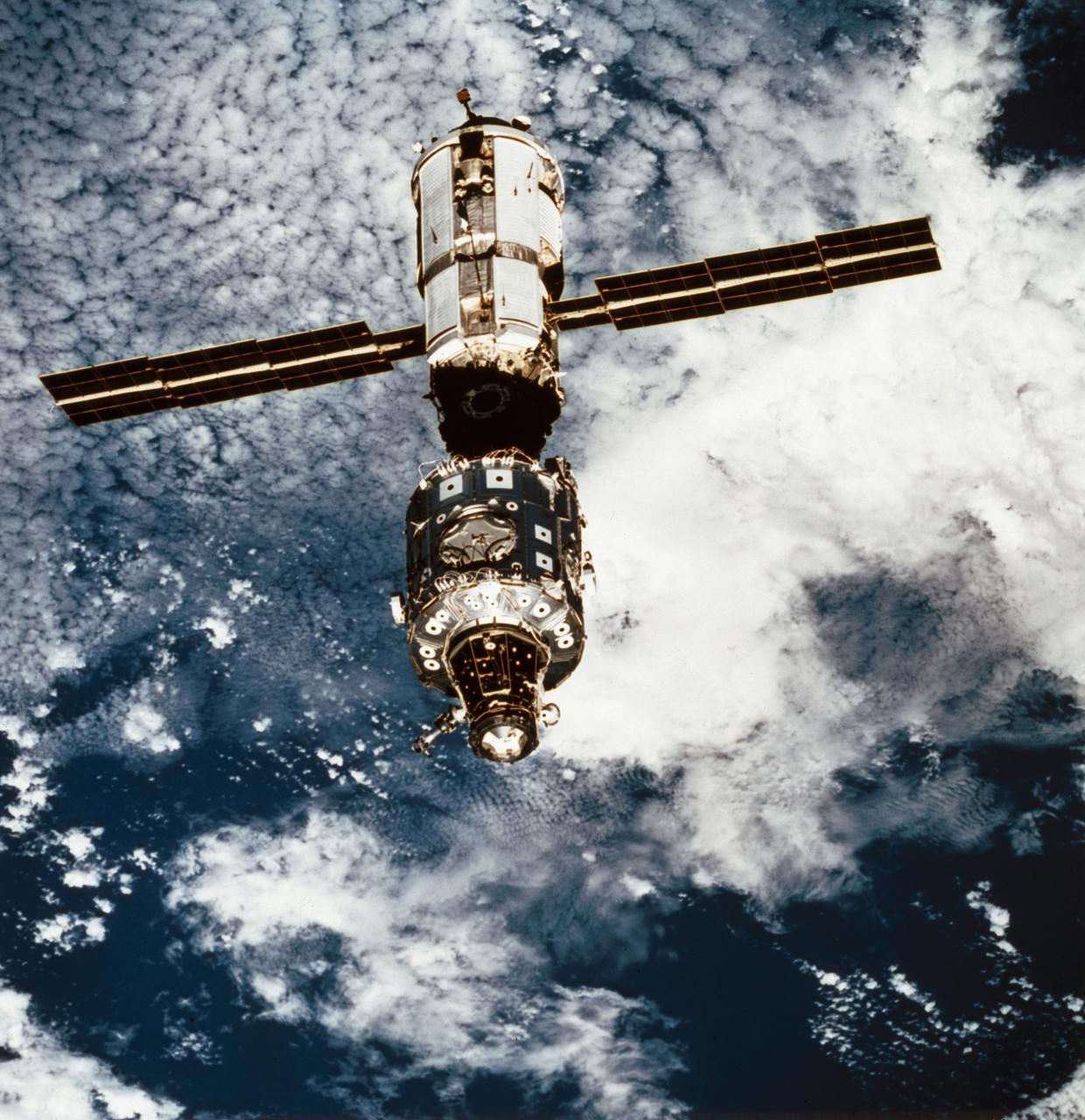

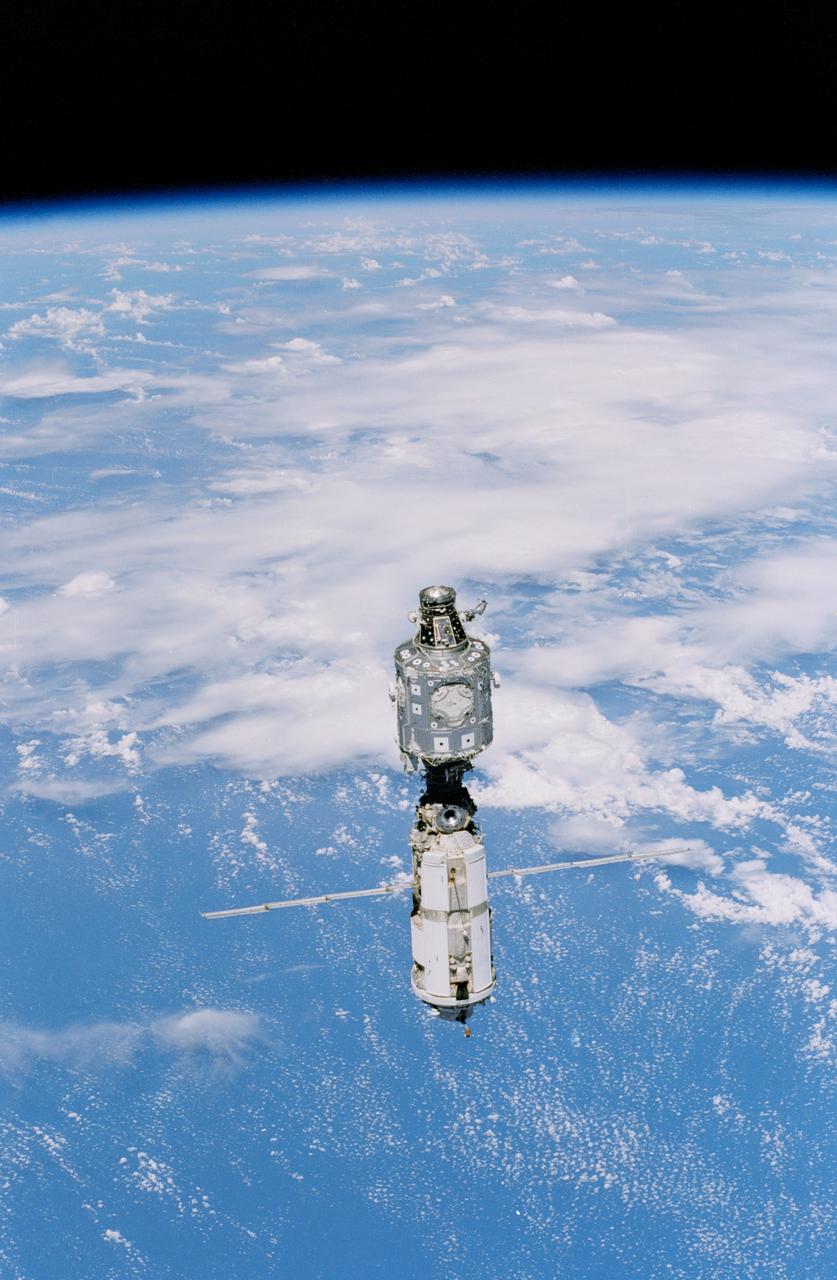
This STS-96 onboard photo of the International Space Station (ISS) was taken from Orbiter Discovery during a fly-around following separation of the two spacecraft. STS-96, the second Space Station assembly and resupply flight, launched on May 27, 1999 for an almost 10 day mission. The Shuttle's SPACEHAB double module carried internal and resupply cargo for station outfitting. Evident in the photo is the newly mounted Russian cargo crane, known as STRELA, which was carried aboard the shuttle in the integrated Cargo Carrir (ICC). The STS-96 flight was the first to perform docking with the ISS.
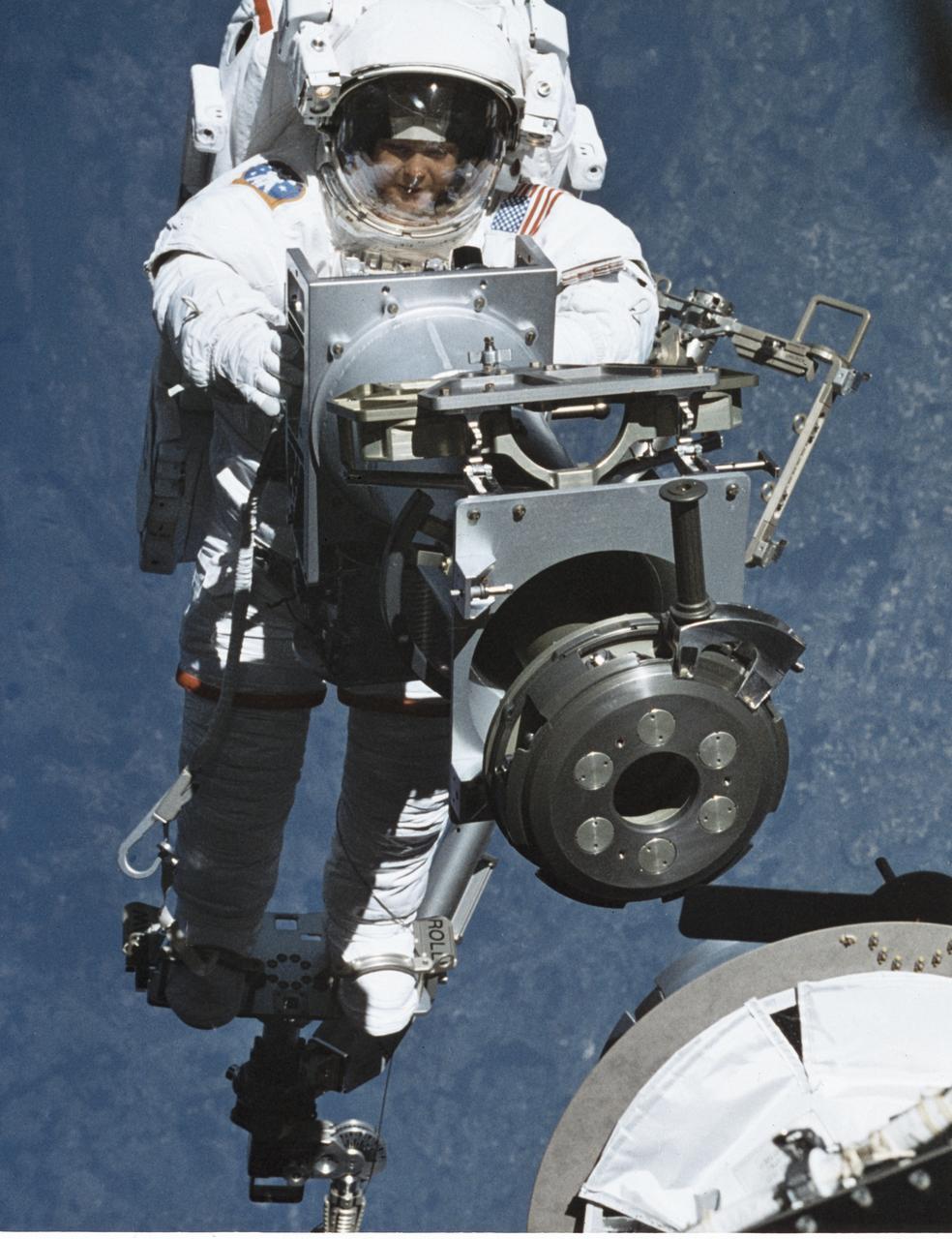

The STS-96 mission, the second International Space Station (ISS) assembly and resupply flight, launched on May 27, 1999 aboard the Orbiter Discovery for an almost 10 day mission. The Shuttle's SPACEHAB double module carried internal and resupply cargo for station outfitting and the Russian cargo crane, STRELA, was carried aboard the shuttle in the integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC). In this STS-96 onboard photo of the first Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA), Mission Specialist Tamara Jernigan totes part of the Russian built crane. Jernigans' feet are anchored on a mobile foot restraint cornected to the Shuttle's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) operated by Mission Specialist Ellen Ochoa. The STS-96 flight was the first to perform docking with the ISS.

S96-E-5020 (30 May 1999) --- Astronaut Tamara Jernigan, backdropped against terrain, totes part of a Russian-built crane, called Strela (a Russian word meaning "arrow"). Jernigan's feet are anchored on a mobile foot restraint connected to Discovery's remote manipulator sytsem (RMS). Astronauts Jernigan and Daniel T. Barry went on to spend over seven hours on the space walk. The photo was recorded with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 06:36:22 GMT, May 30, 1999.
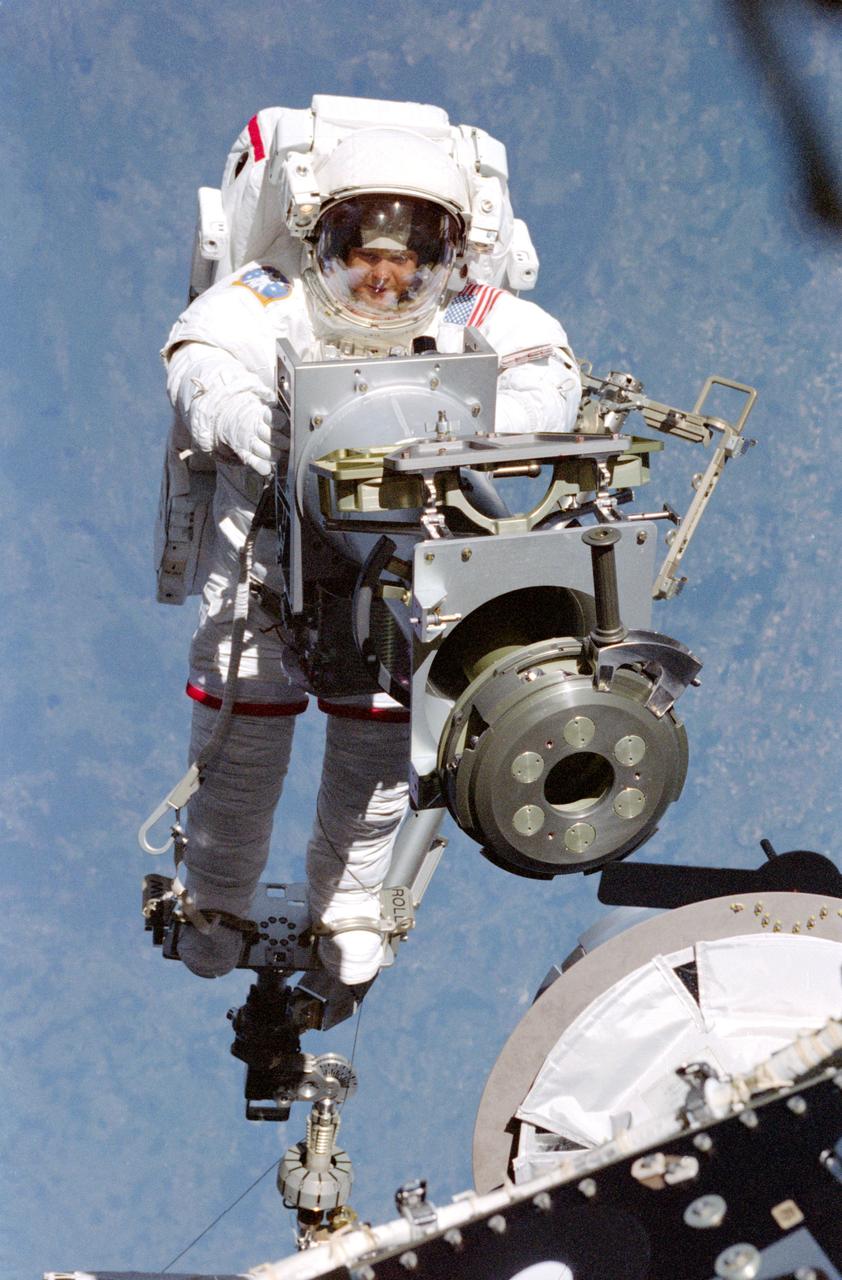

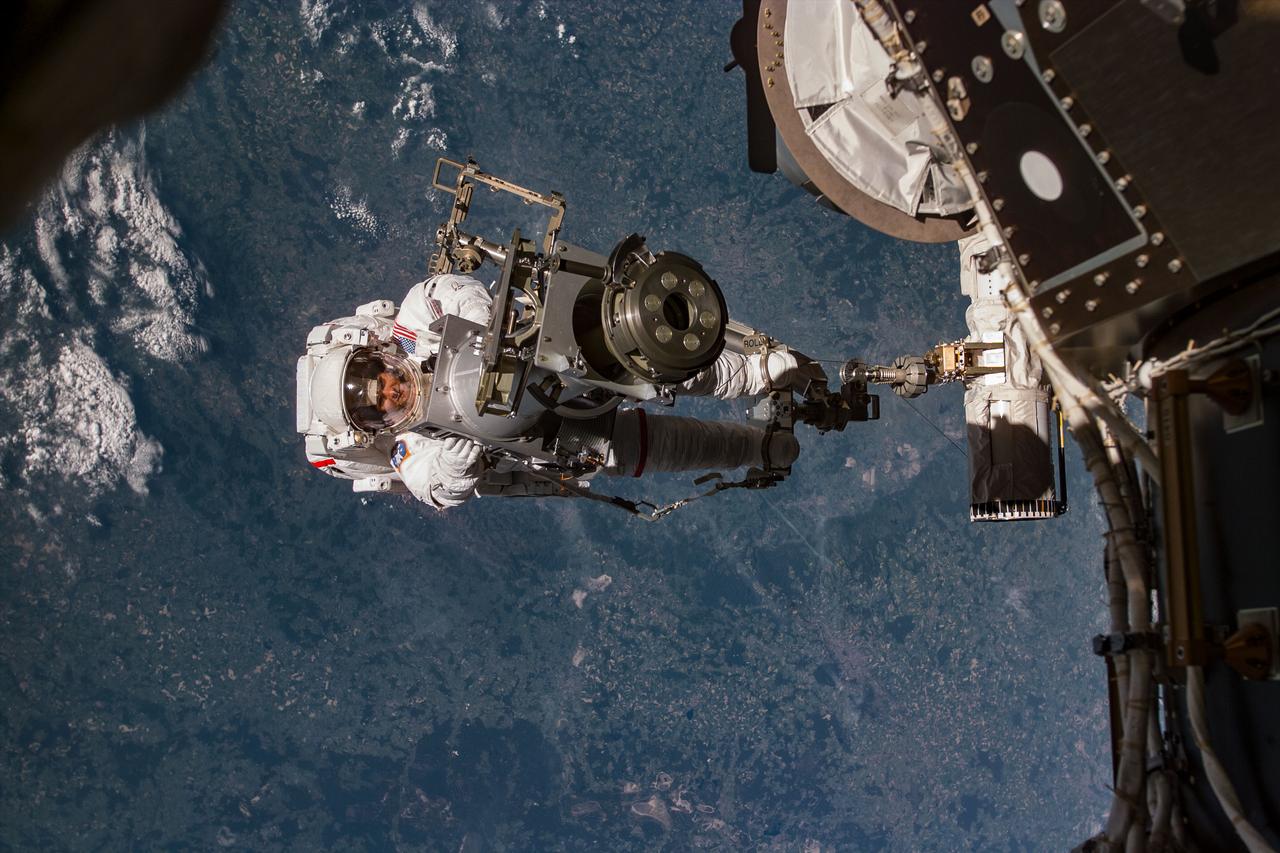
STS096-357-003 (30 May 1999) --- Astronaut Tamara E. Jernigan, backdropped against terrain some 173 nautical miles beneath Discovery, totes part of a Russian-built crane, called Strela (a Russian word meaning "arrow"). Jernigan's feet are anchored on a mobile foot restraint connected to the shuttle's remote manipulator system (RMS). Astronauts Jernigan and Daniel T. Barry eventually spent over seven hours on the space walk.
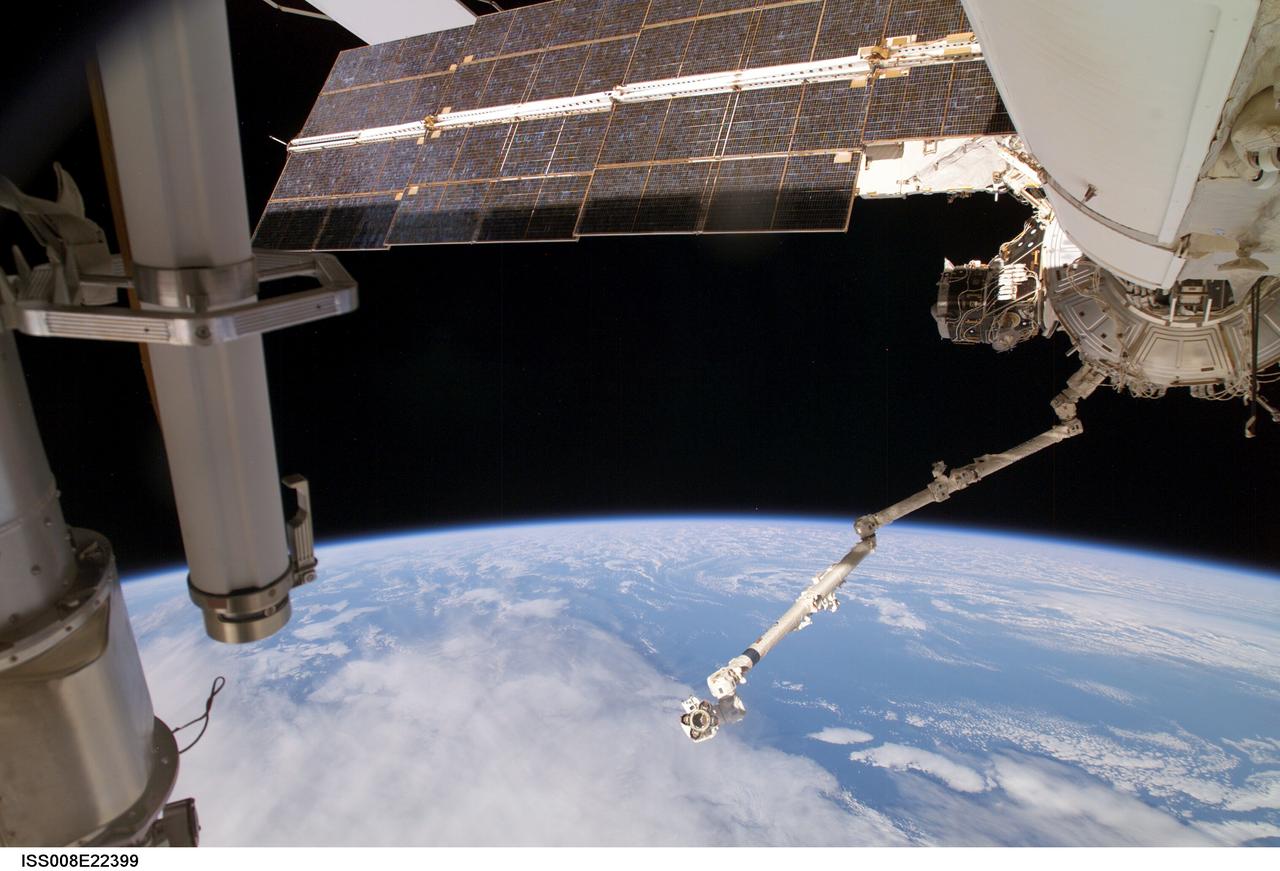

ISS008-E-22399 (28 February 2004) --- This view, taken during Expedition 8 extravehicular activity (EVA), shows the Strela Cargo Boom at left; and the functional cargo block (FGB) or Zarya; Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA-3); Destiny laboratory and Canadarm2, or Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS), at right, backdropped against Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space.
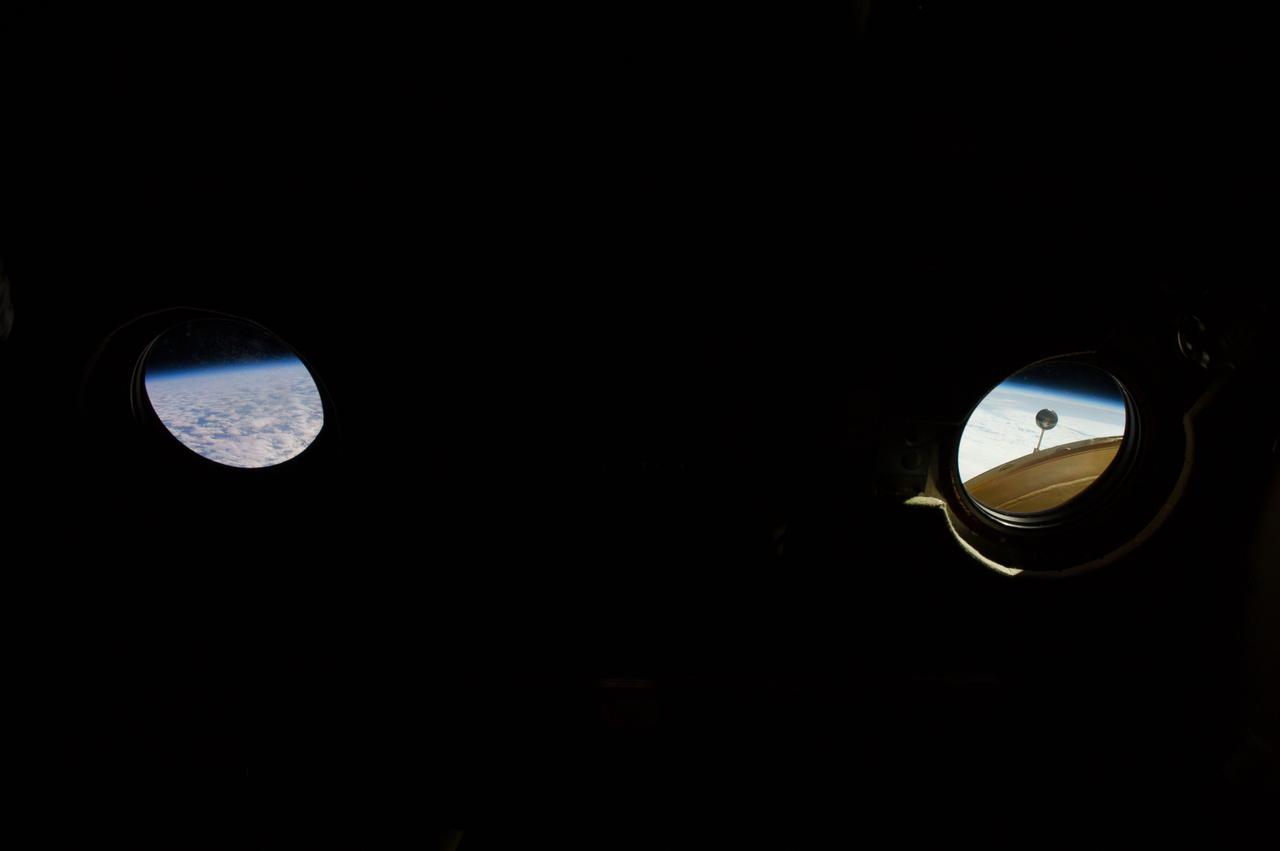

ISS039-E-000021 (11 March 2014) --- With darkness in the Zvezda Service Module, the view outside two windows in the module photographed in the early hours of Expedition 39, an Earth horizon (left) and portions of the Pirs Docking Compartment are visible. In the right window, part of a Strela crane and part of an antenna, both attached to the Pirs, can be seen.
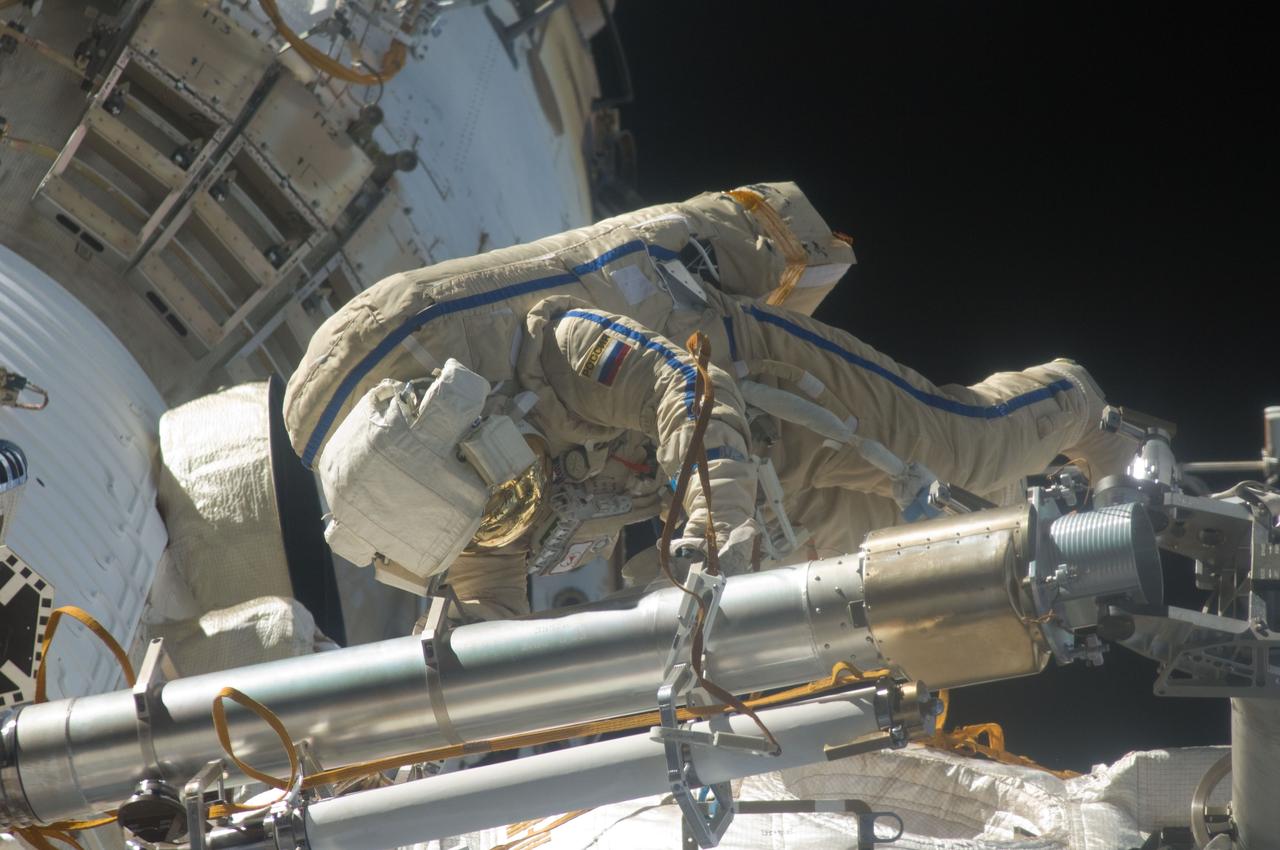

ISS028-E-020924 (3 Aug. 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Sergei Volkov and Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), both Expedition 28 flight engineers, attired in Russian Orlan spacesuits, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Russian segment of the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 23-minute spacewalk, Volkov and Samokutyaev moved a cargo boom from one airlock to another, installed a prototype laser communications system and deployed an amateur radio micro-satellite.
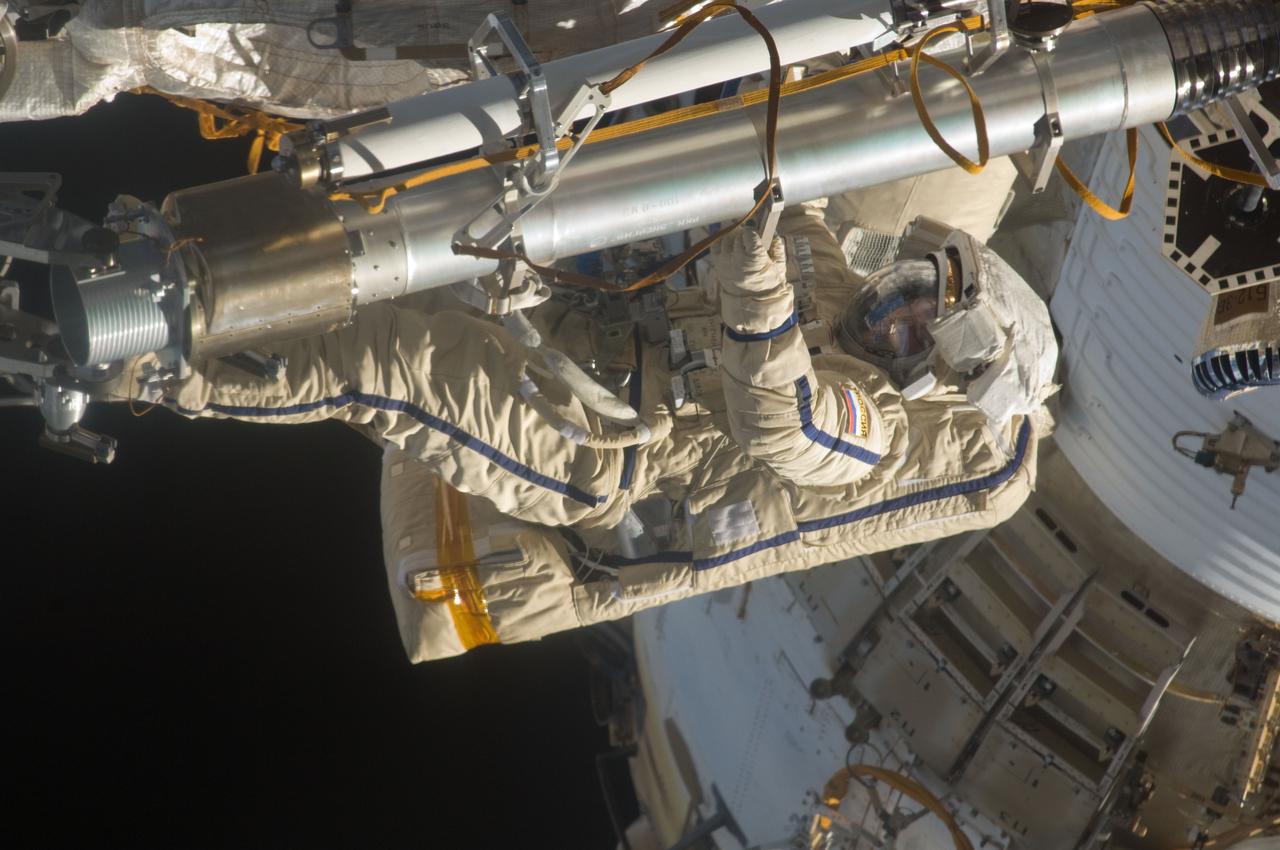

ISS028-E-020911 (3 Aug. 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Sergei Volkov and Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), both Expedition 28 flight engineers, attired in Russian Orlan spacesuits, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Russian segment of the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 23-minute spacewalk, Volkov and Samokutyaev moved a cargo boom from one airlock to another, installed a prototype laser communications system and deployed an amateur radio micro-satellite.
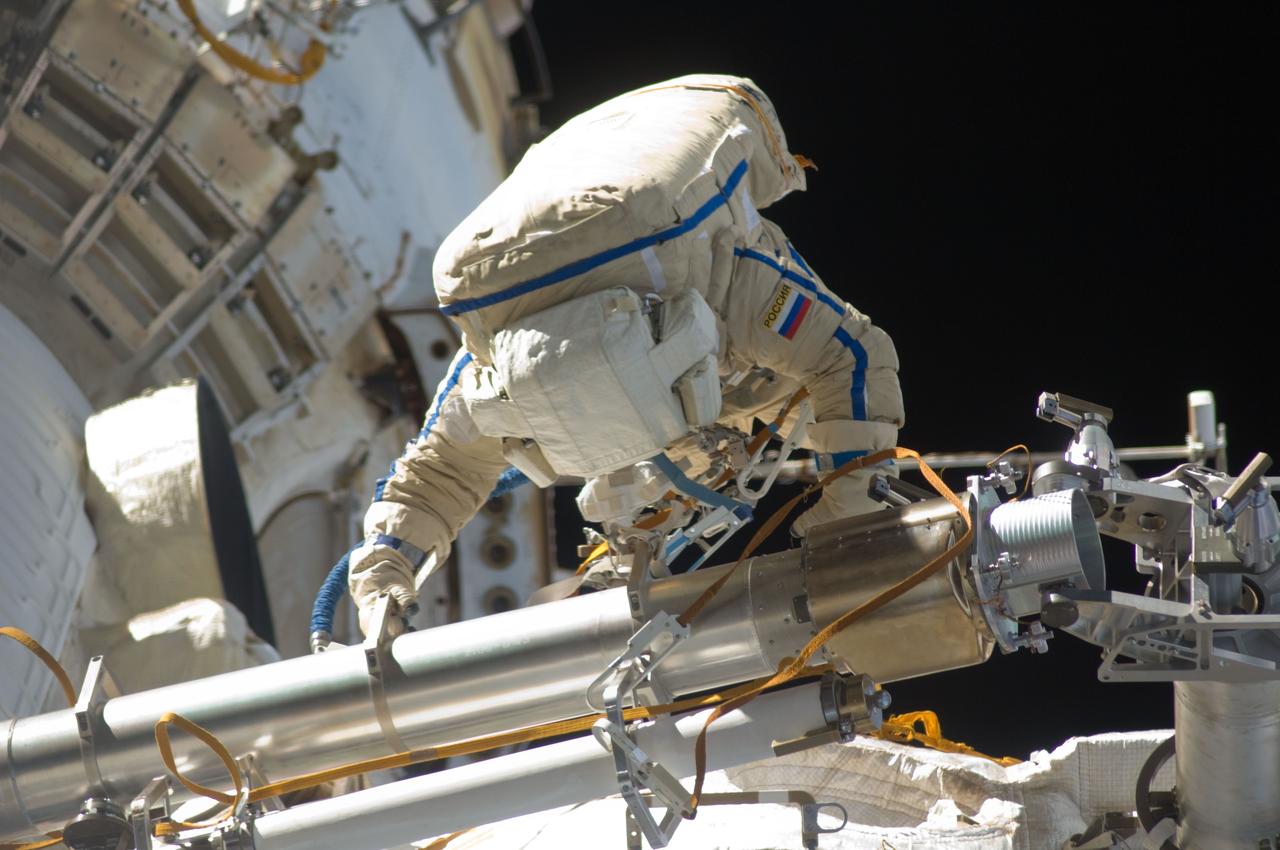

ISS028-E-020926 (3 Aug. 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Sergei Volkov and Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), both Expedition 28 flight engineers, attired in Russian Orlan spacesuits, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Russian segment of the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 23-minute spacewalk, Volkov and Samokutyaev moved a cargo boom from one airlock to another, installed a prototype laser communications system and deployed an amateur radio micro-satellite.
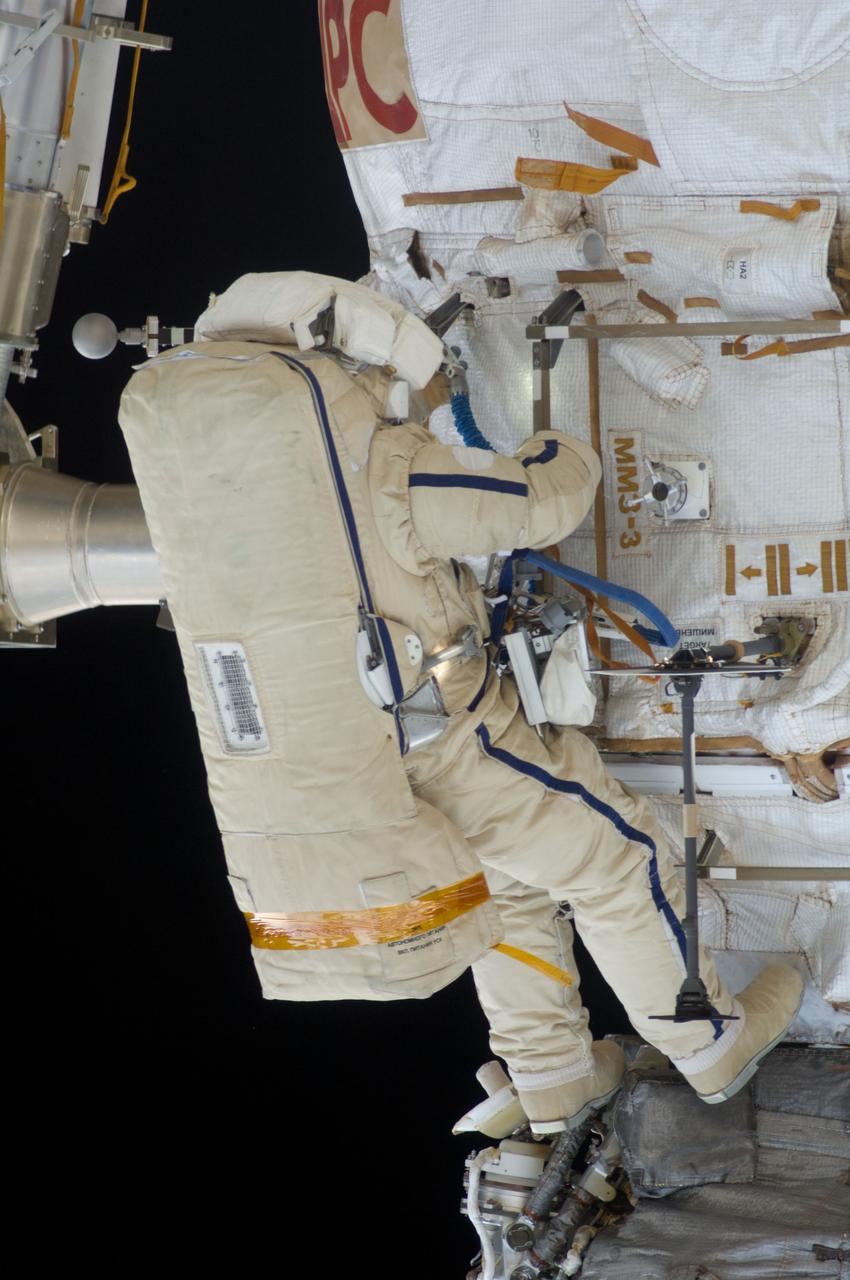

ISS028-E-020929 (3 Aug. 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Sergei Volkov and Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), both Expedition 28 flight engineers, attired in Russian Orlan spacesuits, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Russian segment of the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 23-minute spacewalk, Volkov and Samokutyaev moved a cargo boom from one airlock to another, installed a prototype laser communications system and deployed an amateur radio micro-satellite.
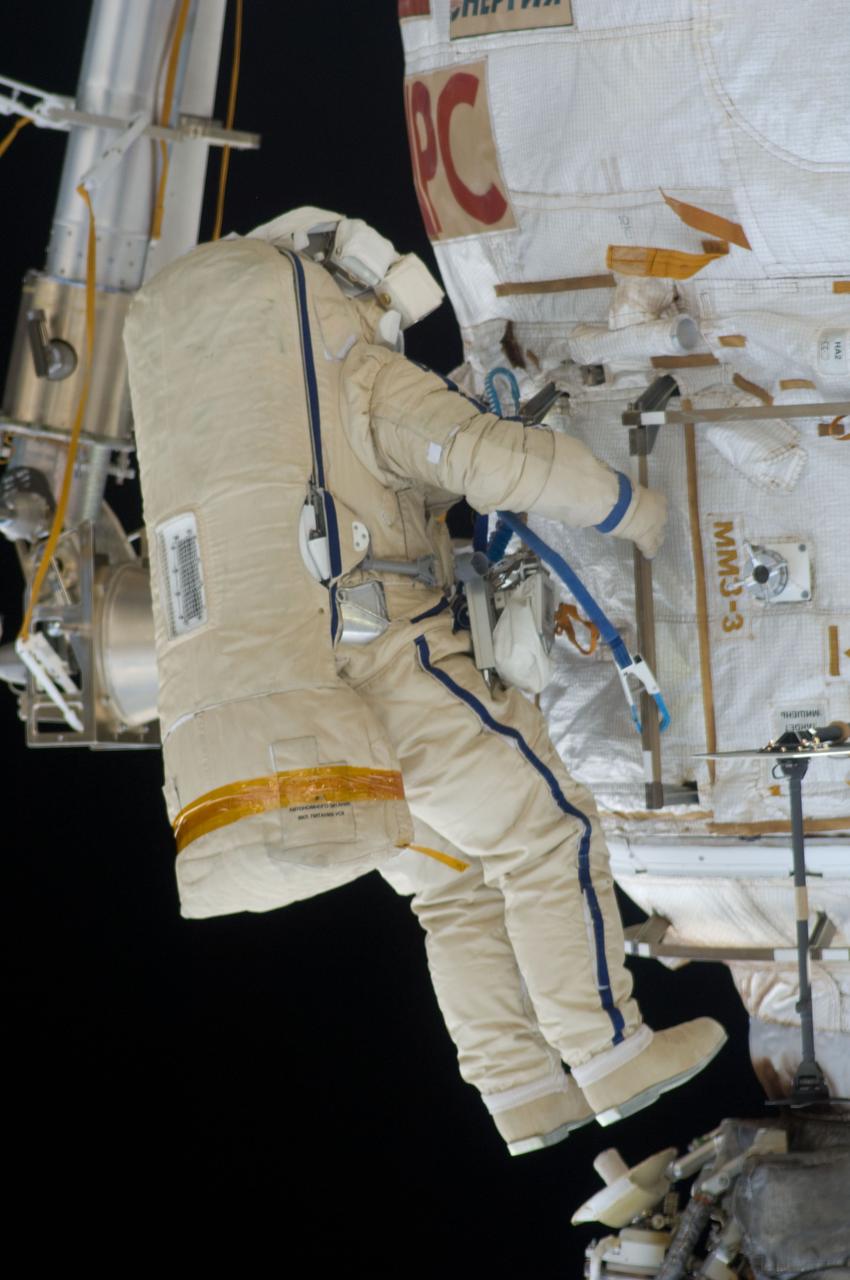

ISS028-E-020928 (3 Aug. 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Sergei Volkov and Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), both Expedition 28 flight engineers, attired in Russian Orlan spacesuits, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Russian segment of the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 23-minute spacewalk, Volkov and Samokutyaev moved a cargo boom from one airlock to another, installed a prototype laser communications system and deployed an amateur radio micro-satellite.
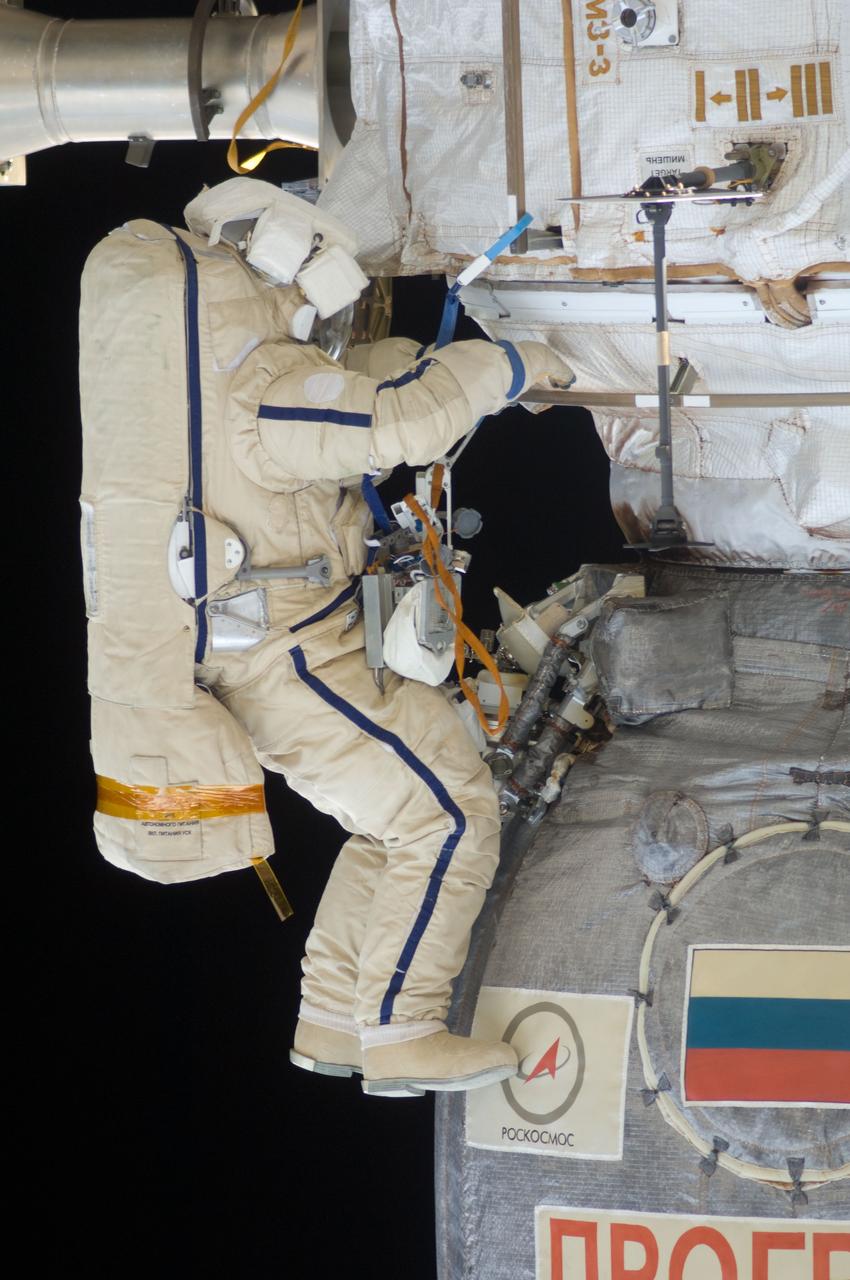

ISS028-E-020931 (3 Aug. 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Sergei Volkov and Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), both Expedition 28 flight engineers, attired in Russian Orlan spacesuits, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Russian segment of the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 23-minute spacewalk, Volkov and Samokutyaev moved a cargo boom from one airlock to another, installed a prototype laser communications system and deployed an amateur radio micro-satellite.
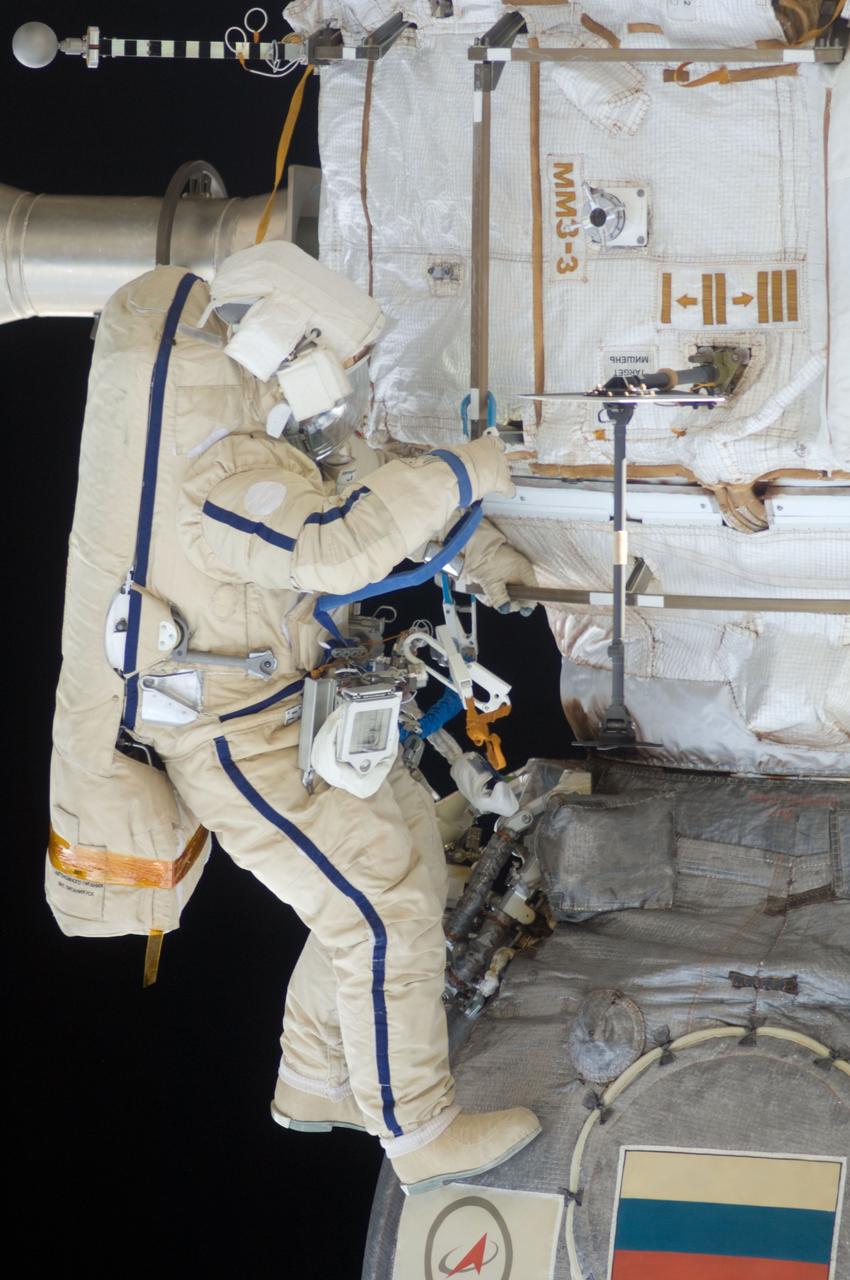

ISS028-E-020930 (3 Aug. 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Sergei Volkov and Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), both Expedition 28 flight engineers, attired in Russian Orlan spacesuits, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Russian segment of the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 23-minute spacewalk, Volkov and Samokutyaev moved a cargo boom from one airlock to another, installed a prototype laser communications system and deployed an amateur radio micro-satellite.
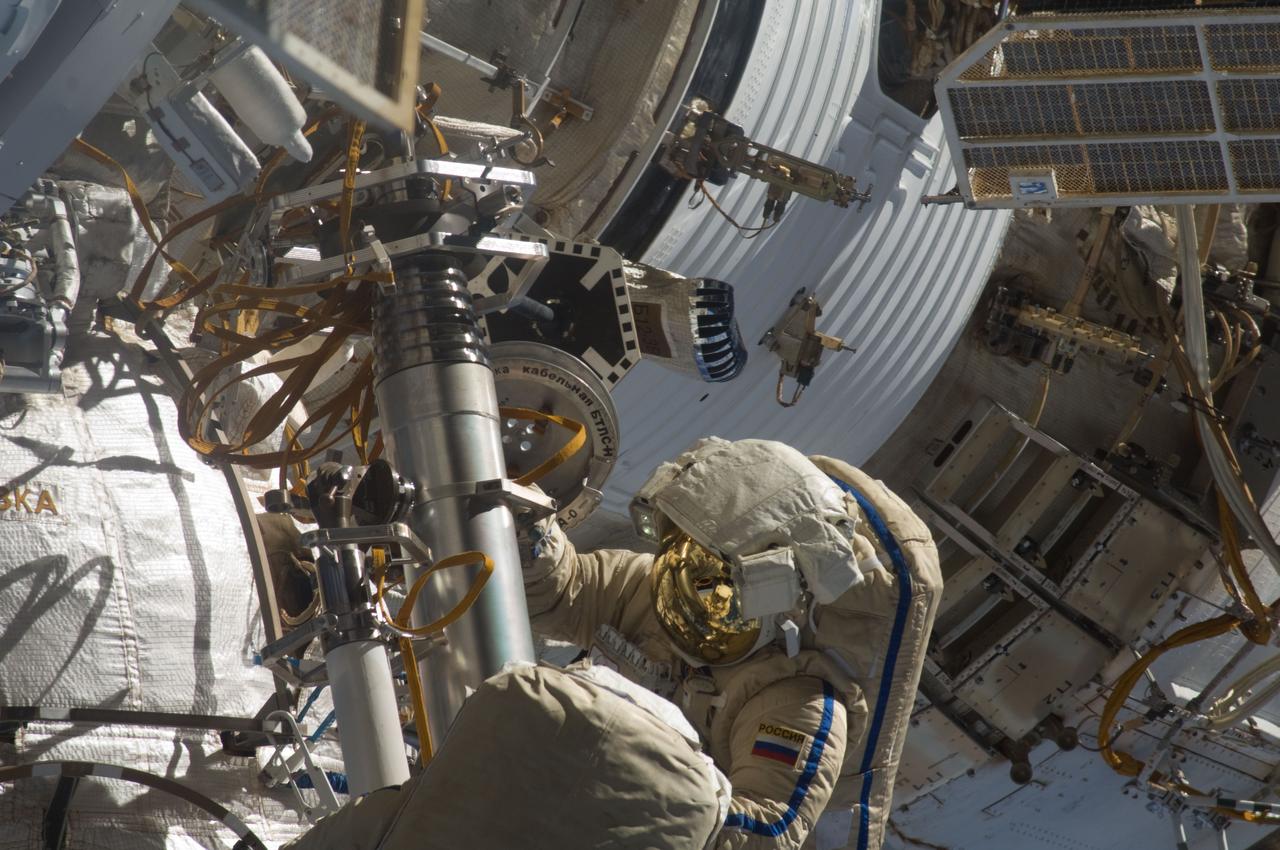

ISS028-E-020919 (3 Aug. 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Sergei Volkov and Alexander Samokutyaev (out of frame), both Expedition 28 flight engineers, attired in Russian Orlan spacesuits, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the Russian segment of the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 23-minute spacewalk, Volkov and Samokutyaev moved a cargo boom from one airlock to another, installed a prototype laser communications system and deployed an amateur radio micro-satellite.
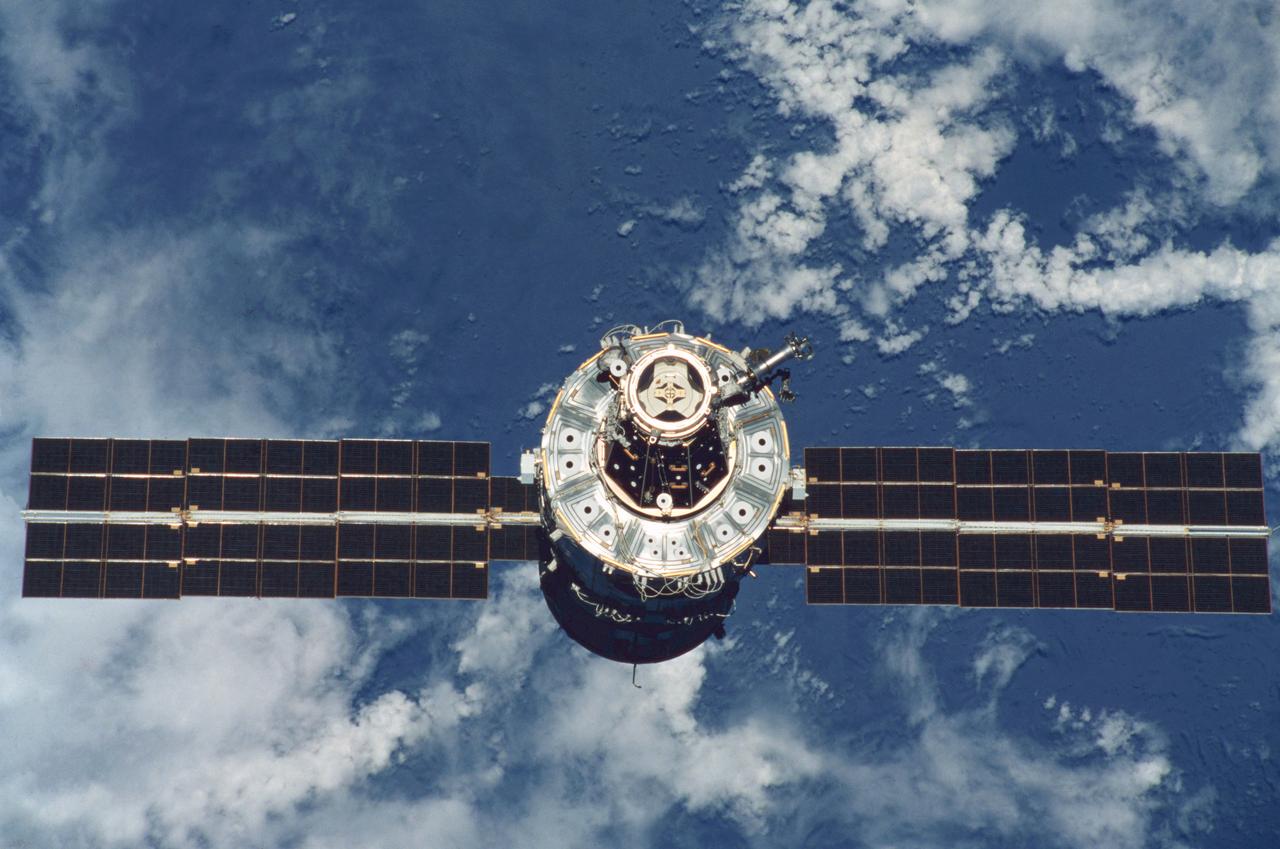

STS096-345-033 (3 June 1999) --- A STS-96 crew member aboard Discovery handling a 35mm camera recorded this image of the International Space Station (ISS) during a fly-around following separation of the two spacecraft. A portion of the work performed on the May 30 space walk by astronauts Tamara E. Jernigan and Daniel T. Barry is evident in the photo, including the installation of the Russian-built crane (called Strela).

STS096-712-034 (3 June 1999) --- A STS-96 crew member aboard Discovery handling a 70mm camera recorded this image of the International Space Station (ISS) during a fly-around following separation of the two spacecraft. A portion of the work performed on the May 30 space walk by astronauts Tamara E. Jernigan and Daniel T. Barry is evident in the photo, including the installation of the Russian-built crane (called Strela).
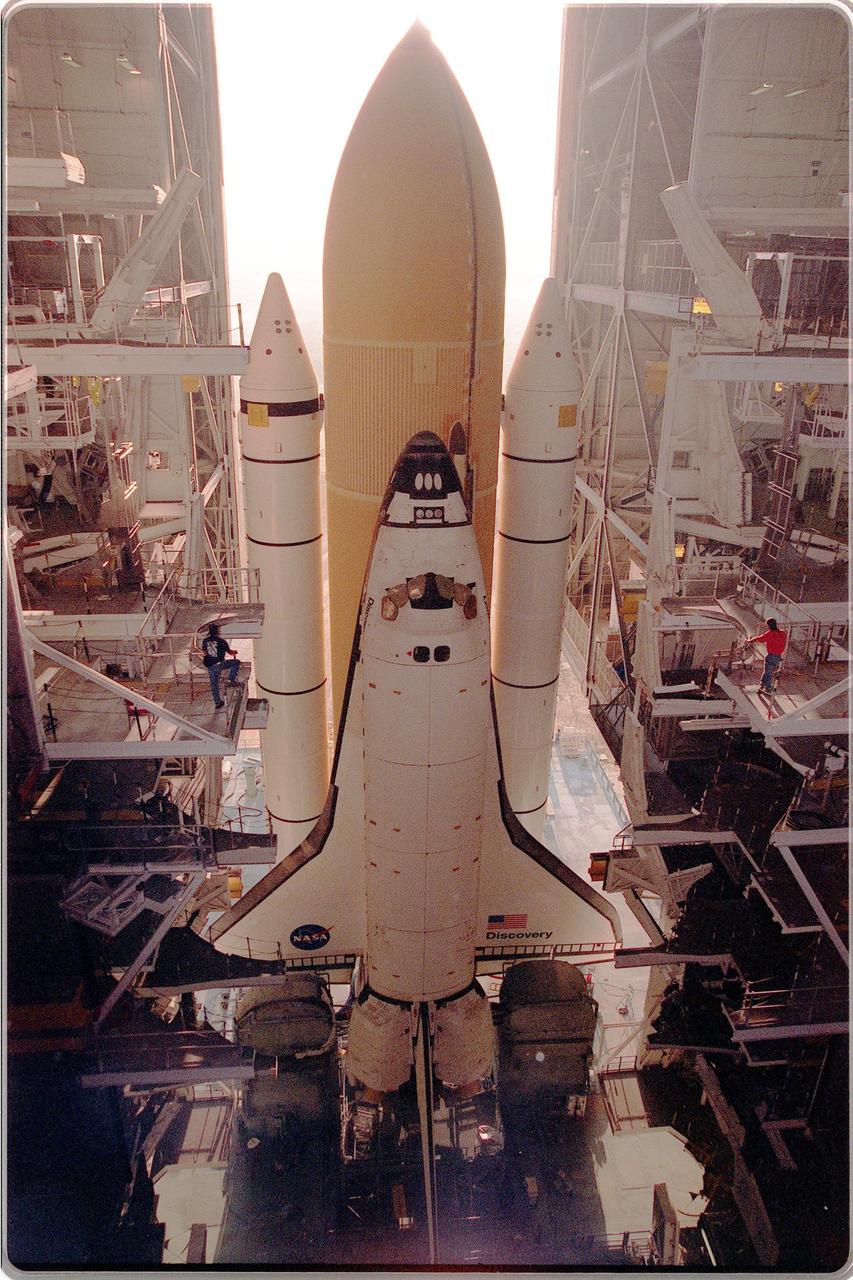

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Inside the Vehicle Assembly Building, Space Shuttle Discovery stands ready for rollout to Launch Pad 39B in preparation for mission STS-96. Liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96 is targeted for May 20 at 9:32 a.m. EDT. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment
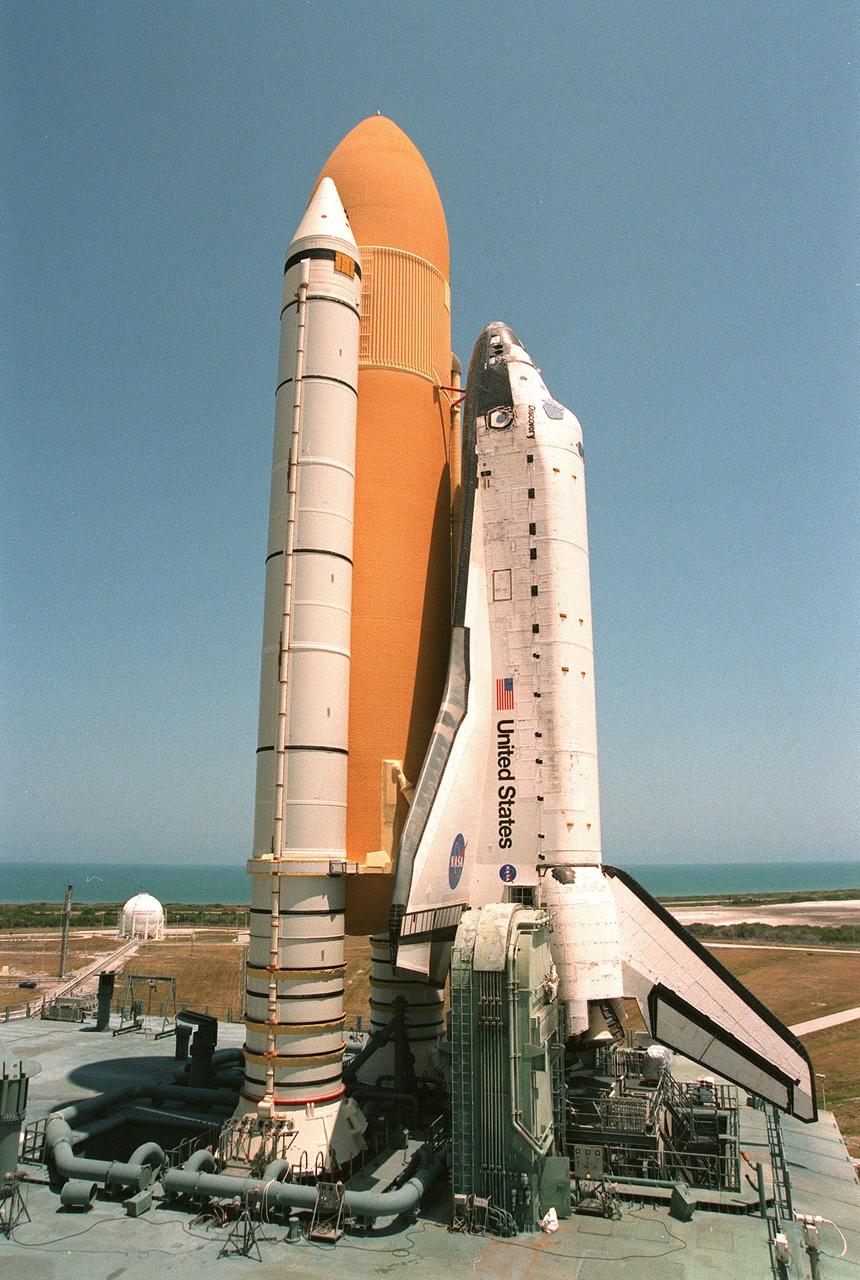

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Against the backdrop of a clear blue sky and the bluer Atlantic Ocean, the Space Shuttle Discovery, on its mobile launcher platform, sits on Launch Pad 39B. Liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96 is targeted for May 20 at 9:32 a.m. EDT. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment
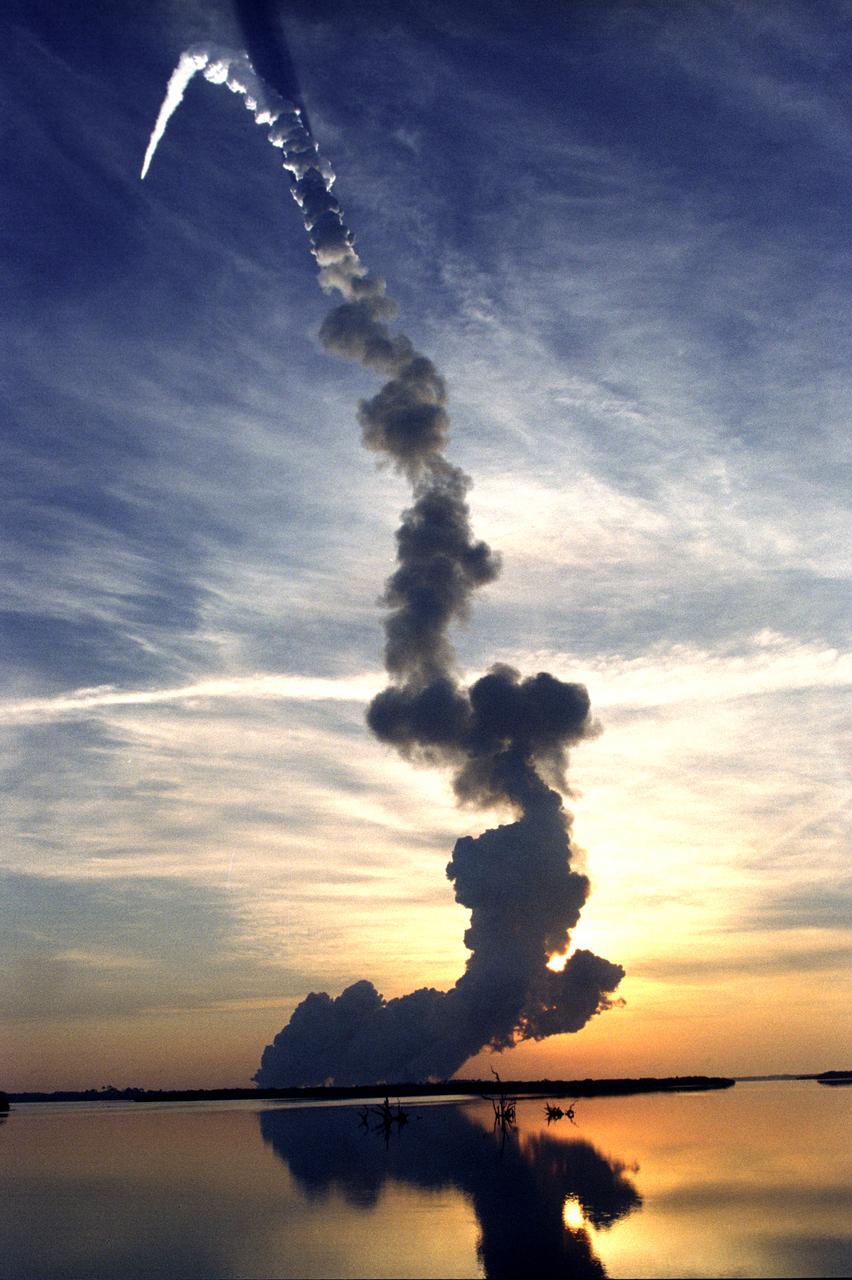

This spectacular photo is of the May 27, 1999 liftoff of the Orbiter Discovery (STS-96). The STS-96 mission, of almost 10 days, was the second International Space Station (ISS) assembly and resupply flight and the first flight to dock with the station. The crew installed foot restraints and the Russian built crane, STRELA. The Shuttle's SPACEHAB double module carried internal and resupply cargo for station outfitting and the Russian cargo crane was carried aboard the shuttle in the integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC).
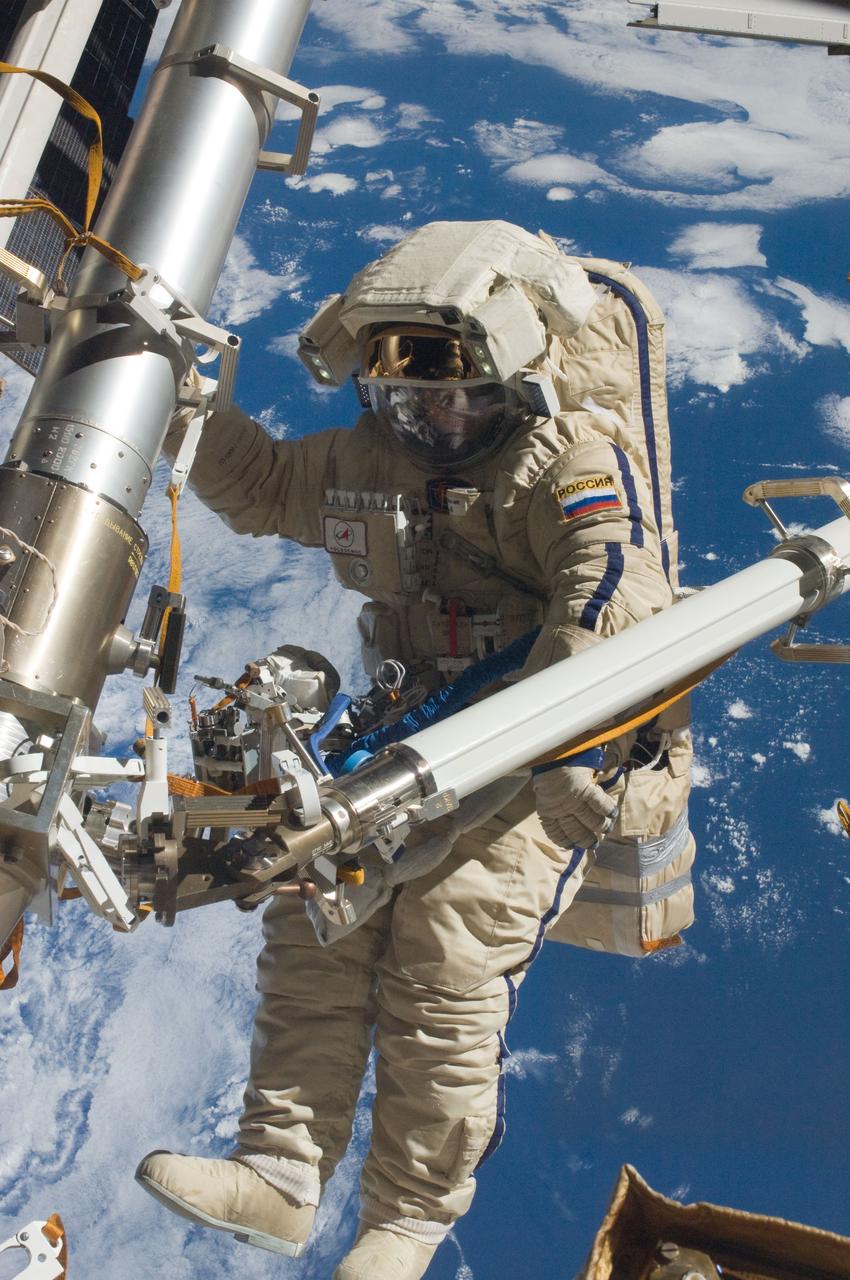

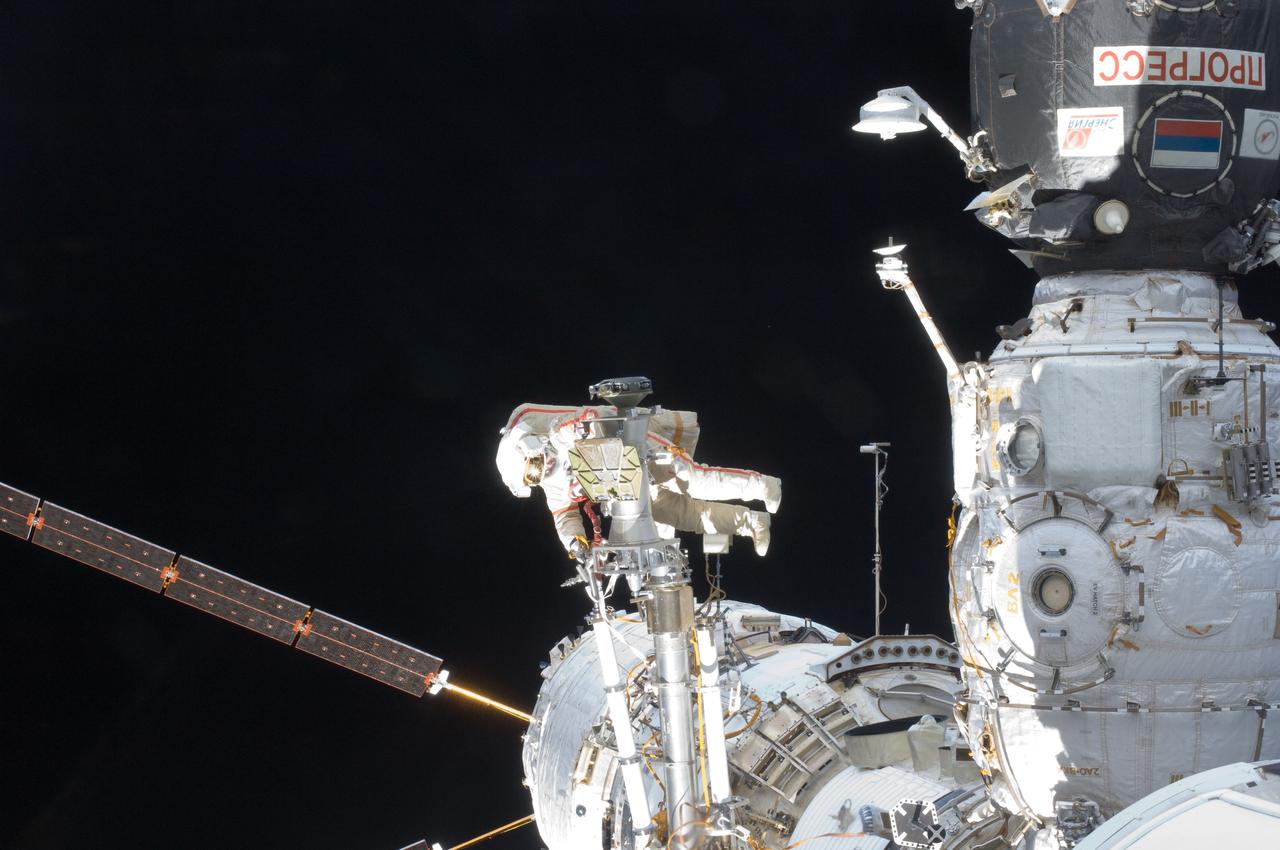
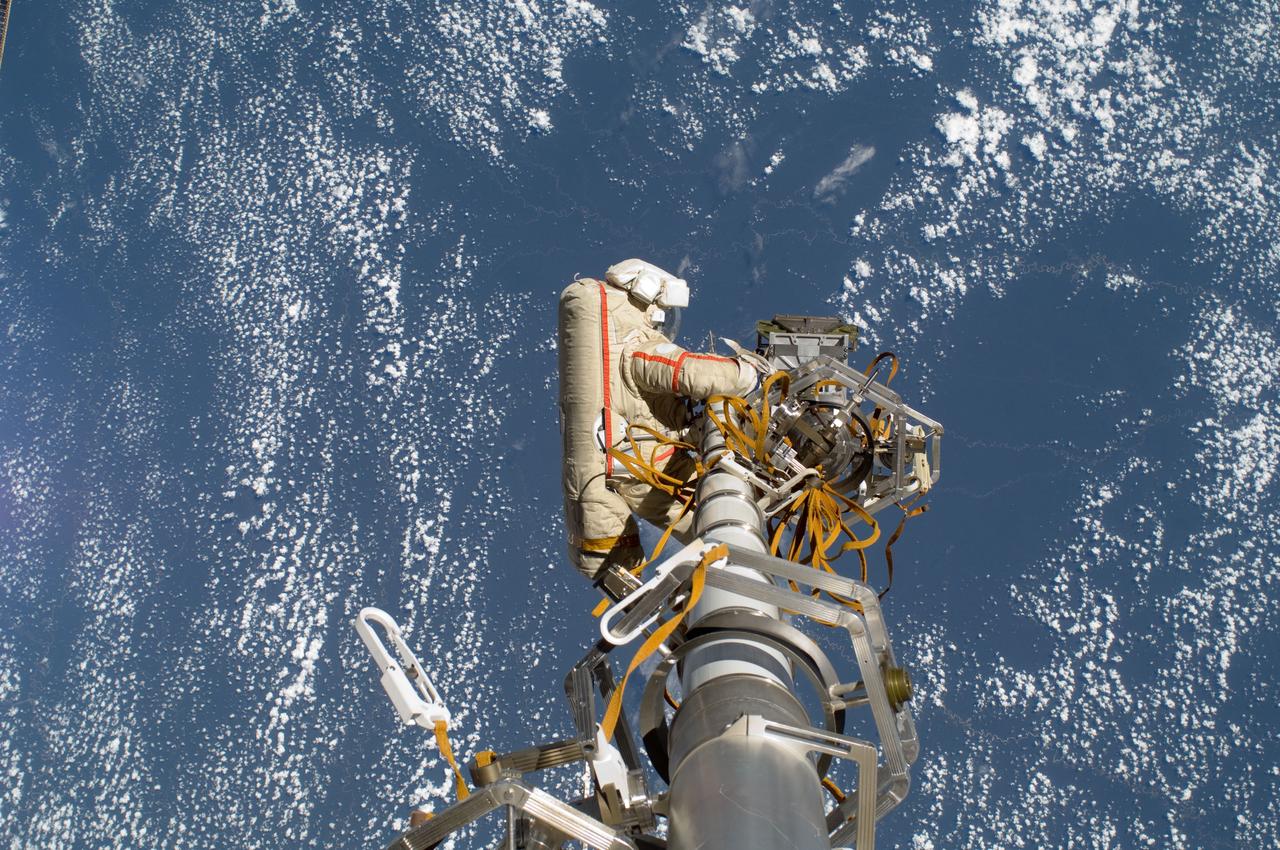
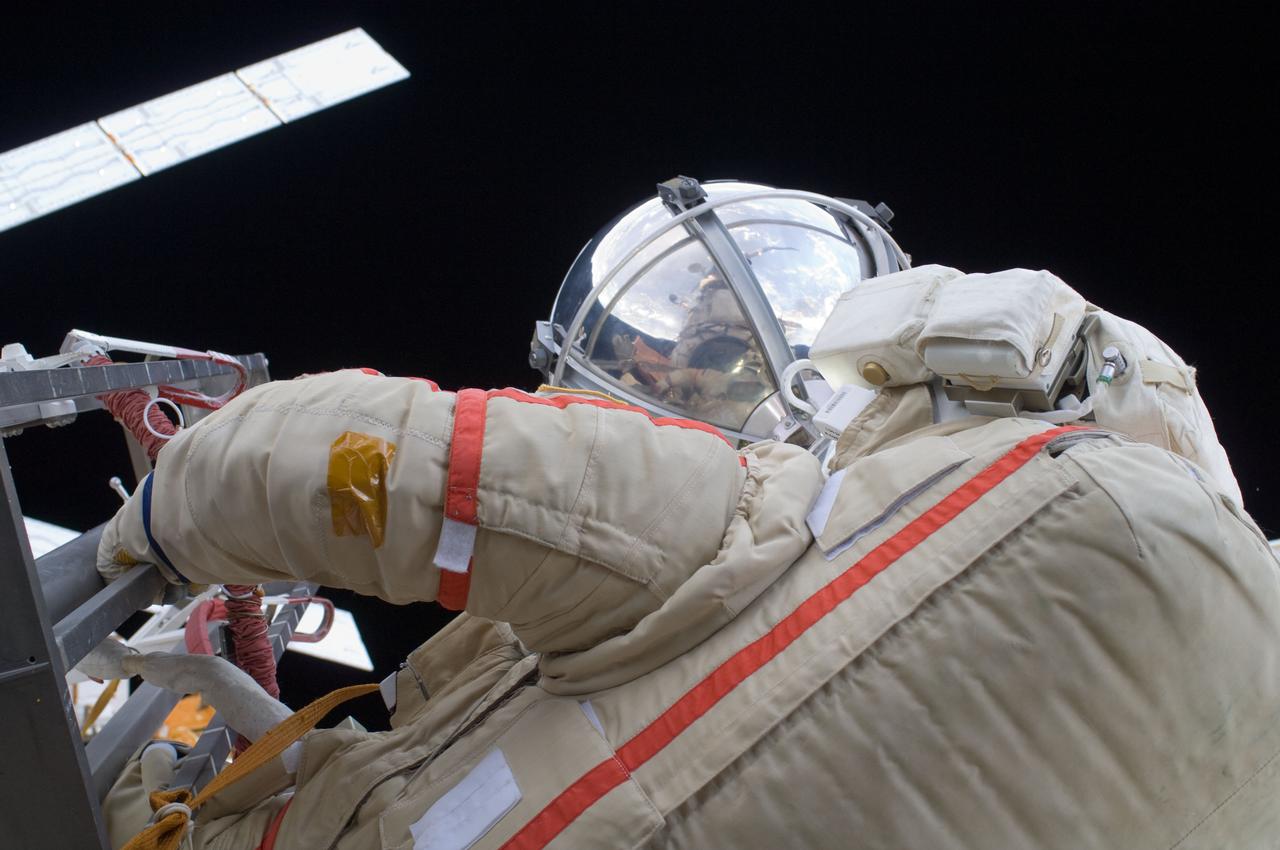
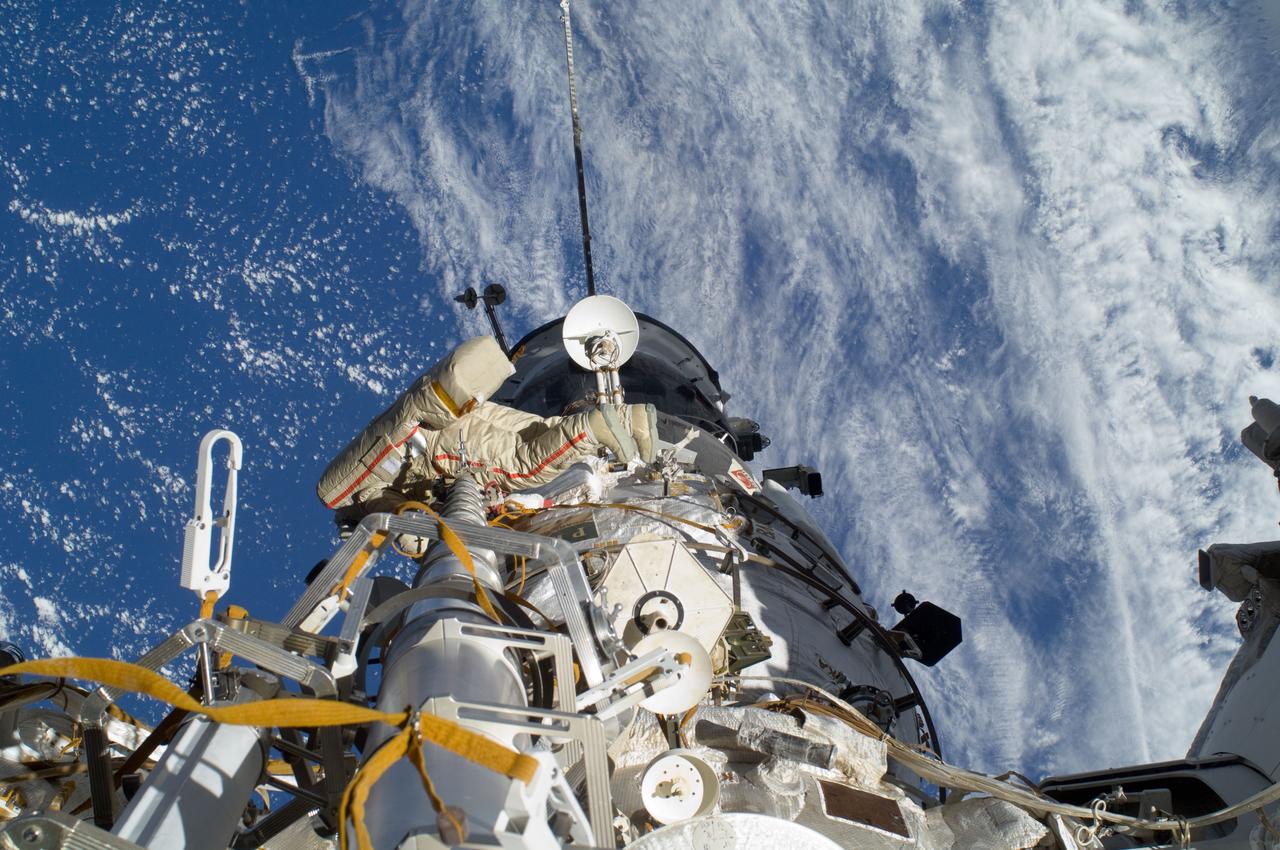
ISS030-E-079955 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
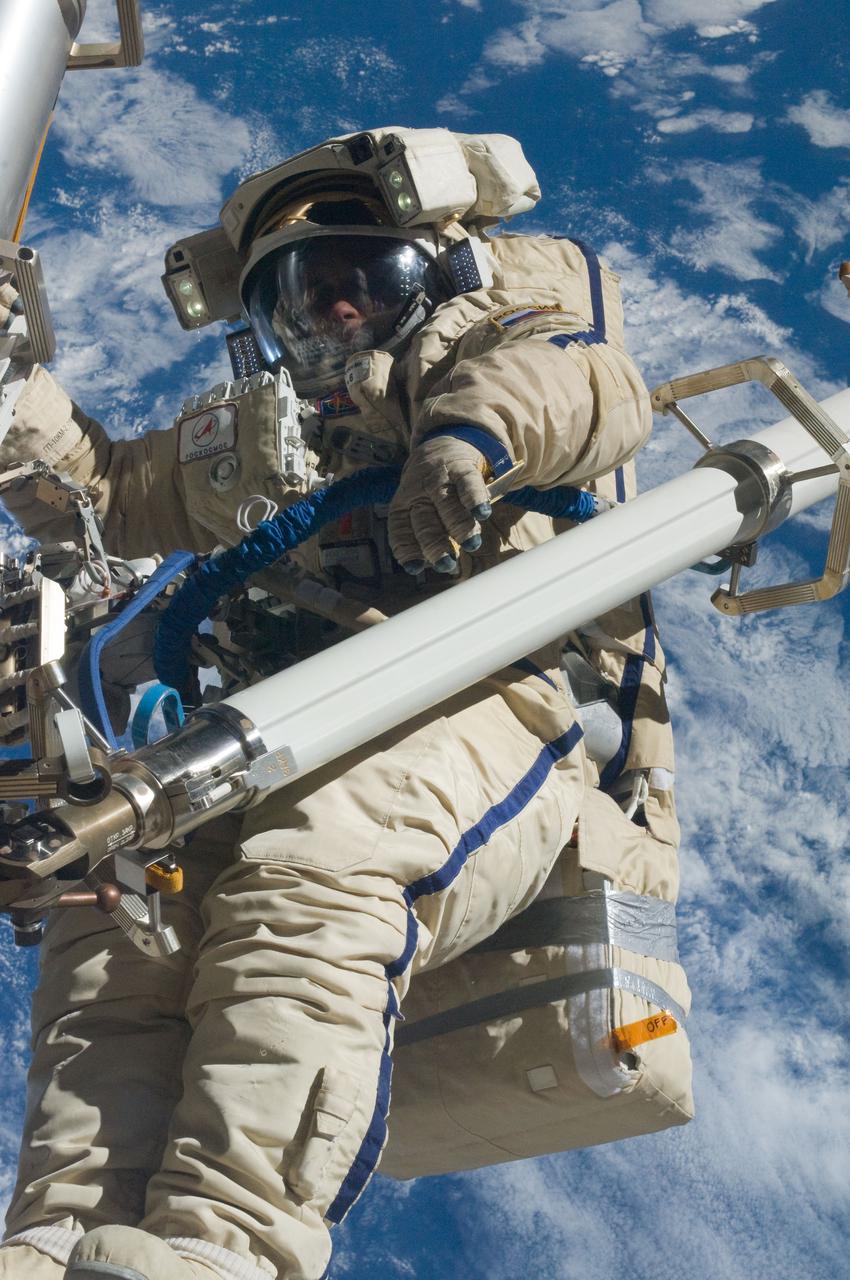

ISS030-E-079949 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
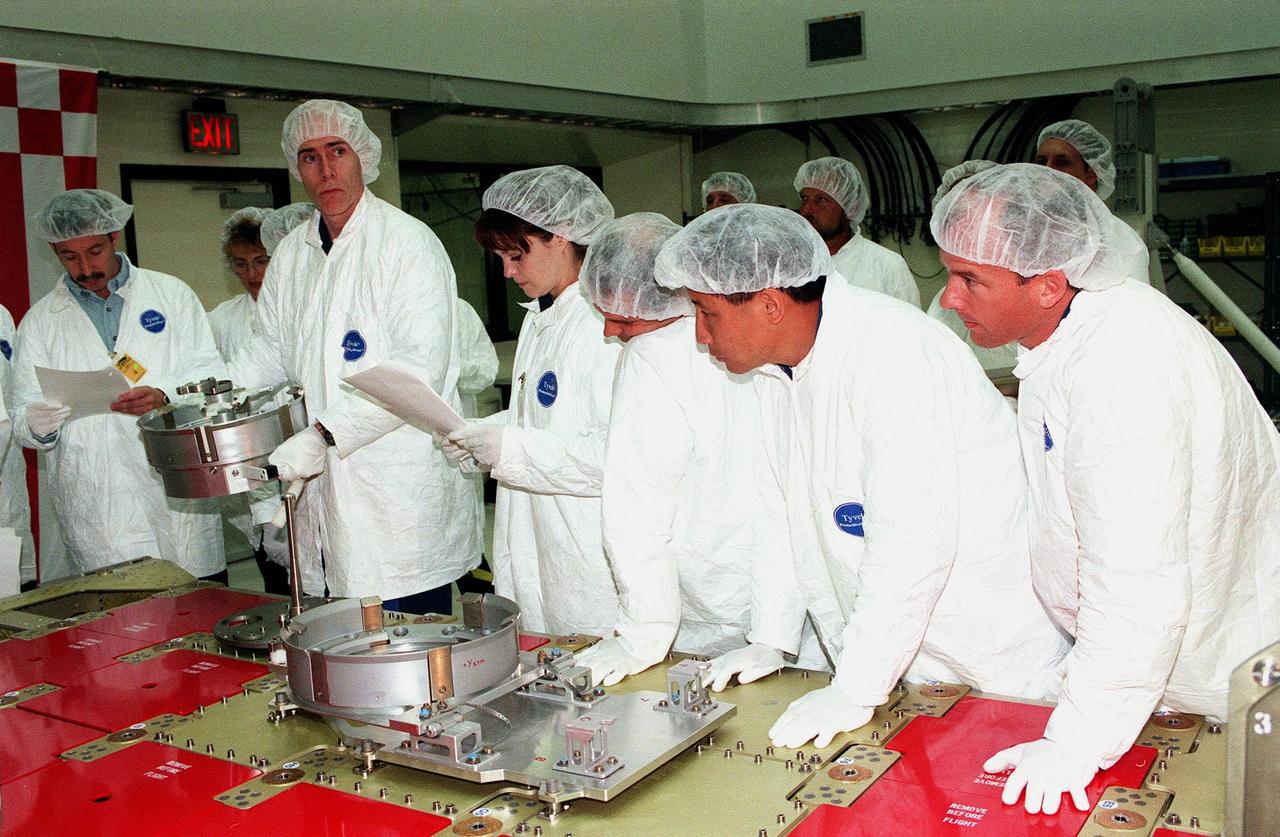

Two Shuttle crews take part in familiarization activities at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla. From left are STS-96 Mission Specialists Daniel T. Barry and Tamara E. Jernigan, and Pilot Rick Douglas Husband; plus STS-101 Mission Specialists Edward Tsang Lu and Jeffrey N. Williams. They are looking at components of a Russian cargo crane, the Strela, to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment on the International Space Station (ISS). Both missions include the SPACEHAB Double Module, carrying internal and resupply cargo for Station outfitting. For the first time, STS-96 will include an Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC) that will carry the Strela; the SPACEHAB Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), which is a logistics items carrier; and a U.S.-built crane (ORU Transfer Device, or OTD) that will be stowed on the station for use during future ISS assembly missions. The ICC can carry up to 6,000 lb of unpressurized payload. It was built for SPACEHAB by DaimlerChrysler Aerospace of Bremen and RSC Energia of Korolev, Russia. STS-96 is targeted for launch on May 24 from Launch Pad 39B. STS-101 is scheduled to launch in early December 1999
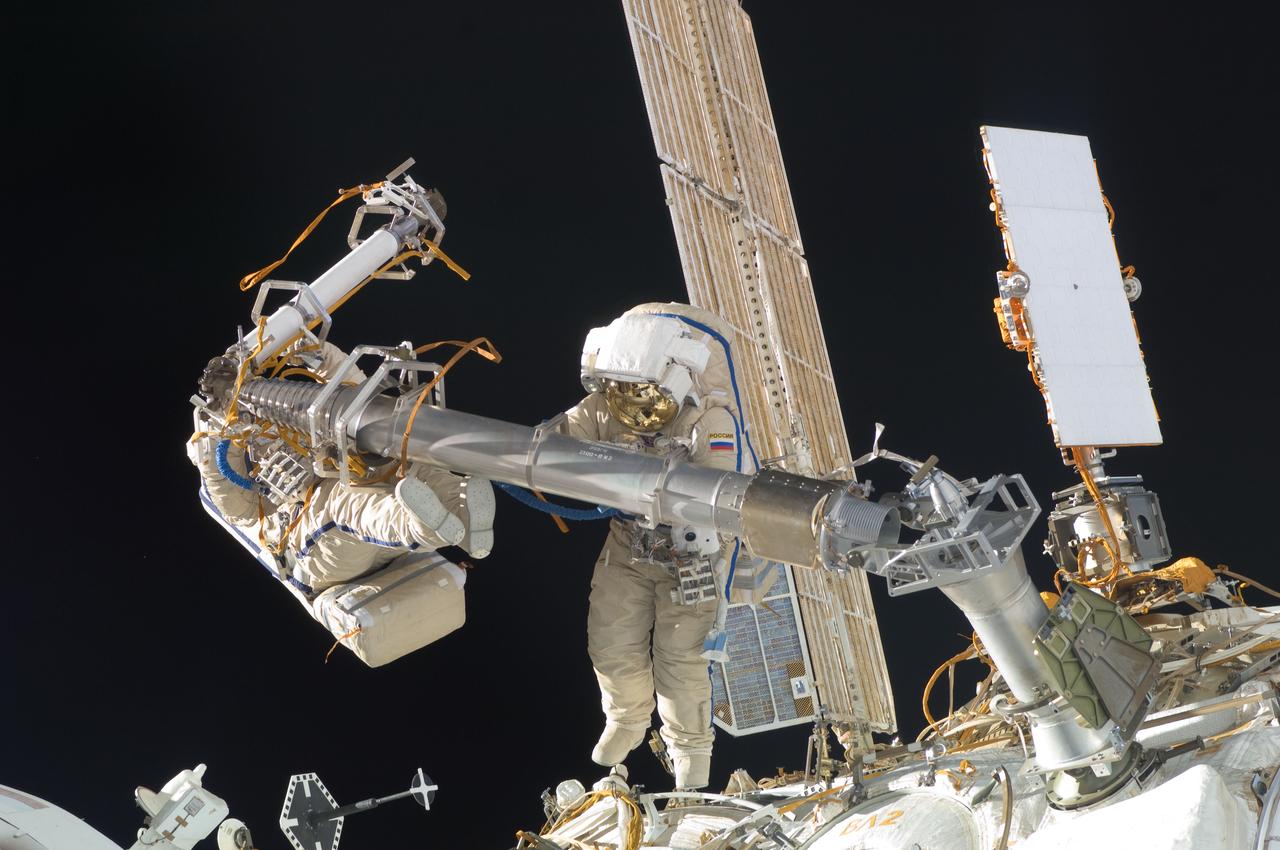

ISS030-E-078377 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
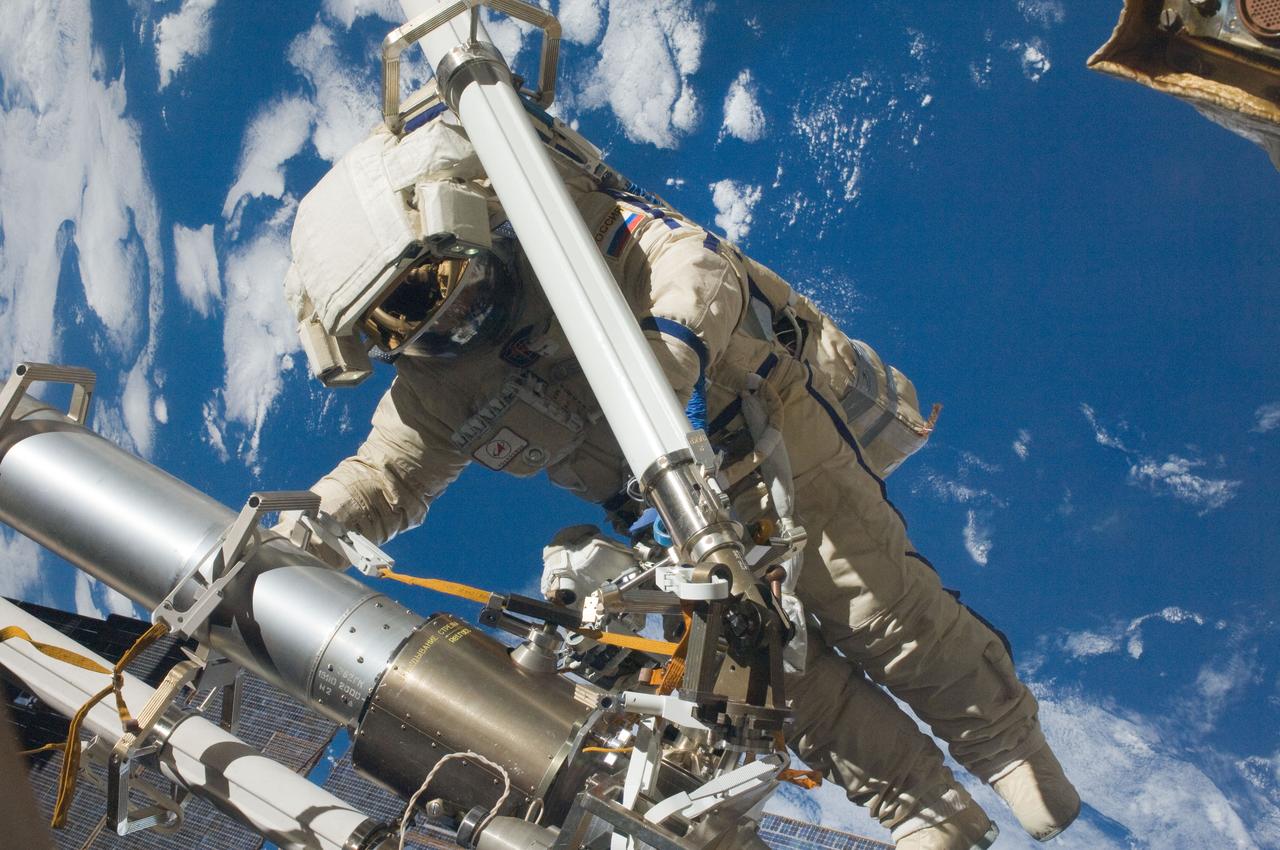

ISS030-E-079956 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
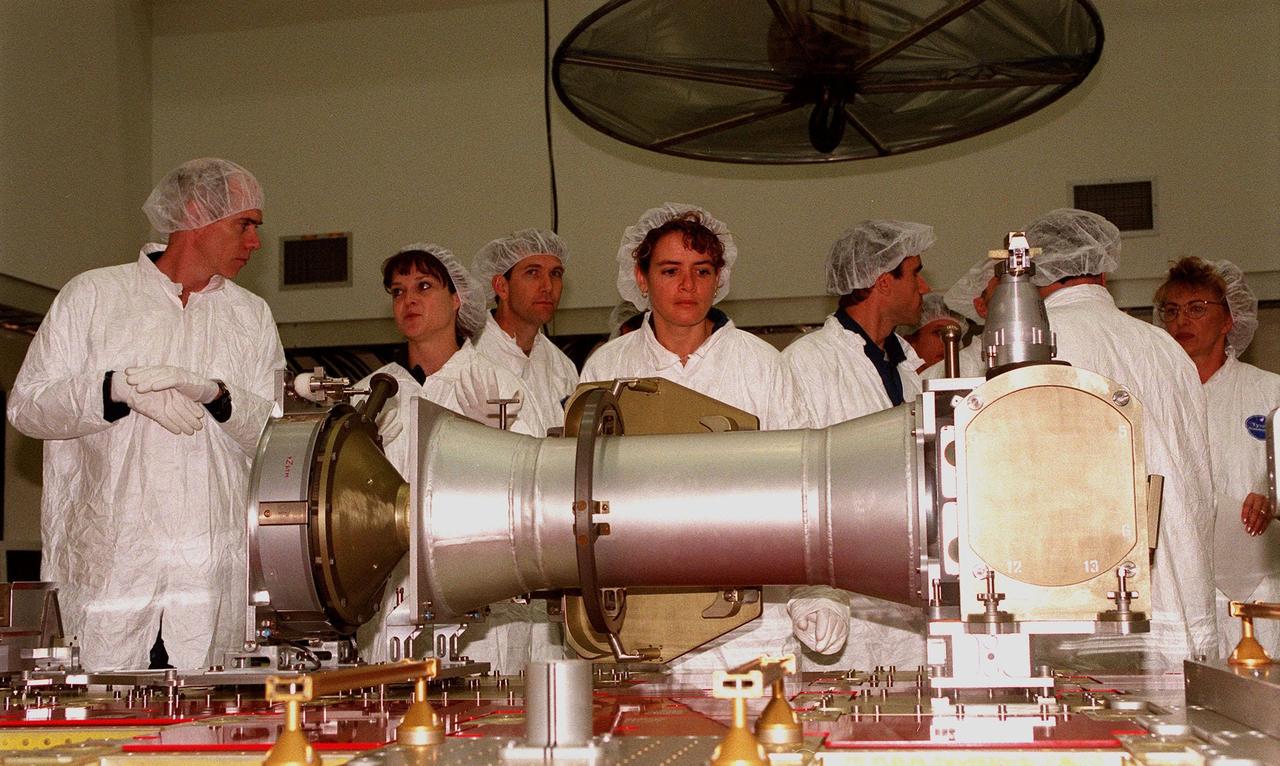

At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., members of two Shuttle crews take a close look at components of a Russian cargo crane, the Strela, to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment on the International Space Station (ISS). From left are STS-96 Mission Specialists Daniel T. Barry and Tamara E. Jernigan, Pilot Rick Douglas Husband, and Mission Specialist Julie Payette; next to them is STS-101 Mission Specialist Yuri Ivanovich Malenchenko, with the Russian Space Agency. Both missions include the SPACEHAB Double Module, carrying internal and resupply cargo for Station outfitting. For the first time, STS-96 will include an Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC) that will carry the Strela; the SPACEHAB Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), which is a logistics items carrier; and a U.S.-built crane (ORU Transfer Device, or OTD) that will be stowed on the station for use during future ISS assembly missions. The ICC can carry up to 6,000 lb of unpressurized payload. It was built for SPACEHAB by DaimlerChrysler and RSC Energia of Korolev, Russia. STS-96 is targeted for launch on May 24 from Launch Pad 39B. STS-101 is scheduled to launch in early December 1999
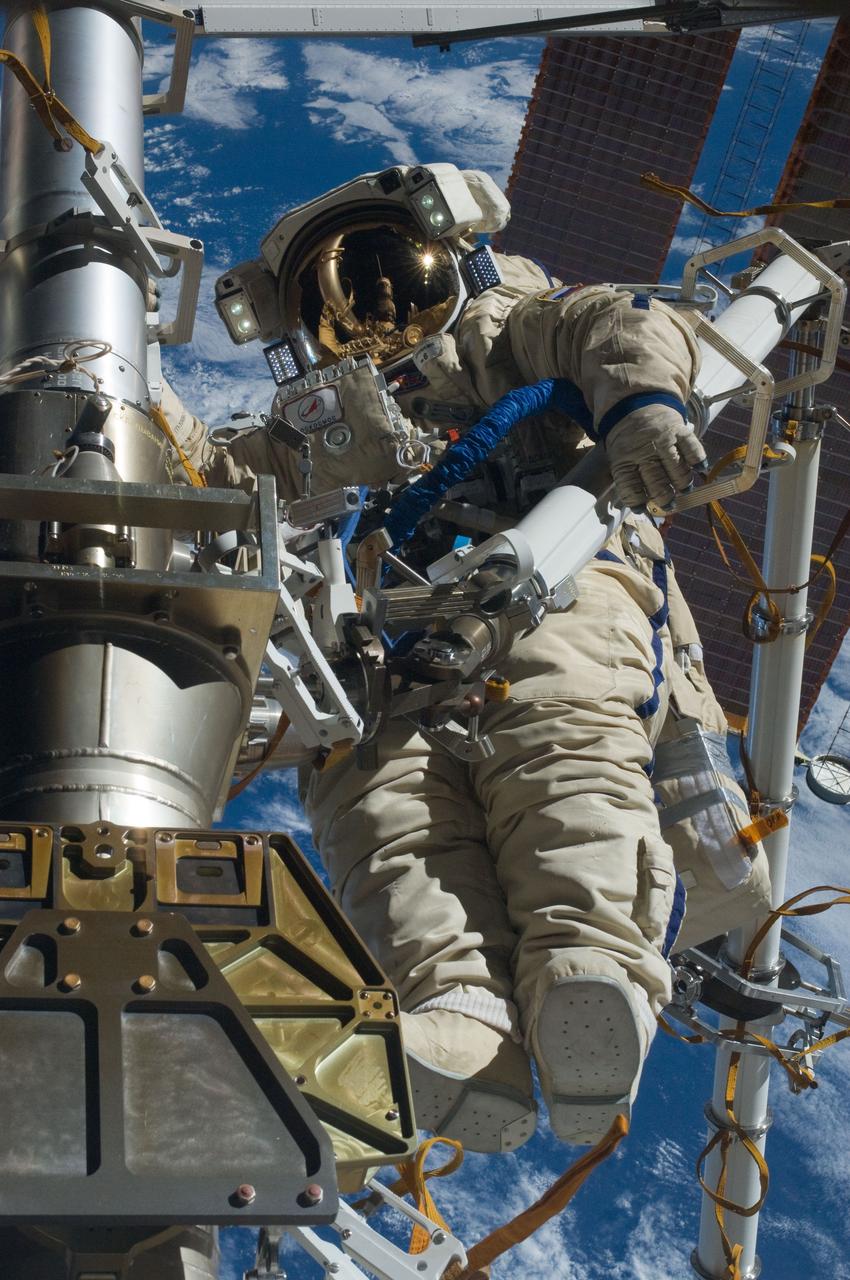

ISS030-E-079943 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
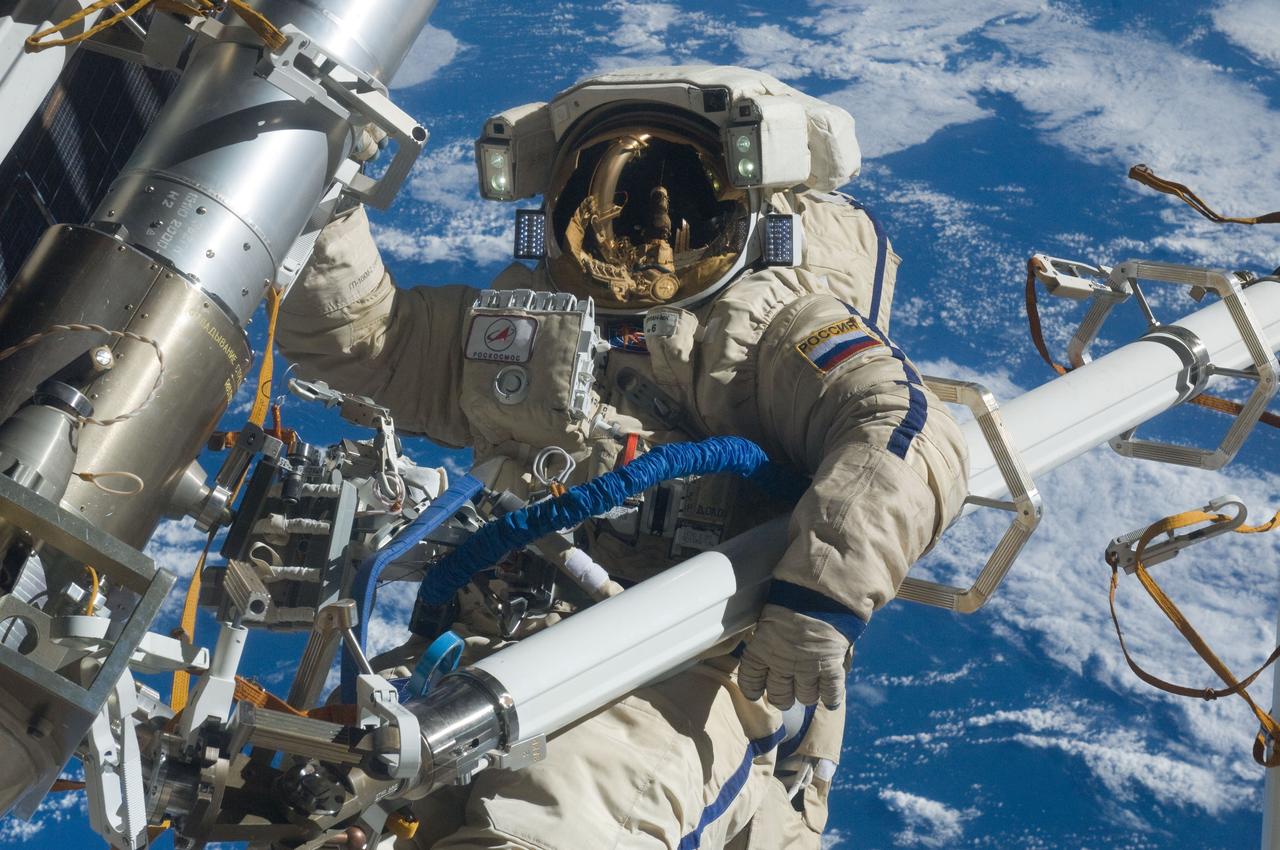

ISS030-E-079939 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
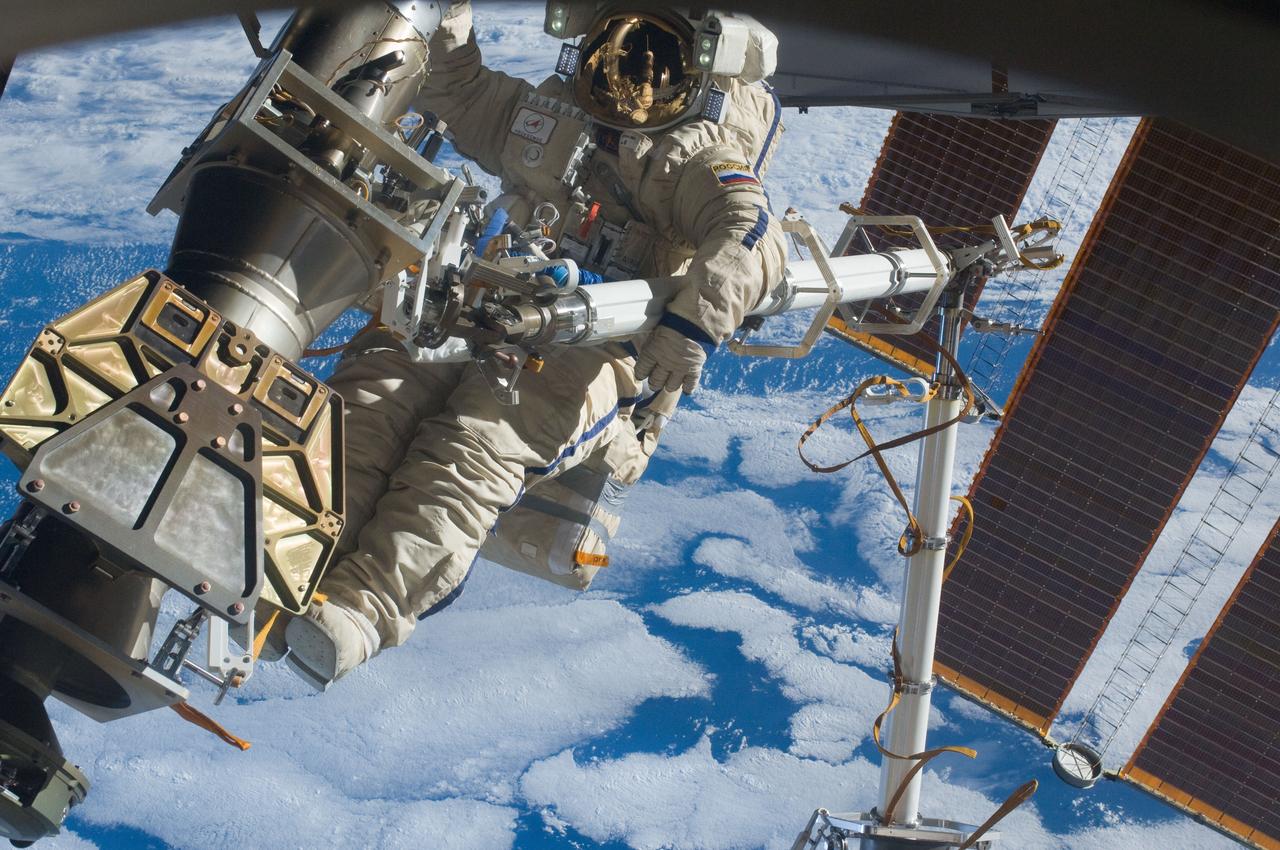

ISS030-E-079930 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
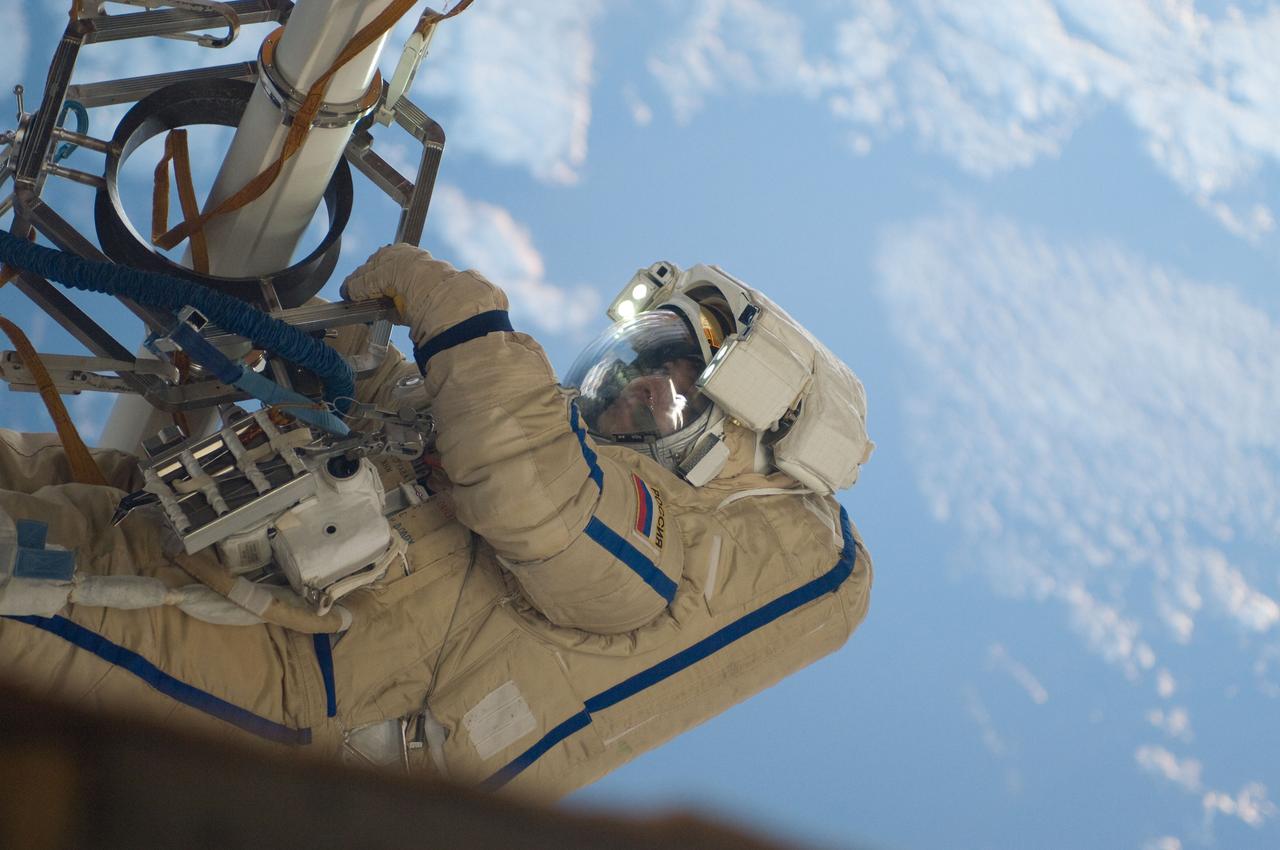

ISS030-E-080048 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
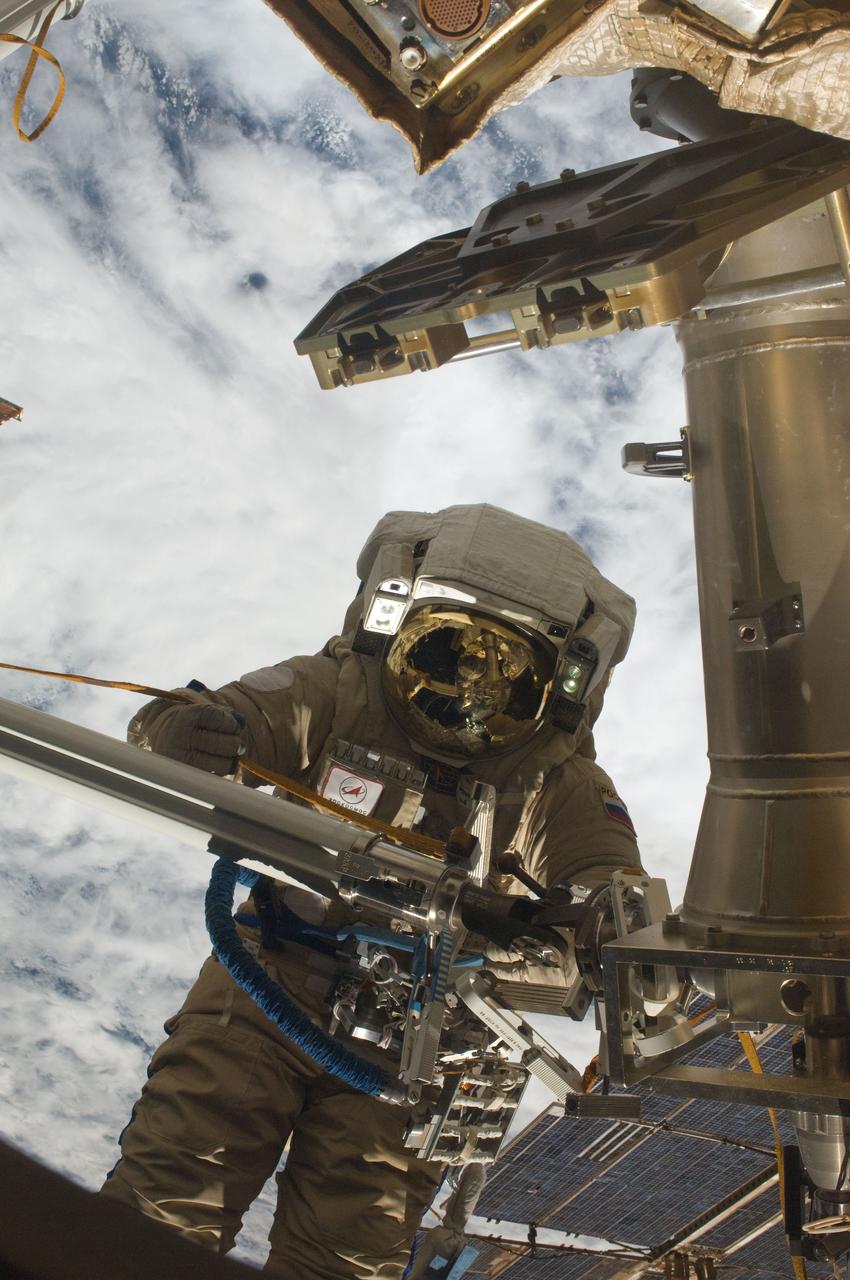

ISS030-E-079991 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
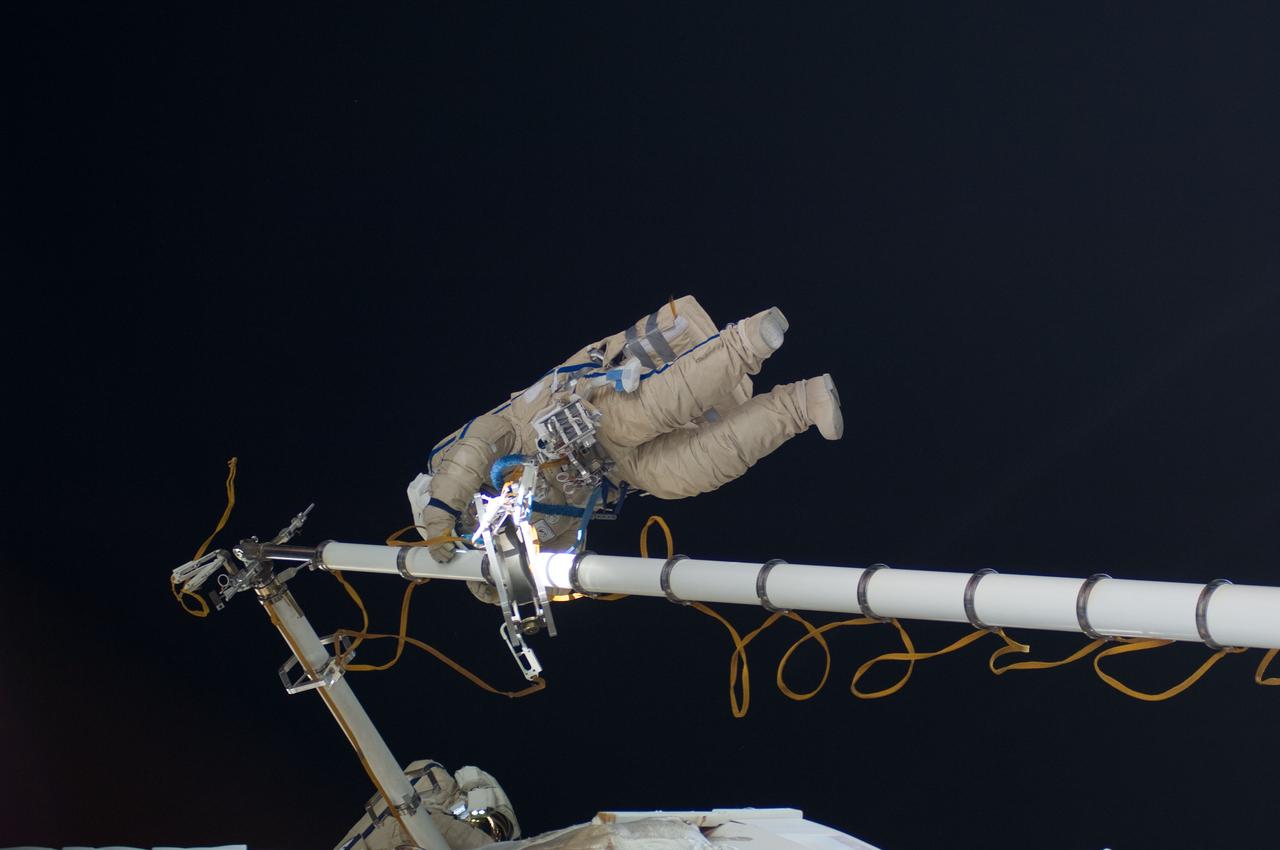

ISS030-E-078488 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
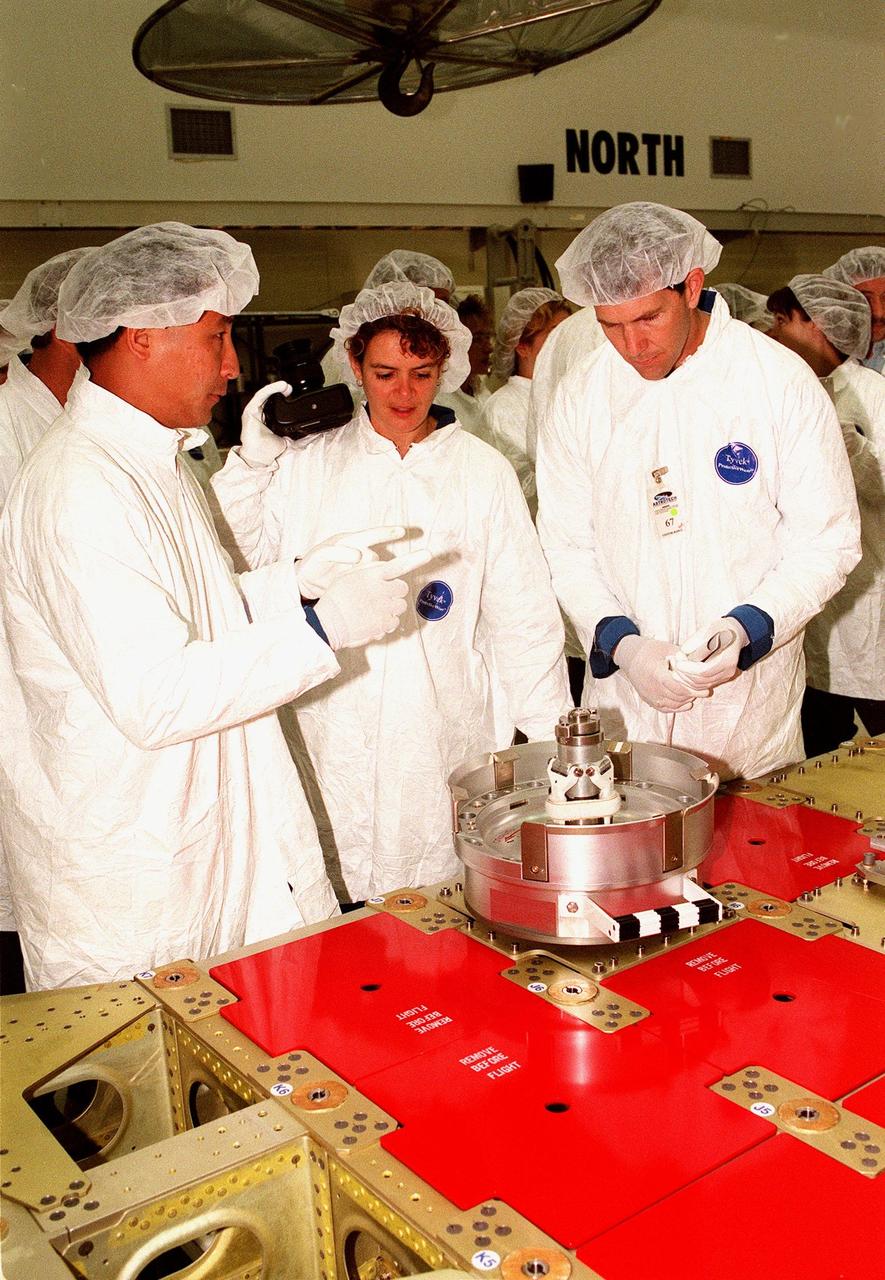

At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., members of two Shuttle crews take a close look at a component of a Russian cargo crane, the Strela, to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment on the International Space Station (ISS). From left, they are STS-101 Mission Specialist Edward Tsang Lu, plus STS-96 Mission Specialist Julie Payette and Pilot Rick Douglas Husband. Payette represents the Canadian Space Agency. Both missions include the SPACEHAB Double Module, carrying internal and resupply cargo for Station outfitting. For the first time, STS-96 will include an Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC) that will carry the Strela; the SPACEHAB Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), which is a logistics items carrier; and a U.S.-built crane (ORU Transfer Device, or OTD) that will be stowed on the station for use during future ISS assembly missions. The ICC can carry up to 6,000 lb of unpressurized payload. It was built for SPACEHAB by DaimlerChrysler and RSC Energia of Korolev, Russia. STS-96 is targeted for launch on May 24 from Launch Pad 39B. STS-101 is scheduled to launch in early December 1999
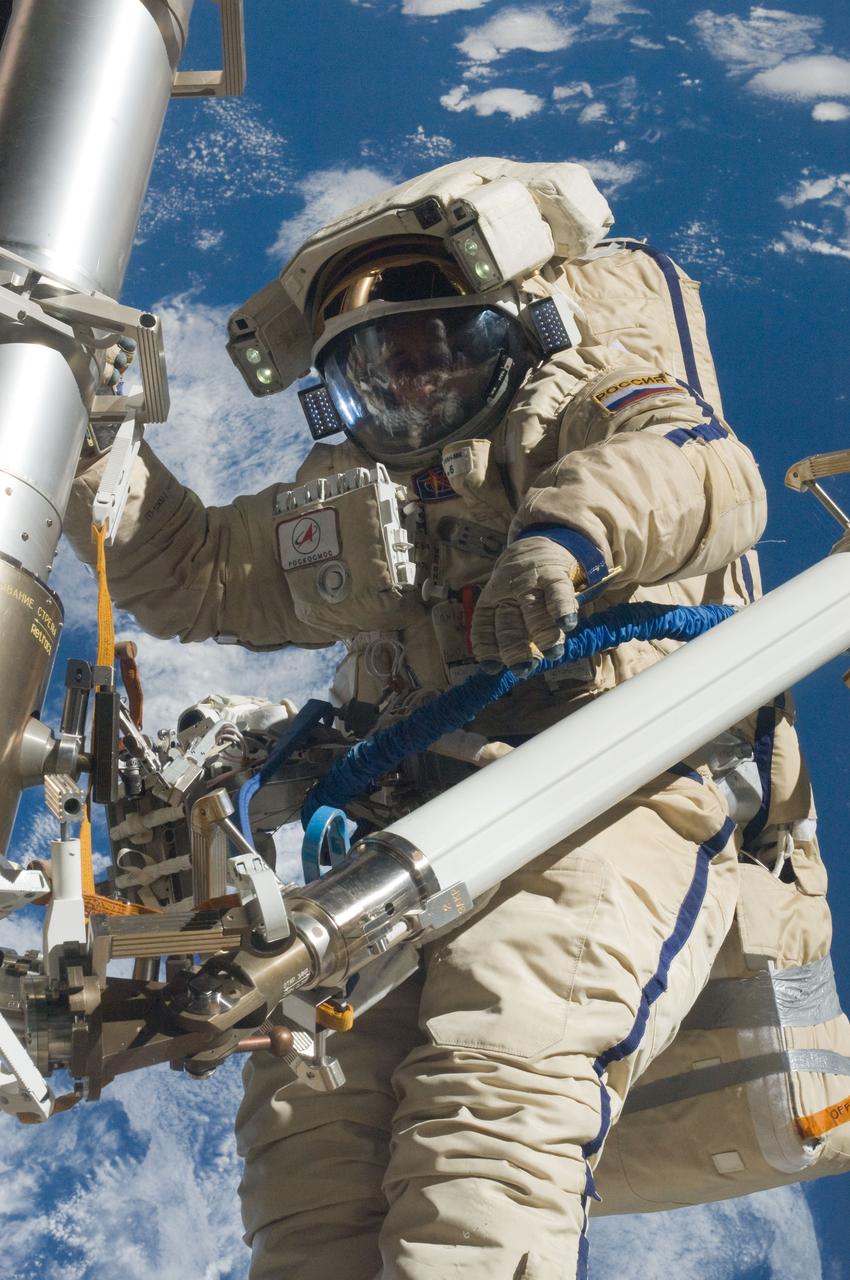

ISS030-E-079953 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
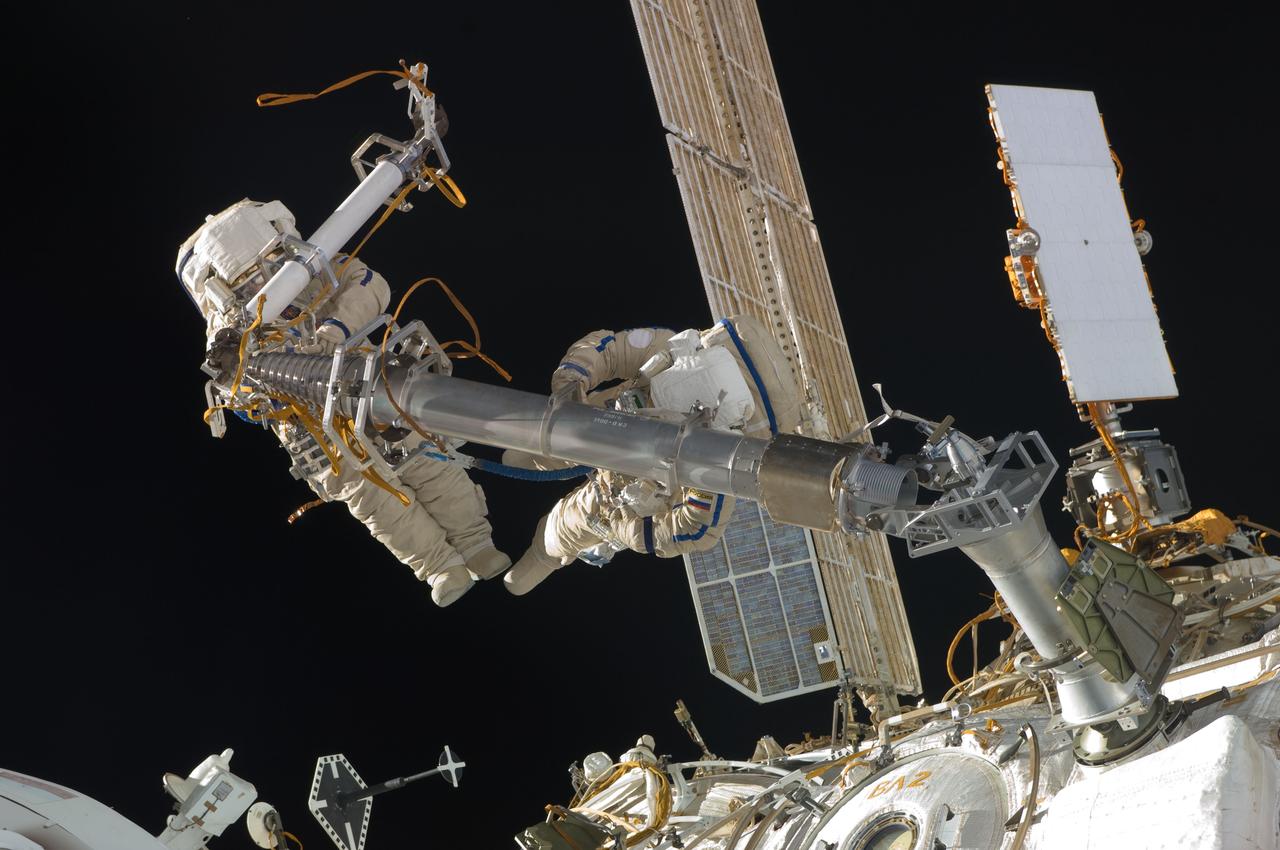

ISS030-E-078381 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
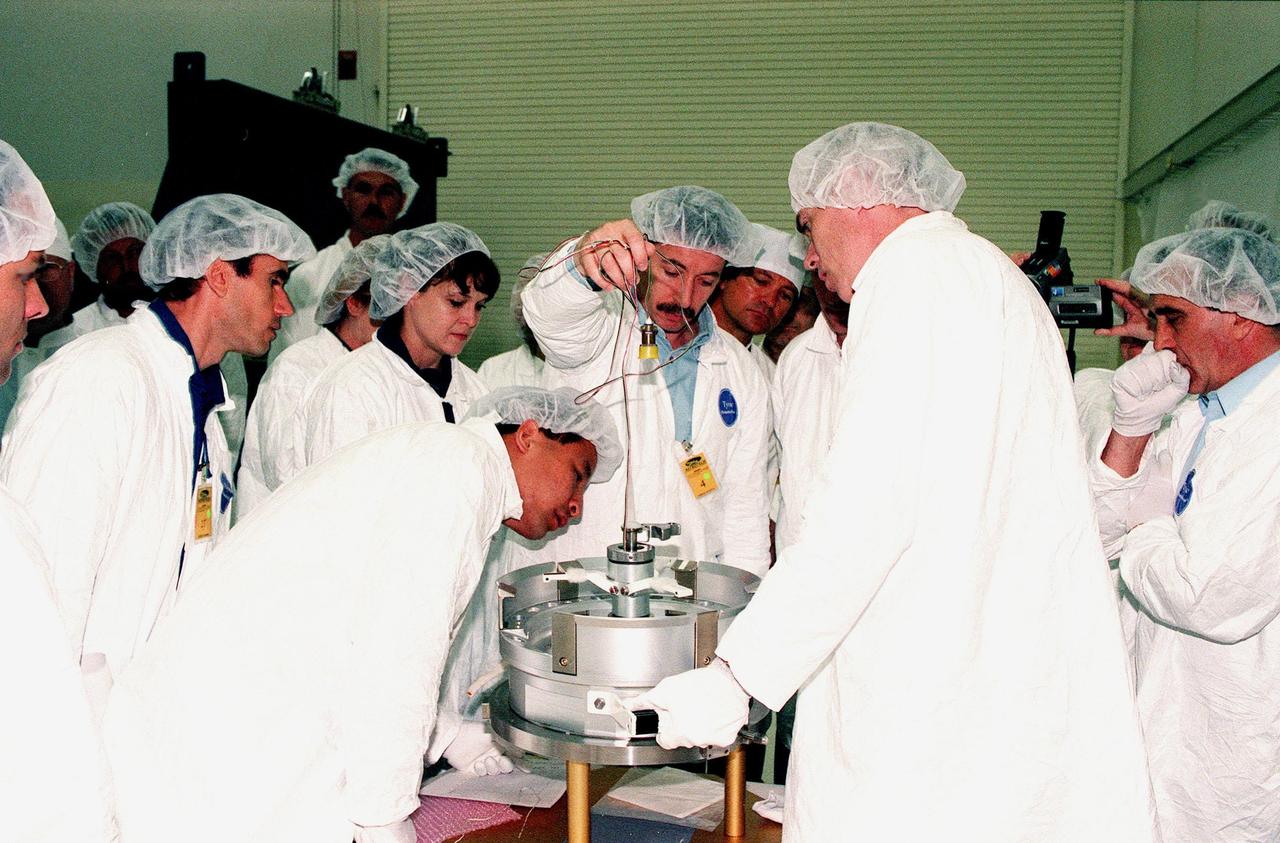

Two Shuttle crews take part in familiarization activities at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla. From left are STS-101 Mission Specialist Jeffrey N. Williams and Yuri Ivanovich Malenchenko, with the Russian Space Agency; STS-96 Mission Specialist Tamara E. Jernigan; STS-101 Mission Specialist Edward Tsang Lu (leaning over); a technician with RSC Energia of Korolev, Russia; Manfred Nordhoff, with DaimlerChrysler Aerospace; STS-96 Mission Specialist Daniel T. Barry; and another technician with RSC Energia. They are looking at components of the Russian cargo crane, Strela, to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment on the International Space Station (ISS). Both missions include the SPACEHAB Double Module, carrying internal and resupply cargo for Station outfitting. For the first time, STS-96 will include an Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC) that will carry the Strela; the SPACEHAB Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), which is a logistics items carrier; and a U.S.-built crane (ORU Transfer Device, or OTD) that will be stowed on the station for use during future ISS assembly missions. The ICC can carry up to 6,000 lb of unpressurized payload. It was built for SPACEHAB by DaimlerChrysler Aerospace of Bremen and RSC Energia of Korolev, Russia. STS-96 is targeted for launch on May 24 from Launch Pad 39B. STS-101 is scheduled to launch in early December 1999
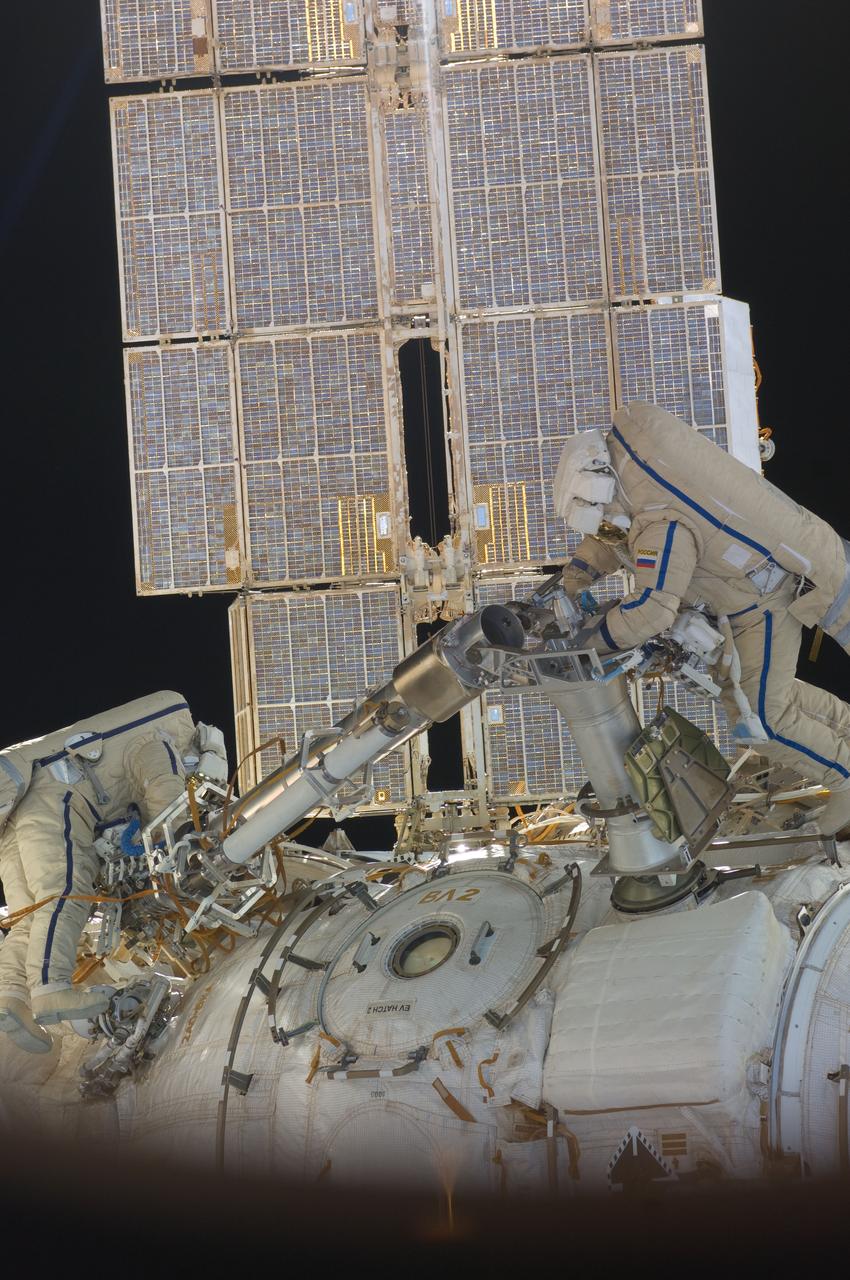

ISS030-E-078393 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
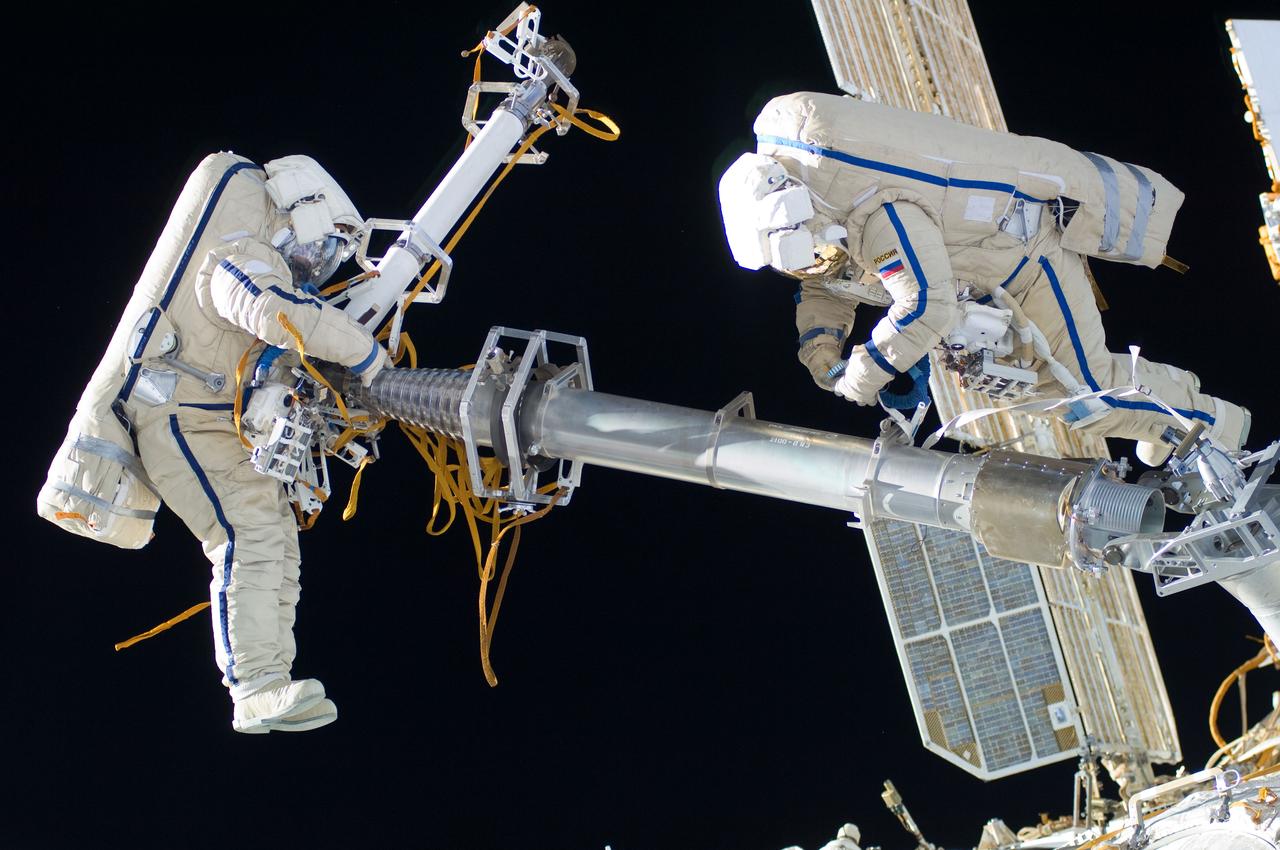

ISS030-E-078533 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
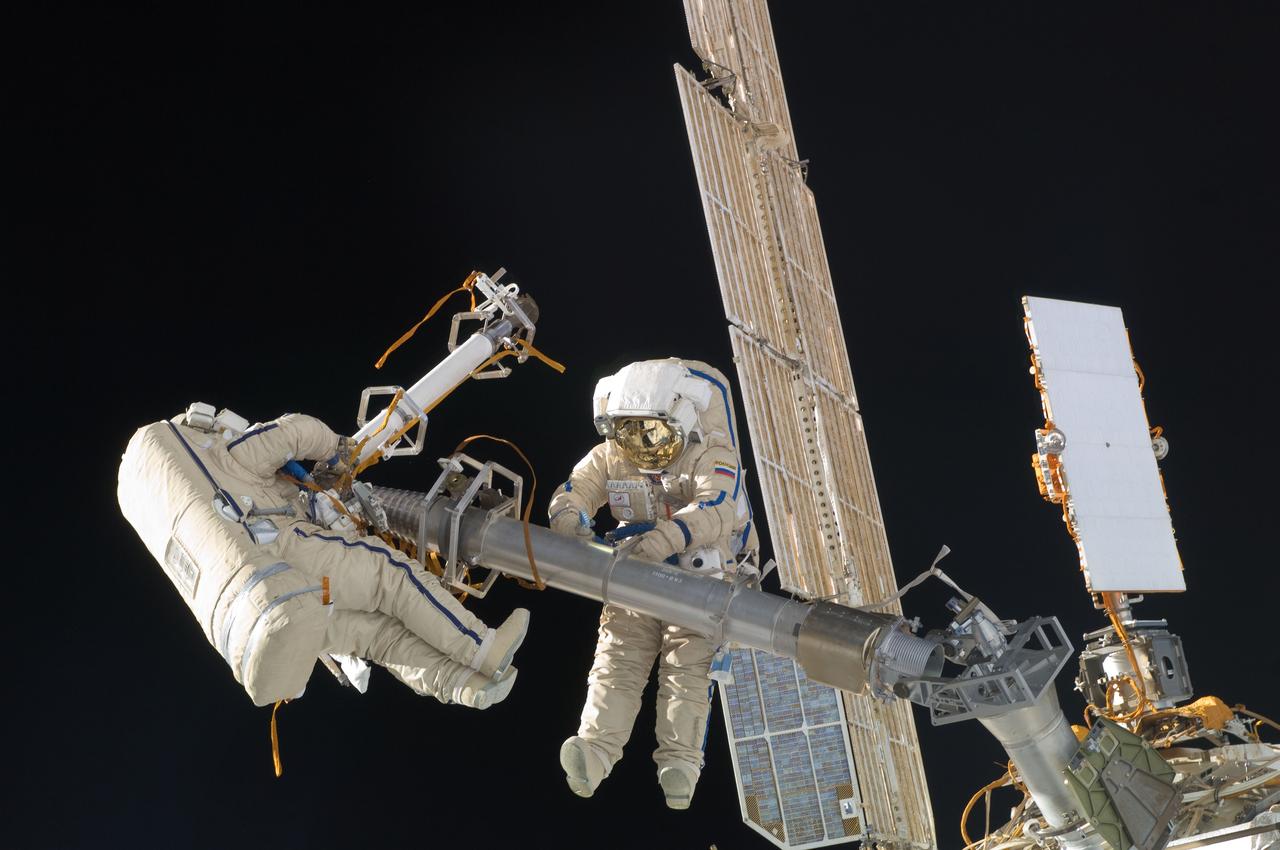

ISS030-E-078372 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
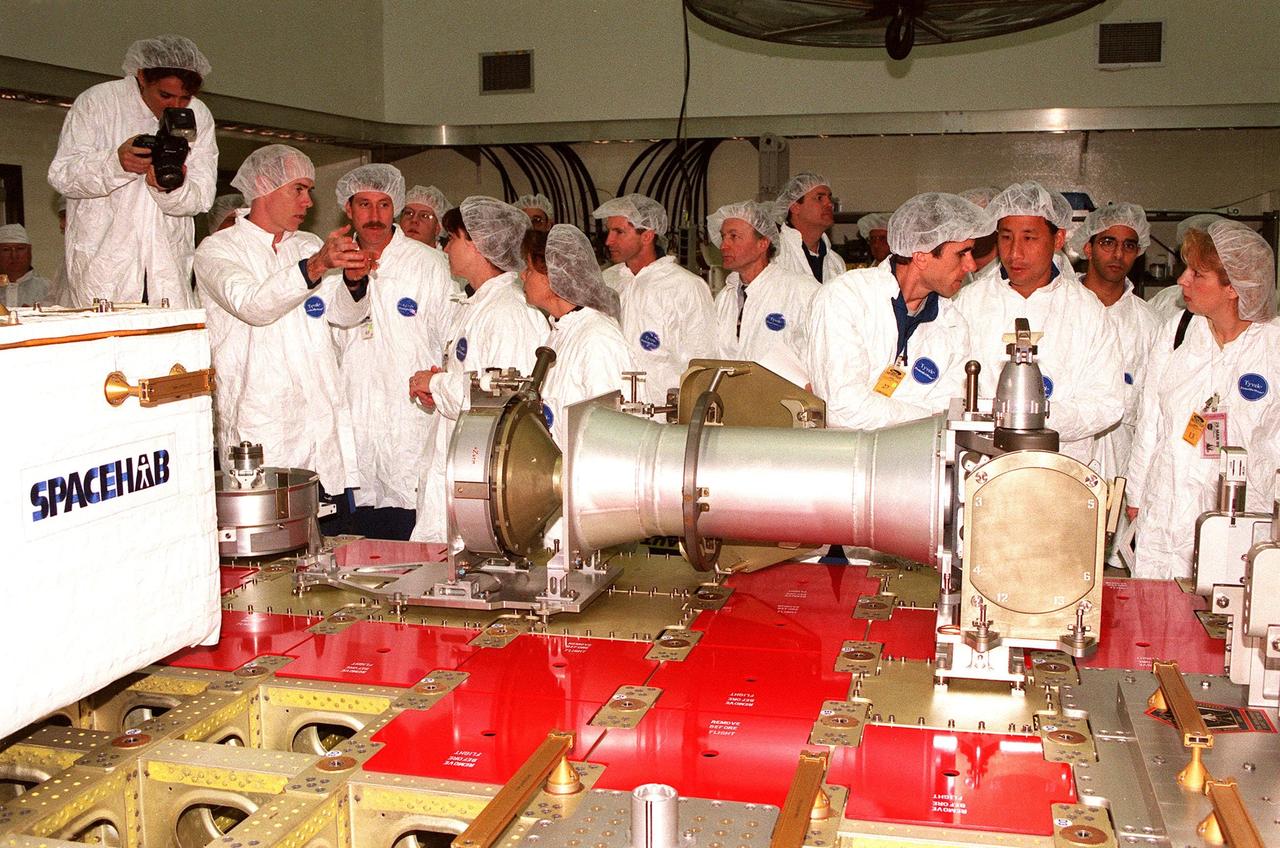

At Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., members of two Shuttle crews look at components of a Russian cargo crane, the Strela, to be mounted to the exterior of the Russian station segment on the International Space Station (ISS). From left are STS-96 Mission Specialist Julie Payette and Daniel T. Barry, Commander Kent V. Rominger and Mission Specialist Tamara E. Jernigan; three technicians from DaimlerChrysler Aerospace; (in the background, facing right) STS-101 Commander James Donald Halsell Jr.; STS-101 Mission Specialists Yuri Ivanovich Malenchenko, with the Russian Space Agency, and Edward Tsang Lu; and two more technicians from DaimlerChrysler. Both missions include the SPACEHAB Double Module, carrying internal and resupply cargo for Station outfitting. For the first time, STS-96 will include an Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC) that will carry the Strela; the SPACEHAB Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), which is a logistics items carrier; and a U.S.-built crane (ORU Transfer Device, or OTD) that will be stowed on the station for use during future ISS assembly missions. The ICC can carry up to 6,000 lb of unpressurized payload. It was built for SPACEHAB by DaimlerChrysler and RSC Energia of Korolev, Russia. STS-96 is targeted for launch on May 24 from Launch Pad 39B. STS-101 is scheduled to launch in early December 1999
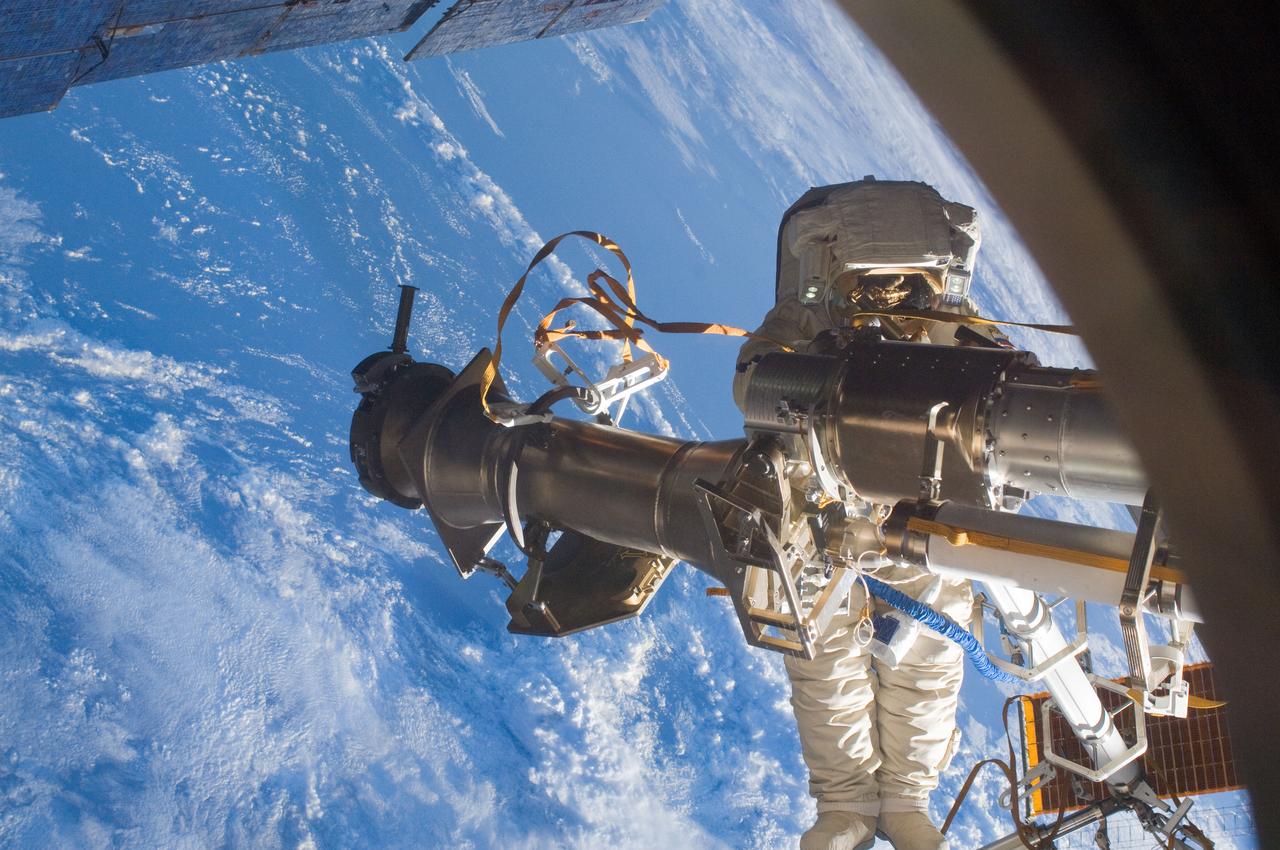

ISS030-E-079919 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
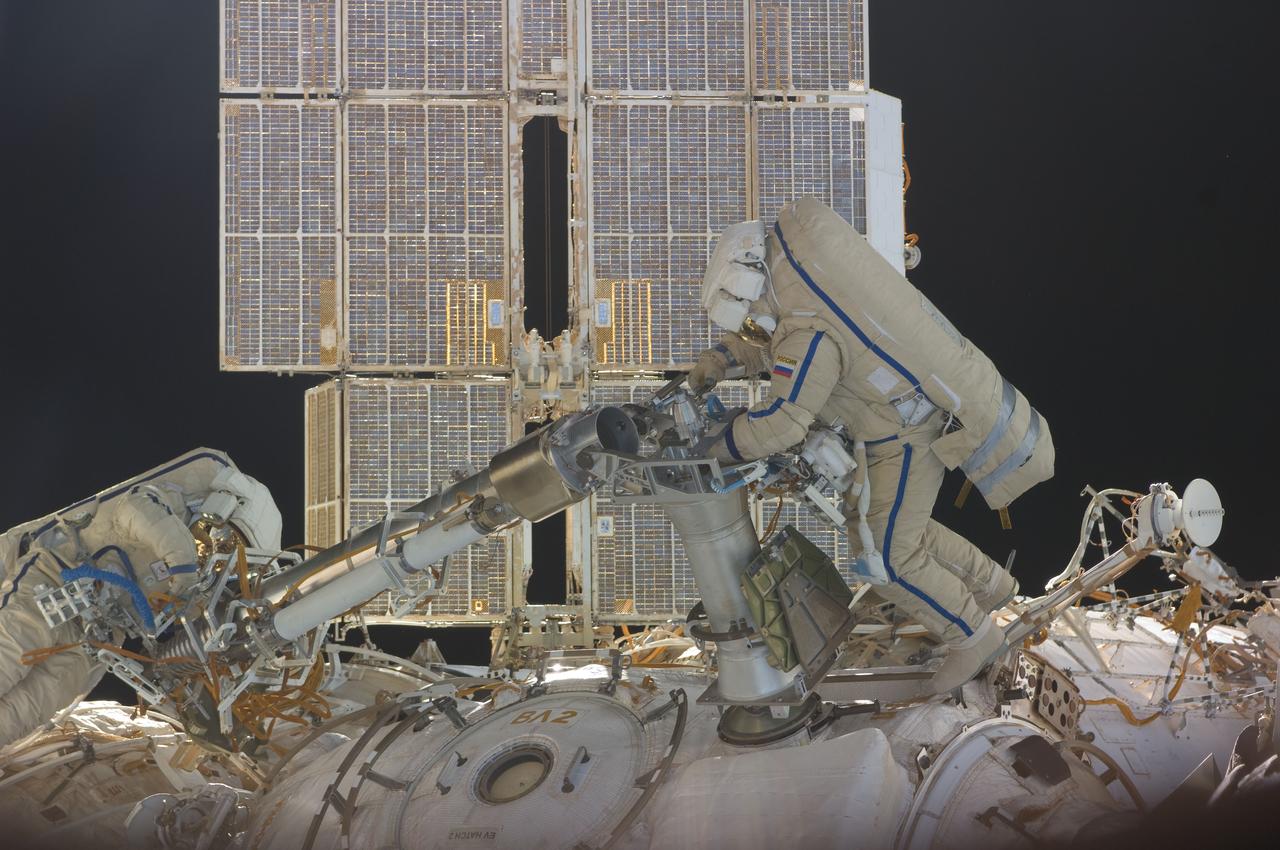

ISS030-E-078391 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.

ISS030-E-078511 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
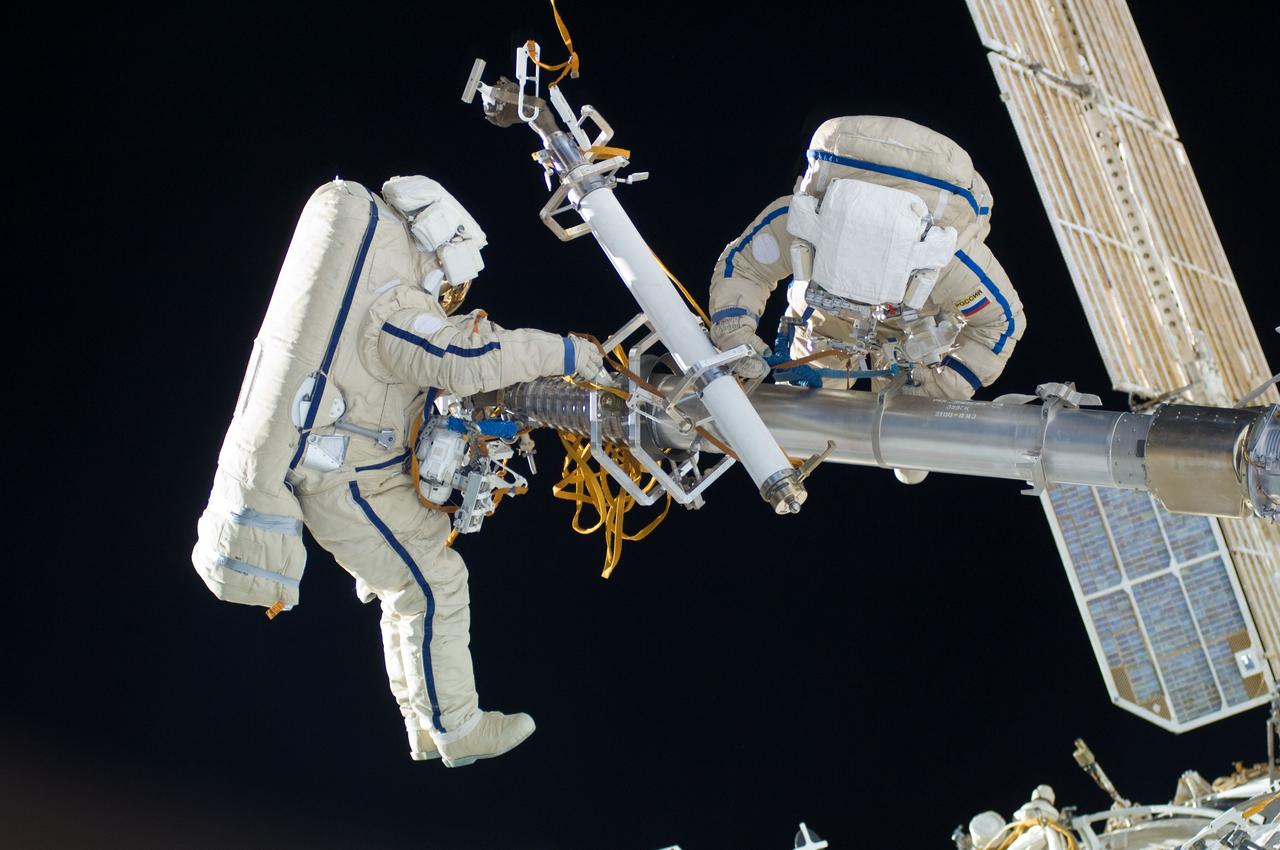

ISS030-E-078537 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
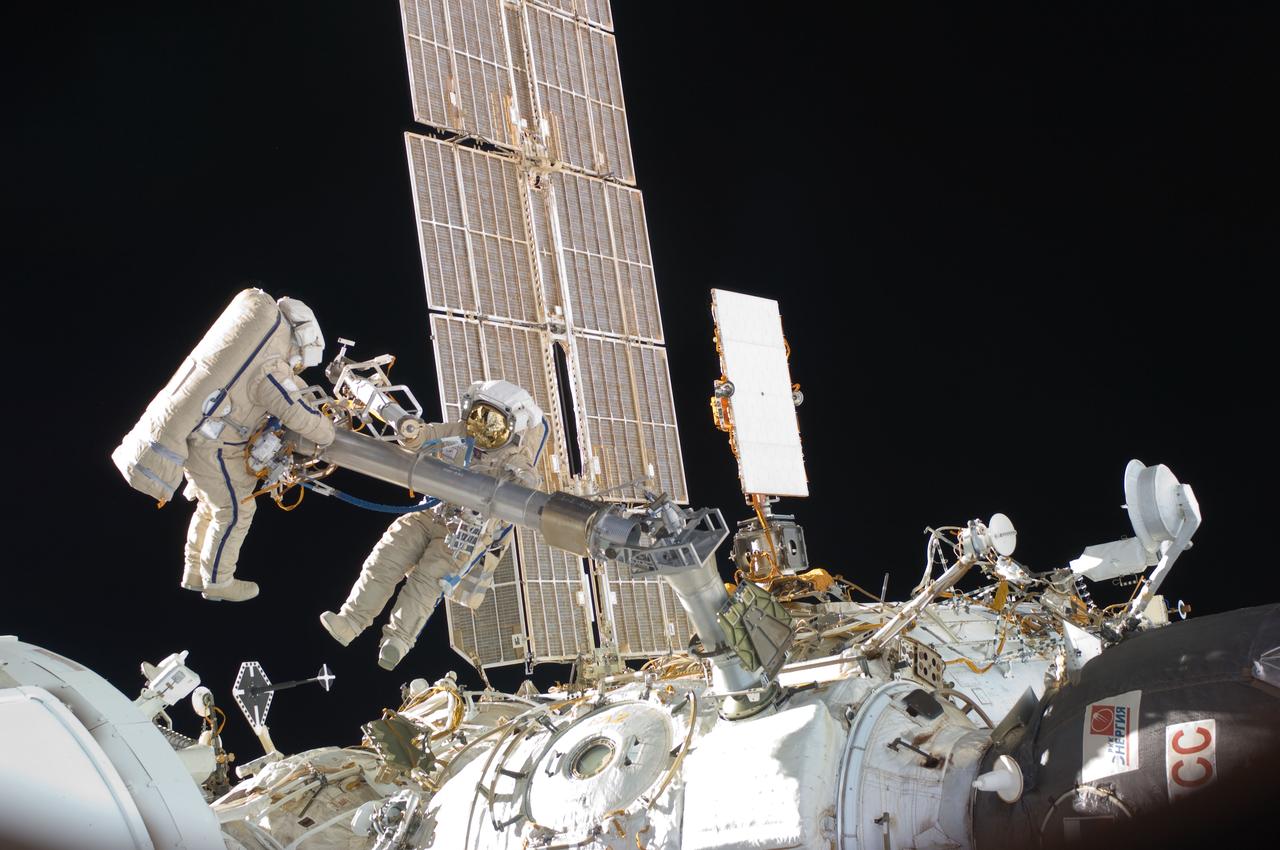

ISS030-E-078385 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
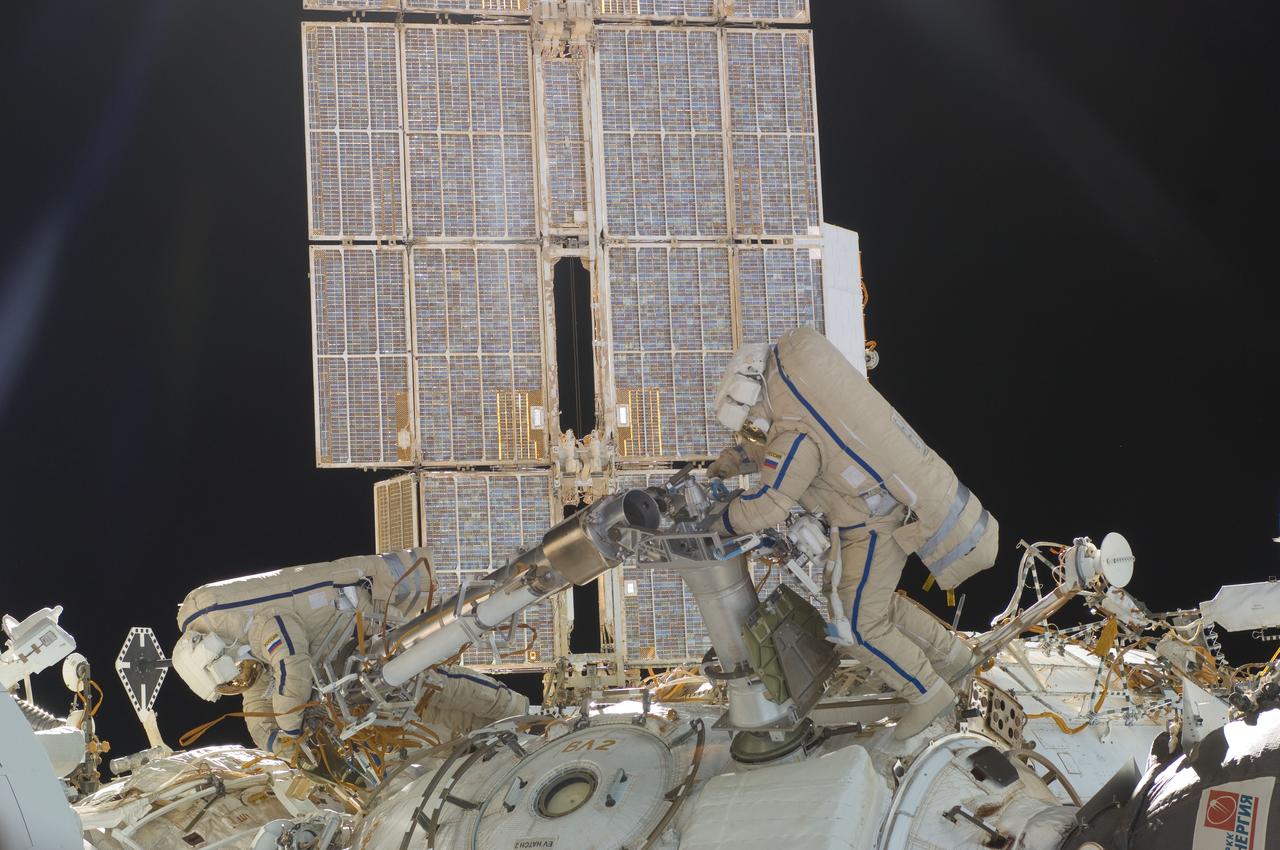

ISS030-E-078388 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
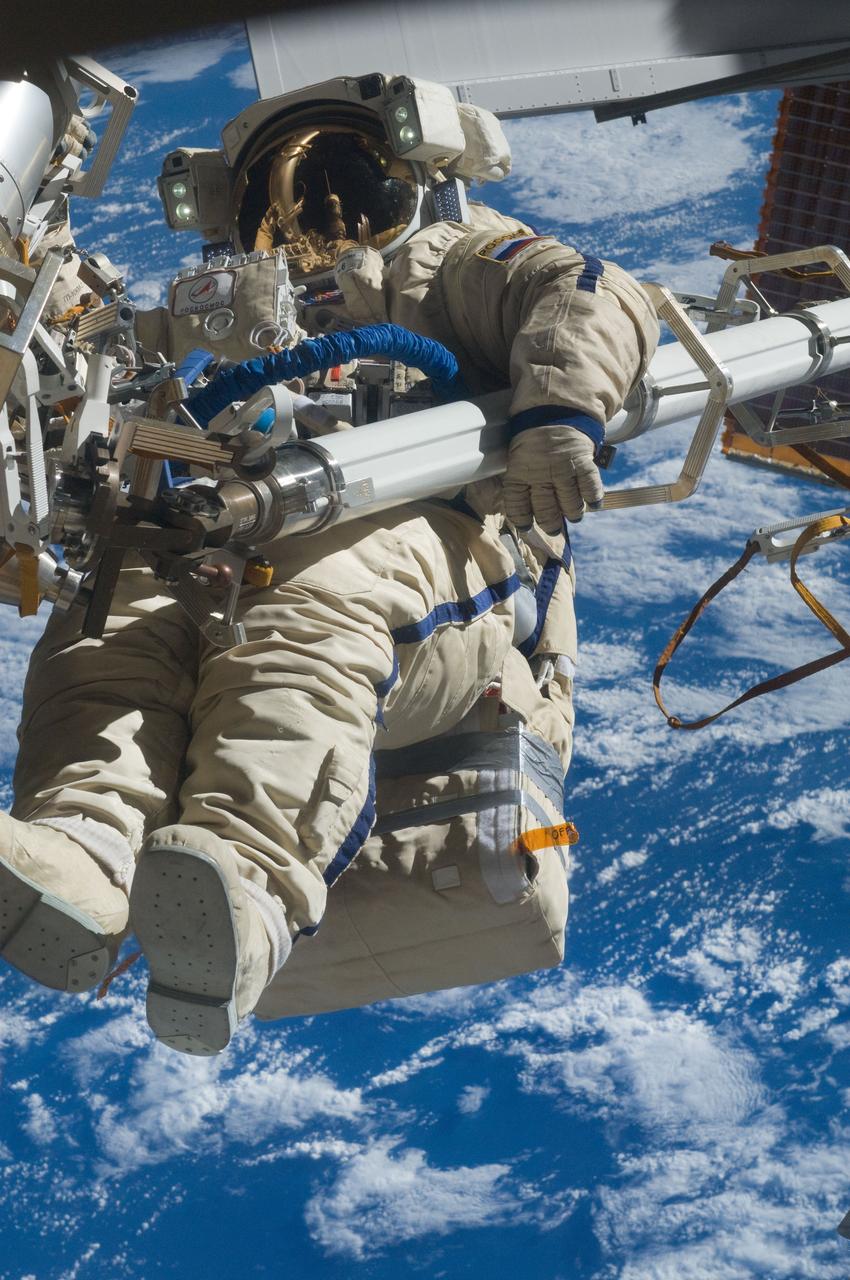

ISS030-E-079937 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Anton Shkaplerov, Expedition 30 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Shkaplerov and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.

ISS030-E-078532 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
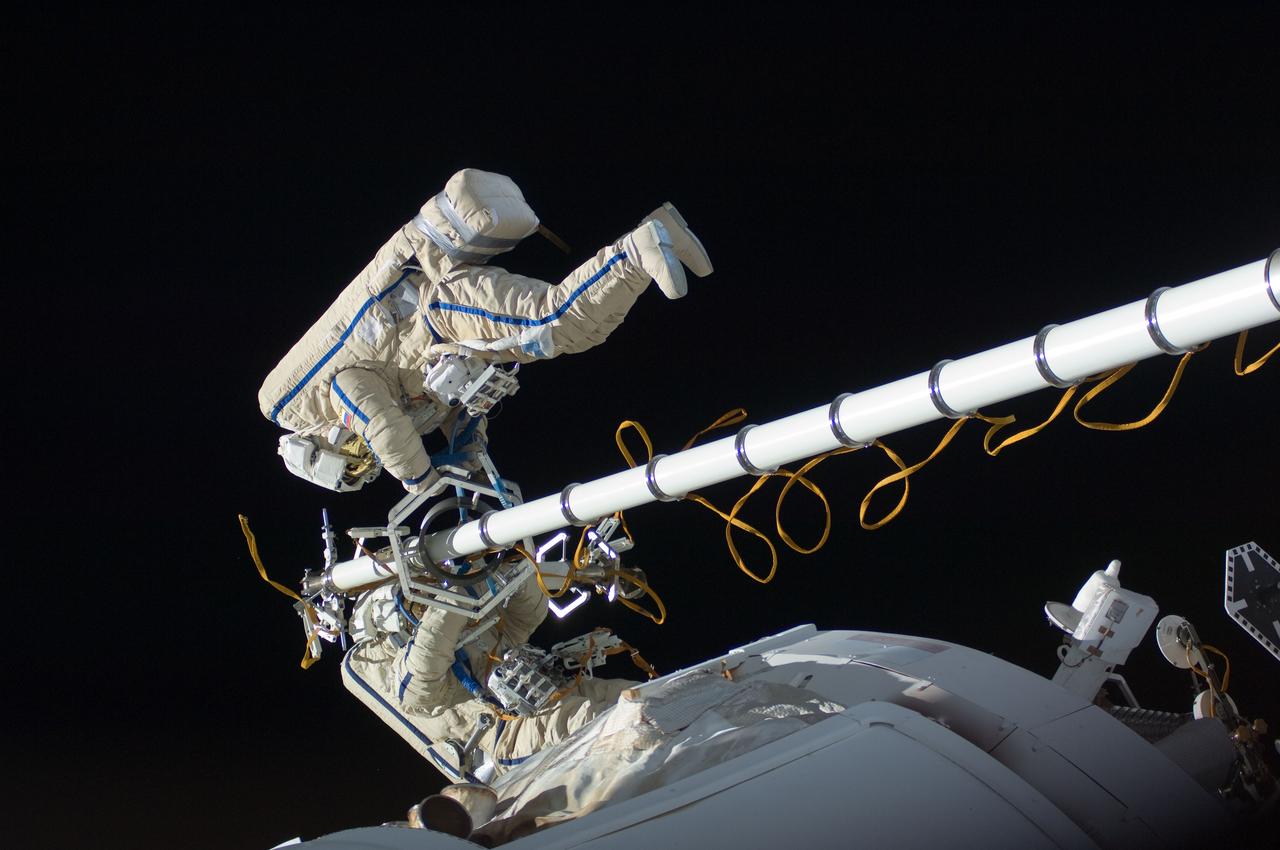

ISS030-E-078522 (16 Feb. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Oleg Kononenko and Anton Shkaplerov, both Expedition 30 flight engineers, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the six-hour, 15-minute spacewalk, Kononenko and Shkaplerov moved the Strela-1 crane from the Pirs Docking Compartment to begin preparing the Pirs for its replacement next year with a new laboratory and docking module. The duo used another boom, the Strela-2, to move the hand-operated crane to the Poisk module for future assembly and maintenance work. Both telescoping booms extend like fishing rods and are used to move massive components outside the station. On the exterior of the Poisk Mini-Research Module 2 (MRM2), they also installed the Vinoslivost Materials Sample Experiment, which will investigate the influence of space on the mechanical properties of the materials. The spacewalkers also collected a test sample from underneath the insulation on the Zvezda Service Module to search for any signs of living organisms. Both spacewalkers wore Russian Orlan spacesuits bearing blue stripes and equipped with NASA helmet cameras.
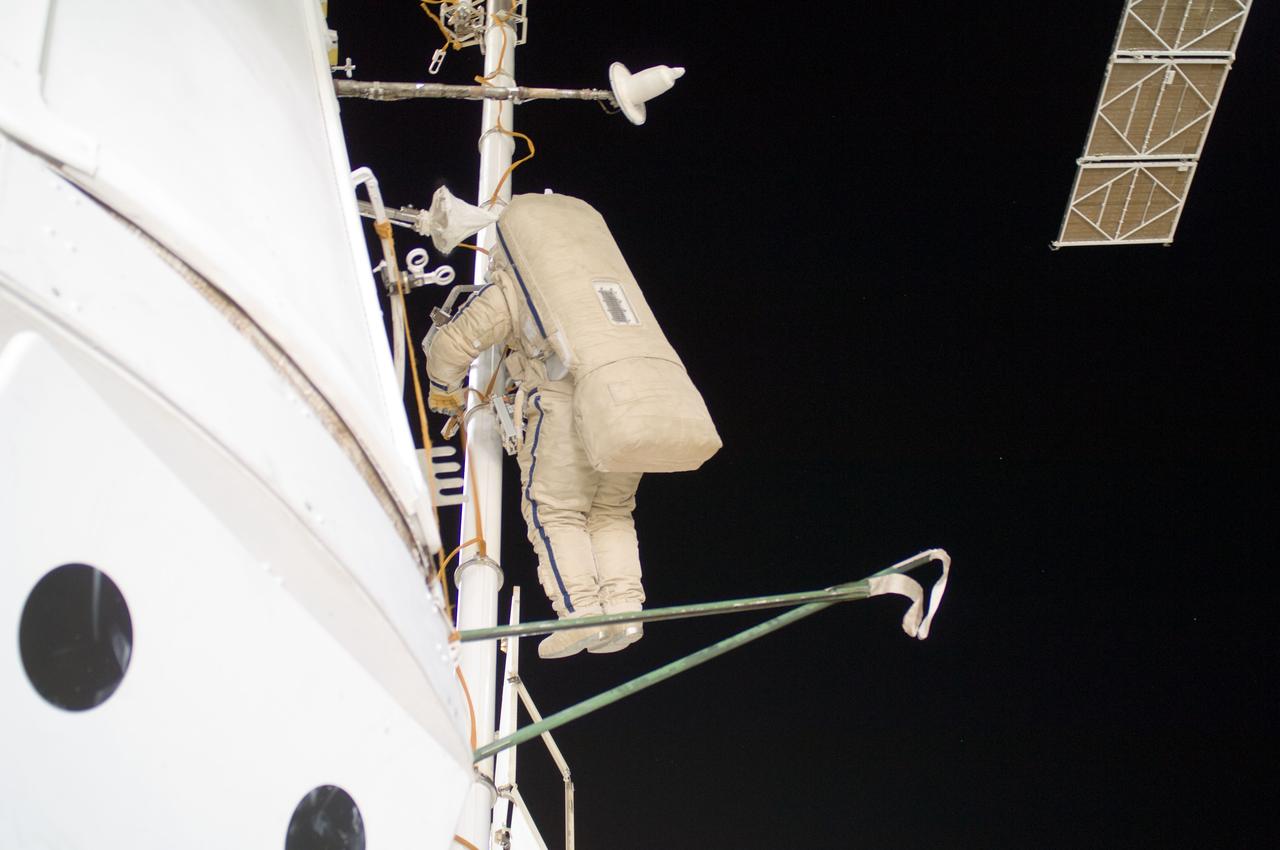

ISS032-E-020884 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
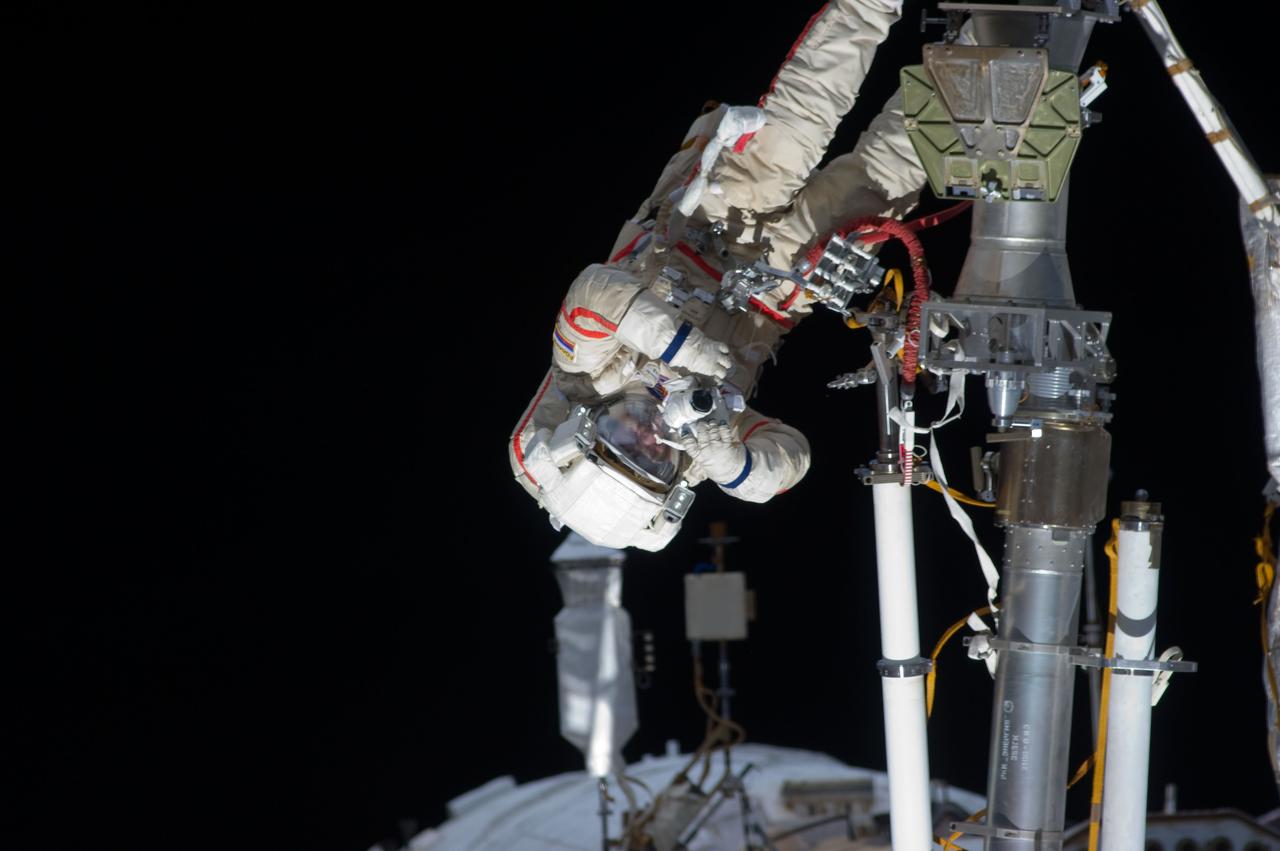

ISS032-E-021078 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, uses a still camera during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

ISS032-E-021054 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
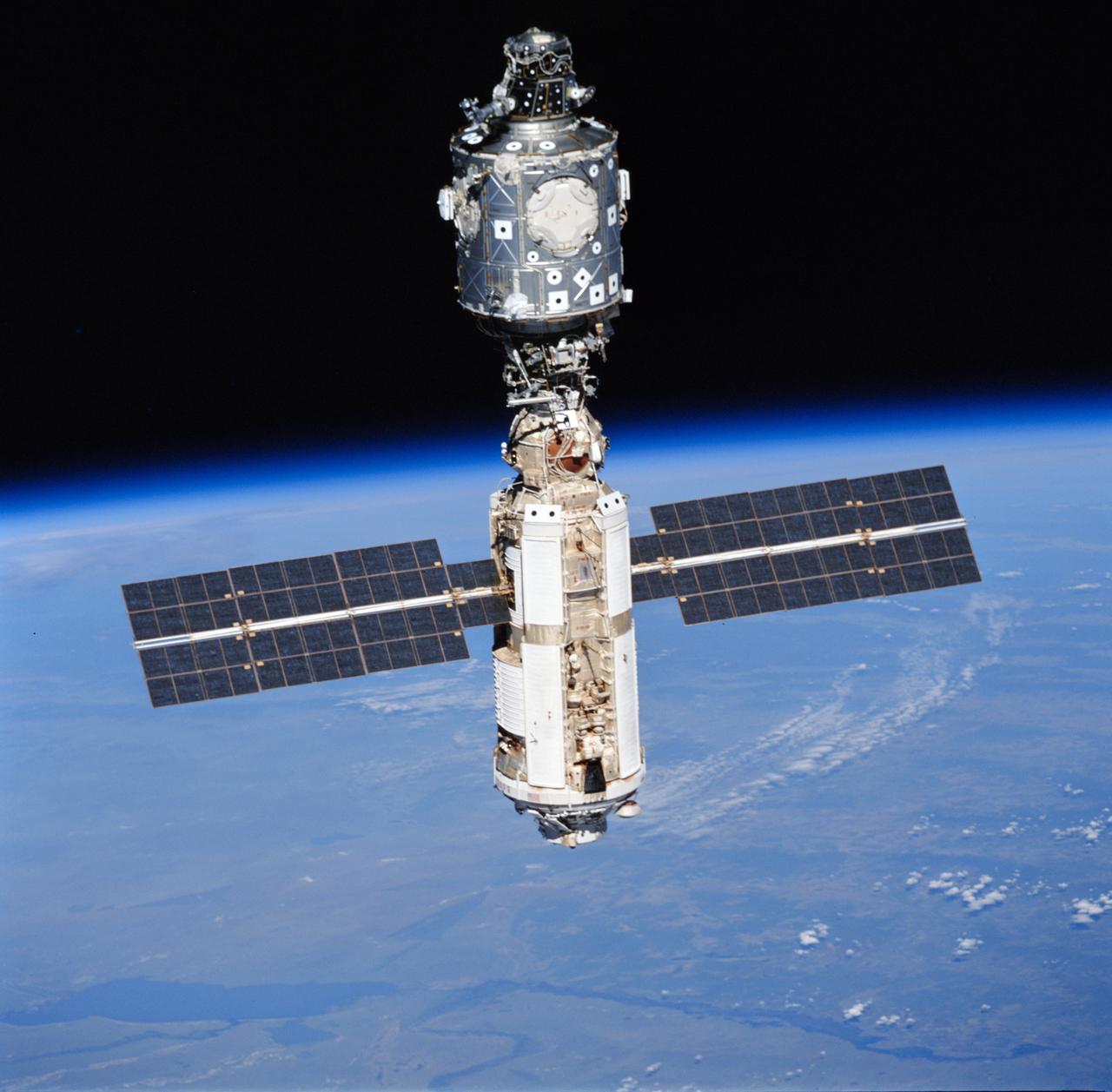

STS096-715-042 (3 June 1999) --- A STS-96 crew member aboard Discovery recorded this image of the International Space Station (ISS) with a 70mm camera during a fly-around following separation of the two spacecraft. Lake Hulun Nur in the People's Republic of China is visible in the lower left portion of the frame. A portion of the work performed on the May 30 space walk by astronauts Tamara E. Jernigan and Daniel T. Barry is evident at various points on the ISS, including the installation of the Russian-built crane (called Strela) and the U.S.-built crane.
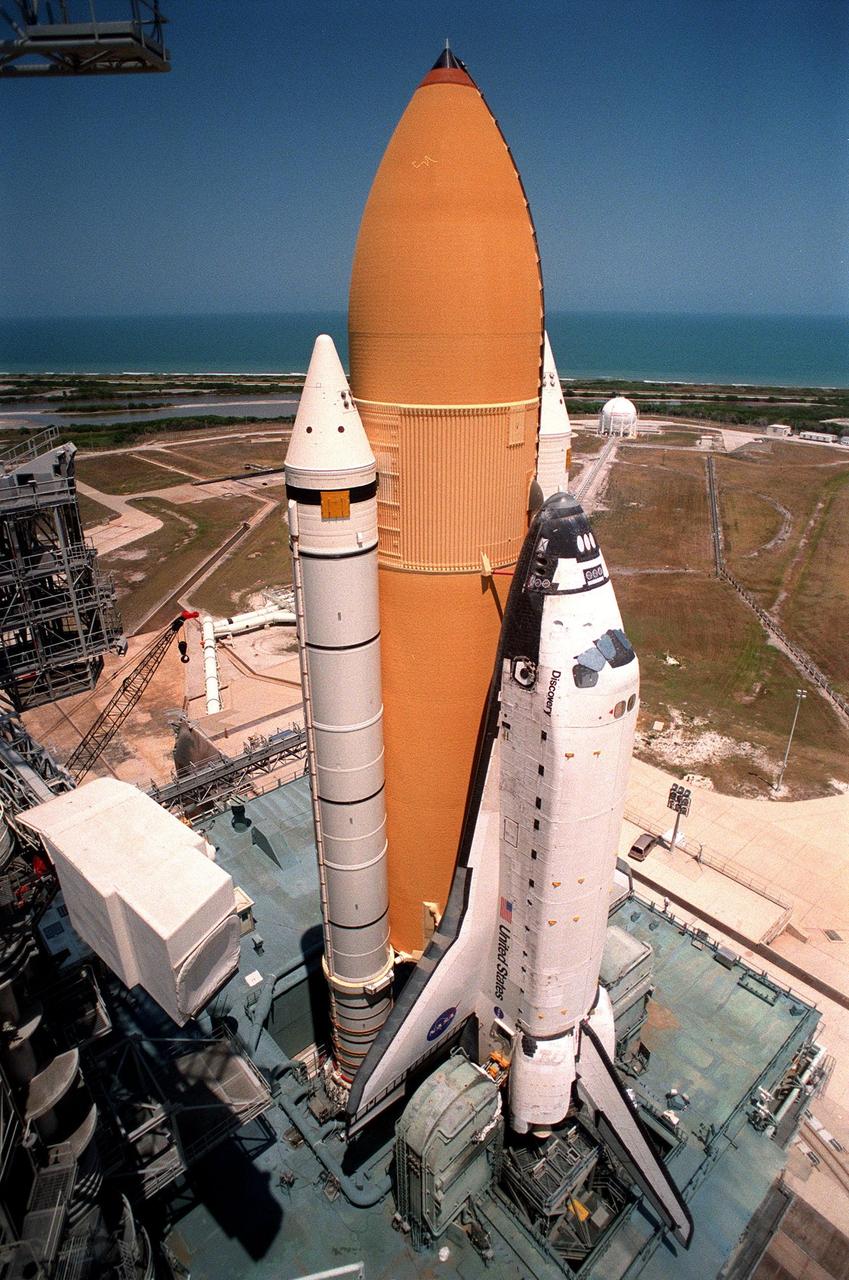

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Space Shuttle Discovery sits on launch Pad 39B, waiting for the rotating service structure to be moved into place for final launch preparations. At the top left of the photo is the end of the hammerhead crane, on the fixed service structure, that provides hoisting services required in pad operations. Liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96 is targeted for May 20 at 9:32 a.m. EDT. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment
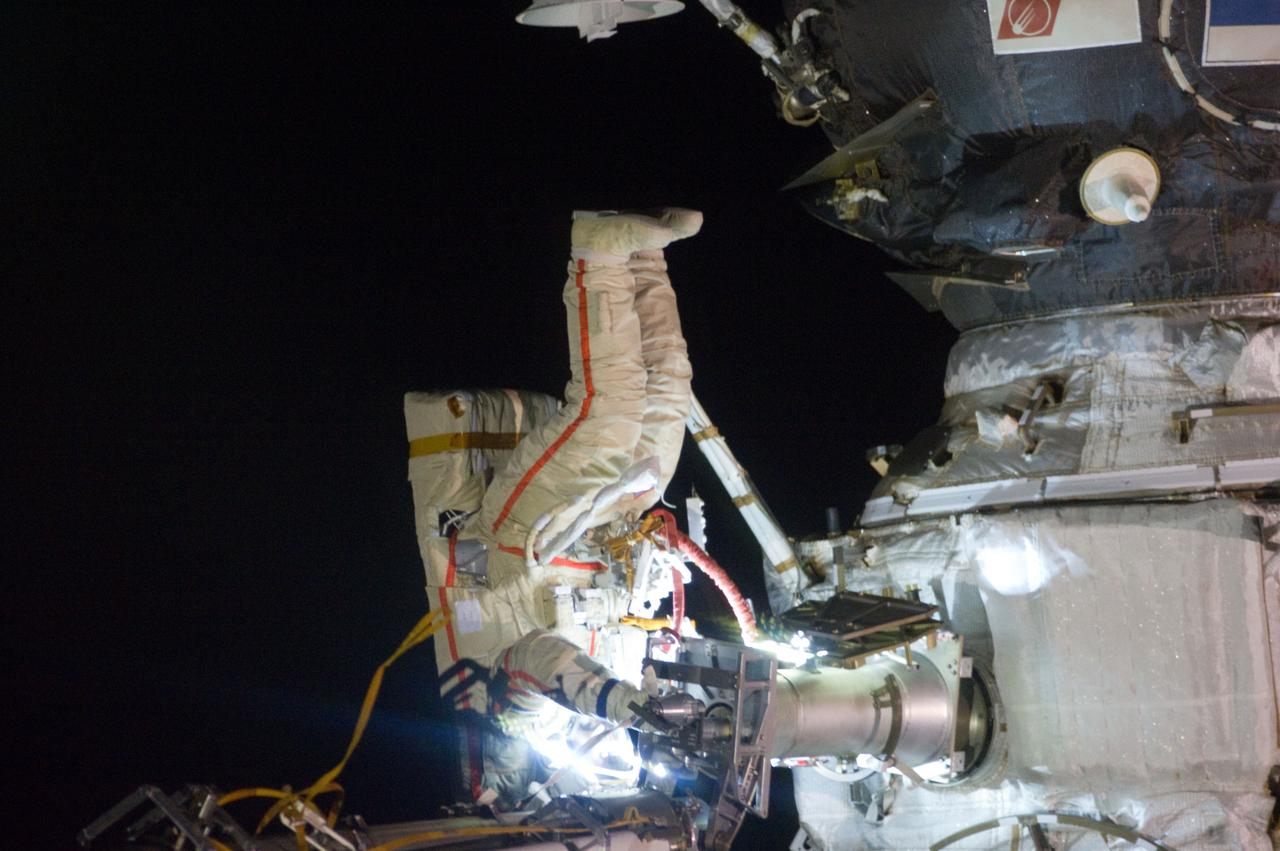

ISS032-E-021037 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
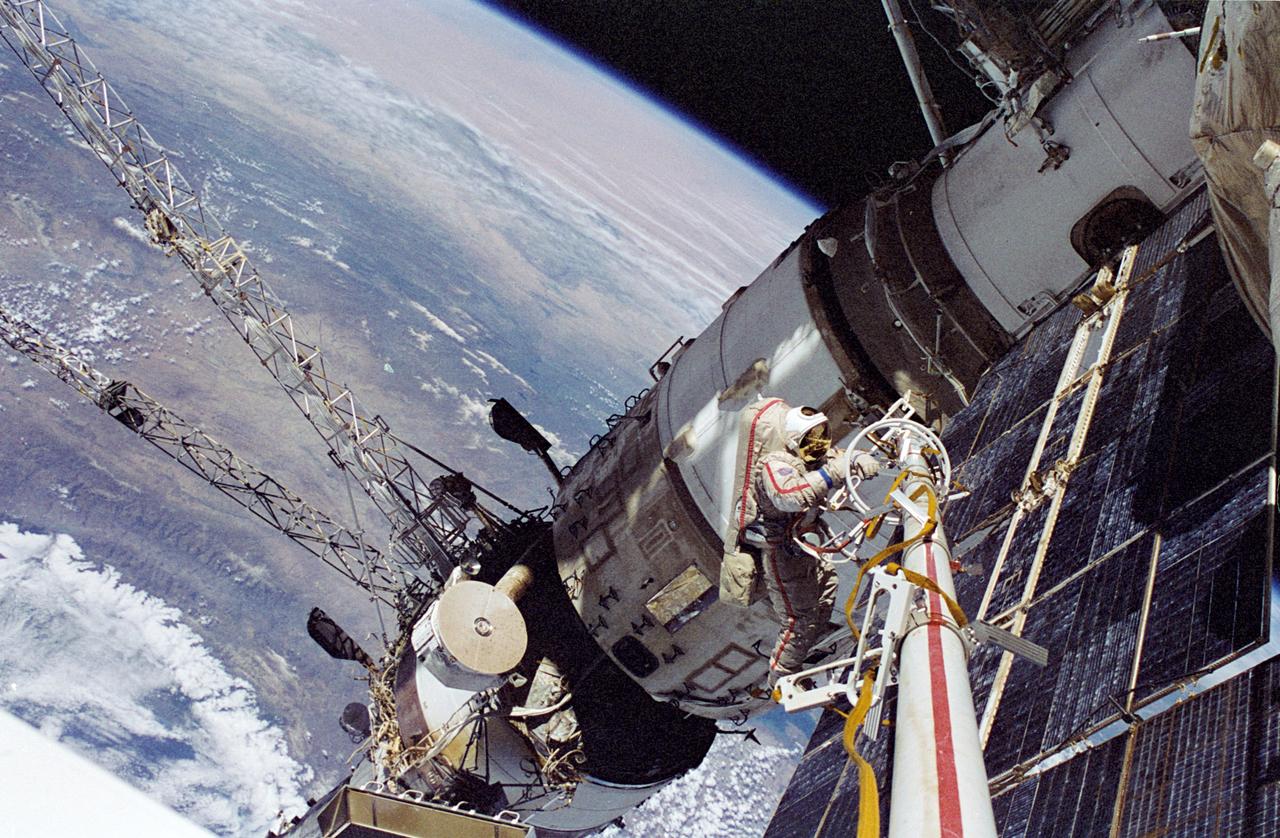

NM23-48-003 (29 April 1997) --- Cosmonaut Vasili V. Tsibliyev, Mir-23 commander, operates at the end of the Russian Mir Space Station’s STRELA boom during a space walk on April 29, 1997. He was joined by United States astronaut Jerry M. Linenger, cosmonaut guest researcher, in an effort to deploy scientific instruments and retrieve other science hardware. At the lower left of the picture is the Kvant-1 module. Hovering above it is the Sofora tower, which was once used for an experiment in attitude control of the Mir.
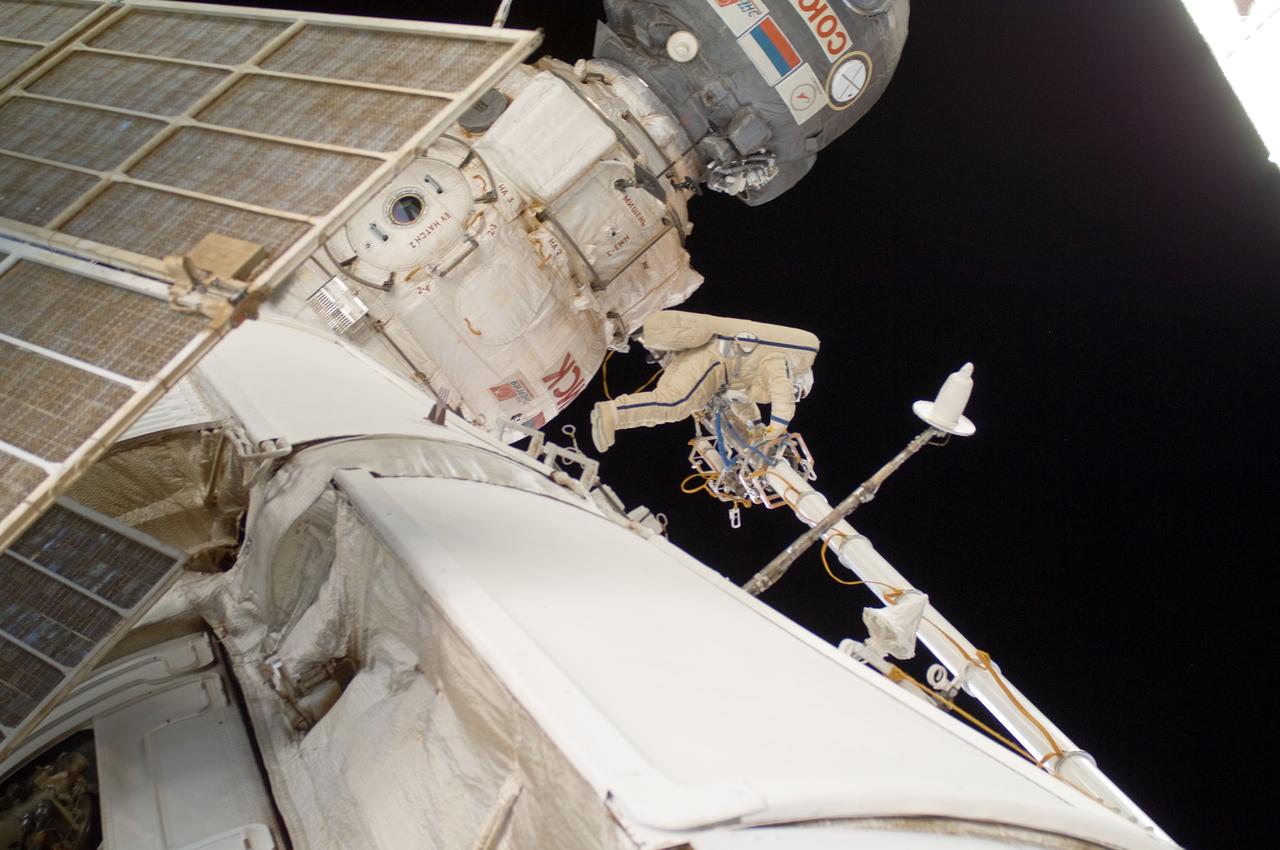

ISS032-E-020892 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
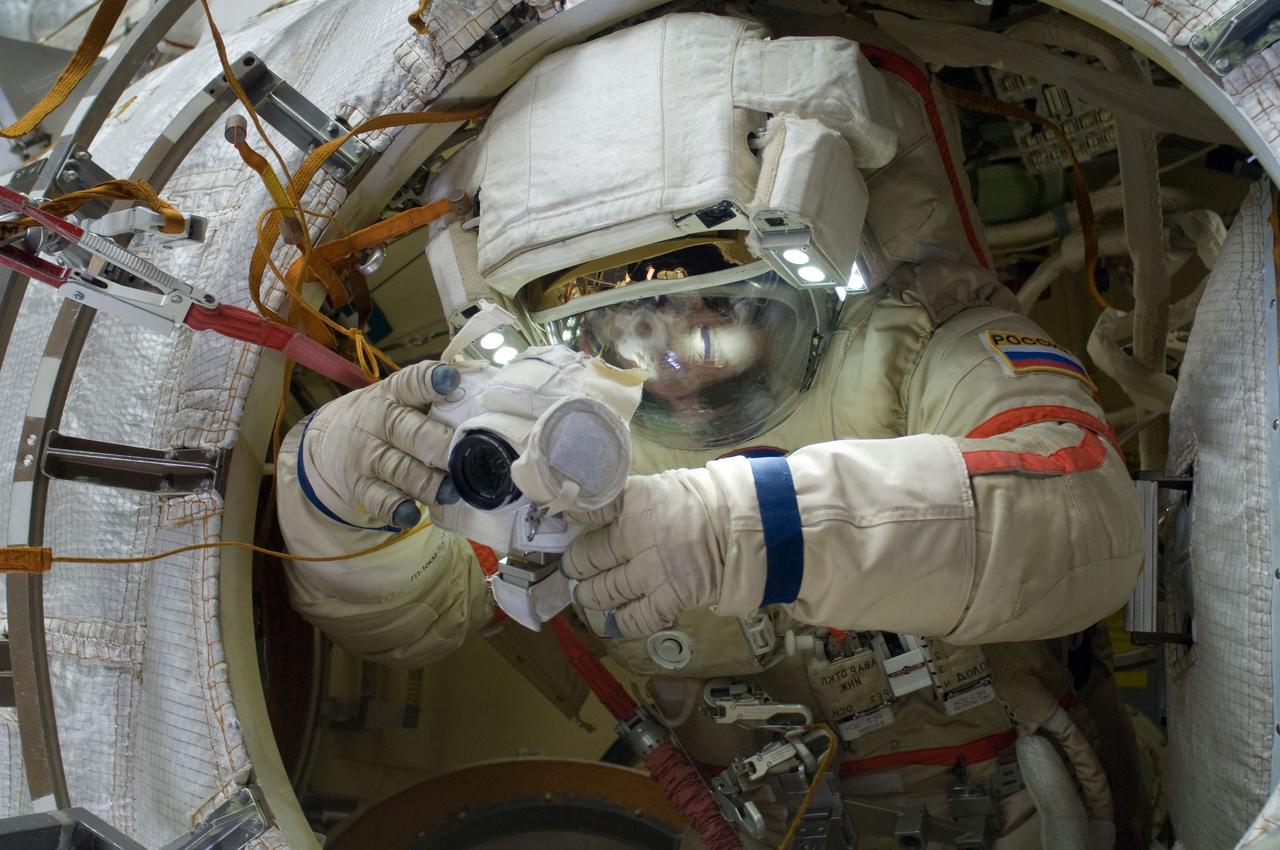

ISS032-E-020619 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, uses a still camera during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
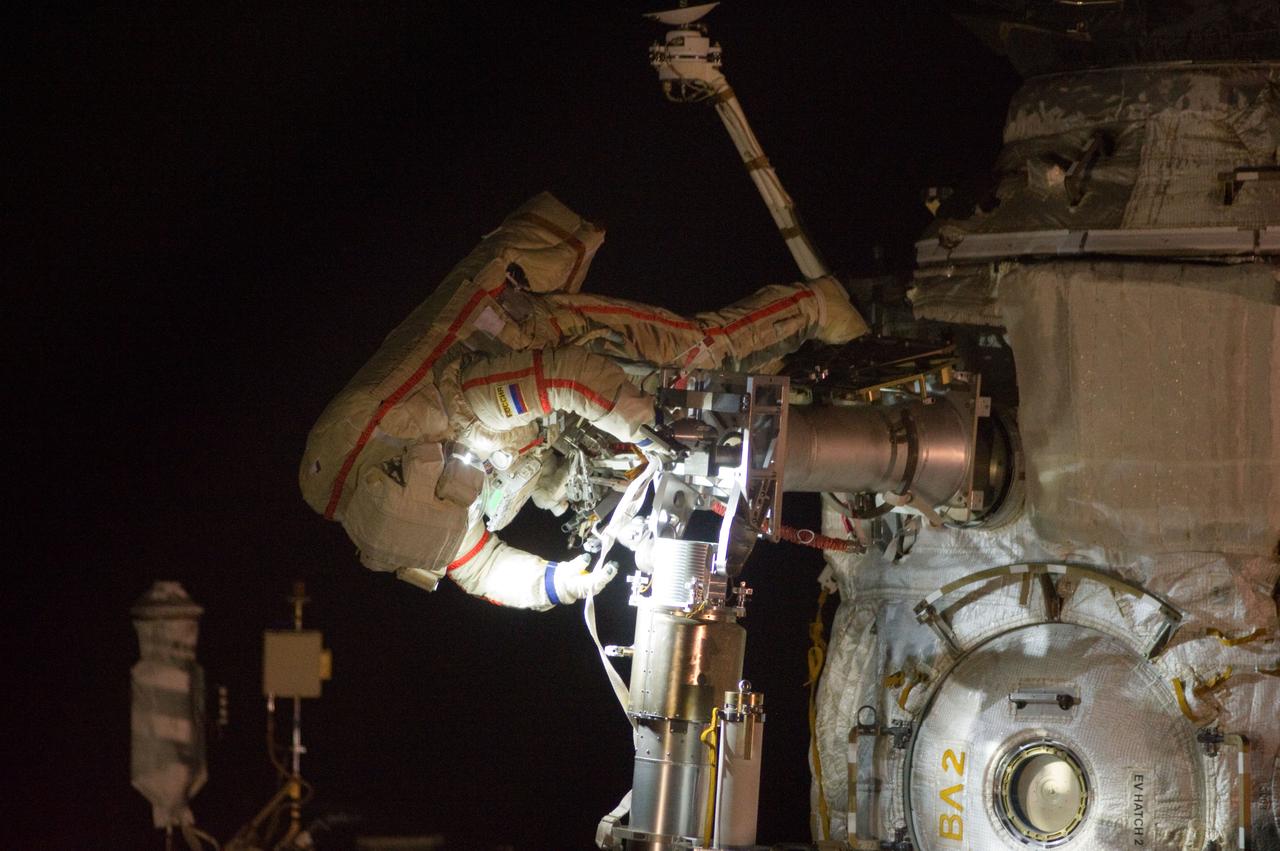

ISS032-E-021024 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
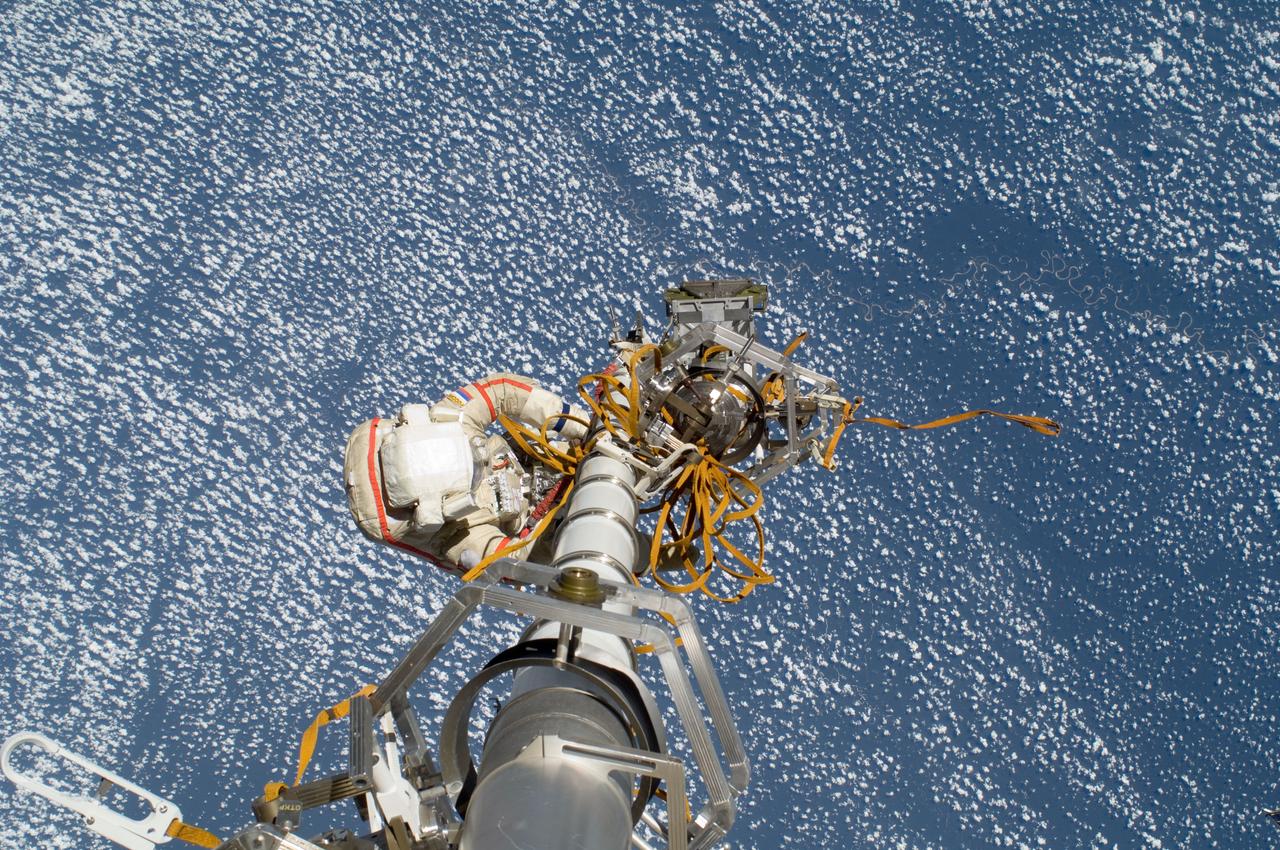

ISS032-E-020581 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
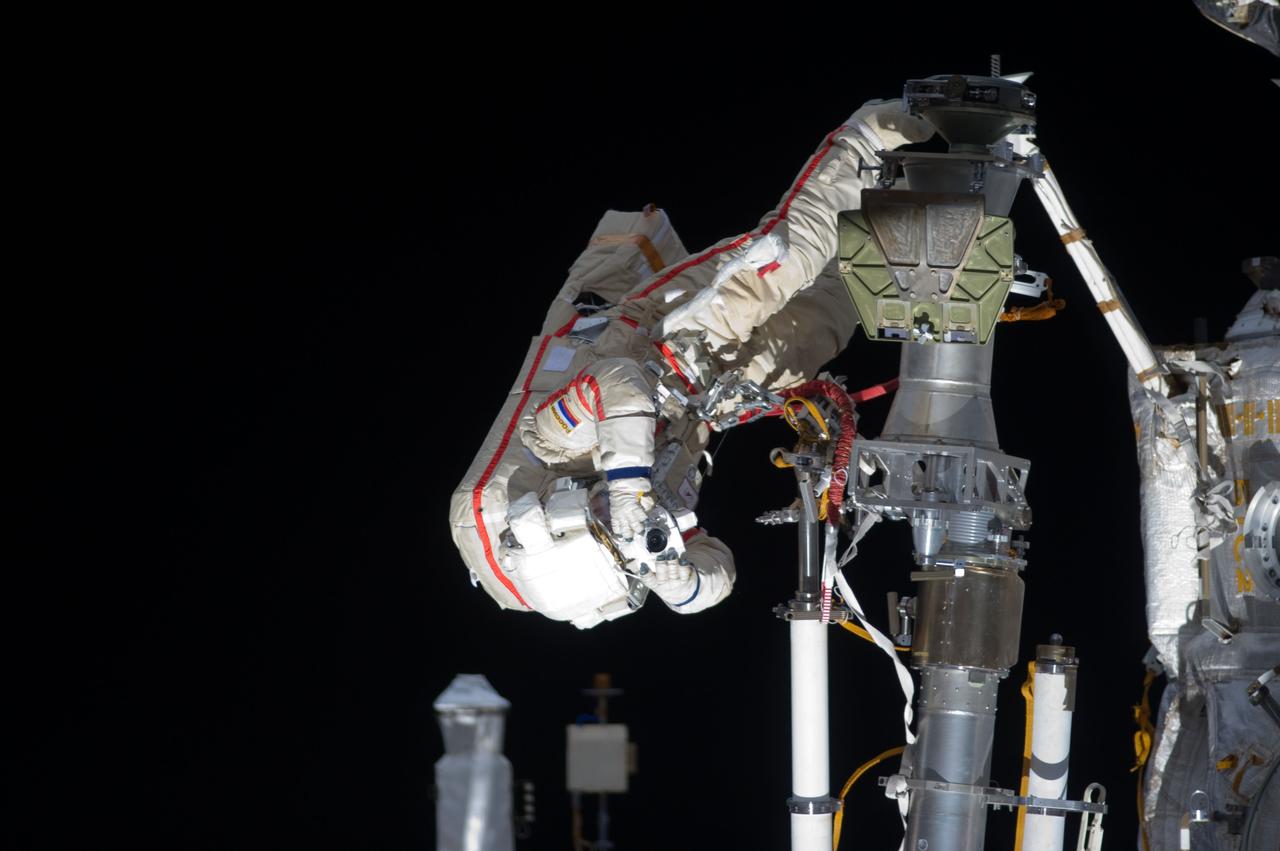
ISS032-E-021072 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, uses a still camera during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
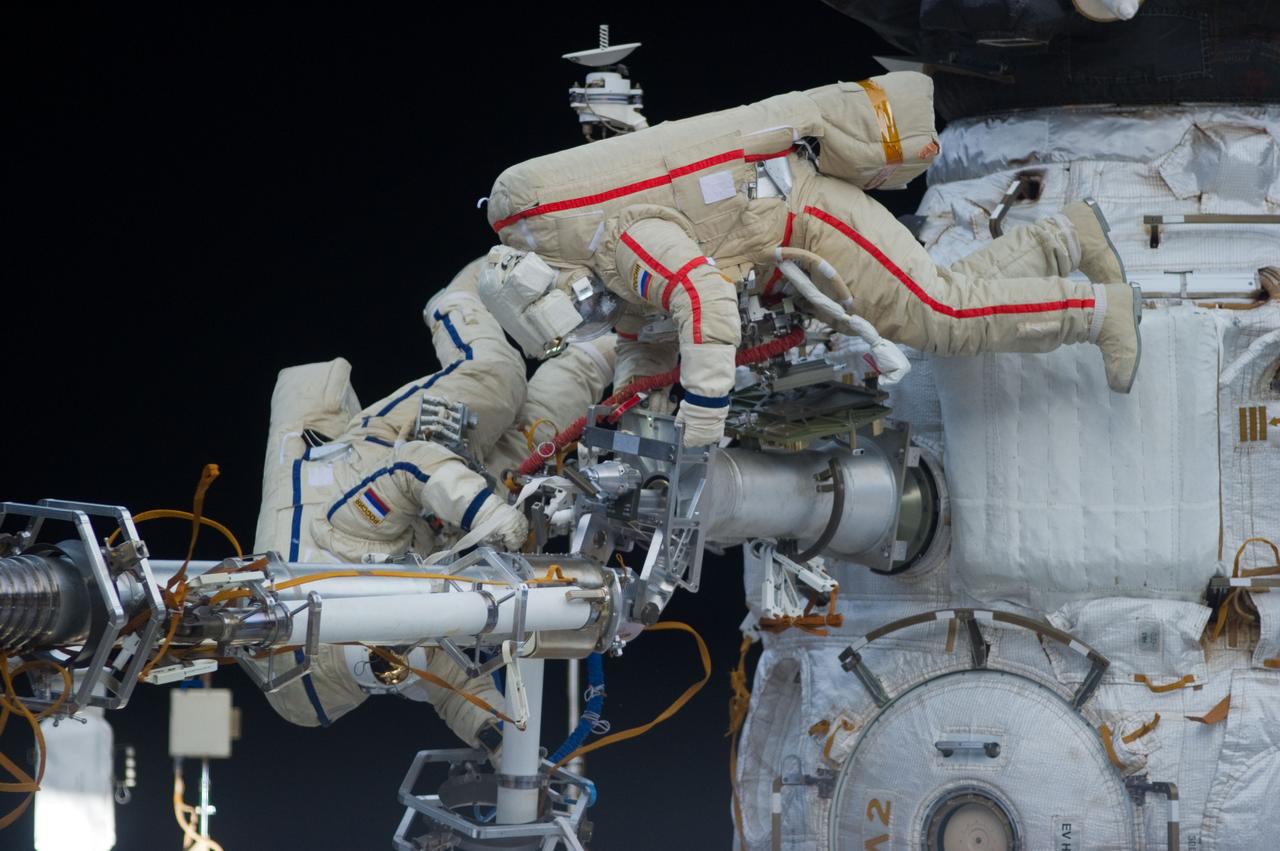

ISS032-E-021061 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
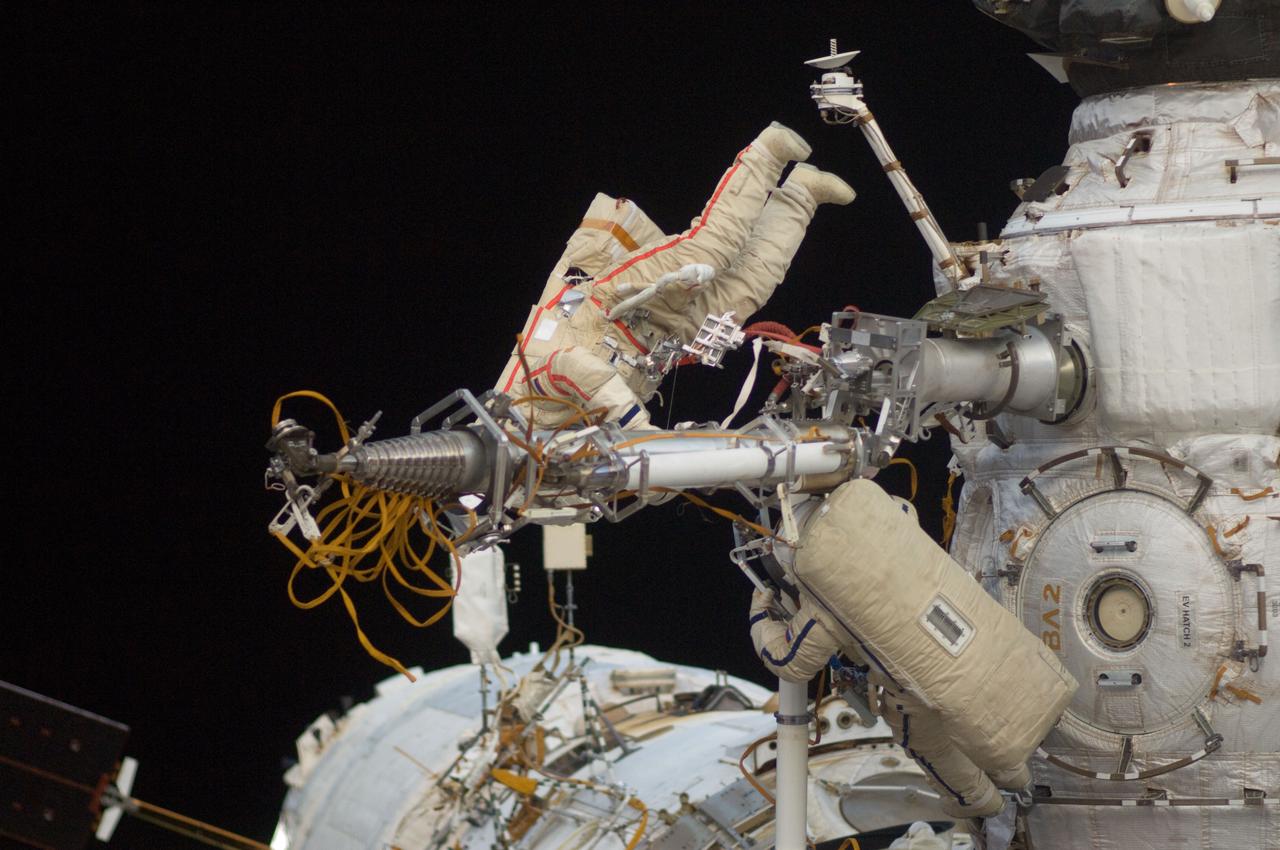

ISS032-E-021286 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
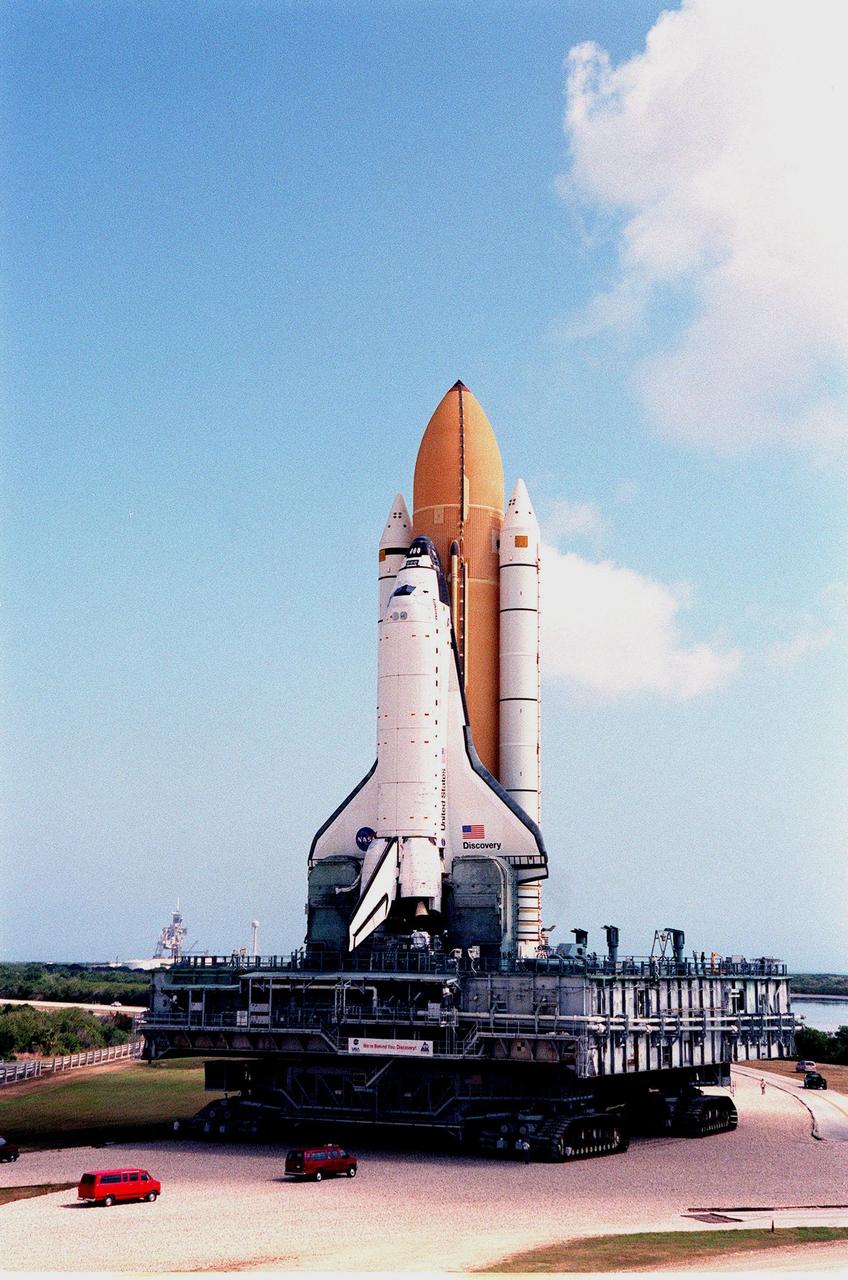
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Discovery, atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler-transporter, approaches the turn in the crawlerway as it creeps to Launch Pad 39B at 1 mph. The crawler-transporter takes about five hours to cover the journey from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. Liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96 is targeted for May 20 at 9:32 a.m. EDT. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment
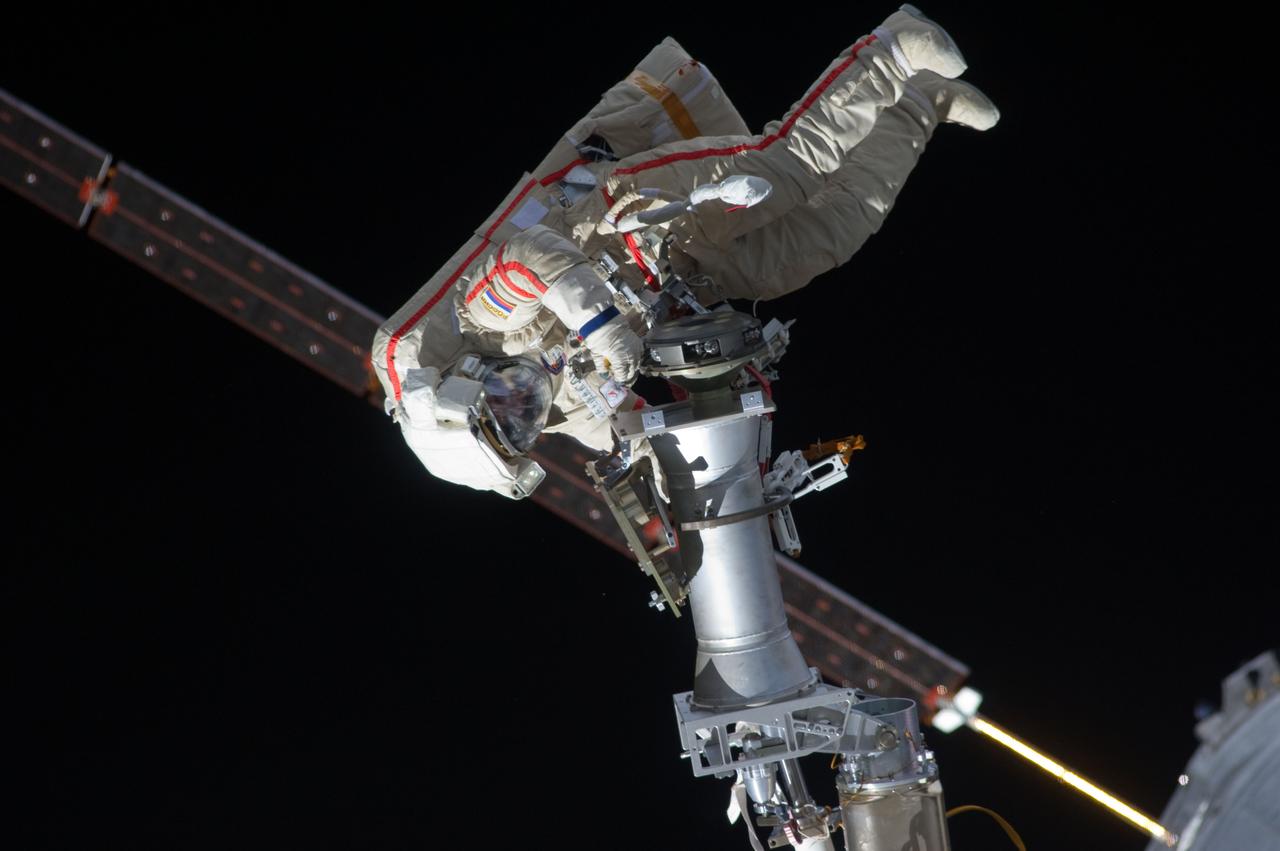

ISS032-E-021085 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

ISS032-E-020683 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
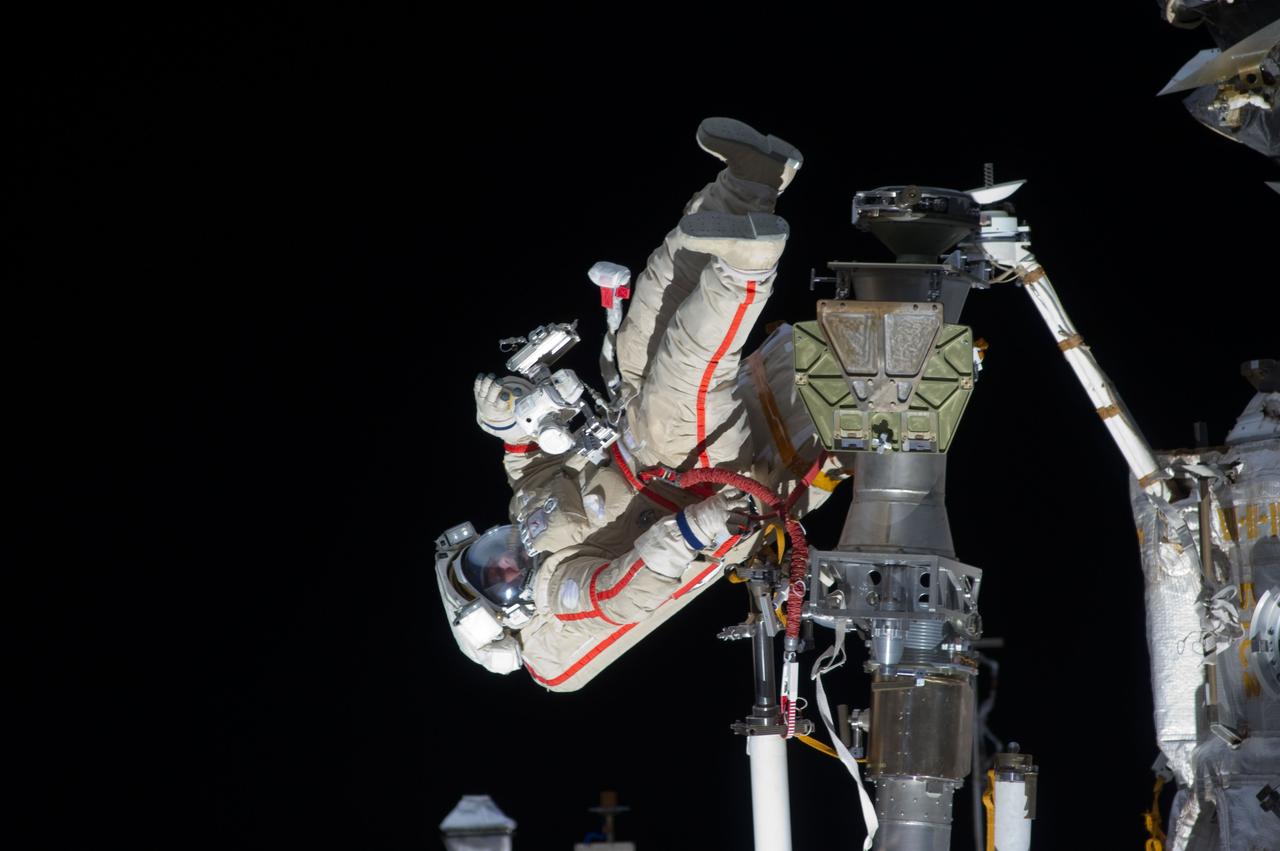
ISS032-E-021080 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

ISS032-E-020576 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
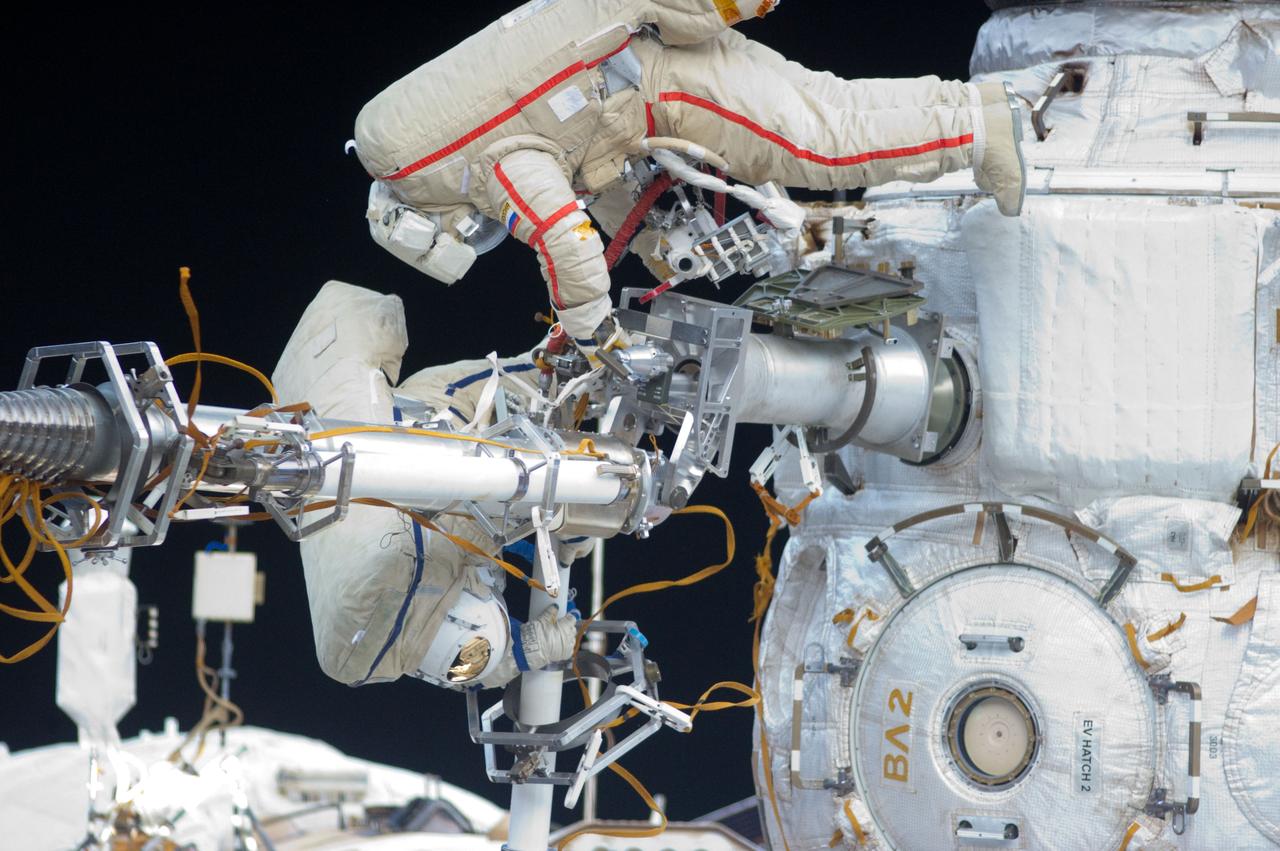
ISS032-E-021060 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

ISS032-E-020596 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, deploys a small ball-shaped science satellite during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, also moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module.
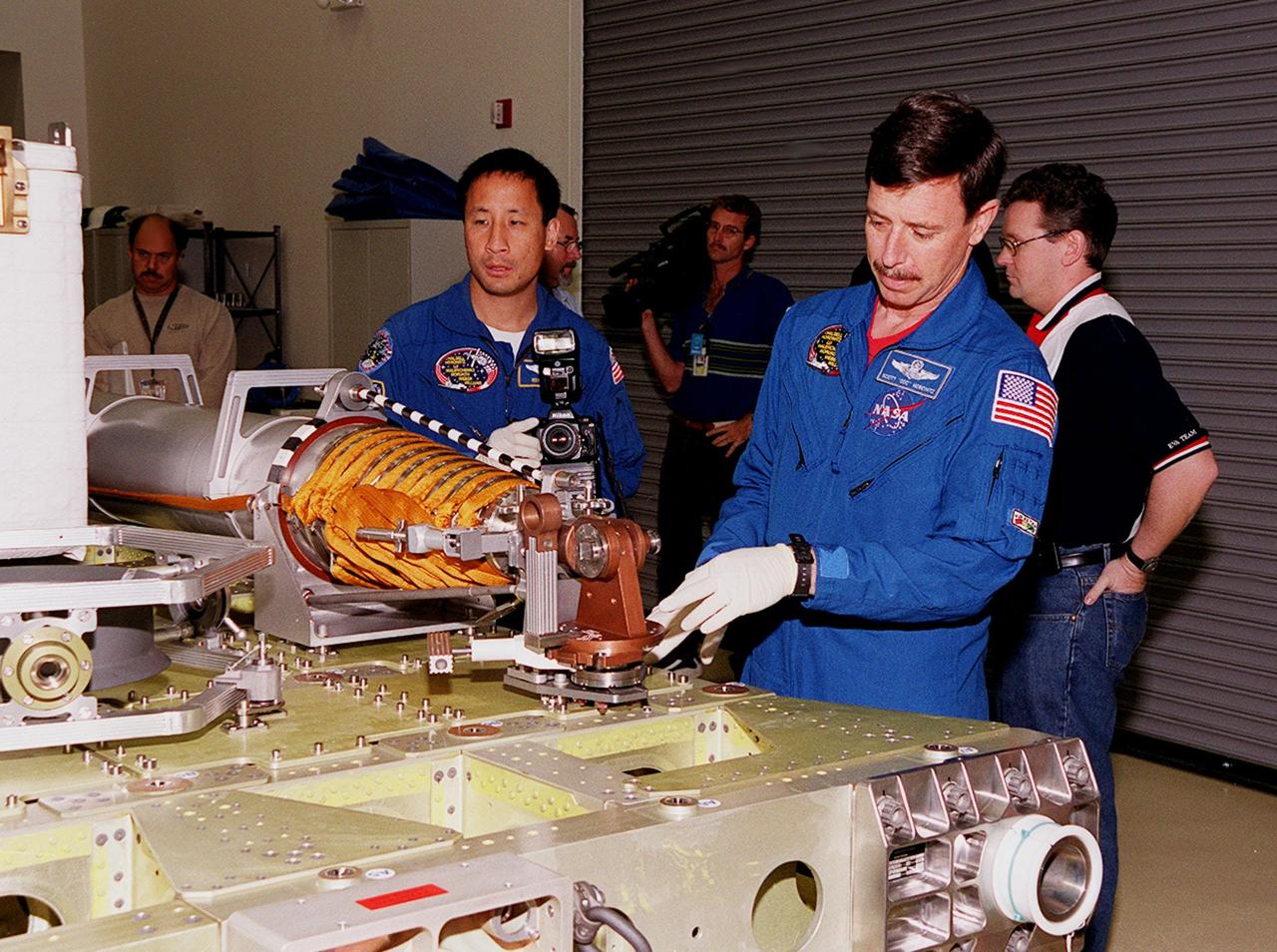

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, in Cape Canaveral, looking over the Russian crane, Strela, are STS-101 Mission Specialist Edward Tsang Lu (left) and Pilot Scott J. "Doc" Horowitz (Ph.D). Lu, Horowitz and other members of the crew are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test, which gives them an opportunity to look over equipment and payloads that will fly on the mission. Space Shuttle Atlantis will be carrying the SPACEHAB Double Module, which carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting. Launch of Atlantis on mission STS-101 is scheduled no earlier than April 13, 2000
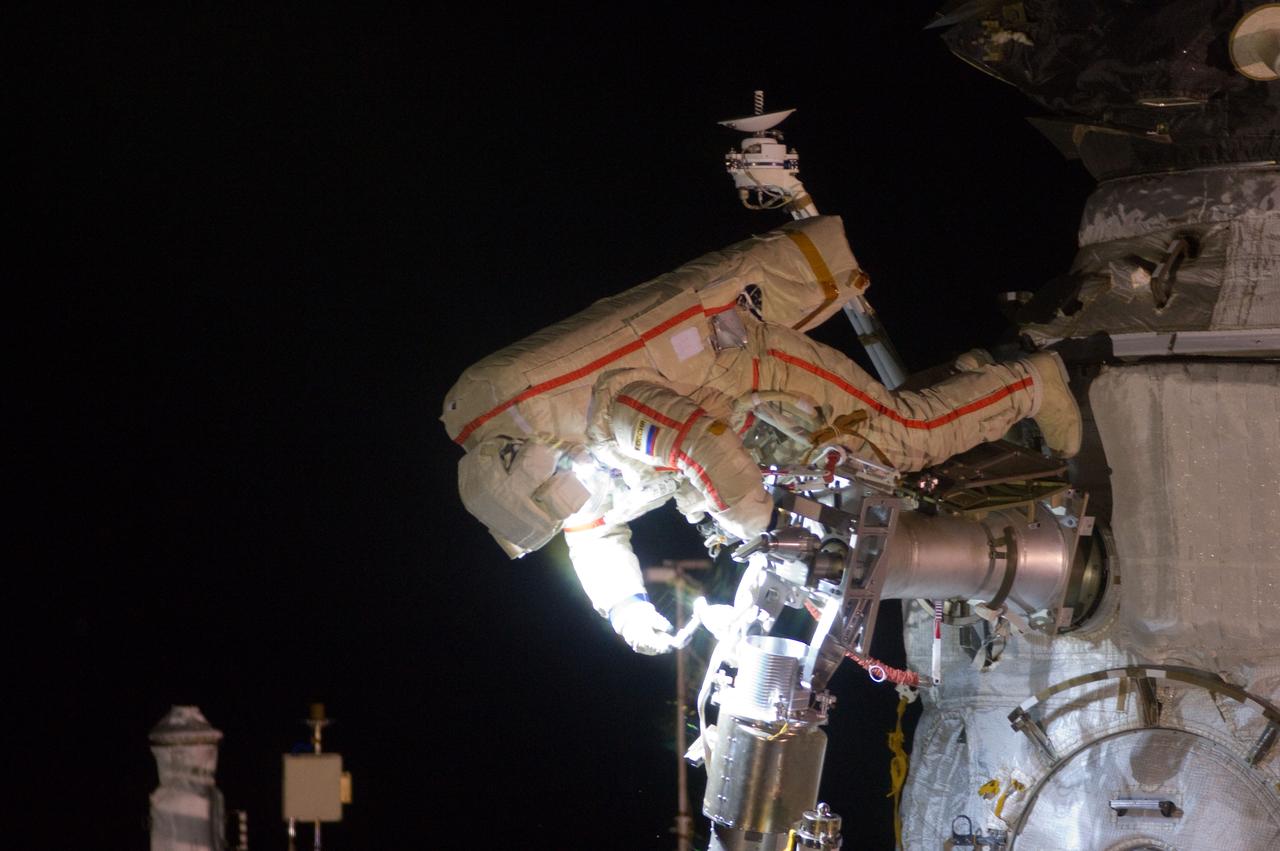

ISS032-E-021028 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
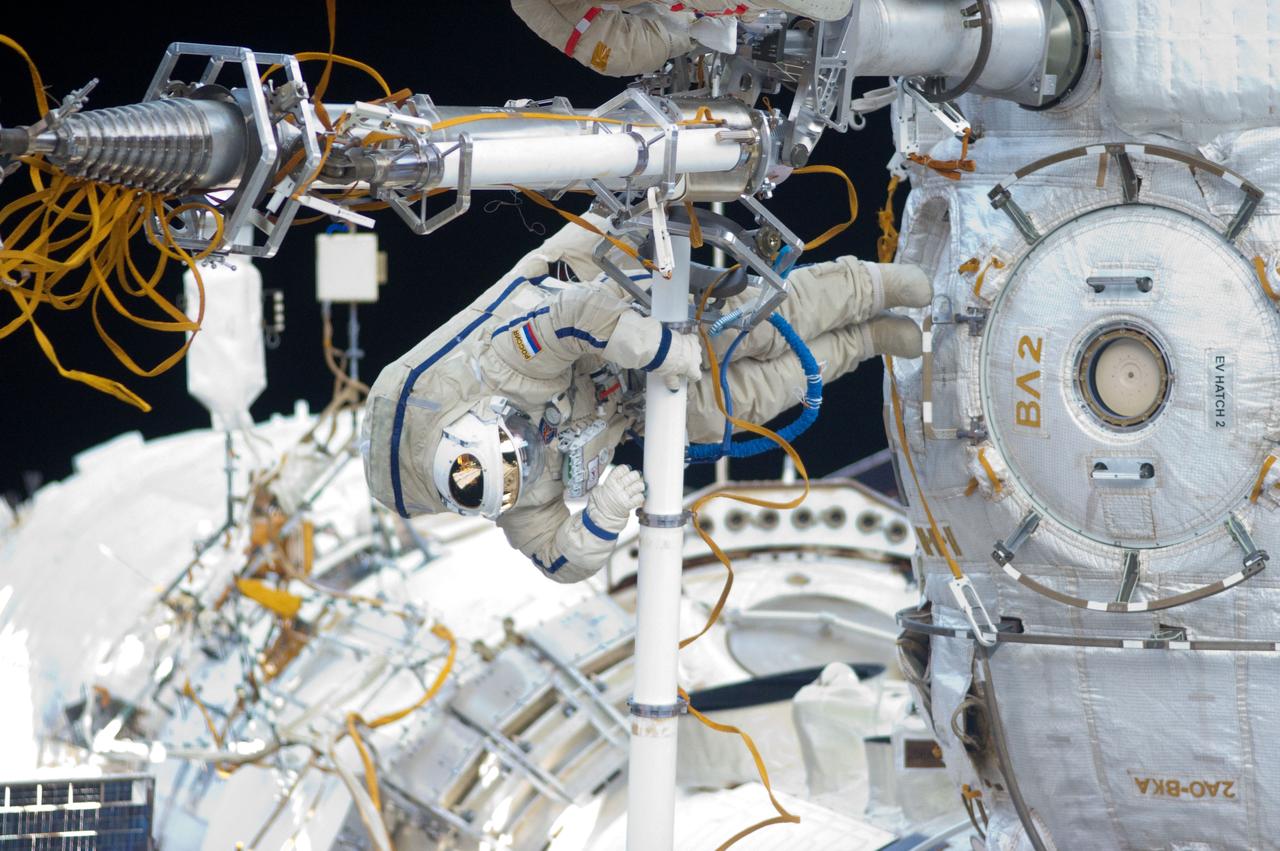

ISS032-E-021058 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

ISS032-E-021044 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
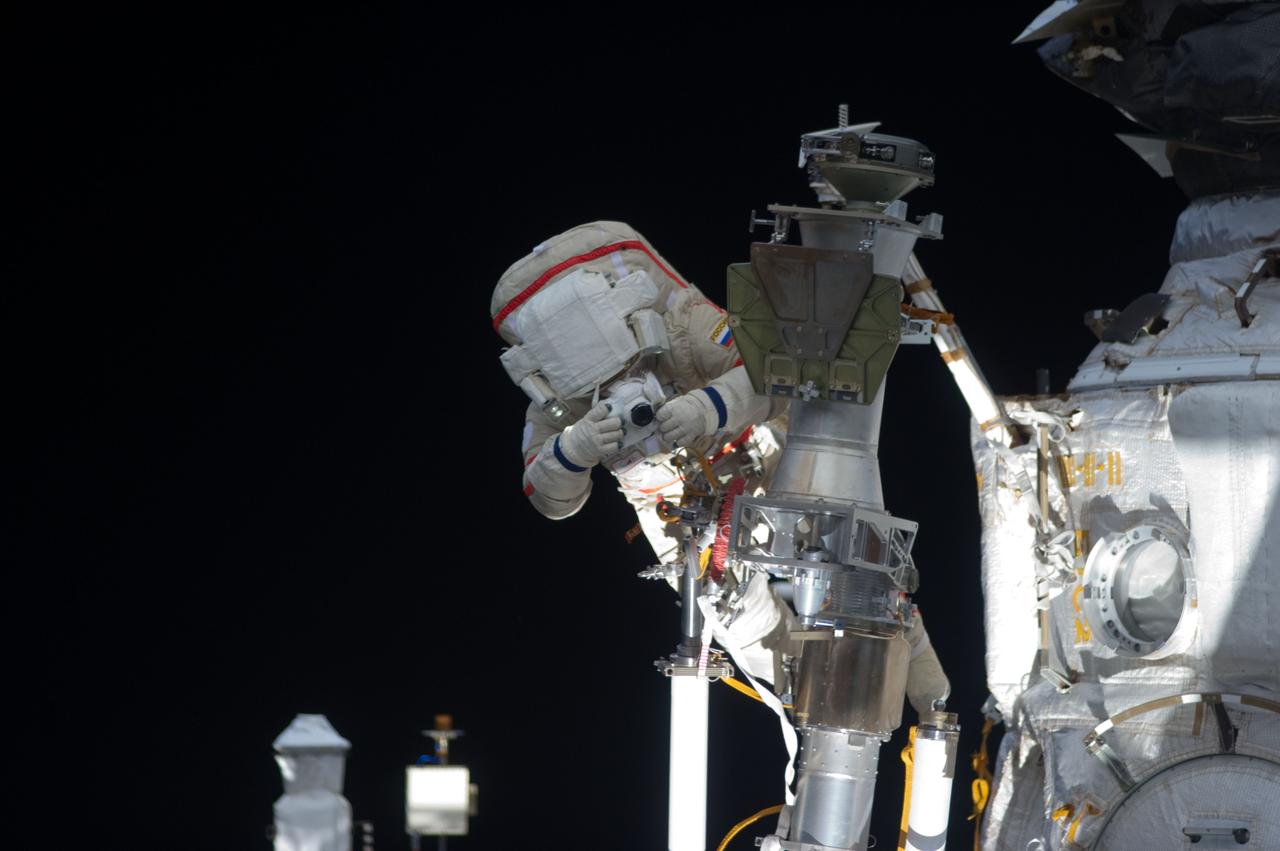

ISS032-E-021067 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, uses a still camera during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
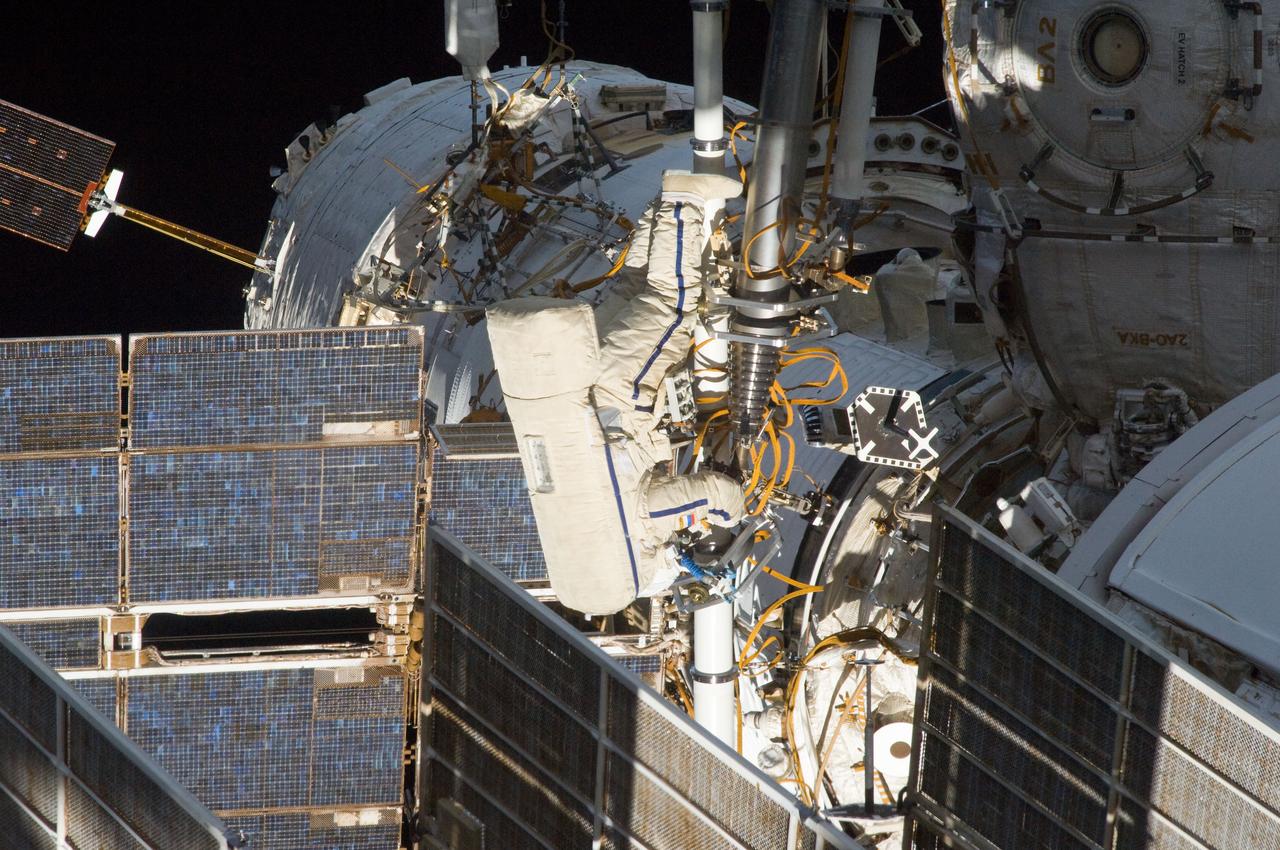

ISS032-E-021293 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

STS096-333-021 (3 June 1999) --- Backdropped against white clouds and blue ocean waters, the International Space Station (ISS) moves away from the Space Shuttle Discovery. The U.S.-built Unity node (left) and the Russian-built Zarya or FGB module (with the solar array panels deployed) were joined during a December 1998 mission. A portion of the work performed on the May 30 space walk by astronauts Tamara E. Jernigan and Daniel T. Barry is evident at various points on the ISS, including the installation of the Russian-built crane (called Strela). A STS-96 crew member aboard Discovery recorded this image with a 35mm camera on June 3, 1999.

ISS032-E-020594 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
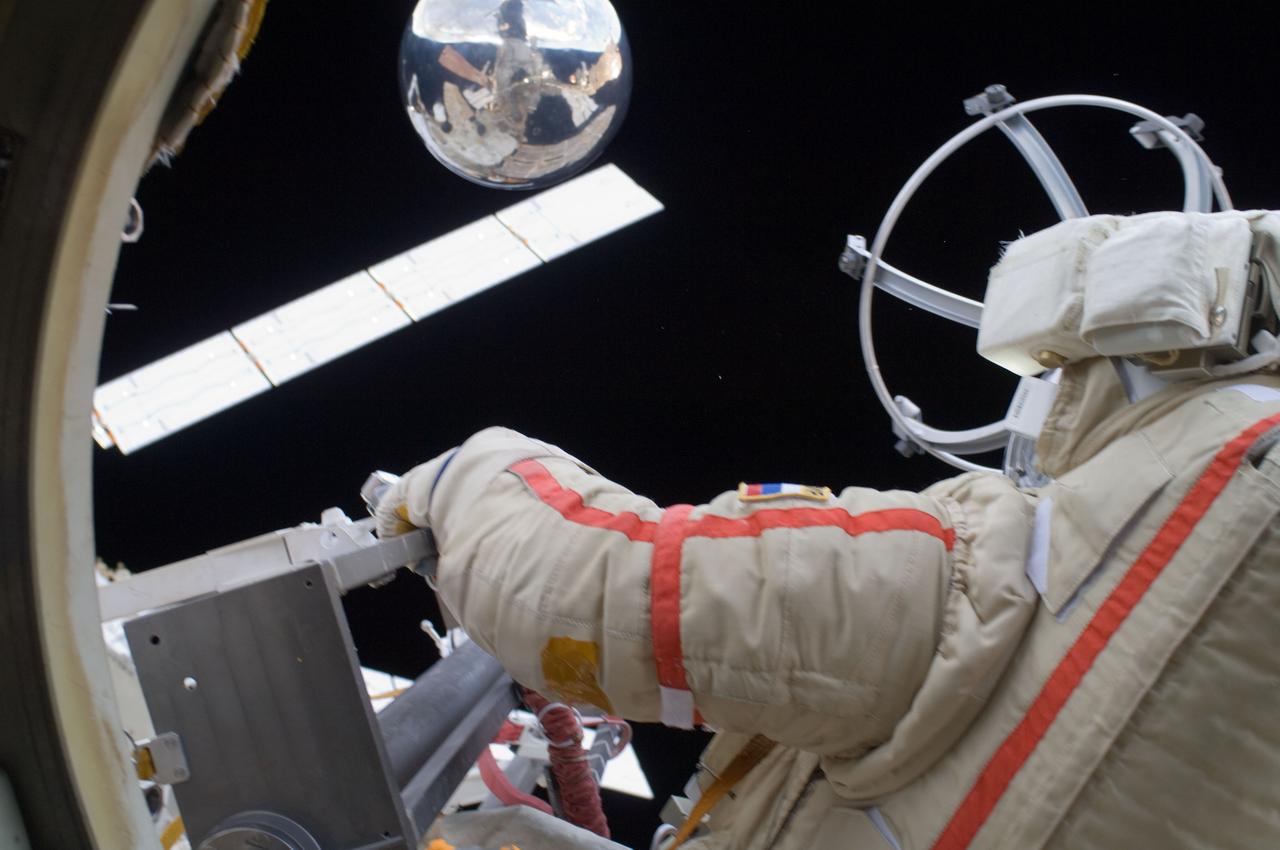

ISS032-E-020601 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, deploys a small ball-shaped science satellite during a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, also moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module.

ISS032-E-021284 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
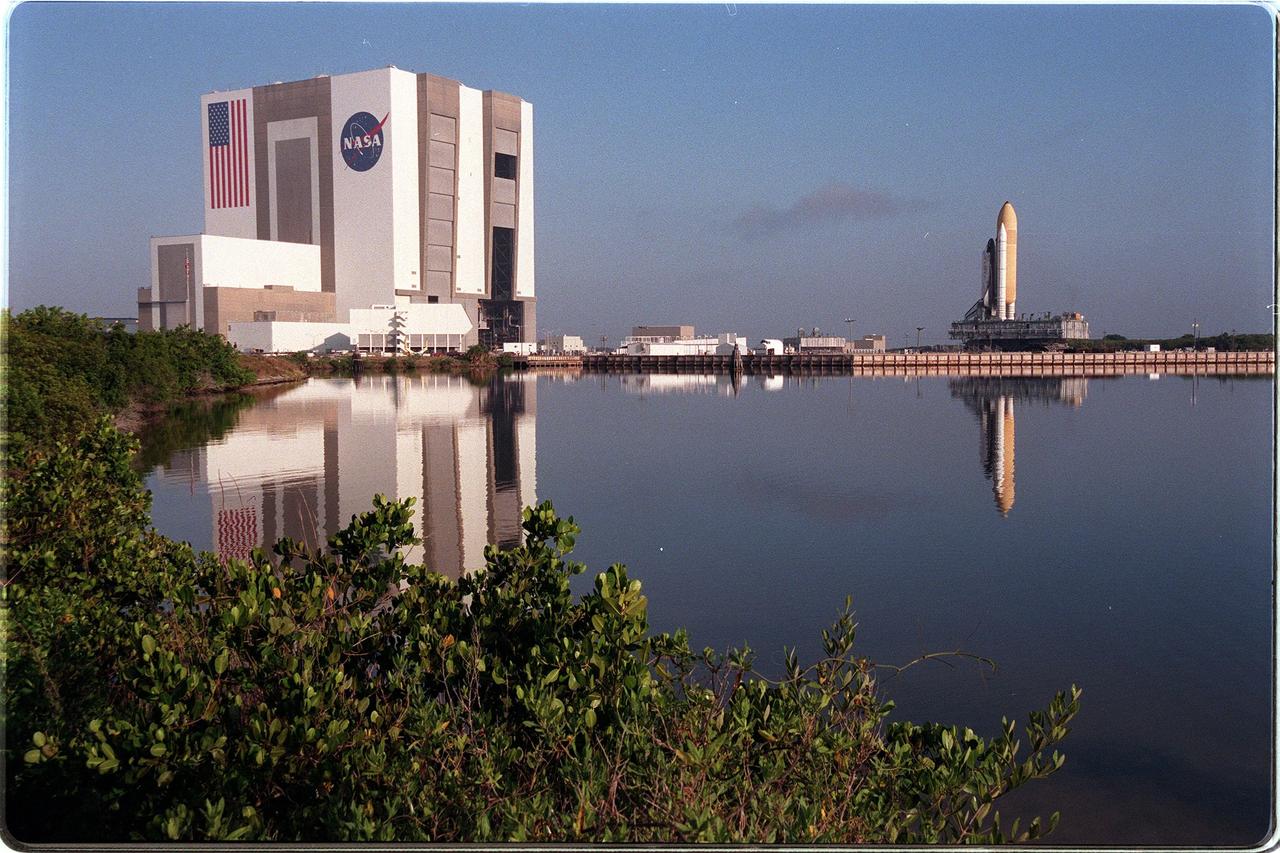

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Reflected in the turn basin at Launch Complex 39 Area, the Space Shuttle Discovery stands atop the crawler-transporter, which carries its cargo at 1 mph to Launch Pad 39B. The vehicle takes about five hours to cover the journey from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. Liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96 is targeted for May 20 at 9:32 a.m. EDT. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment
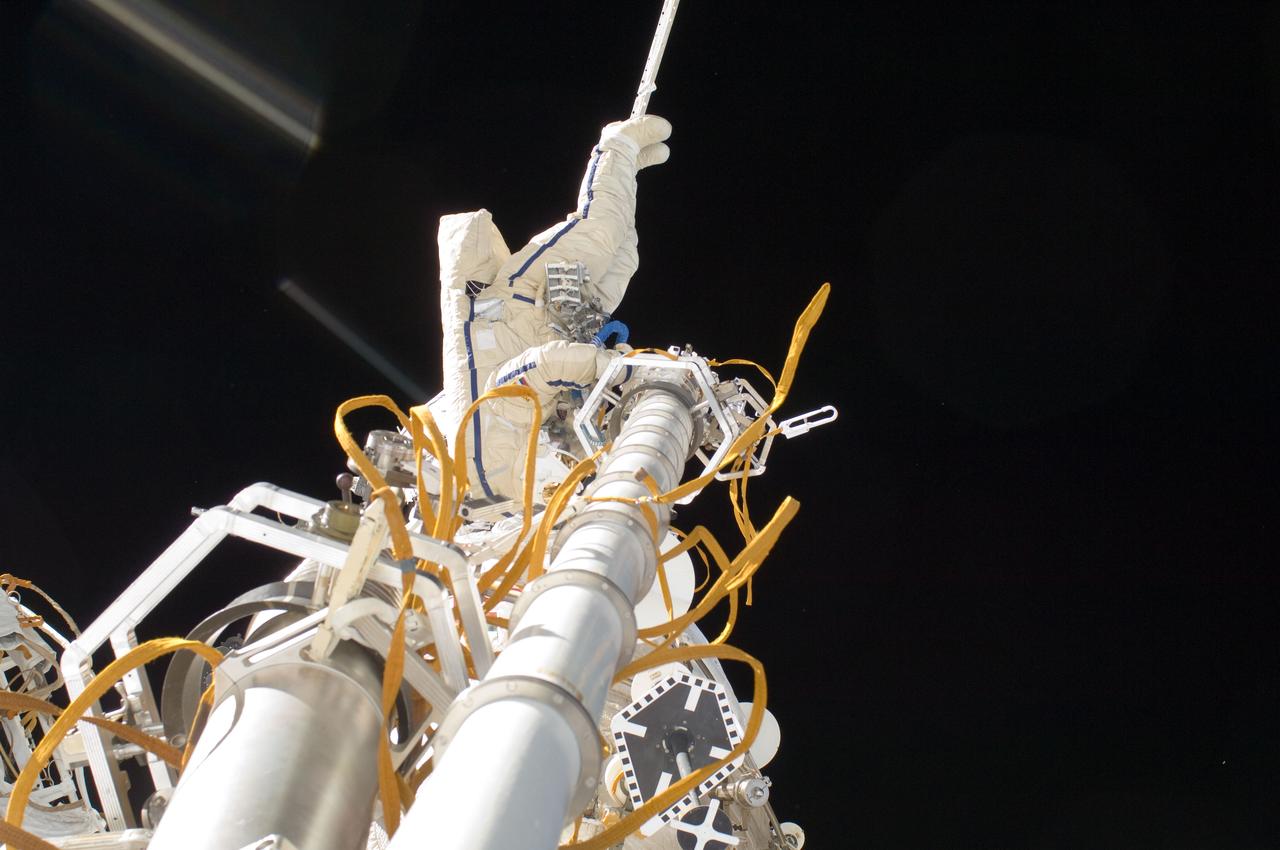

ISS032-E-020856 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko, Expedition 32 flight engineer, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Malenchenko and Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka (out of frame), commander, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
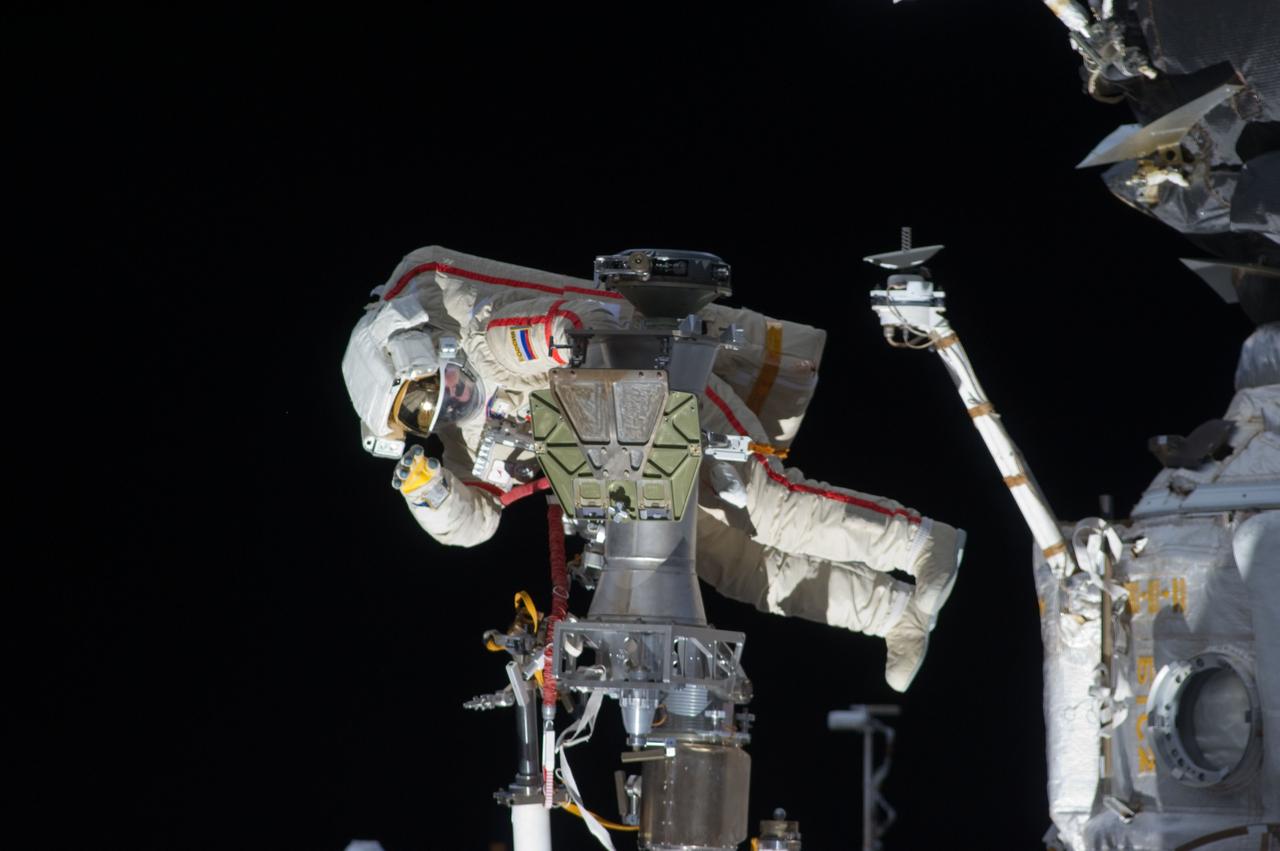

ISS032-E-021081 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.
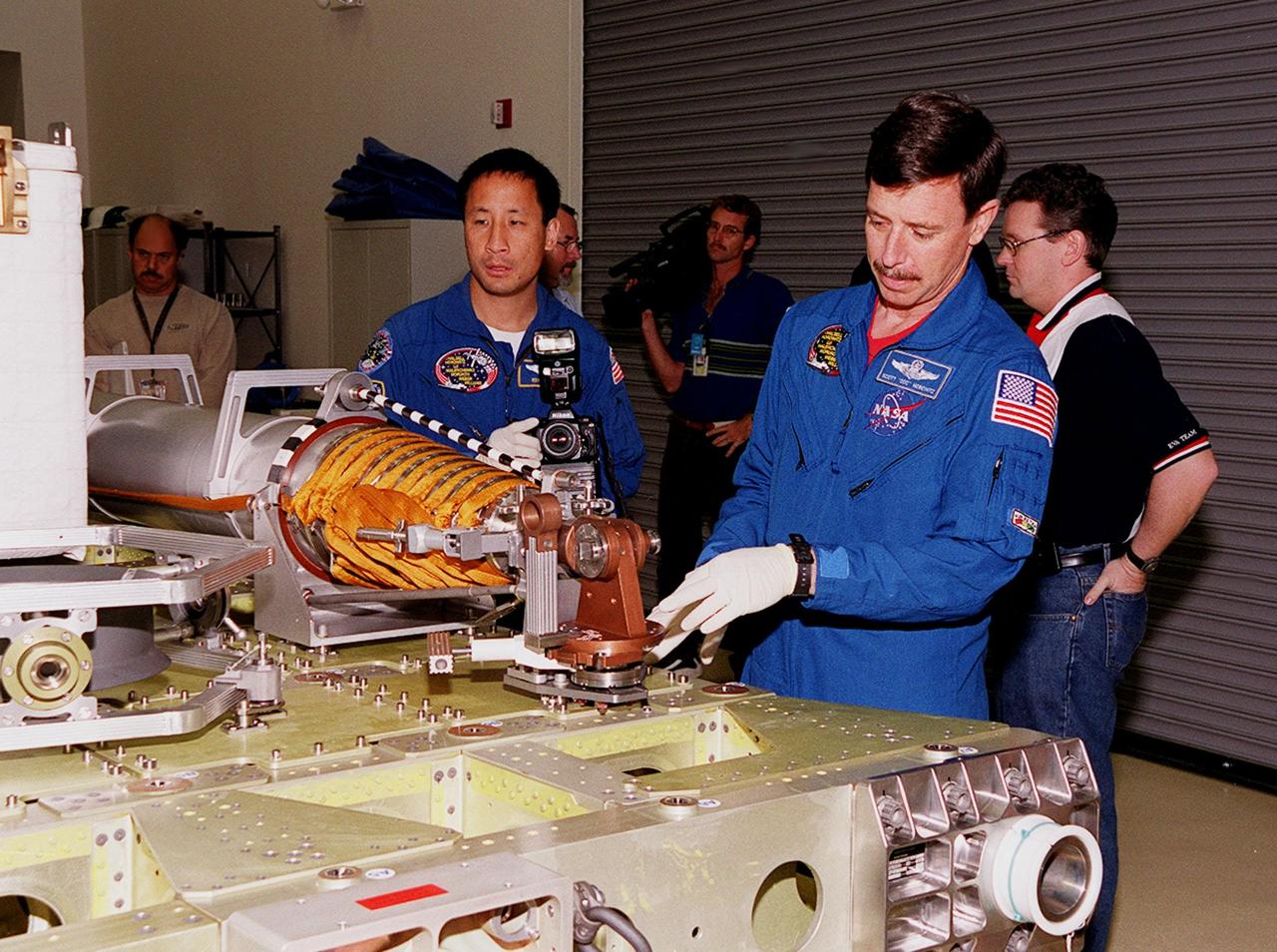

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At SPACEHAB, in Cape Canaveral, looking over the Russian crane, Strela, are STS-101 Mission Specialist Edward Tsang Lu (left) and Pilot Scott J. "Doc" Horowitz (Ph.D). Lu, Horowitz and other members of the crew are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test, which gives them an opportunity to look over equipment and payloads that will fly on the mission. Space Shuttle Atlantis will be carrying the SPACEHAB Double Module, which carries internal logistics and resupply cargo for station outfitting. Launch of Atlantis on mission STS-101 is scheduled no earlier than April 13, 2000
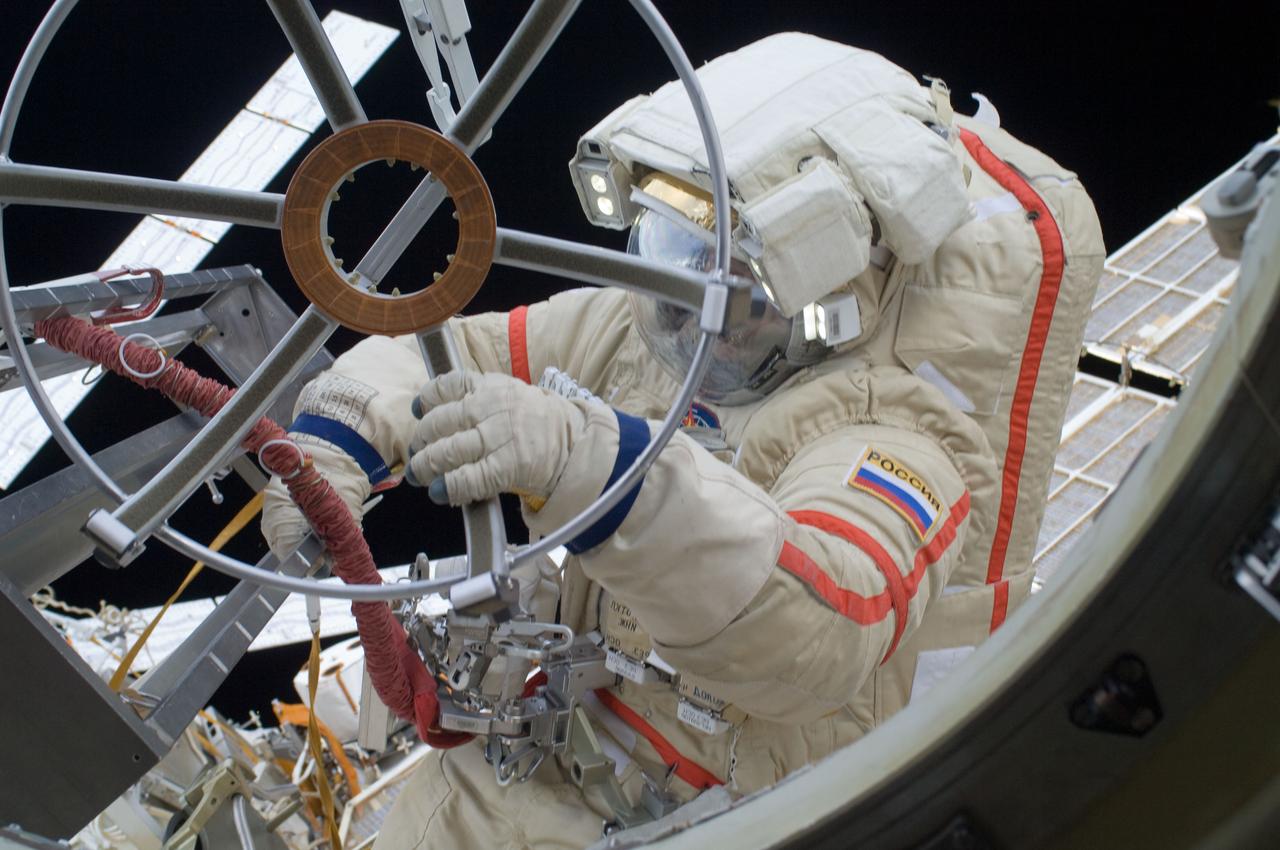

ISS032-E-020610 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

ISS032-E-021046 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonauts Gennady Padalka (top), Expedition 32 commander; and Yuri Malenchenko, flight engineer, participate in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Malenchenko moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The morning sun radiates through an opening between the orbiter Discovery and its external tank at Launch Pad 39B. The Shuttle is returning to the pad after repairs to the hail-damaged external tank. STS-96 is scheduled for liftoff May 27 at 6:48 a.m. EDT, the 94th launch in the Space Shuttle Program. A logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, STS-96 is carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-shared experiment
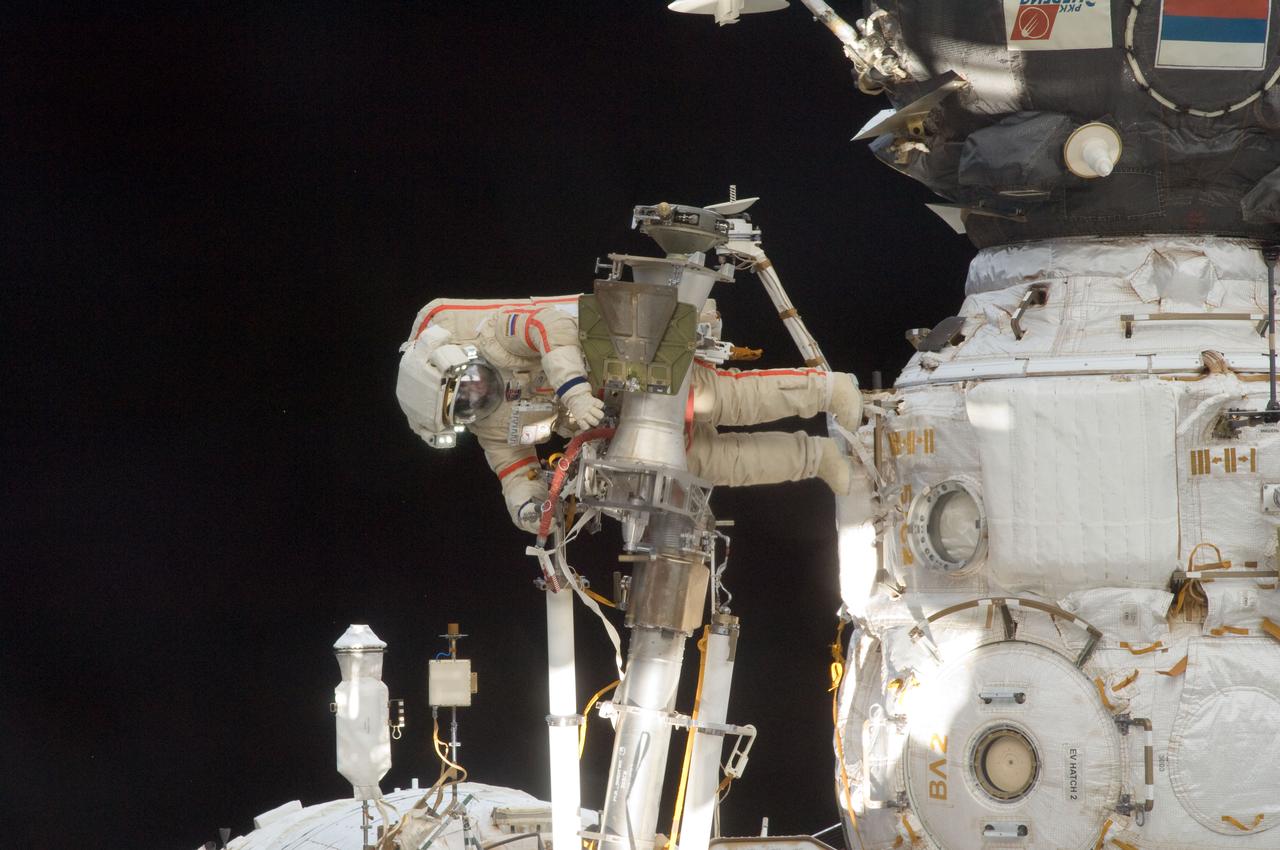

ISS032-E-021296 (20 Aug. 2012) --- Russian cosmonaut Gennady Padalka, Expedition 32 commander, participates in a session of extravehicular activity (EVA) to continue outfitting the International Space Station. During the five-hour, 51-minute spacewalk, Padalka and Russian cosmonaut Yuri Malenchenko (out of frame), flight engineer, moved the Strela-2 cargo boom from the Pirs docking compartment to the Zarya module to prepare Pirs for its eventual replacement with a new Russian multipurpose laboratory module. The two spacewalking cosmonauts also installed micrometeoroid debris shields on the exterior of the Zvezda service module and deployed a small science satellite.

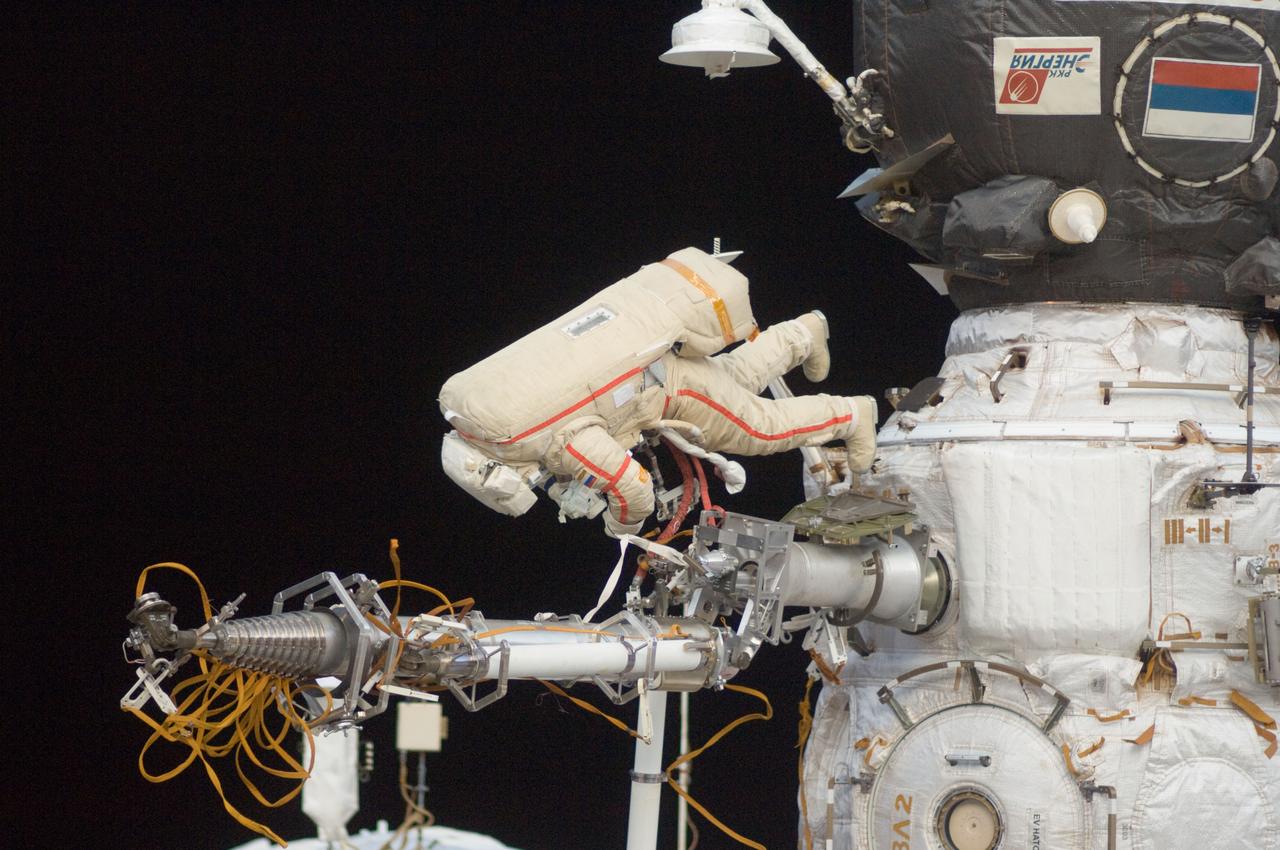
iss057e131572 (Dec. 11, 2018) --- An Expedition 57 crew member inside the cupola photographed Russian spacewalker Oleg Kononenko (suit with red stripes) attached to the Strela boom outside the International Space Station about 250 miles above Earth to inspect the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft. During the spacewalk, he and fellow spacewalker Sergey Prokopyev (out of frame) examined the external hull of the Soyuz crew ship docked to the Rassvet module. The area corresponded with the location of a small hole inside the Soyuz habitation module that was found in August and caused a decrease in the space station’s pressure. The hole was fixed internally with a sealant within hours of its detection. During the spacewalk, Kononenko and Prokopyev collected samples of some of the sealant that extruded through hole to the outer hull before heading back inside the Pirs docking compartment and closing the hatch completing a seven-hour, 45-minute spacewalk.
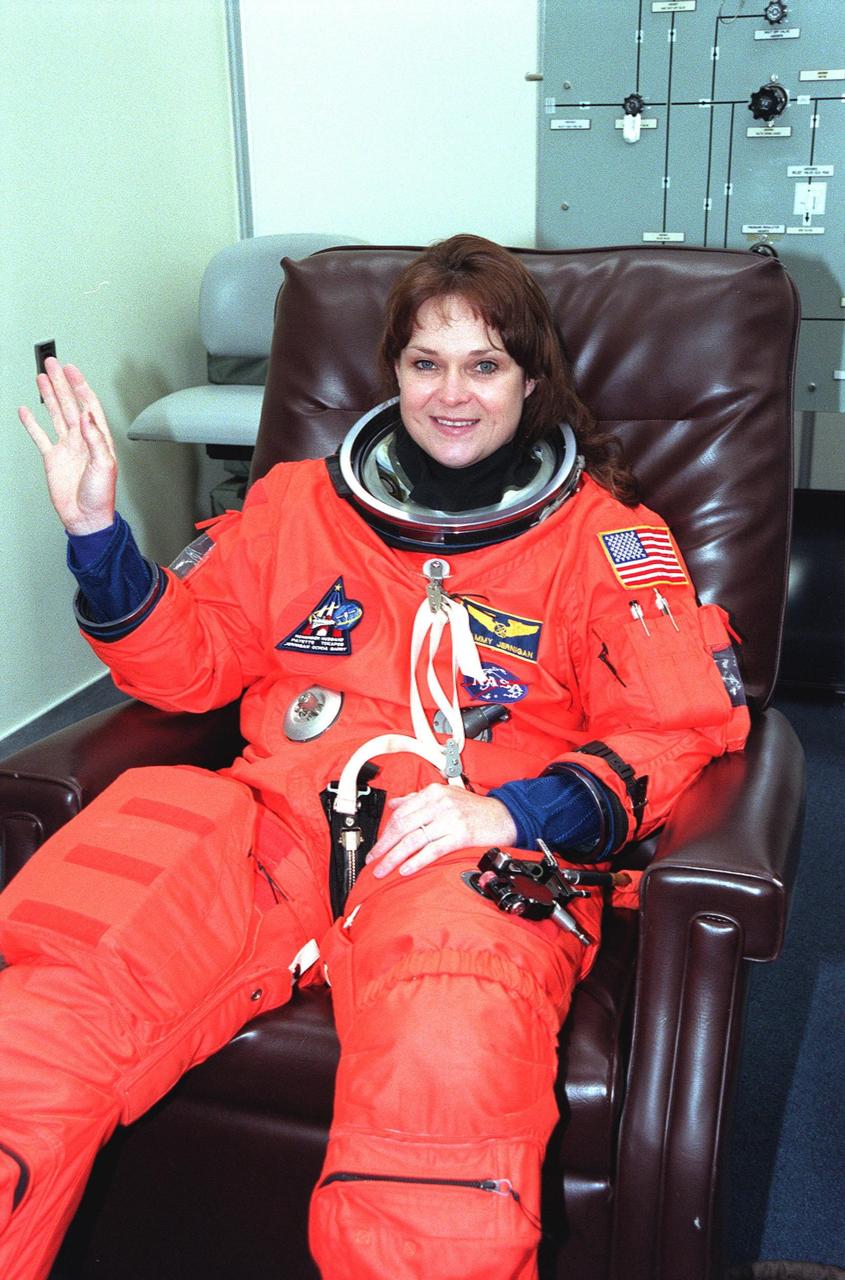

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-96 Mission Specialist Tamara E. Jernigan waves after donning her launch and entry suit during final launch preparations. STS-96 is a 10-day logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying about 4,000 pounds of supplies, to be stored aboard the station for use by future crews, including laptop computers, cameras, tools, spare parts, and clothing. The mission also includes such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-involved experiment. It will include a space walk to attach the cranes to the outside of the ISS for use in future construction.. Space Shuttle Discovery is due to launch today at 6:49 a.m. EDT. Landing is expected at the SLF on June 6 about 1:58 a.m. EDT
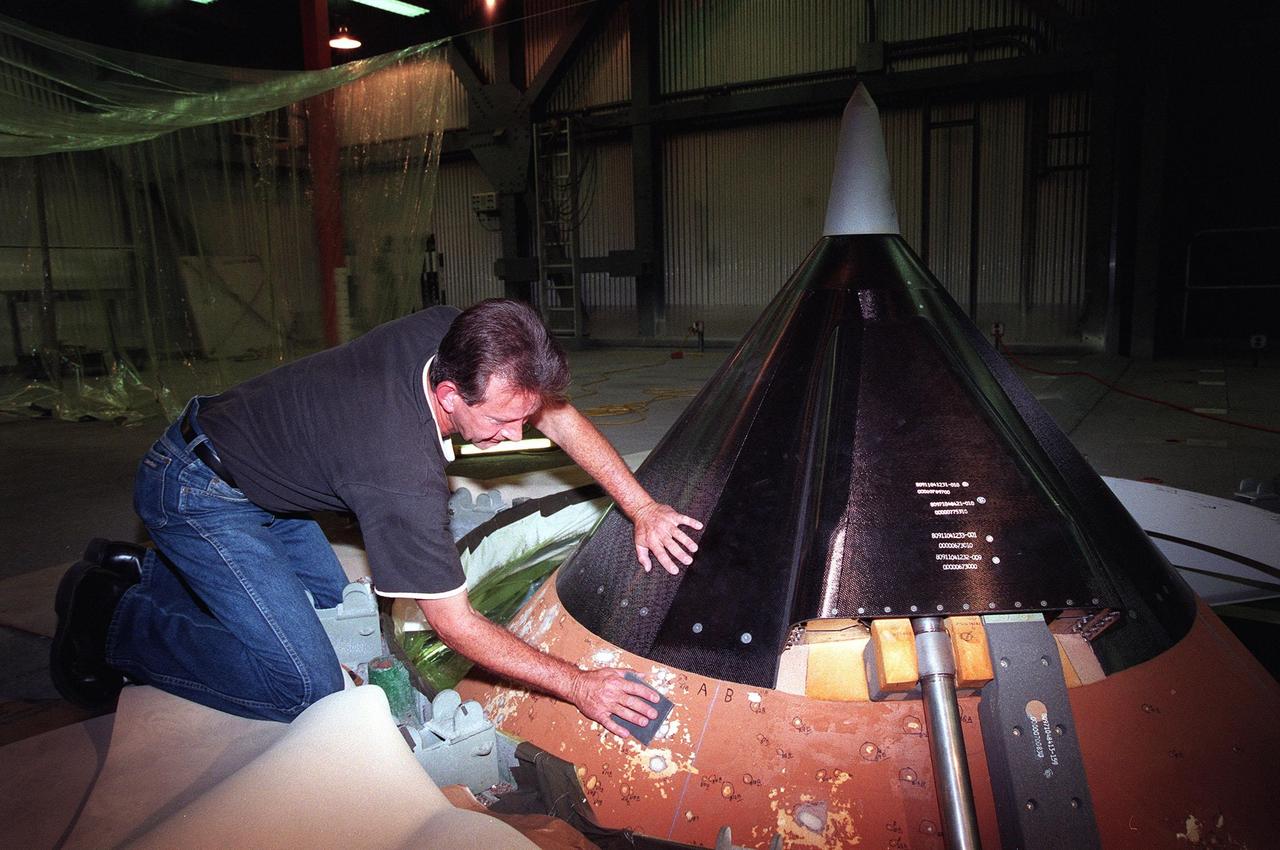

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), United Space Alliance technician Robert Williams sands the repaired areas near the top of Space Shuttle Discovery's external tank. Repairs were required for damage caused by hail during recent storms. Because access to all of the damaged areas was not possible at the pad, the Shuttle was rolled back from Pad 39B to the VAB. The work is expected to take two to three days, allowing Discovery to roll back to the pad late this week for launch of mission STS-96, the 94th launch in the Space Shuttle Program. Liftoff will occur no earlier than May 27. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-shared experiment
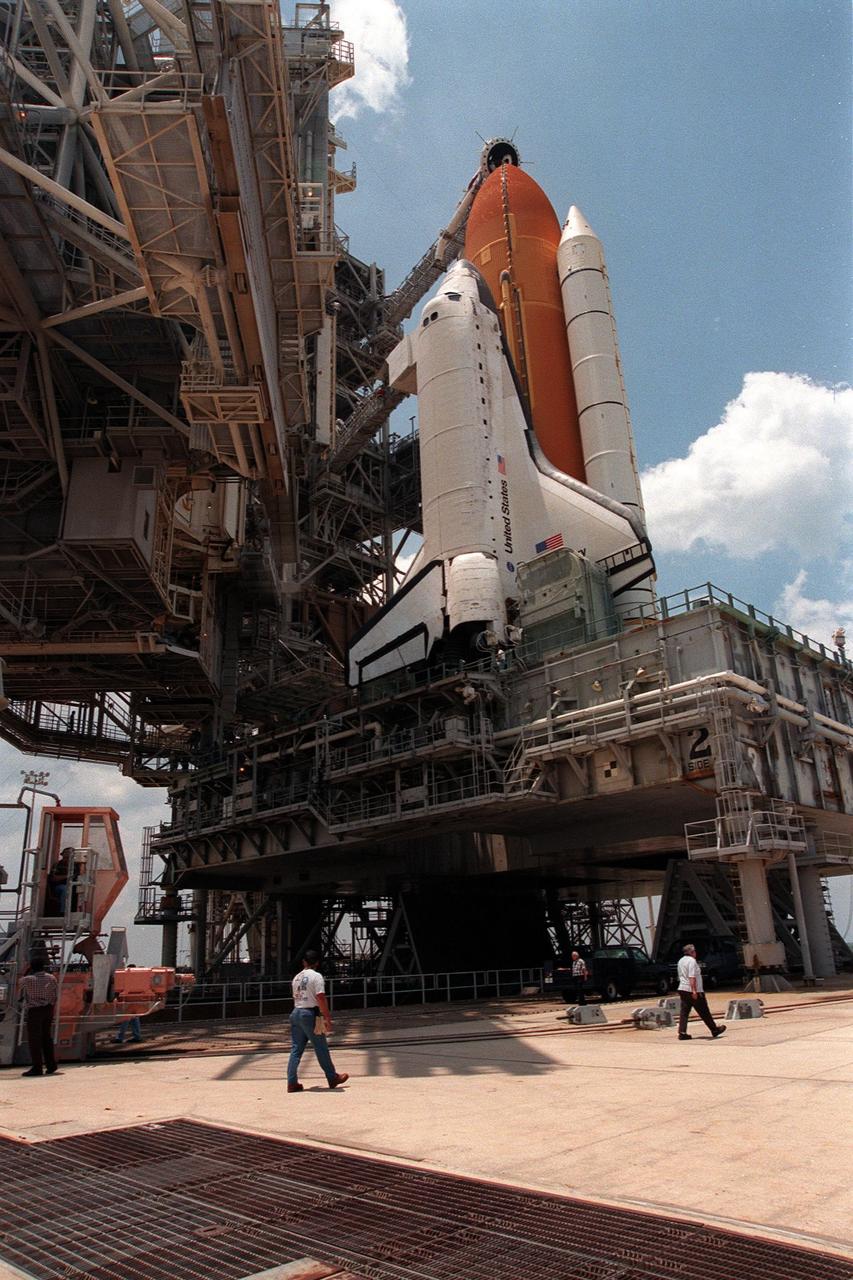

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Rotating Service Structure is rolled back at Launch Pad 39B to reveal the Space Shuttle Discovery, scheduled to launch on mission STS-96 at 6:49 a.m. EDT on May 27. STS-96 is a 10-day logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying about 4,000 pounds of supplies to be stored aboard the station, for use by future crews, including laptop computers, cameras, tools, spare parts, and clothing. The mission also includes such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-involved experiment. The mission will include a space walk to attach the cranes to the outside of the ISS for use in future construction. Space Shuttle Discovery is due to launch on May 27 at 6:49 a.m. EDT. Landing is expected at the SLF on June 6 about 1:58 a.m. EDT
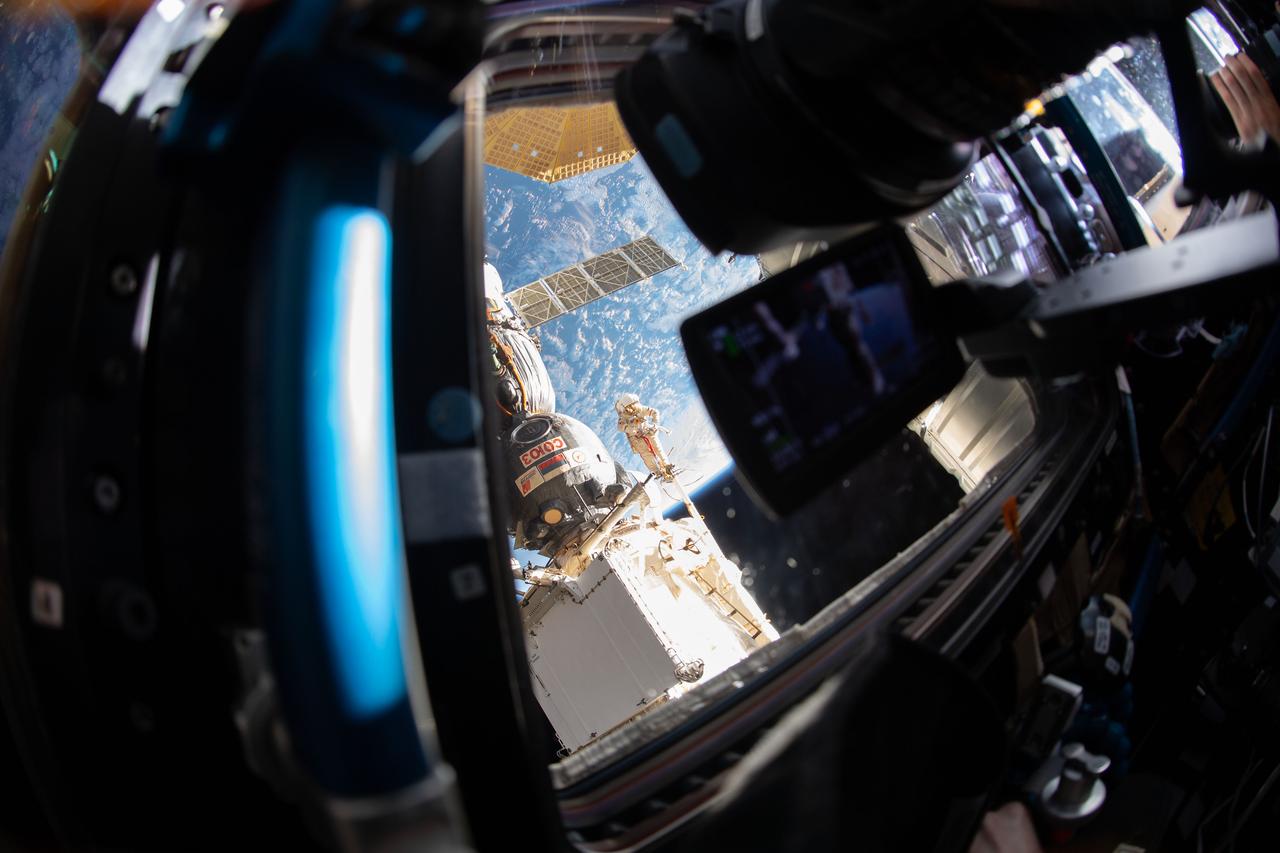

iss057e131556 (Dec. 11, 2018) --- An Expedition 57 crew member inside the cupola photographed Russian spacewalker Oleg Kononenko (suit with red stripes) attached to the Strela boom outside the International Space Station about 250 miles above Earth to inspect the Soyuz MS-09 spacecraft. During the spacewalk, he and fellow spacewalker Sergey Prokopyev (out of frame) examined the external hull of the Soyuz crew ship docked to the Rassvet module. The area corresponded with the location of a small hole inside the Soyuz habitation module that was found in August and caused a decrease in the space station’s pressure. The hole was fixed internally with a sealant within hours of its detection. During the spacewalk, Kononenko and Prokopyev collected samples of some of the sealant that extruded through hole to the outer hull before heading back inside the Pirs docking compartment and closing the hatch completing a seven-hour, 45-minute spacewalk.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Viewed from the top of the rotating service structure, Space Shuttle Discovery rests on the mobile launcher platform and towers over the landscape after rollout to Launch Pad 39B. In the background are portions of the Banana River and the Atlantic Ocean. The lighter spots on the top of the external tank are areas of hail damage that was recently repaired. The Shuttle had to be returned to the VAB for the repairs, making this the second rollout for the Shuttle. Discovery is scheduled for liftoff May 27 at 6:48 a.m. EDT on mission STS-96, the 94th launch in the Space Shuttle Program. A logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, STS-96 is carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-shared experiment

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The morning sun bursts through an opening between the external tank and solid booster rocket on Space Shuttle Discovery aboard the crawler-transporter as it wends its way to Launch Pad 39B. The crawler-transporter carries its cargo at 1 mph, taking about five hours to cover the journey from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the launch pad. Liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96 is targeted for May 20 at 9:32 a.m. EDT. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment
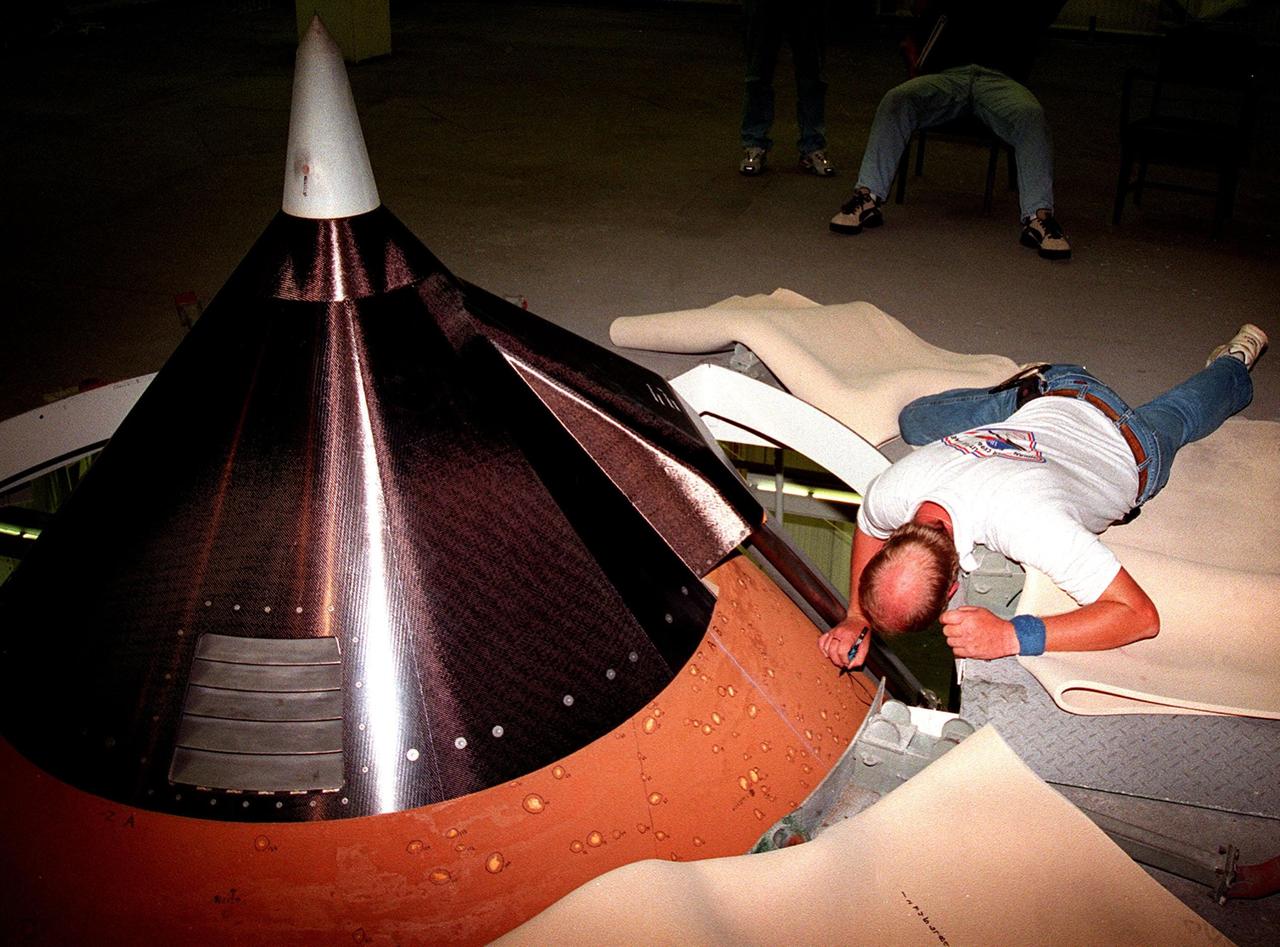

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Inside High Bay 1 of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) Mike Sestile, with United Space Alliance, draws circles around divots in the foam insulation on the top of the external tank of Space Shuttle Discovery. About 150 divots were caused by hail during recent storms. The Shuttle was rolled back from Pad 39B to the VAB for repairs because access to all of the damaged areas was not possible at the pad. The work is expected to take two to three days, allowing Discovery to roll back to the pad as early as May 20 for launch of mission STS-96, the 94th launch in the Space Shuttle Program. Liftoff will occur no earlier than May 27. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-shared experiment
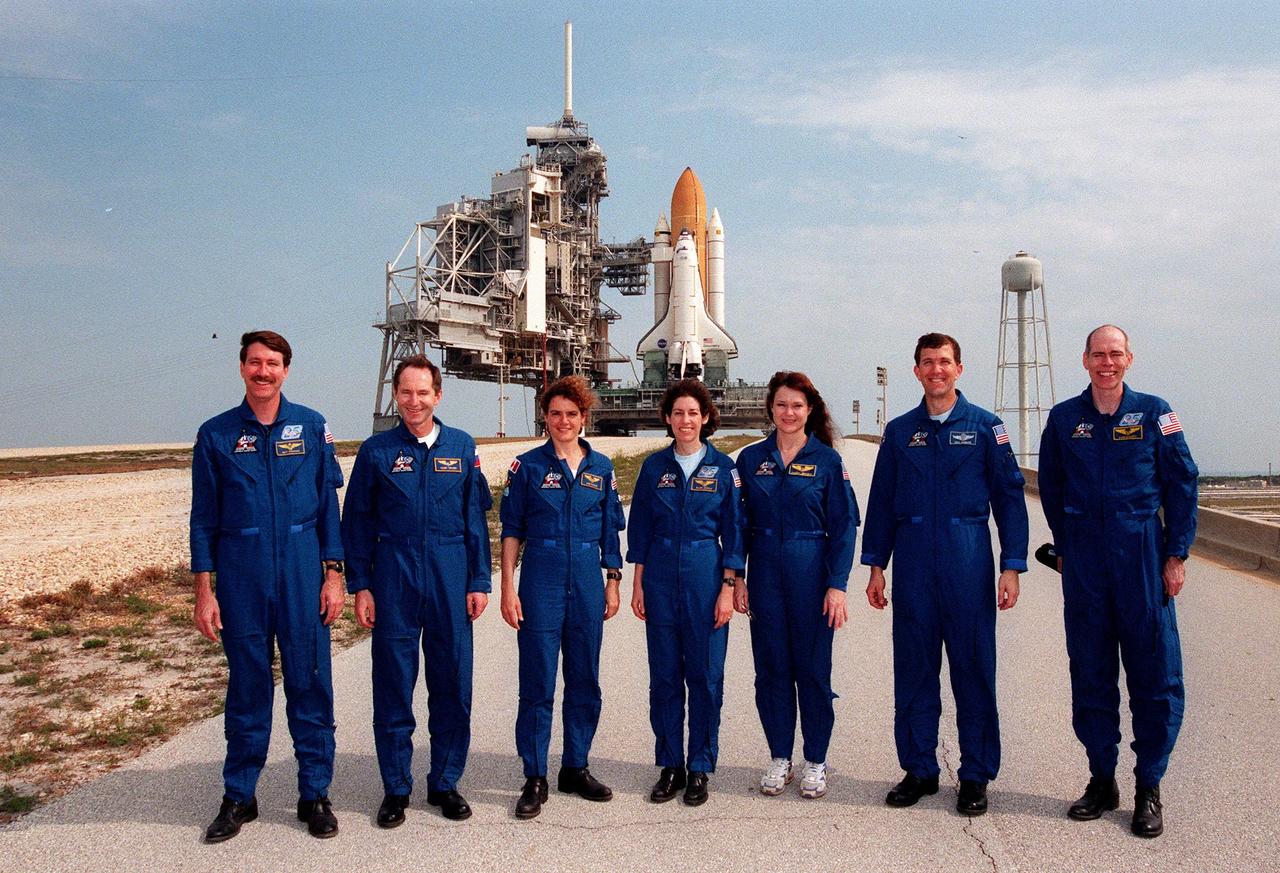

The STS-96 crew visit Launch Pad 39B where Space Shuttle Discovery, in the background, is being prepared for the mission launch on May 20. From left to right are Commander Kent V. Rominger; Mission Specialists Valery Ivanovich Tokarev, Julie Payette, Ellen Ochoa (Ph.D.), and Tamara E. Jernigan (Ph.D.); Pilot Rick Douglas Husband; and Mission Specialist Daniel Barry (M.D., Ph.D.). The crew are taking part in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT provides simulated countdown exercises, emergency egress training, and opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. Mission STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment
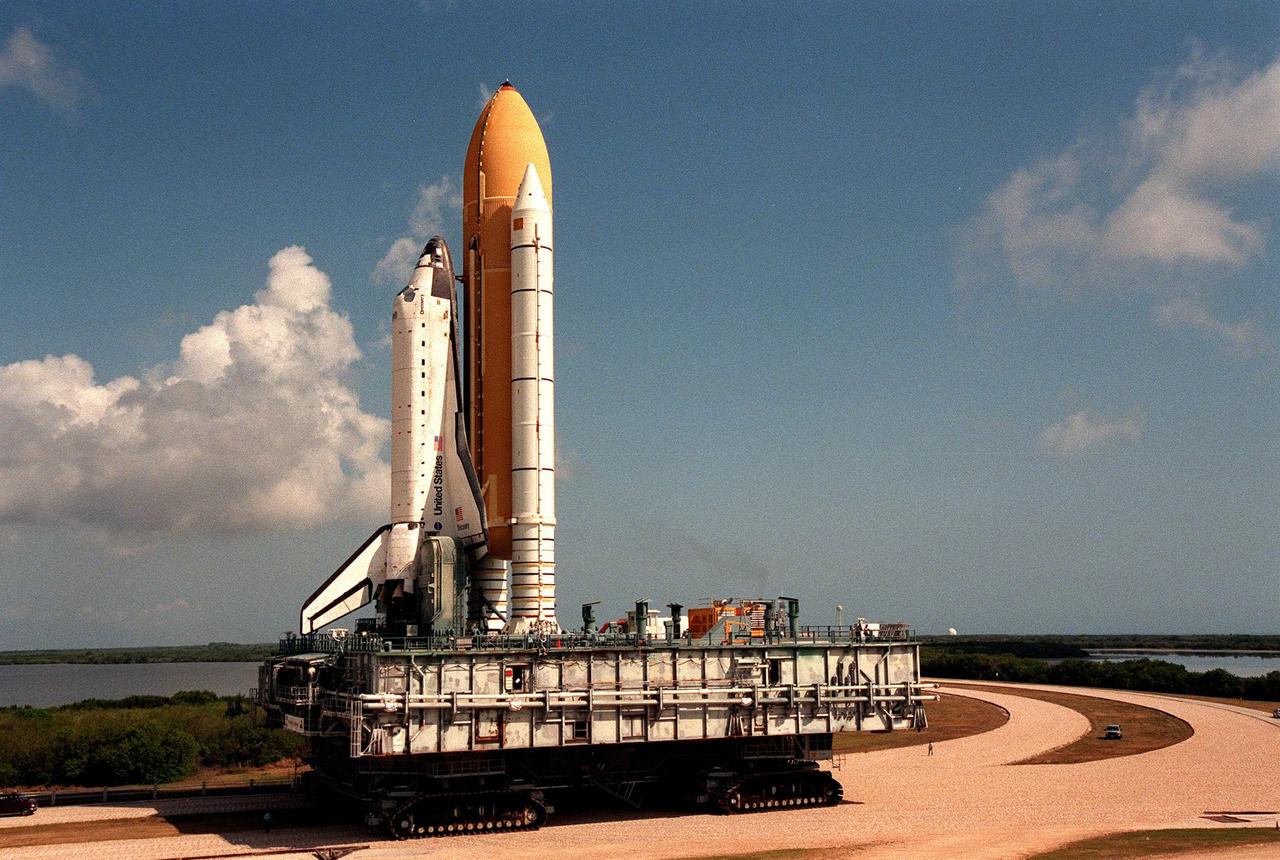

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Discovery, atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler-transporter, dwarfs the car parked at right on the median of the 130-foot-wide crawlerway. Traveling at 1 mph, the crawler-transporter takes about five hours to cover the journey from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39B. Here it is moving toward the turn that will take it to the pad. Liftoff of Discovery on mission STS-96 is targeted for May 20 at 9:32 a.m. EDT. STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment
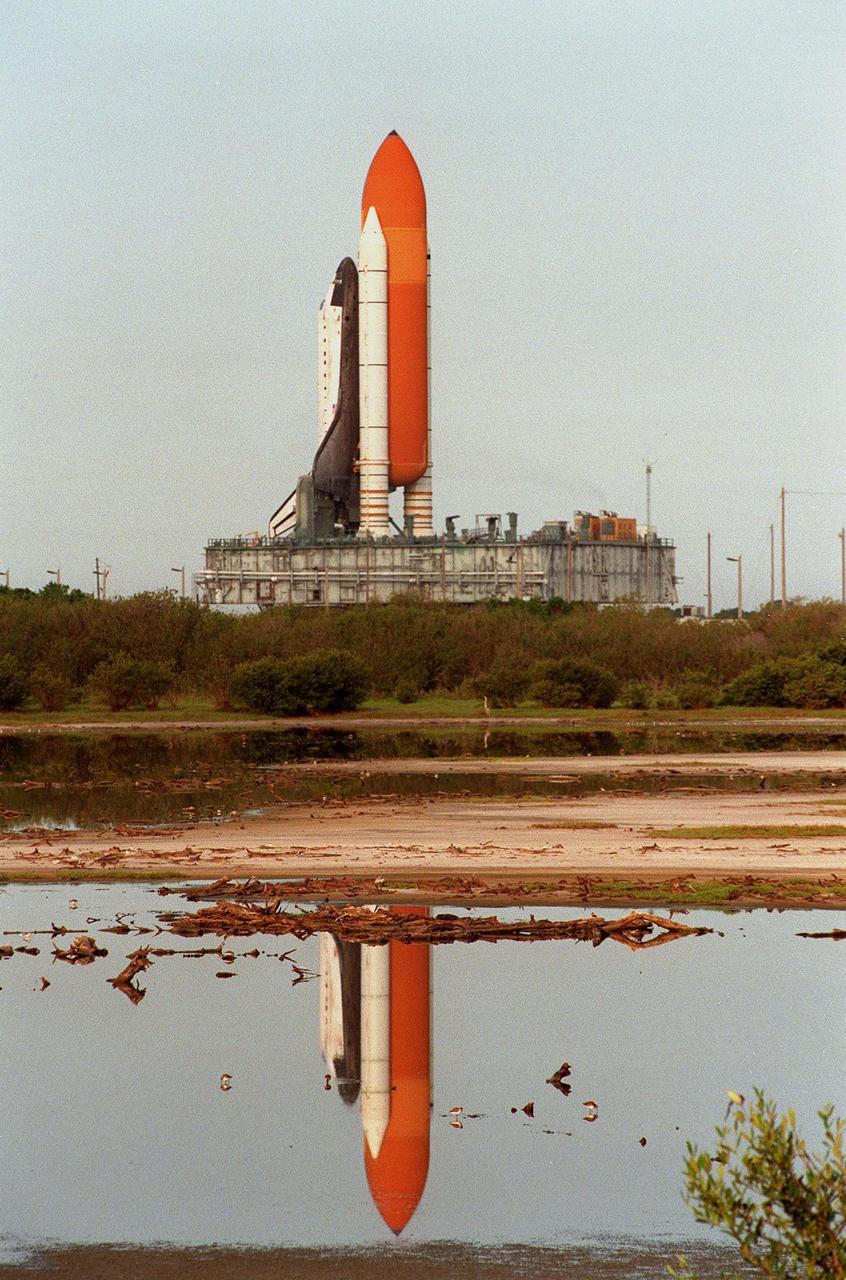

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The avian population (foreground) at this watering site on Kennedy Space Center is undaunted as the 12-million-pound combination of Space Shuttle Discovery, crawler transporter and mobile launcher platform rolls out to Launch Pad 39B from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). Earlier in the week, the Shuttle was rolled back to the VAB from the pad to repair hail damage on the external tank's foam insulation. The trek takes about five hours at the 1-mph speed of the crawler. Mission STS-96, the 94th launch in the Space Shuttle Program, is scheduled for liftoff May 27 at 6:48 a.m. EDT STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-shared experiment
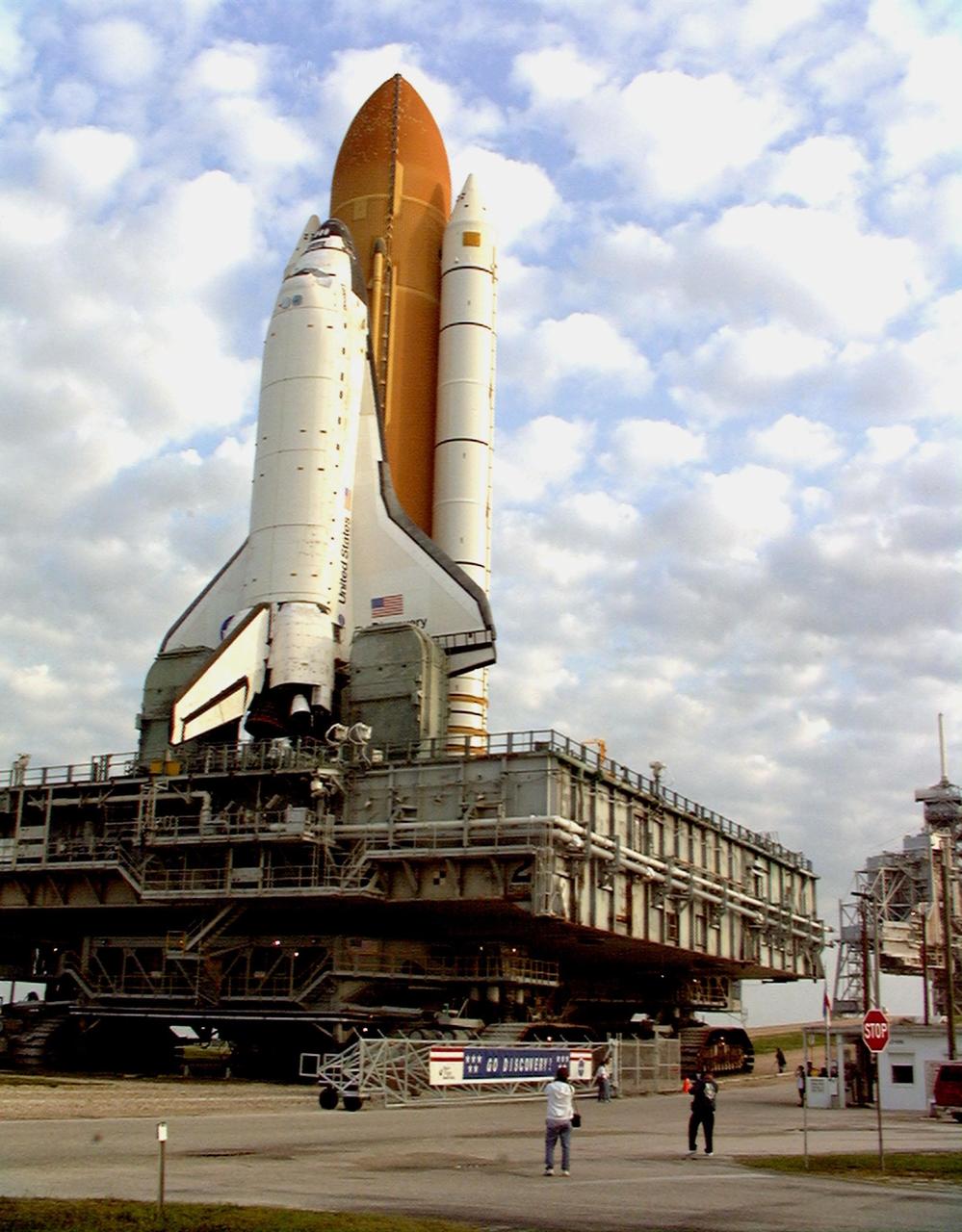

Against a popcorn-clouded blue sky, Space Shuttle Discovery, atop the mobile launcher platform and crawler transporter, ends its five-hour trek from the Vehicle Assembly Building as it crosses through the gate at Launch Pad 39B. Earlier in the week, the Shuttle was rolled back to the VAB from the pad to repair hail damage on the external tank's foam insulation. The 4.2-mile trek takes about five hours at the 1-mph speed of the crawler. Mission STS-96, the 94th launch in the Space Shuttle Program, is scheduled for liftoff May 27 at 6:48 a.m. EDT STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-shared experiment

At Launch Pad 39B, STS-96 Mission Specialist Julie Payette, with the Canadian Space Agency, and Pilot Rick Douglas Husband practice putting on oxygen gas masks as part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT provides the crew with emergency egress traiing, simulated countdown exercises and opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. Other crew members taking part in the TCDT are Commander Kent V. Rominger and Mission Specialists Tamara E. Jernigan (Ph.D.), Daniel Barry (M.D., Ph.D.), Ellen Ochoa (Ph.D.) and Valery Ivanovich Tokarev, with the Russian Space Agency. Scheduled for liftoff on May 20 at 9:32 a.m., STS-96 is a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station, carrying such payloads as a Russian crane, the Strela; a U.S.-built crane; the Spacehab Oceaneering Space System Box (SHOSS), a logistics items carrier; and STARSHINE, a student-led experiment