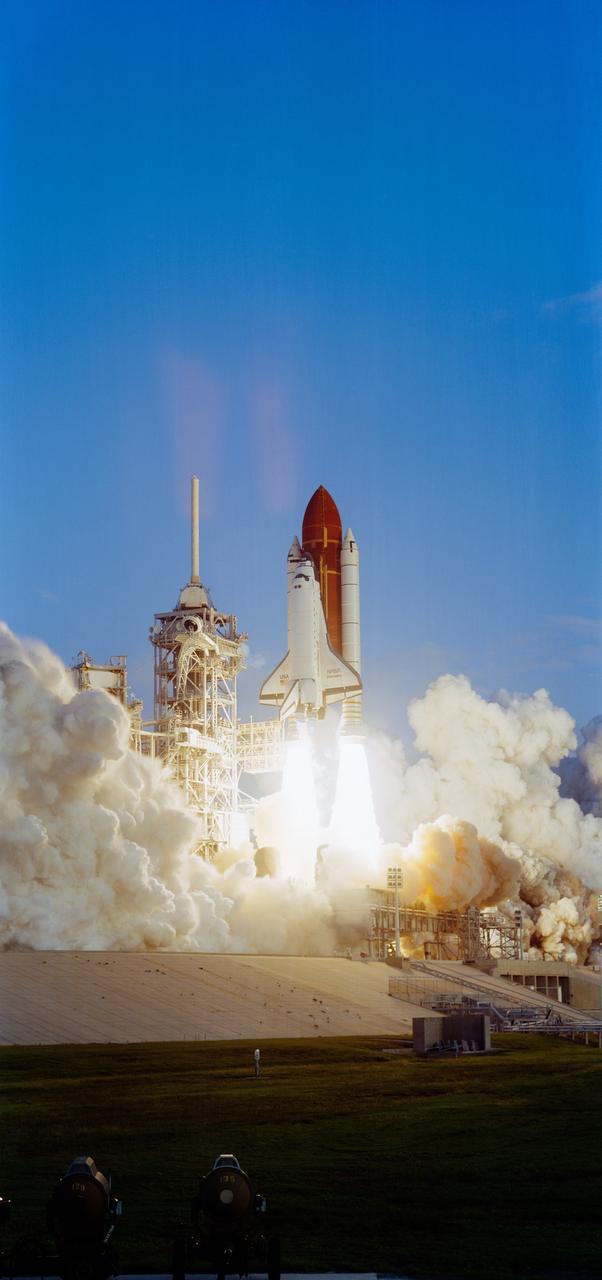

STS-41 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39 mobile launcher platform at 7:47 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). OV-103 riding atop the external tank (ET) and flanked by two solid rocket boosters (SRBs), is captured just moments after liftoff. Not yet clear of the fixed service structure (FSS) tower, OV-103 is highlighted against the cloudless morning sky. Exhaust smoke billows from the SRBs and the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) creating a cloud over the launch pad area.
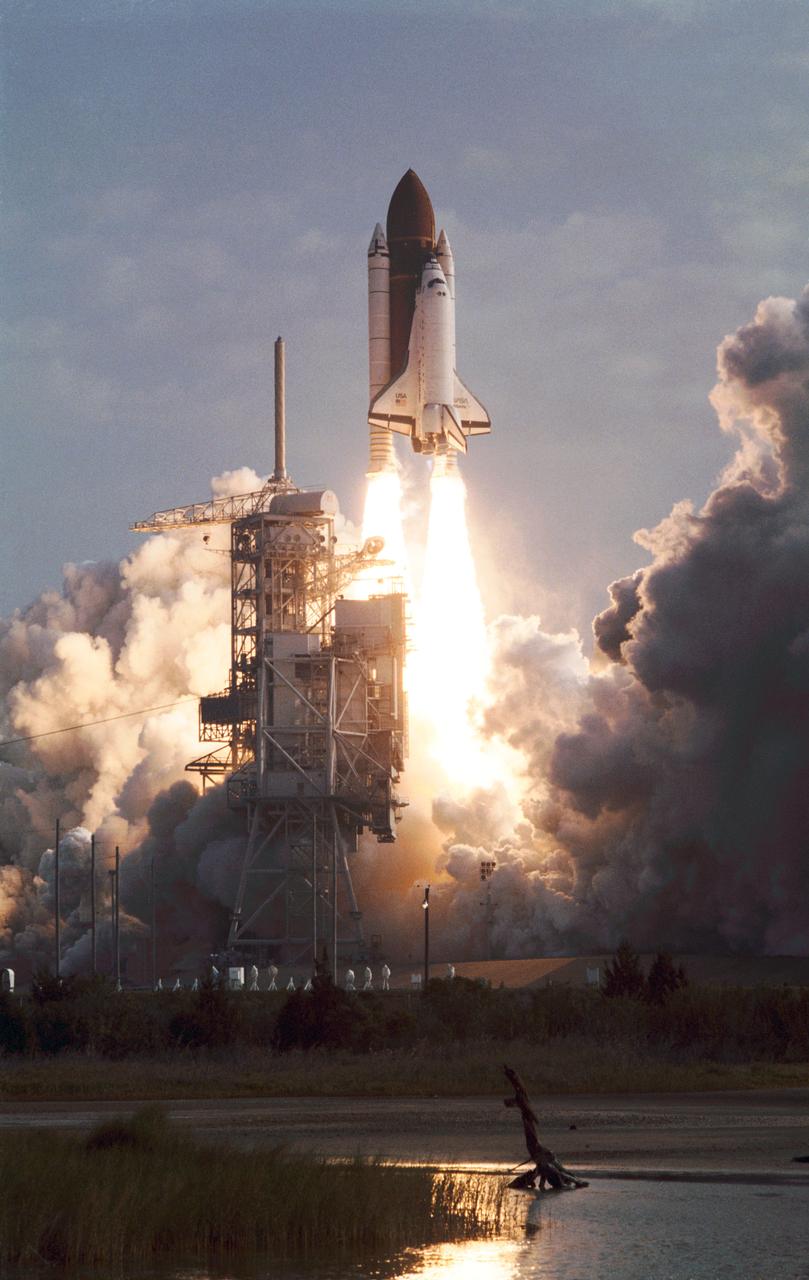

STS-45 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, lifts off from a Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad at 8:13:40:048 am (Eastern Standard Time (EST)). Exhaust billows out the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) as OV-104 atop its external tank (ET) soars above the mobile launcher platform and is nearly clear of the fixed service structure (FSS) tower. The diamond shock effect produced by the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) is visible. The glow of the SRB/SSME firings is reflected in a nearby waterway. An exhaust cloud covers the launch pad area.
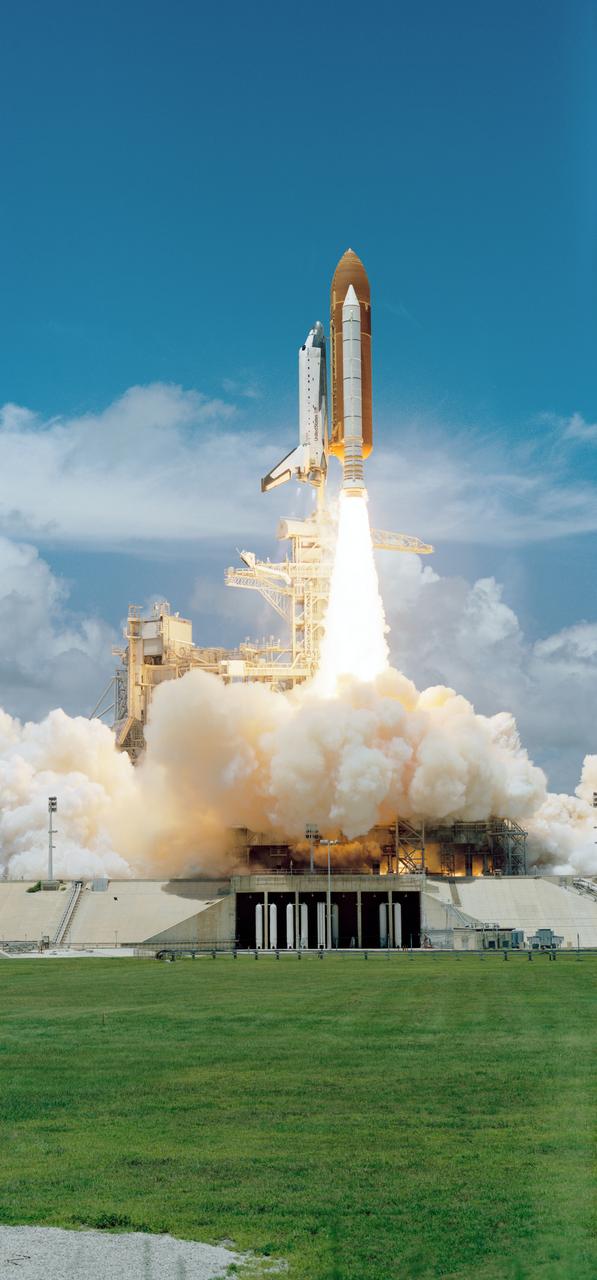

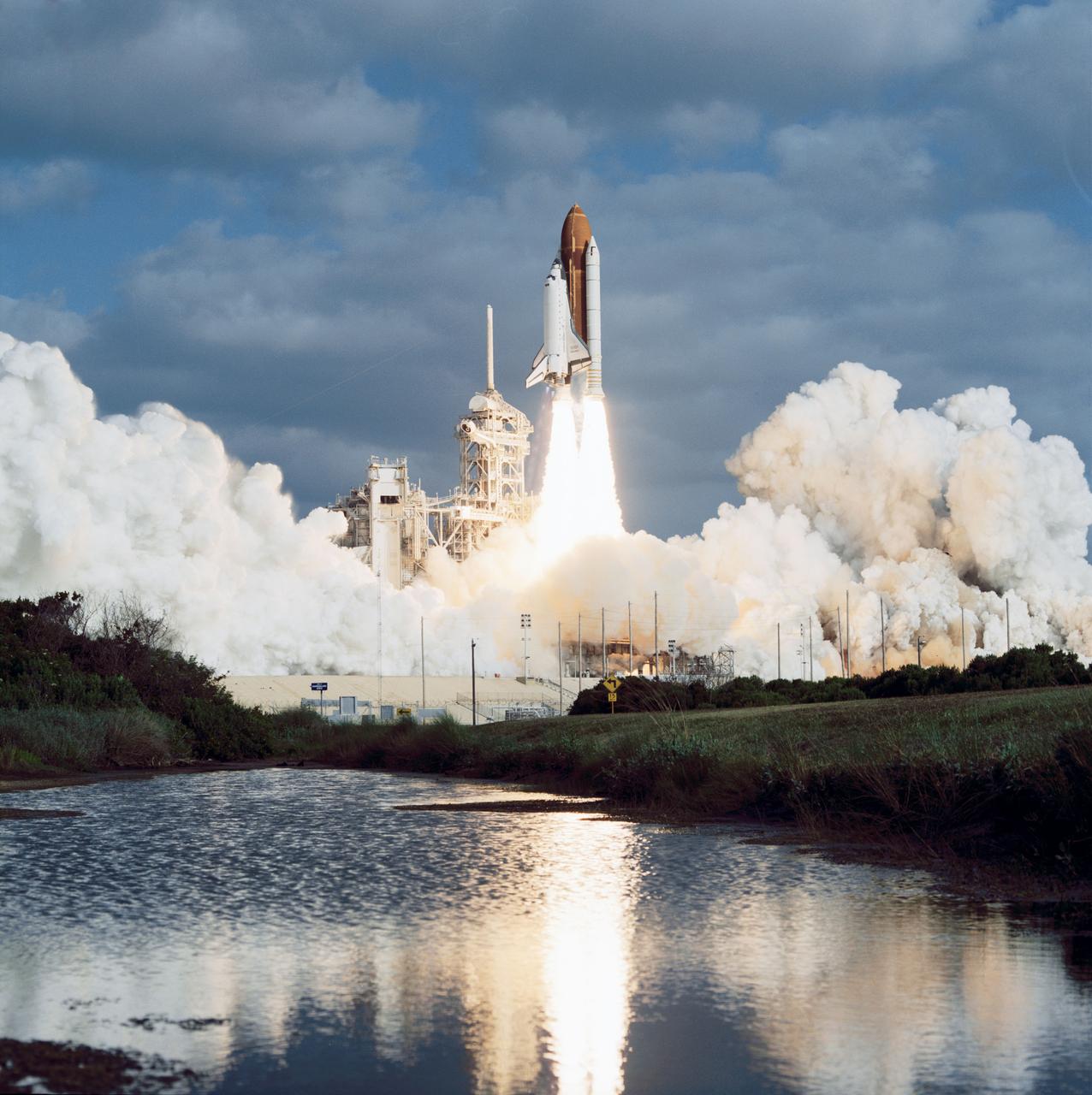
STS065-S-048 (8 July 1994) --- The Space Shuttle Columbia, with six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist aboard, heads toward Earth-orbit. A short time later, the crew began setting up the science module for two weeks of experimentation in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2). Launch occurred at 12:43 p.m. (EDT), July 8, 1994. Onboard were astronauts Robert D. Cabana, James D. Halsell, Jr., Richard J. Hieb, Carl E. Walz, Leroy Chiao, and Donald A. Thomas along with NASDA payload specialist Dr. Chiaki Mukai.

STS029-S-028 (13 March 1989) --- From Launch Pad 39B, the Space Shuttle Discovery is launched on Mission STS-29. Discovery lifted off at 9:57 a.m. (EST), March 13, 1989, carrying the tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS-1) into orbit. Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Michael L. Coats, commander; John E. Blaha, pilot; and James F. Buchli, James P. Bagian and Robert C. Springer, all mission specialists.
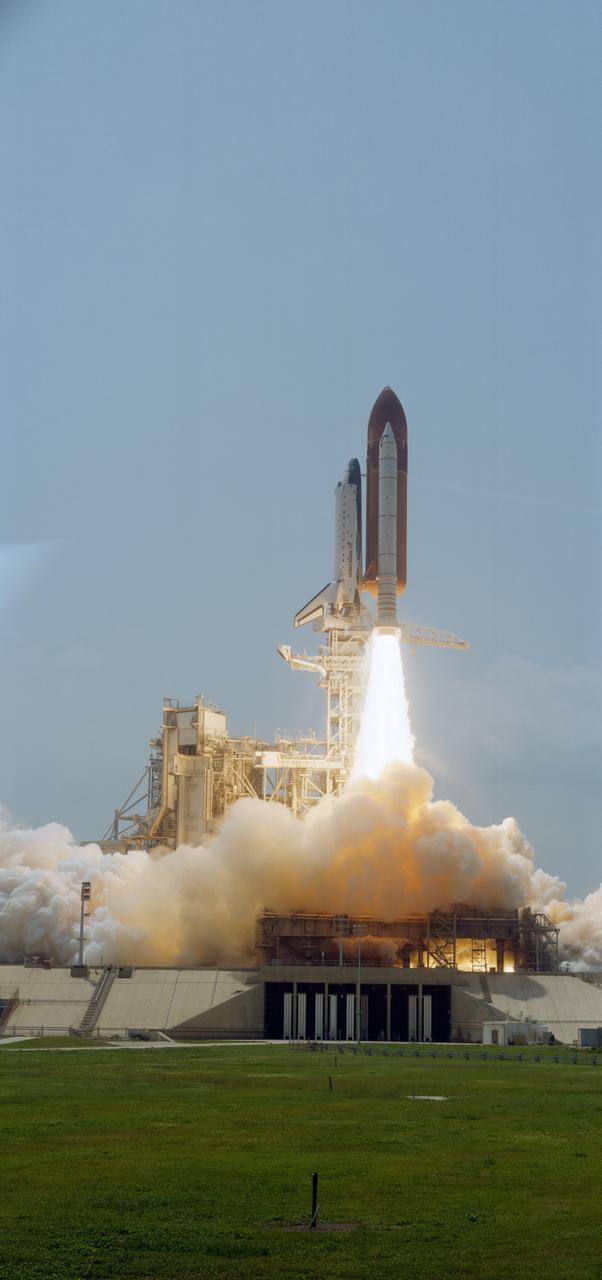

STS030-S-108 (4 May 1989) --- Backdropped against slight gray Florida skies, Space Shuttle Atlantis heads for a four-day mission in earth orbit with five astronaut crewmembers aboard. Onboard were astronauts David. M. Walker, Ronald J. Grabe, Norman E. Thagard, Mary L. Cleave and Mark C. Lee. Launch occurred at 2:46:58 P.M. (EDT), May 4, 1989.
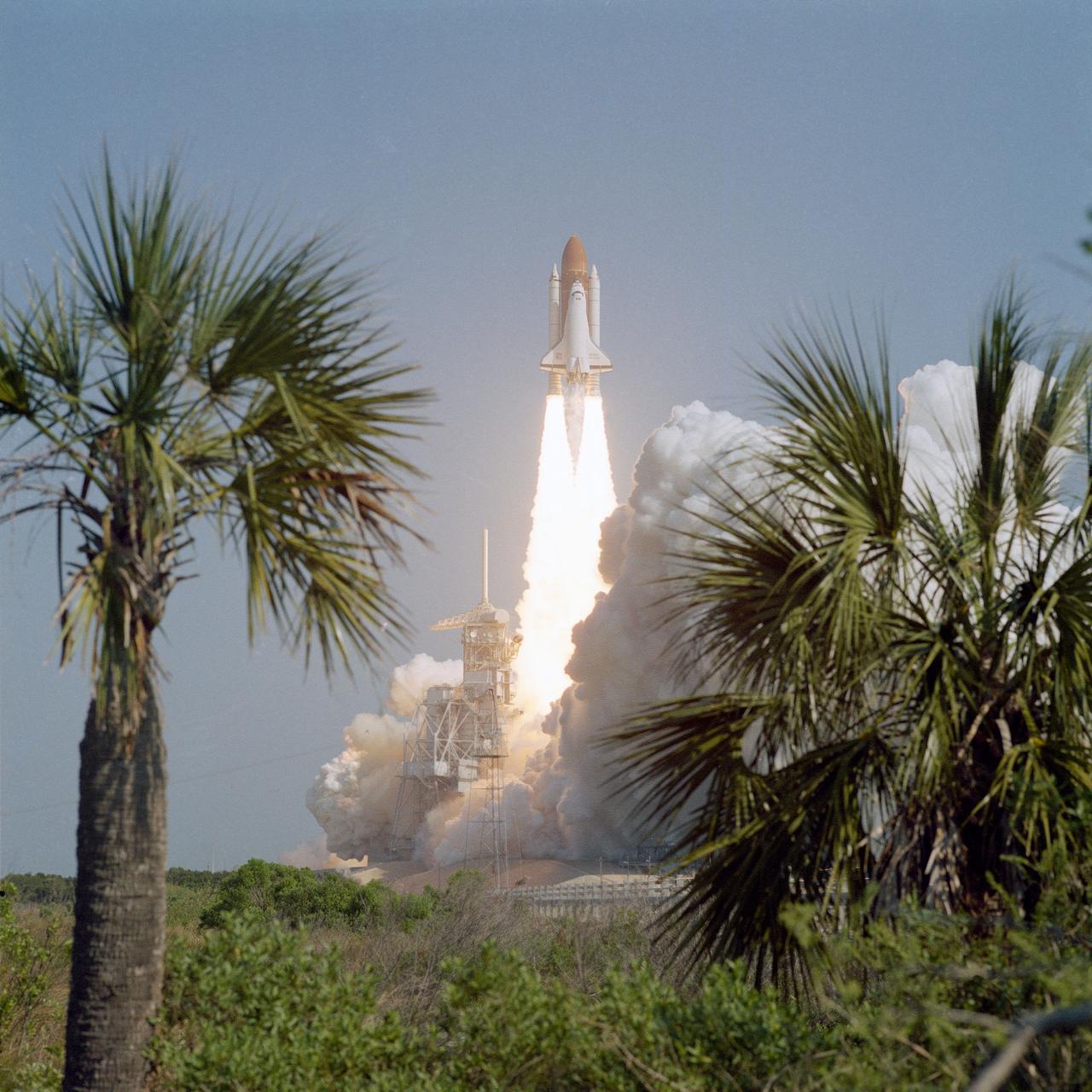

STS029-S-027 (13 March 1989) --- From Launch Pad 39D, the Space Shuttle Discovery is launched on mission STS-29. Discovery lifted off at 9:57 a.m. (EST), March 13, 1989, carrying the tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS-1) into orbit. Florida vegetation frames the launch scene. Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Michael L. Coats, commander; John E. Blaha, pilot; and James F. Buchli, James P. Bagian and Robert C. Springer, all mission specialists.
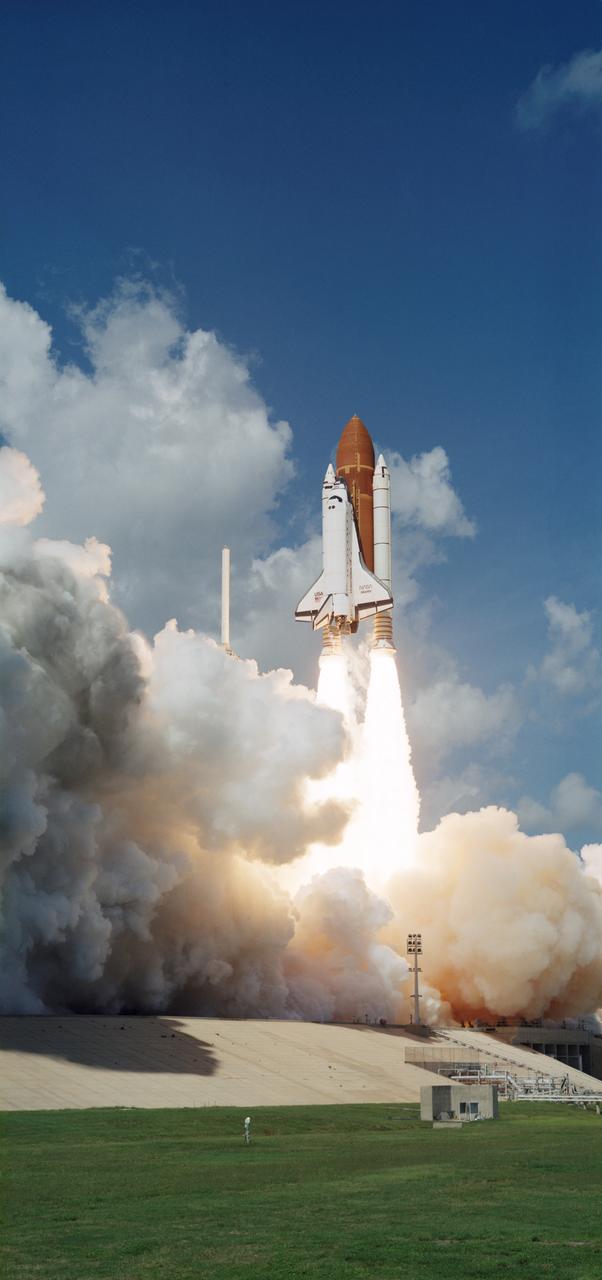

STS034-S-023 (18 Oct. 1989) --- The STS-34 Space Shuttle Atlantis lifts off from Kennedy Space Center’s launch pad 39-B at l2:53:39 p.m. (EDT) on Oct. 18, 1989, marking the beginning of a five-day mission in space. Atlantis carries a crew of five and the spacecraft Galileo. The Jupiter-bound probe will be deployed from Atlantis some six hours after launch. The journey to the giant planet is expected to take over six years. Crewmembers for the mission are astronauts Donald E. Williams, Michael J. McCulley, Shannon W. Lucid, Franklin R. Chang-Diaz and Ellen S. Baker. The scene was recorded with a 70mm camera.
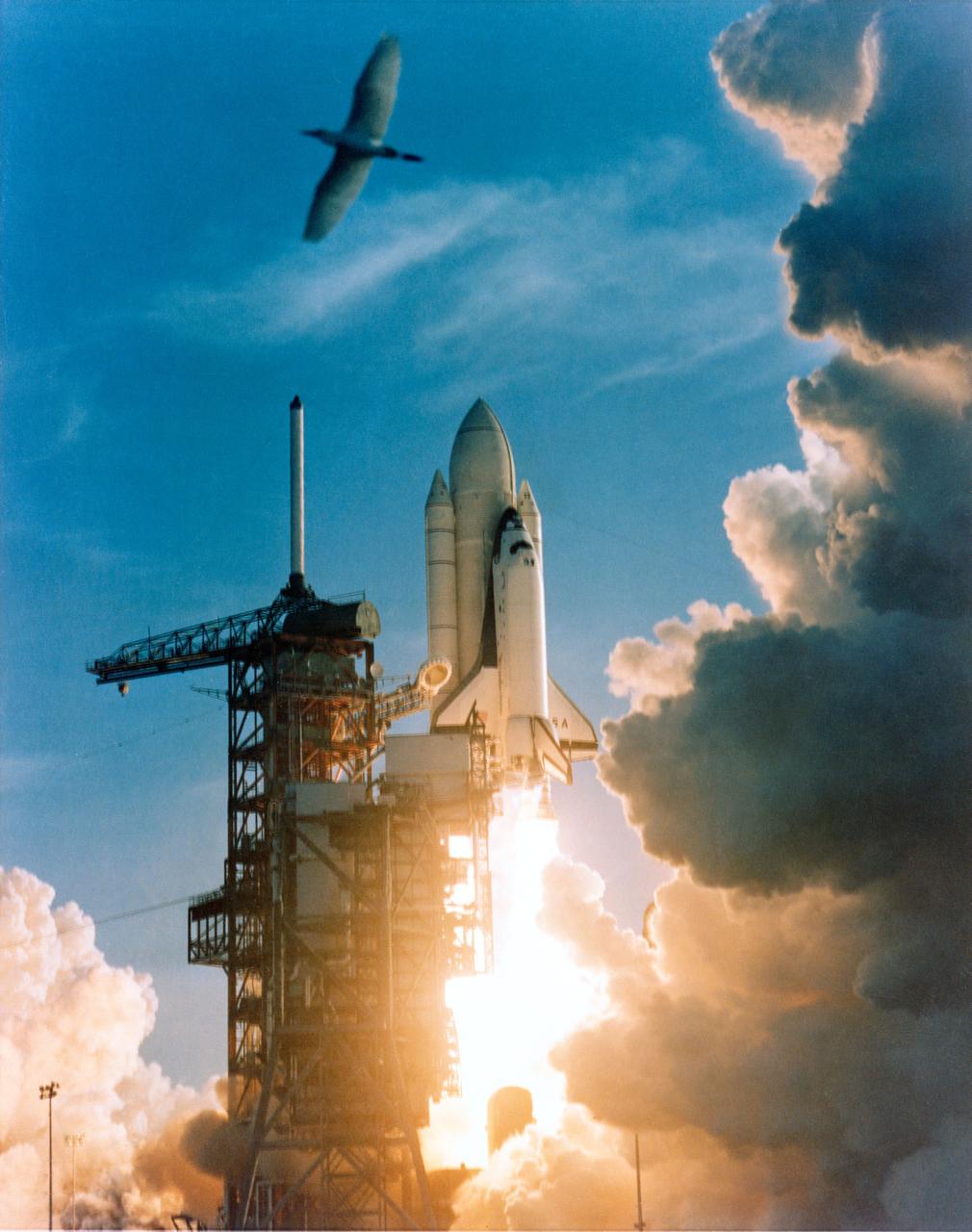

The Space Shuttle Columbia begins a new era of space transportation when it lifts off from NASA Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The reusable Orbiter, its two (2) fuel tanks and two (2) Solid Rocket Boosters (SRB) has just cleared the launch tower. Aboard the spacecraft are Astronauts John W. Young, Commander, and Robert L. Crippen, Pilot . 1. STS-I - LAUNCH KSC, FL KSC, FL Also available in 4x5 BW
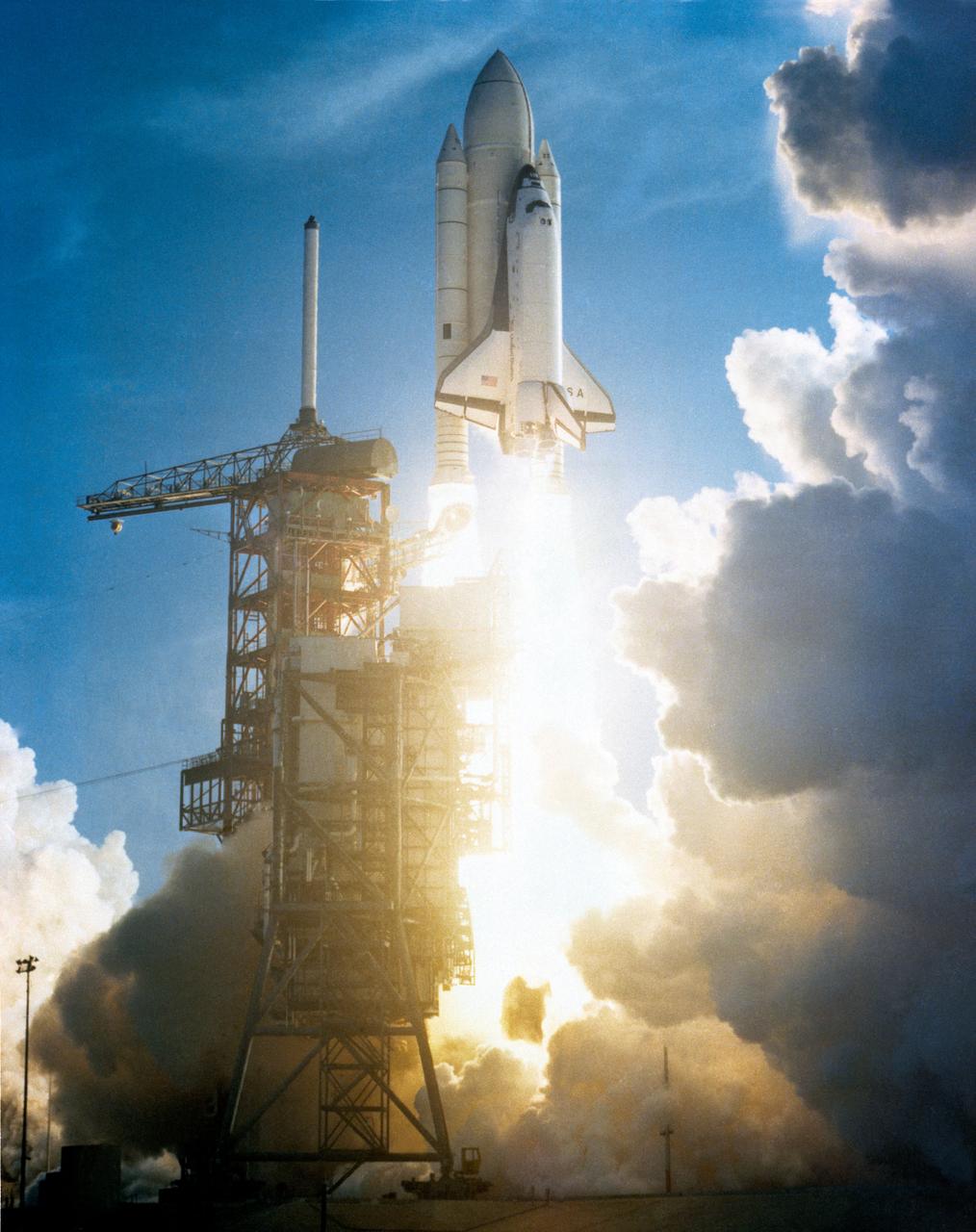

The Space Shuttle Columbia begins a new era of space transportation when it lifts off from NASA Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The reusable Orbiter, its two (2) fuel tanks and two (2) Solid Rocket Boosters (SRB) has just cleared the launch tower. Aboard the spacecraft are Astronauts John W. Young, Commander, and Robert L. Crippen, Pilot . 1. STS-I - LAUNCH KSC, FL KSC, FL Also available in 4x5 BW
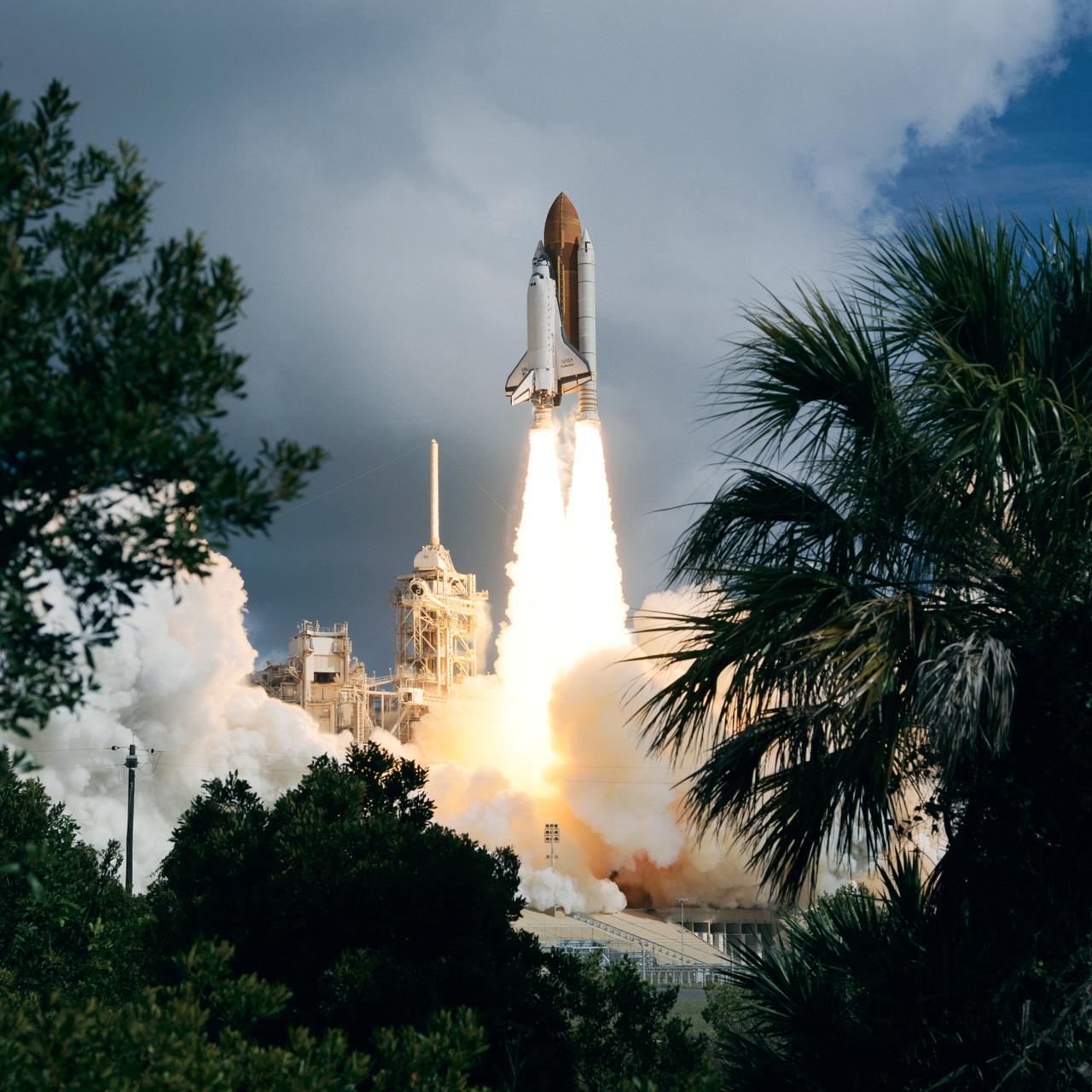

STS057-S-055 (21 June 1993) --- Framed by a variety of flora types, the Space Shuttle Endeavour lifts off Launch Pad 39B to begin the STS-57 mission. Launch occurred at 9:07:22 a.m. (EDT), June 21, 1993. The mission represents the first flight of the commercially developed SPACEHAB laboratory module and also will feature a retrieval of the European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA). Onboard for Endeavour's fourth flight are a crew of six - Ronald J. Grabe, mission commander; Brian Duffy, pilot; G. David Low, payload commander; and Nancy J. Sherlock, Peter J.K. (Jeff) Wisoff and Janice E. Voss, all mission specialists. An earlier launch attempt was scrubbed due to unacceptable weather conditions both at KSC and the overseas contingency landing sites.
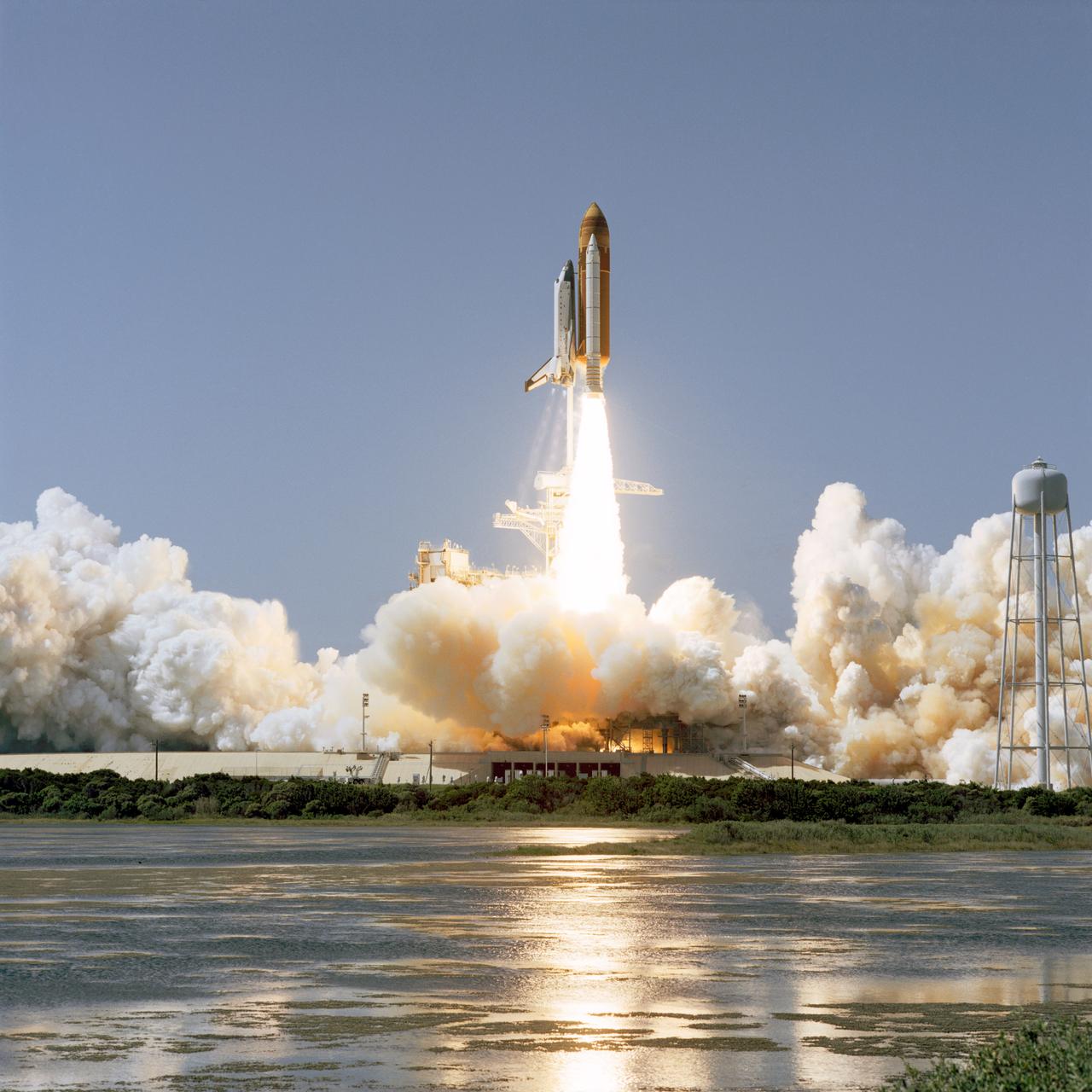

STS052-S-051 (22 Oct 1992) --- This distant 70mm image shows the Space Shuttle Columbia clearing the tower at Launch Pad 39B, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), on its way toward a ten-day Earth-orbital mission with a crew of five NASA astronauts and a Canadian payload specialist. Liftoff occurred at 1:09:39 p.m. (EDT), October 22, 1992. Crew members are astronauts James D. Wetherbee, Michael A. Baker, Tamara E. Jernigan, Charles L. (Lacy) Veach and William M. Shepherd, along with payload specialist Steven G. MacLean. Payloads onboard include the Laser Geodynamic Satellite II (LAGEOS II), which will be deployed early in the mission, a series of Canadian experiments, and the United States Microgravity Payload-1 (USMP-1).
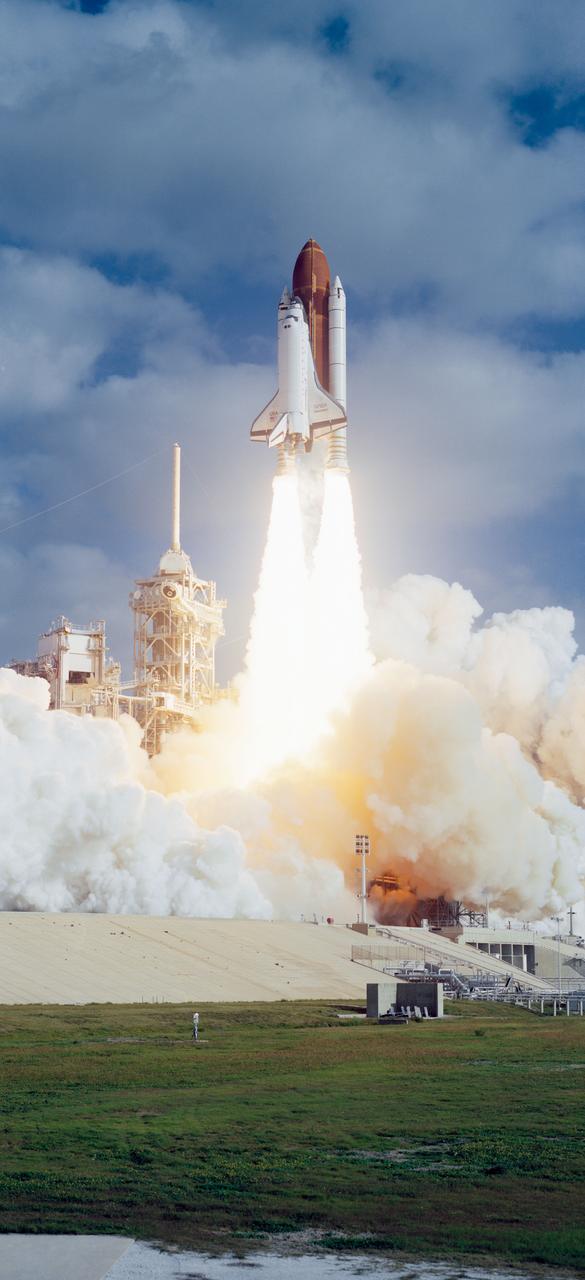

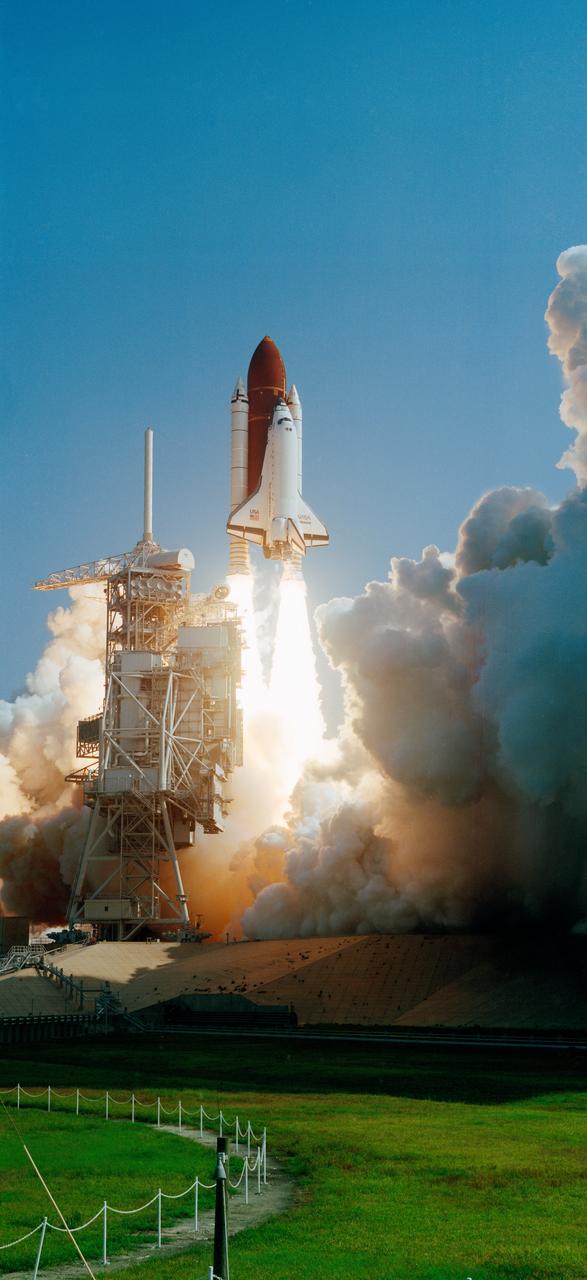
STS031-S-073 (24 April 1990) --? A vertical view of the launch of the STS-31 mission. Onboard Space Shuttle Discovery are the crew of five veteran astronauts and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Official launch time was 8:33:51.0492 a.m. (EDT). Headed for approximately five days in space are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Bruce McCandless, II, Kathryn D. Sullivan, and Steven A. Hawley.

STS053-S-054 (2 Dec 1992) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery, with a crew of five astronauts onboard, launches from Kennedy Space Center?s (KSC) Pad 39A at 8:24:00 a.m. (EST), December 2, 1992. The photograph was taken from the top of the giant Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The all-military crew supporting the Department of Defense (DOD) flight included astronauts David M. Walker, Robert D. Cabana, Guion S. Bluford, Jr., James S. Voss and Michael R. U. (Rick) Clifford.
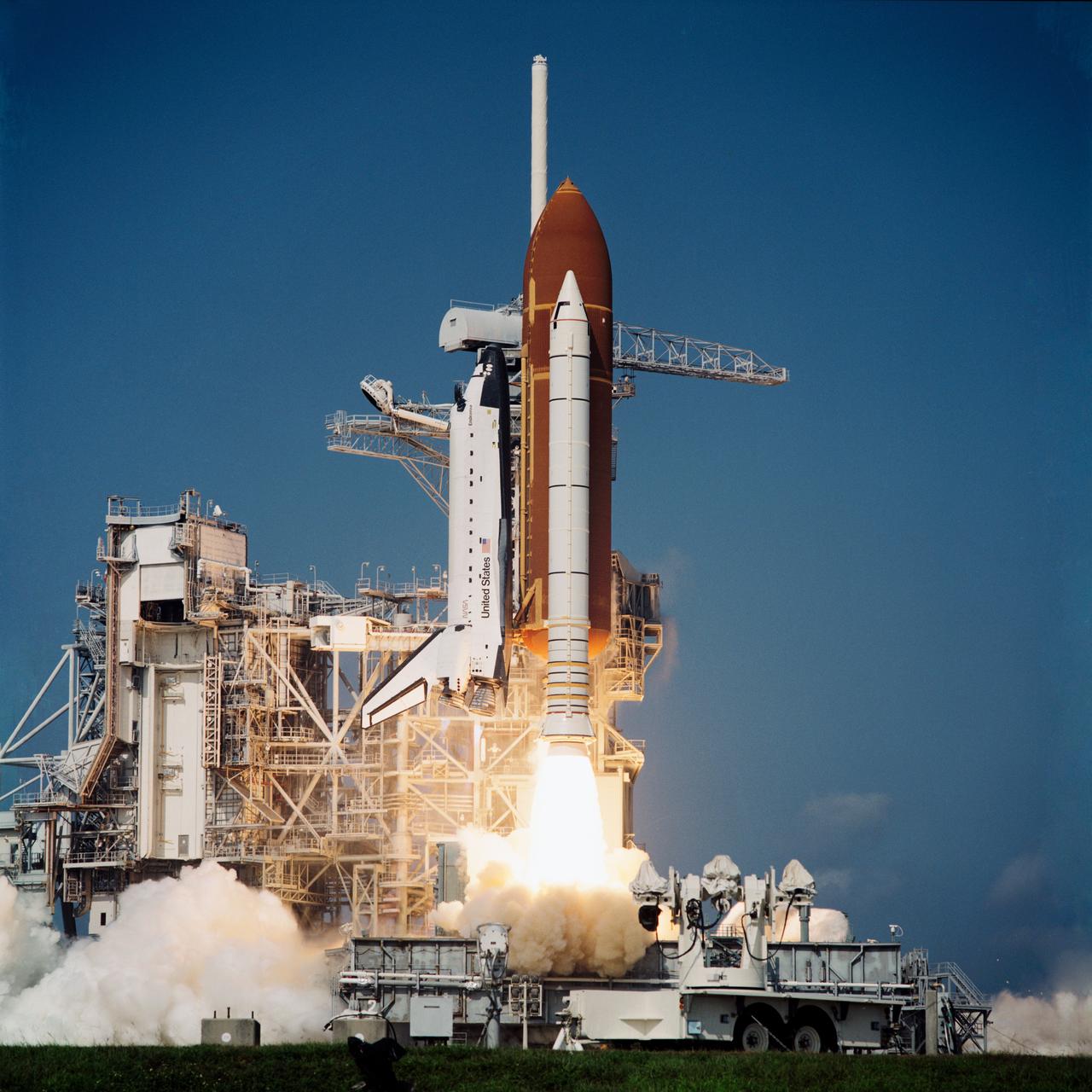

STS047-S-019 (12 Sept 1992) --- With a crew of six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist onboard, the Space Shuttle Endeavour heads for its second trip into space. This trip will be devoted to support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States. Launch occurred at 10:23:00:0680 a.m. (EDT), September 12, 1992. Onboard were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Curtis L. Brown Jr., pilot; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; and Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists; along with payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan.

STS031-S-064 (24 April 1990) --- A horizontal view of the launch of the STS-31 mission. Onboard Space Shuttle Discovery are the crew of five veteran astronauts and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Official launch time was 8:33:51.0492 a.m. (EDT). Headed for approximately five days in space are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Bruce McCandless, II, Kathryn D. Sullivan, and Steven A. Hawley.

STS047-S-021 (12 Sept 1992) --- With a crew of six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist onboard, the Space Shuttle Endeavour heads for its second trip into space. This trip will be devoted to support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States. Launch occurred at 10:23:00:0680 a.m. (EDT), September 12, 1992. Onboard were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Curtis L. Brown Jr., pilot; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; and Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists, along with payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan.
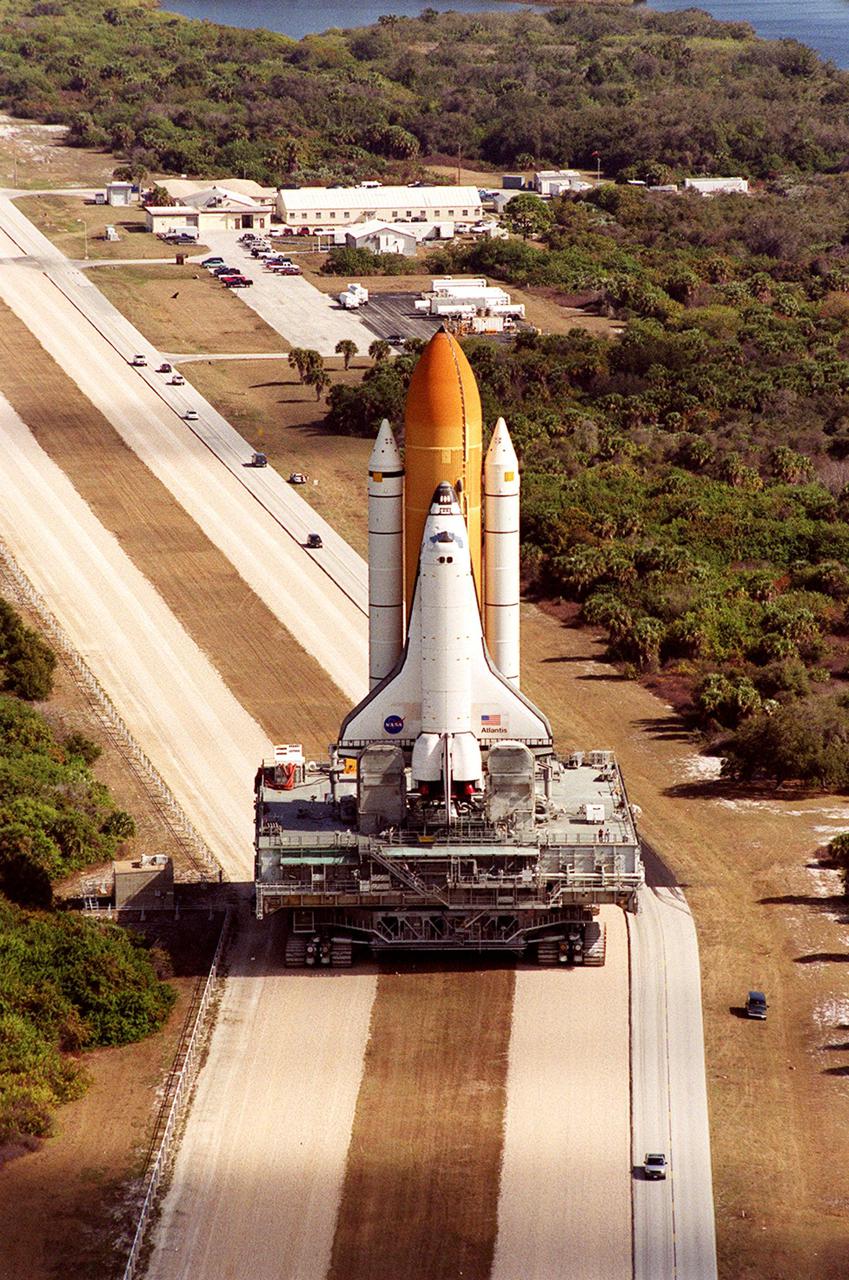

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On its way back from <a href='http:__www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov_kscpao_captions_subjects_lc39a.htm'>Launch Pad 39A,<_a> Space Shuttle <a href='http:__www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov_kscpao_captions_subjects_atlantis.htm'> Atlantis<_a>, towering above the vehicles on the adjacent road, makes the turn on the crawlerway leading to the <a href='http:__www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov_kscpao_captions_subjects_vab.htm'> Vehicle Assembly Building. <_a>In the VAB workers will conduct inspections, make continuity checks and conduct X-ray analysis on the 36 solid rocket booster cables located inside each booster’s external system tunnel. An extensive evaluation of NASA’s SRB cable inventory revealed conductor damage in four (of about 200) cables on the shelf. Shuttle managers decided to prove the integrity of the system tunnel cables already on Atlantis. The launch has been rescheduled no earlier than Feb. 6

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On its way back from <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/captions/subjects/lc39a.htm">Launch Pad 39A,</a> Space Shuttle <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/captions/subjects/atlantis.htm"> Atlantis</a>, towering above the vehicles on the adjacent road, makes the turn on the crawlerway leading to the <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/captions/subjects/vab.htm"> Vehicle Assembly Building. </a>In the VAB workers will conduct inspections, make continuity checks and conduct X-ray analysis on the 36 solid rocket booster cables located inside each booster’s external system tunnel. An extensive evaluation of NASA’s SRB cable inventory revealed conductor damage in four (of about 200) cables on the shelf. Shuttle managers decided to prove the integrity of the system tunnel cables already on Atlantis. The launch has been rescheduled no earlier than Feb. 6
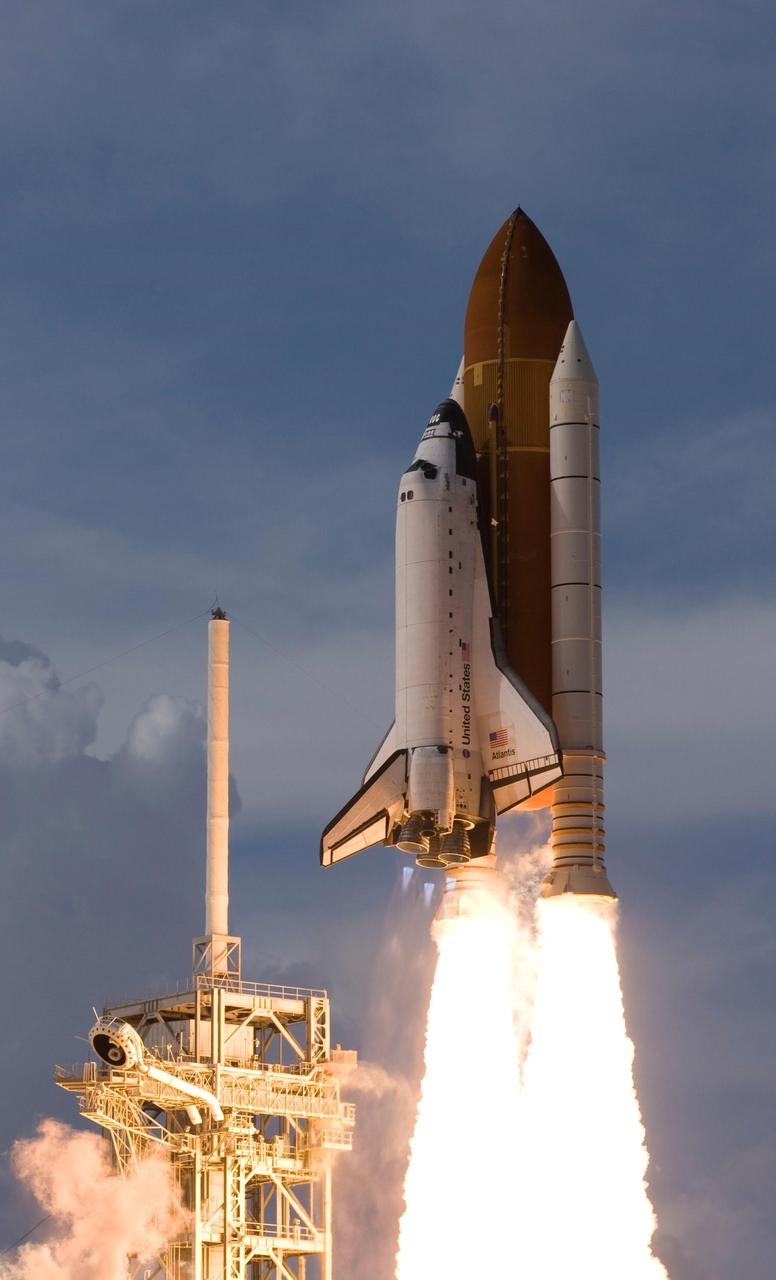

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Boosted by the columns of flame from the solid rocket boosters, space shuttle Atlantis passes the lightning tower on the fixed service structure as it roars into space and a rendezvous with the International Space Station on mission STS-122. Liftoff was on time at 2:45 p.m. EST. This is the third launch attempt for Atlantis since December 2007 to carry the European Space Agency's Columbus laboratory to the station. During the 11-day mission, the crew's prime objective is to attach the laboratory to the Harmony module, adding to the station's size and capabilities. Photo credit: Scott Andrews
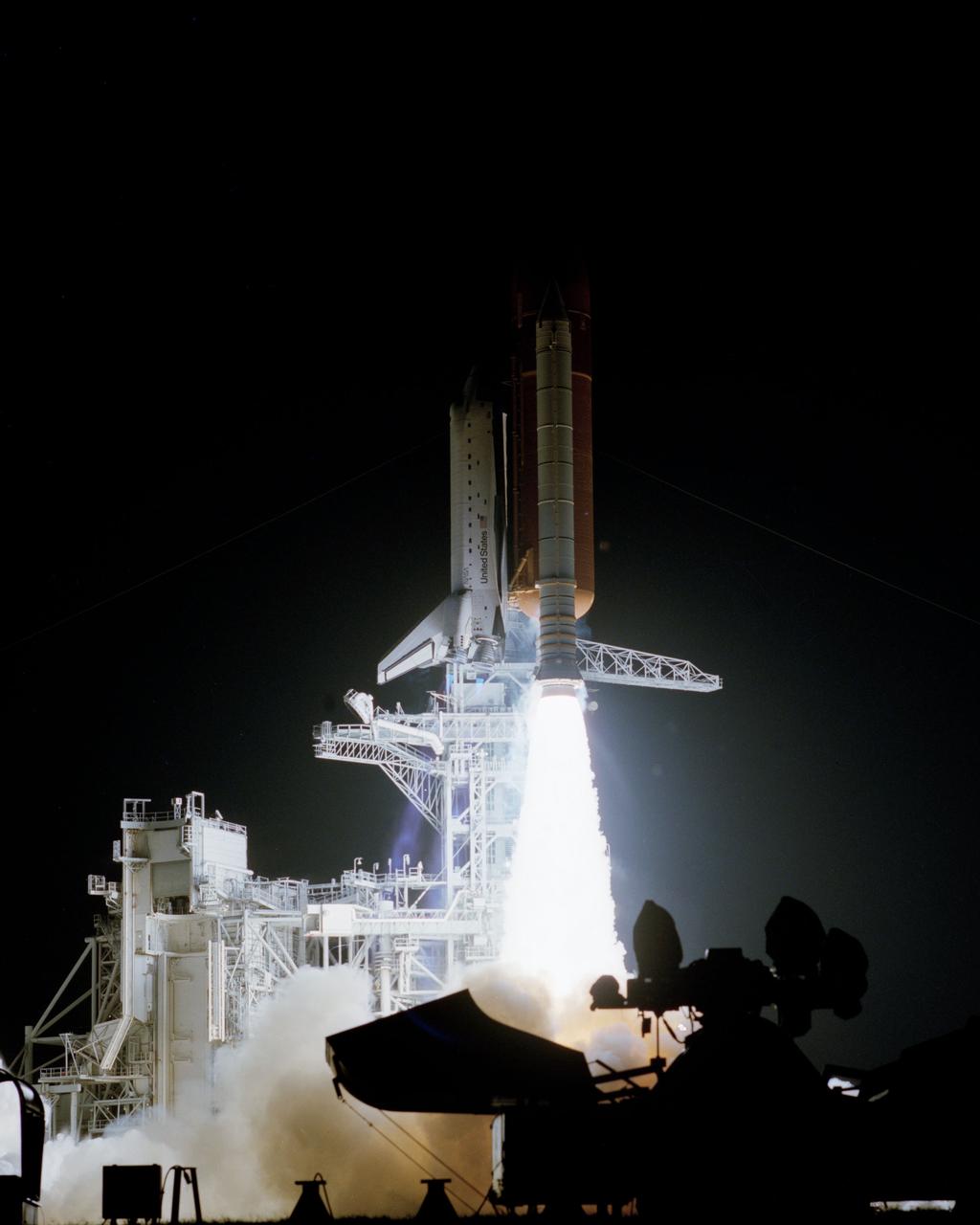

STS-38 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, lifts off from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad at 6:48:15:0639 pm (Eastern Standard Time (EST)) for Department of Defense (DOD)-devoted mission. OV-104, atop the external tank (ET) and flanked by solid rocket boosters (SRBs), is almost clear of the launch tower which is lit up by the SRB and space shuttle main engine (SSME) firings. Spotlight equipment is silhouetted against the SRB/SSME glow in the foreground. The retracted rotating service structure (RSS) is highlighted against the evening darkness by the launch fireworks.
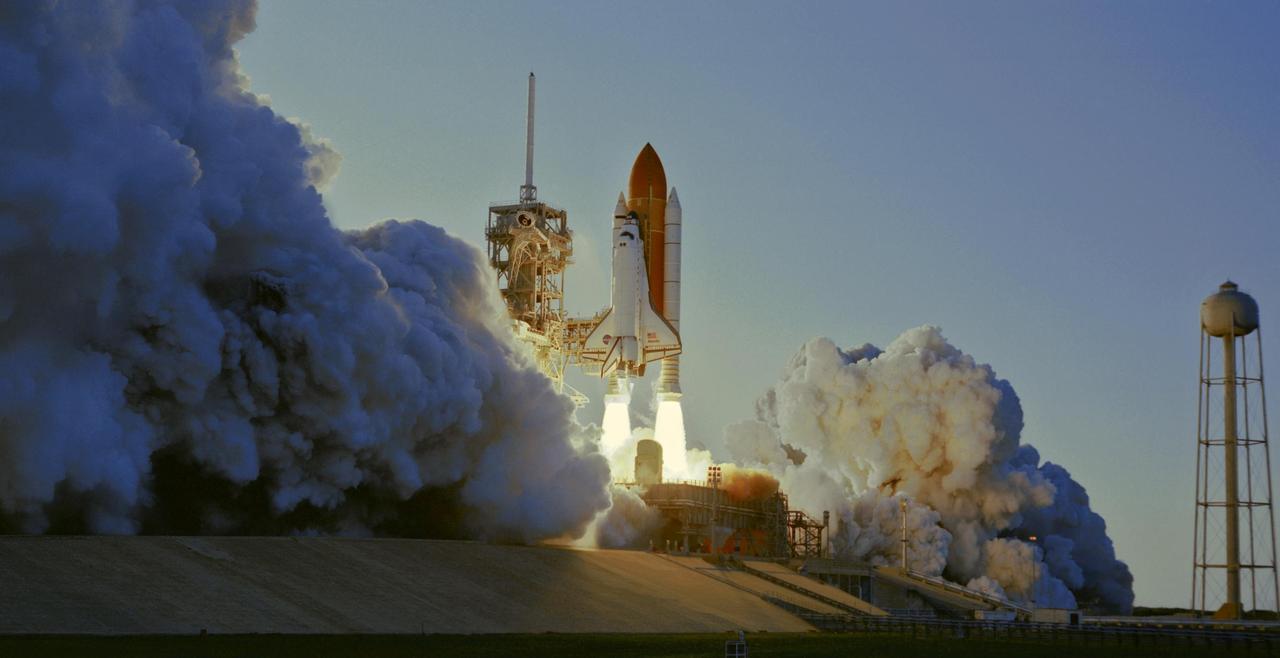

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Smoke and steam billow across Launch Pad 39A as Space Shuttle Atlantis, trailing columns of fire from the solid rocket boosters, hurtles into the sky on mission STS-117 to the International Space Station. At left is the fixed service structure with the 80-foot-tall lightning mast on top. At right is the 290-foot-high water tower that supplies the water for sound suppression. Liftoff was on-time at 7:38:04 p.m. EDT. The shuttle is delivering a new segment to the starboard side of the International Space Station's backbone, known as the truss. Three spacewalks are planned to install the S3/S4 truss segment, deploy a set of solar arrays and prepare them for operation. STS-117 is the 118th space shuttle flight, the 21st flight to the station, the 28th flight for Atlantis and the first of four flights planned for 2007. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray & Don Kight

S82-39532 (11 Nov. 1982) --- Having completed its four-mission test program, the space shuttle Columbia begins a new era of operational flights as it clears the launch tower and heads for Earth orbit. Launch occurred at 7:19 a.m. (EST), November 11, 1982. Aboard the orbiter, mated here to its two solid rocket boosters and external fuel tank, were astronauts Vance D. Brand, STS-5 commander; Robert F. Overmyer, pilot; William B. Lenoir, mission specialist; and Joseph P. Allen, mission specialist. Photo credit: NASA

S82-39532 (11 Nov. 1982) --- Having completed its four-mission test program, the space shuttle Columbia begins a new era of operational flights as it clears the launch tower and heads for Earth orbit. Launch occurred at 7:19 a.m. (EST), November 11, 1982. Aboard the orbiter, mated here to its two solid rocket boosters and external fuel tank, were astronauts Vance D. Brand, STS-5 commander; Robert F. Overmyer, pilot; William B. Lenoir, mission specialist; and Joseph P. Allen, mission specialist. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Space shuttle Discovery clears the tower on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, its two solid rocket boosters and three main engines generating nearly seven million pounds of thrust. Liftoff on the STS-131 mission was on time at 6:21 a.m. EDT April 5. The seven-member crew will deliver the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo, filled with supplies, a new crew sleeping quarters and science racks that will be transferred to the International Space Station's laboratories. The crew also will switch out a gyroscope on the station’s truss, install a spare ammonia storage tank and retrieve a Japanese experiment from the station’s exterior. STS-131 is the 33rd shuttle mission to the station and the 131st shuttle mission overall. For information on the STS-131 mission and crew, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts131_index.html. Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews
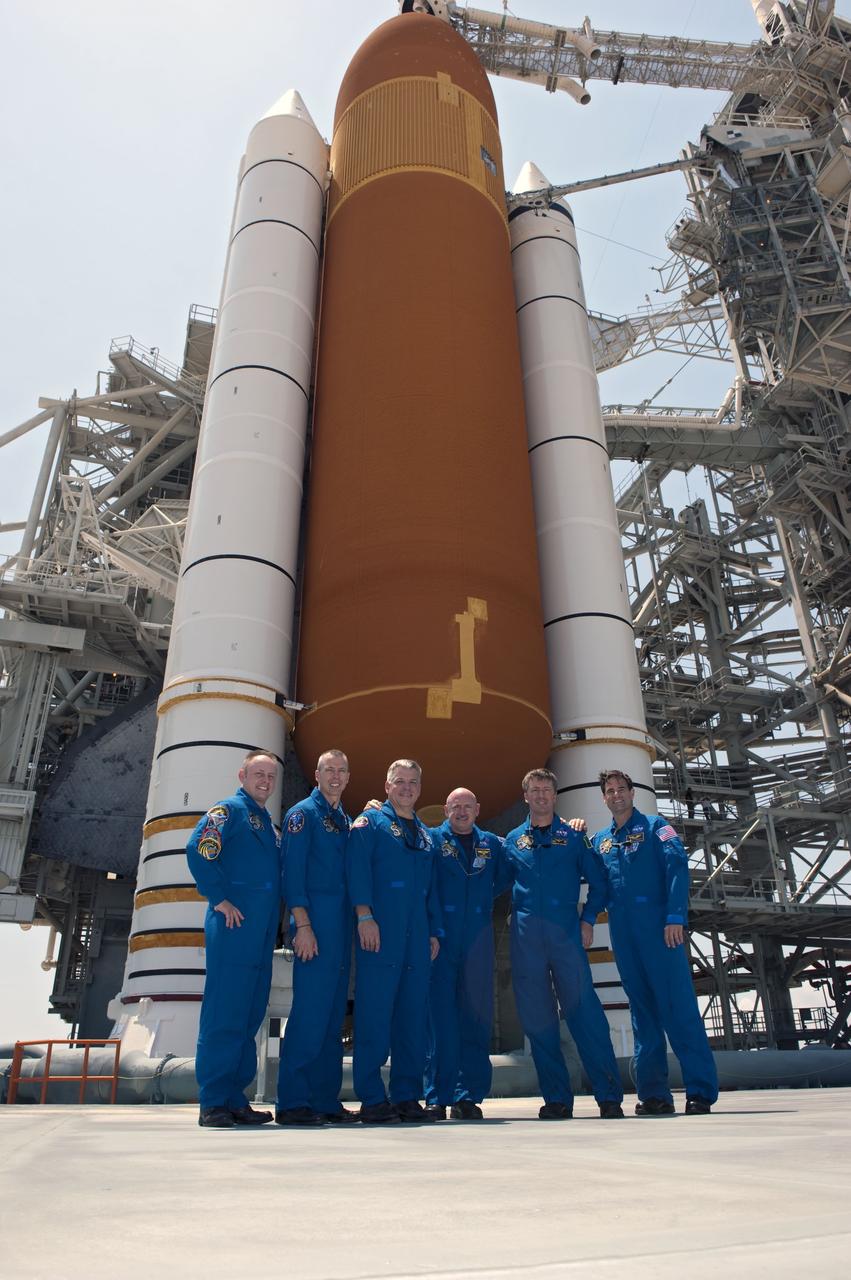

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The STS-134 crew stands together on Launch Pad 39A in front of the towering external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters of space shuttle Endeavour, one day before its final flight, the STS-134 mission, to the International Space Station. From left are Mission Specialists Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel; Pilot Greg H. Johnson, Commander Mark Kelly, European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori and Mission Specialist Greg Chamitoff. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett Endeavour and its crew will deliver the Express Logistics Carrier-3, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS), a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for the Dextre robotic helper to the station. This will be the final spaceflight for Endeavour. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts134/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
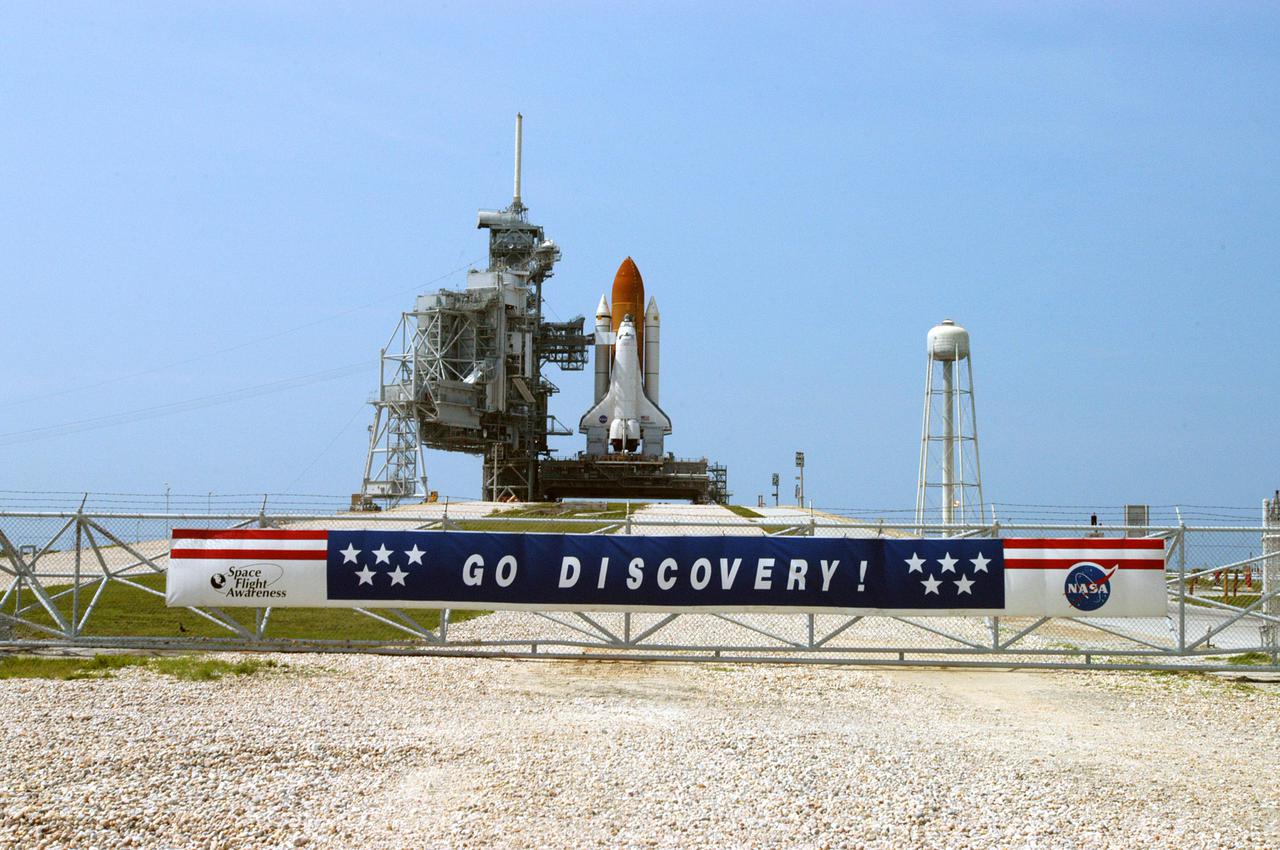

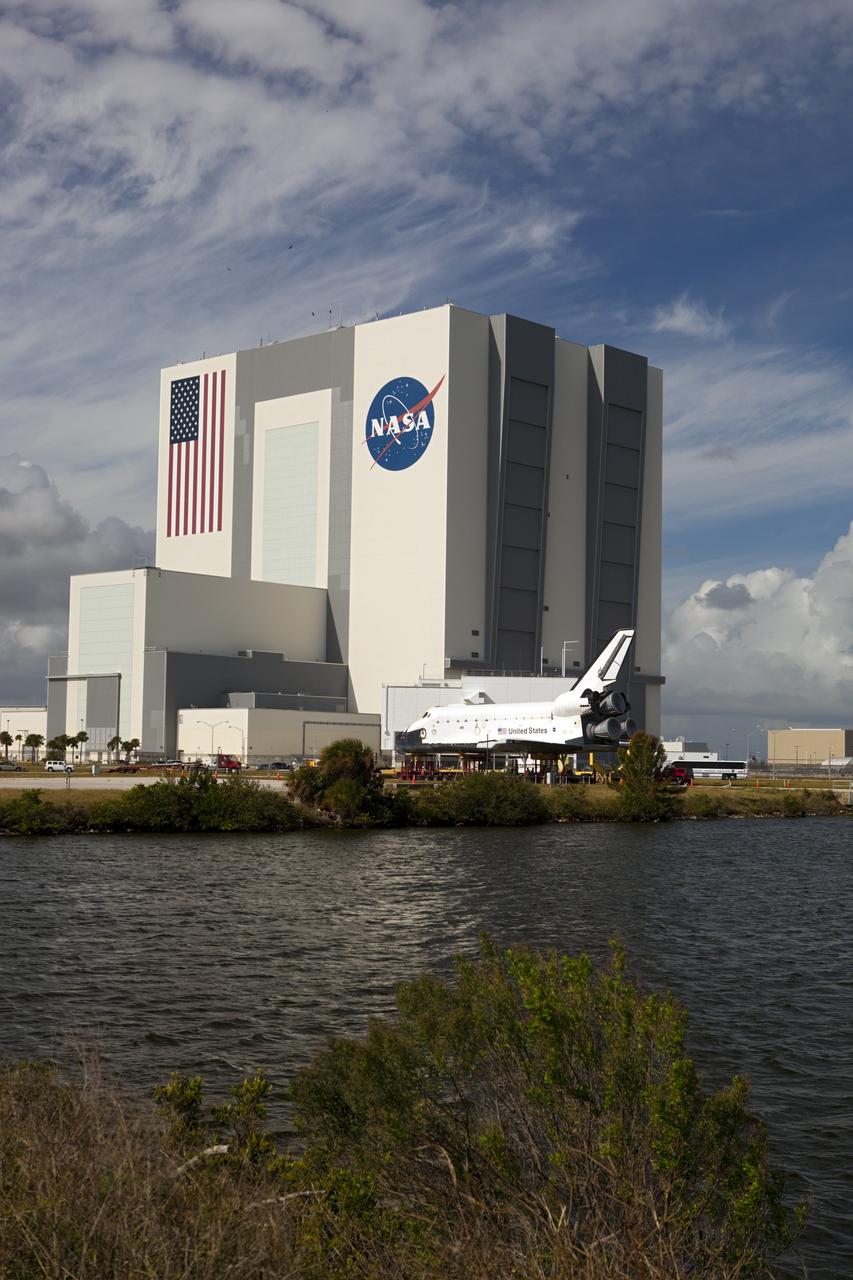
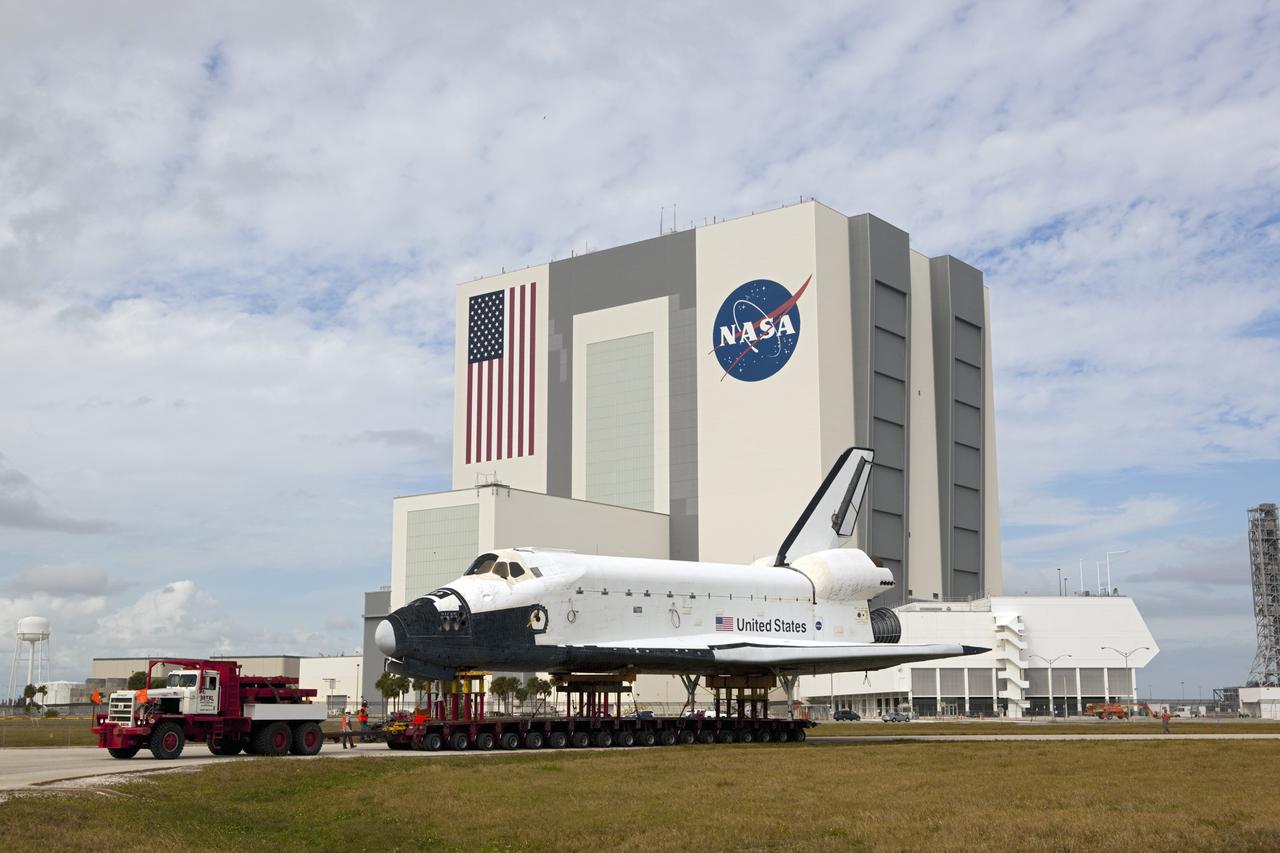
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Discovery is revealed after rollback of the Rotating Service Structure. At right of the pad is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water, part of the sound suppression system during a launch. Discovery will be rolled back to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Once inside the VAB, Discovery will be demated from its External Tank and lifted into the transfer aisle. On or about June 7, Discovery will be lifted and attached to its new tank and Solid Rocket Boosters, which are already in the VAB. Only the 15th rollback in Space Shuttle Program history, the 4.2-mile journey allows additional modifications to be made to the External Tank prior to a safe Return to Flight. Discovery is expected to be rolled back to the launch pad in mid-June for Return to Flight mission STS-114. The launch window extends from July 13 to July 31.
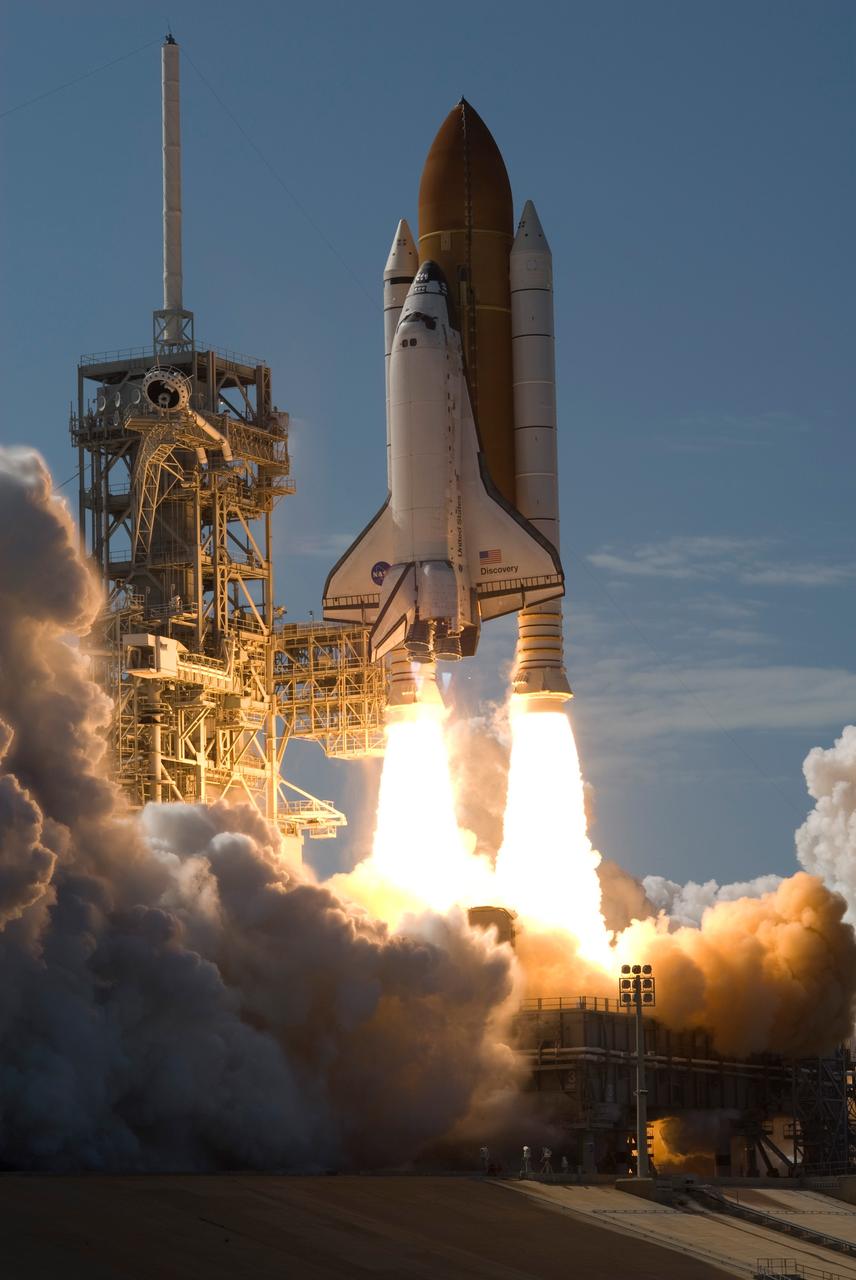

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Smoke and steam billow out from space shuttle Discovery as towers of flame from the solid rocket boosters hurl it into the sky above Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Launch of Discovery on its STS-124 mission was on time at 5:02 p.m. EDT. At left is the fixed service structure with the 80-foot lightning mast on top. Discovery is making its 35th flight. The STS-124 mission is the 26th in the assembly of the space station. It is the second of three flights launching components to complete the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency's Kibo laboratory. The shuttle crew will install Kibo's large Japanese Pressurized Module and its remote manipulator system, or RMS. The 14-day flight includes three spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph, Tony Gray, Robert Murray, Mike Kerley
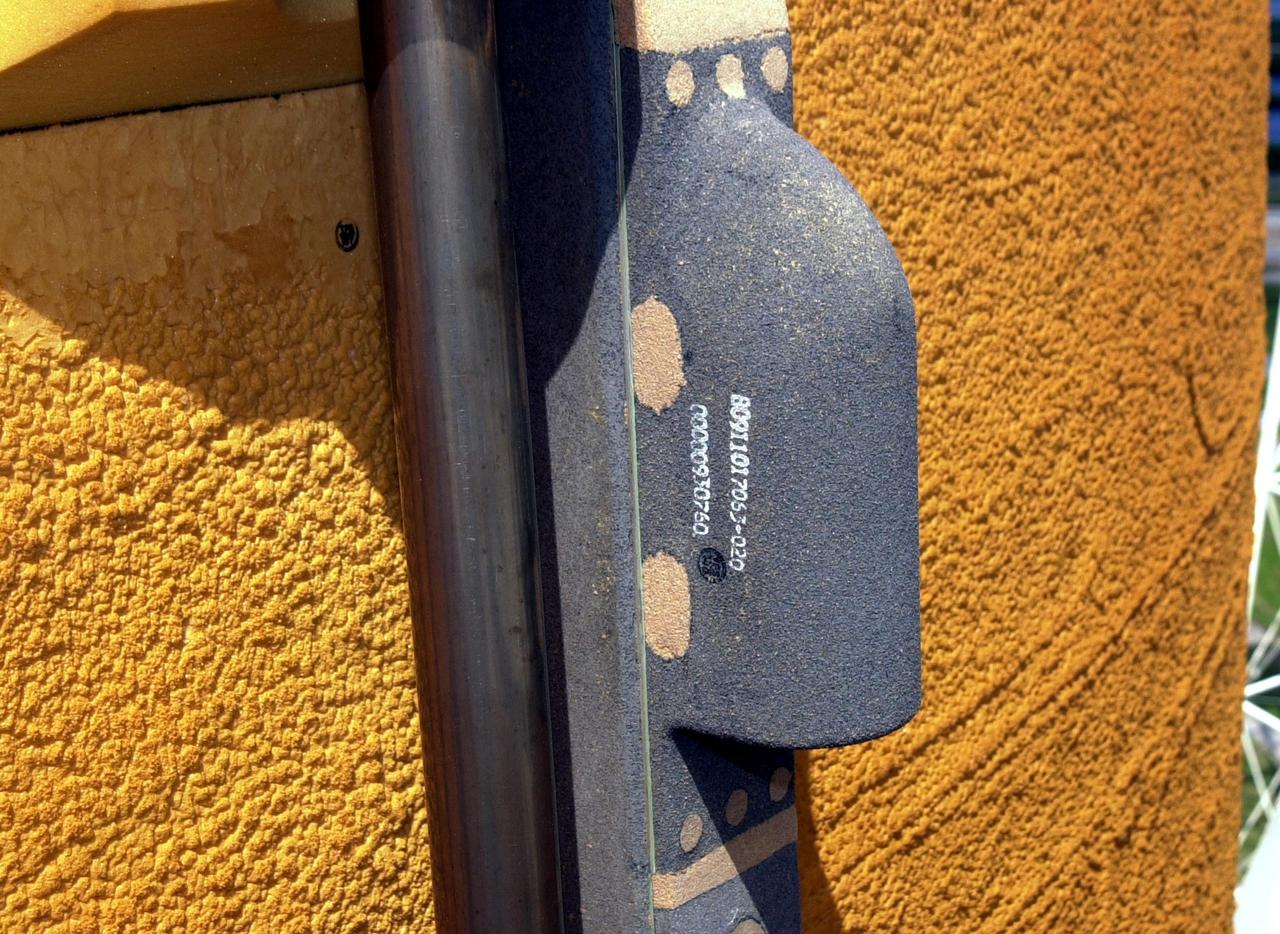

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A closeup view of the camera mounted on the external tank of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The color video camera mounted to the top of Atlantis' external tank will provide a view of the front and belly of the orbiter and a portion of the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) and external tank during the launch of Atlantis on mission STS-112. It will offer the STS-112 team an opportunity to monitor the shuttle's performance from a new angle. The camera will be turned on fifteen minutes prior to launch and will show the orbiter and solid rocket boosters on the launch pad. The video will be downlinked from the external tank during flight to several NASA data-receiving sites and then relayed to the live television broadcast. The camera is expected to operate for about 15 minutes following liftoff. At liftoff, viewers will see the shuttle clearing the launch tower and, at two minutes after liftoff, see the right SRB separate from the external tank. When the external tank separates from Atlantis about eight minutes into the flight, the camera is expected to continue its live feed for about six more minutes although NASA may be unable to pick up the camera's signal because the tank may have moved out of range.
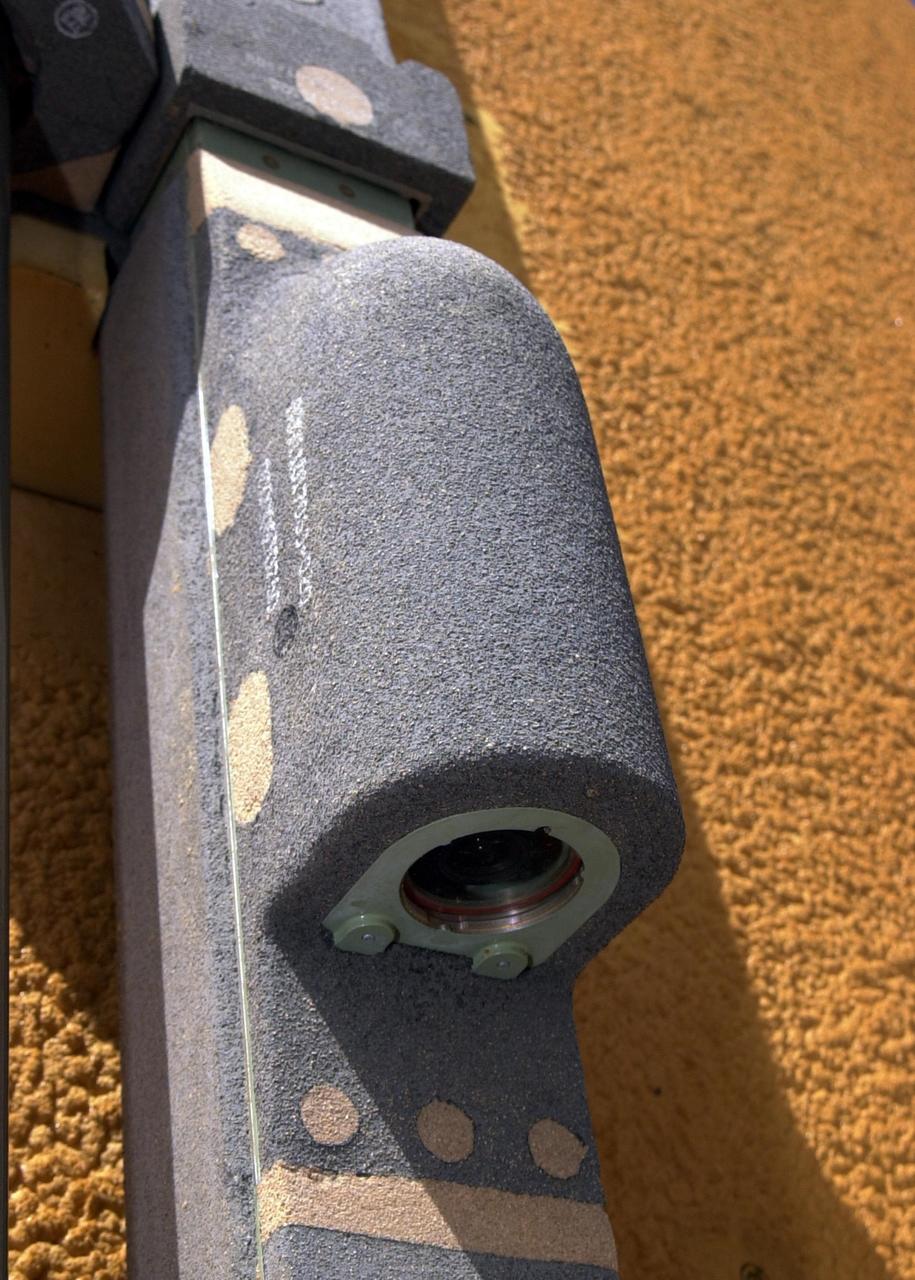

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A closeup view of the camera mounted on the external tank of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The color video camera mounted to the top of Atlantis' external tank will provide a view of the front and belly of the orbiter and a portion of the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) and external tank during the launch of Atlantis on mission STS-112. It will offer the STS-112 team an opportunity to monitor the shuttle's performance from a new angle. The camera will be turned on fifteen minutes prior to launch and will show the orbiter and solid rocket boosters on the launch pad. The video will be downlinked from the external tank during flight to several NASA data-receiving sites and then relayed to the live television broadcast. The camera is expected to operate for about 15 minutes following liftoff. At liftoff, viewers will see the shuttle clearing the launch tower and, at two minutes after liftoff, see the right SRB separate from the external tank. When the external tank separates from Atlantis about eight minutes into the flight, the camera is expected to continue its live feed for about six more minutes although NASA may be unable to pick up the camera's signal because the tank may have moved out of range.
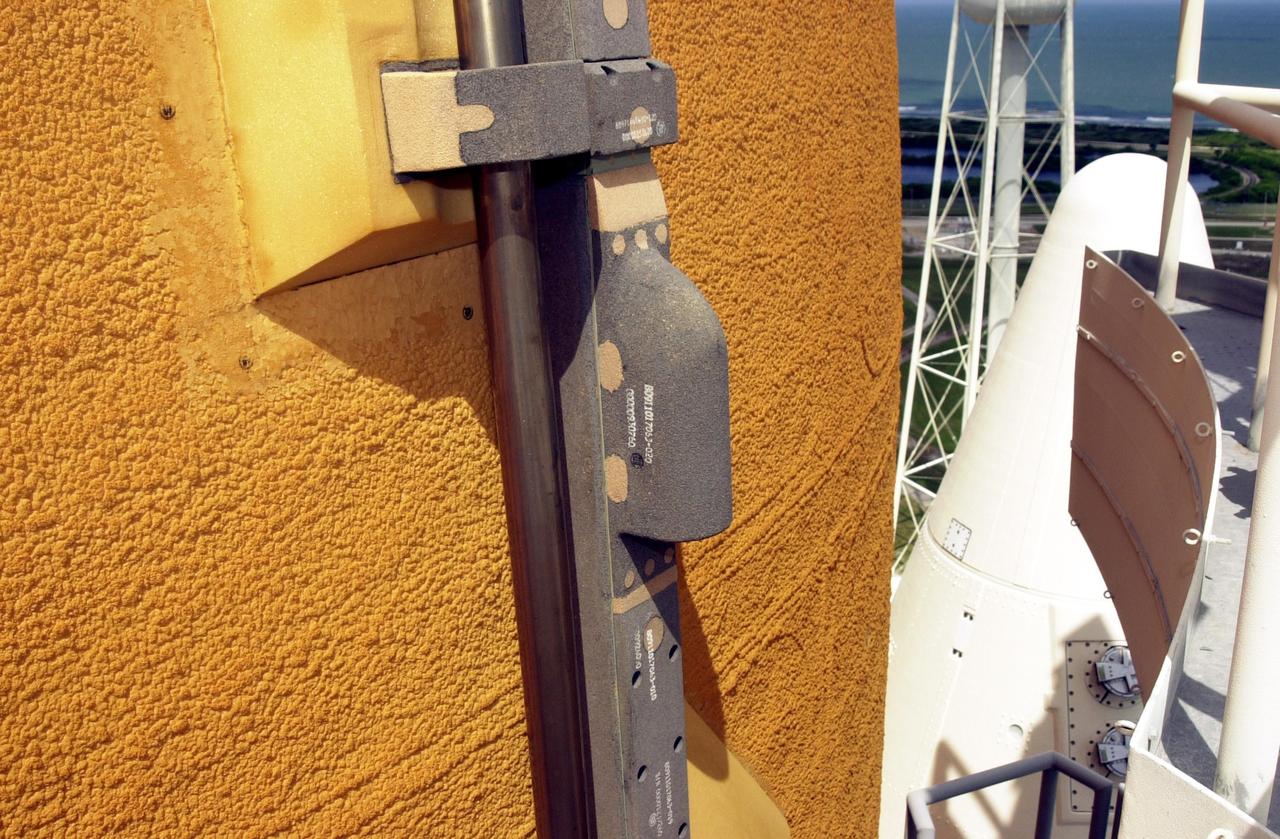

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A view of the camera mounted on the external tank of Space Shuttle Atlantis. The color video camera mounted to the top of Atlantis' external tank will provide a view of the front and belly of the orbiter and a portion of the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) and external tank during the launch of Atlantis on mission STS-112. It will offer the STS-112 team an opportunity to monitor the shuttle's performance from a new angle. The camera will be turned on fifteen minutes prior to launch and will show the orbiter and solid rocket boosters on the launch pad. The video will be downlinked from the external tank during flight to several NASA data-receiving sites and then relayed to the live television broadcast. The camera is expected to operate for about 15 minutes following liftoff. At liftoff, viewers will see the shuttle clearing the launch tower and, at two minutes after liftoff, see the right SRB separate from the external tank. When the external tank separates from Atlantis about eight minutes into the flight, the camera is expected to continue its live feed for about six more minutes although NASA may be unable to pick up the camera's signal because the tank may have moved out of range.
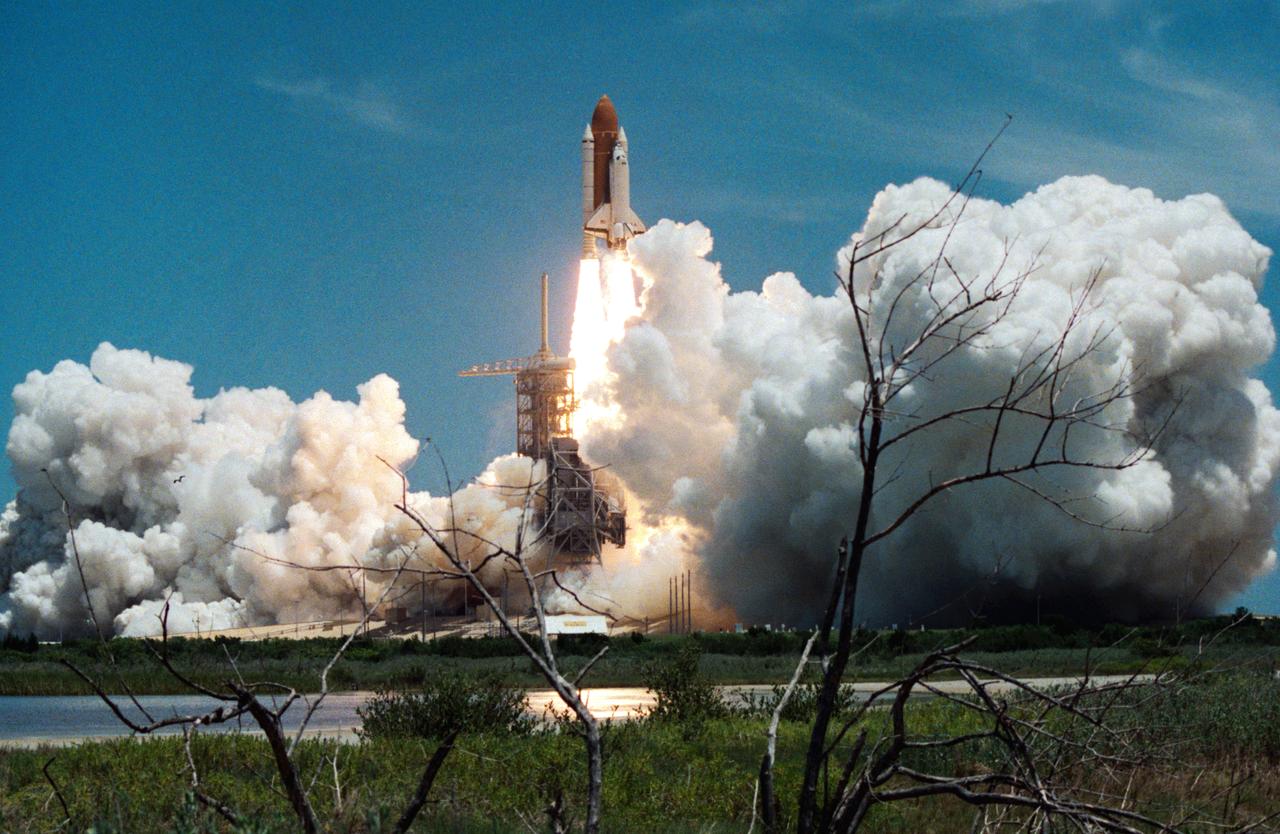

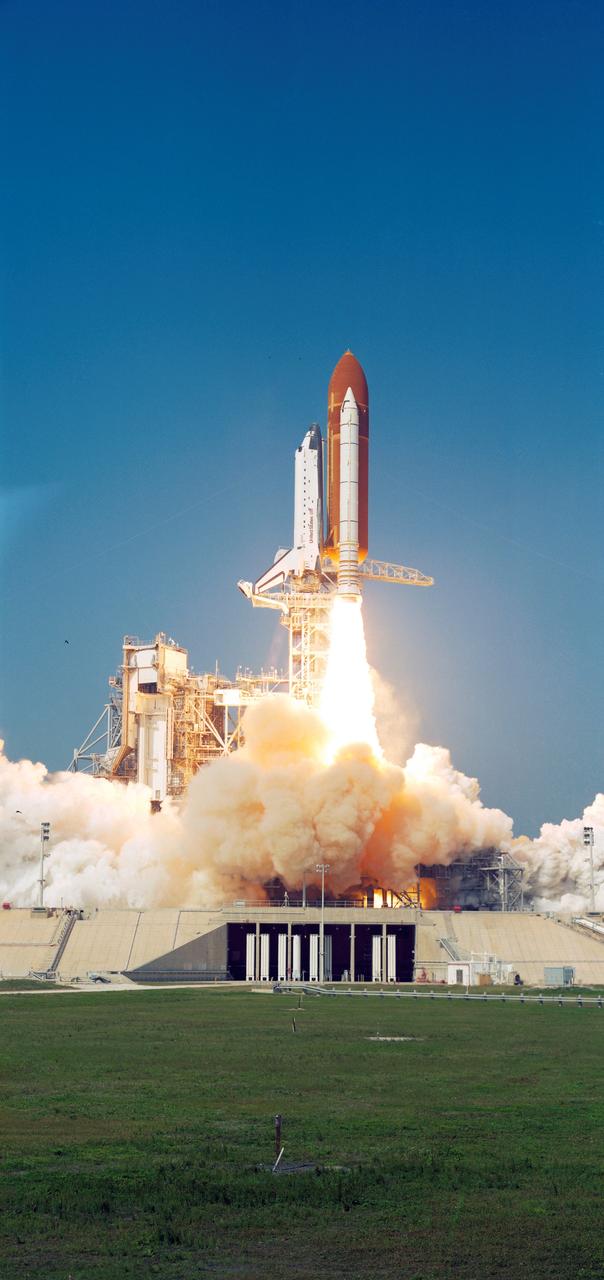
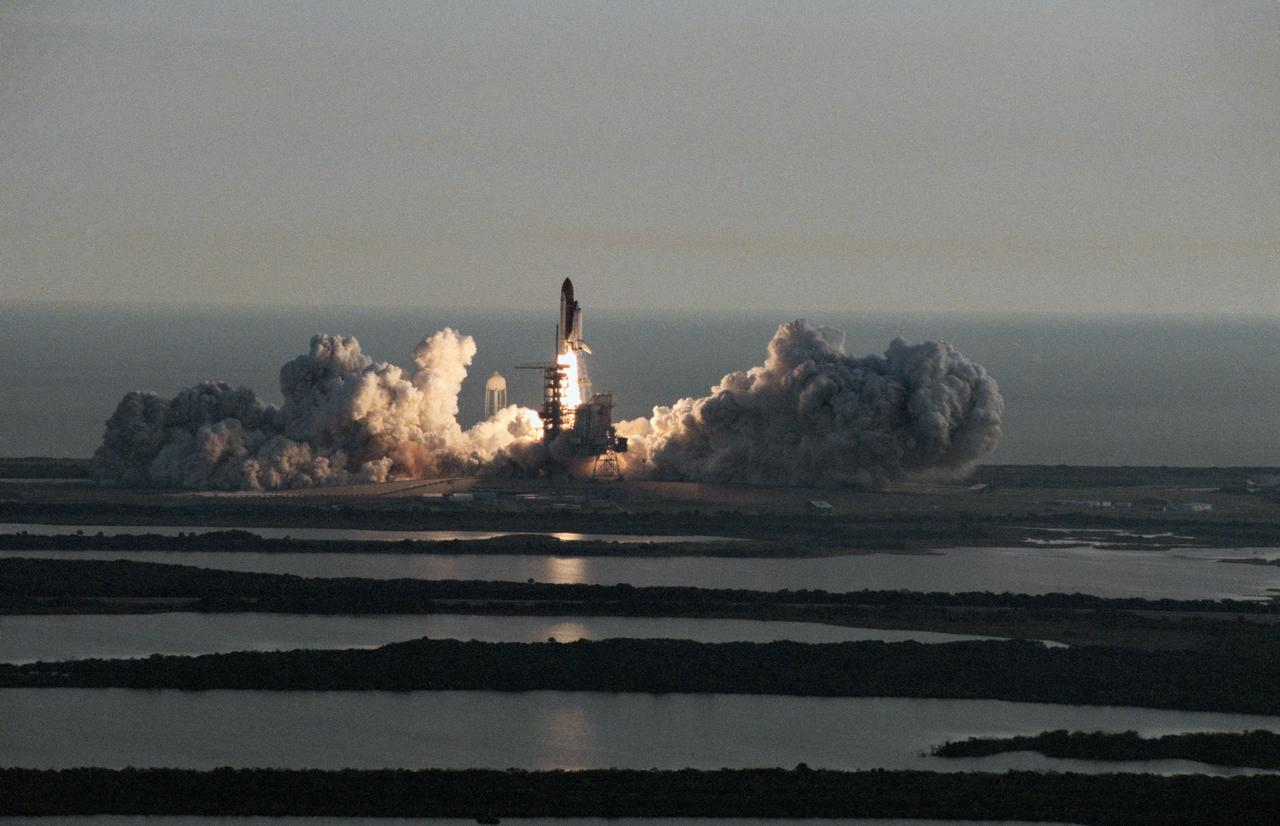
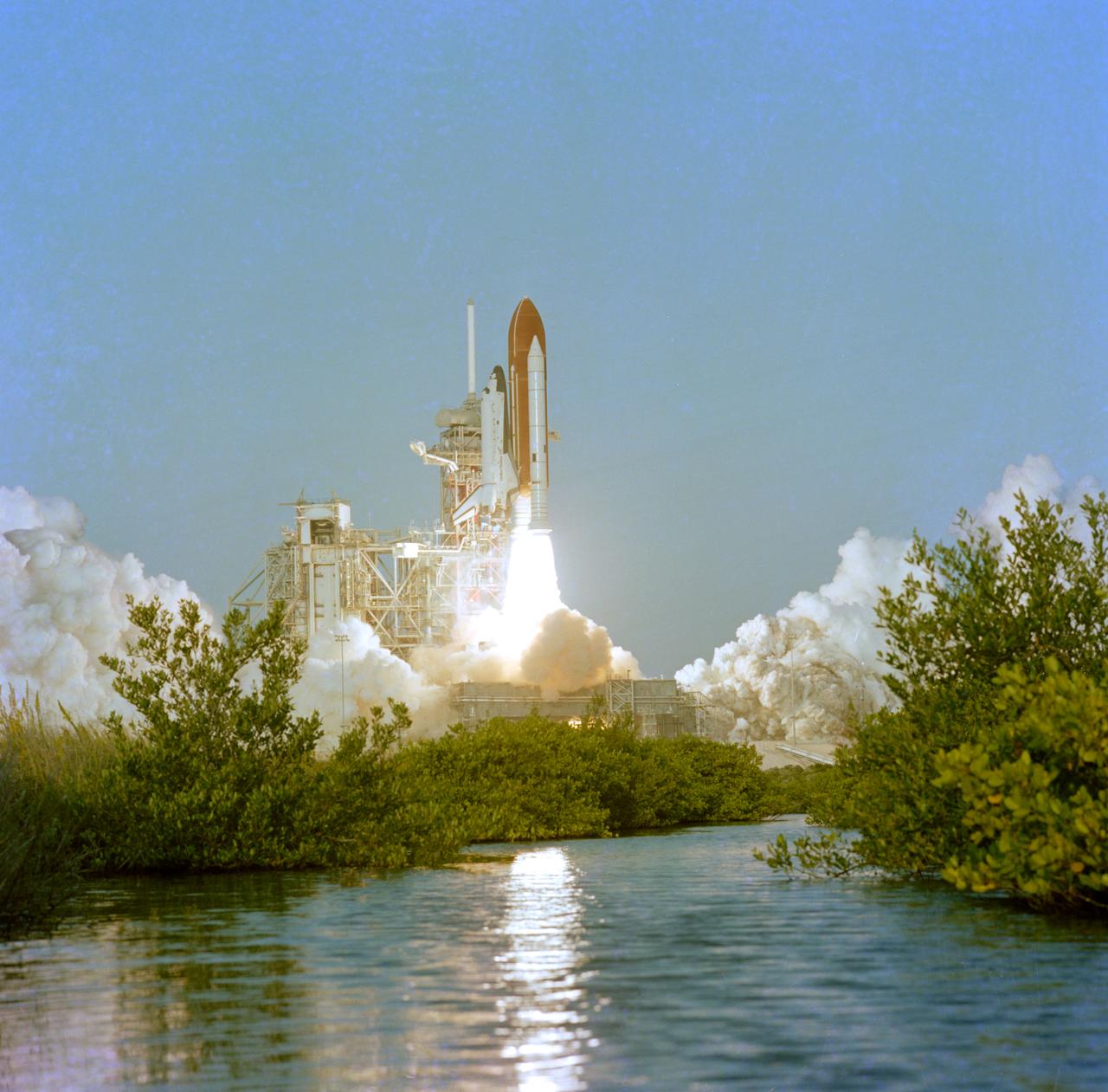
Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, begins its roll maneuver after clearing the fixed service structure (FSS) tower as it rises above Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39A. In the foreground of this horizontal scene is Florida brush and a waterway. Beyond the brush, the shuttle's exhaust cloud envelops the immediate launch pad area. Launch occurred at 12:43 pm Eastern Daylight Time (EDT). The glow of the space shuttle main engine (SSME) and solid rocket booster (SRB) firings is reflected in the nearby waterway. Once in Earth orbit, STS-65's six NASA astronauts and a Japanese Payload Specialist aboard OV-102 will begin two weeks of experimentation in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2).
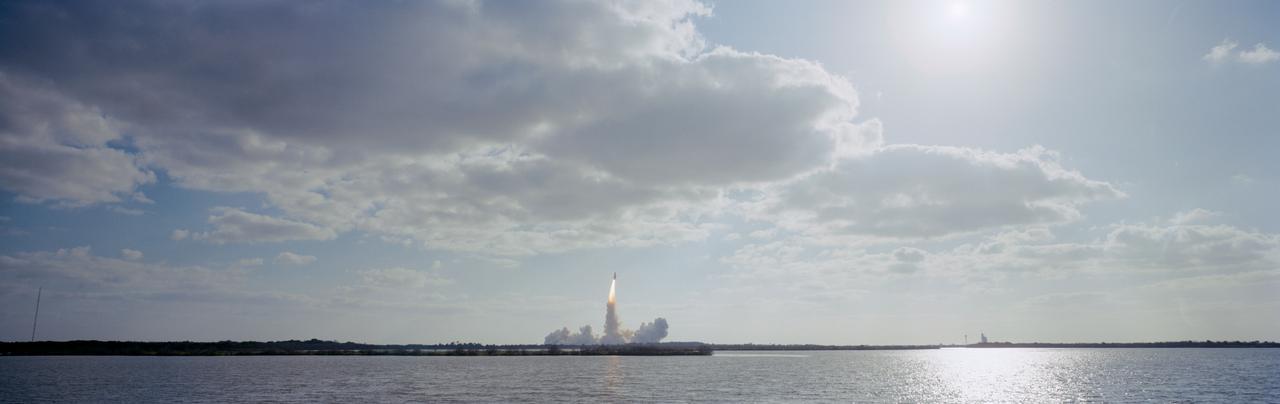

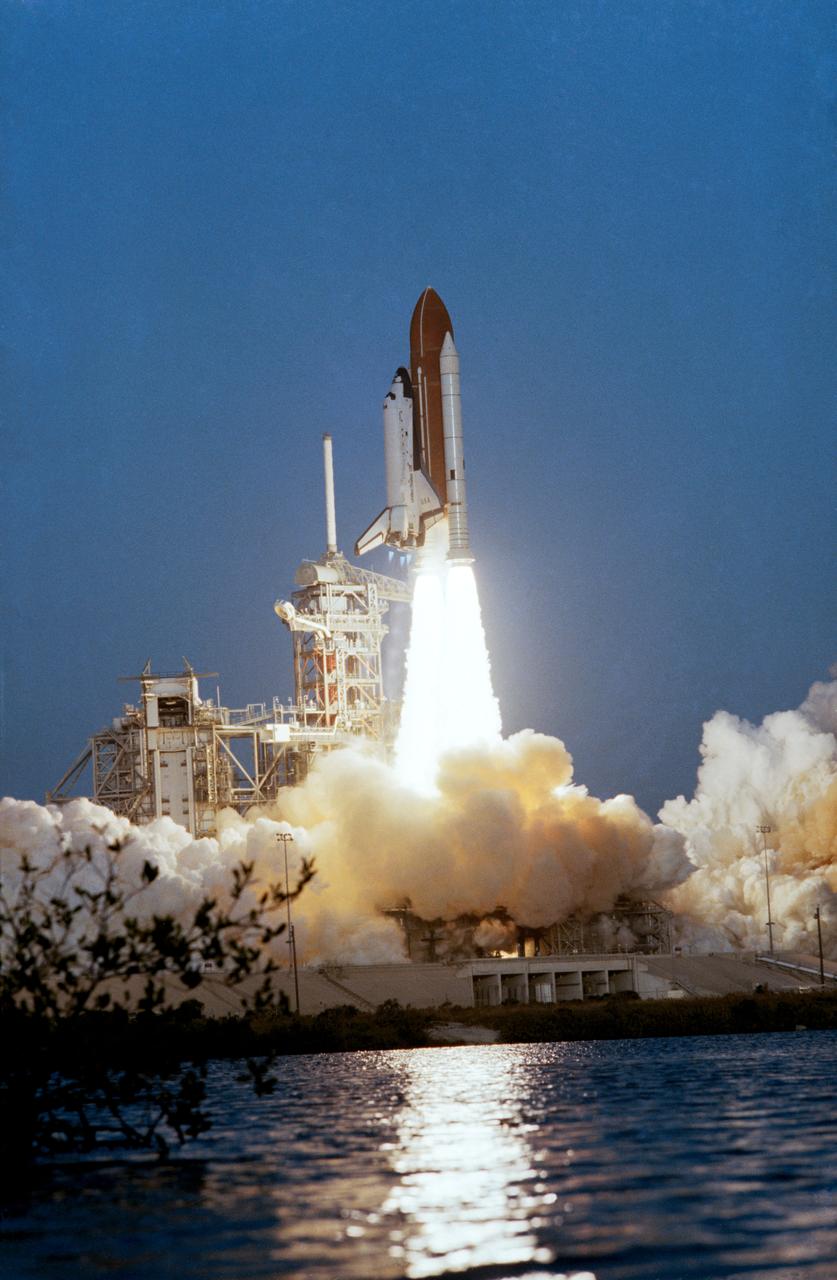
In this distant view, STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is seen as it heads skyward after liftoff from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B at 8:33:51.0492 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). OV-103's silhouette atop the external tank (ET) appears above the glow of the solid rocket booster (SRB) and space shuttle main engine (SSME) firings. An exhaust plume trails behind and covers the launch pad area below the orbiter. A nearby waterway reflects the SRB/SSME glow in the foreground. At the far right and barely discernible is KSC LC Pad 39A and the Sound Supression Water System tower. Columbia, OV-102, is on LC Pad 39A which is separated by a distance of 1.6 miles. This was the first time since January 1986 that there was a shuttle on each pad.
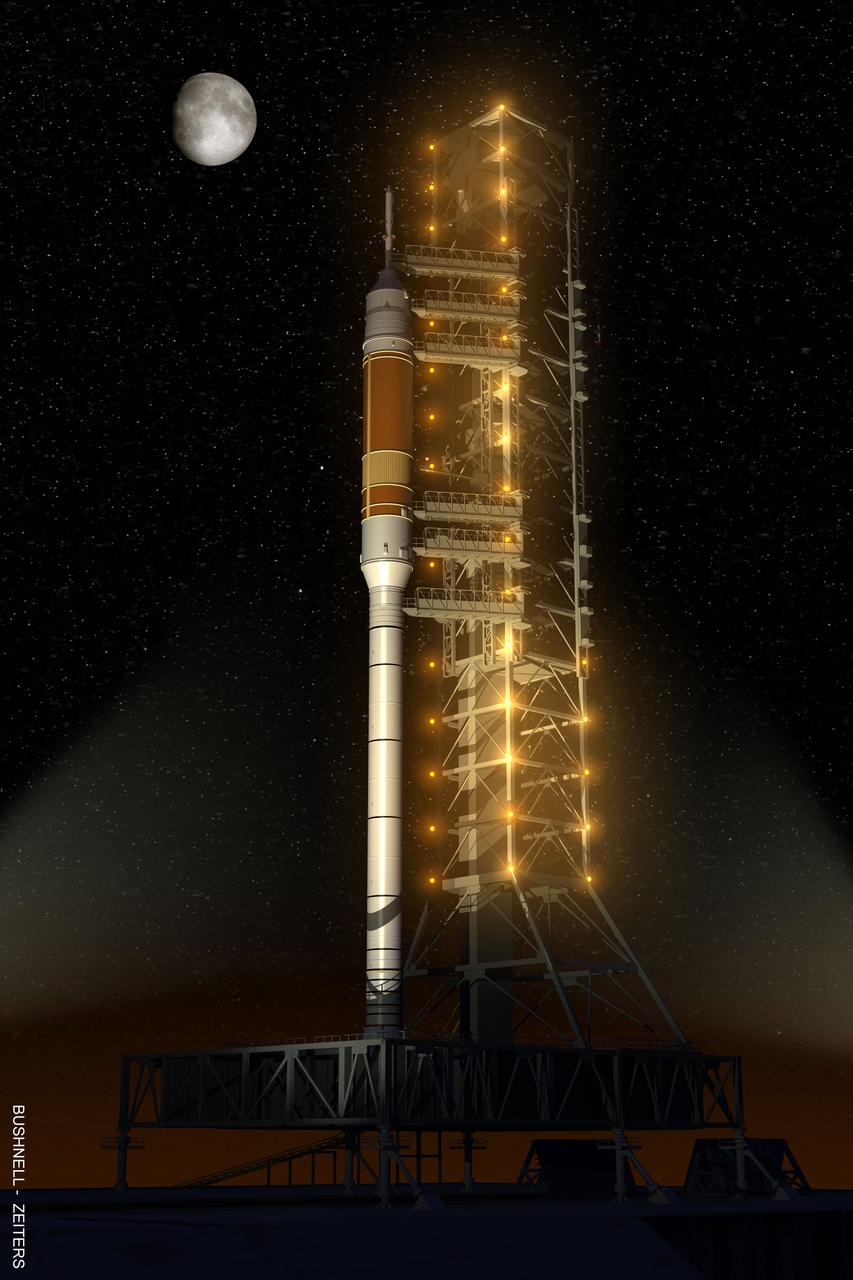
Under the goals of the Vision for Space Exploration, Ares I is a chief component of the cost-effective space transportation infrastructure being developed by NASA's Constellation Program. This transportation system will safely and reliably carry human explorers back to the moon, and then onward to Mars and other destinations in the solar system. Launch Pad 39B of the Kennedy Space Flight Center (KSC), currently used for Space Shuttle launches, will be revised to host the Ares launch vehicles. The fixed and rotating service structures standing at the pad will be dismantled sometime after the Ares I-X test flight. A new launch tower for Ares I will be built onto a new mobile launch platform. The gantry for the shuttle doesn't reach much higher than the top of the four segments of the solid rocket booster. Pad access above the current shuttle launch pad structure will not be required for Ares I-X because the stages above the solid rocket booster are inert. For the test scheduled in 2012 or for the crewed flights, workers and astronauts will need access to the highest levels of the rocket and capsule. When the Ares I rocket rolls out to the launch pad on the back of the same crawler-transporters used now, its launch gantry will be with it. The mobile launchers will nestle under three lightning protection towers to be erected around the pad area. Ares time at the launch pad will be significantly less than the three weeks or more the shuttle requires. This “clean pad” approach minimizes equipment and servicing at the launch pad. It is the same plan NASA used with the Saturn V rockets and industry employs it with more modern launchers. The launch pad will also get a new emergency escape system for astronauts, one that looks very much like a roller coaster. Cars riding on a rail will replace the familiar baskets hanging from steel cables. This artist's concept illustrates the Ares I on launch pad 39B.
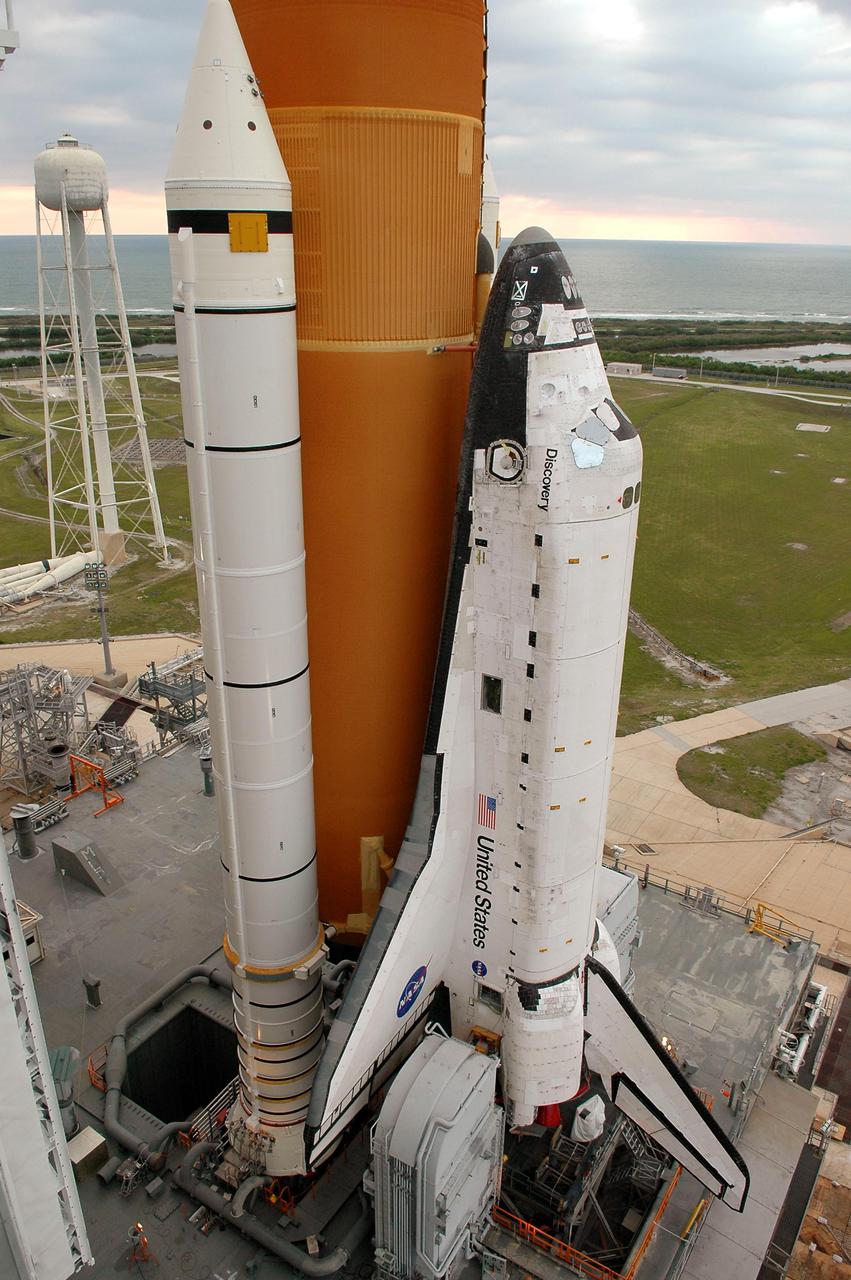

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Under post-dawn cloudy skies that shade the normally bright blue Atlantic Ocean, Space Shuttle Discovery, resting on the Mobile Launcher Platform on Launch Pad 39B, awaits rollback to the Vehicle Assembly Building. To the left of the Solid Rocket Booster is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water, part of the sound suppression system during a launch. Once inside the VAB, Discovery will be demated from its External Tank and lifted into the transfer aisle. On or about June 7, Discovery will be lifted and attached to its new tank and Solid Rocket Boosters, which are already in the VAB. Only the 15th rollback in Space Shuttle Program history, the 4.2-mile journey allows additional modifications to be made to the External Tank prior to a safe Return to Flight. Discovery is expected to be rolled back to the launch pad in mid-June for Return to Flight mission STS-114. The launch window extends from July 13 to July 31.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The high-fidelity space shuttle model which was on display at the NASA Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida arrives at Kennedy's Launch Complex 39 turn basin where it will be prepared for the next leg of its journey. Across the street, the Vehicle Assembly Building towers 525 feet into the sky. The shuttle was part of a display at the visitor complex that also included an external tank and two solid rocket boosters that were used to show visitors the size of actual space shuttle components. The full-scale shuttle model is being transferred from Kennedy to Space Center Houston, NASA Johnson Space Center's visitor center. The model will stay at the turn basin for a few months until it is ready to be transported to Texas via barge. The move also helps clear the way for the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex to begin construction of a new facility next year to display space shuttle Atlantis in 2013. For more information about Space Center Houston, visit http://www.spacecenter.org. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The high-fidelity space shuttle model which was on display at the NASA Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida rolls through the Press Site parking lot toward Kennedy's Launch Complex 39 turn basin. Behind it, the Vehicle Assembly Building towers 525 feet in the air. The shuttle was part of a display at the visitor complex that also included an external tank and two solid rocket boosters that were used to show visitors the size of actual space shuttle components. The full-scale shuttle model is being transferred from Kennedy to Space Center Houston, NASA Johnson Space Center's visitor center. The model will stay at the turn basin for a few months until it is ready to be transported to Texas via barge. The move also helps clear the way for the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex to begin construction of a new facility next year to display space shuttle Atlantis in 2013. For more information about Space Center Houston, visit http://www.spacecenter.org. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The high-fidelity space shuttle model which was on display at the NASA Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida has arrived at Kennedy's Launch Complex 39 turn basin and awaits preparation for the next leg of its journey. Across the street, the Vehicle Assembly Building towers 525 feet into the sky. The shuttle was part of a display at the visitor complex that also included an external tank and two solid rocket boosters that were used to show visitors the size of actual space shuttle components. The full-scale shuttle model is being transferred from Kennedy to Space Center Houston, NASA Johnson Space Center's visitor center. The model will stay at the turn basin for a few months until it is ready to be transported to Texas via barge. The move also helps clear the way for the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex to begin construction of a new facility next year to display space shuttle Atlantis in 2013. For more information about Space Center Houston, visit http://www.spacecenter.org. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
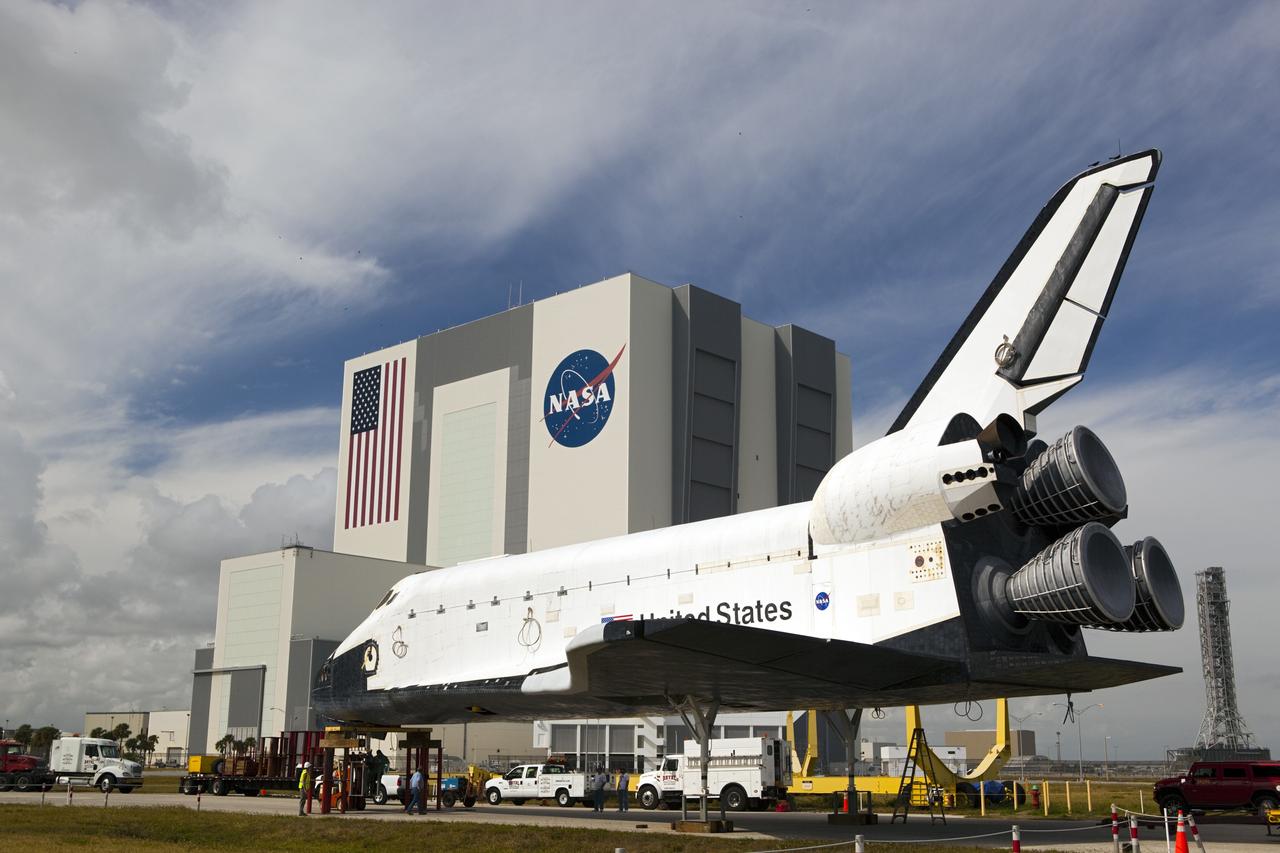

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Pedestals support the high-fidelity space shuttle model which was on display at the NASA Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida following its delivery to Kennedy's Launch Complex 39 turn basin. Behind it, the Vehicle Assembly Building towers 525 feet in the air. The shuttle was part of a display at the visitor complex that also included an external tank and two solid rocket boosters that were used to show visitors the size of actual space shuttle components. The full-scale shuttle model is being transferred from Kennedy to Space Center Houston, NASA Johnson Space Center's visitor center. The model will stay at the turn basin for a few months until it is ready to be transported to Texas via barge. The move also helps clear the way for the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex to begin construction of a new facility next year to display space shuttle Atlantis in 2013. For more information about Space Center Houston, visit http://www.spacecenter.org. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
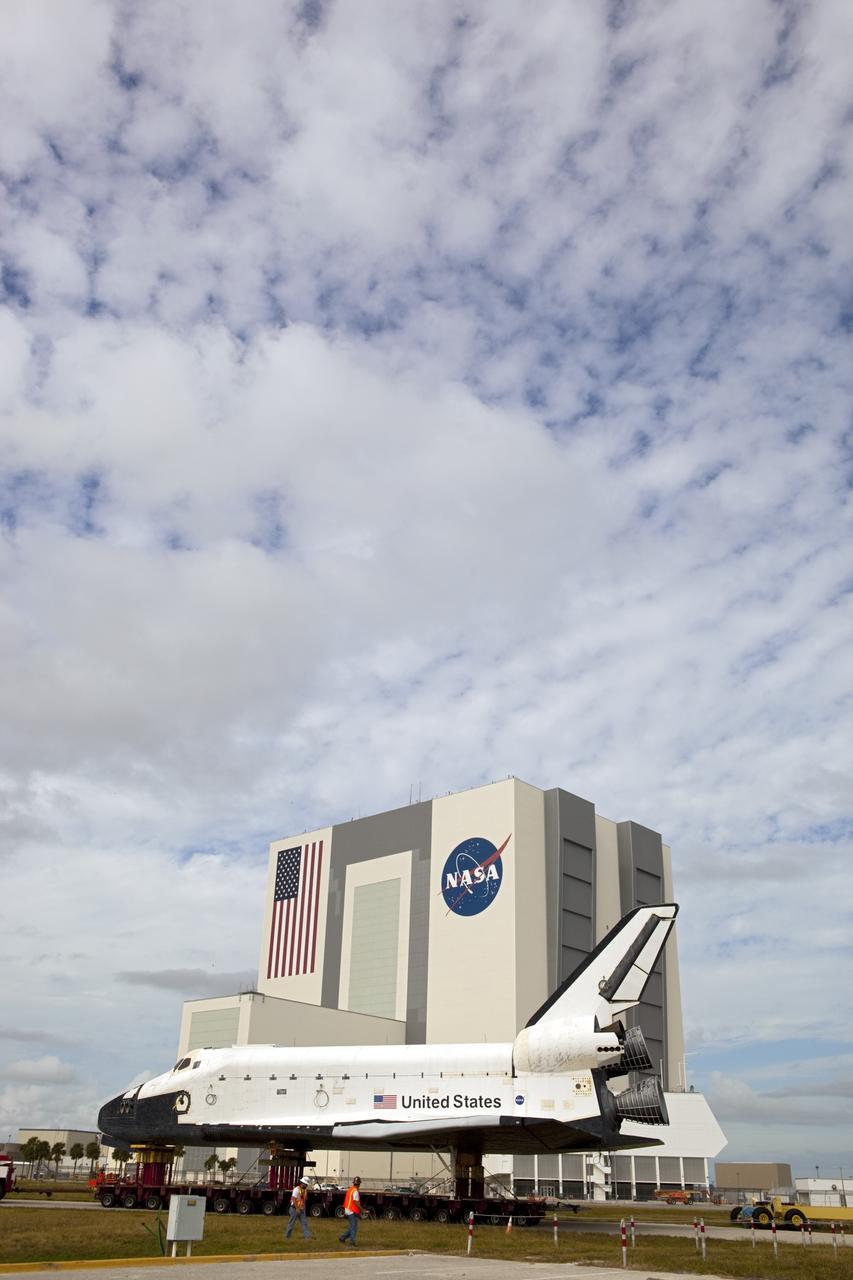

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The high-fidelity space shuttle model which was on display at the NASA Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida backs toward its destination, Kennedy's Launch Complex 39 turn basin. The Vehicle Assembly Building across the street towers 525 feet above it. The shuttle was part of a display at the visitor complex that also included an external tank and two solid rocket boosters that were used to show visitors the size of actual space shuttle components. The full-scale shuttle model is being transferred from Kennedy to Space Center Houston, NASA Johnson Space Center's visitor center. The model will stay at the turn basin for a few months until it is ready to be transported to Texas via barge. The move also helps clear the way for the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex to begin construction of a new facility next year to display space shuttle Atlantis in 2013. For more information about Space Center Houston, visit http://www.spacecenter.org. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
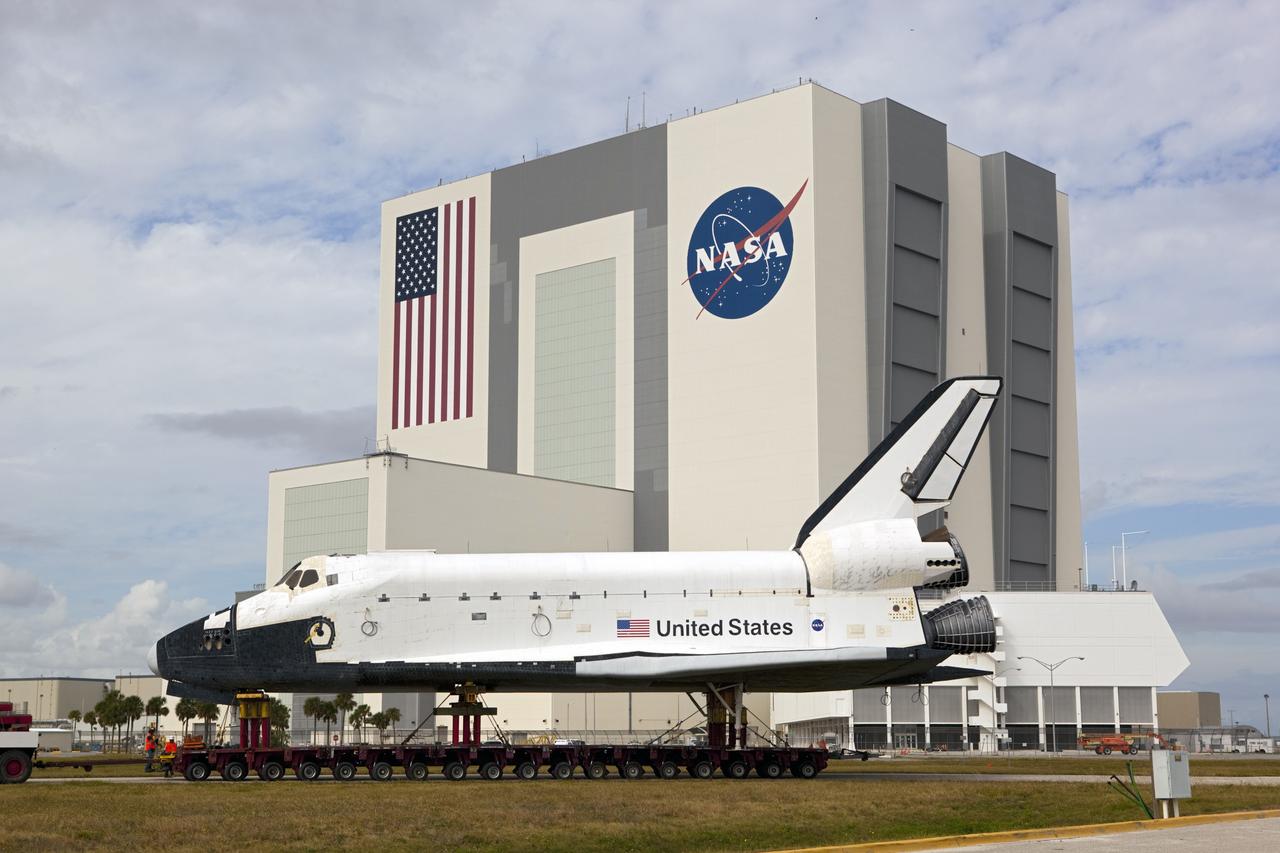

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The high-fidelity space shuttle model which was on display at the NASA Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida backs through the Press Site parking lot toward Kennedy's Launch Complex 39 turn basin. Behind it, the Vehicle Assembly Building towers 525 feet into the sky. The shuttle was part of a display at the visitor complex that also included an external tank and two solid rocket boosters that were used to show visitors the size of actual space shuttle components. The full-scale shuttle model is being transferred from Kennedy to Space Center Houston, NASA Johnson Space Center's visitor center. The model will stay at the turn basin for a few months until it is ready to be transported to Texas via barge. The move also helps clear the way for the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex to begin construction of a new facility next year to display space shuttle Atlantis in 2013. For more information about Space Center Houston, visit http://www.spacecenter.org. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
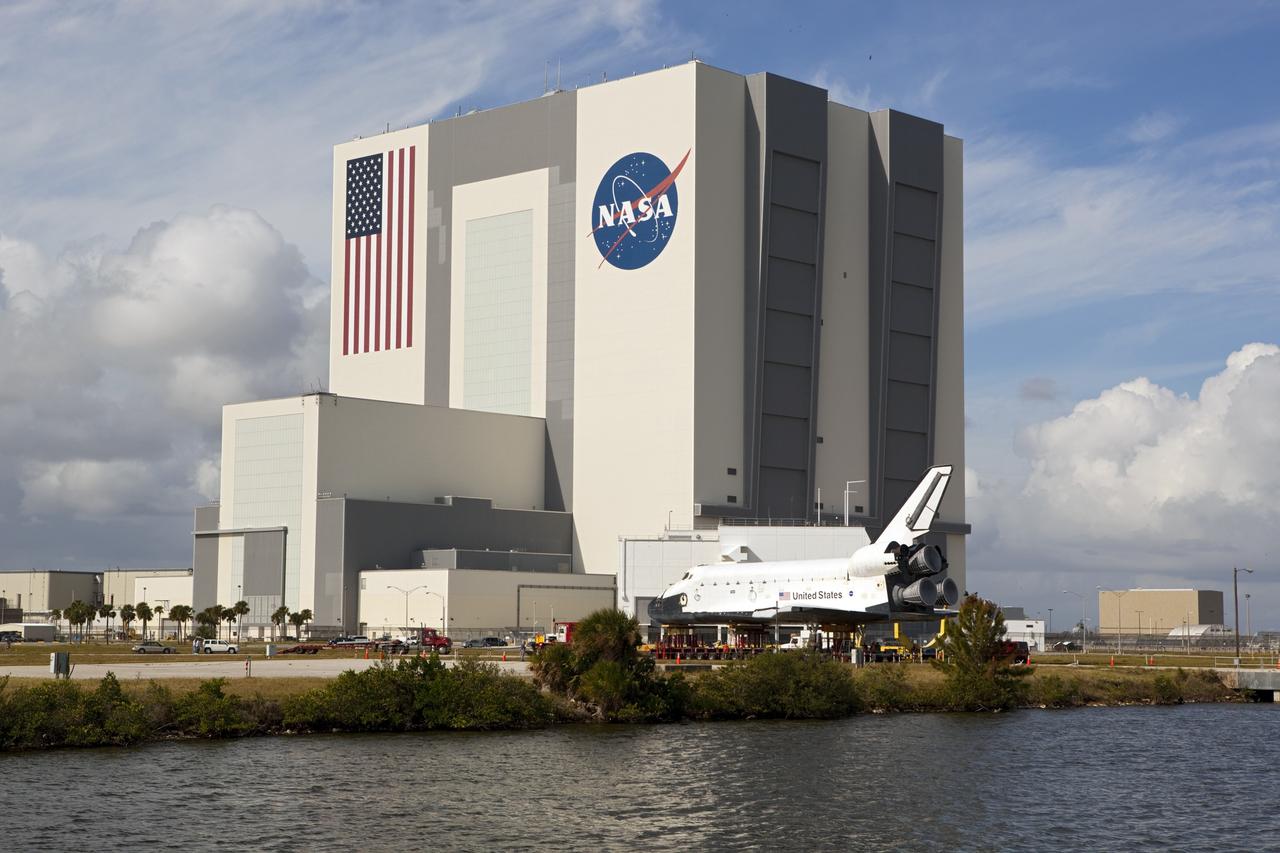

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The high-fidelity space shuttle model which was on display at the NASA Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida seems out of place when viewed across the water of Kennedy's Launch Complex 39 turn basin. The Vehicle Assembly Building across the street towers 525 feet above it. The shuttle was part of a display at the visitor complex that also included an external tank and two solid rocket boosters that were used to show visitors the size of actual space shuttle components. The full-scale shuttle model is being transferred from Kennedy to Space Center Houston, NASA Johnson Space Center's visitor center. The model will stay at the turn basin for a few months until it is ready to be transported to Texas via barge. The move also helps clear the way for the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex to begin construction of a new facility next year to display space shuttle Atlantis in 2013. For more information about Space Center Houston, visit http://www.spacecenter.org. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
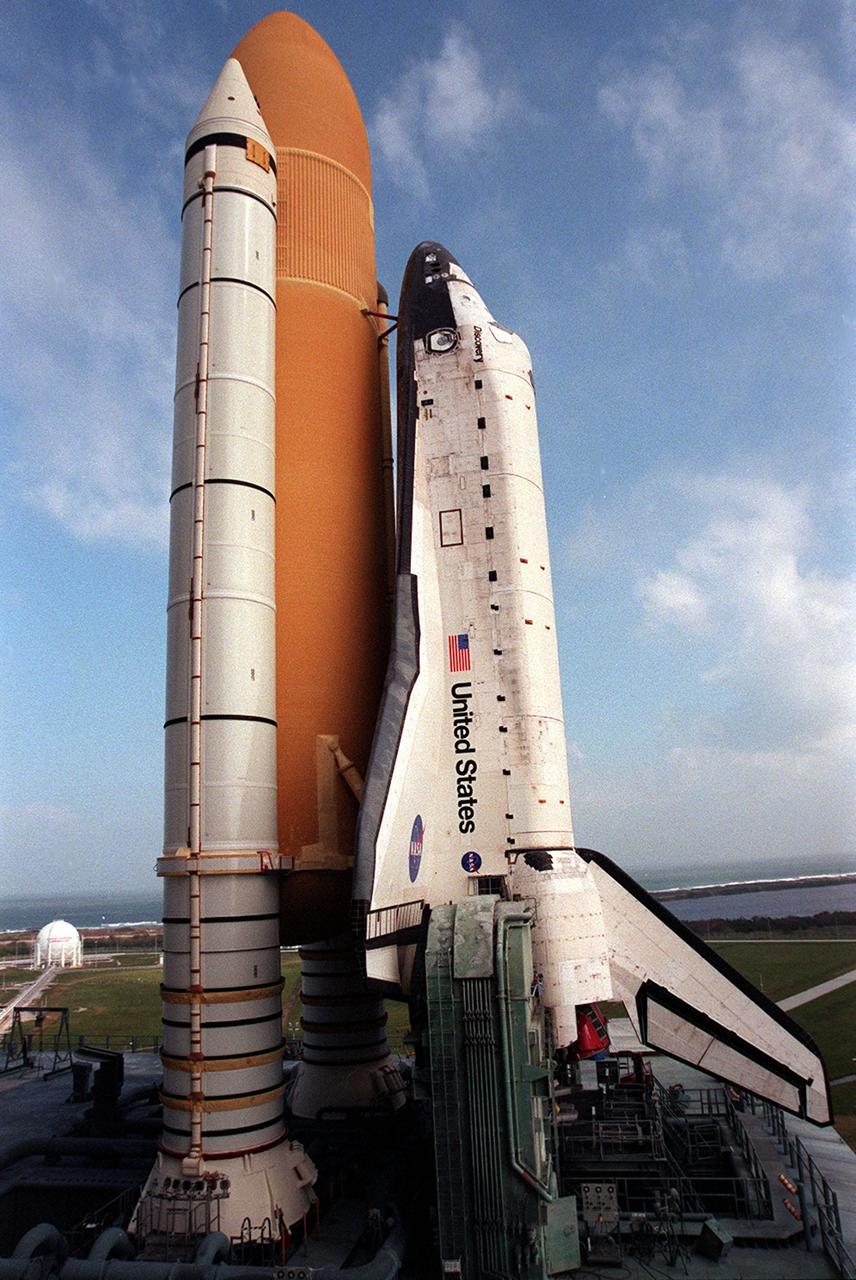

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At Launch Pad 39B, Space Shuttle Discovery towers against the hazy blue sky after a seven-hour trek from the Vehicle Assembly Building. The orbiter, external tank and solid rocket boosters will undergo final preparations for the STS-103 launch. The mission is a "call-up" due to the need to replace and repair portions of the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. The STS-103 crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), and Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France, both with the European Space Agency. The mission is targeted for launch Dec. 6 at 2:37 a.m. EST
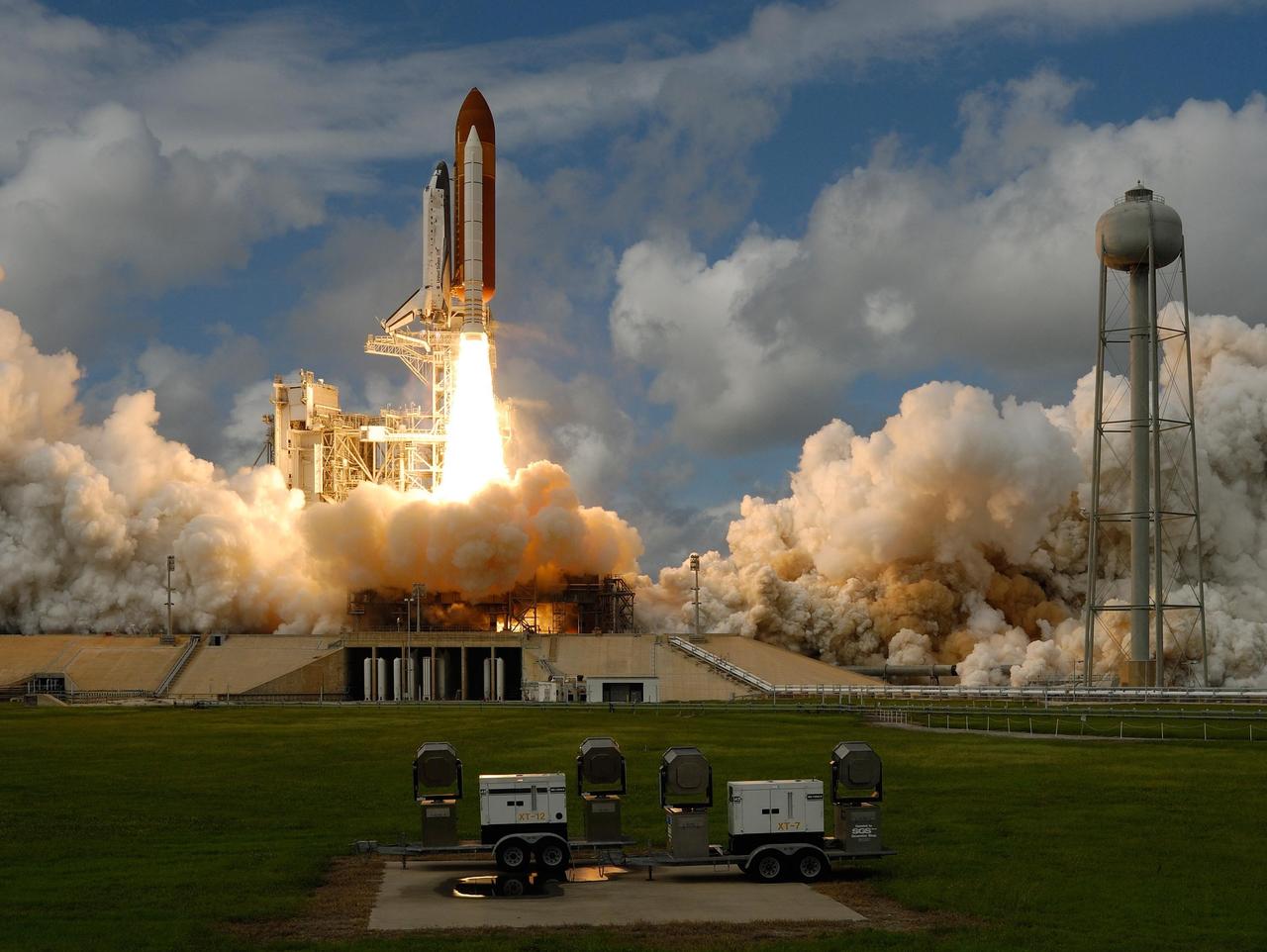

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Moments after liftoff on mission STS-120, space shuttle Discovery's solid rocket boosters spew columns of fire, creating clouds of smoke and steam below on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. At right is the 300,000-gallon water tower that provides water for the sound suppression system during liftoff, which occurred on time at 11:38:19 a.m. EDT. Discovery carries the Italian-built U.S. Node 2, called Harmony. During the 14-day STS-120 mission, the crew will install Harmony and move the P6 solar arrays to their permanent position and deploy them. Discovery is expected to complete its mission and return home at 4:47 a.m. EST on Nov. 6. Photo courtesy of Nikon/Scott Andrews
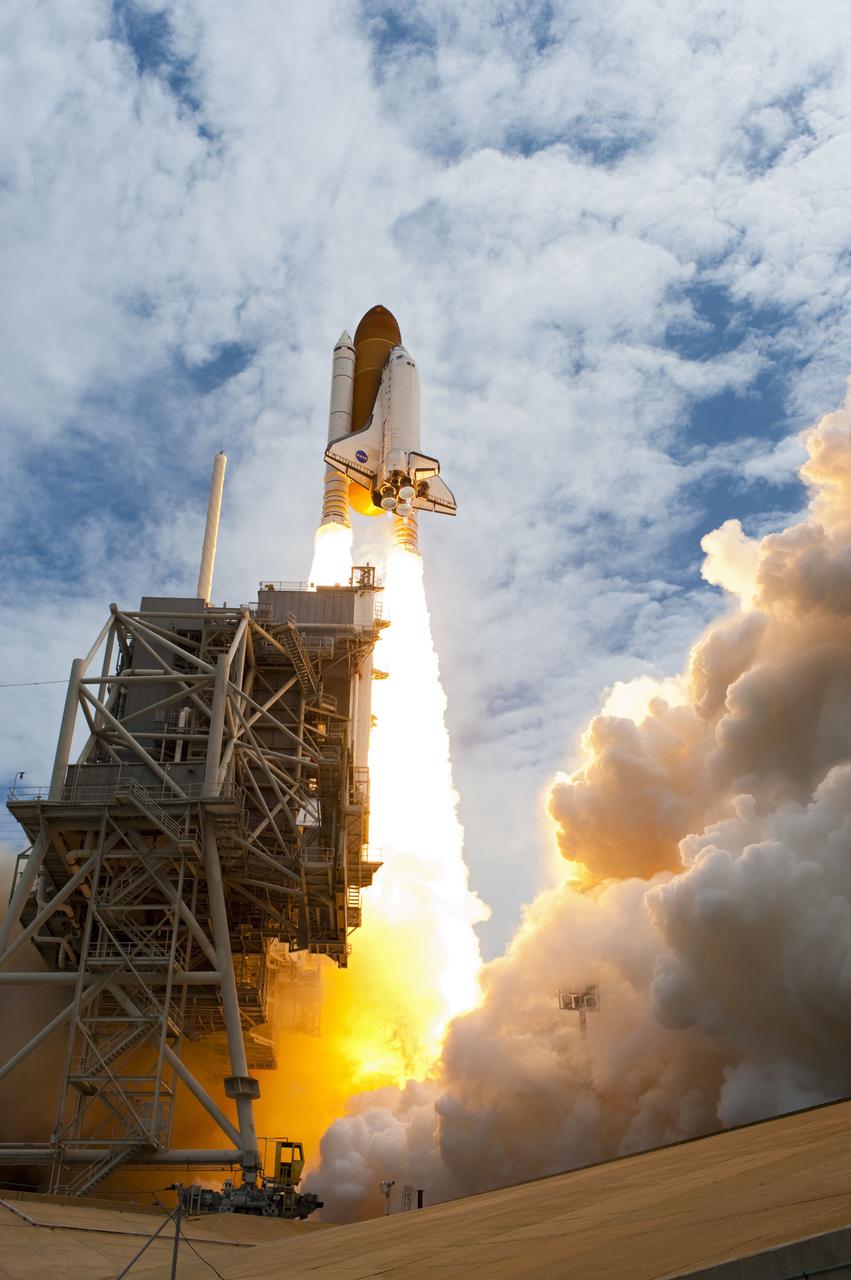

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis' main engines and solid rocket boosters ignite on Launch Pad 39A leaving behind a billow of steam and smoke as it lifts off past the tower on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 will be the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
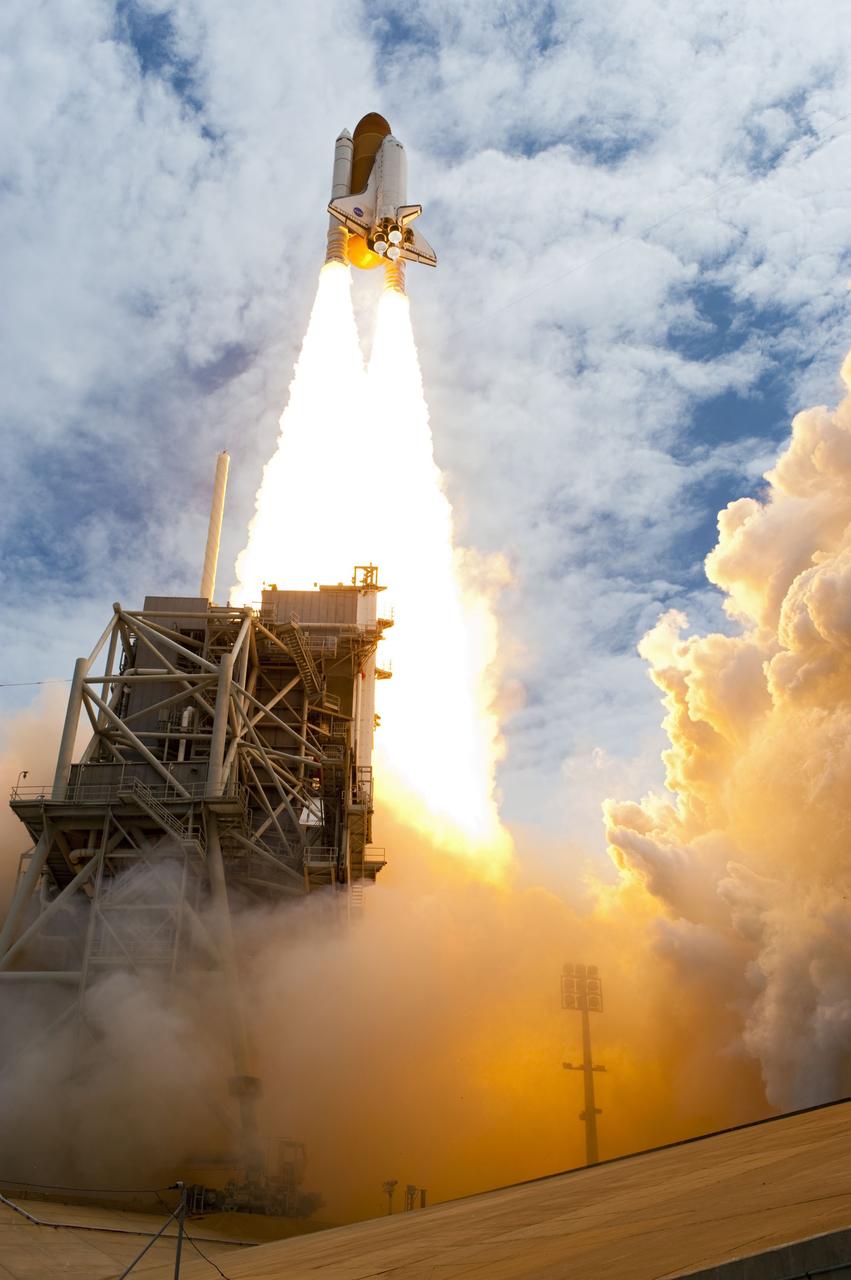

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis' main engines and solid rocket boosters ignite on Launch Pad 39A leaving behind a billow of steam and smoke as it lifts off past the tower into the clouds on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
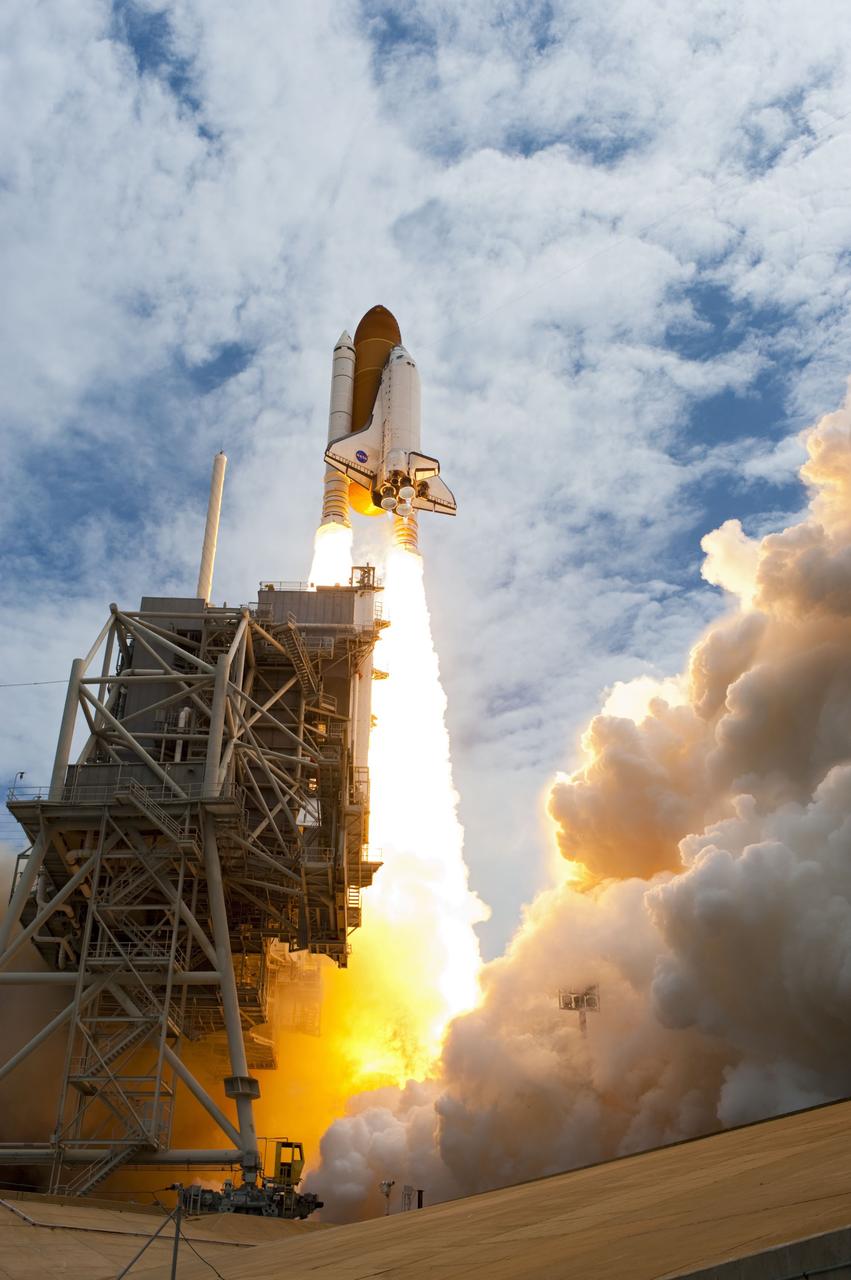

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis' main engines and solid rocket boosters ignite on Launch Pad 39A leaving behind a billow of steam and smoke as it lifts off past the tower on its STS-135 mission to the International Space Station. Atlantis with its crew of four; Commander Chris Ferguson, Pilot Doug Hurley, Mission Specialists Sandy Magnus and Rex Walheim, lifted off at 11:29 a.m. EDT on July 8, 2011 to deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts for the International Space Station. Atlantis also will fly the Robotic Refueling Mission experiment that will investigate the potential for robotically refueling existing satellites in orbit. In addition, Atlantis will return with a failed ammonia pump module to help NASA better understand the failure mechanism and improve pump designs for future systems. STS-135 is the 33rd flight of Atlantis, the 37th shuttle mission to the space station, and the 135th and final mission of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
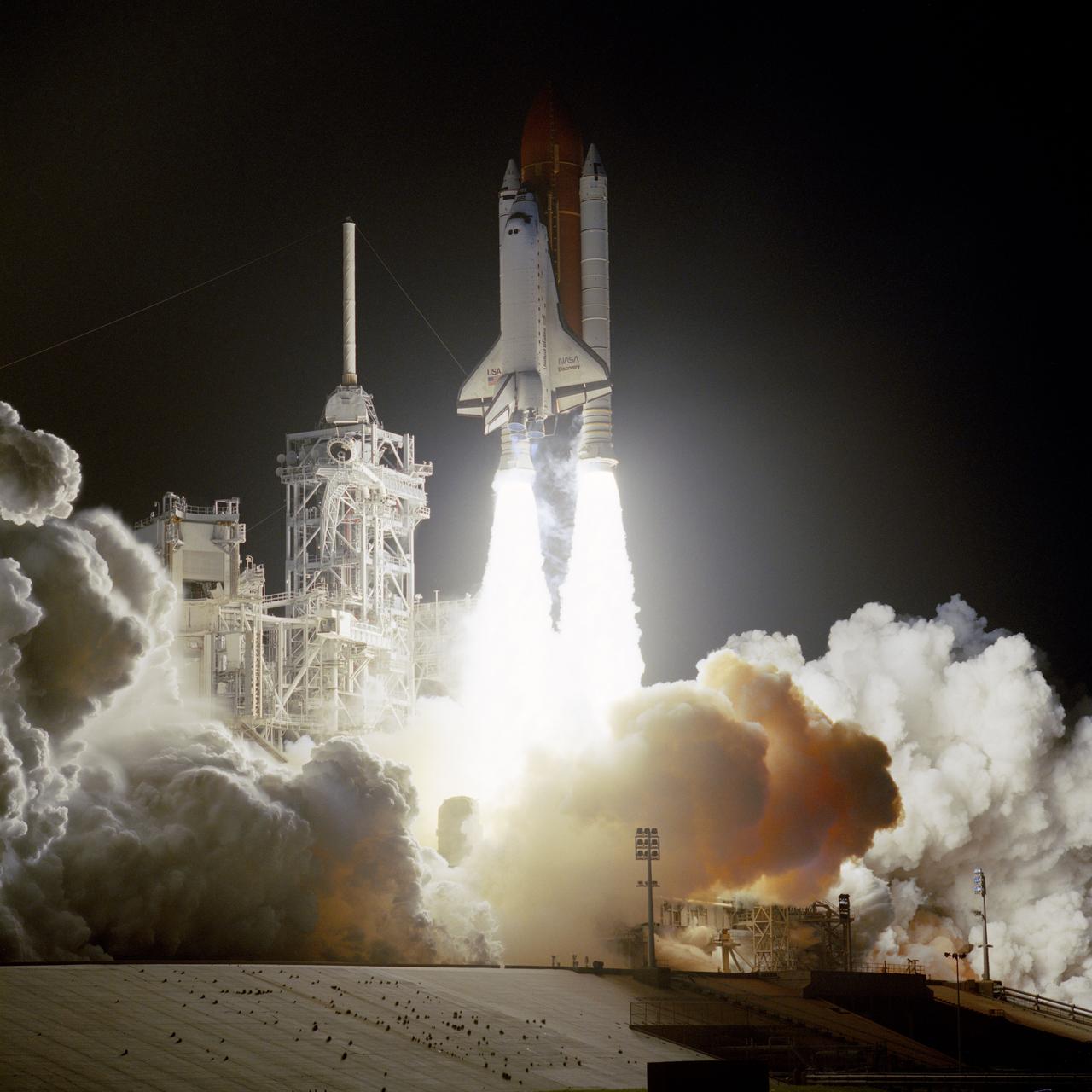

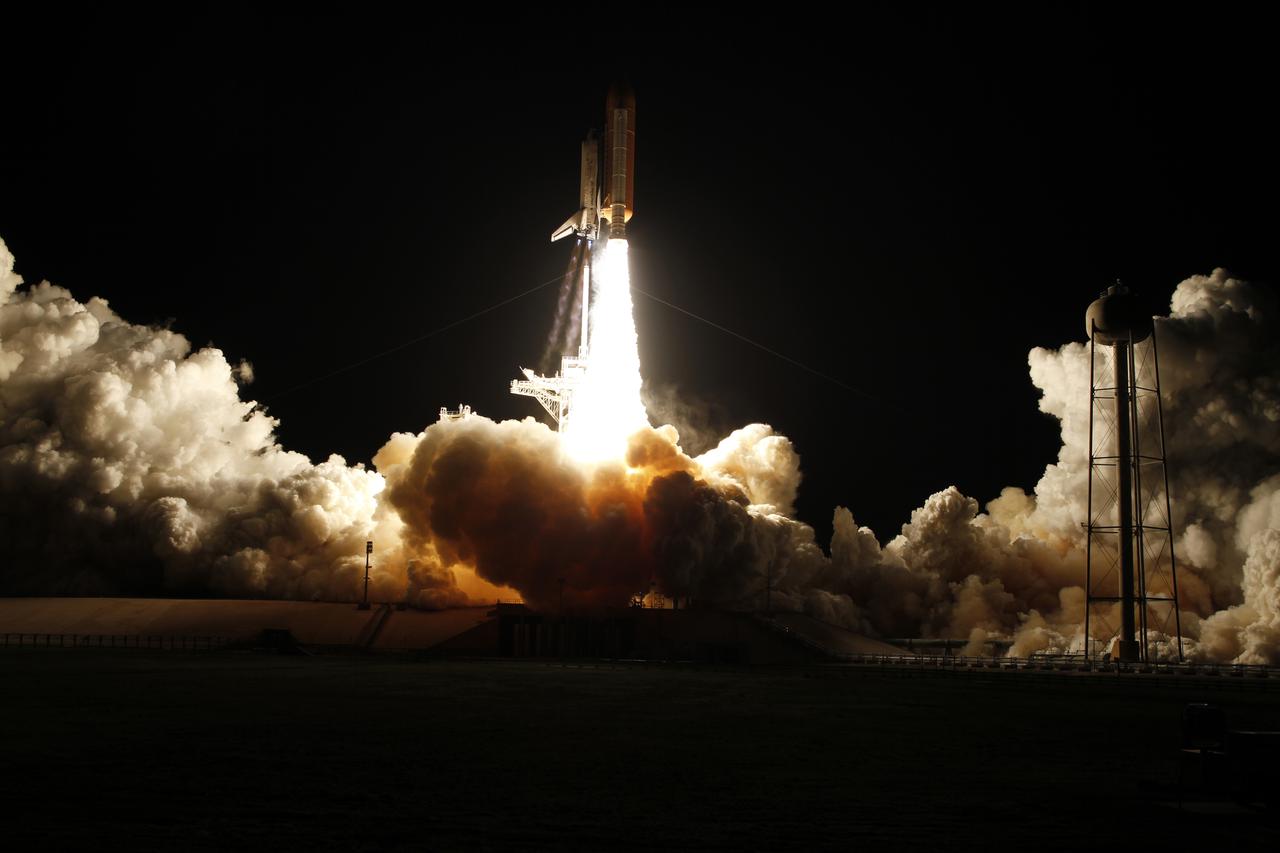
STS-56 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, riding atop its external tank (ET) and flanked by two solid rocket boosters (SRBs), lifts off from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B into the early morning darkness at 1:29 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). In this nocturnal scene, OV-102's nose section is obscured in the shadowy darkness as it clears the fixed service structure (FSS) tower. Exhaust plumes trail from the SRB skirts and cover the launch pad area in a billowy cloud. The SRB / Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME) firings illuminate the FSS and the retracted rotating service structure (RSS). Debris is visible on the base of the launch pad.
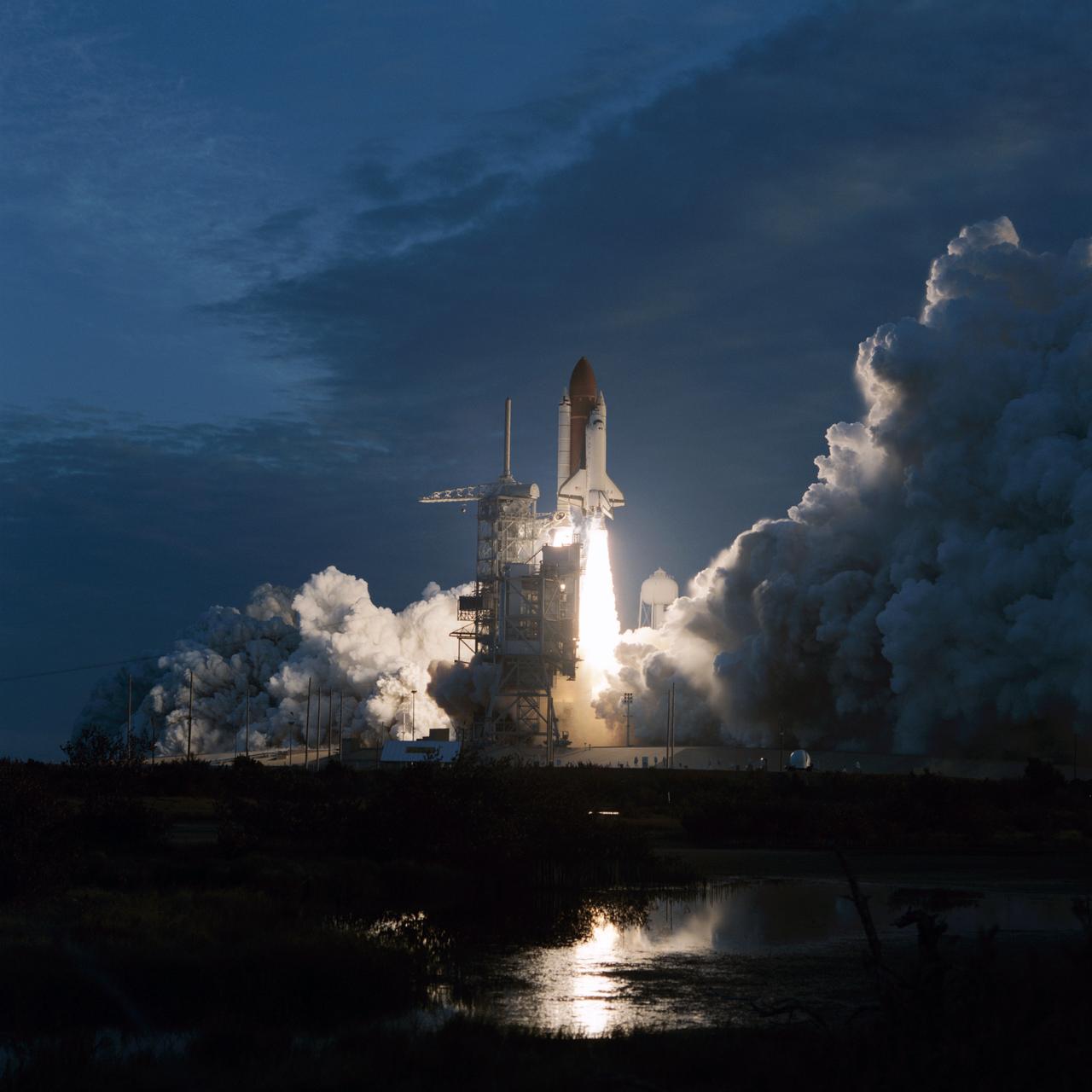

STS-32 Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102, its external tank (ET), and solid rocket boosters (SRBs) rise above the mobile launcher platform and begin to clear fixed service structure (FSS) tower (with rotating service structure (RSS) retracted) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39A. Liftoff occurred at 7:34:59:98 am Eastern Standard Time (EST) some 24 hours after dubious weather at the return-to-landing site (RTLS) had cancelled a scheduled launch. An exhaust cloud covers the launch pad. The firing SRBs and space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) are reflected in a nearby waterway. OV-102's launch is highlighted against the early morning darkness.
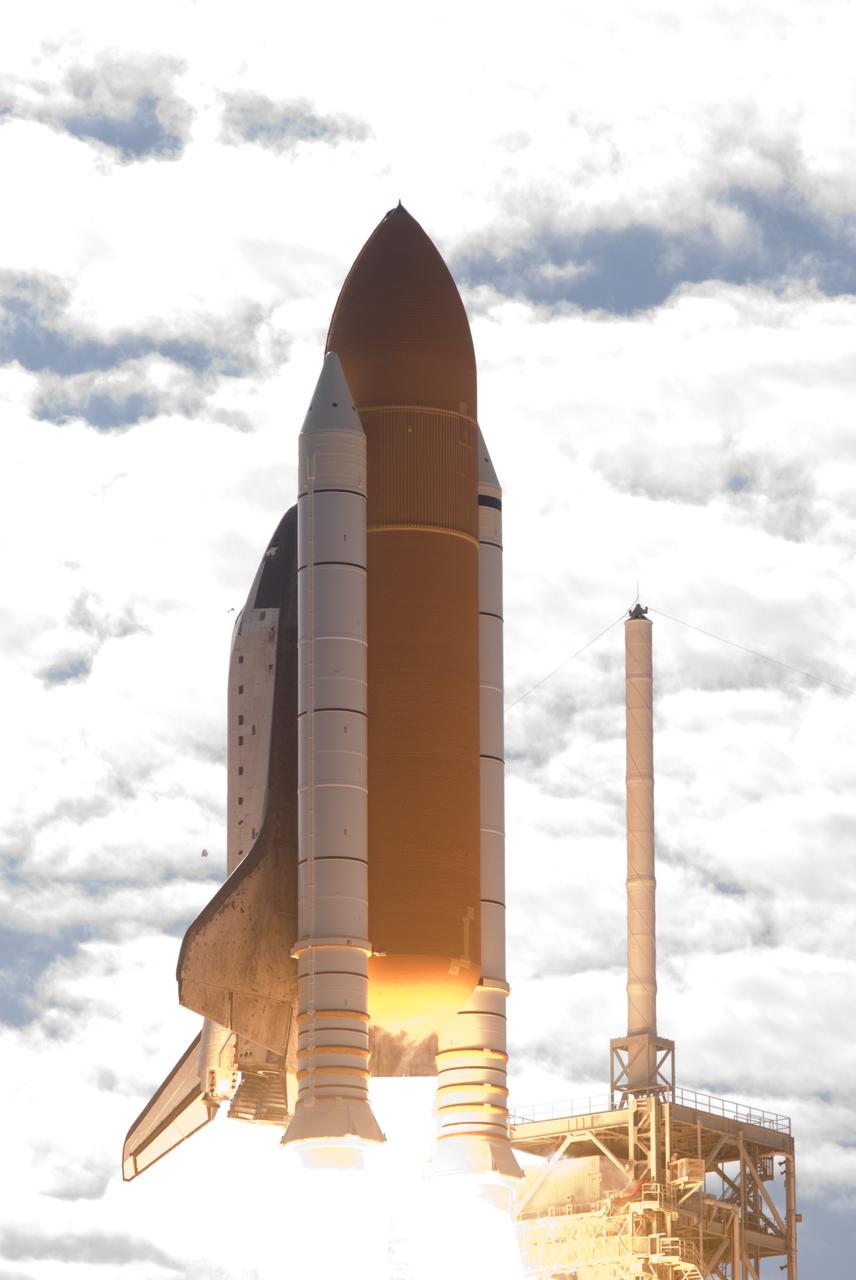

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With nearly 7 million pounds of thrust generated by twin solid rocket boosters and three main engines, space shuttle Atlantis clears the tower on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff on its STS-129 mission came at 2:28 p.m. EST Nov. 16. Aboard are crew members Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; and Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr. On STS-129, the crew will deliver two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers to the International Space Station, the largest of the shuttle's cargo carriers, containing 15 spare pieces of equipment including two gyroscopes, two nitrogen tank assemblies, two pump modules, an ammonia tank assembly and a spare latching end effector for the station's robotic arm. Atlantis will return to Earth a station crew member, Nicole Stott, who has spent more than two months aboard the orbiting laboratory. STS-129 is slated to be the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer
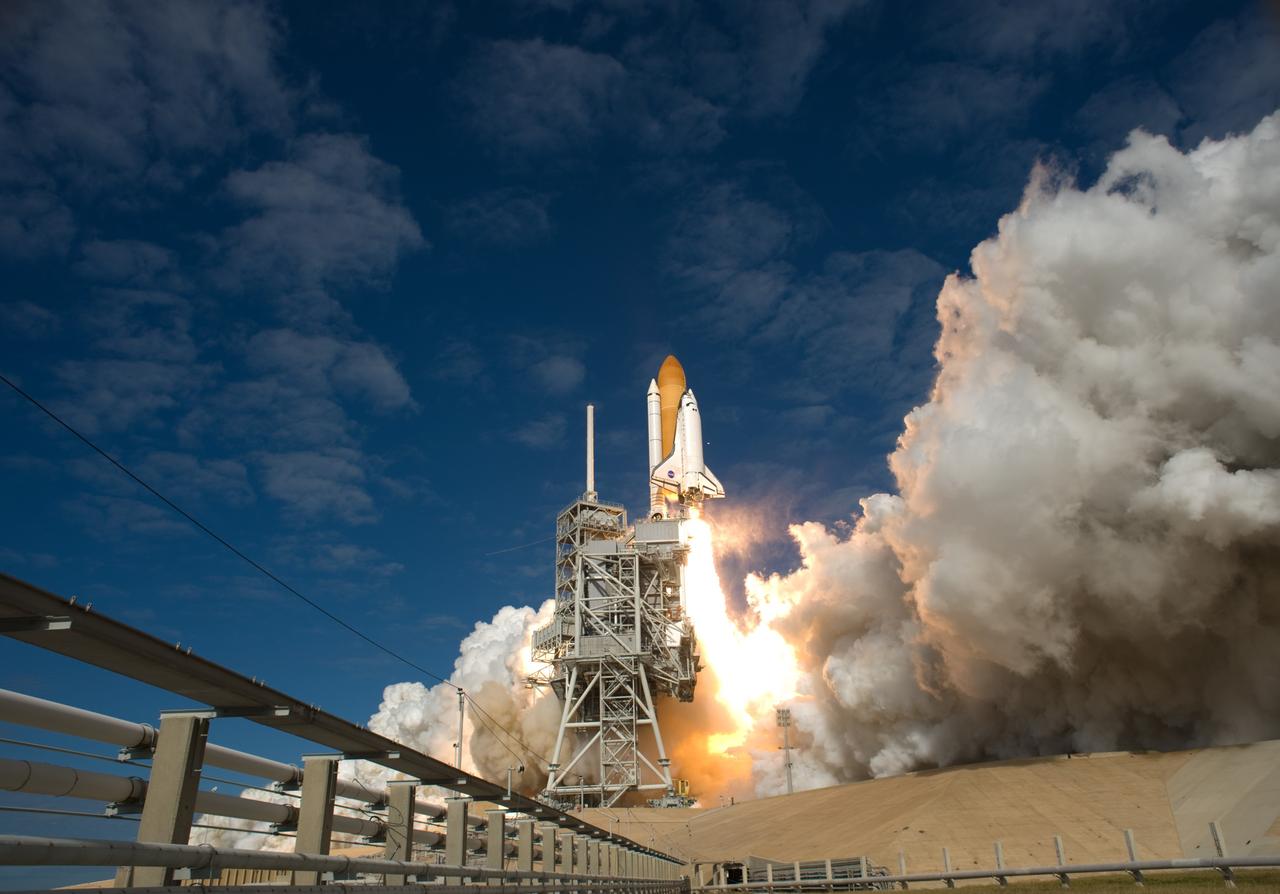

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With nearly 7 million pounds of thrust generated by twin solid rocket boosters and three main engines, space shuttle Atlantis clears the tower on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff on its STS-129 mission came at 2:28 p.m. EST Nov. 16. Aboard are crew members Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; and Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr. On STS-129, the crew will deliver two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers to the International Space Station, the largest of the shuttle's cargo carriers, containing 15 spare pieces of equipment including two gyroscopes, two nitrogen tank assemblies, two pump modules, an ammonia tank assembly and a spare latching end effector for the station's robotic arm. Atlantis will return to Earth a station crew member, Nicole Stott, who has spent more than two months aboard the orbiting laboratory. STS-129 is slated to be the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tom Farrar and Tony Gray
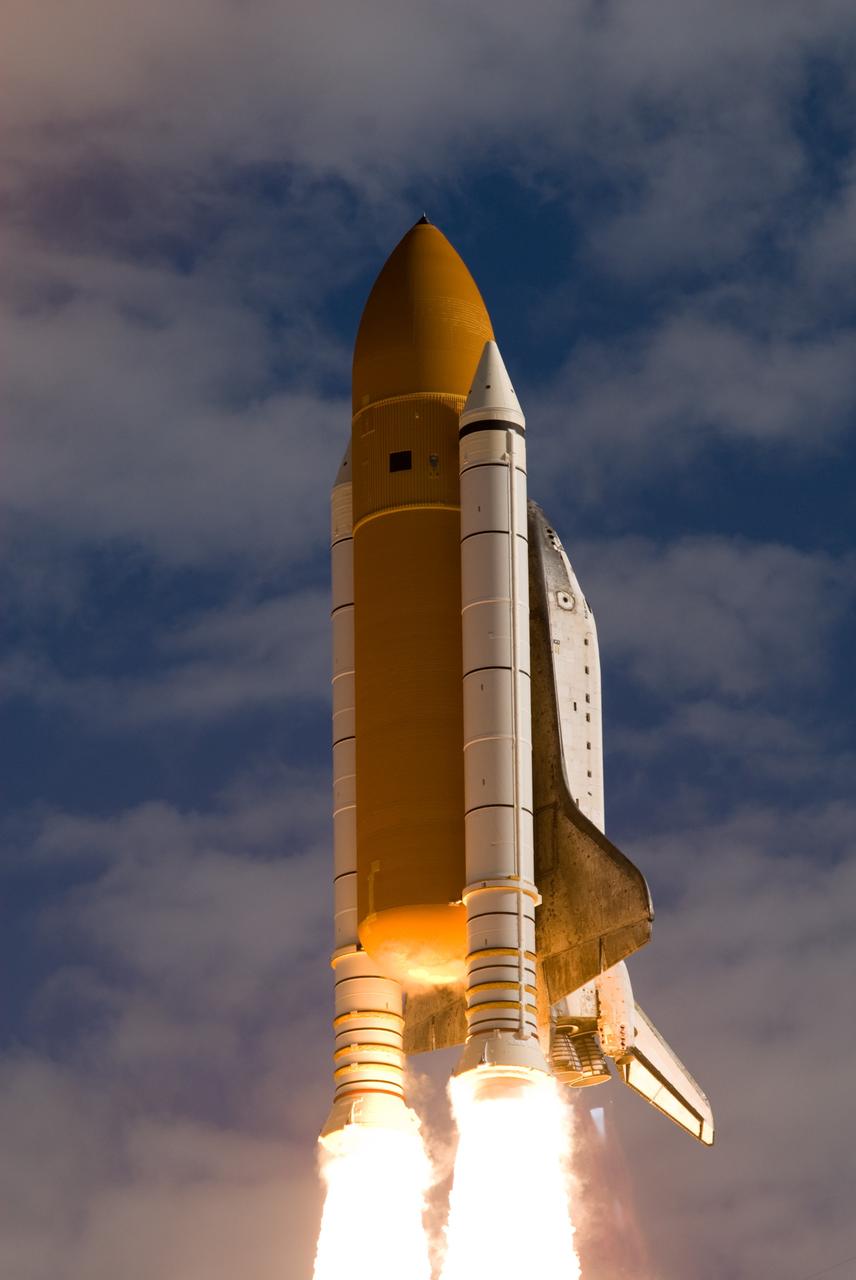

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With nearly 7 million pounds of thrust generated with the aid of twin solid rocket boosters, space shuttle Atlantis clears the tower on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff on its STS-129 mission came at 2:28 p.m. EST Nov. 16. Aboard are crew members Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; and Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr. On STS-129, the crew will deliver two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers to the International Space Station, the largest of the shuttle's cargo carriers, containing 15 spare pieces of equipment including two gyroscopes, two nitrogen tank assemblies, two pump modules, an ammonia tank assembly and a spare latching end effector for the station's robotic arm. Atlantis will return to Earth a station crew member, Nicole Stott, who has spent more than two months aboard the orbiting laboratory. STS-129 is slated to be the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Rusty Backer and Tom Farrar
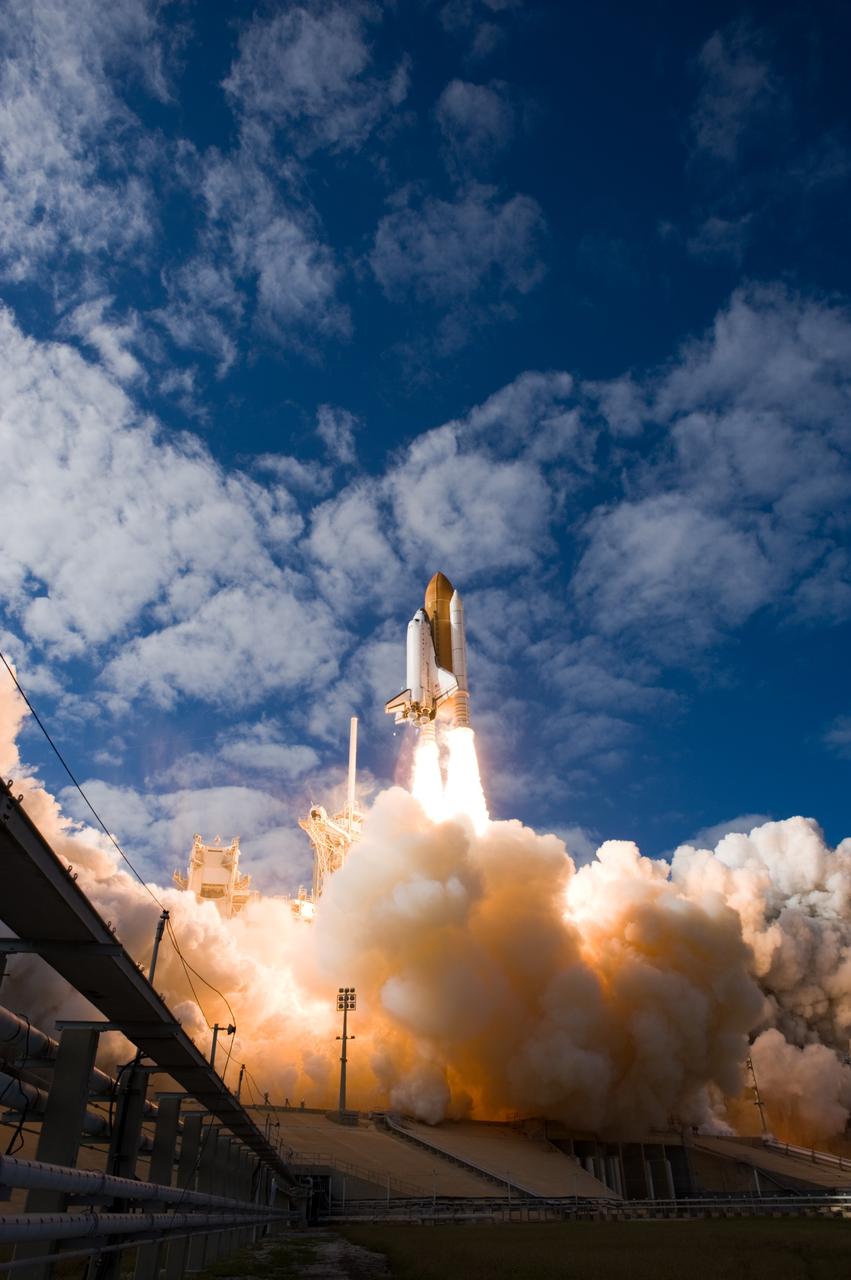

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - With nearly 7 million pounds of thrust generated by twin solid rocket boosters and three main engines, space shuttle Atlantis clears the tower on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Liftoff on its STS-129 mission came at 2:28 p.m. EST Nov. 16. Aboard are crew members Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; and Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr. On STS-129, the crew will deliver two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers to the International Space Station, the largest of the shuttle's cargo carriers, containing 15 spare pieces of equipment including two gyroscopes, two nitrogen tank assemblies, two pump modules, an ammonia tank assembly and a spare latching end effector for the station's robotic arm. Atlantis will return to Earth a station crew member, Nicole Stott, who has spent more than two months aboard the orbiting laboratory. STS-129 is slated to be the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Tom Farrar and Tony Gray

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Just after sundown, the Rotating Service Structure is rolled back to reveal Space Shuttle Endeavour, mated with its solid rocket boosters (left and right) and external tank (center), poised for launch on mission STS-99. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), STS-99 is scheduled to lift off 12:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39A. The SRTM will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. The mission is expected to last about 11days, with Endeavour landing at KSC Friday, Feb. 11, at 4:55 p.m. EST
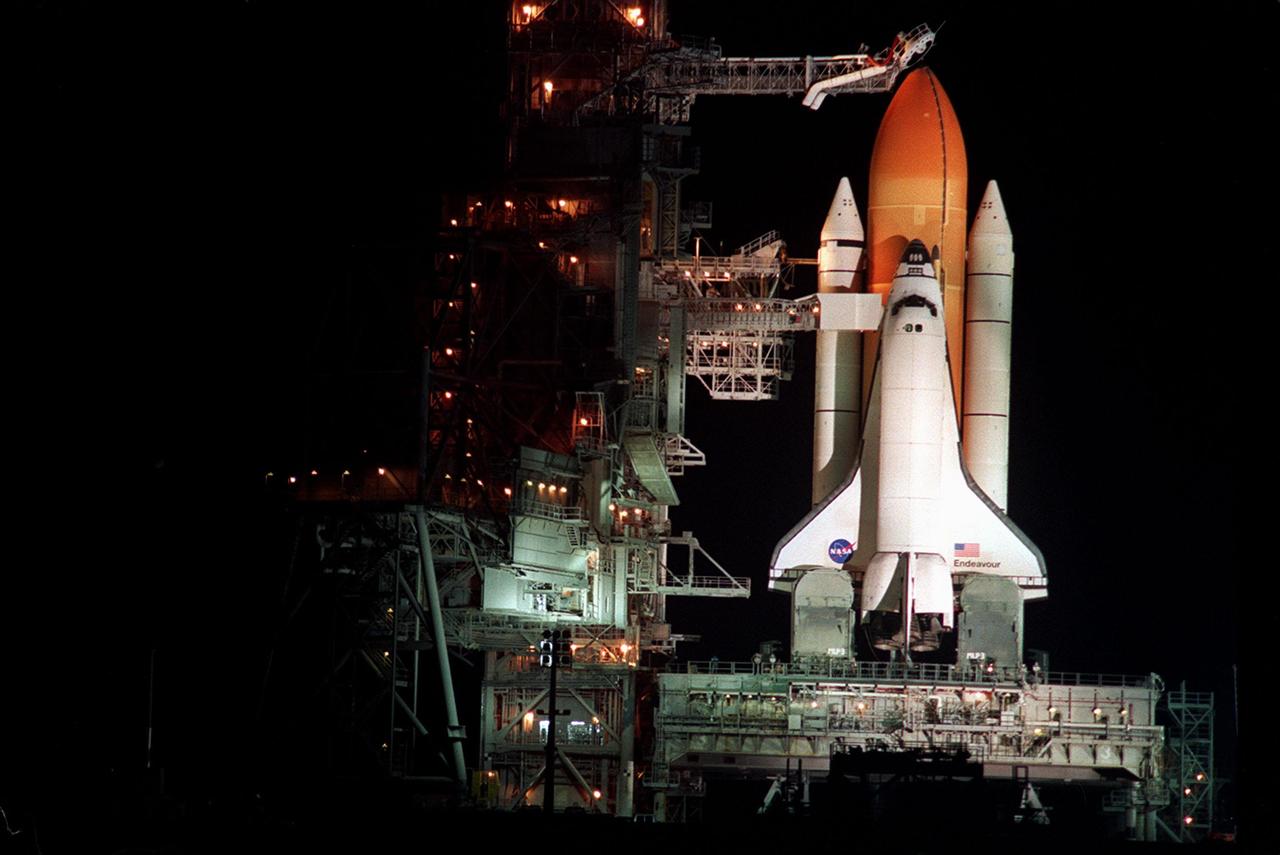

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Just after sundown, the Rotating Service Structure is rolled back to reveal Space Shuttle Endeavour, mated with its solid rocket boosters (left and right) and external tank (center), poised for launch on mission STS-99. Known as the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), STS-99 is scheduled to lift off 12:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39A. The SRTM will chart a new course to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. The mission is expected to last about 11days, with Endeavour landing at KSC Friday, Feb. 11, at 4:55 p.m. EST
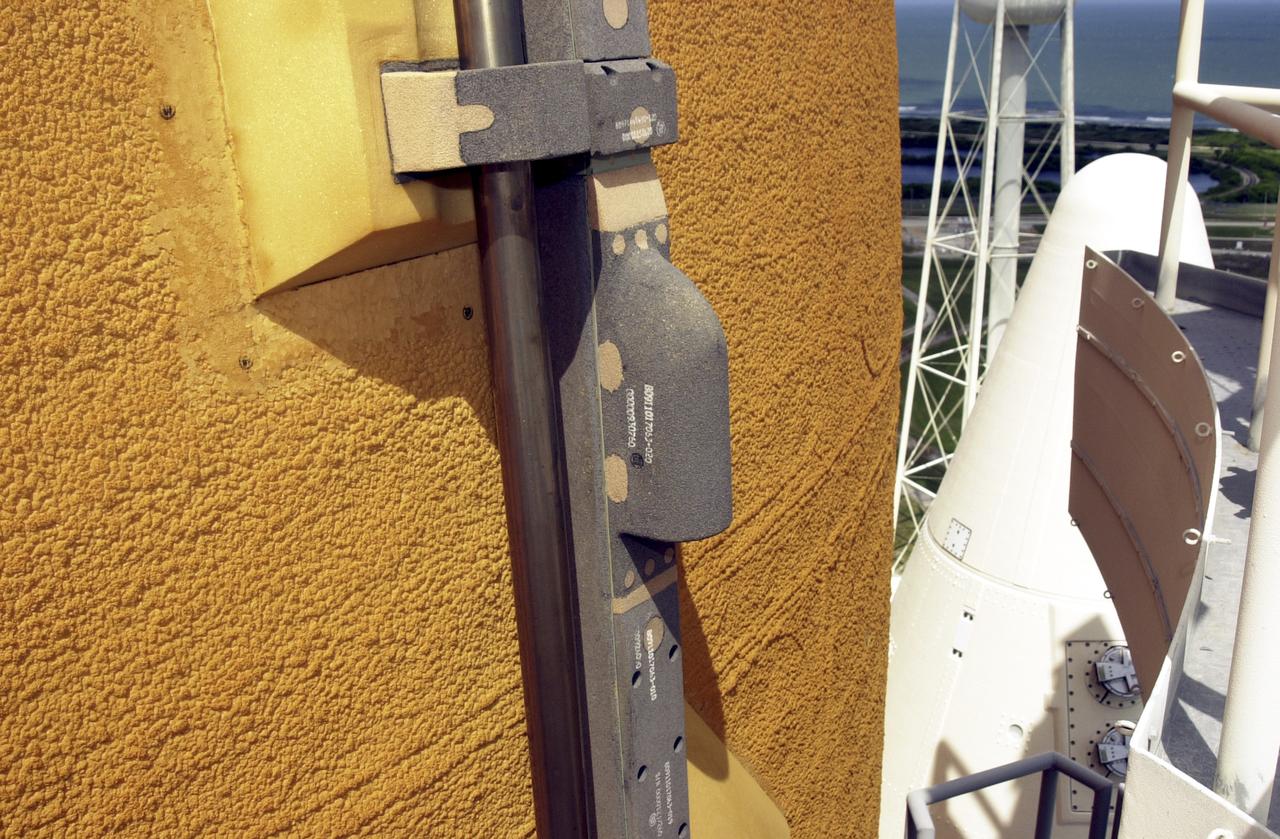

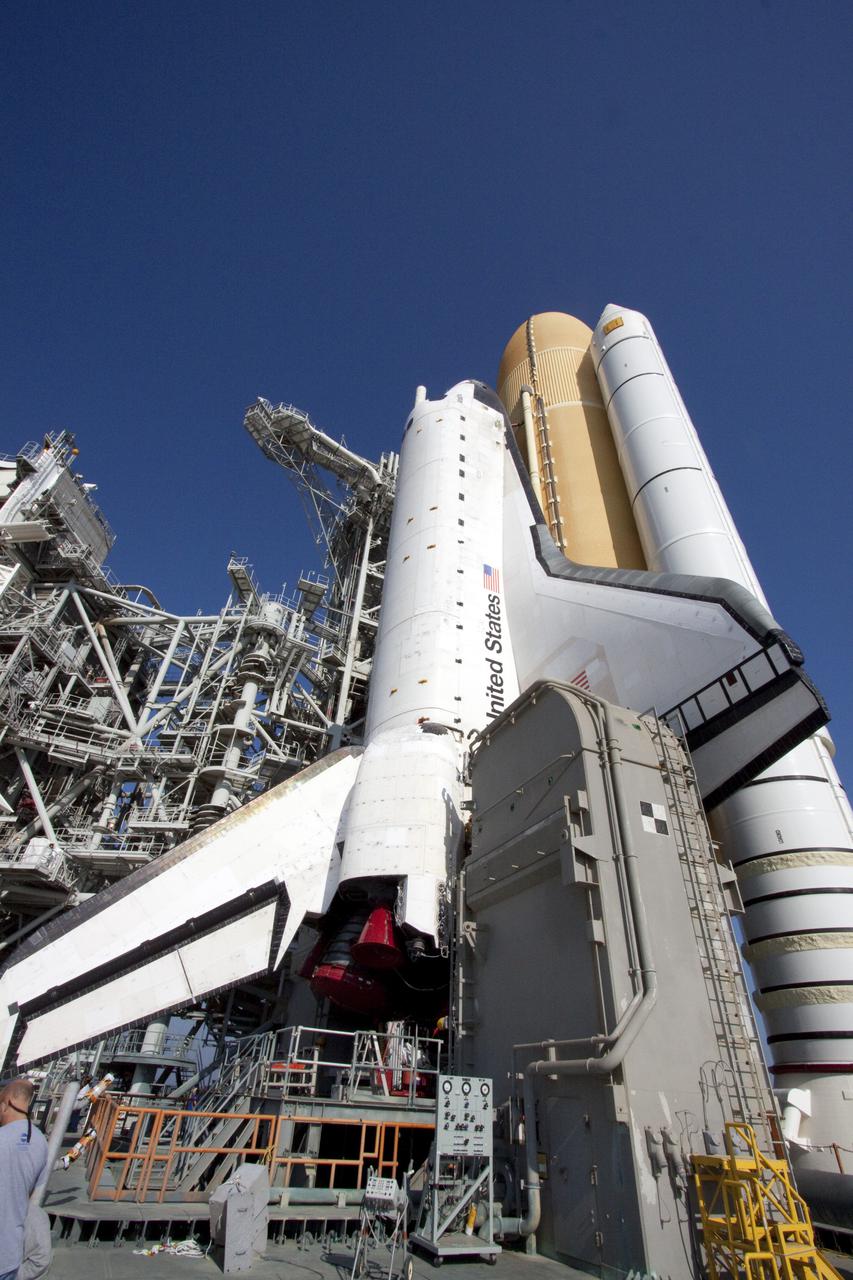
This is a view of the video camera mounted on the External Tank (ET) of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis (STS-112). The camera provided a view of the front and belly of the orbiter, a portion of the Solid Rocket Boosters (SRBs), and ET during the launch. Located high on the ET liquid oxygen tank cable tray, the camera, 6 inches long and resembling a short thin flashlight, is inside an aluminum fairing covered in protective insulating foam. The battery pack and transmitter are contained in an electronics box and mounted in the intertank crossbeam inside the ET. The camera turned on 15 minutes prior to launch and operated for about 15 minutes following liftoff. At liftoff, viewers saw the Shuttle clearing the launch tower and, at 2 minutes after liftoff, saw the right SRB separate from the ET, and ET separation about 8 minutes into the flight. The video was downlinked from the ET during flight to several NASA data-receiving sites and then relayed to the live television broadcast. It provided the STS-112 team an opportunity to monitor the Shuttle's performance from a new angle. Launched on October 7, 2002, Atlantis carried its primary payload, the S1 Truss for the International Space Station.
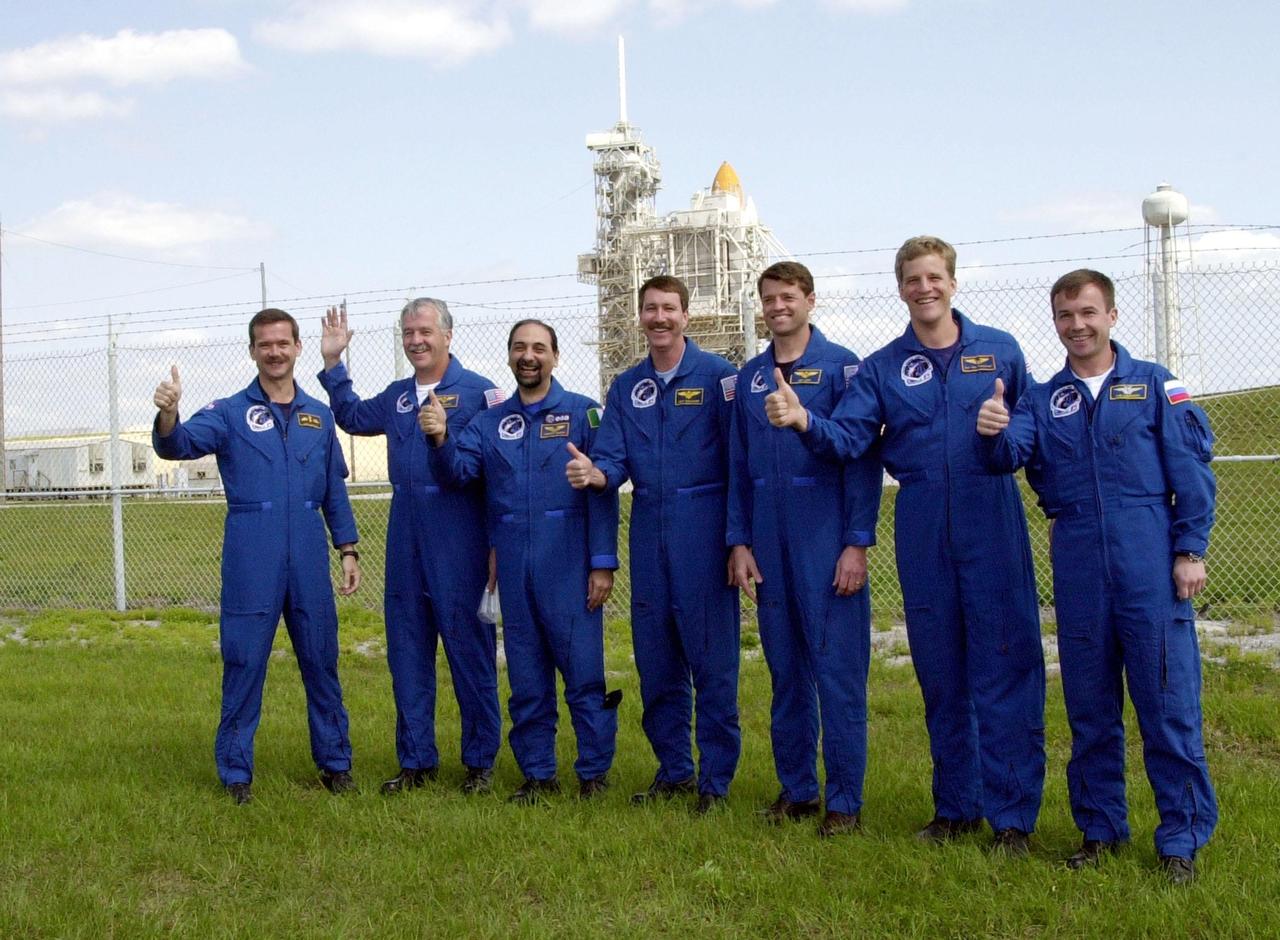

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-100 crew gives thumbs up on launch as they gather near Launch Pad 39A to greet family and friends. Starting at left, they are Mission Specialists Chris A. Hadfield, John L. Phillips and Umberto Guidoni; Commander Kent V. Rominger; Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby; and Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski and Yuri V. Lonchakov. Hadfield is with the Canadian Space Agency; Guidoni is with the European Space Agency; and Lonchakov is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. In the background on the pad can be seen the tips of Space Shuttle Endeavour’s orange external tank and white solid rocket boosters. The 80-foot lightning rod towers above the Shuttle and service structures. The crew is at KSC to complete final flight plan reviews in anticipation of launch. The 11-day mission to the International Space Station will deliver and integrate the Spacelab Logistics Pallet/Launch Deployment Assembly, which includes the Space Station Remote Manipulator system and the UHF Antenna, and the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello. The mission includes two planned spacewalks for installation of the SSRMS. The mission is also the inaugural flight of the MPLM Raffaello, carrying resupply stowage racks and resupply/return stowage platforms. Liftoff on mission STS-100 is scheduled at 2:41 p.m. EDT April 19
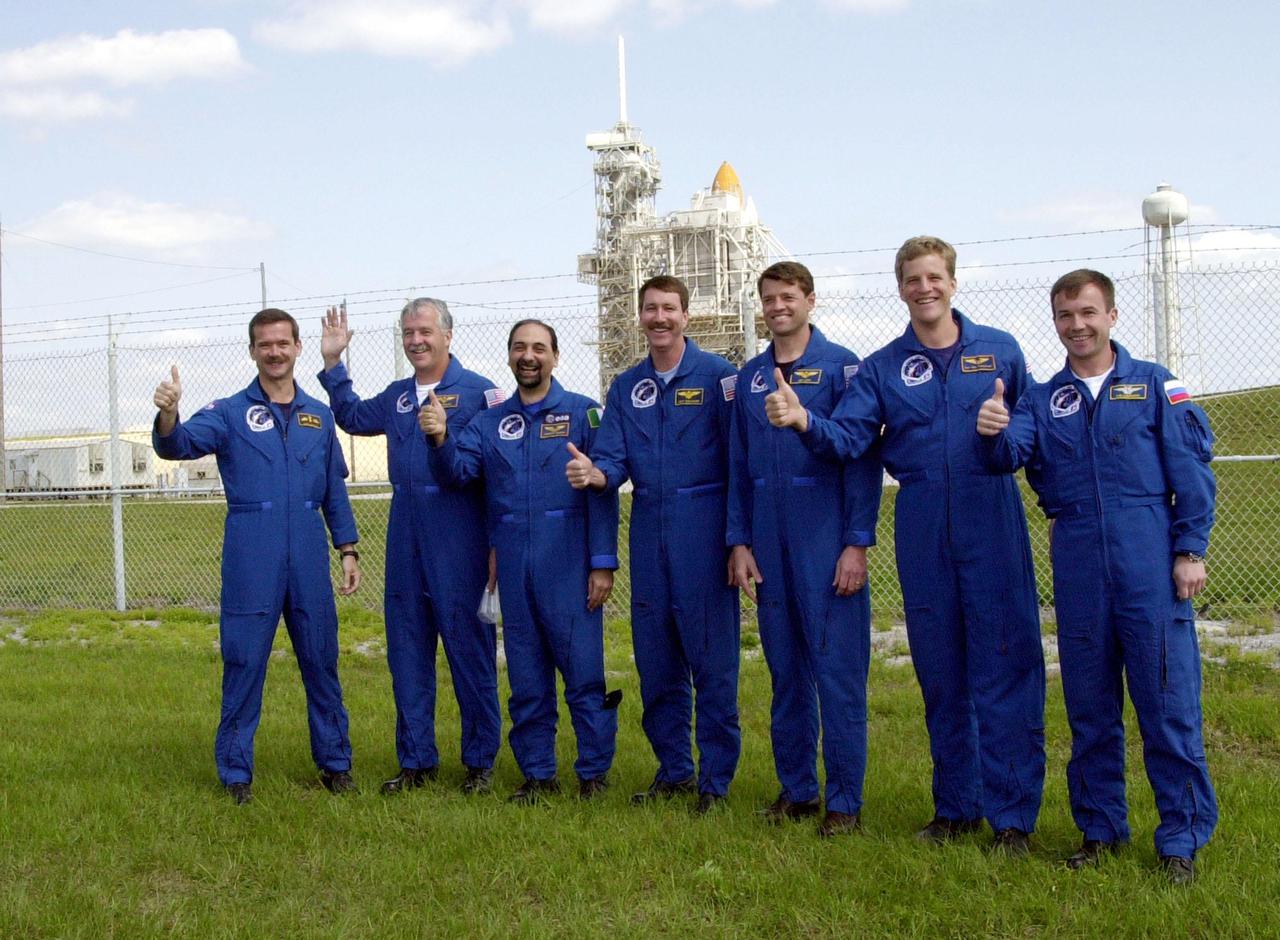

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-100 crew gives thumbs up on launch as they gather near Launch Pad 39A to greet family and friends. Starting at left, they are Mission Specialists Chris A. Hadfield, John L. Phillips and Umberto Guidoni; Commander Kent V. Rominger; Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby; and Mission Specialists Scott E. Parazynski and Yuri V. Lonchakov. Hadfield is with the Canadian Space Agency; Guidoni is with the European Space Agency; and Lonchakov is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. In the background on the pad can be seen the tips of Space Shuttle Endeavour’s orange external tank and white solid rocket boosters. The 80-foot lightning rod towers above the Shuttle and service structures. The crew is at KSC to complete final flight plan reviews in anticipation of launch. The 11-day mission to the International Space Station will deliver and integrate the Spacelab Logistics Pallet_Launch Deployment Assembly, which includes the Space Station Remote Manipulator system and the UHF Antenna, and the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello. The mission includes two planned spacewalks for installation of the SSRMS. The mission is also the inaugural flight of the MPLM Raffaello, carrying resupply stowage racks and resupply_return stowage platforms. Liftoff on mission STS-100 is scheduled at 2:41 p.m. EDT April 19
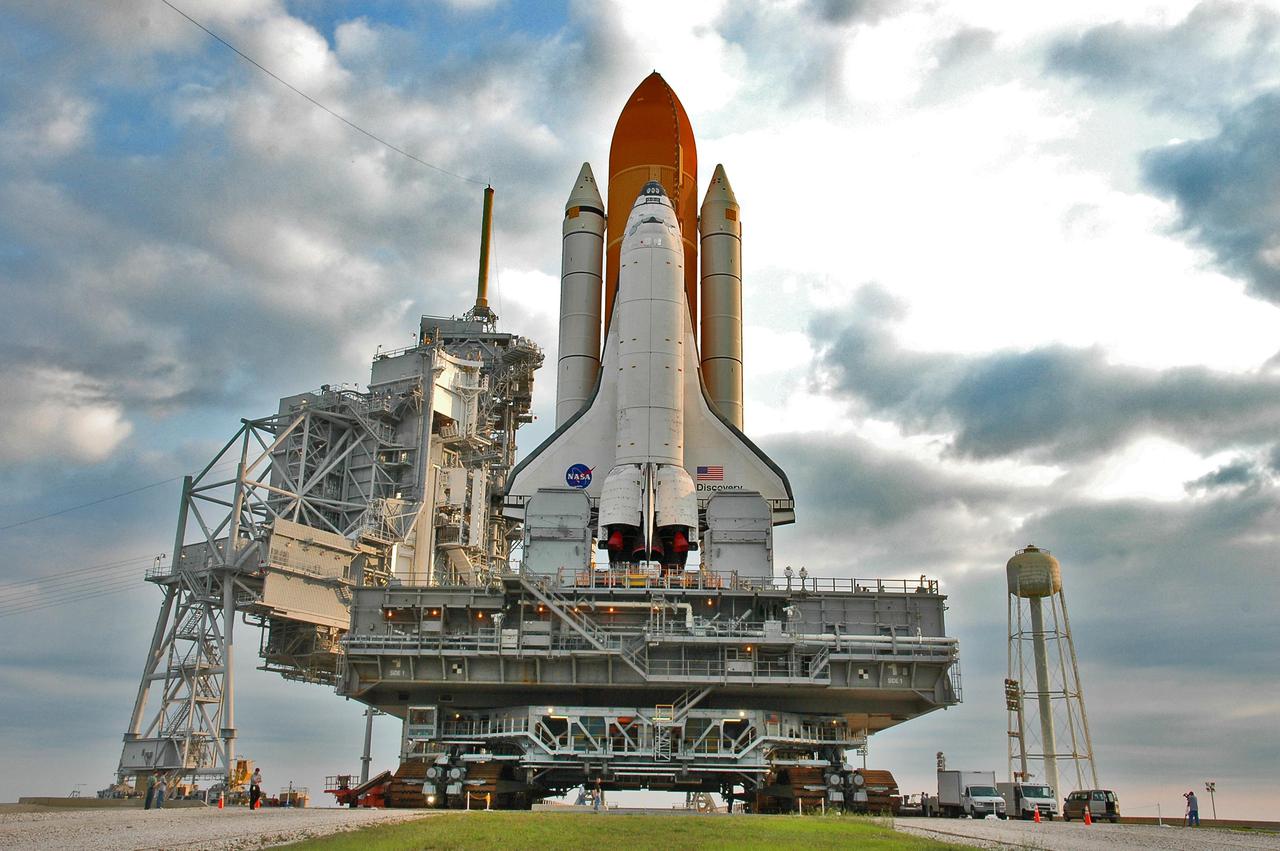

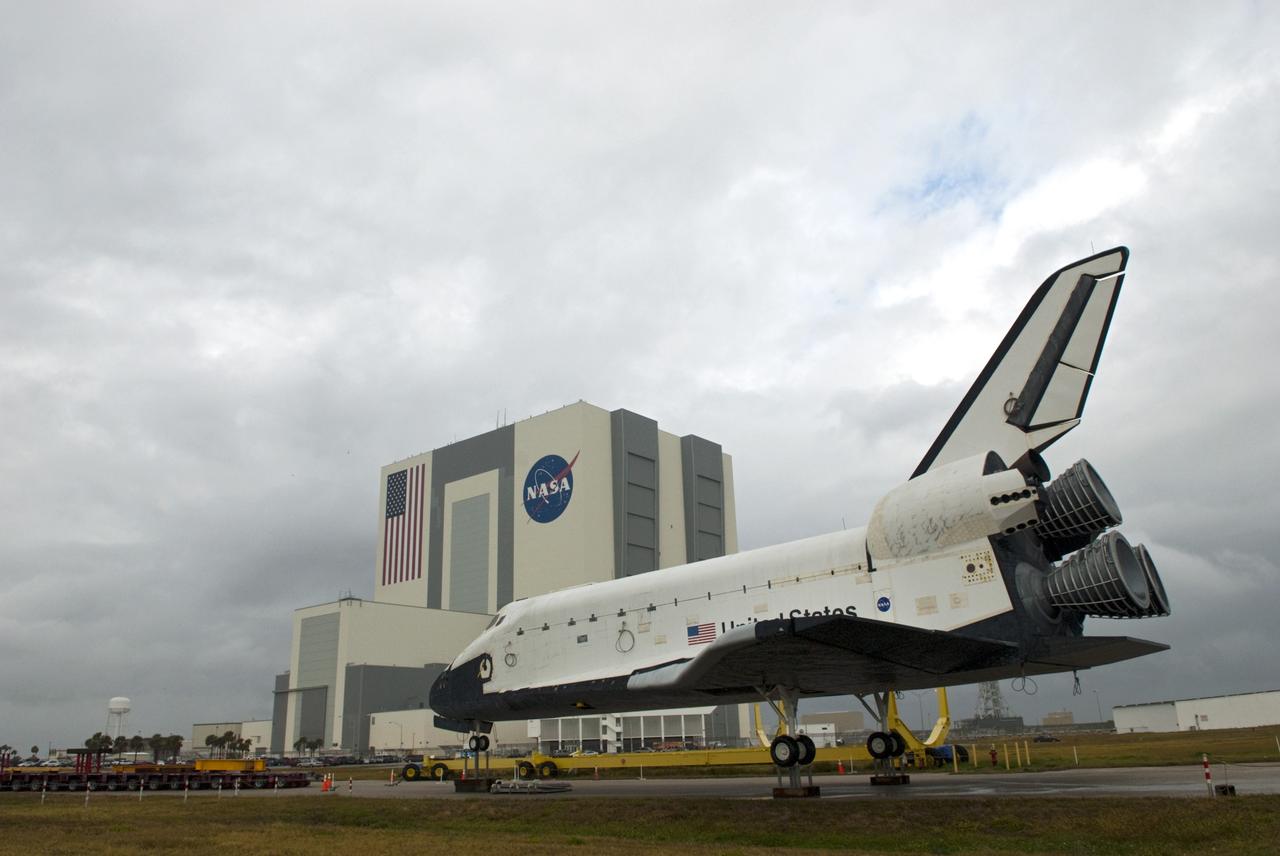
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Under post-dawn cloudy skies, Space Shuttle Discovery, resting on the Mobile Launcher Platform, rolls away from Launch Pad 39B via the Crawler_Transporter underneath. At left are the Rotating and Fixed Service Structures (RSS and FSS). Atop the FSS is the 80-foot lightning mast. At right is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water, part of the sound suppression system during a launch. Discovery is returning to the Vehicle Assembly Buildling where it will be demated from its External Tank and lifted into the transfer aisle. On or about June 7, Discovery will be lifted and attached to its new tank and Solid Rocket Boosters, which are already in the VAB. Only the 15th rollback in Space Shuttle Program history, the 4.2-mile journey allows additional modifications to be made to the External Tank prior to a safe Return to Flight. Discovery is expected to be rolled back to the launch pad in mid-June for Return to Flight mission STS-114. The launch window extends from July 13 to July 31.
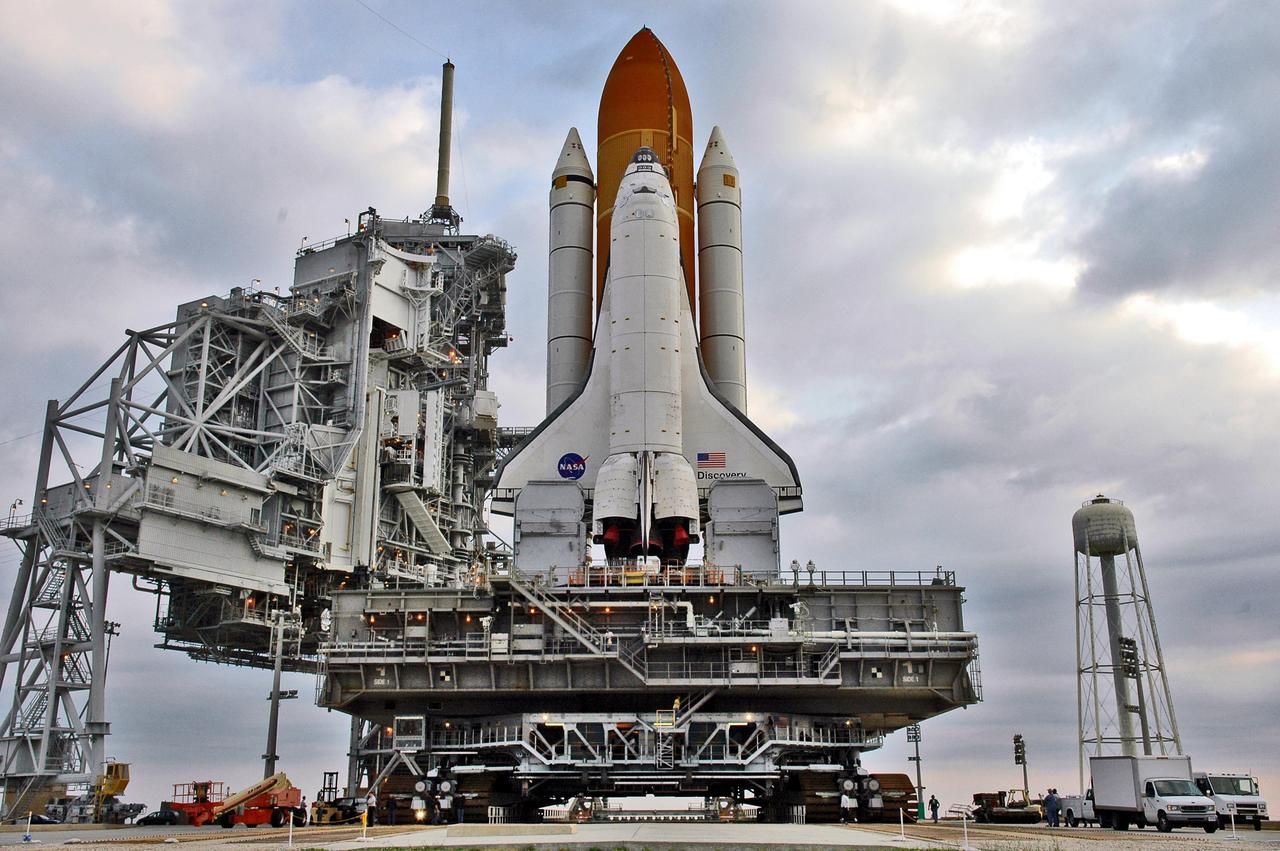

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Under post-dawn cloudy skies, Space Shuttle Discovery, resting on the Mobile Launcher Platform, begins rolling off Launch Pad 39B via the Crawler_Transporter underneath. At left are the Rotating and Fixed Service Structures (RSS and FSS). The 80-foot lightning mast is atop the FSS. At right is the 290-foot-tall water tower that holds 300,000 gallons of water, part of the sound suppression system during a launch. Discovery is returning to the Vehicle Assembly Buildling where it will be demated from its External Tank and lifted into the transfer aisle. On or about June 7, Discovery will be lifted and attached to its new tank and Solid Rocket Boosters, which are already in the VAB. Only the 15th rollback in Space Shuttle Program history, the 4.2-mile journey allows additional modifications to be made to the External Tank prior to a safe Return to Flight. Discovery is expected to be rolled back to the launch pad in mid-June for Return to Flight mission STS-114. The launch window extends from July 13 to July 31.
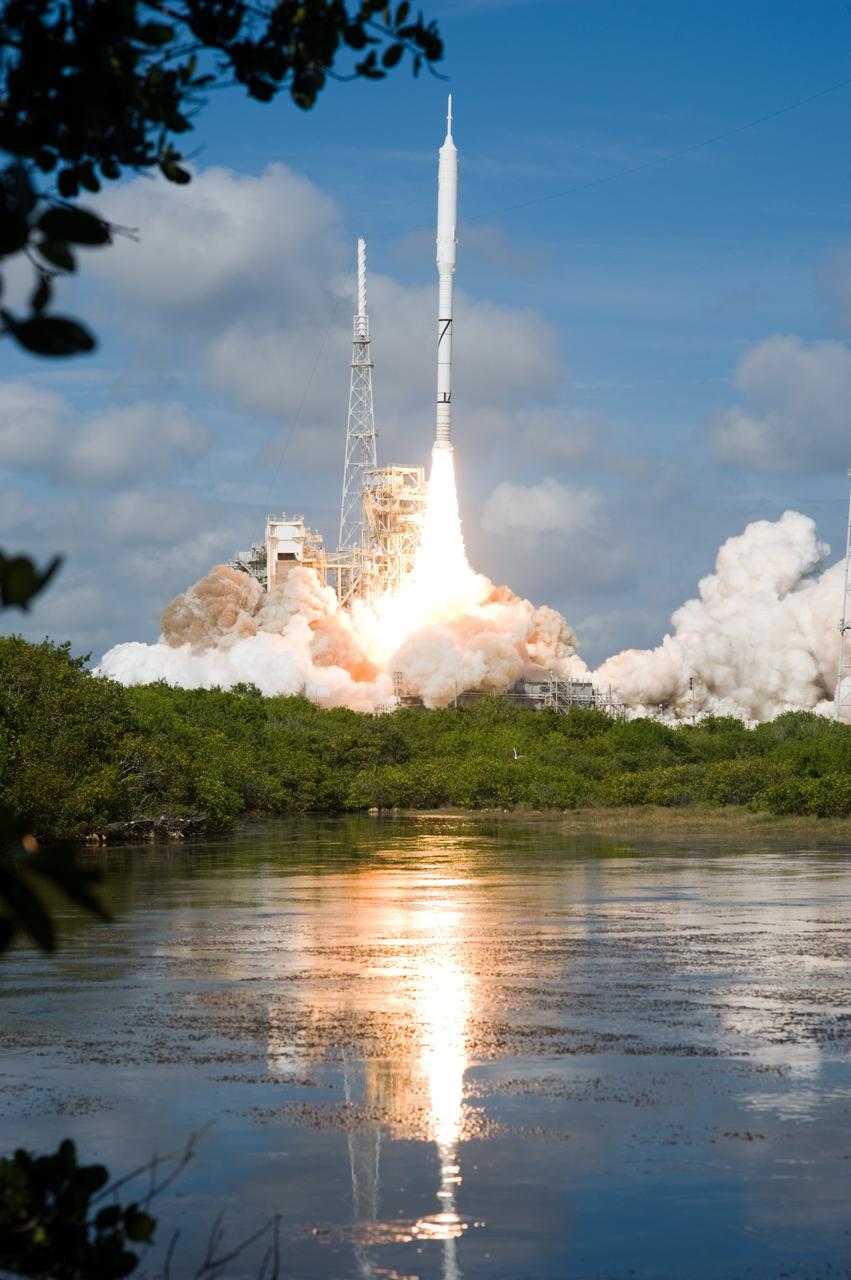

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
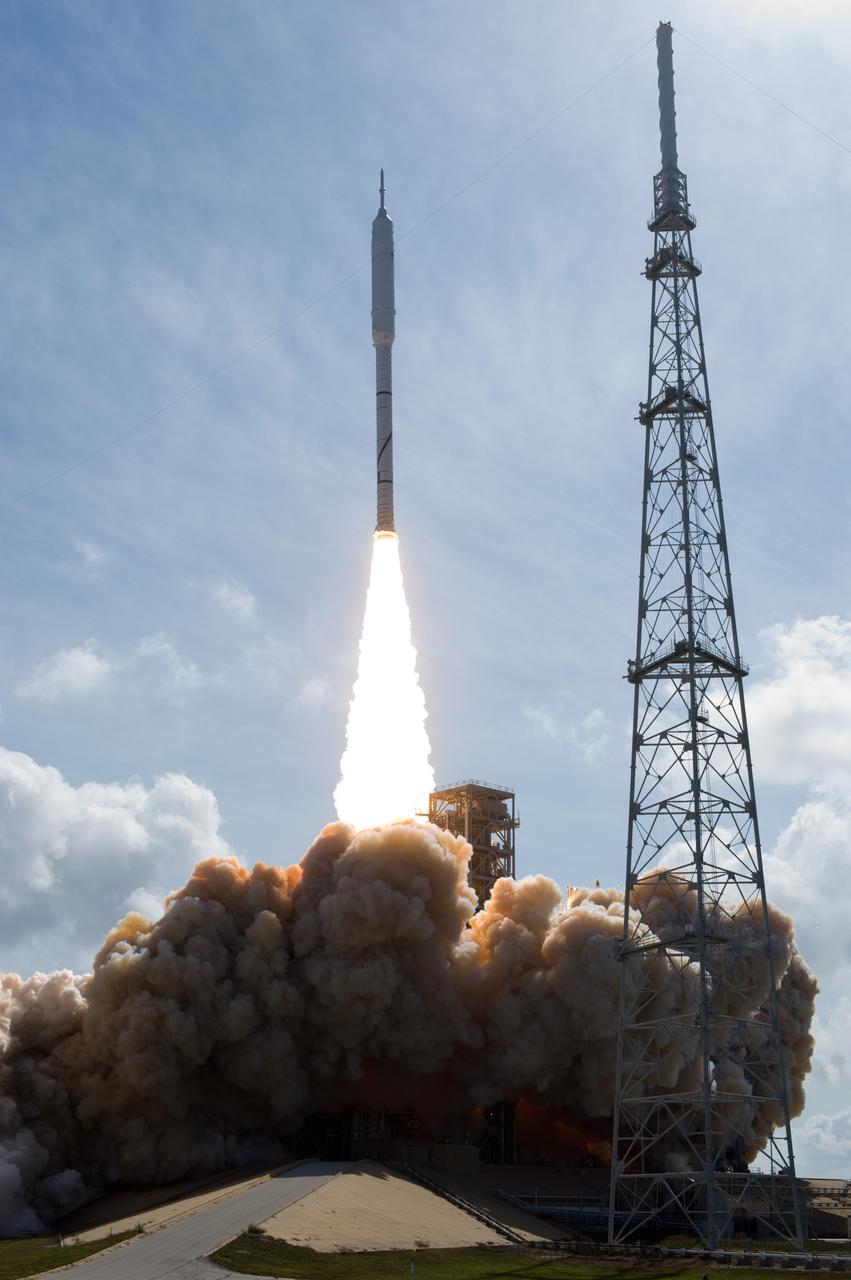

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
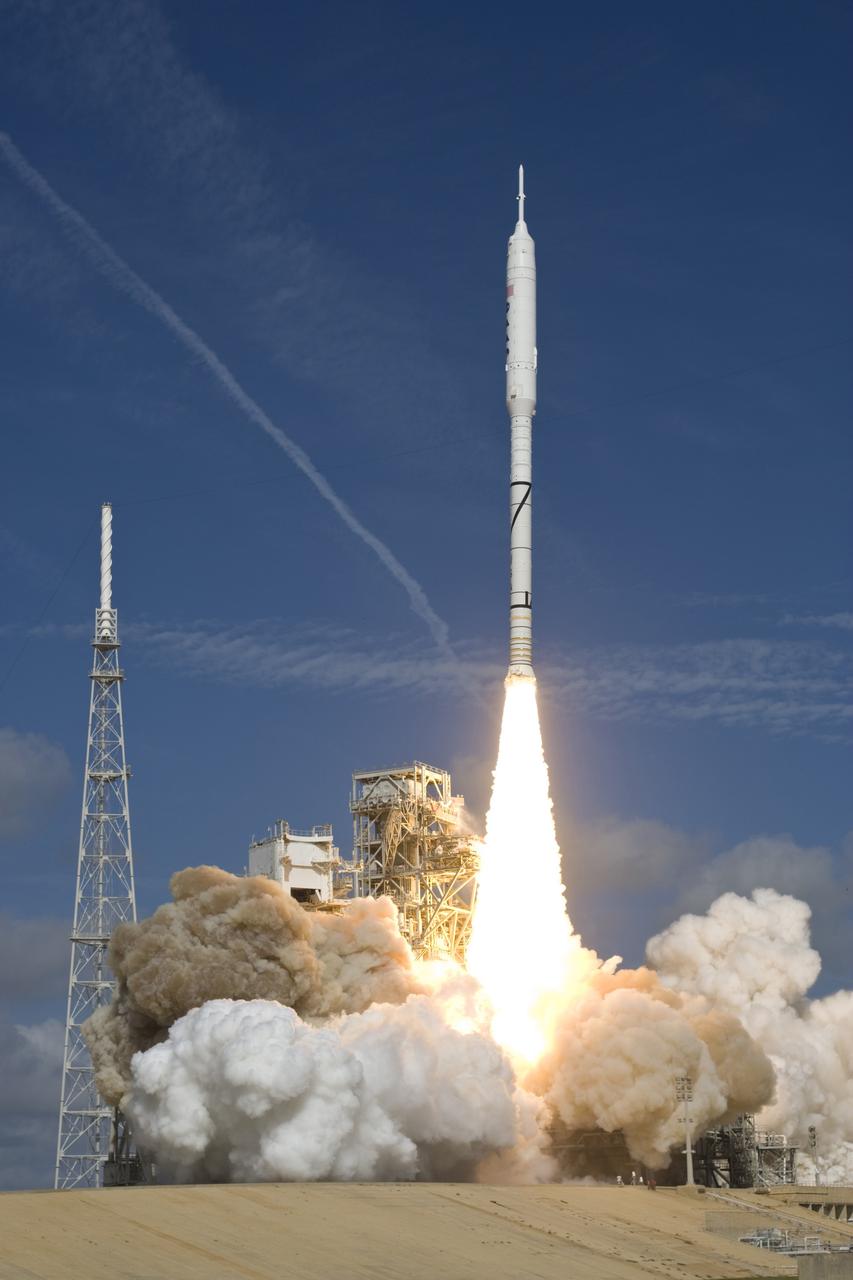

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: Courtesy of Scott Andrews
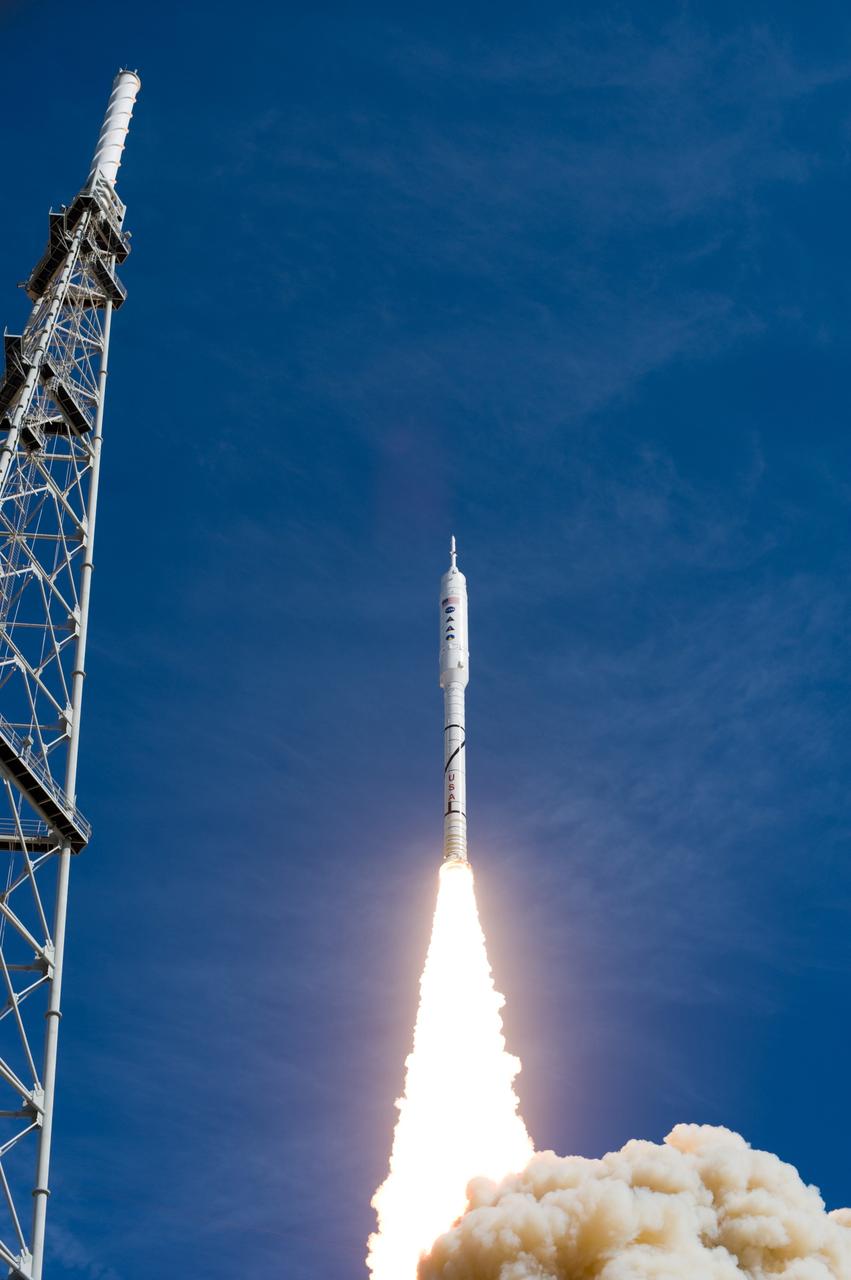

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar
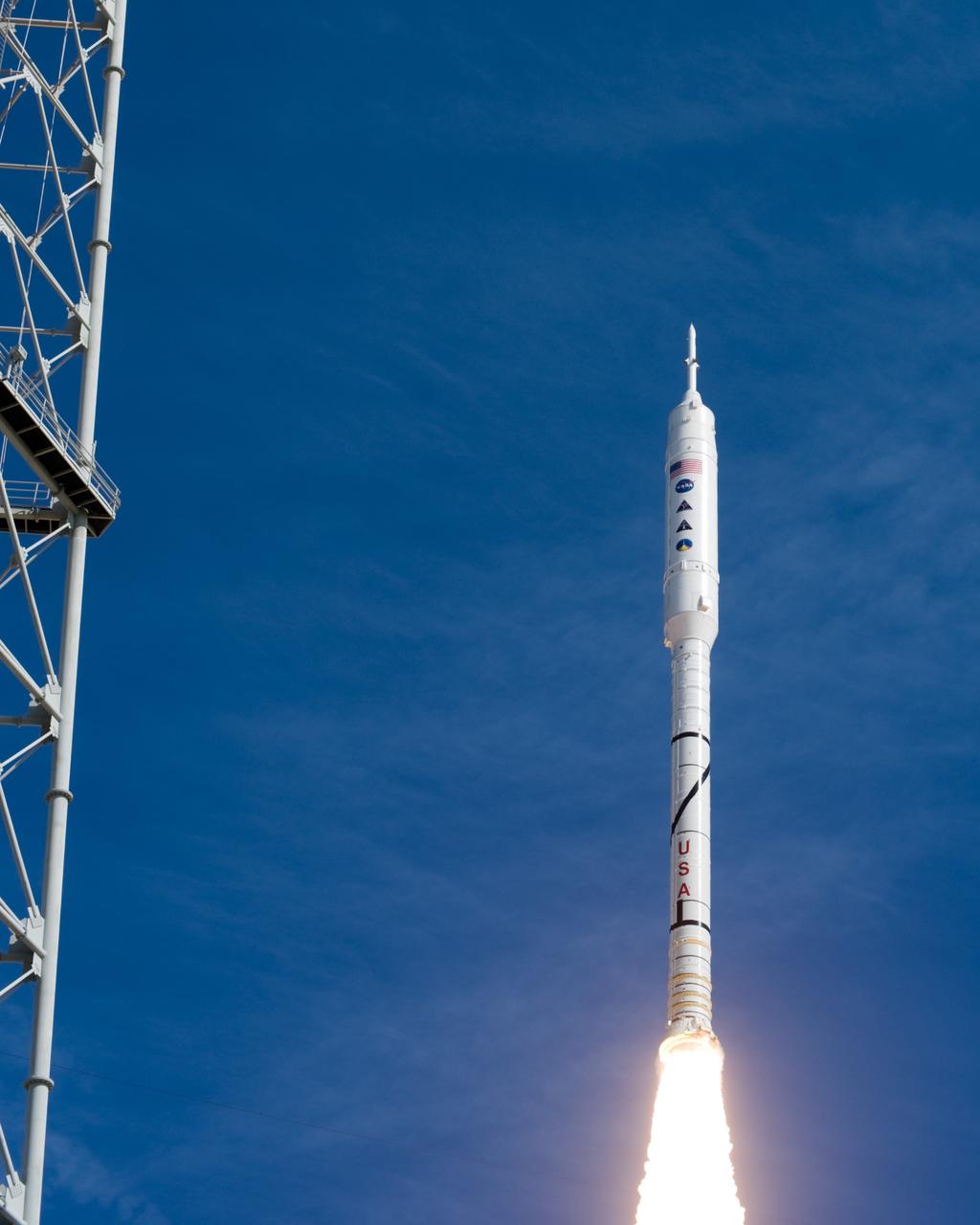

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: Courtesy of Scott Andrews
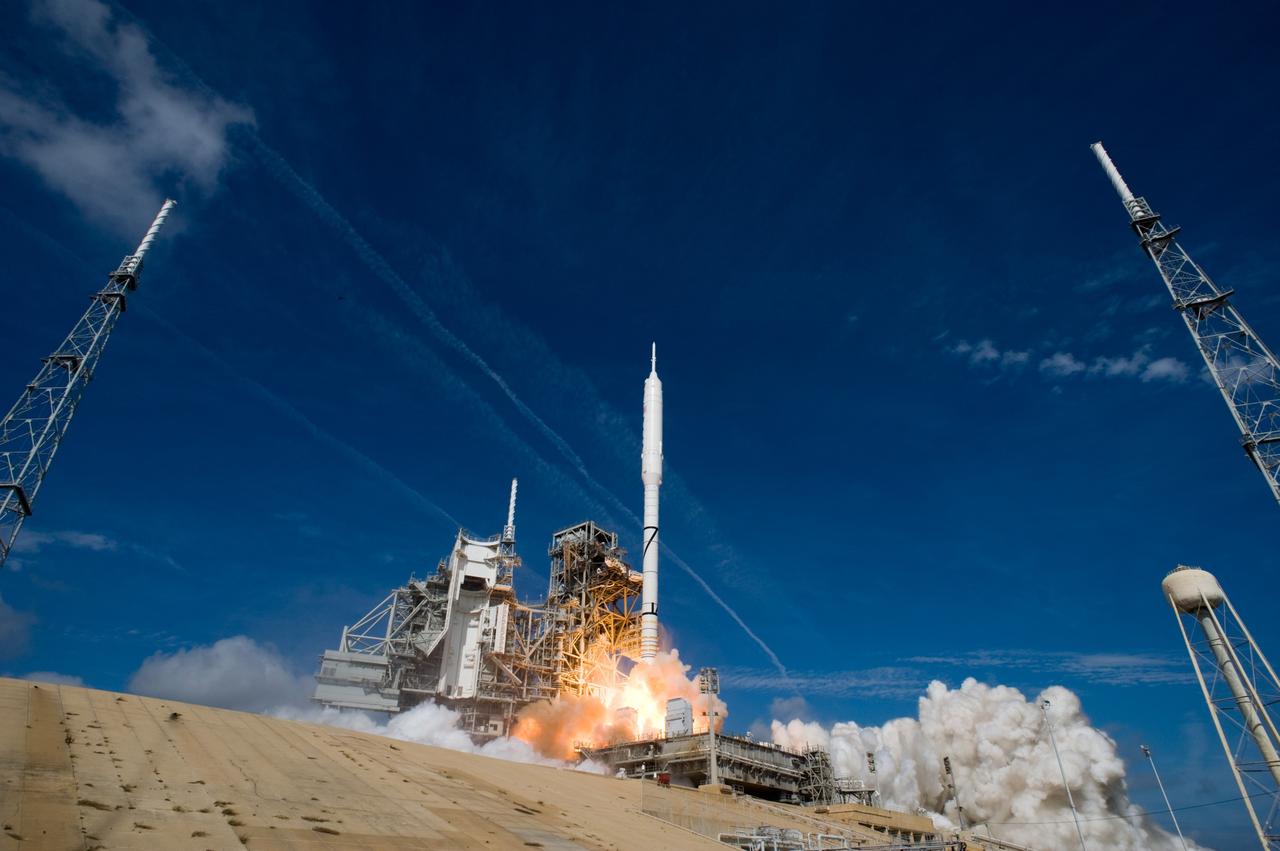

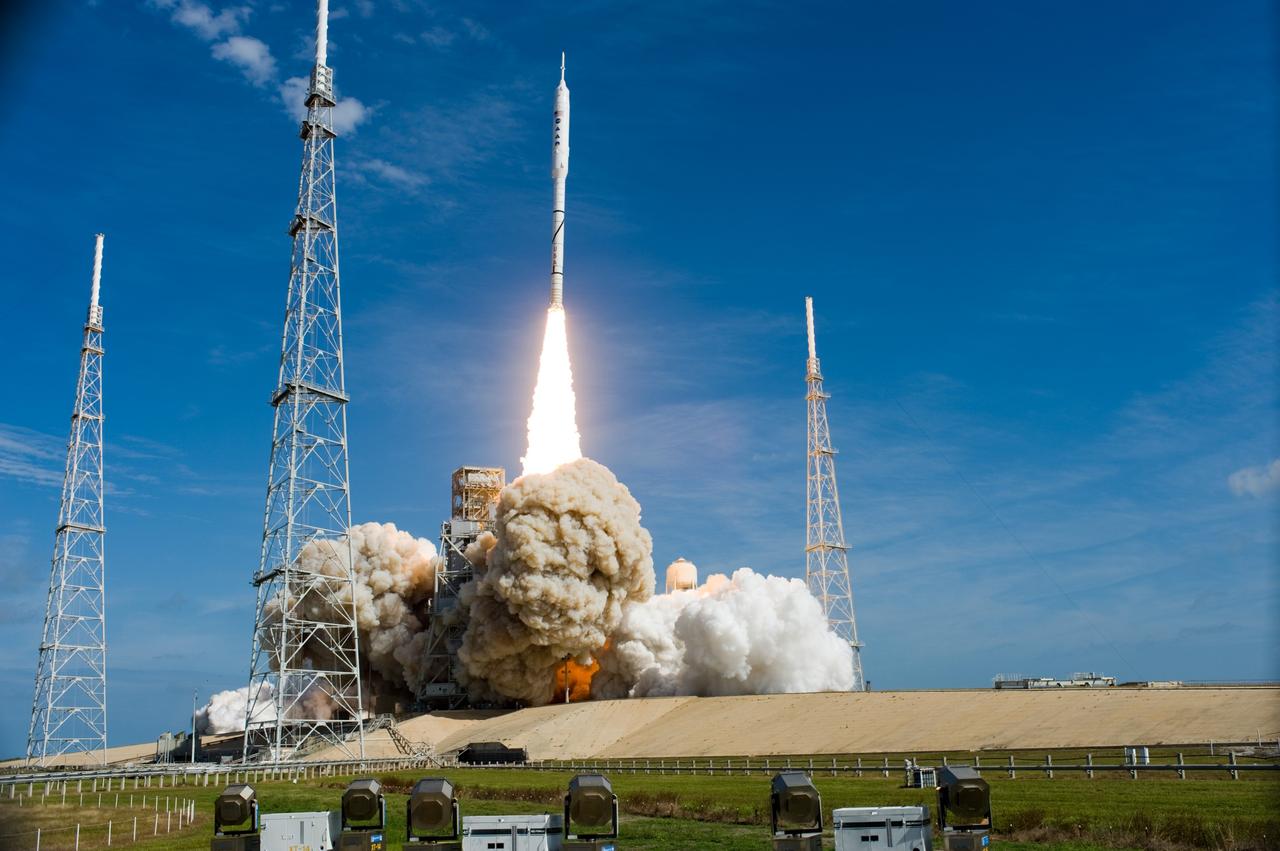
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two of the lightning towers frame the Ares I-X test rocket as it takes off from Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT Oct. 28. NASA’s Constellation Program's 327-foot-tall rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/ Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
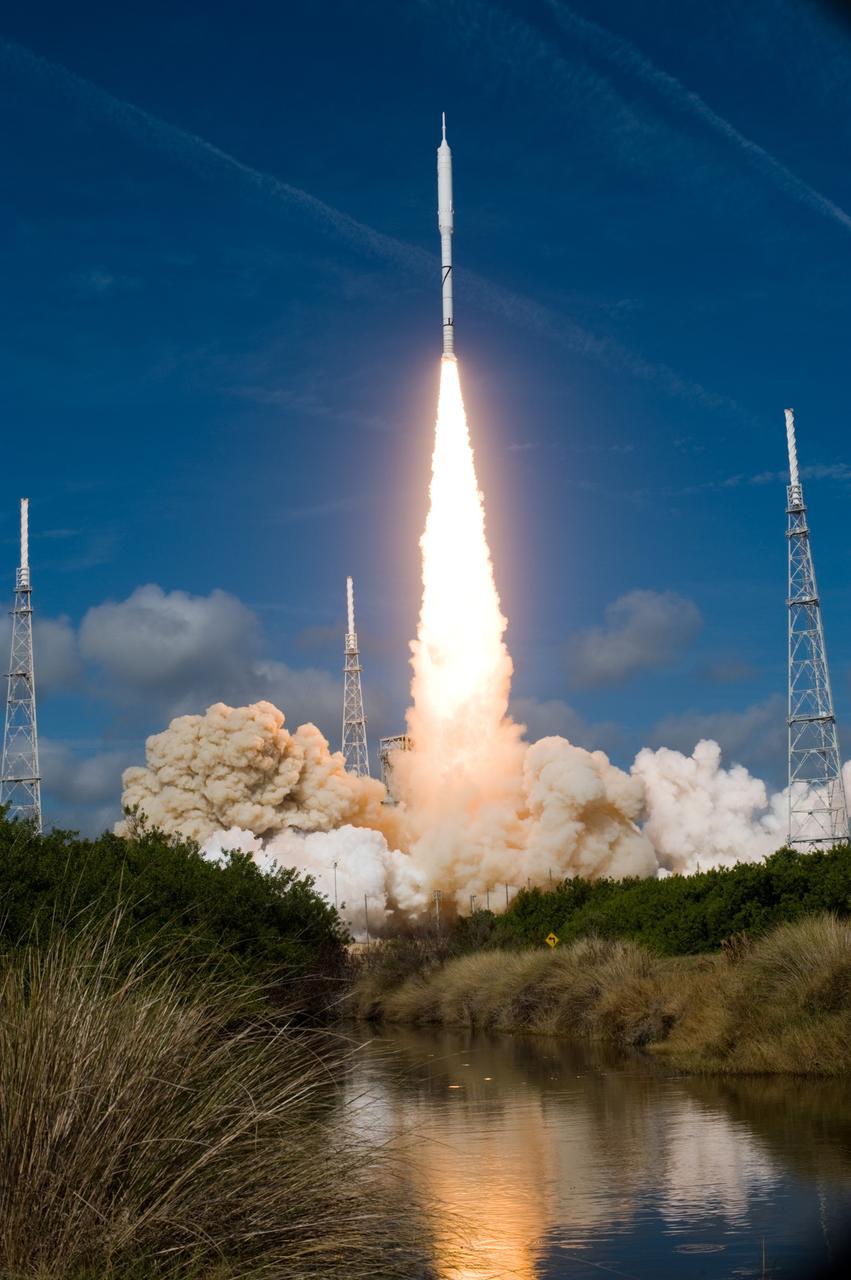

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/ Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
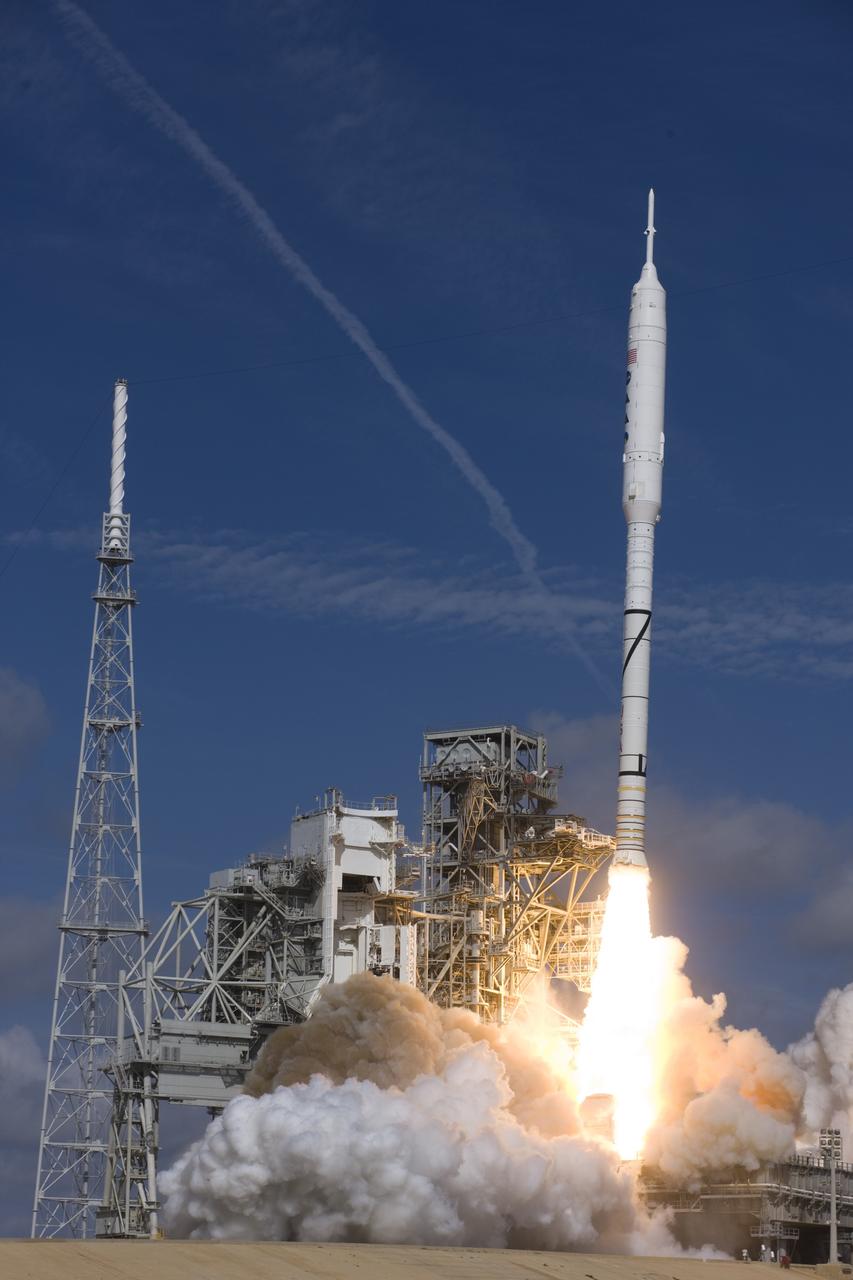

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: Courtesy of Scott Andrews
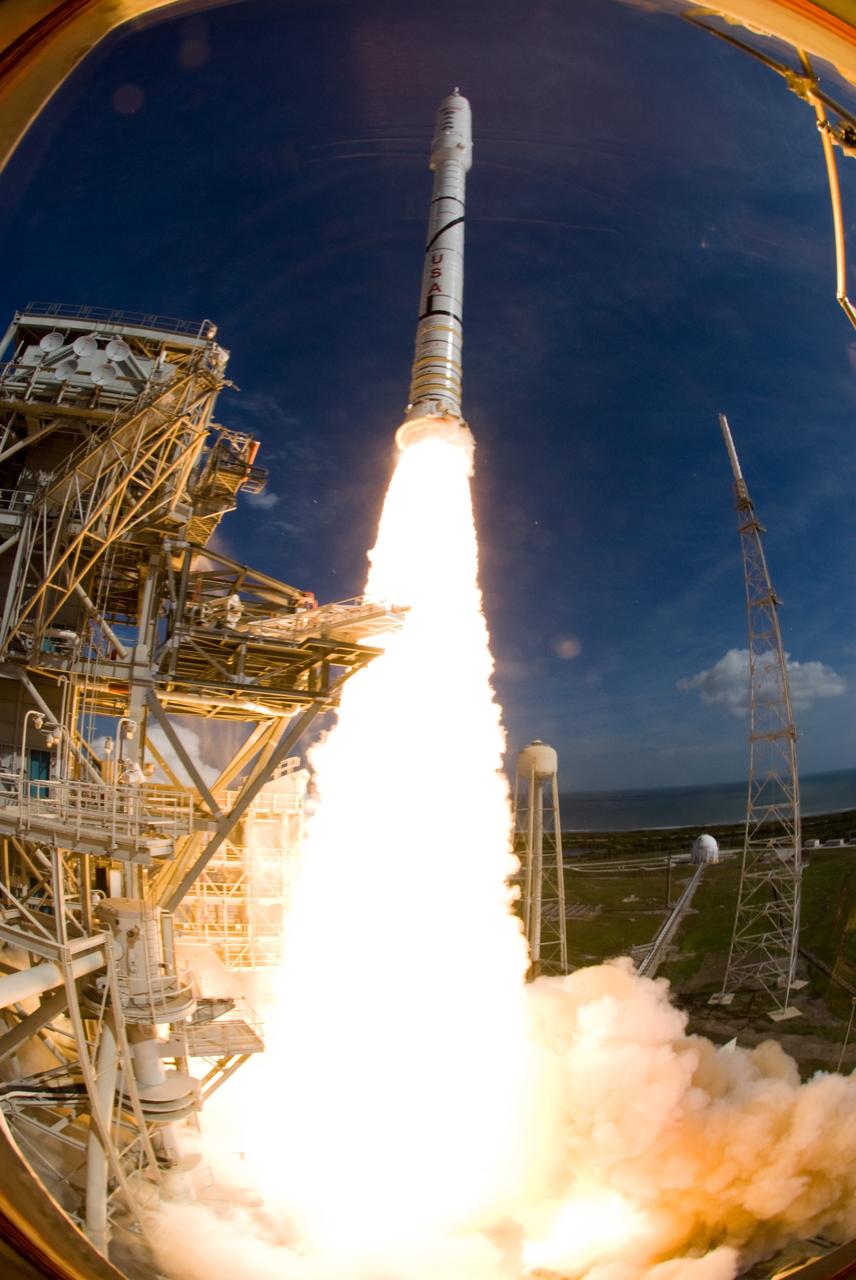

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/ Sandra Joseph and Kevin O'Connell
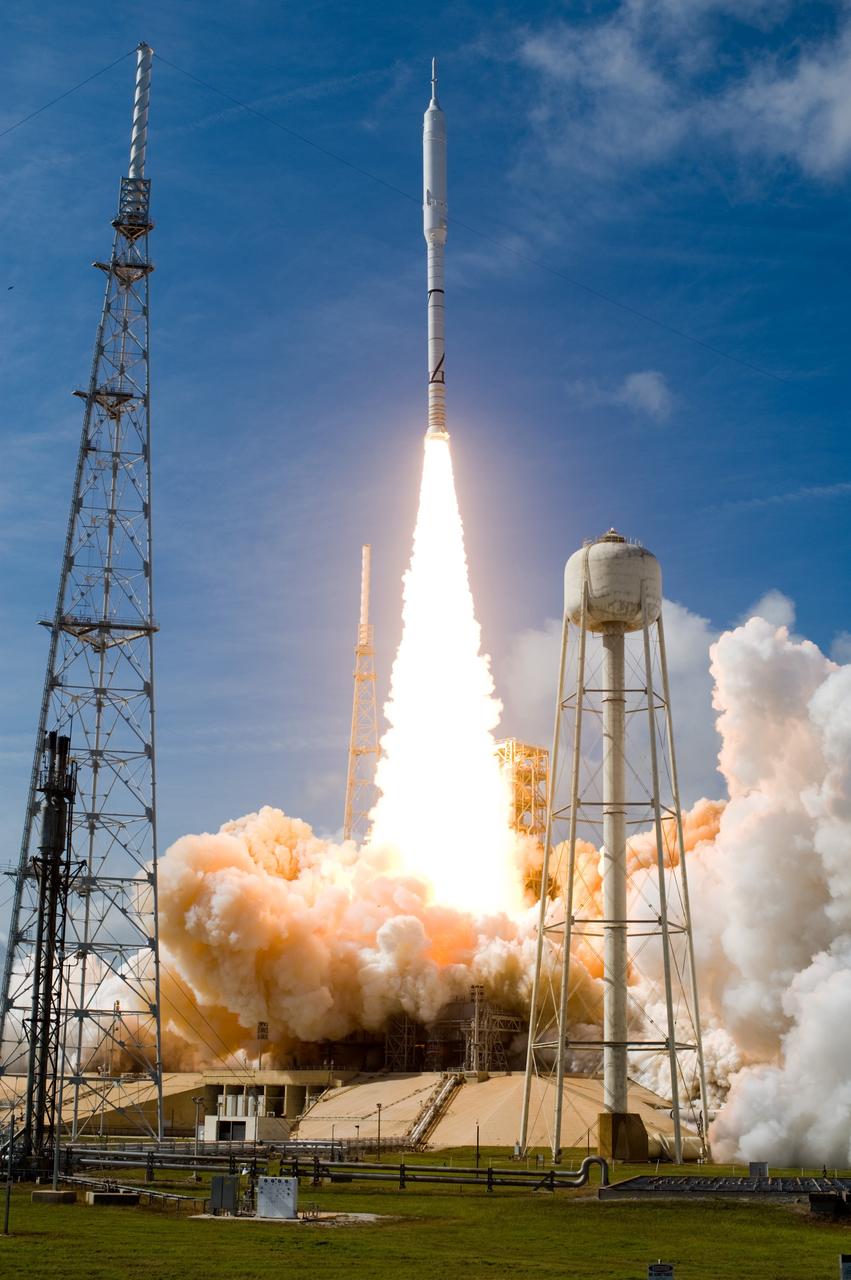

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA’s Ares I-X test rocket clears the tower at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:30 a.m. EDT on Oct. 28. The rocket produces 2.96 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and reaches a speed of 100 mph in eight seconds. This was the first launch from Kennedy's pads of a vehicle other than the space shuttle since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired. The parts used to make the Ares I-X booster flew on 30 different shuttle missions ranging from STS-29 in 1989 to STS-106 in 2000. The data returned from more than 700 sensors throughout the rocket will be used to refine the design of future launch vehicles and bring NASA one step closer to reaching its exploration goals. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray and Tom Farrar

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Towering atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter in the early morning light, Space Shuttle Endeavour arrives at Launch Pad 39A after rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building. At its left are the Rotating Service Structure and the Fixed Service Structure; at the right is the 300,000-gallon water tank, part of the sound suppression water system. While at the pad, the orbiter, external tank and solid rocket boosters will undergo final preparations for the STS-88 launch targeted for Dec. 3, 1998. Mission STS-88 is the first U.S. flight for the assembly of the International Space Station and will carry the Unity connecting module. While on orbit, the flight crew will deploy Unity from the payload bay and connect it to the Russian-built Zarya control module which will be in orbit at that time. Unity will be the main connecting point for later U.S. station modules and components. More than 40 launches are planned over five years involving the resources and expertise of 16 cooperating nations. Comprising the STS-88 crew are Commander Robert D. Cabana, Pilot Frederick W. "Rick" Sturckow, Mission Specialists Nancy J. Currie, Jerry L. Ross, James H. Newman and Russian cosmonaut Sergei Konstantinovich Krikalev. Ross and Newman will make three spacewalks to connect power, data and utility lines and install exterior equipment

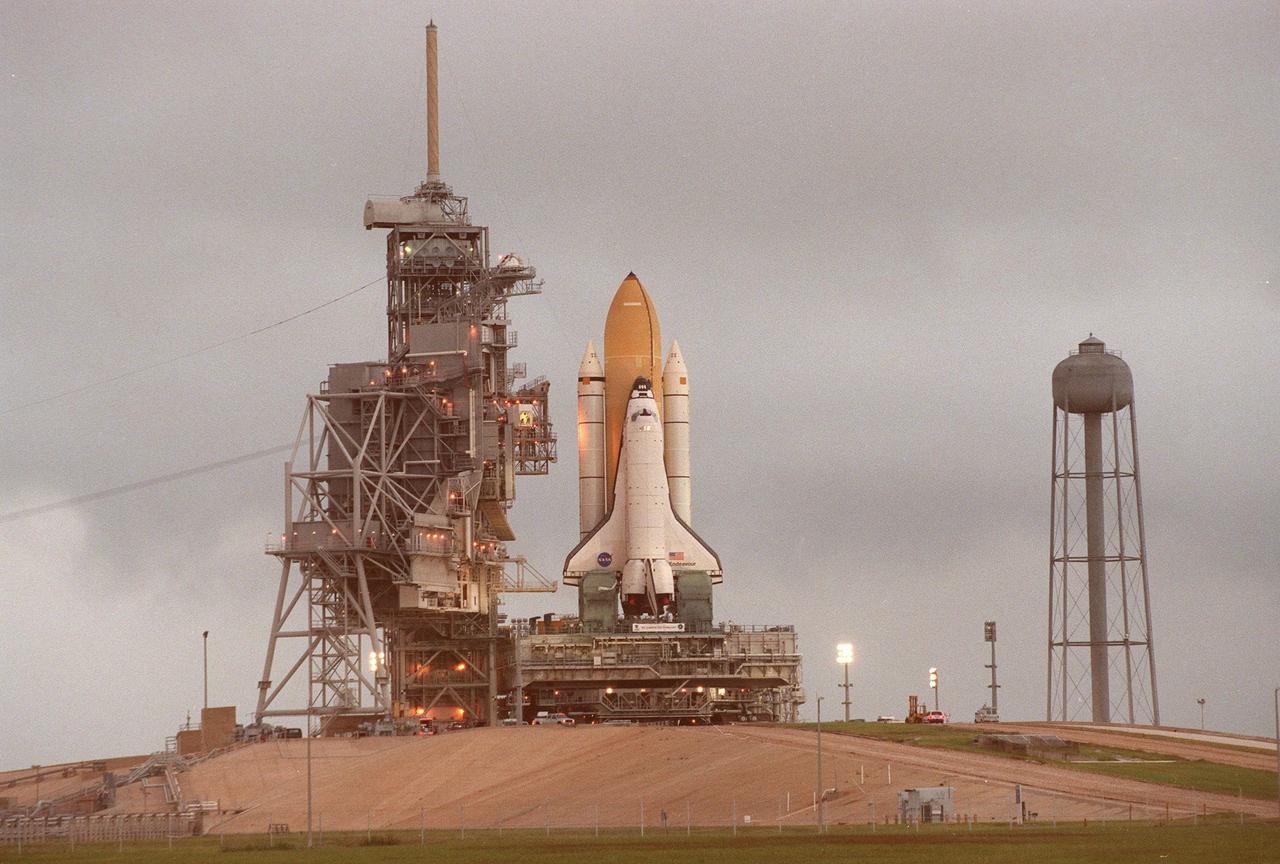
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After a journey of more than 8 hours from the Vehicle Assembly Building, Space Shuttle Atlantis sits on Launch Pad 39B. At left is the Rotating Service Structure, which will roll on its axis to enclose the Shuttle until launch. Towering above the Fixed Service Structure next to it is the 80-foot tall lightning mast that provides protection from lightning strikes. On the right is the elevated water tank with a capacity of 300,000 gallons. Part of the Sound Suppression Water System, the water in the tank is released just before ignition of the orbiter’s three main engines and twin solid rocket boosters and flow through parallel 7-foot-diameter pipes to the pad area. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- After a journey of more than 8 hours from the Vehicle Assembly Building, Space Shuttle Atlantis sits on Launch Pad 39B. At left is the Rotating Service Structure, which will roll on its axis to enclose the Shuttle until launch. Towering above the Fixed Service Structure next to it is the 80-foot tall lightning mast that provides protection from lightning strikes. On the right is the elevated water tank with a capacity of 300,000 gallons. Part of the Sound Suppression Water System, the water in the tank is released just before ignition of the orbiter’s three main engines and twin solid rocket boosters and flow through parallel 7-foot-diameter pipes to the pad area. The Shuttle is targeted for launch no earlier than July 12 on mission STS-104, the 10th flight to the International Space Station. The payload on the 11-day mission is the Joint Airlock Module, which will allow astronauts and cosmonauts in residence on the Station to perform future spacewalks without the presence of a Space Shuttle. The module, which comprises a crew lock and an equipment lock, will be connected to the starboard (right) side of Node 1 Unity. Atlantis will also carry oxygen and nitrogen storage tanks, vital to operation of the Joint Airlock, on a Spacelab Logistics Double Pallet in the payload bay. The tanks, to be installed on the perimeter of the Joint Module during the mission’s spacewalks, will support future spacewalk operations and experiments plus augment the resupply system for the Station’s Service Module

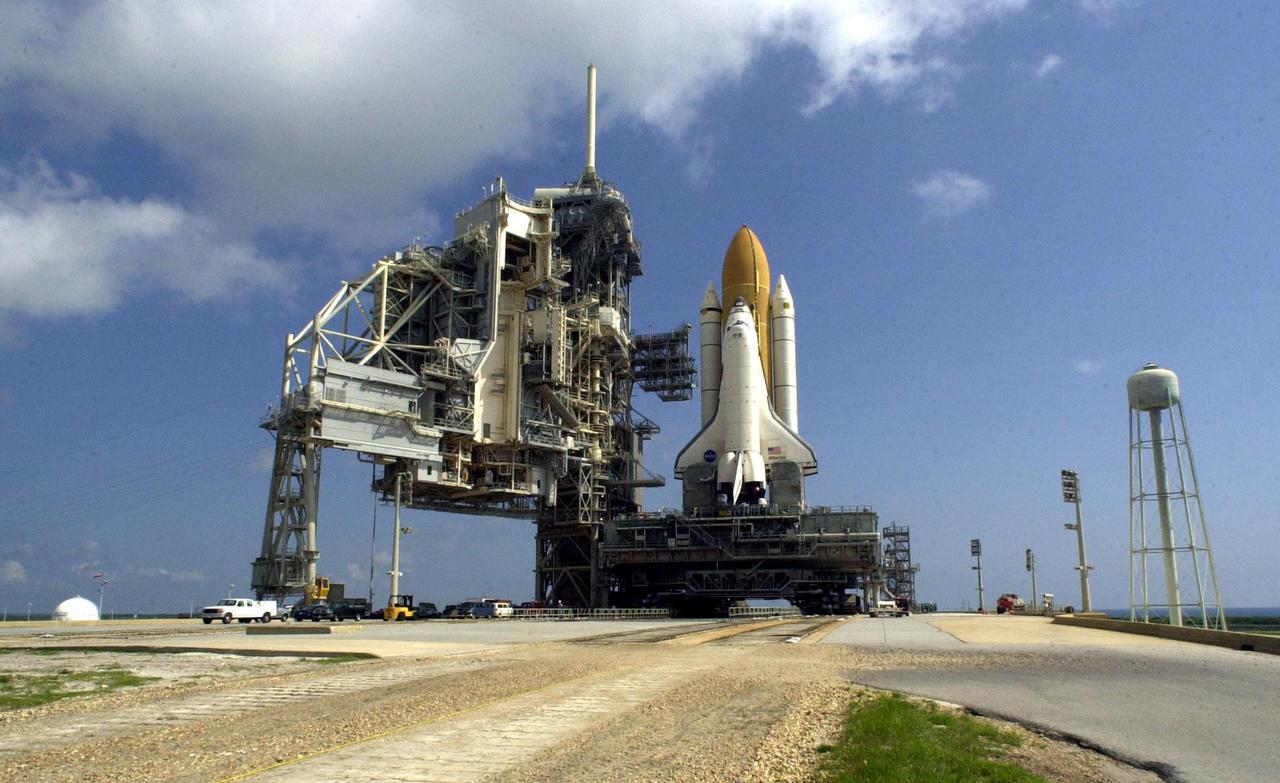
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis, attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, towers above the surface of the mobile launcher platform on which it is secured. From the top of the platform to the tip of the tank is approximately 184 feet. Atlantis' first motion on its 3.4-mile trip from the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 11:31 p.m. EDT April 21. The shuttle was secured, or 'hard down,' on the pad at 6:03 a.m. April 22. Rollout is a significant milestone in launch processing activities. On the STS-132 mission, the six-member crew will deliver an Integrated Cargo Carrier, or ICC, and the Russian-built Mini-Research Module-1, or MRM-1, to the International Space Station. The ICC is an unpressurized flat bed pallet and keel yoke assembly used to support the transfer of exterior cargo from the shuttle to the space station. The MRM-1, known as Rassvet, is the second in a series of new pressurized components for Russia and will be permanently attached to the Earth-facing port of the Zarya control module. Rassvet, which translates to 'dawn,' will be used for cargo storage and will provide an additional docking port to the station. STS-132 is the 34th mission to the station and the 132nd shuttle mission overall. Atlantis is targeted to launch on May 14 at 2:19 p.m. For information on the STS-132 mission, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Jack Pfaller
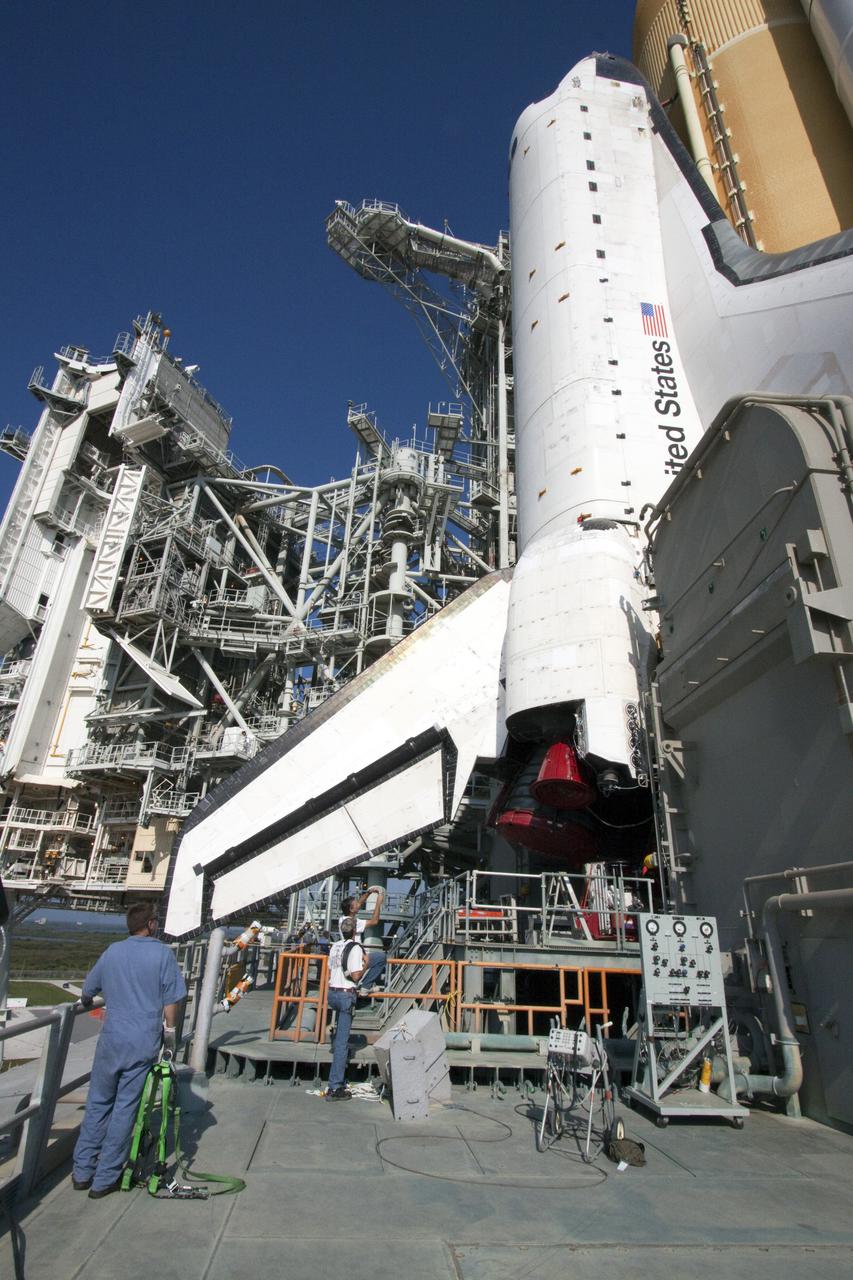

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis, attached to its external fuel tank and solid rocket boosters, towers above the workers on the surface of the mobile launcher platform on which it is secured. From the top of the platform to the tip of the tank is approximately 184 feet. Atlantis' first motion on its 3.4-mile trip from the Vehicle Assembly Building was at 11:31 p.m. EDT April 21. The shuttle was secured, or 'hard down,' on the pad at 6:03 a.m. April 22. Rollout is a significant milestone in launch processing activities. On the STS-132 mission, the six-member crew will deliver an Integrated Cargo Carrier, or ICC, and the Russian-built Mini-Research Module-1, or MRM-1, to the International Space Station. The ICC is an unpressurized flat bed pallet and keel yoke assembly used to support the transfer of exterior cargo from the shuttle to the space station. The MRM-1, known as Rassvet, is the second in a series of new pressurized components for Russia and will be permanently attached to the Earth-facing port of the Zarya control module. Rassvet, which translates to 'dawn,' will be used for cargo storage and will provide an additional docking port to the station. STS-132 is the 34th mission to the station and the 132nd shuttle mission overall. Atlantis is targeted to launch on May 14 at 2:19 p.m. For information on the STS-132 mission, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_mission_pages_shuttle_shuttlemissions_sts132_index.html. Photo credit: NASA_Jack Pfaller

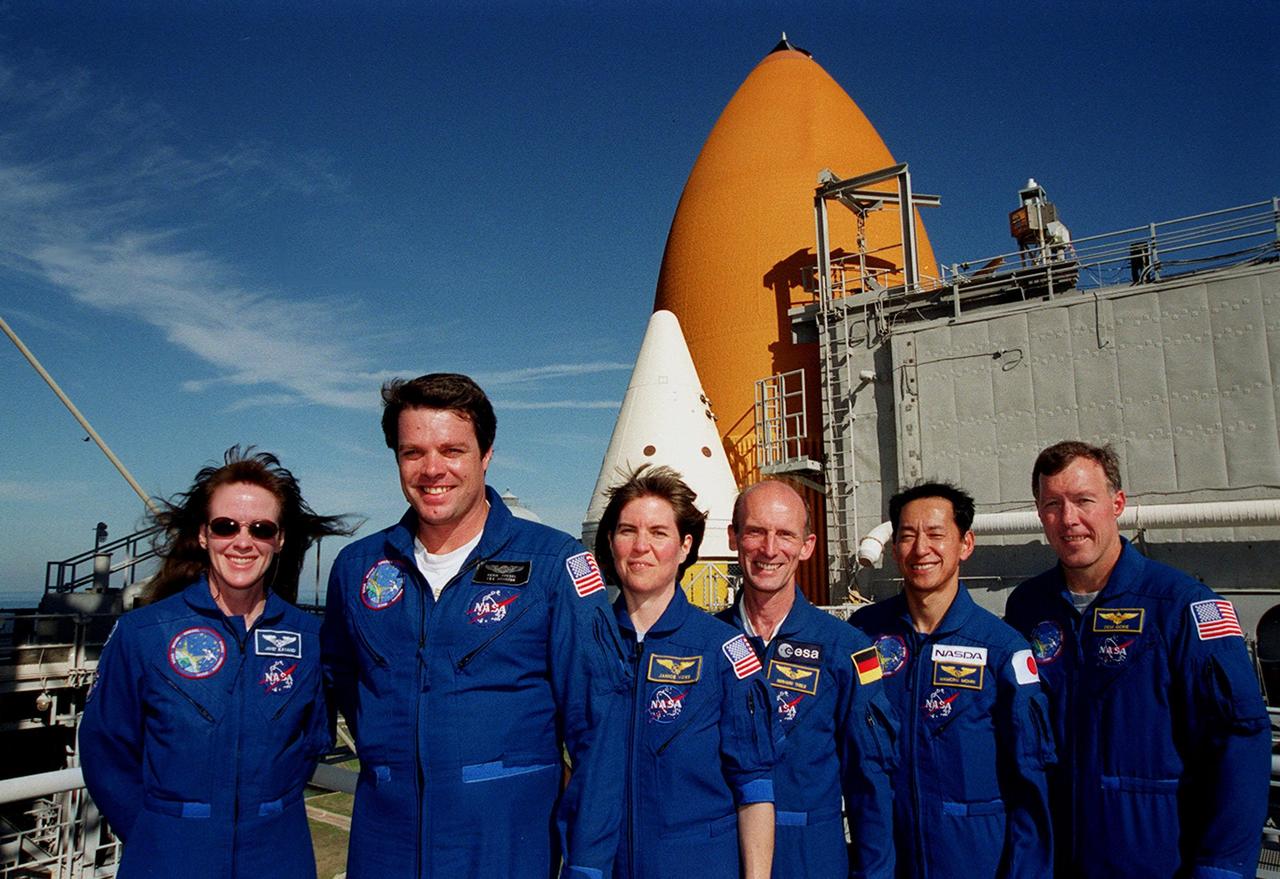
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At the 167-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Pad 39A, the STS-99 crew pose for a photograph during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. Standing left to right are Mission Specialist Janet Lynn Kavandi (Ph.D.), Commander Kevin Kregel, Mission Specialists Janice Voss (Ph.D.), Gerhard Thiele and Mamoru Mohri, and Pilot Dominic Gorie. Thiele is with the European Space Agency and Mohri is with the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan. Behind them are visible the top of a solid rocket booster (white) and external tank (orange). The TCDT provides the crew with simulated countdown exercises, emergency egress training, and opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-99 is the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, which will chart a new course, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. Launch of Endeavour on the 11-day mission is scheduled for Jan. 31 at 12:47 p.m. EST
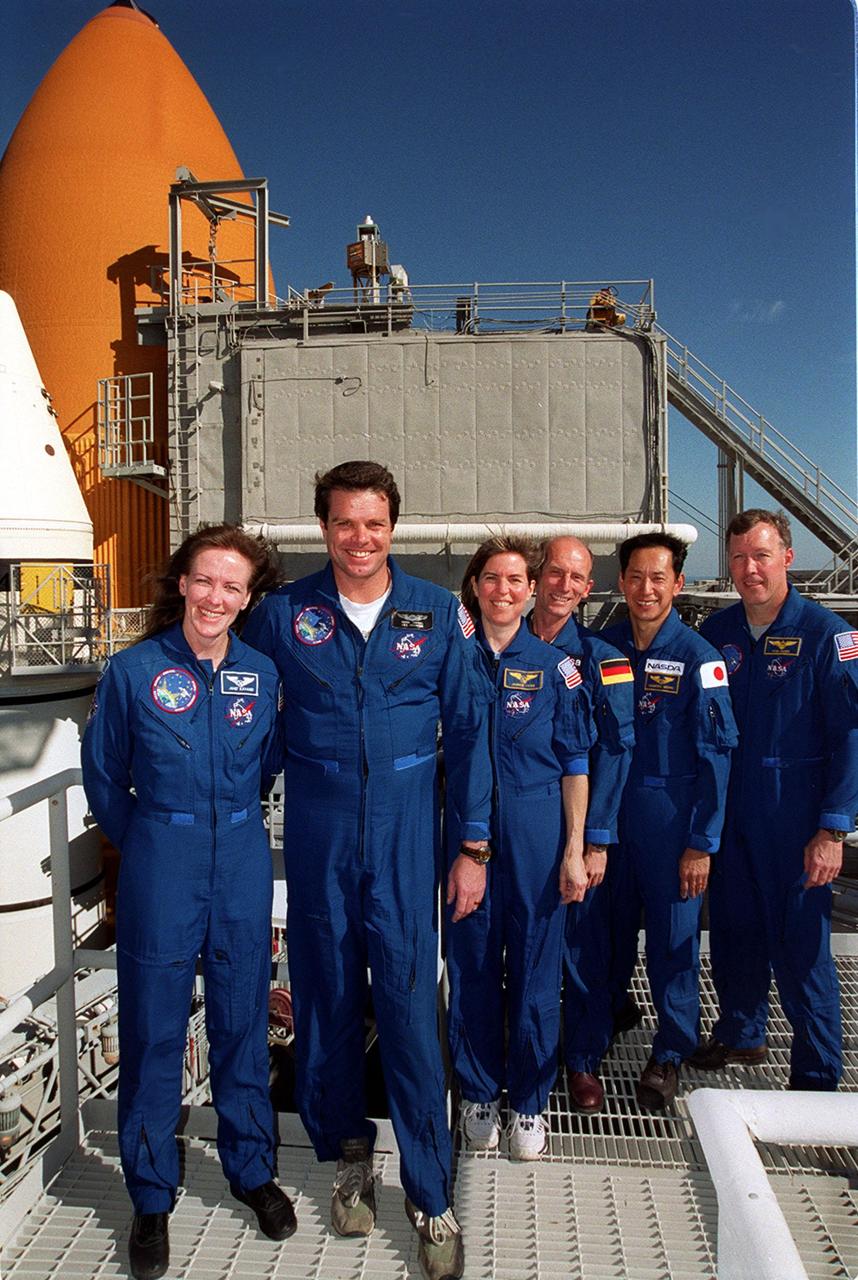

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At the 167-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Pad 39A, the STS-99 crew pose for a photograph during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. Standing left to right are Mission Specialist Janet Lynn Kavandi (Ph.D.), Commander Kevin Kregel, Mission Specialists Janice Voss (Ph.D.), Gerhard Thiele and Mamoru Mohri, and Pilot Dominic Gorie. Thiele is with the European Space Agency and Mohri is with the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan. Behind them (left) are visible the top of a solid rocket booster (white) and external tank (orange). The TCDT provides the crew with simulated countdown exercises, emergency egress training, and opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-99 is the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, which will chart a new course, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. Launch of Endeavour on the 11-day mission is scheduled for Jan. 31 at 12:47 p.m. EST
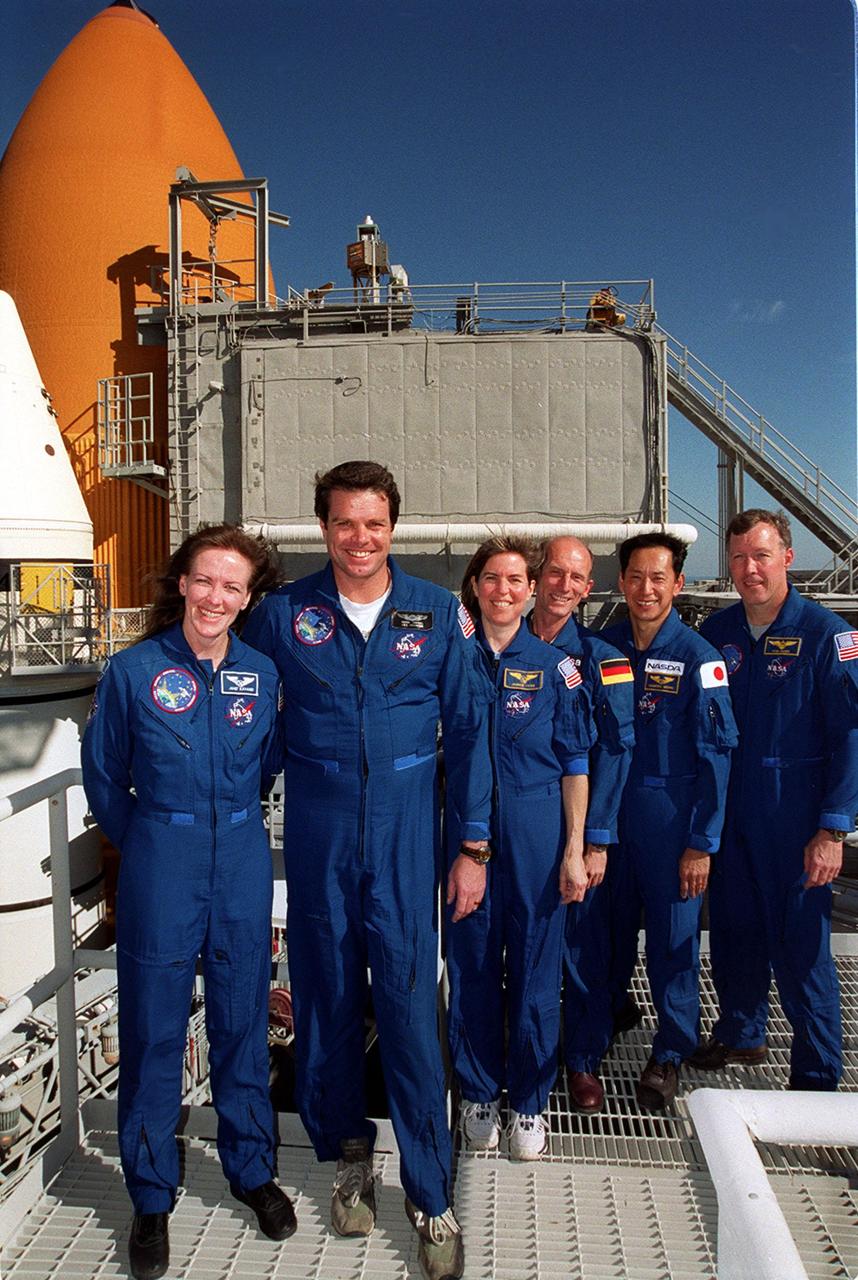

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At the 167-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Pad 39A, the STS-99 crew pose for a photograph during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. Standing left to right are Mission Specialist Janet Lynn Kavandi (Ph.D.), Commander Kevin Kregel, Mission Specialists Janice Voss (Ph.D.), Gerhard Thiele and Mamoru Mohri, and Pilot Dominic Gorie. Thiele is with the European Space Agency and Mohri is with the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan. Behind them (left) are visible the top of a solid rocket booster (white) and external tank (orange). The TCDT provides the crew with simulated countdown exercises, emergency egress training, and opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-99 is the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, which will chart a new course, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. Launch of Endeavour on the 11-day mission is scheduled for Jan. 31 at 12:47 p.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- At the 167-foot level of the Fixed Service Structure on Launch Pad 39A, the STS-99 crew pose for a photograph during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. Standing left to right are Mission Specialist Janet Lynn Kavandi (Ph.D.), Commander Kevin Kregel, Mission Specialists Janice Voss (Ph.D.), Gerhard Thiele and Mamoru Mohri, and Pilot Dominic Gorie. Thiele is with the European Space Agency and Mohri is with the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan. Behind them are visible the top of a solid rocket booster (white) and external tank (orange). The TCDT provides the crew with simulated countdown exercises, emergency egress training, and opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-99 is the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, which will chart a new course, using two antennae and a 200-foot-long section of space station-derived mast protruding from the payload bay to produce unrivaled 3-D images of the Earth's surface. The result of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission could be close to 1 trillion measurements of the Earth's topography. Besides contributing to the production of better maps, these measurements could lead to improved water drainage modeling, more realistic flight simulators, better locations for cell phone towers, and enhanced navigation safety. Launch of Endeavour on the 11-day mission is scheduled for Jan. 31 at 12:47 p.m. EST
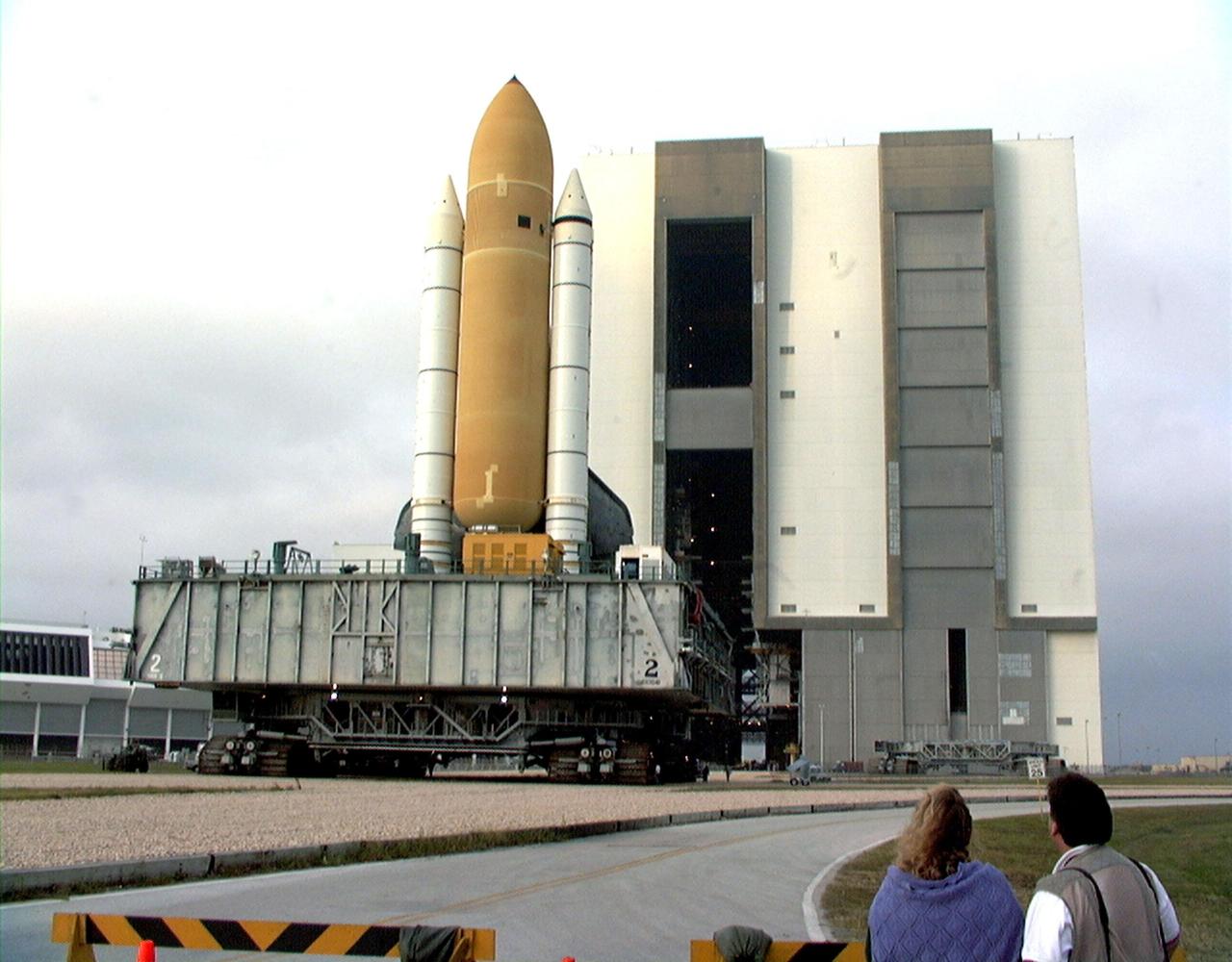

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Towering atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter, Space Shuttle Discovery rolls out of the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Launch Pad 39B. While at the pad, the orbiter, external tank and solid rocket boosters will undergo final preparations for the STS-103 launch targeted for Dec. 6, 1999, at 2:37 a.m. EST. The mission is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system the gyros which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will also be installing a Fine Guidance Sensor, a new enhanced computer, a solid-state digital recorder, and a new spare transmitter to replace older equipment, and replacing degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. Comprising the STS-103 crew are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Mission Specialist Steven L. Smith, Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, with the European Space Agency, and Mission Specialist Jean-François Clervoy of France, with the European Space Agency
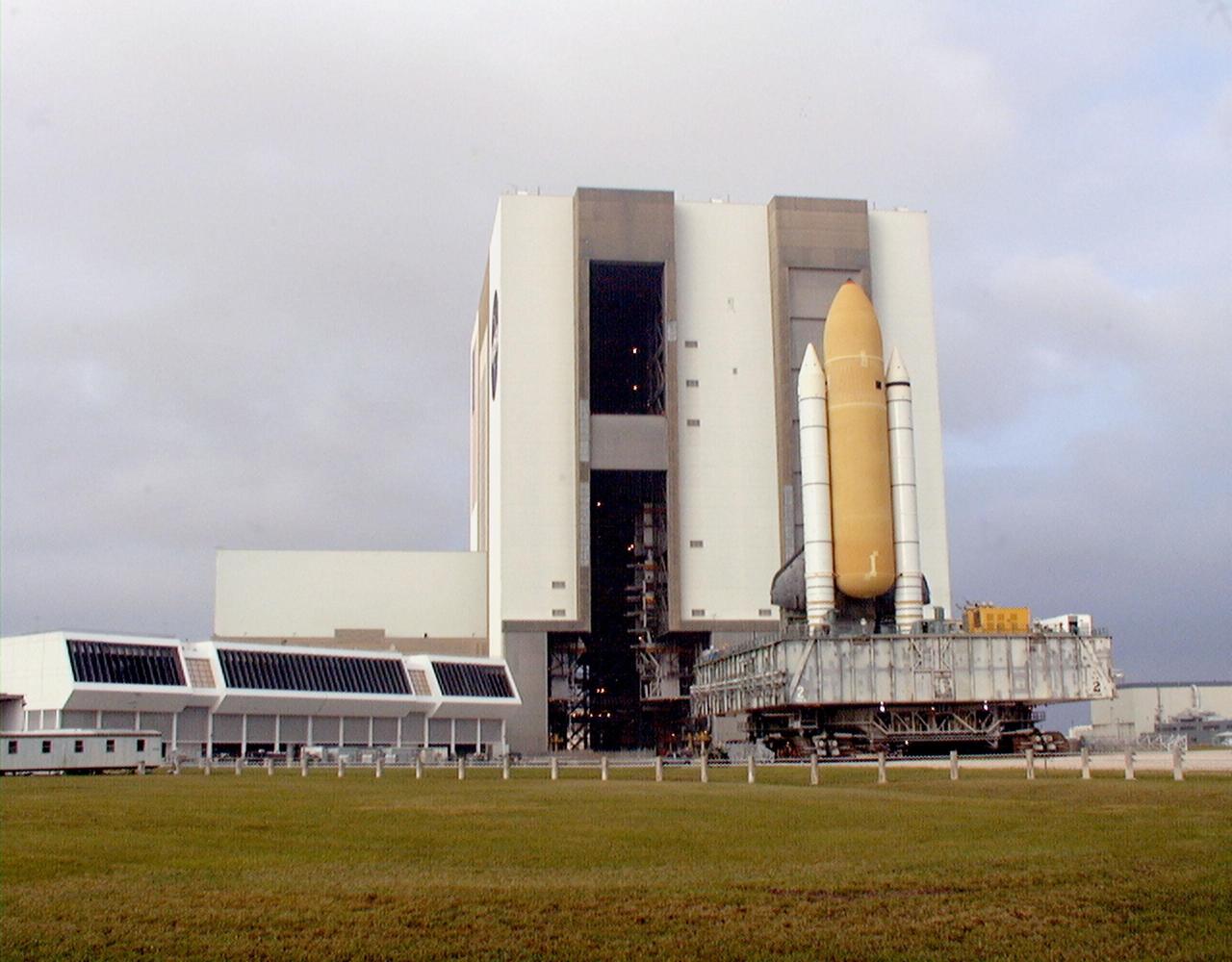
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Towering atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter, Space Shuttle Discovery rolls out of the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Launch Pad 39B which is 4.2 miles (6.8 kilometers) away. While at the pad, the orbiter, external tank and solid rocket boosters will undergo final preparations for the STS-103 launch targeted for Dec. 6, 1999, at 2:37 a.m. EST. The mission is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system the gyros which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will also be installing a Fine Guidance Sensor, a new enhanced computer, a solid-state digital recorder, and a new spare transmitter to replace older equipment, and replacing degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. Comprising the STS-103 crew are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Mission Specialist Steven L. Smith, Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, with the European Space Agency, and Mission Specialist Jean-François Clervoy of France, with the European Space Agency
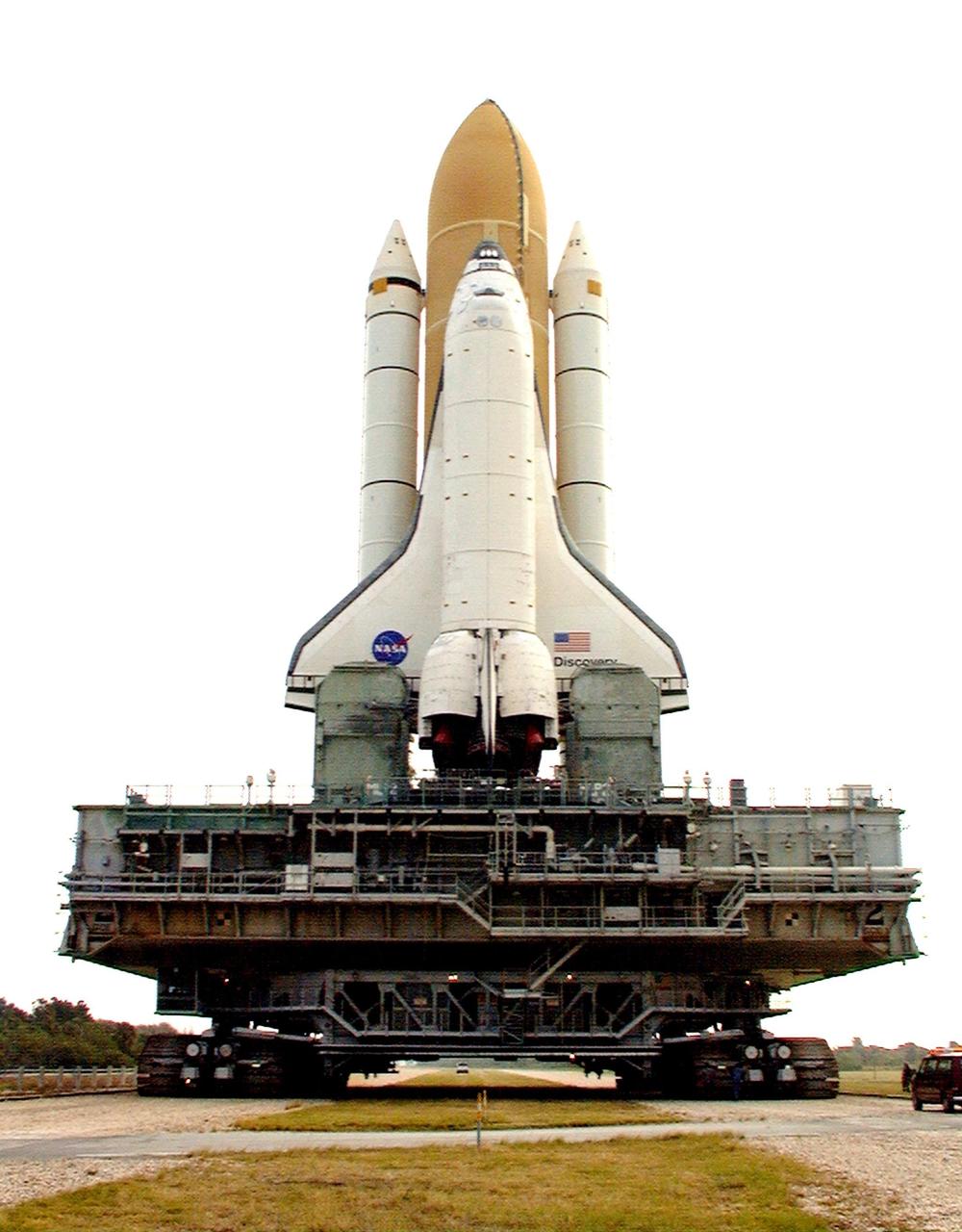
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Towering atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter, Space Shuttle Discovery makes its trek along the stretch of crawlerway between the Vehicle Assembly Building and Launch Pad 39B. Once at the pad, the orbiter, external tank and solid rocket boosters will undergo final preparations for the STS-103 launch targeted for Dec. 6, 1999, at 2:37 a.m. EST. The mission is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system the gyros which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will also be installing a Fine Guidance Sensor, a new enhanced computer, a solid-state digital recorder, and a new spare transmitter to replace older equipment, and replacing degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. Comprising the STS-103 crew are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Mission Specialist Steven L. Smith, Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, with the European Space Agency, and Mission Specialist Jean-François Clervoy of France, with the European Space Agency.
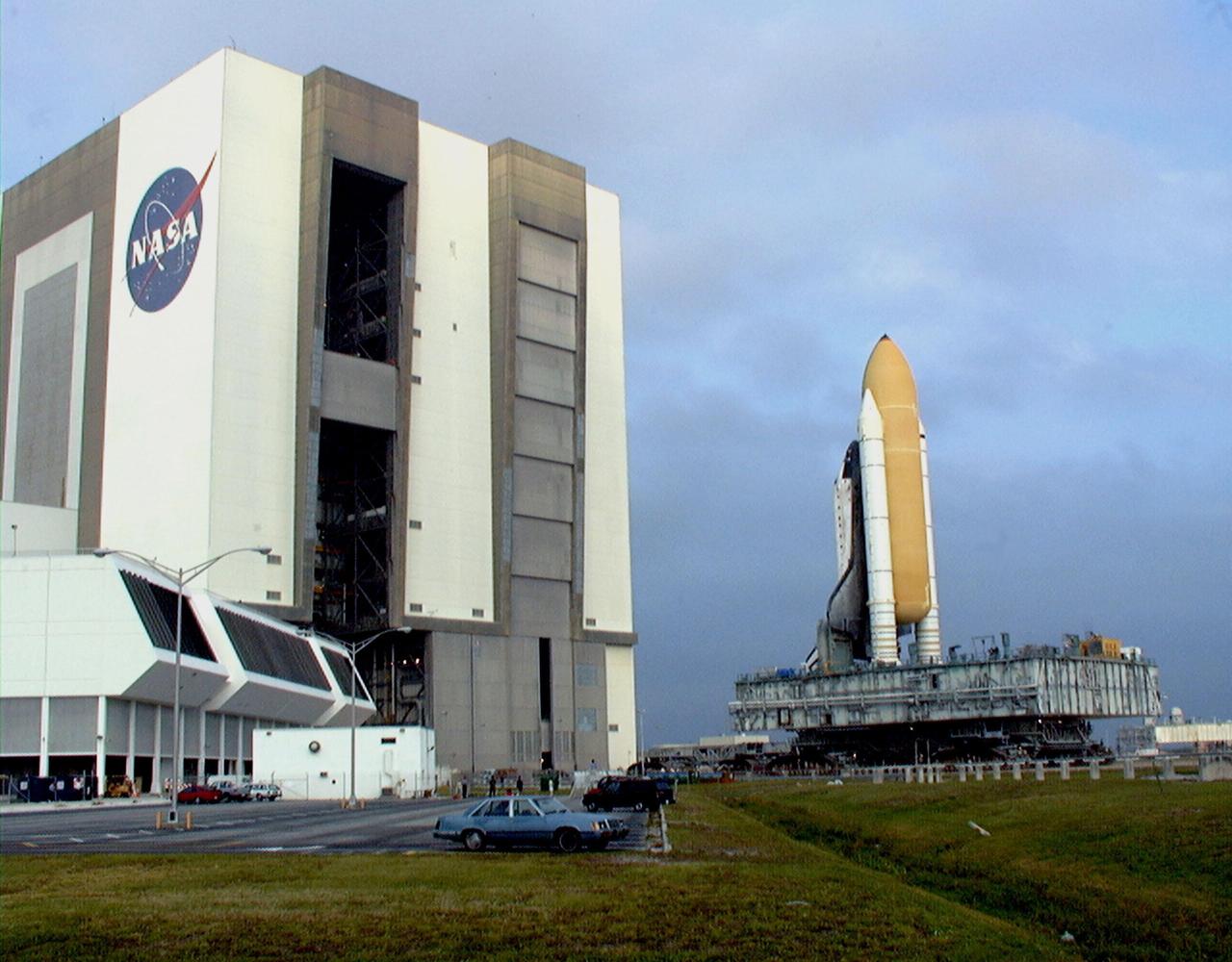

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Towering atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter, Space Shuttle Discovery rolls out of the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Launch Pad 39B which is 4.2 miles (6.8 kilometers) away. While at the pad, the orbiter, external tank and solid rocket boosters will undergo final preparations for the STS-103 launch targeted for Dec. 6, 1999, at 2:37 a.m. EST. The mission is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system the gyros which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will also be installing a Fine Guidance Sensor, a new enhanced computer, a solid-state digital recorder, and a new spare transmitter to replace older equipment, and replacing degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. Comprising the STS-103 crew are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Mission Specialist Steven L. Smith, Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, with the European Space Agency, and Mission Specialist Jean-François Clervoy of France, with the European Space Agency
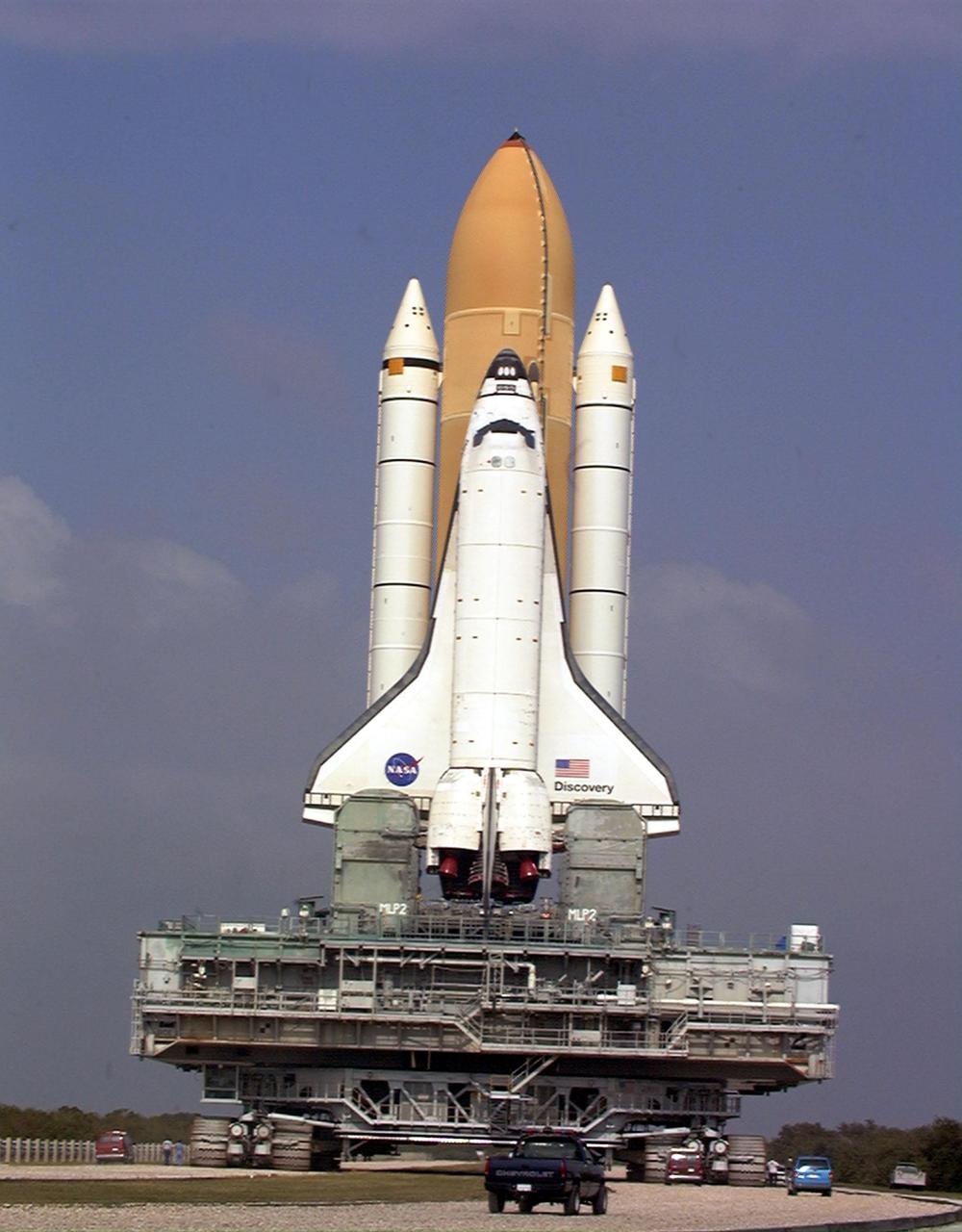

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Towering atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter, Space Shuttle Discovery negotiates a turn in the crawlerway on its trek from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B. While at the pad, the orbiter, external tank and solid rocket boosters will undergo final preparations for the STS-103 launch targeted for Dec. 6, 1999, at 2:37 a.m. EST. The mission is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system the gyros which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will also be installing a Fine Guidance Sensor, a new enhanced computer, a solid-state digital recorder, and a new spare transmitter to replace older equipment, and replacing degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. The STS-103 crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Mission Specialist Steven L. Smith, Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), and Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, and Mission Specialist Jean-François Clervoy of France, both with the European Space Agency