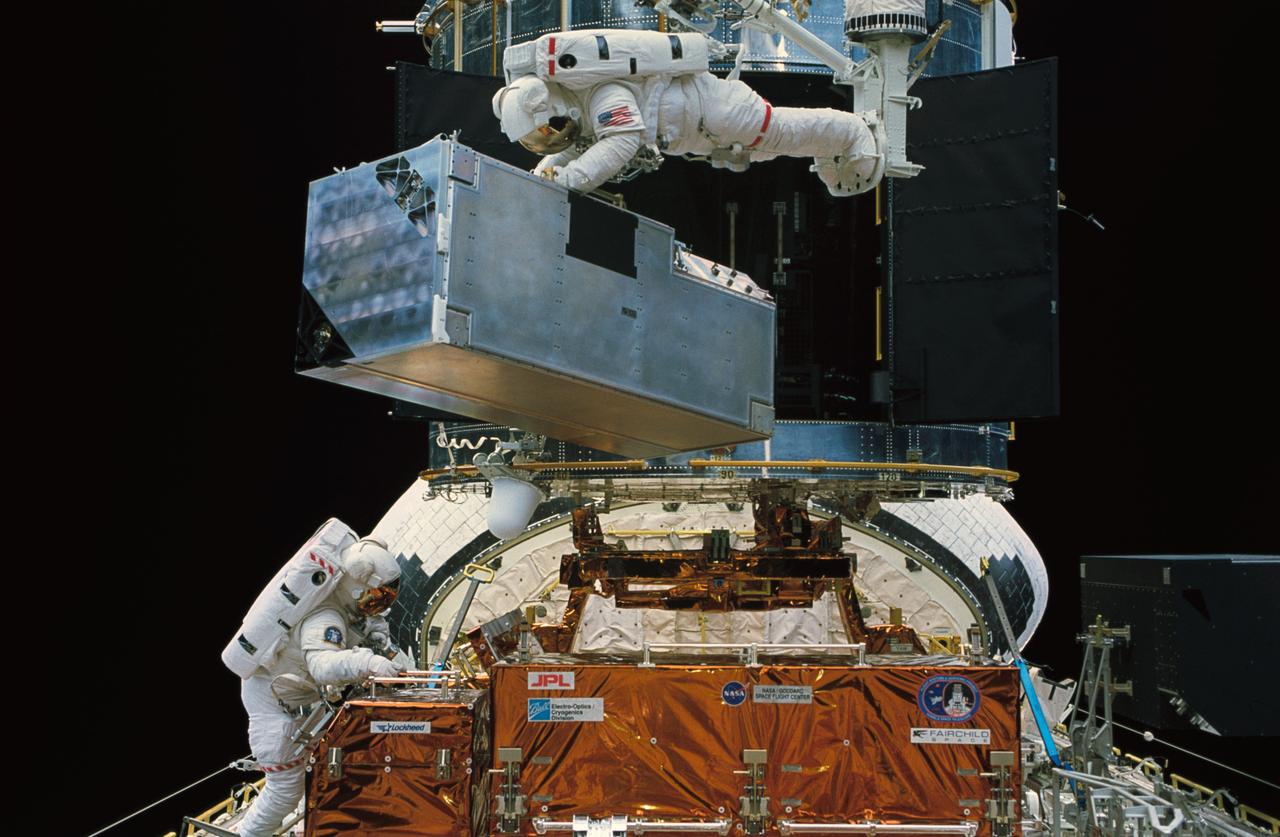
STS061-47-014 (8 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton lifts the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) prior to its installation on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Thornton is anchored to a foot restraint on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. Astronaut Thomas D. Akers, who assisted in the COSTAR installation, is at lower left.
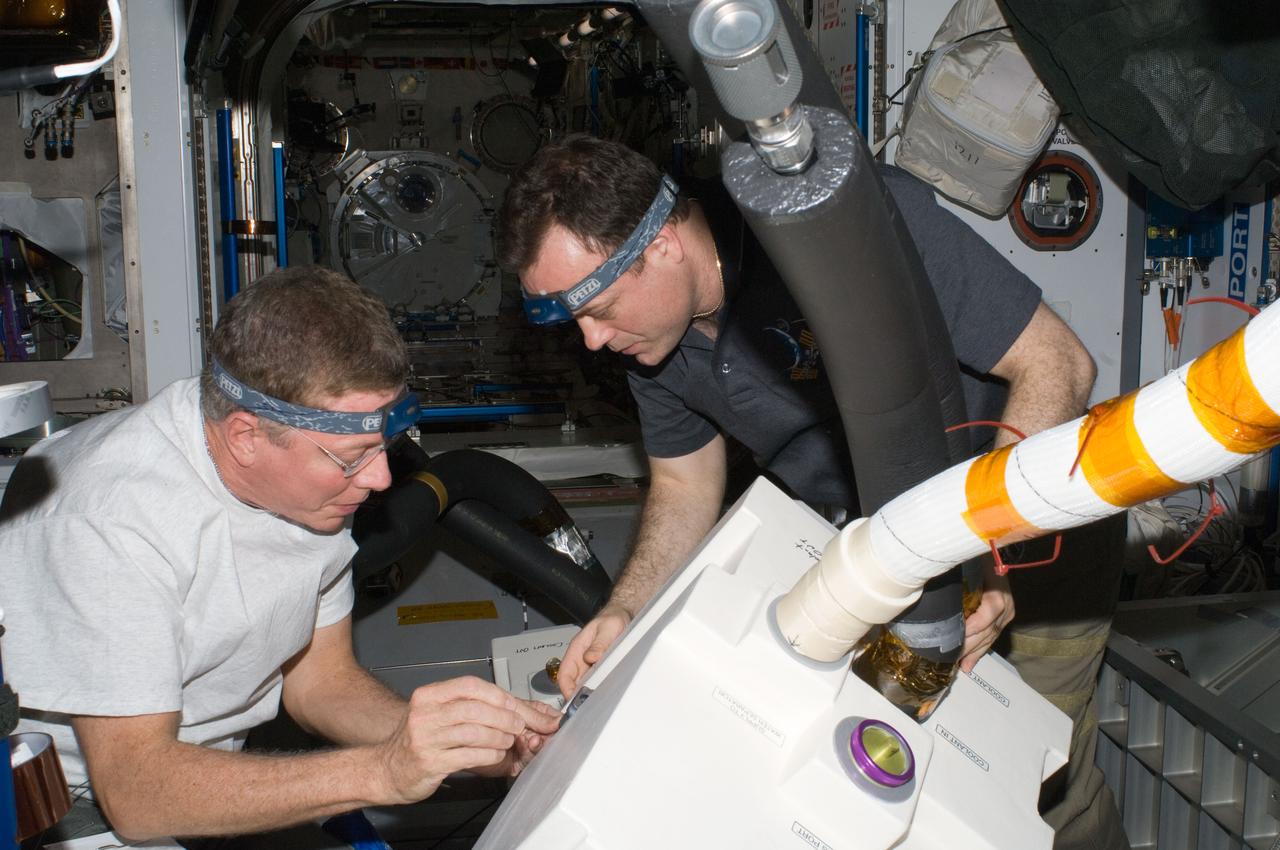

ISS028-E-010781 (30 June 2011) --- NASA astronauts Mike Fossum (left) and Ron Garan, both Expedition 28 flight engineers, perform in-flight maintenance in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. The maintenance involved removing and replacing the failed Common Cabin Air Assembly (CCAA) heat exchanger in the P3 Midbay with a new spare Heat Exchanger Orbit Replaceable Unit (HX ORU) and lines.
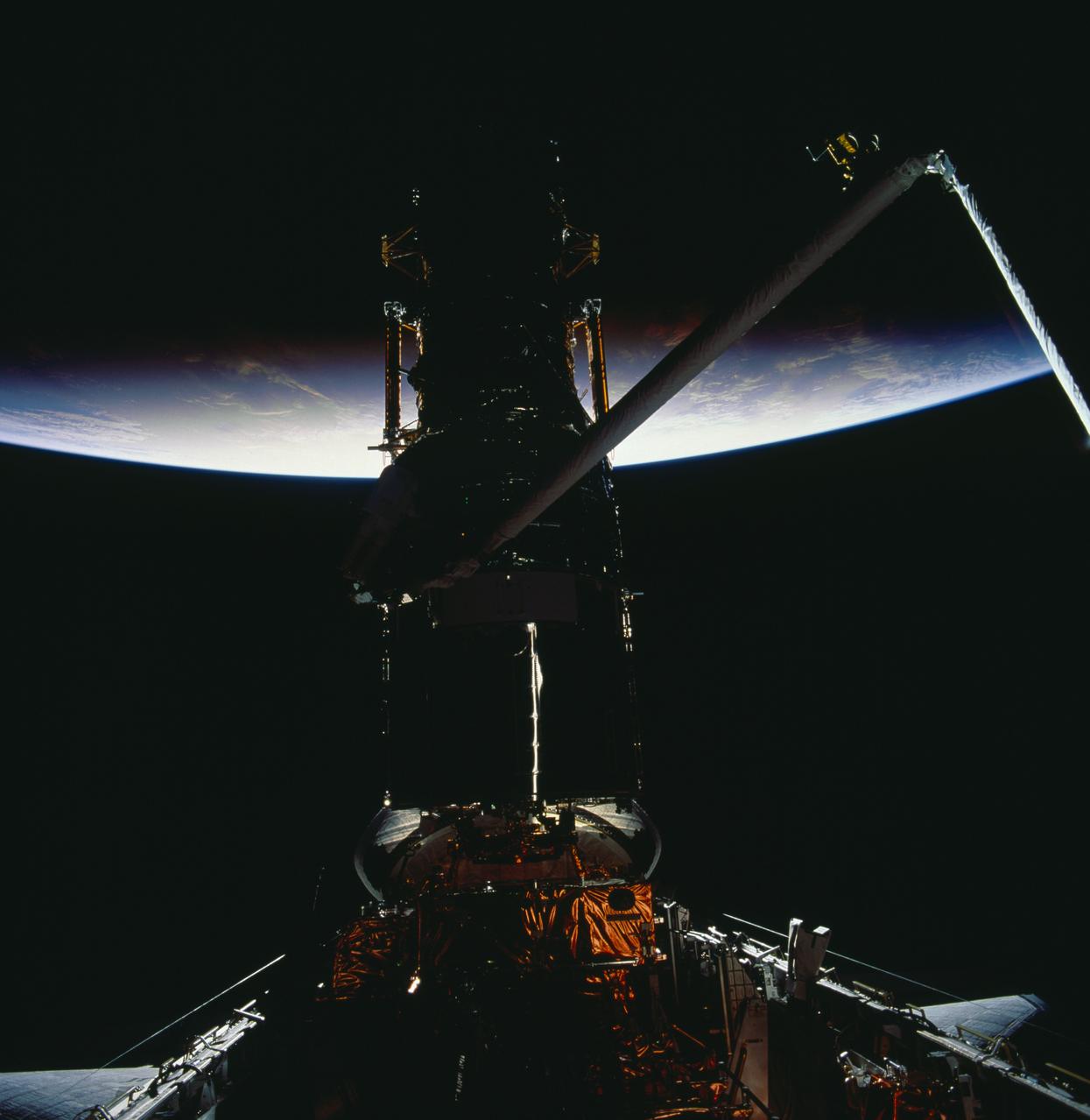

STS061-98-0AR (8 Dec 1993) --- Earth is partially illuminated but the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the Space Shuttle Endeavour are still mostly in darkness, in this 70mm frame photographed during the fourth of five space walks. Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, barely visible above left center in the frame, works to install the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR).
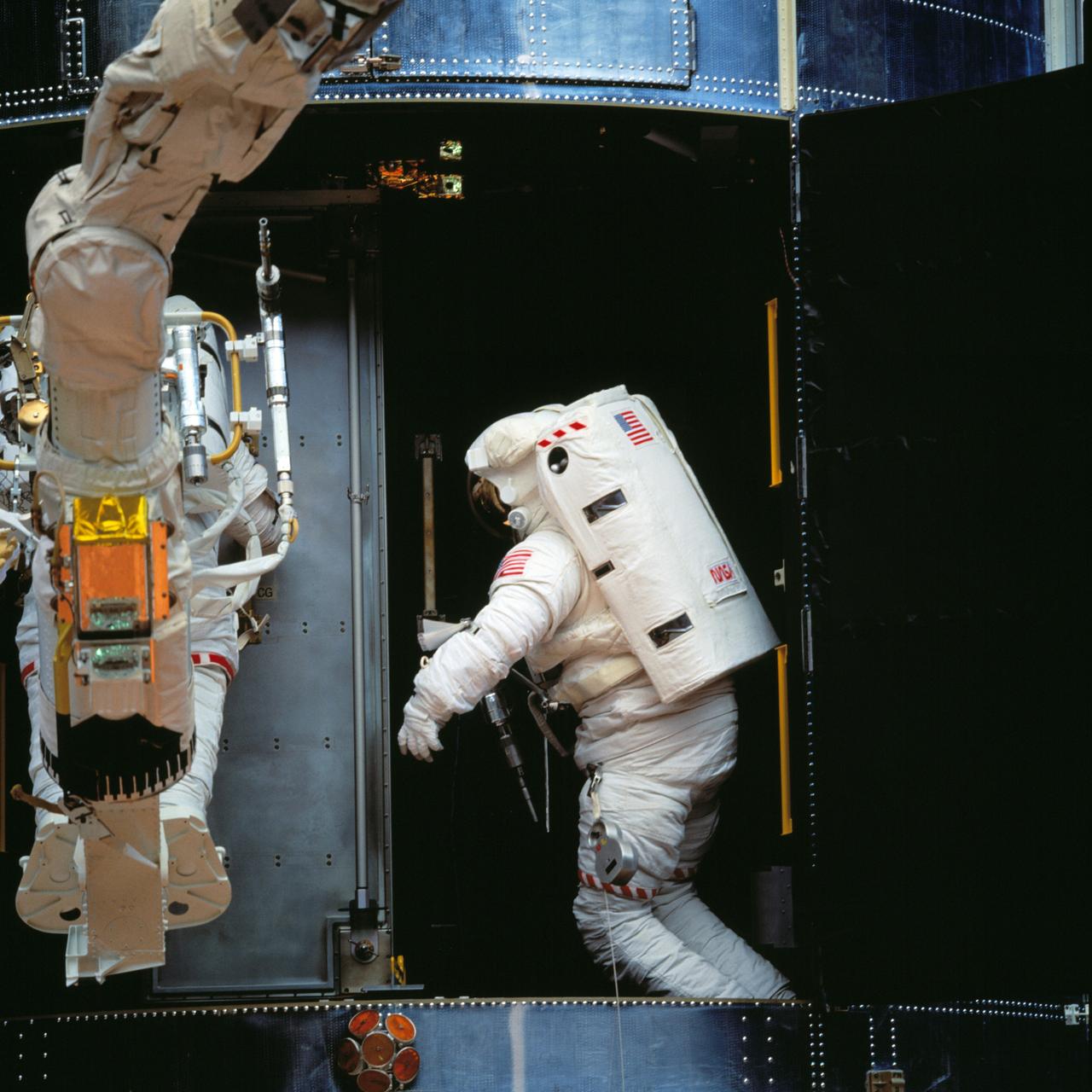
STS061-94-059 (8 Dec. 1993) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers maneuvers inside the bay which will house the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) while assisting astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton with the installation of the 640-pound instrument. Thornton, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is partially visible as she prepares to install the COSTAR.
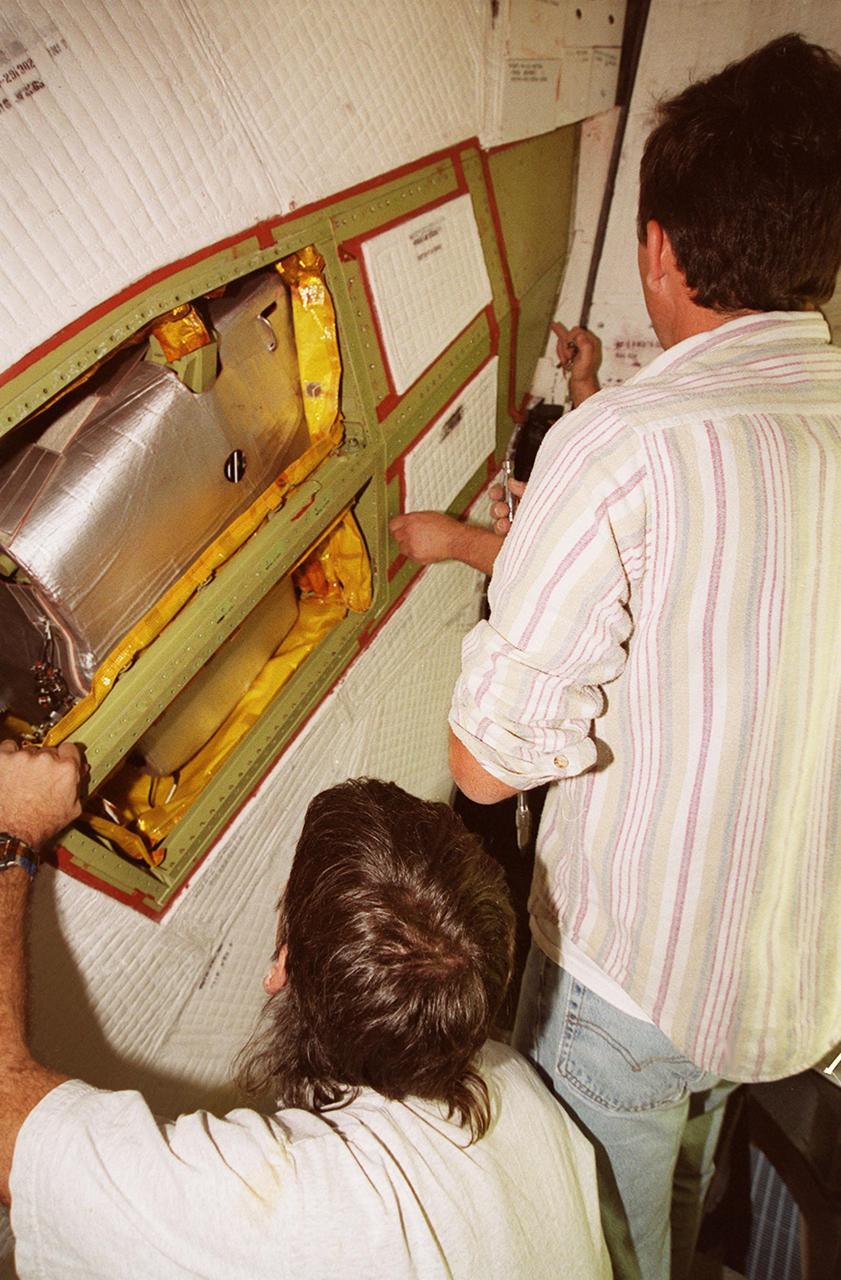

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technicians (left to right) Tod Biddle, Bob Wright and Mark Noel (hidden) remove the coverings from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis to reveal the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
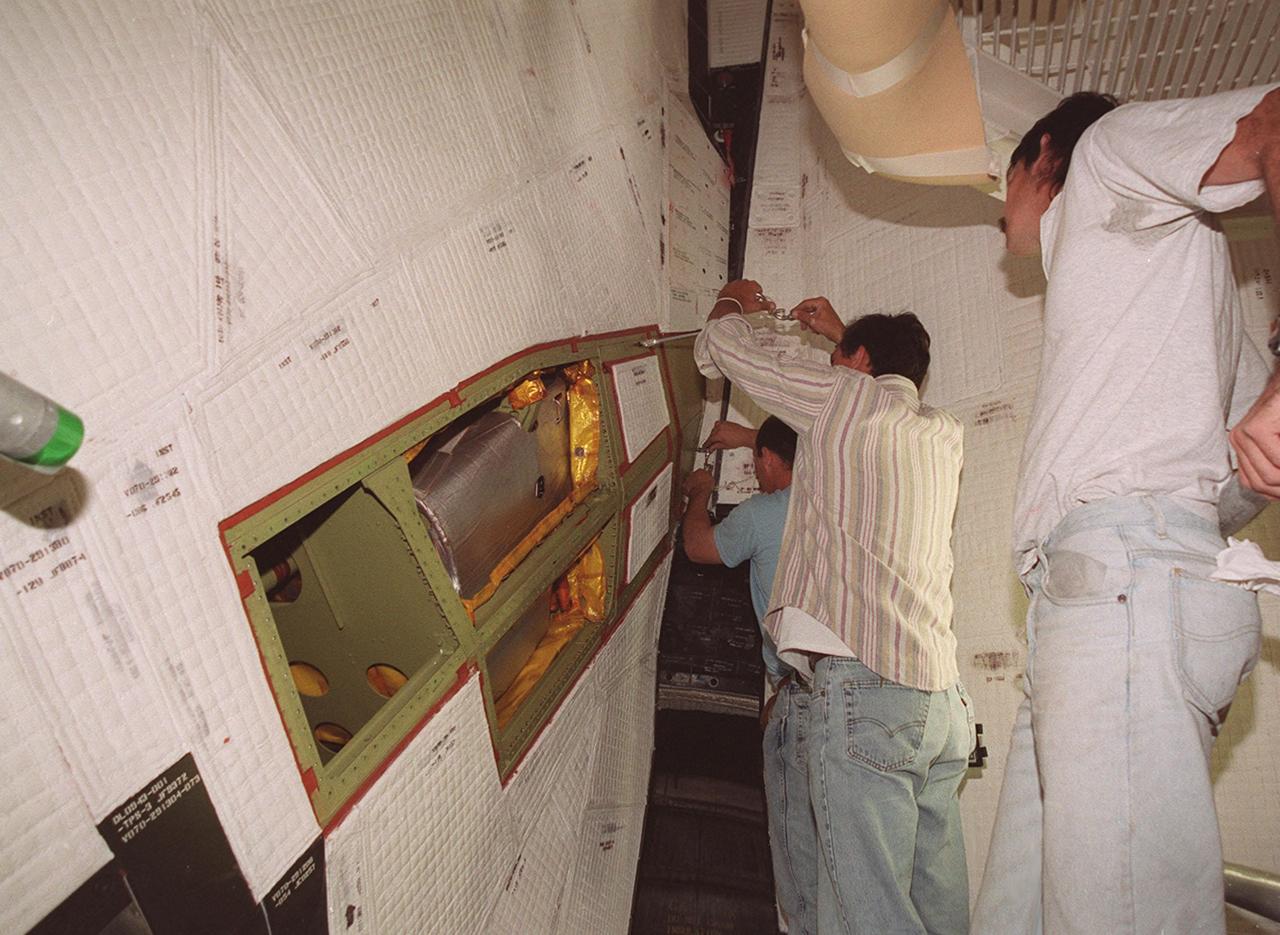

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians at Launch Pad 39A begin removing thermal blankets and panels from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis in order to reach the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. From left to right are Mark Noel, Bob Wright and Tod Biddle, with United Space Alliance. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
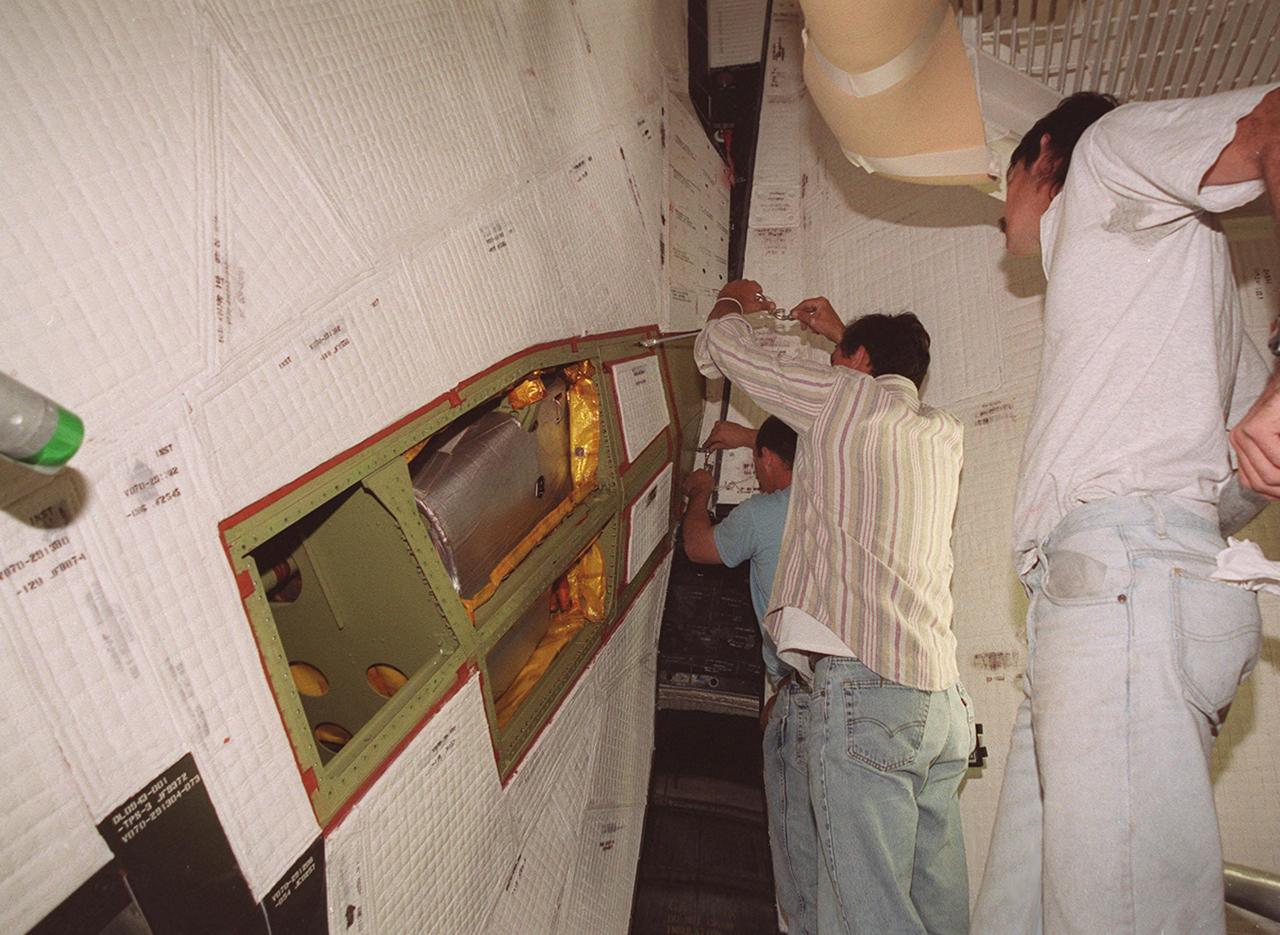

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians at Launch Pad 39A begin removing thermal blankets and panels from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis in order to reach the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. From left to right are Mark Noel, Bob Wright and Tod Biddle, with United Space Alliance. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
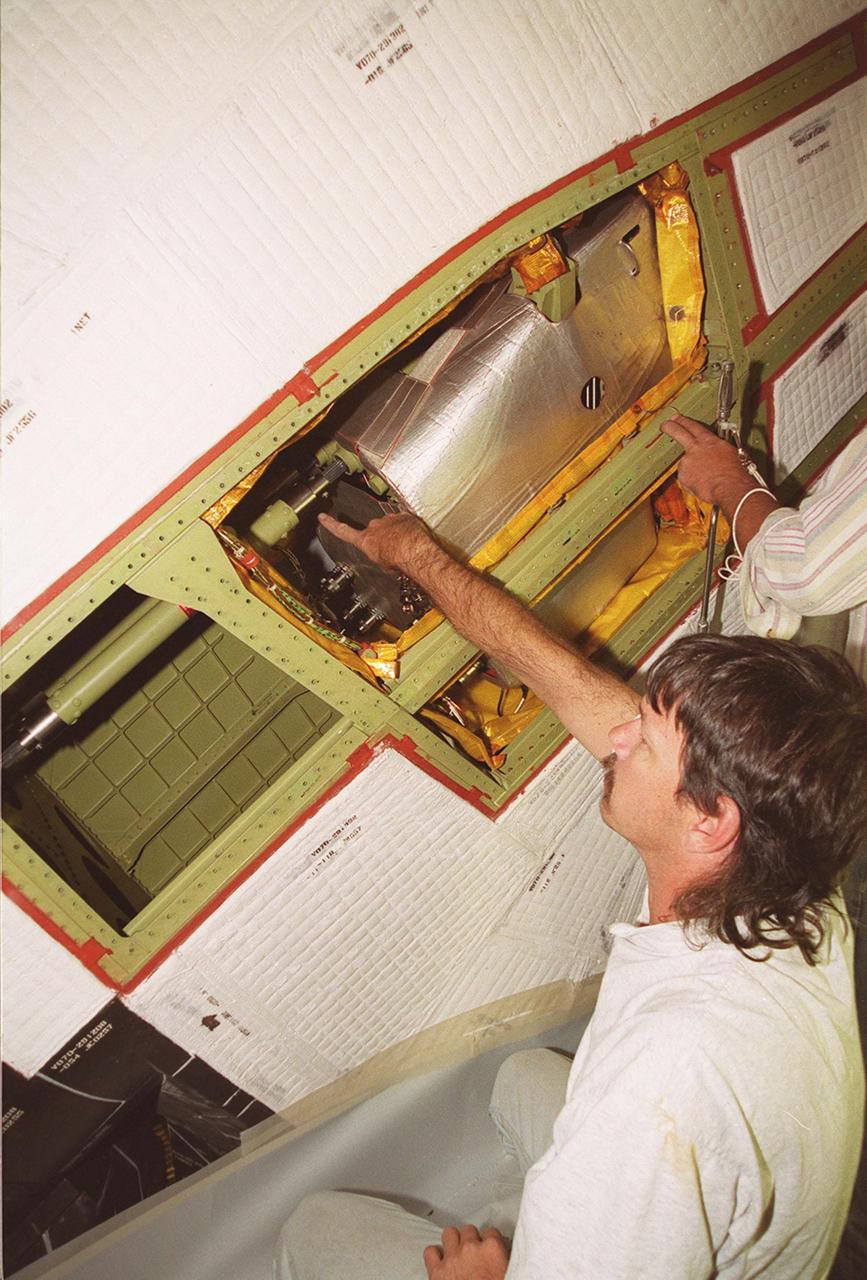

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With coverings removed from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis, Tod Biddle, a United Space Alliance (USA) technician, points to the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. The hands at right belong to Bob Wright, also a USA technician. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
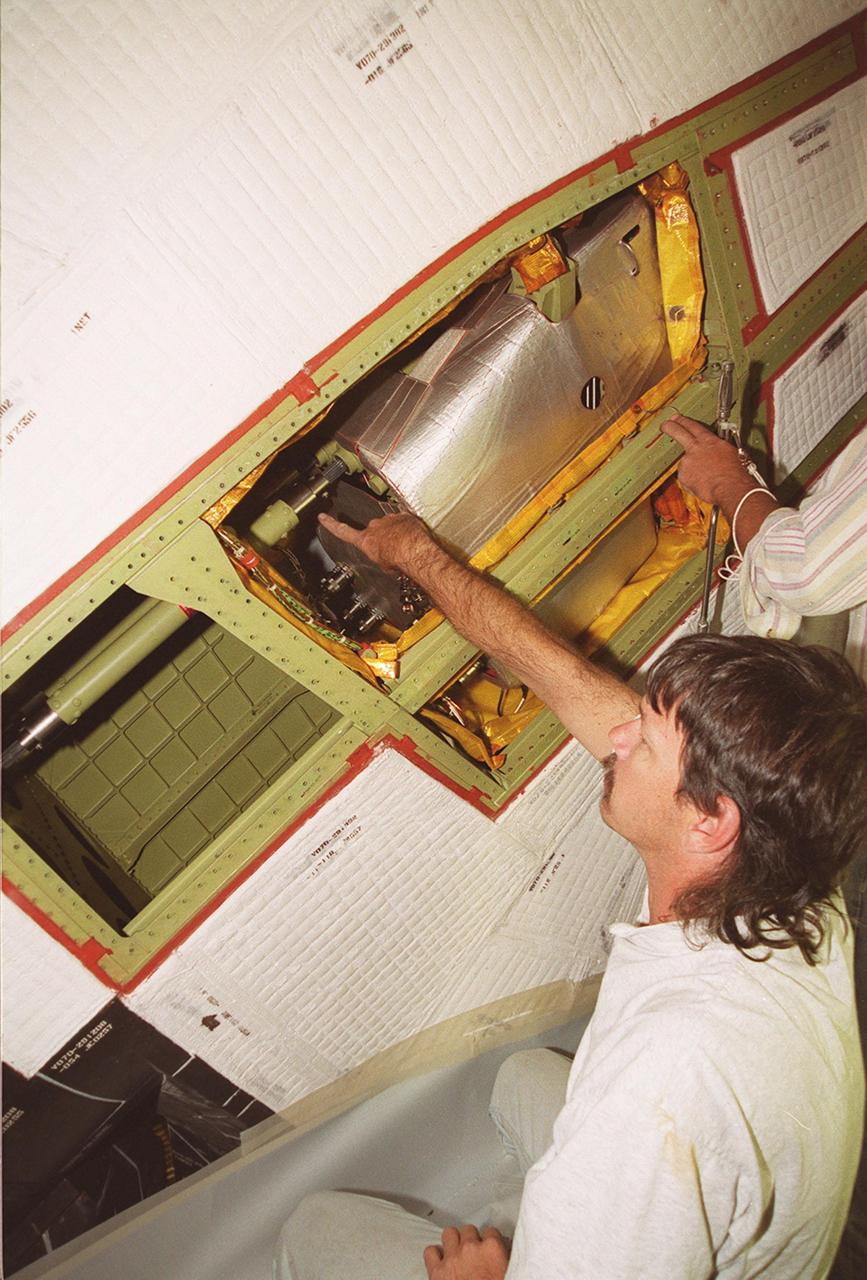

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With coverings removed from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis, Tod Biddle, a United Space Alliance (USA) technician, points to the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. The hands at right belong to Bob Wright, also a USA technician. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
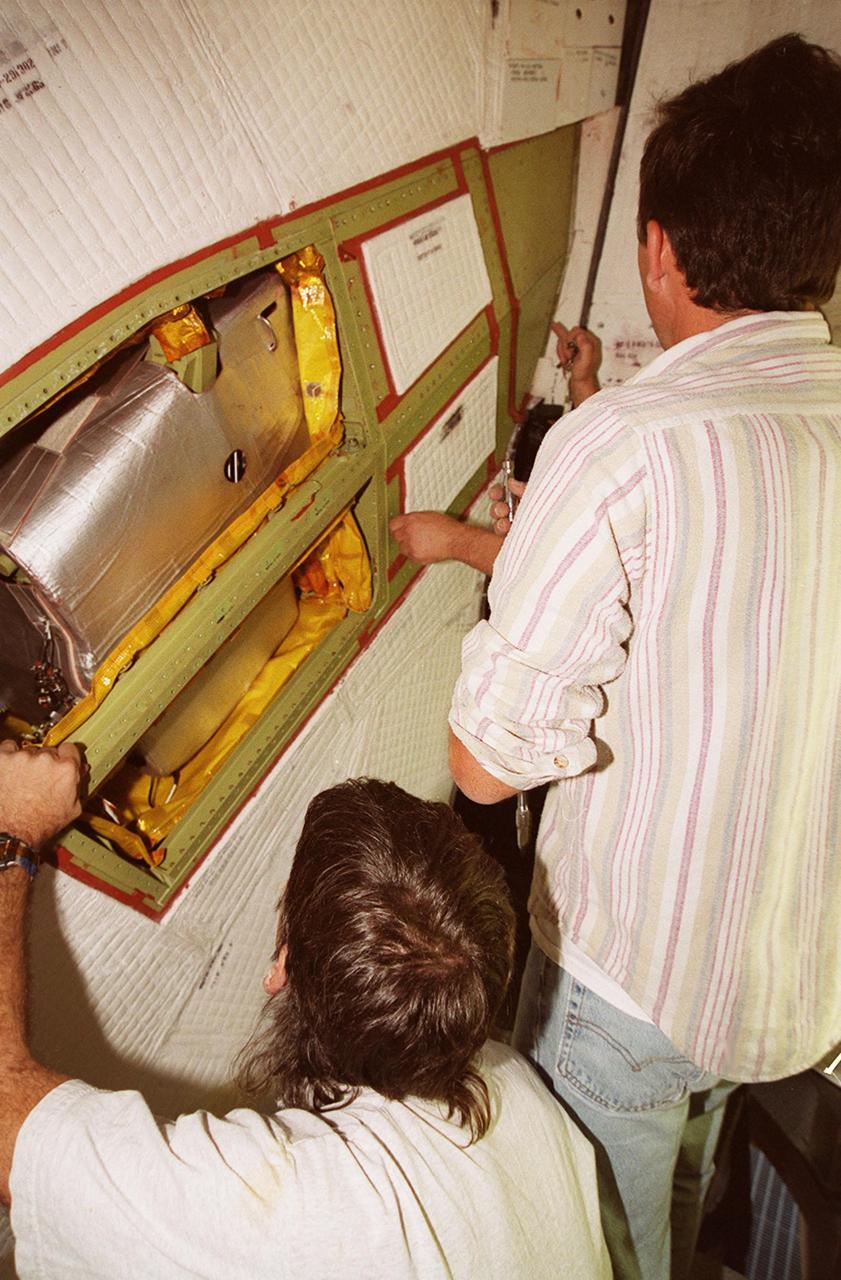

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technicians (left to right) Tod Biddle, Bob Wright and Mark Noel (hidden) remove the coverings from a site near the tail of Space Shuttle Atlantis to reveal the power drive unit (PDU) inside. The PDU controls the rudder/speed brake on the orbiter. Shuttle managers decided to replace the faulty PDU, about the size of an office copy machine, at the launch pad. If successful, launch preparations will continue as planned, with liftoff targeted for April 24 at 4:15 p.m. on mission STS-101. The mission is the third assembly flight for the International Space Station, carrying logistics and supplies to the Space Station, plus the crew will be preparing the Station for the arrival of the Zvezda Service Module, expected to be launched by Russia in July 2000. The crew will conduct one space walk to perform maintenance on the Space Station
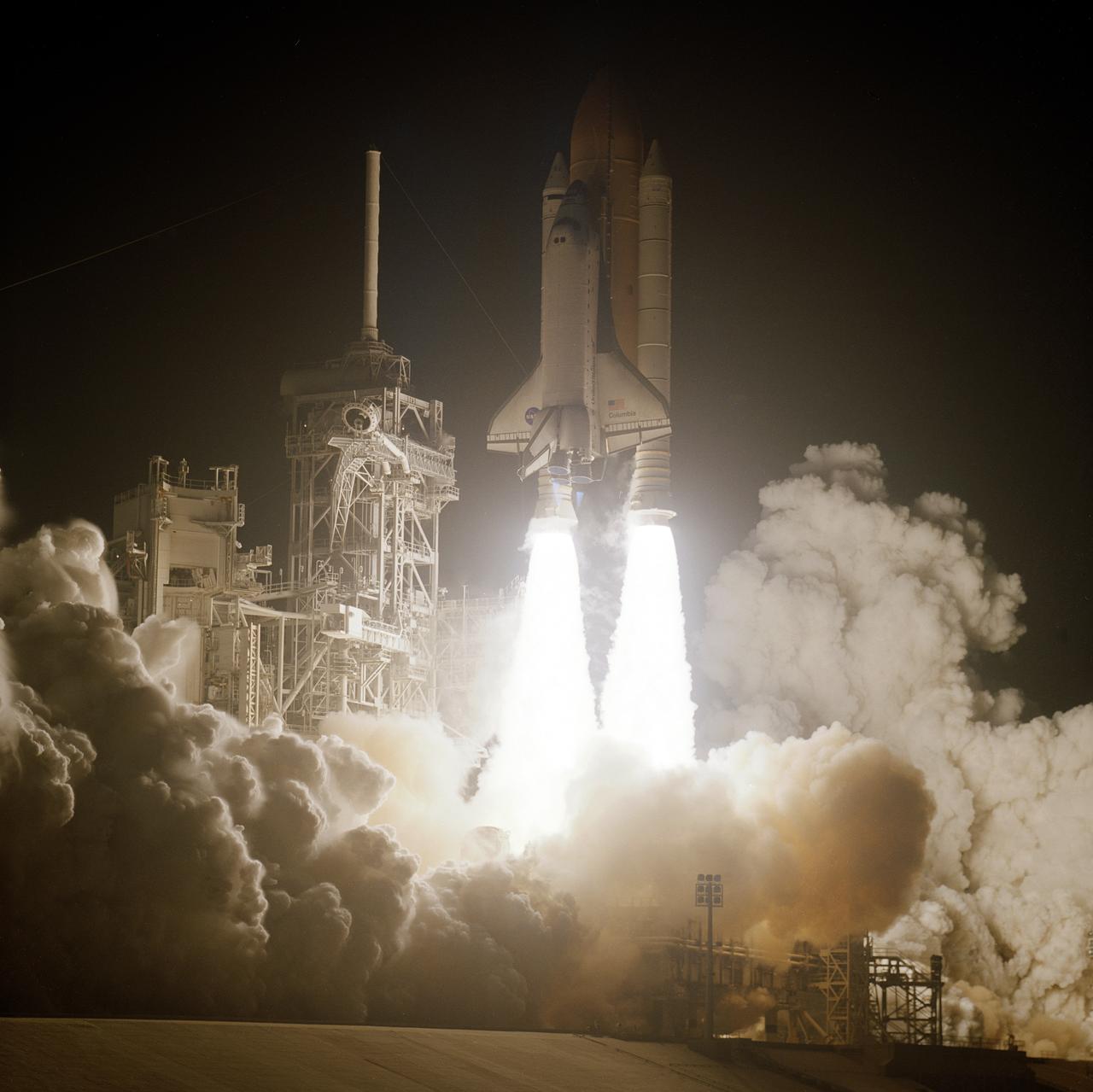

Carrying the STS-109 crew of seven, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia blasted from its launch pad as it began its 27th flight and 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Launched March 1, 2002, the goal of the mission was the maintenance and upgrade of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was developed, designed, and constructed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. Captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm, the HST received the following upgrades: replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the power control unit (PCU); replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when it original coolant ran out. Four of the crewmembers performed 5 space walks in the 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes of the the STS-109 mission.
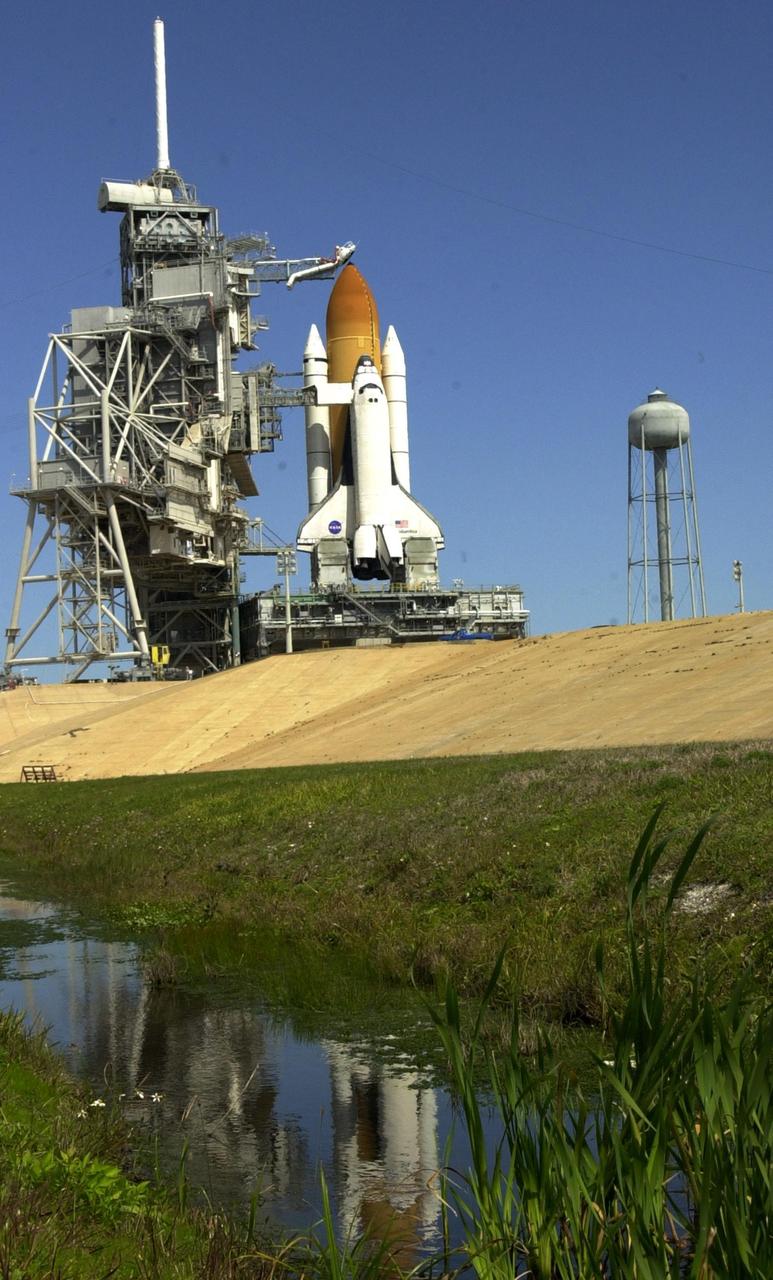

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Rollback of the Rotating Service Structure for the second time, after a scrub of mission STS-109 the day before, provides an unfettered look at Space Shuttle Columbia on Launch Pad 39A. The nearby water gives an impressionistic view. Above the orange-colored external tank is poised the "beanie cap," the gaseous oxygen vent hood. Extending to the side of Columbia is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The White Room provides entry for the crew into the orbiter. Columbia sits atop the Mobile Launcher Platform. At right is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water, part of the sound suppression system during a launch. Columbia is rescheduled for launch on mission STS-109 March 1 at 6:22 a.m. EST (11:22 GMT). The 11-day mission will provide maintenance and upgrade to the Hubble Space Telescope, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, installing the ACS (after removing the Faint Object Camera ), the Near Infrared Camera, the Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and the New Outer Blanket Layer insulation.
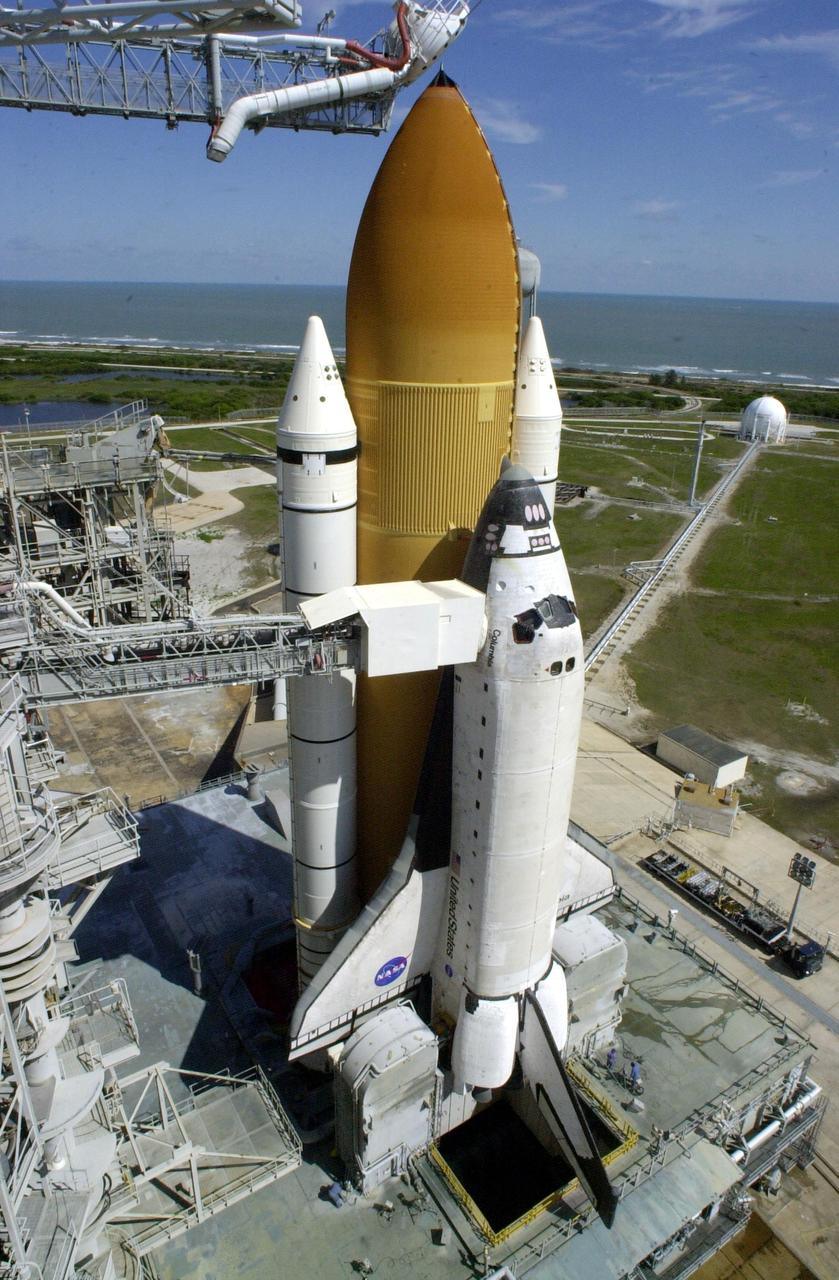

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Rollback of the Rotating Service Structure for the second time after a scrub of mission STS-109 the day before reveals Space Shuttle Columbia on Launch Pad 39A. The clear blue Florida sky and Atlantic Ocean provide a backdrop. Above the orange-colored external tank is poised the "beanie cap," the gaseous oxygen vent hood. Extending to the side of Columbia is the Orbiter Access Arm with the environmentally controlled White Room at the end. The White Room provides entry for the crew into the orbiter. Columbia sits atop the Mobile Launcher Platform which has an opening to the flame trench below. Columbia is rescheduled for launch on mission STS-109 March 1 at 6:22 a.m. EST (11:22 GMT). The 11-day mission will provide maintenance and upgrade to the Hubble Space Telescope, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, installing the ACS (after removing the Faint Object Camera ), the Near Infrared Camera, the Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and the New Outer Blanket Layer insulation.

S123-E-006057 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Garrett Reisman, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Reisman and astronaut Rick Linnehan (out of frame), STS-123 mission specialist, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System. Visible in the reflections in Reisman's visor are various components of the station and the docked Space Shuttle Endeavour.

S123-E-005981 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Garrett Reisman, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the STS-123 mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Reisman and astronaut Rick Linnehan (out of frame), STS-123 mission specialist, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) (top left) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System. The blackness of space and a blue and white Earth provide the backdrop for the scene.
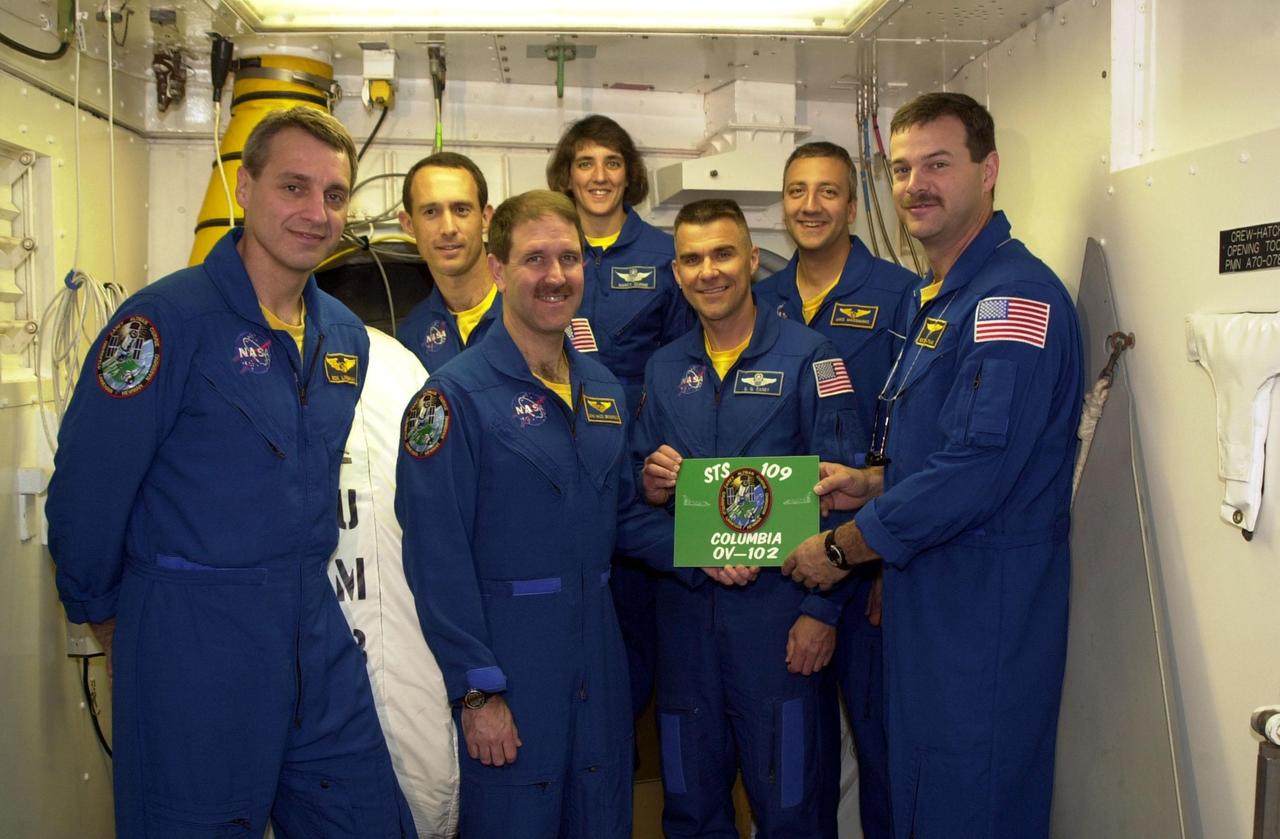

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, the STS-109 crew stands in the White Room, outside the entry into Space Shuttle Columbia, displaying the mission patch and placard. Standing, left to right, are Mission Specialists Richard Linnehan, James Newman, John Grunsfeld and Nancy Currie; Pilot Duane Carey; Mission Specialist Michael Massimino; and Commander Scott Altman. The White Room is an environmentally controlled structure at the end of the Orbiter Access Room that provides access to the orbiter. The crew is taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency egress training and a simulated countdown at the pad. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the ACS, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. . The launch will be the first for Columbia after returning from California where it underwent extensive maintenance, inspections and enhancements. More than 100 upgrades make Columbia safer and more reliable than ever before
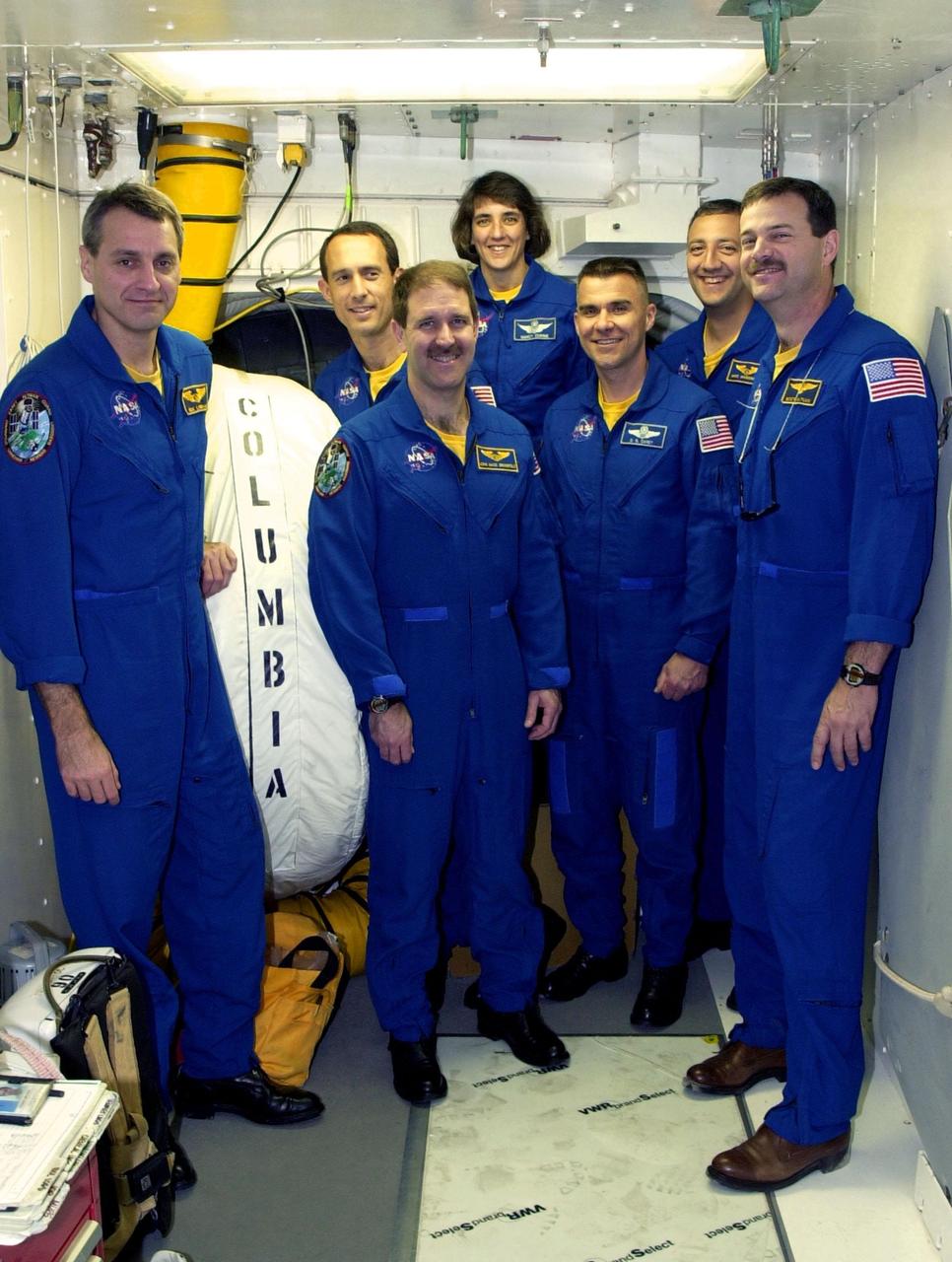

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, the STS-109 crew stands in the White Room, outside the entry into Space Shuttle Columbia. Standing, left to right, are Mission Specialists Richard Linnehan, James Newman, John Grunsfeld and Nancy Currie; Pilot Duane Carey; Mission Specialist Michael Massimino; and Commander Scott Altman. The White Room is an environmentally controlled structure at the end of the Orbiter Access Room that provides access to the orbiter. The crew is taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include emergency egress training and a simulated countdown at the pad. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the ACS, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. . The launch will be the first for Columbia after returning from California where it underwent extensive maintenance, inspections and enhancements. More than 100 upgrades make Columbia safer and more reliable than ever before
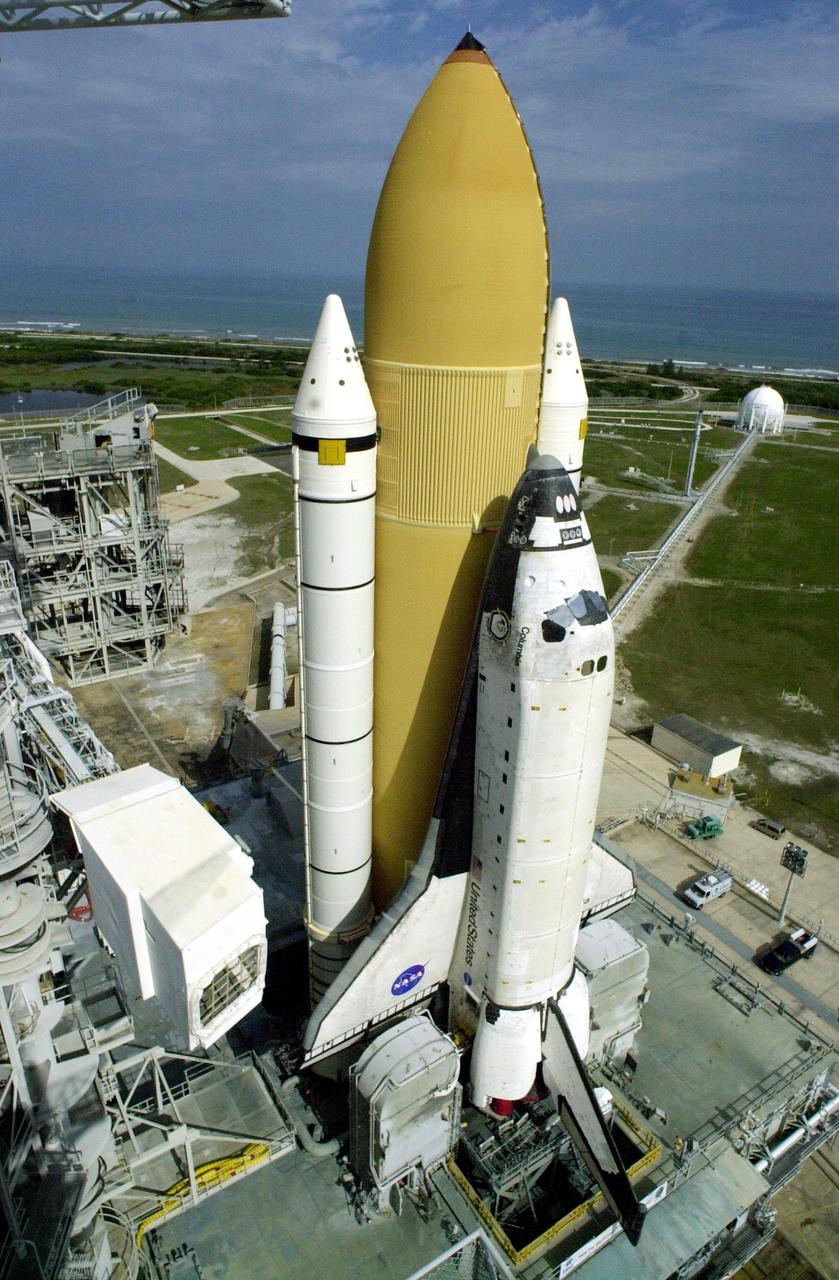

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Columbia, atop its Mobile Launcher Platform, sits on Launch Pad 39A after an early morning rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the distance is seen the Atlantic Ocean. To the left is the "White Room" that provides entry to the cockpit when extended to the orbiter. The environmentally controlled room is at the end of the Orbiter Access Arm, located 147 feet above the pad, on the Fixed Service Structure. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the ACS, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. The launch will be the first for Columbia after returning from California where it underwent extensive maintenance, inspections and enhancements. More than 100 upgrades make Columbia safer and more reliable than ever before
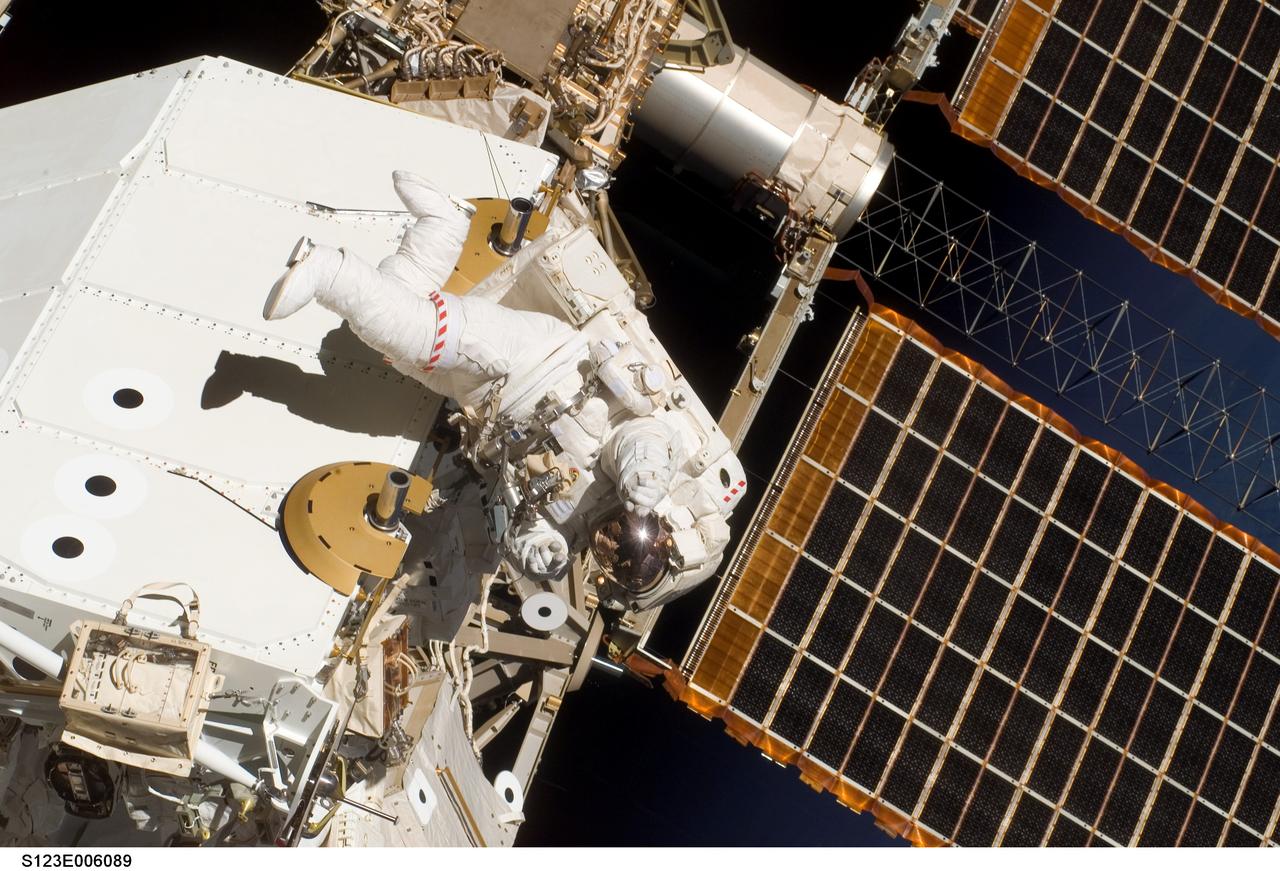

S123-E-006089 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Garrett Reisman, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Reisman and astronaut Rick Linnehan (out of frame), STS-123 mission specialist, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
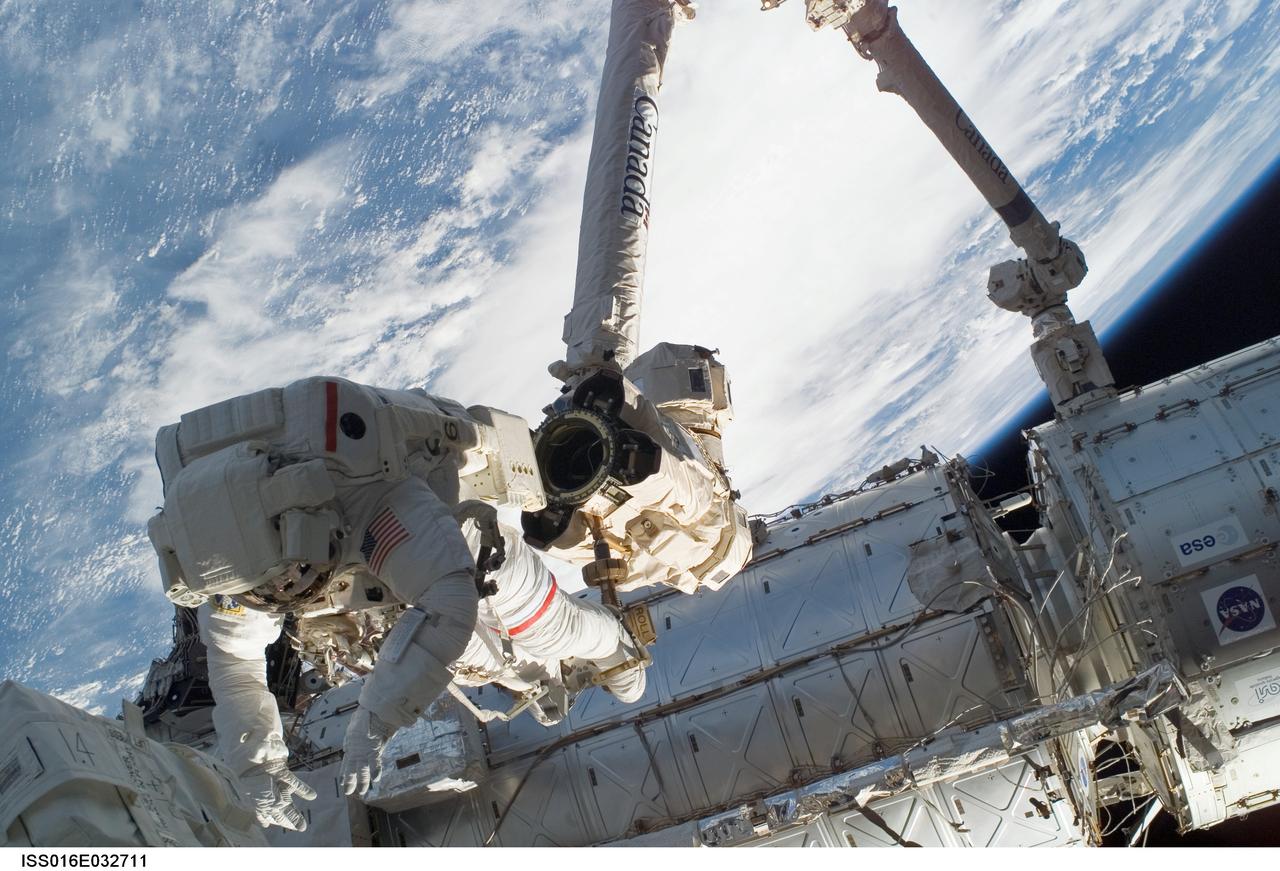

ISS016-E-032711 (13/14 March 2008) --- Anchored to a Canadarm2 mobile foot restraint, astronaut Rick Linnehan, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
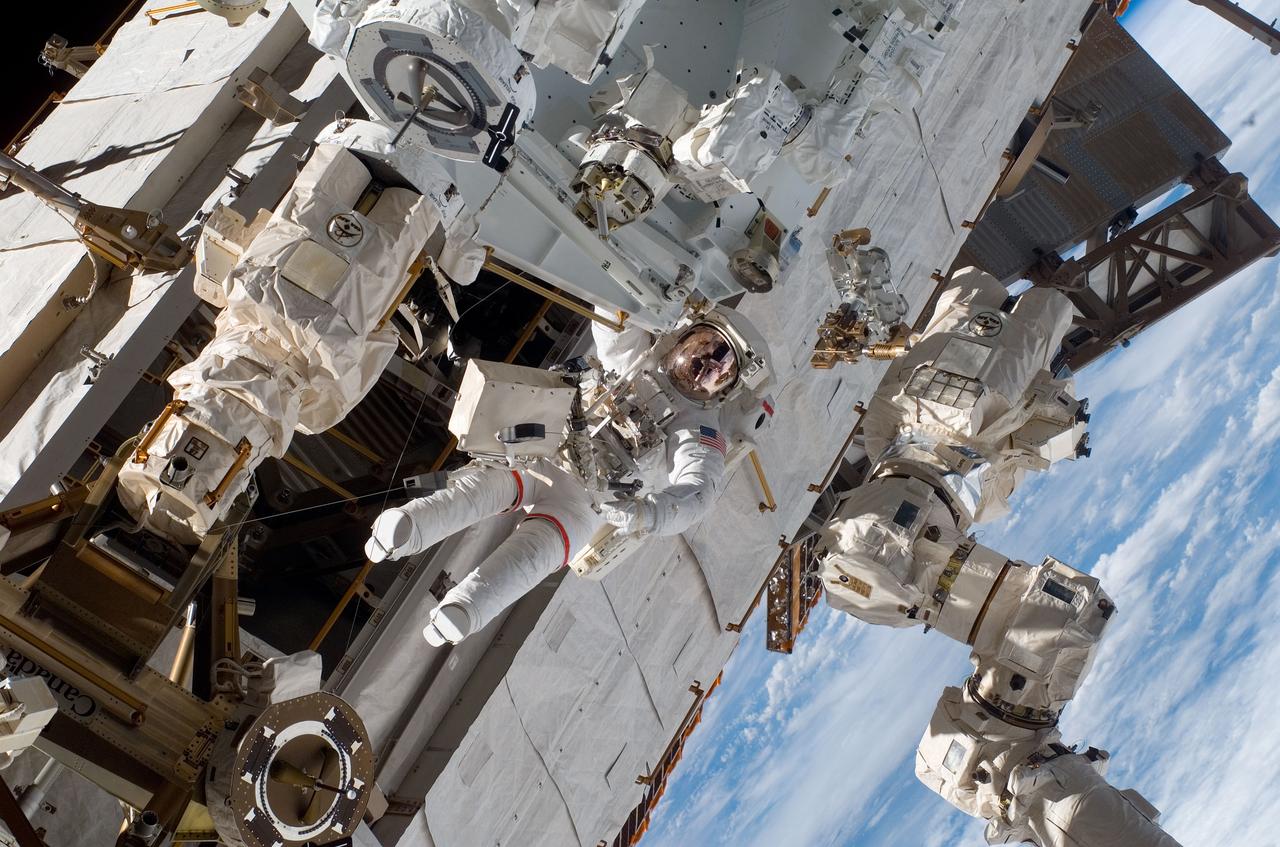

S123-E-006082 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Rick Linnehan, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
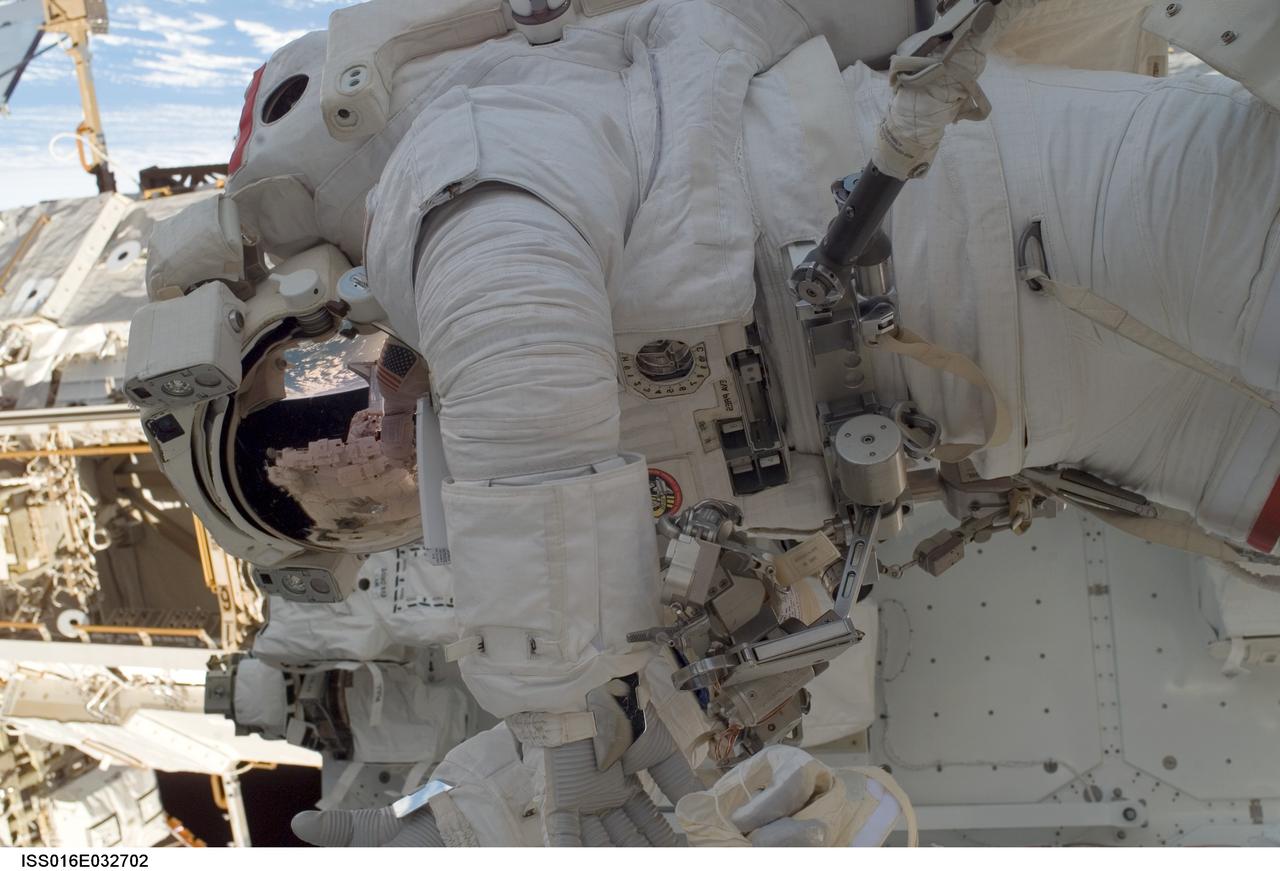

ISS016-E-032702 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Rick Linnehan, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
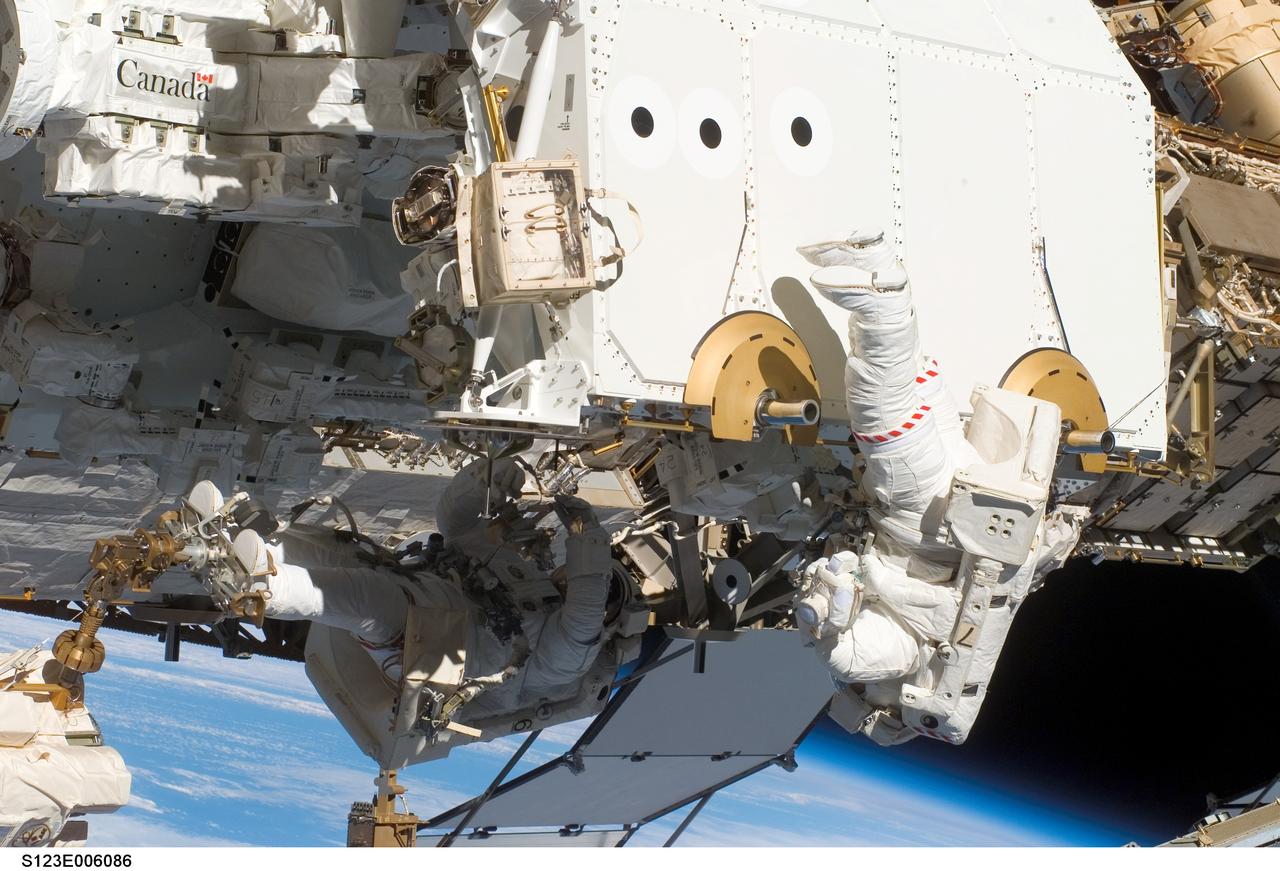

S123-E-006086 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronauts Rick Linnehan (left), STS-123 mission specialist; and Garrett Reisman, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participate in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and Reisman prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
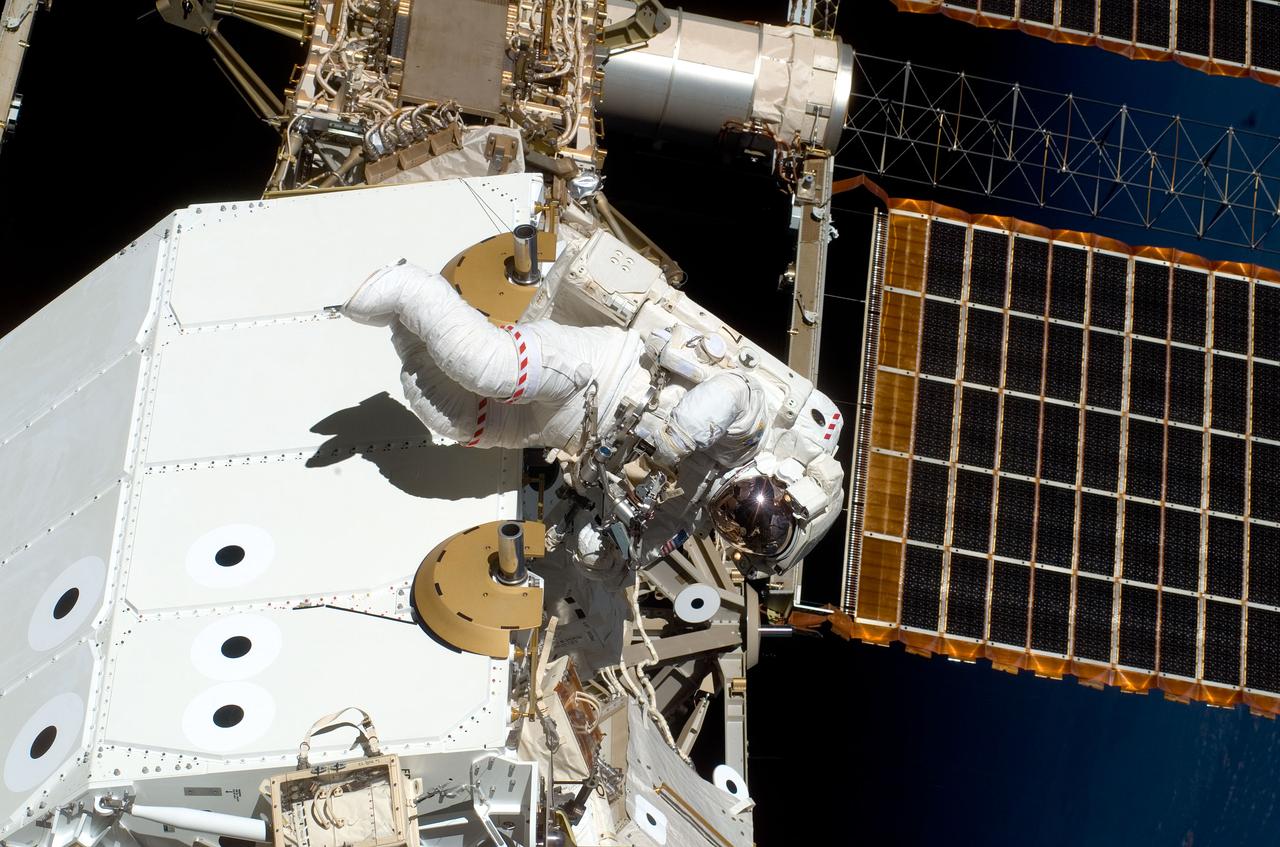

S123-E-006090 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Garrett Reisman, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Reisman and astronaut Rick Linnehan (out of frame), STS-123 mission specialist, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
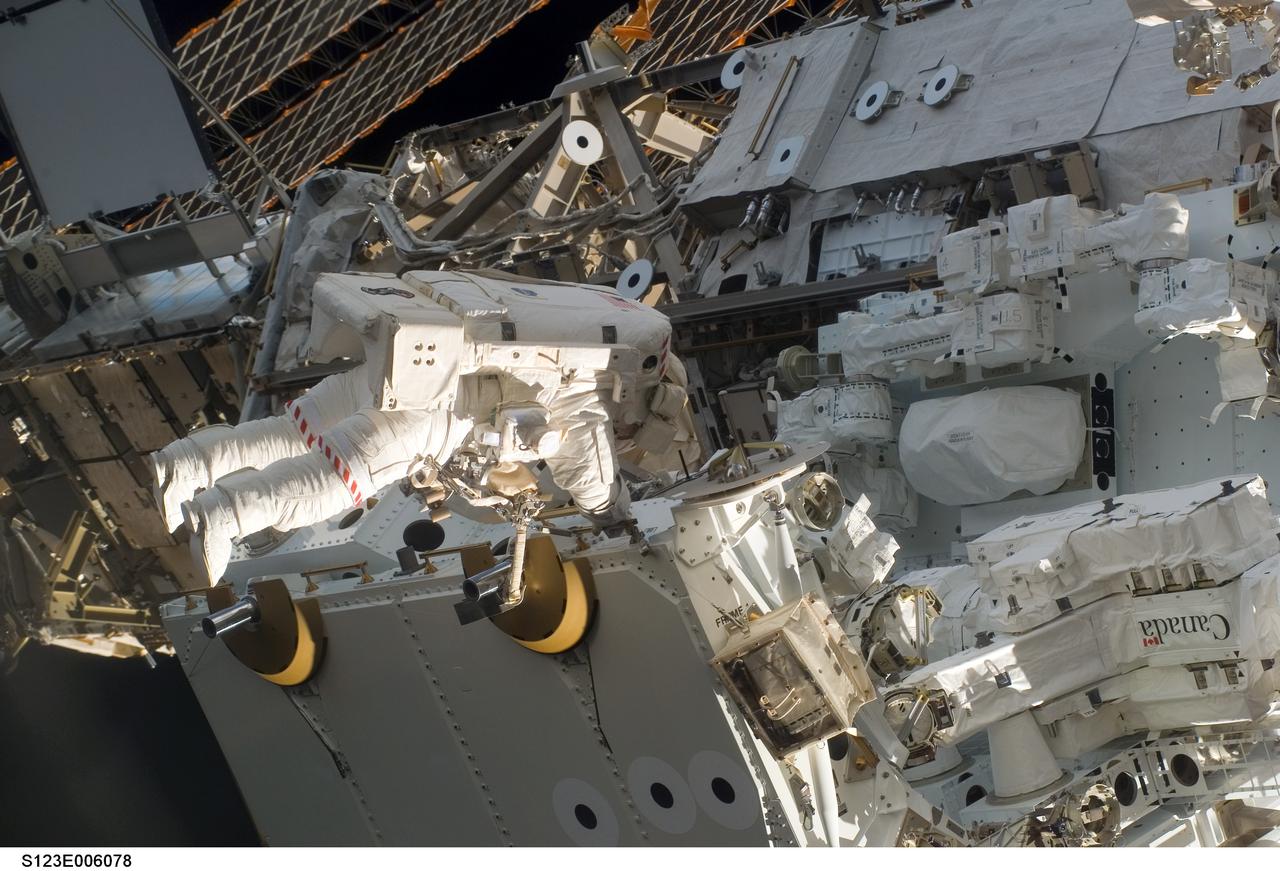

S123-E-006078 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Garrett Reisman, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Reisman and astronaut Rick Linnehan (out of frame), STS-123 mission specialist, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
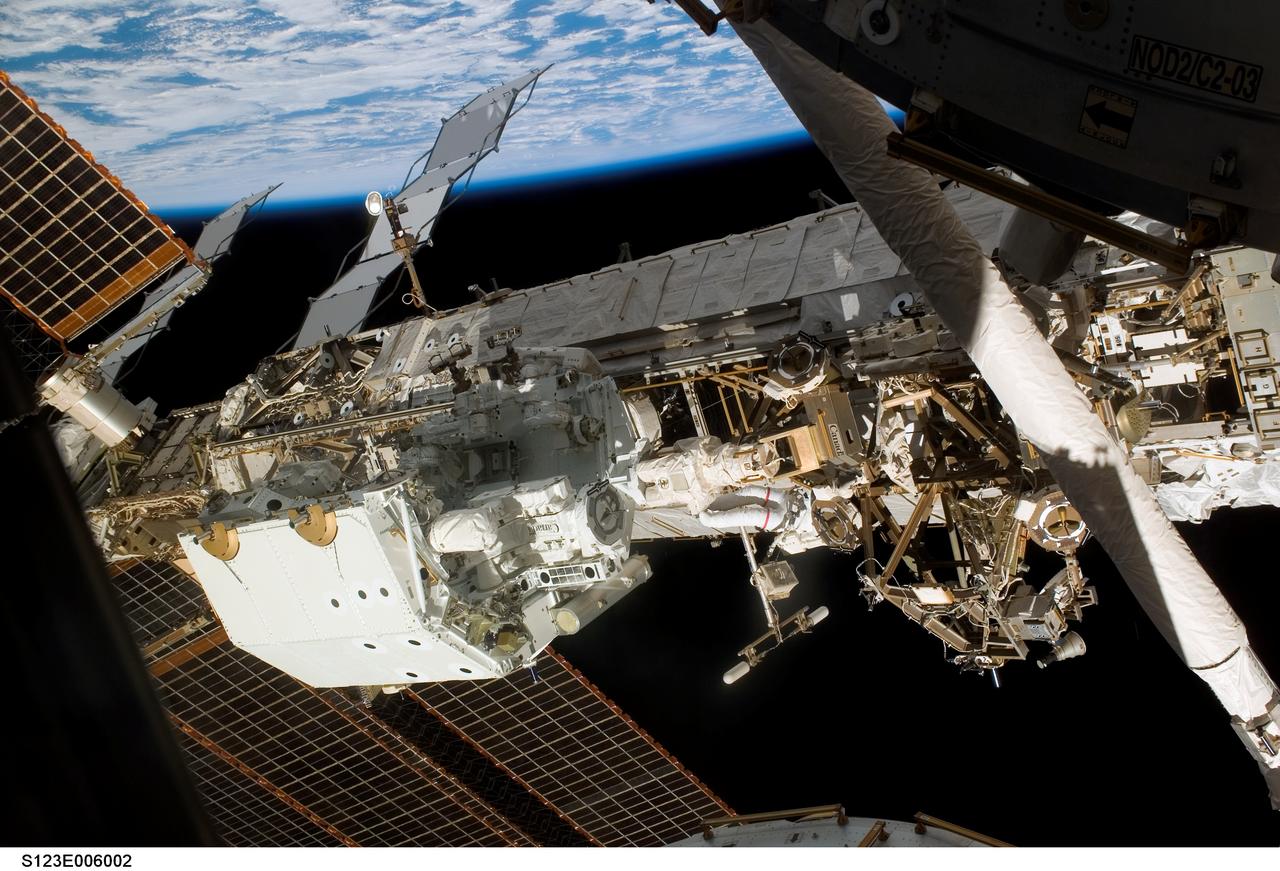

S123-E-006002 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Rick Linnehan (center), STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system (center left), the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
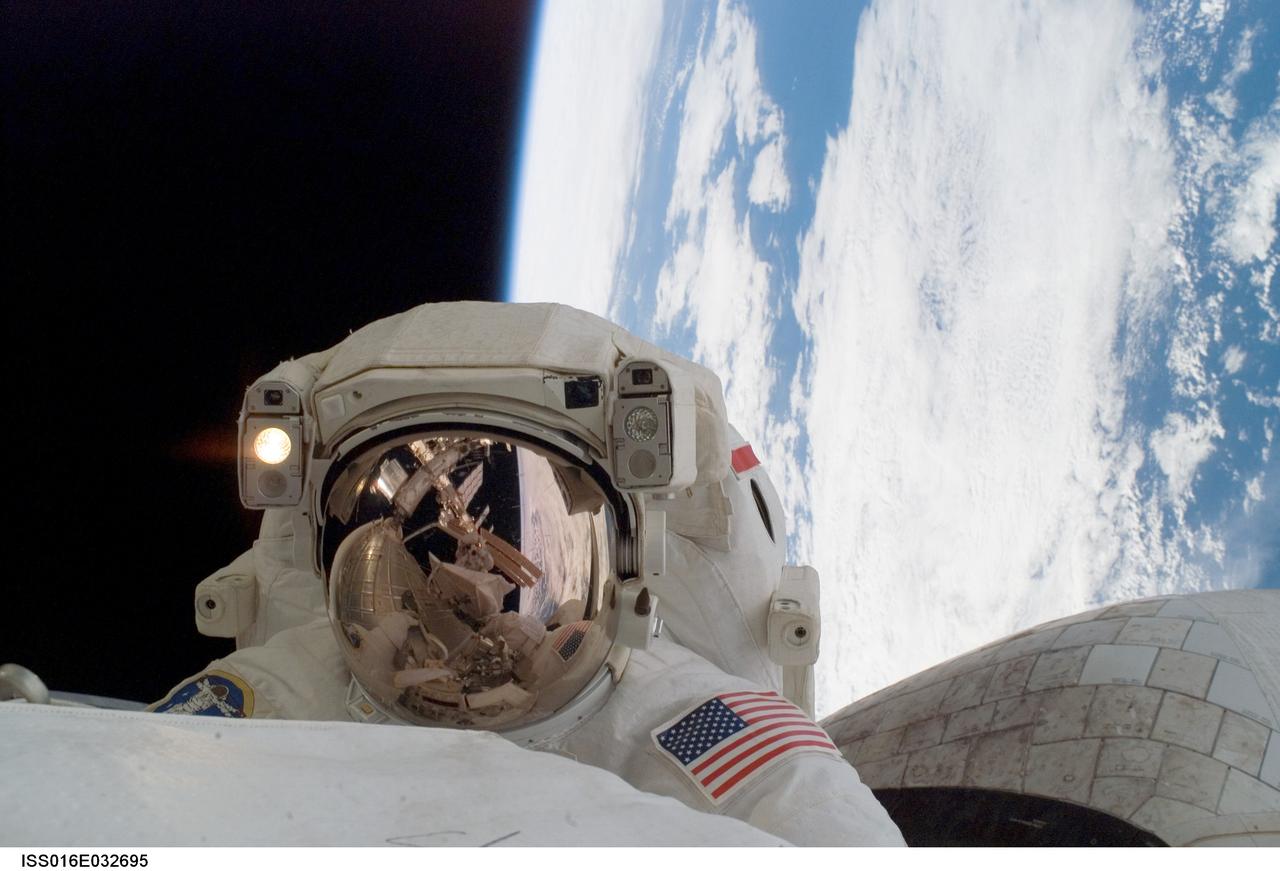

ISS016-E-032695 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Rick Linnehan, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
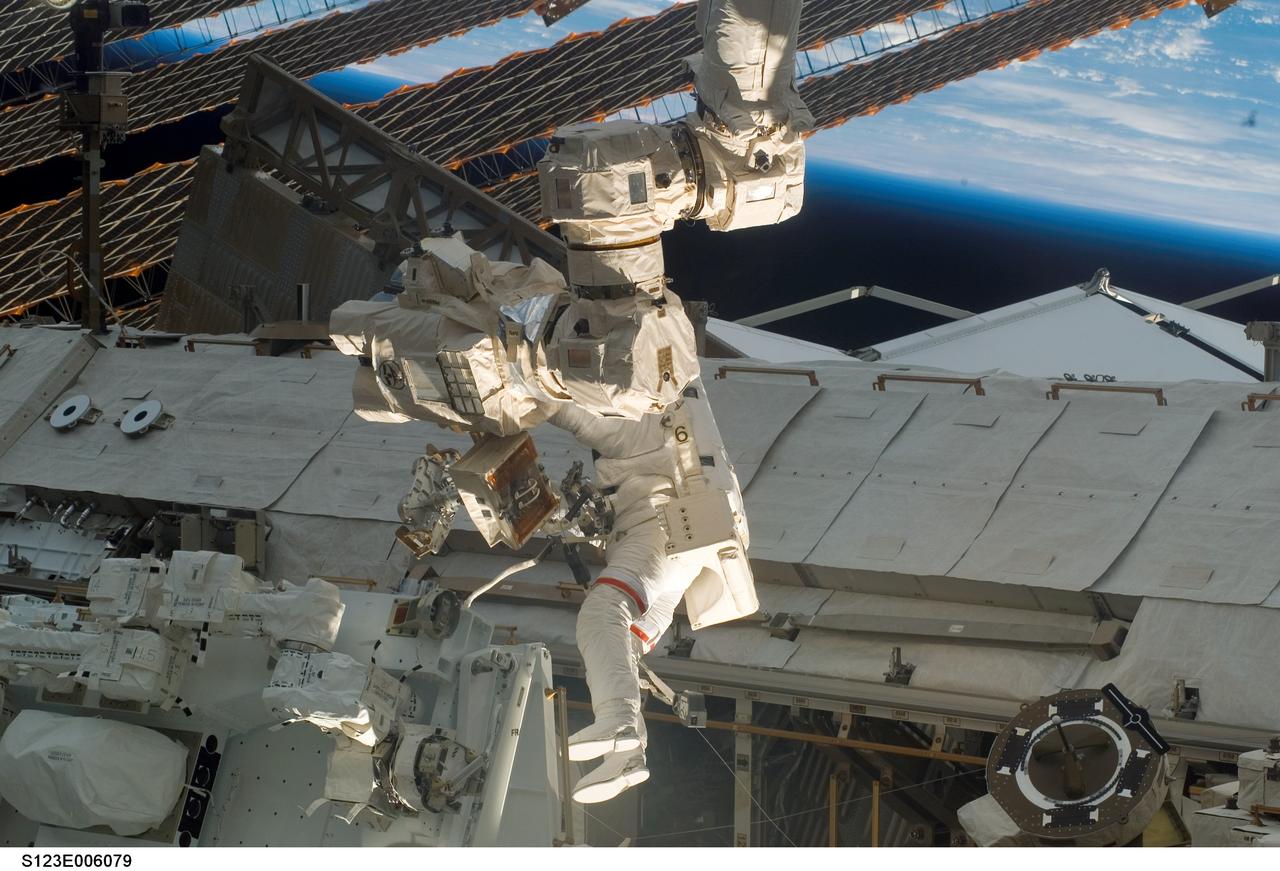

S123-E-006079 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Rick Linnehan, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
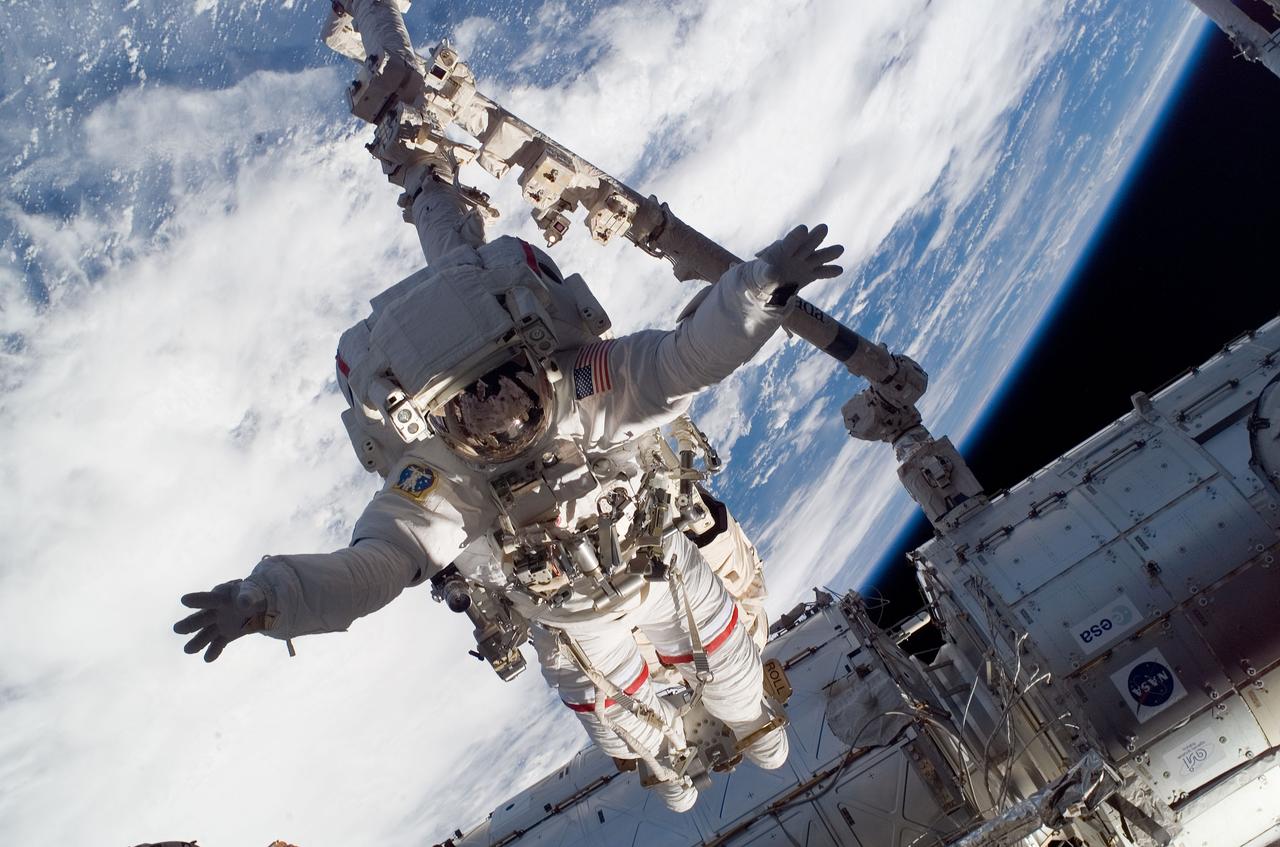

ISS016-E-032708 (13/14 March 2008) --- Anchored to a Canadarm2 mobile foot restraint, astronaut Rick Linnehan, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
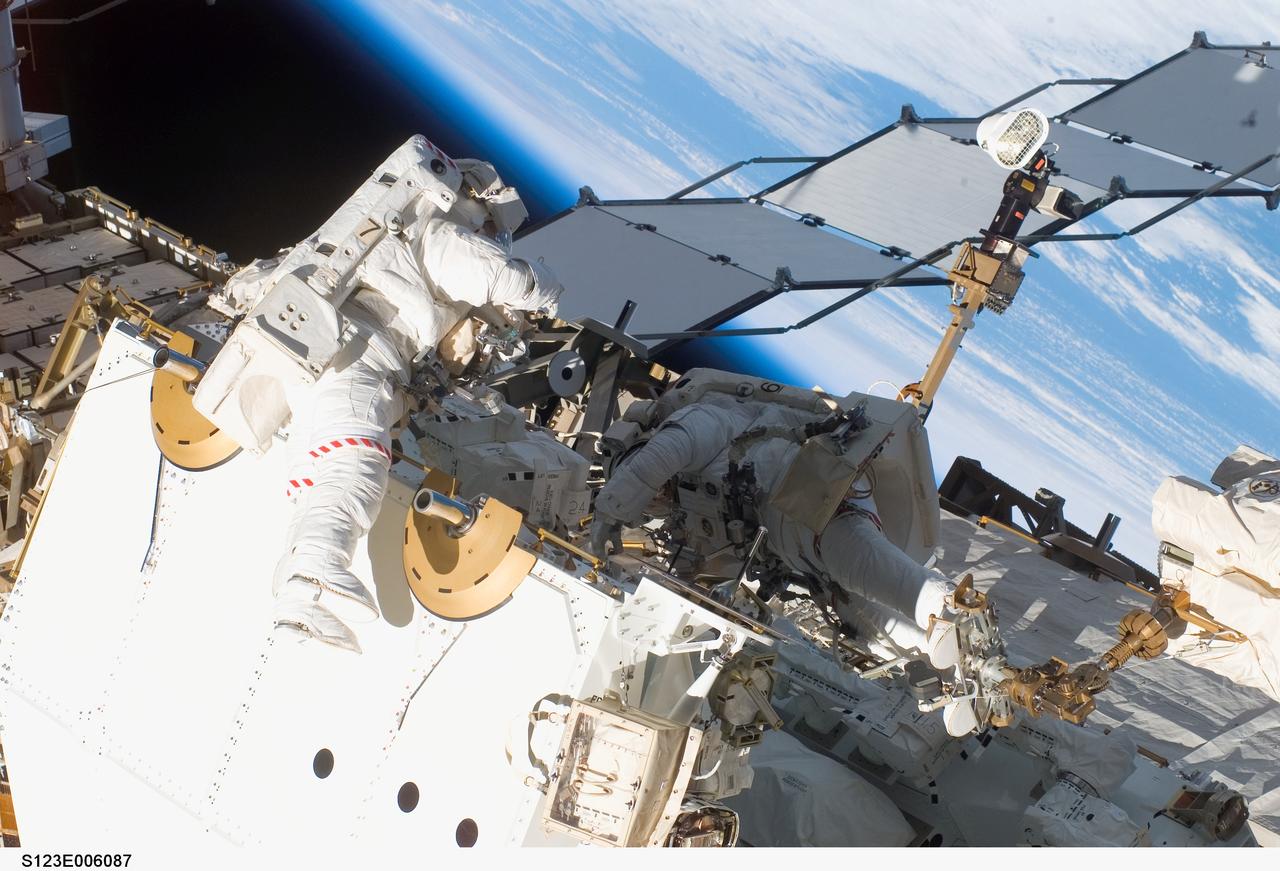

S123-E-006087 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronauts Rick Linnehan (right), STS-123 mission specialist; and Garrett Reisman, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participate in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and Reisman prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
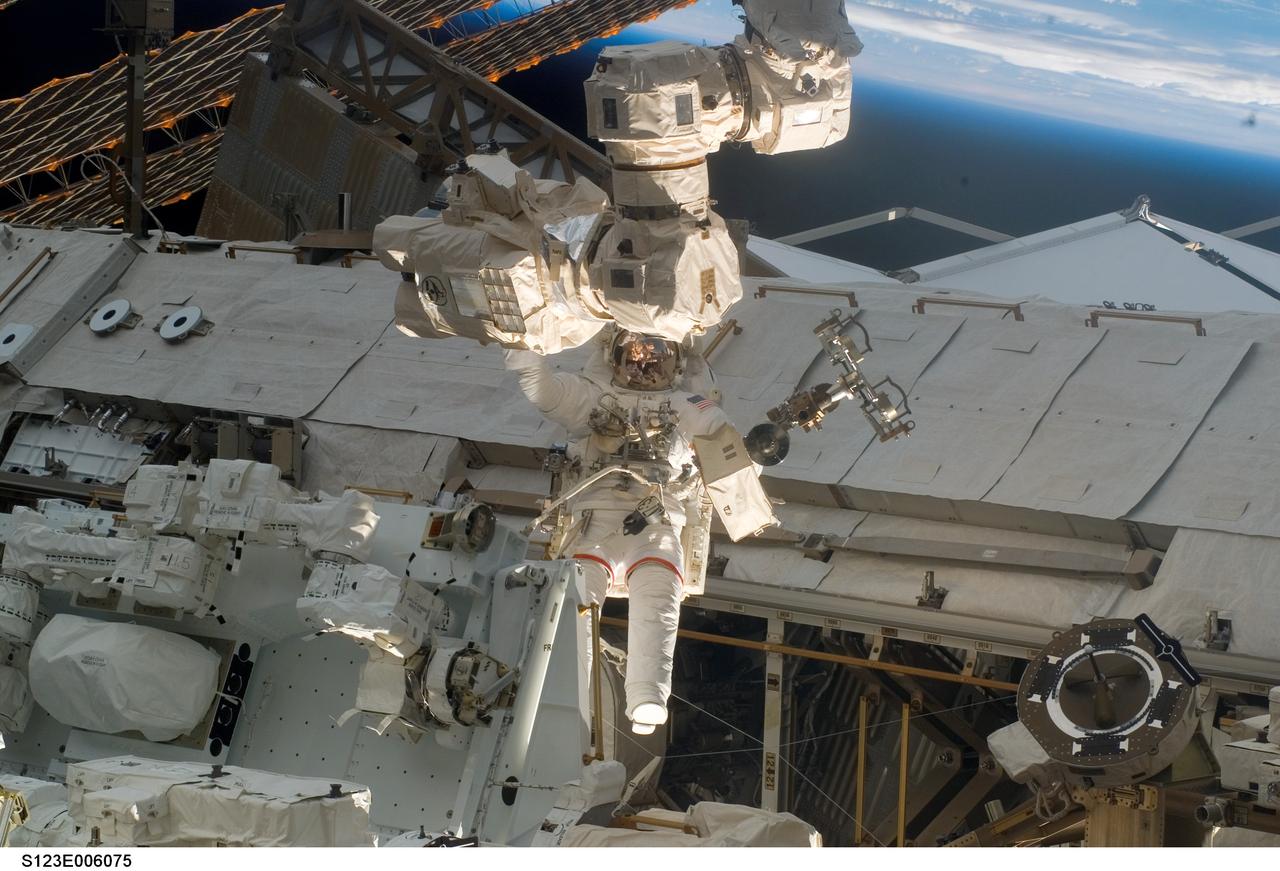

S123-E-006075 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Rick Linnehan, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
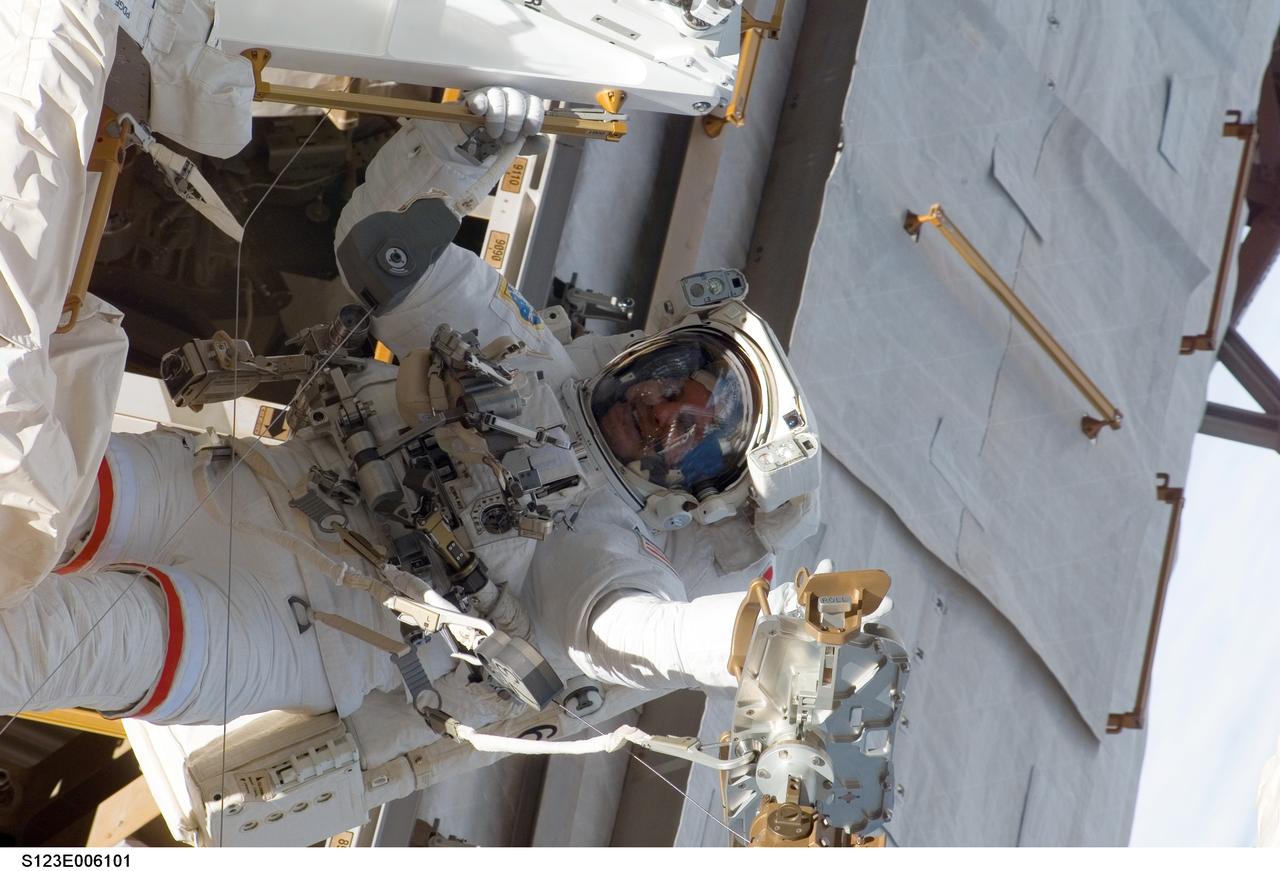

S123-E-006101 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Rick Linnehan, STS-123 mission specialist, participates in the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Linnehan and astronaut Garrett Reisman (out of frame), Expedition 16 flight engineer, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
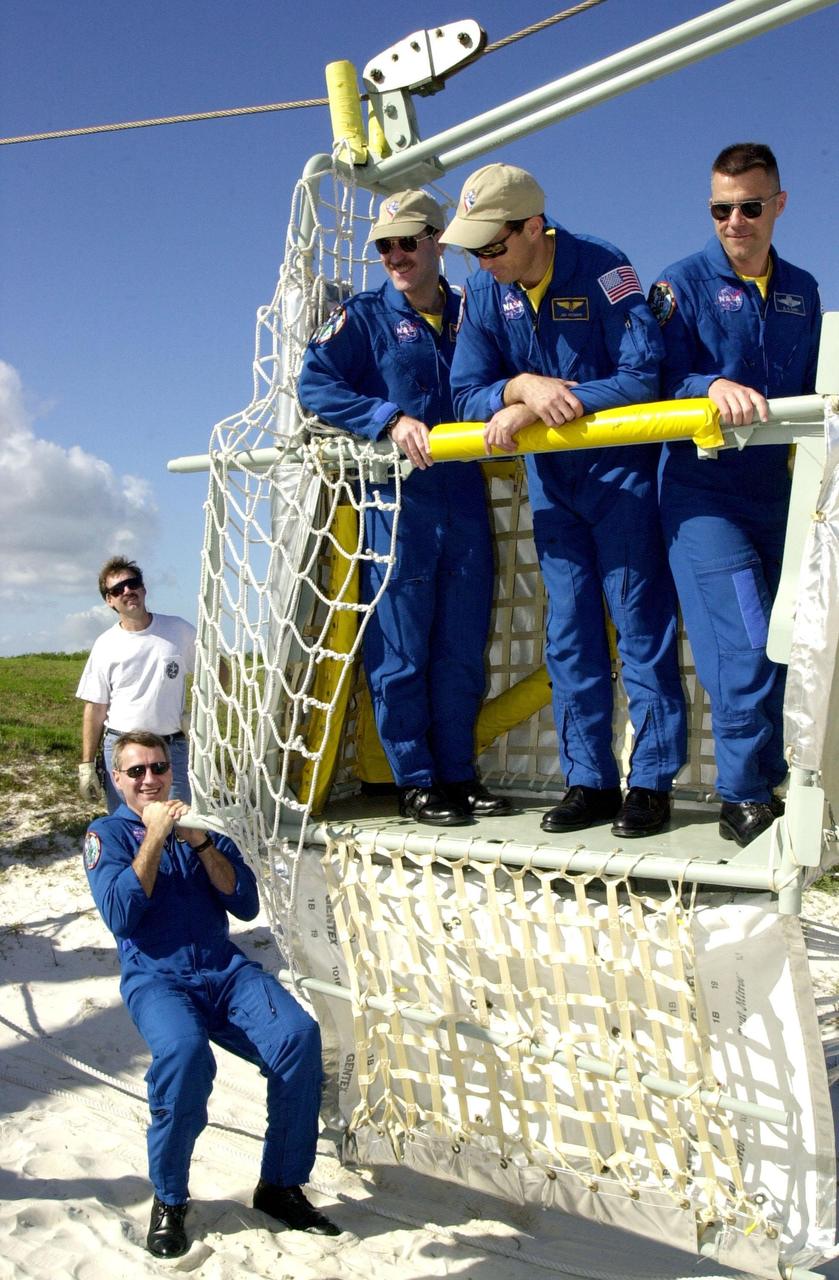

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Near the bunker at the bottom of Launch Pad 39A, Mission Specialist Richard Linnehan steadies the slidewire basket, part of the emergency egress system from the orbiter. In the basket are Mission Specialists John Grunsfeld and James Newman and Pilot Duane Carey. The training is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that include a simulated countdown at the pad. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the ACS, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation. . The launch will be the first for Columbia after returning from California where it underwent extensive maintenance, inspections and enhancements. More than 100 upgrades make Columbia safer and more reliable than ever before

This is the insignia of the STS-109 Space Shuttle mission. Carrying a crew of seven, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia was launched with goals of maintenance and upgrades to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Marshall Space Flight Center had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the HST, which is the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. During the STS-109 mission, the telescope was captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm where four members of the crew performed five spacewalks completing system upgrades to the HST. Included in those upgrades were: The replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the power control unit (PCU); replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when it original coolant ran out. Lasting 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes, the STS-109 mission was the 27th flight of the Orbiter Columbia and the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.
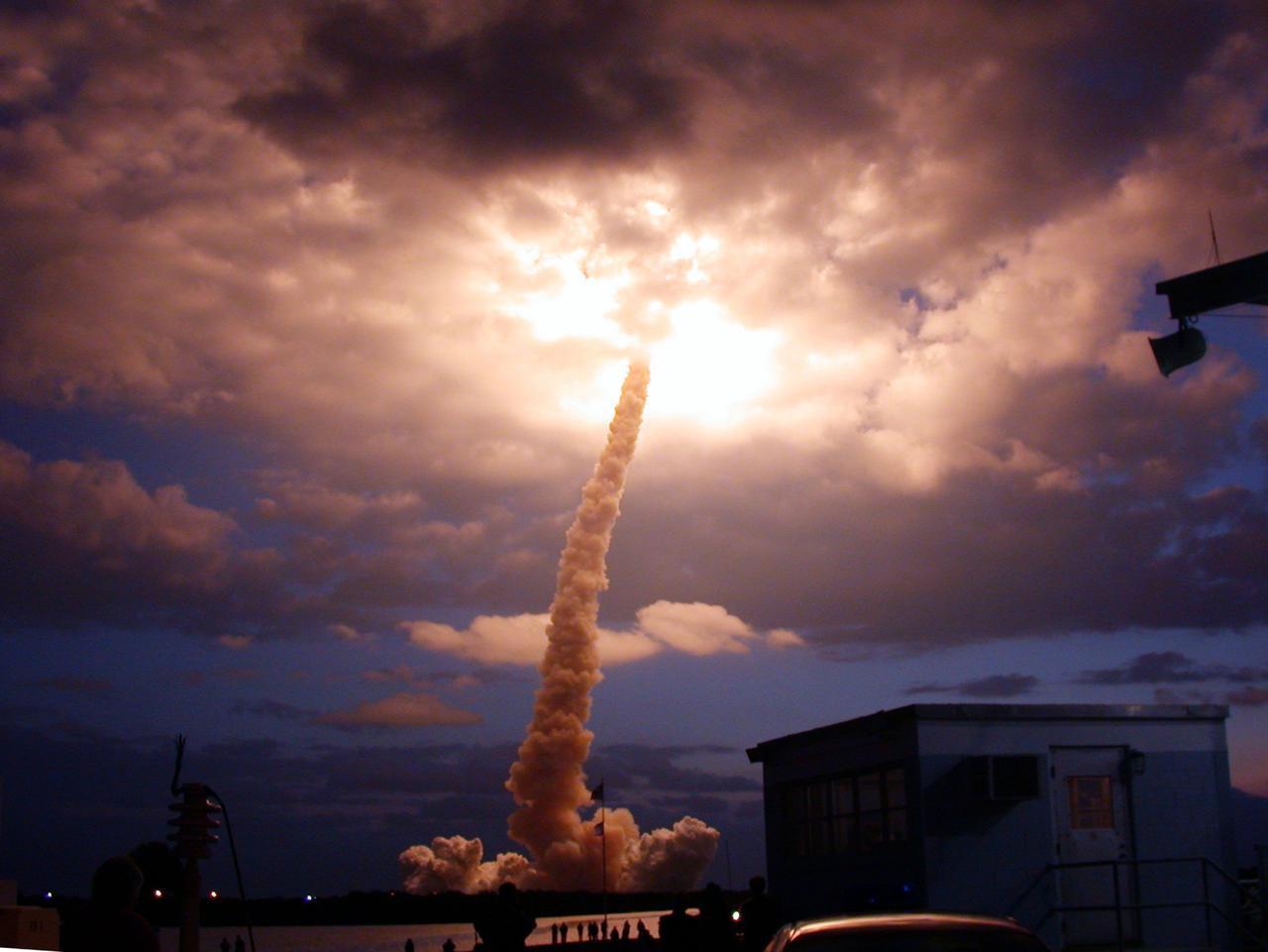

Carrying a crew of seven, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia soared through some pre-dawn clouds into the sky as it began its 27th flight, STS-109. Launched March 1, 2002, the goal of the mission was the maintenance and upgrade of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Marshall Space Flight Center had the responsibility for the design, development, and construction of the HST, which is the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. During the STS-109 mission, the telescope was captured and secured on a work stand in Columbia's payload bay using Columbia's robotic arm. Here four members of the crew performed five spacewalks completing system upgrades to the HST. Included in those upgrades were: replacement of the solar array panels; replacement of the power control unit (PCU); replacement of the Faint Object Camera (FOC) with a new advanced camera for Surveys (ACS); and installation of the experimental cooling system for the Hubble's Near-Infrared Camera and Multi-object Spectrometer (NICMOS), which had been dormant since January 1999 when it original coolant ran out. Lasting 10 days, 22 hours, and 11 minutes, the STS-109 mission was the 108th flight overall in NASA's Space Shuttle Program.
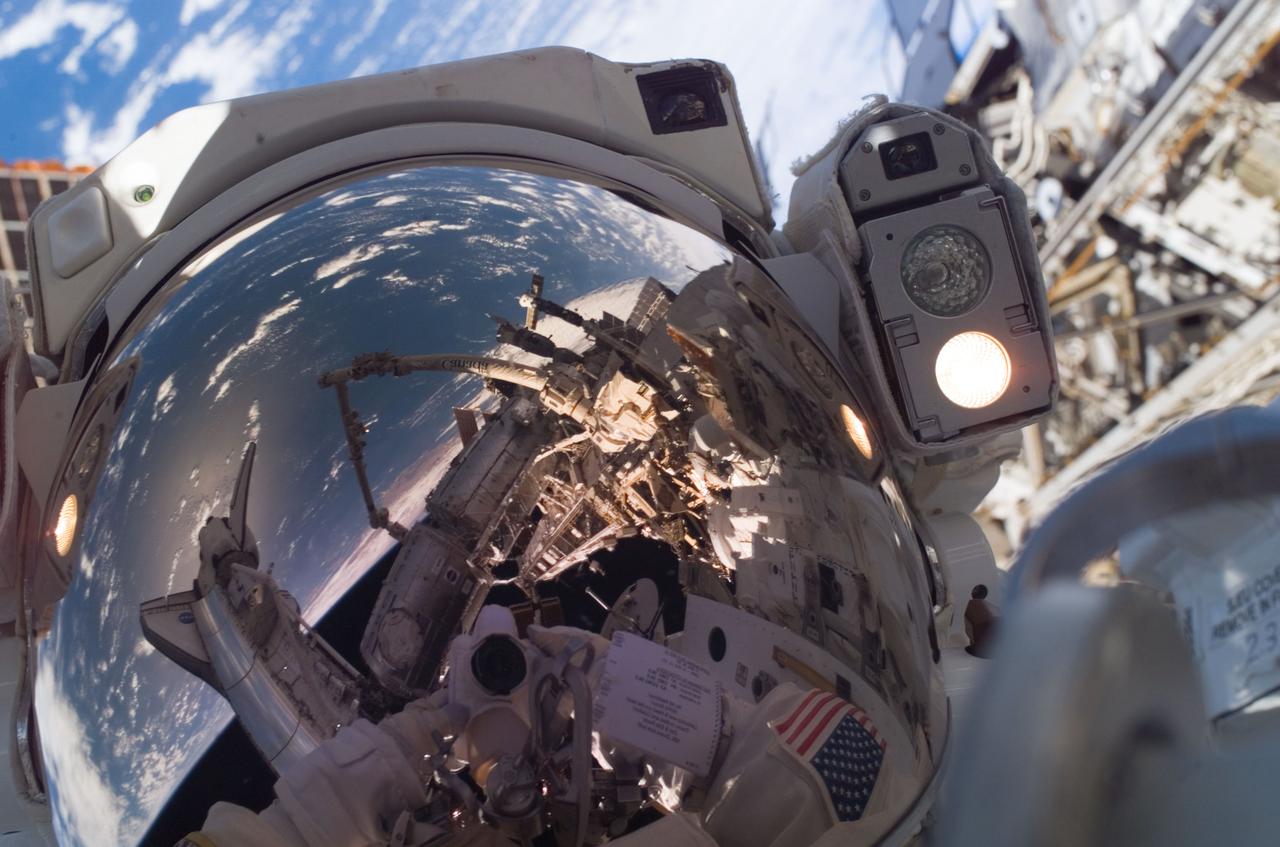

ISS016-E-032705 (13/14 March 2008) --- Astronaut Garrett Reisman, Expedition 16 flight engineer, uses a digital camera to expose a photo of his helmet visor during the mission's first scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. Also visible in the reflections in the visor are various components of the station, the docked Space Shuttle Endeavour and a blue and white portion of Earth. During the seven-hour and one-minute spacewalk, Reisman and astronaut Rick Linnehan (out of frame), STS-123 mission specialist, prepared the Japanese logistics module-pressurized section (JLP) for removal from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay; opened the Centerline Berthing Camera System on top of the Harmony module; removed the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism and installed both the Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) tool change out mechanisms on the Canadian-built Dextre robotic system, the final element of the station's Mobile Servicing System.
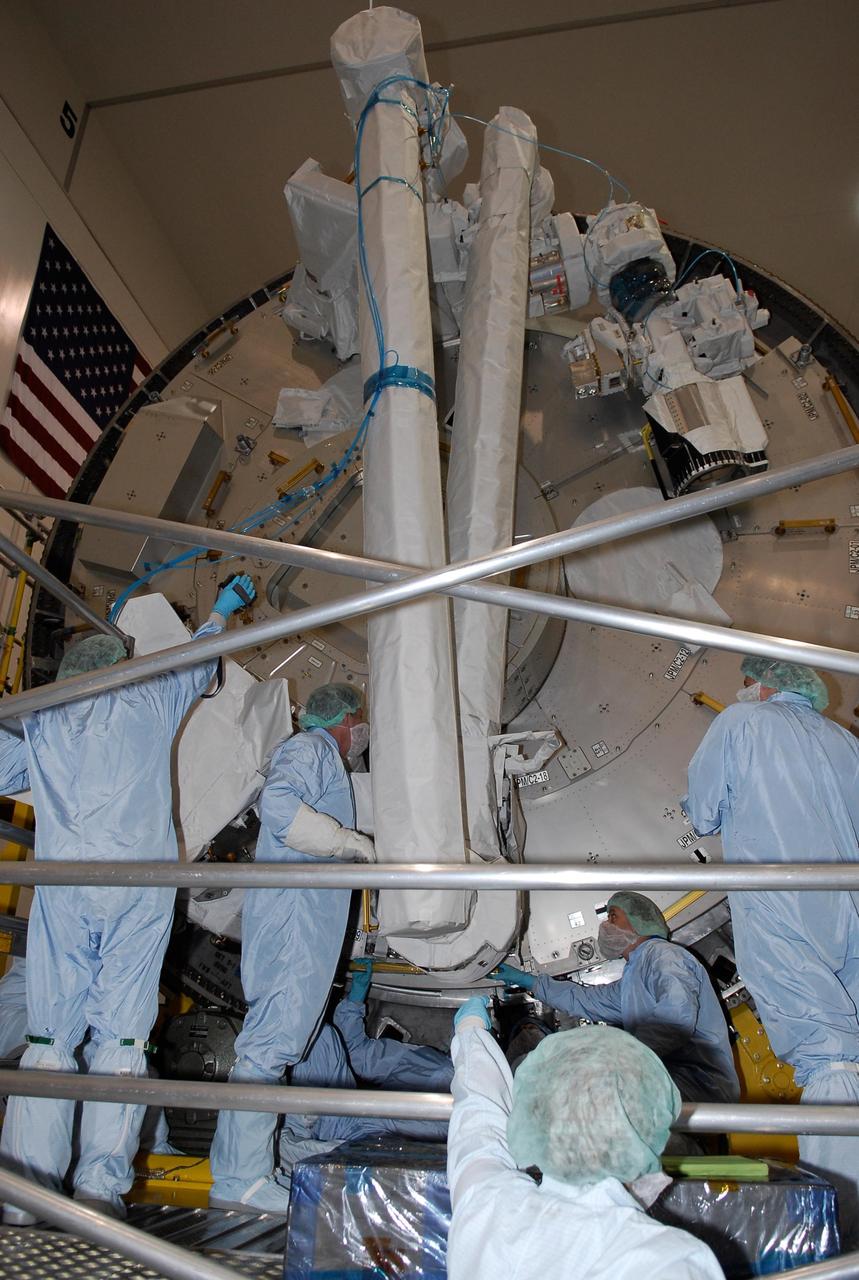

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, members of the STS-124 crew get a close look at the Remote Manipulator System, or RMS, two robotic arms that support operations on the outside of the Japanese Experiment Module, called Kibo. They will be used to exchange experiment payloads or hardware located on the Exposed Facility and Experiment Logistics Module - Exposed Section and from inside the pressurized module through a scientific airlock, support maintenance tasks of Kibo and handle orbital replacement units. Crew members are at Kennedy for a crew equipment interface test that includes familiarization with tools and equipment that will be used on the mission. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights that will launch components to complete the Japanese pressurized module, the Kibo laboratory. The mission will include two spacewalks to install the new lab and its remote manipulator system. The lab's logistics module, which will have been installed in a temporary location during STS-123, will be attached to the new lab. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
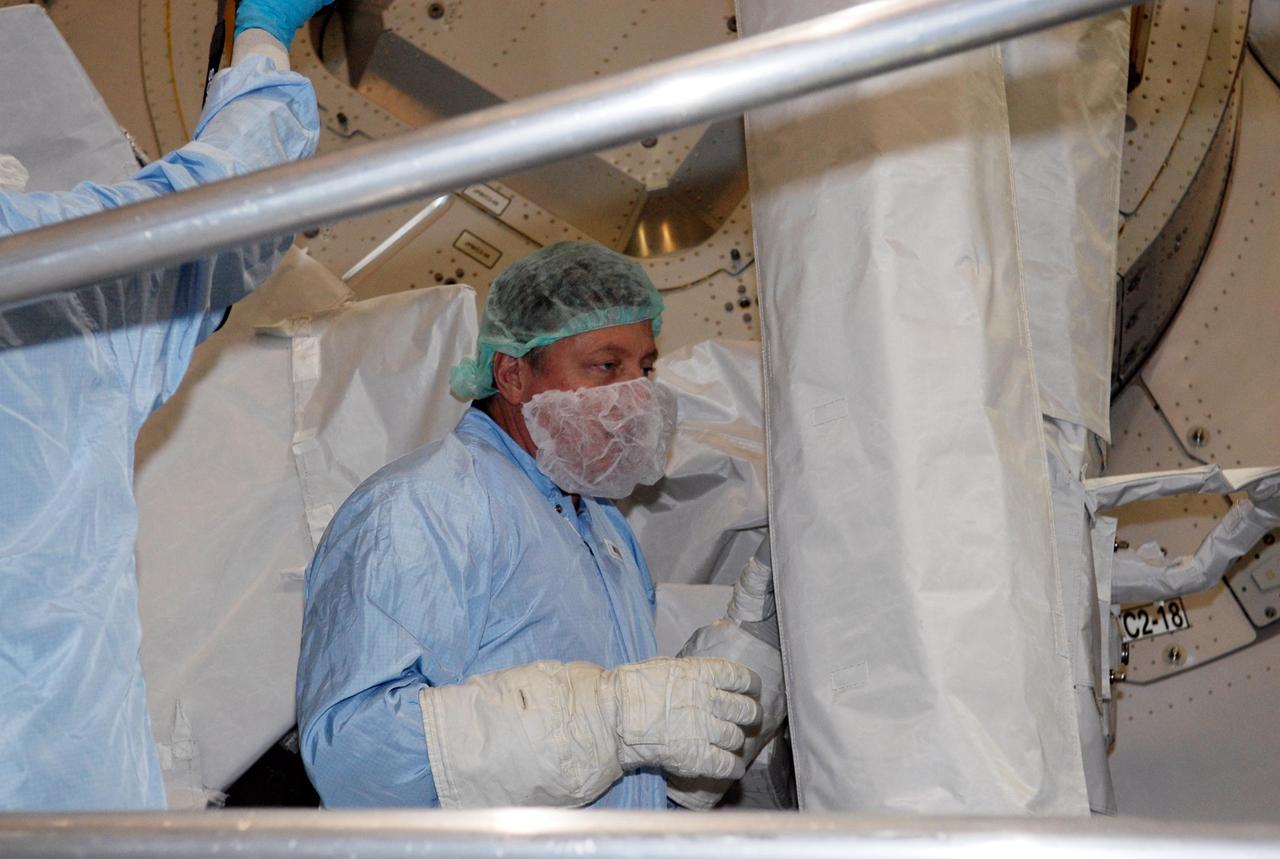
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-124 Mission Specialist Michael Fossum gets a close look at the Remote Manipulator System, or RMS, two robotic arms that support operations on the outside of the Japanese Experiment Module, called Kibo. They will be used to exchange experiment payloads or hardware located on the Exposed Facility and Experiment Logistics Module - Exposed Section and from inside the pressurized module through a scientific airlock, support maintenance tasks of Kibo and handle orbital replacement units. Crew members are at Kennedy for a crew equipment interface test that includes familiarization with tools and equipment that will be used on the mission. The STS-124 mission is the second of three flights that will launch components to complete the Japanese pressurized module, the Kibo laboratory. The mission will include two spacewalks to install the new lab and its remote manipulator system. The lab's logistics module, which will have been installed in a temporary location during STS-123, will be attached to the new lab. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
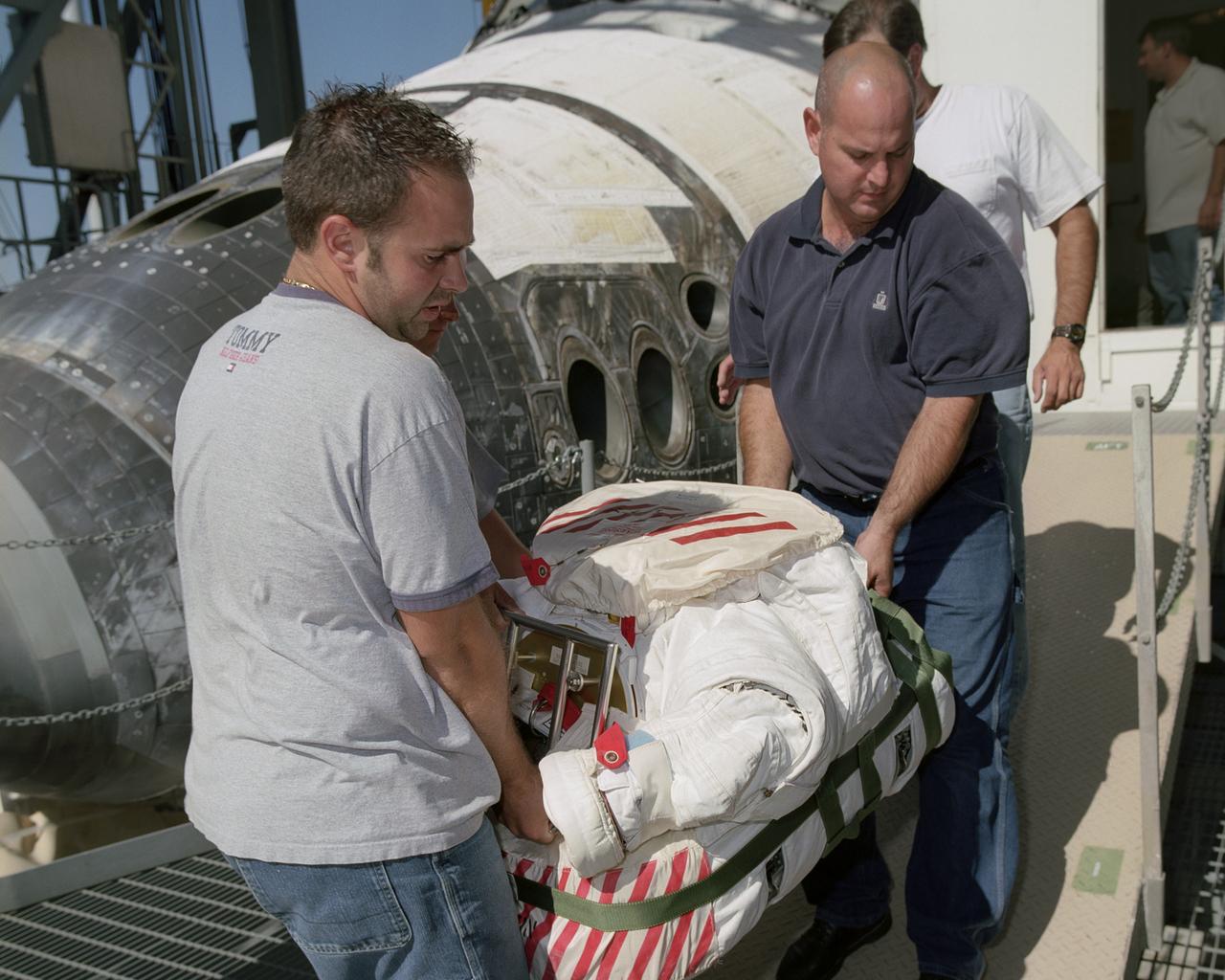

Flight Crew Systems Technicians Ray Smith and Raphael Rodriguez remove one of the Extravehicular Mobility Units, or EMUs, from the Space Shuttle Discovery after it's successful landing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The Space Shuttles receive post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) following landings at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items and returned to Shuttle payload bay. Discovery launched on July 26 and spent almost 14
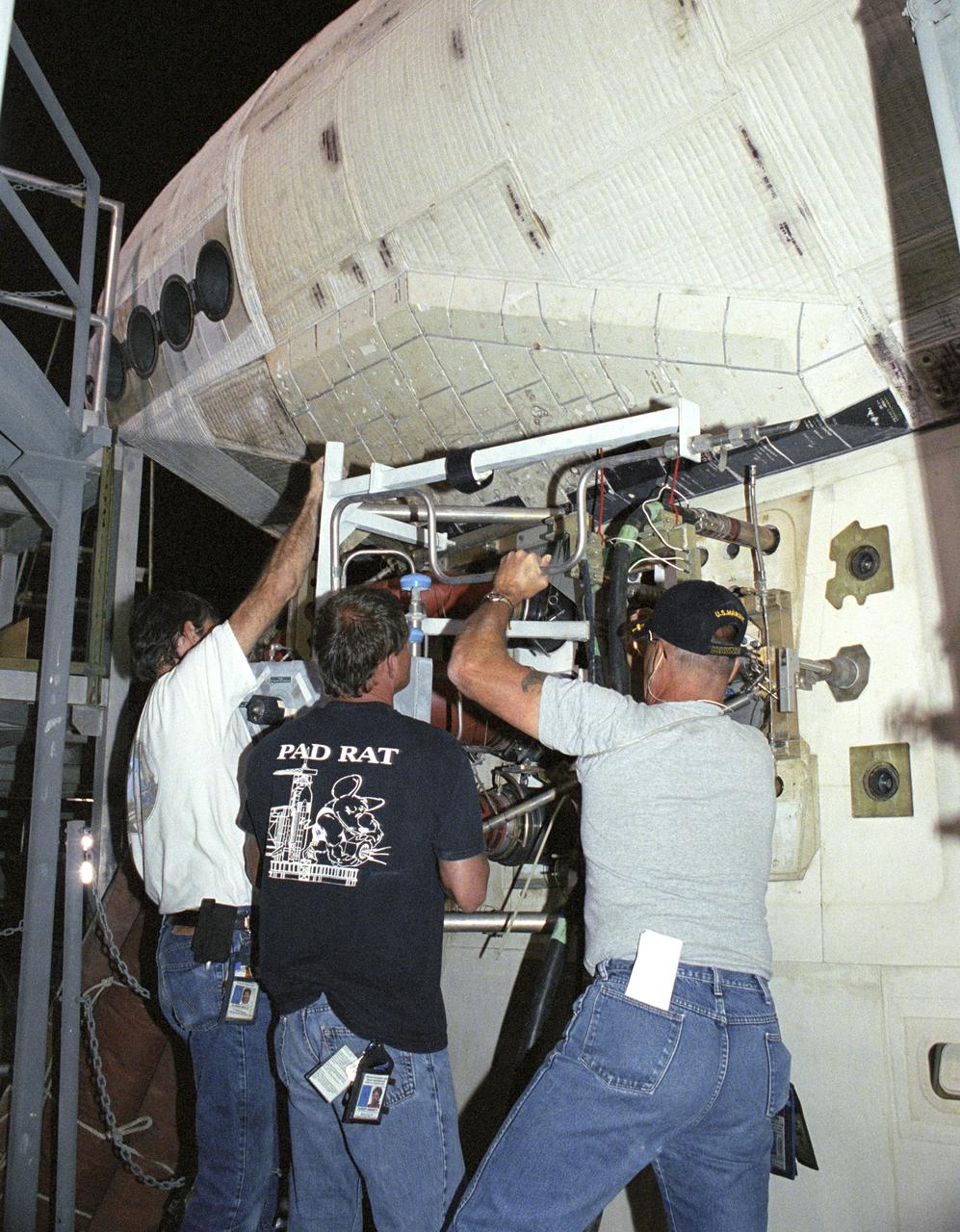

Todd Viddle; APU advanced systems technician, Robert 'Skip' Garrett; main propulsion advanced systems technician, and Dan McGrath; main propulsion systems engineer technician, remove a servicing unit from the Space Shuttle Discovery as part of it's post-flight processing at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center. The Space Shuttles receive post-flight servicing in the Mate-Demate Device (MDD) following landings at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The gantry-like MDD structure is used for servicing the shuttle orbiters in preparation for their ferry flight back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, including mounting the shuttle atop NASA's modified Boeing 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft. Space Shuttle Discovery landed safely at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards Air Force Base in California at 5:11:22 a.m. PDT, August 9, 2005, following the very successful 14-day STS-114 return to flight mission. During their two weeks in space, Commander Eileen Collins and her six crewmates tested out new safety procedures and delivered supplies and equipment the International Space Station. Discovery spent two weeks in space, where the crew demonstrated new methods to inspect and repair the Shuttle in orbit. The crew also delivered supplies, outfitted and performed maintenance on the International Space Station. A number of these tasks were conducted during three spacewalks. In an unprecedented event, spacewalkers were called upon to remove protruding gap fillers from the heat shield on Discovery's underbelly. In other spacewalk activities, astronauts installed an external platform onto the Station's Quest Airlock and replaced one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes. Inside the Station, the STS-114 crew conducted joint operations with the Expedition 11 crew. They unloaded fresh supplies from the Shuttle and the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Before Discovery undocked, the crews filled Raffeallo with unneeded items