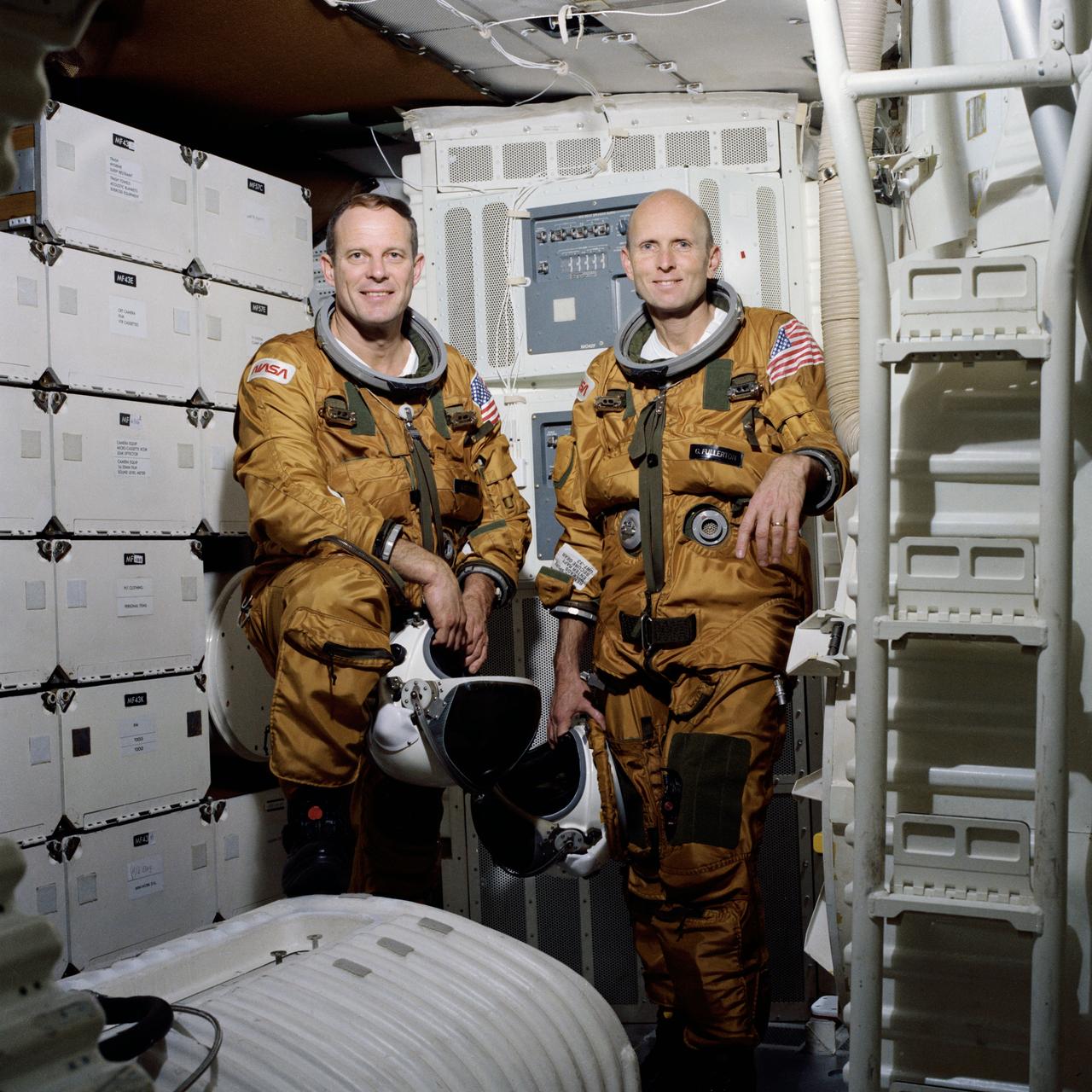

S82-25504 (20 Jan. 1982) --- These two veteran astronauts were named as prime crew members for STS-3 in the space shuttle Columbia. Wearing modified USAF-type altitude pressure garments in their Earth-bound shuttle trainer are astronauts Jack R. Lousma (left), commander, and C. Gordon Fullerton, pilot. Lousma was pilot on the second of three NASA astronaut crews to visit the Earth-orbiting Skylab space station in 1973. Fullerton was pilot for three free flights in the space shuttle Enterprise during approach and landing tests (ALT) in 1977. Photo credit: NASA

S82-28456 (19 Feb. 1982) --- Astronauts Jack R. Lousma, left, STS-3 commander, and C. Gordon Fullerton, pilot, are briefed on emergency procedures at Launch Pad 39A by Buck Tomlinson, a safety instructor with Wackenhut Services, Inc. Also pictured is astronaut Daniel C. Brandenstein, STS-8 pilot. The men were at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) for participation in a countdown demonstration test (CDDT). Photo credit: NASA
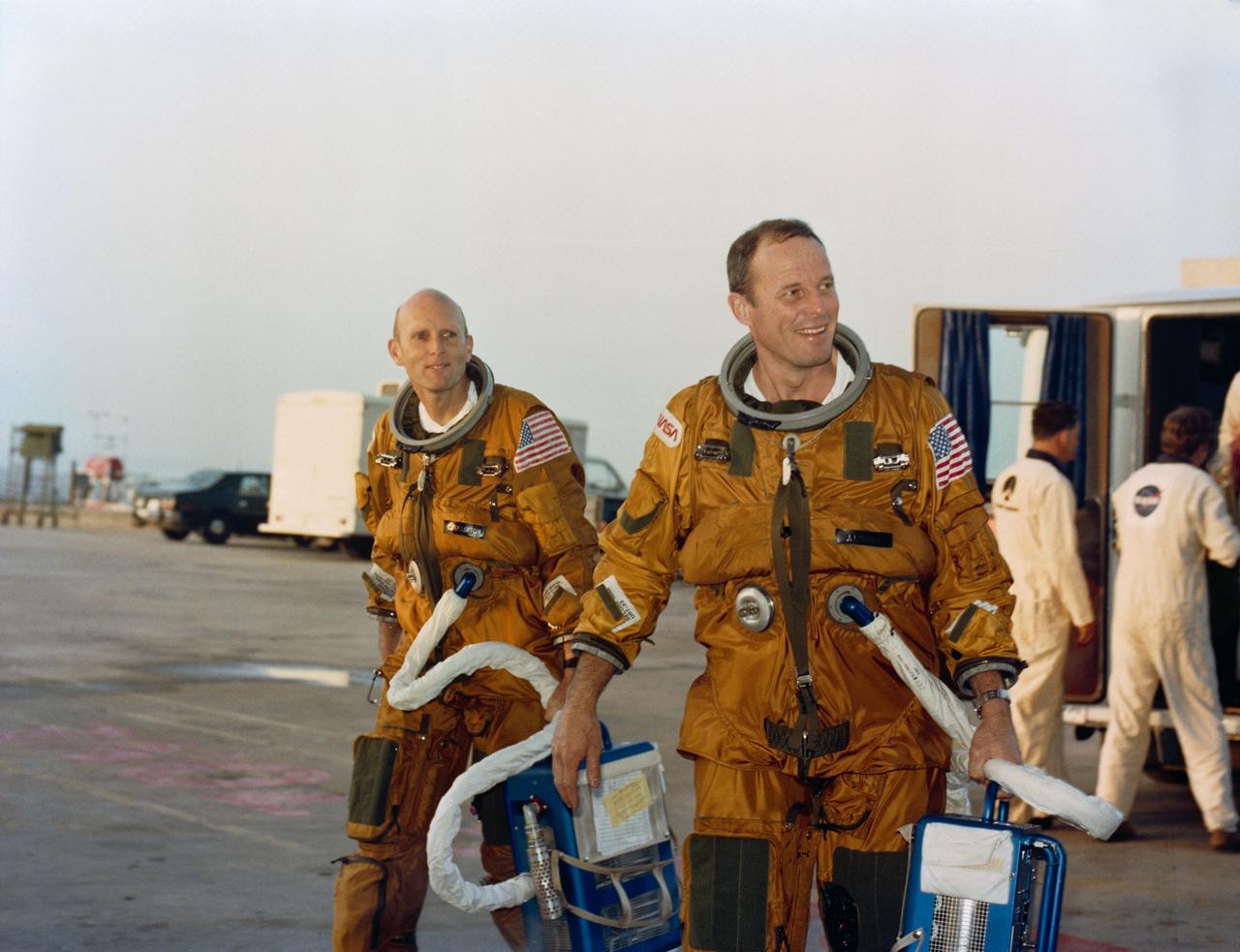

S82-28454 (19 Feb. 1982) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, right, STS-3 commander, and C. Gordon Fullerton, pilot, carry portable spacesuit air controllers as they walk from a transport van to Launch Pad 39A to participate in a simulated countdown and launch. This countdown demonstration test (CDDT) is part of the preparations for NASA?s third orbital flight test in the space shuttle Columbia. The two are scheduled to spend a week orbiting Earth in Columbia this spring. Photo credit: NASA
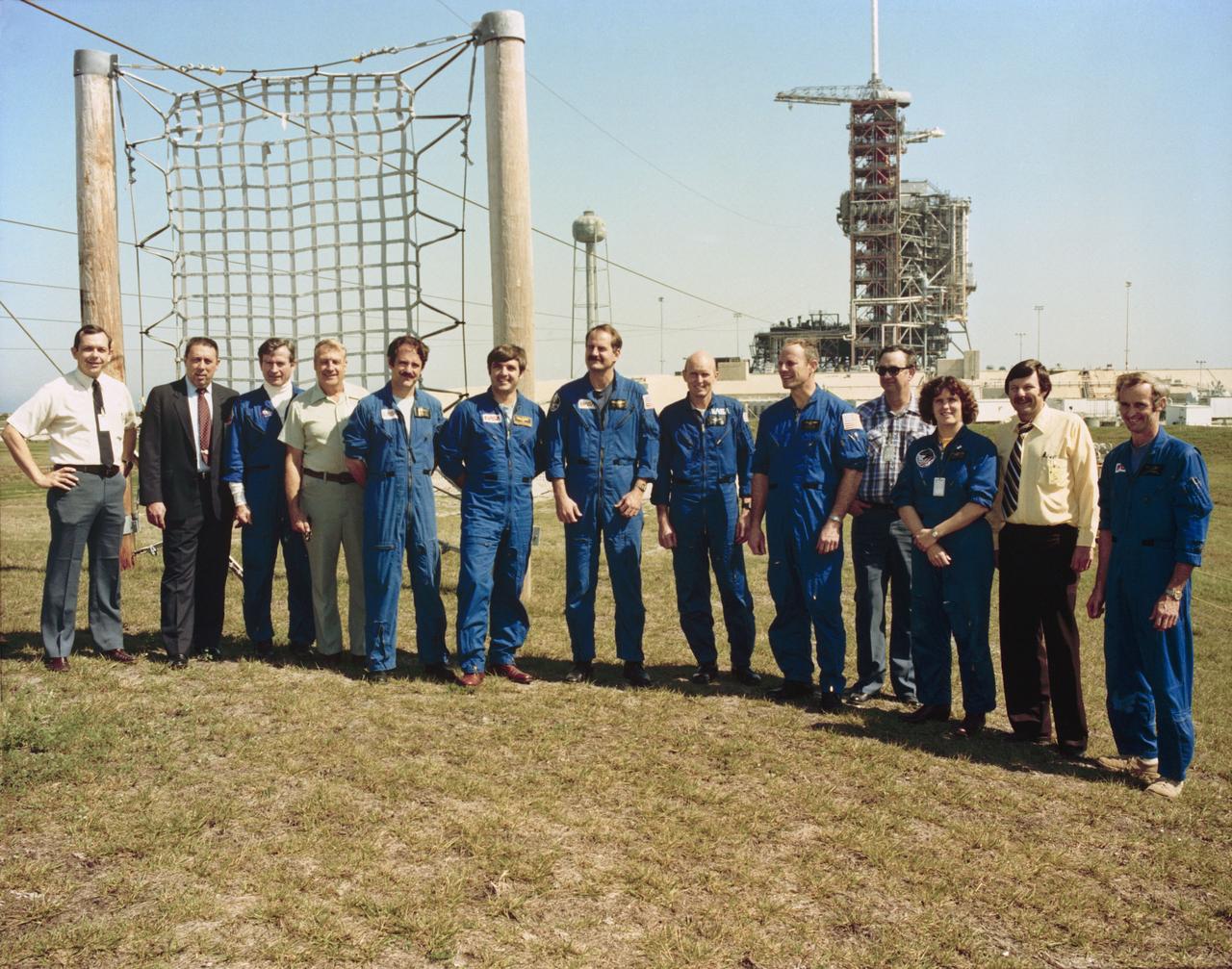

S82-28457 (19 Feb. 1982) --- Member of the JSC astronaut corps., STS-3 vehicle integration test (VIT) team and other personnel pose for a photograph at the completion of a countdown demonstration test (CDDT) and safety briefings at Launch Pad 39A, Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Participants are, from the left, Wilbur J. Etbauer, engineer with the VIT team; George W. S. Abbey, director of flight operations at JSC; astronaut John W. Young, chief of the astronaut office at JSC; Jack Fleming of Rockwell International; mission specialist-astronaut John M. Lounge; astronaut Daniel C. Brandenstein; mission specialist-astronaut James D. Van Hoften; astronauts C. Gordon Fullerton and Jack Lousma, prime crew for STS-3; Olan J. Bertrand, VIT team member; mission specialist-astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan; Richard W. Nygren, head of the VIT team; and astronaut Donald E. Williams. The space shuttle Columbia is obscured by its service structure on Launch Pad 39A in the background. Part of slide-wire type emergency escape system is visible in the picture. Photo credit: NASA
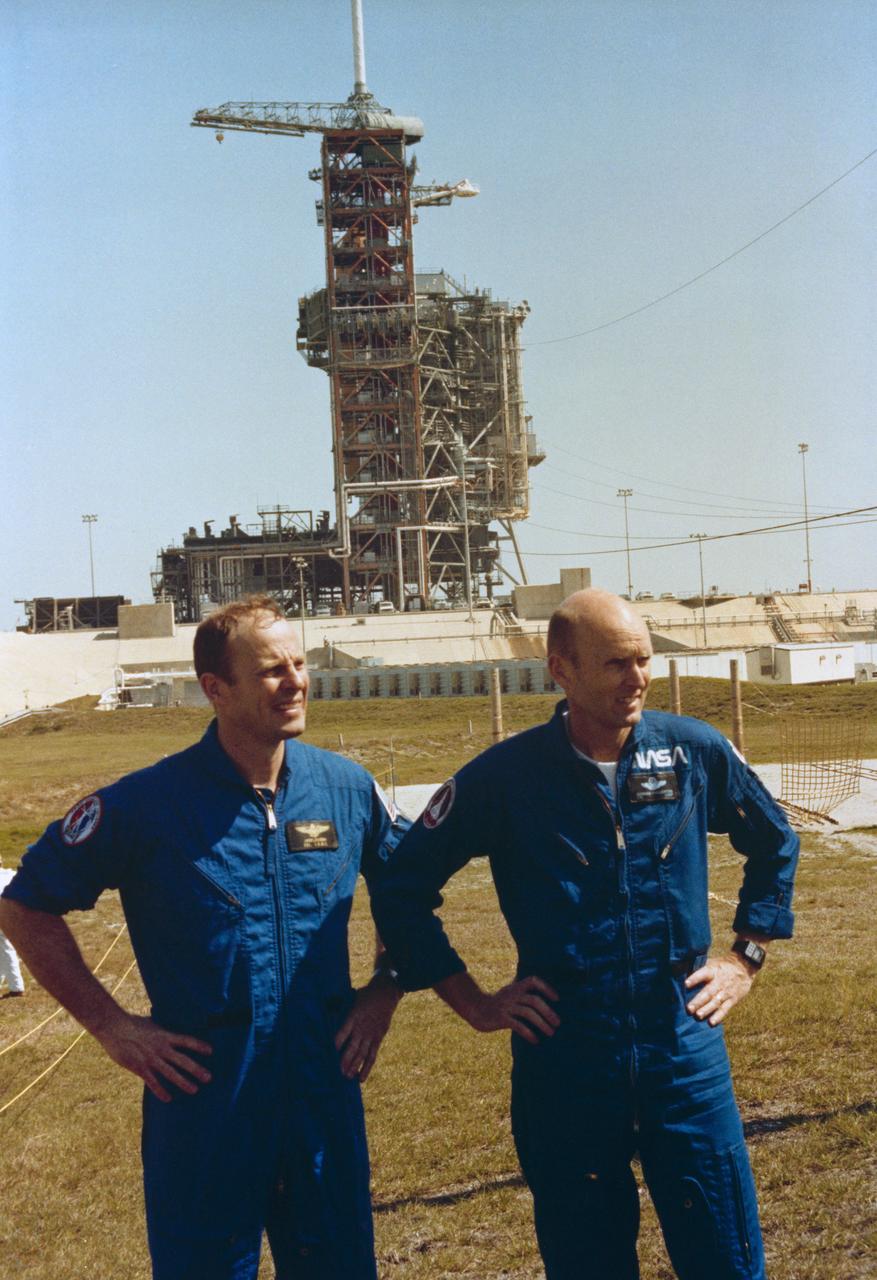

S82-28455 (19 Feb. 1982) --- The prime crew members for STS-3 take a break in their training schedule at KSC to pose for a few pictures. Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, left, is crew commander; and C. Gordon Fullerton, pilot, for STS-3 scheduled to launch this spring. Launch Pad 39A is in the background. Photo credit: NASA
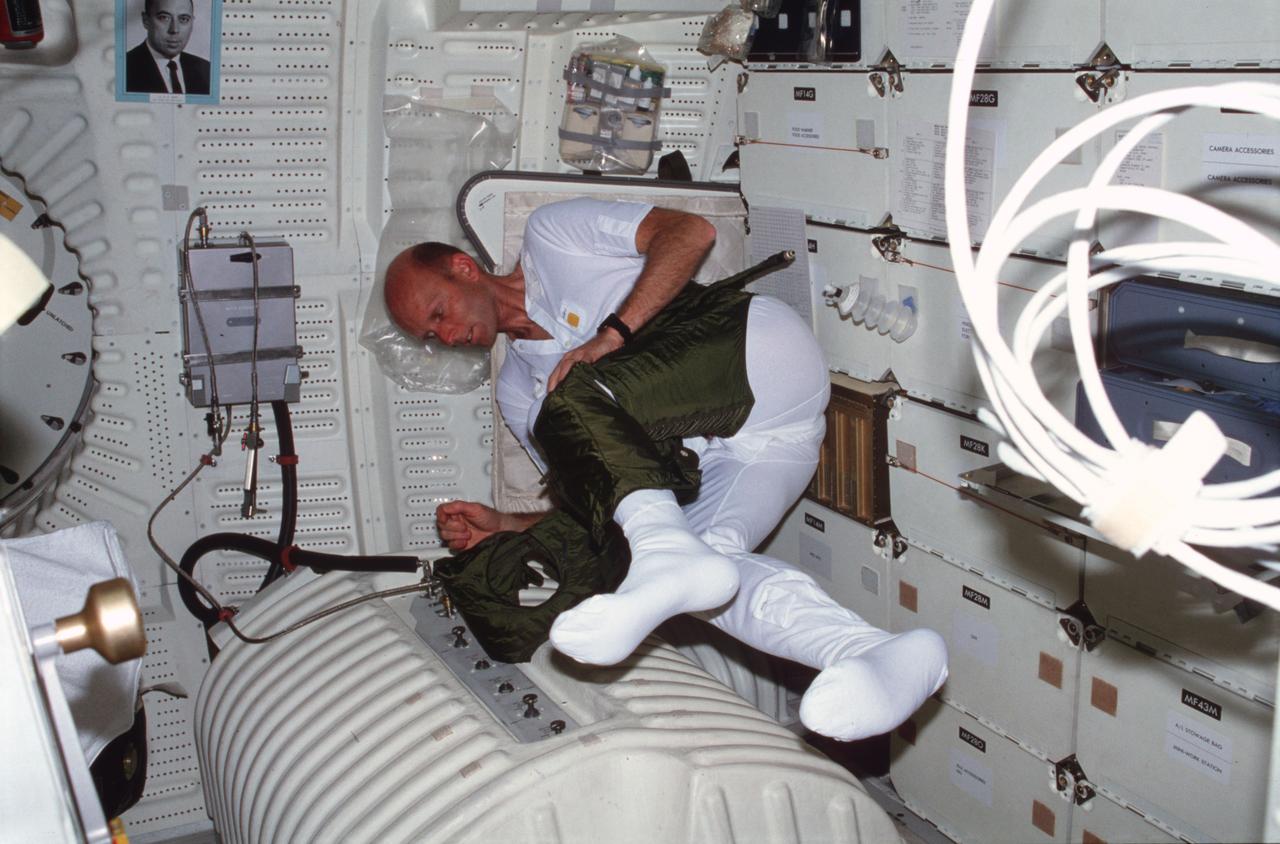

STS003-23-161 (24 March 1982) --- Astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, STS-3 pilot, dons an olive drab inner garment which complements the space shuttle Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit. Since there are no plans for an extravehicular activity (EVA) on the flight, Fullerton is just getting some practice time ?in the field? as he is aboard the Earth-orbiting Columbia. He is in the middeck area of the vehicle. The photograph was taken with a 35mm camera by astronaut Jack R. Lousma, STS-3 commander. Photo credit: NASA
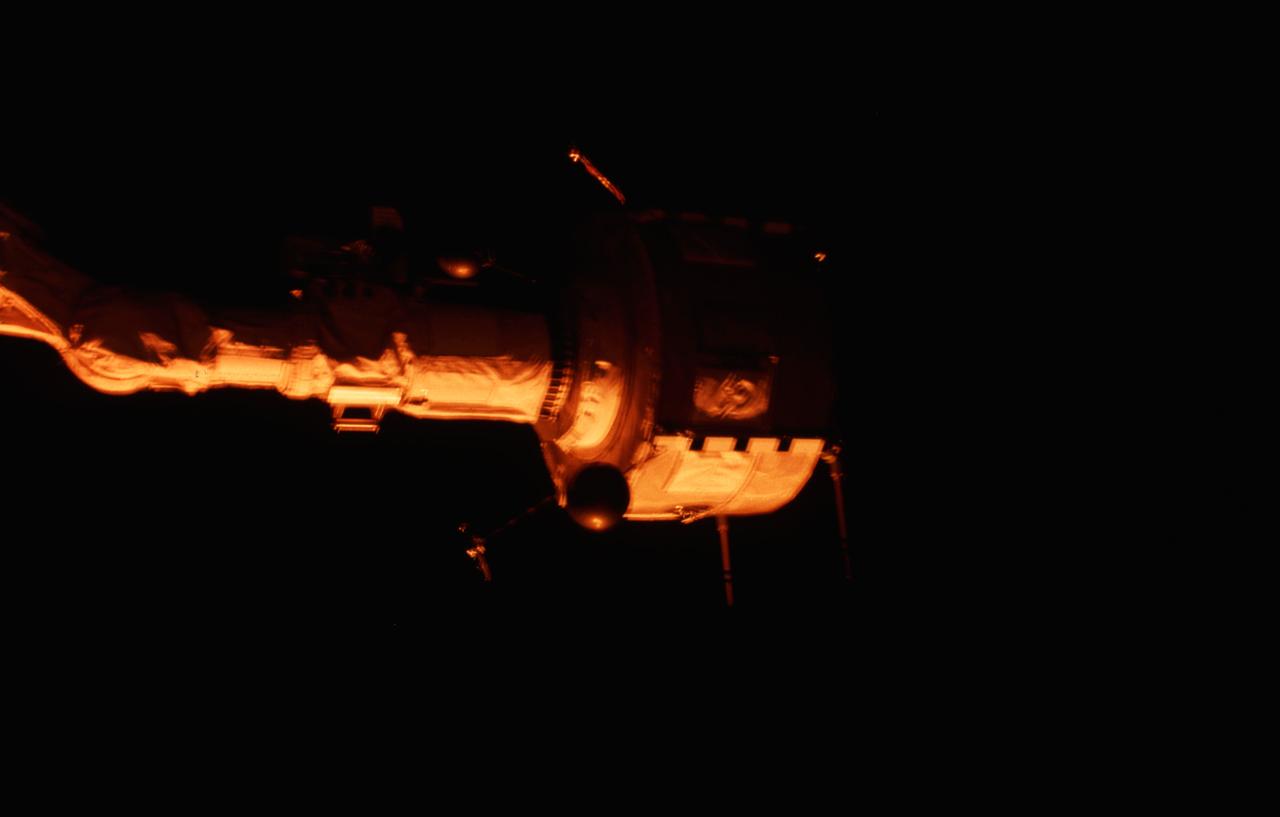

STS003-21-080 (22-30 March 1982) --- Plasma Diagnostics Package (PDP) grappled by remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector is positioned above payload bay (PLB) at sunrise. Photo credit: NASA

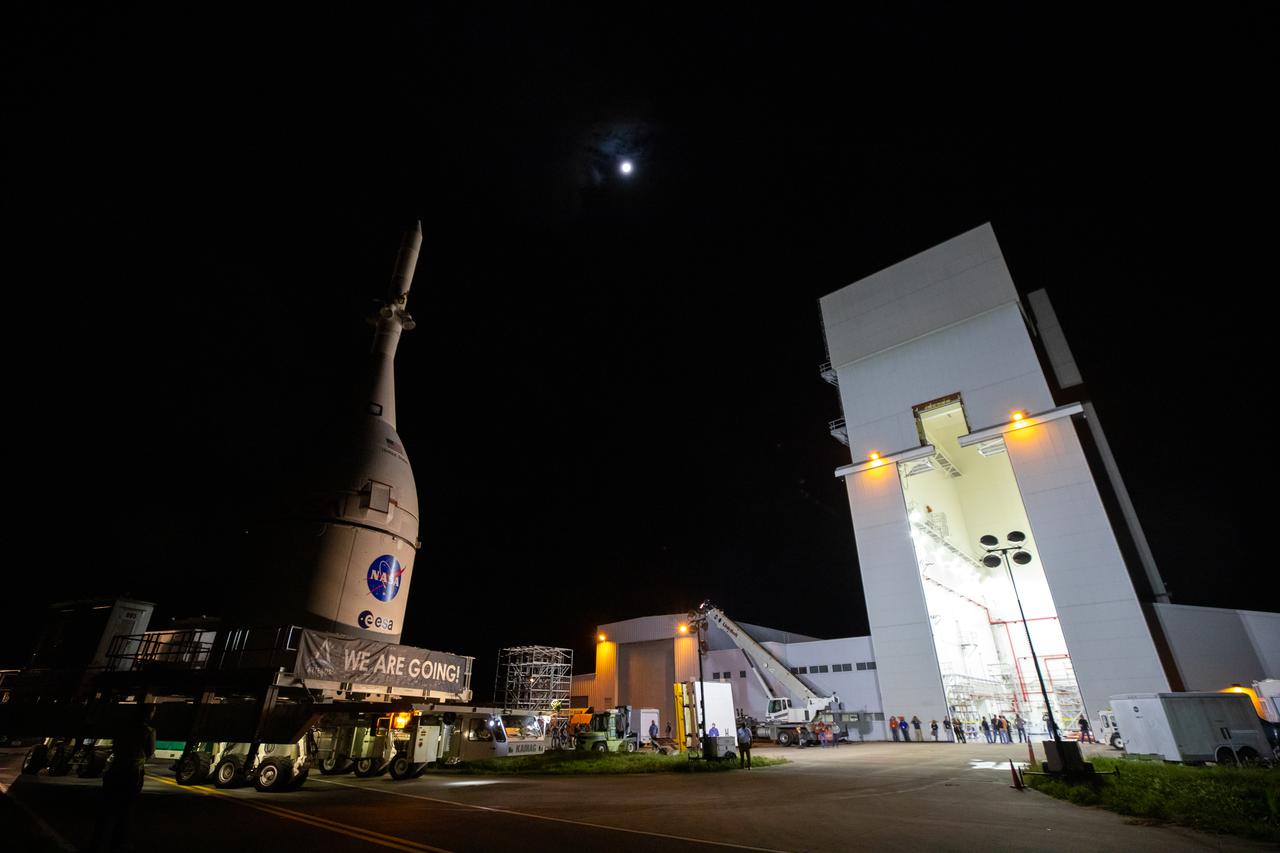
The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, begins the move out of the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 19, 2021. Orion will be transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will join the already stacked flight hardware and be raised into position atop the Space Launch System rocket in High Bay 3. Launching in 2021, Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, moves out of the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 19, 2021. Orion will be transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will join the already stacked flight hardware and be raised into position atop the Space Launch System rocket in High Bay 3. Launching in 2021, Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
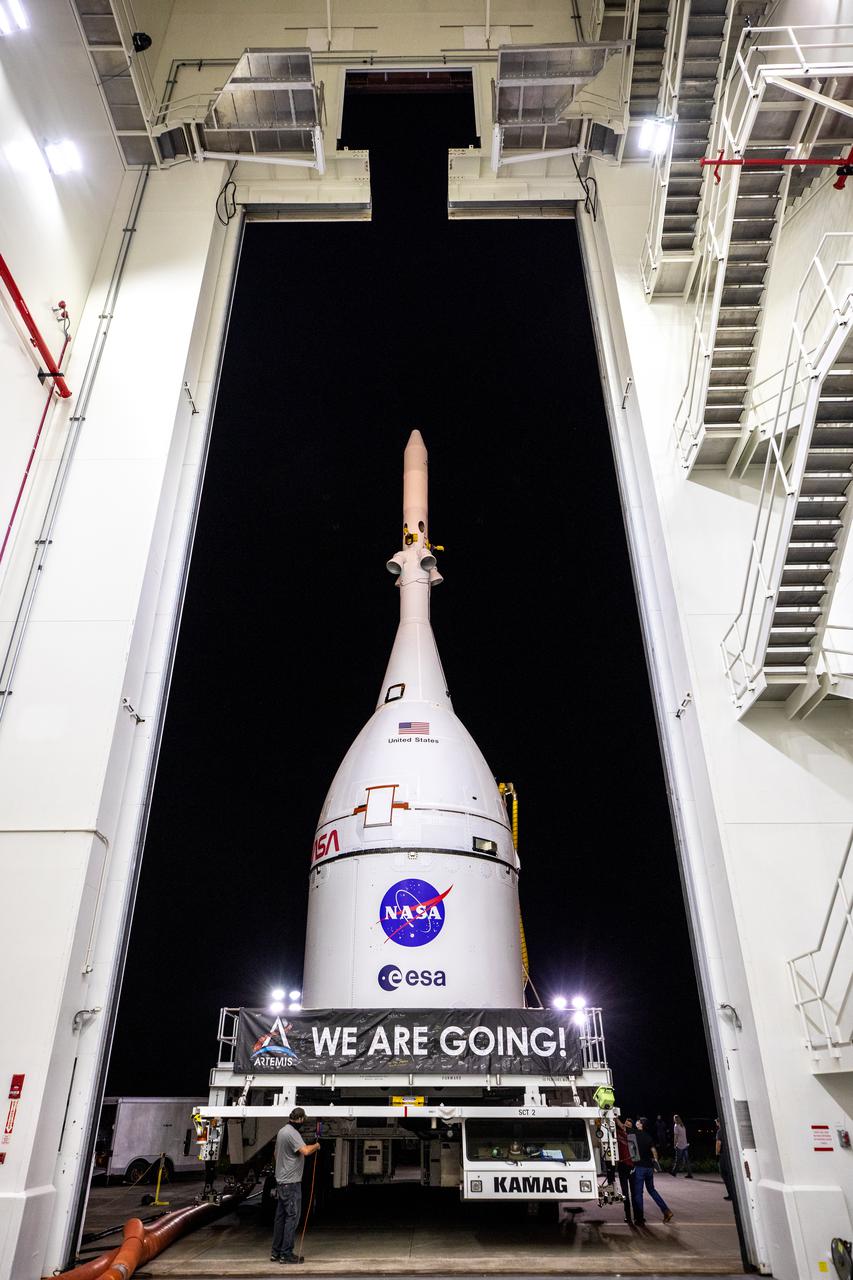

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, begins the move out of the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 19, 2021. Orion will be transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will join the already stacked flight hardware and be raised into position atop the Space Launch System rocket in High Bay 3. Launching in 2021, Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission, fully assembled with its launch abort system, moves out of the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 19, 2021. Orion will be transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will join the already stacked flight hardware and be raised into position atop the Space Launch System rocket in High Bay 3. Launching in 2021, Artemis I will be an uncrewed test flight of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System rocket as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
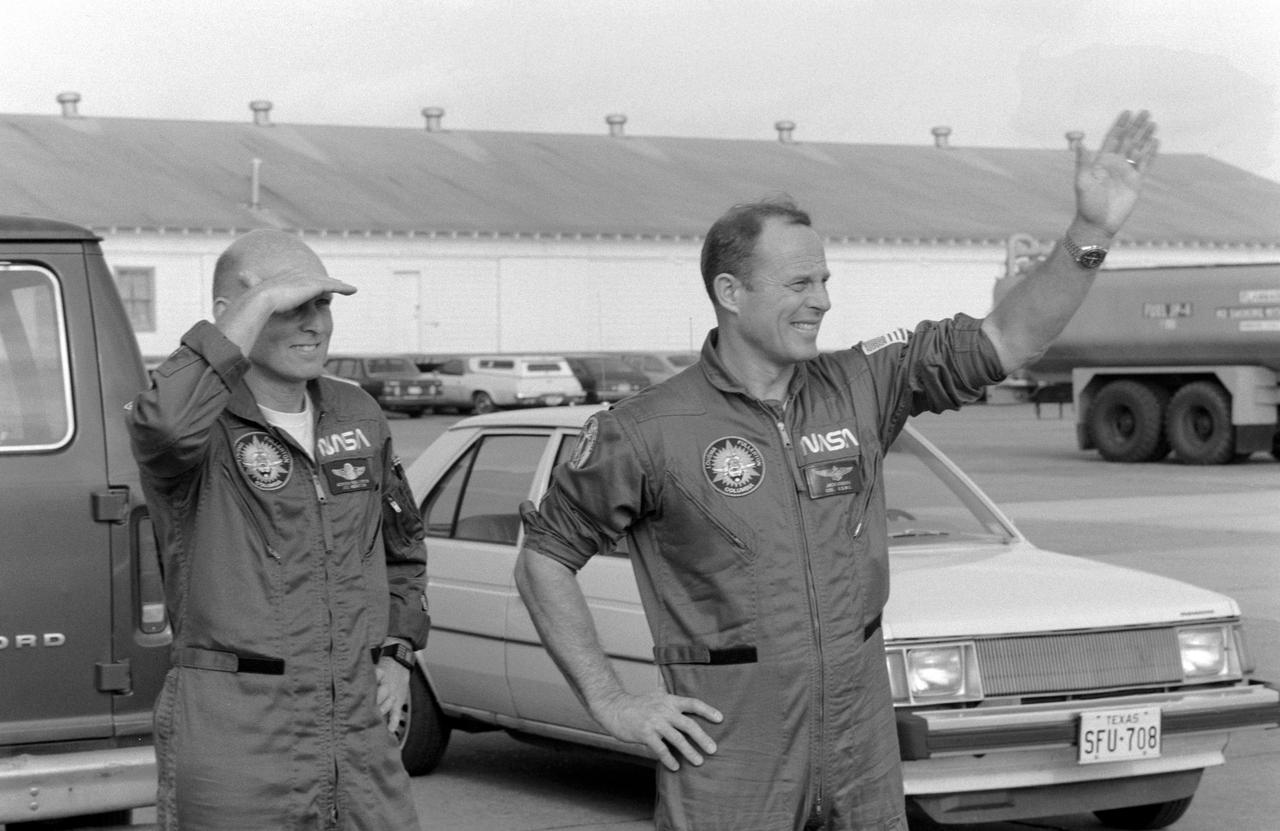

S82-28706 (20 March 1982) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, right, STS-3 commander, and C. Gordon Fullerton, greet a crowd on hand at Ellington Air Force Base to bid them farewell prior to their departure to KSC in a pair of T-38 jet aircraft. The two are scheduled to liftoff in less than 48 hours from the Kennedy Space Center?s Launch Pad 39A, for the third in a series of space transportation system (STS-3) flights. Photo credit: NASA
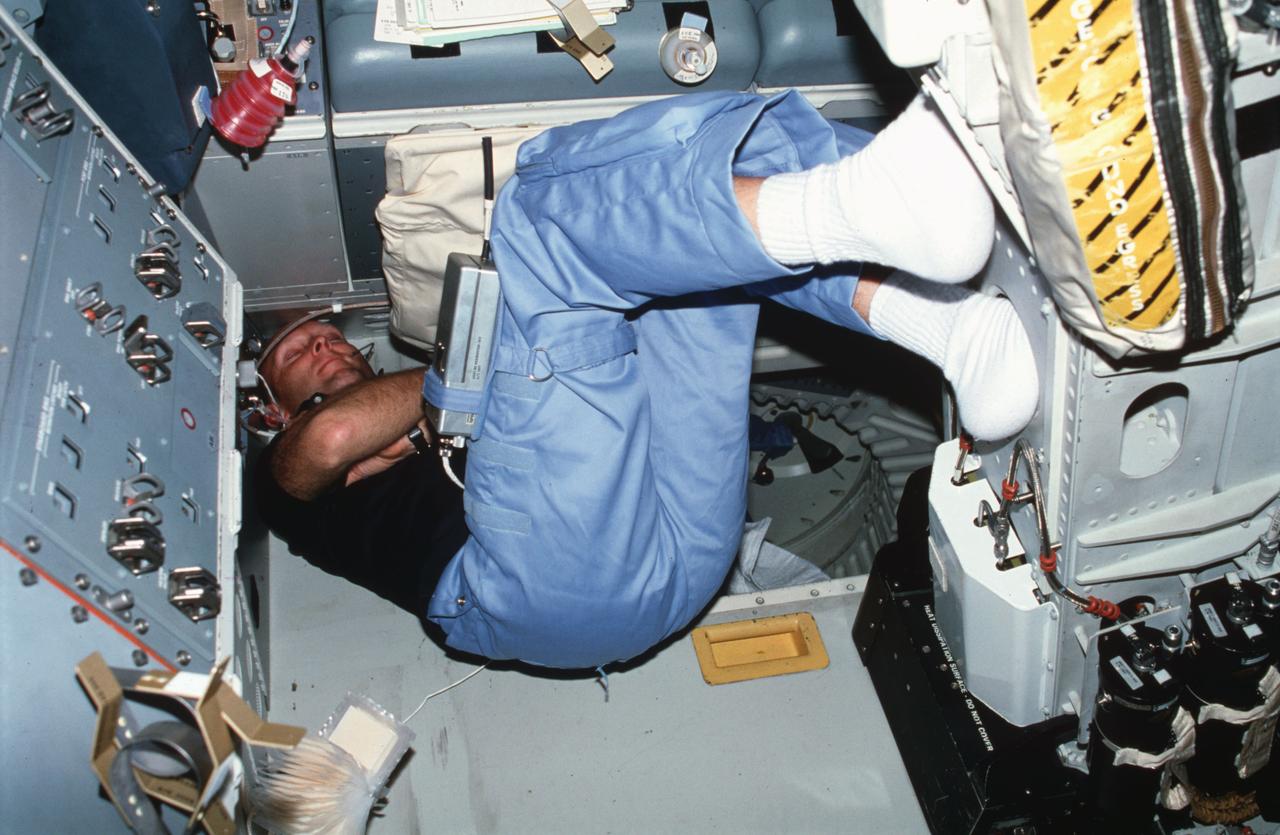
STS003-22-113 (24 March 1982) --- Astronaut Gordon Fullerton, STS-3 pilot, wearing communication kit assembly mini-headset (HDST), sleeps on aft flight deck resting his back against the floor and his feet against commander's ejection seat (S1) back. On-orbit station control panel A8 and payload station panel L15 appear above Fullerton. Special clips for holding notebooks open and beverage containers are velcroed on various panels. Photo credit: NASA
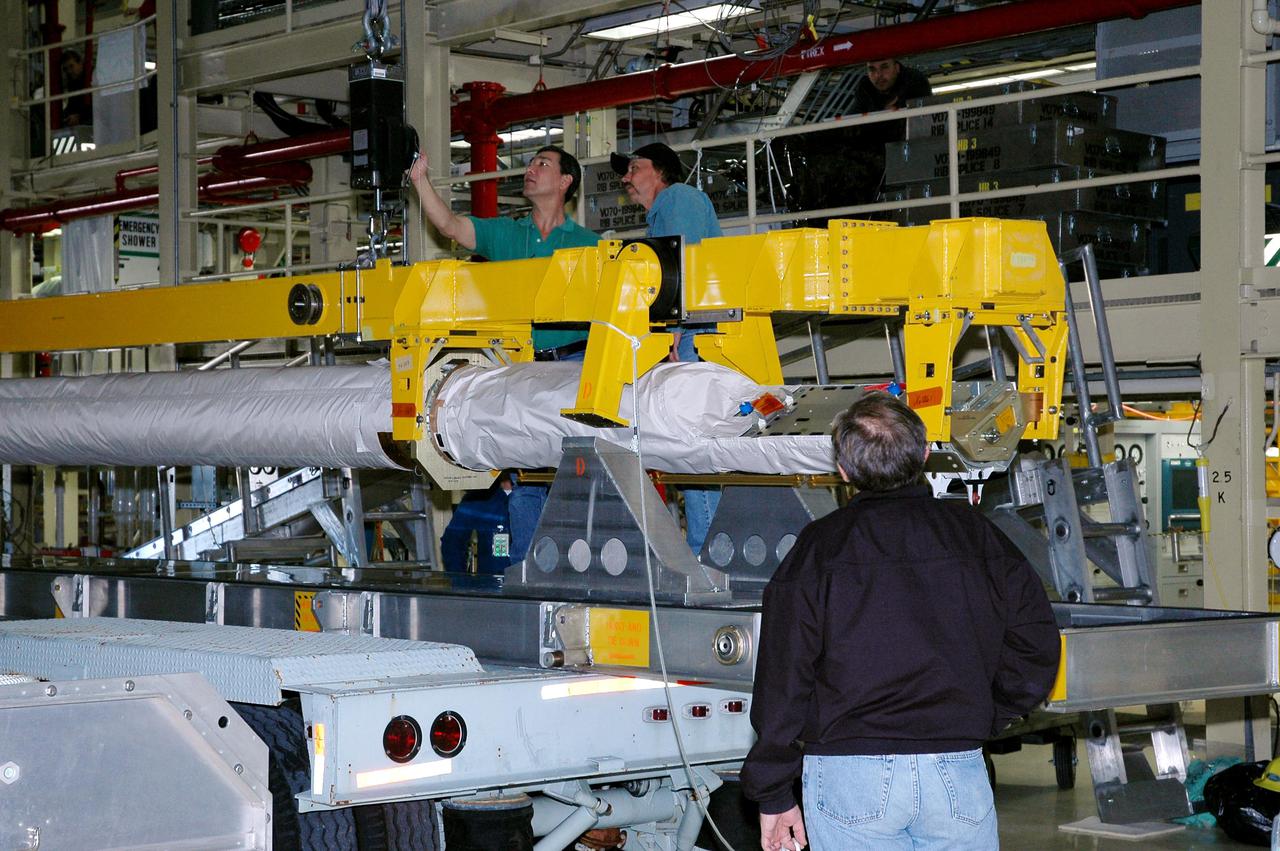

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility high bay, technicians check the crane that will lift the Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS) from its transporter. The OBSS will be installed on the starboard side of the payload bay in the orbiter Discovery. The 50-foot-long OBSS attaches to the Remote Manipulator System, or Shuttle robotic arm, and is one of the new safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the orbiter with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. The Return to Flight mission, STS-114, has a launch window of May 12 to June 3, 2005.
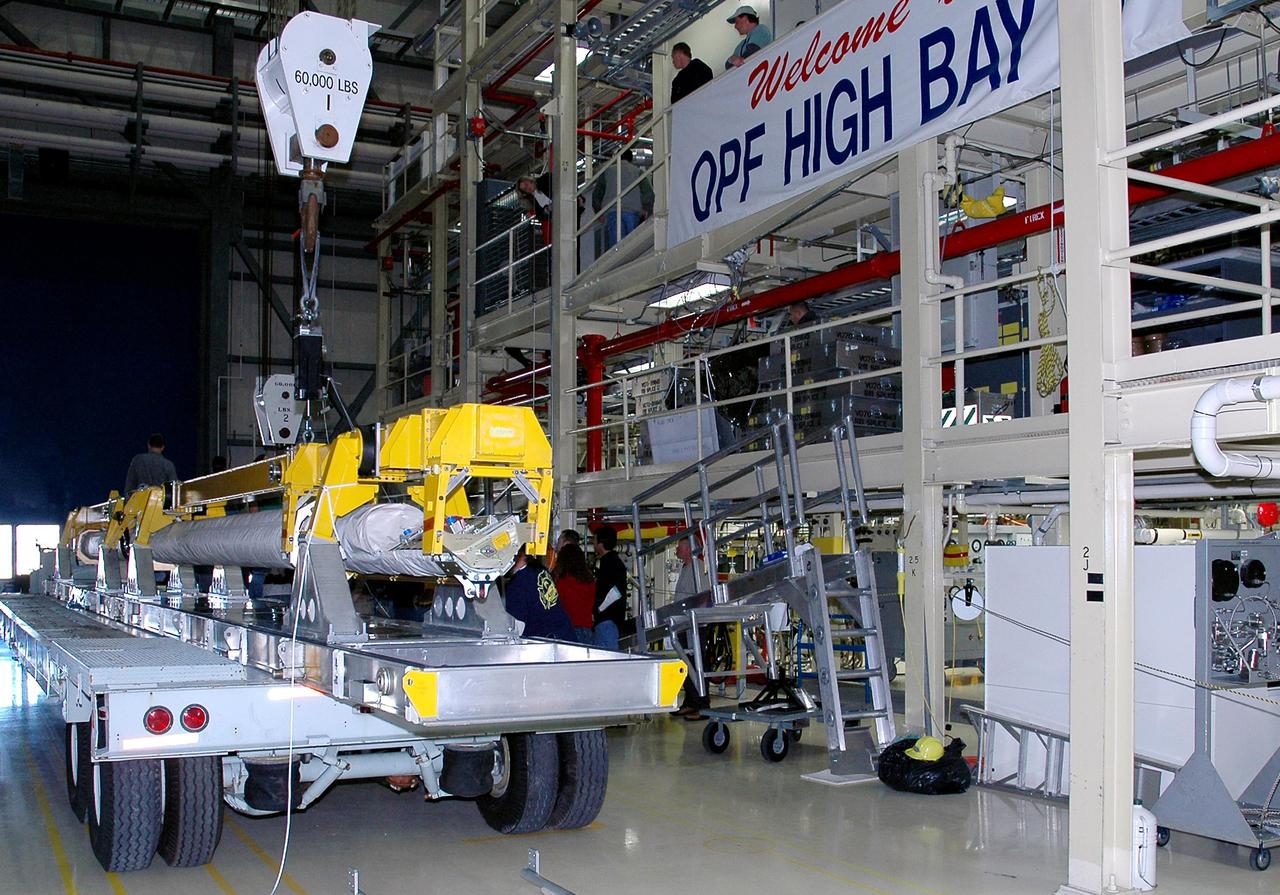

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility high bay, the Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS) is fitted with a crane. After being lifted from its transporter, the OBSS will be installed on the starboard side of the payload bay in the orbiter Discovery. The 50-foot-long OBSS attaches to the Remote Manipulator System, or Shuttle robotic arm, and is one of the new safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the orbiter with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. The Return to Flight mission, STS-114, has a launch window of May 12 to June 3, 2005.
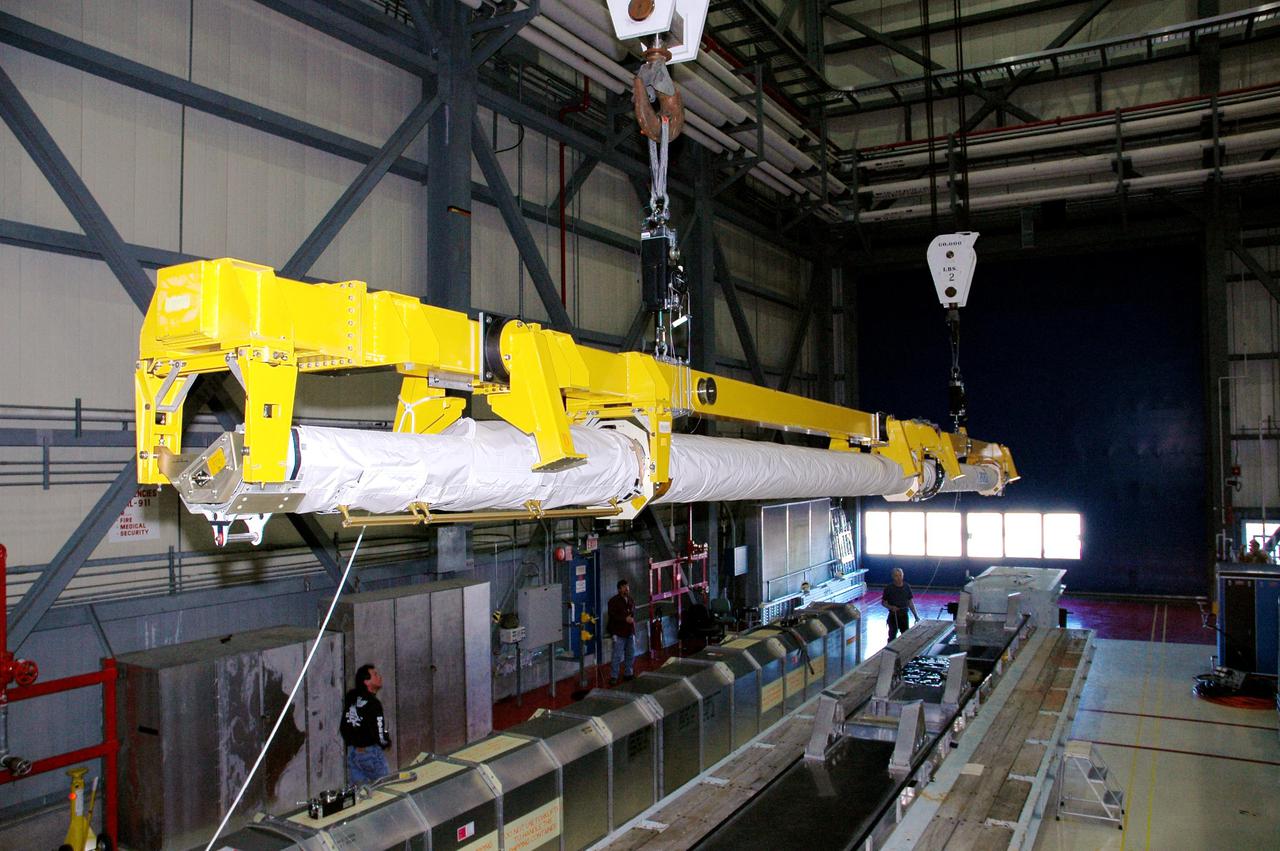

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility high bay, cranes lift the Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS) from its transporter. The OBSS will be installed on the starboard side of the payload bay in the orbiter Discovery. The 50-foot-long OBSS attaches to the Remote Manipulator System, or Shuttle robotic arm, and is one of the new safety measures for Return to Flight, equipping the orbiter with cameras and laser systems to inspect the Shuttle’s Thermal Protection System while in space. The Return to Flight mission, STS-114, has a launch window of May 12 to June 3, 2005.
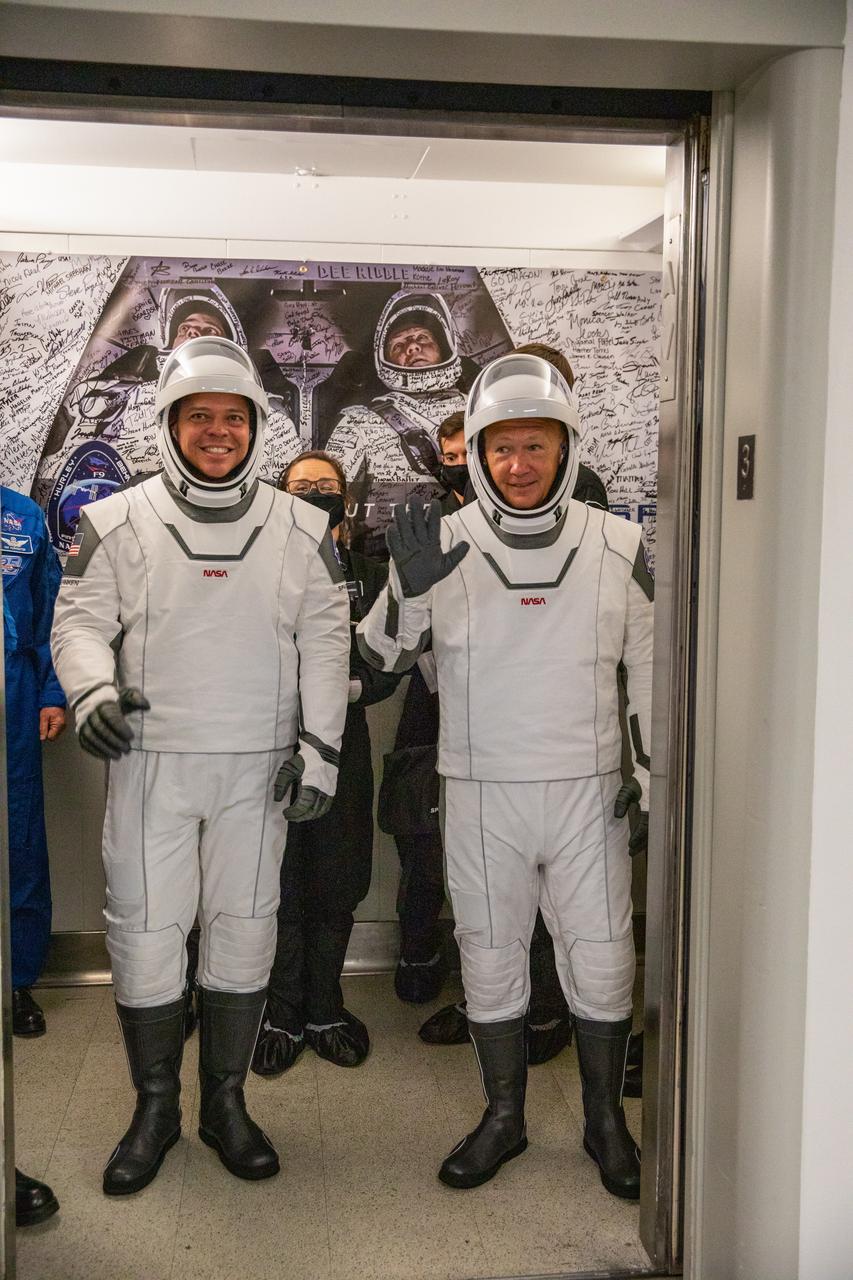

NASA astronauts Robert Behnken (left) and Douglas Hurley depart the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, in preparation for transport to Launch Complex 39A ahead of NASA’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch to the International Space Station from U.S. soil since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Ares I-X rocket stands tall inside NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building High Bay 3, NASA's Ares I-X rocket is ready to undergo its first power-up. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
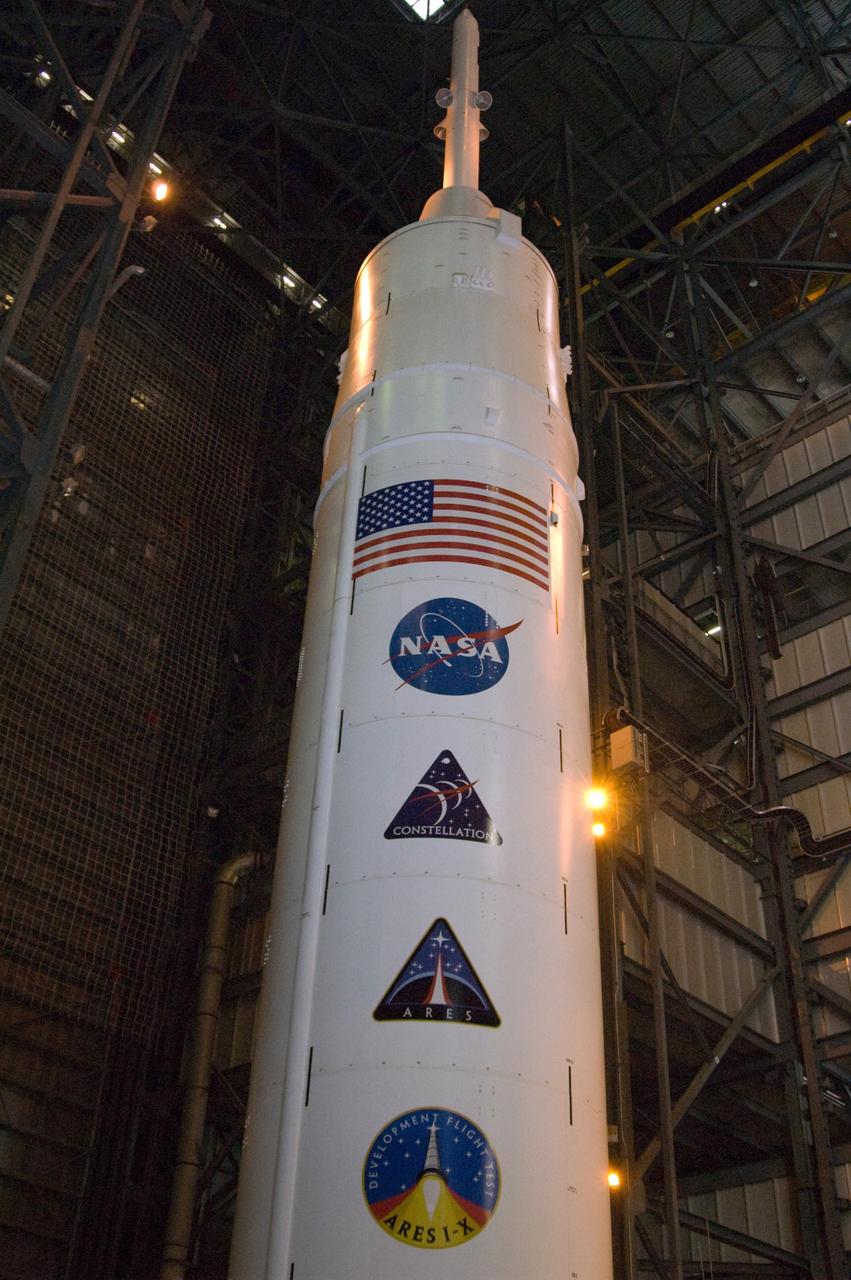

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building High Bay 3, NASA's Ares I-X rocket undergoes its first power-up. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A banner inside NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building captures the excitement building at Kennedy in anticipation of the flight test of the Ares I-X rocket, towering above it in High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system designed to carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/constellation/ares/flighttests/aresIx/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
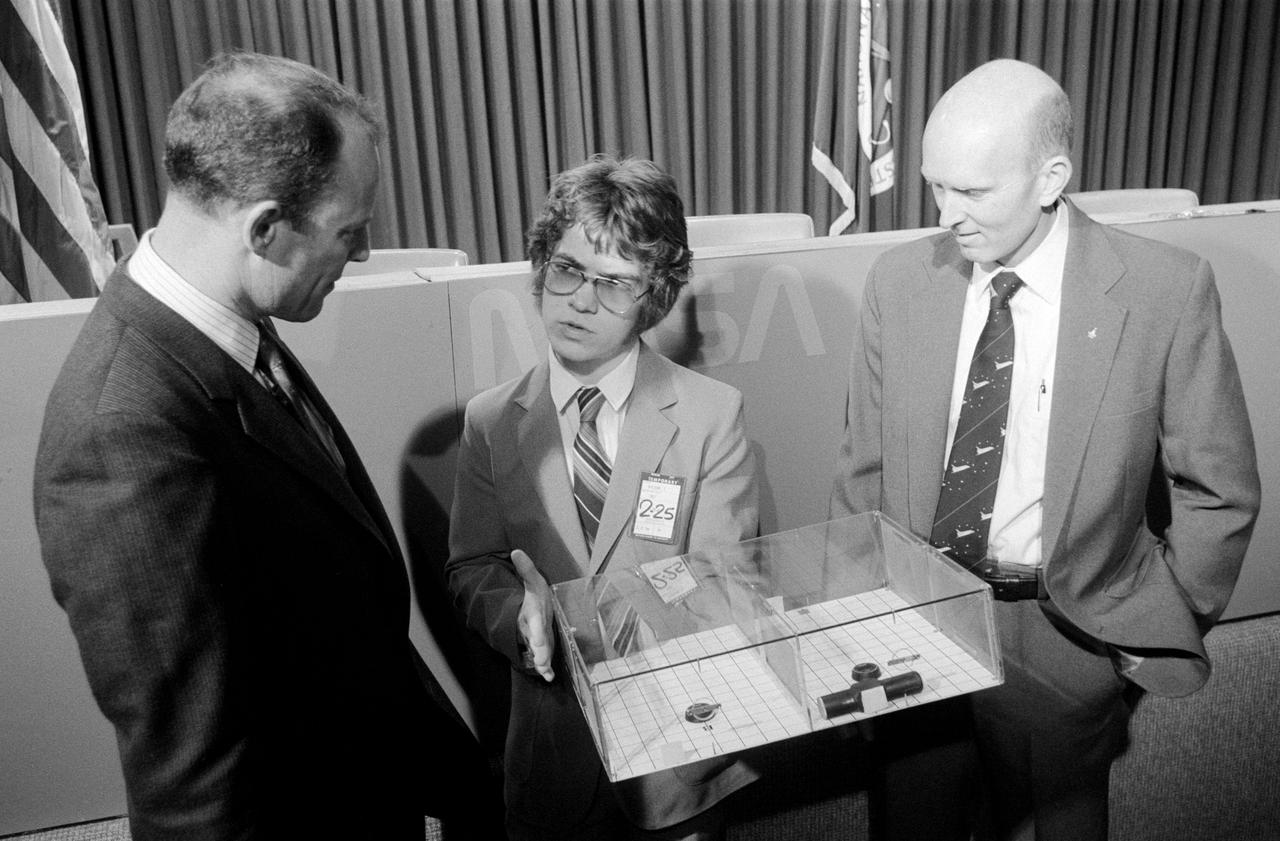

S82-27604 (26 Feb. 1982) --- The astronaut crew members for NASA?s third space transportation system (STS-3) flight meet with Todd E. Nelson, who devised a scientific experiment to fly on their mission. Astronauts Jack R. Lousma, left, commander, and C. Gordon Fullerton, pilot, along with the 18-year-old high school senior, discussed the experiment, entitled ?Insects in Flight Motion Study,? during a press briefing in JSC?s public affairs facility. Photo credit: NASA
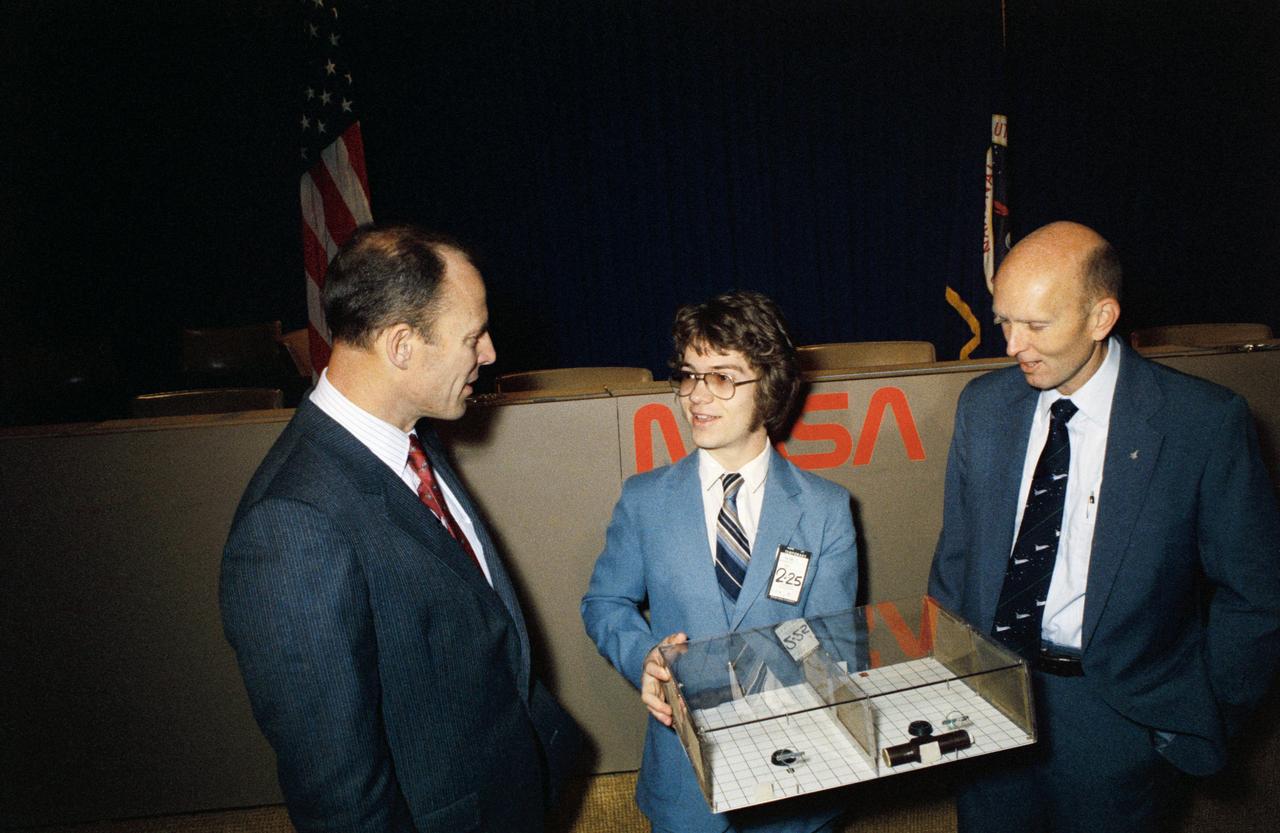

S82-27835 (26 Feb. 1982) --- The astronaut crew members for NASA?s third space transportation system (STS-3) flight meet with Todd E. Nelson, who devised a scientific experiment to fly on their mission. Astronauts Jack R. Lousma, left, commander, and C. Gordon Fullerton, pilot, along with the 18-year-old high school senior, discussed the experiment, entitled ?Insects in Flight Motion Study,? during a press briefing in JSC?s public affairs facility. Photo credit: NASA
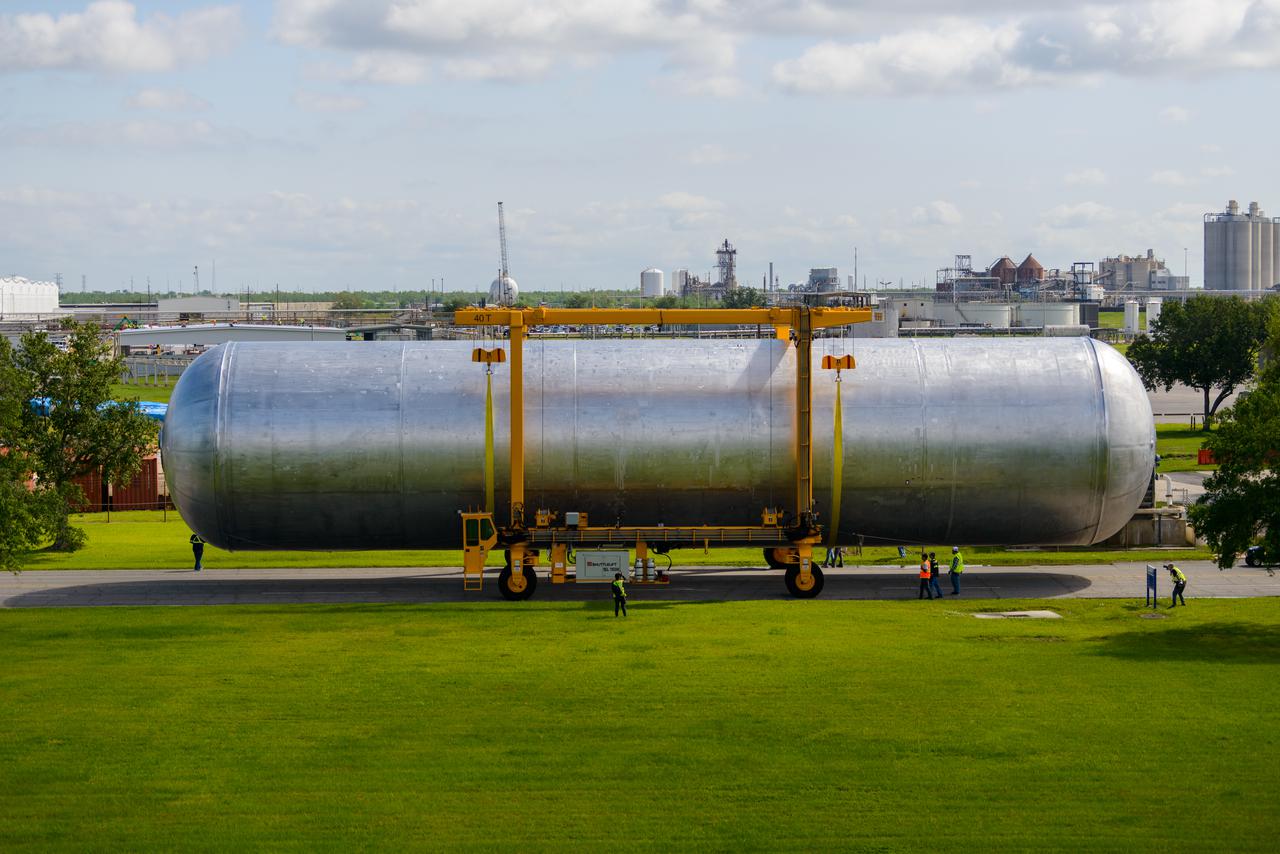

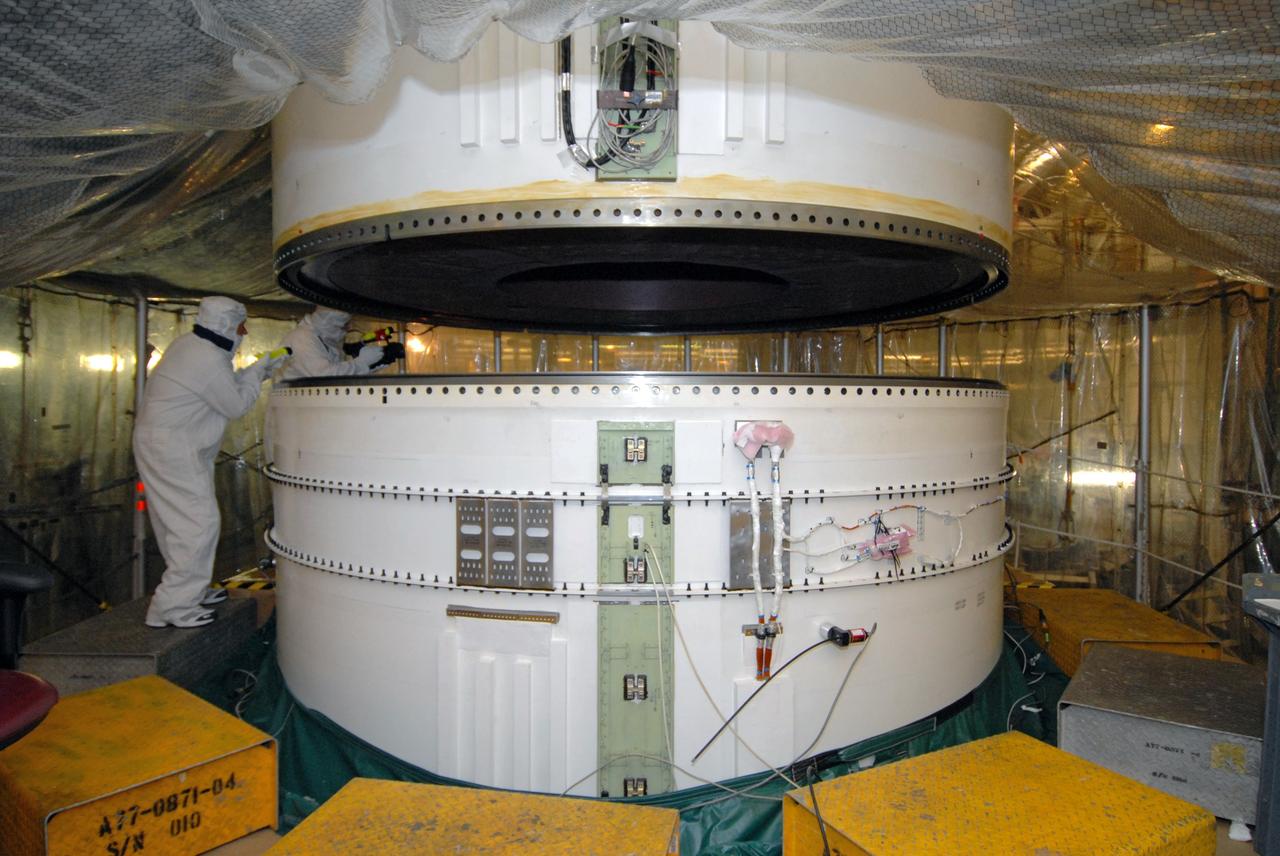
The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022.
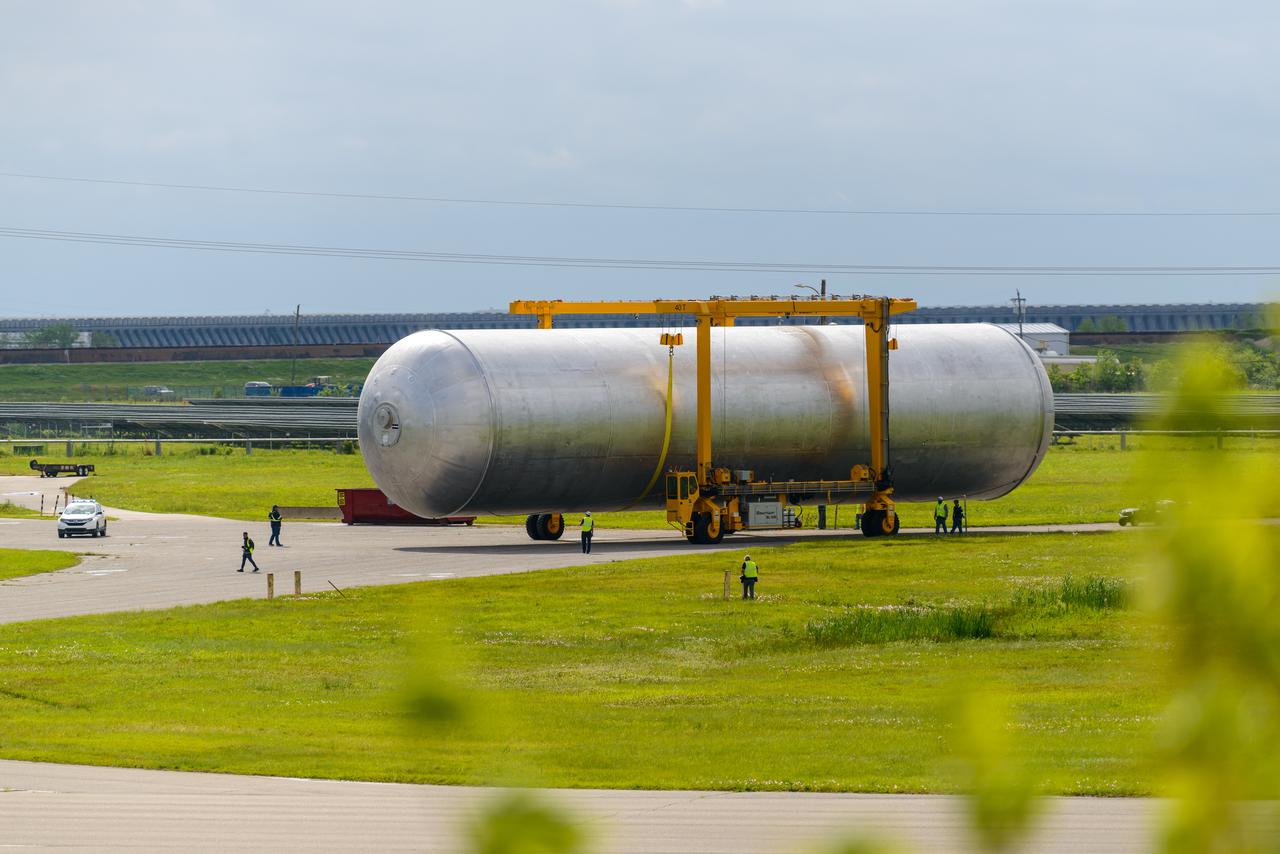

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022.
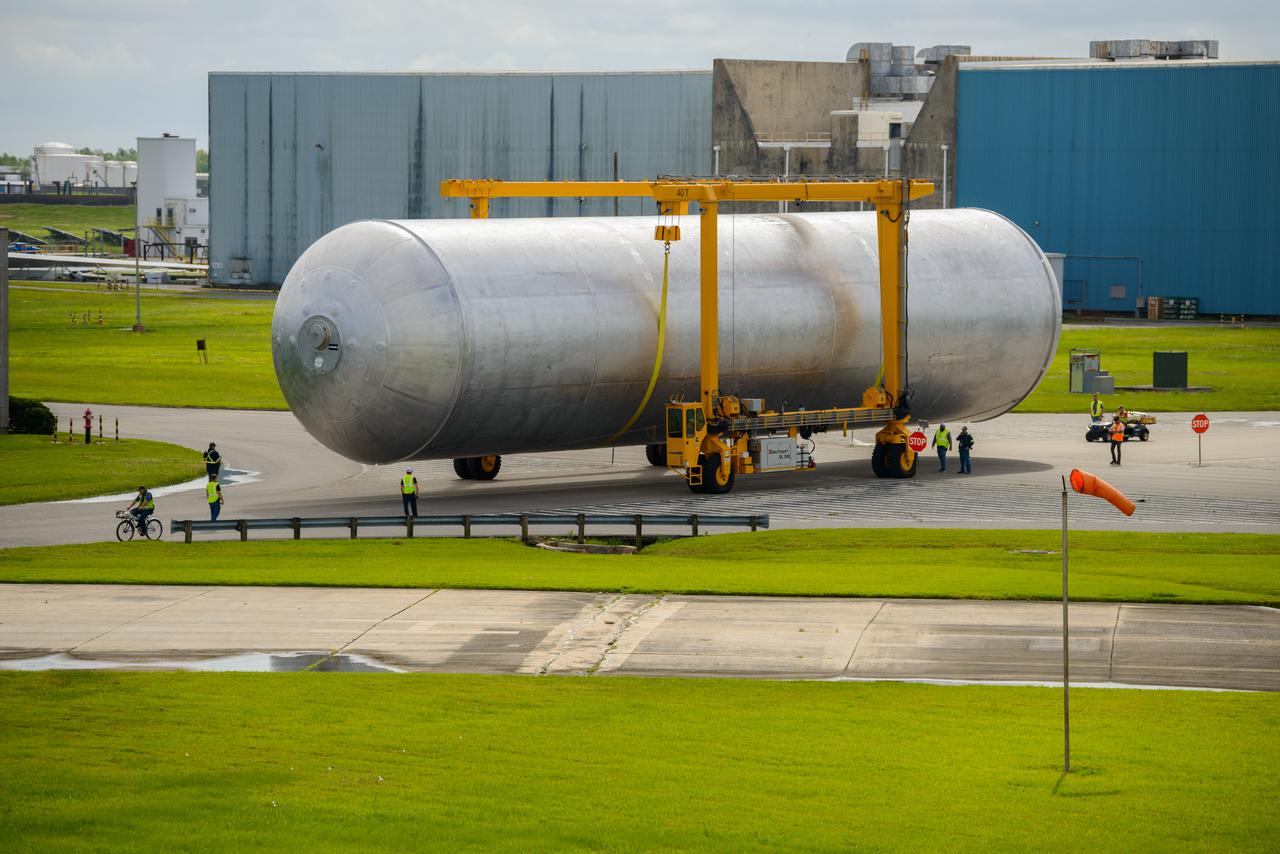

The core stage liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis III mission completed proof testing, and technicians returned it to the main factory building at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where it will undergo more outfitting. As part of proof testing, technicians apply a simple soap solution and check for leaks by observing any bubble formation on the welds. The technician removed the bubble solution with distilled water and then dried the area of application to prevent corrosion. To build the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket’s 130-foot core stage liquid hydrogen tank, engineers use robotic tools to weld five-barrel segments. This process results in a tank with around 1,900 feet, or more than six football fields, of welds that must be tested by hand. After the leak tests, the core stage lead, Boeing, pressurized the SLS tank to further ensure there were no leaks. After it passed proof testing, technicians moved the Artemis III liquid hydrogen tank to Michoud’s main factory. Soon, the technicians will prime and apply a foam-based thermal protection system that protects the tank during launch. Later, the tank will be joined with other parts of the core stage to form the entire 212-foot rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines that produce 2 million pounds of thrust to help launch the rocket. Artemis III will land the first astronauts on the lunar surface. Photographed on Monday, April 18, 2022.
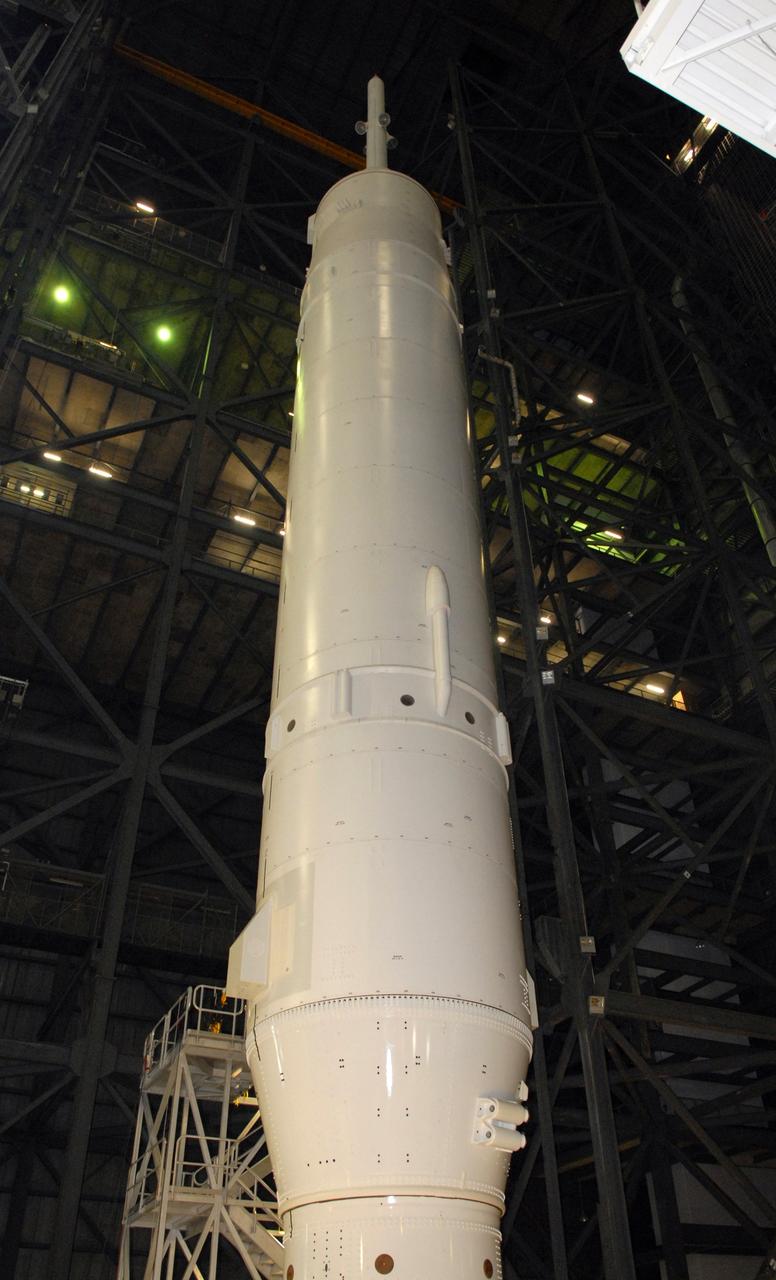

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Processing of the Ares I-X vehicle nears completion in the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Rollout to Launch Pad 39B is targeted for Oct. 19. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system designed to carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/constellation/ares/flighttests/aresIx/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
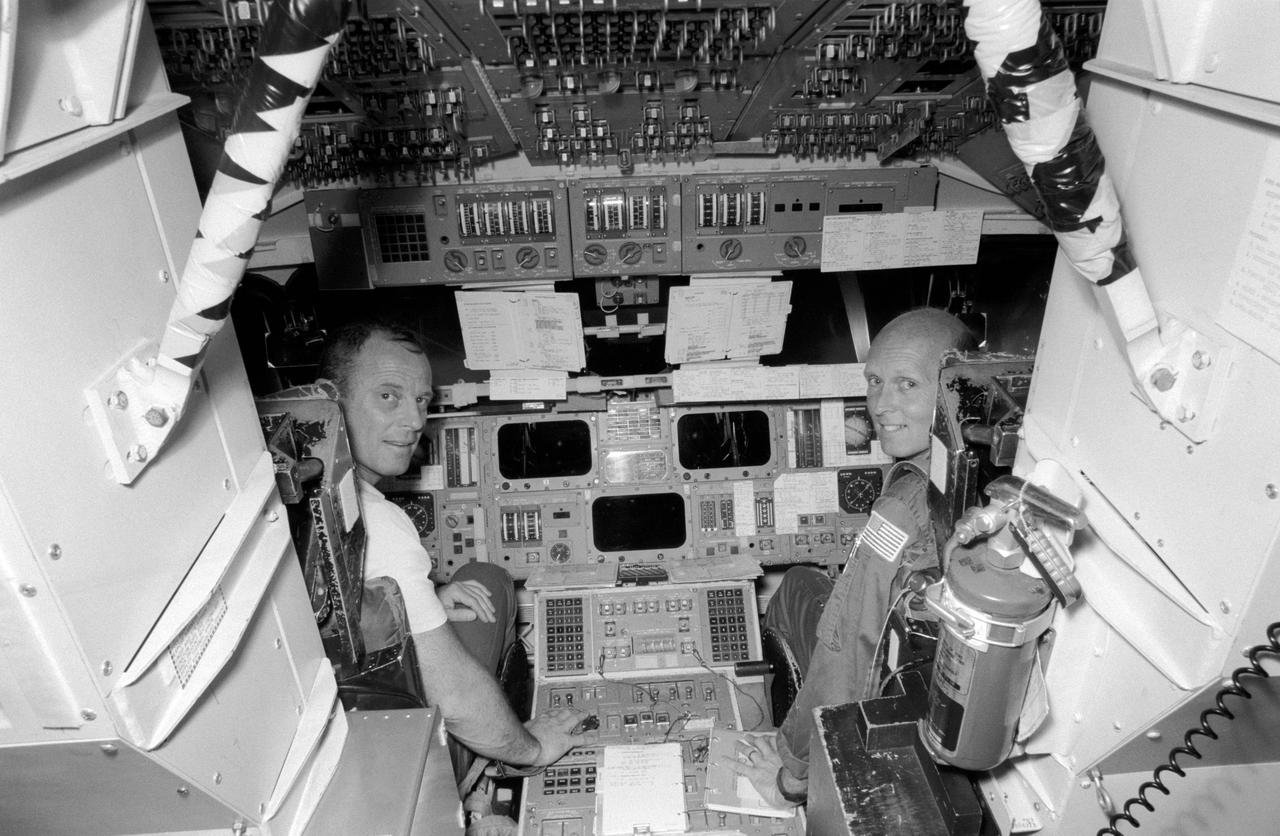

S82-28534 (16 March 1982) --- Astronauts Jack R. Lousma, left, and C. Gordon Fullerton are at the commander and pilot?s station, respectively, in the shuttle mission simulator at the LBJ Space Centers mission simulation and training facility. They have less than a week of training left in preparation for NASA?s third space transportation system (STS-3) flight. Scheduled to launch on March 22, STS-3 in expected to give space shuttle Columbia its longest stay (seven days) thus far. Photo credit: NASA
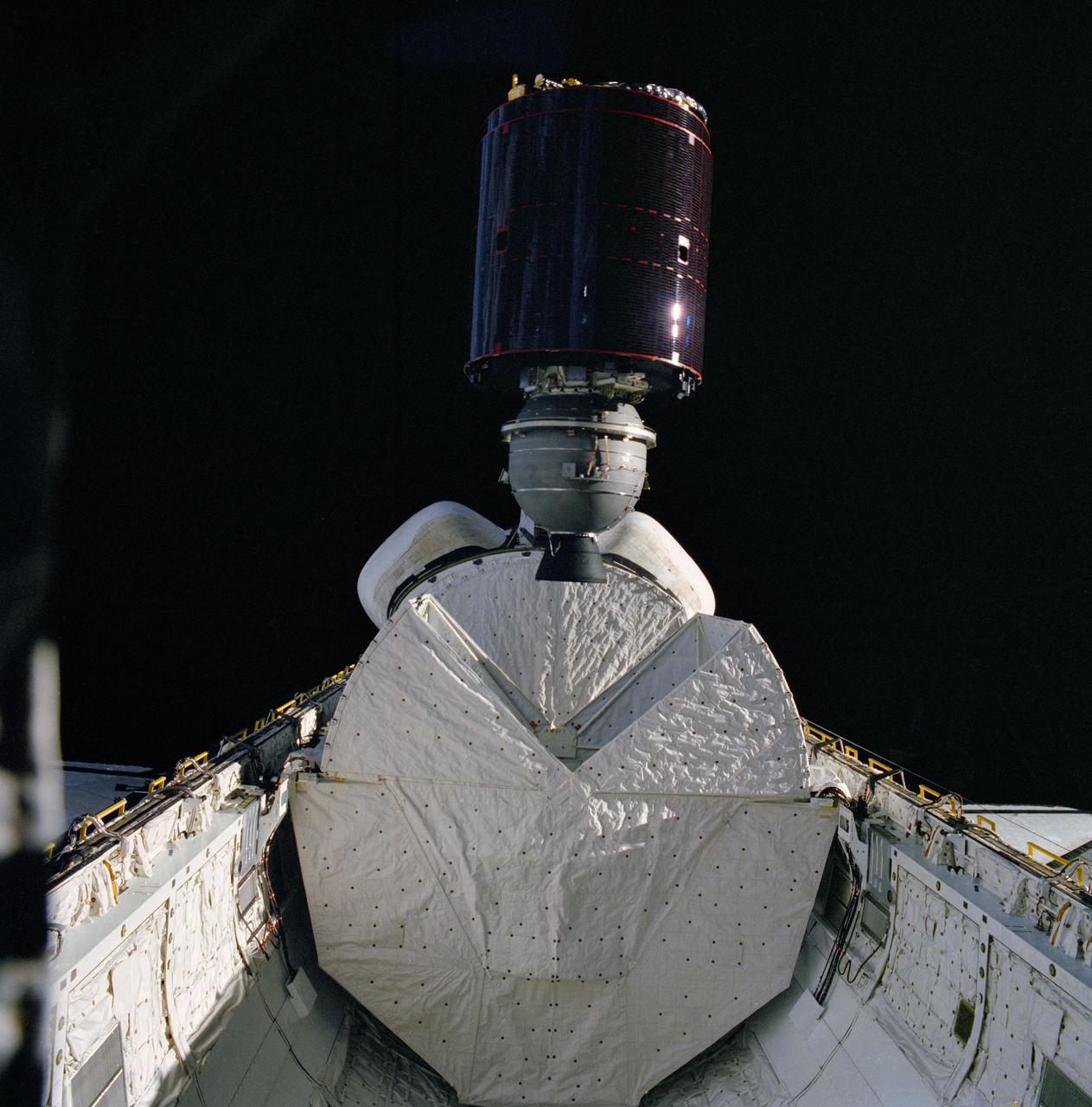

S82-39793 (11 Nov. 1982) --- The Satellite Business Systems (SBS-3) spacecraft springs from its protective ?cradle? in the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia and head toward a series of maneuvers that will eventually place it in a geosynchronous orbit. This moment marks a milestone for the Space Transportation System (STS) program, as the placement of the communications satellites represents the first deployment of a commercial satellite from an orbiting space vehicle. Part of Columbia?s wings can be seen on both the port and starboard sides. Also both orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods are seen at center. The vertical stabilizer is obscured by the satellite. The closed protective cradle device shielding Telesat Canada?s ANIK C-3 spacecraft is seen between the other shield and the OMS pod. ANIK is to be launched on the mission?s second day. This photograph was exposed through the aft windows of the flight deck. Photo credit: NASA
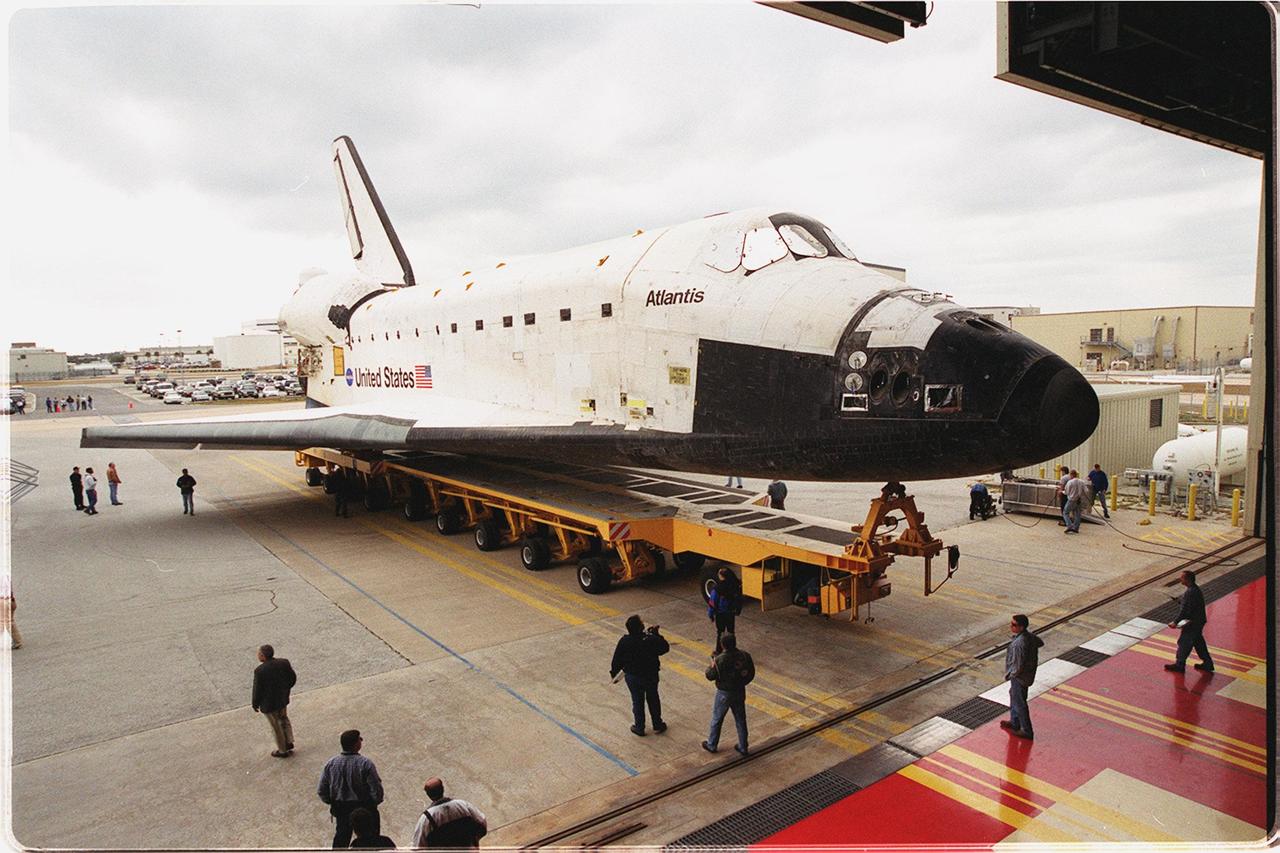

The orbiter Atlantis rolls out of the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3 on its transporter. It is being transferred to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be raised to vertical and lifted up and into high bay 3 for stacking with its external tank and solid rocket boosters. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station. The orbiter will carry in its payload bay the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny, that will have five system racks already installed inside of the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch on Jan. 18, 2001, at 2:44 a.m. EST, with a crew of five
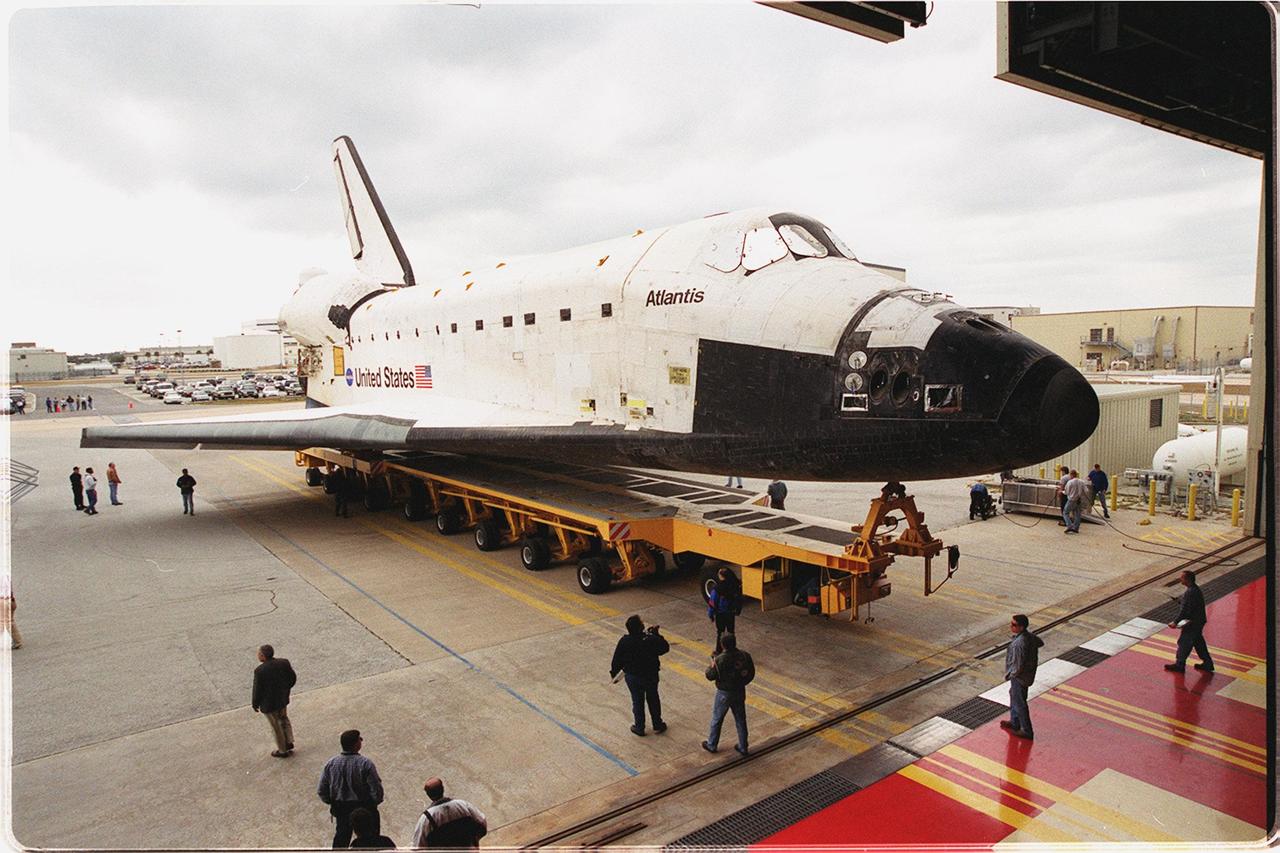

The orbiter Atlantis rolls out of the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3 on its transporter. It is being transferred to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be raised to vertical and lifted up and into high bay 3 for stacking with its external tank and solid rocket boosters. Atlantis will fly on mission STS-98, the seventh construction flight to the International Space Station. The orbiter will carry in its payload bay the U.S. Laboratory, named Destiny, that will have five system racks already installed inside of the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated. Atlantis is scheduled for launch on Jan. 18, 2001, at 2:44 a.m. EST, with a crew of five
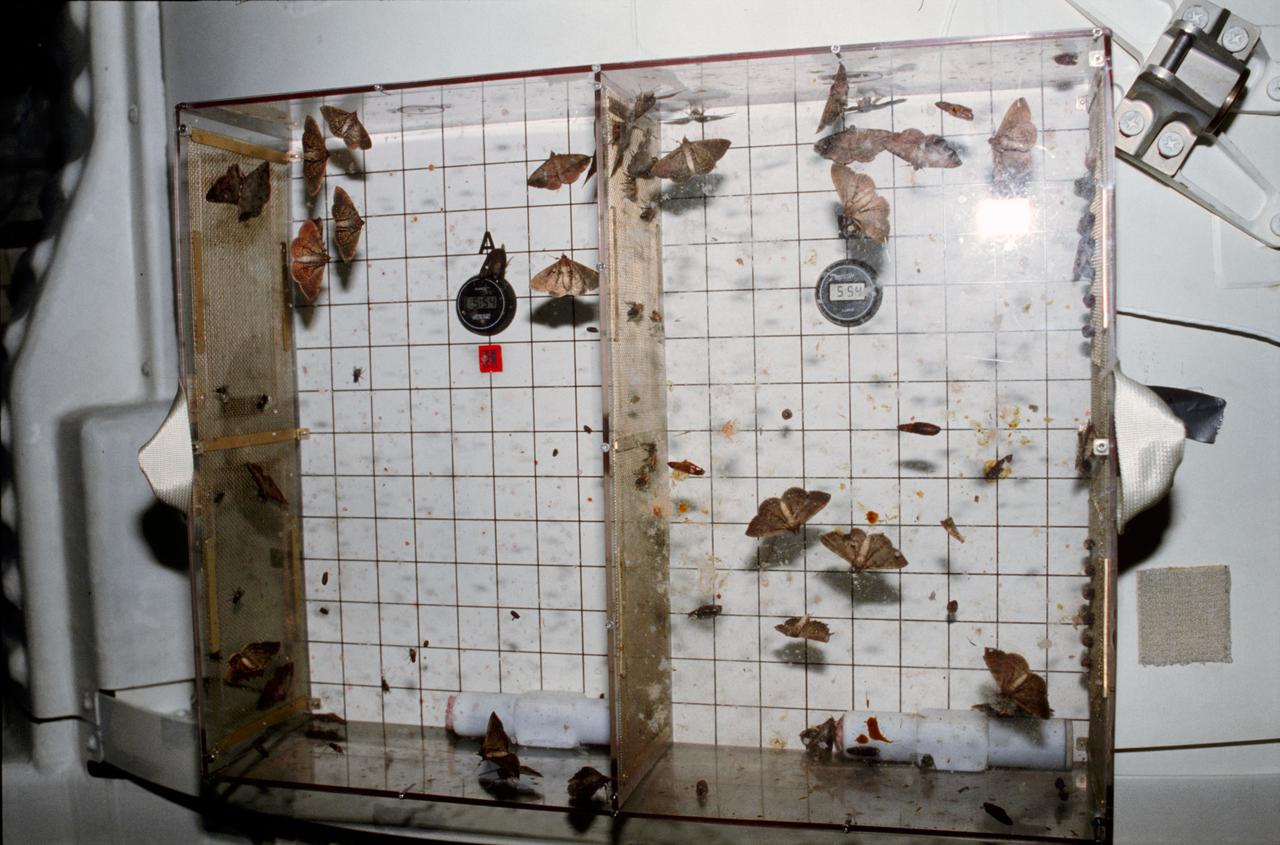

STS003-23-175 (22-30 March 1982) --- Student Experiment 81-8 (SE-81-8) Insect Flight Motion Study taped to the airlock on aft middeck of space shuttle Columbia. Photo credit: NASA
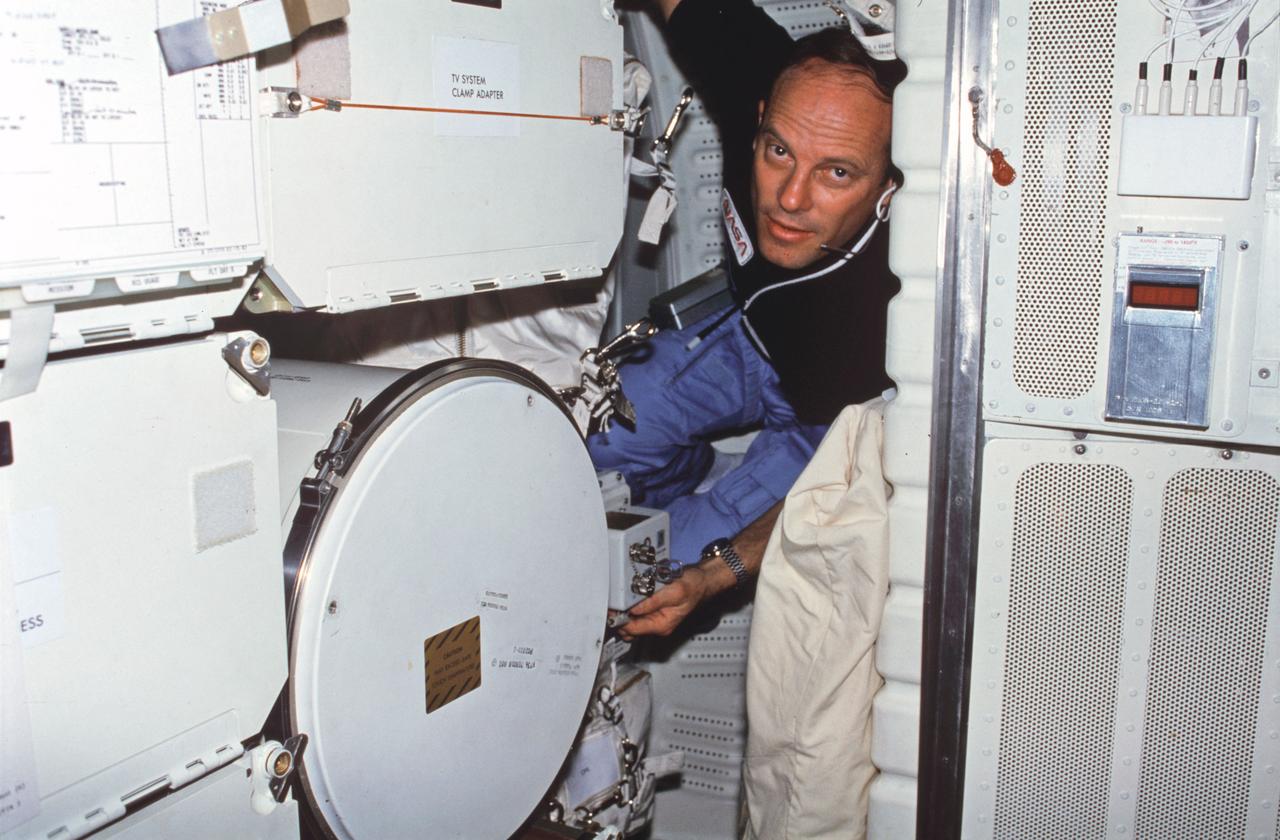

STS003-22-127 (22-30 March 1982) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, STS-3 commander, wearing communications kit assembly (assy) mini-headset, adjusts controls on Monodisperse Latex Reactor (MLR) experiment located in forward middeck lockers MF57H and MF57K. To reach MLR support electronics assy controls, Lousma squeezes in between forward lockers and Development Flight Instrument (DFI) unit on starboard bulkhead. Photo credit: NASA
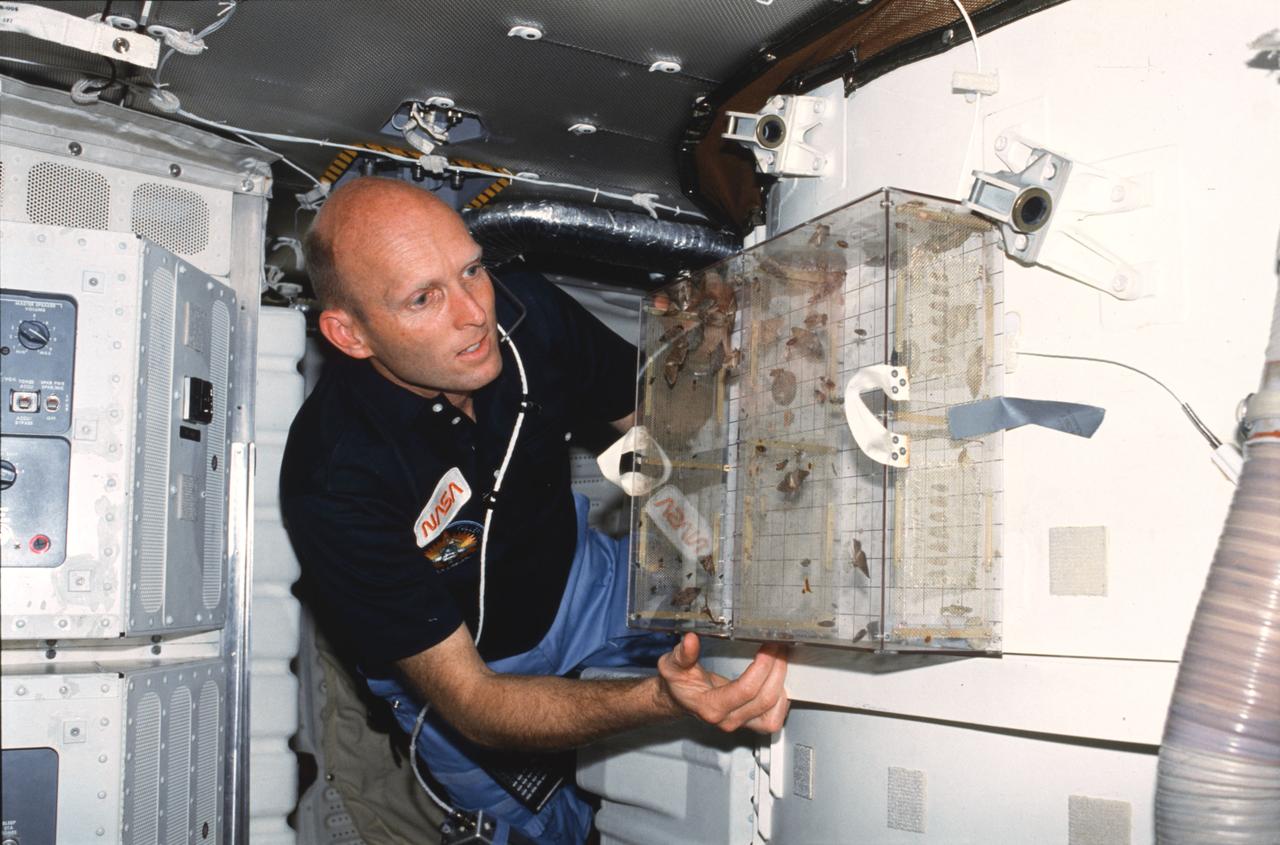

STS003-23-178 (22-30 March 1982) --- Astronaut C. Gordon Fullerton, STS-3 pilot, examines Student Experiment 81-8 (SE-81-8) Insect Flight Motion Study taped to the airlock on aft middeck. Todd Nelson, a high school senior from Minnesota, won a national contest to fly his experiment on this particular flight. Moths, flies, and bees were studied in the near weightless environment. Photo credit: NASA
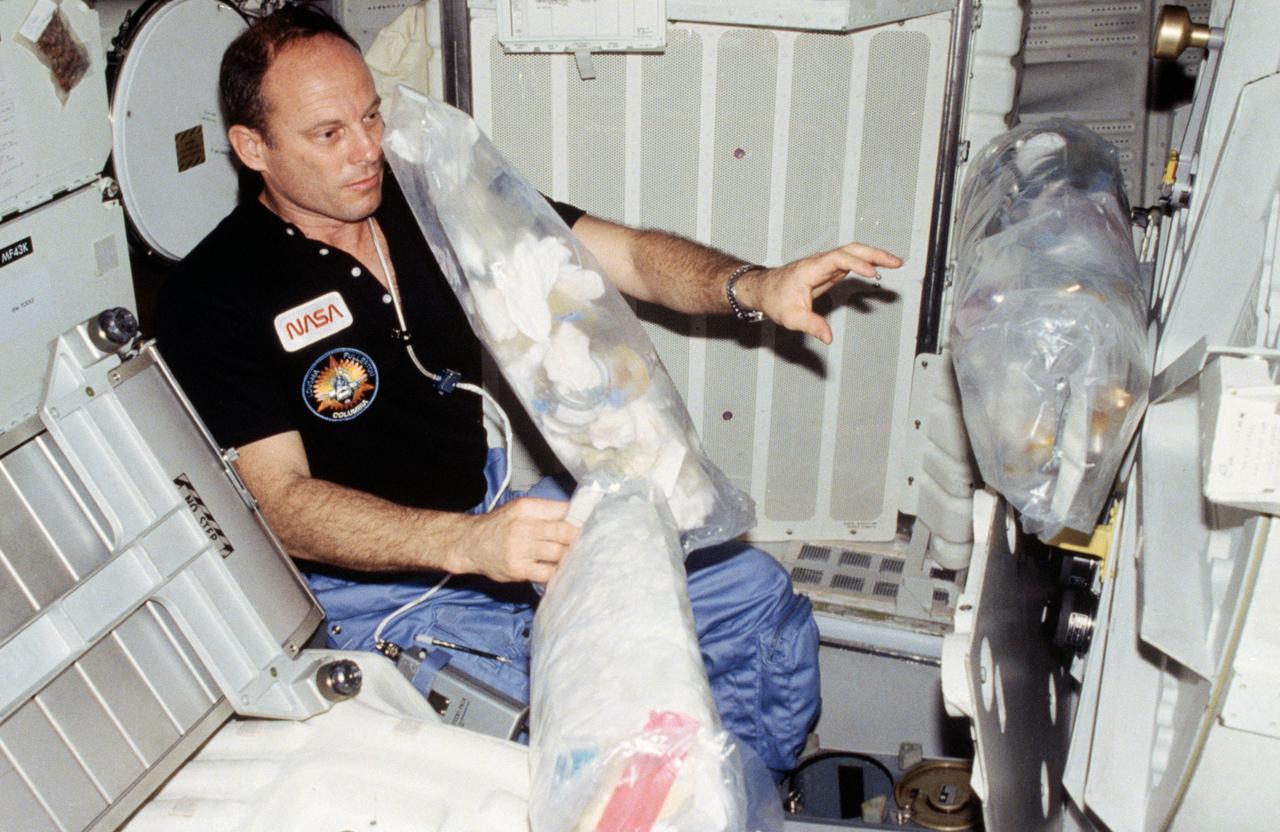

STS003-25-231 (22-30 March 1982) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, STS-3 commander, wearing communication kit assembly mini headset, gathers three freefloating plastic trash bags filled with empty containers, paper towels, straws, etc. Lousma will stow them in a designated stowage volume. Photo credit: NASA
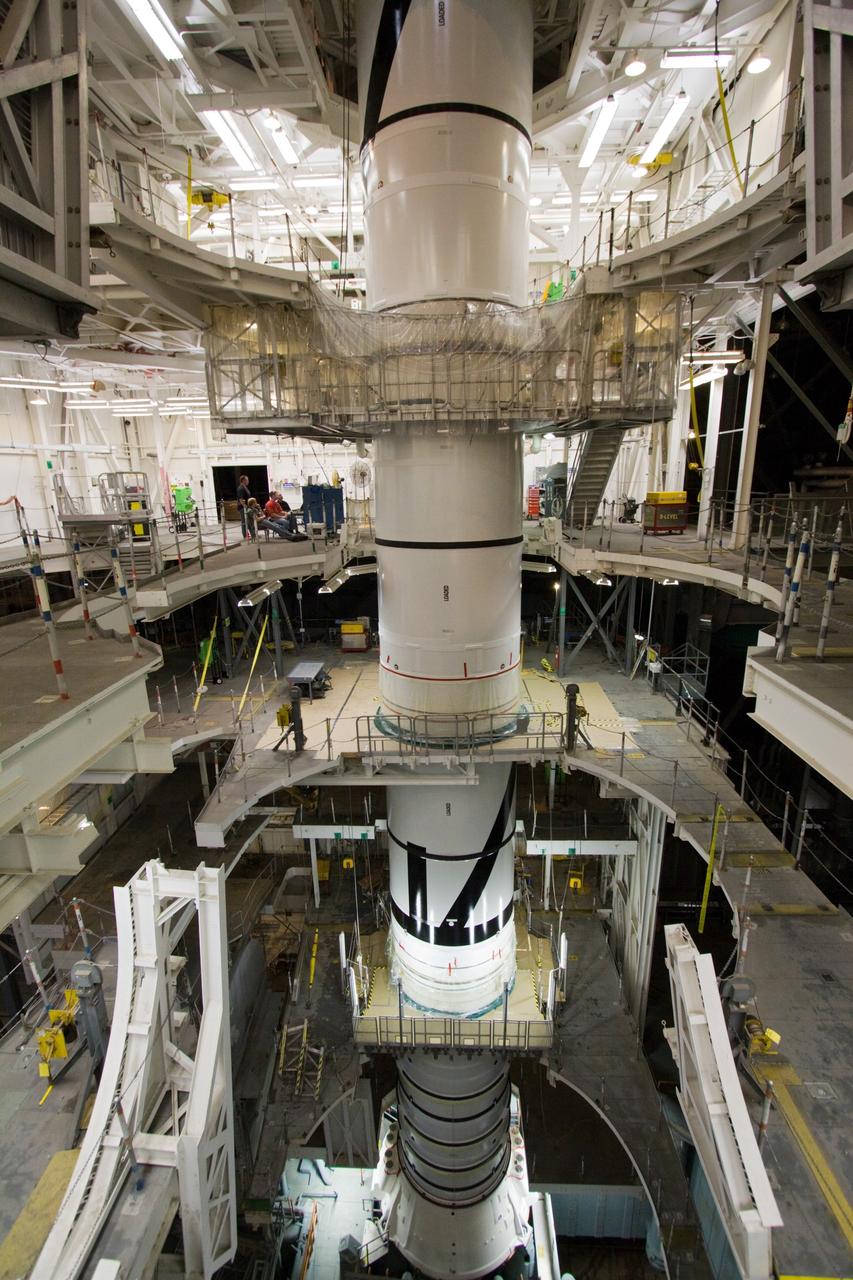

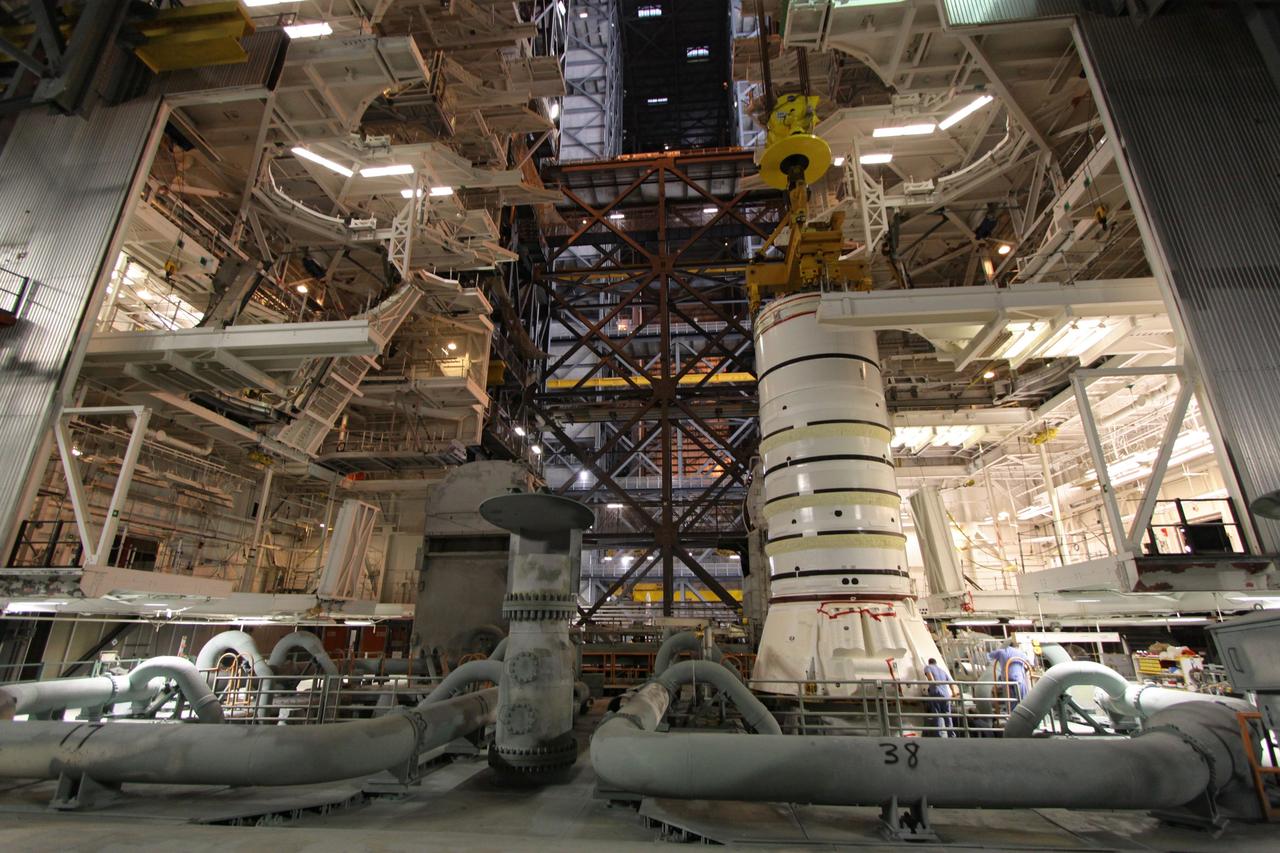
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers secure the attachment, or mating, of the Ares I-X forward segment to the forward center segment atop the aft assembly (aft segment and aft skirt). Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
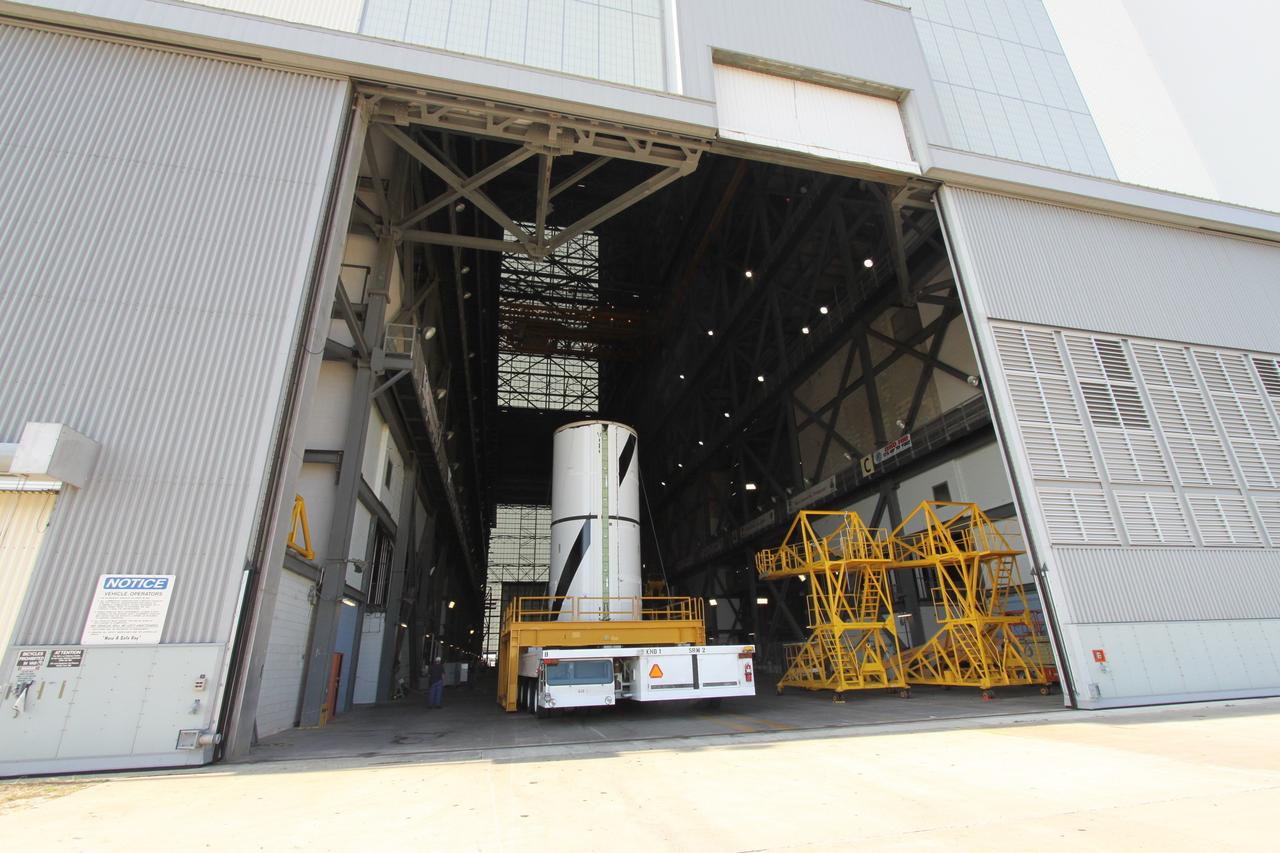

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward center segment moves into the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB. The launch vehicle is being assembled in the VAB's High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the forward segment is mated to the forward center segment atop the aft assembly (aft segment and aft skirt). Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward center segment is moving from the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility to the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB. The launch vehicle is being assembled in the VAB's High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
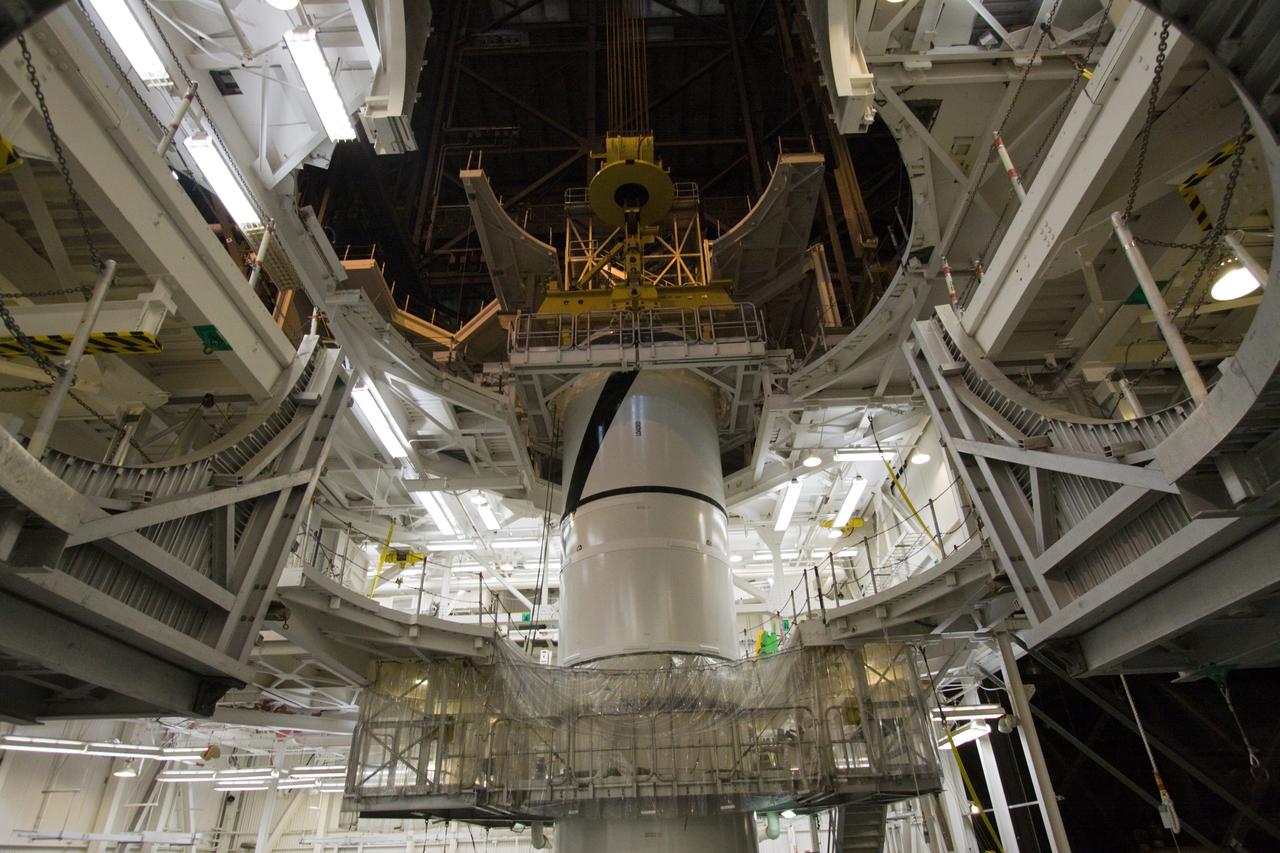

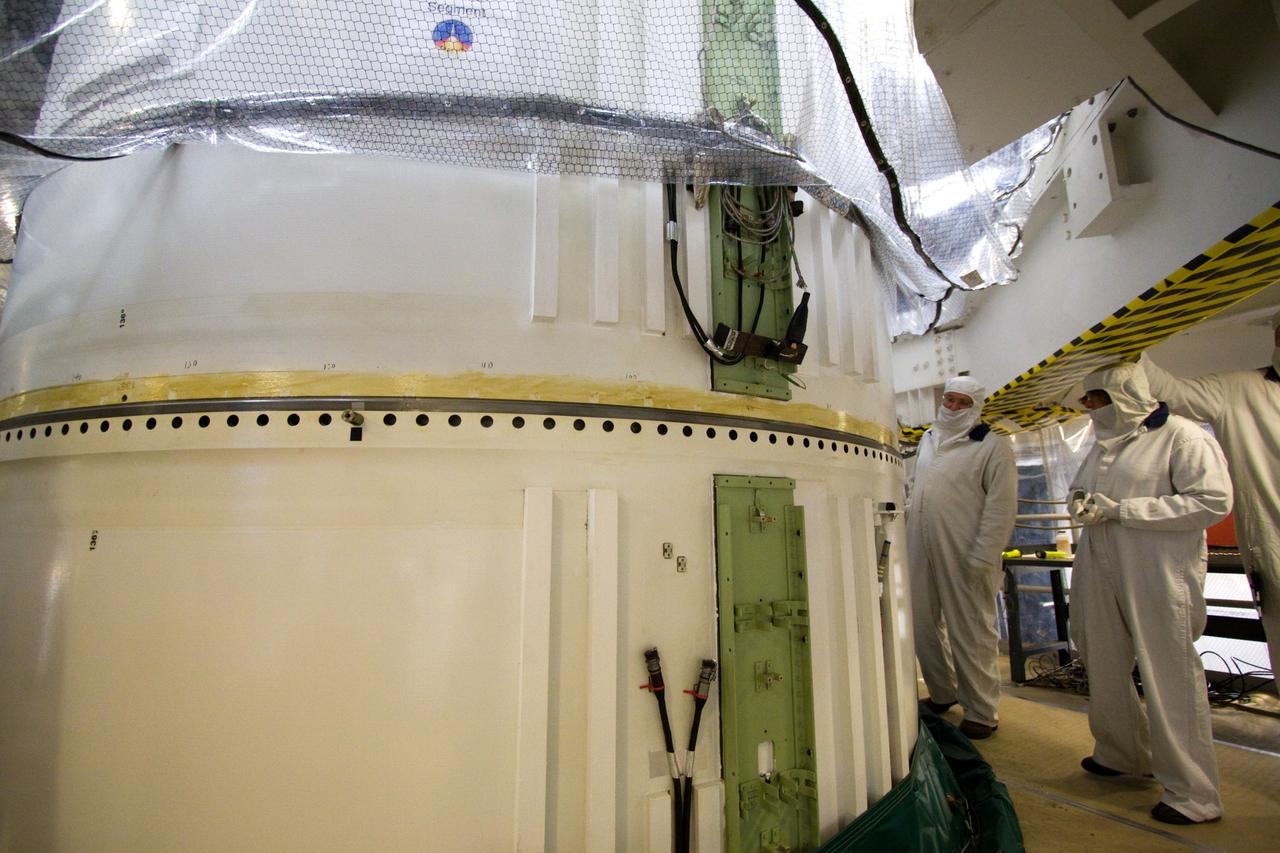
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers check the attachment, or mating, of the Ares I-X forward center segment atop the aft assembly (aft segment and aft skirt). Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
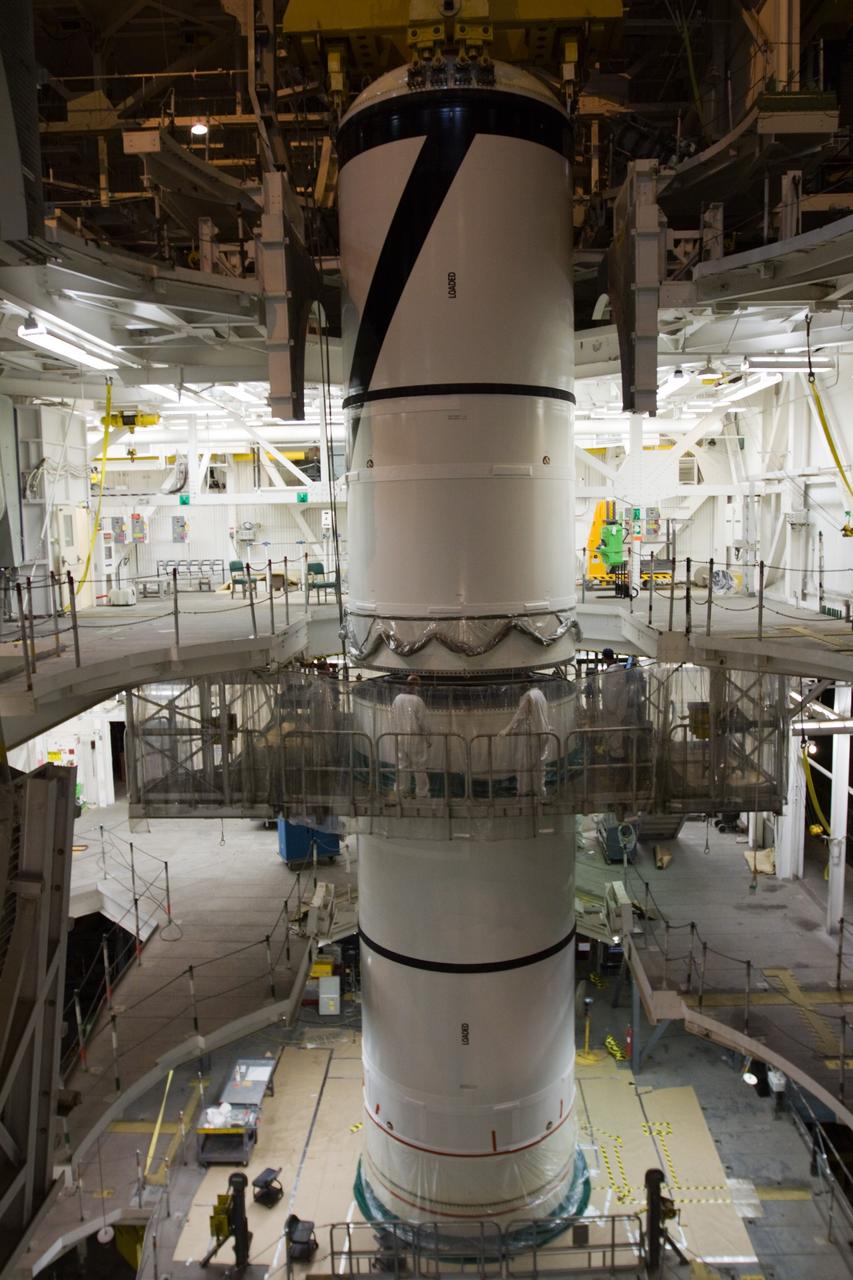

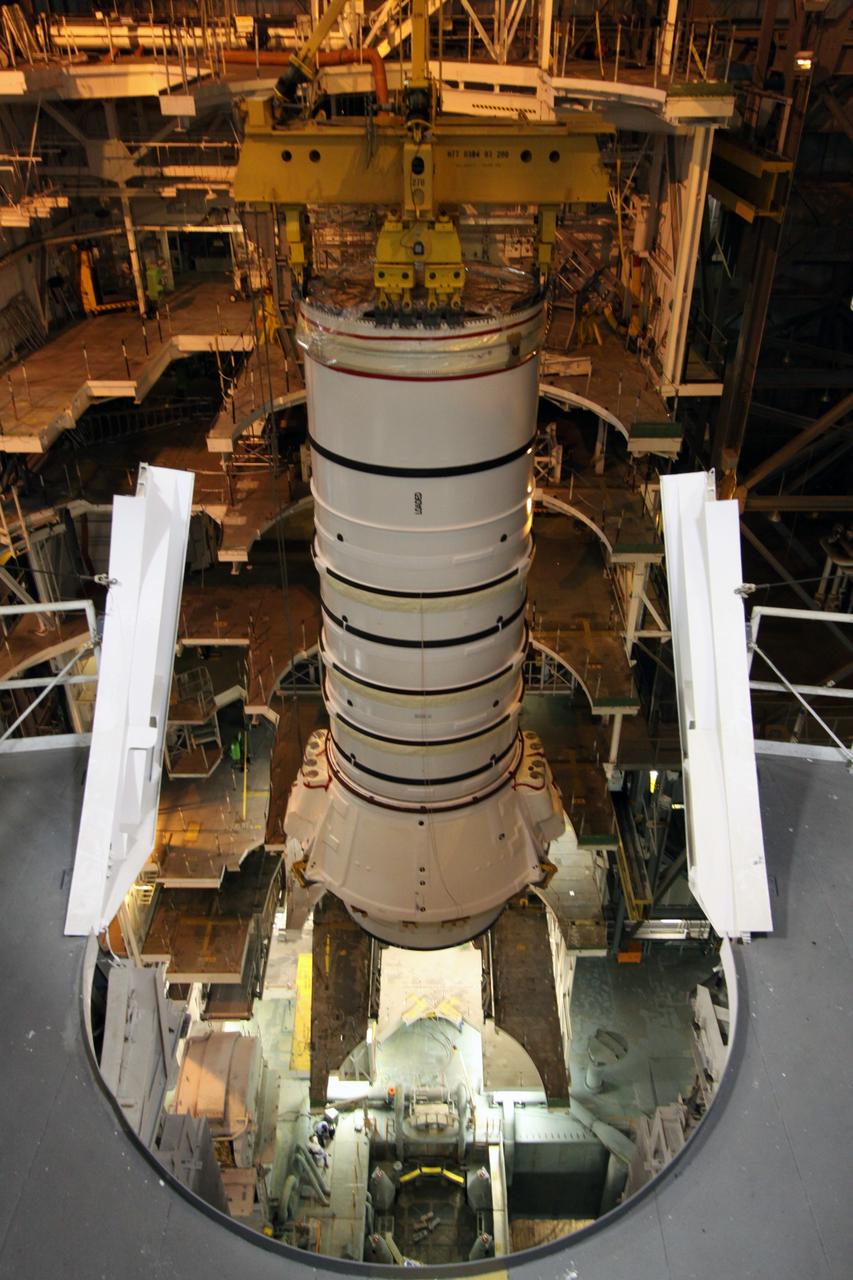
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the High Bay 3 of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building, the Ares I-X forward segment is lowered onto the forward center for mating. The forward center is already mated with the aft center and the aft skirt segments below. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
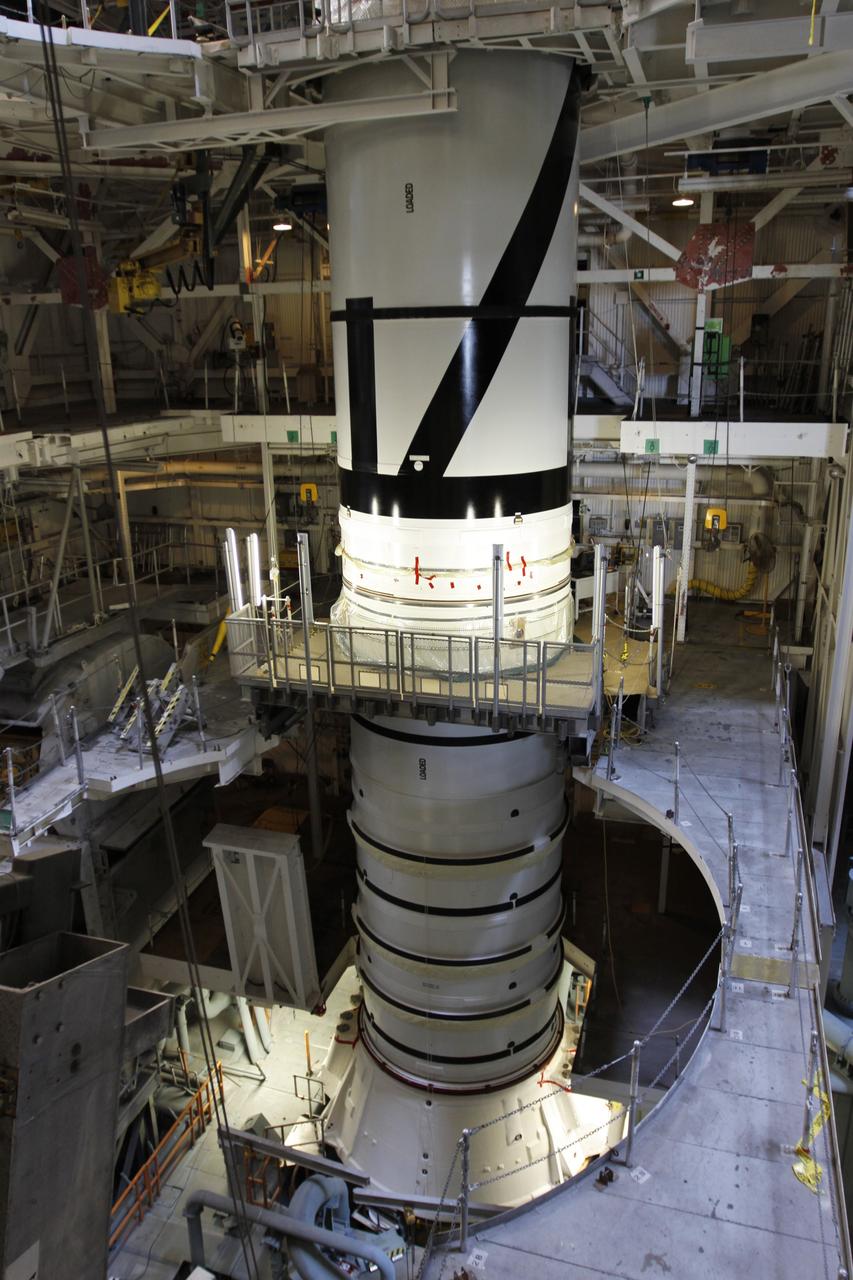

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the stacking of the Ares I-X segments is under way. Seen here are the aft center and the aft skirt segments. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
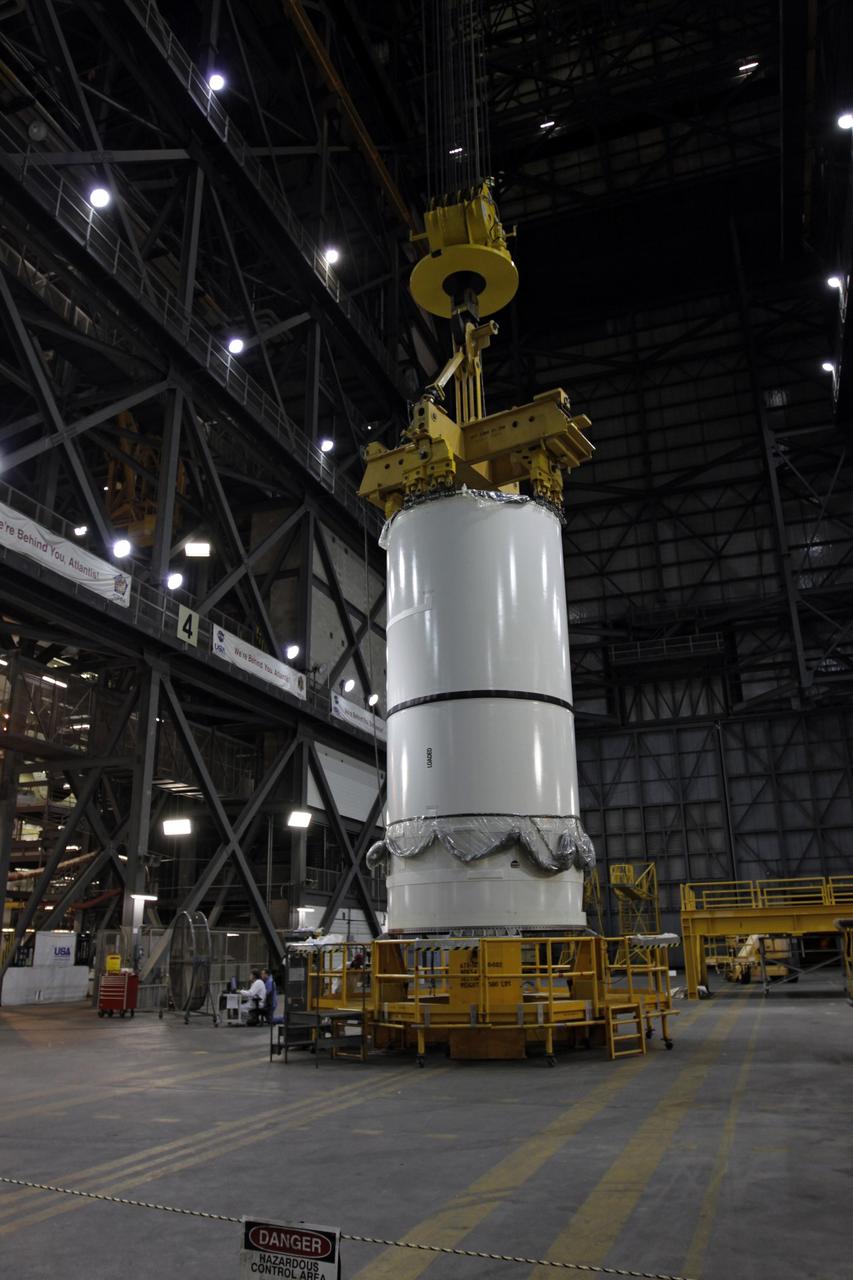

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane is attached to the Ares I-X forward center assembly in NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building. The assembly will be lifted into High Bay 3 for stacking with the aft assembly. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
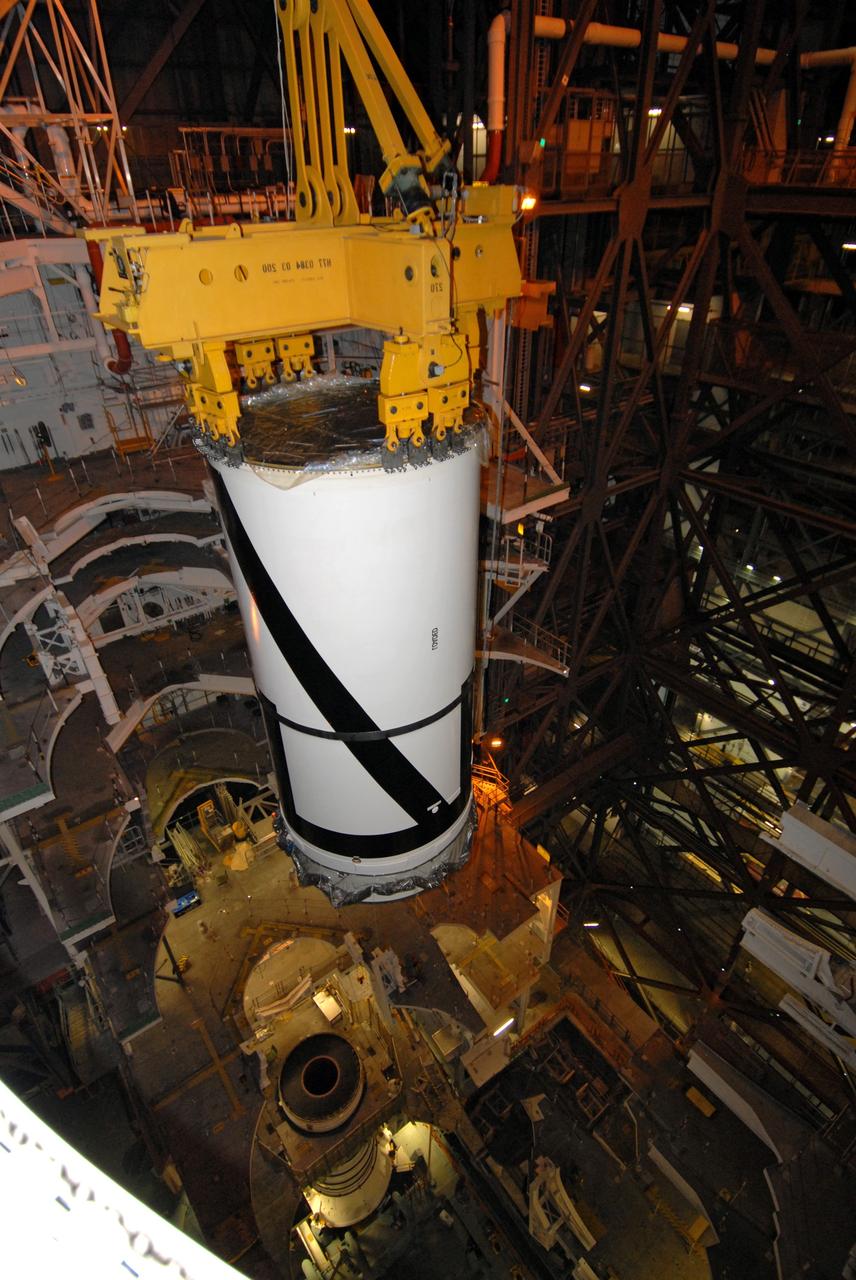

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's transfer aisle at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lowers the Ares I-X aft center booster segment toward the aft booster and skirt in High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The flight test of the Ares I-X is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
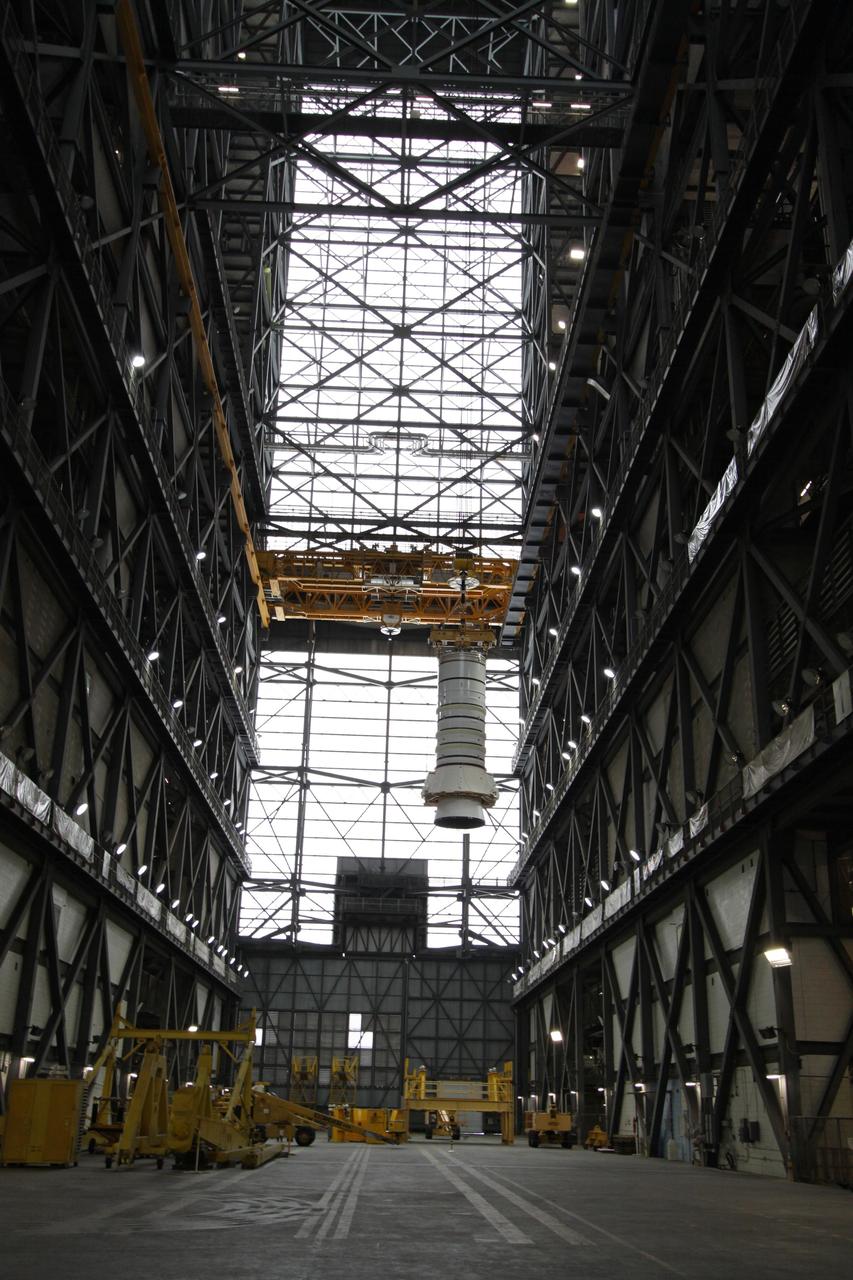

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lifted across the VAB transfer aisle. The stack will be hoisted into the upper regions of the VAB and lowered onto the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft center booster segment is lowered for attachment to the aft booster and skirt. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The flight test of the Ares I-X is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lowered onto the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building High Bay 3, NASA's Ares I-X mission team members Bobby Williams, Trent Smith and Karl Kendall get ready for the rocket's first power-up. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
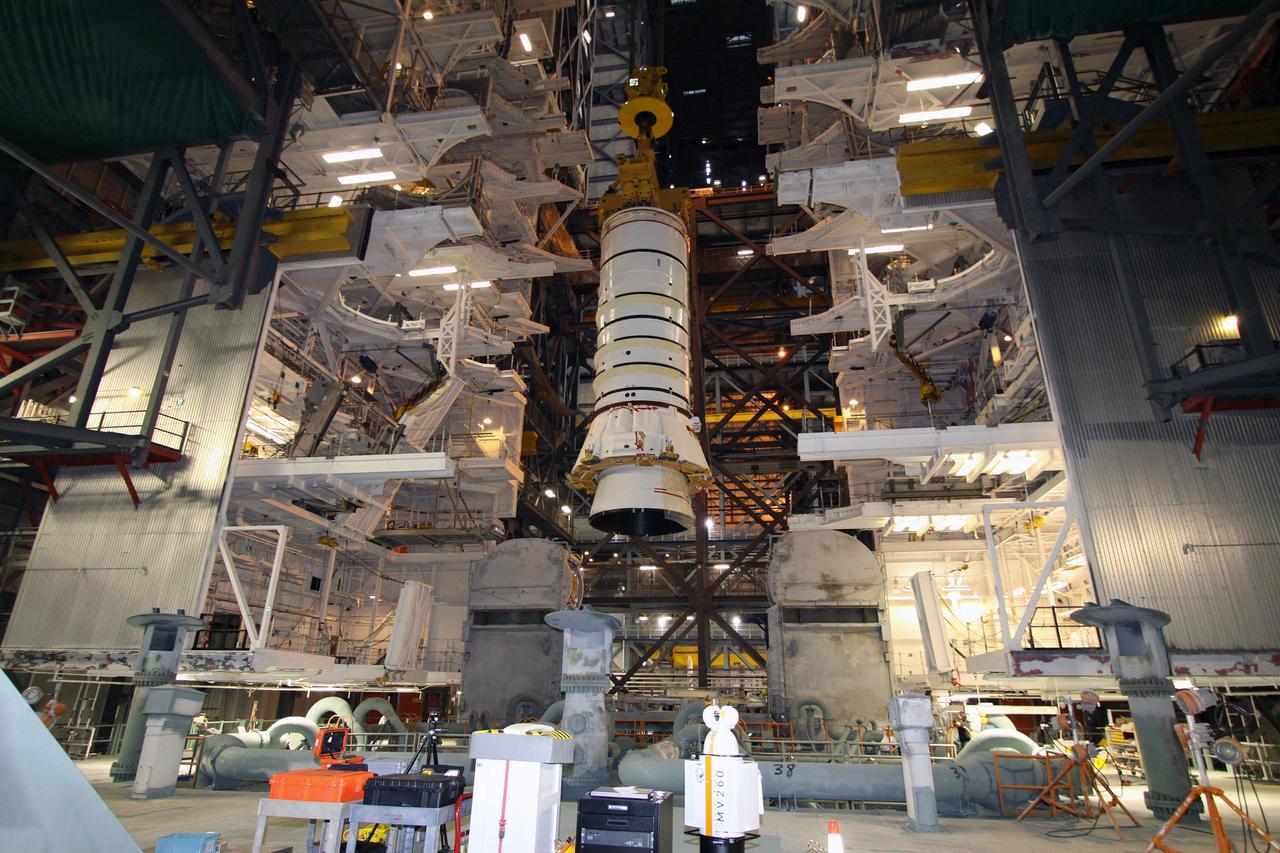

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lowered toward the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building High Bay 3, NASA's Ares I-X mission team members Trent Smith and Karl Kendall get ready for the rocket's first power-up. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
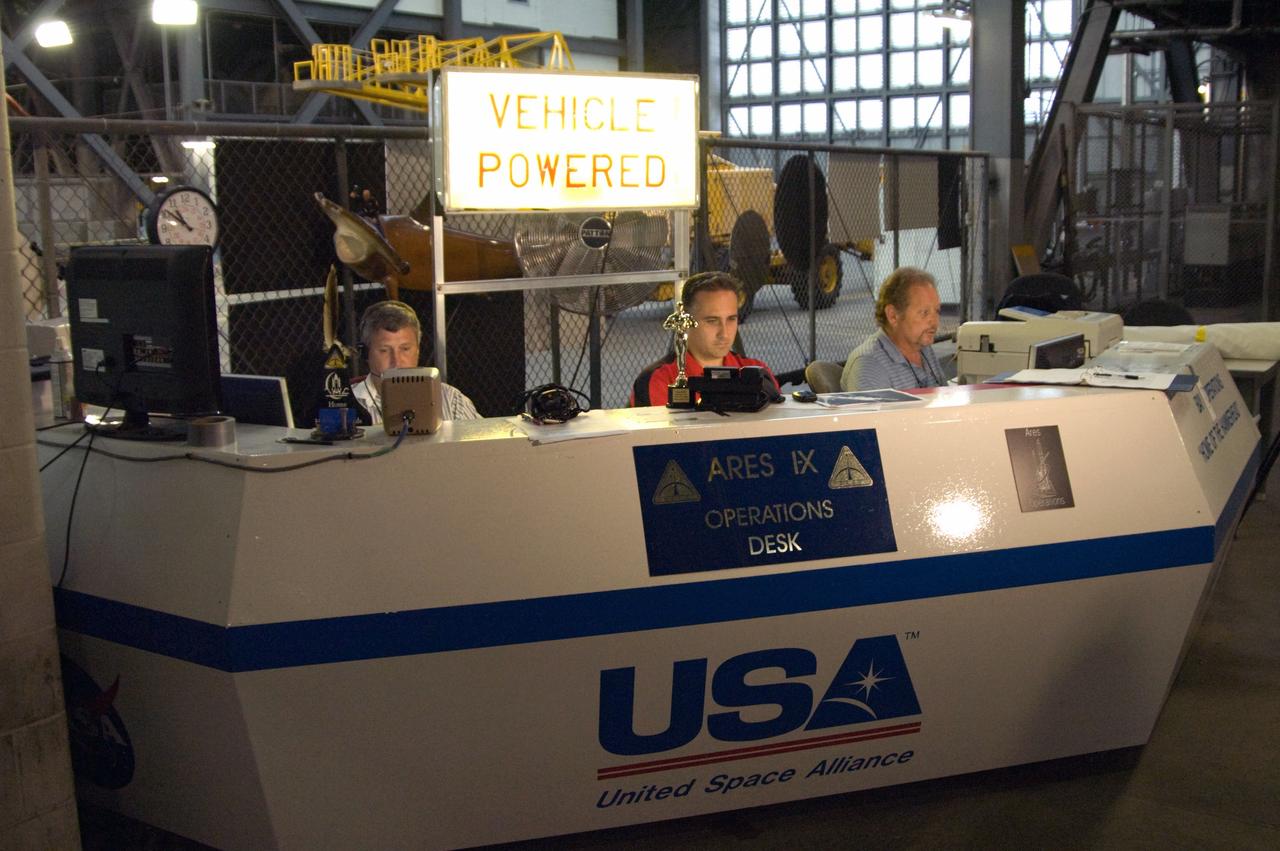

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building High Bay 3, NASA's Ares I-X mission team members Bobby Williams, Trent Smith and Karl Kendall monitor the rocket's first power-up. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
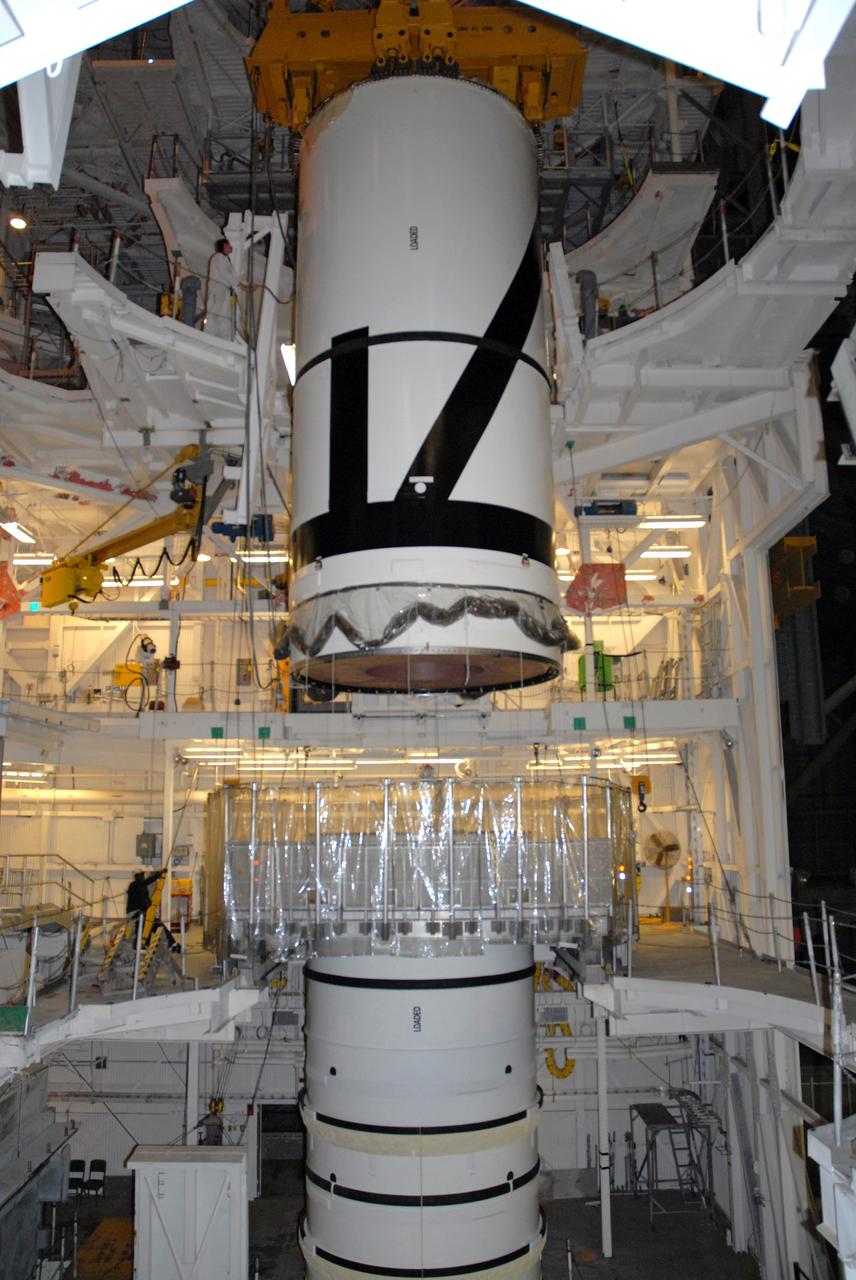
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's transfer aisle at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lowers the Ares I-X aft center booster segment toward the aft booster and skirt in High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The flight test of the Ares I-X is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lowered into High Bay 3. It will be placed on the mobile launch platform. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
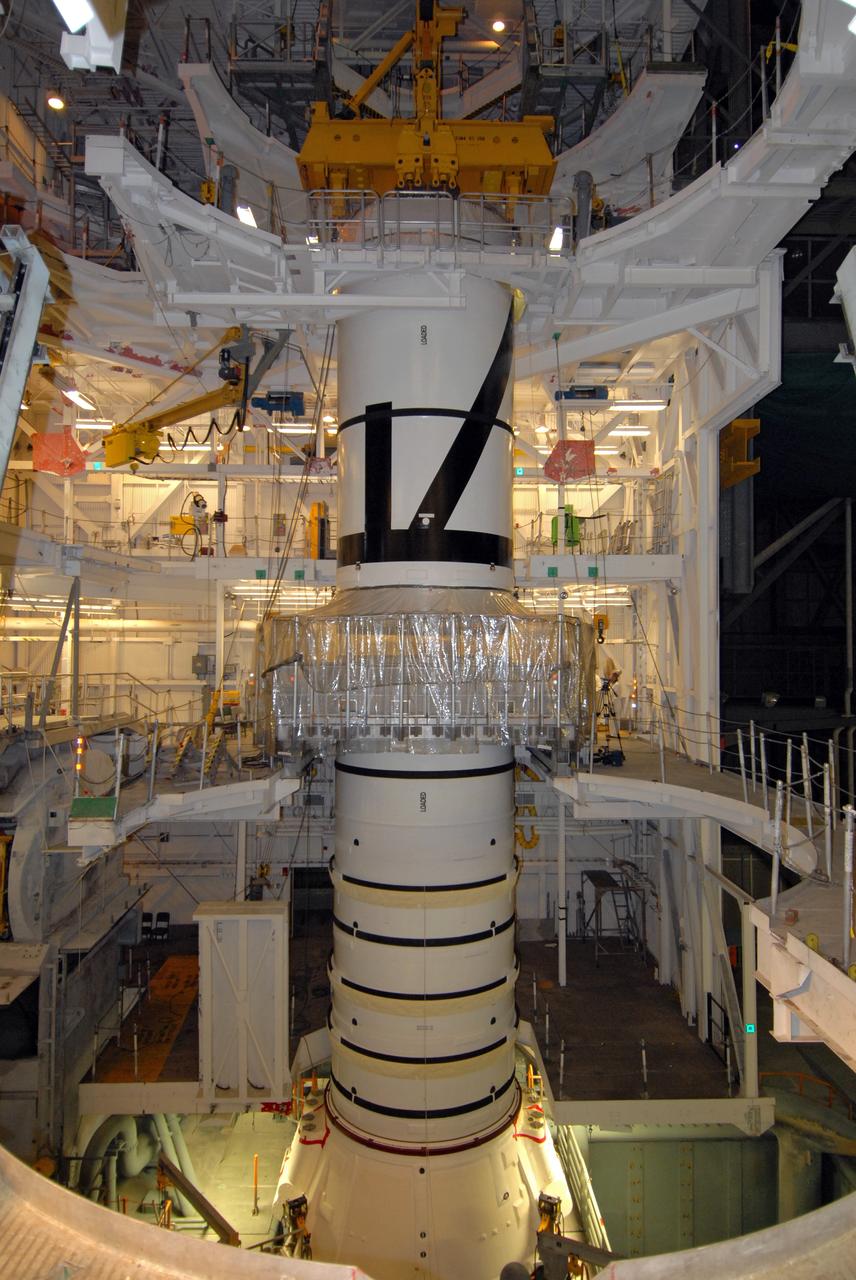
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft center booster segment is lowered onto the aft booster and skirt for mating. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The flight test of the Ares I-X is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
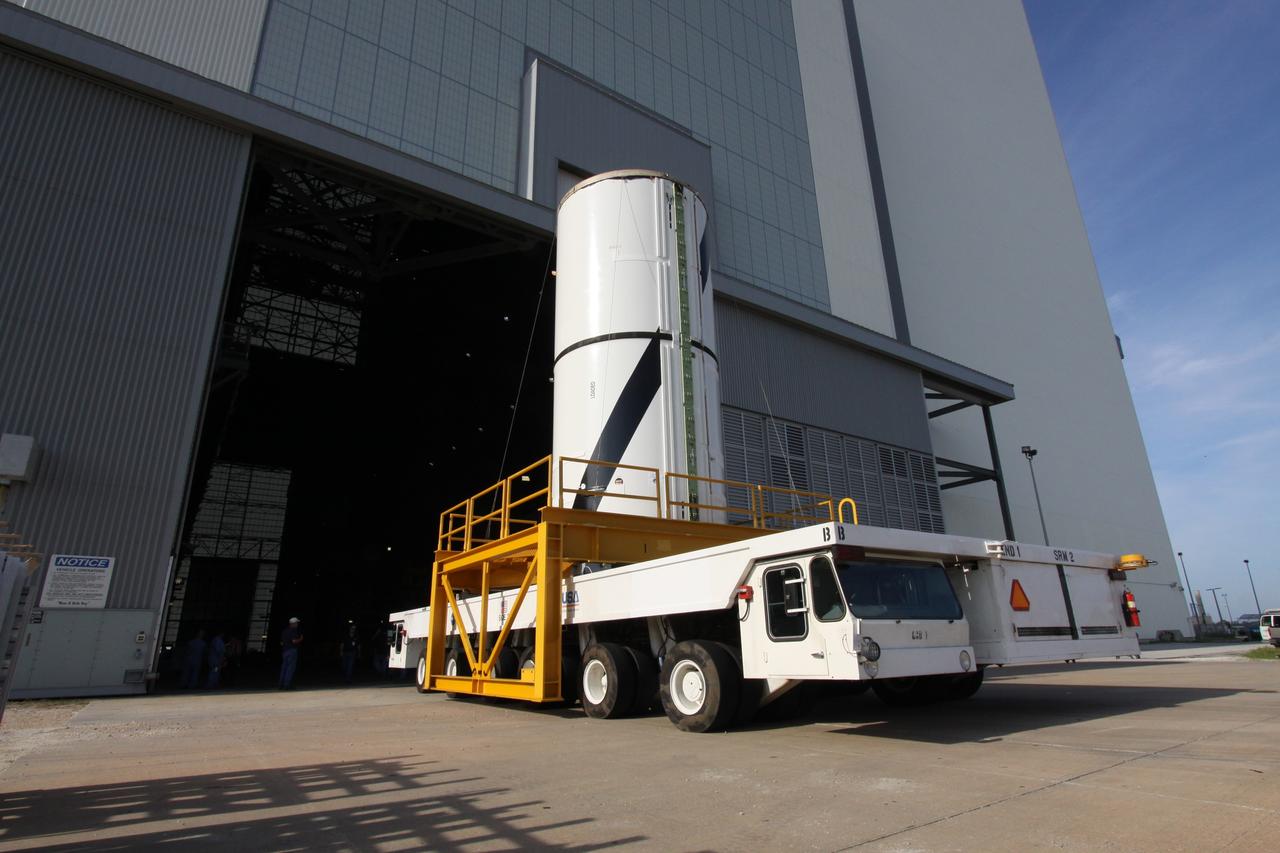

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward center segment heads through the door of the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB. The launch vehicle is being assembled in the VAB's High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
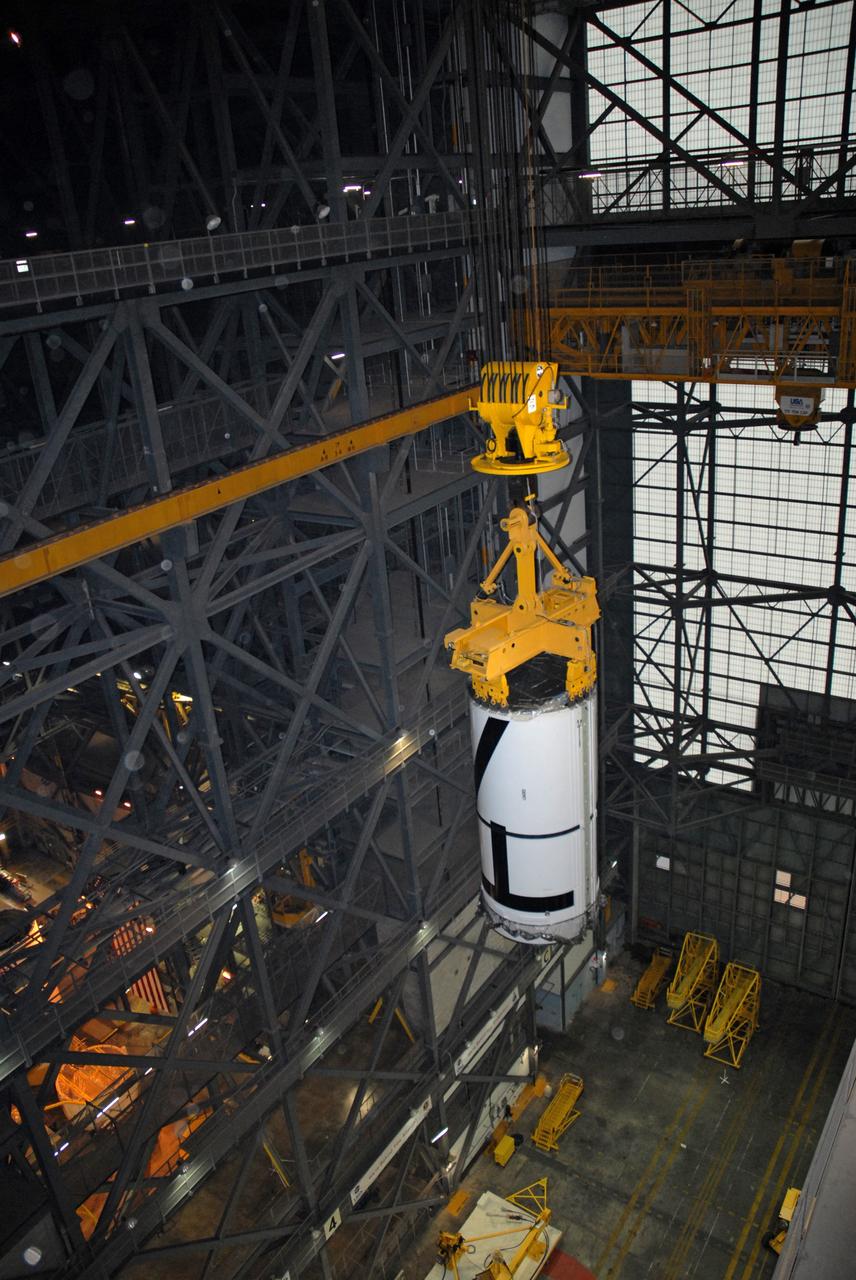

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's transfer aisle at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lifts the Ares I-X aft center booster segment , which will be lifted and then lowered into High Bay 3 for attachment to the aft booster and skirt. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The flight test of the Ares I-X is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
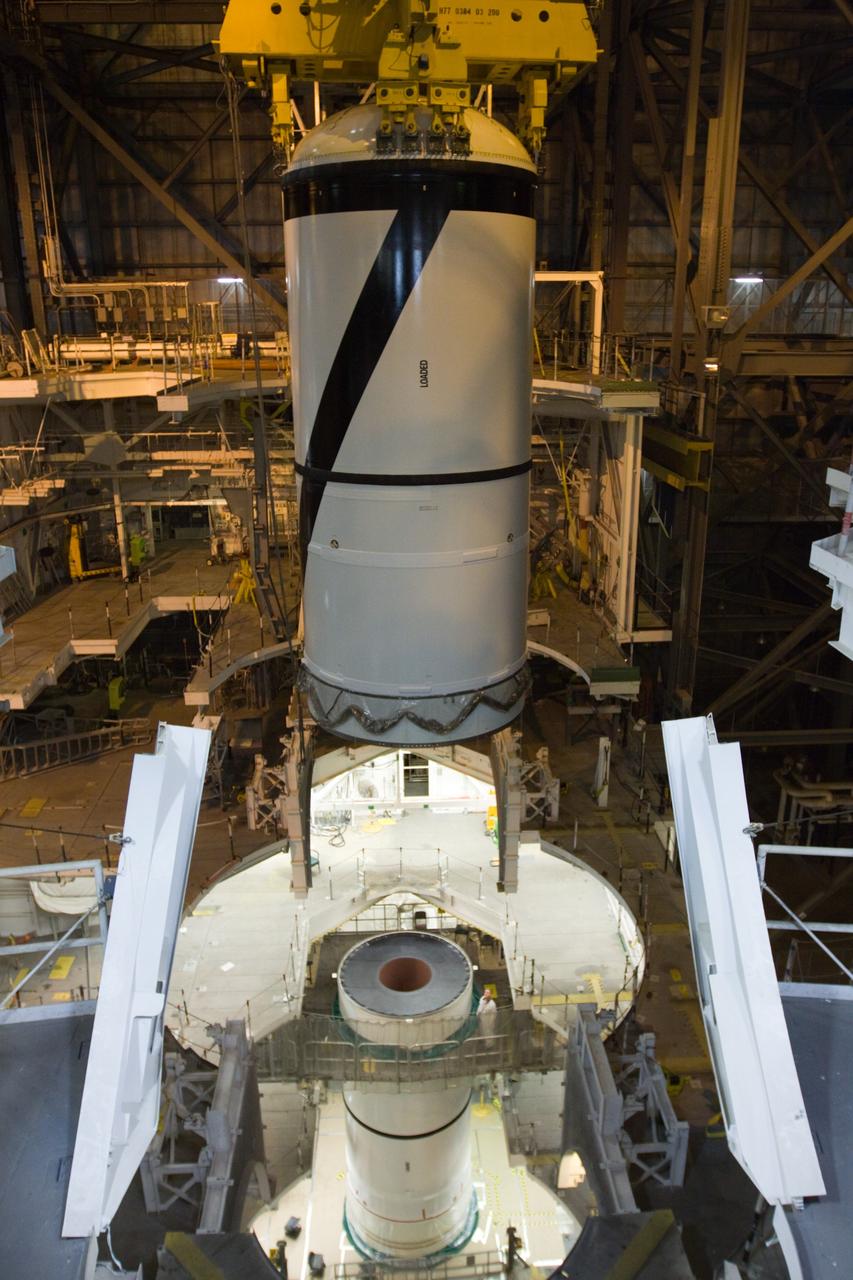

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the High Bay 3 of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building, the Ares I-X forward segment is lowered toward the forward center for mating. The forward center is already mated with the aft center and the aft skirt segments below. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
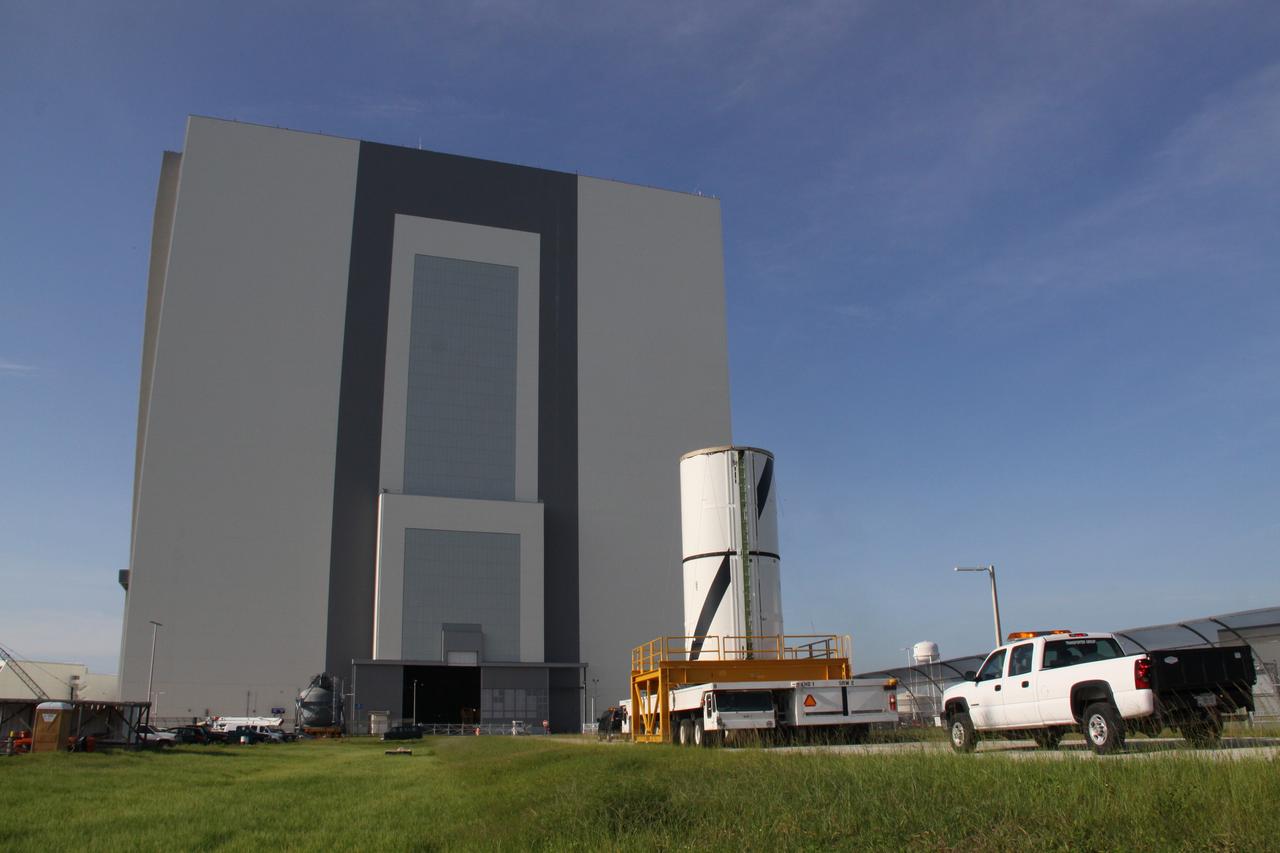

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward center segment approaches the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, after leaving the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility. The launch vehicle is being assembled in the VAB's High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
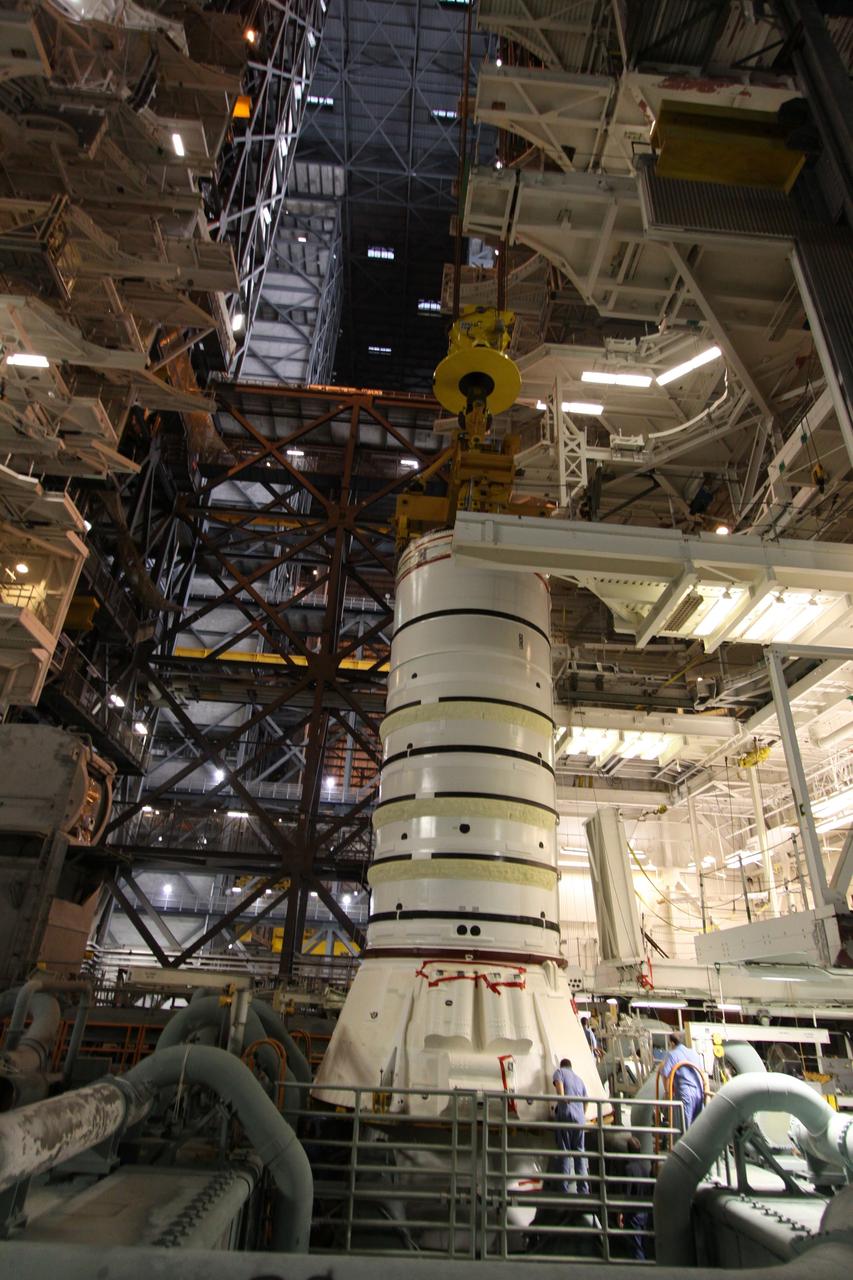

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers keep watch as the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lowered toward the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
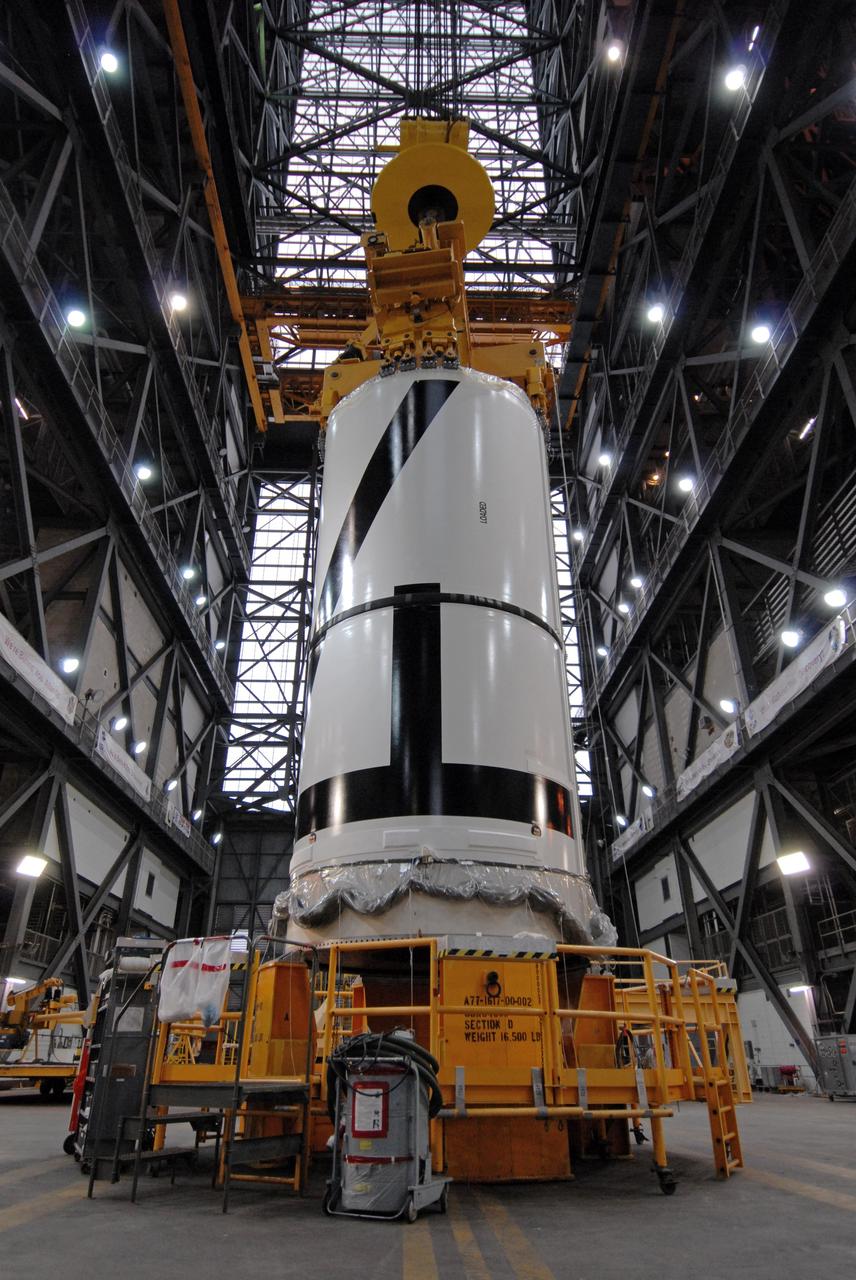

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's transfer aisle at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane is attached to the Ares I-X aft center booster segment. The segment will be lifted and then lowered into High Bay 3 for attachment to the aft booster segment with the aft skirt. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The flight test of the Ares I-X is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
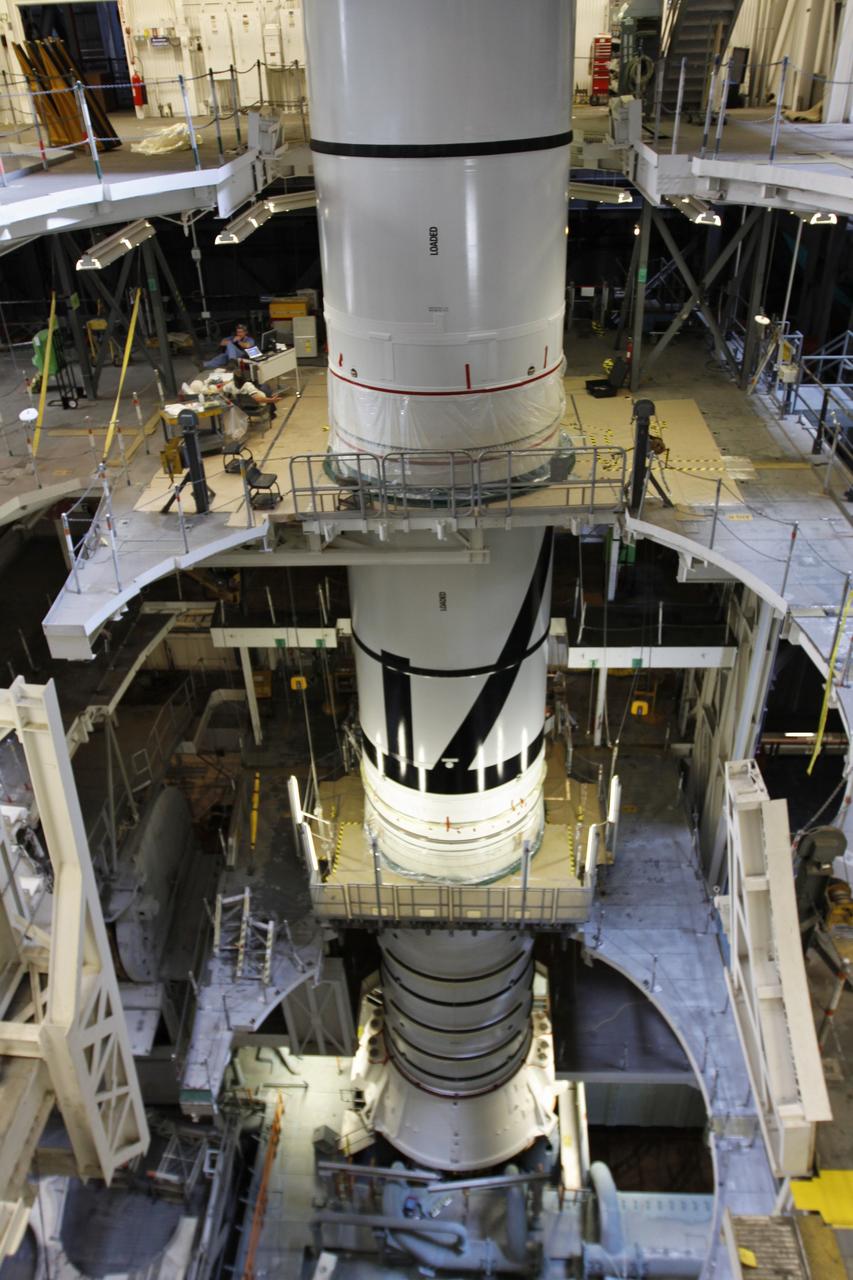

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the stacking of the Ares I-X segments is under way. Here, the forward center segment (top) is lowered onto the aft center and the aft skirt segments. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
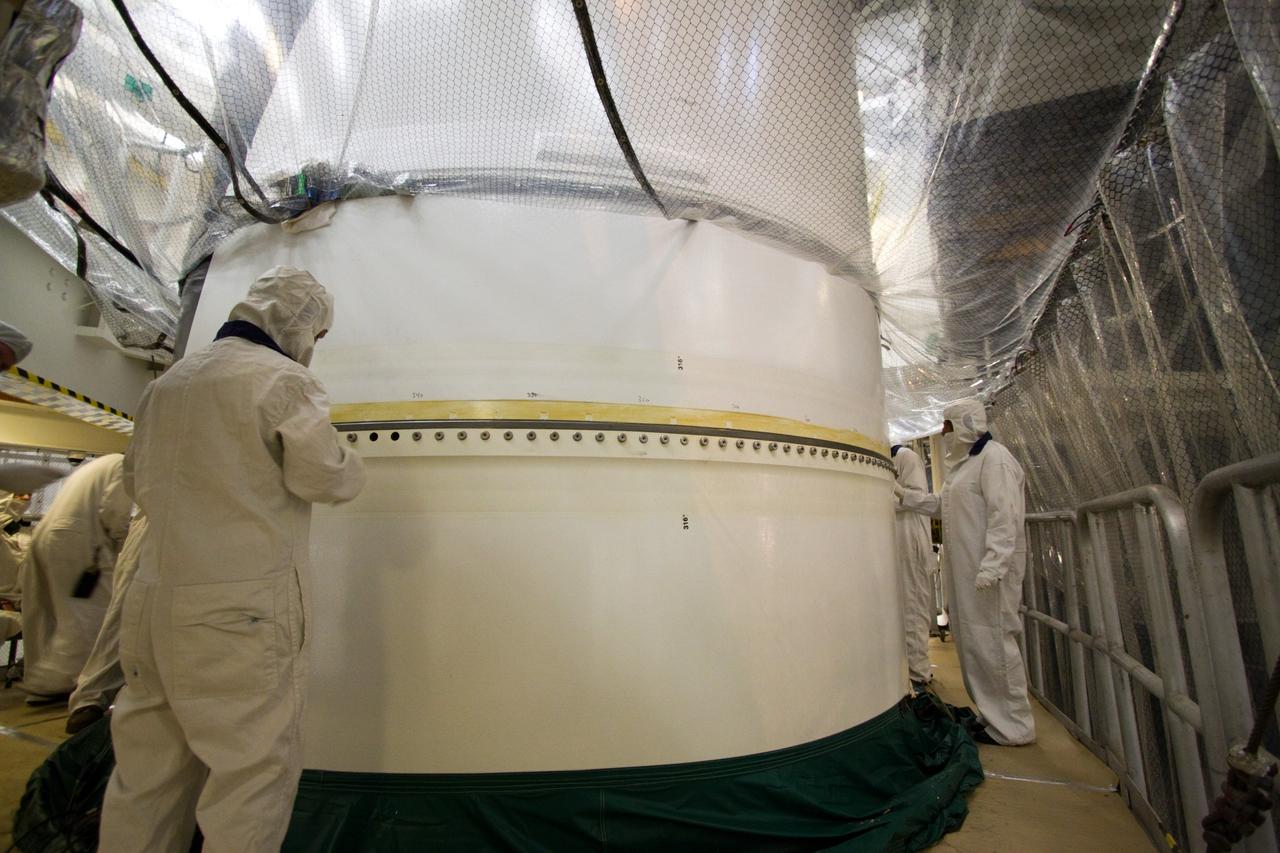

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the forward segment is mated to the forward center segment atop the aft assembly (aft segment and aft skirt). Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
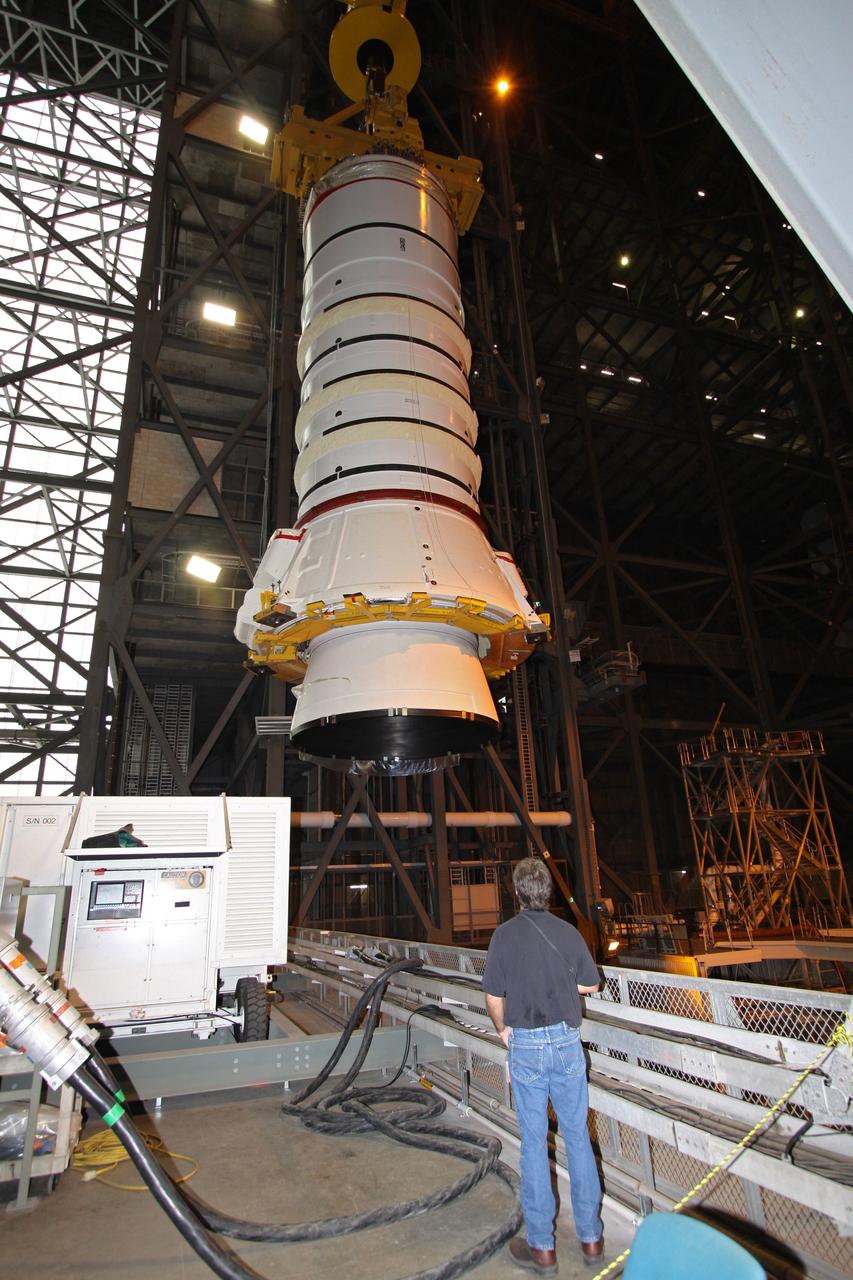

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is moved to High Bay 1 where it will be lowered onto the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
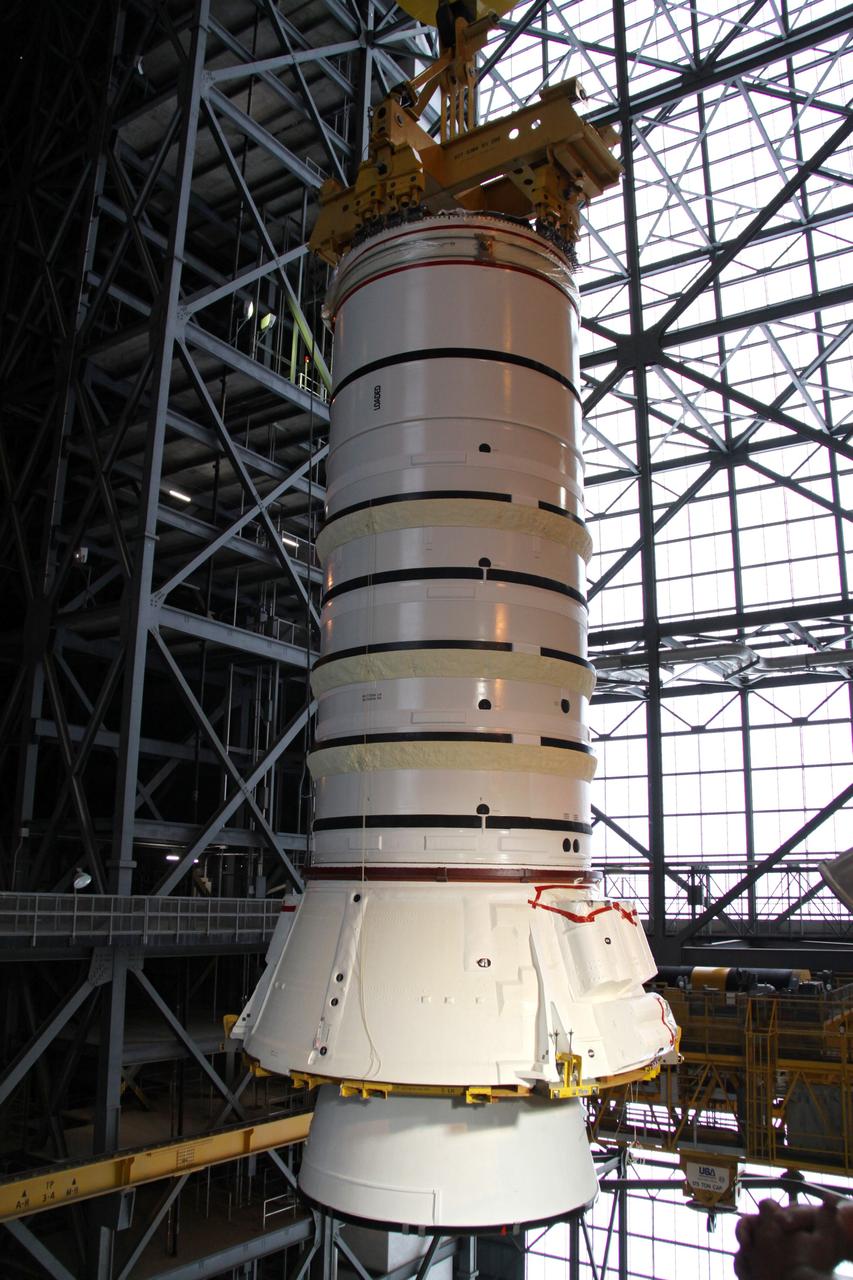

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lifted into the upper regions of the VAB. The stack will be lowered onto the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
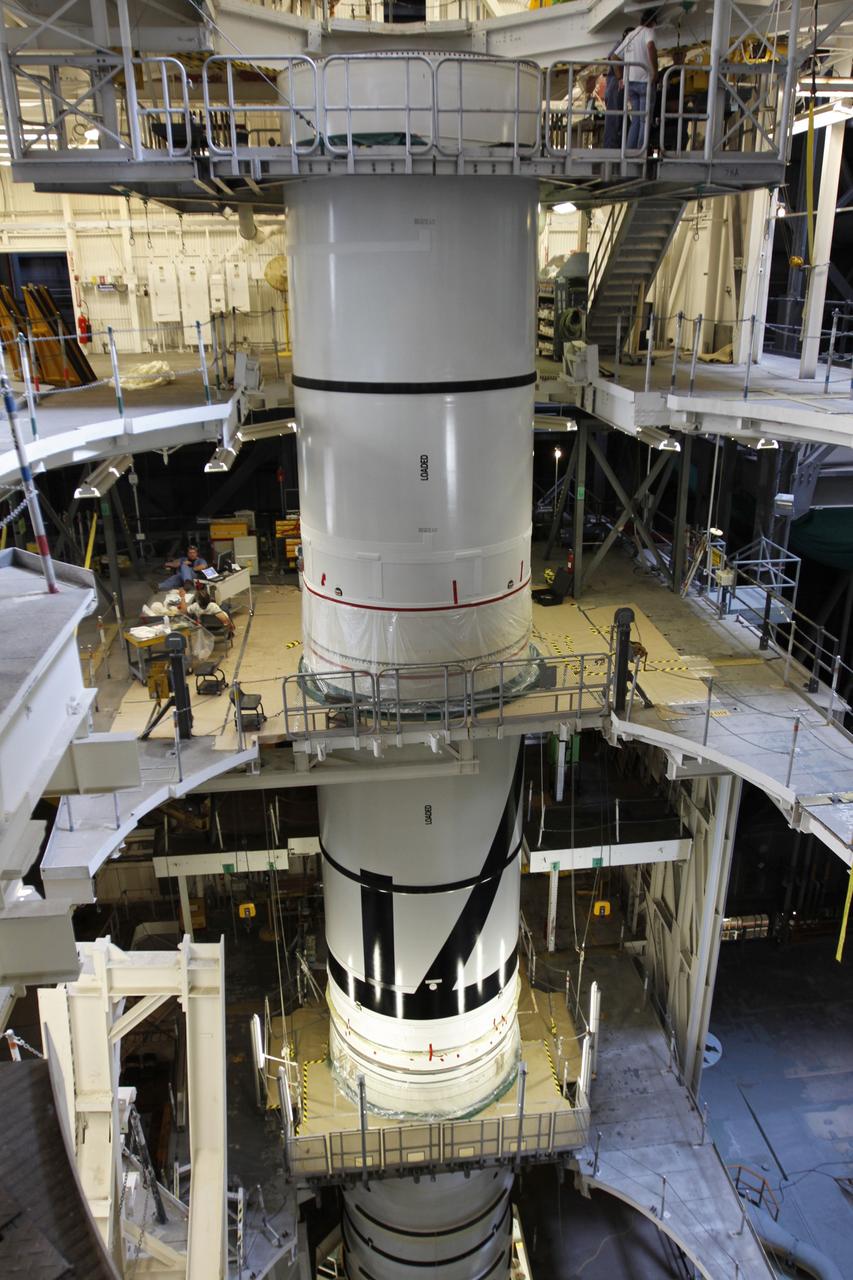

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the stacking of the Ares I-X segments is under way. Here, the forward center segment (top) is lowered onto the aft center and the aft skirt segments. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
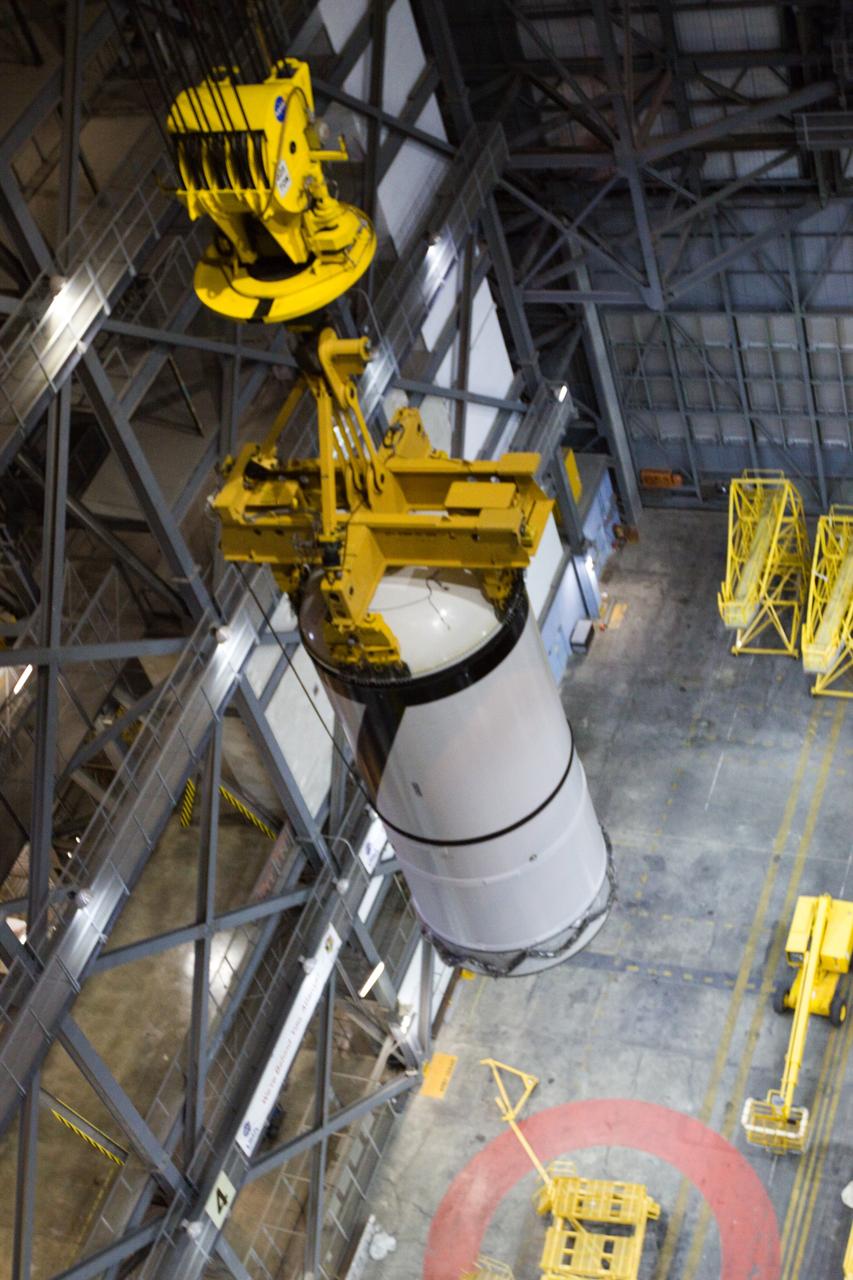

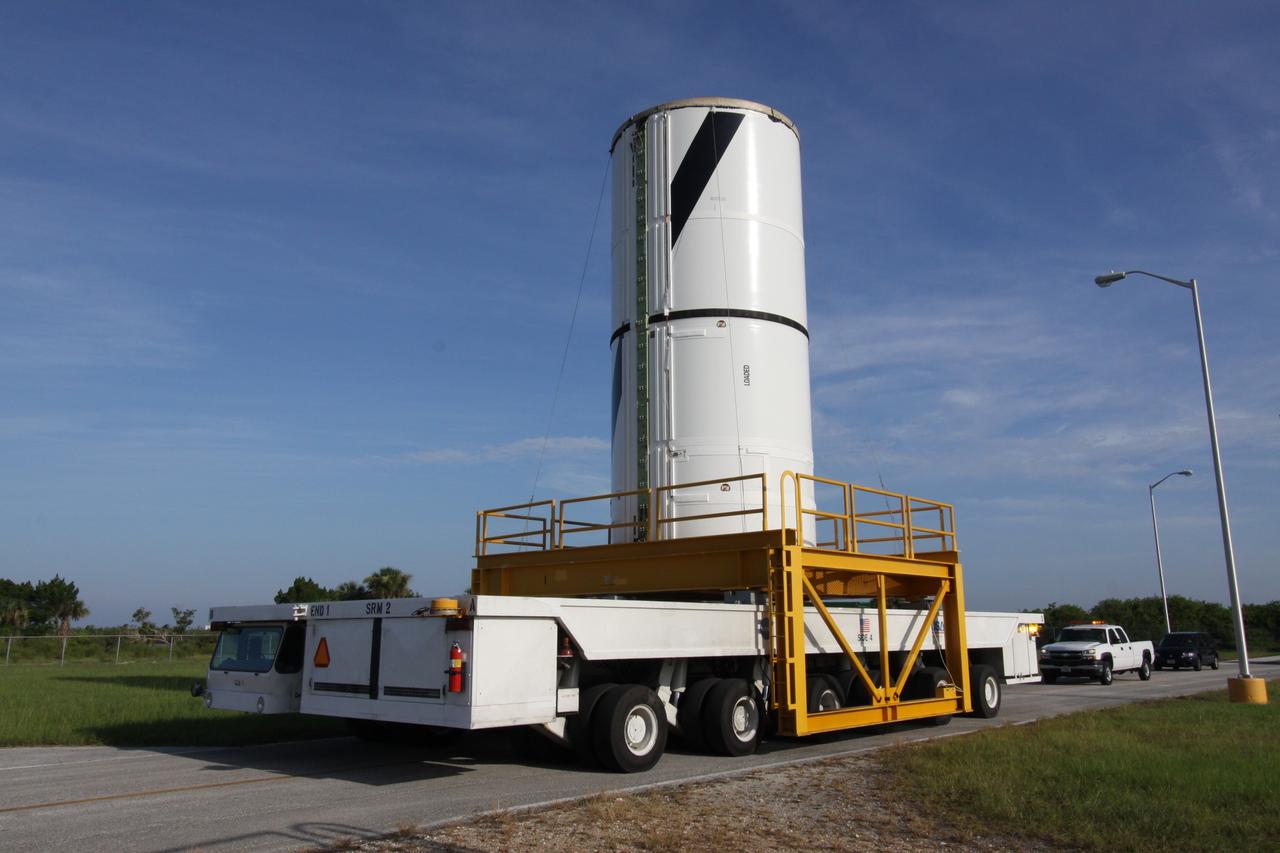
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the transfer aisle of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building, the Ares I-X forward segment is lifted into the upper levels. It will be moved into High Bay 3 for stacking with the forward center, aft center and the aft skirt segments. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
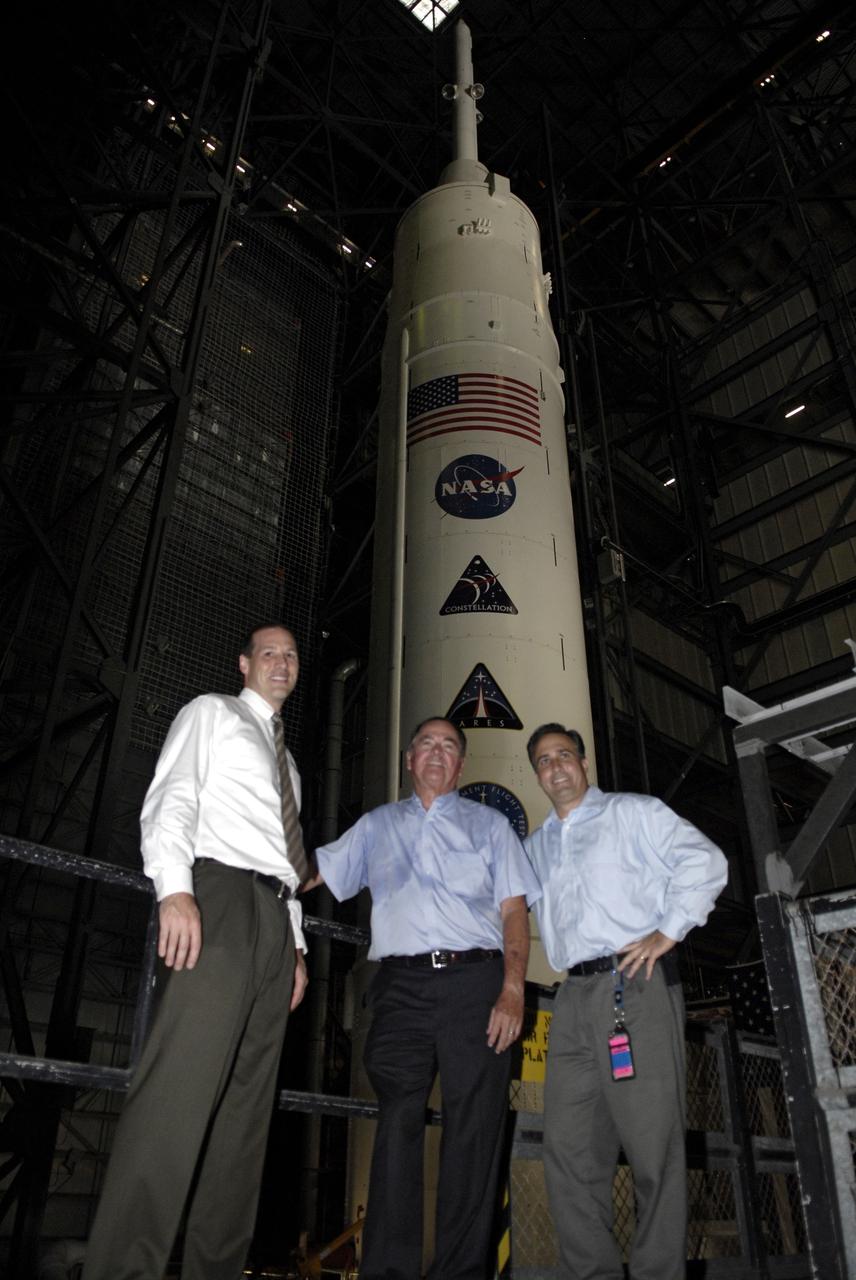

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – – Inside NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building Bay 3, Ares I-X mission manager Bob Ess, former astronaut Robert Crippen and mission team member Trent Smith stand in front of the Ares I-X rocket. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 27. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
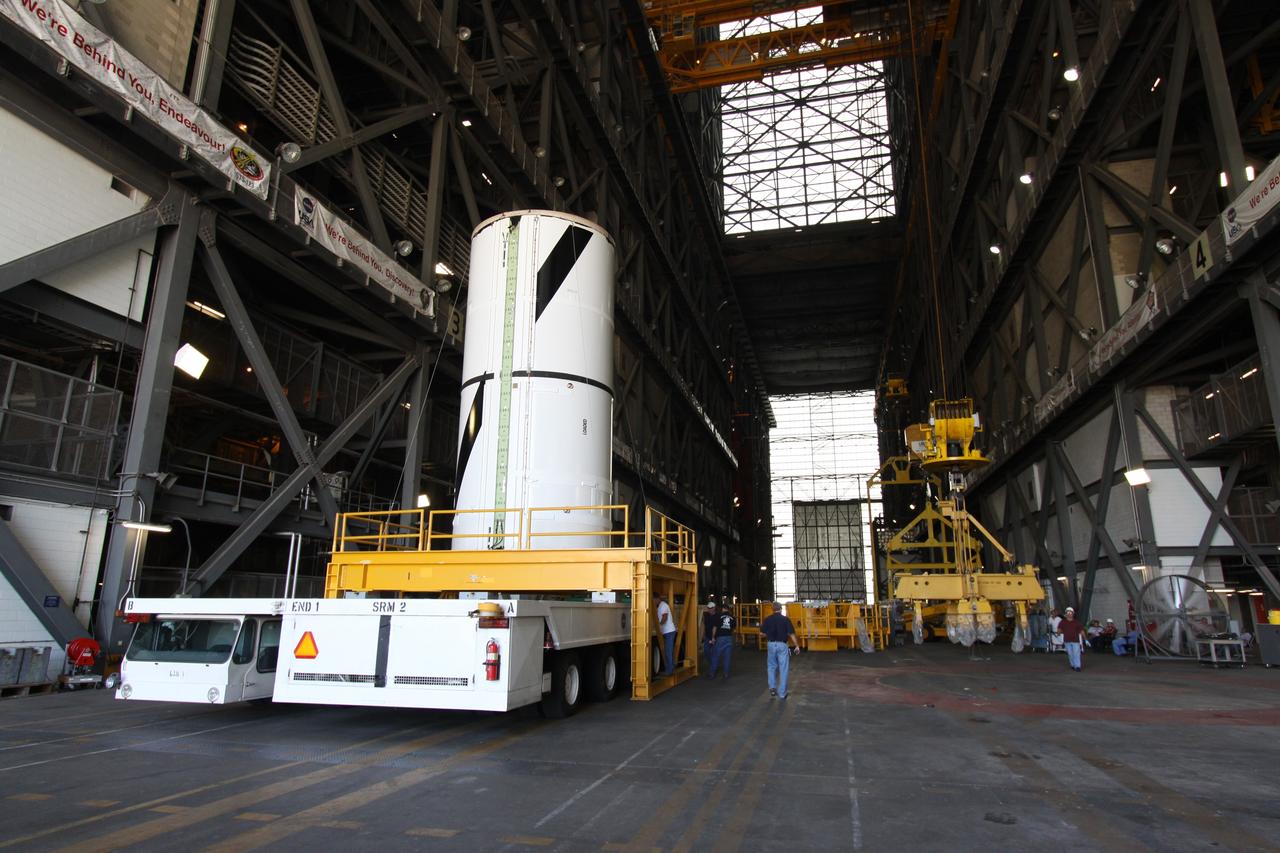

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward center segment arrives in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB. The launch vehicle is being assembled in the VAB's High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
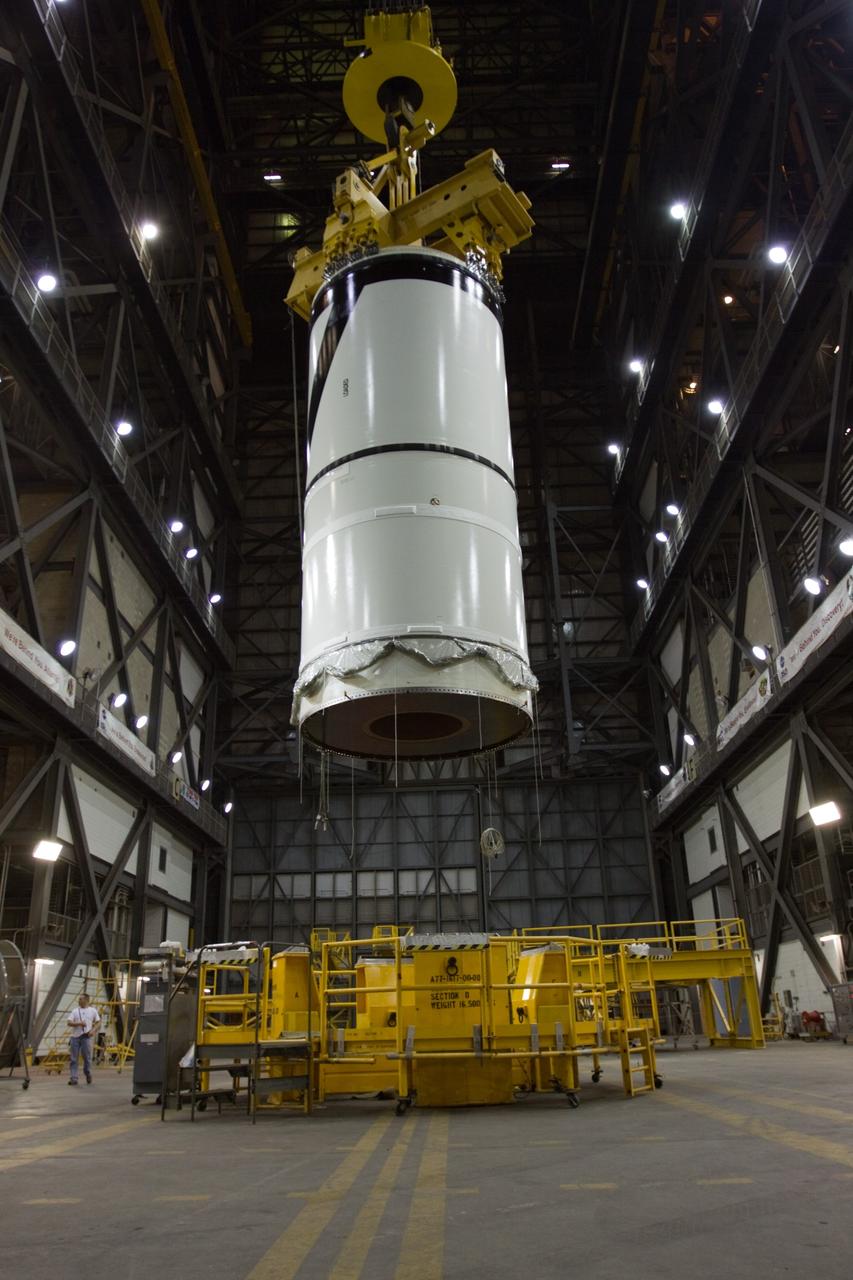

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the transfer aisle of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building, the Ares I-X forward segment is lifted. It will be moved into High Bay 3 for stacking with the forward center, aft center and the aft skirt segments. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
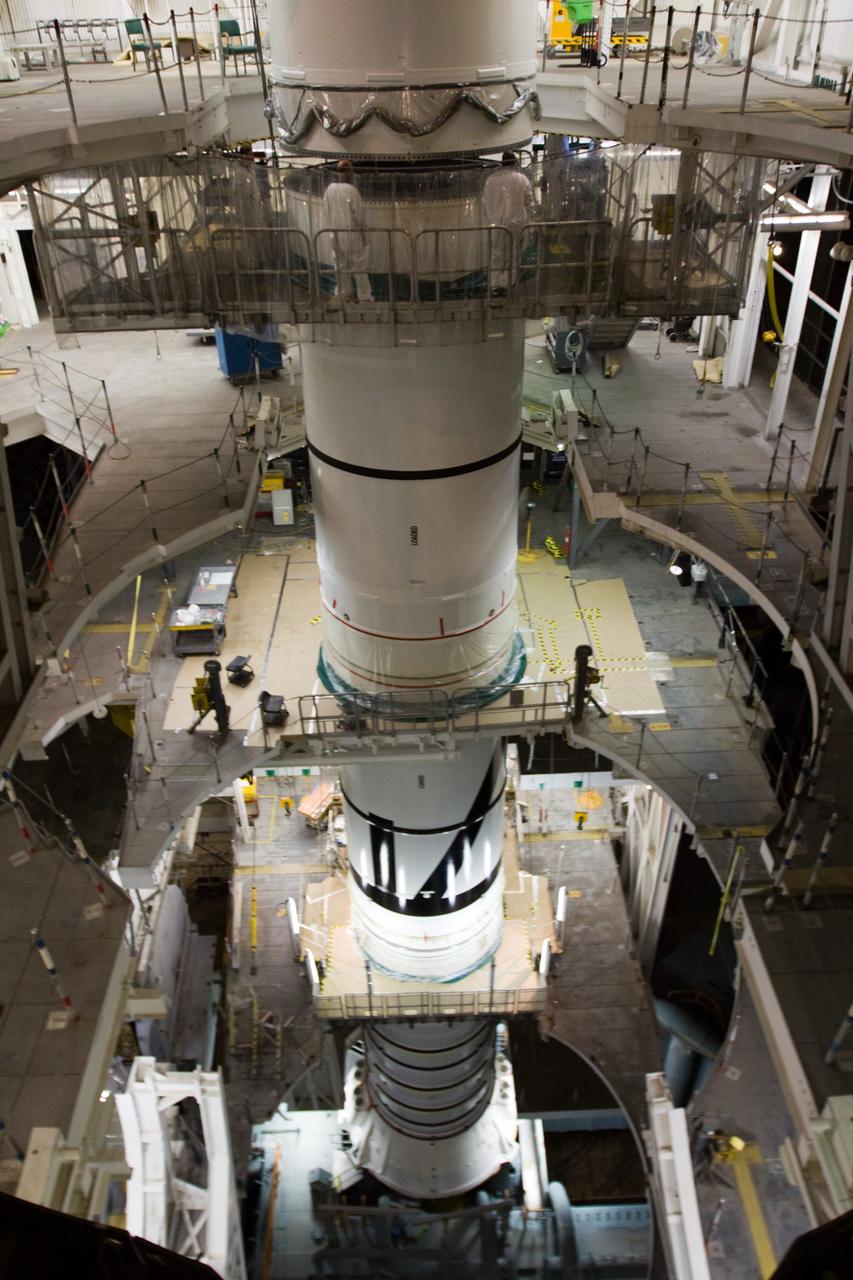

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the High Bay 3 of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building, the Ares I-X forward segment is mated with the forward center segment, already stacked with the aft center and the aft skirt segments below. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
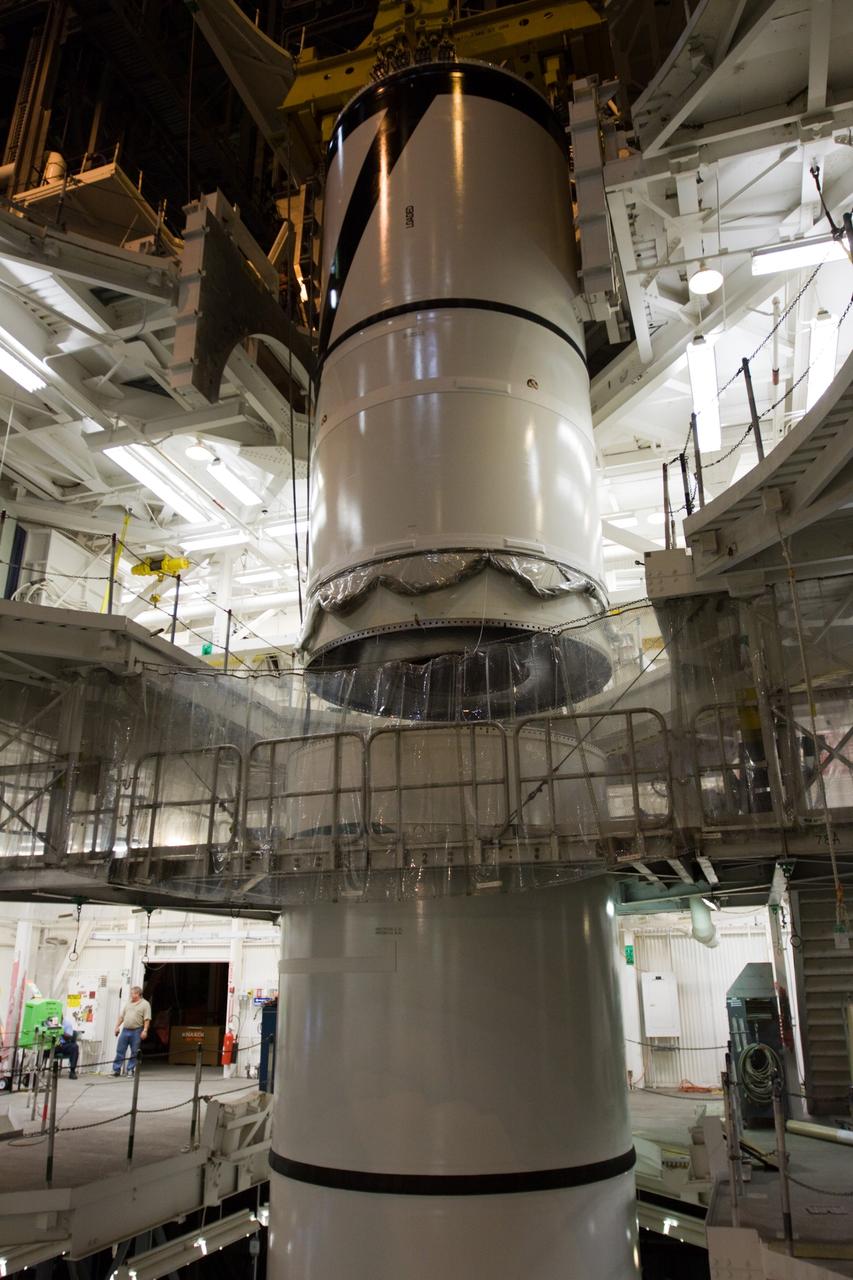

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the High Bay 3 of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building, the Ares I-X forward segment is lowered onto the forward center for mating. The forward center is already mated with the aft center and the aft skirt segments below. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
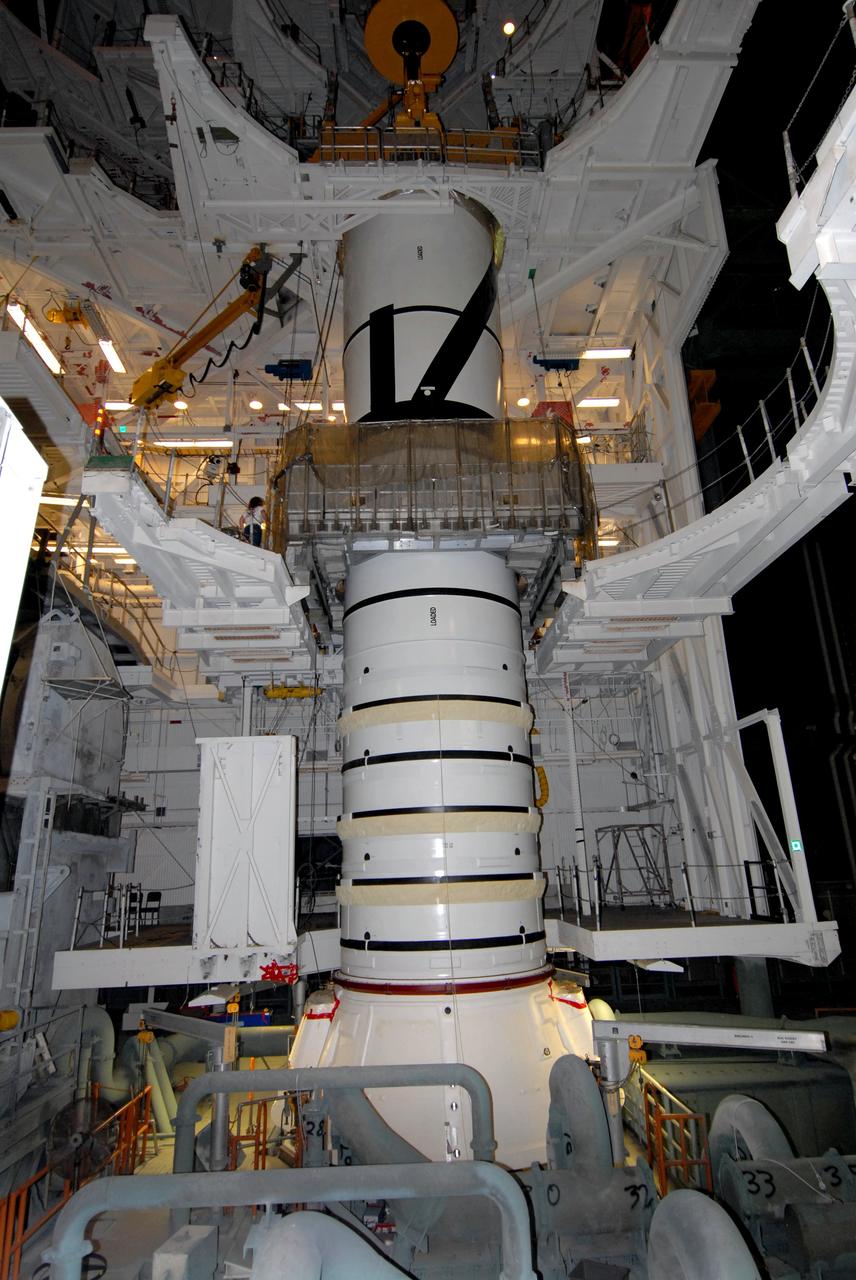

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft center booster segment is mated to the aft booster and skirt. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The flight test of the Ares I-X is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
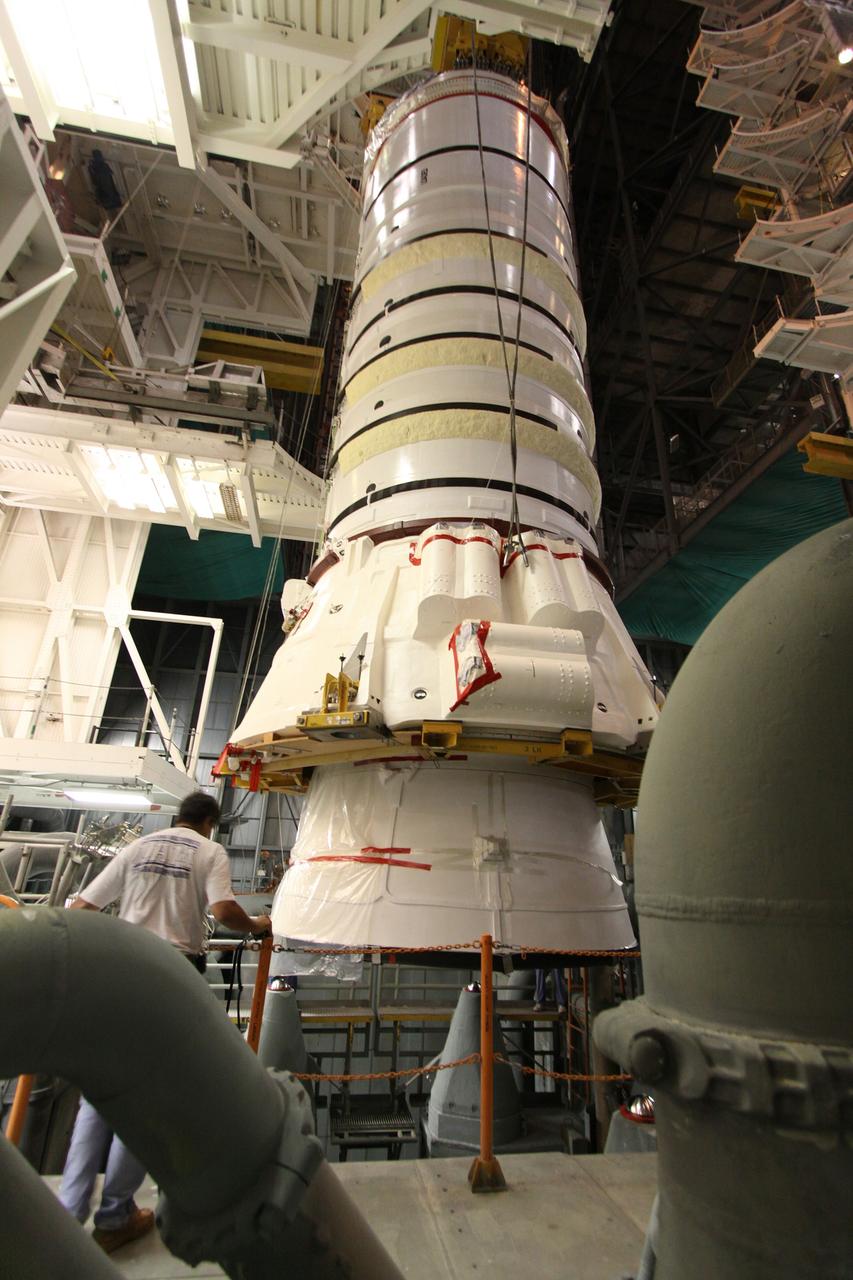

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers keep watch as the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lowered toward the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
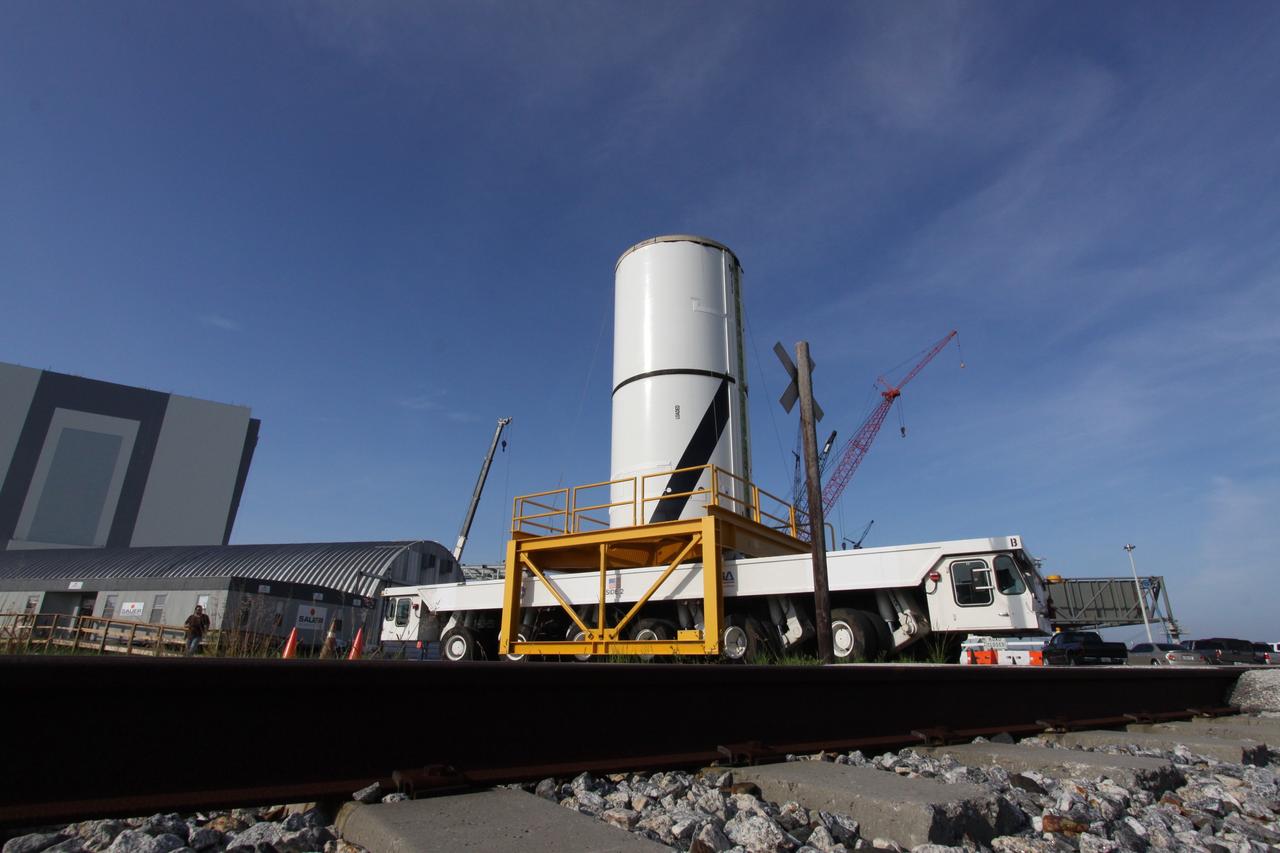

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X forward center segment nears the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, after leaving the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility. The launch vehicle is being assembled in the VAB's High Bay 3. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
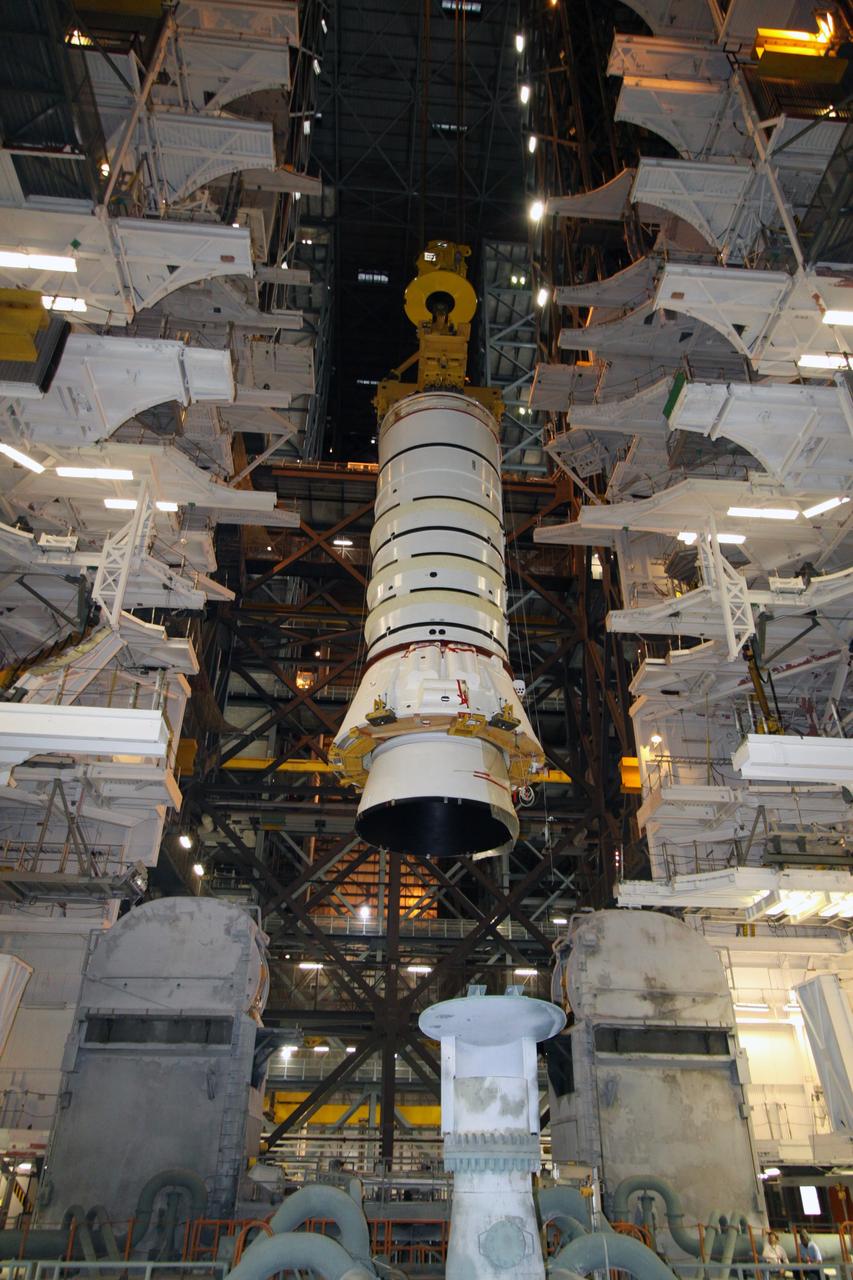

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lowered toward the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
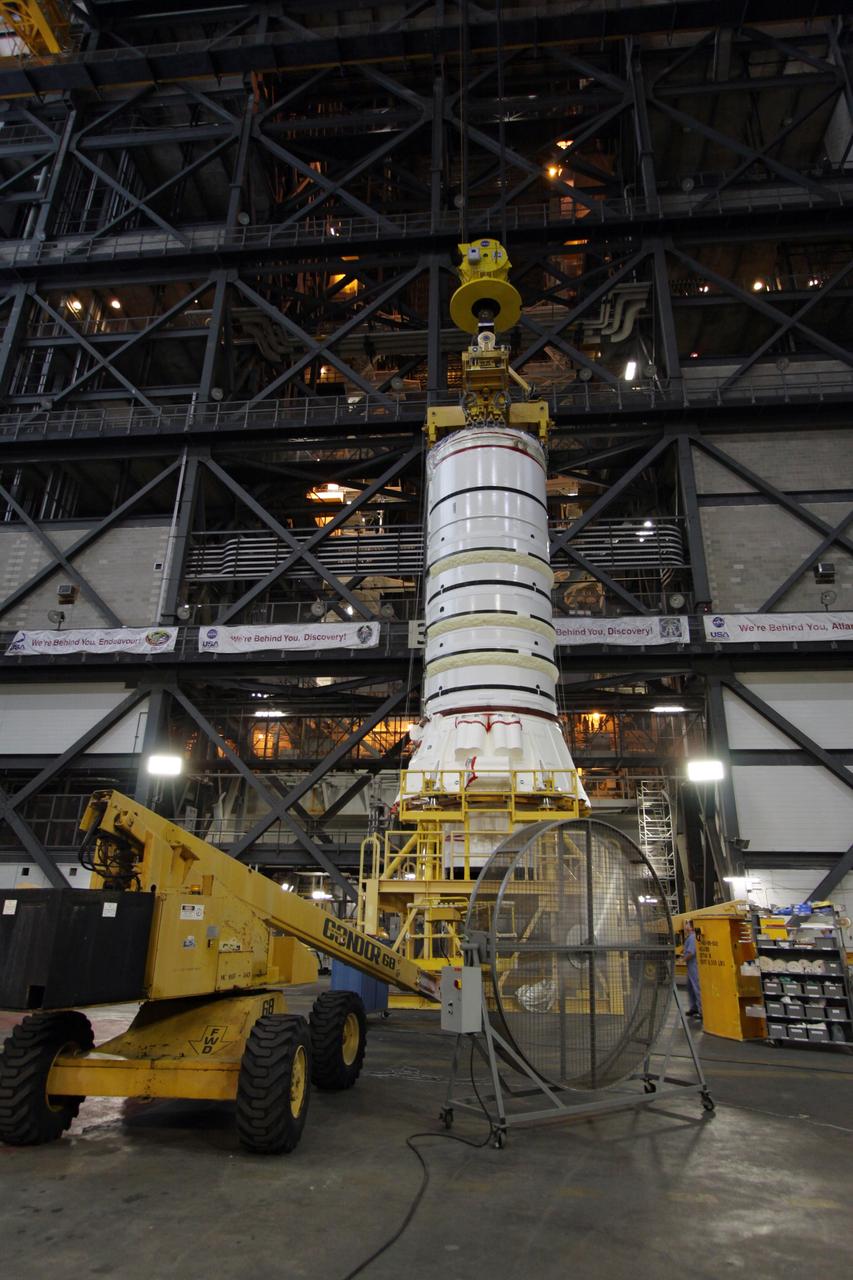

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X aft booster segment with the aft skirt is lifted from its stand. The stack will be hoisted into the upper regions of the VAB and lowered onto the mobile launch platform in High Bay 3. This is the start of the buildup of the Ares I-X launch vehicle for the flight test targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
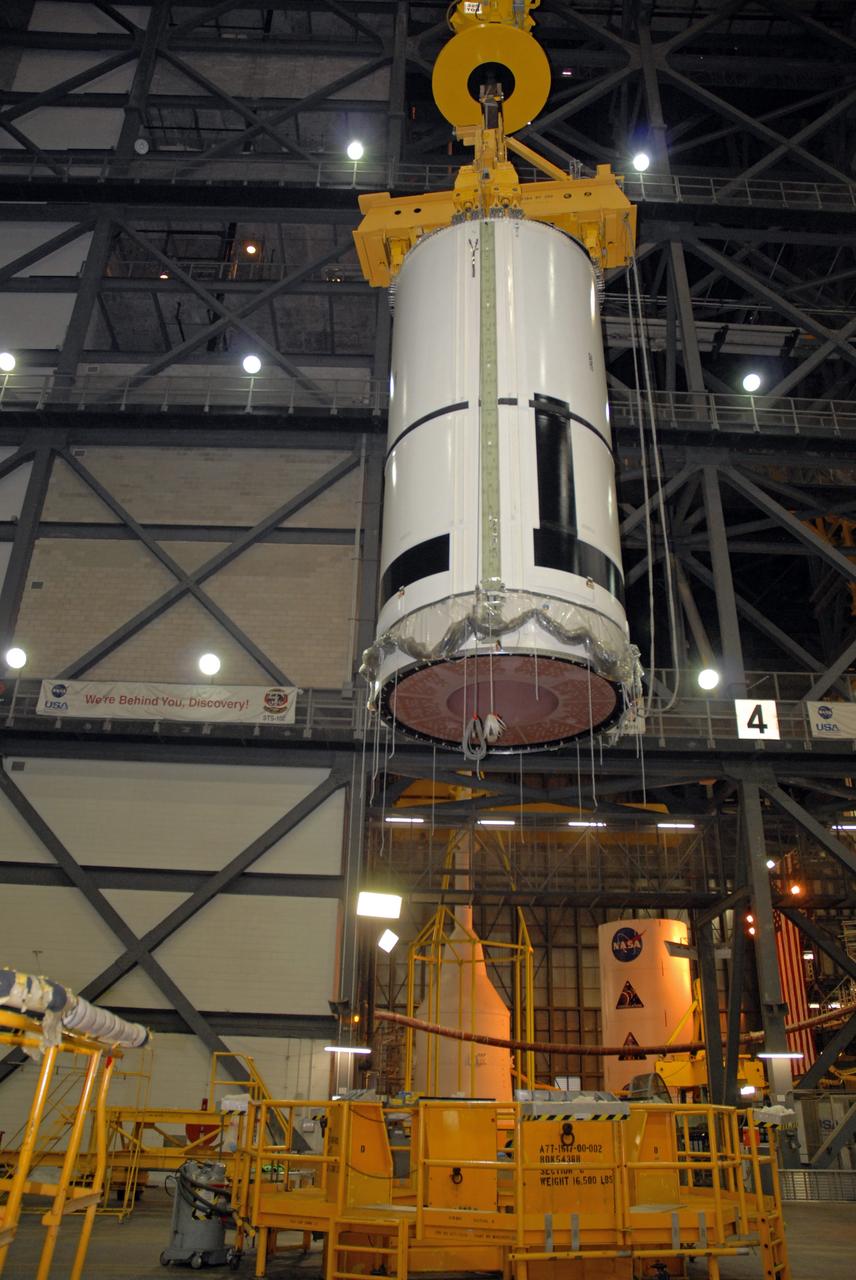

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's transfer aisle at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an overhead crane lifts the Ares I-X aft center booster segment, which will be lifted and then lowered into High Bay 3 for attachment to the aft booster and skirt. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is the essential core of a space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system . The flight test of the Ares I-X is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 30. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
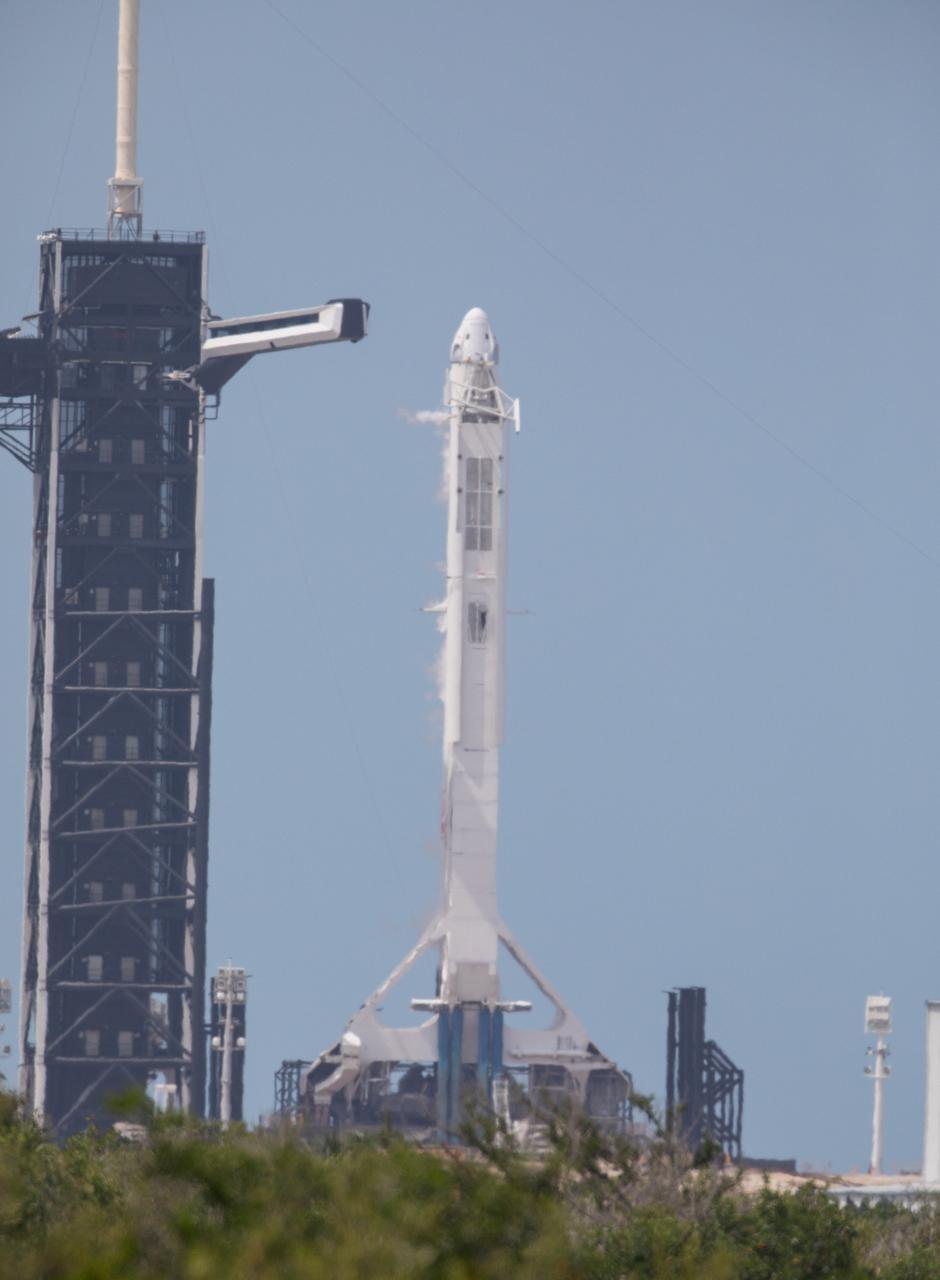

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft stand poised for launch at historic Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
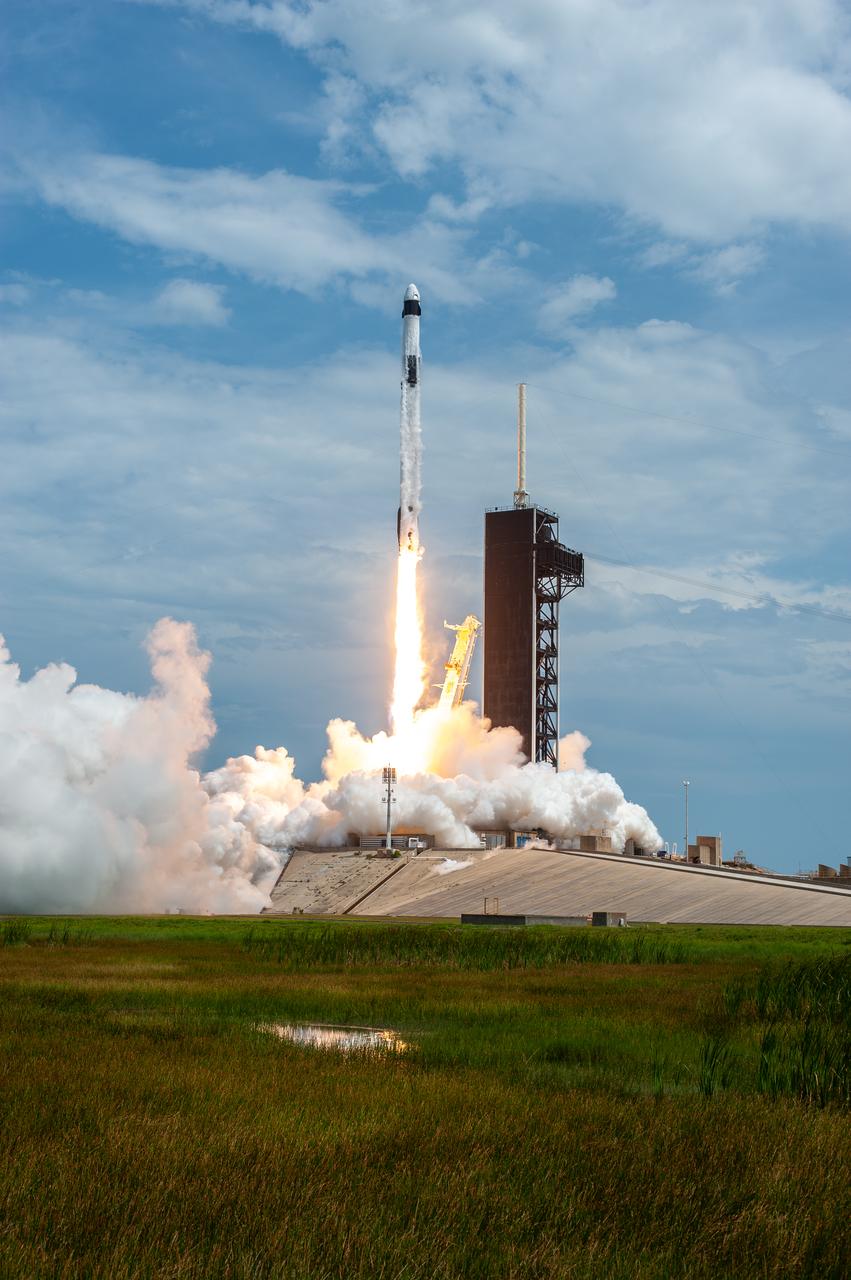

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
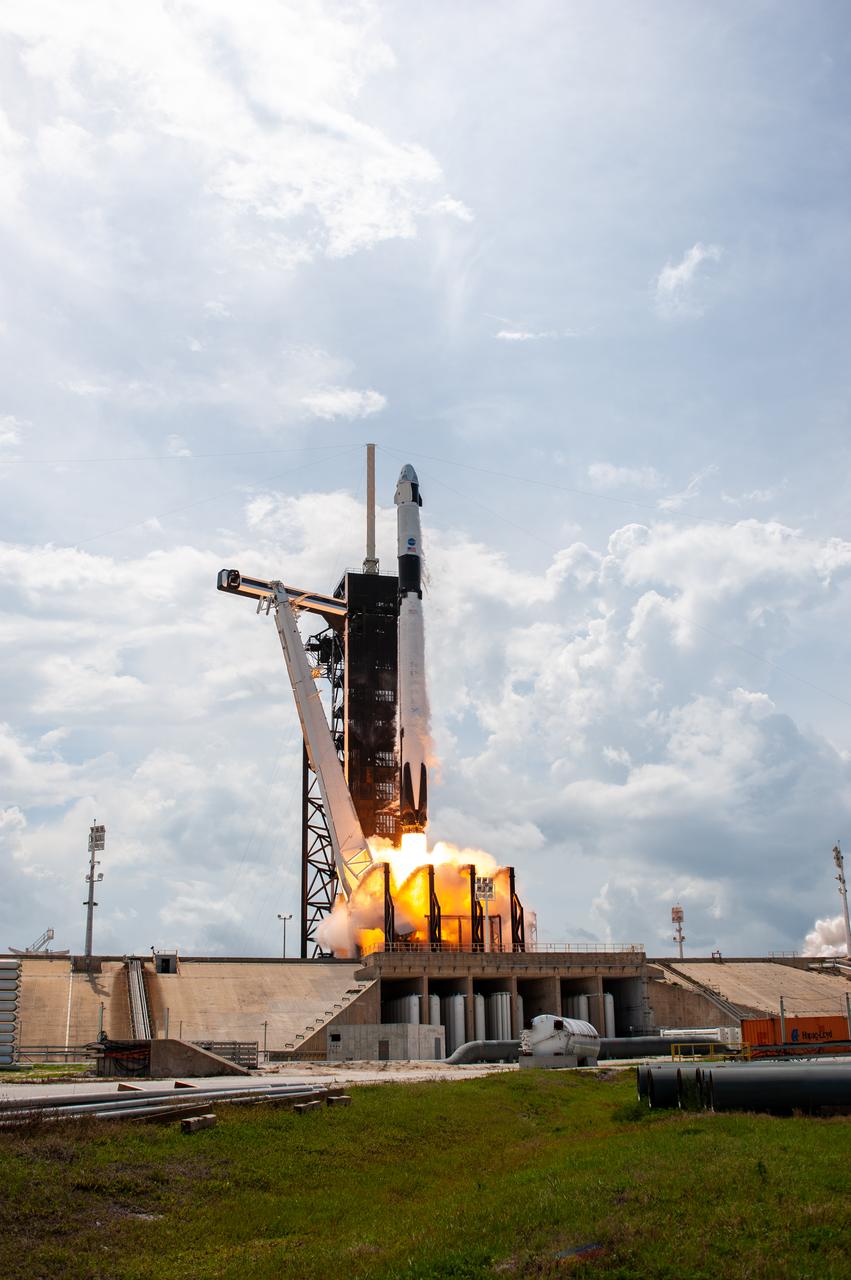

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
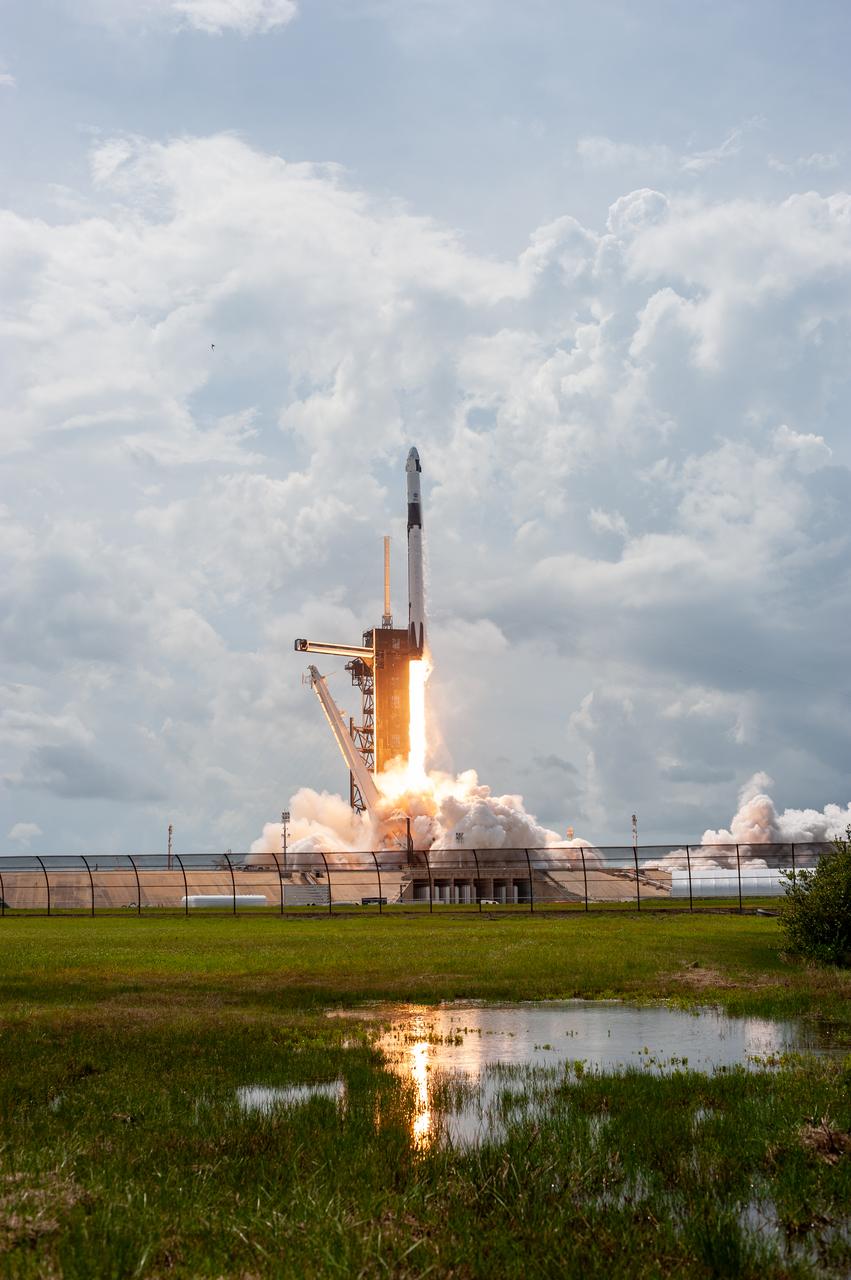

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
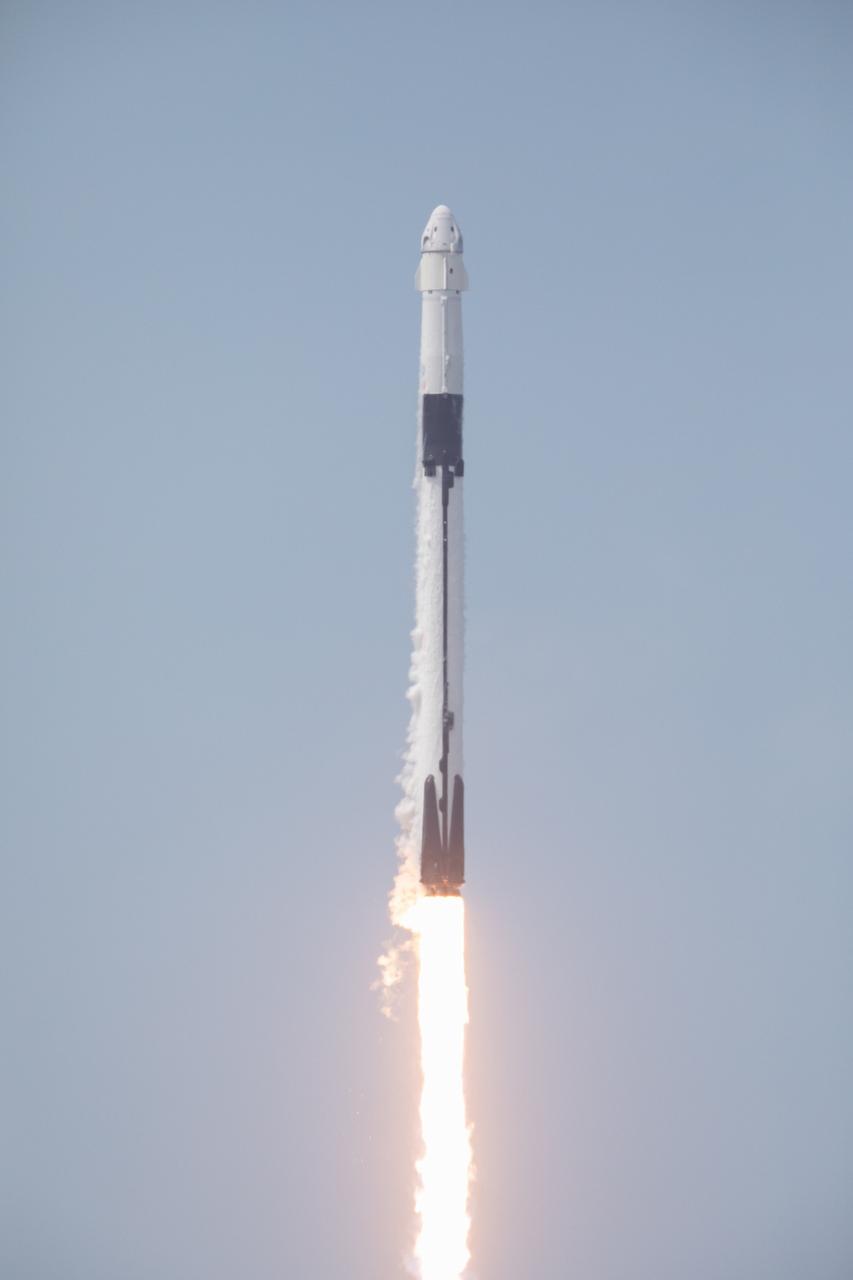

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
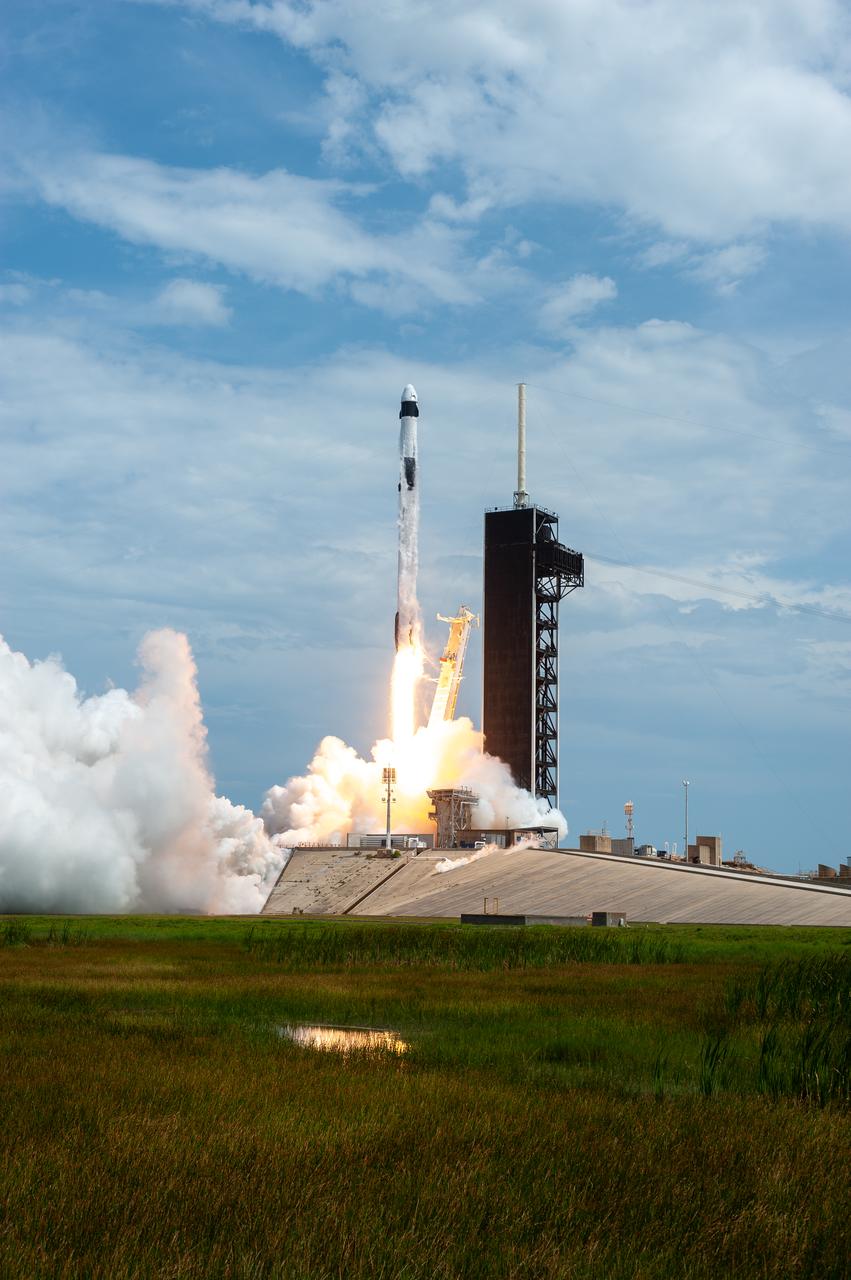

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
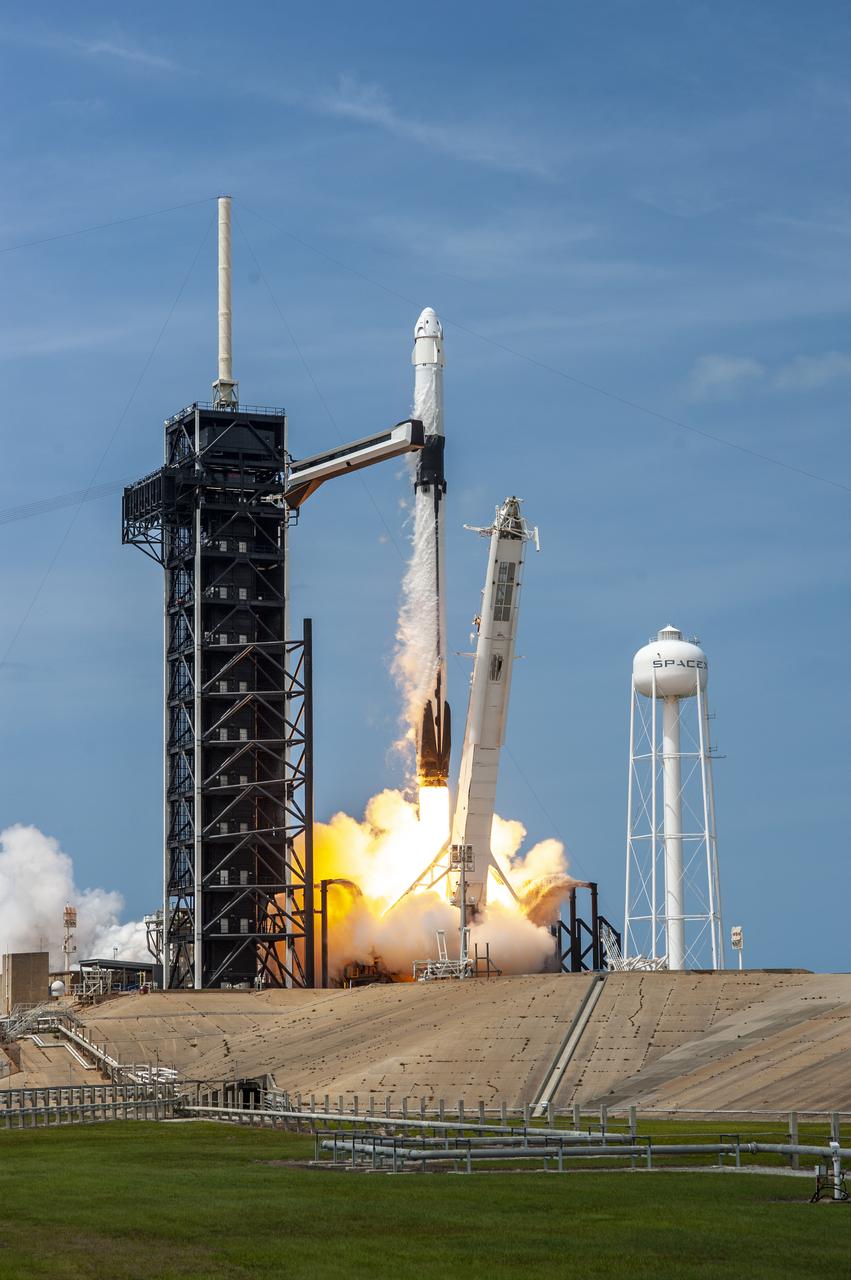

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
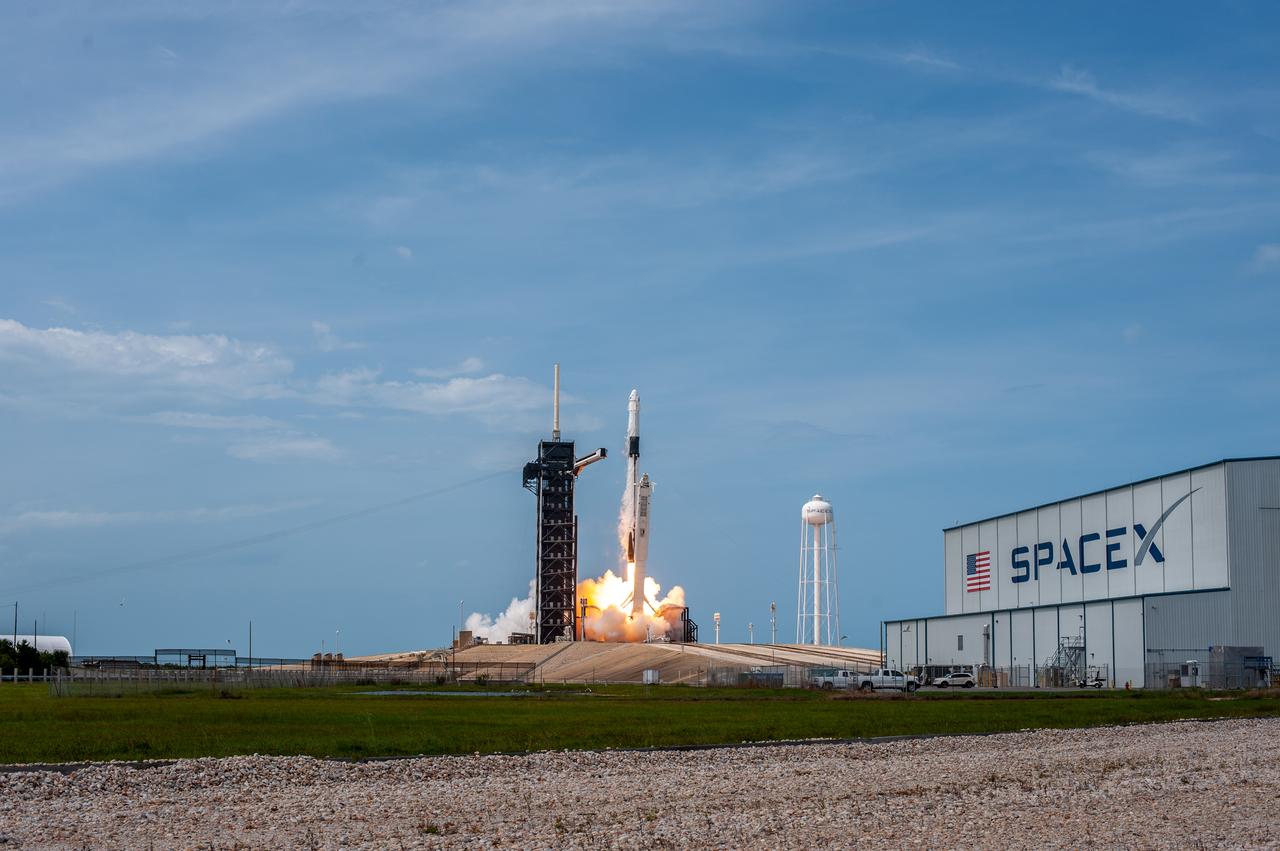

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
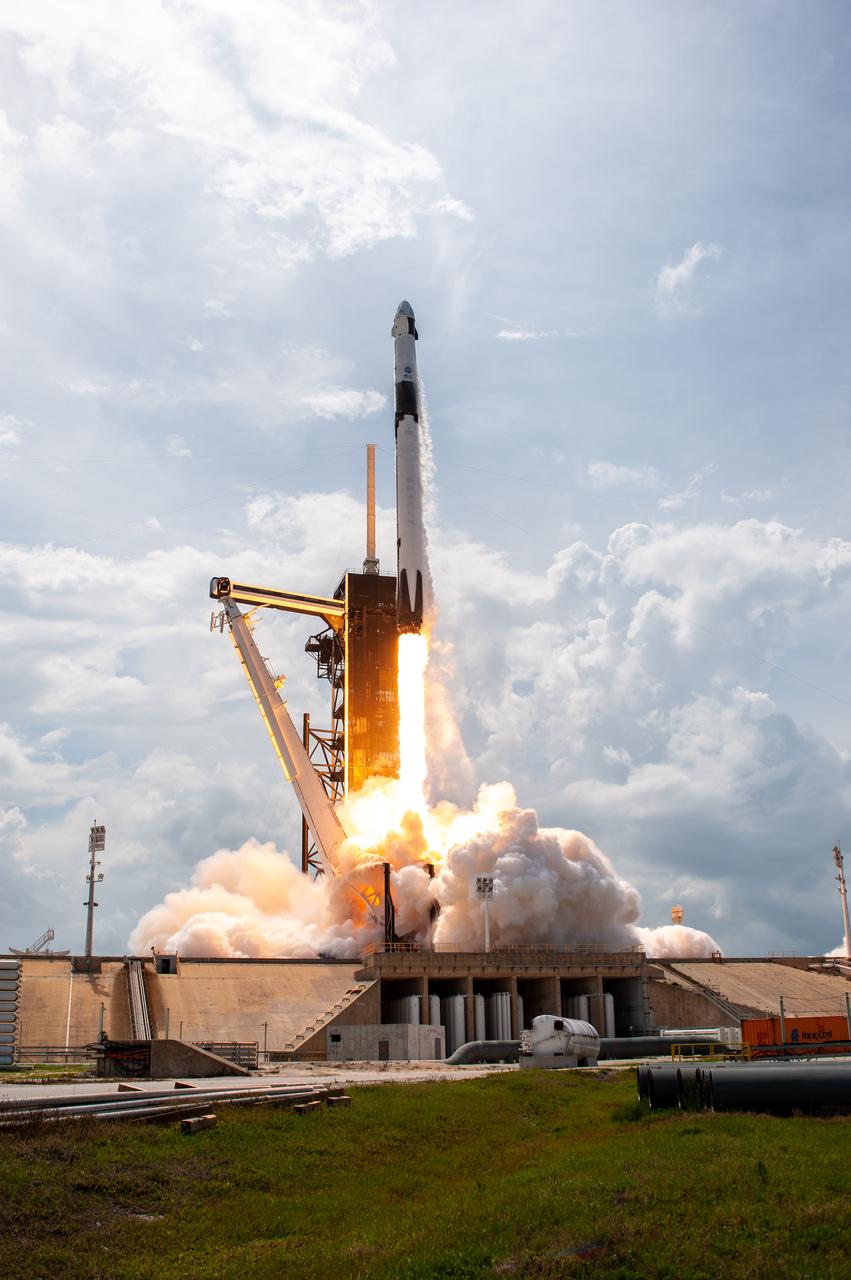

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
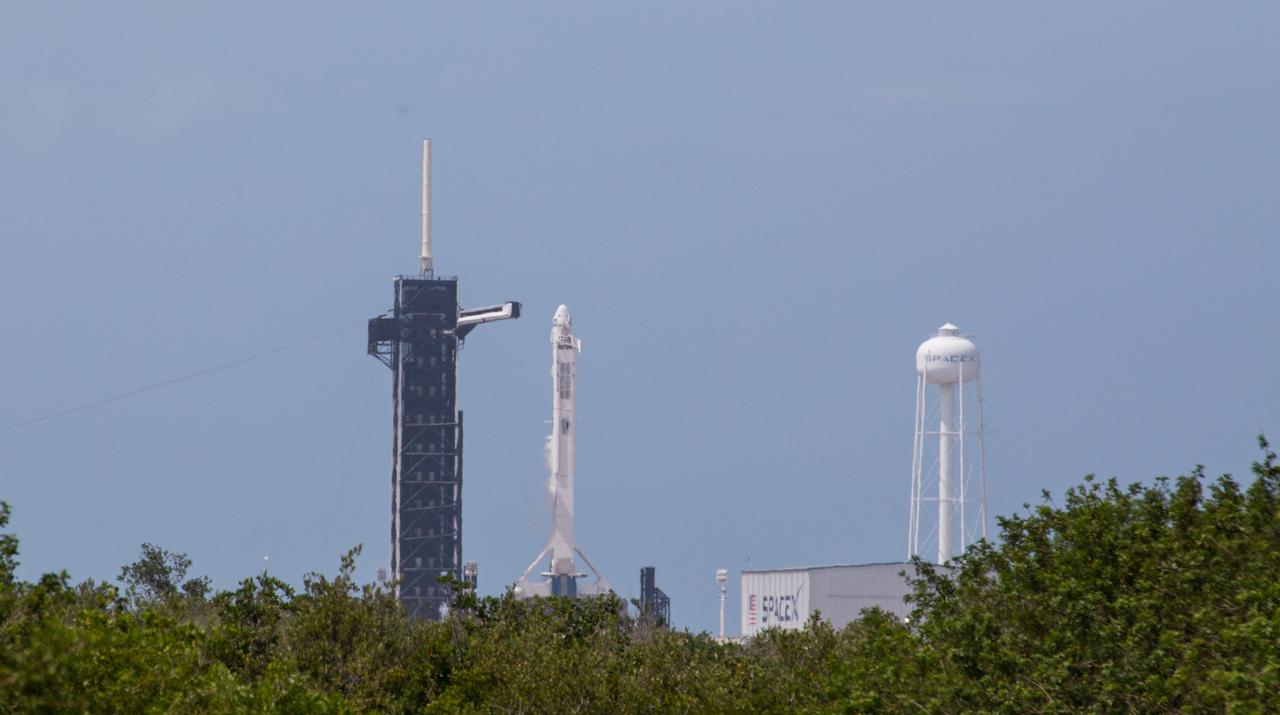

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft stand poised for launch at historic Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
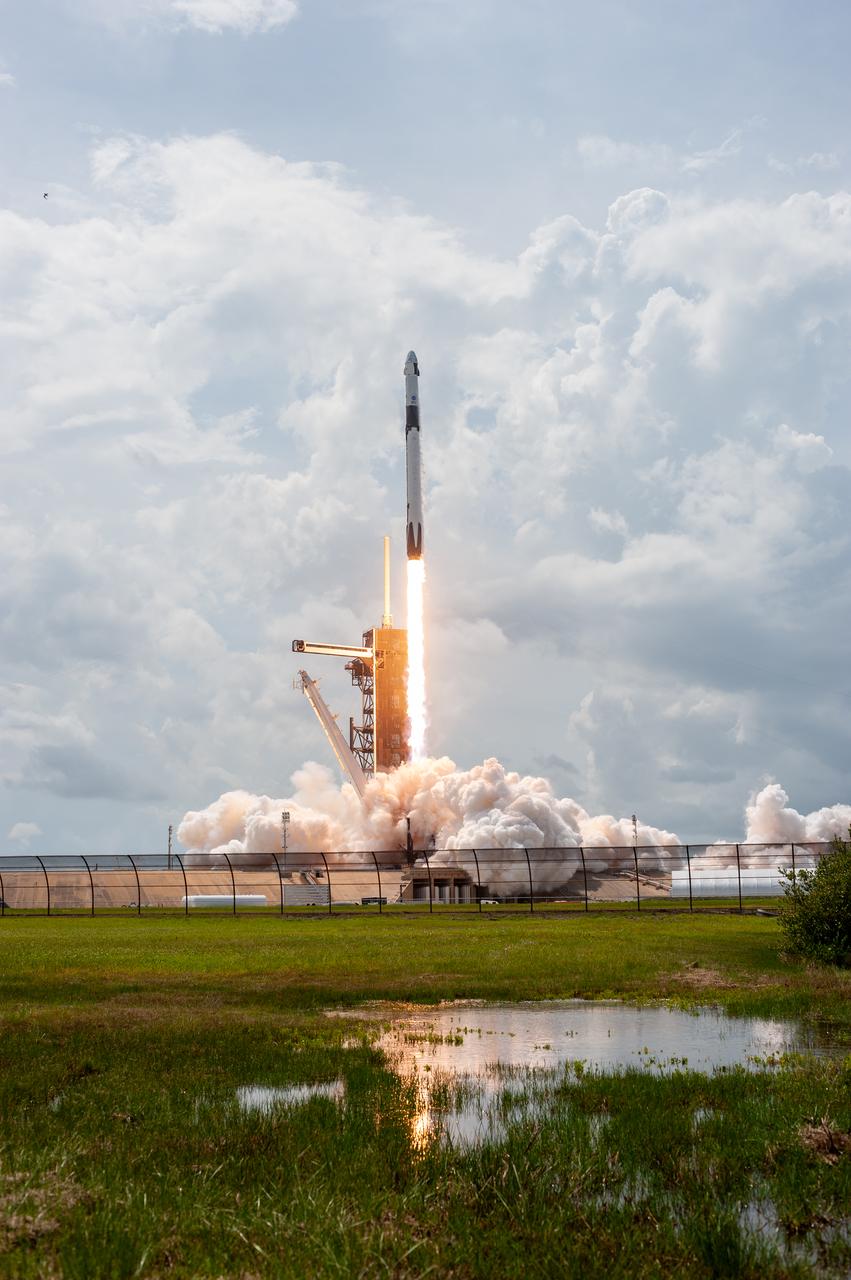

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
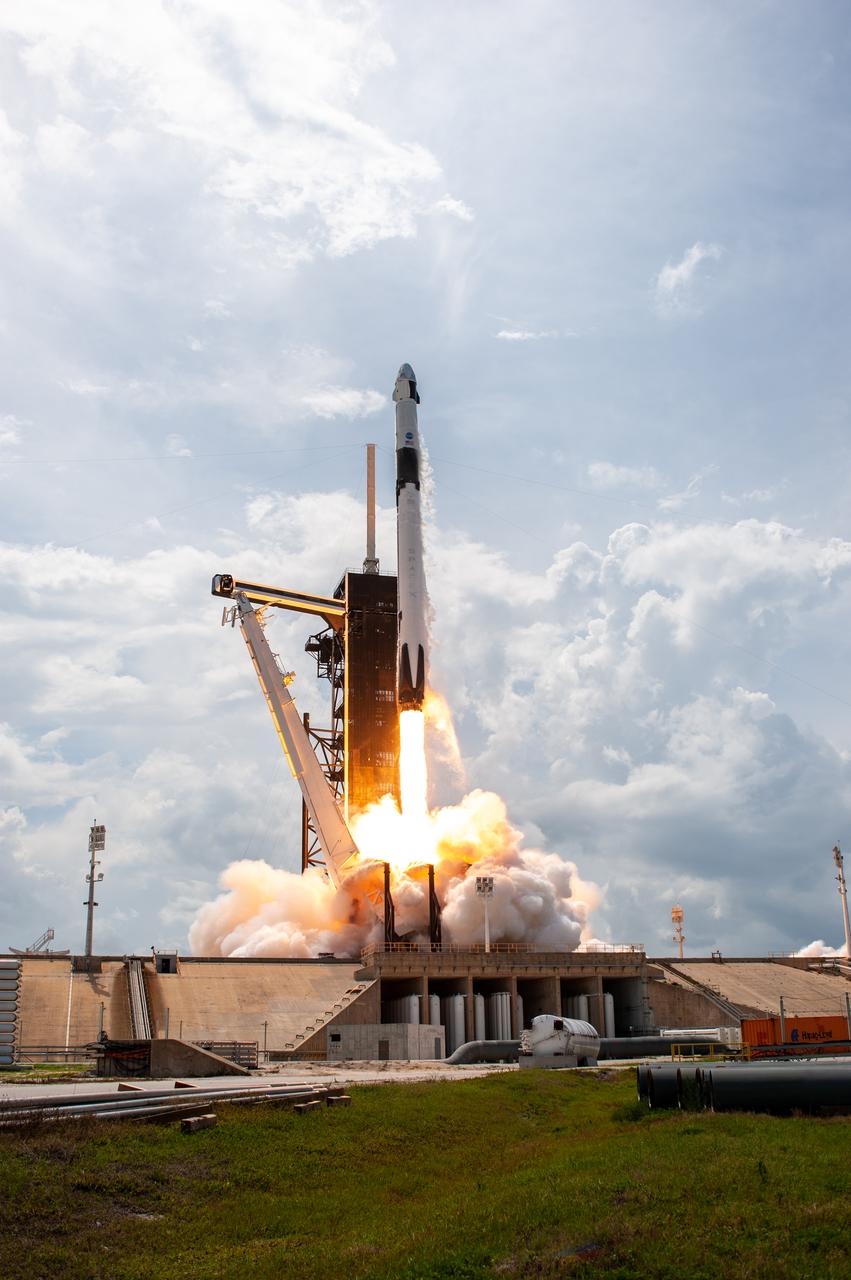

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
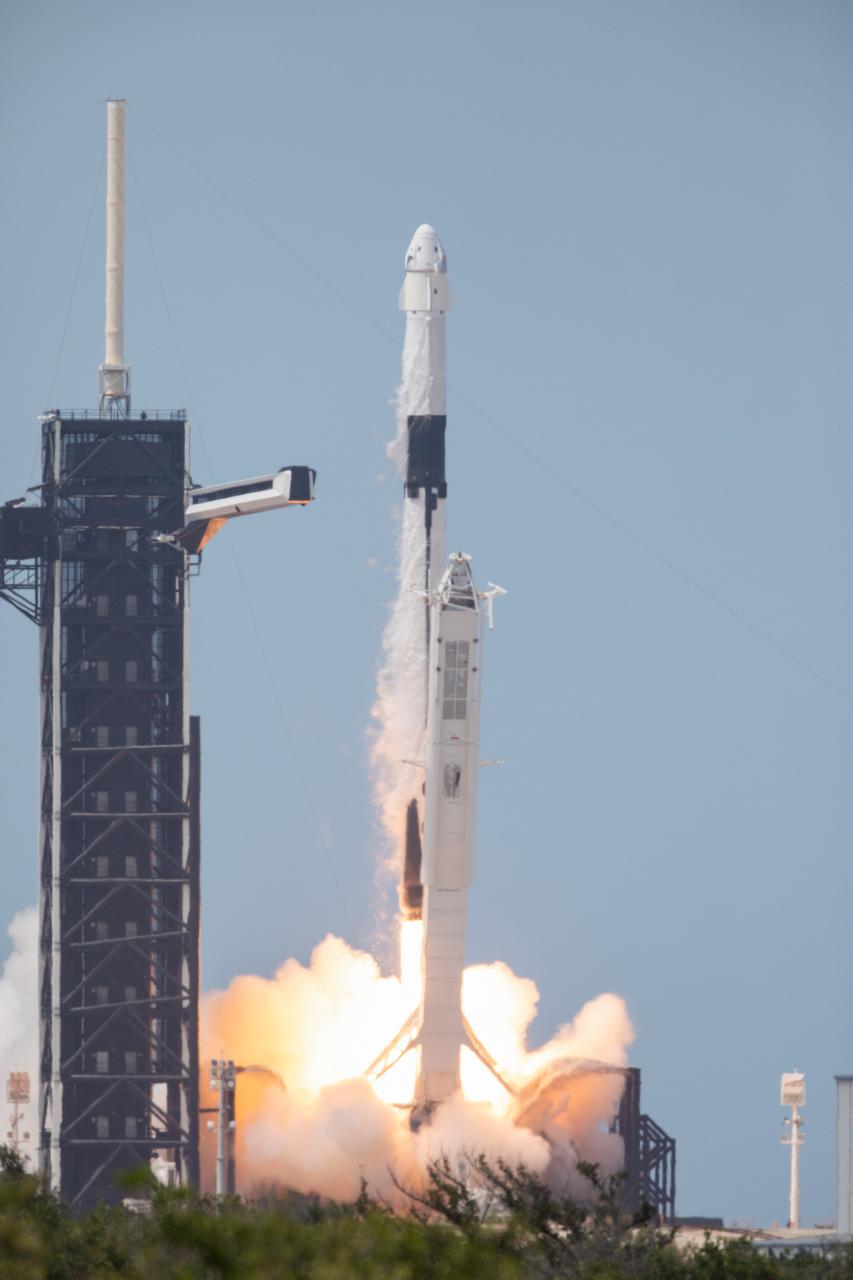

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
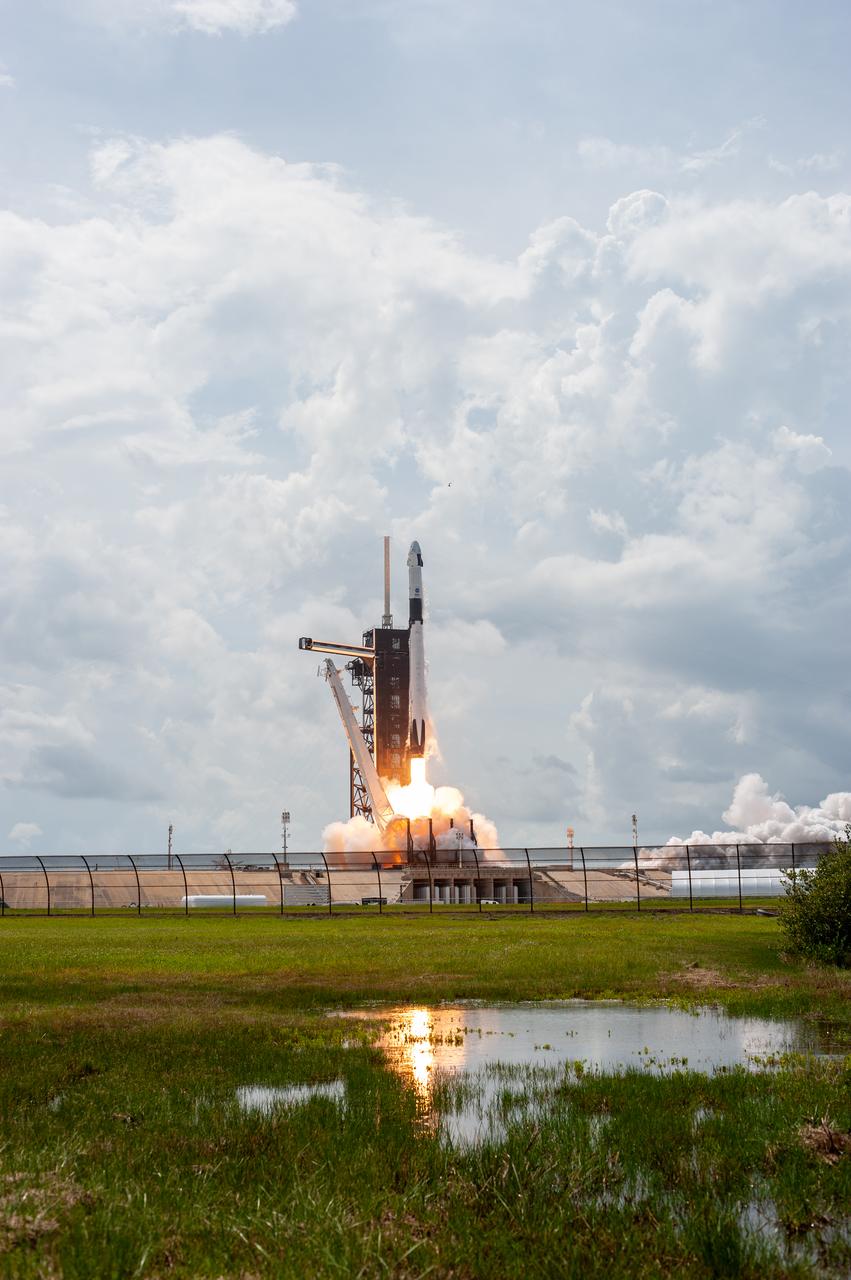

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
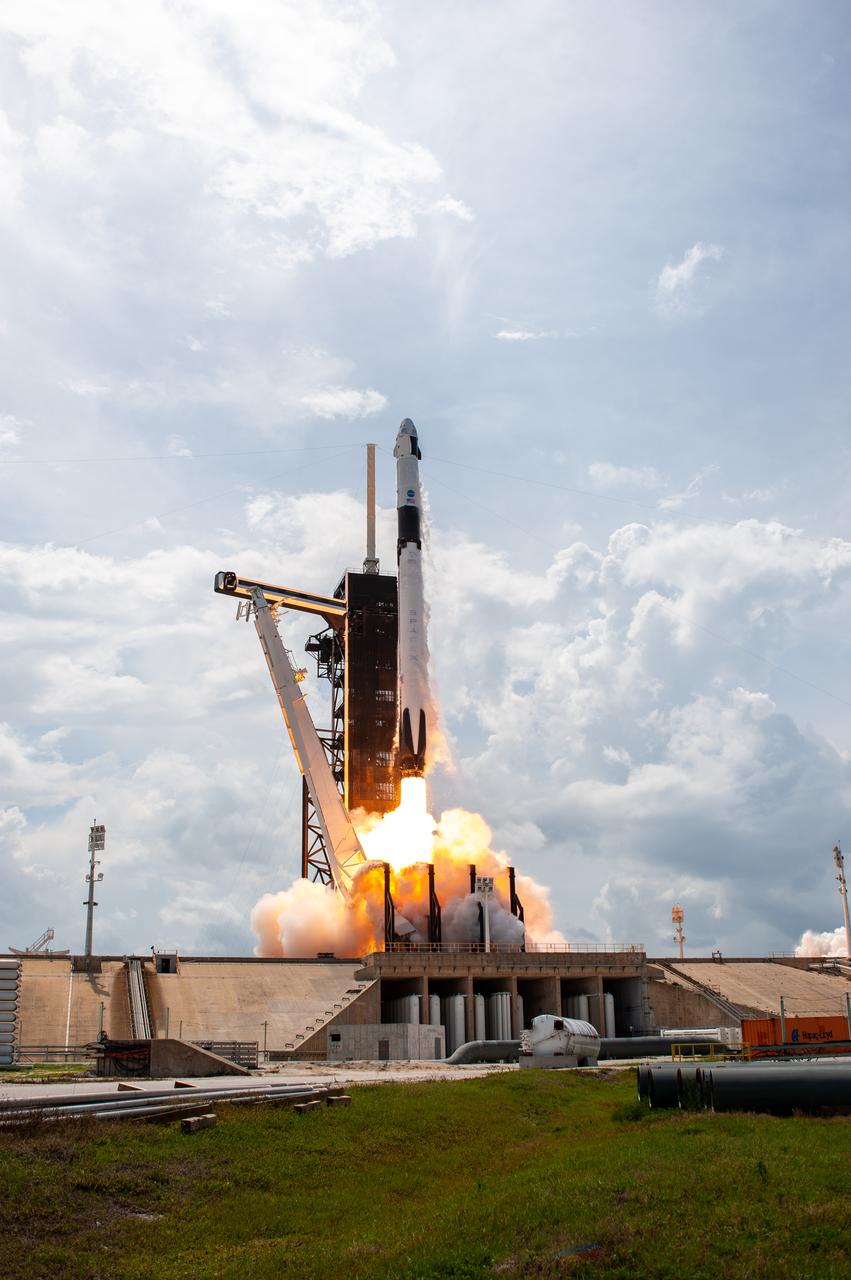

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
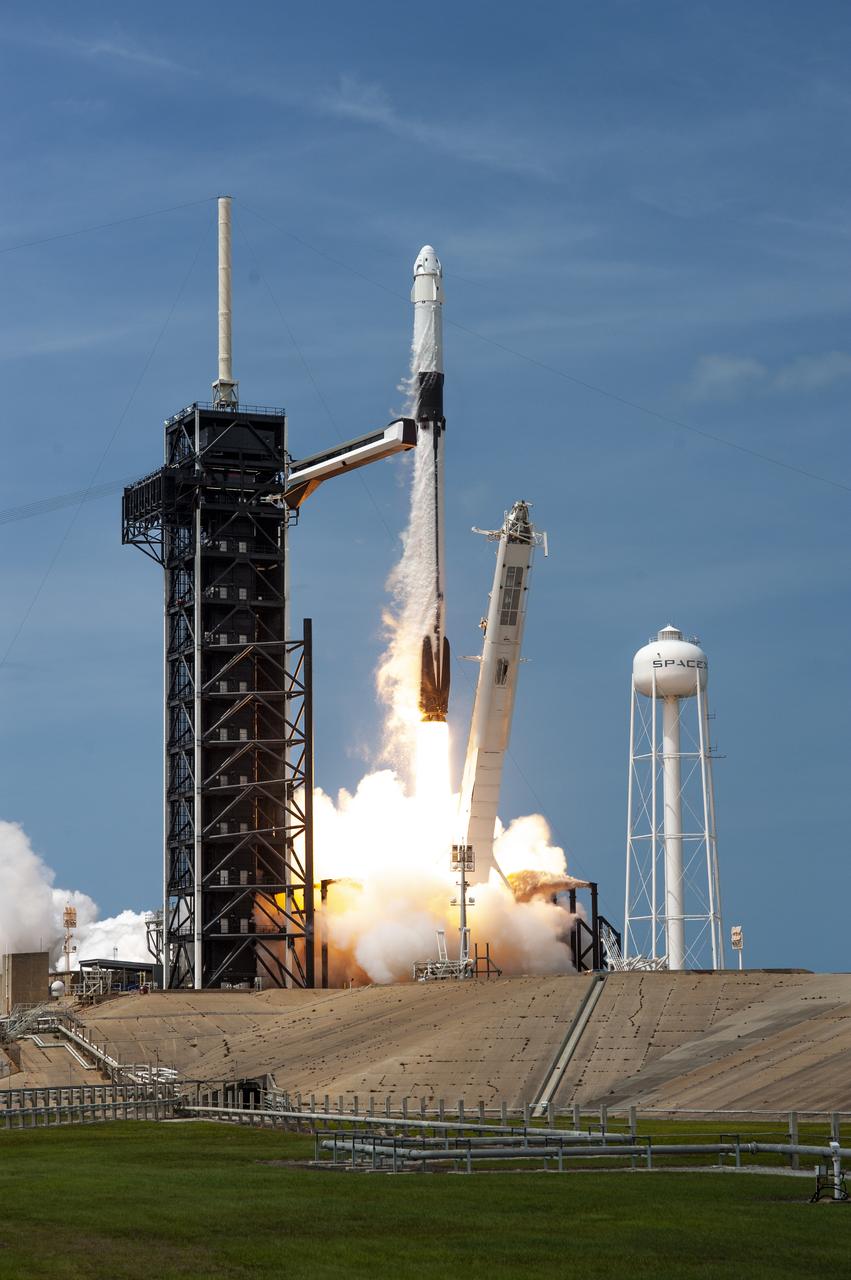

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
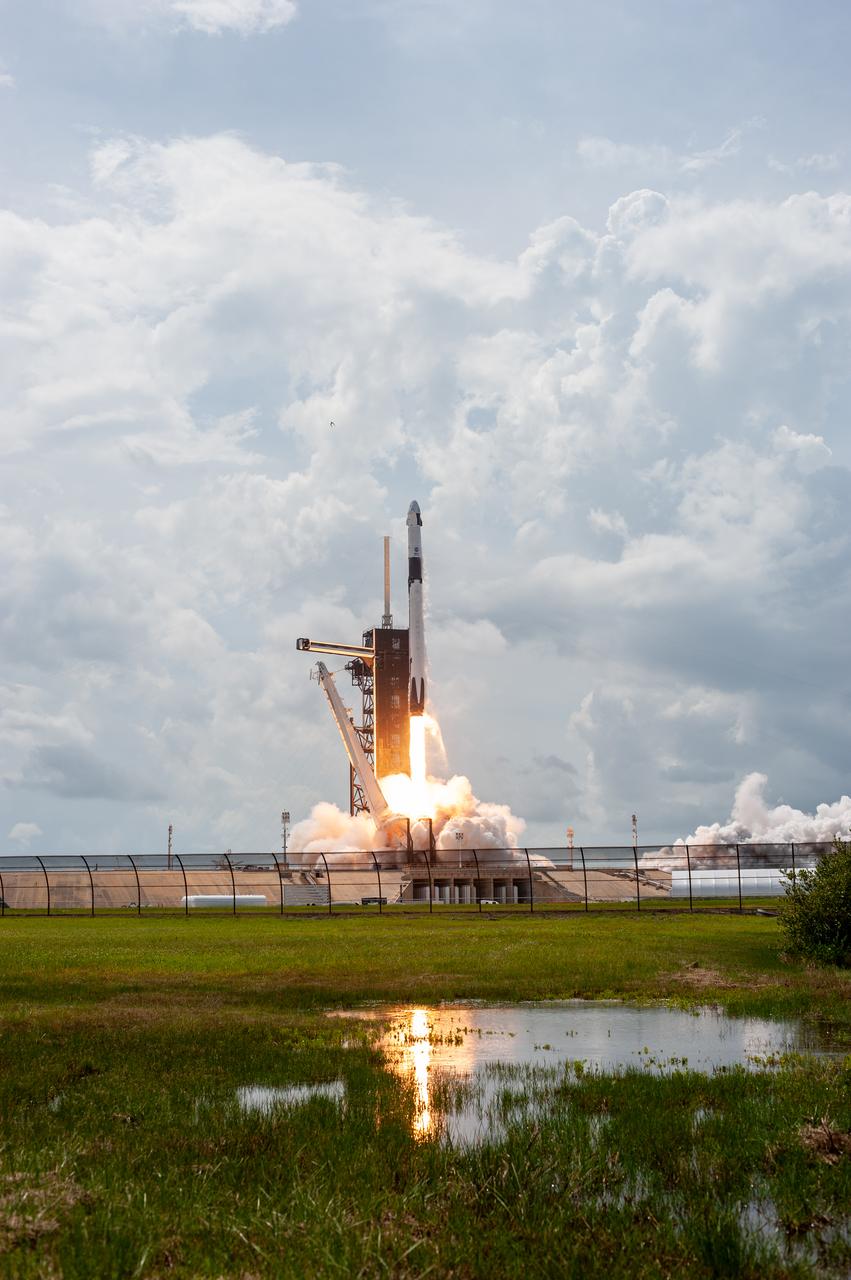

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
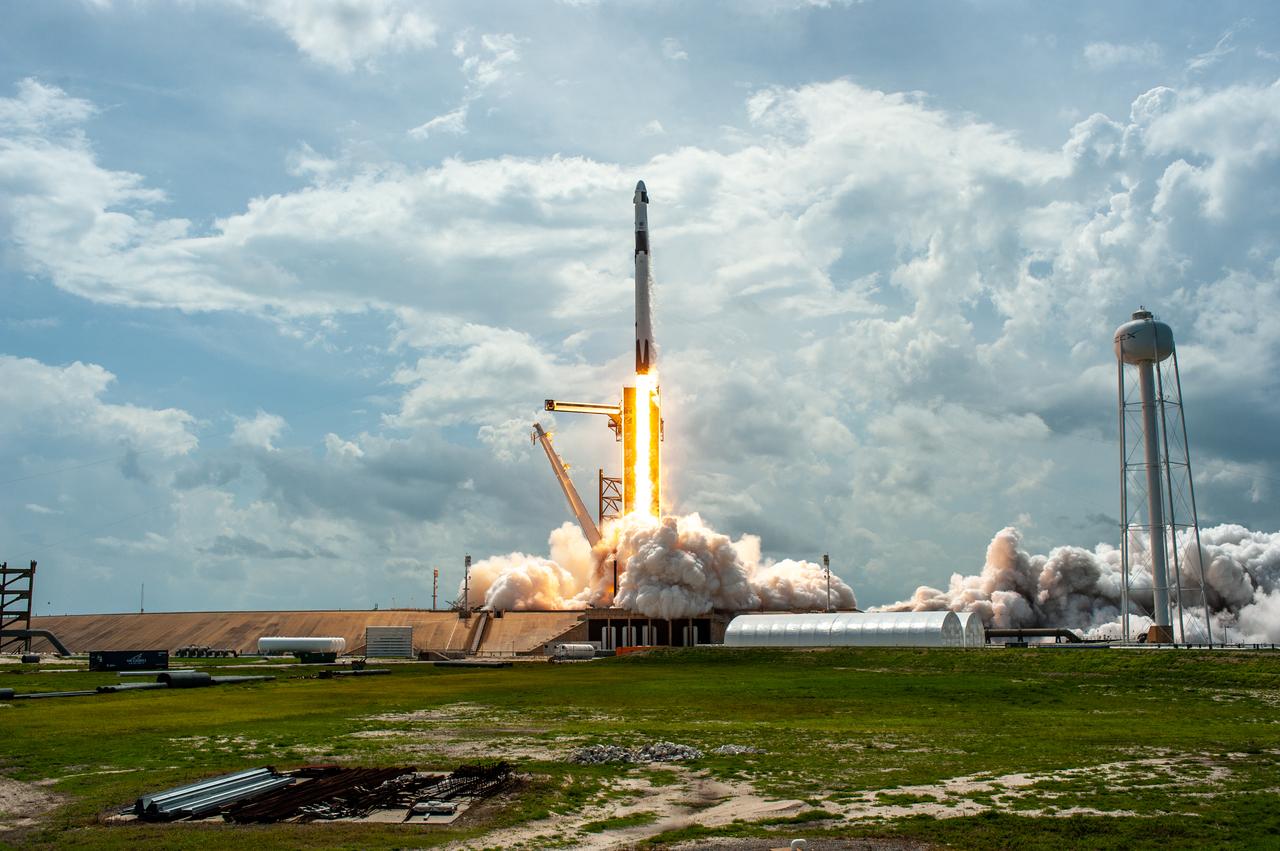

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
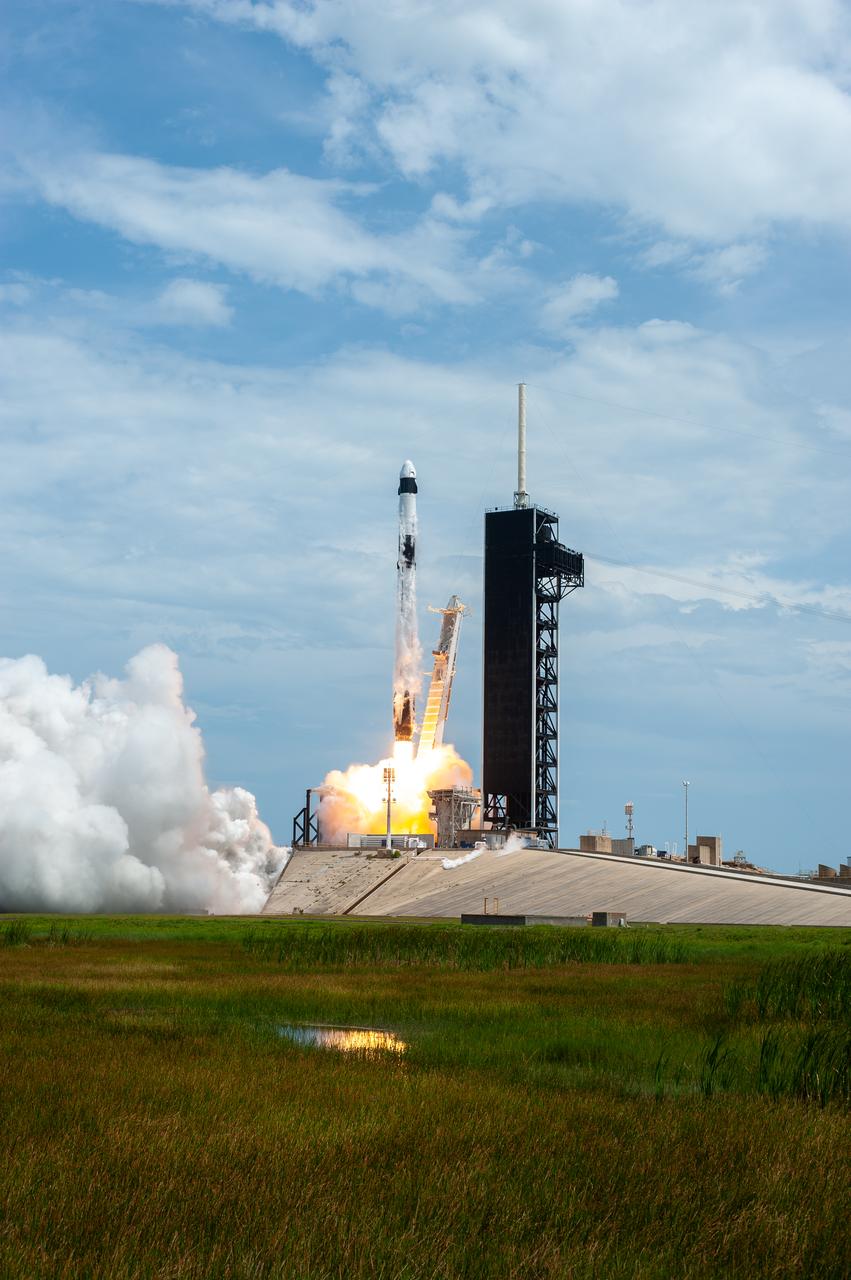

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
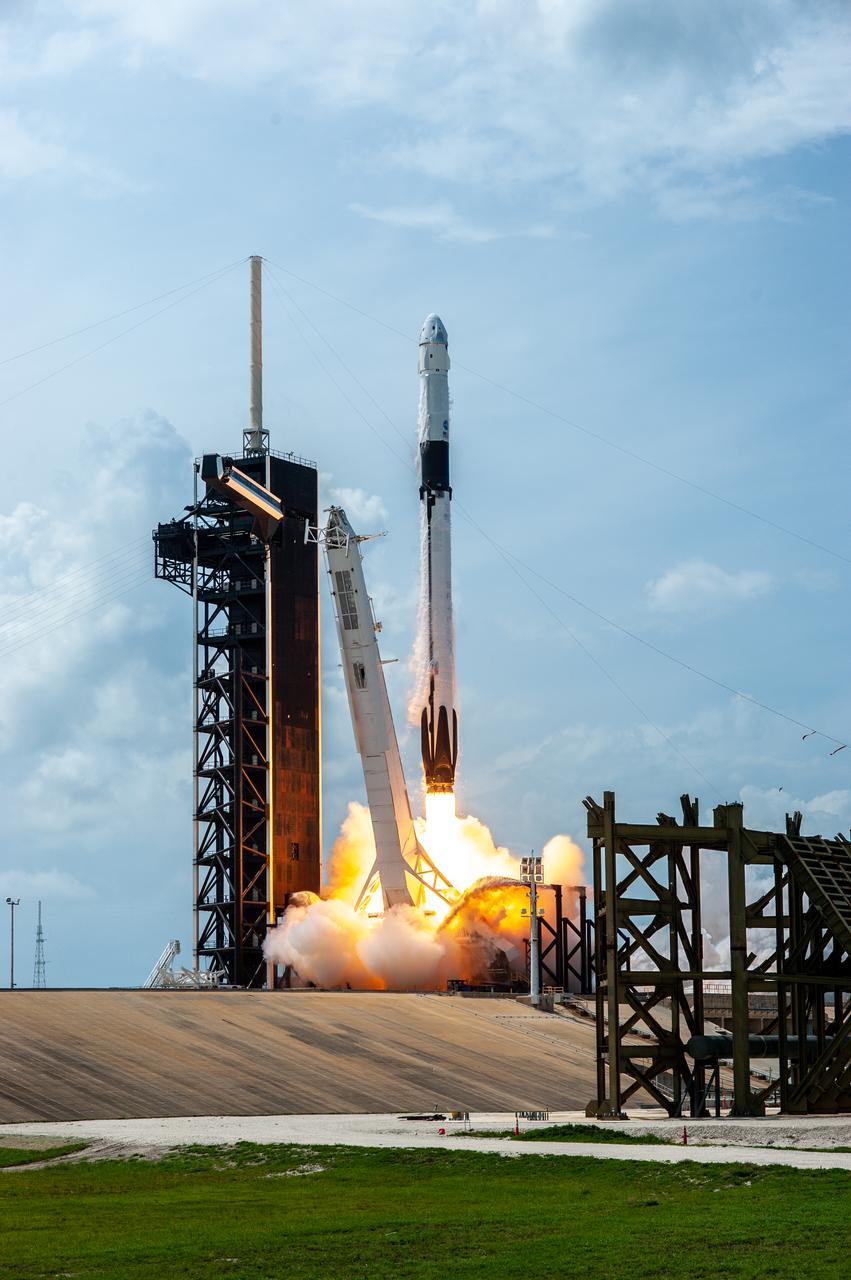

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
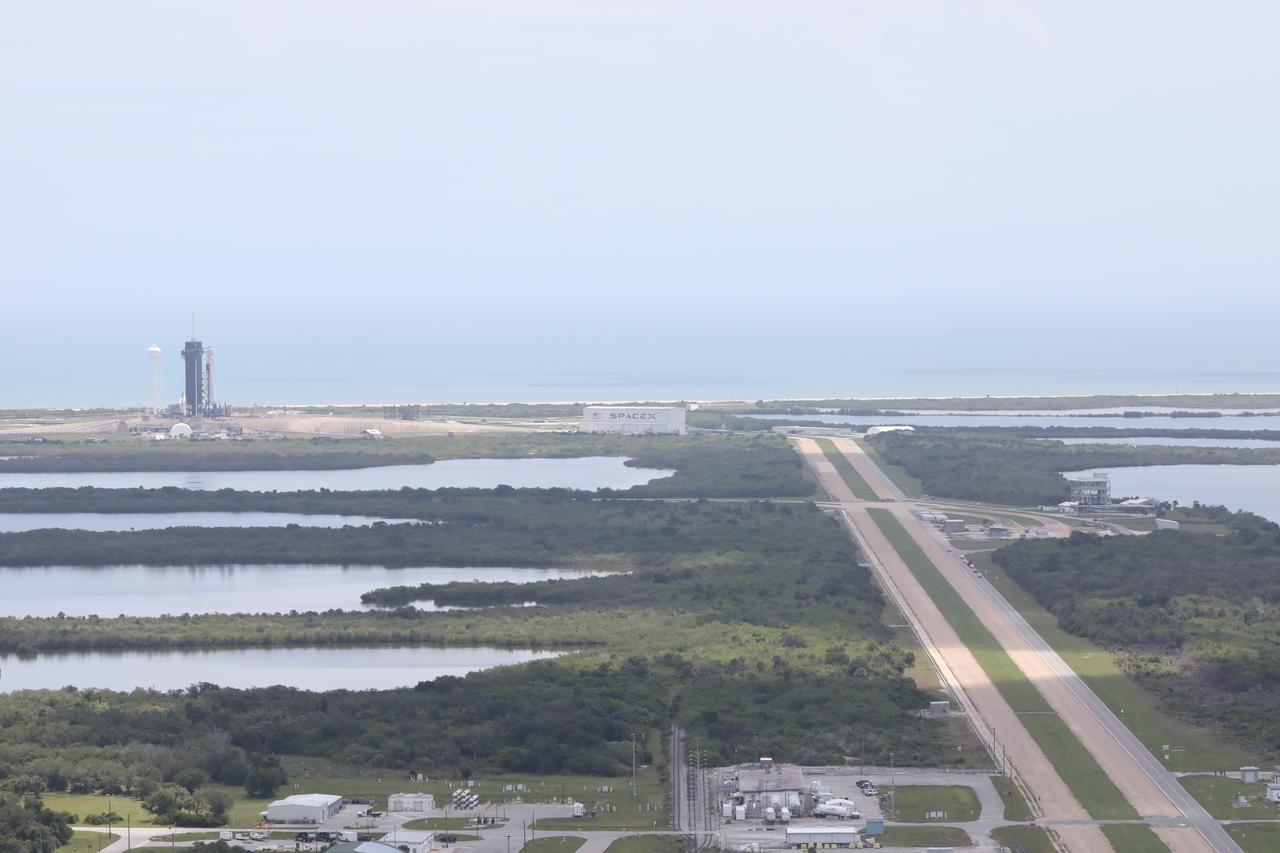

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft stand poised for launch at historic Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
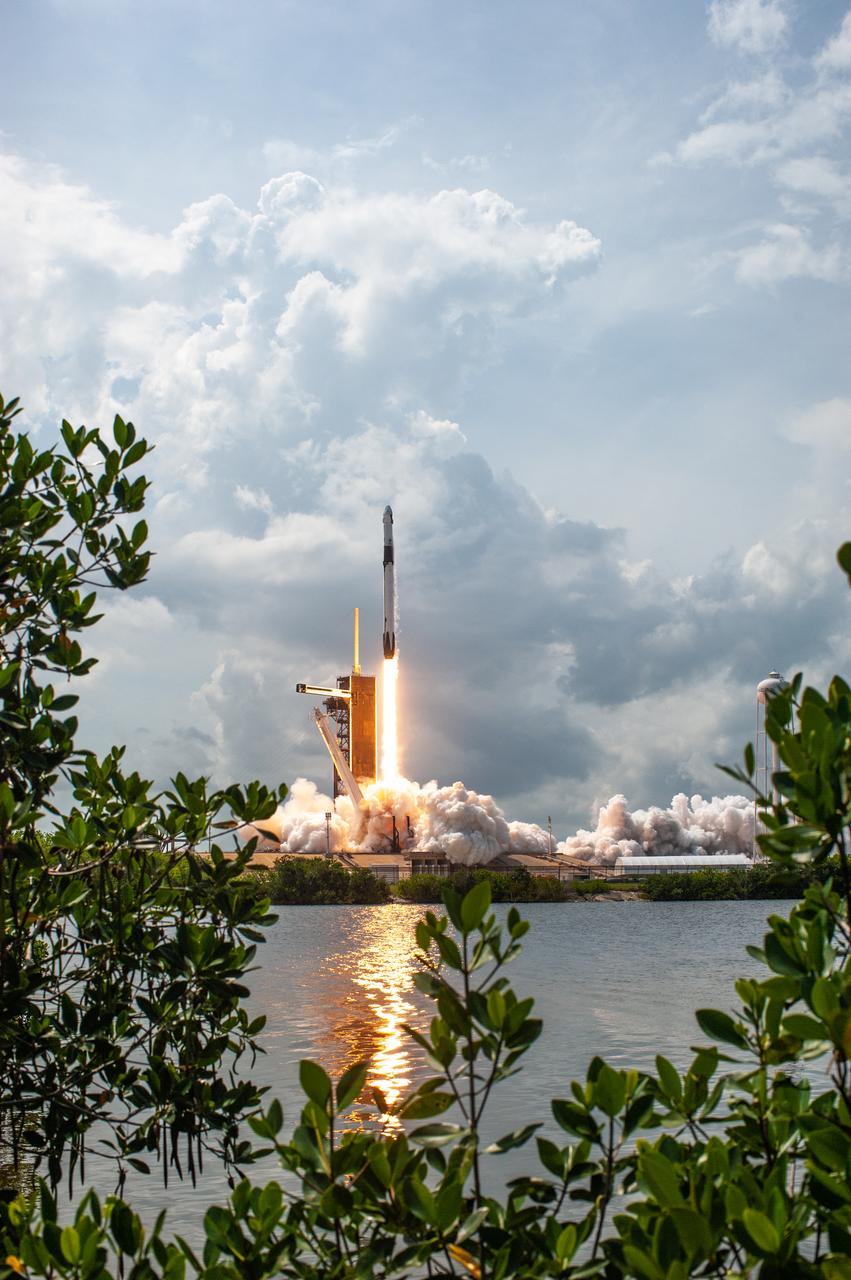

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.