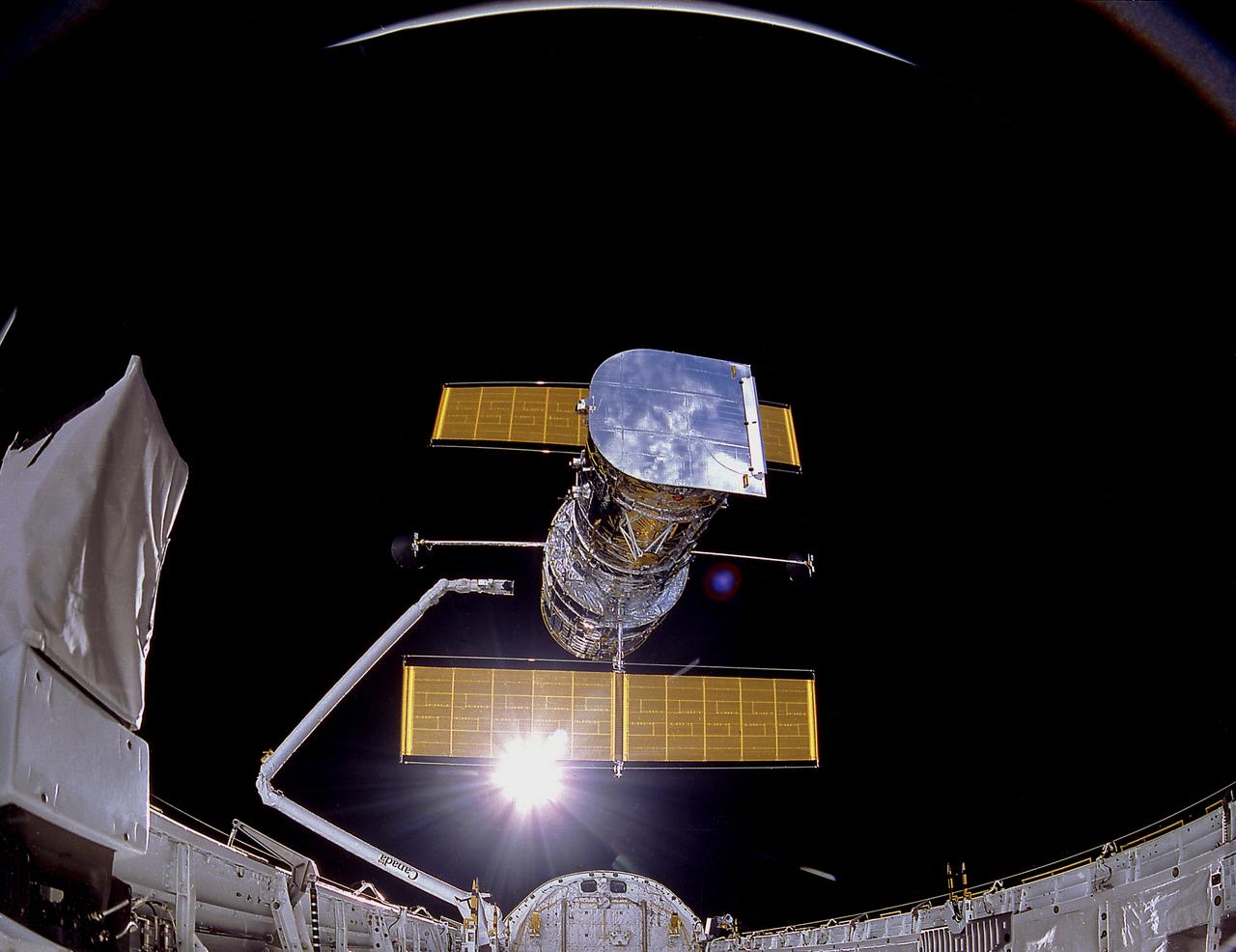

In this photograph, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was being deployed on April 25, 1990. The photograph was taken by the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC) mounted in a container on the port side of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery (STS-31 mission). The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit for 15 years or more. The HST provides fine detail imaging, produces ultraviolet images and spectra, and detects very faint objects. Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. A scheduled Space Service servicing mission (STS-61) in 1993 permitted scientists to correct the problem. During four spacewalks, new instruments were installed into the HST that had optical corrections. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. Photo Credit: NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Lockheed Corporation.
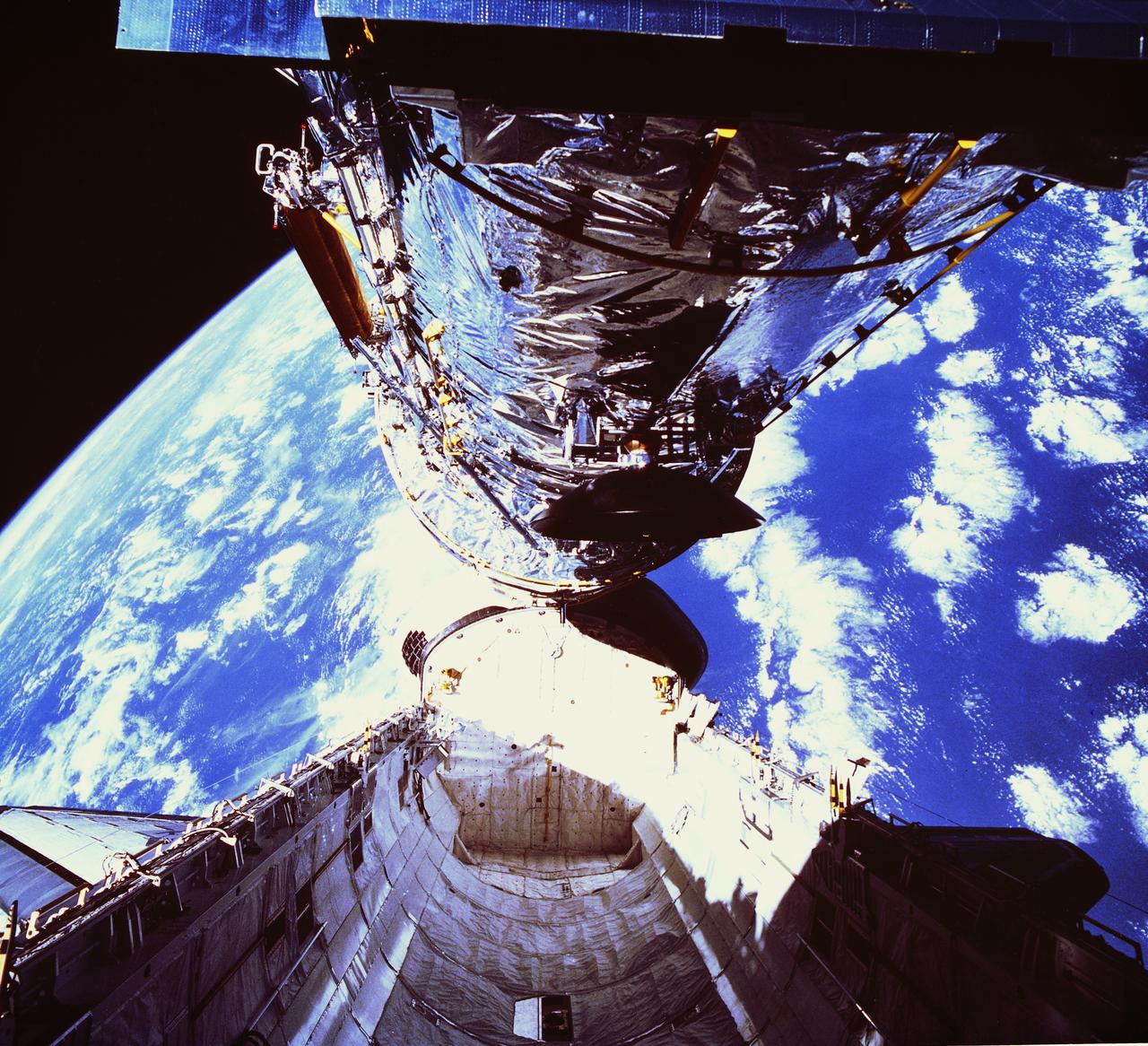

In this photograph, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is clearing the cargo bay during its deployment on April 25, 1990. The photograph was taken by the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC) mounted in a container on the port side of the Space Shuttle orbiter Discovery STS-31 mission. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit for 15 years or more. The HST provides fine detail imaging, produces ultraviolet images and spectra, and detects very faint objects. Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. A scheduled Space servicing mission (STS-61) in 1993 permitted scientists to correct the problem. During four space walks, new instruments were installed into the HST that had optical corrections. A total of four HST servicing missions have taken place since its deployment: STS-61 in December 1993, STS-82 in February 1997, STS-103 in December 1999, and STS-109 in March 2002. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
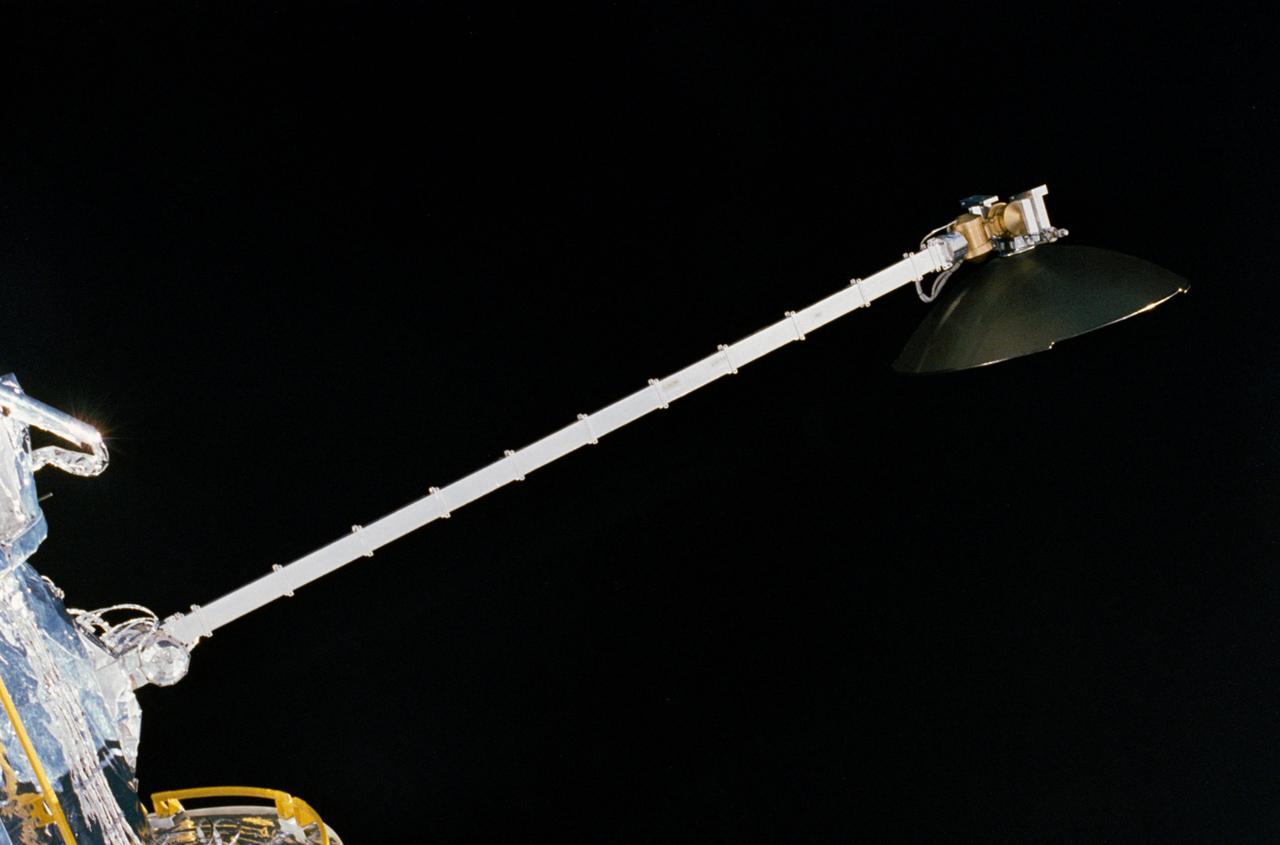

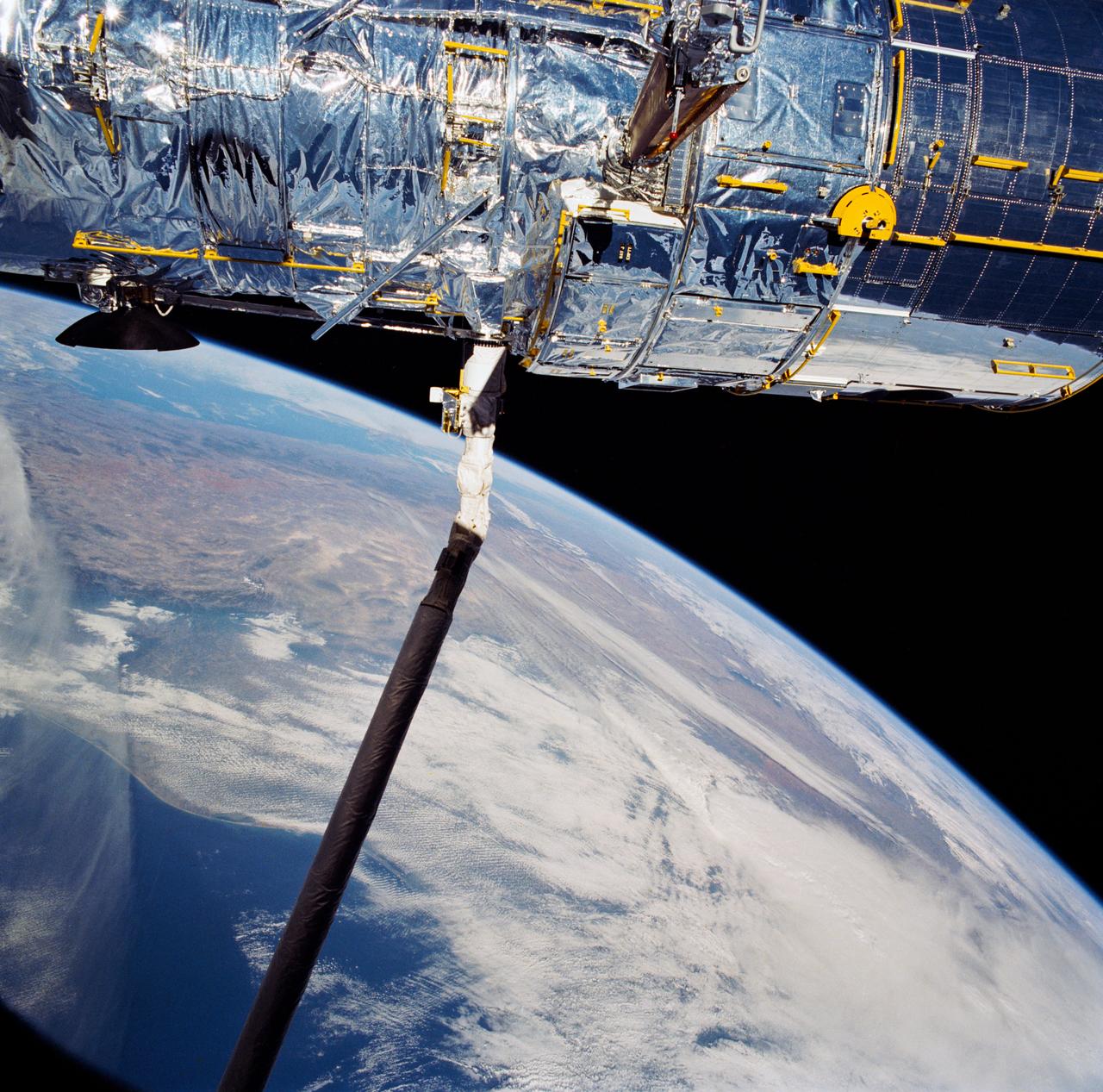
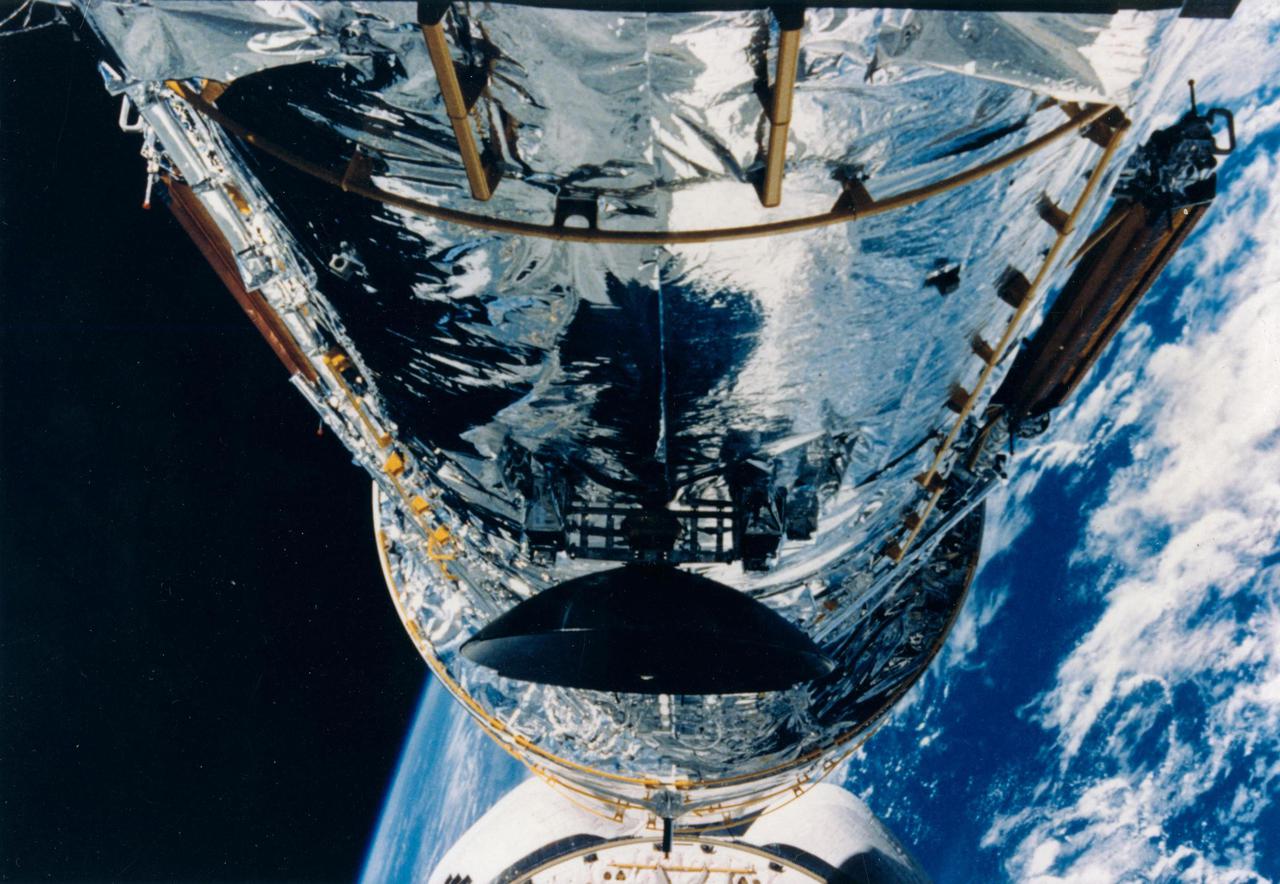
Held in appendage deploy position, the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) high gain antenna (HGA) has been released from its stowed position along the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The STS-31 crew aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) oversees the automatic HGA deployment prior to releasing HST. HST HGA is backdropped against the blackness of space.
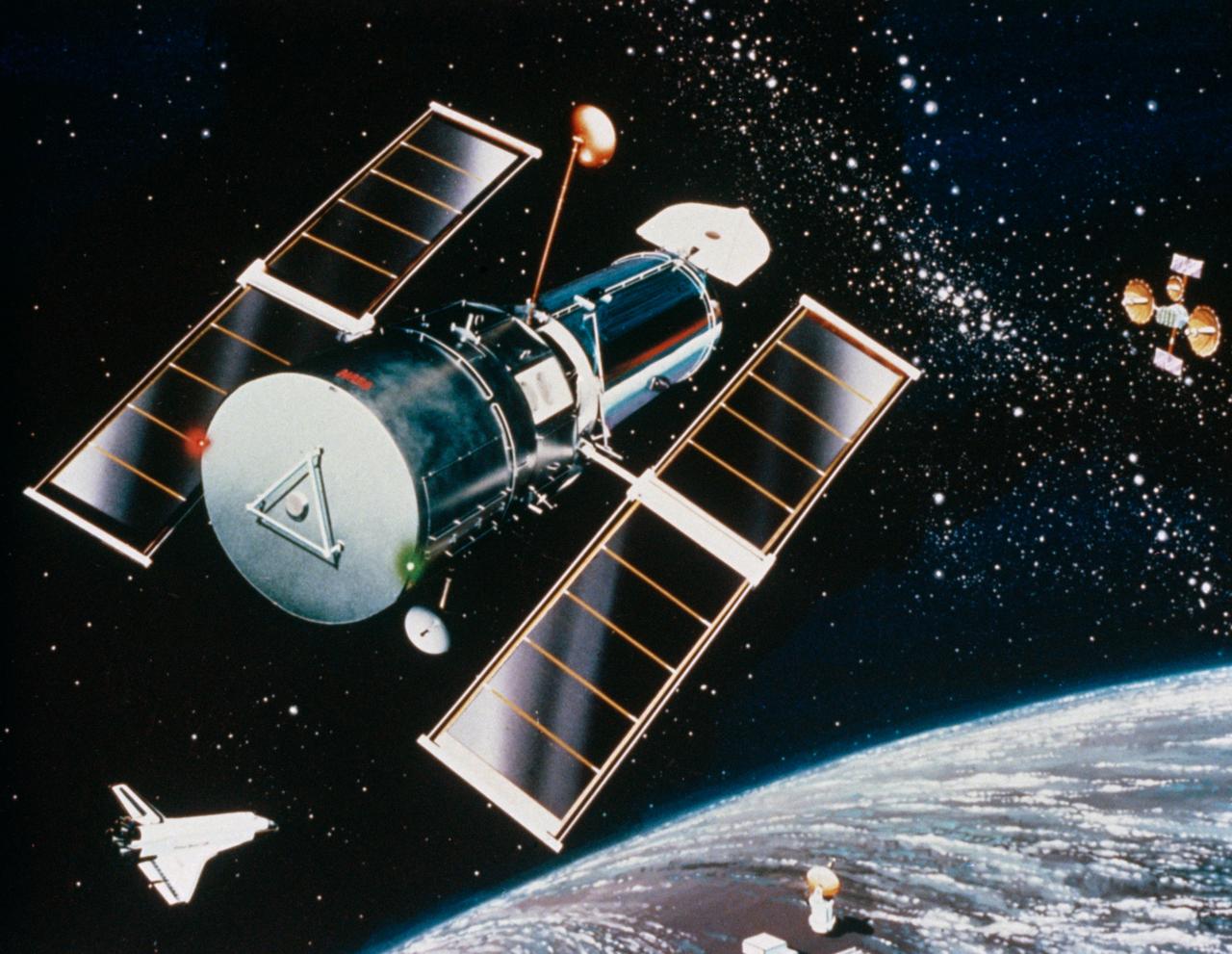

Artist concept shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) placed in orbit above the Earth's distorting layer of atmosphere by Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, during mission STS-31. Tracking and data relay satellite (TDRS) is visible in the background and ground station is visible below on the Earth's surface. HST is the first of the great observatories to go into service and one of NASA's highest priority scientific spacecraft. Capable of observing in both visible and ultraviolet wavelengths, HST has been termed the most important scientific instrument ever designed for use on orbit. It will literally be able to look back in time, observing the universe as it existed early in its lifetime and providing information on how matter has evolved over the eons. The largest scientific payload ever built, the 12 1/2-ton, 43-foot HST was developed by Lockheed Missiles & Space Company, spacecraft prime contractor, and Perkin-Elmer Corporation, prime contractor for the optical assembly. The European Space Agency (ESA) furnished the power generating solar array and one of the system's five major instruments. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) manages the HST project; Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) will be responsible, when the spacecraft is in orbit, for controlling the telescope and processing the images and instrument data returns.

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), is held in a pre-deployment position. During STS-31 checkout procedures, the solar array (SA) panels and the high gain antennae (HGA) will be deployed. The starboard SA (center) and the two HGA are stowed along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The sun highlights HST against the blackness of space.
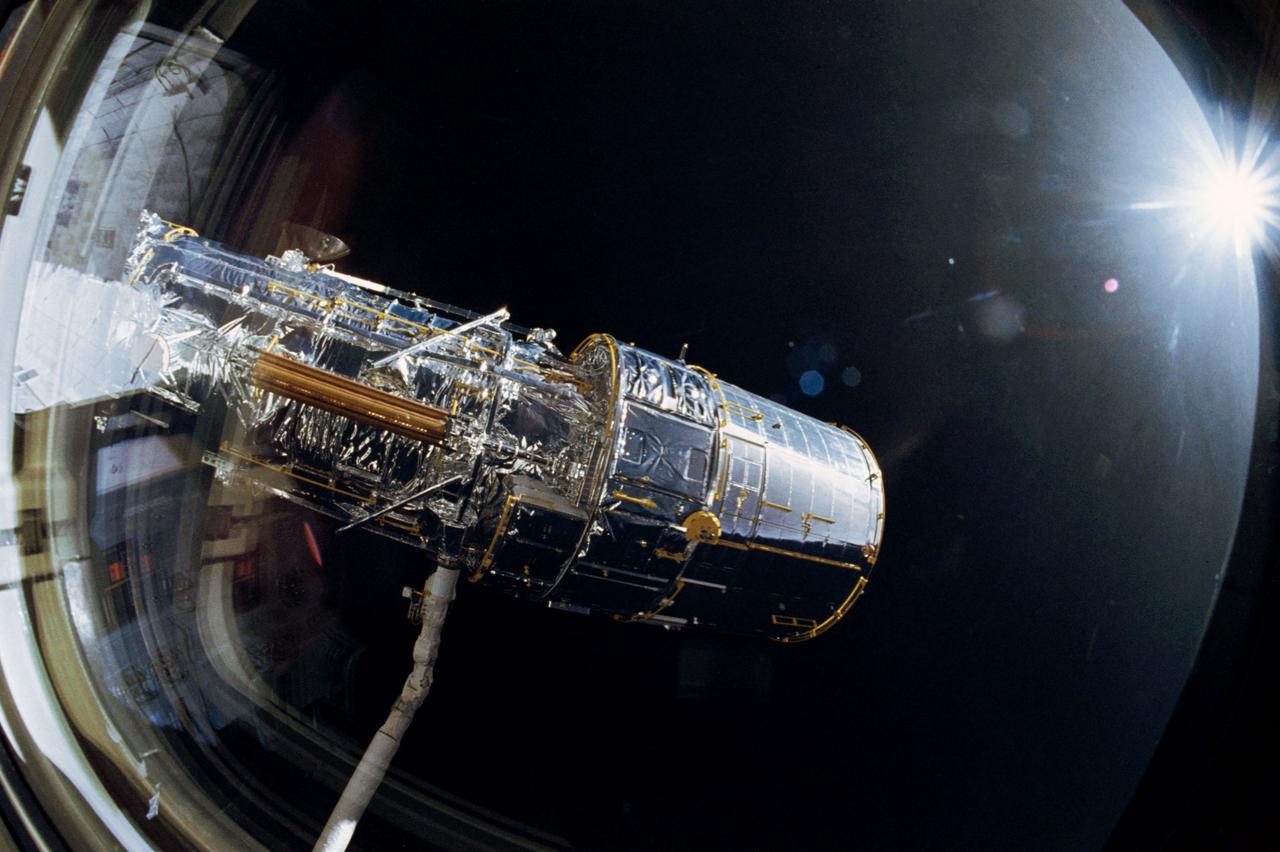
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), is oriented in a 90 degree pitch position during STS-31 pre-deployment checkout procedures. The solar array (SA) panel (center) and high gain antennae (HGA) (on either side) are stowed along the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell prior to deployment. The sun highlights HST against the blackness of space.
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is raised above the payload bay (PLB) in low hover position during STS-31 checkout and pre-deployment procedures aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Stowed along the HST Support System Module (SSM) are the high gain antenna (HGA) (center) and the two solar arrays (one either side). In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's surface.

During STS-31 checkout, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is held in a pre-deployment position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS). The view, taken from the crew cabin overhead window W7, shows the starboard solar array (SA) panel (center) and two high gain antennae (HGA) (on either side) stowed along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The sun highlights HST against the blackness of space.
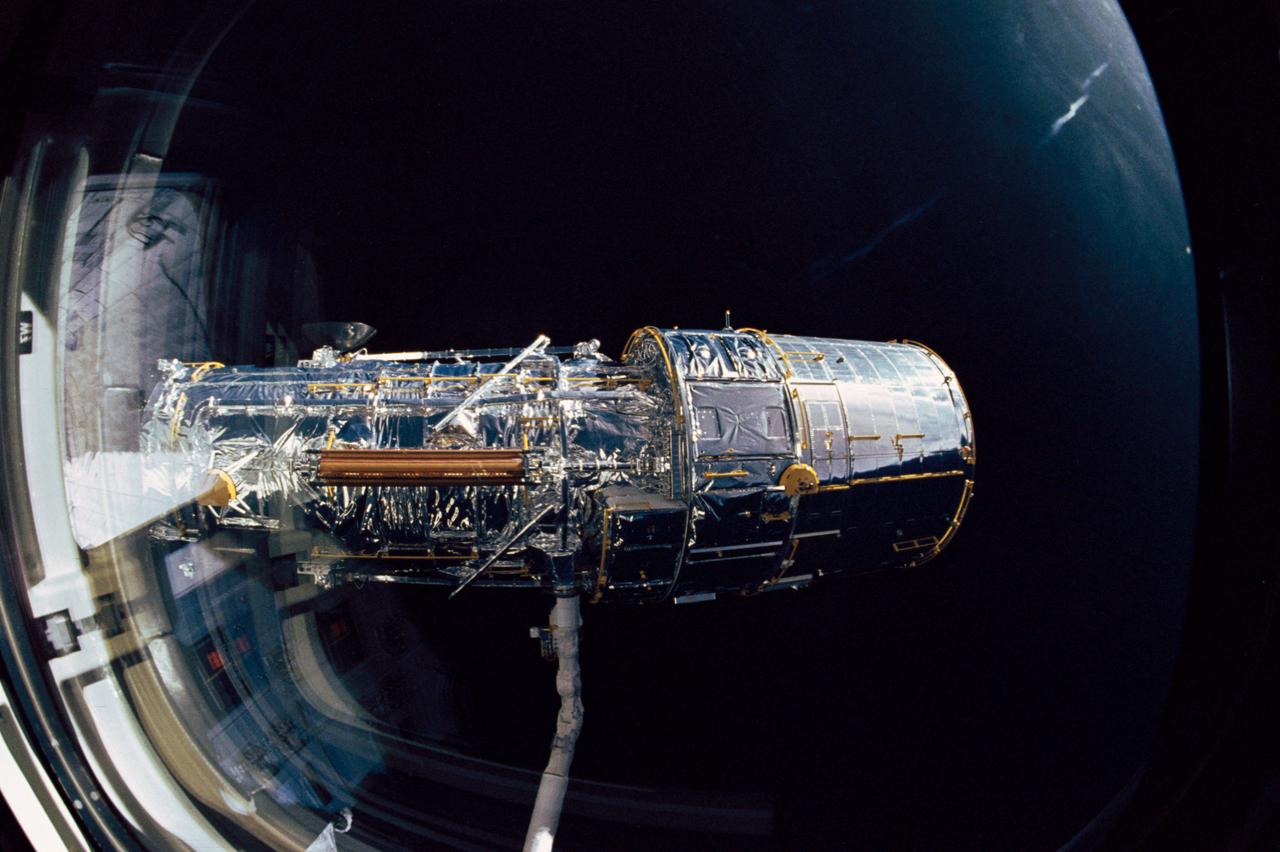
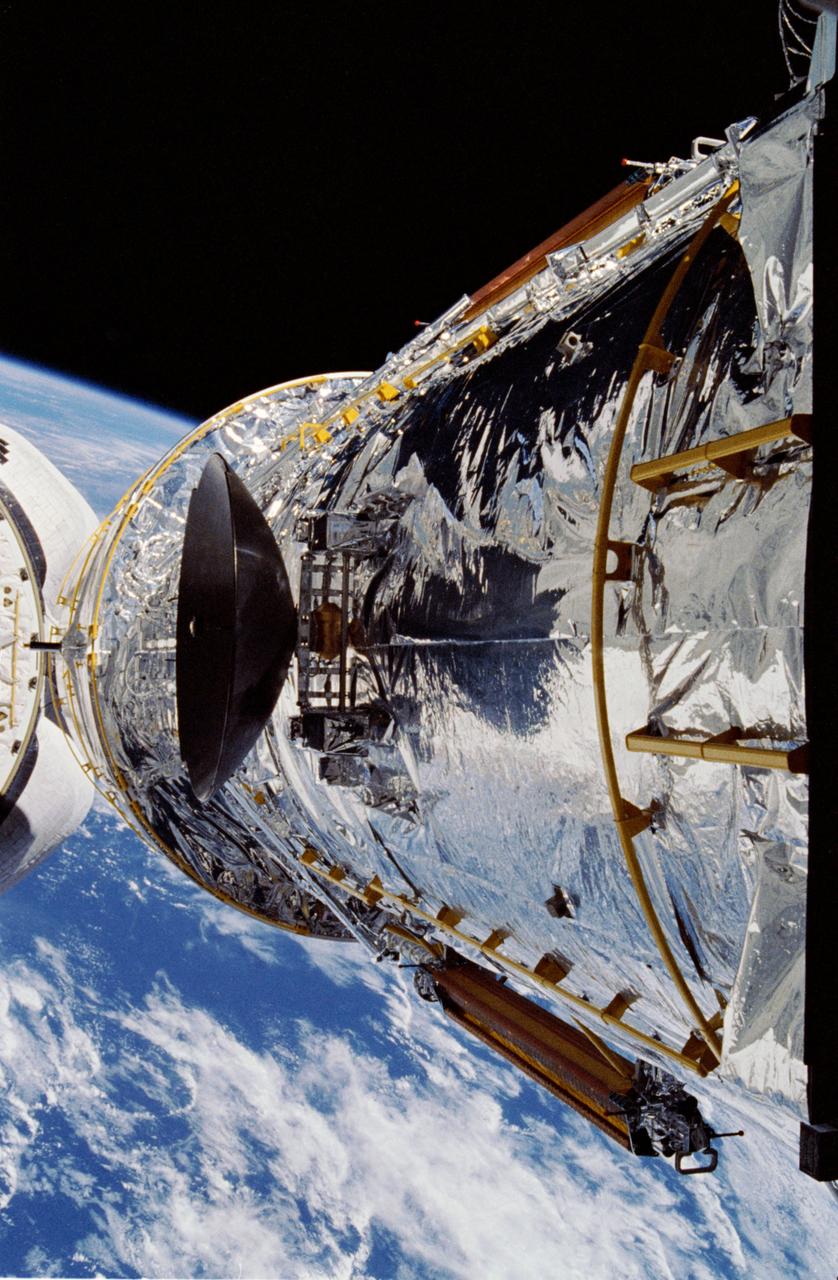
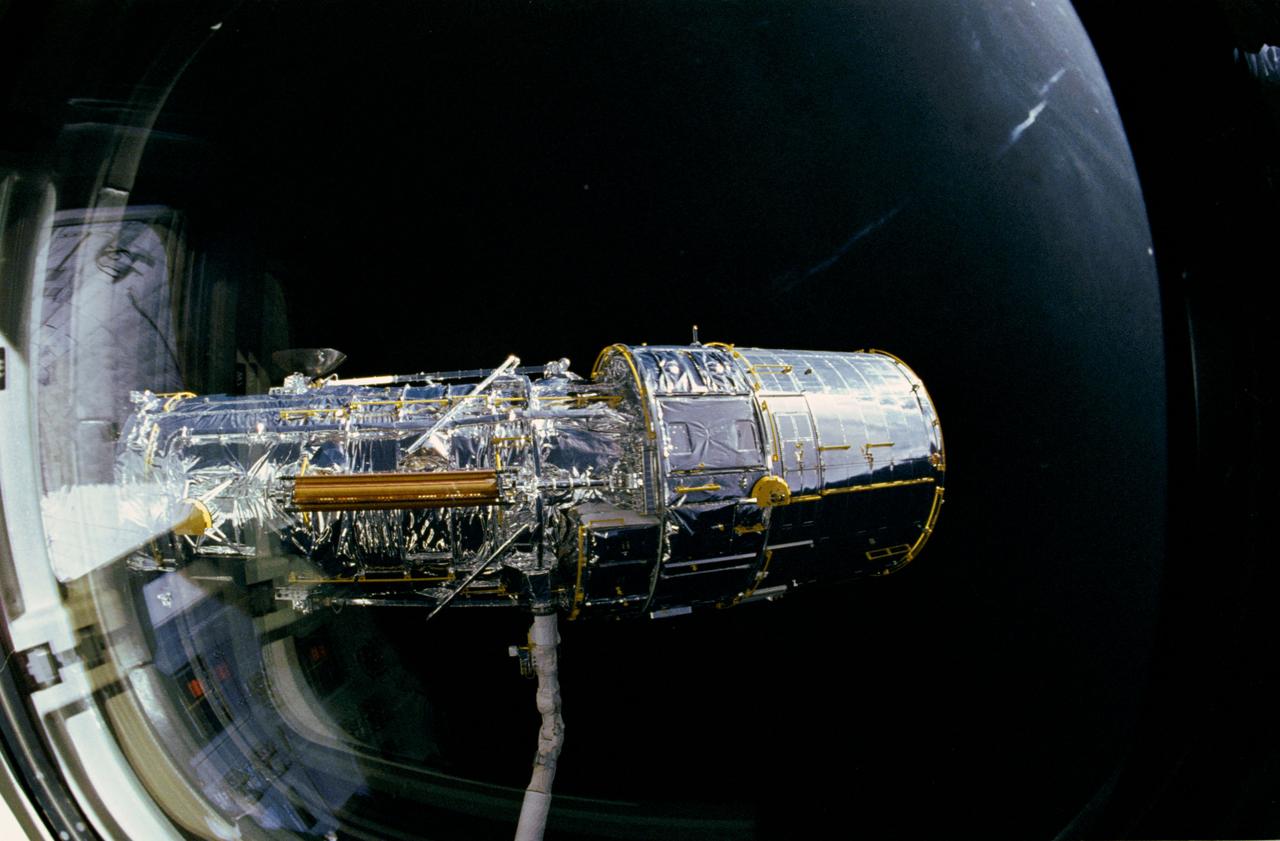
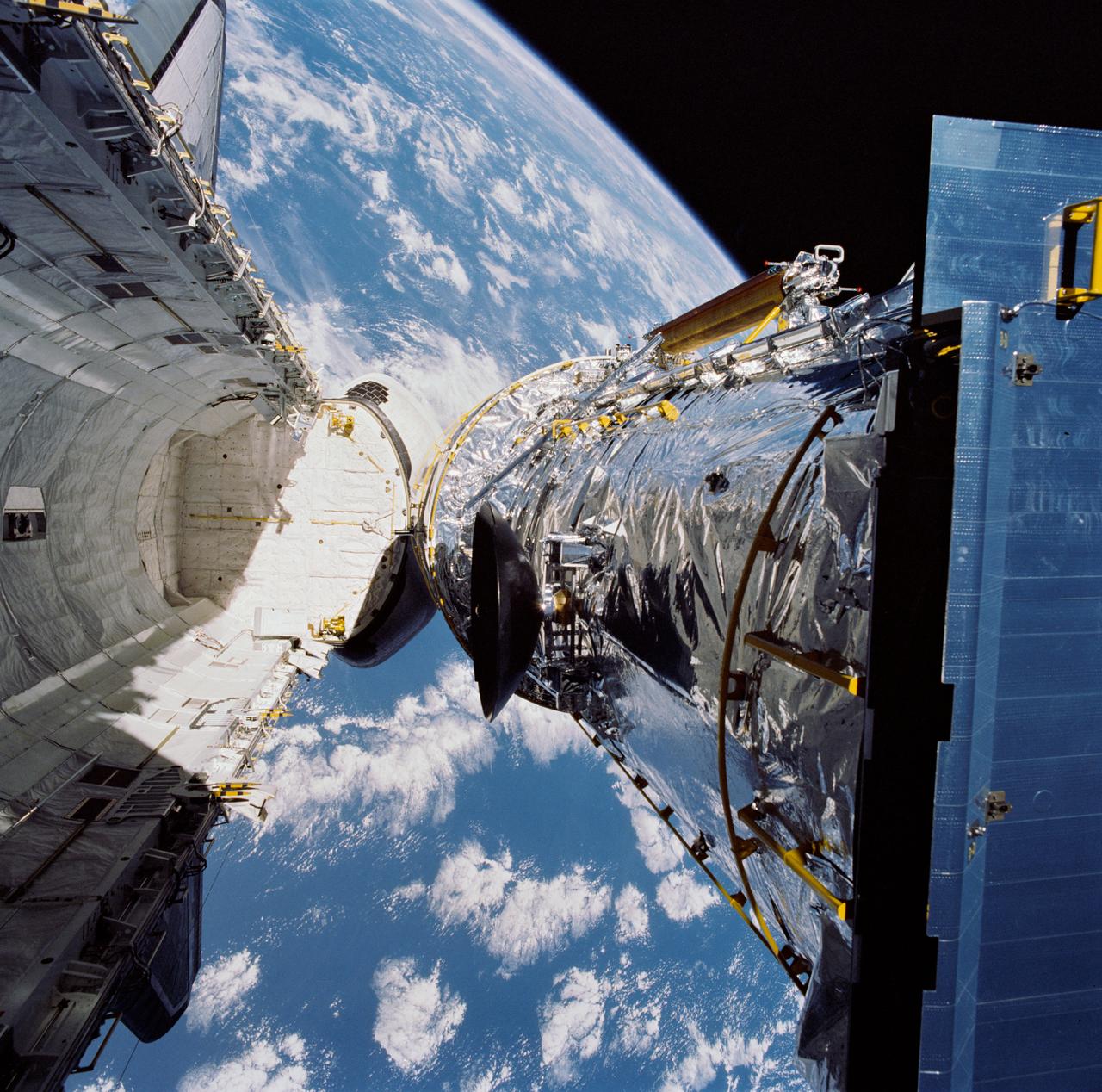
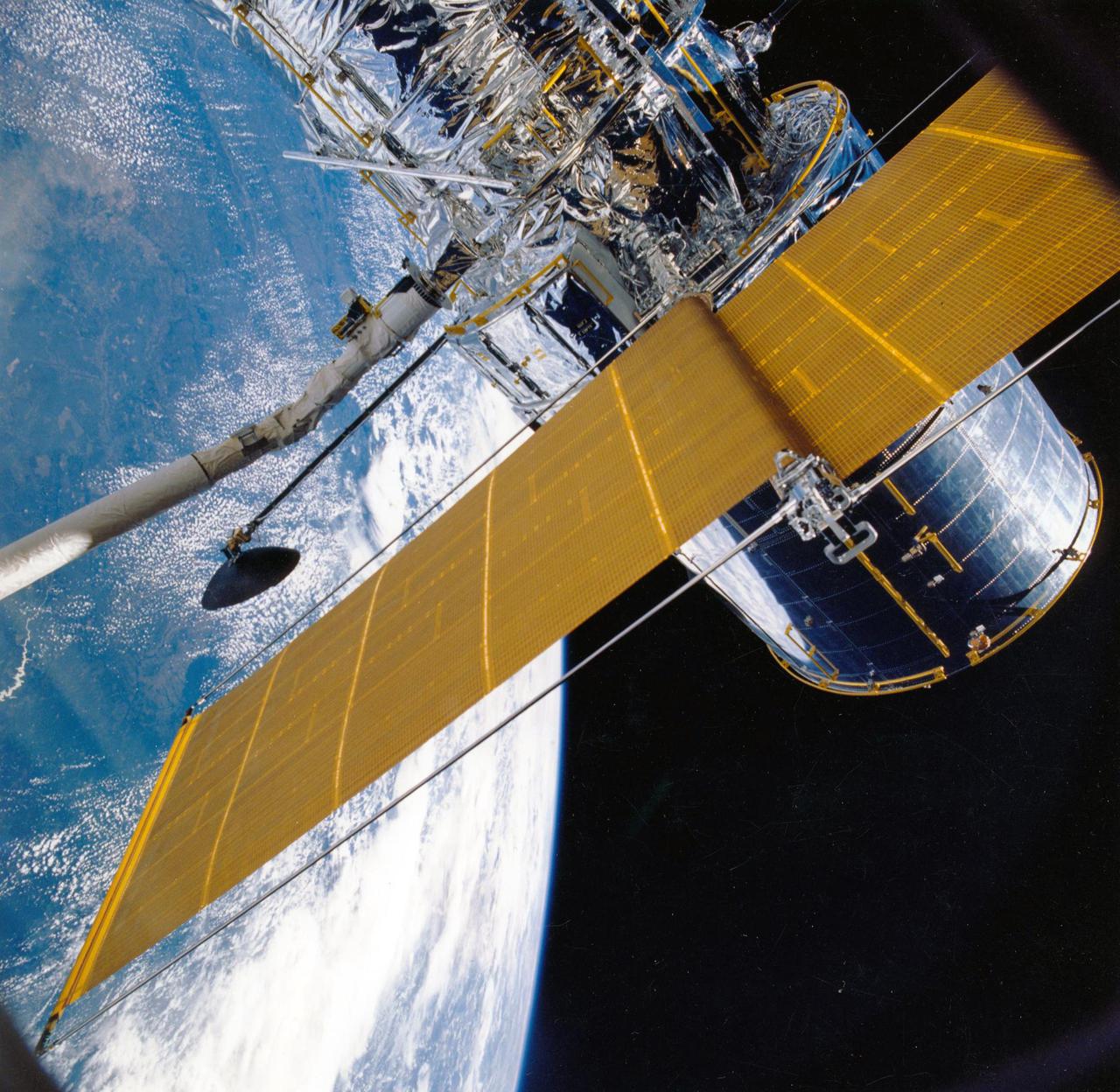
During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector, is held against the blackness of space. The two solar array (SA) wings (large gold panels) are fully extended with bistem cassette and secondary deployment mechanism (SDM) handle clearly visible. The two deployed high gain antennae (HGA) masts are parallel to the SA panels. RMS end effector is positioned on the starboard fixture during the predeployment checkout operations above Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, payload bay (PLB).

During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector is held in appendage deploy position above Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. The solar array (SA) bistem cassette has been released from its latch fittings. The bistem spreader bars begin to unfurl the SA wing. The secondary deployment mechanism (SDM) handle is visible at the SA end. Stowed against either side of the HST System Support Module (SSM) forward shell are the high-gain antennae (HGA). Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic are recognizable at the left of the frame.

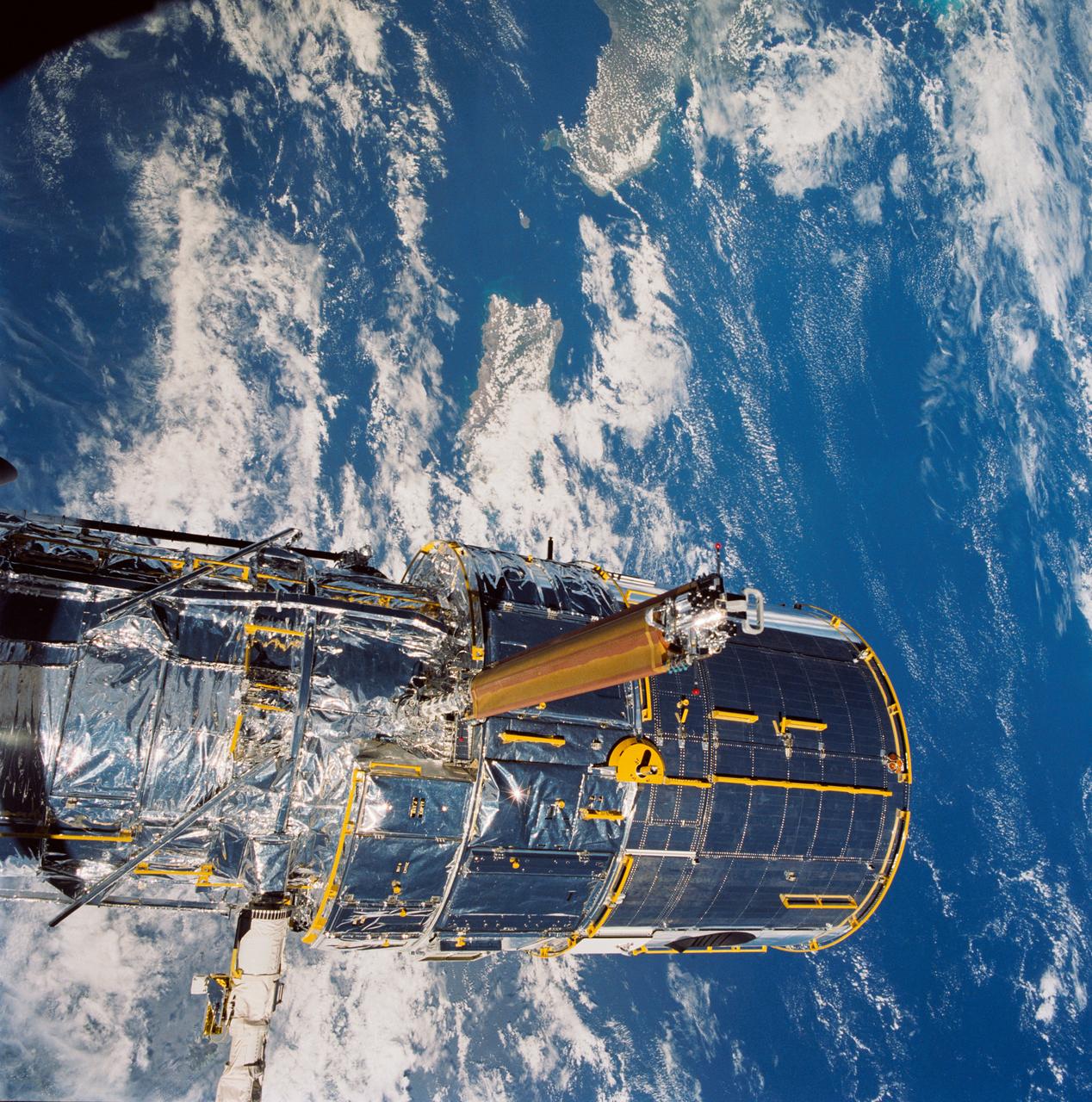
During STS-31, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is held in appendage deploy position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS) above the payload bay (PLB) and crew compartment cabin. While in this position the solar array (SA) wing bistem cassette (HST center) is deployed from its stowed location along side the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. A high gain antenna (HGA) remains stowed along the SSM. The Earth's surface and the Earth limb creates a dramatic backdrop.
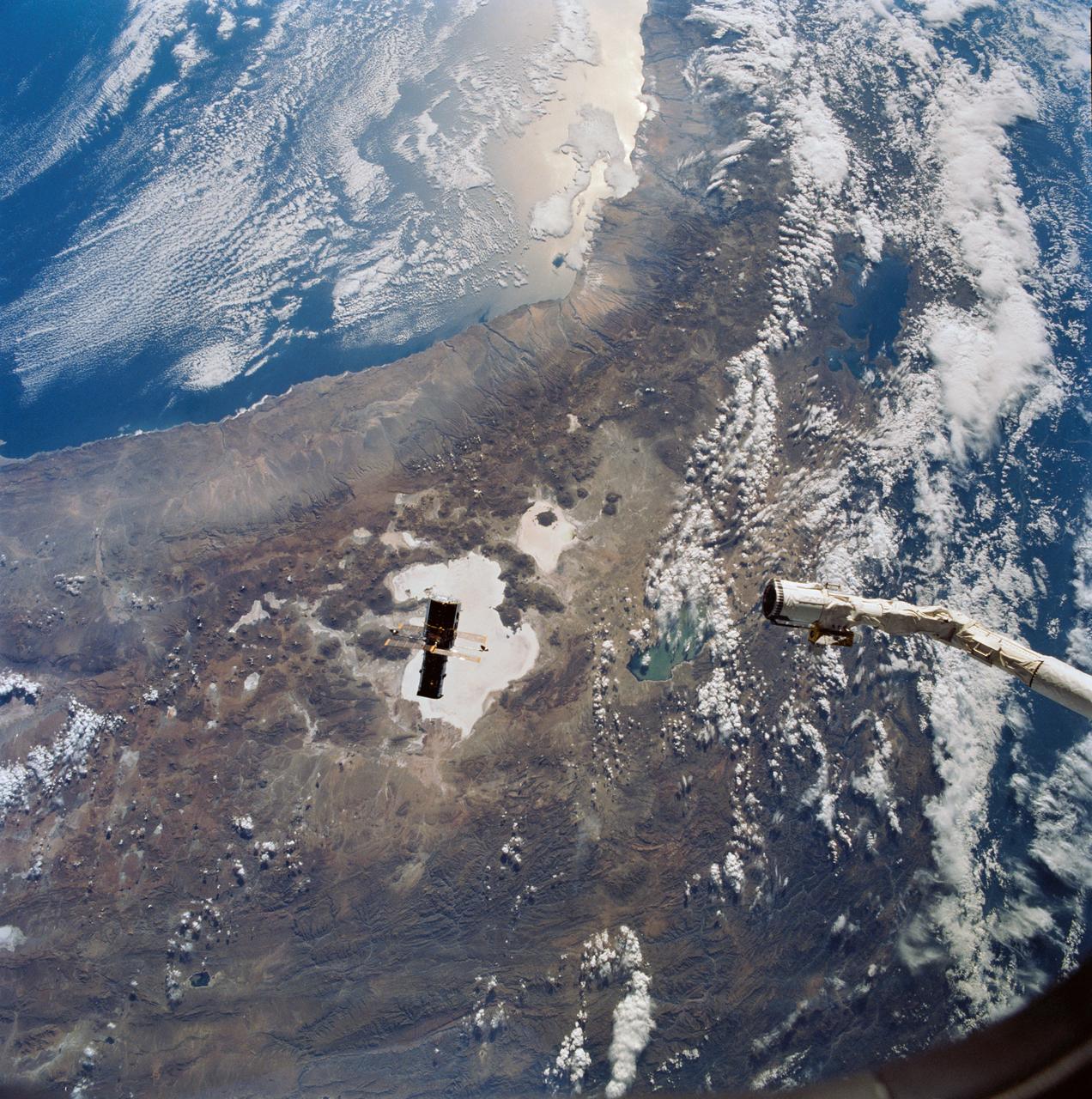

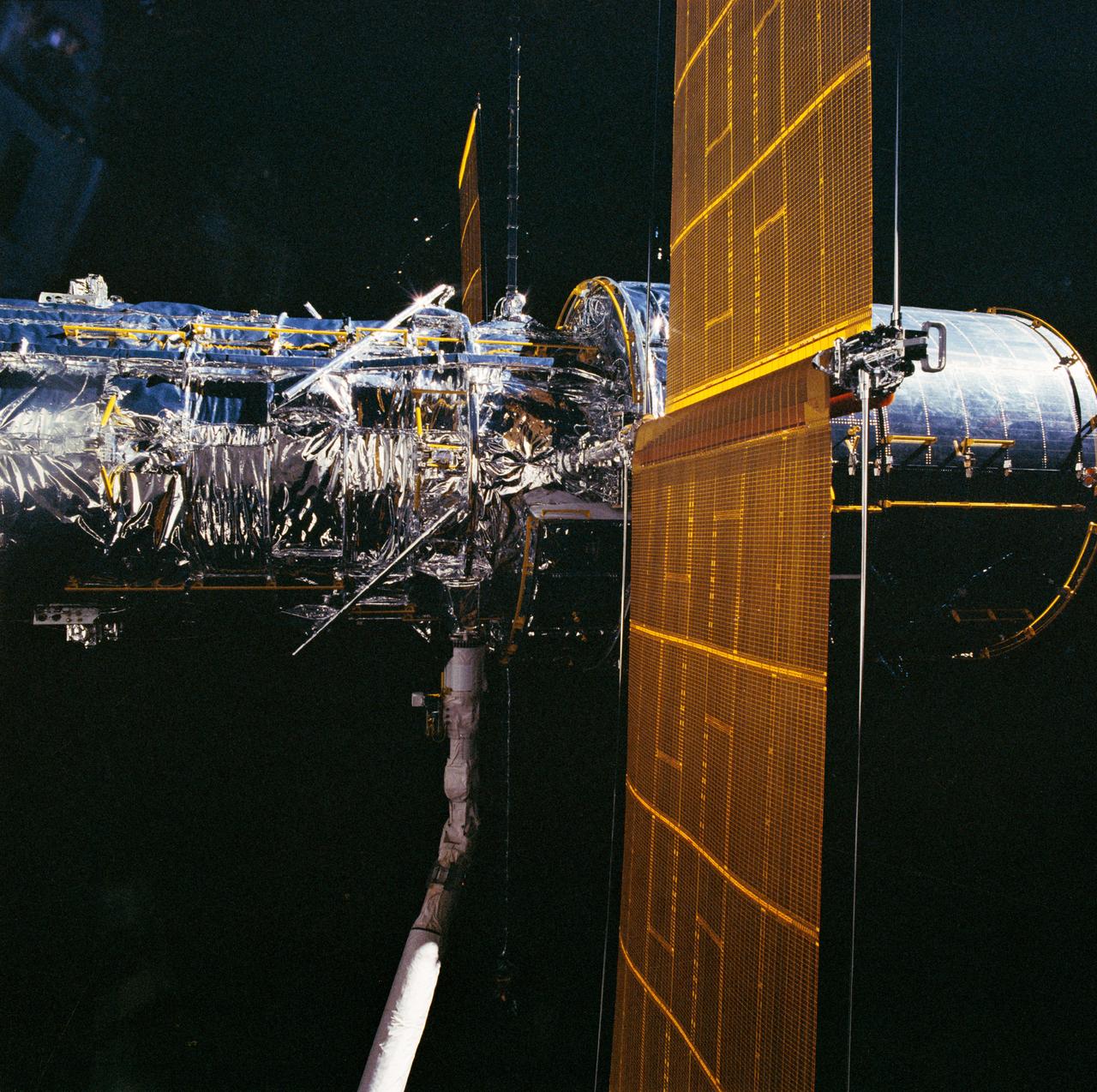
Hubble Space Telescope (HST), with its solar array (SA) wings and high gain antennae (HGA) fully extended,is released from Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector and is set free into Earth orbit by the STS-31 crew. HST drifts away from the end effector over the Andes Mountains.Parts of Bolivia, Peru, Chile, and Argentina are visible. The view covers a huge area of the western half of South America stretching from 14 degrees south latitude to 23 degrees, about 1,000 kilometers.
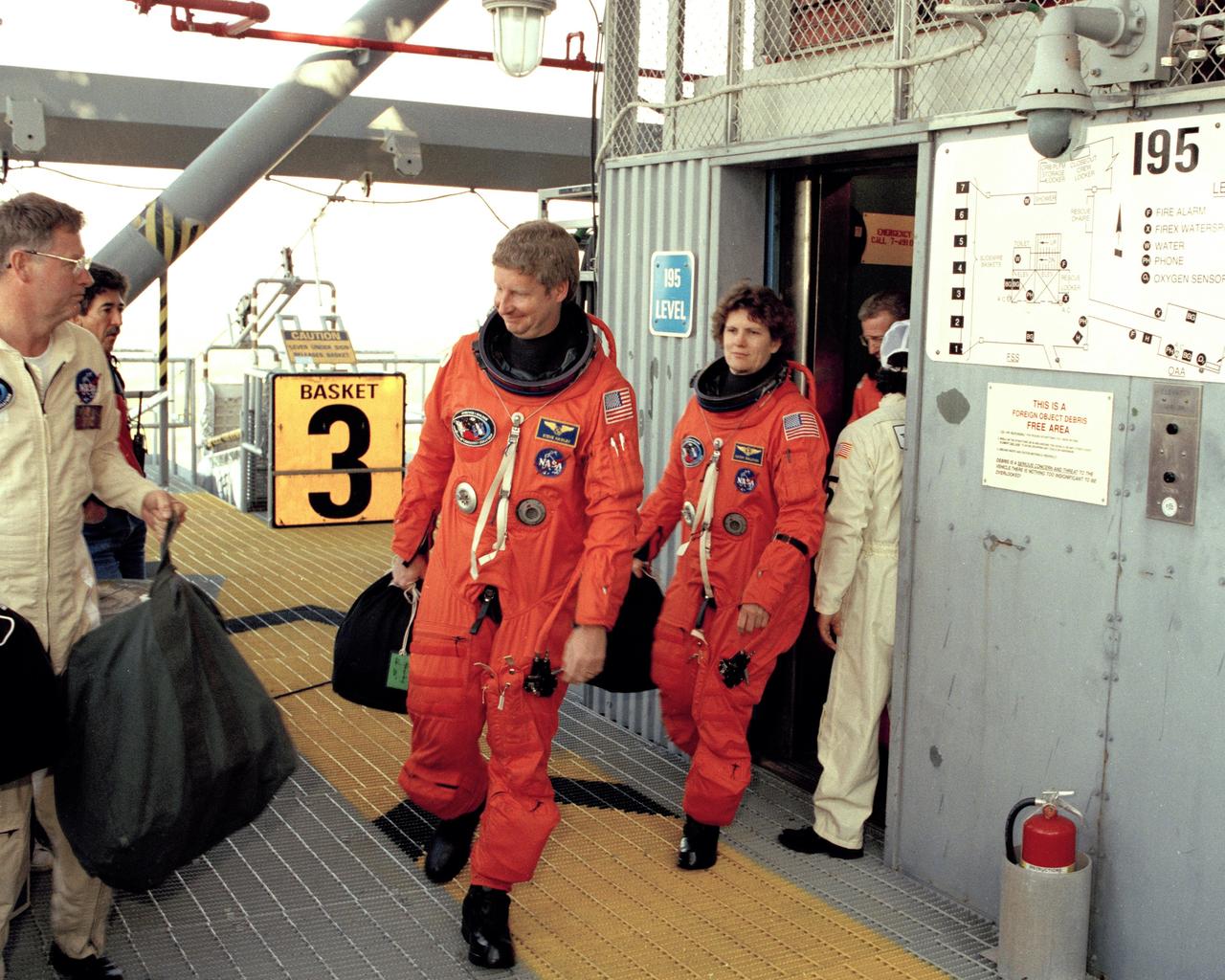

STS-31 Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley (left) and Kathryn D. Sullivan, and Commander Loren J. Shriver prepare to enter the orbiter Discovery from the 195-foot level at Launch Pad 39B during the culmination of the two-day Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT, conducted March 19-20, is a dress rehearsal for launch, simulating final countdown from the T-24 hour mark up to T-5 seconds. Space shuttle mission STS-31 is set to lift off on April 12, carrying a five-member crew and the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo credit: NASA
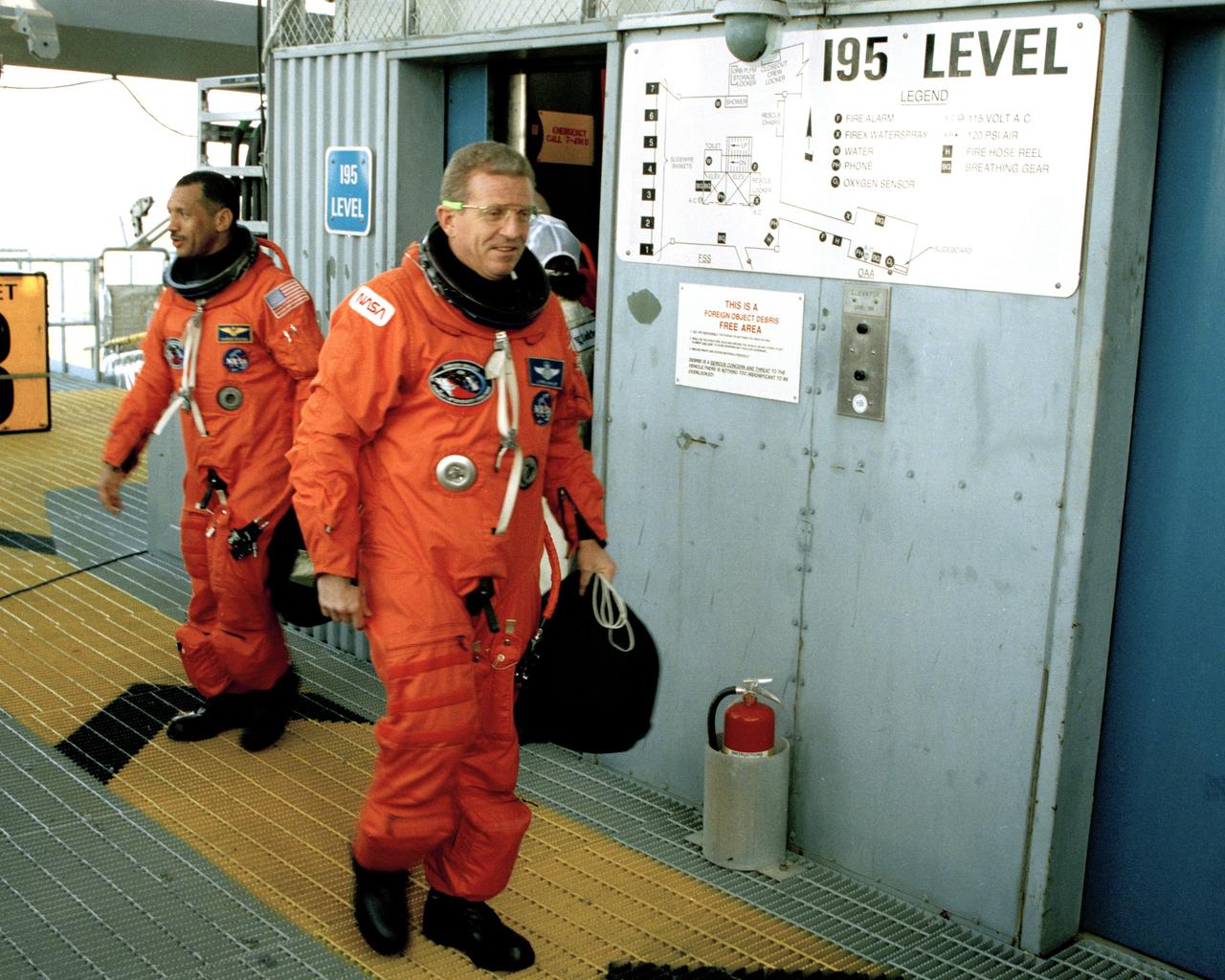

STS-31 Pilot Charles F. Bolden, left, and Commander Loren J. Shriver prepare to enter the orbiter Discovery from the 195-foot level at Launch Pad 39B during the culmination of the two-day Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT). The TCDT, conducted March 19-20, is a dress rehearsal for launch, simulating final countdown from the T-24 hour mark up to T-5 seconds. Space shuttle mission STS-31 is set to lift off on April 12, carrying a five-member crew and the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo credit: NASA
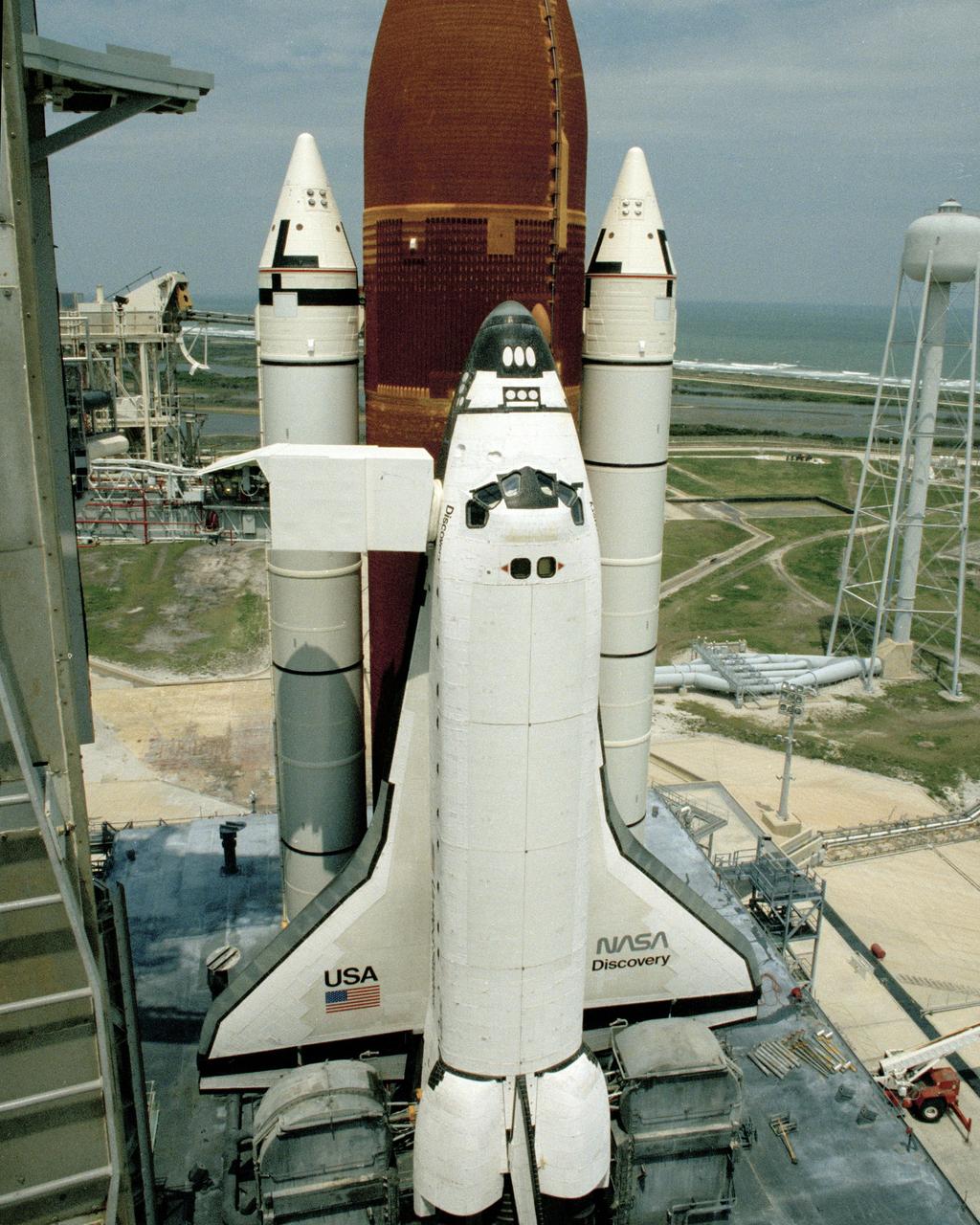

The orbiter Discovery is unveiled as rollback of the Rotating Service Structure begins during final prelaunch preparations at Launch Pad 39B on April 9. Space shuttle mission STS-31, carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope, is set to lift off at 6:47 a.m. EDT, April 10. Photo credit: NASA
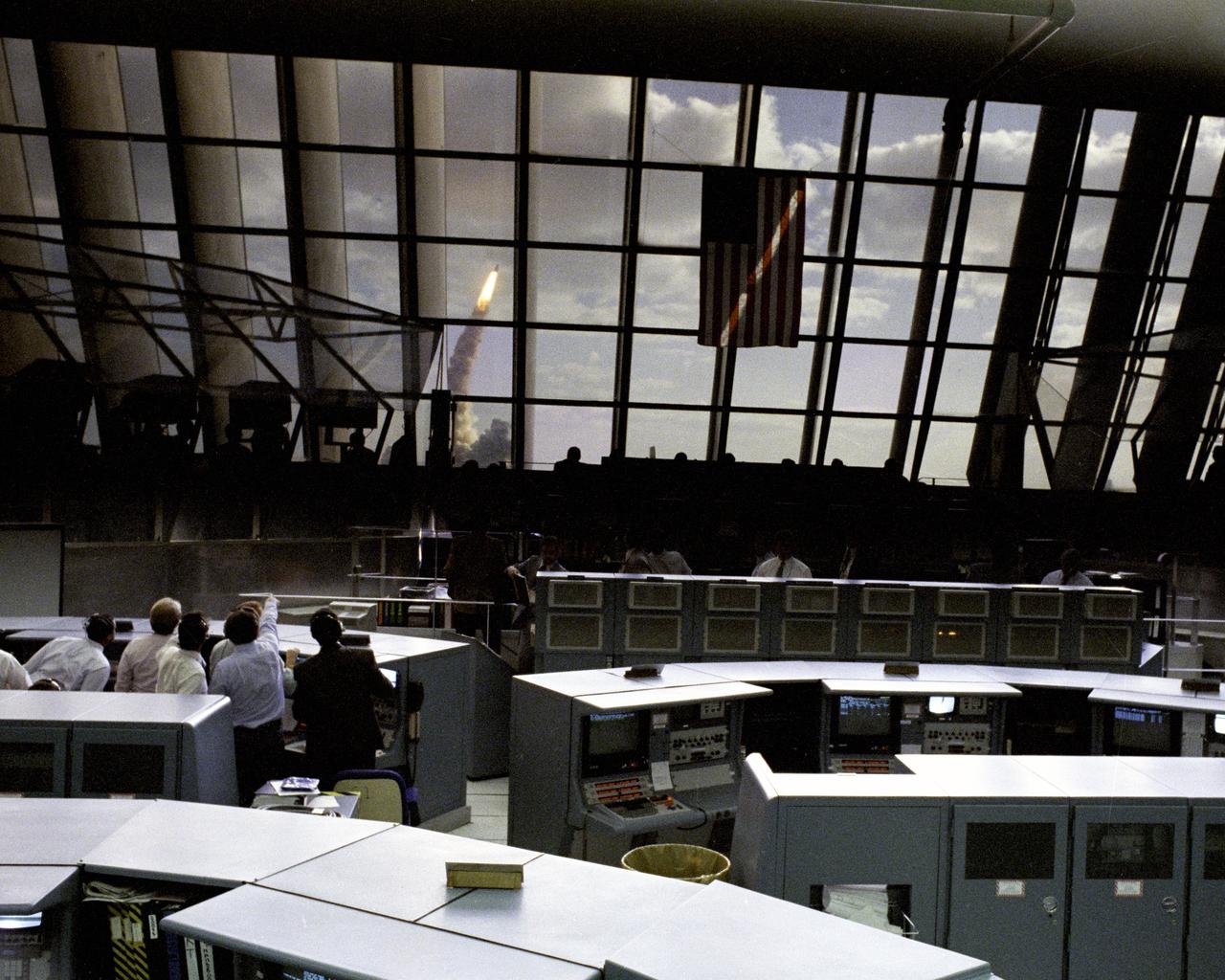

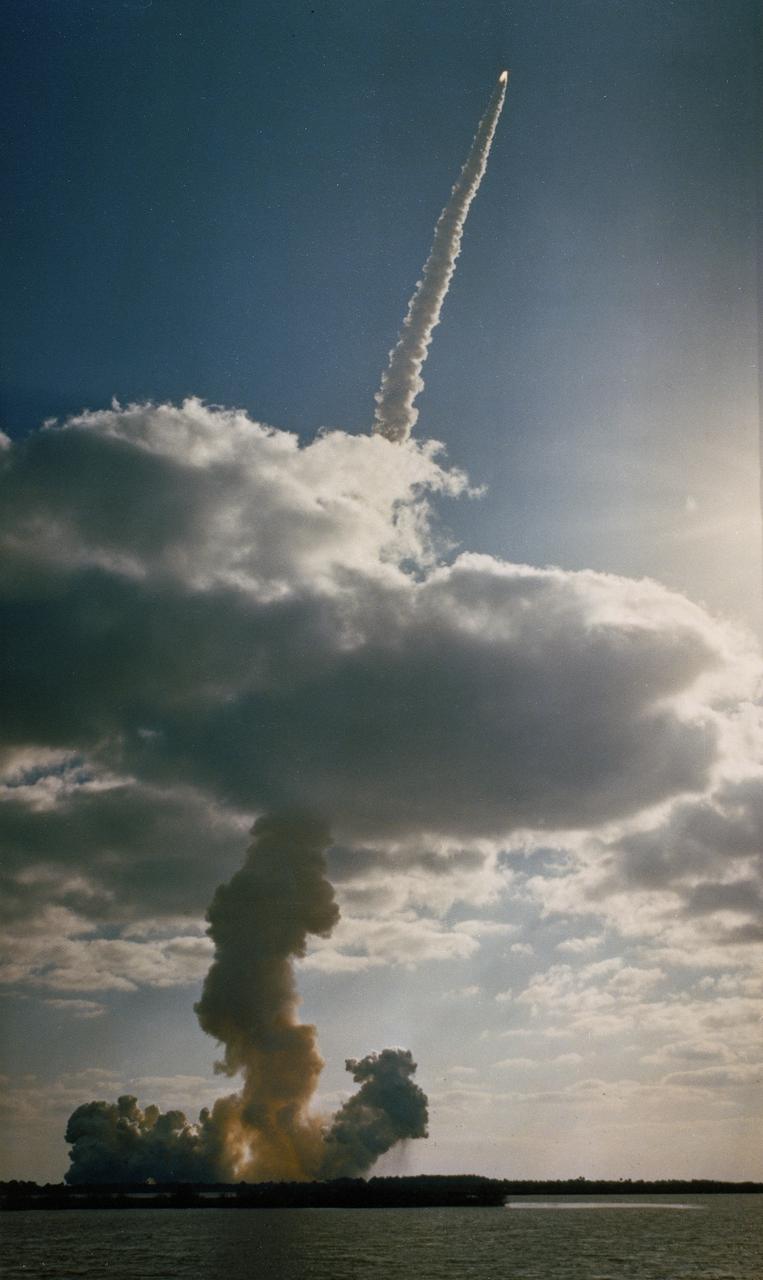
Through the large window panes of Firing Room 1, KSC launch team members reap the rewards of their work with a glimpse of the space shuttle Discovery soaring into the sky. Discovery was launched for the tenth time at 8:34 a.m. EDT on April 24 beginning the five-day STS-31 mission to deploy the Hubble Space Telescope. A ray of morning sunlight highlights the red and white stripes of Old Glory hanging high in the Firing Room. Launch team members overcame a last minute challenge in the STS-31 countdown when software detected a main propulsion system valve was out of position. The situation was quickly corrected and verified by the team from consoles in the Firing Room and the countdown was returned in a matter of minutes. Photo credit: NASA

The space shuttle Discovery lifts off from Launch Pad 39-B at 8:33 a.m. EDT carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope. STS-31 crew members are Commander Loren Shriver, Pilot Charles Bolden and Mission Specialists Steven Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn Sullivan. Photo credit: NASA
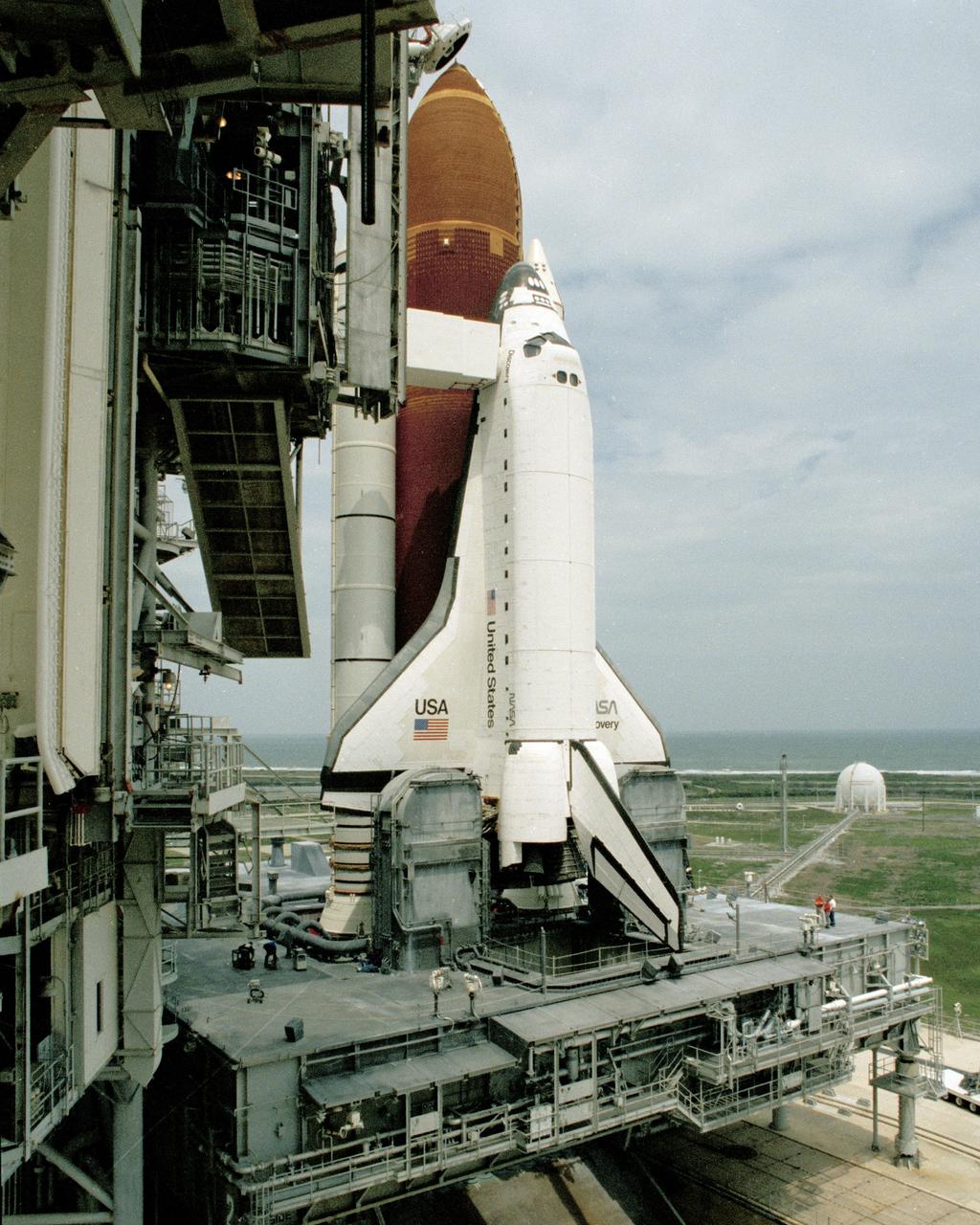

The orbiter Discovery is unveiled as rollback of the Rotating Service Structure begins during final prelaunch preparations at Launch Pad 39B on April 9. Space shuttle mission STS-31, carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope, is set to lift off at 6:47 a.m. EDT, April 10. Photo credit: NASA
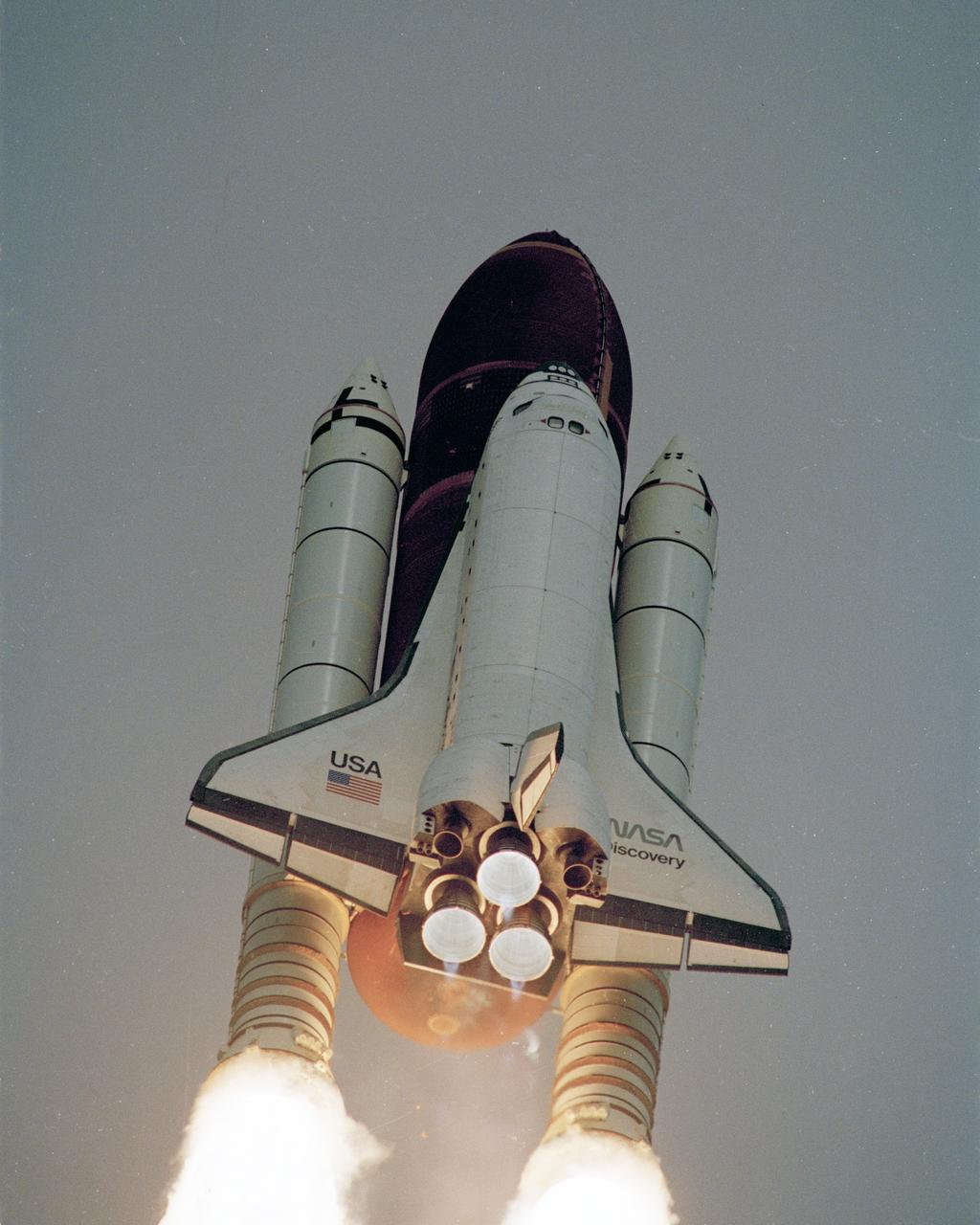

The space shuttle Discovery lifts off from Launch Pad 39-B at 8:33 a.m. EDT carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope. STS-31 crew members are Commander Loren Shriver, Pilot Charles Bolden and Mission Specialists Steven Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn Sullivan. Photo credit: NASA
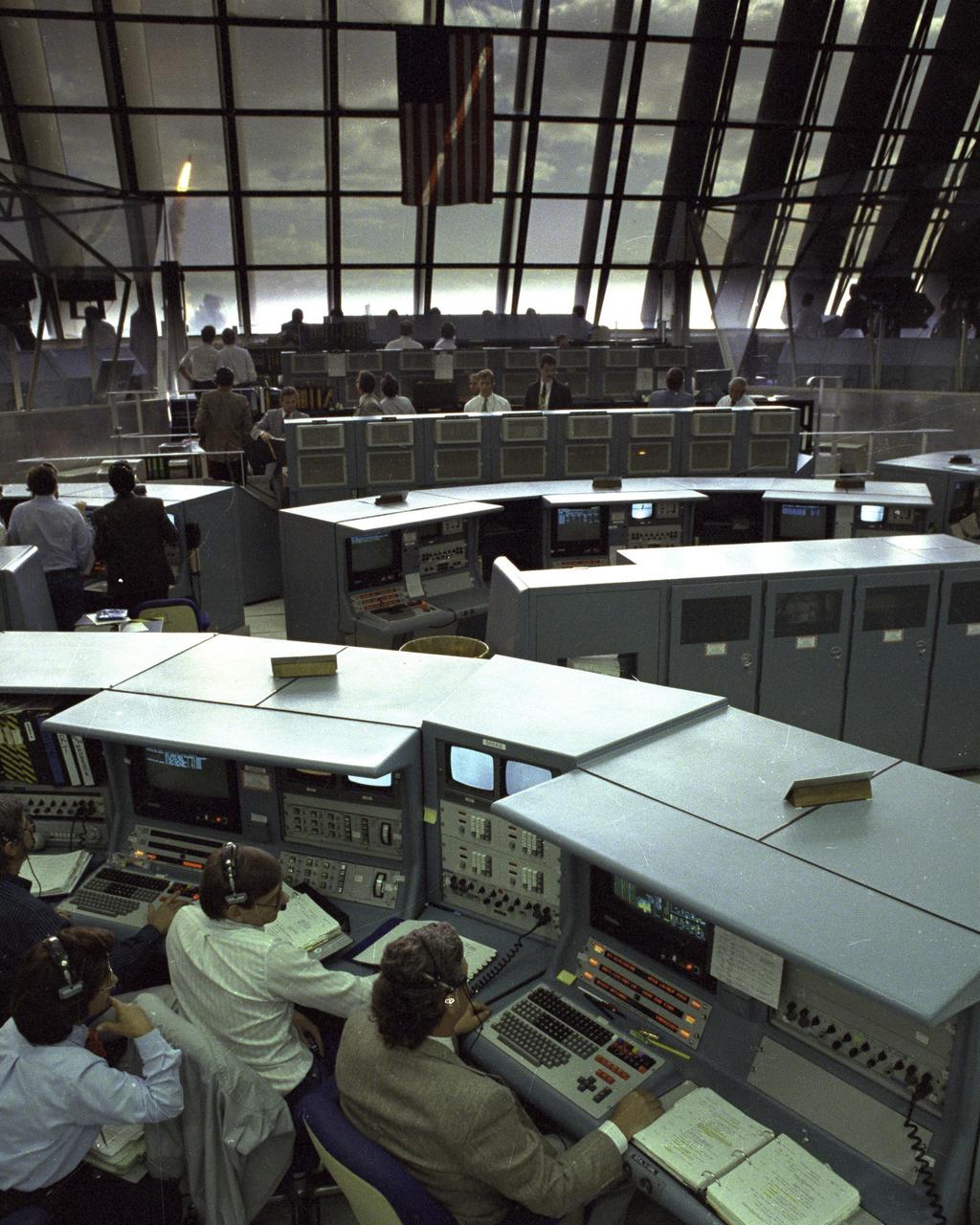

Through the large window panes of Firing Room 1, KSC launch team members reap the rewards of their work with a glimpse of the space shuttle Discovery soaring into the sky. Discovery was launched for the tenth time at 8:34 a.m. EDT on April 24 beginning the five-day STS-31 mission to deploy the Hubble Space Telescope. A ray of morning sunlight highlights the red and white stripes of Old Glory hanging high in the Firing Room. Launch team members overcame a last minute challenge in the STS-31 countdown when software detected a main propulsion system valve was out of position. The situation was quickly corrected and verified by the team from consoles in the Firing Room and the countdown was returned in a matter of minutes. Photo credit: NASA
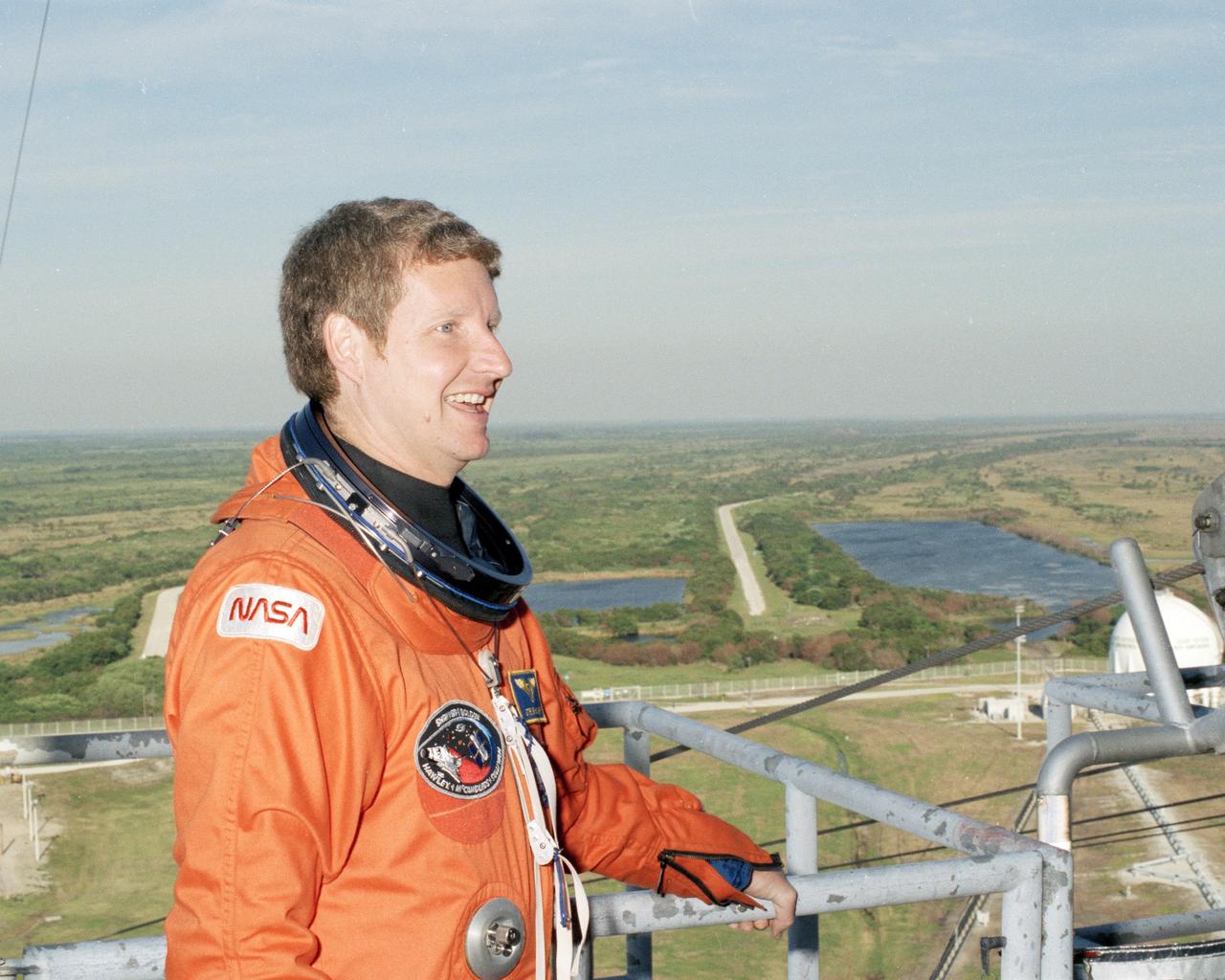

Wide-open Florida terrain creates a dramatic backas STS-31 Mission Specialist Steven A. Hawley stands near the emergency exit system at the 194-foot level of Launch Pad 39B during the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test, or TCDT. Conducted March 19-20, the TCDT is a dress rehearsal for launch, simulating final countdown from the T-24 hour mark up to T-5 seconds. Space shuttle mission STS-31 is set to lift off on April 12, carrying a five-member crew and the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo credit: NASA

Discovery was rolled out to Launch Pad 39-B on March 15-16 for final launch preparations for its 10th mission into space. Launch of the Hubble Space Telescope on the five-day STS-31 mission is targeted for April 12. Photo credit: NASA
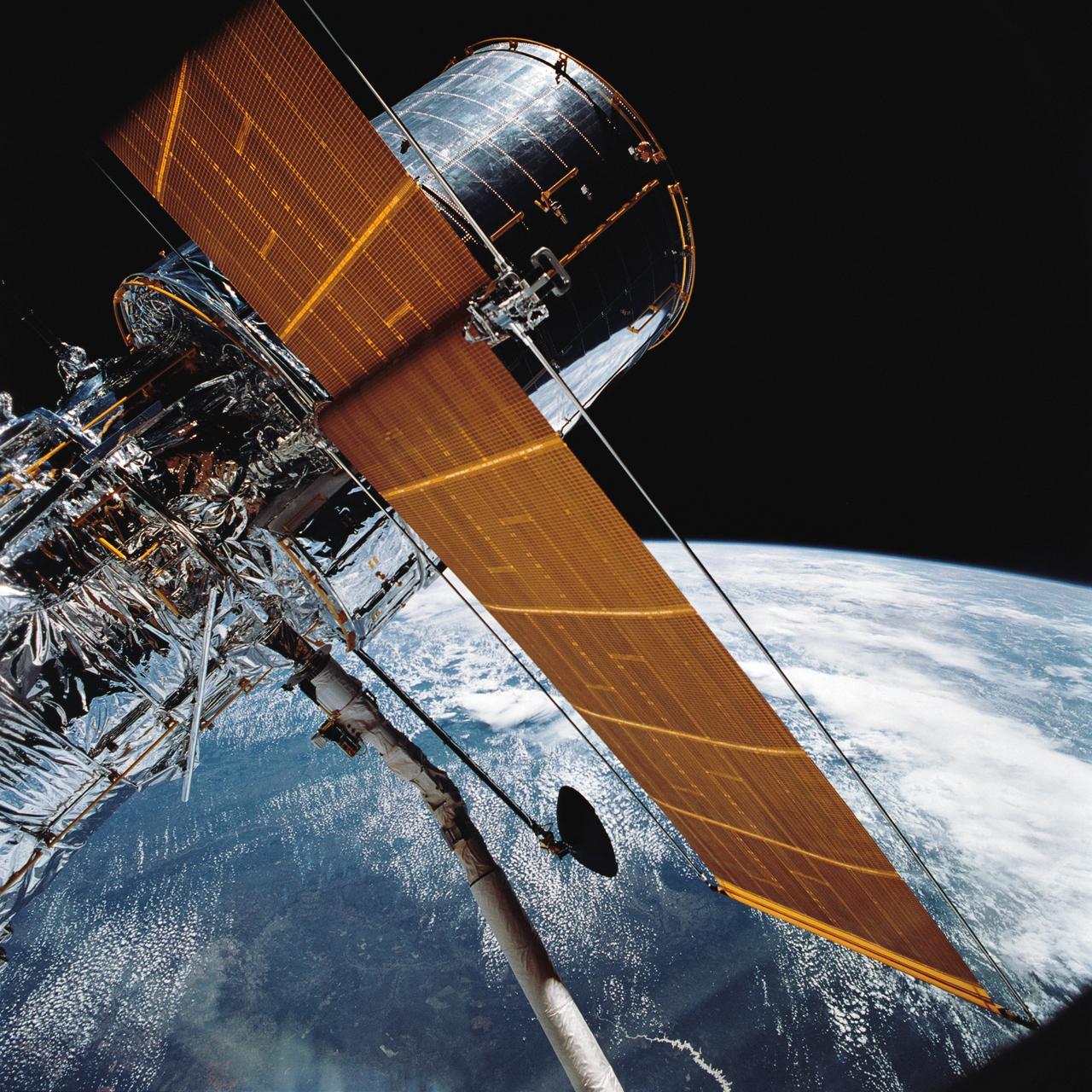

STS031-76-026 (25 April 1990) --- Most of the giant Hubble Space Telescope (HST) can be seen as it is suspended in space by Discovery's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) following the deployment of part of its solar panels and antennae. The photo was taken with a handheld Hasselblad camera. This was among the first photos NASA released on April 30, 1990, from the five-day STS 31 mission.

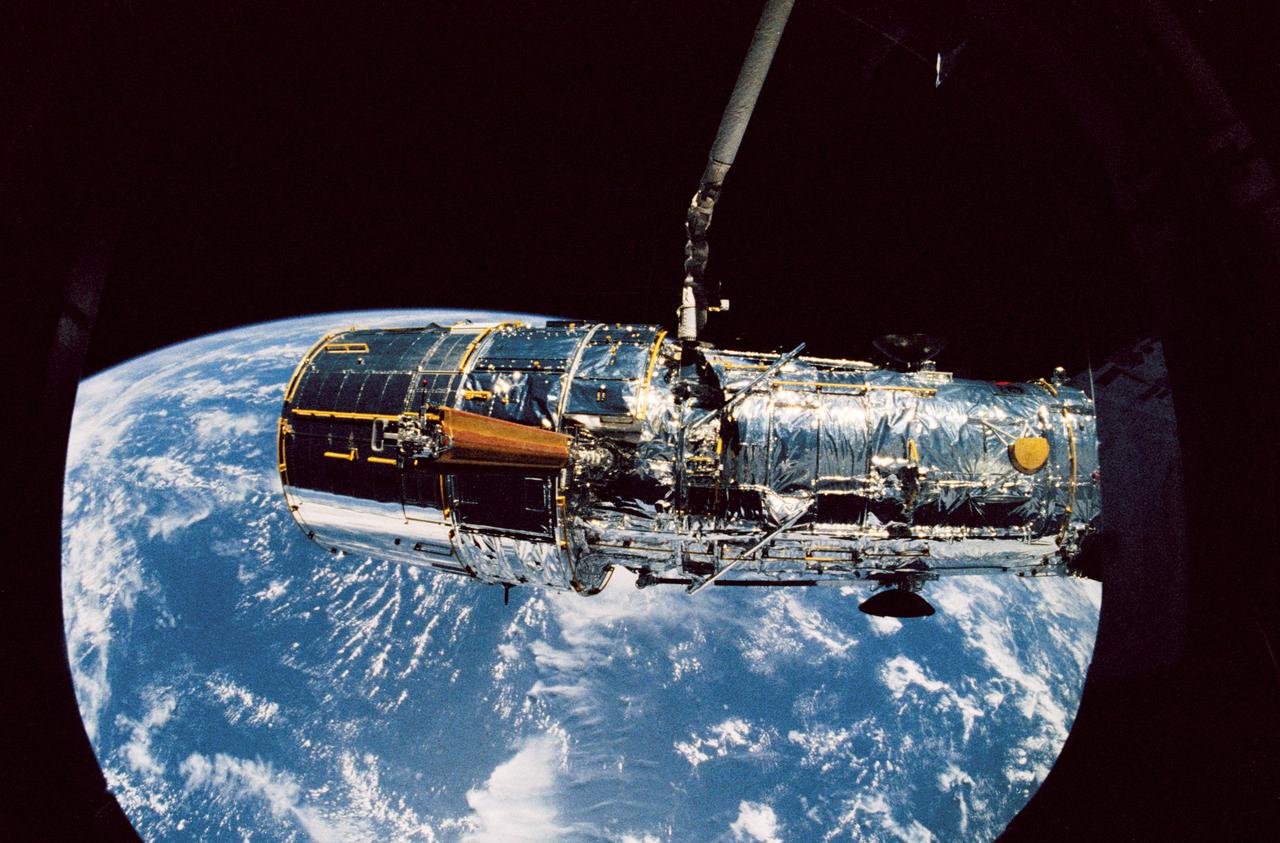
STS031-71-095 (25 April 1990) --- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is suspended above Discovery's cargo bay some 332 nautical miles above Earth. The Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, controlled from in-cabin by the astronaut crew members of STS-31, held the huge telescope in this position during pre-deployment procedures, which included extension of solar array panels and antennae. The photo was made with a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera.
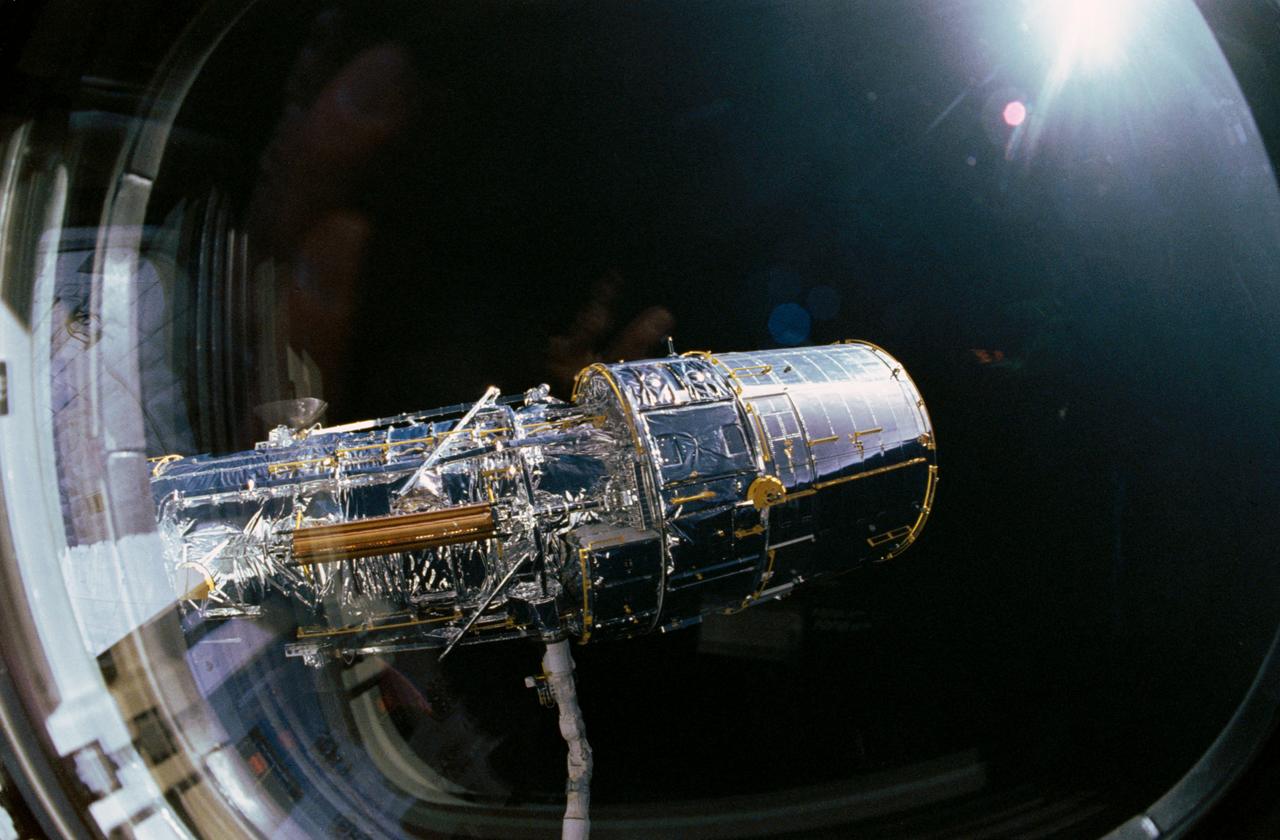
View taken through overhead window W7 aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) and held in a 90 degree pitch position against the blackness of space. The solar array (SA) panel (center) and the high gain antennae (HGA) (on either side) are visible along the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell prior to deployment during STS-31.

Held in appendage deploy position by Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, remote manipulator system (RMS), the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) starboard solar array (SA) bistem cassette is released from its stowed position on the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. The spreader bar & bistem begin to unfurl the SA wing. View was taken by an STS-31 crewmember through an overhead window & is backdropped against the surface of the Earth.
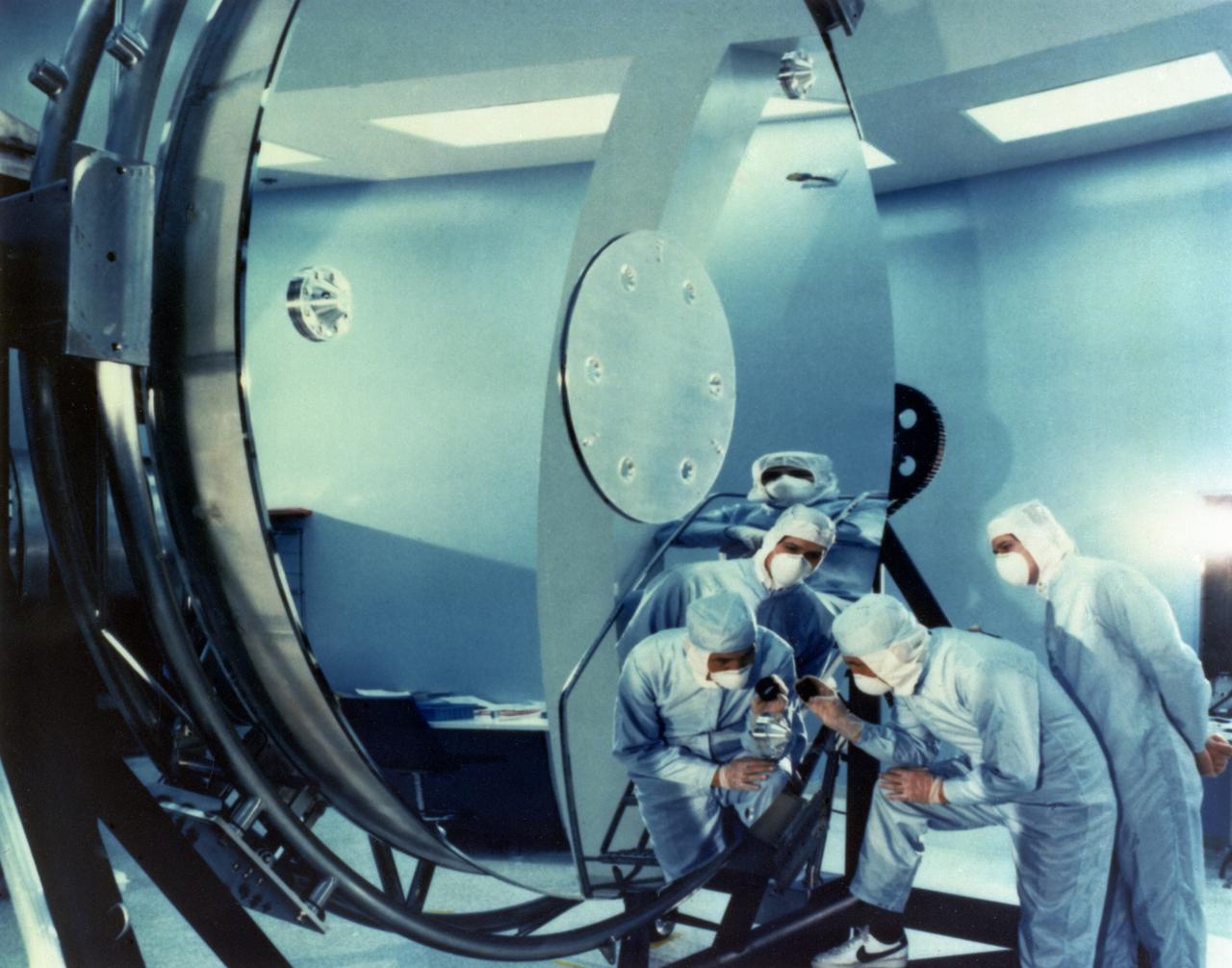
Prior to installation, technicians inspect the primary mirror of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The first in a series of great observatories launched by NASA, the HST was designed to last approximately 15 years. The Marshall Space Flight Center had management responsibility for the development of the HST and played a major role in ground tests and orbital checkout of the telescope. The HST was launched April 24, 1990 aboard Space Shuttle Discovery's STS-31 mission.
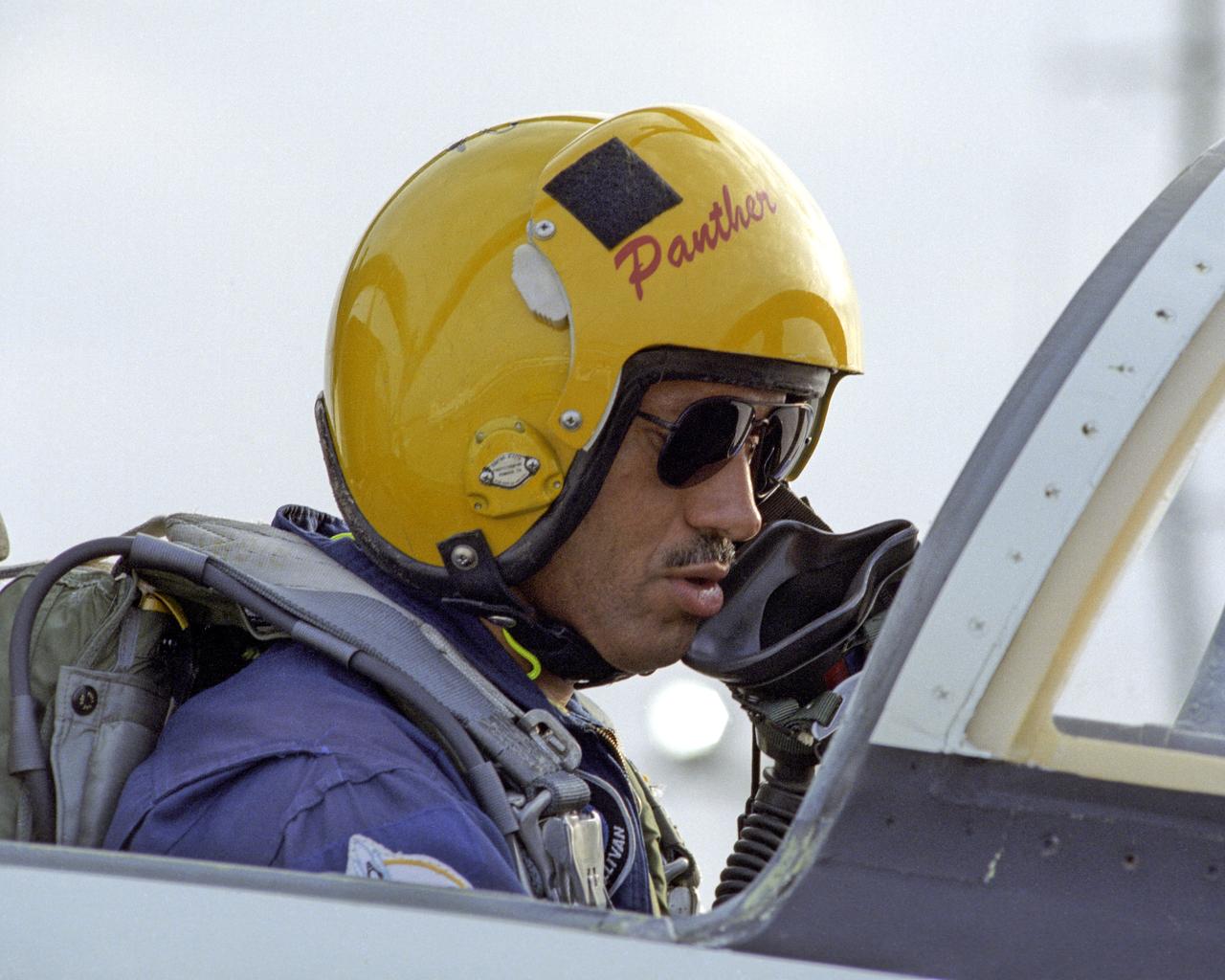

Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Pilot of Space Shuttle Mission STS-31, prepares for rehearsing shuttle contingency landings in the T-38S are among the final pre-launch activities. STS-31, carrying five crew members and the HST is set to liftoff at 8:47 a.m. April 10.

The mission insignia for NASA's STS-31 mission features the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in its observing configuration against a background of the universe it will study. The cosmos includes a stylistic depiction of galaxies in recognition of the contribution made by Sir Edwin Hubble to our understanding of the nature of galaxies and the expansion of the universe. The STS-31 crew points out that is it in honor of Hubble's work that this great observatory in space bears his name. The depicted Space Shuttle trails a spectrum symbolic of both the red shift observations that were so important to Hubble's work and new information which will be obtained with the HST. Encircling the art work, designed by the crew, are the names of its members.
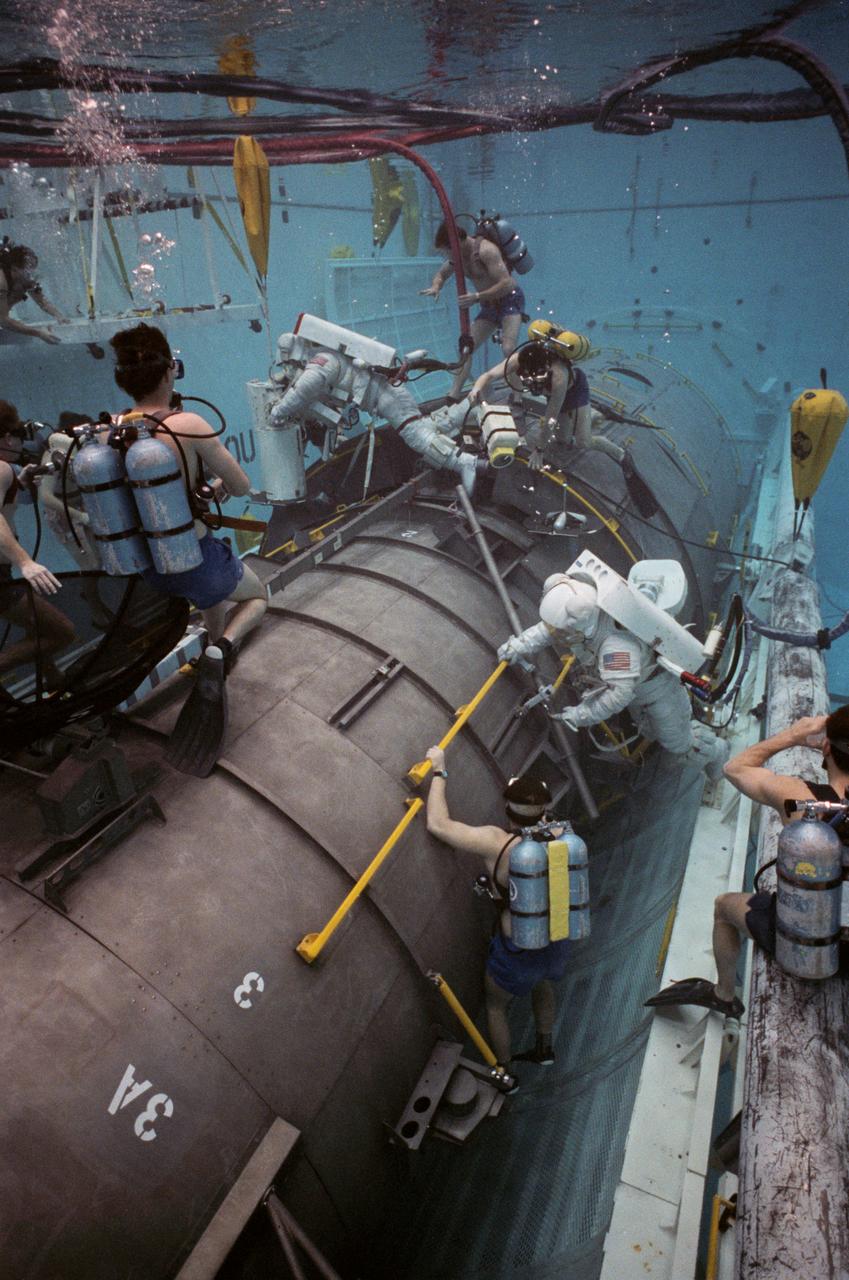

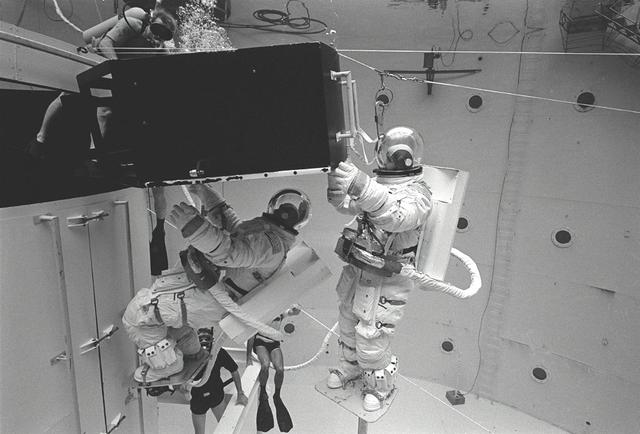
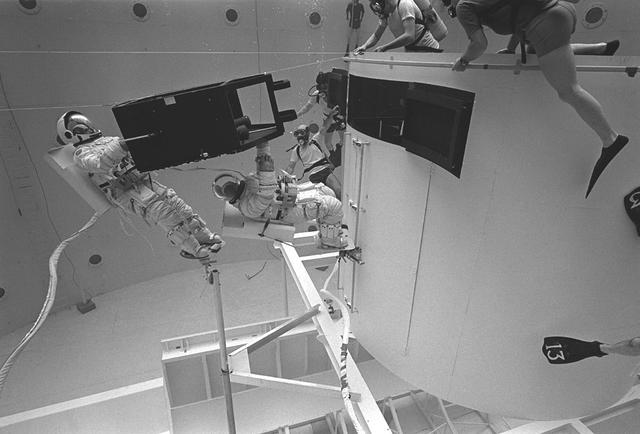
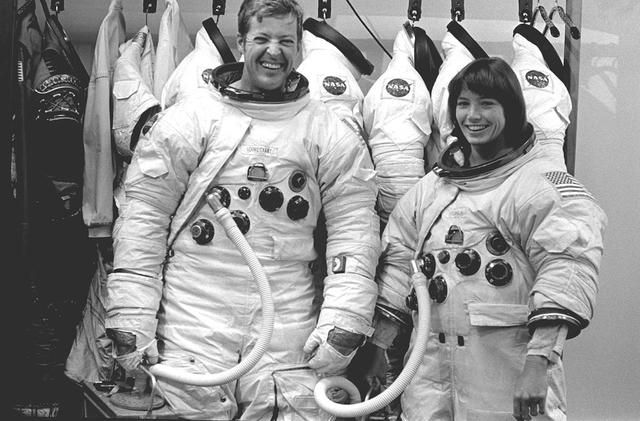
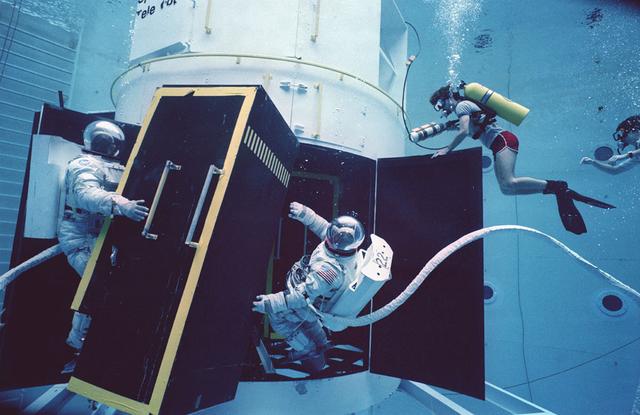
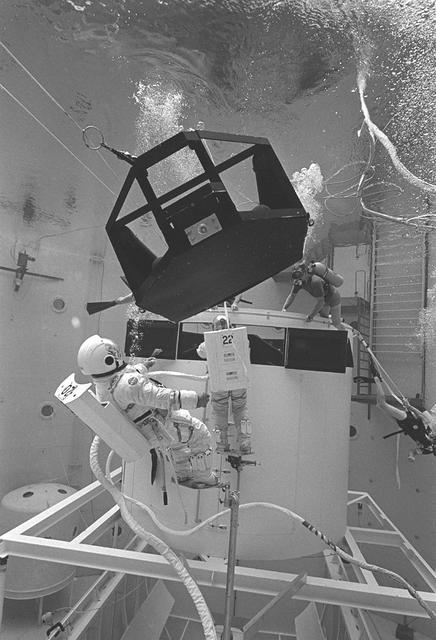
This overall view shows STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II (left) and MS Kathryn D. Sullivan making a practice space walk in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. McCandless works with a mockup of the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector which is attached to a grapple fixture on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) mockup. Sullivan manipulates HST hardware on the Support System Module (SSM) forward shell. SCUBA-equipped divers monitor the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) suited crewmembers during this simulated extravehicular activity (EVA). No EVA is planned for the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment, but the duo has trained for contingencies which might arise during the STS-31 mission aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Photo taken by NASA JSC photographer Sheri Dunnette.
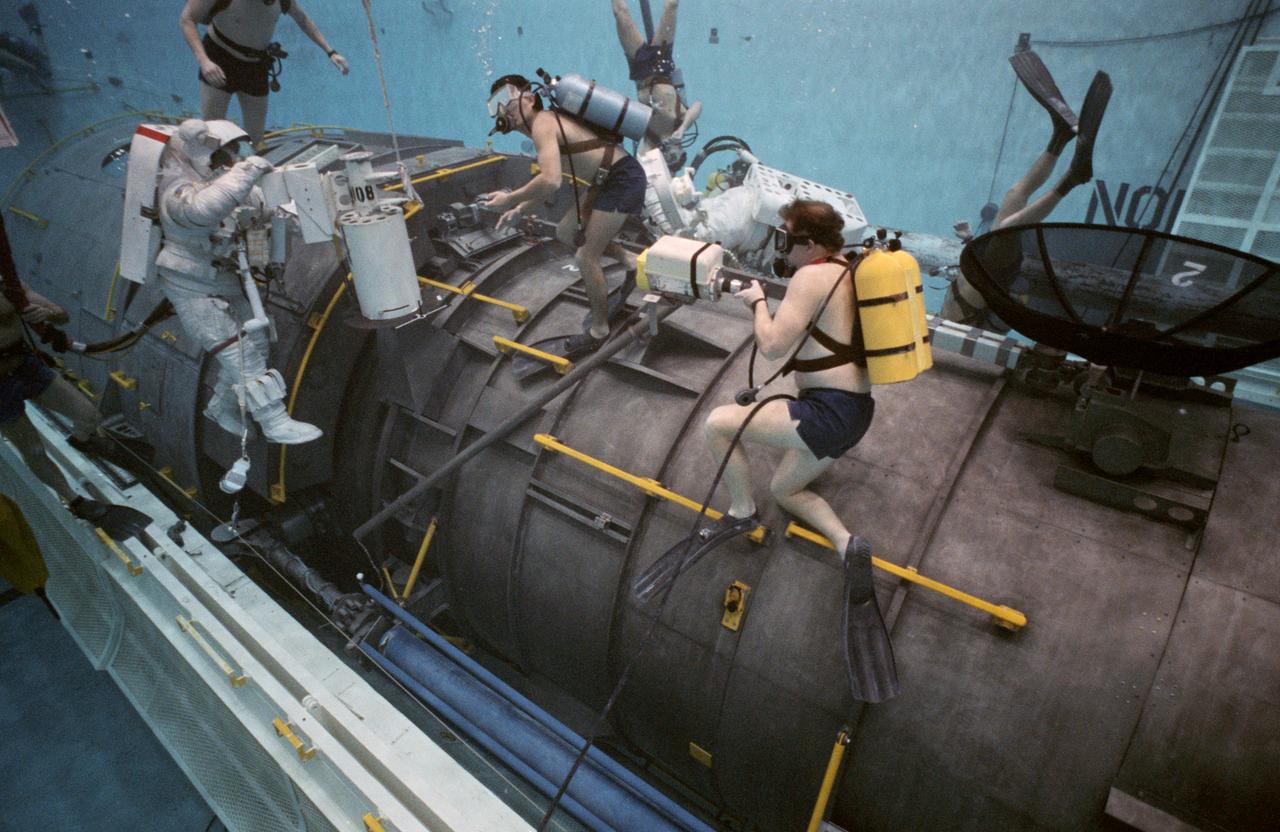

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II (left), wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), maneuvers his way around a mockup of the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector during an underwater simulation in JSC's Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) Bldg 29 pool. The end effector is attached to a grapple fixture on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) mockup. As McCandless performs contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) procedures, fellow crewmember MS Kathryn D. Sullivan, in EMU, works on the opposite side of the HST mockup, and SCUBA-equipped divers monitor the activity. Though no EVA is planned for STS-31, the two crewmembers train for contingencies that would necessitate leaving the shirt sleeve environment of Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, crew cabin and performing chores with the HST payload or related hardware in the payload bay (PLB).
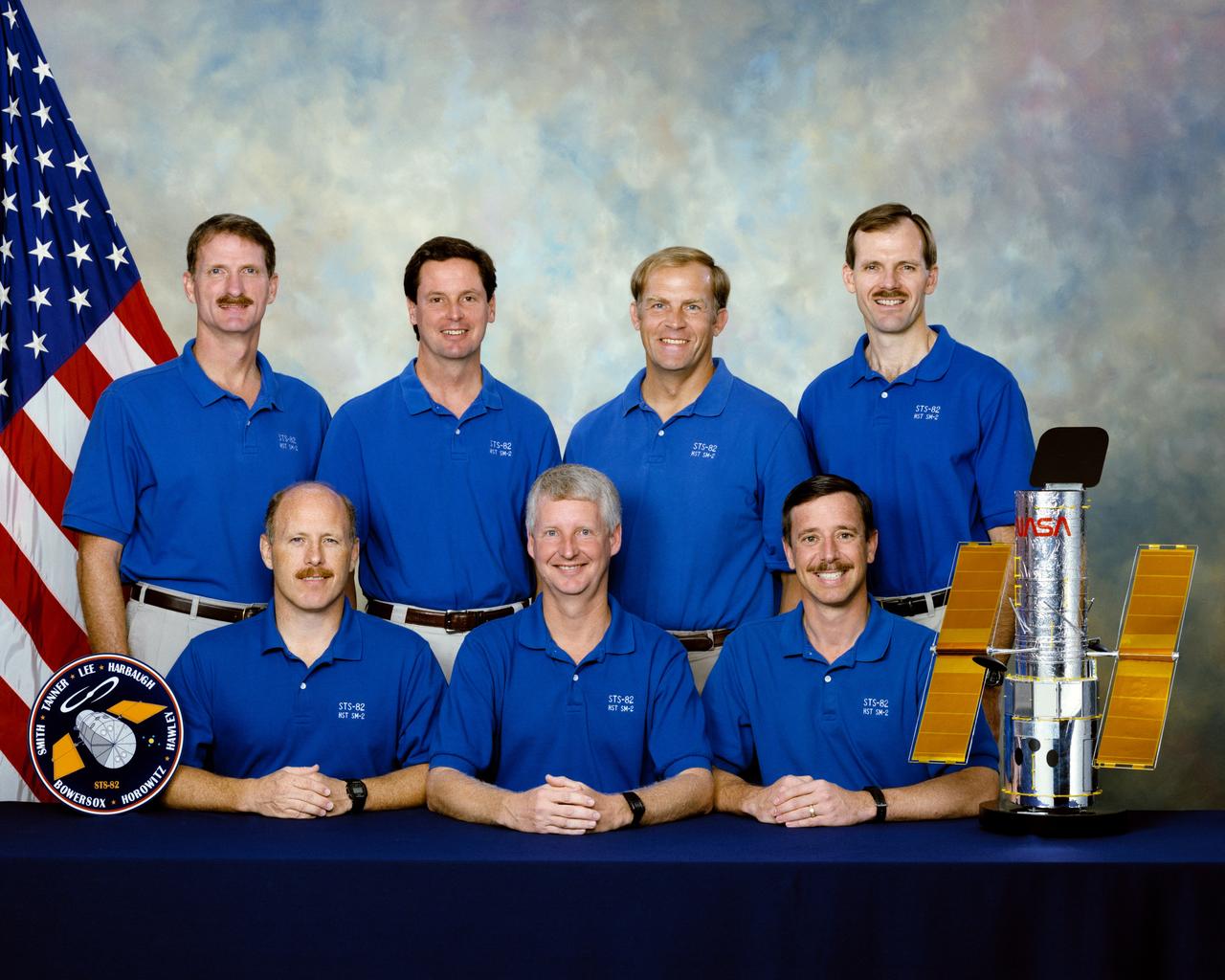

STS082-S-002 (December 1996) --- These seven astronauts are prime crew members for NASA’s STS-82 mission. They are, on the front row, from the left, Kenneth D. Bowersox, Steven A. Hawley and Scott J. Horowitz. On the back row are Joseph R. Tanner, Gregory J. Harbaugh; Mark C. Lee and Steven L. Smith. Bowersox and Horowitz are commander and pilot, respectively, with Lee assigned as payload commander. Hawley, Harbaugh, Smith and Tanner are mission specialists. The seven are pictured with a small model of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), which they will be paying a visit representing the second HST maintenance mission. Bowersox was pilot for the STS-61 mission, which performed the first maintenance on HST. Hawley was a mission specialist on STS-31, the mission whose astronauts originally deployed the HST.
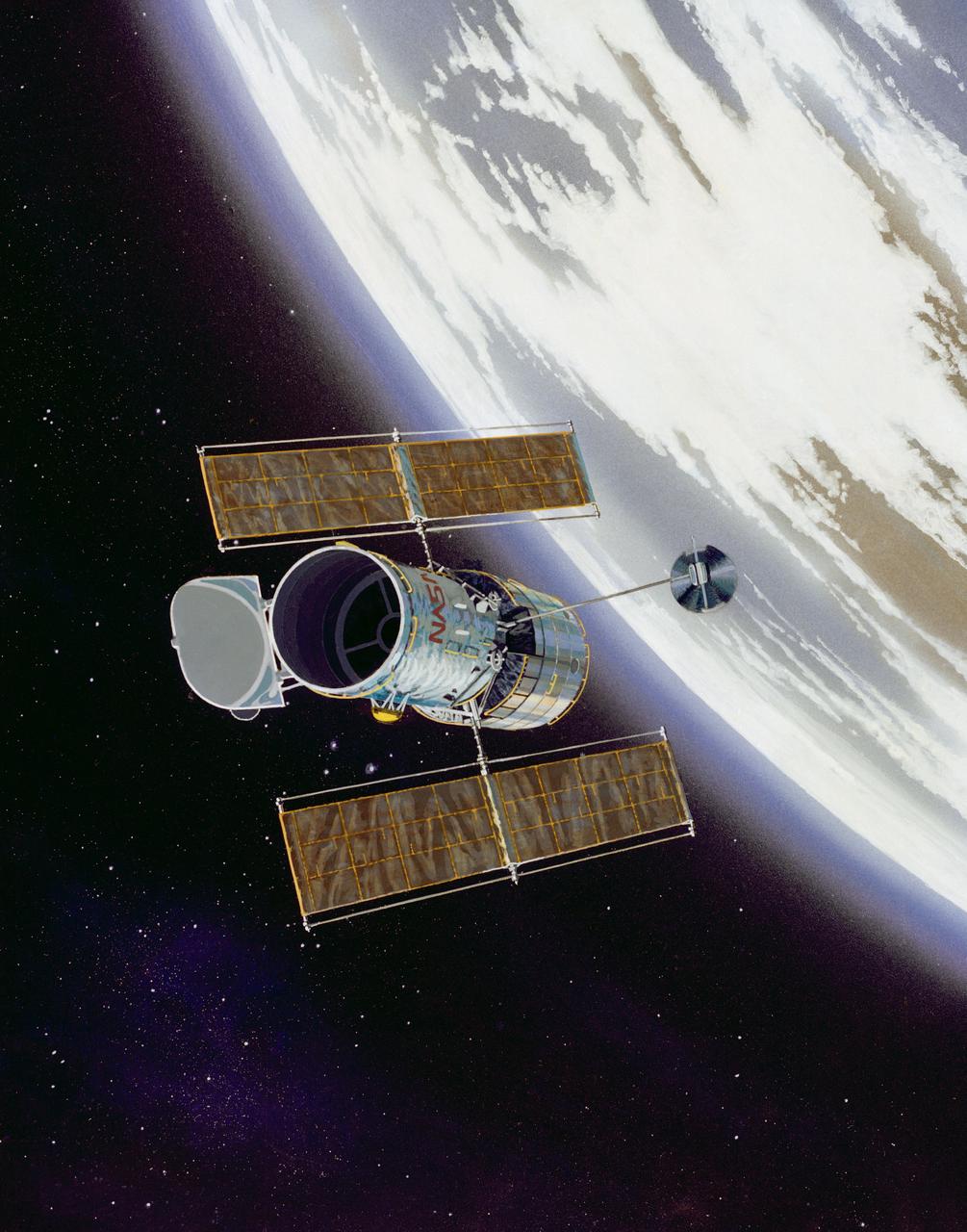

This artist concept shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in operational configuration orbiting the Earth after its deploy from Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103 during STS-31. The high gain antennas (HGAs) and solar arrays (SAs) have been extended. HST's aperature door is open as it views the universe from a vantage point above the Earth's atmosphere. View provided by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
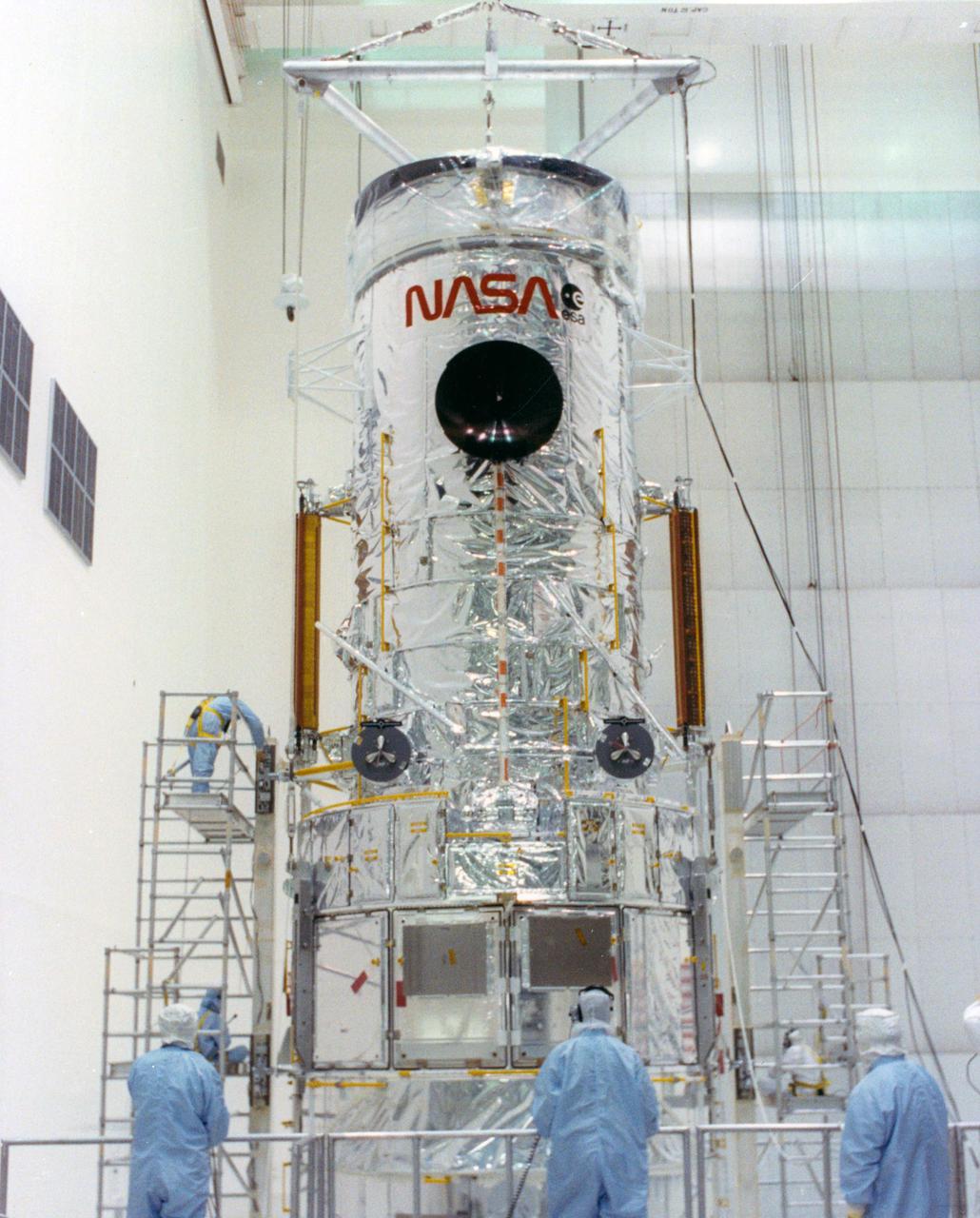

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is lifted into the workstands in the Vertical Processing Facility as work begins at KSC to process the 94-inch primary mirror telescope for launch on Discovery on Space Shuttle Mission STS-31 in March 1990. With HST, astronomers will be able to view 97 percent of the known universe, and will be able to get pictures unlimited and undistorted by the Earth's atmosphere. Compared with earth-based observatories, the HST will be able to view celestial objects that are 50 times fainter, provide images that are 10 times sharper, and see objects that are seven times farther away. .
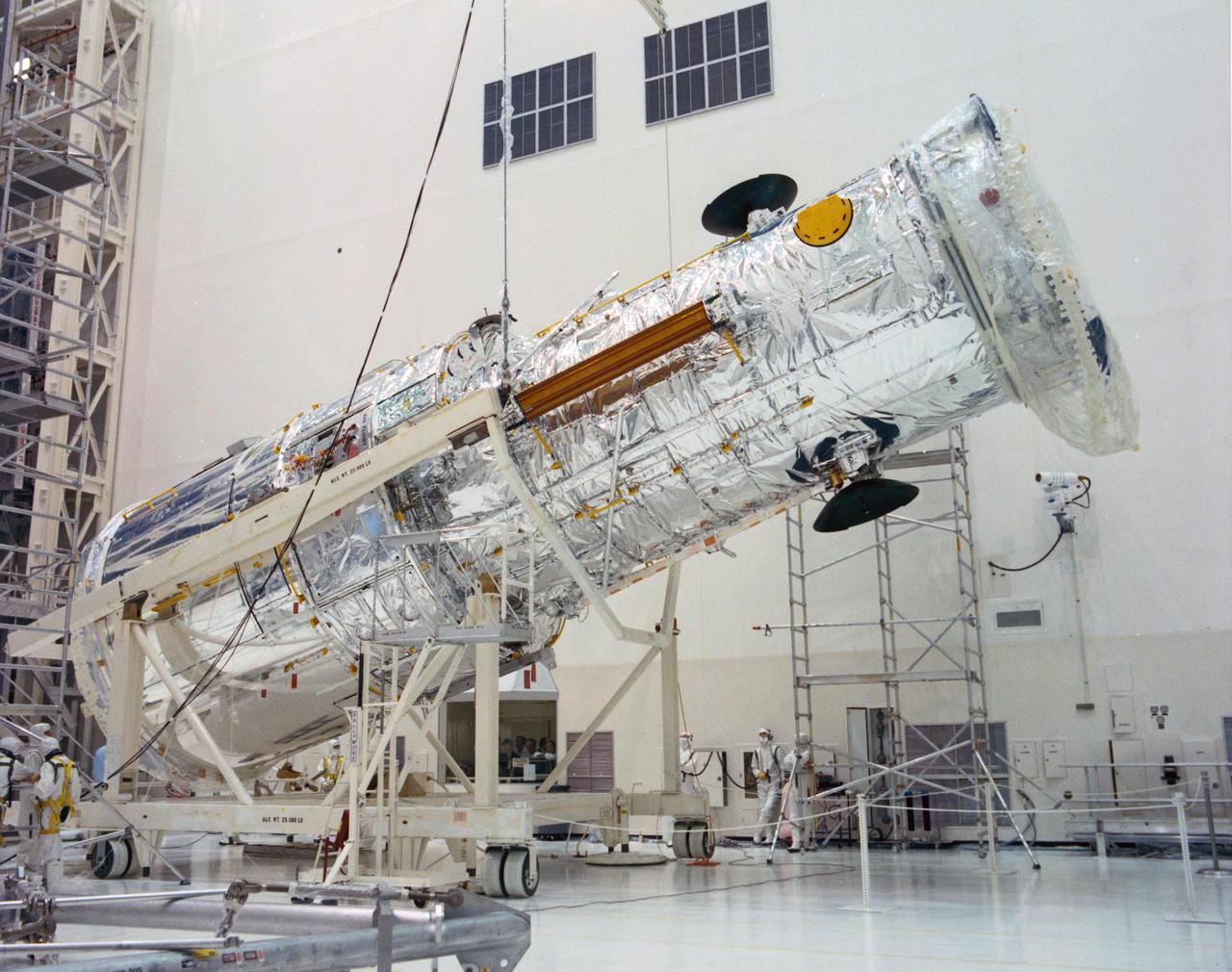

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is lifted into the vertical position in the Vertical Processing Facility as work begins at KSC to process the 94-inch primary mirror telescope for launch on Discovery on Space Shuttle Mission STS-31 in March 1990. With HST, astronomers will be able to view 97 percent of the known universe, and will be able to get pictures unlimited and undistorted by the Earth's atmosphere. Compared with earth-based observatories, the HST will be able to view celestial objects that are 50 times fainter, provide images that are 10 times sharper, and see objects that are seven times farther away. .
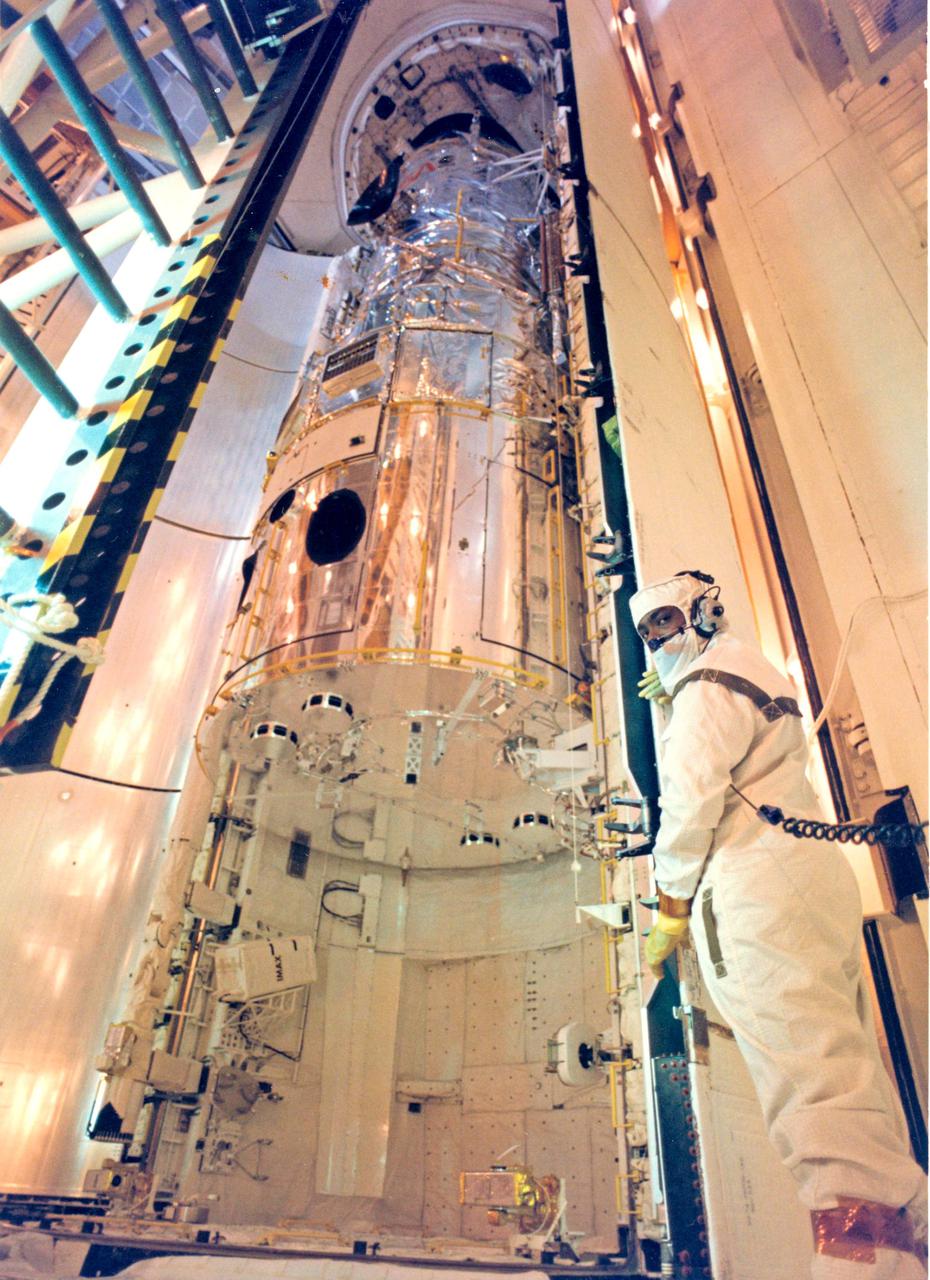

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A technician carefully monitors progress as Discovery's payload bay doors close around the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The payload bay was closed for flight at 6:24 a.m. Sunday, April 8. The STS-31 launch is scheduled for 8:47 a.m. Tuesday, April 10. With HST, astronomers will be able to view 97 percent of the known universe, and will be able to get pictures unlimited and undistorted by the Earth's atmosphere. Compared with earth-based observatories, the HST will be able to view celestial objects that are 50 times fainter, provide images that are 10 times sharper, and see objects that are seven times farther away.
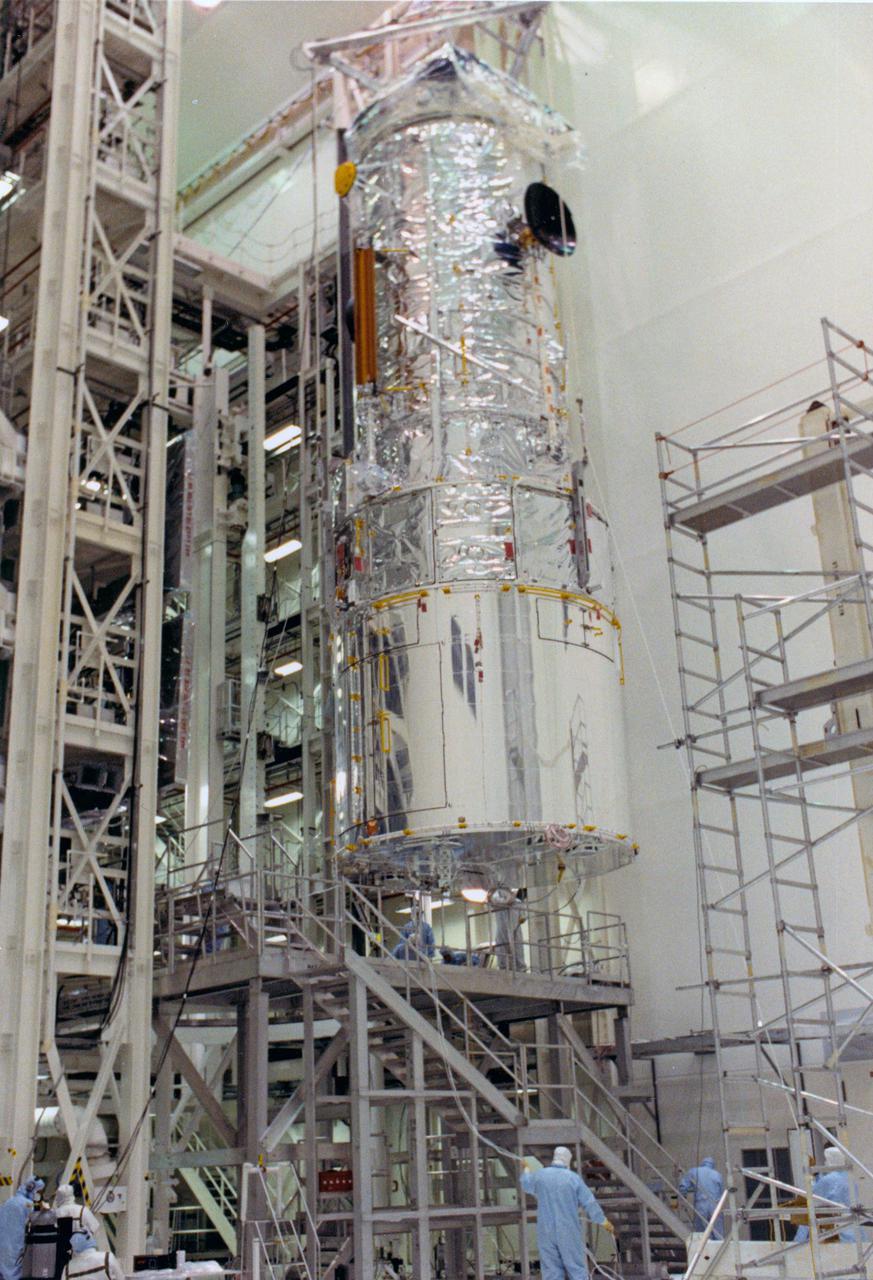

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is lifted into the workstands in the Vertical Processing Facility as work begins at KSC to process the 94-inch primary mirror telescope for launch on Discovery on Space Shuttle Mission STS-31 in March 1990. With HST, astronomers will be able to view 97 percent of the known universe, and will be able to get pictures unlimited and undistorted by the Earth's atmosphere. Compared with earth-based observatories, the HST will be able to view celestial objects that are 50 times fainter, provide images that are 10 times sharper, and see objects that are seven times farther away. .
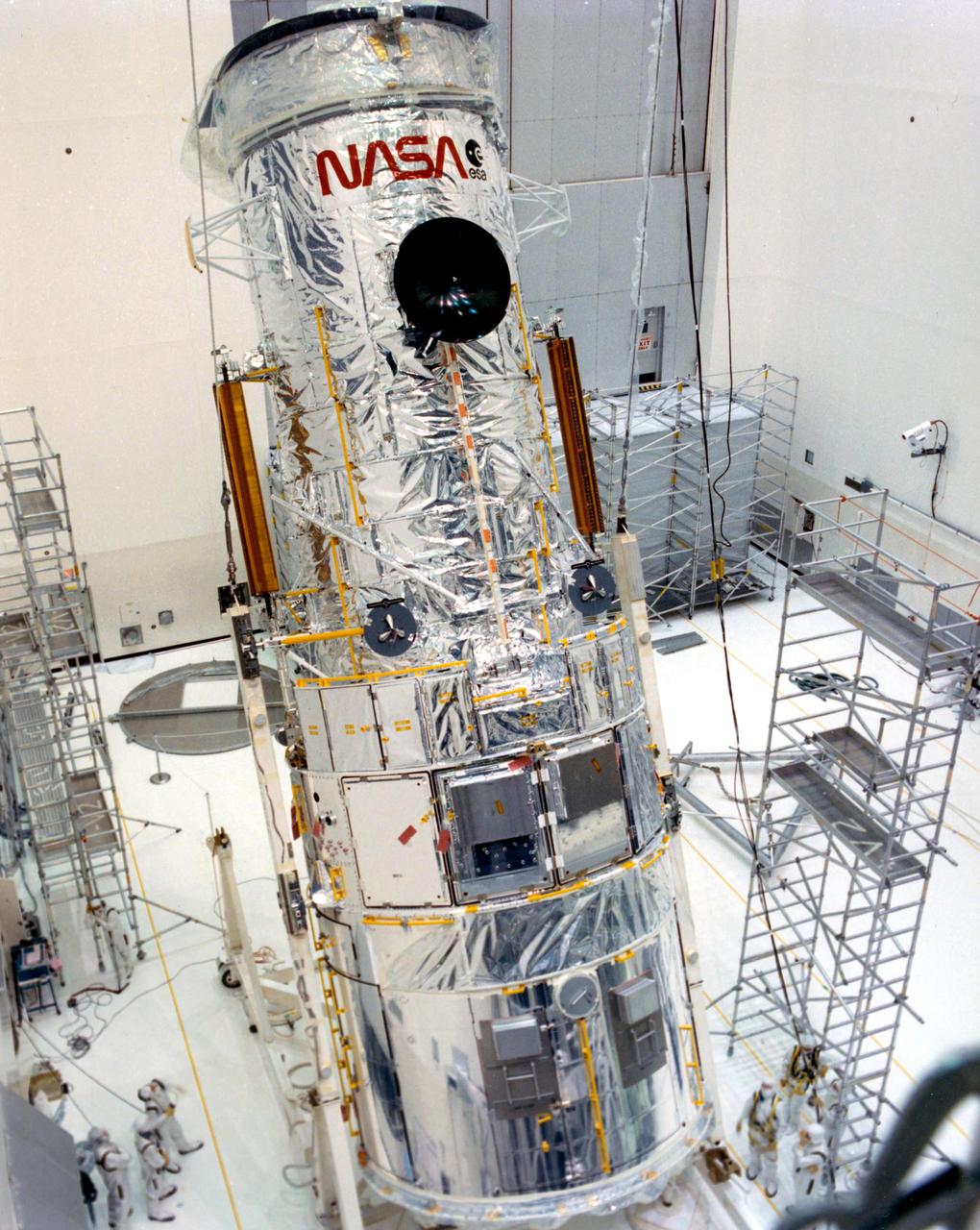
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is lifted into the vertical position in the Vertical Processing Facility as work begins at KSC to process the 94-inch primary mirror telescope for launch on Discovery on Space Shuttle Mission STS-31 in March 1990. With HST, astronomers will be able to view 97 percent of the known universe, and will be able to get pictures unlimited and undistorted by the Earth's atmosphere. Compared with earth-based observatories, the HST will be able to view celestial objects that are 50 times fainter, provide images that are 10 times sharper, and see objects that are seven times farther away. .
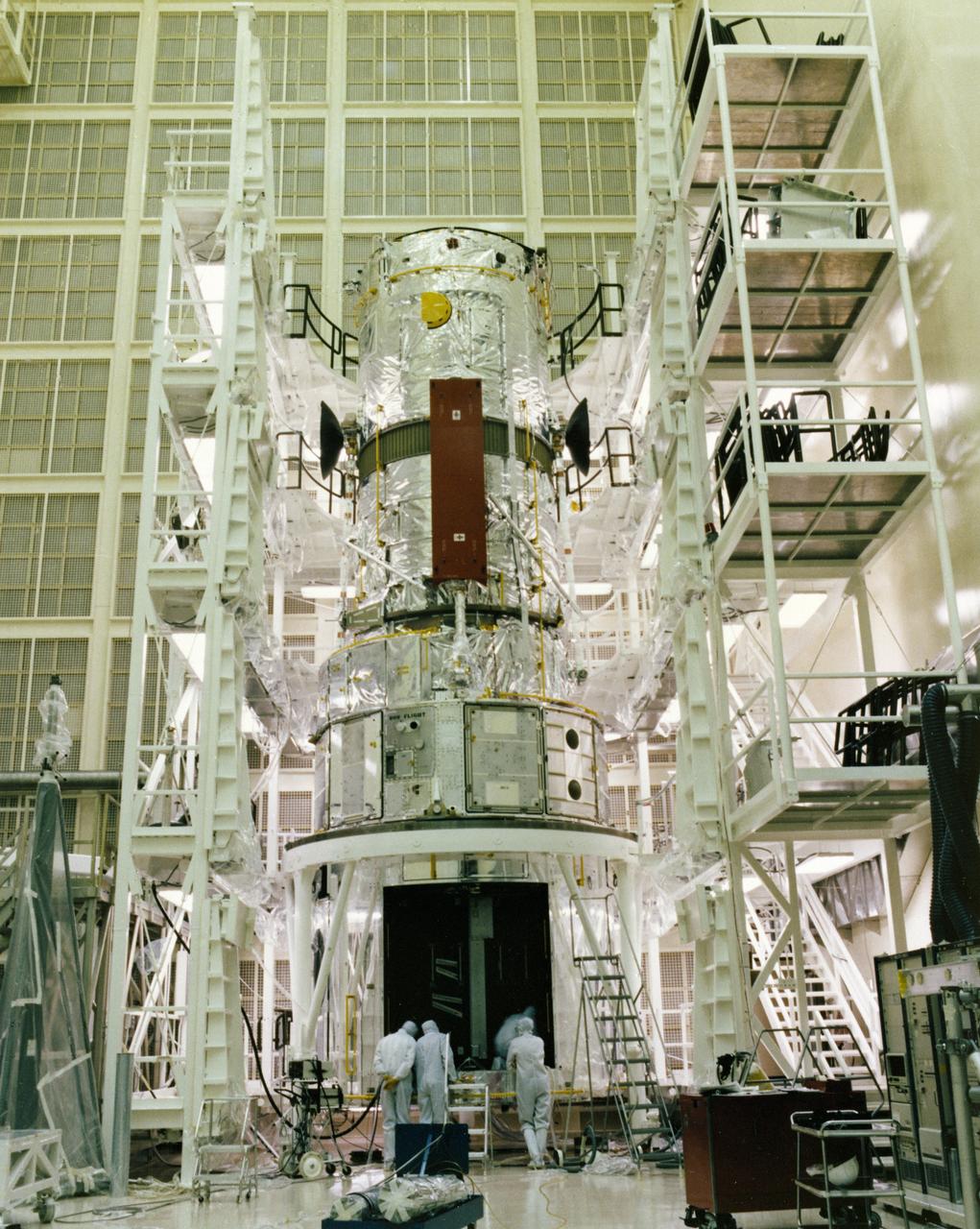
This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) flight article assembly with multilayer insulation, high gain anterna, and solar arrays in a clean room of the Lockheed Missile and Space Company. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS -- STS-31 ONBOARD SCENE -- Most of the giant Hubble Space Telescope (HST) can be seen as it is suspended in space by Discovery's remote manipulator system (RMS), following the deployment of part of its solar panels and antennae. The photo was taken with a handheld Hasselblad camera. This was among the first photos NASA released on April 30 from the five-day STS-31 mission.

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS-- STS-31 ONBOARD SCENE -- A medium closeup view photographed with fish-eye lens on a 35mm camera shooting the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) held above Discovery's cargo bay by the remote manipulator system prior to solar array and antennae deployment.
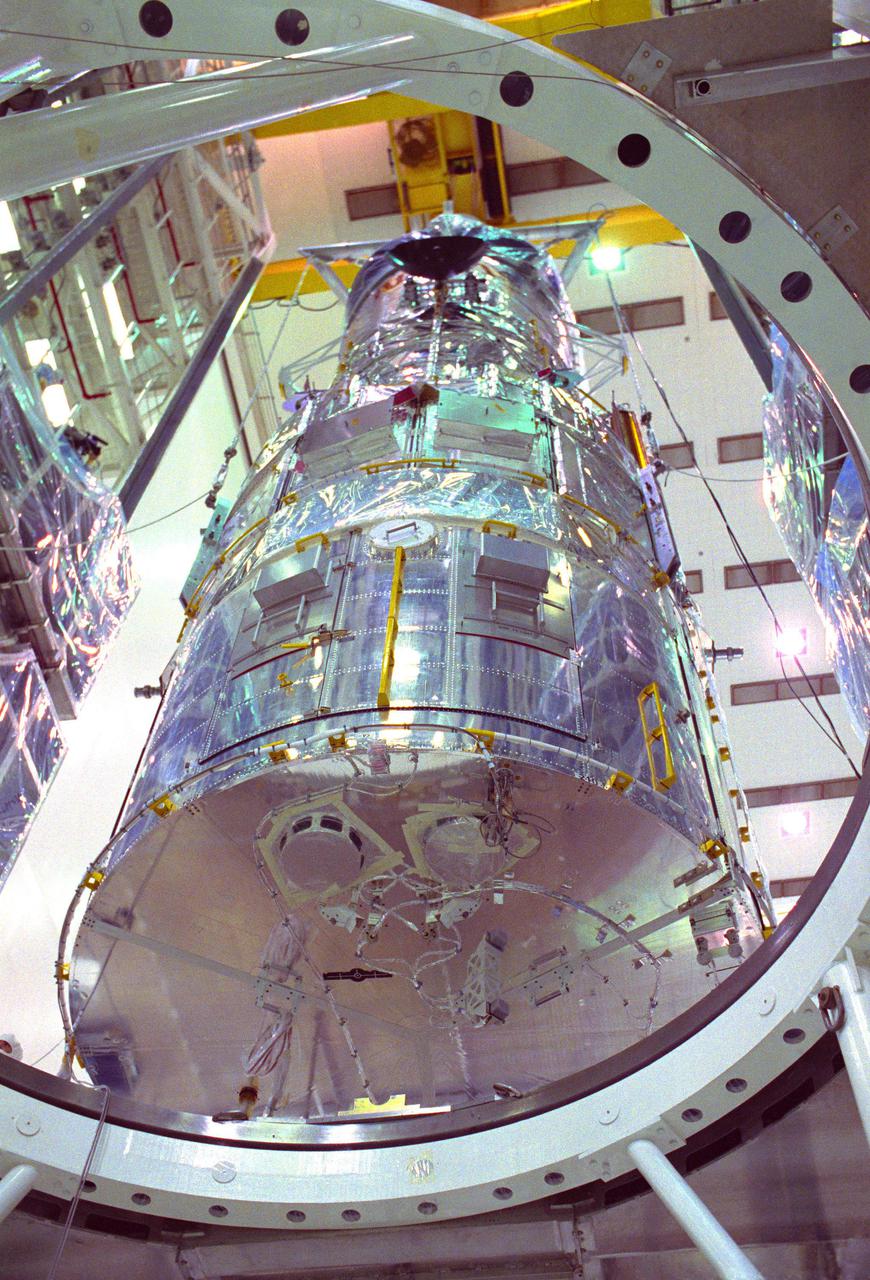
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is lifted into the workstands in the Vertical Processing Facility as work begins at KSC to process the 94-inch primary mirror telescope for launch on Discovery on Space Shuttle Mission STS-31 in March 1990.
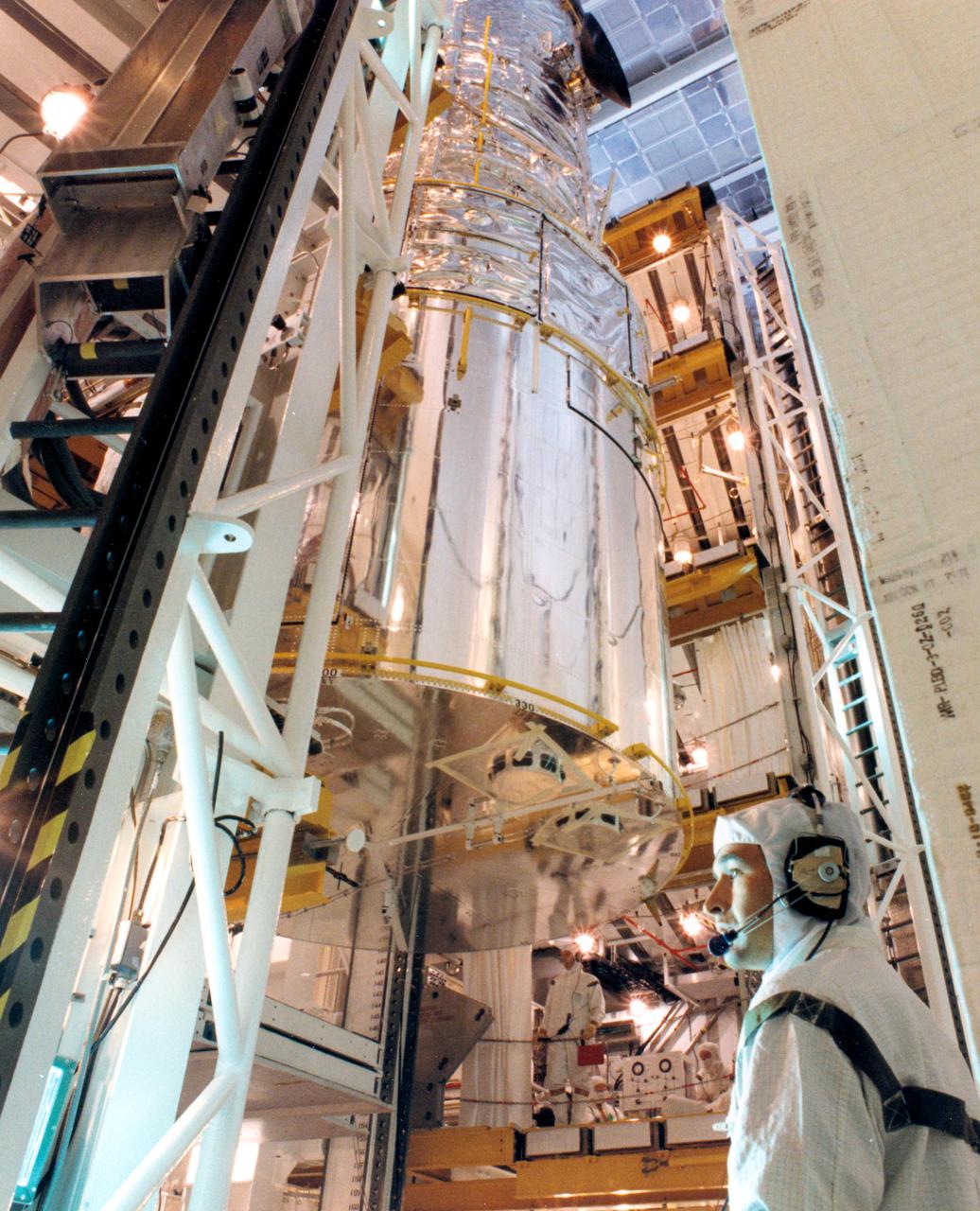
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The bus-size Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is carefully being transferred on March 29 from the surgically clean Payload Changeout Room at Launch Pad 39B into the cargo bay of the orbiter Discovery. The payload ground handling mechanism (left) is a device that extends the HST into the cargo bay (right), allowing workers to fasten it in place with four retention latches. Deployment of Hubble will occur during the five-day flight of Space Shuttle Mission STS-31, set for April 10. With HST, astronomers will be able to view 97 percent of the known universe, and will be able to get pictures unlimited and undistorted by the Earth's atmosphere. Compared with earth-based observatories, the HST will be able to view celestial objects that are 50 times fainter, provide images that are 10 times sharper, and see objects that are seven times farther away. .
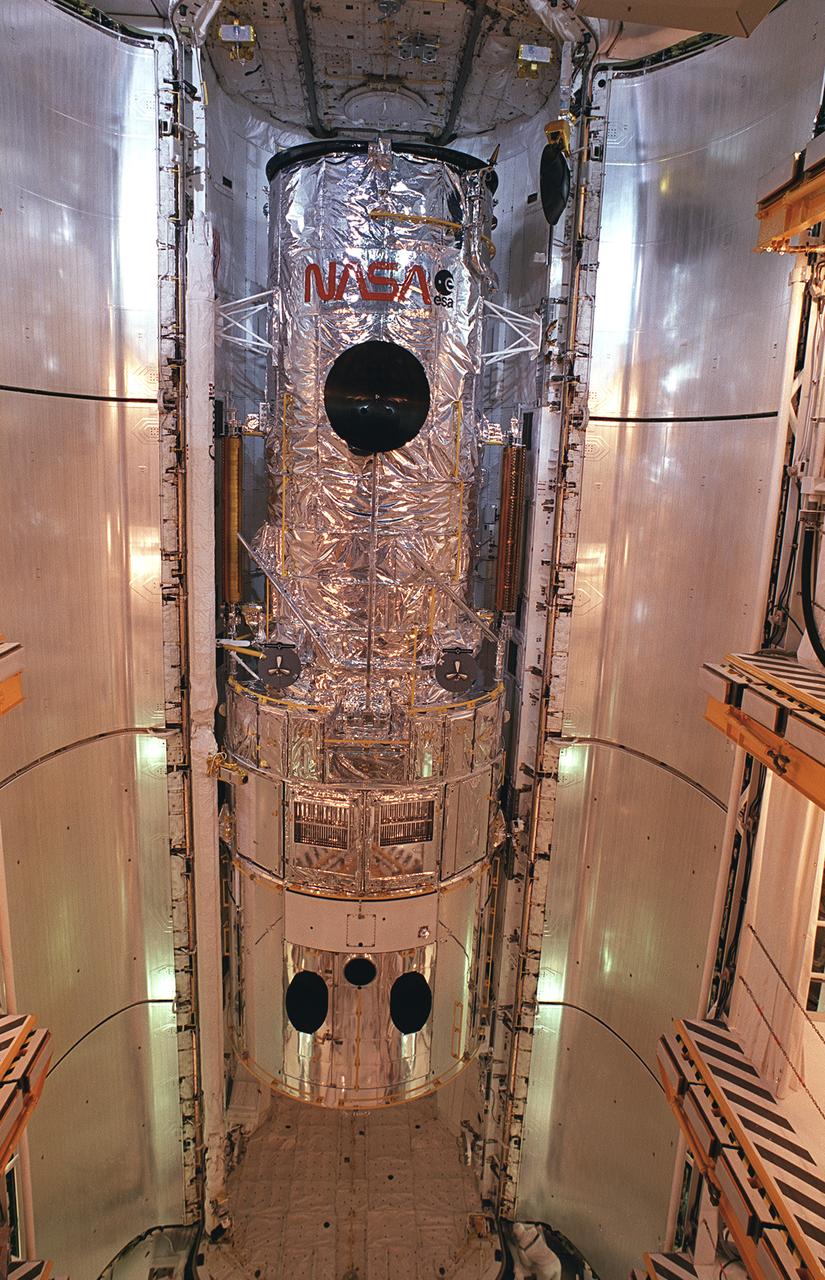

This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) installed in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Discovery for the STS-31 Mission at The Kennedy Space Center prior to launch on April 24, 1990. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
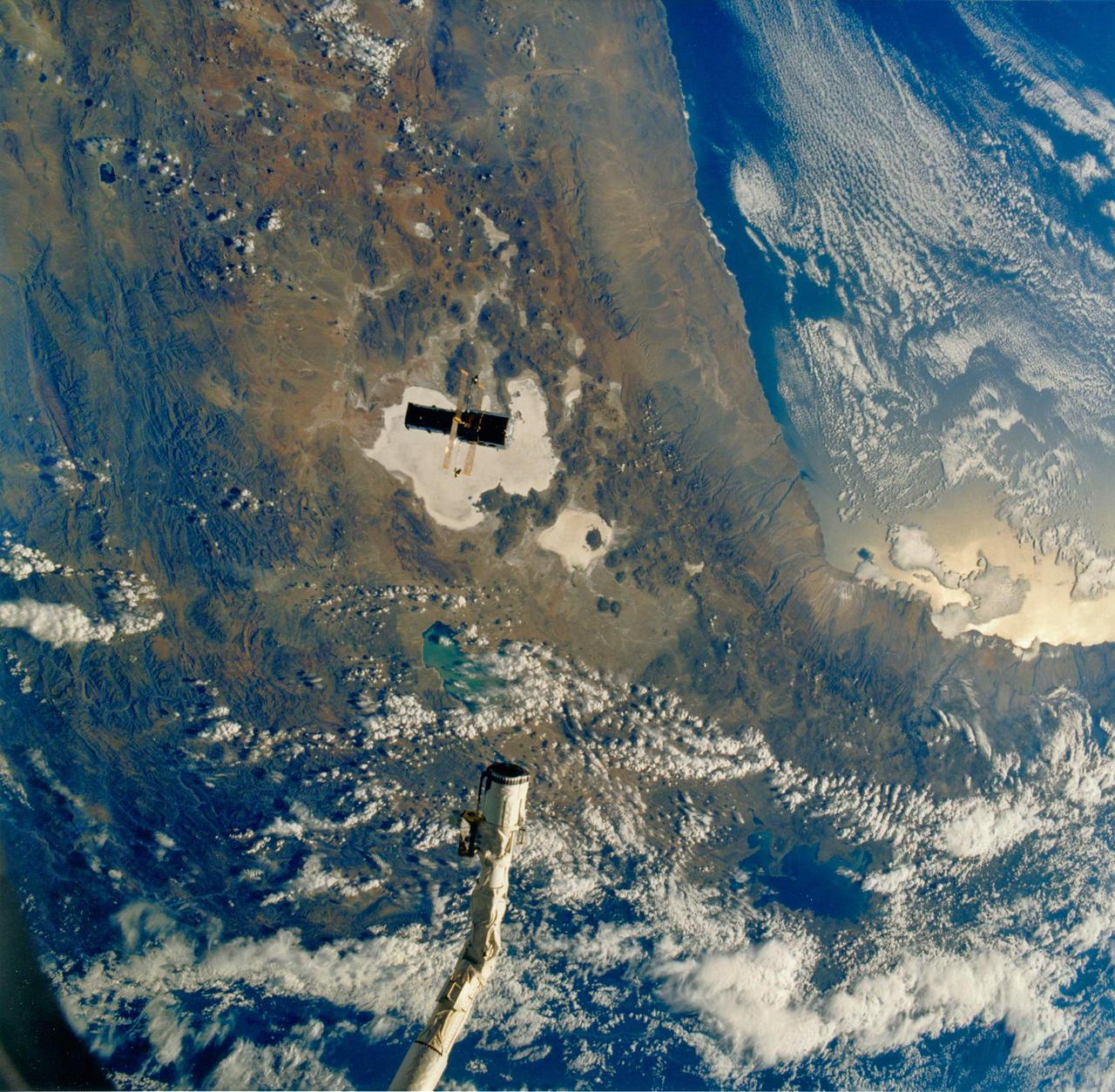

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS -- STS-31 ONBOARD SCENE -- The huge Hubble Space Telescope (HST), backdropped against Bolivian, Chilean and Peruvian topography some 332 nautical miles away, and the Space Shuttle Discovery, represented in this scene by its remote manipulator system (RMS) arm, begin their relative separation in space. The chalk-colored feature directly beneath HST is called Salar de Uyuni. Lake Titicaca is in upper right, and Lake Fuope is under partial cloud cover near the RMS's end effector. This photograph, one of the first eight STS-31 onboard frames to be released by NASA, was taken with a handheld Hasselblad camera by one of the five busy crew members in Discovery's cabin.
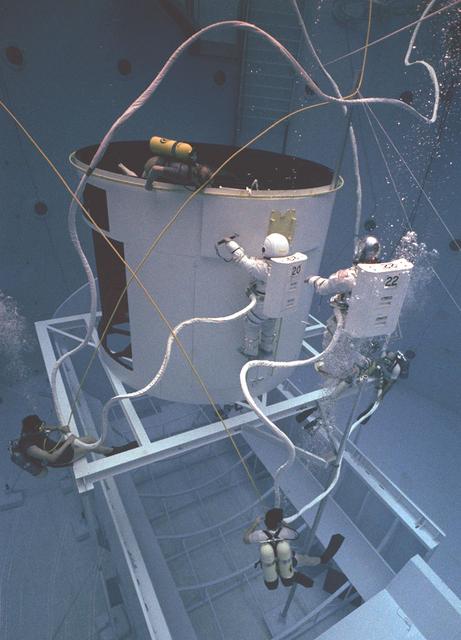

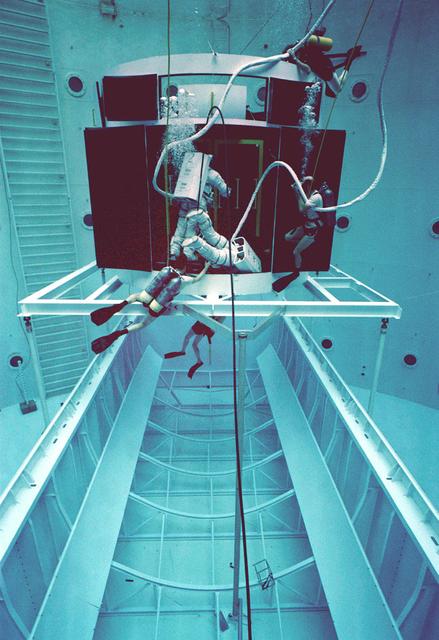
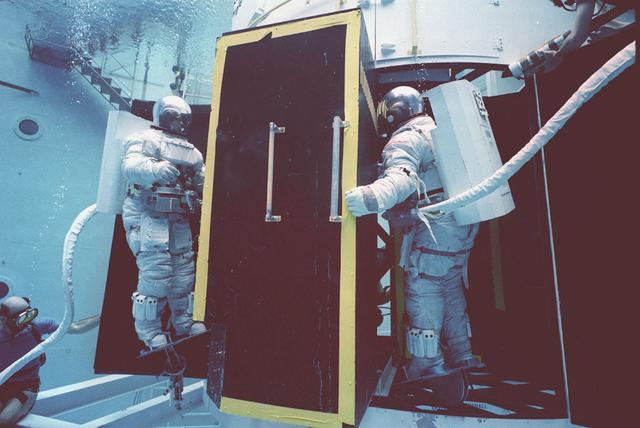
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory; it was the first and flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, HST was finally designed and built; and became operational in the 1990s. HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator which served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is an astronaut training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST in removal/replacement of scientific instruments.
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the first and flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is an astronaut training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST in the removal and replacement of scientific instruments.
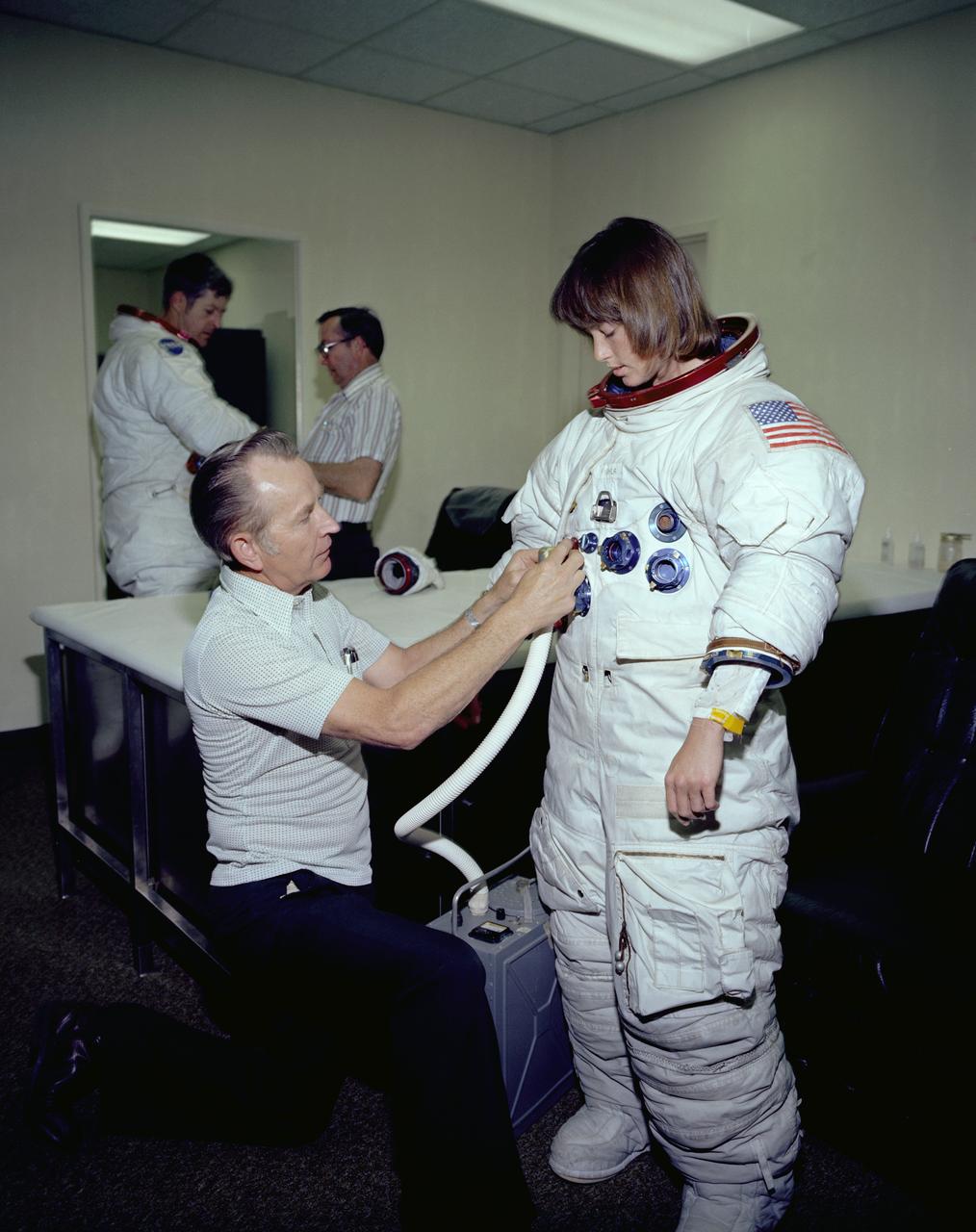

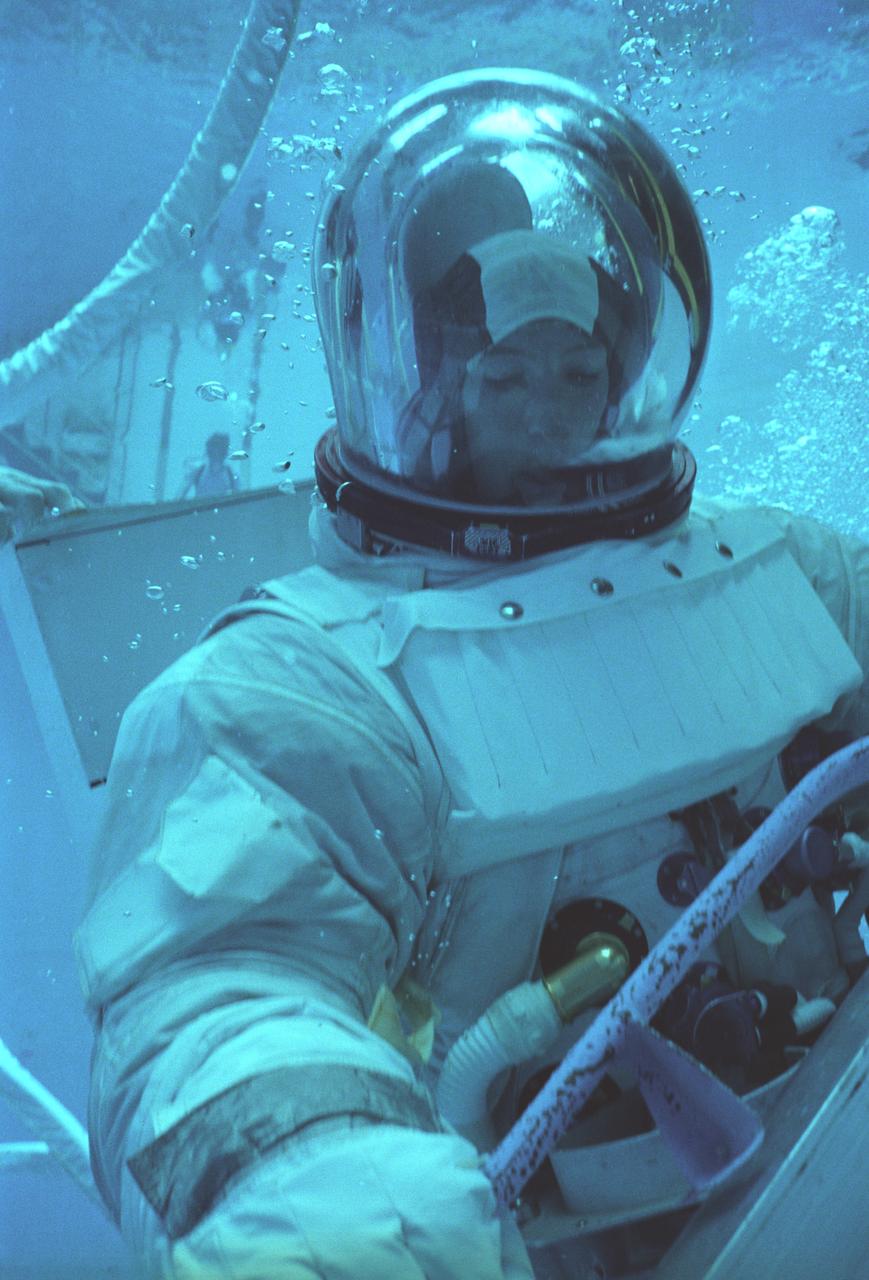
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is astronaut Anna Fisher suiting up for training on a mockup of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument change out.
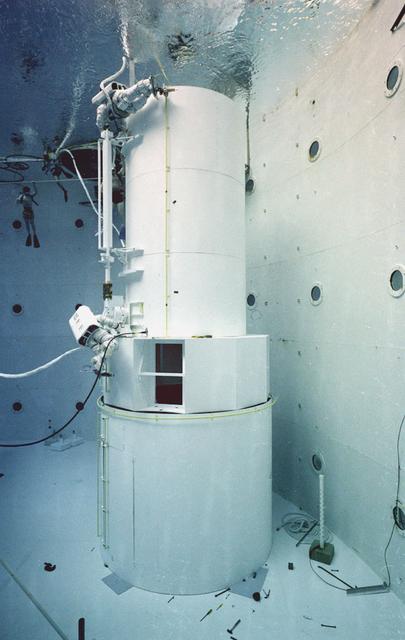

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the first and flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is an astronaut training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST in the removal and replacement of scientific instruments.

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is astronaut Anna Fisher training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument change out.

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the first and flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built and became operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is an astronaut training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST in the removal and replacement of scientific instruments.

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is astronaut Anna Fisher suiting up for training on a mockup of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument change out.

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown are astronauts Arna Fisher and Joe Kerwin training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument changeout.
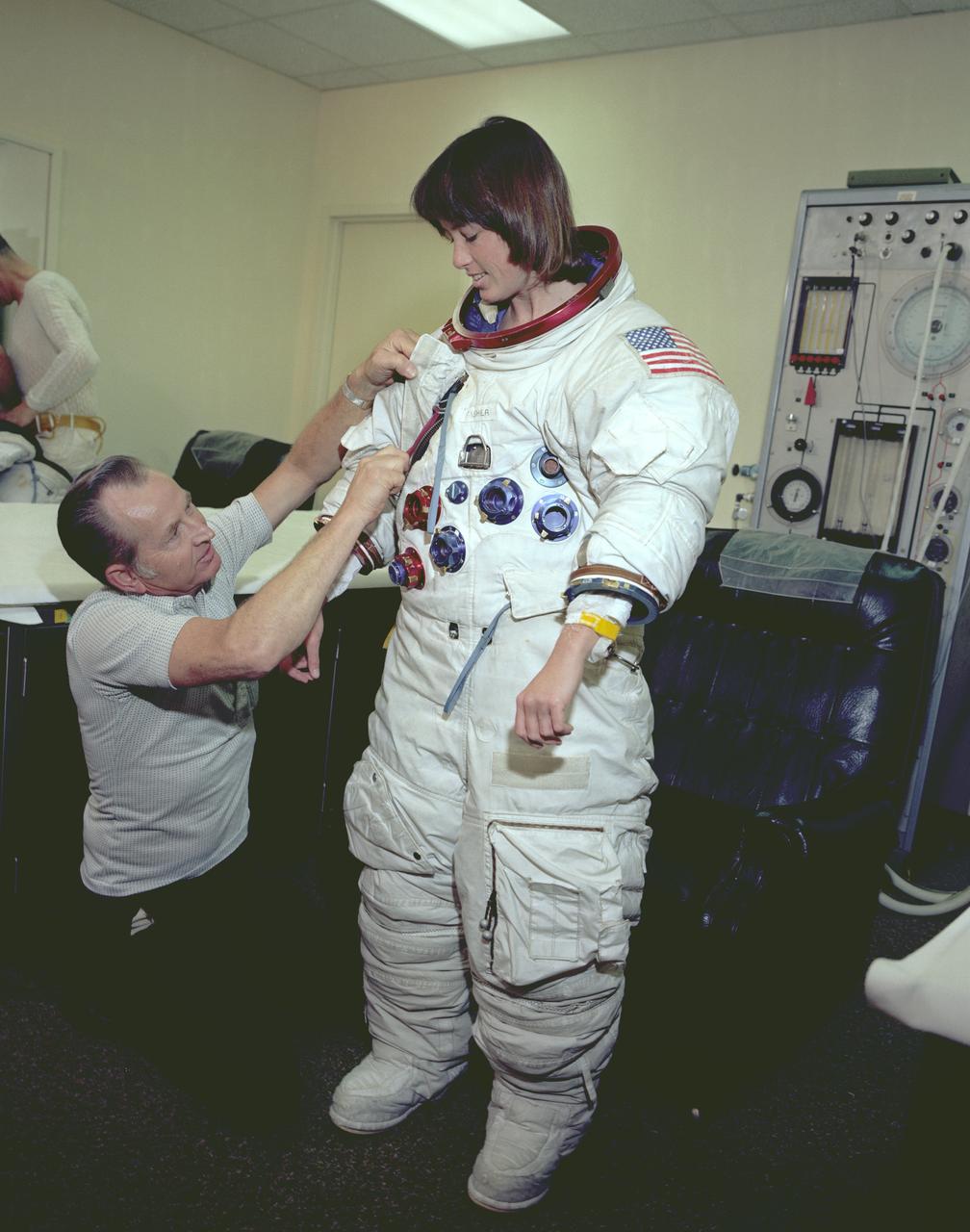
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is astronaut Anna Fisher suiting up for training on a mockup of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument change out.
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory; it was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, HST was finally designed and built; and it finally became operational in the 1990s. HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator which served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown are astronauts McCandless and Nelson training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST in removal/replacement of scientific instruments.
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown are astronauts Arna Fisher and Joe Kerwin training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument changeout.
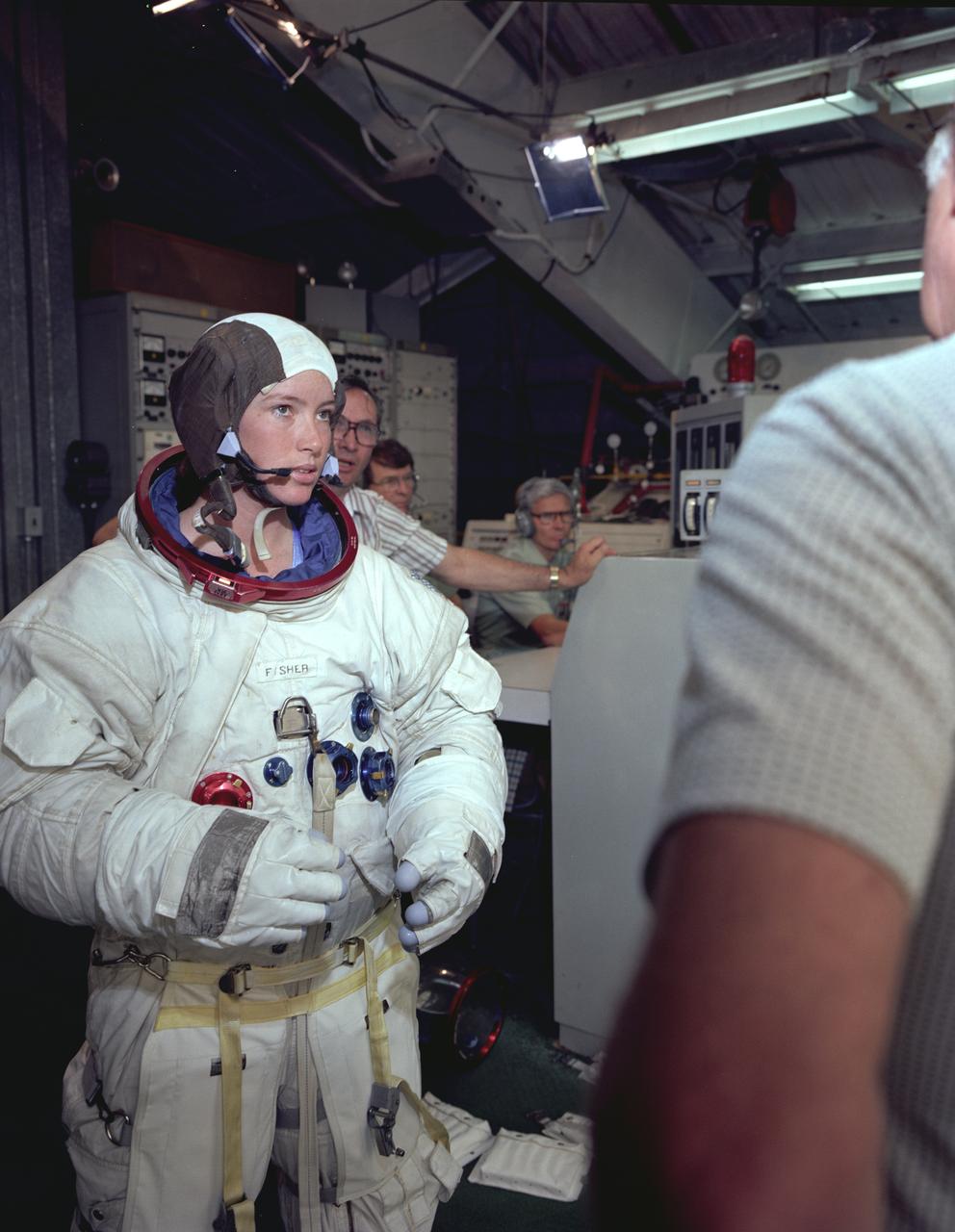

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Marshall SPace Flight Center’s (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is astronaut Anna Fisher suited up for training on a mockup of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument change out.
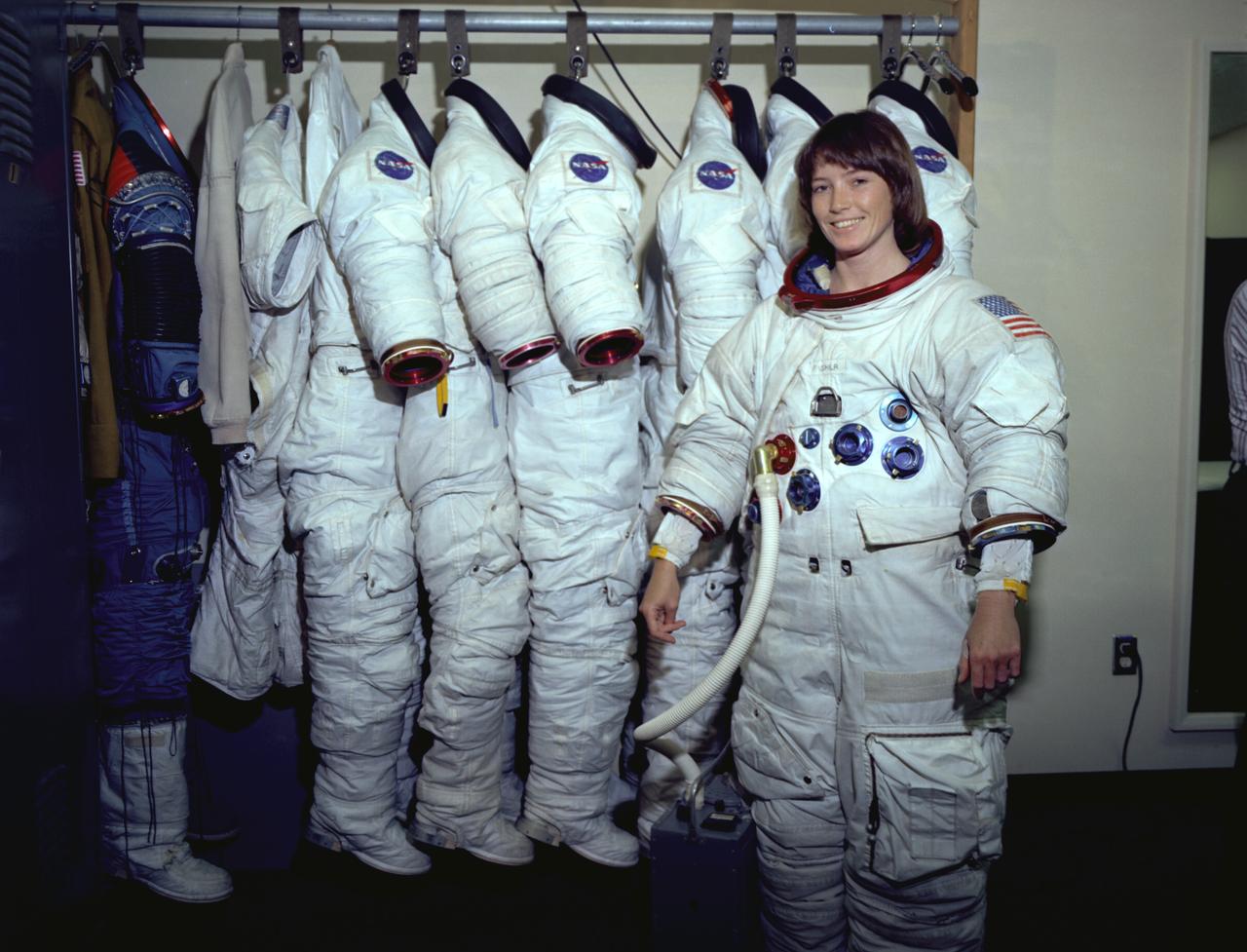

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Marshall Space Flight Center’s (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is astronaut Anna Fisher suited up for training on a mockup of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument change out.

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC's) Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown are astronauts Arna Fisher and Joe Kerwin training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST for an axial scientific instrument changeout.

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory; it was the first and flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, HST was finally designed and built; and became operational in the 1990s. HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator which served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown is an astronaut training on a mock-up of a modular section of the HST in removal/replacement of scientific instruments.

A comparison image of the M100 Galactic Nucleus, taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Wide Field Planetary Camera-1 (WF/PC1) and Wide Field Planetary Camera-2 (WF/PC2). The HST was placed in a low-Earth orbit by the Space Shuttle Discovery, STS-31 mission, in April 1990. Two months after its deployment in space, scientists detected a 2-micron spherical aberration in the primary mirror of the HST that affected the telescope's ability to focus faint light sources into a precise point. This imperfection was very slight, one-fiftieth of the width of a human hair. During four spacewalks, the STS-61 crew replaced the solar panel with its flexing problems; the WF/PC1 with the WF/PC2, with built-in corrective optics; and the High-Speed Photometer with the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR), to correct the aberration for the remaining instruments. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit for 15 years or more. The HST provides fine detail imaging, produces ultraviolet images and spectra, and detects very faint objects.
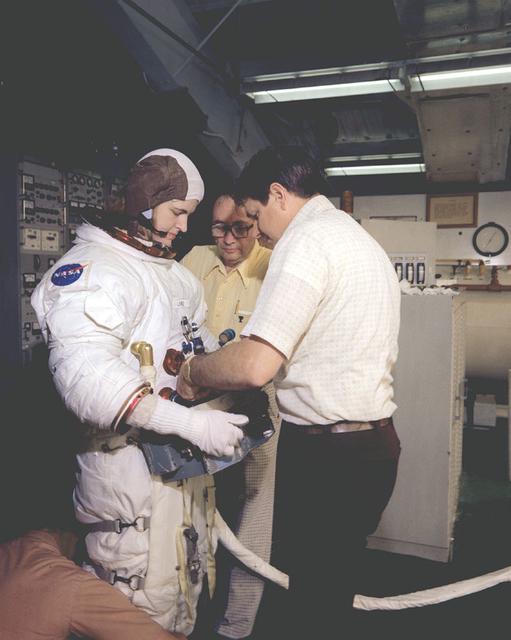

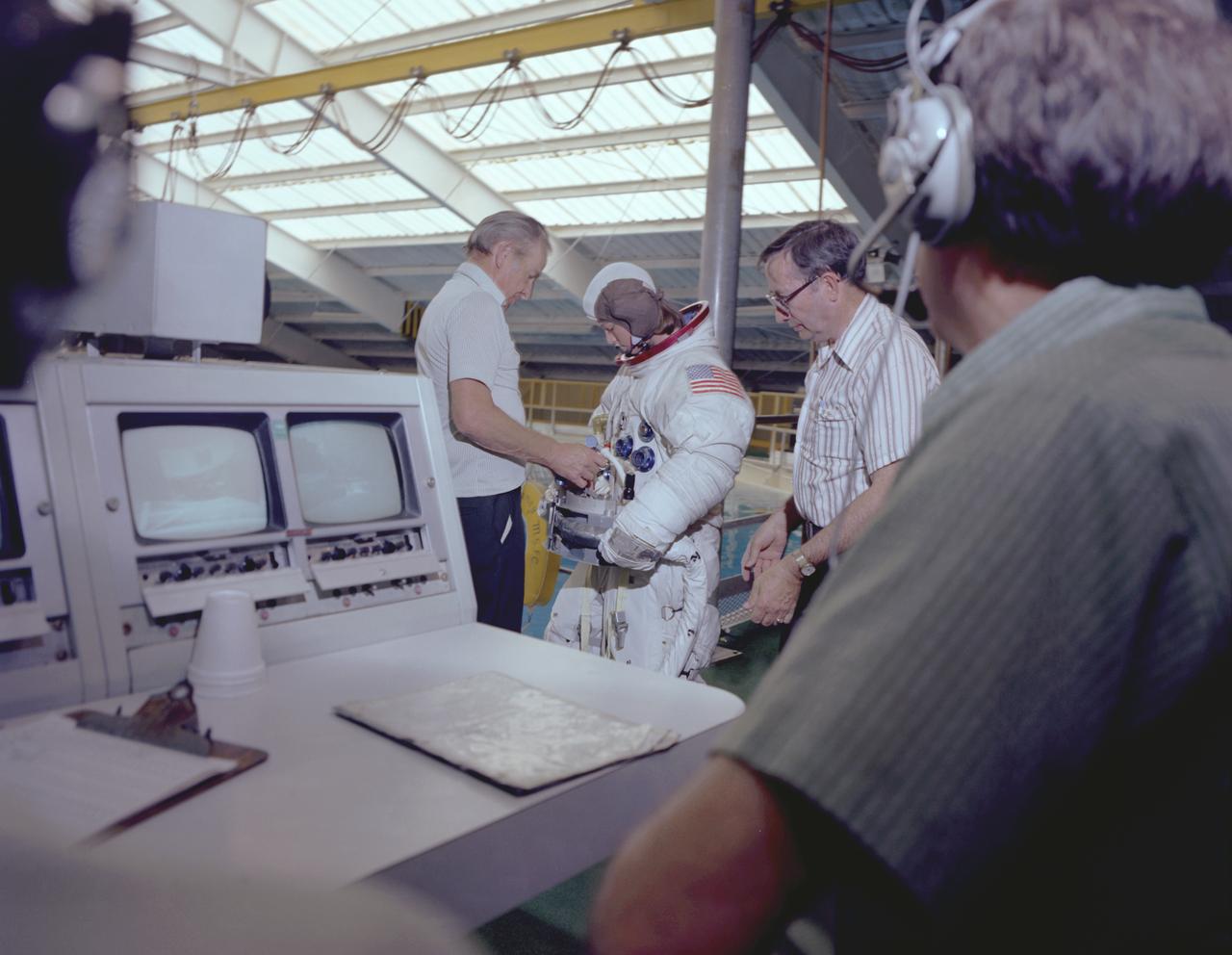
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory; it was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, HST was finally designed and built; and it finally became operational in the 1990s. HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator served as the training facility for shuttle astronauts for Hubble related missions. Shown is astronaut Sharnon Lucid having her life support system being checked prior to entering the NBS to begin training on the space telescope axial scientific instrument changeout.
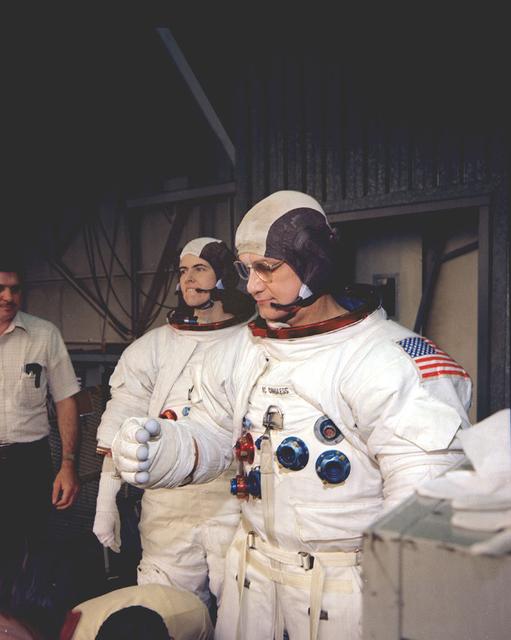

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is a cooperative program of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautical and Space Administration (NASA) to operate a long-lived space-based observatory. It was the flagship mission of NASA's Great Observatories program. The HST program began as an astronomical dream in the 1940s. During the 1970s and 1980s, the HST was finally designed and built becoming operational in the 1990s. The HST was deployed into a low-Earth orbit on April 25, 1990 from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31). The design of the HST took into consideration its length of service and the necessity of repairs and equipment replacement by making the body modular. In doing so, subsequent shuttle missions could recover the HST, replace faulty or obsolete parts and be re-released. Pictured is MSFC's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS) that served as the test center for shuttle astronauts training for Hubble related missions. Shown are astronauts Bruce McCandless and Sharnon Lucid being fitted for their space suits prior to entering the NBS to begin training on the space telescope axial scientific instrument changeout.
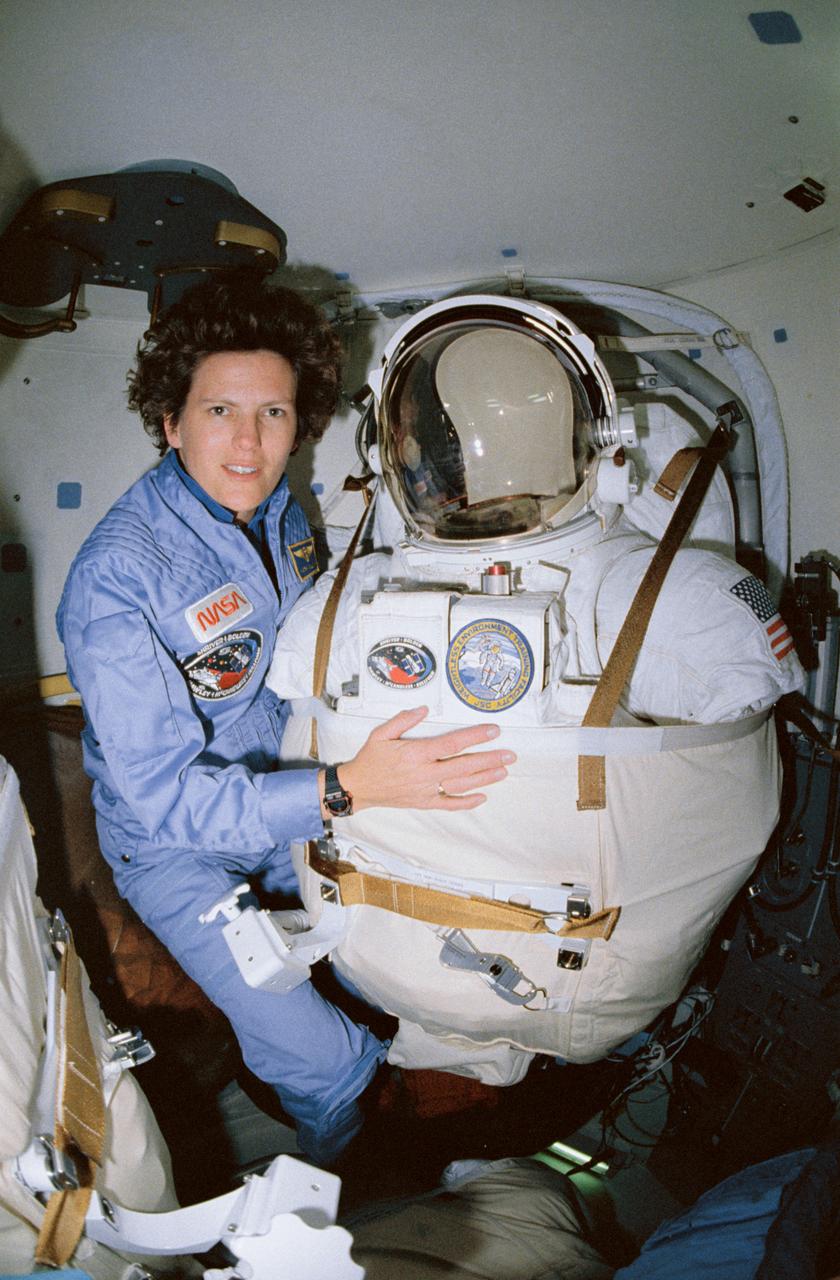

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Kathryn D. Sullivan poses for a picture before beginning extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) donning procedures in the airlock of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Sullivan will remove the lower torso restraint and don EMU which is supported on an airlock adapter plate (AAP). When suited, Sullivan will be ready for contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) in the event that problems arise with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment. Displayed on the front of the EMU are the STS-31 mission insignia and the JSC Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF) insignia.

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS -- STS-31 CREW PATCH – The mission insignia for NASA’s STS-31 mission features the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in its observing configuration against a background of the universe it will study. The cosmos includes a stylistic depiction of galaxies in recognition of the contribution made by Sir Edwin Hubble to our understanding of the nature of galaxies and the expansion of the universe. The STS-31 crew points out that it is in honor of Hubble’s work “that this great observatory in space bears his name.” The depicted Space Shuttle trails a spectrum symbolic of both the red shift observations that were so important to Hubble’s work and now information which will be obtained with the HST. Encircling the art work, designed by the crew, are the names of its members: Loren J. Shriver, mission commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn D. Sullivan, mission specialists. The NASA insignia design for Shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, it will be publicly announced.
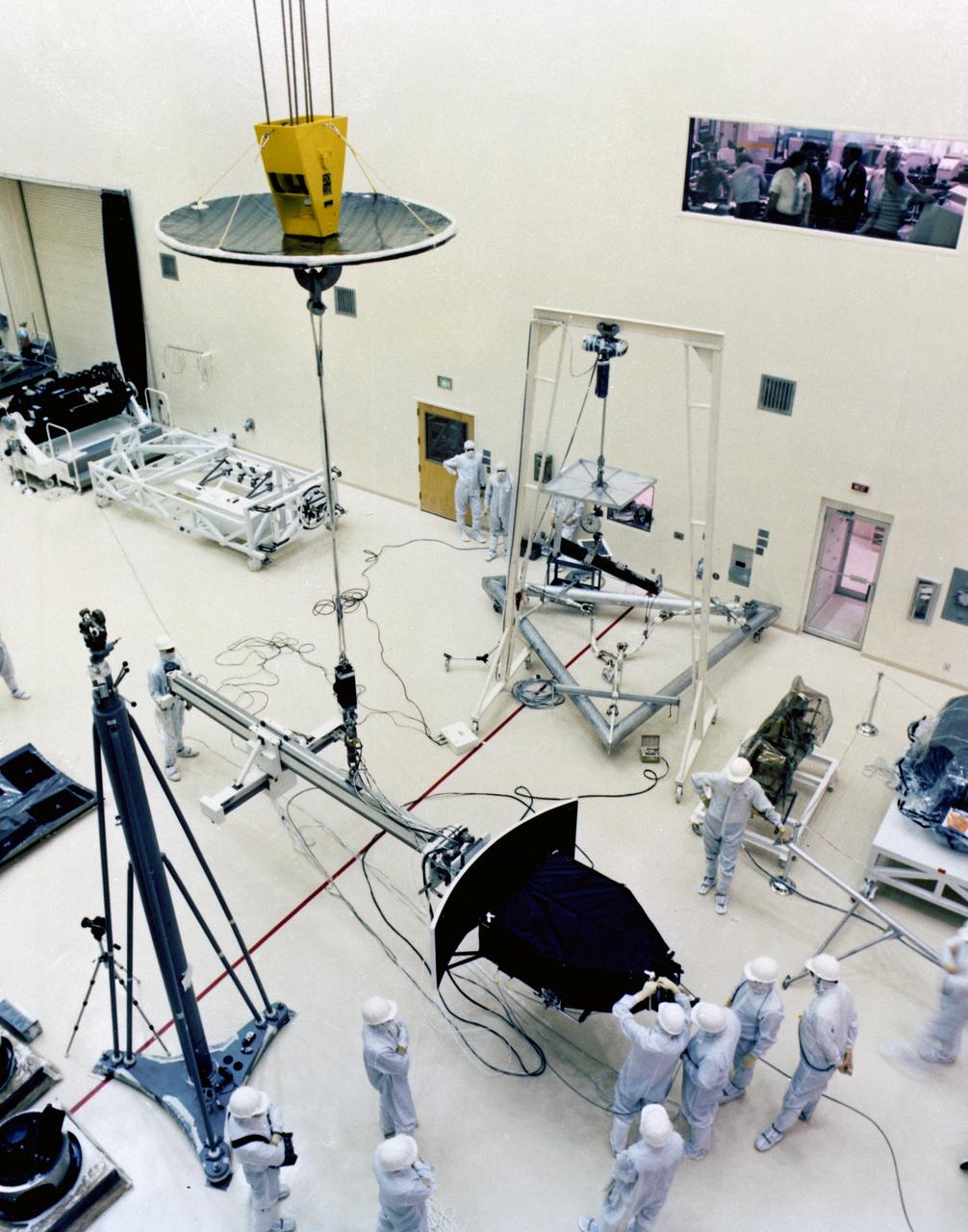

In this photograph, engineers and technicians prepare the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WF/PC) for installation at the Lockheed Missile and Space Company. The WF/PC is designed to investigate the age of the universe and to search for new planetary systems around young stars. It takes pictures of large numbers of galaxies and close-ups of planets in our solar system. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
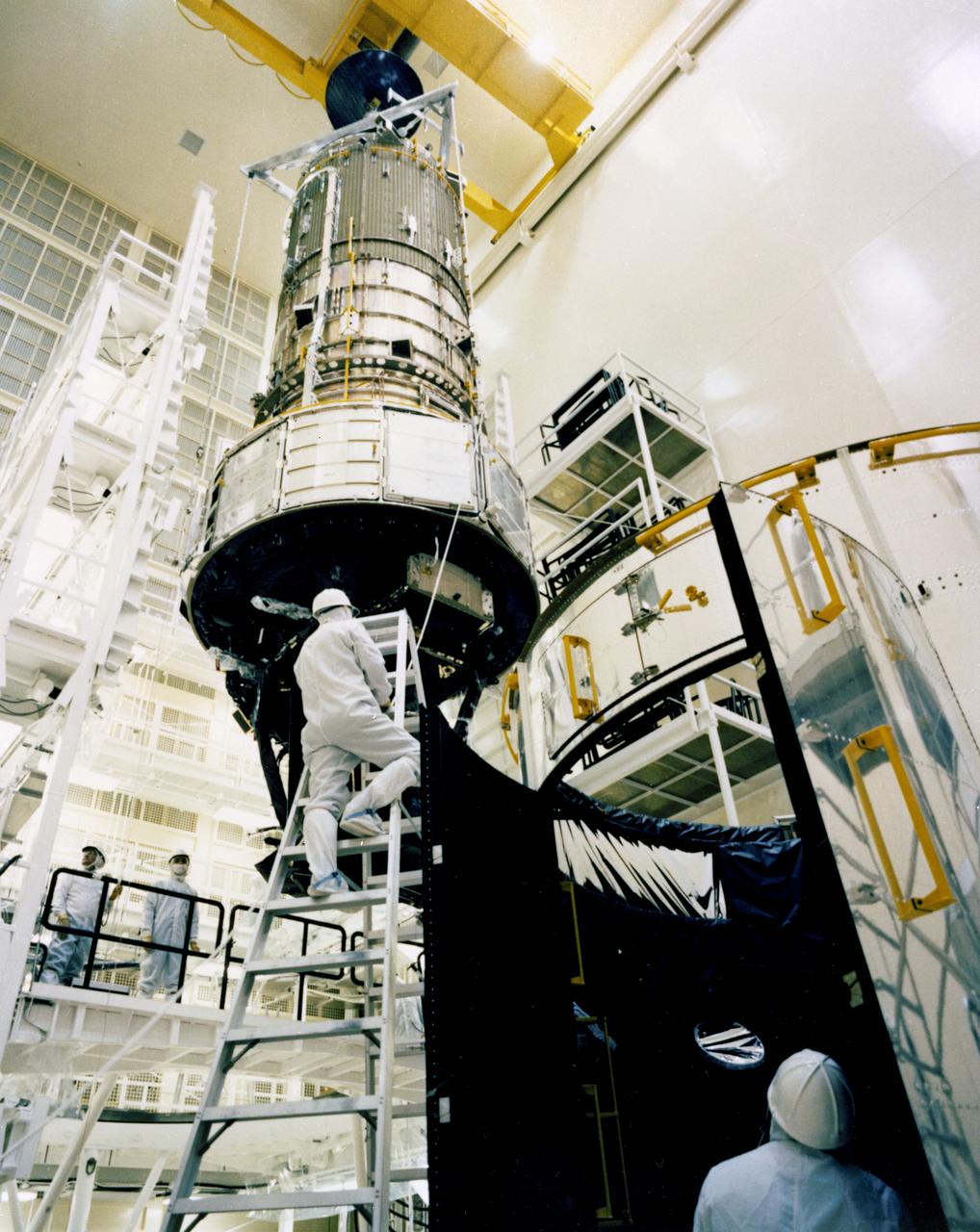

This photograph shows the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being assembled in the clean room of the Lockheed Missile Space Company. The Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA) is being readied for the installation of the AFT shroud. The OTA contains two mirrors, primary and secondary, to collect and focus light from selected celestial objects. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
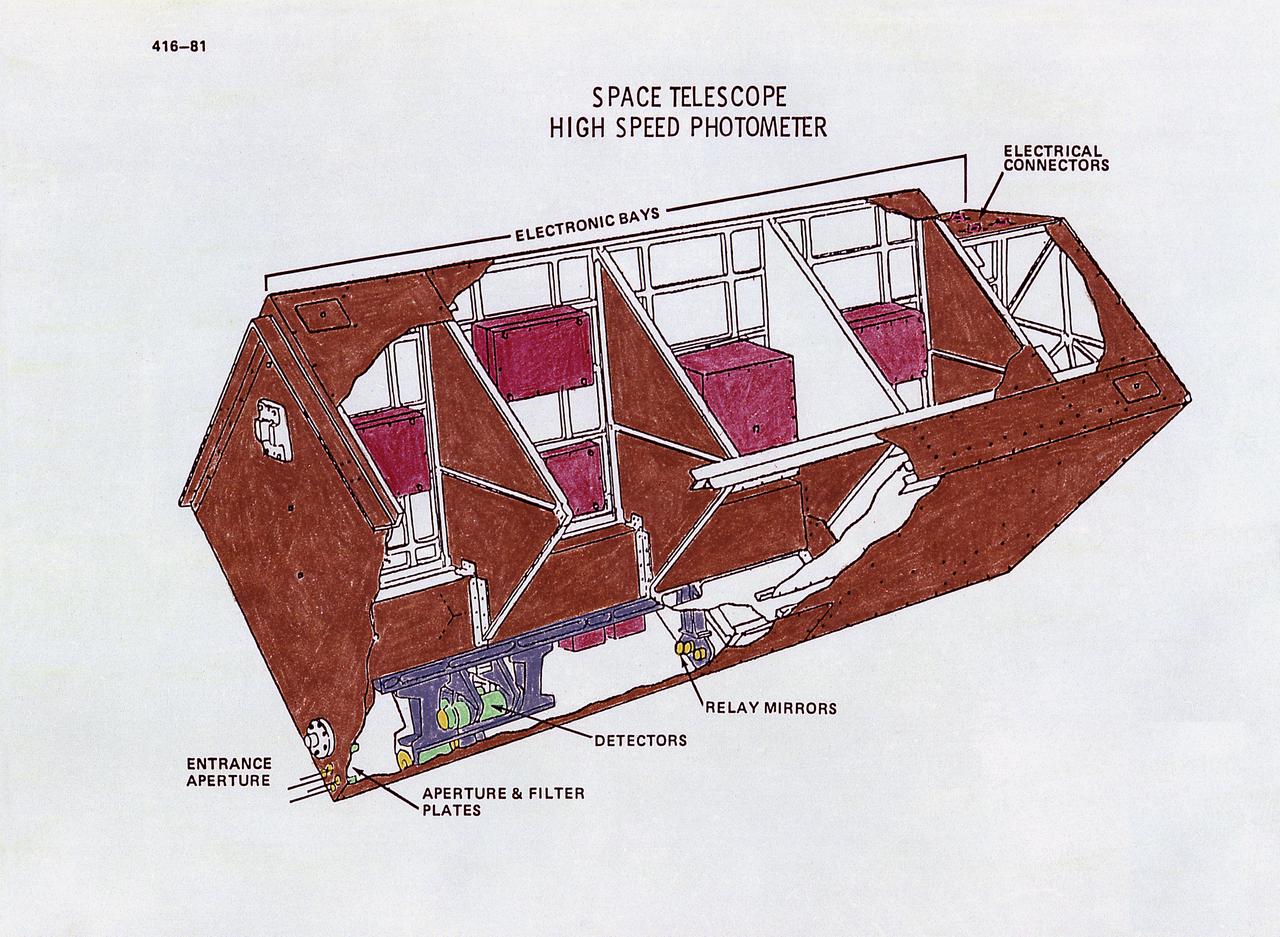
This drawing illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) High Speed Photometer (HSP). The HSP measures the intensity of starlight (brightness), which will help determine astronomical distances. Its principal use will be to measure extremely-rapid variations or pulses in light from celestial objects, such as pulsating stars. The HSP produces brightness readings. Light passes into one of four special signal-multiplying tubes that record the data. The HSP can measure energy fluctuations from objects that pulsate as rapidly as once every 10 microseconds. From HSP data, astronomers expect to learn much about such mysterious objects as pulsars, black holes, and quasars. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
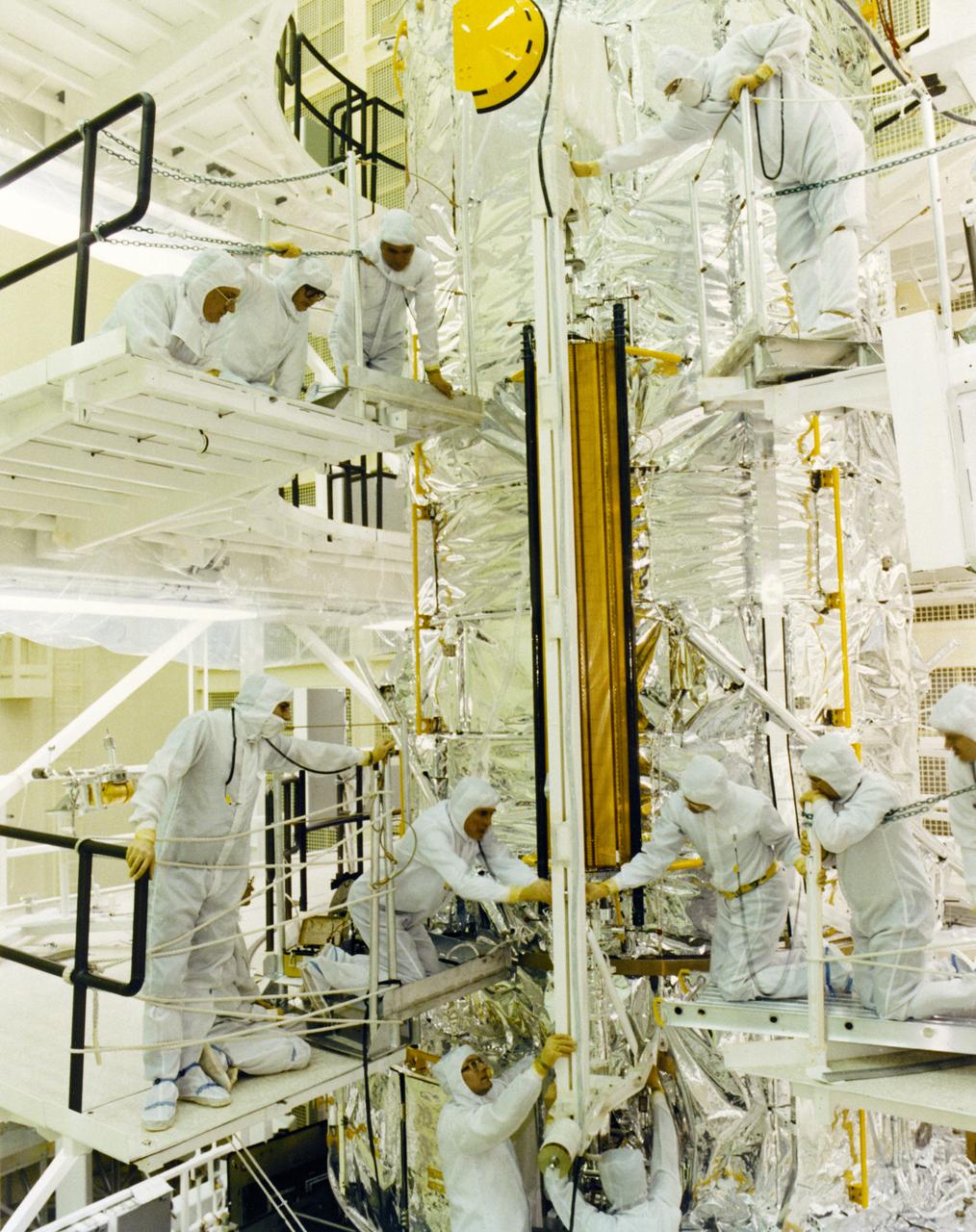

Engineers and technicians conduct a fit check of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Solar Array flight article in a clean room of the Lockheed Missile and Space Company. The Solar Array is 40- feet (12.1-meters) long and 8.2-feet (2.5-meters) wide, and provides power to the spacecraft. The HST is the first of NASA's great observatories and the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made. The purpose of the HST is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit by placing the telescope in space, enabling astronomers to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had overall responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company, Sunnyvale, California, produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

This is an artist's concept of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than is visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
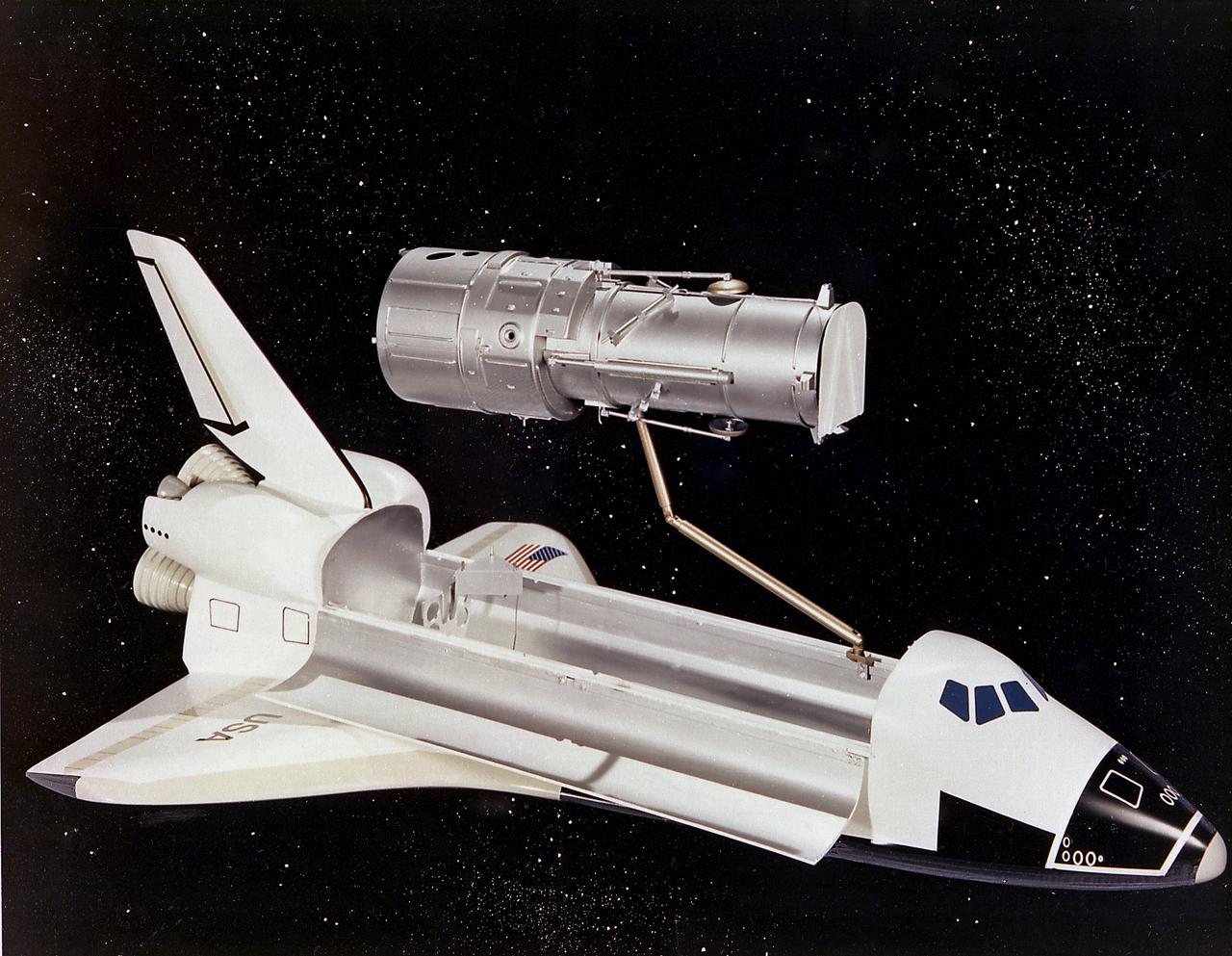
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being positioned for release from the Space Shuttle orbiter by the Remote Manipulator System (RMS). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13- meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
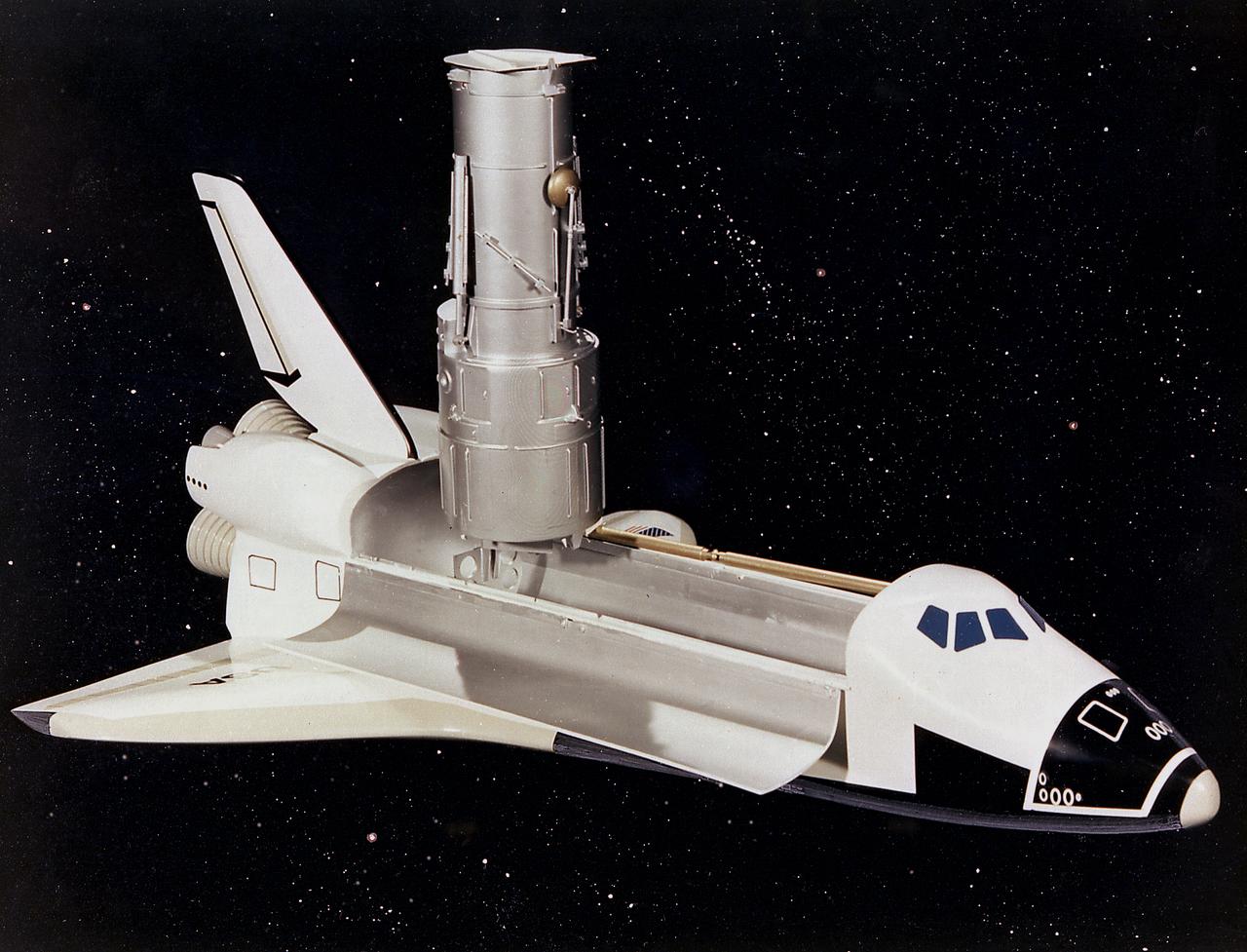
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being raised to a vertical position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
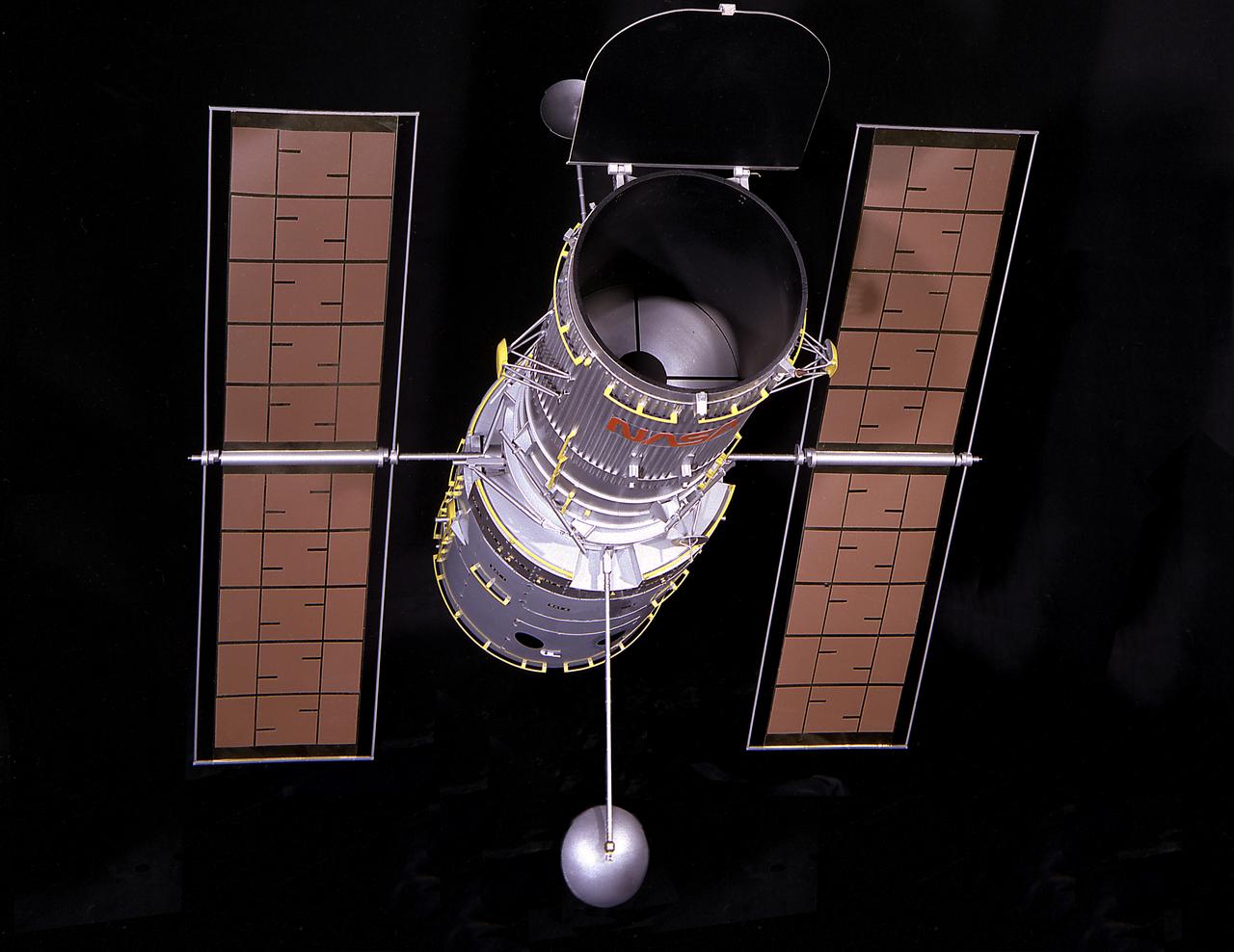
This is a photograph of a 1/15 scale model of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13- meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
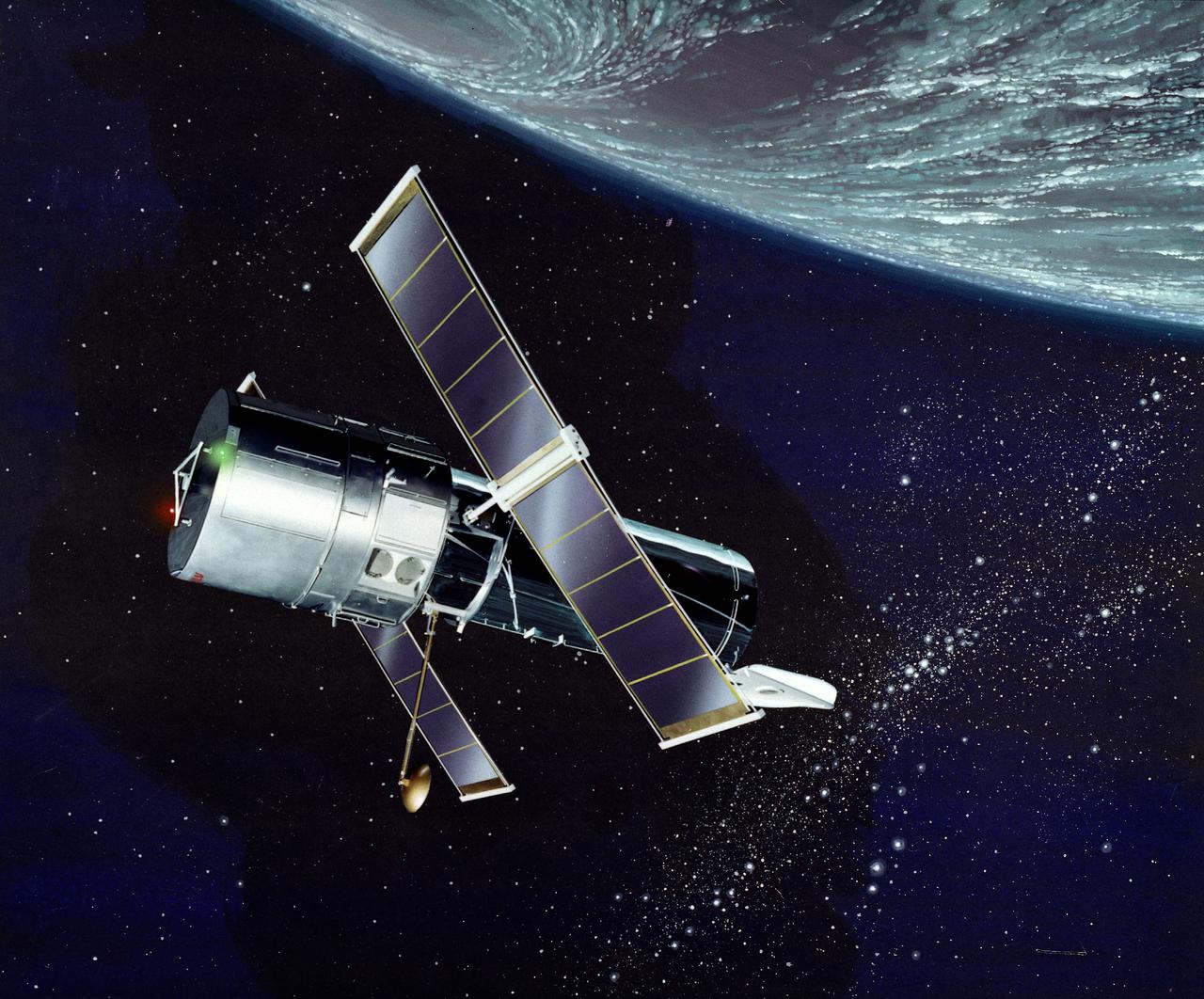

This illustration depicts a side view of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
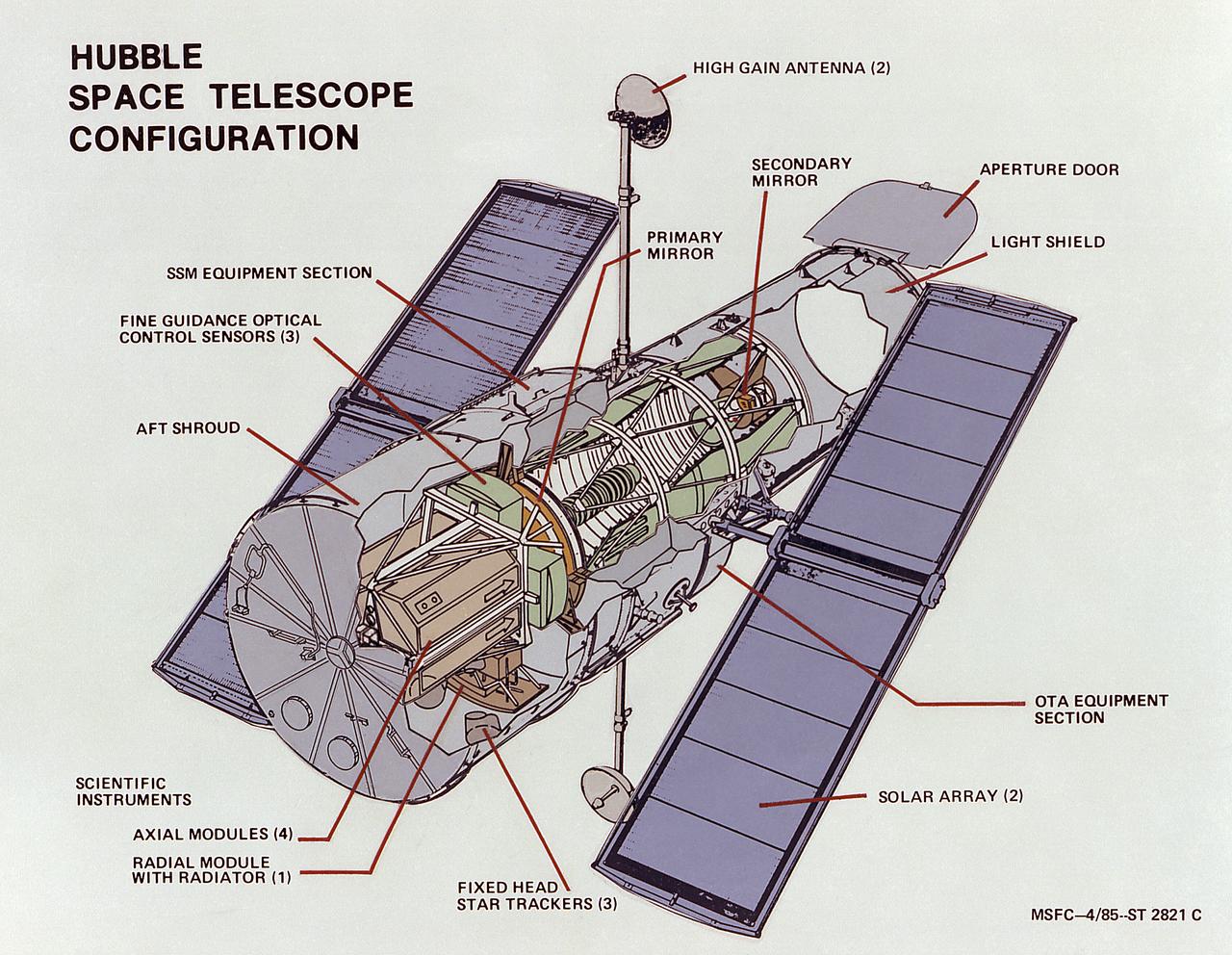
This image illustrates the overall Hubble Space Telescope (HST) configuration. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is approximately the size of a railroad car, with two cylinders joined together and wrapped in a silvery reflective heat shield blanket. Wing-like solar arrays extend horizontally from each side of these cylinders, and dish-shaped anternas extend above and below the body of the telescope. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
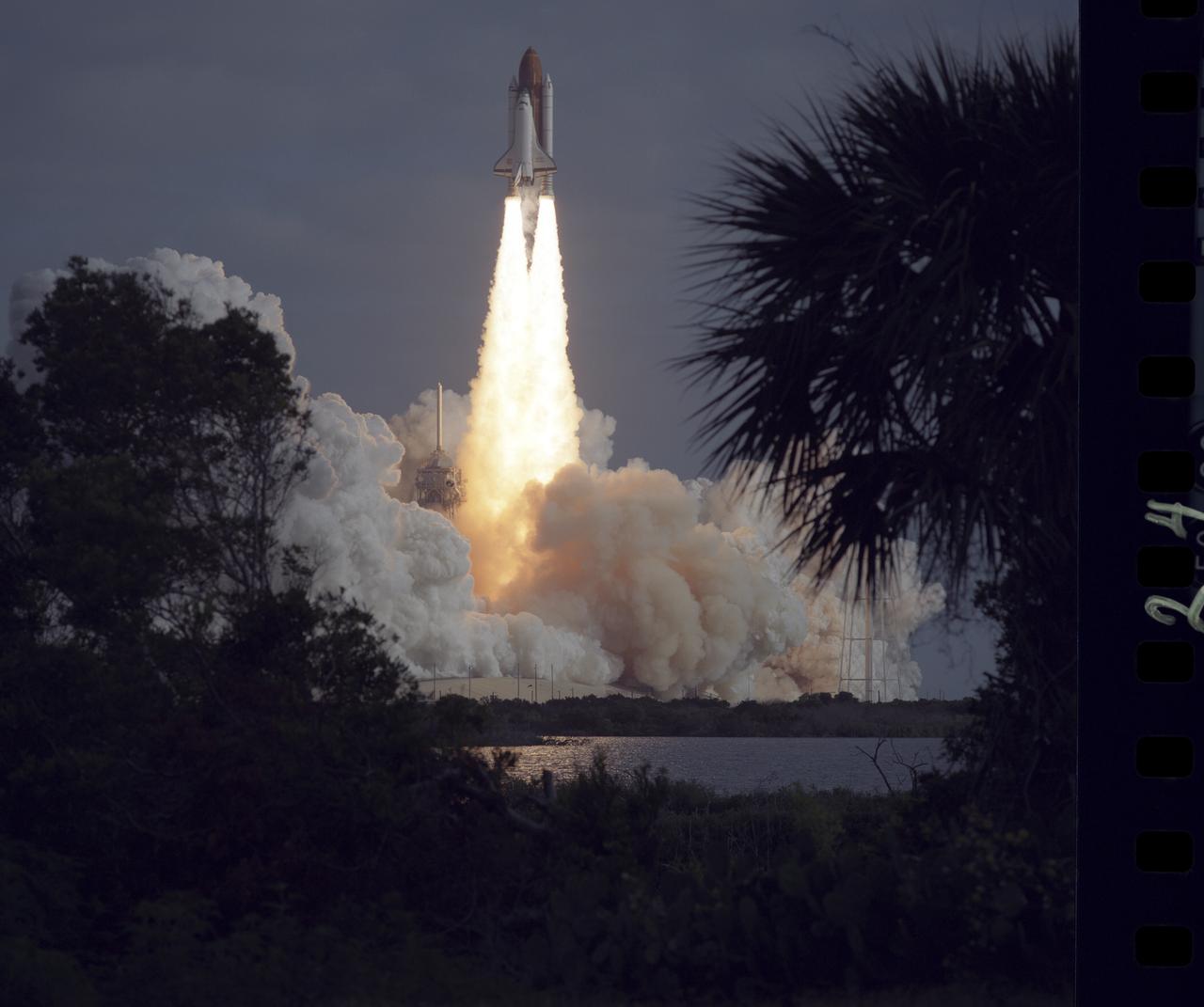

The STS-31 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT). Included in the crew of five were Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists. The primary goal of the mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed program.
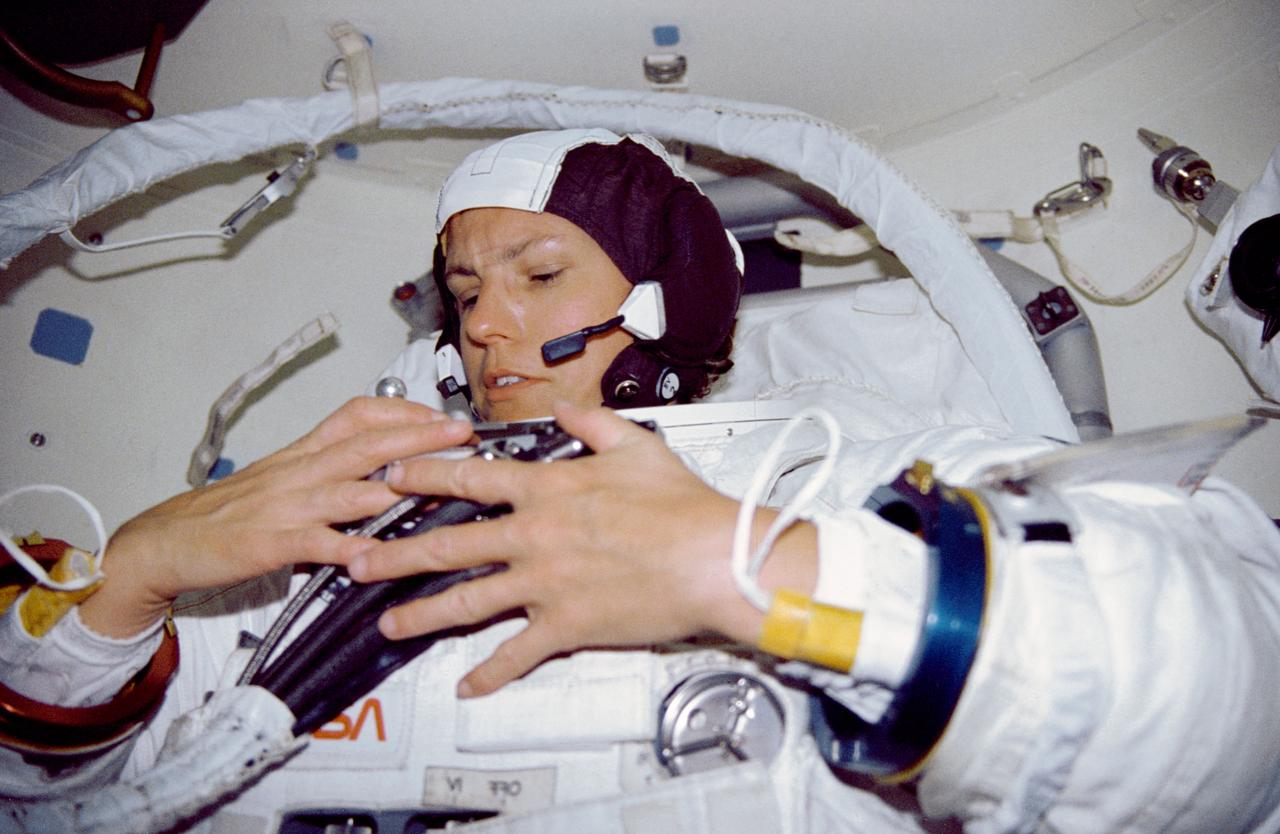
STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Kathryn D. Sullivan, wearing extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) & communications carrier assembly (CCA), attaches service and cooling umbilical (SCU) to the EMU connection on the display & control module (DCM) during contingency extravehicular activity (EVA) preparations in the airlock of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. The procedure was completed in case an EVA was required to support Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment.
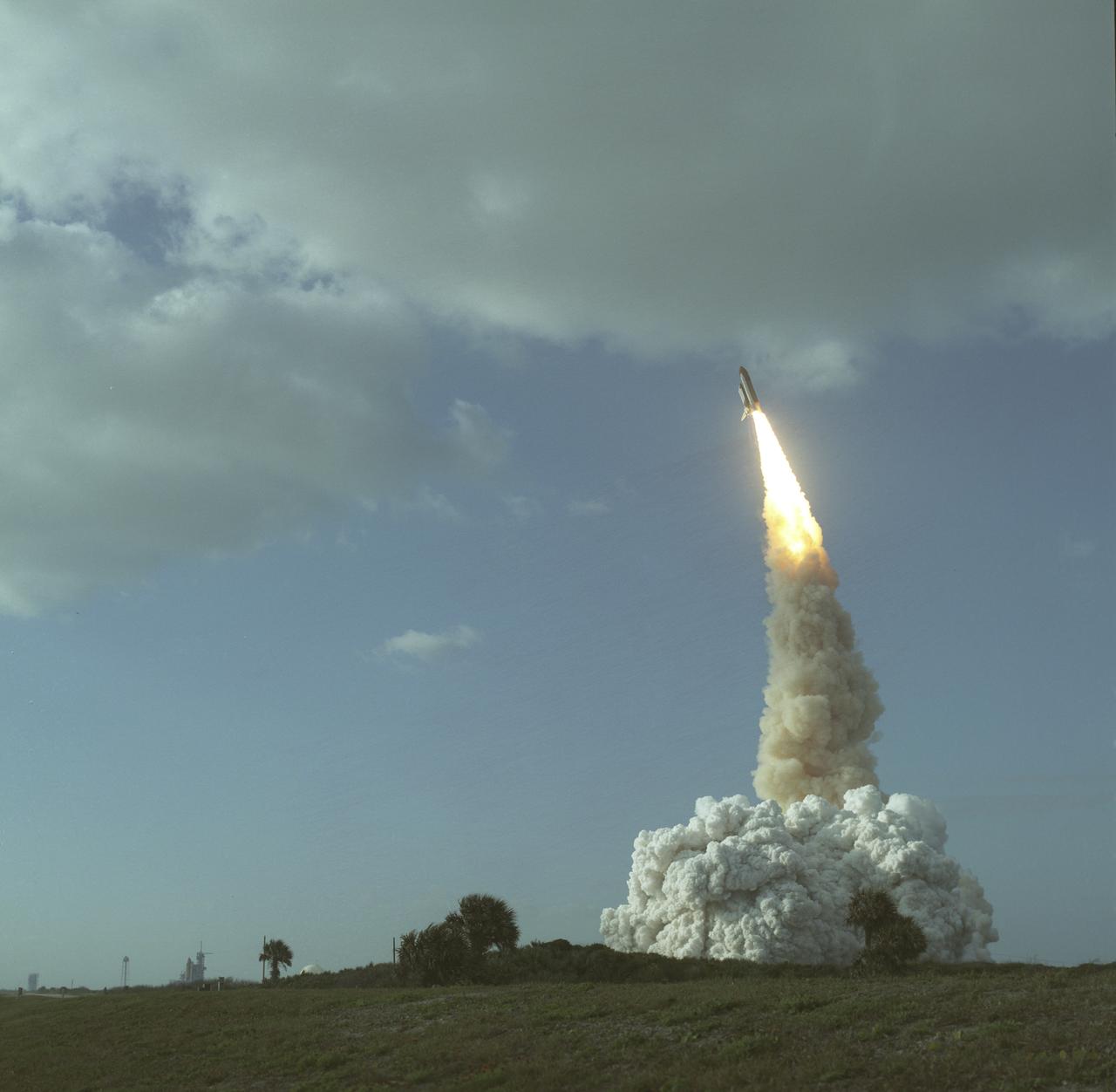

The STS-31 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT). Included in the crew of five were Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists. The primary goal of the mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed program.
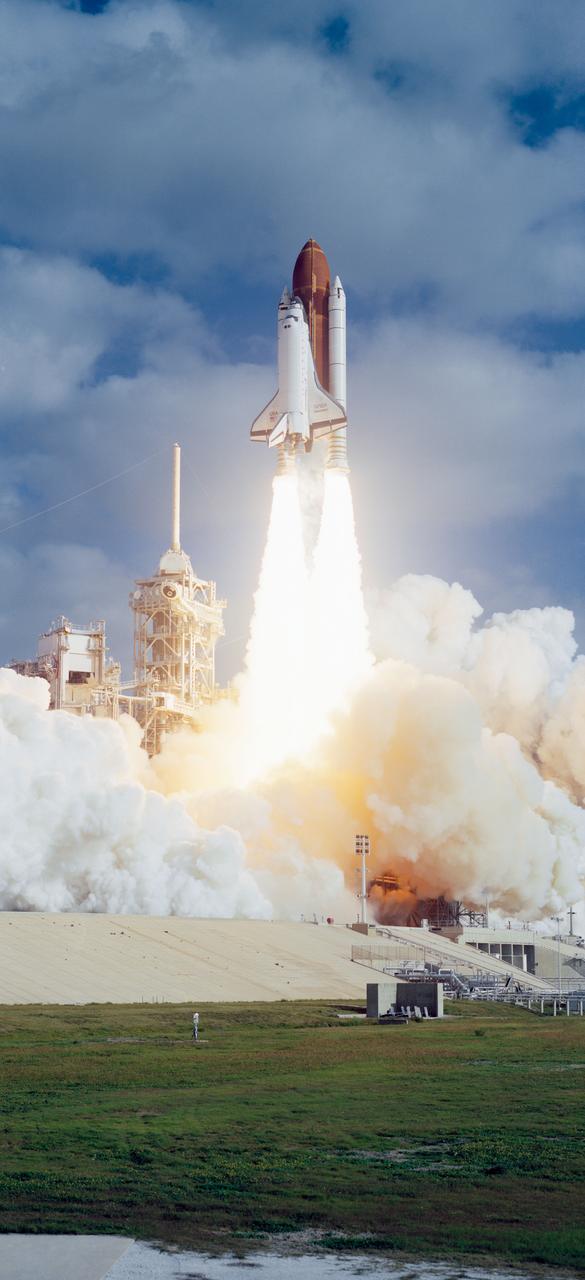

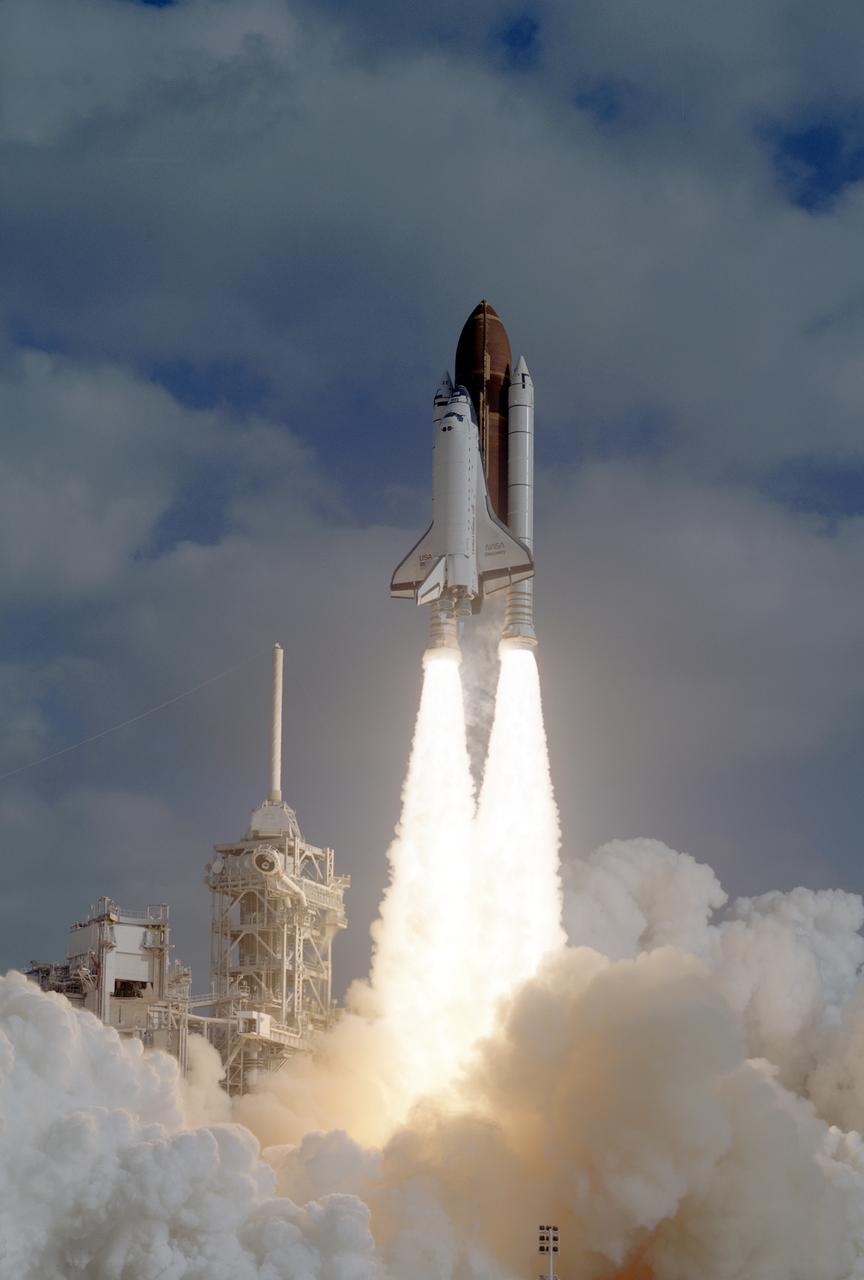
STS031-S-073 (24 April 1990) --? A vertical view of the launch of the STS-31 mission. Onboard Space Shuttle Discovery are the crew of five veteran astronauts and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Official launch time was 8:33:51.0492 a.m. (EDT). Headed for approximately five days in space are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Bruce McCandless, II, Kathryn D. Sullivan, and Steven A. Hawley.
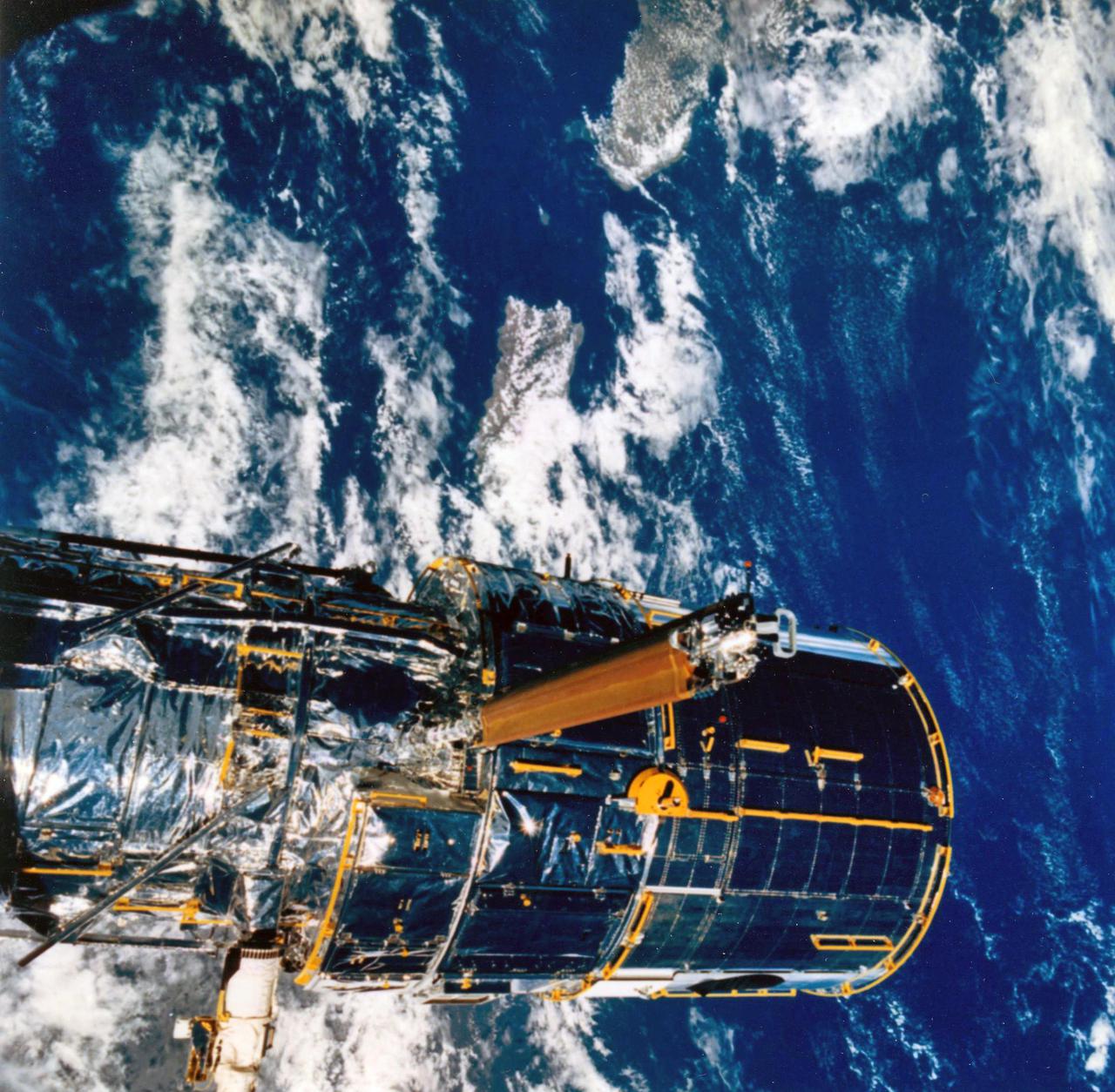

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS-- STS-31 ONBOARD SCENE -- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is suspended in space by Discovery's remote manipulator system prior to deployment of its solar array panels and antennae and its ultimate release. Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic are recognizable at left of the frame. The photo was taken with a handheld Hasselblad camera. This was among the first photos NASA released on April 30 from the five-day mission.
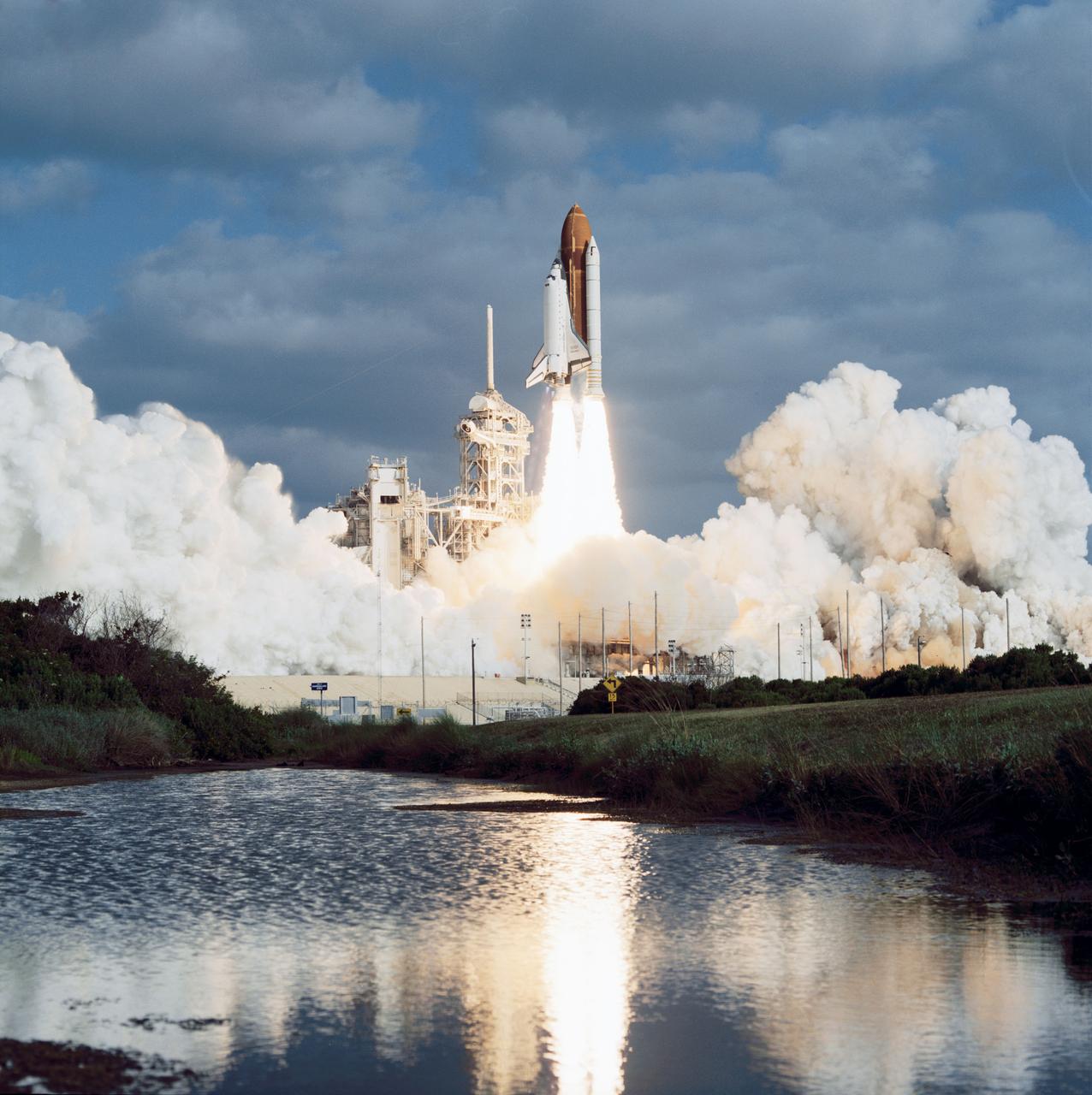

STS031-S-064 (24 April 1990) --- A horizontal view of the launch of the STS-31 mission. Onboard Space Shuttle Discovery are the crew of five veteran astronauts and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Official launch time was 8:33:51.0492 a.m. (EDT). Headed for approximately five days in space are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Bruce McCandless, II, Kathryn D. Sullivan, and Steven A. Hawley.
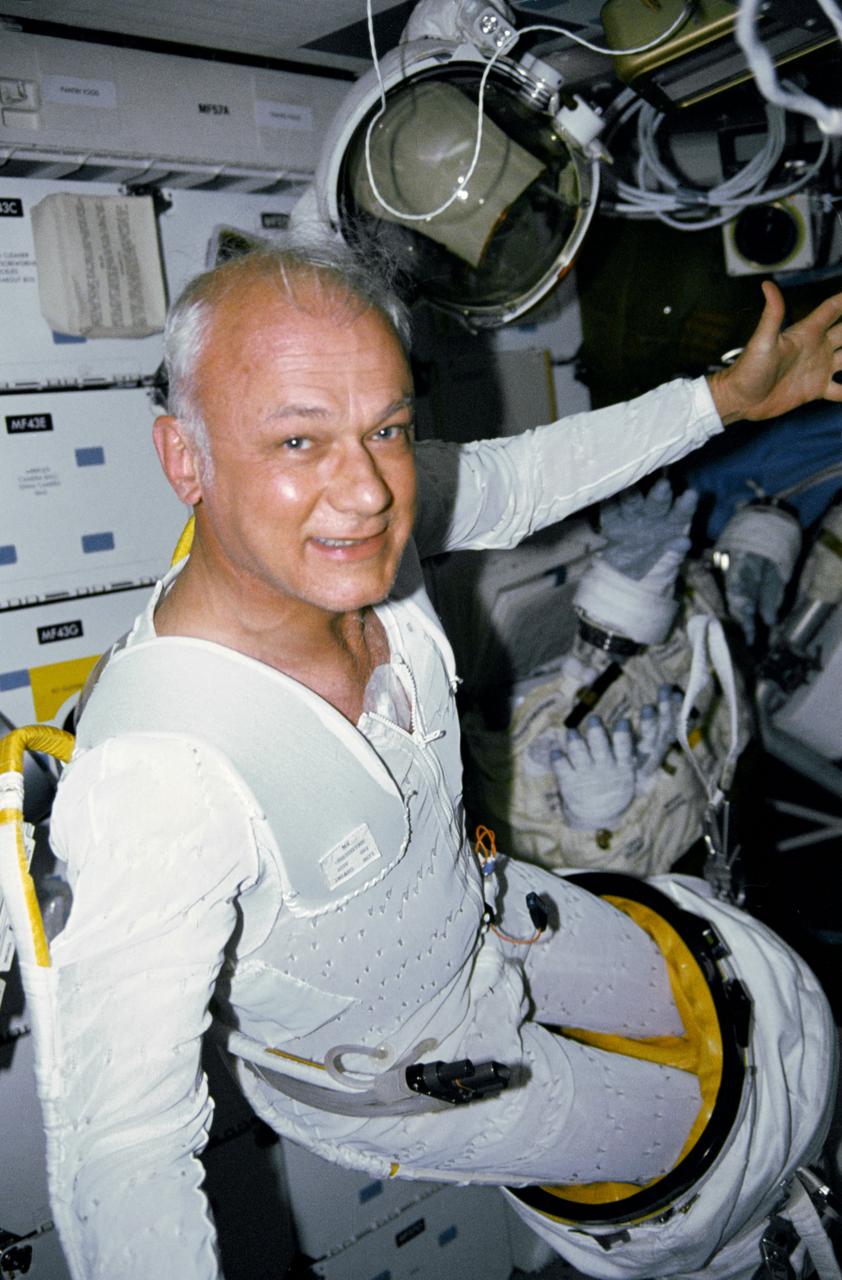

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Bruce McCandless II, wearing liquid cooling and ventilation garment (LCVG), works his way out of the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) lower torso on the middeck of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. McCandless was in a standby mode to perform extravehicular activity (EVA) if needed to support Hubble Space Telescope (HST) deployment and post- deployment tasks. None was needed. His helmet and gloves freefloat in the background.

The STS-31 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT). Included in the crew of five were Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists. The primary goal of the mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed program.

The STS-31 crew launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990 at 8:33:51am (EDT). Included in the crew of five were Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless, and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists. The primary goal of the mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) which was a Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) managed program.
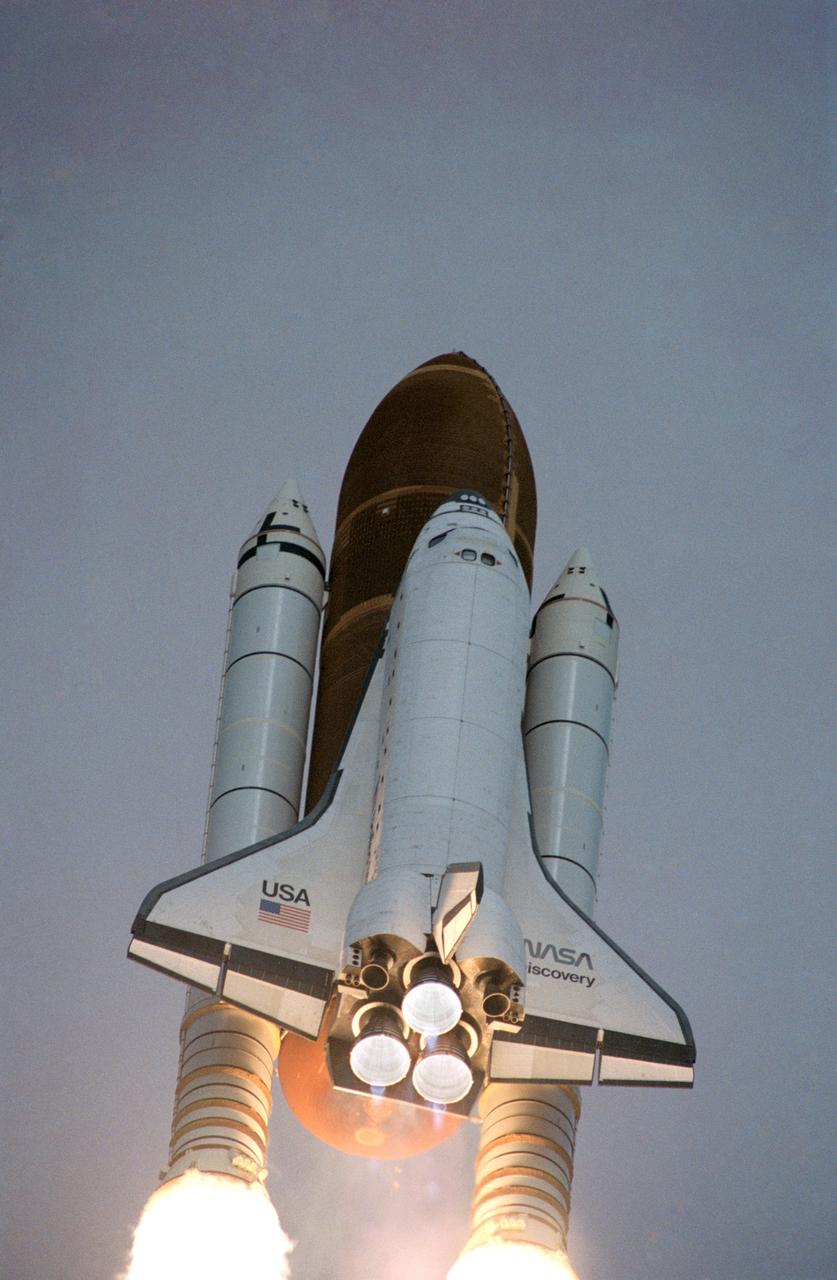
STS031-S-074 (24 April 1990) --- A low-angle view of the launch of the STS-31 mission. Onboard Discovery are a crew of five veteran astronauts and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Official launch time was 8:33:51.0492 a.m. (EDT). Headed for approximately five days in space are astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden Jr., Bruce McCandless II, Kathryn D. Sullivan and Steven S. Hawley.
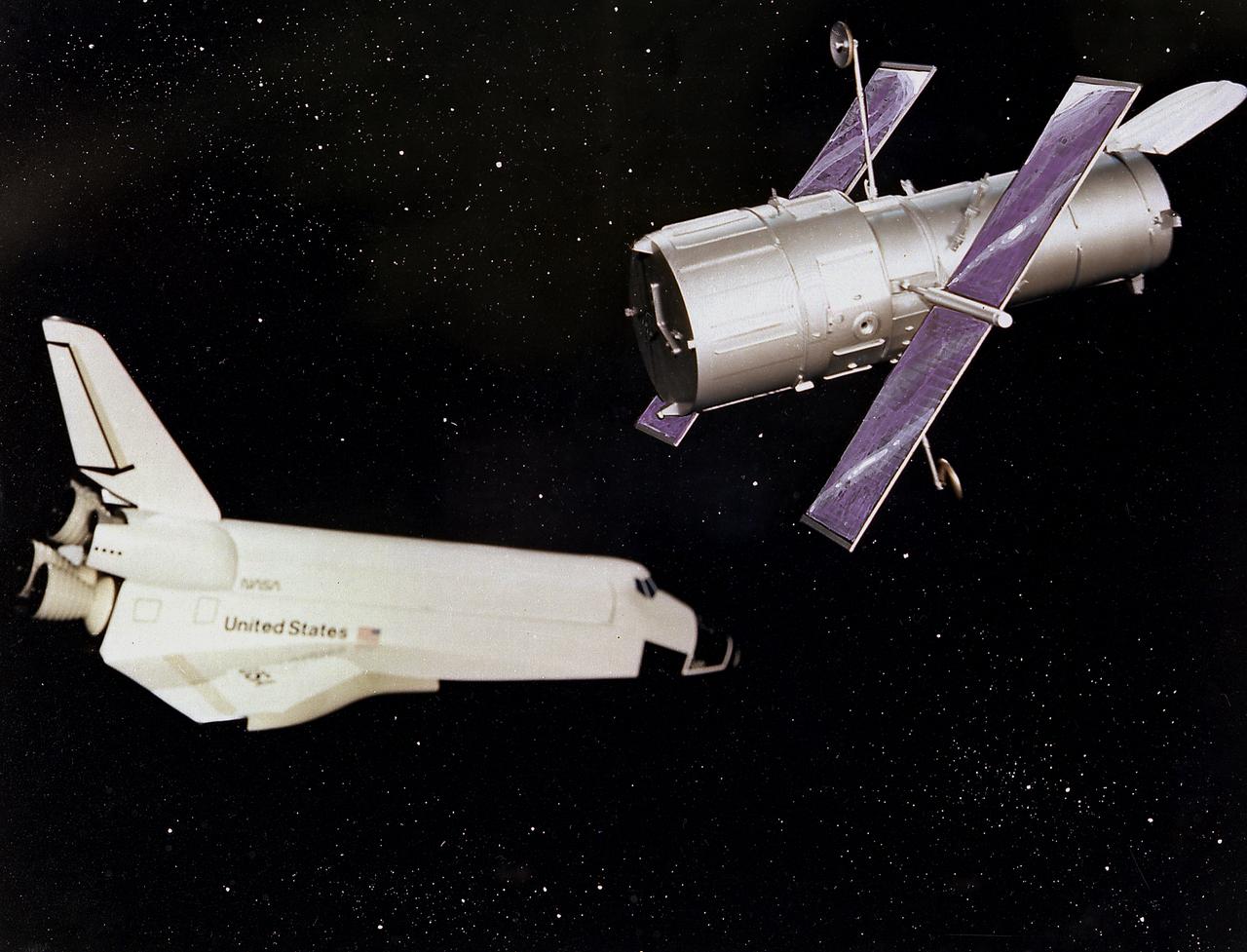
This artist's concept depicts the Hubble Space Telescope after being released into orbit, with the high gain anternas and solar arrays deployed and the aperture doors opened. The HST is the product of a partnership between NASA, European Space Agency Contractors, and the international community of astronomers. It is named after Edwin P. Hubble, an American Astronomer who discovered the expanding nature of the universe and was the first to realize the true nature of galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The major elements of the HST are the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), the Support System Module (SSM), and the Scientific Instruments (SI). The HST is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs about 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

This illustration depicts the design features of the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Support Systems Module (SSM). The SSM is one of the three major elements of the HST and encloses the other two elements, the Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA) and the Scientific Instruments (SI's). The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5-feet (13-meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). Two communication anternas, two solar array panels that collect energy for the HST, and storage bays for electronic gear are on the outside. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Connecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.

S89-40887 (October 1989) --- The mission insignia for NASA?s STS-31 mission features the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) in its observing configuration against a background of the universe it will study. The cosmos includes a stylistic depiction of galaxies in recognition of the contribution made by Sir Edwin Hubble to our understanding of the nature of galaxies and the expansion of the universe. The STS-31 crew points out that it is in honor of Hubble?s work ?that this great observatory in space bears his name.? The depicted space shuttle trails a spectrum symbolic of both the red shift observations that were so important to Hubble?s work and new information which will be obtained with the HST. Encircling the artwork, designed by the crew, are the names of its members: Loren J. Shriver, commander; Charles F. Bolden, pilot; and Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn D. Sullivan, mission specialists. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
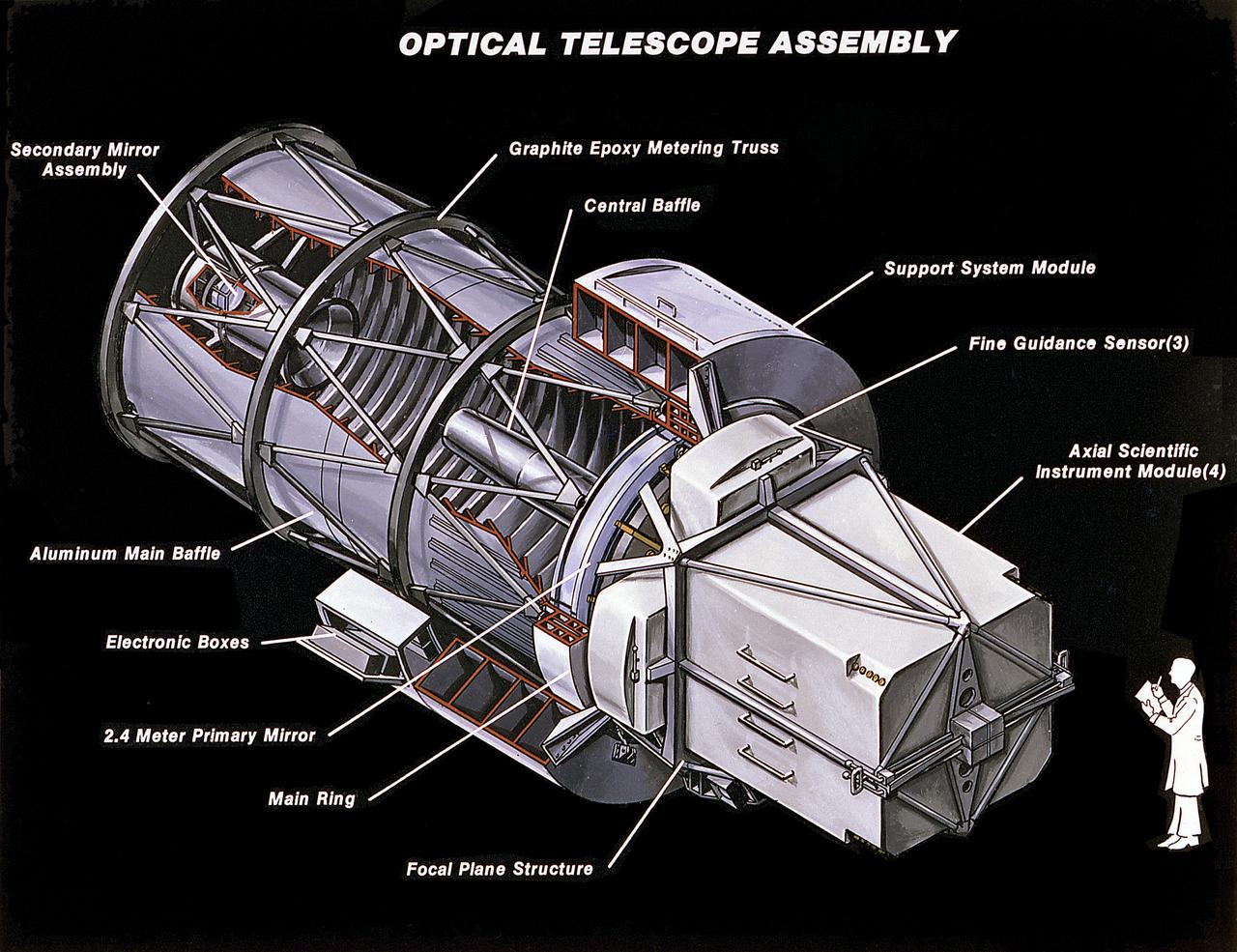
This image illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA). One of the three major elements of the HST, the OTA consists of two mirrors (a primary mirror and a secondary mirror), support trusses, and the focal plane structure. The mirrors collect and focus light from selected celestial objects and are housed near the center of the telescope. The primary mirror captures light from objects in space and focuses it toward the secondary mirror. The secondary mirror redirects the light to a focal plane where the Scientific Instruments are located. The primary mirror is 94.5 inches (2.4 meters) in diameter and the secondary mirror is 12.2 inches (0.3 meters) in diameter. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth Orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from the Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The spacecraft is 42.5 feet (13 meters) long and weighs 25,000 pounds (11,600 kilograms). The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
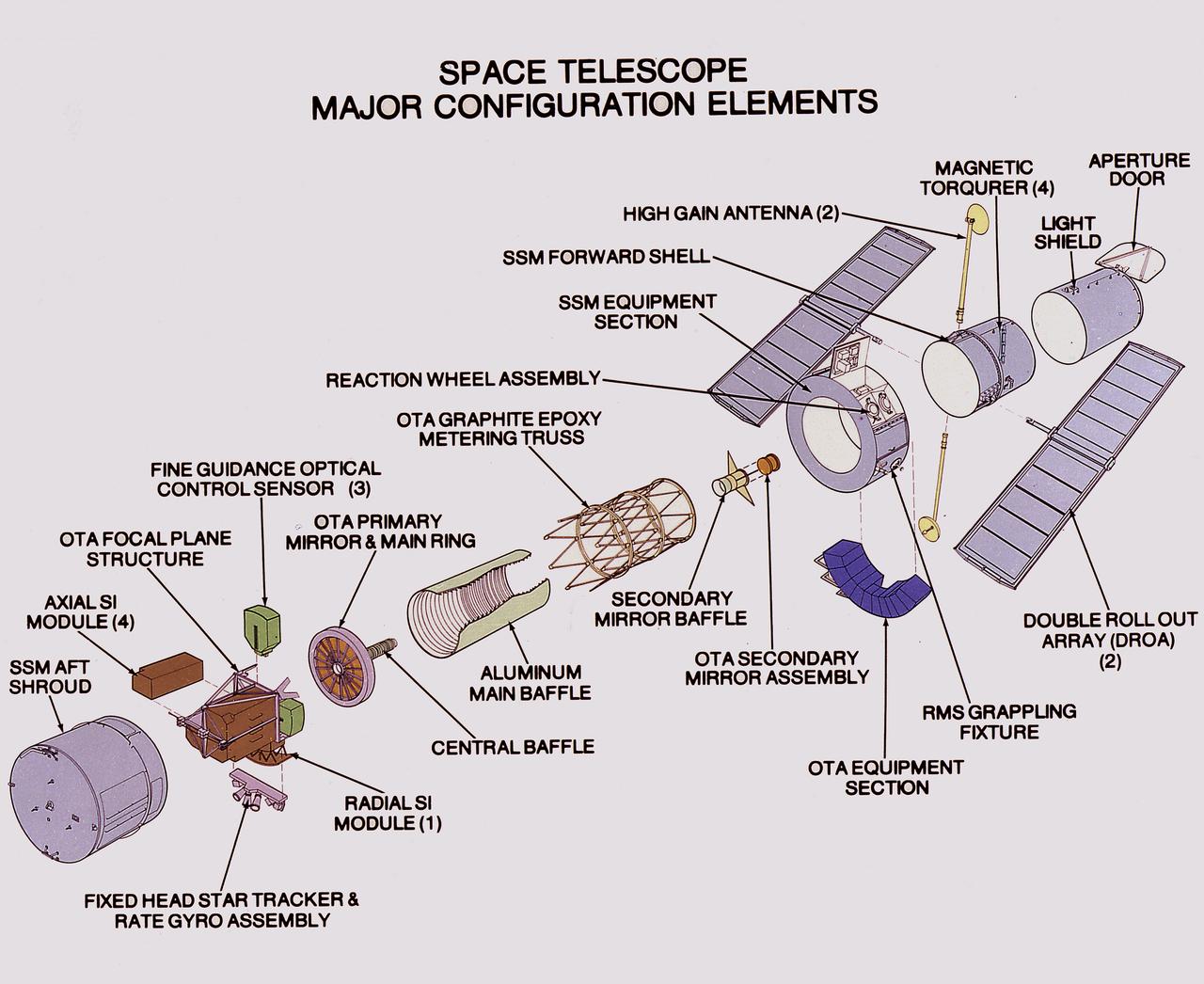
This illustration shows the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's) major configuration elements. The spacecraft has three interacting systems: The Support System Module (SSM), an outer structure that houses the other systems and provides services such as power, communication, and control; The Optical Telescope Assembly (OTA), which collects and concentrates the incoming light in the focal plane for use by the Scientific Instruments (SI); and five SIs. The SI Control and Data Handling (CDH) unit controls the five SI's, four that are housed in an aft section focal plane structure and one that is placed along the circumference of the spacecraft. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors. The Lockheed Missile and Space Company of Sunnyvale, California produced the protective outer shroud and spacecraft systems, and assembled and tested the finished telescope.
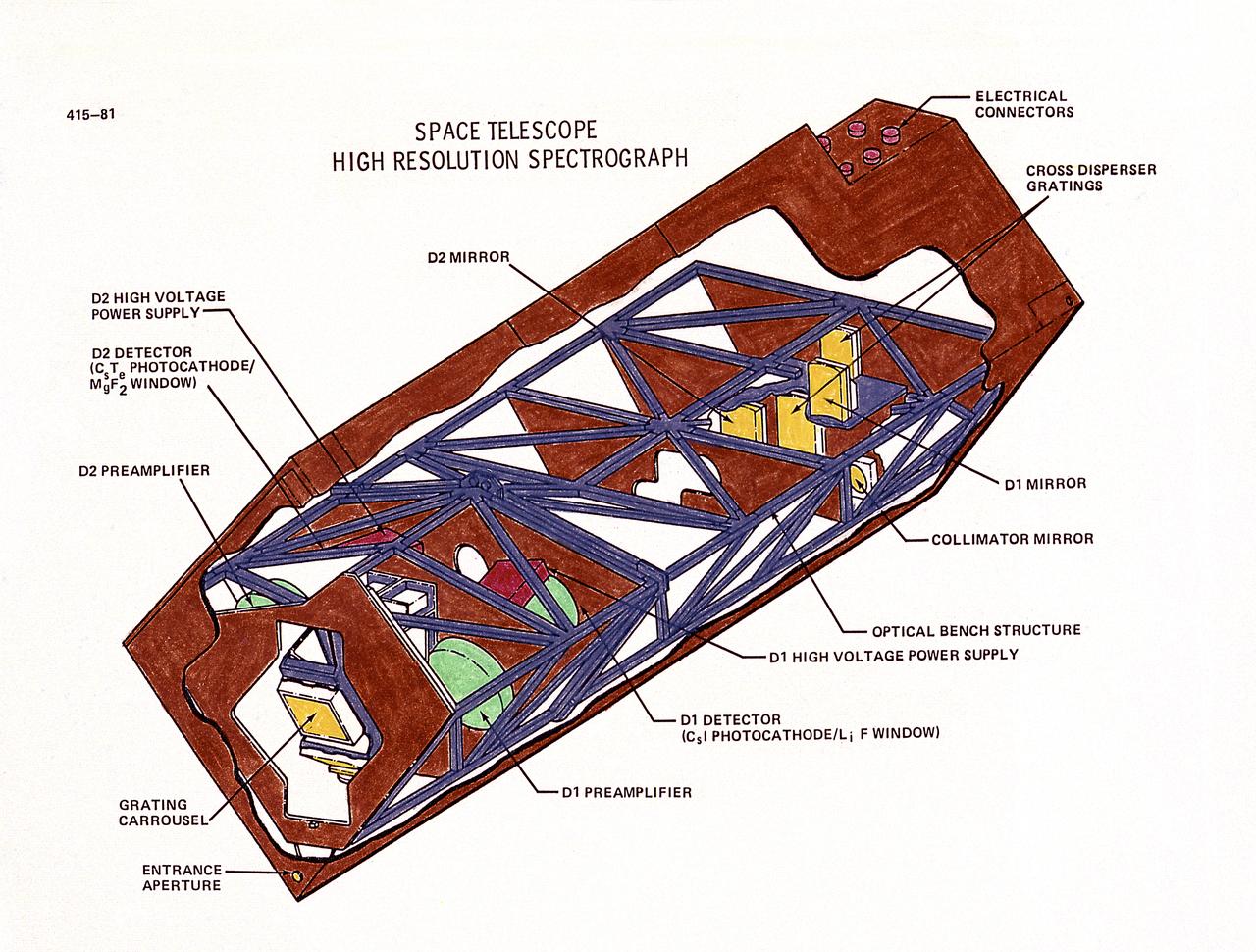
This drawing illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Goddard High-Resolution Spectrograph (GHRS). The HST's two spectrographs, the GHRS and the Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS), can detect a broader range of wavelengths than is possible from Earth because there is no atmosphere to absorb certain wavelengths. Scientists can determine the chemical composition, temperature, pressure, and turbulence of the stellar atmosphere producing the light, all from spectral data. The GHRS can detect fine details in the light from somewhat brighter objects but only ultraviolet light. Both spectrographs operate in essentially the same way. The incoming light passes through a small entrance aperture, then passes through filters and diffraction gratings, that work like prisms. The filter or grating used determines what range of wavelength will be examined and in what detail. Then the spectrograph detectors record the strength of each wavelength band and sends it back to Earth. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
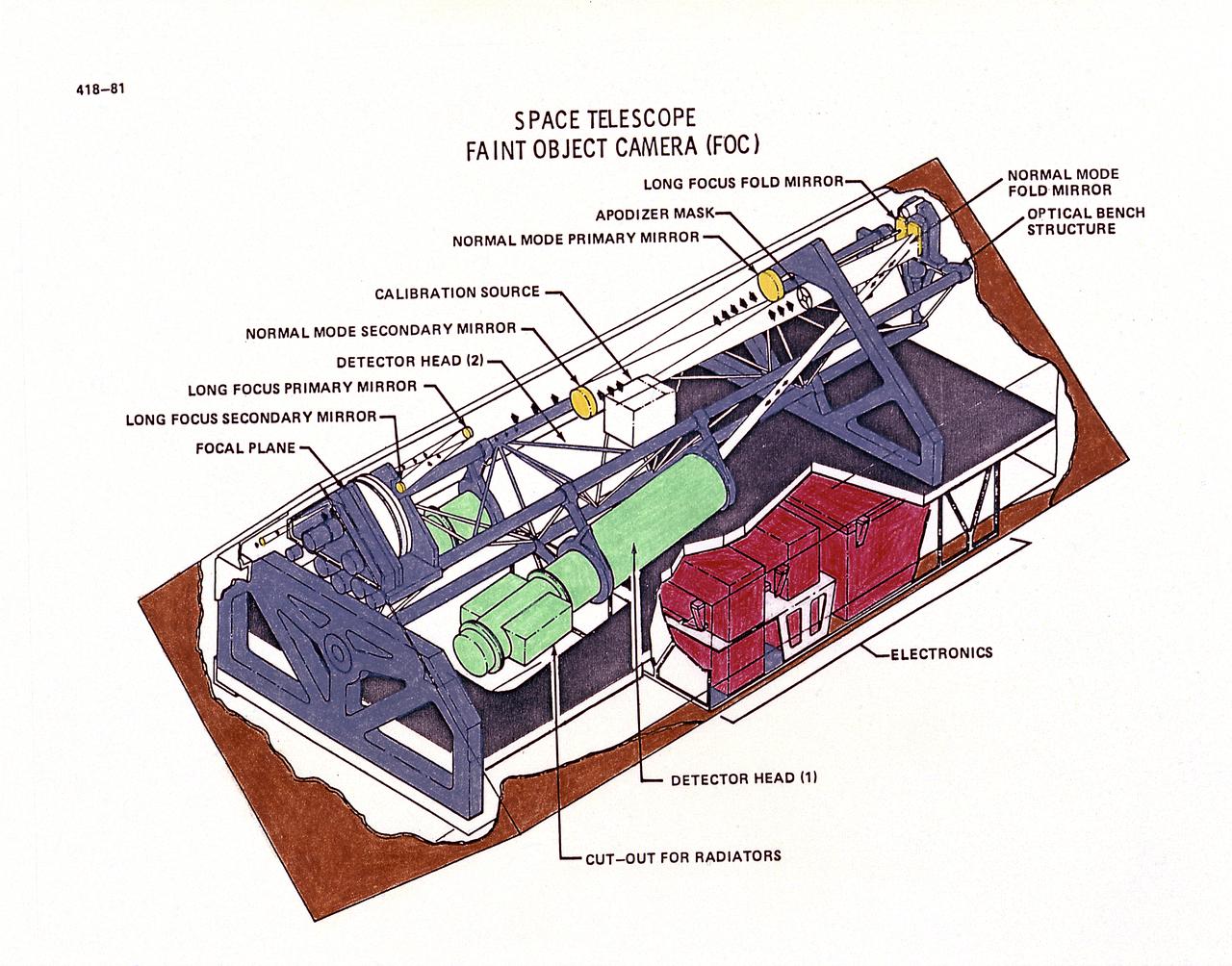
This drawing illustrates Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Faint Object Camera (FOC). The FOC reflects light down one of two optical pathways. The light enters a detector after passing through filters or through devices that can block out light from bright objects. Light from bright objects is blocked out to enable the FOC to see background images. The detector intensifies the image, then records it much like a television camera. For faint objects, images can be built up over long exposure times. The total image is translated into digital data, transmitted to Earth, and then reconstructed. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
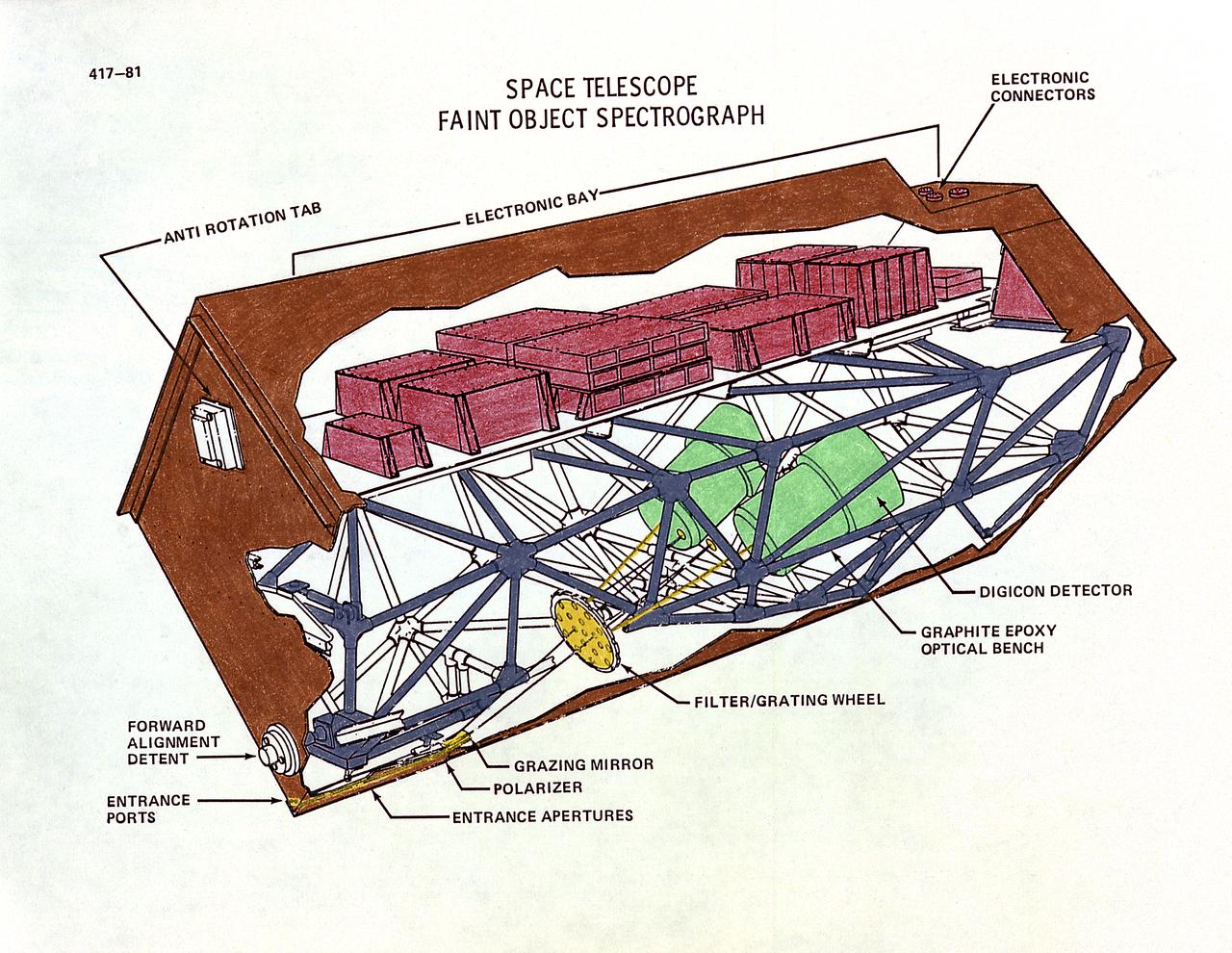
This drawing illustrates the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Faint Object Spectrograph (FOS). The HST's two spectrographs, the Goddard High-Resolution Spectrograph and the FOS, can detect a broader range of wavelengths than is possible from the Earth because there is no atmosphere to absorb certain wavelengths. Scientists can determine the chemical composition, temperature, pressure, and turbulence of the stellar atmosphere producing the light, all from spectral data. The FOC can detect detail in very faint objects, such as those at great distances, and light ranging from ultraviolet to red spectral bands. Both spectrographs operate in essentially the same way. The incoming light passes through a small entrance aperture, then passes through filters and diffraction gratings, that work like prisms. The filter or grating used determines what range of wavelength will be examined and in what detail. Then the spectrograph detectors record the strength of each wavelength band and sends it back to Earth. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.
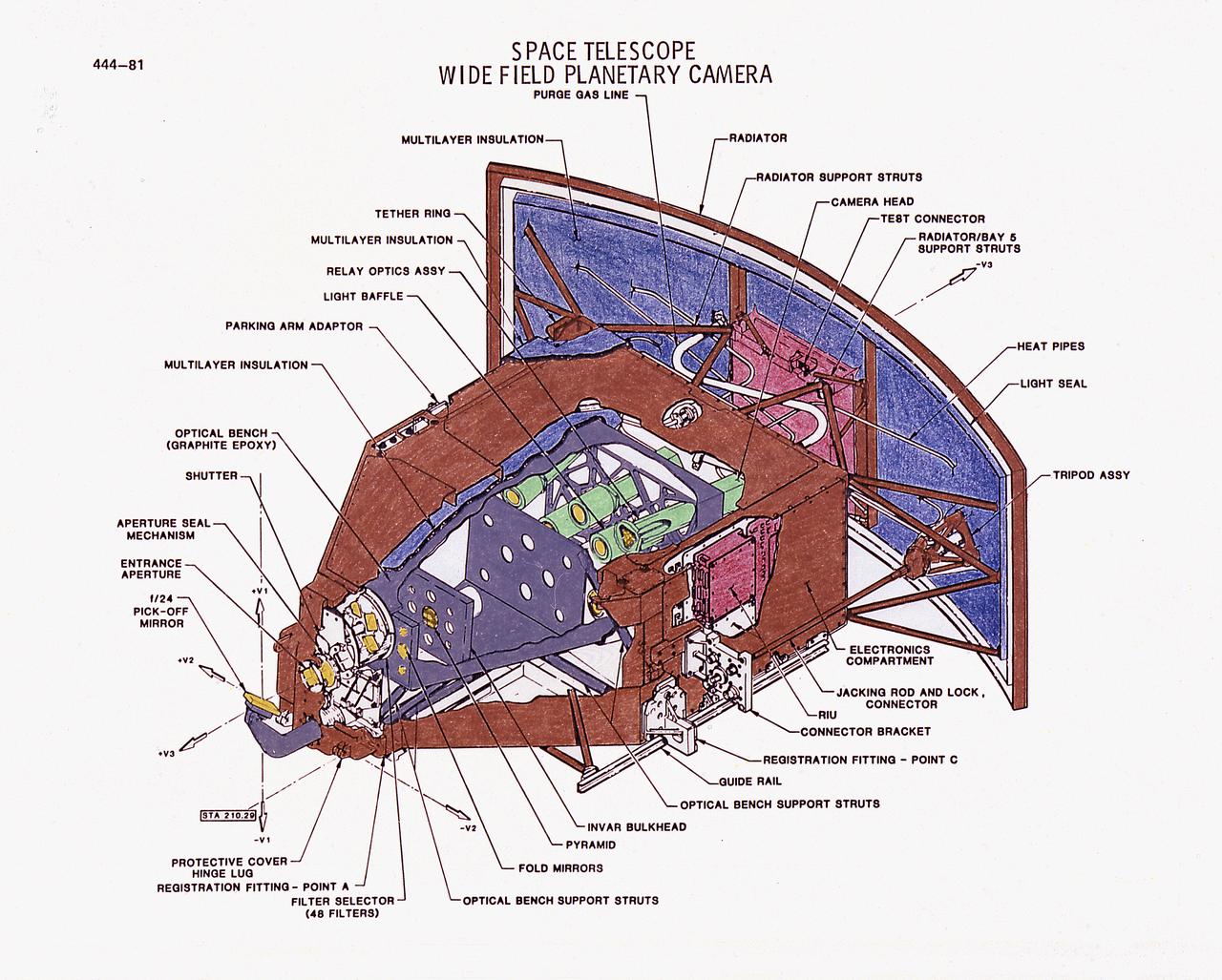
This illustration is a diagram of the Hubble Space Telescope's (HST's), Wide Field Planetary Camera (WF/PC), one of the five Scientific Instruments. The WF/PC uses a four-sided pyramid mirror to split a light image into quarters. It then focuses each quadrant onto one of two sets of four sensors. The sensors are charge-coupled detectors and function as the electronic equivalent of extremely sensitive photographic plates. The WF/PC operates in two modes. The Wide-Field mode that will view 7.2-arcmin sections of the sky, and the Planetary mode that will look at narrower fields of view, such as planets or areas within other galaxies. The purpose of the HST, the most complex and sensitive optical telescope ever made, is to study the cosmos from a low-Earth orbit. By placing the telescope in space, astronomers are able to collect data that is free of the Earth's atmosphere. The HST detects objects 25 times fainter than the dimmest objects seen from Earth and provides astronomers with an observable universe 250 times larger than visible from ground-based telescopes, perhaps as far away as 14 billion light-years. The HST views galaxies, stars, planets, comets, possibly other solar systems, and even unusual phenomena such as quasars, with 10 times the clarity of ground-based telescopes. The HST was deployed from the Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-31 mission) into Earth orbit in April 1990. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibility for design, development, and construction of the HST. The Perkin-Elmer Corporation, in Danbury, Cornecticut, developed the optical system and guidance sensors.

PHOTOS OF STS-31 (DISCOVERY) CREW WITH MODELS OF THE HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE (HST) AND SPACE SHUTTLE AT T-30 (THIRTY DAYS BEFORE LAUNCH) BRIEFING 03/22/90 IN THE AUDITORIUM AND PUBLIC AFFAIRS FACILITY BLDG 2. GROUP PHOTOS OF LOREN J. SHRIVER, CHARLES F. BOLDEN, STEVEN A. HAWLEY, BRUCE MCCANDLESS, AND KATHRYN D. SULLIVAN (32748, 32750, 32758-60 (WIDE ANGLE)) AND INDIVIDUAL PHOTOS OF HAWLEY (32747), MCCANDLESS (32751), SULLIVAN (32753-4), BOLDEN (32755), AND SHRIVER (32757) INCLUDED. ALSO PHOTGRAPHED TOGETHER ARE SULLIVAN, HAWLEY, MCCANDLESS (32749) AND BOLDEN, SHRIVER (32752, 32756).
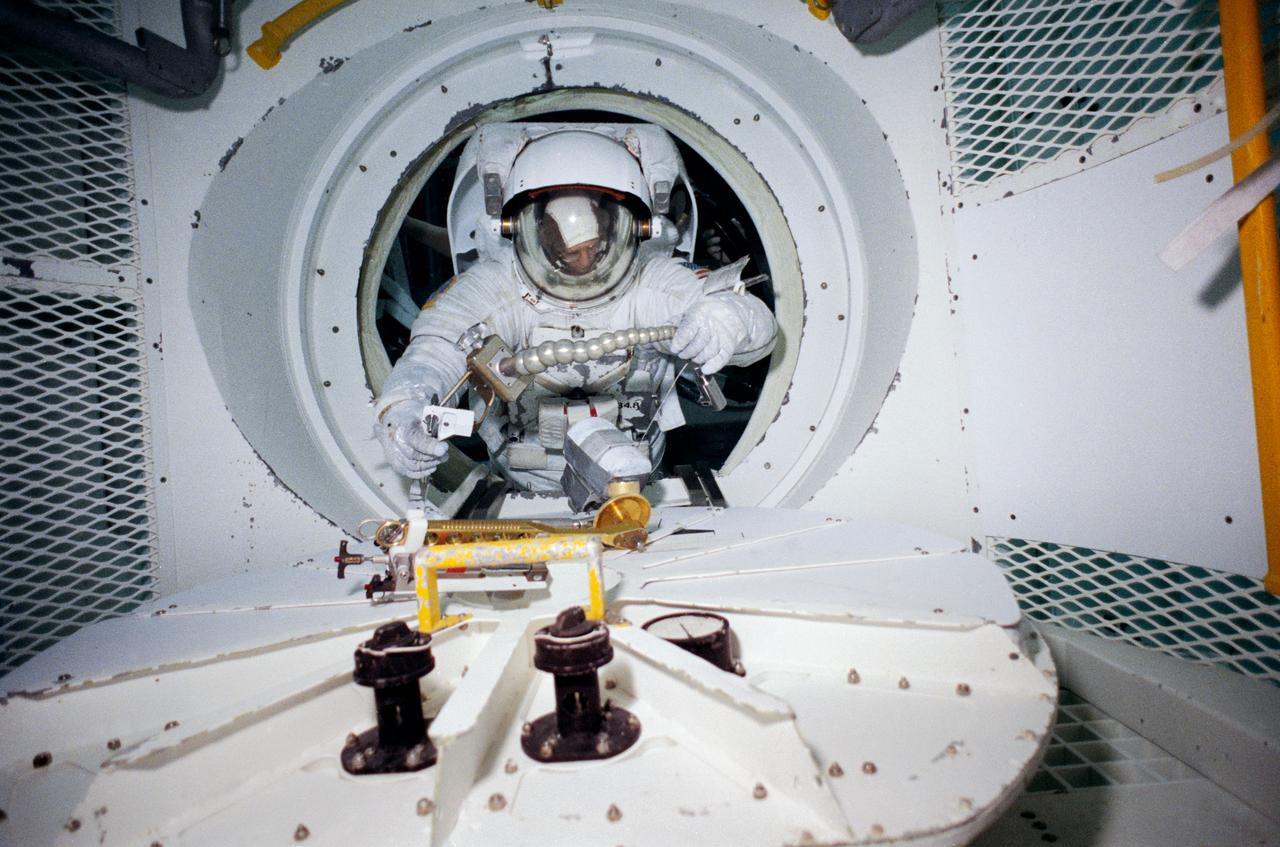
S90-30521 (20 Feb 1990) --- Though no extravehicular activity is planned for STS-31, two crewmembers train for contingencies that would necessitate leaving their shirt sleeve environment of Discovery's cabin and performing chores with their Hubble Space Telescope payload or related hardware. Astronaut Kathryn D. Sullivan, mission specialist, is seen egressing the hatchway of the airlock of a full scale mockup of a Shuttle cabin to interface with an HST mockup in JSC's 25.-ft. deep pool in the weightless environment training facility (WET-F). Two SCUBA-equipped divers who assisted in the training session are also seen. Astronaut Bruce McCandless II, mission specialist, is out of frame.
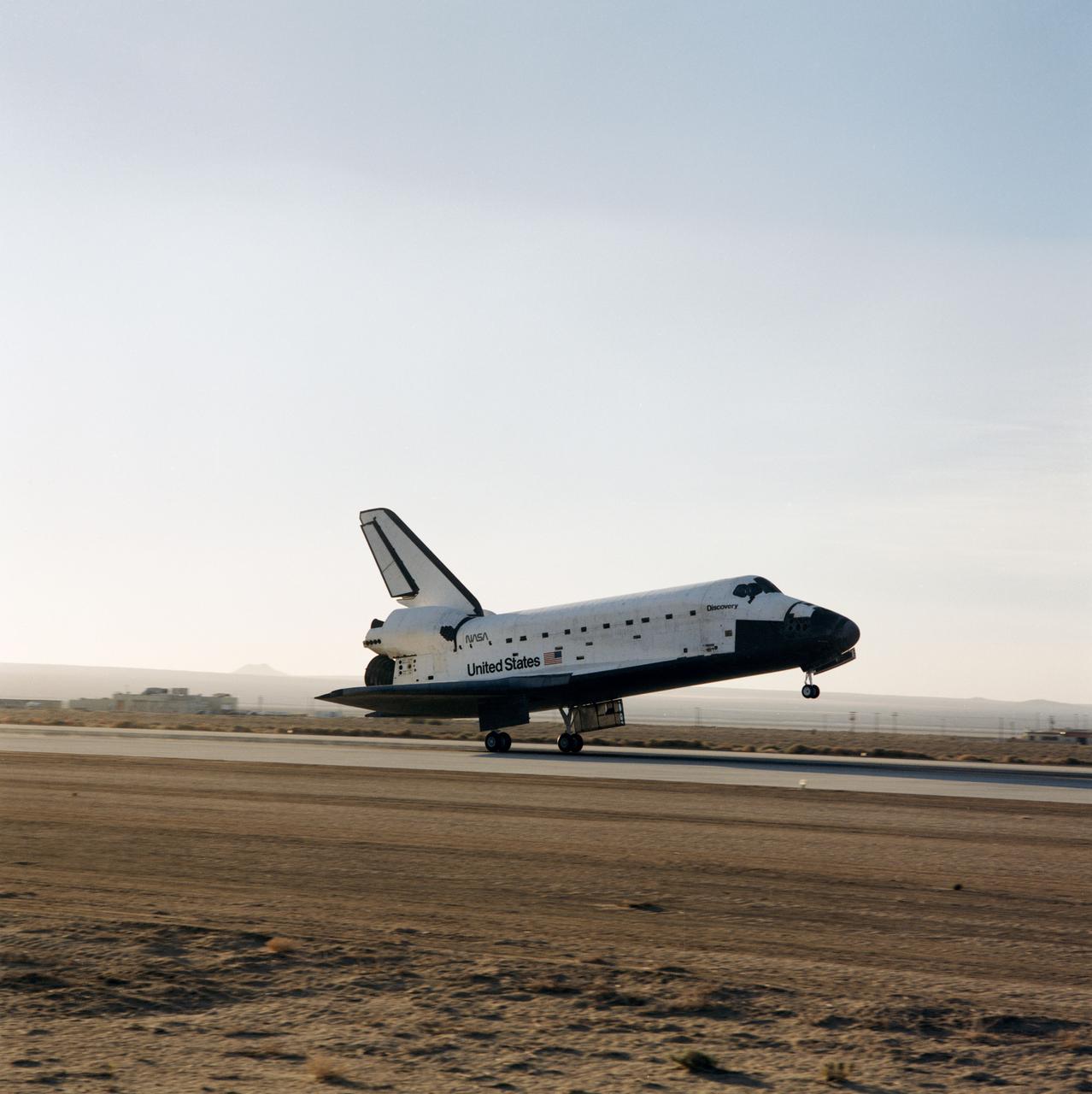

STS031-S-135 (29 April 1990) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery makes a smooth landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base to complete a highly successful five-day mission. It was an Earth orbital flight during which the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was sent toward its 15-year mission. Landing was completed at 6:51 a.m. (PDT), April 29, 1990. Inside the spacecraft for STS-31 were Astronauts Loren J. Shriver, Charles F. Bolden, Bruce McCandless II, Kathryn D. Sullivan and Steven A. Hawley.
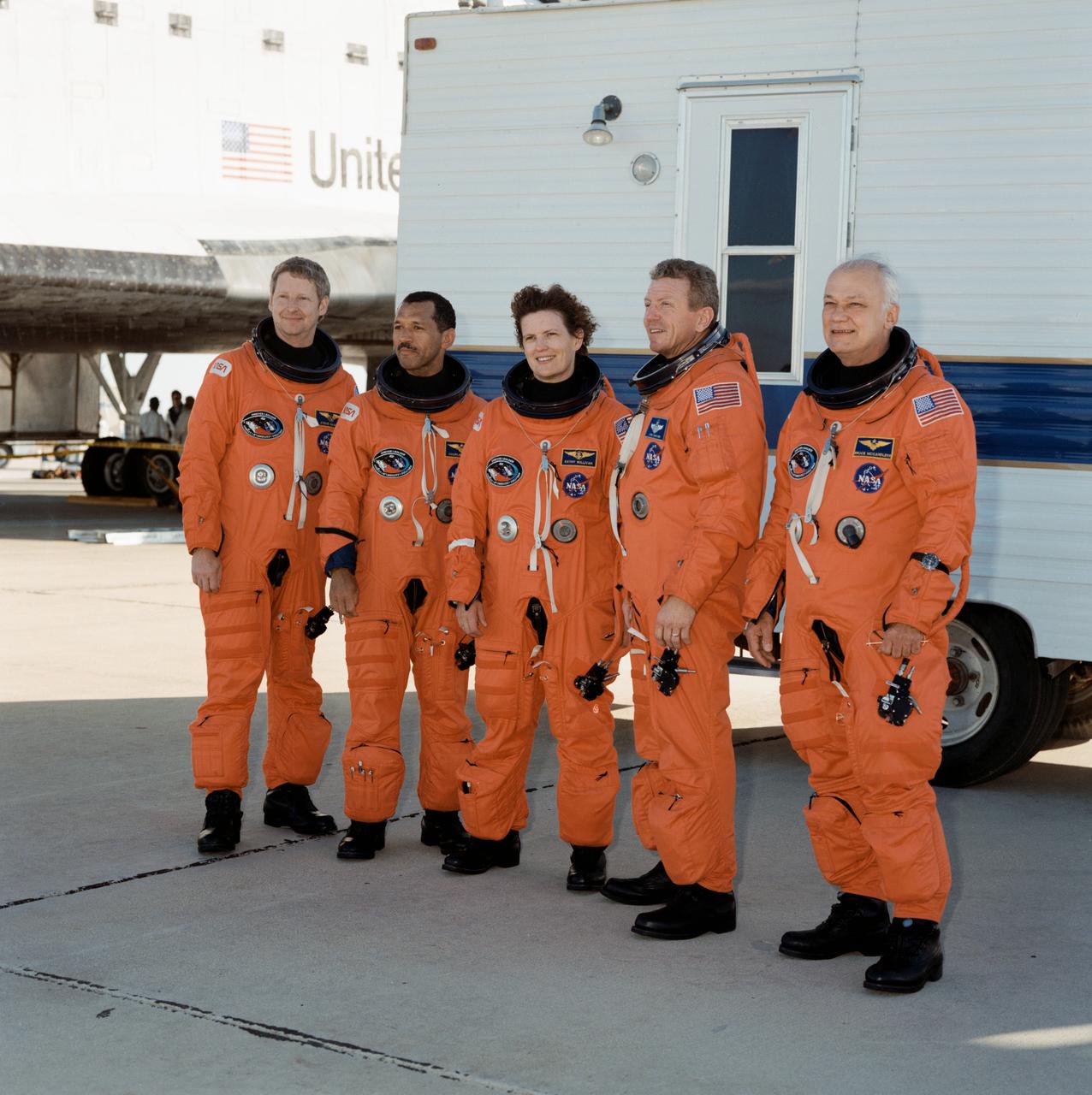

STS031-S-130 (29 April 1990) --- The astronauts of STS-31 pose for a quick photo near the Space Shuttle Discovery following a smooth landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base to complete a highly successful five-day mission. Pictured, left to right, are Astronauts Steven A. Hawley, Charles F. Bolden Jr., Kathryn D. Sullivan, Loren J. Shriver, and Bruce McCandless II. Theirs was an Earth orbital flight during which the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was sent toward its 15-year mission.

STS-31 Mission Specialist (MS) Kathryn D. Sullivan monitors and advises ground controllers of the activity inside the Student Experiment (SE) 82-16, Ion arc - studies of the effects of microgravity and a magnetic field on an electric arc, mounted in front of the middeck lockers aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Pilot Charles F. Bolden uses a video camera and an ARRIFLEX motion picture camera to record the activity inside the special chamber. A sign in front of the experiment reads "SSIP 82-16 Greg's Experiment Happy Graduation from STS-31." SSIP stands for Shuttle Student Involvement Program. Gregory S. Peterson who developed the experiment (Greg's Experiment) is a student at Utah State University and monitored the experiment's operation from JSC's Mission Control Center (MCC) during the flight. Decals displayed in the background on the orbiter galley represent the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), the United States (U.S.) Naval Reserve, Navy Oceanographers, U.S. Navy, and University of Kansas.
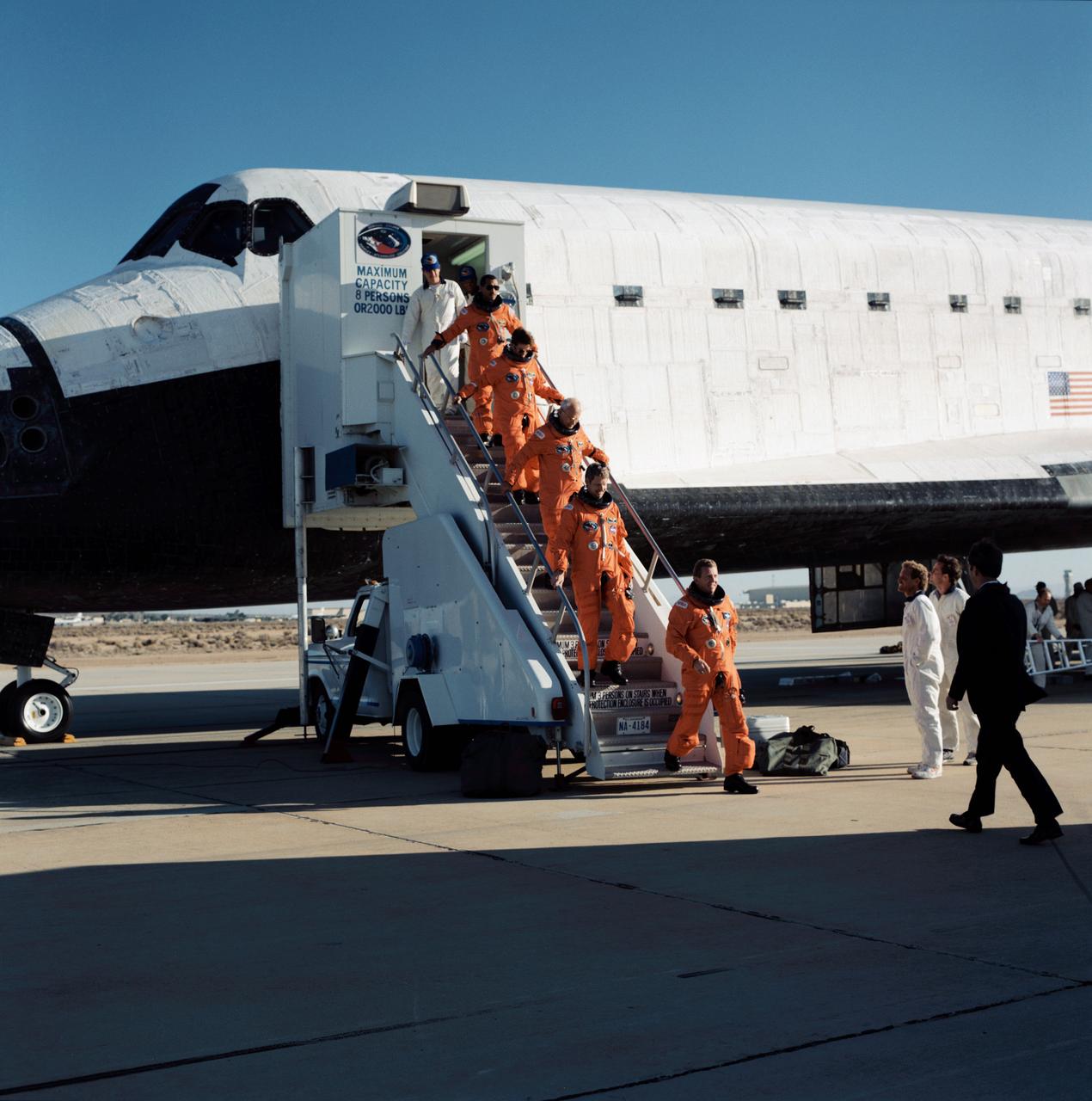

STS031-S-129 (29 April 1990) --- The astronauts of STS-31 egress the Space Shuttle Discovery following a smooth landing on the runway at Edwards Air Force Base to complete a highly successful five-day mission. Approaching from the far right to greet the crew is Dr. William B. Lenoir, NASA's Acting Associate Administrator for Space Flight. Leading the way down the steps is astronaut Loren J. Shriver, mission commander, followed by (in order from bottom of steps) astronauts Steven A. Hawley, Bruce McCandless II and Kathryn D. Sullivan, all mission specialists; and Charles F. Bolden Jr., pilot. Theirs was an Earth-orbital flight during which the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was sent toward its 15-year mission.