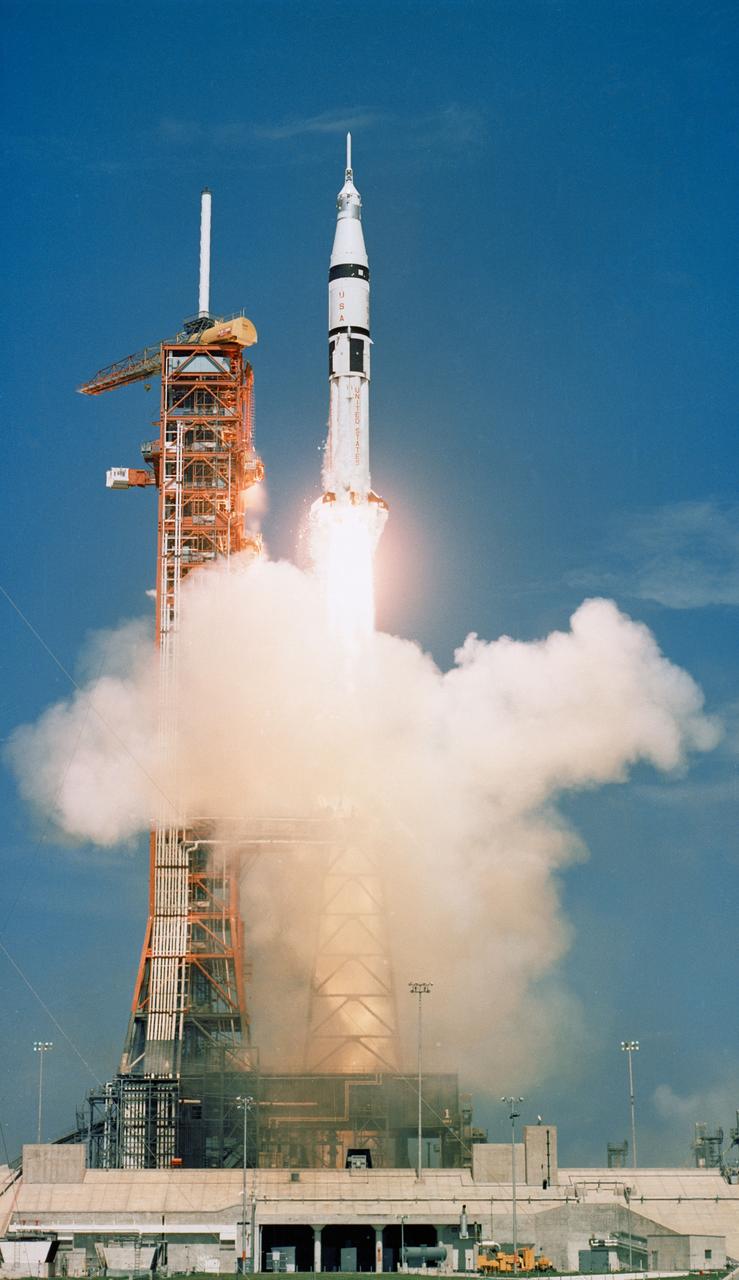

S75-28550 (15 July 1975) --- The Apollo-Soyuz Test Project's (ASTP) NASA Apollo/Saturn 1B space vehicle is launched from Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida, at 3:50 p.m. (EDT), July 15, 1975, to begin Apollo's catch-up journey toward the already Earth-orbiting Soviet Soyuz spacecraft. Aboard the Apollo spacecraft were astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand and Donald K. (Deke) Slayton.

S65-29639 (3 June 1965) --- The Gemini-Titan 4 (GT-4) spaceflight launches from Cape Kennedy's Pad 19 at 10:16 a.m. (EST) on June 3, 1965. The GT-4 spacecraft carried astronauts James A. McDivitt, command pilot, and Edward H. White II, pilot, on a four-day, 62-revolution mission.
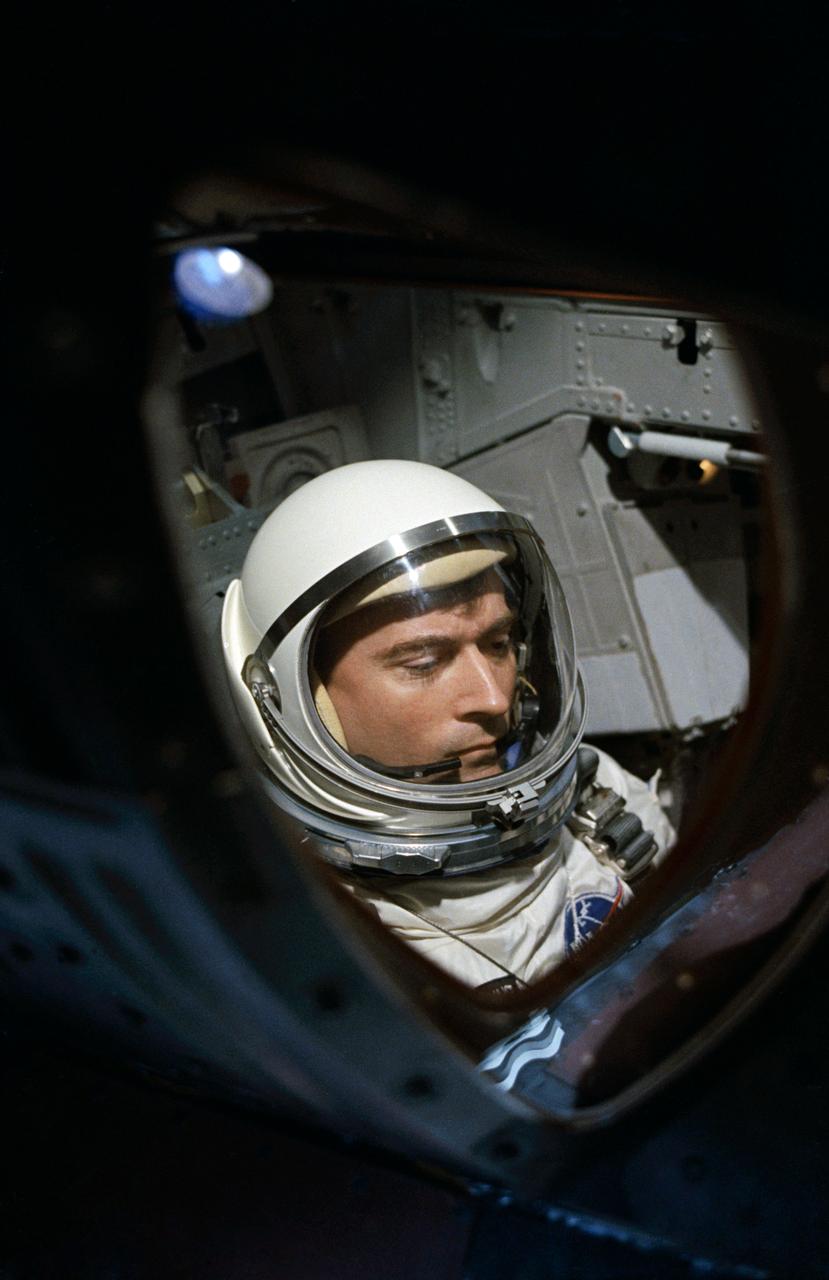

View of Astronaut John W. Young through spacecraft window prior to launch of Gemini-Titan 3 mission.

View of Astronaut Virgil I. Grissom through spacecraft window prior to launch of Gemini-Titan 3 mission.

NASA Juno spacecraft awaits launch from inside the payload fairing atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V-551 launch vehicle. Juno and its rocket are at Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
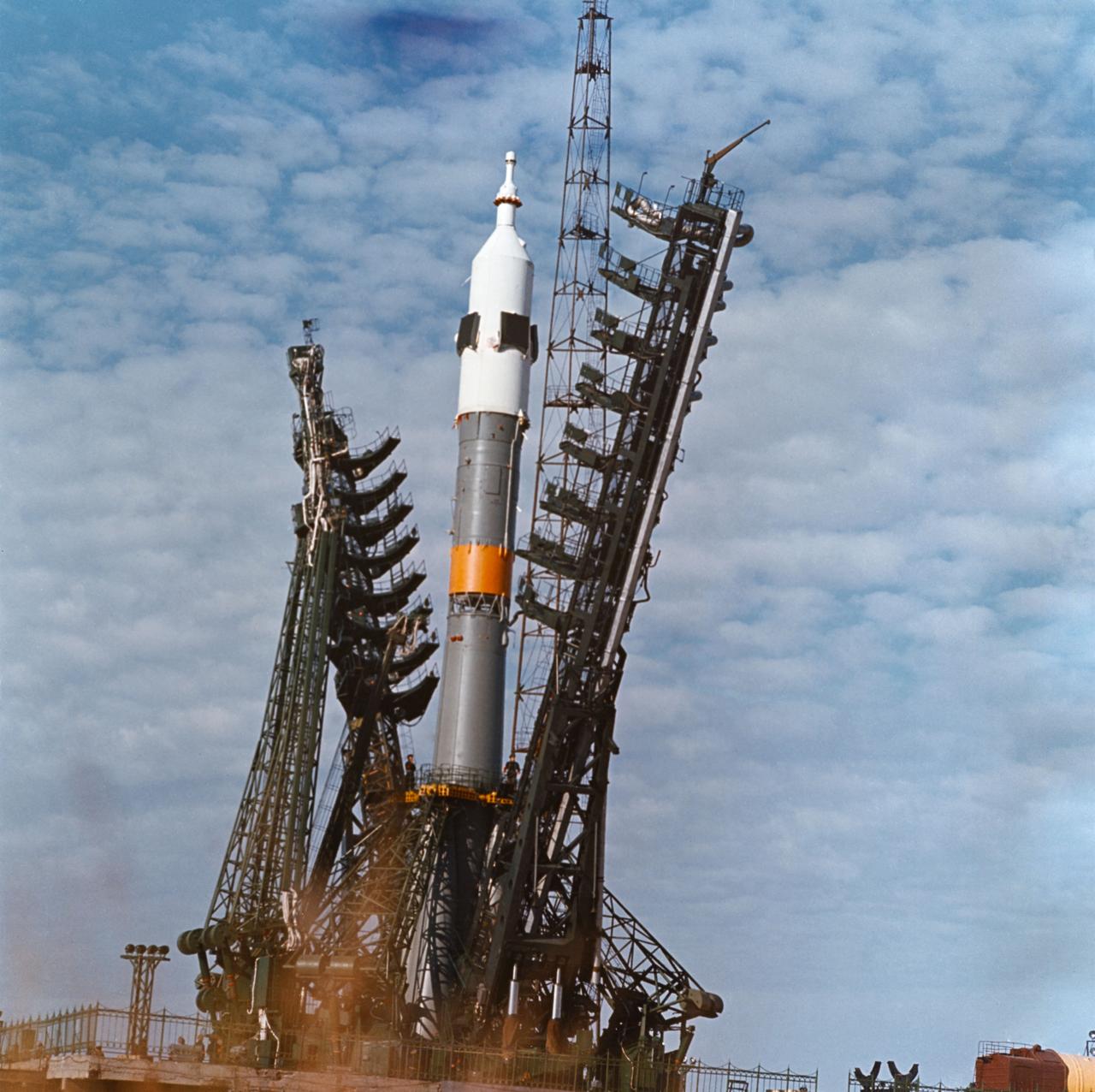

S75-32339 (28 Jan. 1974) --- A low-angle view of a launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan showing the installation of a Soyuz spacecraft and its launch vehicle. The 49.3-meter-high (162 feet) space vehicle is composed of the three-stage booster, a three-module, two-man Soyuz spacecraft and a launch escape system. The weight of the space vehicle at launch is approximately 300,000 kilograms. The first stage vacuum thrust is about 1,000,400 newtons, the second stage is 956,500 newtons, and the third stage is 299,000 newtons. This earlier Soyuz mission illustrates the approximate launch configuration of the Soviet Union?s Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) Soyuz space vehicle. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
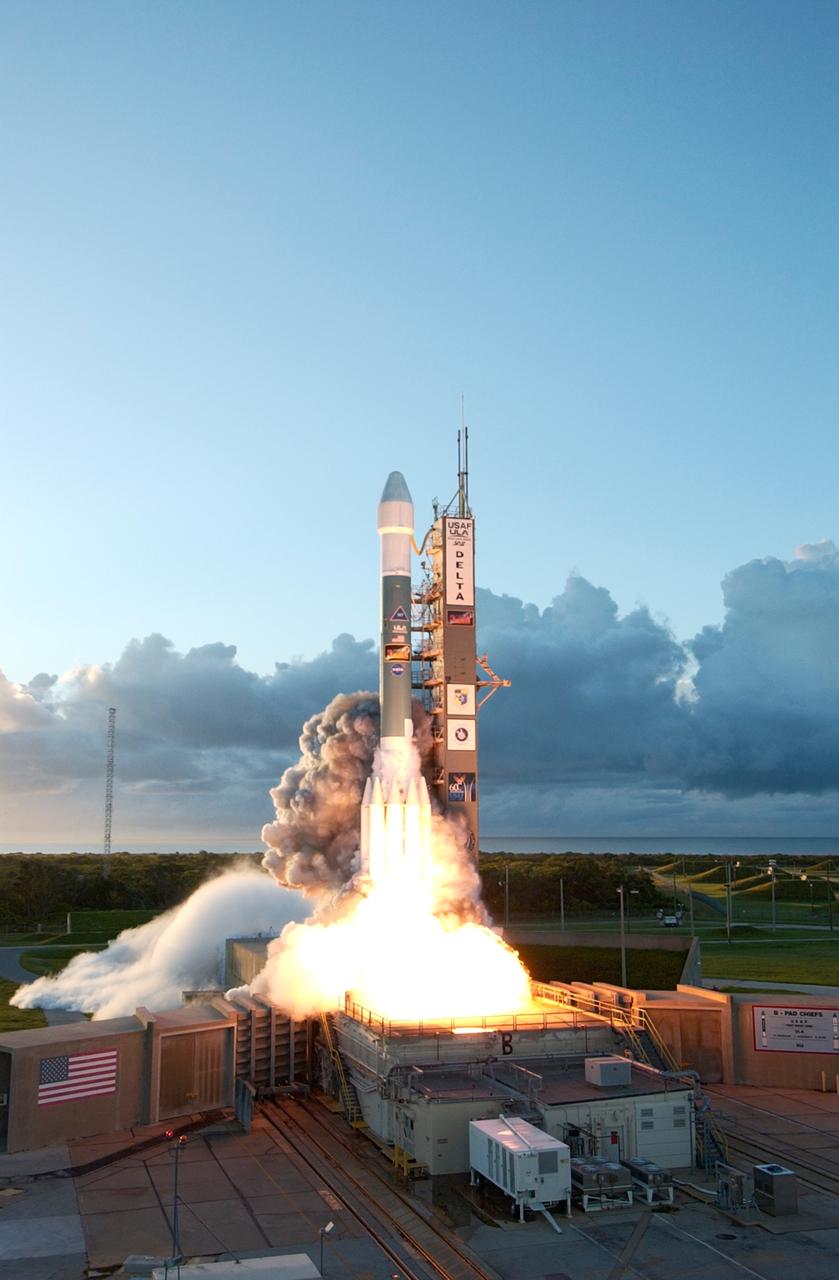

Against a backdrop of clouds on the horizon, the Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Dawn spacecraft rises from the smoke and fire on the launch pad to begin its 1.7-billion-mile journey through the inner solar system to study a pair of asteroids. Liftoff was at 7:34 a.m. EDT from Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Dawn is the ninth mission in NASA's Discovery Program. The spacecraft will be the first to orbit two planetary bodies, asteroid Vesta and dwarf planet Ceres, during a single mission. Vesta and Ceres lie in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. It is also NASA's first purely scientific mission powered by three solar electric ion propulsion engines.
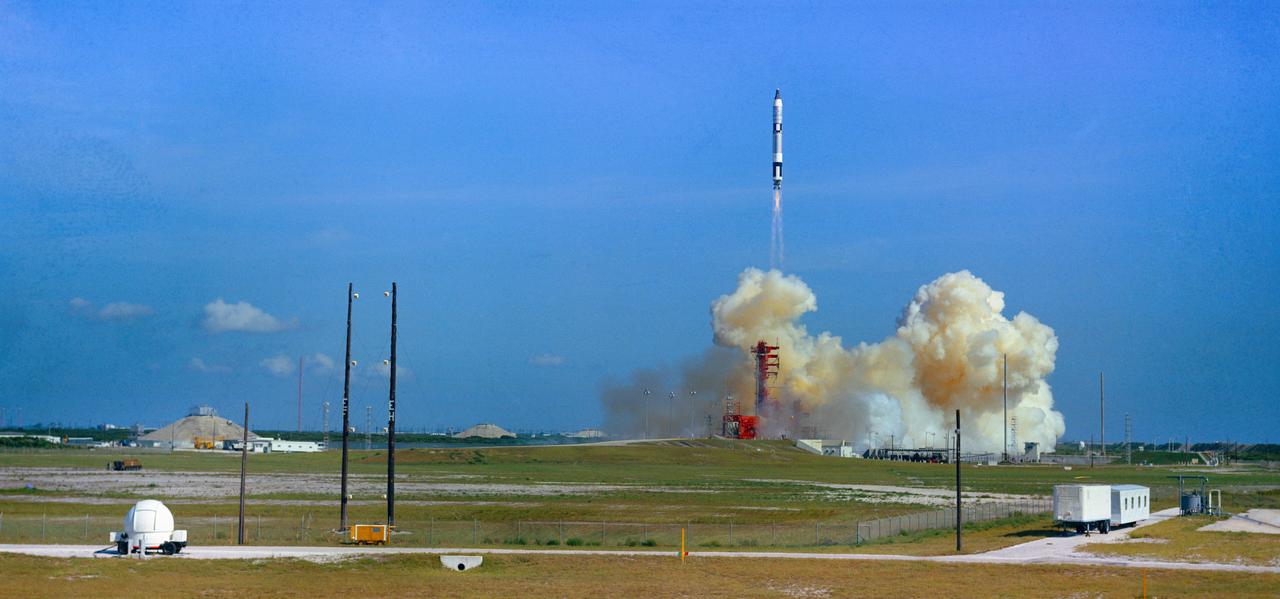

S65-50774 (21 Aug. 1965) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration launched the Gemini-5 spacecraft from Pad 19 at 9 a.m. (EST) Aug. 21, 1965, on a planned eight-day orbital mission. Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper Jr. was the command pilot; and astronaut Charles Conrad Jr. was the pilot. A full duration mission will achieve the longest manned spaceflight to date.

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
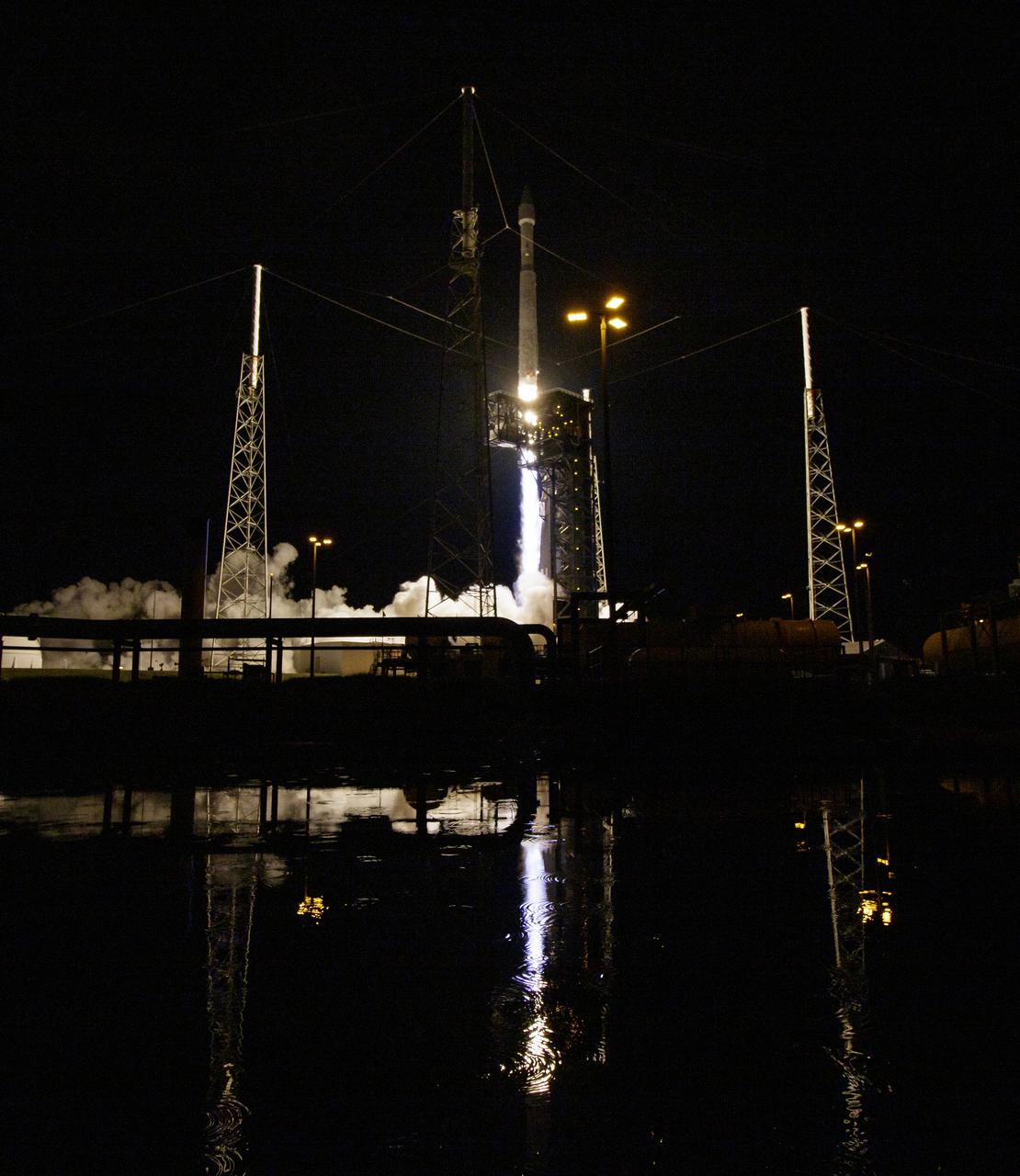

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
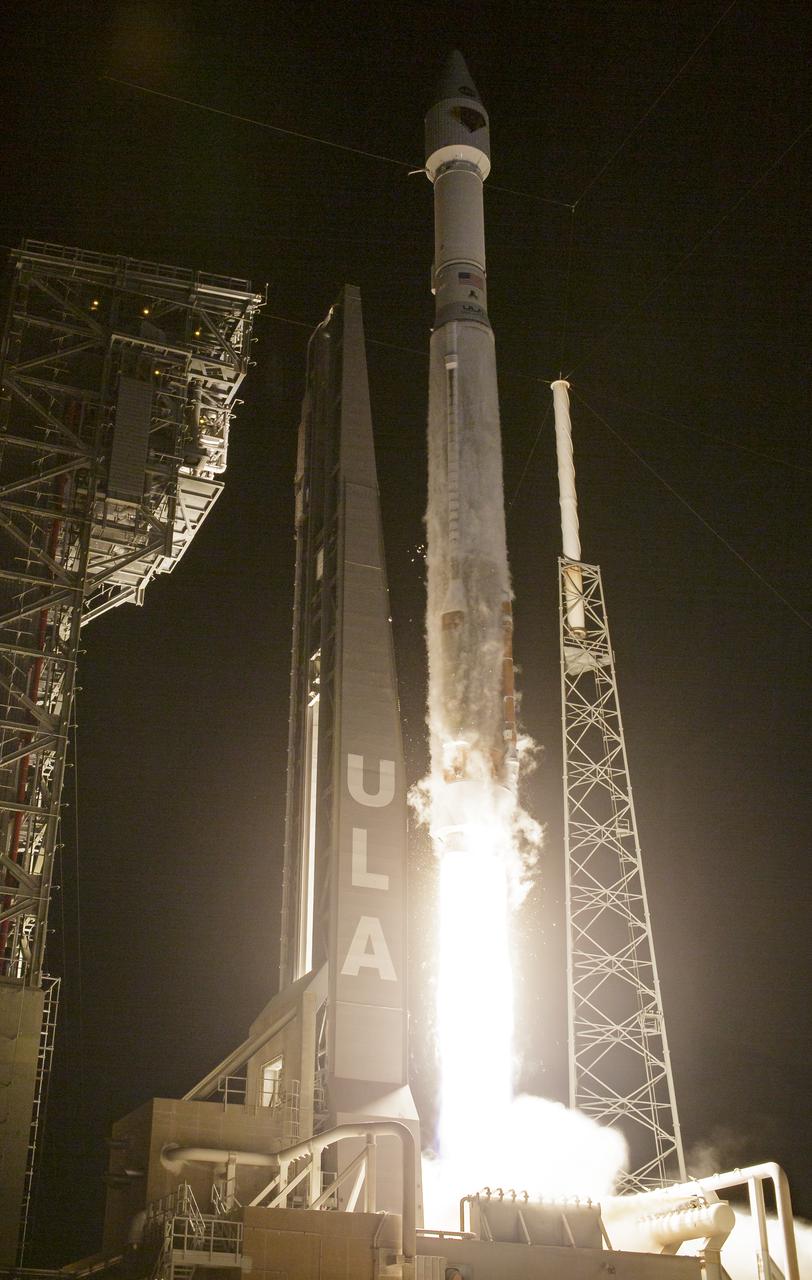

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
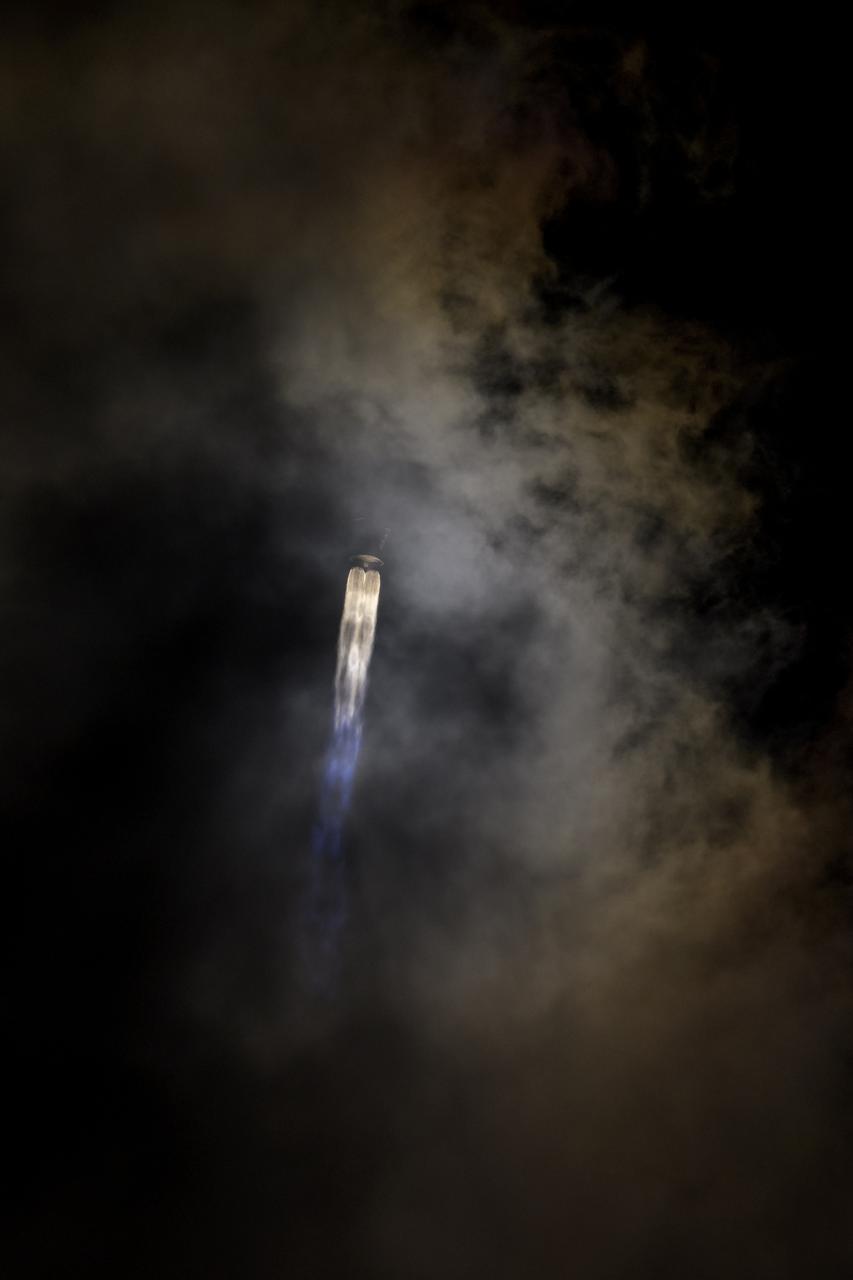

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
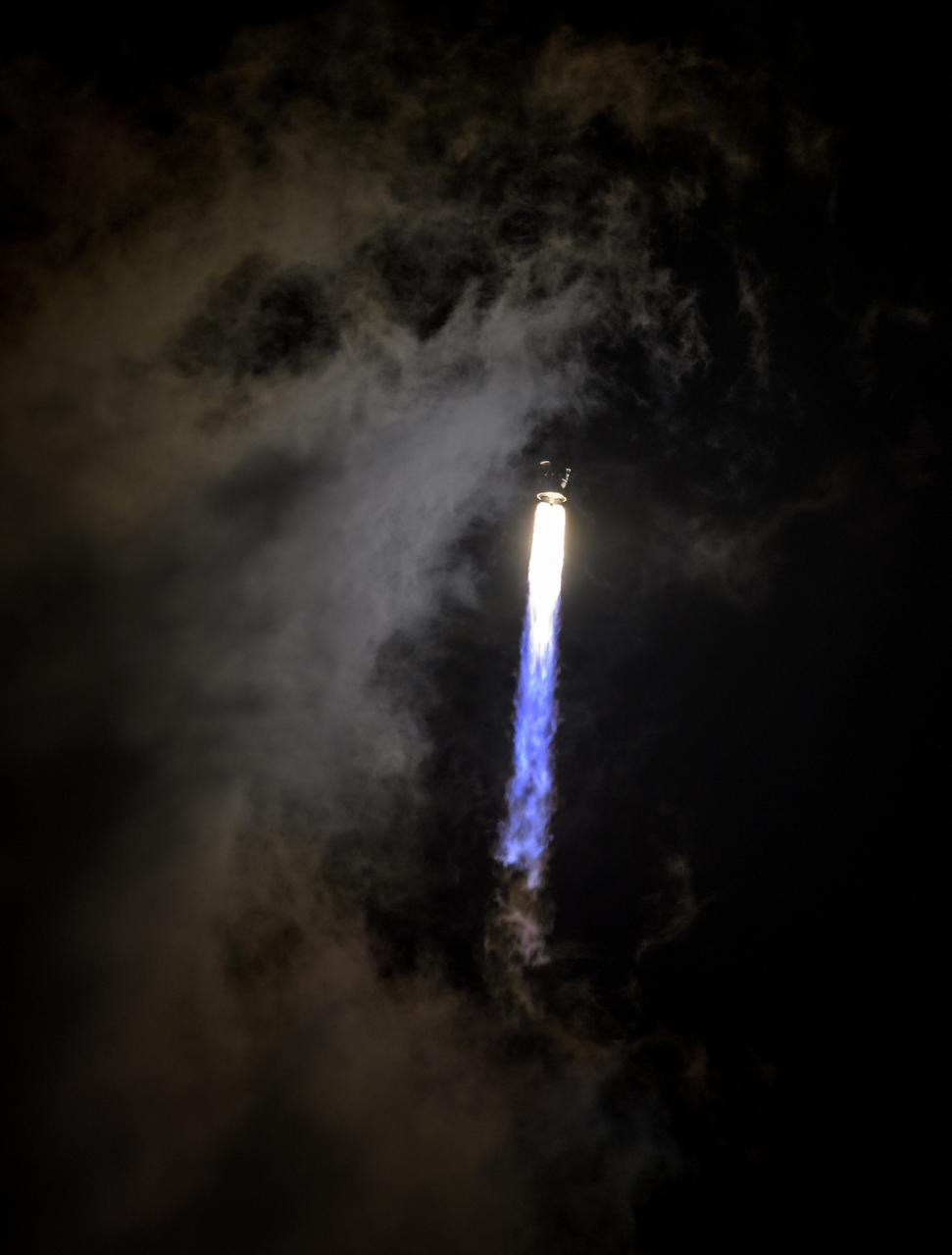

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
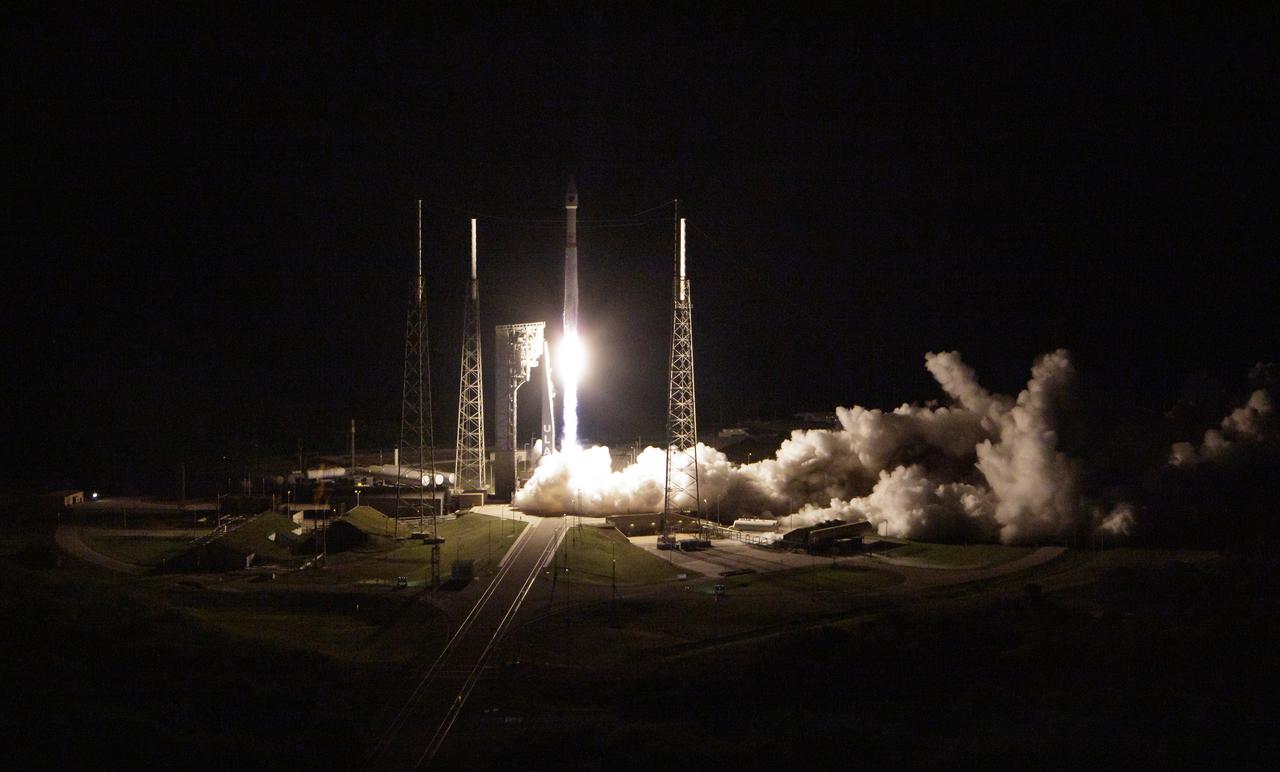

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
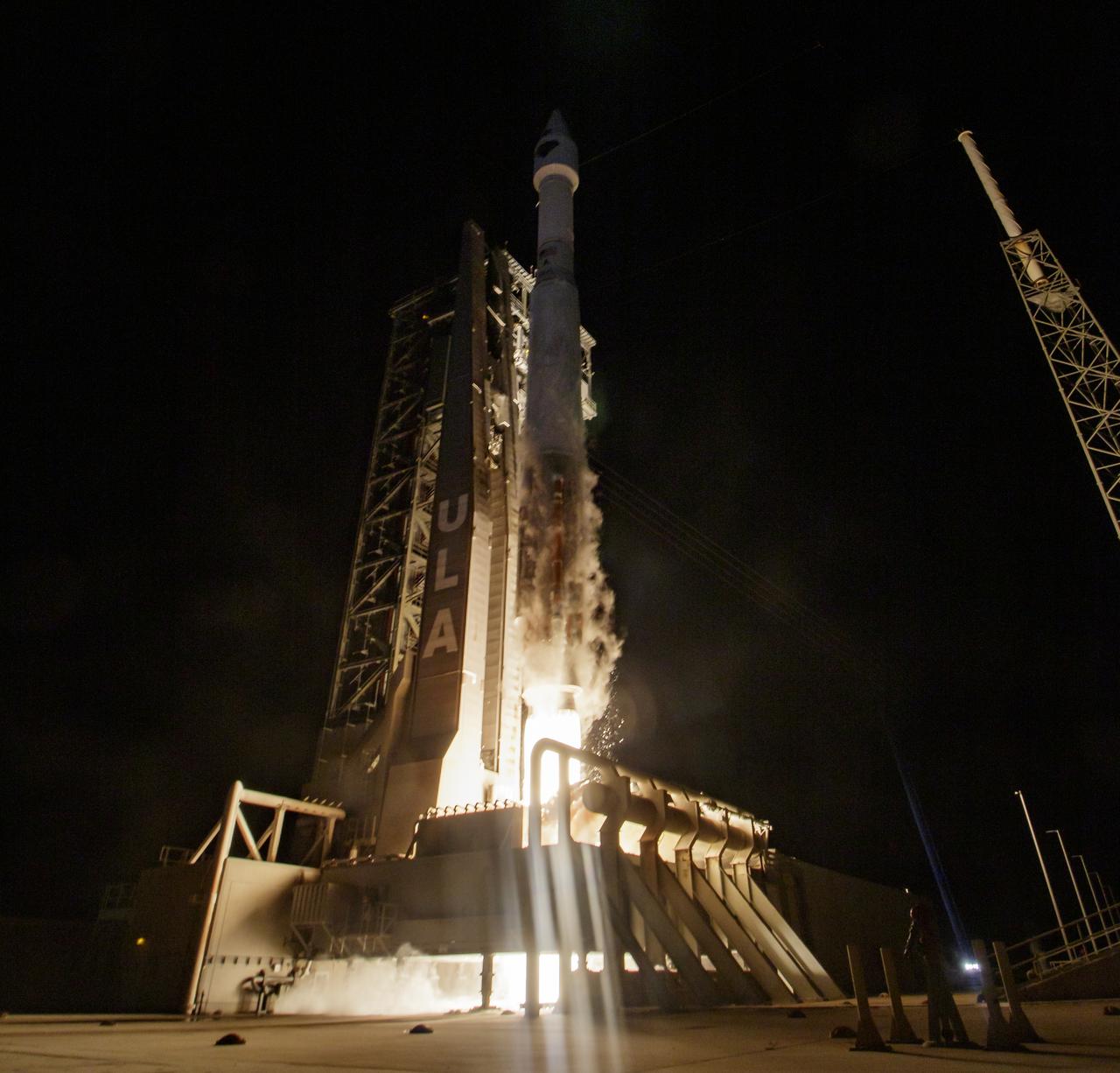

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
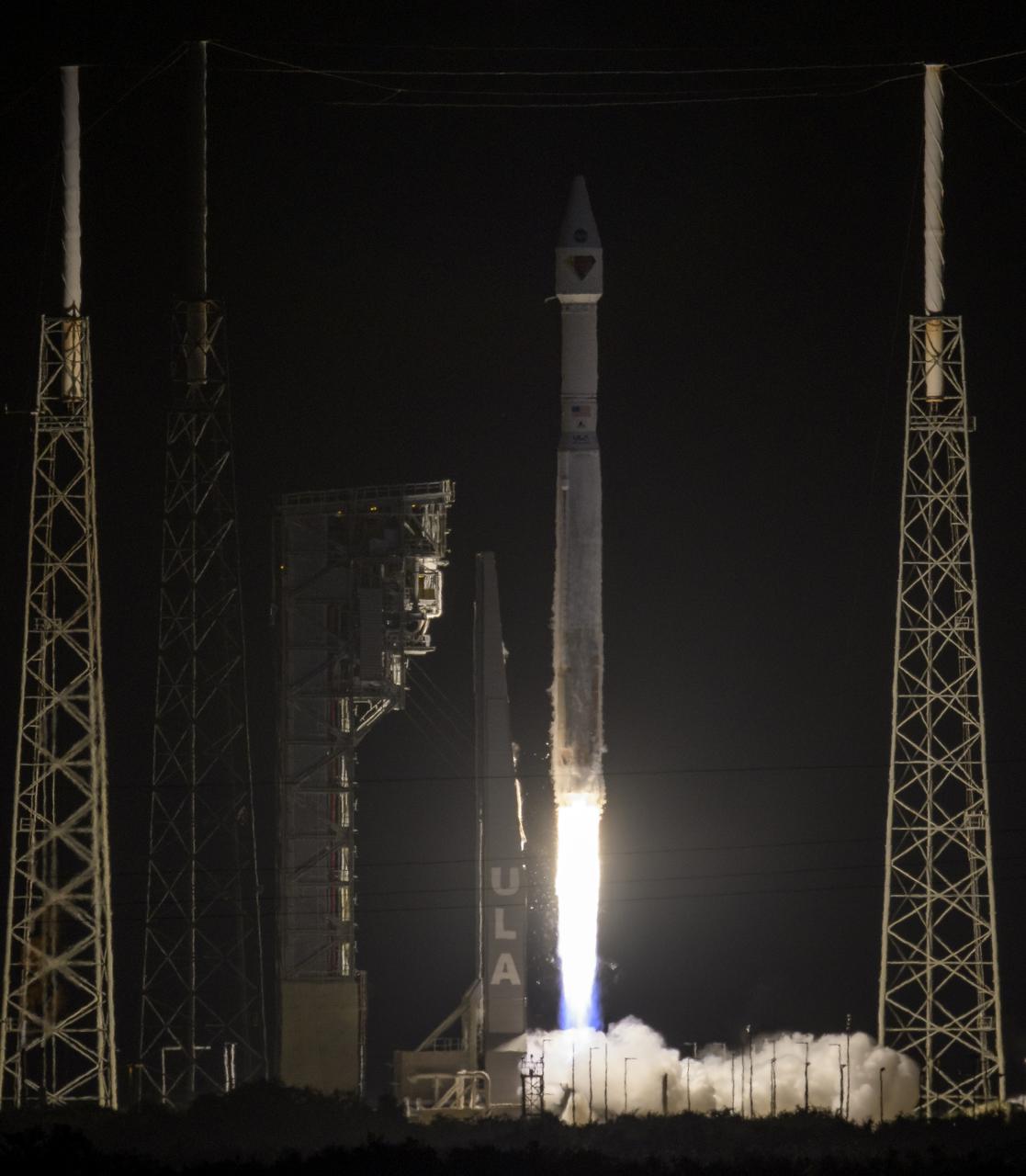

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
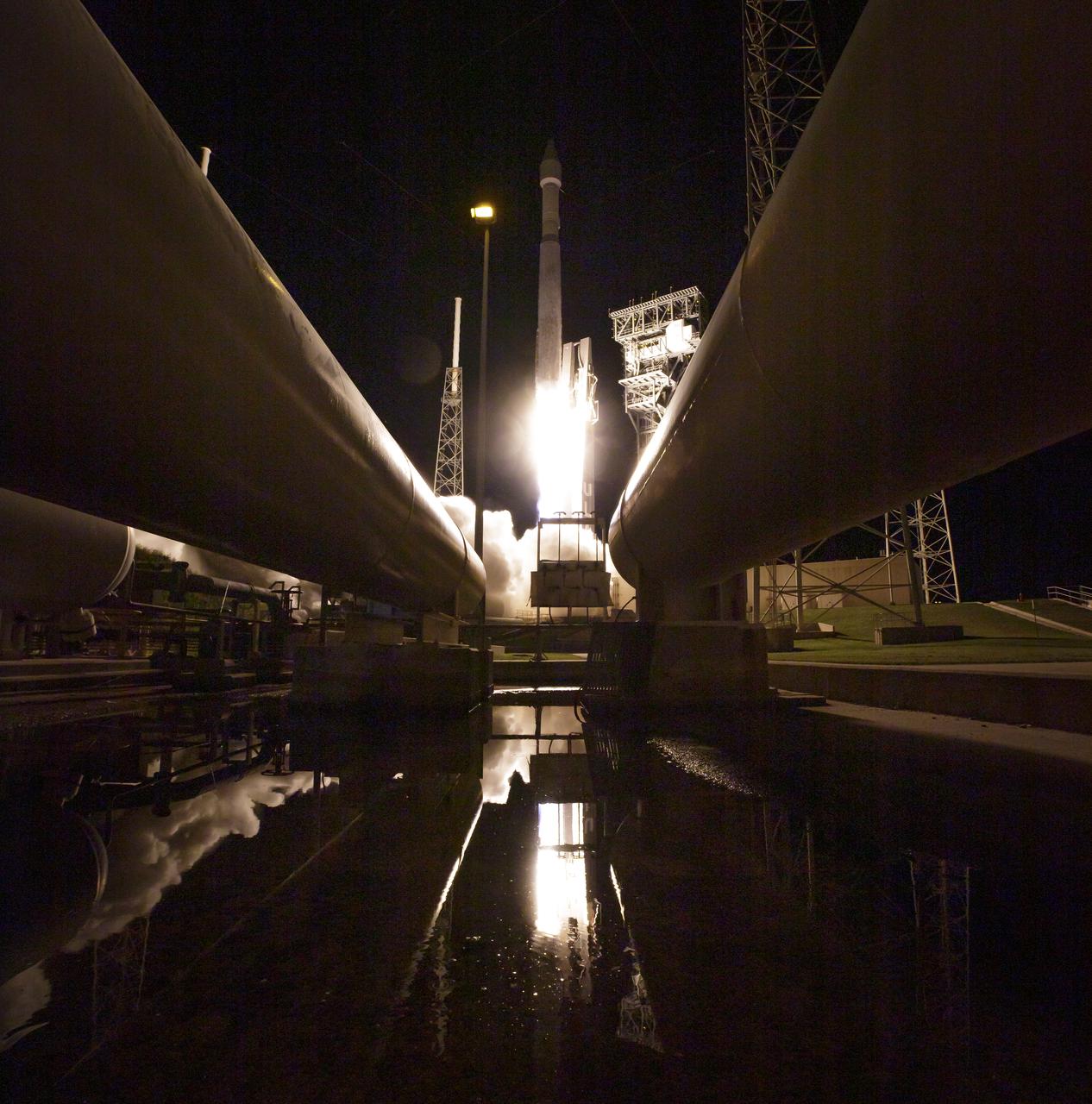

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
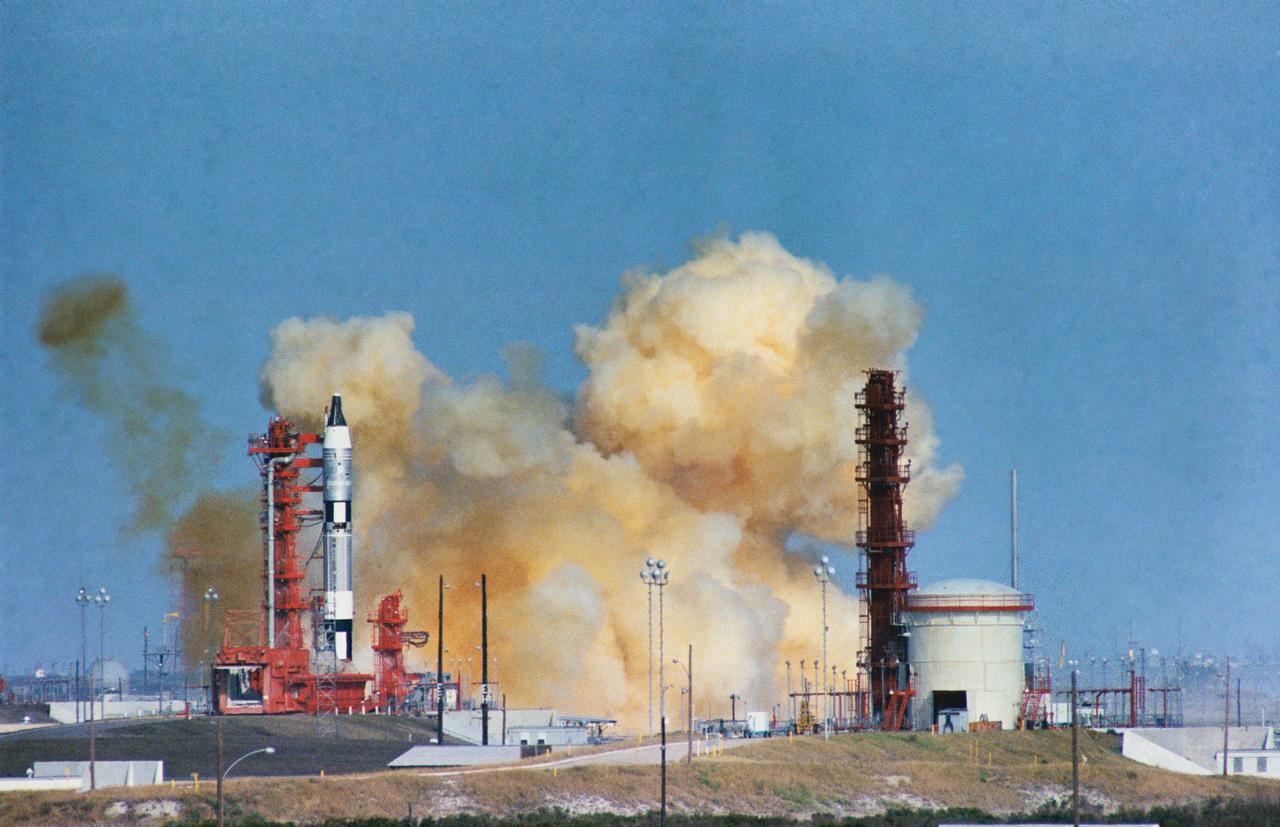

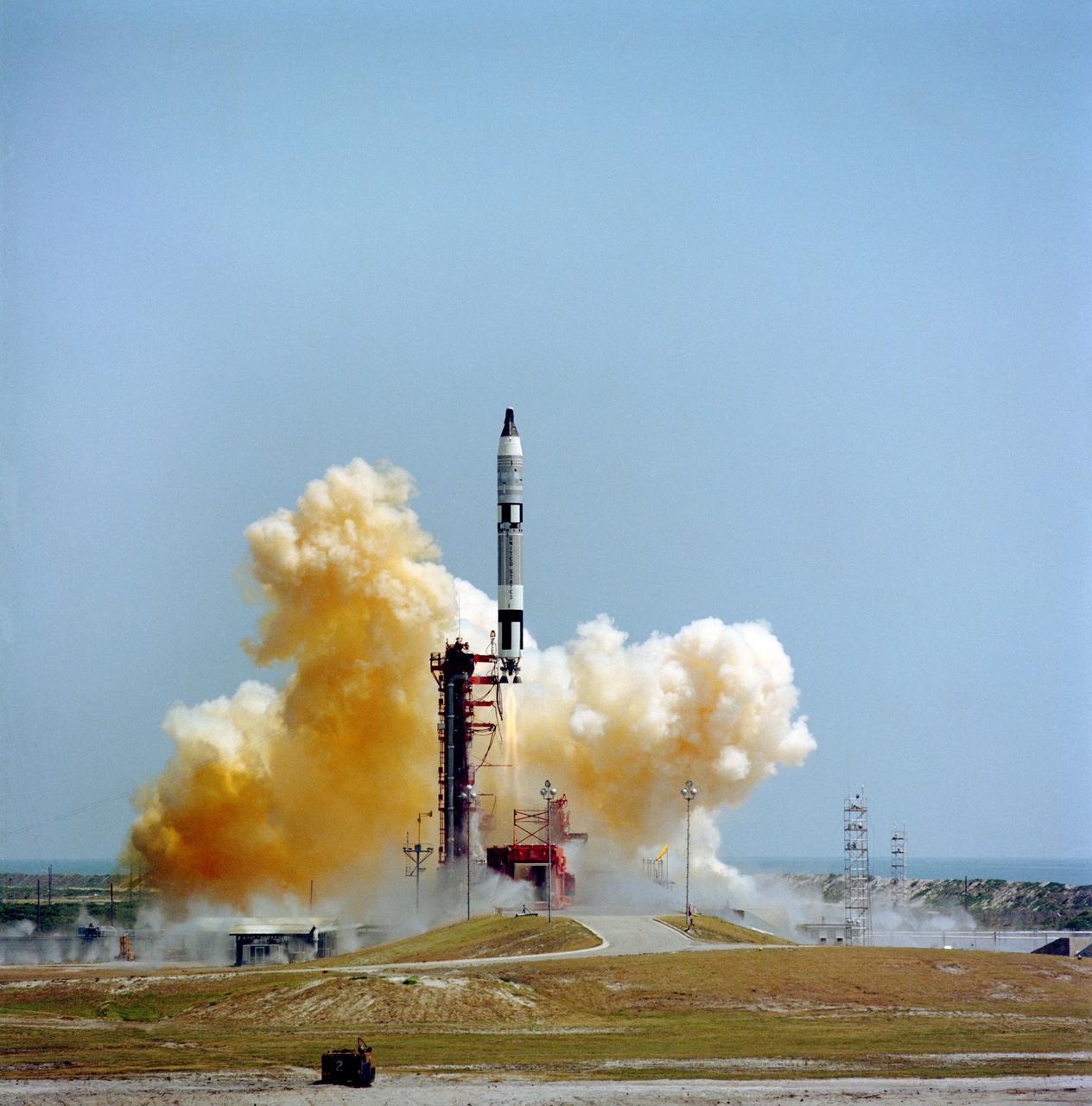
S65-59967 (12 Dec. 1965) --- The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) attempted to launch Gemini-6 at 9:54 a.m. (EST), Dec. 12, 1965. However, seconds after ignition the first stage engine of the Gemini Launch Vehicle 6 shut down due to a faulty release of a liftoff umbilical plug. Inside the spacecraft were astronauts Walter M. Schirra Jr., command pilot, and Thomas P. Stafford, pilot. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
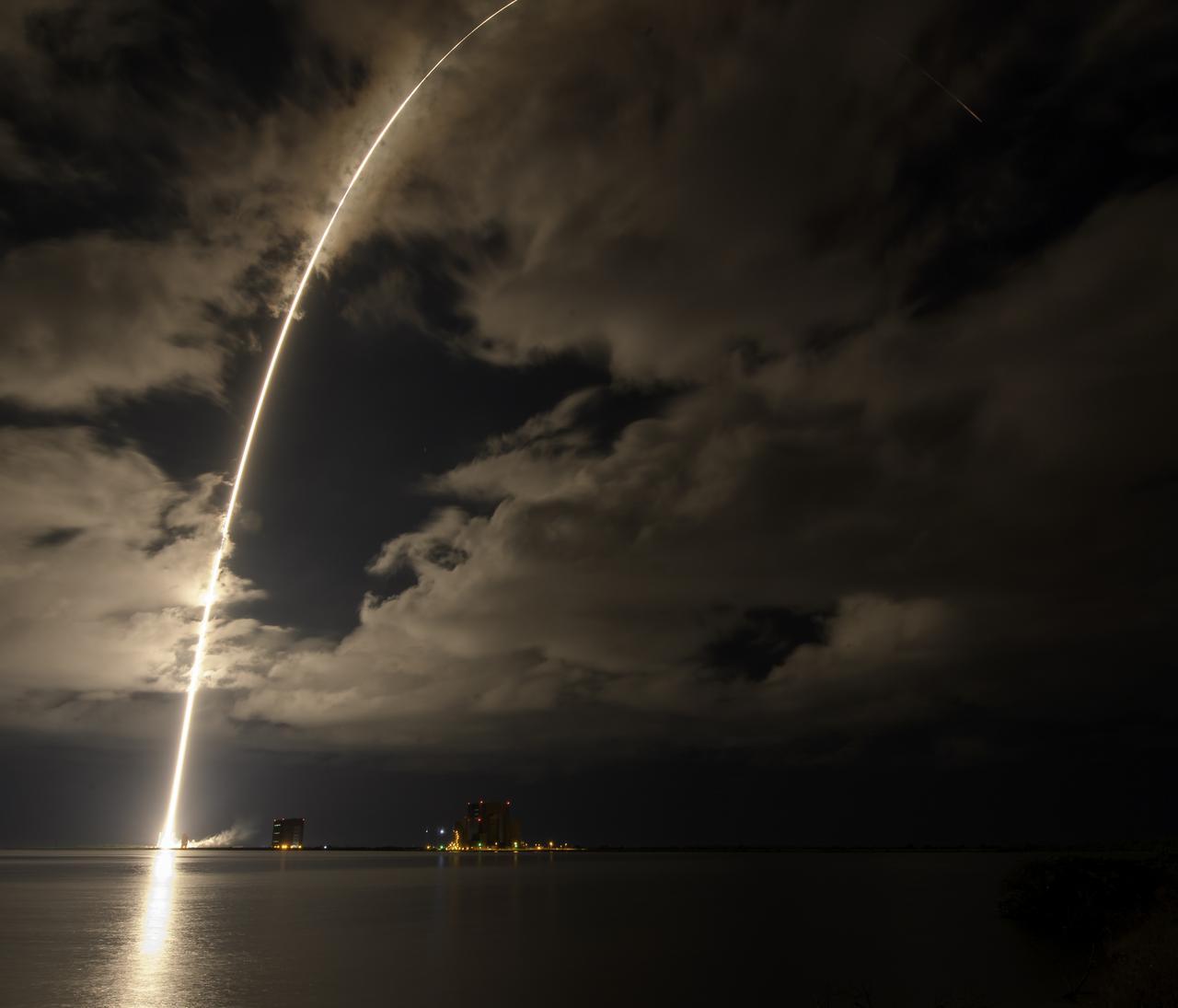

A United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket with the Lucy spacecraft aboard is seen in this 2 minute and 30 second exposure photograph as it launches from Space Launch Complex 41, Saturday, Oct. 16, 2021, at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Lucy will be the first spacecraft to study Jupiter's Trojan Asteroids. Like the mission's namesake – the fossilized human ancestor, "Lucy," whose skeleton provided unique insight into humanity's evolution – Lucy will revolutionize our knowledge of planetary origins and the formation of the solar system. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
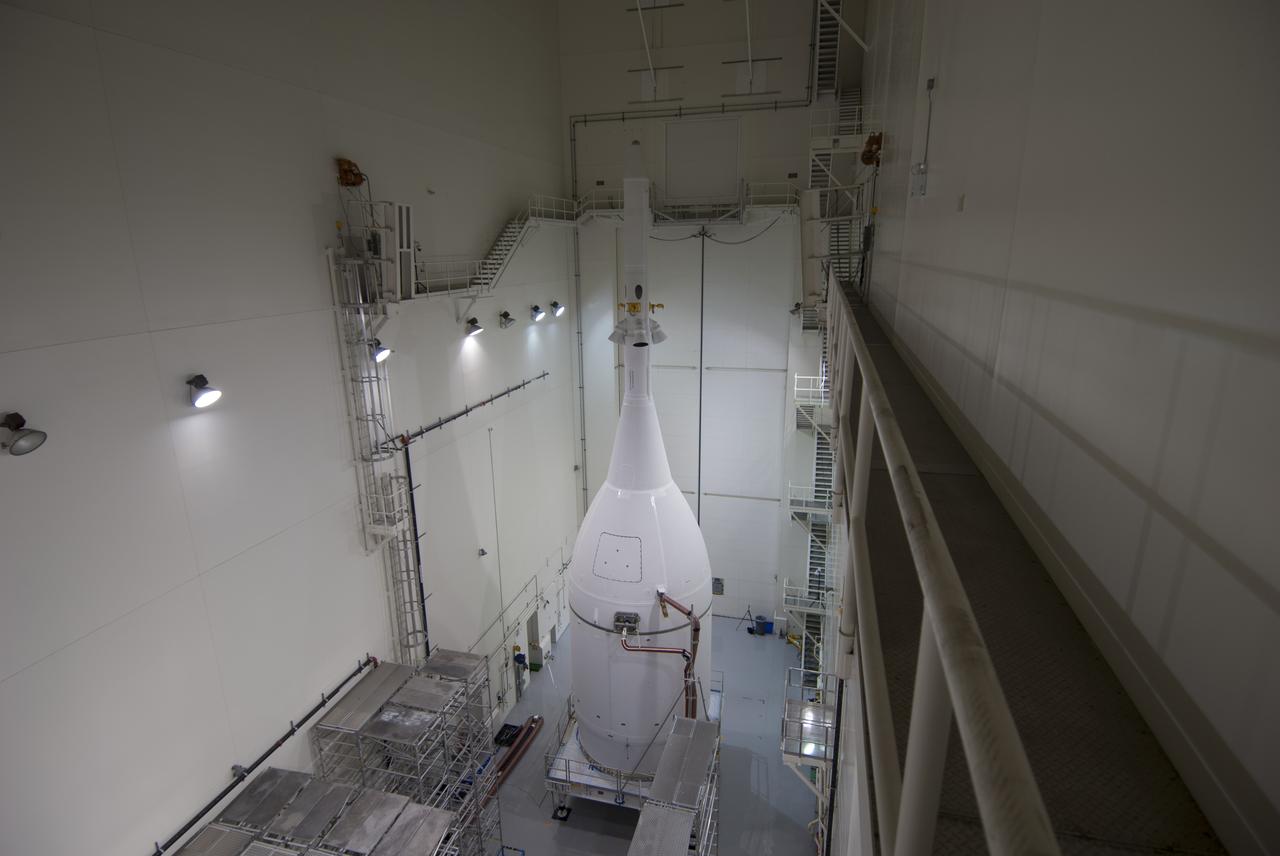

The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
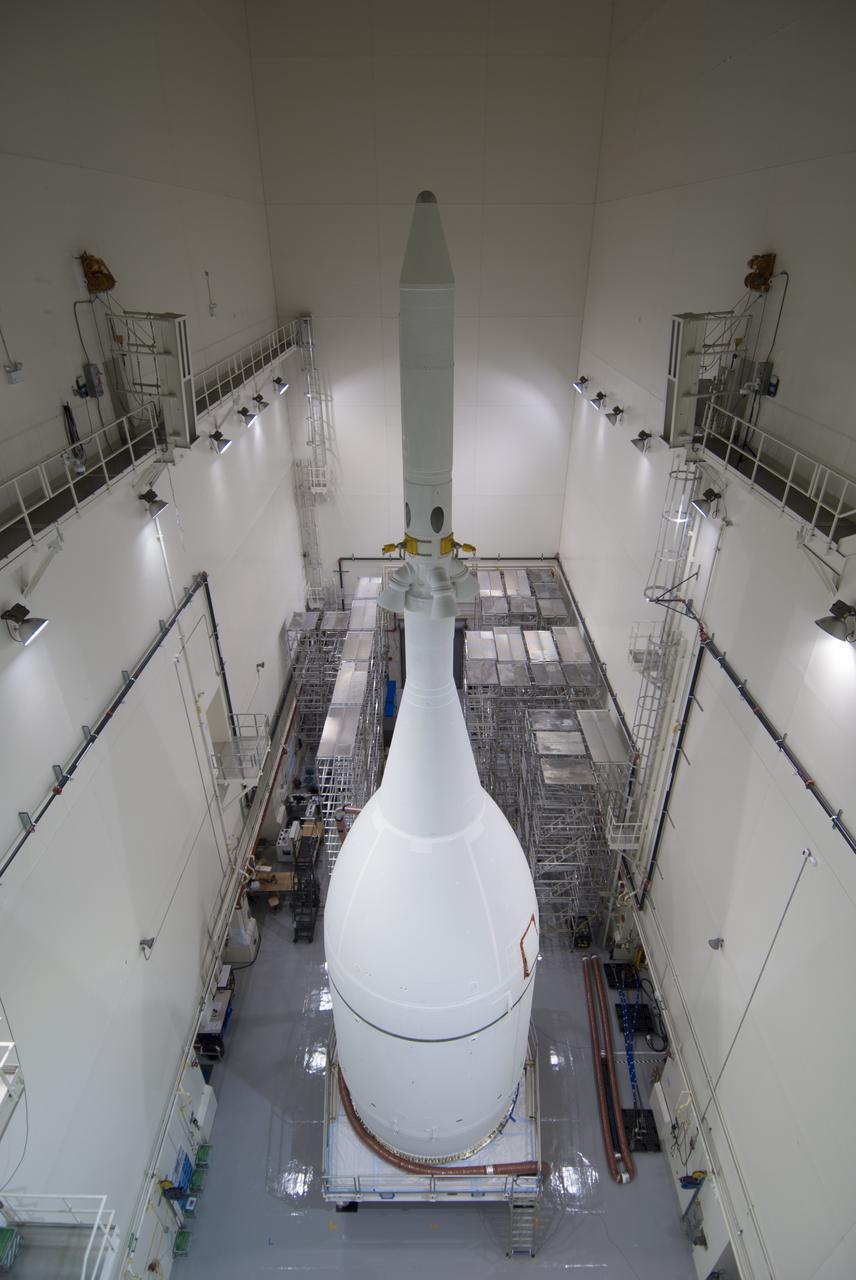

The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
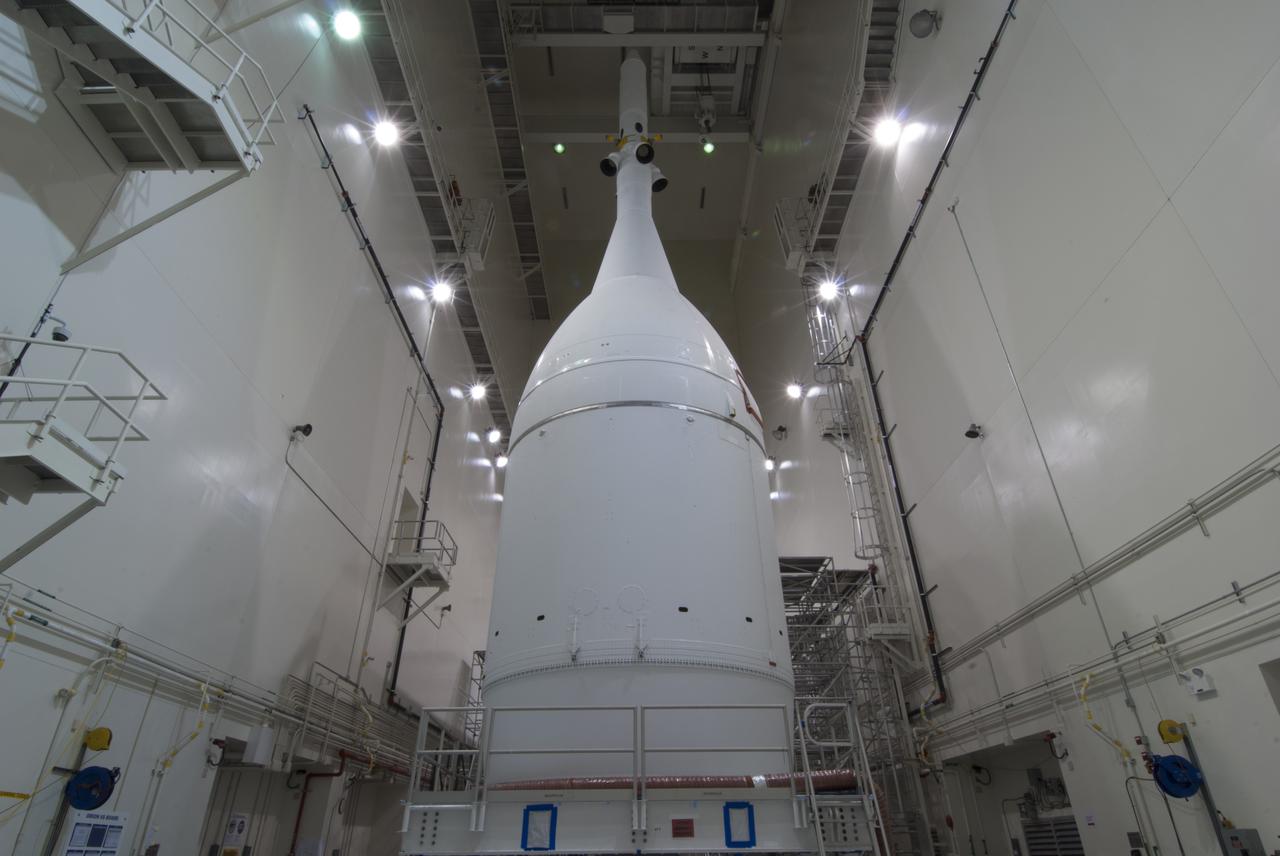

The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
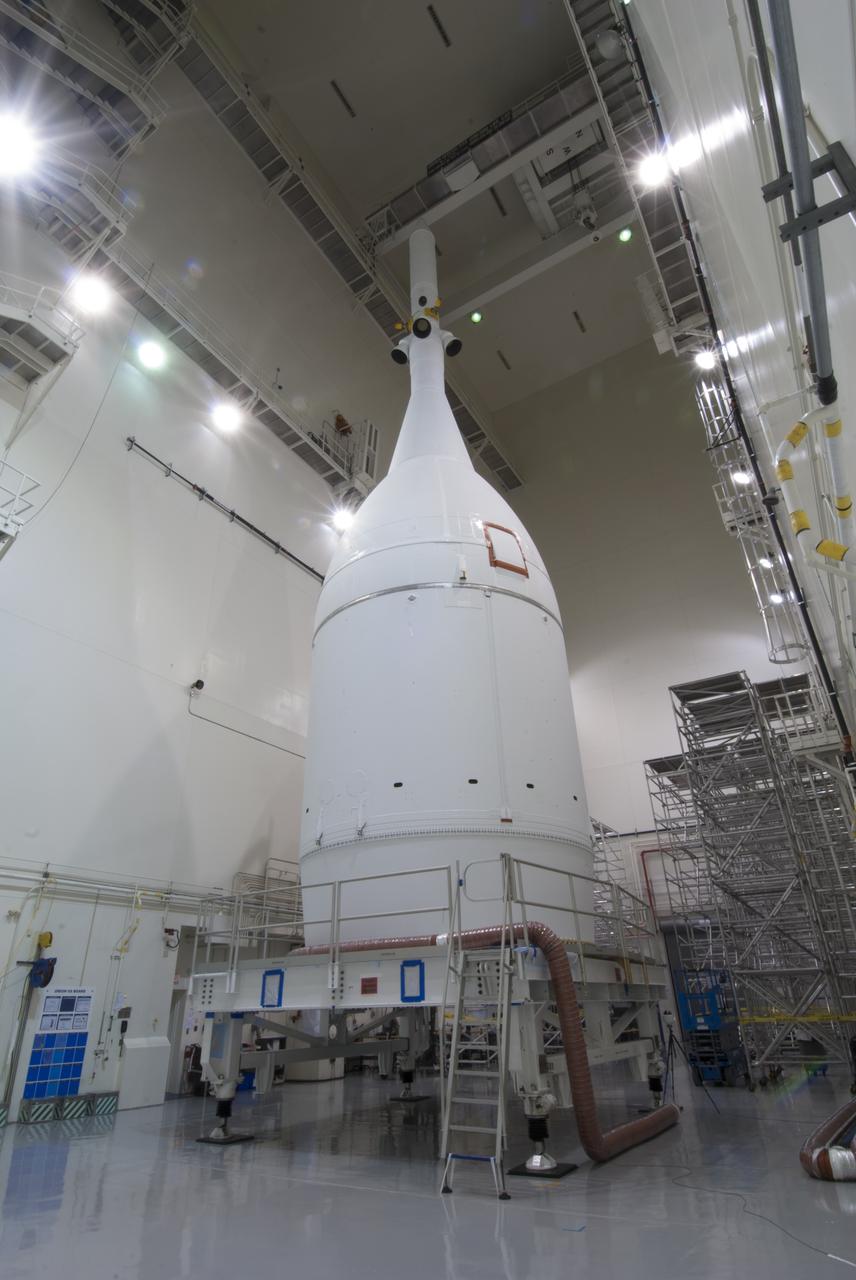

The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
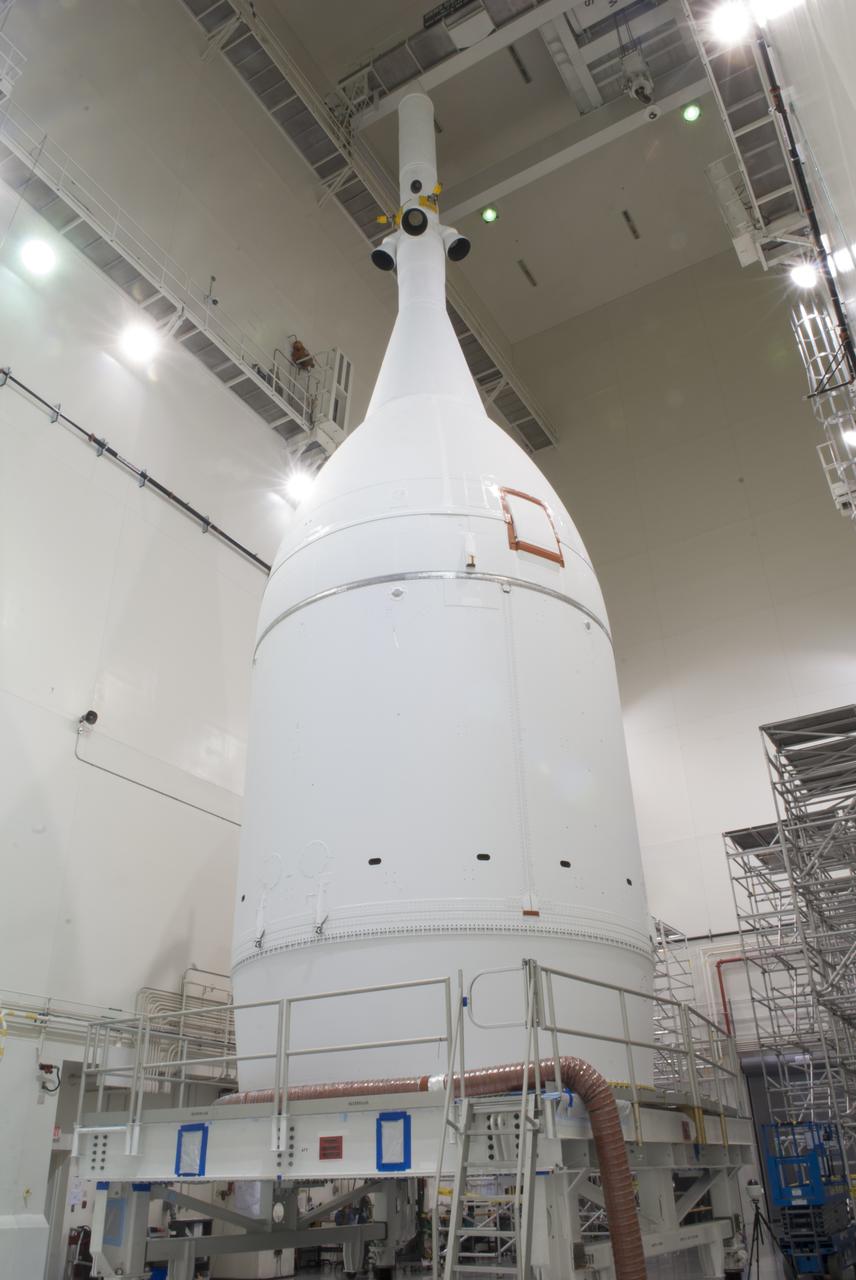

The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
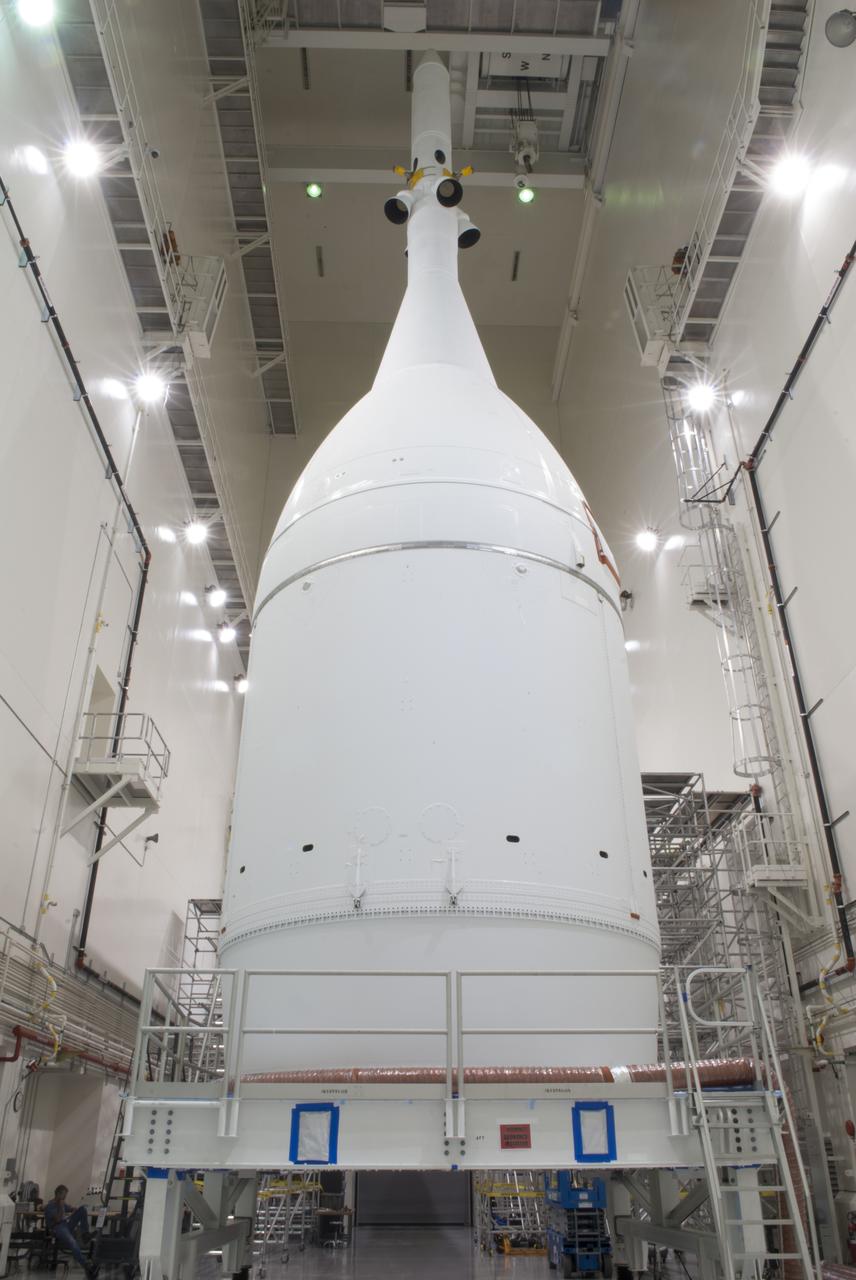

The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.
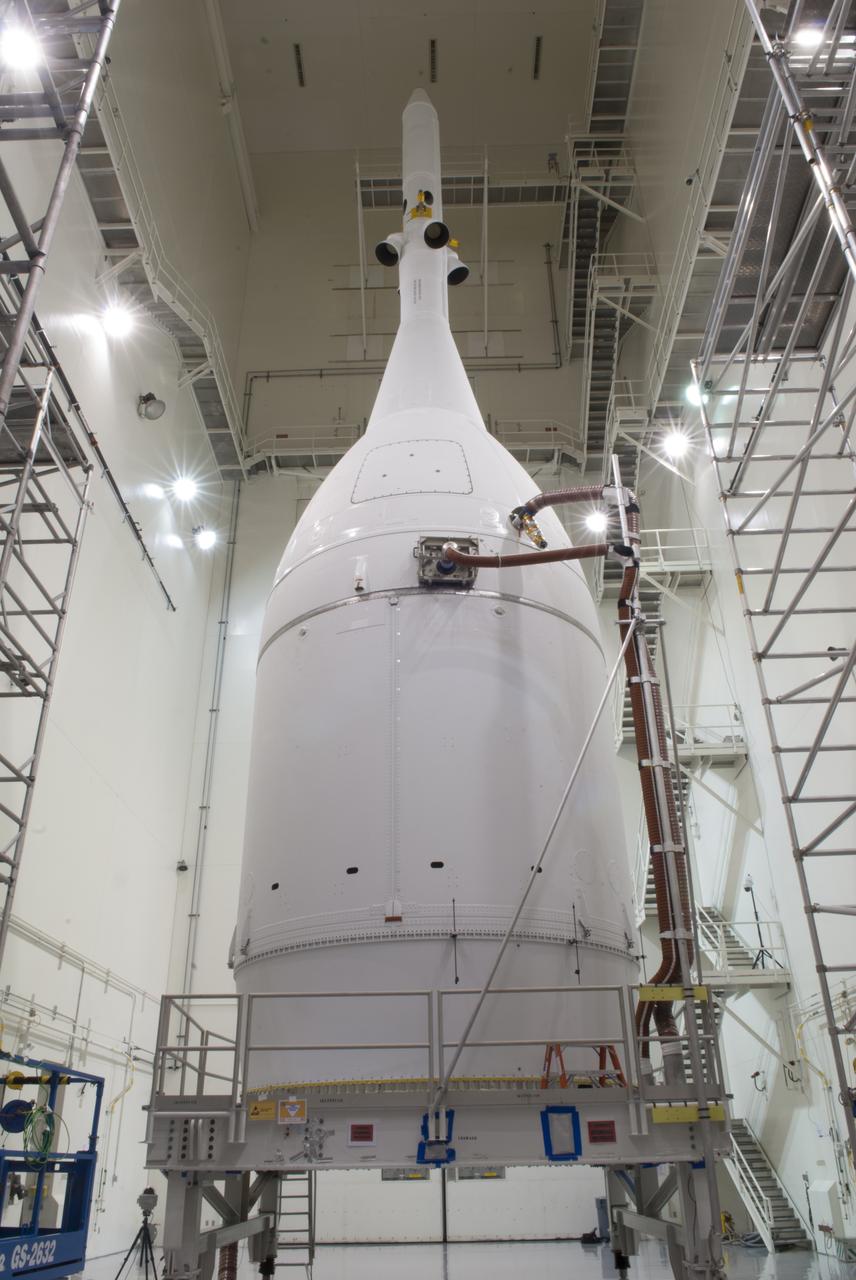

The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft roll out of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the first time on March 17, 2022.

The Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft roll out of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the first time on March 17, 2022.
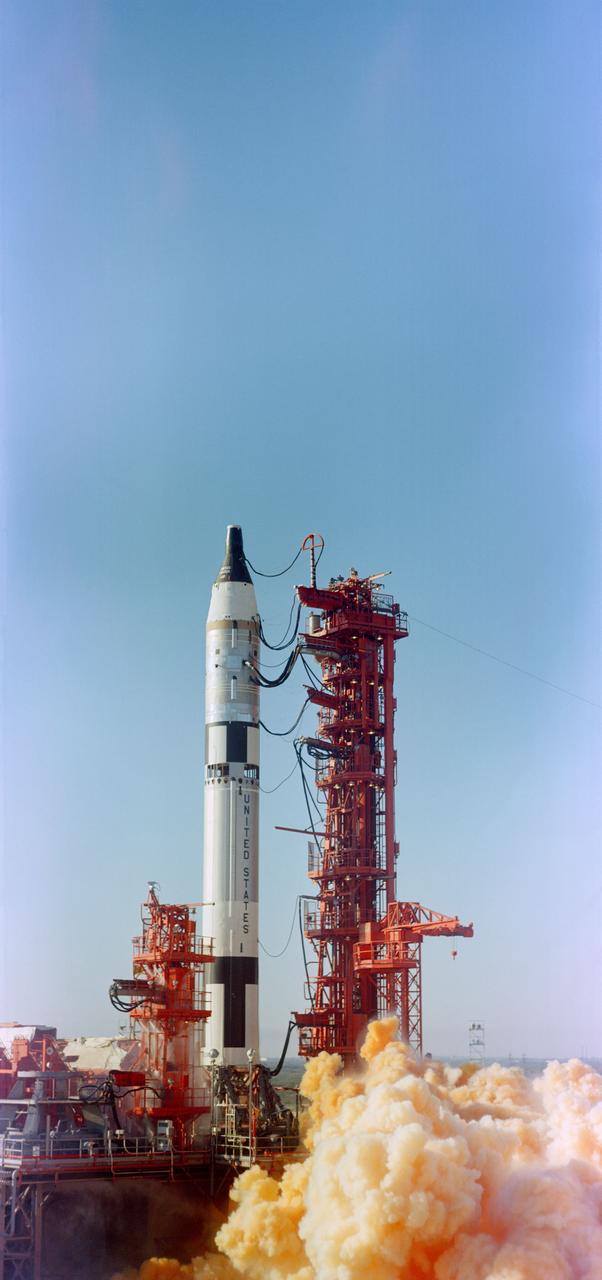

S65-14150 (19 January 1965) --- Launching of the unmanned Gemini 2 flight. The second Titan II Gemini Launch Vehicle (GLV-2) carried the unmanned, instrumented Gemini spacecraft (GT-2) for a suborbital shot preliminary to the first U.S. two-man Gemini mission.
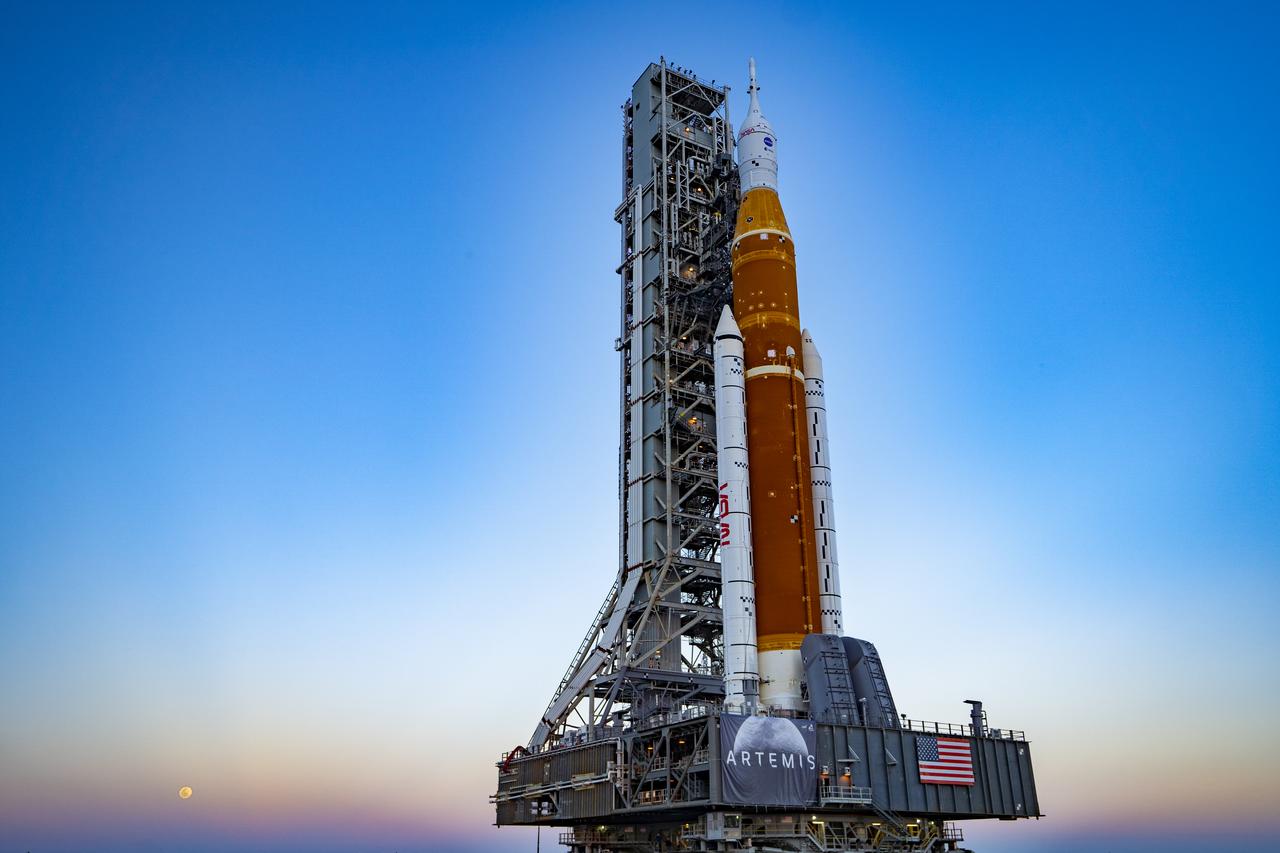

Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft rollout at Kennedy Space Center
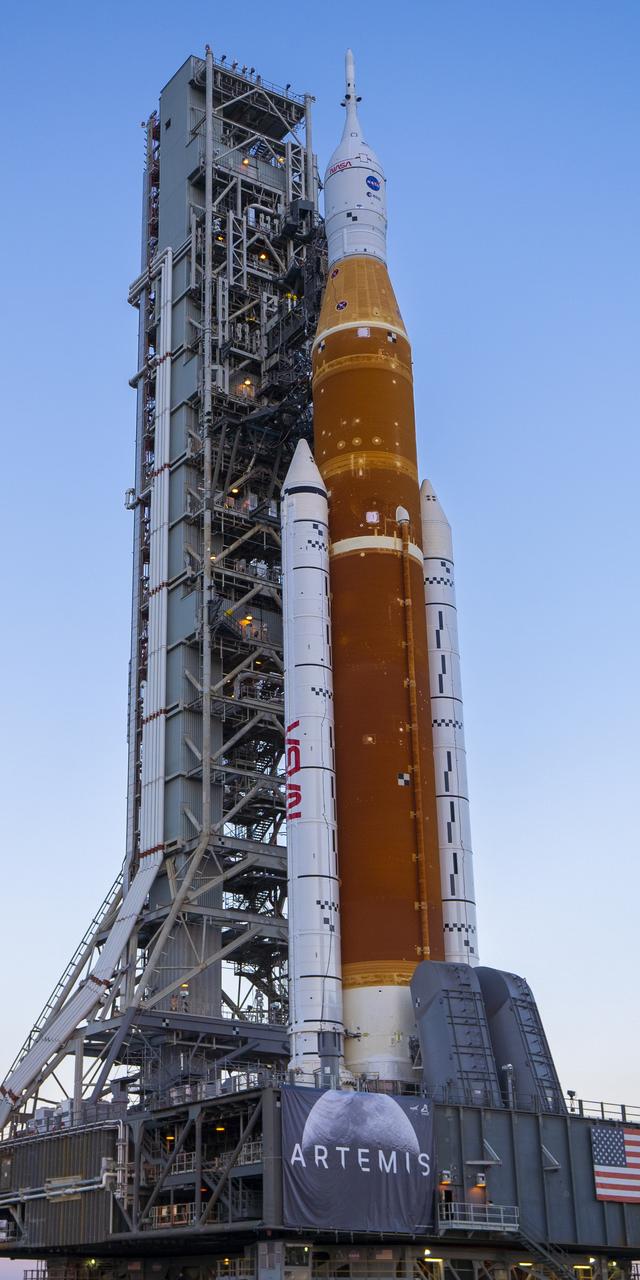

Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion Spacecraft rollout at Kennedy Space Center
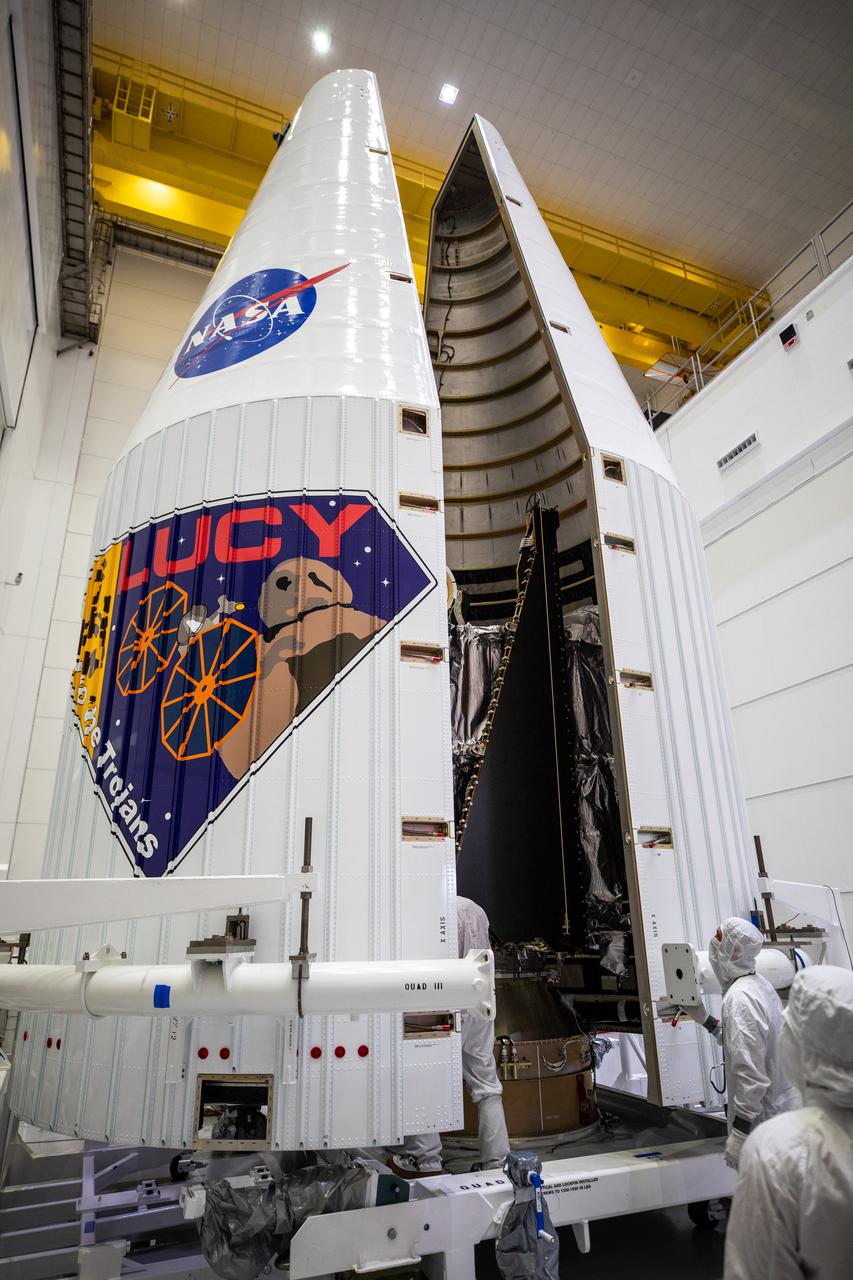

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move both halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing around NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
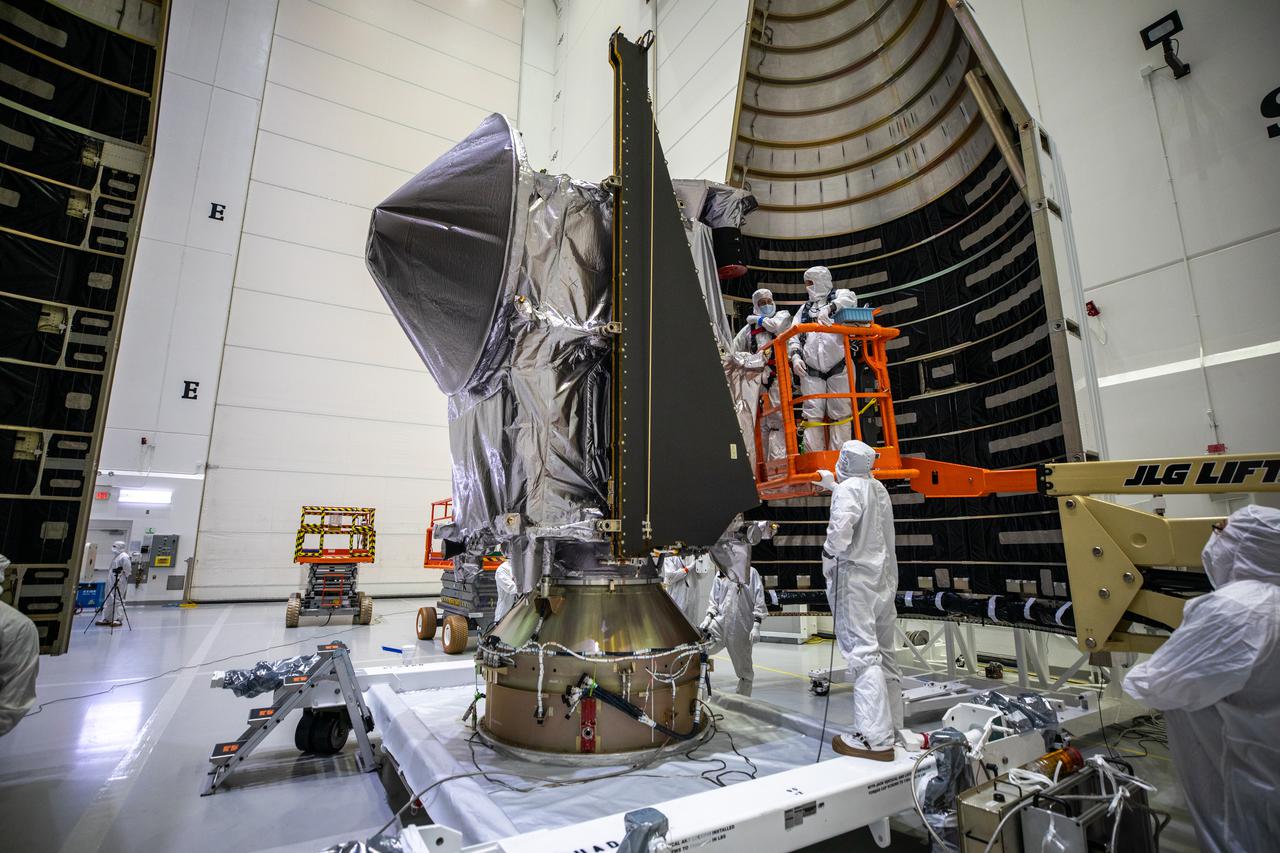
Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
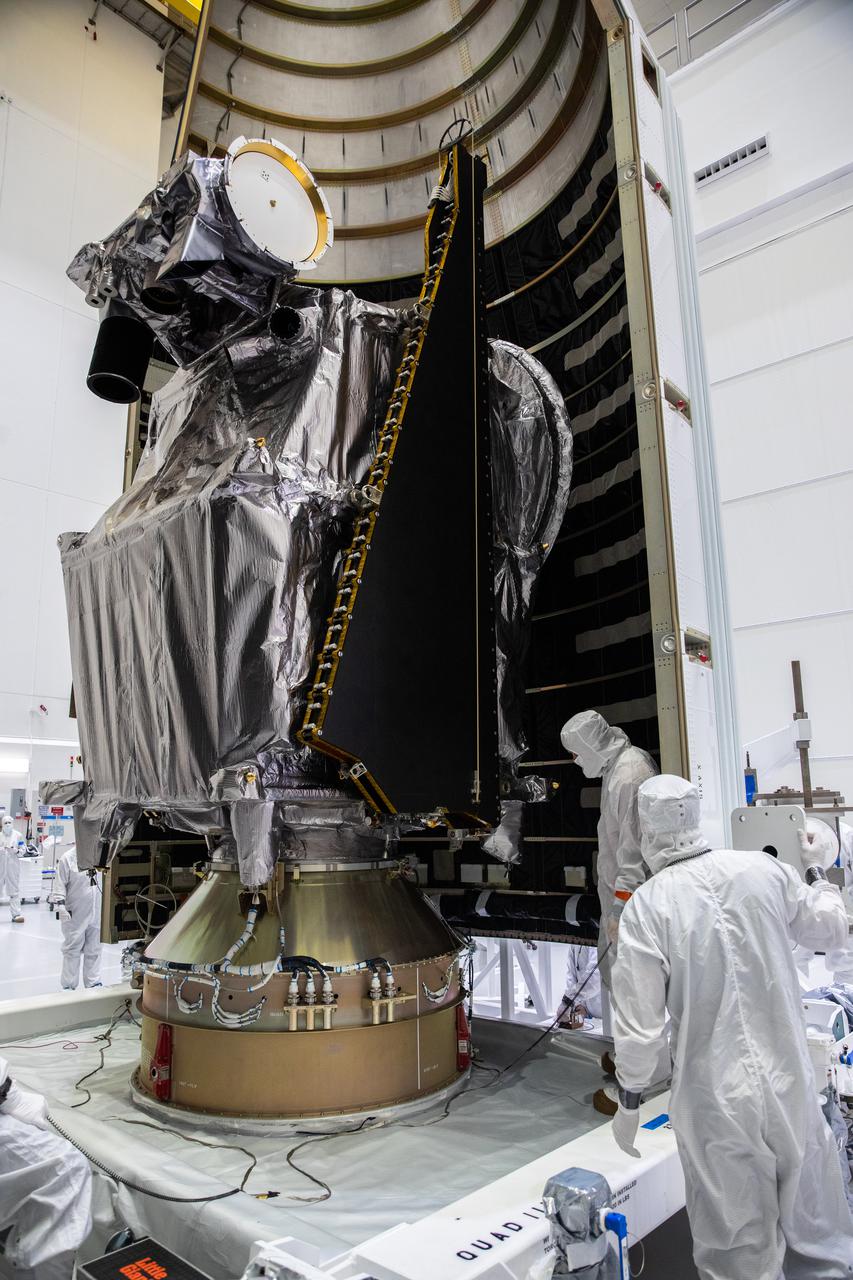

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
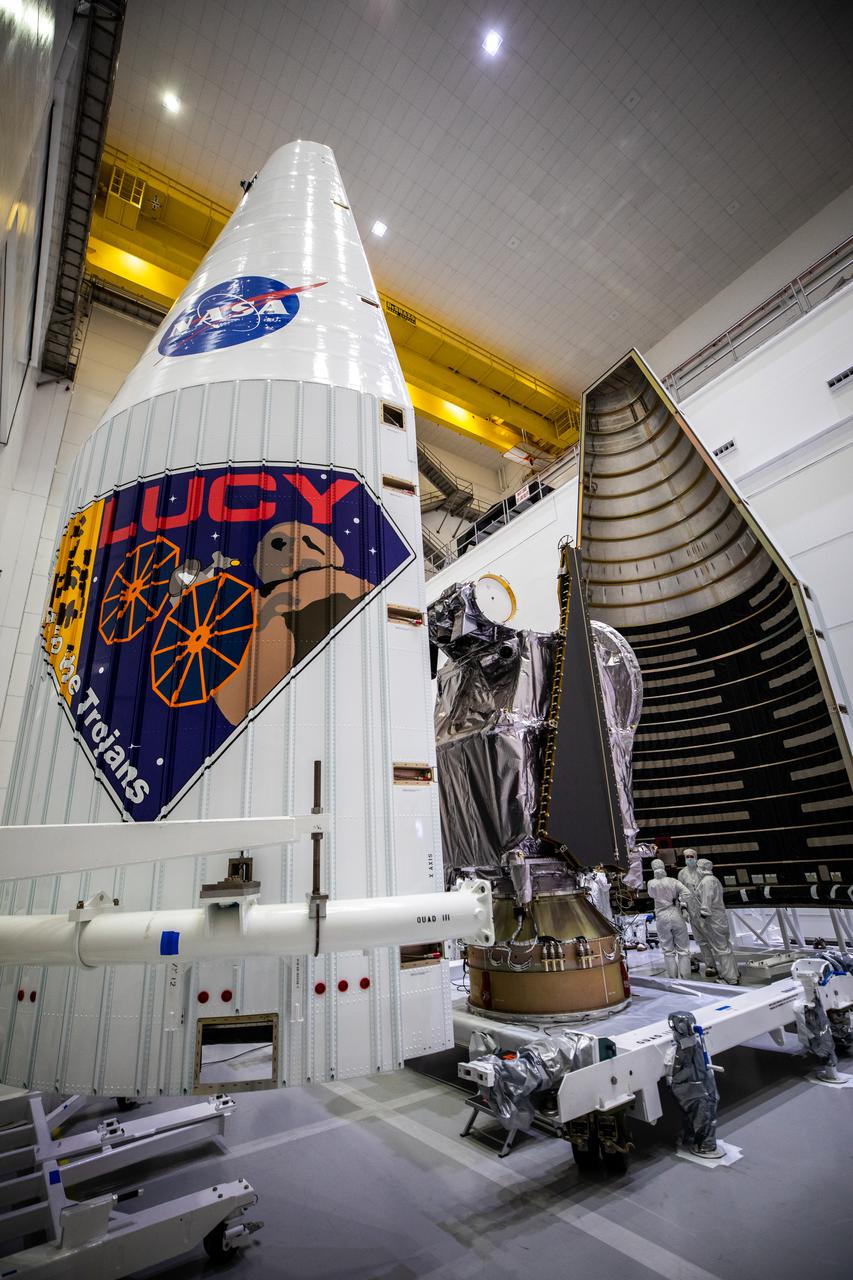

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The other half is in view in the foreground. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
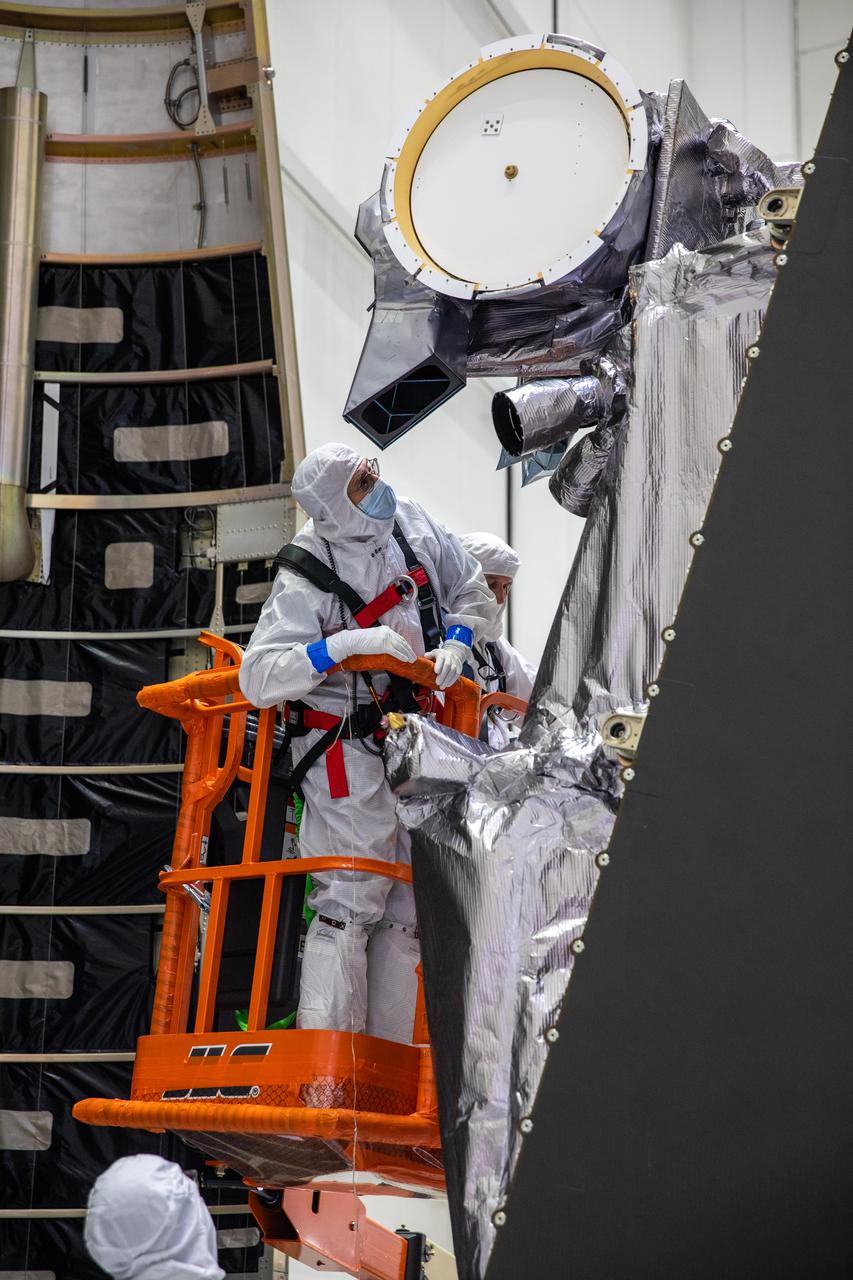

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.

Workers inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, move the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
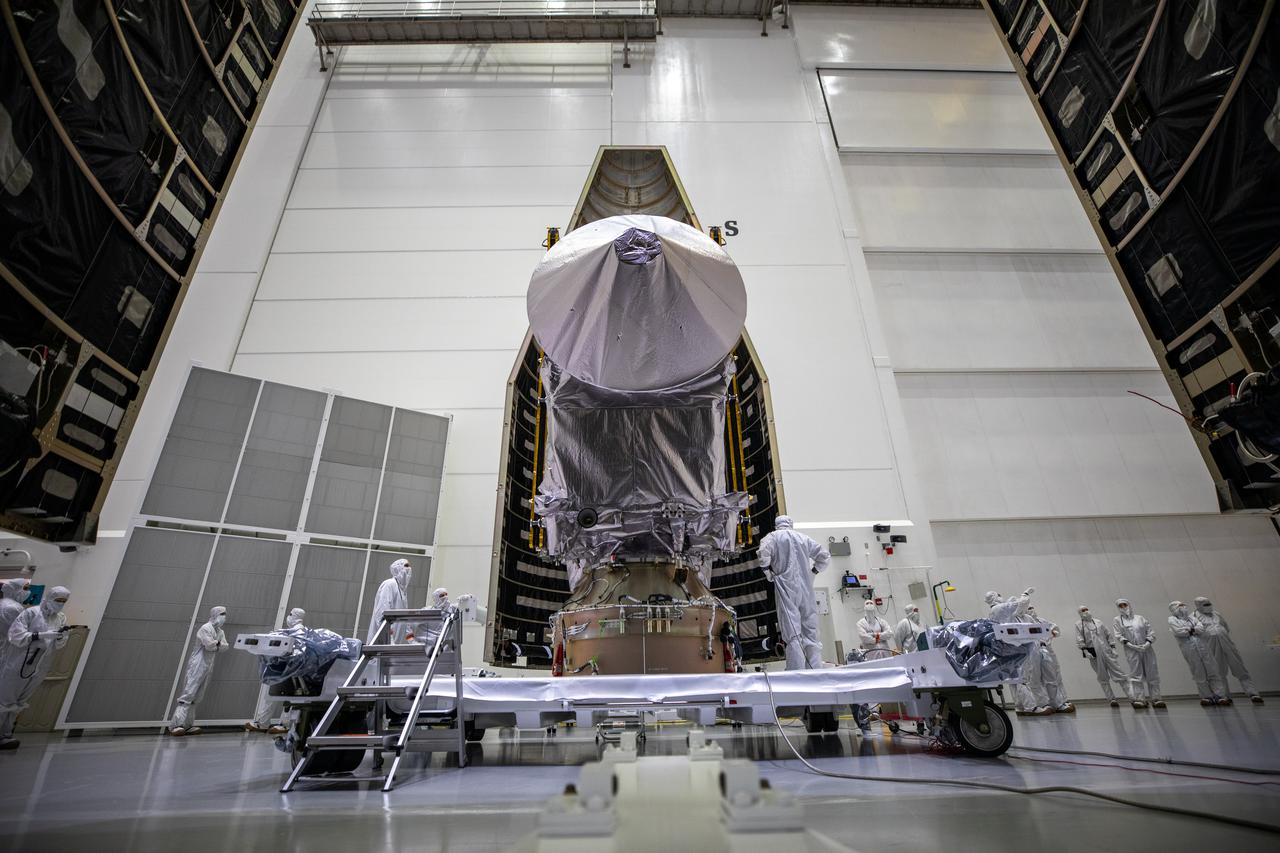

Inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, the first half of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing is moved toward NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
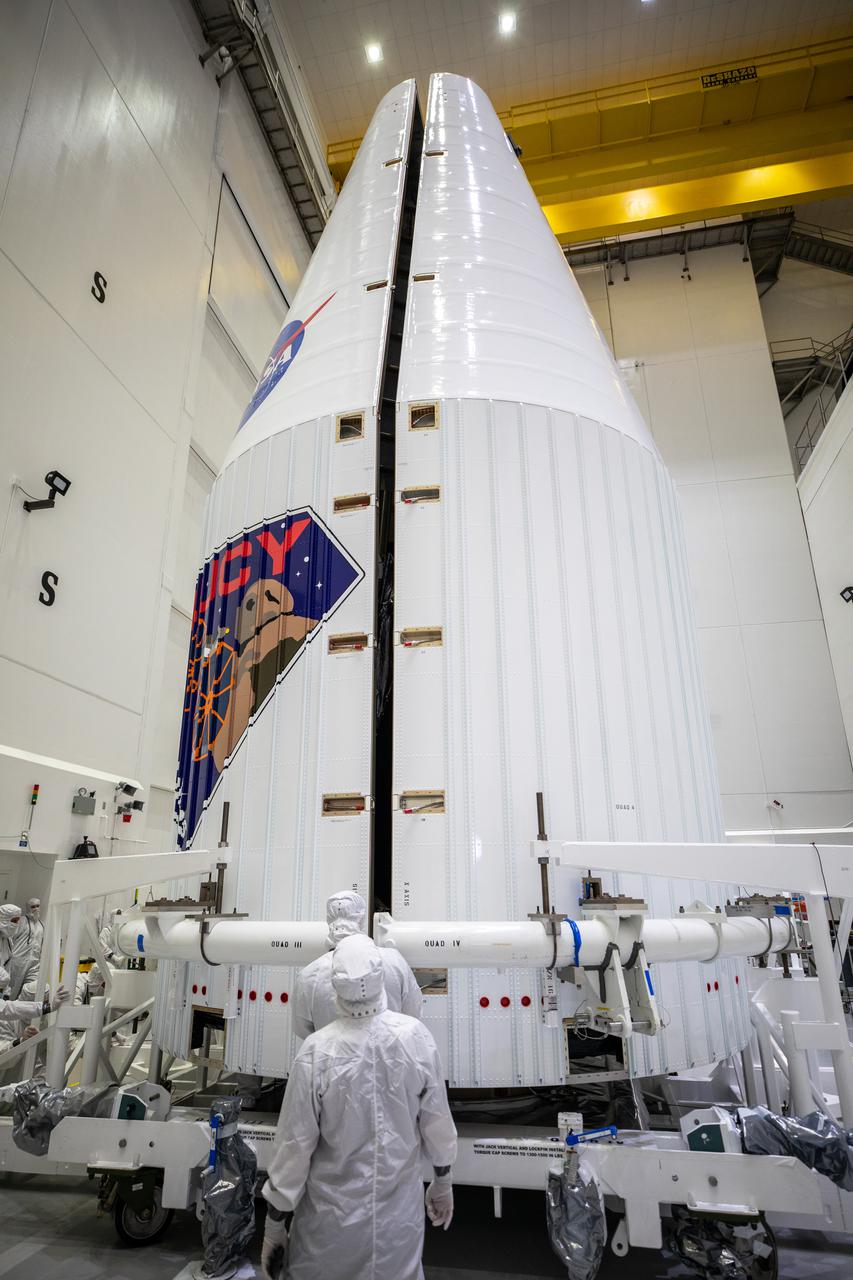

Inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, workers help secure both halves of the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing around NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
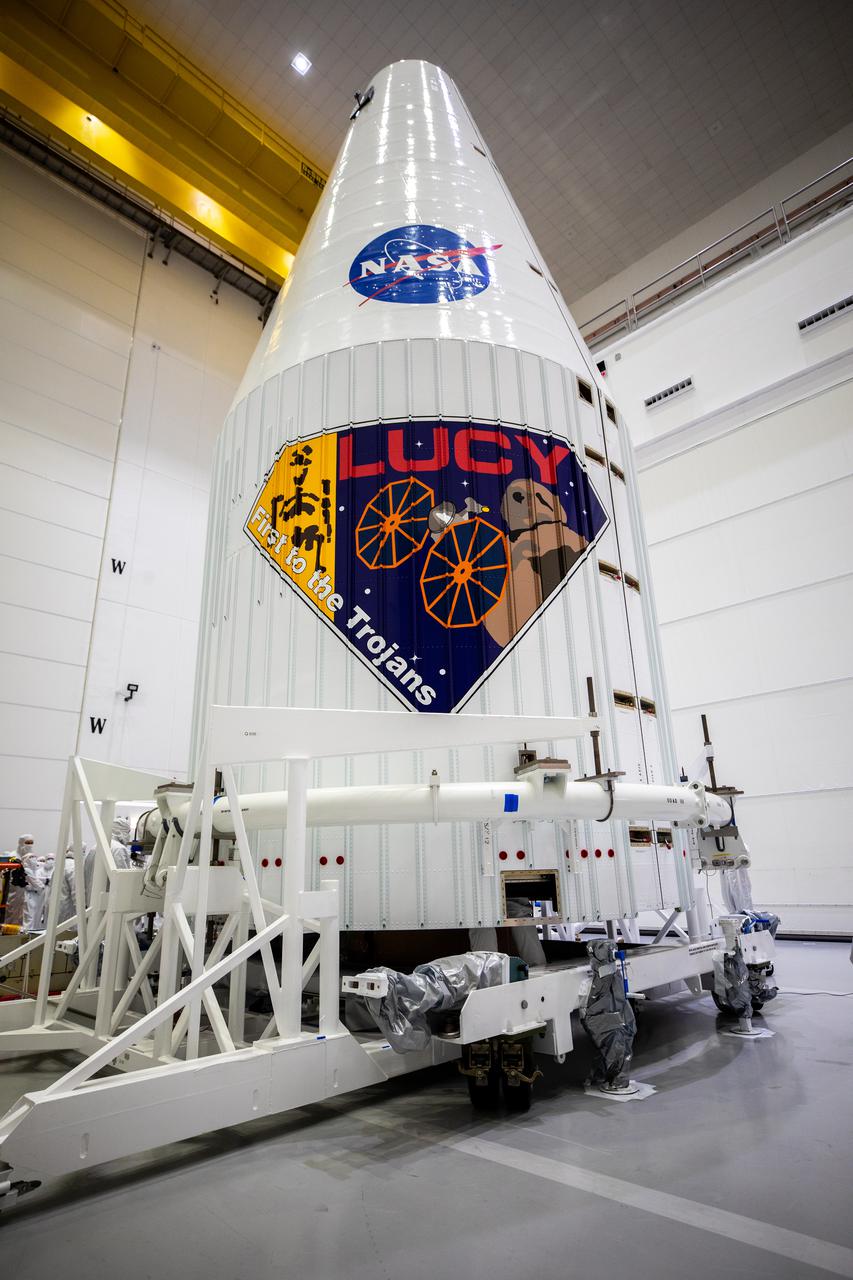

Inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, the United Launch Alliance (ULA) payload fairing has been secured around NASA’s Lucy spacecraft on Sept. 30, 2021. The payload fairing will encapsulate and protect the spacecraft during launch and ascent. Lucy is scheduled to launch no earlier than Saturday, Oct. 16, on a ULA Atlas V 401 rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is managing the launch. Over its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Additionally, Lucy’s path will circle back to Earth three times for gravity assists, making it the first spacecraft ever to return to the vicinity of Earth from the outer solar system.
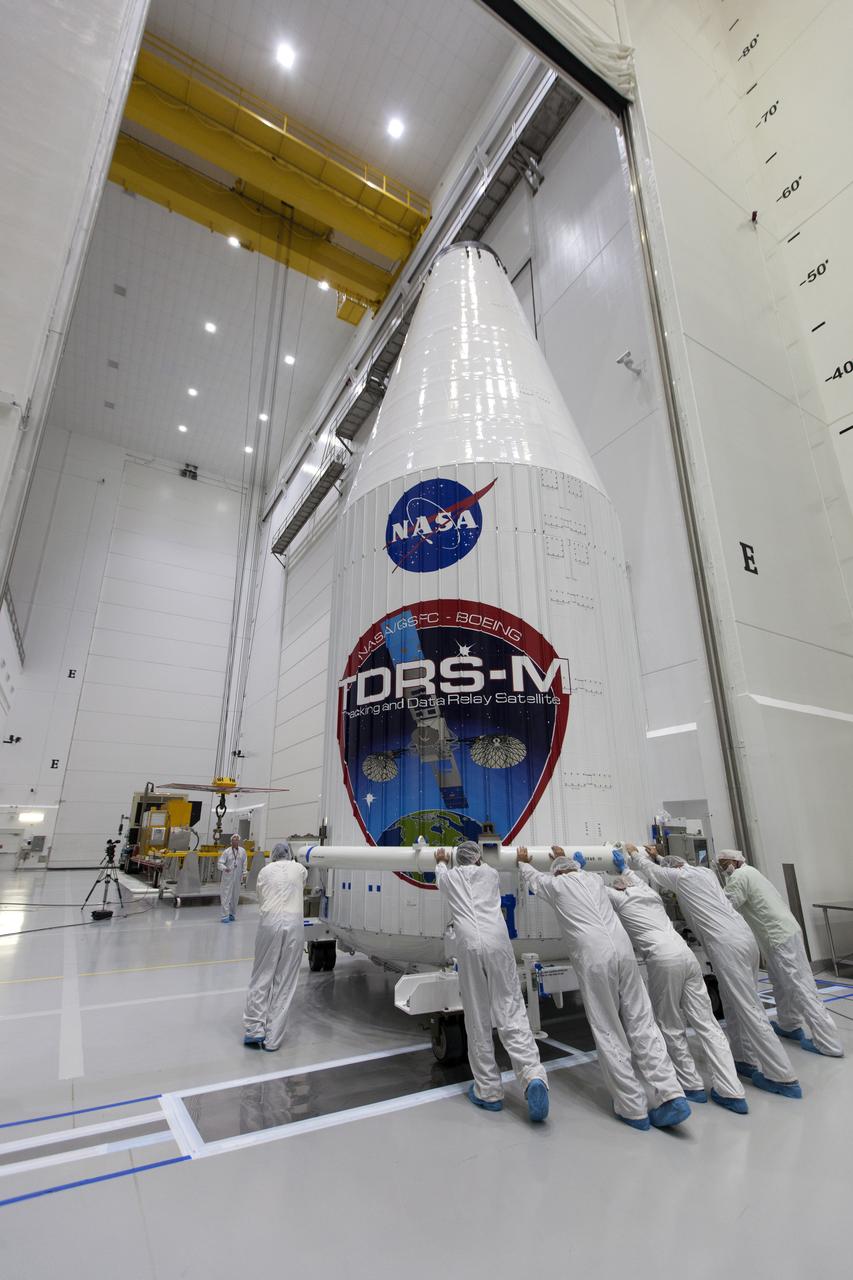

Inside the Astrotech facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians move the agency's TDRS-M satellite, enclosed in its payload fairing, toward a crane for lifting to a transport vehicle. The TDRS-M is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Aug. 18 at 8:03 a.m. EDT.
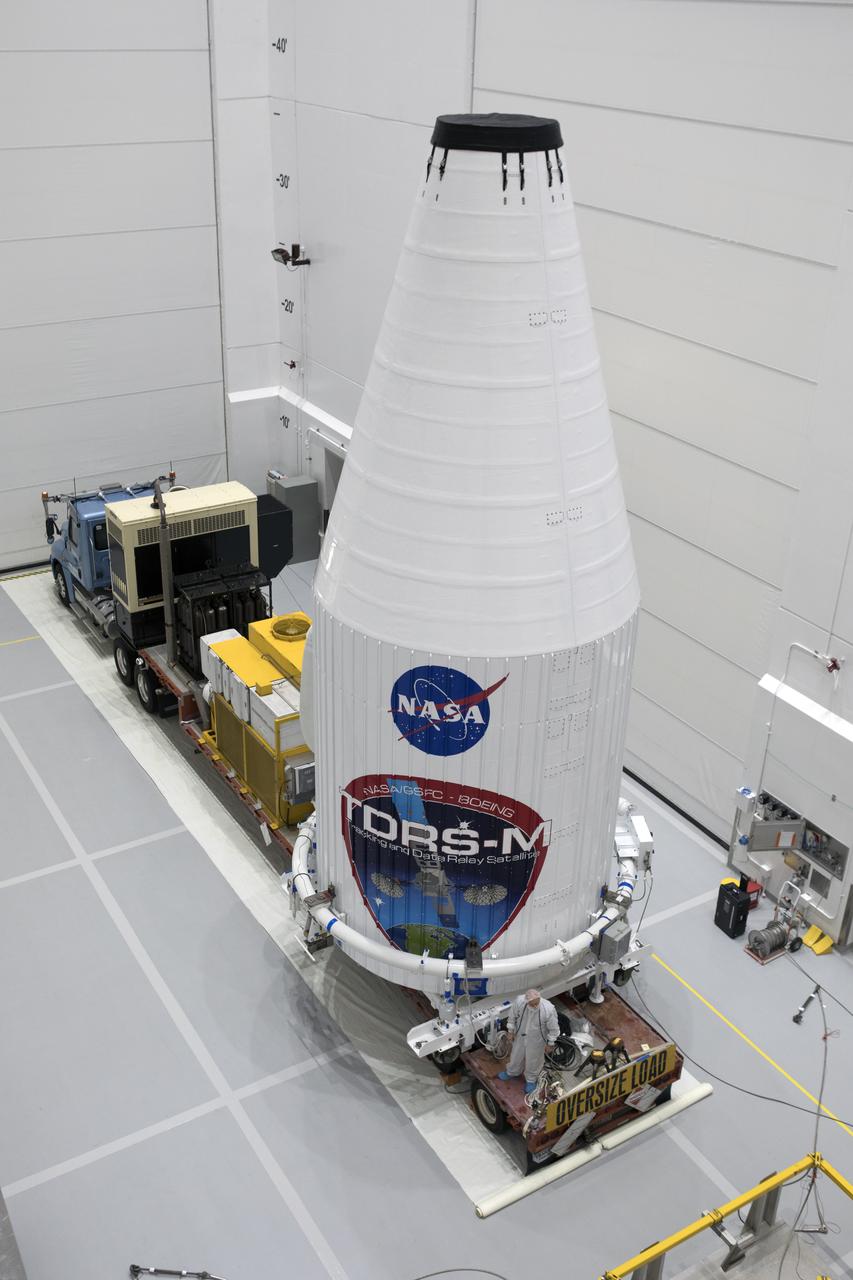

Inside the Astrotech facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's TDRS-M satellite, enclosed in its payload fairing, is secured on a transport vehicle. The TDRS-M is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Aug. 18 at 8:03 a.m. EDT.
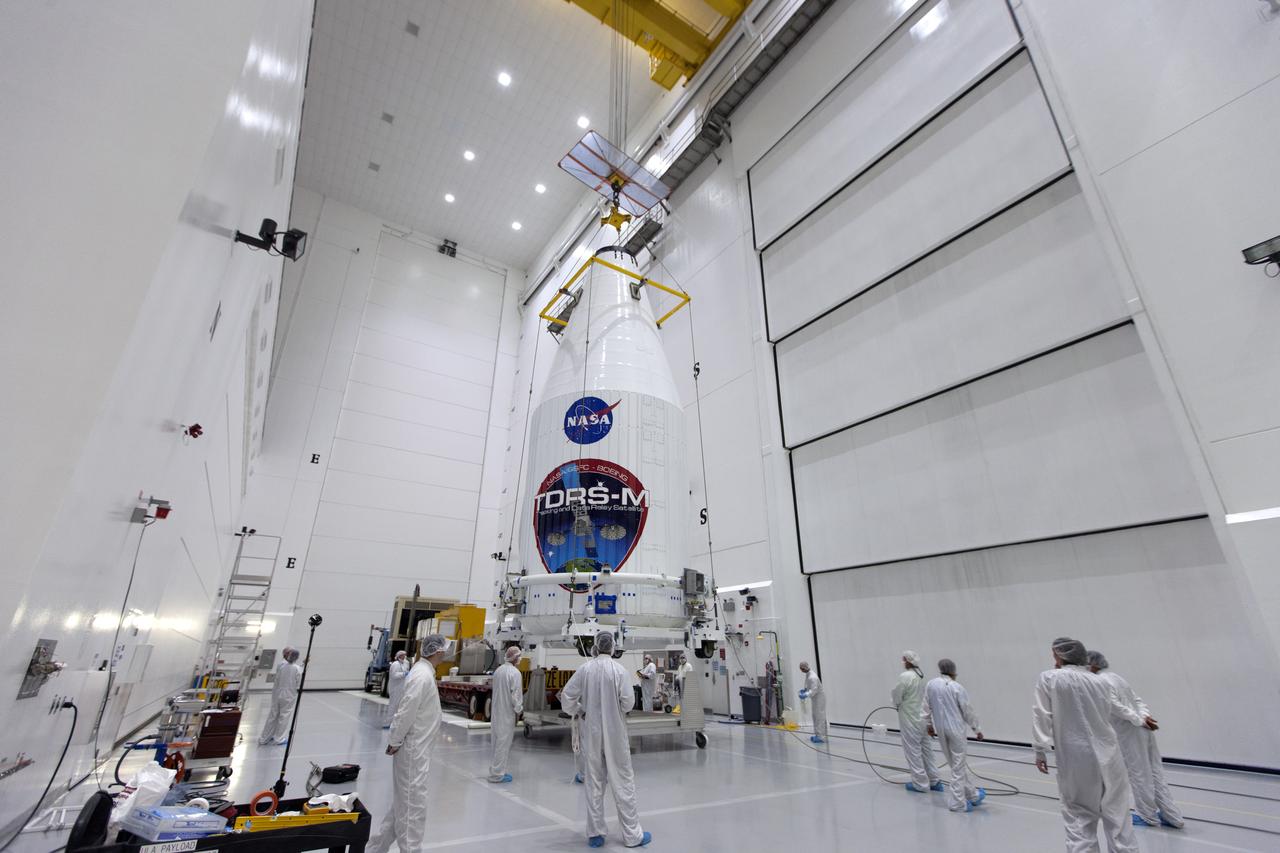

Technicians monitor the progress as NASA's TDRS-M satellite, enclosed in its payload fairing, is lowered onto a transport vehicle inside the Astrotech facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The TDRS-M is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Aug. 18 at 8:03 a.m. EDT.
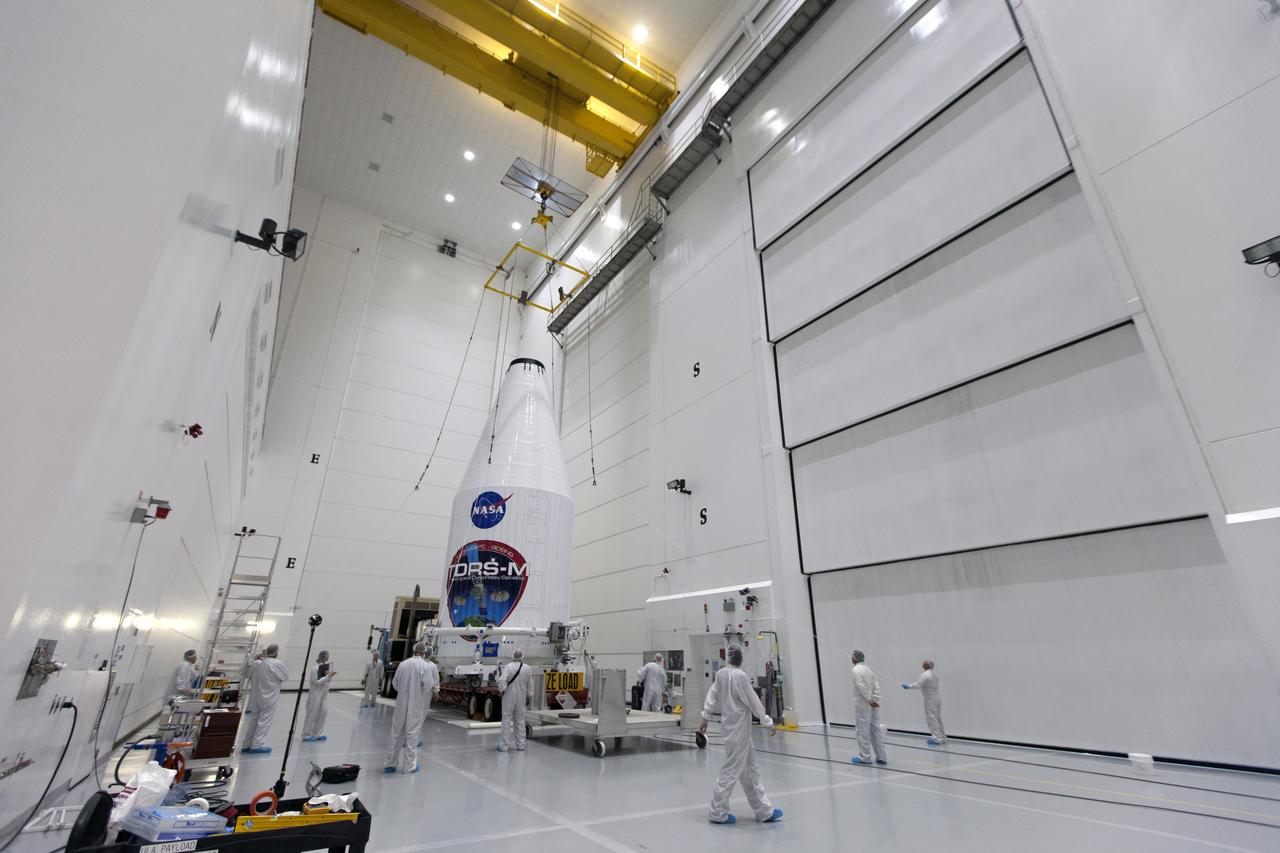

Technicians monitor the progress as NASA's TDRS-M satellite, enclosed in its payload fairing, is lowered onto a transport vehicle inside the Astrotech facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The TDRS-M is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Aug. 18 at 8:03 a.m. EDT.
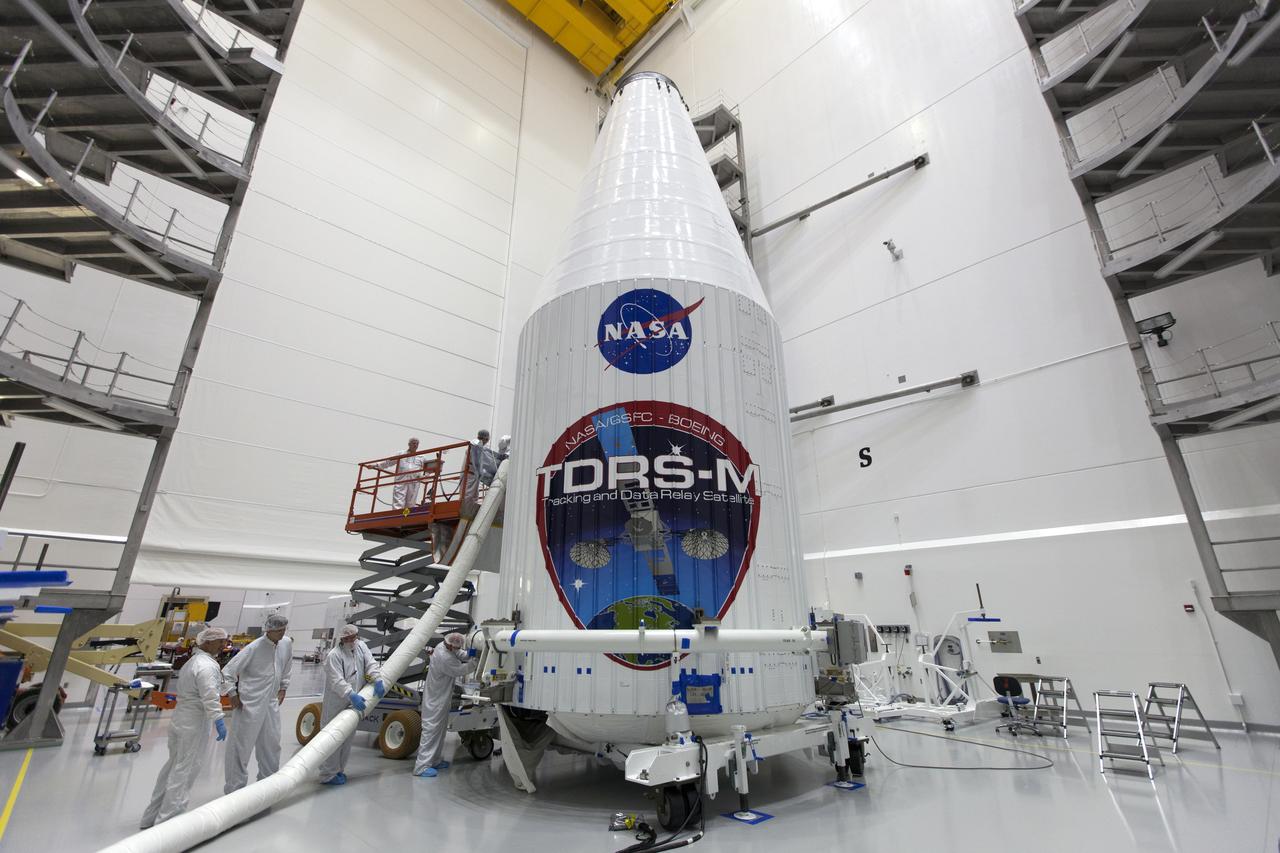

Inside the Astrotech facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's TDRS-M satellite, enclosed in its payload fairing, is being prepared for lifting to a transport vehicle. The TDRS-M is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Aug. 18 at 8:03 a.m. EDT.
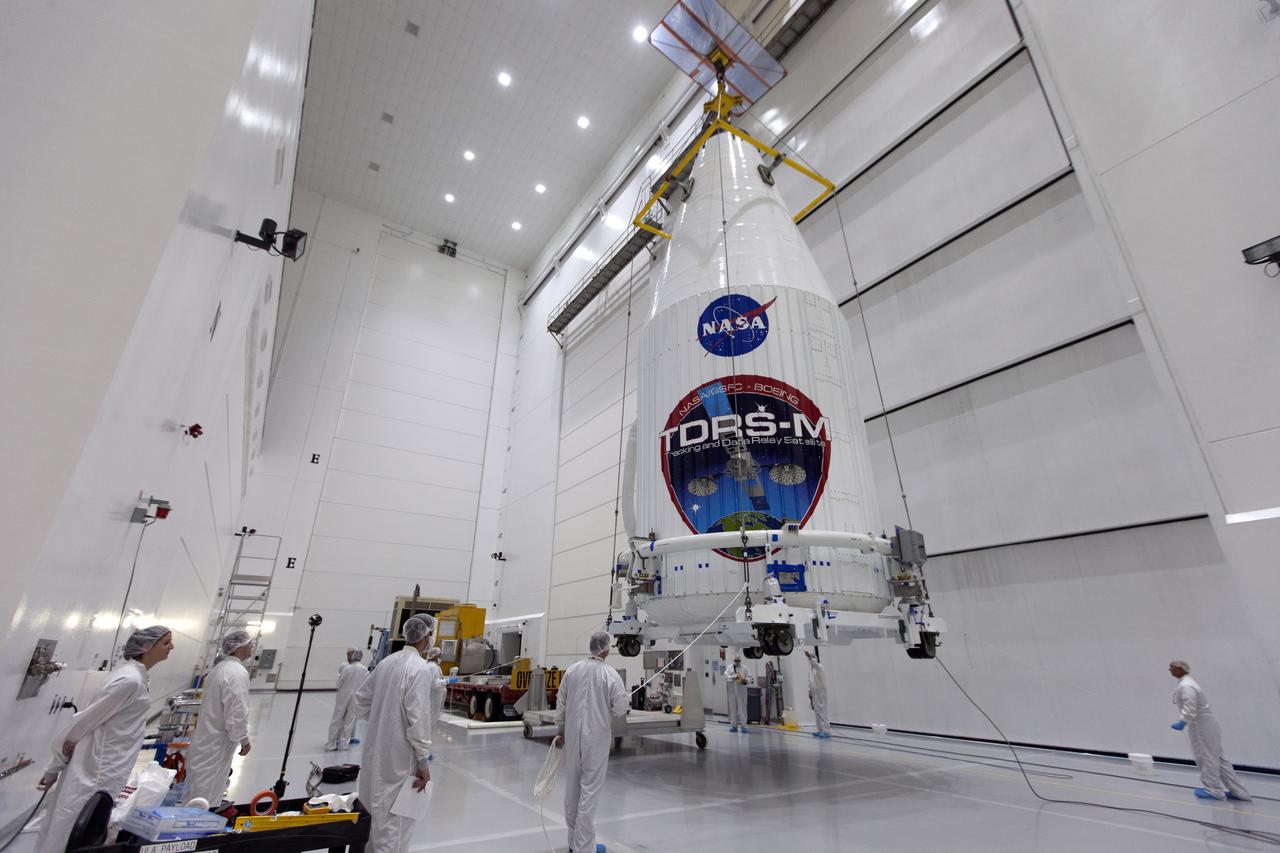

Inside the Astrotech facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's TDRS-M satellite, enclosed in its payload fairing, is lifted by crane and moved to a transport vehicle. The TDRS-M is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Aug. 18 at 8:03 a.m. EDT.
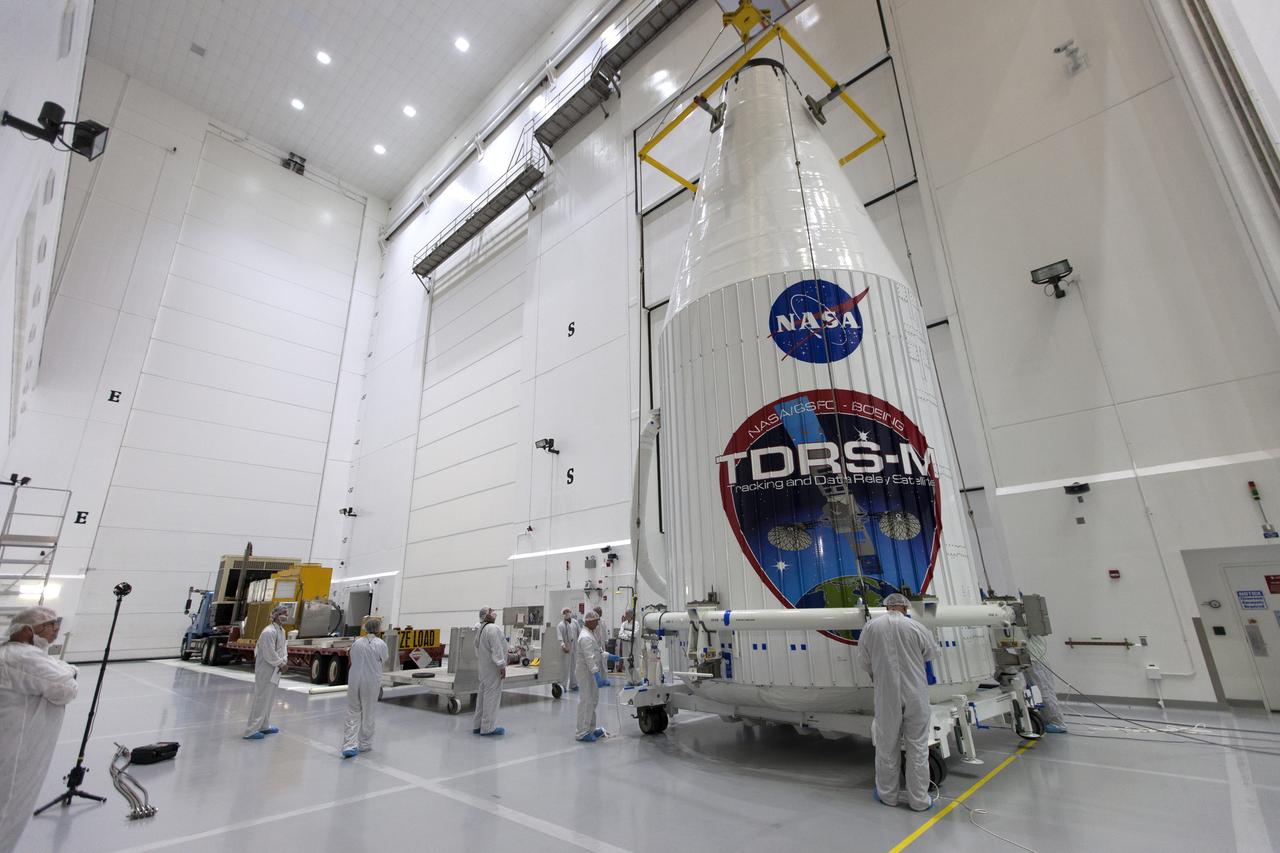

Inside the Astrotech facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's TDRS-M satellite, enclosed in its payload fairing, will be lifted by crane and lowered onto a transport vehicle. The TDRS-M is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Aug. 18 at 8:03 a.m. EDT.
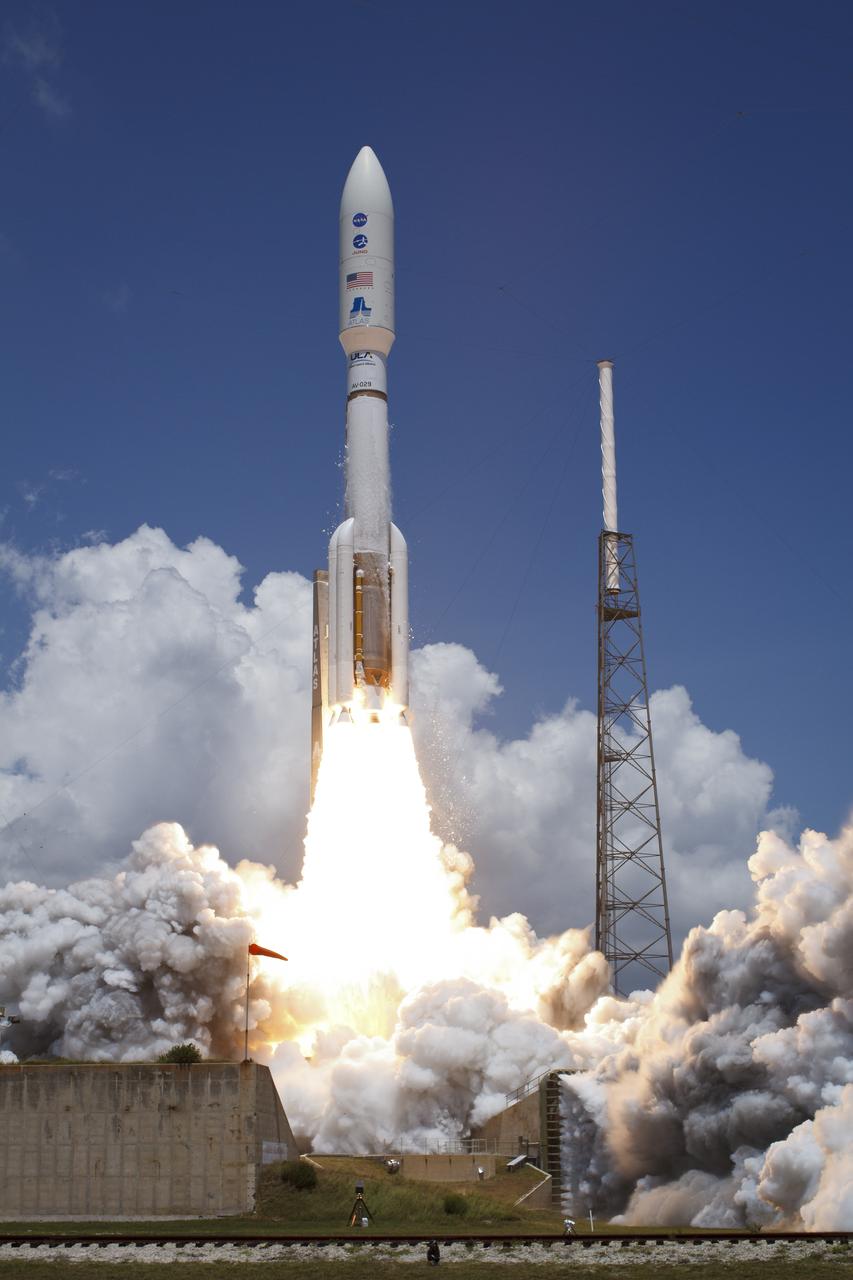

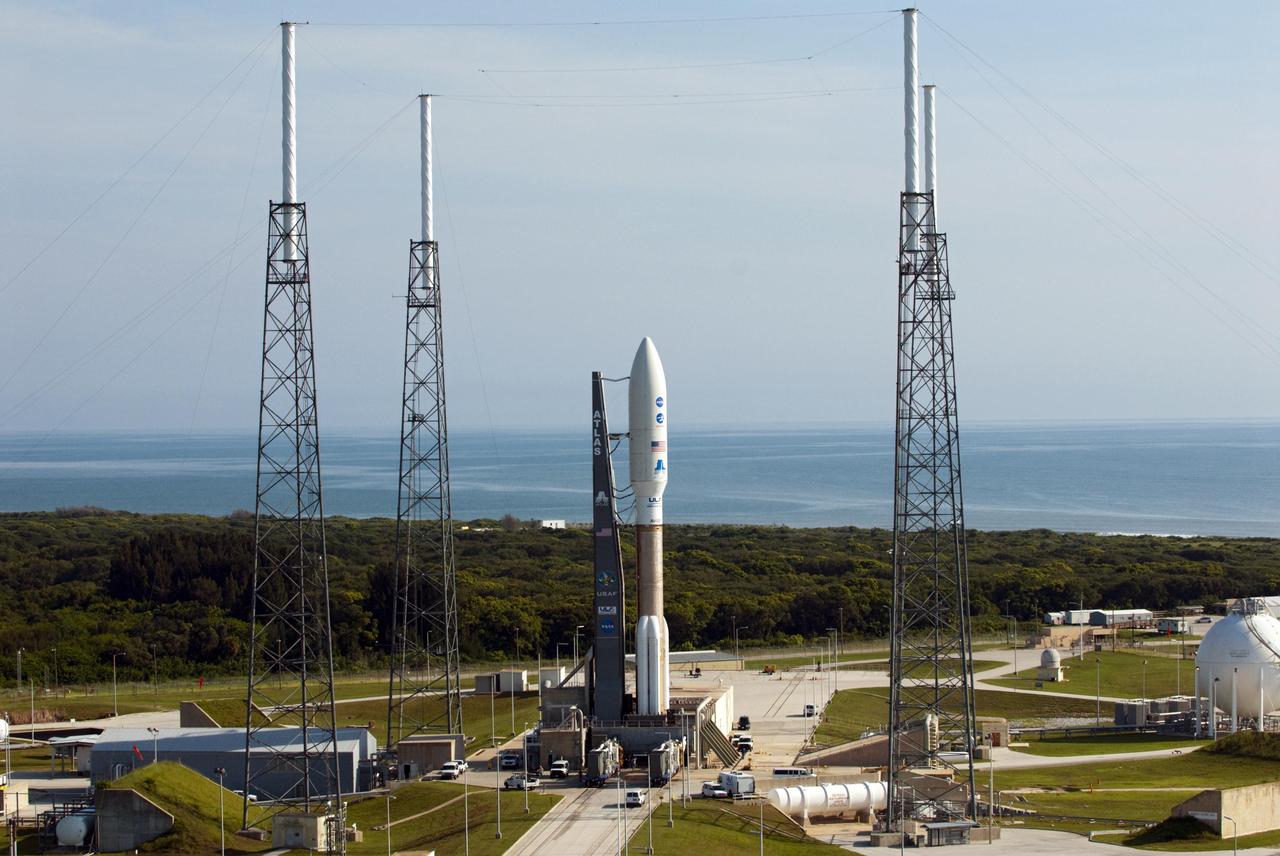
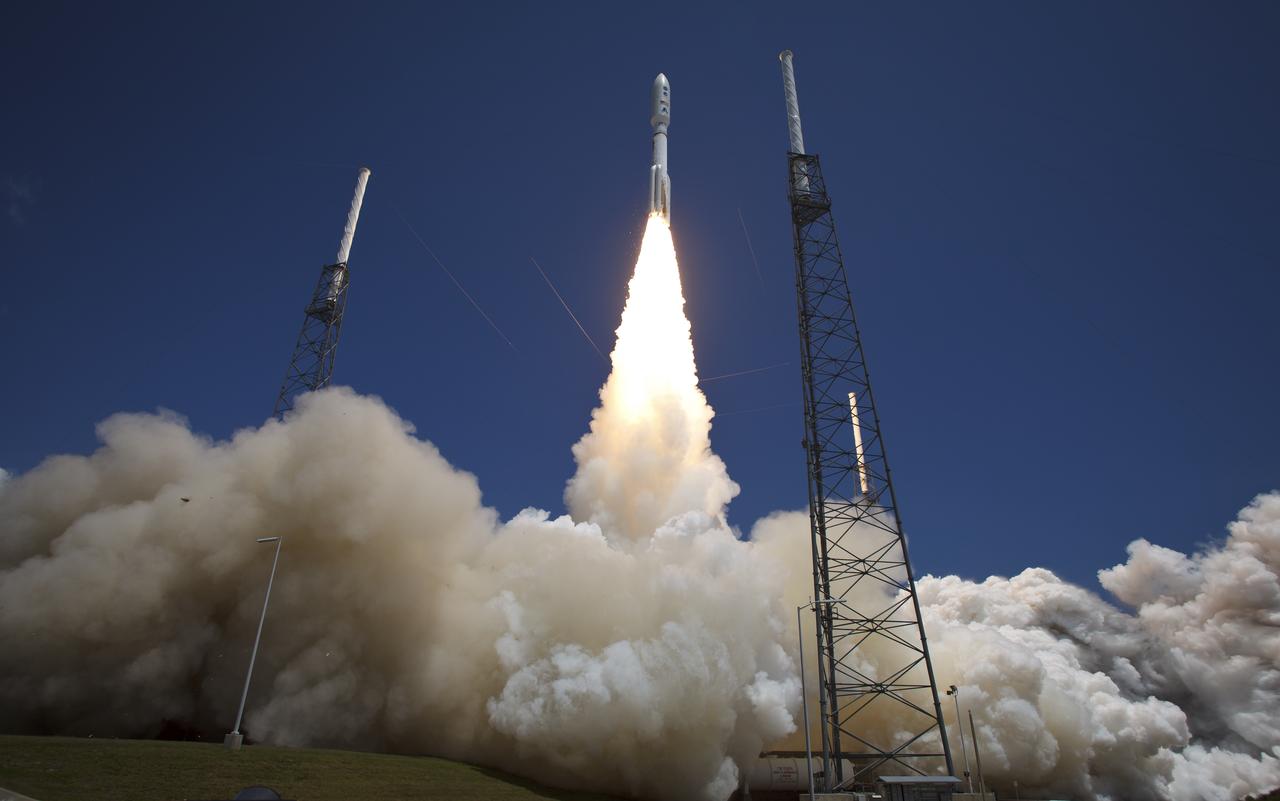
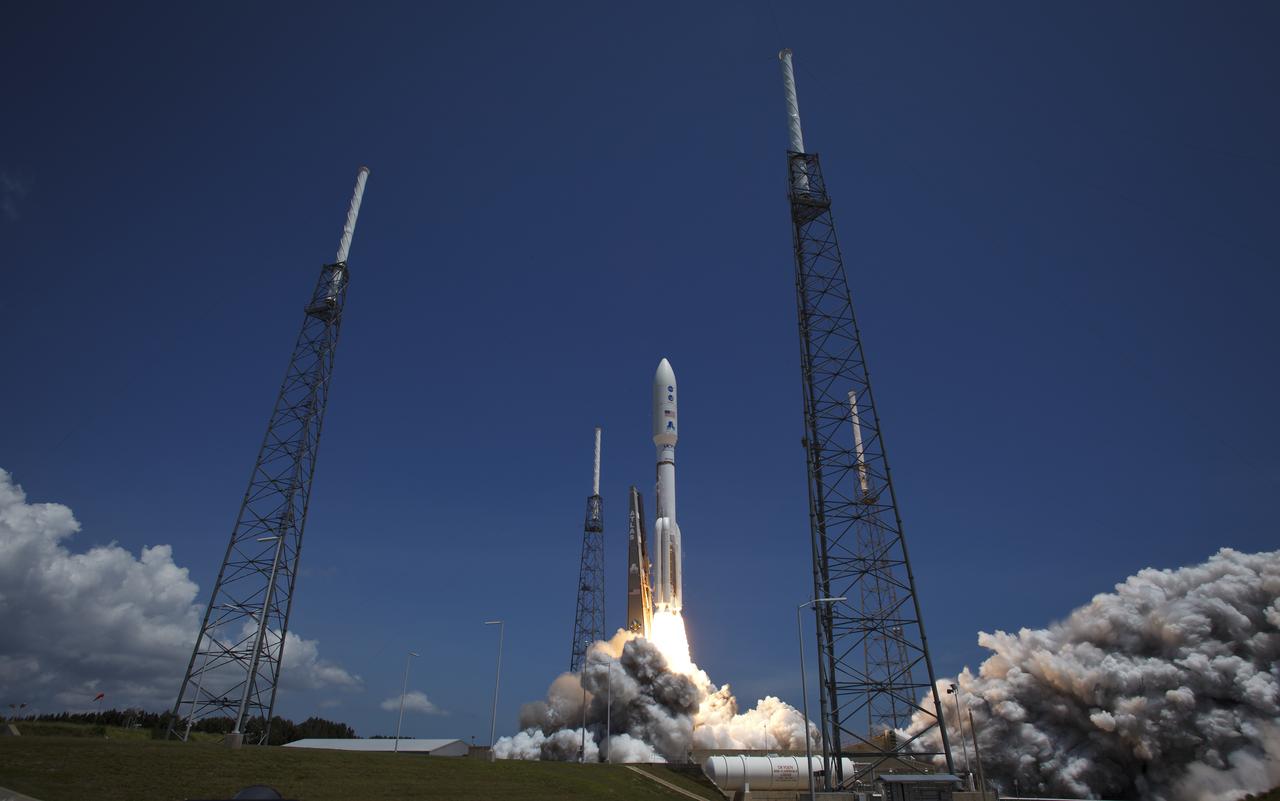
An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
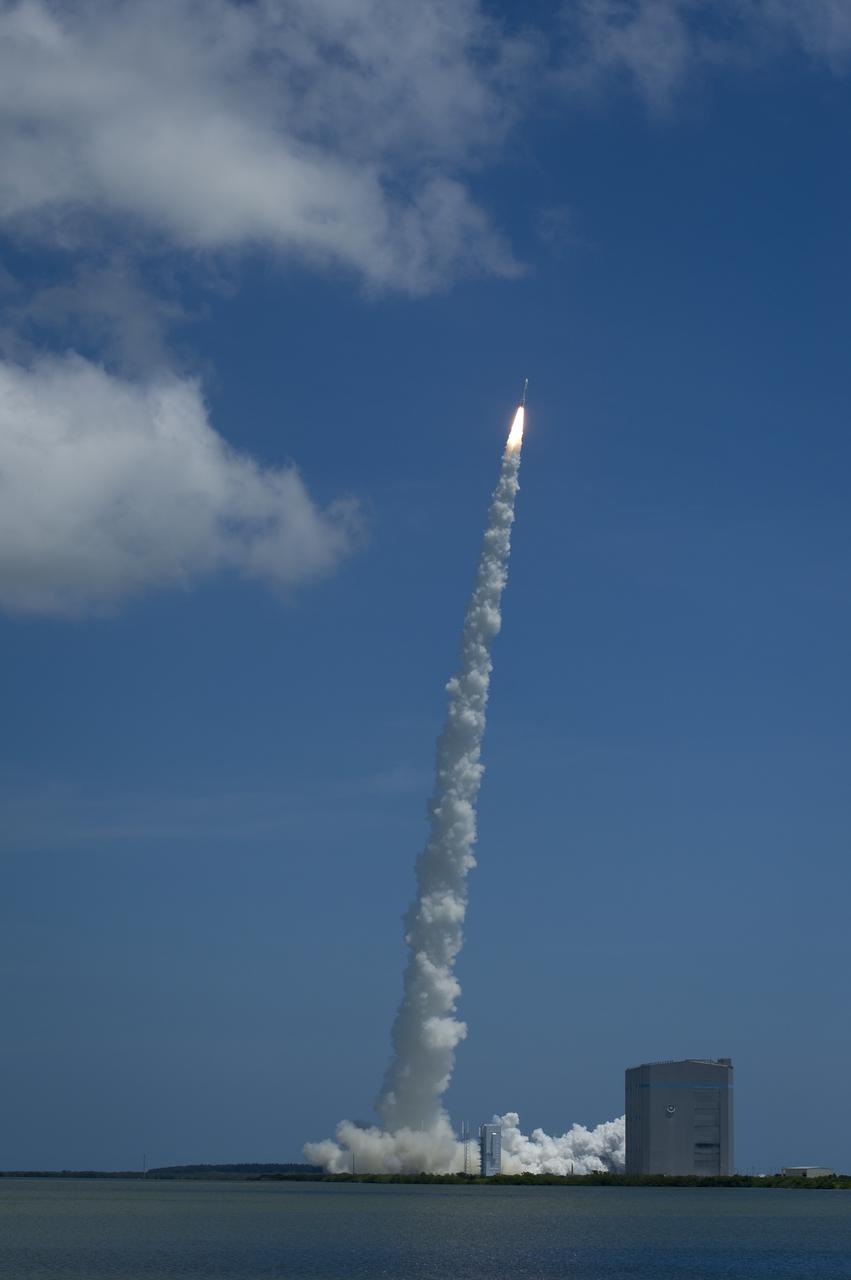

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
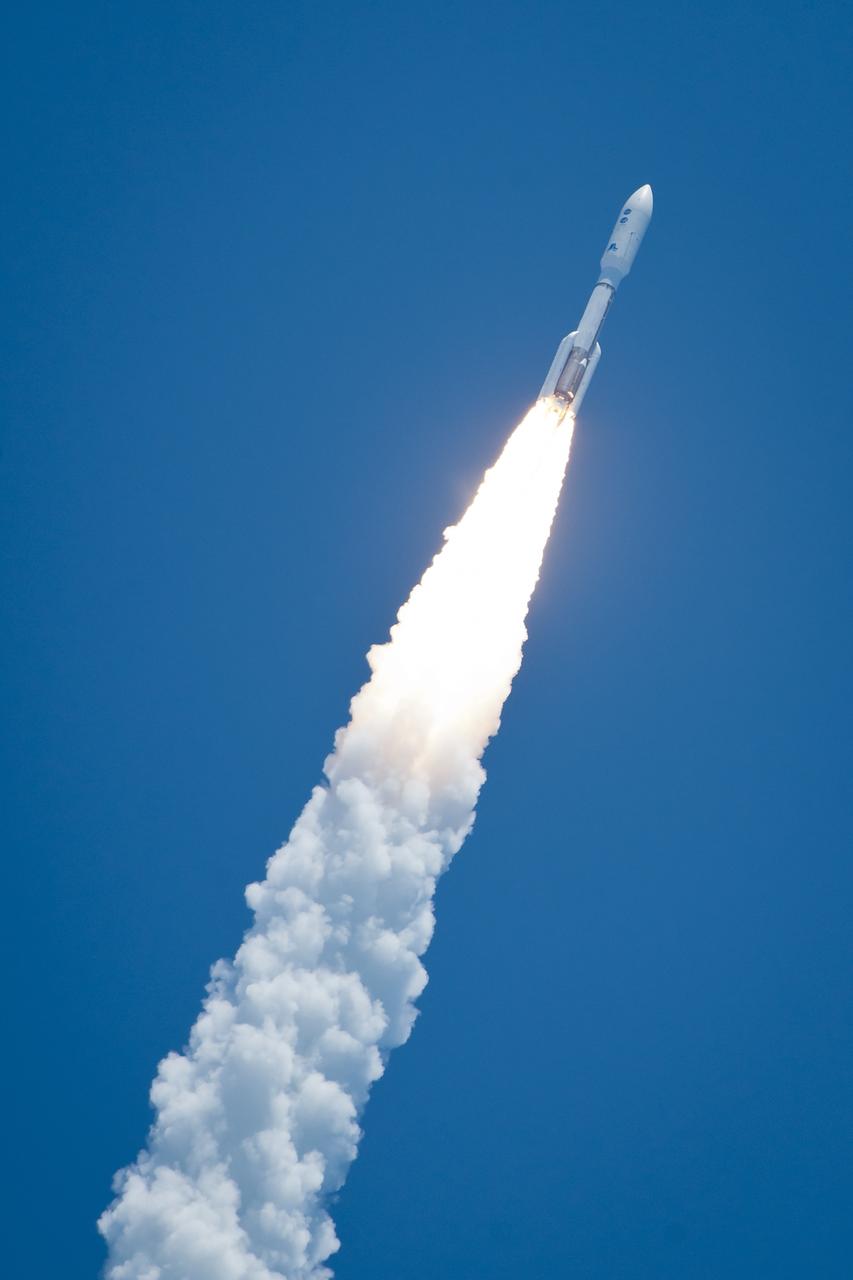

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
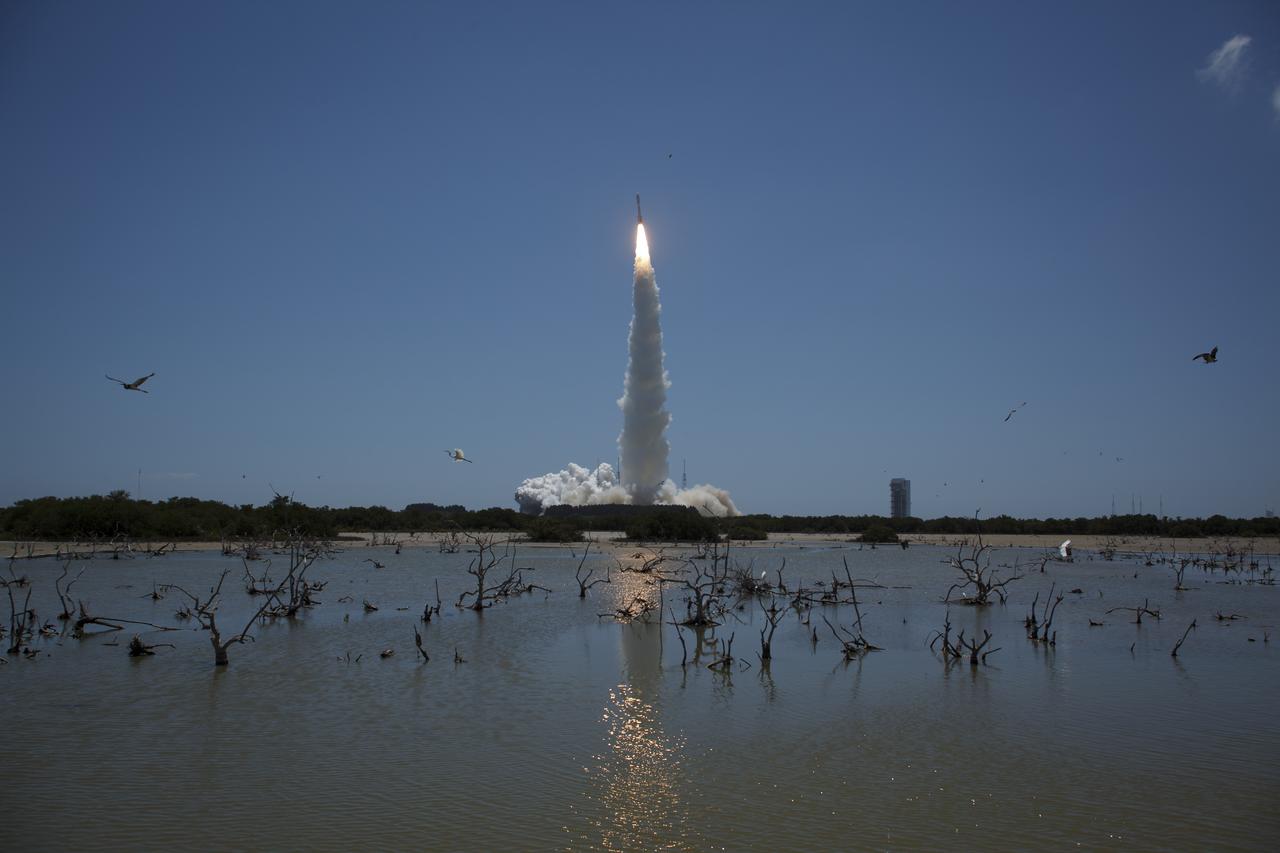

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
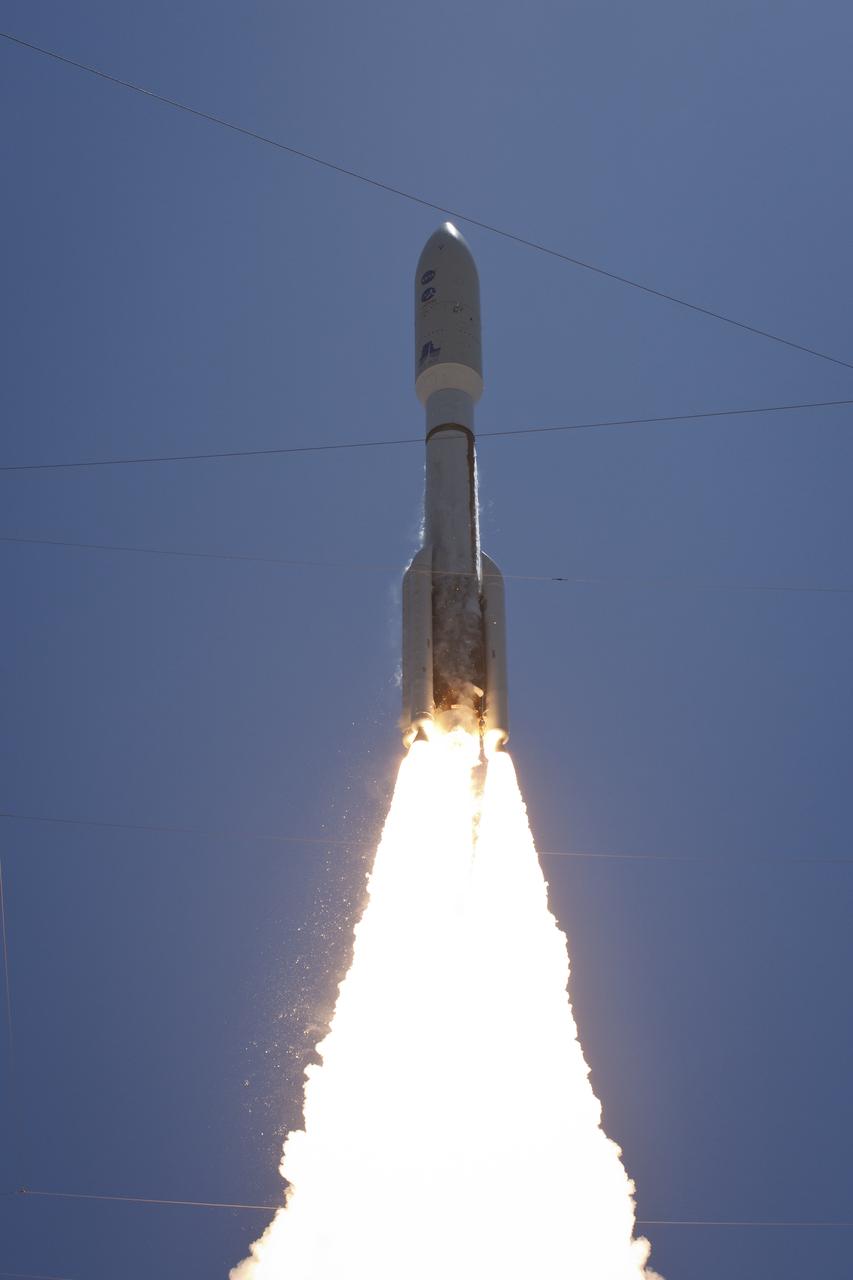

An Atlas V rocket launches with the Juno spacecraft payload from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Friday, August 5, 2011. The Juno spacecraft will make a five-year, 400-million-mile voyage to Jupiter, orbit the planet, investigate its origin and evolution with eight instruments to probe its internal structure and gravity field, measure water and ammonia in its atmosphere, map its powerful magnetic field and observe its intense auroras. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
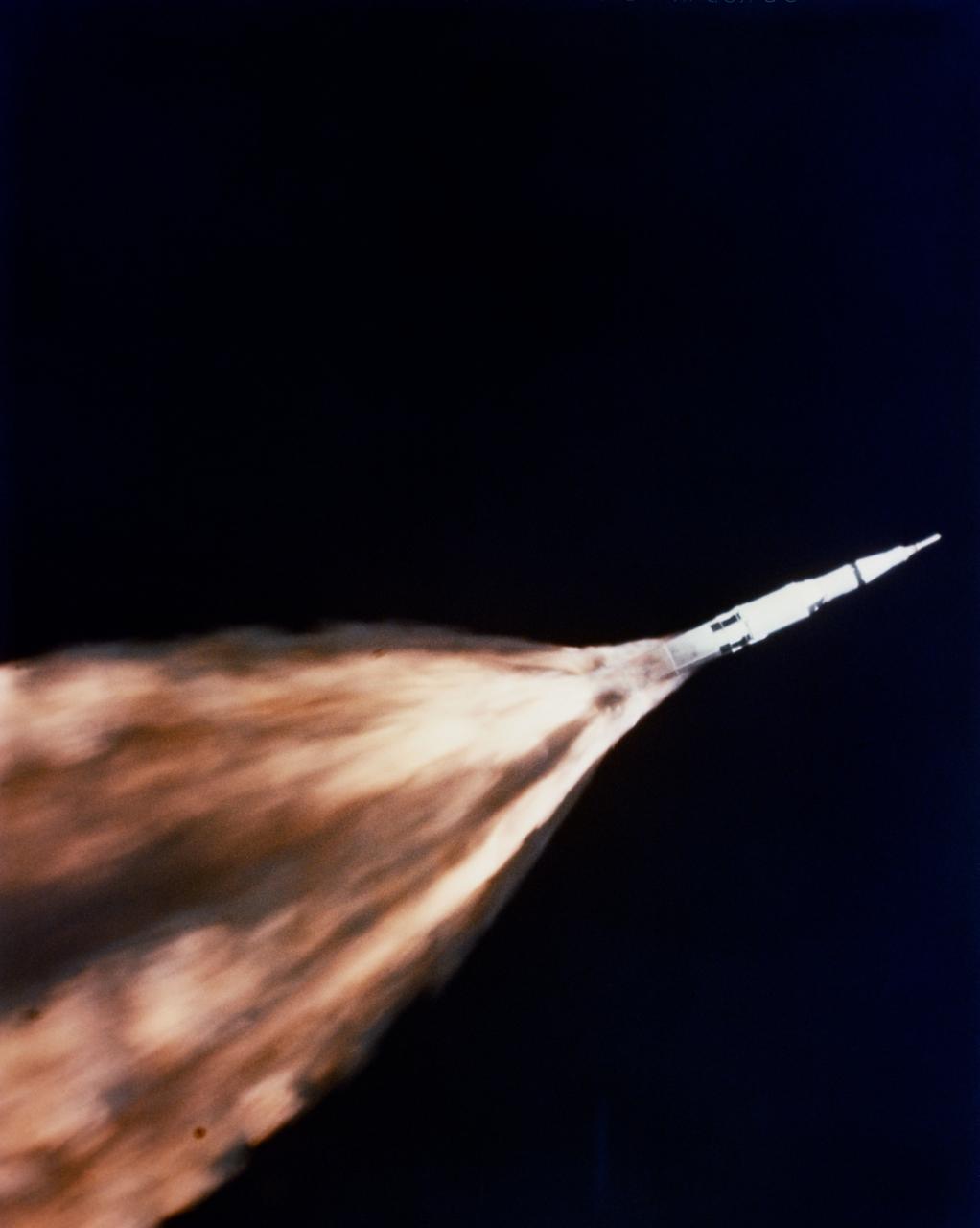

S68-27365 (4 April 1968) --- The five F-1 engines of the huge Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle's first (S-IC) stage leave a gigantic trail of flame in the sky above the Kennedy Space Center seconds after liftoff. The launch of the Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) unmanned space mission occurred at 07:00:01.5 (EST), April 4, 1968. This view of the Apollo 6 launch was taken from a chase plane.
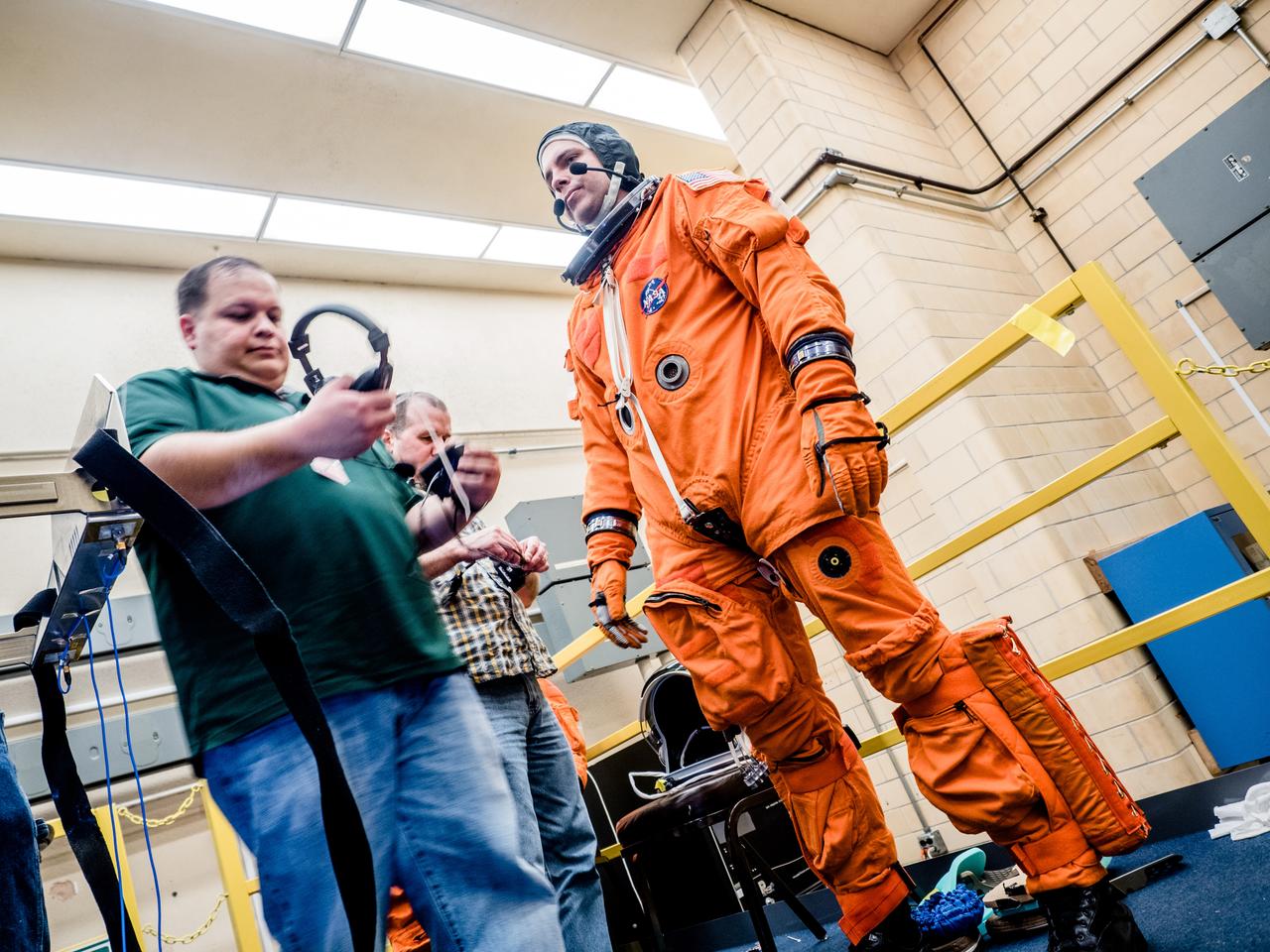

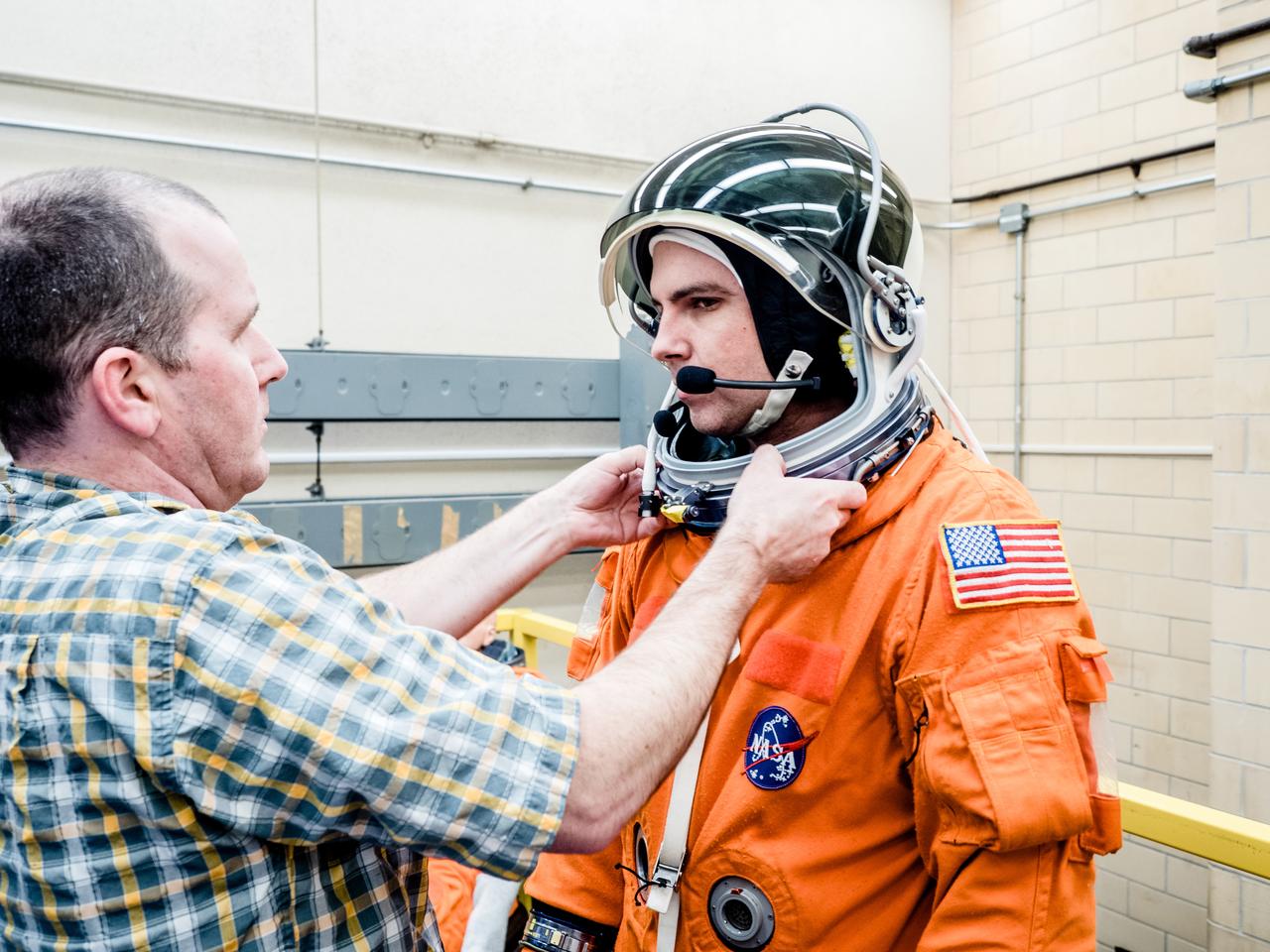
In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.
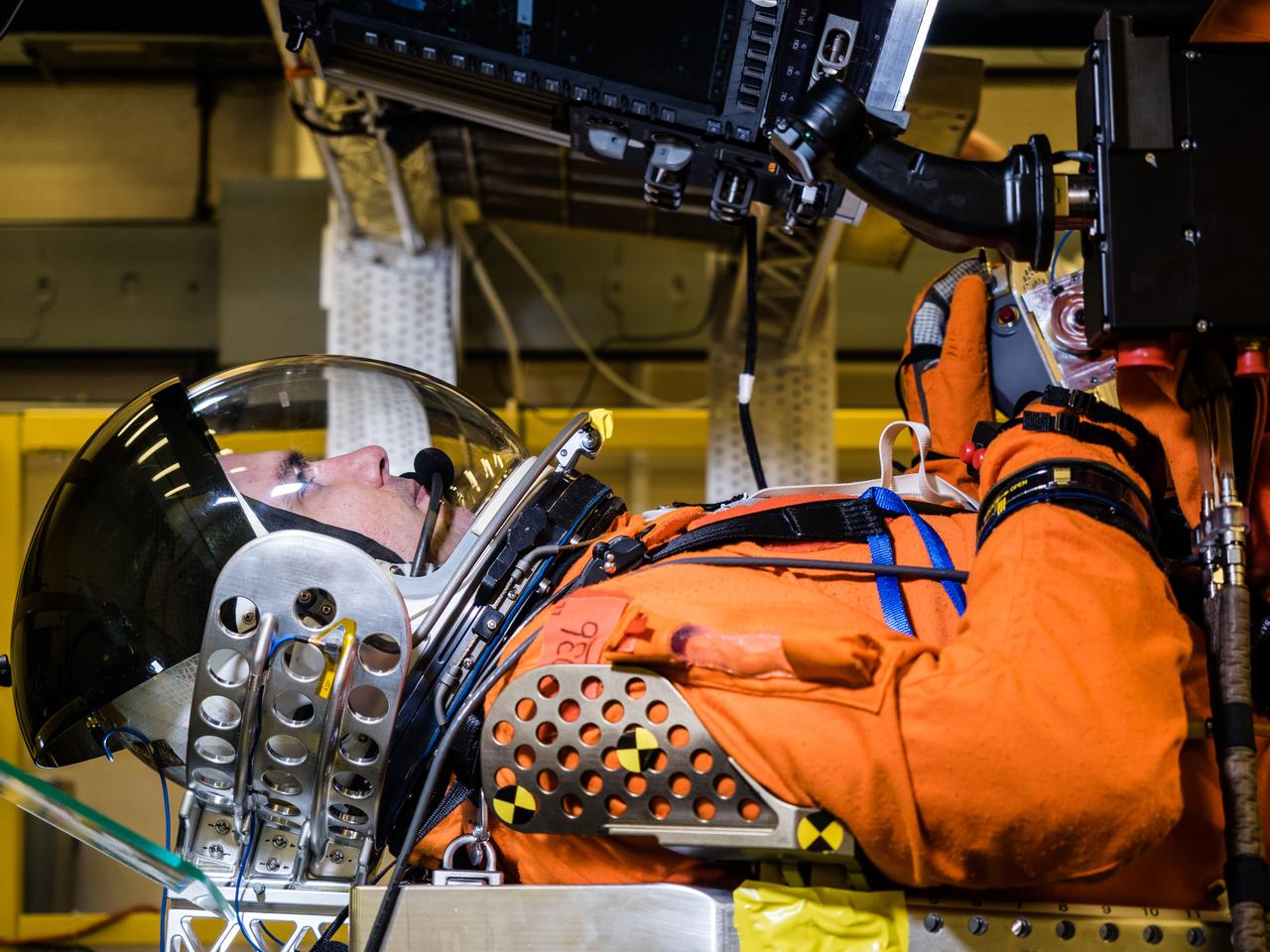

In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.
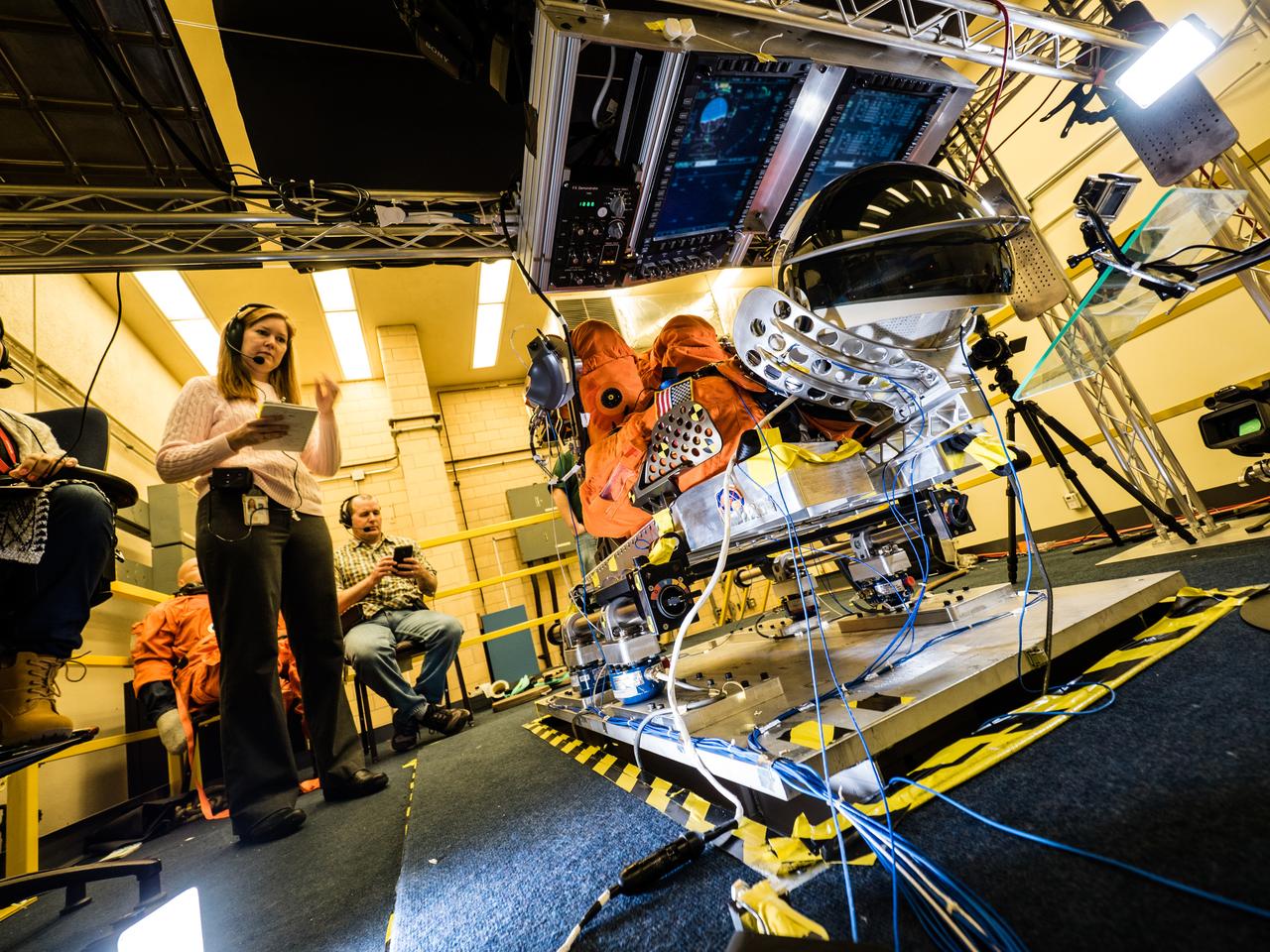
In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.

In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.
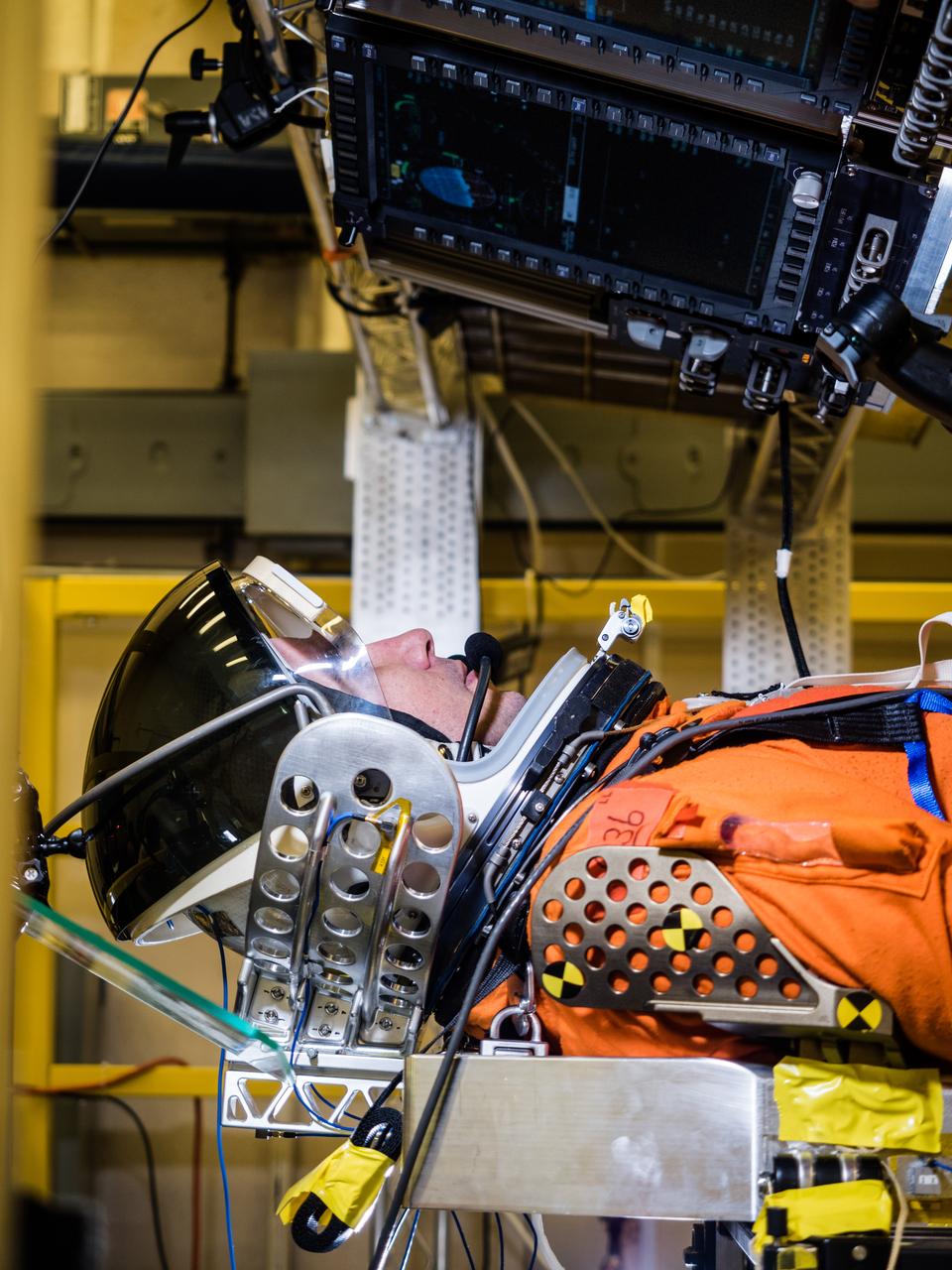

In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.

In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.

In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.
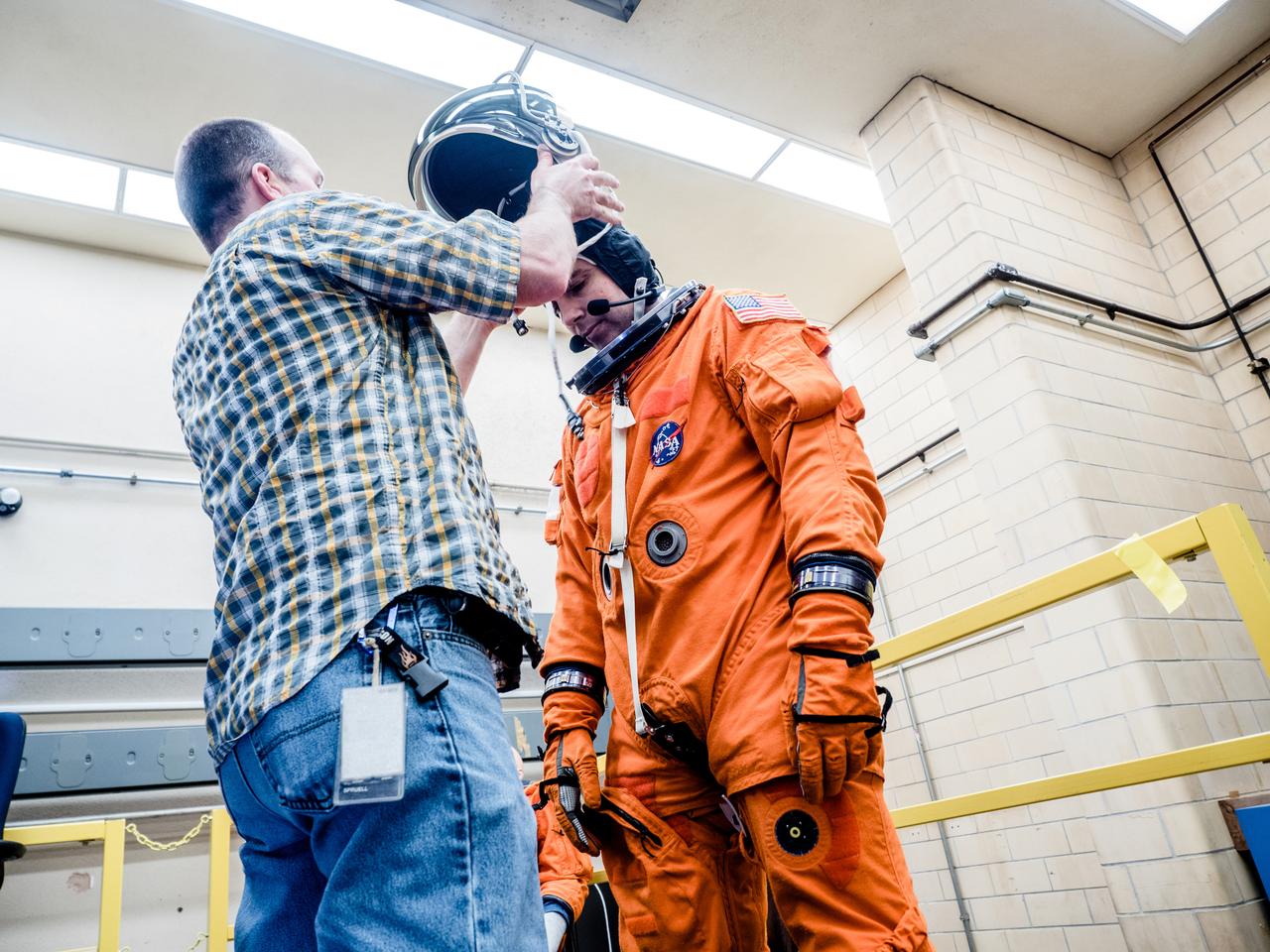

In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.

In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.
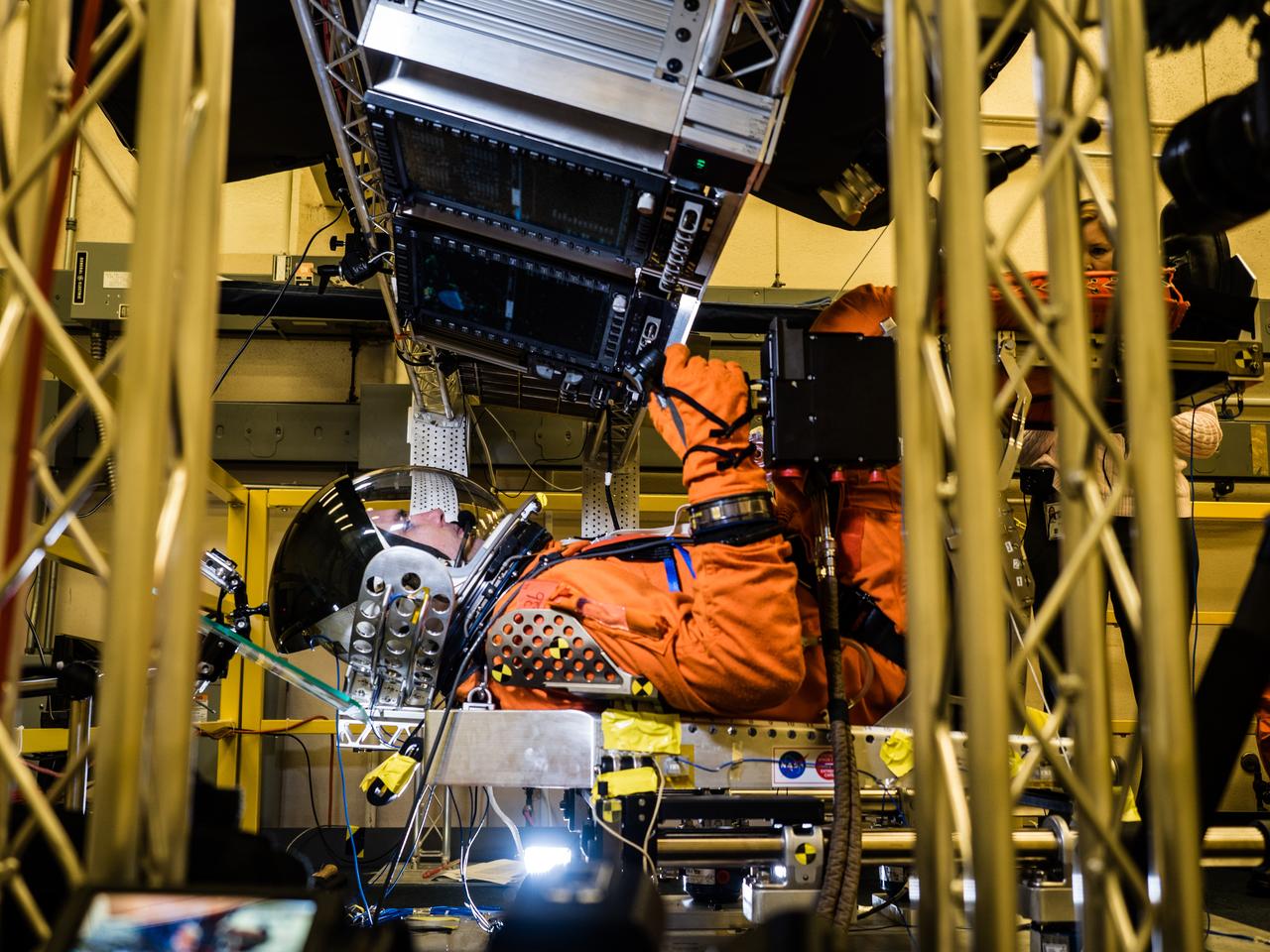

In a lab at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, engineers simulate conditions that astronauts in space suits would experience when the Orion spacecraft is vibrating during launch atop the agency’s powerful Space Launch System rocket on its way to deep space destinations on Jan. 19, 2017. A series of tests occurring this month at Johnson will help human factors engineers assess how well the crew can interact with the displays and controls they will use to monitor Orion’s systems and operate the spacecraft when necessary...Test subjects wore modified advanced crew escape suits that are being developed for astronauts in Orion, and sat in the latest design of the seat atop the crew impact attenuation system. This was the first time this key hardware was brought together to evaluate how launch vibrations may impact the astronaut’s ability to view the displays and controls.
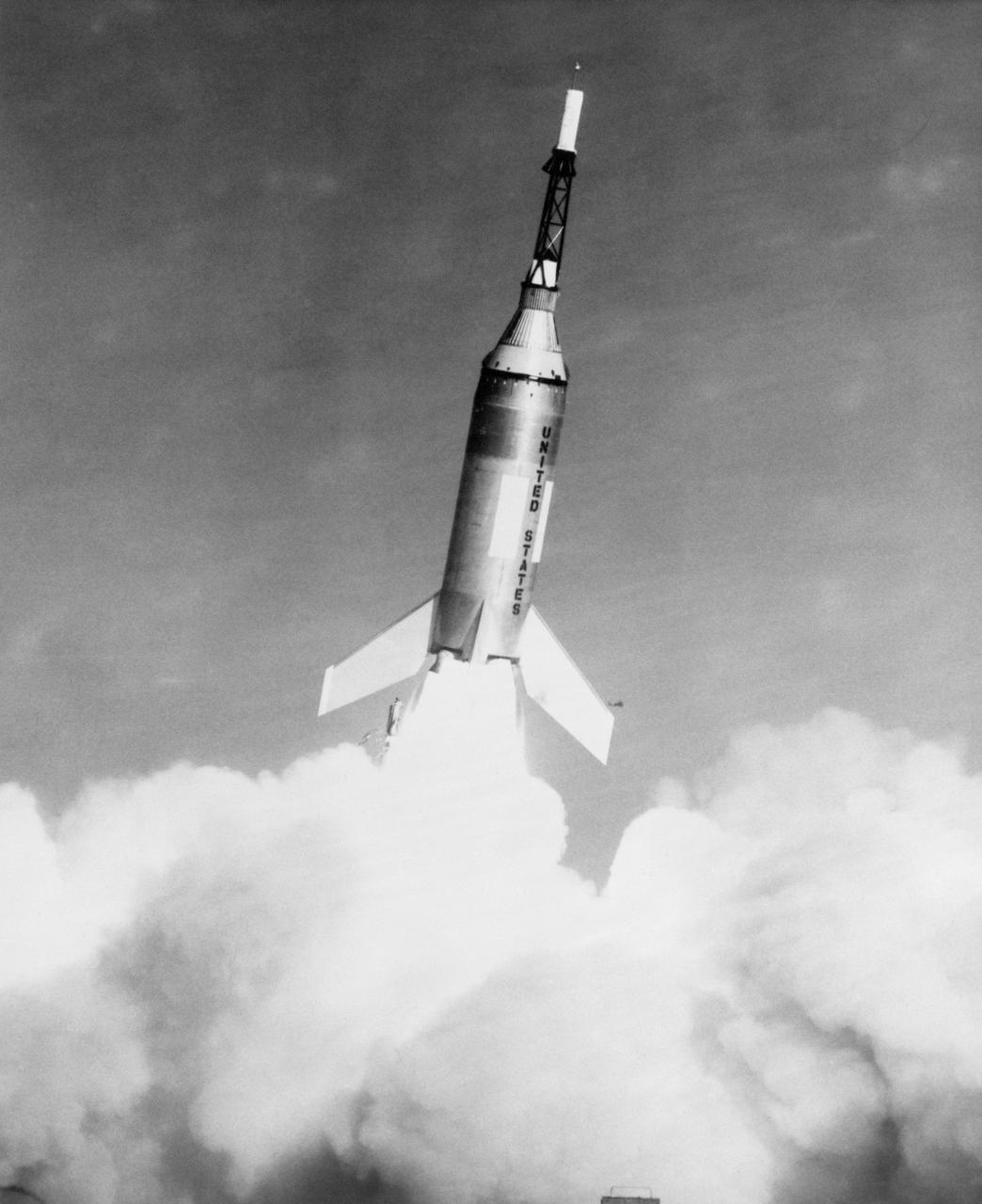
G61-00030 (4 Nov. 1959) --- Launch of Little Joe-2 from Wallops Island carrying Mercury spacecraft test article. The suborbital test flight of the Mercury capsule was to test the escape system. Vehicle functioned perfectly, but escape rocket ignited several seconds too late. Photo credit: NASA
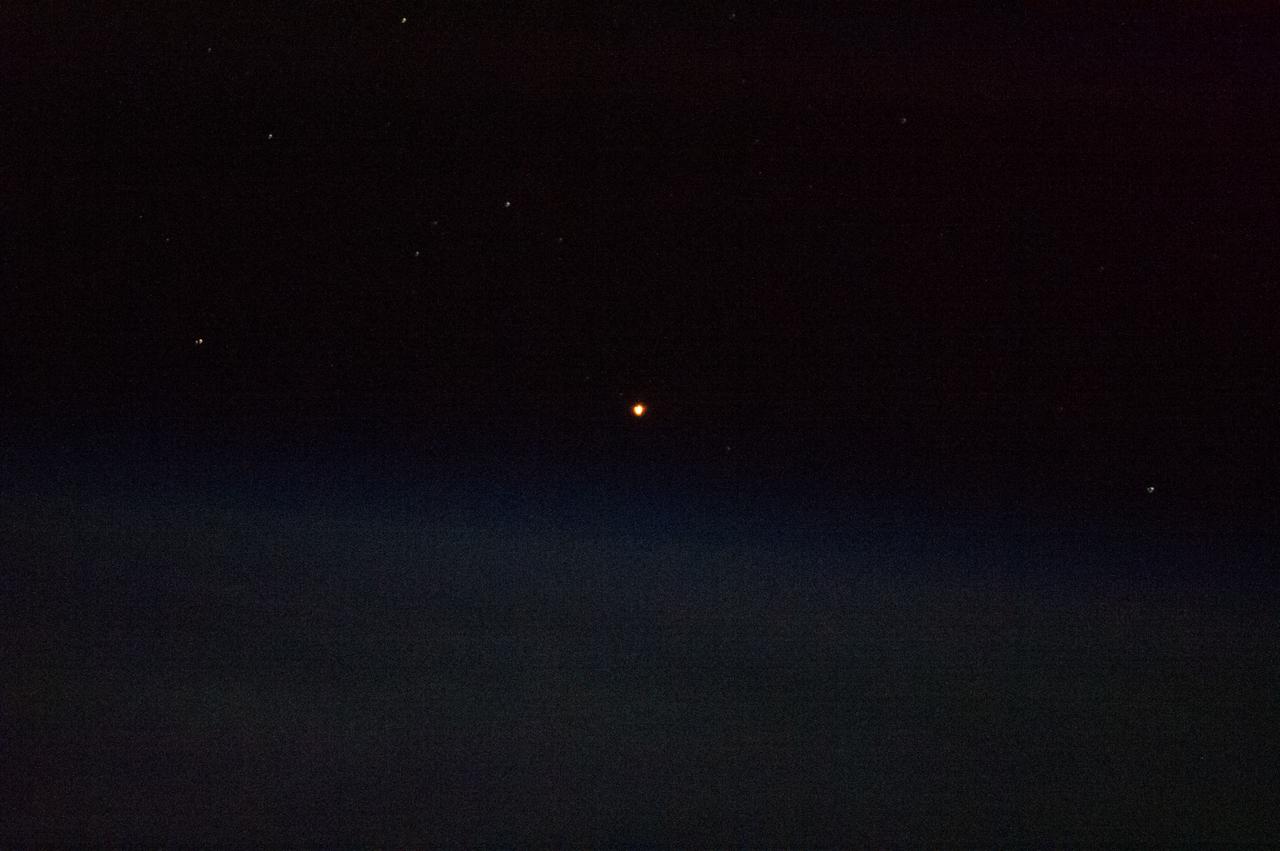

View of the launch of the Soyuz TMA-08M/34S spacecraft as seen by Expedition 35 crewmembers aboard the ISS.
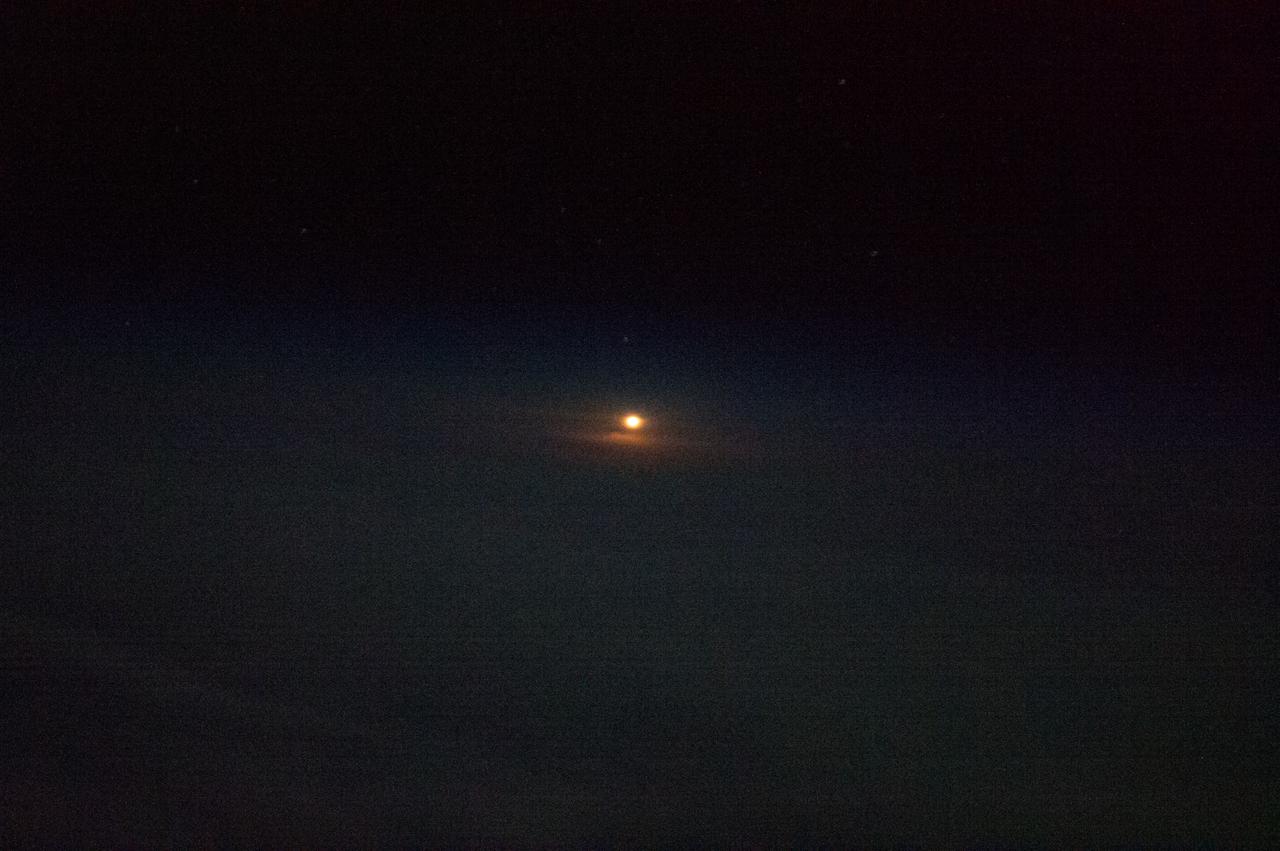

View of the launch of the Soyuz TMA-08M/34S spacecraft as seen by Expedition 35 crewmembers aboard the ISS.

Nighttime view of the launch of the Soyuz TMA-12M spacecraft as seen by Expedition 39 crewmembers aboard the ISS.
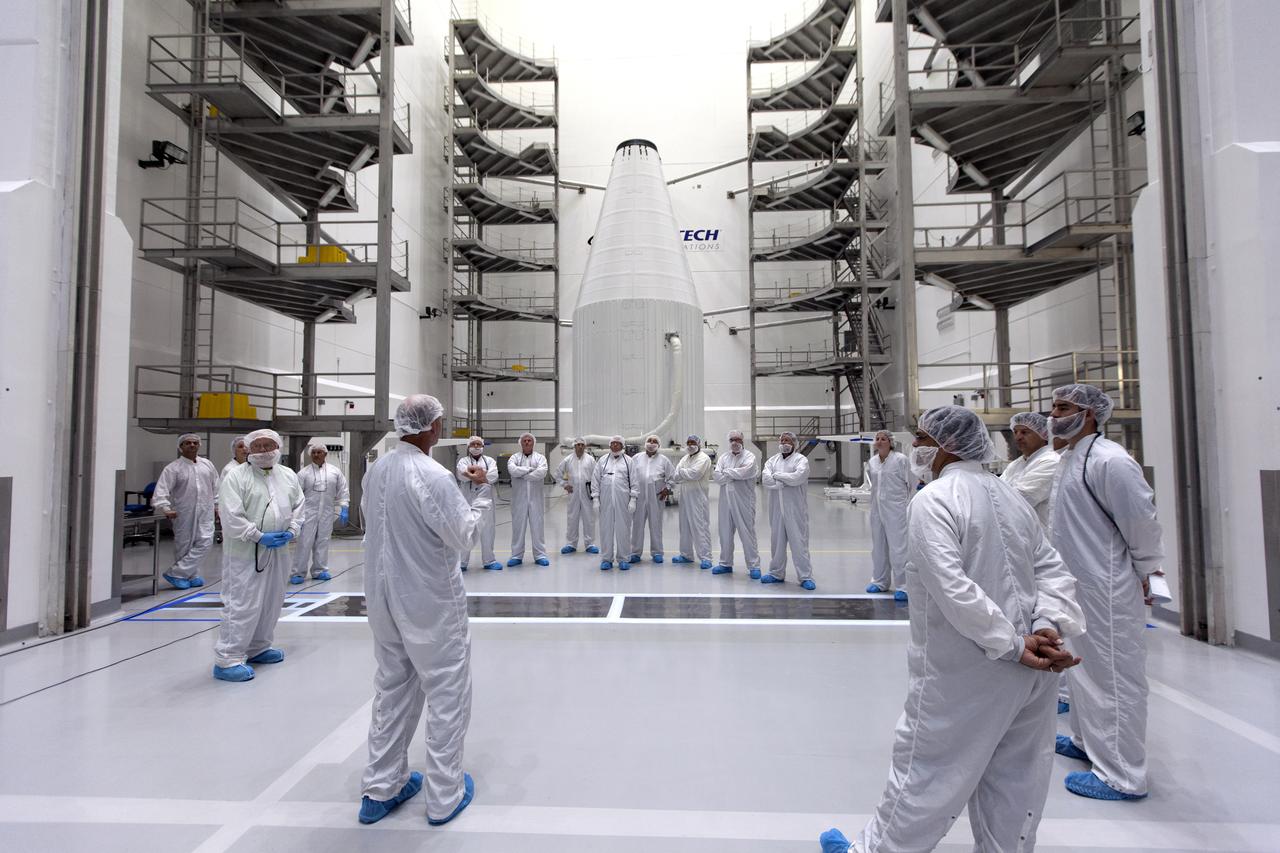

Inside the Astrotech facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's TDRS-M satellite, enclosed in its payload fairing, is being prepared for lifting to a transport vehicle. Engineers and technicians in clean room attire review procedures before the lifting process begins. The TDRS-M is the latest spacecraft destined for the agency's constellation of communications satellites that allows nearly continuous contact with orbiting spacecraft ranging from the International Space Station and Hubble Space Telescope to the array of scientific observatories. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled to take place from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Aug. 18 at 8:03 a.m. EDT.

S68-27364 (4 April 1968) --- The Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) unmanned space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. The liftoff of the huge Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle occurred at 7:00:01.5 a.m. (EST), April 4, 1968.
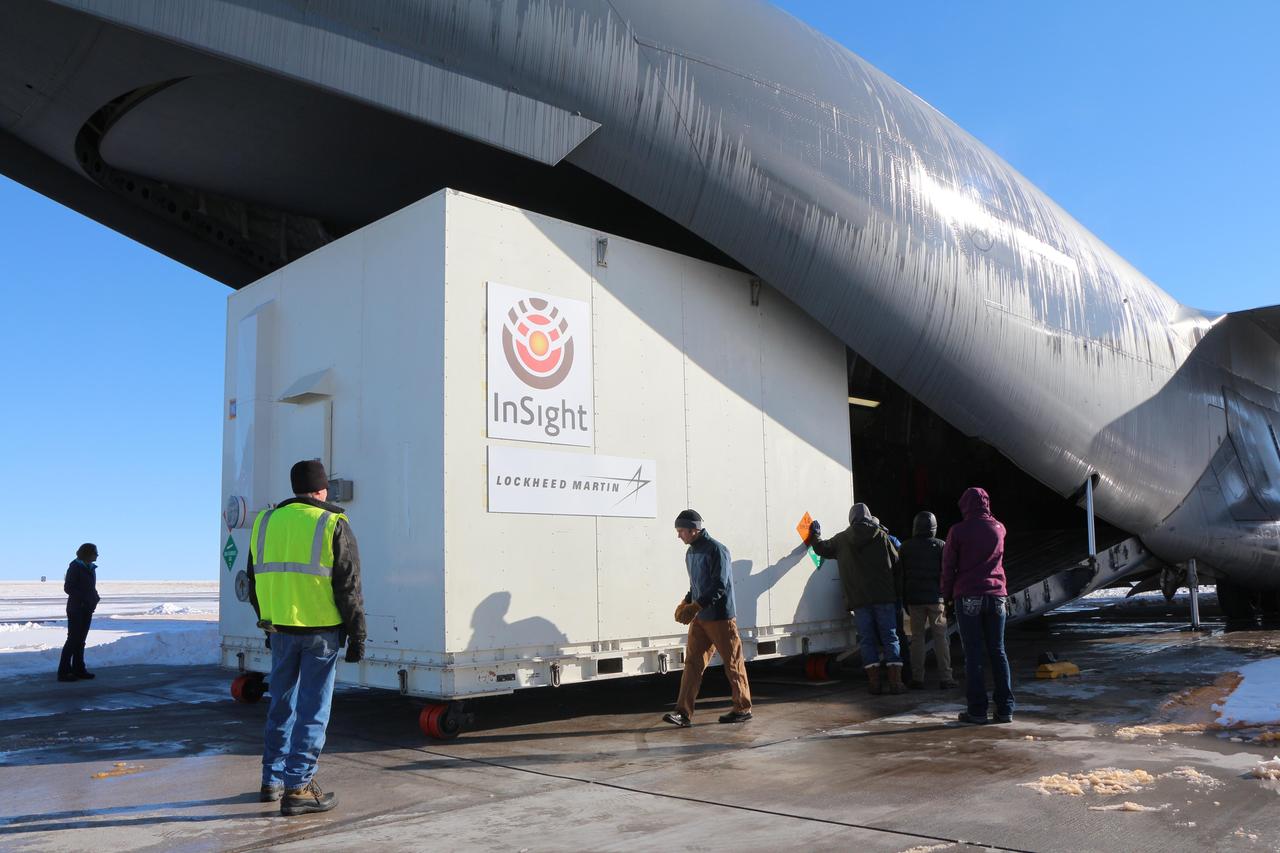

Personnel supporting NASA's InSight mission to Mars load the crated InSight spacecraft into a C-17 cargo aircraft at Buckley Air Force Base, Denver, for shipment to Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. The spacecraft, built in Colorado by Lockheed Martin Space Systems, was shipped Dec. 16, 2015, in preparation for launch from Vandenberg in March 2016. InSight, for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is the first mission dedicated to studying the deep interior of Mars. Its findings will advance understanding of the early history of all rocky planets, including Earth. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20278
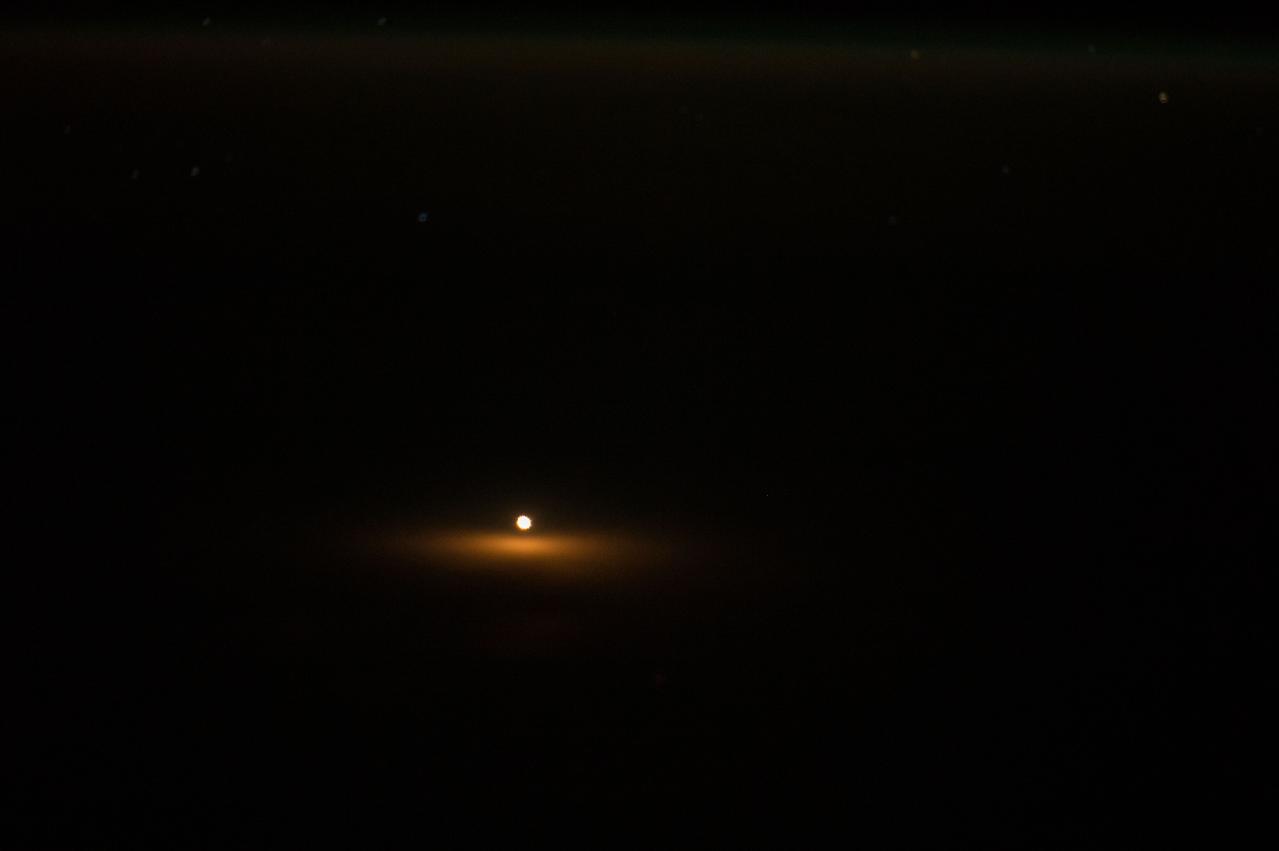

Nighttime view of the launch of the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft as seen by Expedition 42 crewmembers aboard the ISS. Image was released by astronaut on Instagram.
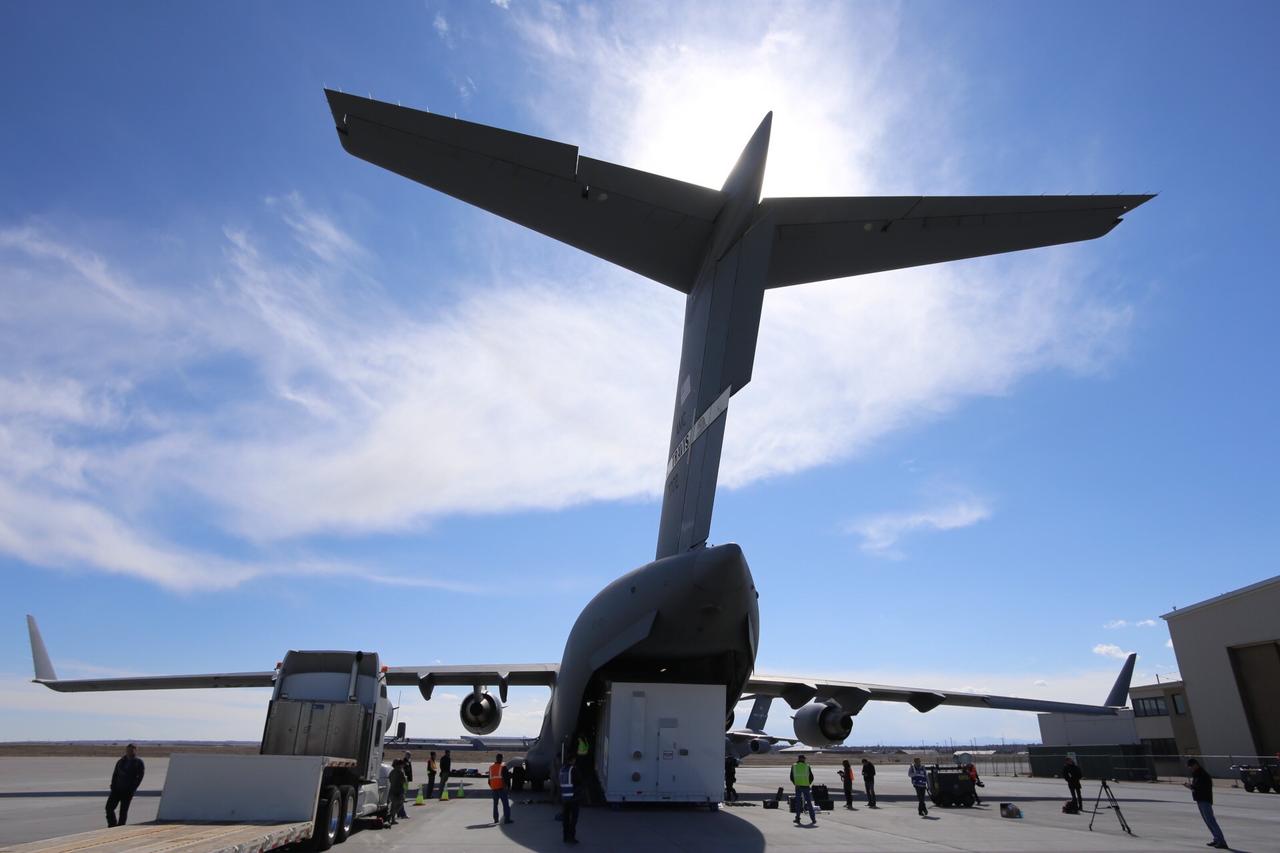

Personnel supporting NASA's InSight mission to Mars load the crated InSight spacecraft into a C-17 cargo aircraft at Buckley Air Force Base, Denver, for shipment to Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. The spacecraft, built in Colorado by Lockheed Martin Space, was shipped February 28, 2018, in preparation for launch from Vandenberg in May 2018. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is the first mission dedicated to studying the deep interior of Mars. Its findings will advance understanding of the early history of all rocky planets, including Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22252
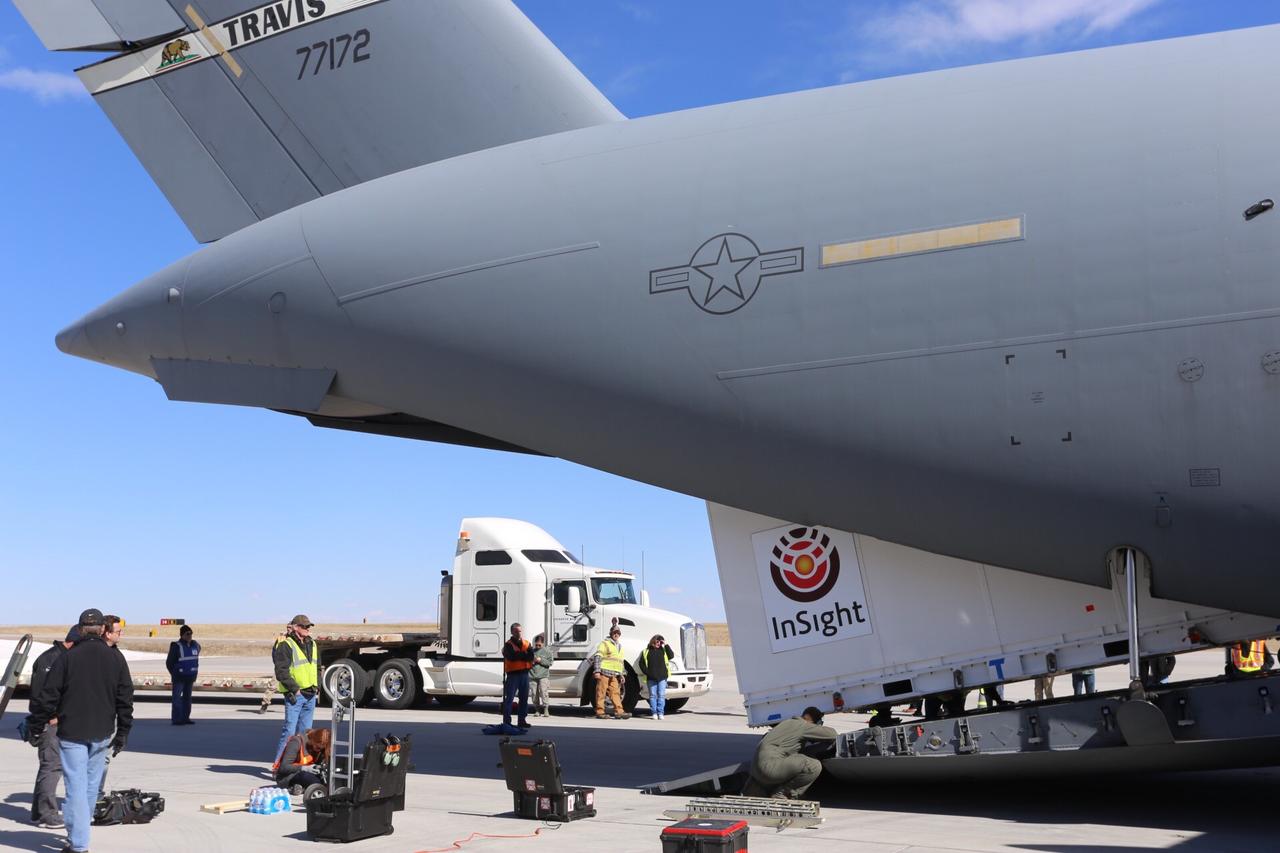

Personnel supporting NASA's InSight mission to Mars load the crated InSight spacecraft into a C-17 cargo aircraft at Buckley Air Force Base, Denver, for shipment to Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. The spacecraft, built in Colorado by Lockheed Martin Space, was shipped February 28, 2018, in preparation for launch from Vandenberg in May 2018. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is the first mission dedicated to studying the deep interior of Mars. Its findings will advance understanding of the early history of all rocky planets, including Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22253
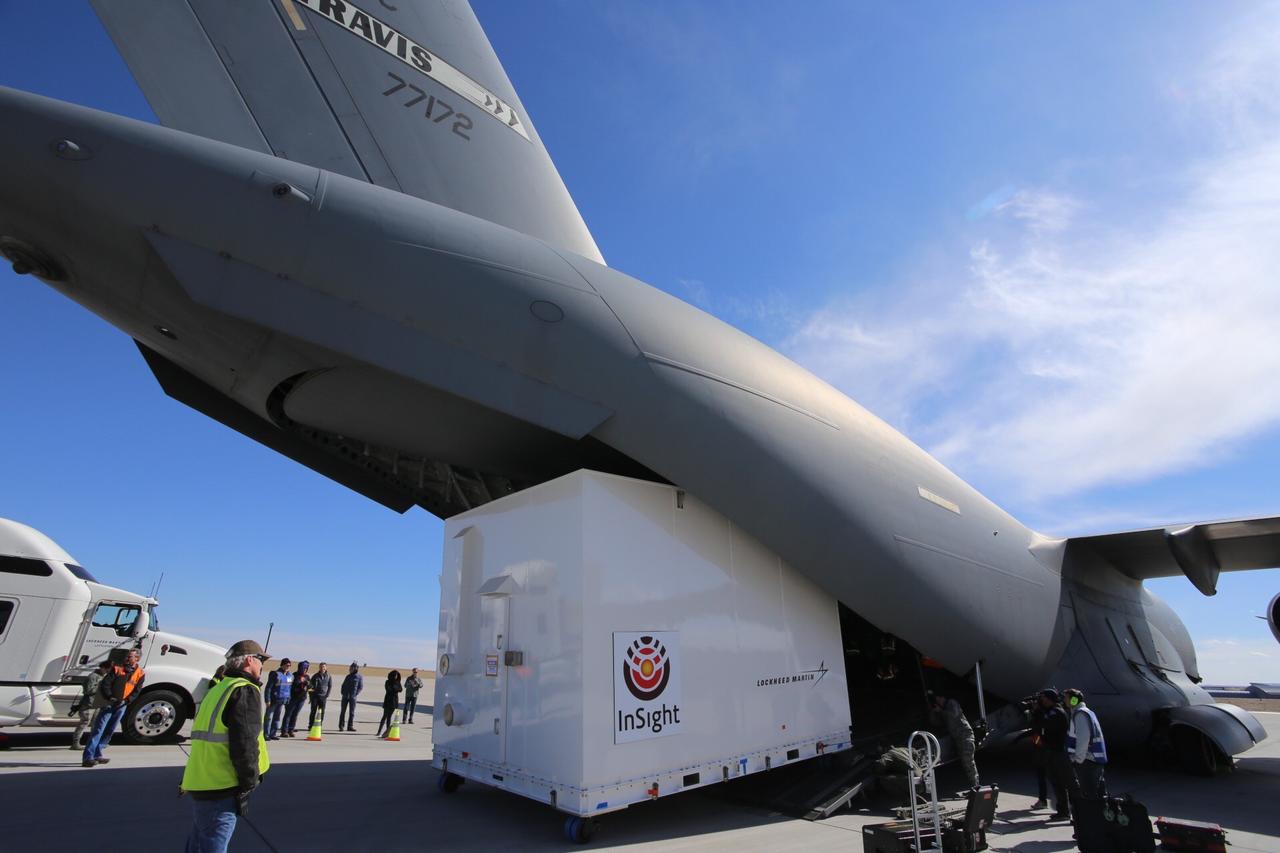

Personnel supporting NASA's InSight mission to Mars load the crated InSight spacecraft into a C-17 cargo aircraft at Buckley Air Force Base, Denver, for shipment to Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. The spacecraft, built in Colorado by Lockheed Martin Space, was shipped February 28, 2018, in preparation for launch from Vandenberg in May 2018. InSight, short for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, is the first mission dedicated to studying the deep interior of Mars. Its findings will advance understanding of the early history of all rocky planets, including Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22220

Flight simulation No. 3 is on the schedule for the Pegasus XL launch vehicle, seen here in Building 1555 on North Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. AIM, which stands for Aeronomy of Ice in the Mesosphere, is being prepared for integrated testing and a flight simulation. The AIM spacecraft will fly three instruments designed to study polar mesospheric clouds located at the edge of space, 50 miles above the Earth's surface in the coldest part of the planet's atmosphere. The mission's primary goal is to explain why these clouds form and what has caused them to become brighter and more numerous and appear at lower latitudes in recent years. AIM's results will provide the basis for the study of long-term variability in the mesospheric climate and its relationship to global climate change. AIM is scheduled to be mated to its launch vehicle, Orbital Sciences' Pegasus XL, during the second week of April, after which final inspections will be conducted. Launch is scheduled for April 25.
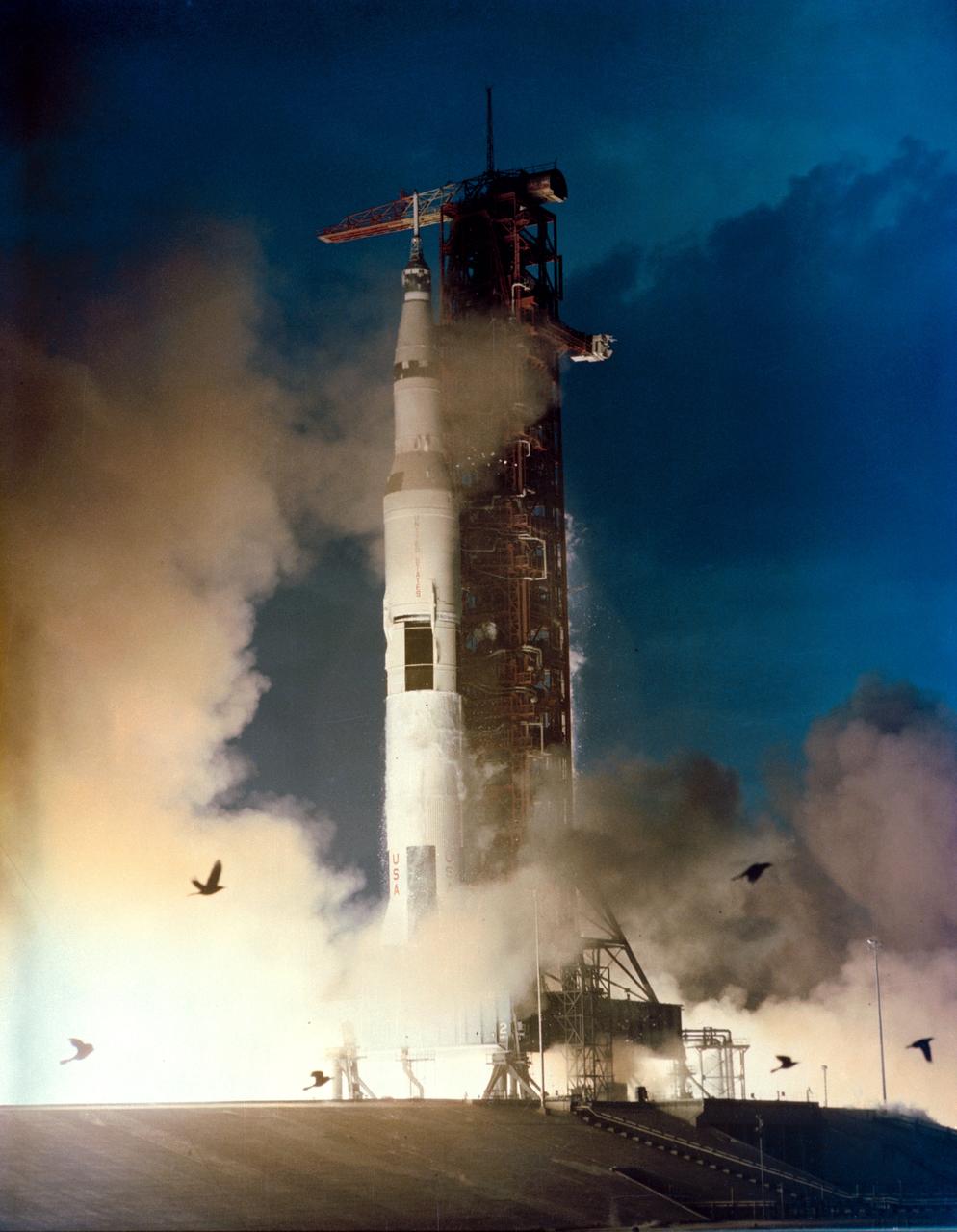

S71-18395 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.
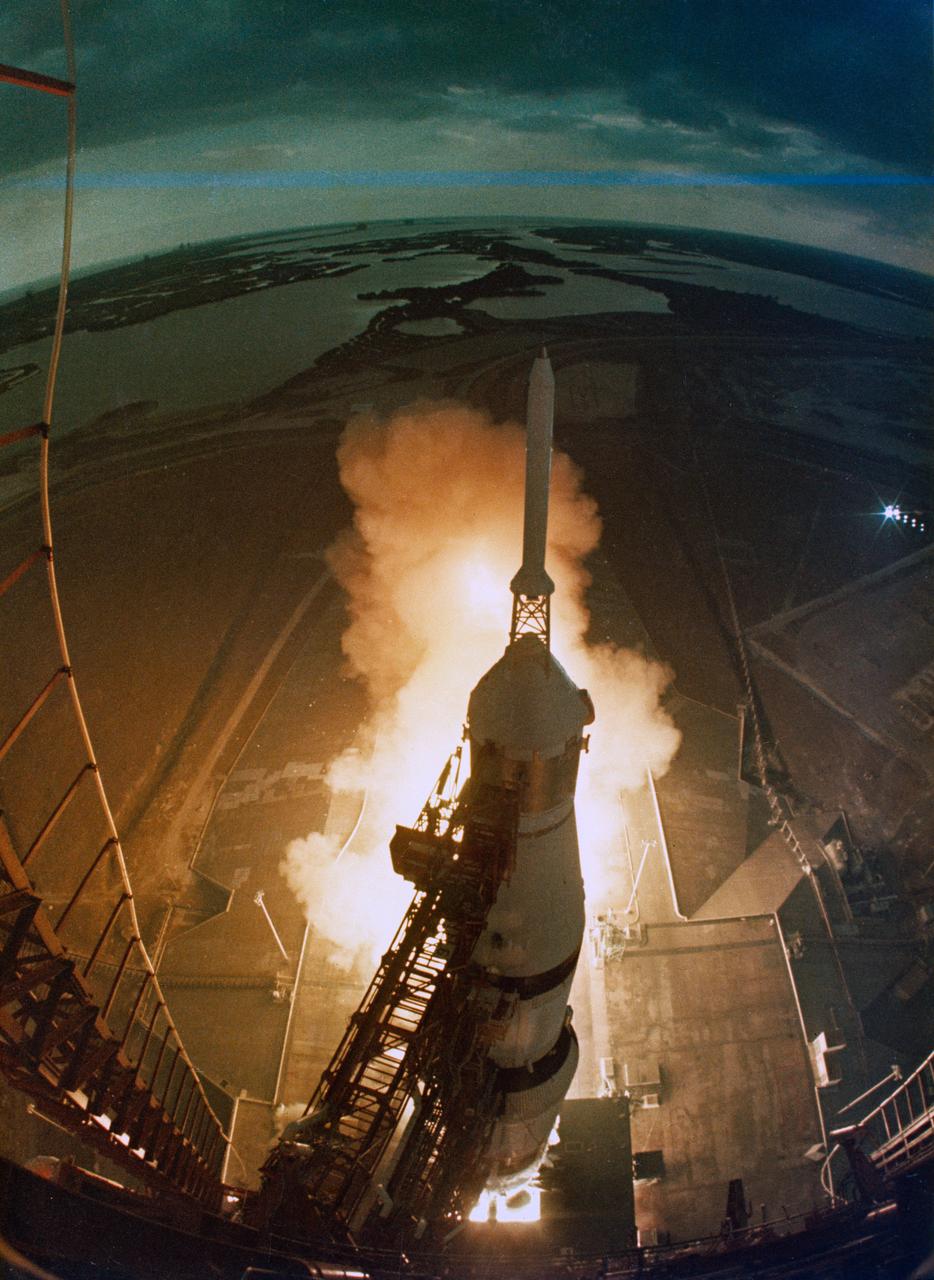

S71-17620 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The huge, 363-feet tall Apollo 14 (Spacecraft 110/Lunar Module 8/Saturn 509) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1981, on a lunar landing mission. This view of the liftoff was taken by a camera mounted on the mobile launch tower. Aboard the Apollo 14 spacecraft were astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot.

S67-43593 (26 Aug. 1967) --- The completely assembled Apollo Saturn 501 launch vehicle mated to the Apollo spacecraft 017 on Launch Complex 39A, Kennedy Space Center. The fully assembled vehicle was transported to the launch complex on the crawler.
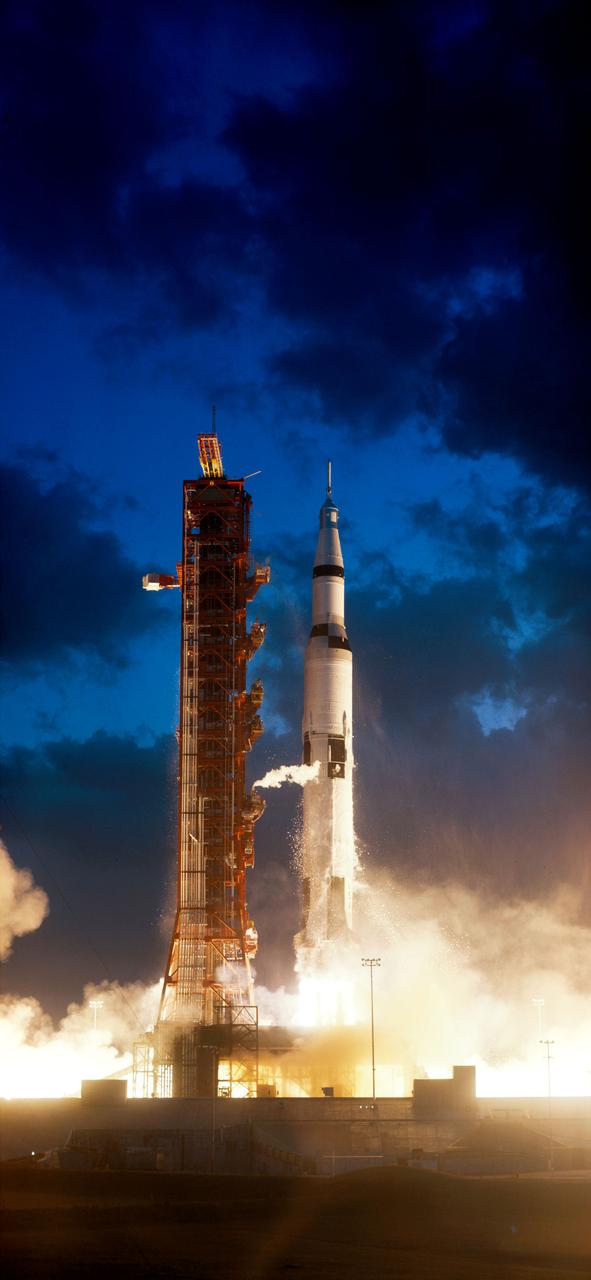

S67-50903 (9 Nov. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) space mission was launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The liftoff of the huge 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was at 7:00:01 a.m. (EST), Nov. 9, 1967. The successful objectives of the Apollo 4 Earth-orbital unmanned space mission obtained included (1) flight information on launch vehicle and spacecraft structural integrity and compatibility, flight loads, stage separation, subsystem operation, emergency detection subsystem, and (2) evaluation of the Apollo Command Module heat shield under conditions encountered on return from a moon mission.
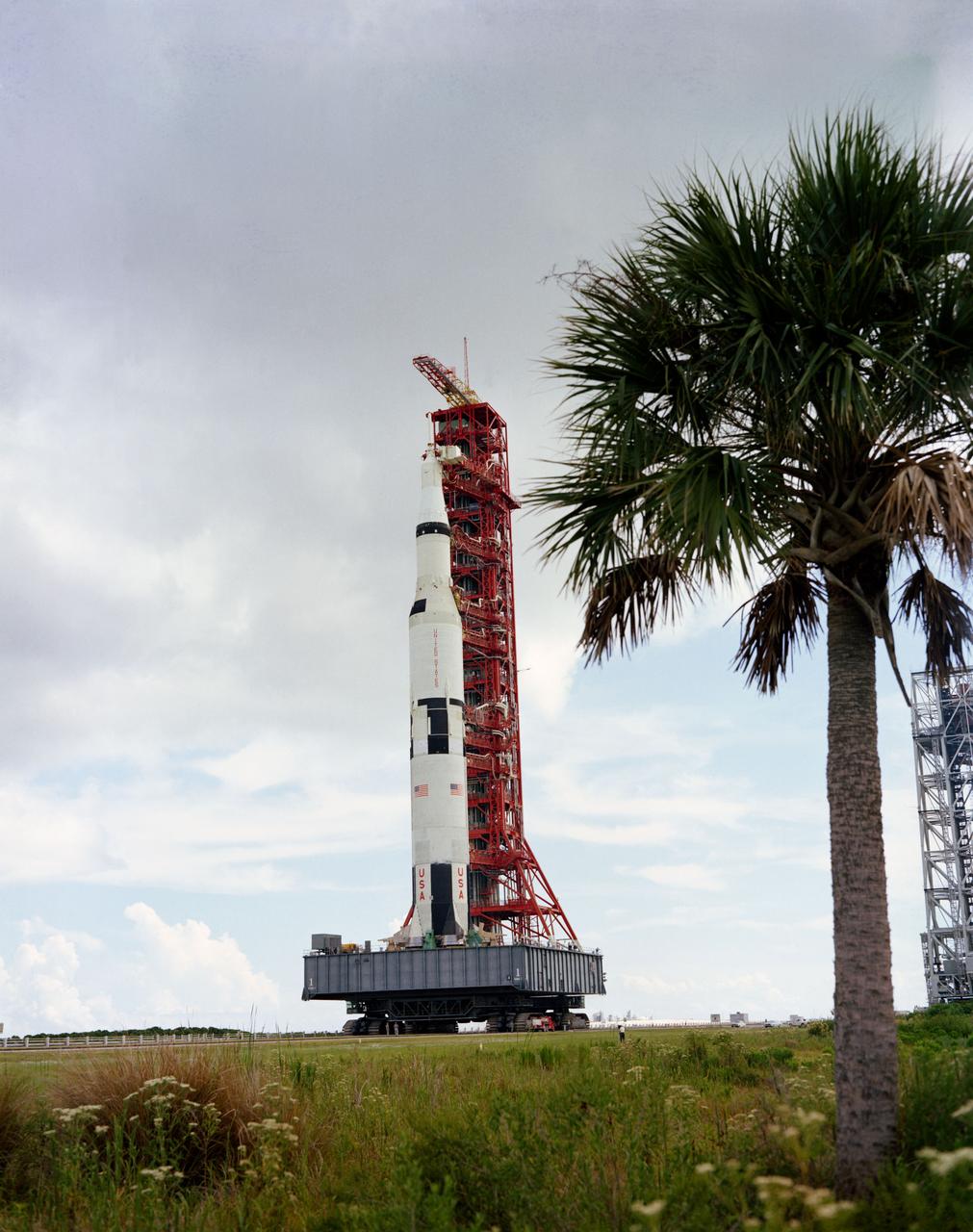

S67-43595 (26 Aug. 1967) --- The Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) stack and its mobile launch tower atop a crawler-transporter moving from the Vehicle Assembly Building toward Pad A, Launch Complex 39.

S68-56001 (21 Dec. 1968) --- The Apollo 8 (Spacecraft 103/Saturn 503) space vehicle is launched from Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, at 7:51 a.m. (EST), Dec. 21, 1968. The crew of the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission is astronauts Frank Borman, commander; James A. Lovell Jr., command module pilot; and William A. Anders, lunar module pilot. Apollo 8 was the first manned Saturn V launch. (Just after ignition)
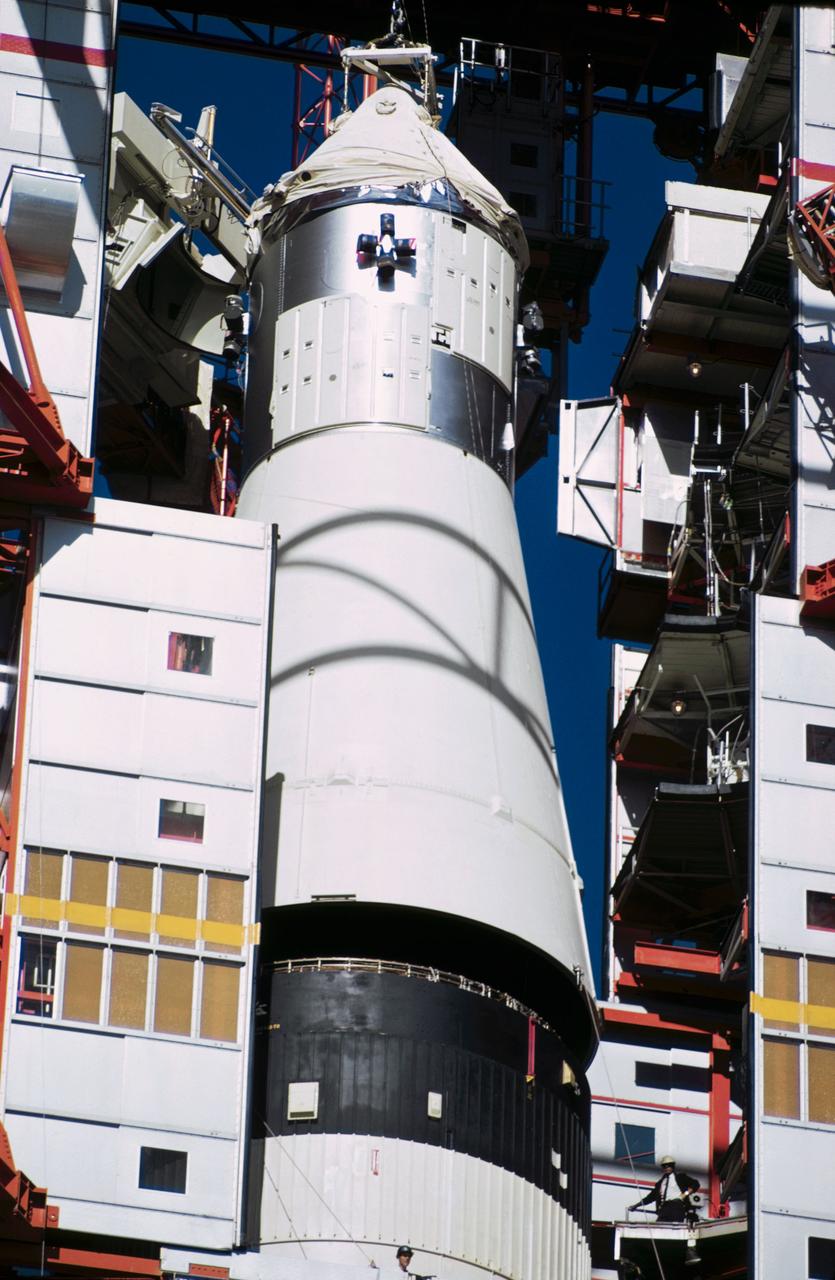

S67-17042 (1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 012 is hoisted to the top of the gantry at Pad 34 during the Apollo/Saturn Mission 204 erection. S/C 012 will be mated with the uprated Saturn I launch vehicle.
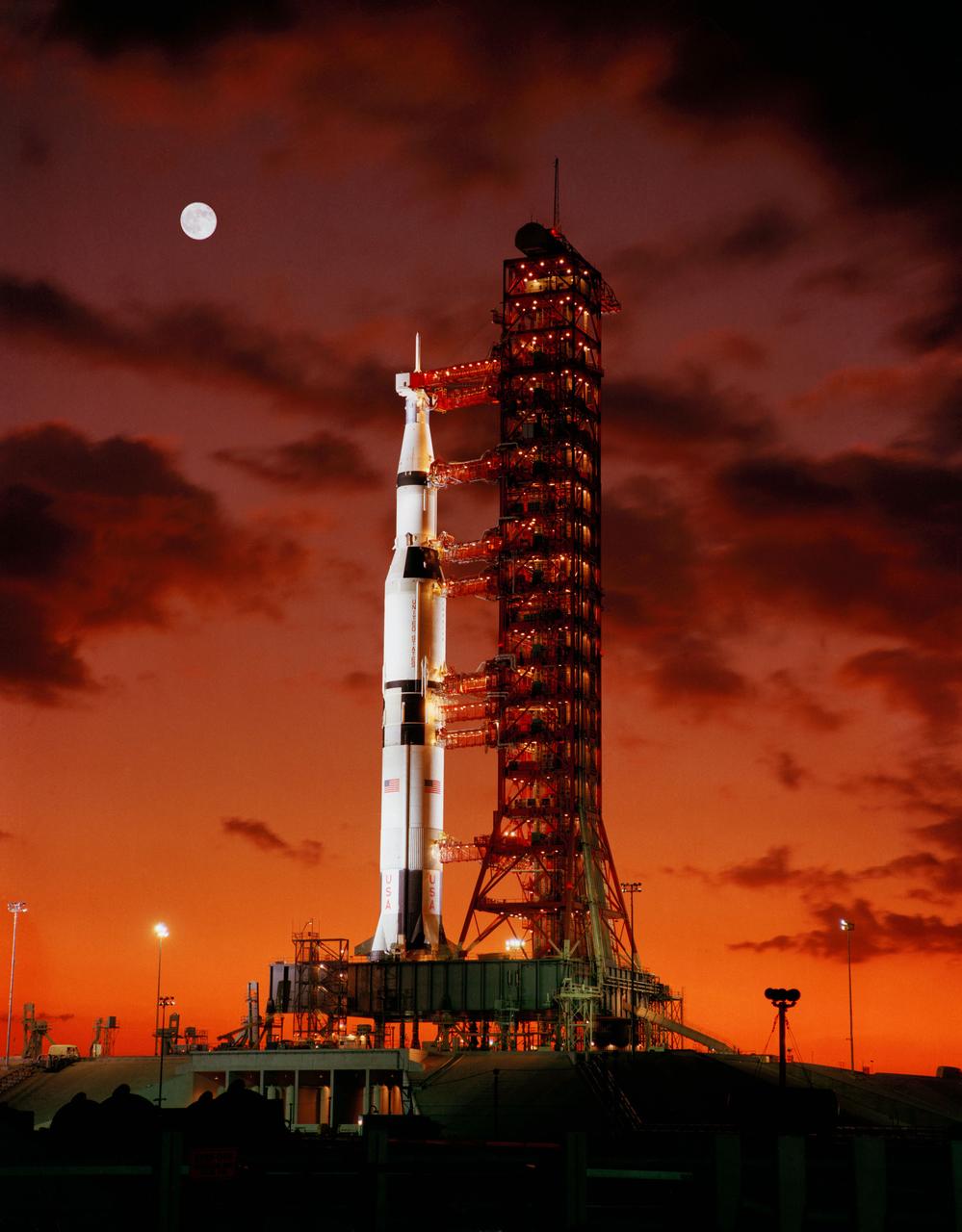

Early morning view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing Apollo 4 (Spacecraft 017/Saturn 501) unmanned, earth-orbital space mission ready for launch, with a full moon in the upper left part of the image. The 363-foot tall Apollo/Saturn V space vehicle was launched at 7:00:01 AM (EST), November 9, 1967.
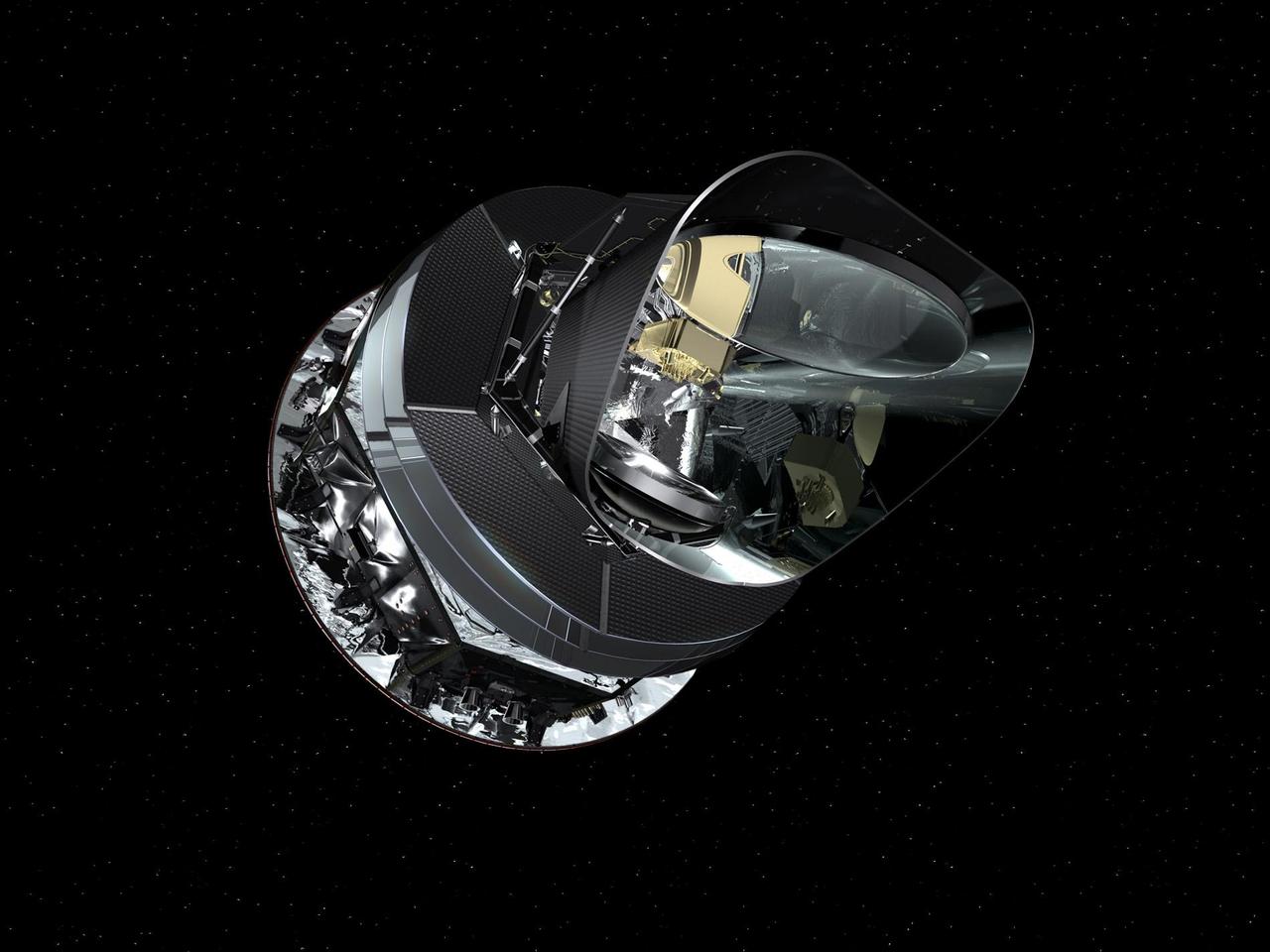

This is an artist concept of the Planck spacecraft. Planck was launched with the Herschel spacecraft, though the two missions separated shortly after launch and operate independently from each other.
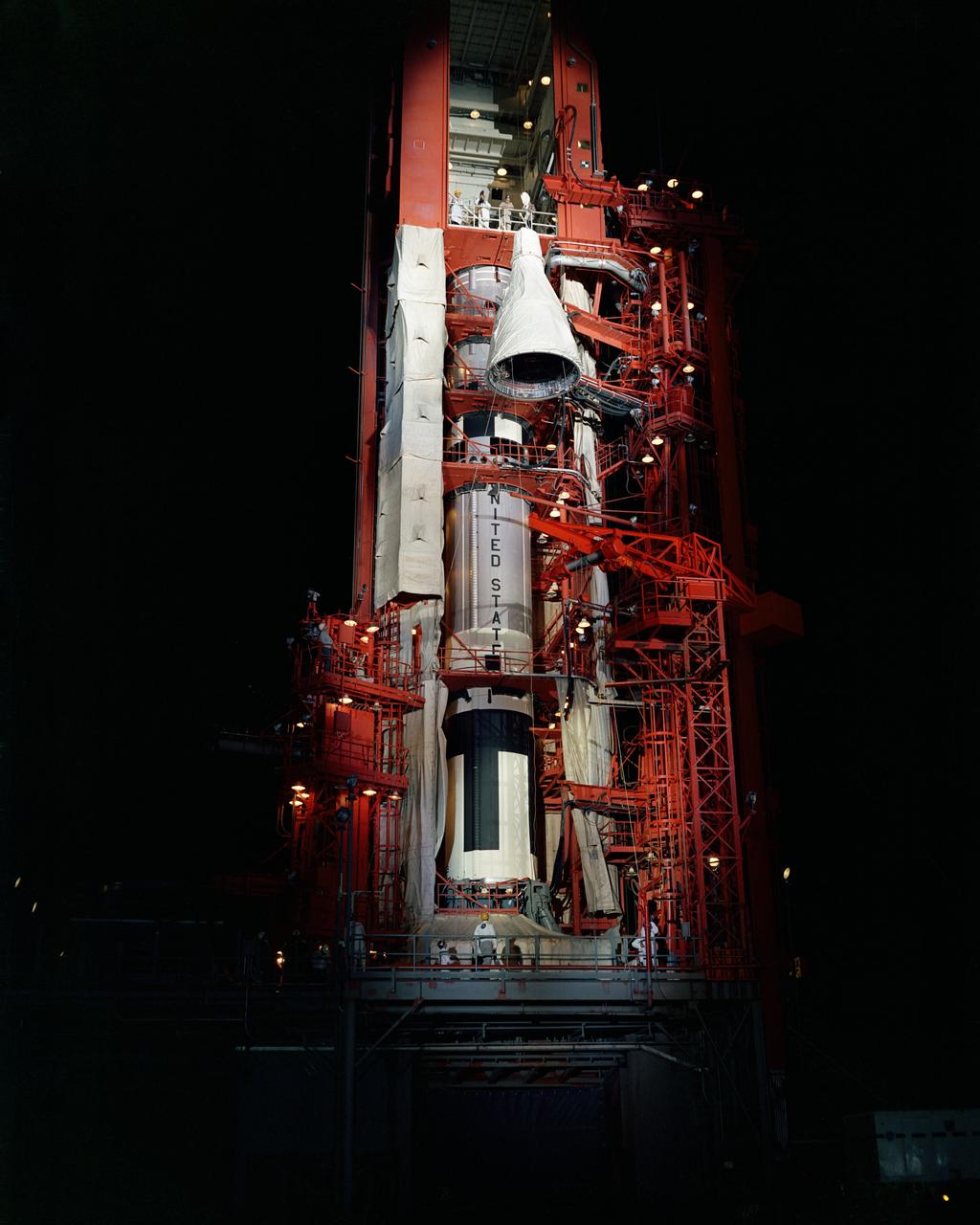

S65-23710 (14 April 1965) --- Nighttime scene showing the Gemini-4 spacecraft being hoisted to the white room at the top of the gantry at Pad 19 for soft mating with the Titan launch vehicle.
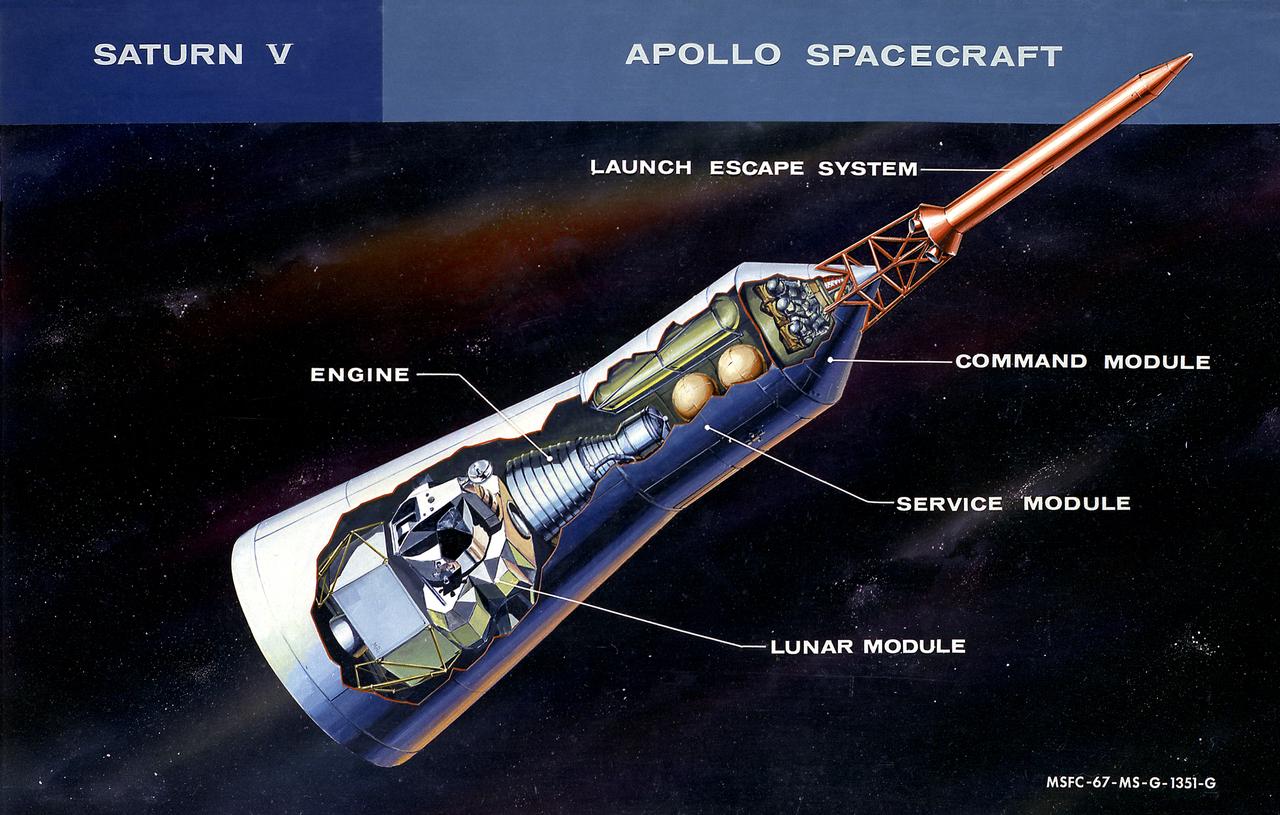
This cutaway illustration shows the Apollo Spacecraft with callouts of the major components. The spacecraft consisted of the lunar module, the service module, the command module, and the launch escape system.
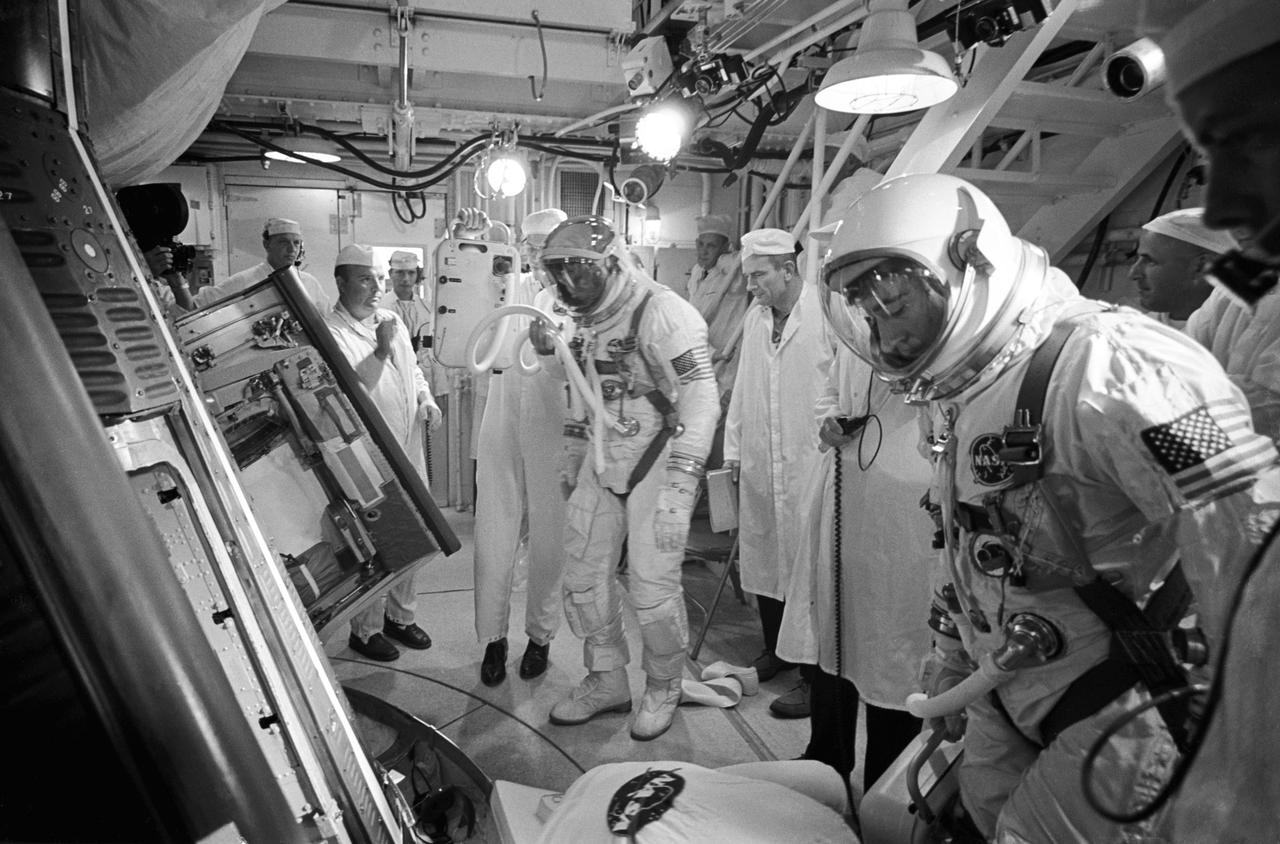
S66-42737 (18 July 1966) --- In the White Room atop the Gemini launch vehicle, astronauts Michael Collins (left), pilot, and John W. Young (right), command pilot, prepare to enter the Gemini-10 spacecraft. Engineers and technicians stand by to assist in the insertion. Photo credit: NASA
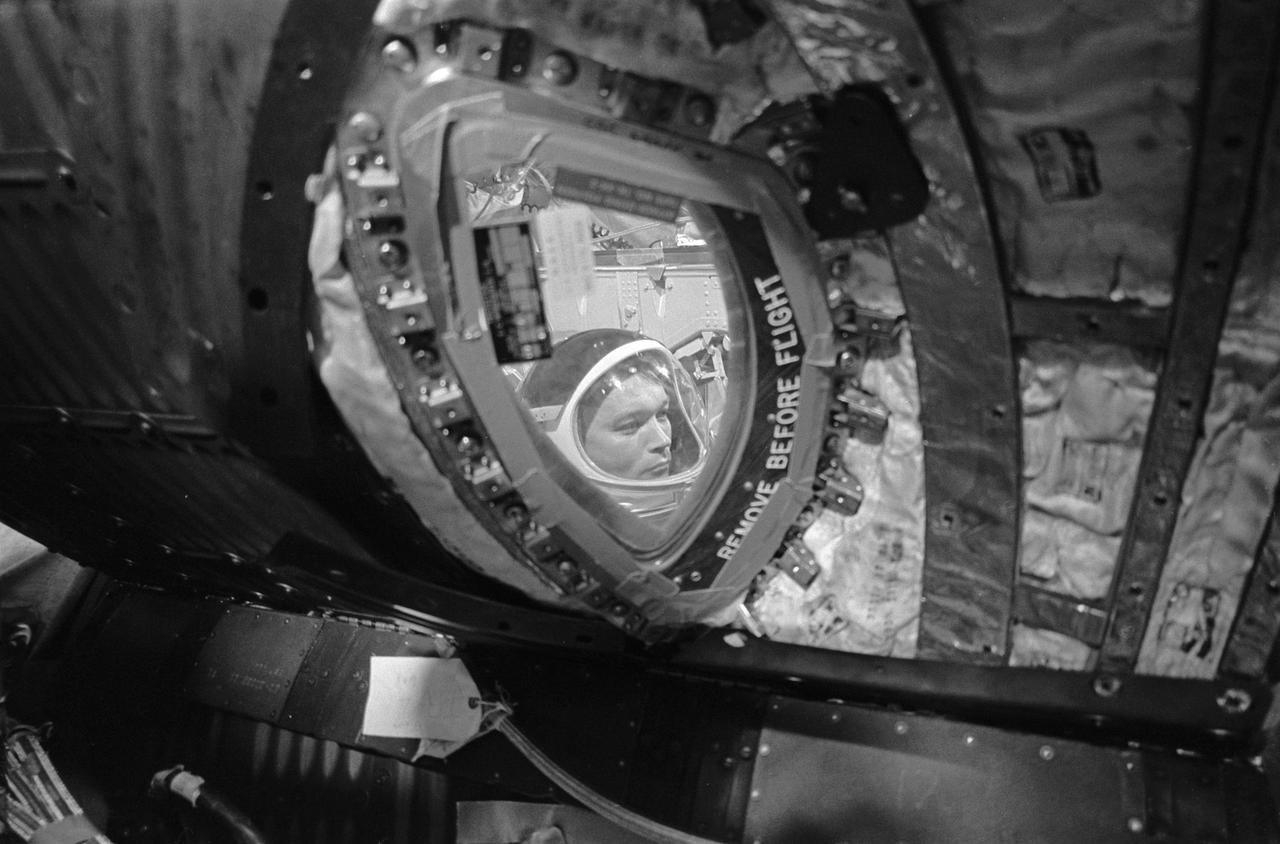

S66-42704 (12 July 1966) --- Astronaut Michael Collins, prime crew pilot for the Gemini-10 spaceflight, is seen through a hatch in the spacecraft during a Simultaneous Launch Demonstration in the White Room atop Pad 19, Cape Kennedy, Florida. Photo credit: NASA
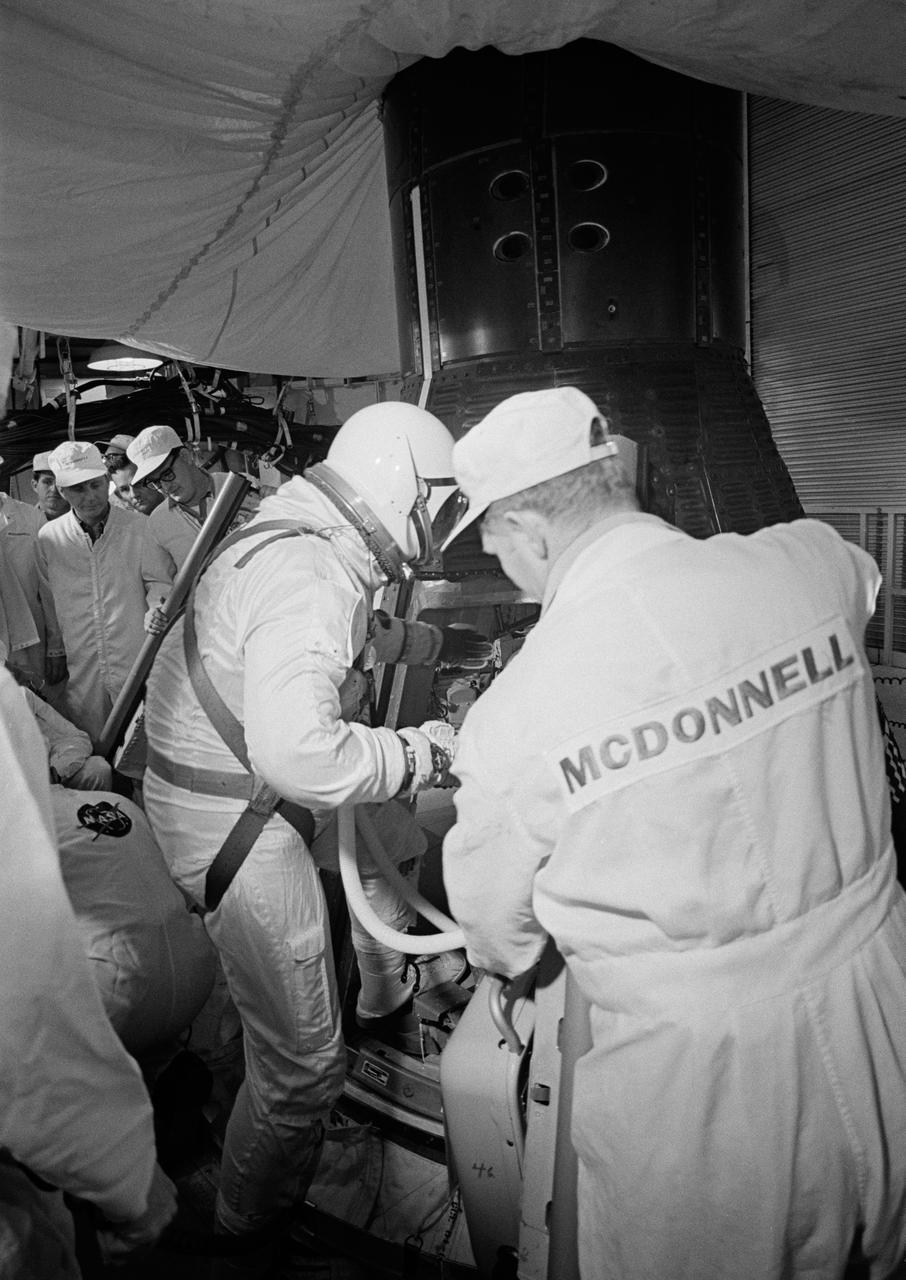
S65-20604 (23 March 1965) --- Astronaut John W. Young, the pilot of the Gemini-Titan 3 three-orbit mission, is assisted by a McDonnell Aircraft Corp. engineer as he enters the Gemini spacecraft in the white room atop the Gemini launch vehicle.
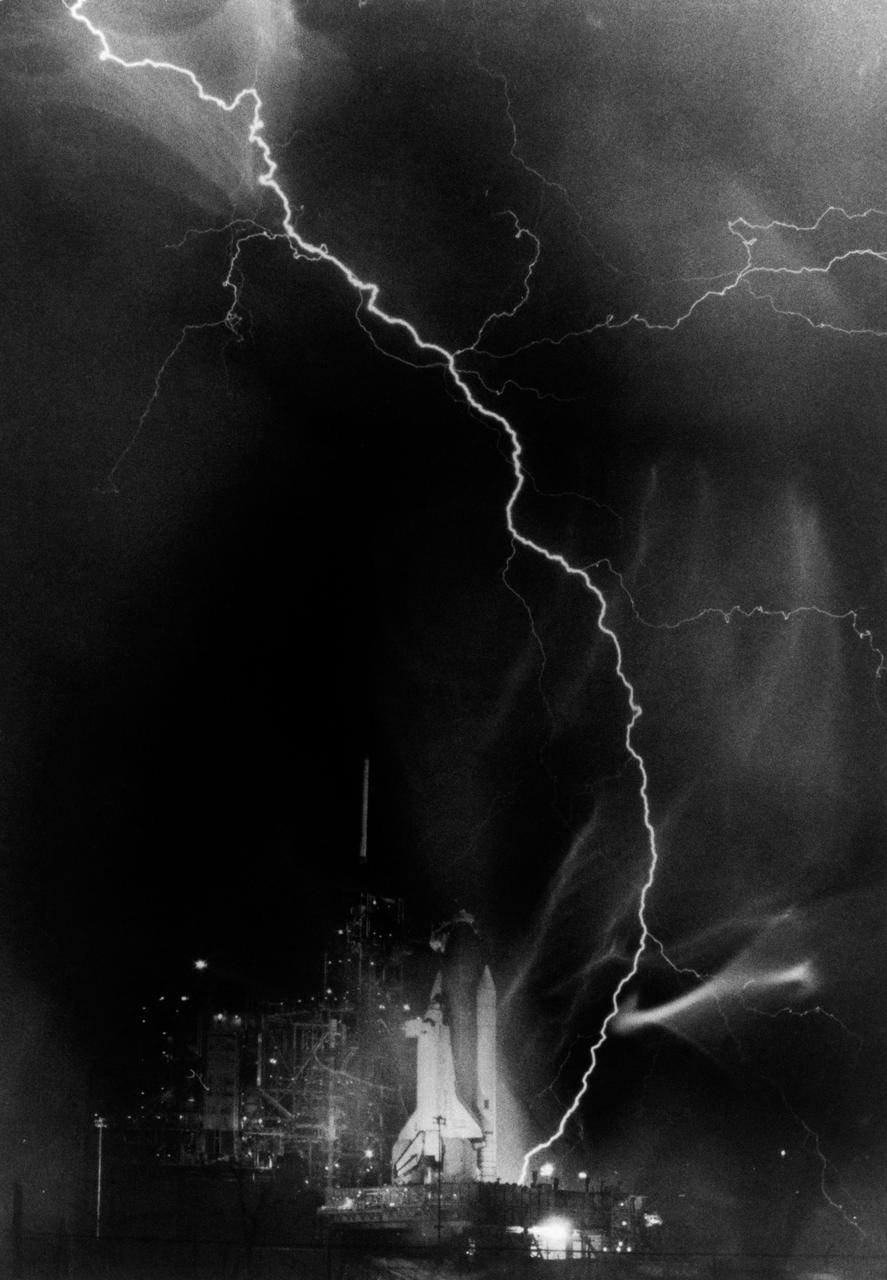

Lightning across the sky with Shuttle at launch pad on 08/30/1983. KSC, FL
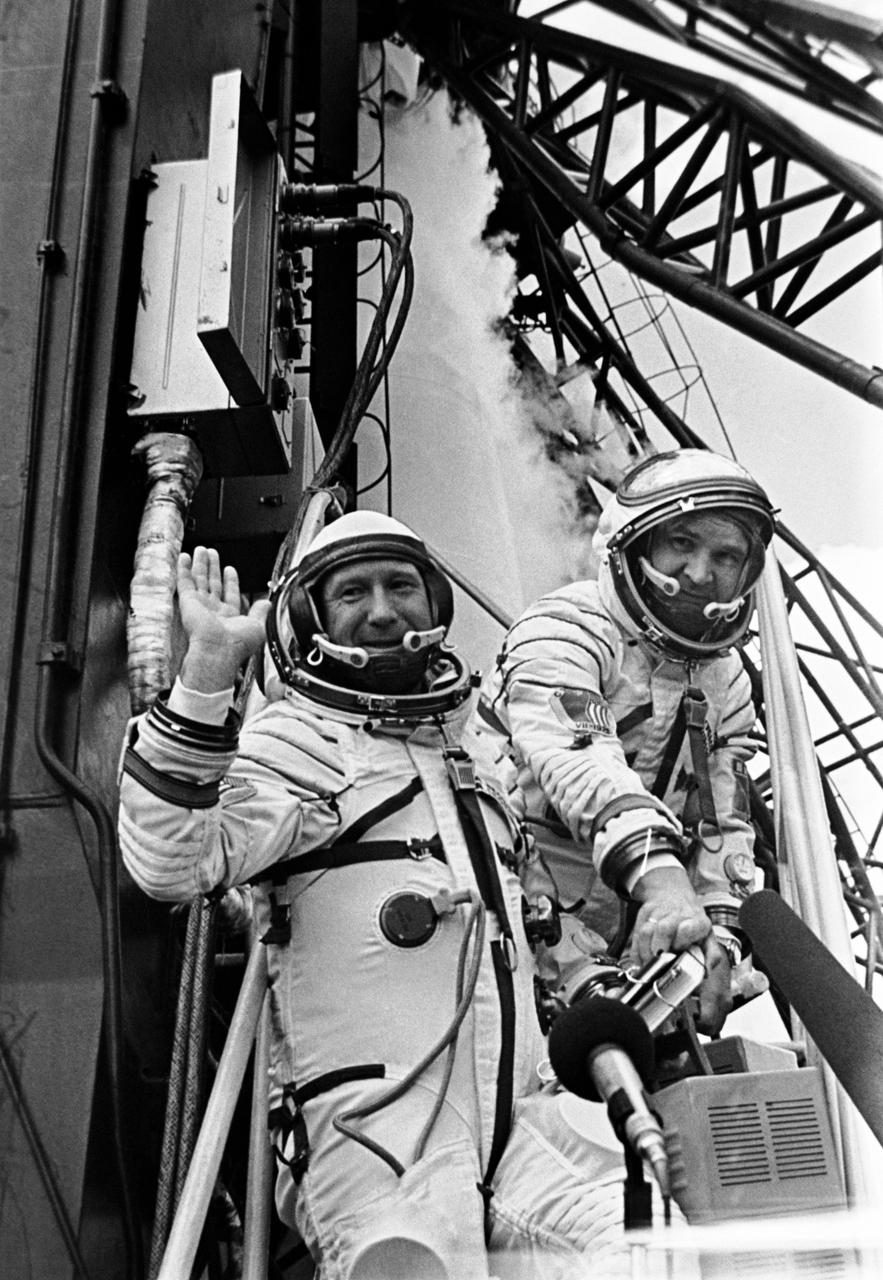

S75-32343 (15 July 1975) --- The two Soviet crewmen for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission are photographed at the launch pad at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on the morning of the Soviet ASTP liftoff on July 15, 1975. They are cosmonauts Aleksey A. Leonov (left), commander; and Valeriy N. Kubasov, flight engineer. Leonov is waving to well-wishers at the launch pad. The Soviet ASTP launch preceded the American ASTP Apollo liftoff by seven and one-half hours. The American and Soviet spacecraft were docked in Earth orbit for a total of about 47 hours on July 17-19, 1975. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
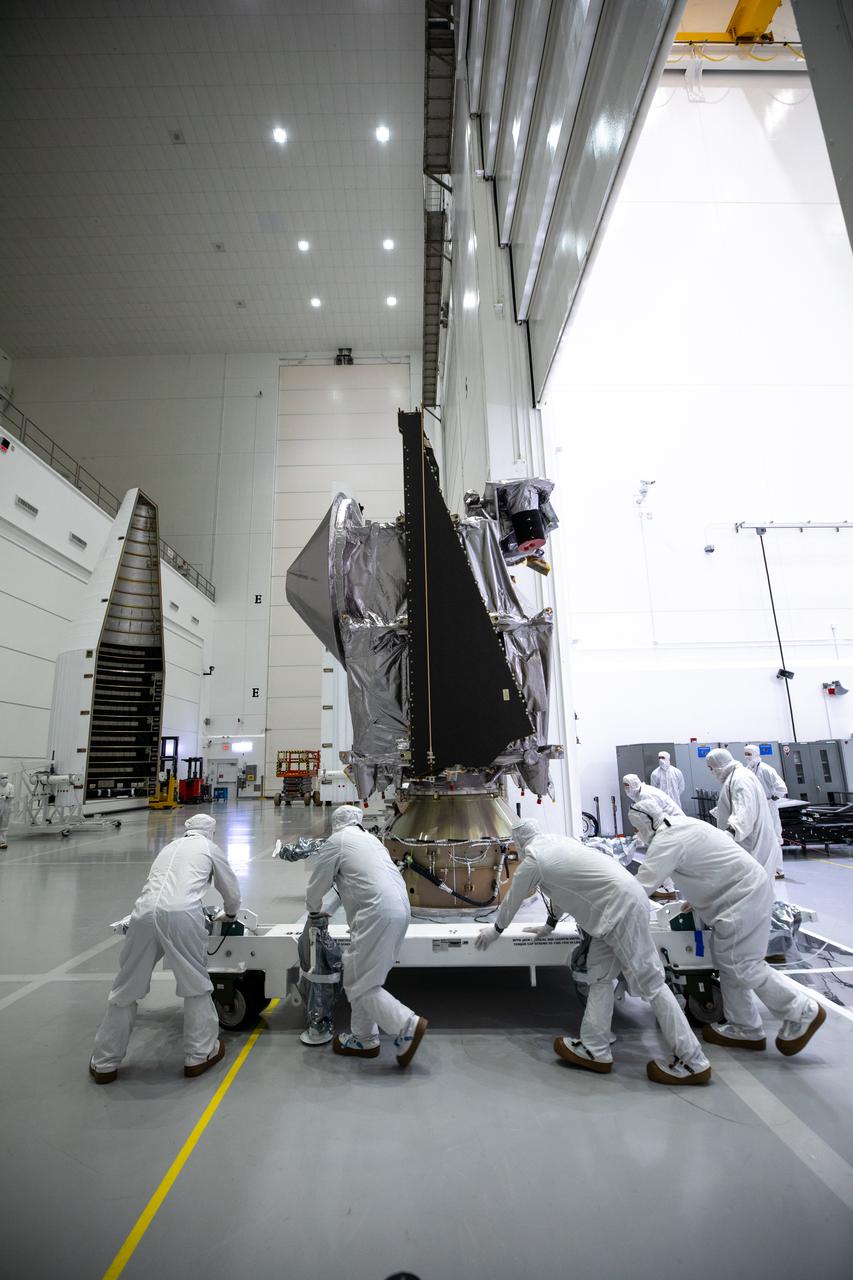

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is moved from the Work Processing Cell to the Airlock inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 29, 2021. A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket roared off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Oct. 16, 2021, at 5:34 a.m. EDT, carrying Lucy into space. During its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Lucy is the first space mission to study the Trojan asteroids, which hold vital clues to the formation of our solar system.
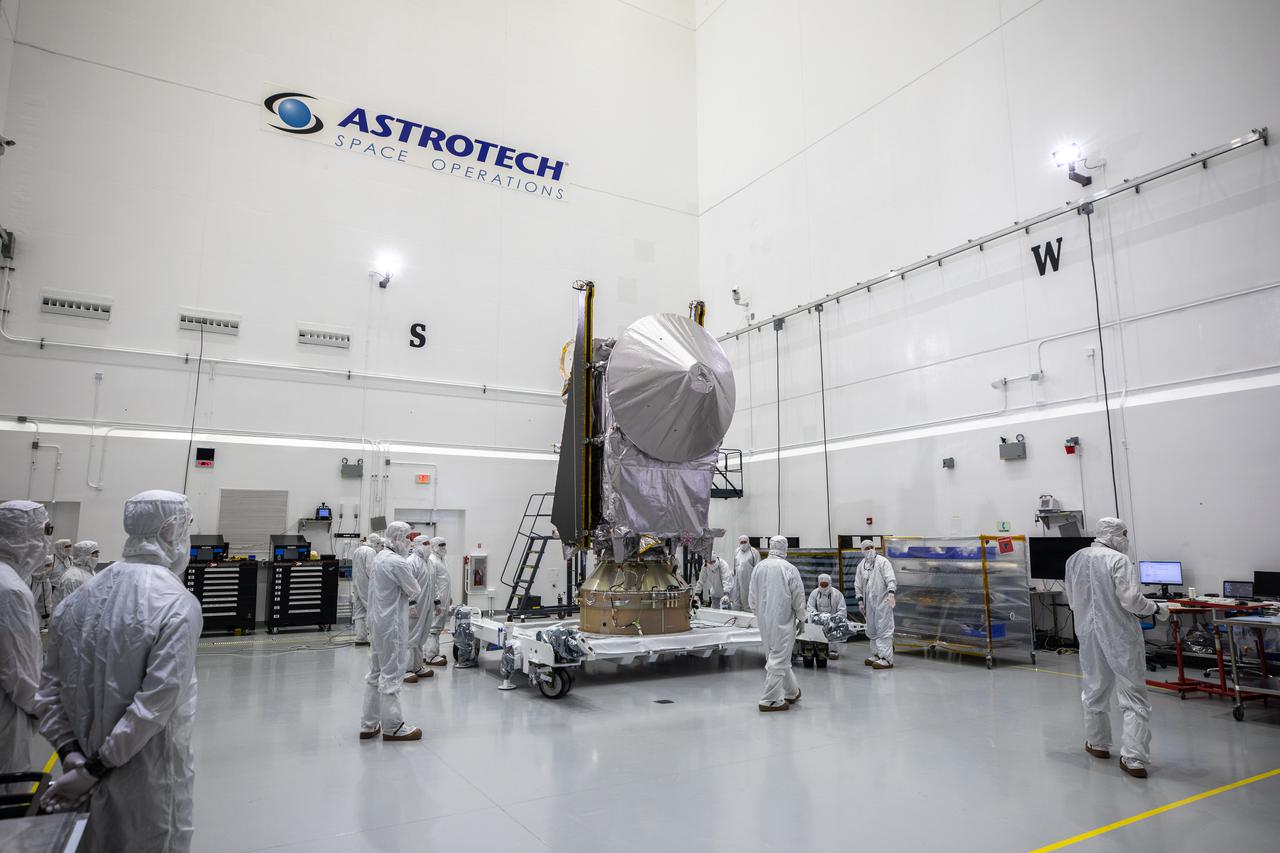

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is prepared to be moved from the Work Processing Cell to the Airlock inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 29, 2021. A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket roared off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Oct. 16, 2021, at 5:34 a.m. EDT, carrying Lucy into space. During its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Lucy is the first space mission to study the Trojan asteroids, which hold vital clues to the formation of our solar system.
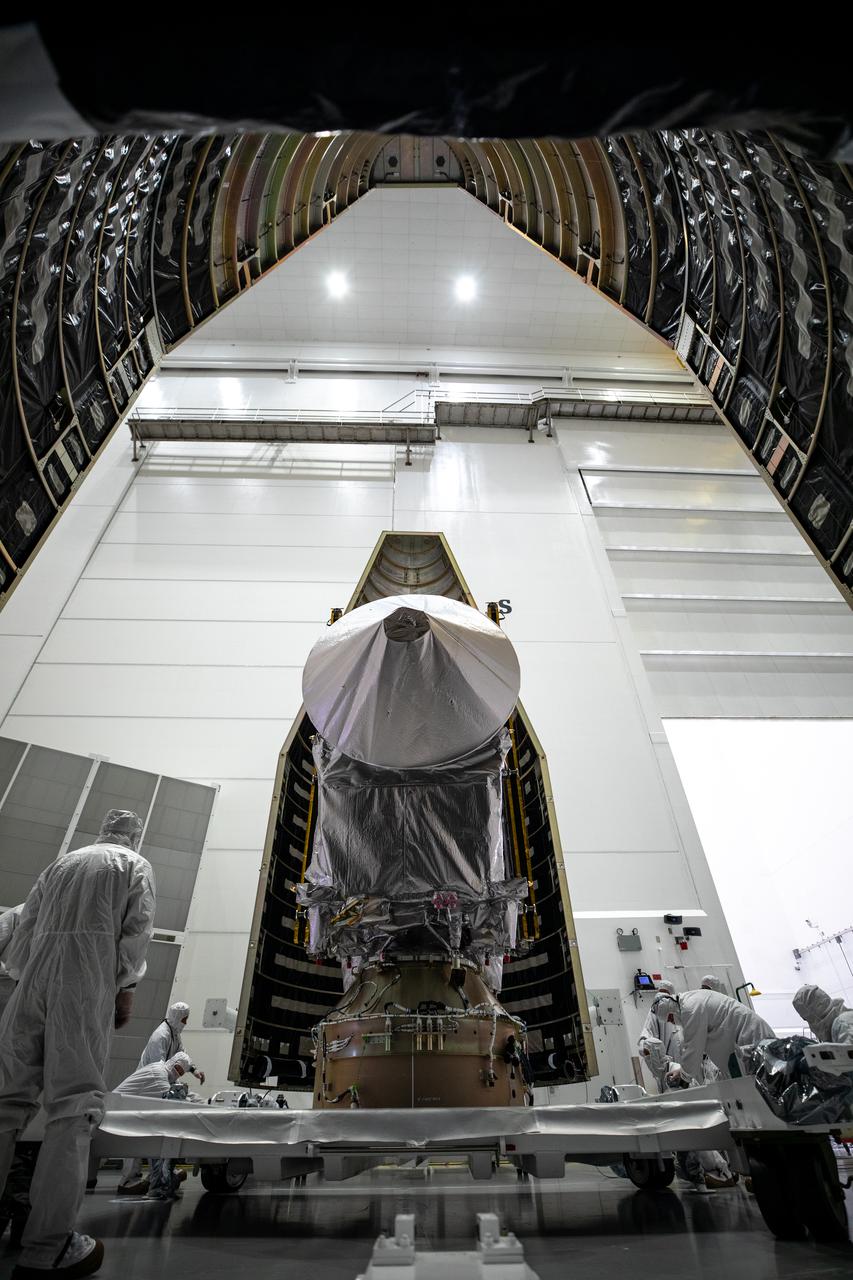

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is moved from the Work Processing Cell to the Airlock inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 29, 2021. A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket roared off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Oct. 16, 2021, at 5:34 a.m. EDT, carrying Lucy into space. During its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Lucy is the first space mission to study the Trojan asteroids, which hold vital clues to the formation of our solar system.
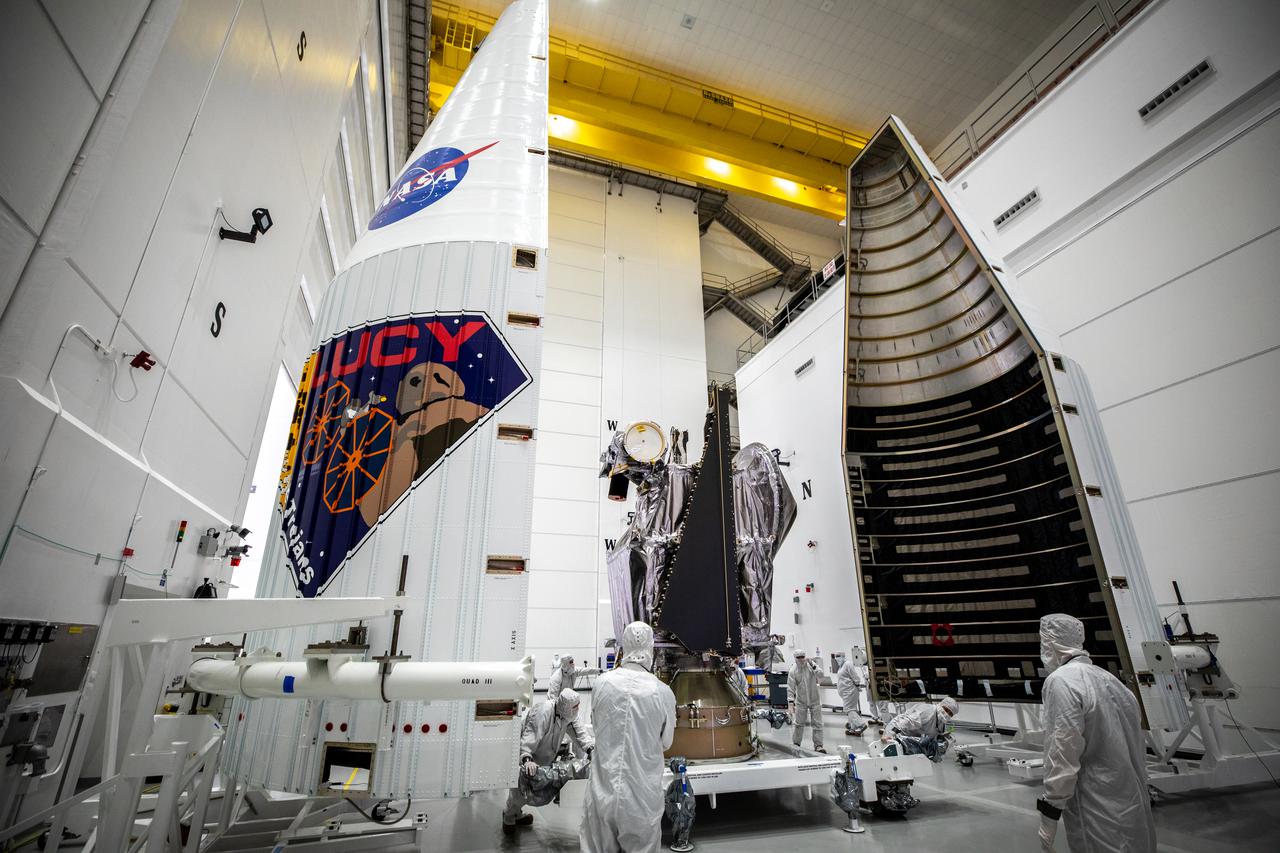

NASA’s Lucy spacecraft is moved from the Work Processing Cell to the Airlock inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville, Florida, on Sept. 29, 2021. A United Launch Alliance V 401 rocket roared off the pad at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41 on Oct. 16, 2021, at 5:34 a.m. EDT, carrying Lucy into space. During its 12-year primary mission, Lucy will explore a record-breaking number of asteroids, flying by one asteroid in the solar system’s main belt and seven Trojan asteroids. Lucy is the first space mission to study the Trojan asteroids, which hold vital clues to the formation of our solar system.