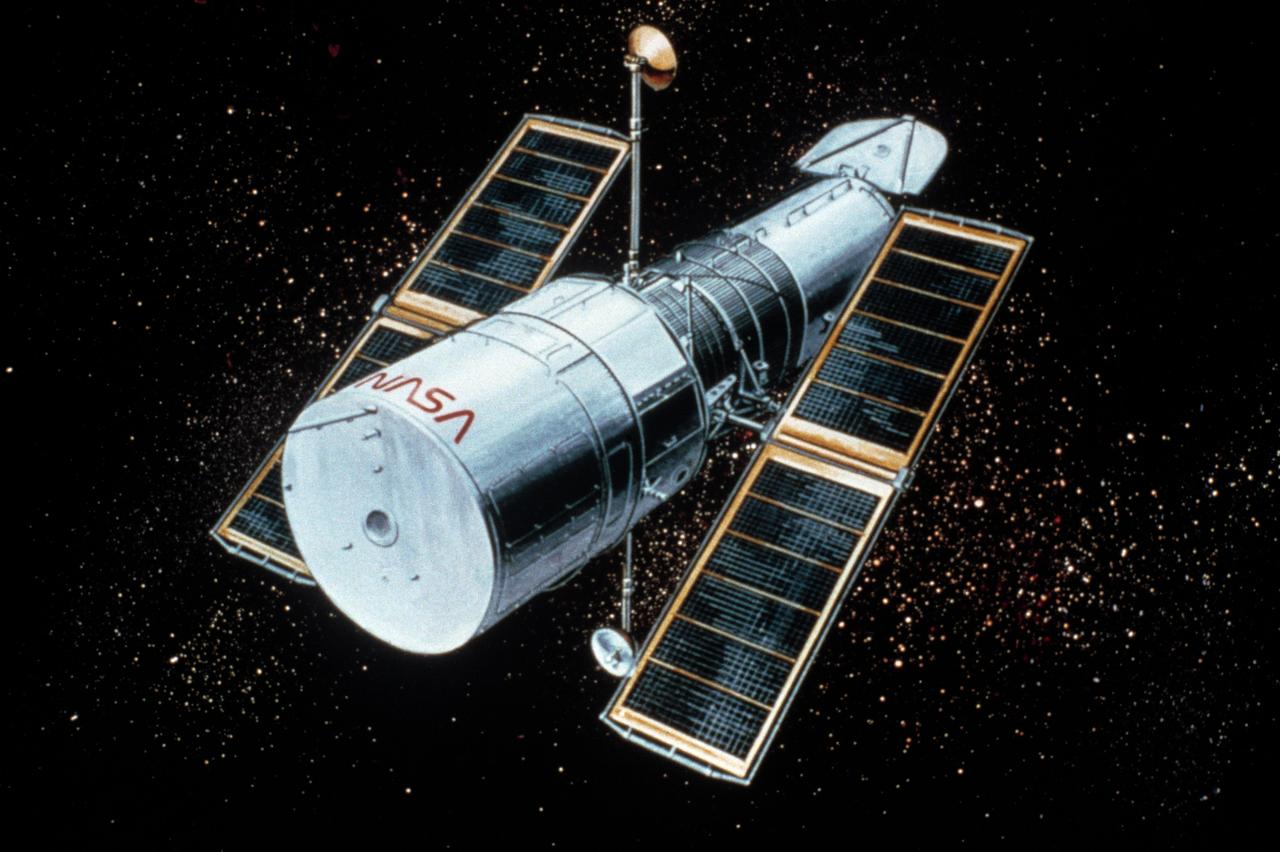

Shuttle related interaction with the space telescope.

The Hyperspectral Imager Suite (HISUI), a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) payload, arrives in its shipping container at the entrance to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 25, 2019. The payload will be packed inside the external trunk of the SpaceX Dragon cargo module at Launch Complex 39A. HISUI will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA in December 2019. HISUI is a spaceborne hyperspectral Earth Imaging System with a reflective telescope and two grating spectrometers.

The Hyperspectral Imager Suite (HISUI), a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) payload, arrives in its shipping container at the entrance to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 25, 2019. The payload will packed inside the external trunk of the SpaceX Dragon cargo module at Launch Complex 39A. HISUI will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA in December 2019. HISUI is a spaceborne hyperspectral Earth Imaging System with a reflective telescope and two grating spectrometers.

The Hyperspectral Imager Suite (HISUI), a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) payload, arrives in its shipping container at the entrance to the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 25, 2019. The payload will be packed inside the external trunk of the SpaceX Dragon cargo module at Launch Complex 39A. HISUI will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA in December 2019. HISUI is a spaceborne hyperspectral Earth Imaging System with a reflective telescope and two grating spectrometers.
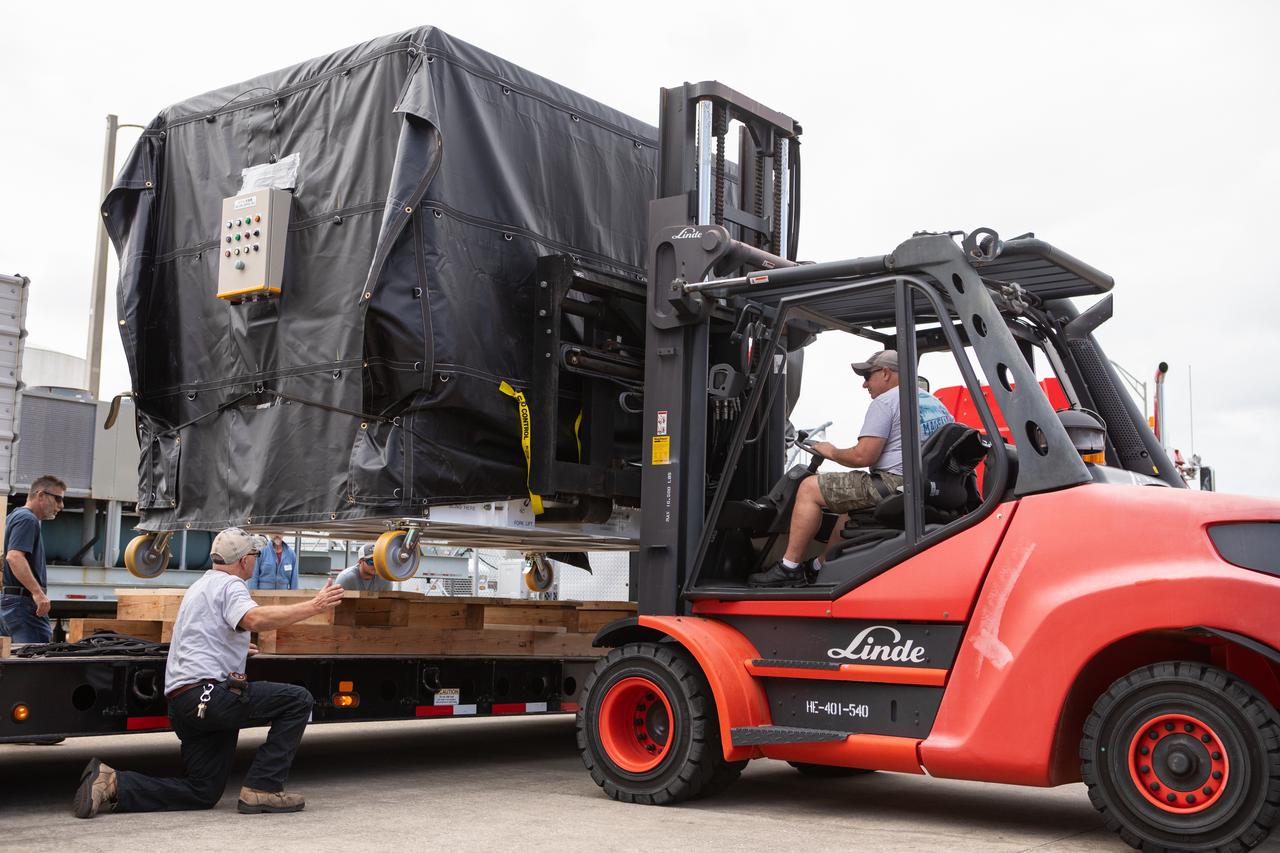

The Hyperspectral Imager Suite (HISUI), a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) payload, is lifted off of its transporter in its shipping container at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 25, 2019. The payload will be packed inside the external trunk of the SpaceX Dragon cargo module at Launch Complex 39A. HISUI will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA in December 2019. HISUI is a spaceborne hyperspectral Earth Imaging System with a reflective telescope and two grating spectrometers.
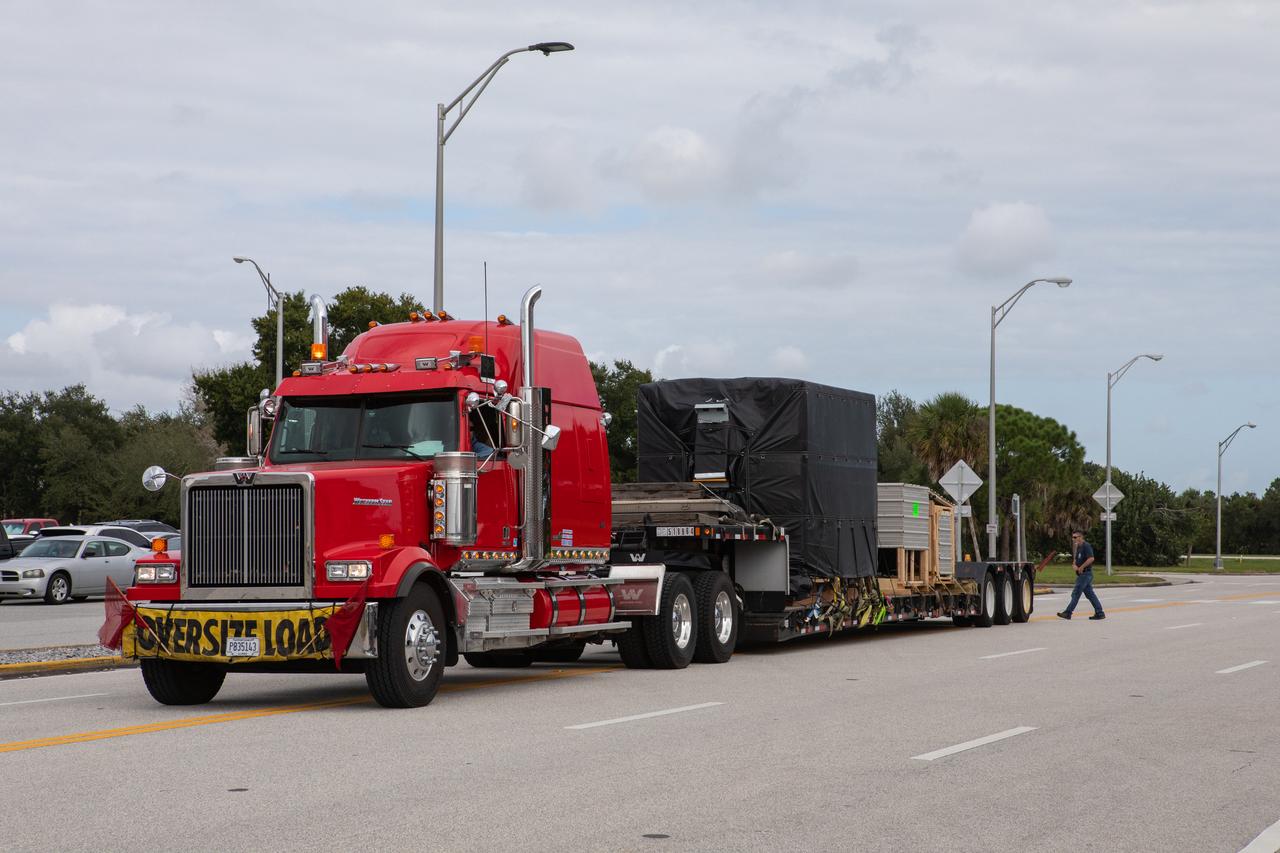

The Hyperspectral Imager Suite (HISUI), a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) payload, arrives in its shipping container on a flatbed truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 25, 2019. The payload will be packed inside the external trunk of the SpaceX Dragon cargo module at Launch Complex 39A. HISUI will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA in December 2019. HISUI is a spaceborne hyperspectral Earth Imaging System with a reflective telescope and two grating spectrometers.
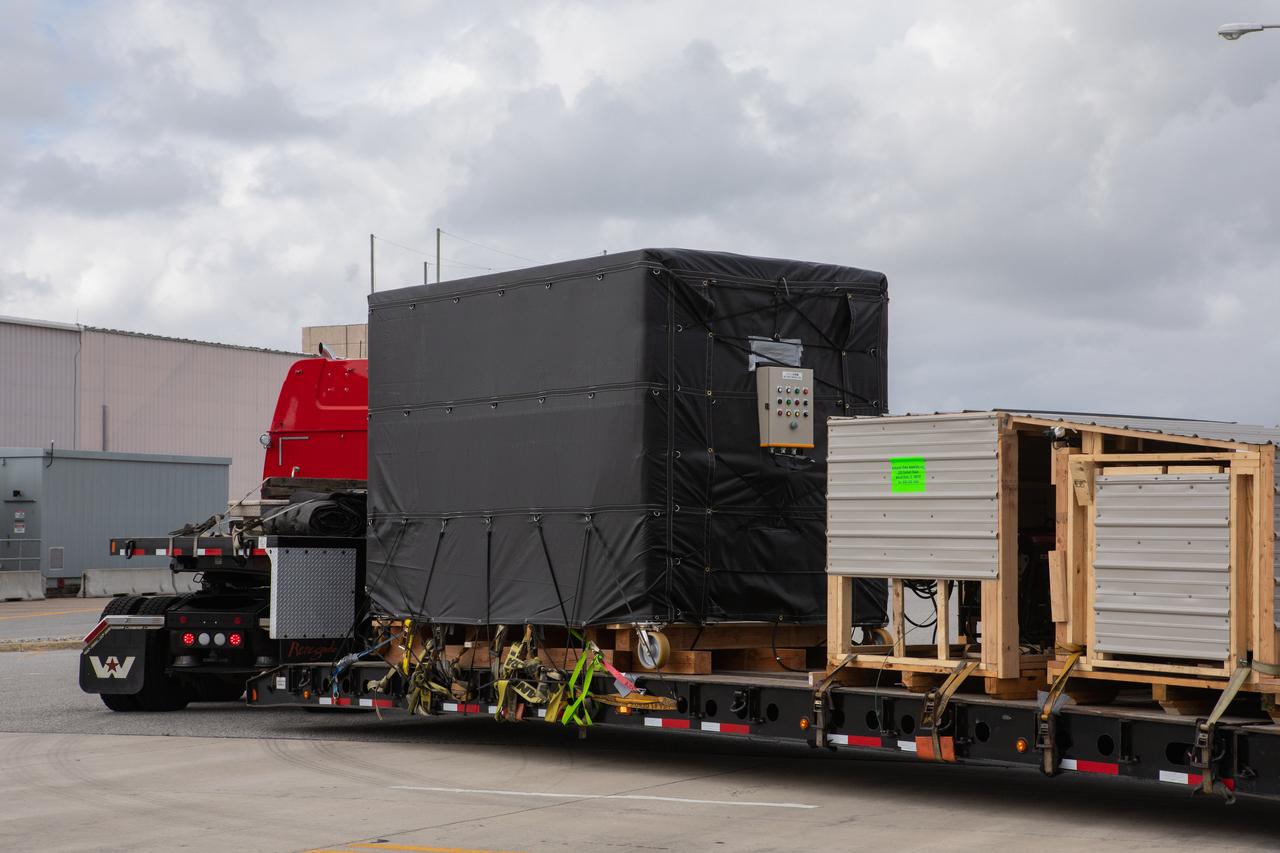

The Hyperspectral Imager Suite (HISUI), a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) payload, arrives in its shipping container on a flatbed truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 25, 2019. The payload will be packed inside the external trunk of the SpaceX Dragon cargo module at Launch Complex 39A. HISUI will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 19th Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASA in December 2019. HISUI is a spaceborne hyperspectral Earth Imaging System with a reflective telescope and two grating spectrometers.
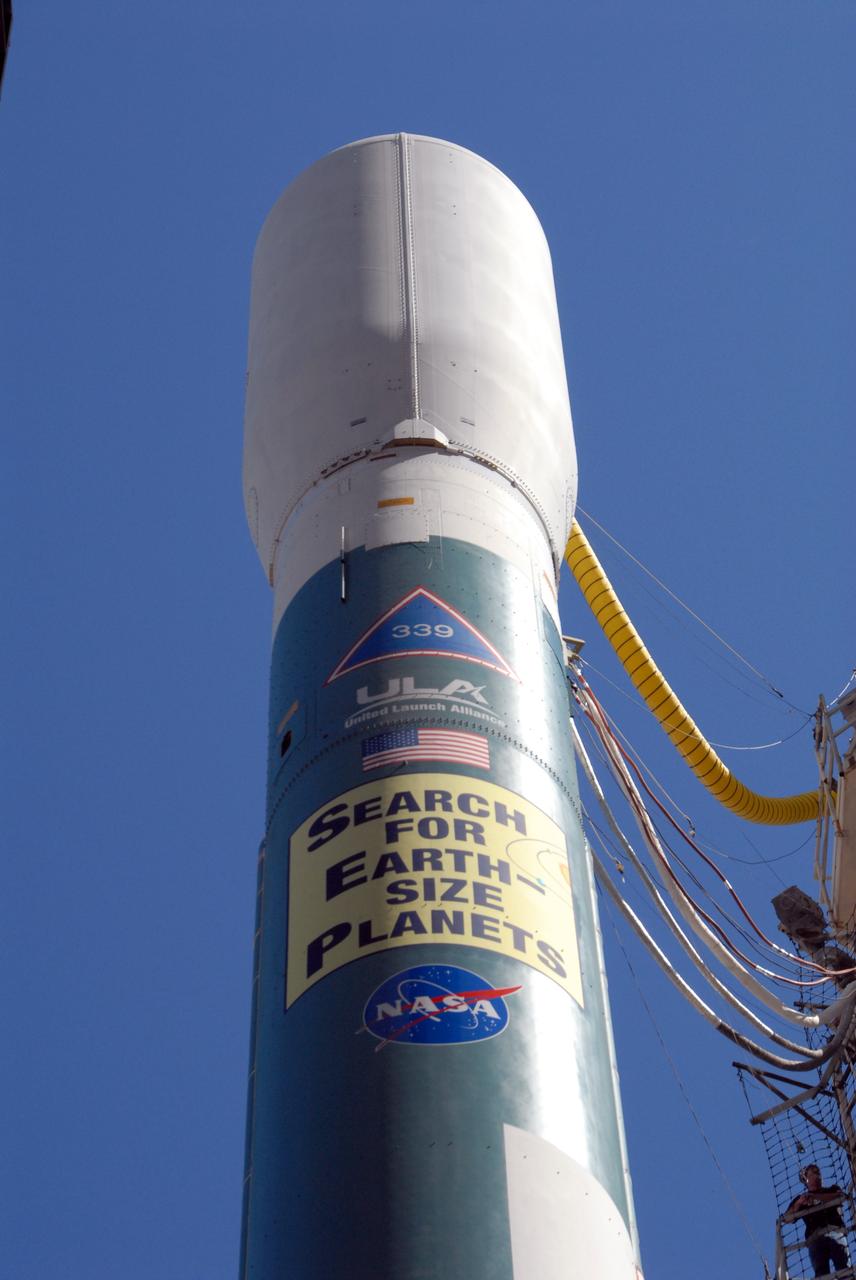

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
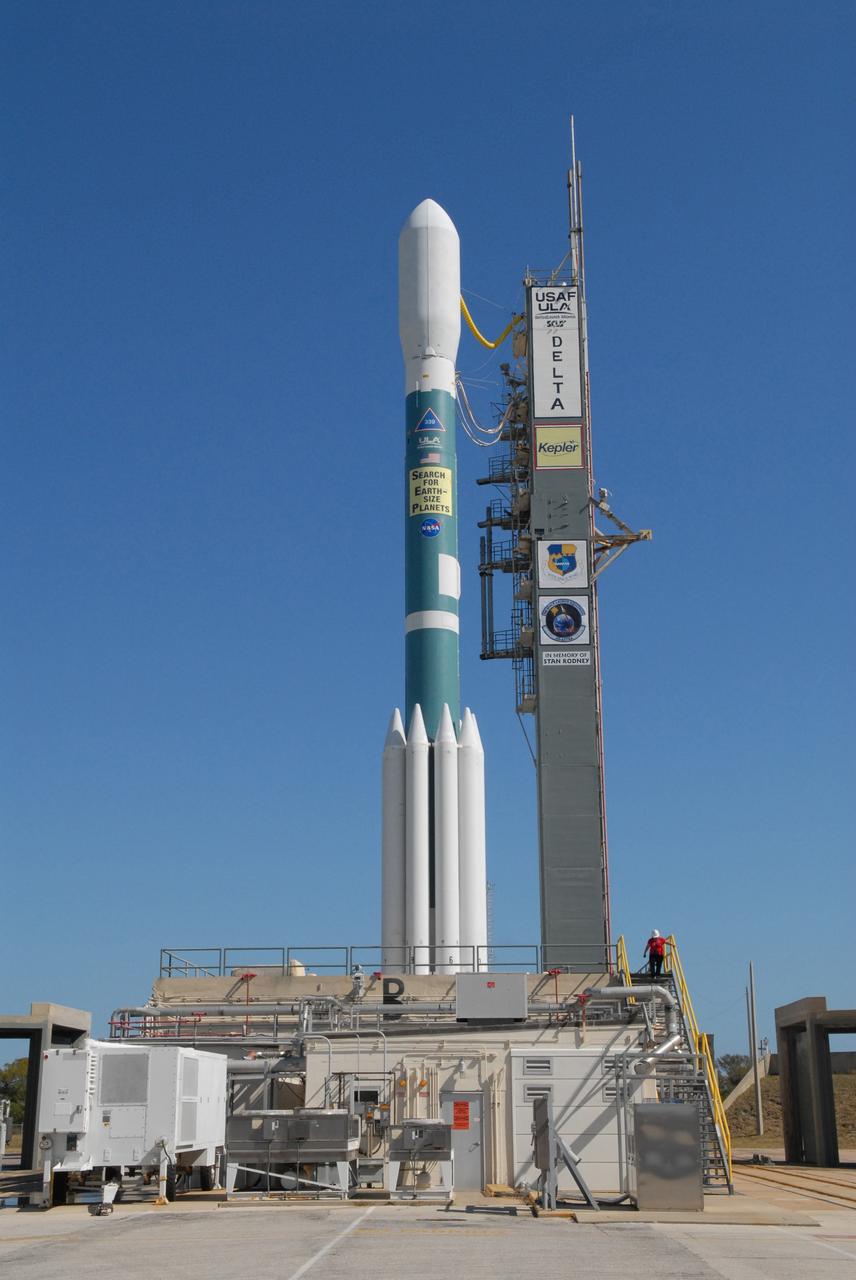

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
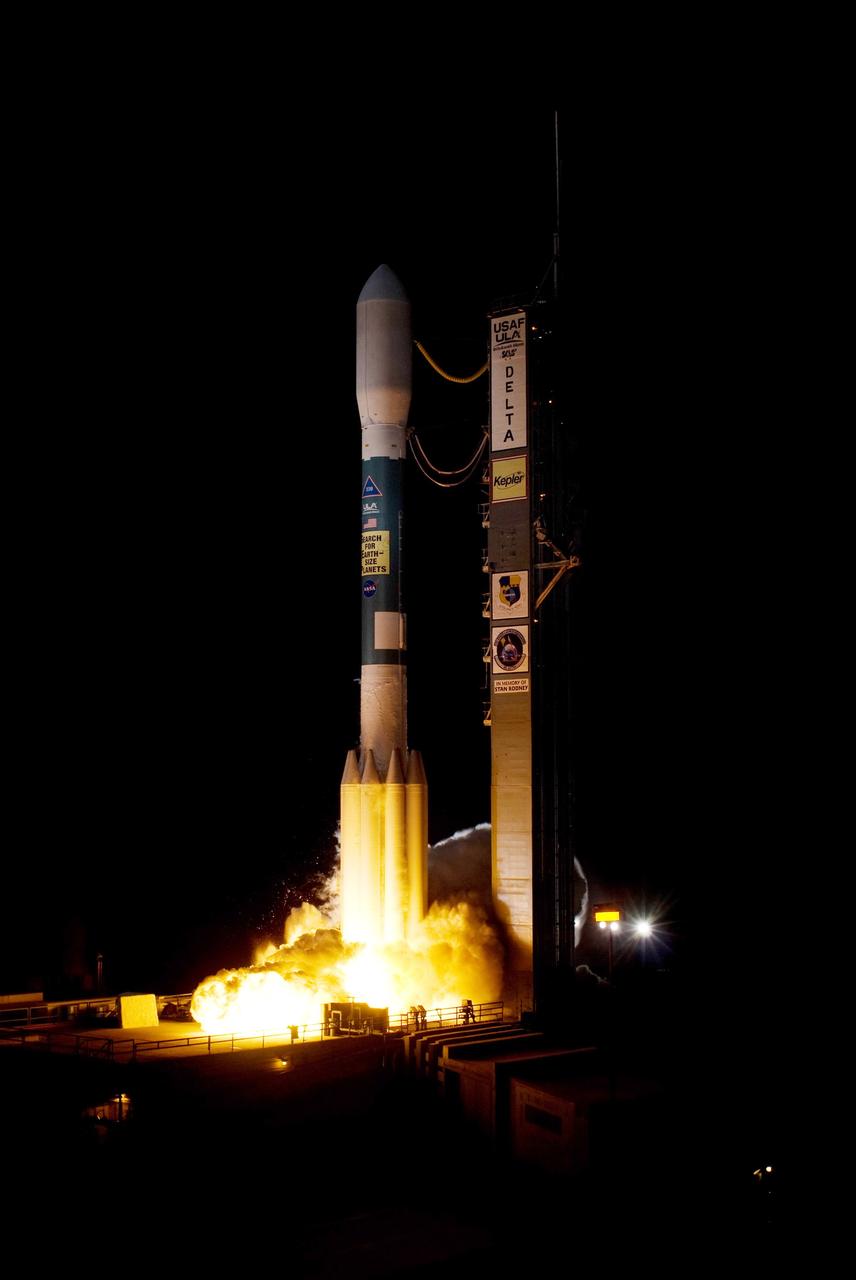

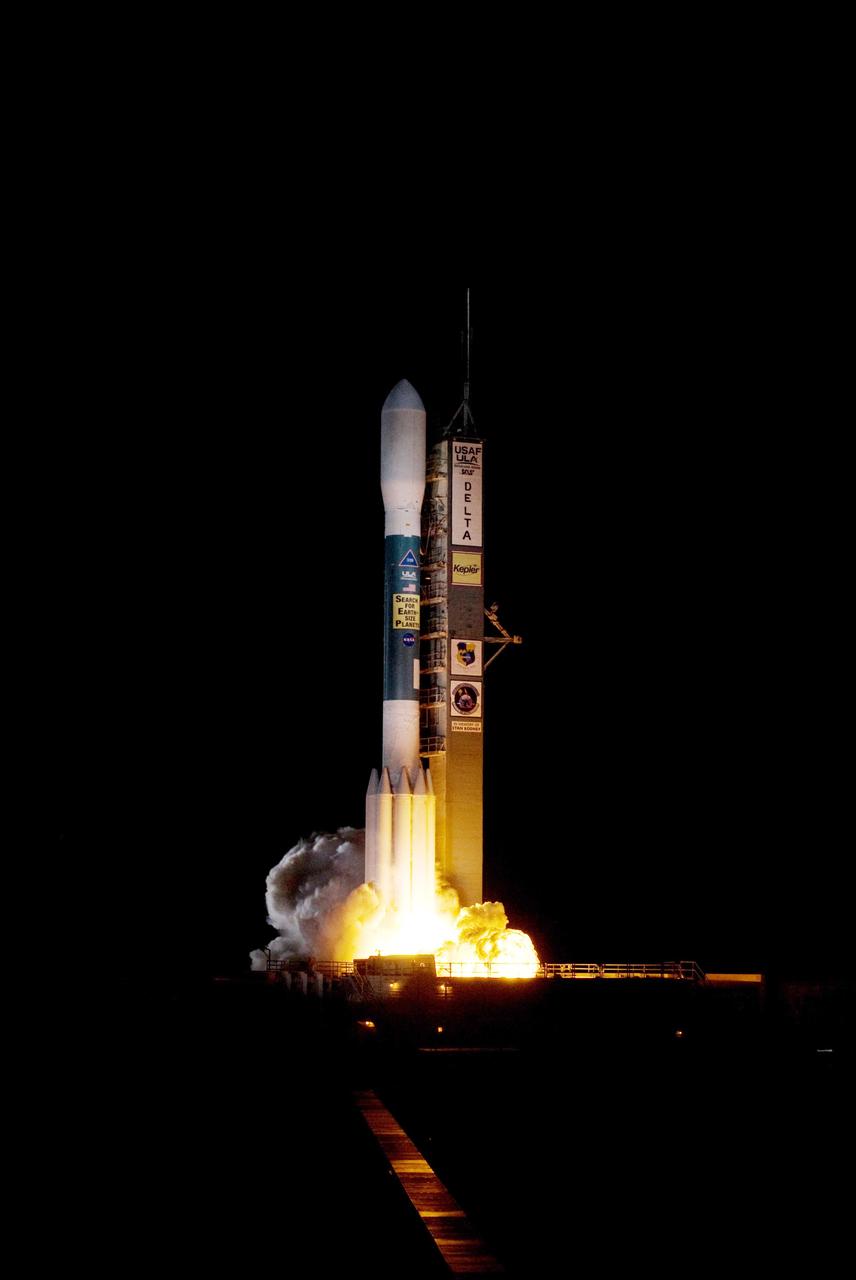
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the engines on United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft ignite. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray
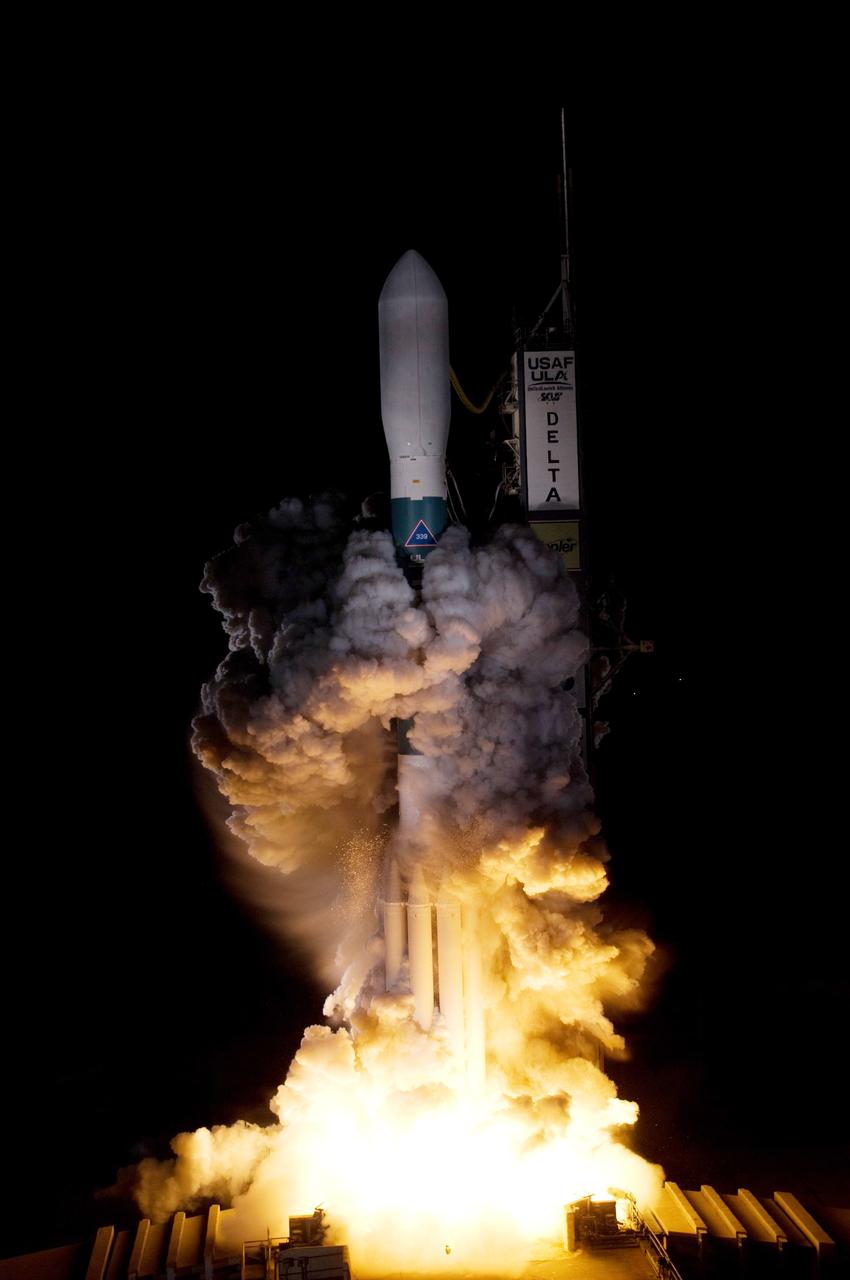

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft rises through the exhaust cloud created by the firing of the rocket’s engines. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Regina Mitchell-Ryall, Tom Farrar
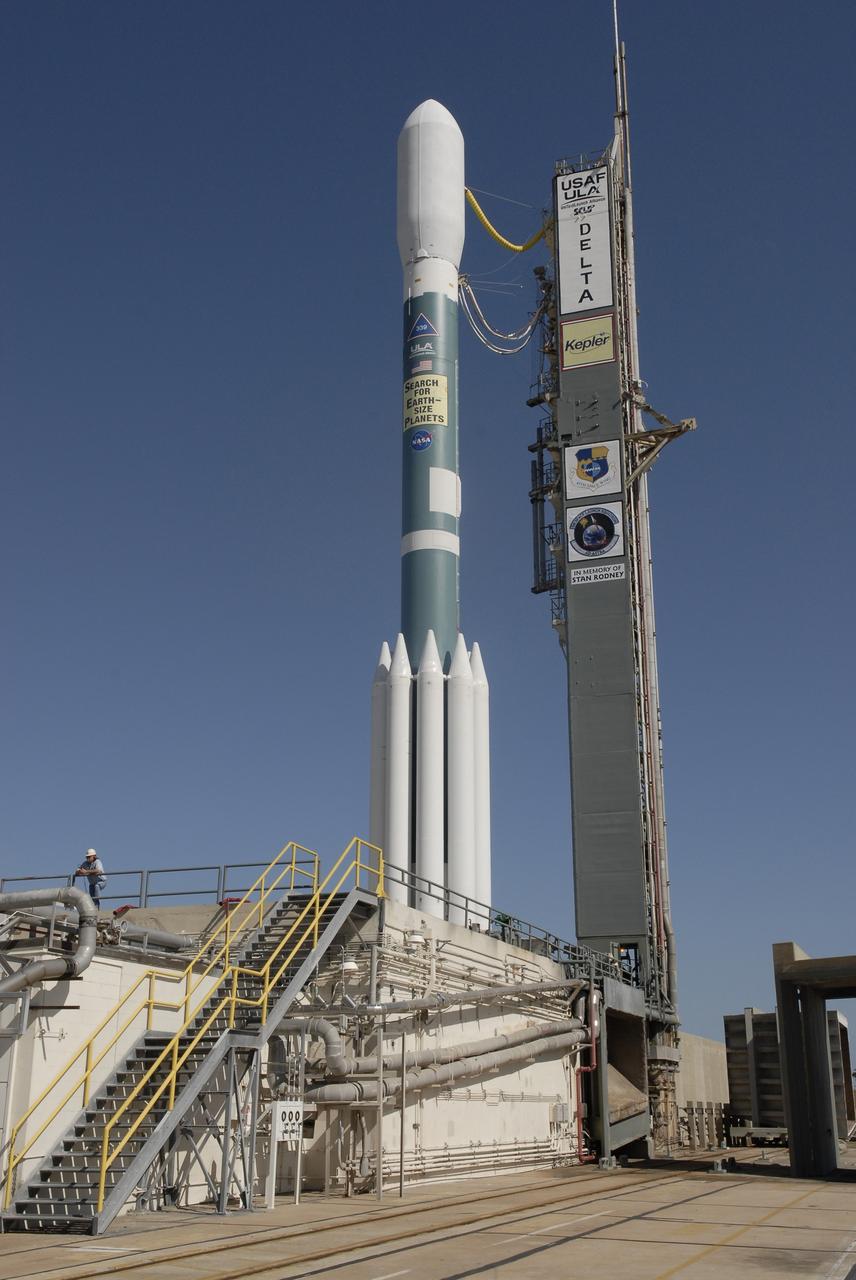

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
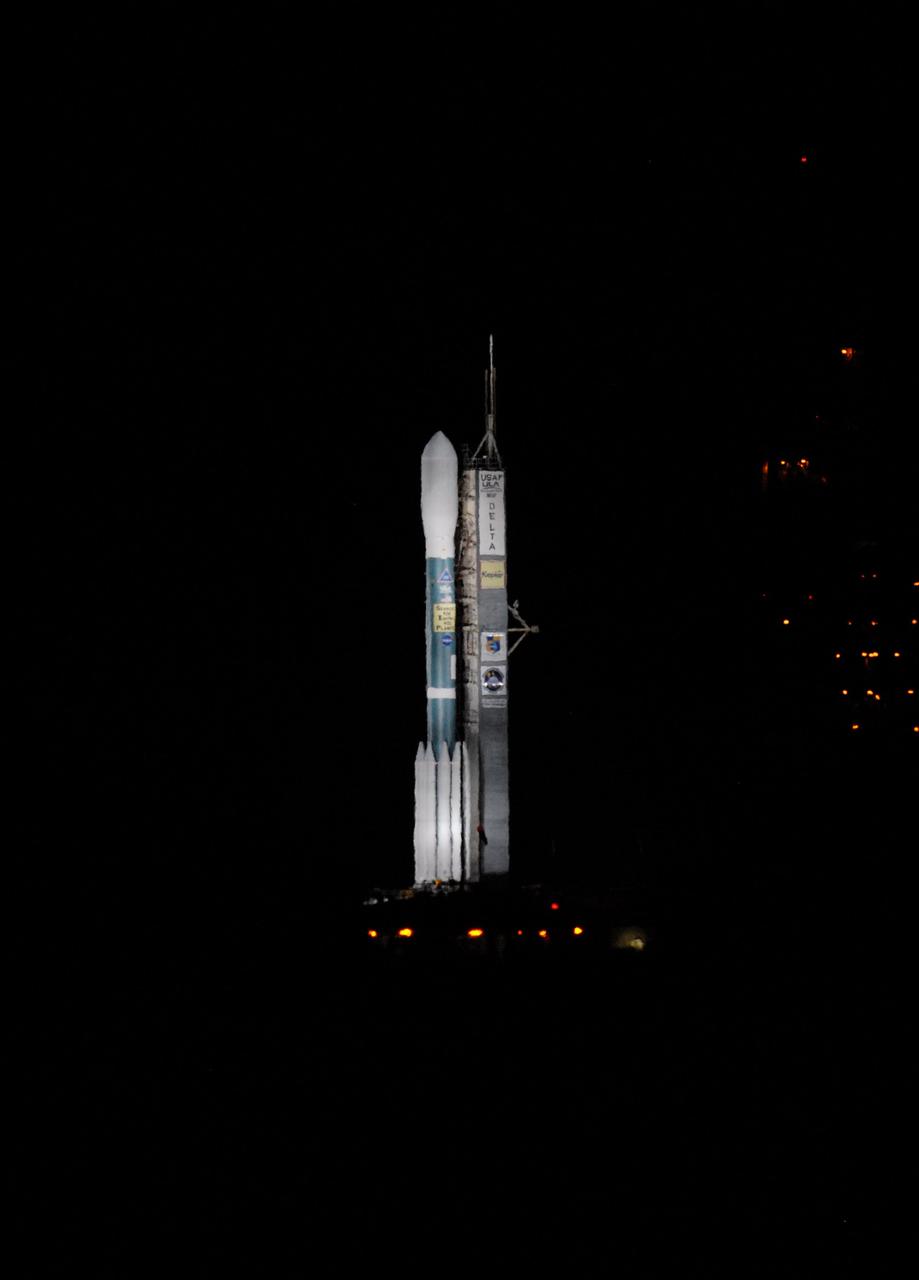

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket, with NASA's Kepler spacecraft aboard, is bathed in light on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida prior to launch. Liftoff is planned for 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
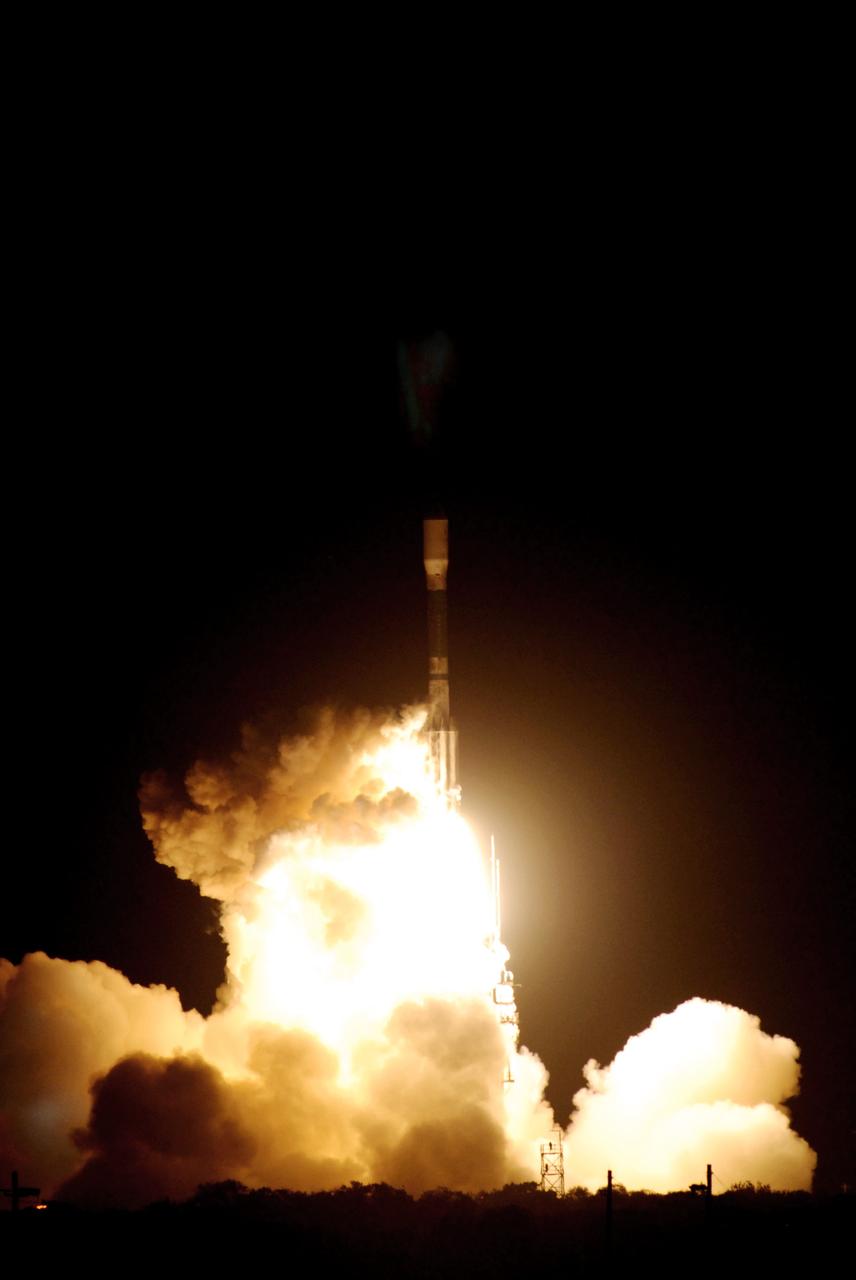

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket roars into the night sky carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
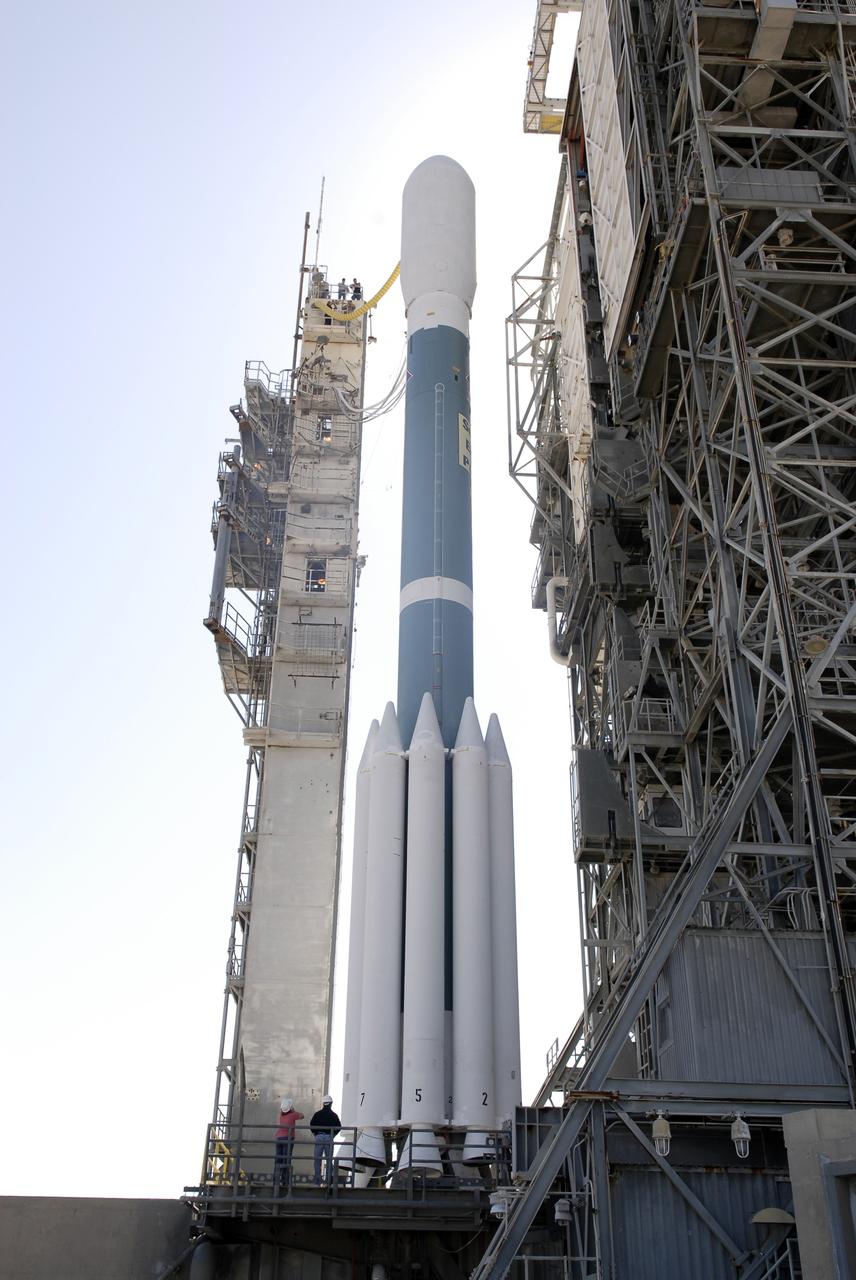

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
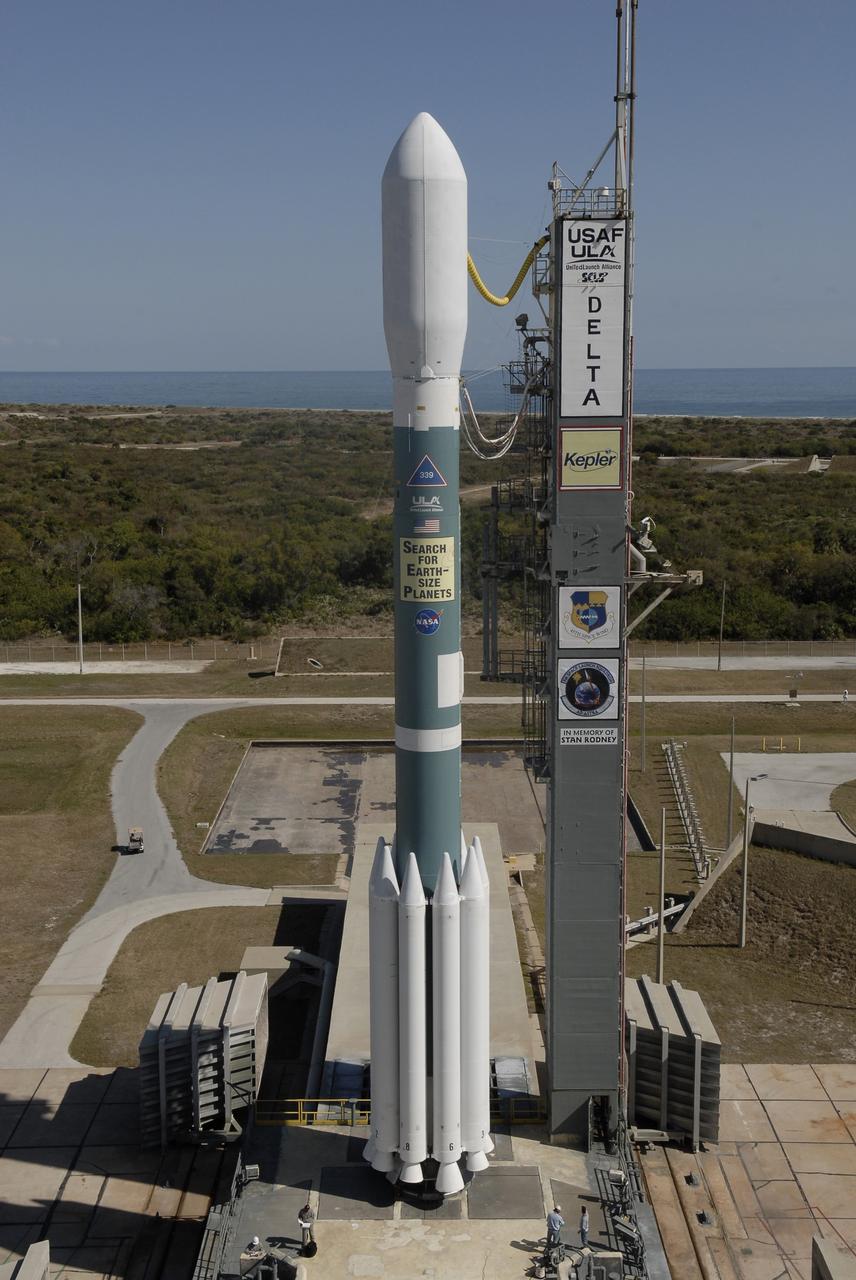

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B, in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, exhaust clouds cascade around the base of United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft as the rocket’s engines ignite. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph, Kevin O'Connell
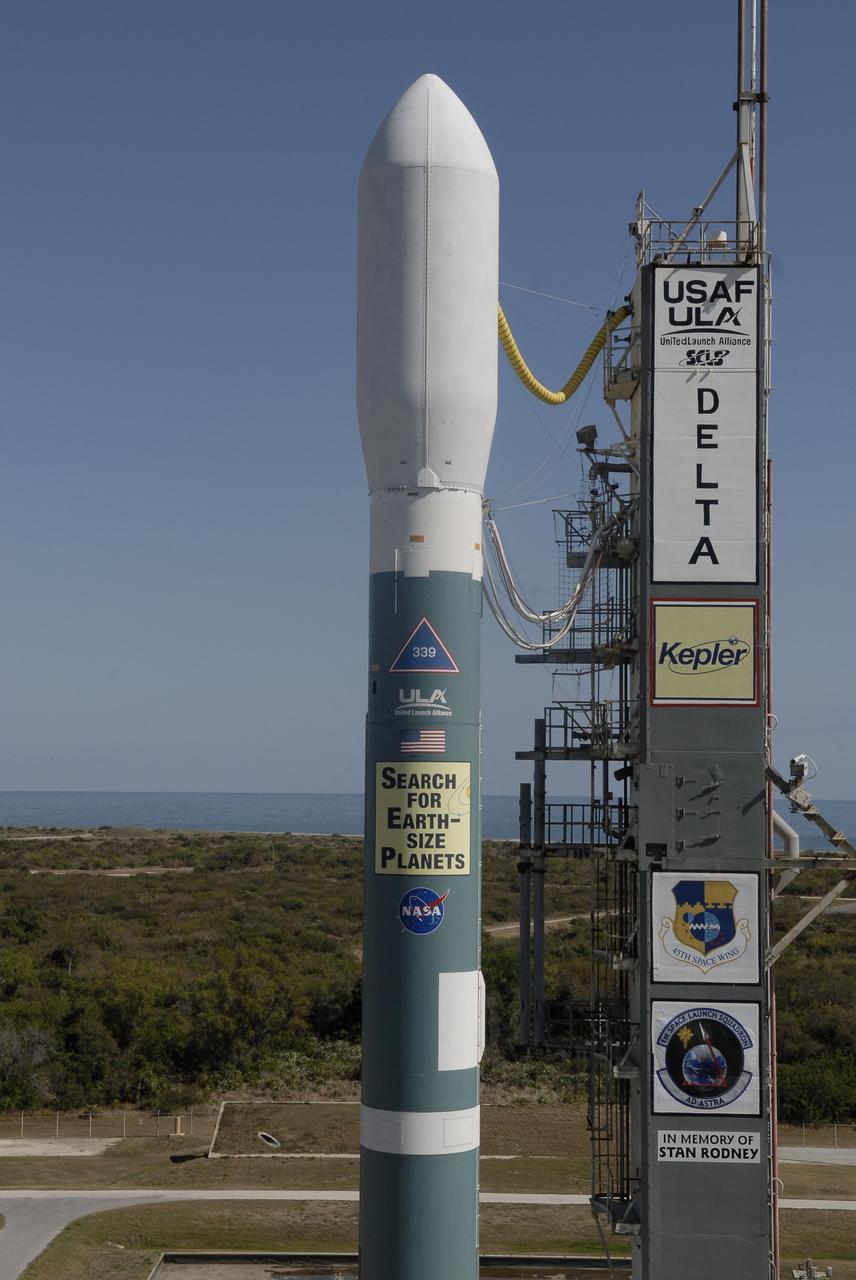

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Against the backdrop of the Atlantic Ocean, the Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
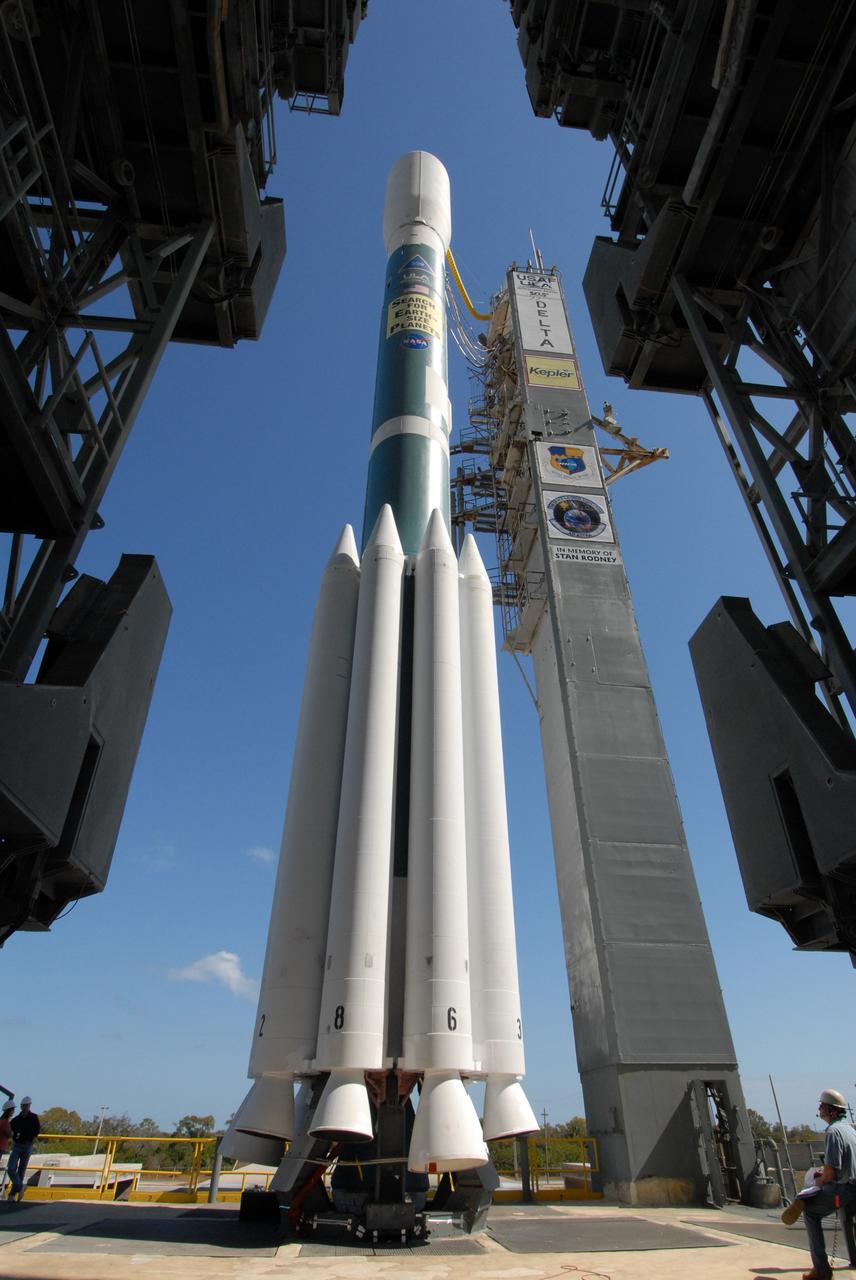

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
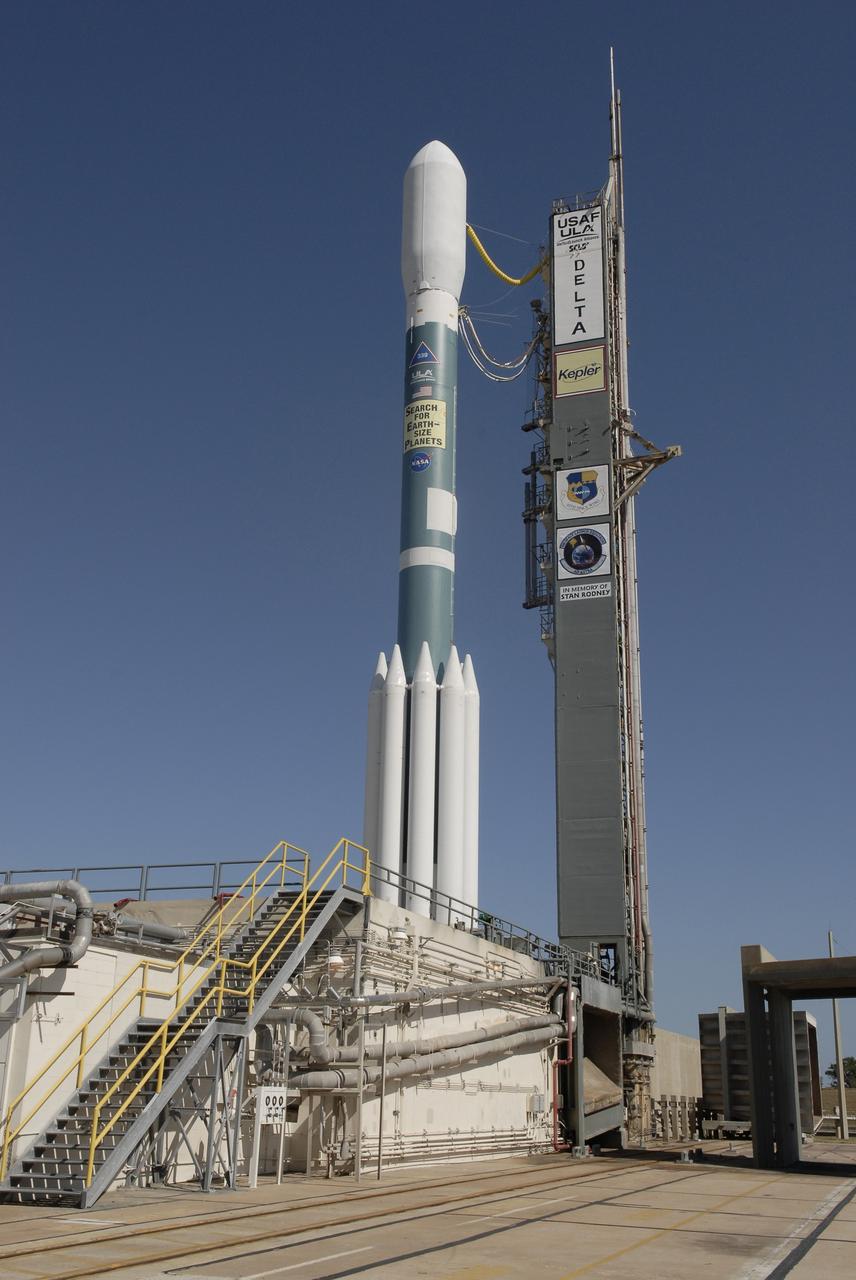

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The gantry on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida shows the various logos of NASA's Kepler spacecraft launch. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
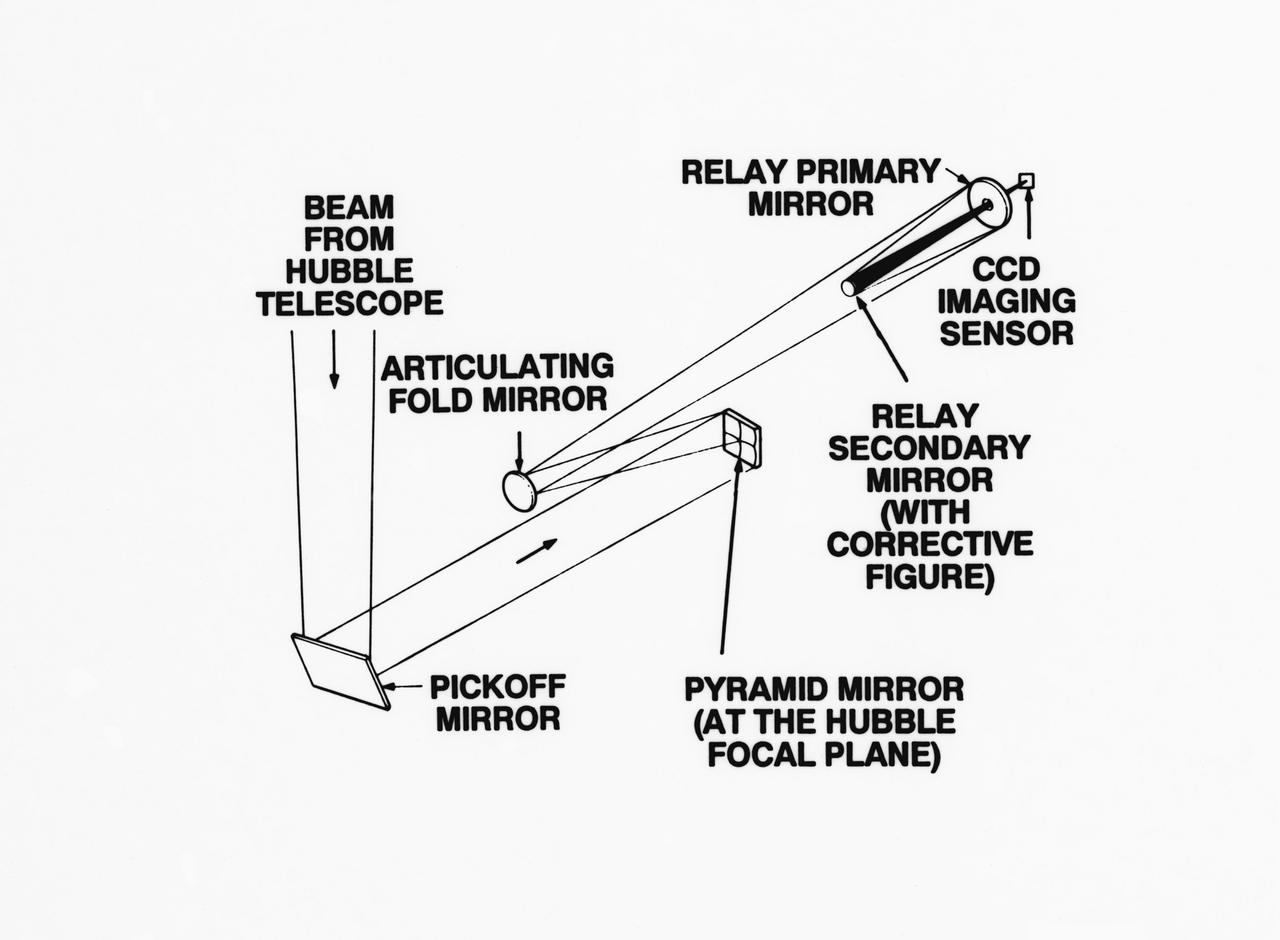
S93-33258 (15 Mar 1993) --- An optical schematic diagram of one of the four channels of the Wide Field\Planetary Camera-2 (WF\PC-2) shows the path taken by beams from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) before an image is formed at the camera's charge-coupled devices. A team of NASA astronauts will pay a visit to the HST later this year, carrying with them the new WF/PC-2 to replace the one currently on the HST. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California has been working on the replacement system for several months. See NASA photo S93-33257 for a close-up view of tiny articulating mirrors designed to realign incoming light in order to make certain the beams fall precisely in the middle of the secondary mirrors.
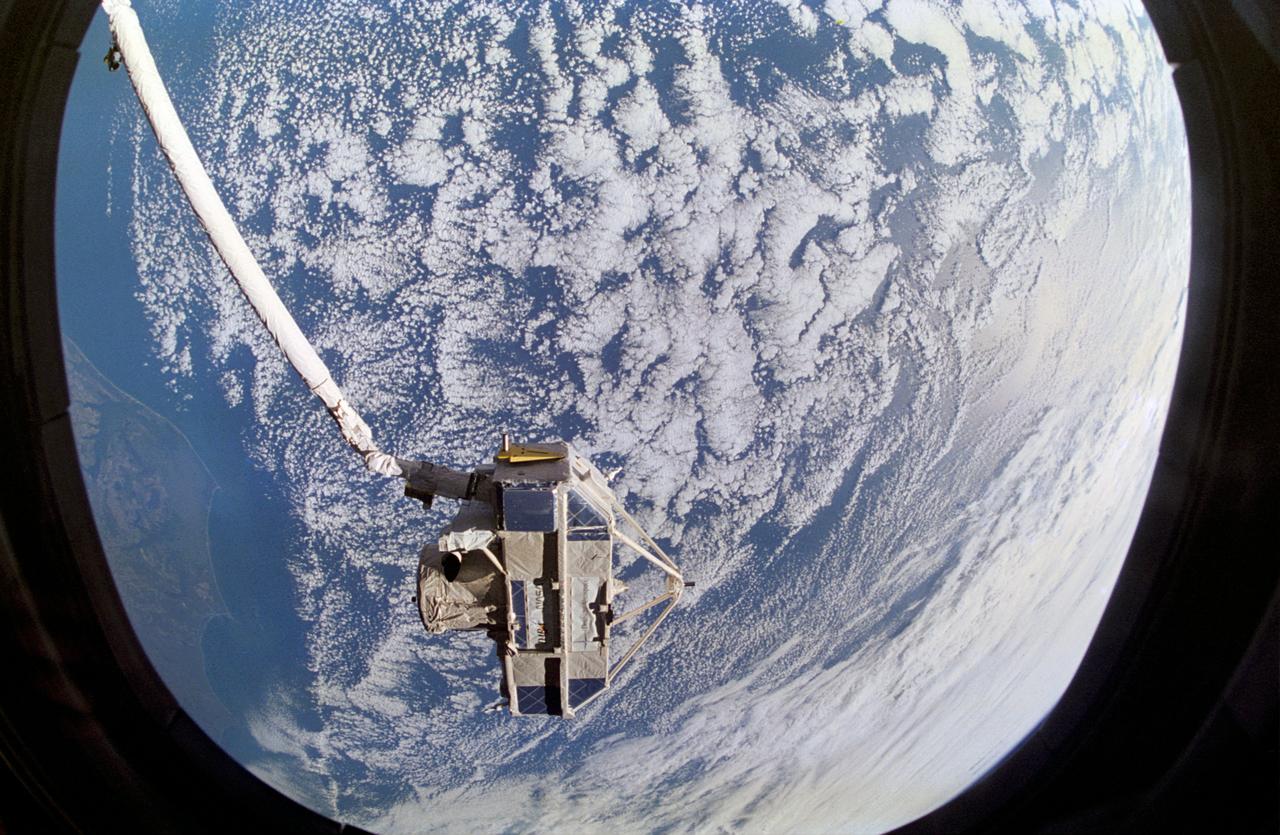

Clouds over the Atlantic Ocean serve as the backdrop for this 70mm scene of the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere (CRISTA), attached to the Shuttle Pallet System (SPAS). CRISTA-SPAS was in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Atlantis Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The crew deployed the Crista-SPAS on November 4, 1994 and the tandem remained in free-flight until November 12, 1994 when it was retrieved by the Canadian-built RMS, controlled by payload commander Ellen Ochoa.

Scientist-Astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot of the Skylab 3 mission, is stationed at the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM) console in the Multiple Docking Adapter of the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. From this console the astronauts actively control the ATM solar physics telescope.
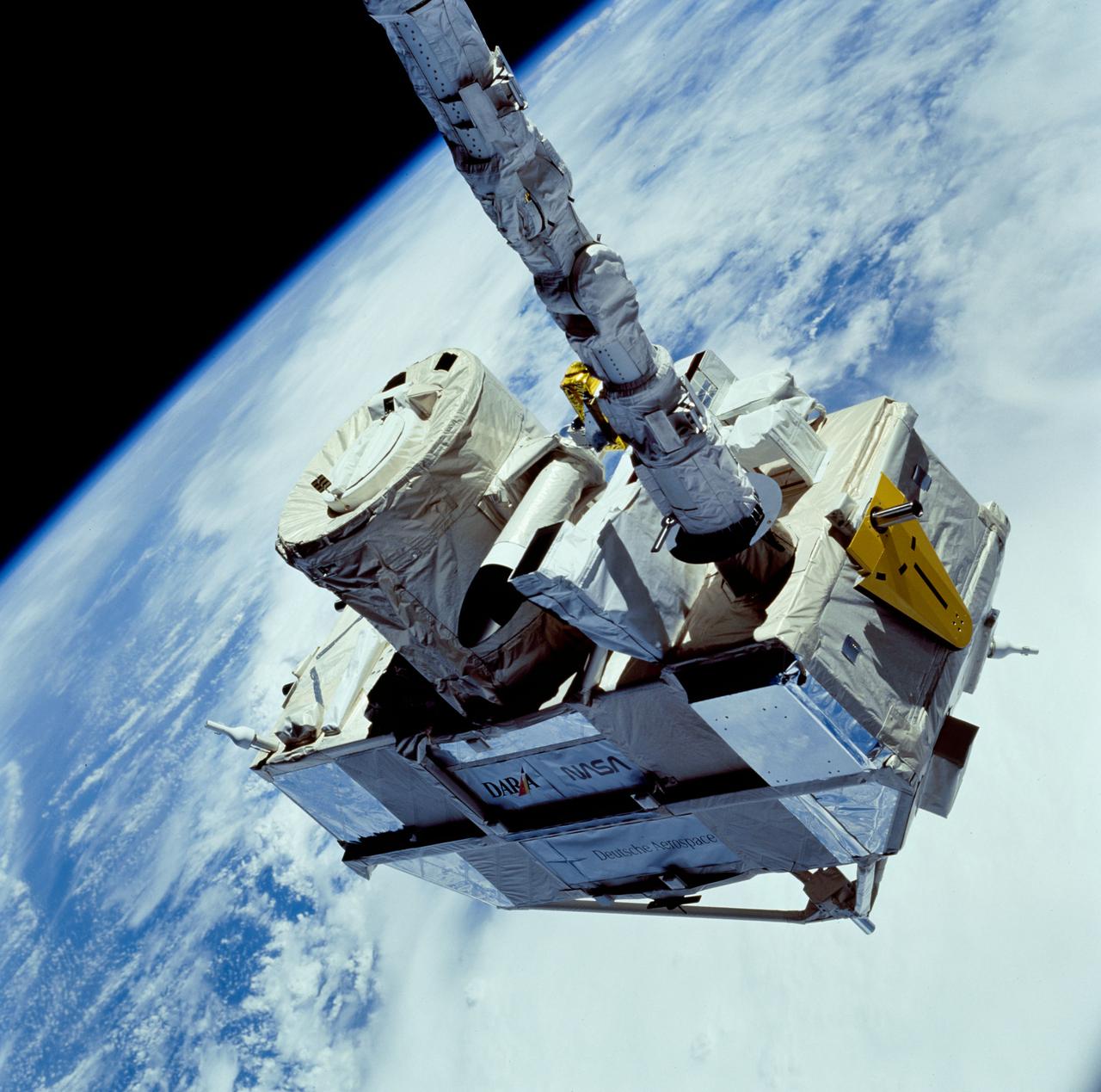

STS066-96-030 (3-14 Nov 1994) --- Masses of clouds serve as the backdrop for this close-up 70mm scene of the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere (CRISTA), attached to the Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS). CRISTA-SPAS was in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Atlantis' Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The crew deployed the CRISTA-SPAS on November 4, 1994 and the spacecraft remained in free-flight until November 12, 1994 when it was retrieved by the Canadian-built RMS, controlled by payload commander Ellen Ochoa. Other crew members onboard Atlantis were astronauts Donald R. McMonagle, Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Scott E. Parazynski and Joseph R. Tanner, along with Jean-Francois Clervoy of ESA. The six astronauts spent 11-days in Earth-orbit in support of the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.
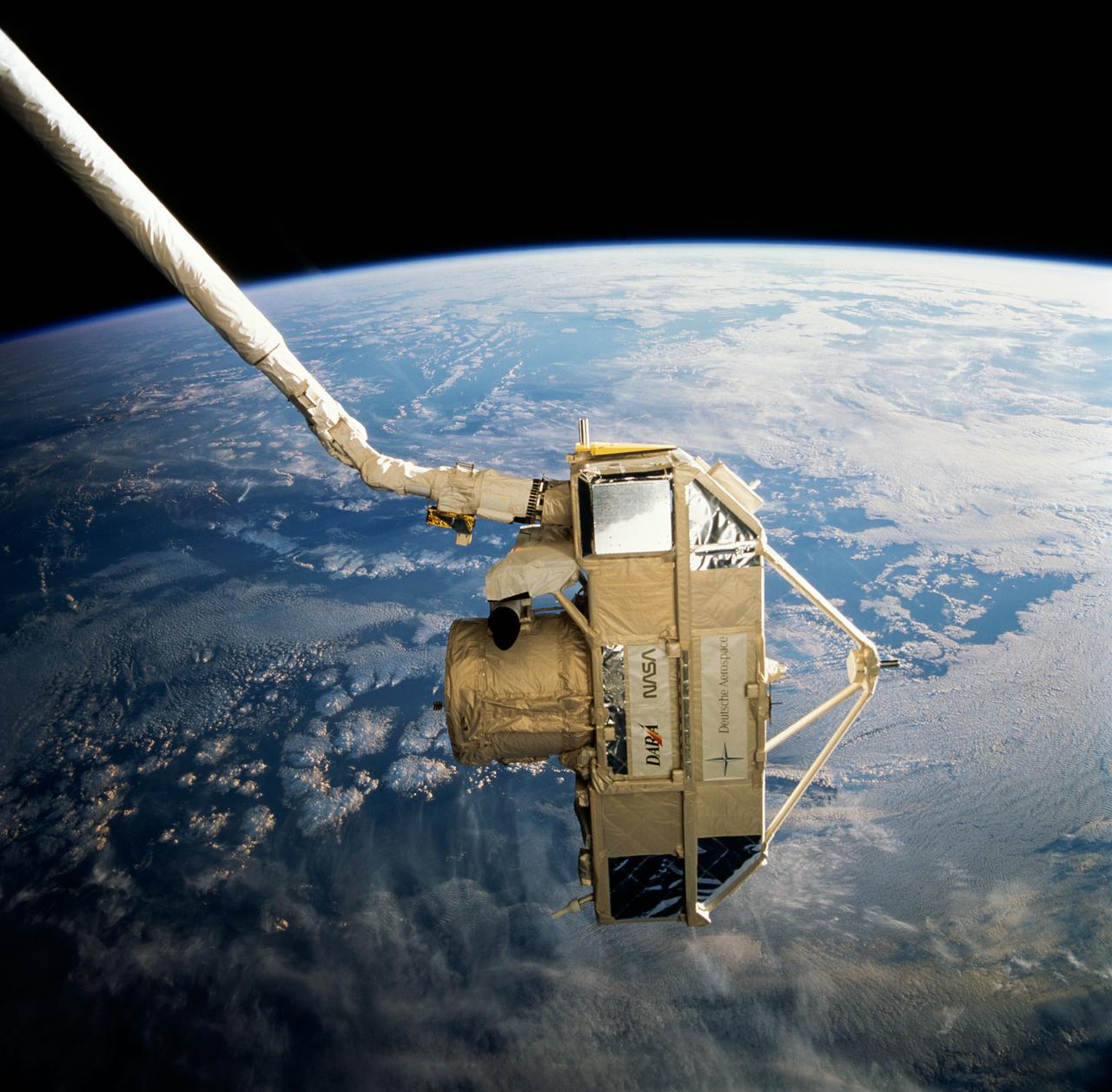

STS066-129-043 (3-14 Nov 1994) --- Clouds over the Atlantic Ocean serve as the backdrop for this 70mm scene of the Cryogenic Infrared Spectrometers and Telescopes for the Atmosphere (CRISTA), attached to the Shuttle Pallet System (SPAS). CRISTA-SPAS was in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Atlantis' Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. The crew deployed the CRISTA-SPAS on November 4, 1994 and the tandem remained in free-flight until November 12, 1994 when it was retrieved by the Canadian-built RMS, controlled by payload commander Ellen Ochoa. Other crew members onboard Atlantis were astronauts Donald R. McMonagle, Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Scott E. Parazynski and Joseph R. Tanner, along with Jean-François Clervoy of the European Space Agency (ESA). The six astronauts spent 11-days in Earth-orbit in support of the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.
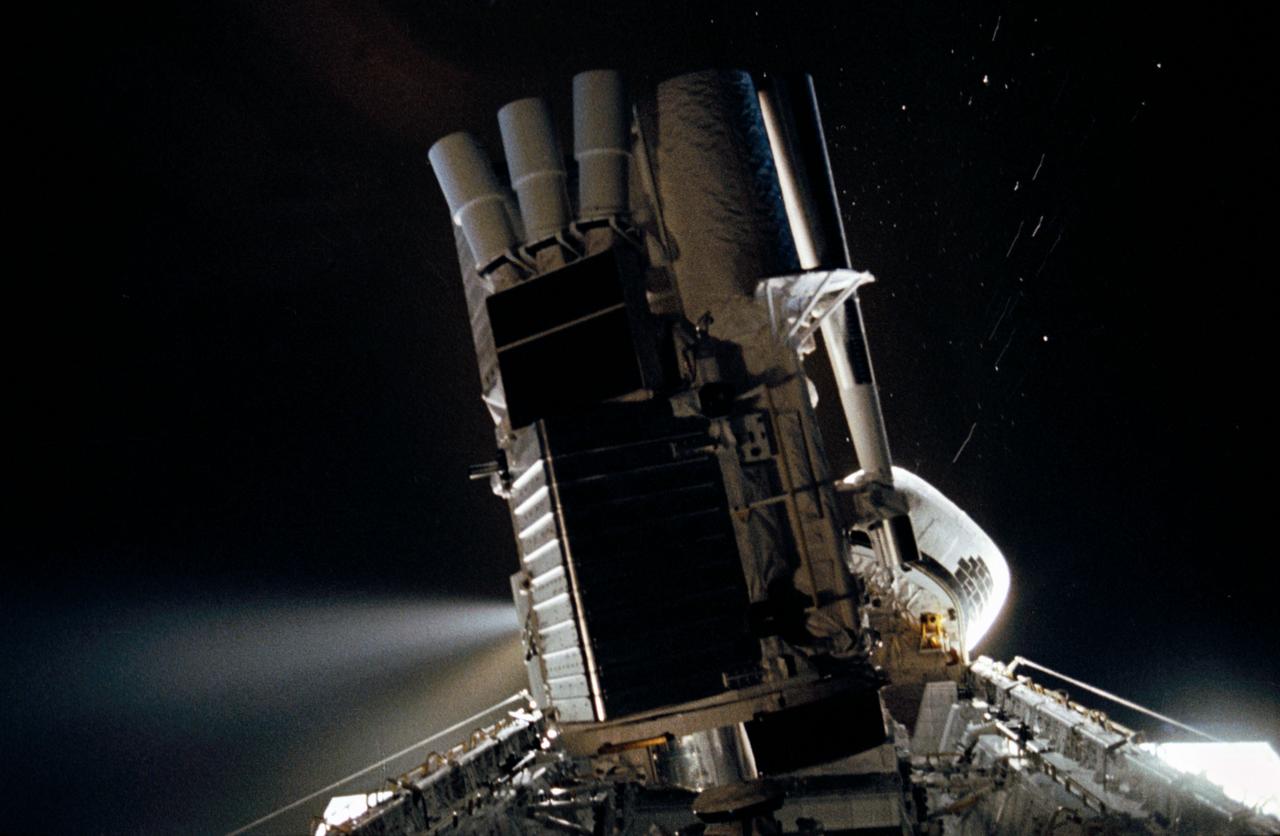
STS035-35-007 (2-10 Dec 1990) --- During the STS-35 mission, the Astronomy Laboratory 1 (ASTRO-1) payload, in its on-orbit operating configuration in the payload bay (PLB), is silhouetted against the firing of a reaction control system (RCS) jet. In the center of the frame, three ultraviolet telescopes are mounted and precisely co-aligned on a common structure, called the cruciform, that is attached to the instrument pointing system (IPS). Visible on the cruciform are Integrated Radiator System (IRS) (silver box on left), the Optical Sensor Package (OSP) (above IRS), the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT), and the star tracker (S TRK) (far right). A right RCS jet is fired during this maneuver of Columbia, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 102.
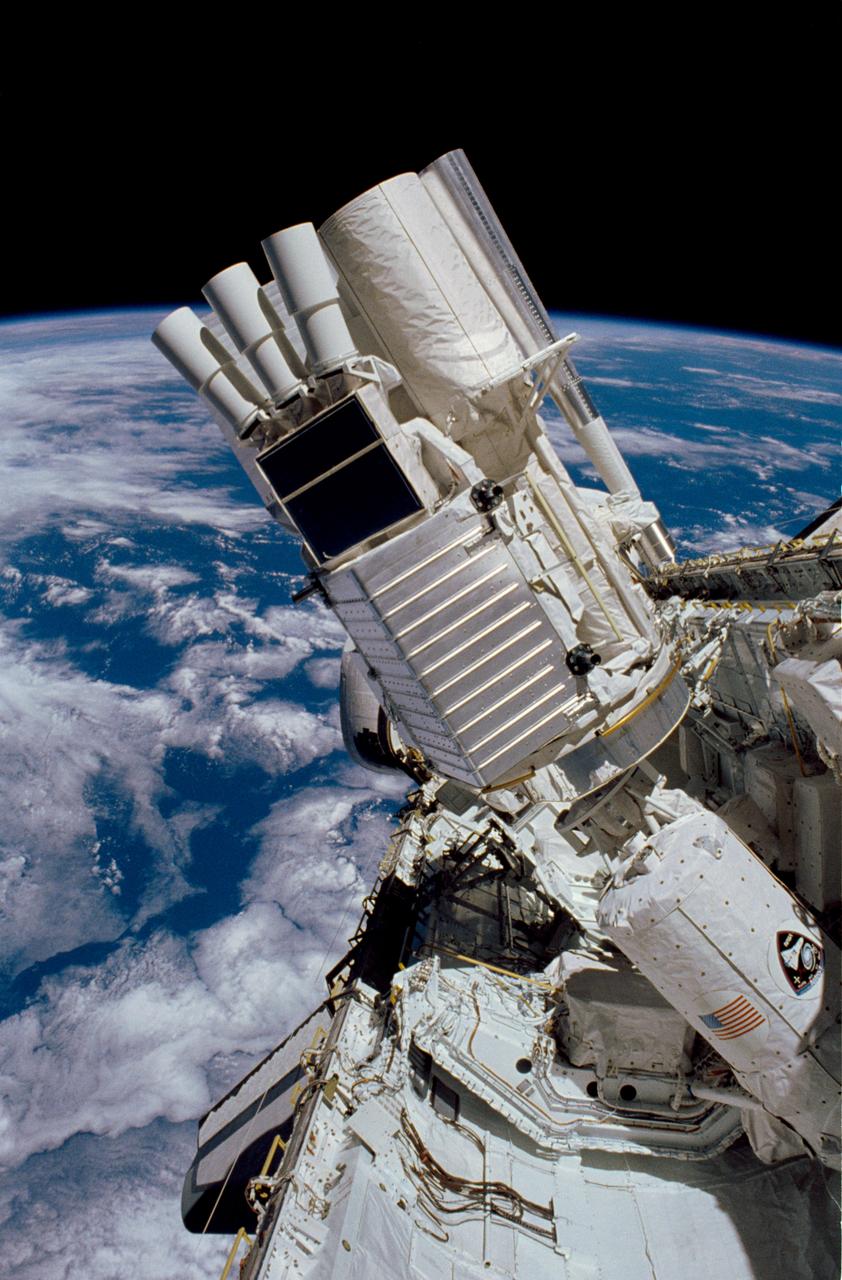

STS035-13-008 (2-10 Dec. 1990) --- The various components of the Astro-1 payload are seen backdropped against the blue and white Earth in this 35mm scene photographed through Columbia's aft flight deck windows. Parts of the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT) and the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE) are visible on the Spacelab Pallet in the foreground. The Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT) is behind this pallet and is not visible in this scene. The smaller cylinder in the foreground is the "Igloo," which is a pressurized container housing the Command and Data Management System, which interfaces with the in-cabin controllers to control the Instrument Pointing System (IPS) and the telescopes.
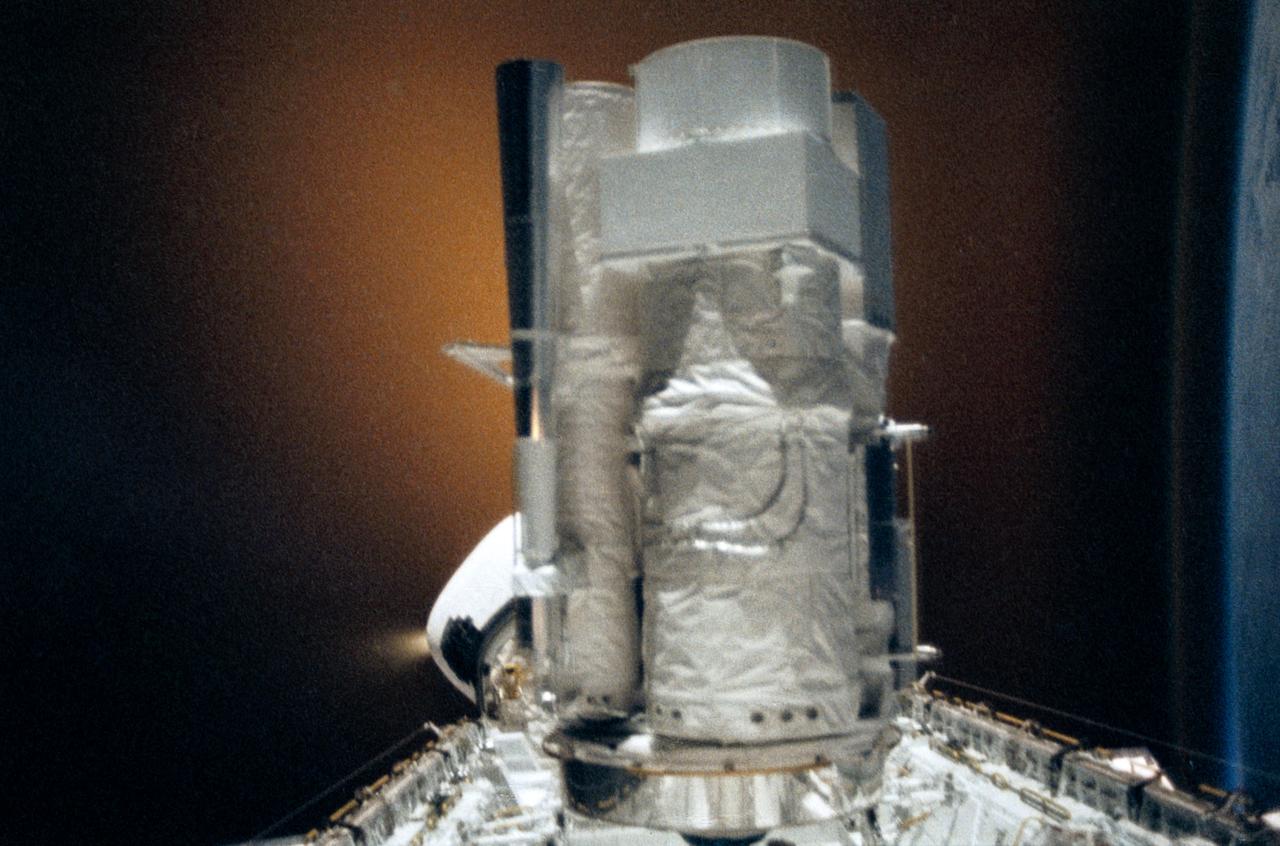
STS035-28-006 (2-10 Dec 1990) --- STS-35 Astronomy Laboratory 1 (ASTRO-1) telescopes, in on-orbit operating position in the payload bay (PLB), are silhouetted against an reaction control system (RCS) right thruster firing. Three ultraviolet telescopes are mounted and precisely co-aligned on a common structure, called the cruciform, that is attached to the instrument pointing system (IPS). Here the IPS holds the telescopes in a position that is parallel to the Earth's limb below. Visible on the cruciform are the star tracker (S TRK) (silver cone at the top), the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT) (behind S TRK), and the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope(HUT).