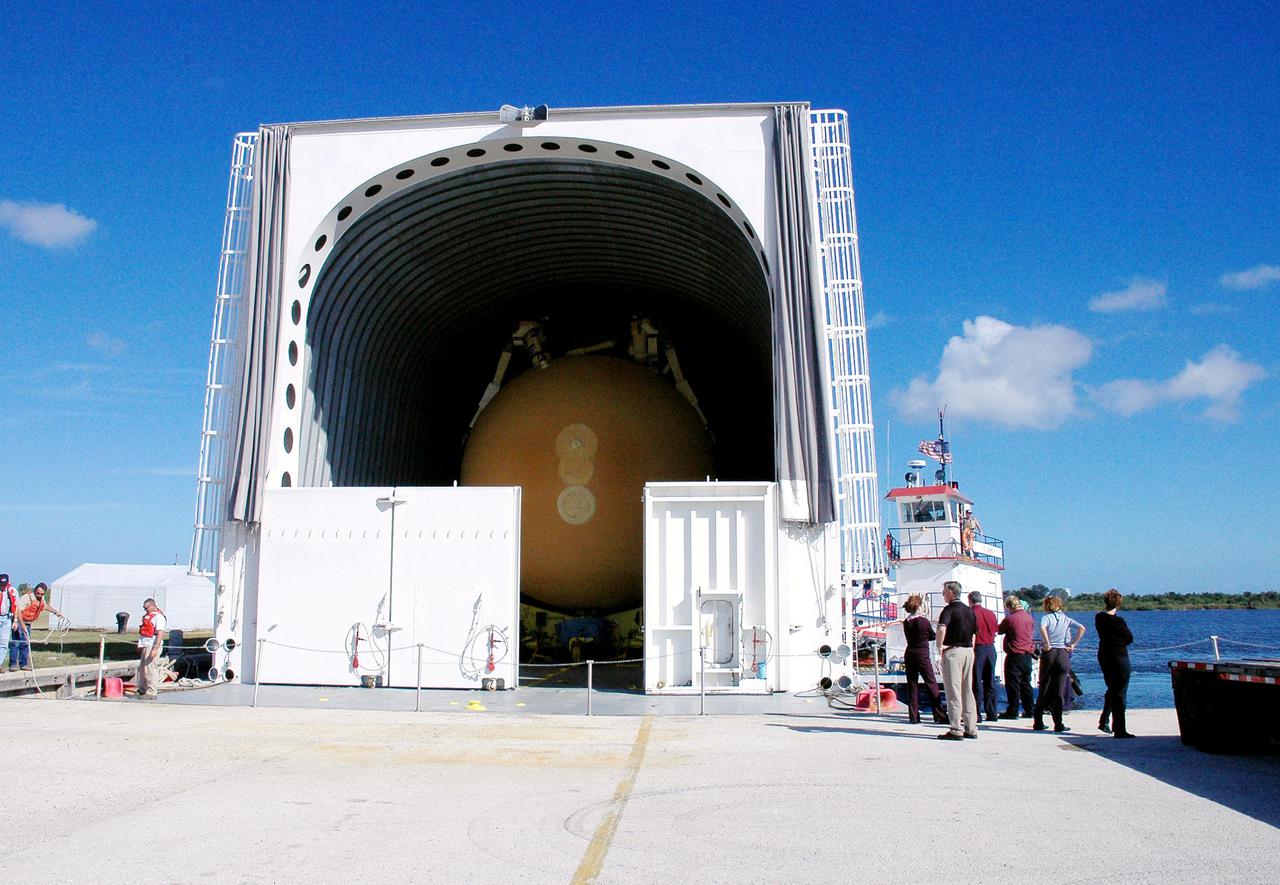

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank (ET), designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, is finally docked at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin. The ET can be seen inside the barge. The External Tank arrived safely early this morning at Port Canaveral, Fla., after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea. It departed from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Dec. 31 and was transported on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, pulled by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At the port, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
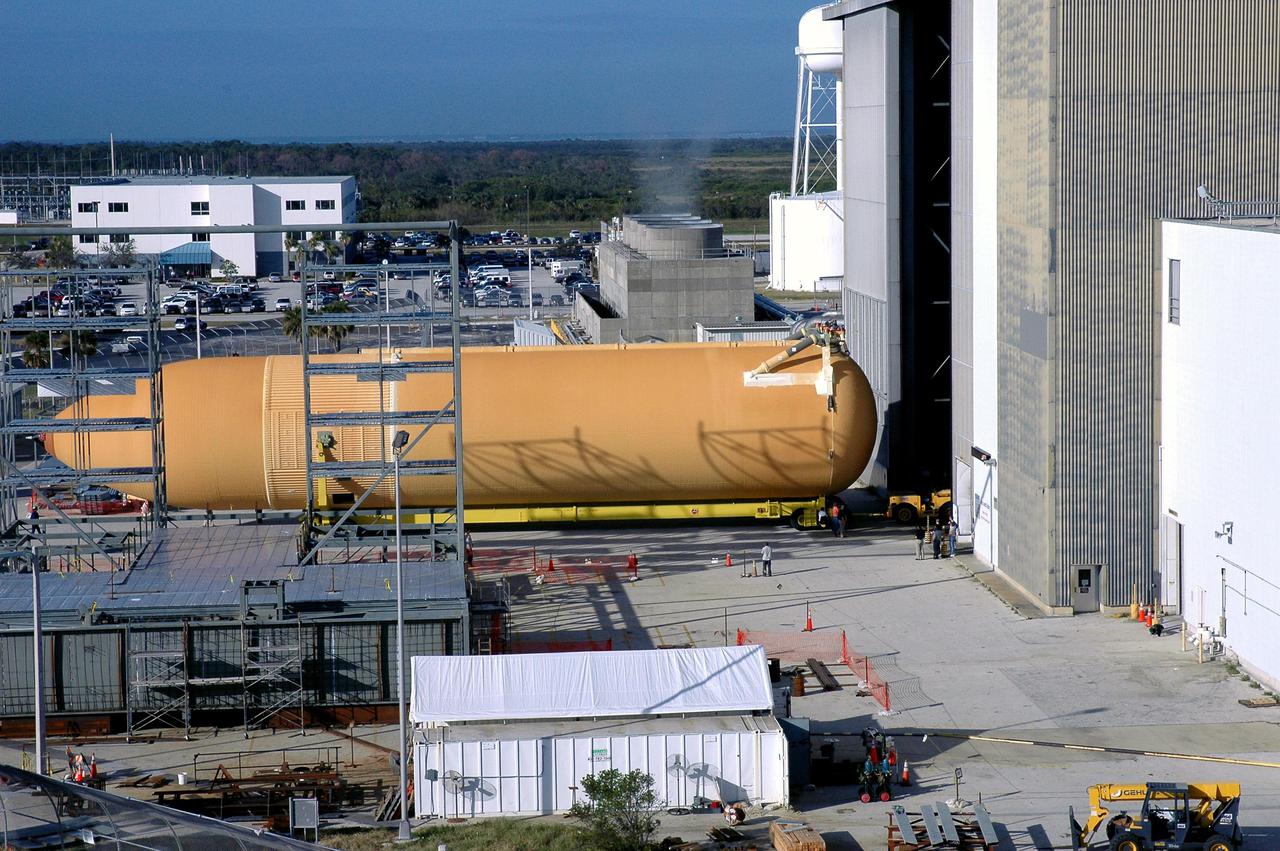

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Viewed from the roof of the Launch Control Center in the Launch Complex 39 Area, the newly redesigned External Tank is seen moving into the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank, designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, moves slowly toward its destination, the dock at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin, propelled by two tugboats. At left in the background is Launch Pad 39A. The External Tank arrived safely early this morning at Port Canaveral, Fla., after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea. It departed from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Dec. 31 and was transported on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, pulled by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At the port, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey to the Turn Basin. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
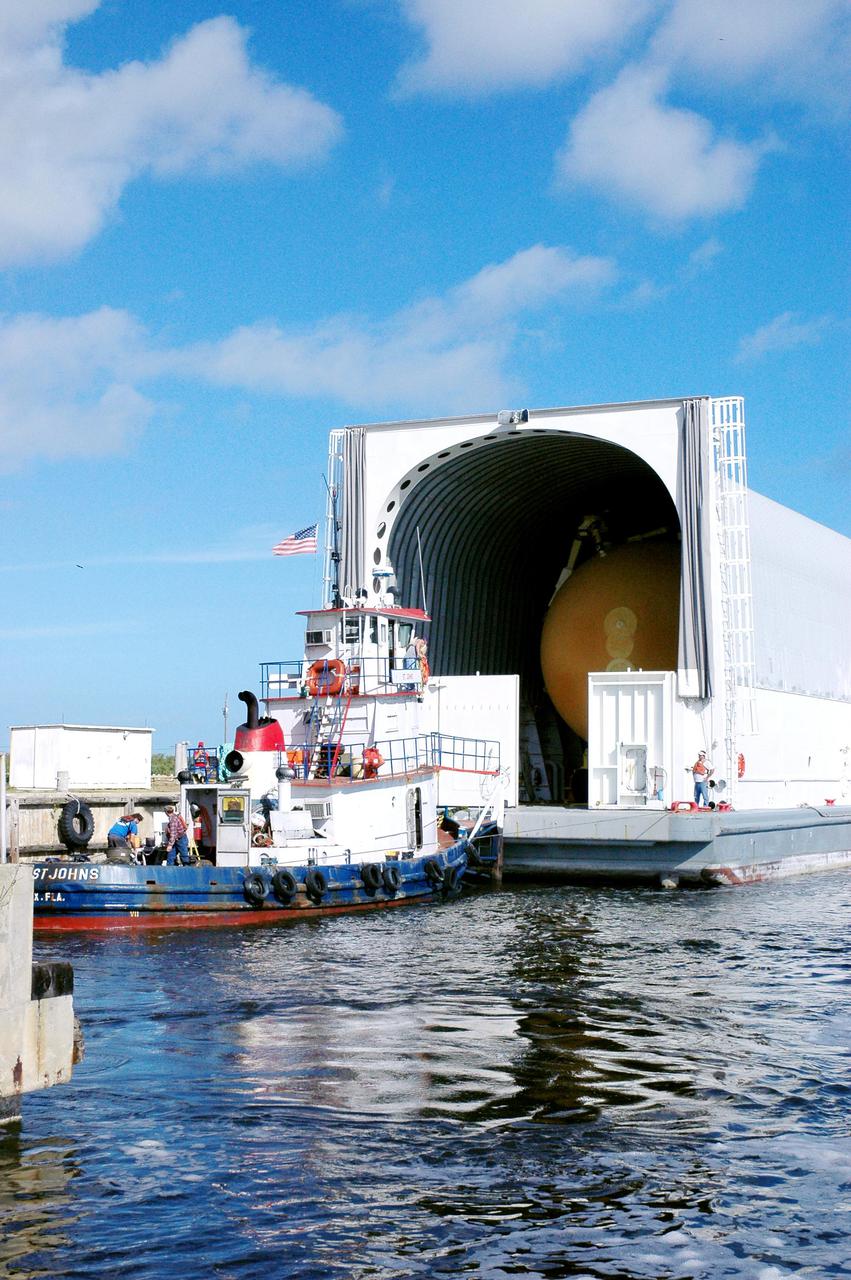

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Tugboats maneuver the barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank (ET), designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, closer to the dock at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin. The ET can be seen inside the barge. The External Tank arrived safely early this morning at Port Canaveral, Fla., after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea. It departed from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Dec. 31 and was transported on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, pulled by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At the port, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey to the Turn Basin. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
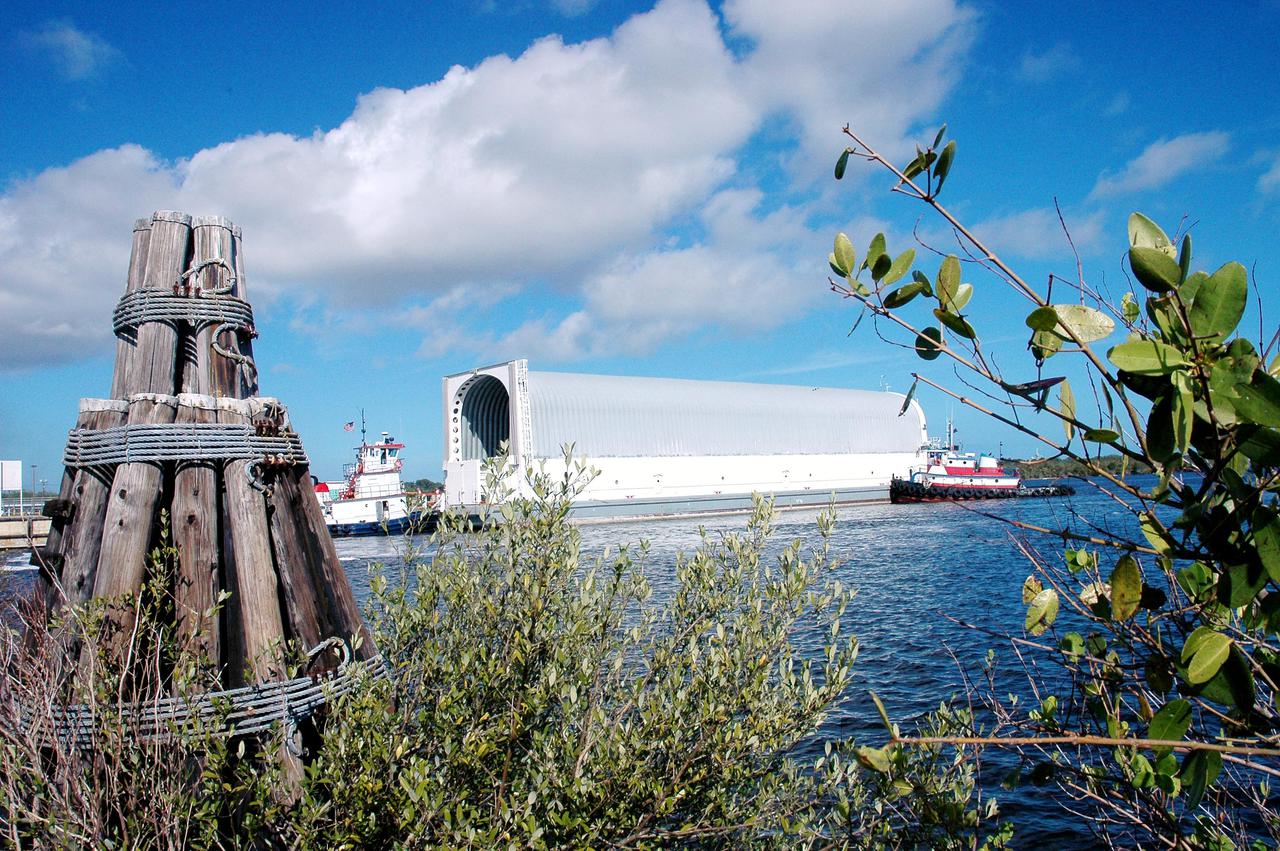

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - Tugboats maneuver the barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank, designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, toward the dock at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin at Kennedy. The barge arrived after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. It left the facility Dec. 31 on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, towed by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At Port Canaveral, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
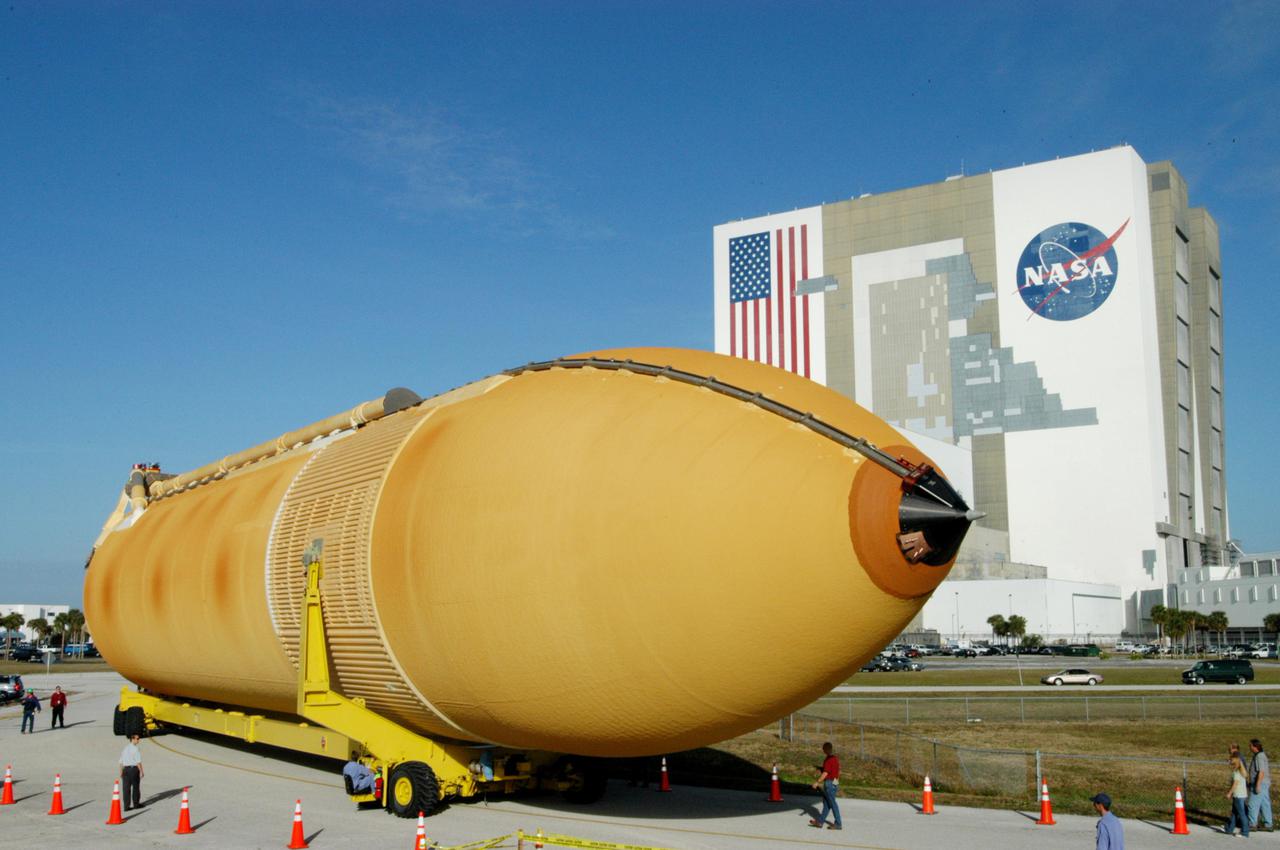

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank turns the corner of the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin parking area on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen at right. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
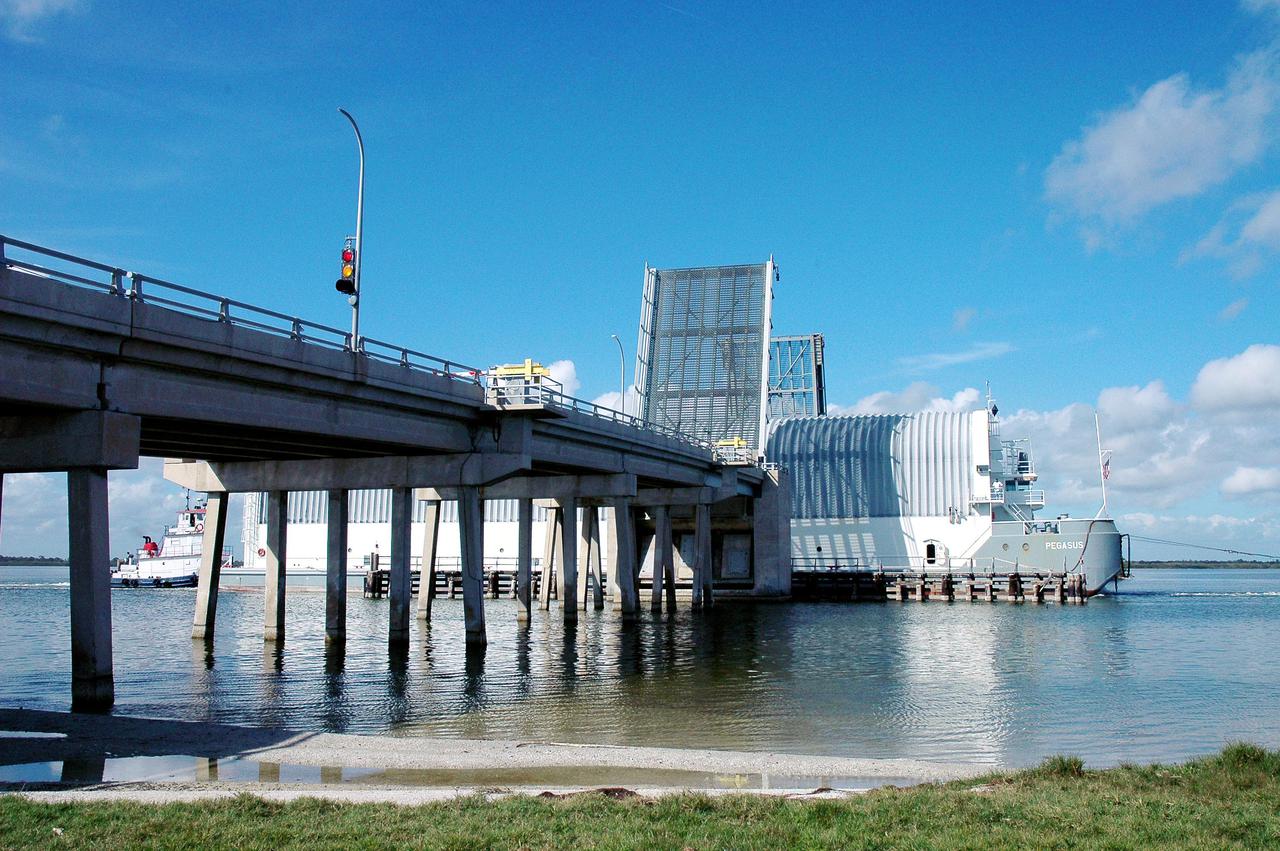

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The tugboat towing the barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank, designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, passes through a drawbridge on its voyage to the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin at Kennedy. The barge arrived after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. It left the facility Dec. 31 on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, towed by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At Port Canaveral, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey to the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin at Kennedy. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
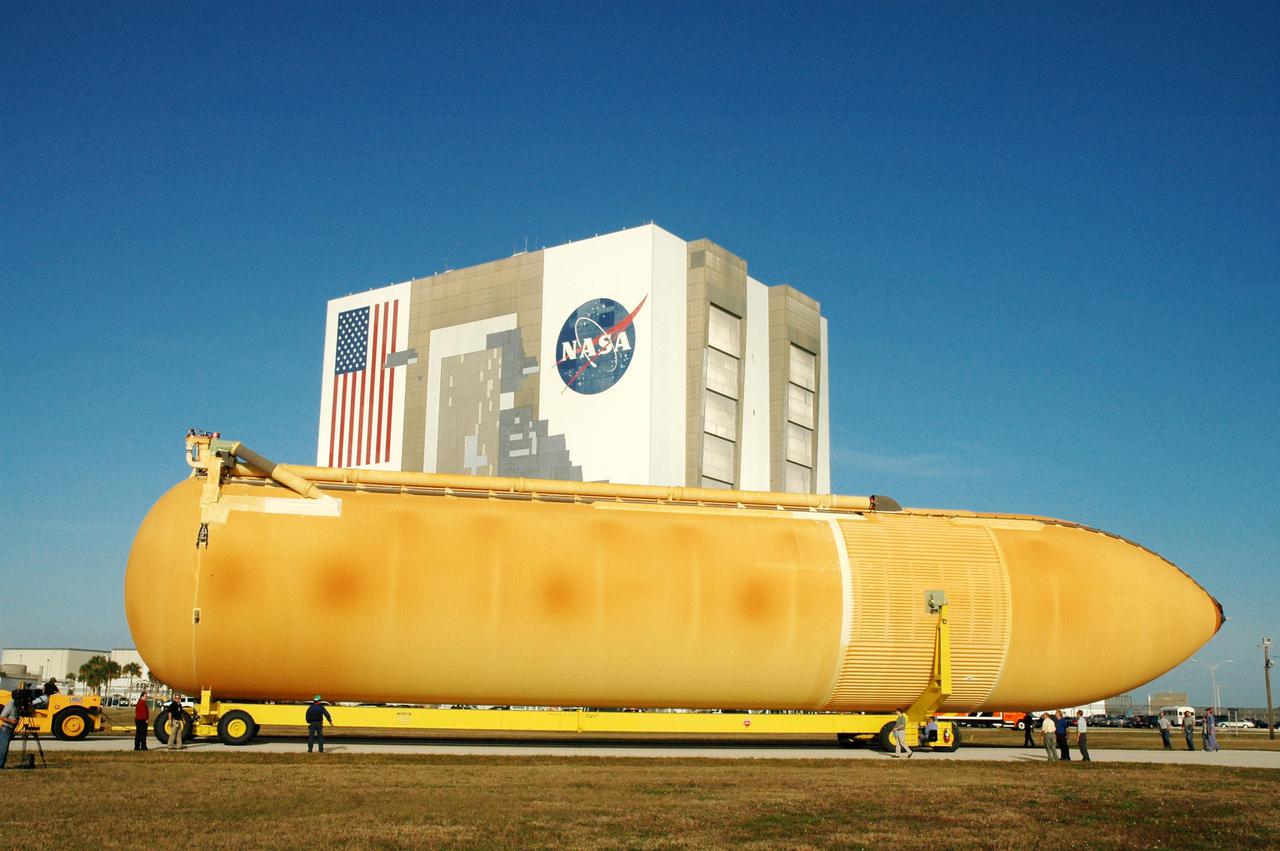

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank wends its way through the parking area at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen behind it. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
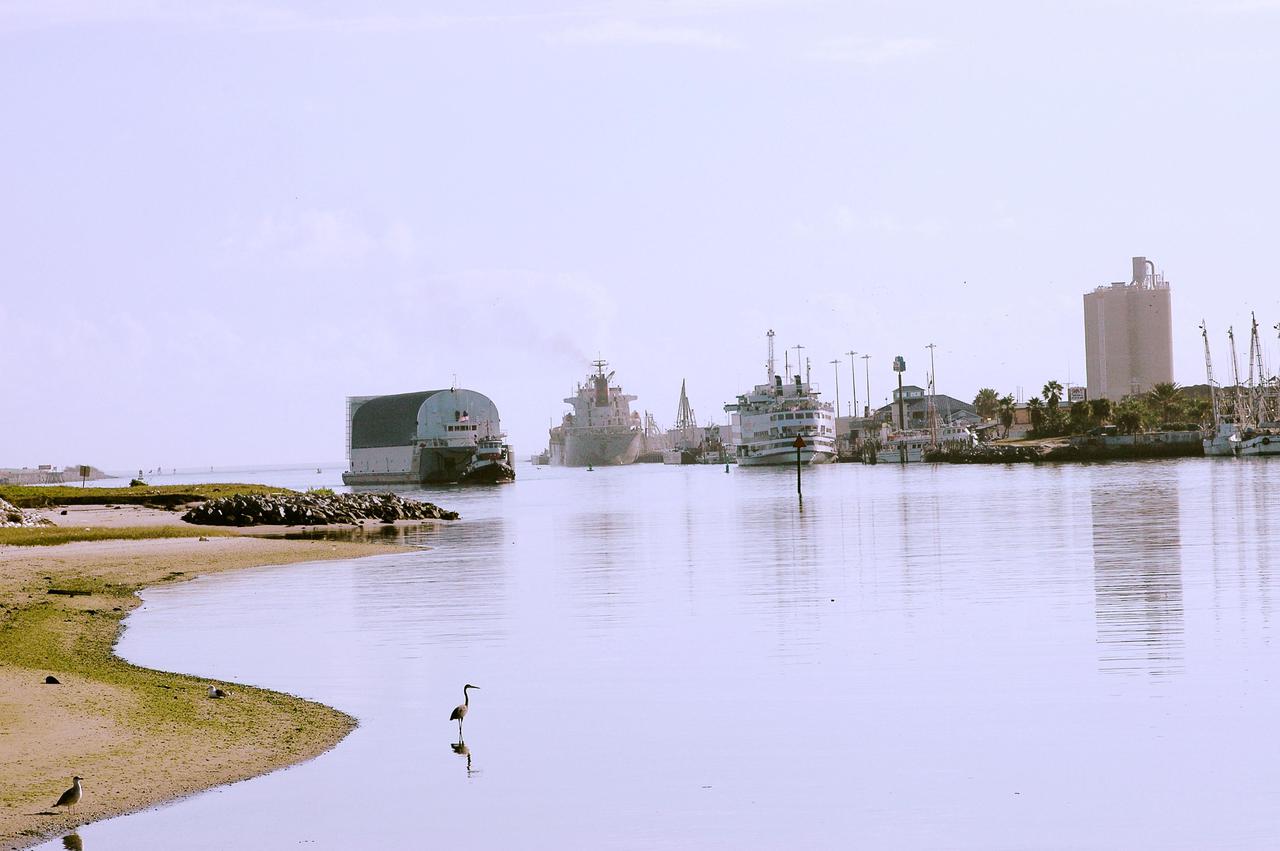

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank, designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, passes cruise ships as it enters Port Canaveral, Fla. The barge arrived after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. It left the facility Dec. 31 on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, towed by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At Port Canaveral, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey to the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin at Kennedy. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
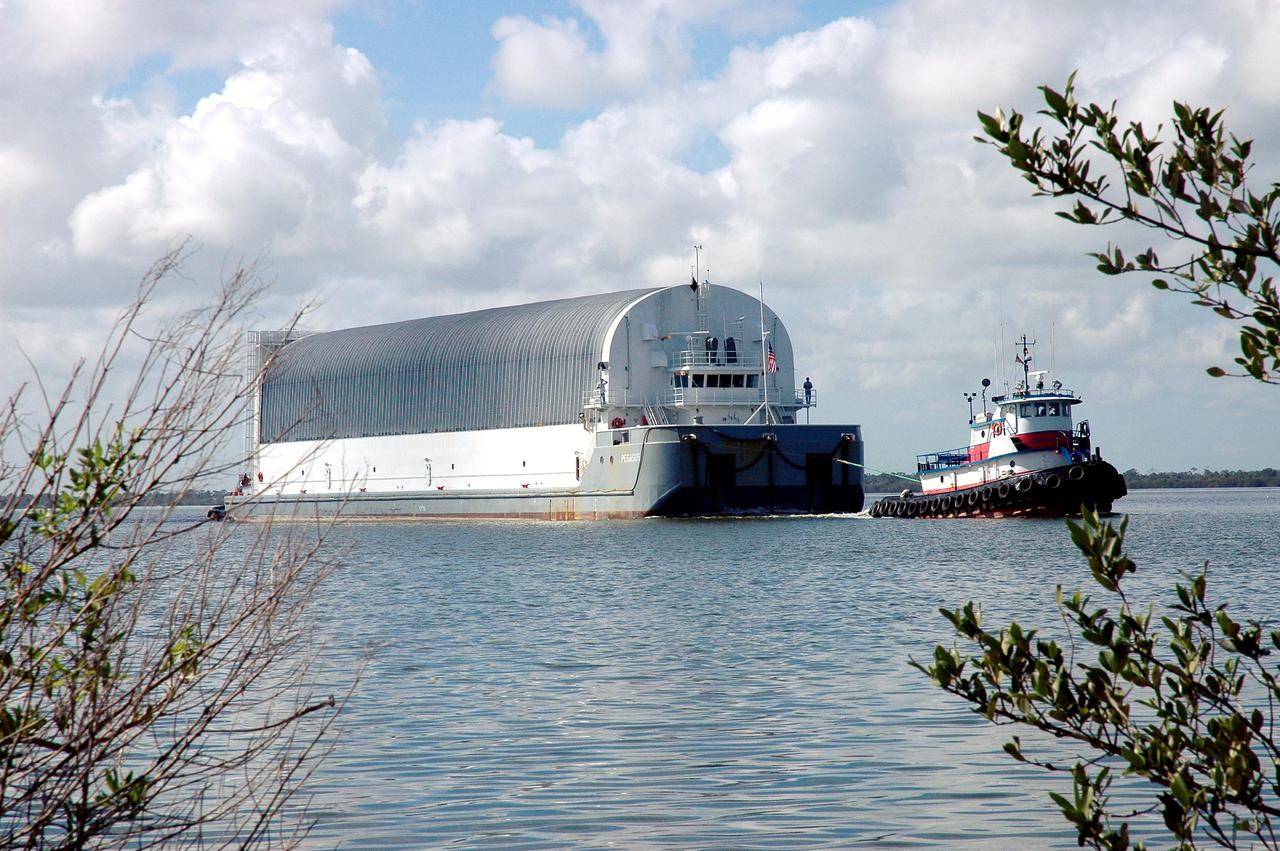

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A tugboat tows the barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank, designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, to the dock at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin at Kennedy. The barge arrived after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. It left the facility Dec. 31 on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, towed by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At Port Canaveral, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey to the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin at Kennedy. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
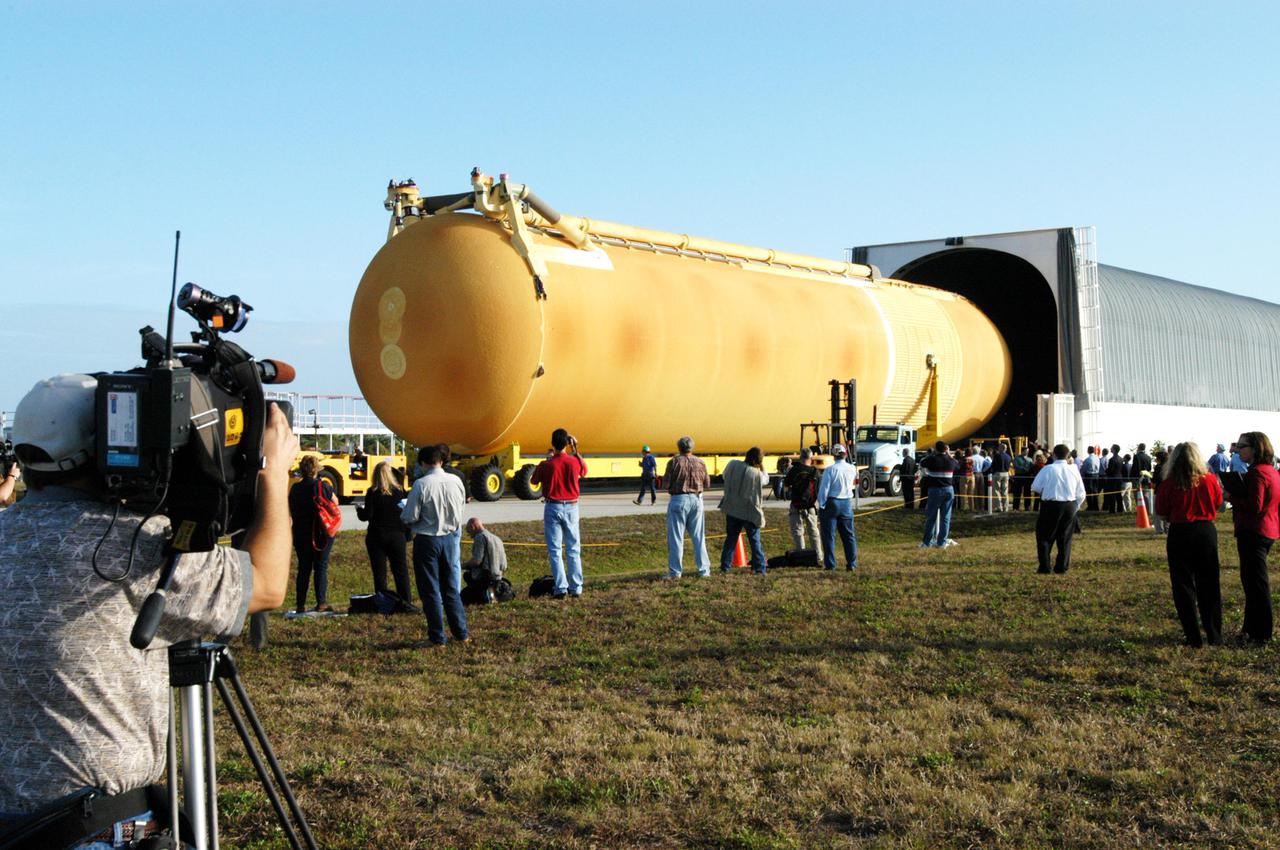

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Media view the newly redesigned External Tank as it is off-loaded from the barge that carried it from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank is being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
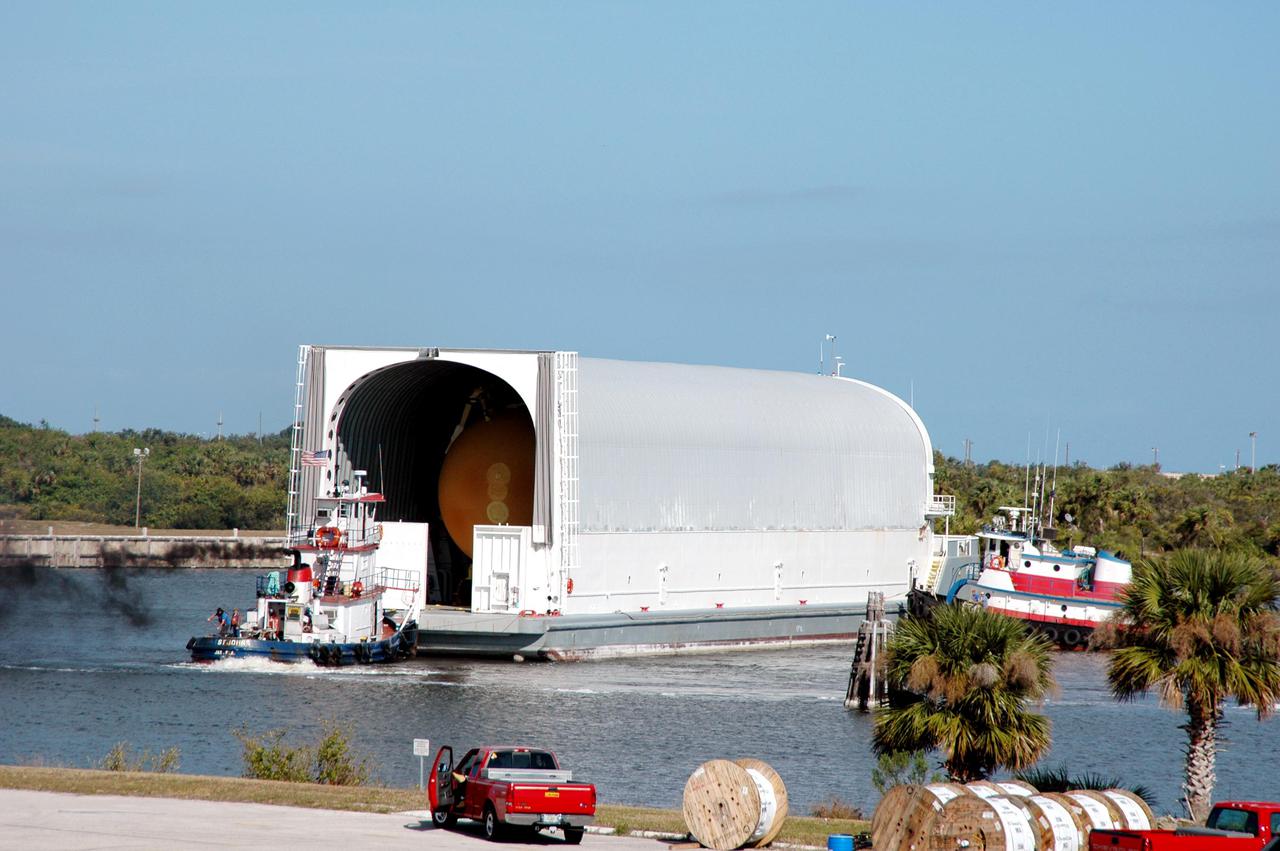

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Tugboats maneuver the barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank (ET), designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, closer to the dock at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin. The ET can be seen inside the barge. The External Tank arrived safely early this morning at Port Canaveral, Fla., after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea. It departed from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Dec. 31 and was transported on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, pulled by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At the port, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey to the Turn Basin. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
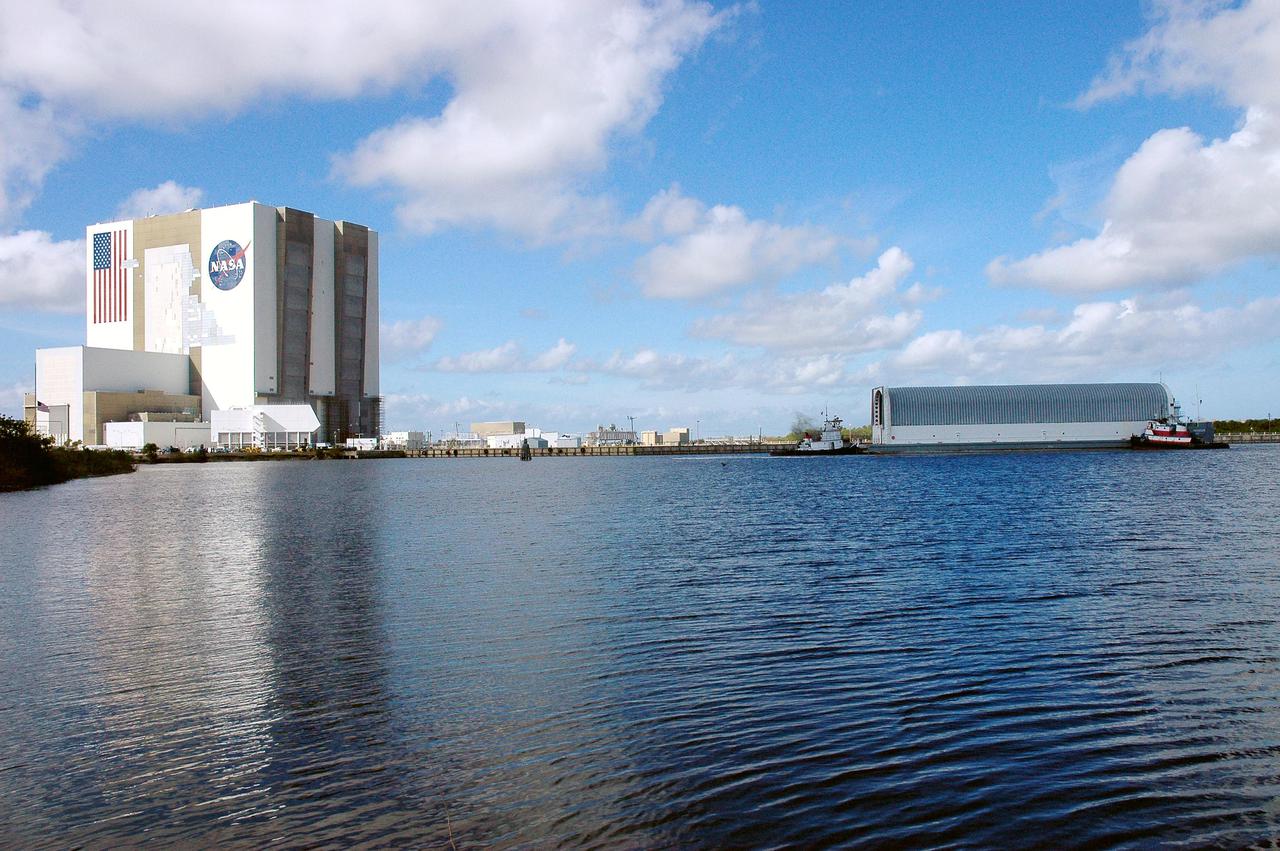

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank, designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, is towed toward the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin at Kennedy. At left is the Vehicle Assembly Building. The barge arrived after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. It left the facility Dec. 31 on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, towed by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At Port Canaveral, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.

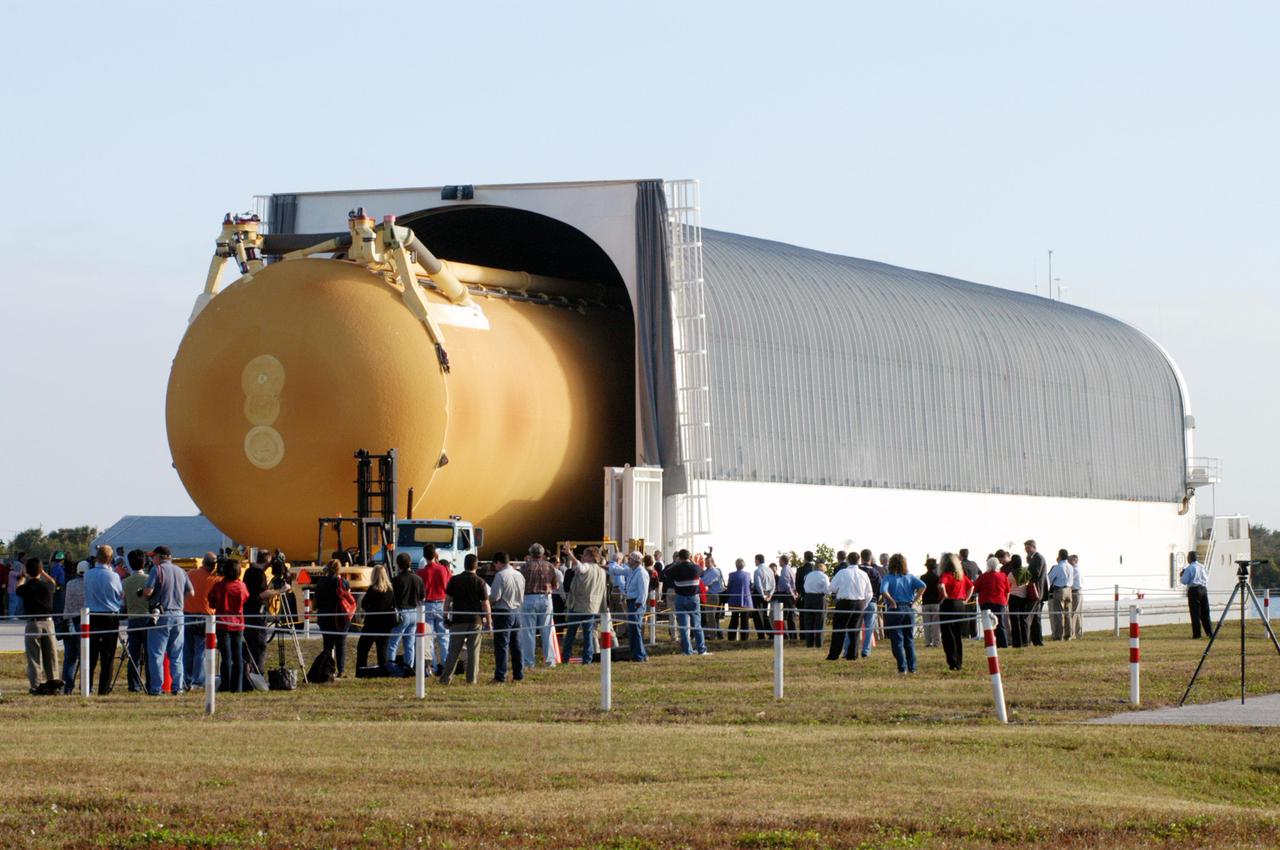
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank heads for the open doors of the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen behind it. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Viewed from the roof of the Launch Control Center in the Launch Complex 39 Area, the newly redesigned External Tank is seen moving past the parking area on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building. Behind the tank is Operations Support Building II, currently under construction. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Media view the newly redesigned External Tank as it is off-loaded from the barge that carried it from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank is being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - KSC employees accompany the newly redesigned External Tank as it wends its way through the parking area at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin. The tank is being moved to the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen behind it. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
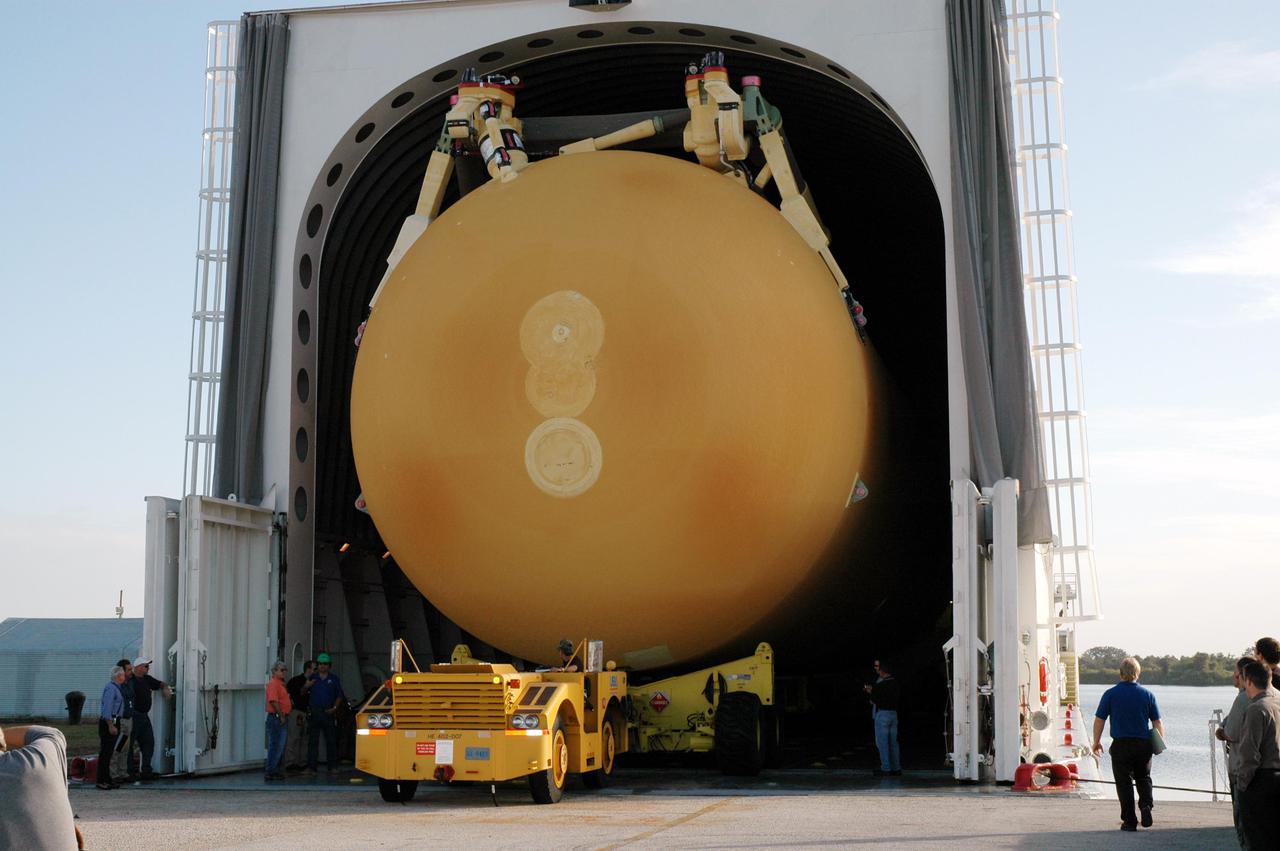

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Media view the newly redesigned External Tank as a transporter begins off-loading it from the barge that carried it from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank is being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
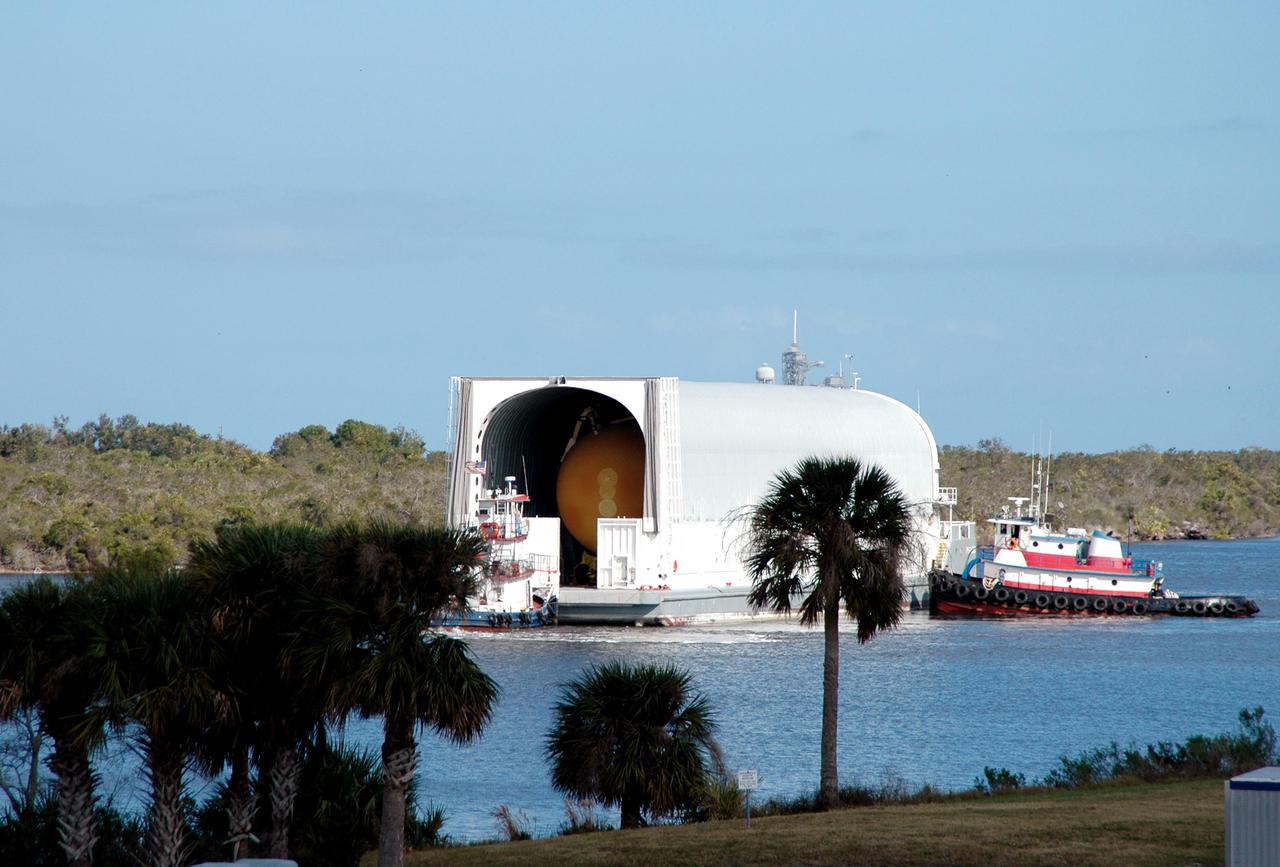

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A tugboat maneuvers the barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank (ET), designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, toward the dock at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin. The ET can be seen inside the barge. The External Tank arrived safely early this morning at Port Canaveral, Fla., after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea. It departed from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Dec. 31 and was transported on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, pulled by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At the port, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey to the Turn Basin. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Media view the newly redesigned External Tank after its off-loading from the barge that carried it from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank is being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
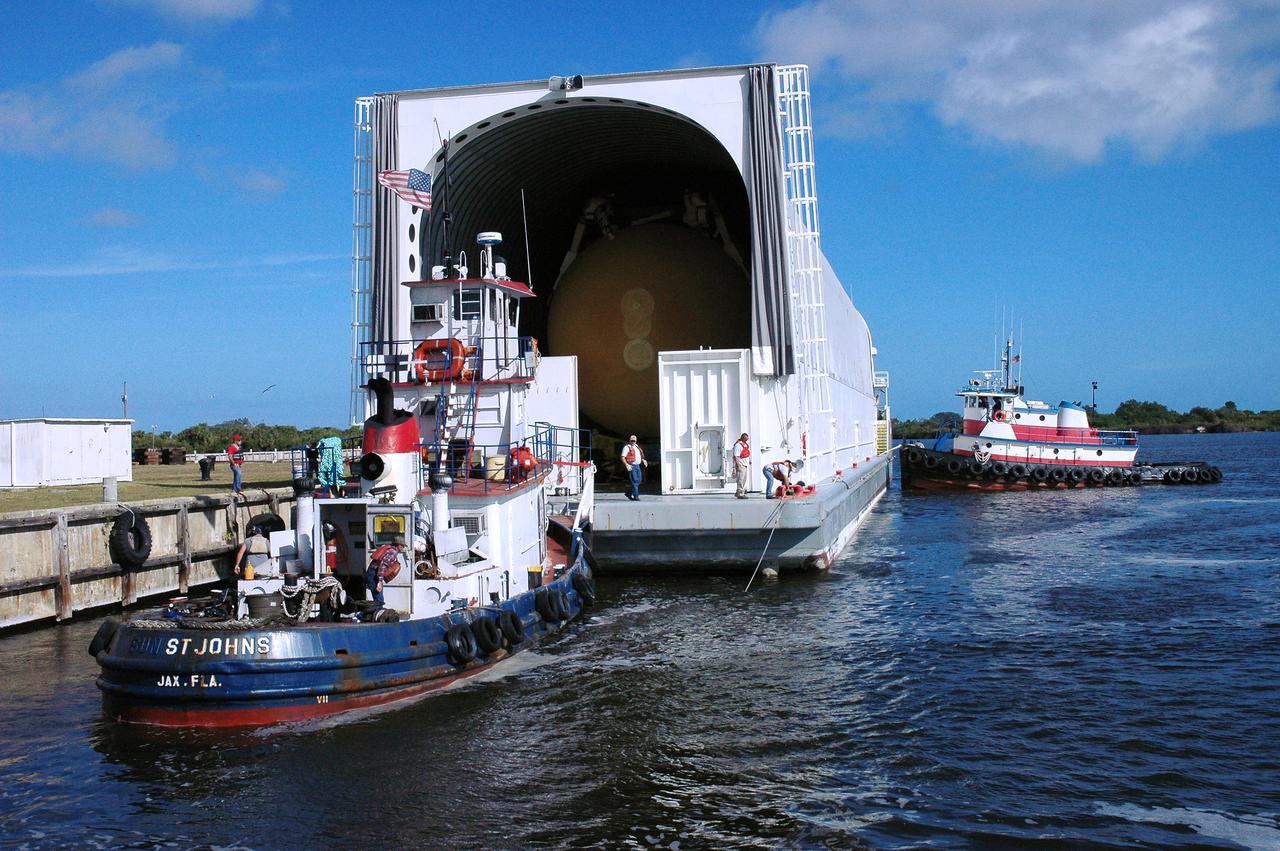

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Tugboats maneuver the barge carrying the newly redesigned External Tank (ET), designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, closer to the dock at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin. The ET can be seen inside the barge. The External Tank arrived safely early this morning at Port Canaveral, Fla., after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea. It departed from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Dec. 31 and was transported on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, pulled by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At the port, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
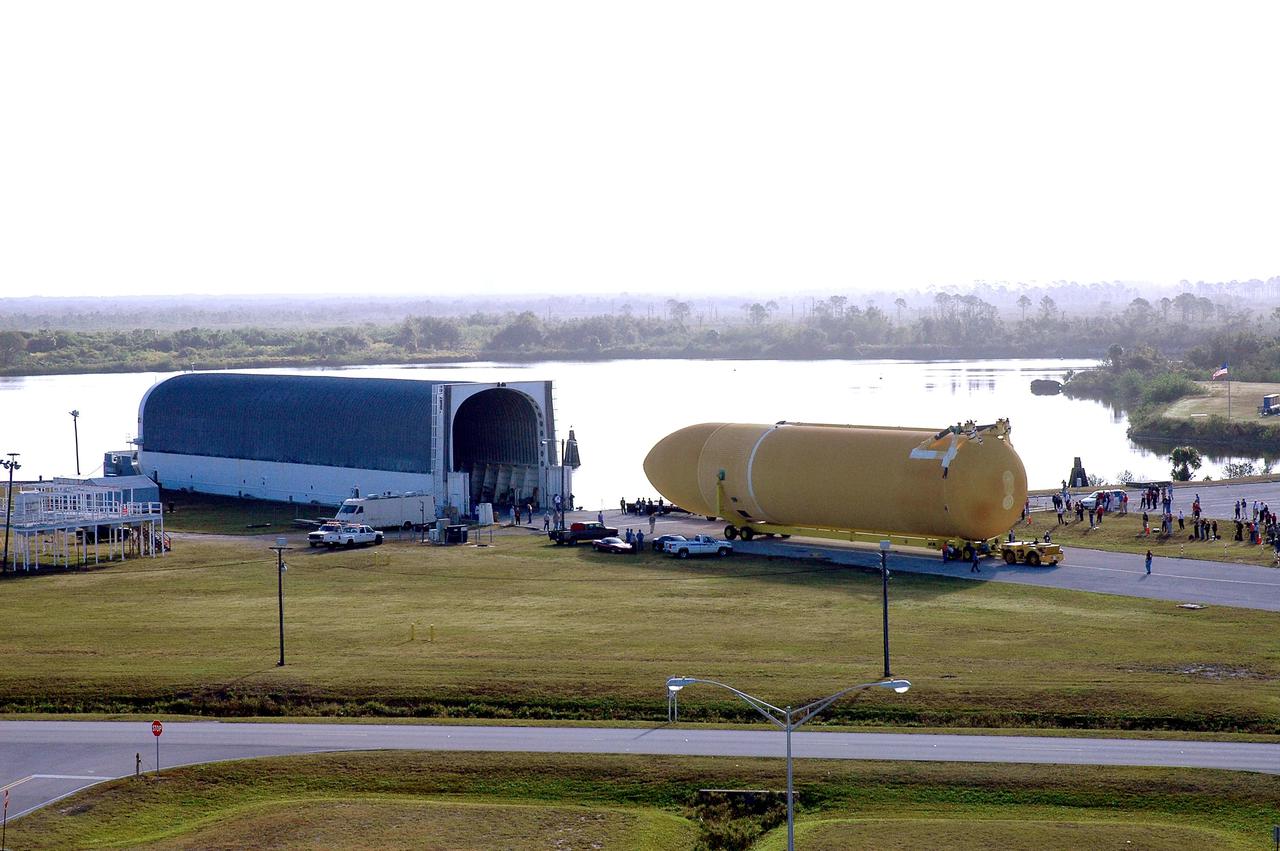

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Viewed from the roof of the Launch Control Center, the newly redesigned External Tank is seen after being off-loaded from NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, which delivered it from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank is being transferred to the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
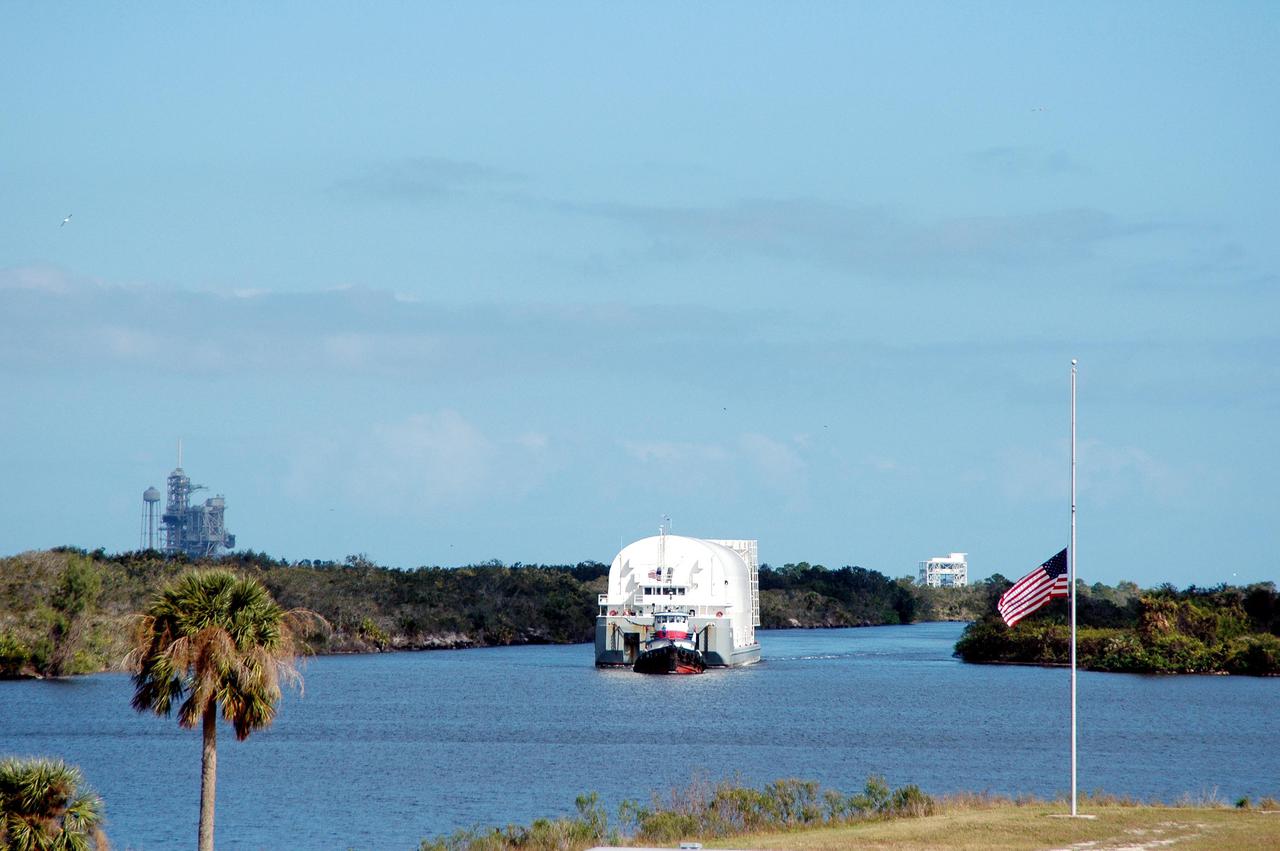

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank, designated for use on Return to Flight mission STS-114, moves slowly toward its destination, the dock at the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin, propelled by two tugboats. At left in the background is Launch Pad 39A. The External Tank arrived safely early this morning at Port Canaveral, Fla., after an approximately 900-mile journey at sea. It departed from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans Dec. 31 and was transported on the Pegasus, NASA’s specially designed barge, pulled by Solid Rocket Booster retrieval ship Liberty Star. At the port, the barge was then hooked up to the tugs for the last part of the journey to the Turn Basin. Next, the External Tank will be off-loaded from the barge and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for its final checkout and mating to the twin Solid Rocket Boosters and orbiter Discovery. NASA and Lockheed Martin Corp. spent nearly two years modifying the 15-story, bronze-colored tank to make it safer for liftoff. Among dozens of changes is a redesigned forward bipod fitting -- a design that meets the recommendation of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board to reduce the risk to the Space Shuttle from falling debris during ascent. STS-114 is targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
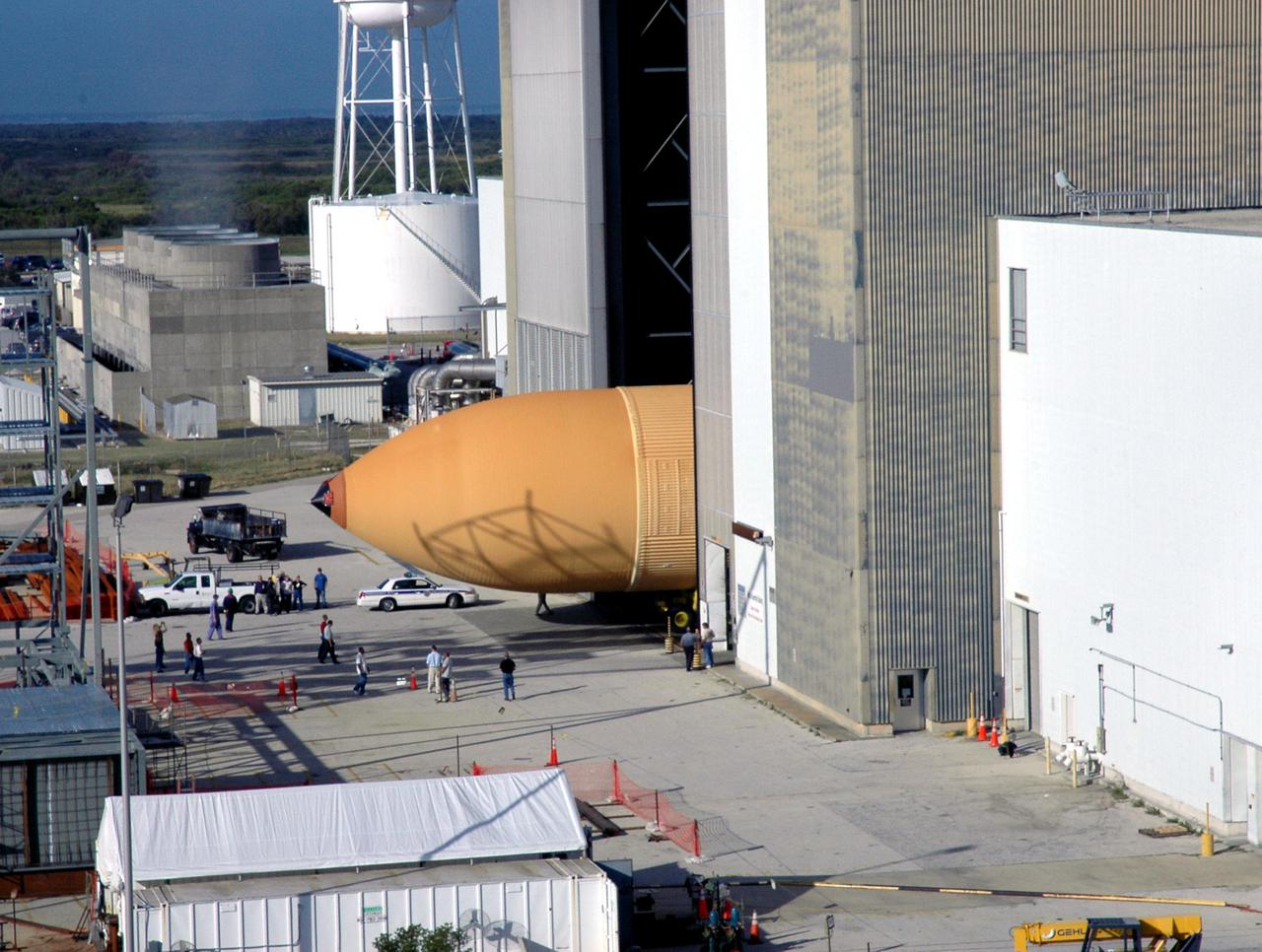

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Viewed from the roof of the Launch Control Center in the Launch Complex 39 Area, the newly redesigned External Tank disappears into the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
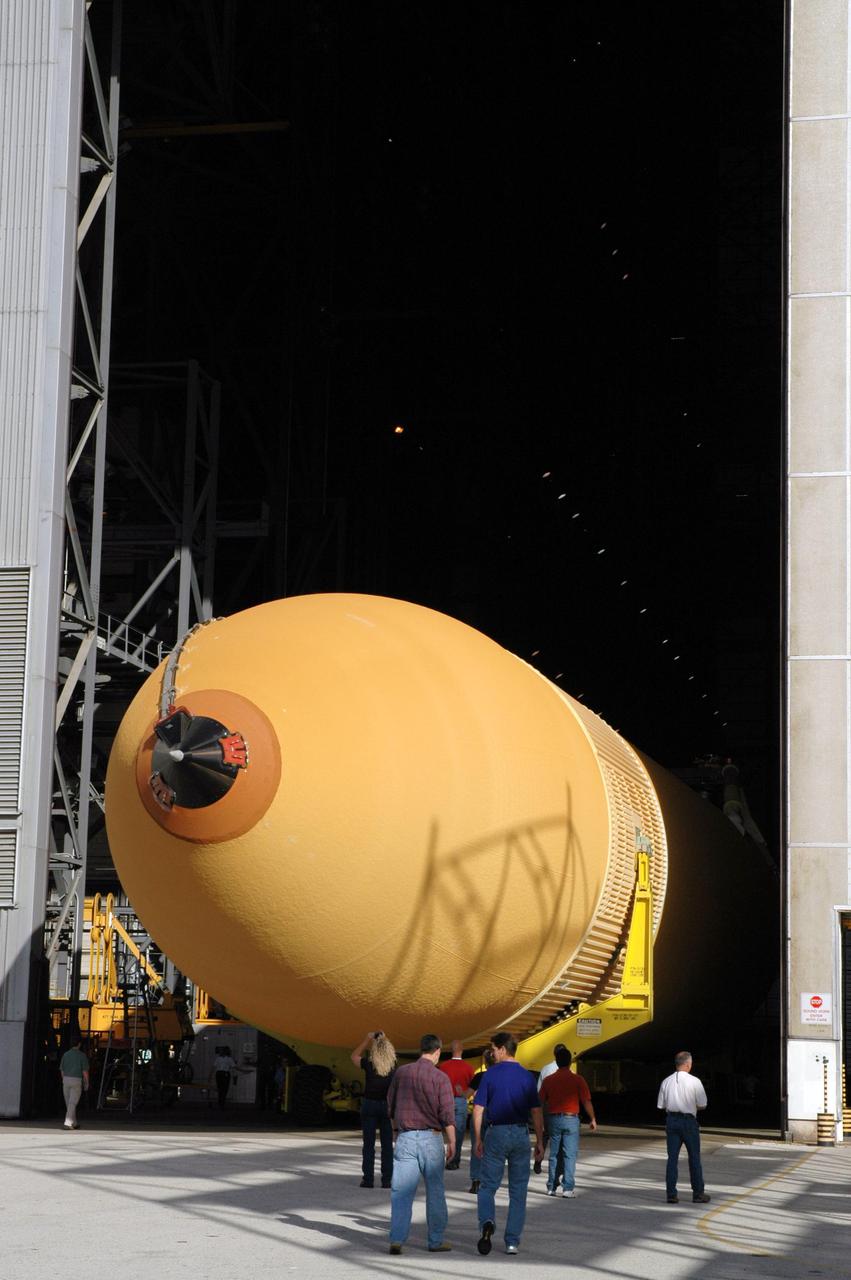
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Accompanied by KSC employees, the newly redesigned External Tank rolls into the Vehicle Assembly Building. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
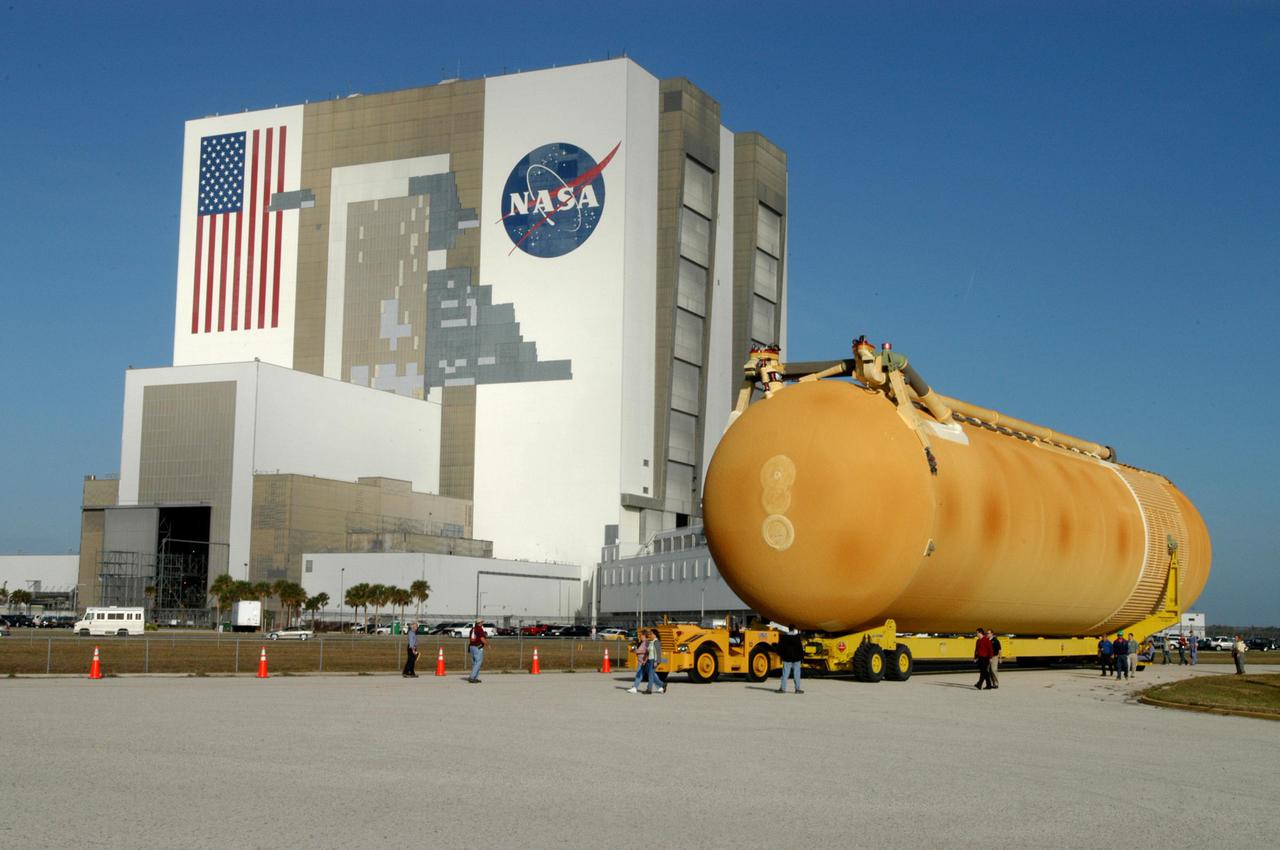

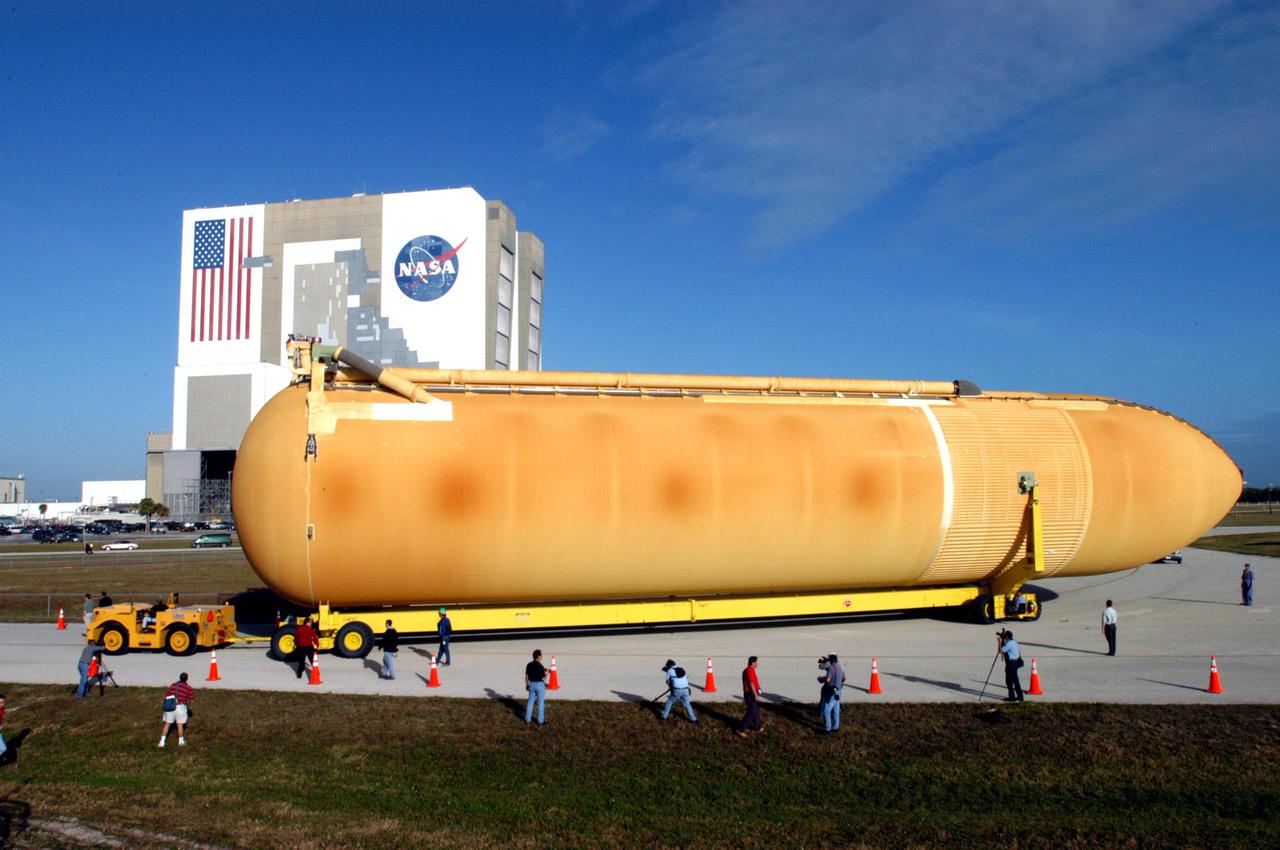
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank is slowly moved from the dock in the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen at left. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
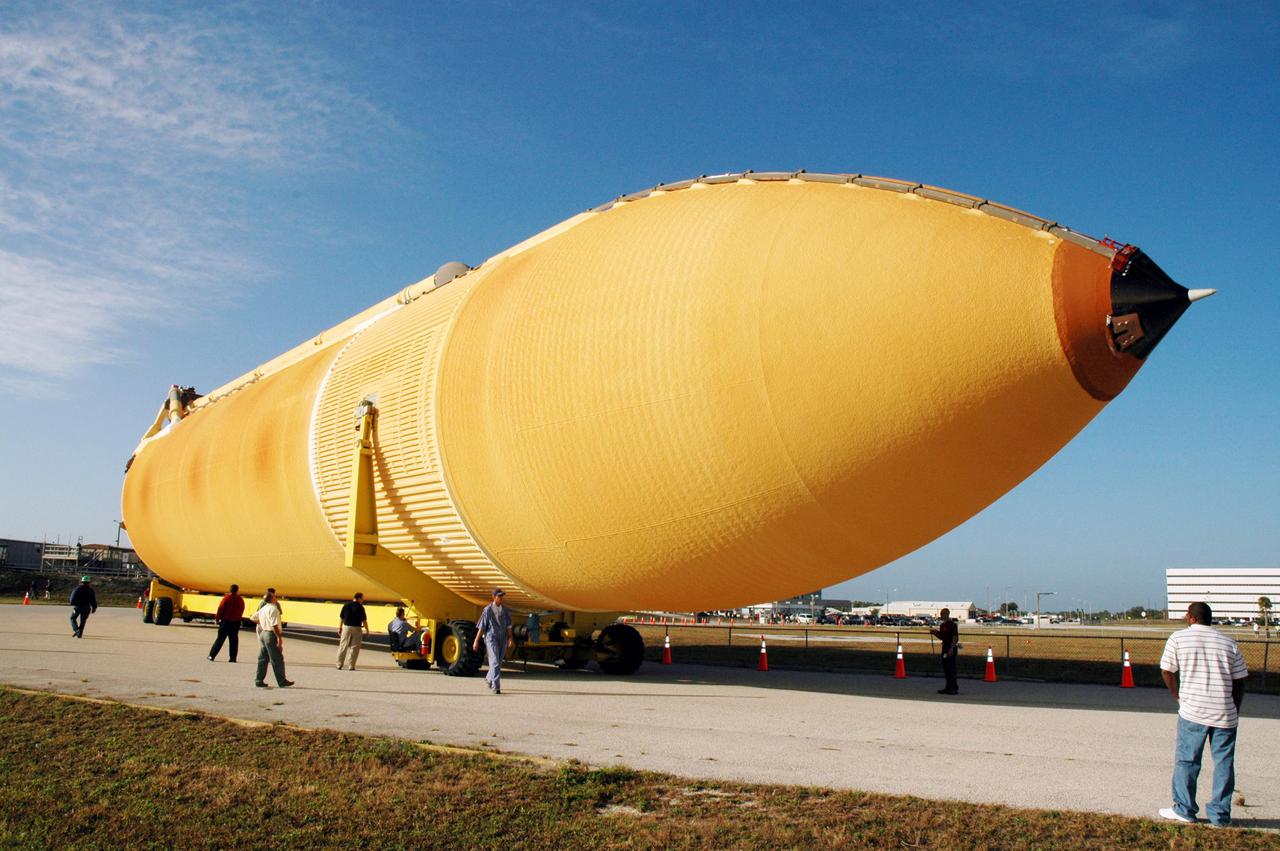

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank turns the corner of the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin parking area on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen at right. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
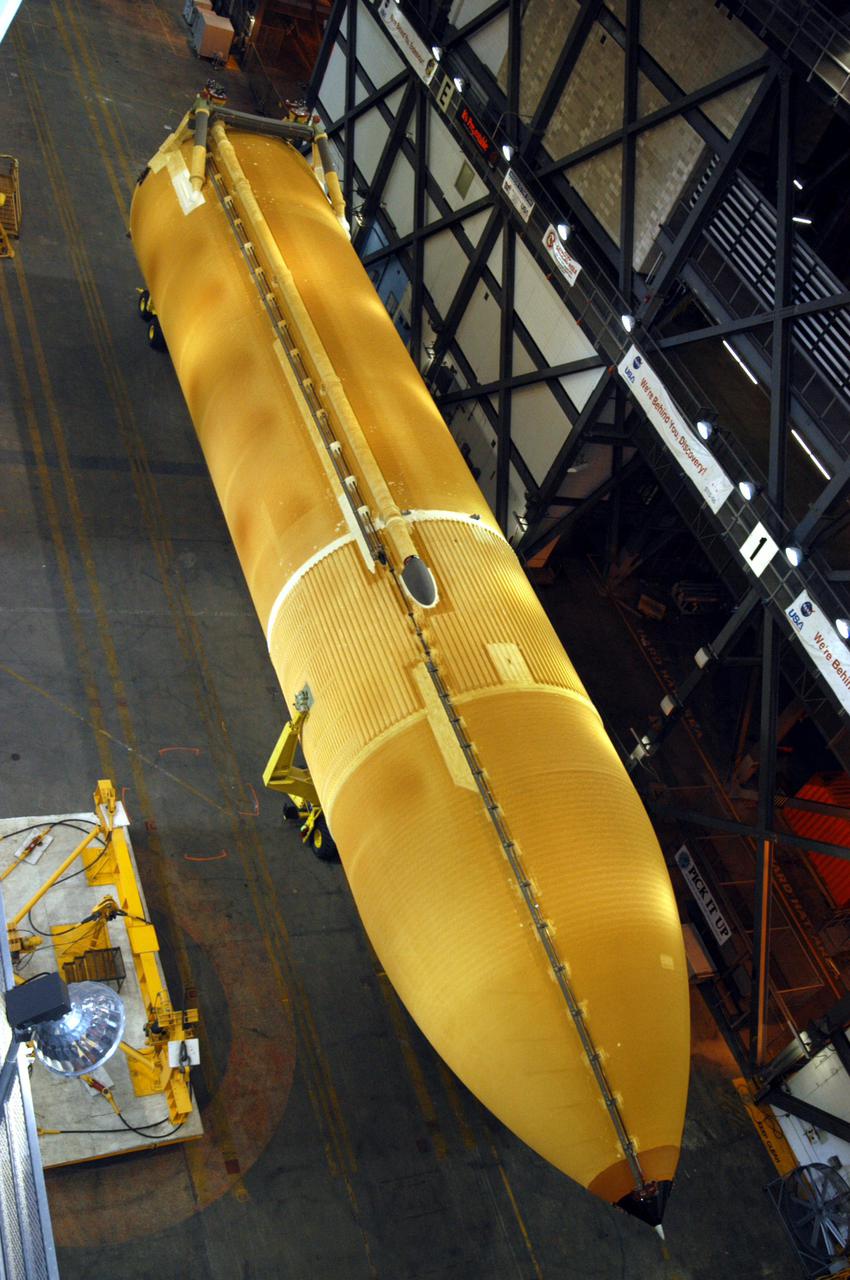

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, the redesigned External Tank to be used on Return to Flight mission STS-114 waits in the transfer aisle after its move from the barge in the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin. The tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from redesign of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform.
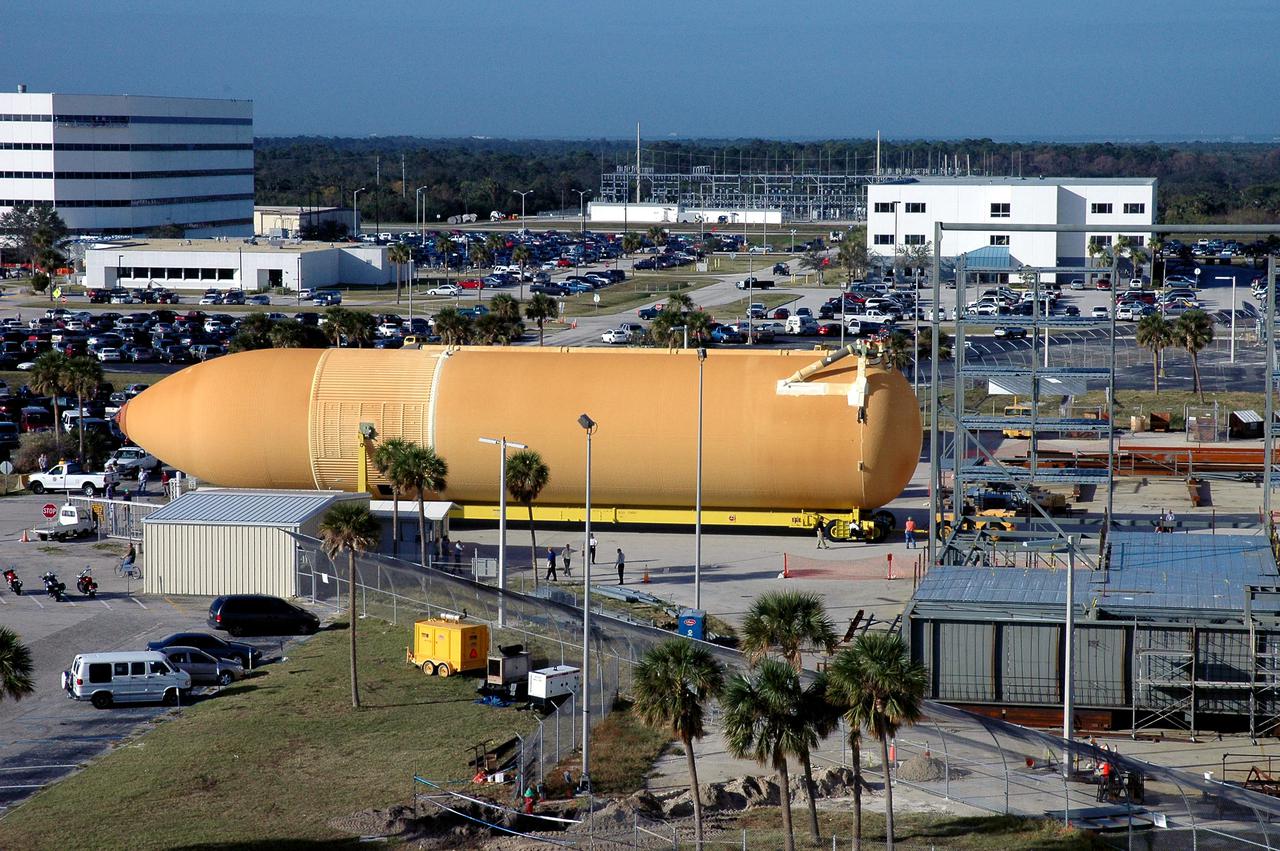

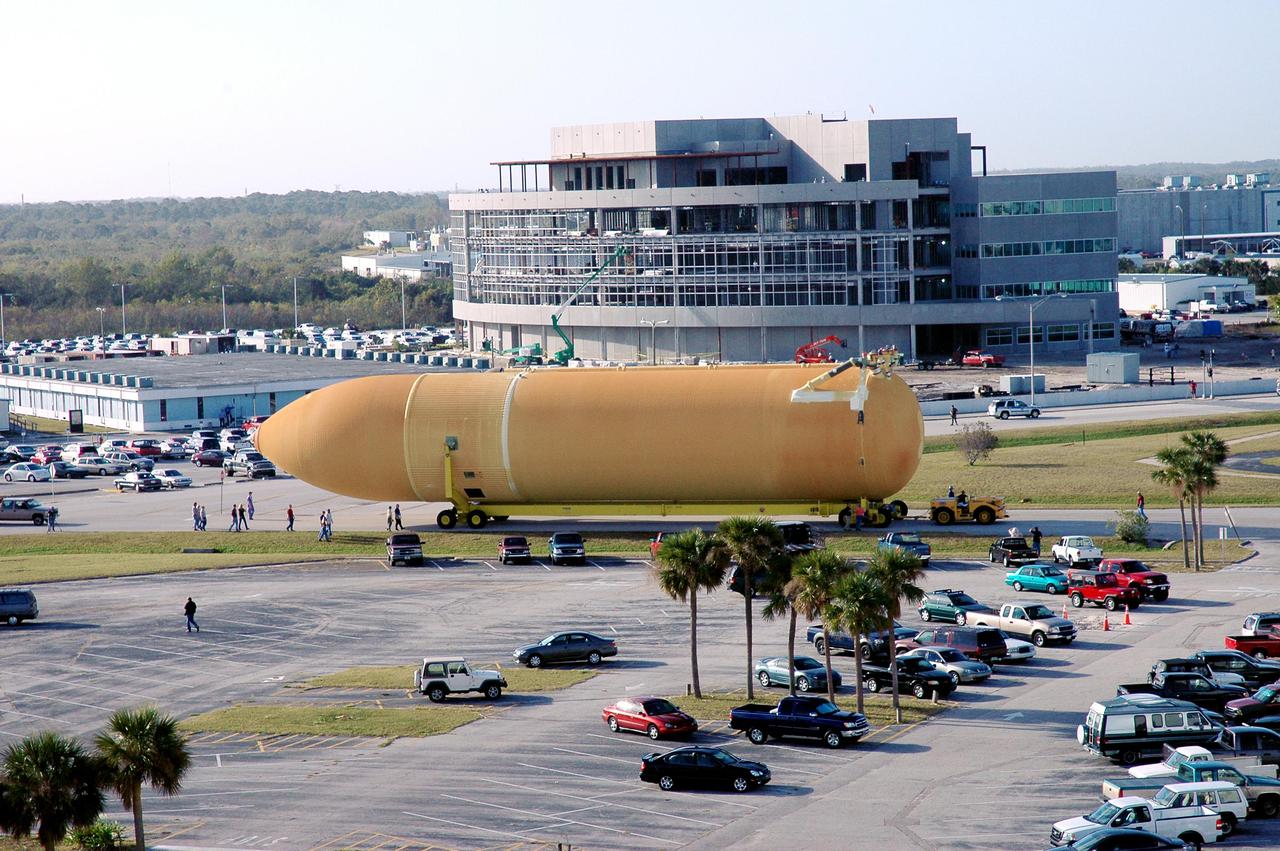
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Viewed from the roof of the Launch Control Center in the Launch Complex 39 Area, the newly redesigned External Tank is seen moving along the roadway on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the background, at left, is the Operations Support Building I. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
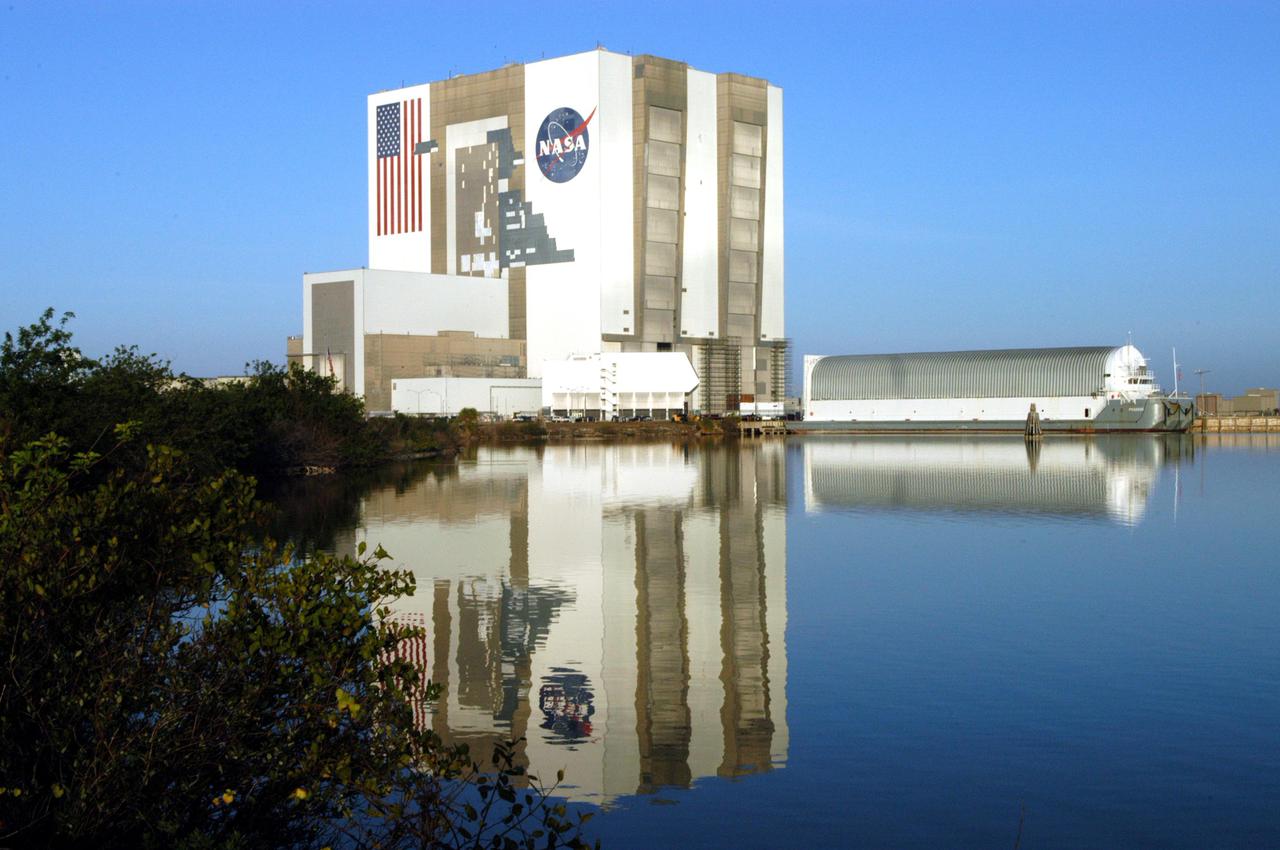

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, is docked in the Launch Complex 39 Area Turn Basin with its cargo of the newly redesigned External Tank. The barge was towed from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank will be off-loaded and transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen at left of the barge. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
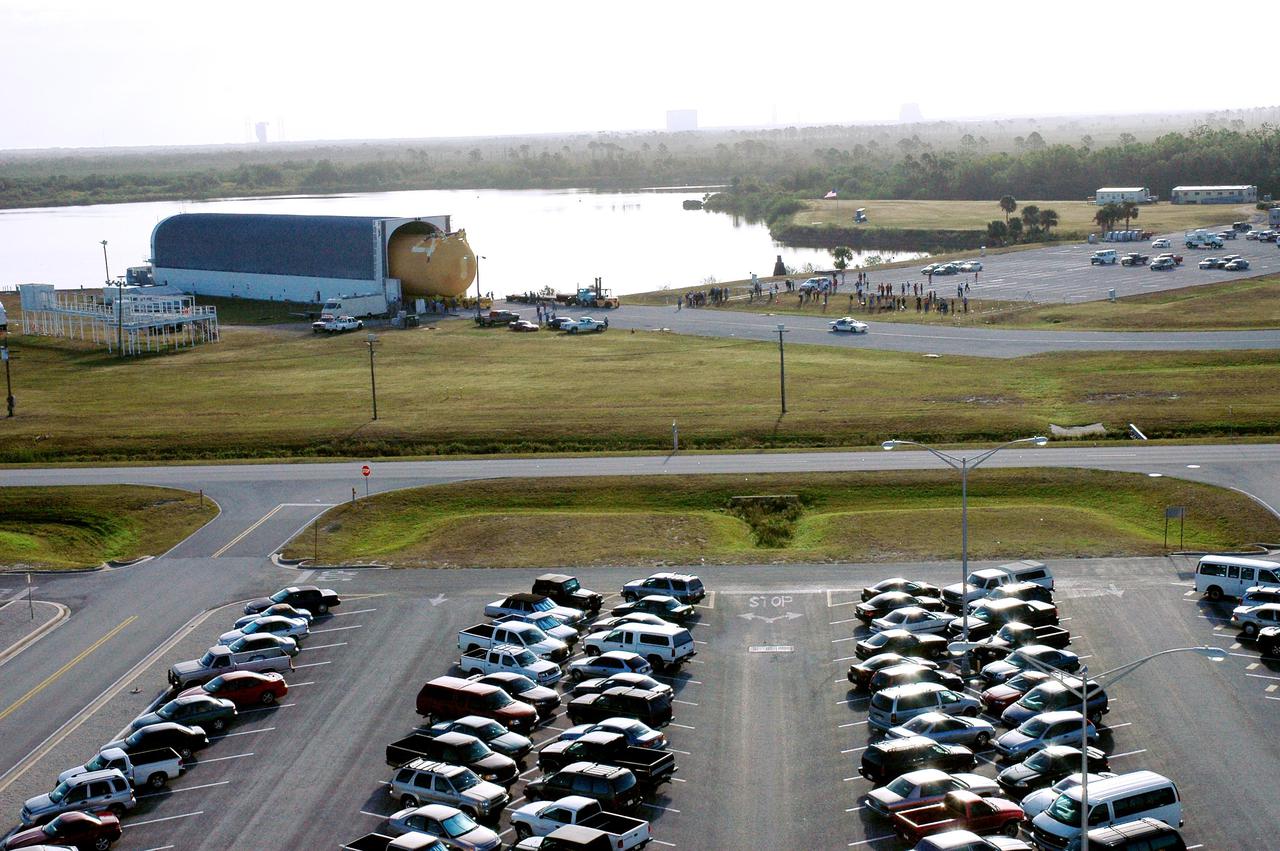

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Viewed from the top of the Launch Control Center, the newly redesigned External Tank is seen moving out of NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, which delivered it from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. The tank is being transferred to the Vehicle Assembly Building. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
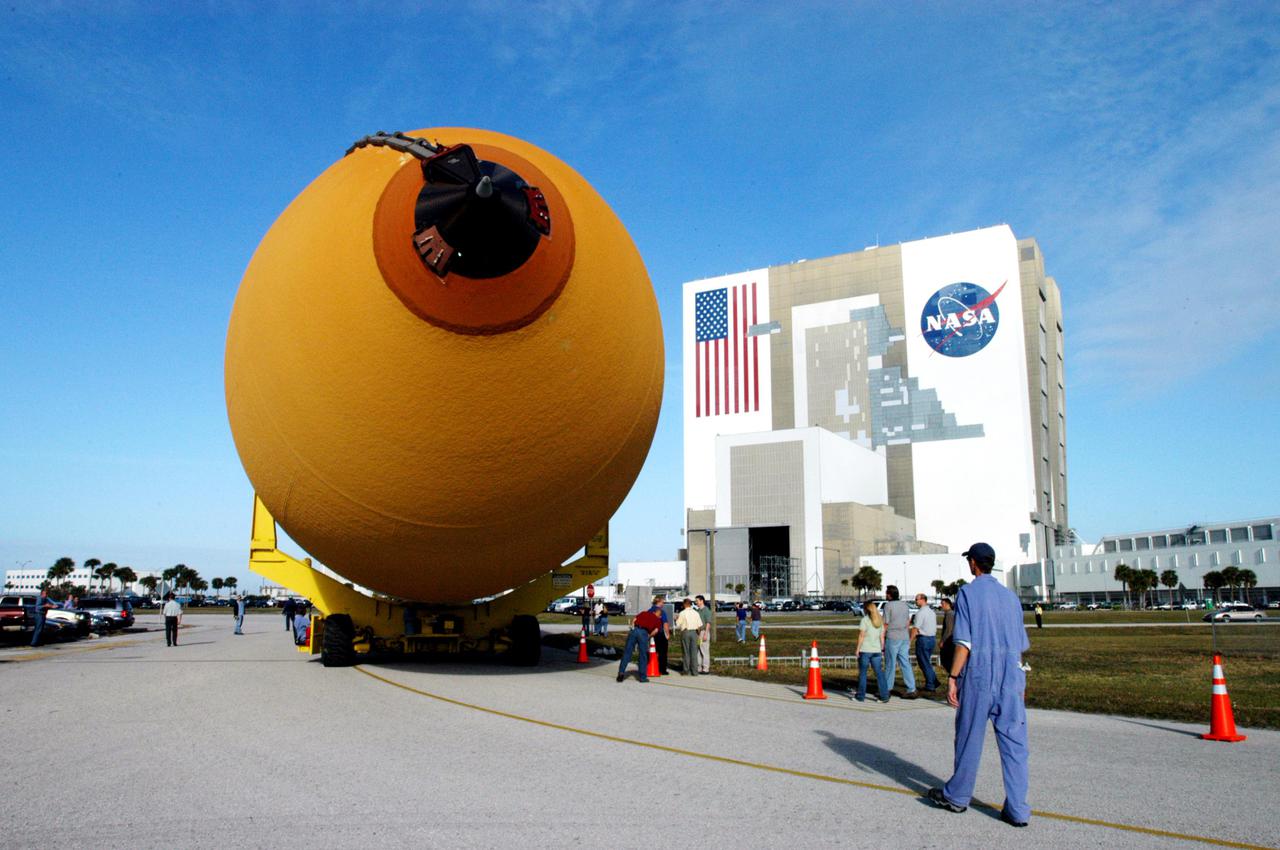

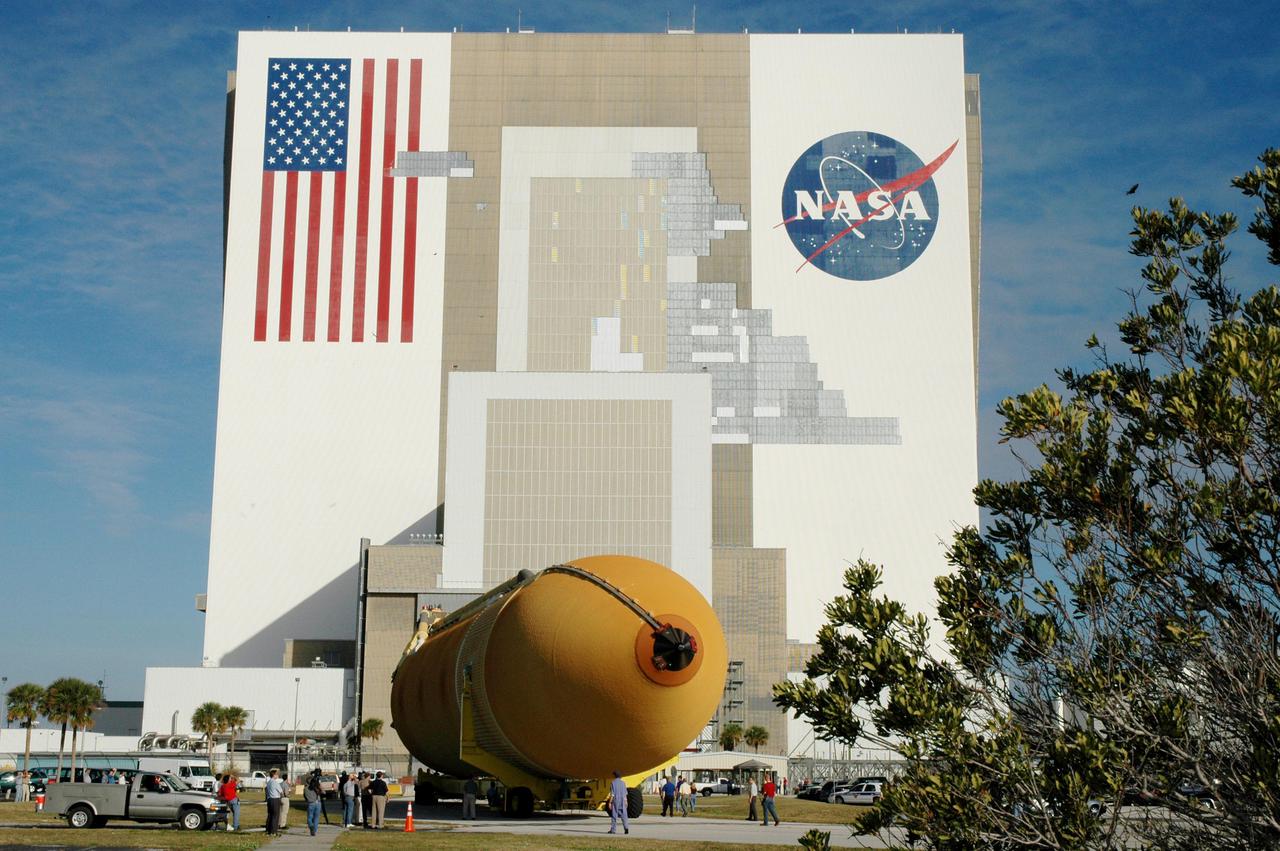
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank slowly moves toward the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen at right. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
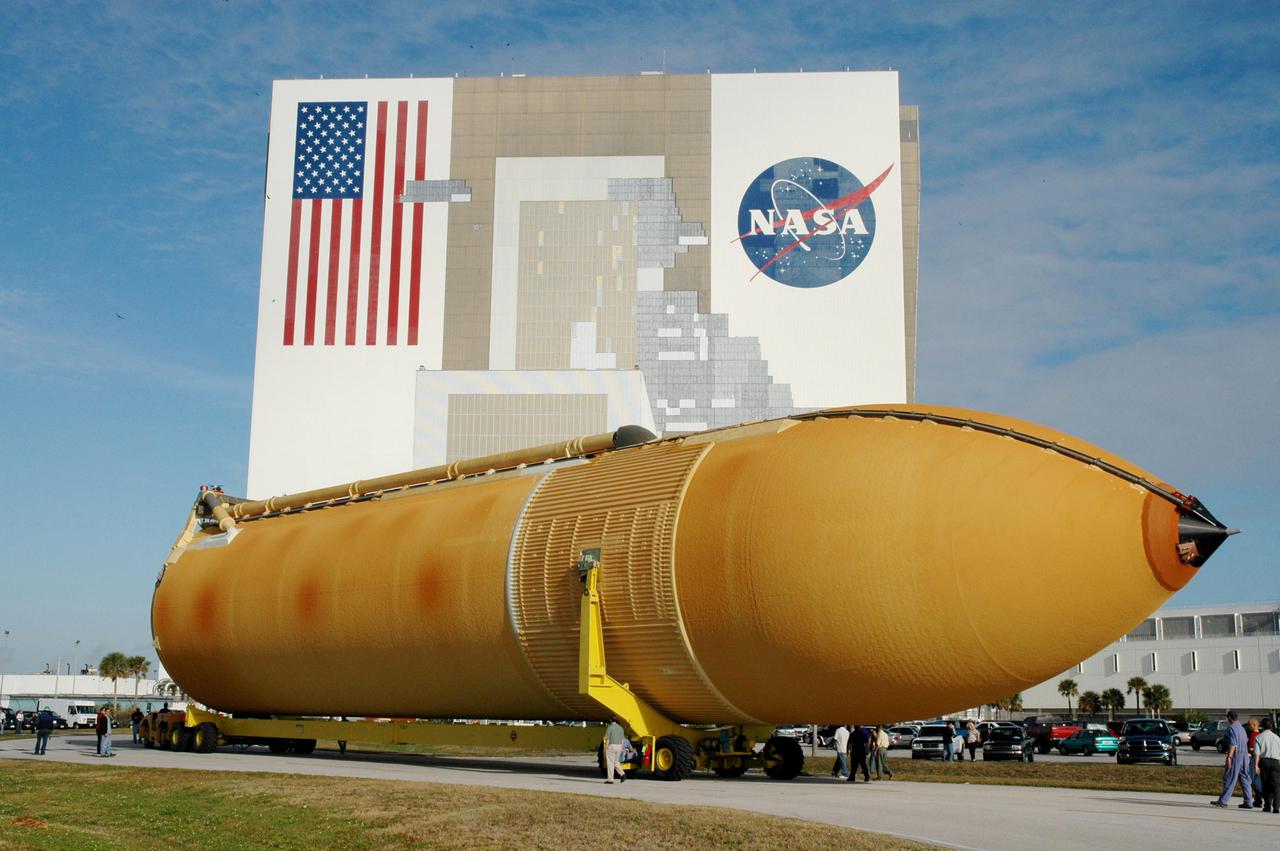

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The newly redesigned External Tank moves closer to its destination, the Vehicle Assembly Building, seen behind it. The tank arrived Jan. 5 after a 900-mile sea voyage aboard NASA’s specially designed barge, Pegasus, from the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. In the transfer aisle of the VAB, the tank will be raised from a horizontal to a vertical position, then lifted high up into a storage cell, or “checkout cell,” where it will undergo inspections of the mechanical, electrical and thermal protection systems. New processing activities resulting from re-design of the tank include inspection of the bipod heater and External Tank separation camera, which includes charging the camera batteries. The tank will be then prepared for mating to the Solid Rocket Boosters. When preparations are complete, the tank will be lifted from the checkout cell, moved across the transfer aisle and into High Bay 1, where it will be lowered and attached to the boosters, which are sitting on the Mobile Launch Platform. The tank is designated for the Return to Flight mission, STS-114, targeted for a launch opportunity beginning in May. The seven-member Discovery crew will fly to the International Space Station primarily to test and evaluate new procedures for flight safety, including Space Shuttle inspection and repair techniques.
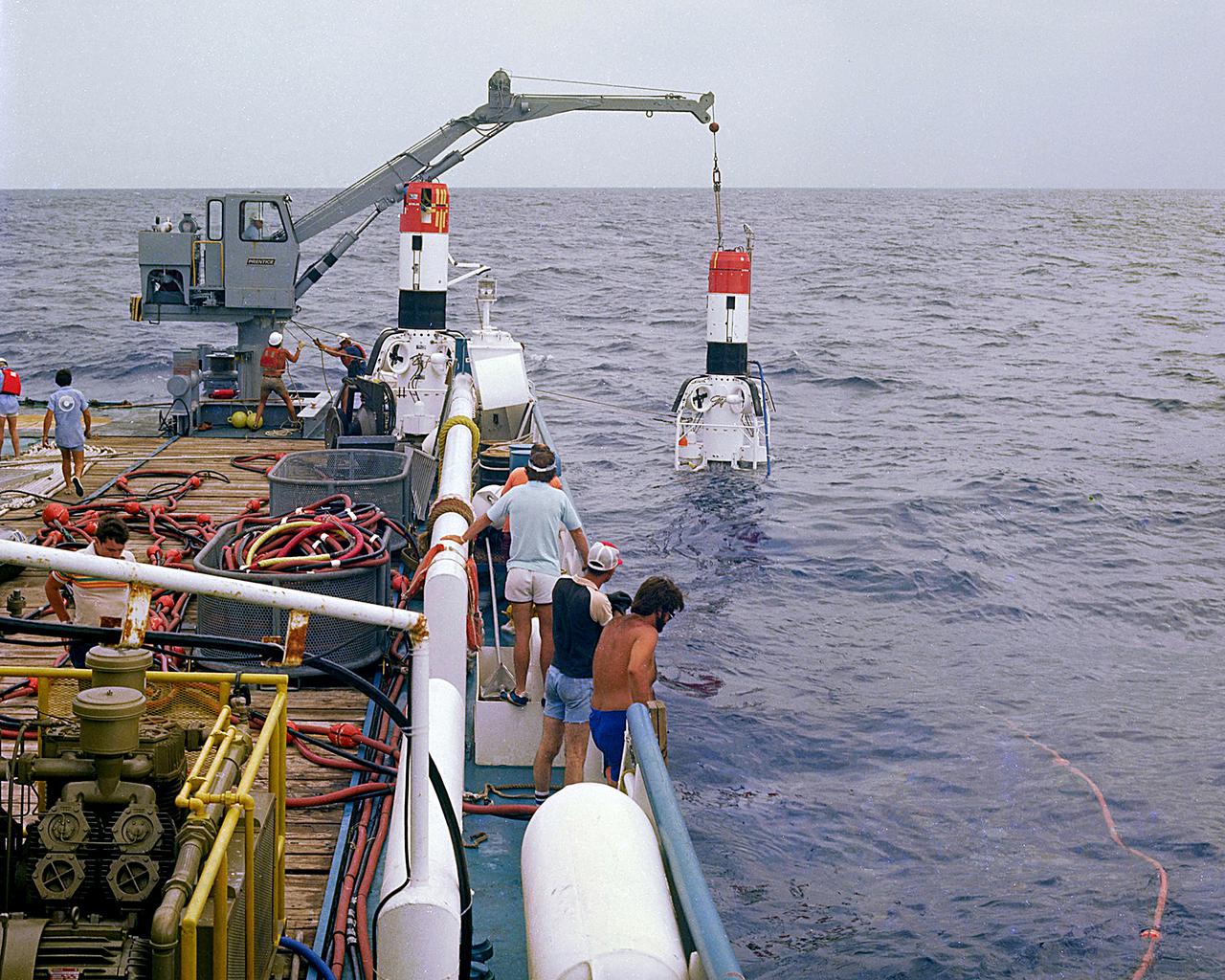

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Shuttle SRB retrieval acceptance test at sea.
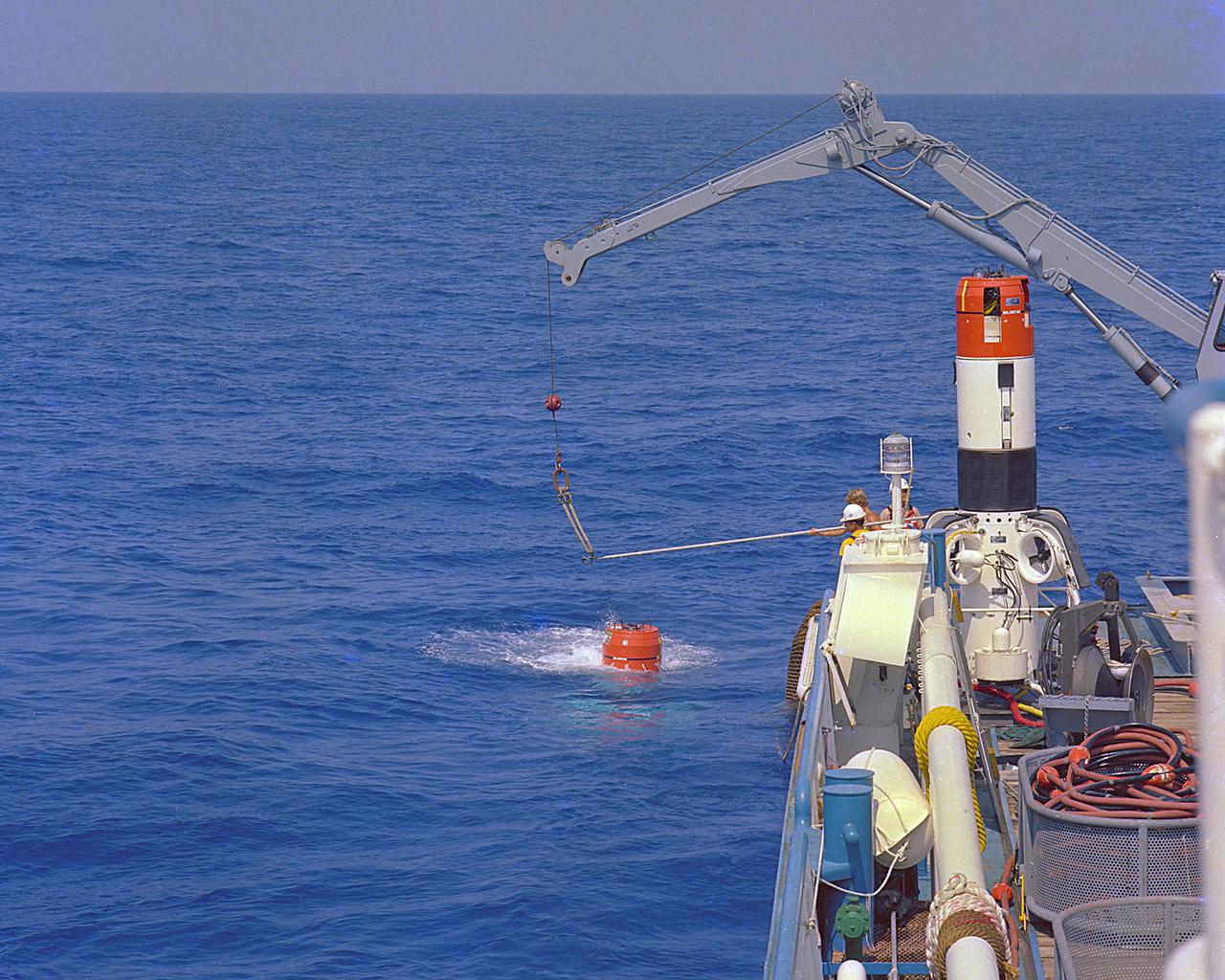

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Shuttle SRB retrieval acceptance test at sea.