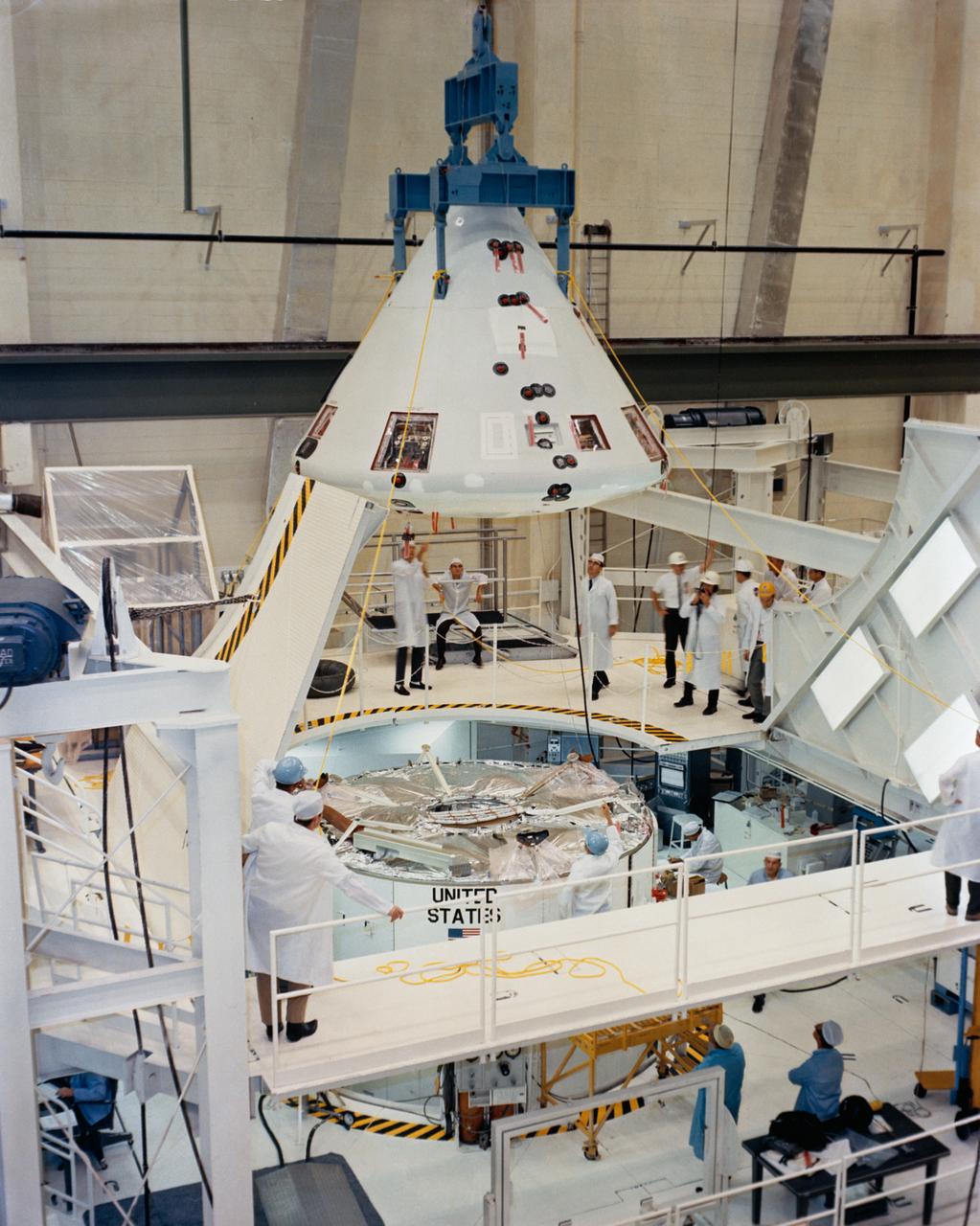

S68-17301 (6 Dec. 1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 020 Command Module is hoisted into position for mating with Service Module in the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building. Spacecraft 020 will be flown on the Apollo 6 (Spacecraft 020/Saturn 502) unmanned, Earth-orbital space mission.
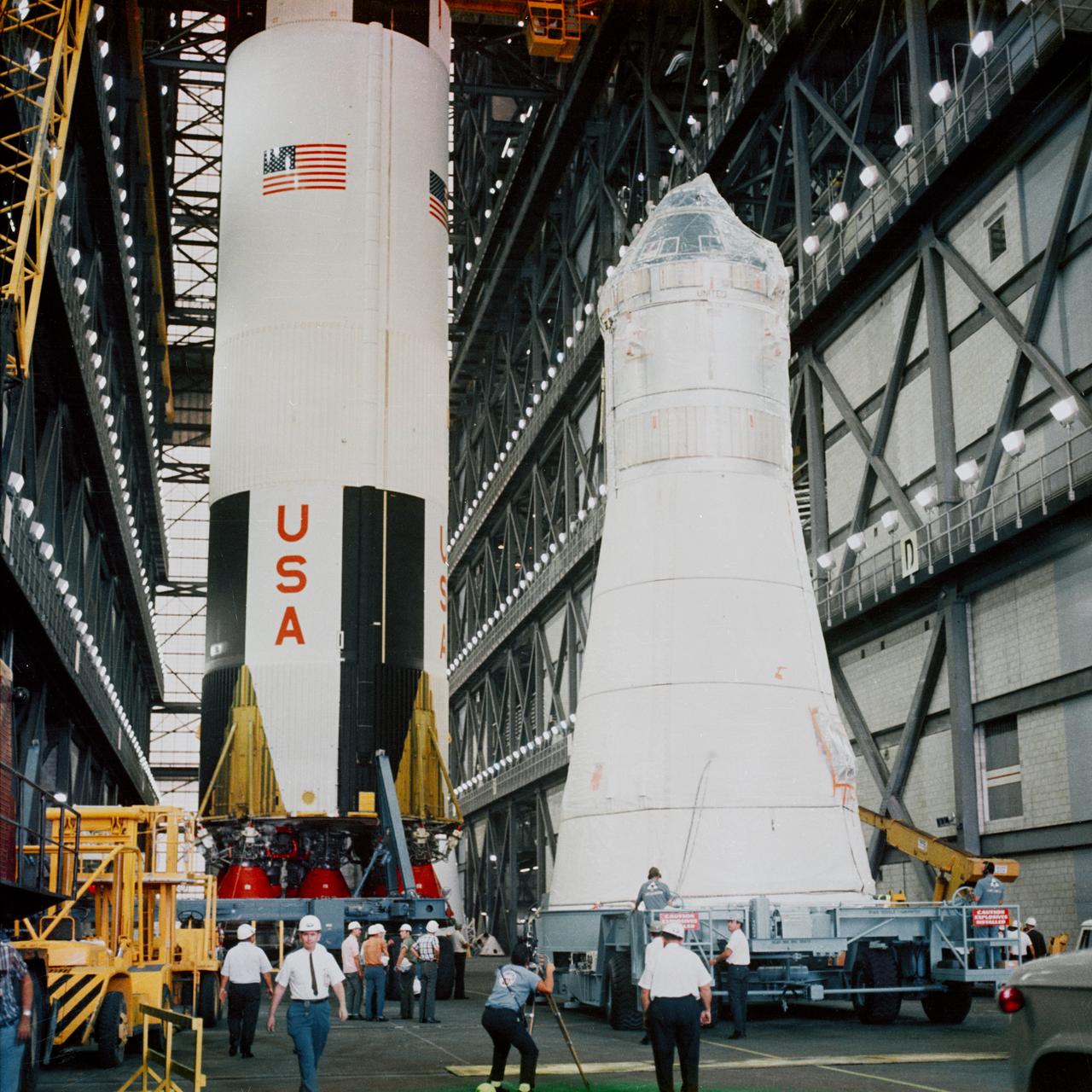

Apollo Spacecraft 104 Command/Service Module and Lunar Module 3 arrive at the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) for mating atop the Saturn 504 launch vehicle. The Saturn 504 stack is out of view. The Saturn V first (S-IC) stage in left background is scheduled for a later flight.
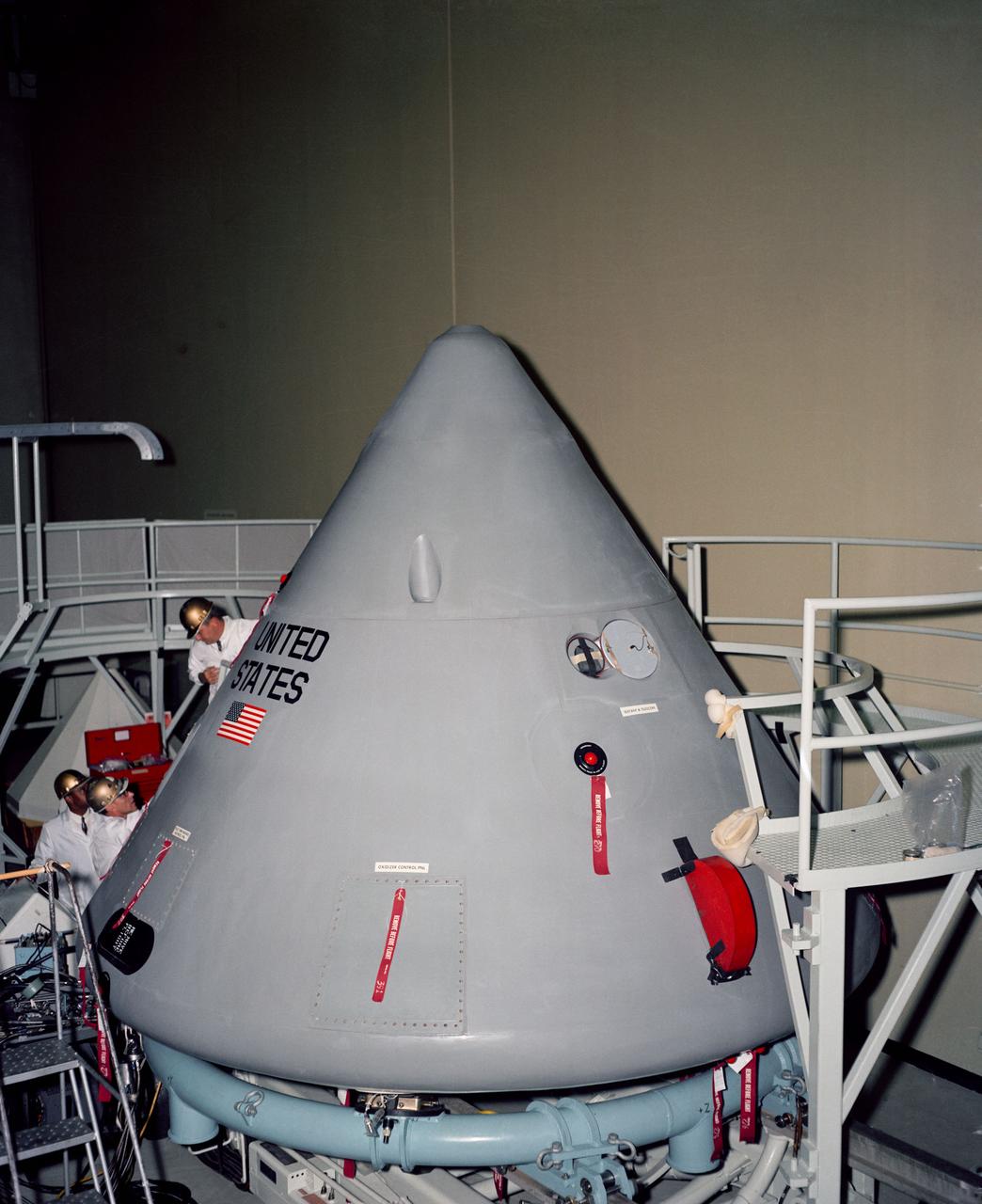

S66-53655 (1966) --- High angle view of Apollo Spacecraft 012 Command Module looking toward +Z axis during pre-shipping operations in south air lock of Systems Integration and Checkout Facility.
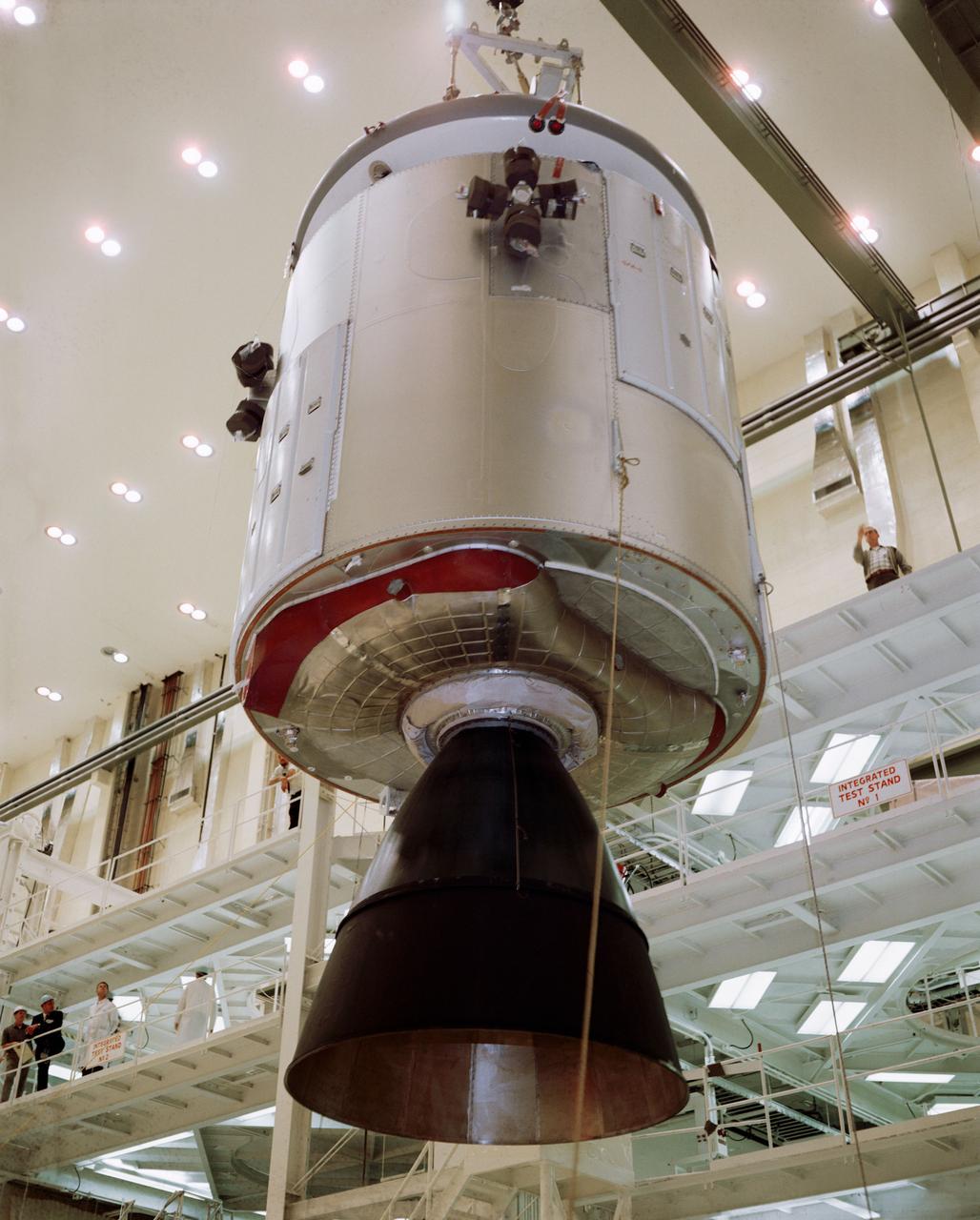

S67-15704 (3 Jan. 1967) --- Transfer of Apollo Spacecraft 012 Command/Service Module (CSM) for mating with the Saturn Lunar Module (LM) Adapter No.05 in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building. Spacecraft 012 will be flown on the Apollo/Saturn 1 (204) mission. Photo credit: NASA
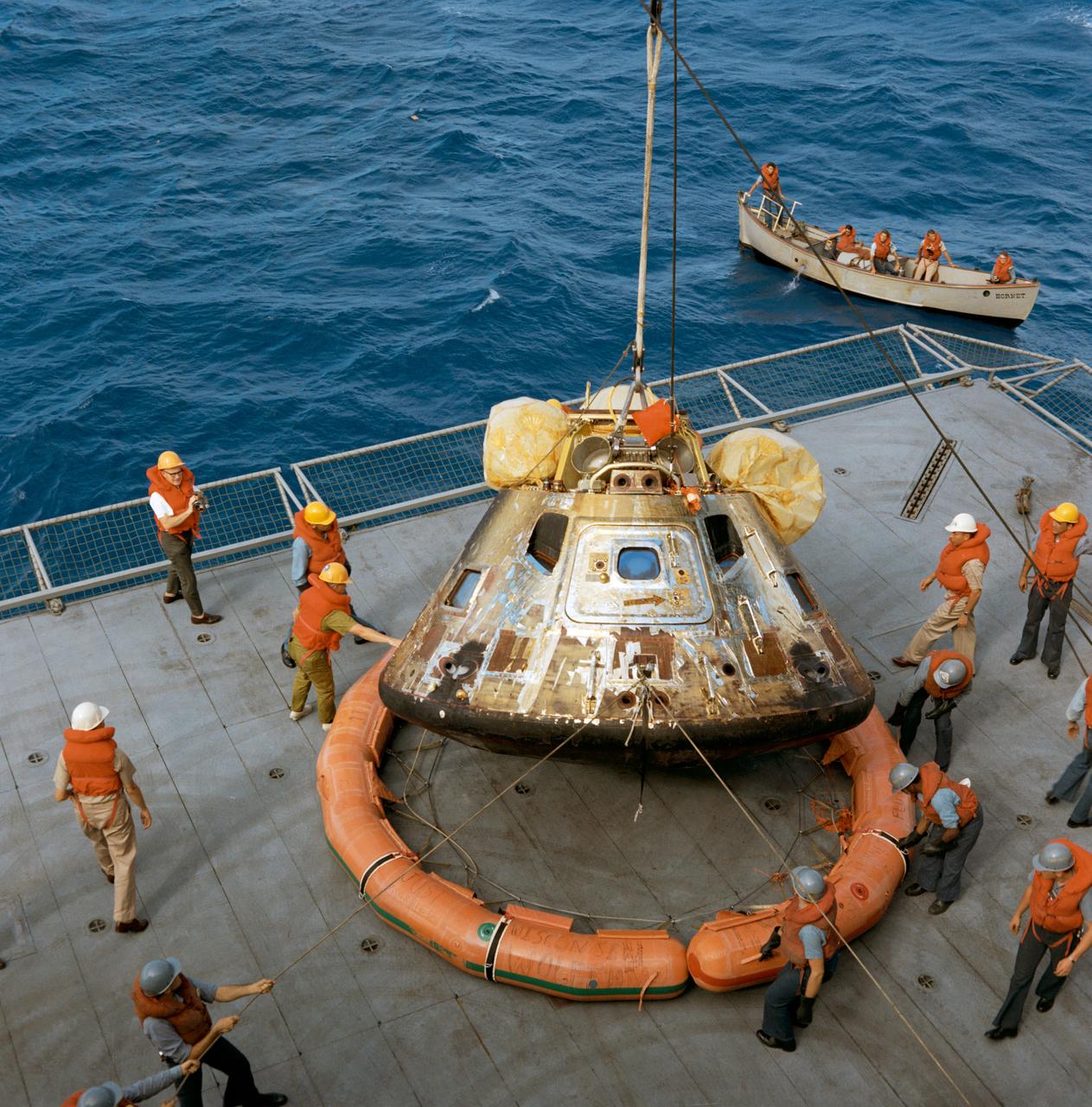

The Apollo 11 spacecraft Command Module is photographed being lowered to the deck of the U.S.S. Hornet, prime recovery ship for the historic lunar landing mission. Note the flotation ring attached by Navy divers has been removed from the capsule.
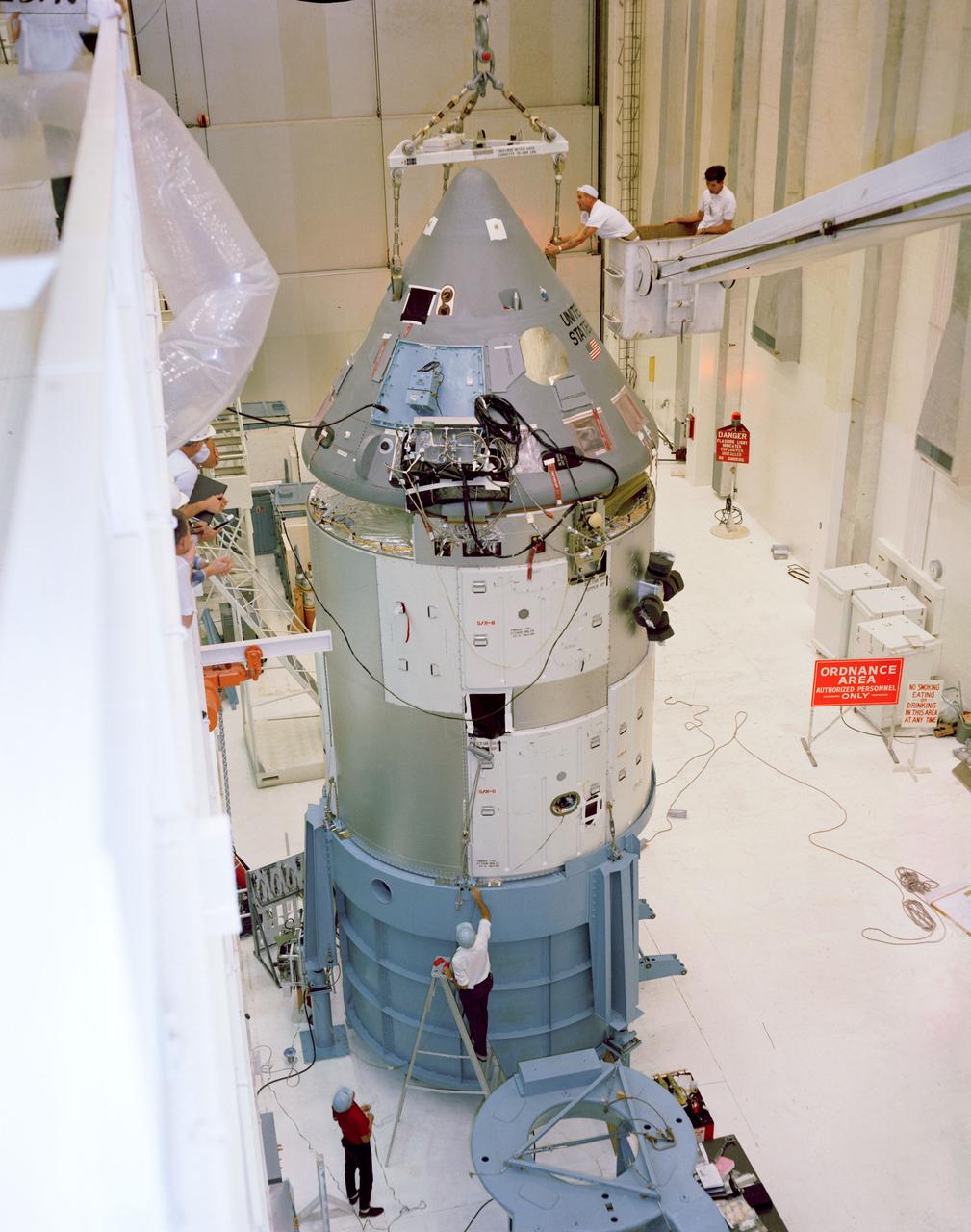

S67-15717 (1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 012 Command/Service Module is moved from H-134 to east stokes for mating to the Saturn Lunar Module Adapter No. 05 in the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building. S/C 012 will be flown on the Apollo/Saturn 204 mission.
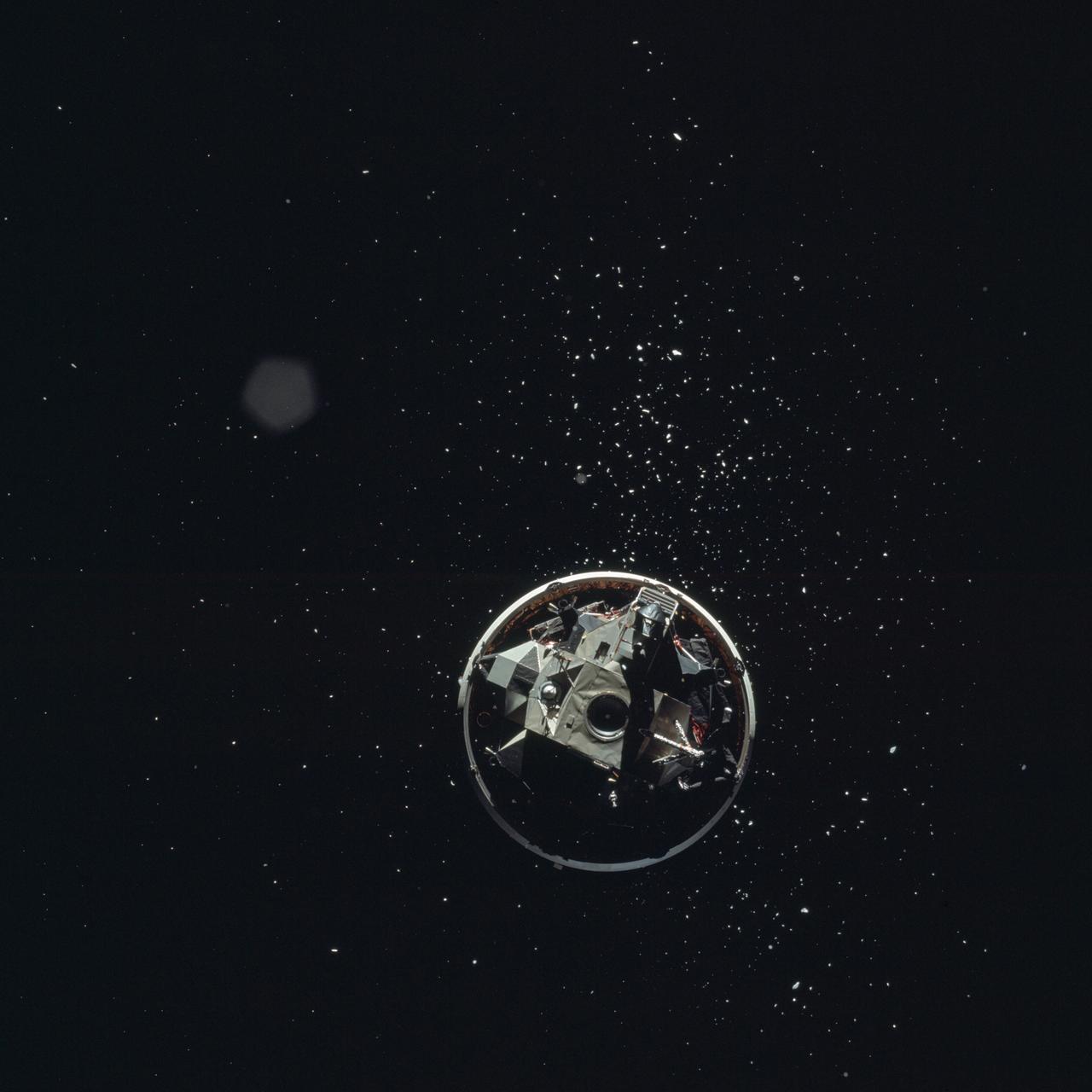

AS17-148-22688 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- View of the Lunar Module from the Apollo 17 spacecraft after transposition/docking maneuvers. The white dots surrounding the Lunar Module are debris from the Saturn S-IVB stage separation.
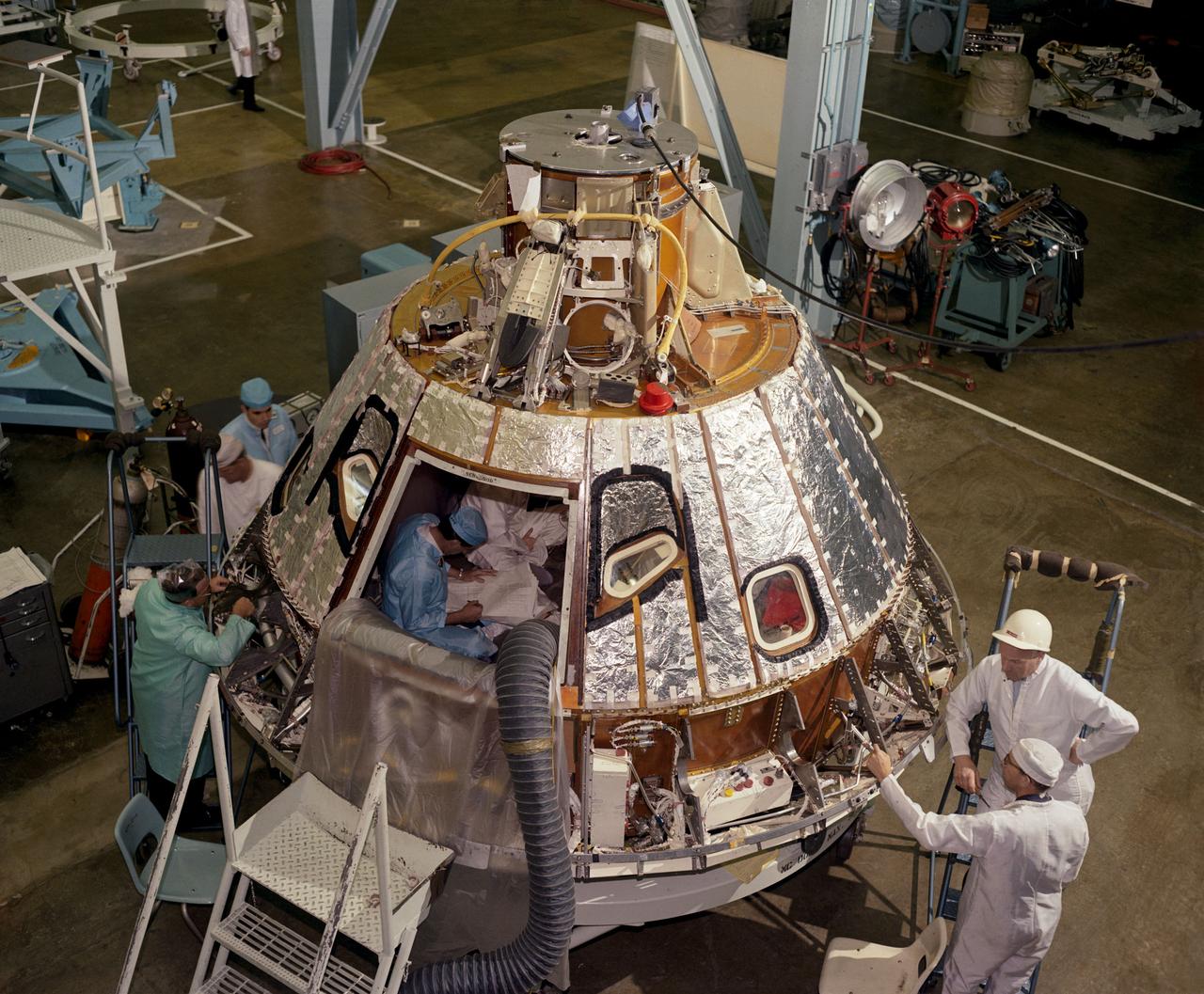
S66-41851 (1966) --- High angle view of Spacecraft 012 Command Module, looking toward -Z axis, during preparation for installation of the crew compartment heat shield, showing mechanics working on aft bay.
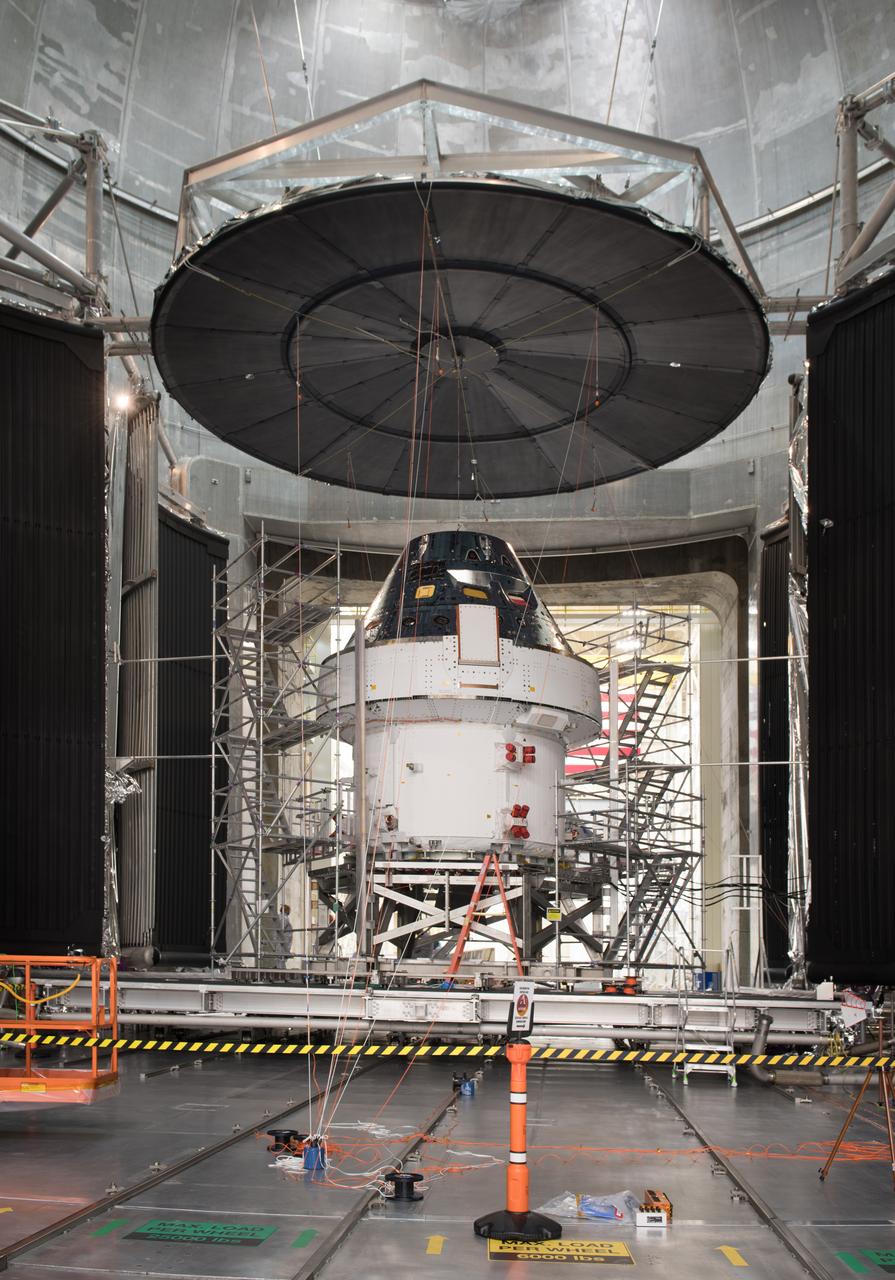

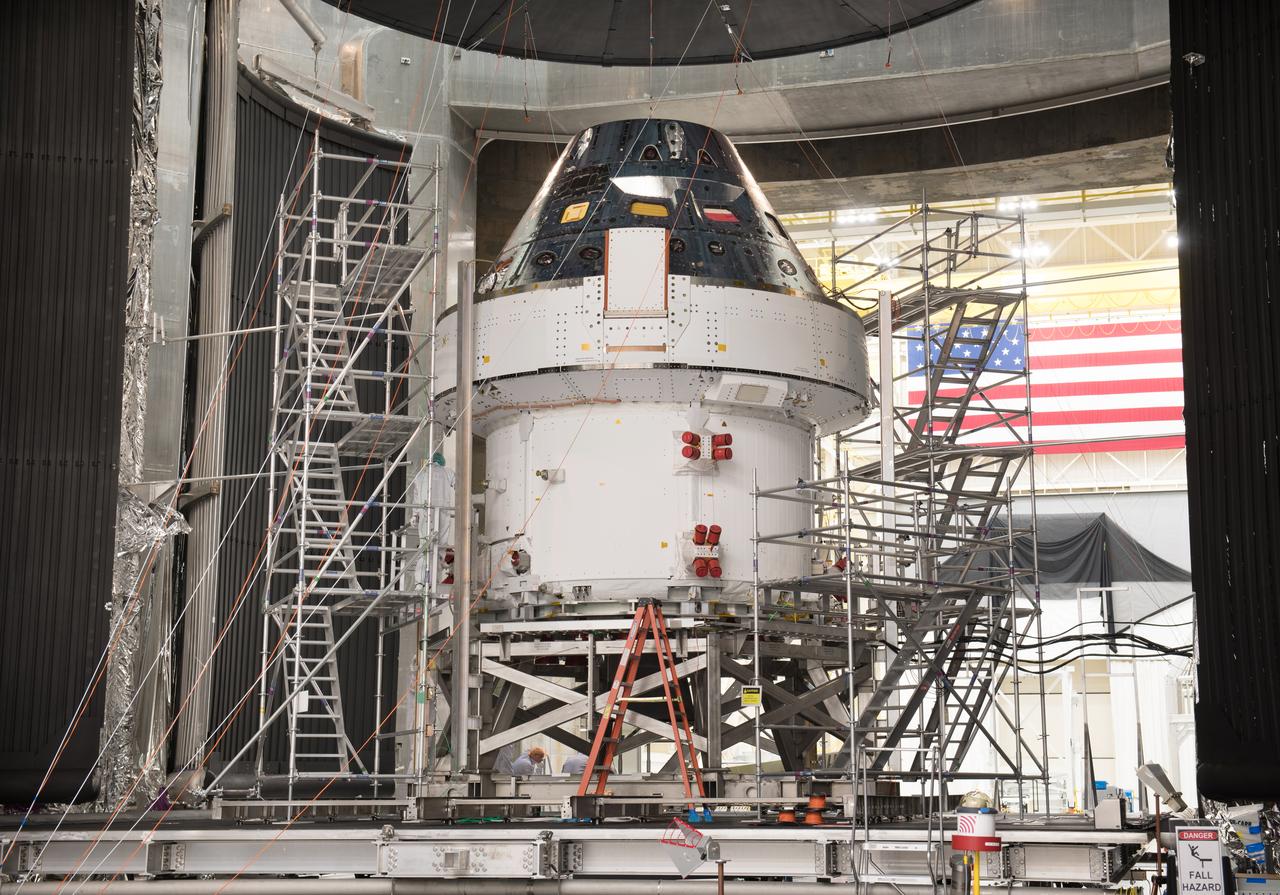
The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
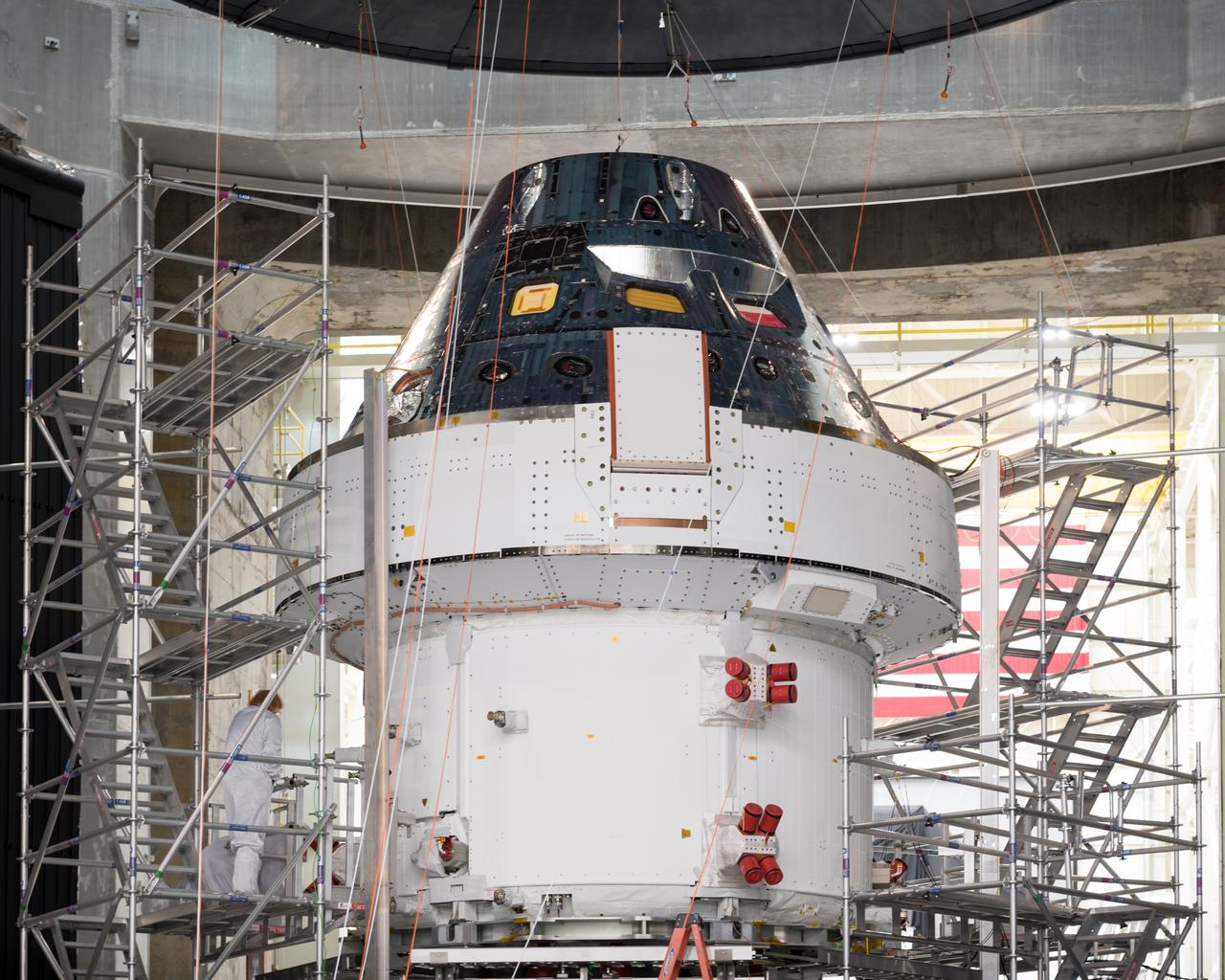

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
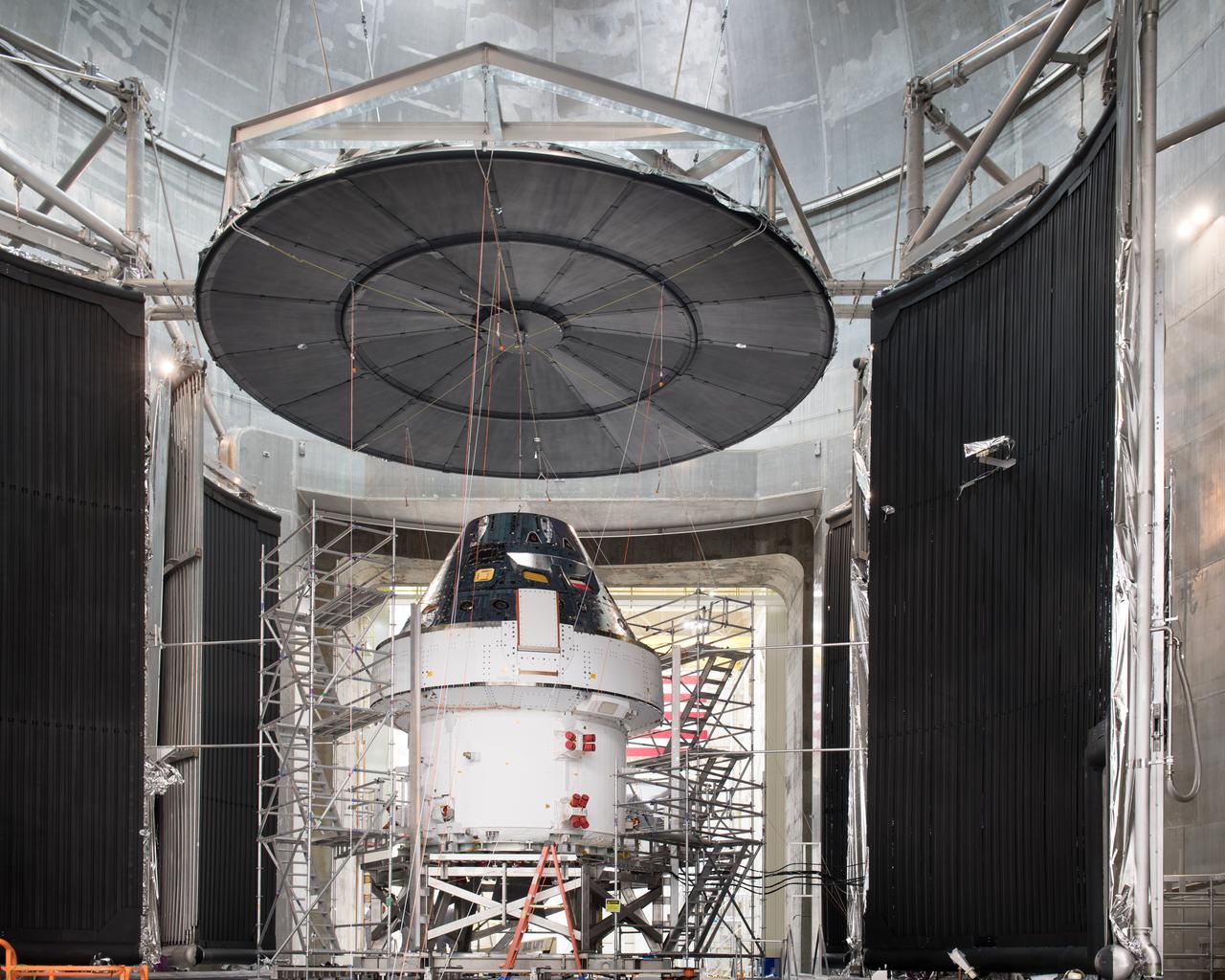

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
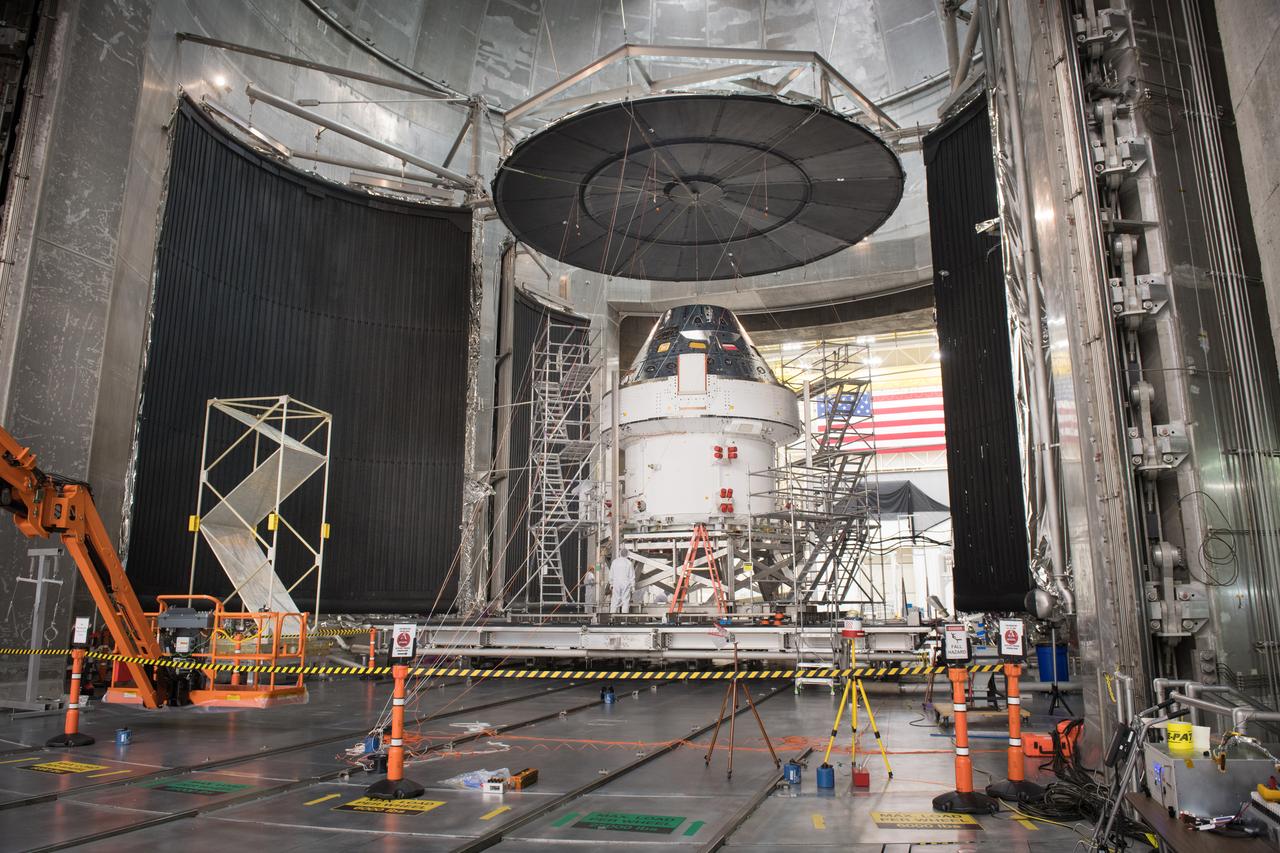
The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
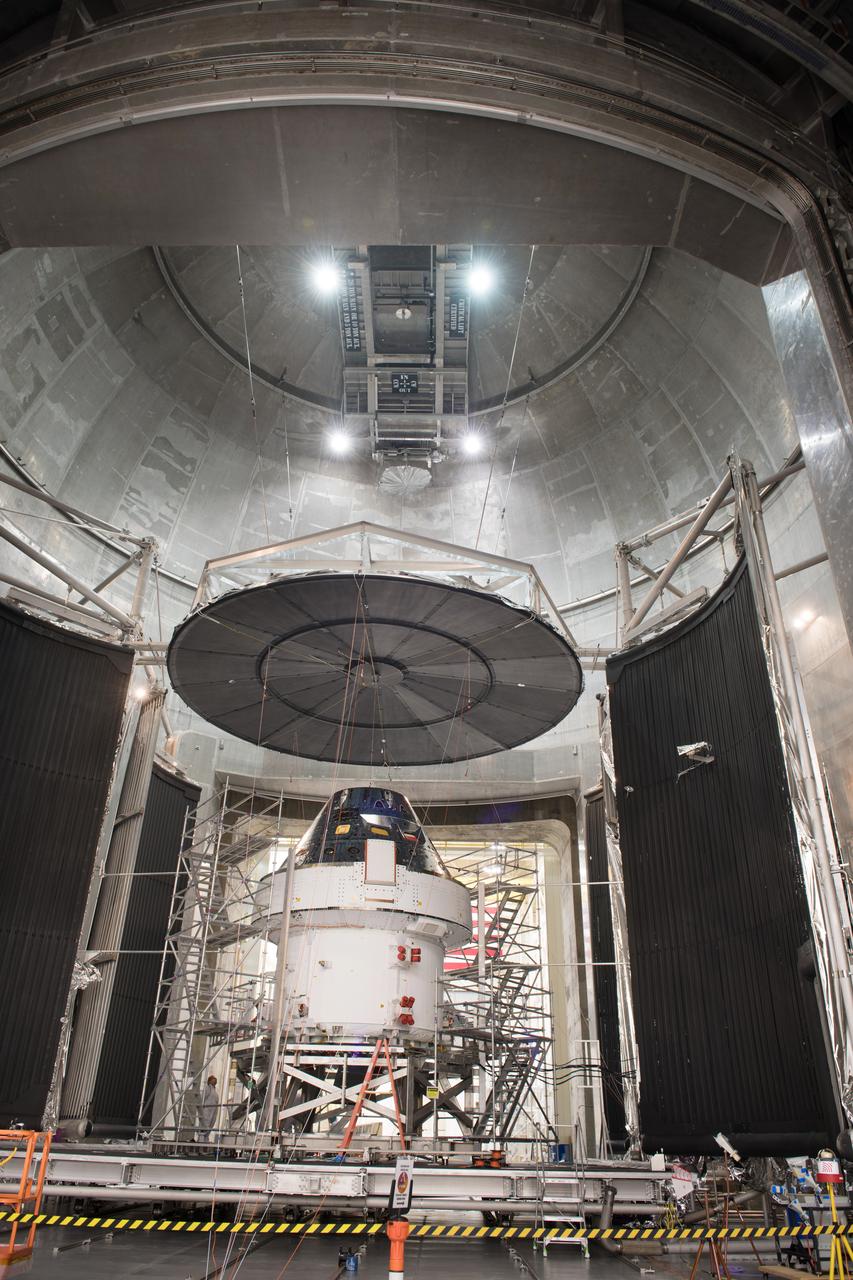

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
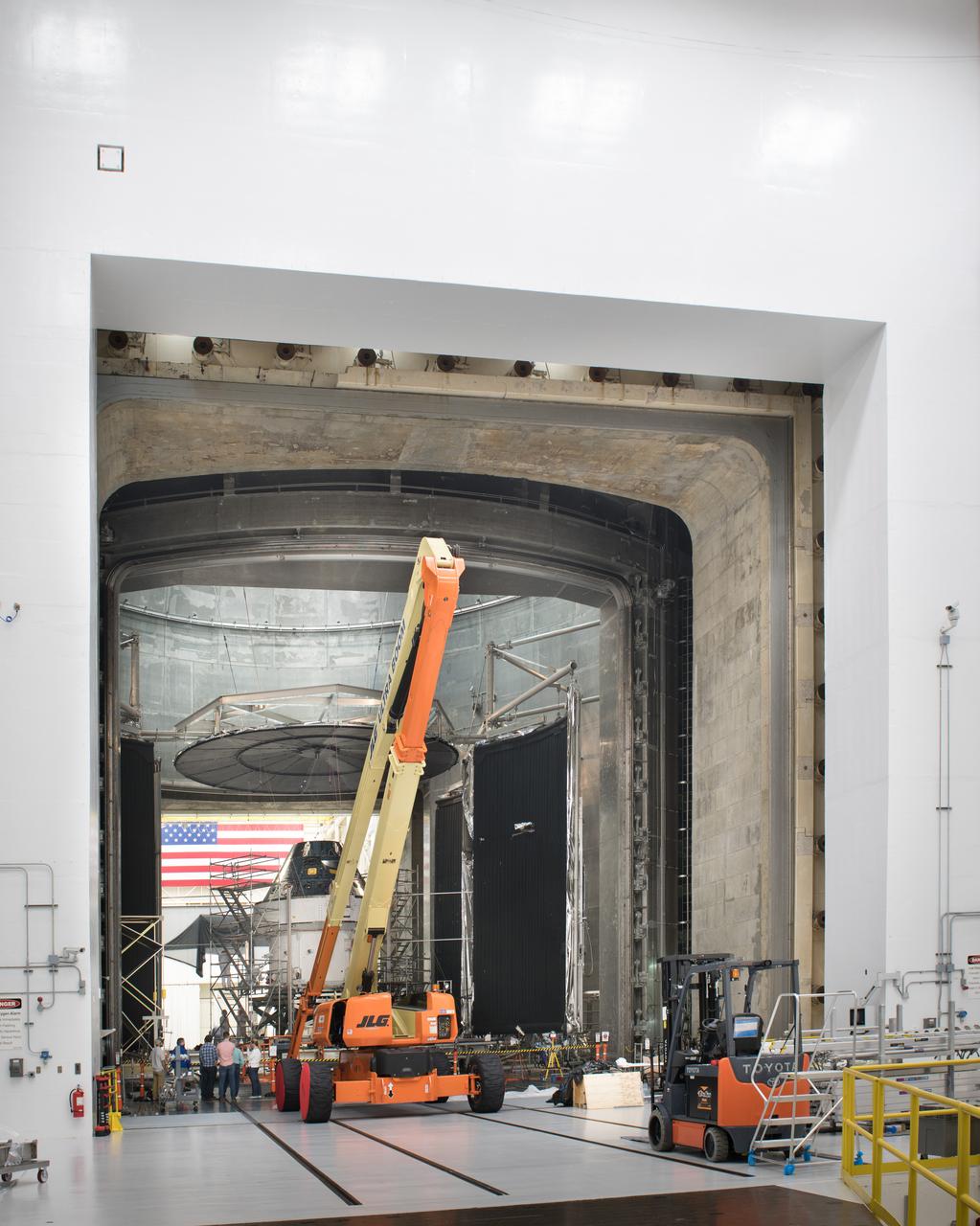

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
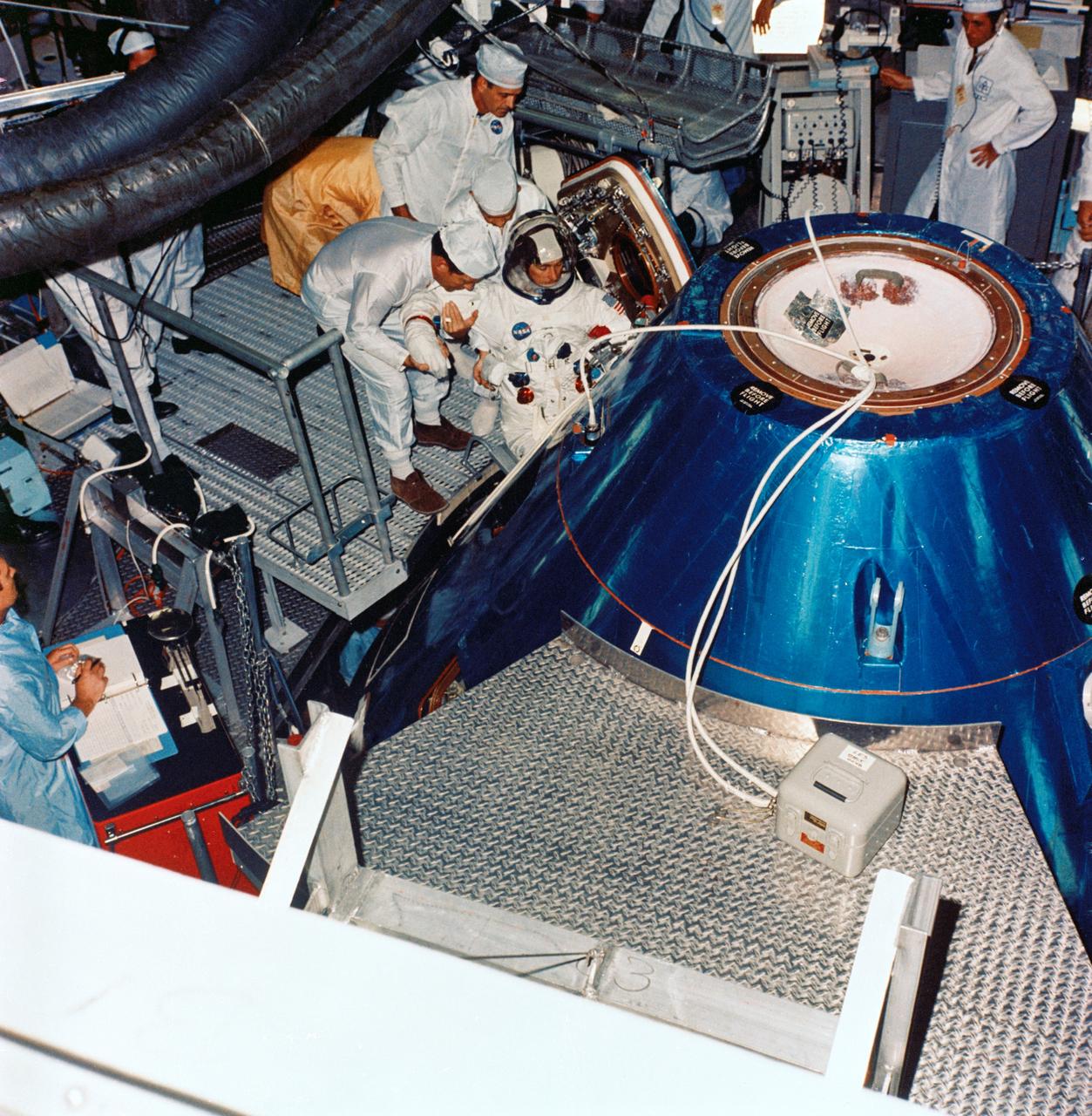
S68-40875 (5 July 1968) --- Astronaut John W. Young, Apollo 7 backup command module pilot, ingresses Apollo Spacecraft 101 Command Module during simulated altitude runs at the Kennedy Space Center's Pad 34.
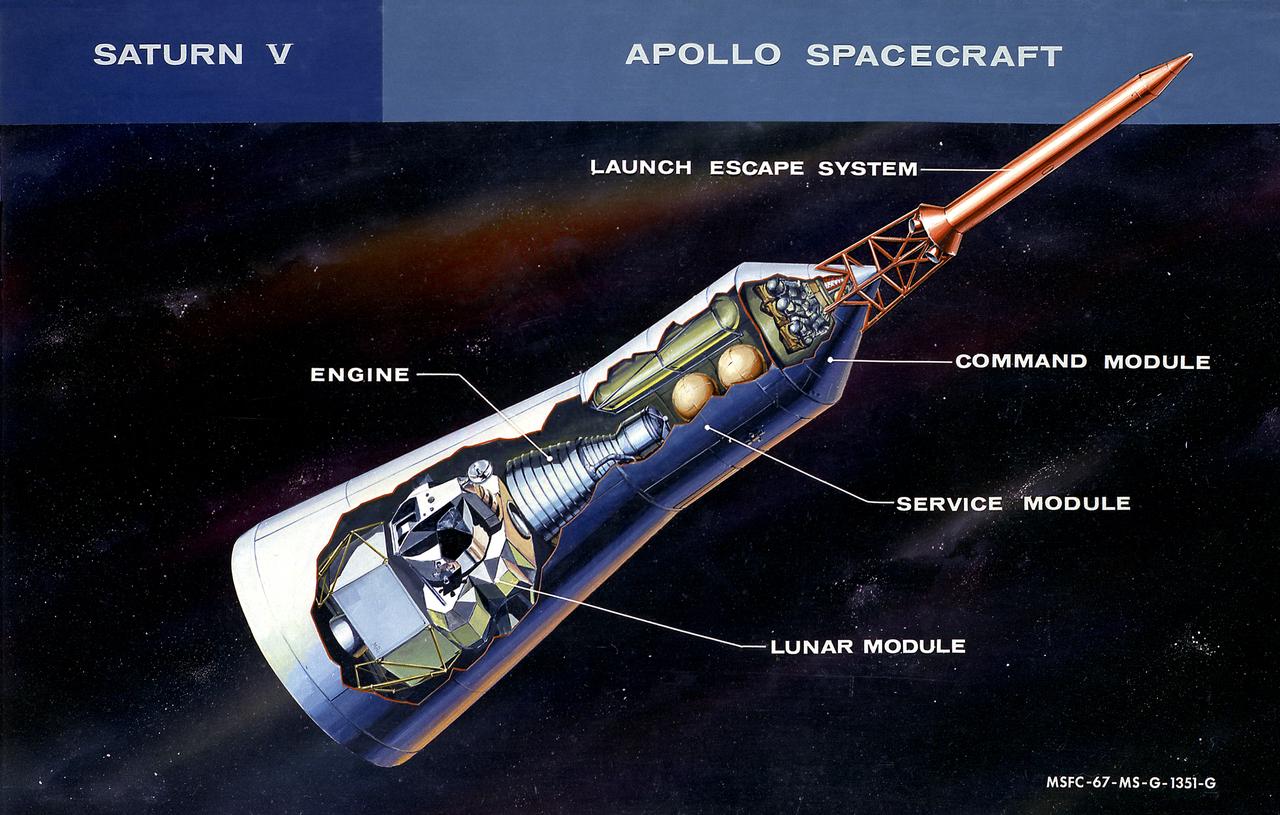
This cutaway illustration shows the Apollo Spacecraft with callouts of the major components. The spacecraft consisted of the lunar module, the service module, the command module, and the launch escape system.
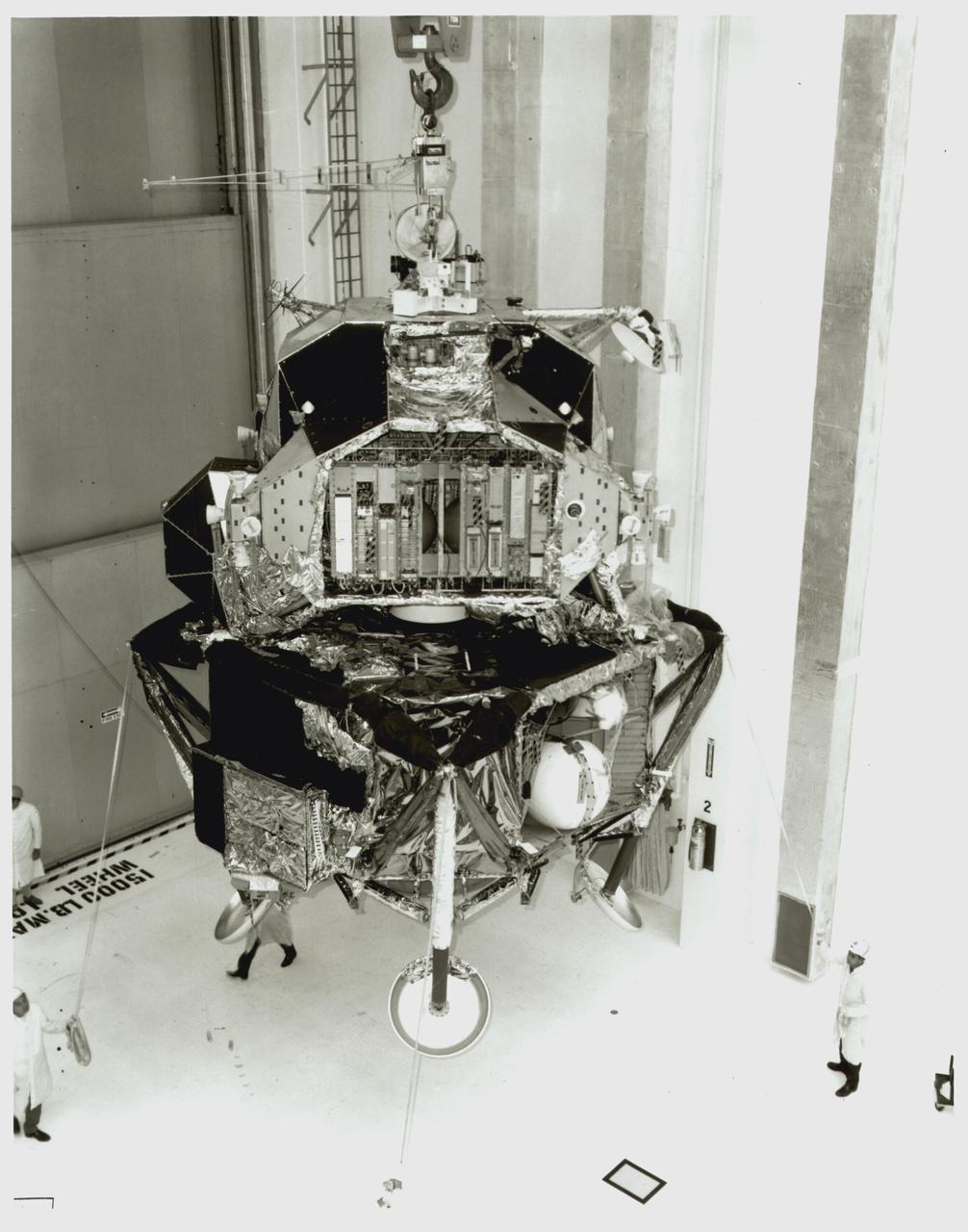
The Lunar Module for Apollo 11 moves from the landing gear fixture and mate to the spacecraft-lunar module adapter.
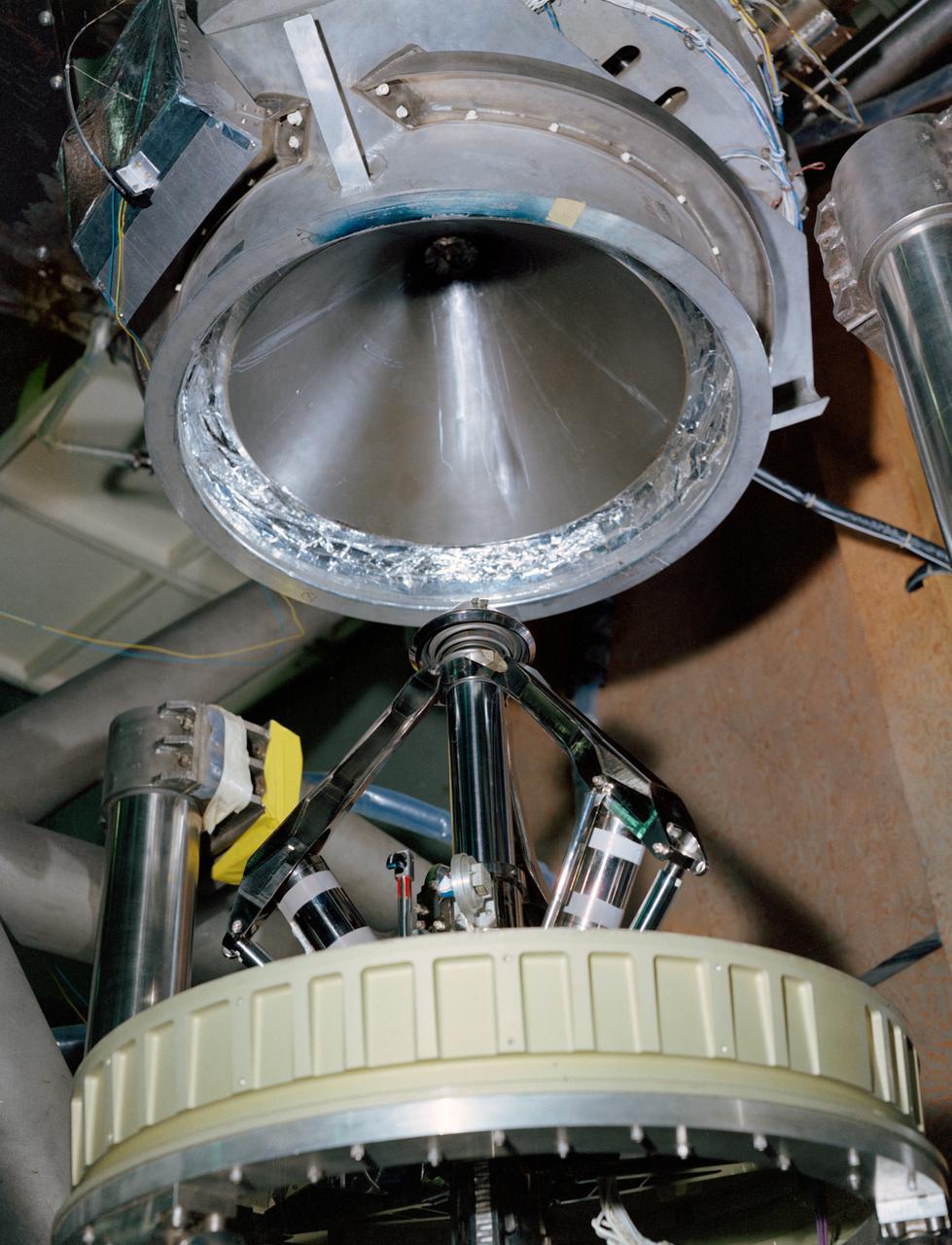
S68-50869 (1968) --- An engineering set up illustrating the docking system of the Apollo spacecraft. During docking maneuvers the docking probe on the Command Module engages the cone-shaped drogue of the Lunar Module. The primary docking structure is the tunnel through which the astronauts transfer from one module to the other. This tunnel is partly in the nose of the Command Module and partly in the top of the Lunar Module. Following CSM/LM docking the drogue and probe are removed to open the passageway between the modules.

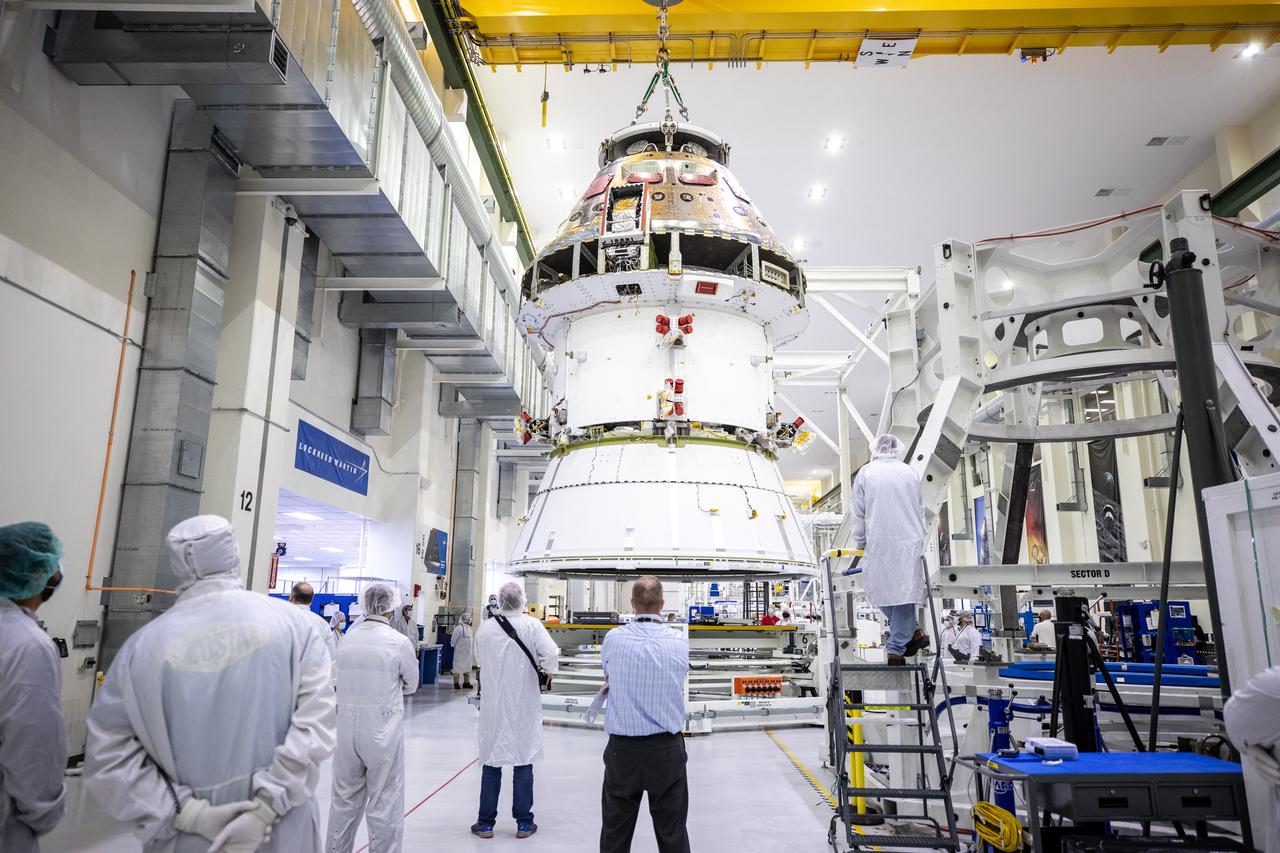
S69-19197 (1969) --- Interior view of the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Manned Spacecraft Operations Building (MSOB) showing Apollo Spacecraft 106 Command and Service Modules (CSM) being moved to integrated work stand number one for mating to Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) 13. Spacecraft 106 will be flown on the Apollo 10 (Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space mission.
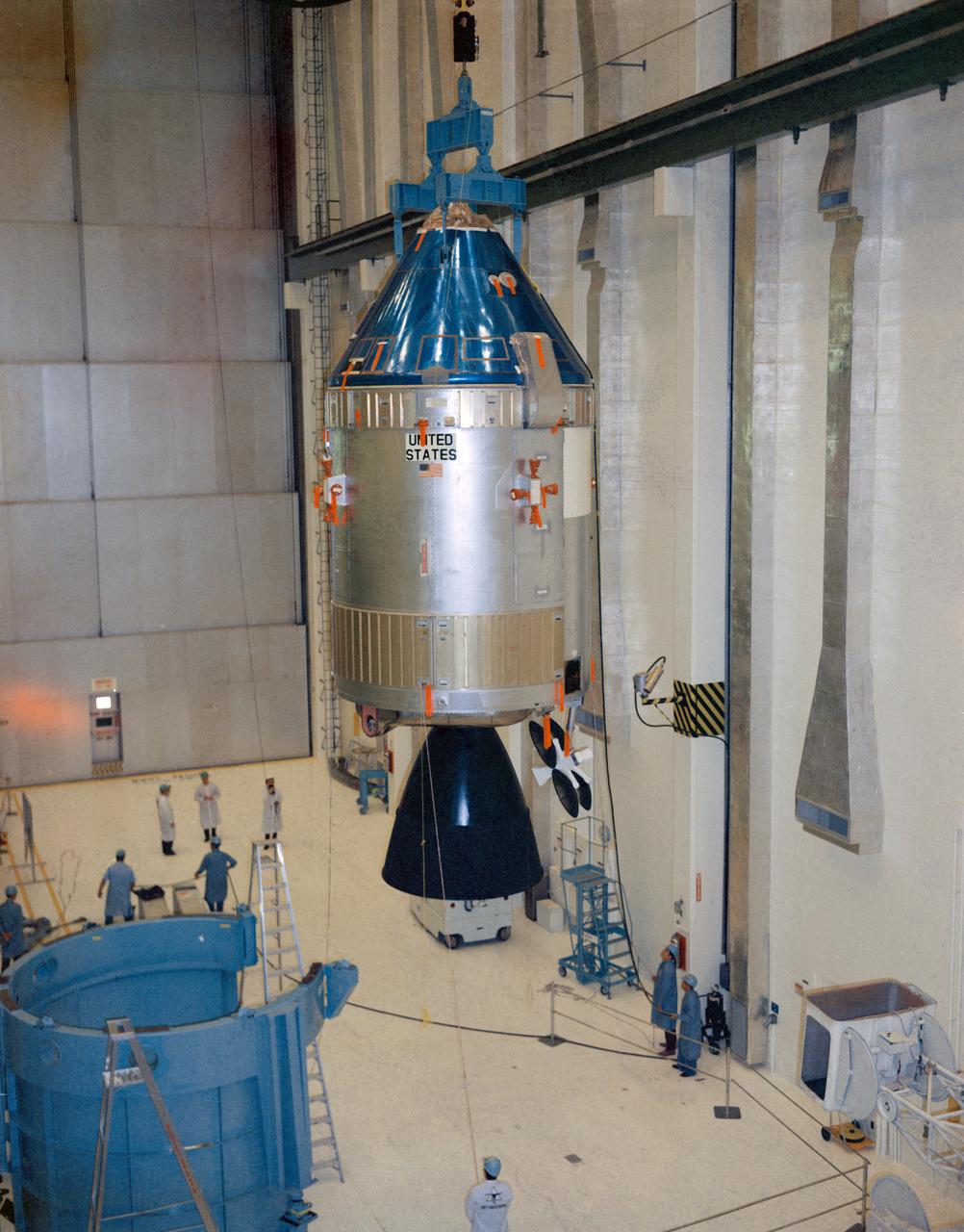

S69-19190 (31 Jan. 1969) --- Interior view of the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building showing Apollo Spacecraft 106/Command/Service Module being moved to integrated work stand number one for mating to Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) 13. Spacecraft 106 will be flown on the Apollo 10 (Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space mission.
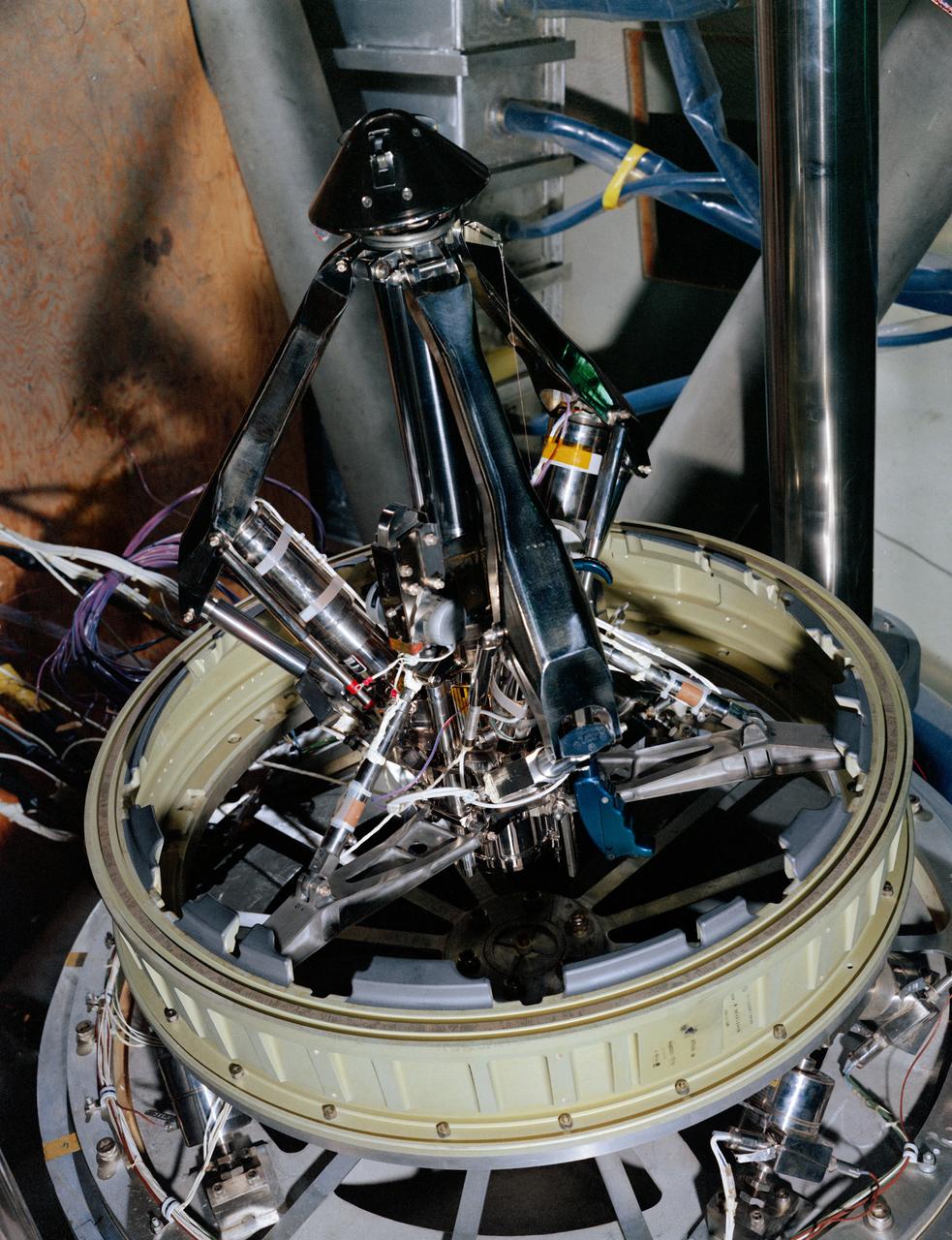

S68-50870 (1968) --- An engineering set up illustrating the probe portion of the docking system of the Apollo spacecraft. During docking maneuvers the docking probe on the Command Module (CM) engages the cone shaped drogue of the Lunar Module (LM). The primary docking structure is the tunnel through which the astronauts transfer from one module to the other. This tunnel is partly in the nose of the CM and partly in the top of the LM. Following CSM/LM docking the drogue and probe are removed to open the passageway between the modules.
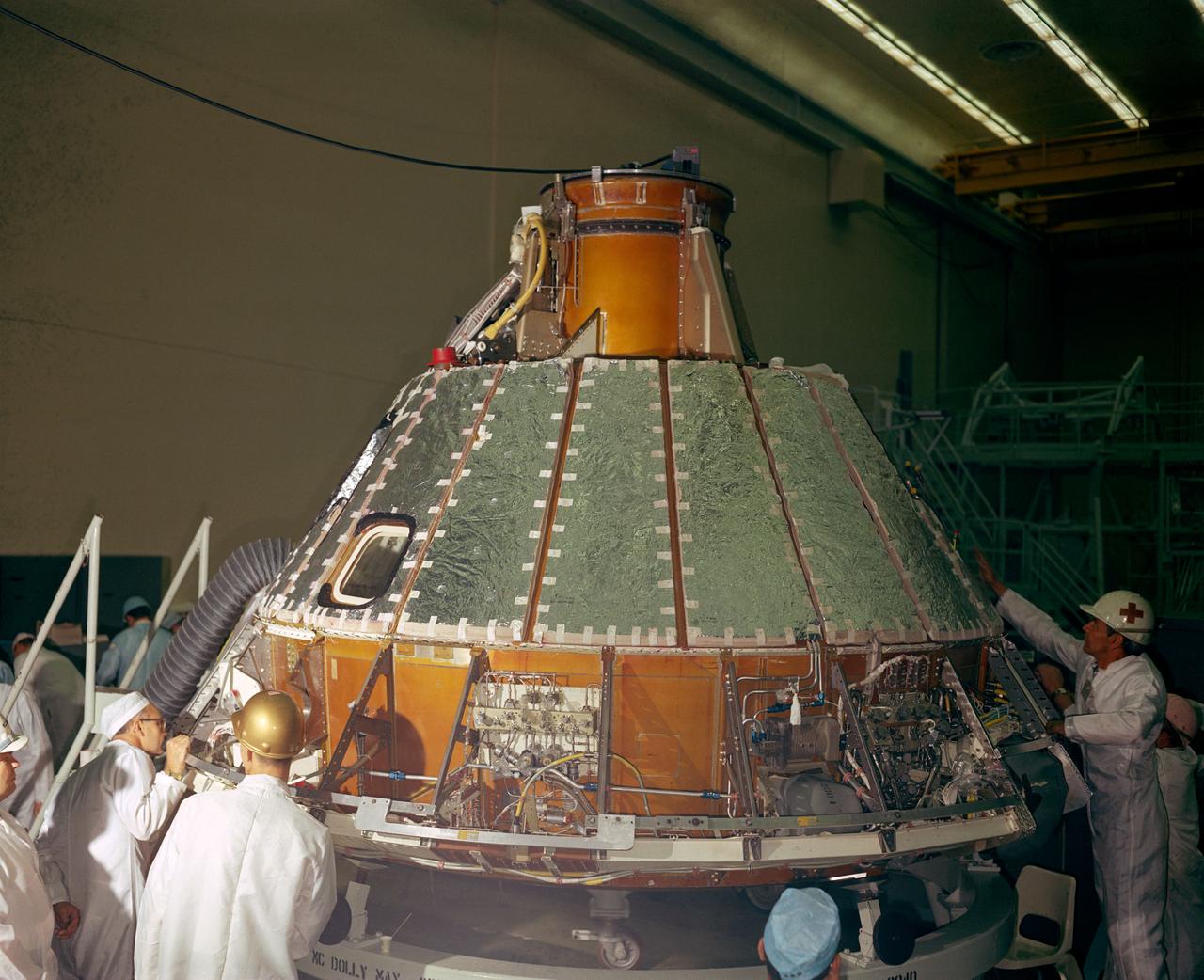

S66-41852 (1966) --- Spacecraft 012 looking toward -Y axis during installation of heat shield. Note uprighting system compressor in aft bay, at right, and Reaction Control System (RCS) valve module panel, center of photo.
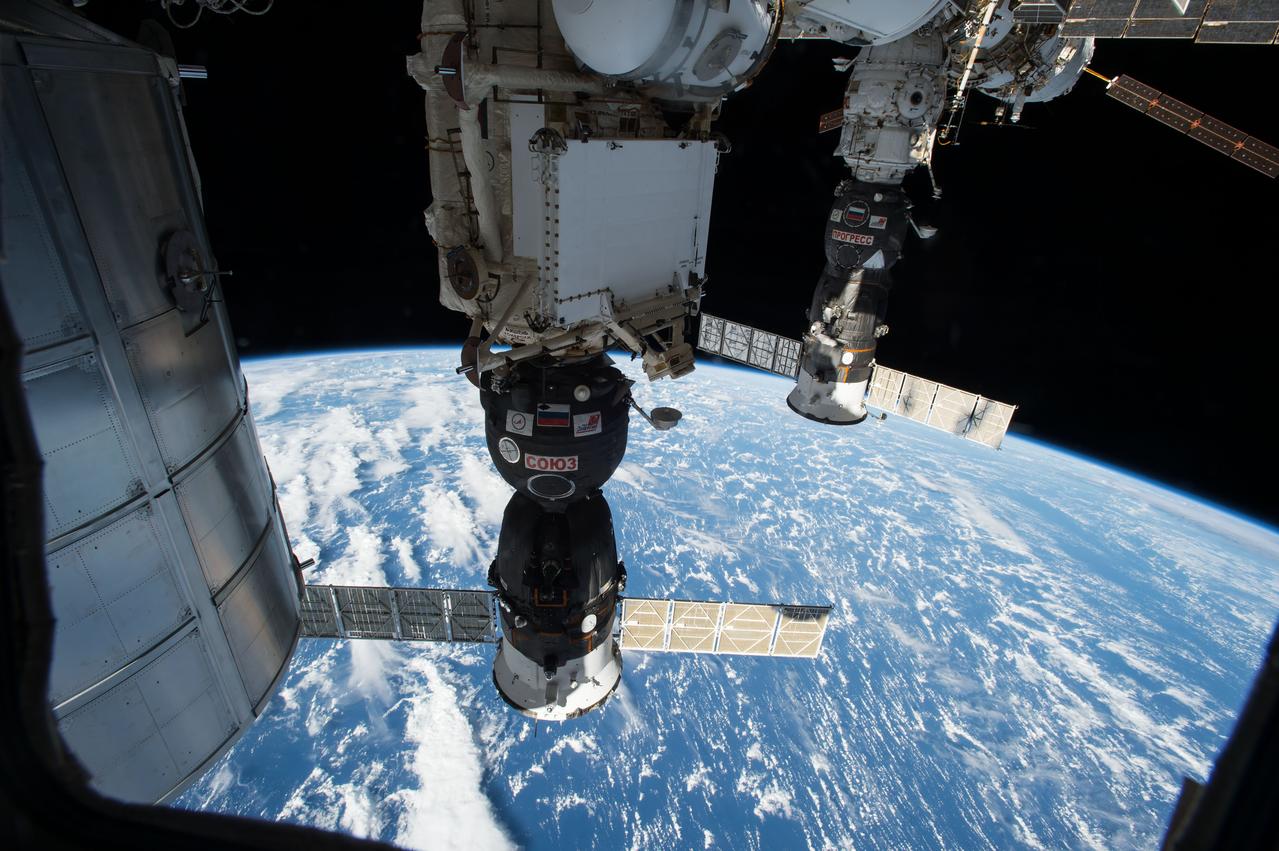

View of the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft docked to Rassvet Mini-Research Module 1 (MRM1) and the Progress 57P spacecraft docked to Pirs Docking Compartment (DC1). Portions of the Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module (PMM), aft ISS, and an Earth limb are in view. Image was released by astronaut on Twitter.
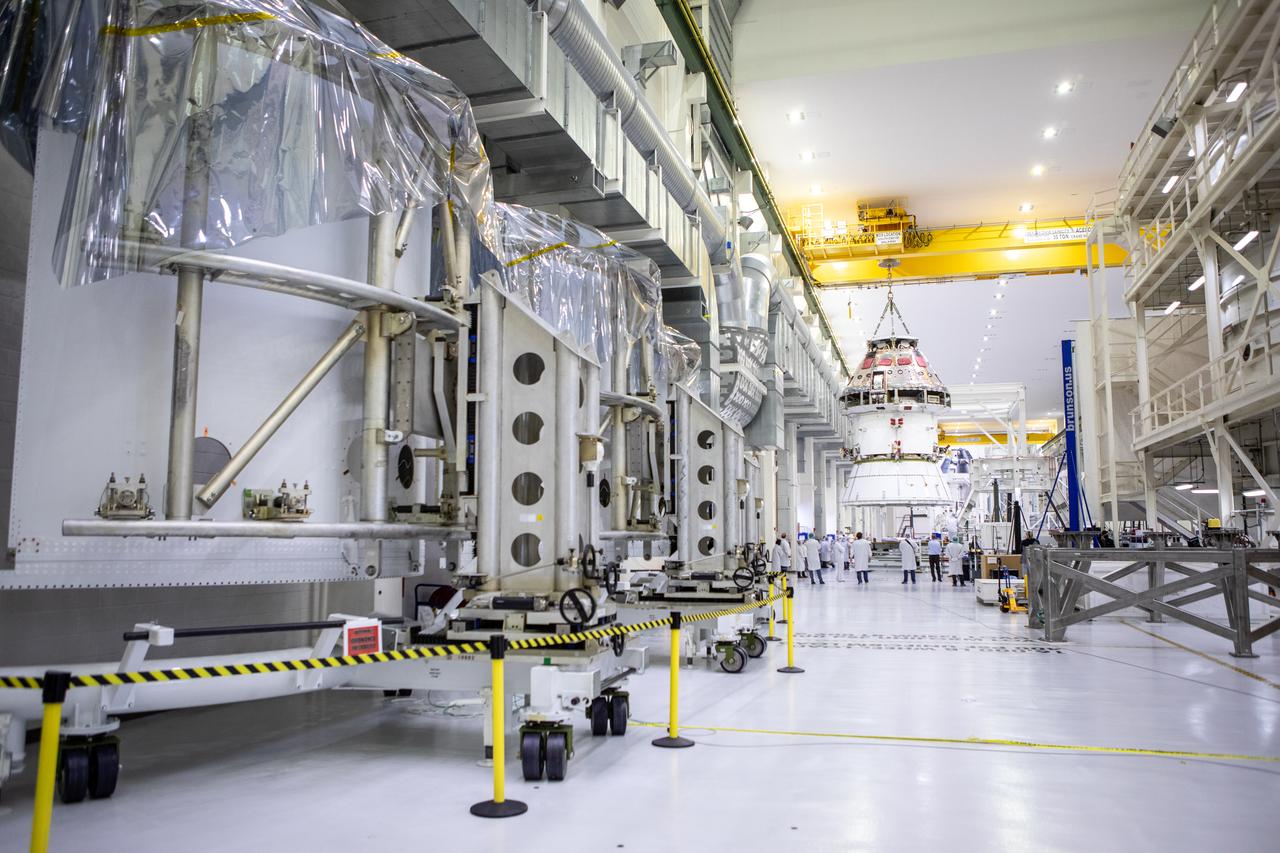

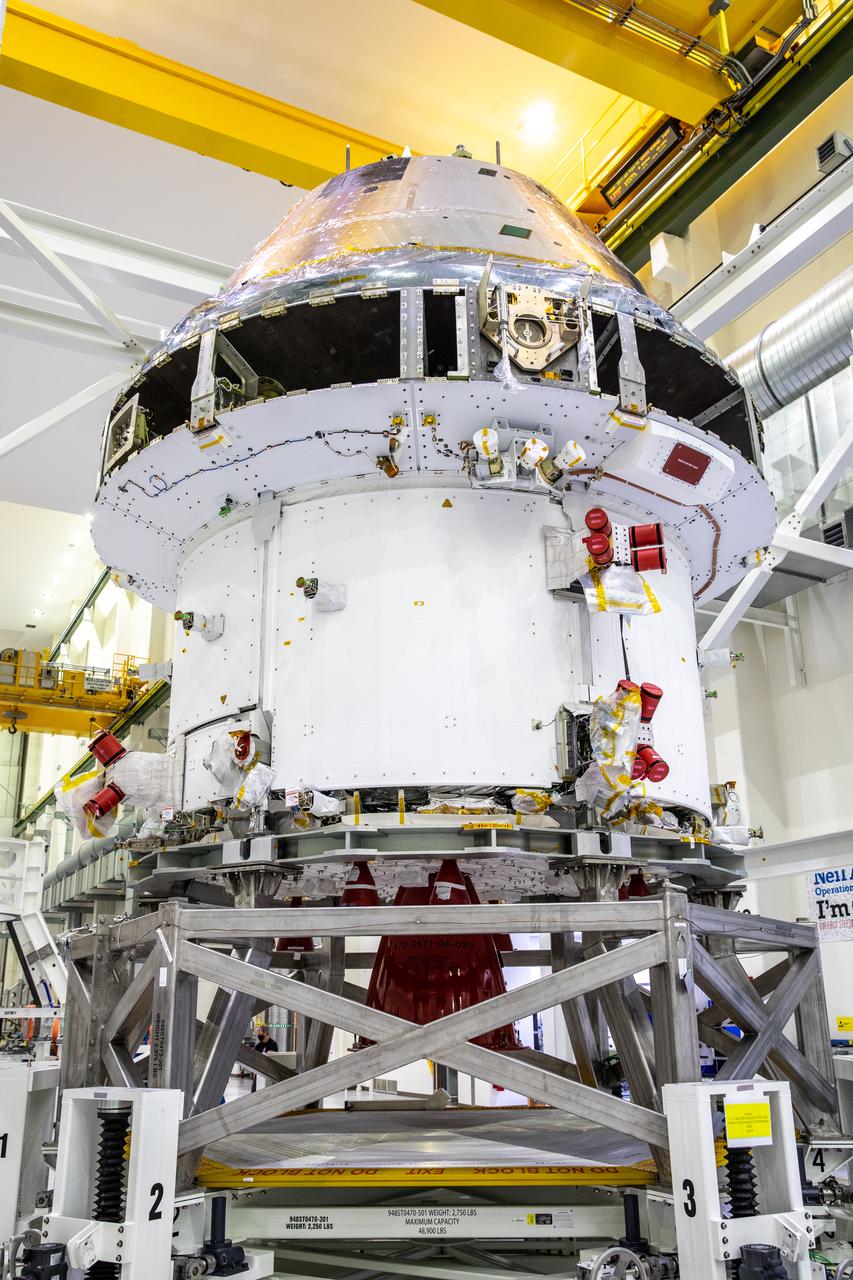
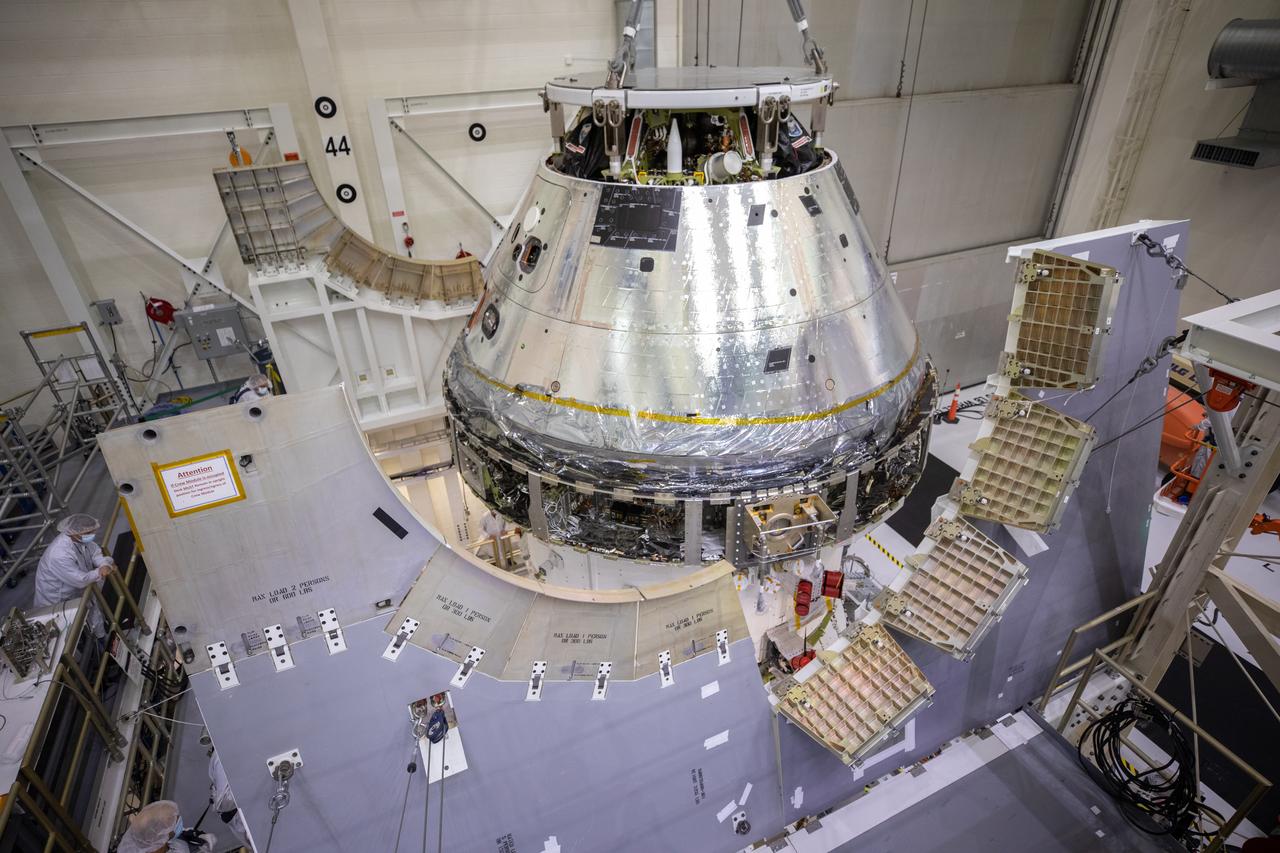
Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). In view at left in the foreground are the Spacecraft Adapter Jettison Fairing panels that will protect Orion’s service module from the environment around it during the ascent. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
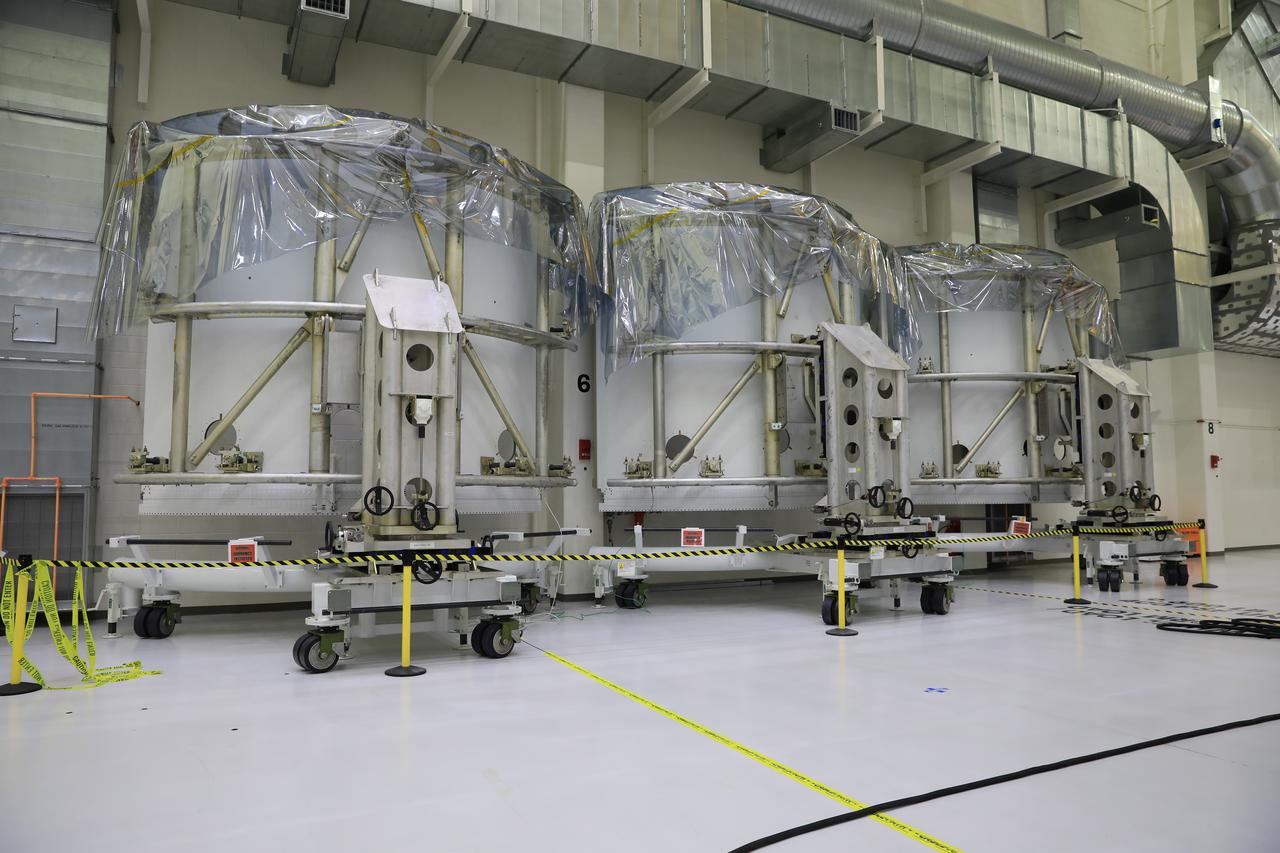

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
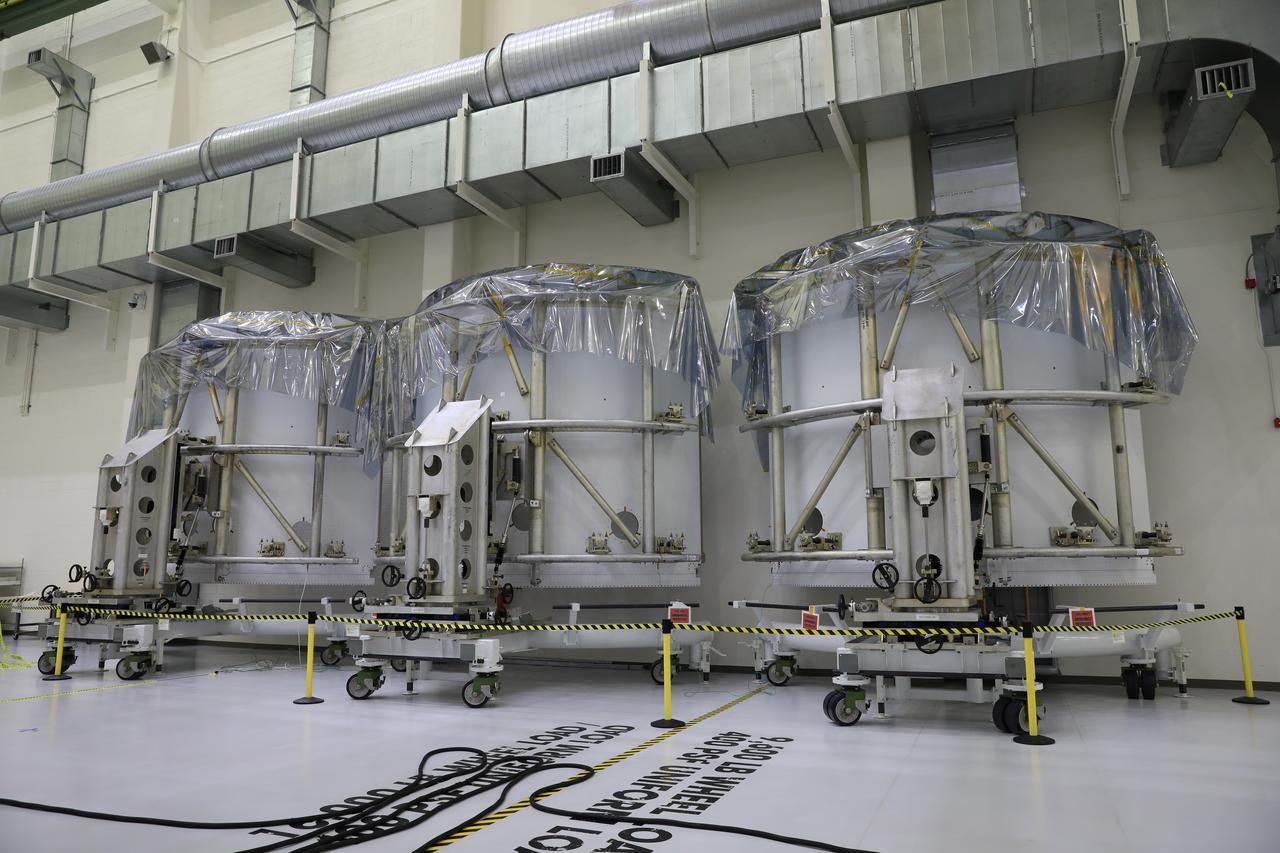

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
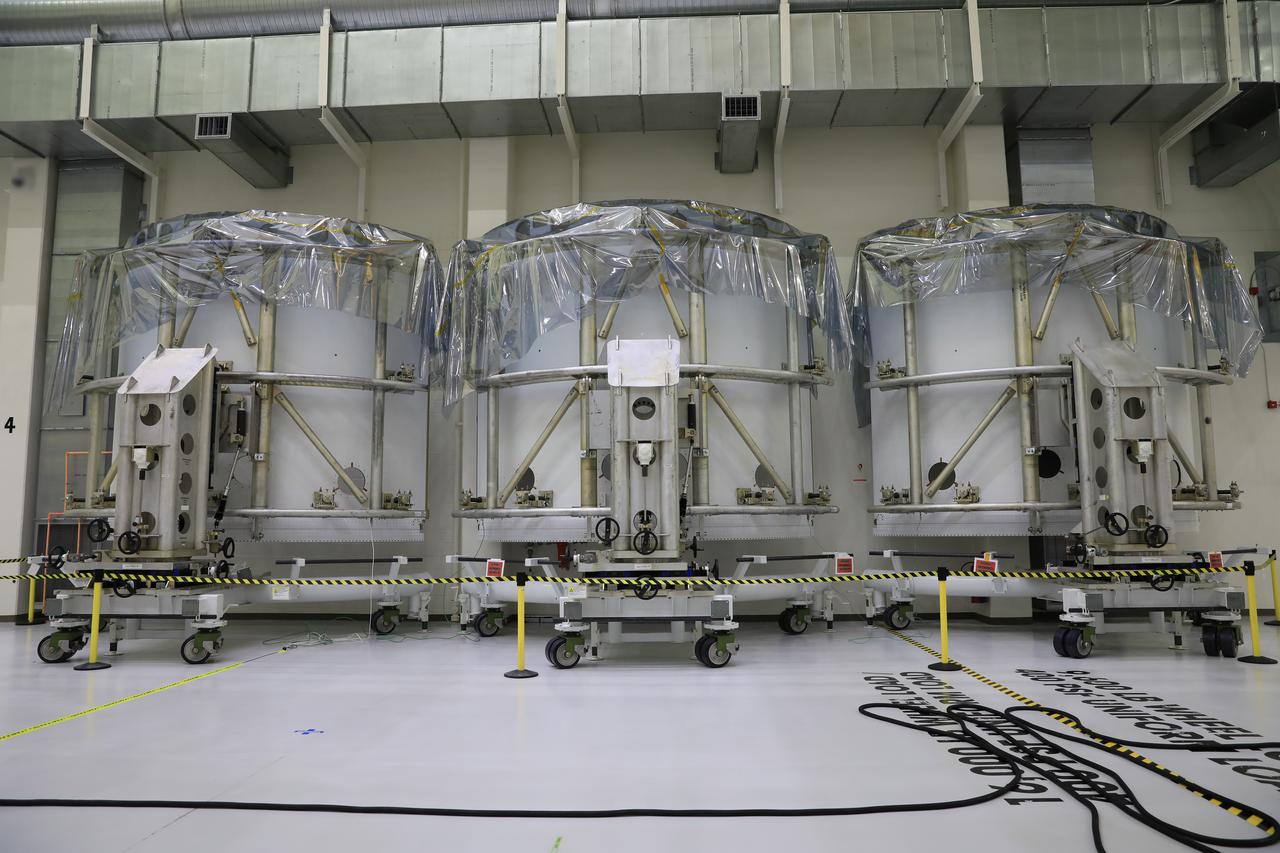

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
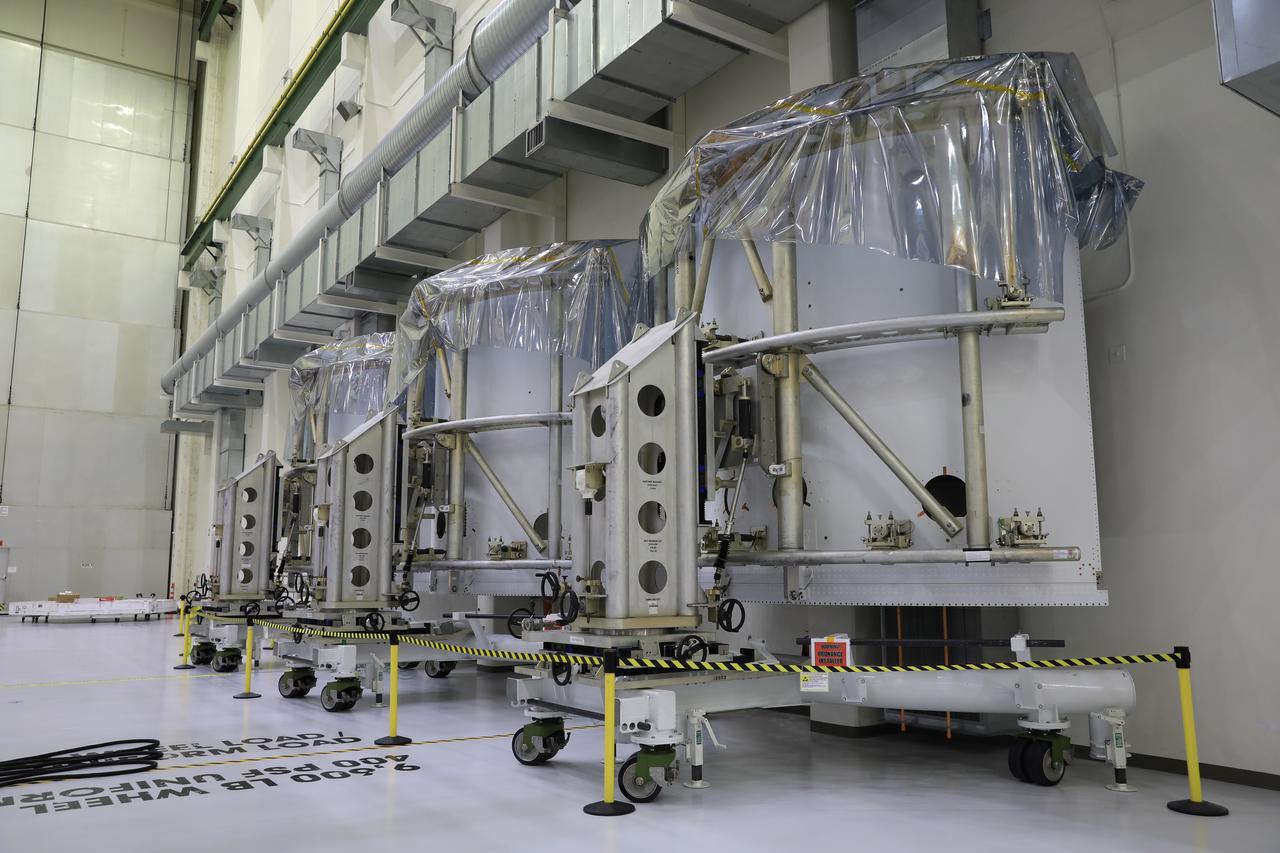

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

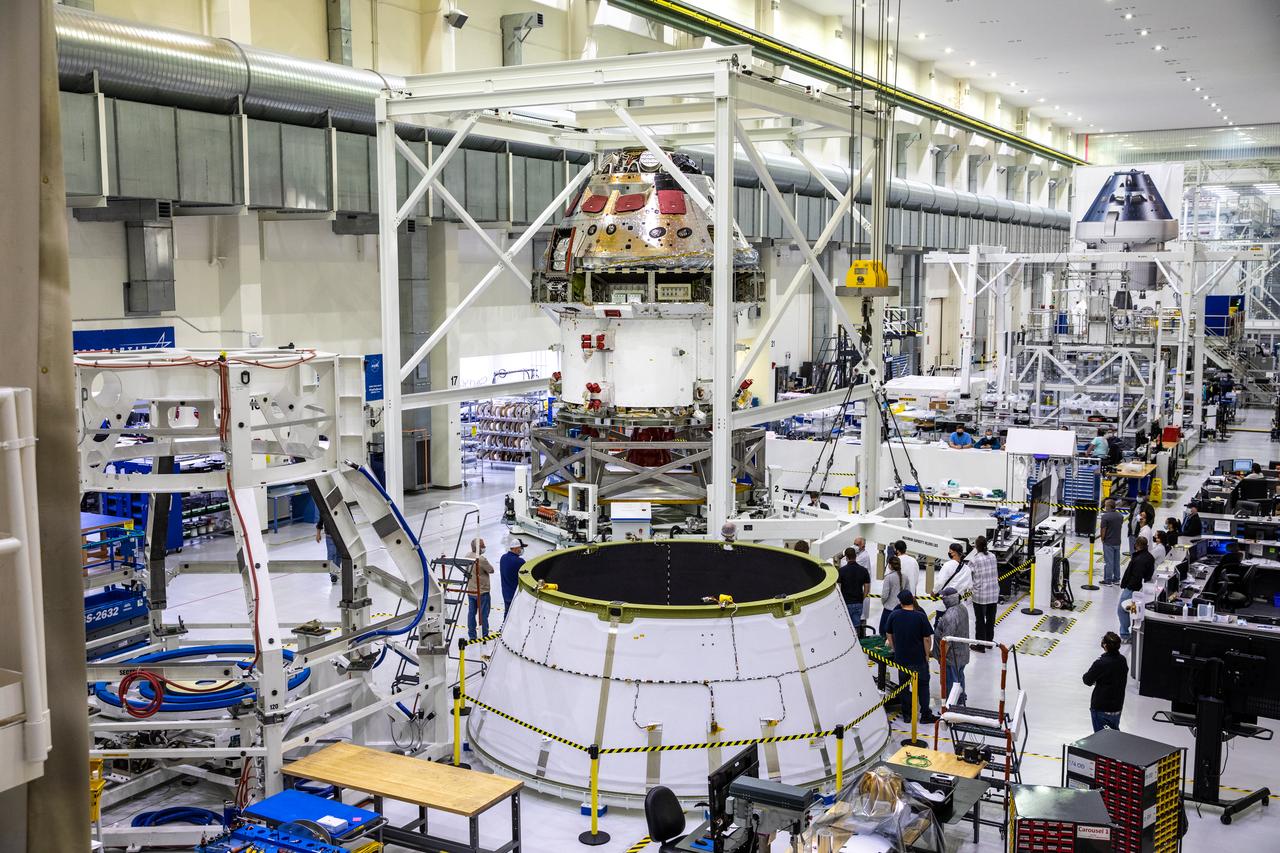
Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
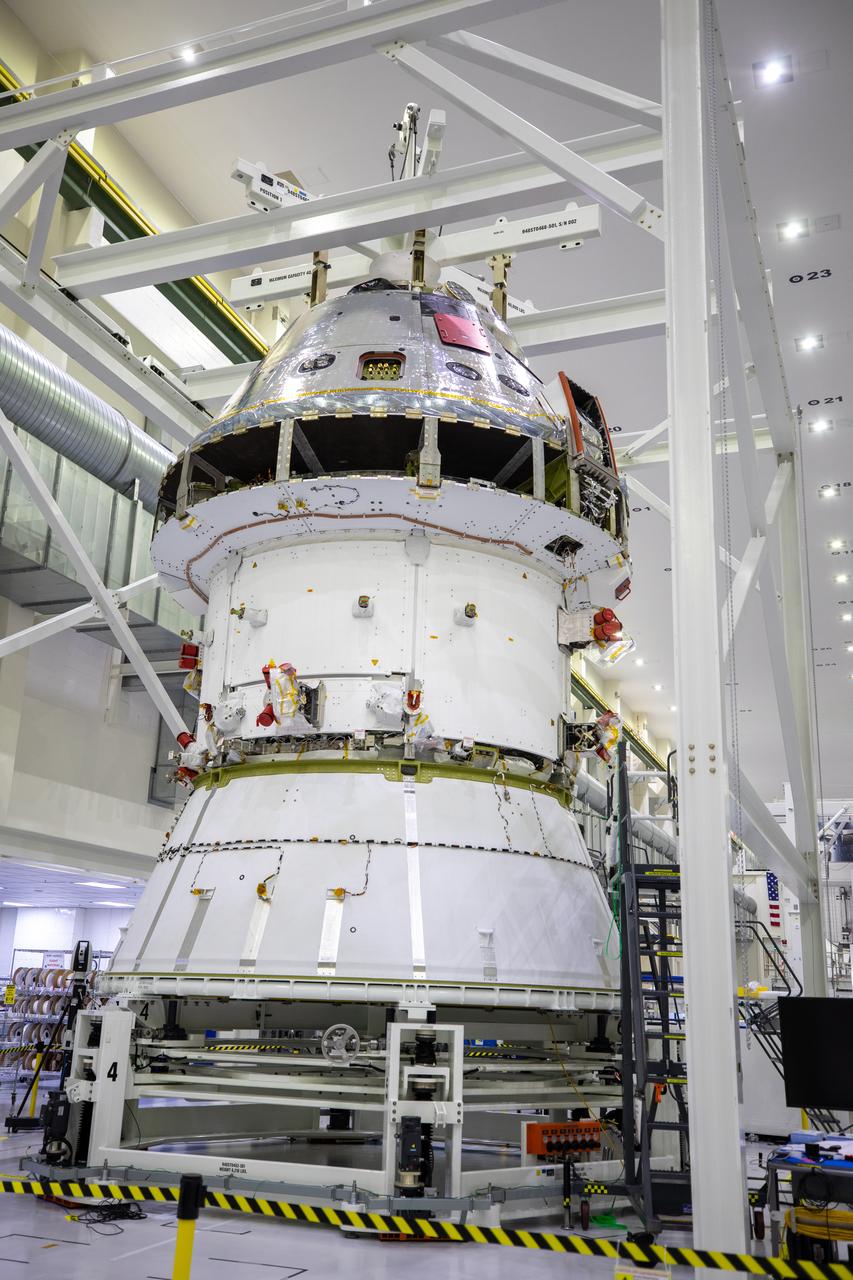

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
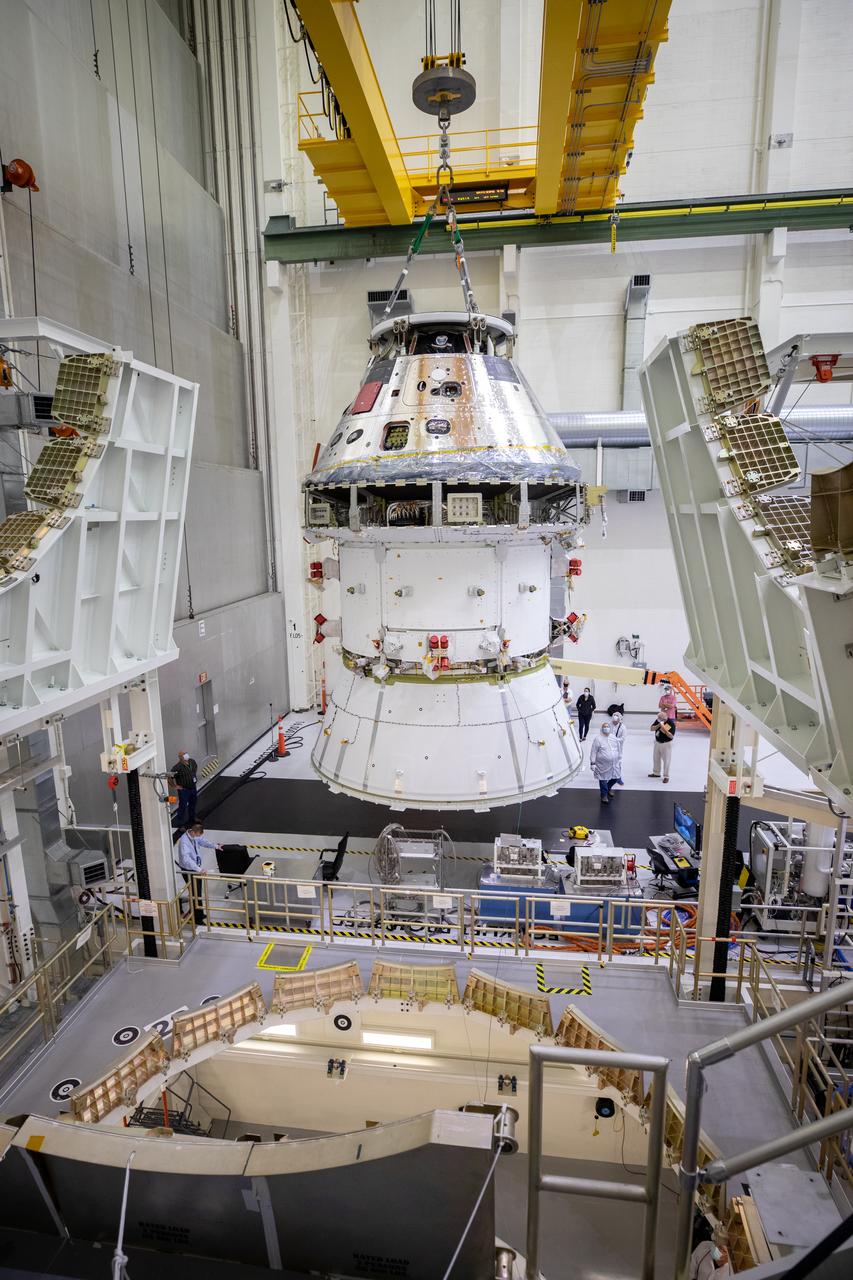

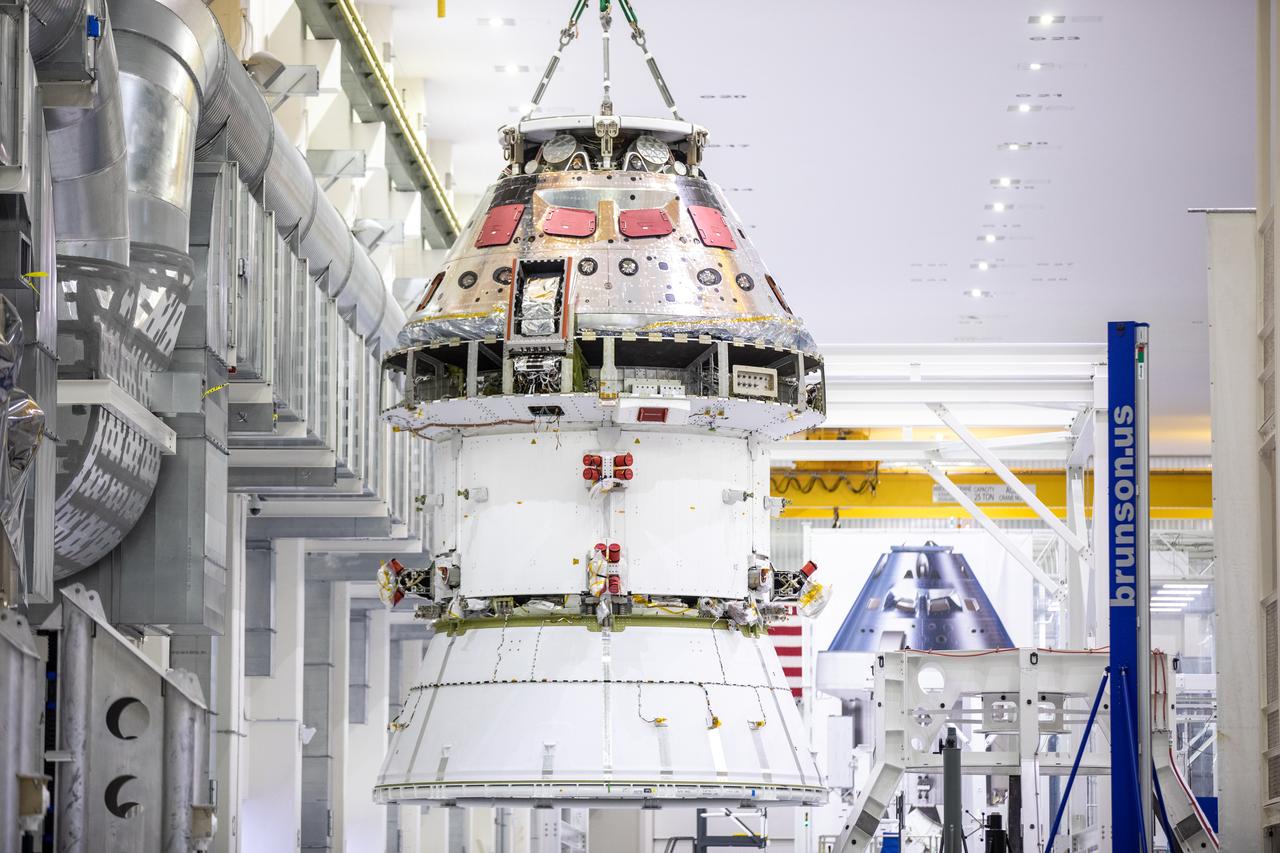
The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane into the FAST cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
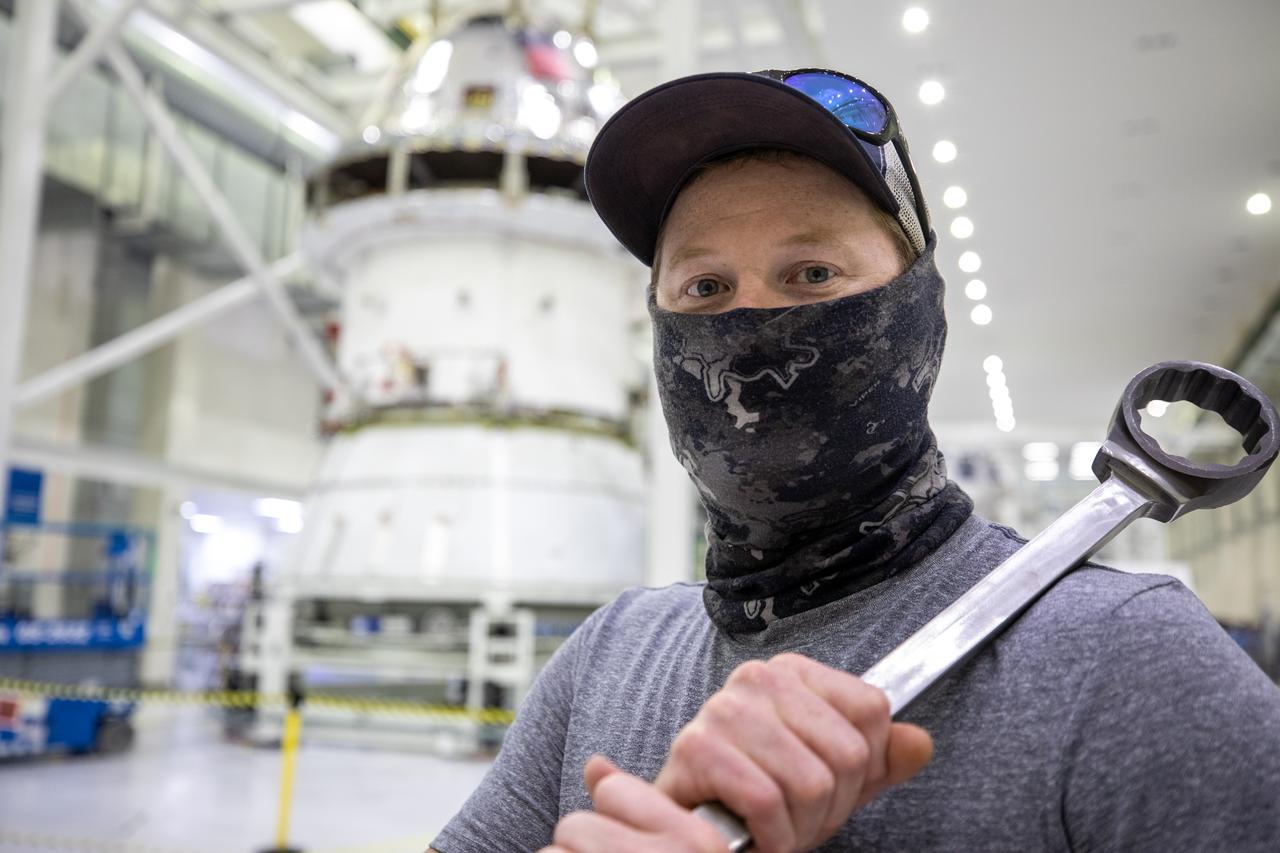

ASRC technician Chris Slack assists with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
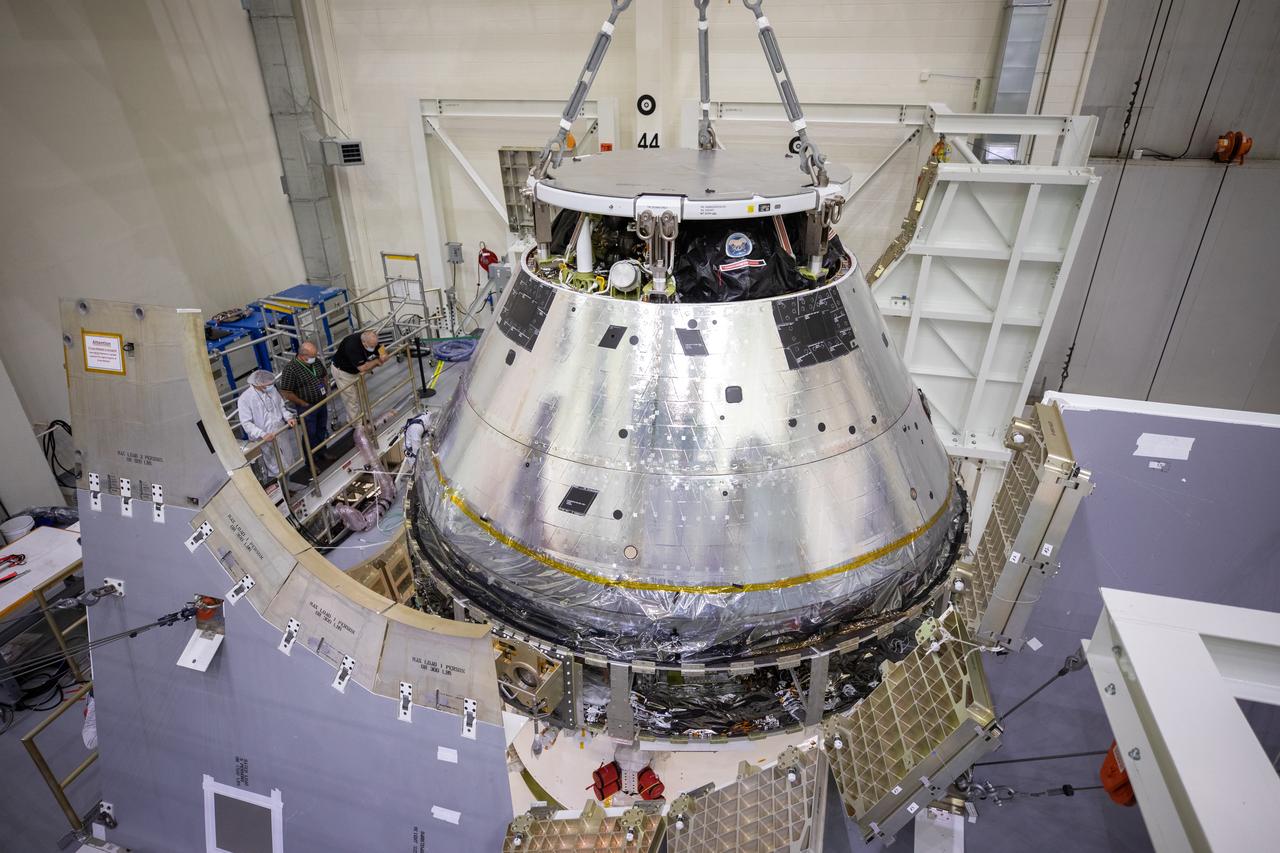

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft is lowered by crane into the FAST cell after installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone was completed inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
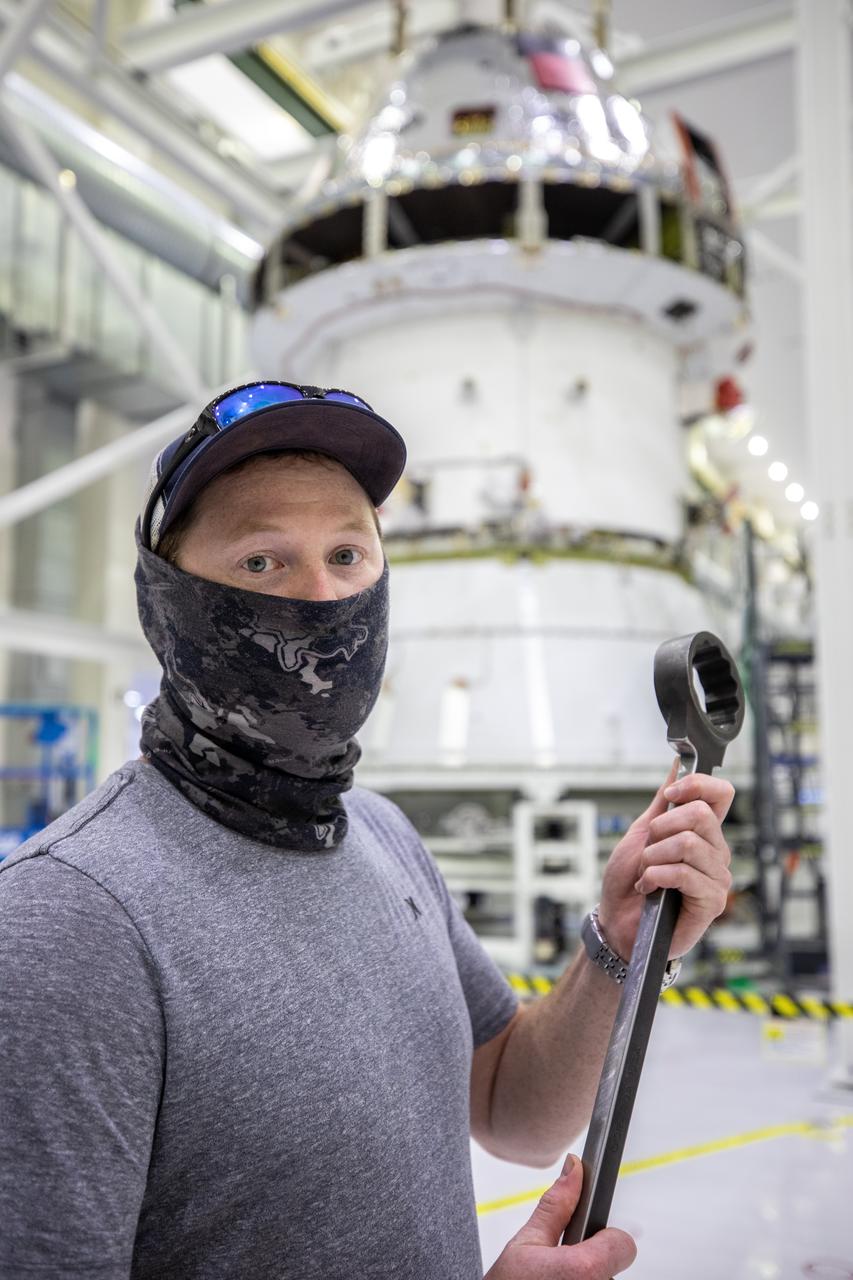

ASRC technician Chris Slack assists with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
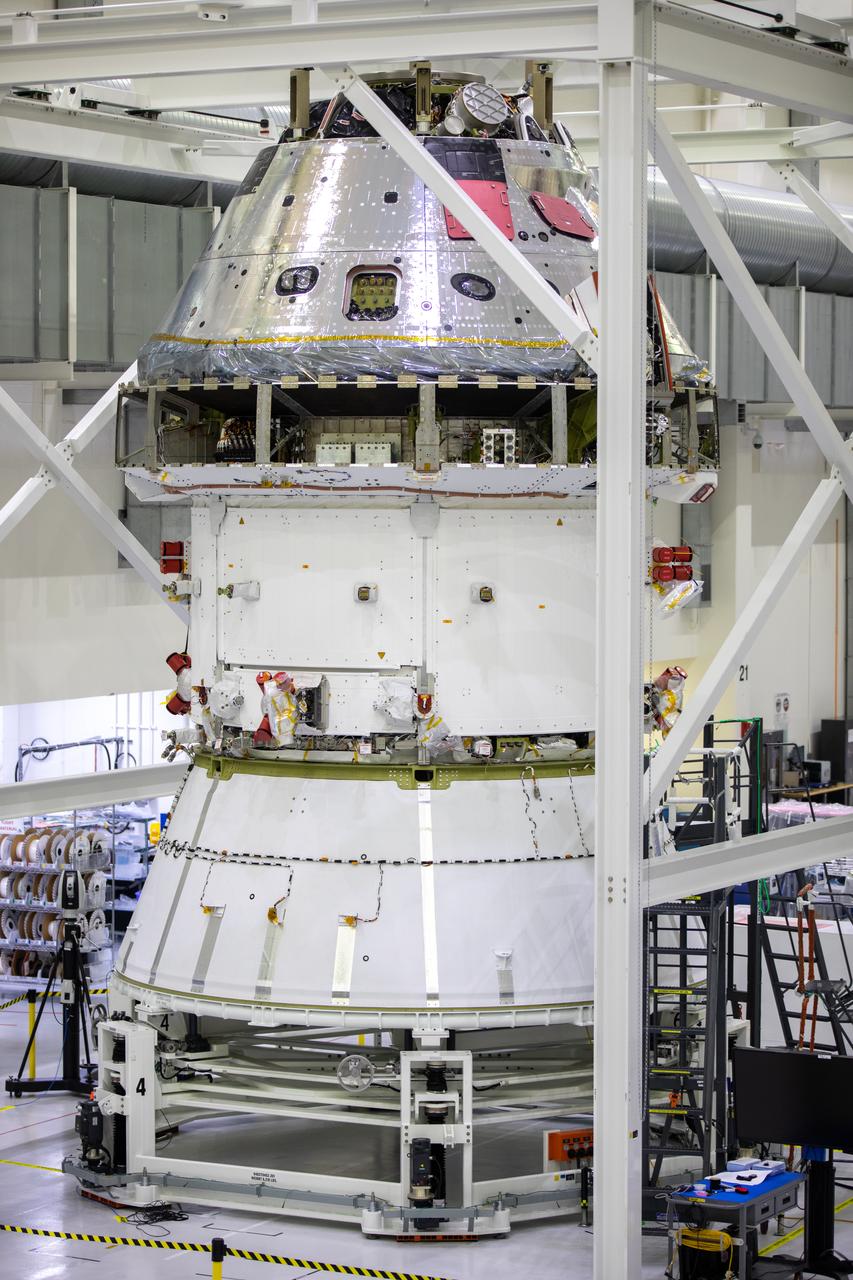

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
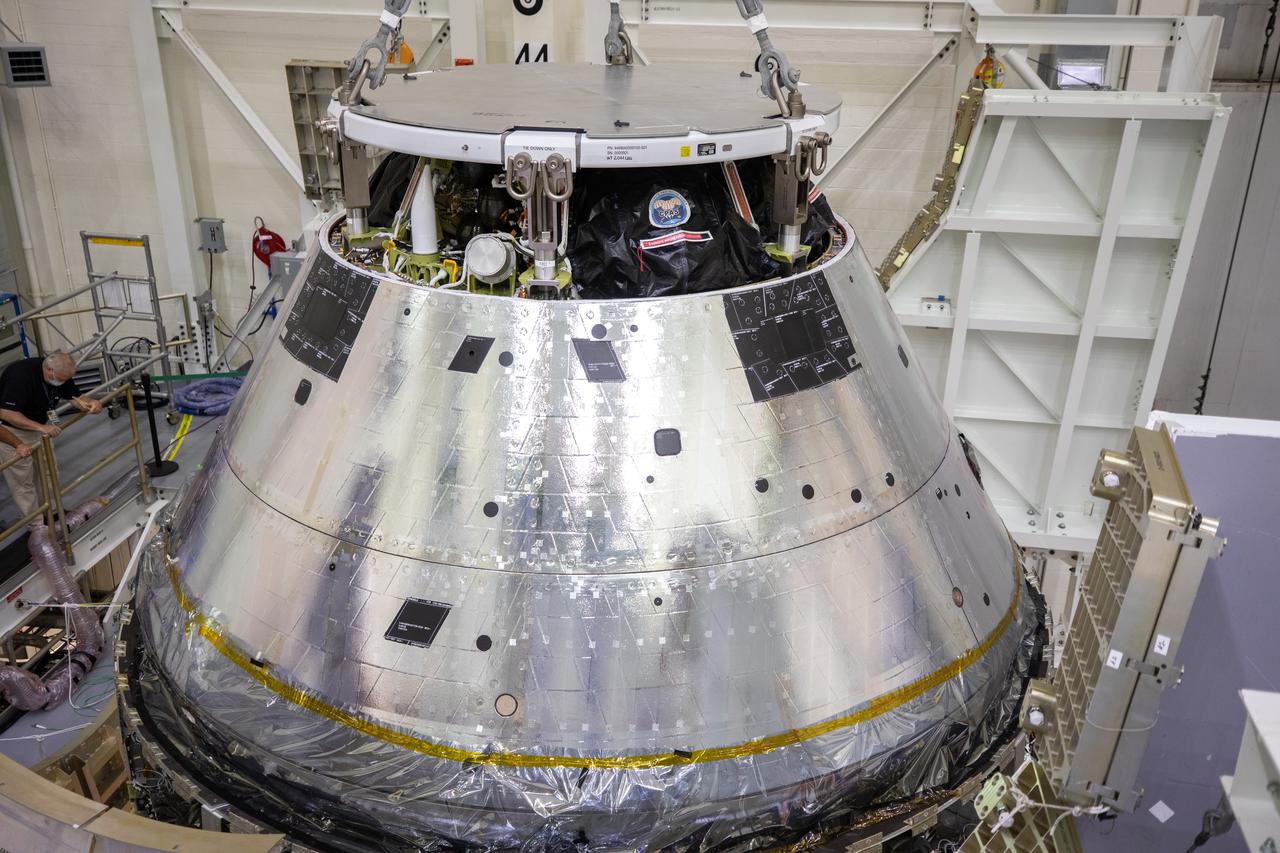

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft is lowered by crane into the FAST cell after installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone was completed inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
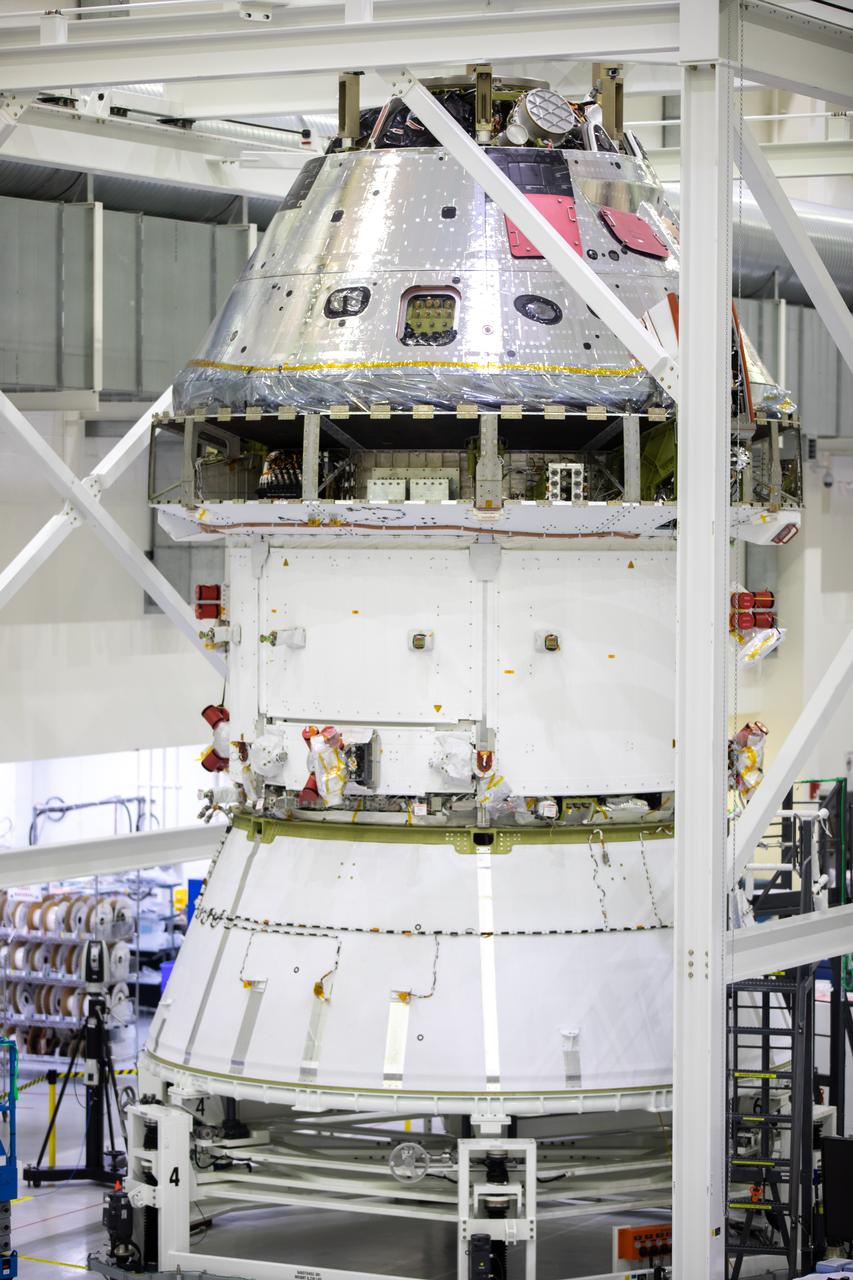

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
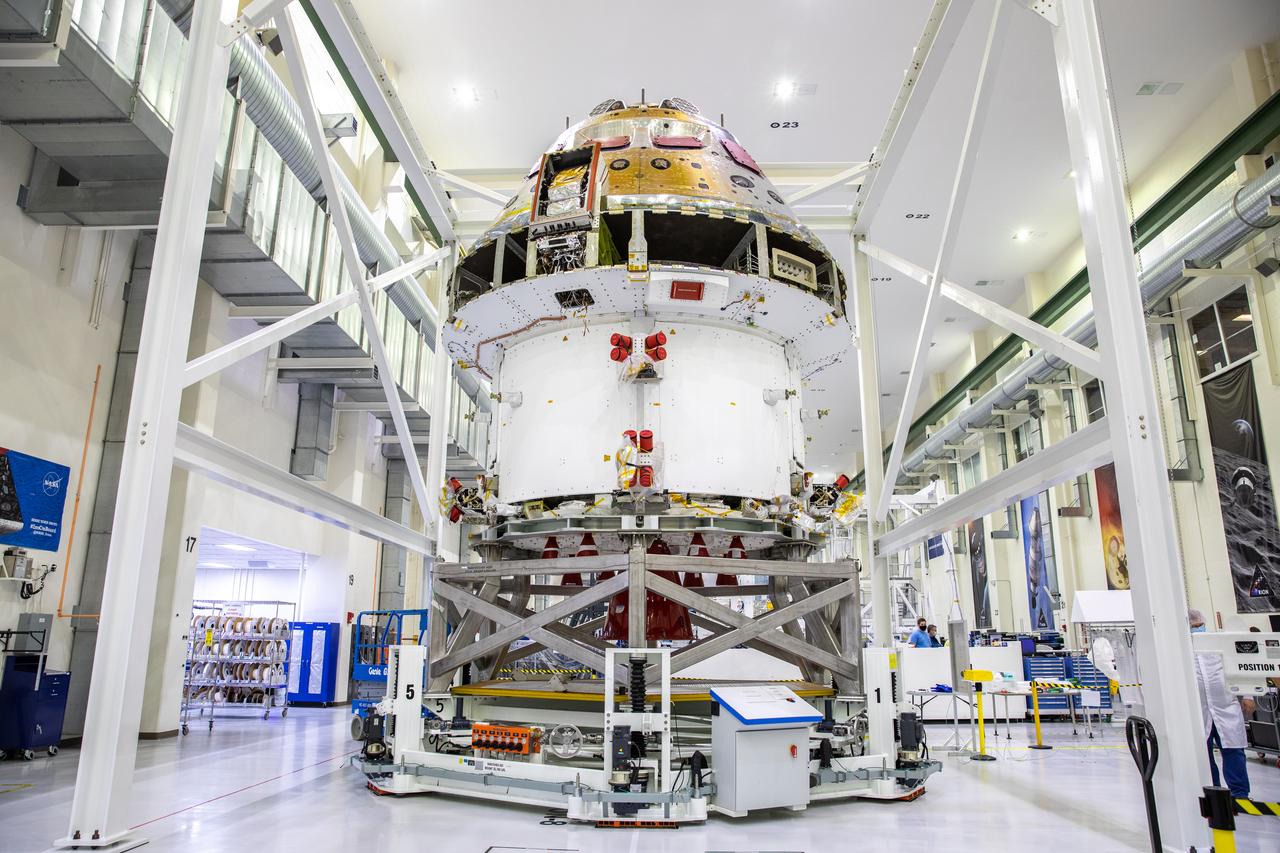

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
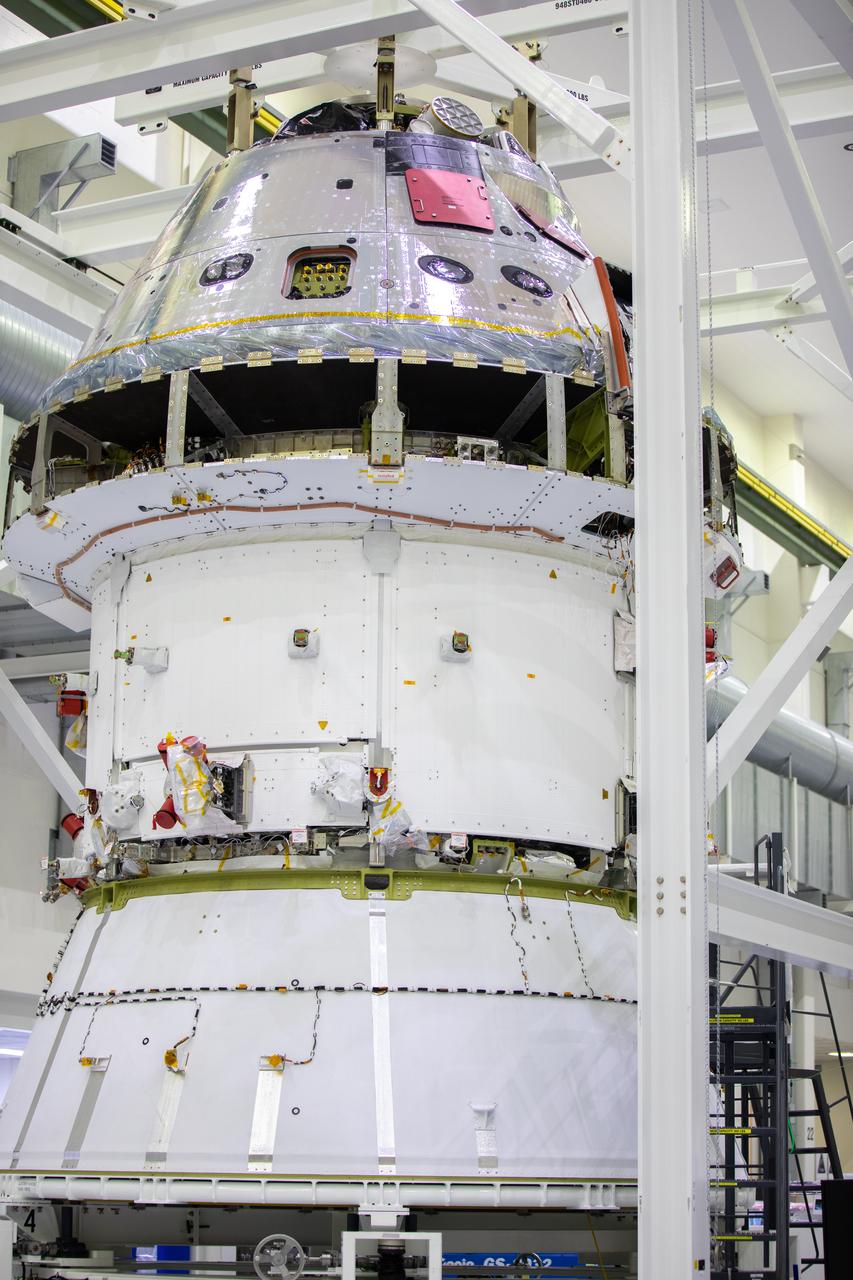

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
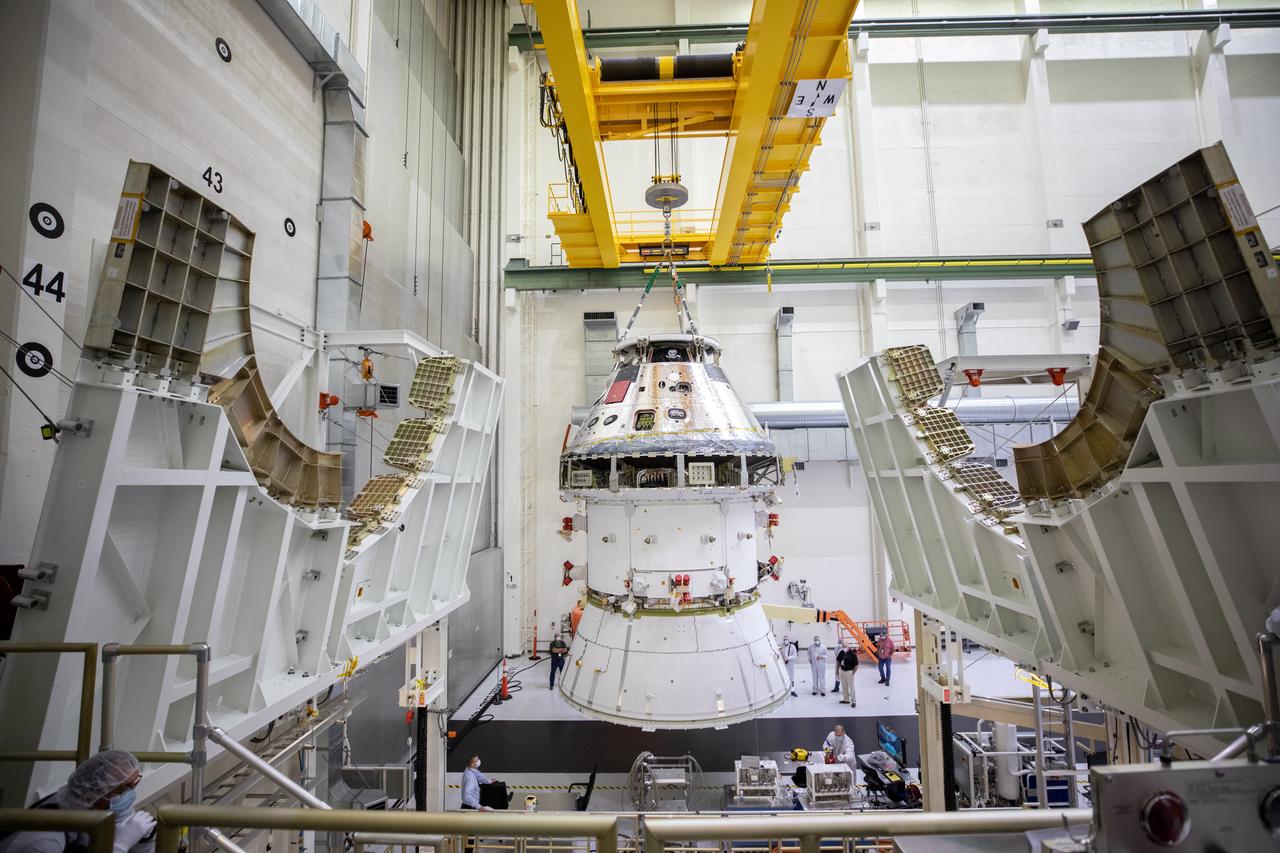

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane into the FAST cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
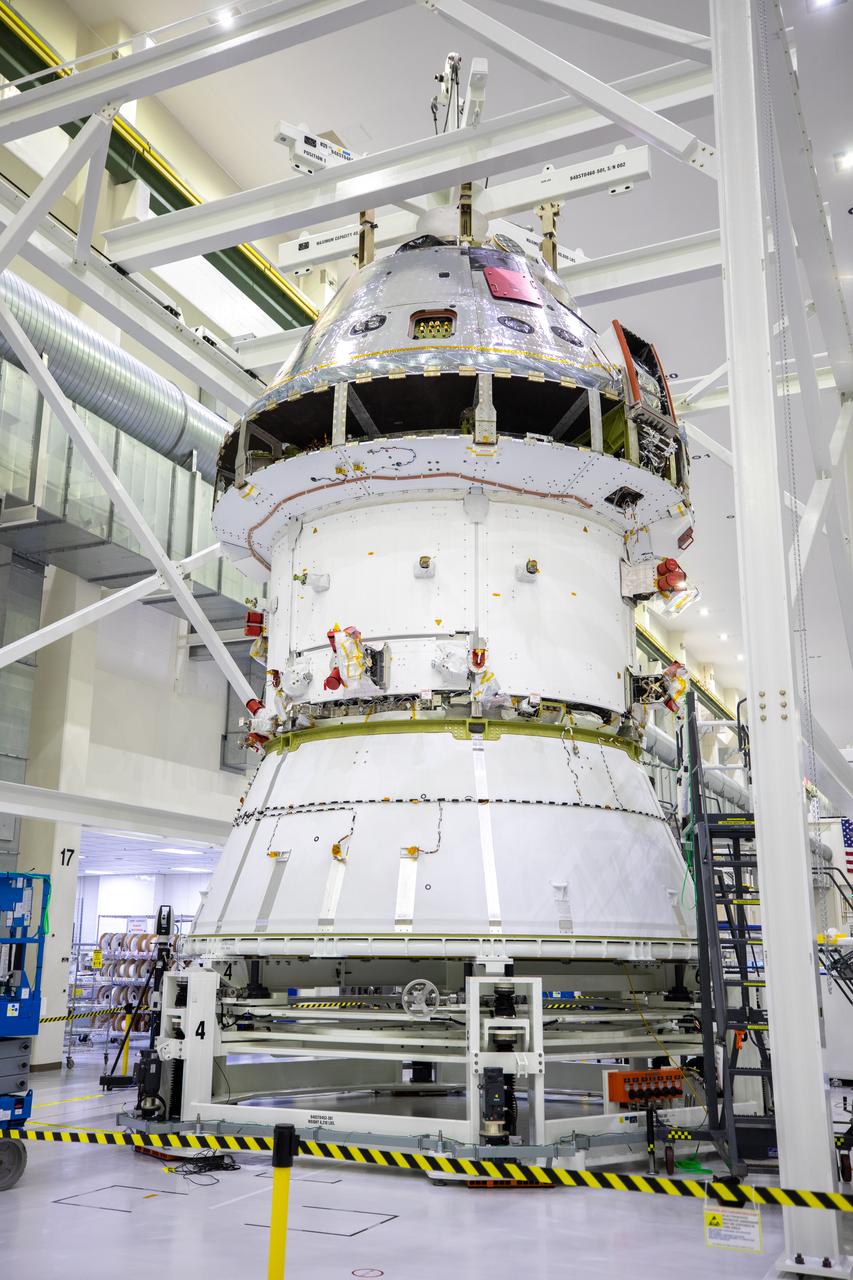

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft shown in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
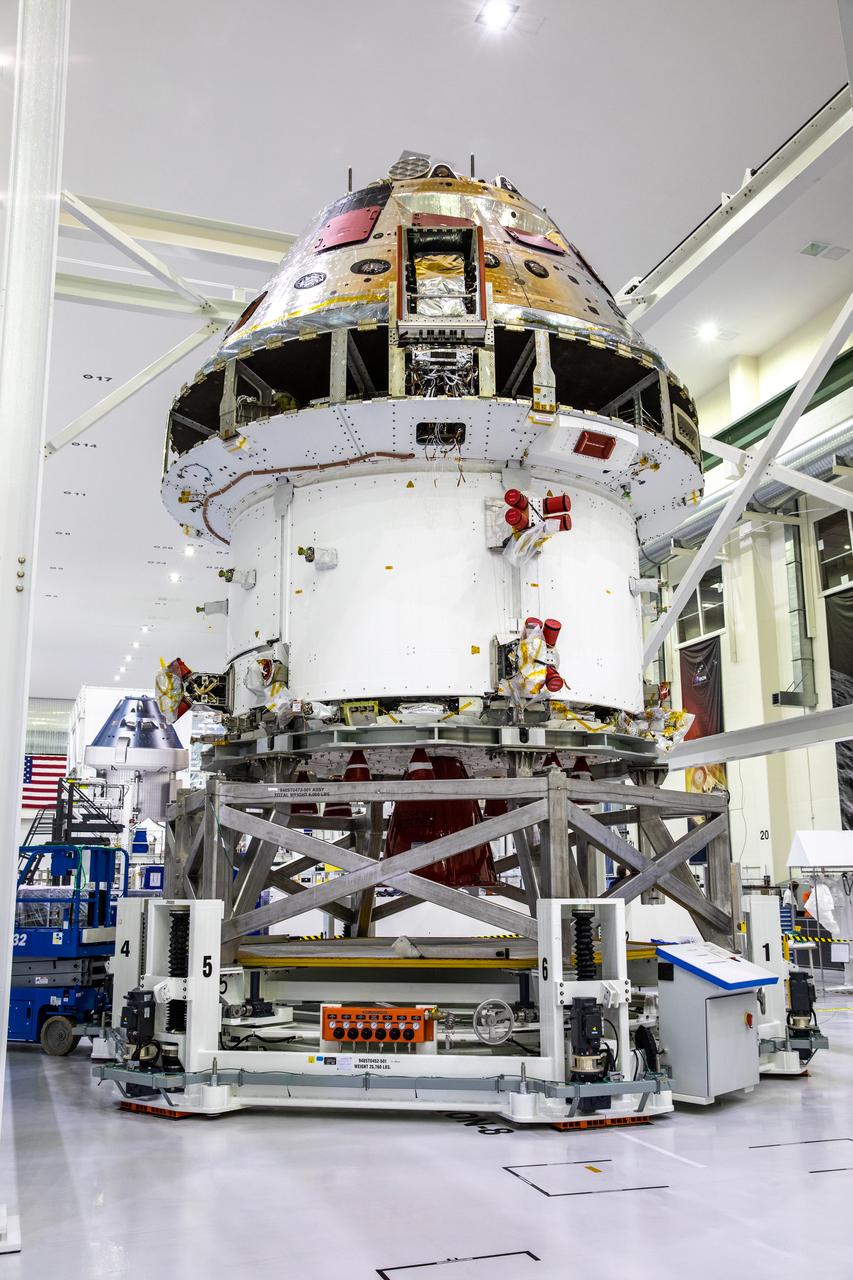

Installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
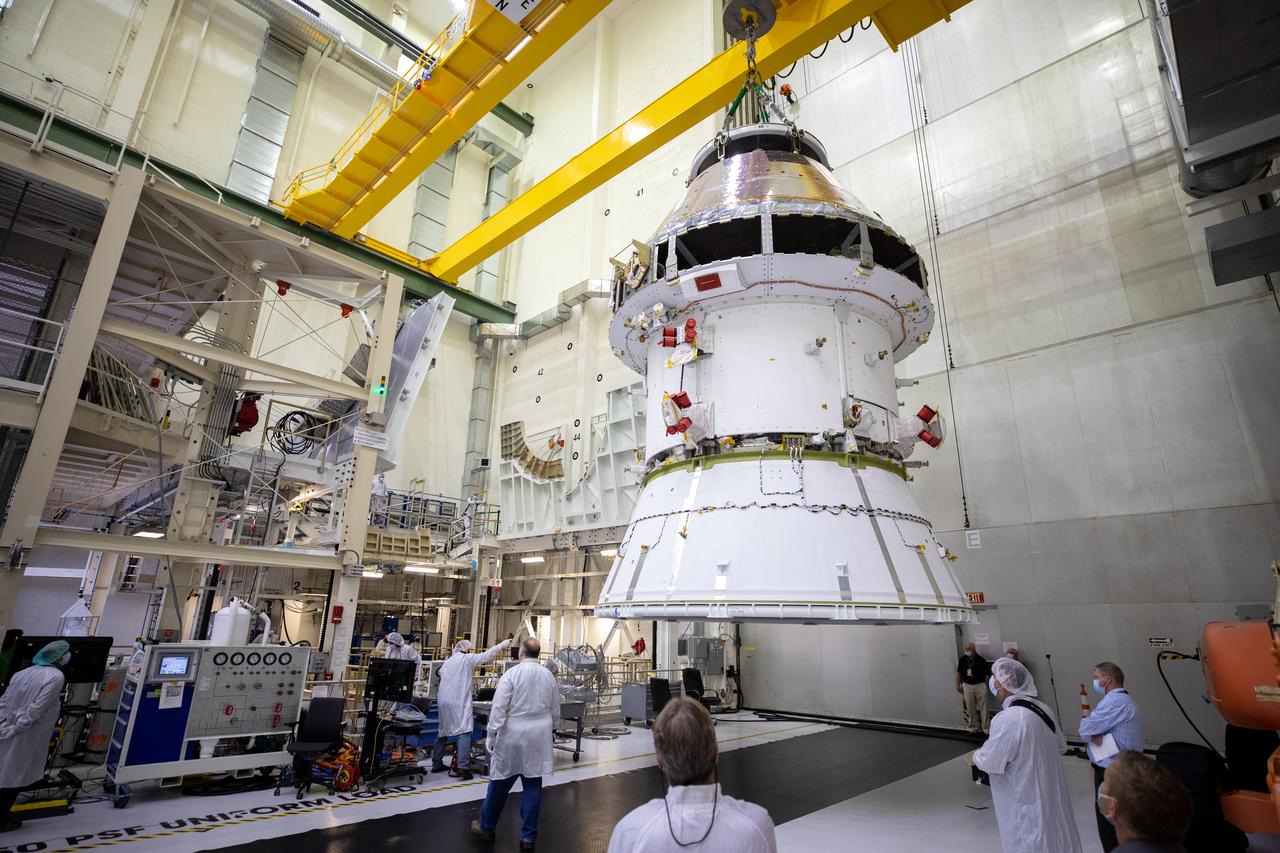

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
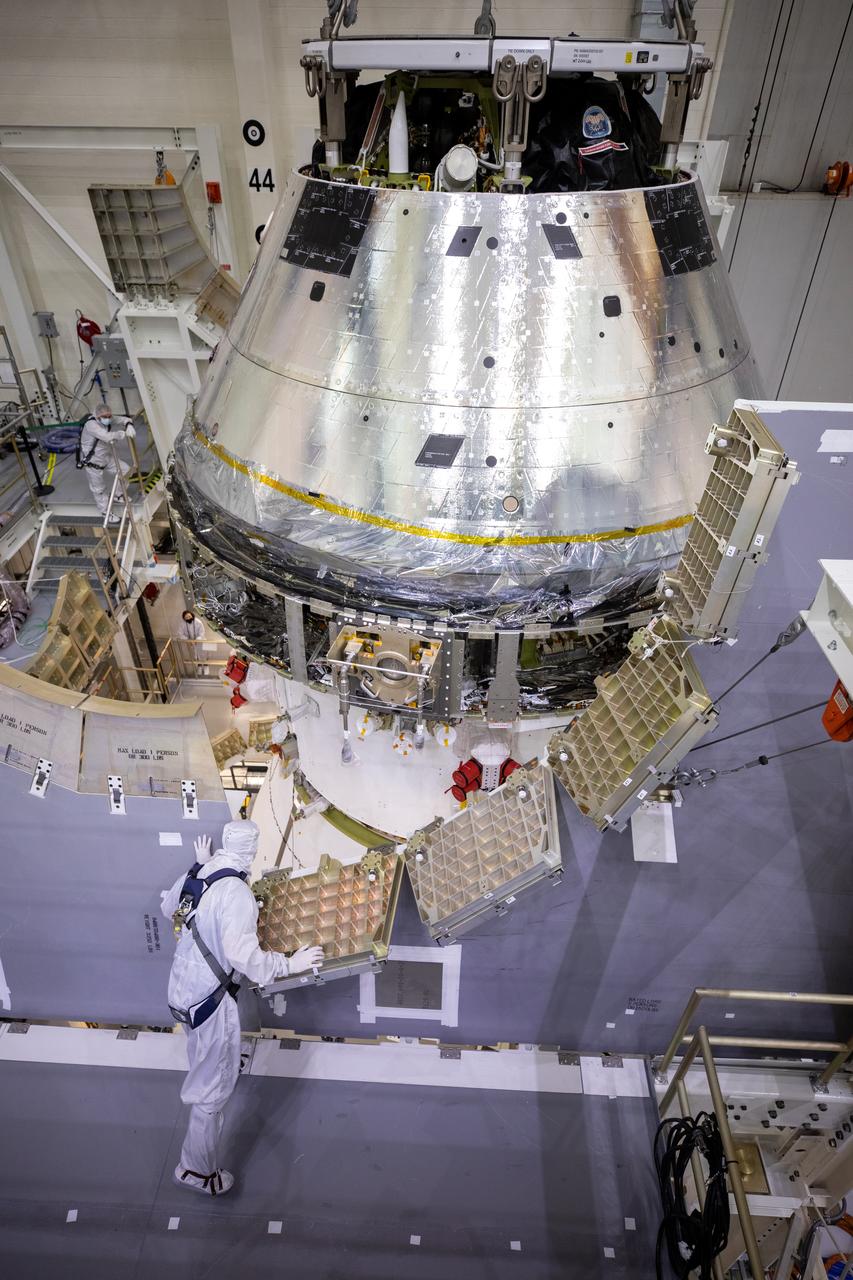

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely lower the Artemis I Orion spacecraft into the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely lower the Artemis I Orion spacecraft into the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
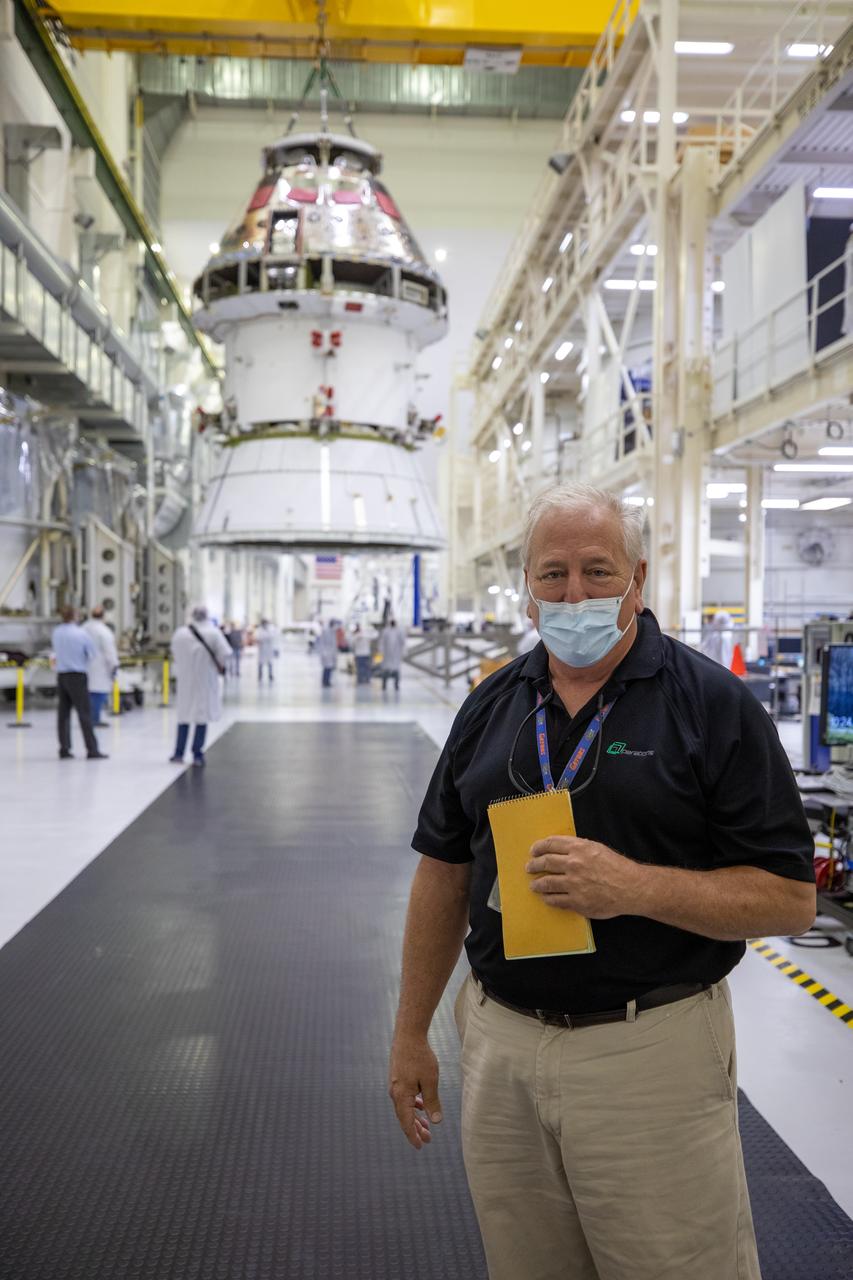

Bill Ruff, Lockheed Martin Safety manager, stands inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. Technicians are working to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the high bay. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
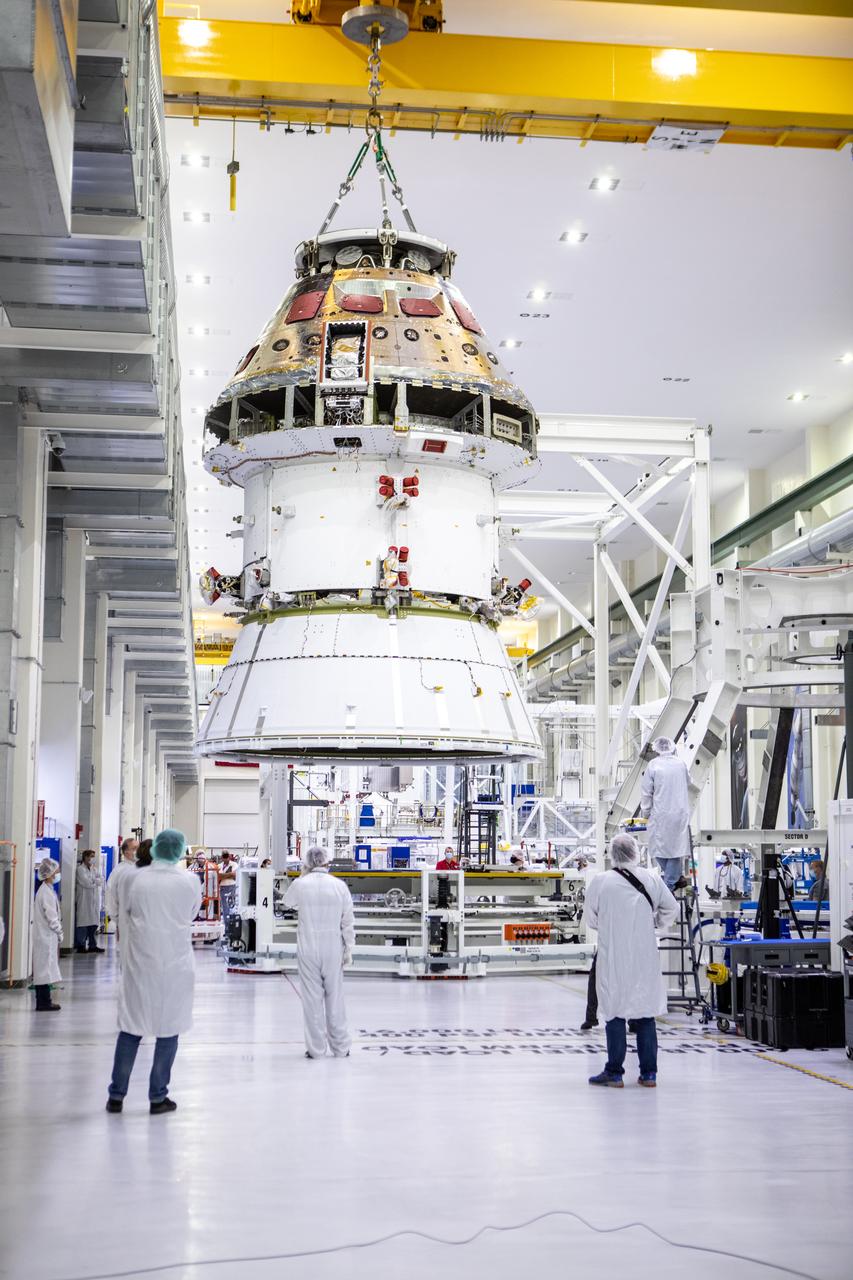

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
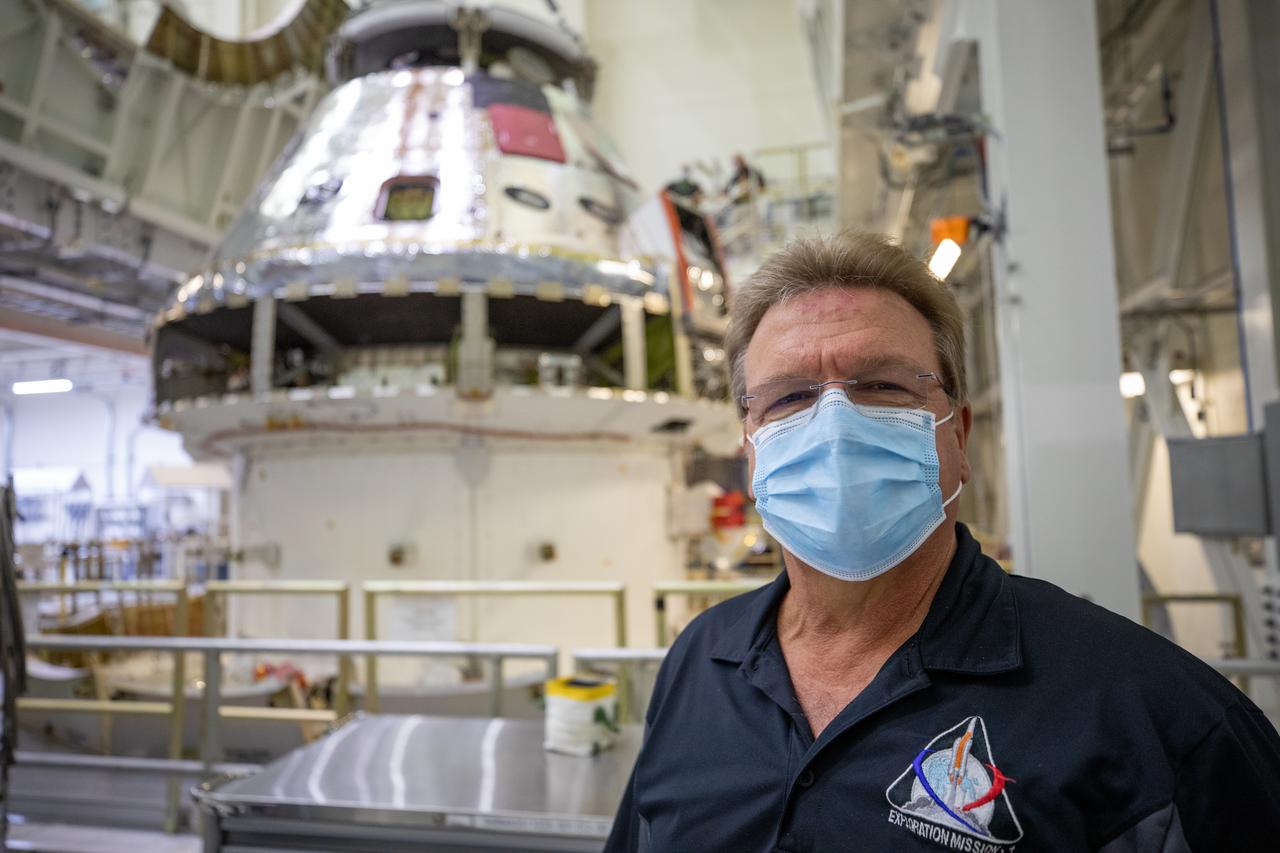

Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Assembly, Test and Launch Operations director, is shown inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay in front of the FAST cell as the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is lowered by crane after installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone was completed on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
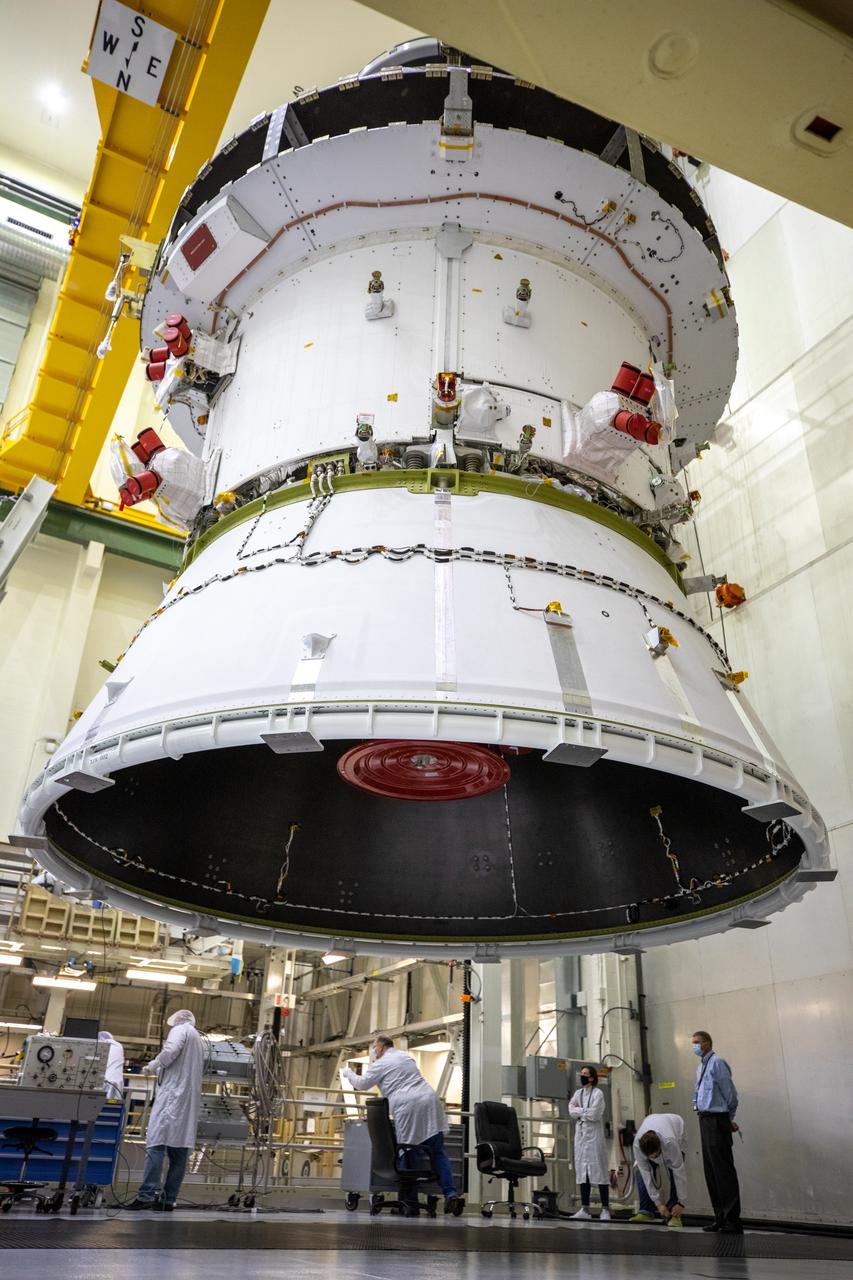

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
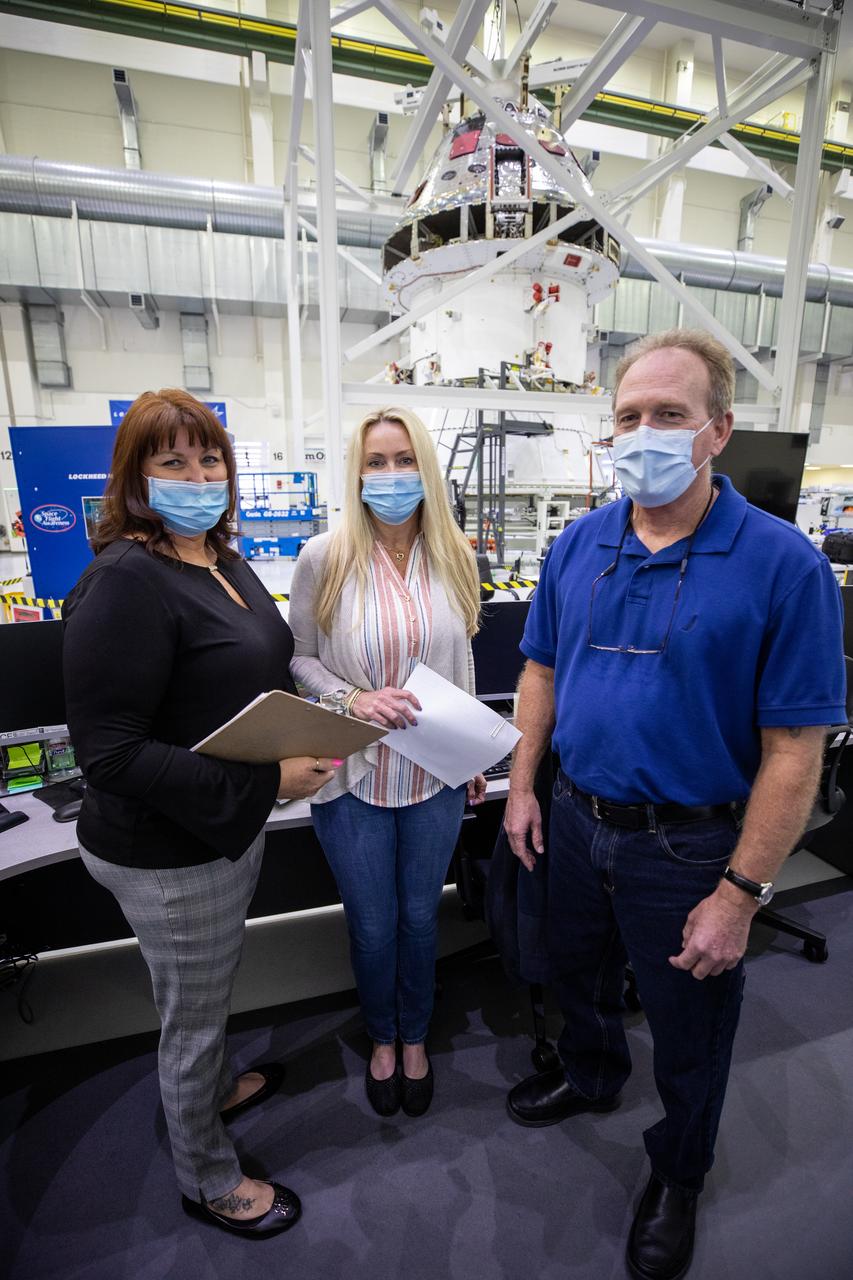

From left, Michelle Clontz and Sharon Prisco, with Lockheed Martin security operations, and Newt Allen, ASRC operations, assist with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
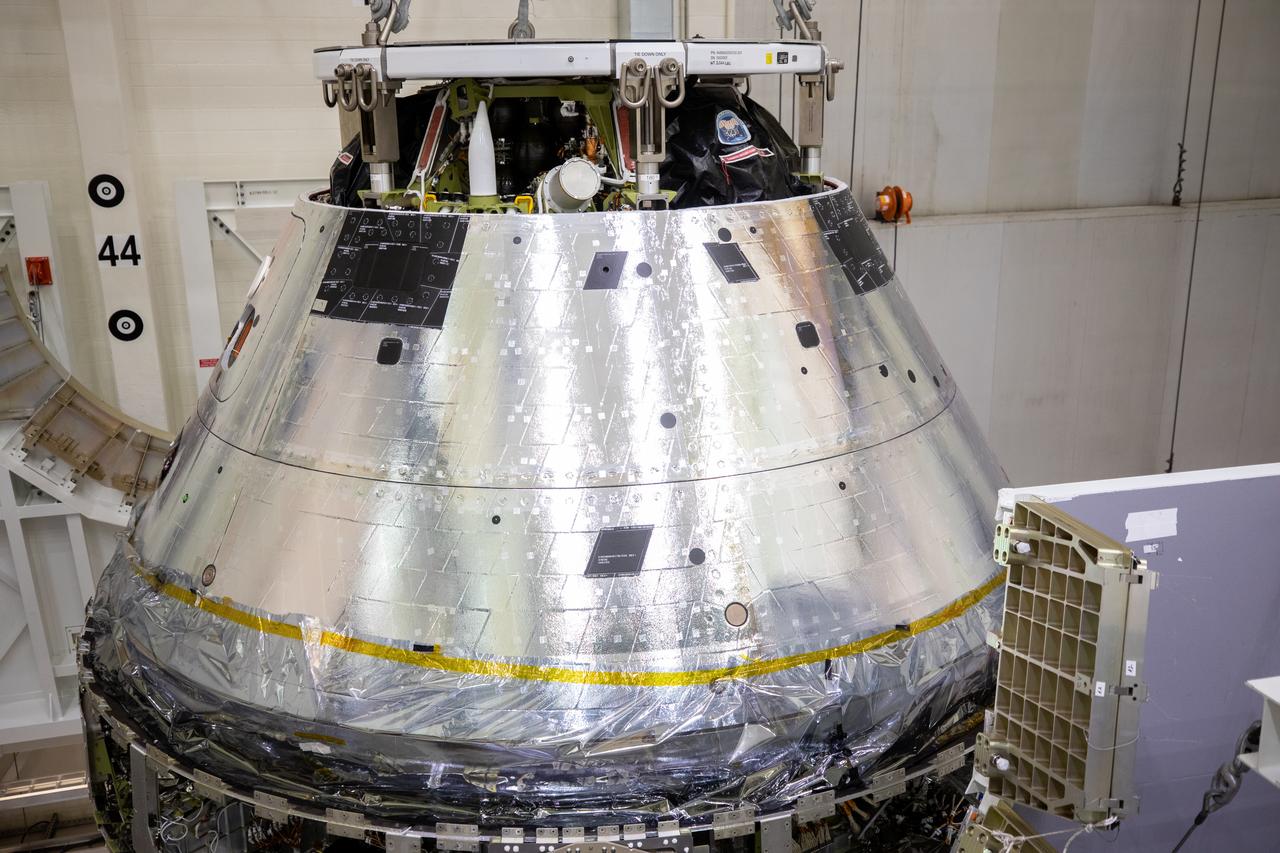

A close-up view of the Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is shown being lowered into the FAST cell inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
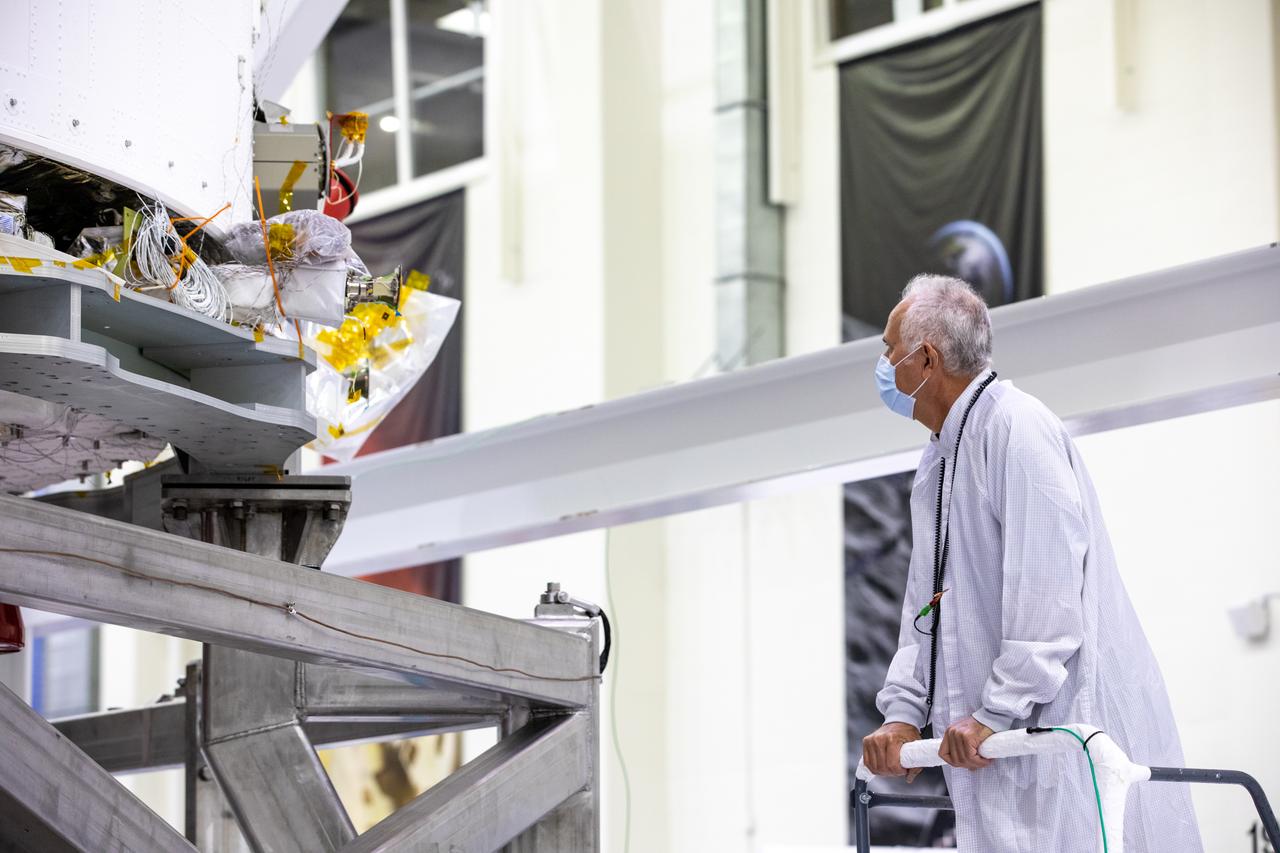

Vince Nichols, Lockheed Martin Floor Operations, inspects the Artemis I Orion spacecraft in preparation for installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
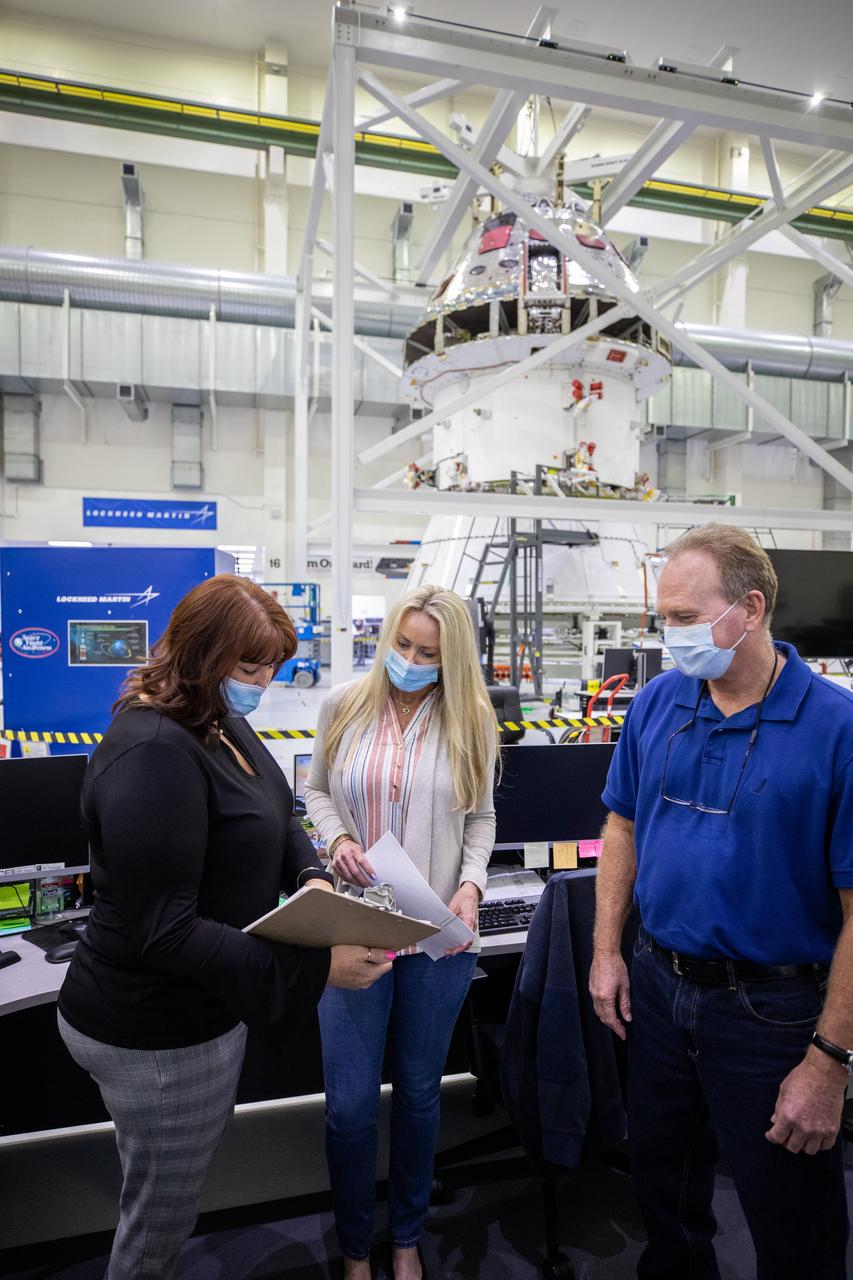

From left, Michelle Clontz and Sharon Prisco, with Lockheed Martin security operations, and Newt Allen, ASRC operations, assist with the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
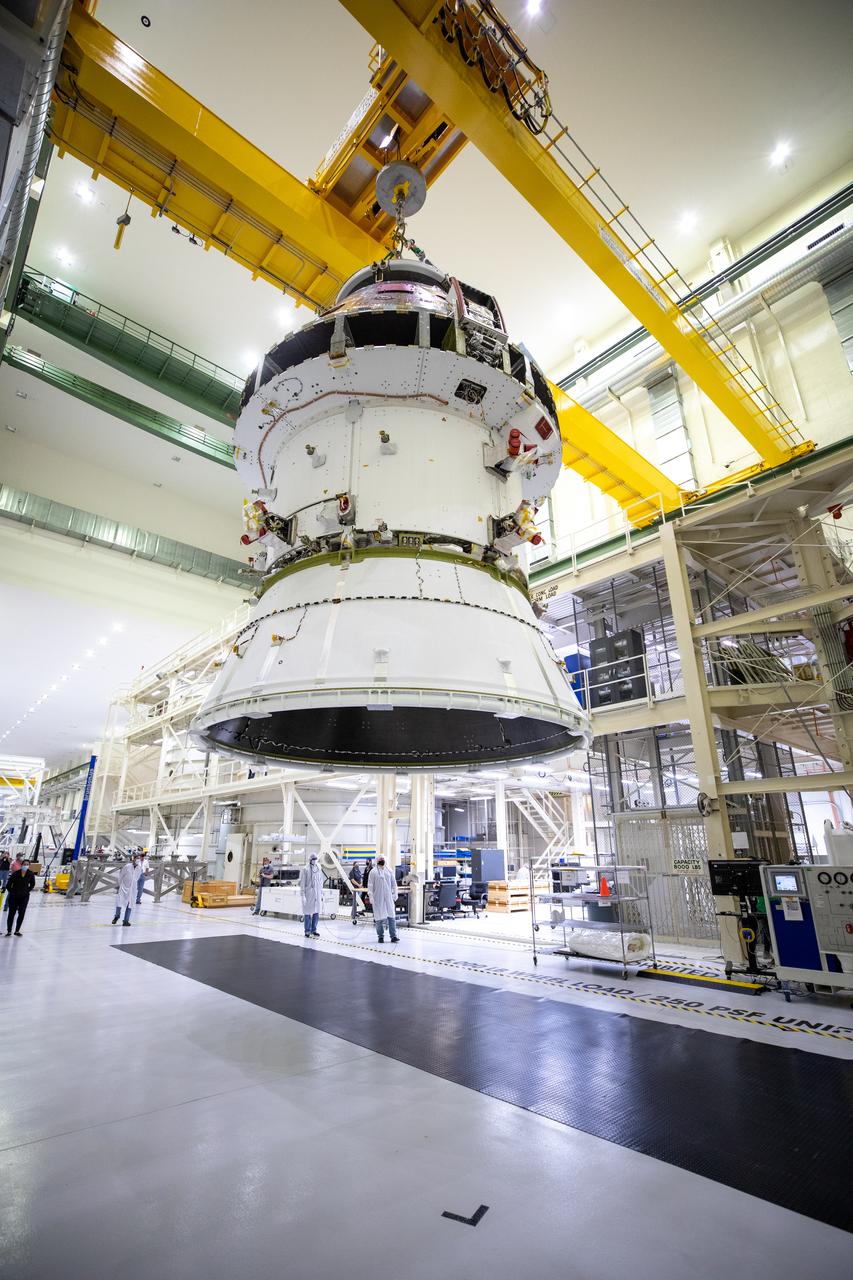

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
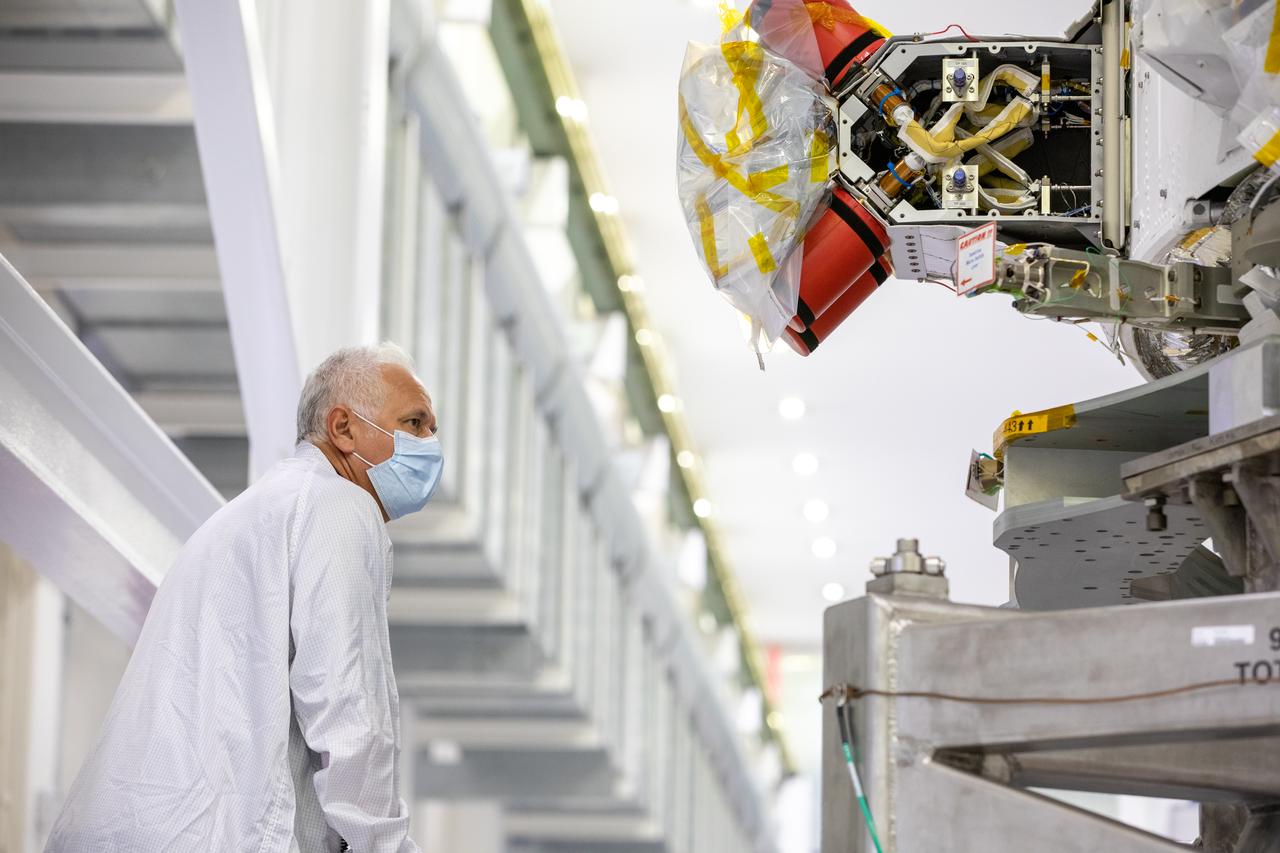

Vince Nichols, Lockheed Martin Floor Operations, inspects the Artemis I Orion spacecraft in preparation for installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
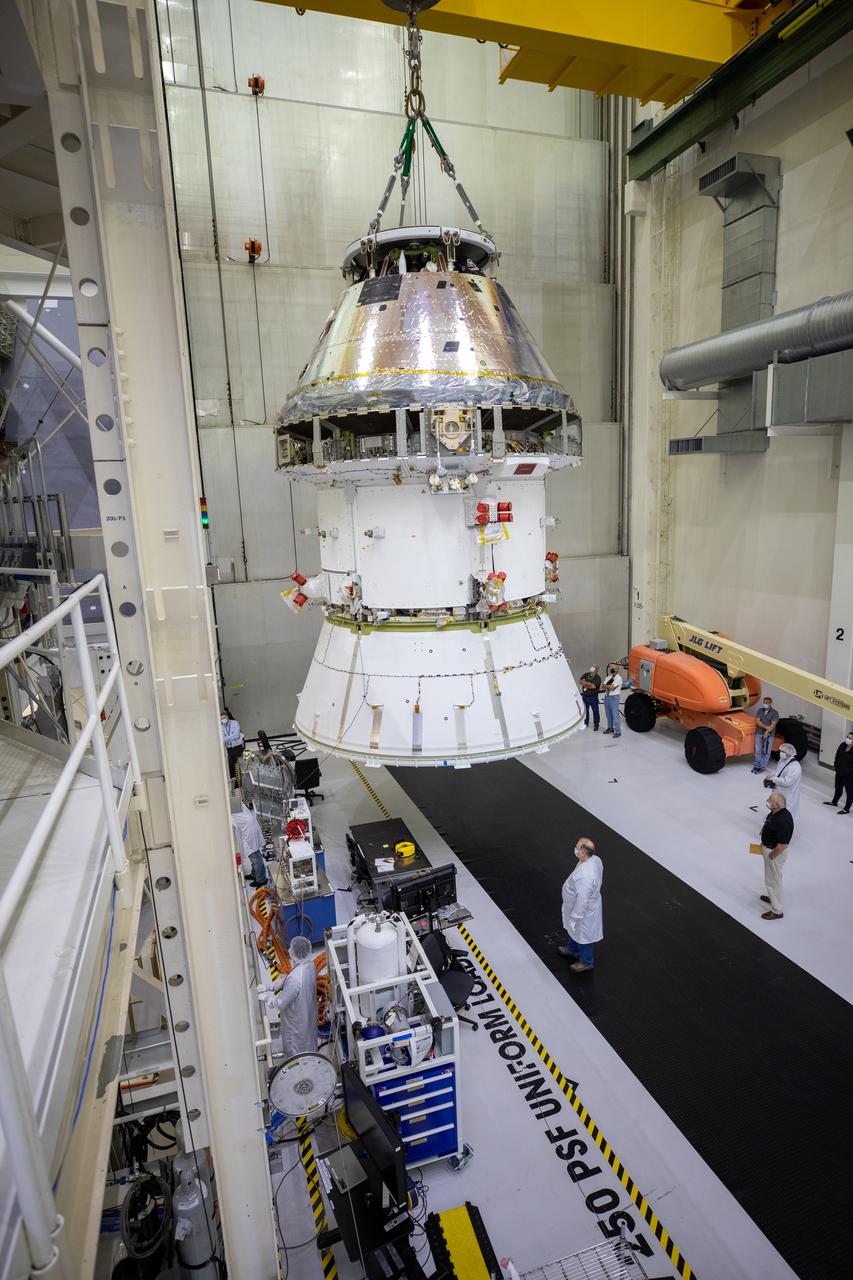

The Artemis I Orion spacecraft with its spacecraft adapter cone attached, is moved by crane along the high bay inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
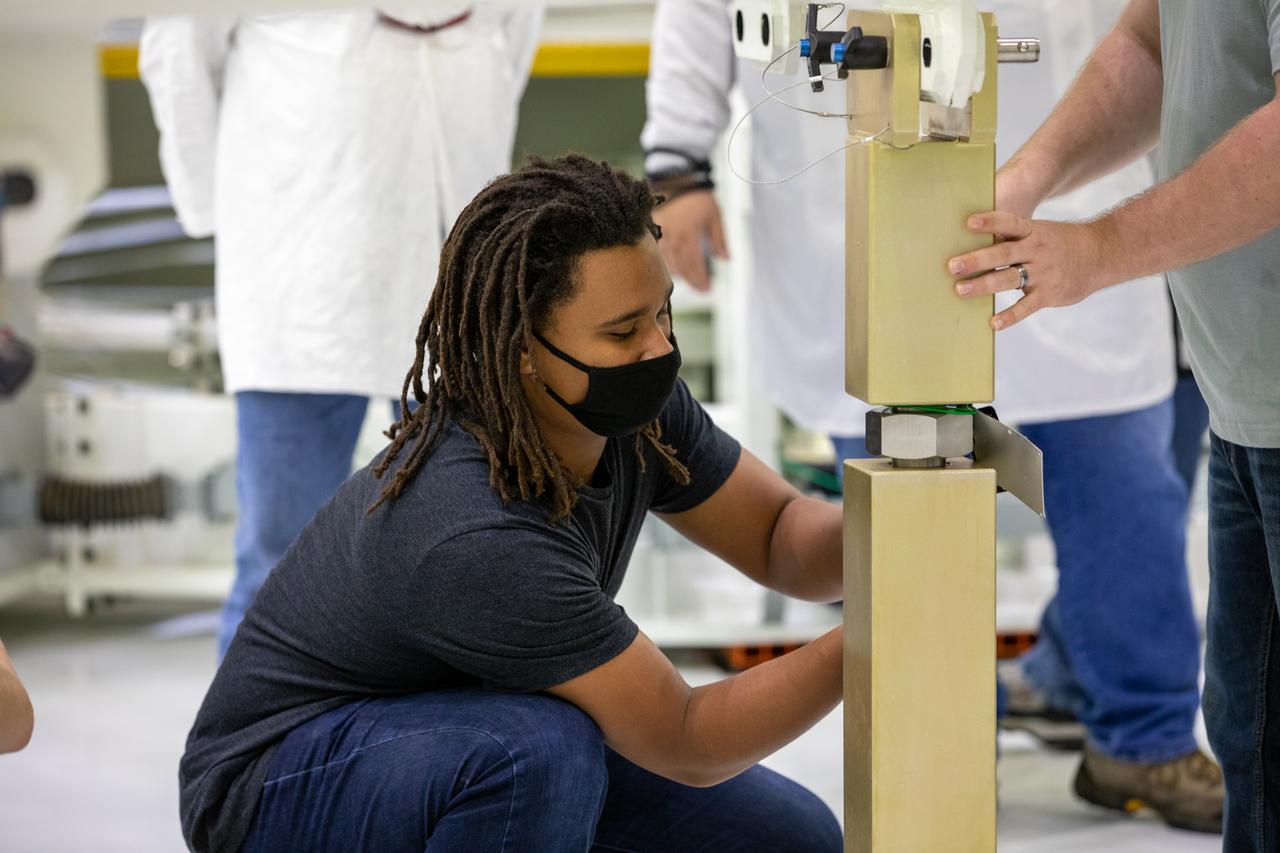

ASRC technician Nathaniel Bowman works to ready the Super Station fixture that will support the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
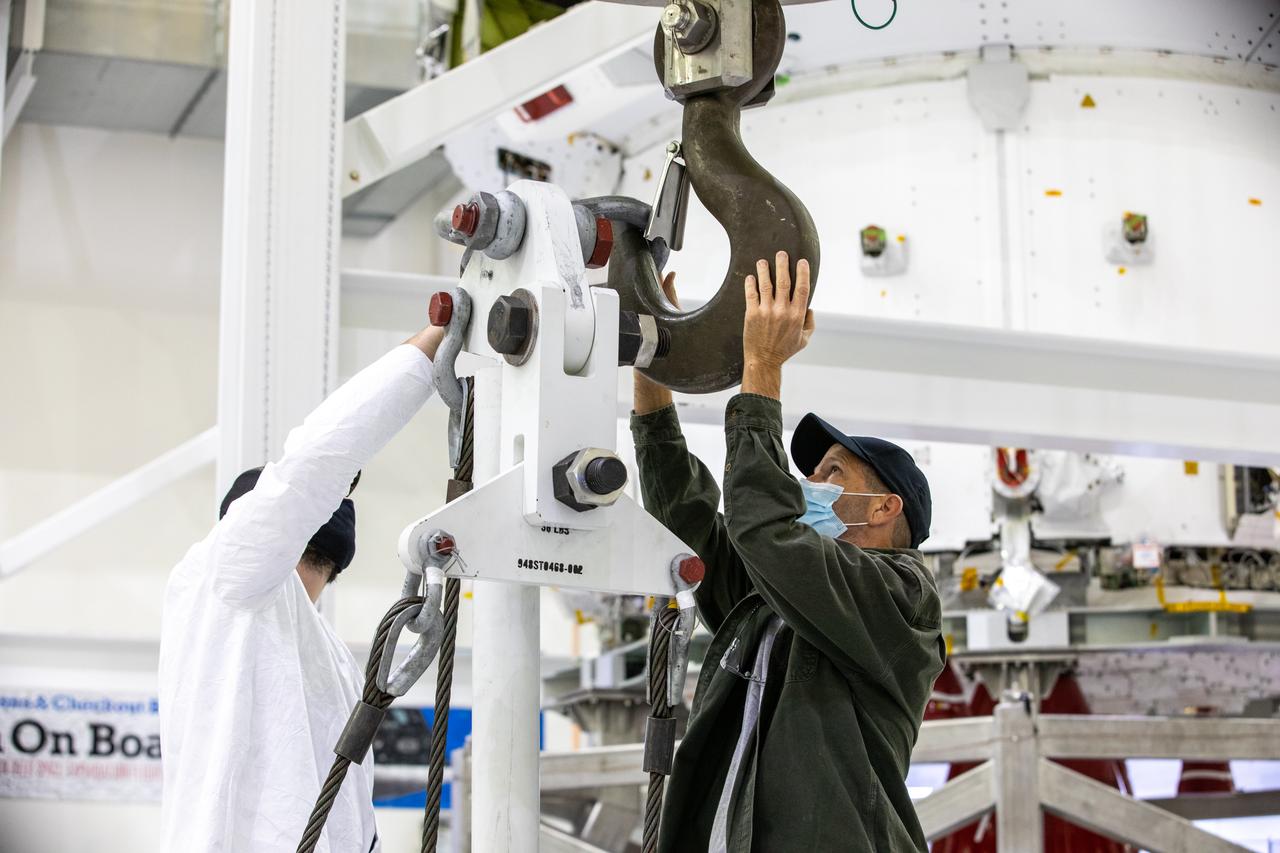

ASRC technicians Dustin Swickert, to the left. and John Nesbitt, to the right, work to attach the crane that lifts the Artemis I Orion spacecraft in preparation for installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
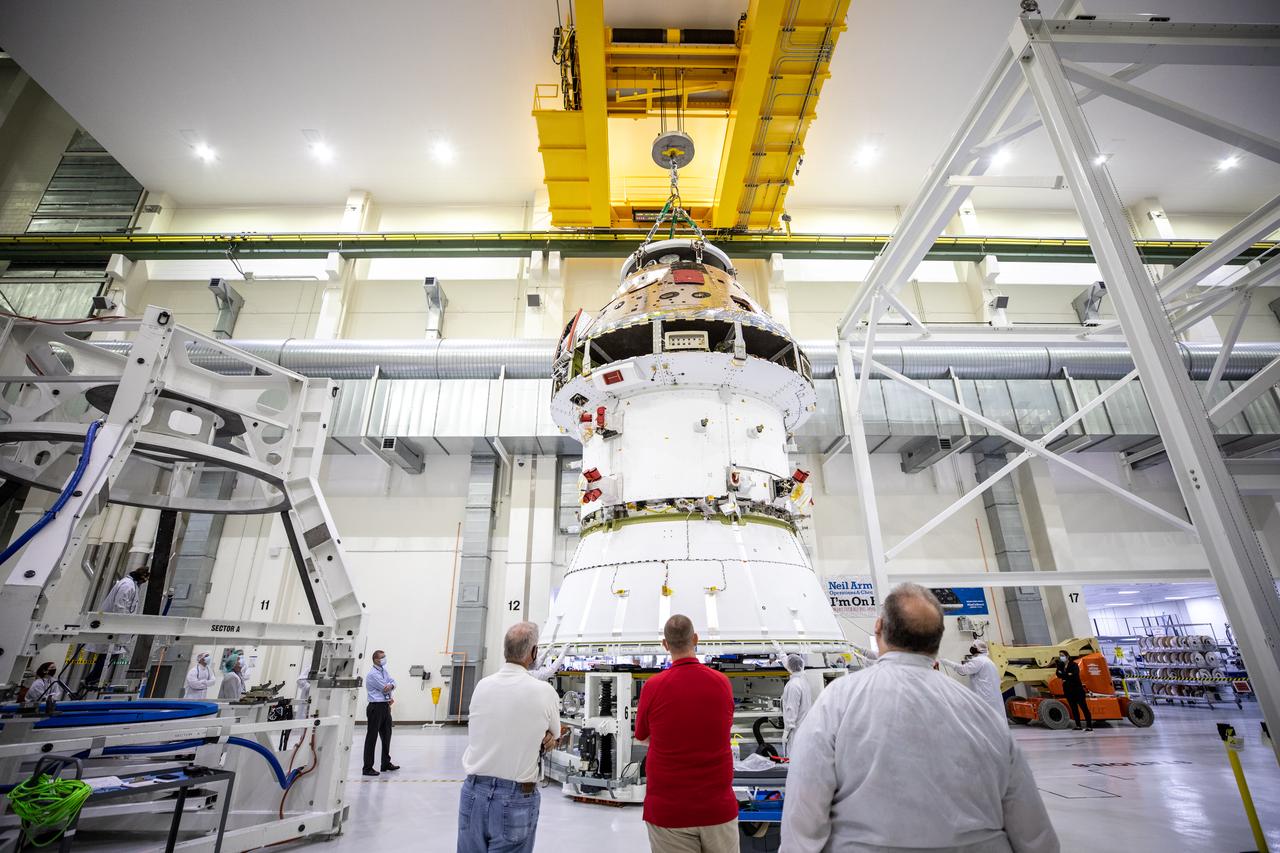

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to safely return the Artemis I Orion spacecraft to the FAST cell after completing the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 20, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
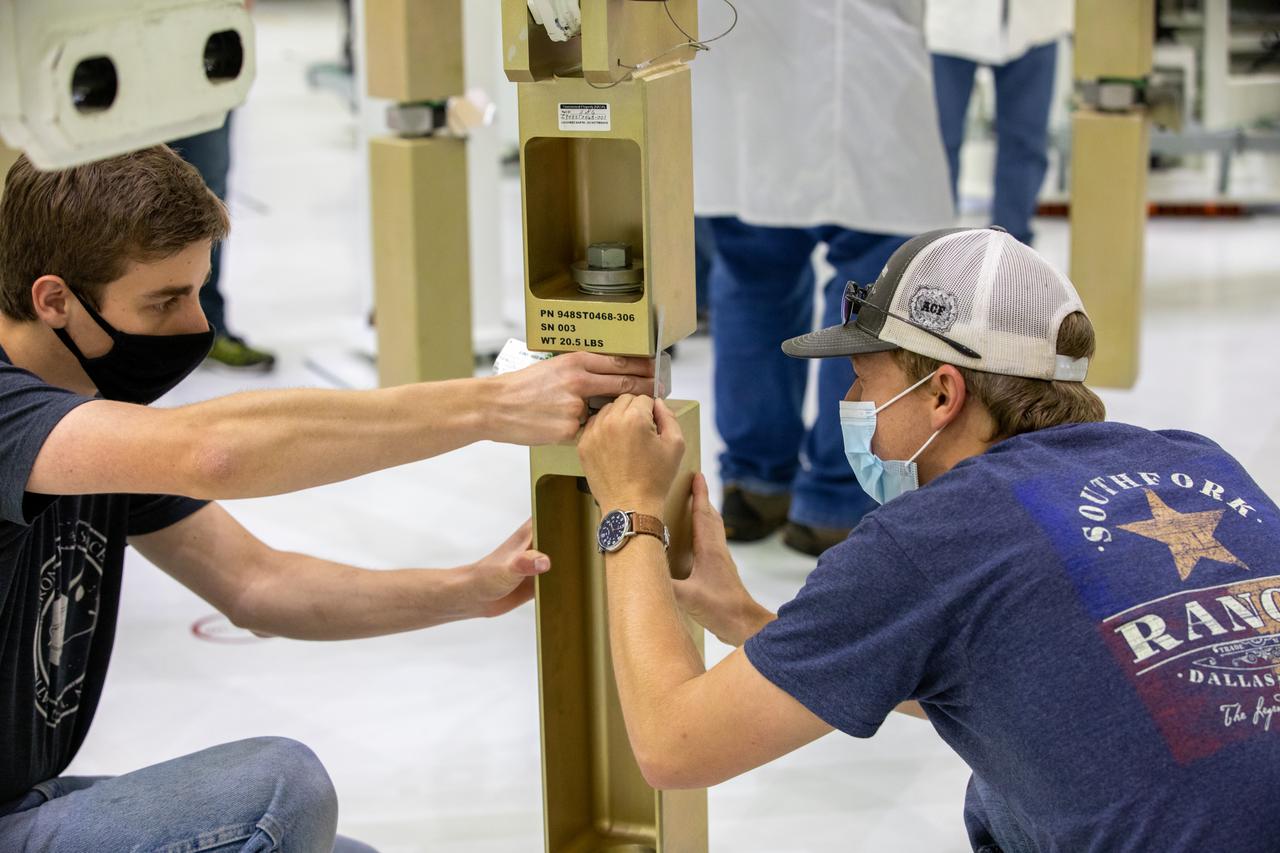

ASRC technicians William Coddington, to the left and Cameron Fitch, to the right, work to ready the Super Station fixture that will support the installation of the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft is in progress inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
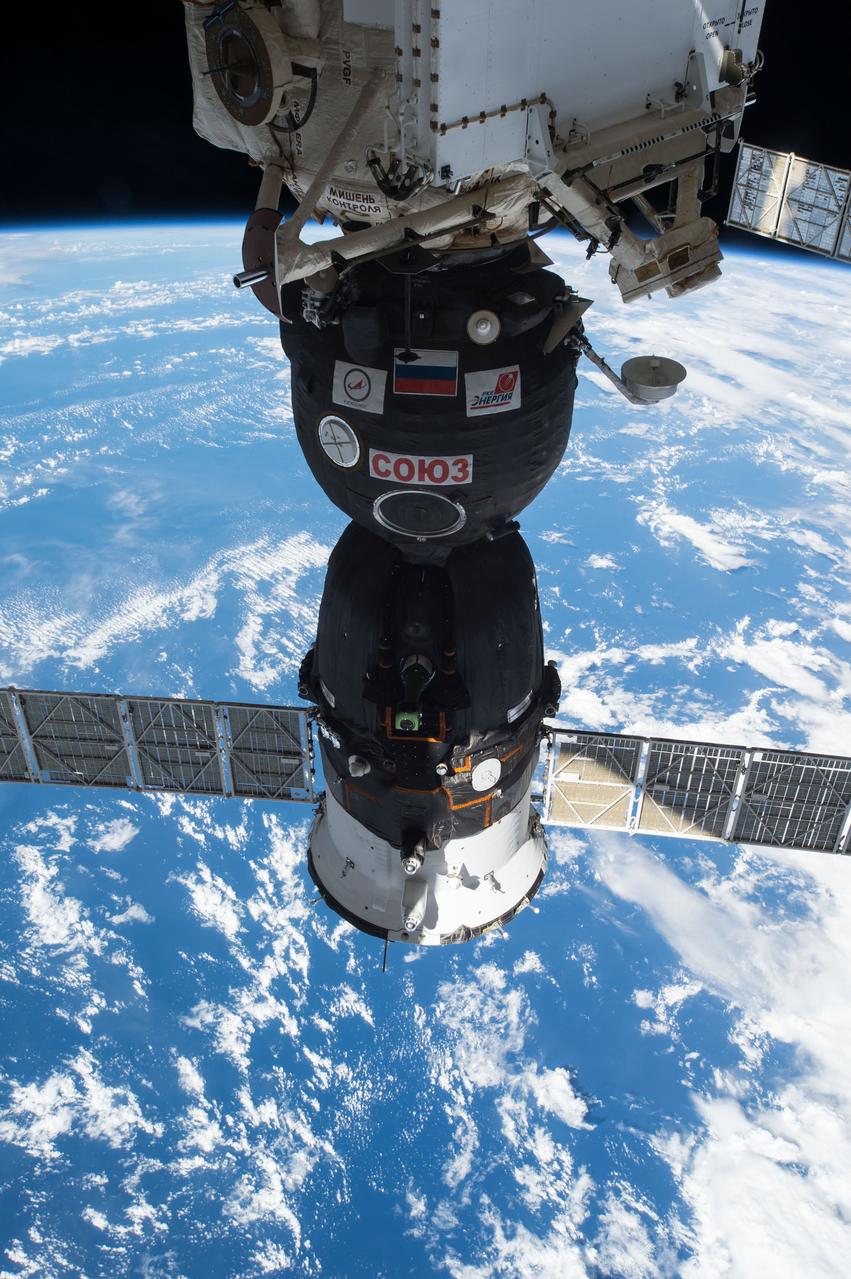

View of the Soyuz TMA-15M spacecraft docked to Rassvet Mini-Research Module 1 (MRM1) An Earth limb is in view.

S68-26989 (4 April 1968) --- The Apollo 6 Spacecraft 020 Command Module is hoisted aboard the USS Okinawa.
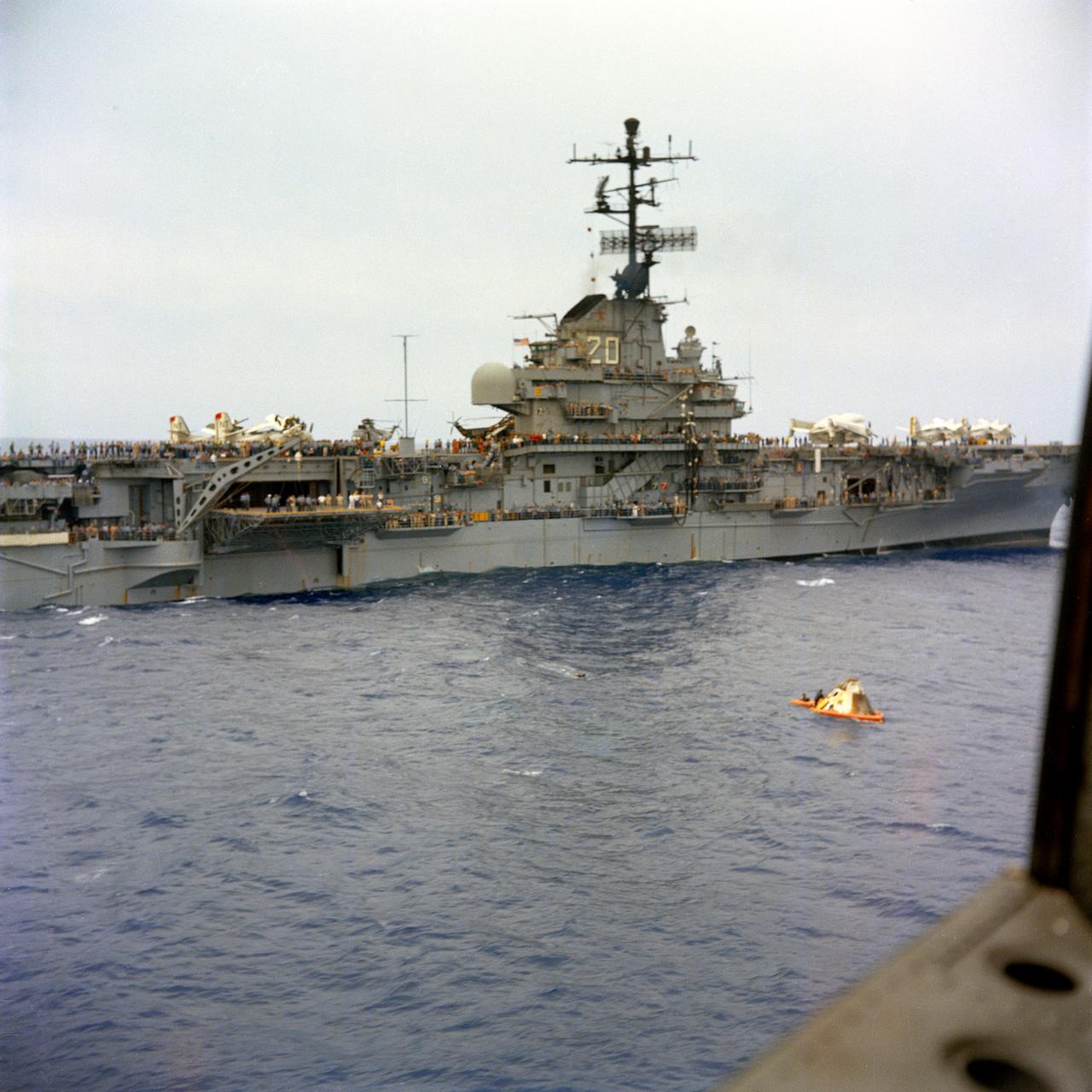

U.S.S. Bennington comes alongside the floating Apollo spacecraft 017 Command Module during recovery operations in the mid-Pacific Ocean. The Command Module splashed down at 3:37 p.m., November 9, 1967, 934 nautical miles northwest of Honolulu, Hawaii.
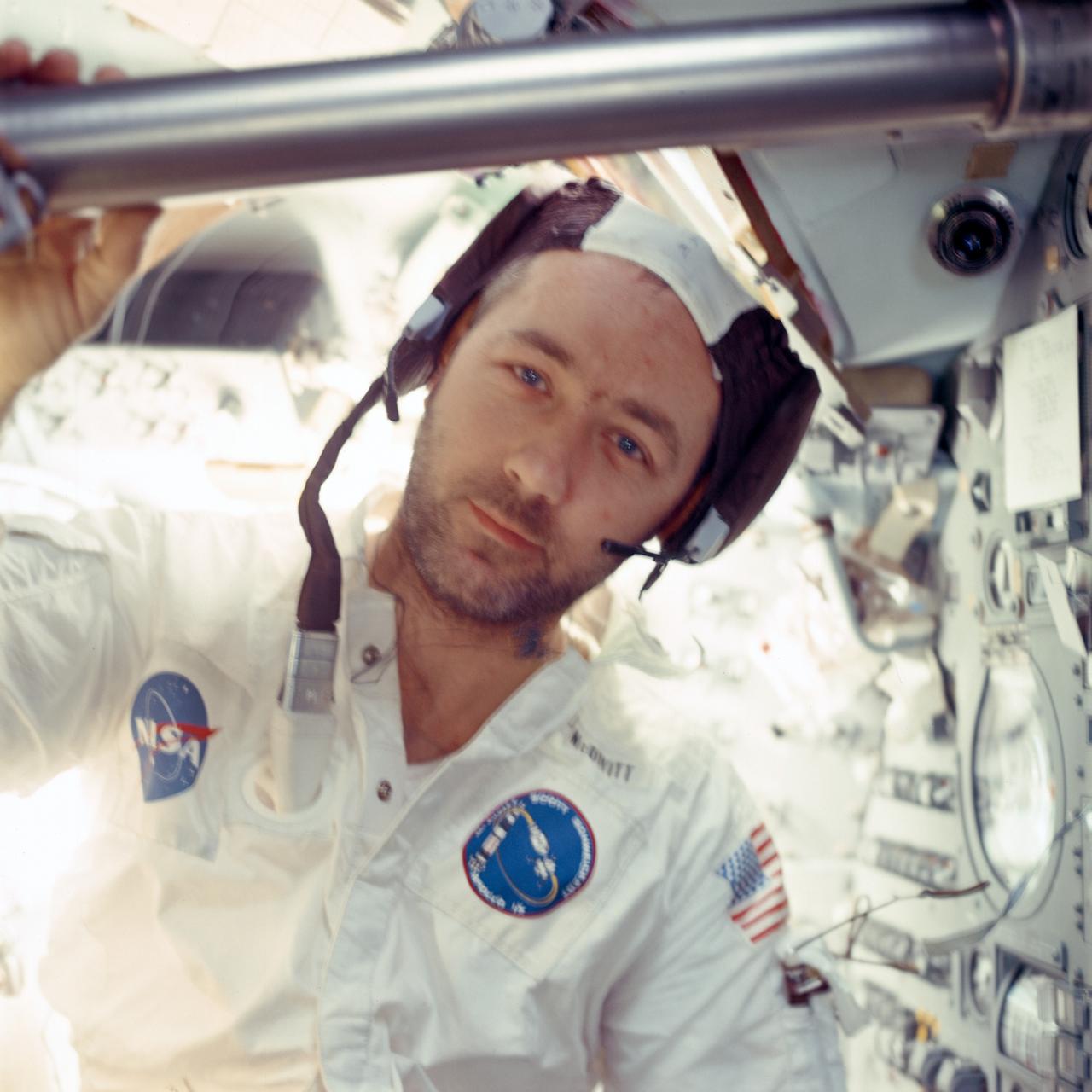

AS09-20-3154 (3-13 March 1969) --- This close-up view of astronaut James A. McDivitt shows several days' beard growth. The Apollo 9 mission commander was onboard the Lunar Module (LM) "Spider" in Earth orbit, near the end of the flight. He was joined on the mission by astronauts David R. Scott, command module pilot, and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Schweickart took this picture while Scott remained in the Command Module (CM) "Gumdrop." In Earth orbit, the three tested the transposition and docking systems of the lunar module and command module. On a scheduled lunar landing mission later this year, a team of three astronauts and ground controllers will use what this crew and its support staff have learned in handling the systems of the two spacecraft.
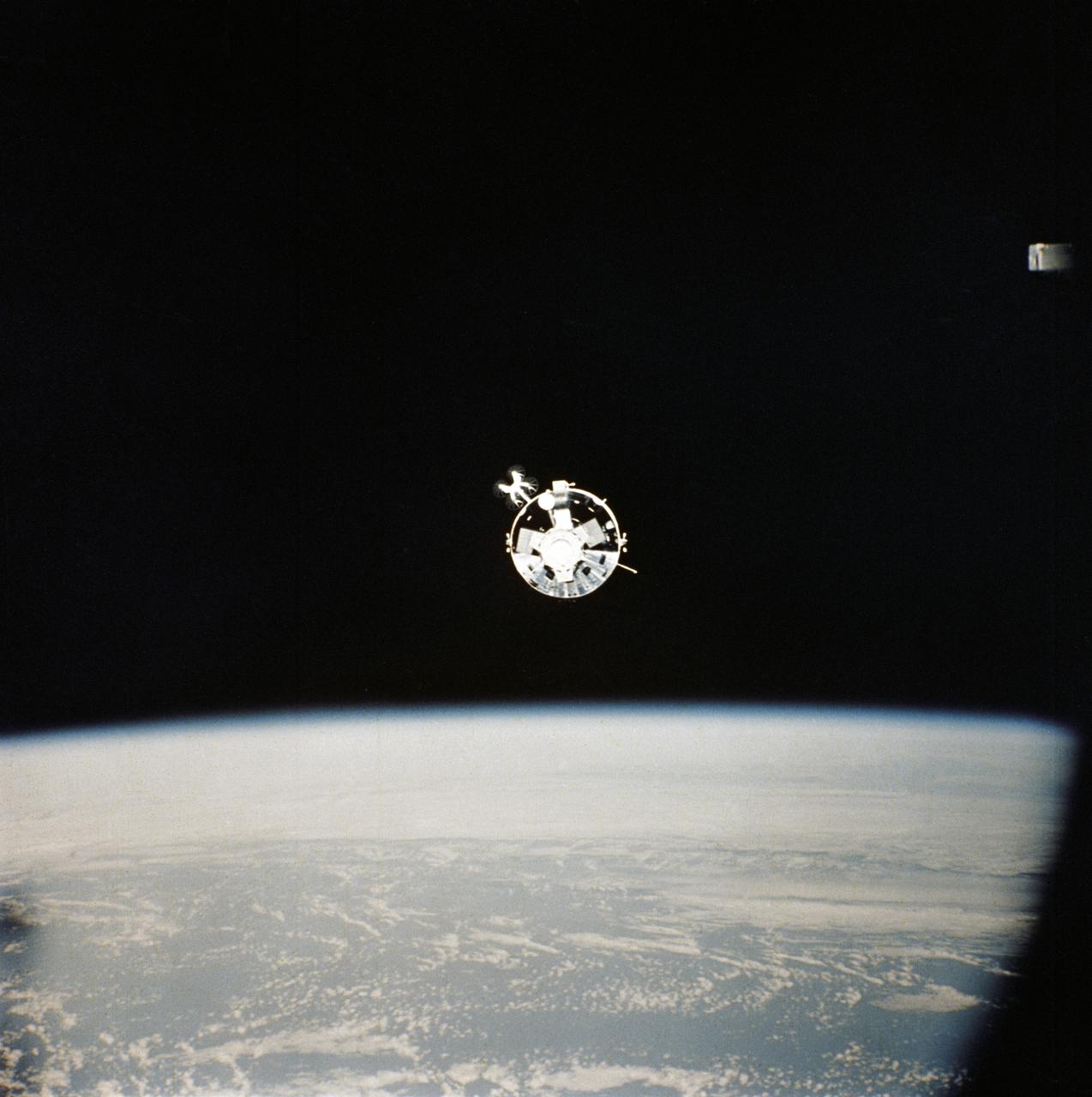

AST-32-2675 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module and Docking Module are contrasted against a black-sky background. This is a "head on" view of the Apollo. The horizon of Earth is below. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17-18-19, 1975. Note the docking mechanism on the Docking Module. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
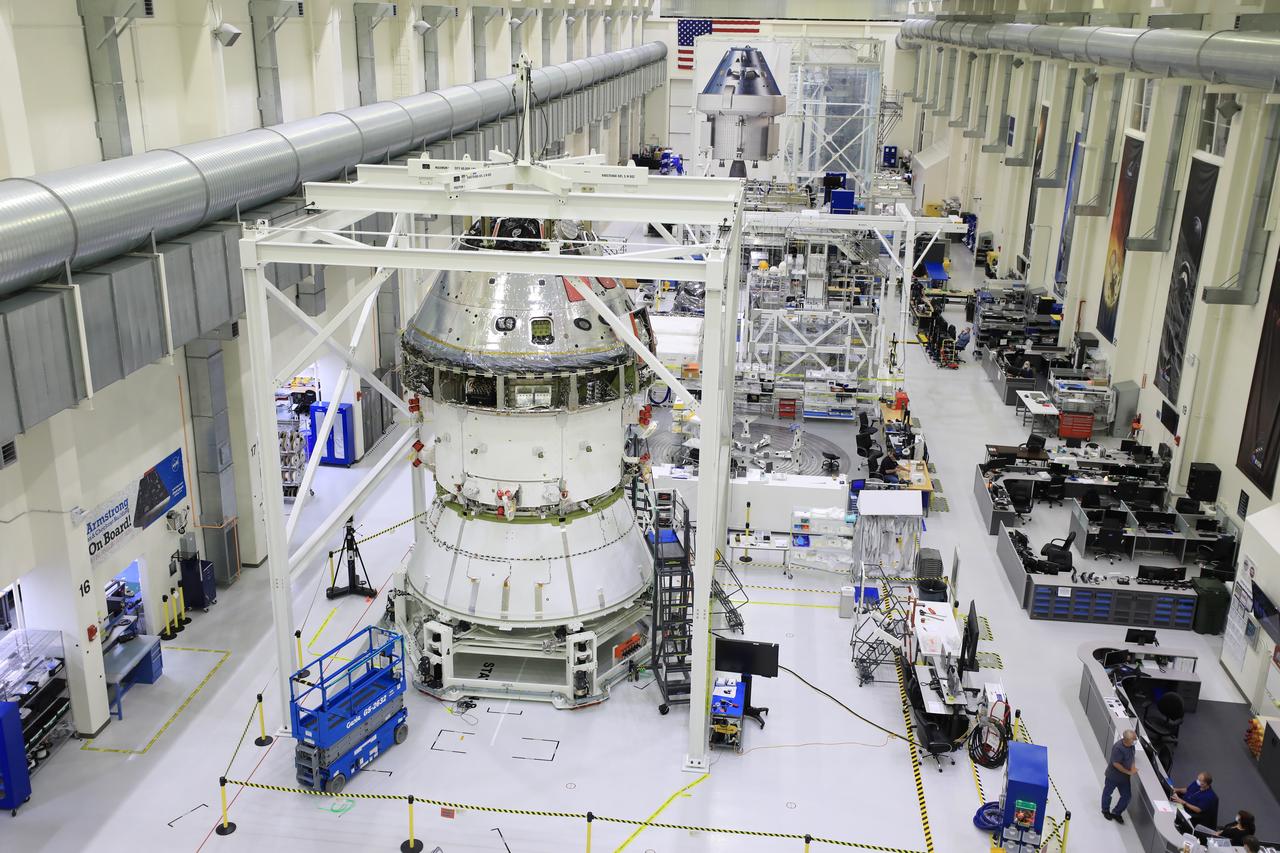
Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to install the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
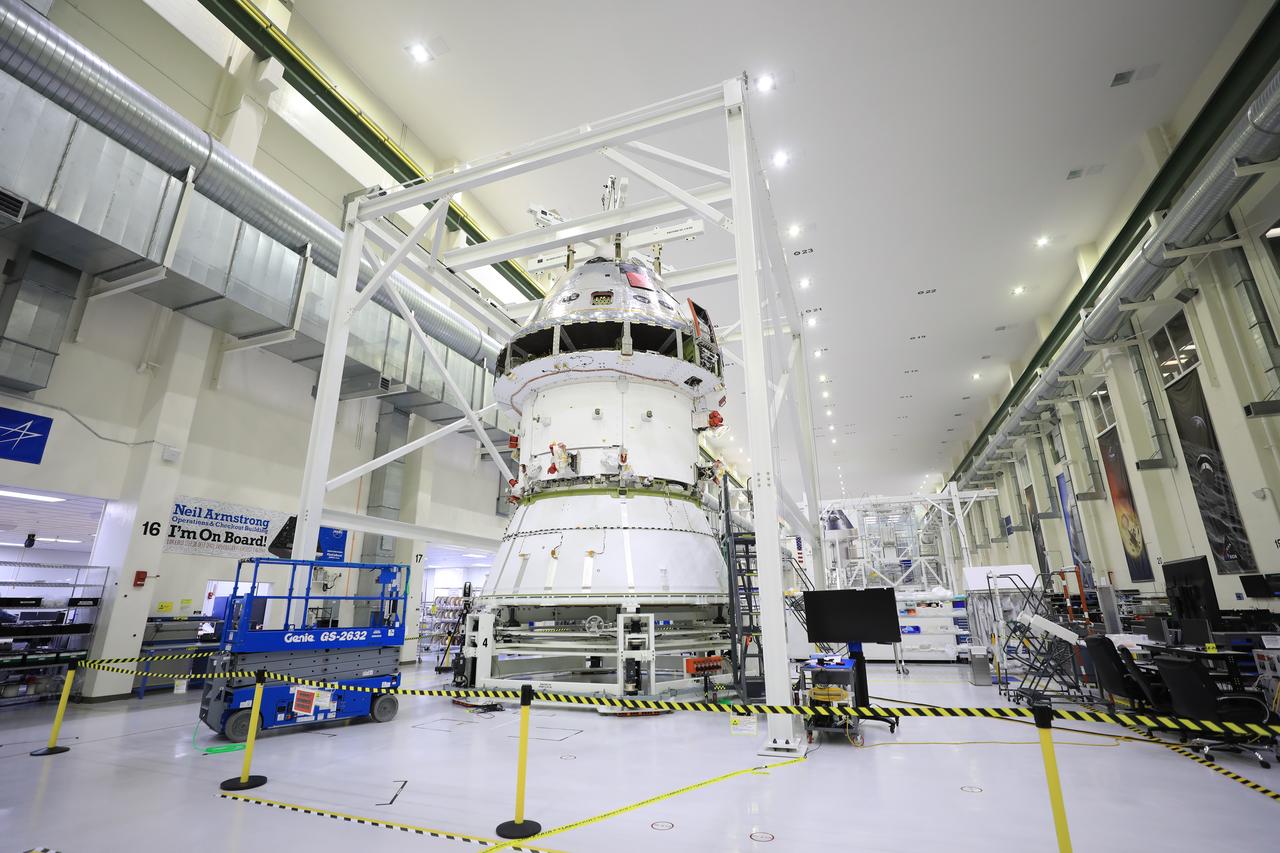

Technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work to install the spacecraft adapter (SA) cone to the Artemis I Orion spacecraft inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Aug. 10, 2020. This is one of the final major hardware operations the spacecraft will undergo during closeout processing prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in preparation for the first Artemis mission. The spacecraft adapter cone connects the bottom portion of Orion’s service module to the top part of the rocket known as the interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS). Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
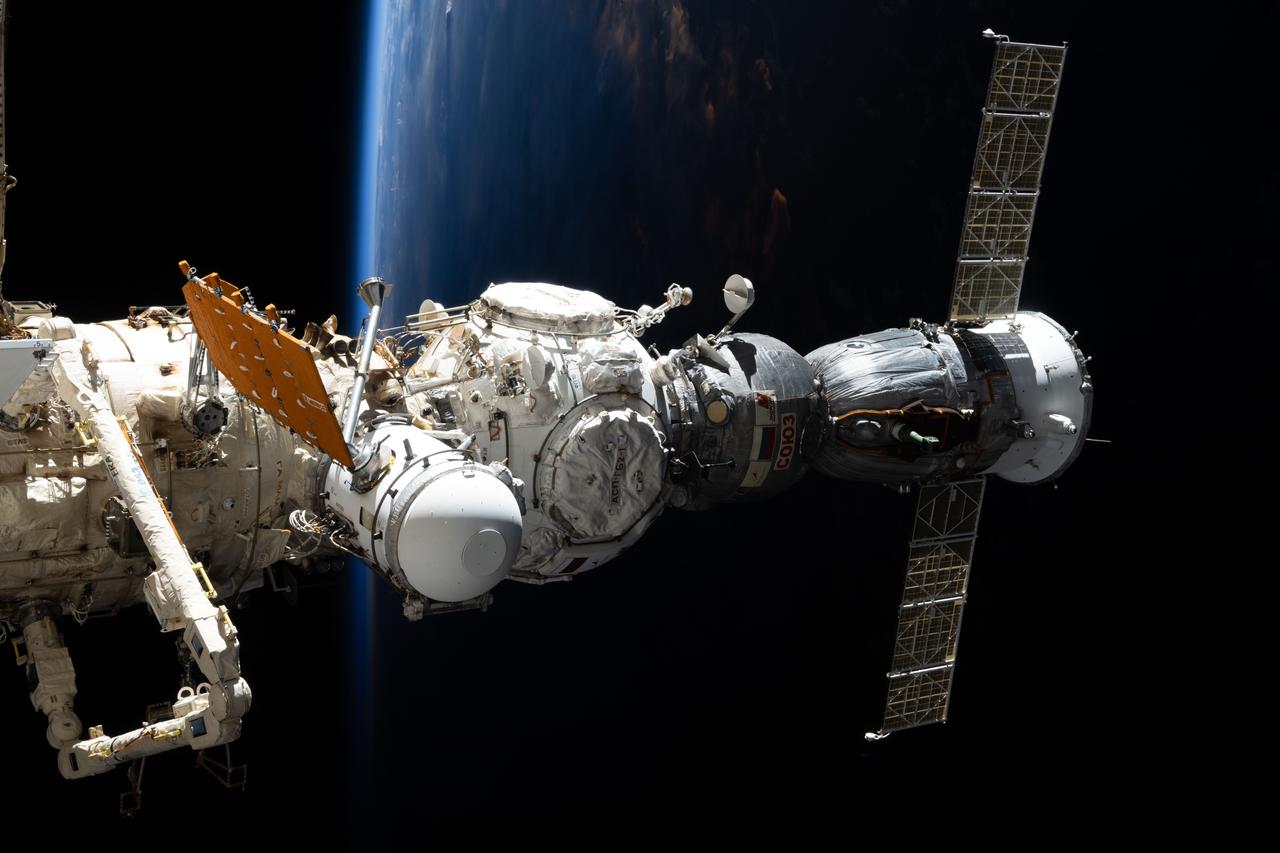

iss073e0775529 (Sept. 8, 2025) --- The Soyuz MS-27 spacecraft, which launched three Expedition 73 crew members to the International Space Station, is pictured docked to the Prichal module. Prichal is itself connected to the Nauka science module on the station’s Roscosmos segment. Below, the Pacific Ocean fades from view as an orbital sunset descends 258 miles beneath the orbiting complex.

iss073e0775543 (Sept. 8, 2025) --- The Soyuz MS-27 spacecraft, which launched three Expedition 73 crew members to the International Space Station, is pictured docked to the Prichal module. Prichal is itself connected to the Nauka science module on the station’s Roscosmos segment. Below, the Pacific Ocean fades from view as an orbital sunset descends 258 miles beneath the orbiting complex.

AST-32-2691 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module and Docking Module are contrasted against a black-sky background. This is a near "head on" view of the Apollo. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. Note the docking mechanism and docking target on the Docking Module. The four dish-like reflectors of the unified S-band high-gain antenna protrude from the side of the Service Module. The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17-18-19, 1975. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES

AST-32-2695 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module and Docking Module are contrasted against a black-sky background. The horizon of Earth is below. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. The bell-shaped engine nozzle of the service propulsion system protrudes from the rear of the Service Module. Note the docking mechanism on the Docking Module. The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17-18-19, 1975. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
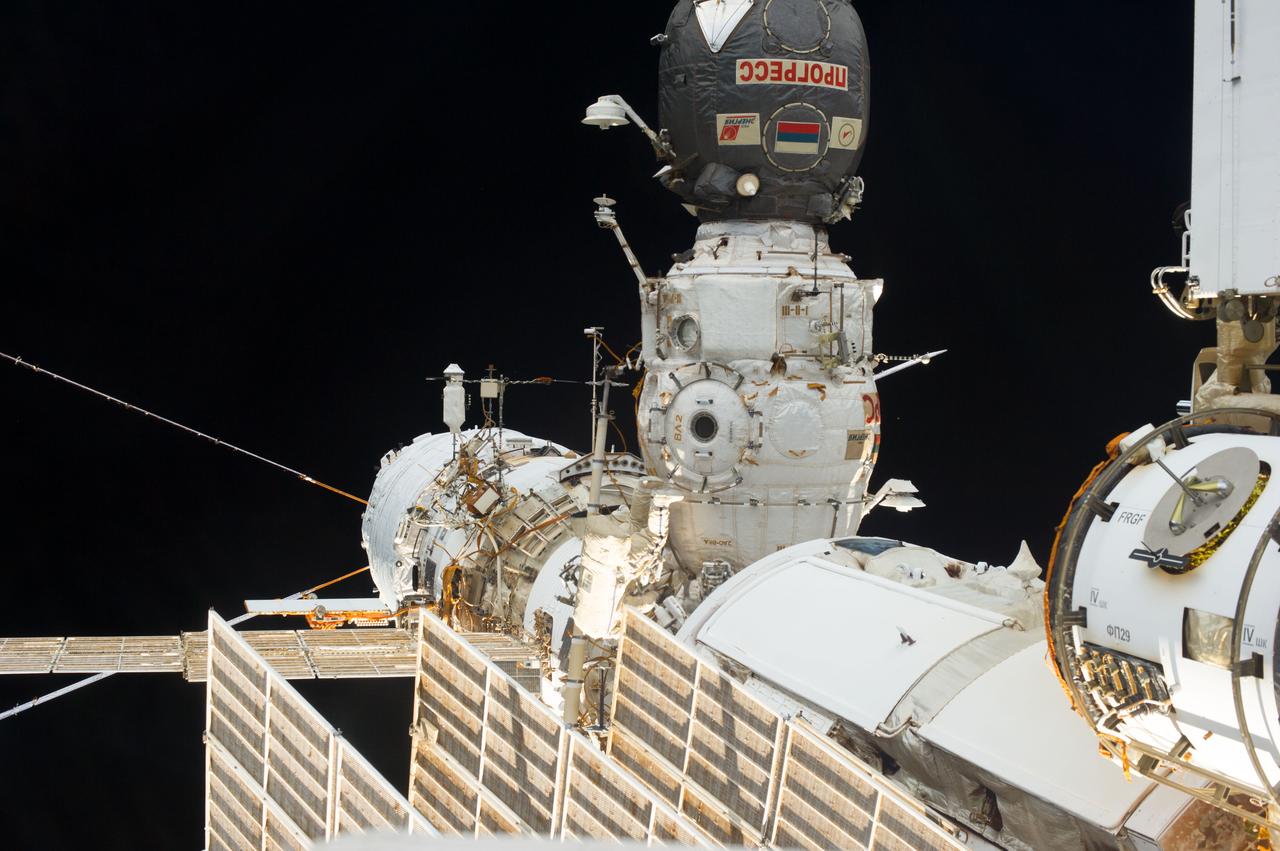

View of Russian cosmonaut Alexander Misurkin (bottom center), Expedition 36 flight engineer, participating in Russian extravehicular activity (EVA) 33. Also visible are the Progress spacecraft docked to the Pirs Docking Compartment (DC1) with the Service Module (SM) .
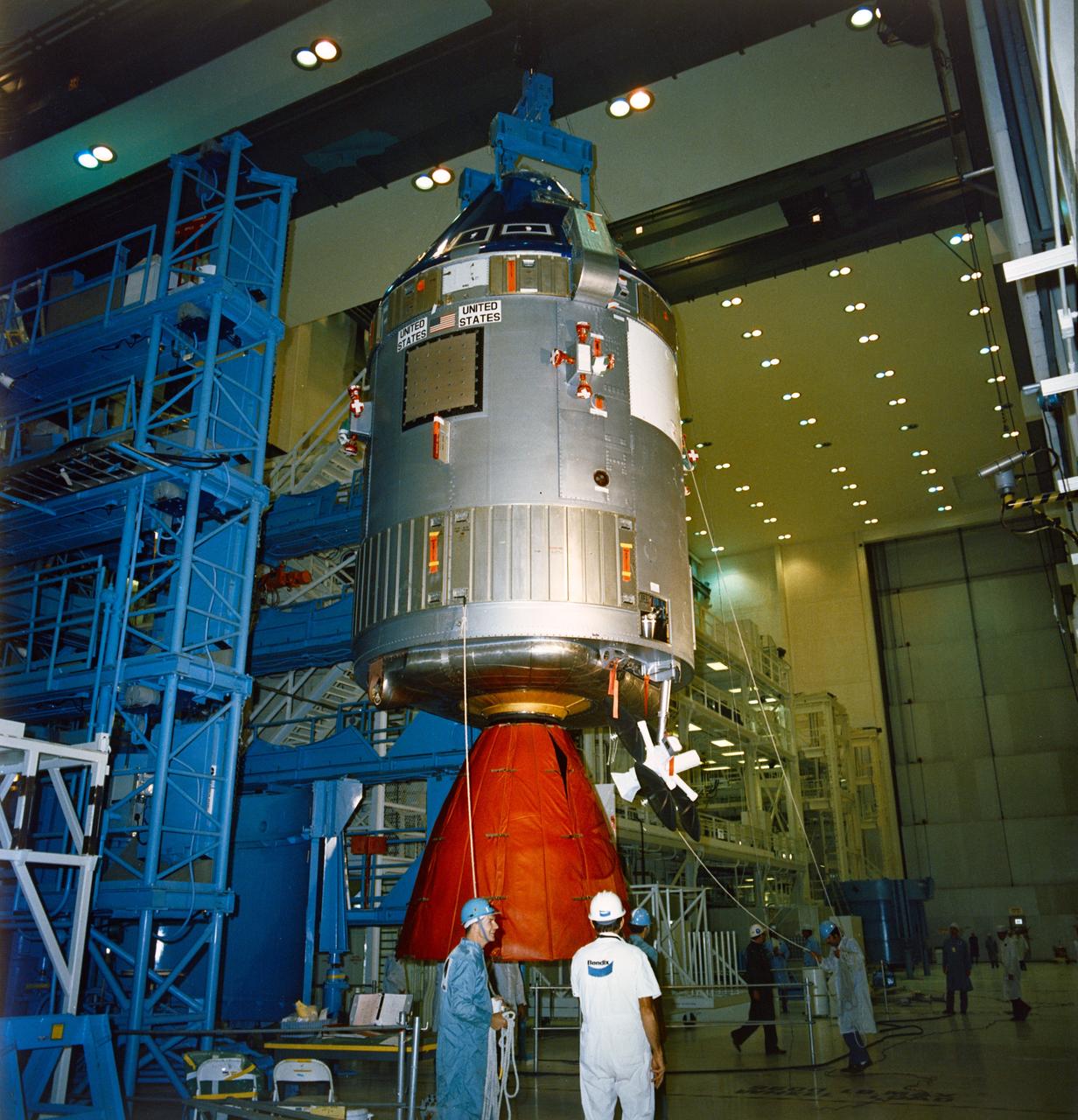
S75-26904 (27 Jan. 1975) --- The flight article Apollo spacecraft (Command Module-111 and Service Module-111) for the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission goes through prelaunch checkout procedures in the high bay area of the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Later, Spacecraft-111 was mated to the spacecraft launch vehicle adapter (SLA-18) in the MSOB before being moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building where it was mated to the Saturn 1B launch vehicle. The joint U.S.-USSR ASTP docking mission in Earth orbit is scheduled for July 1975.
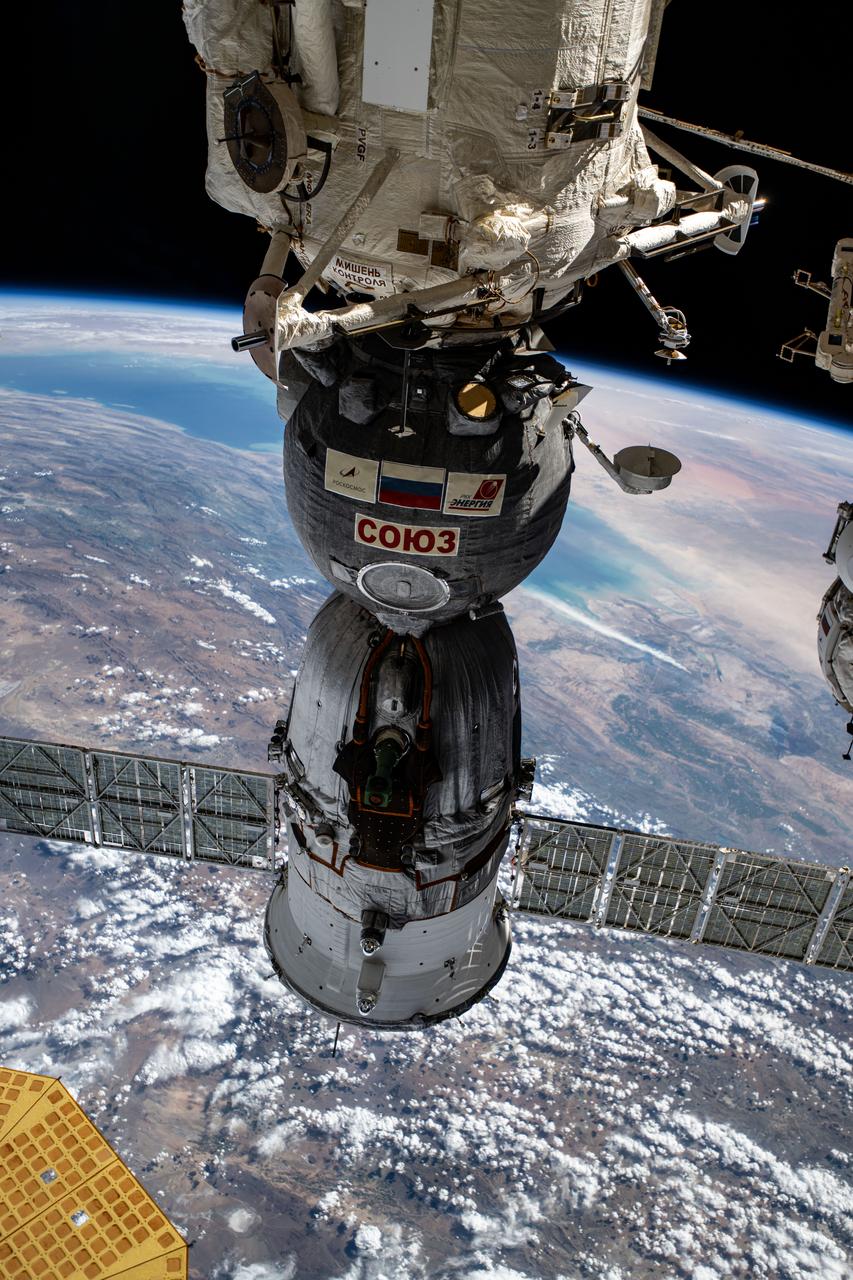

iss072e838106 (March 24, 2025) --- The Soyuz MS-26 spacecraft that launched NASA astronaut Don Pettit and Roscosmos cosmonauts Alexey Ovchinin and Ivan Vagner to the International Space Station is pictured docked to the Rassvet module. The orbiting lab was soaring 260 miles above Turkmenistan near the Caspian Sea.
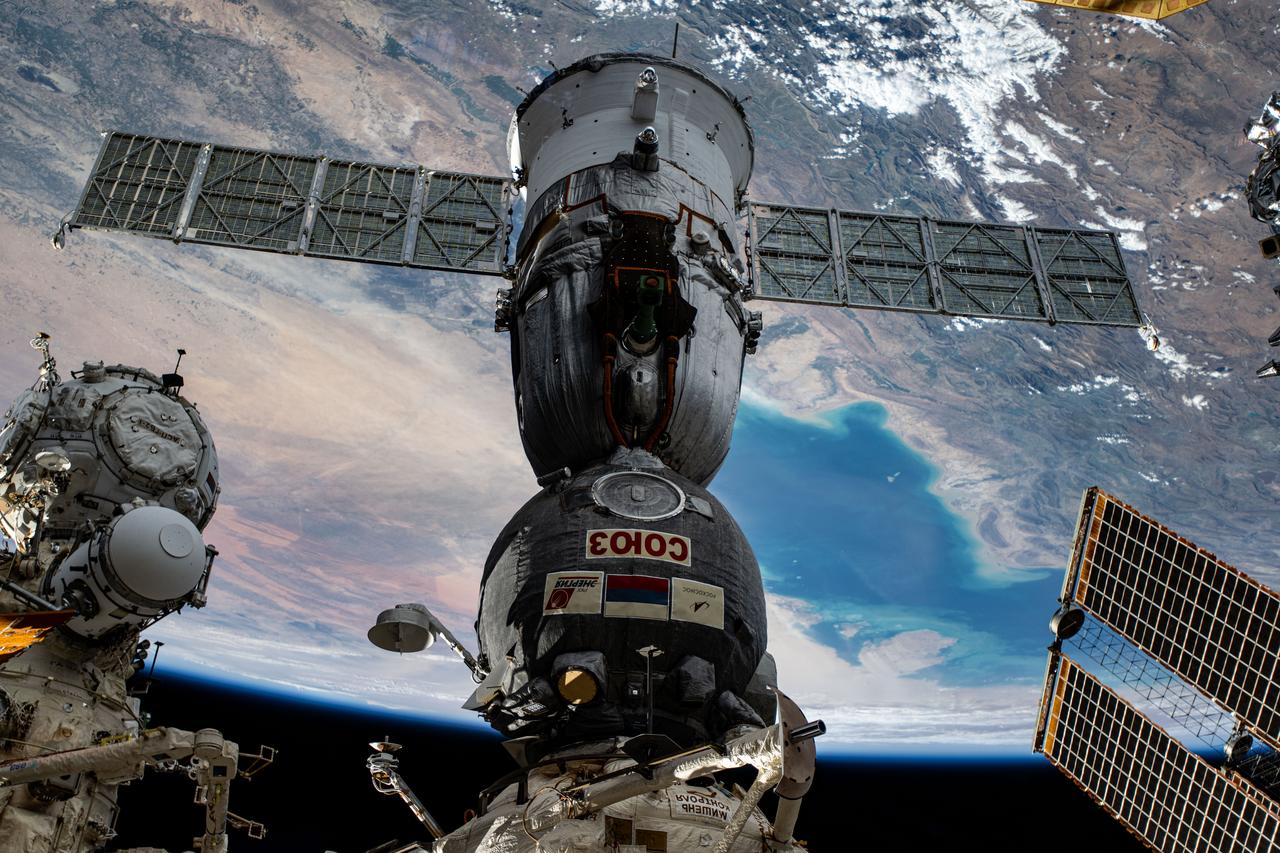

iss072e838101 (March 24, 2025) --- The Soyuz MS-26 spacecraft that launched NASA astronaut Don Pettit and Roscosmos cosmonauts Alexey Ovchinin and Ivan Vagner to the International Space Station is pictured docked to the Rassvet module. The orbiting lab was soaring 260 miles above Turkmenistan near the Caspian Sea.
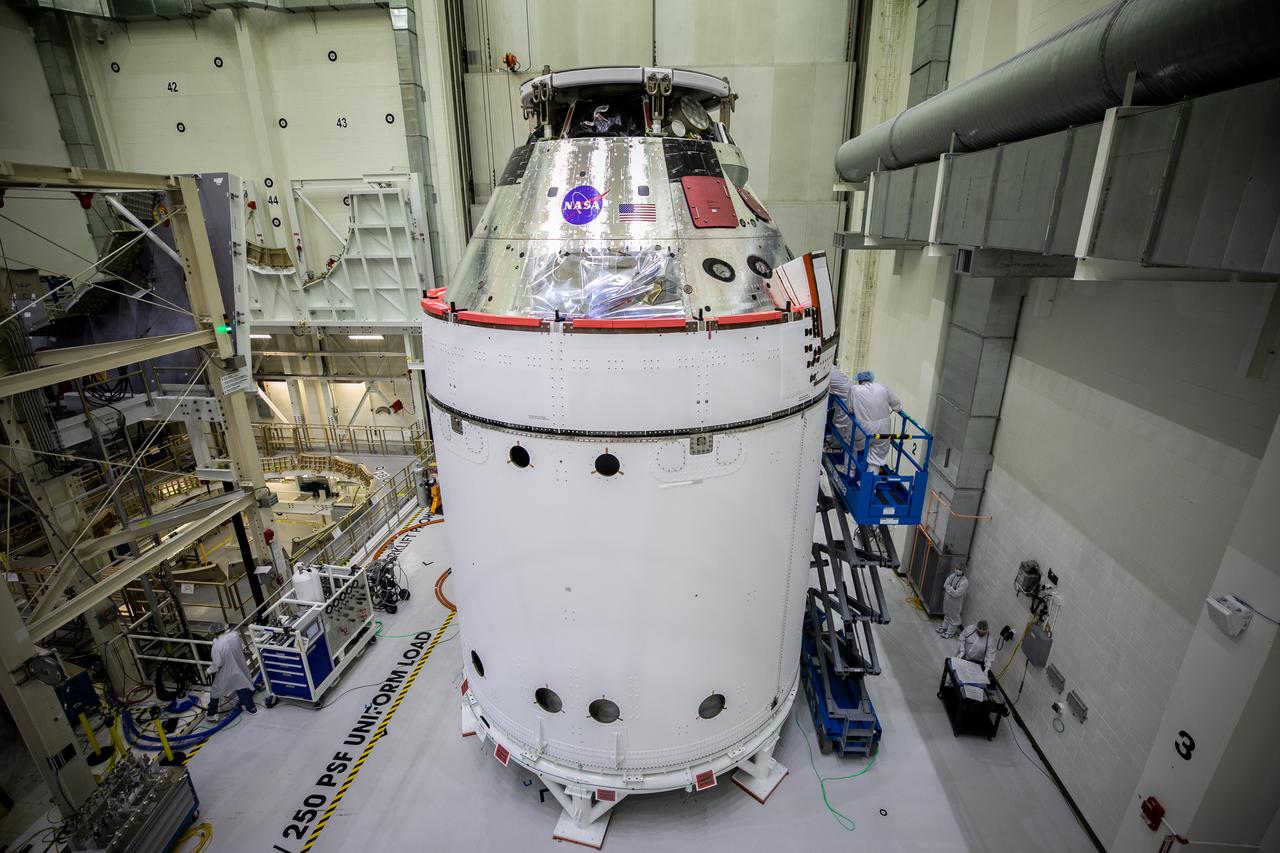

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis I mission is in view inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Oct. 28, 2020, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag have been applied to the Orion crew module back shell. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Todd Biddle, ASRC technician, is shown in the foreground with the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission behind him inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2020. The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and American Fag have been applied to the Orion crew module back shell. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.

Shawn Corwin, at left, ASRC technician, Shawn Corwin, at left, points to the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 28, 2020. At right is Eric Nolan, ASRC technician. The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and American Flag have been applied to the Orion crew module back shell. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
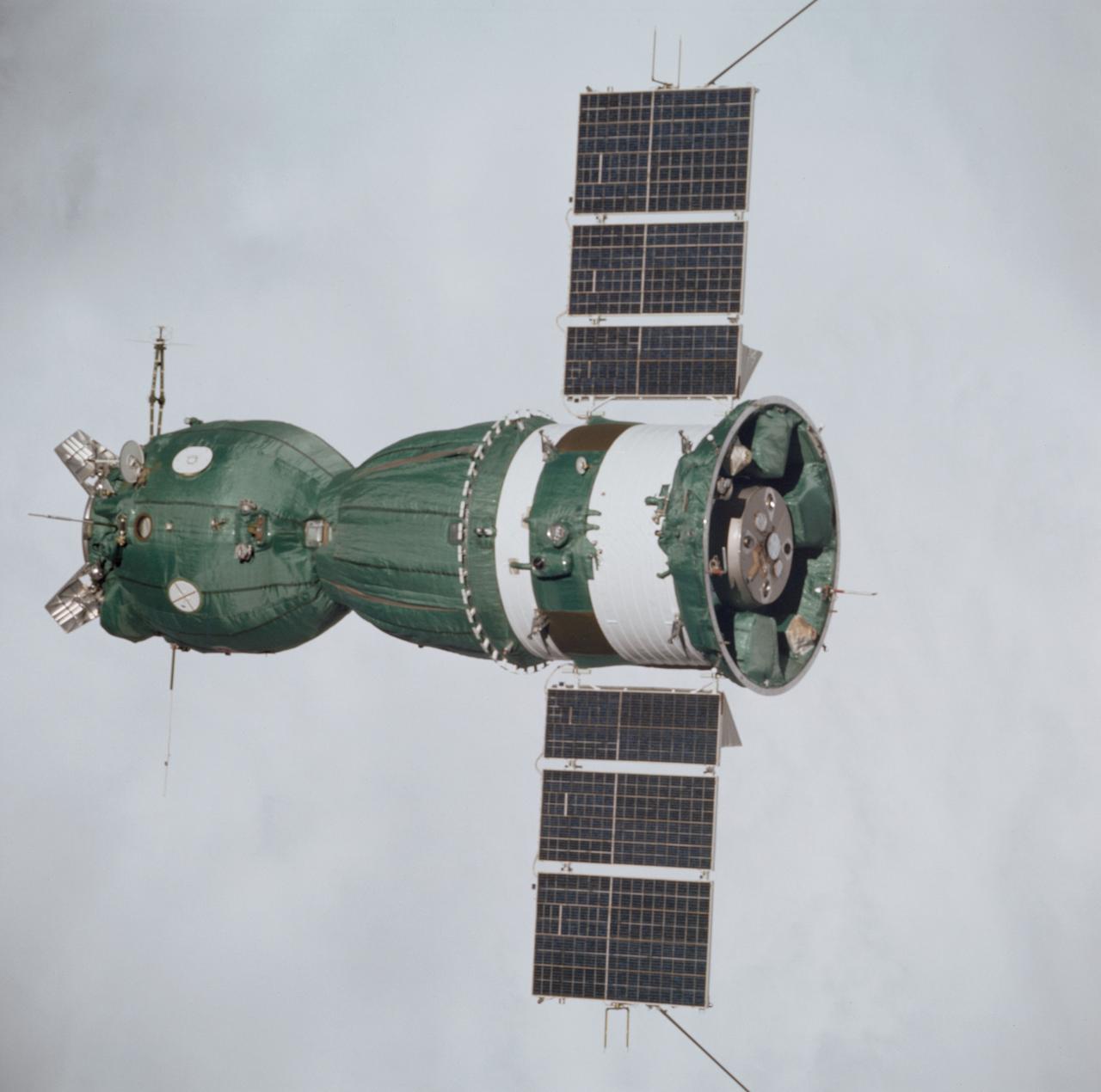

AST-01-056 (18 July 1975) --- An excellent view of the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft in Earth orbit, photographed from the American Apollo spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) docking mission in Earth orbit. The Soyuz is contrasted against a white-cloud background in this overhead view. The three major components of the Soyuz are the spherical-shaped Orbital Module, the bell-shaped Descent Vehicle and the cylindrical-shaped instrument Assembly Module from which two solar panels protrude. The docking system on the Orbital Module was specially designed to interface with the docking system on the Apollo's Docking Module. The ASTP astronauts and cosmonauts visited each other's spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo were docked in Earth orbit for two days. The Apollo crew consisted of astronauts Stafford, commander; Donald K. "Deke" Slayton, docking module pilot; and Vance D. Brand, command module pilot. The Soyuz 19 crew consisted of cosmonauts Leonov, command pilot; and Valeri N. Kubasov, flight engineer.
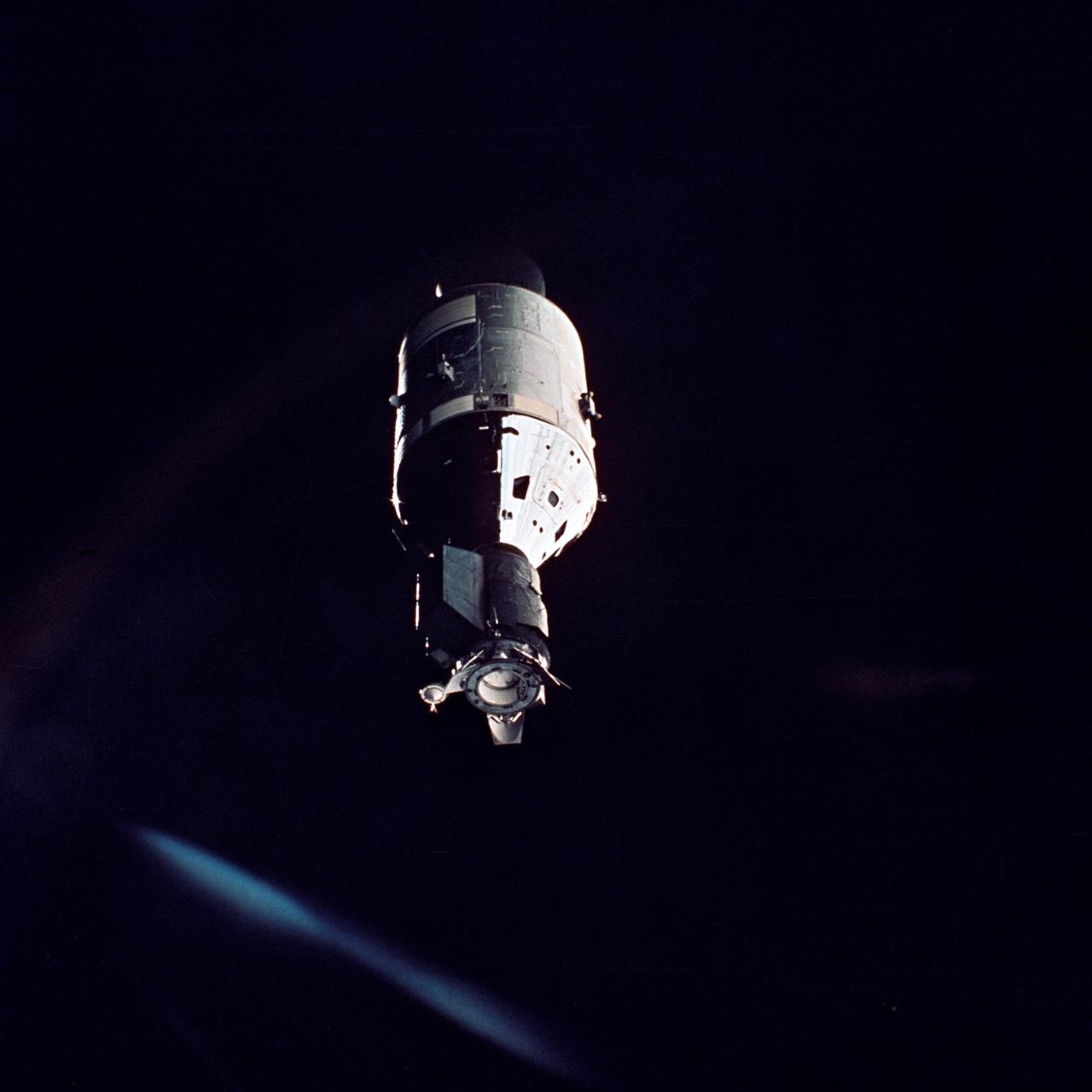

AST-32-2686 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz 19 spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) mission. The Command and Service Module (CSM) and Docking Module (DM) are contrasted against a black-sky background. Light reflected in the camera streaks the image. Note the docking mechanism and docking target on the DM. On the left the bell-shaped engine nozzle of the service propulsion system protrudes from the rear of the Service Module (SM). The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17, 18, 19, 1975. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. The Apollo crew consisted of astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; Donald K. "Deke" Slayton, docking module pilot; and Vance D. Brand, command module pilot. The Soyuz 19 crew consisted of cosmonauts Aleksei A. Leonov, command pilot; and Valeri N. Kubasov, flight engineer.
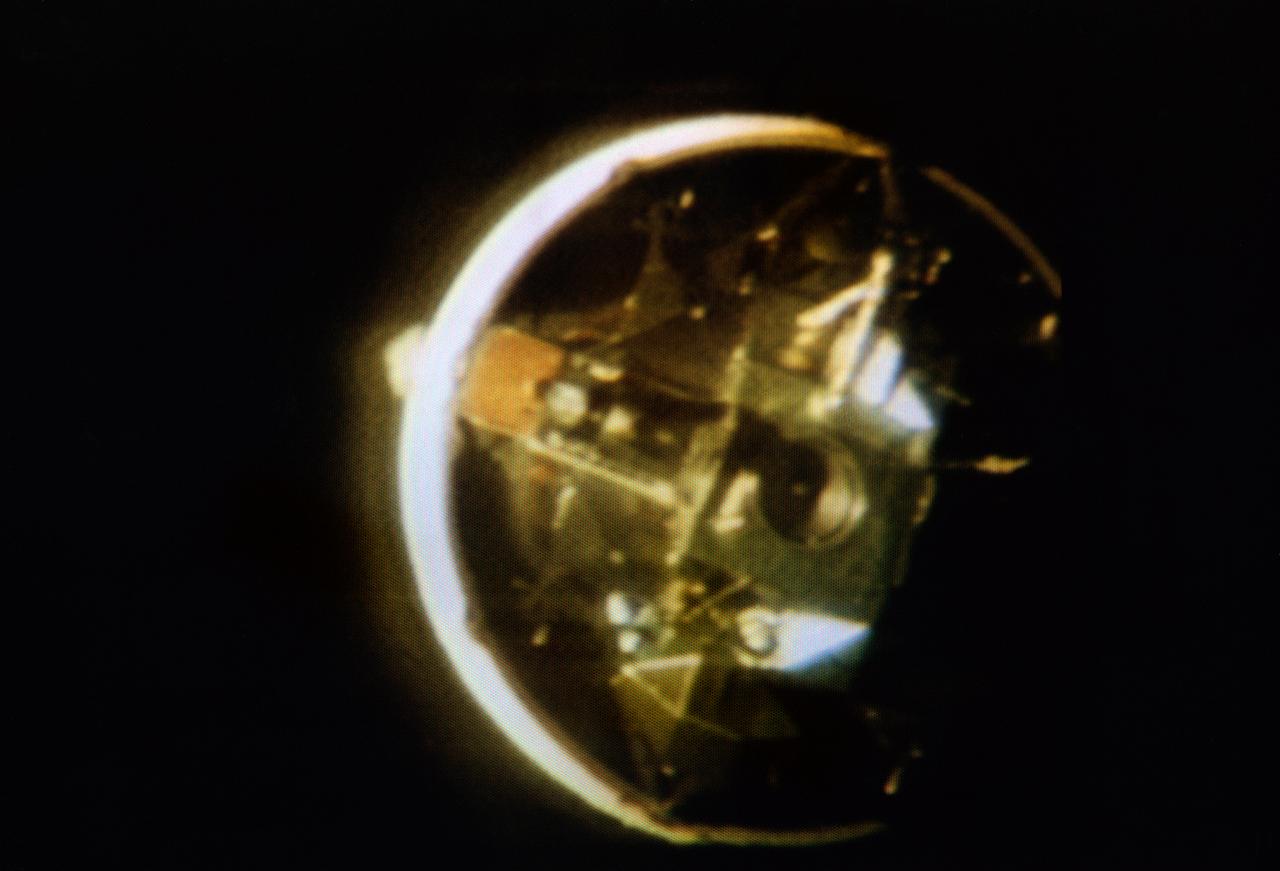

S69-33994 (18 May 1969) --- The Apollo 10 Lunar Module, still attached to the Saturn IVB stage, is seen in this color reproduction taken from the first television transmission made by the color television camera aboard the Apollo 10 spacecraft. This picture was made following CSM/LM-S-IVB separation, and prior to LM extraction from the S-IVB. The Command and Service Modules were making the docking approach to the LM/S-IVB. The circular object is the docking drogue assembly on the LM. Aboard the Command Module were astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.

The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag are applied to the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
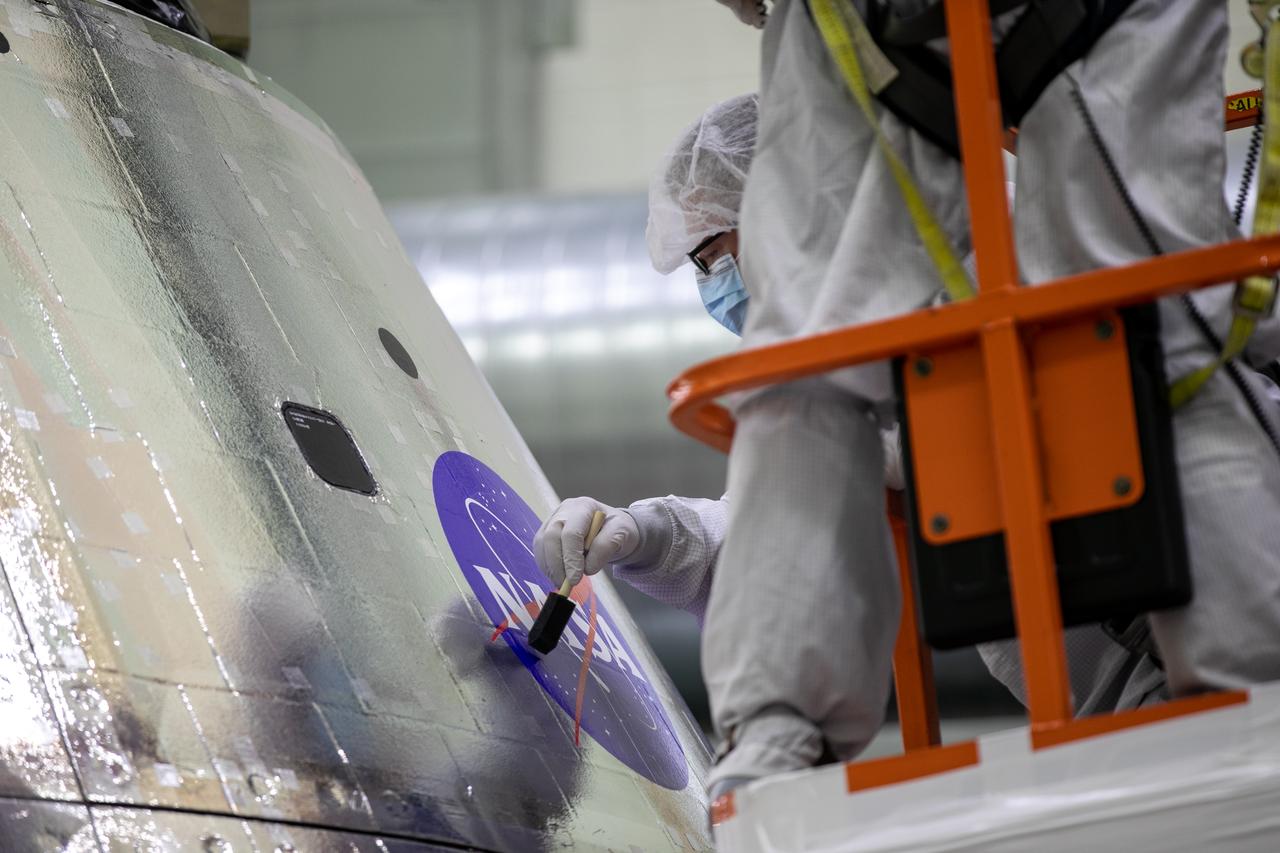

Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, paints a clear adhesive over the NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” on the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The American Flag also has been added. Attached below Orion (not in view) are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
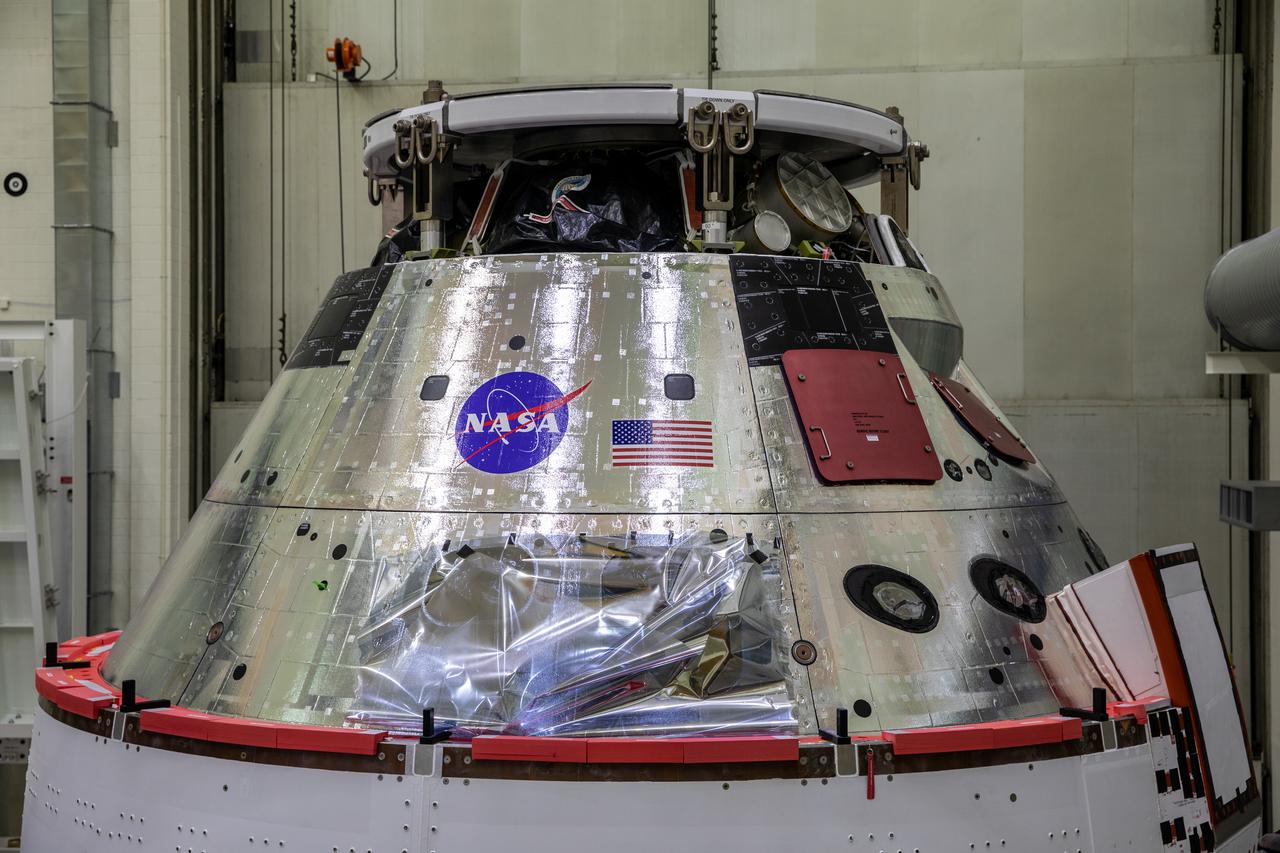

The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag are applied to the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
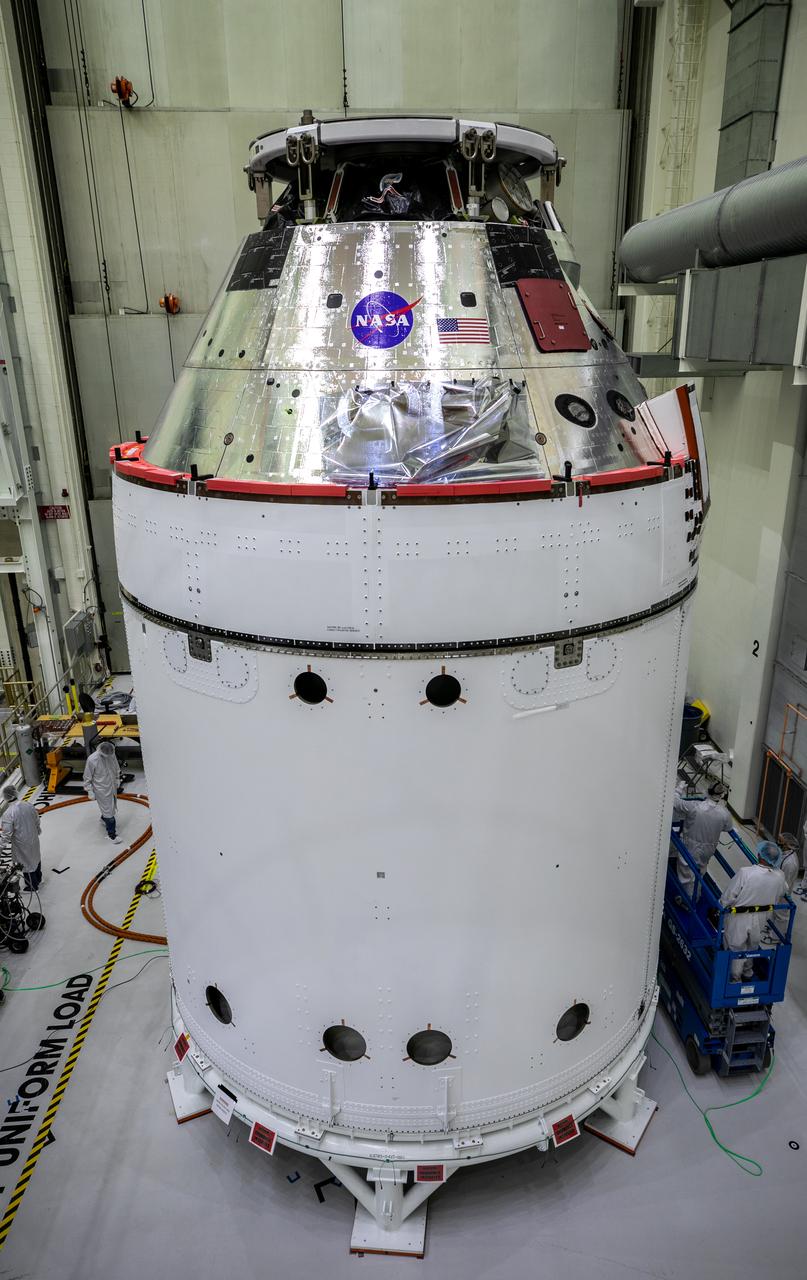

The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag are applied to the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
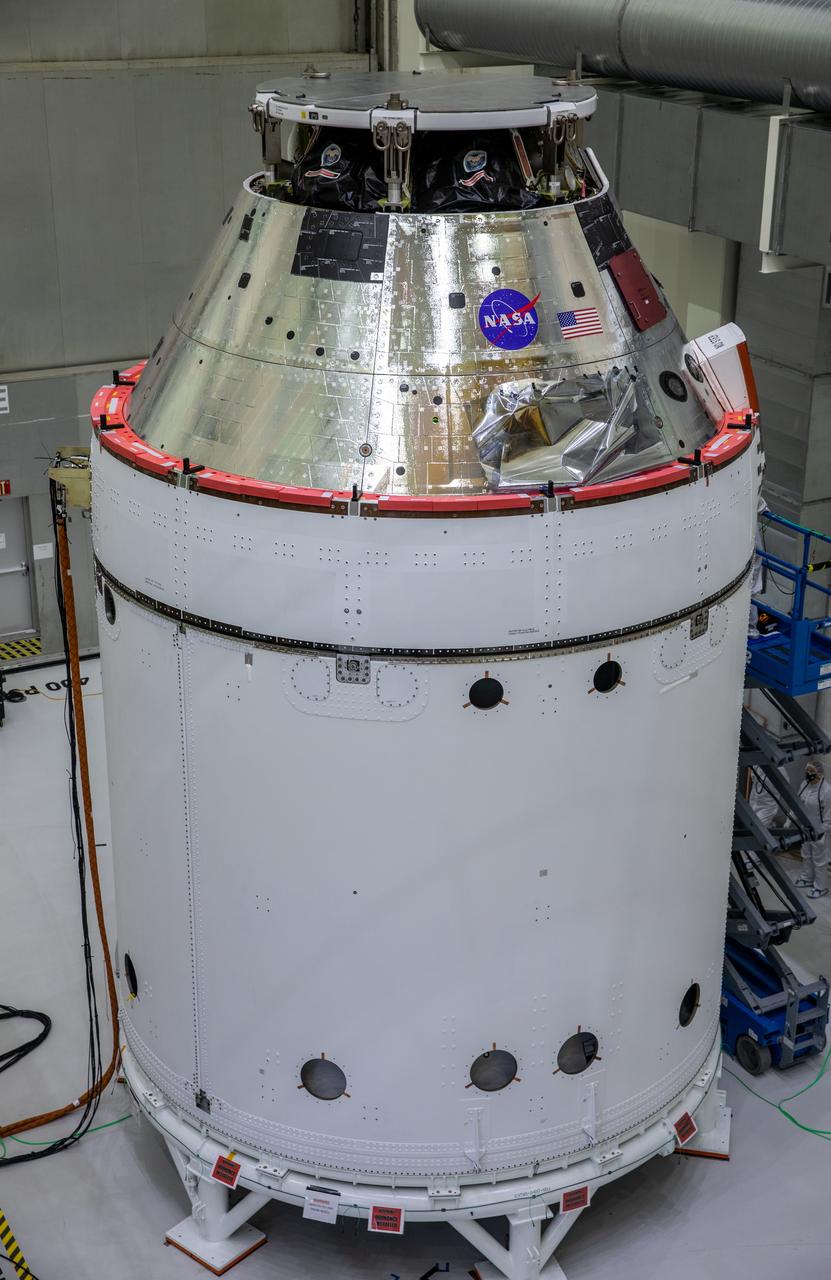

The NASA insignia, also called the “meatball,” and the American Flag are applied to the Orion crew module back shell for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
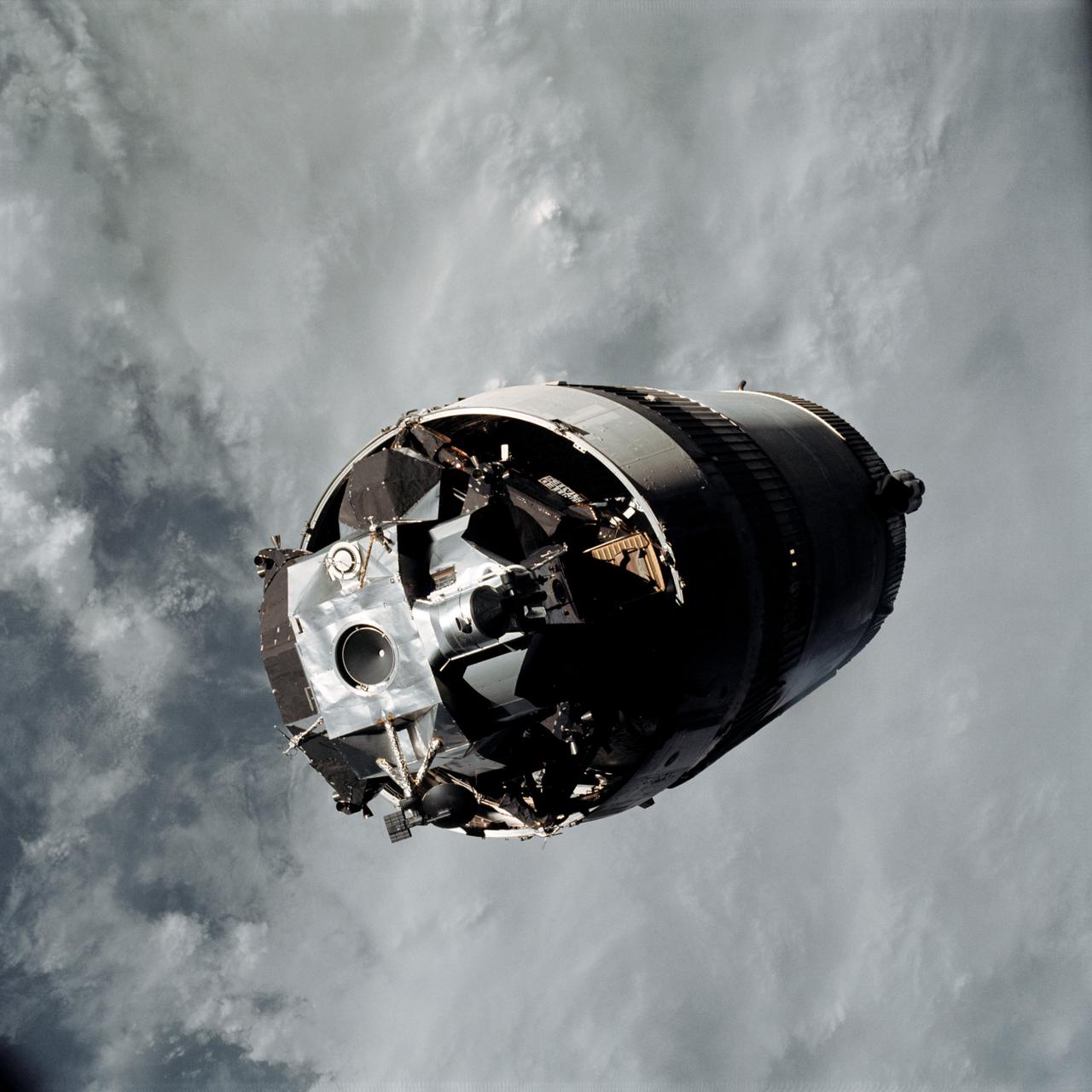

AS09-19-2919 (3 March 1969) --- The Lunar Module (LM) "Spider", still attached to the Saturn V third (S-IVB) stage, is photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Gumdrop" on the first day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. This picture was taken following CSM/LM-S-IVB separation and prior to LM extraction from the S-IVB. The Spacecraft Lunar Module Adapter (SLA) panels have already been jettisoned. Inside the Command Module were astronauts James A. McDivitt, commander; David R. Scott, command module pilot; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot.
Izeal Battle, ASRC technician, is shown in the foreground with the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I mission on Oct. 28, 2020, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building (O&C) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attached below Orion (not in view) are the crew module adapter and the European Service Module (ESM) with spacecraft adapter jettison fairings installed. Recently, teams from across the globe installed the four solar array wings, which are housed inside the protective covering of the fairings. The fairing panels will encapsulate the ESM to protect it from harsh environments such as heat, wind, and acoustics as the spacecraft is propelled out of Earth’s atmosphere atop the Space Launch System rocket during NASA’s Artemis I mission.
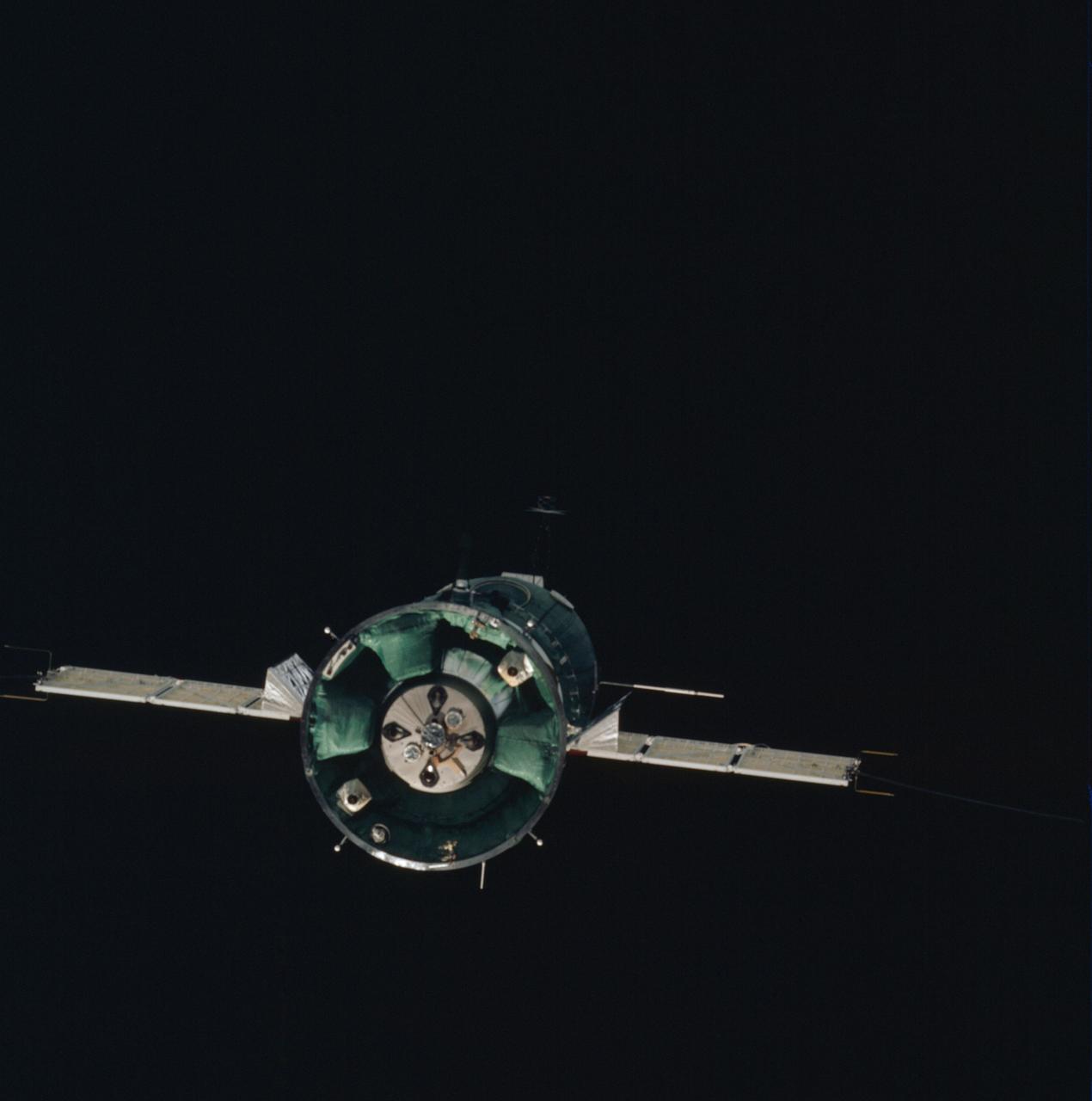

AST-01-053 (17-19 July 1975) --- The Soviet Soyuz spacecraft is contrasted against a black-sky background in this photograph taken in Earth orbit. This view is looking toward the aft end of the Soyuz. Two solar panels protrude out from the spacecraft's Instrument Assembly Module. The ASTP astronauts and cosmonauts visited each other's spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo were docked in Earth orbit for two days.
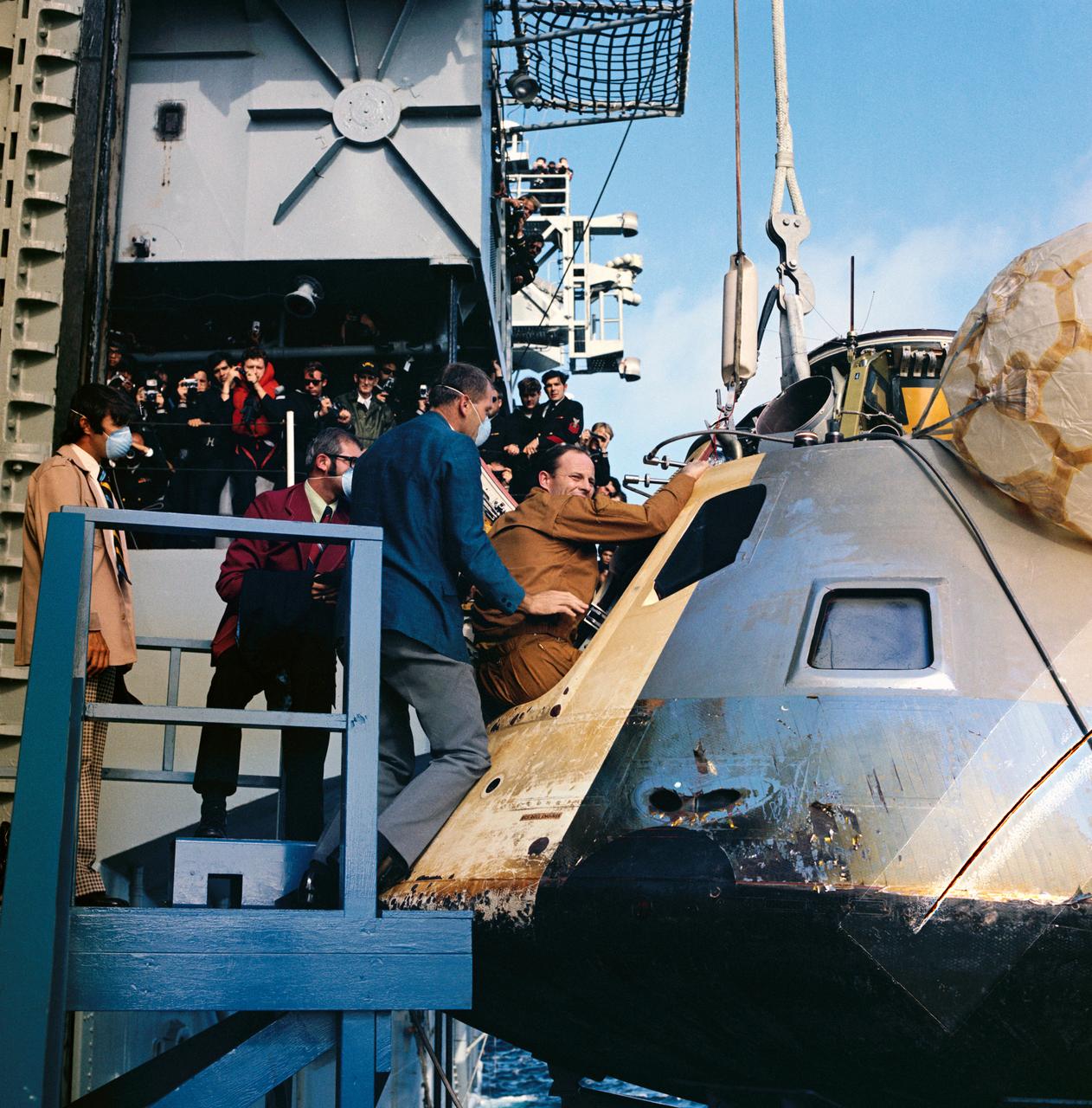

S73-36435 (25 Sept. 1973) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Skylab 3 pilot, egresses the Skylab 3 Command Module aboard the prime recovery ship, USS New Orleans, during recovery operations in the Pacific Ocean. Astronauts Lousma; Alan L. Bean, commander; and Owen L. Garriott, science pilot, had just completed a successful 59-day visit to the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The Skylab 3 spacecraft splashed down in the Pacific about 230 miles southwest of San Diego, California. Photo credit: NASA
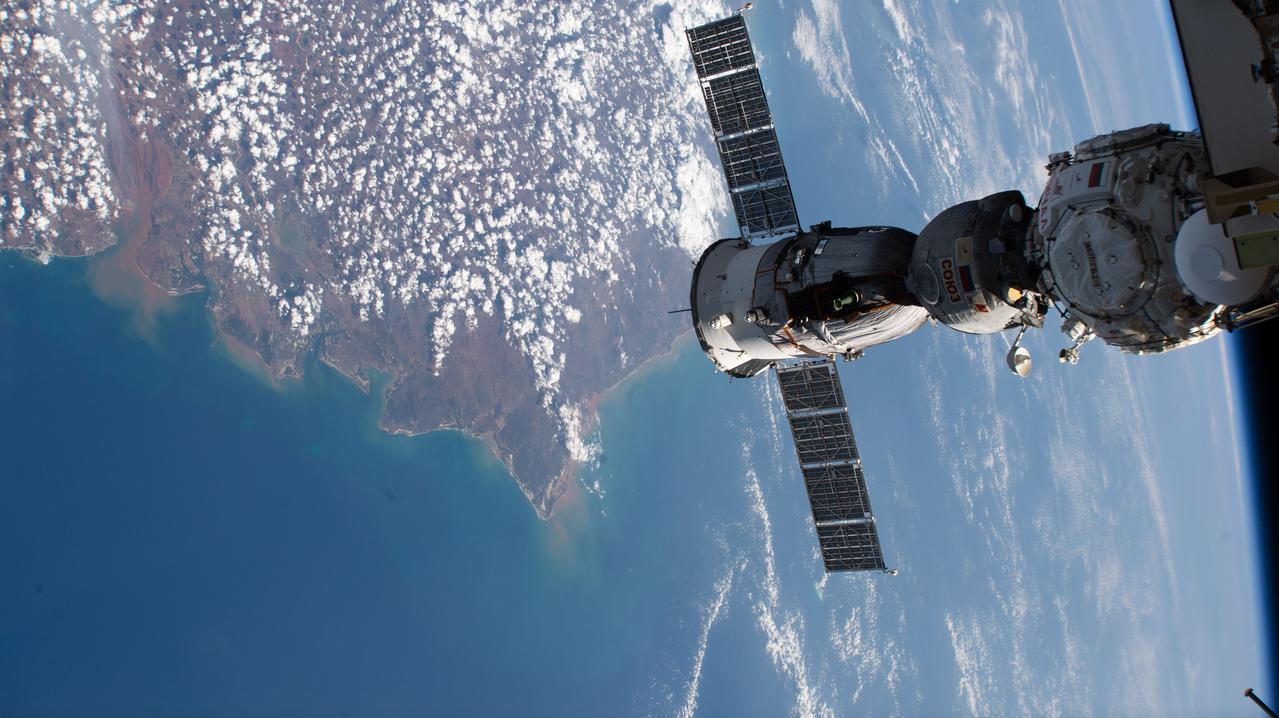

iss073e0659744 (Sept. 14, 2025) --- The Soyuz MS-27 spacecraft is pictured docked to the International Space Station's Prichal module as the orbital outpost soared 259 miles above the northern coast of Madagascar.
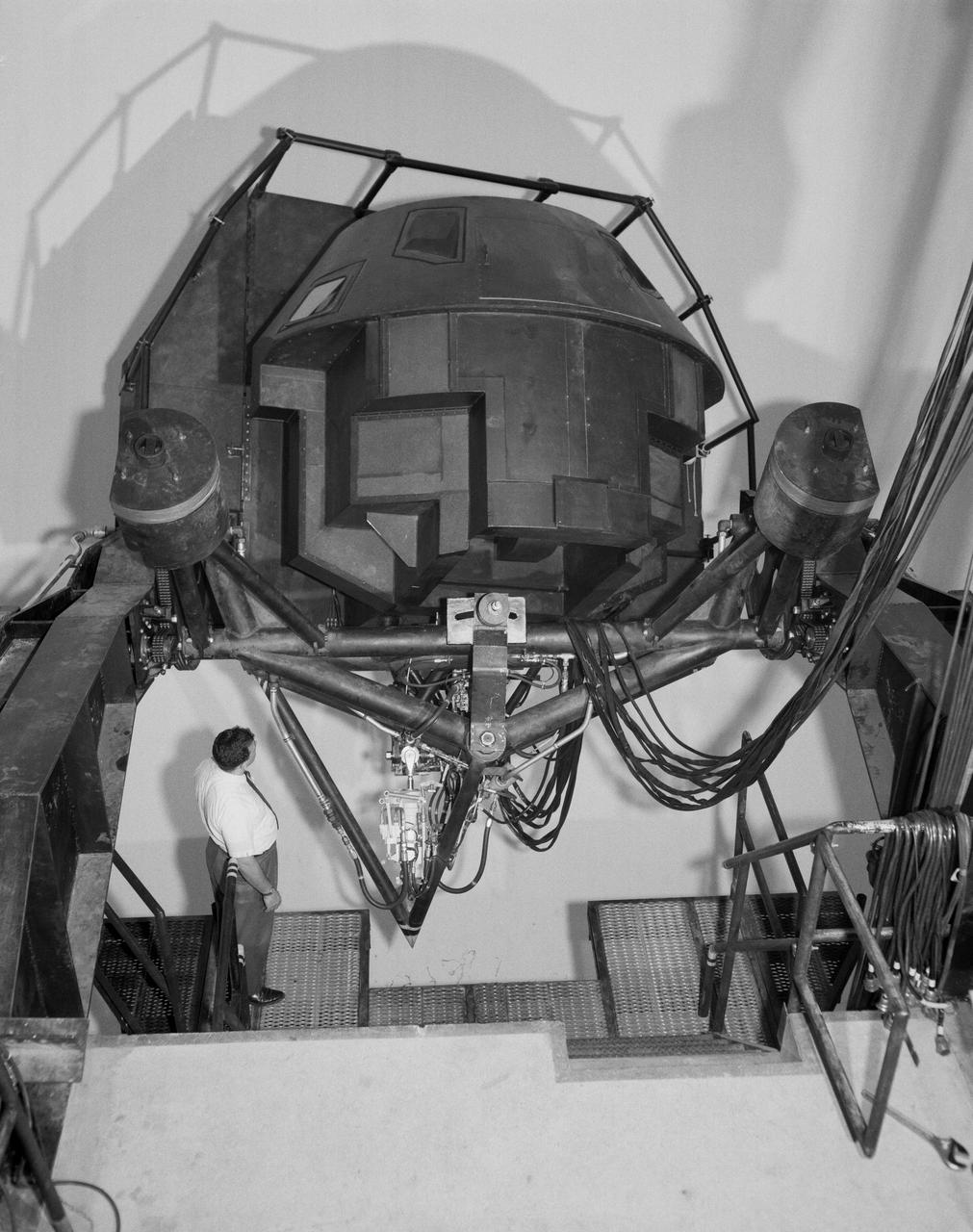
S66-21296 (1967) --- This is a medium exterior view of the Dynamic Crew Procedures Trainer, Command Module configuration, one of the Apollo astronaut training components located in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility, Building 5, Manned Spacecraft Center, Houston, Texas. Photo credit: NASA