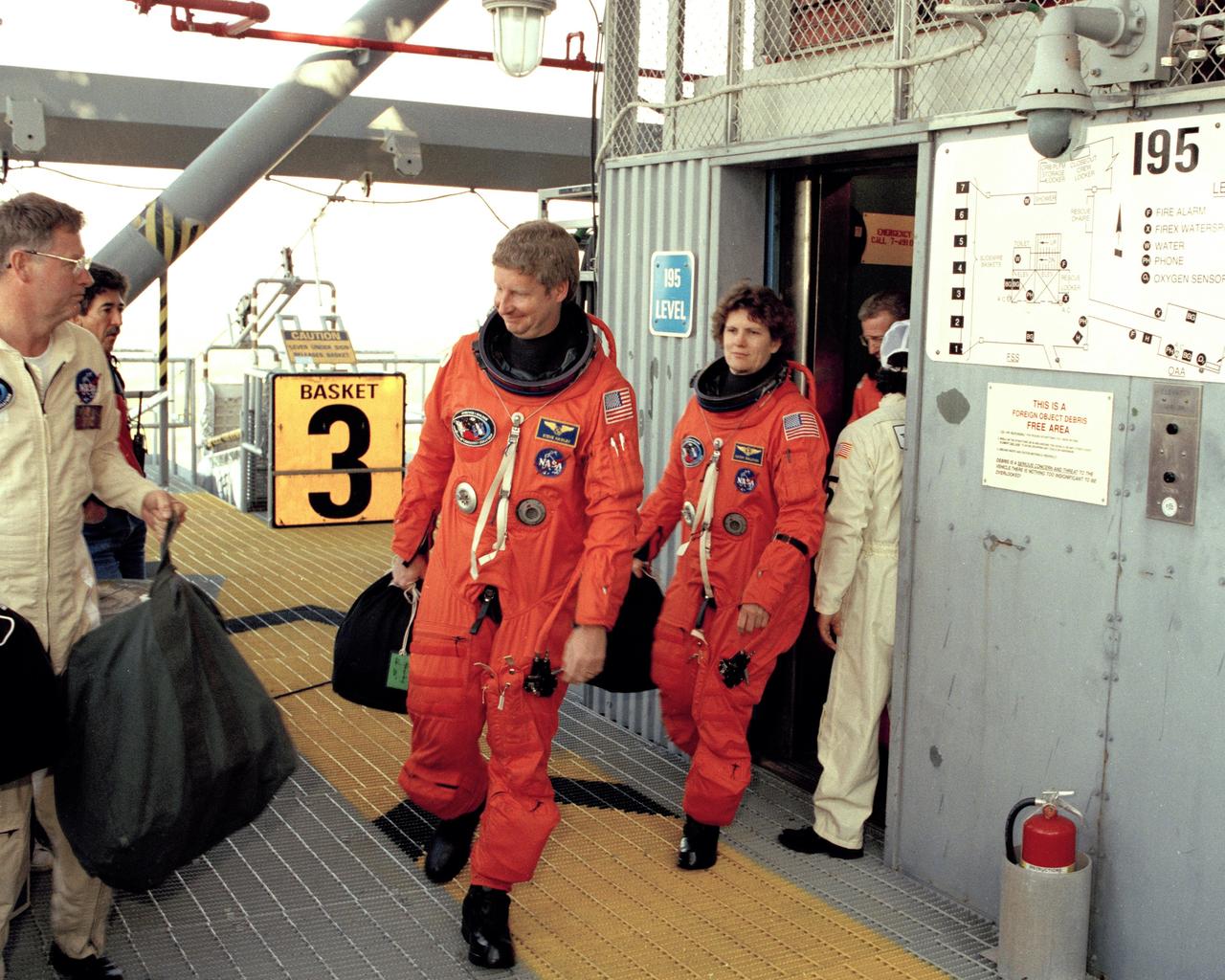

STS-31 Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley (left) and Kathryn D. Sullivan, and Commander Loren J. Shriver prepare to enter the orbiter Discovery from the 195-foot level at Launch Pad 39B during the culmination of the two-day Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT, conducted March 19-20, is a dress rehearsal for launch, simulating final countdown from the T-24 hour mark up to T-5 seconds. Space shuttle mission STS-31 is set to lift off on April 12, carrying a five-member crew and the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo credit: NASA
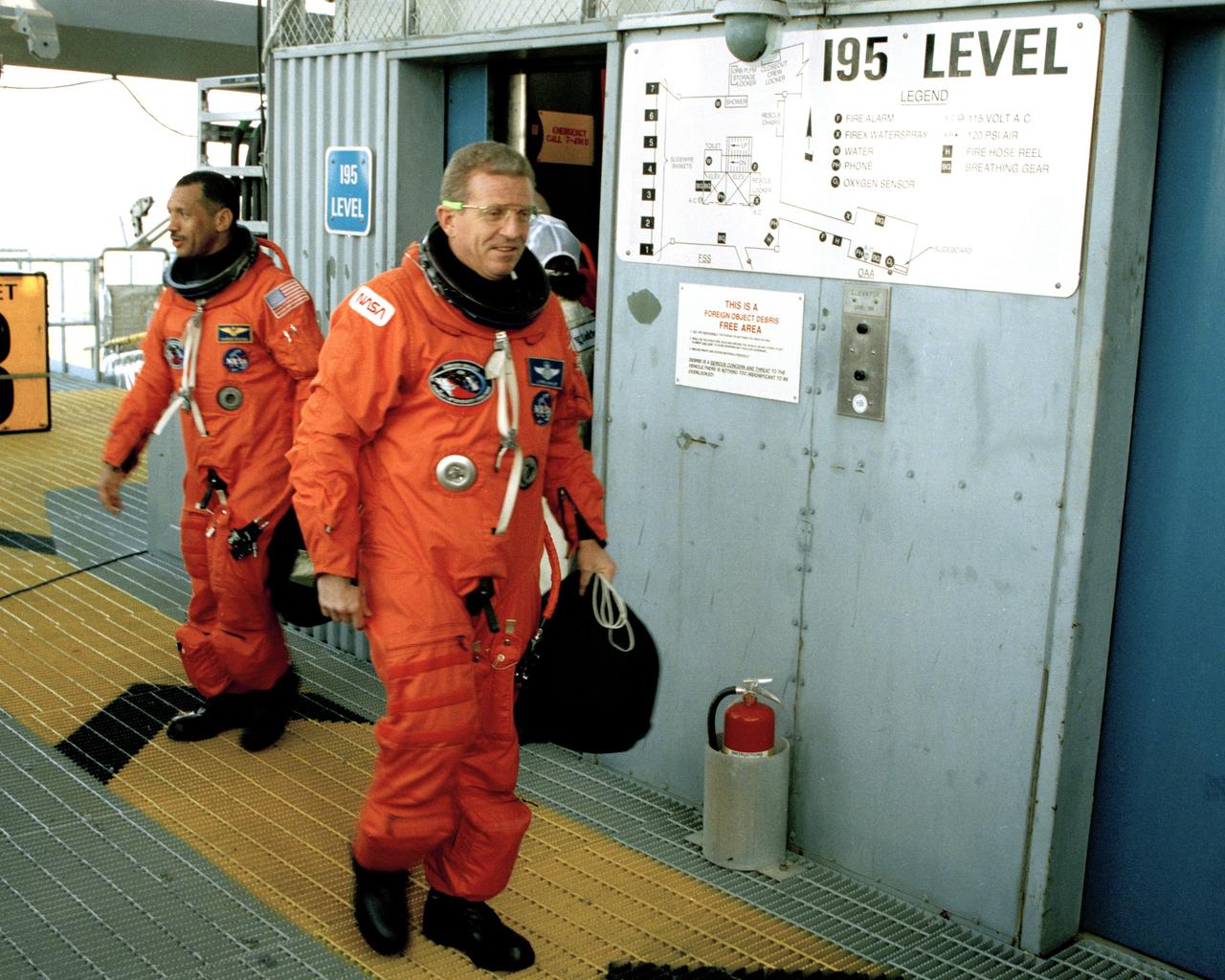

STS-31 Pilot Charles F. Bolden, left, and Commander Loren J. Shriver prepare to enter the orbiter Discovery from the 195-foot level at Launch Pad 39B during the culmination of the two-day Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT, conducted March 19-20, is a dress rehearsal for launch, simulating final countdown from the T-24 hour mark up to T-5 seconds. Space shuttle mission STS-31 is set to lift off on April 12, carrying a five-member crew and the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo credit: NASA
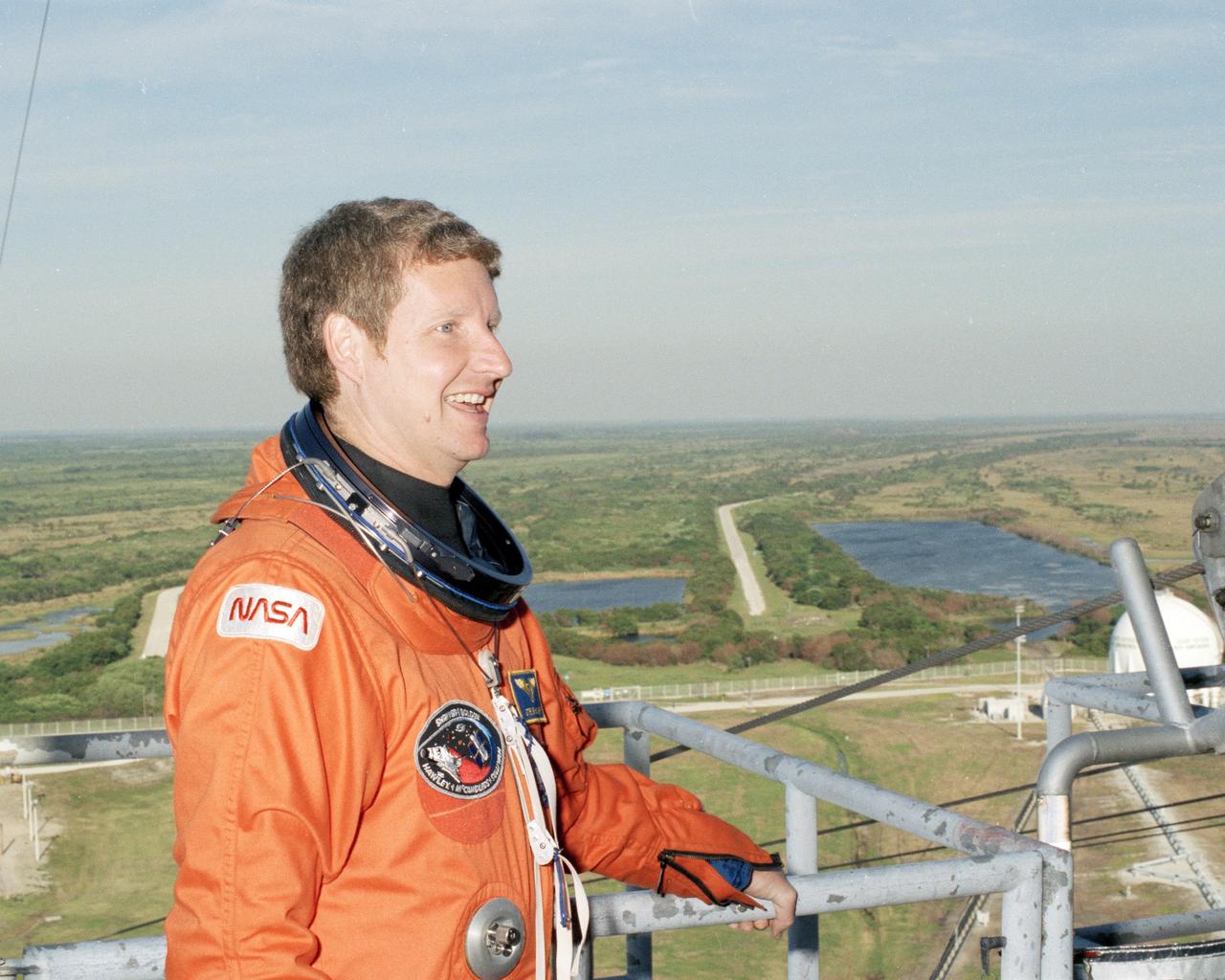

Wide-open Florida terrain creates a dramatic backas STS-31 Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley stands near the emergency exit system at the 194-foot level of Launch Pad 39B during the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test, or TCDT. Conducted March 19-20, the TCDT is a dress rehearsal for launch, simulating final countdown from the T-24 hour mark up to T-5 seconds. Space shuttle mission STS-31 is set to lift off on April 12, carrying a five-member crew and the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo credit: NASA
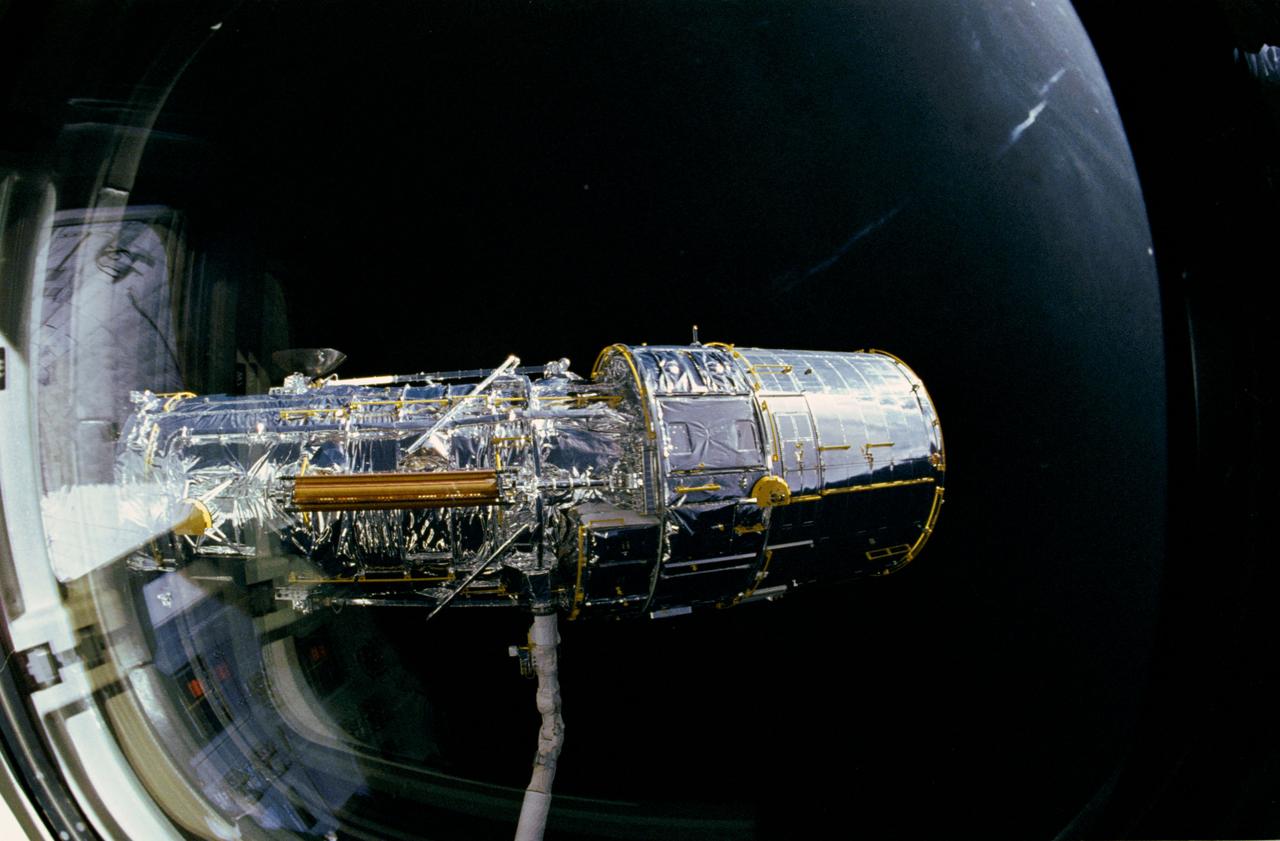

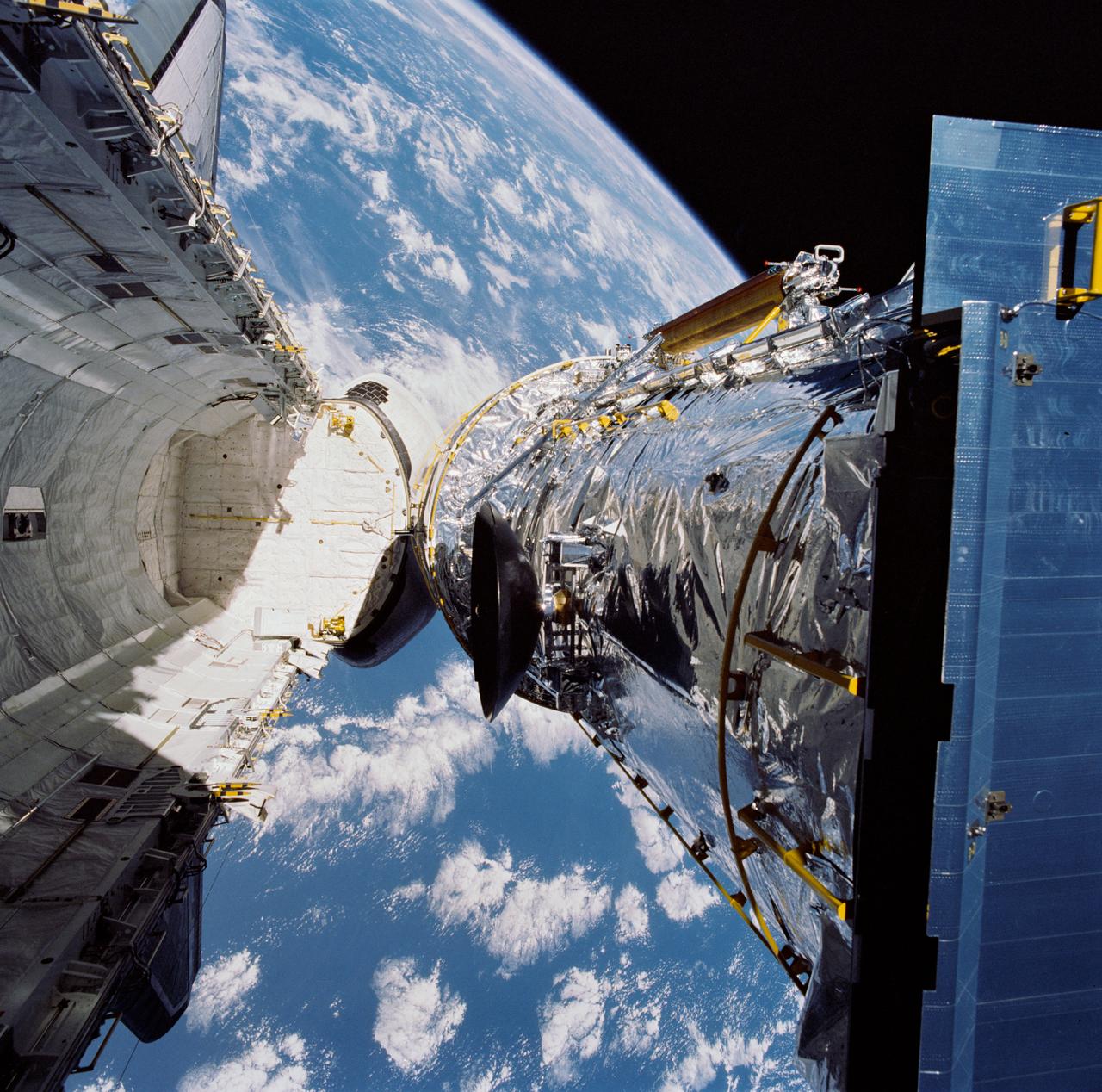
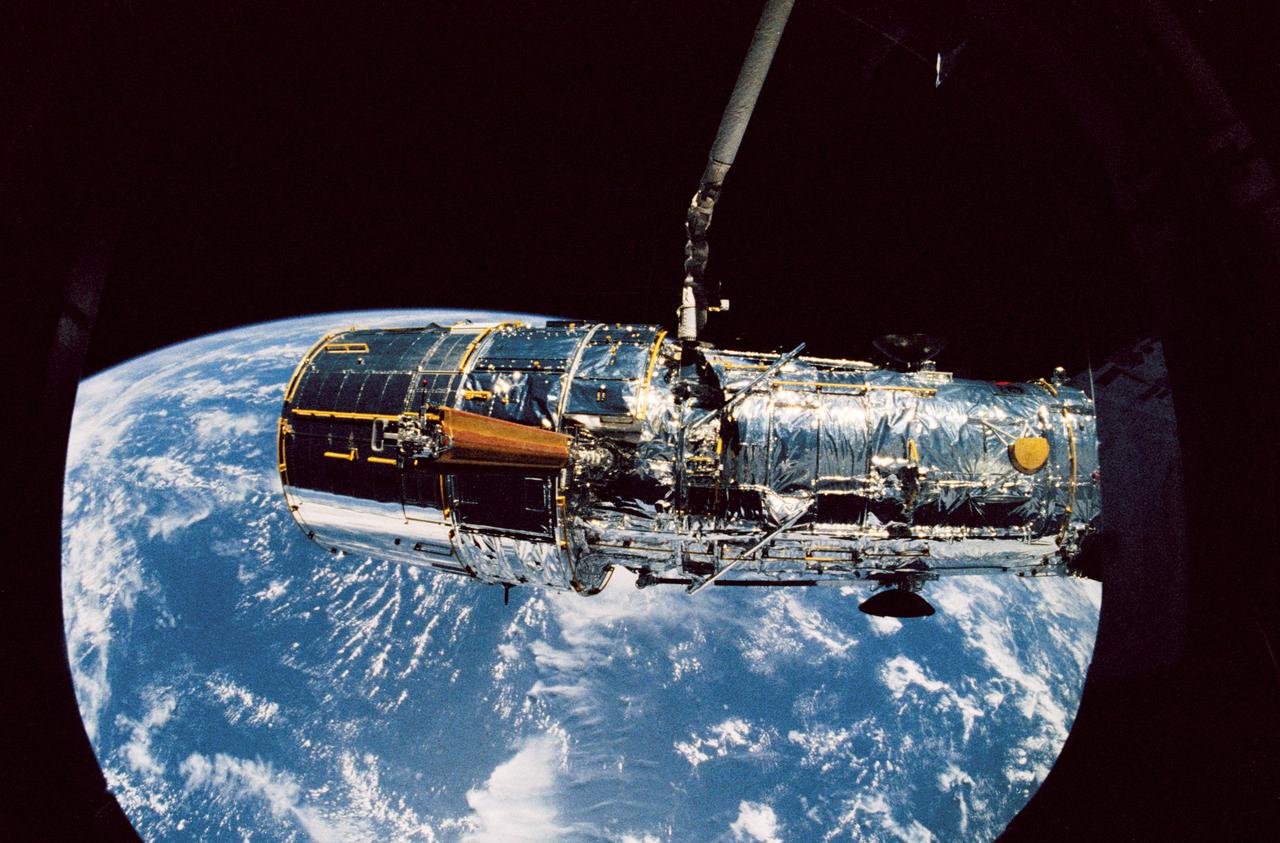
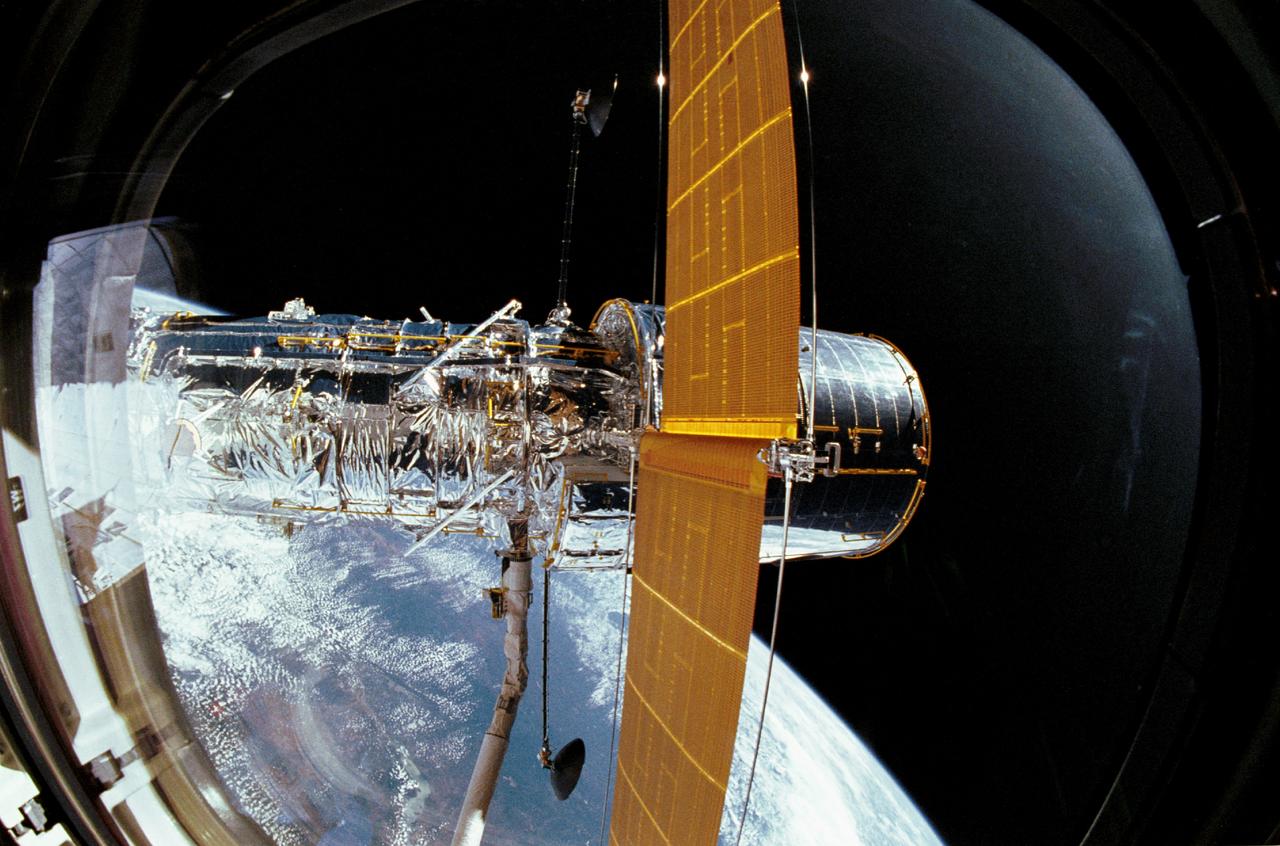
During STS-31 checkout, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is held in a pre-deployment position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS). The view, taken from the crew cabin overhead window W7, shows the starboard solar array (SA) panel (center) and two high gain antennae (HGA) (on either side) stowed along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The sun highlights HST against the blackness of space.
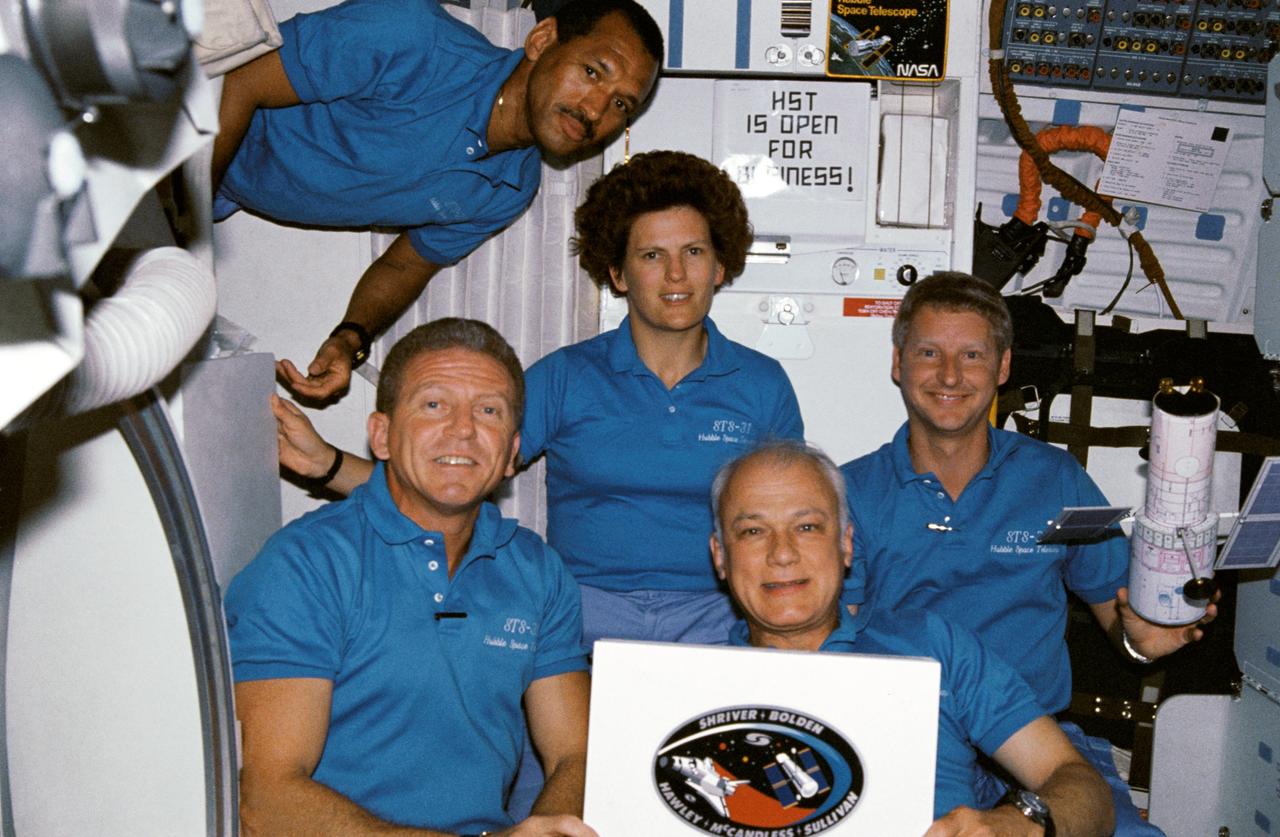

STS031-12-031 (24-29 April 1990) --- On Discovery's middeck, the STS-31 crew poses for a traditional in-flight portrait. Astronaut Loren J. Shriver, mission commander, is at lower left. Astronaut Charles F. Bolden, pilot, floats above. Others, left to right, are Kathryn D. Sullivan, Bruce McCandless II and Steven A. Hawley, all mission specialists. Photo credit: NASA
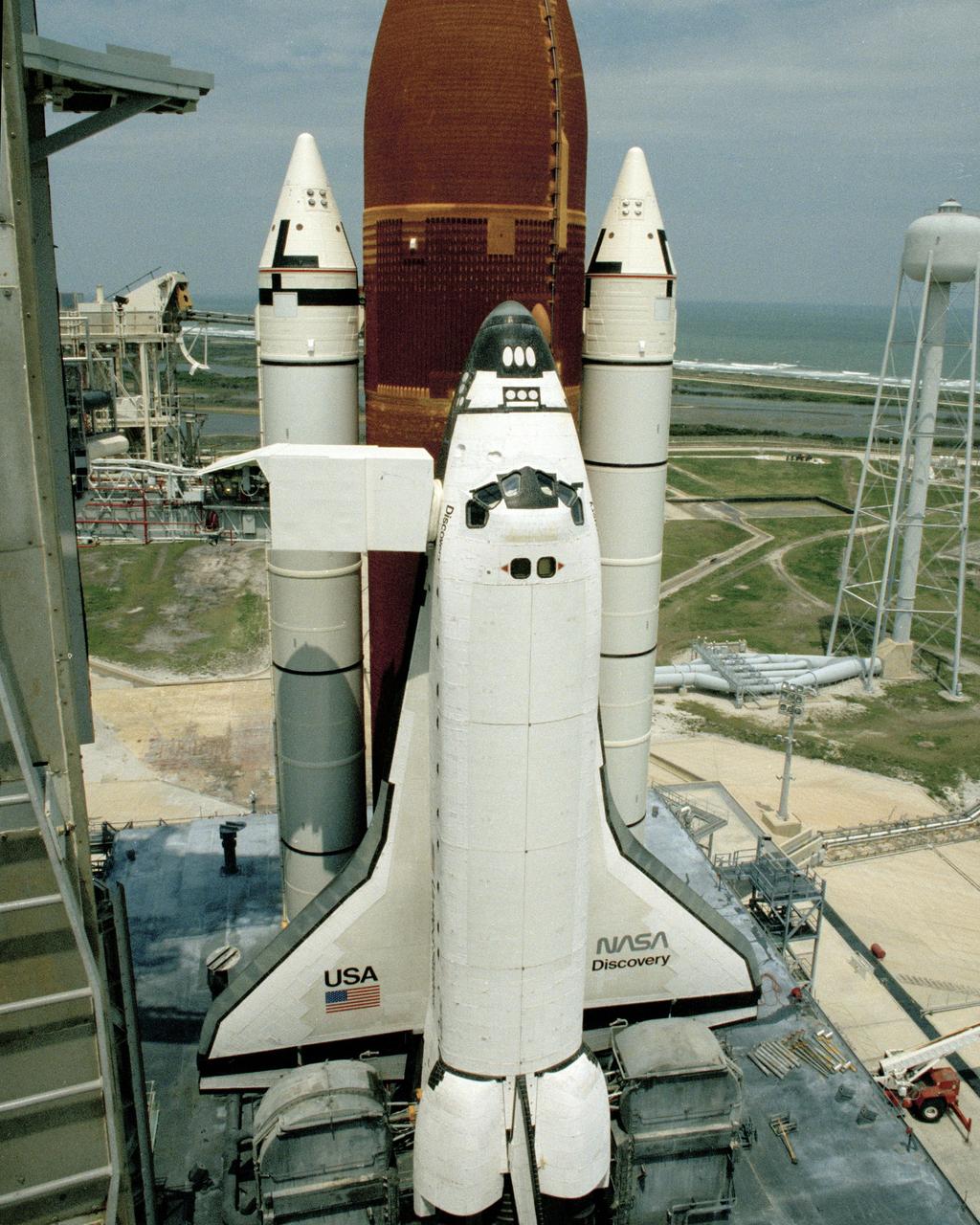

The orbiter Discovery is unveiled as rollback of the Rotating Service Structure begins during final prelaunch preparations at Launch Pad 39B on April 9. Space shuttle mission STS-31, carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope, is set to lift off at 6:47 a.m. EDT, April 10. Photo credit: NASA
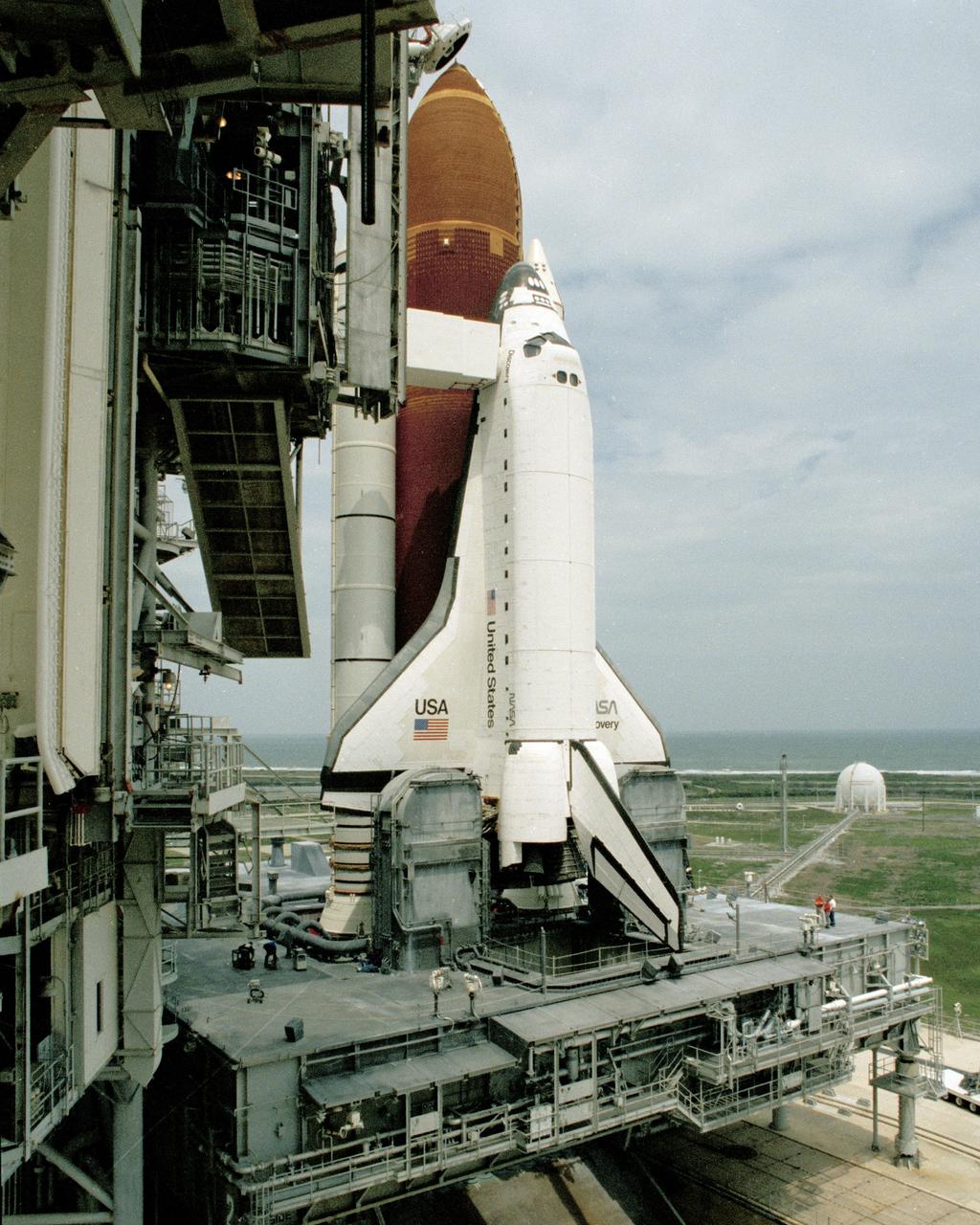

The orbiter Discovery is unveiled as rollback of the Rotating Service Structure begins during final prelaunch preparations at Launch Pad 39B on April 9. Space shuttle mission STS-31, carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope, is set to lift off at 6:47 a.m. EDT, April 10. Photo credit: NASA

Discovery was rolled out to Launch Pad 39-B on March 15-16 for final launch preparations for its 10th mission into space. Launch of the Hubble Space Telescope on the five-day STS-31 mission is targeted for April 12. Photo credit: NASA
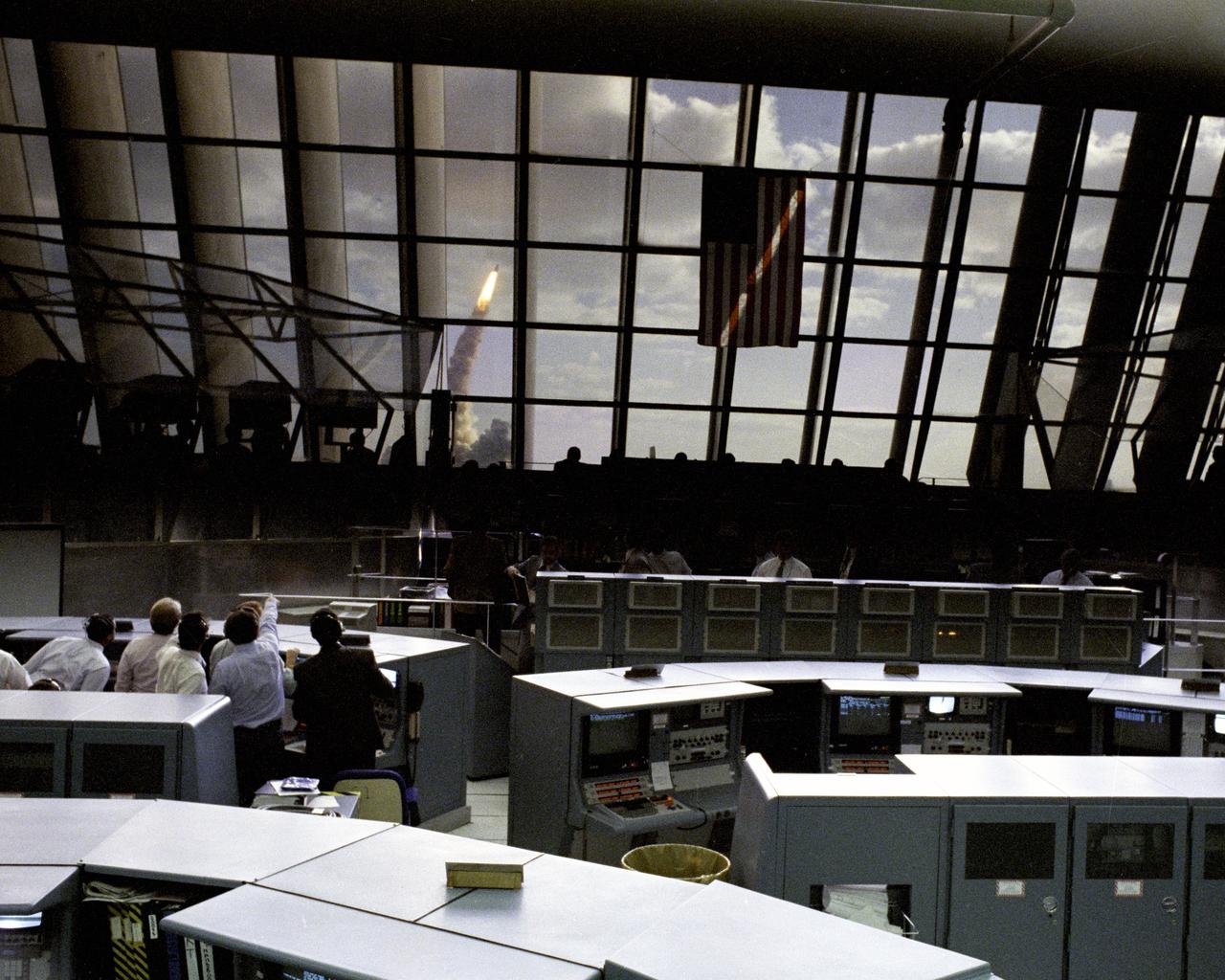

Through the large window panes of Firing Room 1, KSC launch team members reap the rewards of their work with a glimpse of the space shuttle Discovery soaring into the sky. Discovery was launched for the tenth time at 8:34 a.m. EDT on April 24 beginning the five-day STS-31 mission to deploy the Hubble Space Telescope. A ray of morning sunlight highlights the red and white stripes of Old Glory hanging high in the Firing Room. Launch team members overcame a last minute challenge in the STS-31 countdown when software detected a main propulsion system valve was out of position. The situation was quickly corrected and verified by the team from consoles in the Firing Room and the countdown was returned in a matter of minutes. Photo credit: NASA
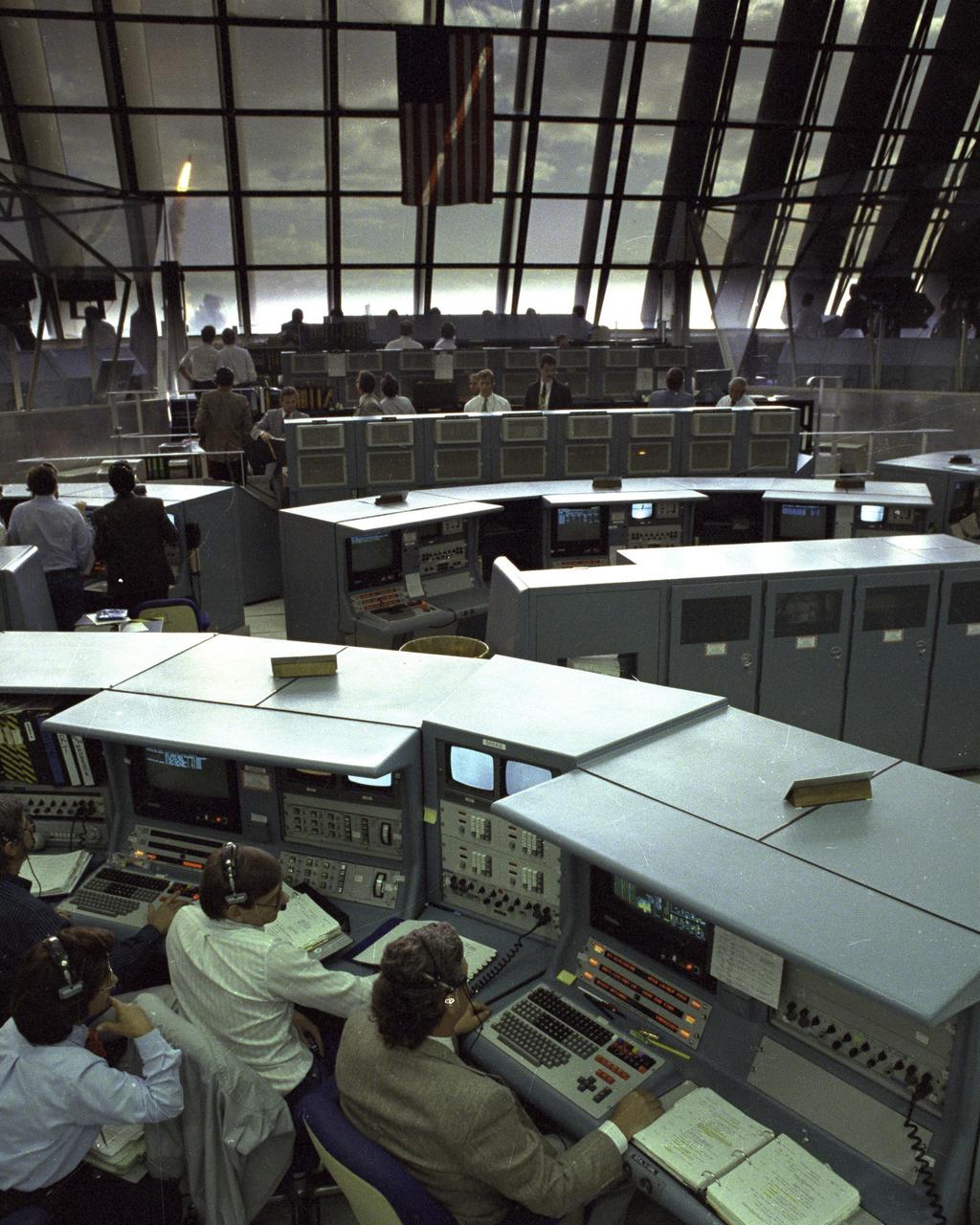

Through the large window panes of Firing Room 1, KSC launch team members reap the rewards of their work with a glimpse of the space shuttle Discovery soaring into the sky. Discovery was launched for the tenth time at 8:34 a.m. EDT on April 24 beginning the five-day STS-31 mission to deploy the Hubble Space Telescope. A ray of morning sunlight highlights the red and white stripes of Old Glory hanging high in the Firing Room. Launch team members overcame a last minute challenge in the STS-31 countdown when software detected a main propulsion system valve was out of position. The situation was quickly corrected and verified by the team from consoles in the Firing Room and the countdown was returned in a matter of minutes. Photo credit: NASA
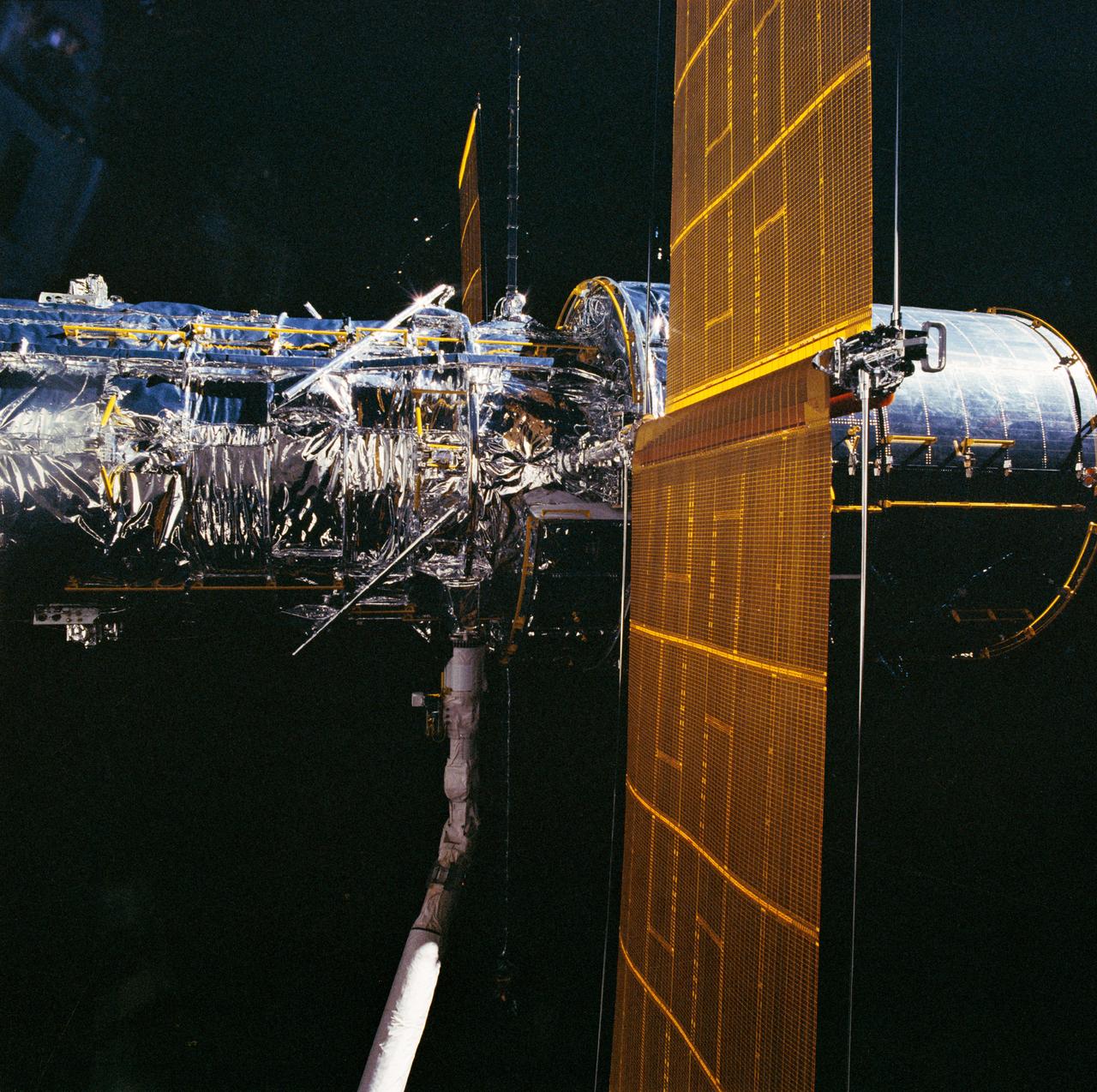
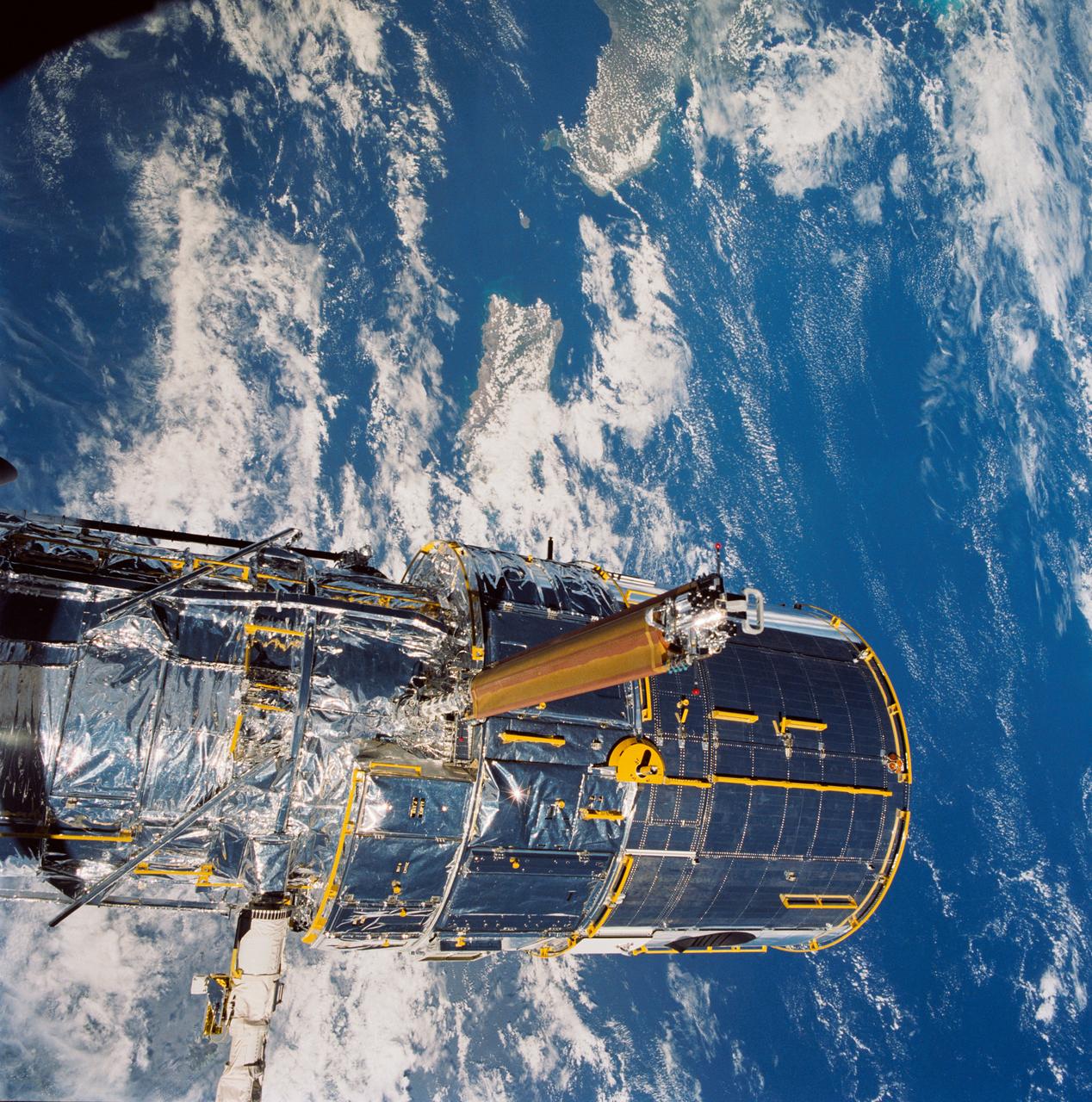
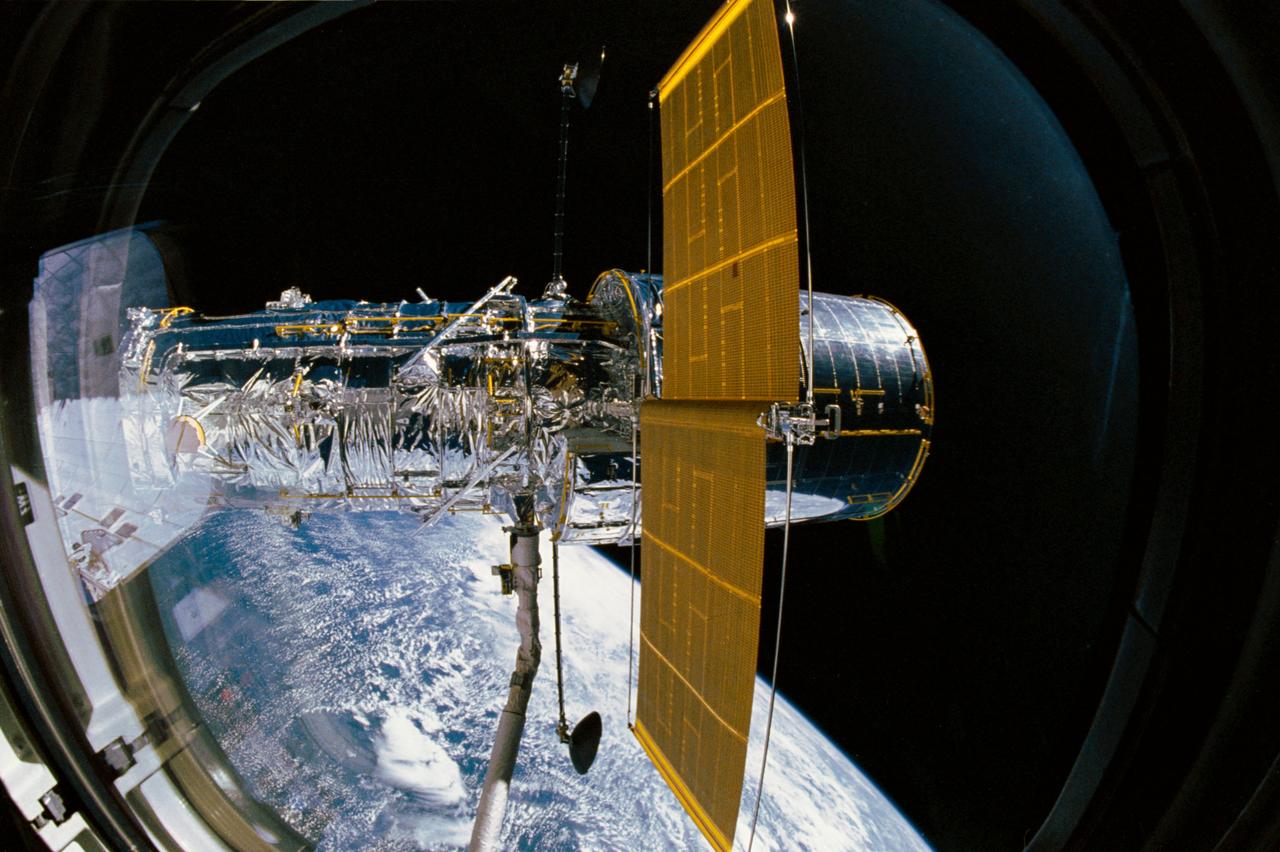
During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector, is held against the blackness of space. The two solar array (SA) wings (large gold panels) are fully extended with bistem cassette and secondary deployment mechanism (SDM) handle clearly visible. The two deployed high gain antennae (HGA) masts are parallel to the SA panels. RMS end effector is positioned on the starboard fixture during the predeployment checkout operations above Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, payload bay (PLB).
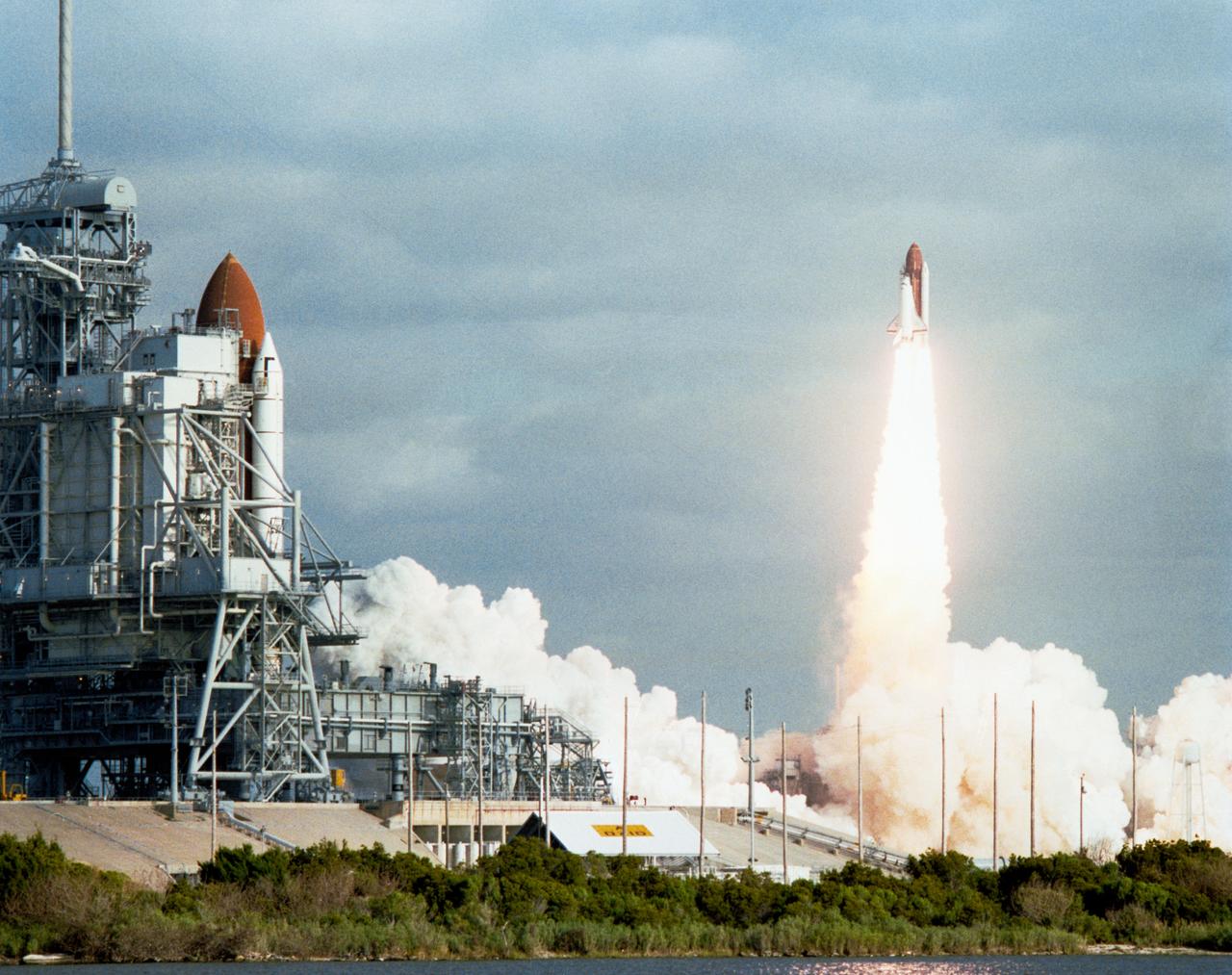

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, lifts off from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) 39 Pad B. In the foreground STS-35 Columbia, OV-102, is visible on launch pad 39A. This event marked the first time since January 1986 that there was an orbiter on each pad. LC 39 pads are separated by 1.6 miles. View provided by KSC with alternate number KSC-90PC-610.
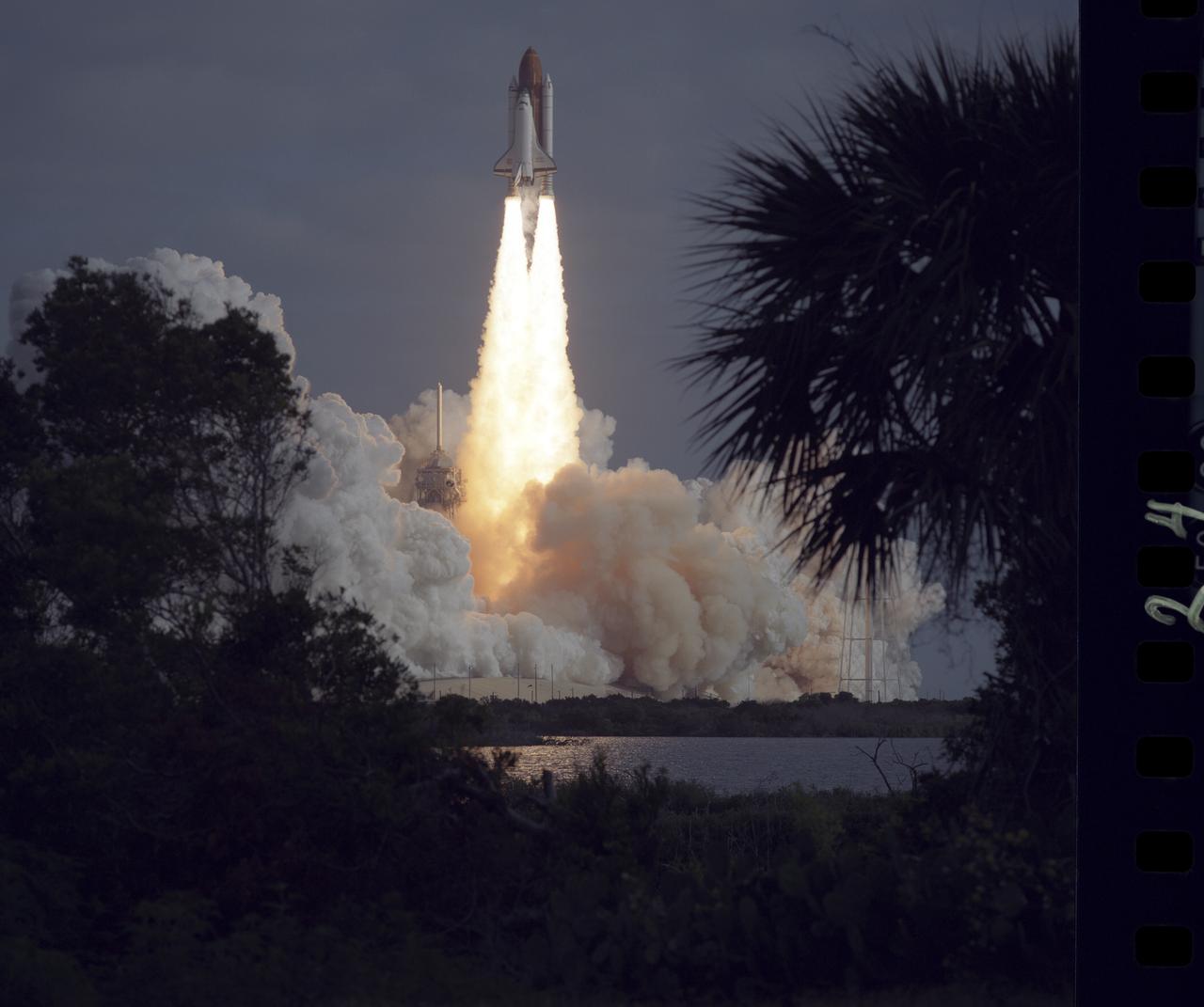

The STS-31 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT). Included in the crew of five were Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists. The primary goal of the mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed program.

The STS-31 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT). Included in the crew of five were Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists. The primary goal of the mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed program.

The space shuttle Discovery lifts off from Launch Pad 39-B at 8:33 a.m. EDT carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope. STS-31 crew members are Commander Loren Shriver, Pilot Charles Bolden and Mission Specialists Steven Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn Sullivan. Photo credit: NASA
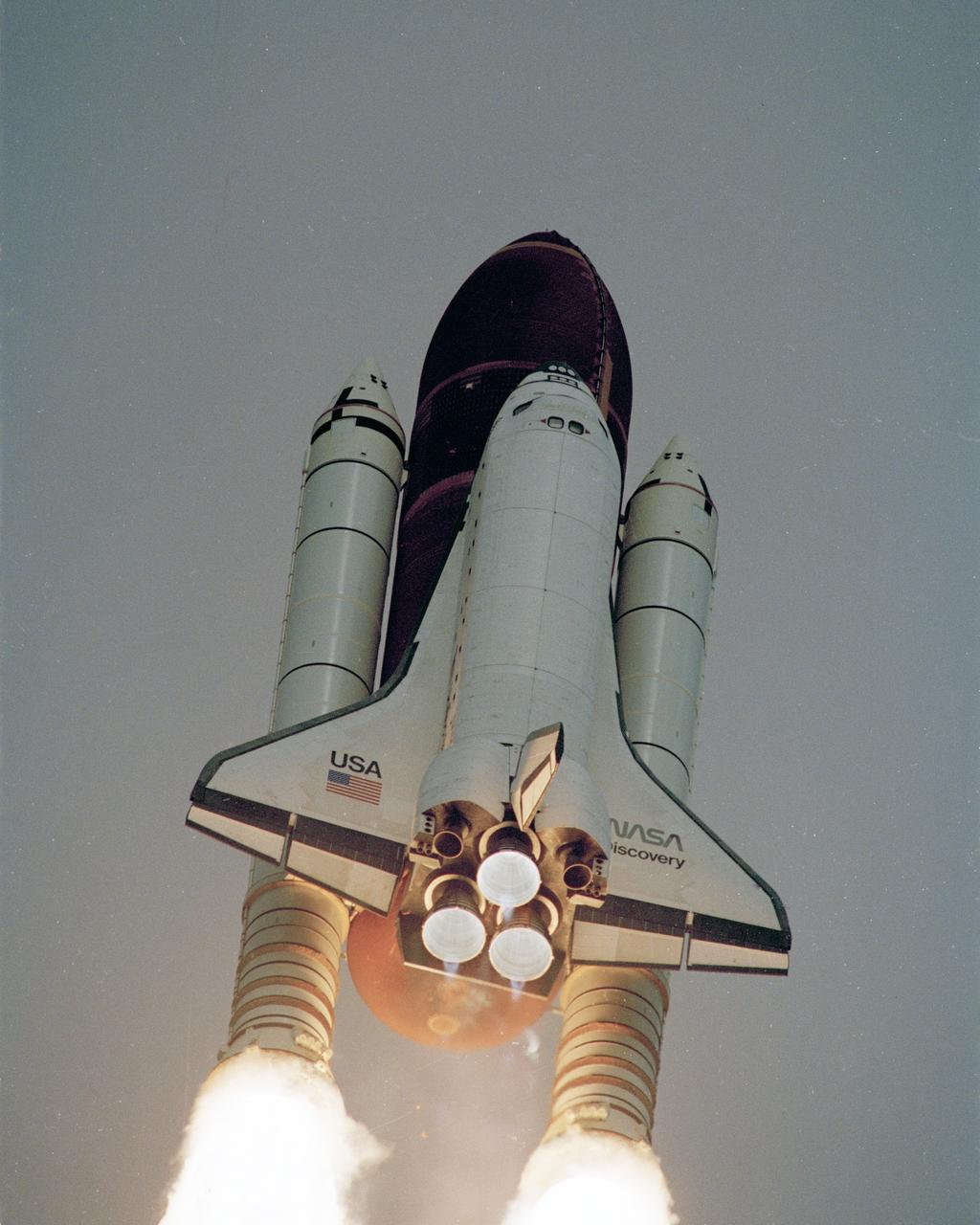

The space shuttle Discovery lifts off from Launch Pad 39-B at 8:33 a.m. EDT carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope. STS-31 crew members are Commander Loren Shriver, Pilot Charles Bolden and Mission Specialists Steven Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn Sullivan. Photo credit: NASA
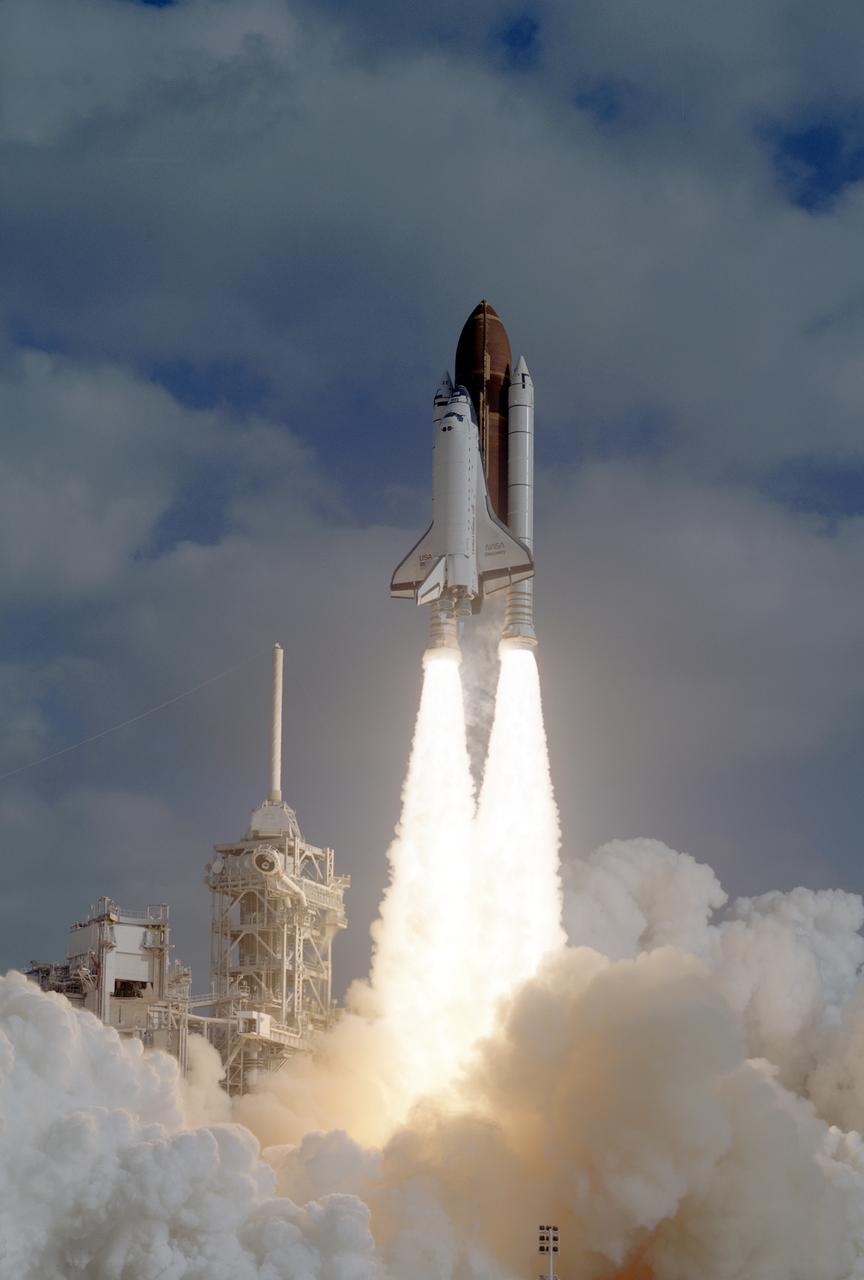

The STS-31 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT). Included in the crew of five were Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists. The primary goal of the mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed program.
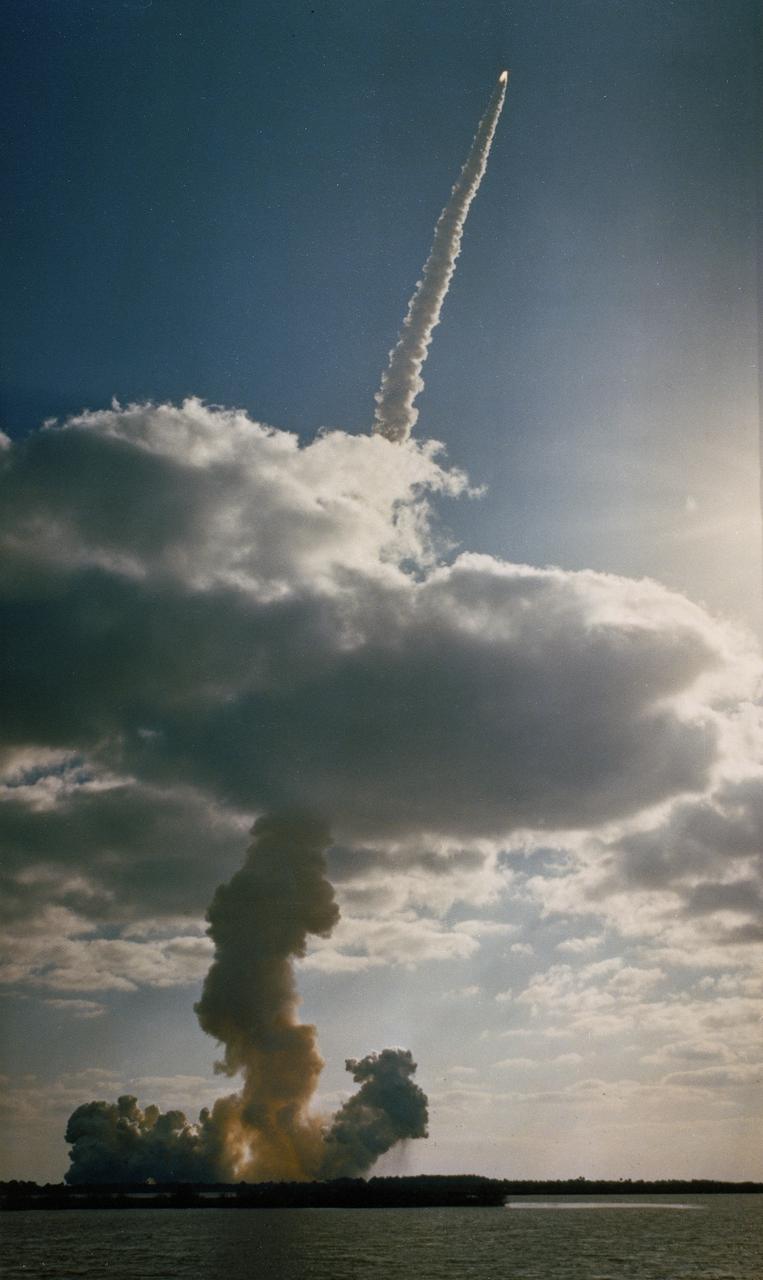

The STS-31 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT). Included in the crew of five were Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists. The primary goal of the mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed program.
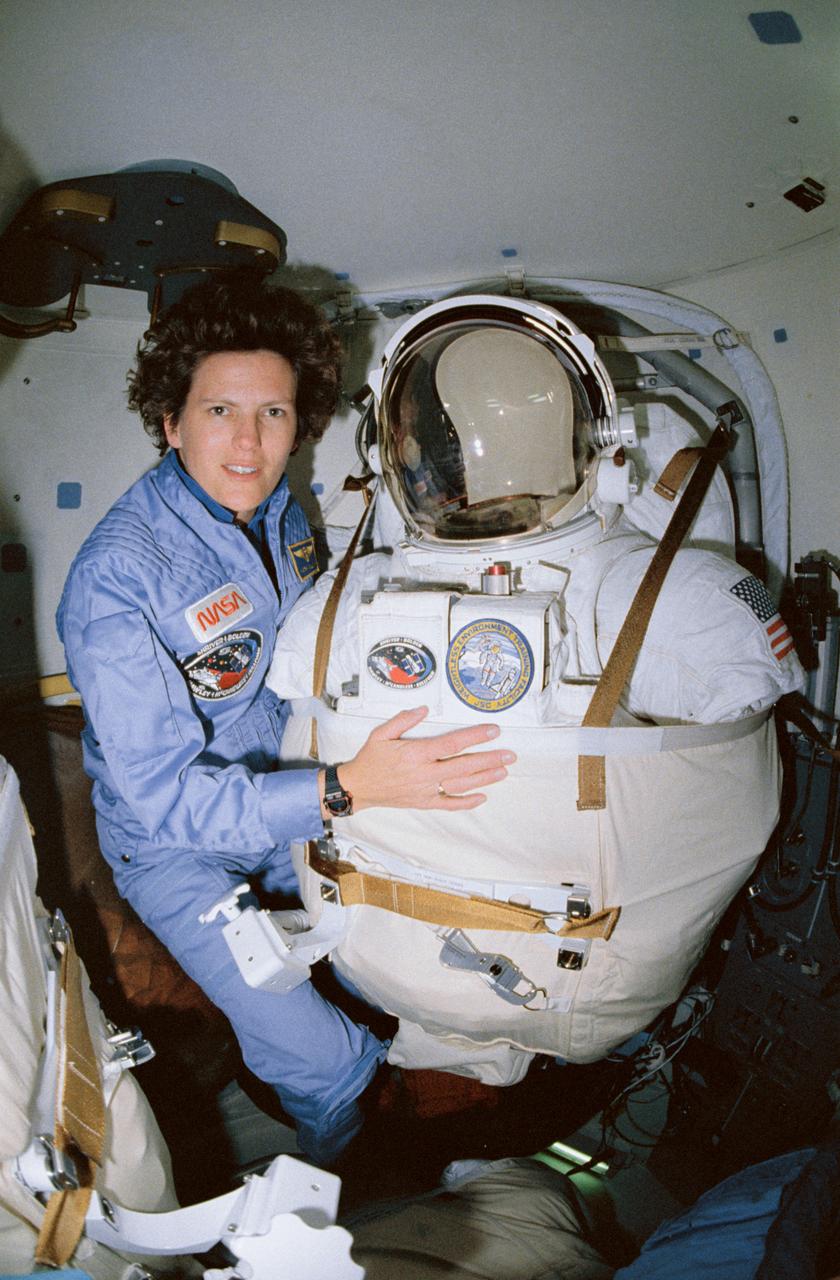

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Kathryn D. Sullivan poses for a picture before beginning extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) donning procedures in the airlock of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Sullivan will remove the lower torso restraint and don EMU which is supported on an airlock adapter plate (AAP). When suited, Sullivan will be ready for contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) in the event that problems arise with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment. Displayed on the front of the EMU are the STS-31 mission insignia and the JSC Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) insignia.

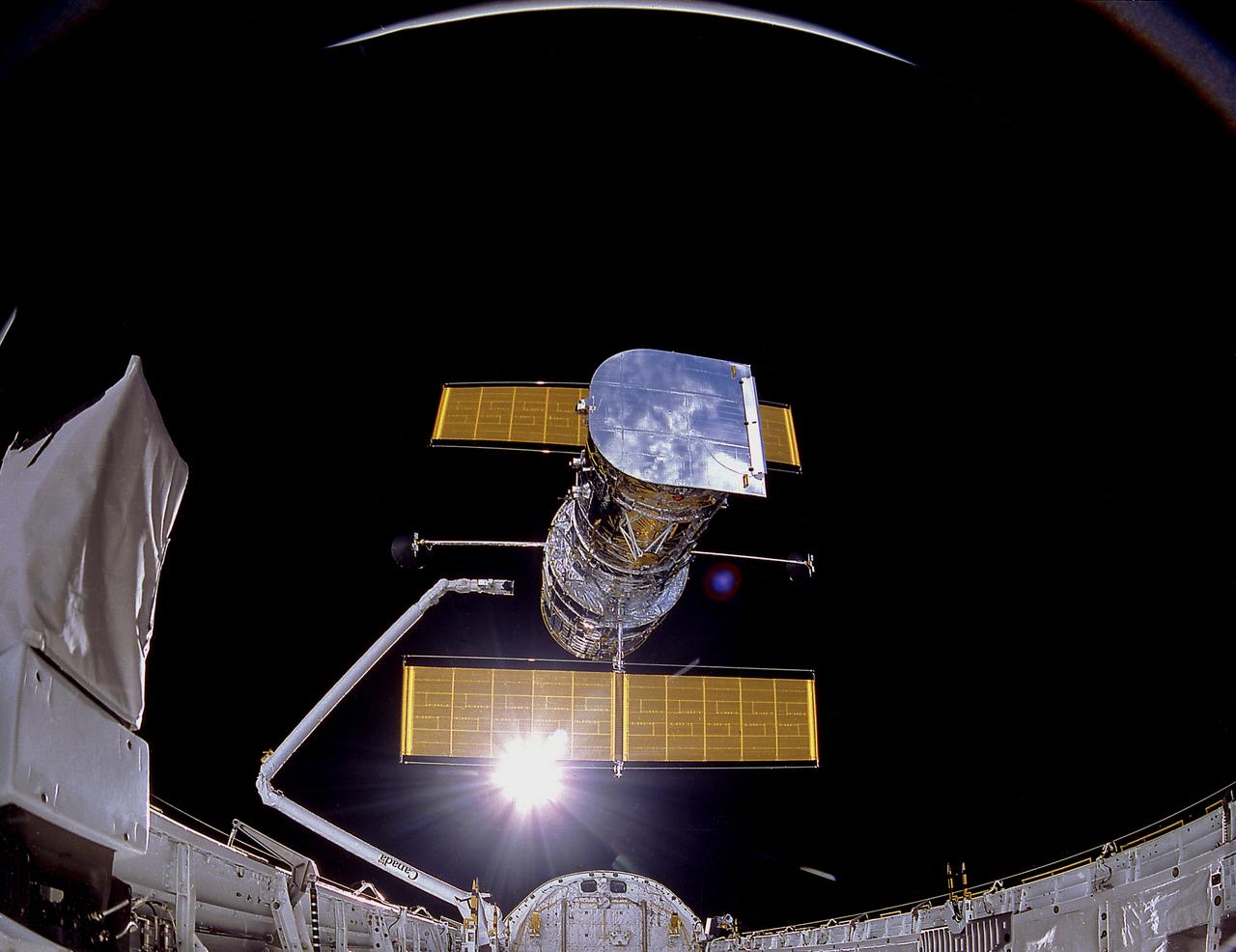
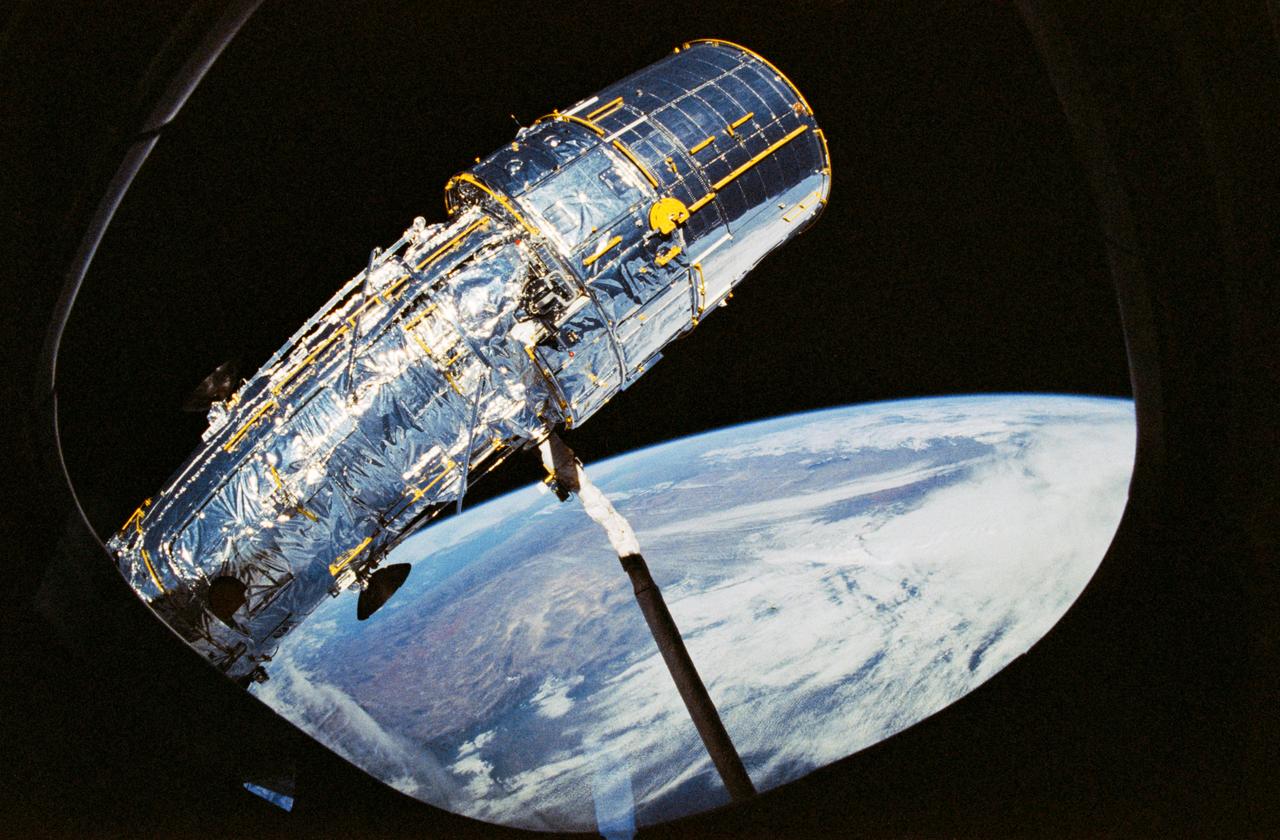
STS031-71-095 (25 April 1990) --- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is suspended above Discovery's cargo bay some 332 nautical miles above Earth. The Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, controlled from in-cabin by the astronaut crew members of STS-31, held the huge telescope in this position during pre-deployment procedures, which included extension of solar array panels and antennae. The photo was made with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera.
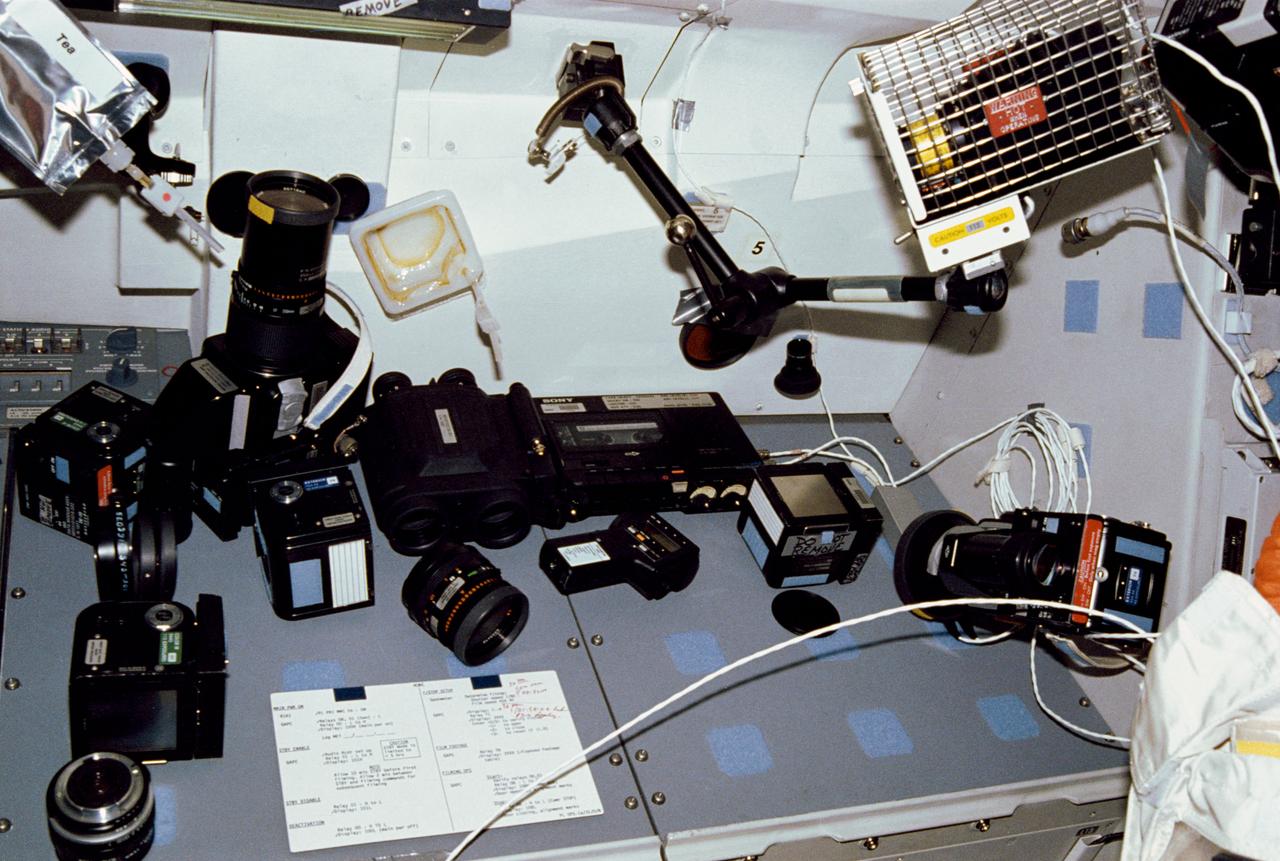

This array of photographic equipment, displayed on the aft flight deck payload station, represents just a part of the imaging and recording hardware which was carried aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, for STS-31's five day mission. Lenses, film magazines, cassettes, recorders, camera chassis, a pair of binoculars, spot meter, tape recorder, and a bracket-mounted light fixture are included among the array.
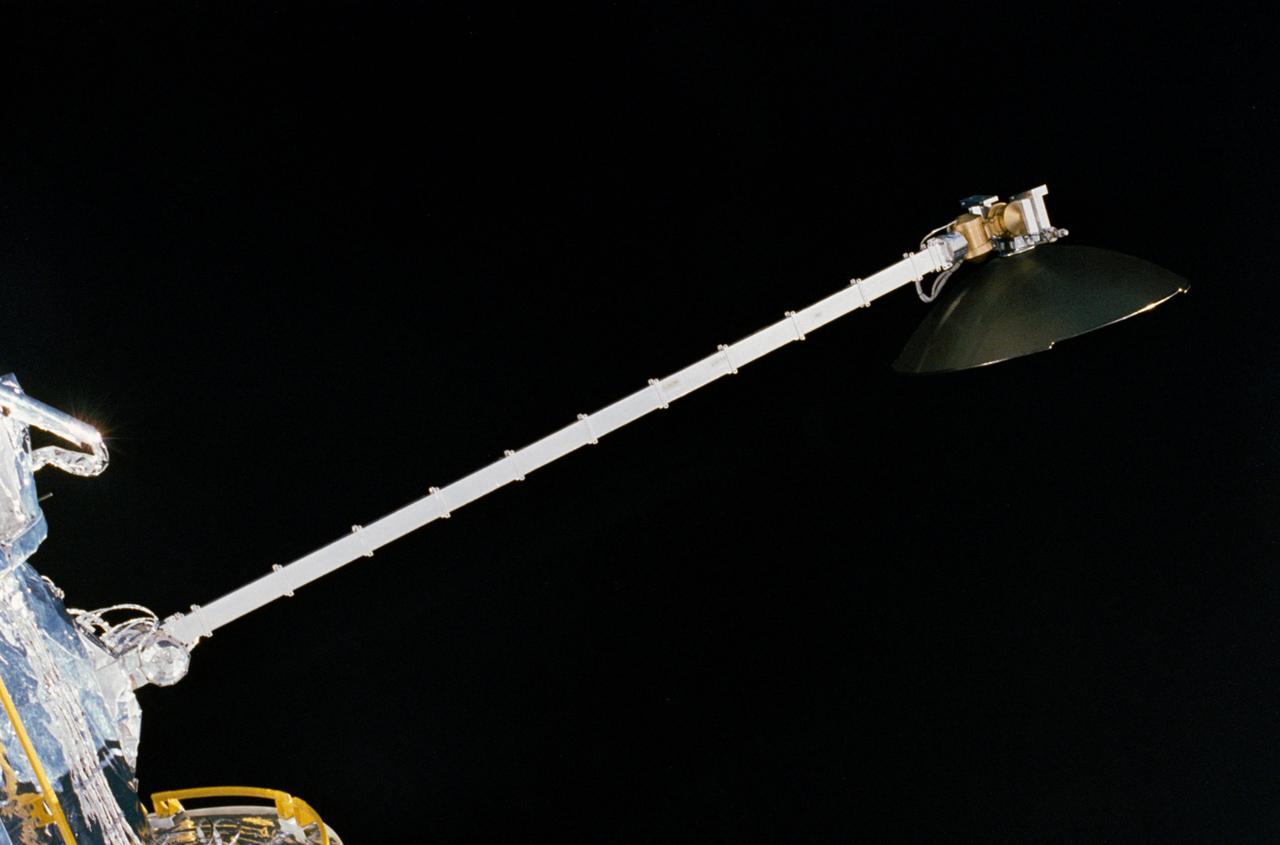

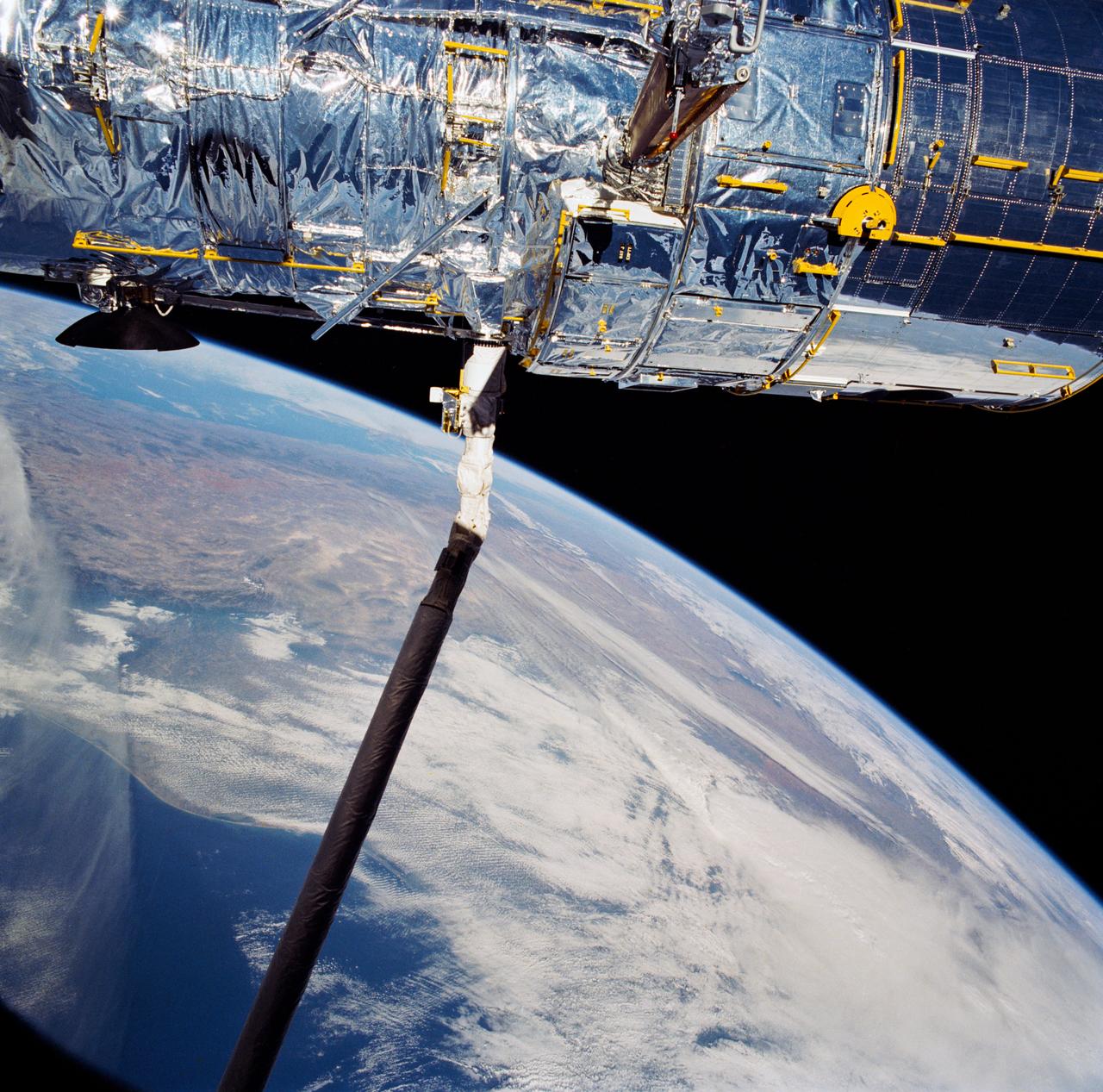
Held in appendage deploy position, the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) high gain antenna (HGA) has been released from its stowed position along the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The STS-31 crew aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) oversees the automatic HGA deployment prior to releasing HST. HST HGA is backdropped against the blackness of space.

The mission insignia for NASA's STS-31 mission features the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in its observing configuration against a background of the universe it will study. The cosmos includes a stylistic depiction of galaxies in recognition of the contribution made by Sir Edwin Hubble to our understanding of the nature of galaxies and the expansion of the universe. The STS-31 crew points out that is it in honor of Hubble's work that this great observatory in space bears his name. The depicted Space Shuttle trails a spectrum symbolic of both the red shift observations that were so important to Hubble's work and new information which will be obtained with the HST. Encircling the art work, designed by the crew, are the names of its members.
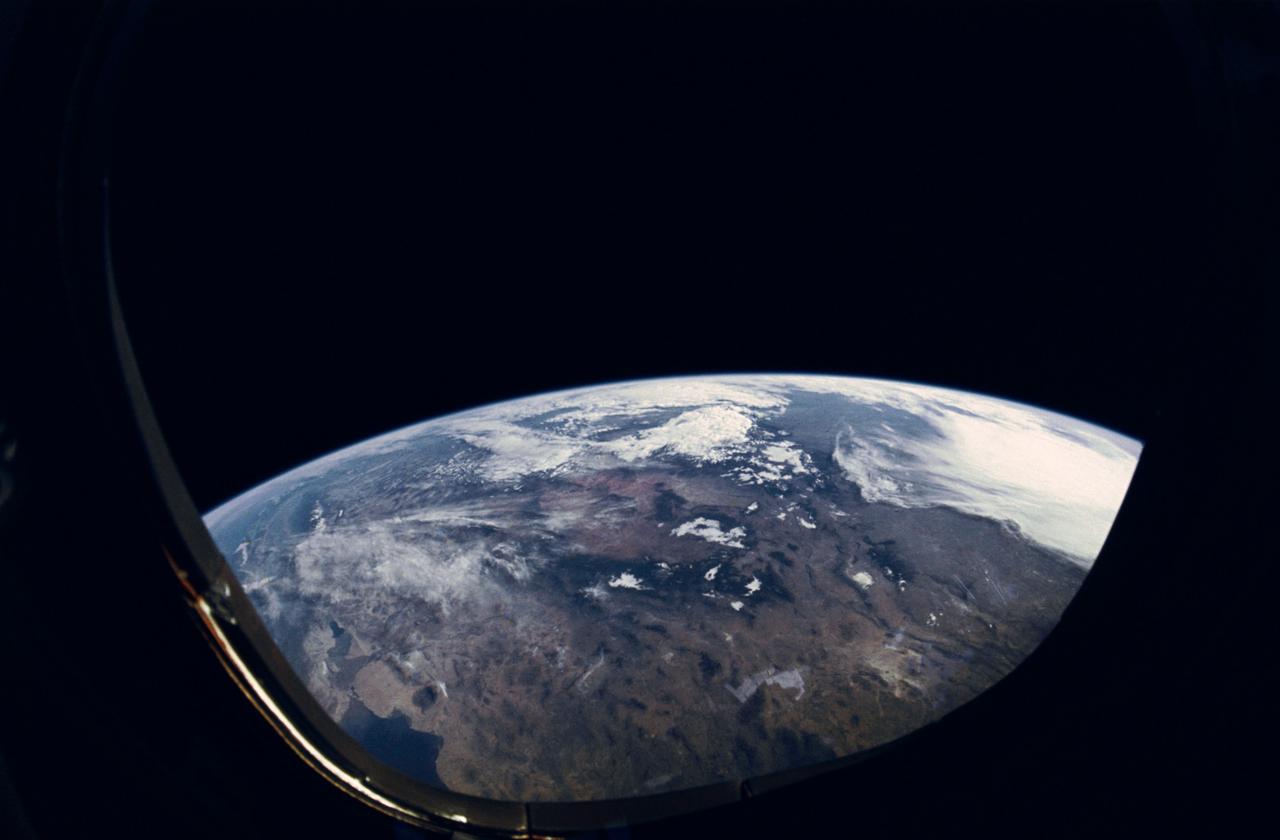

STS-31 Earth observation taken aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is of the western United States with the Salton Sea and Imperial Valley area recognizable at the lower left. The view is framed in a flight deck window and was photographed using a fish-eye lens.
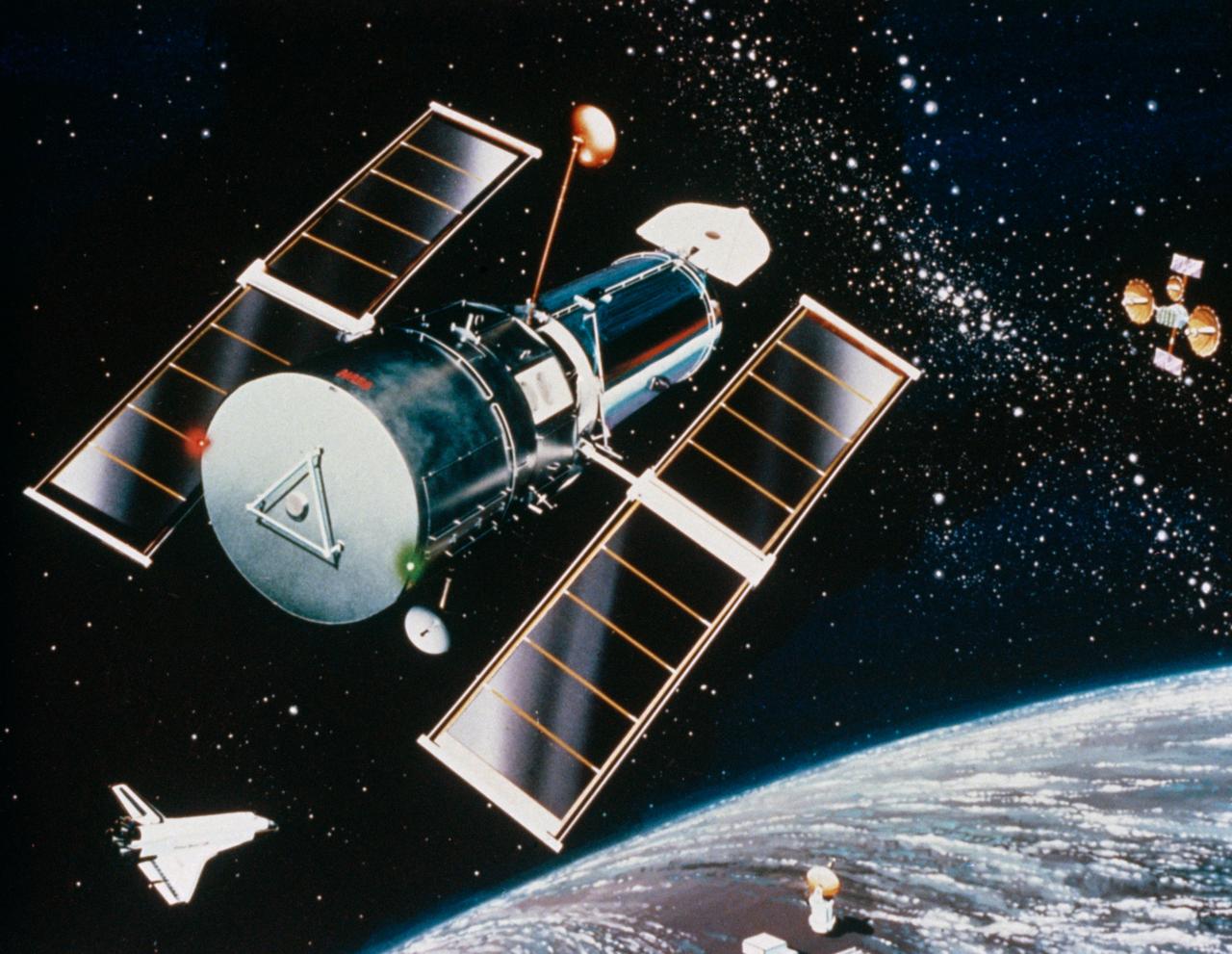

Artist concept shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) placed in orbit above the Earth's distorting layer of atmosphere by Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, during mission STS-31. Tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is visible in the background and ground station is visible below on the Earth's surface. HST is the first of the great observatories to go into service and one of NASA's highest priority scientific spacecraft. Capable of observing in both visible and ultraviolet wavelengths, HST has been termed the most important scientific instrument ever designed for use on orbit. It will literally be able to look back in time, observing the universe as it existed early in its lifetime and providing information on how matter has evolved over the eons. The largest scientific payload ever built, the 12 1/2-ton, 43-foot HST was developed by Lockheed Missiles & Space Company, spacecraft prime contractor, and Perkin-Elmer Corporation, prime contractor for the optical assembly. The European Space Agency (ESA) furnished the power generating solar array and one of the system's five major instruments. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) manages the HST project; Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) will be responsible, when the spacecraft is in orbit, for controlling the telescope and processing the images and instrument data returns.
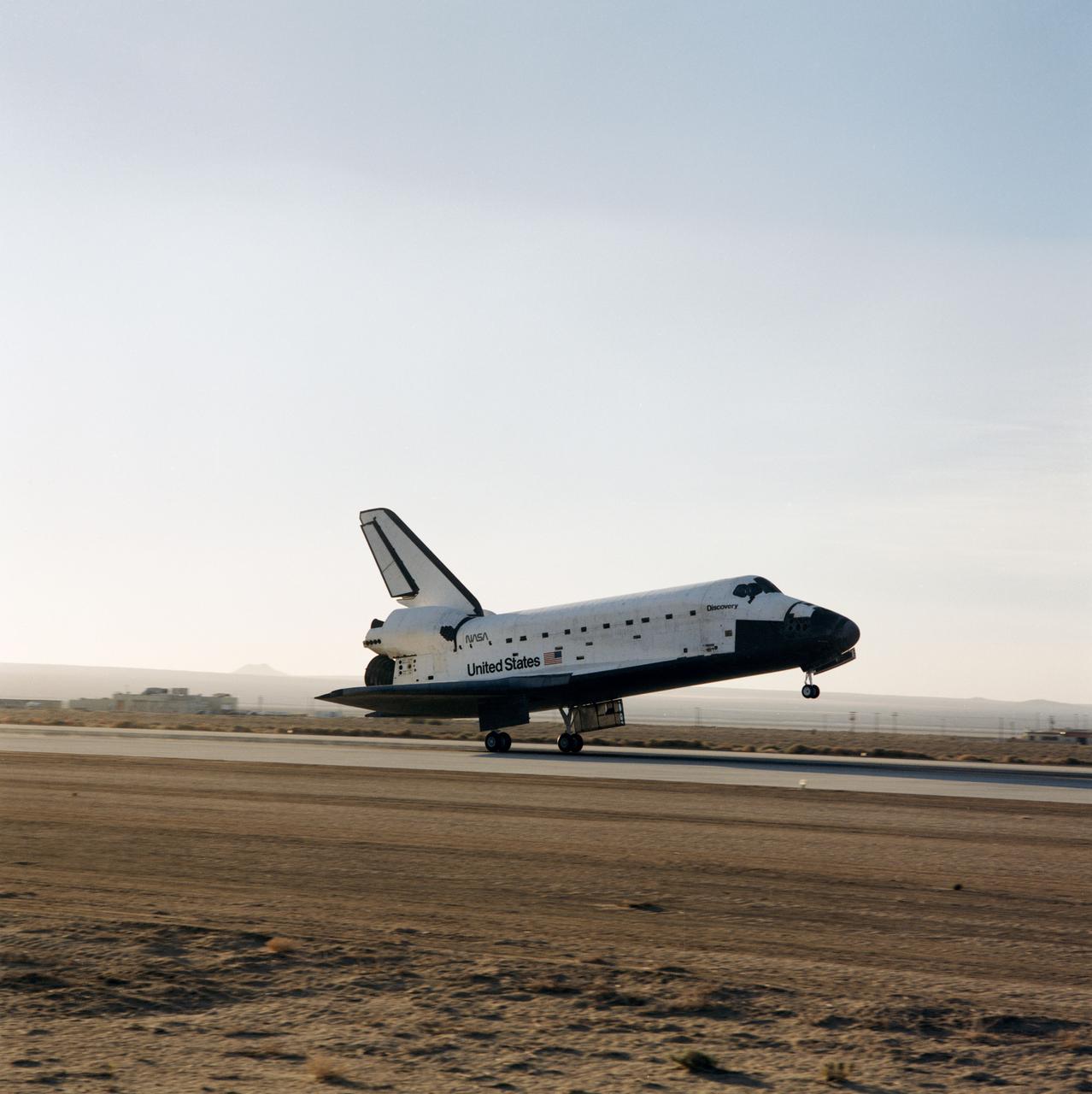

STS031-S-135 (29 April 1990) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery makes a smooth landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base to complete a highly successful five-day mission. It was an Earth orbital flight during which the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was sent toward its 15-year mission. Landing was completed at 6:51 a.m. (PDT), April 29, 1990. Inside the spacecraft for STS-31 were Astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Bruce McCandless II, Kathryn D. Sullivan and Steven A. Hawley.

Views of the STS-31/61B Crew during Emergency Egress Training, Bldg. 9A, 10/28/1985; and, the Crew Preflight Press Conference, Bldg. 2, 10/24/1985. 1. STS-31/61B - CREW TRAINING (EMERGENCY EGRESS) JSC, HOUSTON, TX
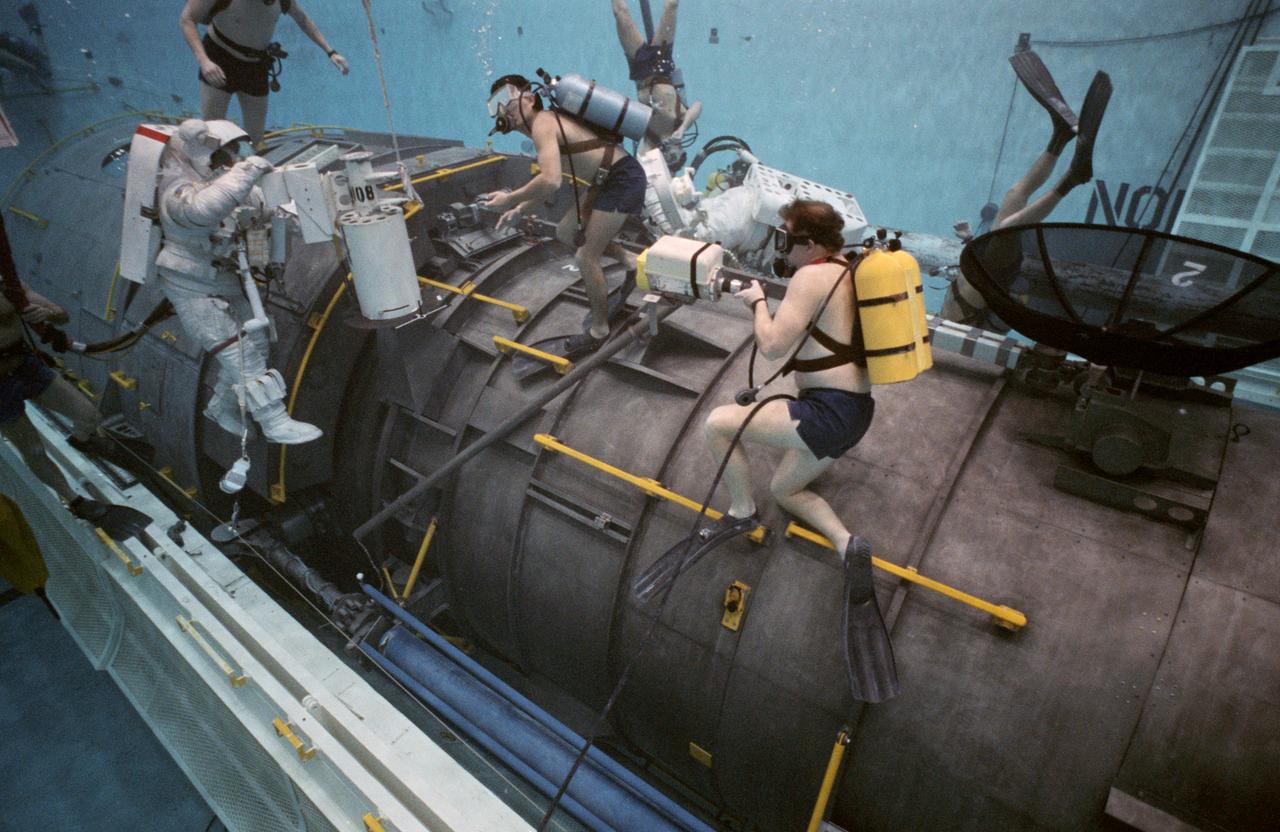

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II (left), wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), maneuvers his way around a mockup of the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector during an underwater simulation in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. The end effector is attached to a grapple fixture on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) mockup. As McCandless performs contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) procedures, fellow crewmember MS Kathryn D. Sullivan, in EMU, works on the opposite side of the HST mockup, and SCUBA-equipped divers monitor the activity. Though no EVA is planned for STS-31, the two crewmembers train for contingencies that would necessitate leaving the shirt sleeve environment of Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, crew cabin and performing chores with the HST payload or related hardware in the payload bay (PLB).
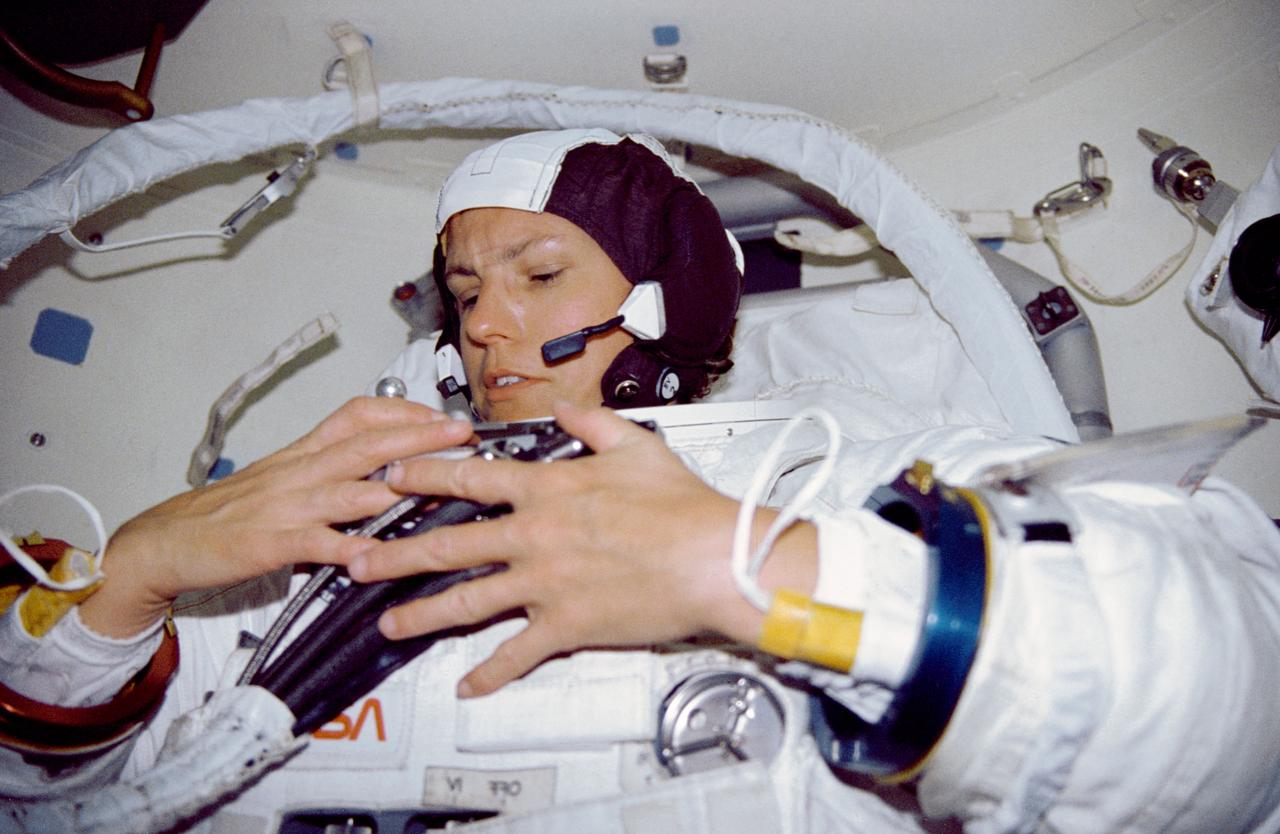
STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Kathryn D. Sullivan, wearing extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) & communications carrier assembly (CCA), attaches service and cooling umbilical (SCU) to the EMU connection on the display & control module (DCM) during contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) preparations in the airlock of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. The procedure was completed in case an EVA was required to support Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment.
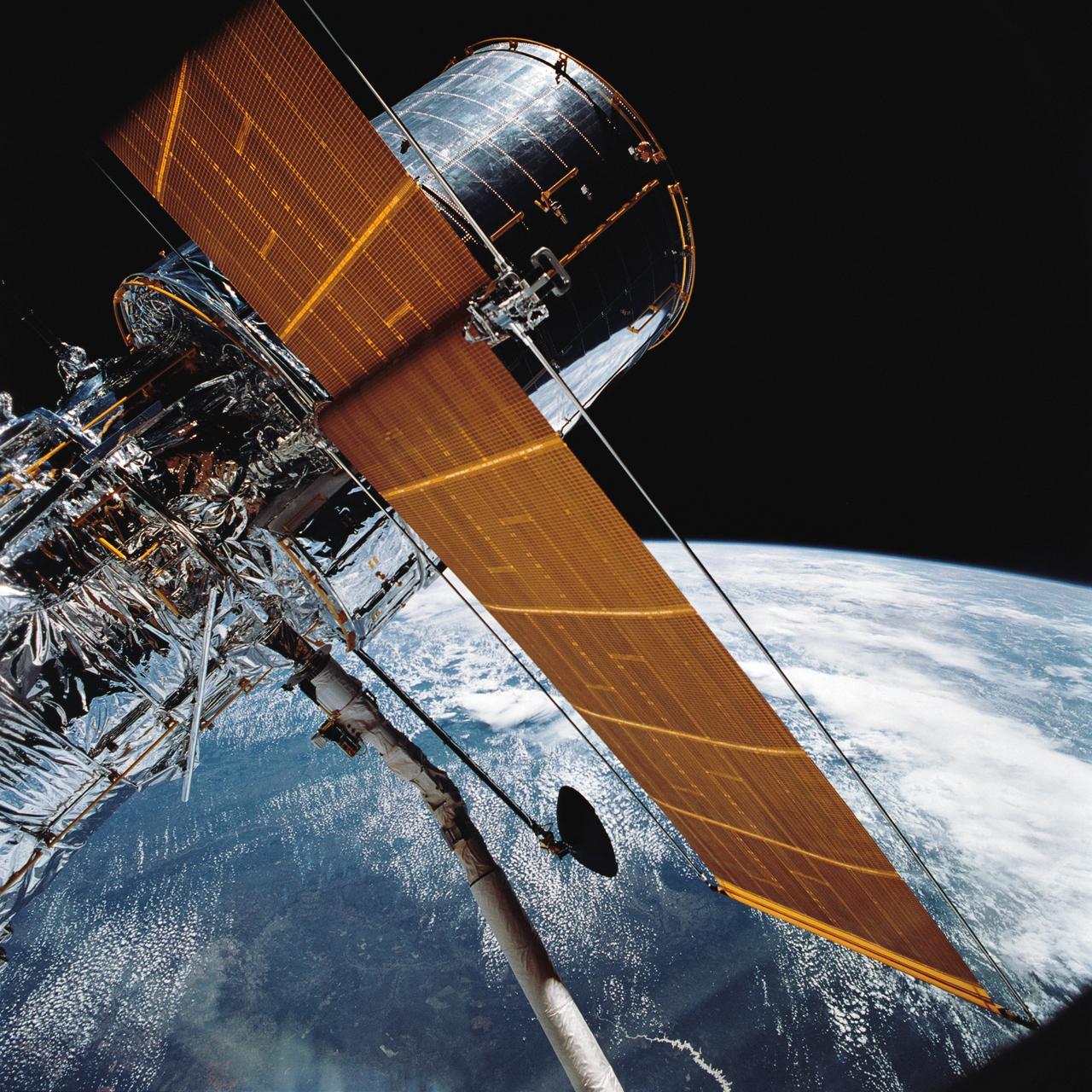

STS031-76-026 (25 April 1990) --- Most of the giant Hubble Space Telescope (HST) can be seen as it is suspended in space by Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) following the deployment of part of its solar panels and antennae. The photo was taken with a handheld Hasselblad camera. This was among the first photos NASA released on April 30, 1990, from the five-day STS 31 mission.
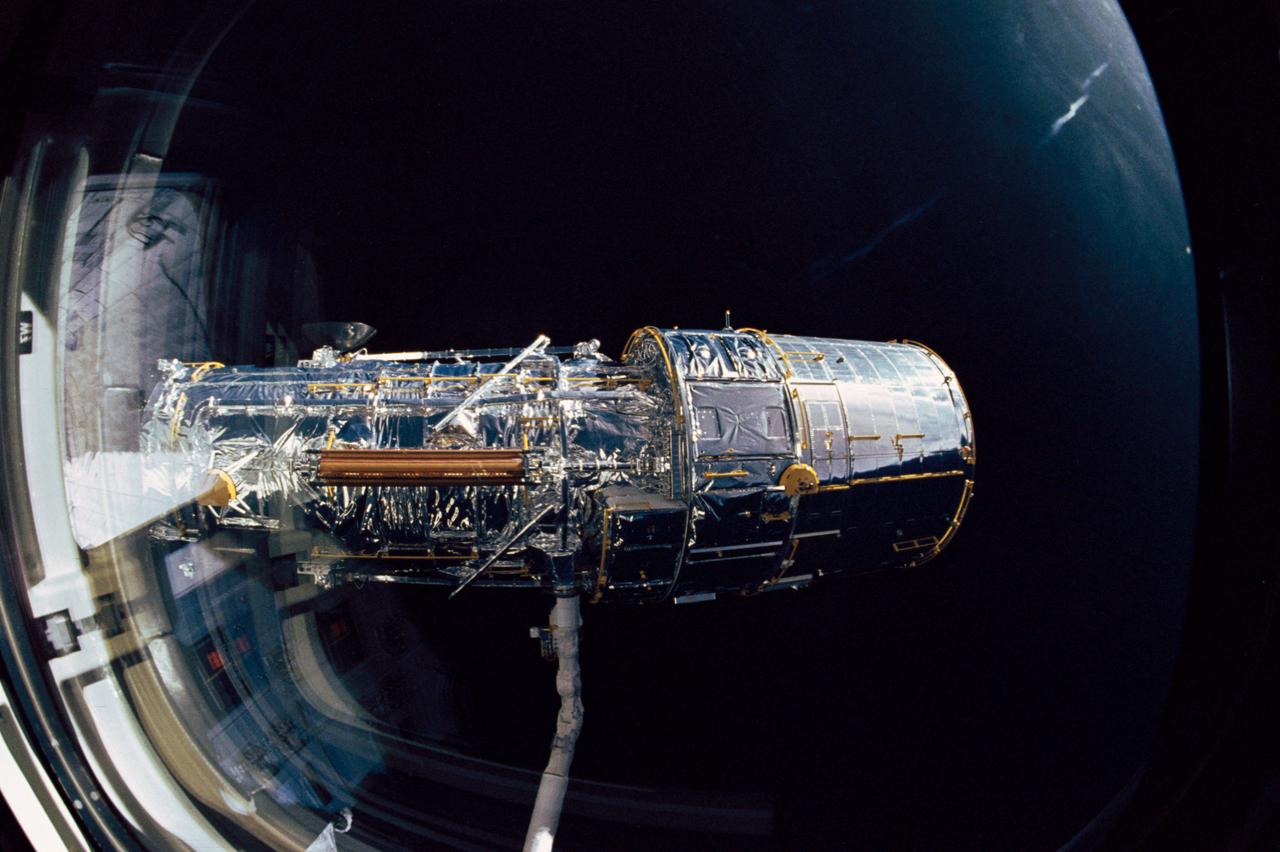

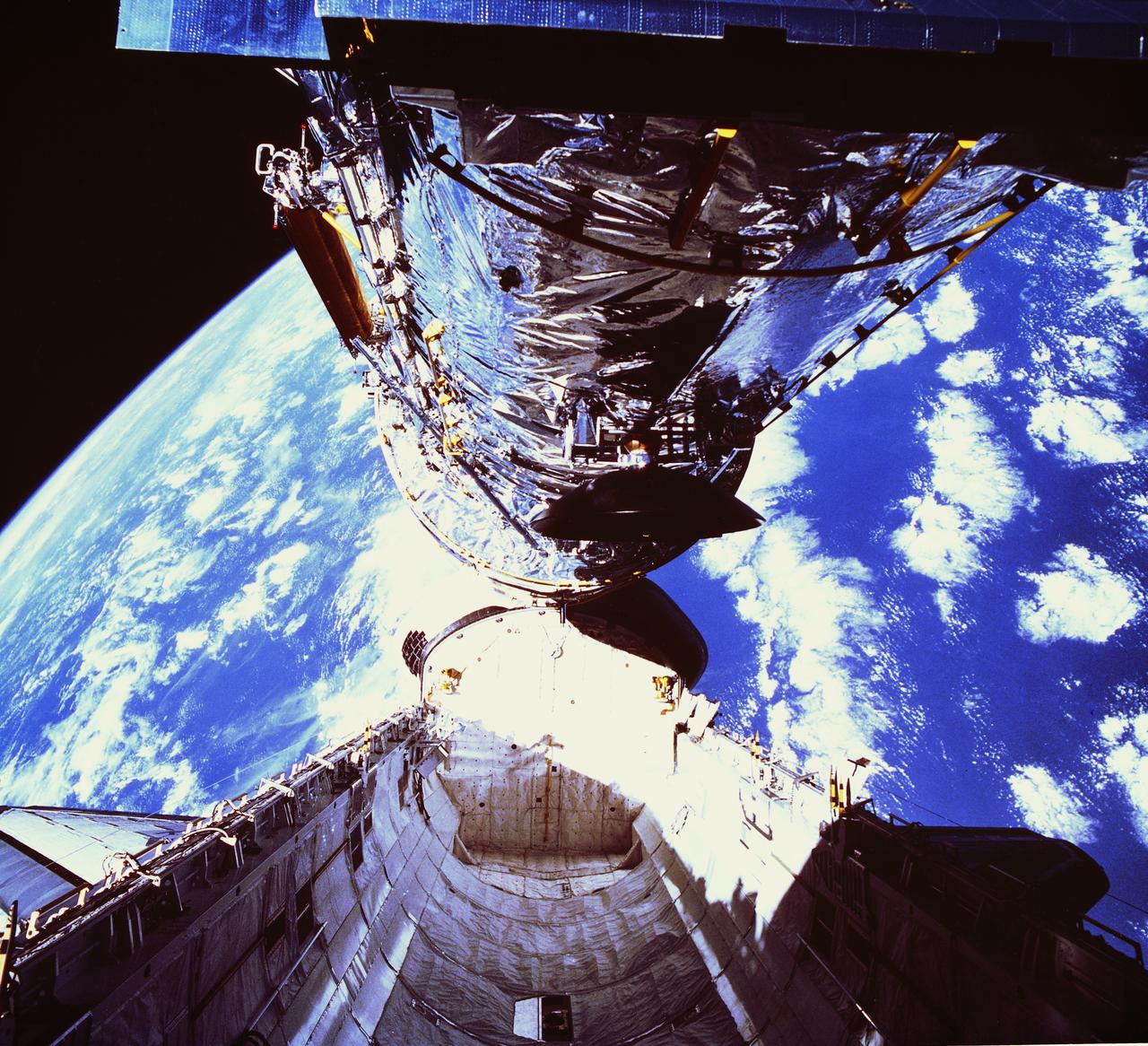
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), is held in a pre-deployment position. During STS-31 checkout procedures, the solar array (SA) panels and the high gain antennae (HGA) will be deployed. The starboard SA (center) and the two HGA are stowed along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The sun highlights HST against the blackness of space.
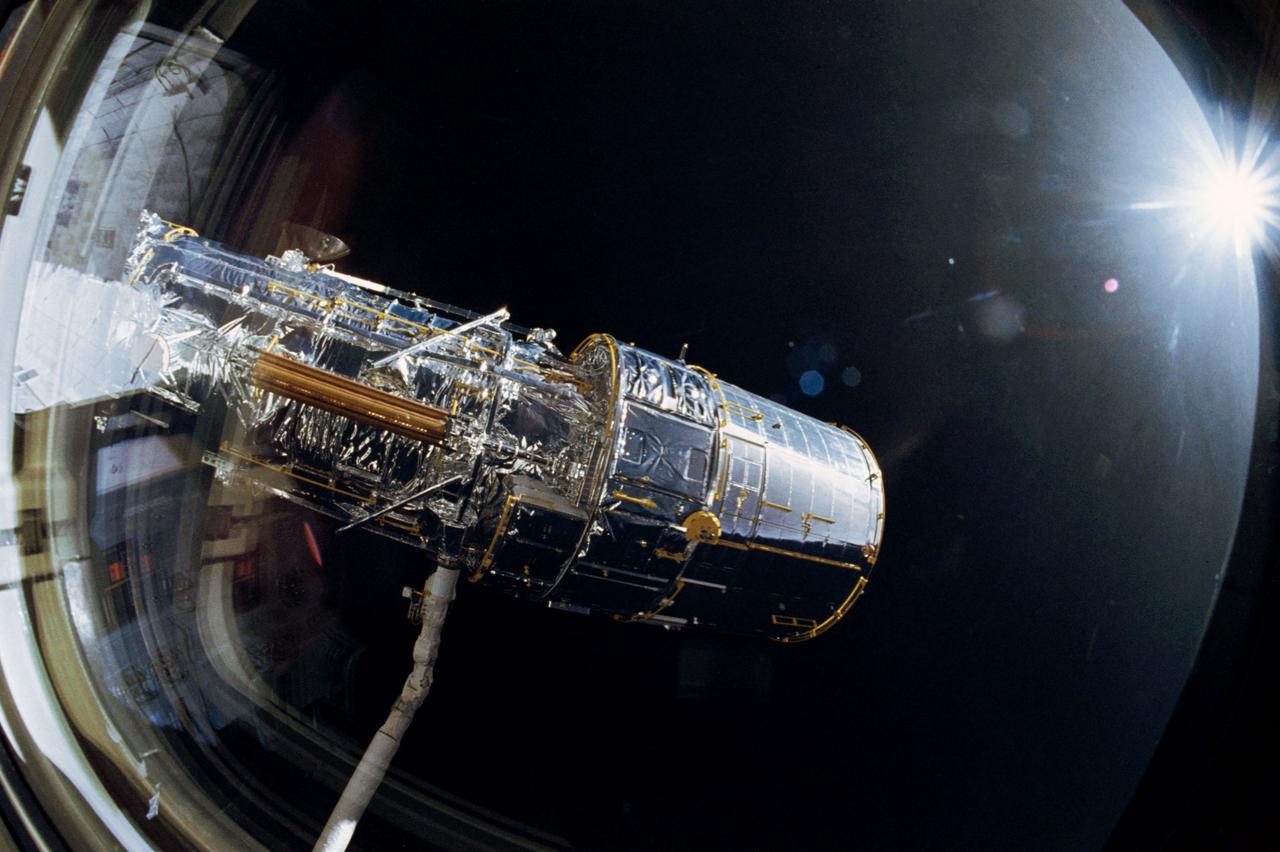
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), is oriented in a 90 degree pitch position during STS-31 pre-deployment checkout procedures. The solar array (SA) panel (center) and high gain antennae (HGA) (on either side) are stowed along the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell prior to deployment. The sun highlights HST against the blackness of space.
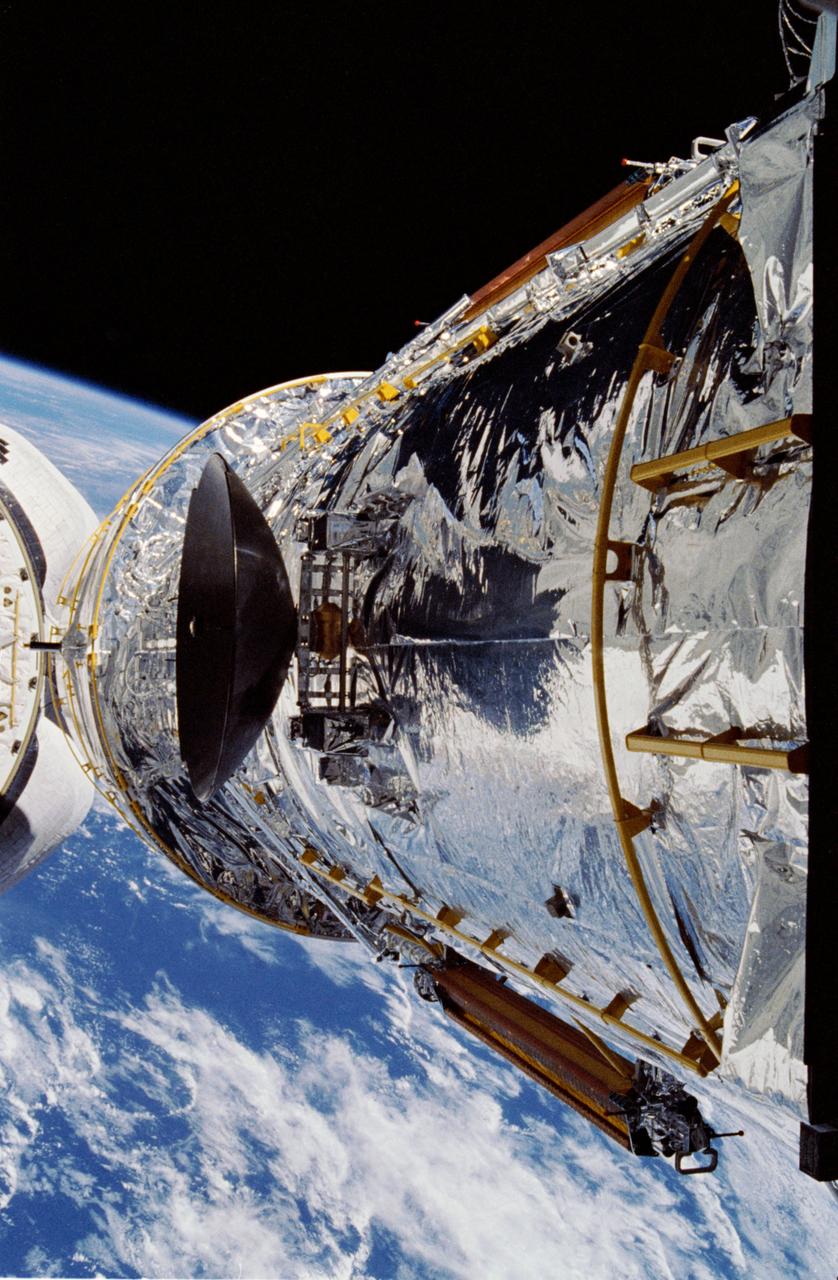
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is raised above the payload bay (PLB) in low hover position during STS-31 checkout and pre-deployment procedures aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Stowed along the HST Support System Module (SSM) are the high gain antenna (HGA) (center) and the two solar arrays (one either side). In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's surface.
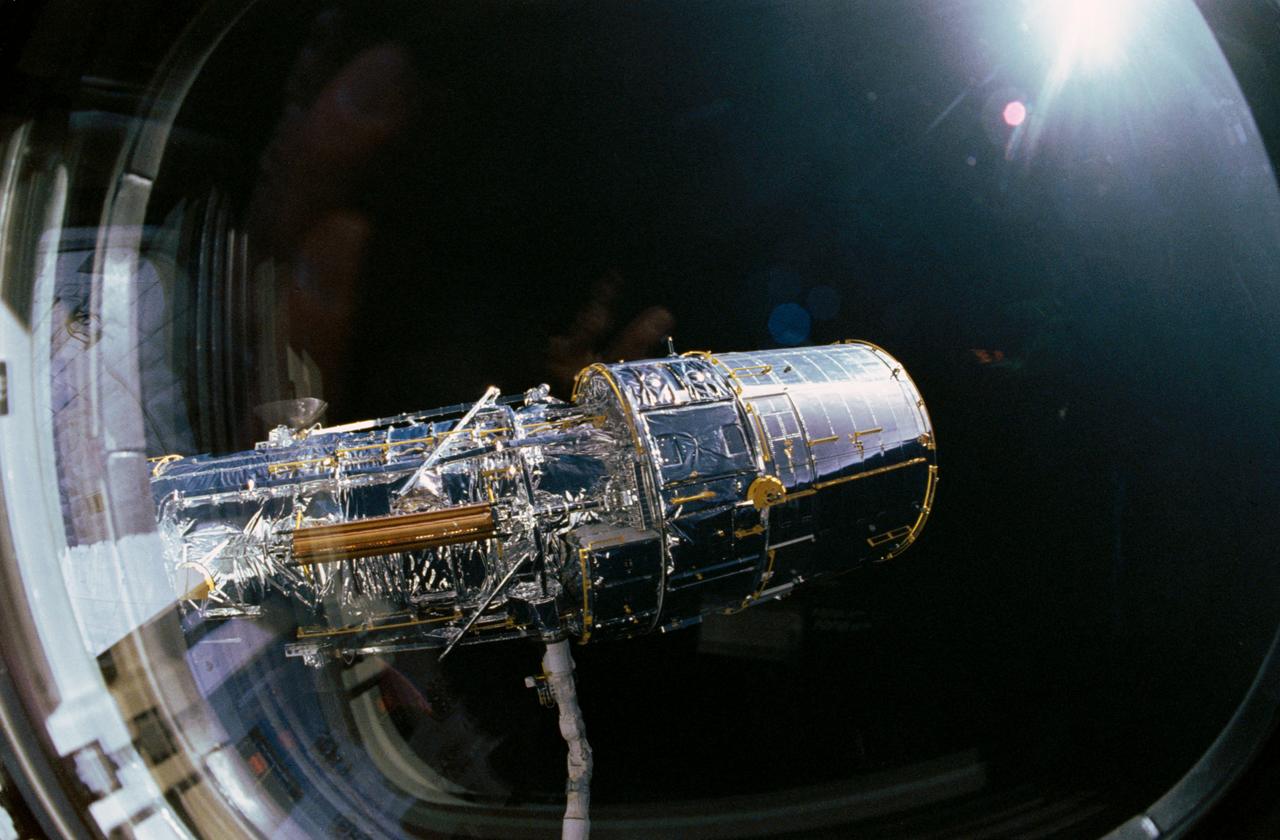
View taken through overhead window W7 aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) and held in a 90 degree pitch position against the blackness of space. The solar array (SA) panel (center) and the high gain antennae (HGA) (on either side) are visible along the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell prior to deployment during STS-31.
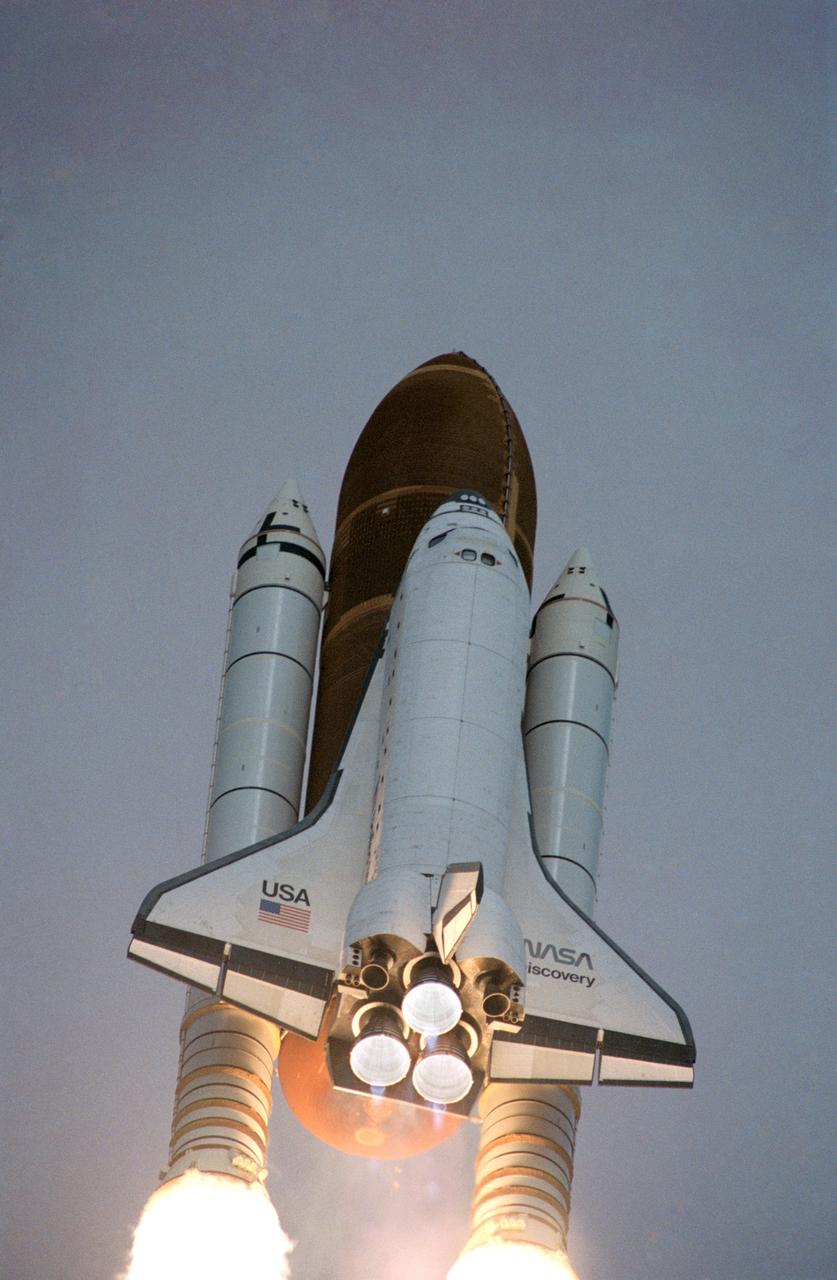
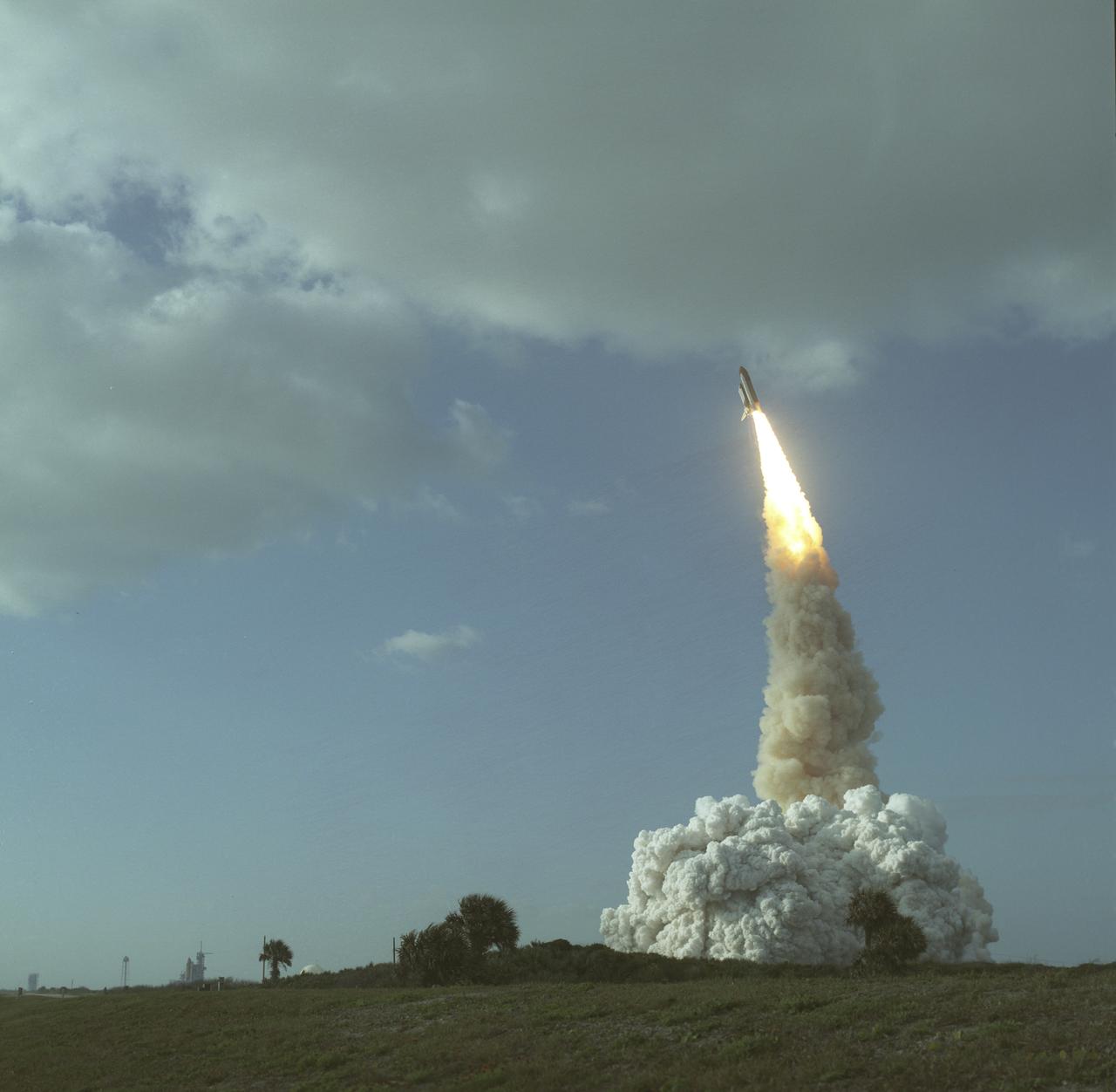
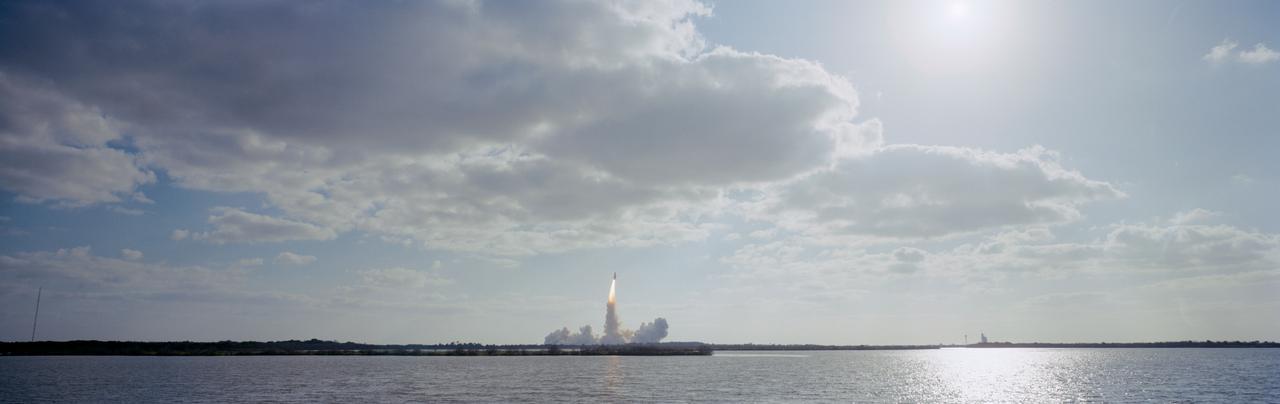
STS031-S-074 (24 April 1990) --- A low-angle view of the launch of the STS-31 mission. Onboard Discovery are a crew of five veteran astronauts and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Official launch time was 8:33:51.0492 a.m. (EDT). Headed for approximately five days in space are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden Jr., Bruce McCandless II, Kathryn D. Sullivan and Steven S. Hawley.
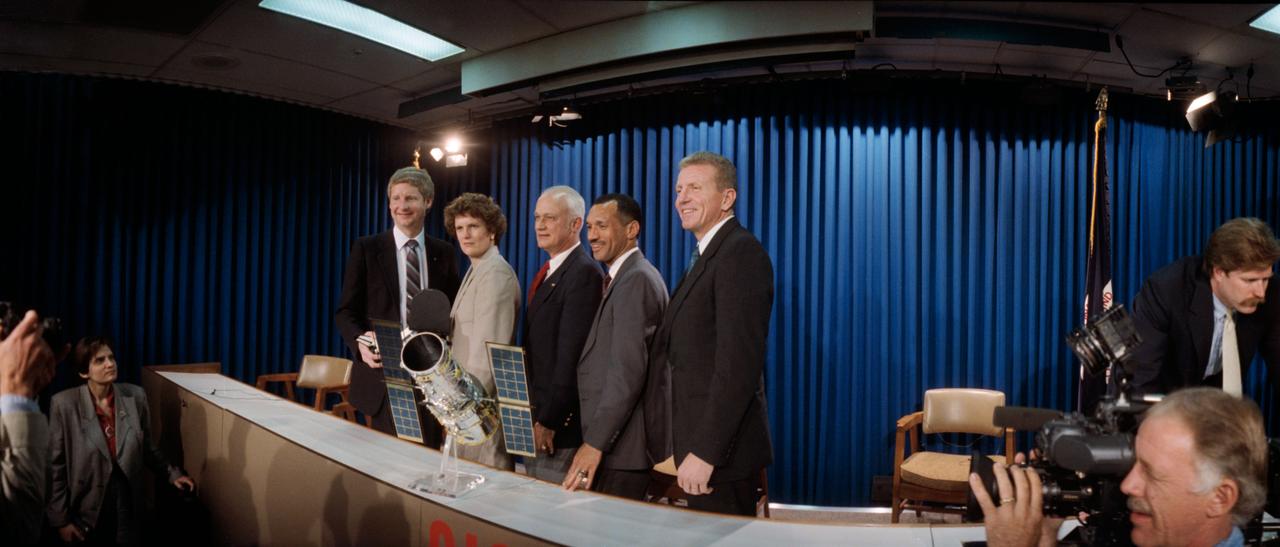

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, crewmembers pose for an informal portrait after the T-30 (thirty days before launch) briefing at JSC's Auditorium and Public Affairs Facility Bldg 2. Standing behind the conference table are (left to right) Mission Specialist (MS) Steven A. Hawley, MS Kathryn D. Sullivan, MS Bruce McCandless II, Pilot Charles F. Bolden, and Commander Loren J. Shriver.
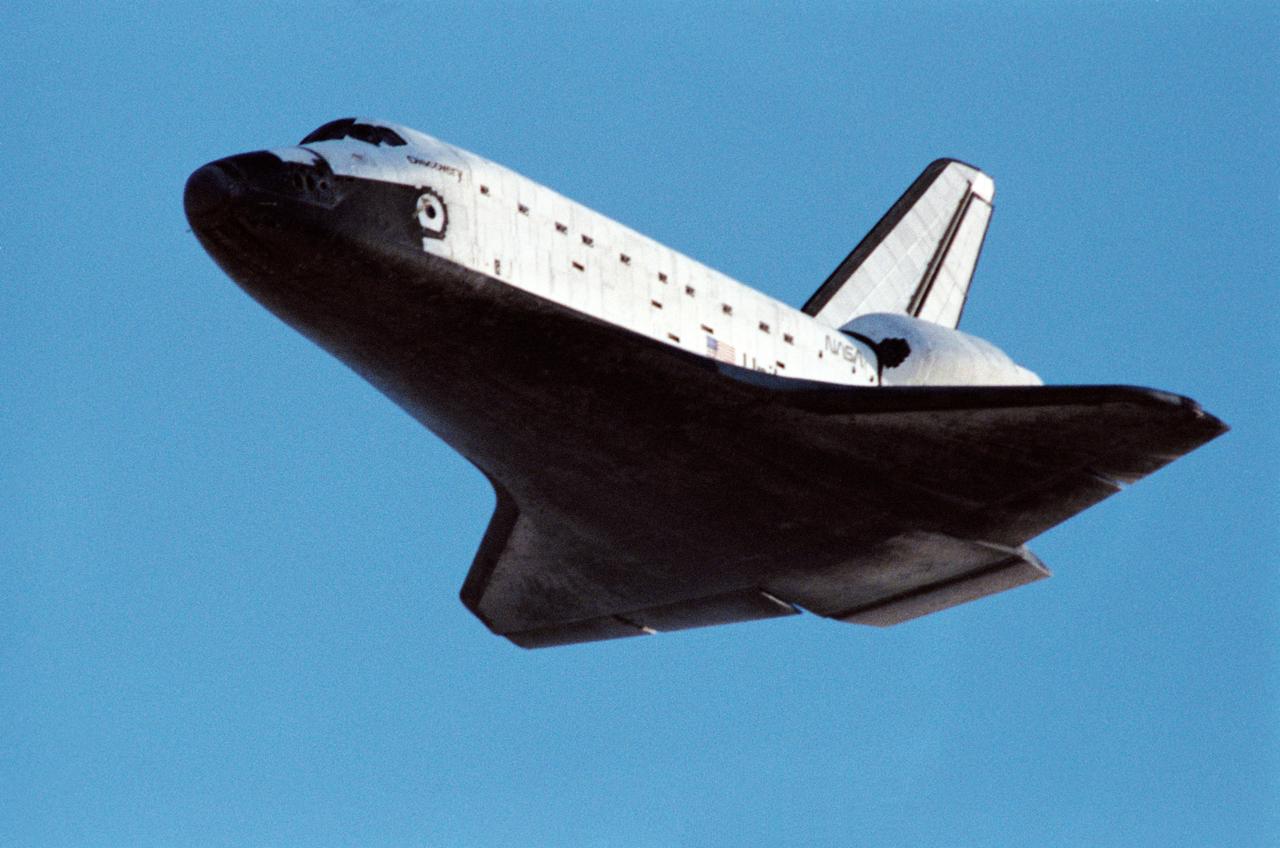

STS031-S-131 (29 April 1990) --- Low angle view of the Space Shuttle Discovery as it approaches for landing on a concrete runway at Edwards Air Force Base to complete a highly successful five-day mission. It was a long awaited Earth orbital flight during which the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was sent toward its 15-year mission. Discovery's wheels came to a complete stop at 6:51:00 a.m. (PDT), April 29, 1990. The landing gear was deployed just moments after this frame was exposed. Inside the spacecraft for STS-31 were astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Bruce McCandless II, Kathryn D. Sullivan and Steven A. Hawley.
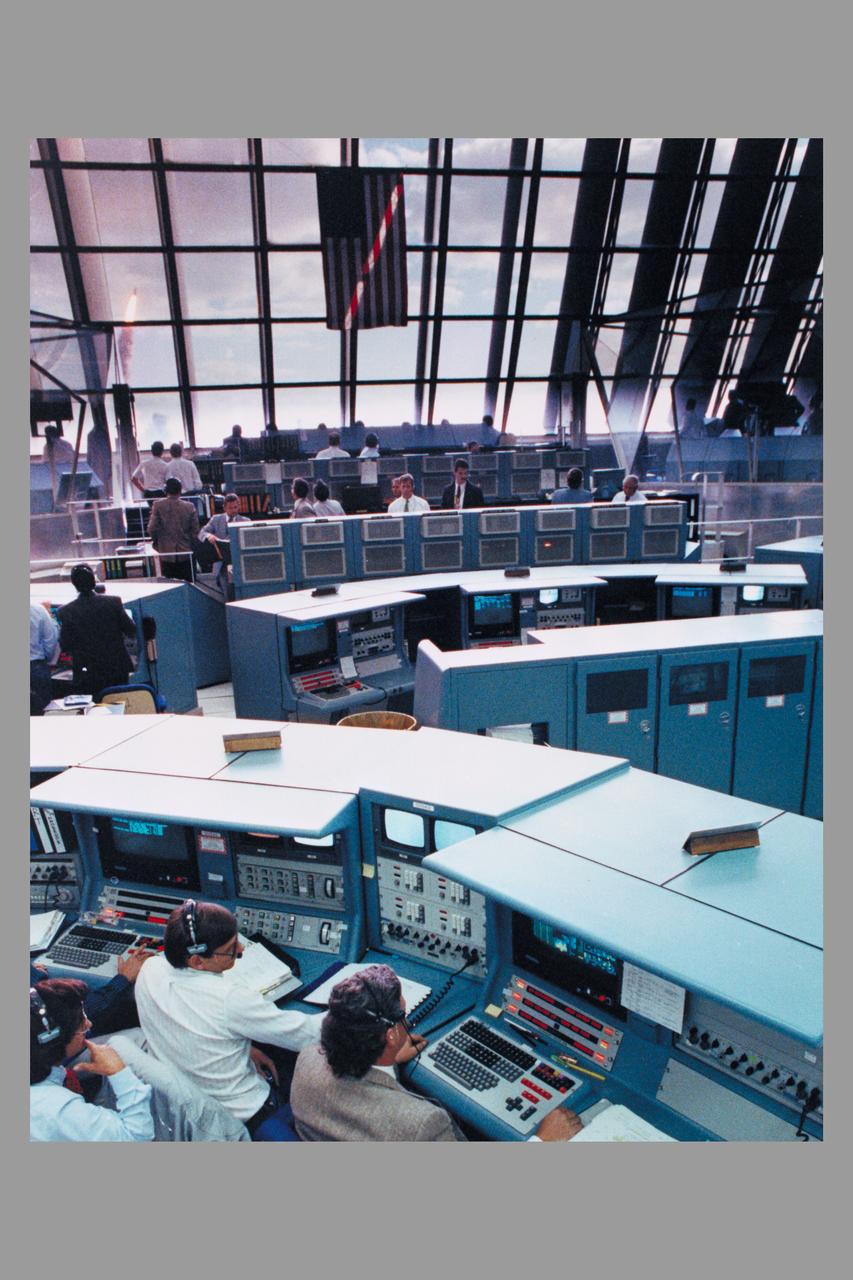

Kennedy Space Center Firing room during launch of Space Shuttle Discovery Hubble Space Telescope deployment Mission STS-31 (The Shuttle can be seen through window) (ref: KSC-90PC-626)
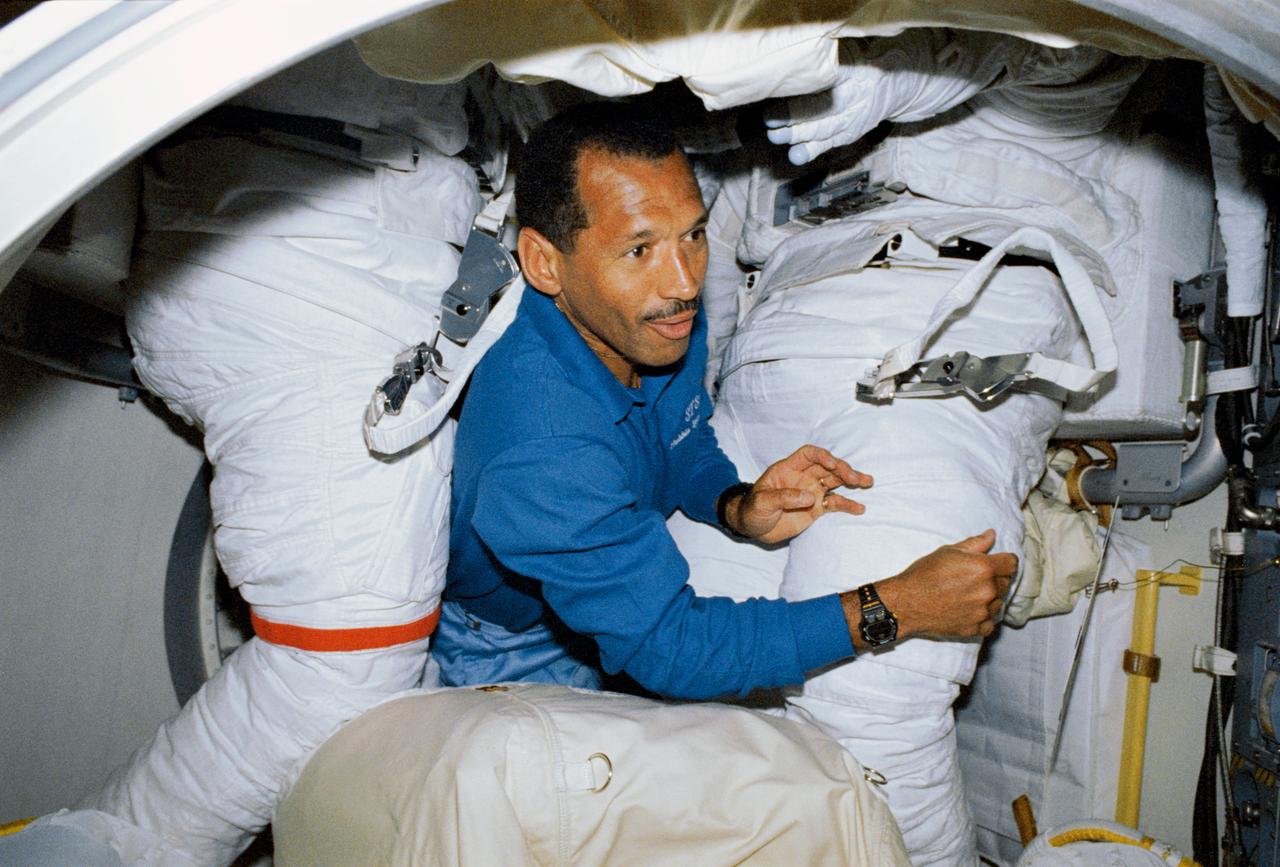

STS031-02-021 (24-29 April 1990) --- STS-31 pilot Charles F. Bolden, is surrounded by extravehicular mobility unit spacesuits in the airlock of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Discovery. The suits did not get used outside the spacecraft as the mission's spacewalk was cancelled. Bolden's role in the spacewalk, had it happened, would have kept him inside the orbiter, supporting the efforts of two crewmates. Photo credit: NASA
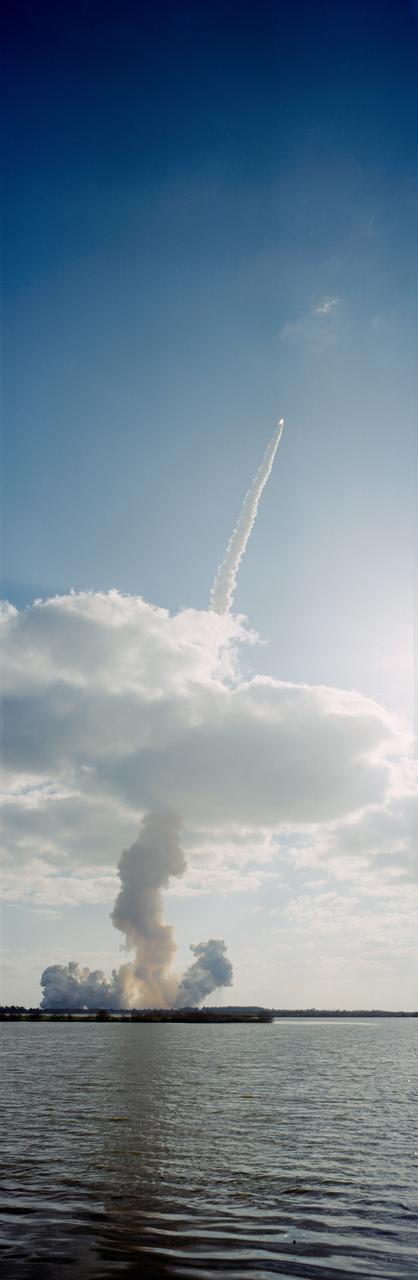

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, rides above the firey glow of the solid rocket boosters (SRBs) and space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) and a long trail of exhaust as it heads toward Earth orbit. Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B is covered in an exhaust cloud moments after the liftoff of OV-103 at 8:33:51.0492 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). The exhaust plume pierces the low-lying clouds as OV-103 soars into the clear skies above. A nearby waterway appears in the foreground.
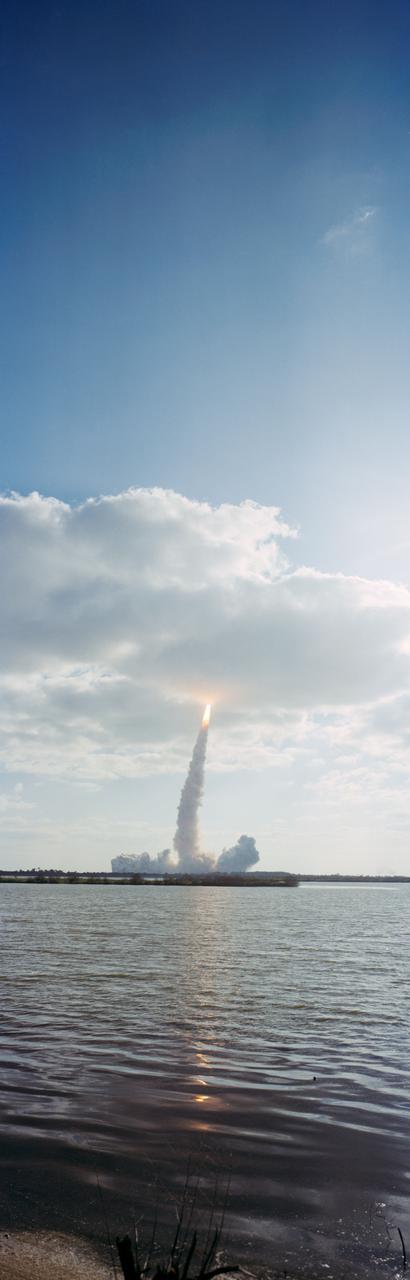

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is hidden in low-lying cloud cover as it rises above Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B just after its liftoff at 8:33:51.0492 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). The glow of the solid rocket booster (SRB) and the space shuttle main engine (SSME) firings appears just below the cloud cover and is reflected in the nearby waterway (foreground). An exhaust plume trails from OV-103 and its SRBs and covers the launch pad area.
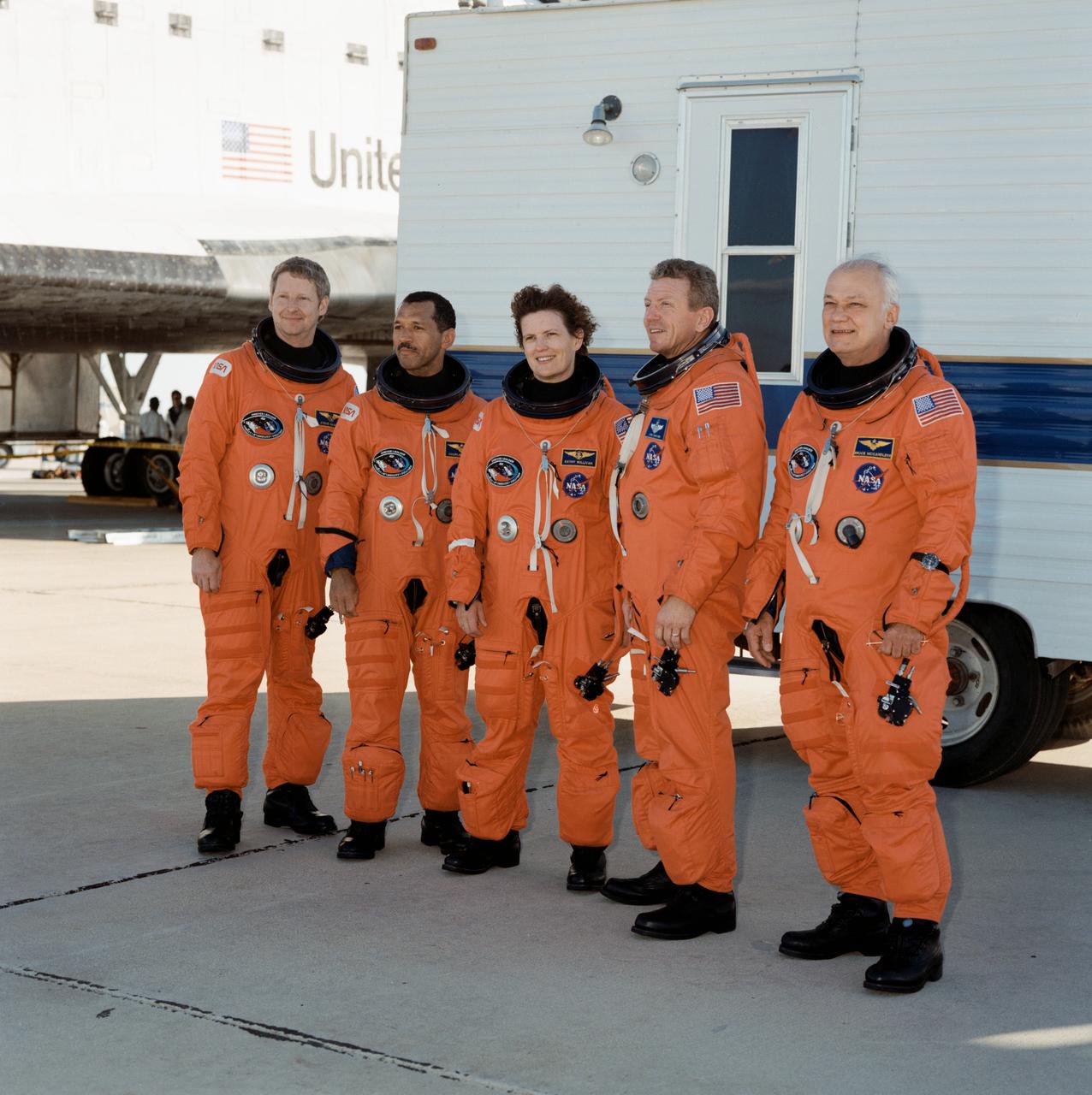

STS031-S-130 (29 April 1990) --- The astronauts of STS-31 pose for a quick photo near the Space Shuttle Discovery following a smooth landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base to complete a highly successful five-day mission. Pictured, left to right, are Astronauts Steven A. Hawley, Charles F. Bolden Jr., Kathryn D. Sullivan, Loren J. Shriver, and Bruce McCandless II. Theirs was an Earth orbital flight during which the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was sent toward its 15-year mission.
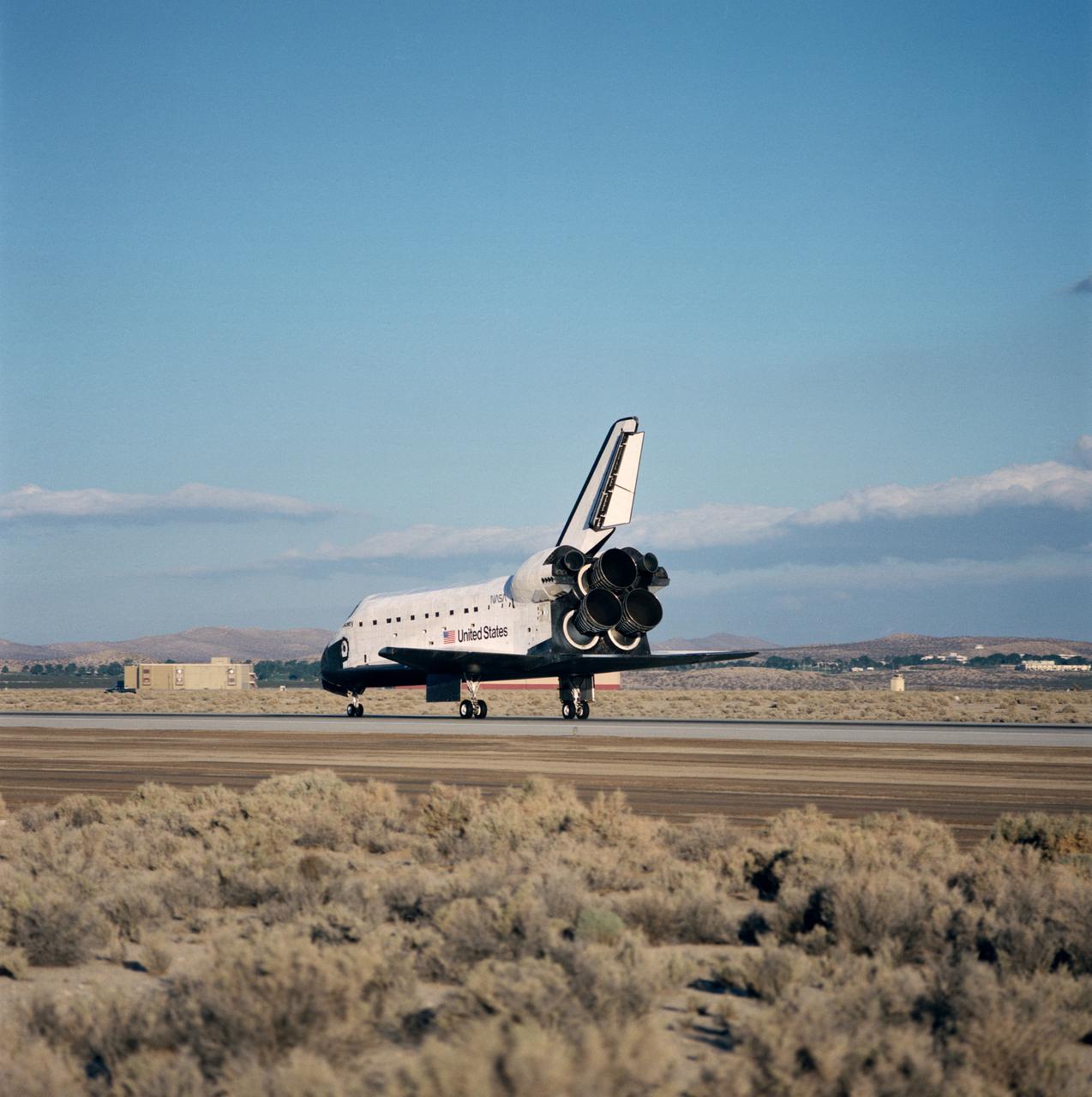

STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, rolls along concrete runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base (EAFB), California, after nose landing gear (NLG) and main landing gear (MLG) touchdown. This view looks down OV-103's port side from the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) to the nose section. The SSMEs are gimbaled to their descent position and the rudder/speedbrake is deployed on the vertical stabilizer. Wheel stop occurred at 6:51 am (Pacific Daylight Time (PDT)). In the distance EAFB facilities are visible.
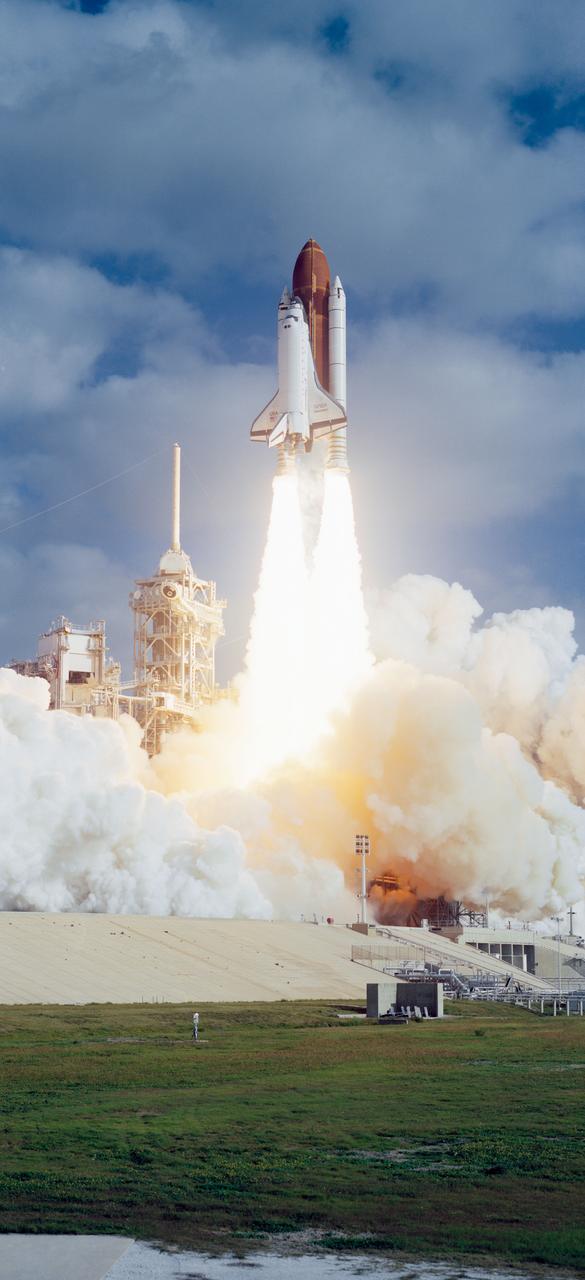

STS031-S-073 (24 April 1990) --? A vertical view of the launch of the STS-31 mission. Onboard Space Shuttle Discovery are the crew of five veteran astronauts and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Official launch time was 8:33:51.0492 a.m. (EDT). Headed for approximately five days in space are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Bruce McCandless, II, Kathryn D. Sullivan, and Steven A. Hawley.
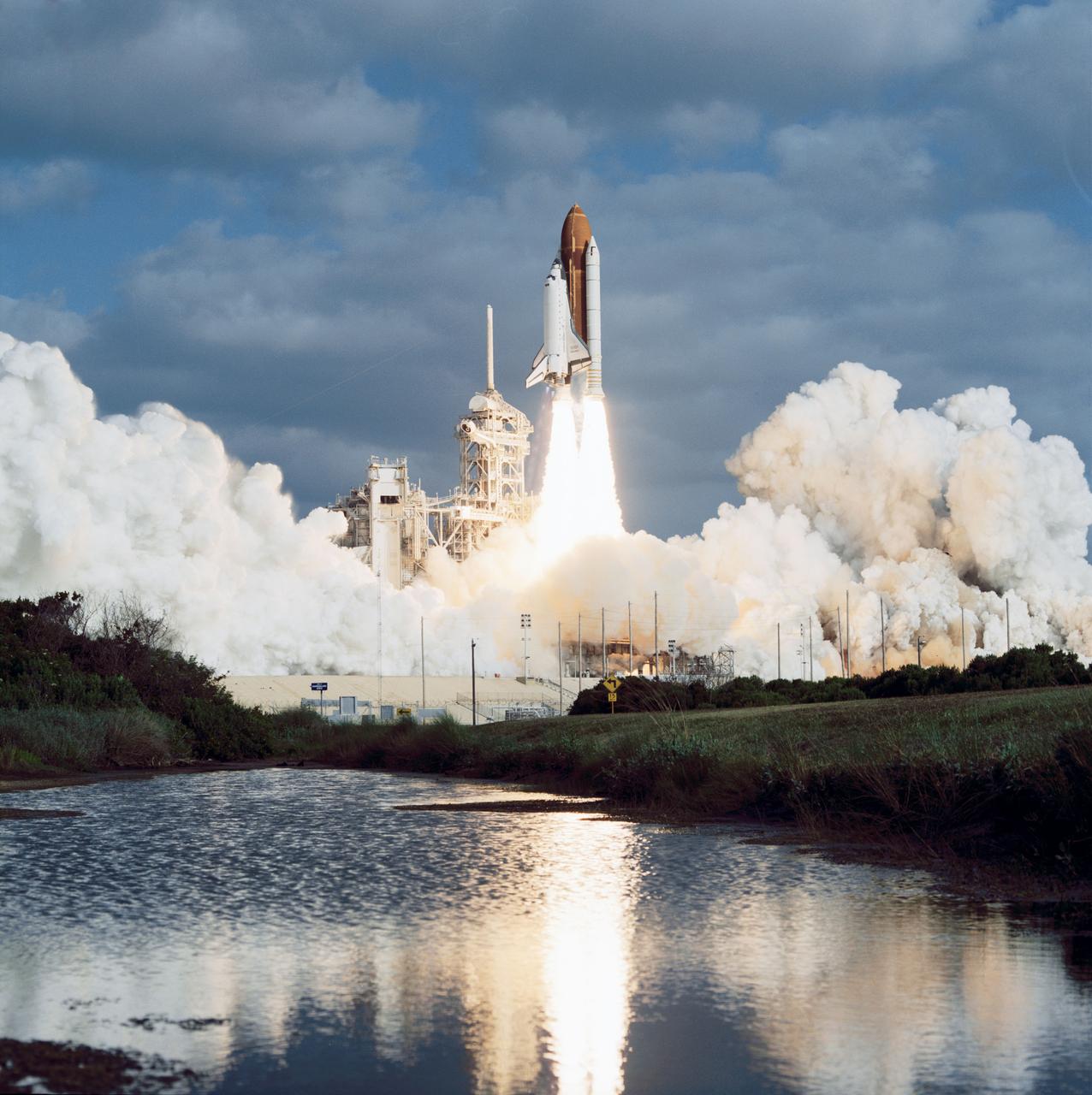

STS031-S-064 (24 April 1990) --- A horizontal view of the launch of the STS-31 mission. Onboard Space Shuttle Discovery are the crew of five veteran astronauts and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Official launch time was 8:33:51.0492 a.m. (EDT). Headed for approximately five days in space are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Bruce McCandless, II, Kathryn D. Sullivan, and Steven A. Hawley.
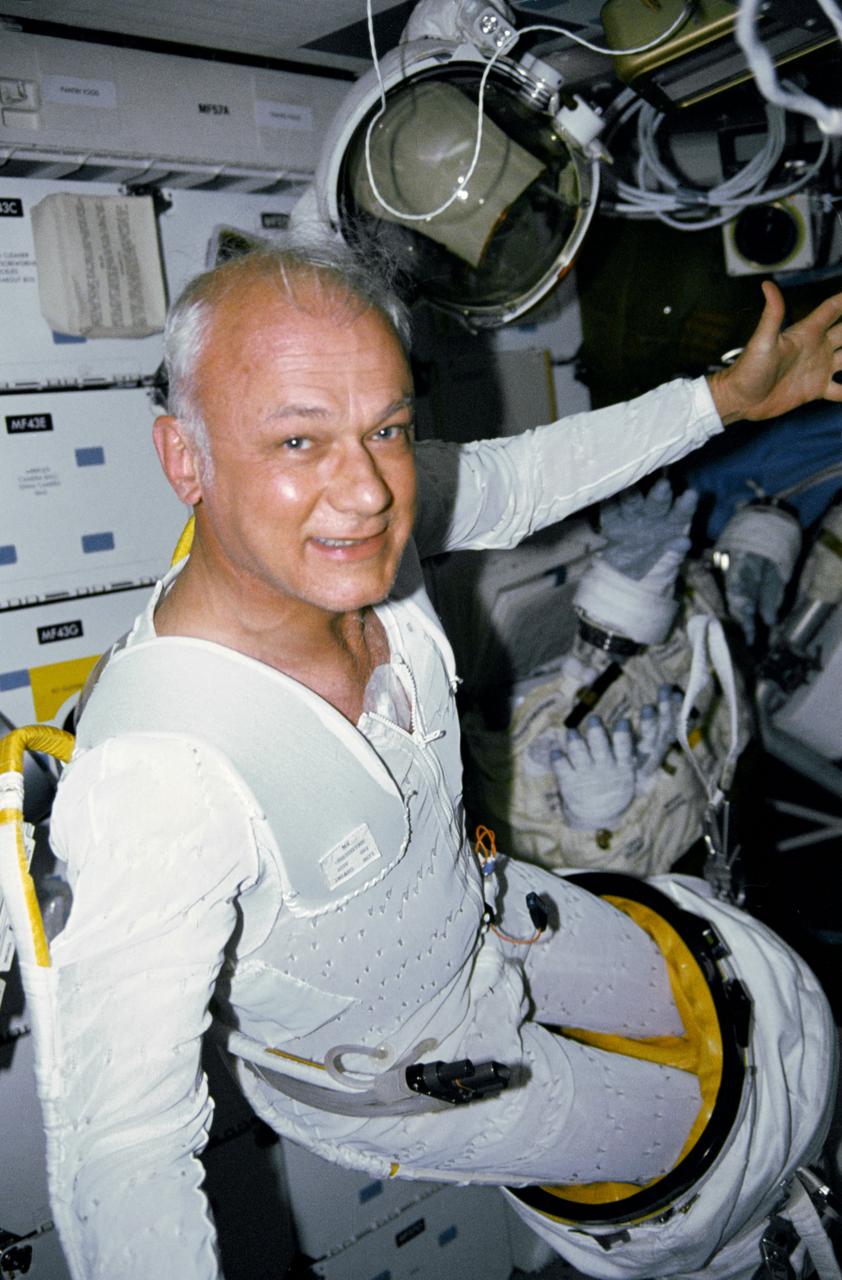

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II, wearing liquid cooling and ventilation garment (LCVG), works his way out of the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) lower torso on the middeck of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. McCandless was in a standby mode to perform extravehicular activity (EVA) if needed to support Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment and post- deployment tasks. None was needed. His helmet and gloves freefloat in the background.

Held in appendage deploy position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) starboard solar array (SA) bistem cassette is released from its stowed position on the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The spreader bar & bistem begin to unfurl the SA wing. View was taken by an STS-31 crewmember through an overhead window & is backdropped against the surface of the Earth.
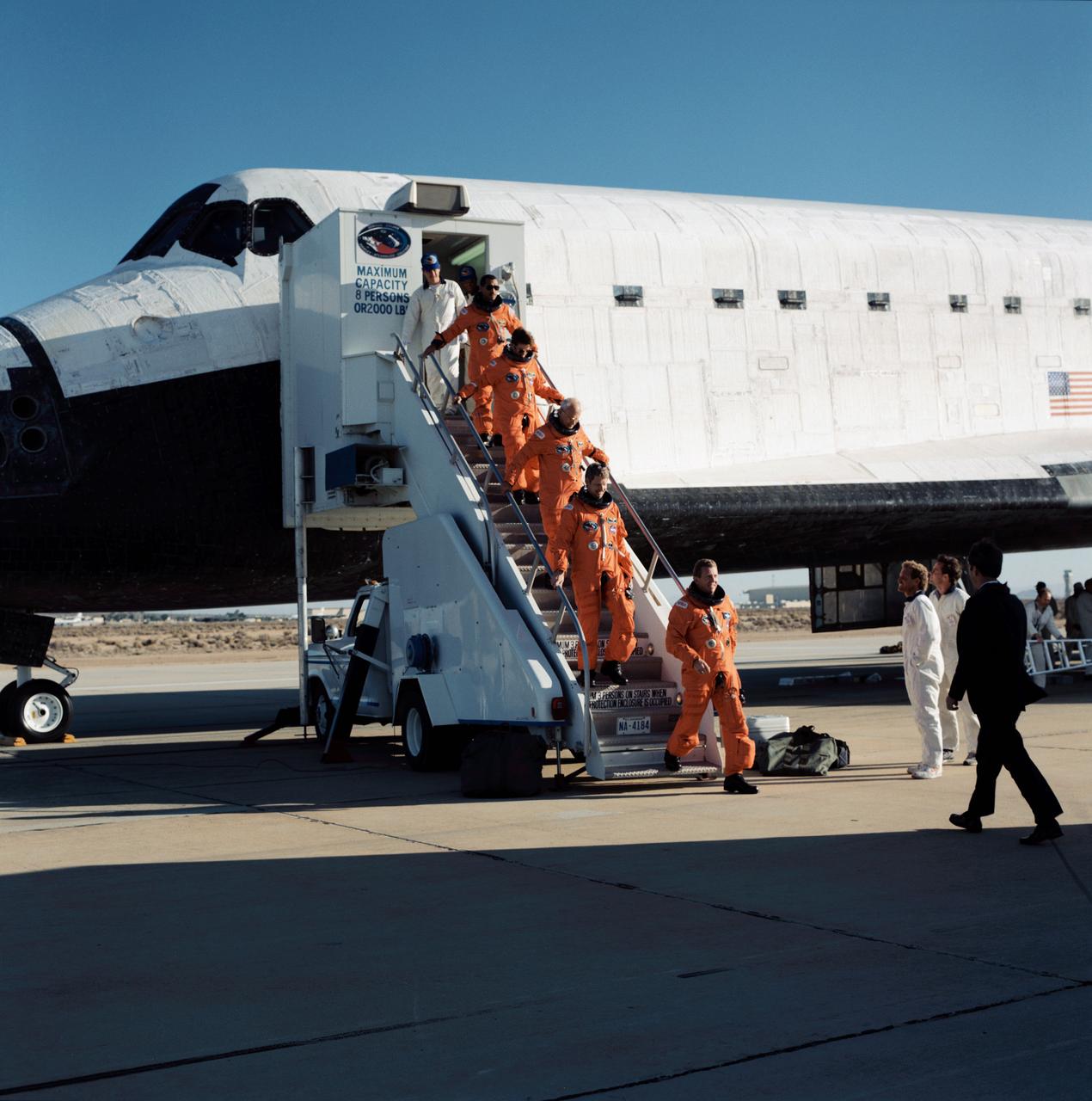

STS031-S-129 (29 April 1990) --- The astronauts of STS-31 egress the Space Shuttle Discovery following a smooth landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base to complete a highly successful five-day mission. Approaching from the far right to greet the crew is Dr. William B. Lenoir, NASA's Acting Associate Administrator for Space Flight. Leading the way down the steps is astronaut Loren J. Shriver, mission commander, followed by (in order from bottom of steps) astronauts Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists; and Charles F. Bolden Jr., pilot. Theirs was an Earth-orbital flight during which the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was sent toward its 15-year mission.

In this distant view, STS-31 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is seen as it heads skyward after liftoff from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39B at 8:33:51.0492 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). OV-103's silhouette atop the external tank (ET) appears above the glow of the solid rocket booster (SRB) and space shuttle main engine (SSME) firings. An exhaust plume trails behind and covers the launch pad area below the orbiter. A nearby waterway reflects the SRB/SSME glow in the foreground. At the far right and barely discernible is KSC LC Pad 39A and the Sound Supression Water System tower. Columbia, OV-102, is on LC Pad 39A which is separated by a distance of 1.6 miles. This was the first time since January 1986 that there was a shuttle on each pad.
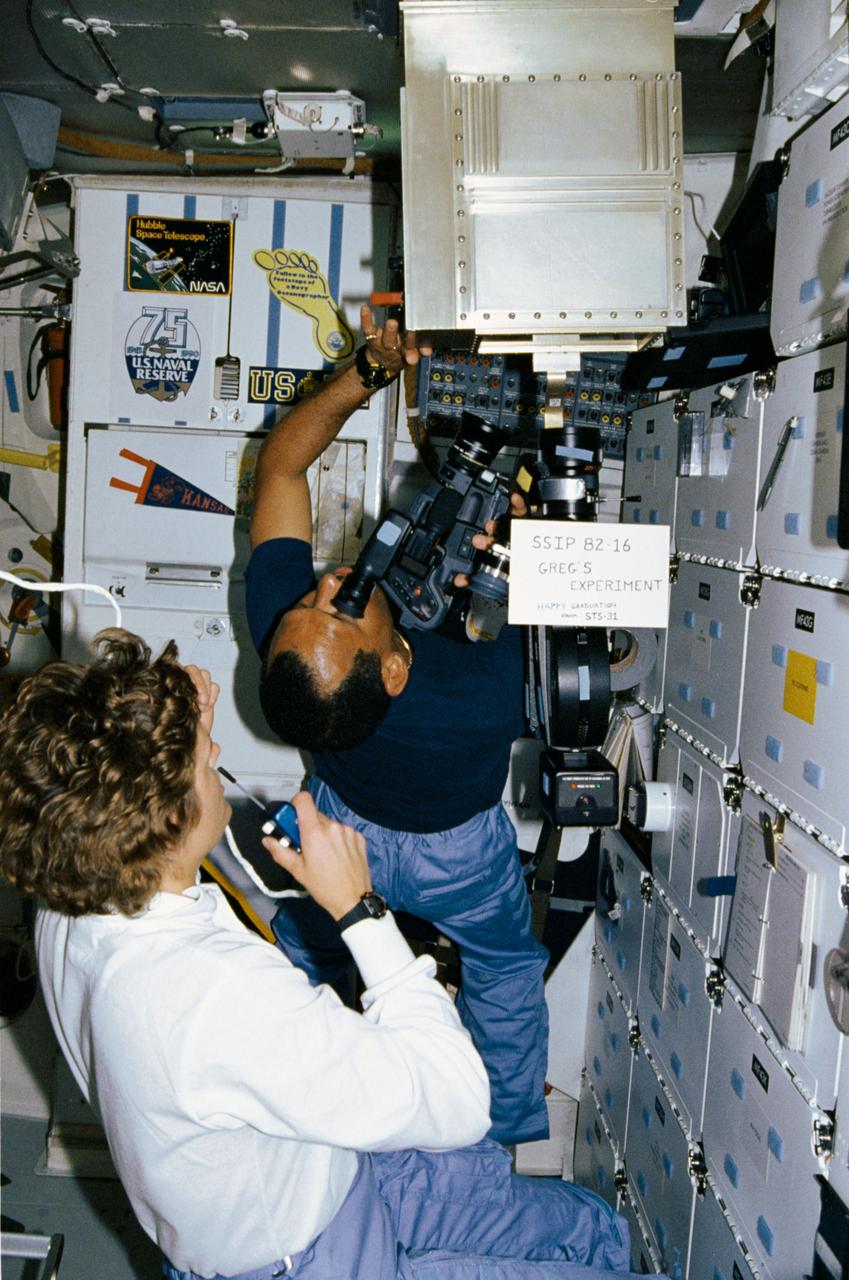

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Kathryn D. Sullivan monitors and advises ground controllers of the activity inside the Student Experiment (SE) 82-16, Ion arc - studies of the effects of microgravity and a magnetic field on an electric arc, mounted in front of the middeck lockers aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Pilot Charles F. Bolden uses a video camera and an ARRIFLEX motion picture camera to record the activity inside the special chamber. A sign in front of the experiment reads "SSIP 82-16 Greg's Experiment Happy Graduation from STS-31." SSIP stands for Shuttle Student Involvement Program. Gregory S. Peterson who developed the experiment (Greg's Experiment) is a student at Utah State University and monitored the experiment's operation from JSC's Mission Control Center (MCC) during the flight. Decals displayed in the background on the orbiter galley represent the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), the United States (U.S.) Naval Reserve, Navy Oceanographers, U.S. Navy, and University of Kansas.
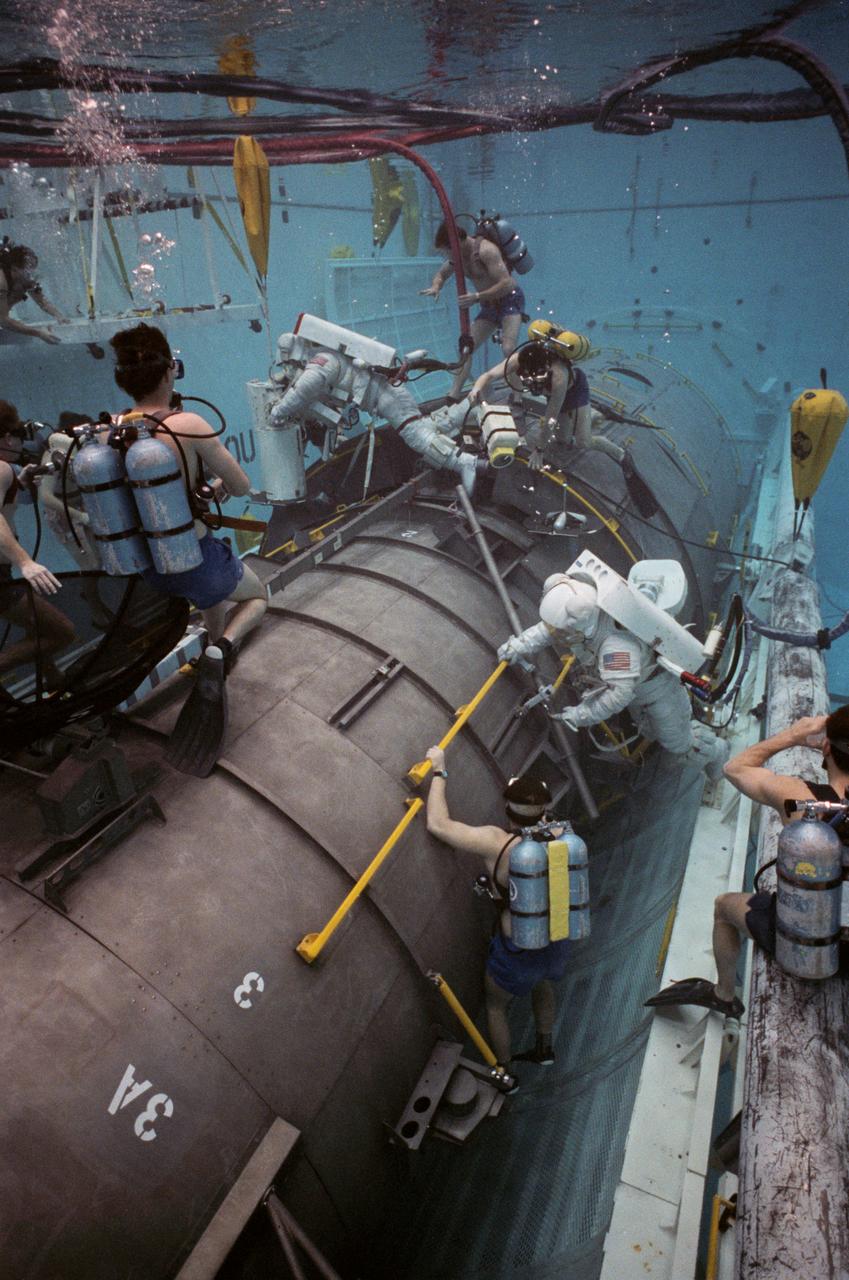

This overall view shows STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II (left) and MS Kathryn D. Sullivan making a practice space walk in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. McCandless works with a mockup of the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector which is attached to a grapple fixture on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) mockup. Sullivan manipulates HST hardware on the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. SCUBA-equipped divers monitor the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) suited crewmembers during this simulated extravehicular activity (EVA). No EVA is planned for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment, but the duo has trained for contingencies which might arise during the STS-31 mission aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Photo taken by NASA JSC photographer Sheri Dunnette.

During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector is held in appendage deploy position above Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. The solar array (SA) bistem cassette has been released from its latch fittings. The bistem spreader bars begin to unfurl the SA wing. The secondary deployment mechanism (SDM) handle is visible at the SA end. Stowed against either side of the HST System Support Module (SSM) forward shell are the high-gain antennae (HGA). Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic are recognizable at the left of the frame.

During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is held in appendage deploy position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS) above the payload bay (PLB) and crew compartment cabin. While in this position the solar array (SA) wing bistem cassette (HST center) is deployed from its stowed location along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. A high gain antenna (HGA) remains stowed along the SSM. The Earth's surface and the Earth limb creates a dramatic backdrop.
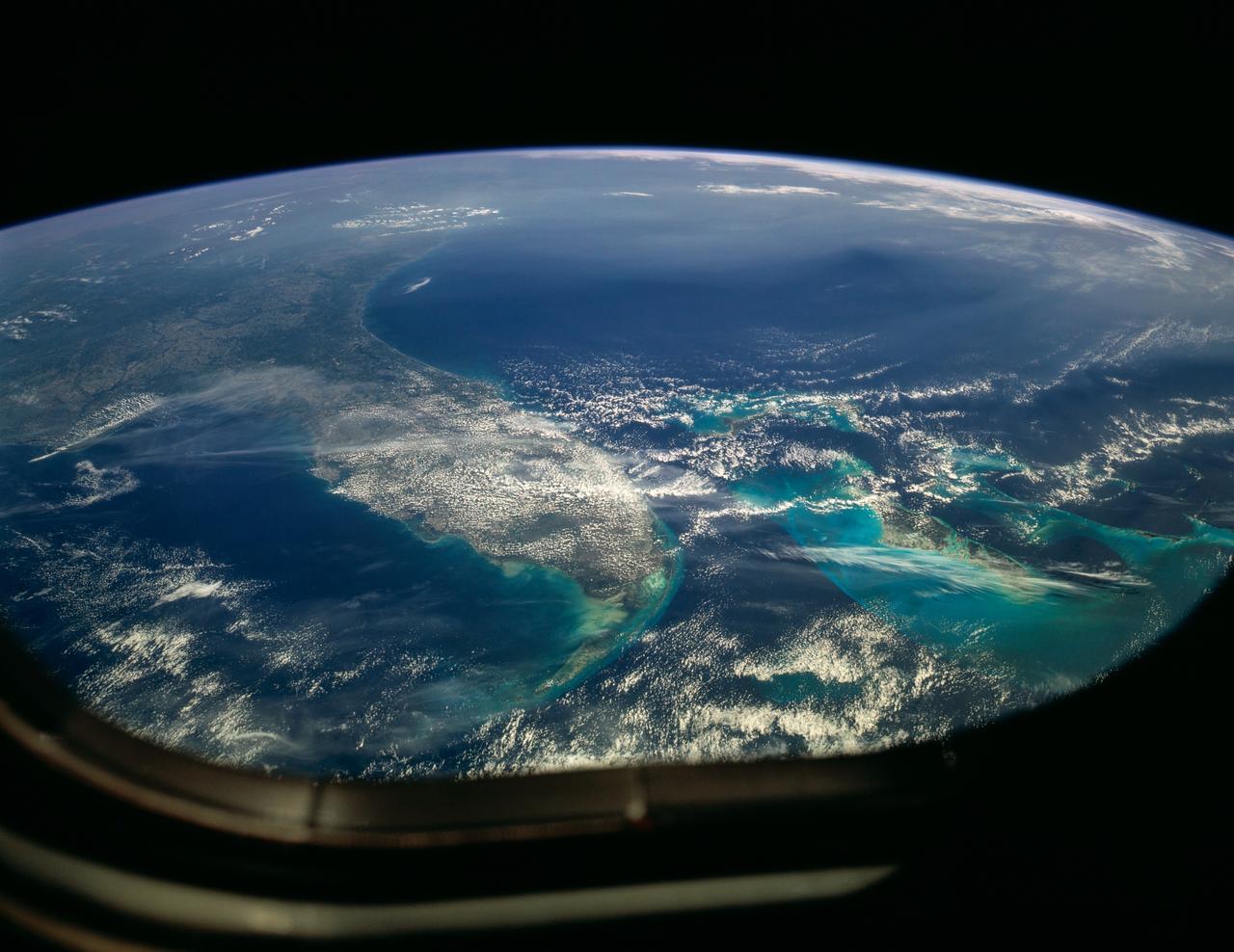

STS031-151-155 (26 April 1990) --- The Florida peninsula and smog over the northeastern U.S. coast are featured in this image photographed by a Space Shuttle Discovery crewmember during STS-31 mission. According to scientists, a mass of aerosol haze stretches across the top of the entire view. Meteorological, visibility and sulfate-content data showed that the haze was indeed industrial smog haze, rather than cloud. The air mass was transported west to east (left to right) around the north limb of a high pressure cell. It moved offshore for at least 1500 kilometers reaching the Atlantic islands of Bermuda. The leading edge of the haze mass can be detected far to the south, near the Bahamas--indicating that aerosols from the industrial Northeast were transported around the high, back directly toward the large population centers of Florida.

In this photograph, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is clearing the cargo bay during its deployment on April 25, 1990. The photograph was taken by the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC) mounted in a container on the port side of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery STS-31 mission. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit for 15 years or more. The HST provides fine detail imaging, produces ultraviolet images and spectra, and detects very faint objects. Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. A scheduled Space servicing mission (STS-61) in 1993 permitted scientists to correct the problem. During four space walks, new instruments were installed into the HST that had optical corrections. A total of four HST servicing missions have taken place since its deployment: STS-61 in December 1993, STS-82 in February 1997, STS-103 in December 1999, and STS-109 in March 2002. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.

In this photograph, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was being deployed on April 25, 1990. The photograph was taken by the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC) mounted in a container on the port side of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery (STS-31 mission). The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit for 15 years or more. The HST provides fine detail imaging, produces ultraviolet images and spectra, and detects very faint objects. Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. A scheduled Space Service servicing mission (STS-61) in 1993 permitted scientists to correct the problem. During four spacewalks, new instruments were installed into the HST that had optical corrections. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. Photo Credit: NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Lockheed Corporation.
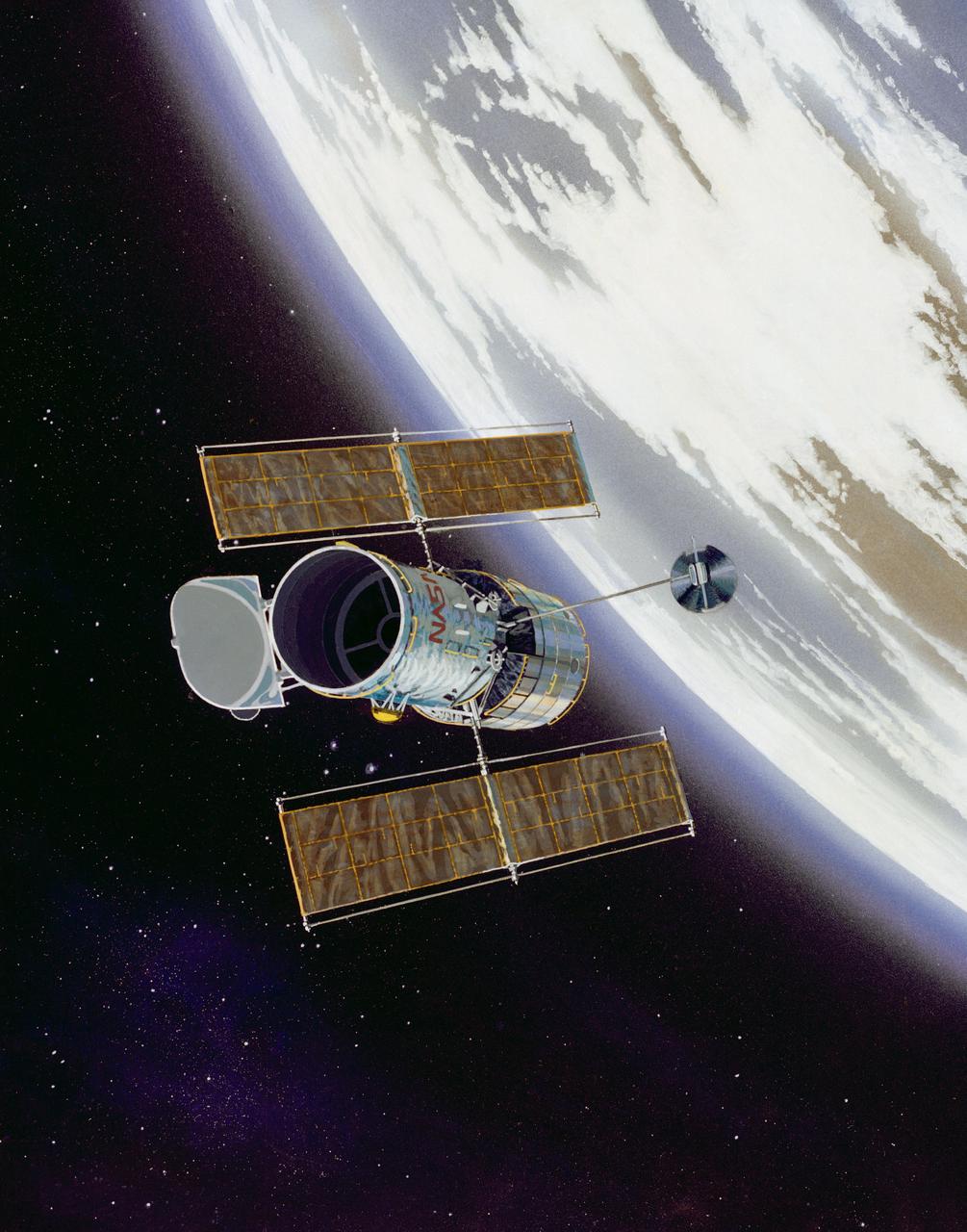

This artist concept shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in operational configuration orbiting the Earth after its deploy from Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103 during STS-31. The high gain antennas (HGAs) and solar arrays (SAs) have been extended. HST's aperature door is open as it views the universe from a vantage point above the Earth's atmosphere. View provided by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).

The STS-31 crew of five included (left to right) Charles F. Bolden, pilot; Steven A. Hawley, mission specialist; Loren J. Shriver, commander; Bruce McCandless, mission specialist; and Kathryn D. Sullivan, mission specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT), the primary payload was the Hubble Space Telescope. This was the first flight to use carbon brakes at landing.

STS031-83-090 (24-29 April 1990) --- This late afternoon scene over the Andes Mountains features sun glare, heavy cloud illumination and sunglint against the Pacific Ocean. This photo was among those selected by the crew members for showing at their May 9, 1990, Post-Flight Press Conference (PFPC) at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) Public Affairs Office (PAO) Facility briefing room. Onboard the Space Shuttle Discovery for the flight, which lifted off on April 24, 1990, and landed on April 29, 1990, were astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Bruce McCandless II, Kathryn D. Sullivan and Steven A. Hawley. Some of the slides were not actually shown due to a shortage of time.
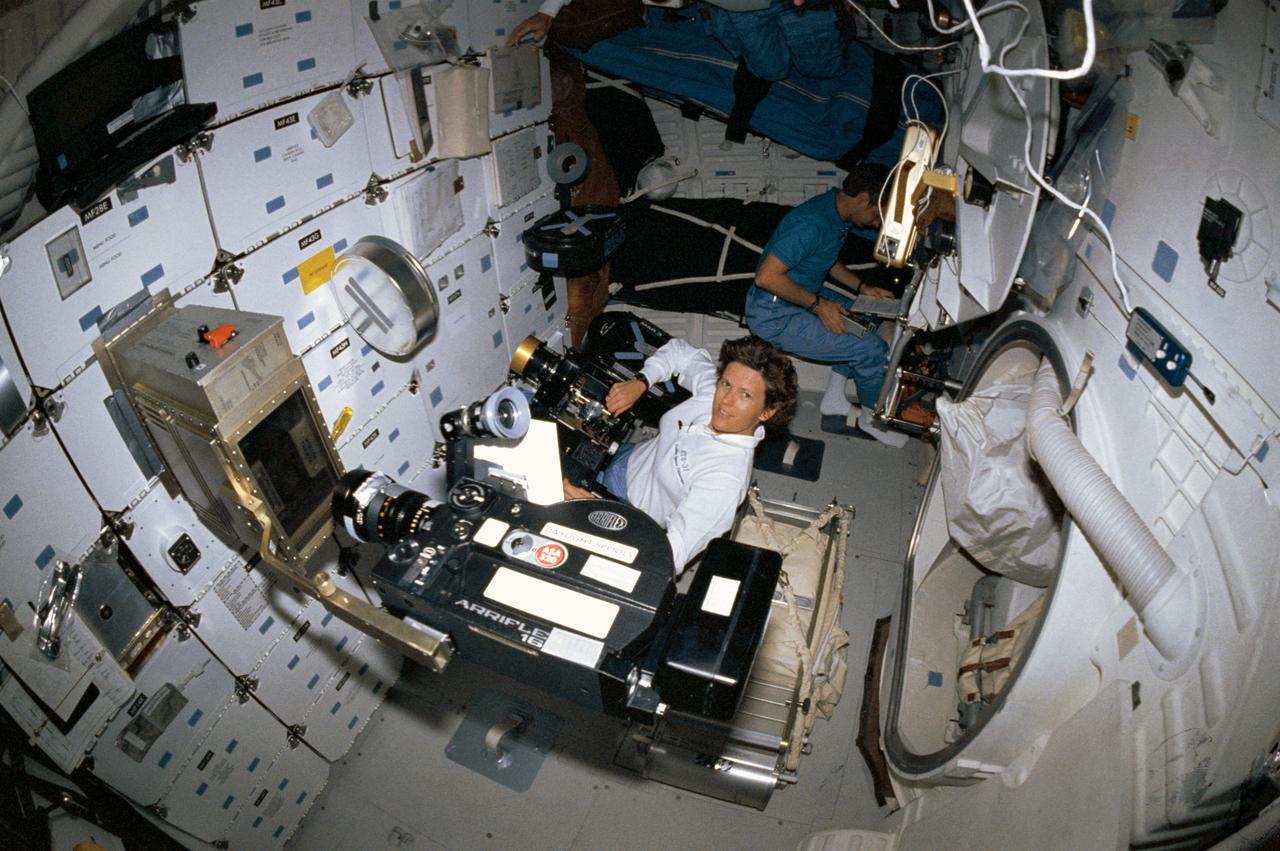

STS031-05-002 (24-29 April 1990) --- A 35mm camera with a "fish eye" lens captured this high angle image on Discovery's middeck. Astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan works with the IMAX camera in foreground, while Astronaut Steven A. Hawley consults a checklist in corner. An Arriflex motion picture camera records student ion arc experiment in apparatus mounted on stowage locker. The experiment was the project of Gregory S. Peterson, currently a student at Utah State University.
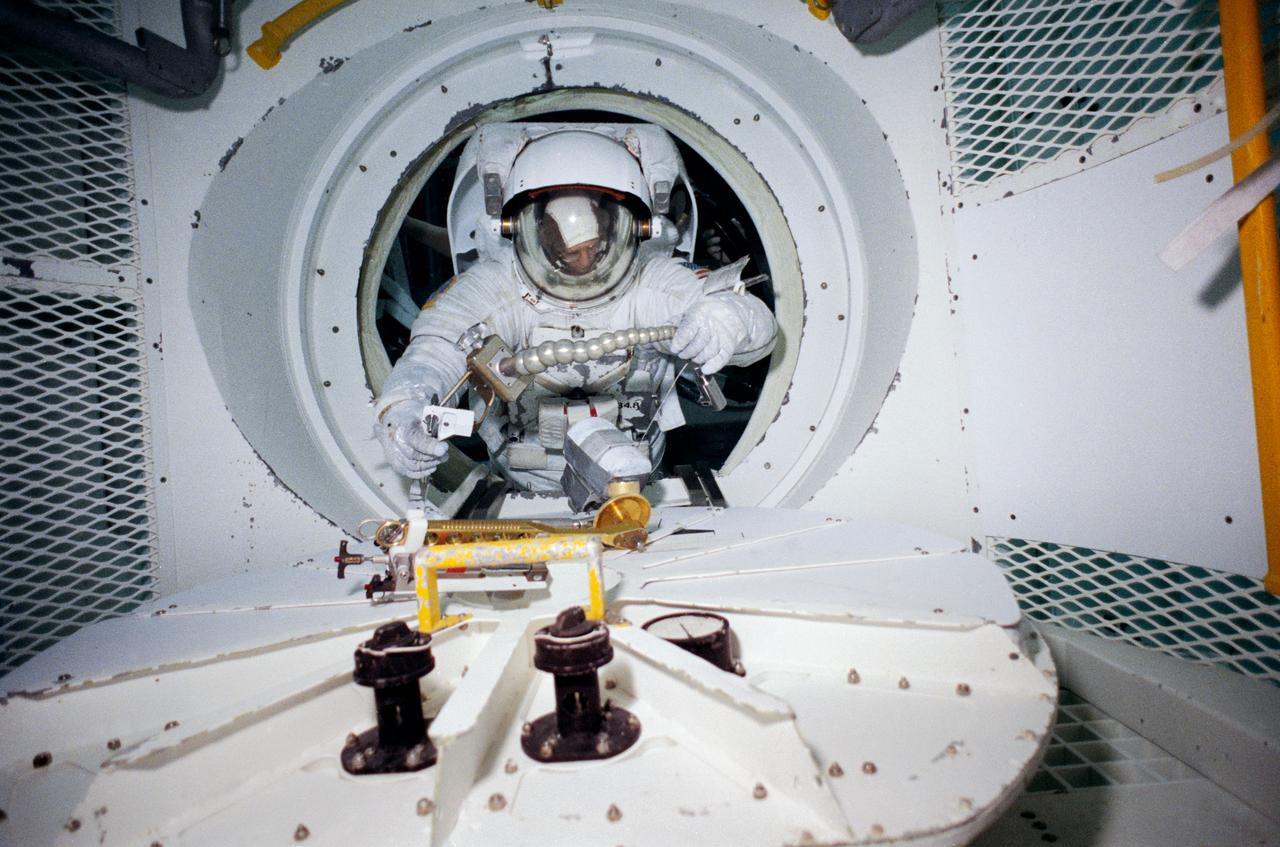
S90-30521 (20 Feb 1990) --- Though no extravehicular activity is planned for STS-31, two crewmembers train for contingencies that would necessitate leaving their shirt sleeve environment of Discovery's cabin and performing chores with their Hubble Space Telescope payload or related hardware. Astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan, mission specialist, is seen egressing the hatchway of the airlock of a full scale mockup of a Shuttle cabin to interface with an HST mockup in JSC's 25.-ft. deep pool in the weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Two SCUBA-equipped divers who assisted in the training session are also seen. Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, mission specialist, is out of frame.
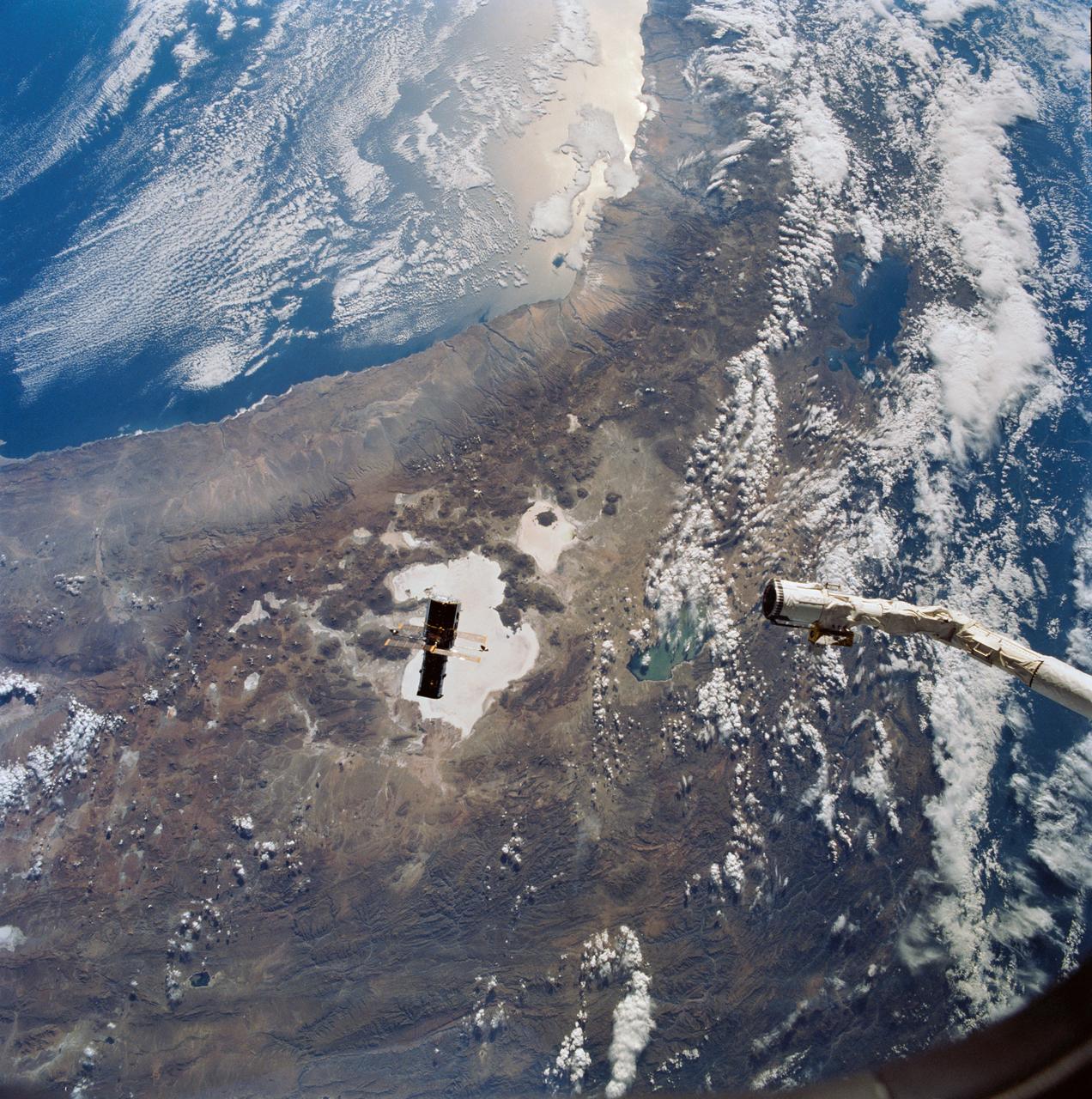

Hubble Space Telescope (HST), with its solar array (SA) wings and high gain antennae (HGA) fully extended,is released from Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector and is set free into Earth orbit by the STS-31 crew. HST drifts away from the end effector over the Andes Mountains.Parts of Bolivia, Peru, Chile, and Argentina are visible. The view covers a huge area of the western half of South America stretching from 14 degrees south latitude to 23 degrees, about 1,000 kilometers.

S89-40887 (October 1989) --- The mission insignia for NASA?s STS-31 mission features the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in its observing configuration against a background of the universe it will study. The cosmos includes a stylistic depiction of galaxies in recognition of the contribution made by Sir Edwin Hubble to our understanding of the nature of galaxies and the expansion of the universe. The STS-31 crew points out that it is in honor of Hubble?s work ?that this great observatory in space bears his name.? The depicted space shuttle trails a spectrum symbolic of both the red shift observations that were so important to Hubble?s work and new information which will be obtained with the HST. Encircling the artwork, designed by the crew, are the names of its members: Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn D. Sullivan, mission specialists. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
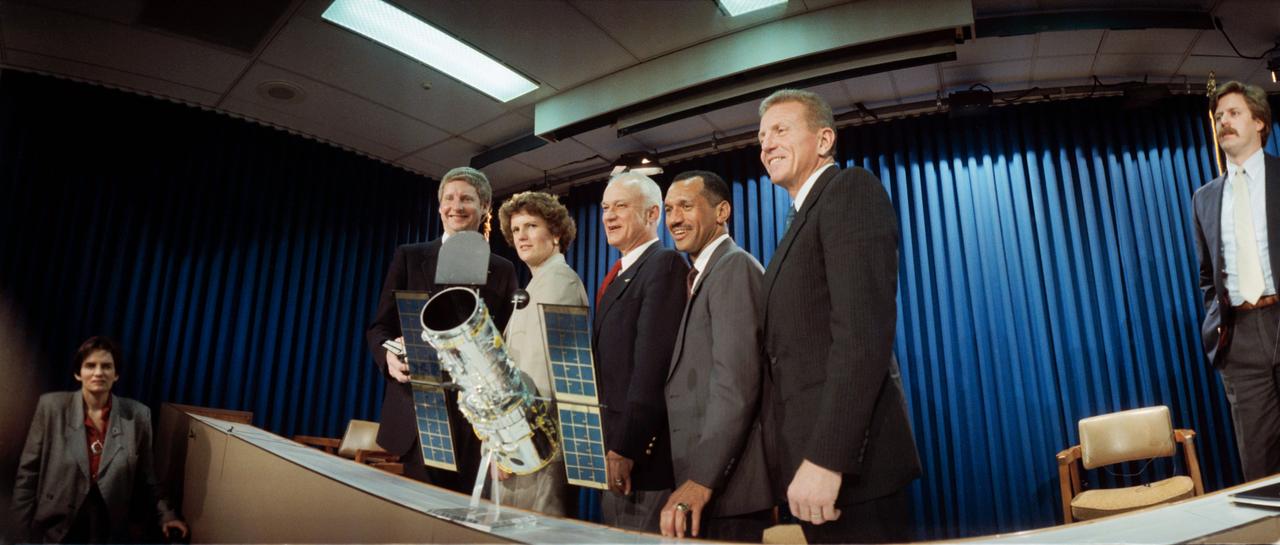

PHOTOS OF STS-31 (DISCOVERY) CREW WITH MODELS OF THE HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE (HST) AND SPACE SHUTTLE AT T-30 (THIRTY DAYS BEFORE LAUNCH) BRIEFING 03/22/90 IN THE AUDITORIUM AND PUBLIC AFFAIRS FACILITY BLDG 2. GROUP PHOTOS OF LOREN J. SHRIVER, CHARLES F. BOLDEN, STEVEN A. HAWLEY, BRUCE MCCANDLESS, AND KATHRYN D. SULLIVAN (32748, 32750, 32758-60 (WIDE ANGLE)) AND INDIVIDUAL PHOTOS OF HAWLEY (32747), MCCANDLESS (32751), SULLIVAN (32753-4), BOLDEN (32755), AND SHRIVER (32757) INCLUDED. ALSO PHOTGRAPHED TOGETHER ARE SULLIVAN, HAWLEY, MCCANDLESS (32749) AND BOLDEN, SHRIVER (32752, 32756).

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
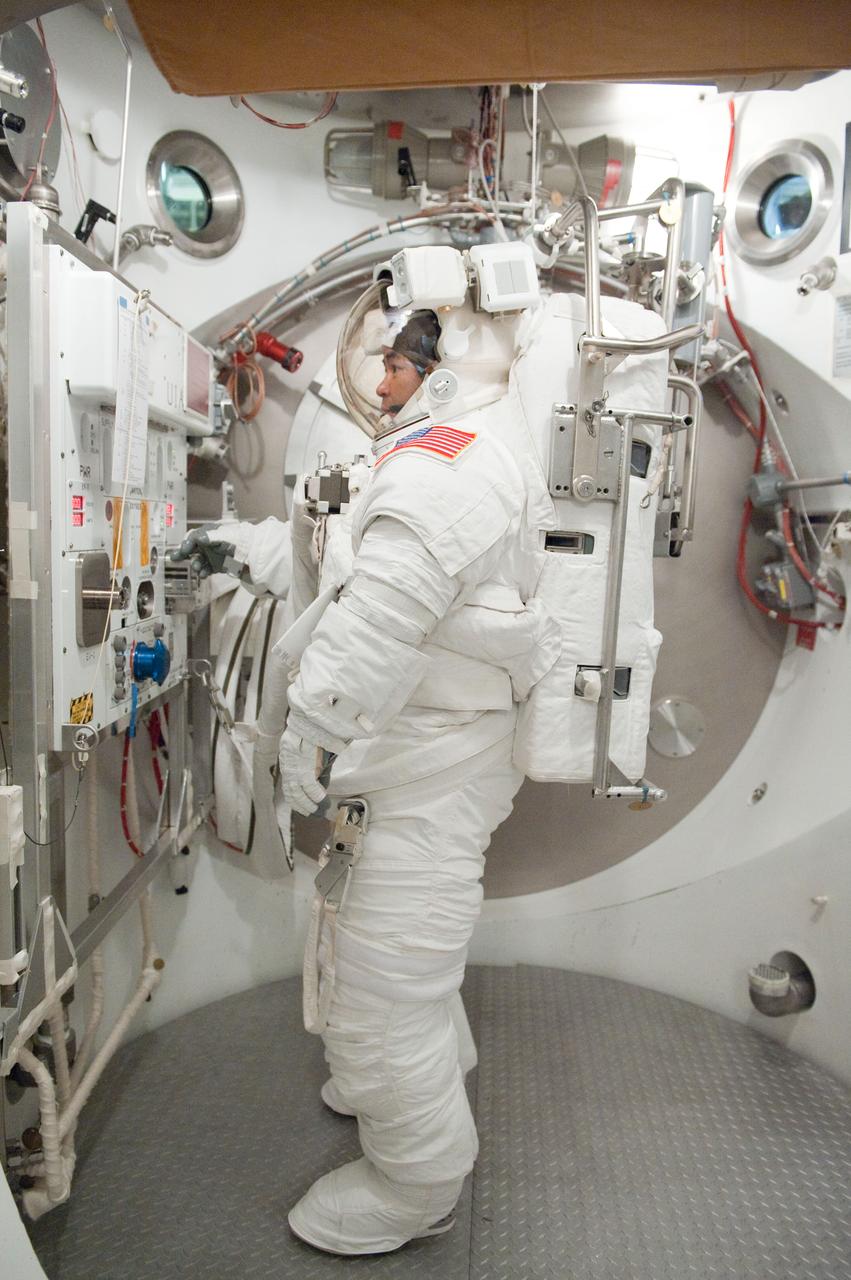

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
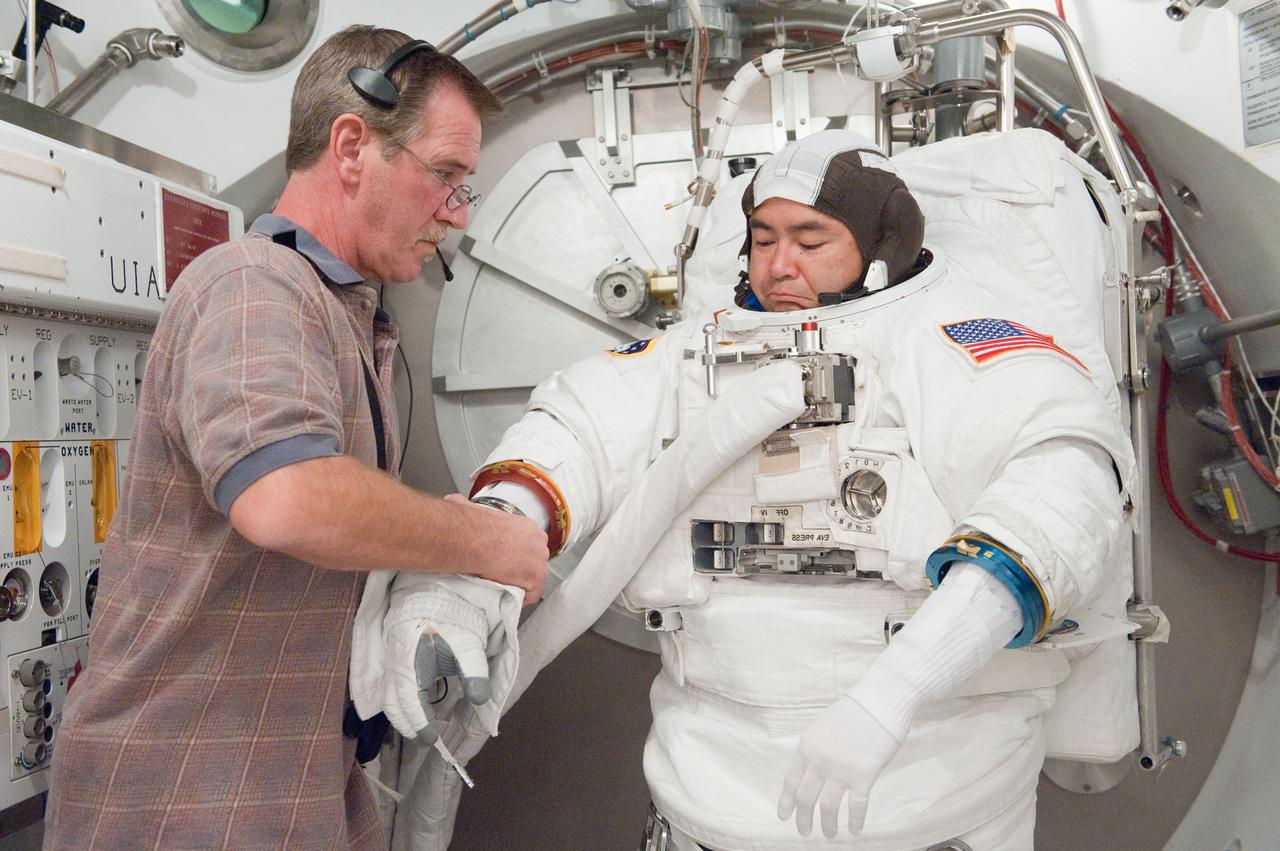

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
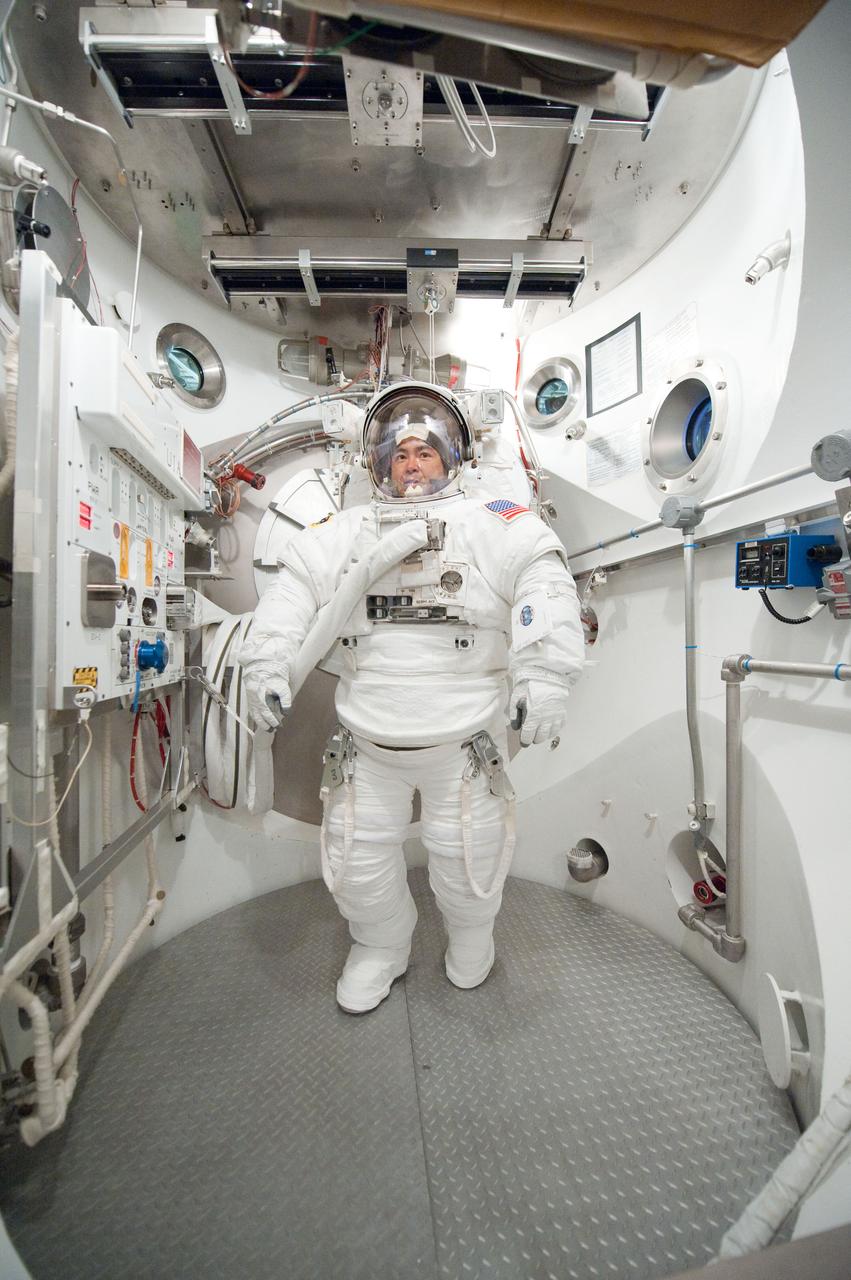

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
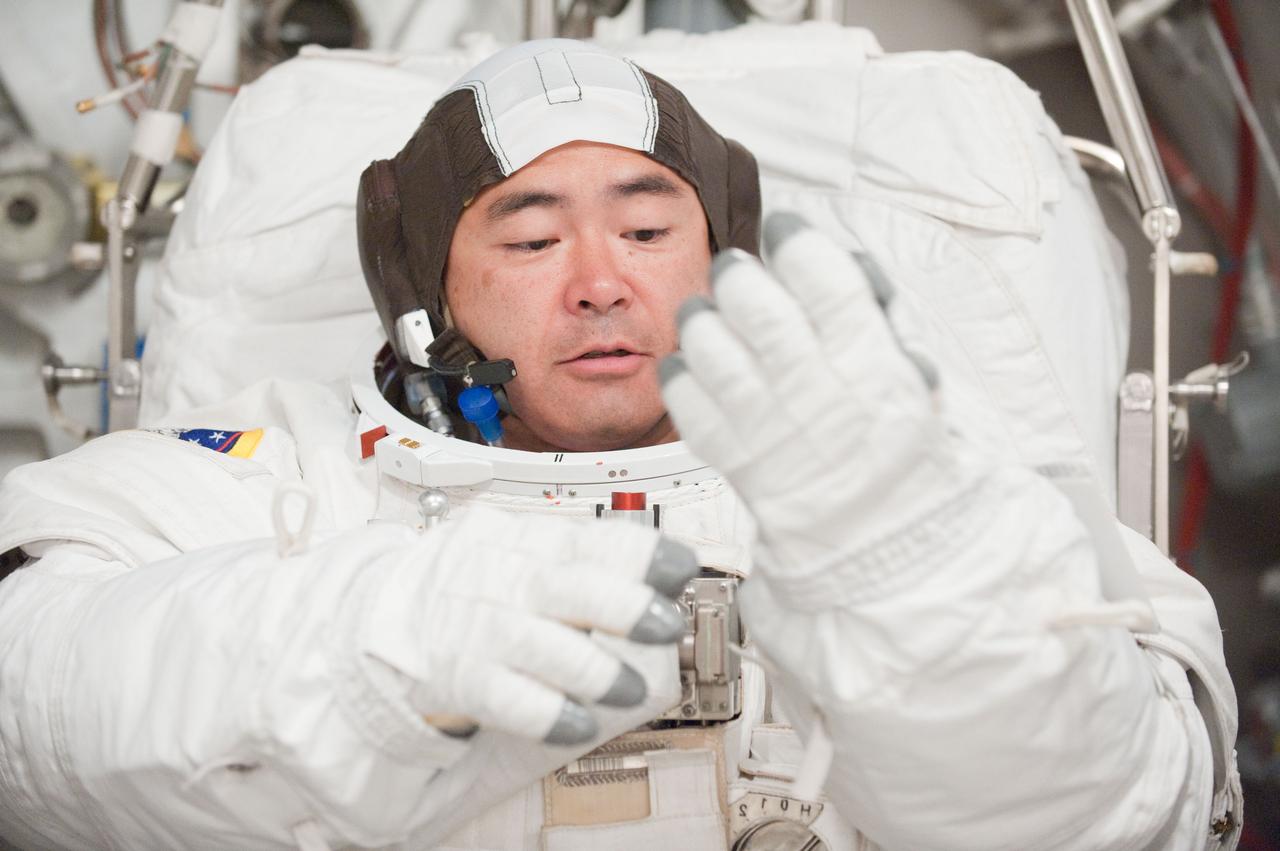

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
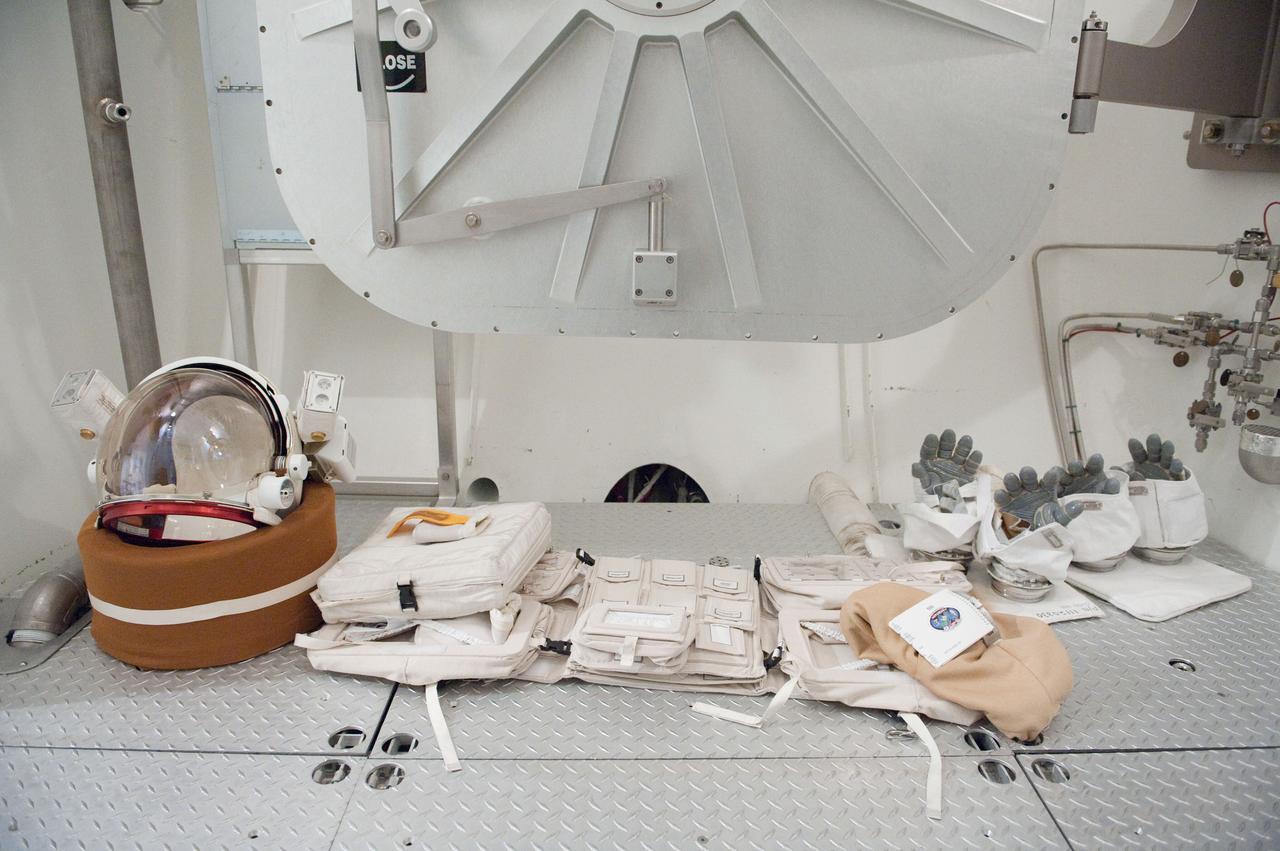

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
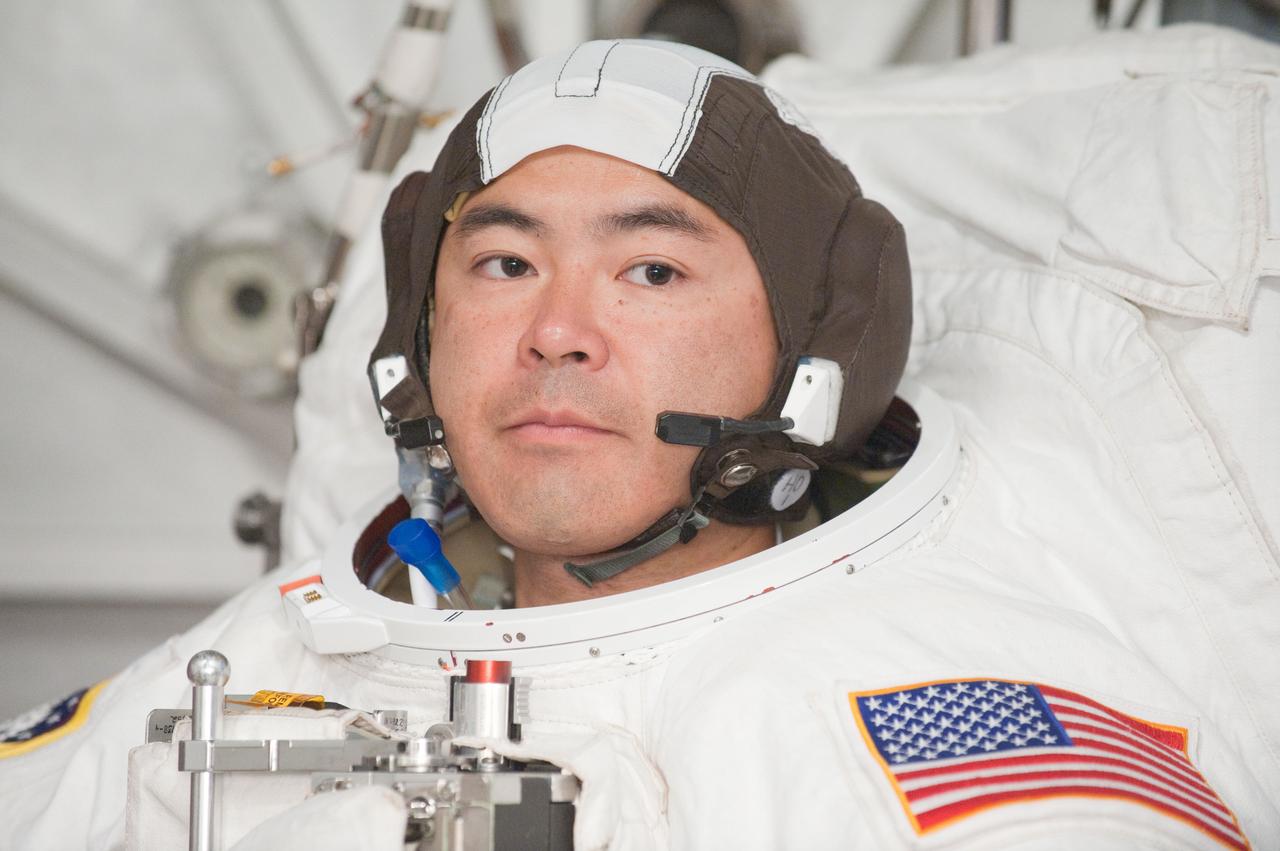

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
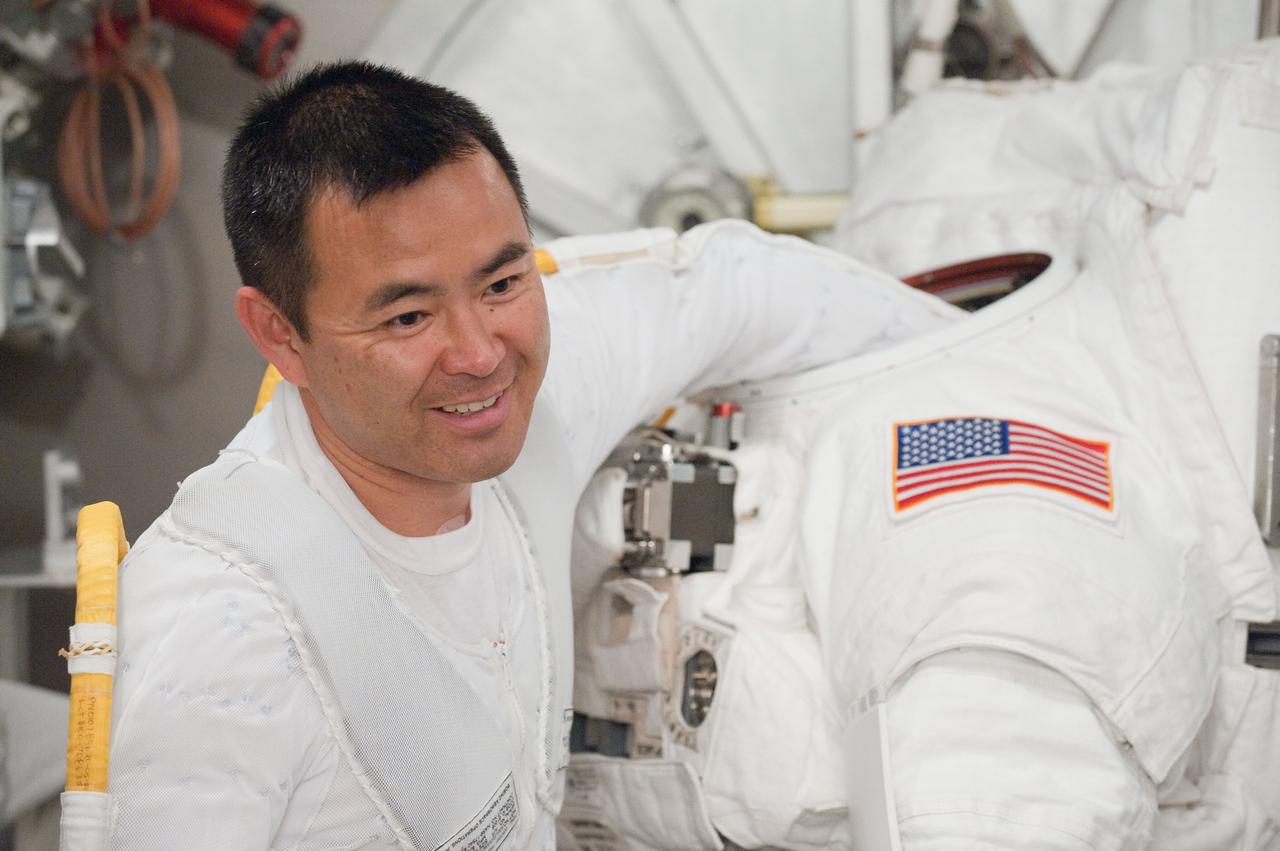

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
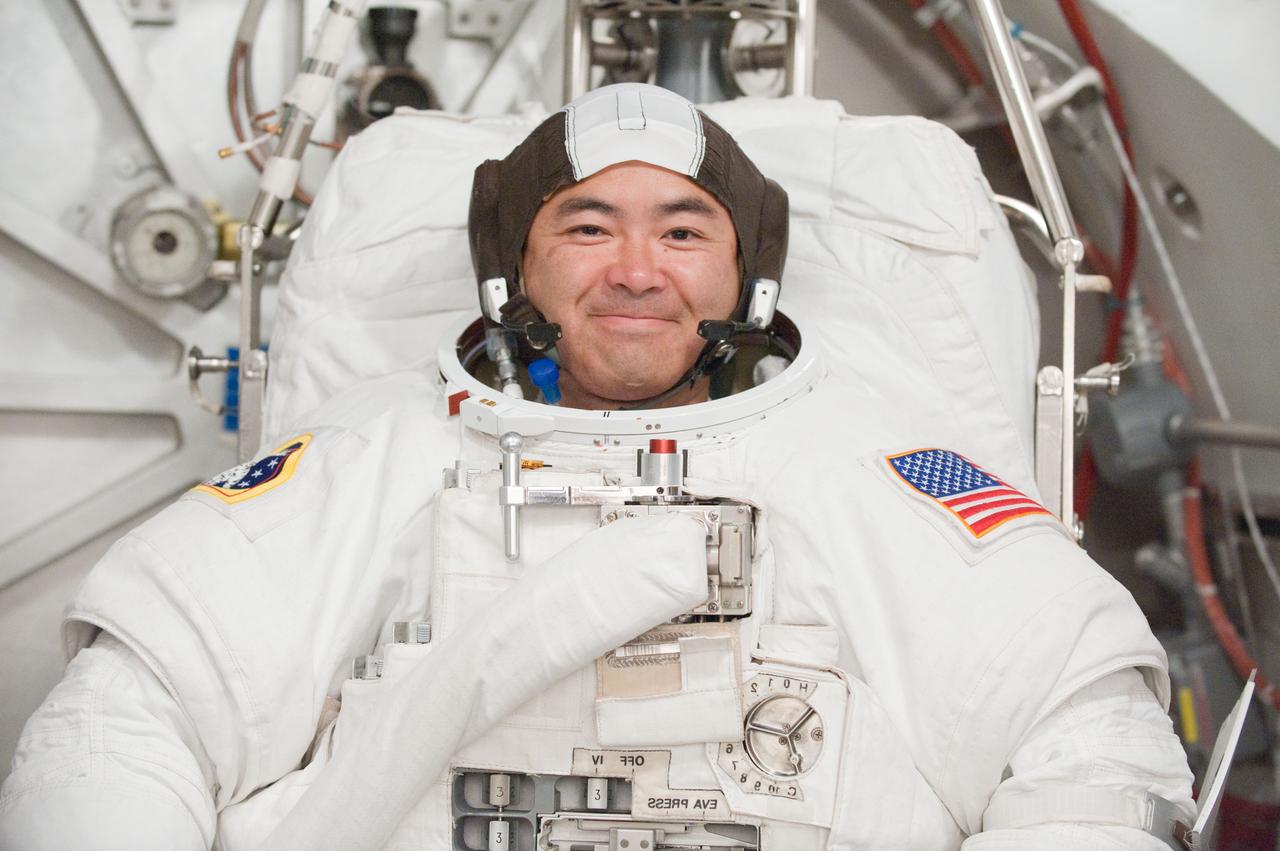

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
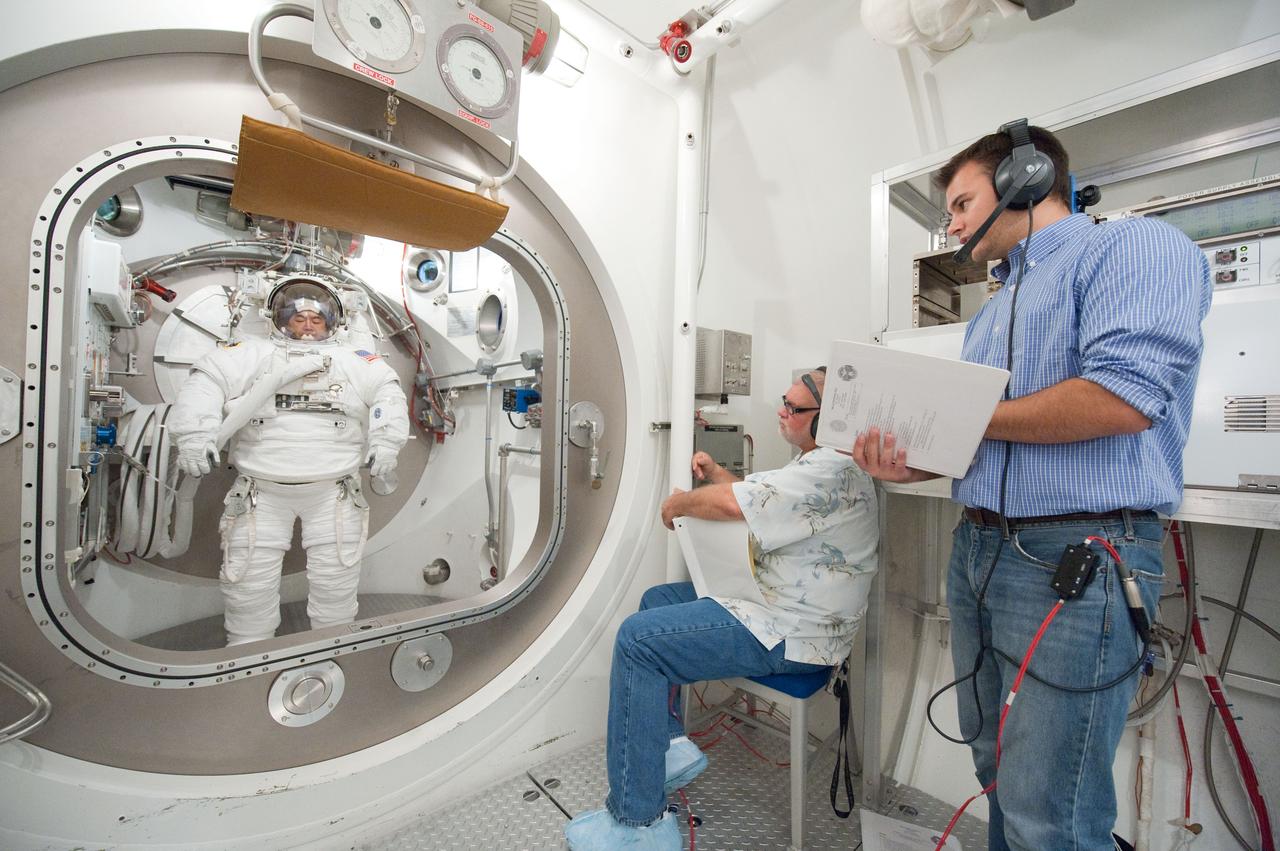

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
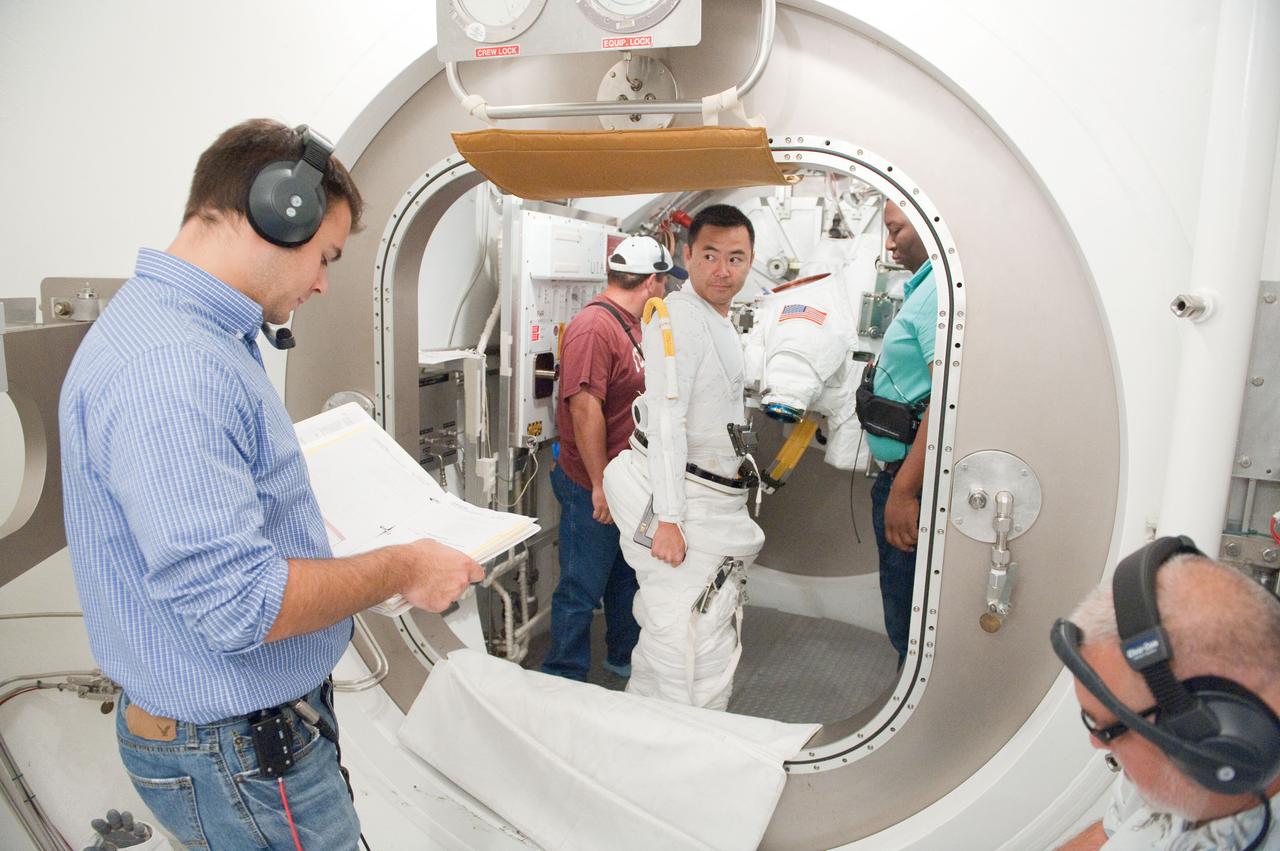

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
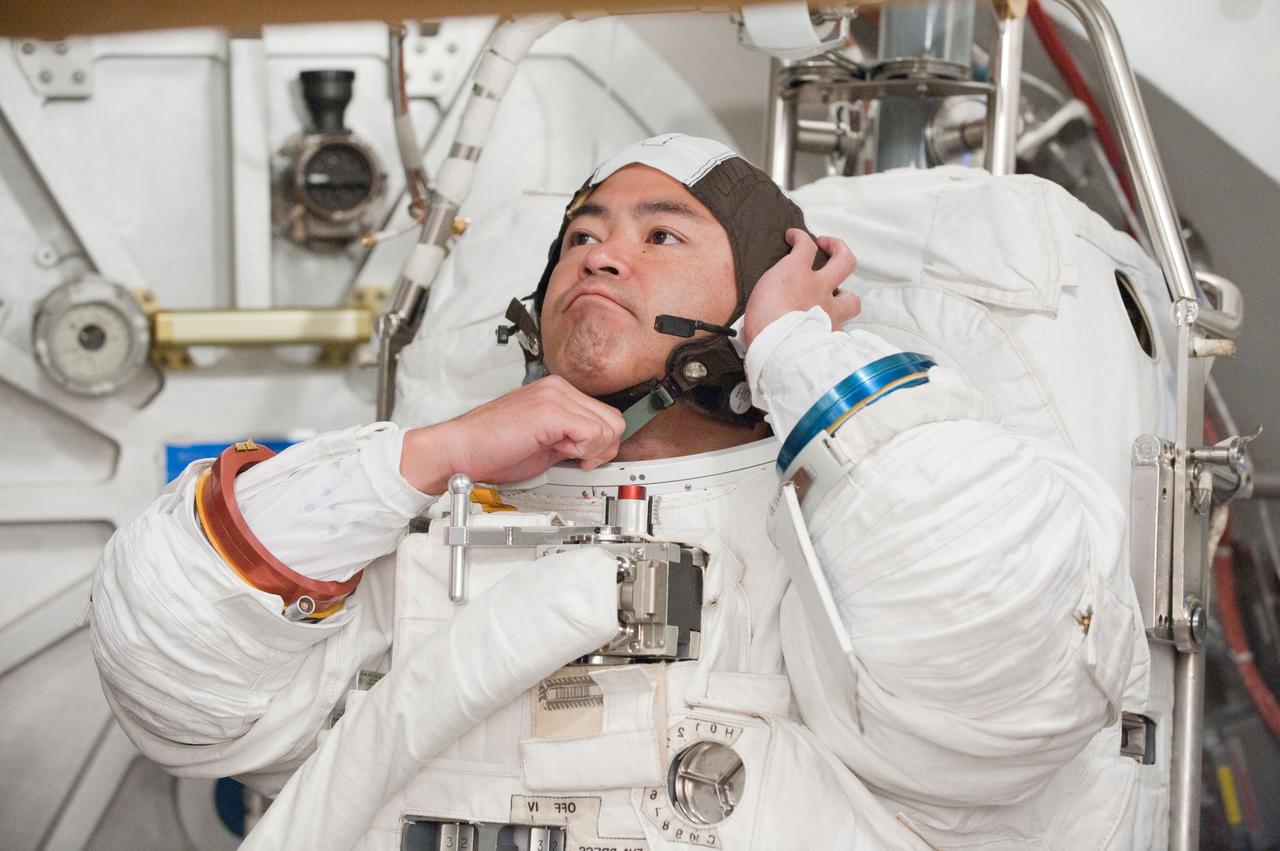

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
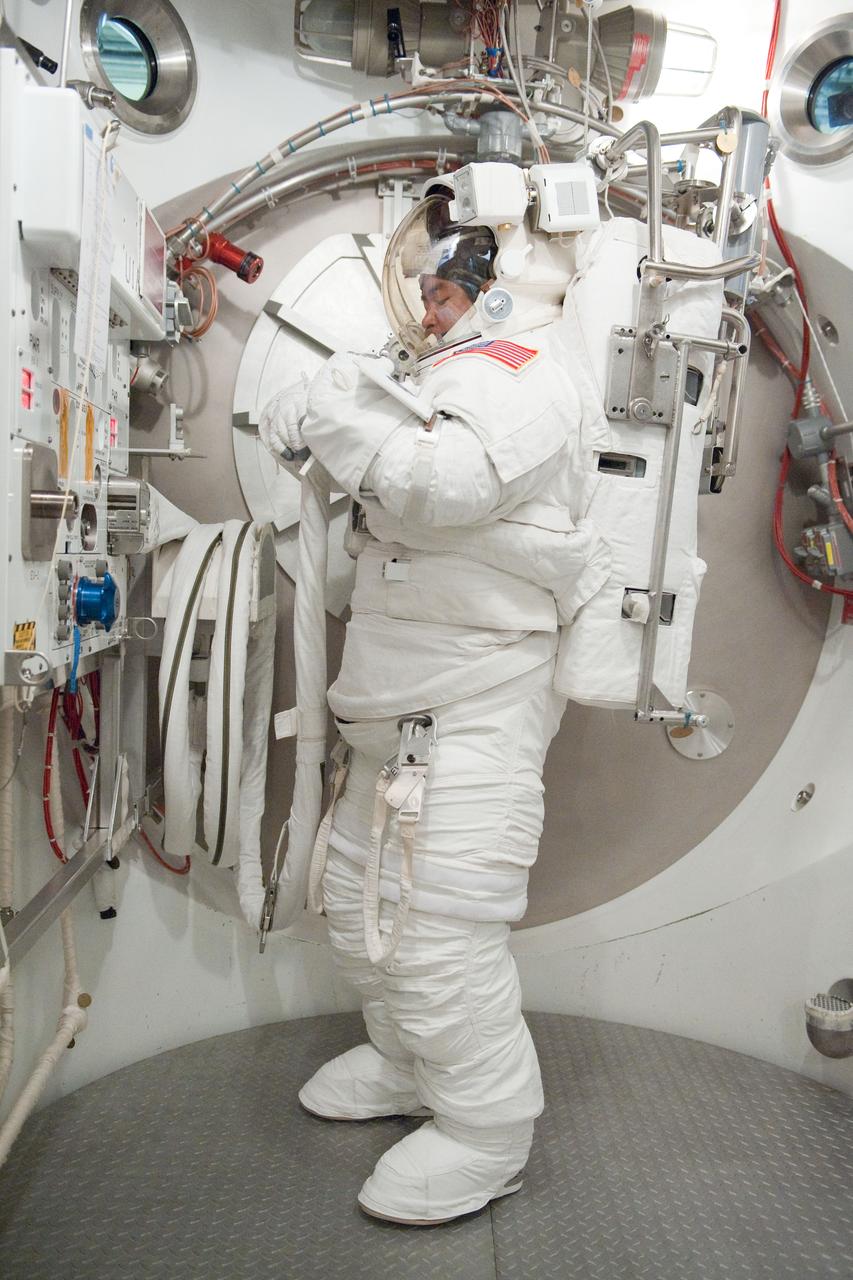

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
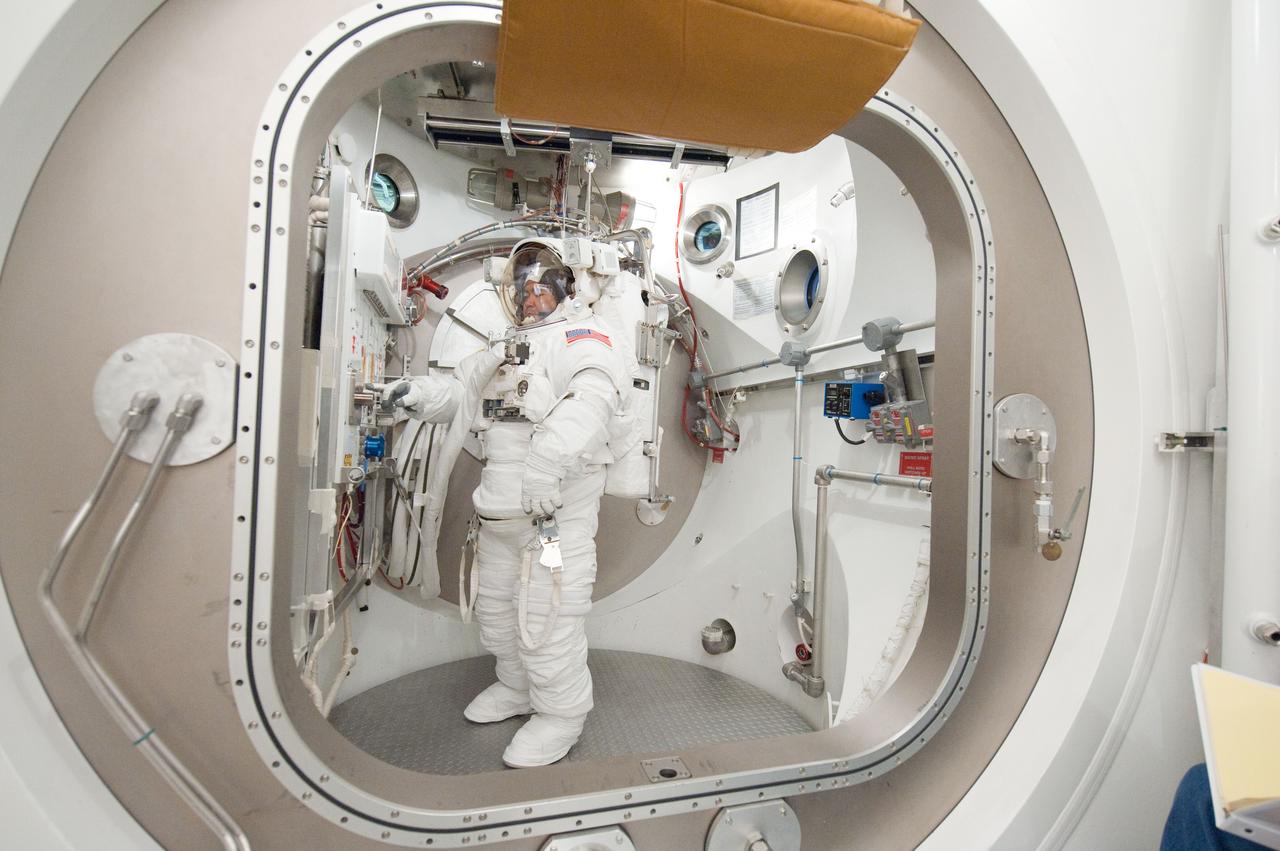

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
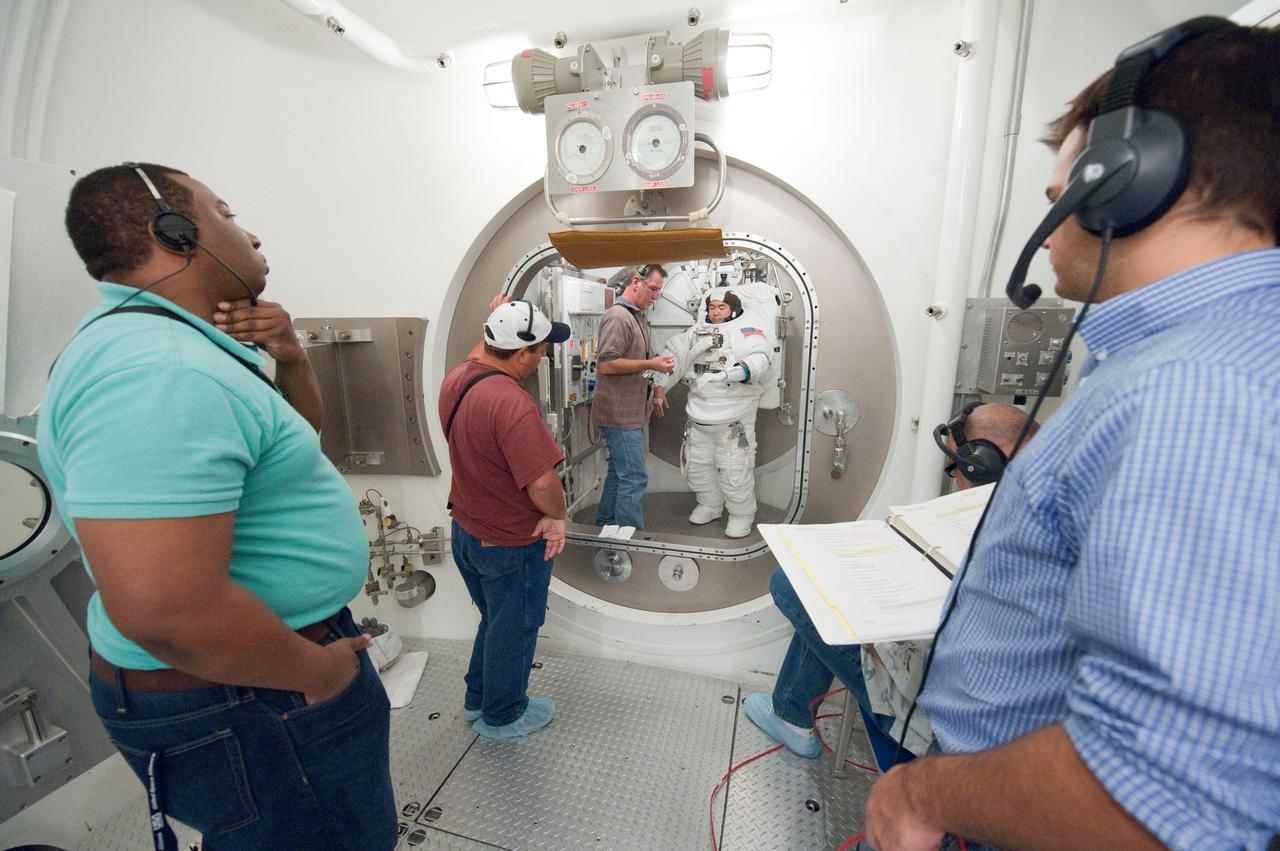

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
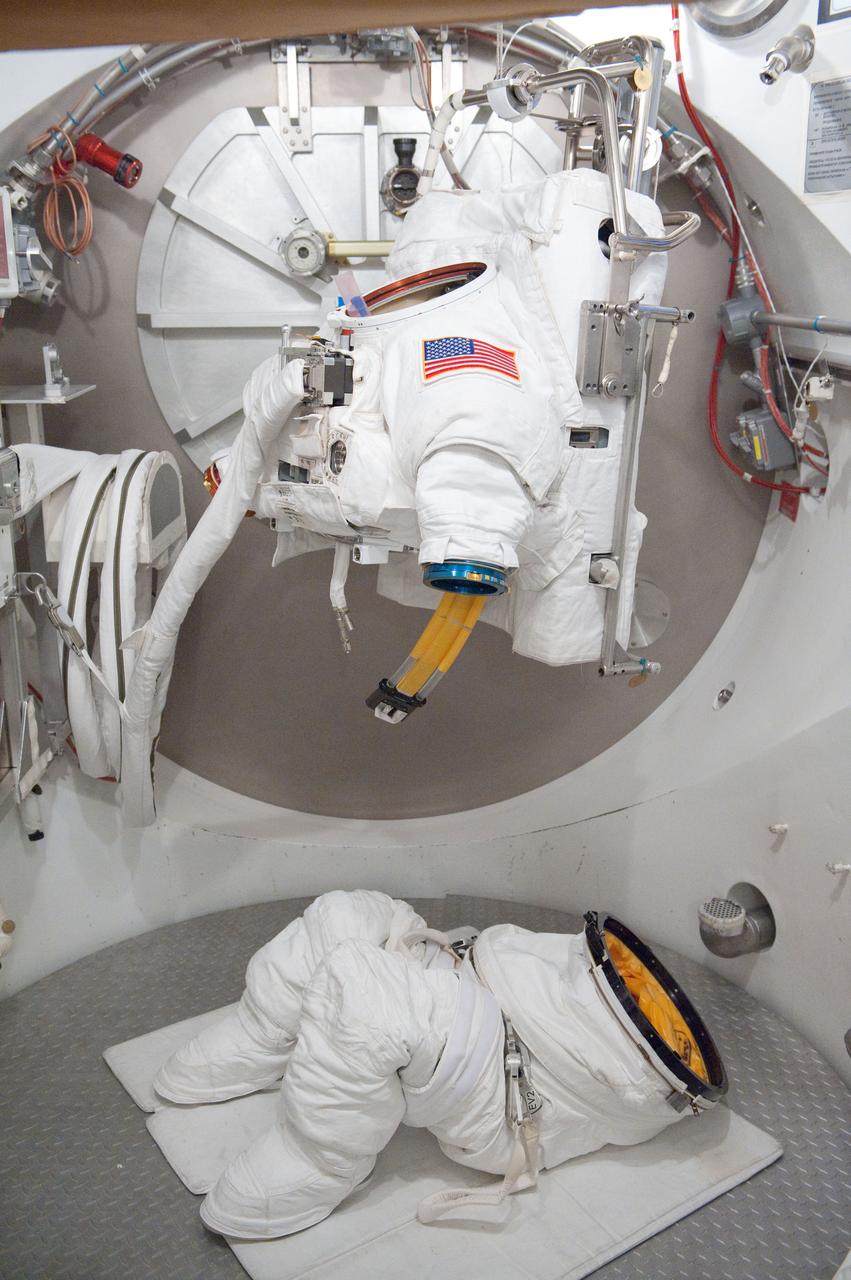

PHOTO DATE: 31 August 2011 LOCATION: Bldg. 7, SSATA Chamber SUBJECT: Expedition 32 crew member and JAXA astronaut, Akihiko Hoshide in SSATA Chamber during Dry Run. STB-ST-942. PHOTOGRAPHER: Mark Sowa
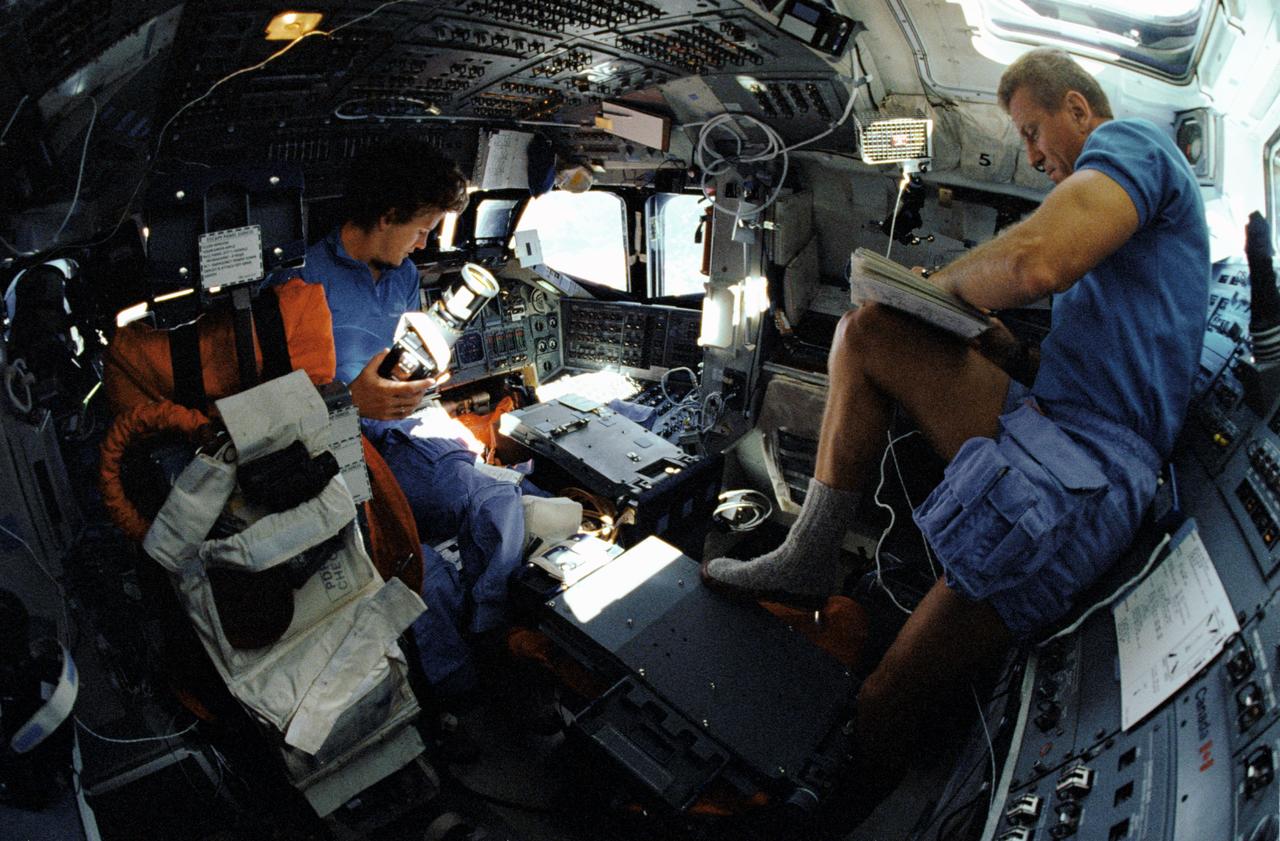

STS031-101-053 (24-29 April 199) --- A 35mm camera equipped with a "fish-eye" lens captured this view on Discovery's flight deck featuring astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan with a Hasselblad camera on forward flight deck and astronaut Loren J. Shriver, pen in hand, amending flight data on aft flight deck.

STS031-03-014 (25 April 1990) --- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), still in the grasp of Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS), is backdropped over Earth some 332 nautical miles below. In this scene, HST has deployed one of its solar array panels but is yet to have extended the second. This scene was captured with a 35mm camera aimed through an overhead window on aft the flight deck.

STS031-03-009 (25 April 1990) --- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), still in the grasp of Discovery's remote manipulator system (RMS), is backdropped over Earth some 332 nautical miles below. In this scene, HST has deployed one of its solar array panels but is yet to have extended the second. This scene was captured with a 35mm camera aimed through an overhead window on the aft flight deck.
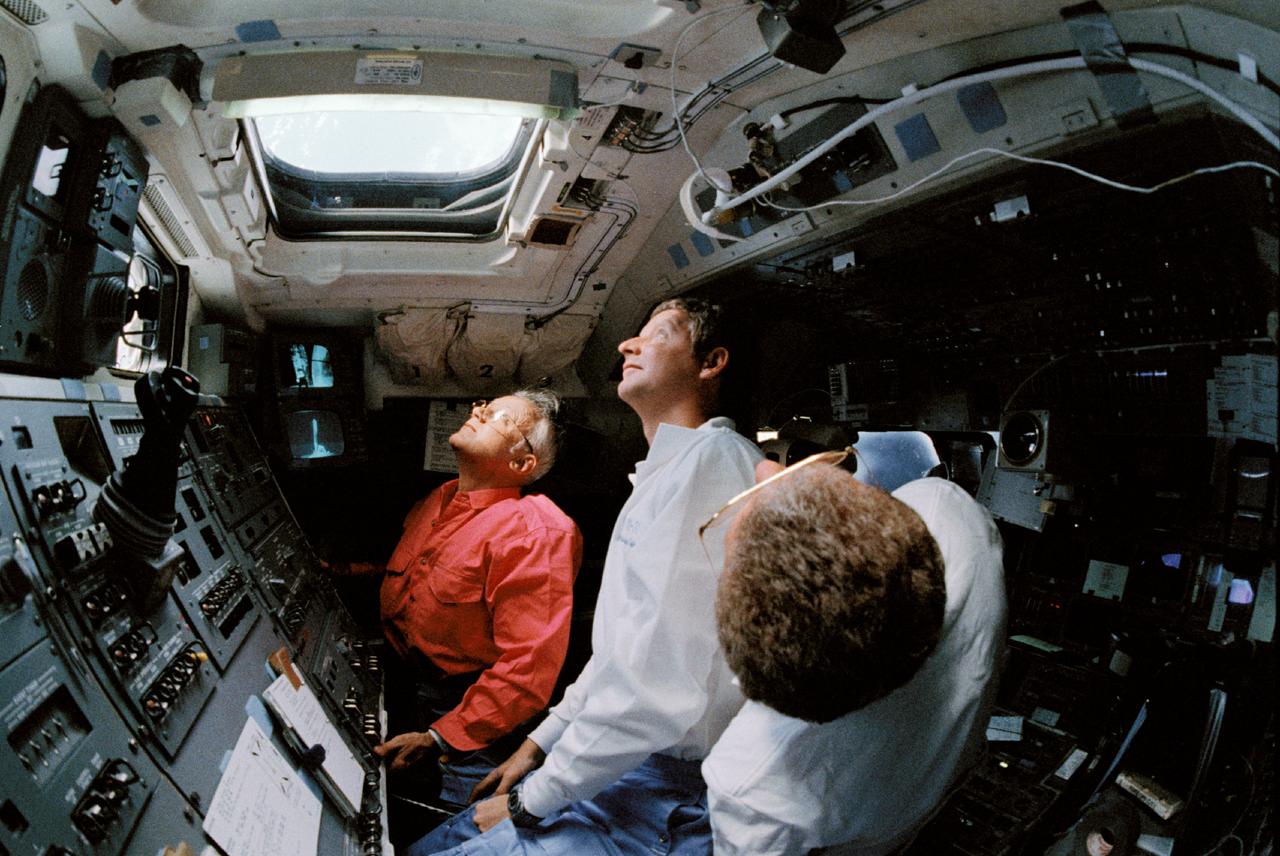

STS031-10-027 (24-29 April 1990) --- A "fish eye" lens captured this overall view of the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Discovery while the crewmembers were monitoring the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment checkout procedures. From front to back are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, commander, and Steven A. Hawley and MS Bruce McCandless II, both mission specialists, looking up at overhead windows and the HST on the remote manipulator system (RMS) outside them.

STS031-10-023 (25 April 1990) --- View of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on the end of Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm prior to deployment of its antennae and solar array panels.
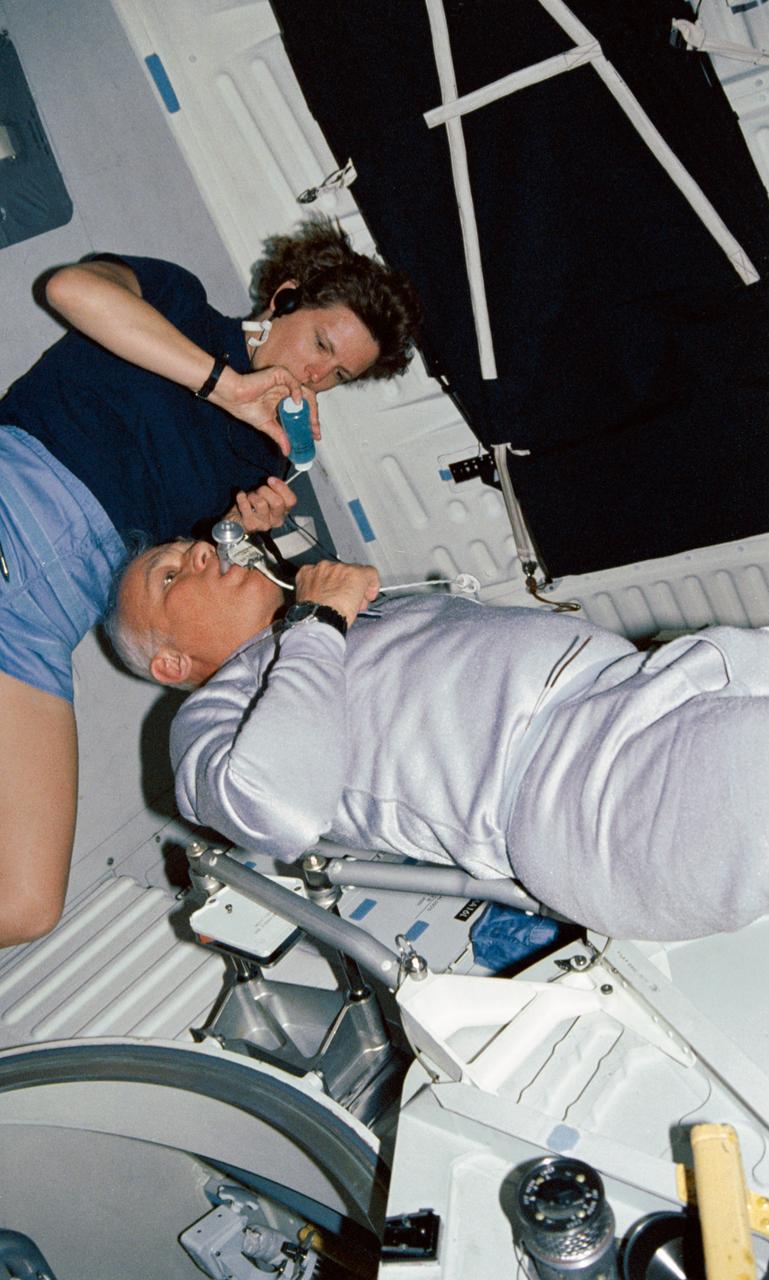
STS031-04-002 (24-29 April 1990) --- Astronauts Kathryn D. Sullivan and Bruce McCandless II, mission specialists, work together to perform one of the mission's medical experiments. The experiment is Detailed Supplementary Objective (DSO) 462, Non invasive Estimation of Central Venous Pressure During Spaceflight. Sullivan applies a gel substance to a transducer which will be placed on McCandless' jugular vein to collect the sought data. The cable links to a data recorder.

This high oblique view shows the majority of the island of Madagascar (19.0S, 47.5E). This Texas sized island is now largely deforested and is suffering from severe soil erosion as well as a declining biological species diversity and productivity. At the turn of the century, the island was almost totally forested but now, forests cover only about 10 percent of the surface. Evidence of soil erosion can be seen in the offshore sediment plumes.
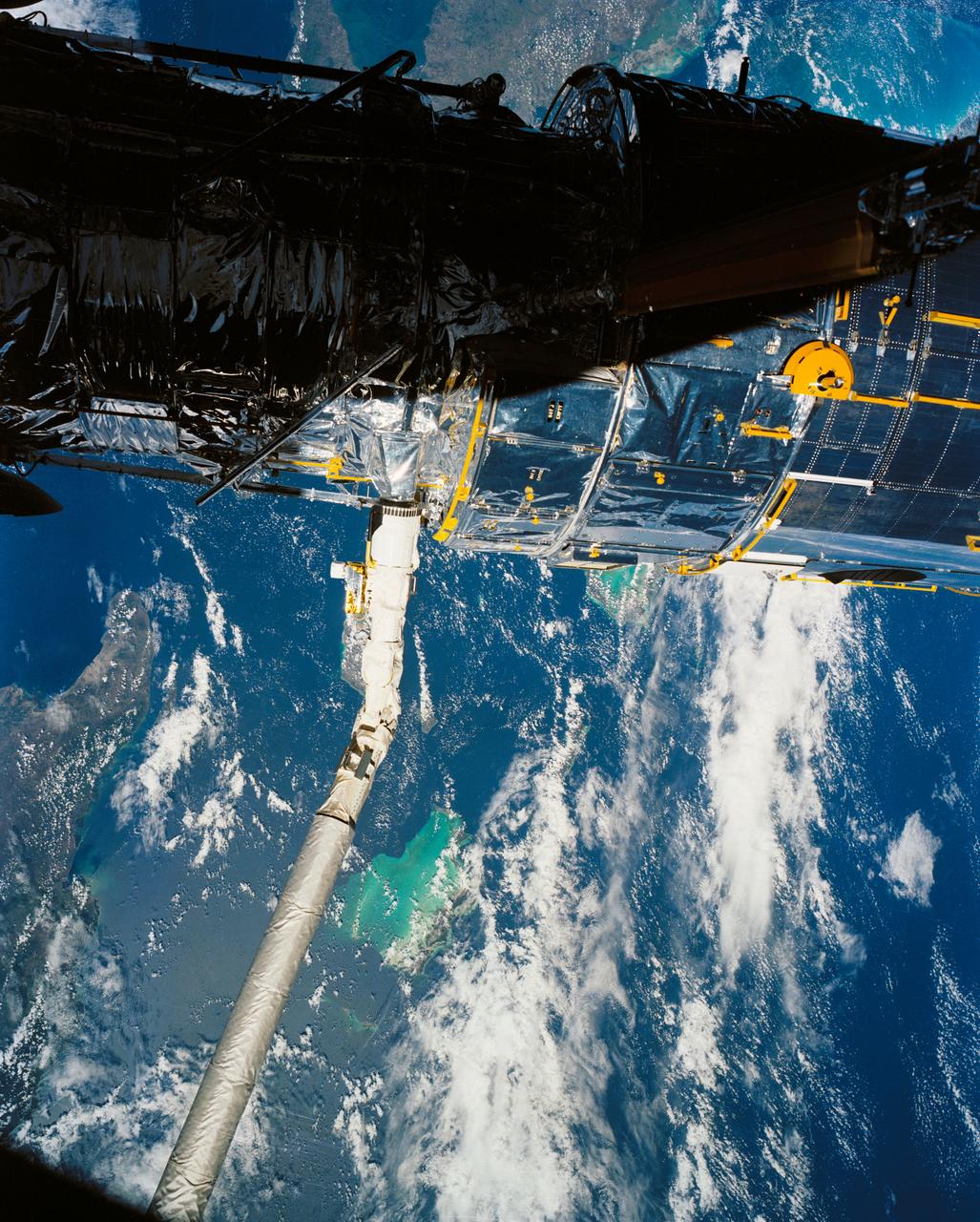

A close up deploy view of the Hubble Space Telescope on the end of the space shuttle remote manipulator system (RMS) with Eastern Cuba, (20.0N, 74.0W) seen on the left side of the telescope and northern Haiti seen on the right side of the telescope. The light colored blue feature in the water north of Haiti is the shallow waters of the Caicos Bank.
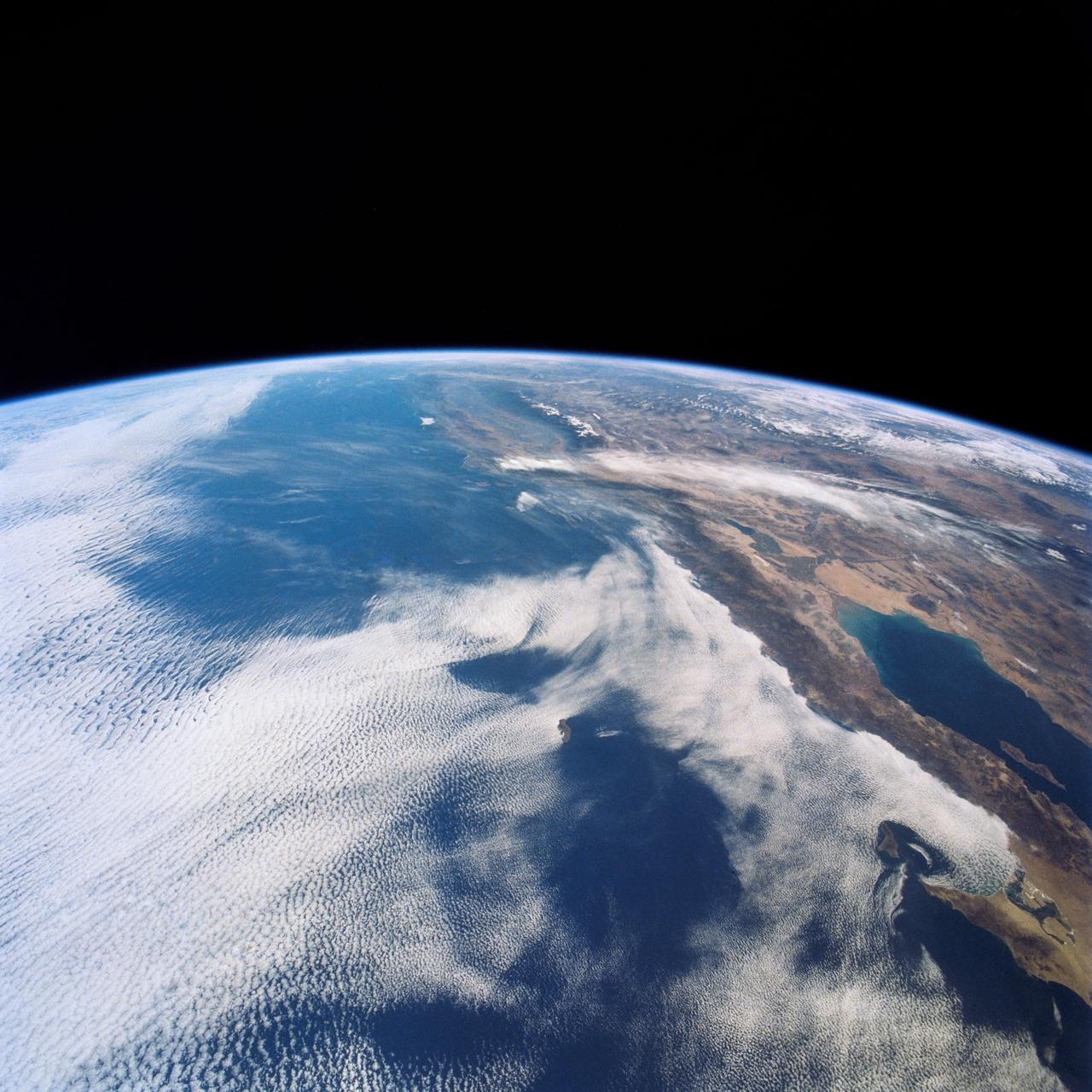

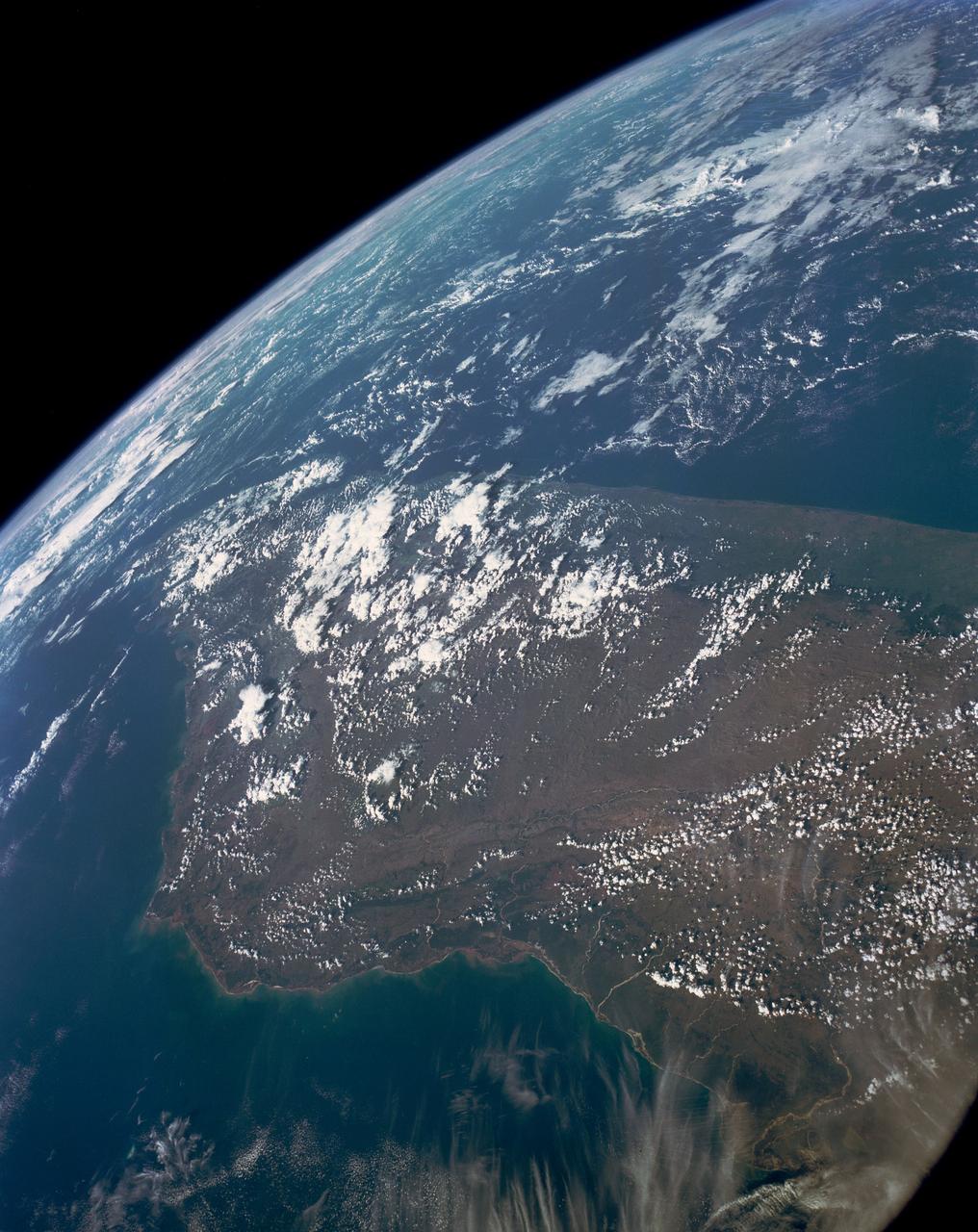
This view shows the west coast of the United States and Mexico (32.5N, 118.0W) and gives an indication of the range of view from orbital altitude. The visual range of this particular scene is from Skammon's Lagoon on Baja to the northern tip of California's Central Valley and Sierra Nevada, a range of over 15 degrees of latitude. Coastal fog drapes over southern California and northern Baja California. White Sands, New Mexico is at far right center.
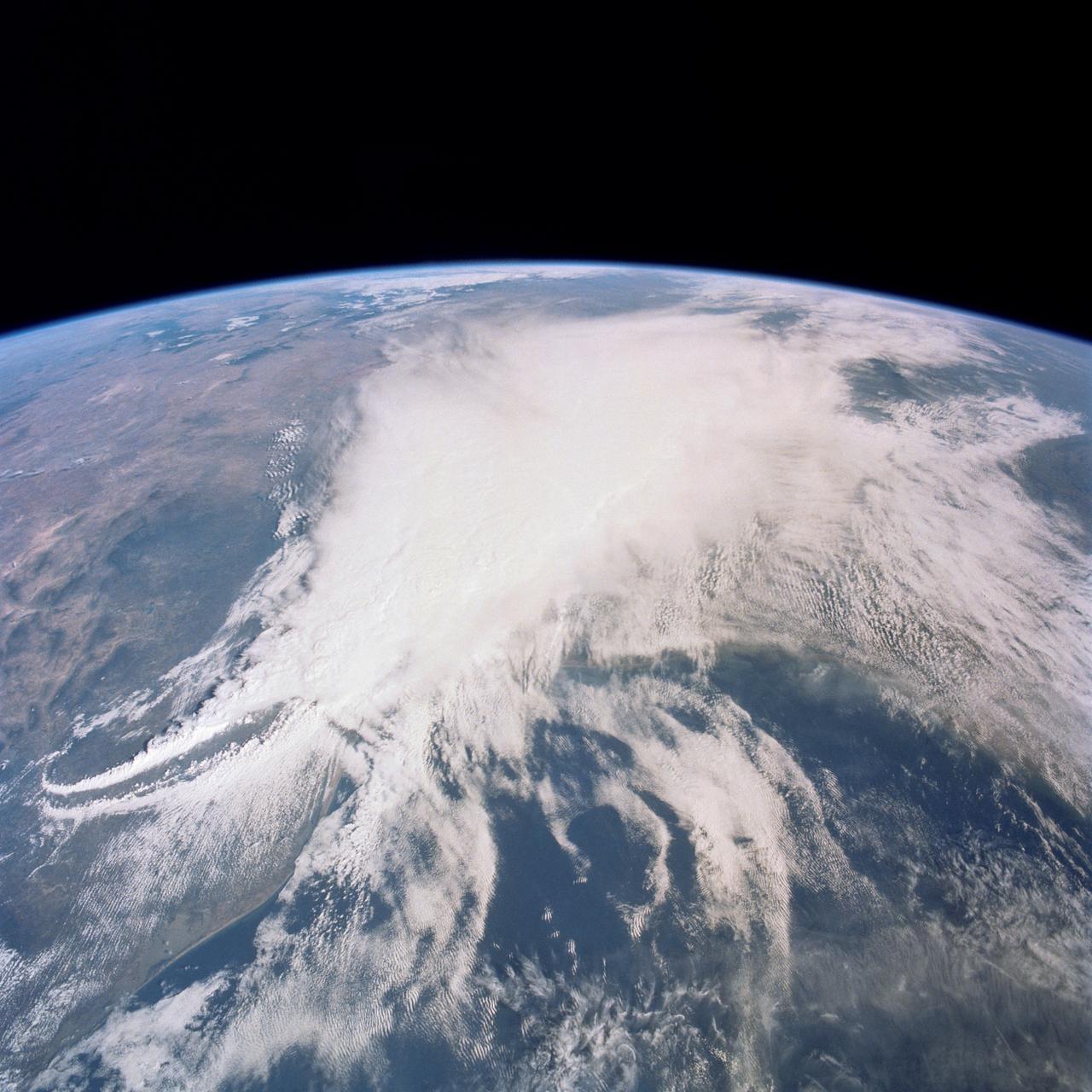

This thunderstorm along the Texas Gulf Coast (29.0N, 95.0W), USA is seen as the trailing edge of a large cloud mass formed along the leading edge of a spring frontal system stretching northwest to southeast across the Texas Gulf Coast. This system brought extensive severe weather and flooding to parts of Texas and surrounding states. Muddy water discharging from coastal streams can be seen in the shallow Gulf of Mexico as far south as Lavaca Bay.
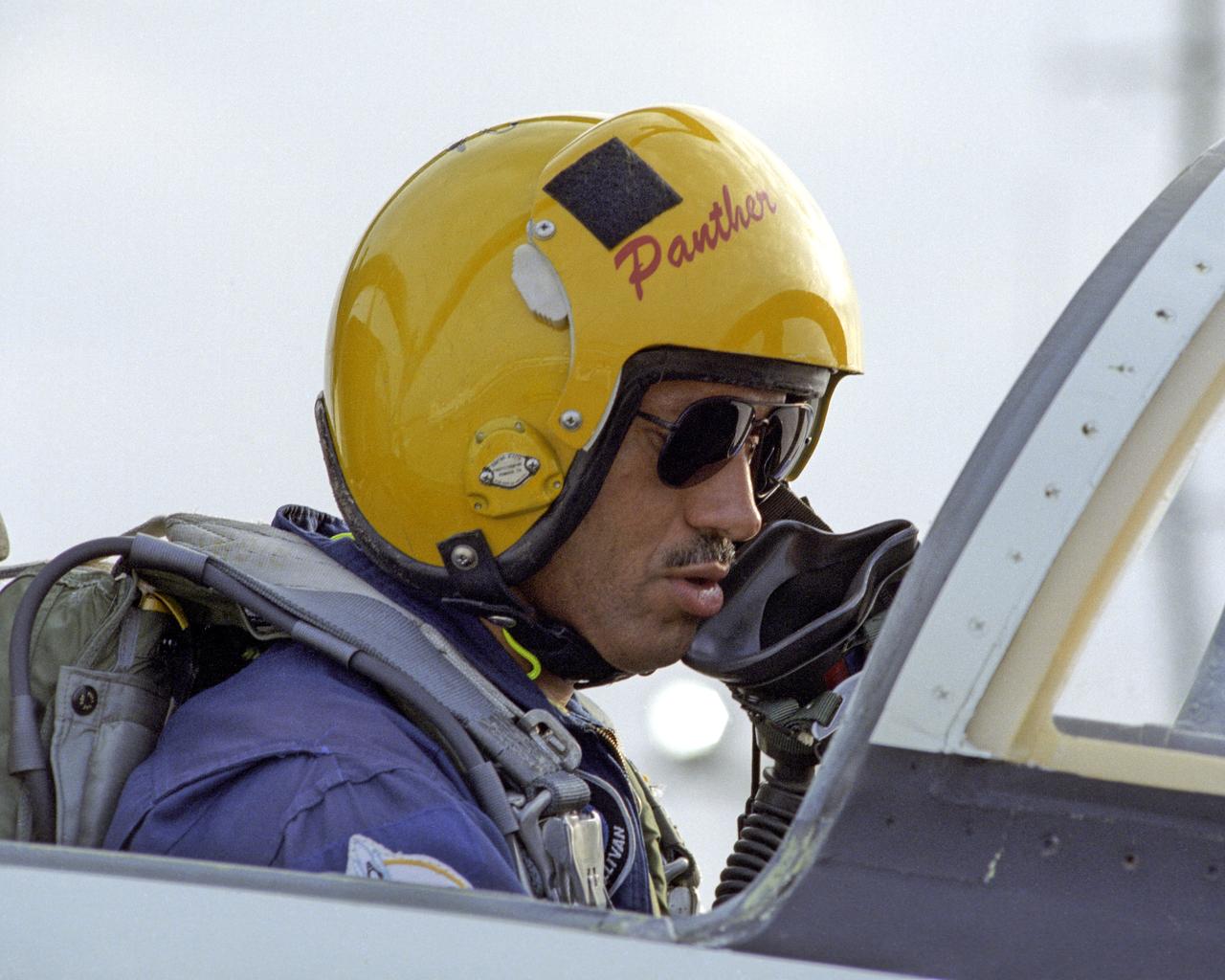

Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Pilot of Space Shuttle Mission STS-31, prepares for rehearsing shuttle contingency landings in the T-38S are among the final pre-launch activities. STS-31, carrying five crew members and the HST is set to liftoff at 8:47 a.m. April 10.
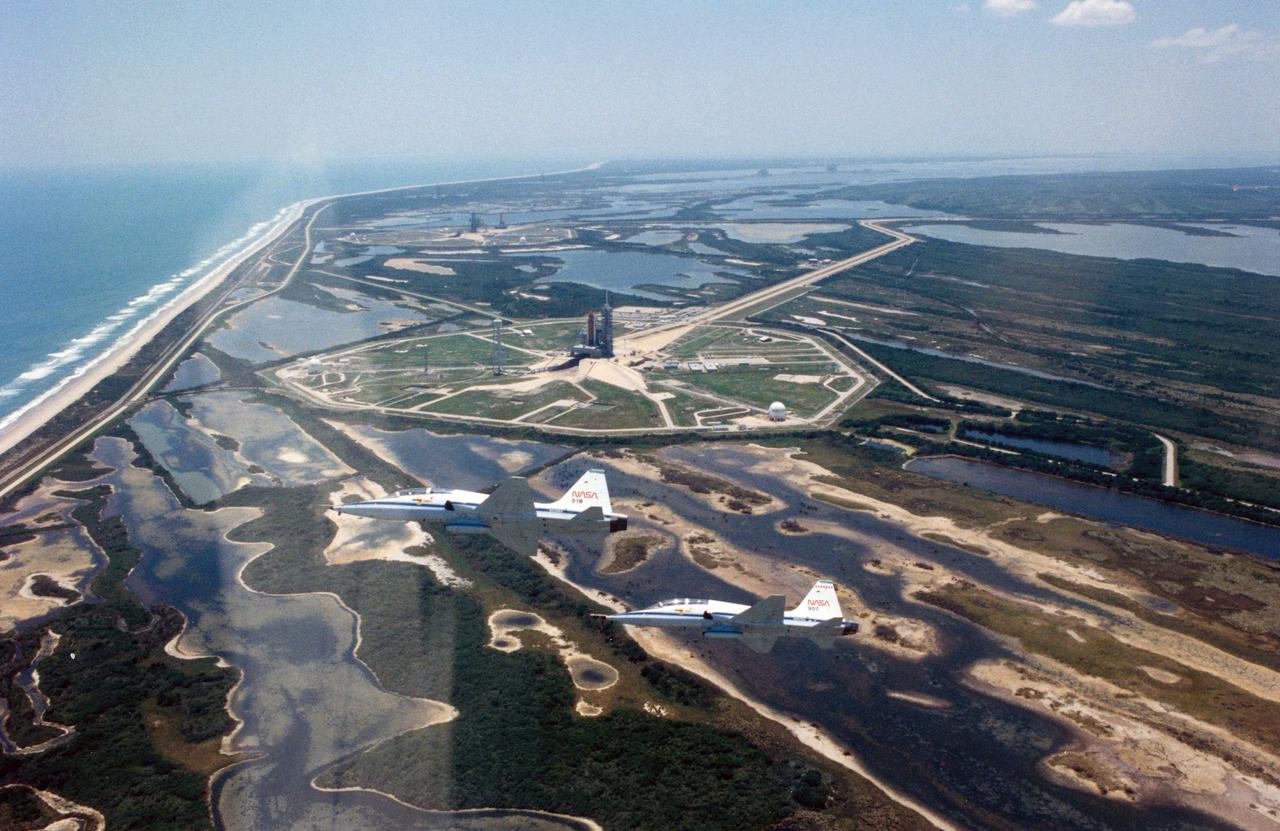

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Mission Specialist Kathryn D. Sullivan's camera skills show that the view of Launch Pads 39A and 39B from a T-30 trainer is unforgettable. Sullivan took the pictures as she and fellow Space Shuttle Mission STS-31 crew members flew into KSC on April 22. In the foreground, the Shuttle Discovery is poised on Pad B, and in the distance, Columbia rolls out to Pad A. While Sullivan flew with STS-31 Pilot Charles F. Bolden Jr., Mission Commander Loren J. Shriver and Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley flew alongside in T-38 #918, and Mission Specialist Bruce McCandless II and NASA Pilot Mario Runco flew in T-38 #907. STS-31 is set to lift off from Pad B at 8:31 a.m. EDT, April 24.

STS076-E-05264 (22-31 March 1996) --- STS-76 KidSat Earth View (Morocco)

STS076-E-05275 (22-31 March 1996) --- STS-76 KidSat Earth View (Canada)
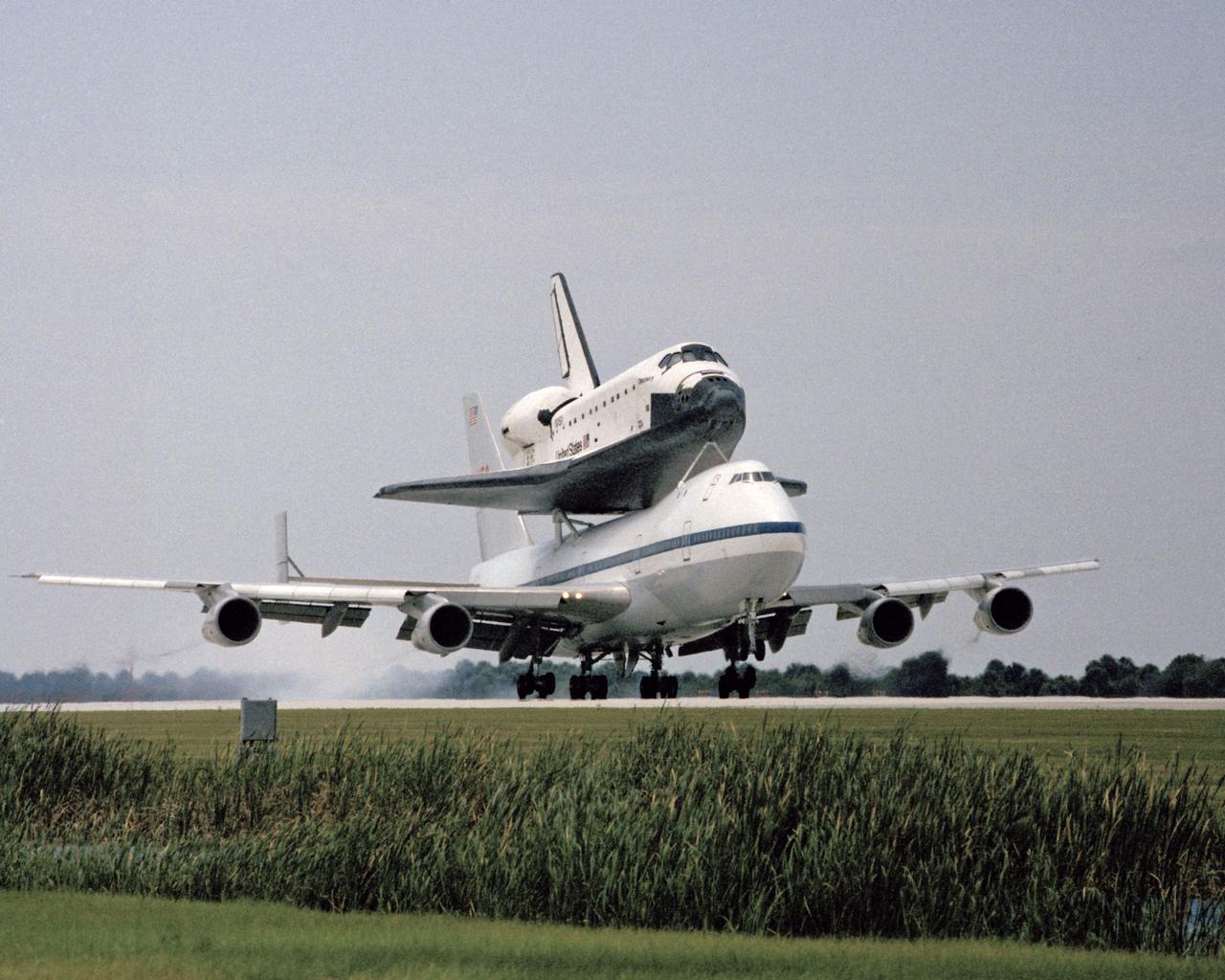

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- STS-31. Return of the space shuttle Discovery at the SLF. Photo credit: NASA

Aerial, ground level and night views of STS-2 Rollout to and on Pad 39A, 08/31/1981. KSC, FL
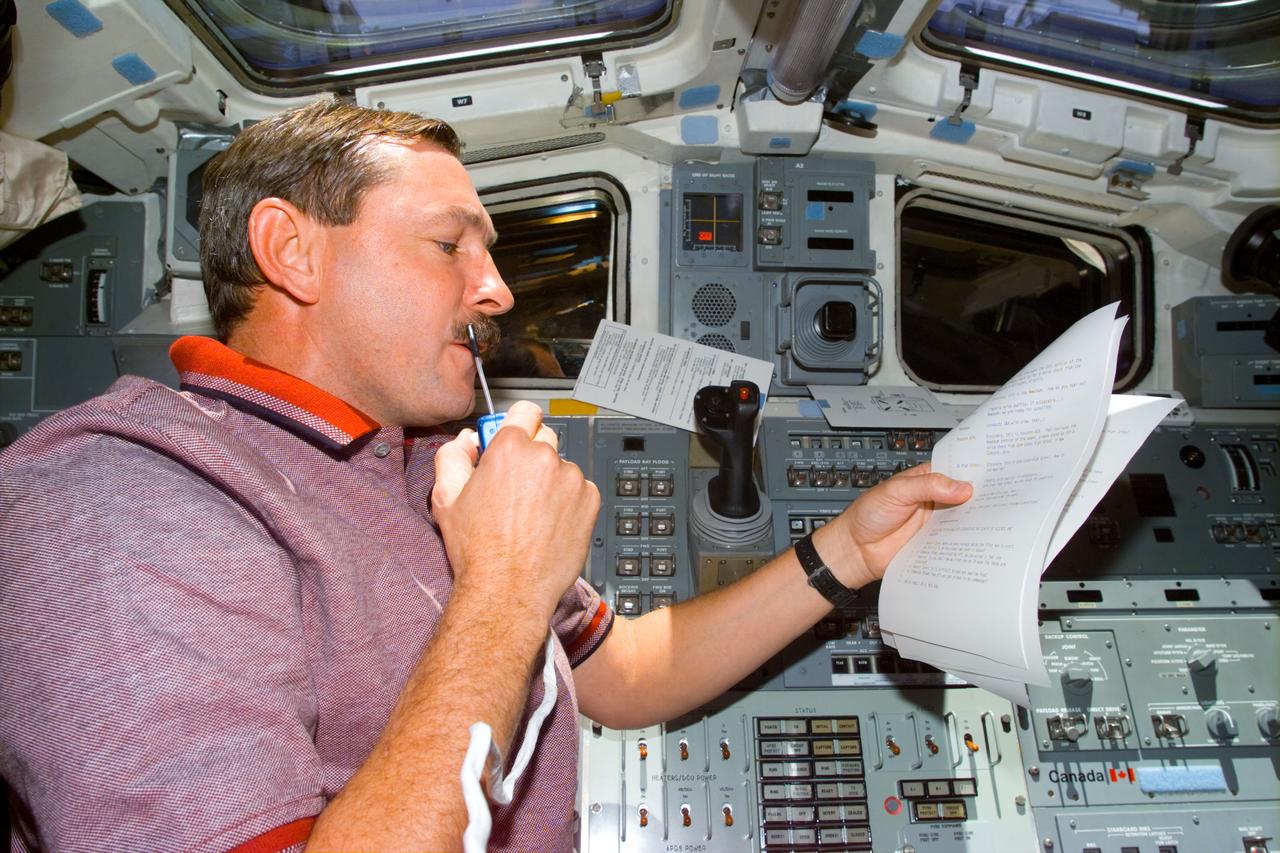

STS095-E-5177 (31 Oct. 1998) --- On Discovery's aft flight deck, astronaut Curtis L. Brown Jr., STS-95 commander, checks over notes with ground controllers in Houston. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 00:41:51 GMT, Oct. 31.
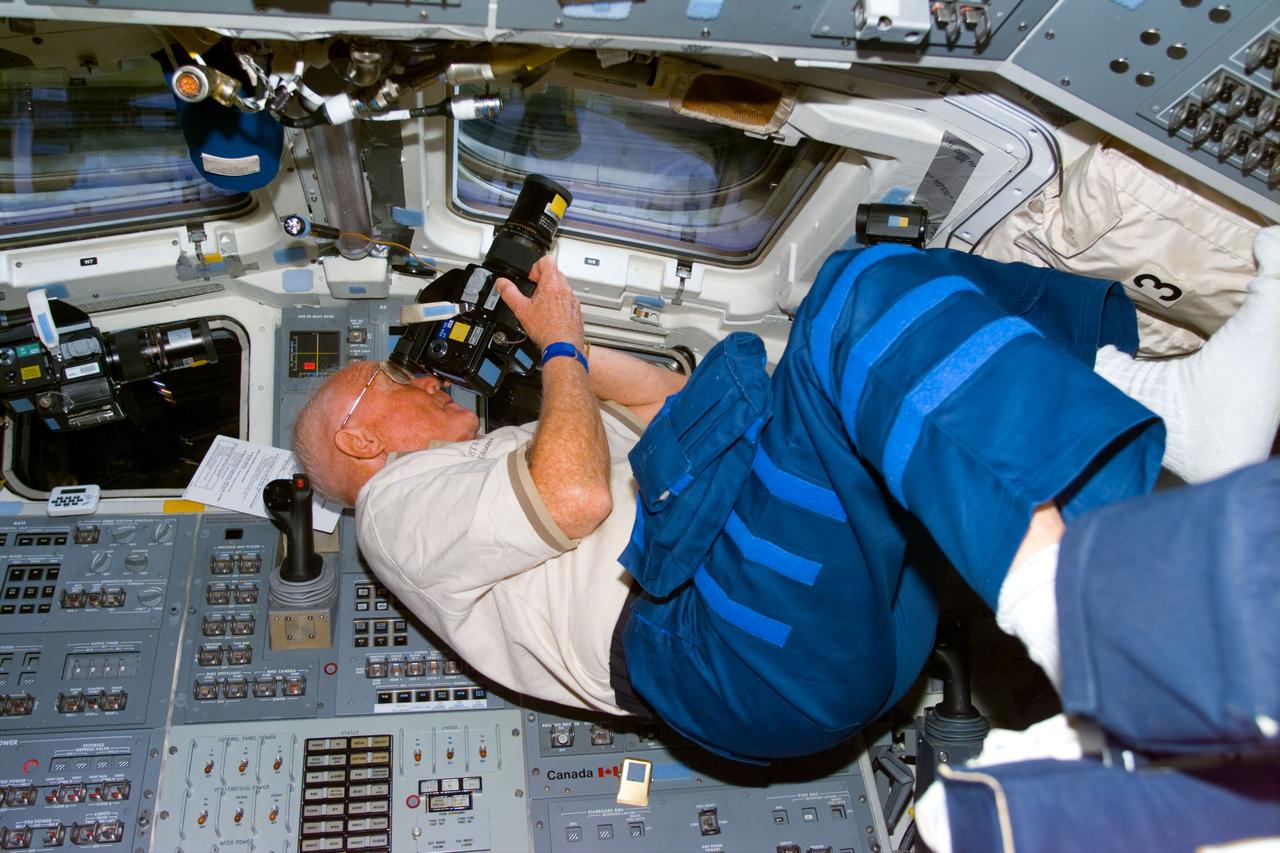

STS095-E-5190 (31 Oct. 1998) --- U.S. Sen. John H. Glenn Jr., STS-95 payload specialist, focuses in on a target of opportunity as he participates in earth observations photography. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 02:21:14 GMT, Oct. 31. Photo credit: NASA
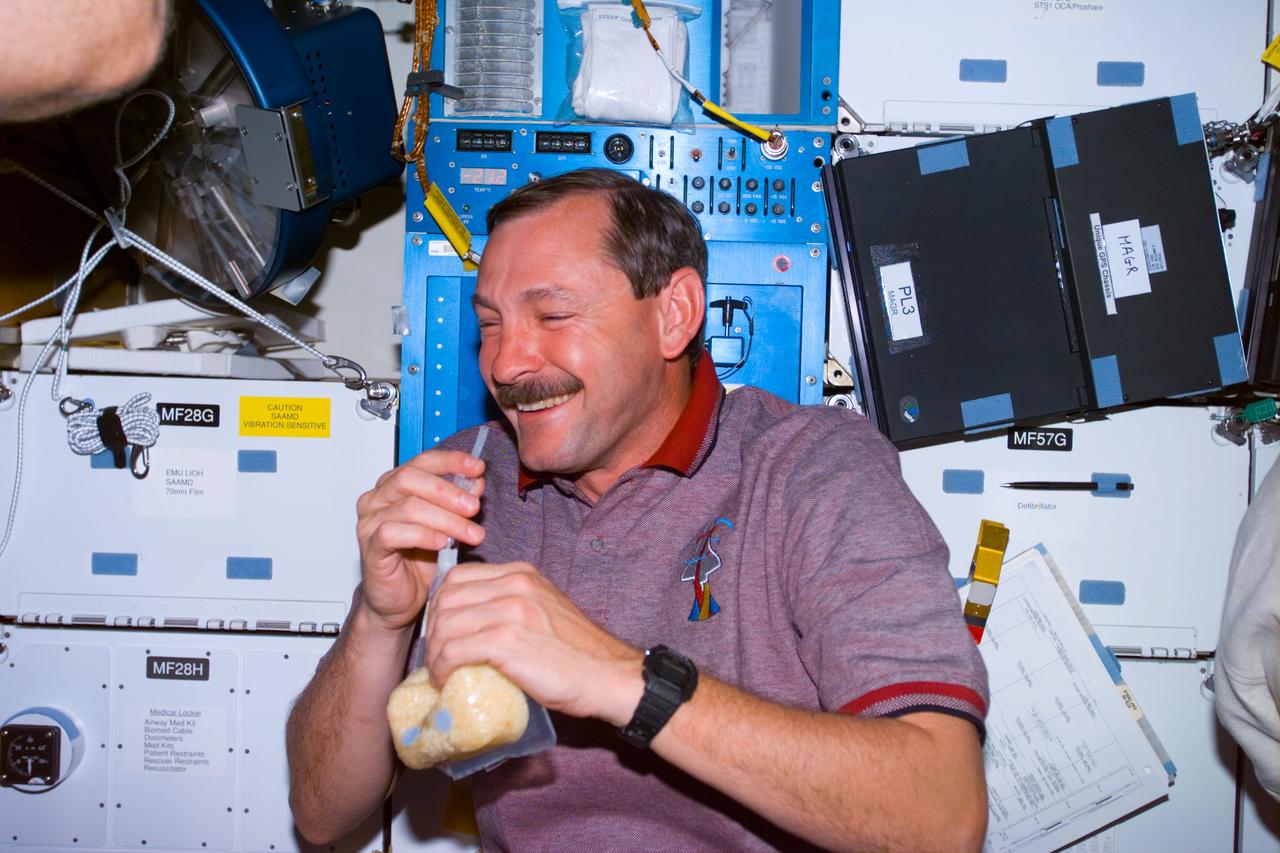

STS095-E-5125 (31 Oct. 1998) --- Astronaut Curtis L. Brown Jr., STS-95 commander, has just added water to a snack at Discovery's galley on the middeck. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 9:52:32, Oct. 31.