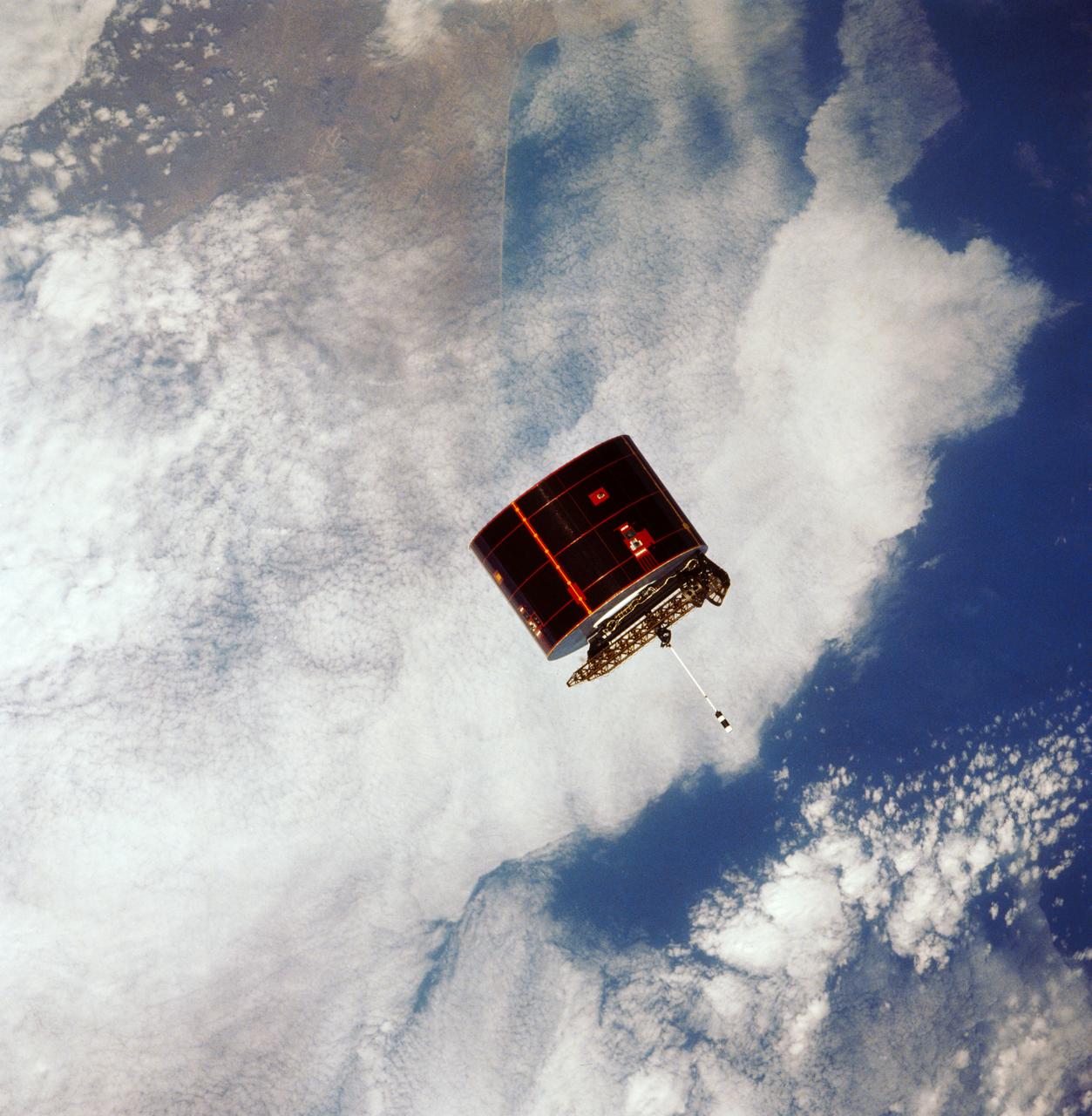

41D-32-067 (31 Aug 1984) --- The Atlantic Oceans coastline of Angola forms the backdrop for this scene of the Syncom IV (Leasat-2) spacecraft as it and the Space Shuttle Discovery begin their relative separation on Day Two of a busy-six-day 41-D mission. Moments, earlier in a Frisbee-like fashion, the spacecraft departed the Discovery’s cargo bay, marking the second of three scheduled satellite placements for the spacecraft’s maiden voyage. The scene was photographed with a 70mm camera aimed through the aft windows on the flight deck.
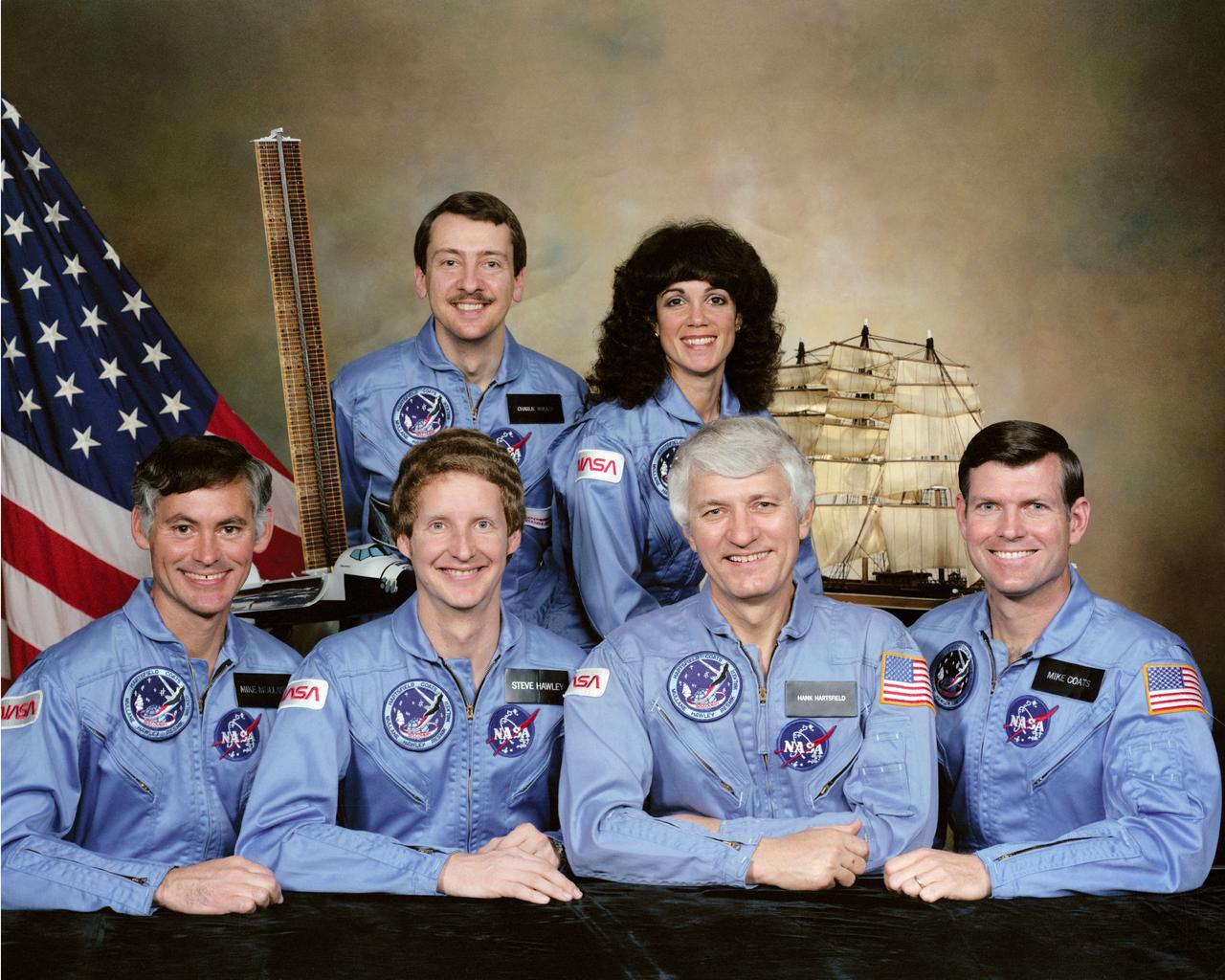

S84-30259 (April 1984) --- NASA's Discovery will carry these six STS51-D crew members into space on an early summer mission. Astronaut Henry W. Hartsfield Jr. (second right, front row) is crew commander; and Michael L. Coats, right, is pilot. Astronauts Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, left; Steven A. Hawley (second left) and Judith A. Resnik are mission specialists. Charles D. Walker (back row) is payload specialist. Both the early ocean-going Discovery and the debuting spacecraft are depicted in the backdrop. The conspicuous payload in the cargo bay of the spacecraft is that of NASA's Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology (OAST-1). Photo credit: NASA
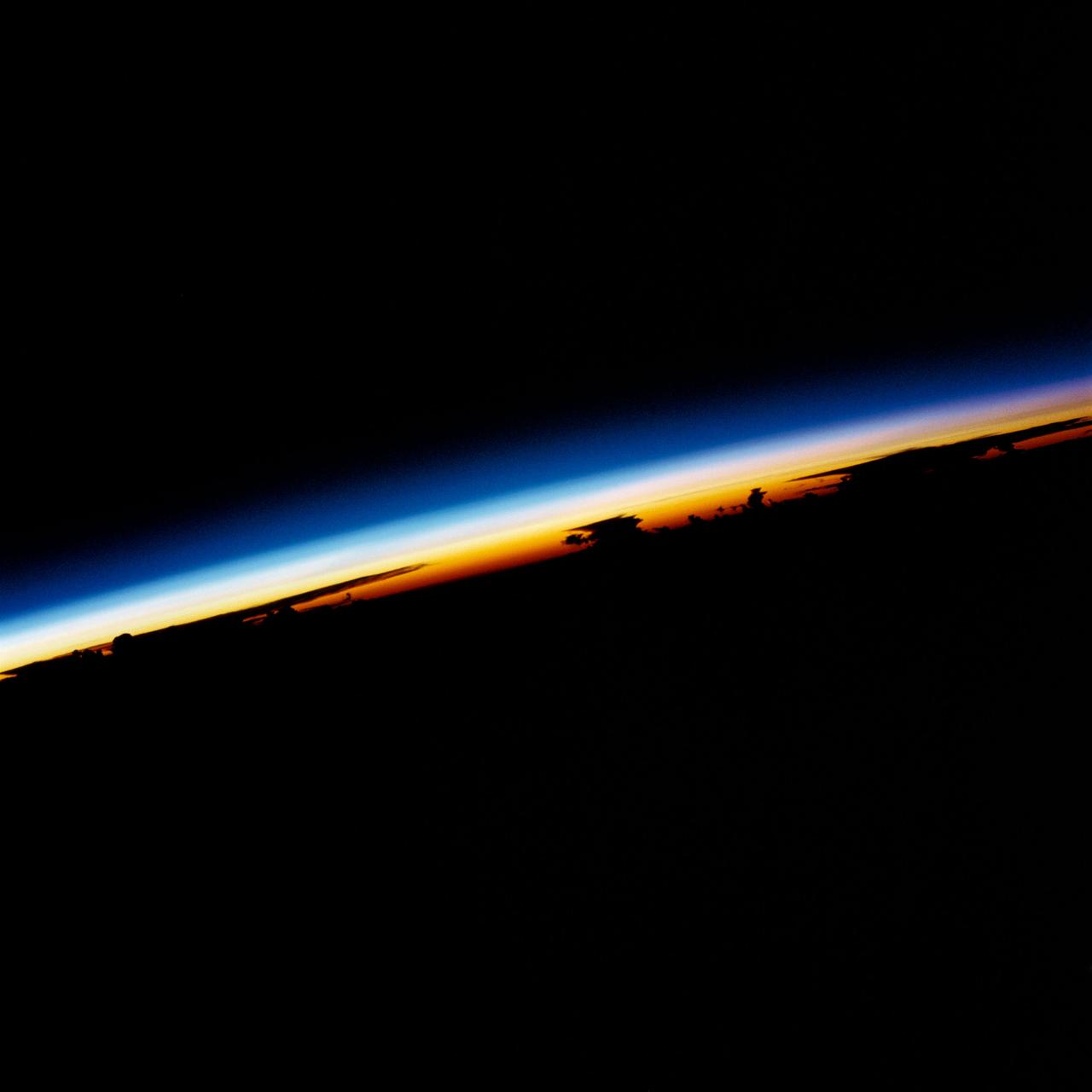

41D-32-14 (30 Aug 1984) --- A rainbow-like sunrise over the Philippine Sea greeted the six crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery on its first day in space. A 70mm camera was used to record the scene at 3:08:14 p.m. (CDT), August 30, 1984, during Discovery's sixth orbit of a six-day mission. The spacecraft was above a position on Earth centered at 21.1 degrees north and 12.9 degrees east (about 250 miles north - northeast of the Philippine Islands). The scene was shown as one of the Post-Flight Press Conference (PFPC) visuals by the crew on September 12, 1984.
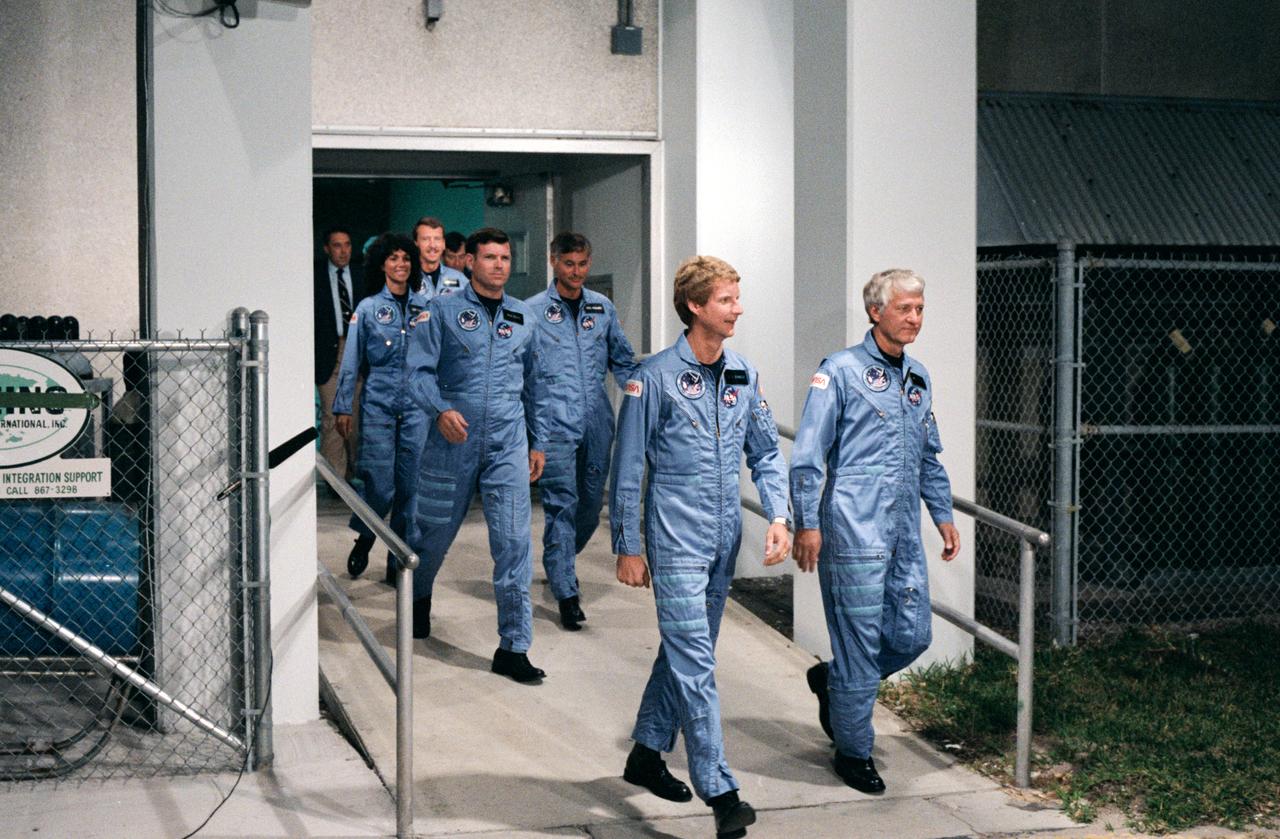

41D-3194 (30 Aug 1984)--- The six members of the 41-D Discovery crew leave the operations and checkout building at Kennedy Space to marke their way to Launch Pad 39A and a date with space. Leading the group is Henry W. hartsfield Jr., commander. Michael L. Coats, pilot, is left center. The mission specialists are Steven A. Hawley, second right, Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, right center, and Judith A. Resnik. Charles D. Walker, payload specialist, follows Resnik. Behind the blue-suited crewmembers are George W.S. Abbey, left, director of flight crew operations and John W. Young, chief of the astronaut office.
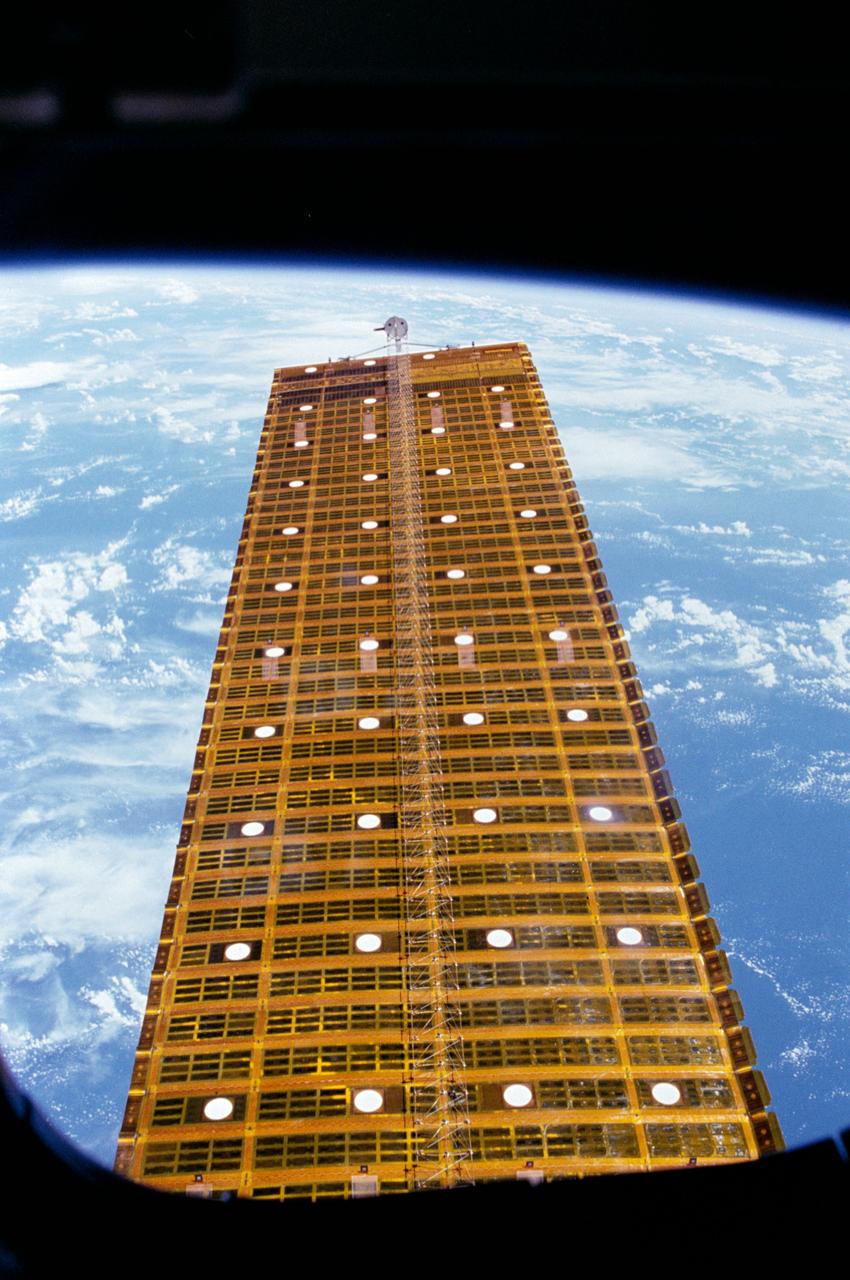

Scene of an extended solar array experiment (SAE) panel during the OAST-1 experiment. View was shot from the orbiter window by one of the STS 41-D crewmembers.
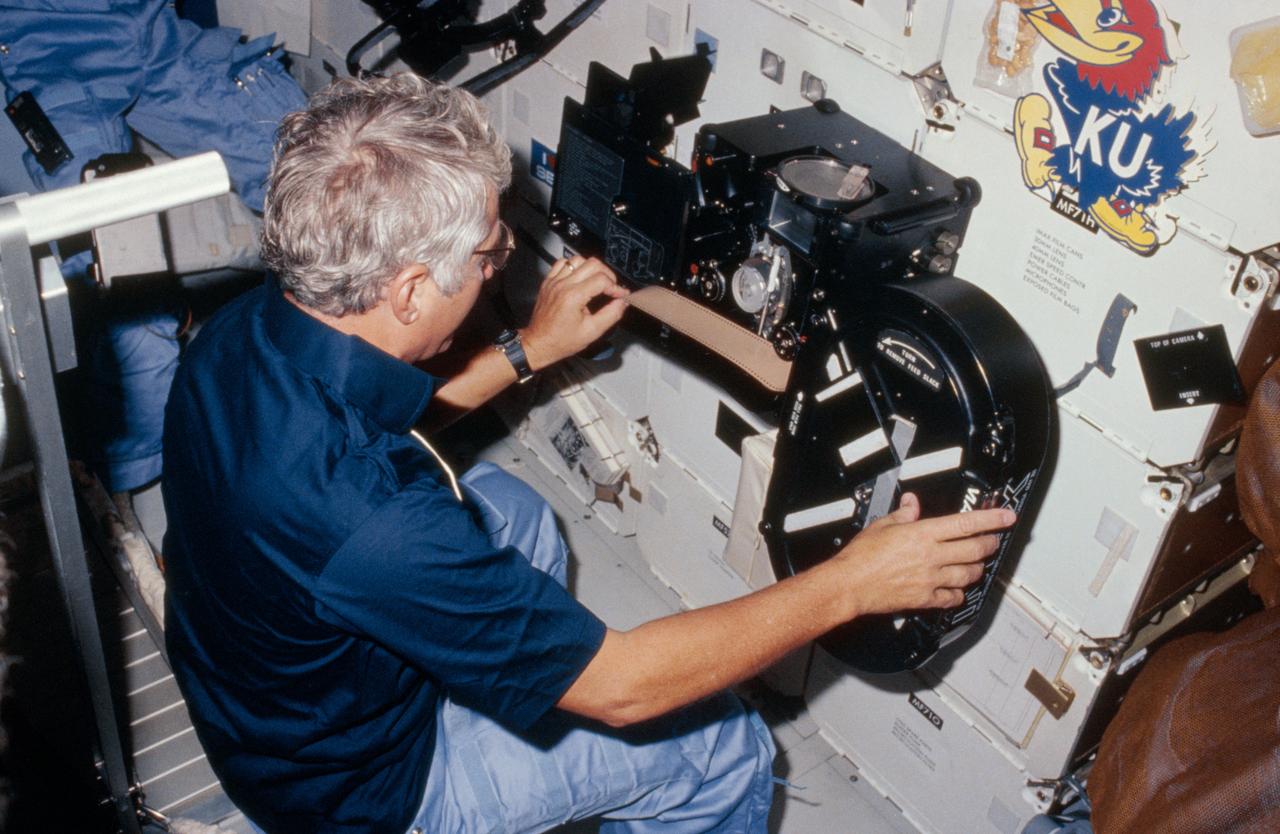

41D-11-004 (8 September 1984 --- View of Crew Commander Henry Hartsfield Jr. loading film into the IMAX camera during the 41-D mission. The camera is floating in front of the middeck lockers. Above it is a sticker of the University of Kansas mascott, the Jayhawk.
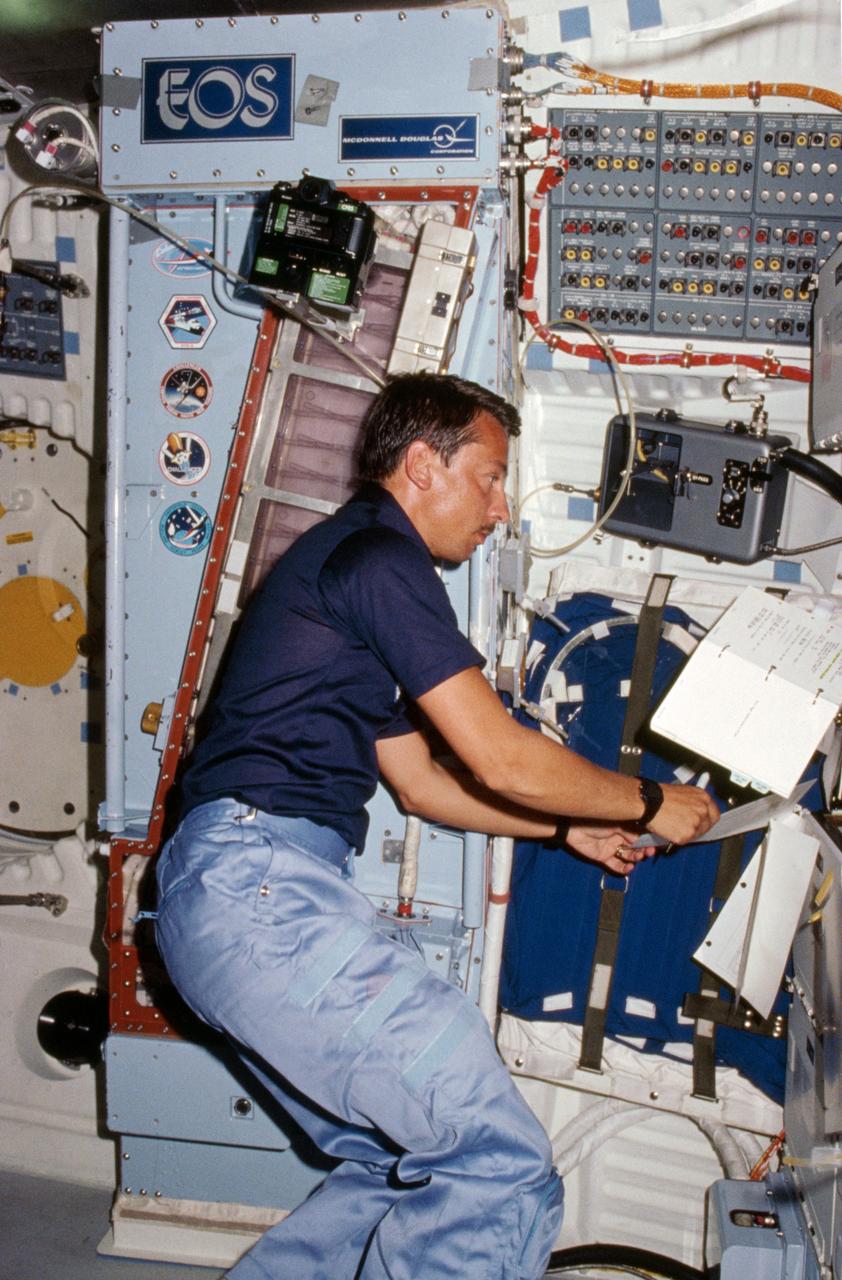

41D-06-013 (6 Sept 1984) --- Payload specialist Charles Walker works with the continuous flow electrophoresis systems (CFES) experiment, located in the middeck.
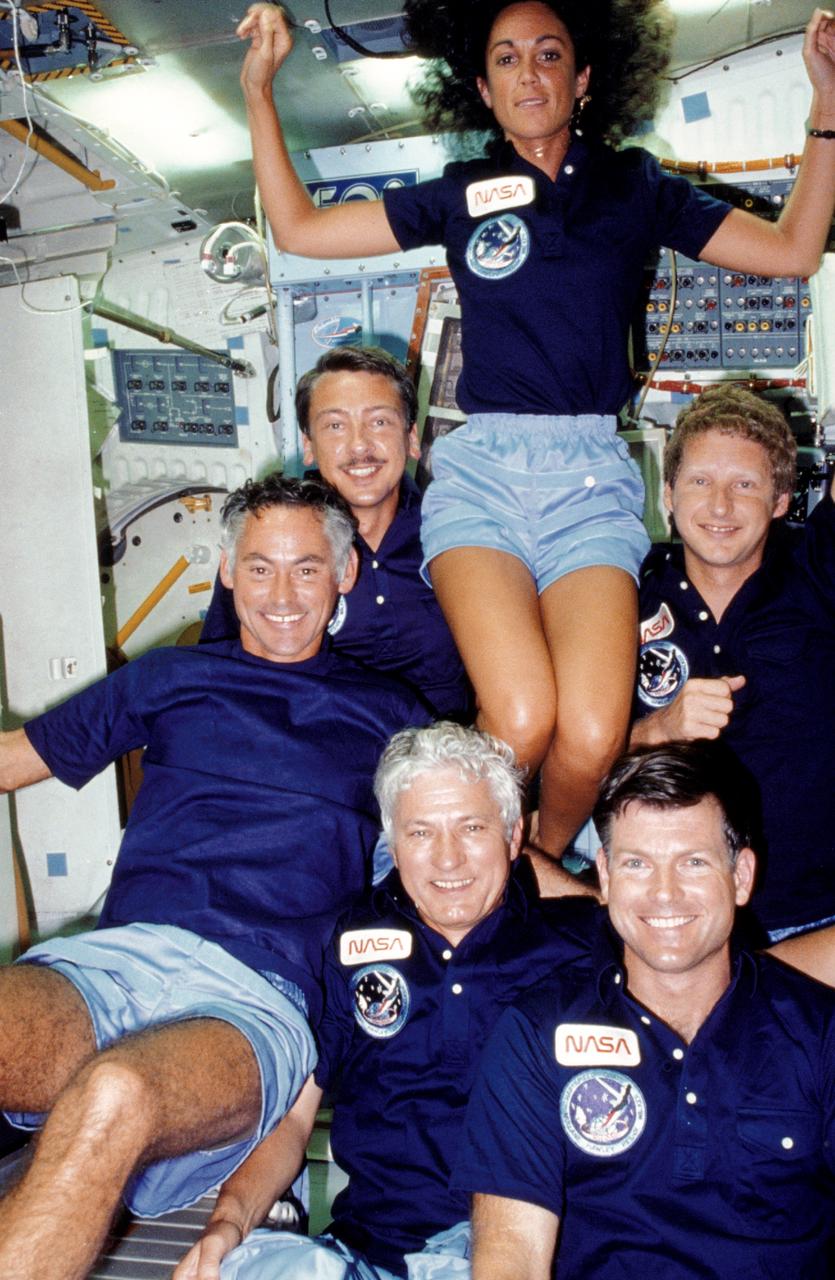

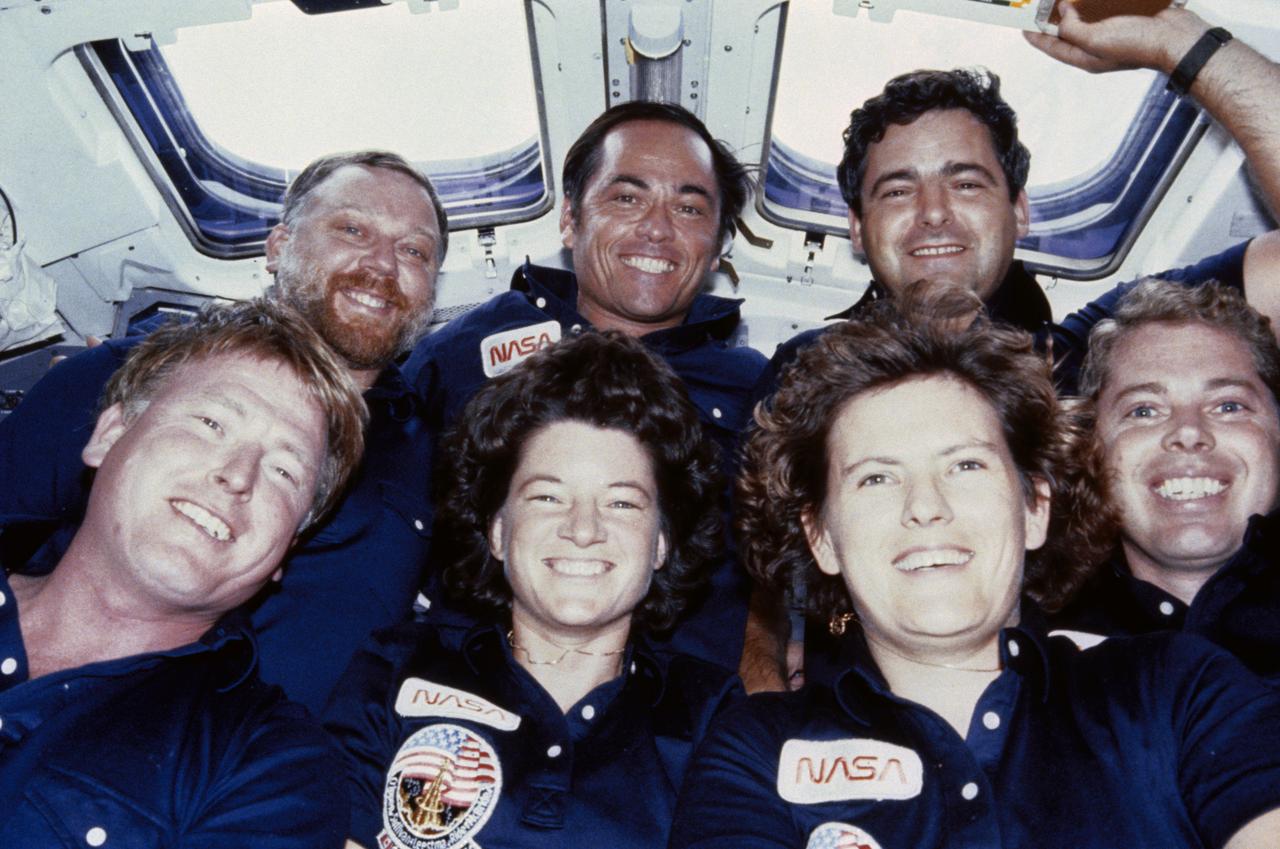
41D-12-034 (30 Aug.- 5 Sept. 1984) --- Following the completion of their six-day mission in space, the six crew members of NASA's 41-D mission mentioned that though a great deal of work was accomplished, there were "fun" moments too. From all appearance this group shot was one of the lighter moments aboard the Discovery. Crew members are (counter-clockwise from center) Henry W. Hartsfield Jr., crew commander; Michael L. Coats, pilot; Steven A. Hawley and Judith A. Resnik, both mission specialists; Charles D. Walker, payload specialist; and Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, mission specialist. A pre-set 35mm camera was used to expose the frame. Walker stands near the project that occupied the majority of his time onboard--the continuous flow electrophoresis systems (CFES) experiment. Photo credit: NASA
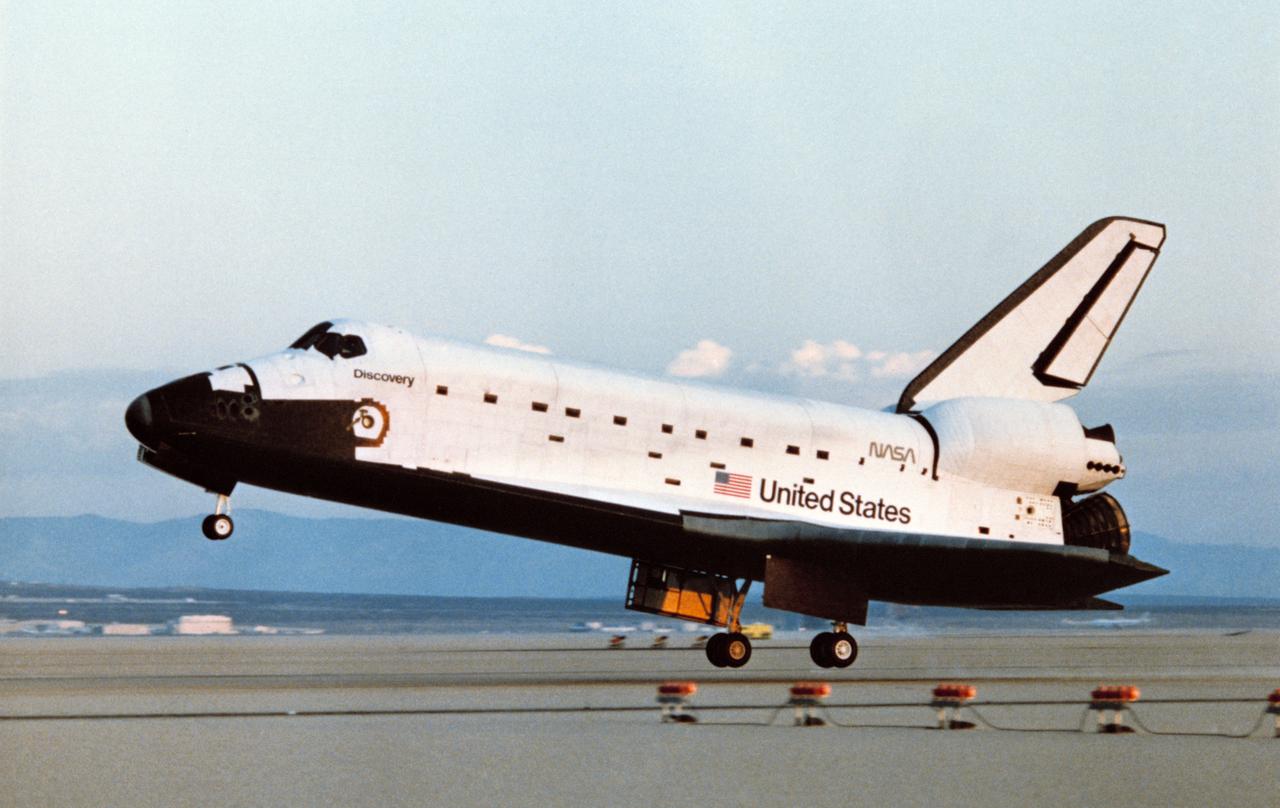

41D-3299 (5 Sept 1984) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery was captured on film just prior to touchdown on Runway 17 at Edwards Air Force Base to successfully complete a six-day mission in space. Inside were Henry W. Hartsfield, Jr., Michael L., Coats, Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, Steven A. Hawley, Judith A. Resnik and Charles D. Walker. Mission duration time was six days, 56 minutes and four seconds.
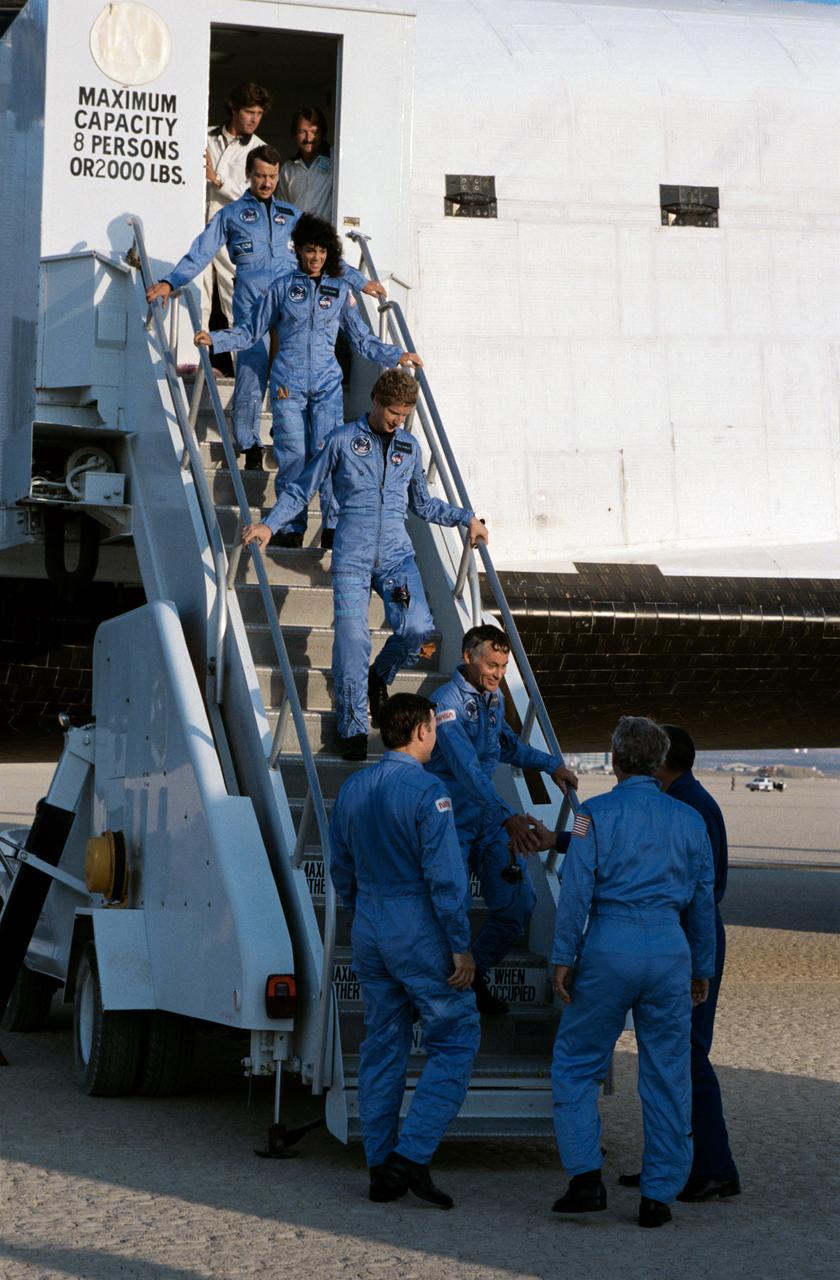

The crew of the STS 41-D mission exit the orbiter after landing at Edwards Air Force Base in California. Starting at the top of the ladder is Astronaut Charles D. Walker, payload specialist; Judith A. Resnik, mission specialist; Steven A. Hawley, mission specialist; and Richard M. Mike Mullane, mission specialist. Waiting at the bottom of the ramp are Astronaut Mike Coats (left), pilot and Henry W. Hartsfield, Jr. (center), crew commander.
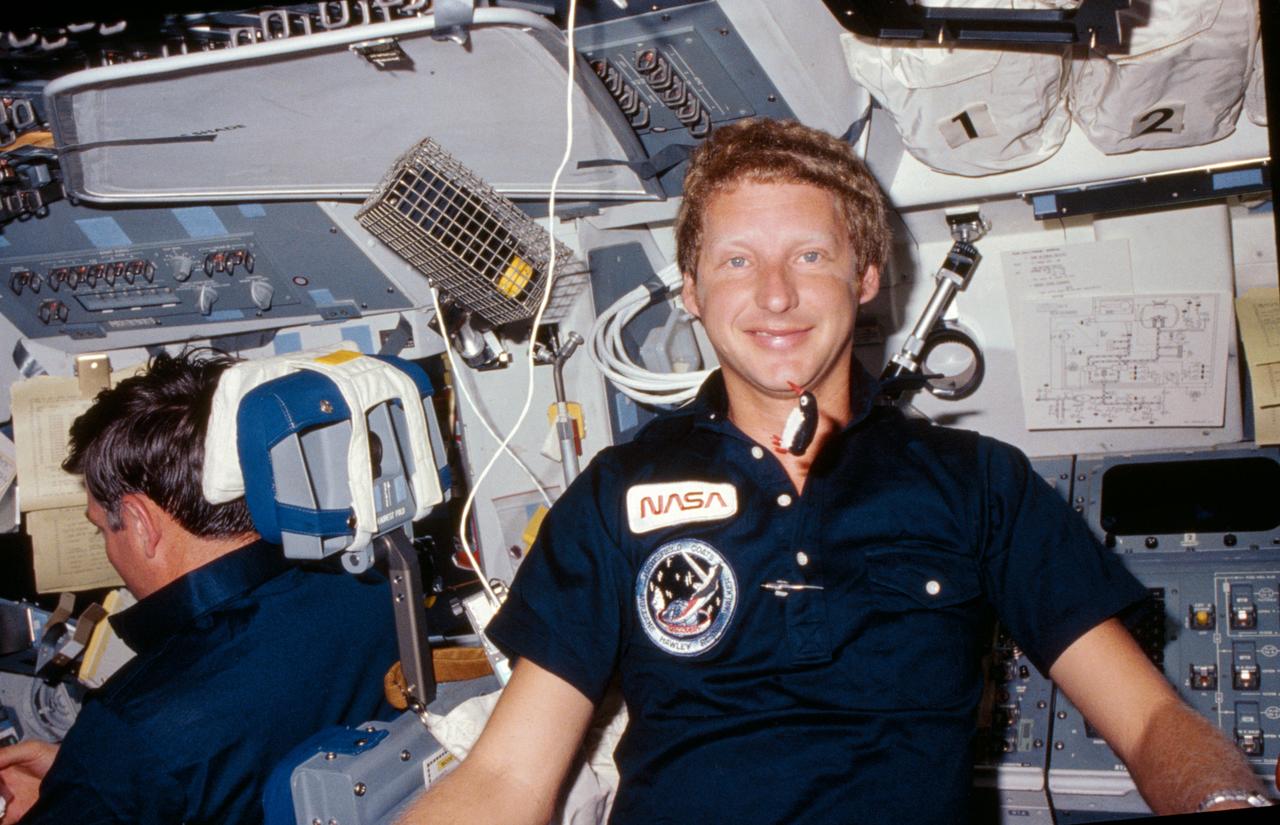

A tiny stuffed penguin floats in front of Mission specialist Steven Hawley as he sits at the mission specialists position behind the pilot on the flight deck.

41D-12-020 (6 Sept 1984) --- Astronaut Judith A. Resnik, mission specialist, anchors herself on the flight deck (out of frame) to take a peek at mid-deck activity aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery. Among the many stationary and portable cameras onboard the flight are (left to right) TV camera, a data acquisition motion picture camera and the IMAX.
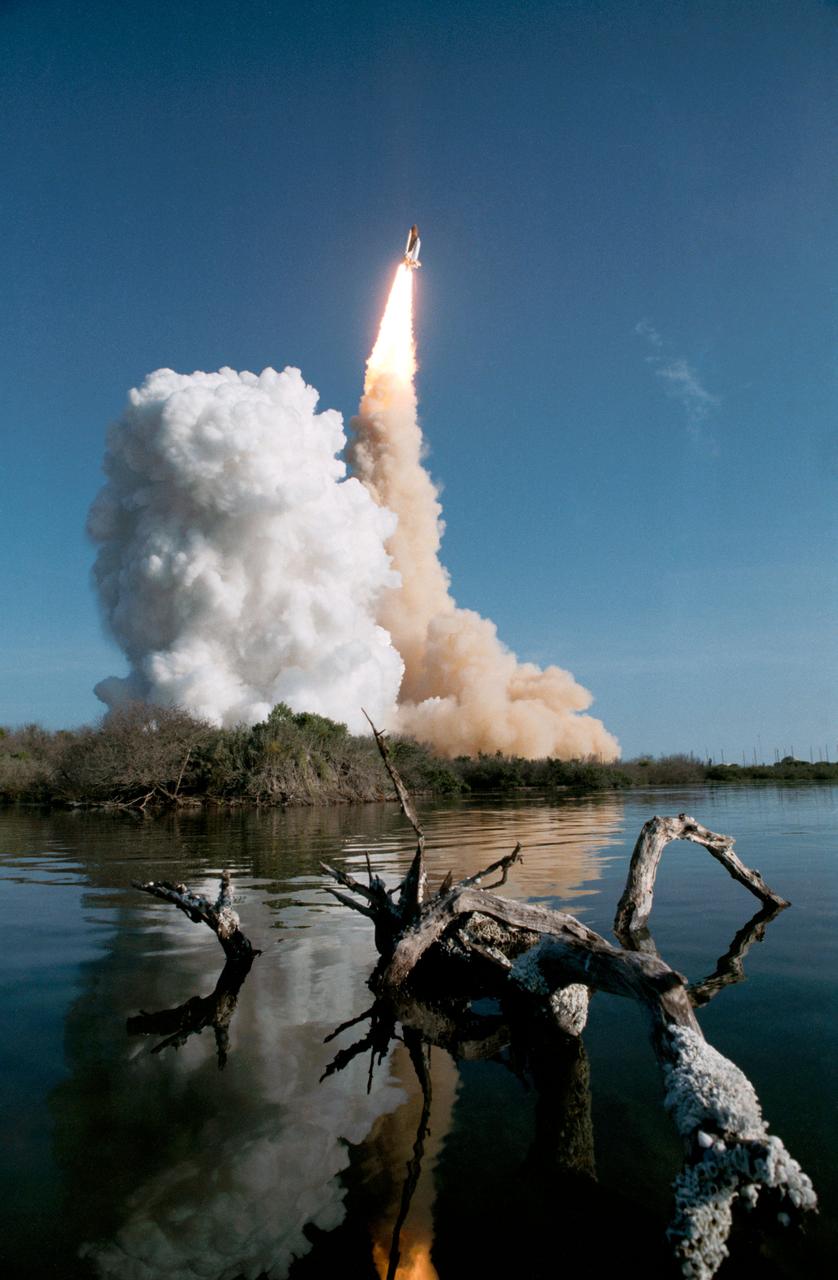

View of the launch of the shuttle Discovery and the 41-D mission. The orbiter and its plume of smoke are photographed from across the river in the early stages of liftoff (3085,3087); The orbiter can be seen just clearing the pad, with a cloud of smoke billowing to the left of the frame. The orbiters two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and external tank are visible along with the orbiter (3086).
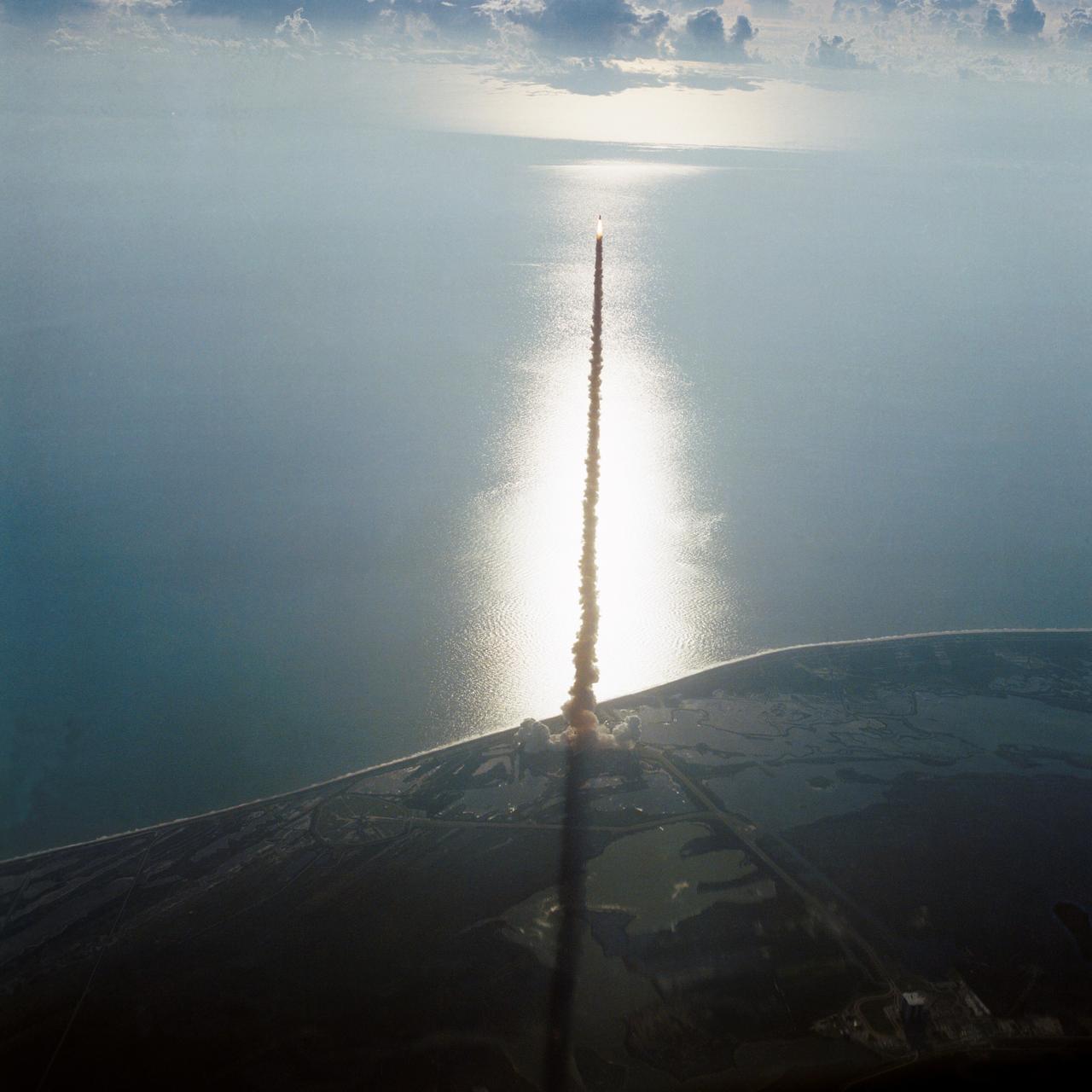

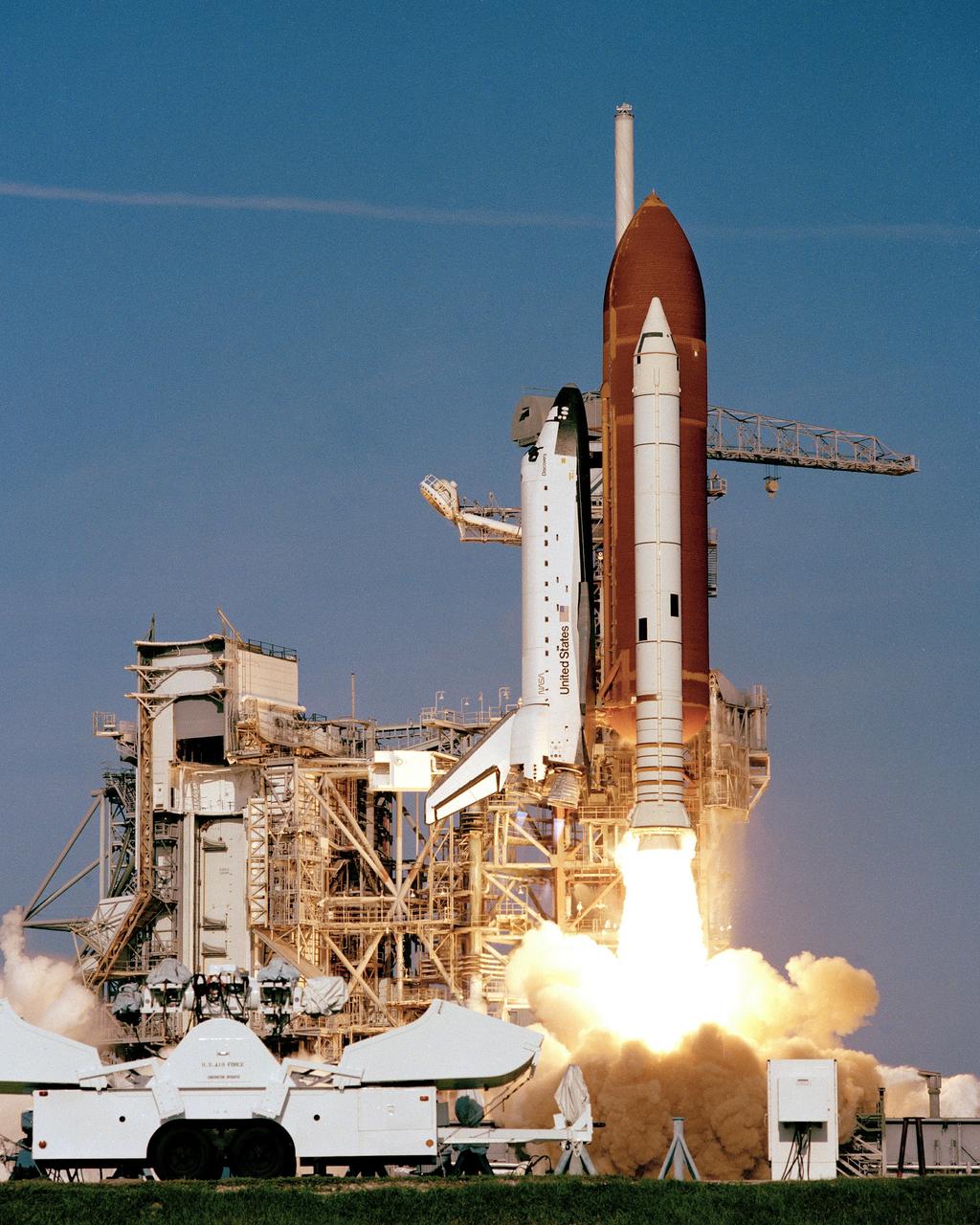
41D-3063 (30 Aug. 1984) --- The space shuttle Discovery climbs toward Earth orbit following a successful liftoff from KSC's Pad 39A at 8:41:50 a.m. (EDT), Aug. 30, 1984. Inside the spacecraft are six crewmembers looking forward to a busy week in space. The scene was photographed by astronaut John W. Young in the Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA). Photo credit: NASA
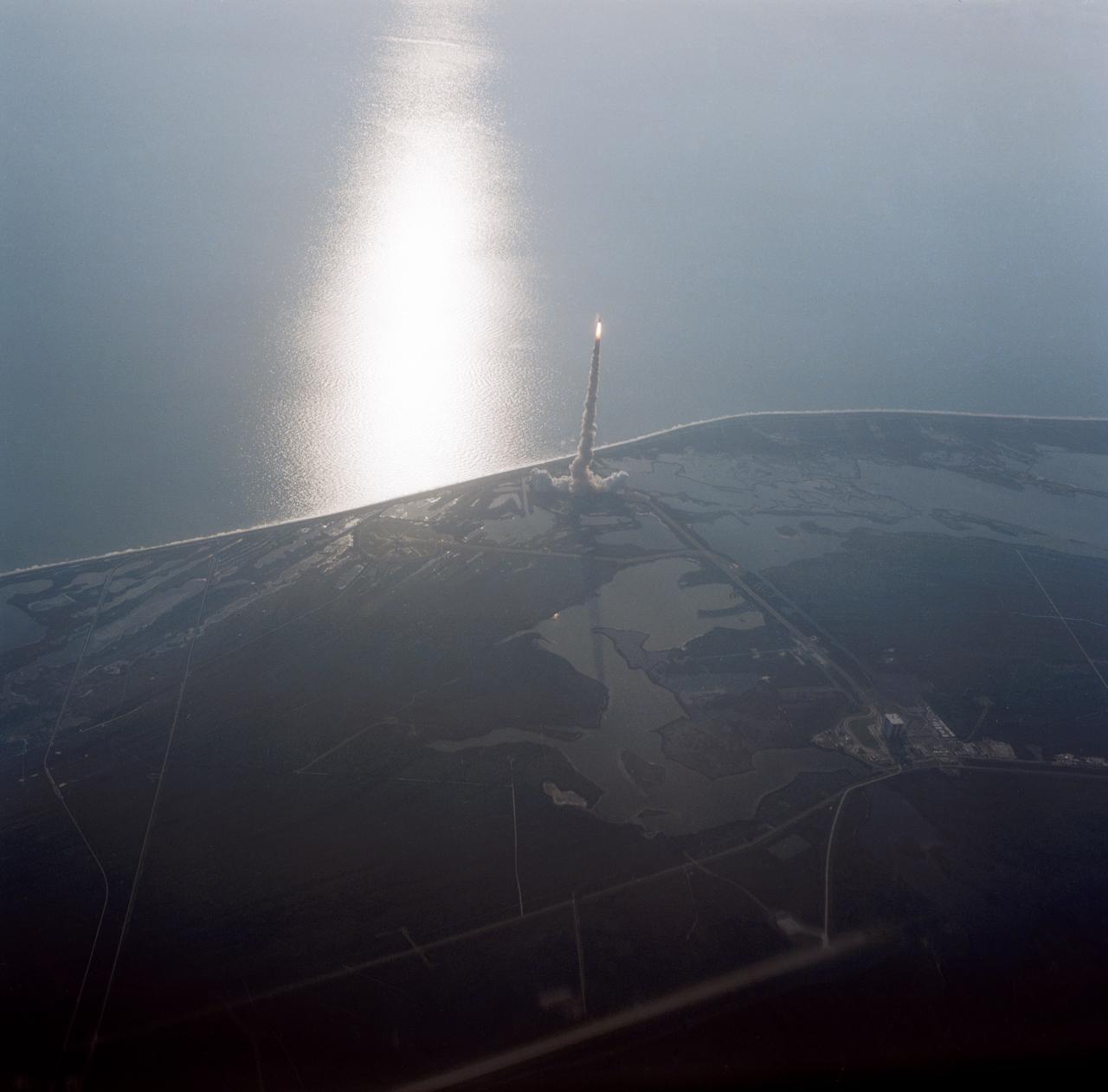

41D-3071 (30 Aug. 1984) --- The space shuttle Discovery climbs toward Earth orbit following a successful liftoff from KSC's Pad 39A at 8:41:50 a.m. (EDT), Aug. 30, 1984. Inside the spacecraft are six crewmembers looking forward to a busy week in space. The scene was photographed by astronaut John W. Young in the Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA). Photo credit: NASA
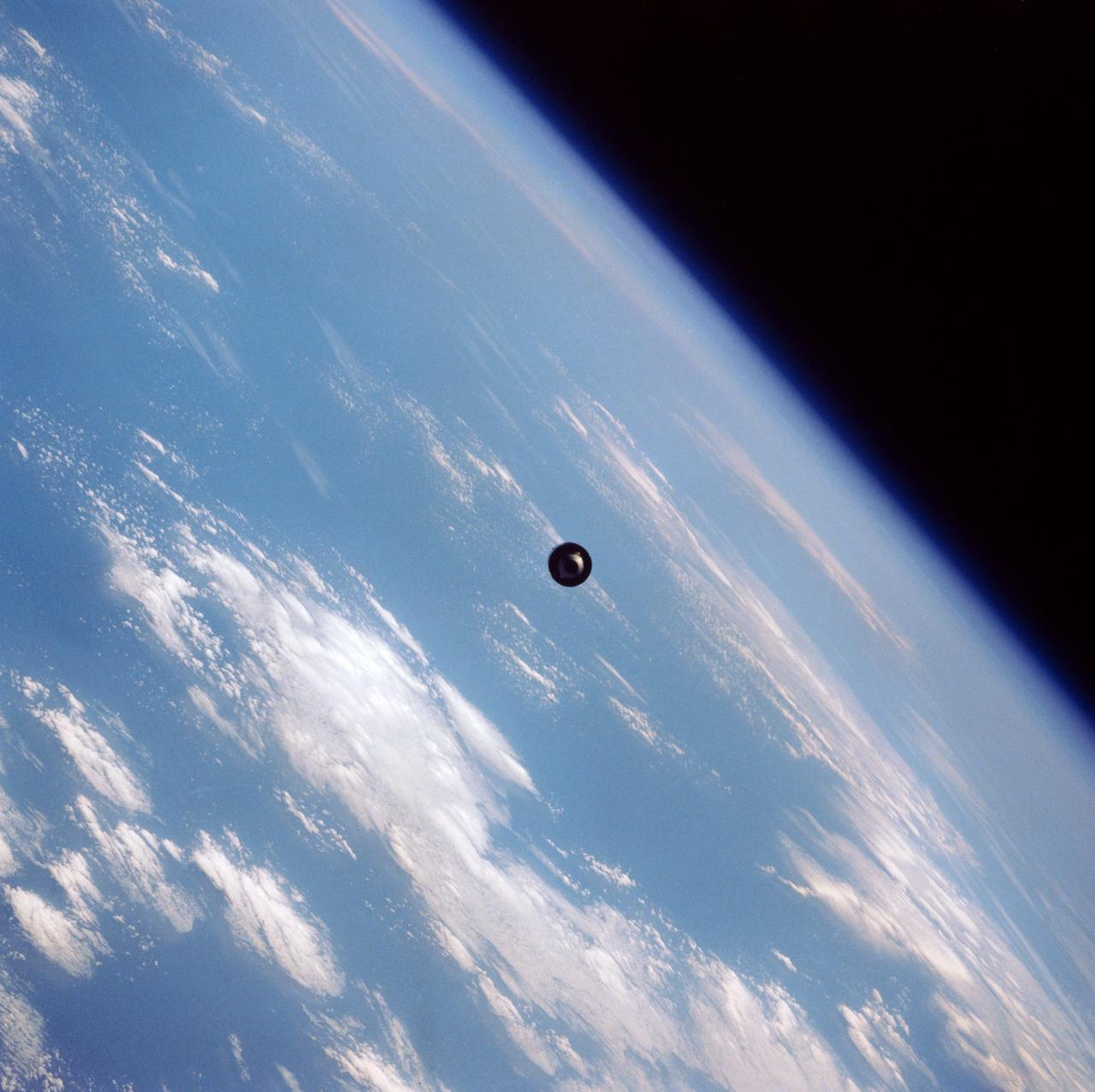

41D-39-068 (1 Sept 1984) --- Quickly moving away from the Space Shuttle Discovery is the Telstar 3 communications satellite, deployed September 1, 1984. The 41-D crew successfully completed three satellite placements, of which this was the last. Telstar was the second 41-D deployed satellite to be equipped with a payload assist module (PAM-D). The frame was exposed with a 70mm camera.

41D-3391 (10 April 1984) --- Astronaut Michael L. Coats positions himself for a photographic briefing during a training session for 41-D crew members in the shuttle one-g trainer at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Coats will assume pilot duties aboard the space shuttle Discovery for the scheduled seven-day 41-D mission in late June. This photograph was taken for NASA by Otis Imboden.
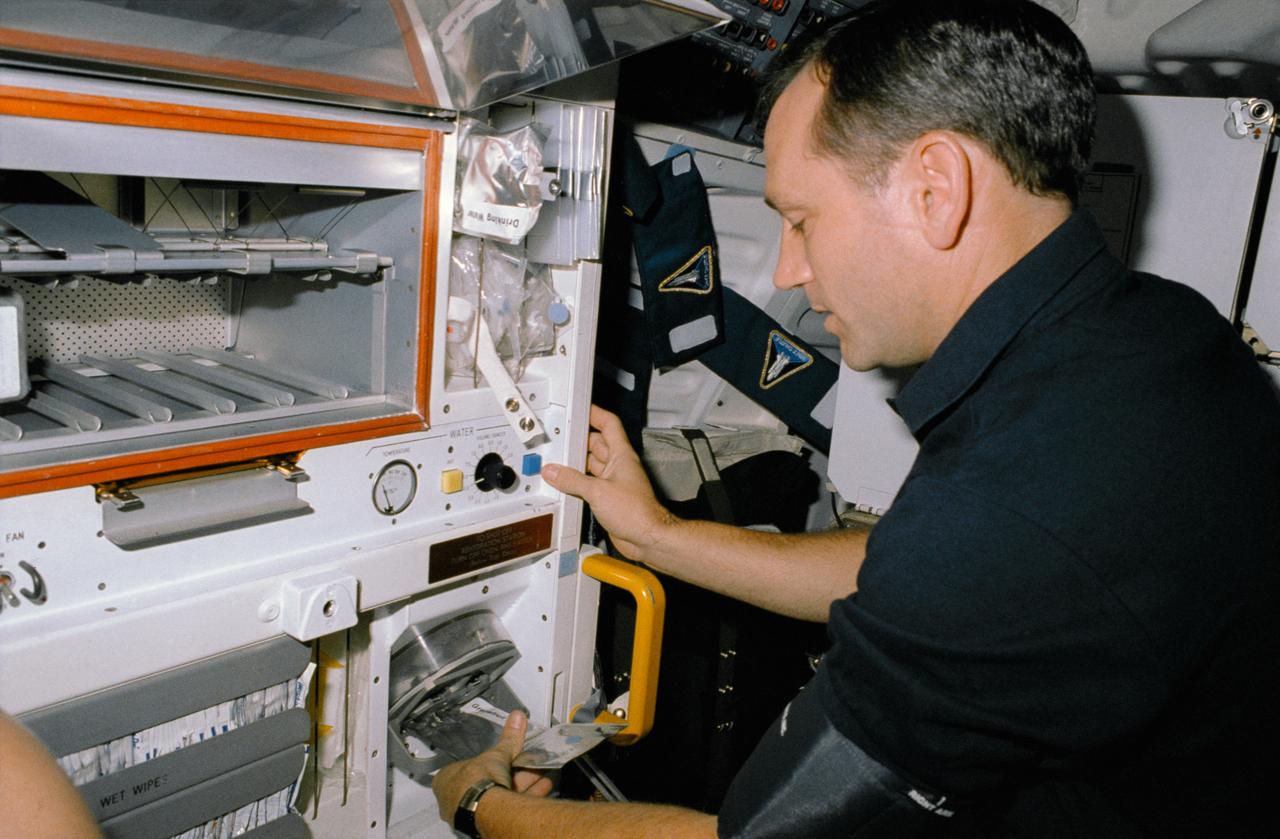

STS041-06-004 (6-10 Oct 1990) --- A 35mm scene of astronaut Thomas D. Akers, STS-41 mission specialist, using Space Shuttle Discovery?s galley water feed to rehydrate a package of food.

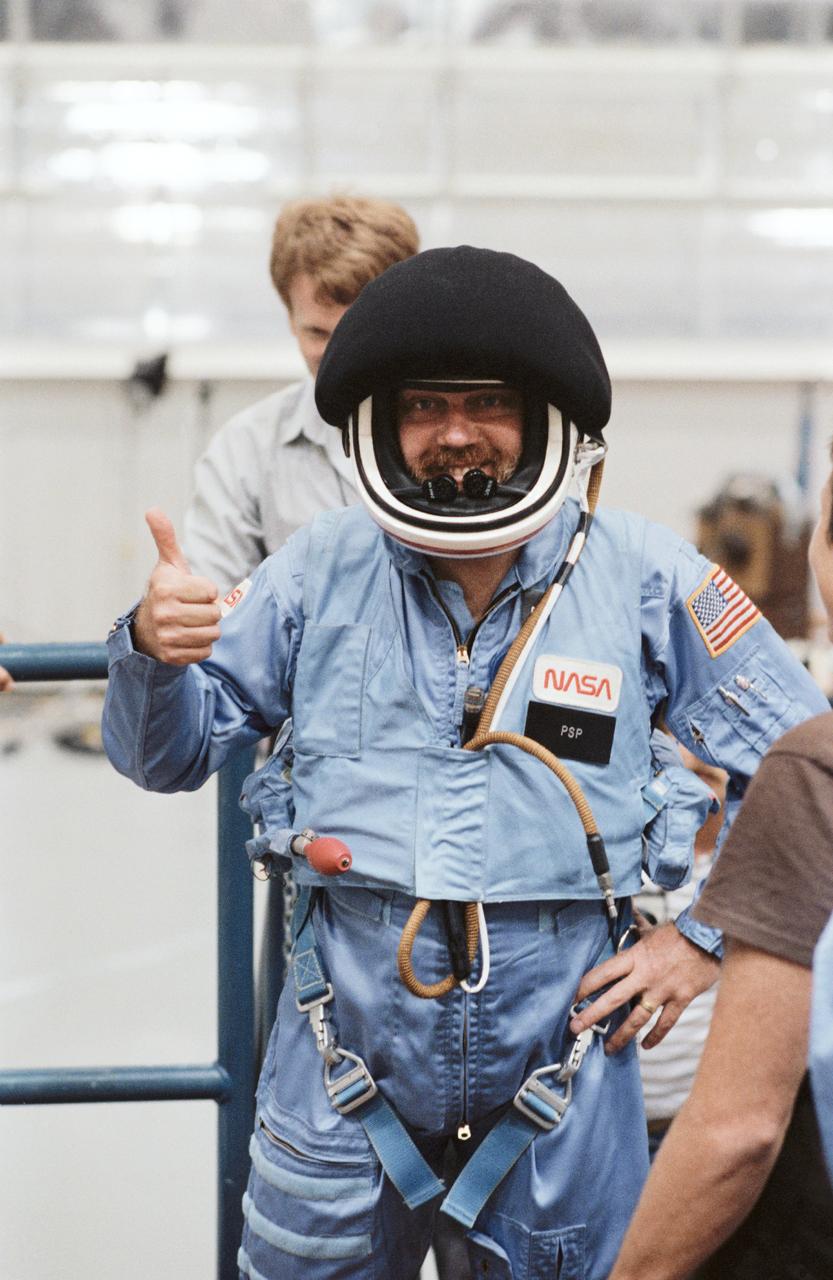
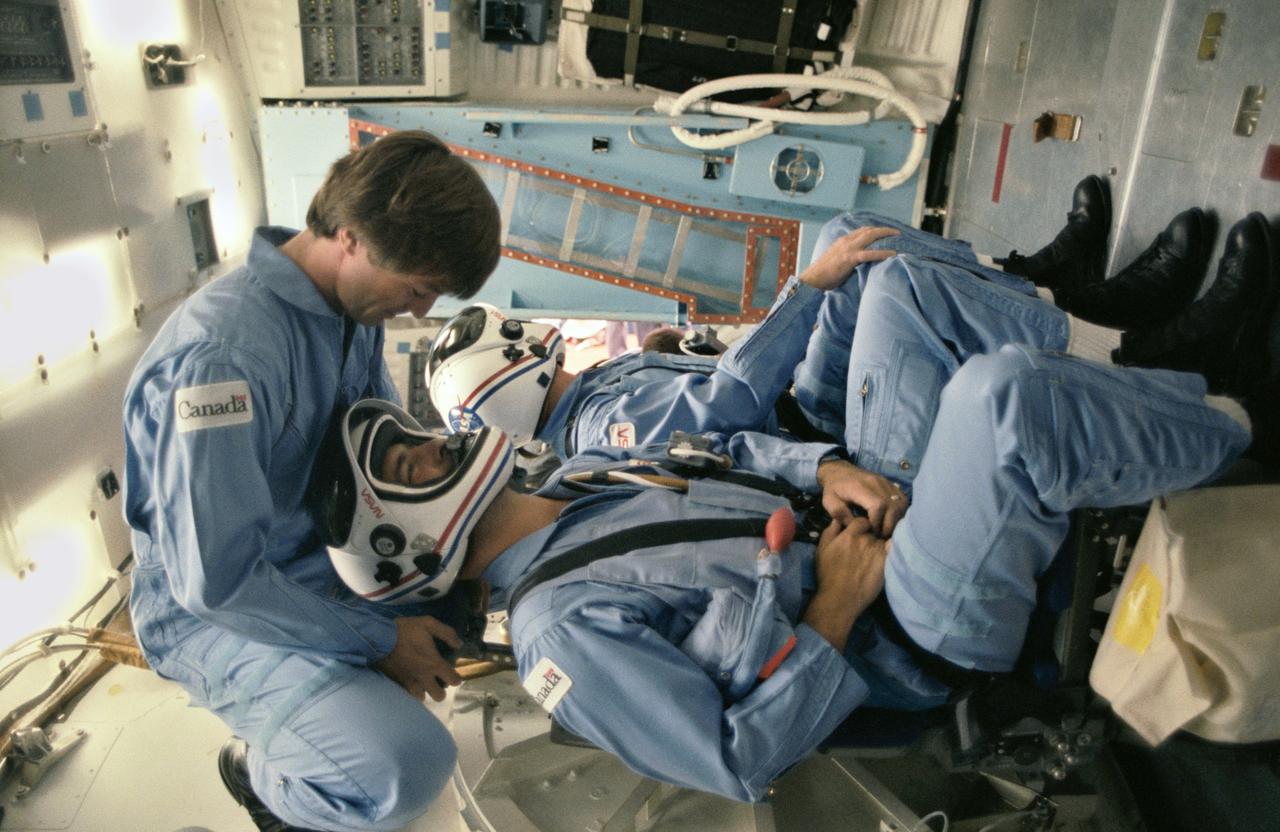
The 41-D crewmembers participate in suiting exercises in the weightless environment of the KC-135 aircraft.
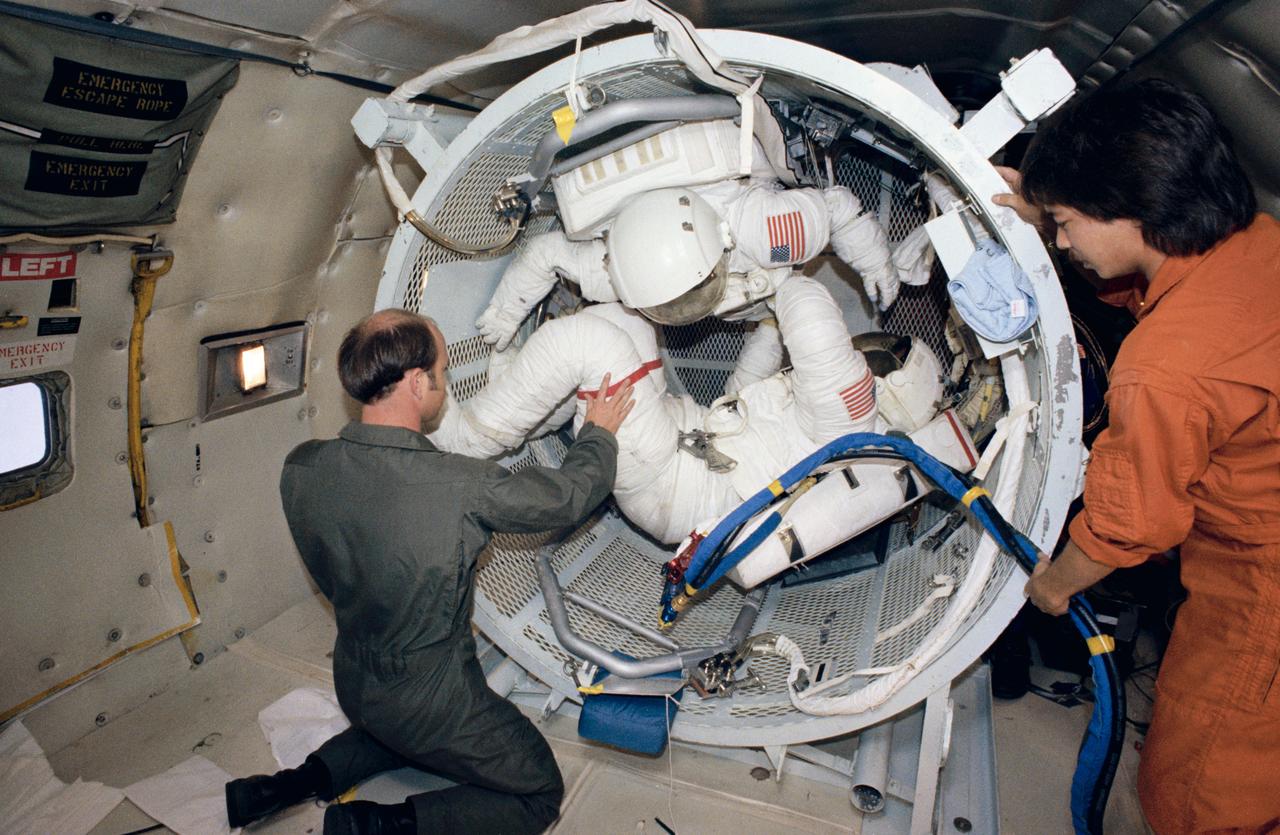
The 41-D crewmembers participate in suiting exercises in the weightless environment of the KC-135 aircraft.
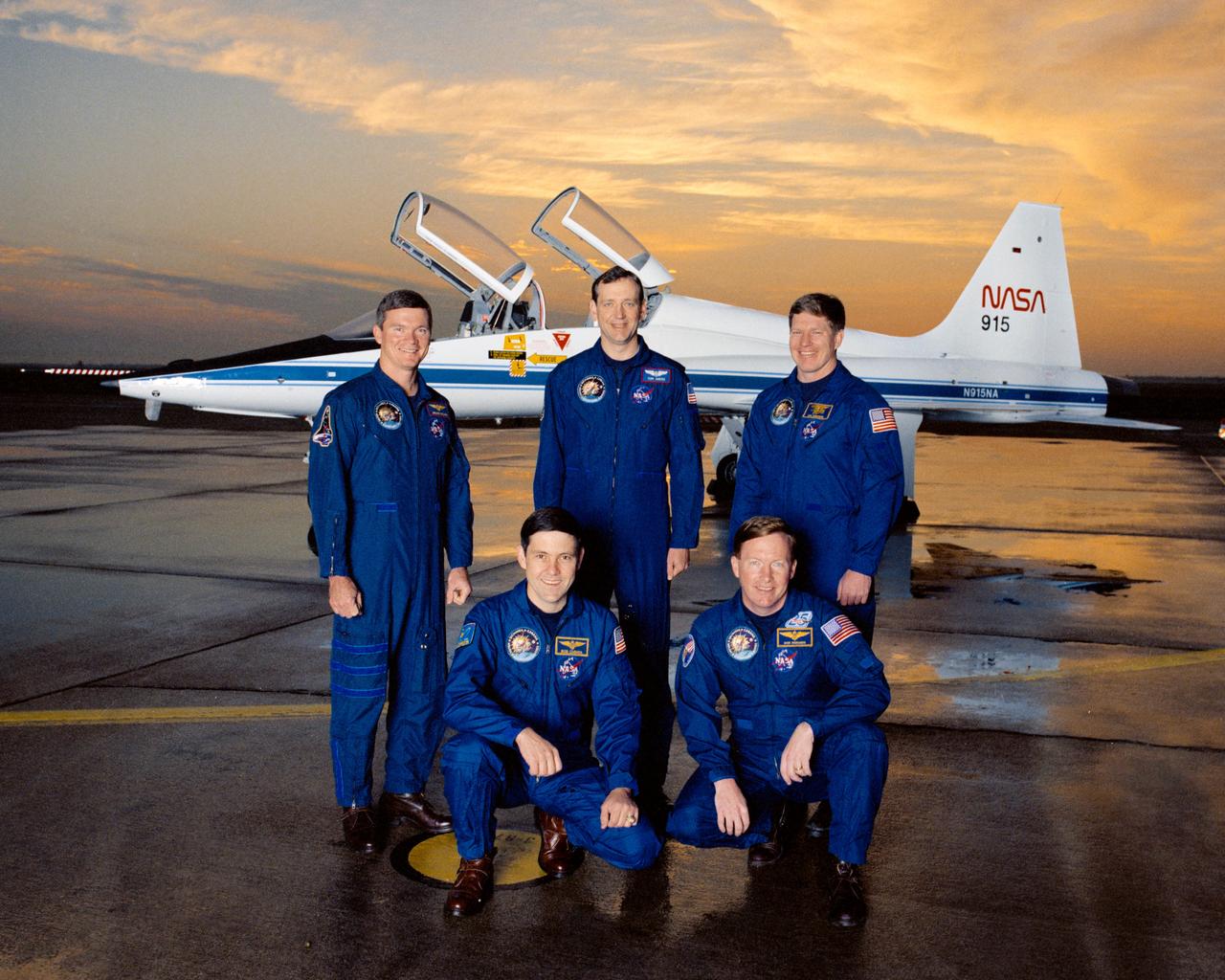

STS041-S-002 (7 May 1990) --- These five astronauts have been assigned to fly the STS-41 mission for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Pictured near the flight line at Ellington Field prior to an early morning flight in NASA T-38s are (kneeling, from the left) Robert D. Cabana, pilot; and Richard N. Richards, mission commander; and (standing, from left) Bruce E. Melnick, Thomas D. Akers and William M. Shepherd, all mission specialists. Primary payload for the Space Shuttle Discovery on the STS 41 mission is Ulysses.
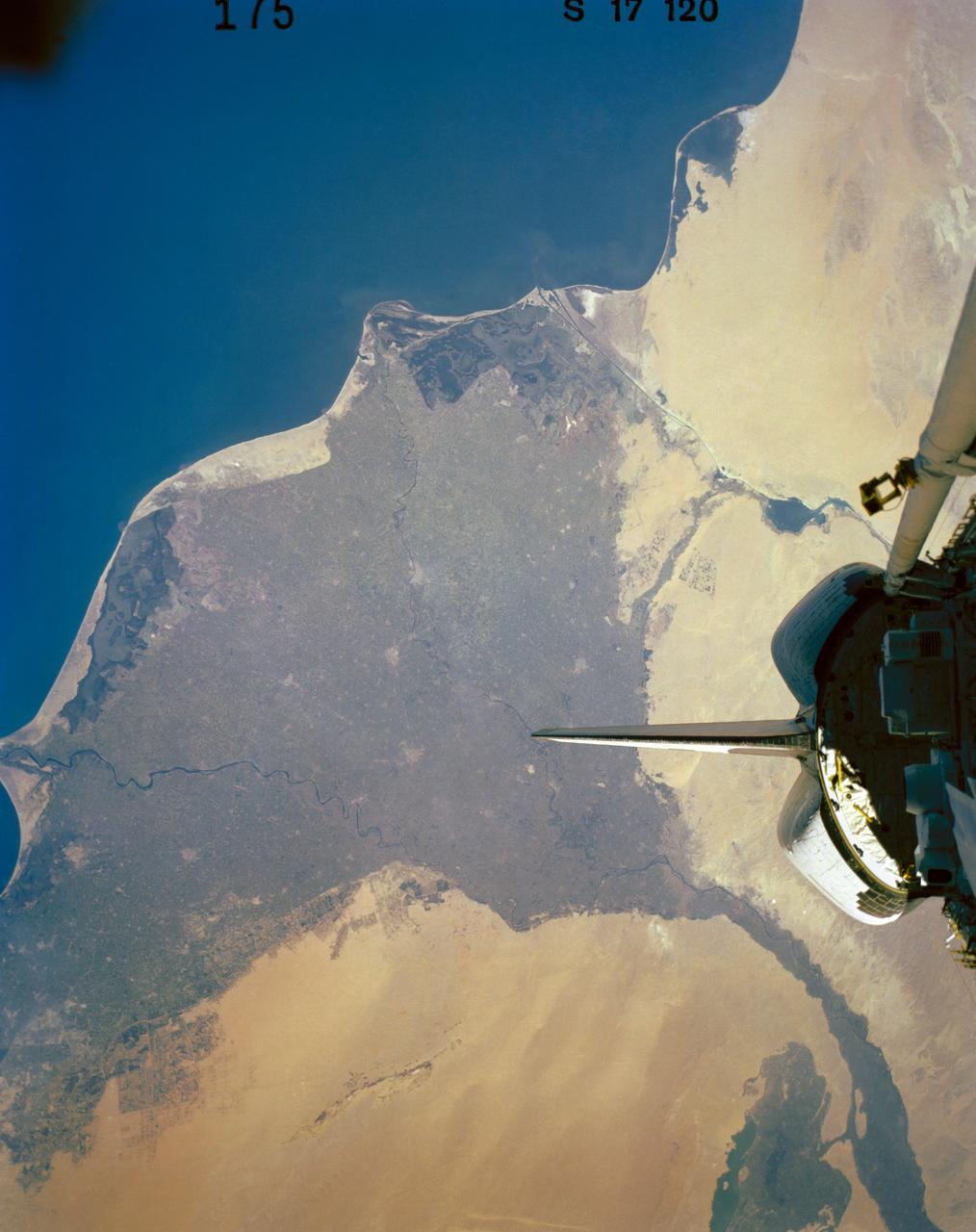

41G-120-175 (5-13 Oct. 1984) --- Egypt and the Nile River Delta are easily recognizable in this 250mm frame photographed by one of the seven 41-G crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger. Cairo and the Egyptian pyramids are also visible in the lower left side of this photograph. The 41-G crew consisted of astronauts Robert L. Crippen, commander, Jon A. McBride, pilot; Mission Specialists Kathryn D. Sullivan, Sally K. Ride, and David D. Leestma; along with Canadian astronaut Marc Garneau; and Paul D. Scully-Power, both payload specialists. Photo credit: NASA
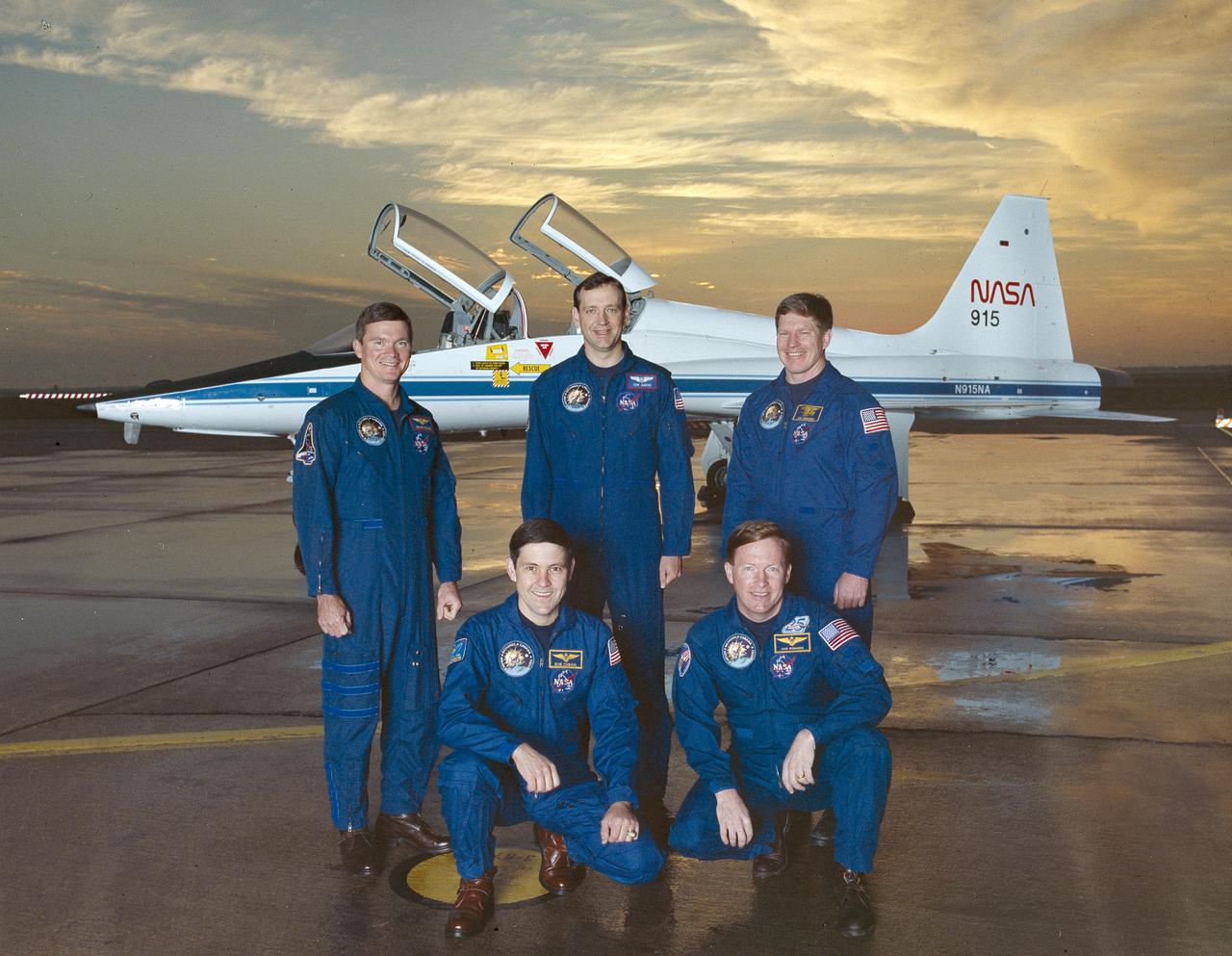

The 5 member crew of the STS-41 mission included (left to right): Bruce E. Melnick, mission specialist 2; Robert D. Cabana, pilot; Thomas D. Akers, mission specialist 3; Richard N. Richards, commander; and William M. Shepherd, mission specialist 1. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on October 6, 1990 at 7:47:15 am (EDT), the primary payload for the mission was the ESA built Ulysses Space Craft made to explore the polar regions of the Sun. Other main payloads and experiments included the Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet (SSBUV) experiment and the INTELSAT Solar Array Coupon (ISAC).
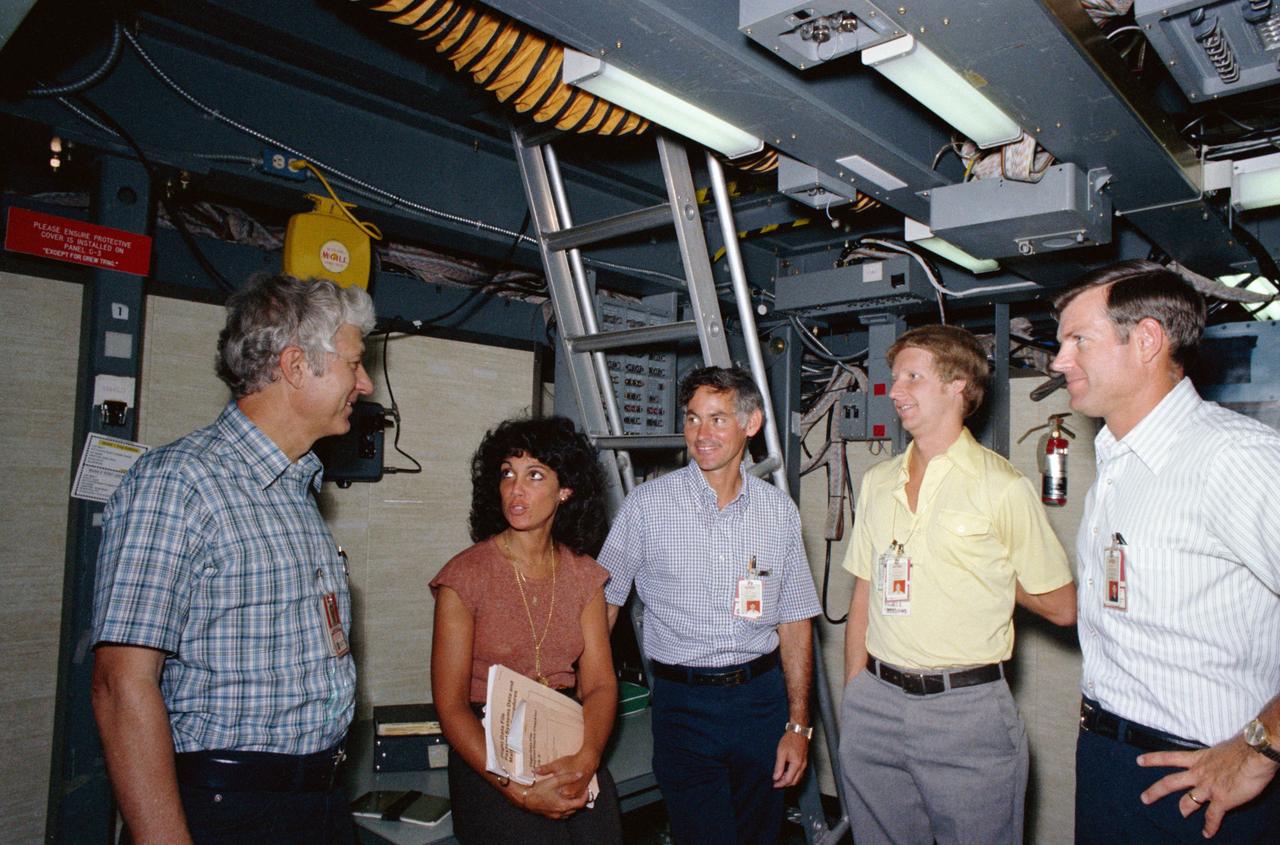

View of STS 41-D mission crew training in Shuttle Mission simulator. From left to right are Henry Hartsfield, Jr., commander; mission specialists Judith Resnik, Richard Mullane, and Steven Hawley; and Michael Coats, pilot. They appear to be standing in the middeck mockup, preparing for training.
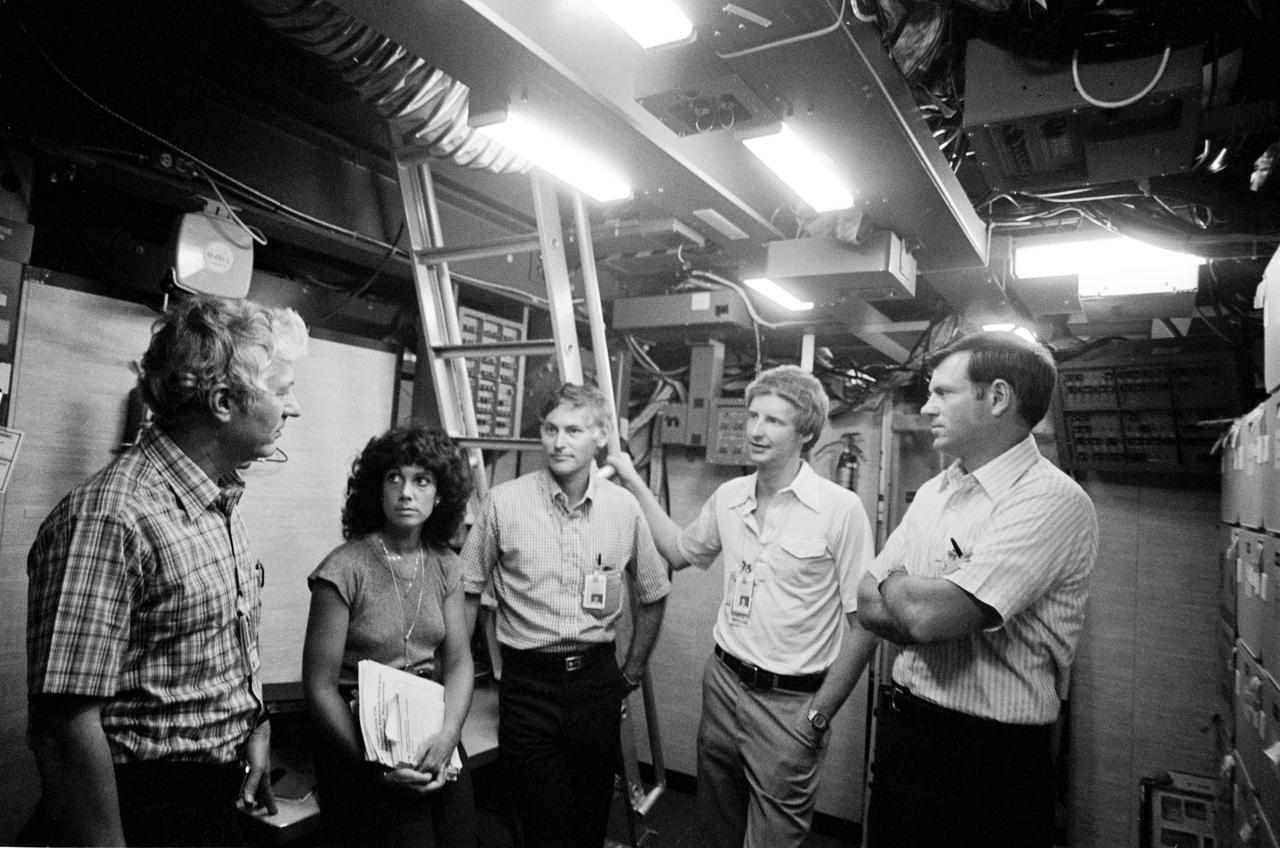

View of STS 41-D mission crew training in Shuttle Mission simulator. From left to right are Henry Hartsfield, Jr., commander; mission specialists Judith Resnik, Richard Mullane, and Steven Hawley; and Michael Coats, pilot. They appear to be standing in the middeck mockup, preparing for training.
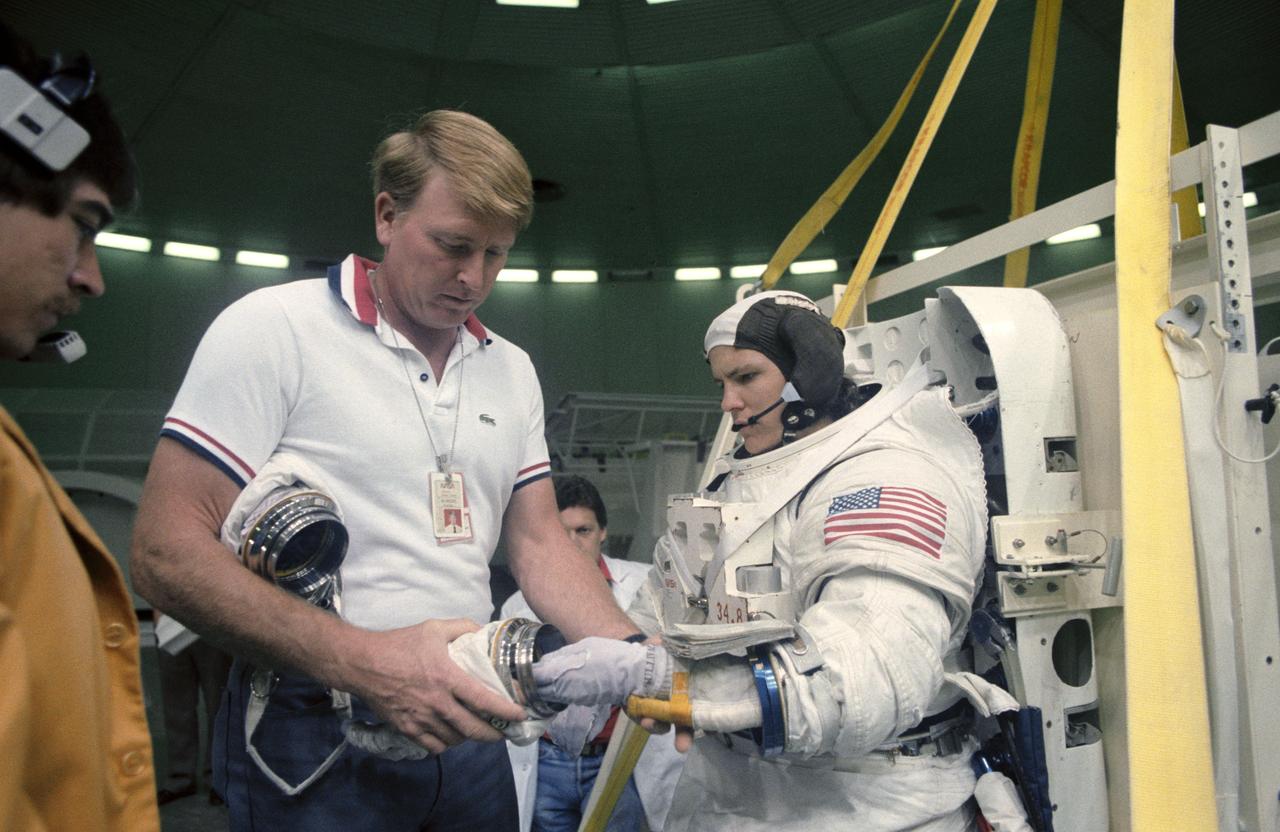

S84-33898 (21 May 1984) --- Astronaut Jon A. McBride, 41-G pilot, assists his crewmate, Astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan with the glove portion of her extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) prior to Dr. Sullivan's underwater session in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Mission specialists Sullivan and David C. Leestma are scheduled for extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Columbia for NASA's 17th scheduled flight.
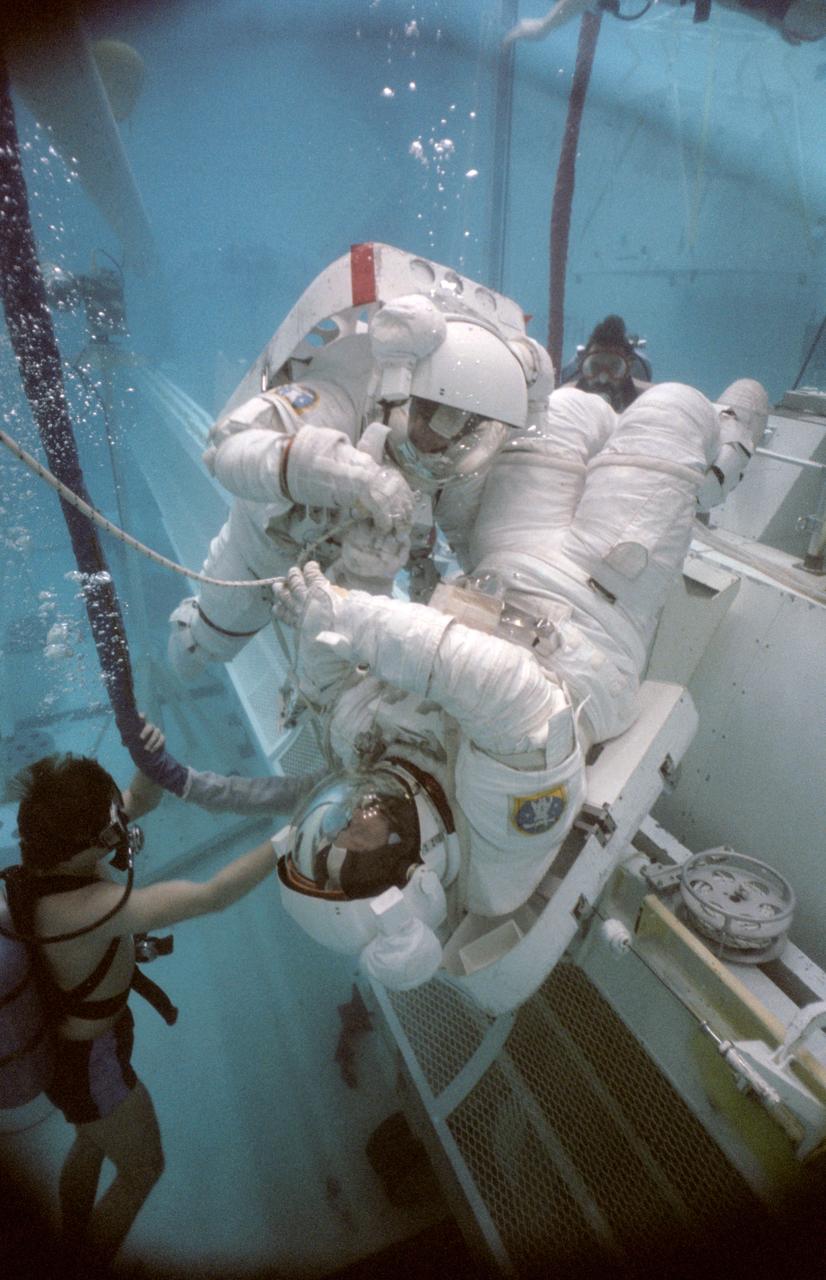

S84-28206 (26 Feb 1984) --- Astronauts Richard M. (Mike) Mullane (with striped suit and PLSS) and Steven A. Hawley participate in and underwater simulation of a 41-D contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F). All Shuttle crews, many of which are not scheduled for definite EVAs, possess team members trained to perform in space certain tasks normally done remotely in the event of systems failures. Among those contingent tasks is the manual closing of the payload bay doors. Mullane and Hawley are two of three mission specialists assigned duty on the seven-day 41-D flight. This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
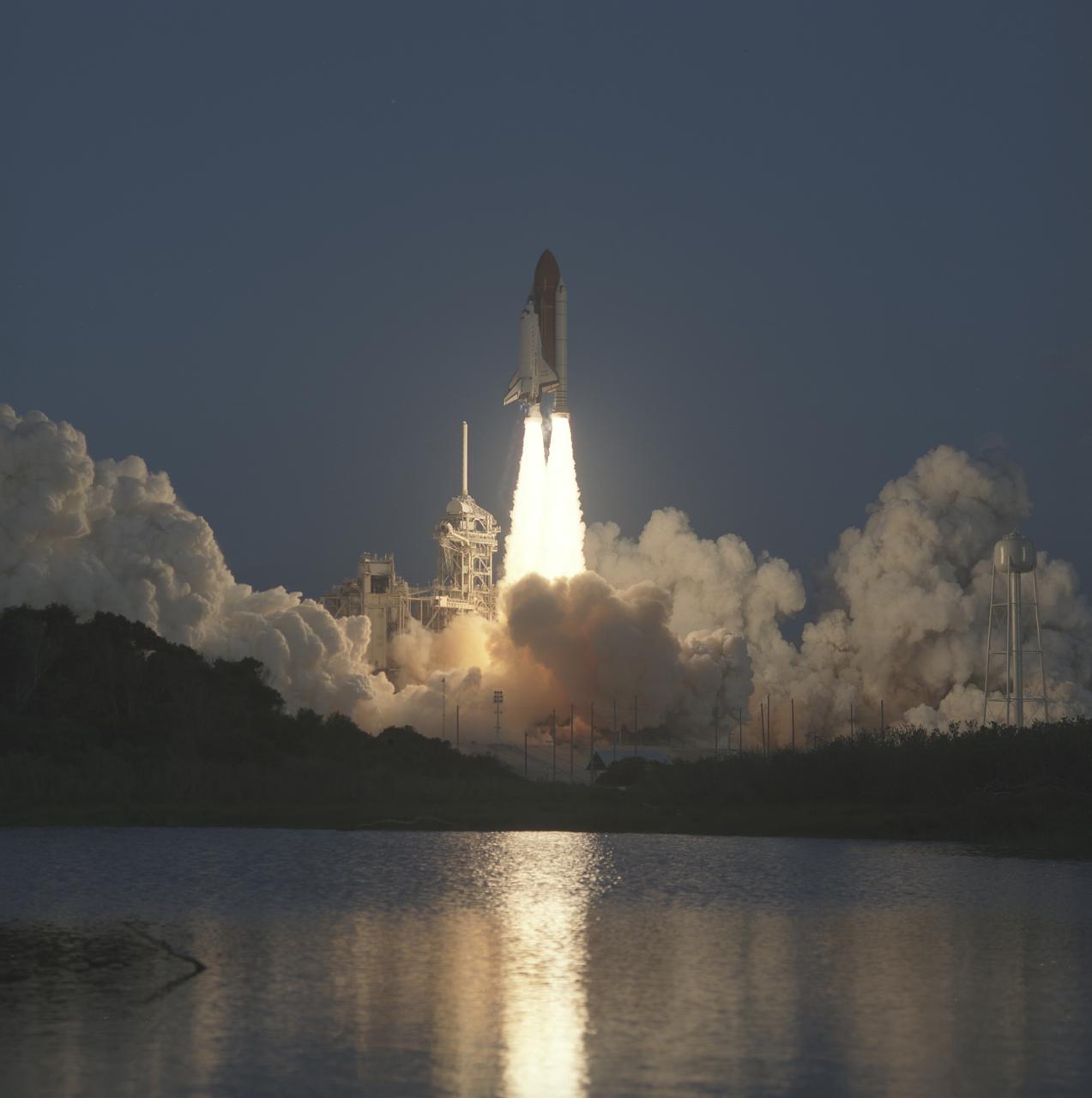

Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on October 6, 1990 at 7:47:15 am (EDT), the STS-41 mission consisted of 5 crew members. Included were Richard N. Richards, commander; Robert D. Cabana, pilot; and Bruce E. Melnick, Thomas D. Akers, and William M. Shepherd, all mission specialists. The primary payload for the mission was the European Space Agency (ESA) built Ulysses Space Craft made to explore the polar regions of the Sun. Other main payloads and experiments included the Shuttle Solar Backscatter Ultraviolet (SSBUV) experiment and the INTELSAT Solar Array Coupon (ISAC).
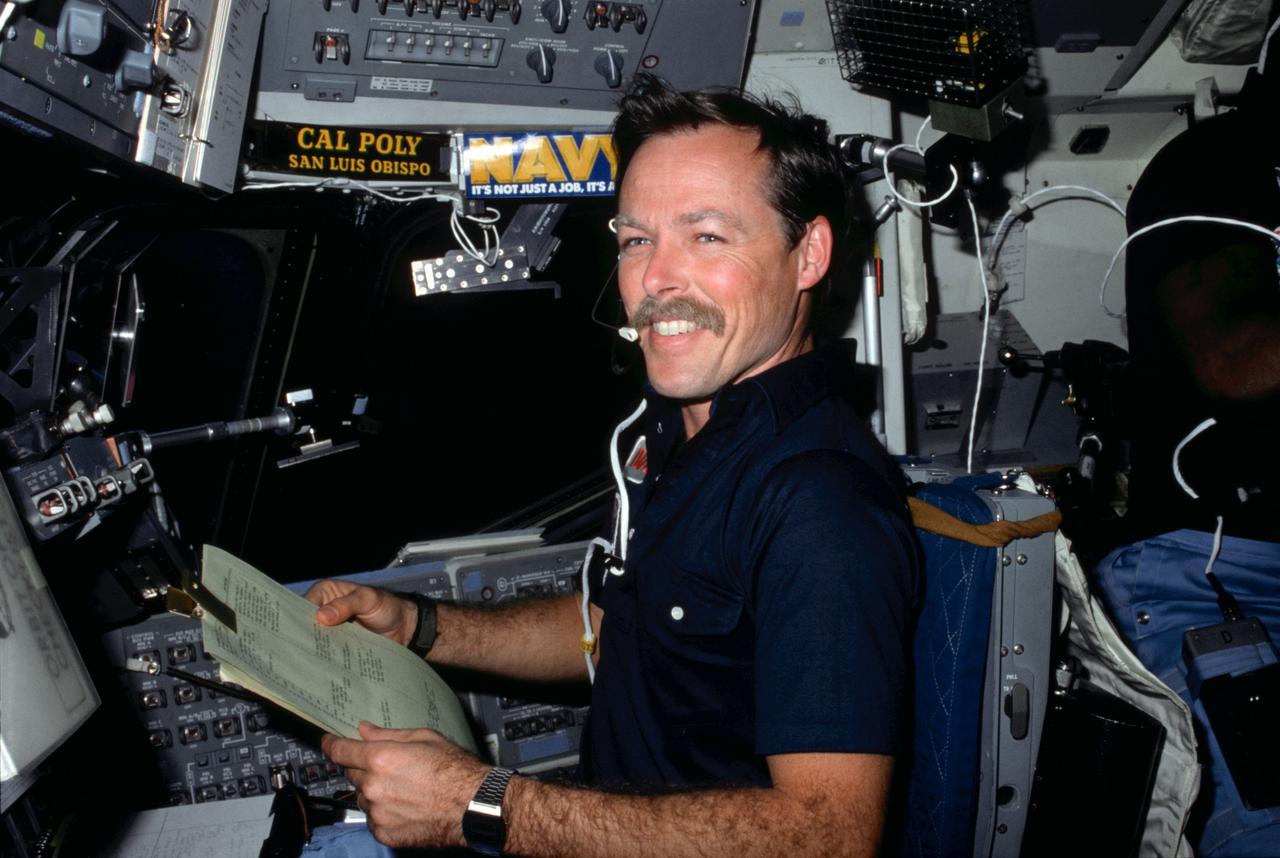

41B-07-230 (S84-27027) (3-11 February 1984) ---Astronaut Robert L. Gibson, 41-B pilot, reviews some teleprinter copy on the flight deck?s starboard station during the eight-day 41-B Space Shuttle mission. Four other astronauts share the Challenger with Gibson. They are Astronauts Vance D. Brand, commander; and Ronald E. McNair, Bruce McCandless II and Robert L. Stewart, all mission specialists. The photograph was taken from the commander?s station with a 35mm camera.
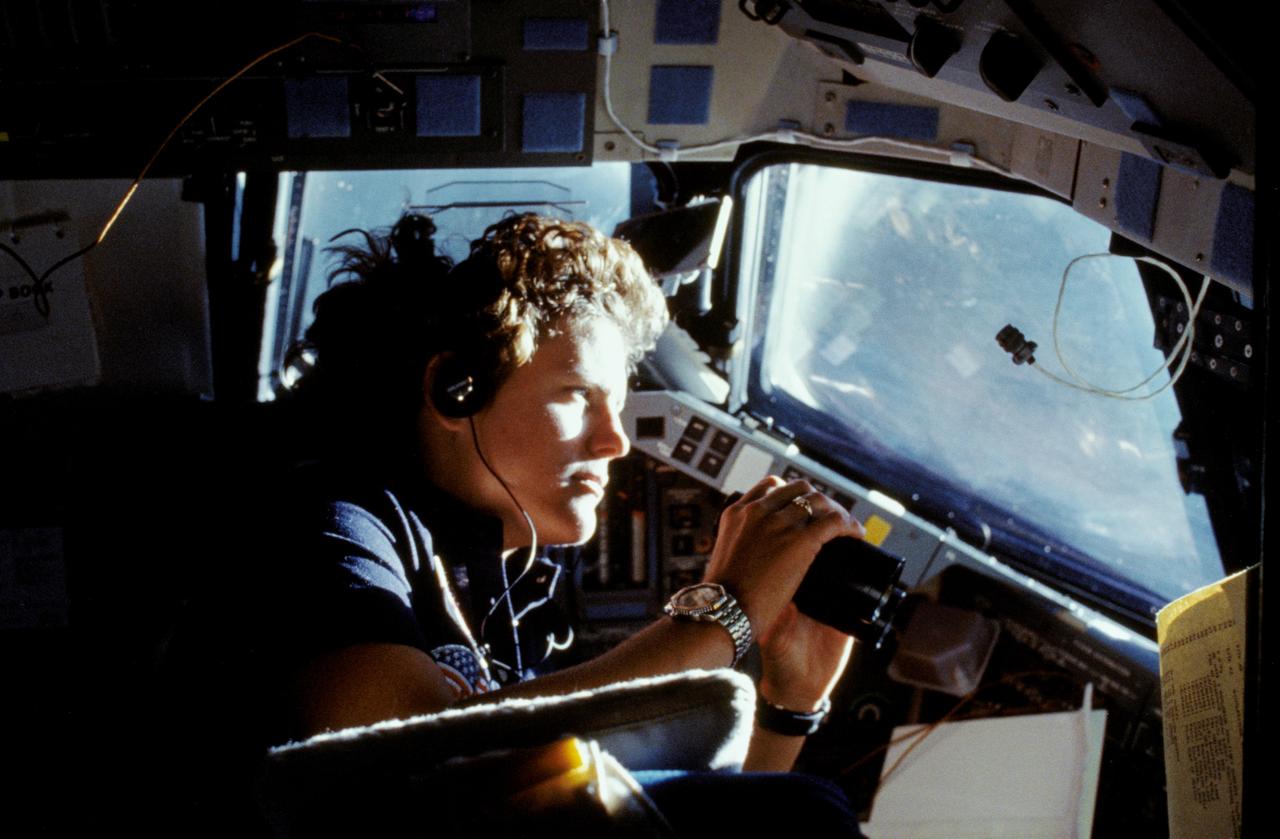

41G-11-027 (14 Oct. 1984) --- Kathryn D. Sullivan, 41-G mission specialist, uses a pair of binoculars to do some magnified viewing through the forward cabin windows of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger. The 35mm frame was part of the first photographic release from the eight-day 41-G mission on Oct. 14, 1984. Photo credit: NASA
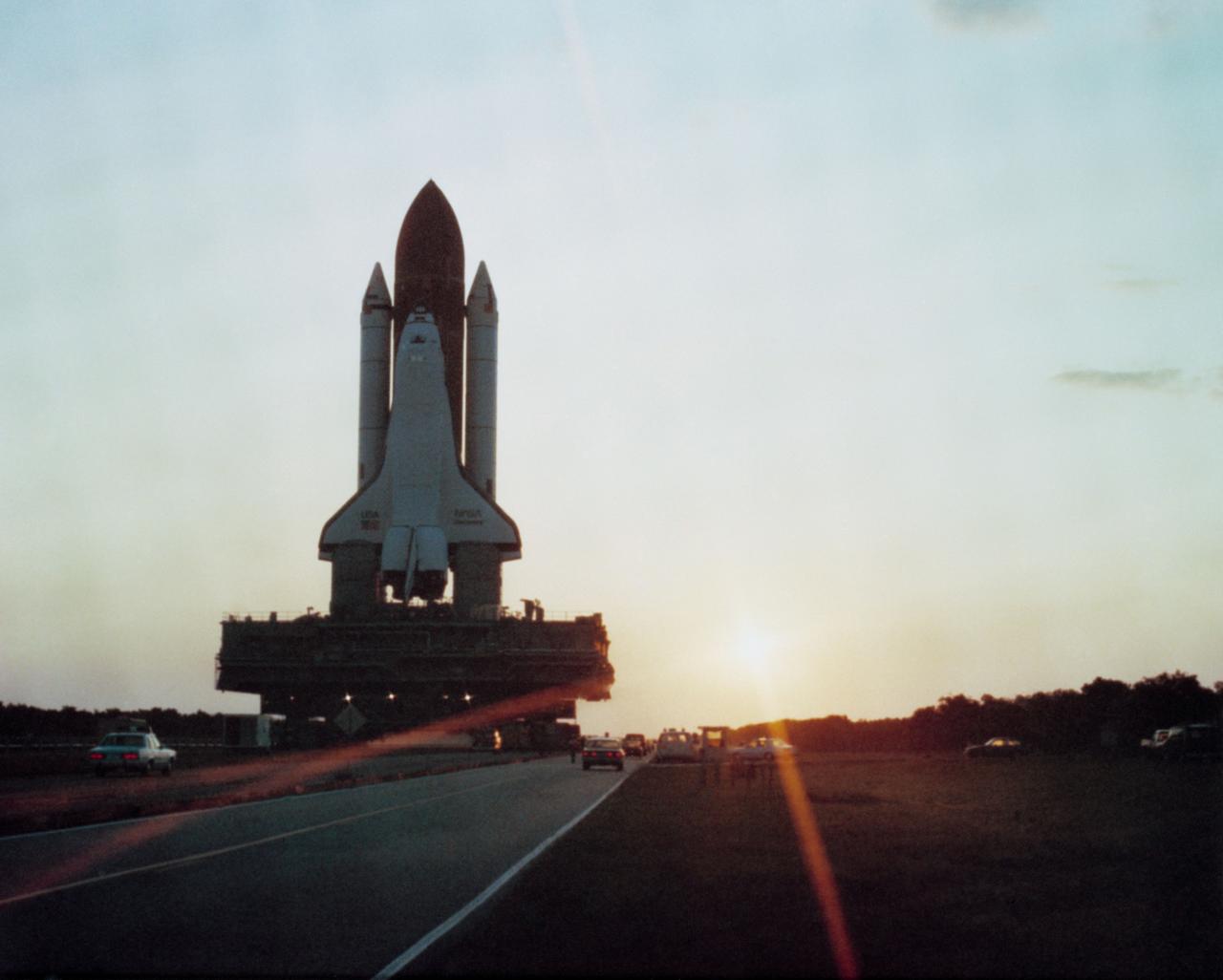

S86-41700 (19 May 1984) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery moves towards Pad A on the crawler transporter for its maiden flight. Discovery will be launched on its first mission no earlier than June 19, 1984. Flight 41-D will carry a crew of six; Commander Henry Hartsfield, Pilot Mike Coats, Mission Specialists Dr. Judith Resnik, Dr. Steven Hawley and Richard Mullane and Payload Specialist Charles Walker. Walker is the first payload specialist to fly aboard a space shuttle. He will be running the materials processing device developed by McDonnell Douglas as part of its Electrophoresis Operations in Space project. Mission 41-D is scheduled to be a seven-day flight and to land at Edwards Air Force Base in California. The Syncom IV-1 (LEASAT) will be deployed from Discovery's cargo bay and the OAST-1, Large Format Camera, IMAX and Cinema 360 cameras will be aboard.

The official mission insignia for the 41-D Space Shuttle flight features the Discovery - NASA's third orbital vehicle - as it makes its maiden voyage. The ghost ship represents the orbiter's namesakes which have figured prominently in the history of exploration. The Space Shuttle Discovery heads for new horizons to extend that proud tradition. Surnames for the crewmembers of NASA's eleventh Space Shuttle mission encircle the red, white, and blue scene.
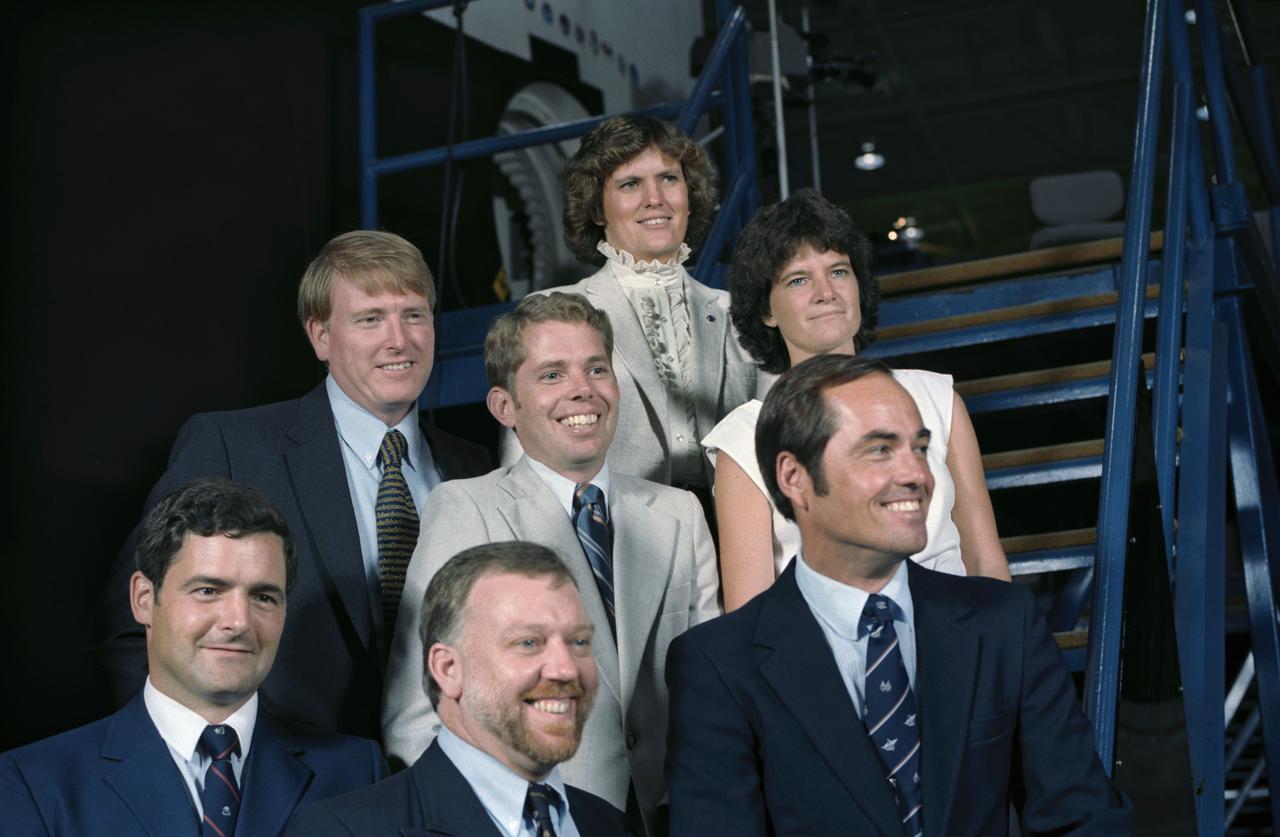

41D-3277 (S14-3277) (4 Sept 1984) --- Having met the press for the first time as a group, members of the STS 41-G crew pose for photographs in the Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory at the Johnson Space Center. They are (bottom row, left, to right) Marc Garneau and Paul D. Scully-Power, both payload specialists; and Robert L. Crippen, crew commander; (second row, l.-r.) Astronauts Jon A. McBride, pilot; David C. Leestma and Sally K. Ride, both mission specialists; and Kathryn D. Sullivan, mission specialist. They are scheduled for an October 5, 1984 launch aboard the Space Shuttle Challenger.
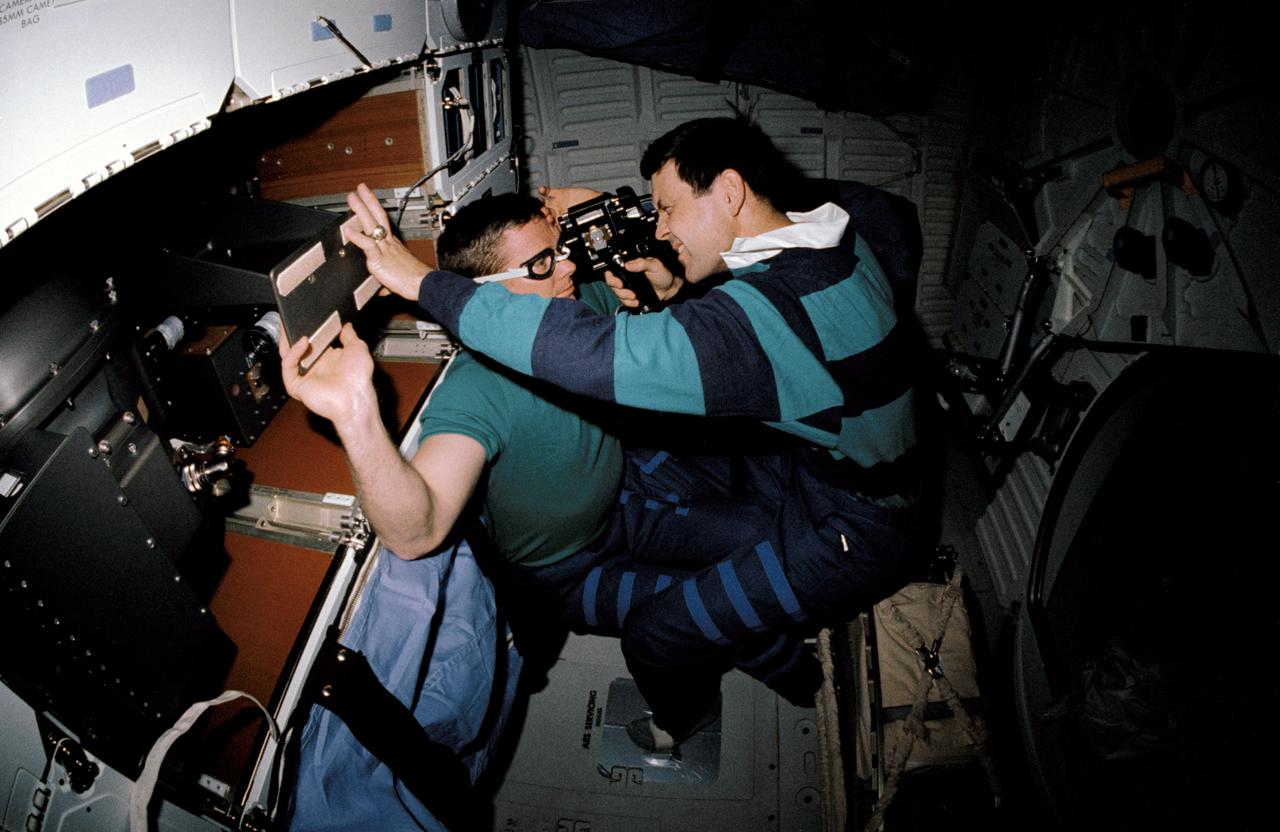

STS041-02-015 (6-10 Oct. 1990) --- A 35mm scene showing astronauts Robert D. Cabana (right), STS-41 pilot, and Bruce E. Melnick, mission specialist, participating in a detailed supplemental objective for STS-41 involving retinal photography. The hypothesis of this experiment is that retinal photographs taken on orbit will show evidence of increased intracranial pressure (ICP) and the evidence of increased ICP and the development of Space Adaptation Syndrome (SAS) will be correlated. SAS has been a subject of on-orbit analysis since the early days of space shuttle.
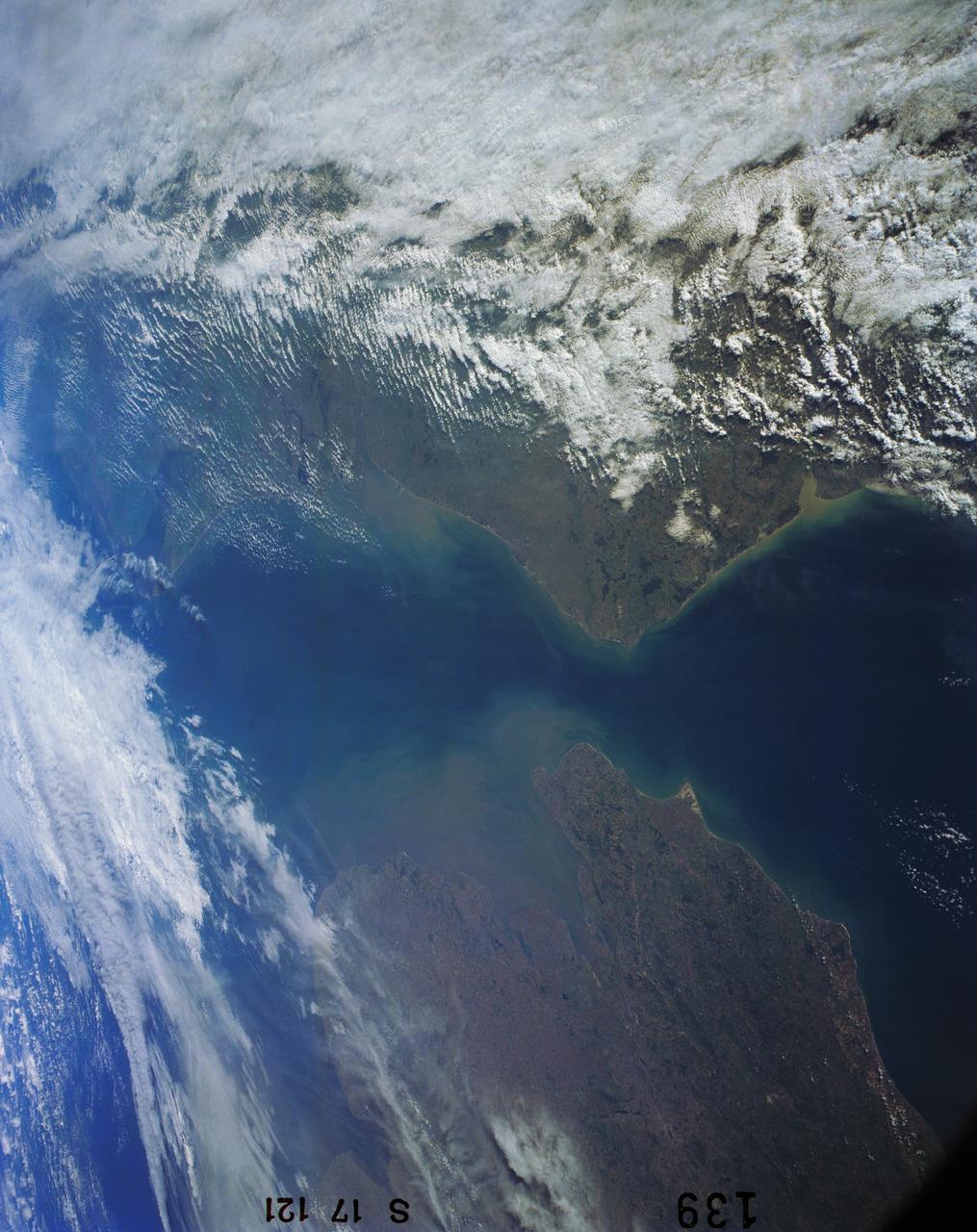

41G-121-139 (5-13 Oct. 1984) --- The Strait of Dover and London, seldom seen in space photography, can be delineated in this medium format camera's scene showing parts of England and France from onboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger. Parts of the Thames River can also be traced in the frame. The 41-G crew consisted of astronauts Robert L. Crippen, commander; Jon A. McBride, pilot; and Mission Specialists Kathryn D. Sullivan, Sally K. Ride, and David D. Leestma; along with Canadian astronaut Marc Garneau; and Paul D. Scully-Power, both payload specialists. Photo credit: NASA
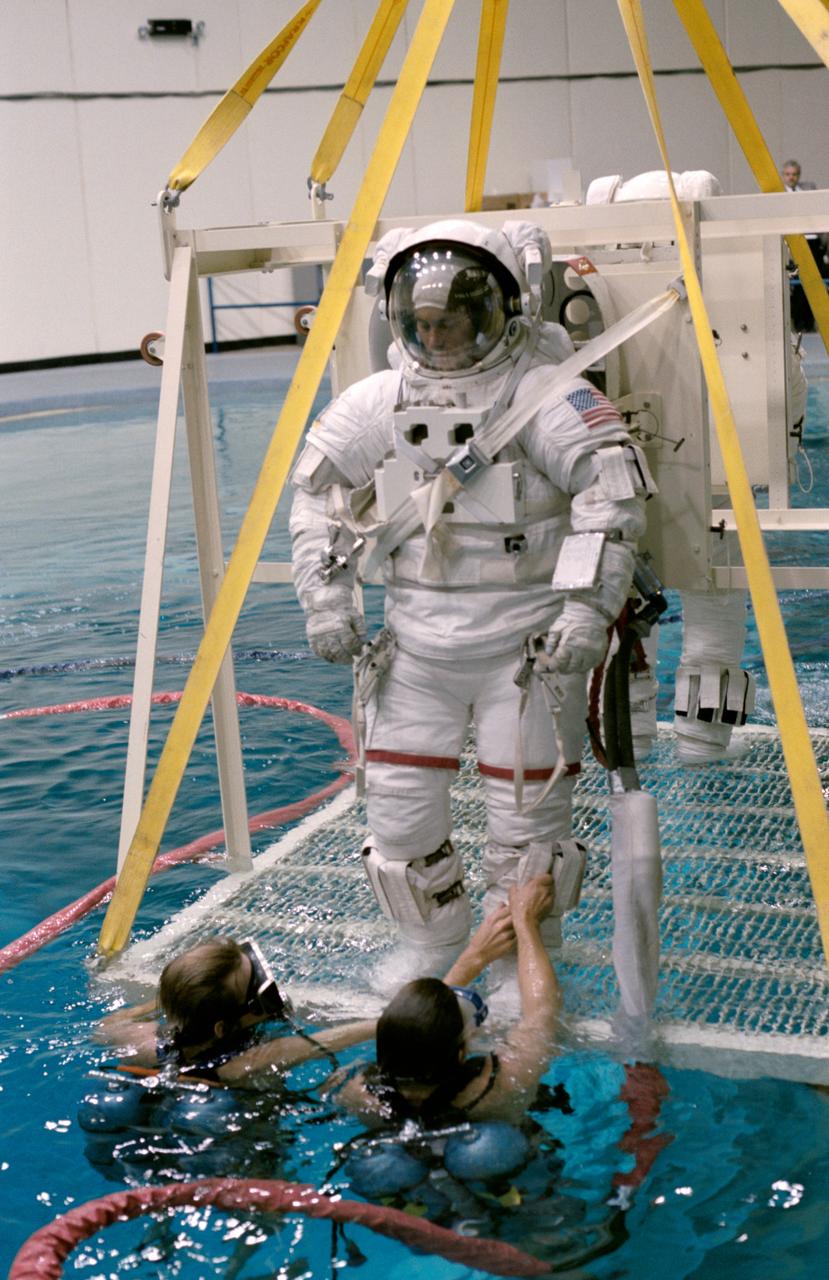

S84-28204 (26 Feb 1984) --- Astronaut Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, one of three 41-D mission specialists, is almost ready for submerging in the 25 ft. deep facility used to simulate space tasks on earth. Moments later, the 41-D crewmember was floating around a submerged Shuttle mockup simulating a contignency EVA for his seven-day flight. Partially pictured in the background is Astronaut Steven A. Hawley, who would share EVA duties with Mullane in the event an EVA was deemed necessary. All Shuttle crews, many of which are not scheduled for definite EVAs, possess team members trained to perform in space certain tasks normally done remotely in the event of systems failures. Among those contingent tasks is the manual closing of the Shuttle's cargo bay doors. This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.
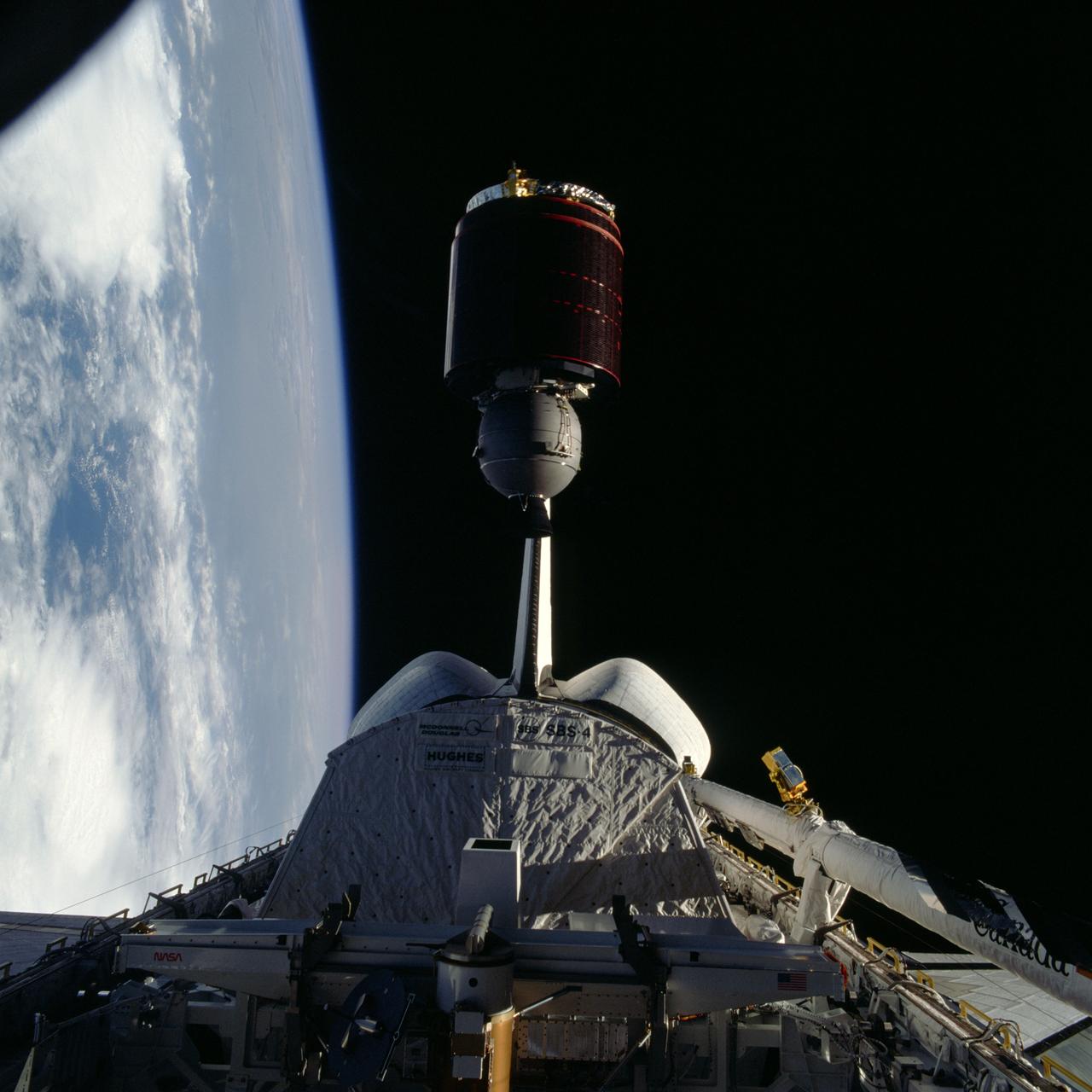

41D-37-050 (1 Sept 1984) --- Telstar, the third of three satellites to be placed into space via the Earth-orbiting Discovery, departs from the cargo bay of the manned vehicle during 41-D's third day in space. The scene was photographed at 9:35 a.m. (CDT), Sept. 1, 1984, with a 70mm handheld hasselblad camera aimed through the windows on the flight deck. Heavy clouds cover much of the water and land mass of Earth in the background.
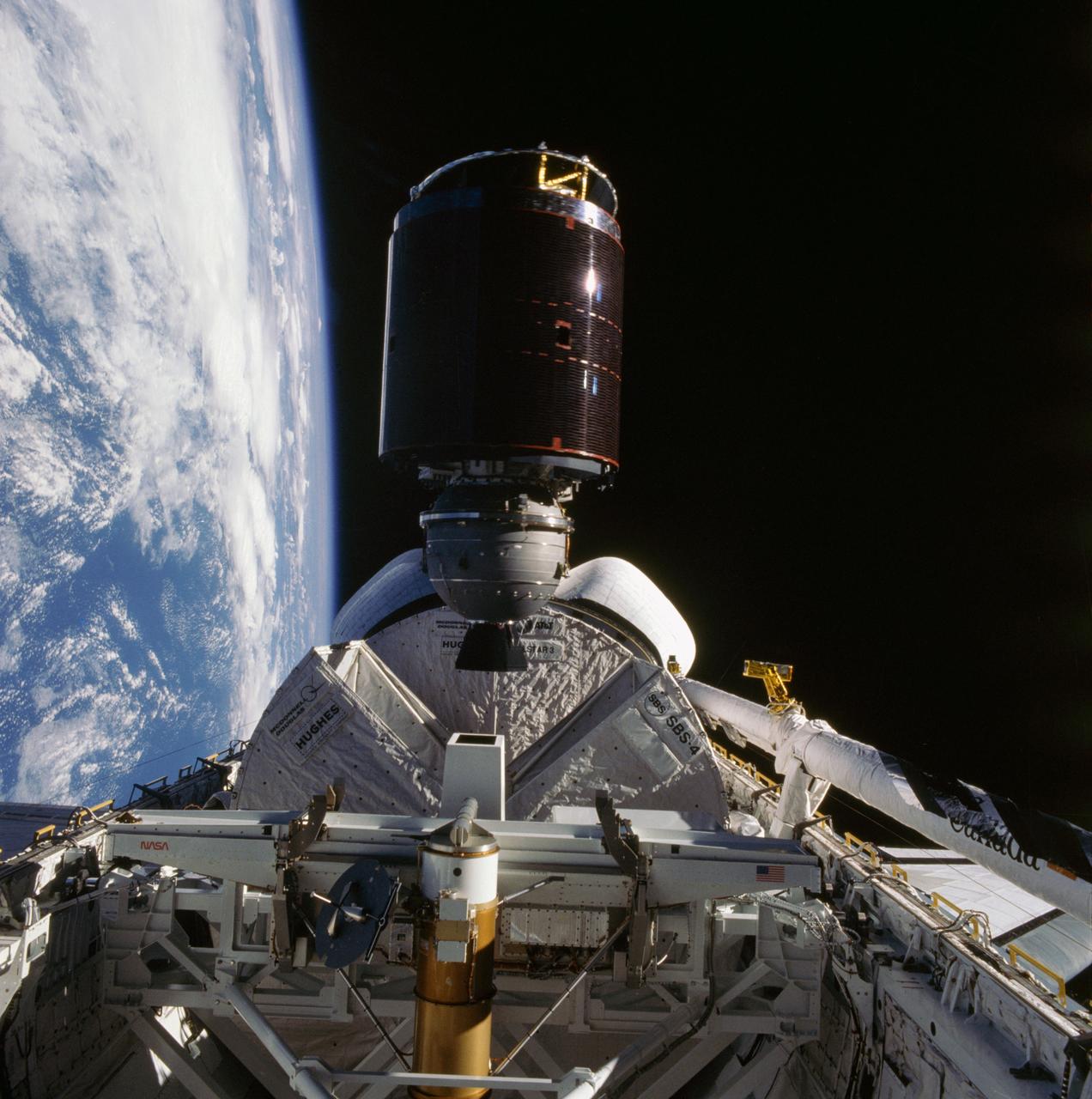

41D-36-034 (30 Aug 1984) --- Less than nine hours after the first launch of the Discovery, its astronaut crewmembers photographed deployment of the SBS-4 communications satellite. The cylindrical spacecraft spins and rises from its cradle-like protective shield to begin life in space. A number of maneuvers will place it in its desired orbit. A 70mm camera, aimed through the spacecraft’s aft flight deck windows, was used to expose the frame.
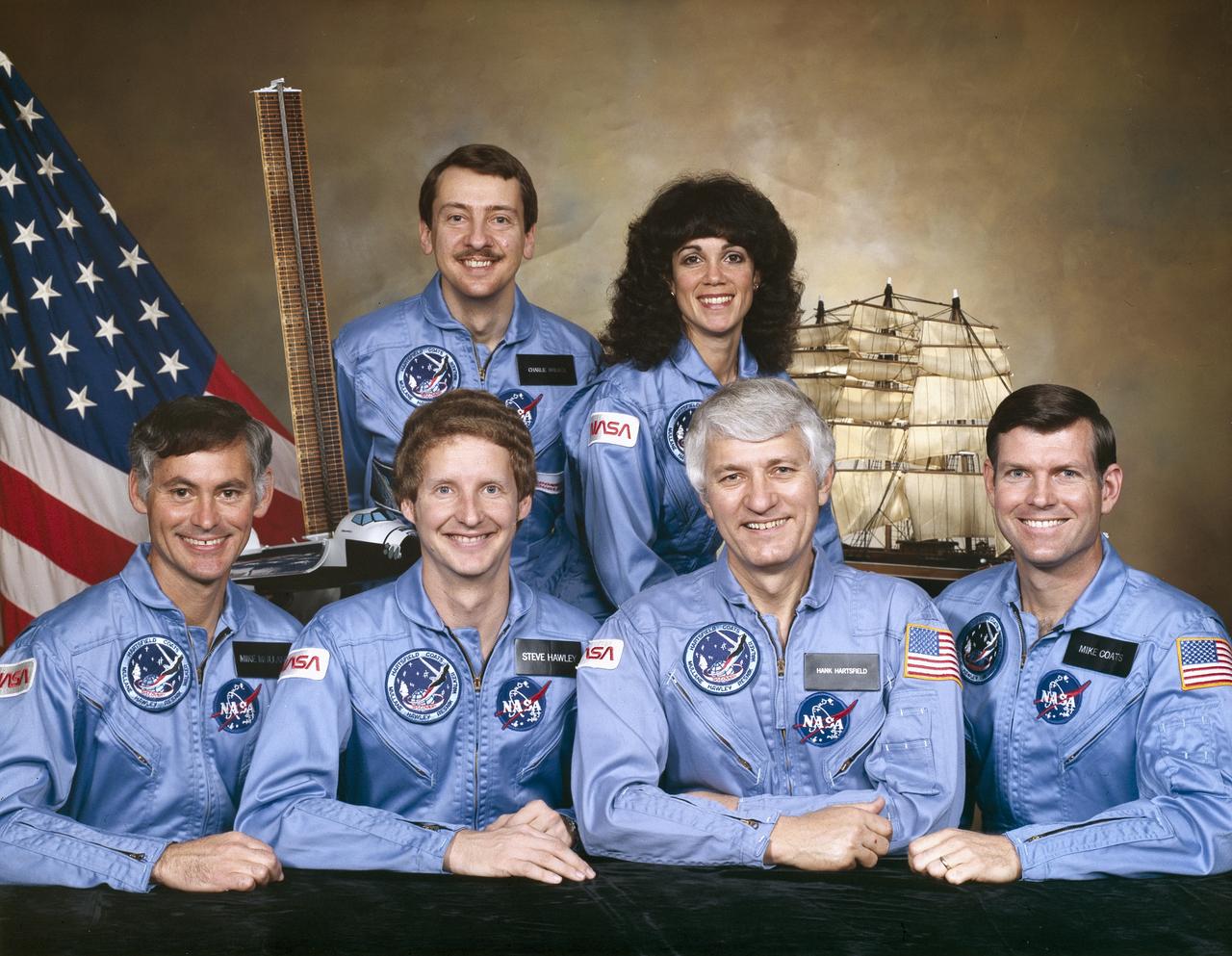

The crew assigned to the STS-41D mission included (seated left to right) Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, mission specialist; Steven A. Hawley, mission specialist; Henry W. Hartsfield, commander; and Michael L. (Mike) Coats, pilot. Standing in the rear are Charles D. Walker, payload specialist; and Judith A. (Judy) Resnik, mission specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery August 30, 1984 at 8:41:50 am (EDT), the STS-41D mission deployed three satellites: the Satellite Business System SBS-D; the SYCOM IV-2 (also known as LEASAT-2); and the TELSTAR.
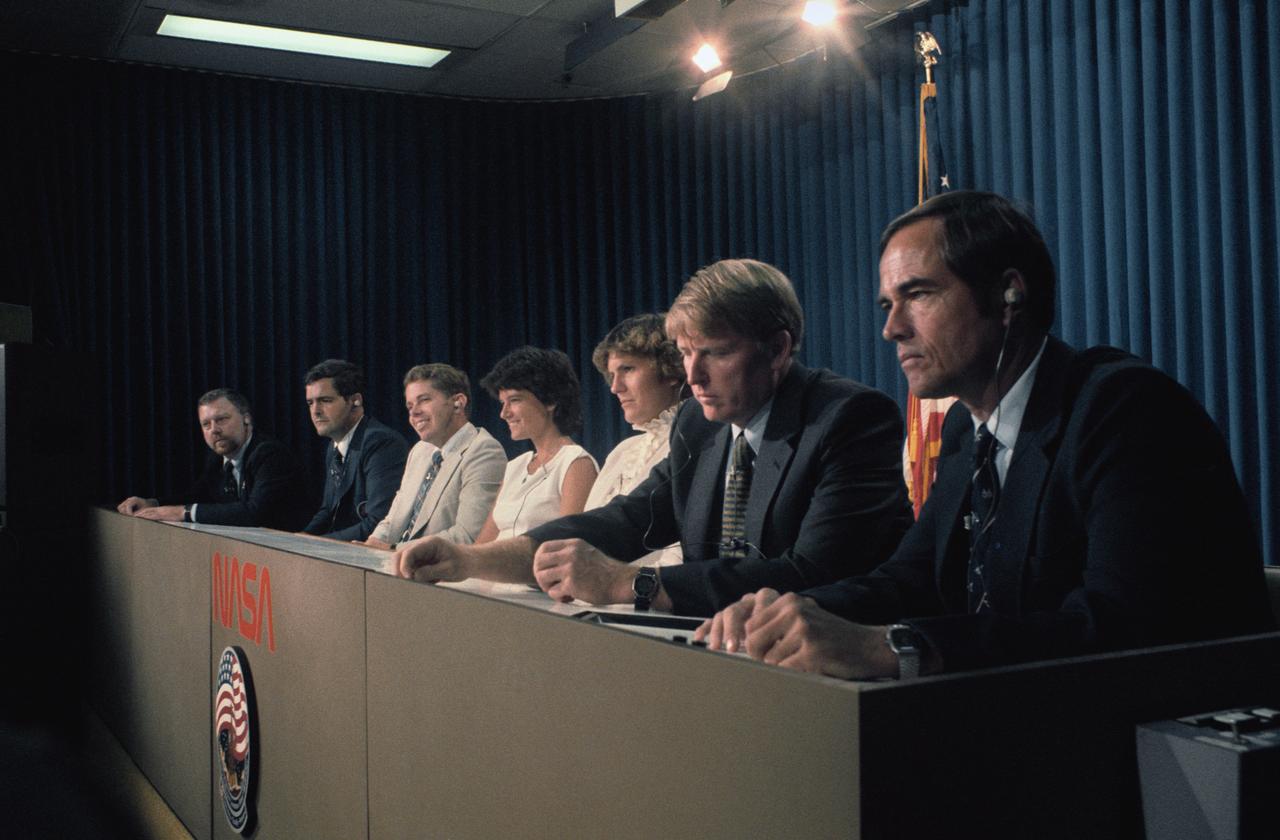

S84-41580 (3 Sept 1984) --- Assembled together publicly for the first time, the seven crewmembers for NASA's 41-G Space Shuttle mission field questions from the press corps at the Johnson Space Center. Pictured (foreground right to left) are Robert L. Crippen, crew commander ;Jon A. McBride, pilot; Kathryn D. Sullivan, Sally K. Ride and David C. Leestma--all mission specialists; Marc Garneau, representing the Canadian National Research Council, and Paul D. Scully-Power, U.S. Navy oceanographer, both payload specialists. Their flight is scheduled for early October.
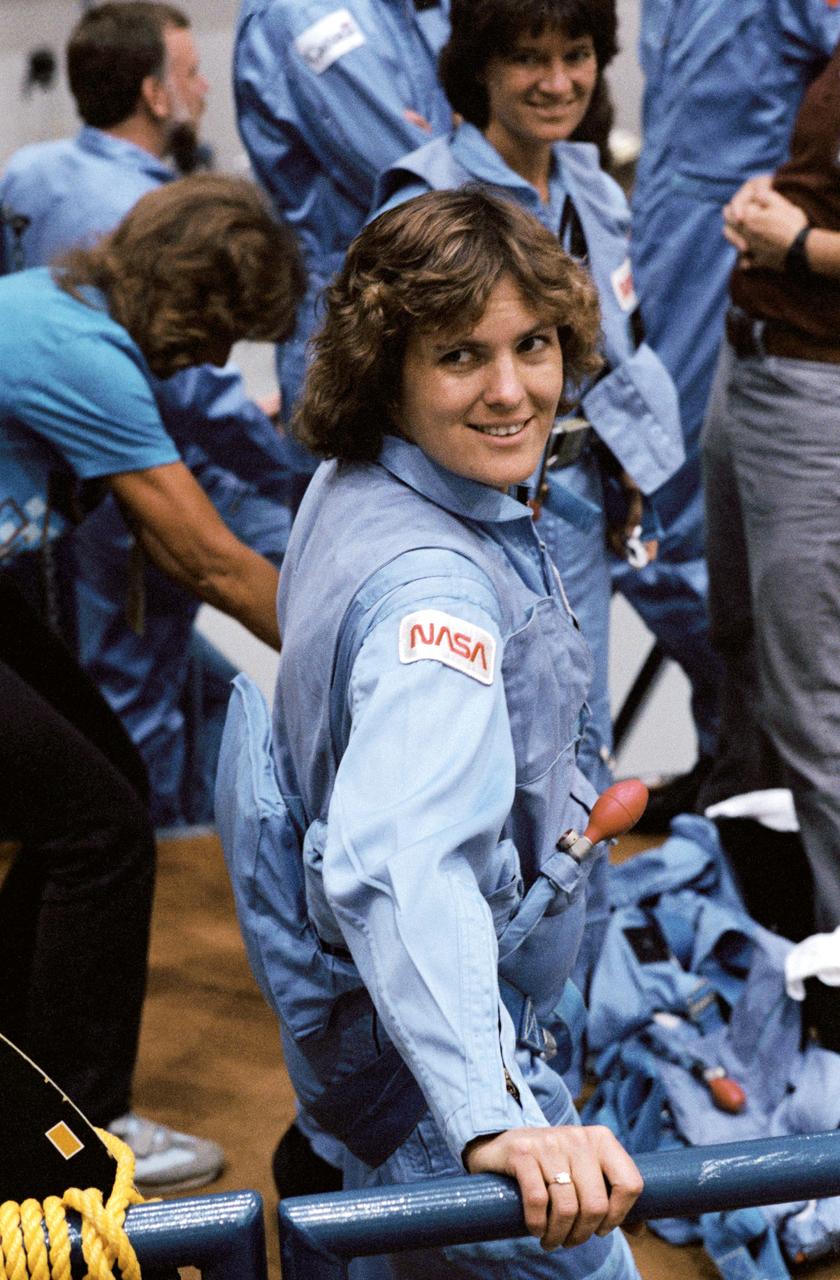

41D-3188 (2 September 1984) --- Astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan, 41-G mission specialist, joins with other members of the seven-person crew prior to a training session in the Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory at the Johnson Space Center. Dr. Sullivan will be the first American woman to perform an extravehicular activity (EVA) in space when she joins Astronaut David C. Leestma for some outside-the-Challenger duty on October 9. The mission is scheduled for an October 5, 1984 launch.

41D-3183 (2 Sept. 1984) --- Paul D. Scully-Power, 41-G payload specialist, appears ready to participate in the eight-day space shuttle mission in this photograph taken during a pause in training in the Johnson Space Center's mockup and integration laboratory. The U.S. Navy oceanographer and a Canadian will join five NASA astronauts for a busy stay in space aboard the Challenger next month. The team was practicing for emergency egress. Photo credit: NASA (Editor's note: Please ignore the odd photo identification number for this image. This is a 41-G training image.)

41G-19-006 (5-13 Oct. 1984) --- The seven-member 41-G crew assembles for a group shot on the flight deck of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger. Robert L. Crippen, commander, is in center of the back row. Others pictured are (front row, l.-r.) Jon A. McBride, pilot; Sally K. Ride, Kathryn D. Sullivan and David C. Leestma, all mission specialists; and Paul D. Scully-Power (left) and Marc Garneau, both payload specialists, on the back row. Garneau represents the National Research Council of Canada and Scully-Power is a civilian oceanographer with the U.S. Navy. Photo credit: NASA

41D-3139 (2 Sept 1984) --- Two prime crew member payload specialist and a backup for NASA's 41-G Space Shuttle mission participate in launch phase simulations at the Johnson Space Center. Securing themselves in temporary stations in the middeck of a trainer are Marc Garneau, representing the Canadian National Research Council (NRC), and Paul D. Scully-Power (background), a U.S. Navy oceanographer. Robert Thirsk, also with the NRC, is a backup payload specialist. This photograph was taken by Otis Imboden.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, The space shuttle Discovery lifts off from Launch Pad 39A for its maiden flight at 8:42 a.m. EDT. The crew members for the 41-D flight are commander Henry w. Hartsfield, pilot Michael L. Coats, mission specialists Judith A. Resnik, Steven A. Hawley, Richard M. Mullane, and payload specialist Charles W. Walker. Photo Credit: NASA

41G-102-047 (13 Oct. 1984) --- An unusual picture, photographed by astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan, shows the beginning and ending location of her eight-day mission in space with six other 41-G crew members aboard the space shuttle Challenger. The picture was made moments before touchdown at the KSC landing facility. Dr. Sullivan aimed a 35mm camera through the port hole in Challenger's hatch. The five ground features represented as circles or pentagonals are launch areas. Photo credit: NASA
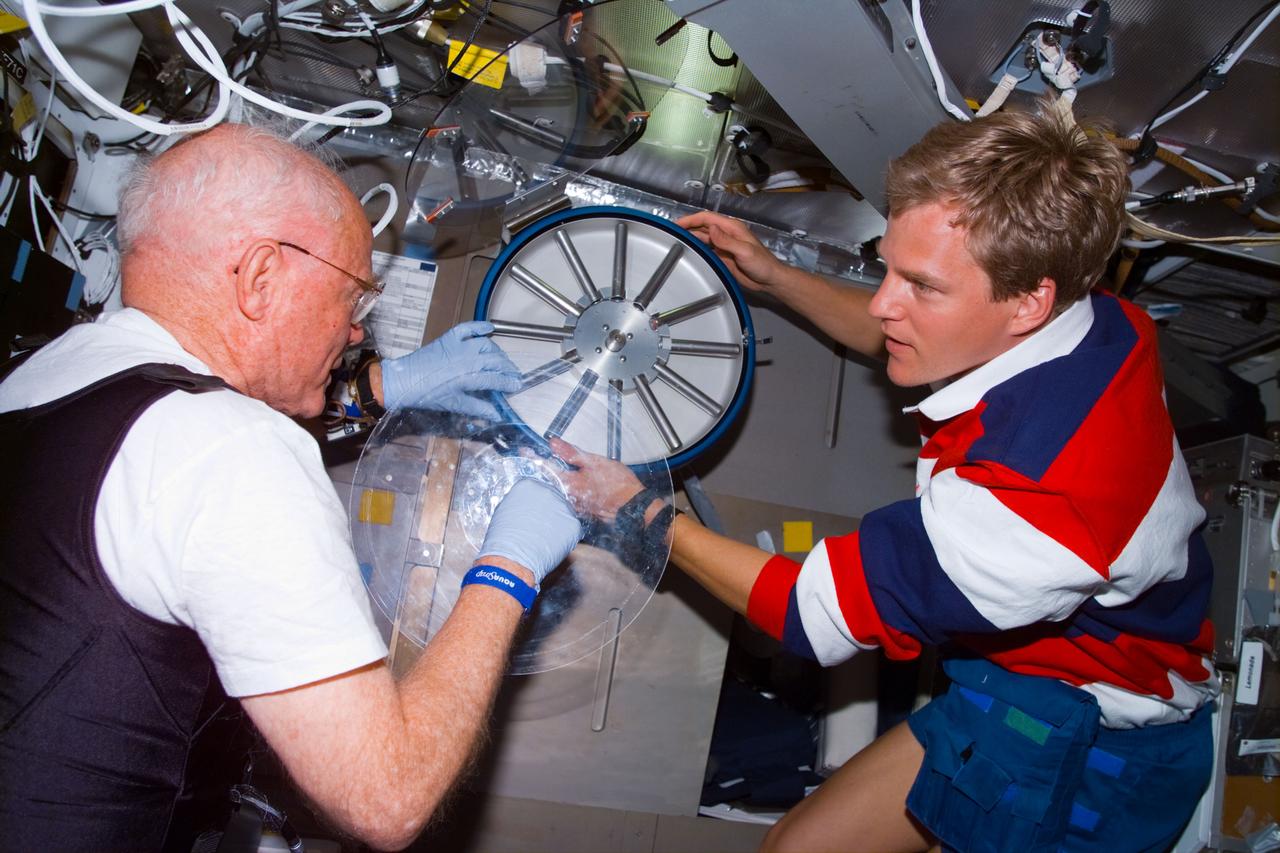

STS095-E-5239 (4 Nov. 1998) --- Astronaut Scott E. Parazynski (right), STS-95 mission specialist, assists U.S. Sen. John H. Glenn Jr. (D.-Ohio), payload specialist, with a chore onboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 18:41:20 GMT, Nov. 4.
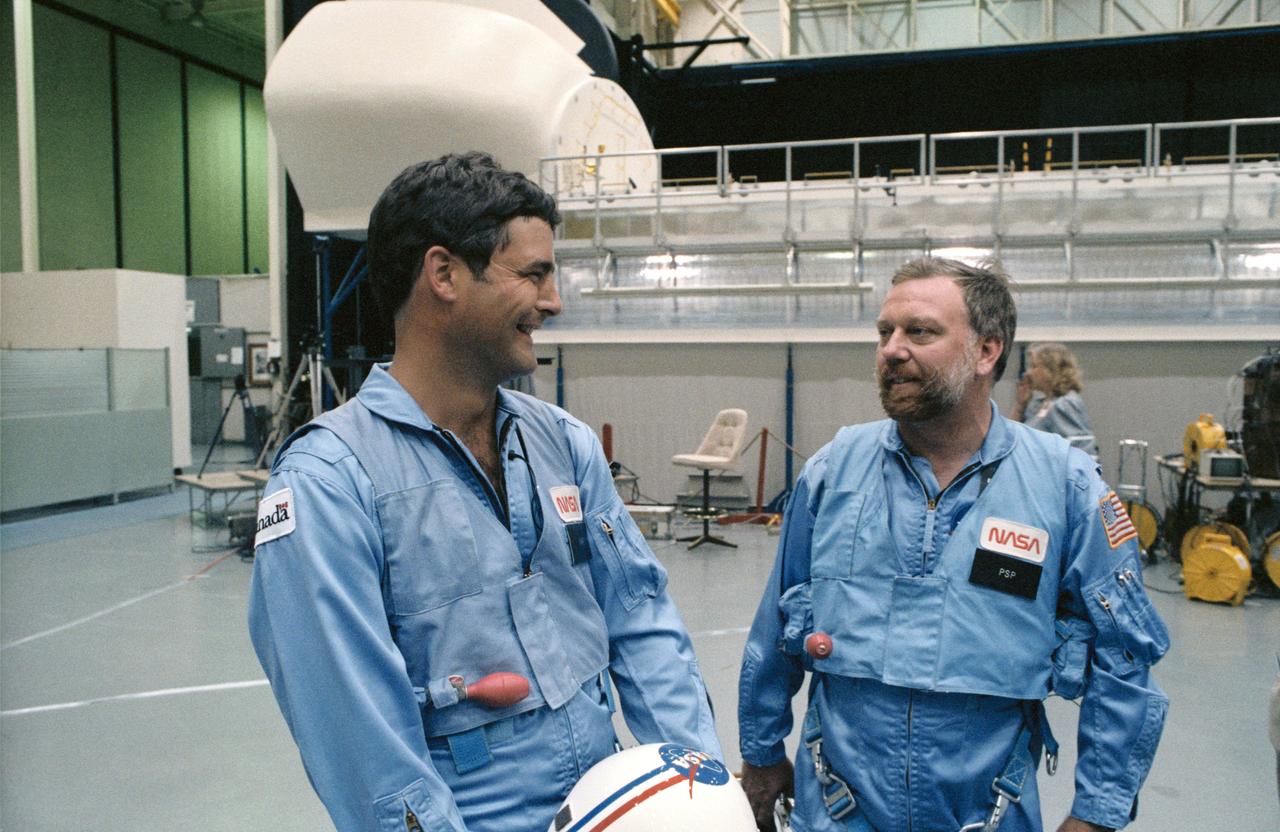

41D-3185 (S14-3185) (4 Sept 1984) --- The two payload specialists for NASA's 41-G mission aboard the Challenger chat prior to a simulation session in the Shuttle mockup and integration laboratory at the Johnson Space Center. They are Marc Garneau, left, representing the Canadian National Research Council, and Paul D. Scully-Power, an oceanographer with the U.S. Navy. They are standing near the manipulator development facility (MDF), pictured in background.
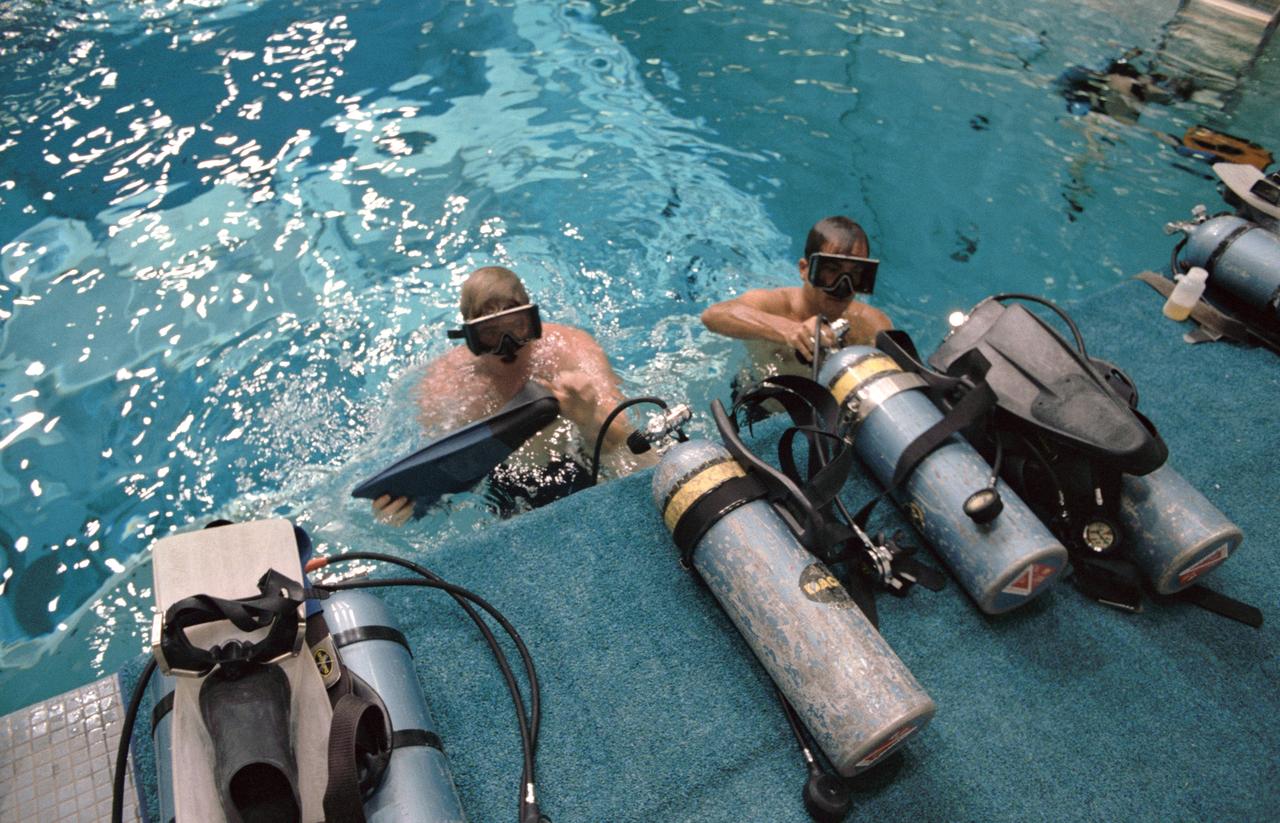

S84-36900 (29 June 1984) ---Astronauts Robert L. Crippen (right) and Jon A. McBride, crew commander and pilot, respectively, for NASA's 41-G Space Shuttle mission, don self contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) gear prior to their underwater to observe a simulation of an extravehicular activity (EVA) to be performed on their mission. Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan and David C. Leestma, two of three mission specialists on the seven-member crew, are scheduled for the EVA. The underwater training took place in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F).

S84-36898 (29 June 1984) --- Astronauts Robert L. Crippen (left) and Jon A. McBride, crew commander and pilot, respectively for NASA's 41-G Space Shuttle mission, await the delivery of self contained underwater breathing apparatus (SCUBA) gear prior to their going underwater to observe a simulation of an extravehicular activity (EVA) scheduled for their mission. The EVA will be performed by Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan and David C. Leestma, two of three mission specialists named for the seven-member crew. The underwater training took place in the Johnson Space Center's weightless environment training facility (WET-F).

S84-26391 (3 April 1984) --- The official mission insignia for the 41-D space shuttle flight features the Discovery--NASA's third orbital vehicle--as it makes its maiden voyage. The ghost ship represents the orbiter's namesakes which have figured prominently in the history of exploration. The space shuttle Discovery heads for new horizons to extend that proud tradition. Surnames for the crew members of NASA's eleventh space shuttle mission encircle the red, white and blue scene. They are astronauts Henry W. Hartsfield Jr., commander; Michael L. Coats, pilot; Judith A. Resnik, Steven A. Hawley and Richard M. (Mike) Mullane, all mission specialists; and Charles D. Walker, payload specialist. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
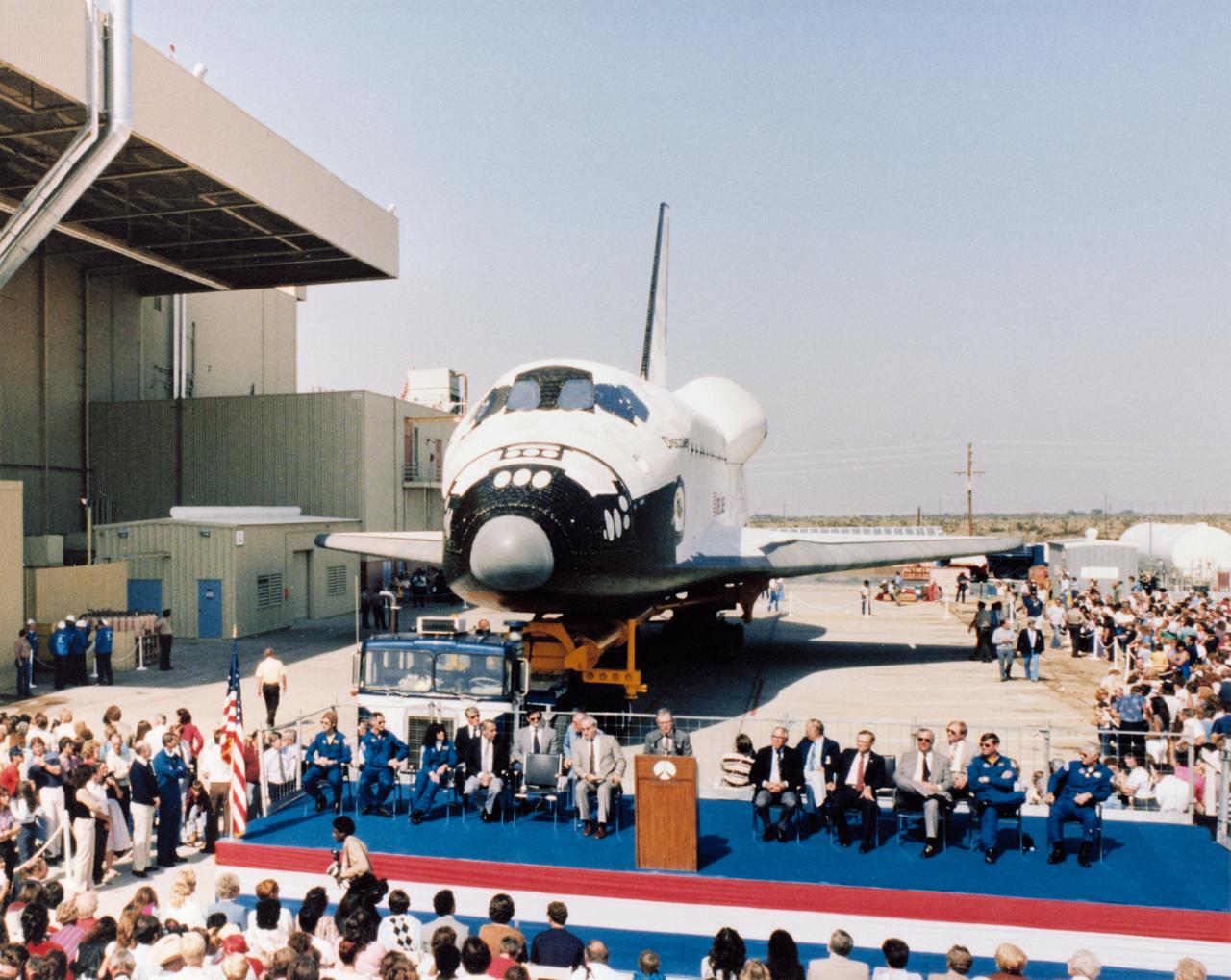

S84-30898 (16 Oct 1983) --- NASA Space Shuttle Orbiter 103, Discovery, is rolled out in formal ceremonies at the Rockwell International Palmdale, California, facility. On hand to greet the vehicle and the public are members of the 41-D crew--the first team of astronauts to man the new vehicle. Scheduled for a spring or summer flight in 1984 are astronauts Henry W. Hartsfield (right), commander; Michael L. Coats (second right), pilot; and Judith A. Resnik, Richard M. (Mike) Mullane and Steven A. Hawley (on left of stage), all mission specialists. Don Beall of Rockwell International (at lectern) prepares to introduce Dr. Rocco A. Petrone, president of Rockwell's Space Transportation Systems Division.
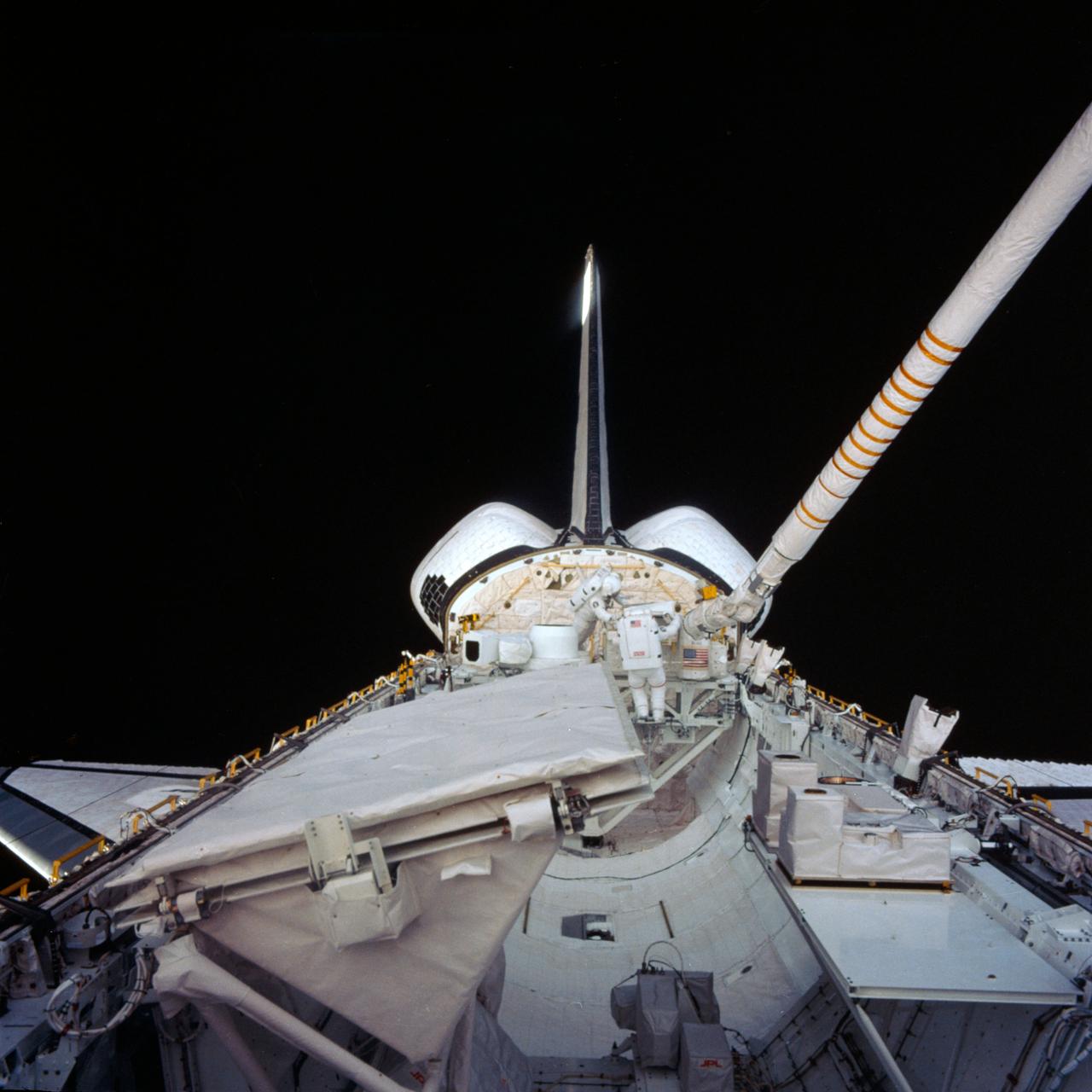

S84-43432 (11 Oct. 1984) --- Appearing small in the center background of this image, astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan, left, and David C. Leestma, both 41-G mission specialists, perform an in-space simulation of refueling another spacecraft in orbit. Their station on the space shuttle Challenger is the orbital refueling system (ORS), positioned on the mission peculiar support structure (MPR ESS). The Large Format Camera (LFC) is left of the two mission specialists. In the left foreground is the antenna for the shuttle imaging radar (SIR-B) system onboard. The Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS) is positioned to allow close-up recording capability of the busy scene. A 50mm lens on a 70mm camera was used to photograph this scene. Photo credit: NASA
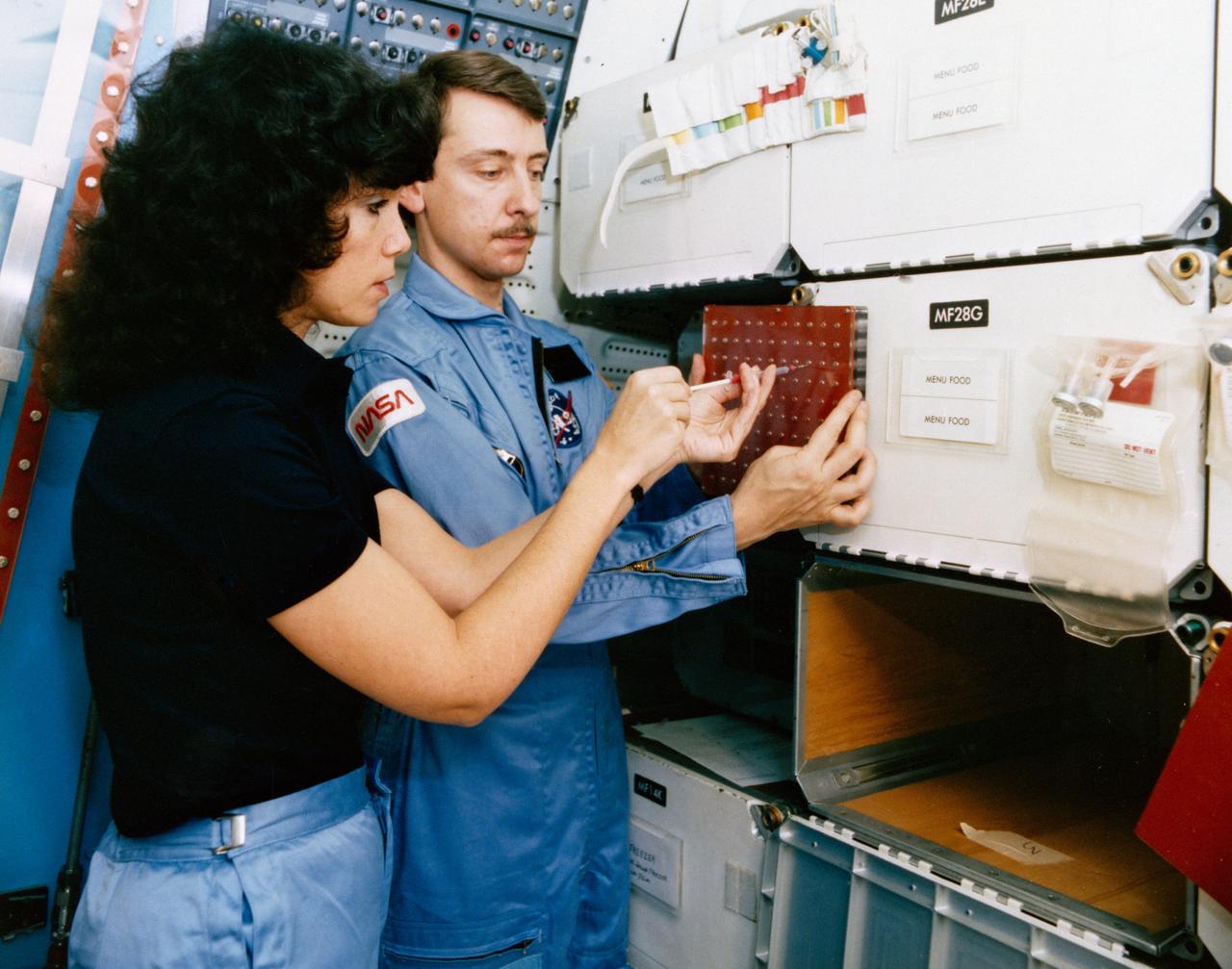

S84-35757 (May 1984) --- Astronaut Judith A. Resnik, 41-D mission specialist, and Charles Walker, payload specialist for that June 1984 flight, prepare for some scheduled intravehicular activity involving the continuous flow electrophoresis systems (CFES) experiment. CFES will join the six-member crew aboard the Earth-orbiting Discovery for a seven day mission. The two share in preparing a sample to be processed by the CFES. In the background are stowage lockers and a CFES trainer-- part of the Shuttle one-g trainer at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). Walker, an engineer at McDonnell Douglas Astronautics Co. in St. Louis, Missouri, will be the first Shuttle payload specialist to represent a project designed for commercial purposes. As payload specialist, his job will be to run the materials electrophoresis-operations-in-space project. The project is aimed at separating large quantities of biological materials in space for ultimate use in new pharmaceuticals. The photo was taken by a McDonnell Douglas photographer.
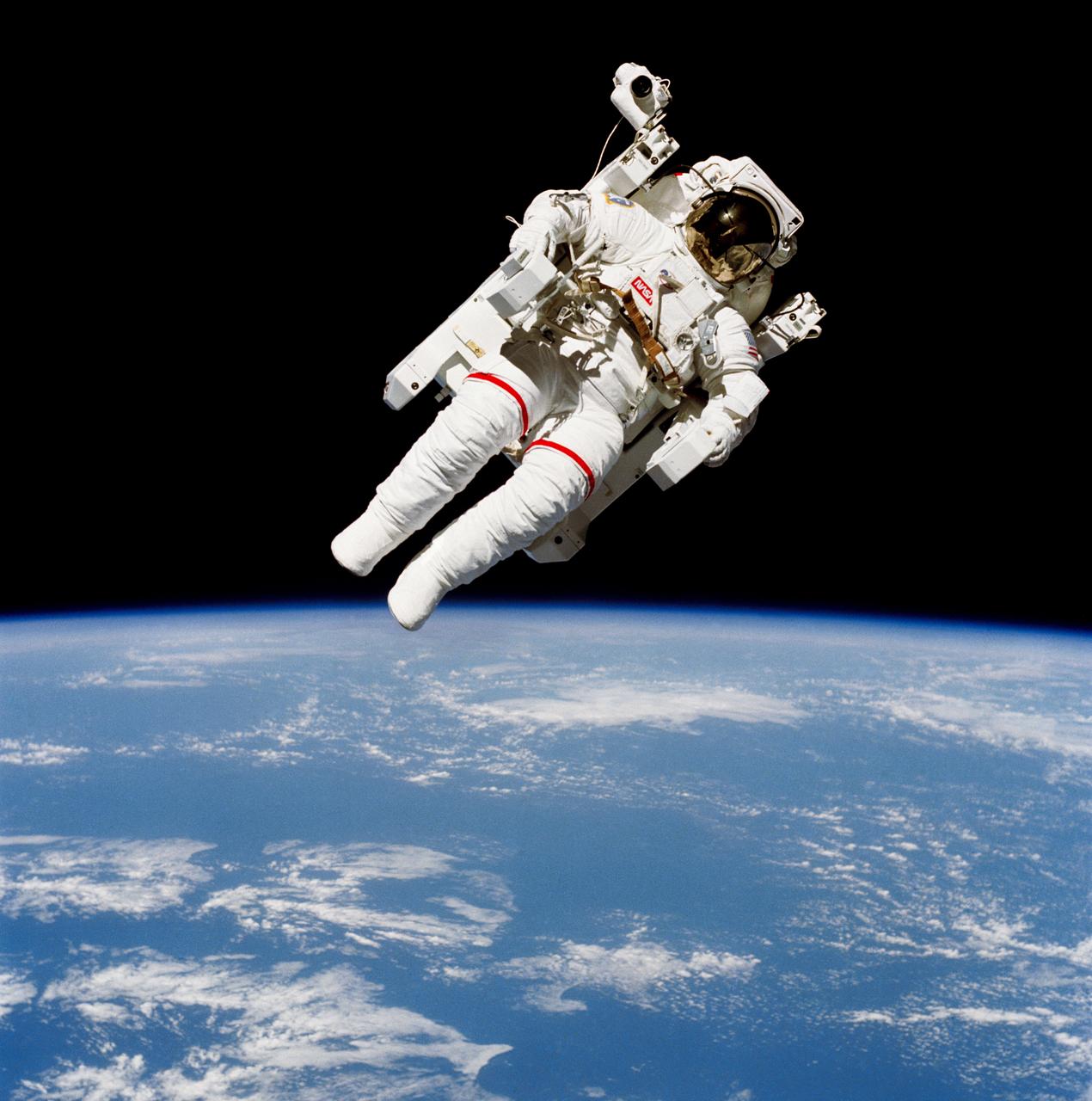

S84-27017 (7 Feb. 1984) --- Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, one of two 41-B mission specialist, participating in a historical Extravehicular Activity (EVA), is a few meters away from the cabin of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Challenger in this 70mm frame. This EVA represented the first use of a nitrogen-propelled, hand-controlled device called the Manned Maneuvering Unit (MMU), which allows for much greater mobility than that afforded previous spacewalkers who had to use restrictive tethers. Robert L. Stewart, mission specialist, later tried out the MMU McCandless is using here. The two of them tested another similar unit two days later. Inside the spacecraft were astronauts Vance D. Brand, commander; Robert L. Gibson, pilot; and Ronald E. McNair, mission specialist. Photo credit: NASA
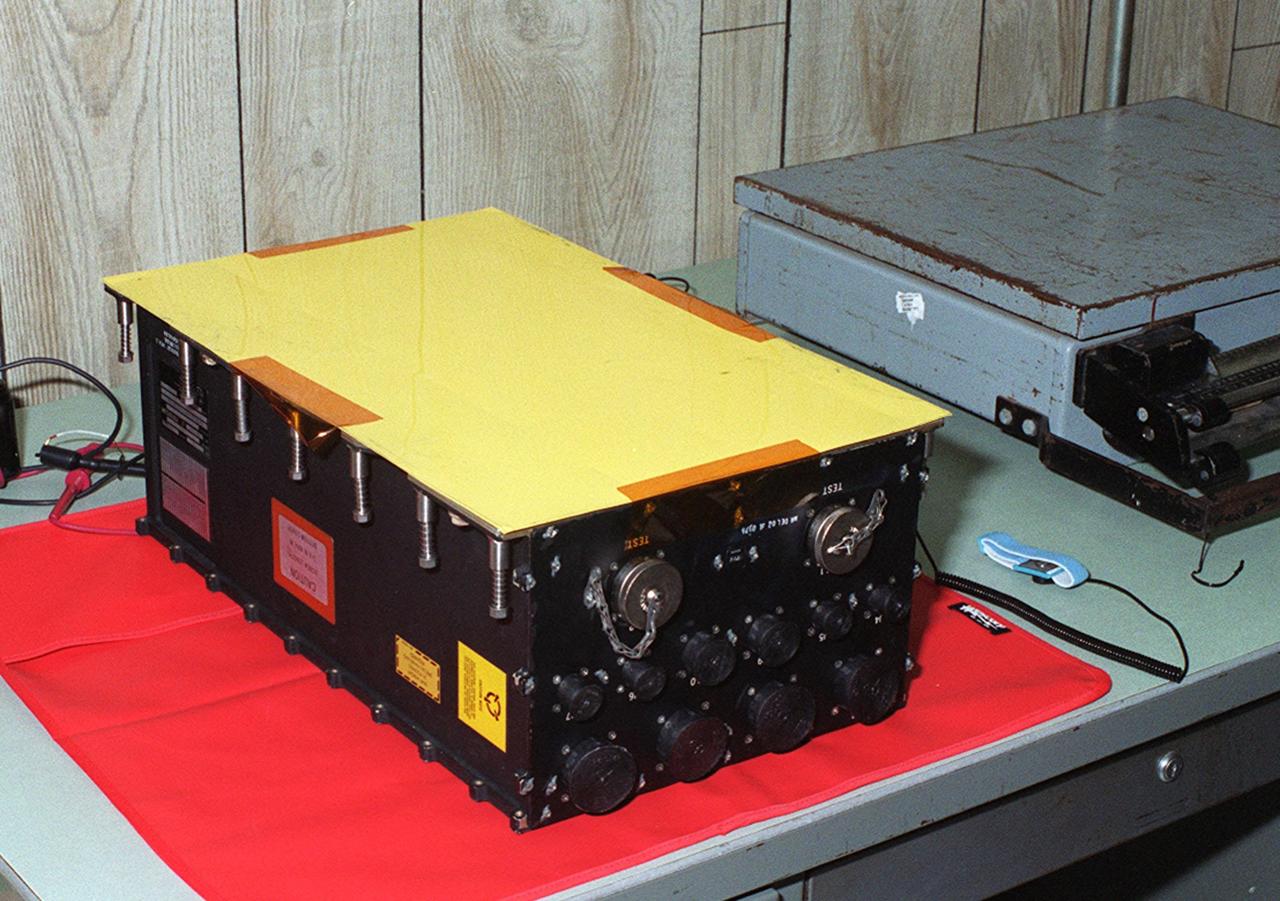

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A new Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) for Shuttle Endeavour sits on a table in a Quality trailer in the Launch Pad 39B area. The original E-MEC in Endeavour became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. The E-MECs are located in the orbiter's aft compartment and both are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. Before workers can begin E-MEC replacement efforts at the launch pad, cryogenic reactants must be offloaded from the orbiter and Space Shuttle ordnance disconnected. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST
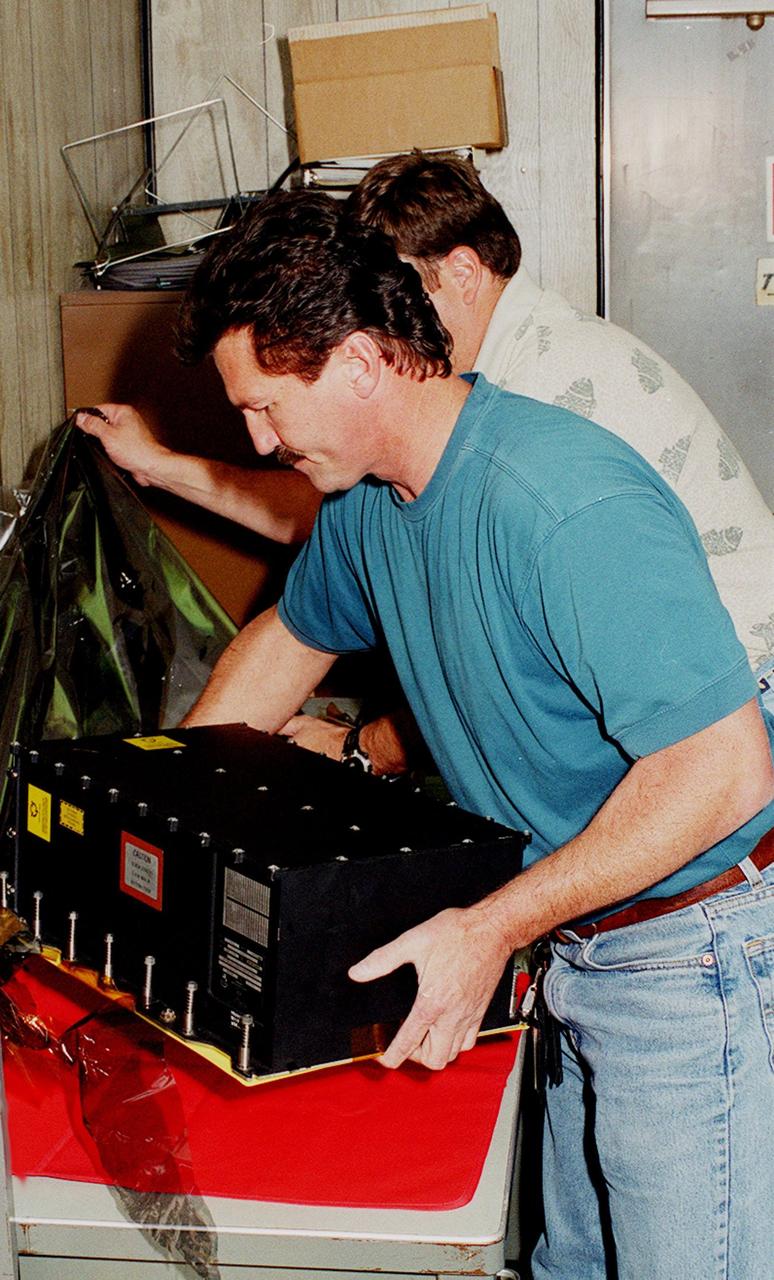

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in a Quality trailer in the Launch Pad 39B Area unwrap a new Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) to be installed in Shuttle Endeavour. The original E-MEC in Endeavour became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. The E-MECs are located in the orbiter's aft compartment and both are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. Before workers can begin E-MEC replacement efforts at the launch pad, cryogenic reactants must be offloaded from the orbiter and Space Shuttle ordnance disconnected. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in a Quality trailer in the Launch Pad 39B Area unwrap a new Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) to be installed in Shuttle Endeavour. The original E-MEC in Endeavour became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. The E-MECs are located in the orbiter's aft compartment and both are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. Before workers can begin E-MEC replacement efforts at the launch pad, cryogenic reactants must be offloaded from the orbiter and Space Shuttle ordnance disconnected. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST
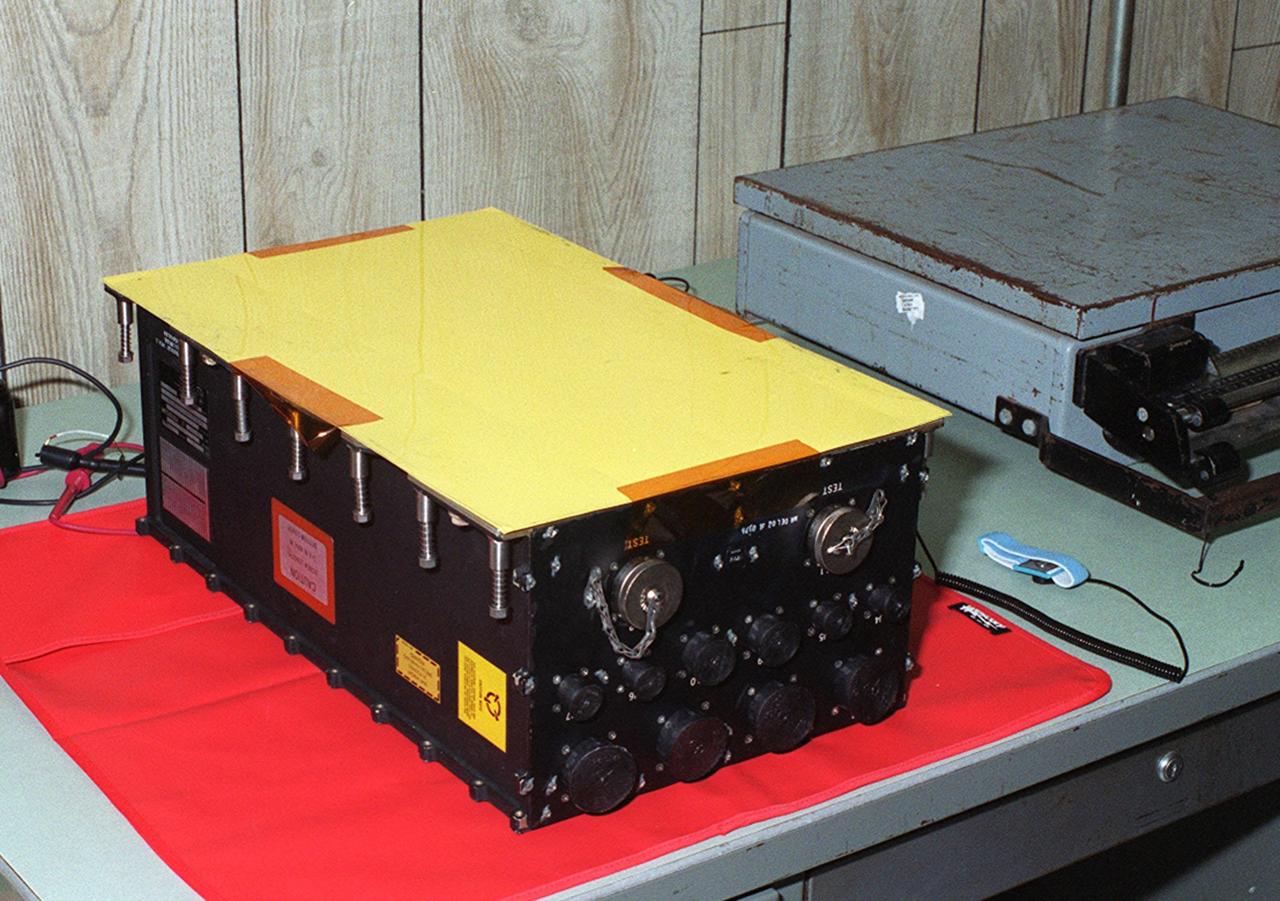

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A new Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) for Shuttle Endeavour sits on a table in a Quality trailer in the Launch Pad 39B area. The original E-MEC in Endeavour became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. The E-MECs are located in the orbiter's aft compartment and both are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. Before workers can begin E-MEC replacement efforts at the launch pad, cryogenic reactants must be offloaded from the orbiter and Space Shuttle ordnance disconnected. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST
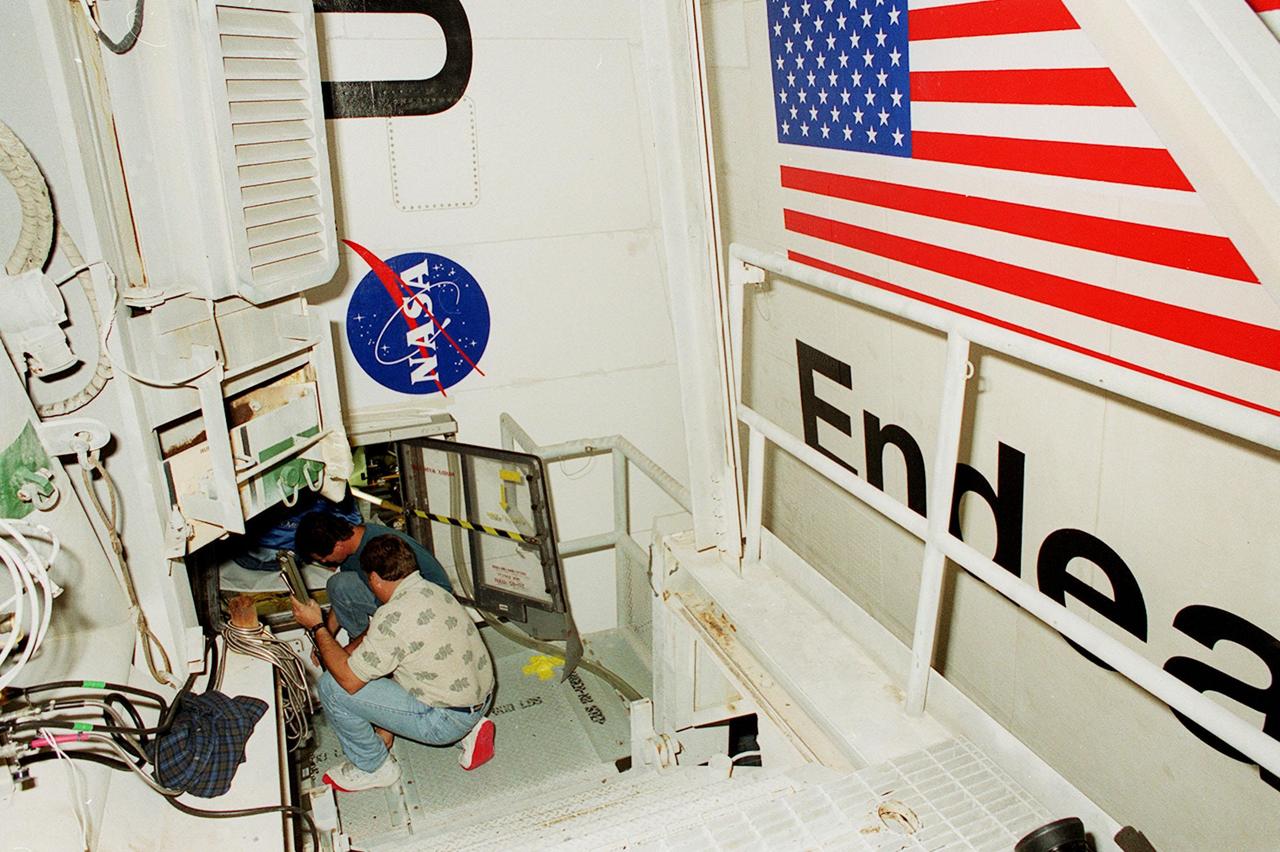

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians work in the aft compartment of Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay, where a new Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) will be installed. The original E-MEC in Endeavour became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. Before workers can begin E-MEC replacement efforts at the launch pad, cryogenic reactants had to be offloaded from the orbiter and Space Shuttle ordnance disconnected. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians work in the aft compartment of Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay, where a new Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) will be installed. The original E-MEC in Endeavour became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. Before workers can begin E-MEC replacement efforts at the launch pad, cryogenic reactants had to be offloaded from the orbiter and Space Shuttle ordnance disconnected. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST
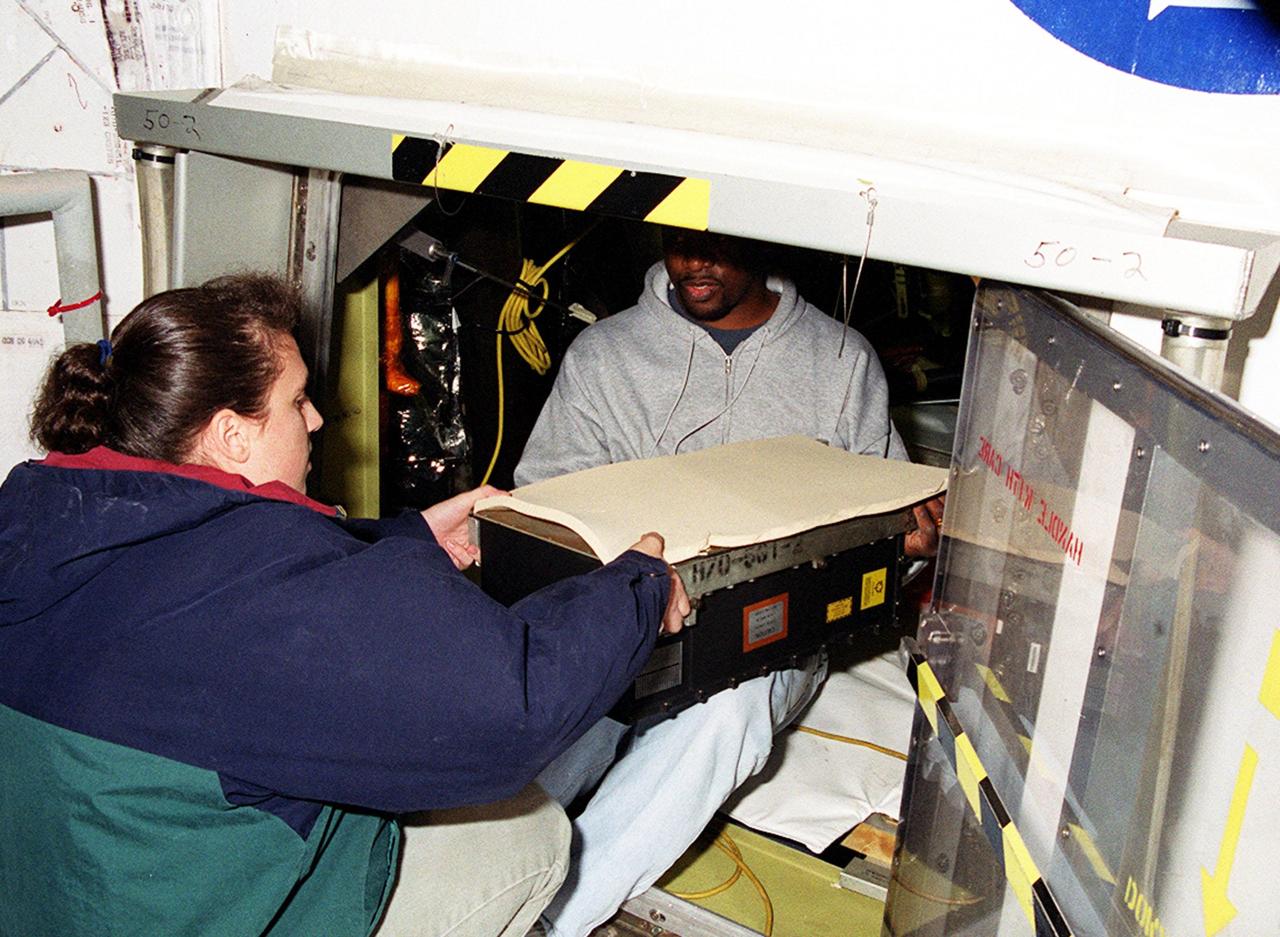

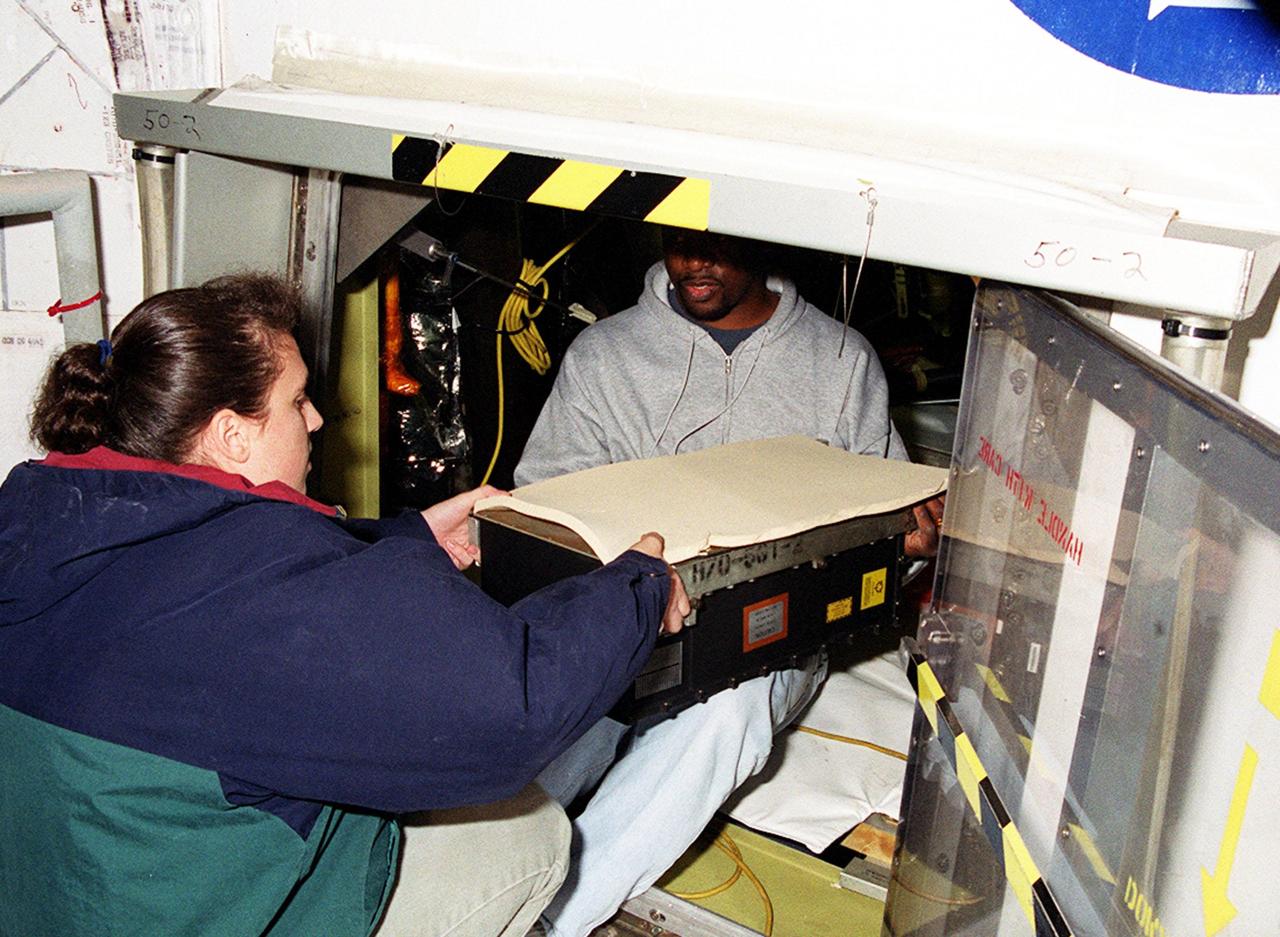
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers move the replacement Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) into Shuttle Endeavour's aft compartment in the payload bay. The original E-MEC became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST
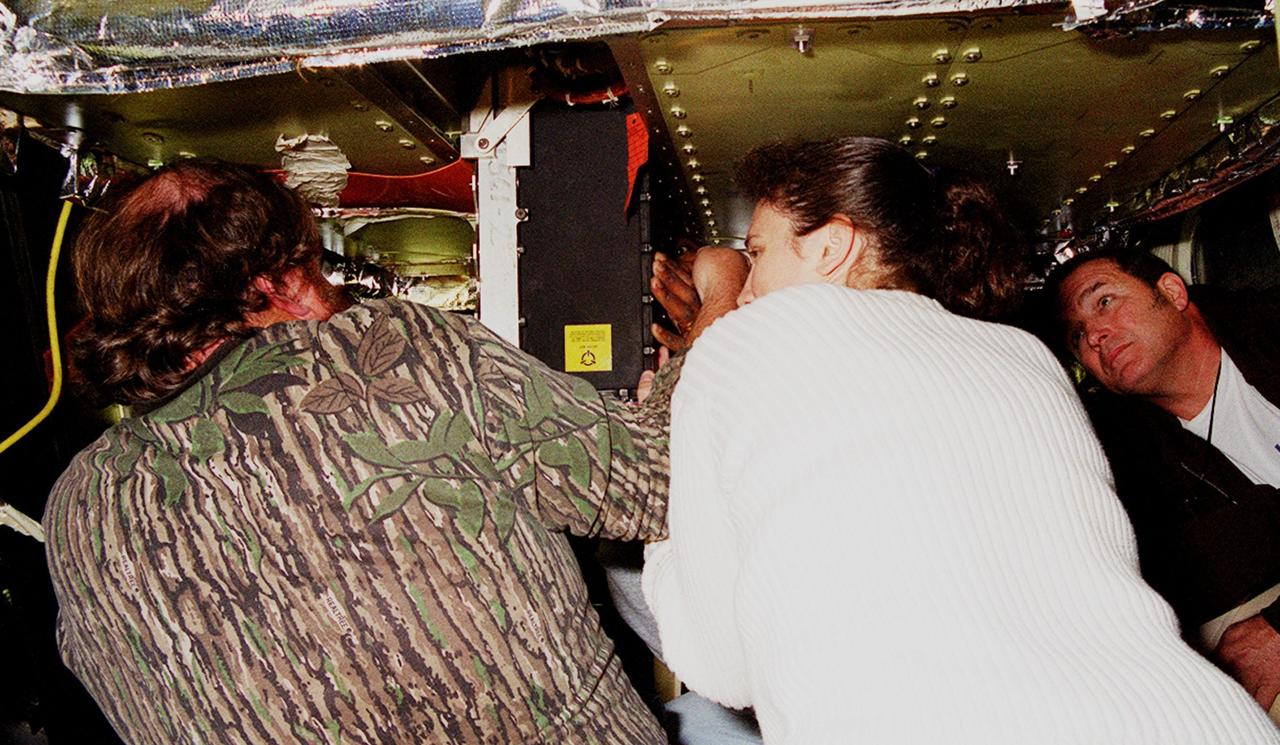

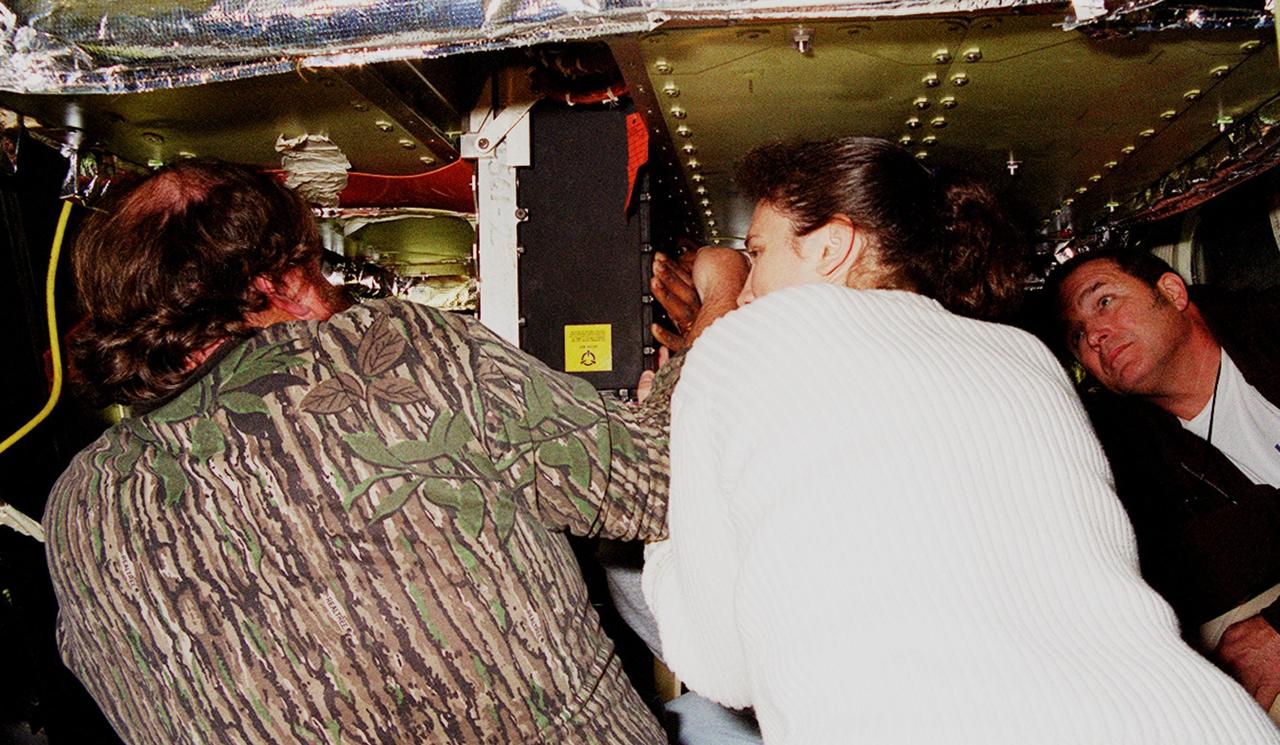
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians remove a faulty Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) from Shuttle Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A. The E-MEC became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST
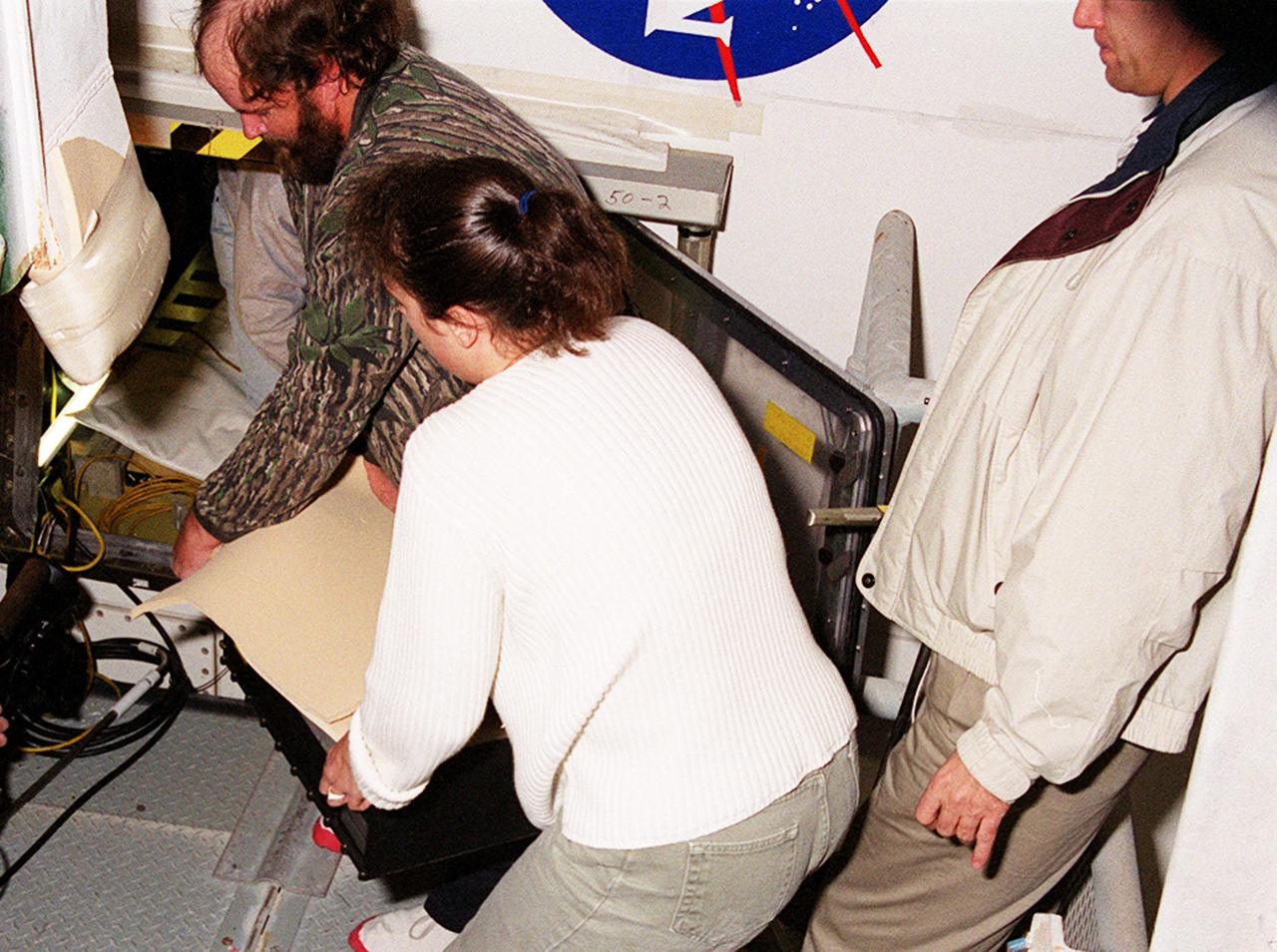

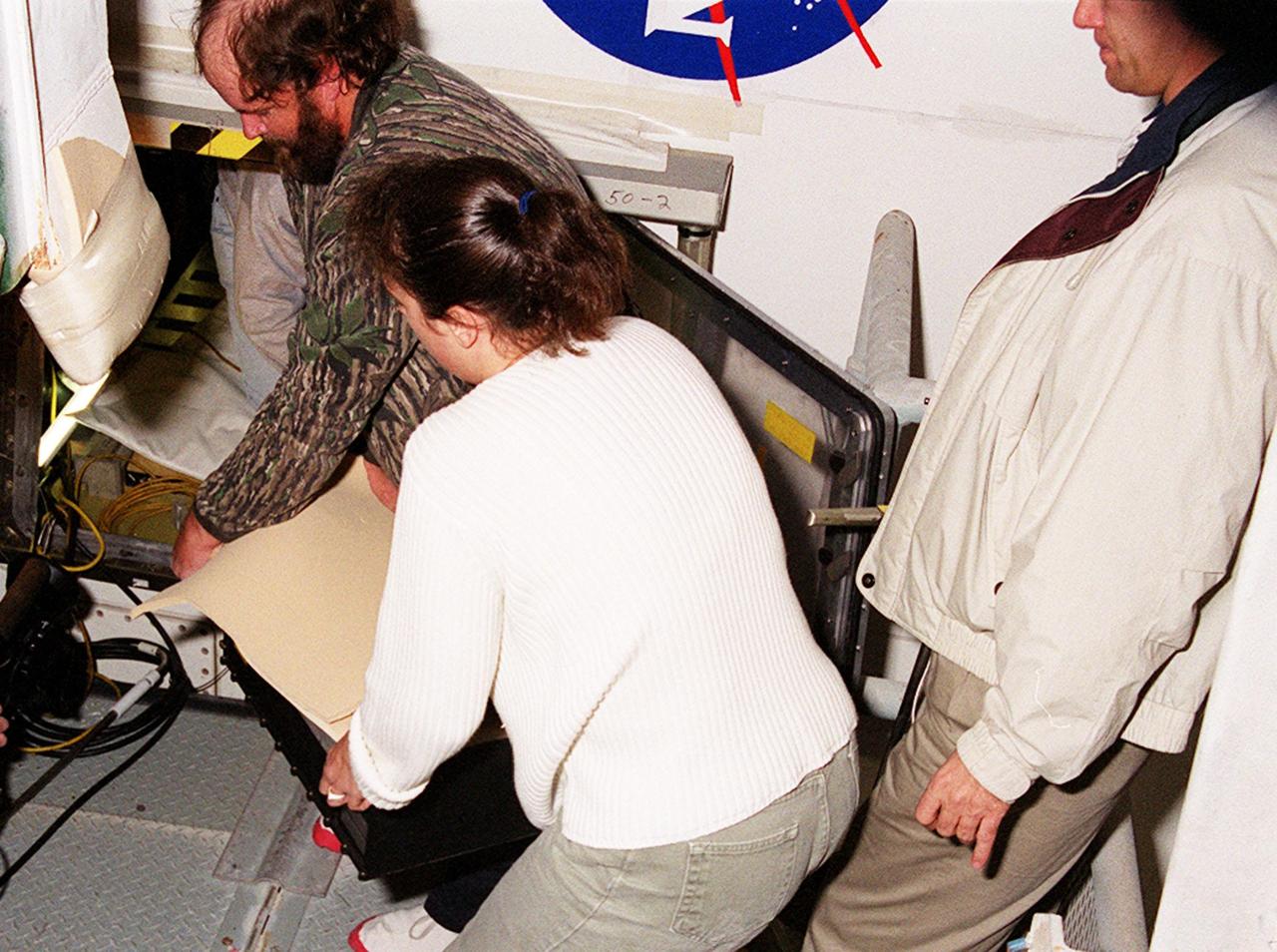
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers carry away the faulty Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) from Shuttle Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A. The E-MEC became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST
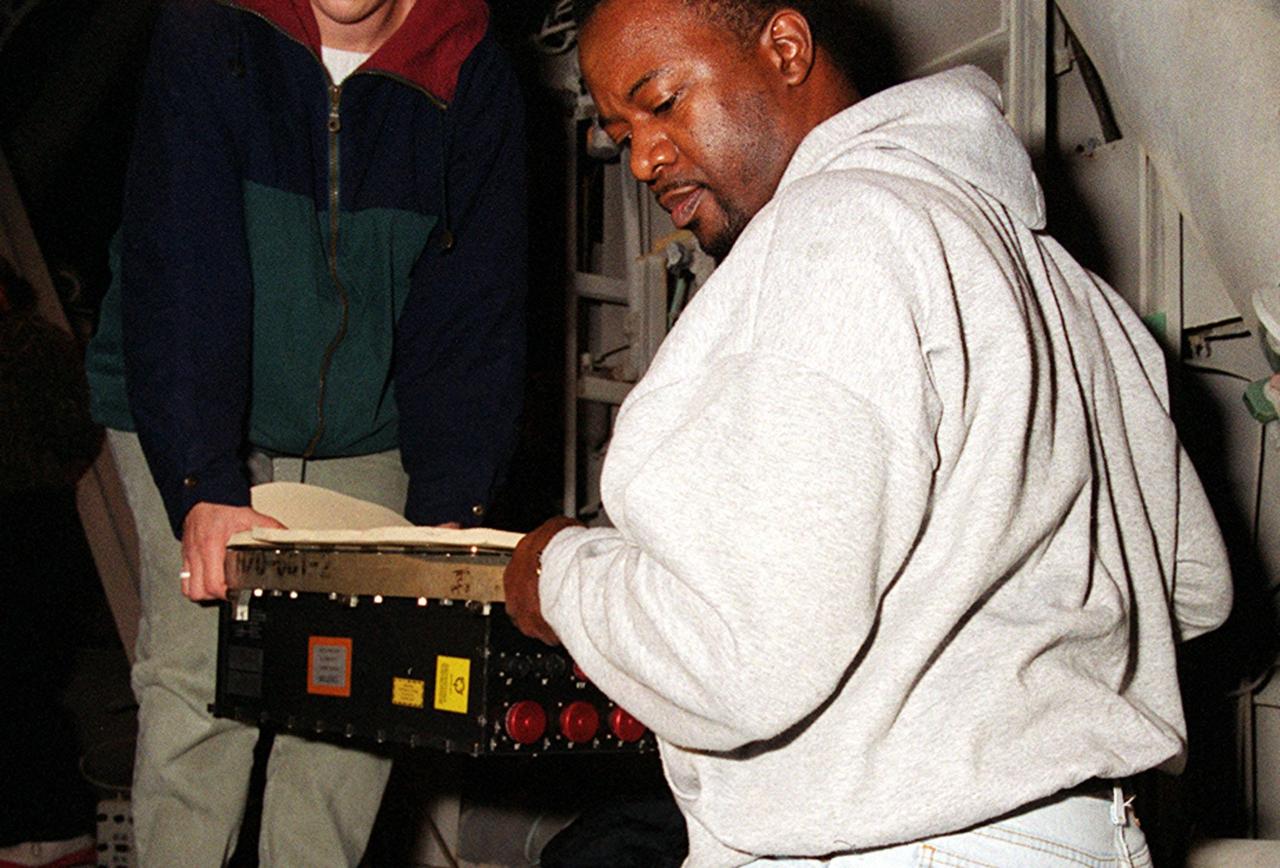

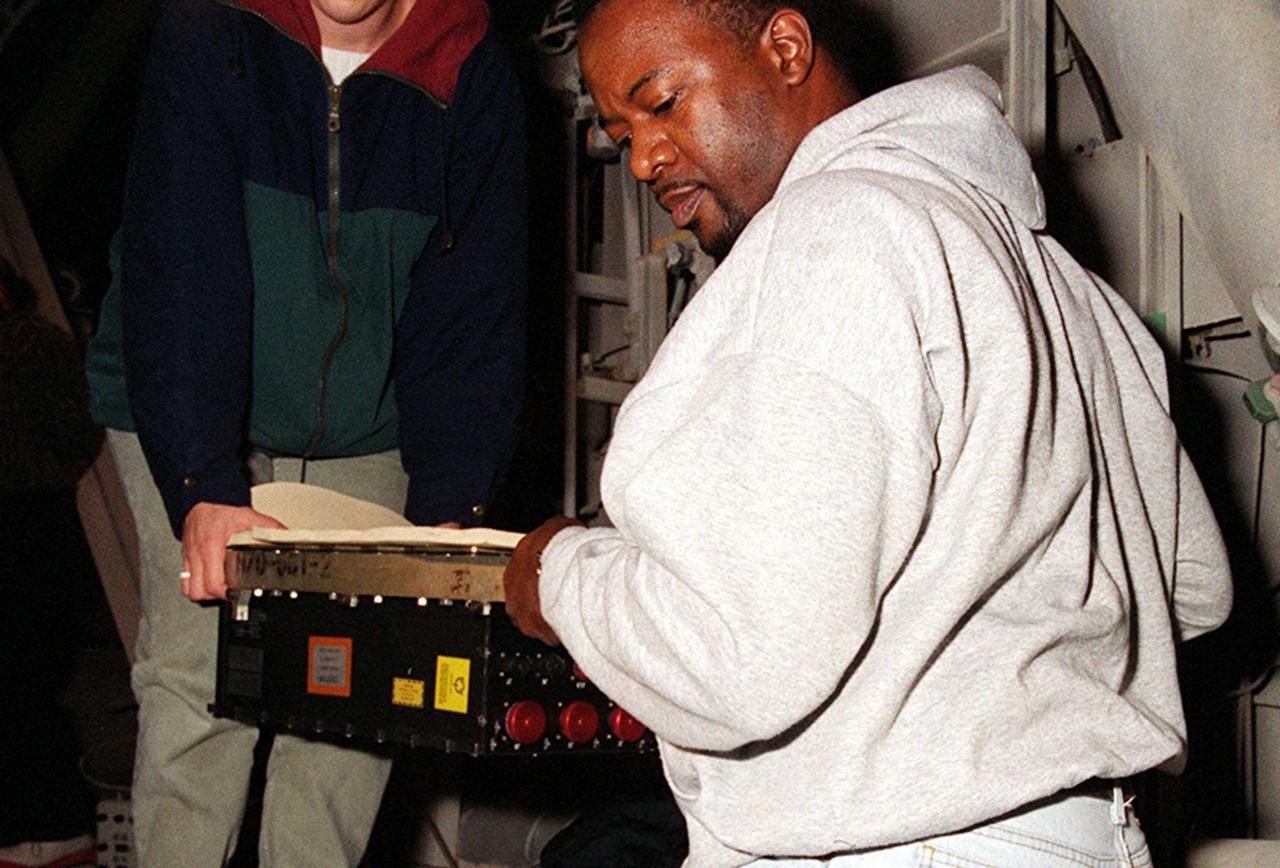
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers carry the replacement Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) to Shuttle Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A for installation in the aft compartment of the payload bay. The original E-MEC became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians remove a faulty Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) from Shuttle Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A. The E-MEC became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers carry away the faulty Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) from Shuttle Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A. The E-MEC became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers carry the replacement Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) to Shuttle Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A for installation in the aft compartment of the payload bay. The original E-MEC became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Pad 39A, workers move the replacement Enhanced Main Events Controller (E-MEC) into Shuttle Endeavour's aft compartment in the payload bay. The original E-MEC became suspect during the Jan. 31 launch countdown and mission STS-99 was delayed when NASA managers decided to replace it. Each Shuttle carries two enhanced master events controllers (E-MECs), which provide relays for onboard flight computers to send signals to arm and fire pyrotechnics that separate the solid rockets and external tank during assent. Both E-MECs are needed for the Shuttle to be cleared for flight. Currently Endeavour and Columbia are the only two orbiters with the E-MECs. Built by Rockwell's Satellite Space Electronics Division, Anaheim, Calif., each unit weighs 65 pounds and is approximately 20 inches long, 13 inches wide and 8 inches tall. Previously, three Shuttle flights have been scrubbed or delayed due to faulty MECs: STS-73, STS-49 and STS-41-D. The next scheduled date for launch of STS-99 is Feb. 11 at 12:30 p.m. EST