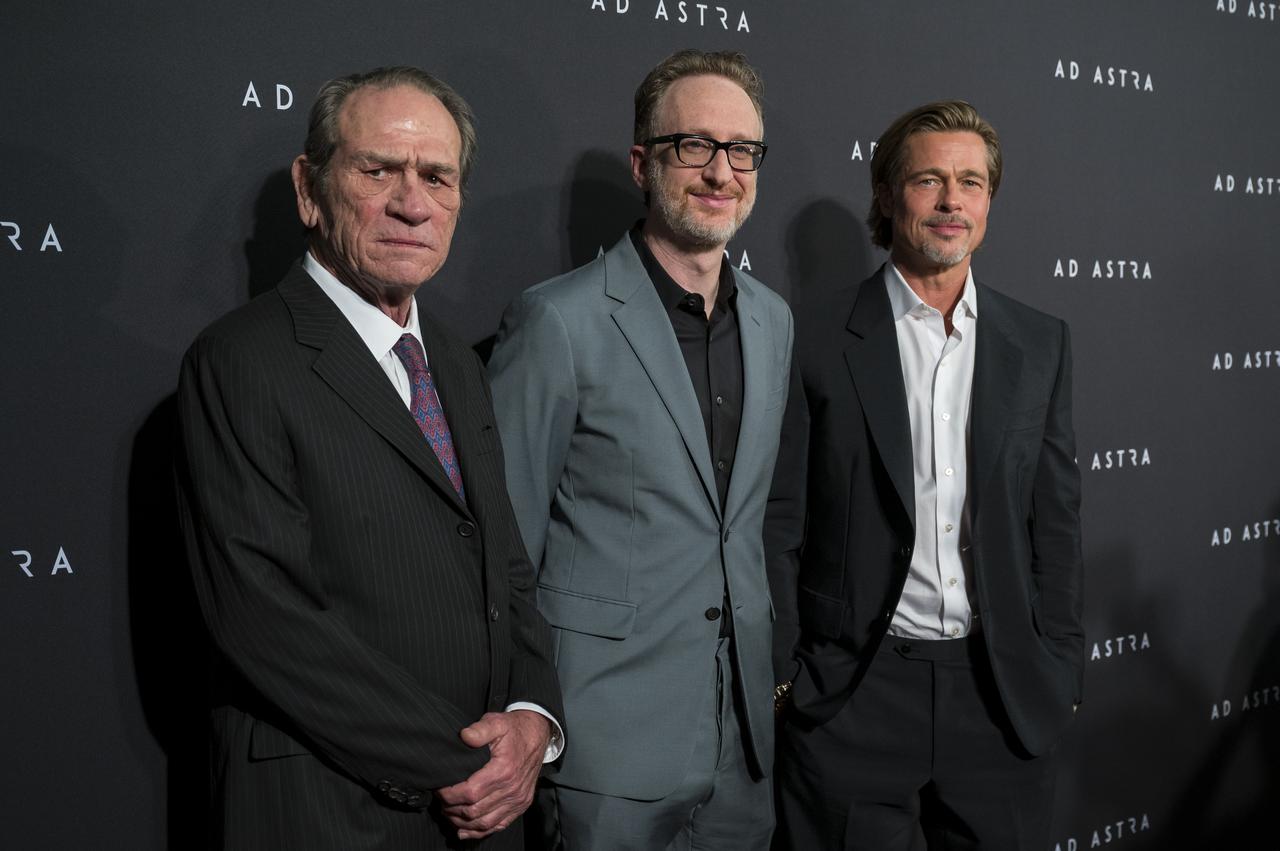

From left to right, actor Tommy Lee Jones, film producer, co-writer, and director James Gray, and actor Brad Pitt arrive on the red carpet for a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Pitt, Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Jay Phillips, a research physicist in the Kennedy Space Center's Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory, left, and Dr. Carlos Calle, lead scientist in the lab, are modifying an electrostatic precipitator to help remove dust from simulated Martian atmosphere. NASA's Journey to Mars requires cutting-edge technologies to solve the problems explorers will face on the Red Planet. Scientists are developing some of the needed solutions by adapting a device to remove the ever-present dust from valuable elements in the Martian atmosphere. Those commodities include oxygen, water and methane.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks before a screening of "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Tommy Lee Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
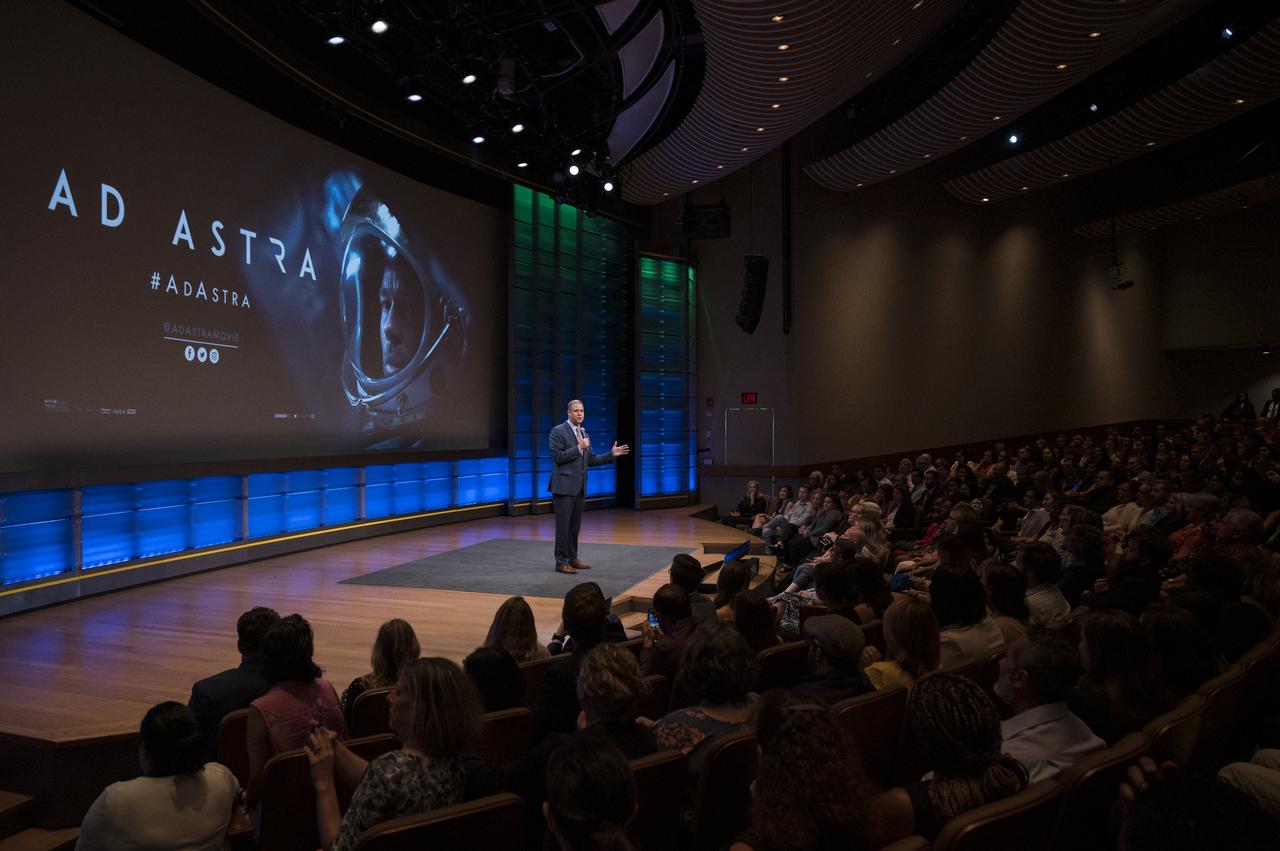

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks before a screening of "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Tommy Lee Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NACA Laboratory Computers Help Compile Handbook: ''Monroe Methods for Algebra, " a new booklet describing short-cuts that can be used in solving frequently-used algebraic formulas with a calculating machine, is undergoing its first trial at the hands of Laboratory computers. Several Monro-matics were purchased recently by NACA. In photo are W.H. Rankins discusses the "Monroe Methods for Algebra" with Gladys Storey (seated) and Ferne Gapcynski, both of 16 foot Hight Speed Tunnel. NACA Air Scoop August 17,1951 Page 4.
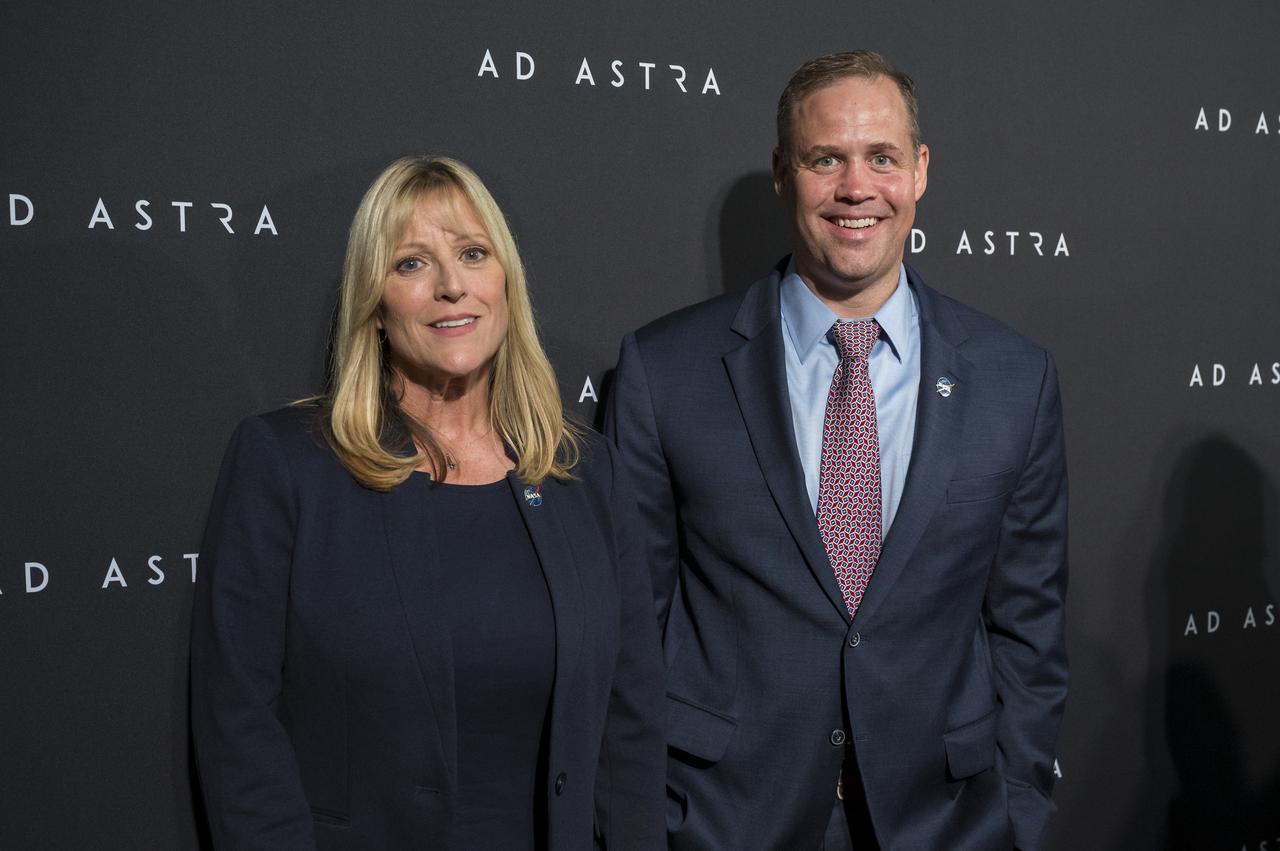
Former NASA astronaut Kay Hire and NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine pose for a photo on the red carpet during a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film was produced, co-written, and directed by James Gray and stars Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
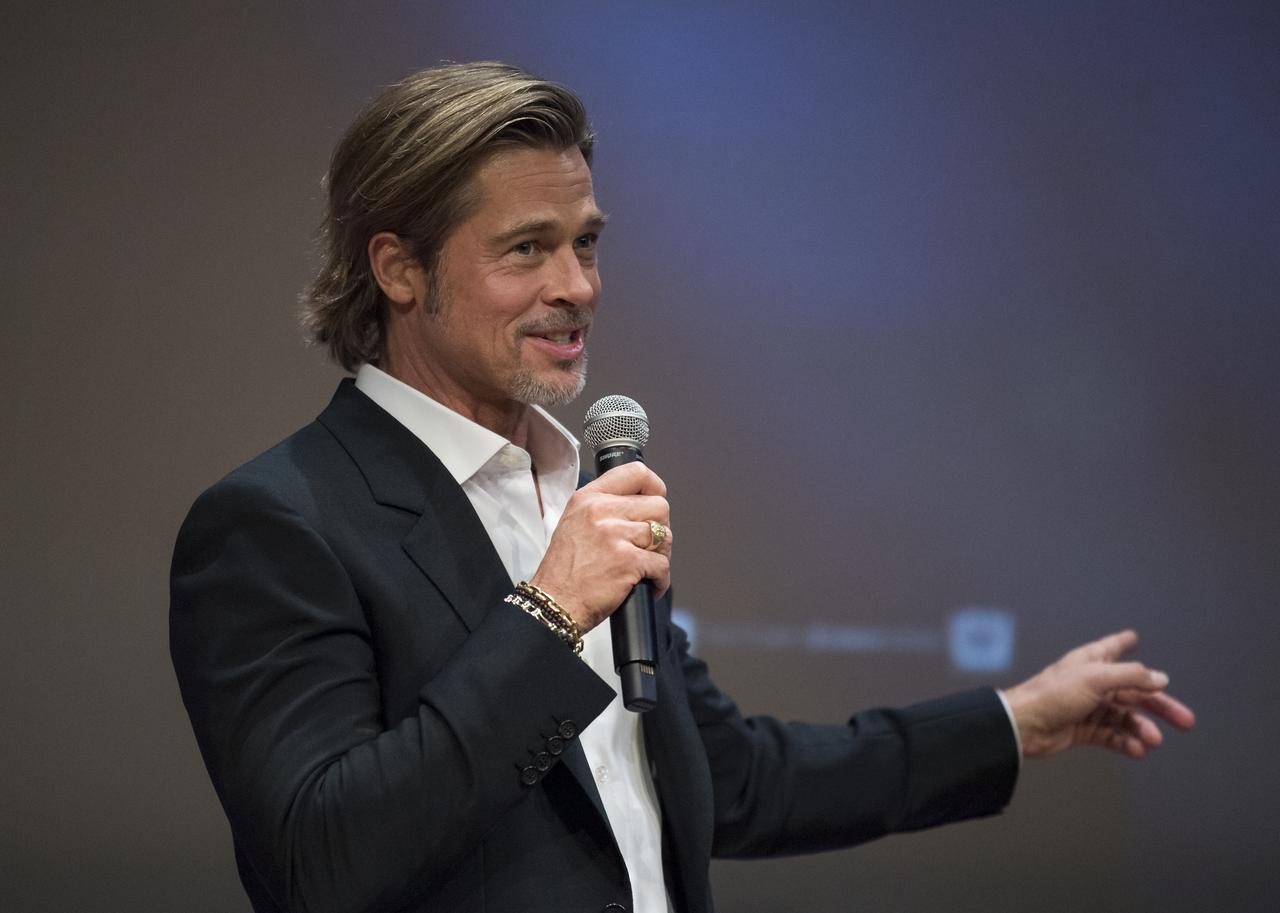

Actor Brad Pitt speaks before a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film was produced, co-written, and directed by James Gray and stars Pitt, Tommy Lee Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NACA Laboratory Computers Help Compile Handbook: ''Monroe Methods for Algebra, " a new booklet describing short-cuts that can be used in solving frequently-used algebraic formulas with a calculating machine, is undergoing its first trial at the hands of Laboratory computers. Several Monro-matics were purchased recently by NACA. NACA Air Scoop August 17,1951 Page 4.
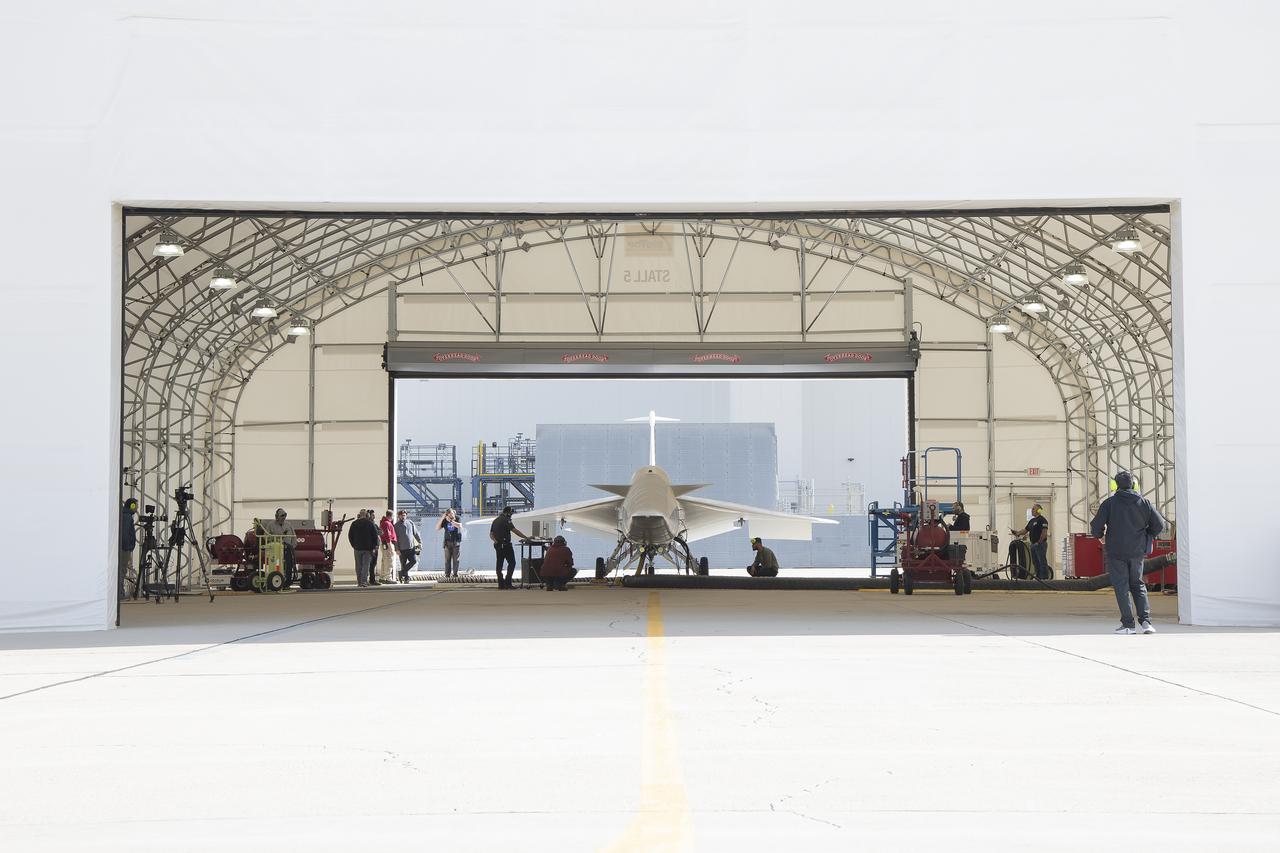

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in its run stall at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, prior to its first engine run. Engine runs are part of a series of integrated ground tests needed to ensure safe flight and successful achievement of mission goals. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land by making sonic booms quieter.
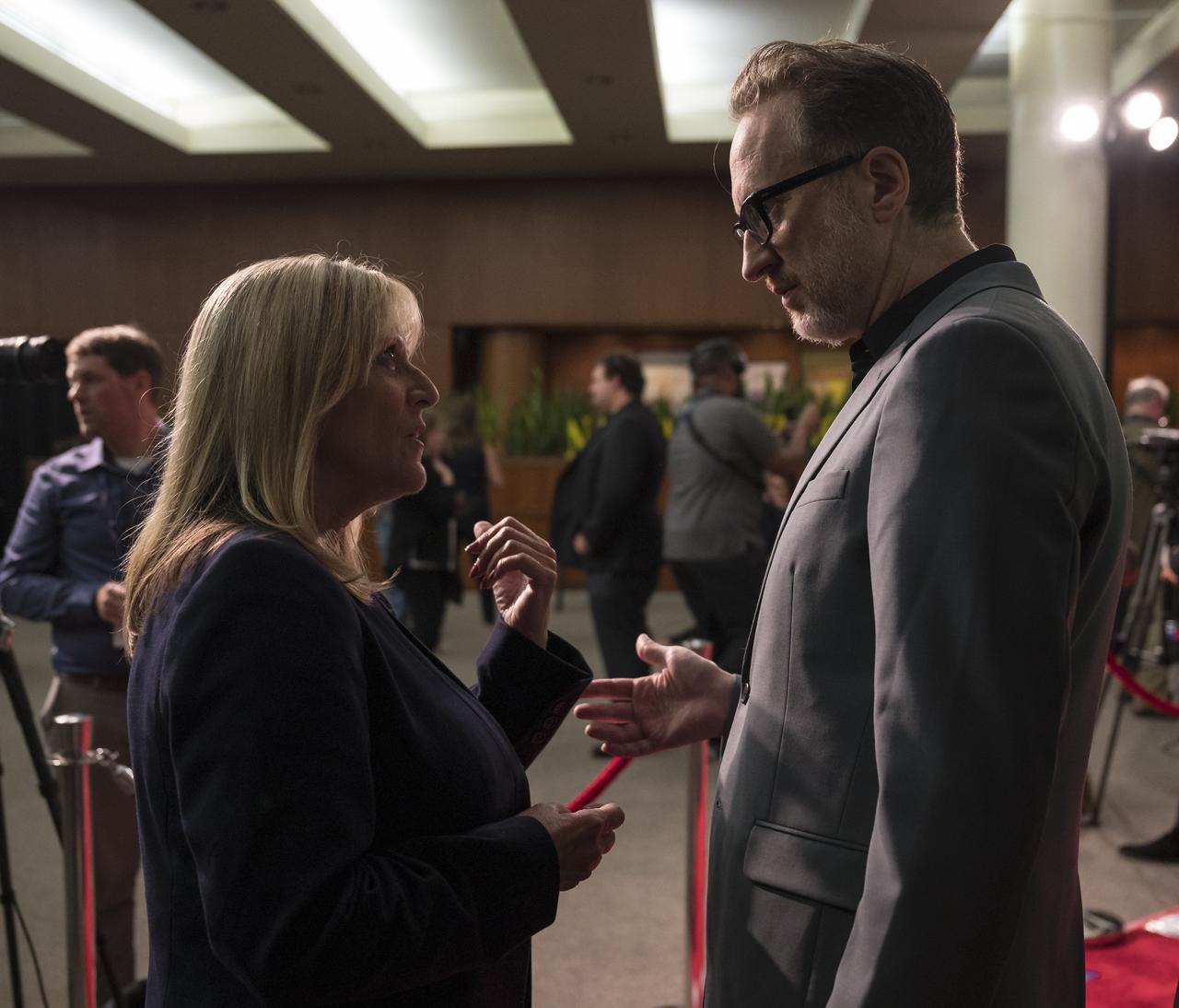

Former NASA astronaut Kay Hire, left, speaks with film producer, co-writer, and director James Gray at a screening of "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. It stars Tommy Lee Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
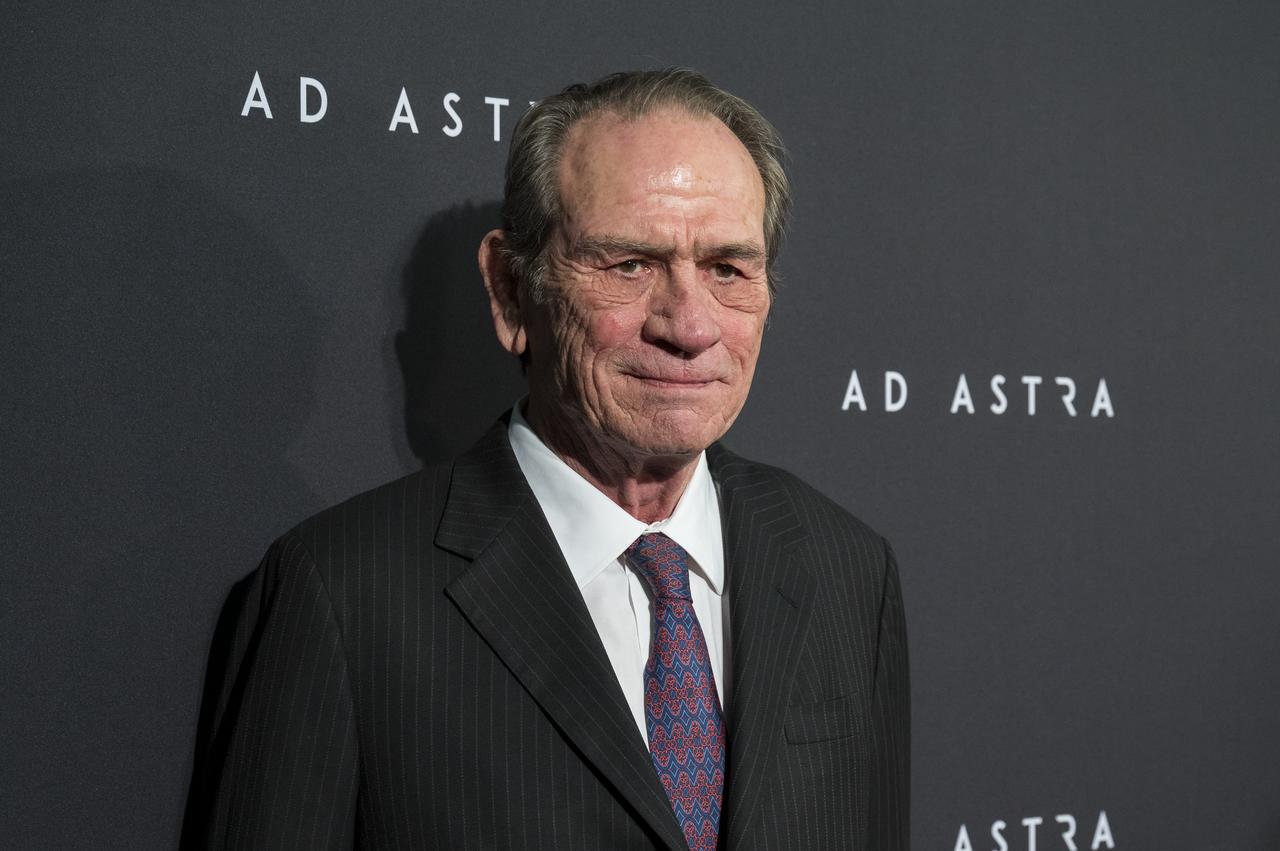

Actor Tommy Lee Jones arrives on the red carpet for a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film was produced, co-written, and directed by James Gray and stars Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
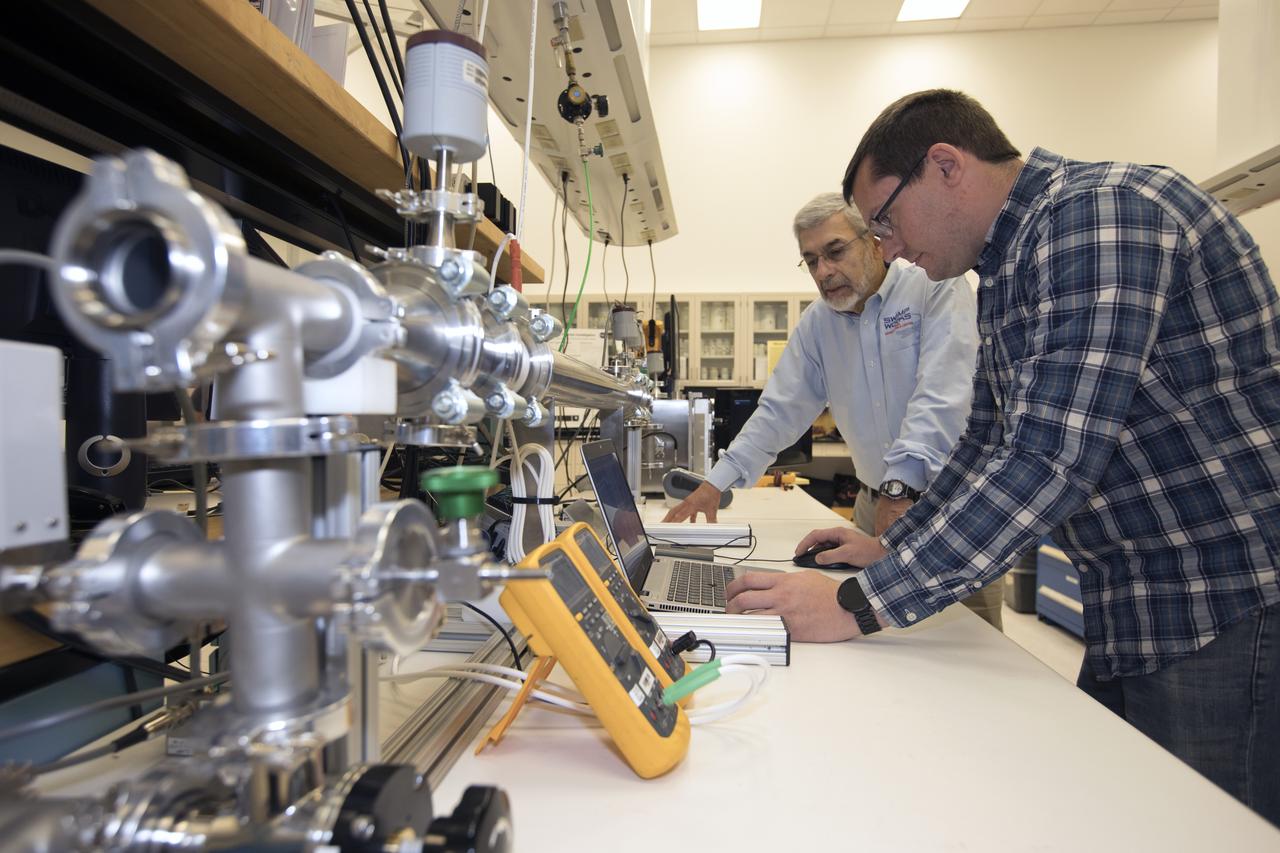
Dr. Carlos Calle, lead scientist in the Kennedy Space Center's Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory, left, and Jay Phillips, a research physicist, are modifying an electrostatic precipitator to help remove dust from simulated Martian atmosphere. NASA's Journey to Mars requires cutting-edge technologies to solve the problems explorers will face on the Red Planet. Scientists are developing some of the needed solutions by adapting a device to remove the ever-present dust from valuable elements in the Martian atmosphere. Those commodities include oxygen, water and methane.
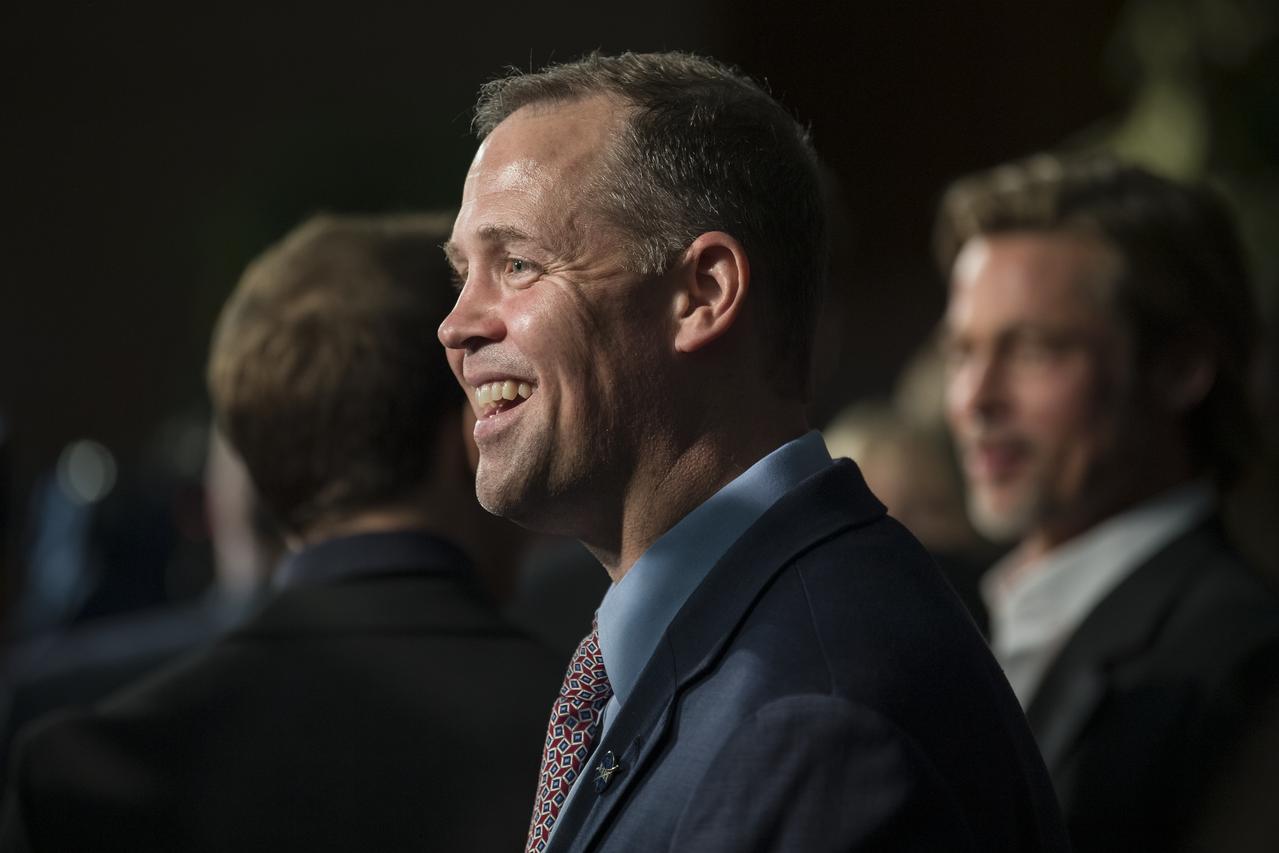

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, arrives on the red carpet at a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Tommy Lee Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
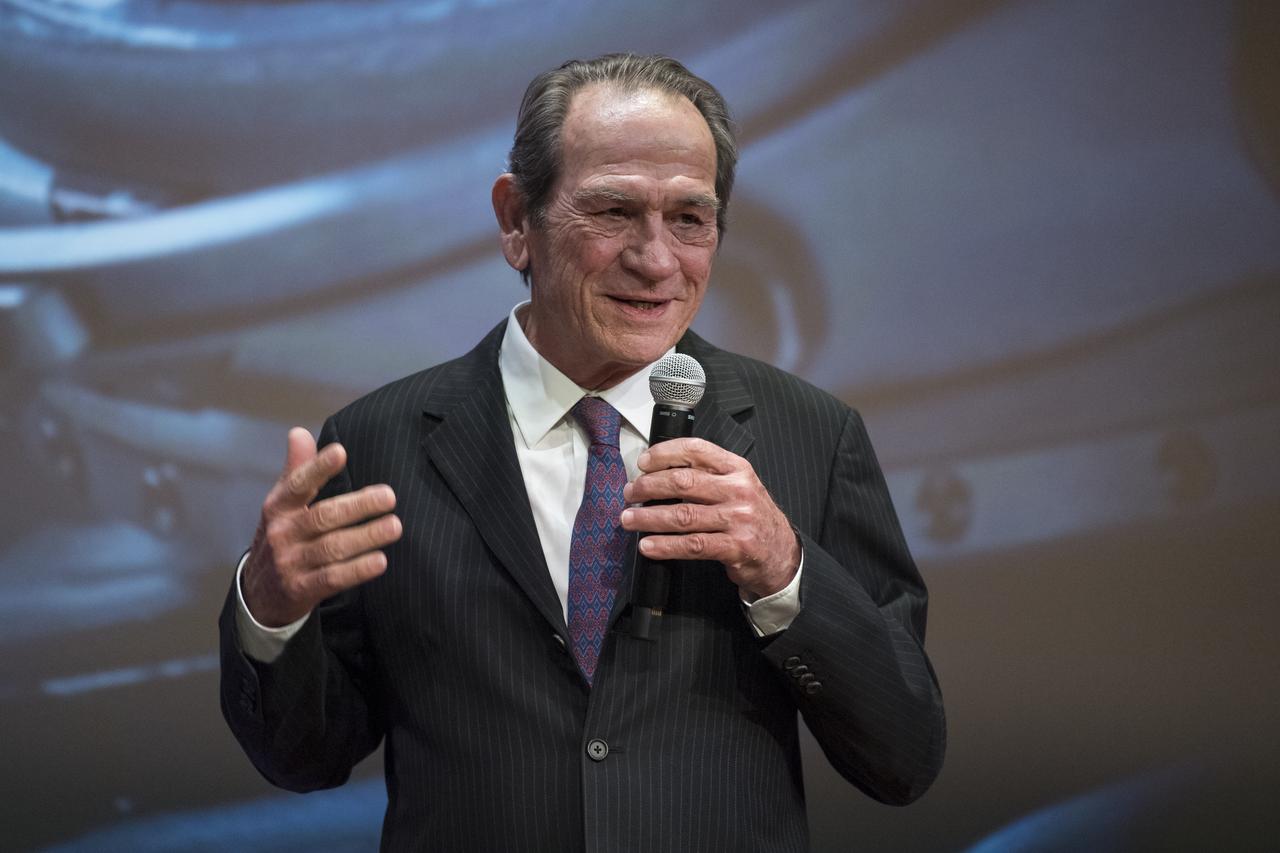

Actor Tommy Lee Jones speaks before a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film was produced, co-written, and directed by James Gray and stars Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
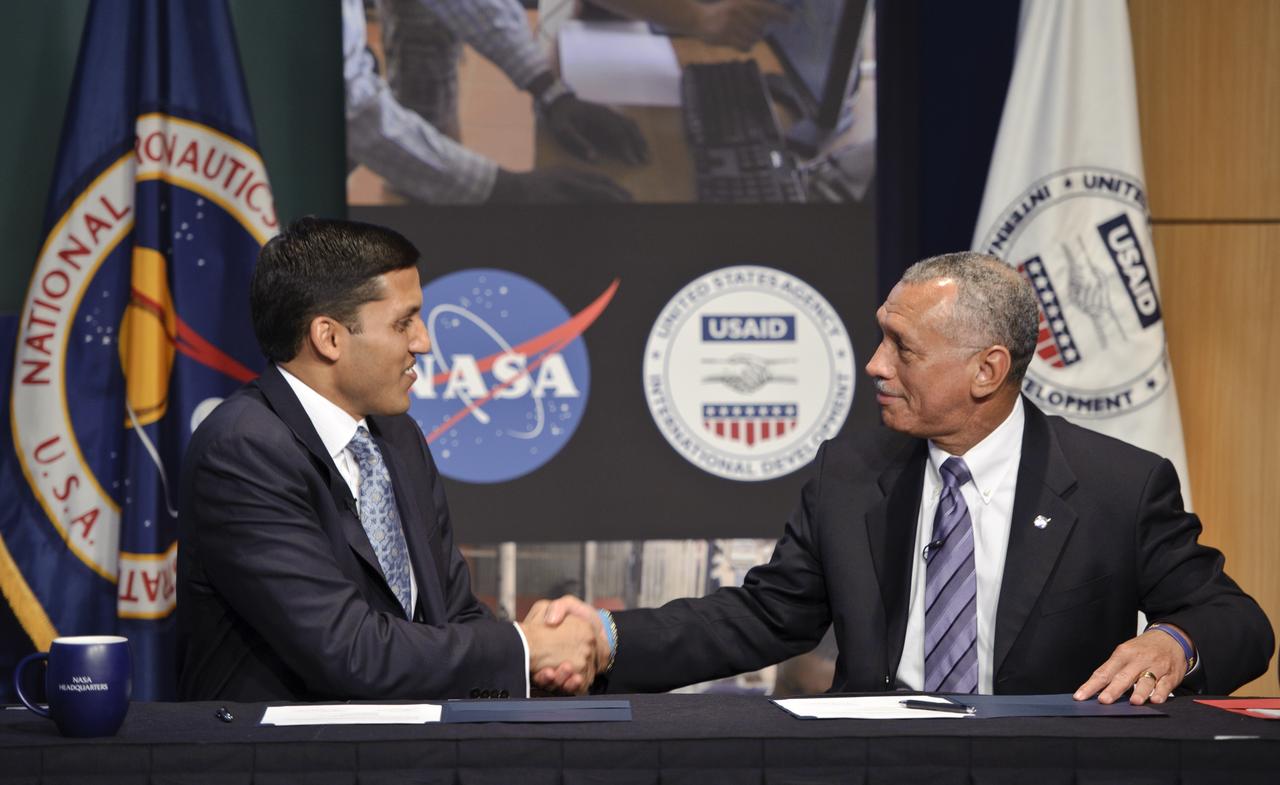

USAID Administrator Rajiv Shah, left, and NASA Administrator Charles Bolden shake hands after signing a five-year memorandum of understanding, Monday, April 25, 2011, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agreement formalizes ongoing agency collaborations that use Earth science data to address developmental challenges, and to assist in disaster mitigation and humanitarian responses. The agreement also encourages NASA and USAID to apply geospatial technologies to solve development challenges affecting the United States and developing countries. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
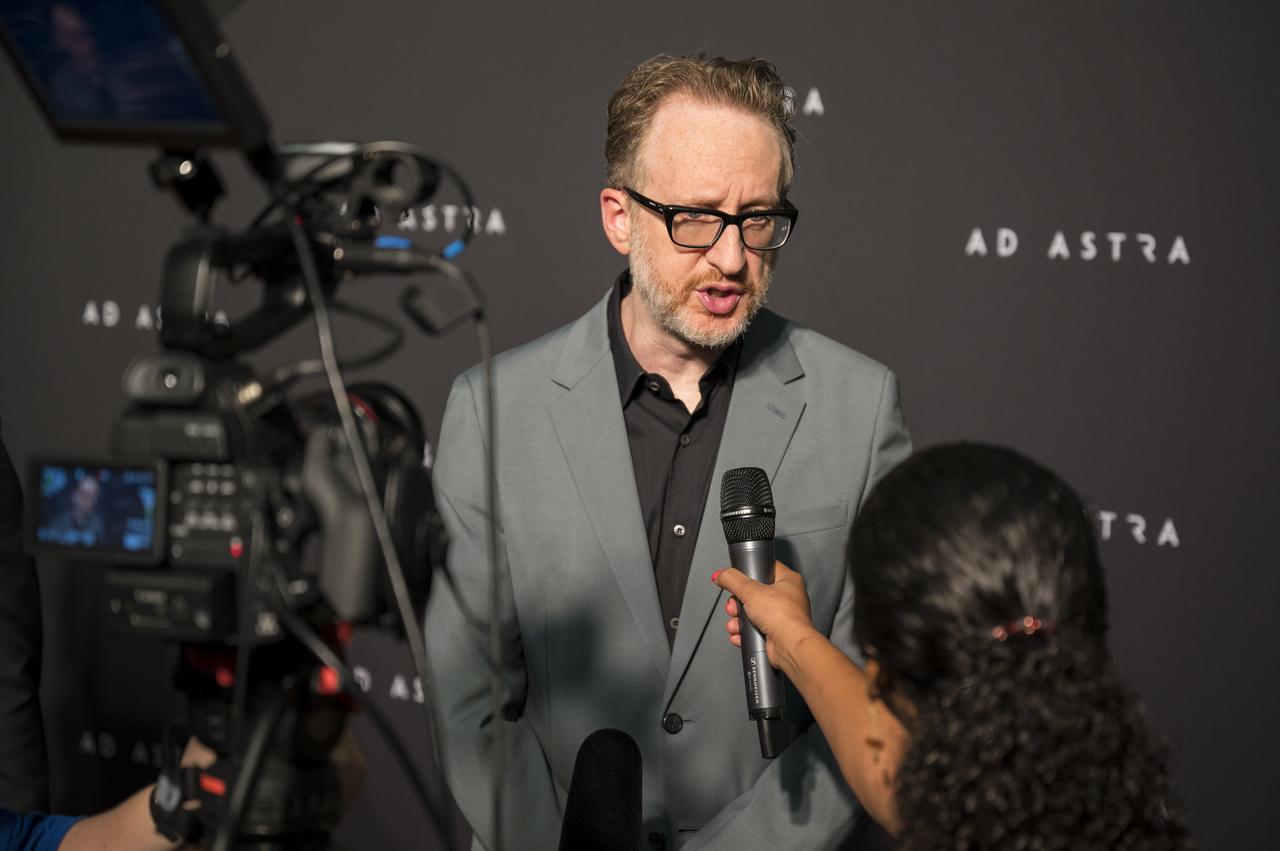

Producer, co-writer, and director James Gray is interviewed by NASA television on the red carpet during a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Tommy Lee Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
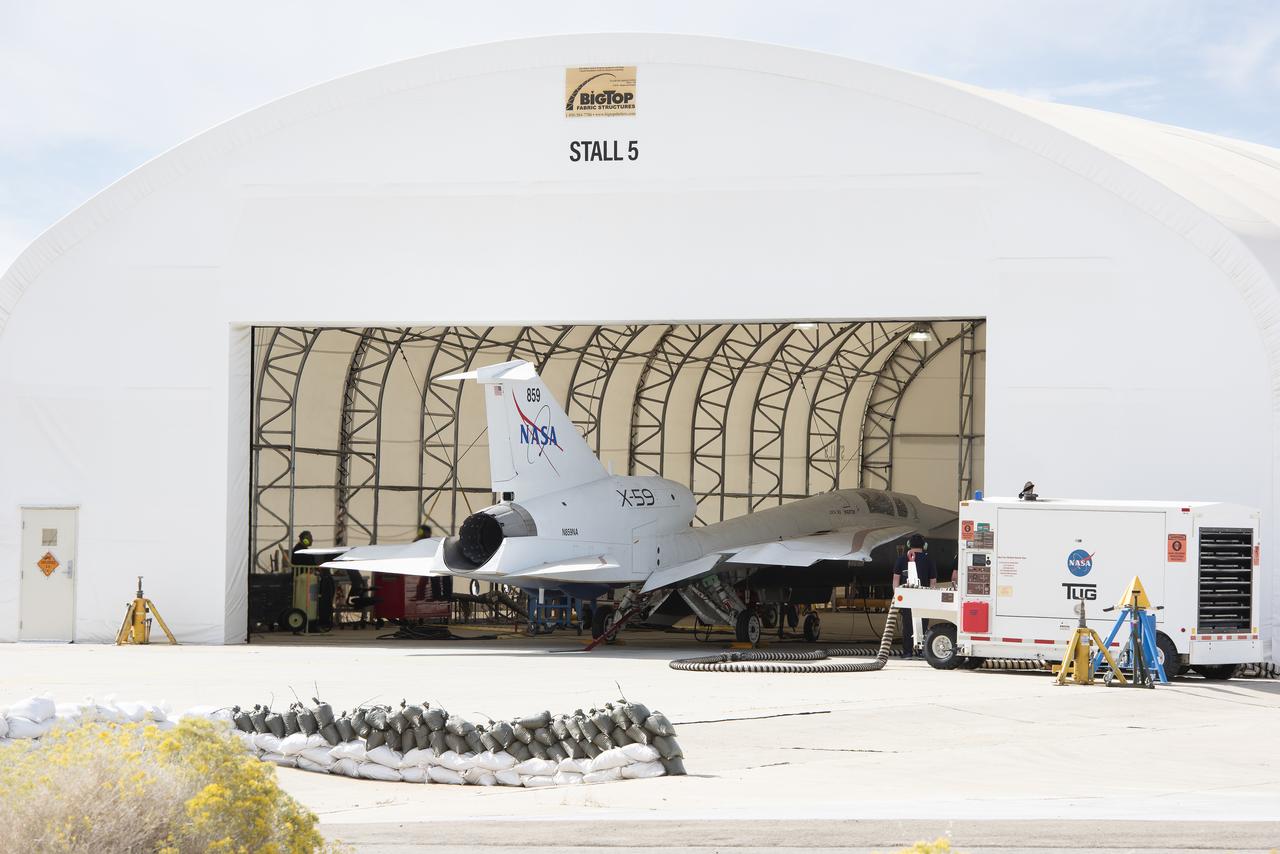

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in its run stall at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, firing up its engine for the first time. These engine-run tests start at low power and allow the X-59 team to verify the aircraft’s systems are working together while powered by its own engine. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land by making sonic booms quieter.
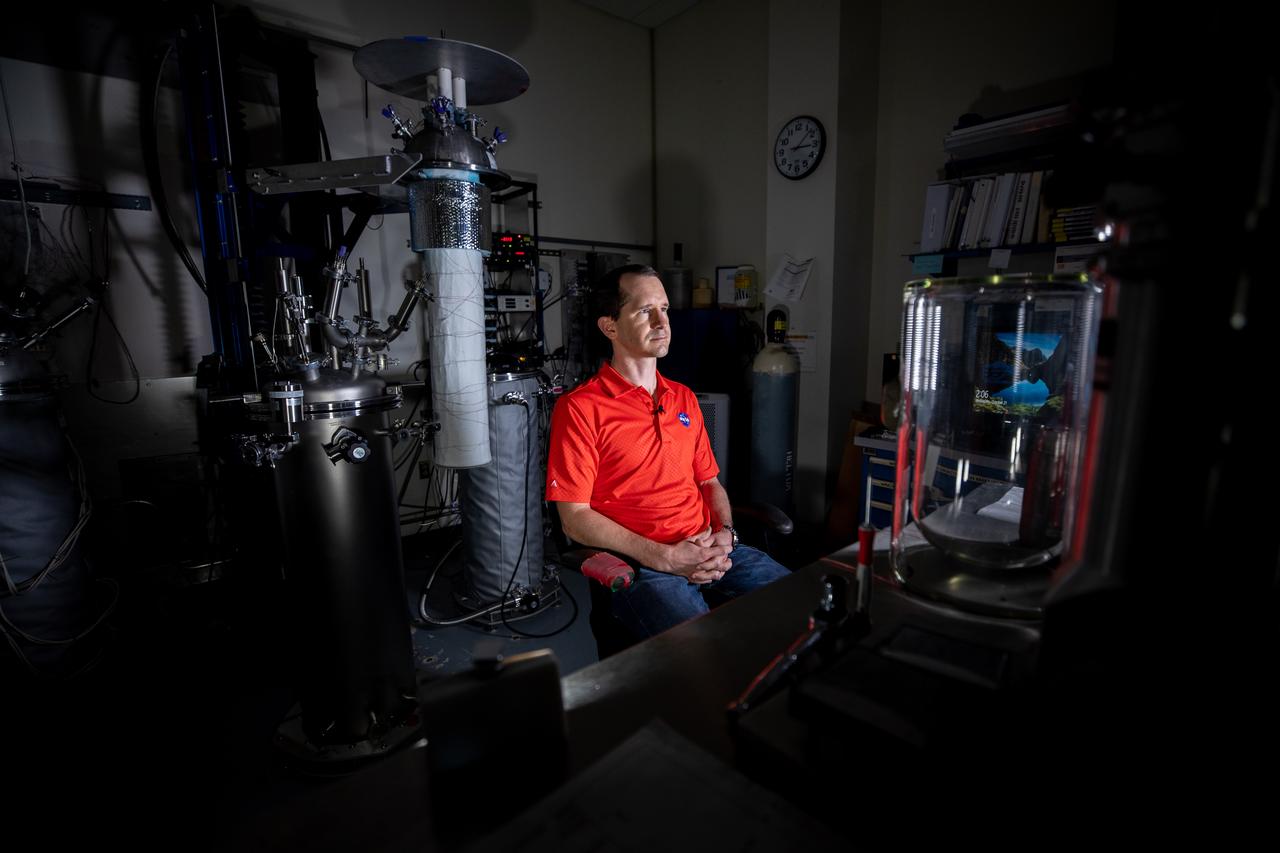

Adam Swanger, NASA engineer, is inside the Cryogenics Test Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. Established in 2000, the Cryogenics Test Laboratory provides a one-of-a kind capability for research, development and application of cross-cutting technologies to meet the needs of industry and government. The test lab provides cryogenic expertise, experimental testing, technical standards development, prototype construction and practical problem-solving for technology development with research institutions and commercial partners.

NACA Laboratory Computers Help Compile Handbook: ''Monroe Methods for Algebra, " a new booklet describing short-cuts that can be used in solving frequently-used algebraic formulas with a calculating machine, is undergoing its first trial at thehands of Laboratory computers. Several Monro-matics were purchased recently by NACA. In photo are W.H. Rankins discusses the "Monroe Methods for Algebra" with Gladys Storey (seated) and Ferne Gapcynski, both of 16 foot Hight Speed Tunnel. NACA Air Scoop August 17,1951 Page 4.
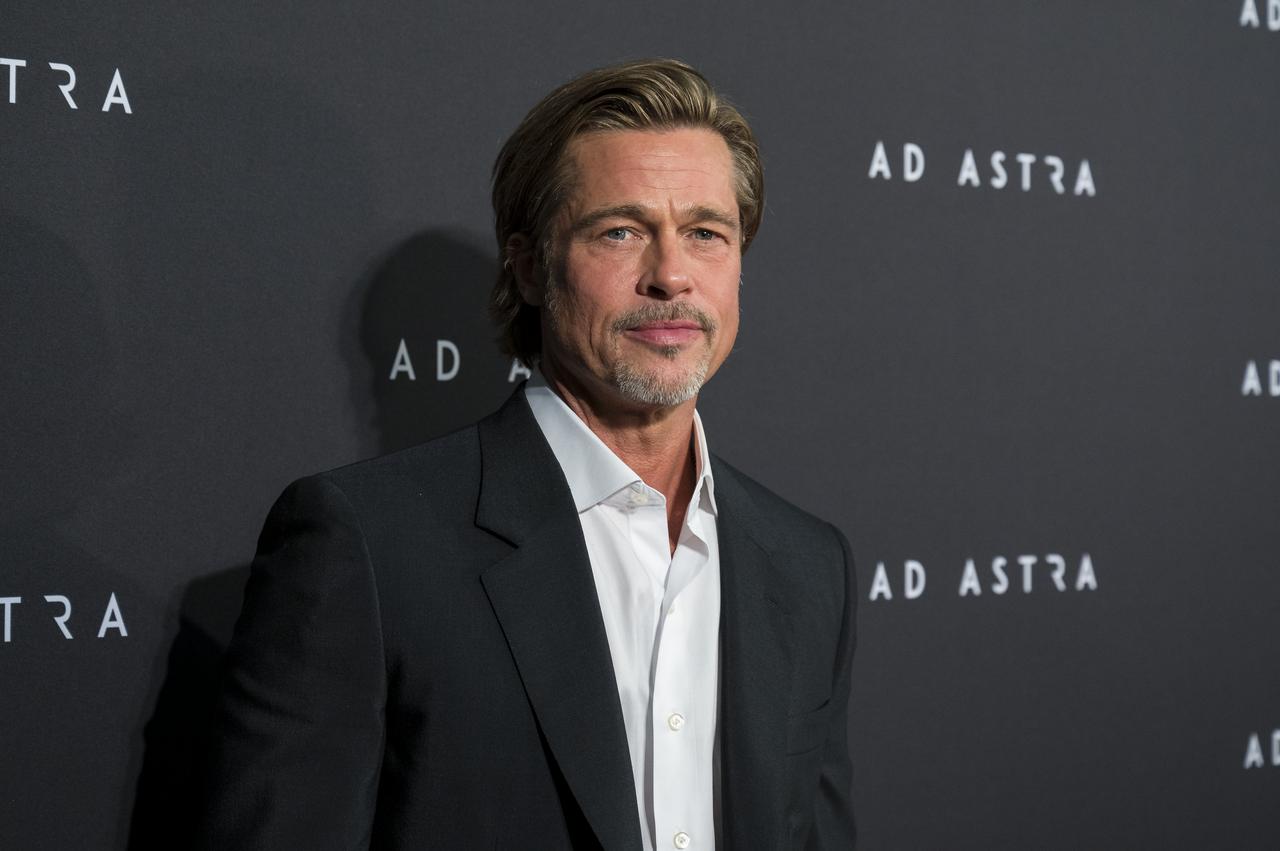

Actor Brad Pitt arrives on the red carpet for a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film was produced, co-written, and directed by James Gray and stars Pitt, Tommy Lee Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
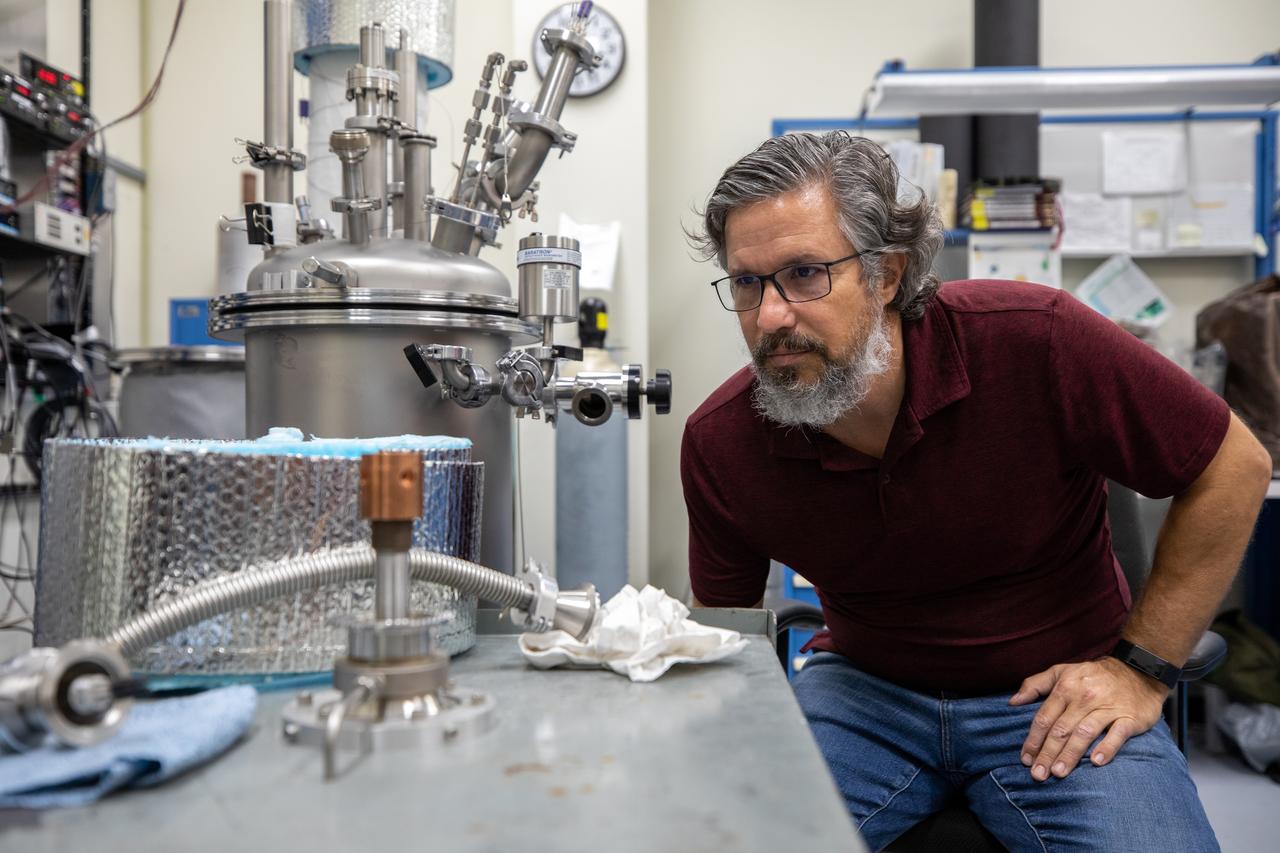
Jared Sass, NASA engineer, monitors a test inside the Cryogenics Test Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. Established in 2000, the Cryogenics Test Laboratory provides a one-of-a kind capability for research, development and application of cross-cutting technologies to meet the needs of industry and government. The test lab provides cryogenic expertise, experimental testing, technical standards development, prototype construction and practical problem-solving for technology development with research institutions and commercial partners.
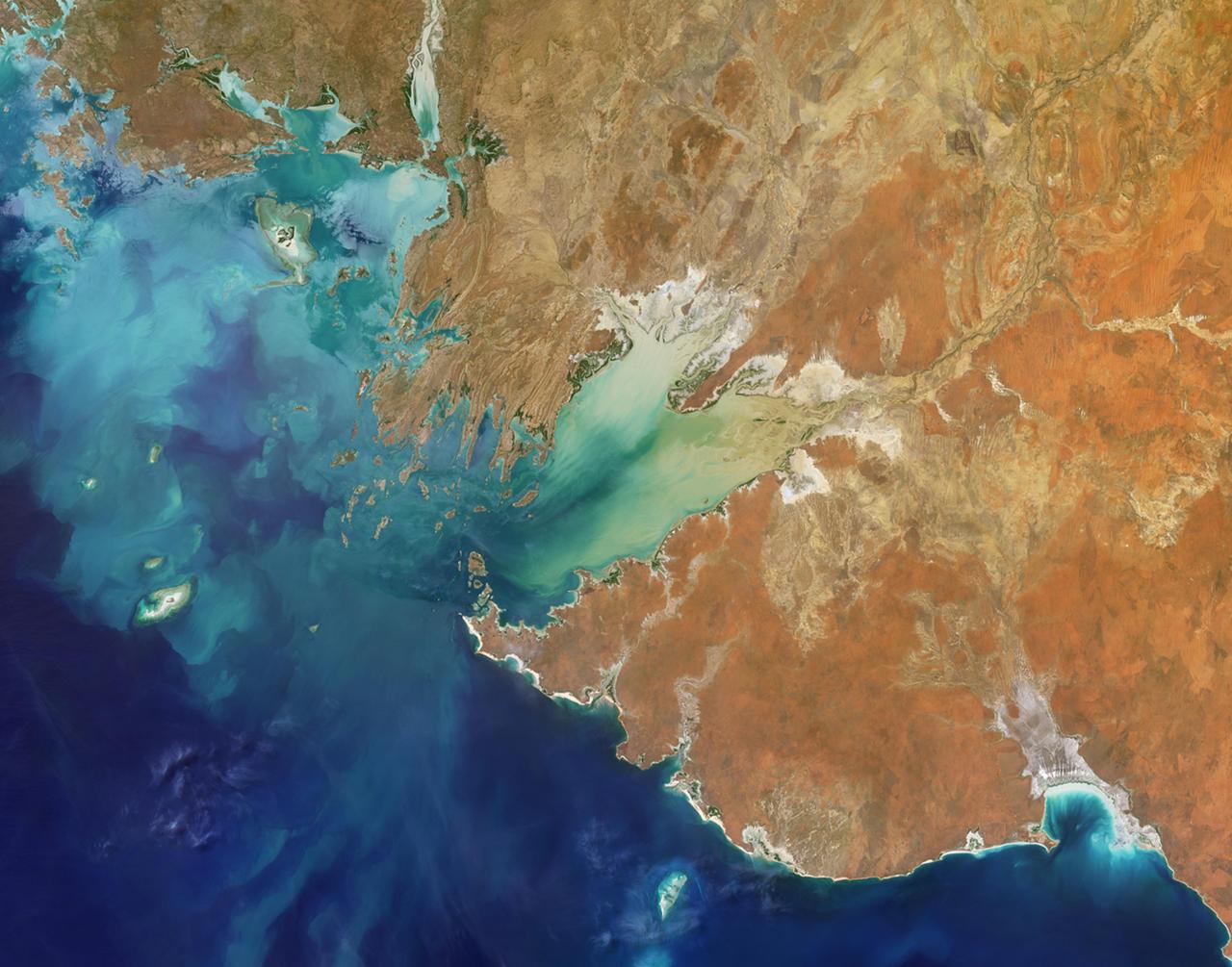

Are you ready for a challenge? Become a geographical detective and solve the latest mystery quiz from NASA's MISR Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument onboard the Terra satellite. Prize submissions for perfect scores accepted until Wednesday, June 28, at 4:00 p.m. PDT. Happy sleuthing! Take the quiz here http://climate.nasa.gov/quizzes/misr_quiz_29. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21762
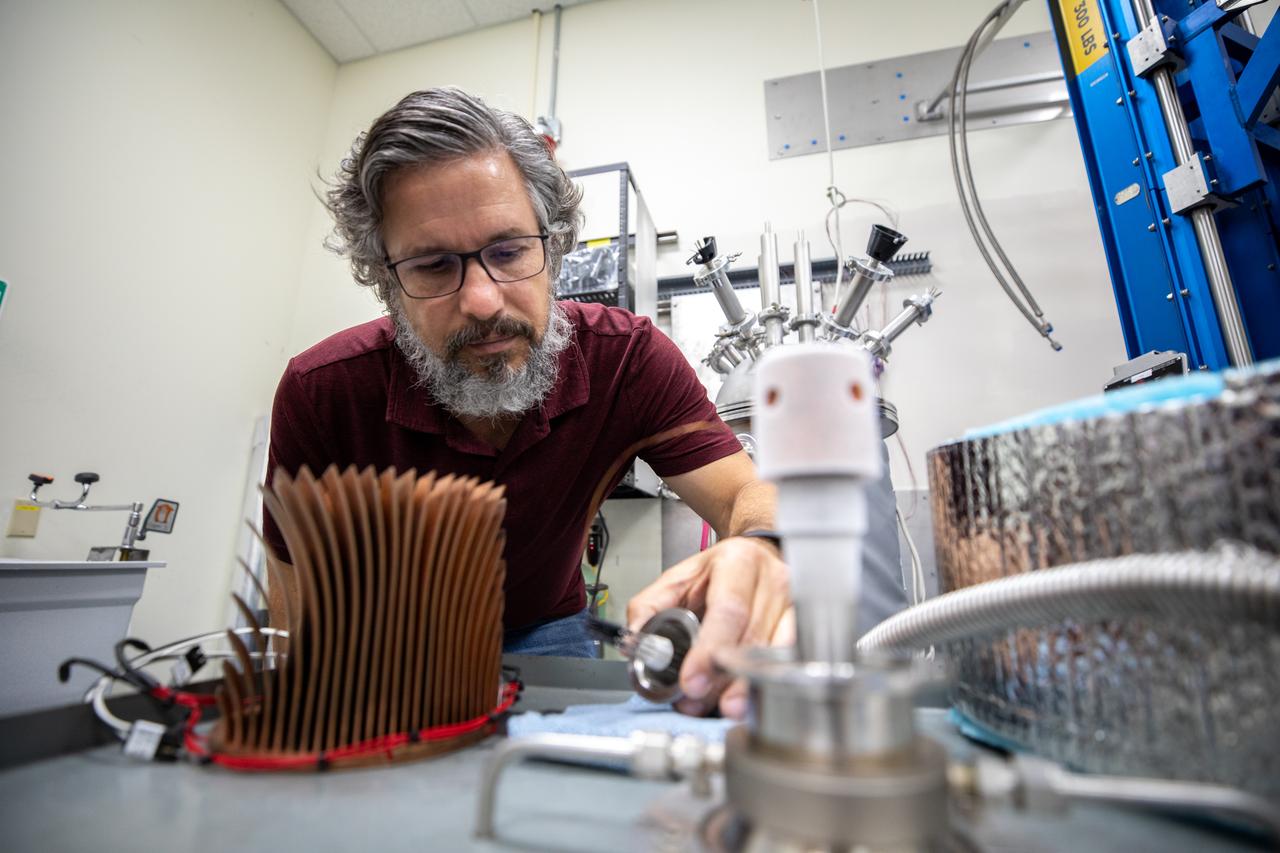
Jared Sass, NASA engineer, monitors a test inside the Cryogenics Test Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 21, 2020. Established in 2000, the Cryogenics Test Laboratory provides a one-of-a kind capability for research, development and application of cross-cutting technologies to meet the needs of industry and government. The test lab provides cryogenic expertise, experimental testing, technical standards development, prototype construction and practical problem-solving for technology development with research institutions and commercial partners.

Actor Brad Pitt is interviewed by Entertainment Tonight after arriving on the red carpet for a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Pitt, Tommy Lee Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
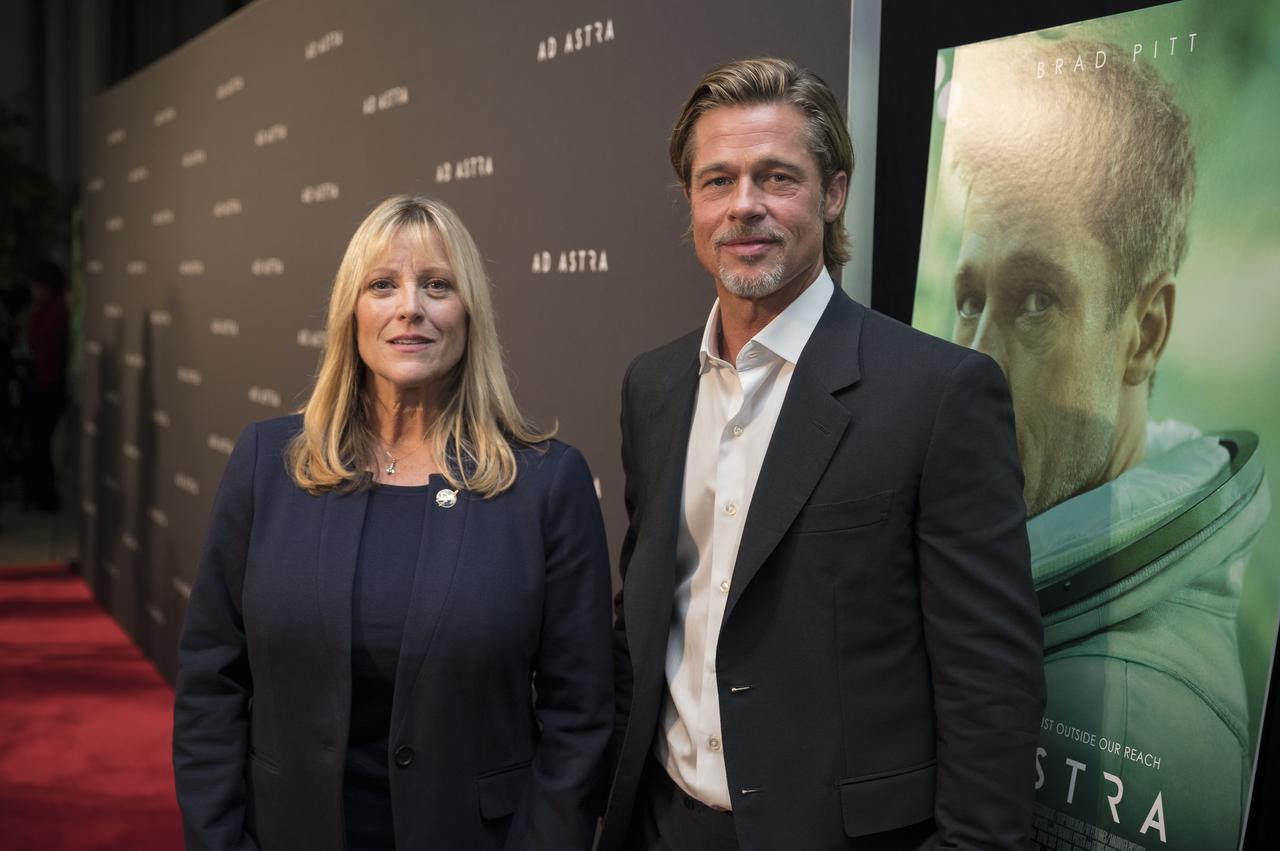

Former NASA astronaut Kay Hire poses for a photo with actor Brad Pitt, at a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Pitt, Tommy Lee Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Producer, co-writer, and director James Gray speaks before a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Tommy Lee Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
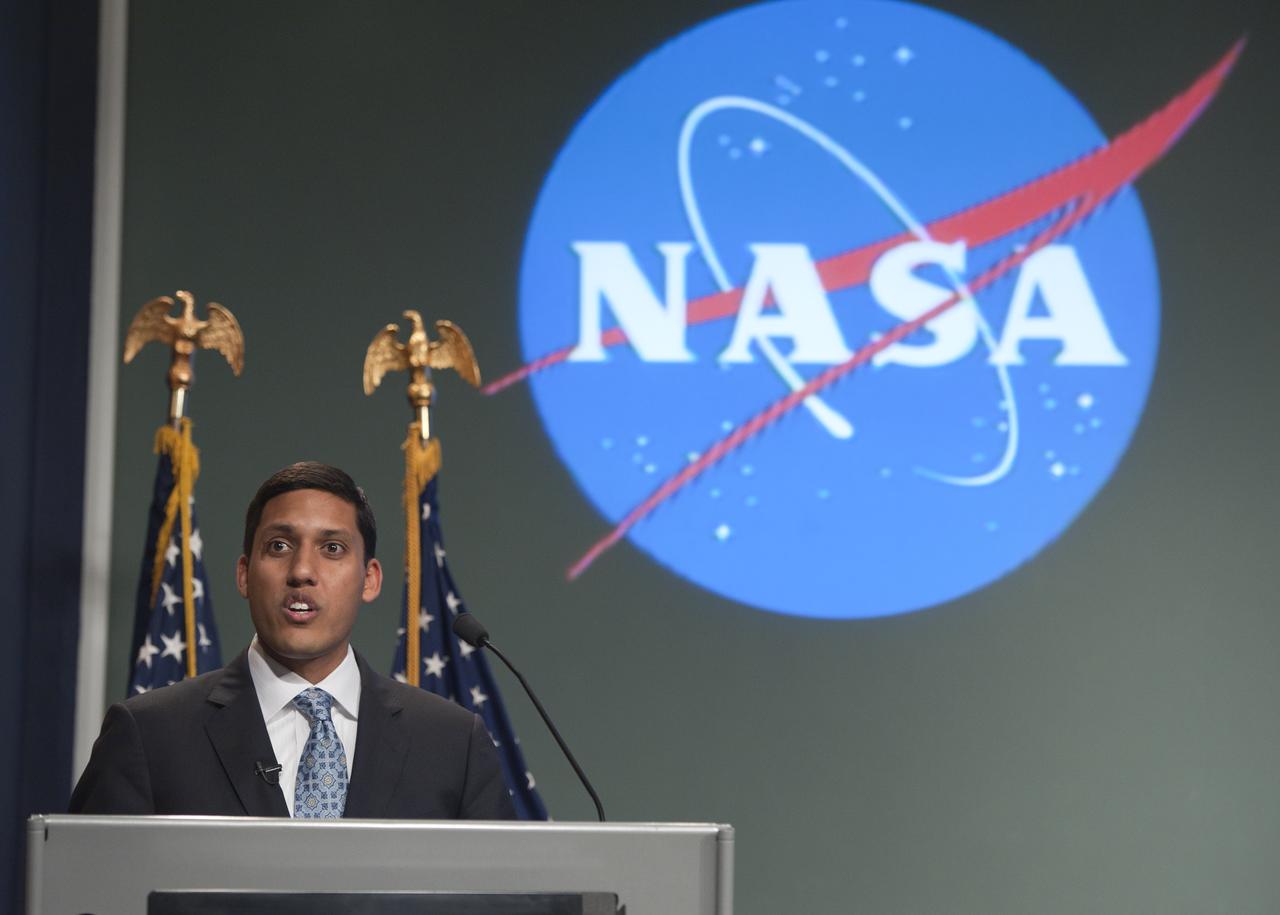

USAID Administrator Rajiv Shahspeaks prior to signing a five-year memorandum of understanding with NASA, Monday, April 25, 2011, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agreement formalizes ongoing agency collaborations that use Earth science data to address developmental challenges, and to assist in disaster mitigation and humanitarian responses. The agreement also encourages NASA and USAID to apply geospatial technologies to solve development challenges affecting the United States and developing countries. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
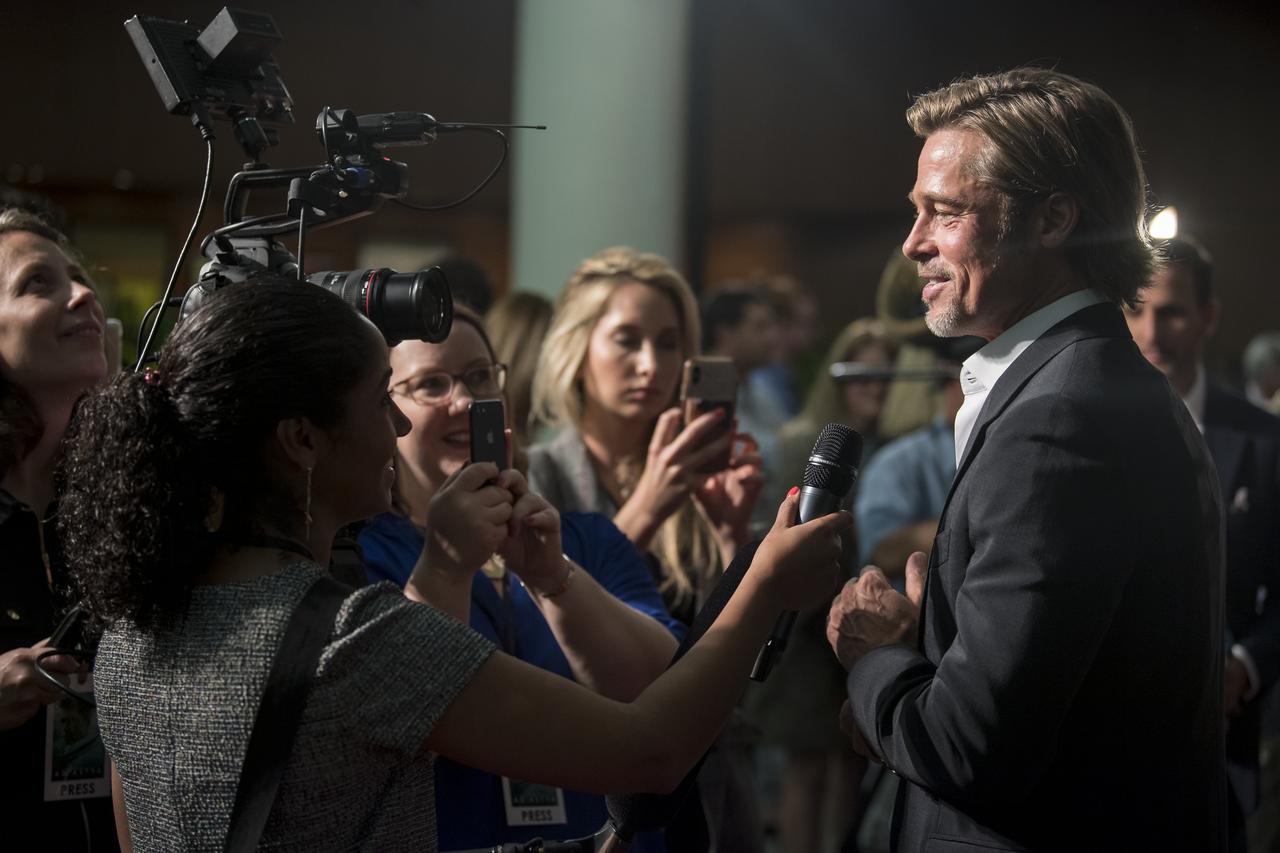

Actor Brad Pitt is interviewed by NASA television on the red carpet during a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film was produced, co-written, and directed by James Gray and stars Pitt, Tommy Lee Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

S73-26128 (1973) --- An artist's concept of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit illustrating the deployment of the twin pole thermal shield to shade the Orbital Workshop (OWS) from the sun. This is one of the sunshade possibilities considered to solve the problem of the overheated OWS. In this view the Skylab astronauts have partially deployed the sunshade. Photo credit: NASA

NACA Laboratory Computers Help Compile Handbook: ''Monroe Methods for Algebra, " a new booklet describing short-cuts that can be used in solving frequently-used algebraic formulas with a calculating machine, is undergoing its first trial at the hands of Laboratory computers. Several Monro-matics were purchased recently by NACA. NACA Air Scoop August 17,1951 Page 4.
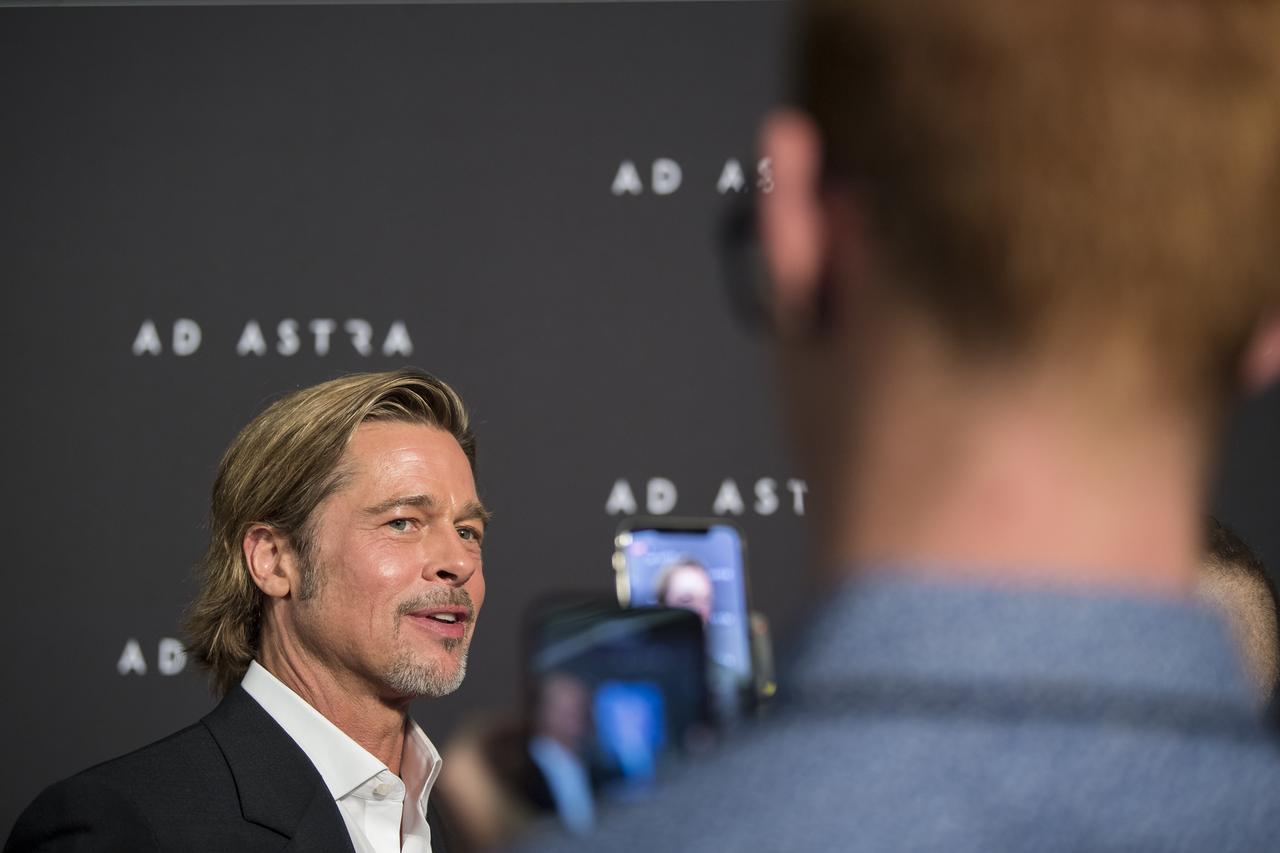

Actor Brad Pitt arrives on the red carpet for a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film was produced, co-written, and directed by James Gray and stars Pitt, Tommy Lee Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
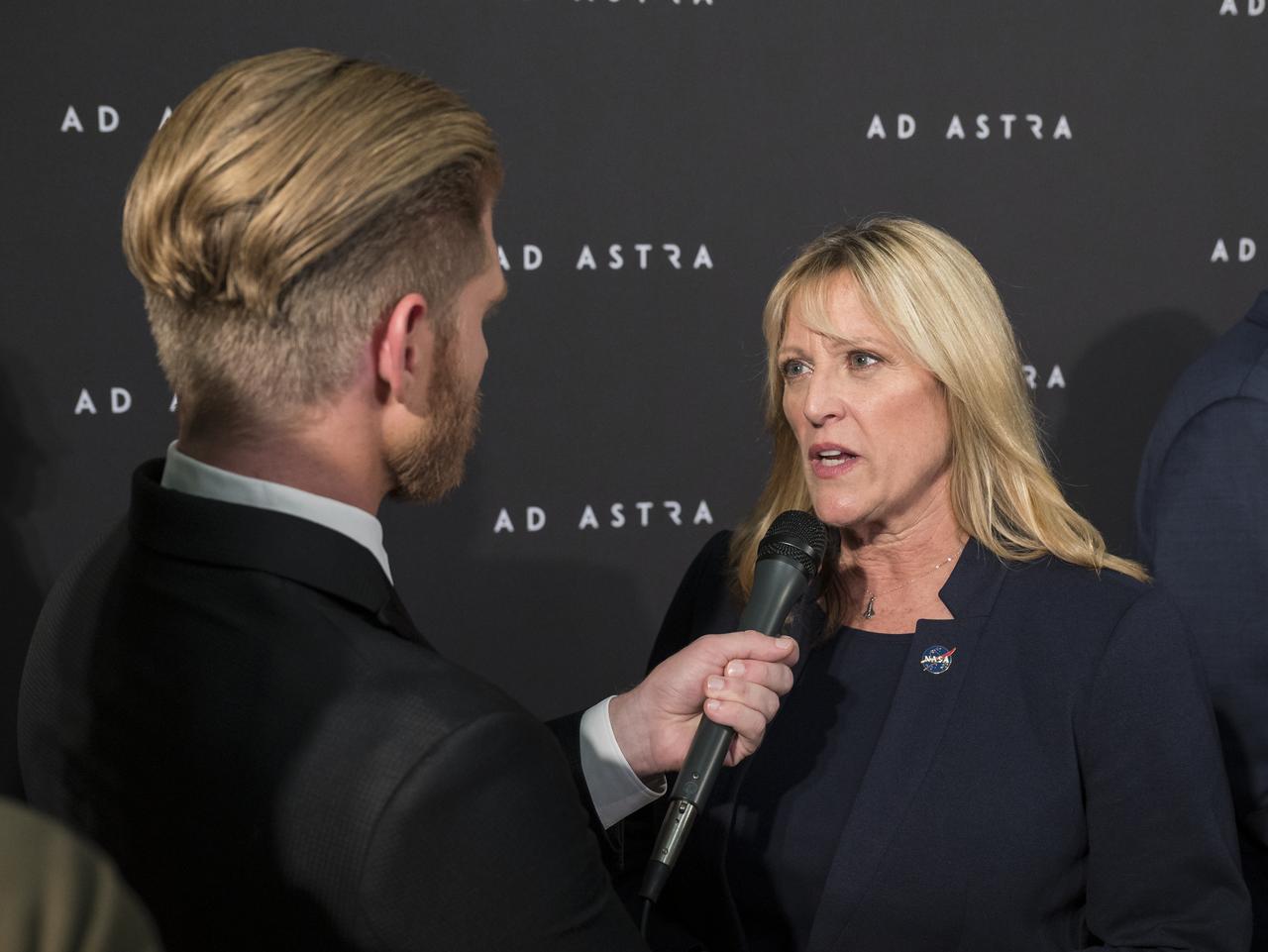

Former NASA astronaut Kay Hire is interviewed on the red carpet during a screening of the film "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film was produced, co-written, and directed by James Gray and stars Brad Pitt, Tommy Lee Jones, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

S73-26127 (1973) --- An artist's concept of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit illustrating the deployment of the twin pole thermal shield to shade the Orbital Workshop (OWS) from the sun. This is one of the sunshade possibilities considered to solve the problem of the overheated OWS. Here the two Skylab 2 astronauts have completely deployed the sunshade. Note the evidence of another Skylab problem - the solar panels on the OWS are not deployed as required. Photo credit: NASA
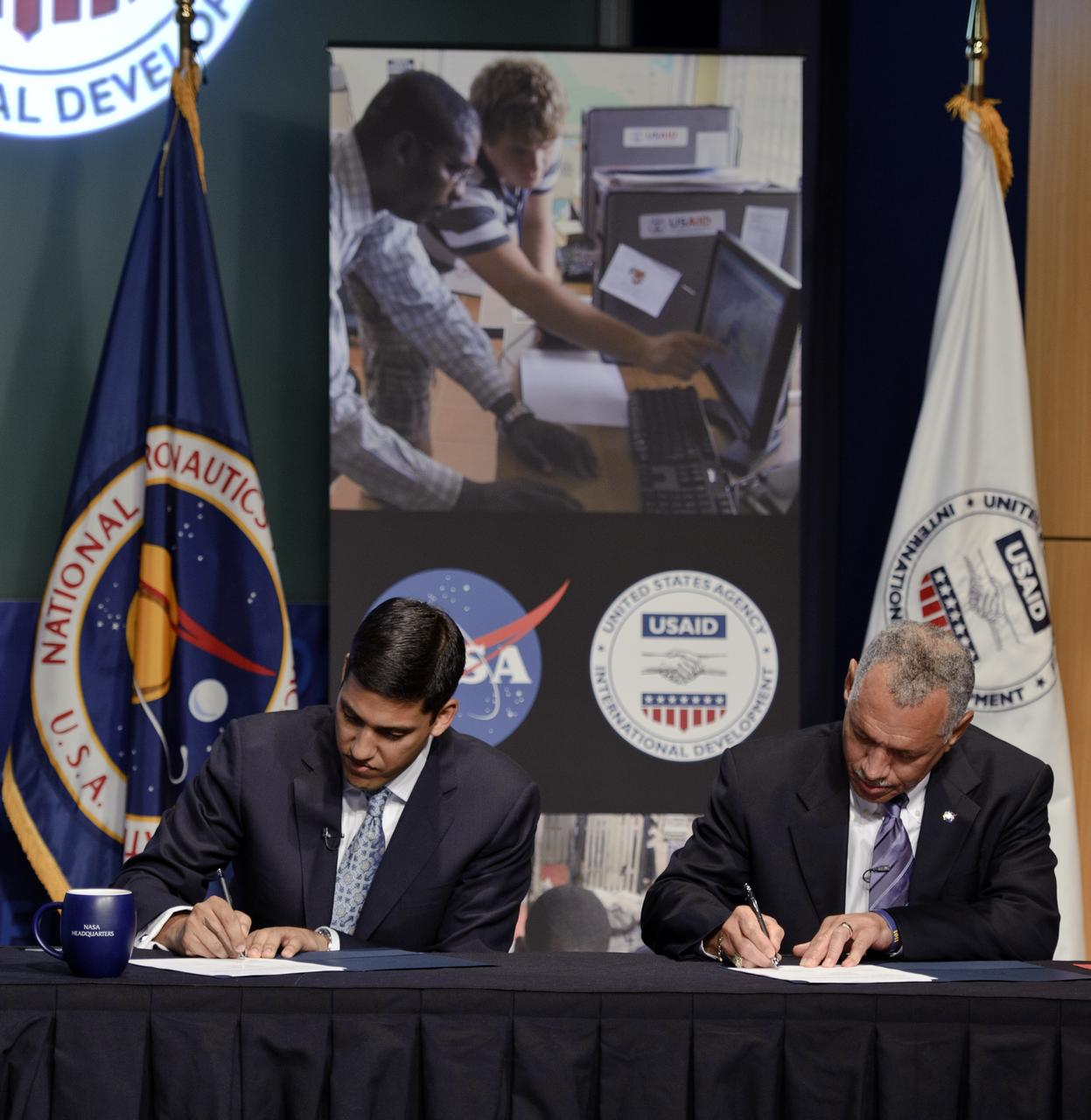

USAID Administrator Rajiv Shah, left, and NASA Administrator Charles Bolden sign a five-year memorandum of understanding, Monday, April 25, 2011, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The agreement formalizes ongoing agency collaborations that use Earth science data to address developmental challenges, and to assist in disaster mitigation and humanitarian responses. The agreement also encourages NASA and USAID to apply geospatial technologies to solve development challenges affecting the United States and developing countries. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
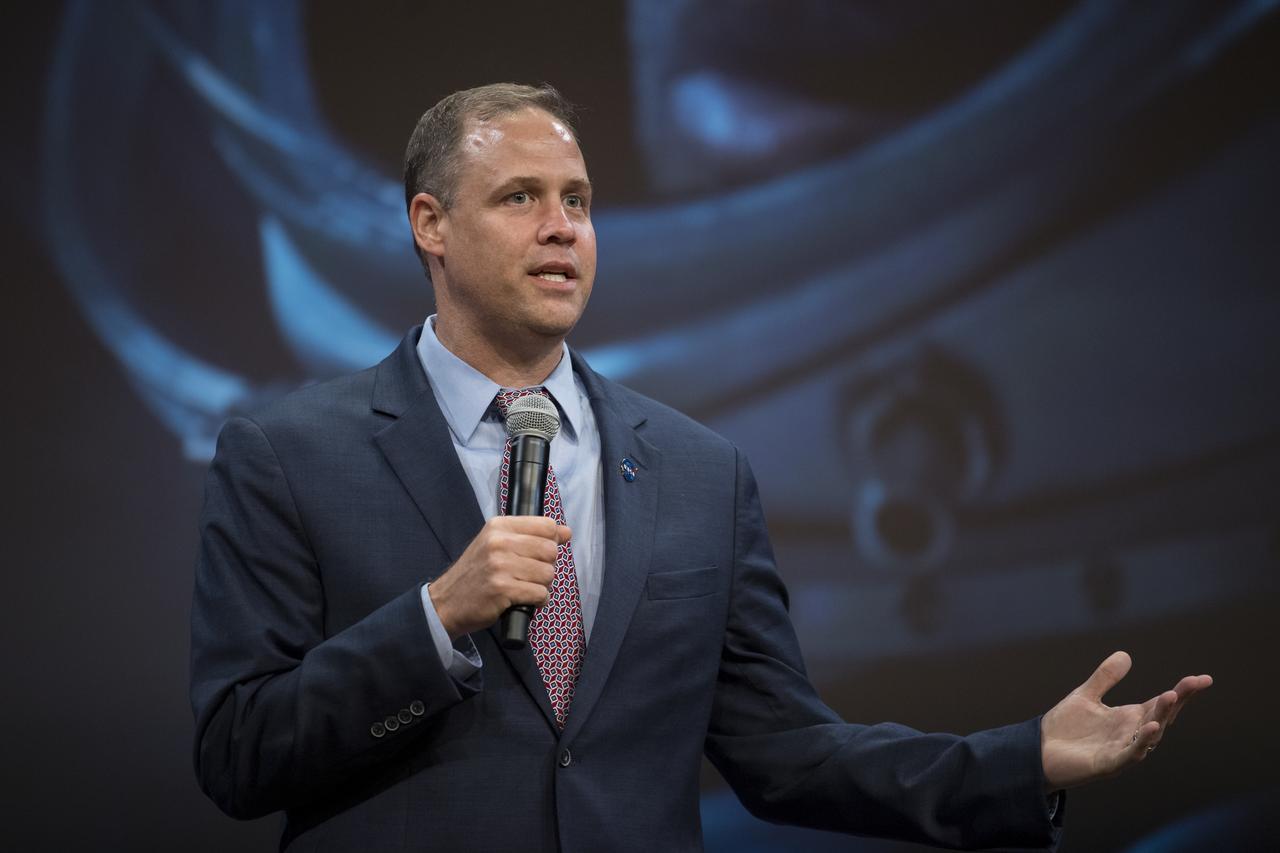

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine speaks before a screening of "Ad Astra" at National Geographic Society, Monday, September 16, 2019 in Washington. The film stars Tommy Lee Jones, Brad Pitt, Ruth Negga, Liv Tyler, and Donald Sutherland. Pitt stars as astronaut Roy McBride who travels deep into the solar system in hopes of solving a mystery that threatens life on Earth. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
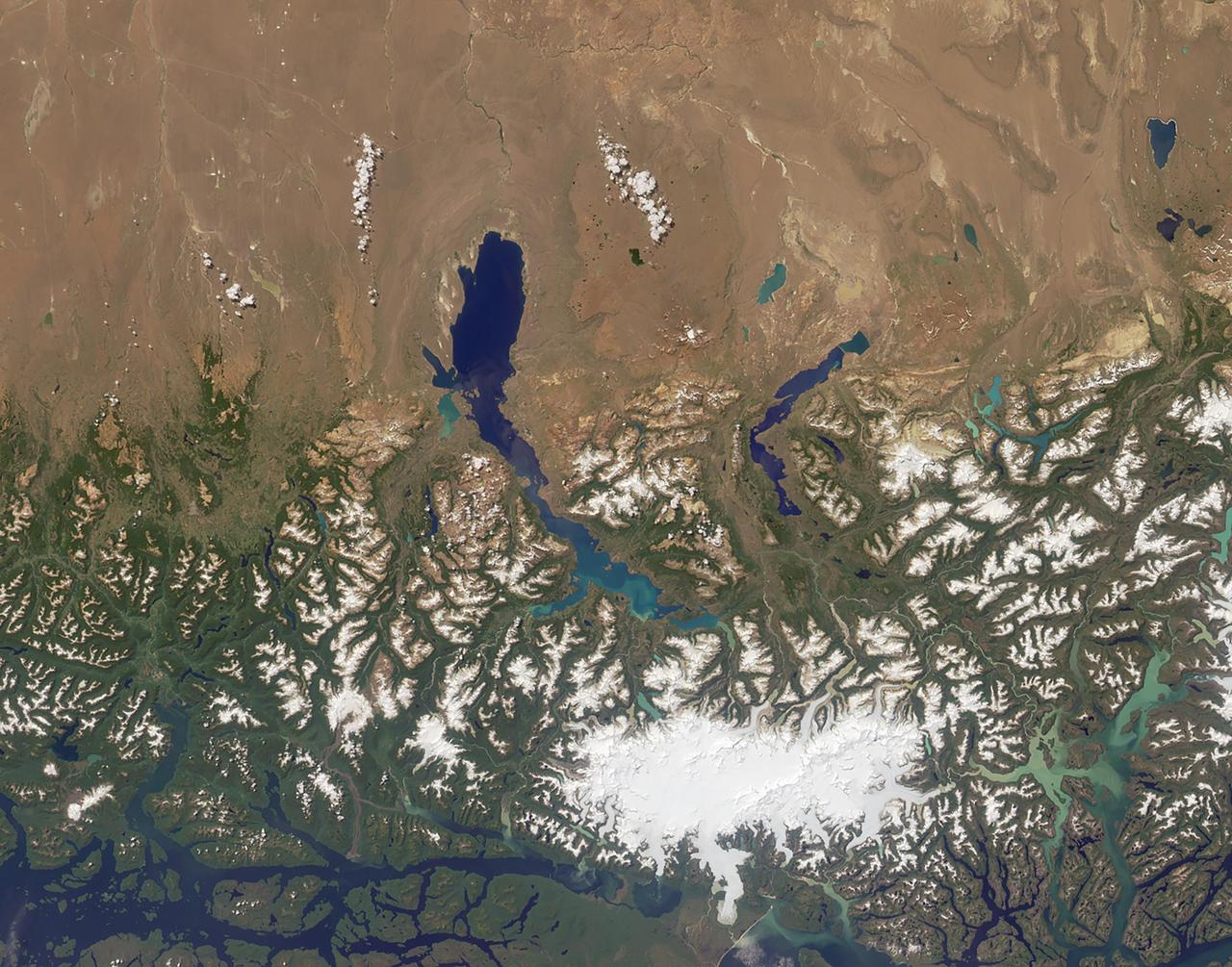

Are you ready for a challenge? Become a geographical detective and solve the latest mystery quiz from NASA's MISR (Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer) instrument onboard the Terra satellite. Prize submissions for perfect scores accepted until Wednesday, November 23, at 4:00 p.m. PST. Happy sleuthing! Take the quiz here http://climate.nasa.gov/quizzes/misr_quiz_28. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA15375

Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Vice President and General Manager John Clark speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Associate Administrator for the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate Bob Pearce speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Associate Administrator for the Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate Bob Pearce speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
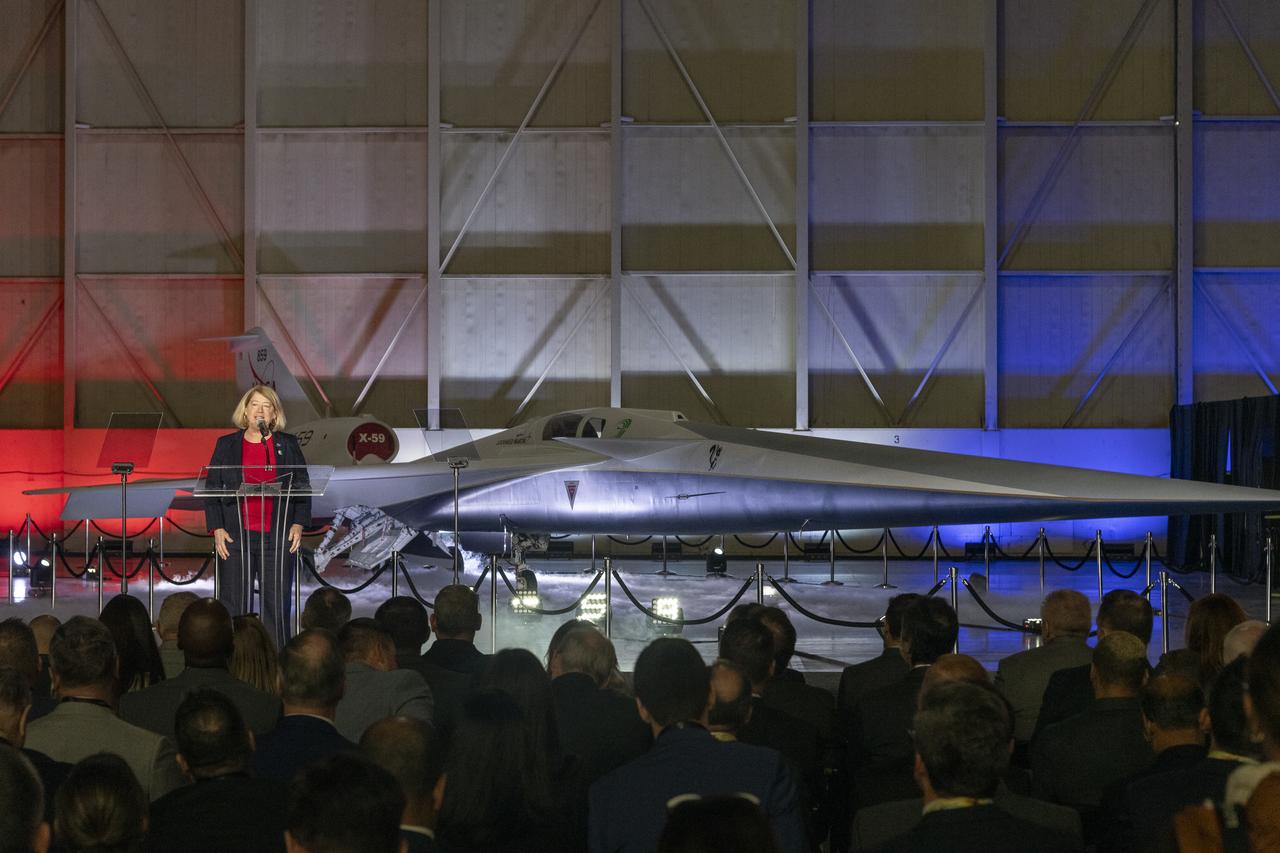

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage immediately following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
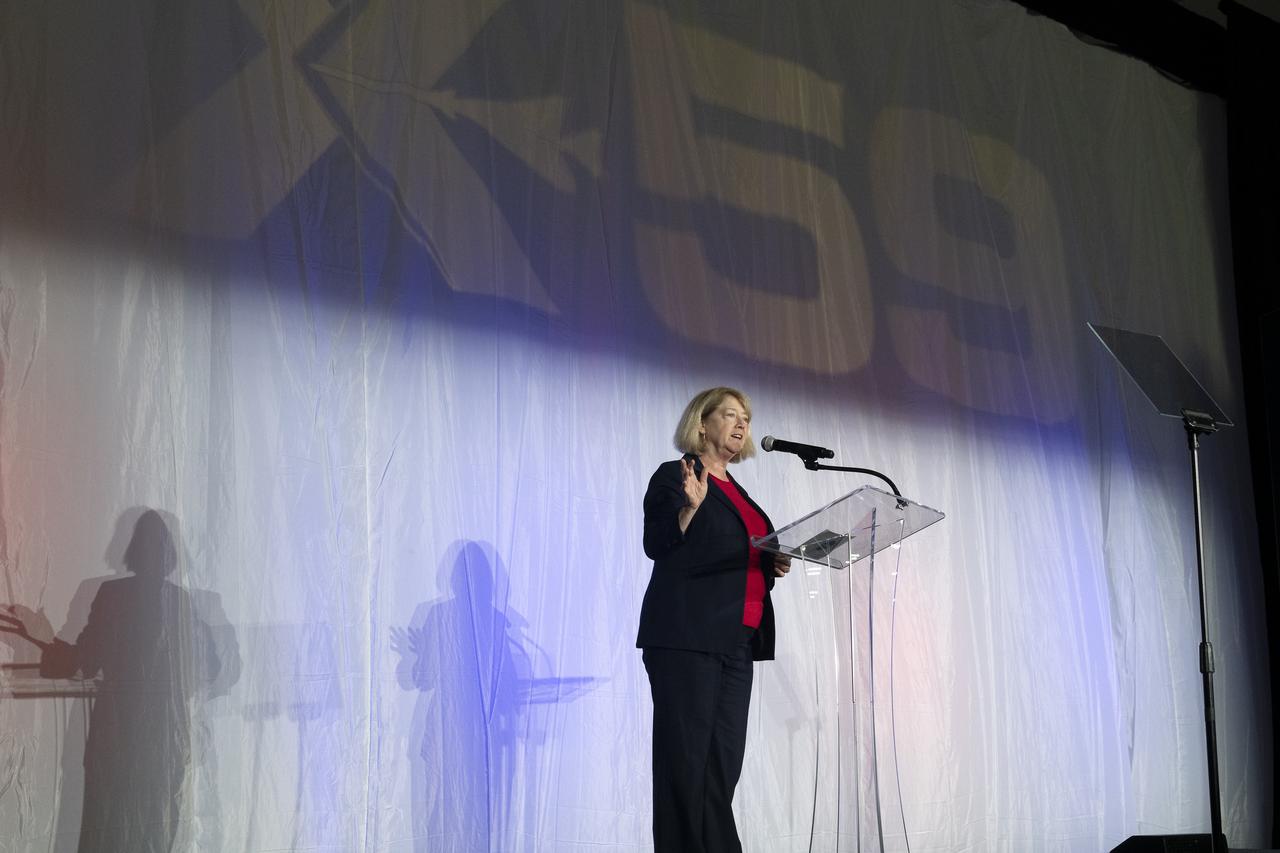

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage prior to the official unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
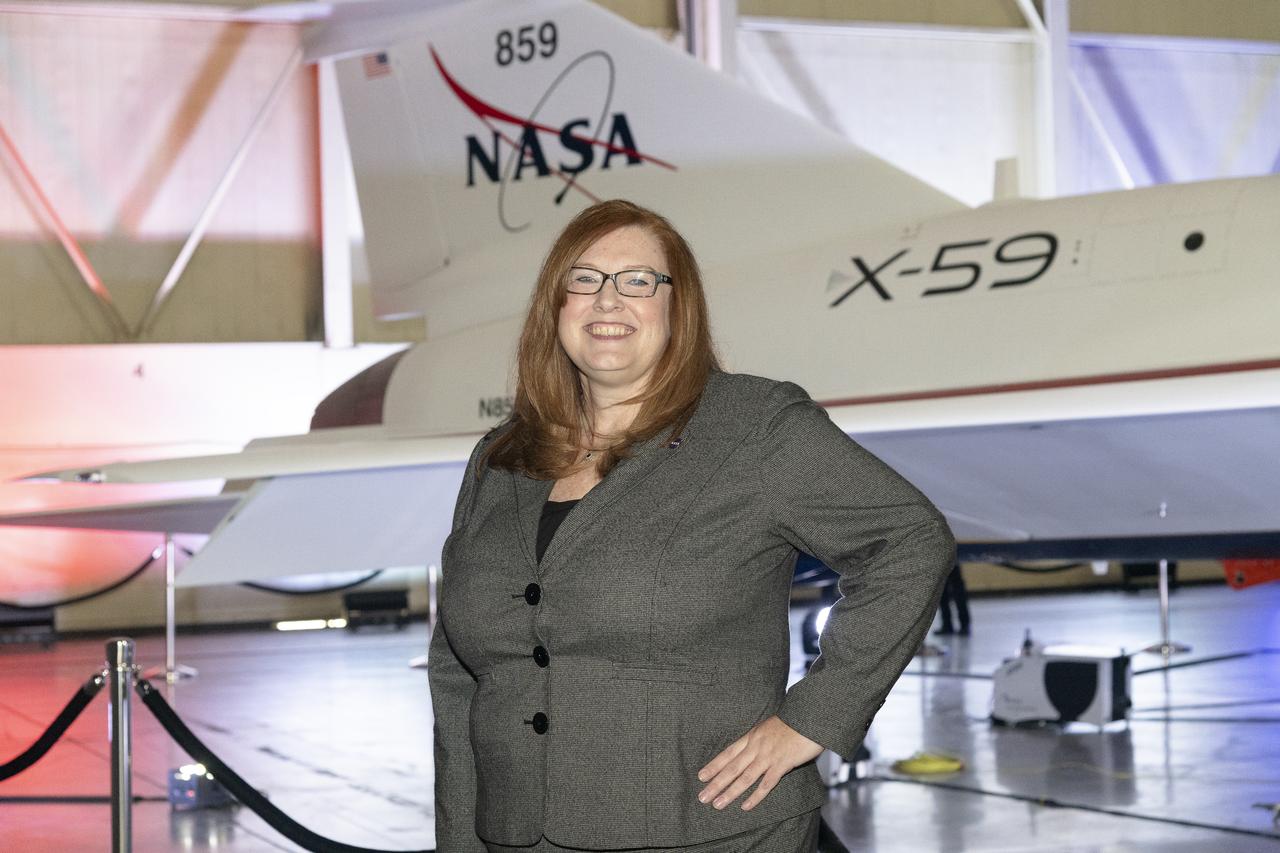

NASA’s project manager for the Low Boom Flight Demonstrator project, Cathy Bahm, poses in front of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
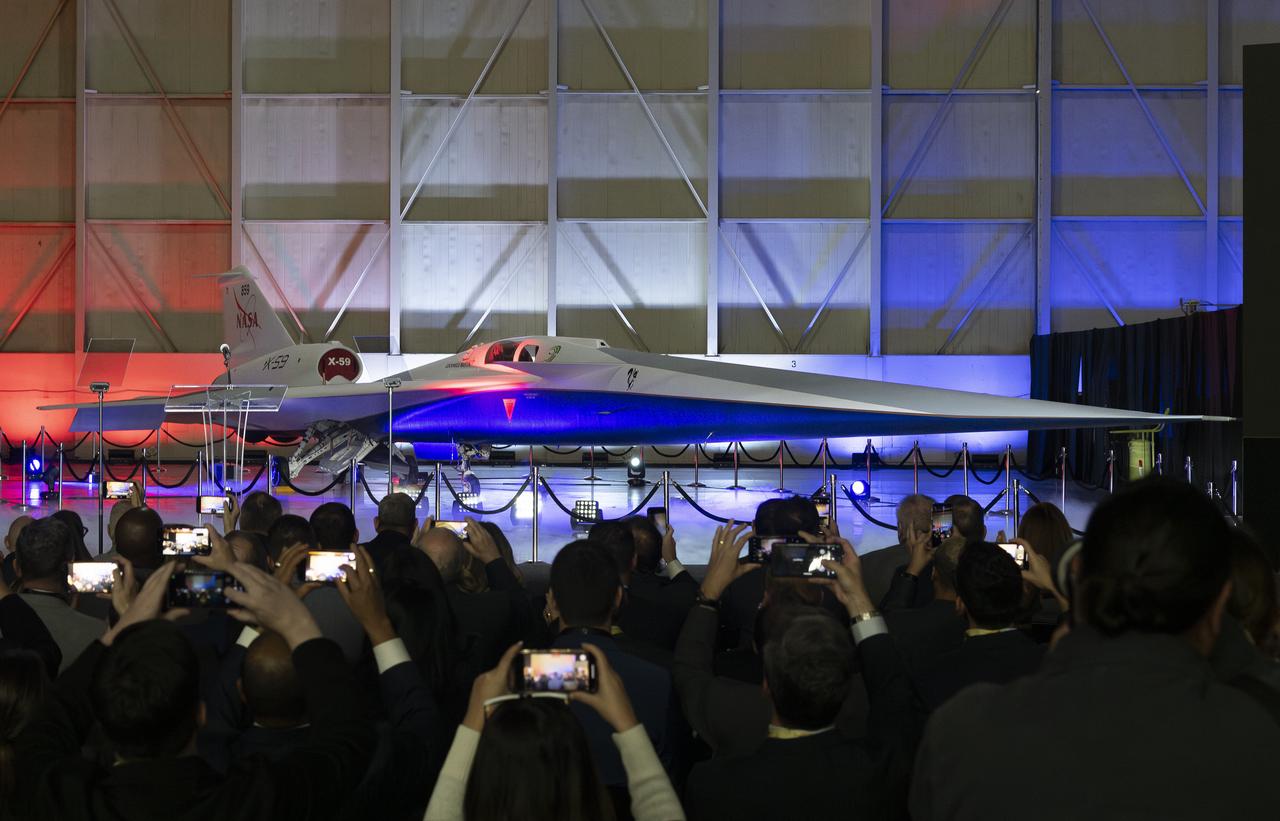

NASA and Lockheed Martin publicly unveil the X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a ceremony in Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
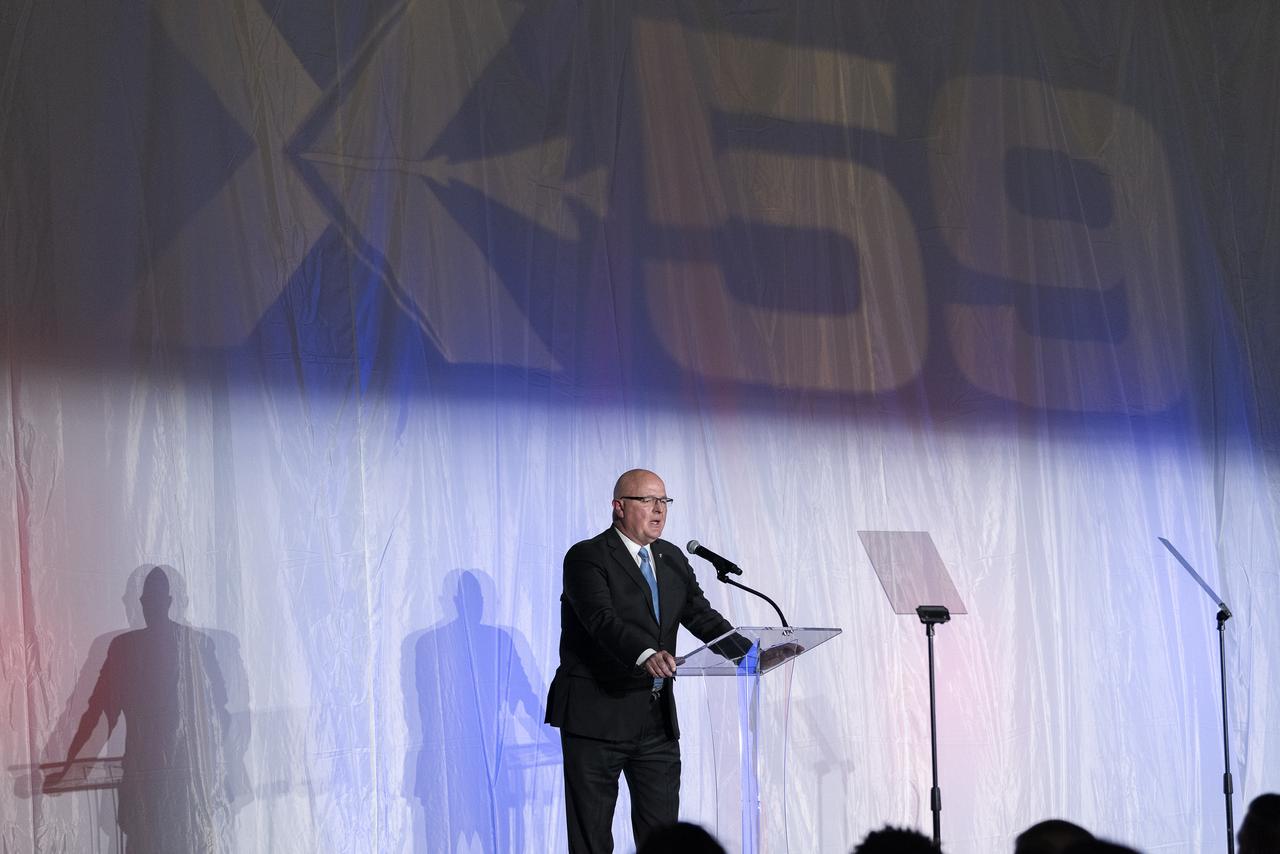

Lockheed Martin Skunk Works Director of Government Affairs Eric Fox speaks on stage prior to the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
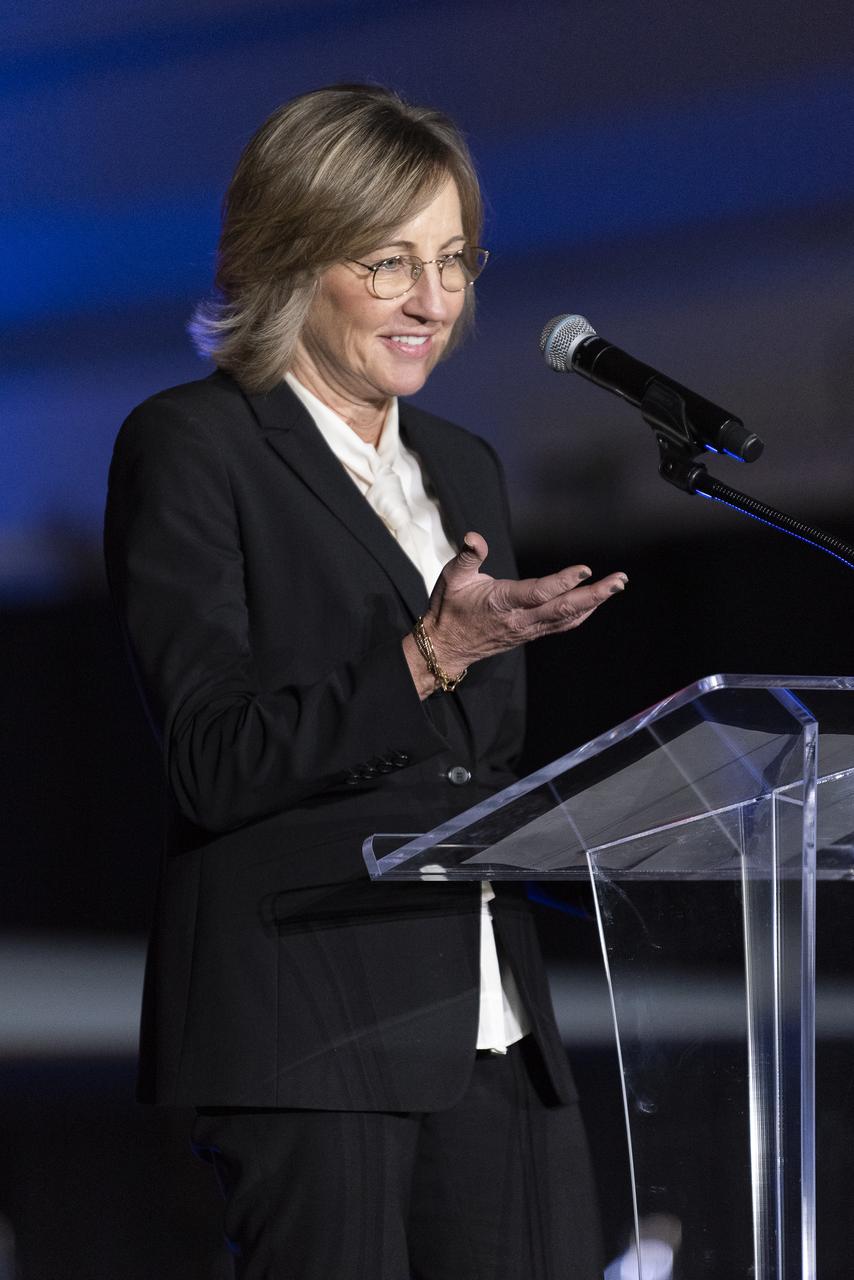

California Senior Economic Advisor to the Governor Dee Dee Myers speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
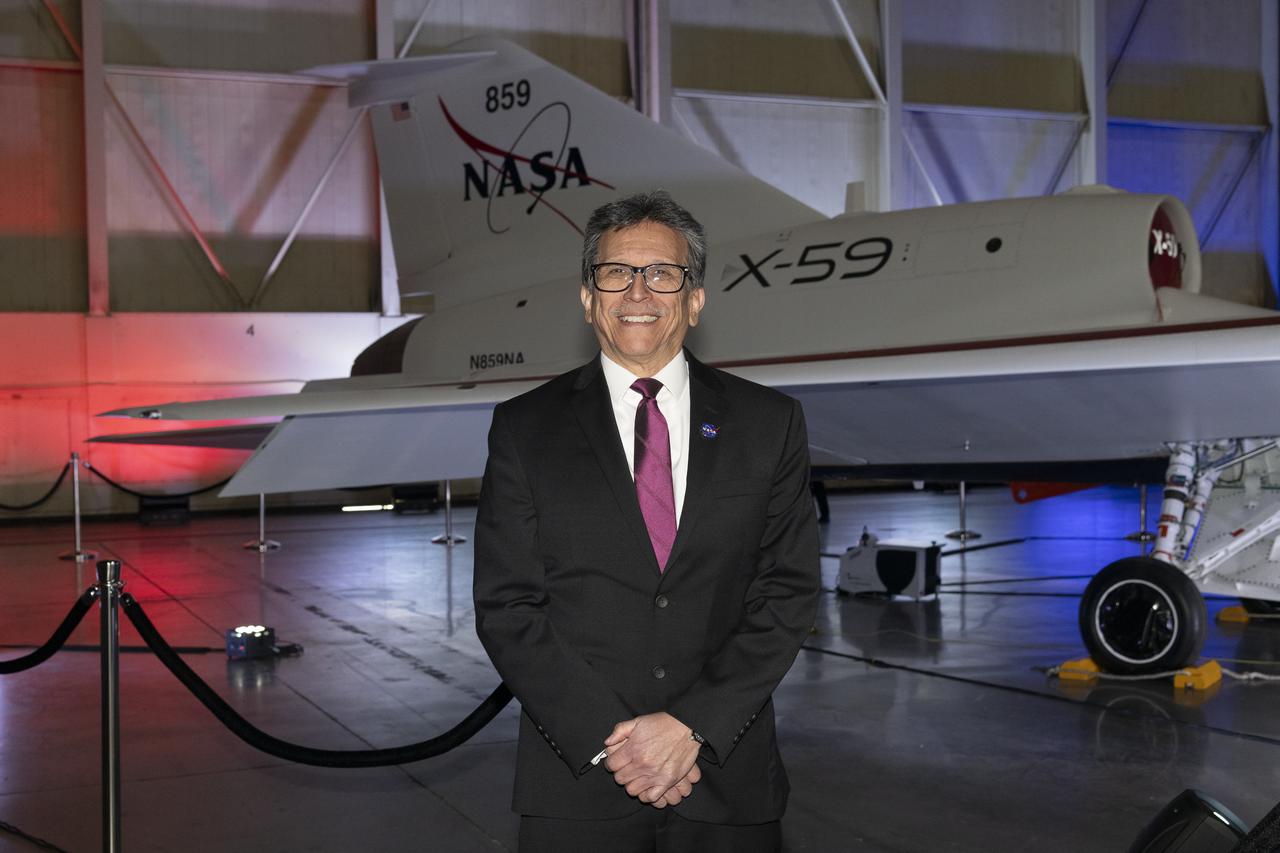

NASA’s structures lead for the X-59, Dr. Walt Silva, poses in front of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage immediately following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
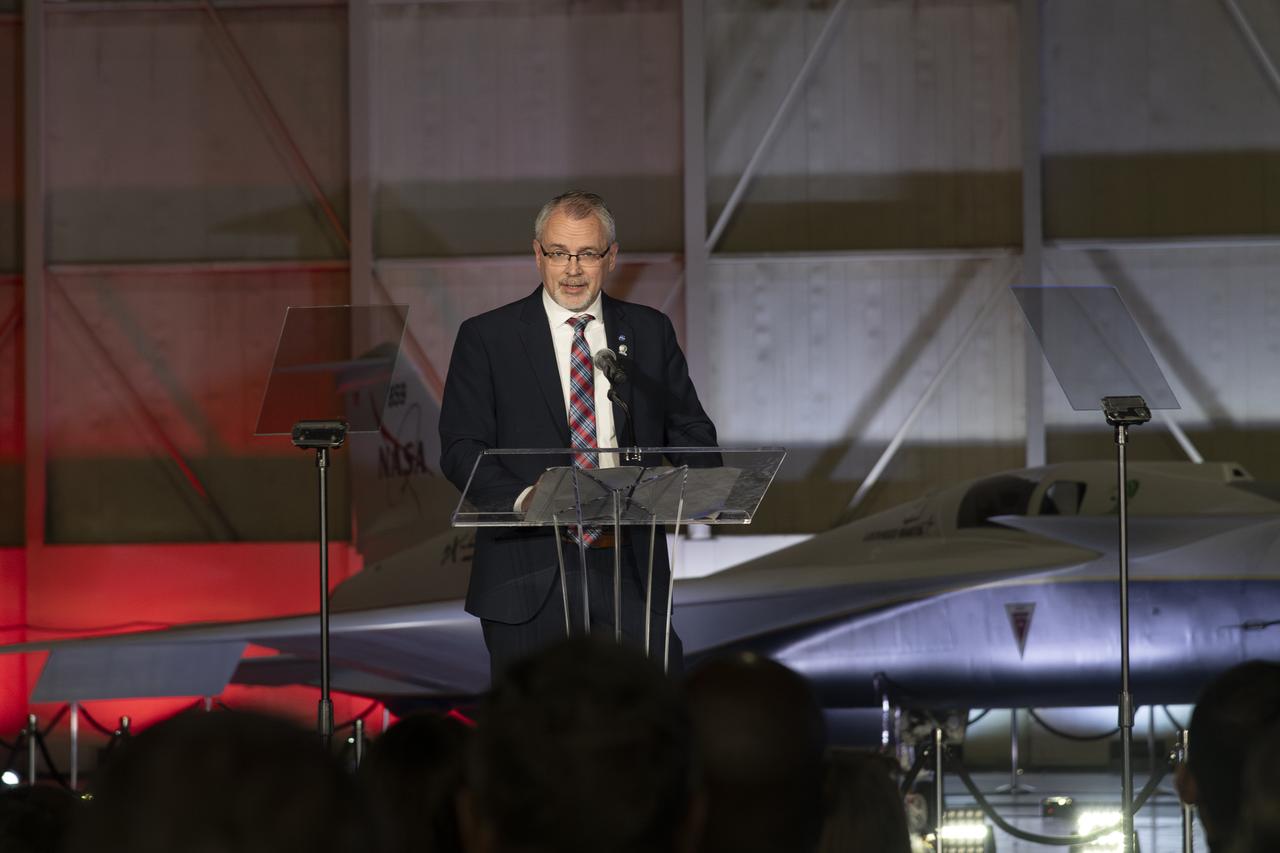

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
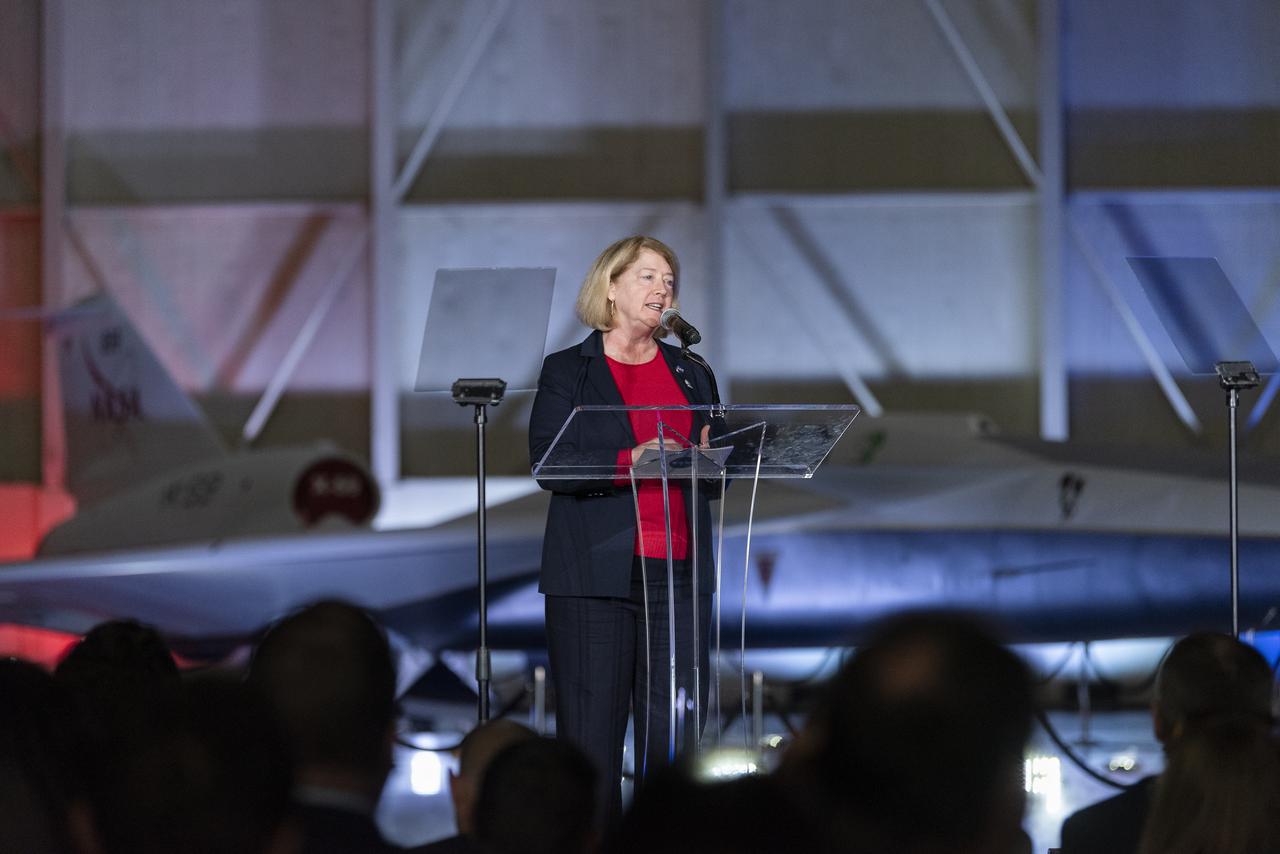

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage immediately following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
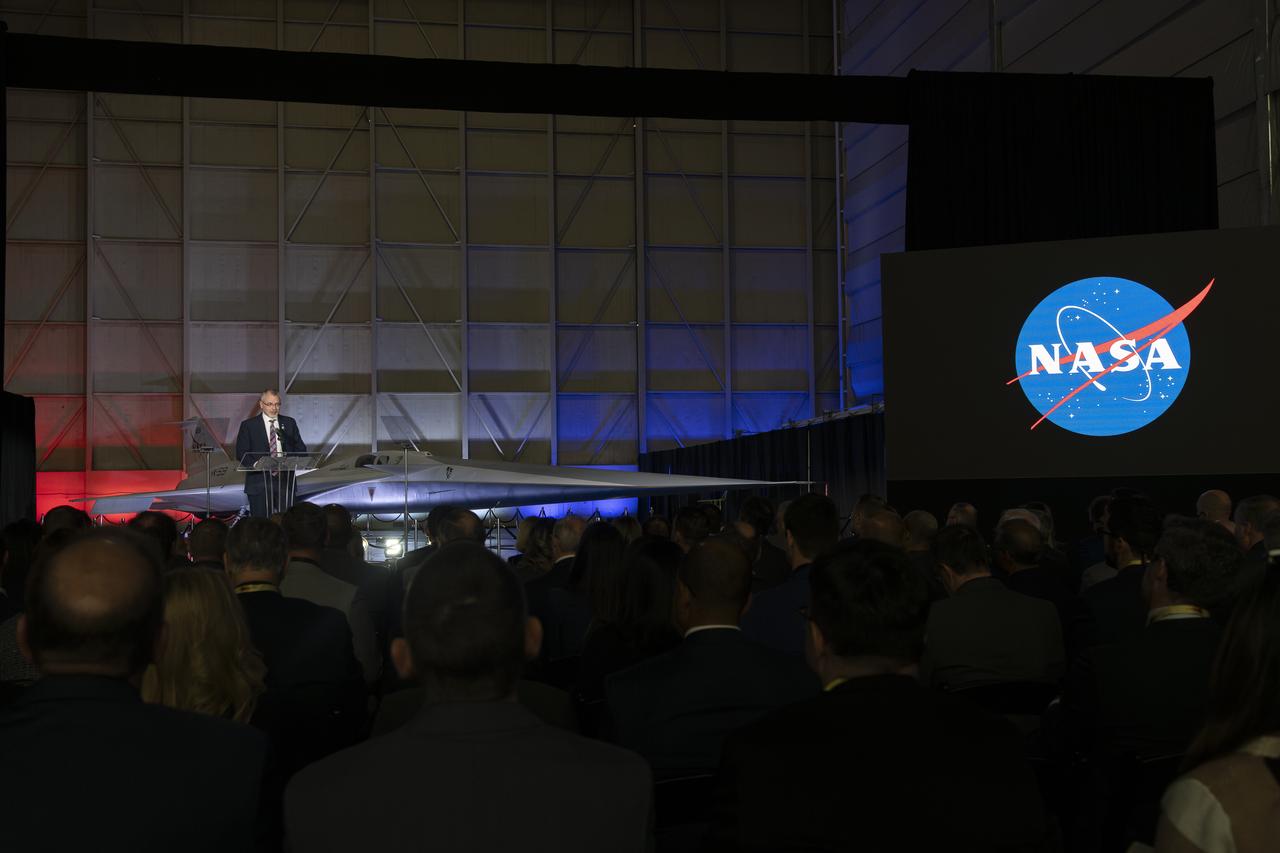

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free speaks on stage following the unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
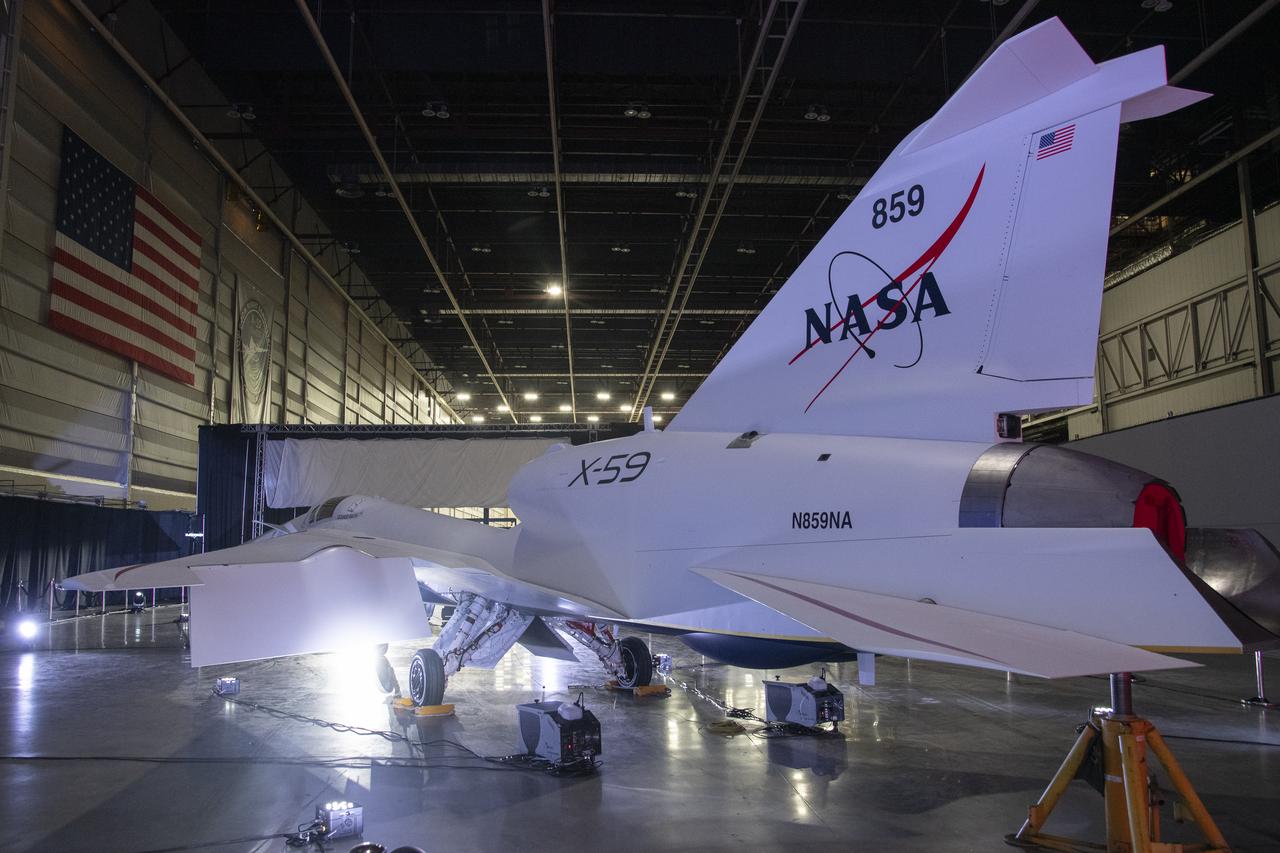

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits in position inside a hangar at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California prior to its January 12, 2024 unveiling. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
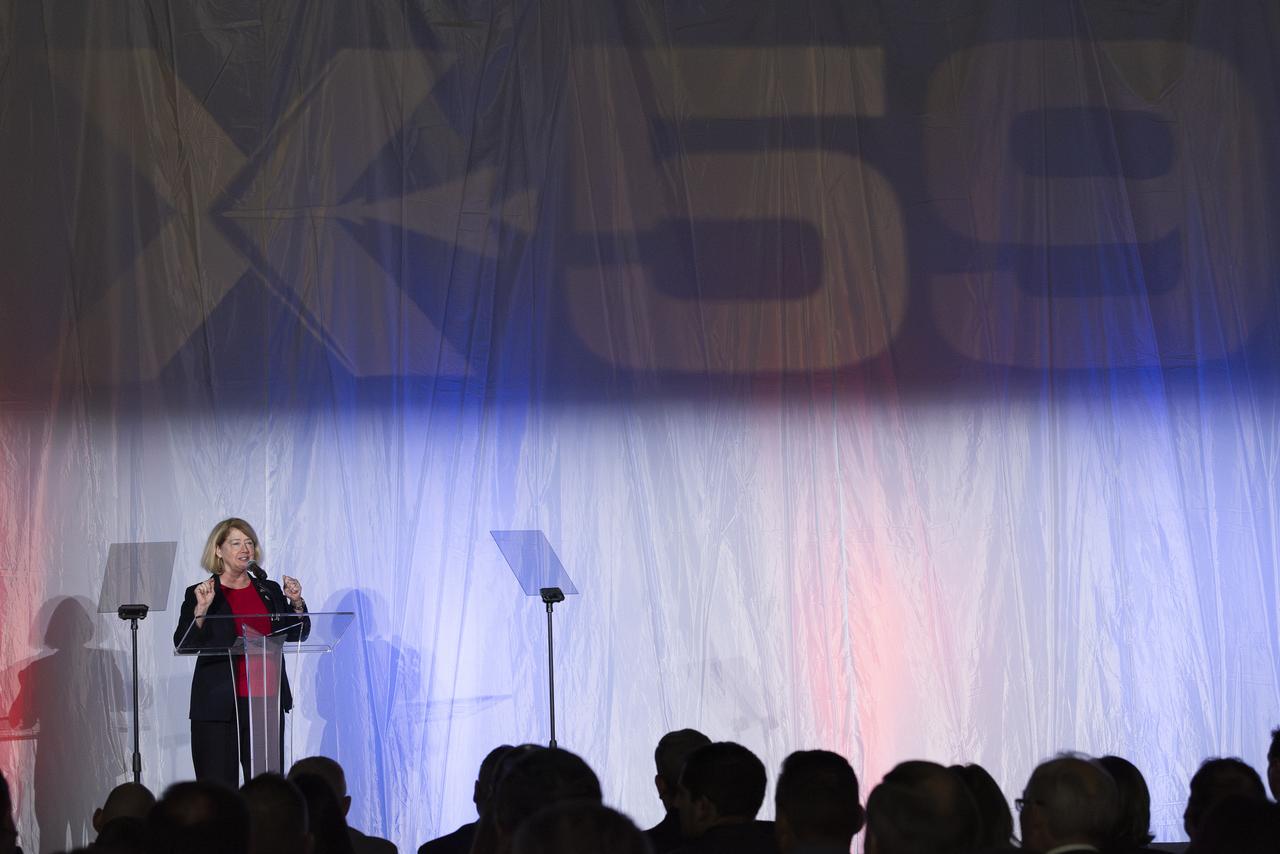

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy speaks on stage prior to the official unveiling of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
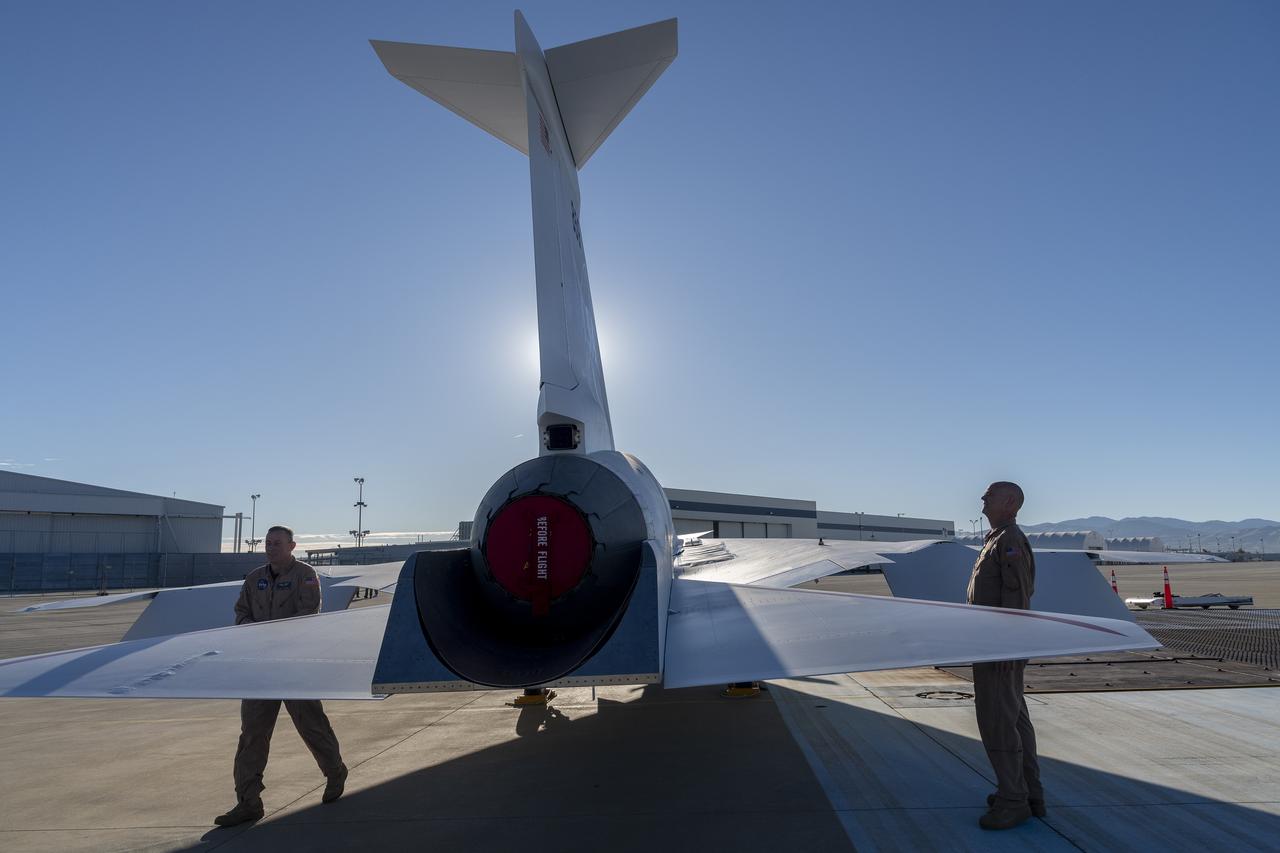

NASA and Lockheed Martin test pilots inspect the painted X-59 as it sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
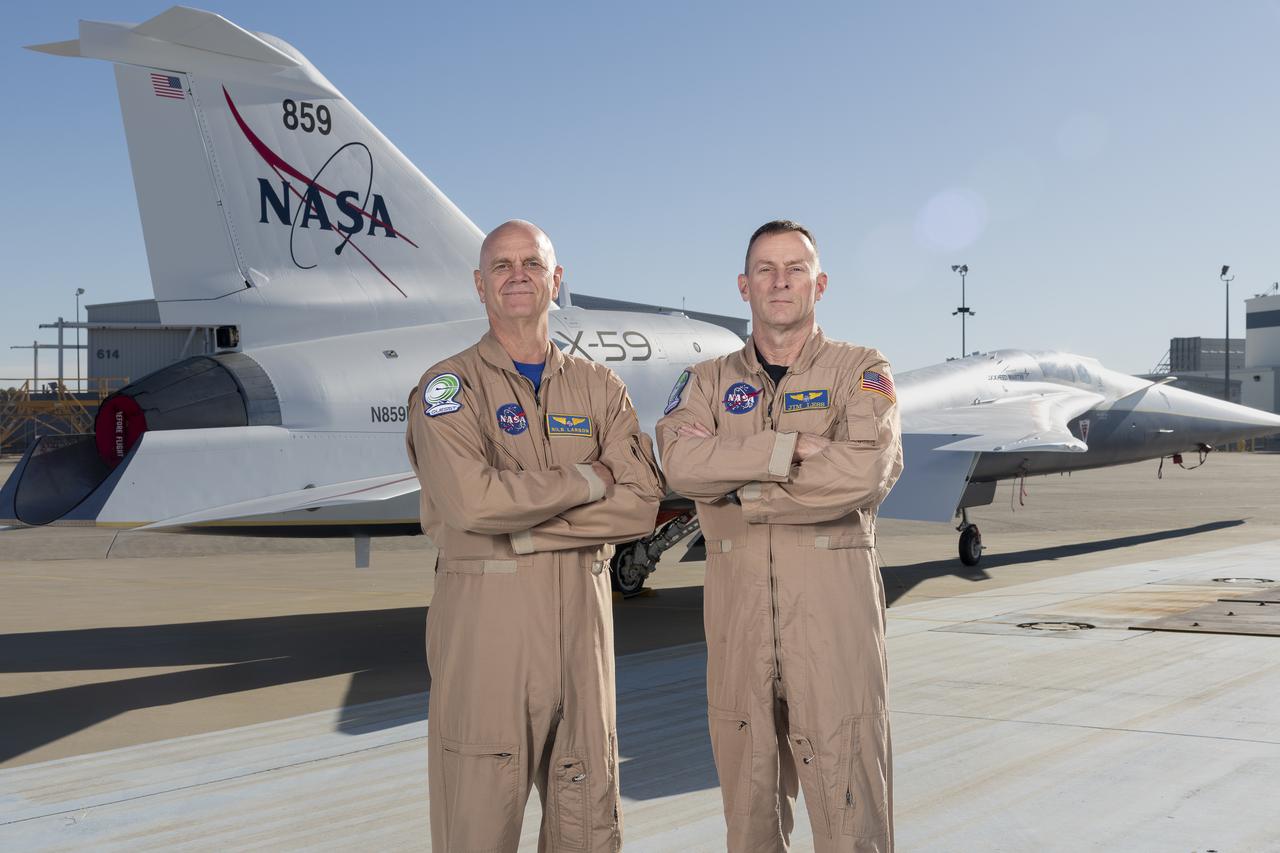

NASA test pilots Nils Larson (left) and Jim “Clue” Less (right) pose with the newly-painted X-59 as it sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
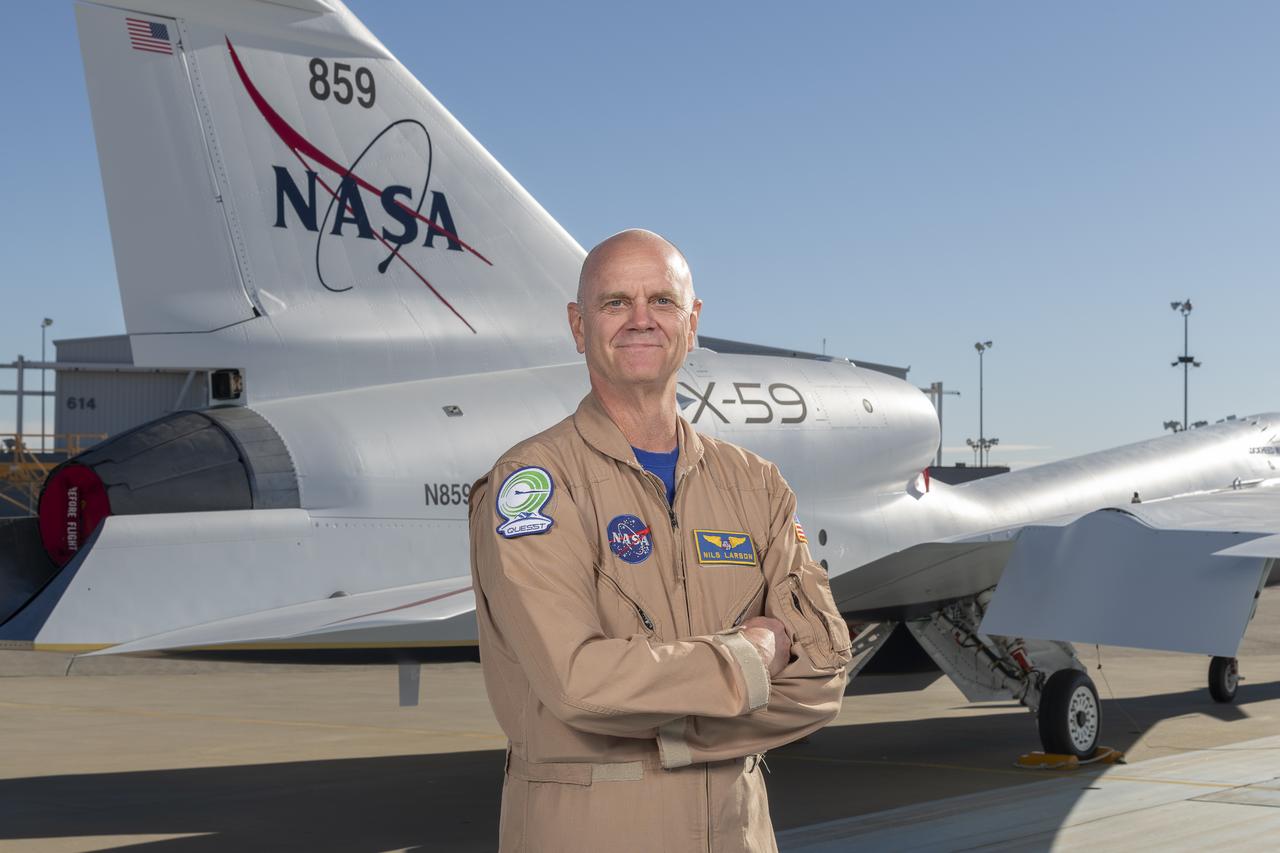

NASA test pilot Nils Larson poses with the newly-painted X-59 as it sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
