
S81-26158 (Feb 1981) --- A close-up view of a training version of a STS-40/SLS-1 blood kit. Blood samples from crewmembers are critical to a number of Space Life Sciences-1 (SLS-1) investigations. One day's collection equipment, color coded for each crewmember, is neatly organized in the kit.
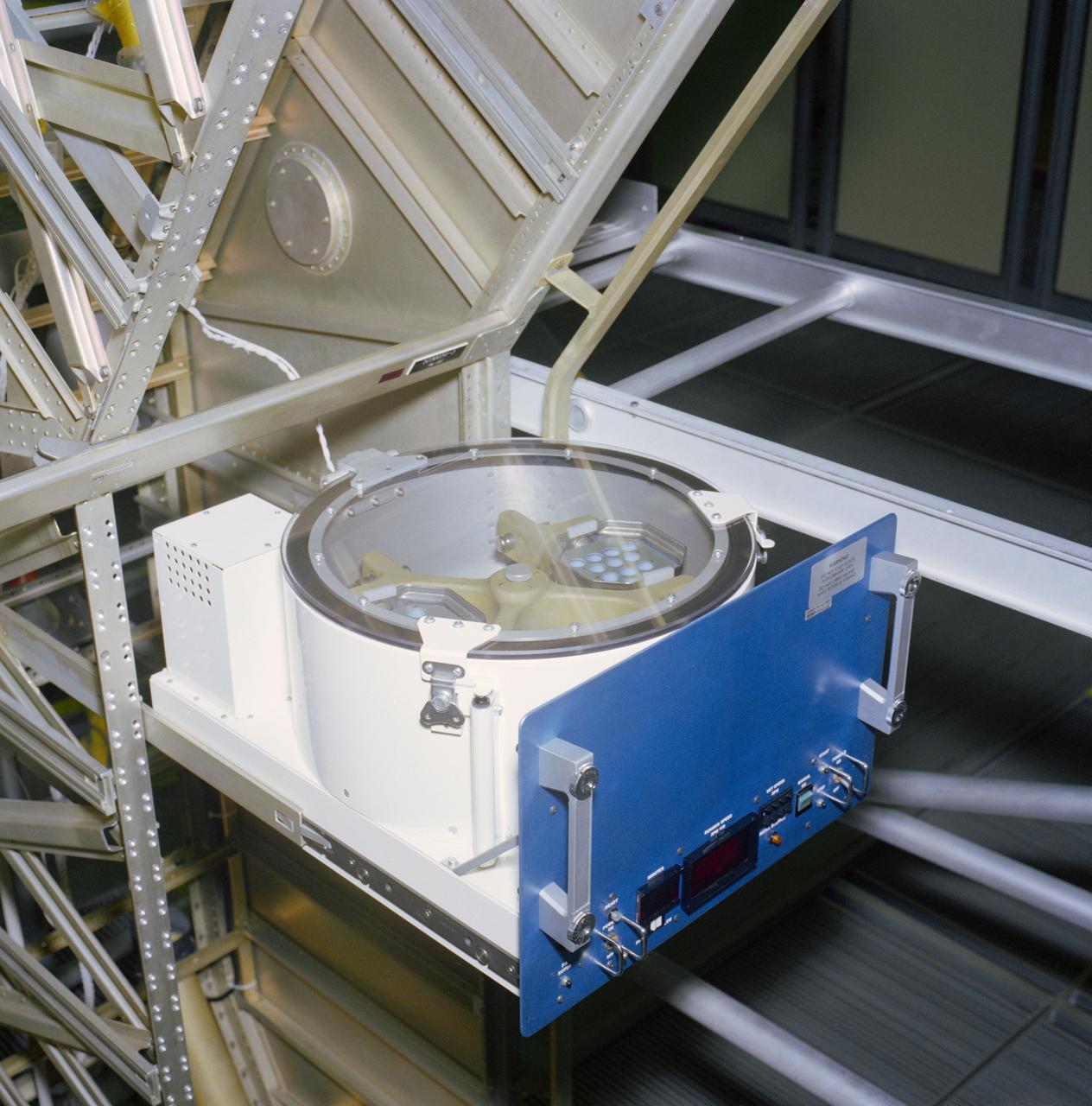

S81-25565 (Feb 1981) --- Expected to be a busy item of flight hardware on the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) mission is this low-gravity centrifuge. To be flown onboard Columbia for STS-40, the centrifuge is able to simulate several gravity levels (0.5 g, 1.0 g, 1.5 g. and 2.0 g). Blood samples, taken during the flight, will be placed in the centrifuge, fixed for post flight analysis and transferred to a freezer.
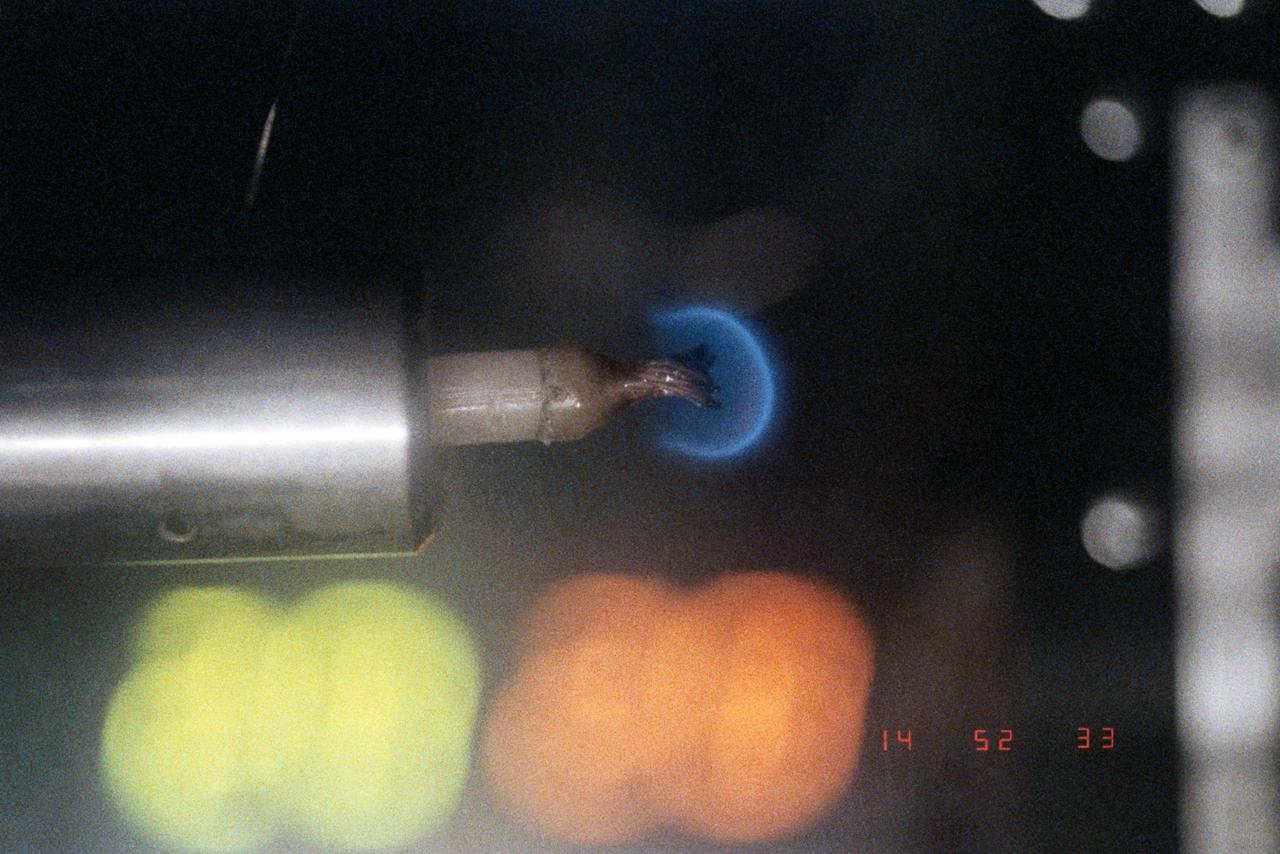
Closeup view inside glovebox showing a candle flame. The Candle Flames in Microgravity experiment is carried onboard Columbia to examine whether candle flames can be sustained in space; to study the interaction and physical properties of diffusion flames. In space, where buoyancy-driven convection is reduced, the role diffusion plays in sustaining candle flames can be isolated. Results have implications for other diffusion flame studies. Diffusion flames are the most common type of flame on Earth.
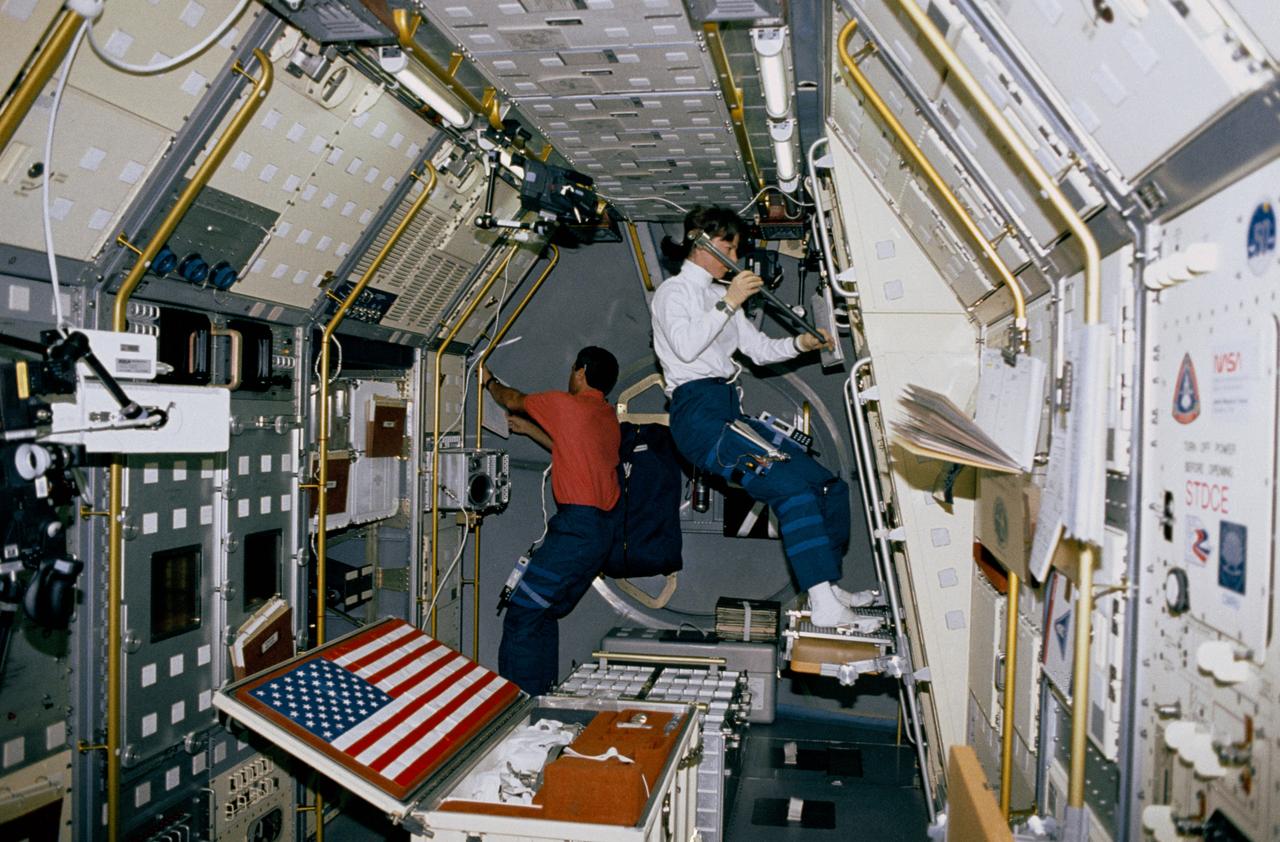

STS050-02-001 (9 July 1992) --- View showing Payload Specialists Bonnie Dunbar and Larry DeLucas in the aft section of the U. S. Microgravity Laboratory-1. Dunbar is preparing to load a sample in the Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) Integrated Furnace Experiment Assembly (IFEA) in rack 9 of the Microgravity Laboratory. DeLucas is checking out the multipurpose Glovebox Facility.
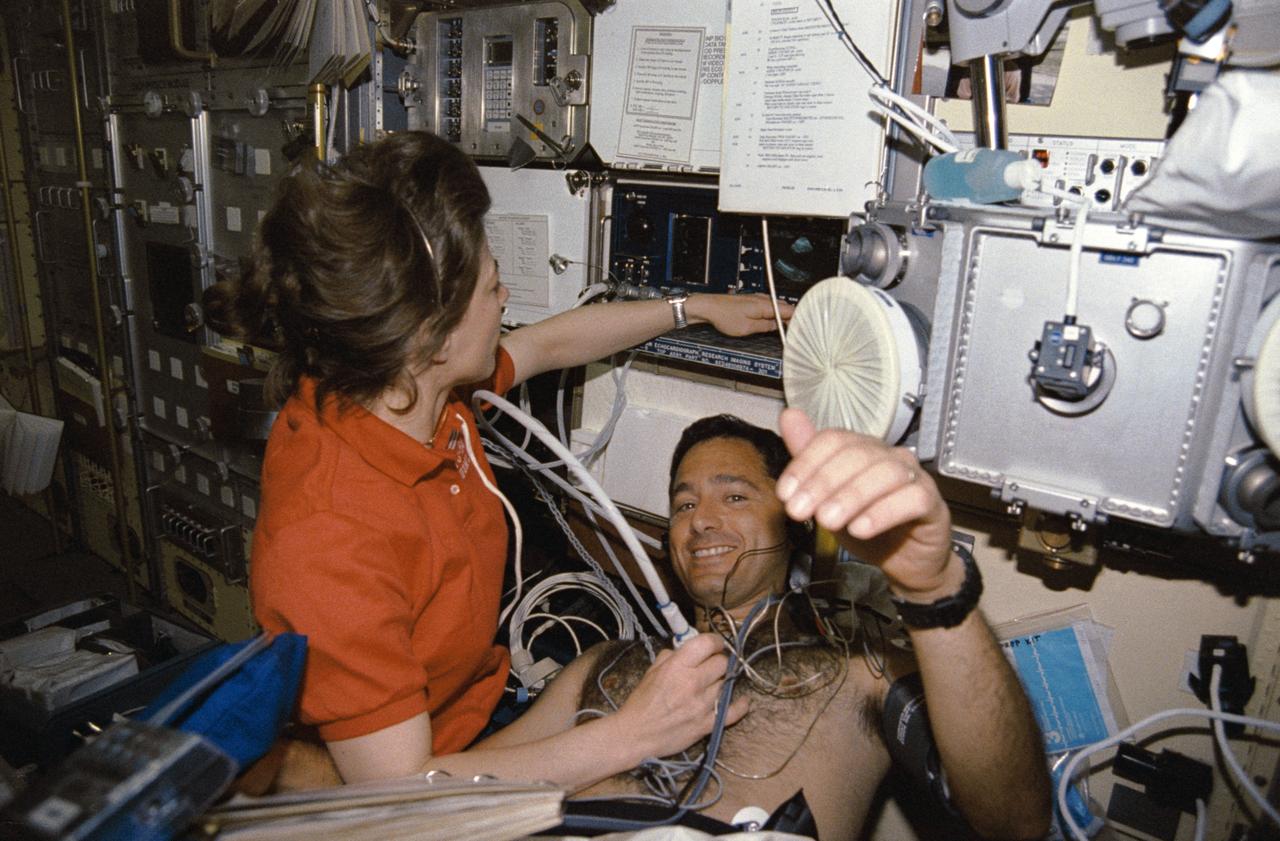
STS050-291-027 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar uses a Doppler to collect medical data from Lawrence J. DeLucas, payload specialist, during his diagnostic "run" in the Lower Body Negative Pressure device (LBNP). The Doppler is used to pick up high-frequency sound waves from the surface of the heart, thus producing pictures on the monitor of the American Flight Echocardiograph (AFE). The result of the LBNP procedure is expected to be an increased tolerance of orthostatis - or standing upright - upon return to Earth's gravity. LBNP has been used a number of times in the United States space program, as early as the Skylab missions. STS-50 is the fourth flight of the current collapsible unit. Researchers are refining the LBNP protocol which will be used operationally on future 13 through 16 day missions.

STS050-02-023 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, payload commander, unstows United States Microgravity Laboratory 1 (USML-1) experiment paraphernalia in early stages of the mission. The Multipurpose Glove Box (MPGB) is at upper left. And, at right center, is the Space Station design foot restraint, making its first flight aboard a Space Shuttle on the record-setting 14-day mission.
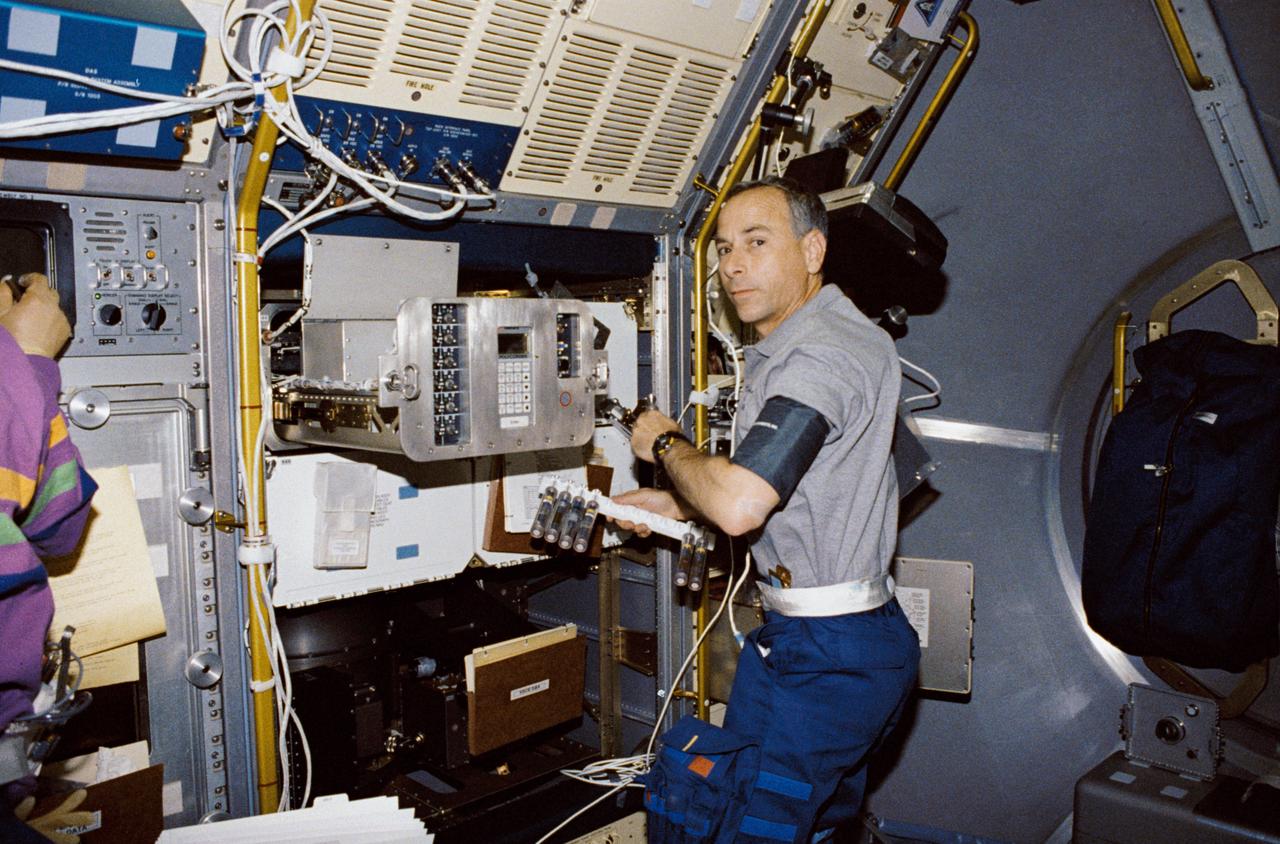

STS050-301-001 (25 June-9July 1992) --- Astronaut Carl J. Meade, mission specialist, works with the Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus in the science module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Payload specialist Eugene H. Trinh is partially visible (left), monitoring an experiment in the Drop Physics Module (DPM). The two joined four other astronauts and a second scientist from the private sector for 14-days of scientific data-gathering.
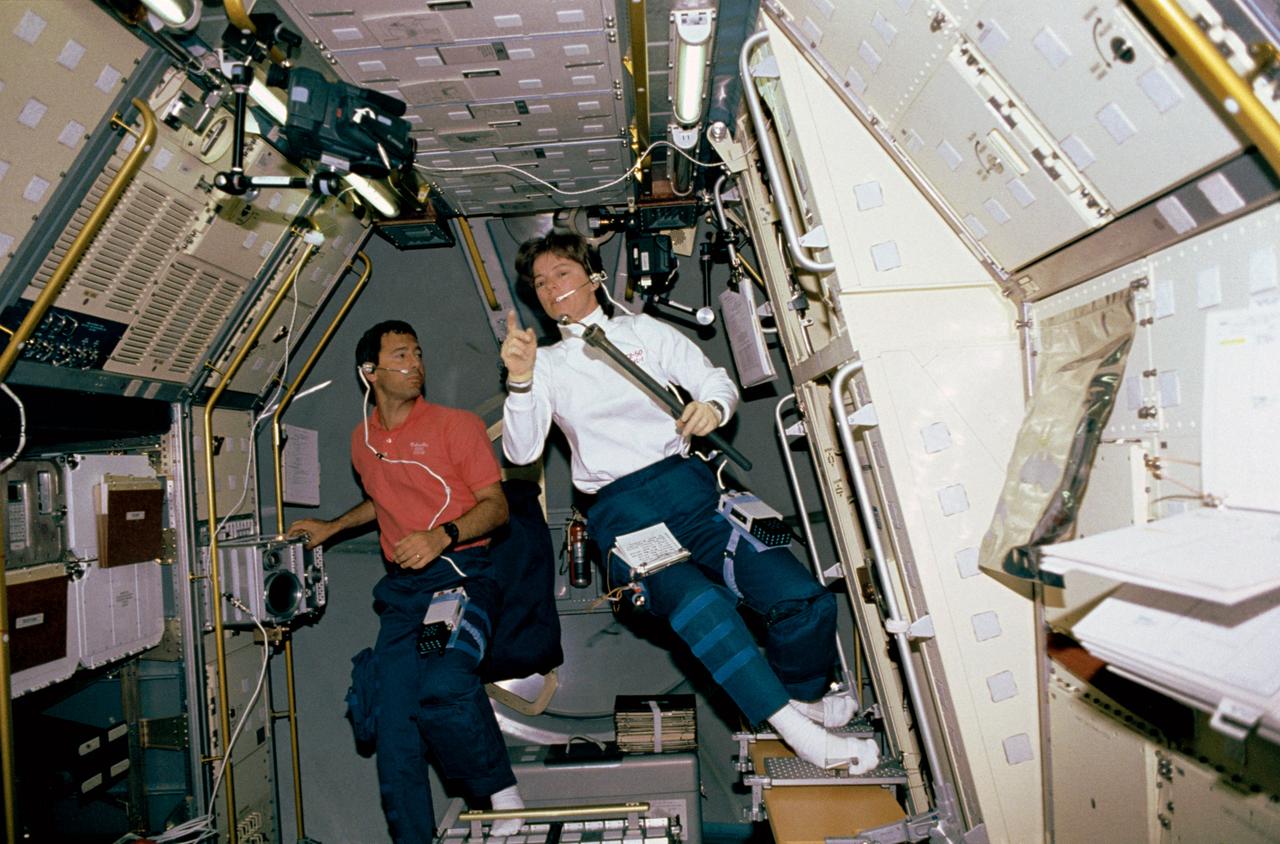

View showing Payload Specialists Bonnie Dunbar and Larry DeLucas in the aft section of the U. S. Microgravity Laboratory-1. Dunbar prepares to load a sample in the Crystal Growth Furnace (CGF) Integrated Furnace Experiment Assembly (IFEA) in rack 9 of the Microgravity Laboratory, while DeLucas checks out the multi-purpose Glovebox Facility.
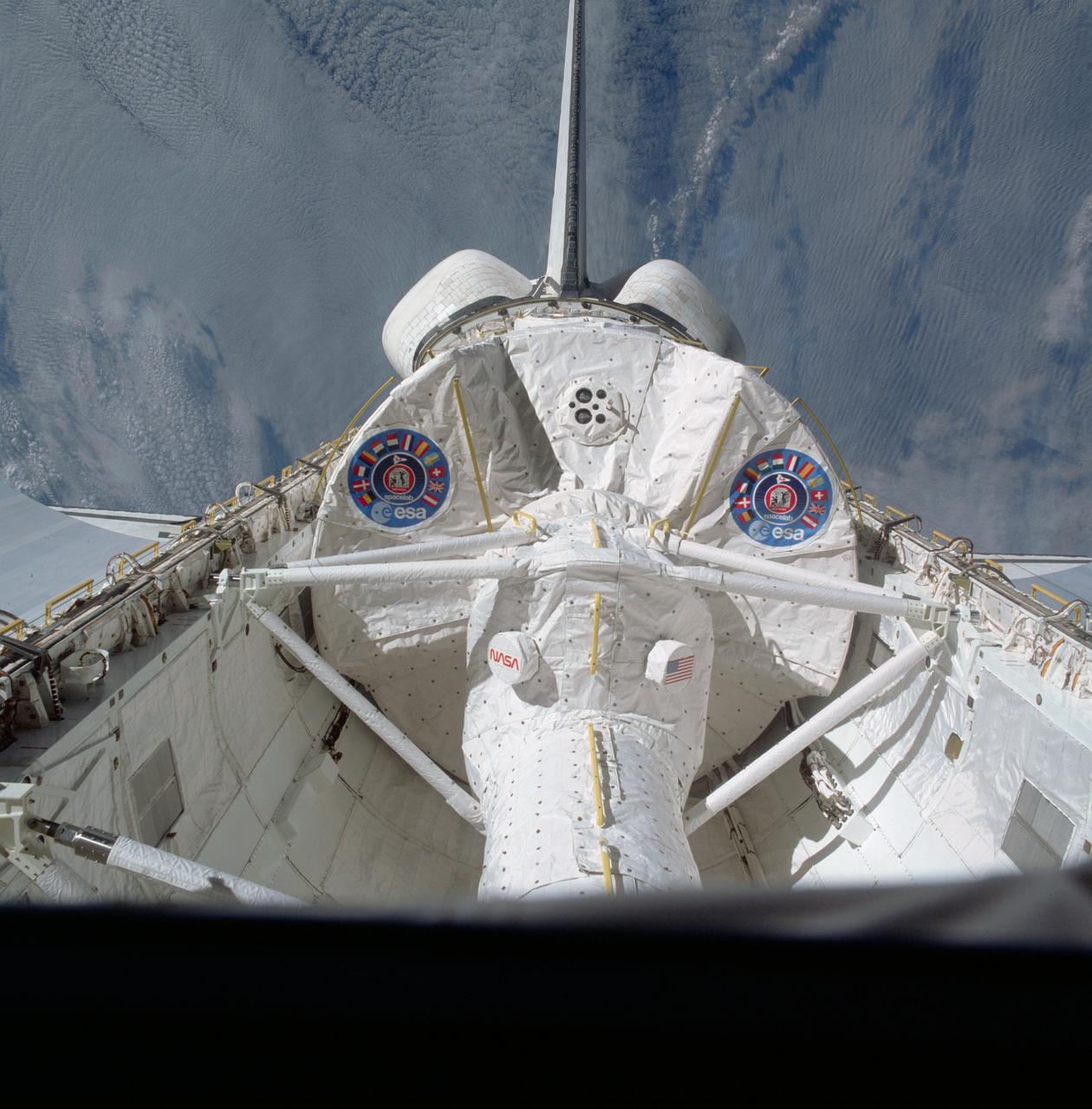

STS009-32-1112 (28 Nov-8 Dec 1983) --- A handheld Hasselblad camera was aimed through the aft windows on the flight deck of Columbia for this initially released scene of the active Spacelab module in the cargo bay. The docking tunnel, leading from the shirt-sleeve environment of the orbiter to the equally comfortable environment of Spacelab, is in the foreground.
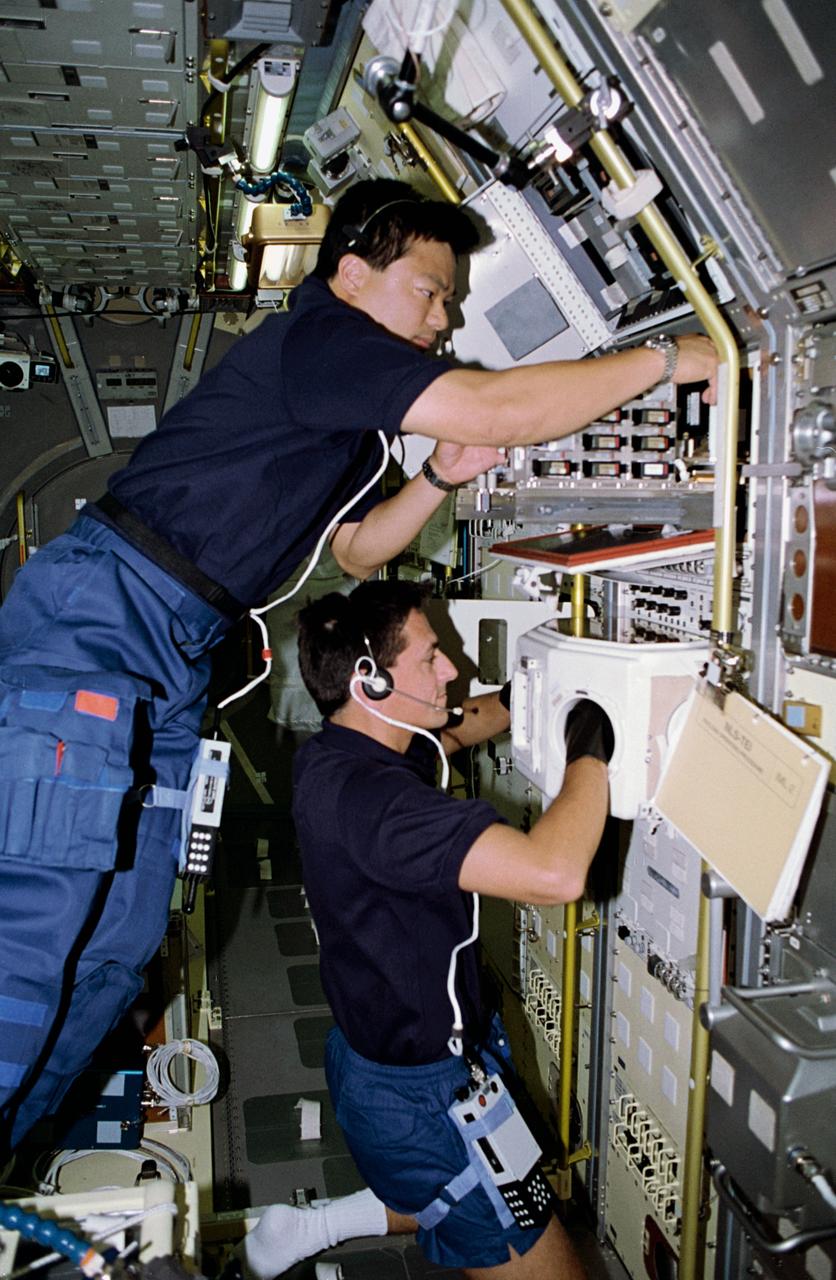

STS-65 Mission Specialist (MS) Leroy Chiao (top) and MS Donald A. Thomas are seen at work in the International Microgravity Laboratory 2 (IML-2) spacelab science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102. The two crewmembers are conducting experiments at the IML-2 Rack 5 Biorack (BR). Chiao places a sample in the BR incubator as Thomas handles another sample inside the BR glovebox. The glovebox is used to prepare samples for BR and slow rotating centrifuge microscope (NIZEMI) experiments.
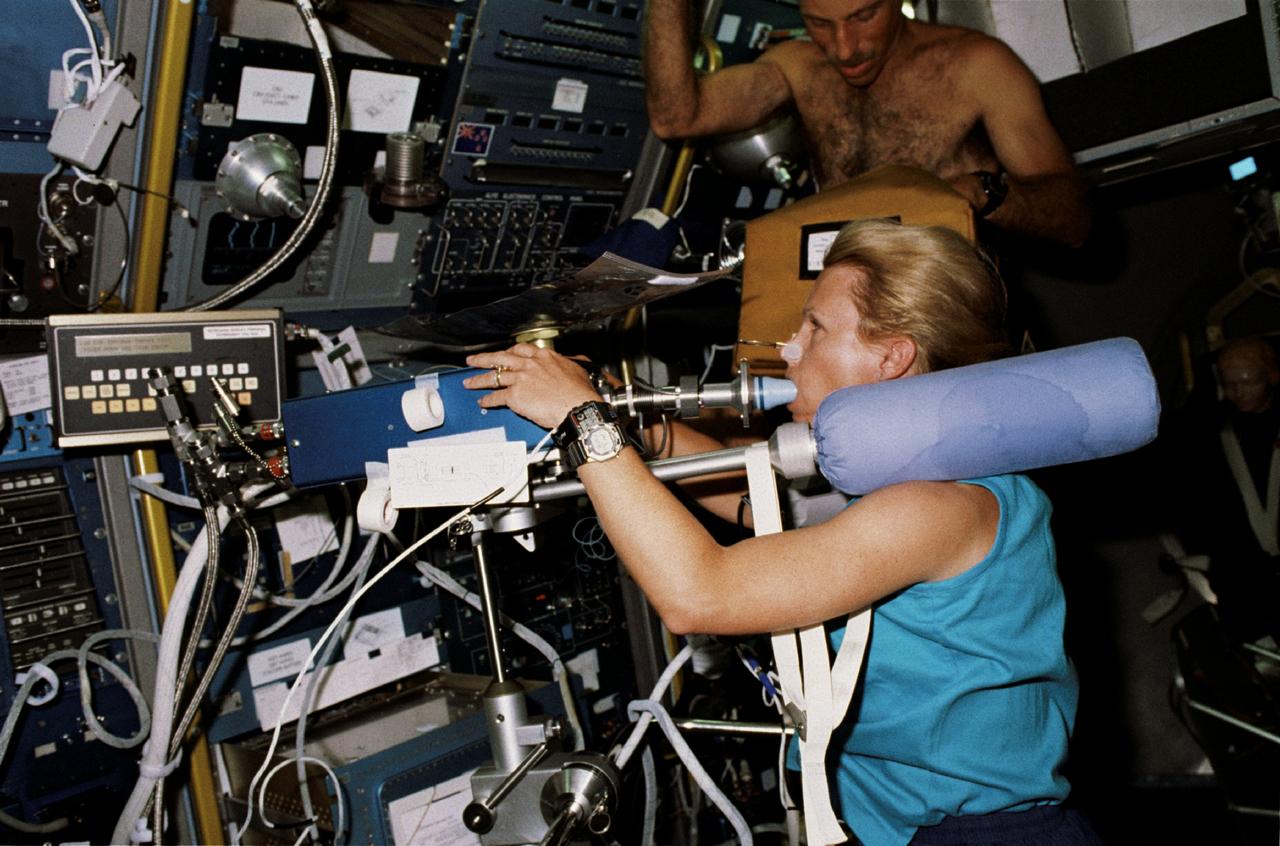

STS040-211-019 (5-14 June 1991) --- Astride the bicycle ergometer, astronaut Rhea Seddon, mission specialist, breathes into the cardiovascular re-breathing unit during the exercise phase of an experiment. The investigation, In-flight Study of Cardiovascular Deconditioning (Experiment 066), was developed by Dr. Leon E. Farhi of the State University of New York in Buffalo. It focuses on the deconditioning of the heart and lungs and changes in cardiopulmonary function that occur upon return to Earth. By using non-invasive techniques of prolonged expiration and re-breathing, investigators can determine the amount of blood pumped out of the heart (cardiac output), the ease with which blood flows through all the vessels (total peripheral resistance), oxygen used and carbon dioxide released by the body, and lung function and volume changes. Measurements are made both while crew members are resting and while they pedal the exercise bicycle, as Dr. Seddon is doing here. This scene was photographed with a 35mm camera.
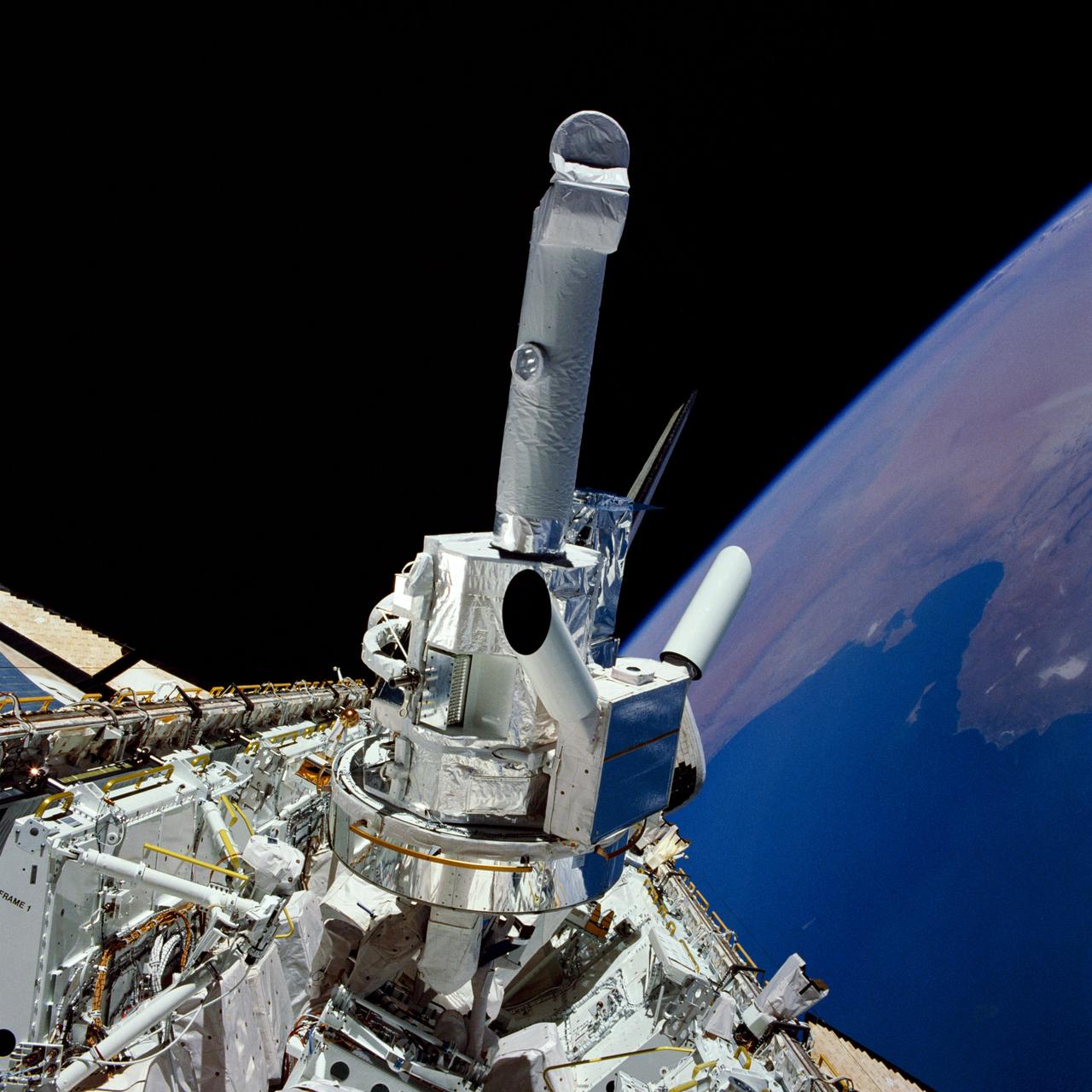

51F-33-005 (29 July - 6 August 1985) --- Experiments and the instrument pointing system (IPS) for Spacelab 2 are backdropped against the Libya/Tunisia Mediterranean coast and black space in this 70mm view photographed through the aft flight deck windows of the Space Shuttle Challenger. Also partially visible among the cluster of Spacelab 2 hardware are the solar optical universal polarimeter (SOUP) experiment and the coronal helium abundance experiment (CHASE).
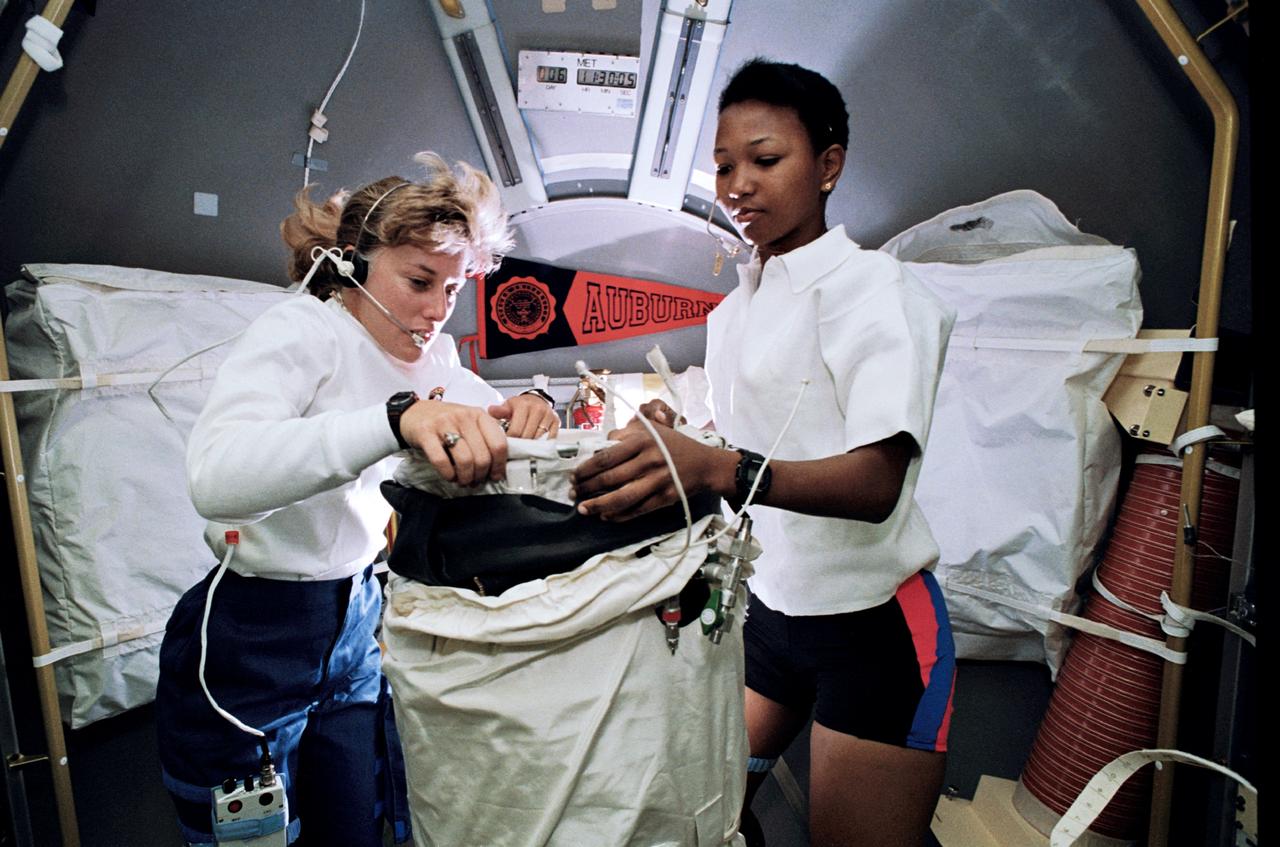
STS047-46-027 (12-20 Sept. 1992) --- Astronauts N. Jan Davis (left) and Mae C. Jemison, STS-47 mission specialists, prepare to deploy the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) apparatus in this 35mm frame photographed in the Science Module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Making their first flight in space, the two were joined by four other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for eight days of research. The Spacelab-J mission is a joint effort between Japan and the United States of America.
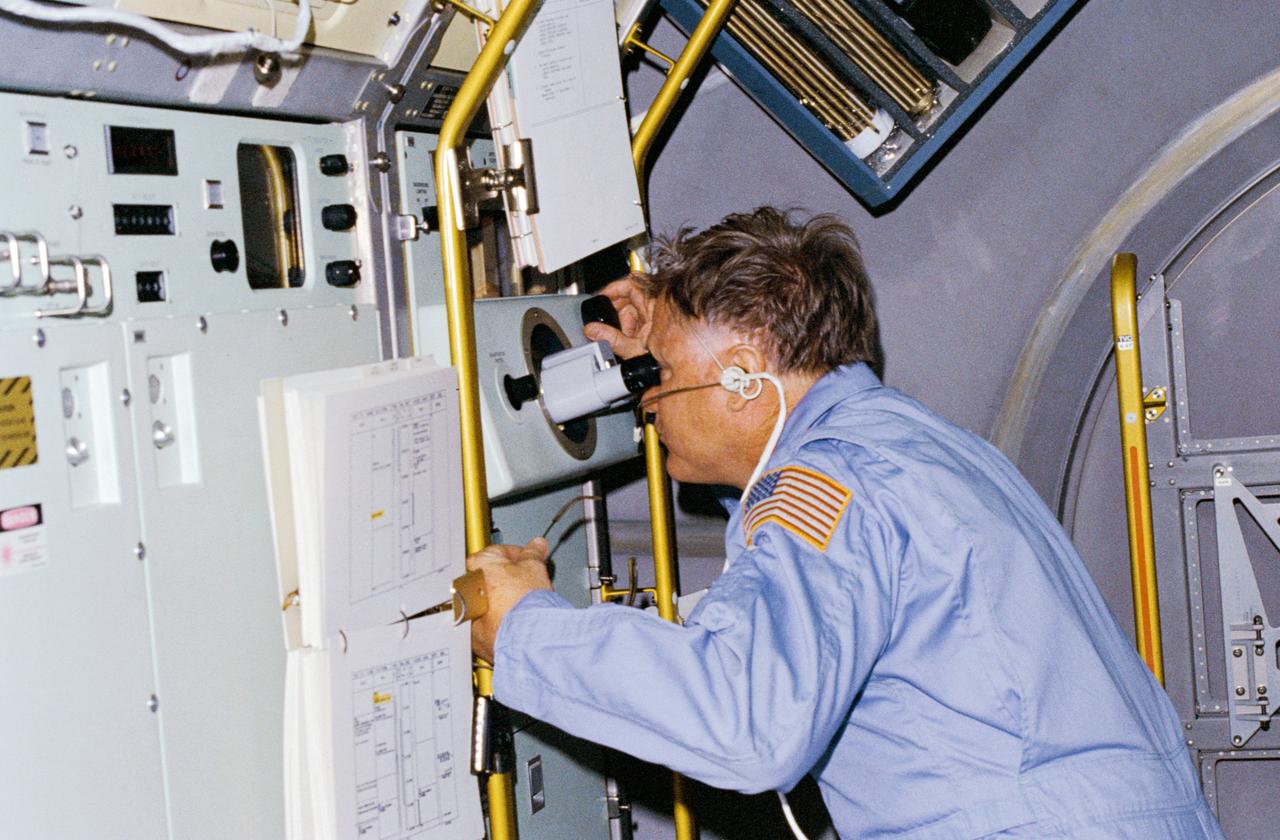

51B-01-007 (30 April 1985) --- Astronaut Don L. Lind, 51-B Spacelab 3 mission specialist, observes the growth of mercuric iodide crystal in the vapor crystal growth system (VCGS) on the Spacelab 3 science module aboard the orbiter Challenger.
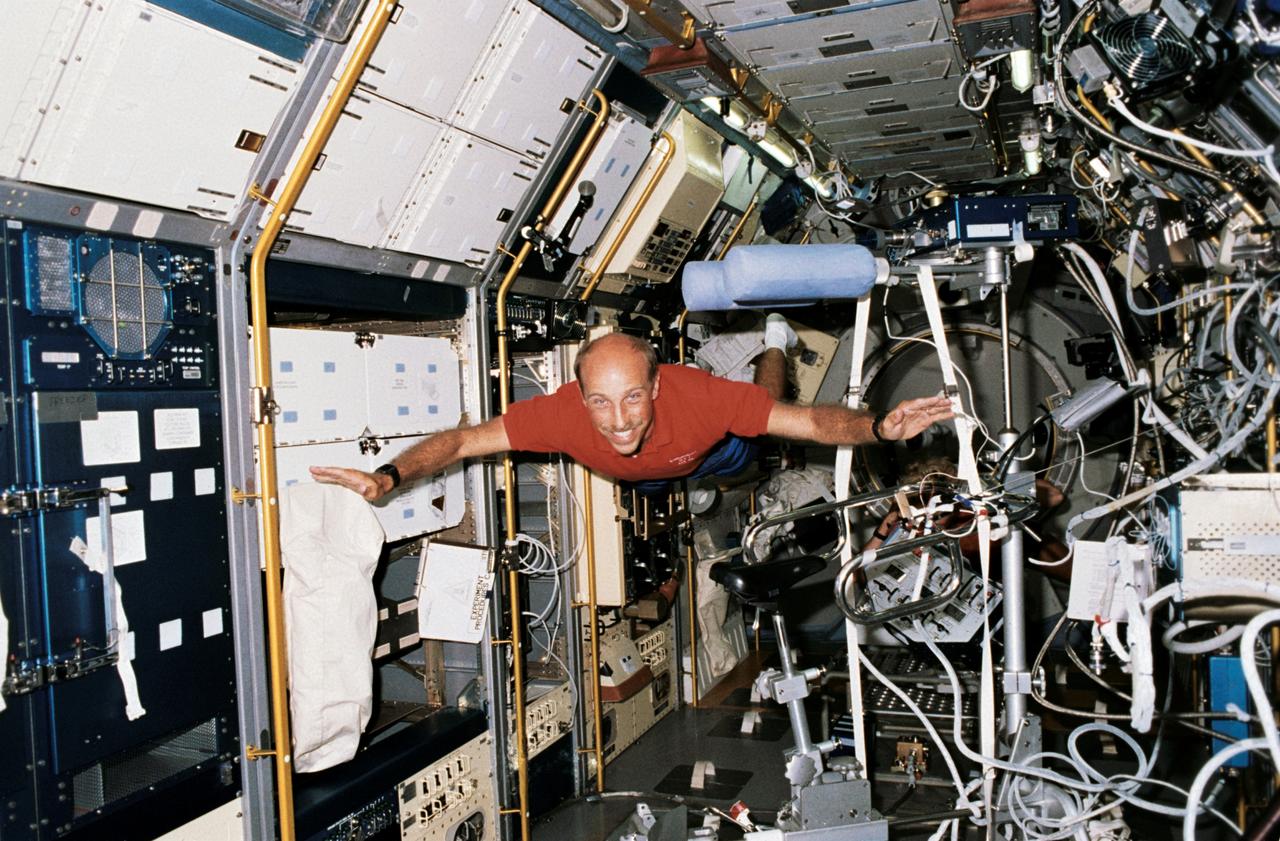

STS040-212-004 (5-14 June 1991) --- Astronaut James P. Bagian, STS-40 mission specialist, floats through the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Bagian and six other crew members spent over nine-days in space conducting life sciences research.
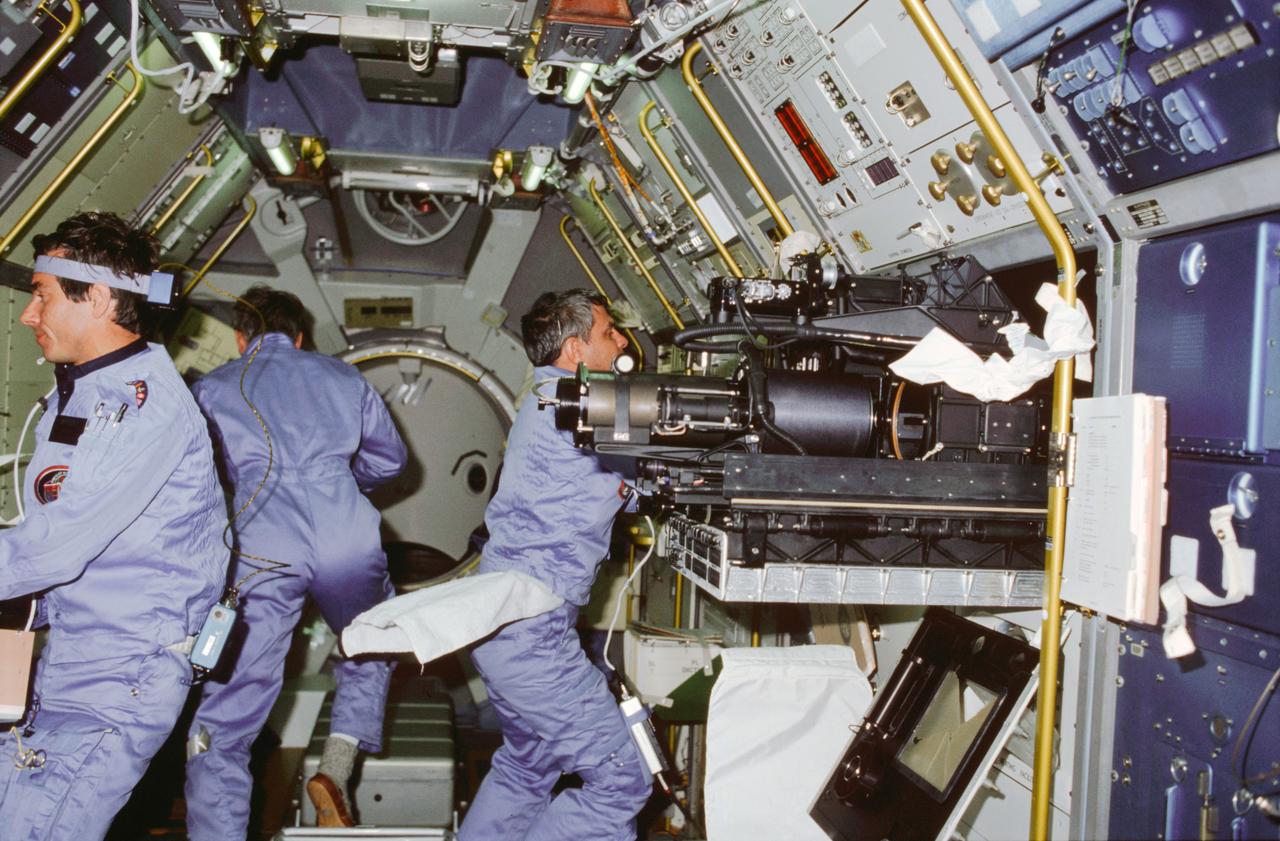

STS009-03-093 (28 Nov-8 Dec 1983) --- A mission specialist and two payload specialists busy themselves in the Spacelab 1 module aboard the Earth orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Left to right are Payload Specialist Robert A. R. Parker. Parker is partially obscured by a deployed instrument of the fluid physics module at the materials sciences double rack. Merbold, a physicist from Max-Planck Institute in the Federal Republic of Germany, wears a head band-like device and a recorder as part of an overall effort to learn more about space adaptation. Both Space lab 1 payload specialists wore the devices during most of their waking hours on this 10-day flight. The frame was exposed with a 35mm camera.
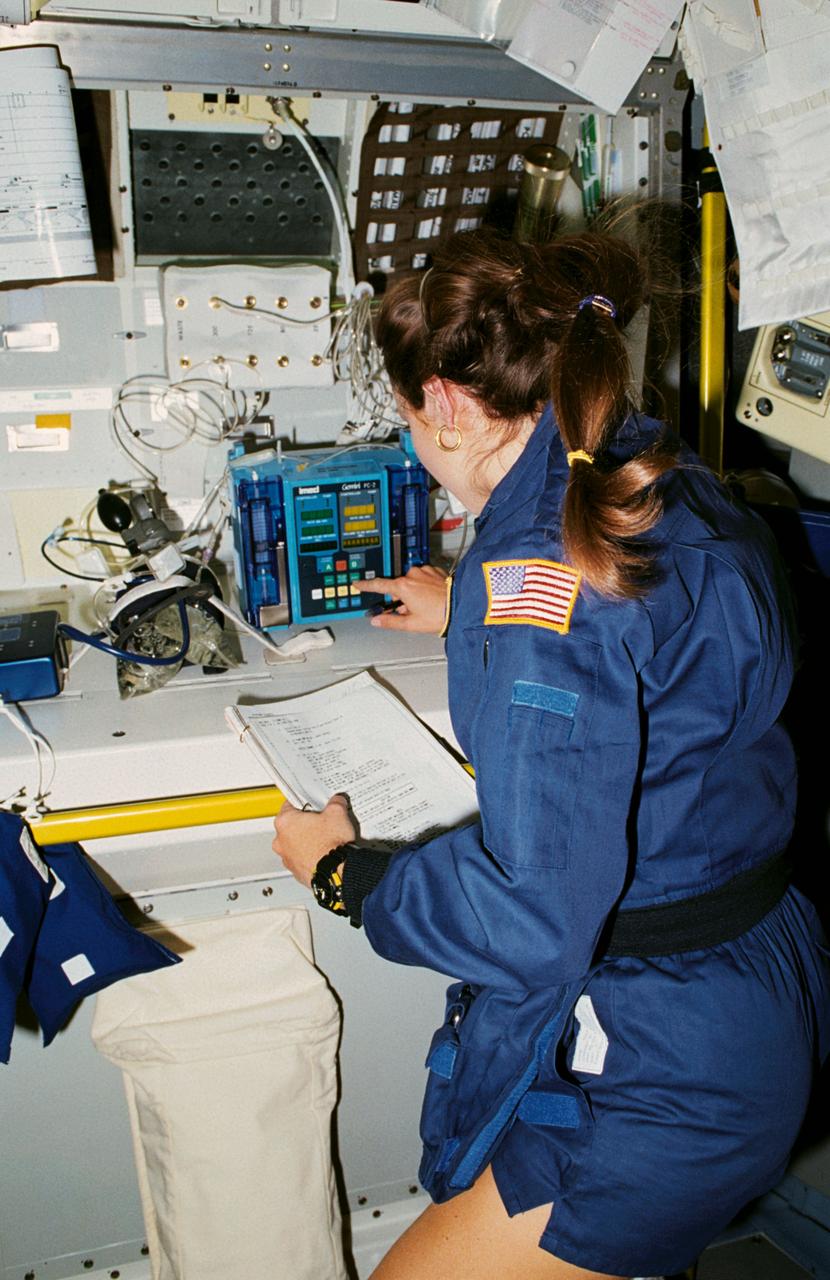

STS040-30-008 (5-14 June 1991) --- Astronaut Tamara E. Jernigan, after applying a blood pressure cuff to an experiment, watches it in operation. The experiment is the intravenous infusion pump. The device is being considered for use on Space Station Freedom's Health Maintenance Facility. Dr. Jernigan is one of seven crew members supporting the nine-day Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) mission aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia.
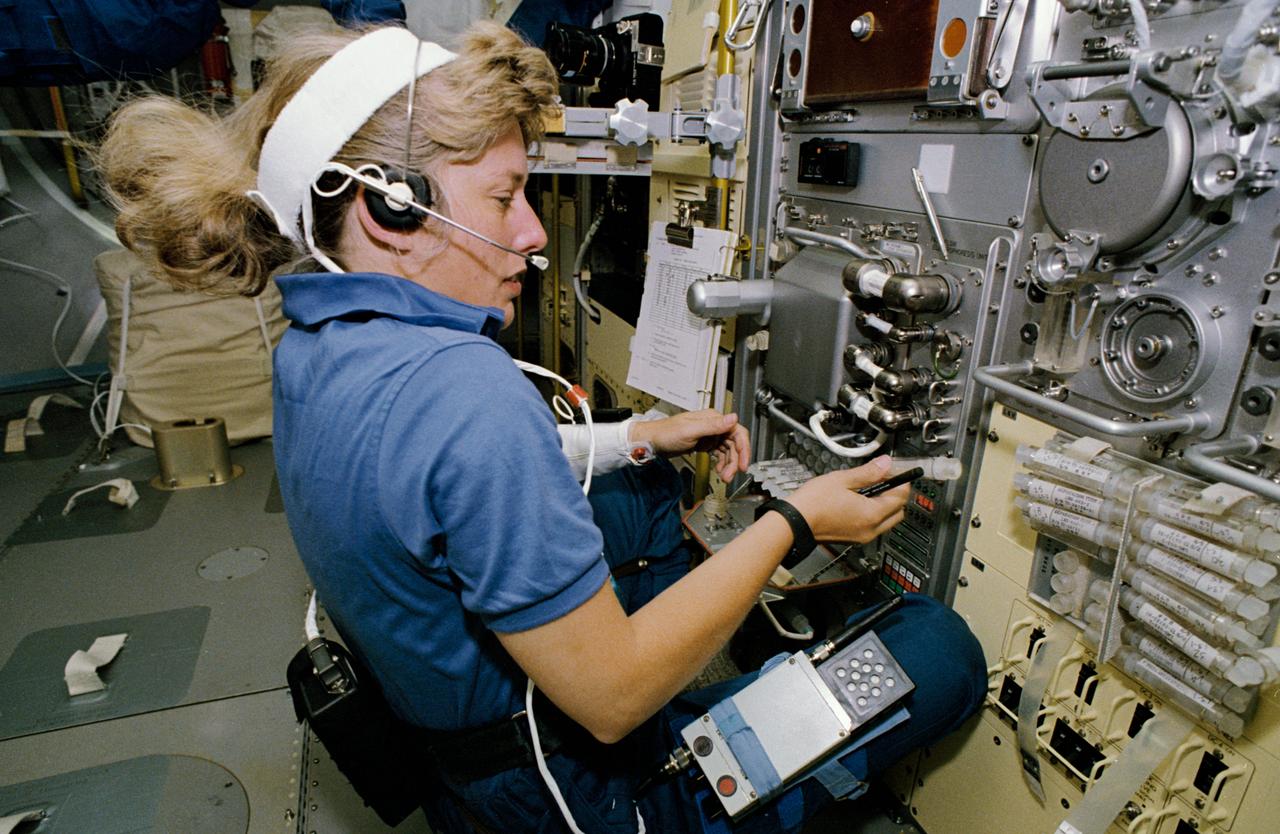

STS047-03-024 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronaut N. Jan Davis, mission specialist, talks to ground controllers as she works with the Free Flow Electrophoresis Unit (FFEU) in the Science Module of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Davis joined five other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for eight days of scientific research onboard Endeavour.
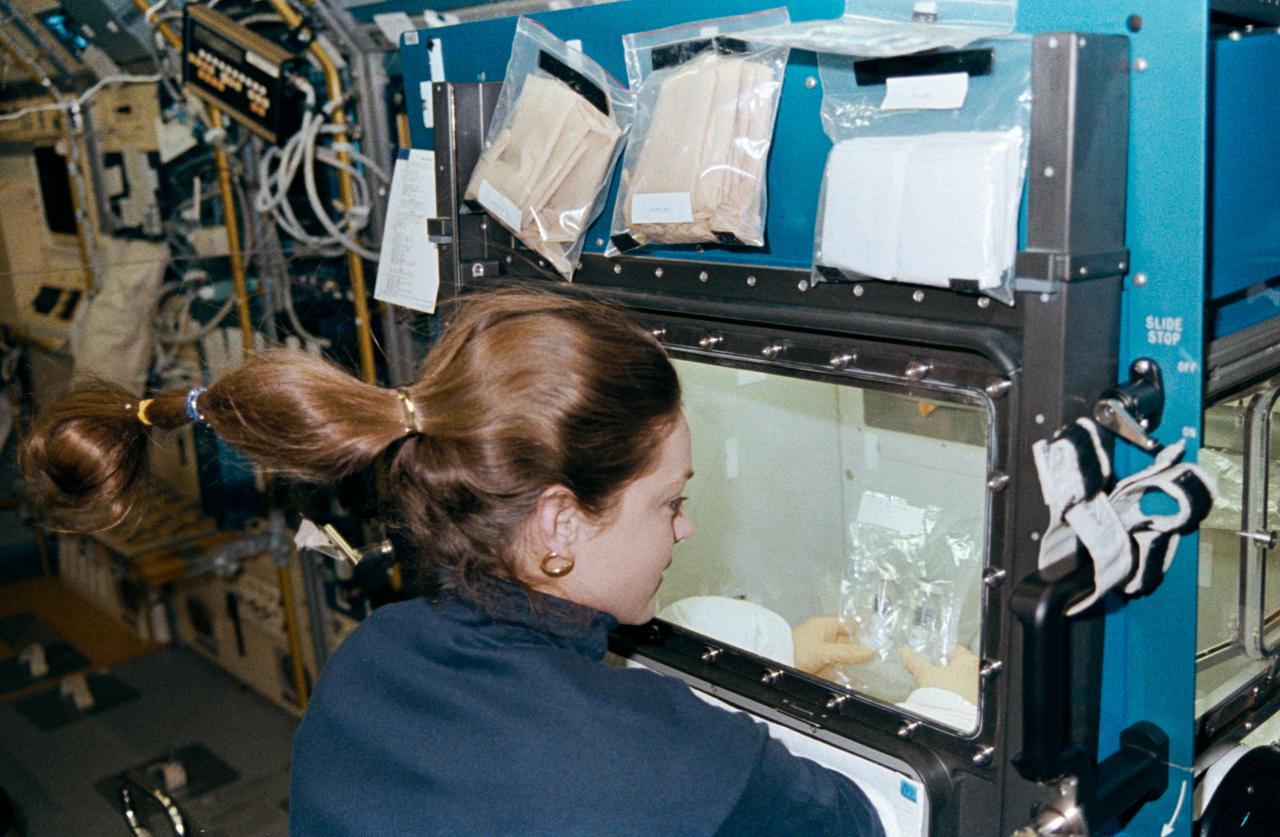

STS040-224-005 (5-14 June 1991) --- Astronaut Tamara E. Jernigan, STS-40 mission specialist, conducts an evaluation of the General Purpose Work Station (GPWS) in the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) module onboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. The photograph was taken with a 35mm camera.
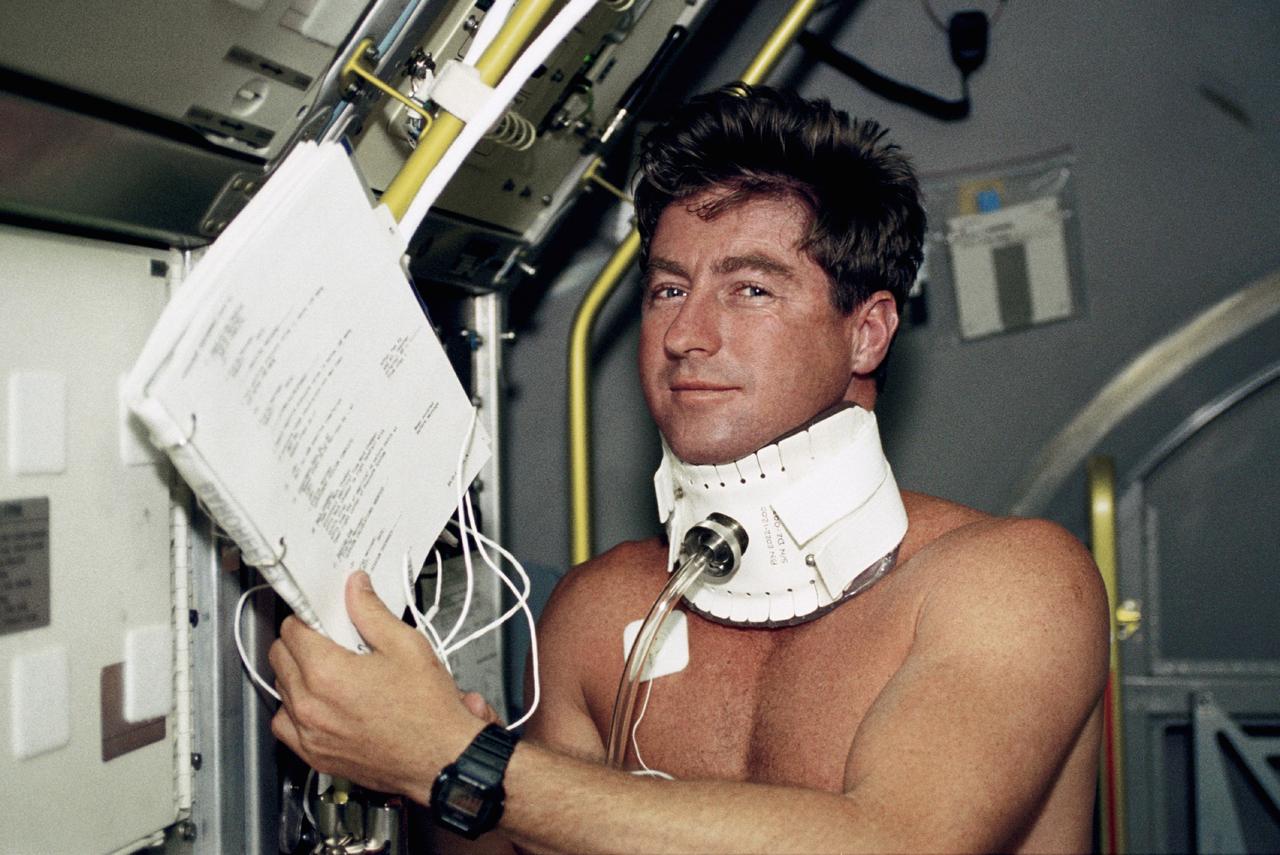
STS055-233-019 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Terence T. (Tom) Henricks, STS-55 pilot, wears a special collar for a space adaptation experiment in the science module onboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. The Baroreflex (BA) experiment is designed to investigate the theory that light-headedness and a reduction in blood pressures upon standing after landing may arise because the normal reflex system regulating blood pressure behaves differently after having adapted to a microgravity environment. These space-based measurements of the baroreflex will be compared to ground measurements to determine if microgravity affects the reflex.
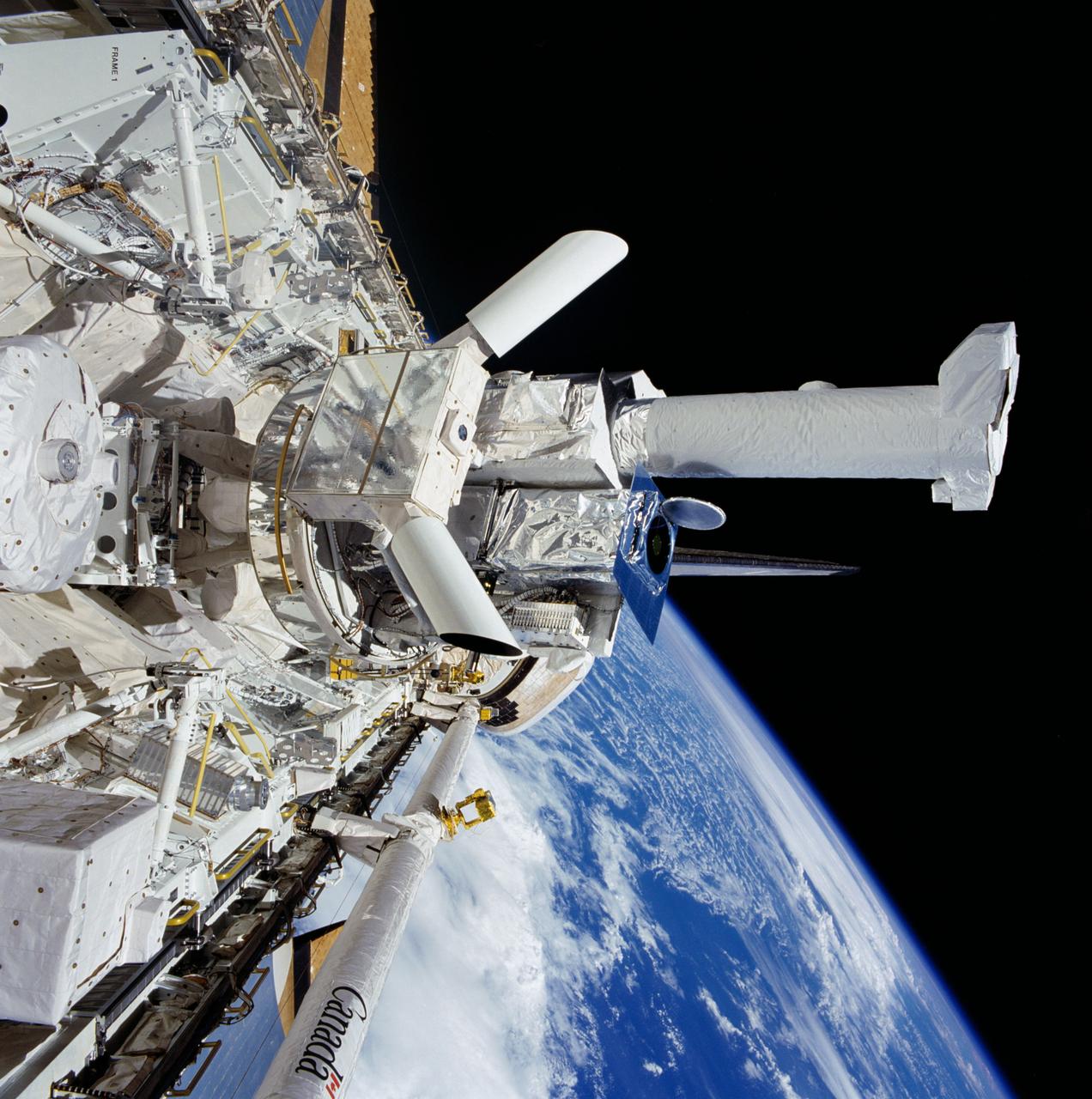

51F-42-069 (29 July-6 Aug 1985) --- The solar optical universal polarimeter (SOUP) experiment is visible among the cluster of Spacelab 2 hardware in the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger, backdropped against a curtain of white clouds over ocean waters. Various components of the instrument positioning system (IPS) are conspicuous at the center of the frame. Now resting, the remote manipulator system (RMS) was used at various points during the mission with the plasma diagnostics package (PDP) and as a support service structure for television cameras covering various activities of the busy science-oriented Spacelab 2 mission.
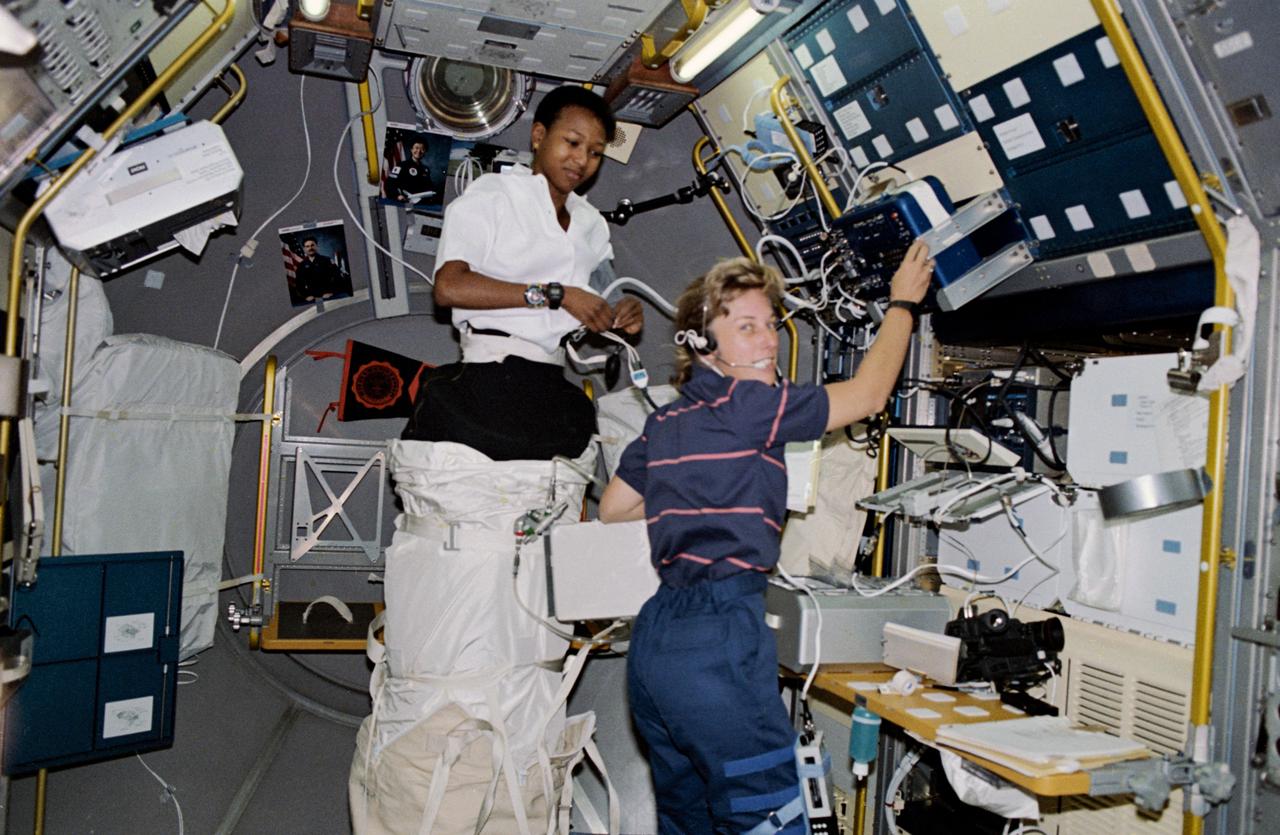

STS047-230-030 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronauts Mae C. Jemison (left) and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists, are pictured in the Spacelab-J science module preparing to conduct a session with the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) experiment. The two joined four other NASA astronauts and a payload specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA) aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour for eight days of Spacelab-J research.
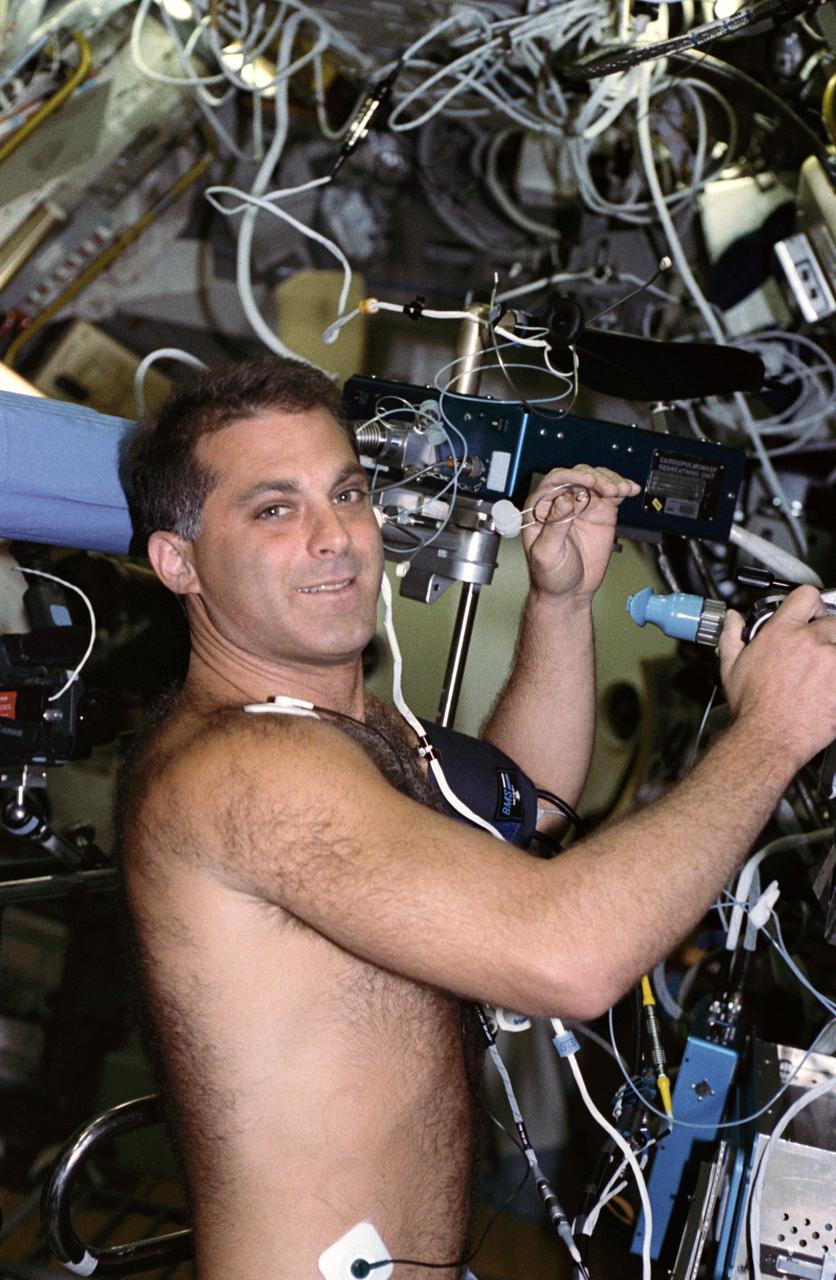

STS058-204-014 (18 Oct.-1 Nov. 1993) --- Astronaut David A. Wolf, mission specialist, participates in an experiment that investigates in-space distribution and movement of blood and gas in the pulmonary system. The data gathered during the two-week flight will be compared with results of tests performed on Earth to determine the changes that occur in pulmonary functions. Photo credit: NASA
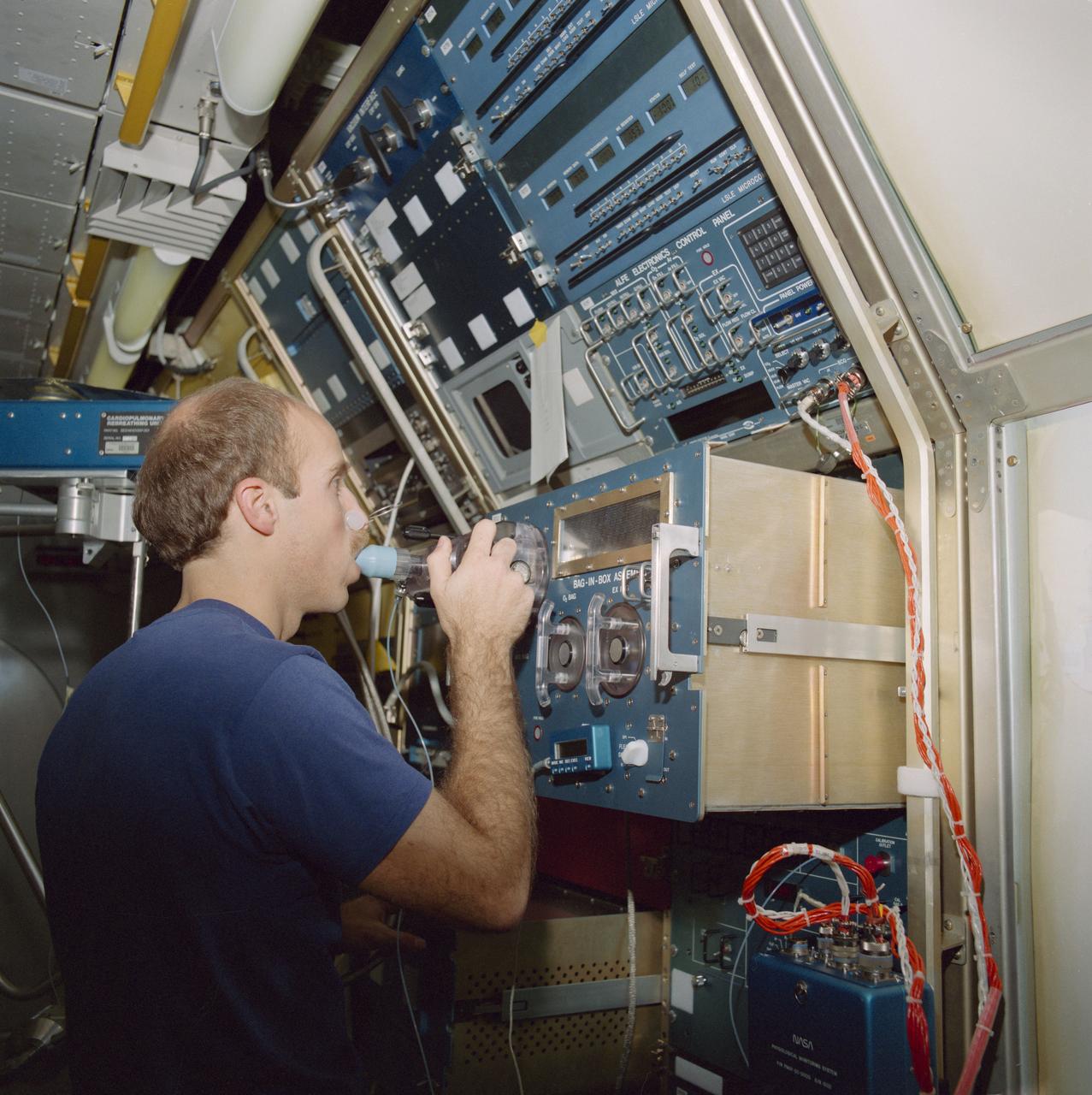

S85-26582 (Feb 1985) --- Training on the rebreathing assembly, astronaut James P. Bagian, STS-40 mission specialist, inhales a predetermined gas composition. A gas analyzer mass spectrometer determines the composition of the gases he exhales. The rebreathing assembly and gas analyzer system are part of an investigation that explores how lung function is altered. Dr. Bagian will be joined by two other mission specialists, the mission commander, the pilot and two payload specialists for the scheduled 10-day Spacelab Life Sciences-1 (SLS-1) mission. The flight is totally dedicated to biological and medical experimentation.
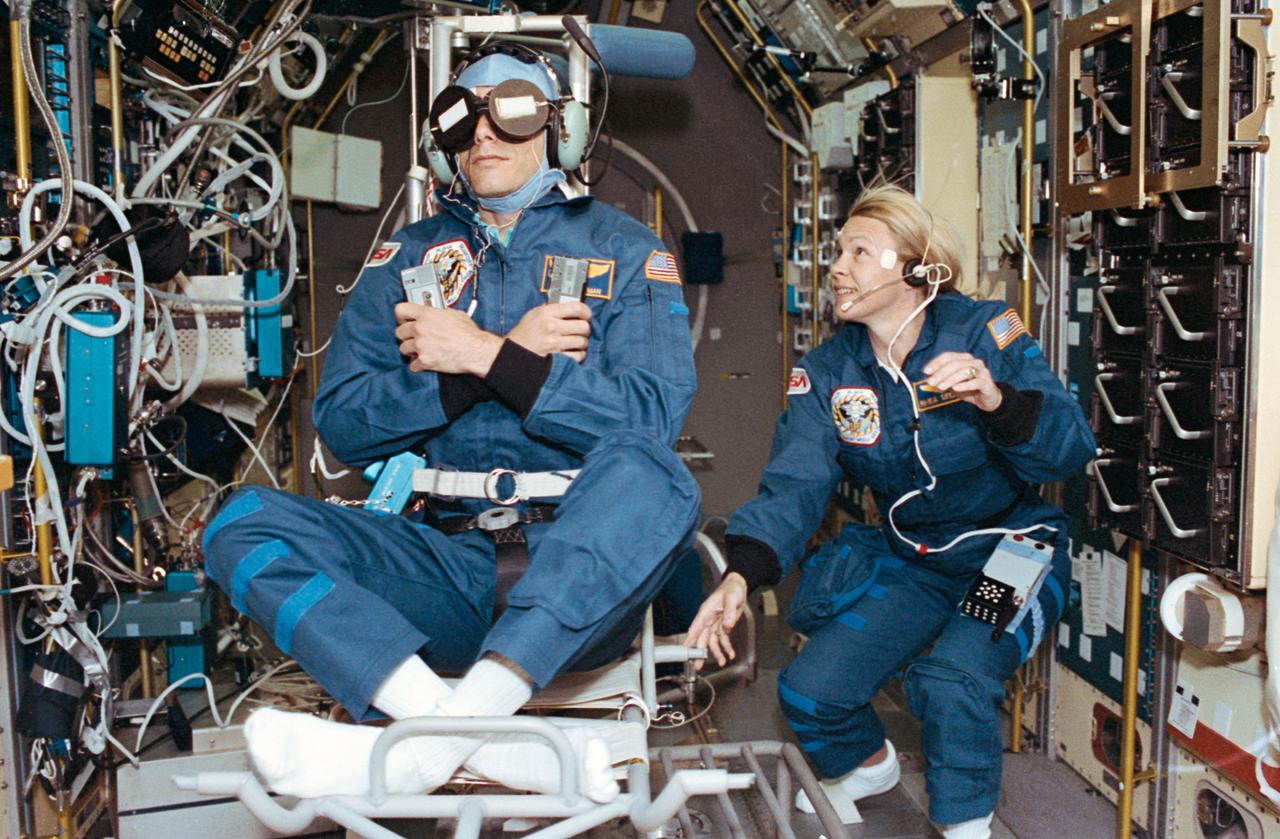

STS058-202-002 (18 Oct.-1 Nov. 1993) --- Astronaut Rhea Seddon, STS-58 payload commander, spins the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-2) rotating chair as payload specialist Martin J. Fettman serves as test subject. The two joined five NASA astronauts for fourteen days of medical research aboard the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia. Photo credit: NASA
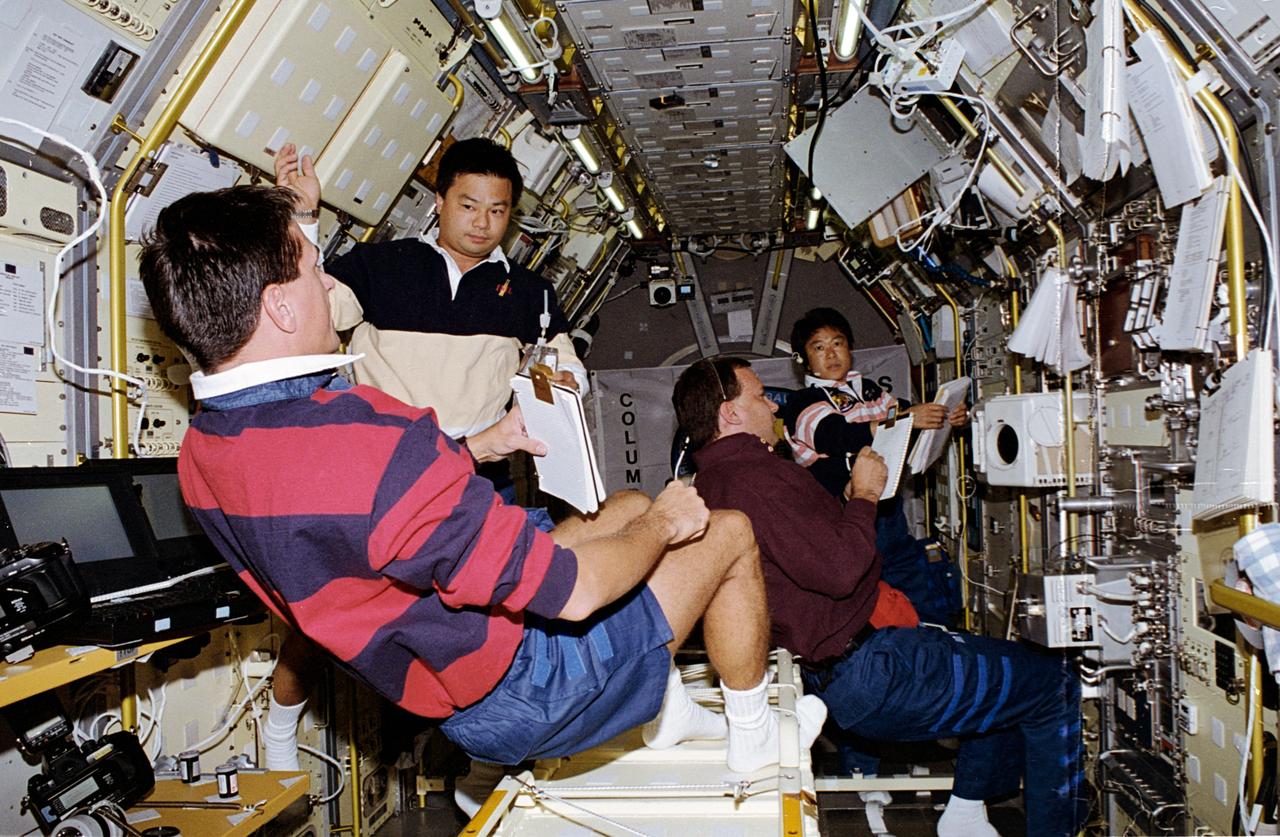

STS065-05-037 (8-23 July 1994) --- In the science module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, four members of the crew busy themselves with experiments in support of the second International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-2) mission. Left to right are Donald A. Thomas and Leroy Chiao, both mission specialists; Richard J. Hieb, payload commander, and Dr. Chiaki Mukai of NASDA, payload specialist.
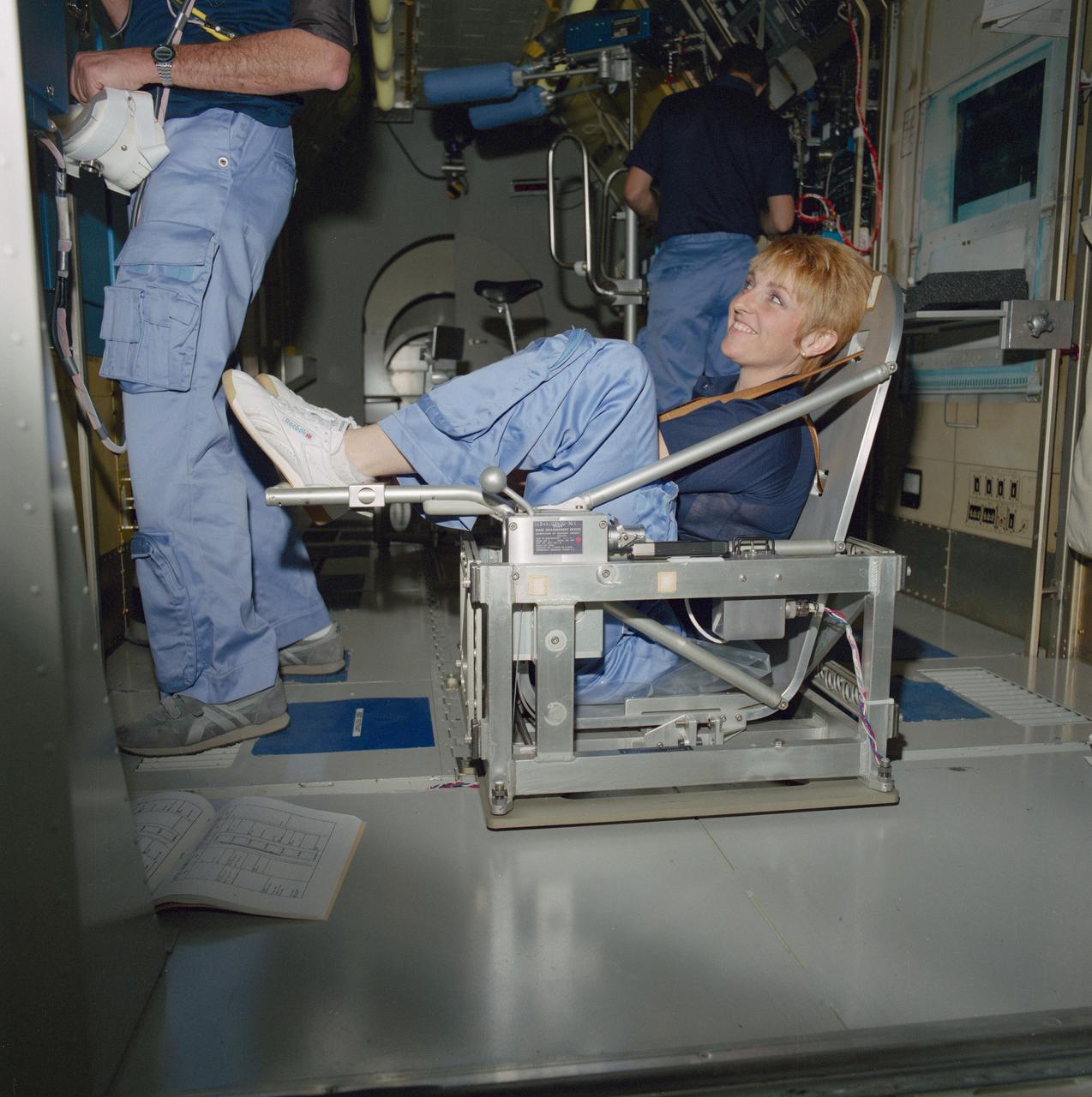
S85-26553 (Feb 1985) --- STS-40/SLS-1 payload specialist Millie Hughes-Fulford sits strapped in the special device scientists have developed for determining mass on orbit. As the chair swings back and forth, a timer records how much the crewmember's mass retards the chair's movement. Dr. Hughes-Fulford will be joined by three mission specialists, the mission commander, the pilot and a second payload specialist for the scheduled 10-day Spacelab Life Sciences-1 (SLS-1) mission. The flight is totally dedicated to biological and medical experimentation.
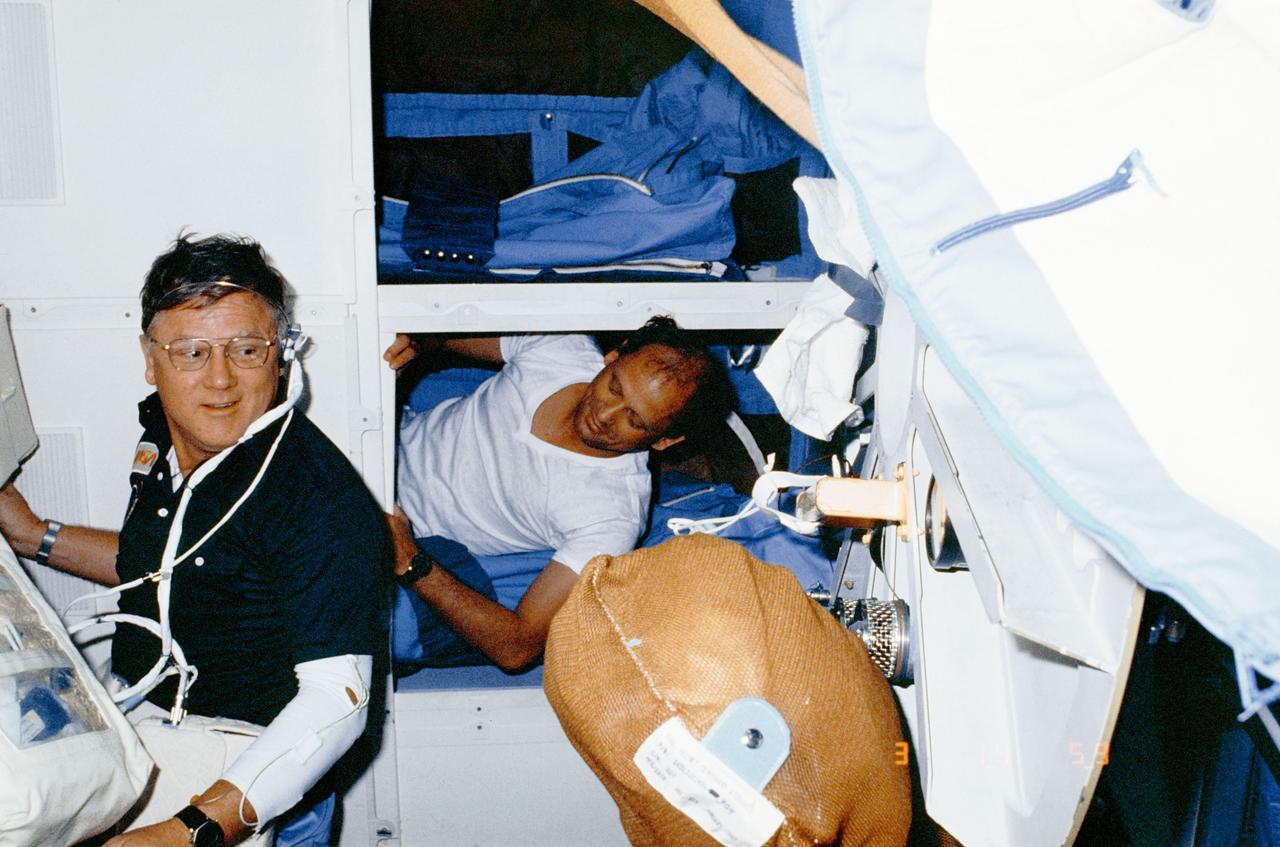
Astronaut Norman E. Thagard, mission specialist for the "silver" team, rests on the middeck while the "gold" team is on duty in the science module. Don L. Lind, left, "gold" team member, meanwhile participates in autogenic feedback training (AFT), designed to help flight crewmembers overcome the effects of zero-gravity adaptation.
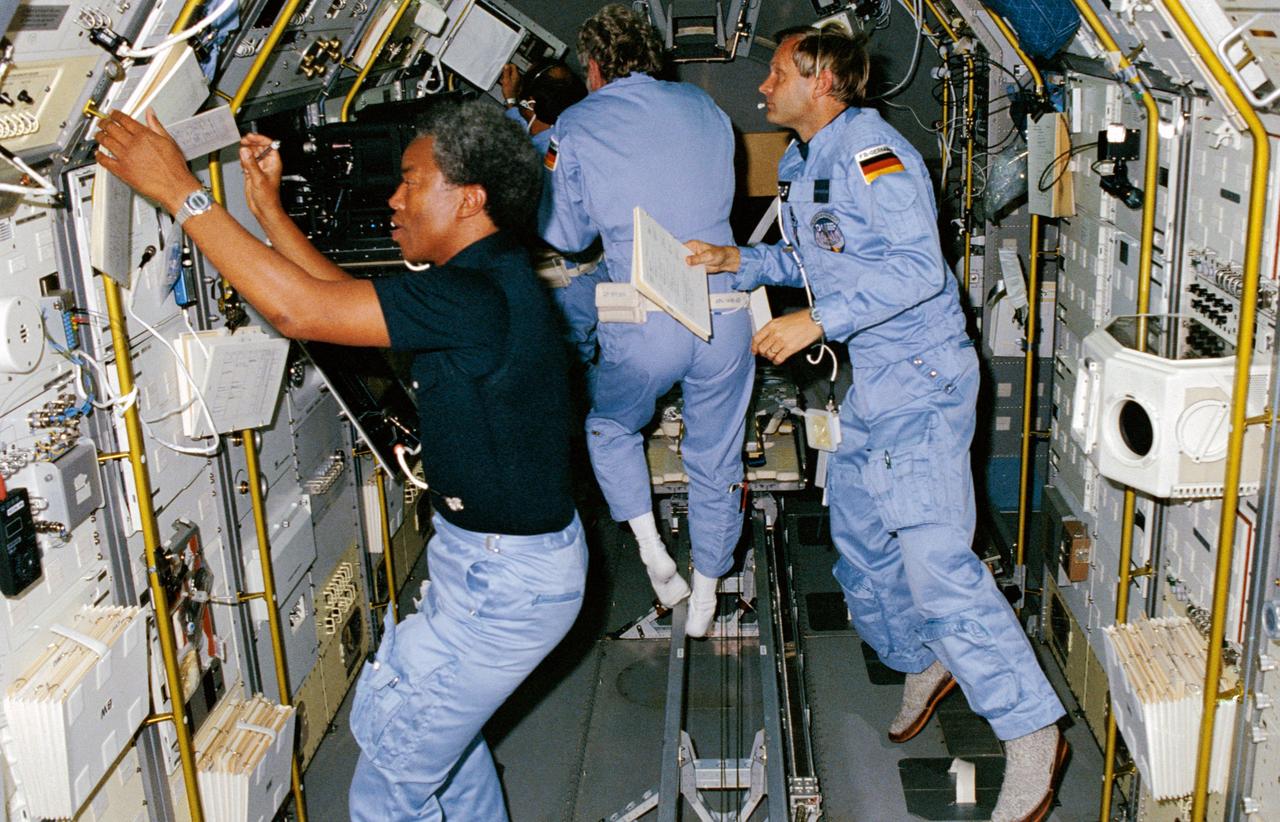

61A-01-030 (30 Oct.-6 Nov. 1985) --- Mission specialist Guion S. Bluford prepares to perform a physics experiment onboard the D-1 science module in the cargo bay of the earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger. In the backgroud, three European payload specialists busy themselves with experiment chores: (L-R) Wubbo J. Ockels (partially obscured), Reinhard Furrer and Ernst Messerschmid.
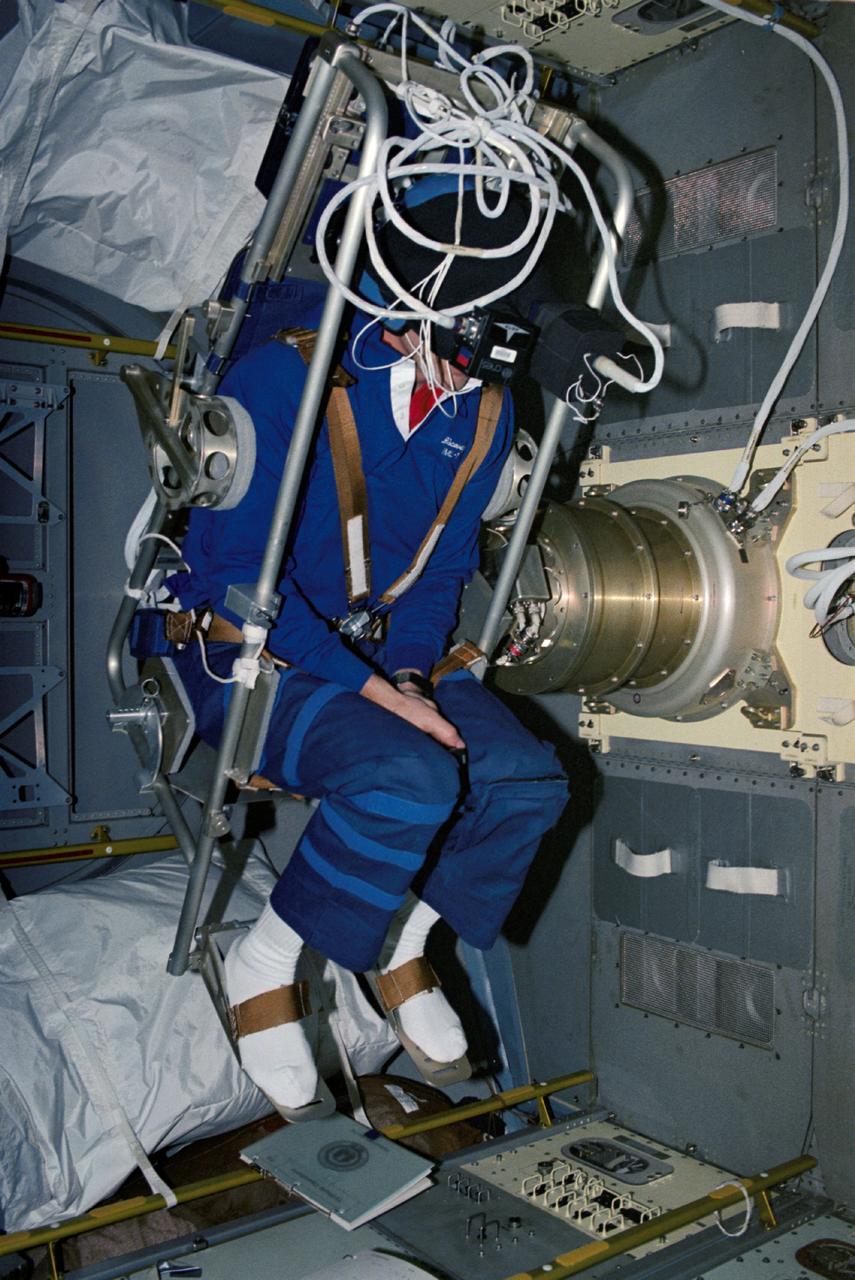

STS042-27-037 (22-30 Jan. 1992) --- Astronaut David C. Hilmers, STS-42 mission specialist, wearing a helmet assembly, sits in the Microgravity Vestibular Investigation (MVI) rotating chair. The scene is in the International Microgravity Laboratory (IML-1) science module aboard Discovery. Hilmers, a mission specialist, and six other crewmembers spent more than eight days in Earth-orbit conducting experiments. Hilmer's helmet assembly is outfitted with accelerometers to measure head movements and visors that fit over each eye independently to provide visual stimuli. The chair system has three movement patterns: "sinusoidal" or traveling predictably back and forth over the same distance at a constant speed; "pseudorandom" or moving back and forth over the varying distances; and "stepped" or varying speeds beginning and stopping suddenly.
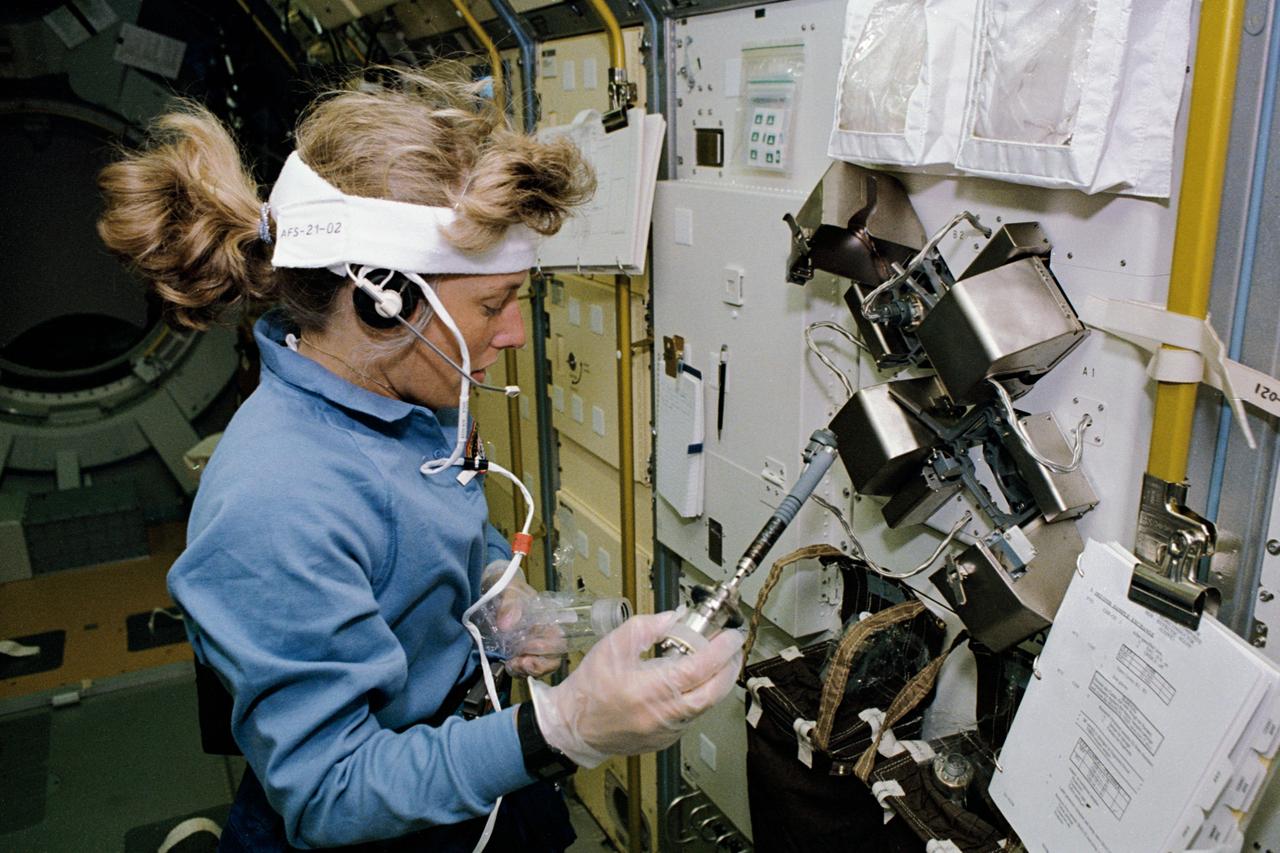

STS047-02-003 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronaut N. Jan Davis, mission specialist, works at the Continuous Heating Furnace (CHF) in the Spacelab-J Science Module. This furnace provided temperatures up to 1,300 degrees Celsius and rapid cooling to two sets of samples concurrently. The furnace accommodated in-space experiments in the Fabrication of Si-As-Te:Ni Ternary Amorphous Semiconductor and the Crystal Growth of Compound Semiconductors. These were two of the many experiments designed and monitored by Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA).
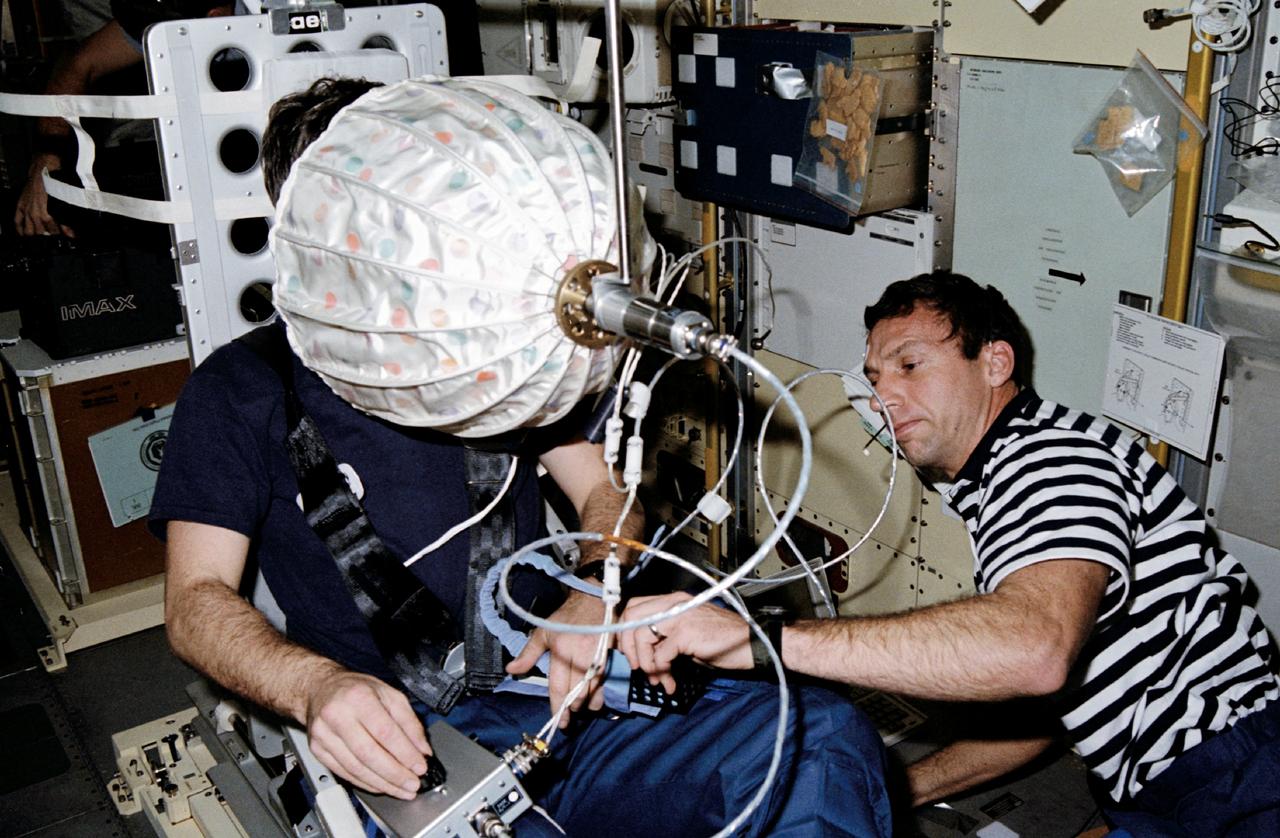

STS042-203-024 (22-30 Jan. 1992) --- Astronaut David C. Hilmers (right), STS-42 mission specialist, assists European Space Agency (ESA) payload specialist Ulf Merbold with the visual stimulator experiment on the Space Shuttle Discovery's middeck. This particular test is part of an ongoing study of the Space Adaptation Syndrome (SAS). Seated in a stationary mini-sled, Merbold (or any other subject for this test) stares at an umbrella-shaped rotating dome with a pattern of colored dots on its interior. While observing the rotating dome, the subject turns a knob to indicate his perception of body rotation. The strength of circular vection is calculated by comparing the signals from the dome and the knob. The greater the false sense of circular vection, the more the subject is relying on visual information instead of otolith information.
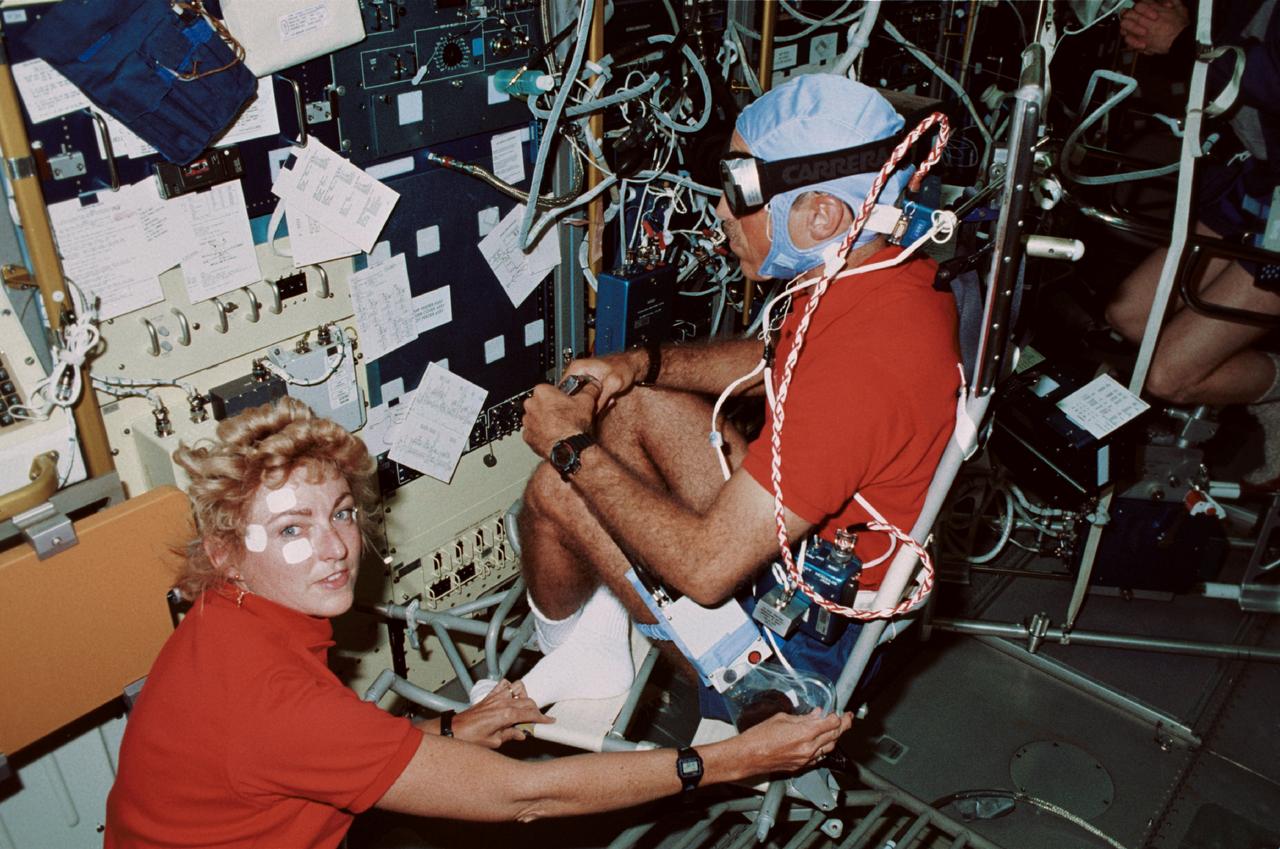

STS040-211-020 (5-14 June 1991) --- Vestibular experiment activities were captured onboard Columbia's Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) module in this 35mm scene. Astronaut James P. Bagian, STS-40 mission specialist, is in a rotating chair while wearing an accelometer and electrodes to record head motion and horizontal and vertical eye movements during the rotations. Payload specialist Millie Hughes-Fulford, lower left, assists with the test.
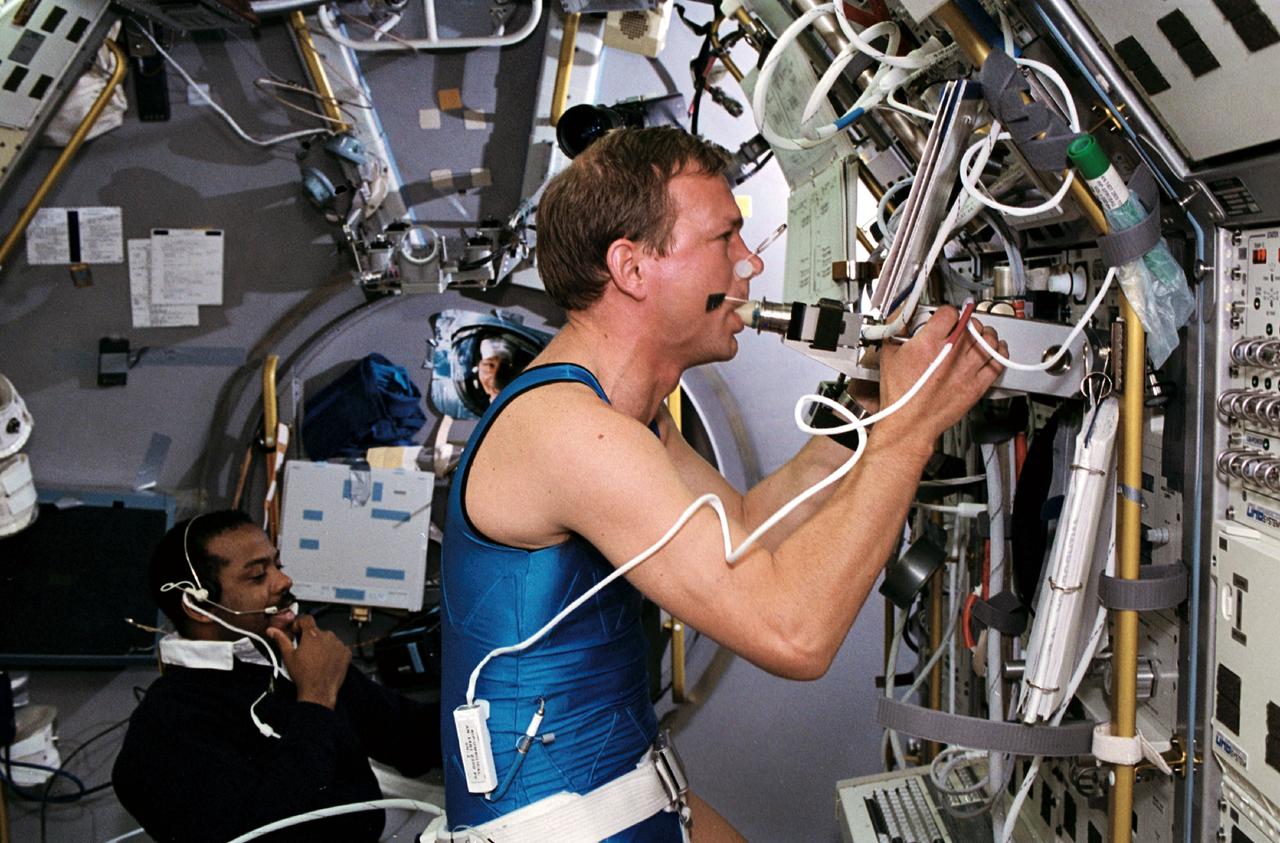

STS055-45-017 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Hans Schlegel (foreground) participates in the ongoing investigation of human physiology under microgravity conditions as he works out on the ergometer at the Anthrorack. Monitoring the "run" is astronaut Bernard A. Harris, Jr., STS-55 mission specialist. Schlegel is one of two payload specialists representing the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DLR) on the Spacelab D-2 mission.
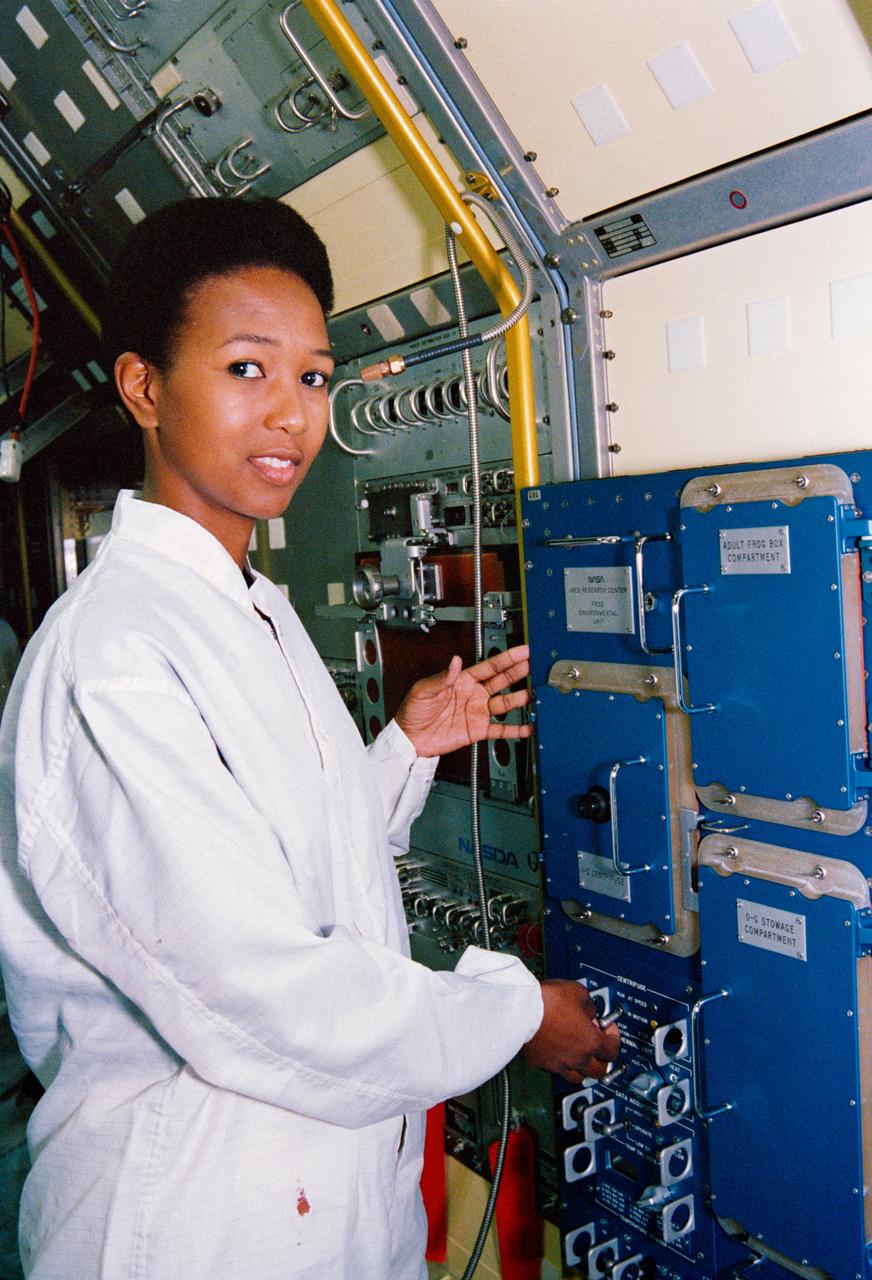

S92-44302 (25 July 1992) --- Astronaut Mae C. Jemison, mission specialist, examines the interior of the Spacelab-J laboratory module installed in Endeavour's cargo bay. The STS-47 crewmembers visited Endeavour, currently undergoing pre-flight processing in a high bay area of the Orbiter Processing Facility at the Kennedy Space Center. The Spacelab-J mission is currently scheduled for September of this year.
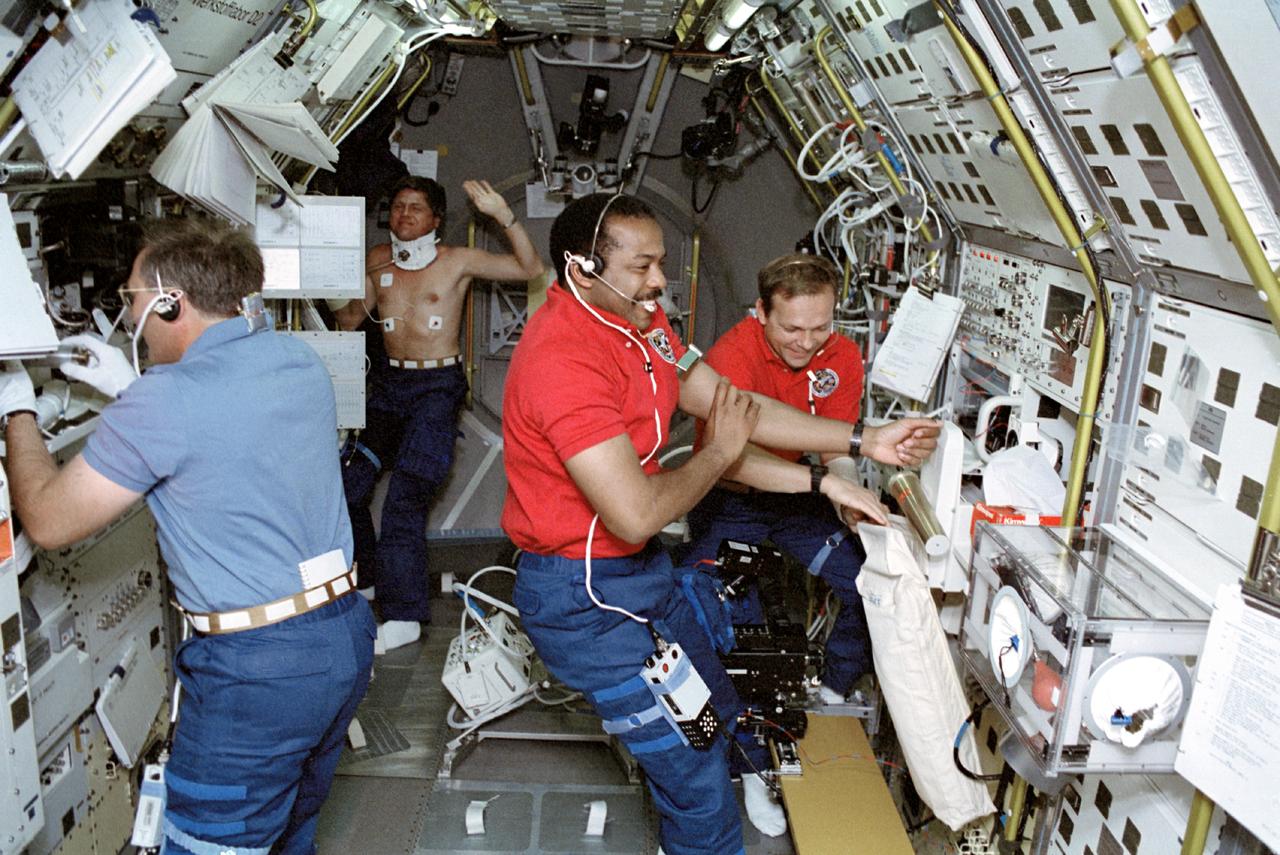

STS055-22-004 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Four of the seven crew members who spent 10 days aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia are pictured during a brief shift overlap period in the Spacelab D-2 Science Module. Left to right are Jerry L. Ross, Ulrich Walter, Bernard A. Harris, Jr. and Hans Schlegel. Ross, STS-55 payload commander, is changing a sample in a materials processing furnace; Walter, a German payload specialist is in the midst of a baroreflex test and fellow payload specialist Schlegel assists mission specialist and physician Harris with a physiological test at the "Anthrorack".
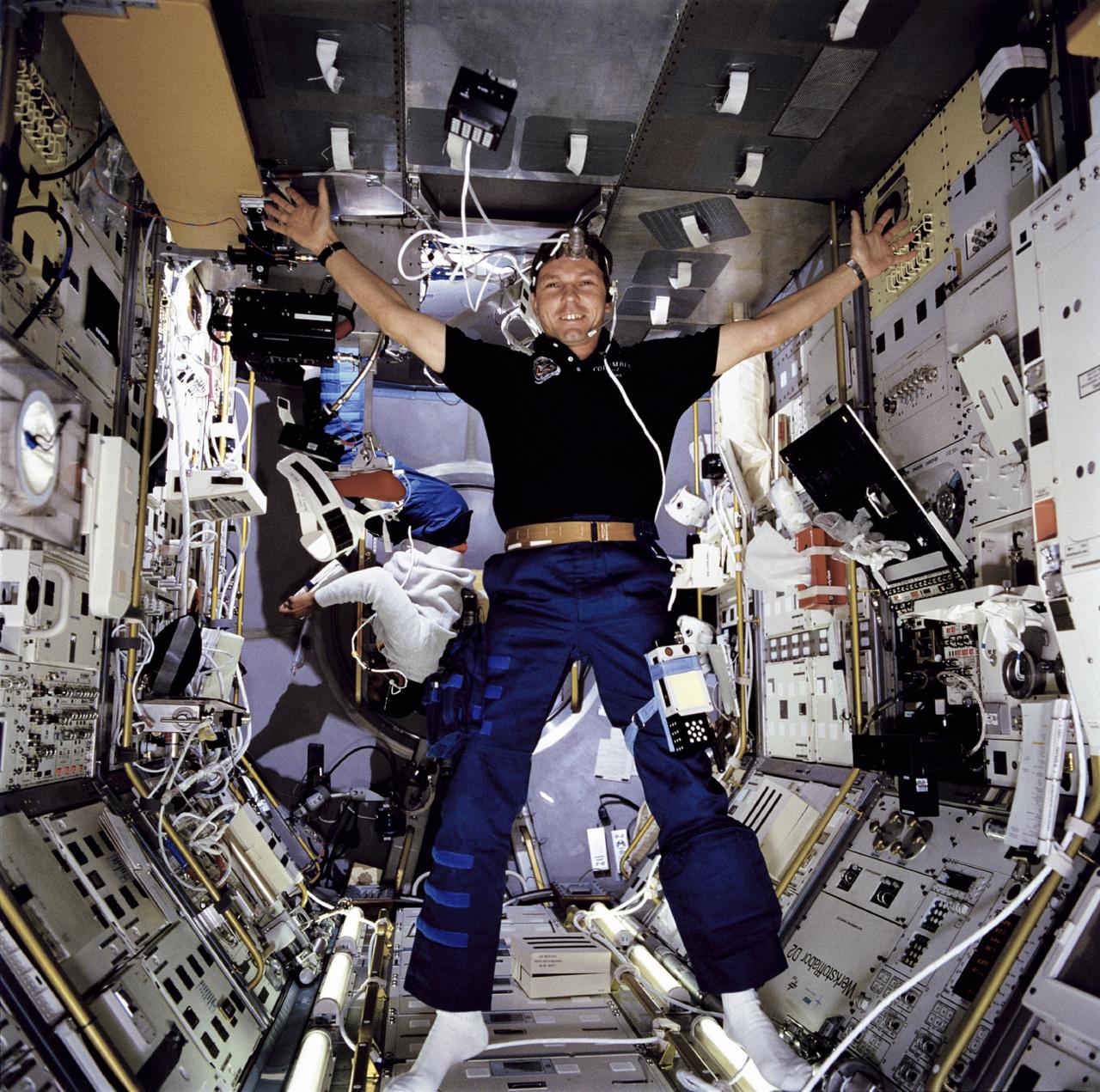

STS055-106-090 (26 April- 6 May 1993) --- Hans Schlegel, one of two STS-55 payload specialists representing the German Aerospace Research Establishment (DLR) onboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, finds plenty of room to "spread out" while participating in a Tissue experiment. Astronaut Bernard A. Harris, Jr., mission specialist, monitors an experiment in the background.

STS055-203-034 (26 April-6 May 1993) --- Astronaut Steven R. Nagel, STS-55 mission commander, has found an isolated station in the D-2 science module from which to talk to students on Earth. Like many before it, the seven member crew participated in communications with students and licensed radio operators via the Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment (SAREX). Photo credit: NASA
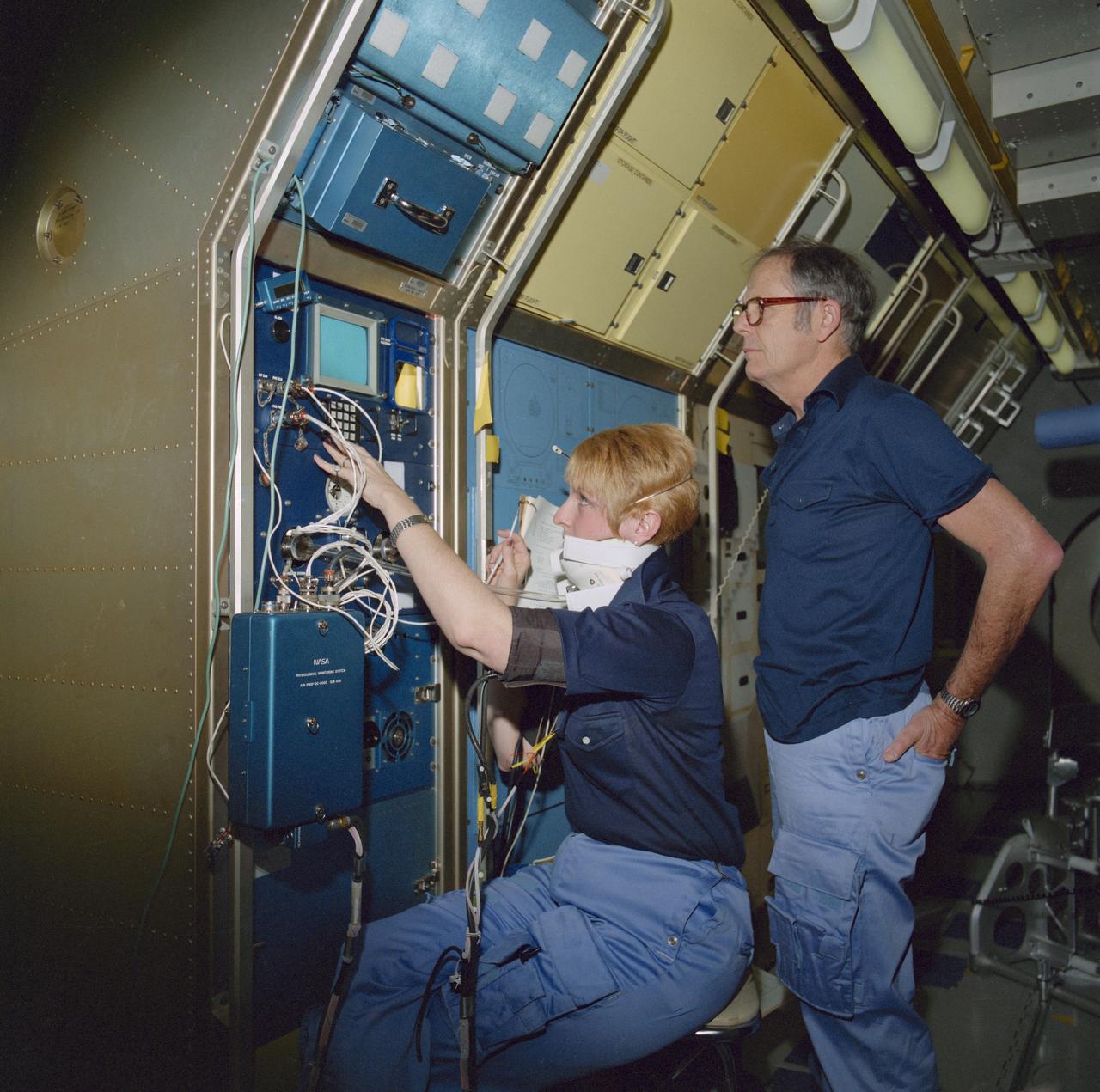

S85-26571 (Feb 1985) --- Wearing a special collar, Millie Hughes-Fulford, payload specialist, practices medical test operations scheduled for the Spacelab Life Sciences (SLS-1) mission. Robert Ward Phillips, backup payload specialist, looks on. The collar, called the baroflex neck pressure chamber, is designed to stimulate the bioceptors in the carotid artery, one of the two main arteries that supply blood to the head.
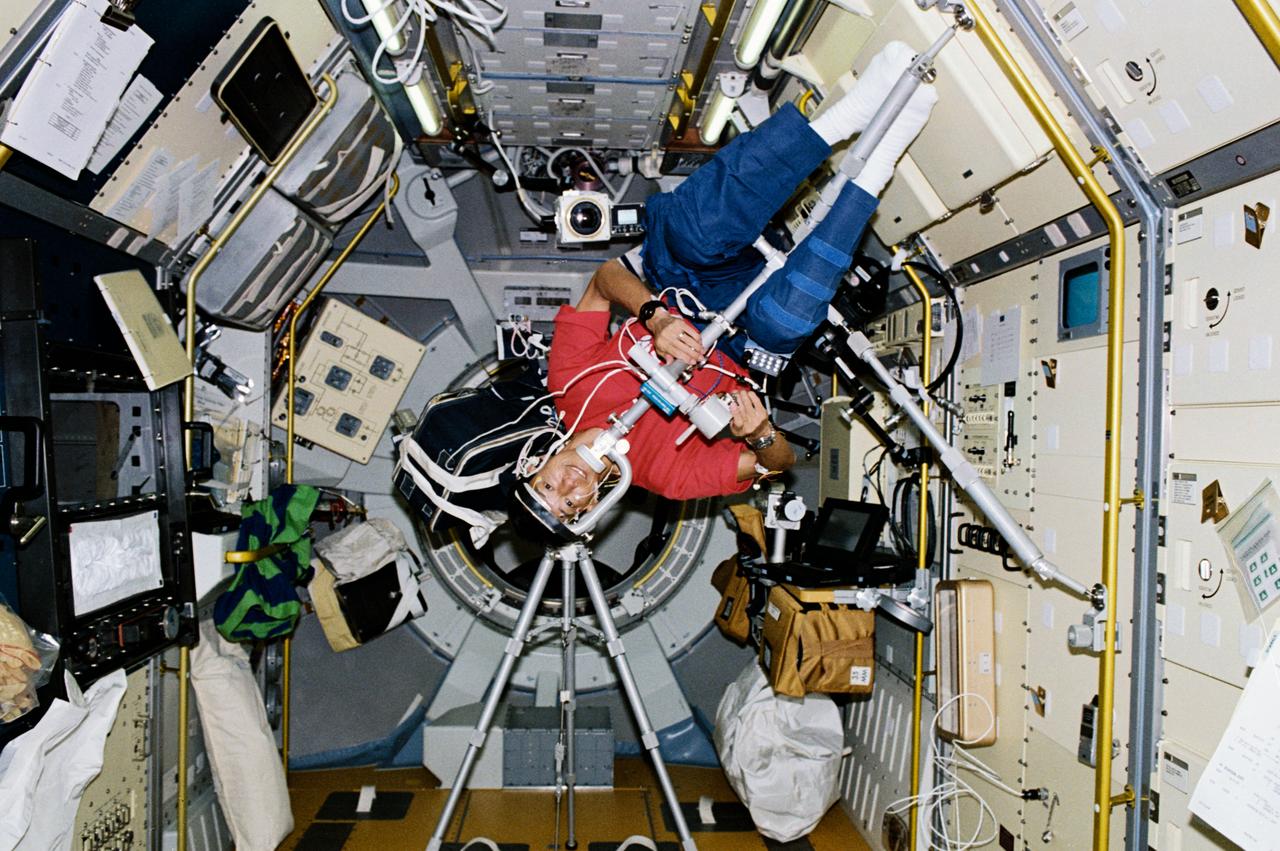

STS047-204-006 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Dr. Mamoru Mohri, payload specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA), participates in an experiment designed to learn more about Space Adaptation Syndrome (SAS). The experiment is titled, "Comparative Measurement of Visual Stability in Earth and Cosmic Space." During the experiment, Dr. Mohri tracked a flickering light target while eye movements and neck muscle tension were measured. This 45-degree angle position was one of four studied during the eight-day Spacelab-J mission.