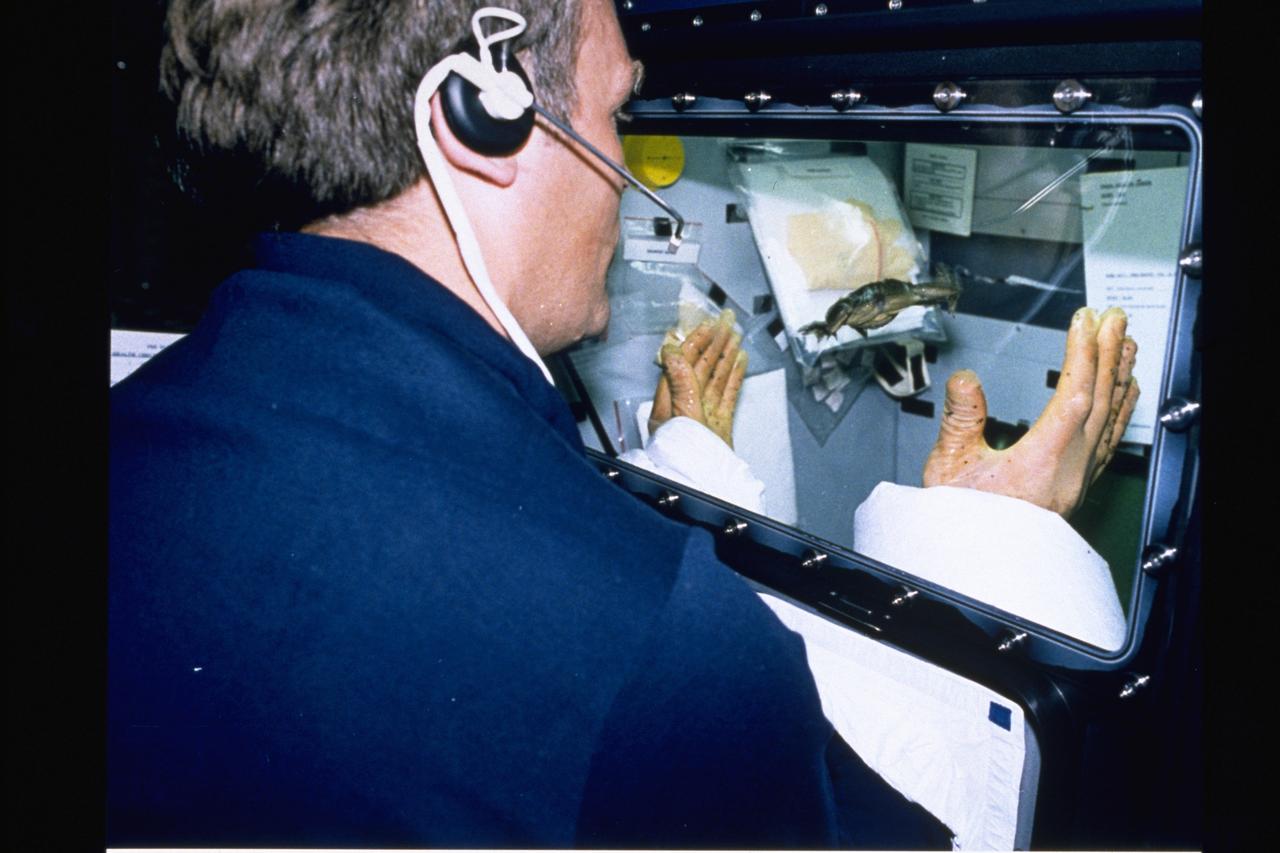

Space Shuttle Endeavour STS-47 Spacelab J mission: Frog Embryology Experiment, Astronaut works with adult frog in 0 gravity using the glovebox to contain and protect the frog during procedures
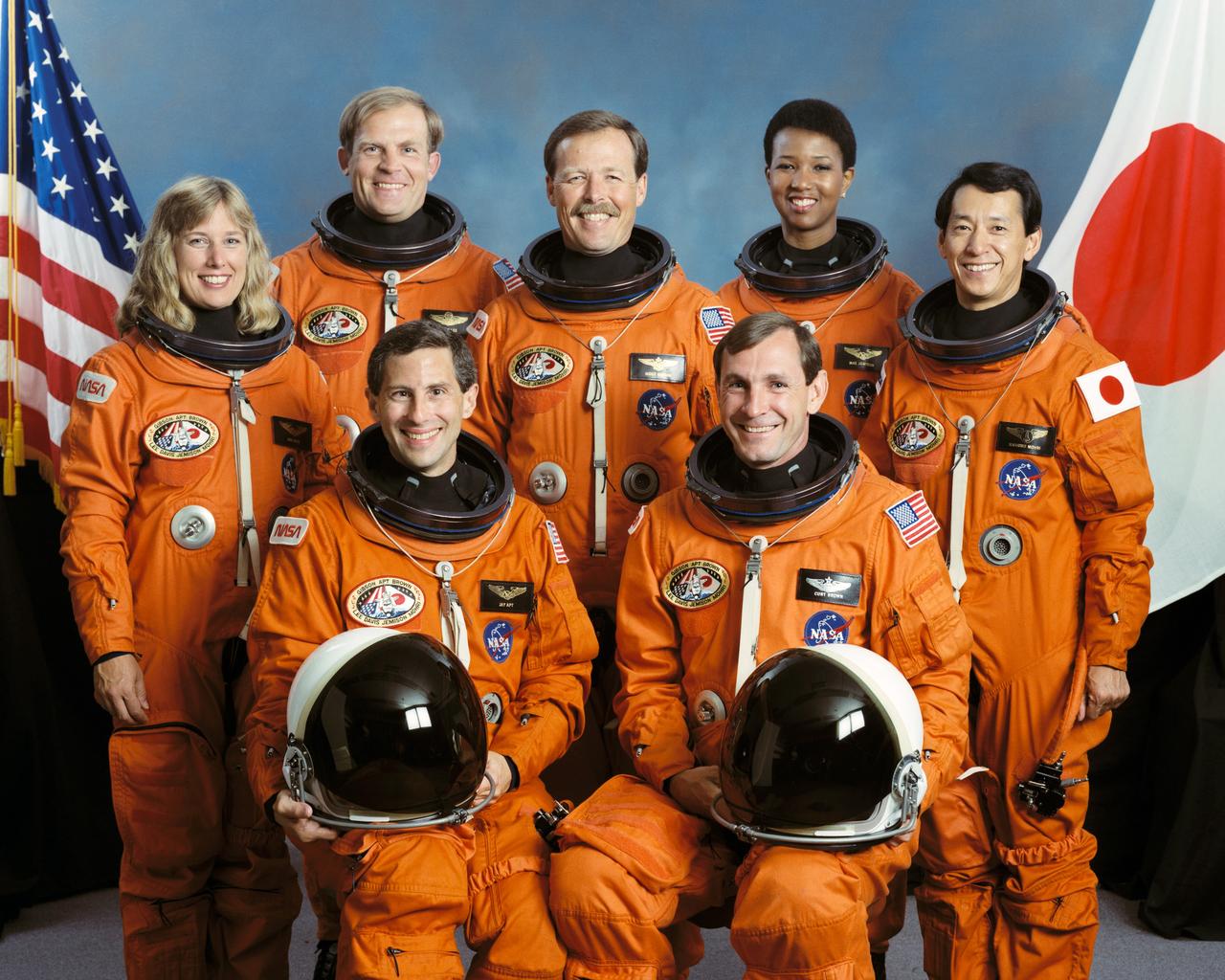

STS047-S-002 (June 1992) --- These seven crew members are currently in training for the STS-47/Spacelab J mission scheduled for later this year. Pictured are (left to right, front) Jerome (Jay) Apt, mission specialist; Curtis L. Brown, pilot; and (left to right, rear) N. Jan Davis, mission specialist; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Mae C. Jemison, mission specialist; and Mamoru Mohri, payload specialist, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). This is the Space Shuttle Endeavour's second scheduled mission.
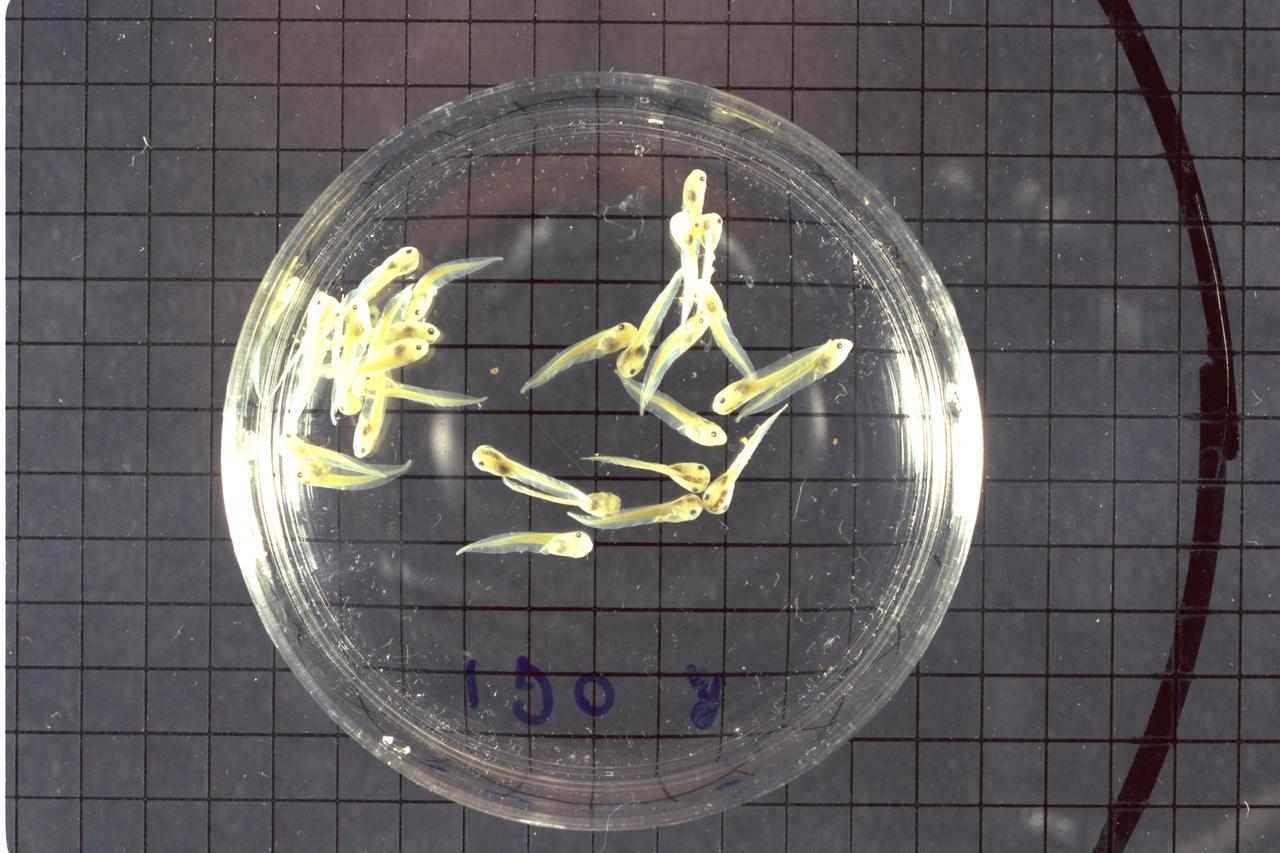
STS-47 Spacelab-J - post flight tadpoles
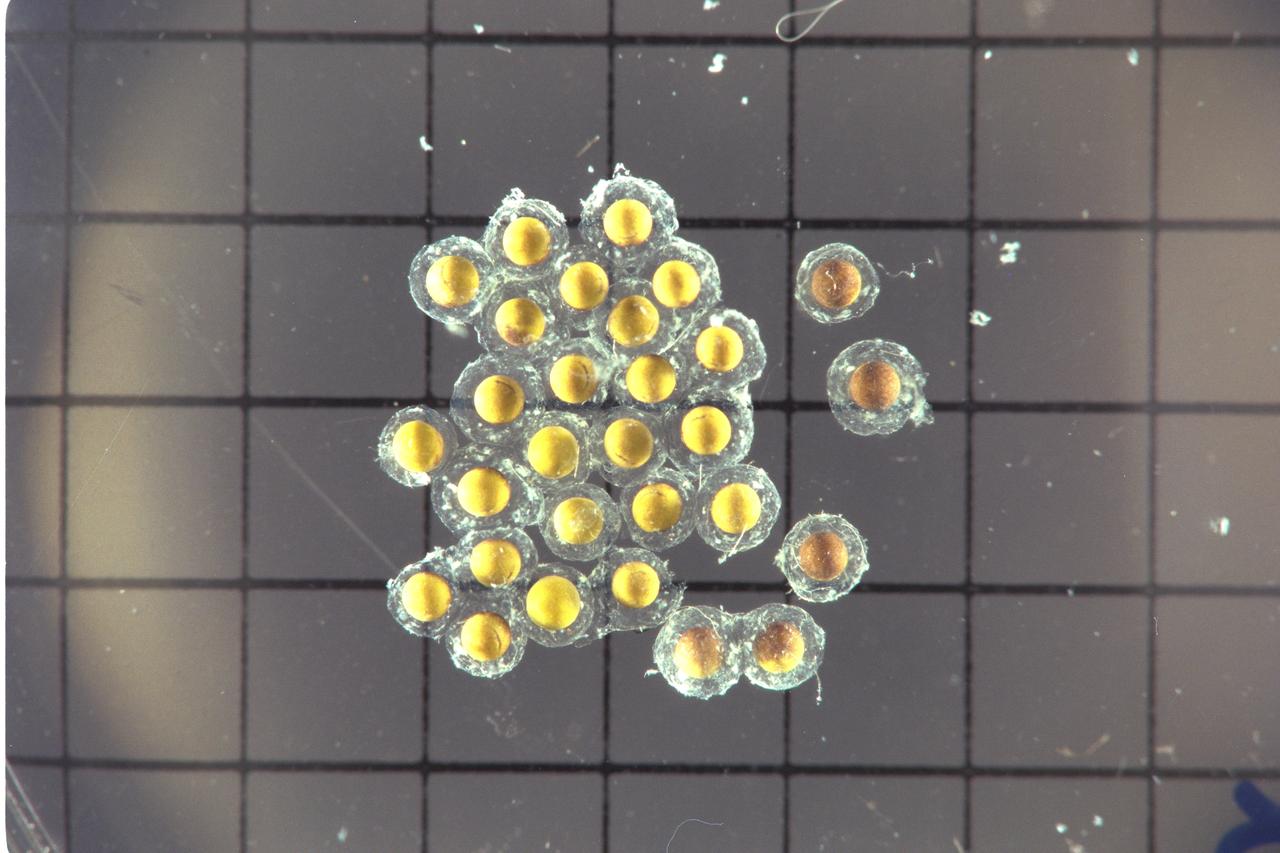
STS-47 Spacelab-J - eggs - post flight data
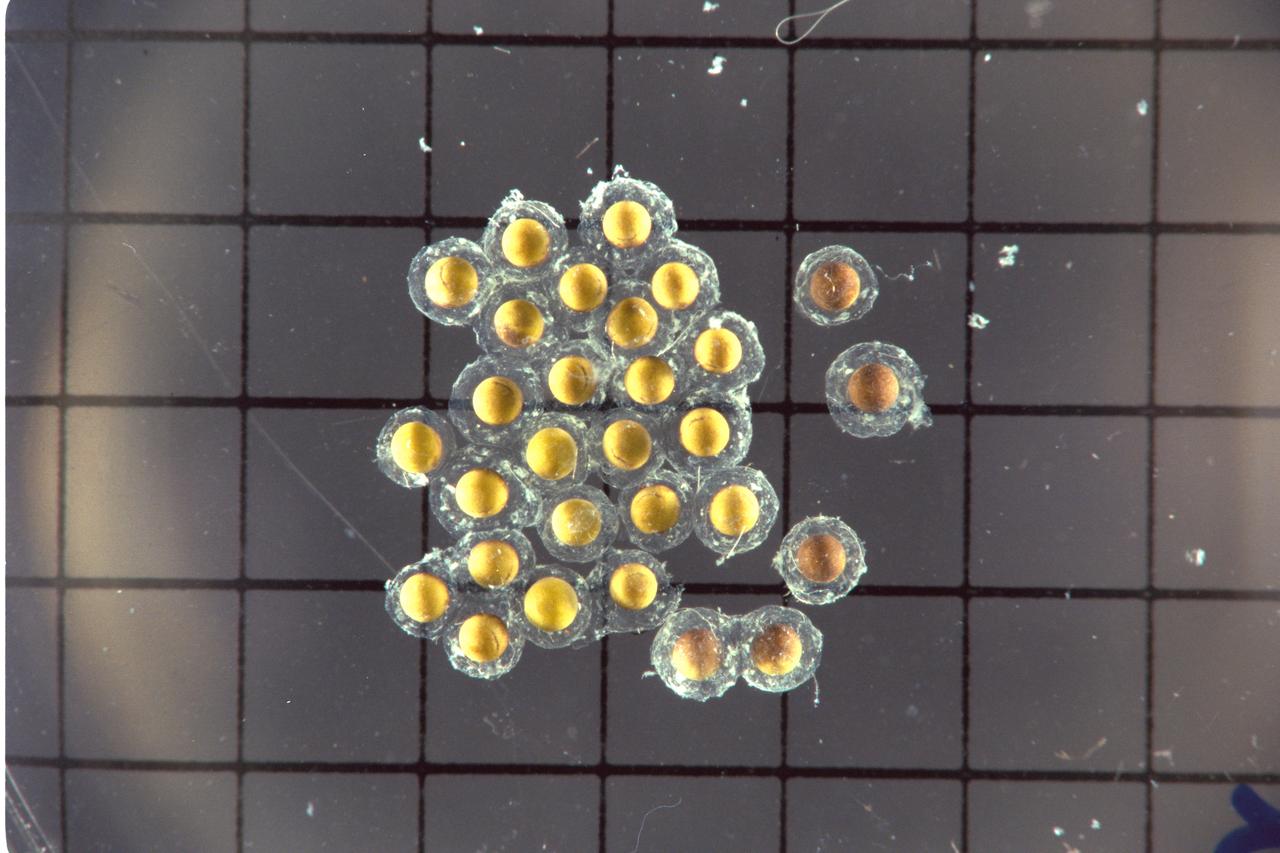
STS-47 Spacelab-J - eggs - post flight data
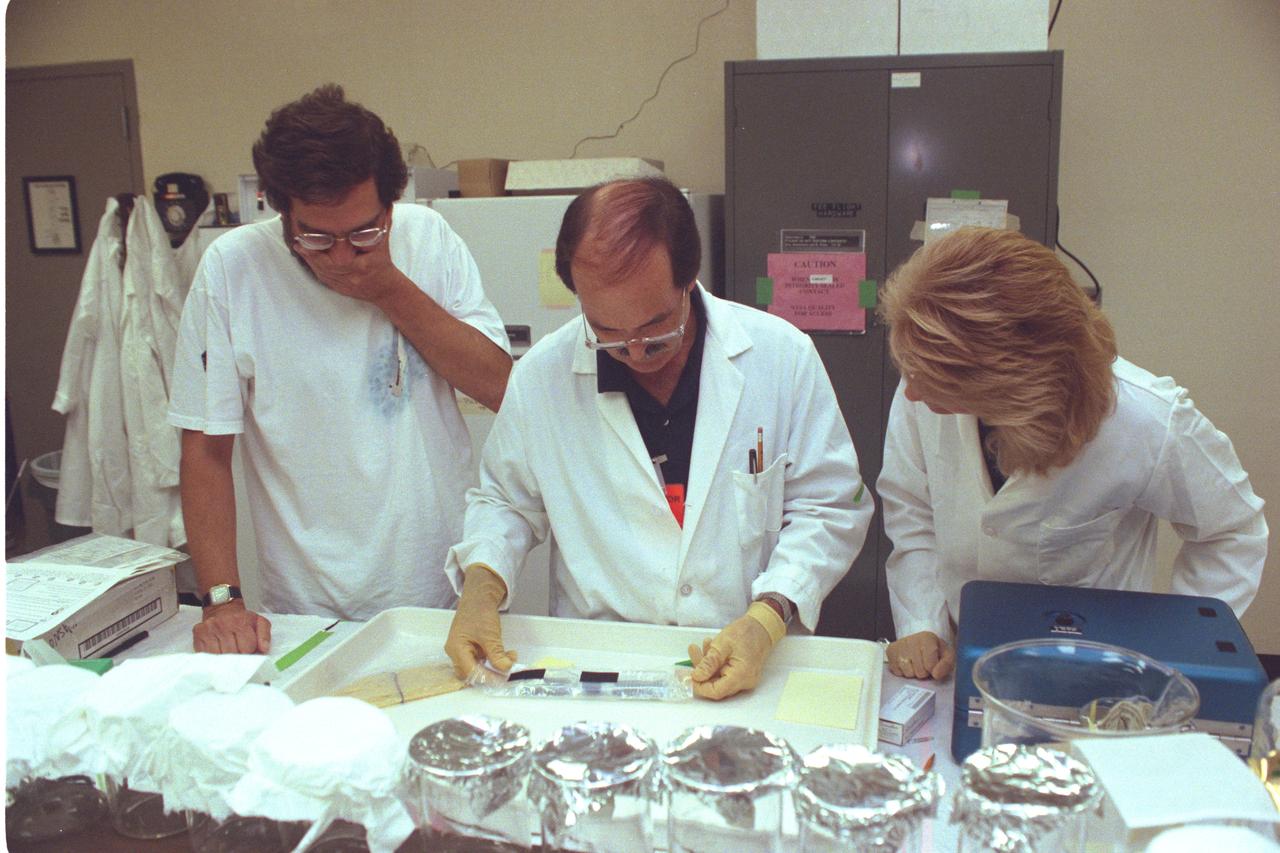

STS-47 Spacelab-J - Ken Souza and team during post flight work at KSC
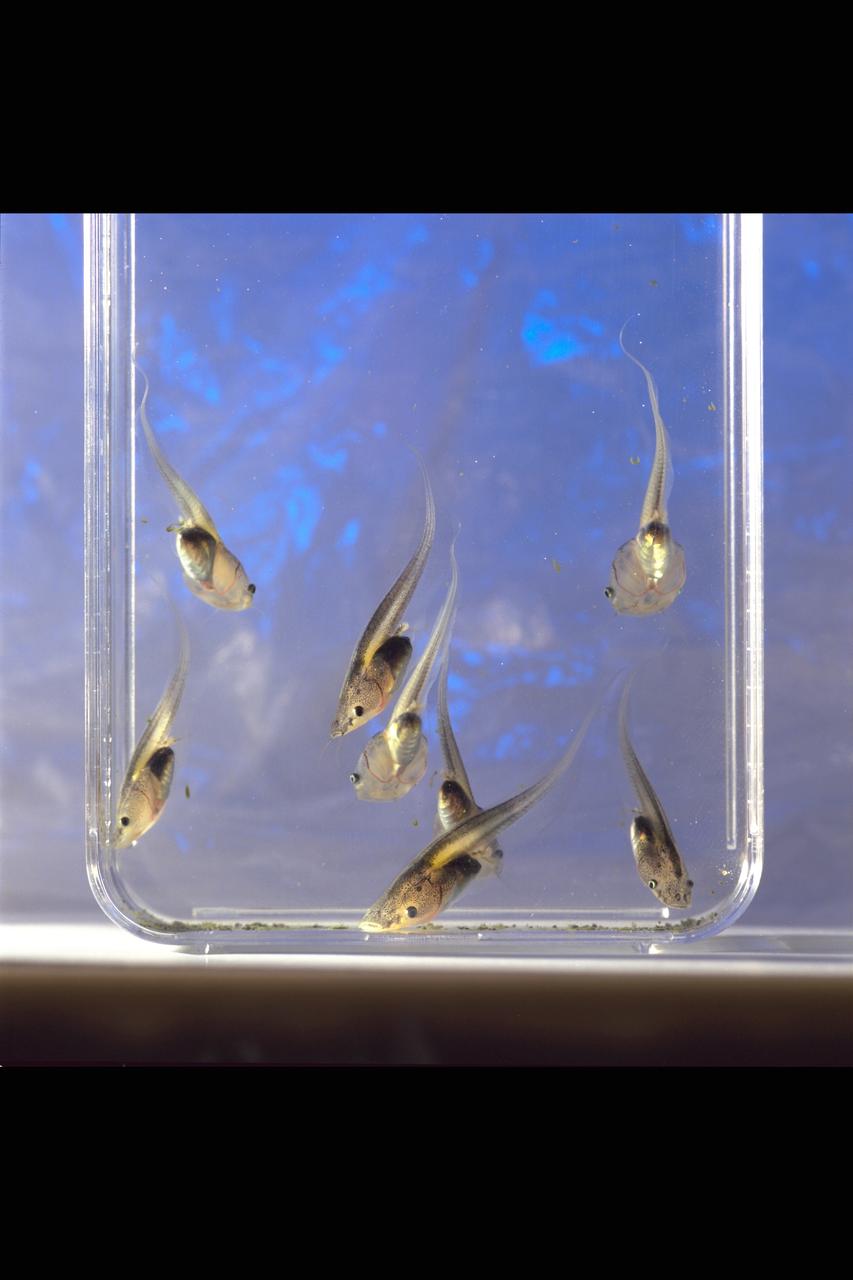

STS-47 Spacelab-J FFE (Frog Embryology Experiment) post flight data - flight frogs from SL-J, ground control tadpoles
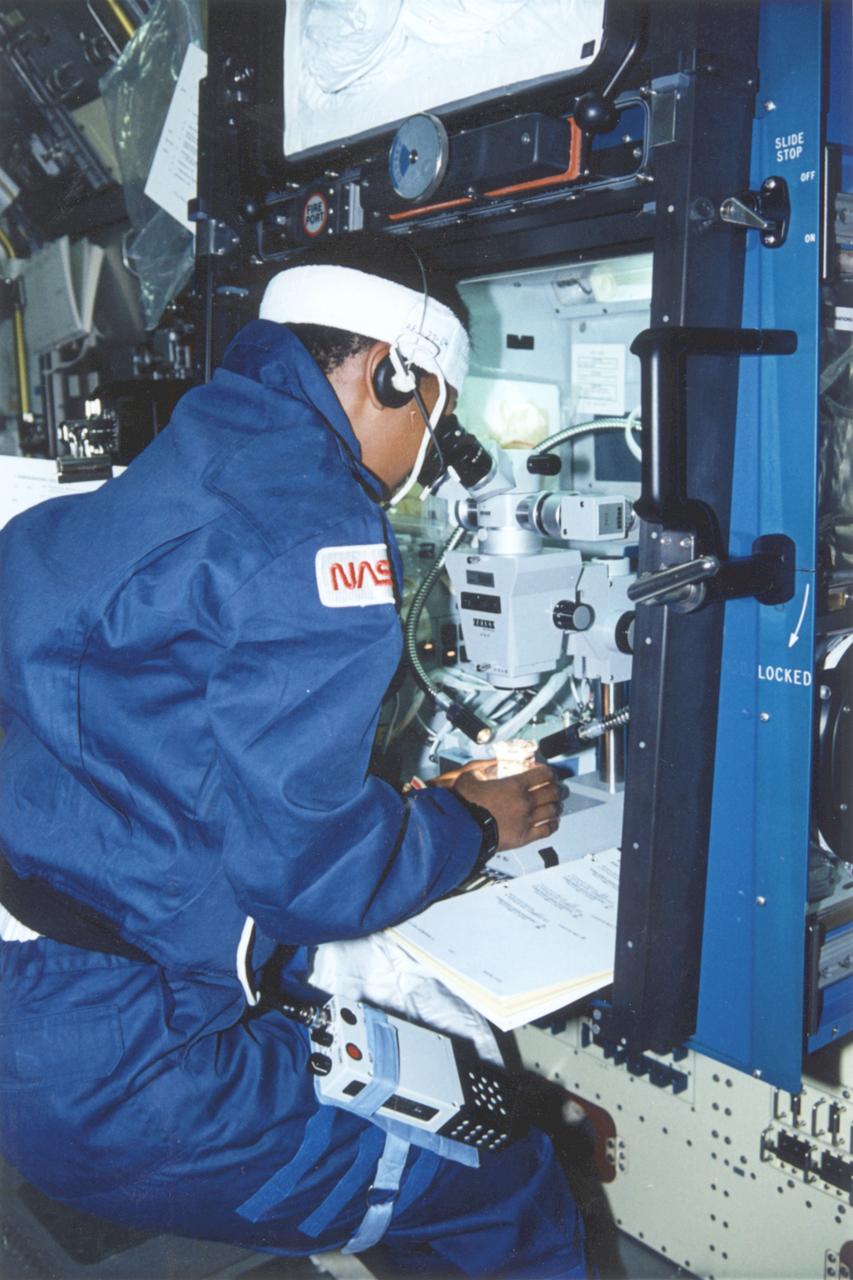

Astronaut Mae Jemison using the Glovebox microscope onboard STS-47.
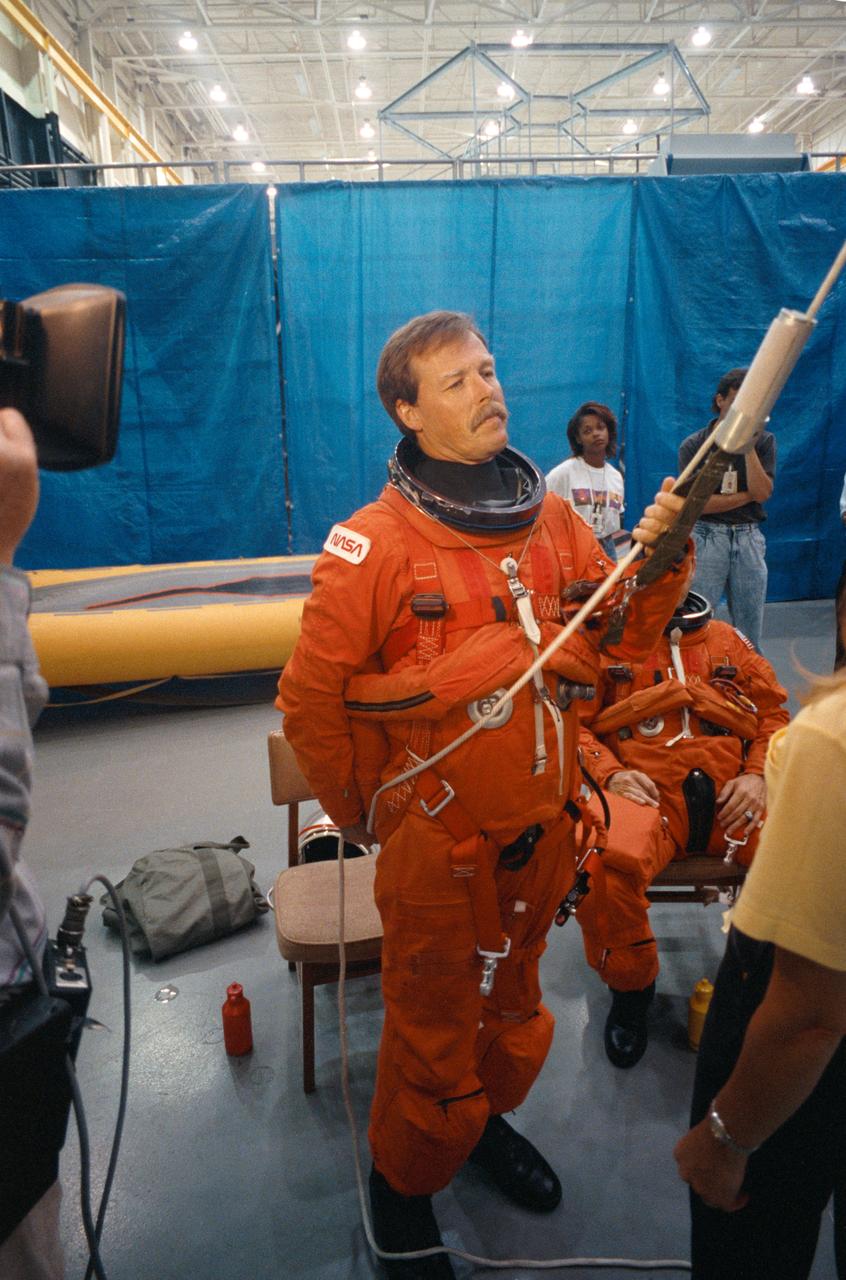

STS-47 Endeavour, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 105, Spacelab Japan (SLJ) Commander Robert L. Gibson, wearing launch and entry suit (LES), holds sky genie equipment in proper position while listening to a training instructor's directions. Gibson along with the other STS-47 crewmembers is participating in post landing emergency egress procedures at JSC's Mockup and Integration Laboratory (MAIL) Bldg 9NE.
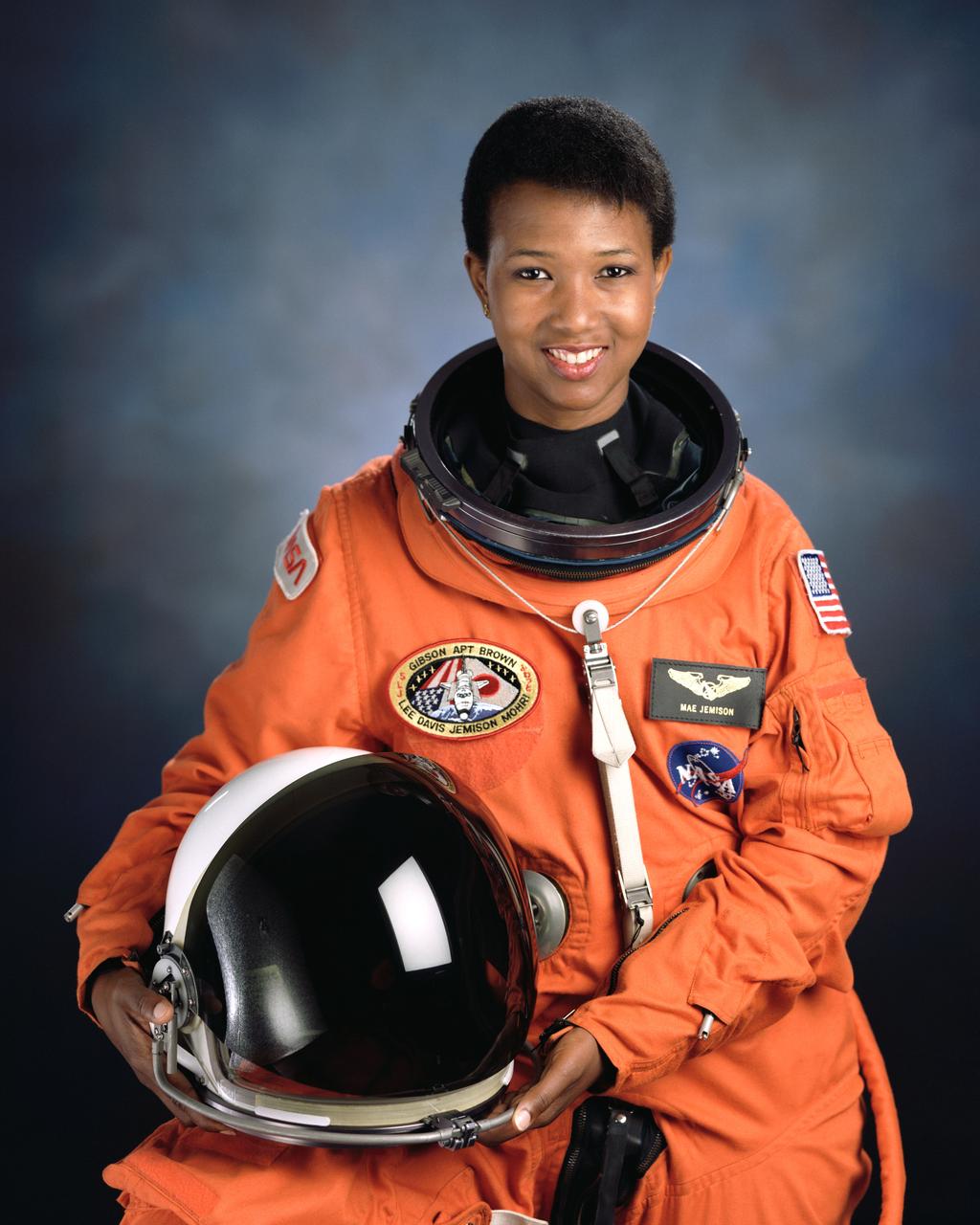

S92-40463 (July 1992) --- Astronaut Mae C. Jemison, M.D., mission specialist.
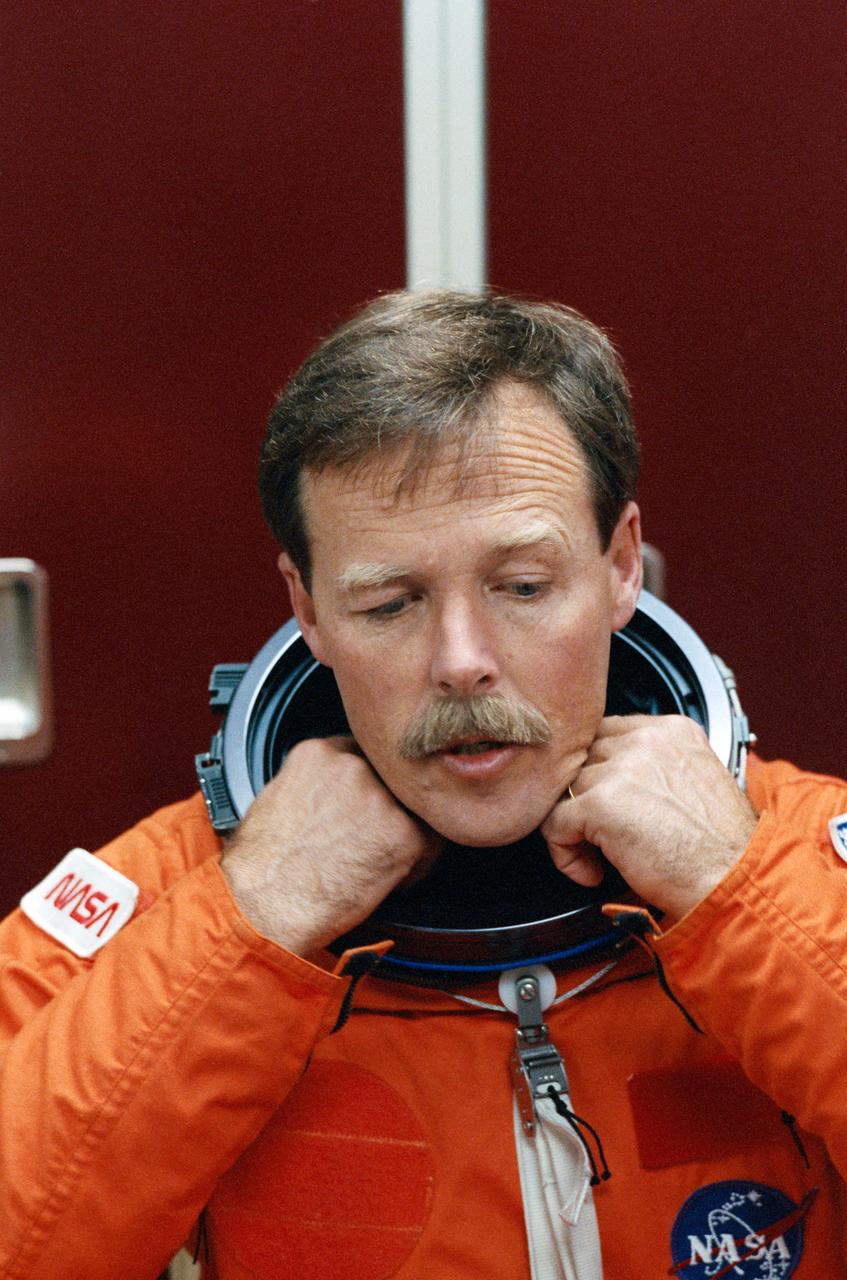

STS-47 Endeavour, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 105, Commander Robert L. Gibson adjusts the launch and entry suit (LES) neck dam during suit donning in JSC's Mockup and Integration Laboratory (MAIL) Bldg 9A. Gibson is preparing for launch emergency egress (bailout) exercises in the Crew Compartment Trainer (CCT).
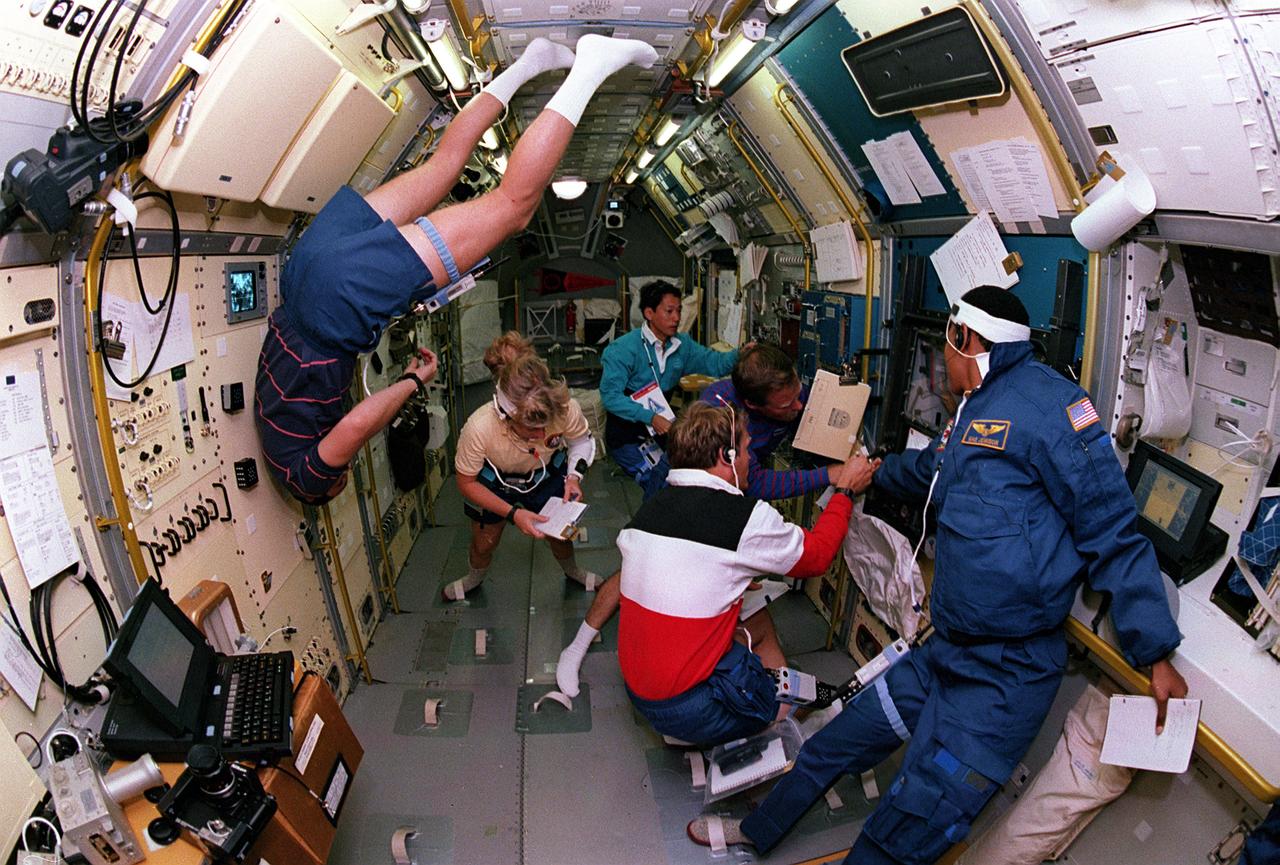

Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) onboard photo of crew members working in the Spacelab-J module.
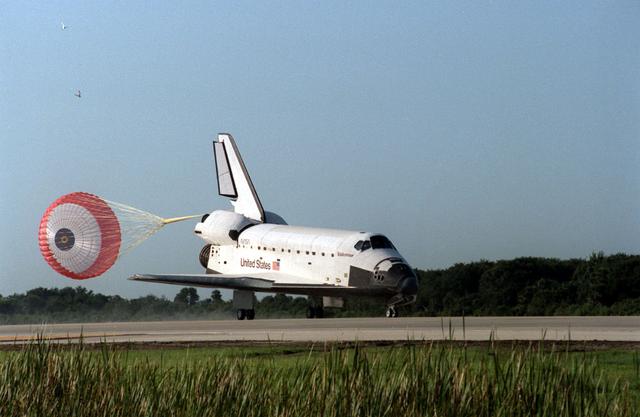

After completion of a seven-day flight mission, the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour (STS-47) landed at Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility. Spacelab-J, a joint research venture between NASA and NASDA (National Space Development Agency of Japan) completed a successful mission.
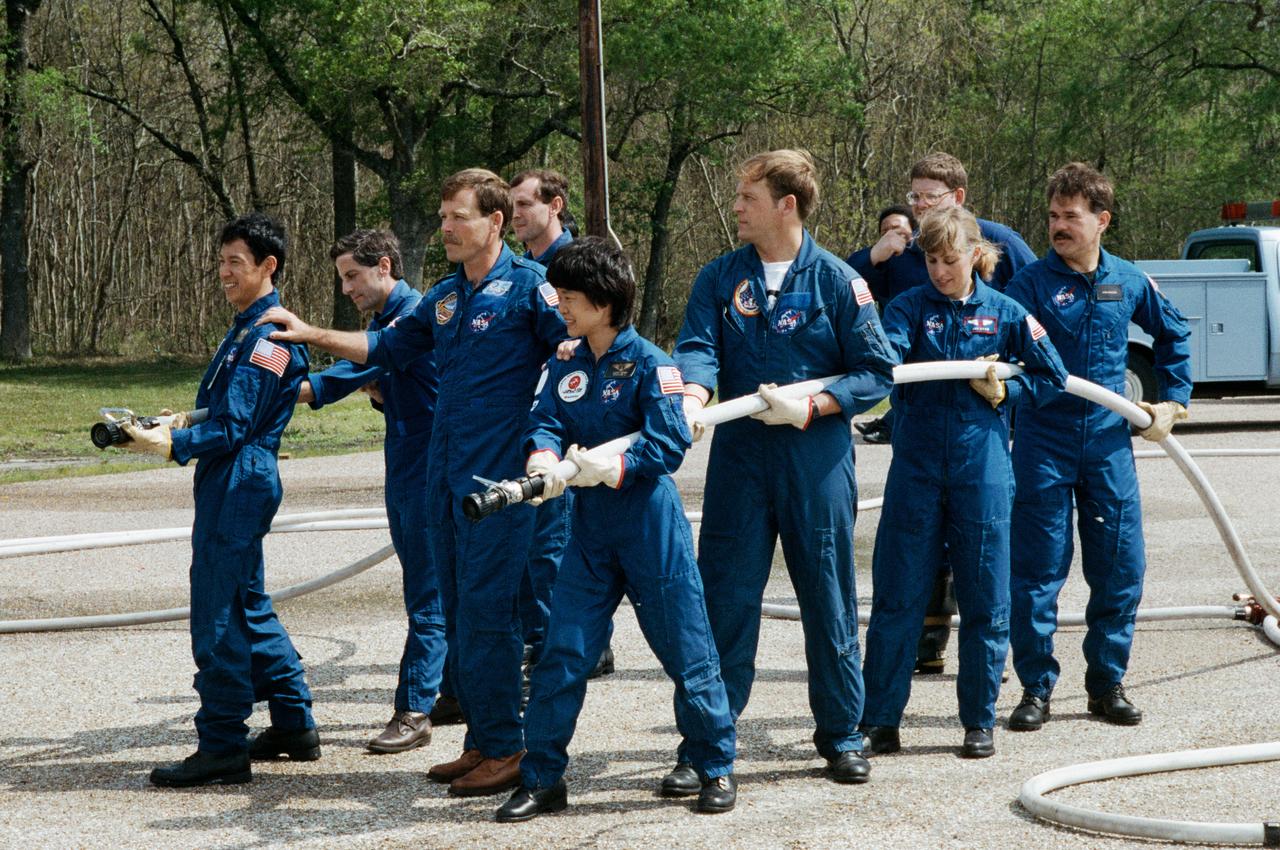

STS-47 Endeavour, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 105, crewmembers led by Commander Robert L. Gibson (center) prepare to extinguish a blaze in JSC's Fire Training Pit. Lined up along the water hoses are: (on left) Payload Specialist Mamoru Mohri, holding the hose nozzle, followed by Mission Specialist (MS) Jerome Apt, and Pilot Curtis L. Brown, Jr; and (on right) backup Payload Specialist Chiaki Naito-Mukai, holding the hose nozzle, followed by MS and Payload Commander (PLC) Mark C. Lee, MS N. Jan Davis, and backup Payload Specialist Stan Koszelak. A veteran fire fighter and the instructor, positioned between the two hoses, looks on. Mohri and Mukai represent Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA). The Fire Training Pit is located across from the Gilruth Center Bldg 207.
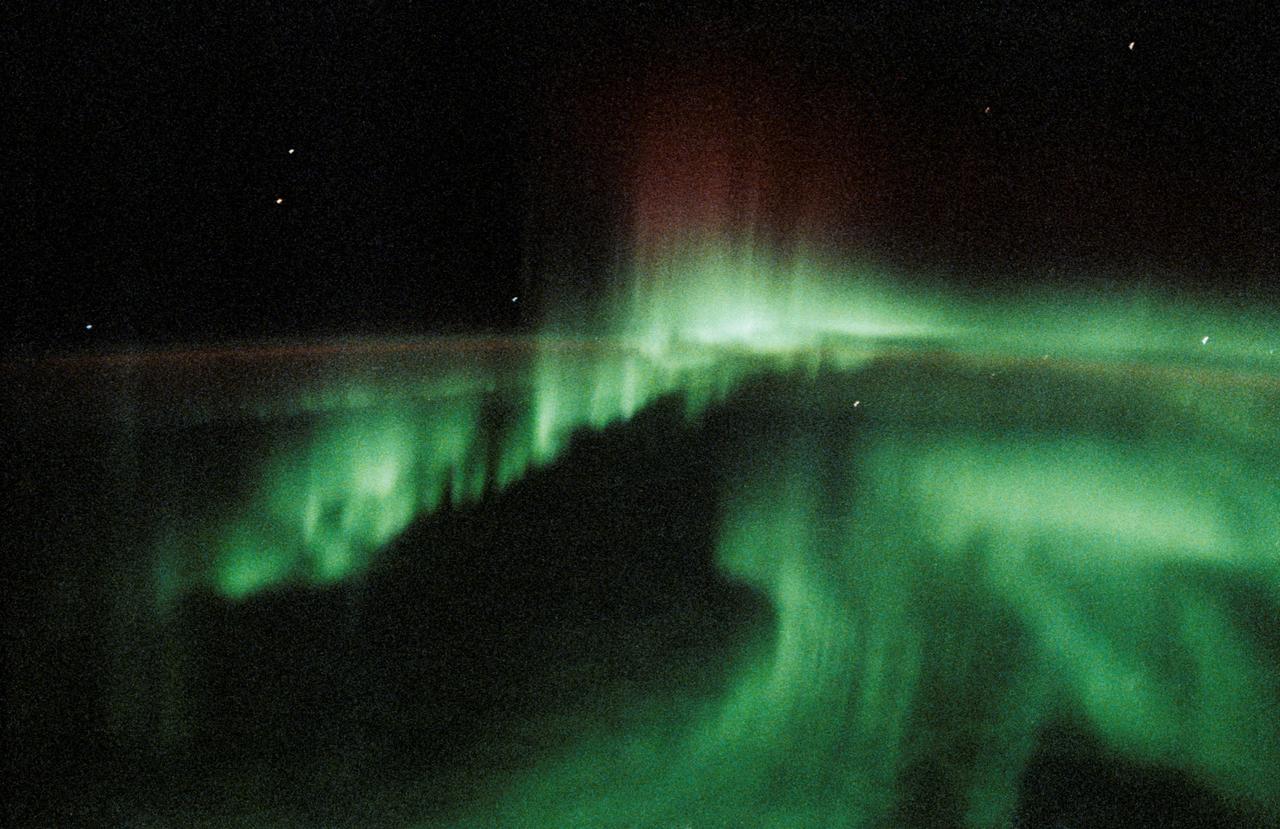

STS047-20-015 (12-20 Sept. 1992) --- This 35mm frame represents one of the more spectacular views of Aurora Australis, photographed by the crew. The crew observed and photographed a great deal of auroral activity from the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour during the eight-day Spacelab-J mission.
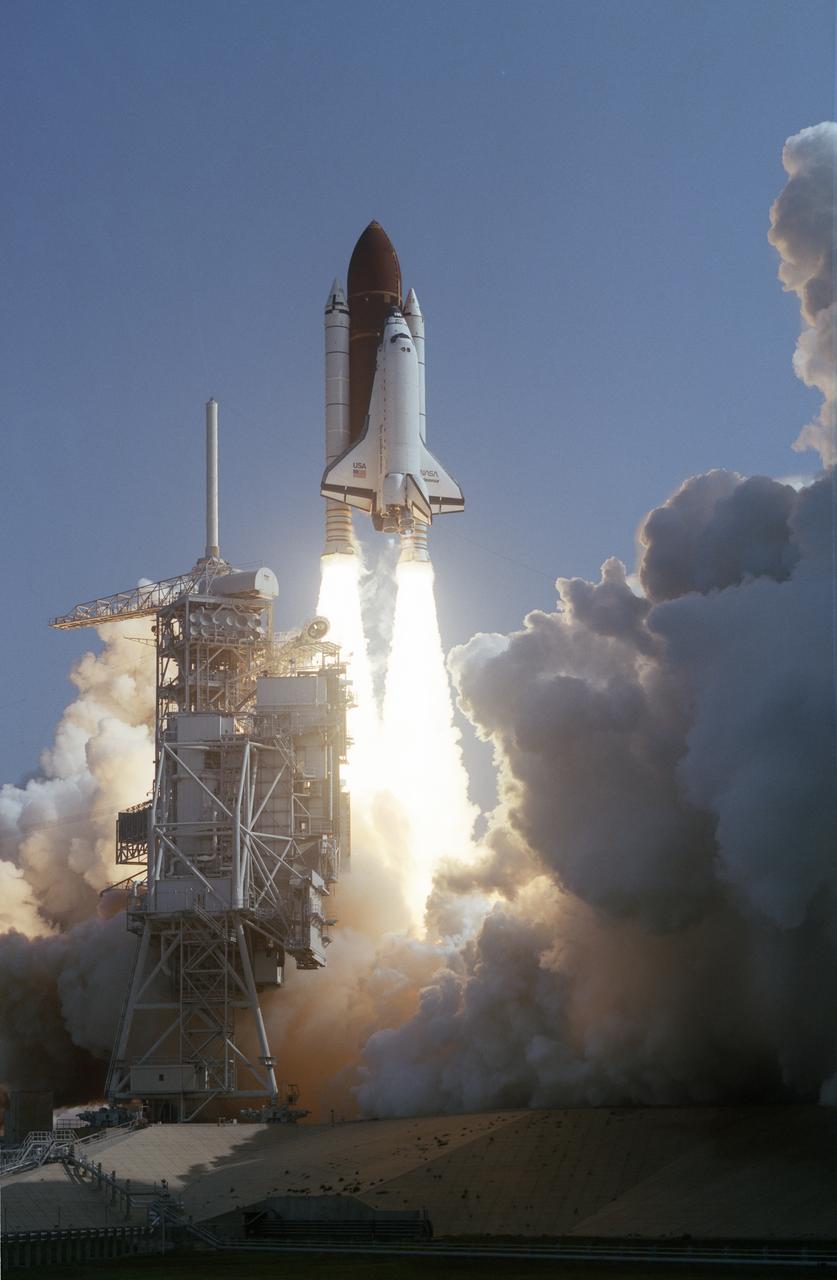

A smooth countdown culminated in a picture-perfect launch as the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour (STS-47) climbed skyward atop a ladder of billowing smoke on September 12, 1992. The primary payload for the plarned seven-day flight was the Spacelab-J science laboratory. The second flight of Endeavour marks a number of historic firsts: the first space flight of an African-American woman, the first Japanese citizen to fly on a Space Shuttle, and the first married couple to fly in space.
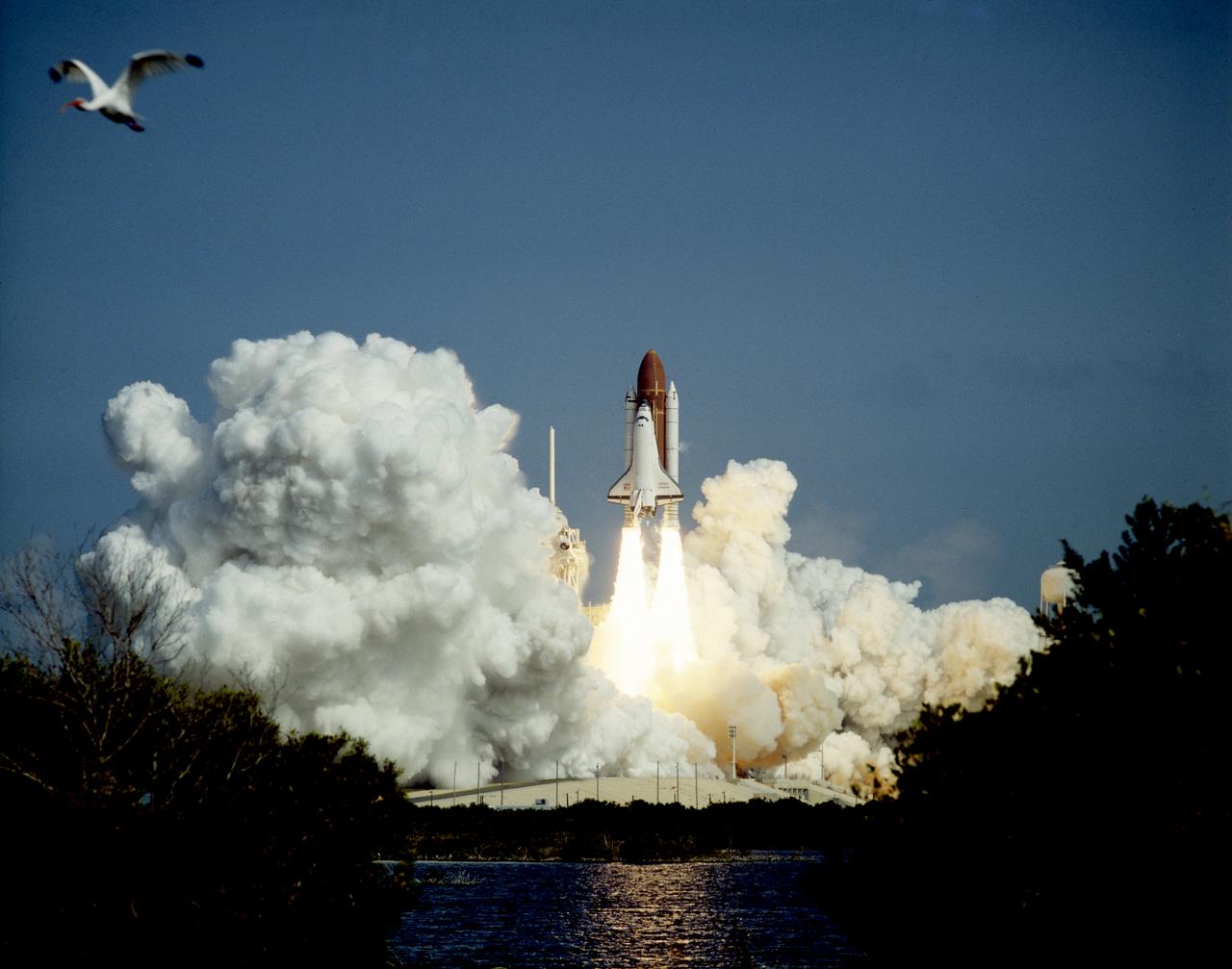

A smooth countdown culminated in a picture-perfect launch as the Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) climbed skyward atop a ladder of billowing smoke. Primary payload for the plarned seven-day flight was Spacelab-J science laboratory. The second flight of Endeavour marks a number of historic firsts: the first space flight of an African-American woman, the first Japanese citizen to fly on a Space Shuttle, and the first married couple to fly in space.

Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) onboard photo of Astronaut Mae Jemison working in Spacelab-J module. Spacelab-J is a combined National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) and NASA mission. The objectives included life sciences, microgravity and technology research.
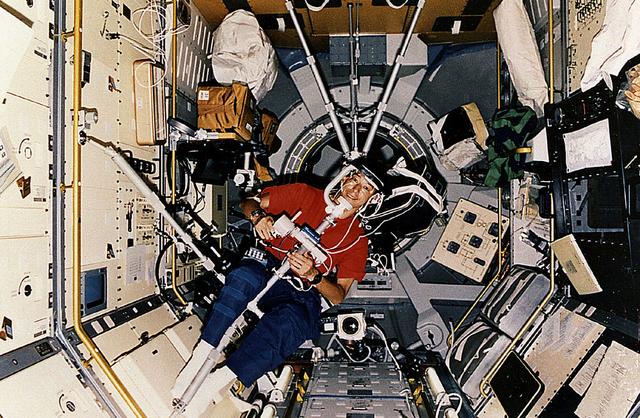

Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) onboard photo of Japanese Payload Specialist Dr. Mamoru Mohri participating in Comparative Measurement of Visual Stability in Earth Cosmic Space experiment to learn more about Space Adaptation Syndrome (SAS).
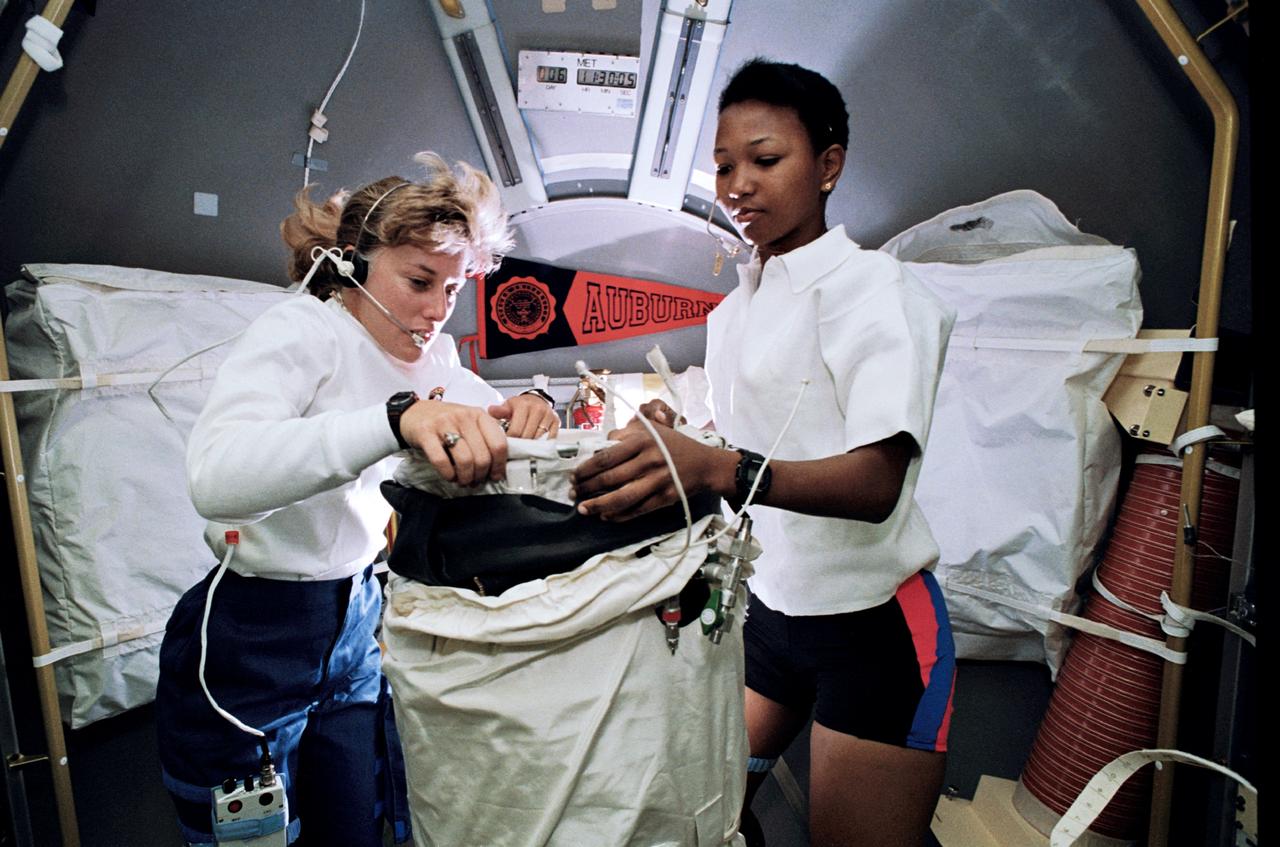
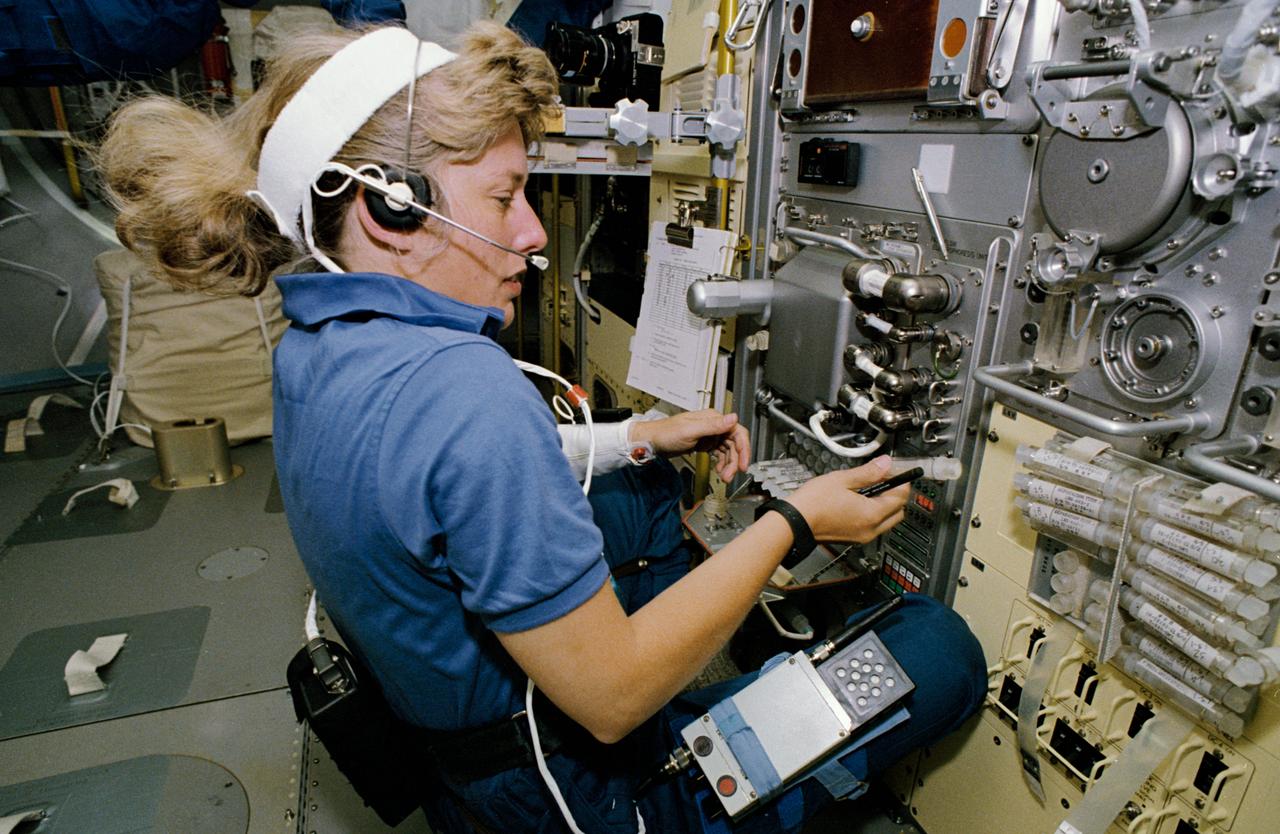
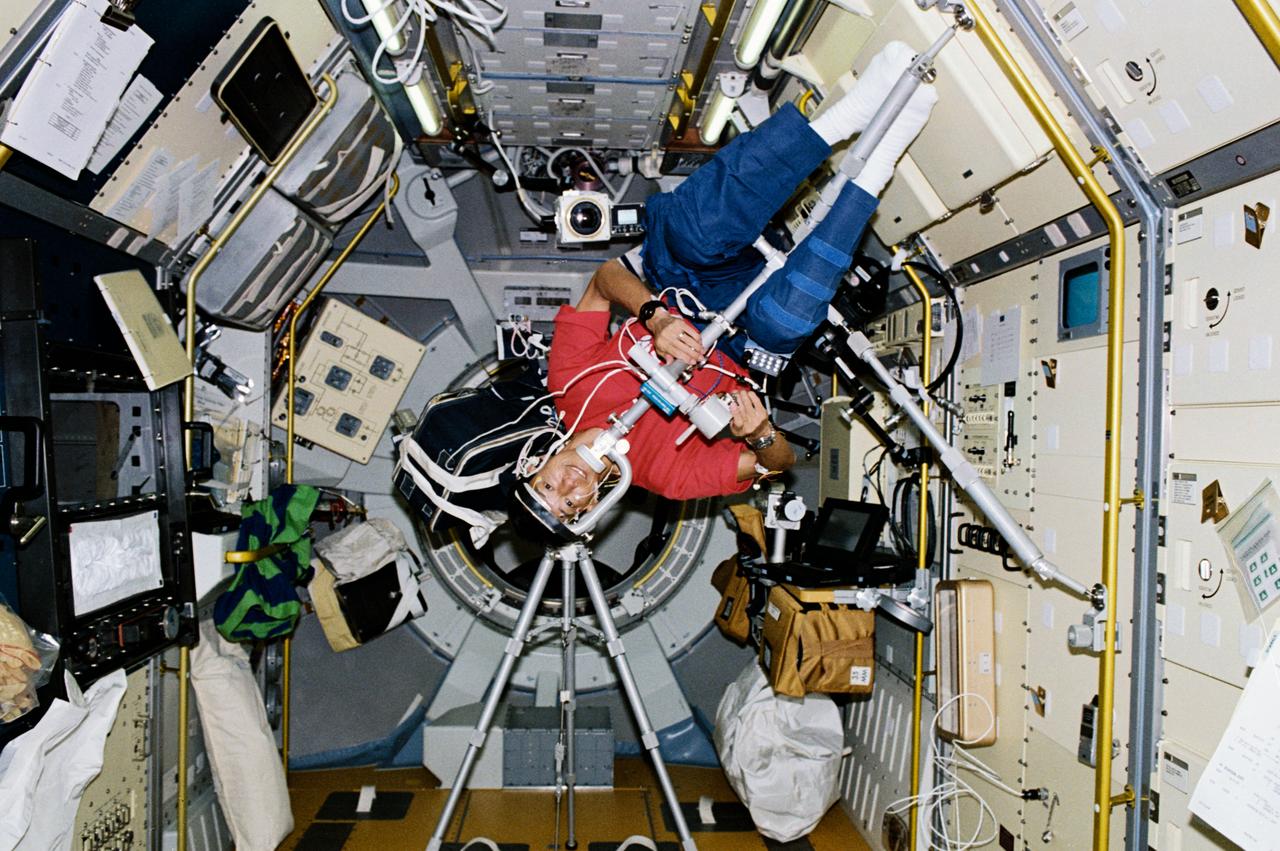
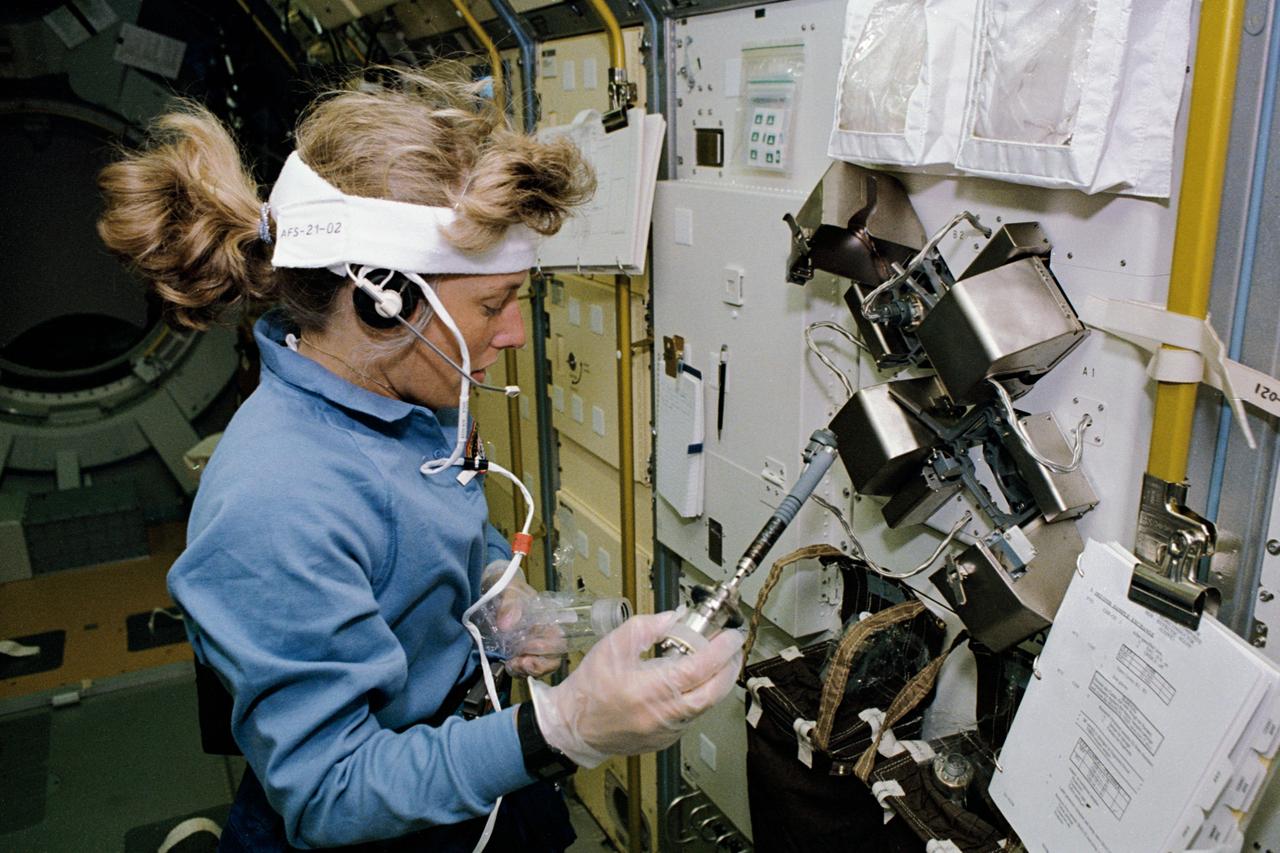
STS047-46-027 (12-20 Sept. 1992) --- Astronauts N. Jan Davis (left) and Mae C. Jemison, STS-47 mission specialists, prepare to deploy the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) apparatus in this 35mm frame photographed in the Science Module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Making their first flight in space, the two were joined by four other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for eight days of research. The Spacelab-J mission is a joint effort between Japan and the United States of America.
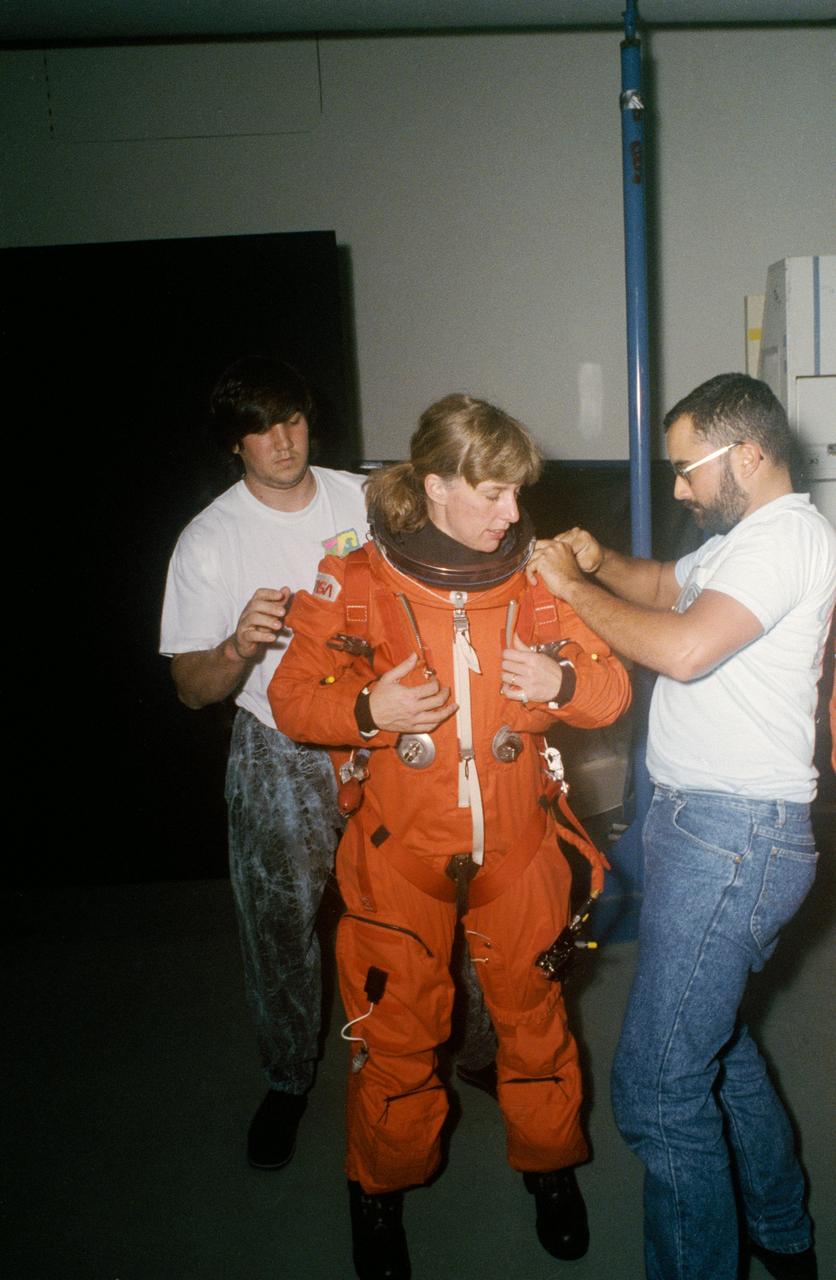

STS-47 Endeavour, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 105, Mission Specialist (MS) N. Jan Davis, wearing a launch and entry suit (LES), looks on as technicians adjust her LES parachute pack prior to launch emergency egress (bailout) exercises in JSC's Mockup and Integration Laboratory (MAIL) Bldg 9A. Davis is making her first flight in space.
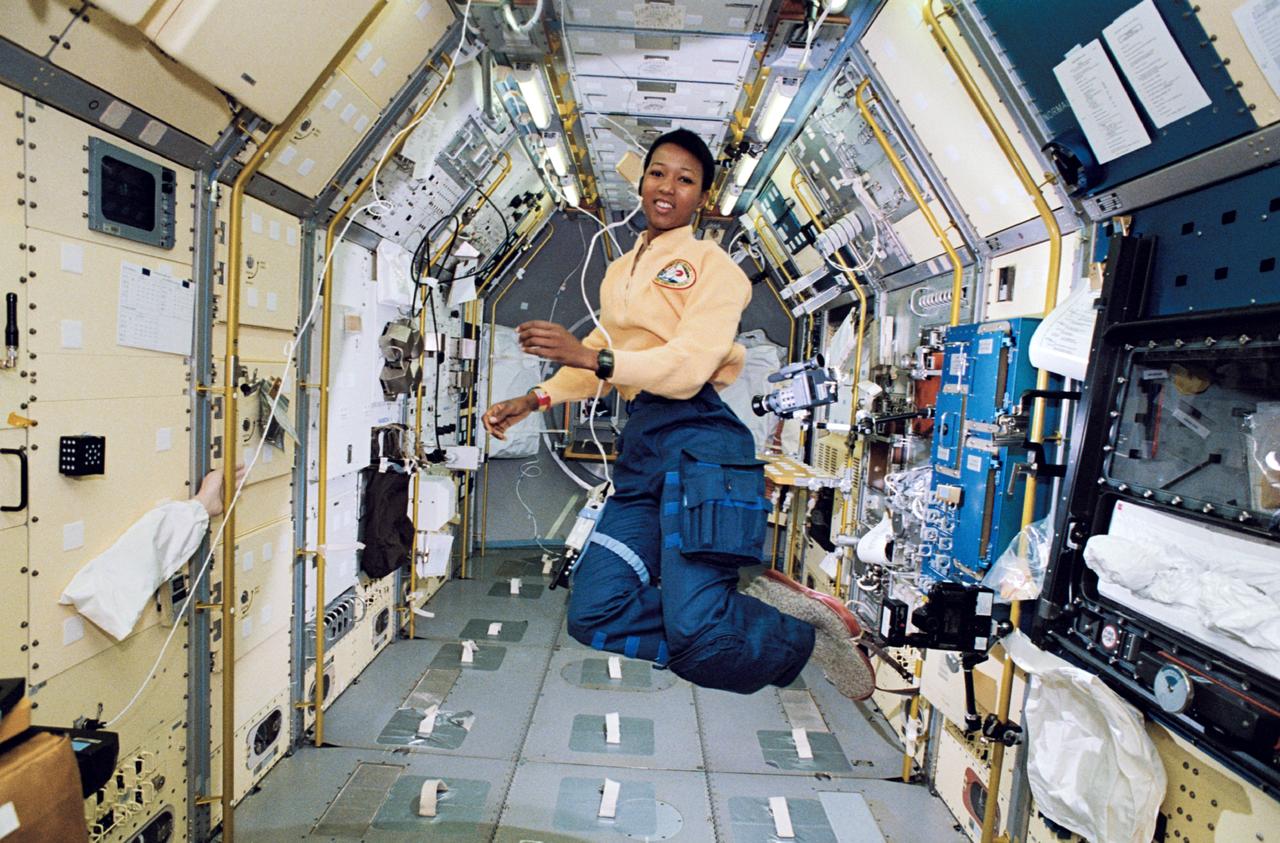

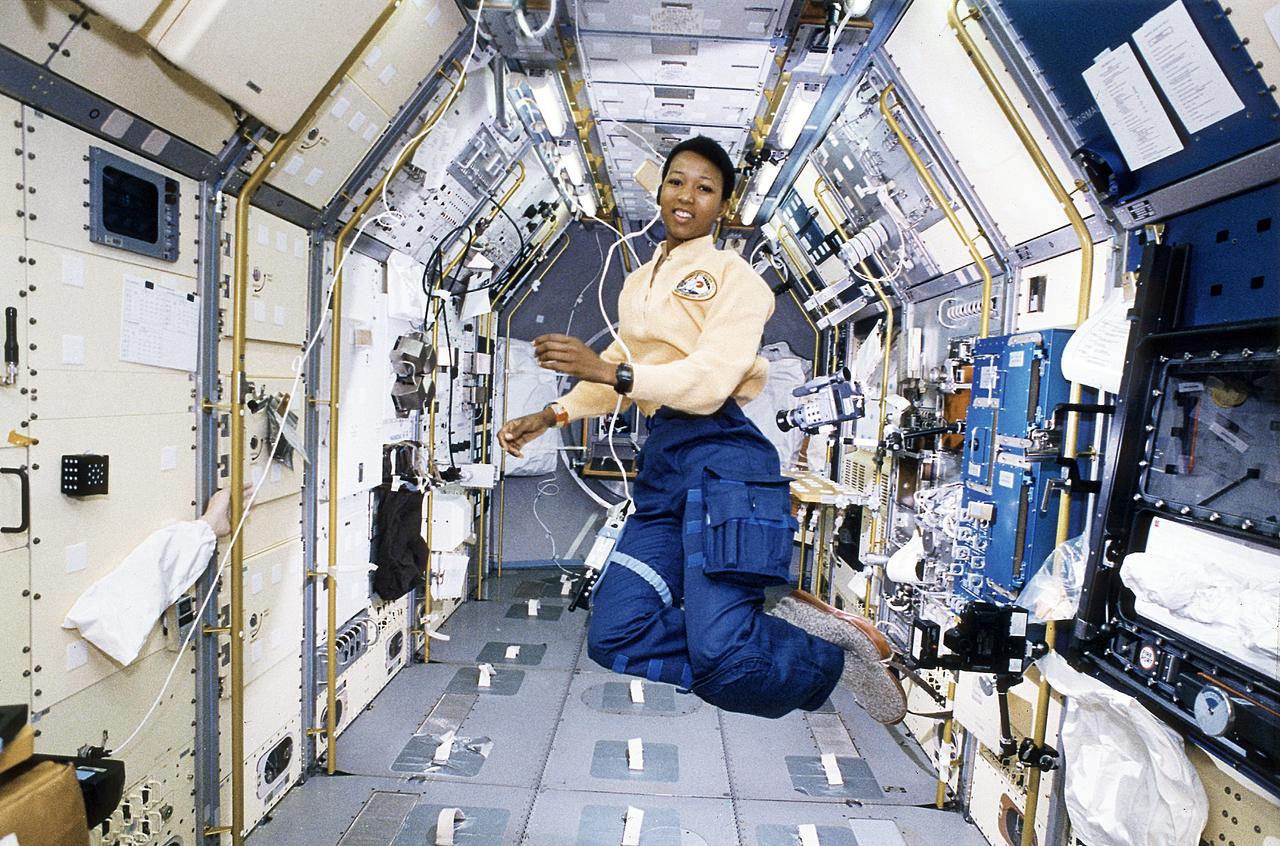
STS047-37-003 (12-20 Sept. 1992) --- Astronaut Mae C. Jemison, STS-47 mission specialist, appears to be clicking her heels in zero-gravity in this 35mm frame photographed in the Science Module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Making her first flight in space, Dr. Jemison was joined by five other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for eight days of research in support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States.
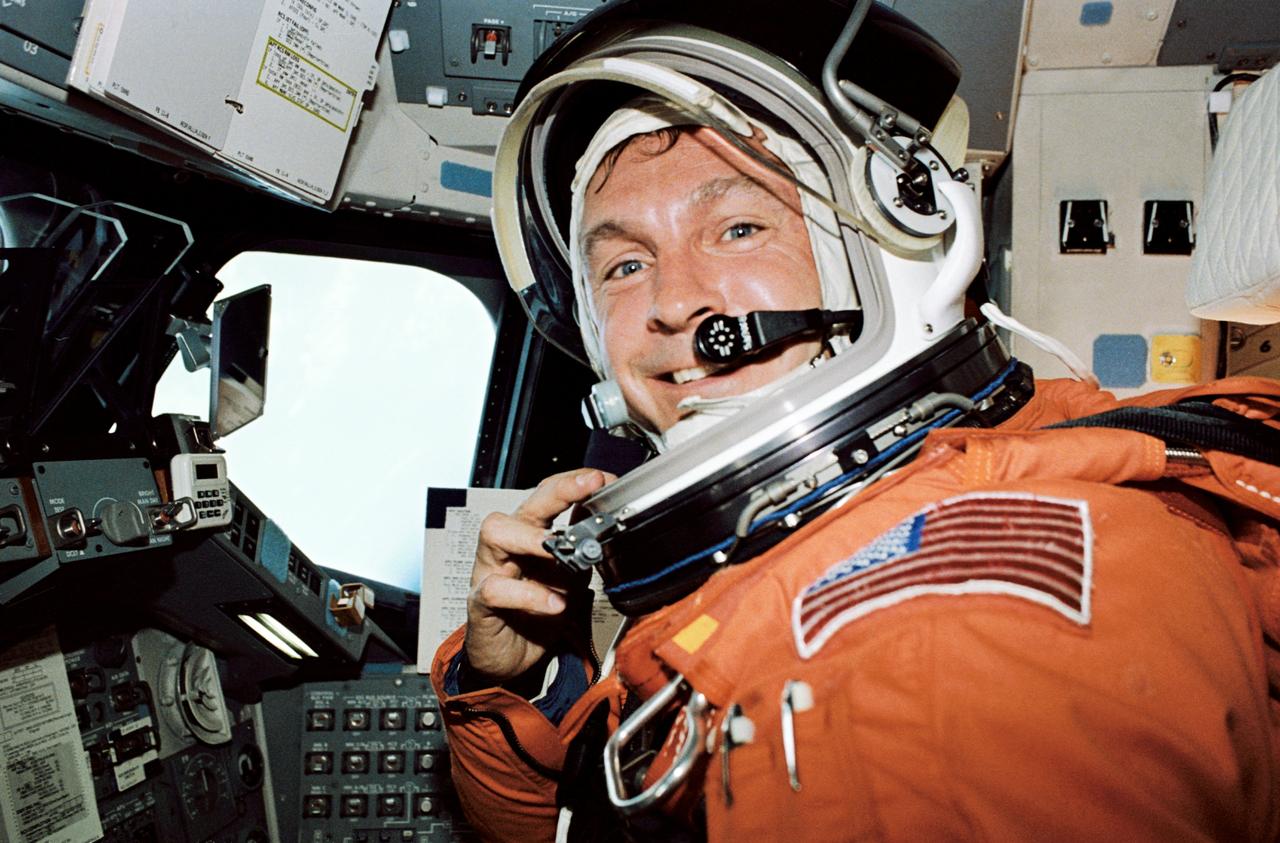

STS047-28-002 (20 Sept. 1992) --- Astronaut Curtis L. Brown, Jr., STS-47 pilot, is photographed at the Space Shuttle Endeavour's pilot station about ten minutes after main engine cutoff on launch day of the eight-day Spacelab-J mission. Wearing the partial-pressure launch and entry suit, Brown shared the forward cabin with astronaut Robert L. Gibson (out of frame at left), mission commander. Endeavour was beginning its second mission in space, this one devoted to research supporting the Spacelab-J mission.
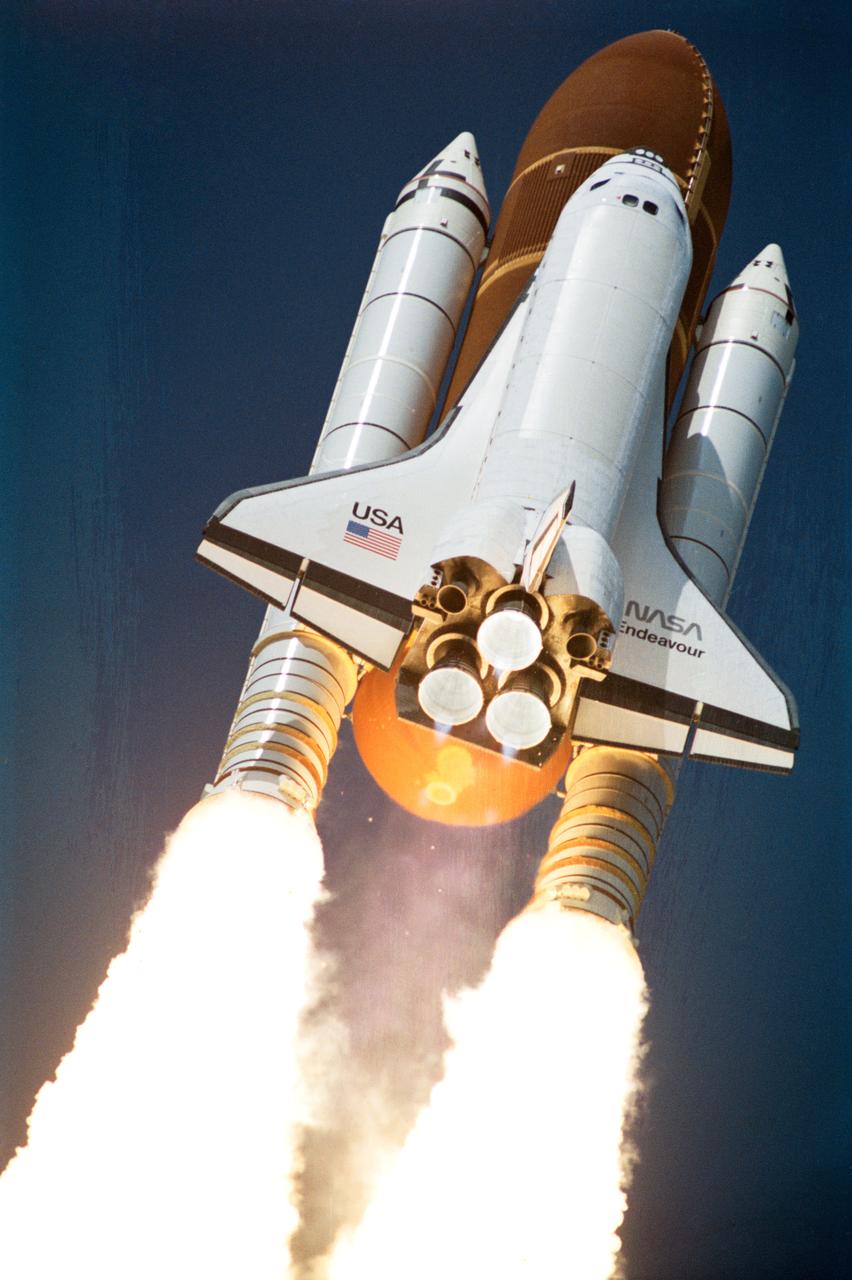

STS047-S-039 (12 Sept 1992) --- A 35mm camera was used to record this low-angle view of the STS-47 launch. With a crew of six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist onboard, the Space Shuttle Endeavour was heading for its second trip into space. This mission will be devoted to support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States. Launch occurred at 10:23:00:0680 a.m. (EDT), September 12, 1992. Onboard were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Curtis L. Brown Jr., pilot; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; and Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists; along with payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan.
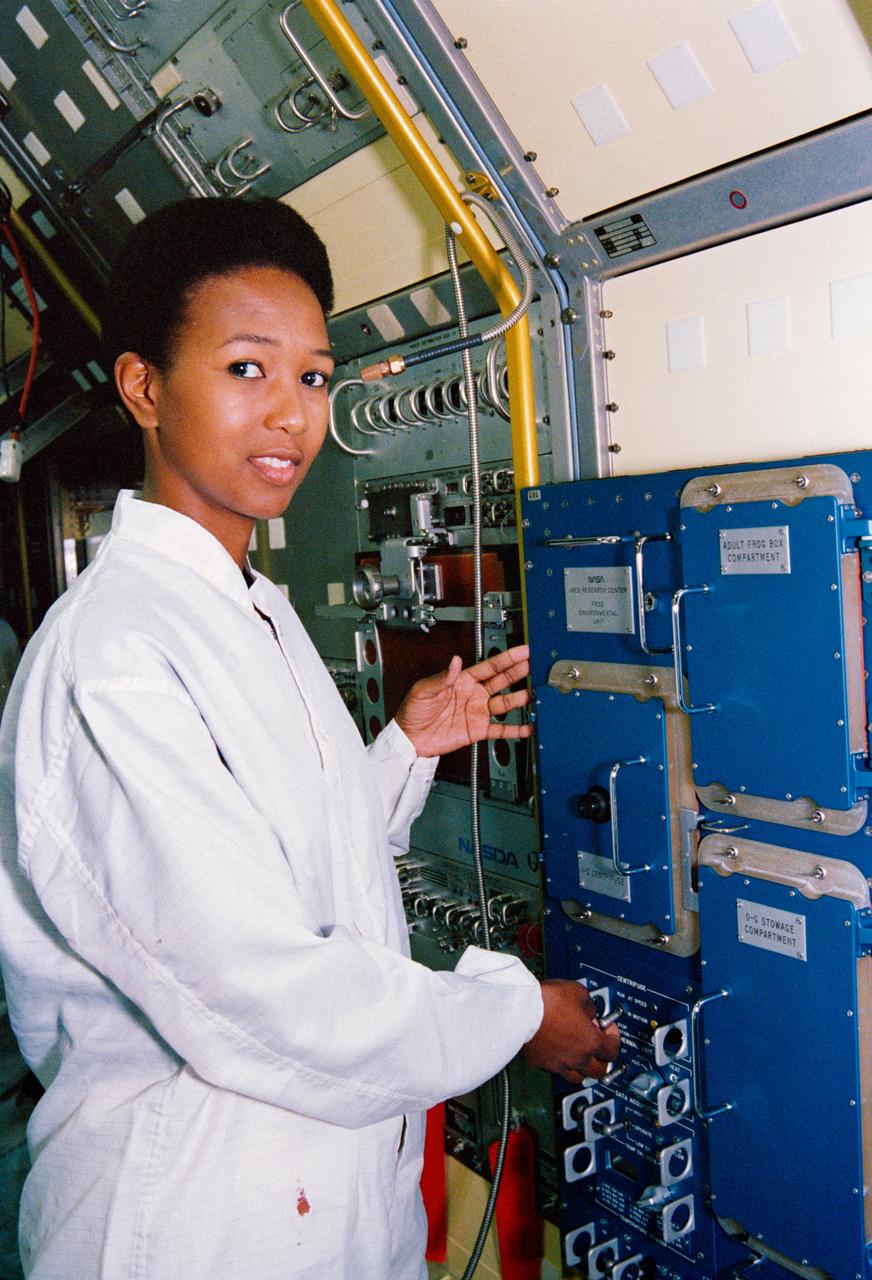

S92-44302 (25 July 1992) --- Astronaut Mae C. Jemison, mission specialist, examines the interior of the Spacelab-J laboratory module installed in Endeavour's cargo bay. The STS-47 crewmembers visited Endeavour, currently undergoing pre-flight processing in a high bay area of the Orbiter Processing Facility at the Kennedy Space Center. The Spacelab-J mission is currently scheduled for September of this year.
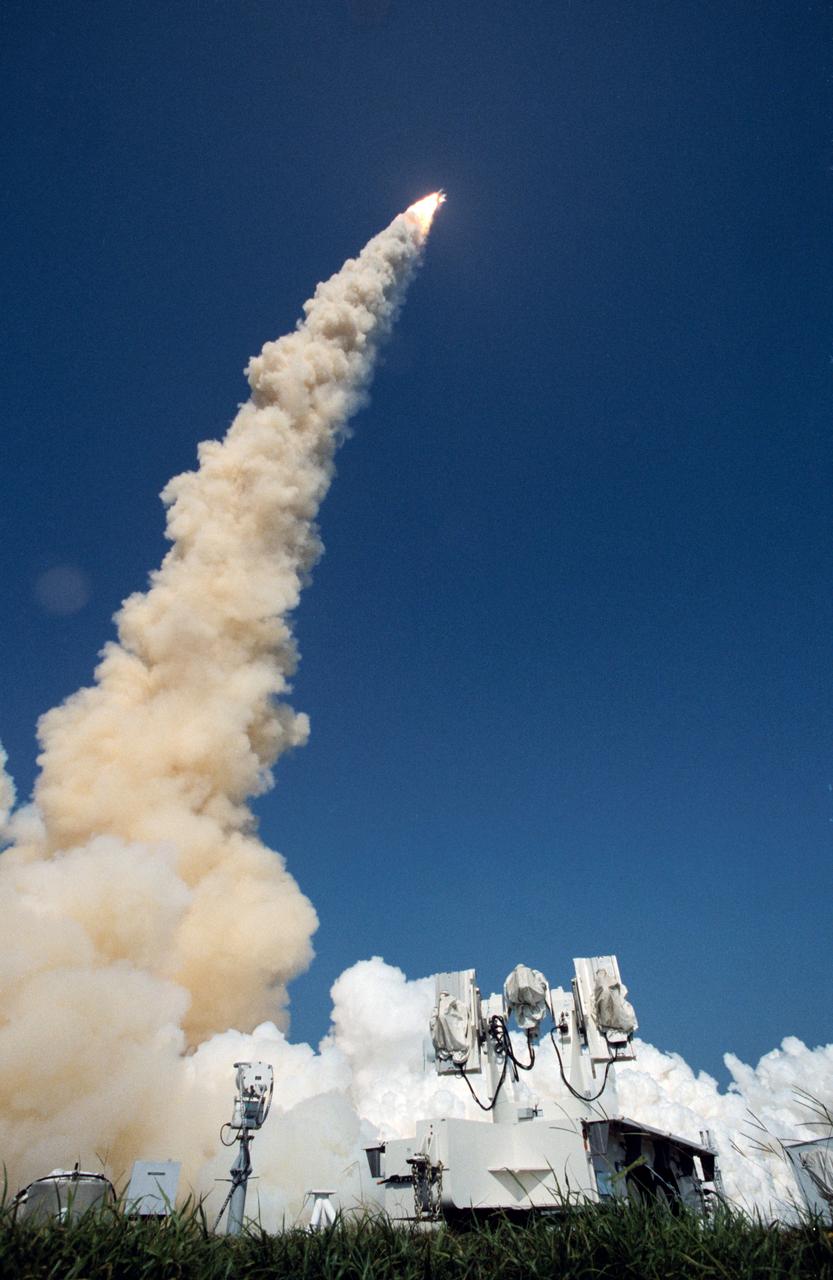

STS047-S-040 (12 Sept 1992) --- A 35mm camera was used to record this distant, low-angle view of the STS-47 launch. With a crew of six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist onboard, the Space Shuttle Endeavour was heading for its second trip into space. This mission is devoted to support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States. Launch occurred at 10:23:00:0680 a.m. (EDT), September 12, 1992. Onboard were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Curtis L. Brown Jr., pilot; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; and Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists; along with payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan.
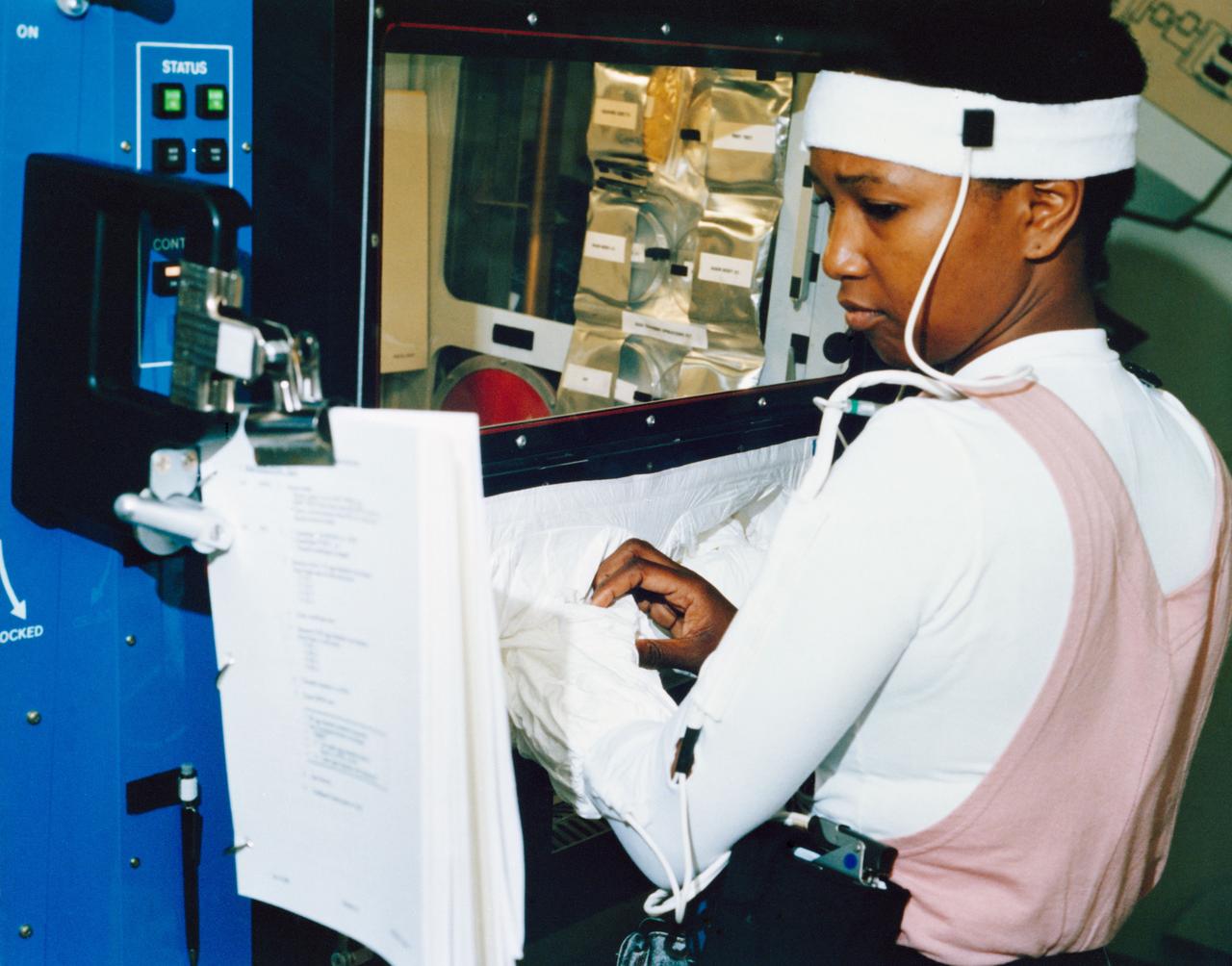

S92-45761 --- Astronaut Mae C. Jemison, mission specialist for the STS-47 mission, participates in a training exercise at the Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
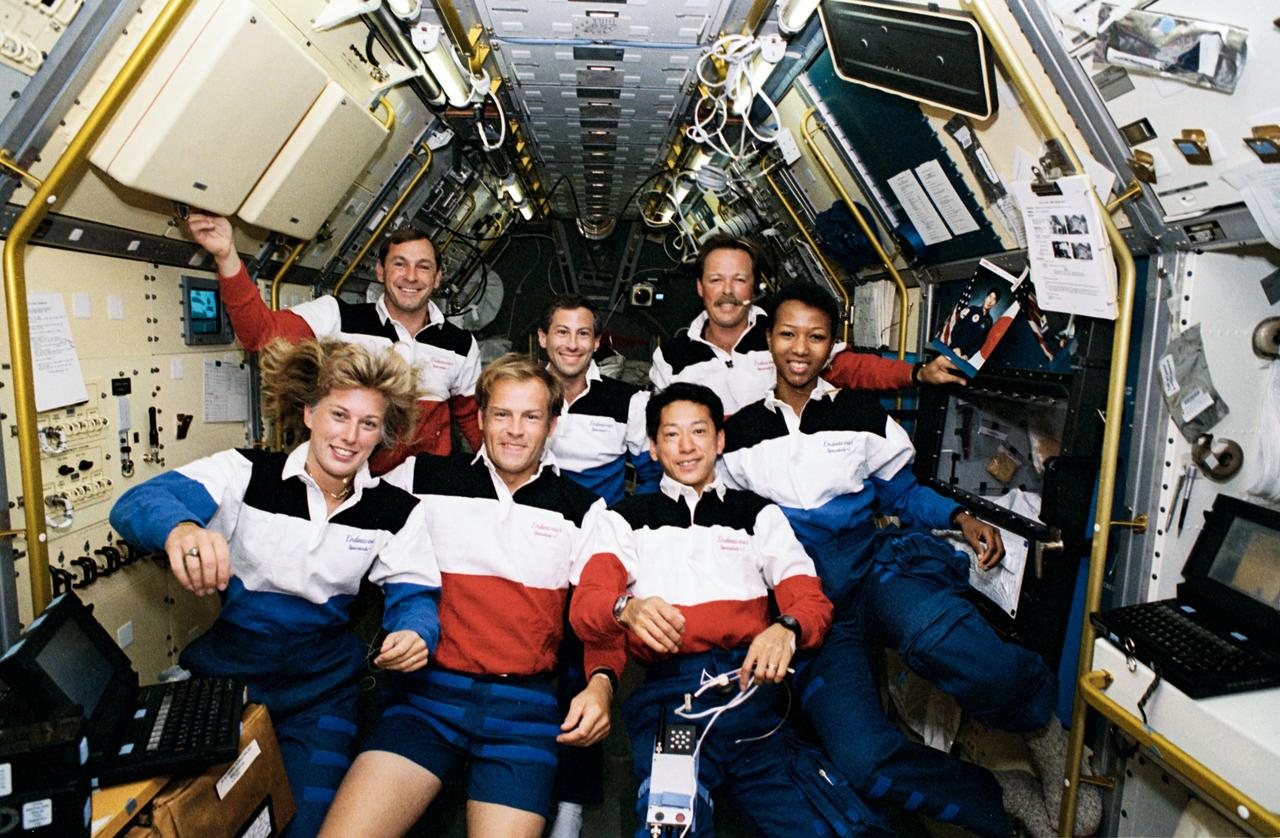

STS047-12-002 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- The crew members assemble for their traditional in-flight portrait in this 35mm frame photographed in the Science Module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Left to right (front) are N. Jan Davis, Mark C. Lee and Mamoru Mohri; and (rear) Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Jerome (Jay) Apt, Robert L. Gibson and Mae C. Jemison. The seven spent eight days in space in support of the Spacelab-J mission.
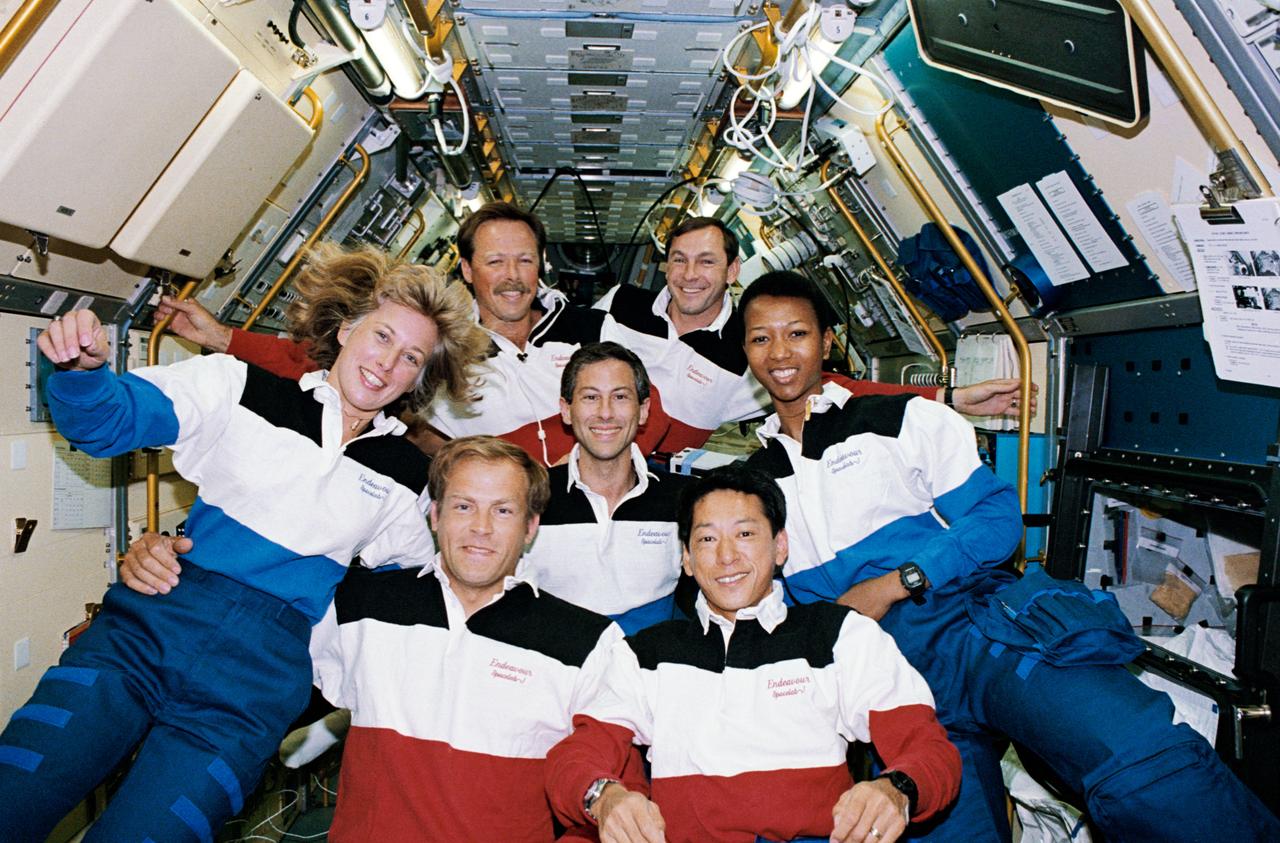

STS047-09-009 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- The seven crew members sharing eight days of research in support of Spacelab-J pose for the traditional inflight portrait in the Science Module. Pictured, left to right, back row, are Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; and Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot; middle row, N. Jan Davis, Jerome (Jay) Apt and Mae C. Jemison, all mission specialists; and front row, Mark C. Lee, payload commander, and Mamoru Mohri, payload specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA).
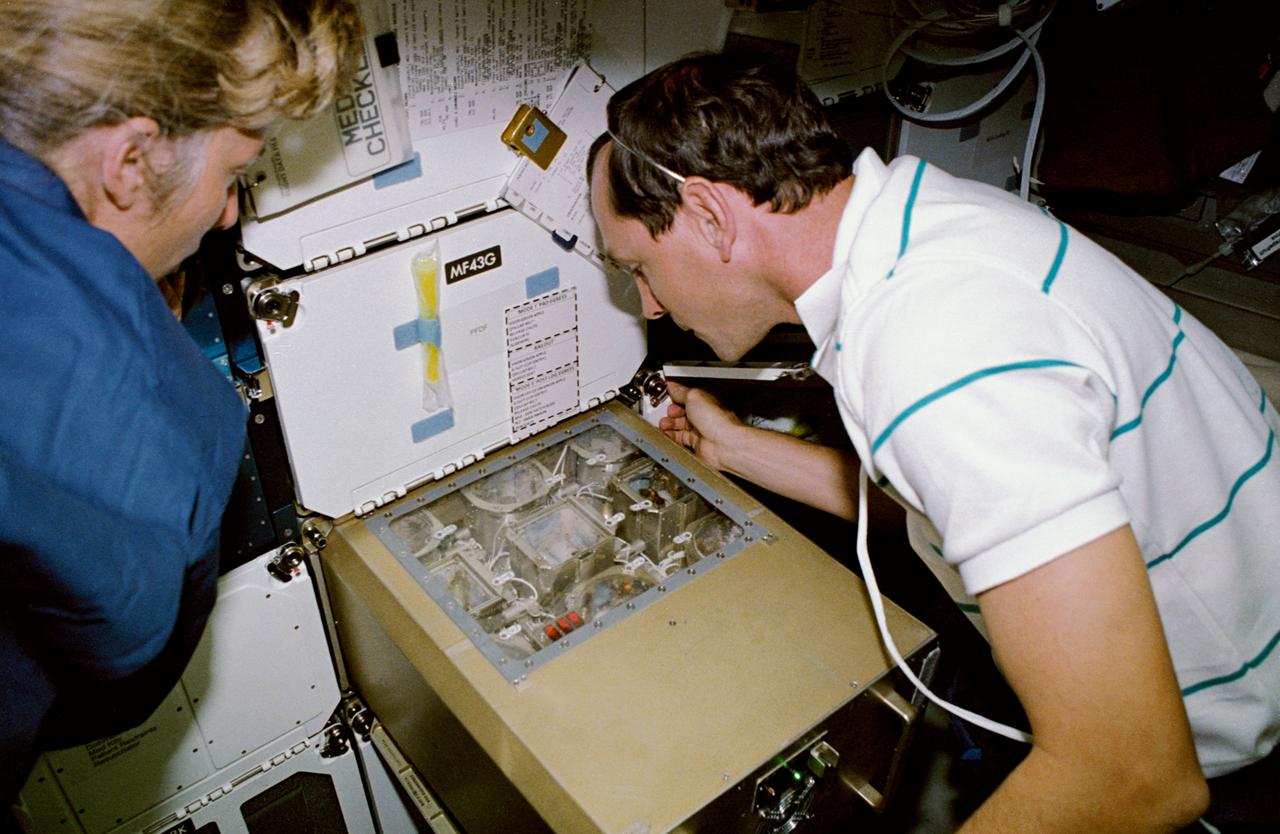

STS047-02-018 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronauts N. Jan Davis, mission specialist, and Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot, oversee the progress of some of the 180 female Oriental Hornets onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The insects are part of the Israeli Space Agency Investigation About Hornets (ISAIAH) experiment. The objective of this experiment is to examine the effects of microgravity on the orientation, reproductive capability and social activity of the hornets. Also, the direction of comb-building by hornet workers in microgravity, as well as the structural integrity of the combs, will be examined.
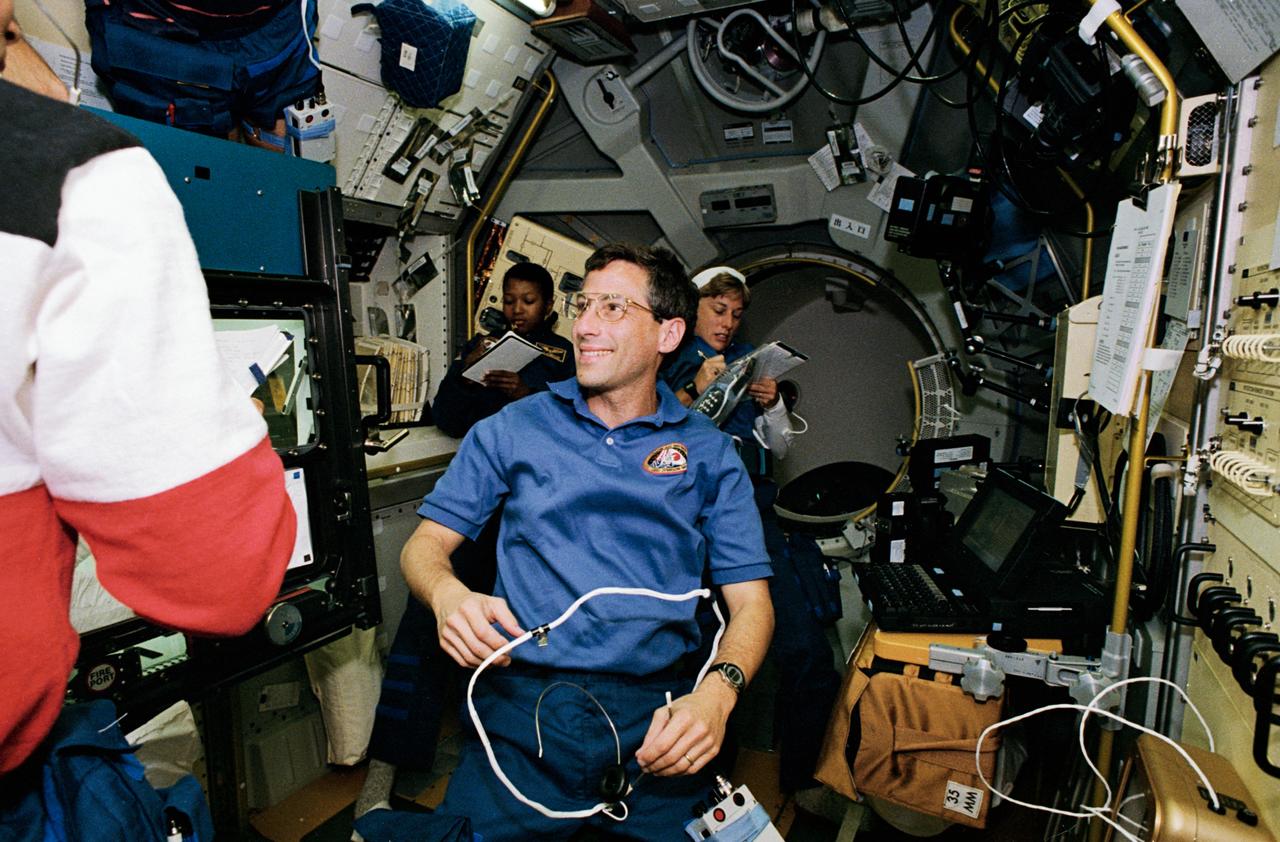

STS047-05-019 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronaut Jerome (Jay) Apt, mission specialist, responds to a crew mate's query during a shift change in the Spacelab-J Science Module aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Others pictured, left to right, are astronauts Mark C. Lee (immediate foreground, partially out of frame), payload commander; Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists. The four joined two other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for eight days aboard Endeavour in support of the joint Japanese-American effort.
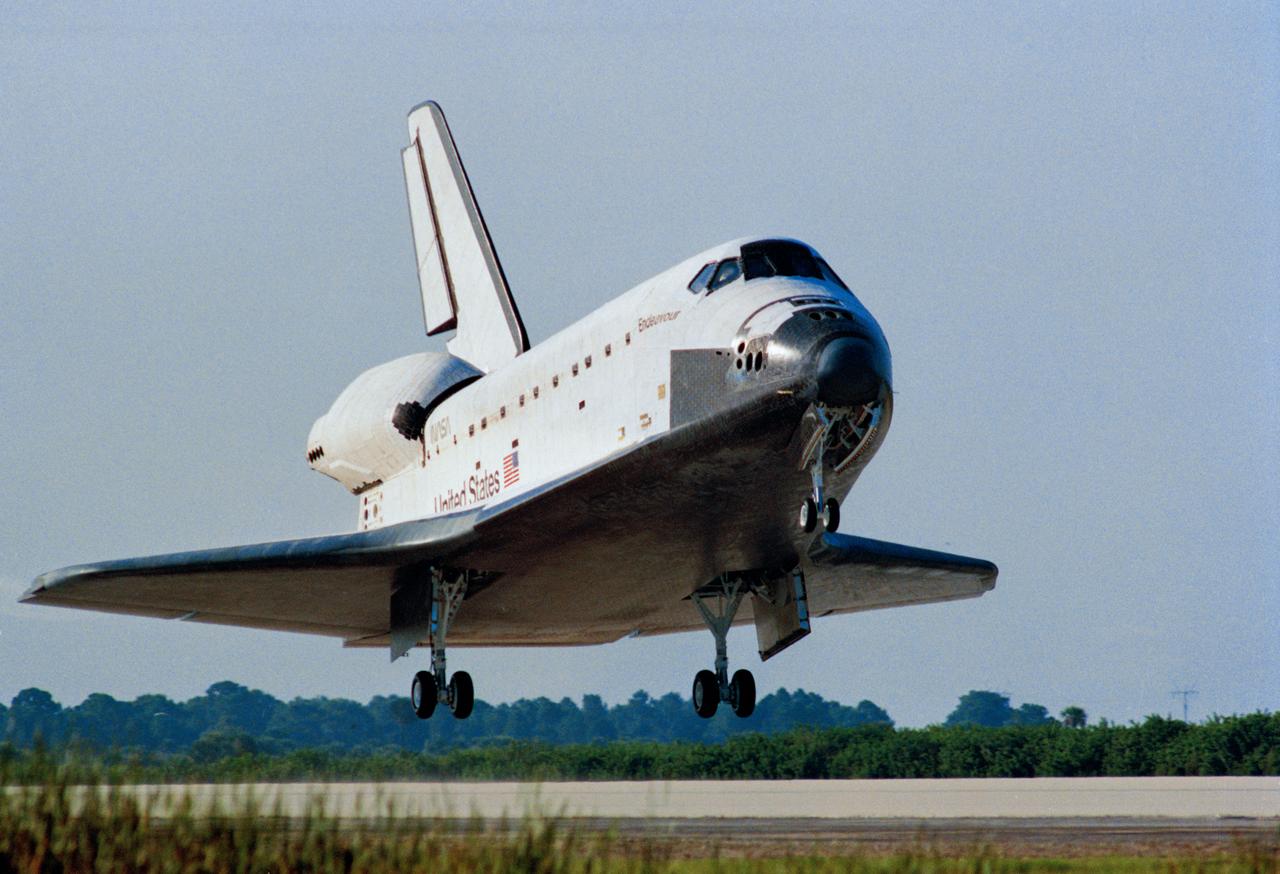

STS047-S-116 (20 Sept 1992) --- The Space Shuttle Endeavour prepares to land on the Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle landing facility runway. The successful landing marked the completion of an eight-day Earth-orbital mission for the orbiter, its seven-member crew and the Spacelab-J payload. Landing occurred at 8:53 a.m. (EDT), September 20, 1992. Onboard the spacecraft were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, Curtis L. Brown Jr., Mark C. Lee, Jerome (Jay) Apt, N. Jan Davis and Mae C. Jemison, along with Japanese payload specialist Dr. Mamoru Mohri.
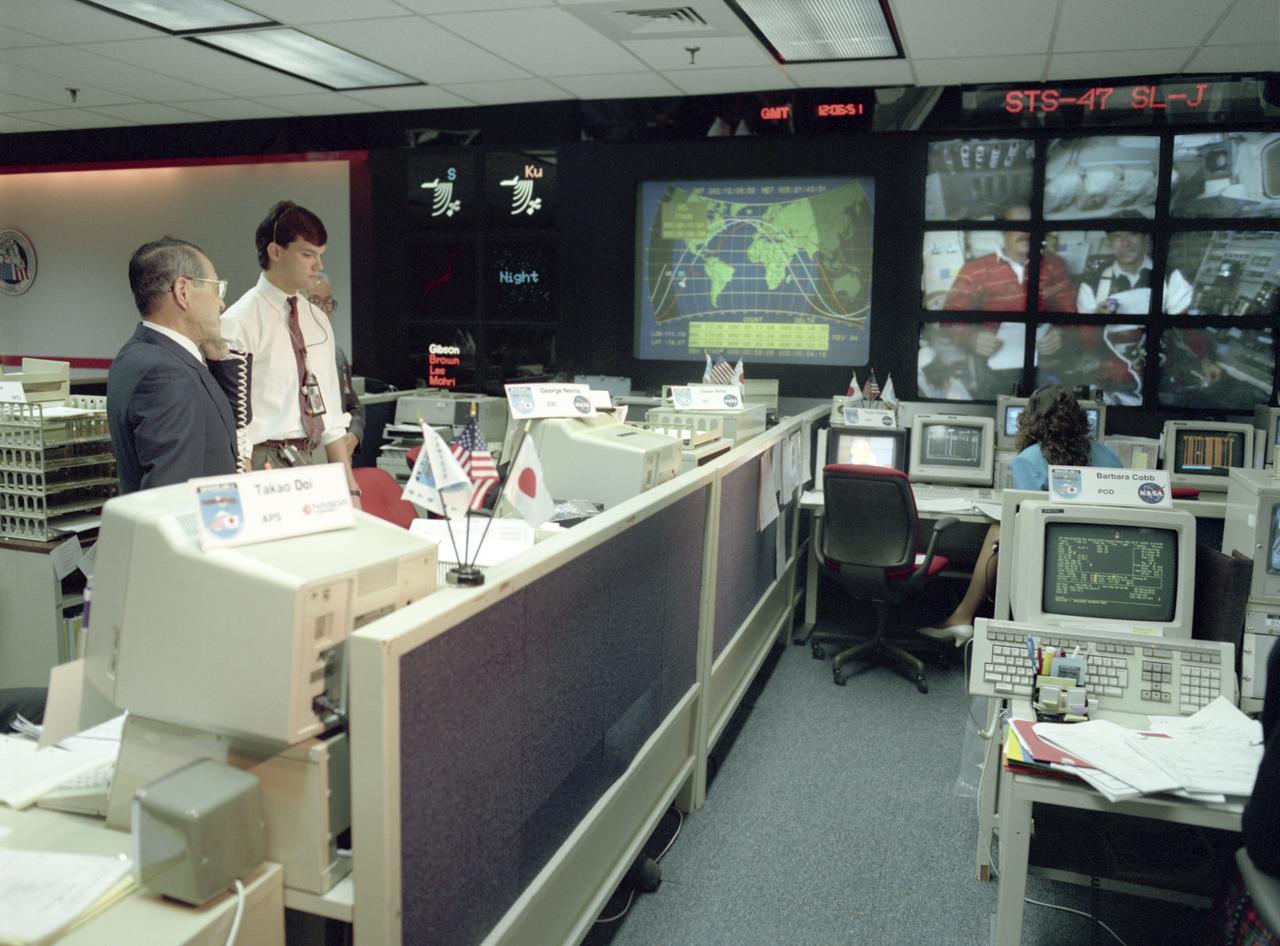

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. From the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC), NASDA President, Mr. Yamano, speaks to Payload Specialist Mamoru Mohri, a Japanese crew member aboard the STS-47 Spacelab J mission.
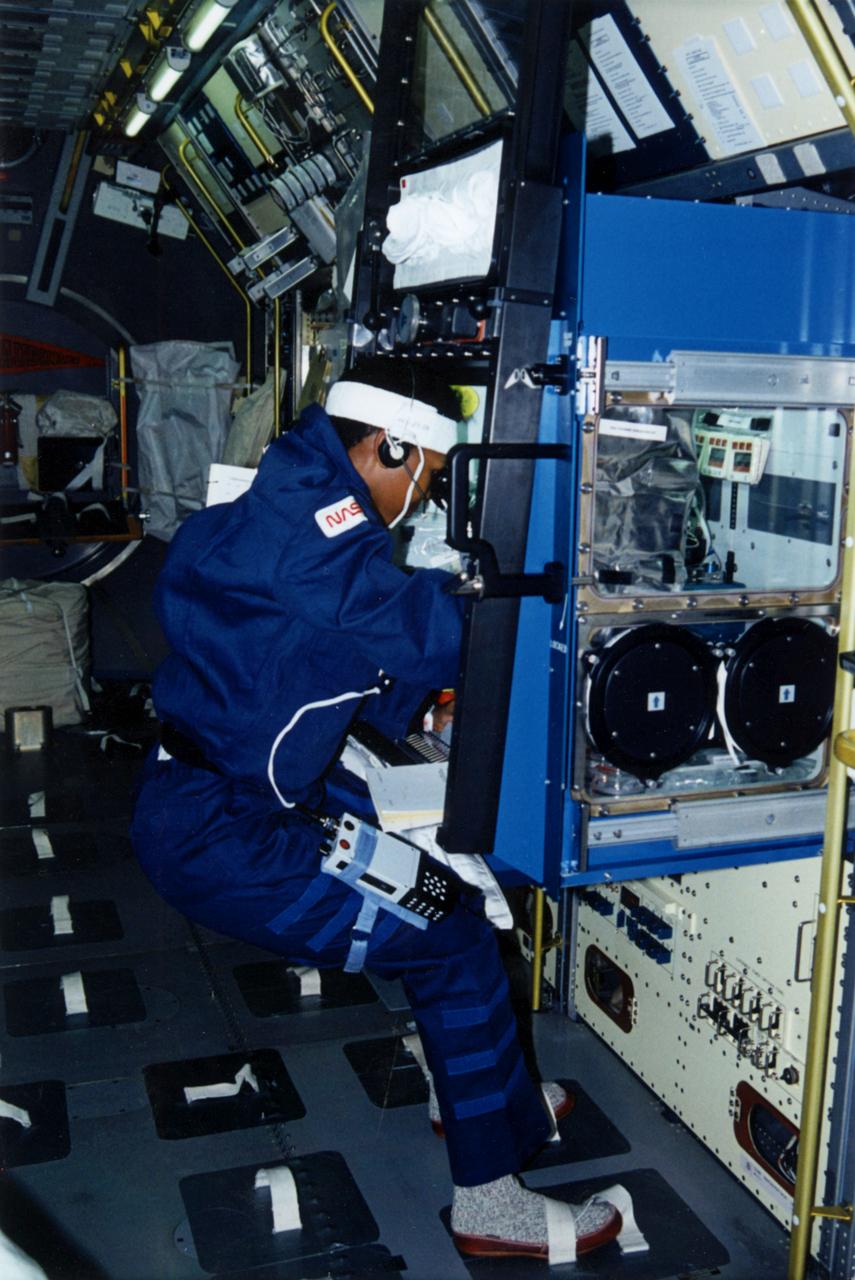

Astronaut Mae Jemison working on Glovebox experiment.
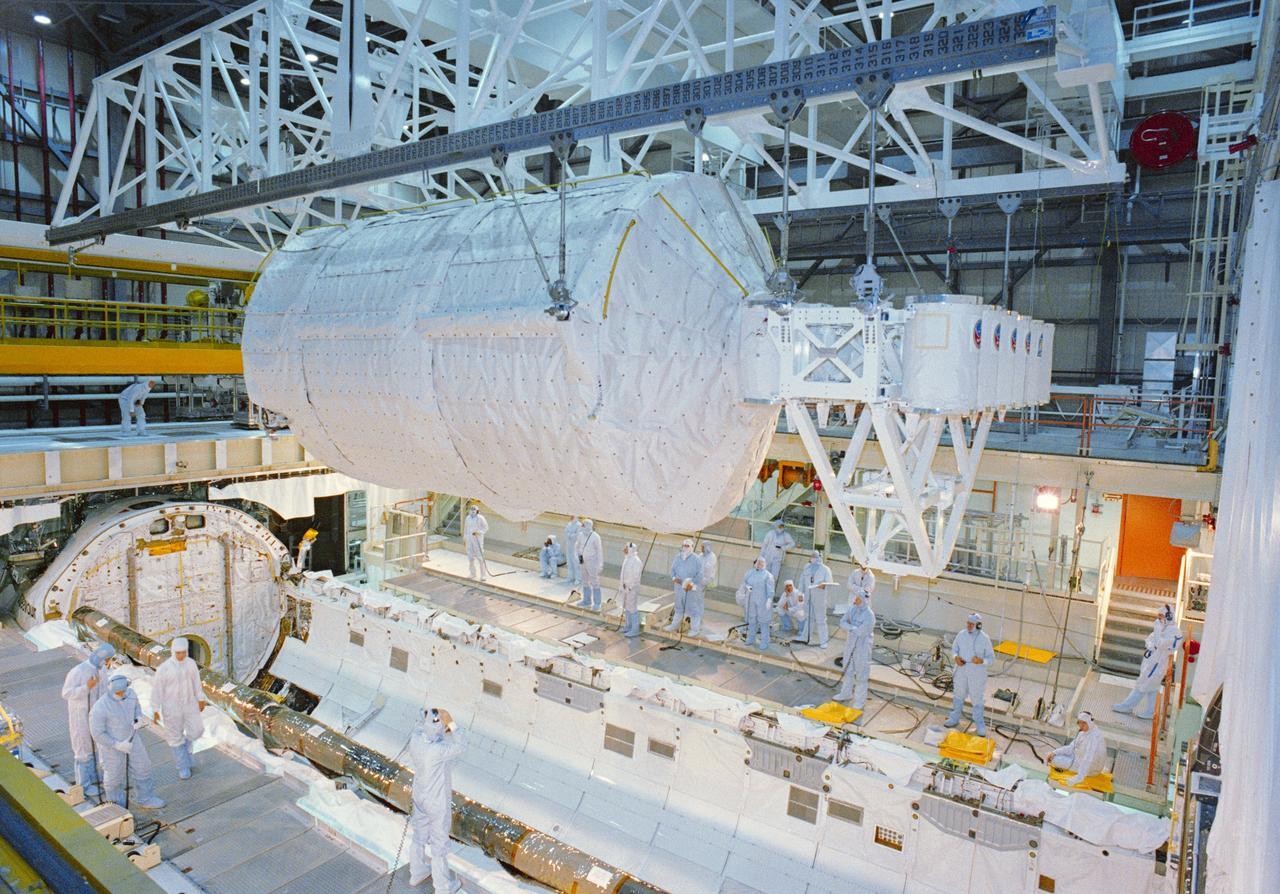

S92-44307 (25 July 1992) --- Technicians, engineers and flight crewmembers look on as the Spacelab-J laboratory module and experiment canister bridge are lowered into Endeavour's cargo bay. The STS-47 crewmembers visited Endeavour, currently undergoing pre-flight processing in a high bay area of the Orbiter Processing Facility at the Kennedy Space Center. The Spacelab-J mission is currently scheduled for September of this year.
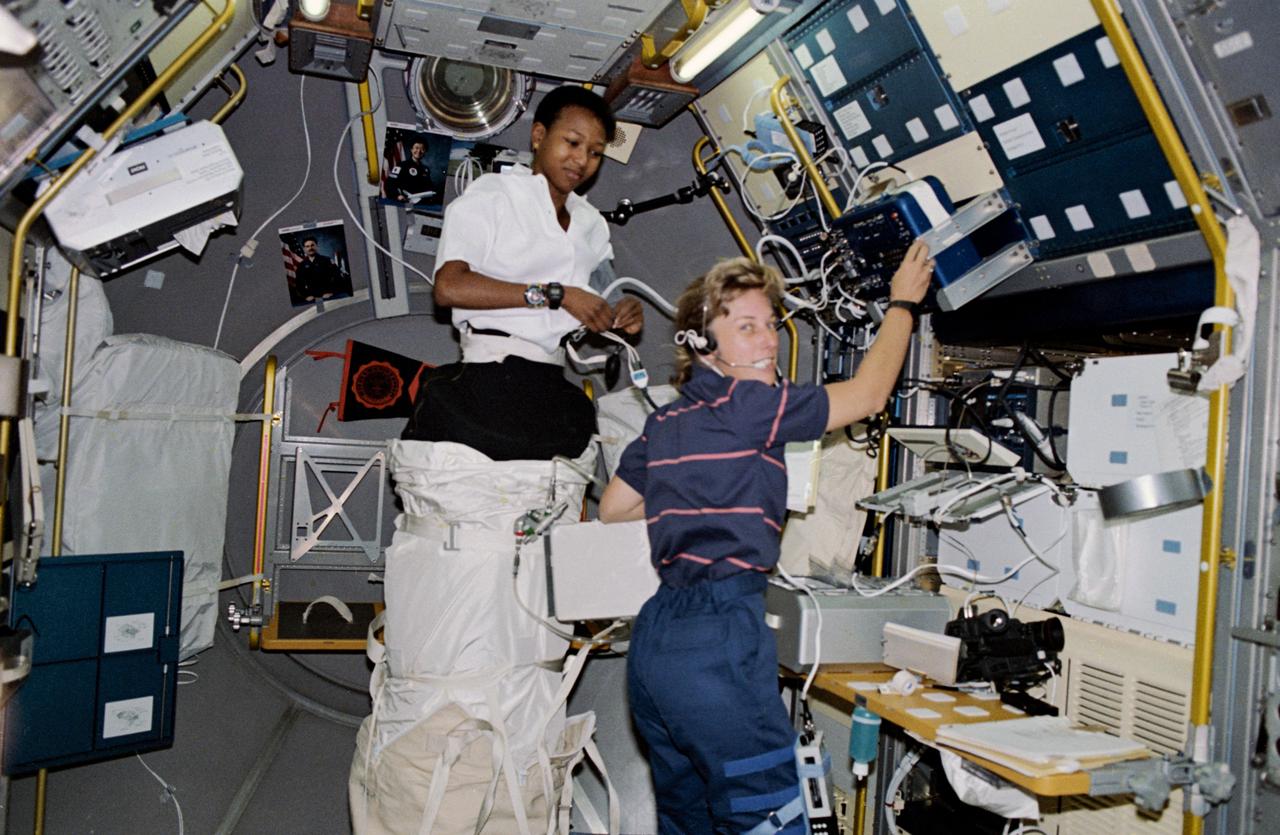

STS047-230-030 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronauts Mae C. Jemison (left) and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists, are pictured in the Spacelab-J science module preparing to conduct a session with the Lower Body Negative Pressure (LBNP) experiment. The two joined four other NASA astronauts and a payload specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA) aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour for eight days of Spacelab-J research.

STS047-35-022 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot, and N. Jan Davis, mission specialist, team up to cure a high humidity problem in the hornet experiment in the Spacelab-J Science Module of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Via a jury-rigged hose hook-up, the two were able to blow air from a spacesuit fan into the experiment, thus eliminating condensation that obscured the viewing of the Israeli hornet experiment. The experiment examined the effects of microgravity on the orientation, reproductive capability and social activity of 180 female Oriental Hornets.

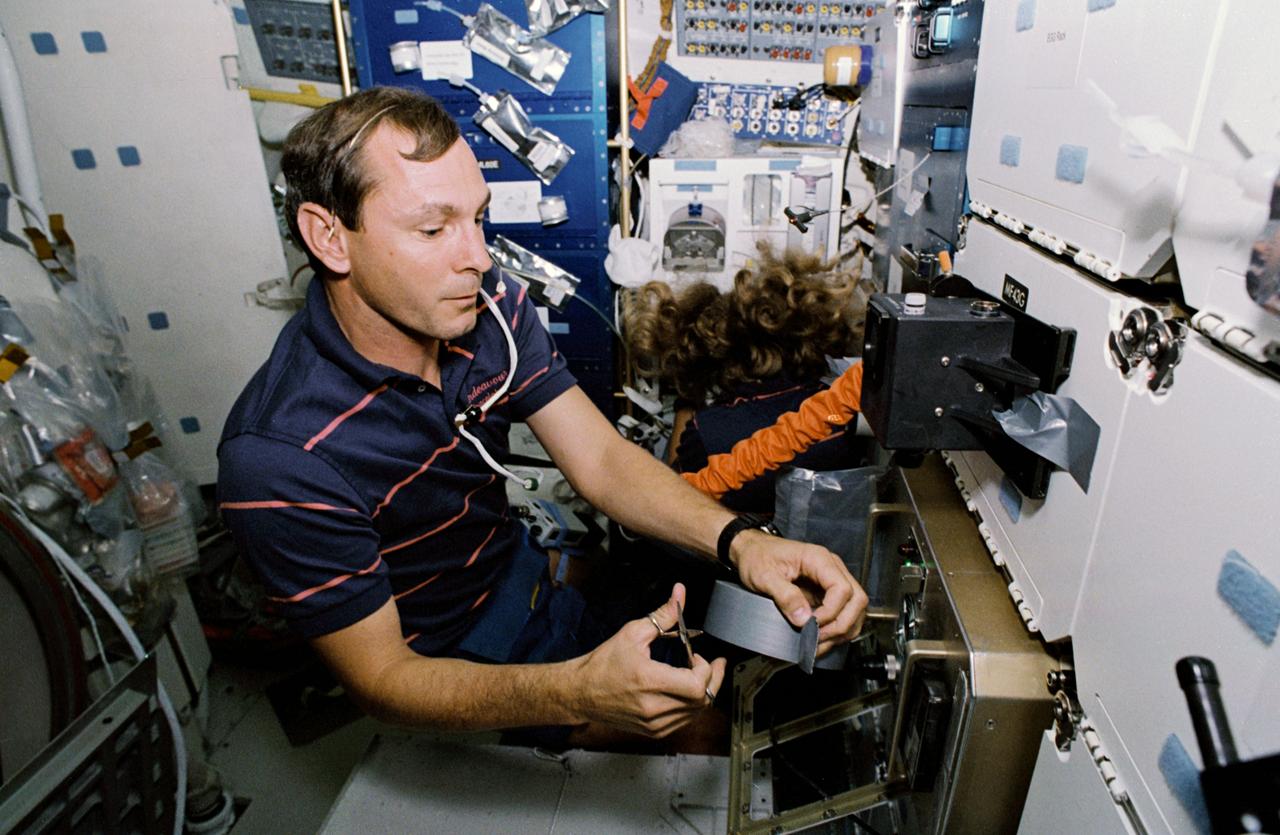
STS047-03-024 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronaut N. Jan Davis, mission specialist, talks to ground controllers as she works with the Free Flow Electrophoresis Unit (FFEU) in the Science Module of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. Davis joined five other NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist for eight days of scientific research onboard Endeavour.

STS047-S-001 (June 1992) --- Designed by its crew members, the STS-47 mission emblem depicts the space shuttle orbiter with the Spacelab module in the cargo bay against a backdrop of the flags of the United States and Japan. The flags symbolize the side-by-side cooperation of the two nations in this mission. The land masses of Japan and Alaska are represented on the emblem, emphasizing the multi-national aspect of the flight as well as the high inclination orbit of 57 degrees. The initials "SLJ" on the left border of the emblem stand for Spacelab Japan; the name generally used for the mission is Spacelab-J. The Japanese characters on the right border form the word Fuwatto which means "weightlessness." The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
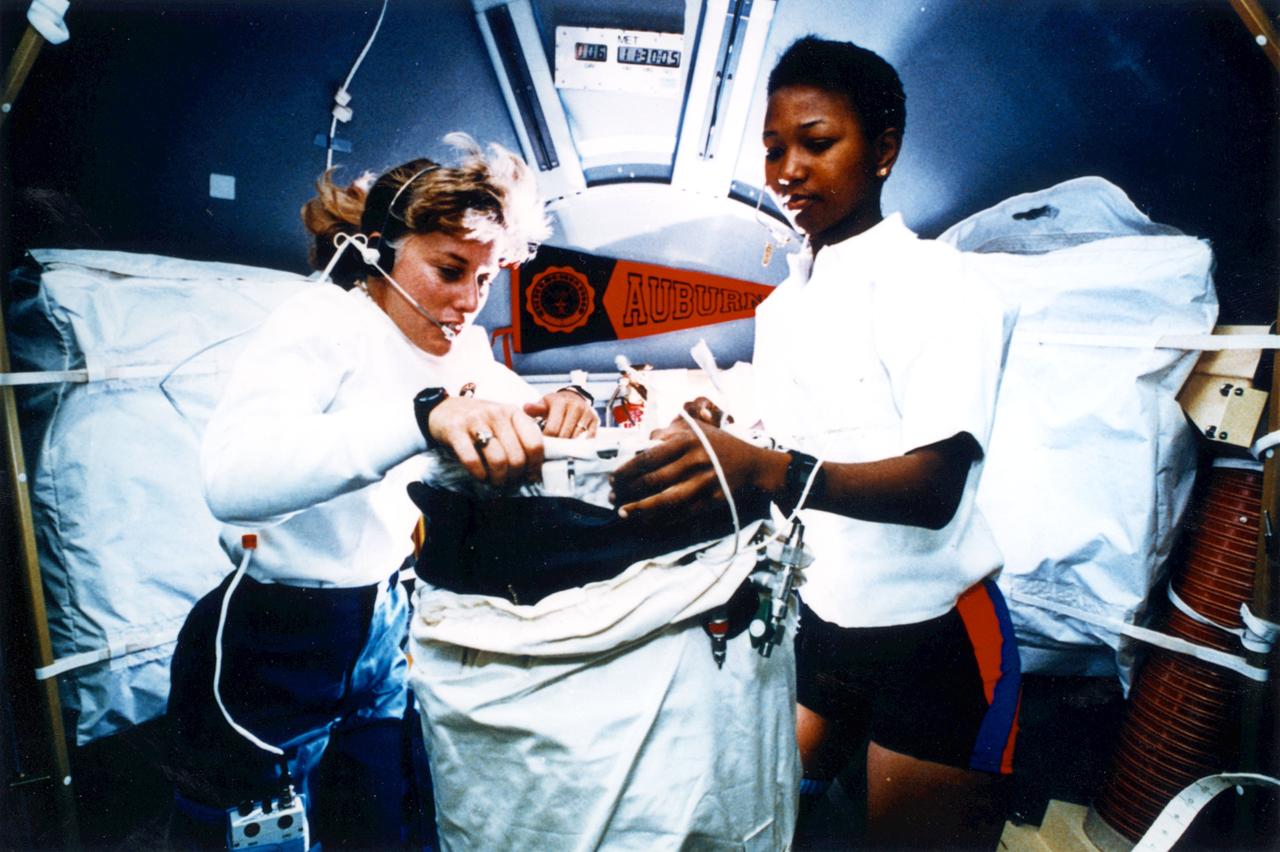

Jan Davis and Mae Jemison working on experiments.
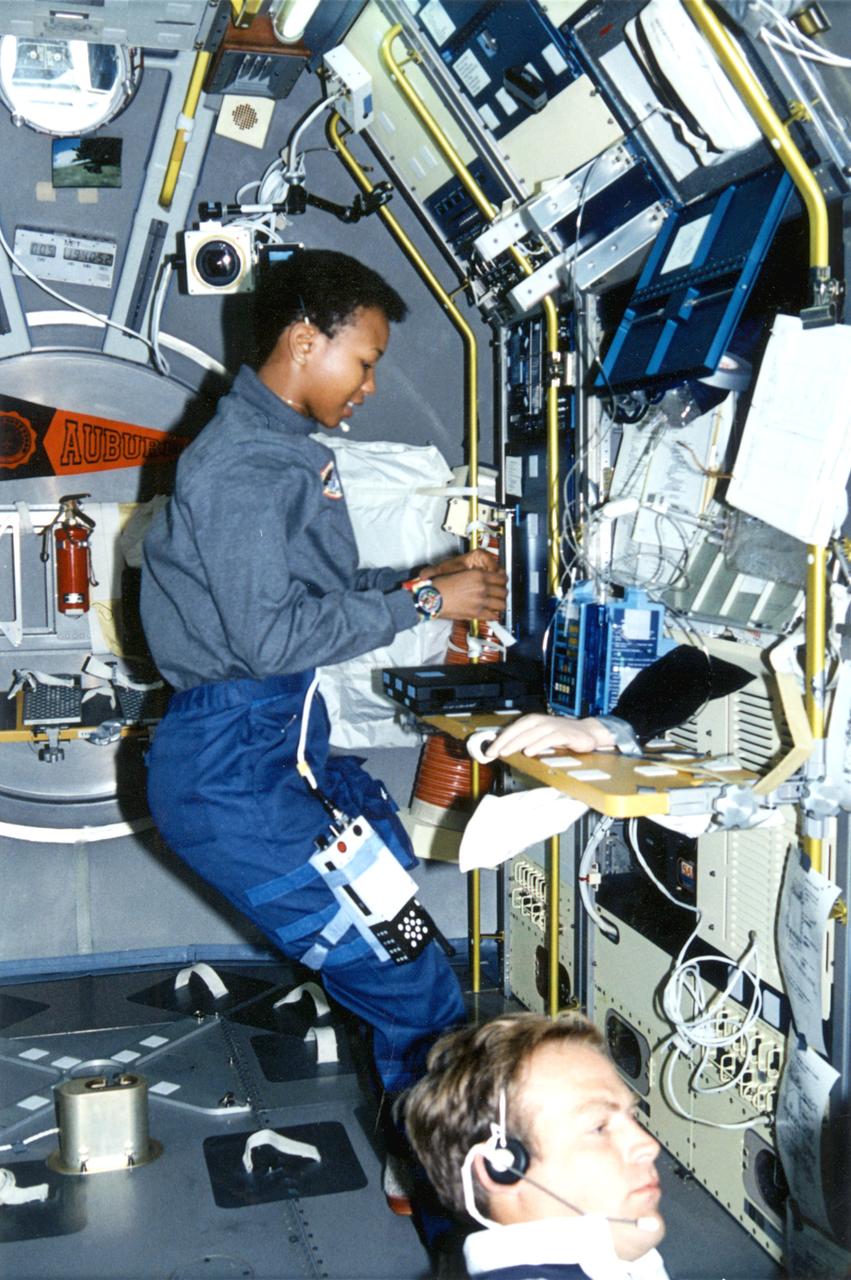

Astronaut Mae Jemison on Spacelab-J.
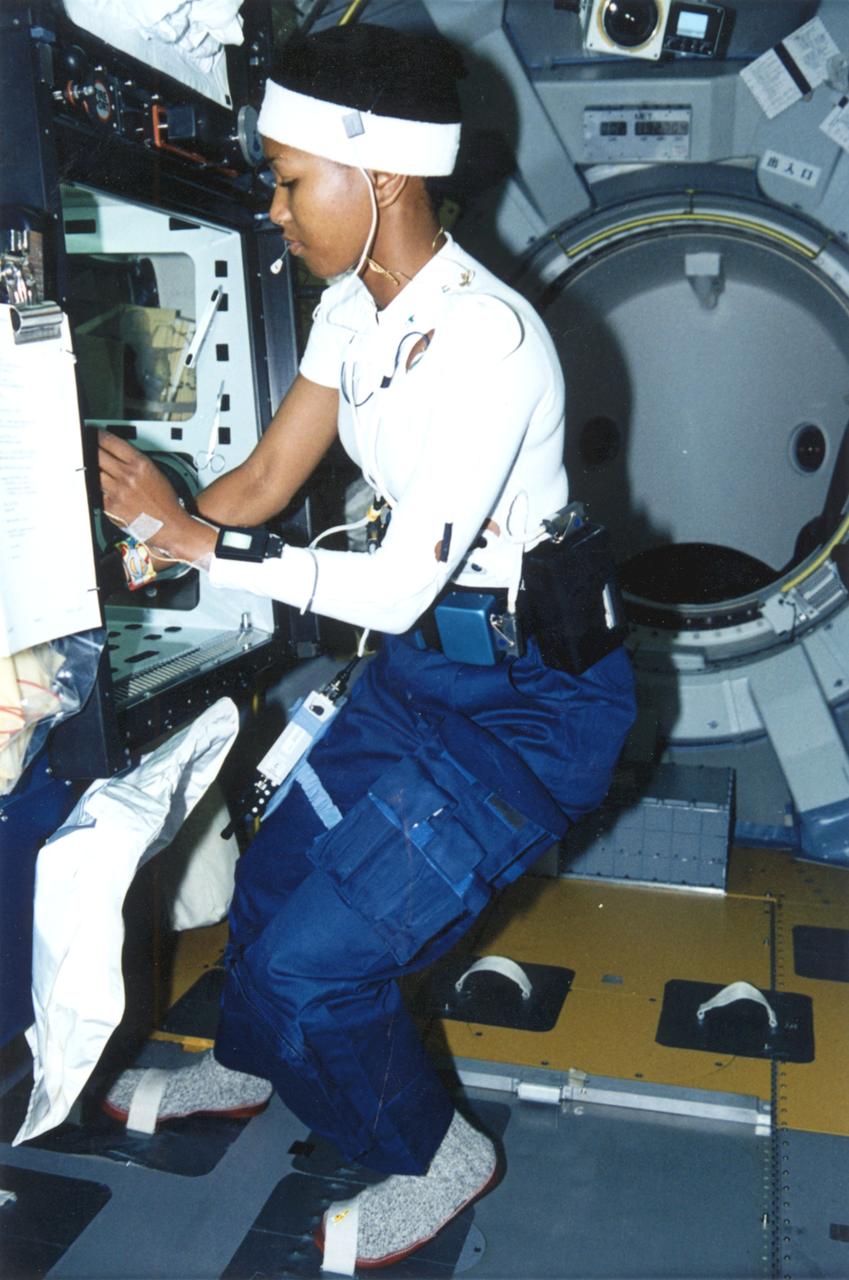

Astronaut Mae Jemison working on experiment.

STS047-204-006 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Dr. Mamoru Mohri, payload specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA), participates in an experiment designed to learn more about Space Adaptation Syndrome (SAS). The experiment is titled, "Comparative Measurement of Visual Stability in Earth and Cosmic Space." During the experiment, Dr. Mohri tracked a flickering light target while eye movements and neck muscle tension were measured. This 45-degree angle position was one of four studied during the eight-day Spacelab-J mission.
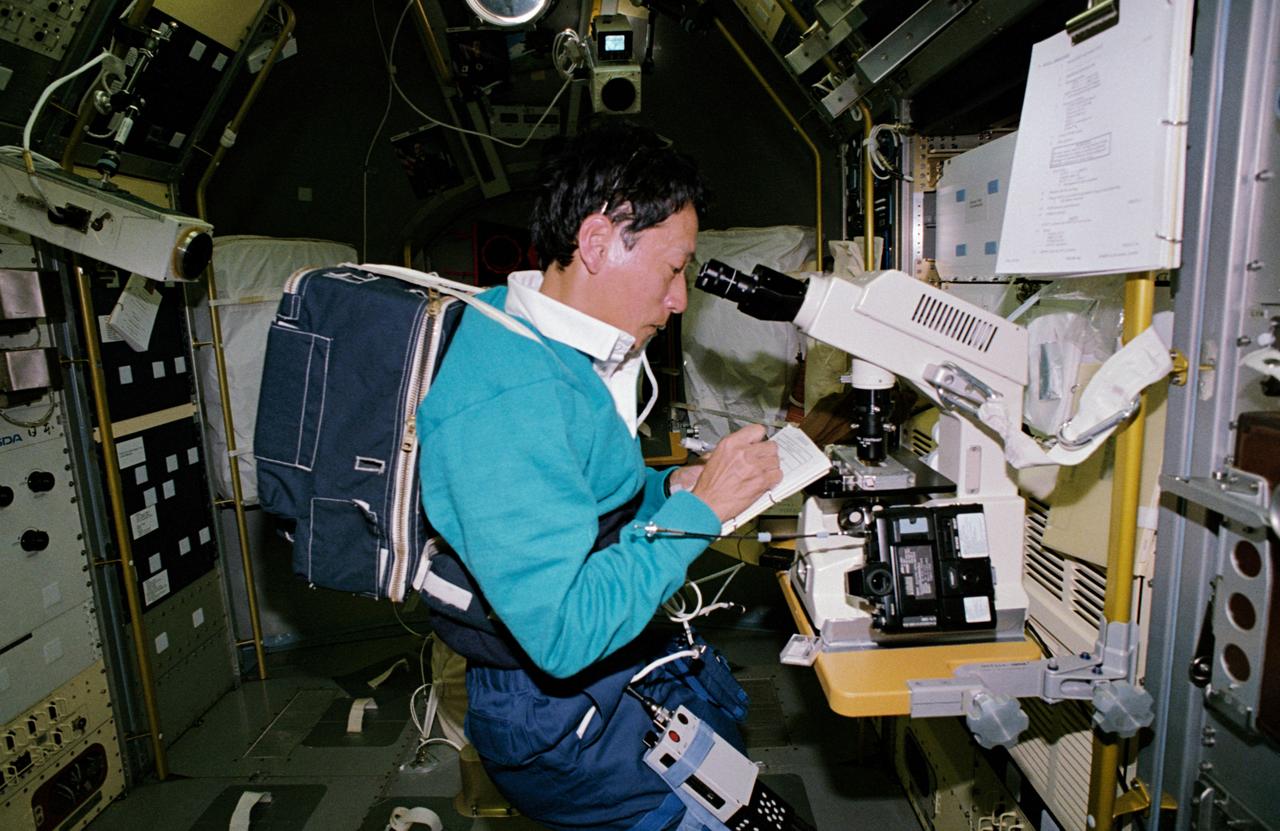

STS047-05-025 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA), uses a microscope to produce photomicrographs of mammalian cells. The mammal cell structure experiment is one of a large number of tests that were performed during the eight-day Spacelab-J mission. On his back, Dr. Mohri totes a health monitoring experiment. The primary objective of the physiological monitoring system is to observe the health condition of the Japanese payload specialist so that good health can be maintained during and after the spaceflight.
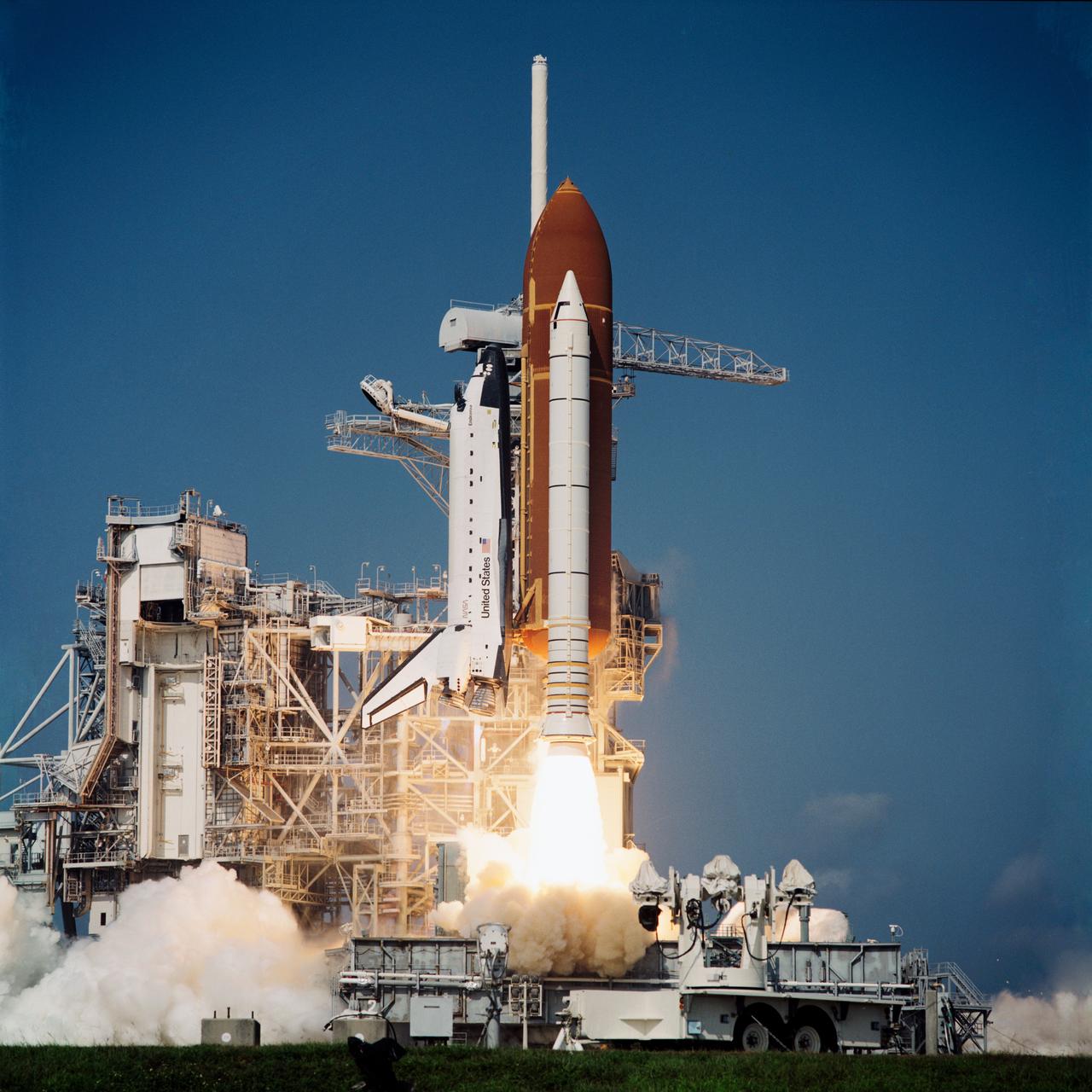

STS047-S-019 (12 Sept 1992) --- With a crew of six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist onboard, the Space Shuttle Endeavour heads for its second trip into space. This trip will be devoted to support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States. Launch occurred at 10:23:00:0680 a.m. (EDT), September 12, 1992. Onboard were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Curtis L. Brown Jr., pilot; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; and Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists; along with payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan.

STS047-02-003 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- Astronaut N. Jan Davis, mission specialist, works at the Continuous Heating Furnace (CHF) in the Spacelab-J Science Module. This furnace provided temperatures up to 1,300 degrees Celsius and rapid cooling to two sets of samples concurrently. The furnace accommodated in-space experiments in the Fabrication of Si-As-Te:Ni Ternary Amorphous Semiconductor and the Crystal Growth of Compound Semiconductors. These were two of the many experiments designed and monitored by Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA).
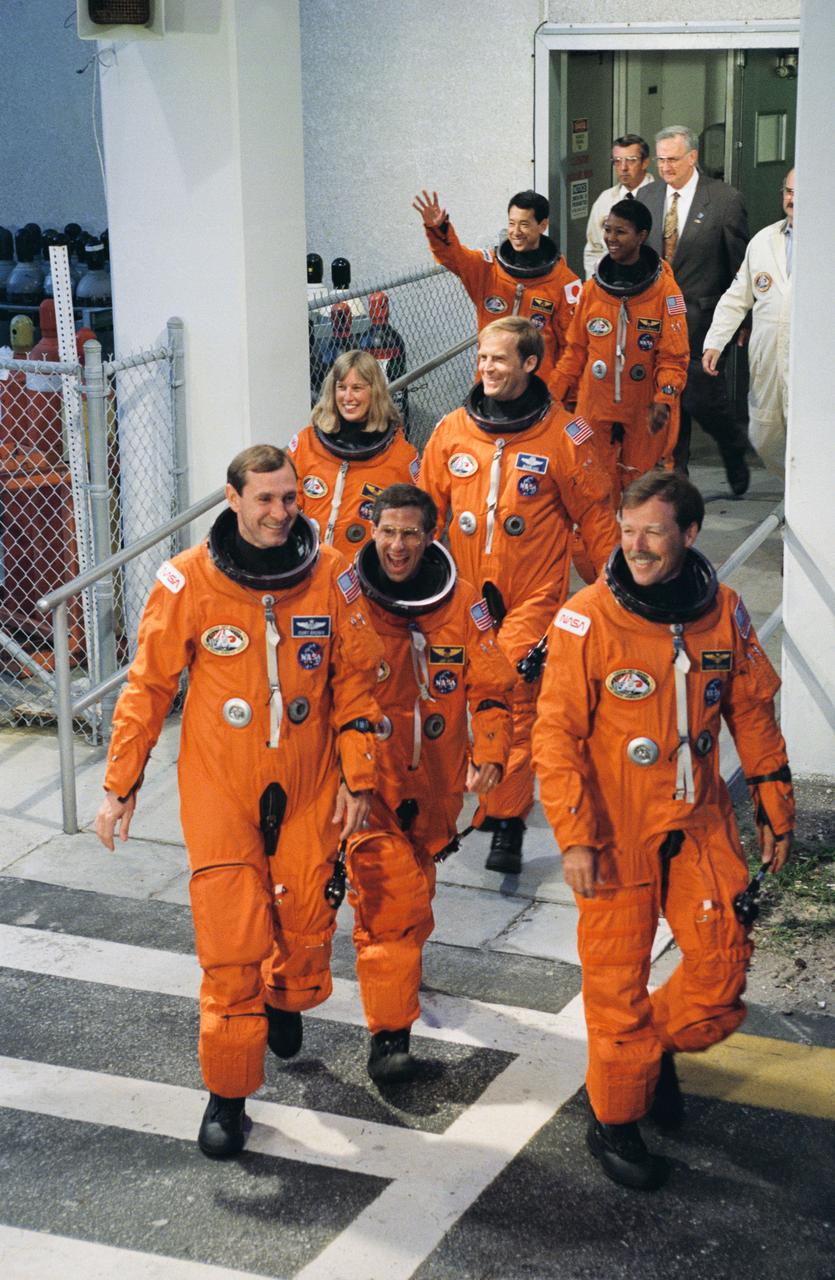

STS047-S-038 (12 Sept 1992) --- The seven crewmembers who will be aboard for Endeavour's second trip into space leave the Operations and Checkout Building to board a van headed for Launch Complex 39. This mission will be devoted to support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States. Launch occurred at 10:23:00:0680 a.m. (EDT), September 12, 1992. Onboard were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Curtis L. Brown Jr., pilot; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; and Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists; along with payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan.
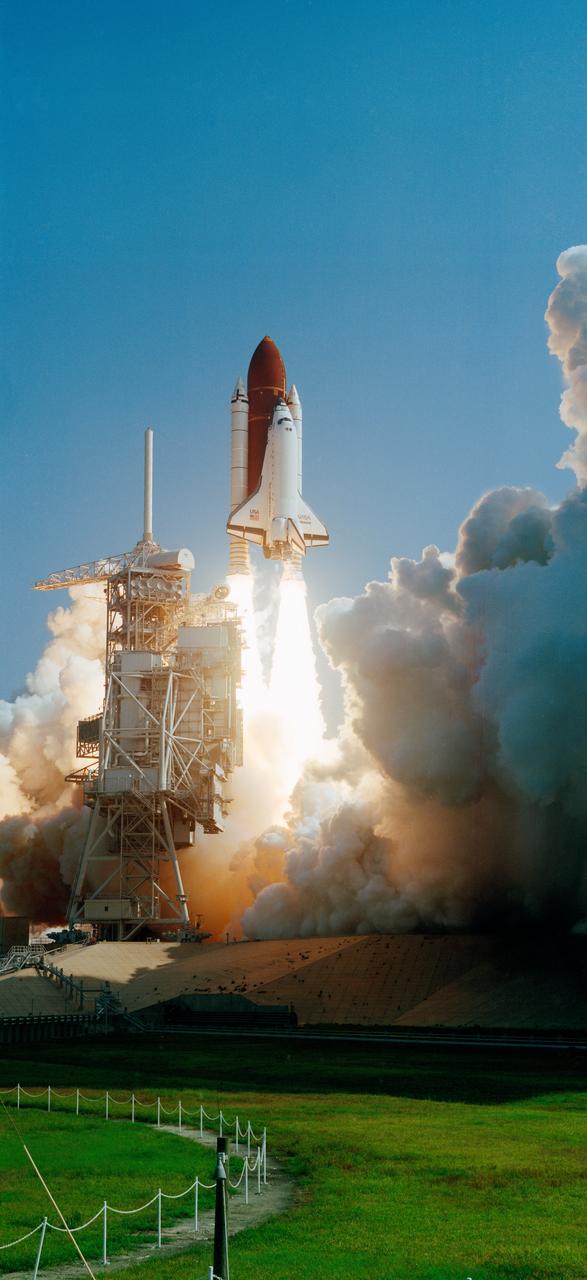

STS047-S-021 (12 Sept 1992) --- With a crew of six NASA astronauts and a Japanese payload specialist onboard, the Space Shuttle Endeavour heads for its second trip into space. This trip will be devoted to support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States. Launch occurred at 10:23:00:0680 a.m. (EDT), September 12, 1992. Onboard were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Curtis L. Brown Jr., pilot; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; and Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists, along with payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing the National Space Development Agency of Japan.
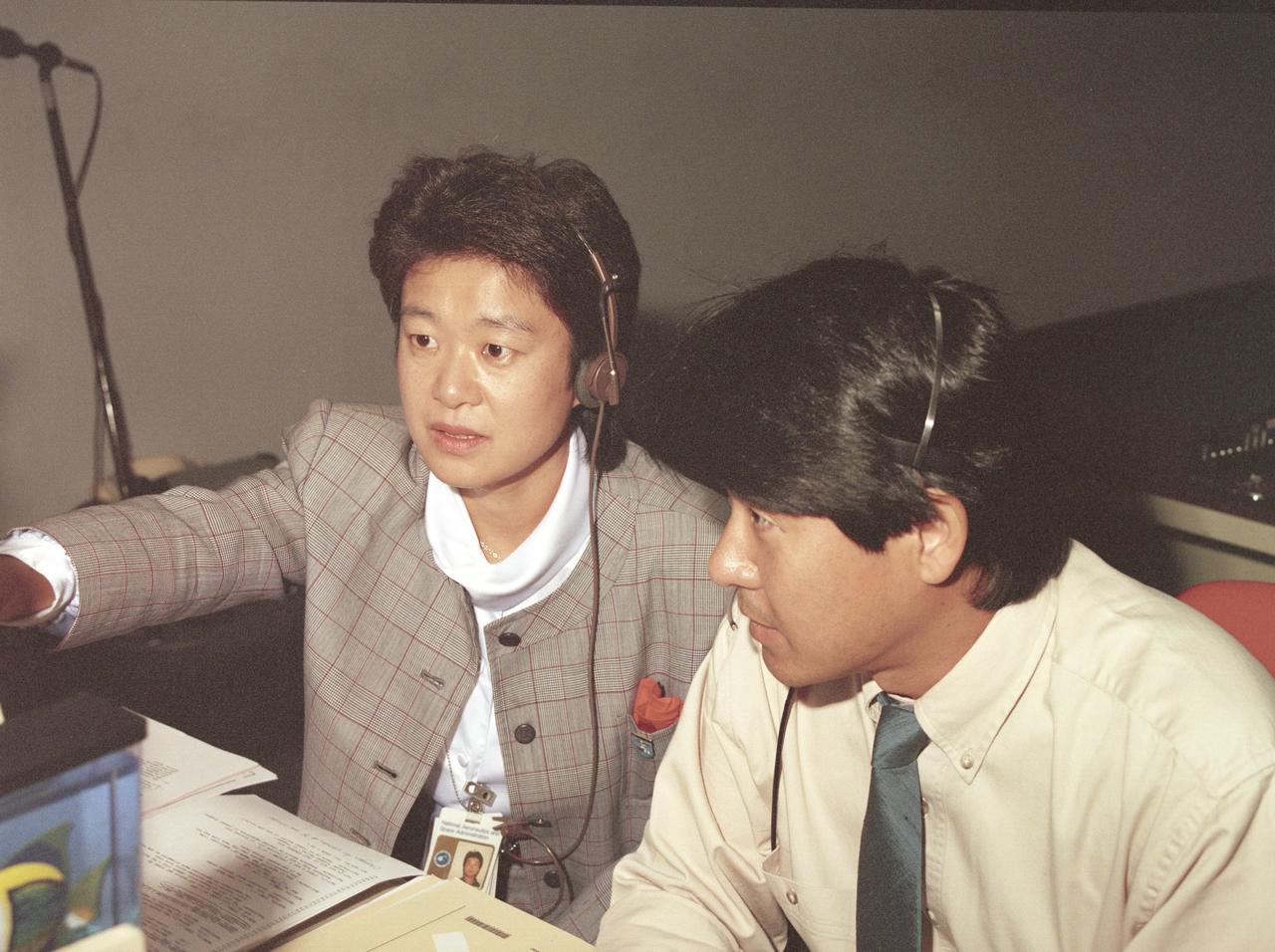

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Pictured in the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) are NASDA alternate payload specialists Dr. Doi and Dr. Mukai.
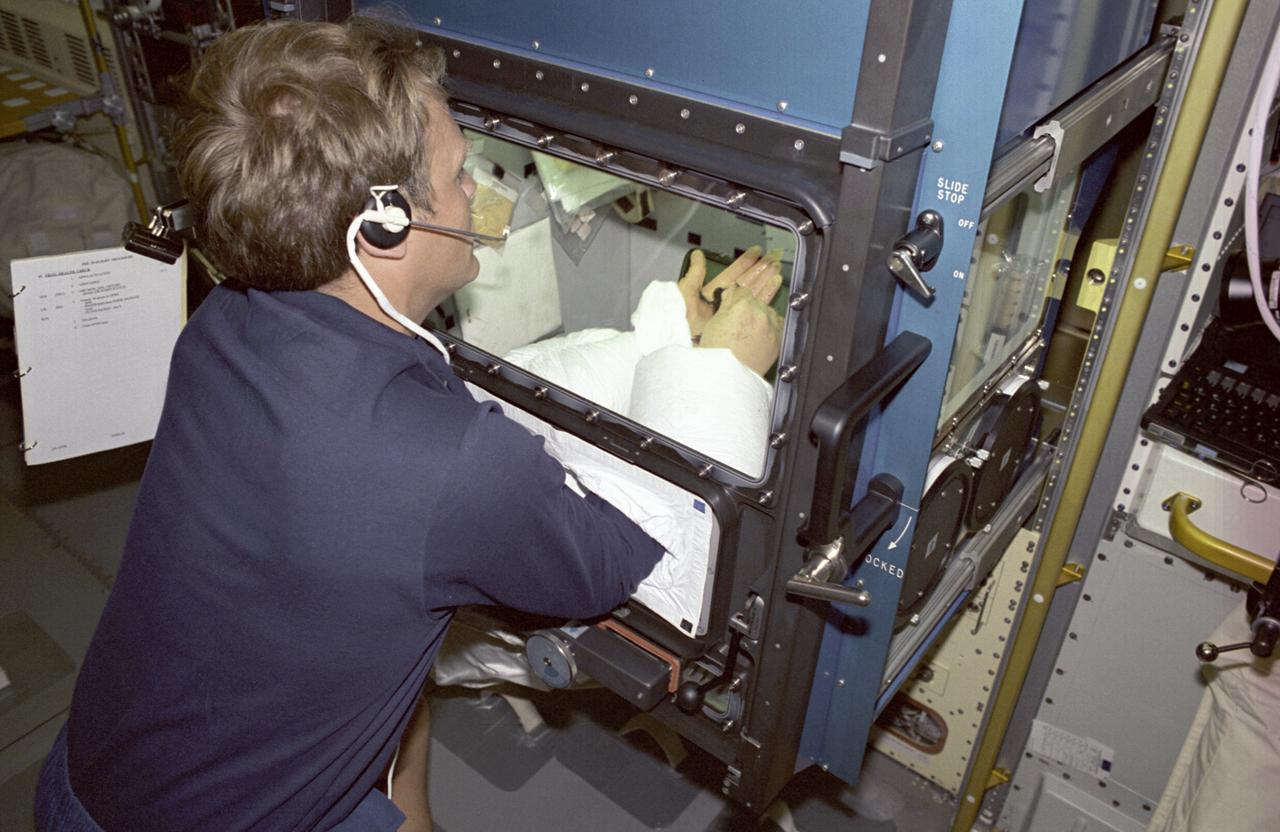

The Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Before long-term space ventures are attempted, numerous questions must be answered: how will gravity play in the early development of an organism, and how will new generations of a species be conceived and develop normally in microgravity. The Effects of Weightlessness on the Development of Amphibian Eggs Fertilized in Space experiment aboard SL-J examined aspects of these questions. To investigate the effect of microgravity on amphibian development, female frogs carried aboard SL-J were induced to ovulate and shed eggs. These eggs were then fertilized in the microgravity environment. Half were incubated in microgravity, while the other half were incubated in a centrifuge that spins to simulate normal gravity. This photograph shows astronaut Mark Lee working with one of the adult female frogs inside the incubator. The mission also examined the swimming behavior of tadpoles grown in the absence of gravity. The Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
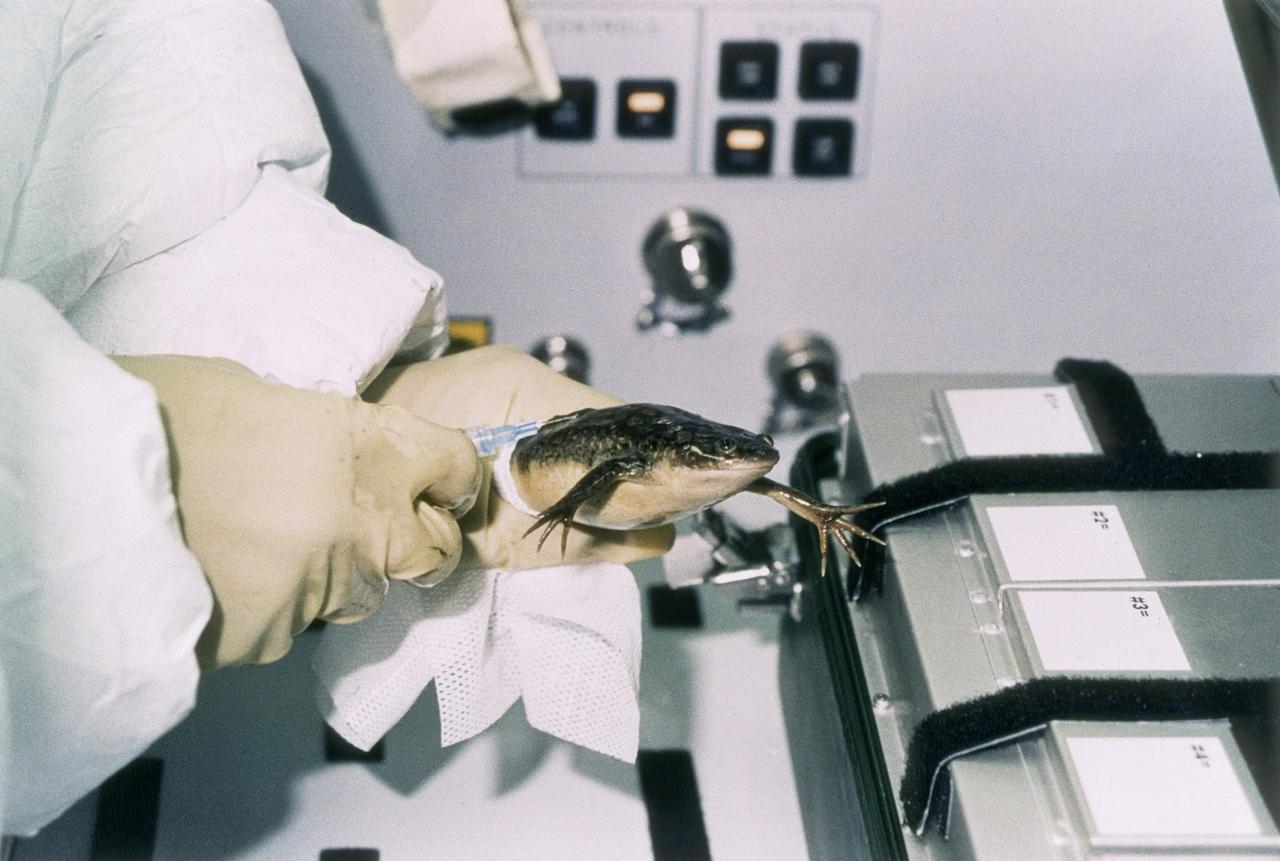
The Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Before long-term space ventures are attempted, numerous questions must be answered: how will gravity play in the early development of an organism, and how will new generations of a species be conceived and develop normally in microgravity. The Effects of Weightlessness on the Development of Amphibian Eggs Fertilized in Space experiment aboard SL-J examined aspects of these questions. To investigate the effect of microgravity on amphibian development, female frogs carried aboard SL-J were induced to ovulate and shed eggs. These eggs were then fertilized in the microgravity environment. Half were incubated in microgravity, while the other half were incubated in a centrifuge that spins to simulate normal gravity. This photograph shows an astronaut working with one of the adult female frogs inside the incubator. The mission also examined the swimming behavior of tadpoles grown in the absence of gravity. The Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
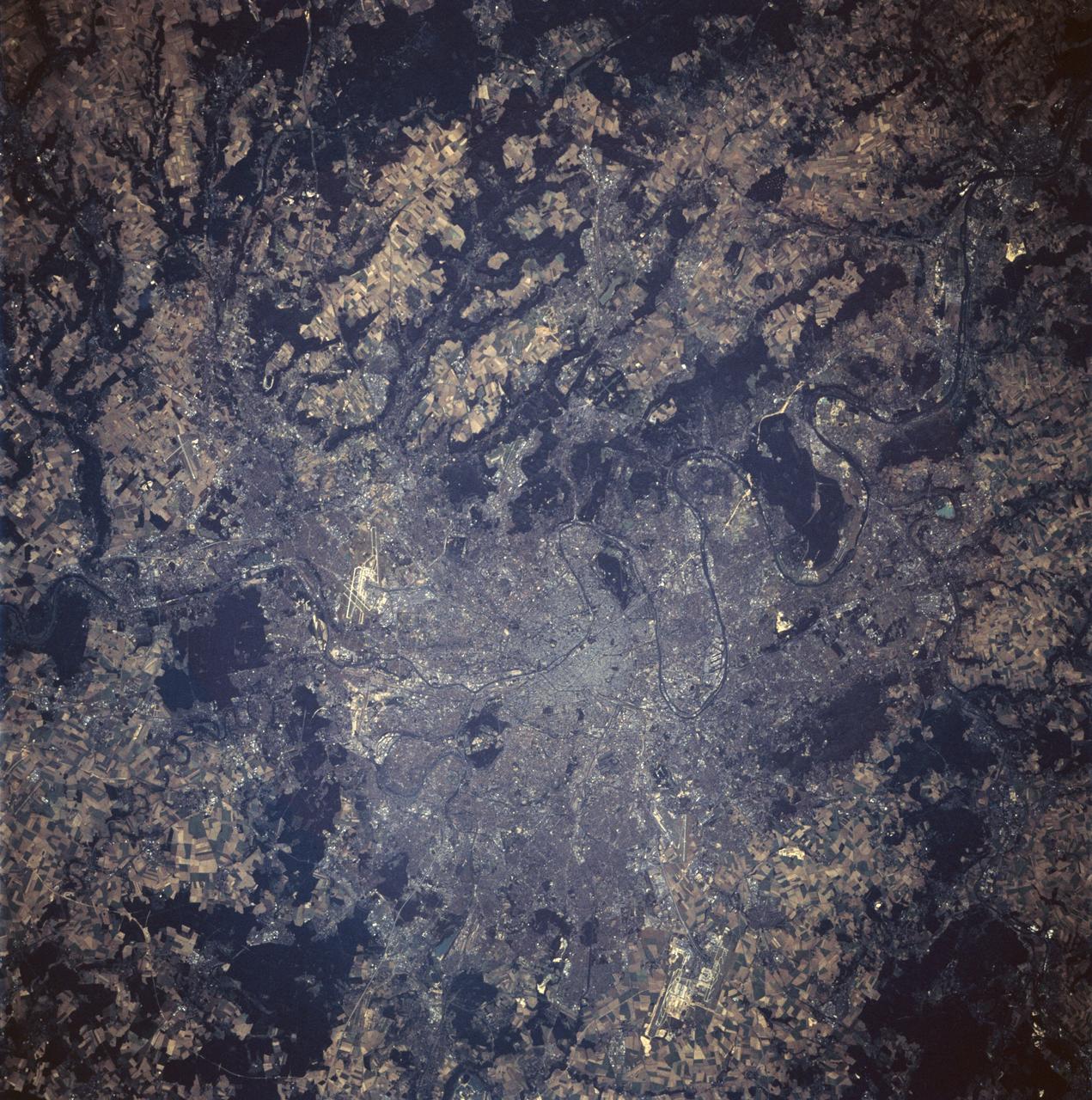

STS047-94-010 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- This 250mm Hasselblad color photo of Paris, France recorded during this mission, shows urban land uses in great detail. Several airports are clear, including the two major international airports of Orly and Le Bourget. Paris was founded in pre-Roman times on an island in the Seine River and continued as a Roman outpost. The easily defensible location was one of the keys to the growth of this island city. The city expanded from its island state to become a major urban center in Europe because of its location, its easy access by river traffic, and its productive hinterland.
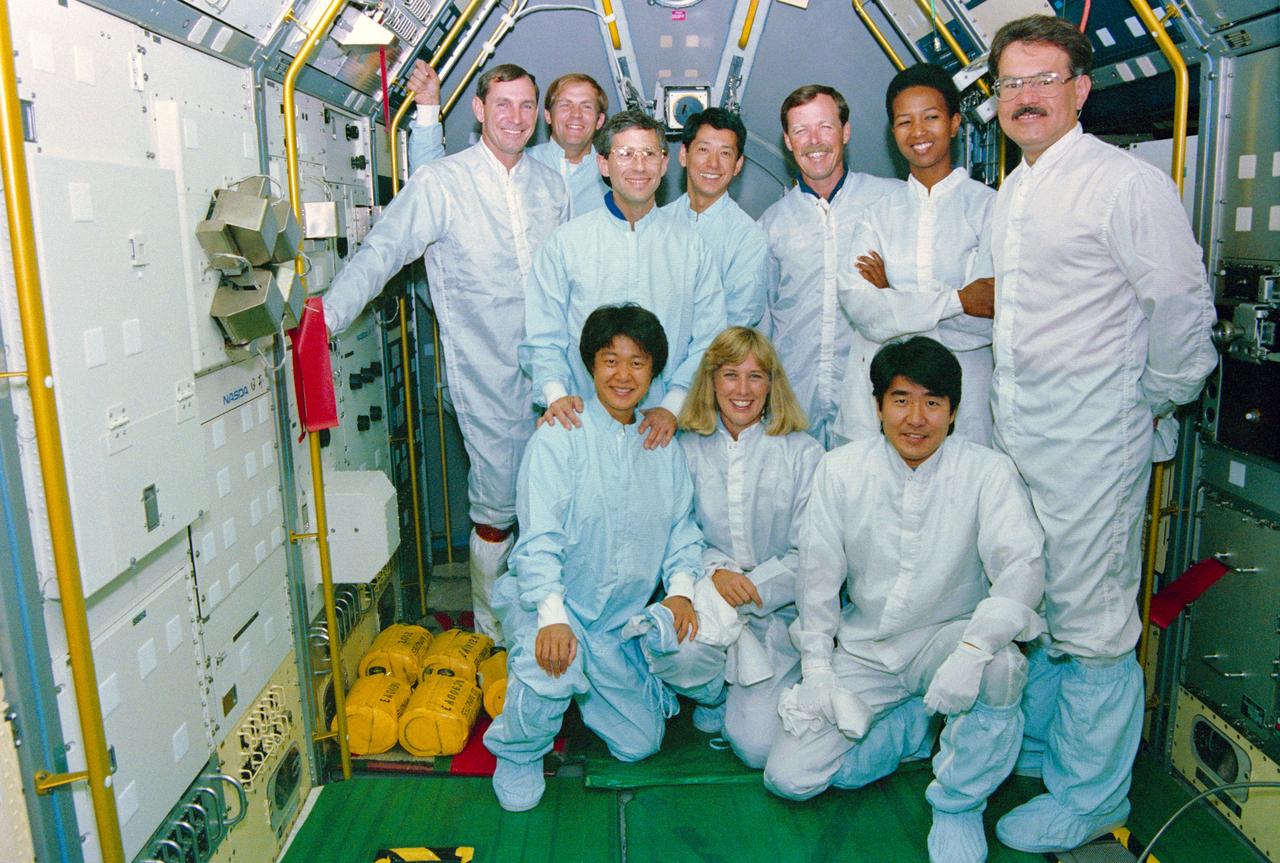

S92-44303 --- STS-47 Endeavour, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 105, crew members and back-up payload specialists, wearing clean suits, pose for a group portrait in the Spacelab Japan (SLJ) module. The team is at the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC's) Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) to inspect SLJ configuration and OV-105 preparations. Kneeling, from left, are back-up Payload Specialist Chiaki Naito-Mukai; Mission Specialist N. Jan Davis; and backup Payload Specialist Takao Doi. Standing, from the left, are Pilot Curtis L. Brown,Jr; Payload Commander Mark C. Lee; Jerome Apt; Payload Specialist Mamoru Mohri; Commander Robert L. Gibson; Mae C. Jemison; and back-up Payload Specialist Stanely L. Koszelak. Mohri, Mukai, and Doi represent the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). View provided by KSC with alternate KSC number KSC-92PC-1647. Photo credit: NASA
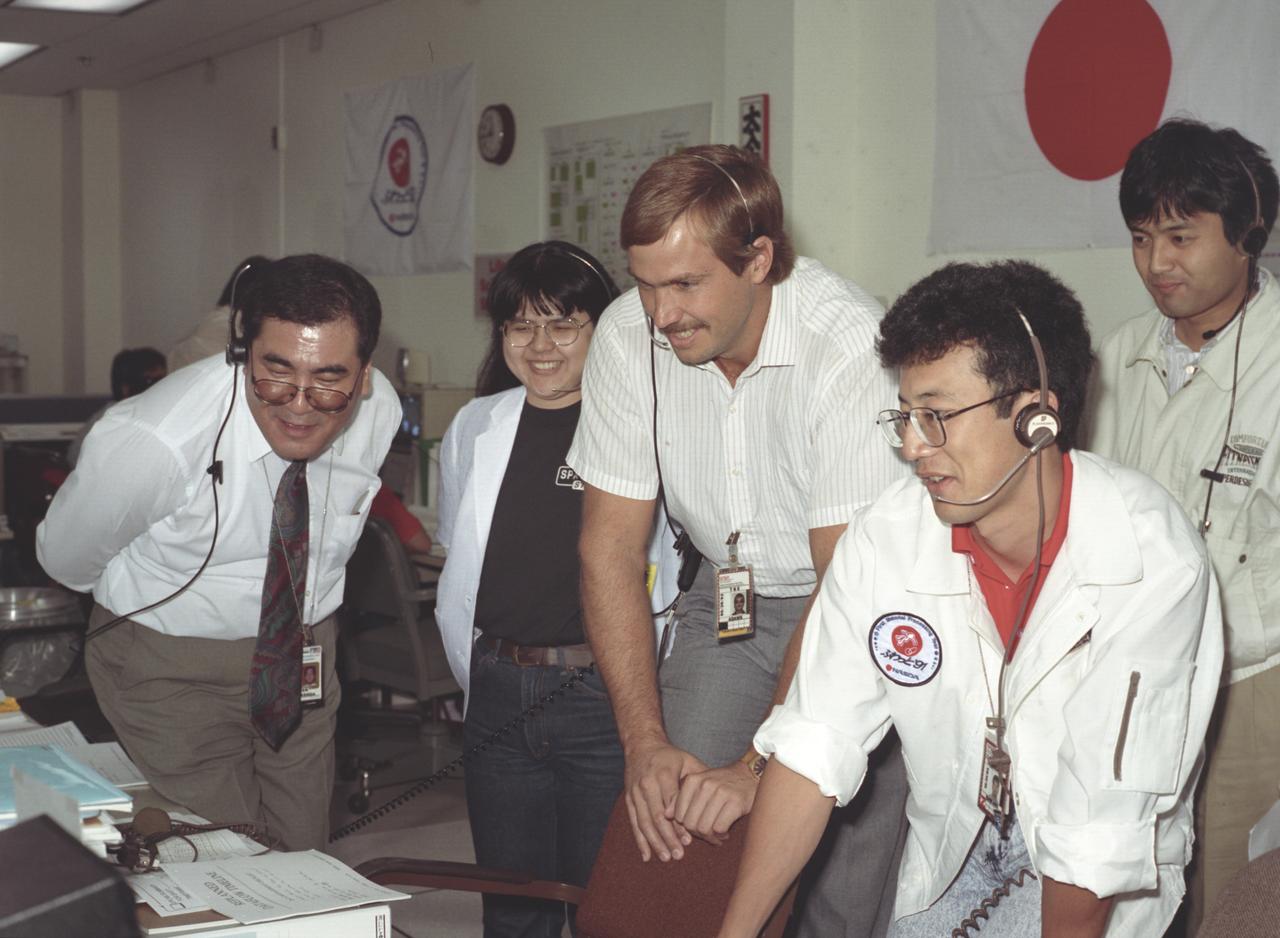

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Featured together in joint ground activities during the SL-J mission are NASA/NASDA personnel at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
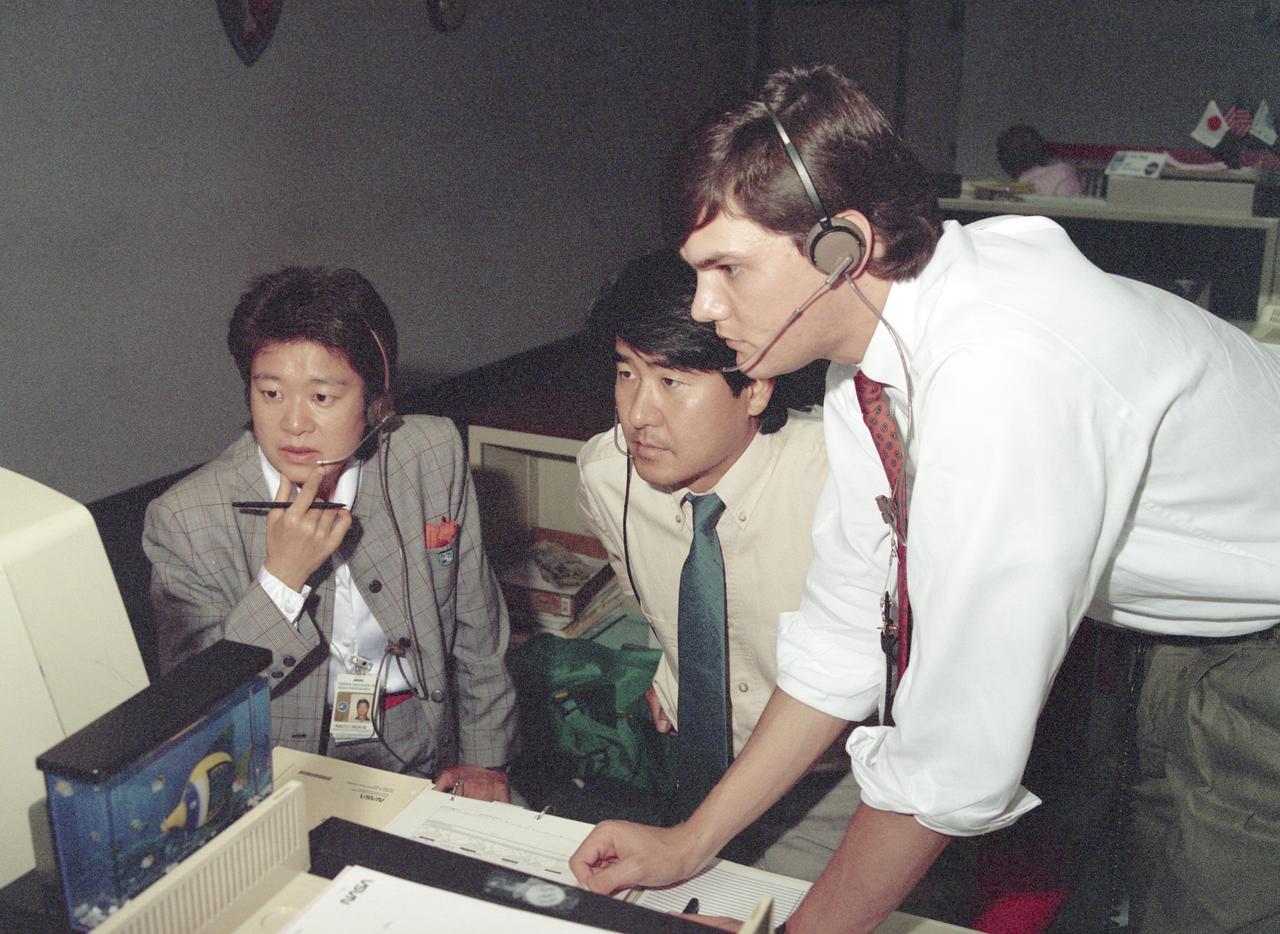

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Pictured along with George Norris in the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) are NASDA alternate payload specialists Dr. Doi and Dr. Mukai.
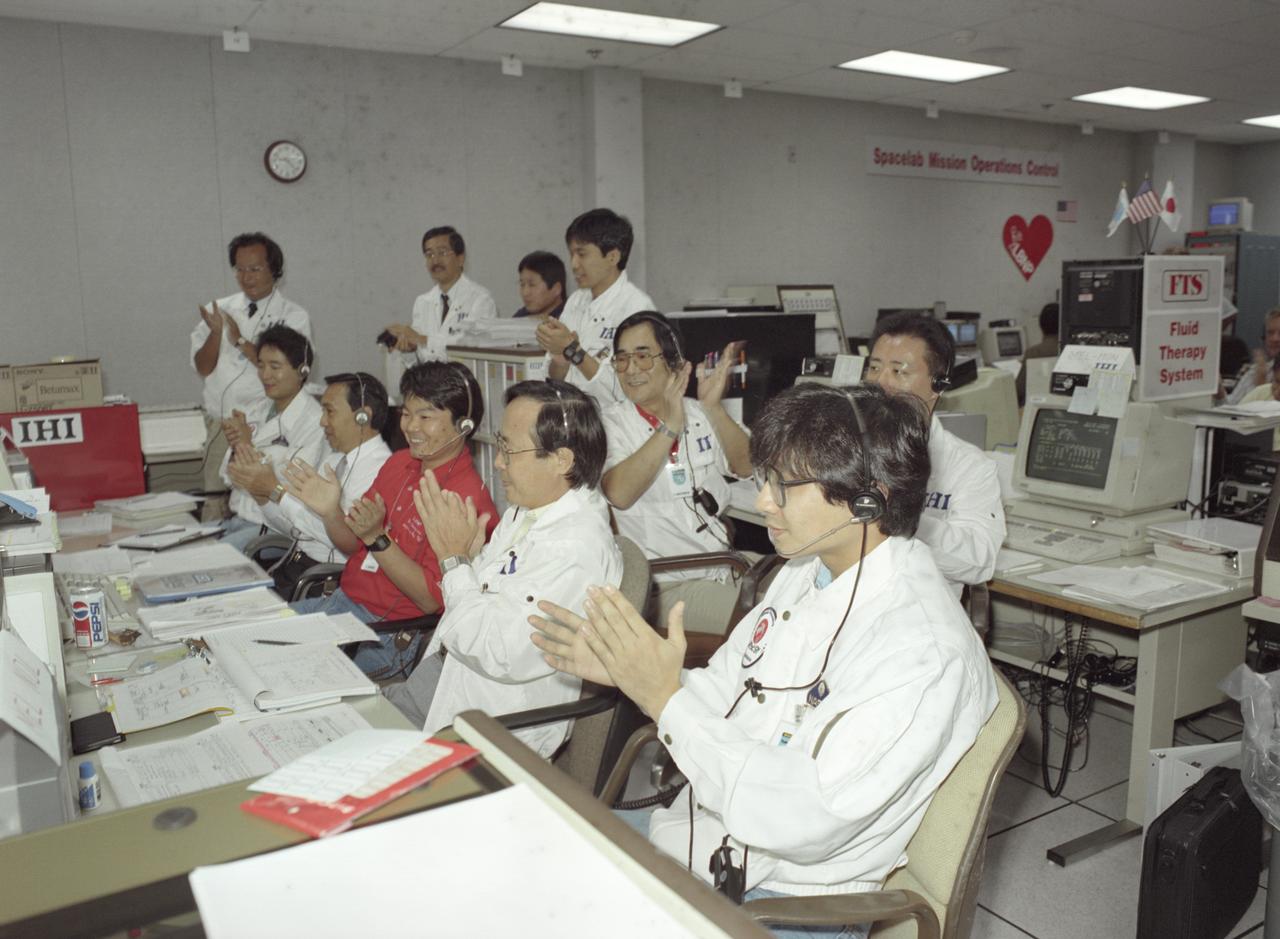

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Featured together in the Science Operation Area (SOA) are payload specialists’ first Materials Processing Test during NASA/NASDA joint ground activities at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
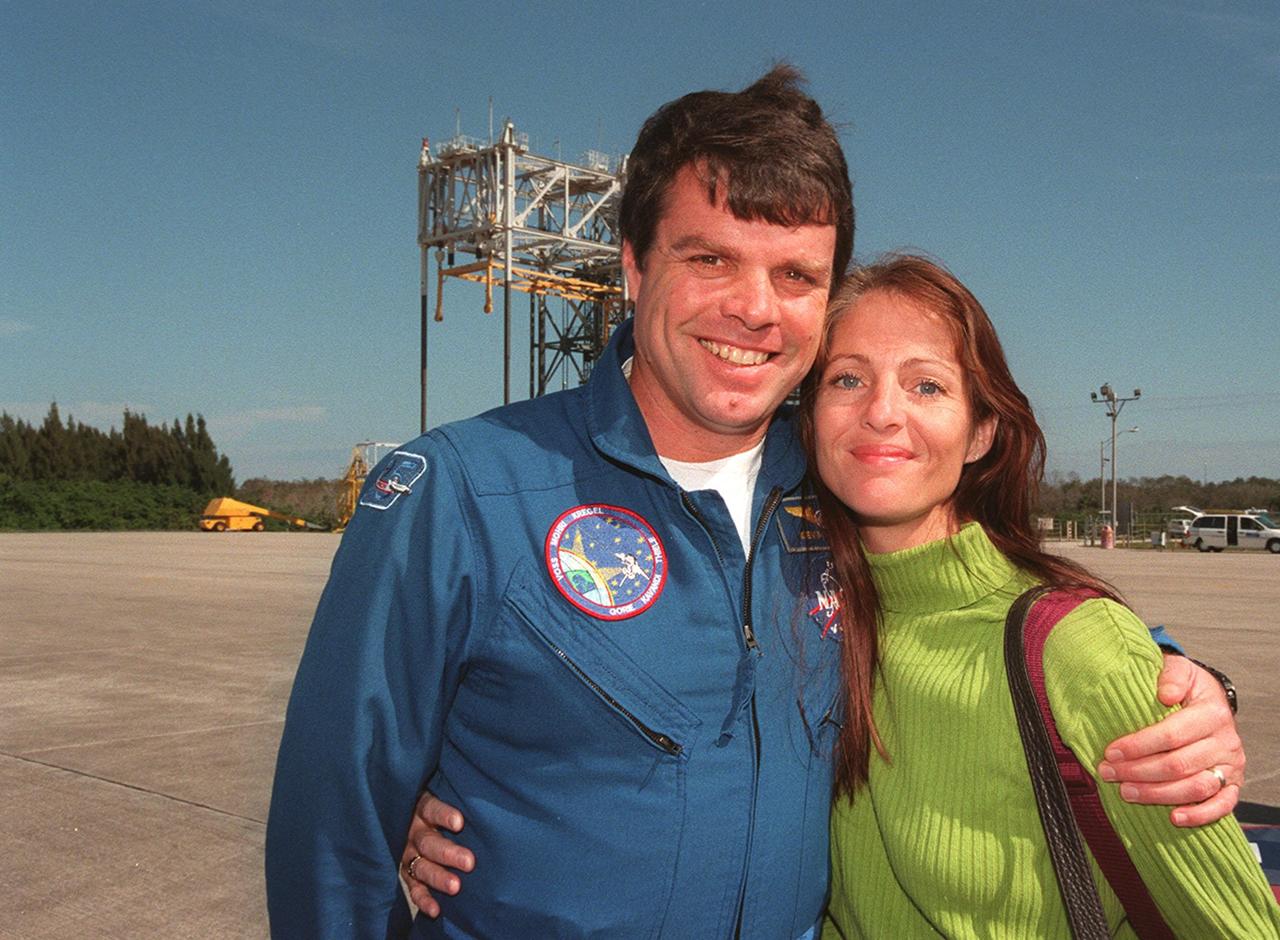

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 Commander Kevin Kregel is joined by his wife, Jeanne, before their departure for Houston. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
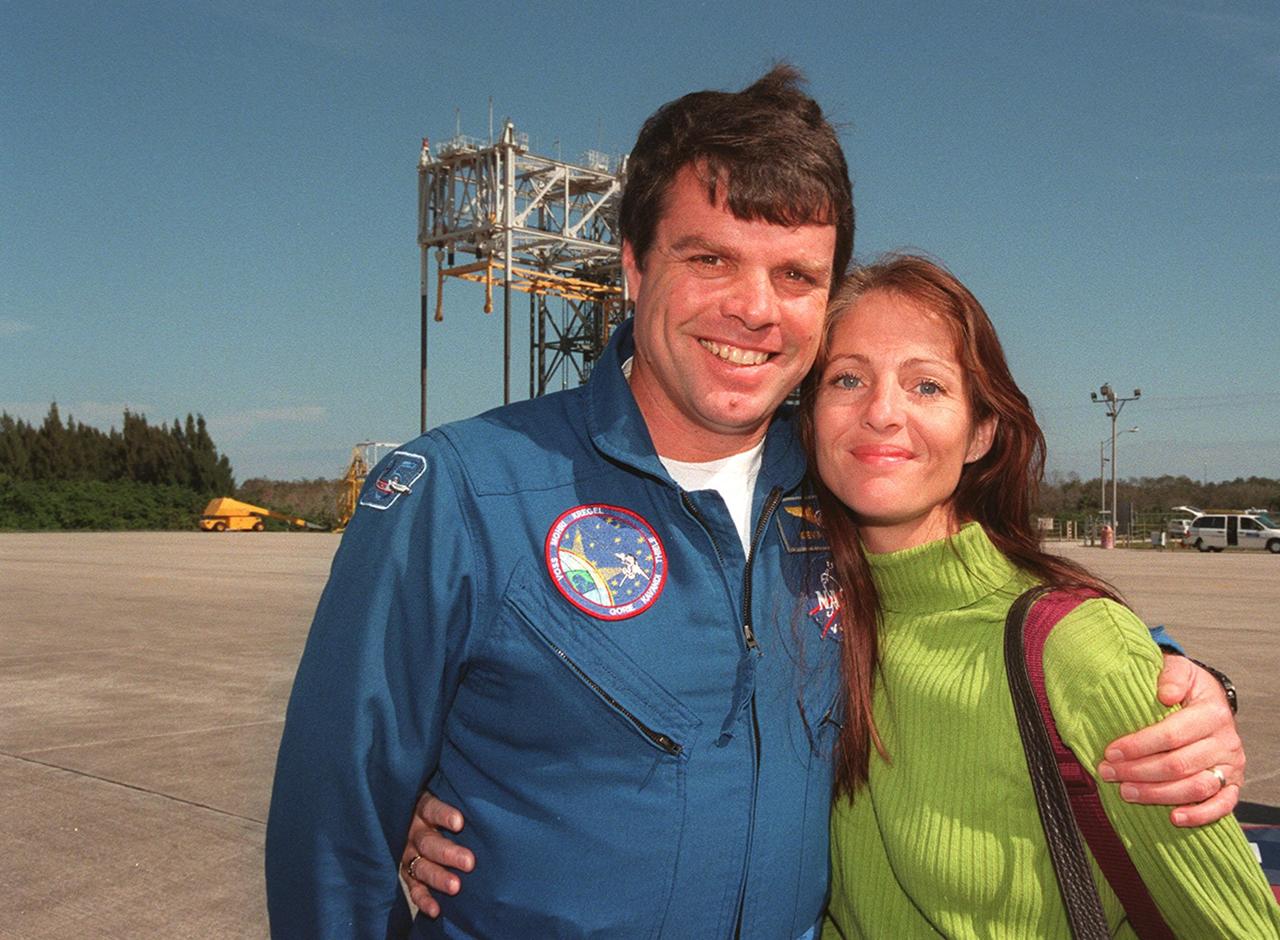

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 Commander Kevin Kregel is joined by his wife, Jeanne, before their departure for Houston. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
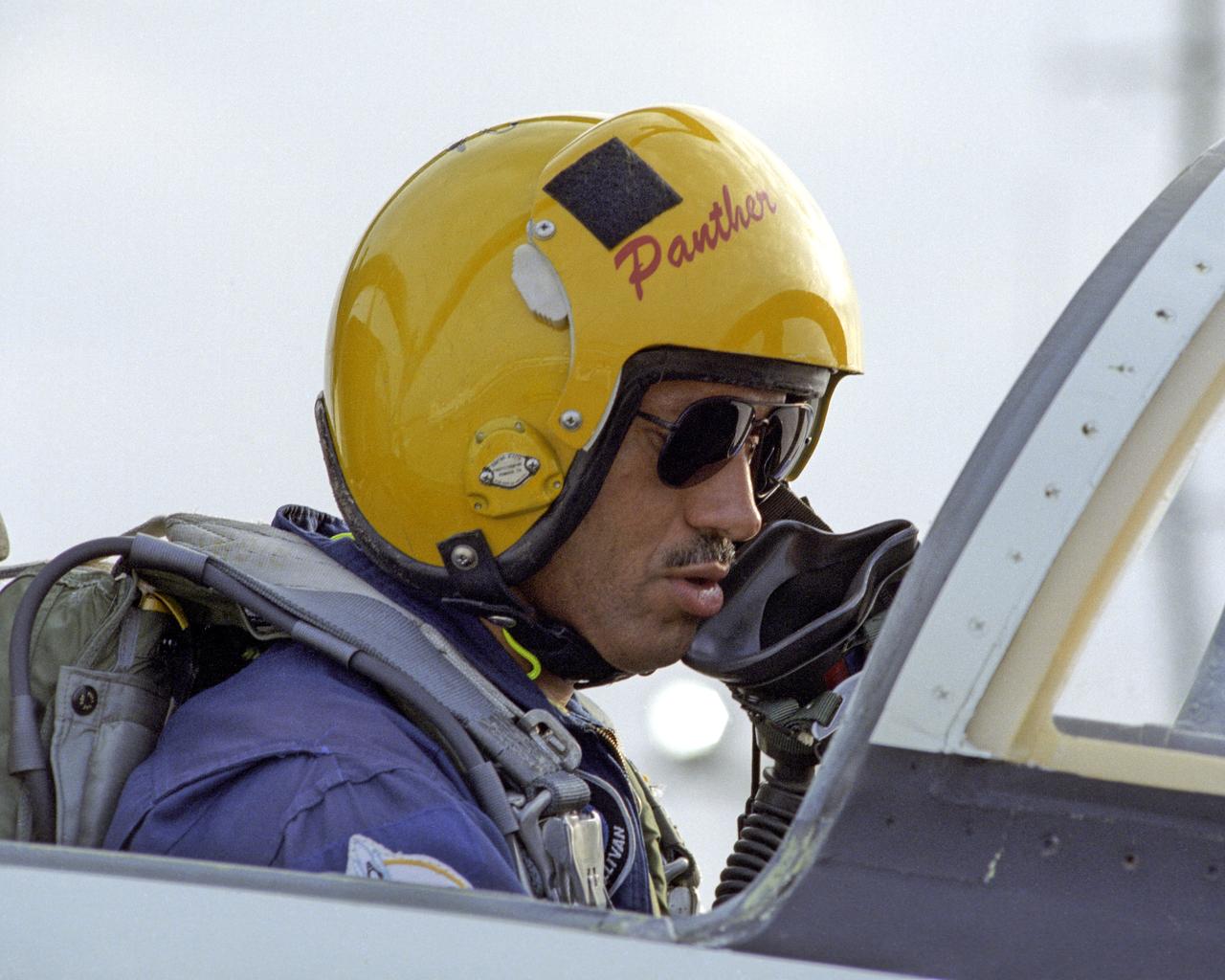

Charles F. Bolden, Jr., Pilot of Space Shuttle Mission STS-31, prepares for rehearsing shuttle contingency landings in the T-38S are among the final pre-launch activities. STS-31, carrying five crew members and the HST is set to liftoff at 8:47 a.m. April 10.
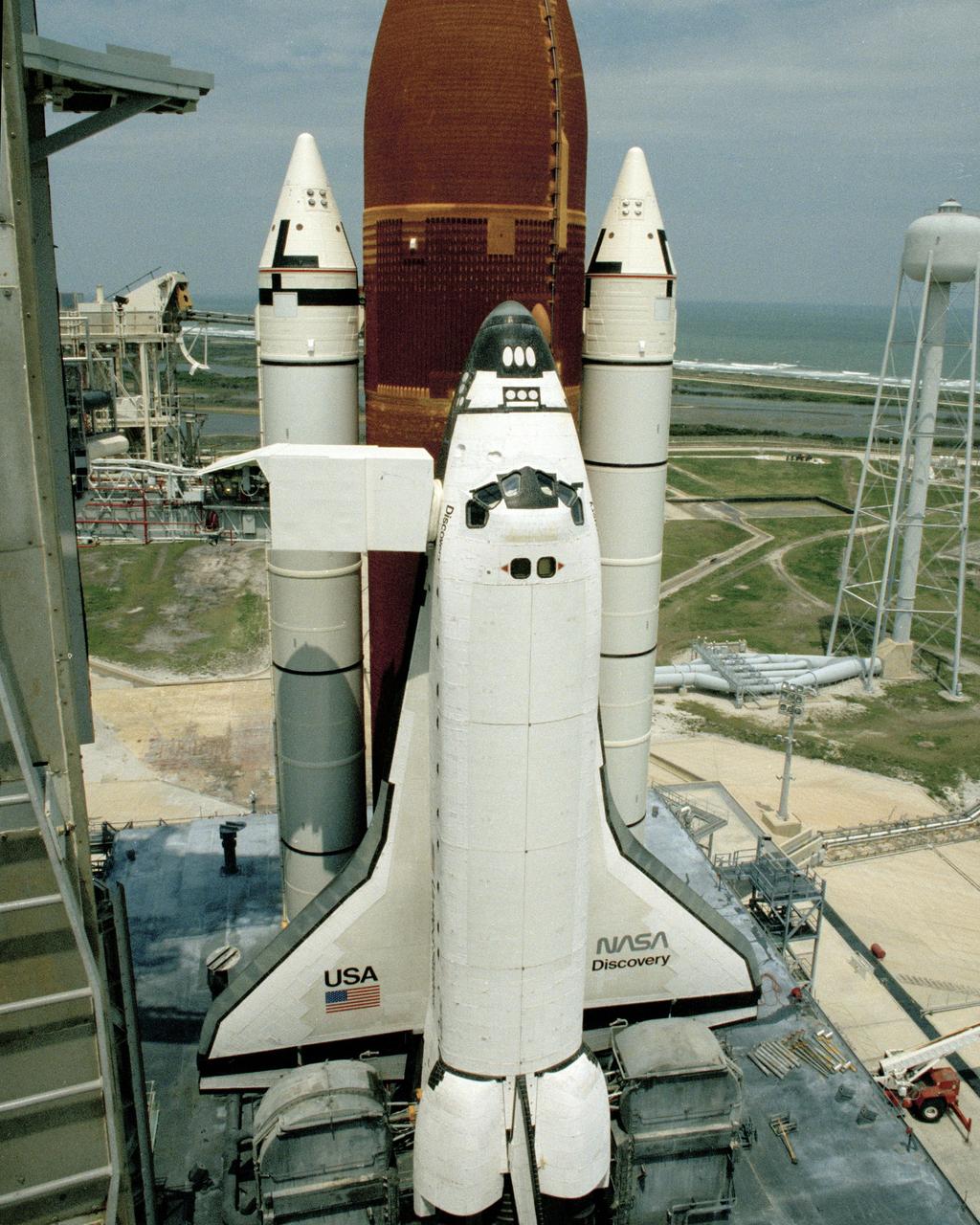

The orbiter Discovery is unveiled as rollback of the Rotating Service Structure begins during final prelaunch preparations at Launch Pad 39B on April 9. Space shuttle mission STS-31, carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope, is set to lift off at 6:47 a.m. EDT, April 10. Photo credit: NASA
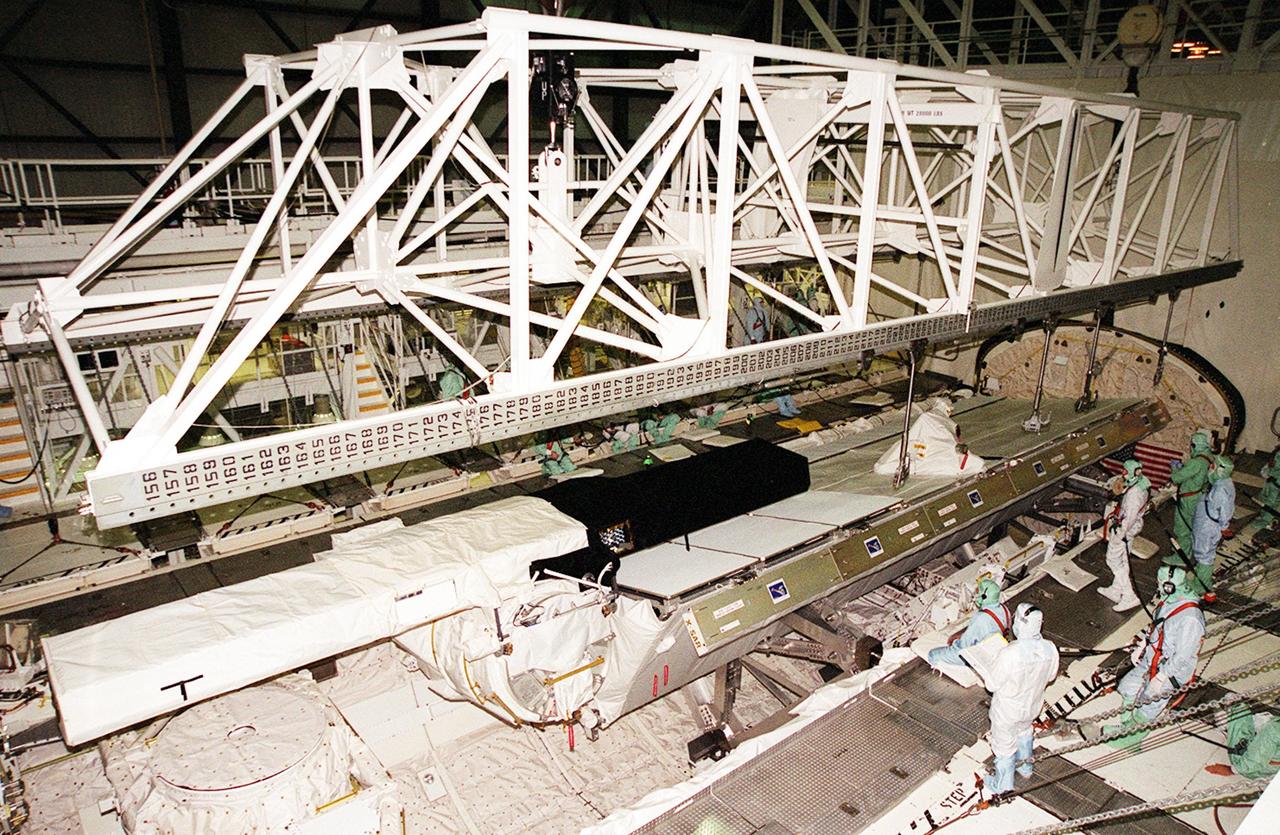

In OPF bay 2, the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) payload is lifted out of Endeavour's payload bay for transport to the Space Station Processing Facility. The SRTM mapped more than 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface on mission STS-99, which landed Feb. 22, 2000
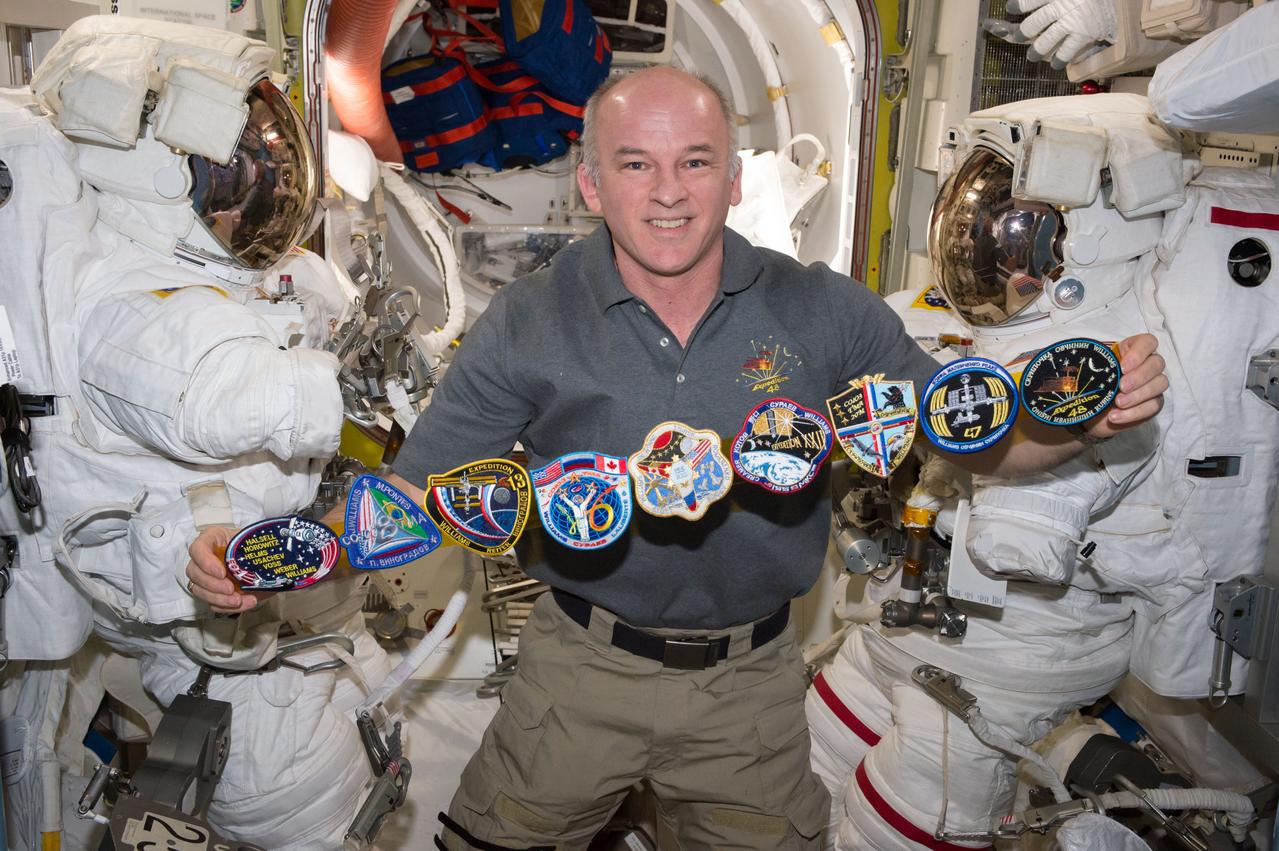

Commander Jeff Williams poses for a photo in the Quest Airlock (A/L) with all of his mission patches. The patches are, from left, STS-101, Soyuz TMA-8, Expedition 13, Soyuz TMA-16, Expedition 21, Expedition 22, Soyuz TMA-20M, Expedition 47, and Expedition 48.
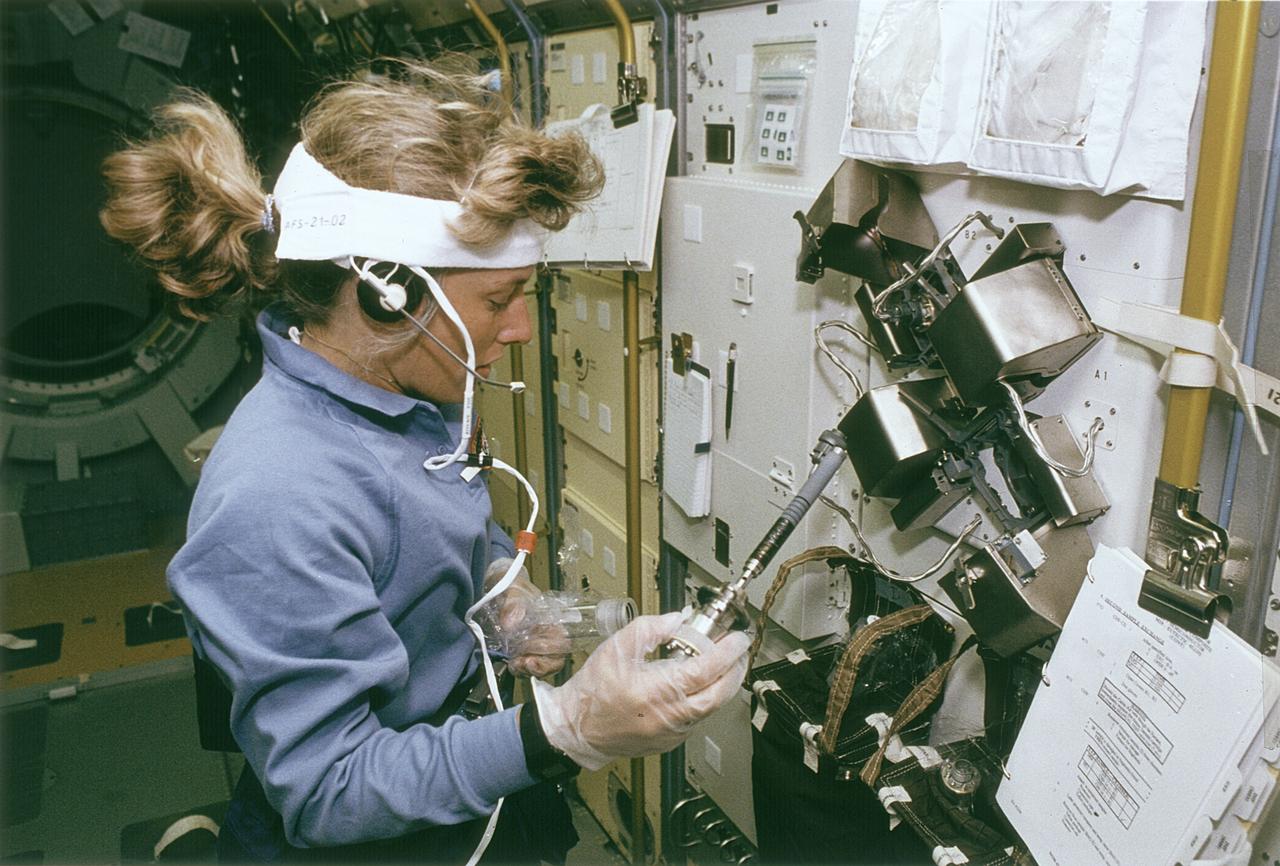

Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) onboard photo of Astronaut N. Jan Davis at work at the Continuous Heating Furnace (CHF) in the Spacelab-J Science Module. Spacelab-J is a combined National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) and NASA mission. The objectives included life sciences, microgravity and technology research.
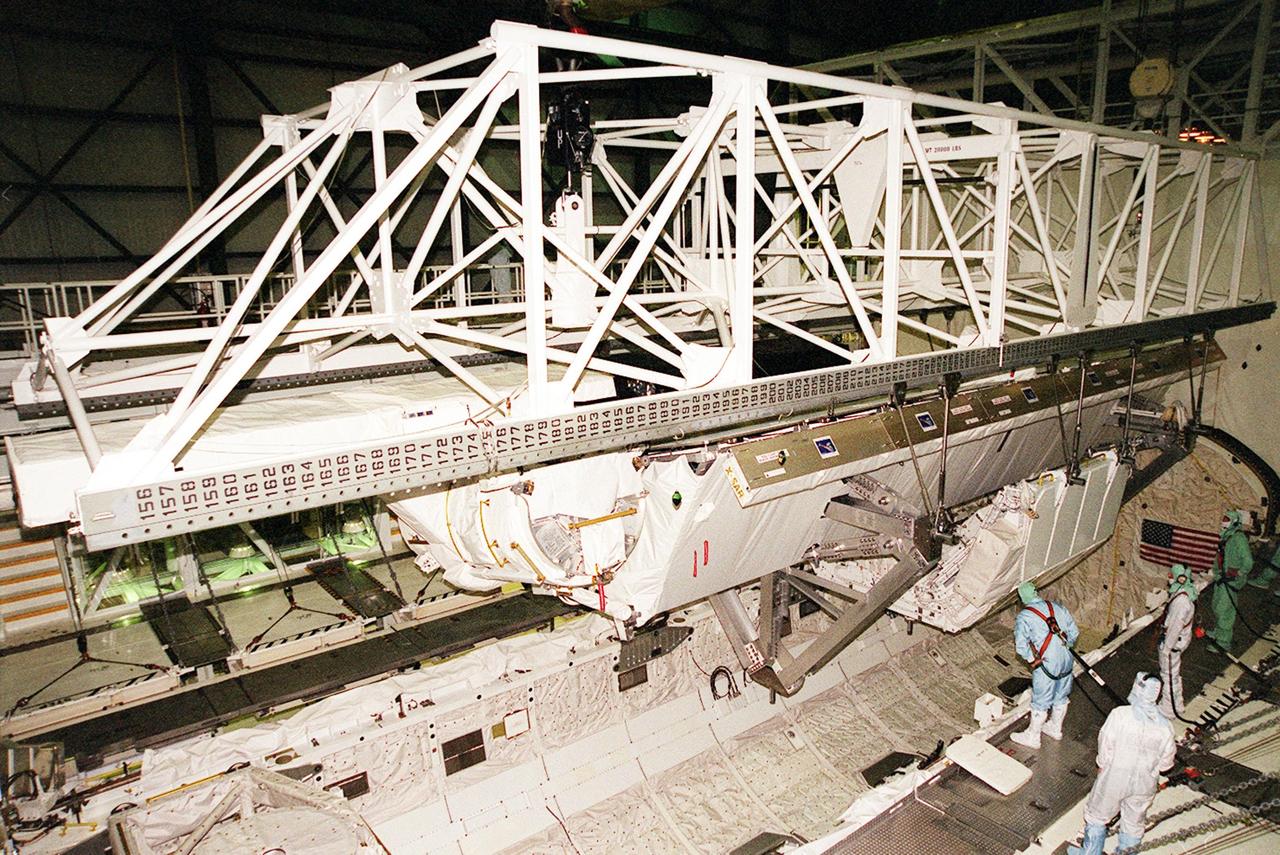

In OPF bay 2, an overhead crane lifts the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) payload out of Endeavour's payload bay for transport to the Space Station Processing Facility. The SRTM mapped more than 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface on mission STS-99, which landed Feb. 22, 200
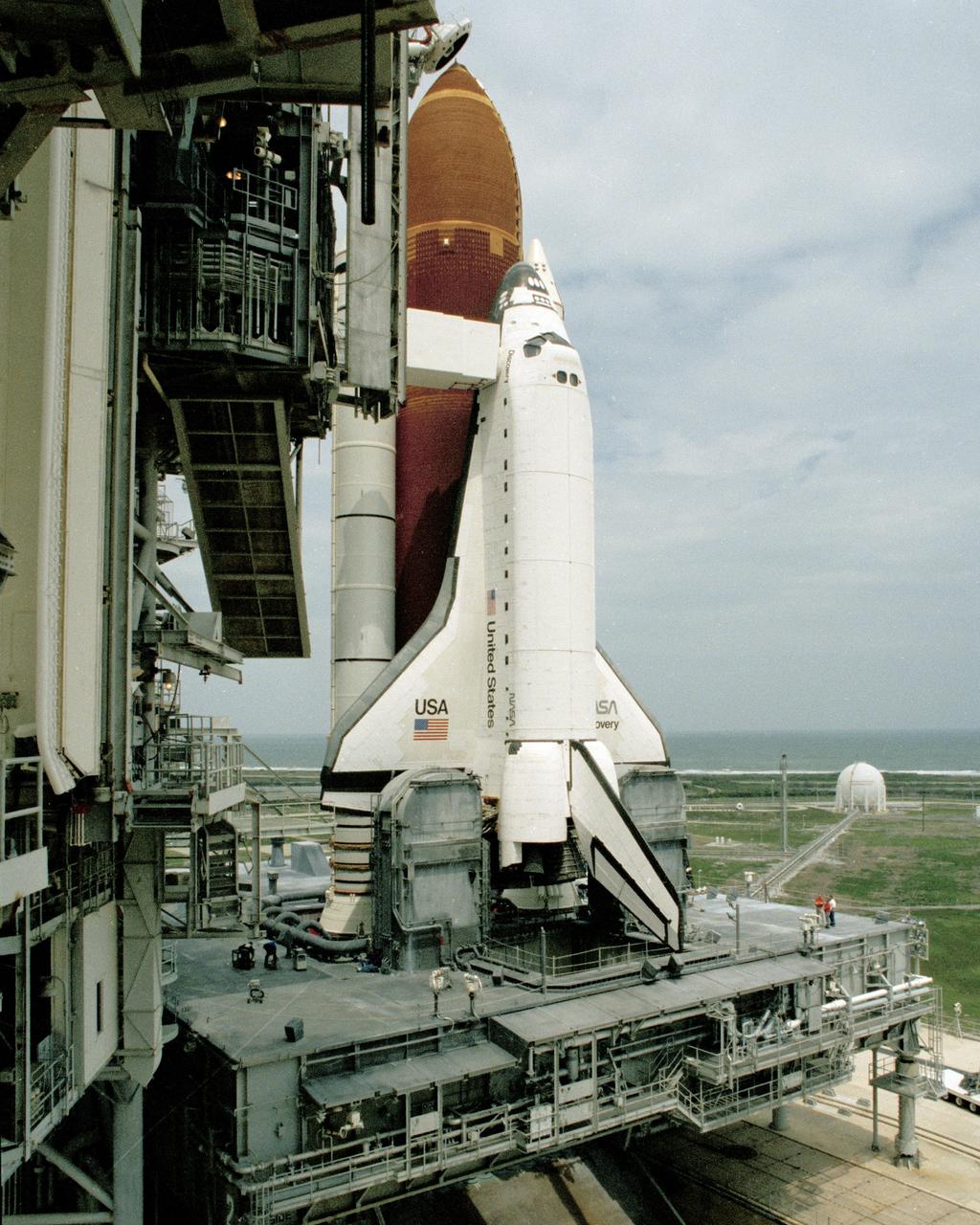

The orbiter Discovery is unveiled as rollback of the Rotating Service Structure begins during final prelaunch preparations at Launch Pad 39B on April 9. Space shuttle mission STS-31, carrying a crew of five and the Hubble Space Telescope, is set to lift off at 6:47 a.m. EDT, April 10. Photo credit: NASA
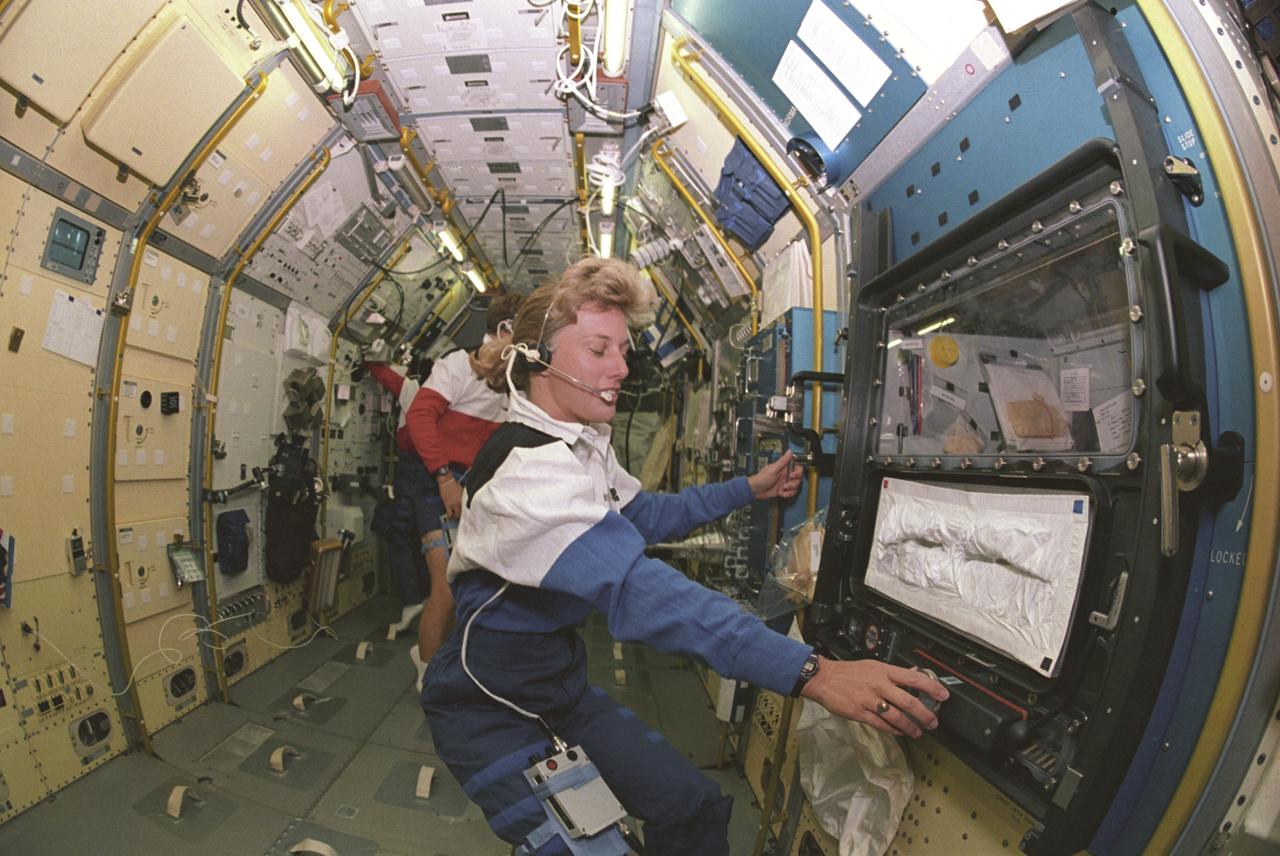

Space Shuttle Endeavour (STS-47) onboard photo of Astronaut Jan Davis inside the Spacelab-J module. Spacelab-J is a combined National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) and NASA mission. The objectives included life sciences, microgravity and technology research.
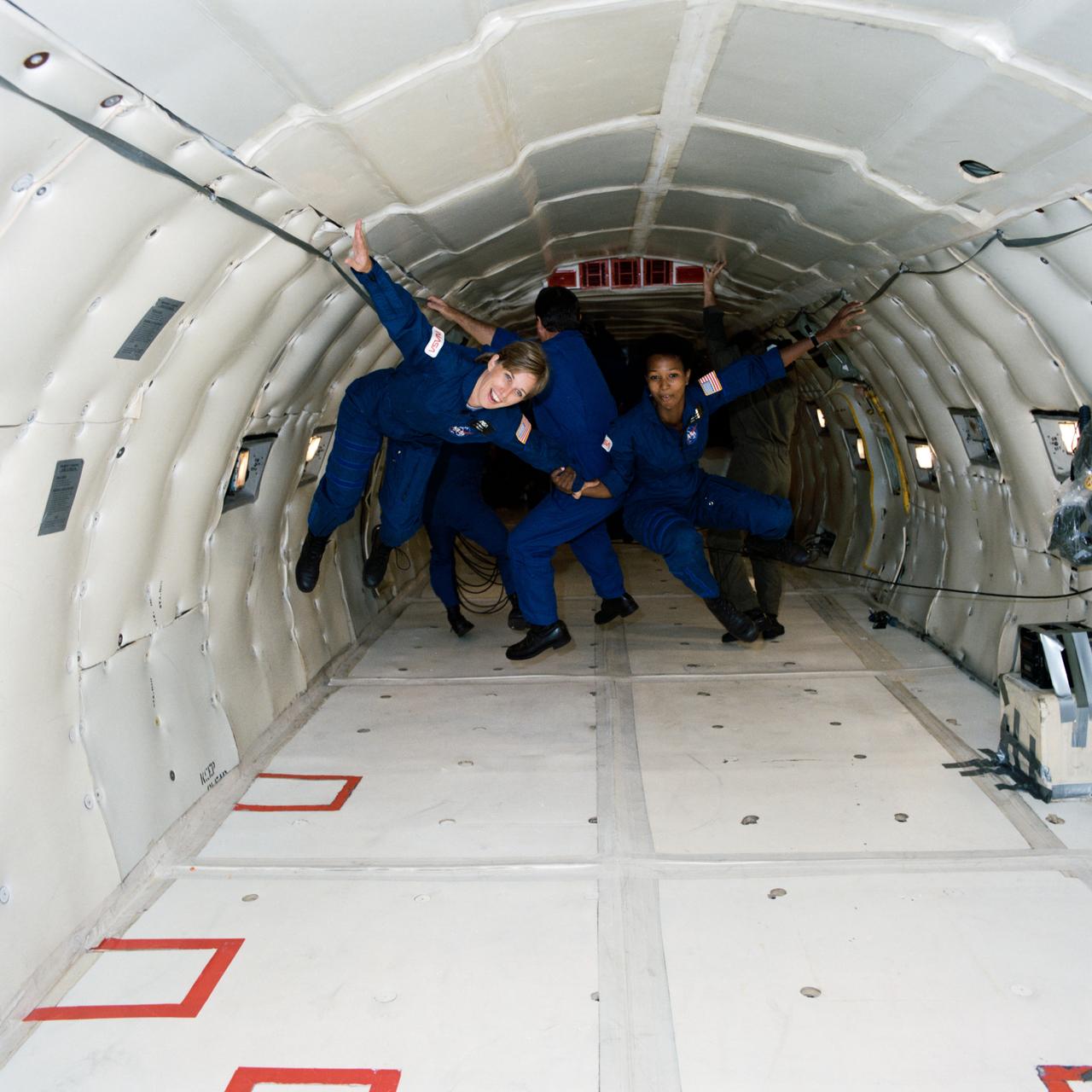

S87-44950 --- Group 12, 1987 Astronaut Class, candidates (ASCANs) N. Jan Davis (left) and Mae C. Jemison freefloat during the seconds of microgravity created aboard the KC-135 NASA 930 aircraft's parabolic flight. Davis and Jemison, two of the recently-named ASCANs, were taking a familiarization flight aboard the KC-135 "zero gravity" aircraft. Photo credit: NASA
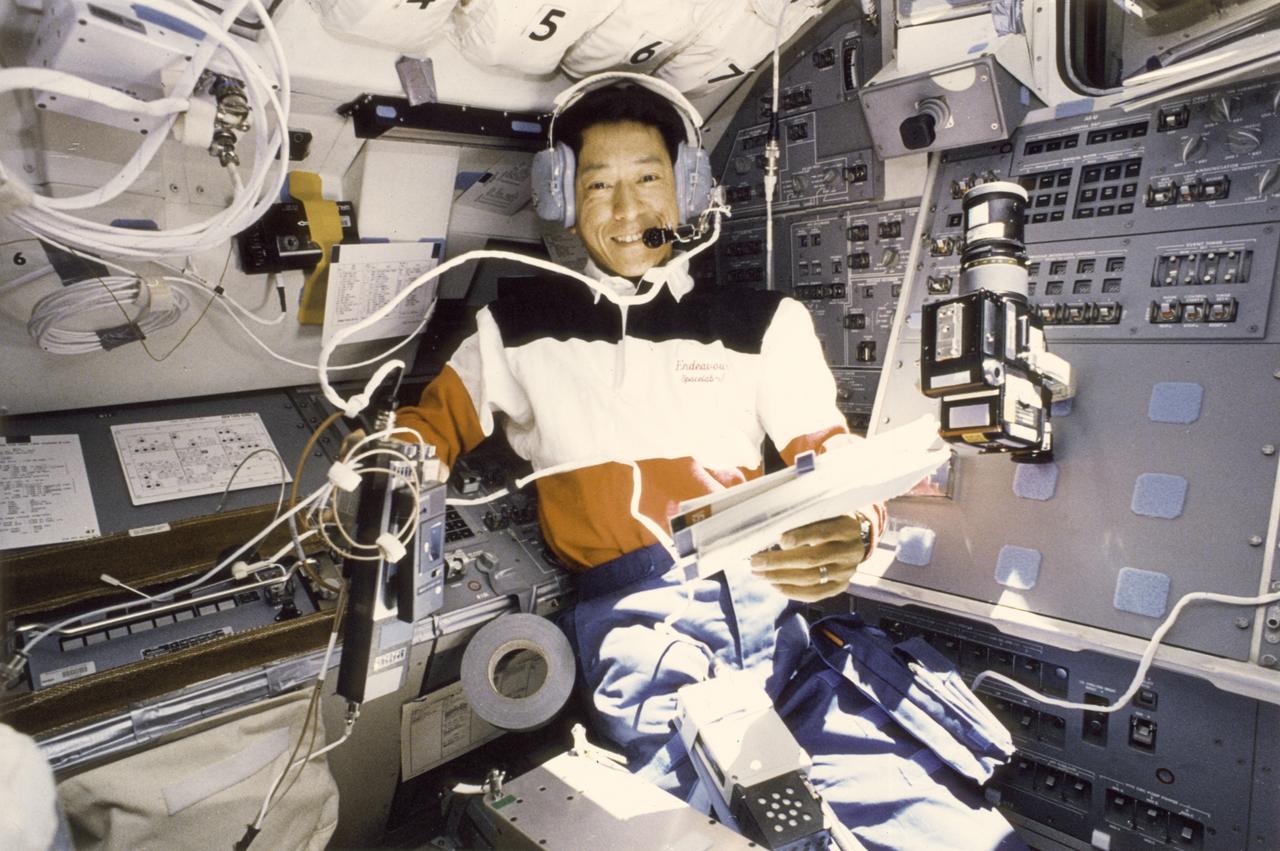

Japanese astronaut, Mamoru Mohri, talks to Japanese students from the aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour during the Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission. The SL-J mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
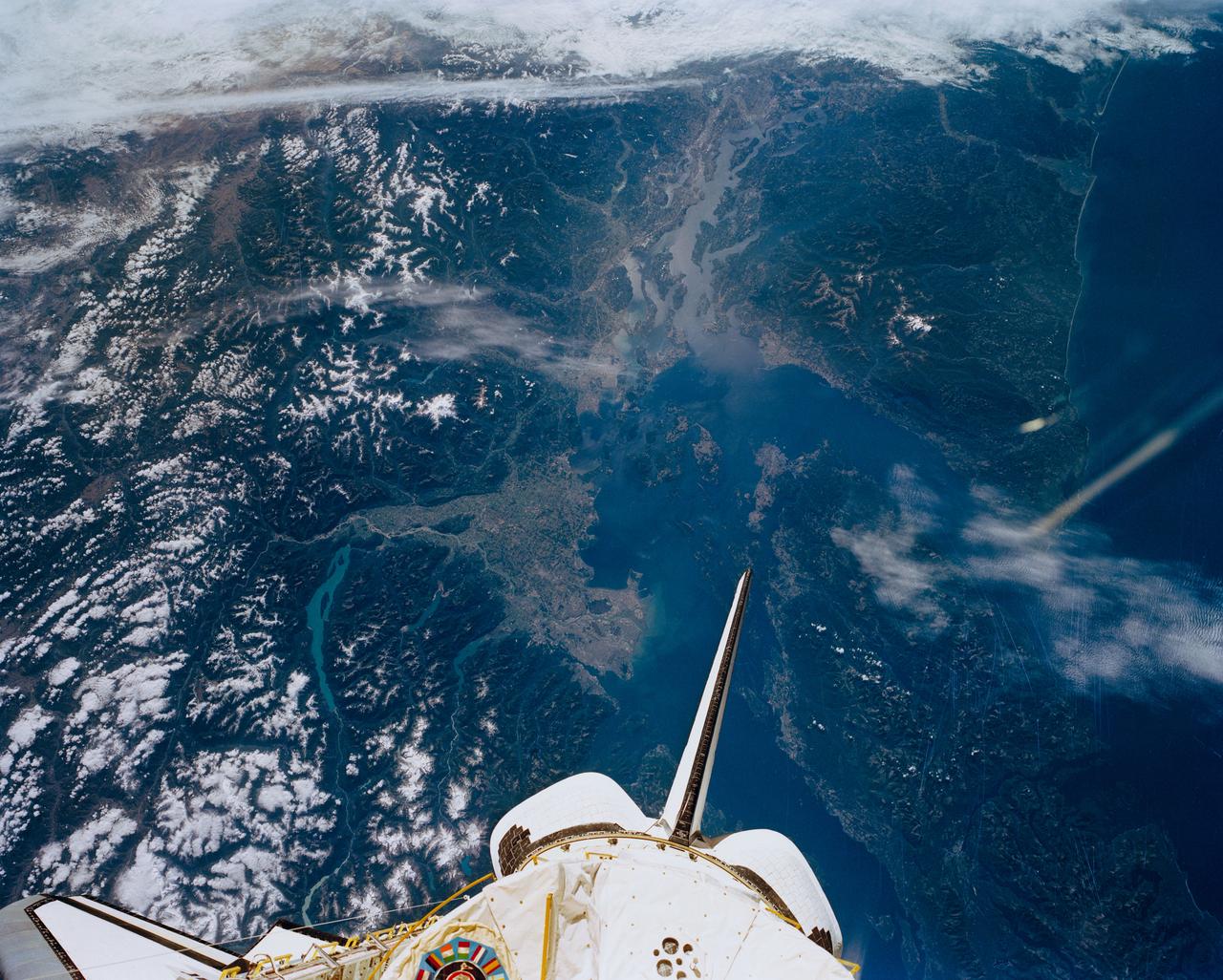

STS047-151-488 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- In this large format camera image, the forested Cascade Range appears along the left side; the Pacific Ocean, on the right. The frame was photographed as the Space Shuttle Endeavour flew north to south over Vancouver and Seattle. Many peaks in the Cascades reach altitudes greater than 9,000 feet and remain snowcapped even in mid-summer. The Strait of Juan de Fuca separates the Olympic Peninsula (top right) from Vancouver Island (bottom right). Snowcapped Mt. Olympus (7,965 feet) is one of the wettest places in the continental United States, with rainfall in excess of 120 inches per year. The port cities of Seattle and Tacoma occupy the heavily indented coastline of Puget Sound (top center). They appear as light-colored areas on the left side of the Sound. The angular street pattern of Tacoma is visible at the top of the picture. The international boundary between Canada and the United States of America runs across the middle of the view. The city of Victoria (center) is the light patch on the tip of Vancouver Island. Canada's Fraser River Delta provides flat topography on which the cities of Vancouver, Burnaby, and New Westminster were built. These cities appear as the light-colored area just left of center. The Fraser River can be seen snaking its way out of the mountains at the apex of the delta. Numerous ski resorts dot the slopes of the mountains (bottom left) that rise immediately to the north of Vancouver. In the same area the blue water of Harrison and other, smaller lakes fills some of the valleys that were excavated by glaciers in the "recent" geological past, according to NASA scientists studying the photography. A Linhof camera was used to expose the frame.
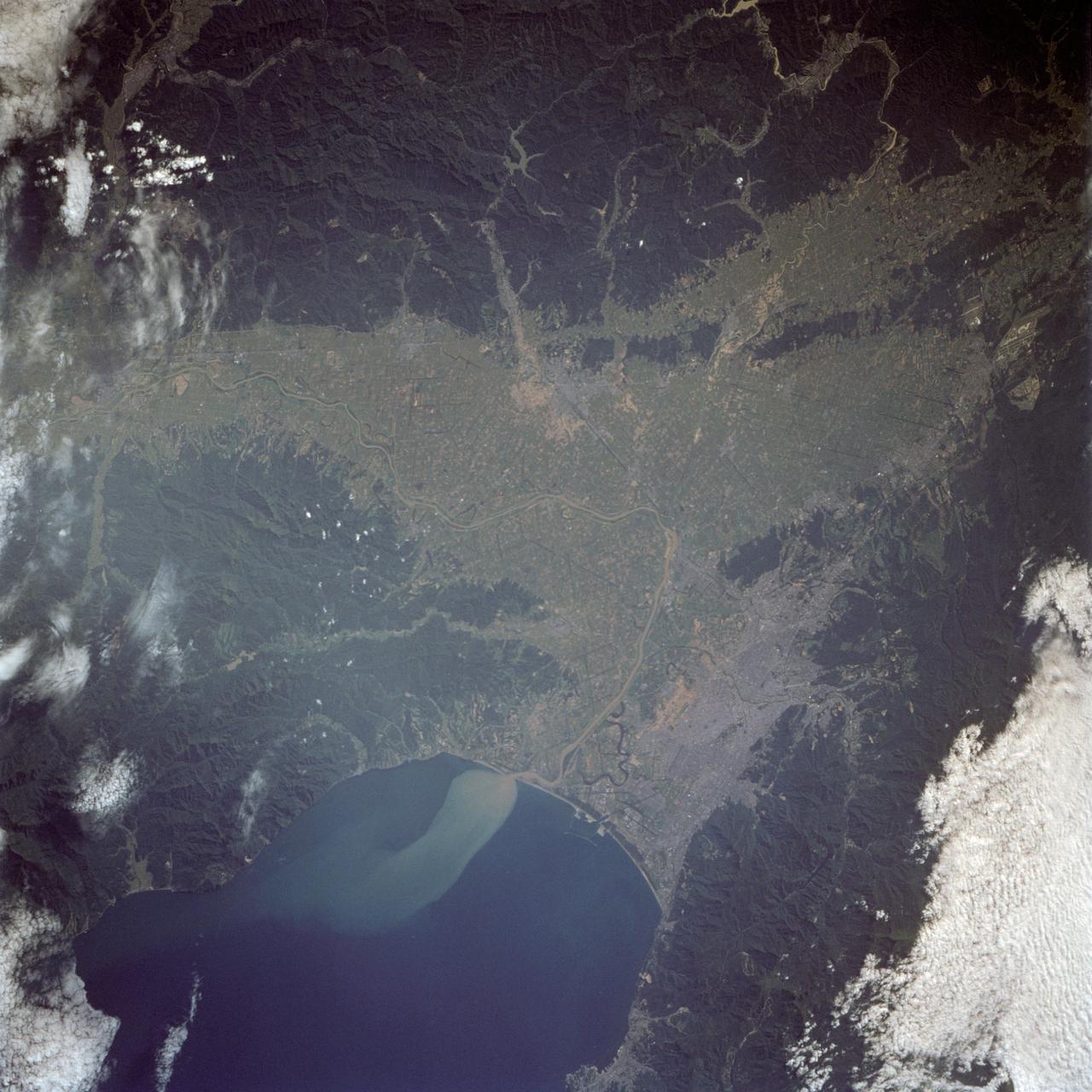

The city of Sapporo on the northernmost of the Japanese Home Island of Hokkaido (43.5N, 141.5E), host to the 1986 Winter Olympic Games is situated along the margin of a large valley which extends across the island from the Sea of Japan to the Pacific Ocean. The Valley is largely cultivated (the lighter green of the cultivated land distinguishes it from the gray urban development of Sapporo), but much of the island remains heavily forested.
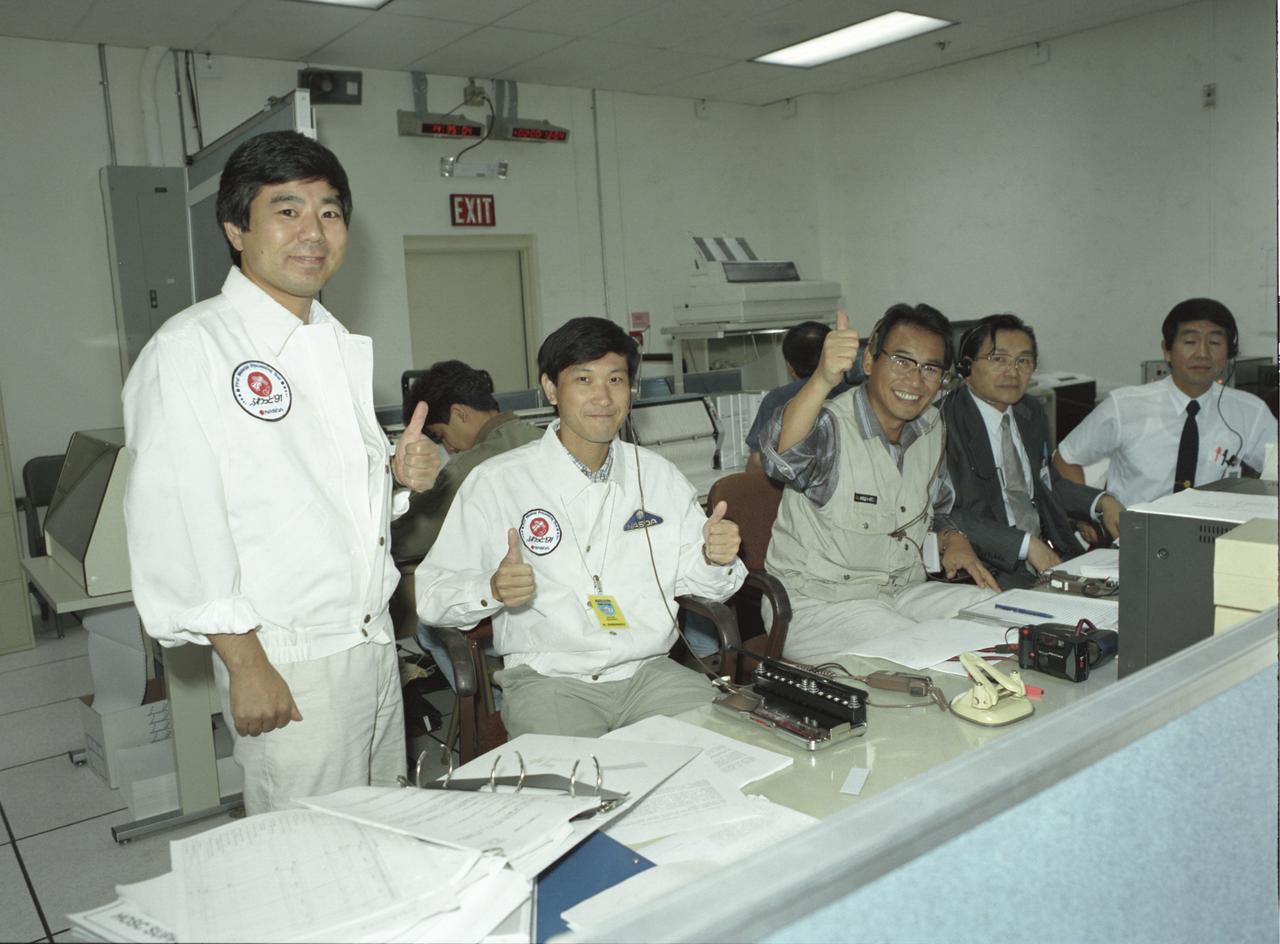

The group of Japanese researchers of the Spacelab-J (SL-J) were thumbs-up in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center after the successful launch of Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour that carried their experiments. The SL-J was a joint mission of NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. The mission conducted microgravity investigations in materials and life sciences. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, frogs, and frog eggs. The POCC was the air/ground communications channel between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The Spacelab science operations were a cooperative effort between the science astronaut crew in orbit and their colleagues in the POCC. Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
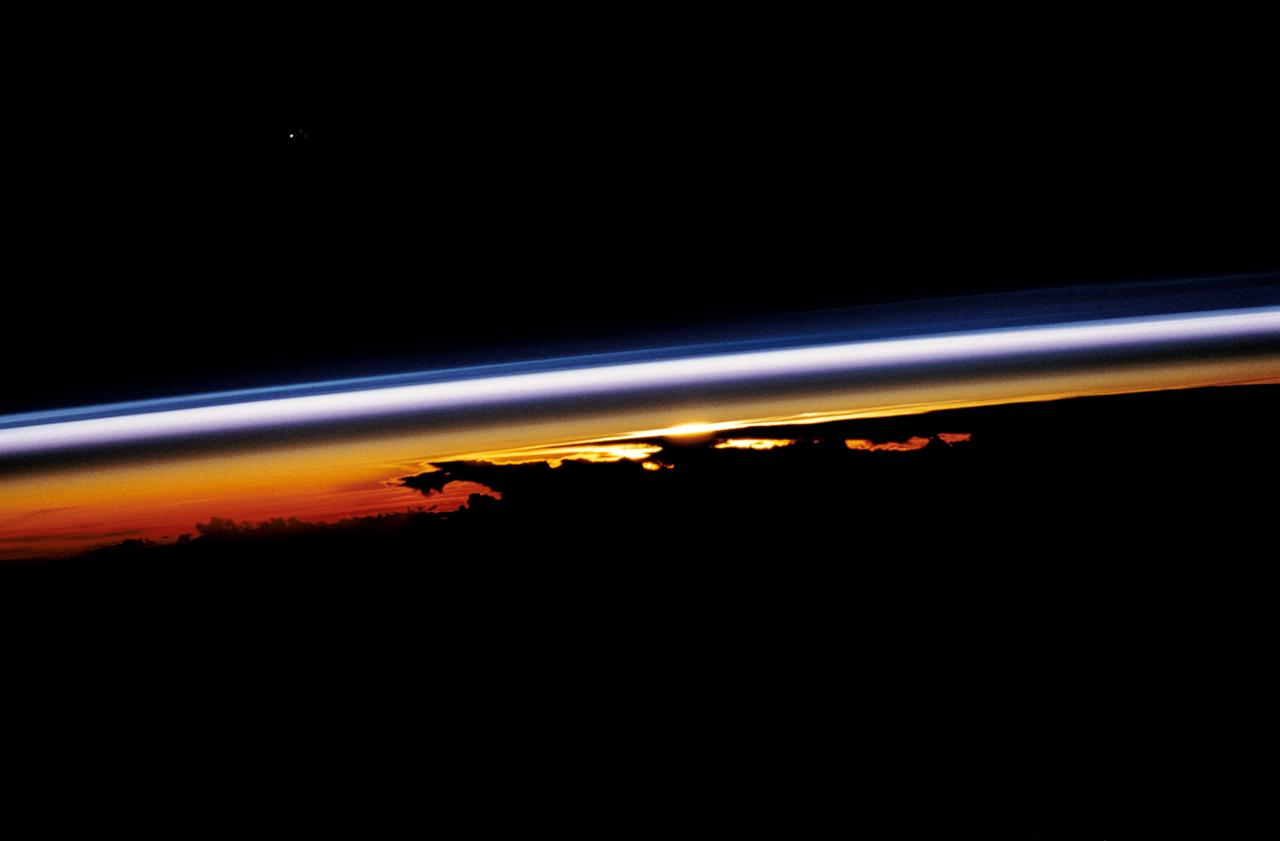

STS047-54-018 (12-20 Sept. 1992) --- The colors in this photograph provide insight into the relative density of the atmosphere. The crew members had many opportunities to witness sunrises and sunsets, considering they orbit the Earth every 90 minutes, but few, they said, compared to this scene. It captures the silhouette of several mature thunderstorms with their cirrus anvil tops spreading out against the tropopause (the top of the lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere) at sunset. The lowest layer (troposphere) is the densest and refracts light at the red end of the visible spectrum (7,400 Angstroms), while the blues (4,000 Angstroms) are separated in the least dense portion of the atmosphere (middle and upper atmosphere, or stratosphere and mesosphere). Several layers of blue can be seen. NASA scientists studying the photos believe this stratification to be caused by the scattering of light by particulate trapped in the stratosphere and mesosphere particulate that generally originate from volcanic eruptions, such as those of Mt. Pinatubo in the Philippines and, most recently, Mt. Spurr in Alaska.
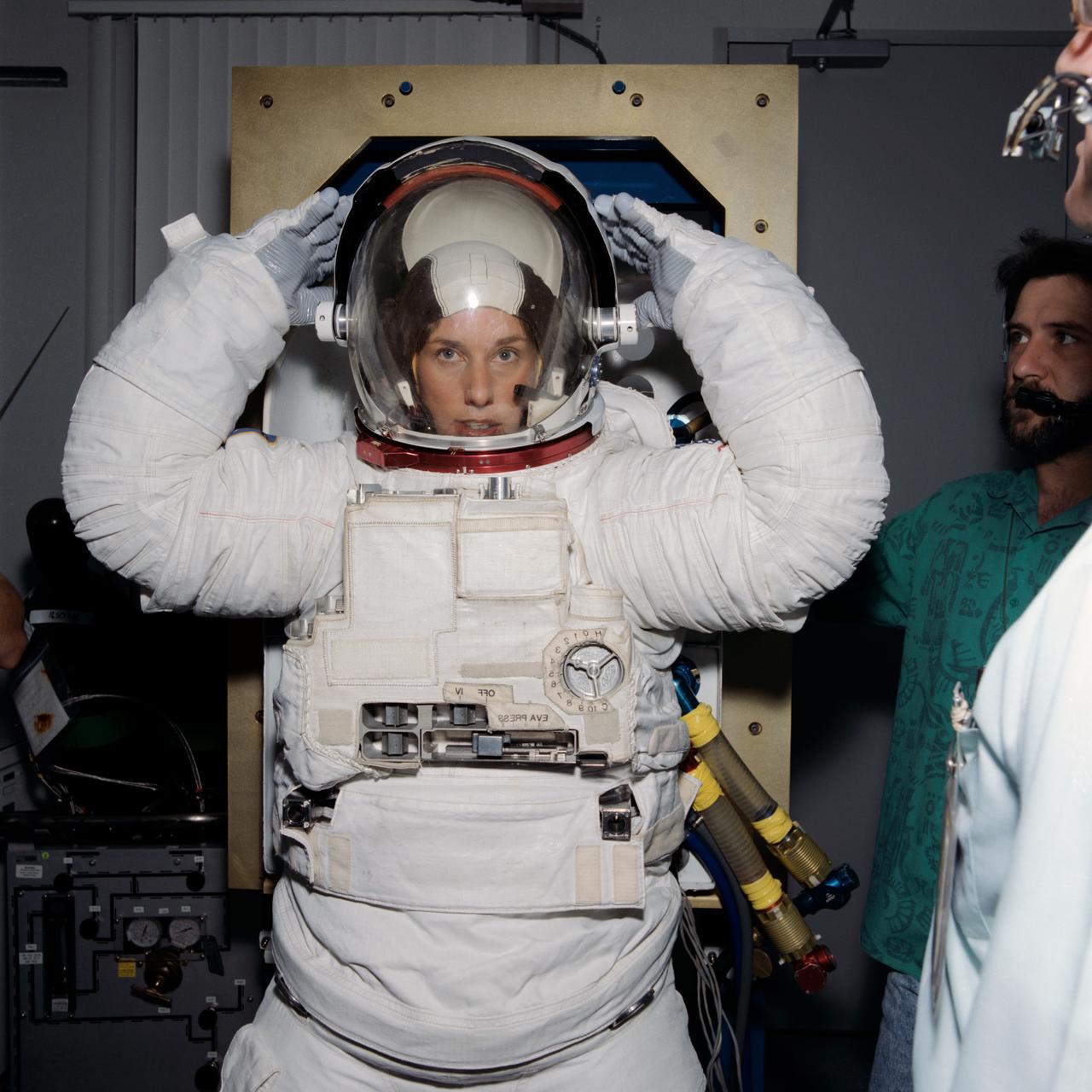

Astronaut N. Jan Davis, with her arms over her head, adjusts her helmet visor during crewmember shuttle suit fit check conducted at JSC's Crew Systems Laboratory Bldg 7.
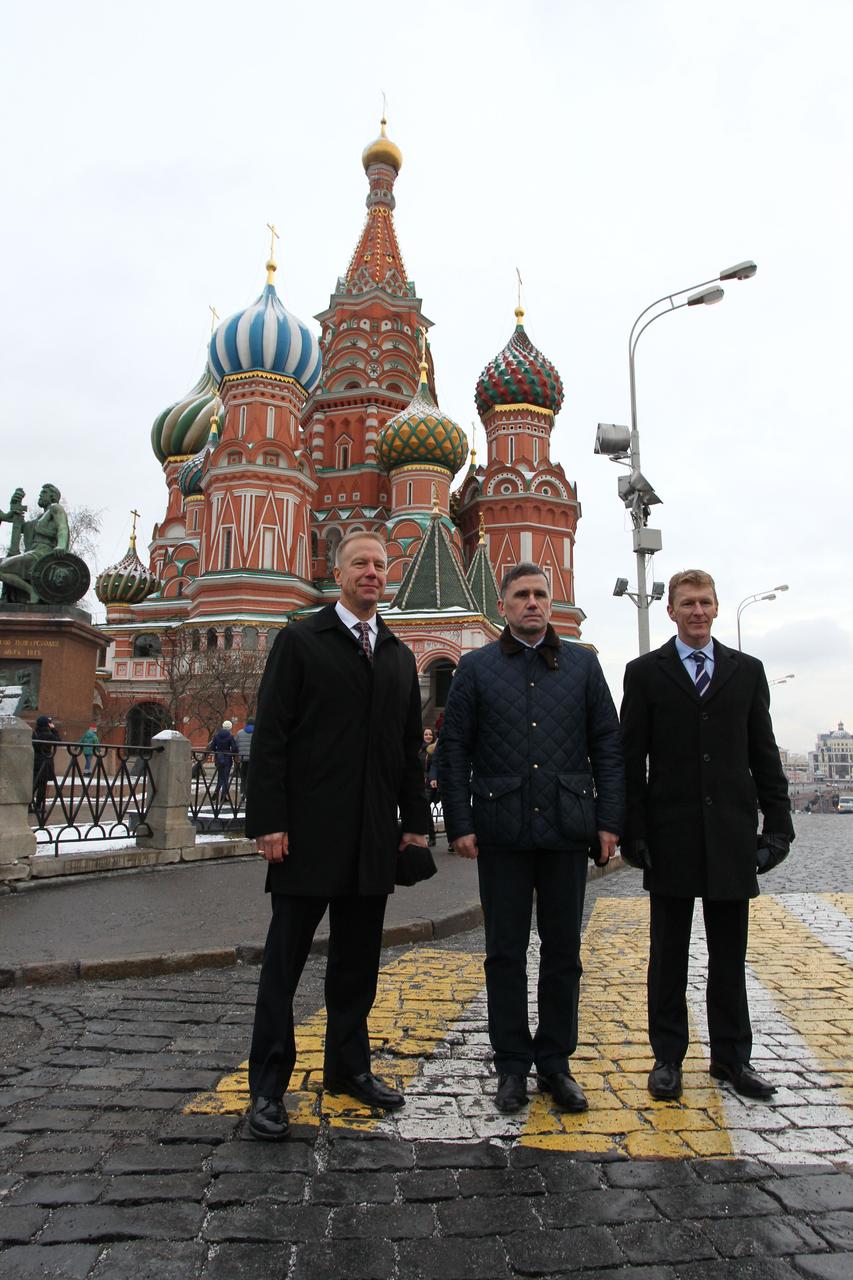

With St. Basil’s Cathedral in Red Square in Moscow serving as a backdrop, Expedition 46-47 crewmembers Tim Kopra of NASA (left), Yuri Malenchenko of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos, center) and Tim Peake of the European Space Agency (right) pose for pictures Nov. 23 after laying flowers at the Kremlin Wall where Russian space icons are interred. Peake, Malenchenko and Kopra will launch on Dec. 15 on the Soyuz TMA-19M spacecraft from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan for a six-month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Seth Marcantel

STS047-31-009 (12-20 Sept 1992) --- Two NASA astronauts prepare to try their hand at a new method of eating an in-space meal as chopsticks are called upon by a third crew member. Pictured left to right, are Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot; payload specialist Mamoru Mohri representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA); and Robert L. Gibson, mission commander. Several months of training, as well as the eight-days of sharing research on the Spacelab-J mission, allowed the astronauts and payload specialist to learn a great deal about the two cultures.
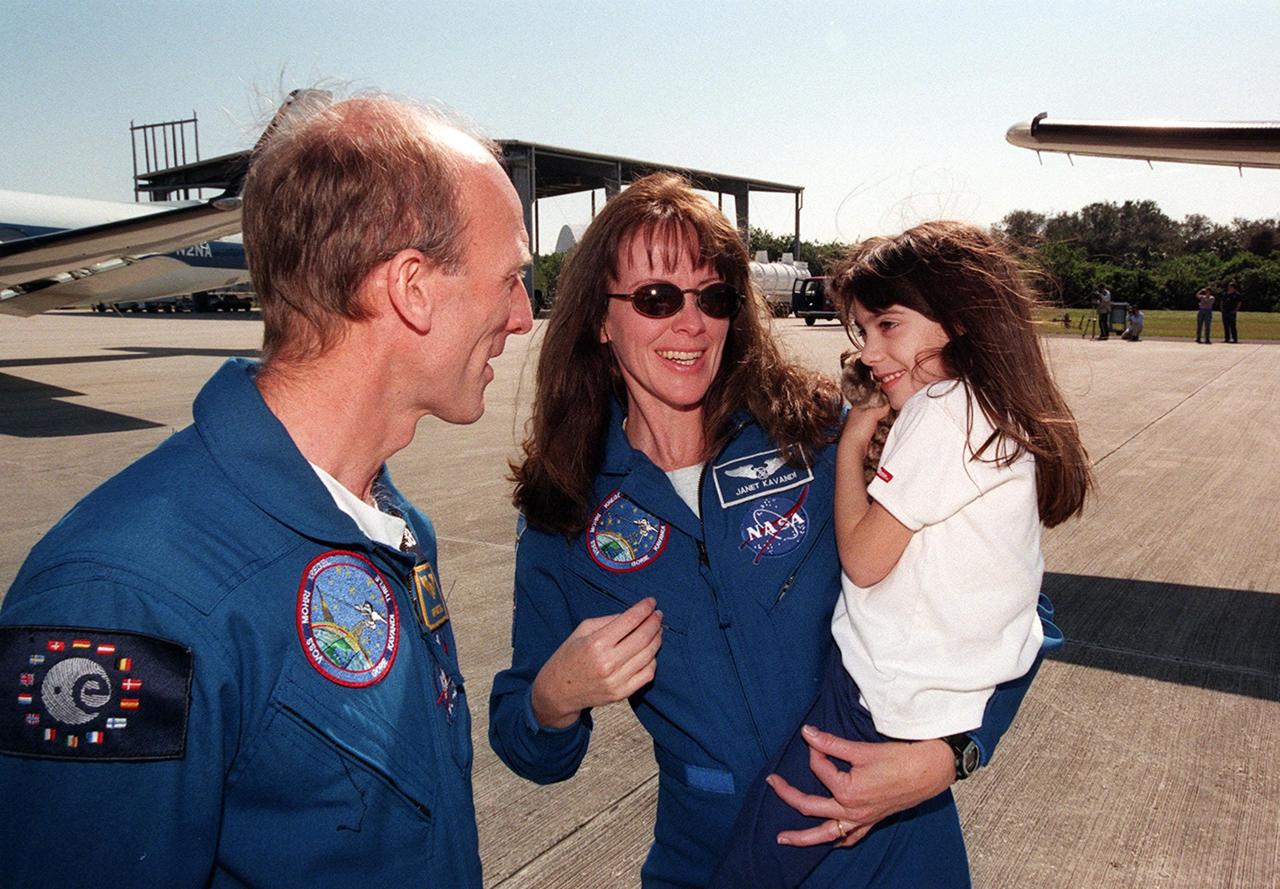

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele (left) joins Mission Specialist Janet Kavandi with her daughter before their departure for Houston. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
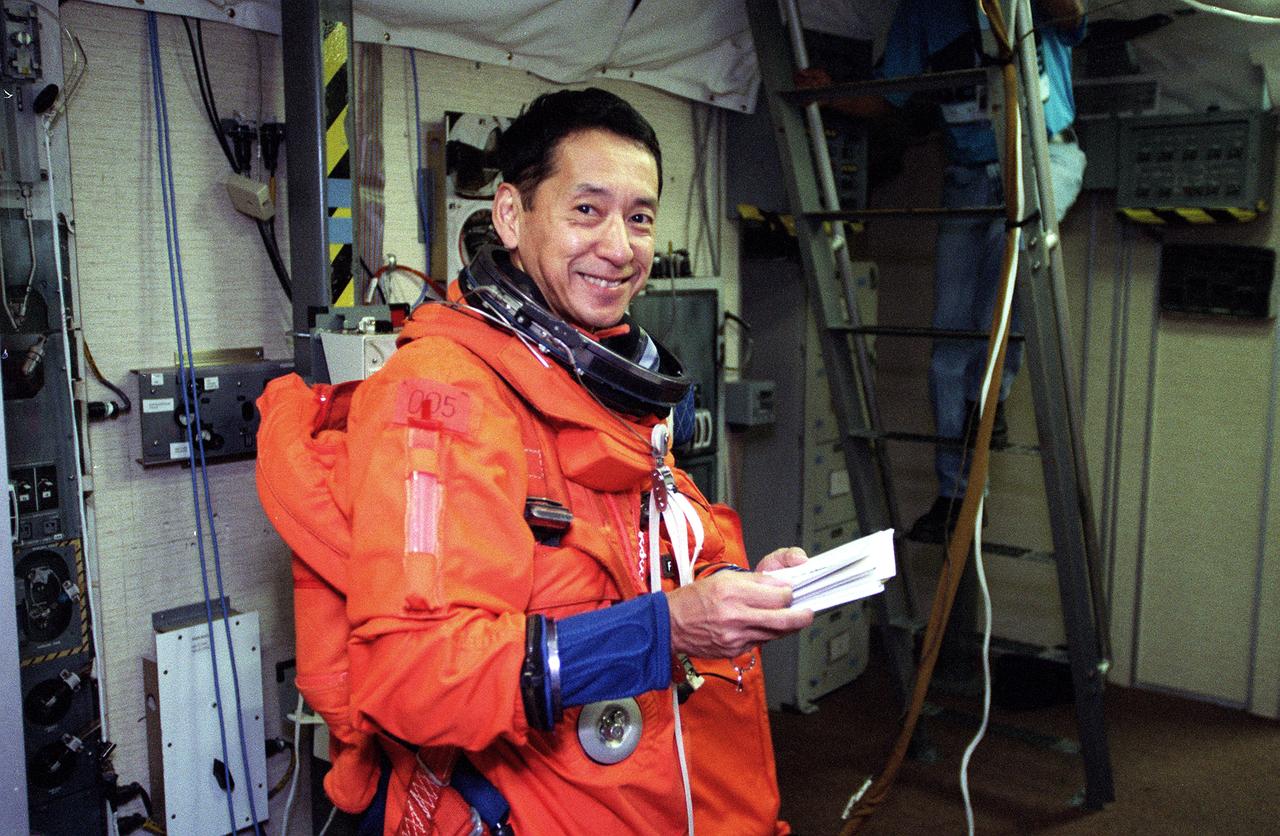

S99-10565 (24 August 1999) --- Astronaut Mamoru Mohri, STS-99 mission specialist, goes over a checklist on the mid deck of a shuttle trainer at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Mohri represents Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA). He will be making his second flight in space and his second flight aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour, having flown as a payload specialist on the STS-47 mission in 1992.
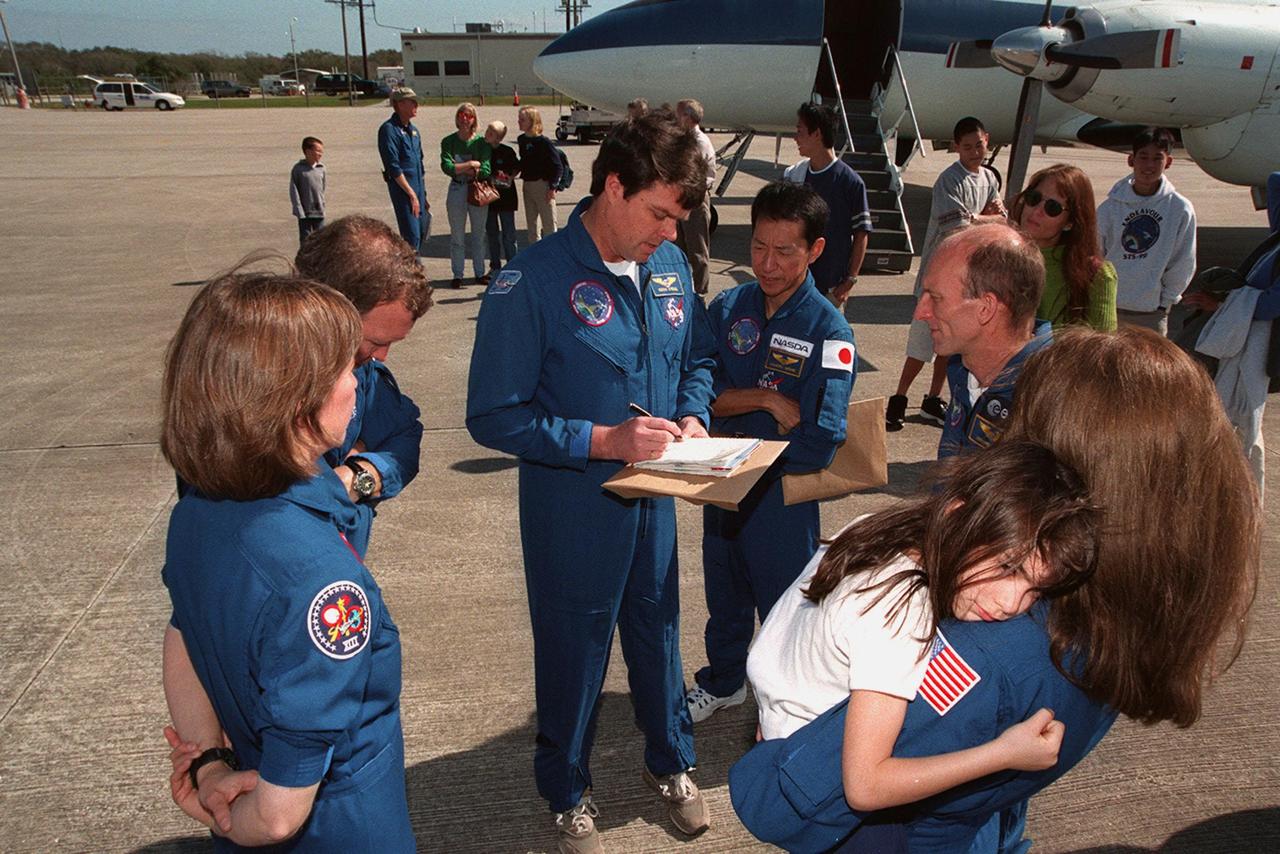

The STS-99 crew get ready to leave KSC with their families for a return trip to Houston. From left are Mission Specialist Janice Voss, Pilot Dominic Gorie, Commander Kevin Kregel, and Mission Specialists Mamoru Mohri of Japan, Gerhard Thiele of Germany, and Janet Kavandi, holding her daughter. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
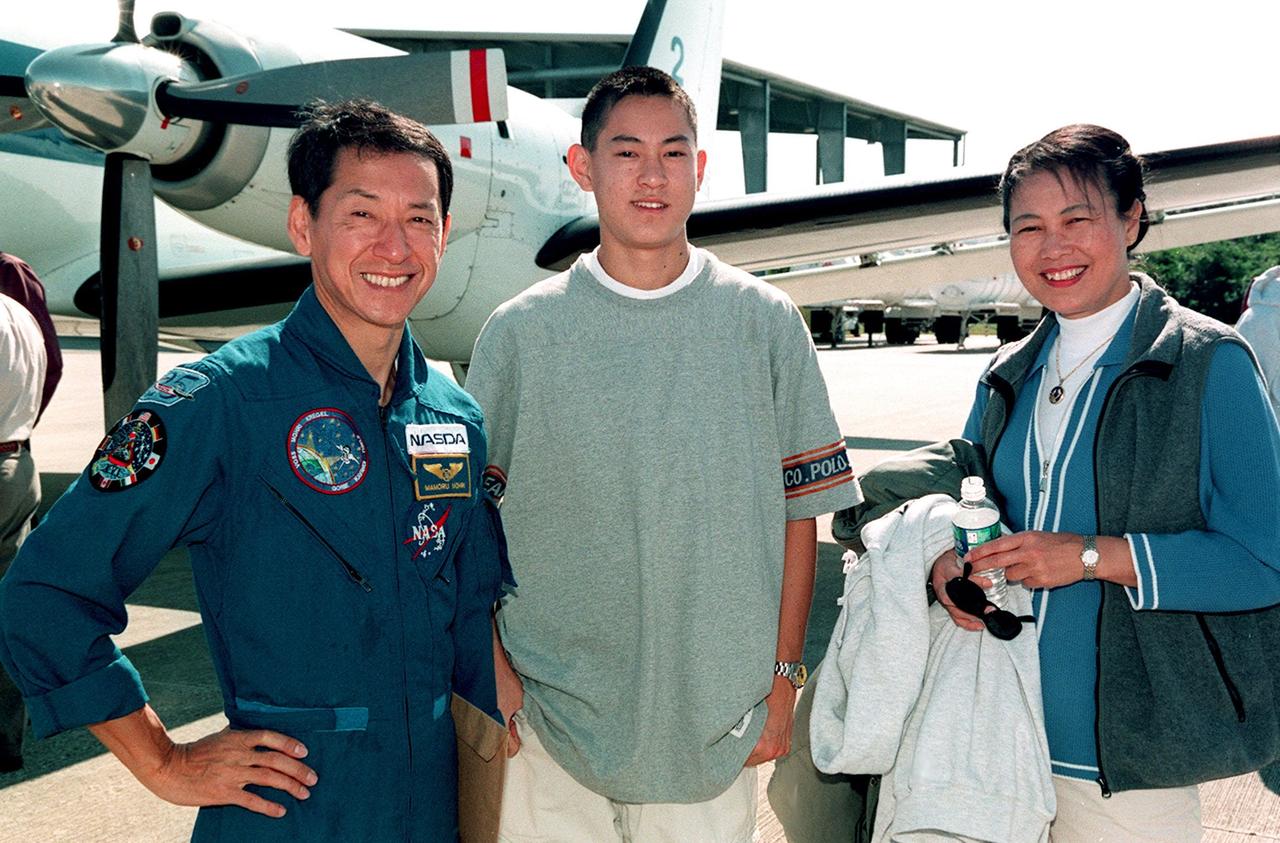

STS-99 Mission Specialist Mamoru Mohri (left) is joined by his son and wife, Akiko, at the Shuttle Landing Facility before their departure for Houston. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
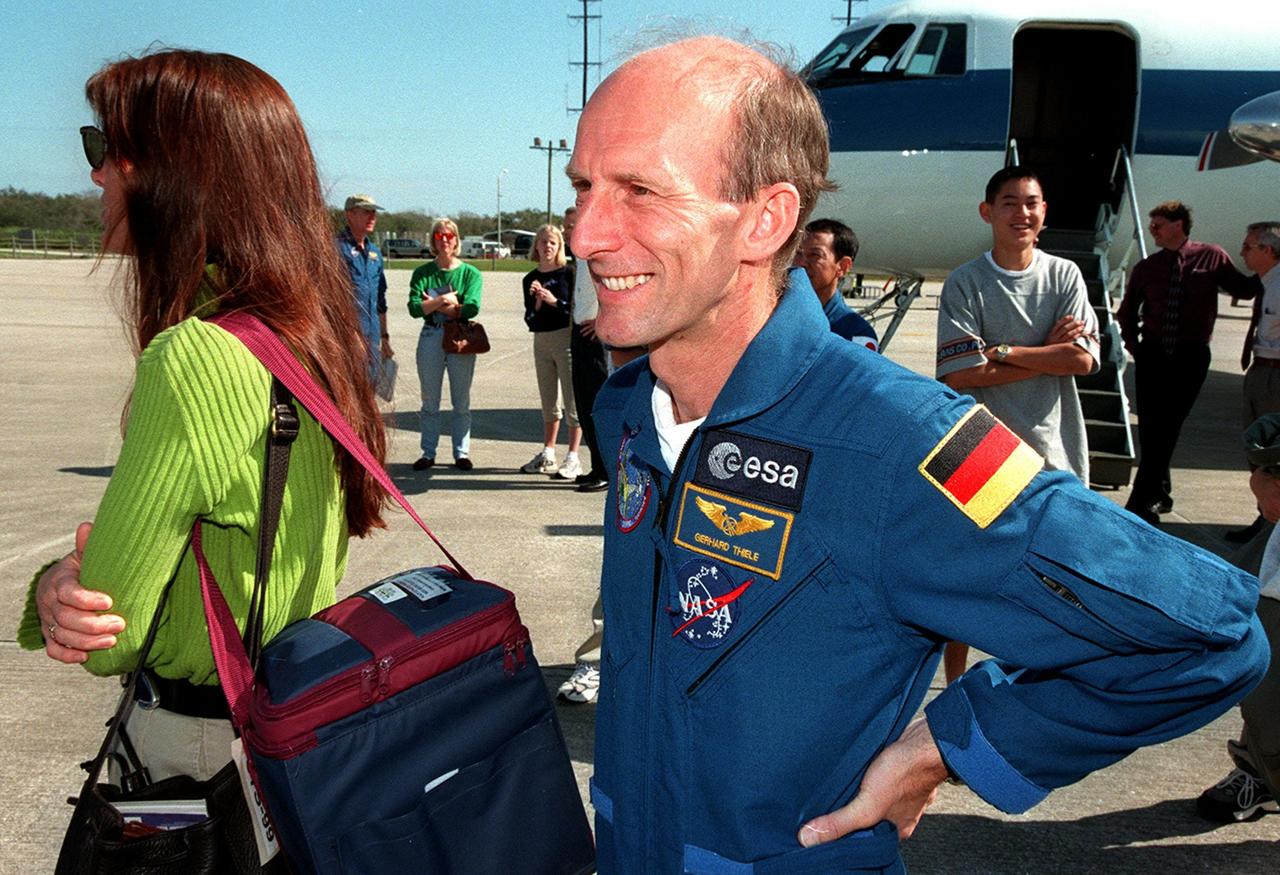

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 crew members join family members for their return trip to Houston. At left is Jeanne Kregel, wife of Commander Kevin Kregel. At right is Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele of Germany. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
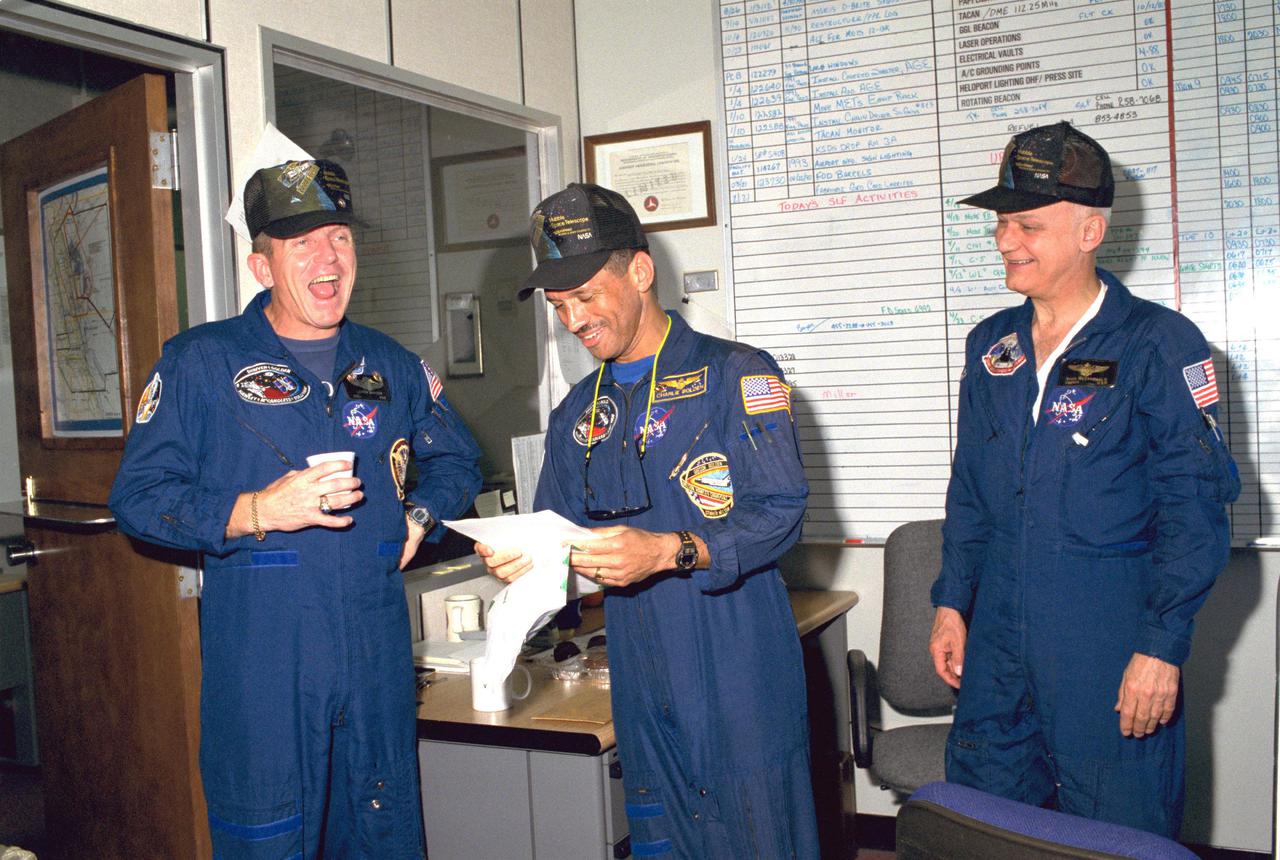

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Loren J. Shriver (left), commander of Space Shuttle Mission STS-31, enjoys a laugh with fellow crew members Pilot Charles F. Bolden Jr. and Mission Specialist Bruce McCandless II after practice runs in the Shuttle Training Aircraft. STS-31 is set to lift off April 10 at 8:47 a.m. EDT.
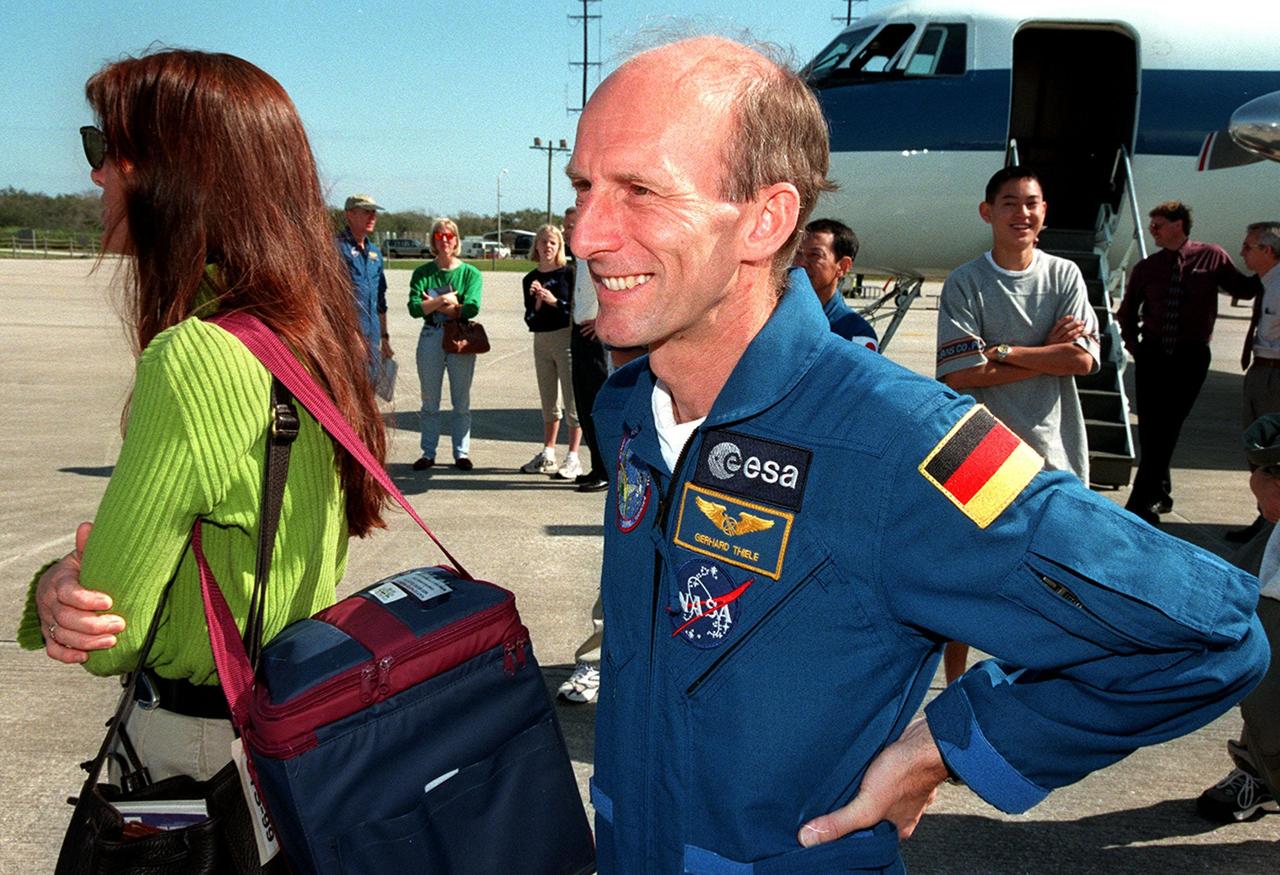

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 crew members join family members for their return trip to Houston. At left is Jeanne Kregel, wife of Commander Kevin Kregel. At right is Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele of Germany. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
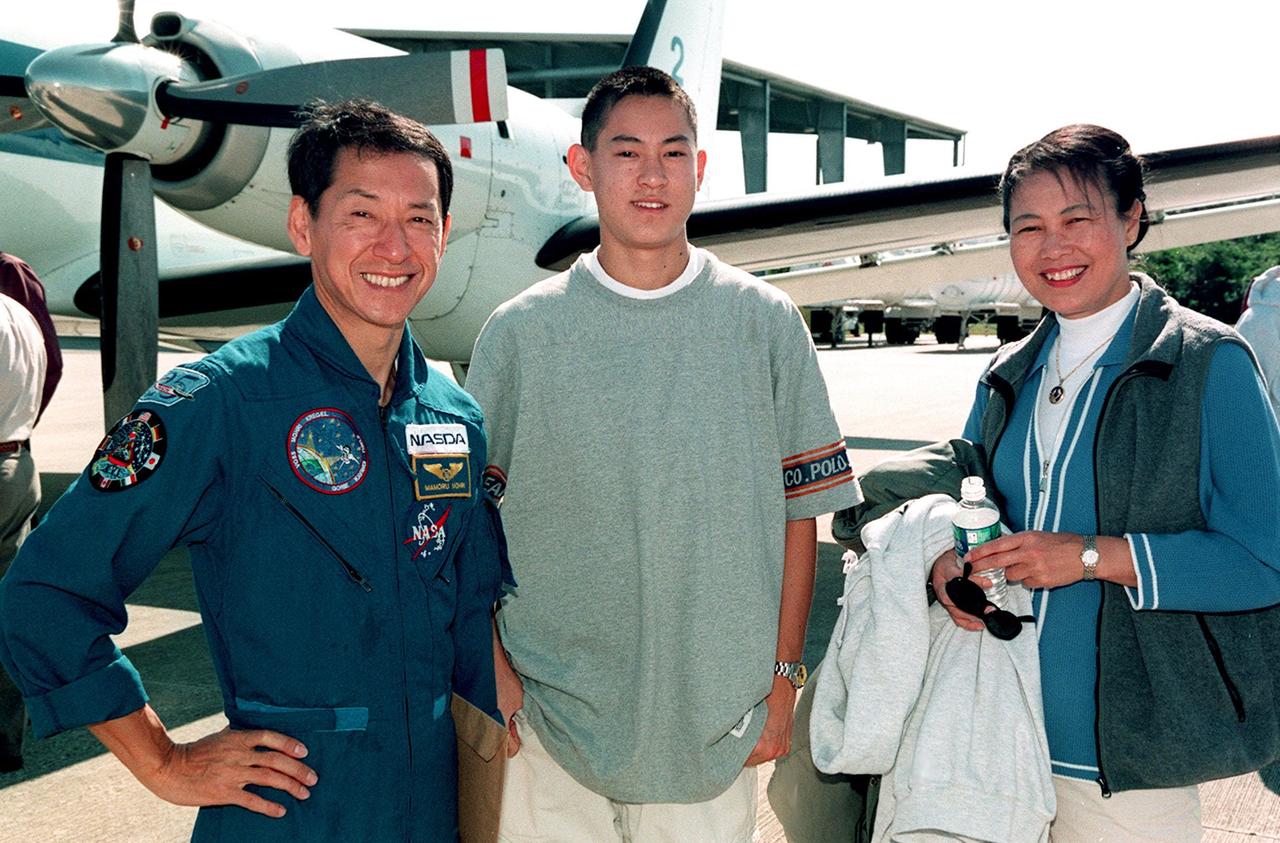

STS-99 Mission Specialist Mamoru Mohri (left) is joined by his son and wife, Akiko, at the Shuttle Landing Facility before their departure for Houston. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
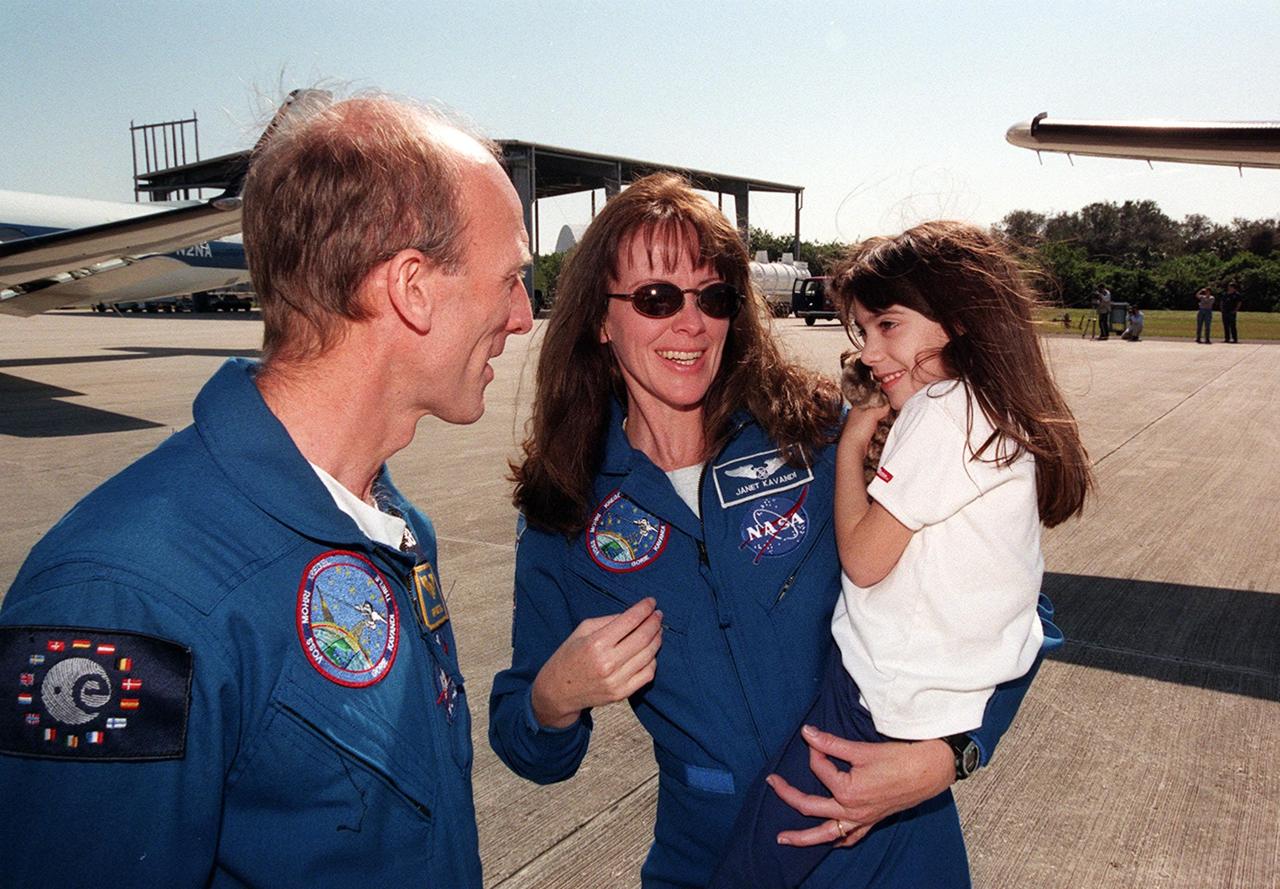

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-99 Mission Specialist Gerhard Thiele (left) joins Mission Specialist Janet Kavandi with her daughter before their departure for Houston. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
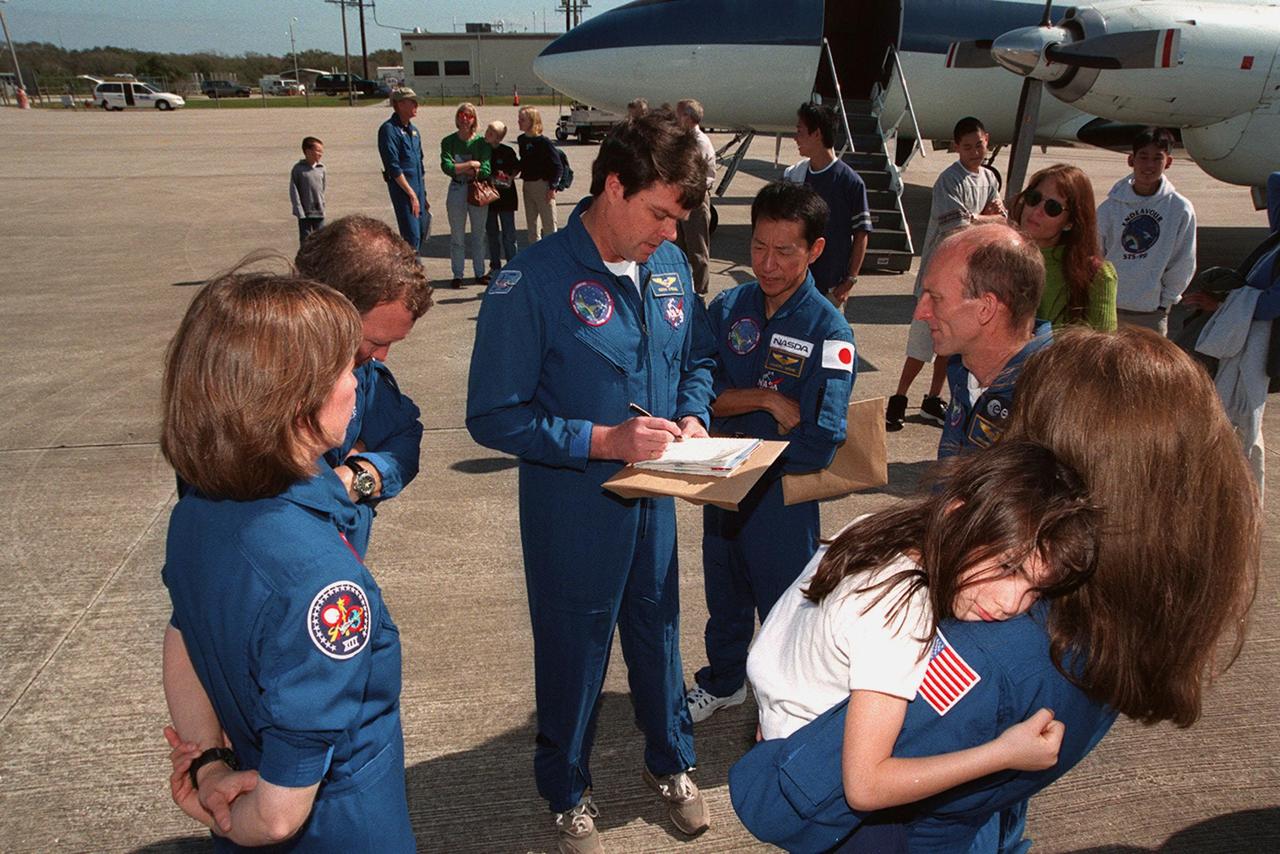

The STS-99 crew get ready to leave KSC with their families for a return trip to Houston. From left are Mission Specialist Janice Voss, Pilot Dominic Gorie, Commander Kevin Kregel, and Mission Specialists Mamoru Mohri of Japan, Gerhard Thiele of Germany, and Janet Kavandi, holding her daughter. The STS-99 crew completed a successful 11-day Shuttle Radar Topography Mission mapping 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface before landing at KSC Feb. 22
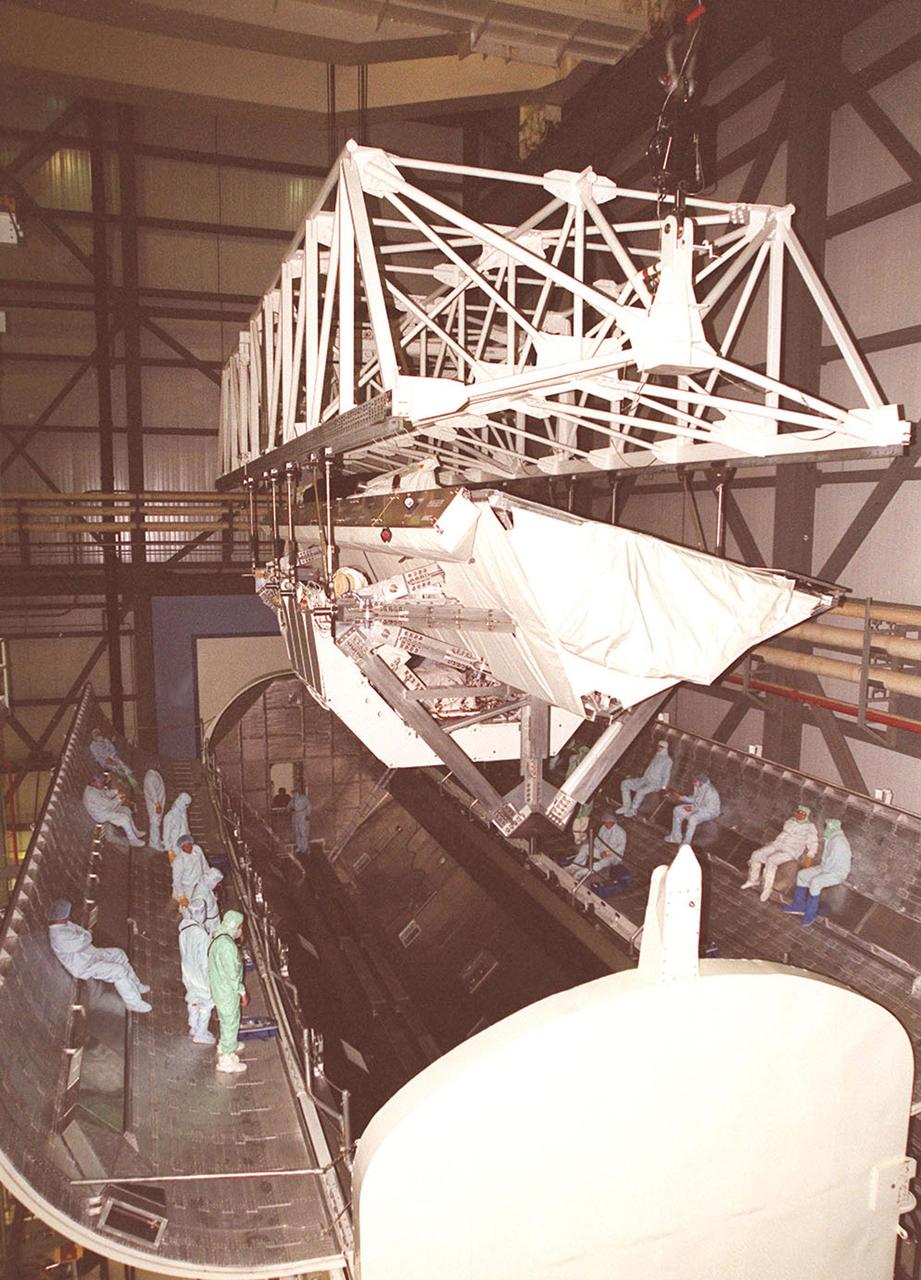
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In OPF bay 2, after lifting the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) payload out of Endeavour's payload bay, a crane moves it into a payload canister for transport to the Space Station Processing Facility. The SRTM mapped more than 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface on mission STS-99, which landed Feb. 22, 2000
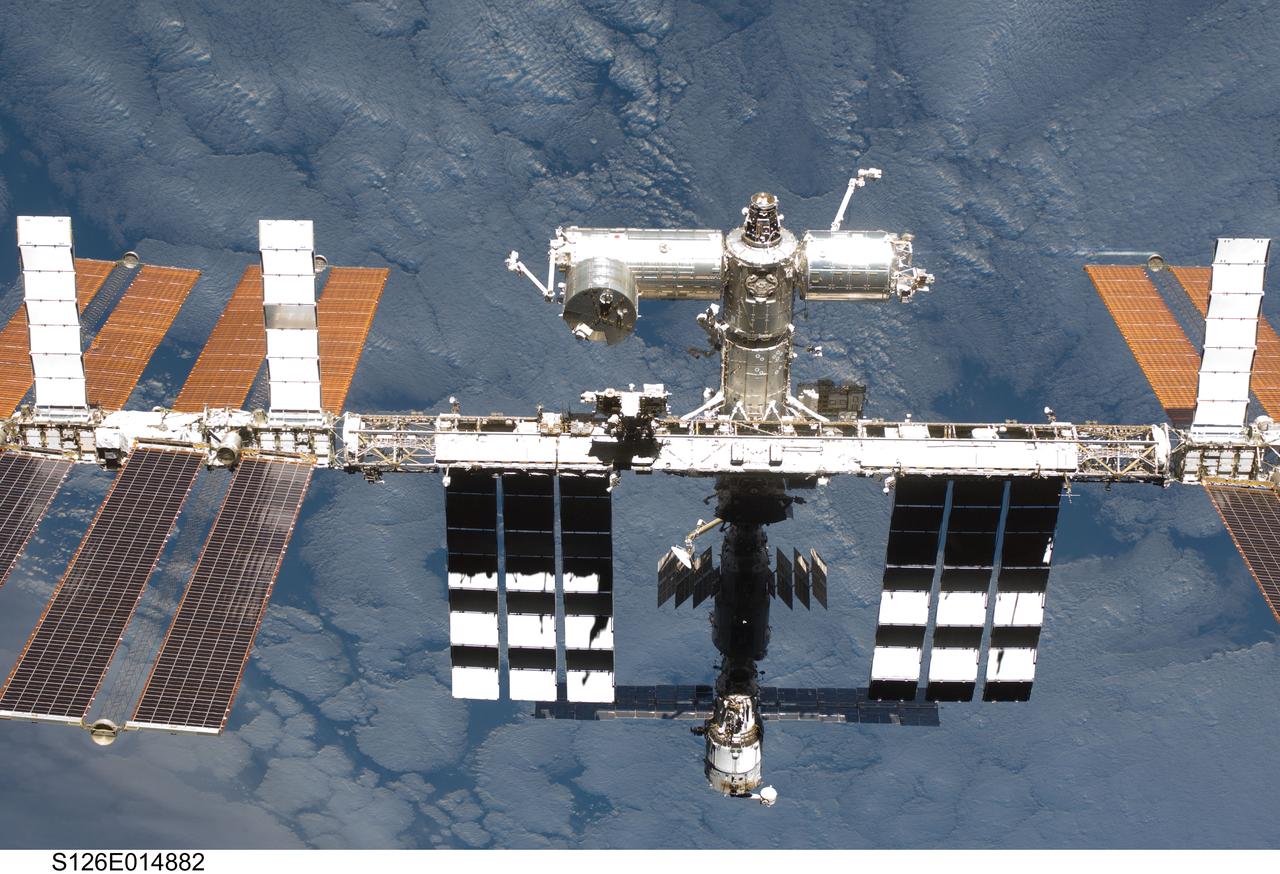
S126-E-014882 (28 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped by a cloud-covered part of Earth, the International Space Station is seen from Space Shuttle Endeavour as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. Earlier the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crews concluded 11 days, 16 hours and 46 minutes of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 8:47 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 28, 2008.
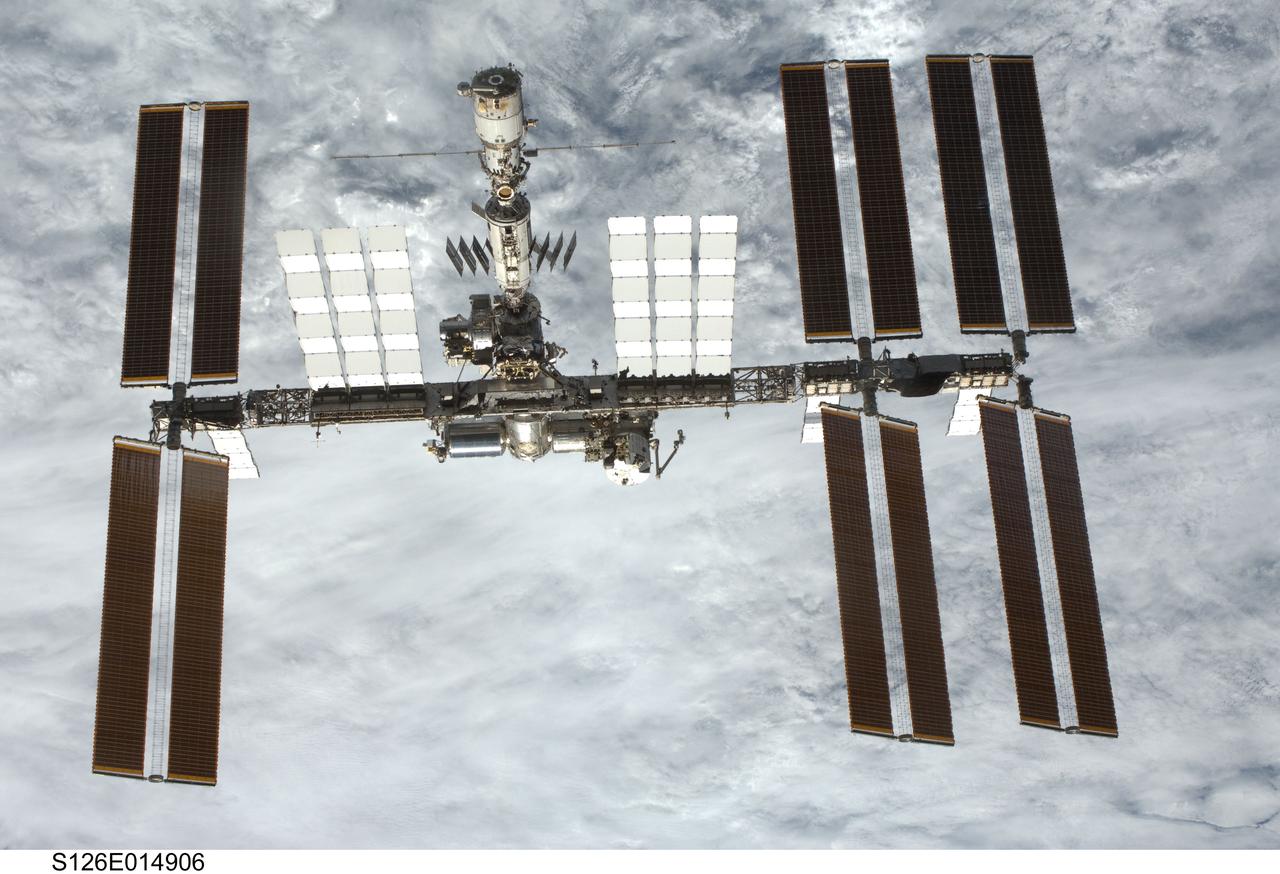

S126-E-014906 (28 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped by a cloud-covered part of Earth, the International Space Station is seen from Space Shuttle Endeavour as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. Earlier the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crews concluded 11 days, 16 hours and 46 minutes of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 8:47 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 28, 2008.
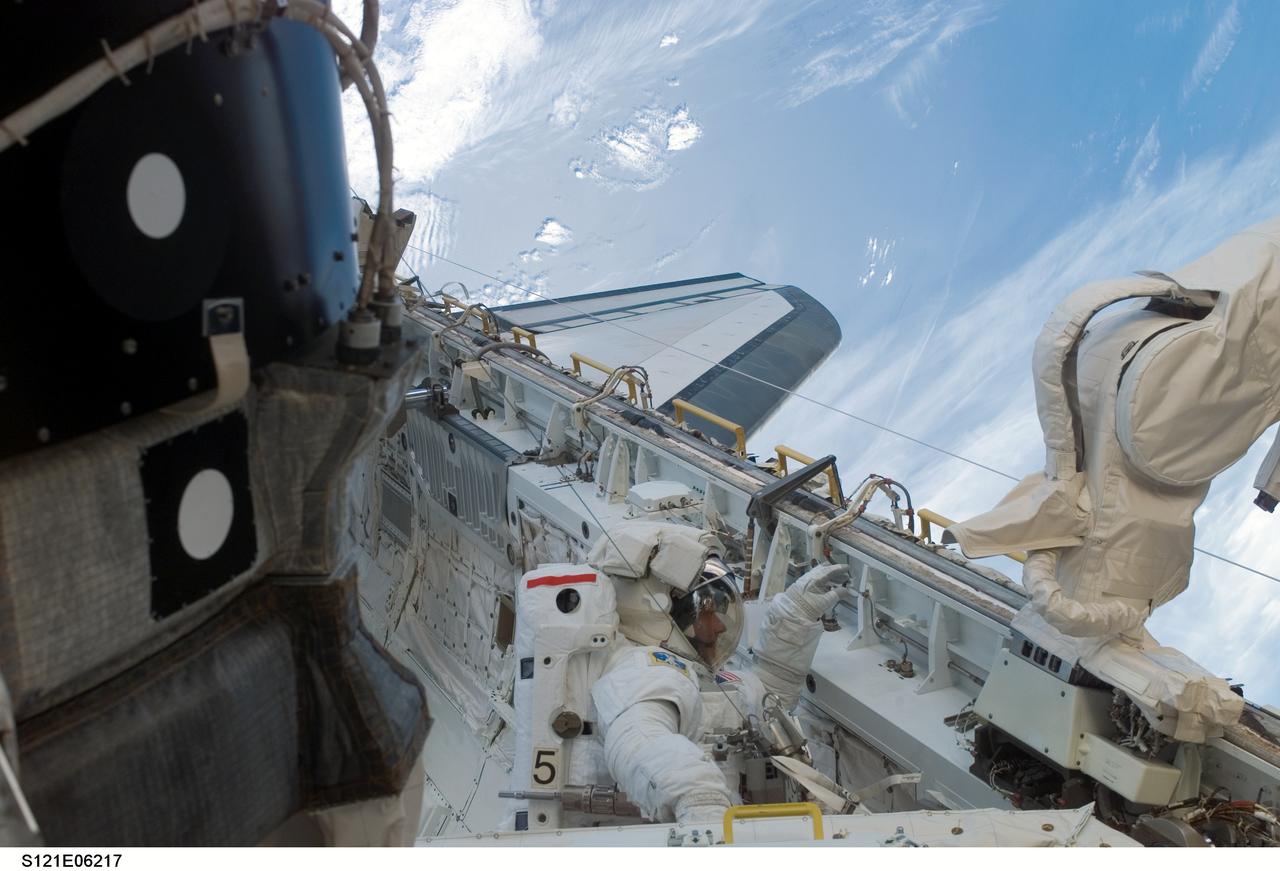

S121-E-06217 (10 July 2006) --- Astronaut Piers J. Sellers, STS-121 mission specialist, works in the Space Shuttle Discovery's cargo bay during the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA). During today's six-hour 47-minute spacewalk, Sellers and astronaut Michael E. Fossum (out of frame), mission specialist, restored the International Space Station's Mobile Transporter rail car to full operation and delivered a spare pump module for the station's cooling system.
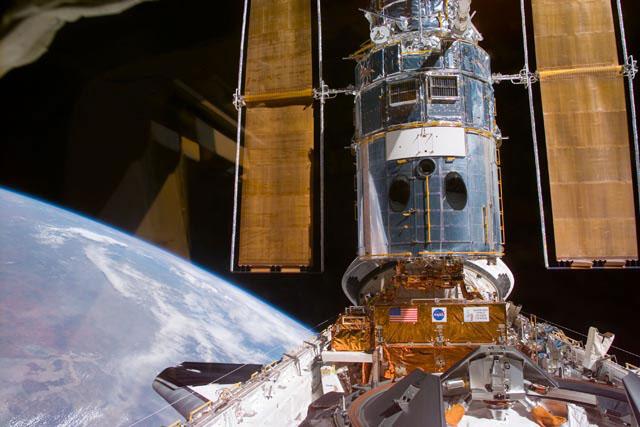

S103-E-5159 (21 December 1999) --- This electronic still camera's view and others in this series showing the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) being berthed in Discovery's bay were recorded during and soon after capture; and they were downlinked at the completion of the mission's first space walk on the following day by the busy STS-103 astronauts. The image was recorded at 19:47:02 GMT, Dec. 21, 1999.
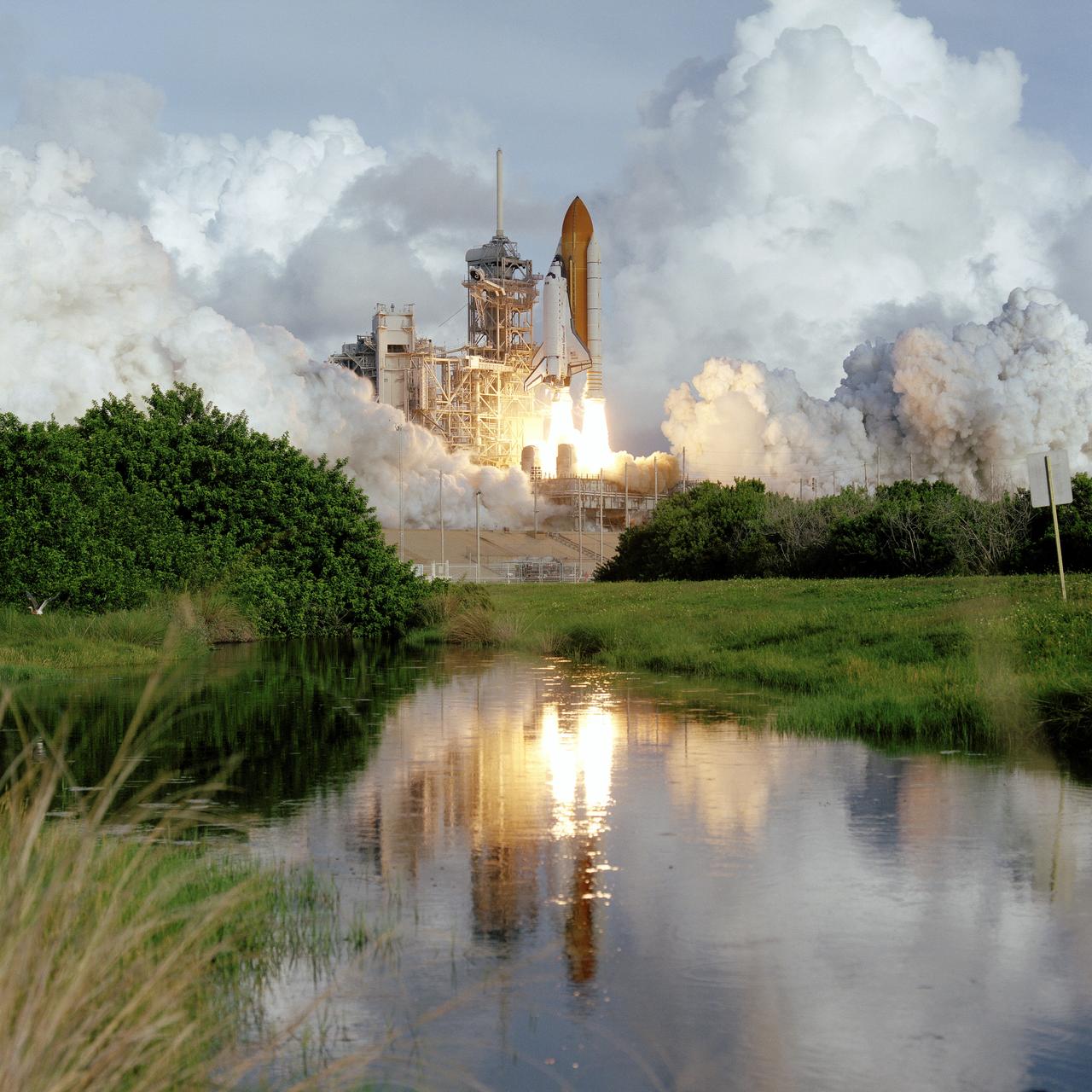

STS106-S-010 (8 Sept. 2000) --- The Space Shuttle Atlantis is mirrored in nearby marsh waters as it makes its 22nd launch into space. The perfect on-time liftoff for STS-106 occurred at 8:45:47 a.m. (EDT), Sept. 8, 2000. Onboard the shuttle were astronauts Terrence W. Wilcutt, Scott D. Altman, Edward T. Lu, Richard A. Mastracchio and Daniel C. Burbank, along with cosmonauts Yuri I. Malenchenko and Boris V. Morukov who represent the Russian Aviation and Space Agency.
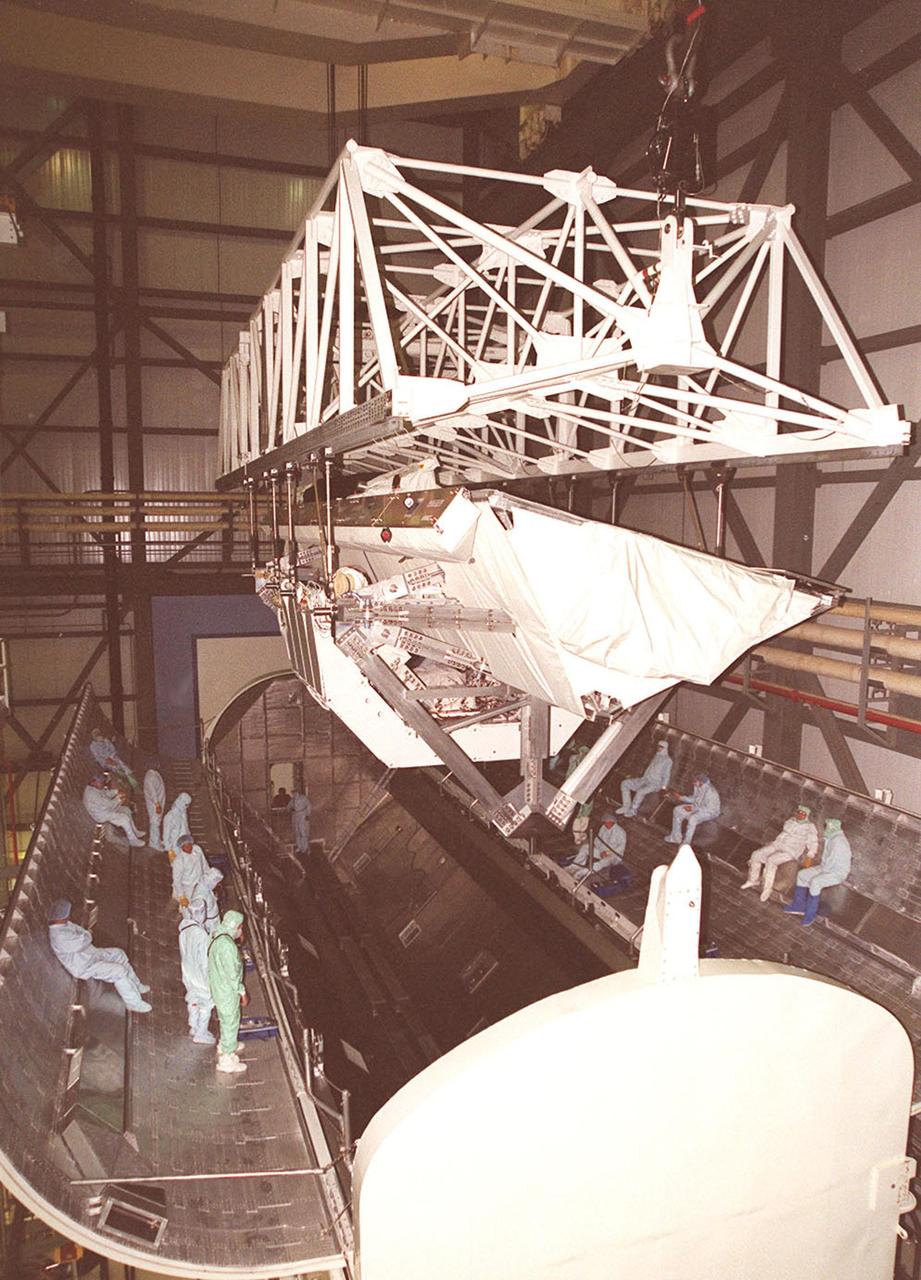
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In OPF bay 2, after lifting the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) payload out of Endeavour's payload bay, a crane moves it into a payload canister for transport to the Space Station Processing Facility. The SRTM mapped more than 47 million square miles of the Earth's surface on mission STS-99, which landed Feb. 22, 2000
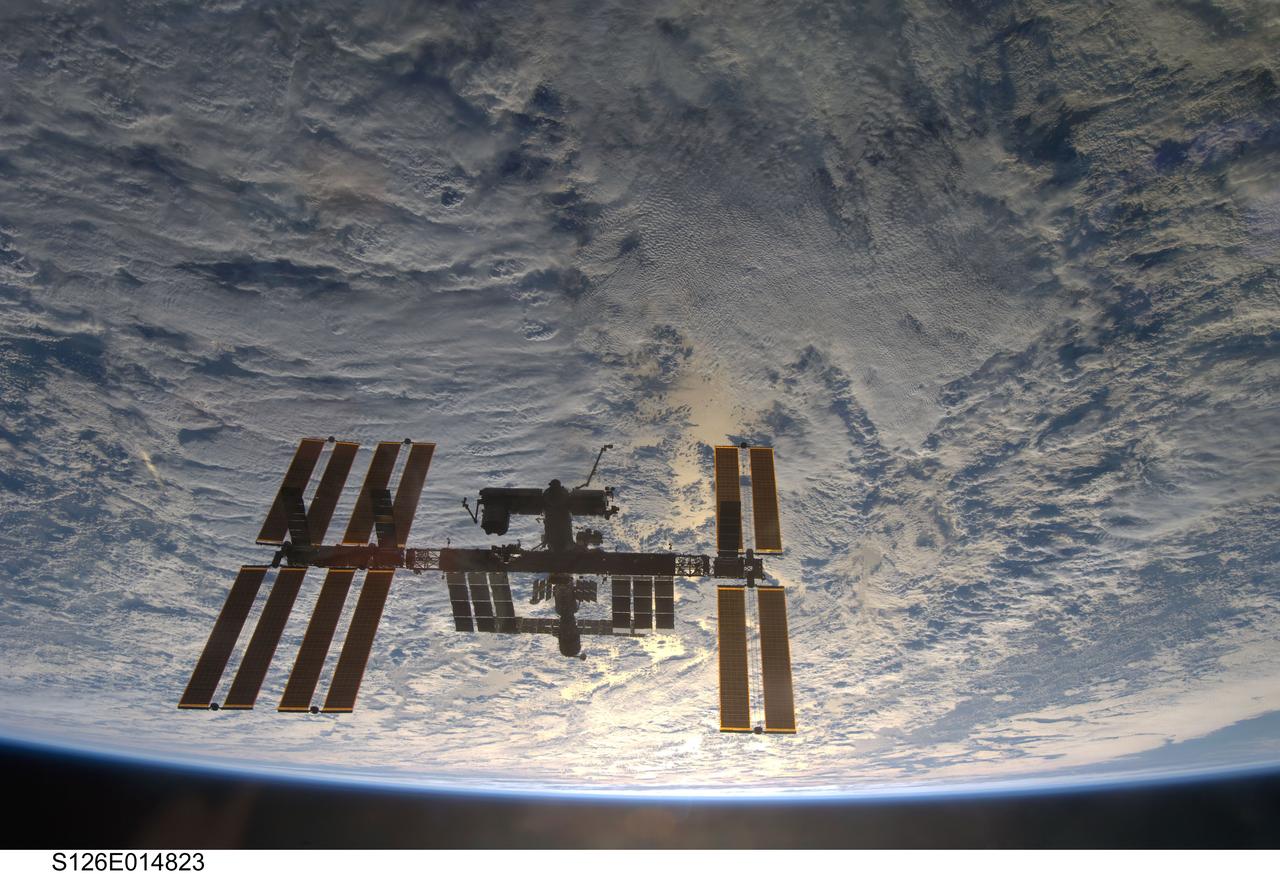

S126-E-014823 (28 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped by a cloud-covered part of Earth, the International Space Station is seen from Space Shuttle Endeavour as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. Earlier the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crews concluded 11 days, 16 hours and 46 minutes of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 8:47 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 28, 2008.
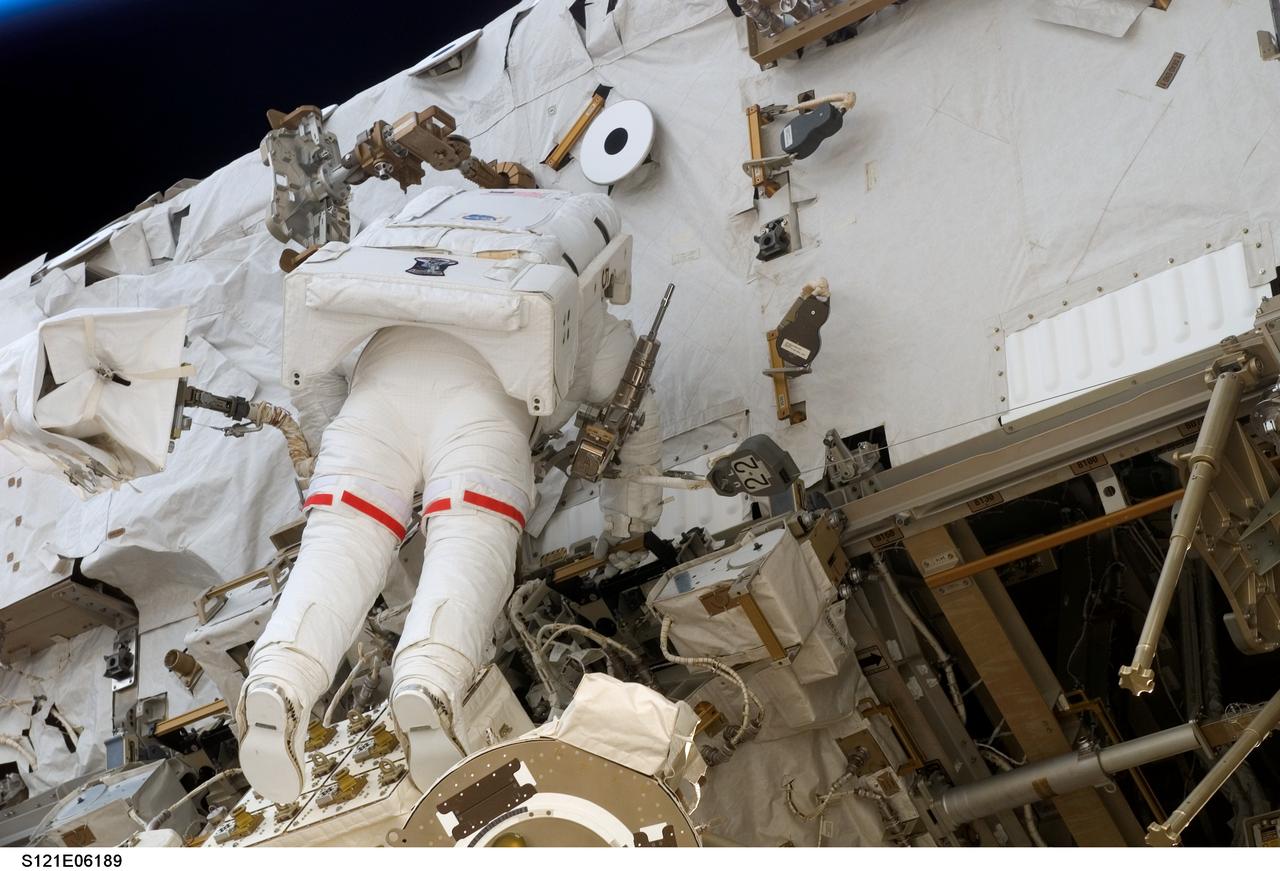

S121-E-06189 (10 July 2006) --- Astronaut Piers J. Sellers, STS-121 mission specialist, participates in the mission's second session of extravehicular activity (EVA). During today's six-hour 47-minute spacewalk, Sellers and astronaut Michael E. Fossum (out of frame), mission specialist, restored the International Space Station's Mobile Transporter rail car to full operation and delivered a spare pump module for the station's cooling system.

S88-E-5149 (12-13-98) --- Astronaut Robert D. Cabana, STS-88 mission commander, looks toward the mated Russian-built Zarya and the U.S.-built Unity module in Endeavour's cargo bay several hours prior to release of the ISS components. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 05:11:47 GMT, Dec. 13.
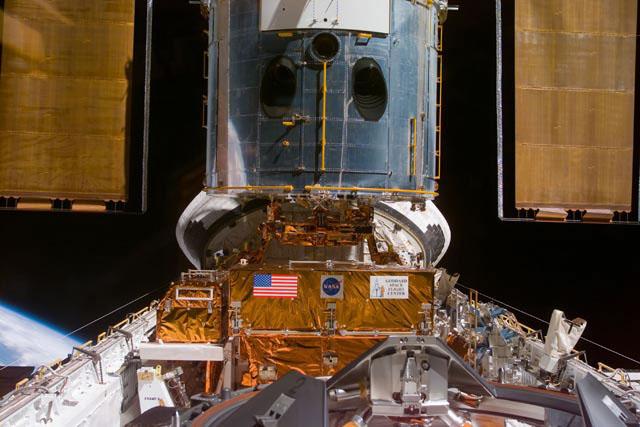

S103-E-5165 (21 December 1999) --- This electronic still camera's view and others in this series showing the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) berthed in Discovery's bay were recorded soon after capture and downlinked at the completion of the mission's first space walk on the following day by the busy STS-103 astronauts. The image was recorded at 19:47:57 GMT, Dec. 21, 1999.
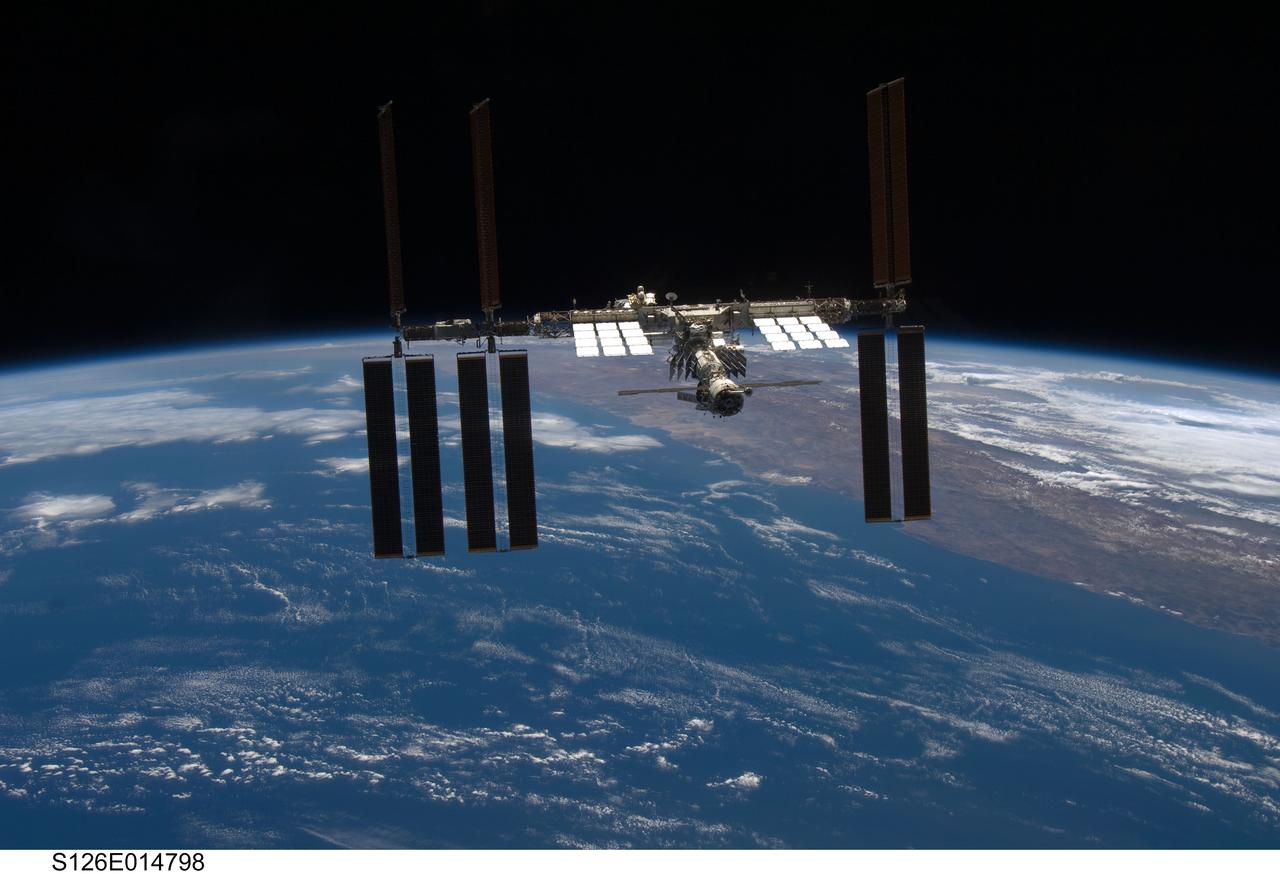

S126-E-014798 (28 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped by a colorful Earth and the blackness of space, the International Space Station is seen from Space Shuttle Endeavour as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. Earlier the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crews concluded 11 days, 16 hours and 46 minutes of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 8:47 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 28, 2008.
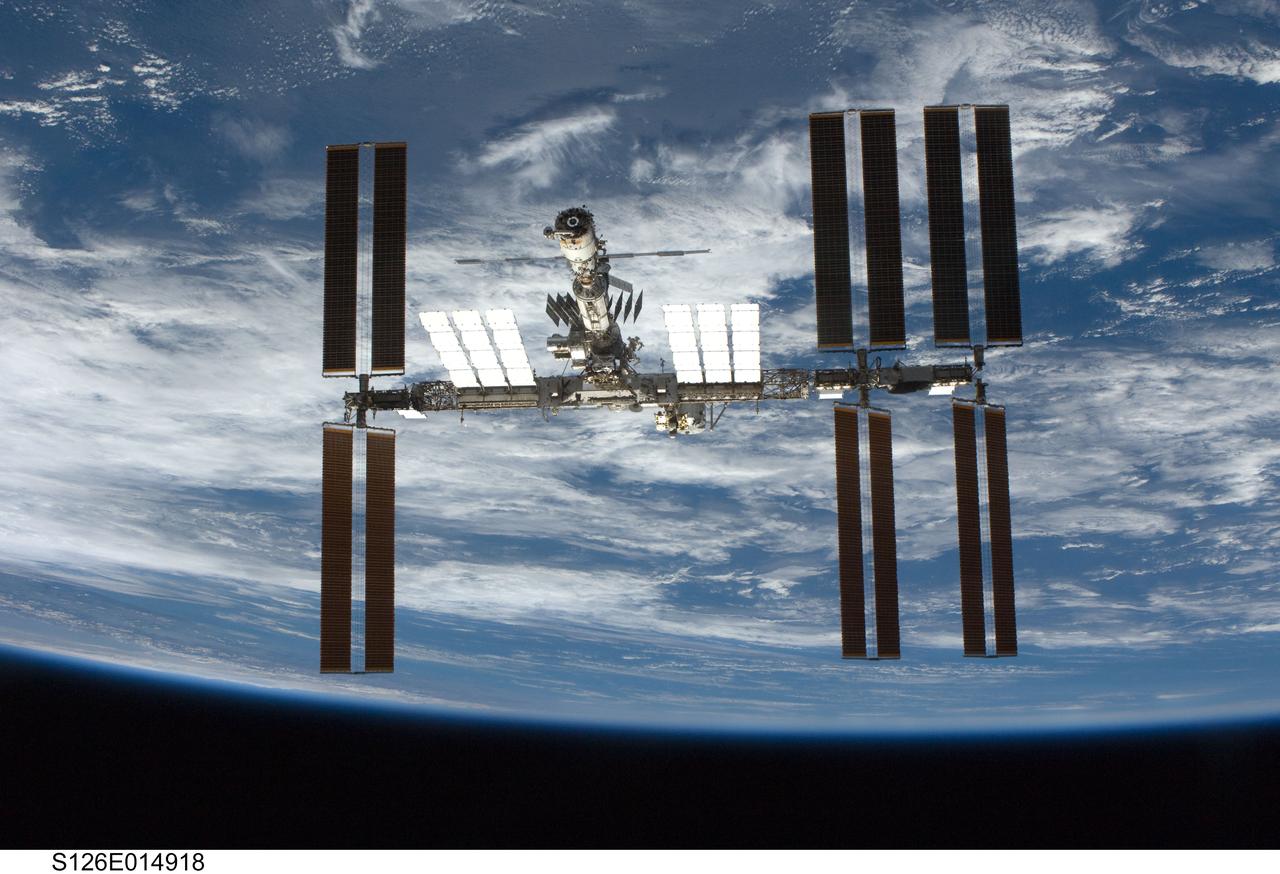

S126-E-014918 (28 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped by a blue and white Earth and the blackness of space, the International Space Station is seen from Space Shuttle Endeavour as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. Earlier the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crews concluded 11 days, 16 hours and 46 minutes of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 8:47 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 28, 2008.
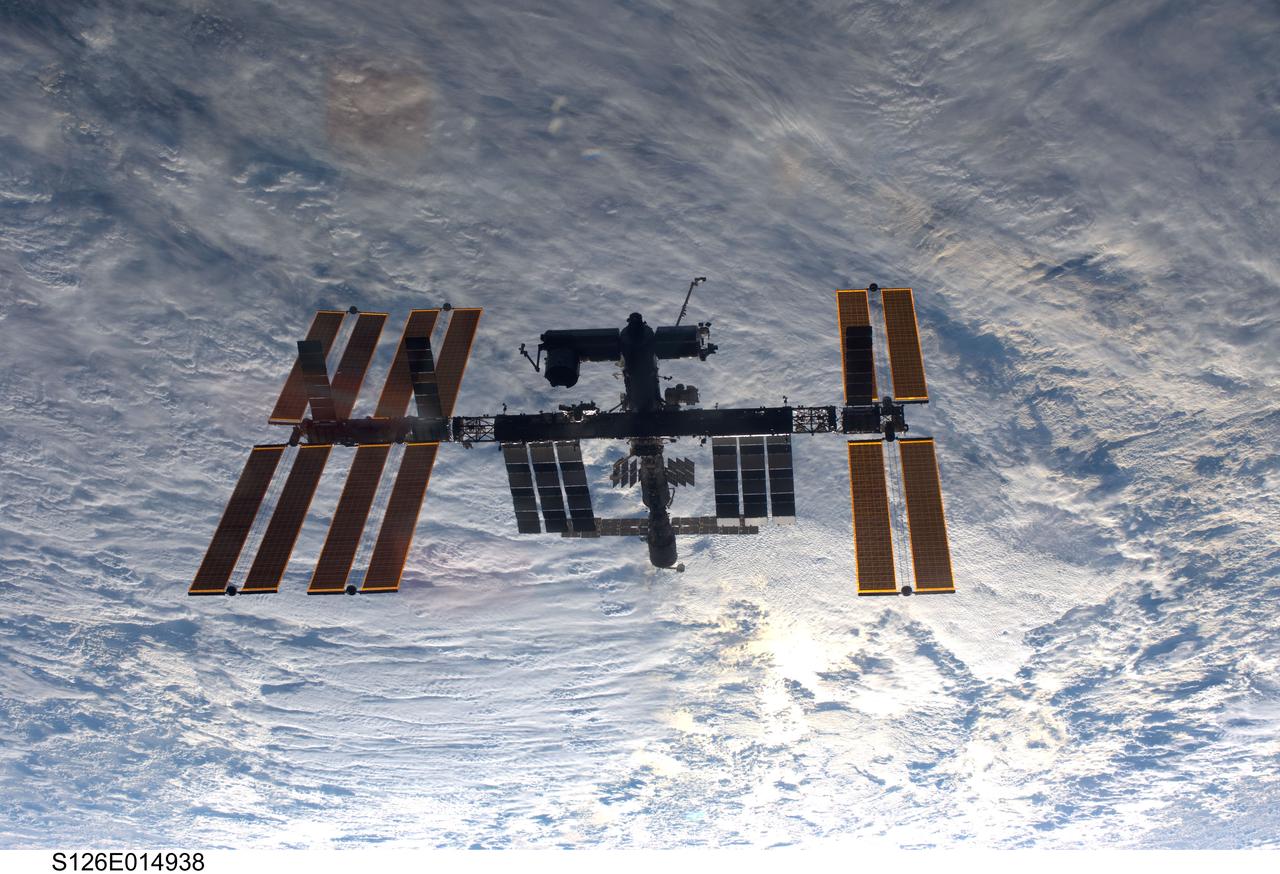

S126-E-014938 (28 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped by a cloud-covered part of Earth, the International Space Station is seen from Space Shuttle Endeavour as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. Earlier the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crews concluded 11 days, 16 hours and 46 minutes of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 8:47 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 28, 2008.
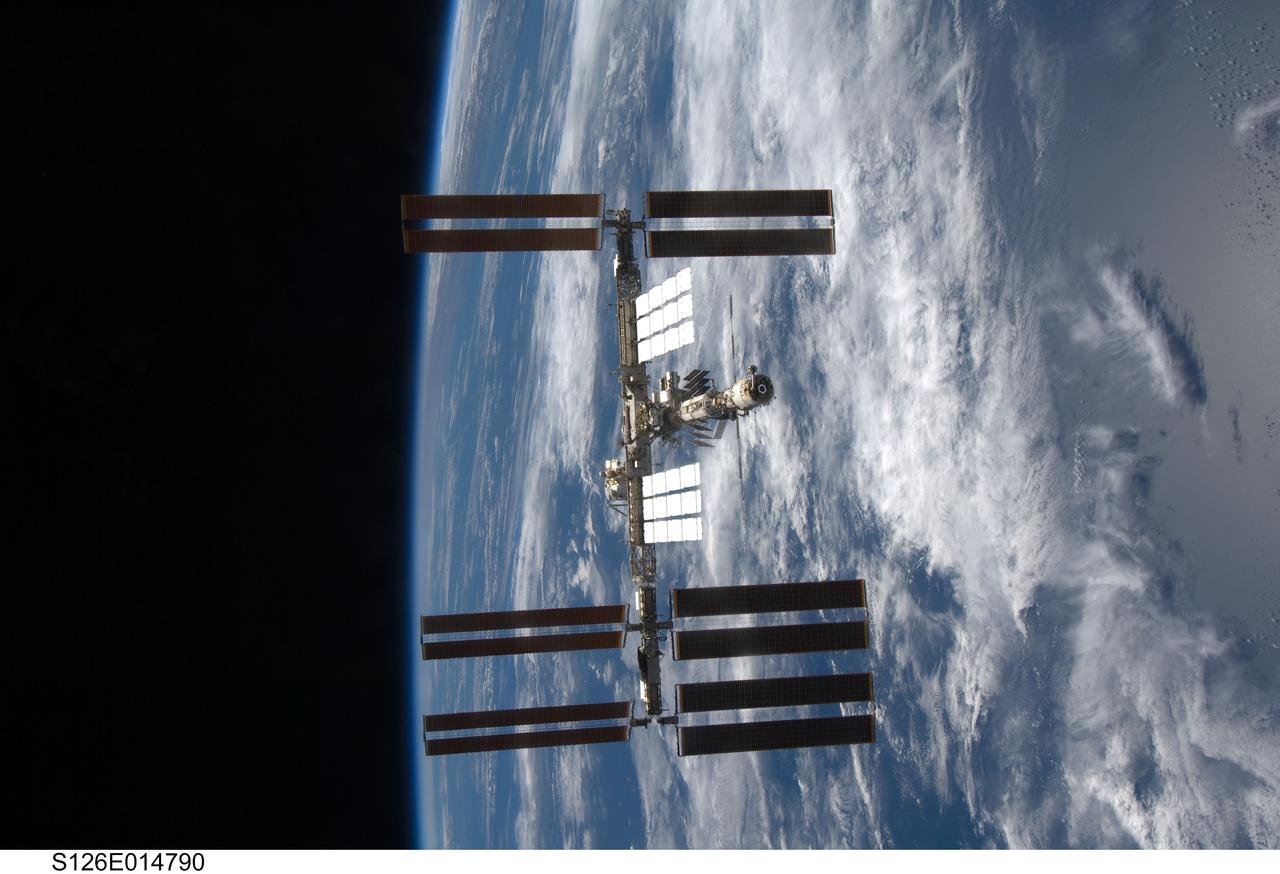

S126-E-014790 (28 Nov. 2008) --- Backdropped by a blue and white Earth and the blackness of space, the International Space Station is seen from Space Shuttle Endeavour as the two spacecraft begin their relative separation. Earlier the STS-126 and Expedition 18 crews concluded 11 days, 16 hours and 46 minutes of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station. Undocking of the two spacecraft occurred at 8:47 a.m. (CST) on Nov. 28, 2008.