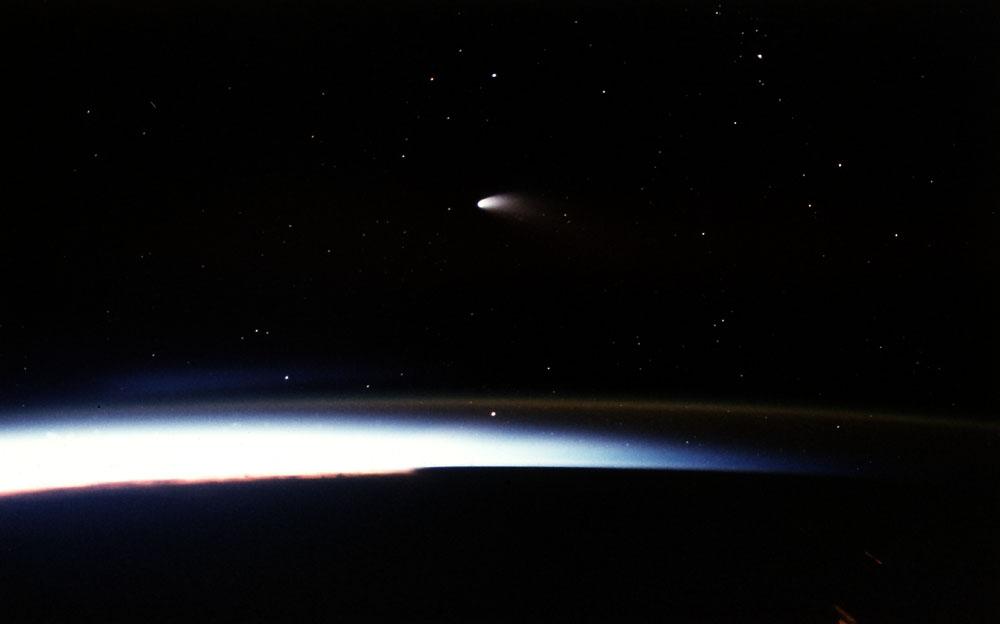

This is a Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MLS-1) onboard STS-83 photo of the most recent comet to date, Hale-Bopp, which passed by Earth during the spring and summer of 1997. In this view, the comet is visible during sunset. The streaks and distorted lights seen in the bottom of the photo are city lights and petroleum fires.

The crew patch for NASA's STS-83 mission depicts the Space Shuttle Columbia launching into space for the first Microgravity Sciences Laboratory 1 (MSL-1) mission. MSL-1 investigated materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology, and combustion science in the microgravity environment of space, experiments that were conducted in the Spacelab Module in the Space Shuttle Columbia's cargo bay. The center circle symbolizes a free liquid under microgravity conditions representing various fluid and materials science experiments. Symbolic of the combustion experiments is the surrounding starburst of a blue flame burning in space. The 3-lobed shape of the outermost starburst ring traces the dot pattern of a transmission Laue photograph typical of biotechnology experiments. The numerical designation for the mission is shown at bottom center. As a forerunner to missions involving International Space Station (ISS), STS-83 represented the hope that scientific results and knowledge gained during the flight will be applied to solving problems on Earth for the benefit and advancement of humankind.
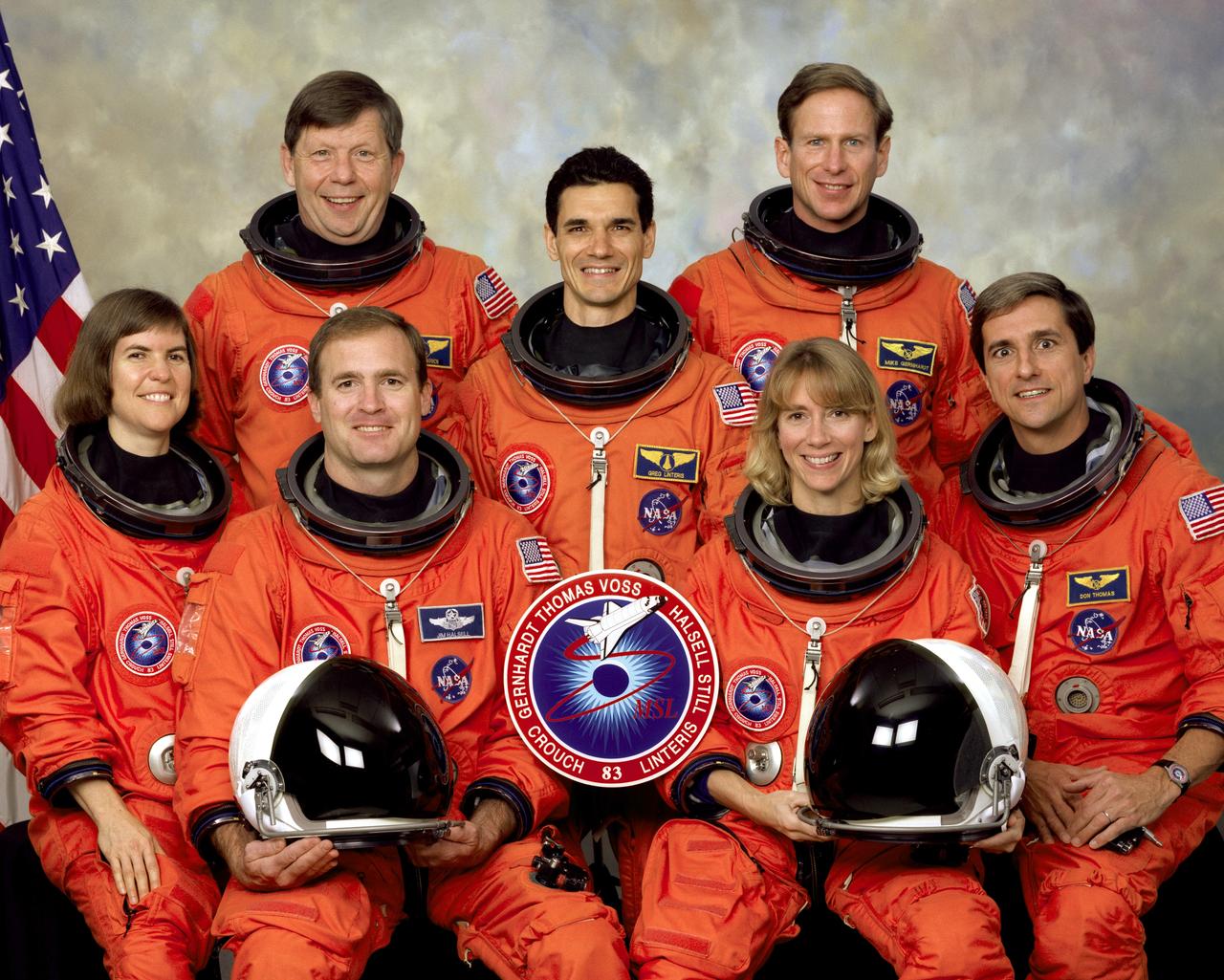

Five NASA astronauts and two scientists comprised the crew for the STS-83 mission in support of the first Microgravity Sciences Laboratory 1 (MSL-1). Pictured on the front row (left to right) are Janice E. Voss, payload commander; James D. Halsell, commander; Susan L. Still, pilot; and Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist. On the back row (left to right) are payload specialists Roger K. Crouch, and Gregory T. Linteris; and Michael L. Gernhardt, mission specialist. Dr. Crouch and Dr. Linteris are experts in several disciplines treated on MSL-1. STS-83 launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on April 4, 1997. The five launched again in July 1997 for the STS-94 mission.

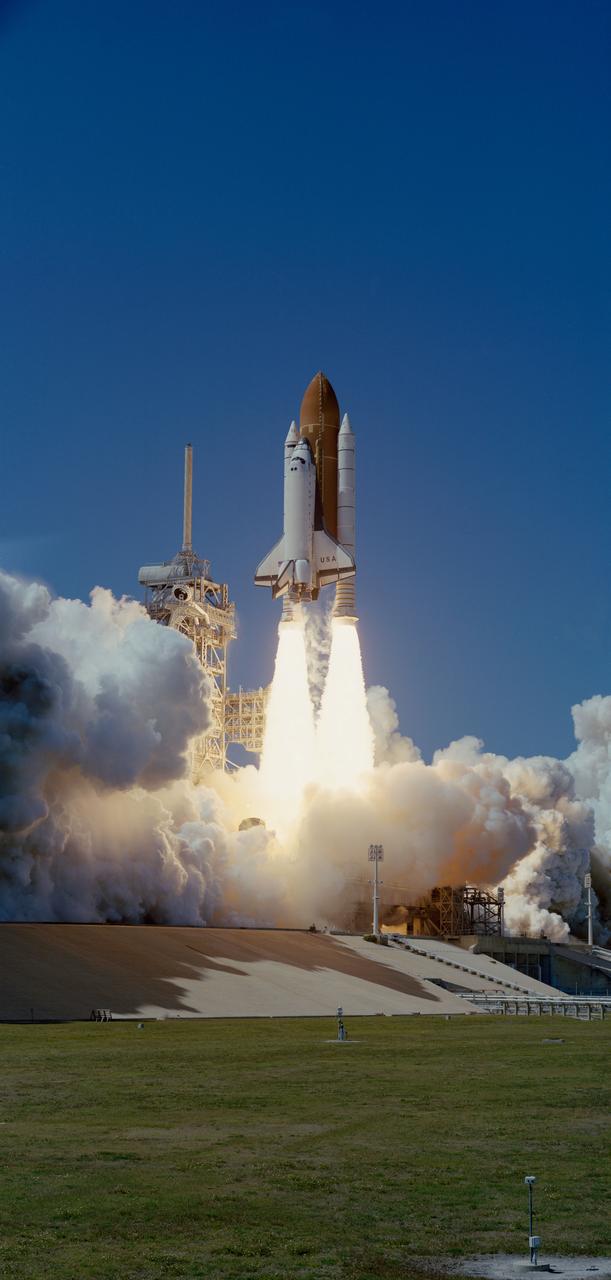
STS083-S-001 008

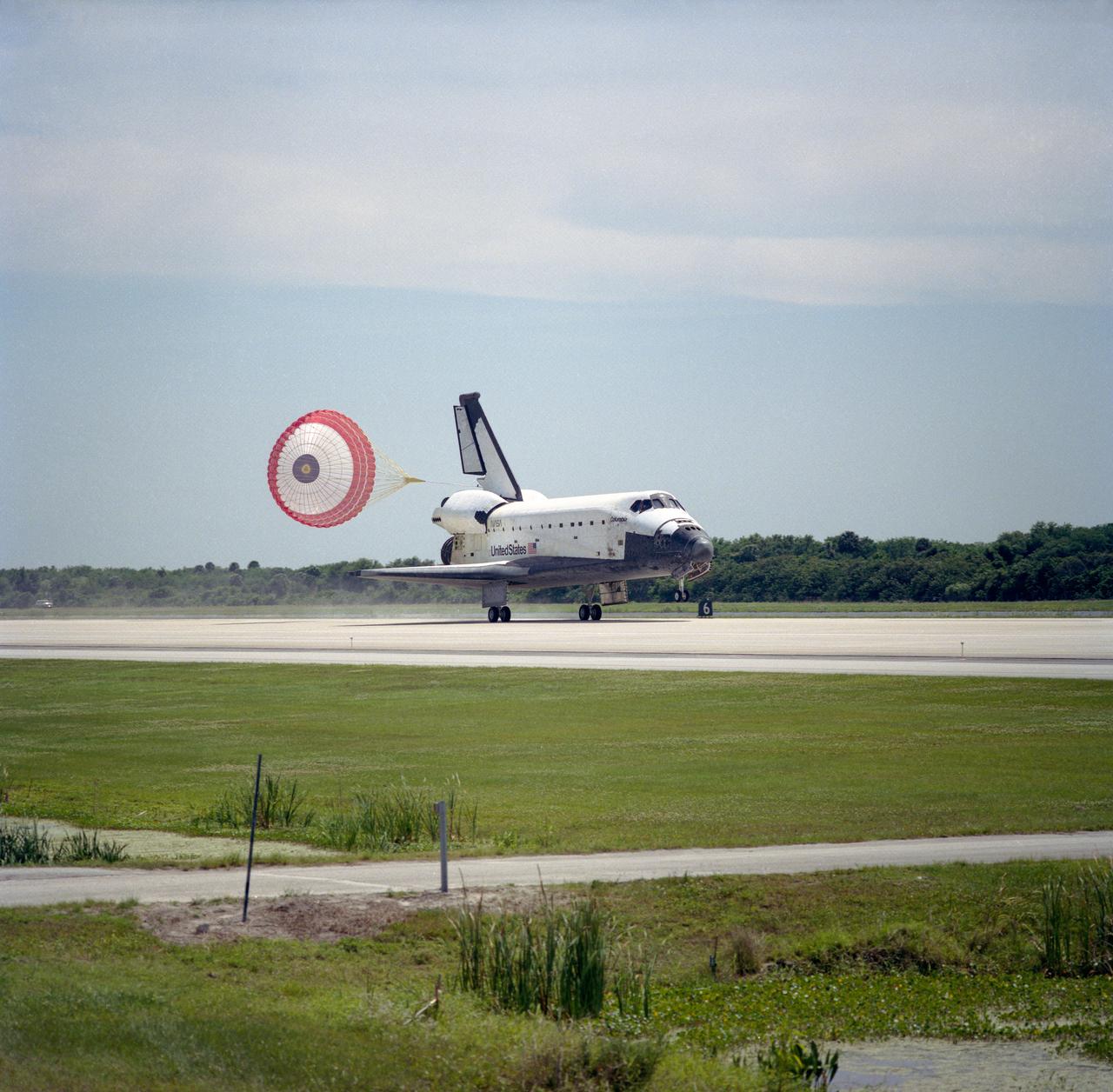
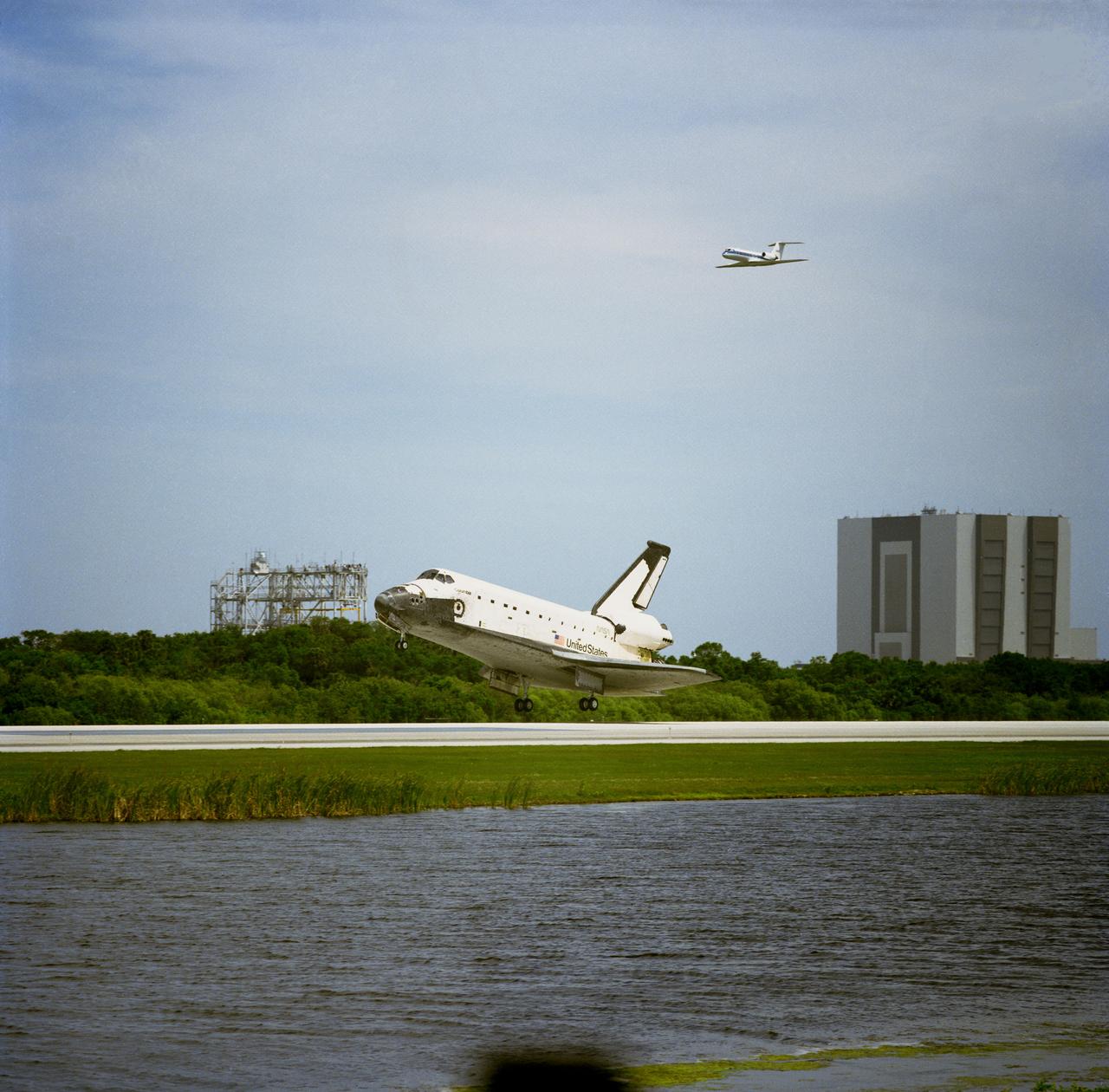
STS083-S-010 (8 April 1997) --- The main landing gear of the Space Shuttle Columbia touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) runway at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), after completing almost four days of a scheduled 16-day mission in Earth-orbit. A problem with one of three fuel cells led to an early landing for the seven-member Microgravity Science Laboratory 1 (MSL-1) crew. Touchdown occurred at 1:33:11 p.m. (EDT), April 8, 1997. Onboard Columbia were James D. Halsell, Jr., Susan L. Still, Janice E. Voss, Donald A. Thomas, Michael L. Gernhardt, Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris.
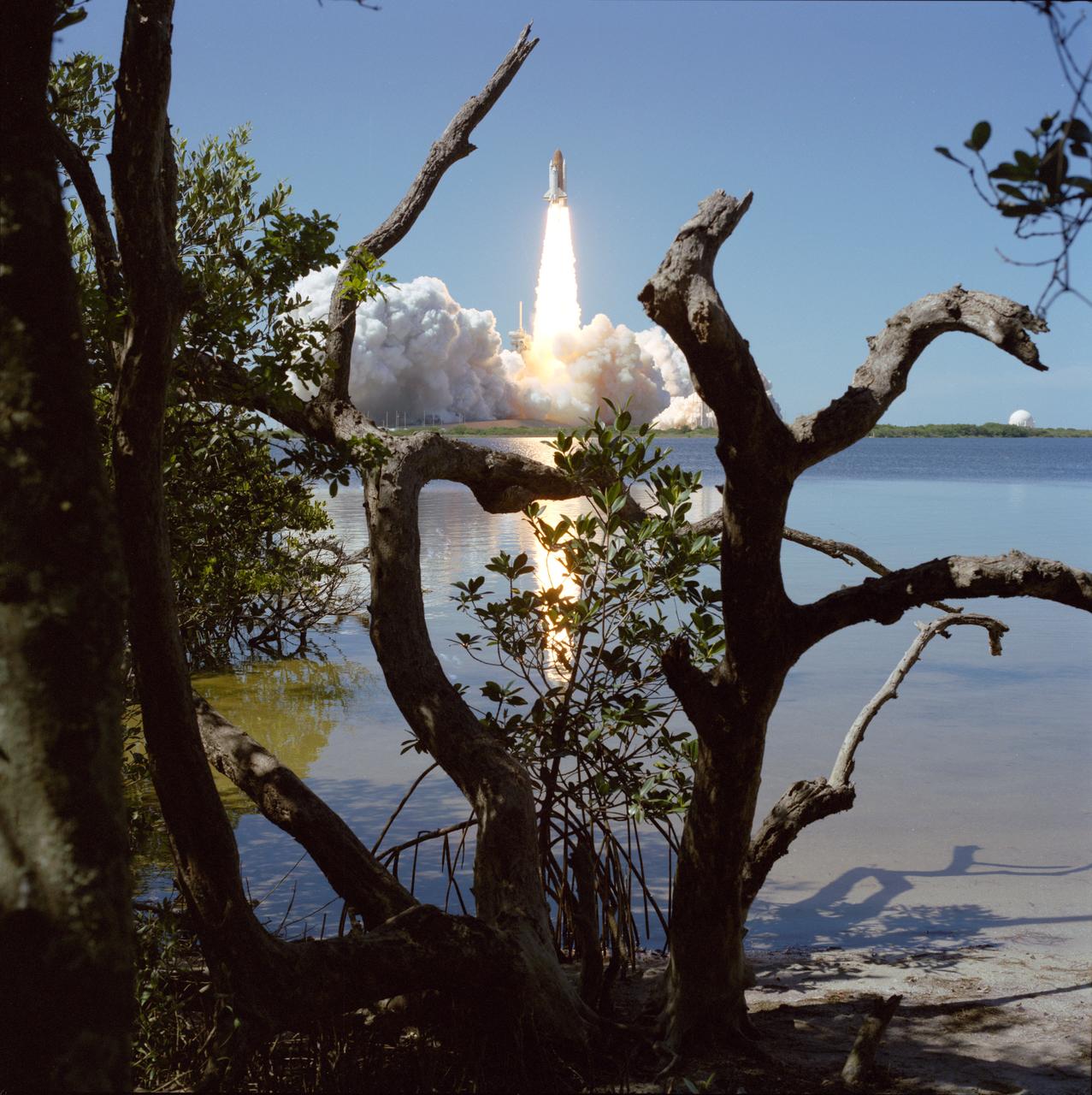

STS083-S-001 005
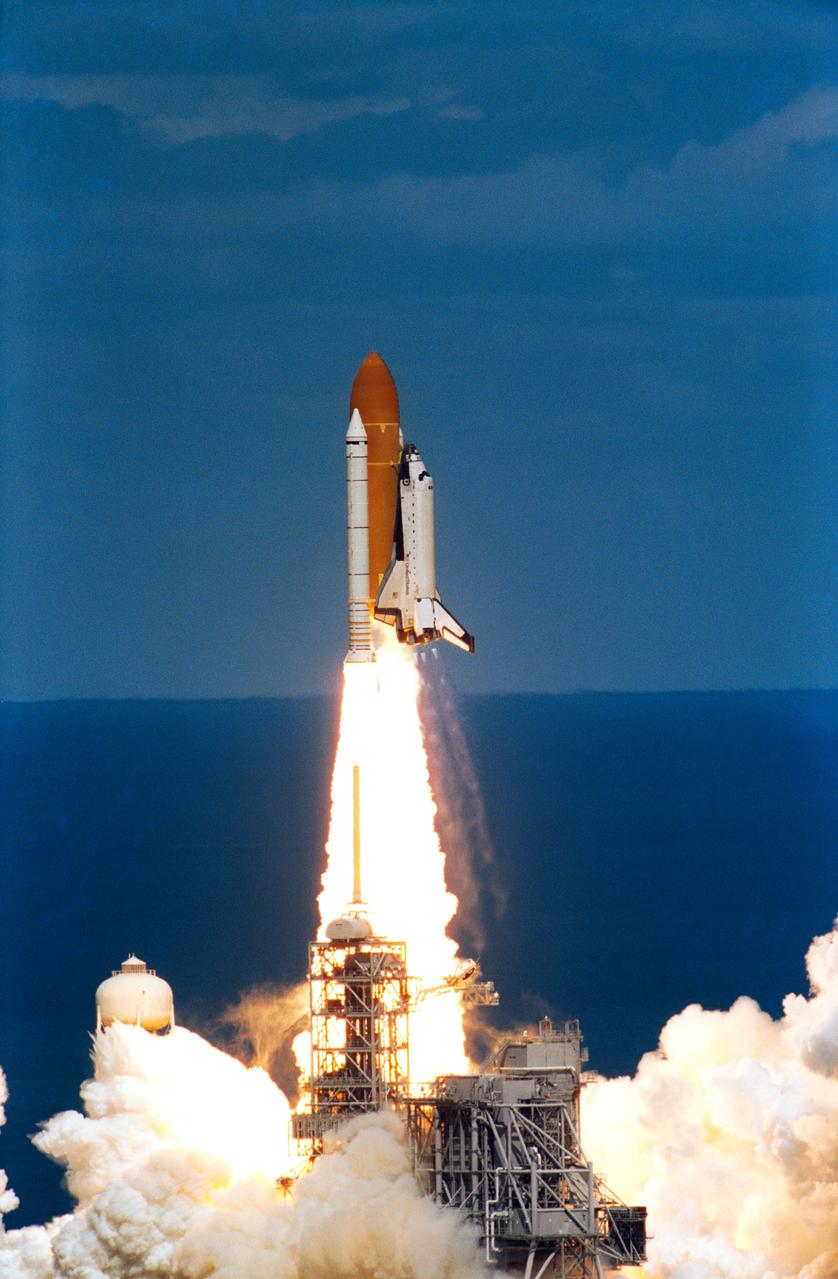
STS083-S-003 (4 April 1997)--- With the Atlantic Ocean in the background, the Space Shuttle Columbia heads toward Earth-orbit from Launch Pad 39A at 2:20:32 p.m. (EST), April 4, 1997, from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Onboard the spacecraft to support the Microgravity Science Laboratory 1 (MSL-1) mission were astronauts James D. Halsell, commander; Susan L. Still, pilot; Janice E. Voss, payload commander; Michael L. Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas, both mission specialists; along with payload specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. A problem with a fuel cell caused the crew to cut the mission short and return to Earth on April 8, 1997.

STS083-S-001 006

STS083-S-007 (4 April 1997)--- The Space Shuttle Columbia heads toward Earth-orbit from Launch Pad 39A at 2:20:32 p.m. (EST), April 4, 1997, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Onboard the spacecraft to support the Microgravity Science Laboratory 1 (MSL-1) mission were astronauts James D. Halsell, commander; Susan L. Still, pilot; Janice E. Voss, payload commander; Michael L. Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas, both mission specialists; along with payload specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. A problem with a fuel cell caused the crew to cut the mission short and return to Earth on April 8, 1997.
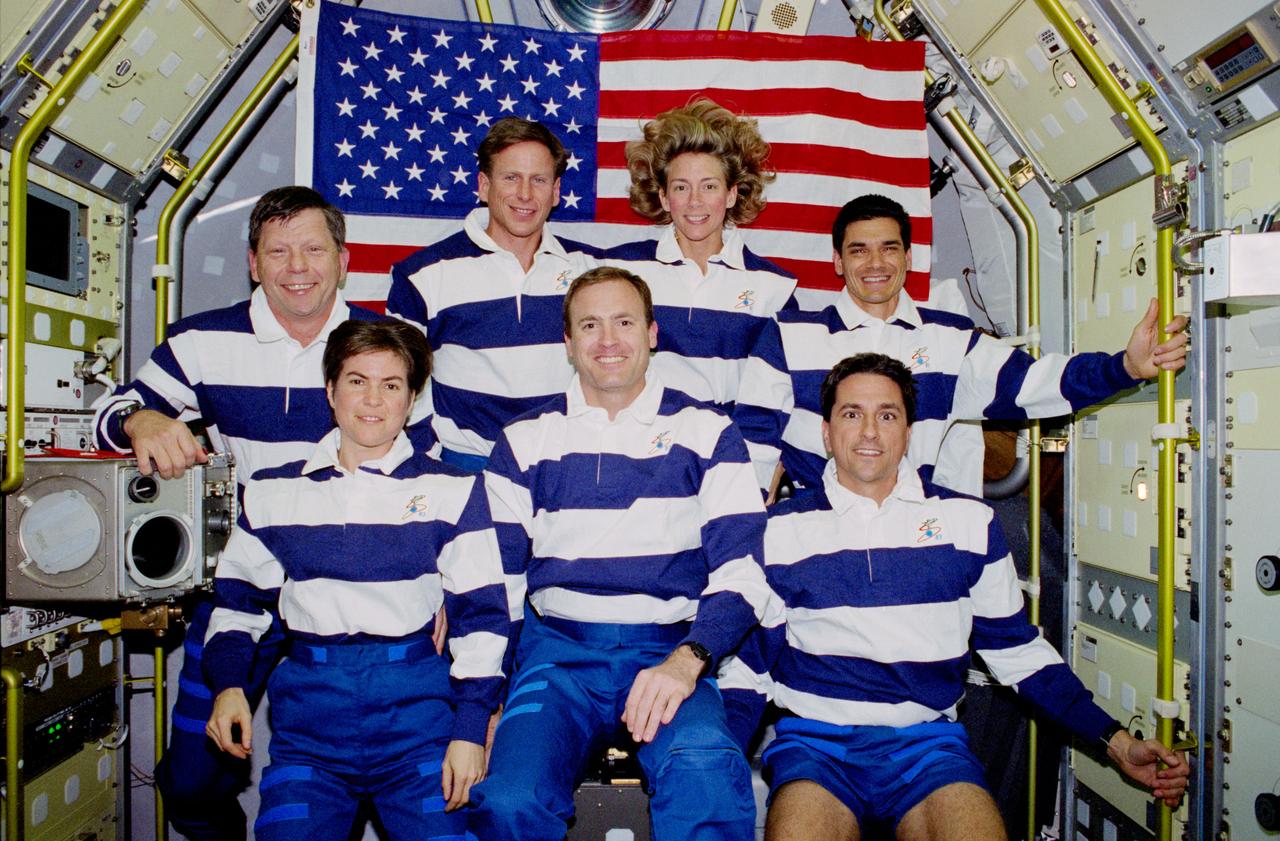

STS083-325-004 (4-8 April 1997) --- Five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists pose for the traditional inflight crew portrait during a Microgravity Science Laboratory 1 (MSL-1) shift changeover in the Spacelab Module aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. In front (from the left) are astronauts Janice E. Voss, James D. Halsell, Jr. and Donald A. Thomas. From left to right in the rear are Roger K. Crouch, along with astronauts Michael L. Gernhardt and Susan L. Still, and Gregory T. Linteris. Crouch and Linteris are payload specialists.
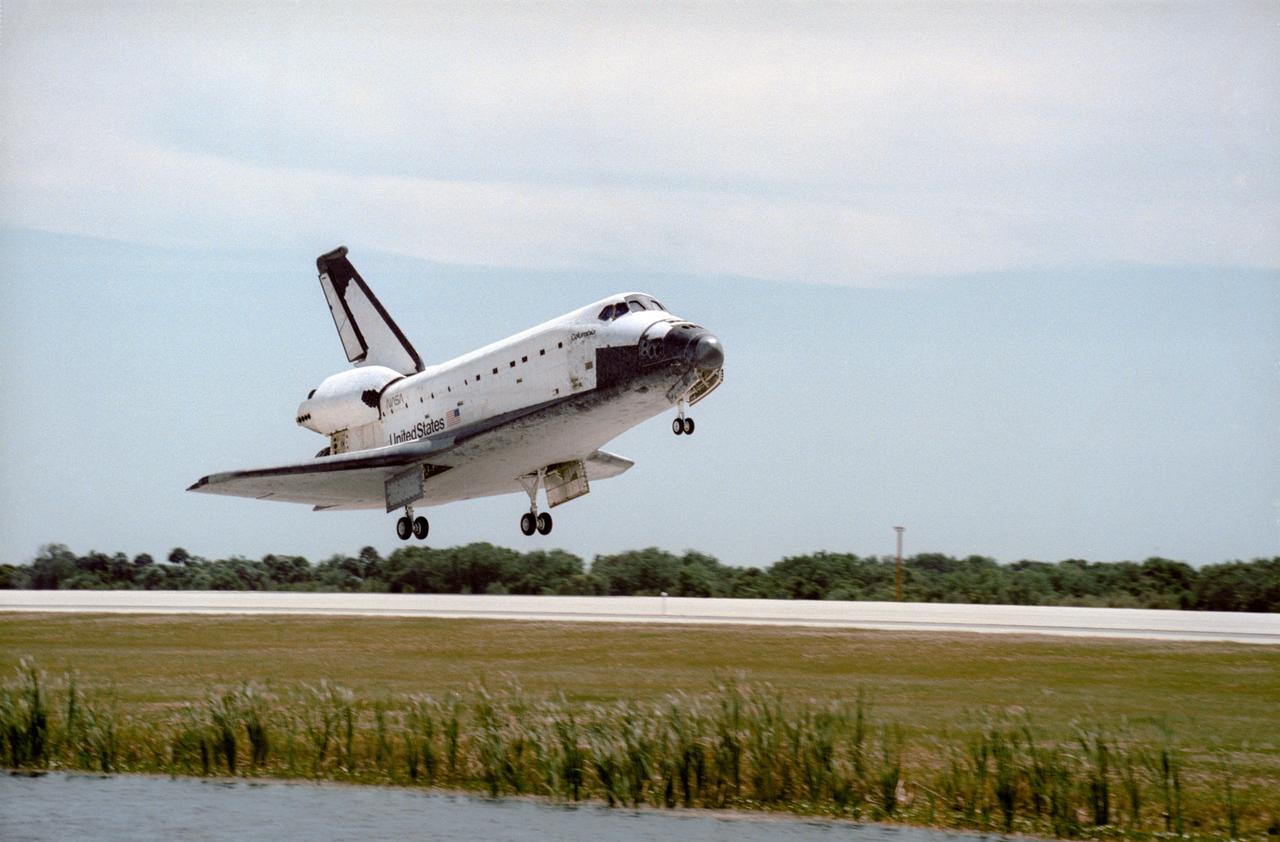

STS083-S-009 (8 April 1997) --- The Space Shuttle Columbia nears touchdown on the Shuttle Landing Facility (SLF) runway at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), after completing almost four days of a scheduled 16-day mission in Earth-orbit. A problem with one of three fuel cells led to an early landing for the seven-member Microgravity Science Laboratory 1 (MSL-1) crew. Touchdown occurred at 1:33:11 p.m. (EDT), April 8, 1997. Onboard Columbia were James D. Halsell, Jr., Susan L. Still, Janice E. Voss, Donald A. Thomas, Michael L. Gernhardt, Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-83 Payload Commander Janice E. Voss prepares to enter the Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Pad 39A after getting assistance from the White Room closeout crew that included Bob Saulnier (right).
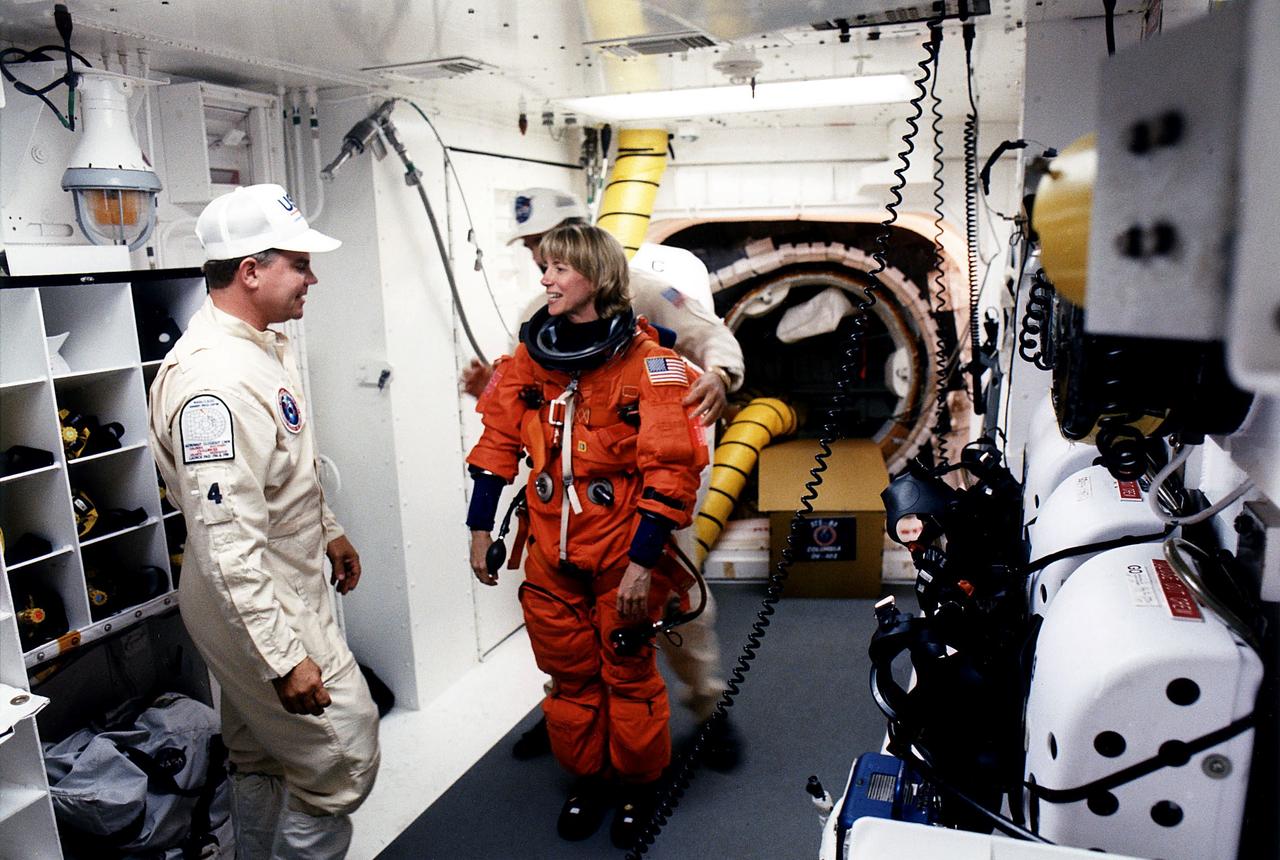

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-83 Pilot Susan L. Still chats with White Room closeout crew member Rene Arriens as she prepares to enter the Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Pad 39A with assistance from closeout crew worker Bob Saulnier (behind Still).
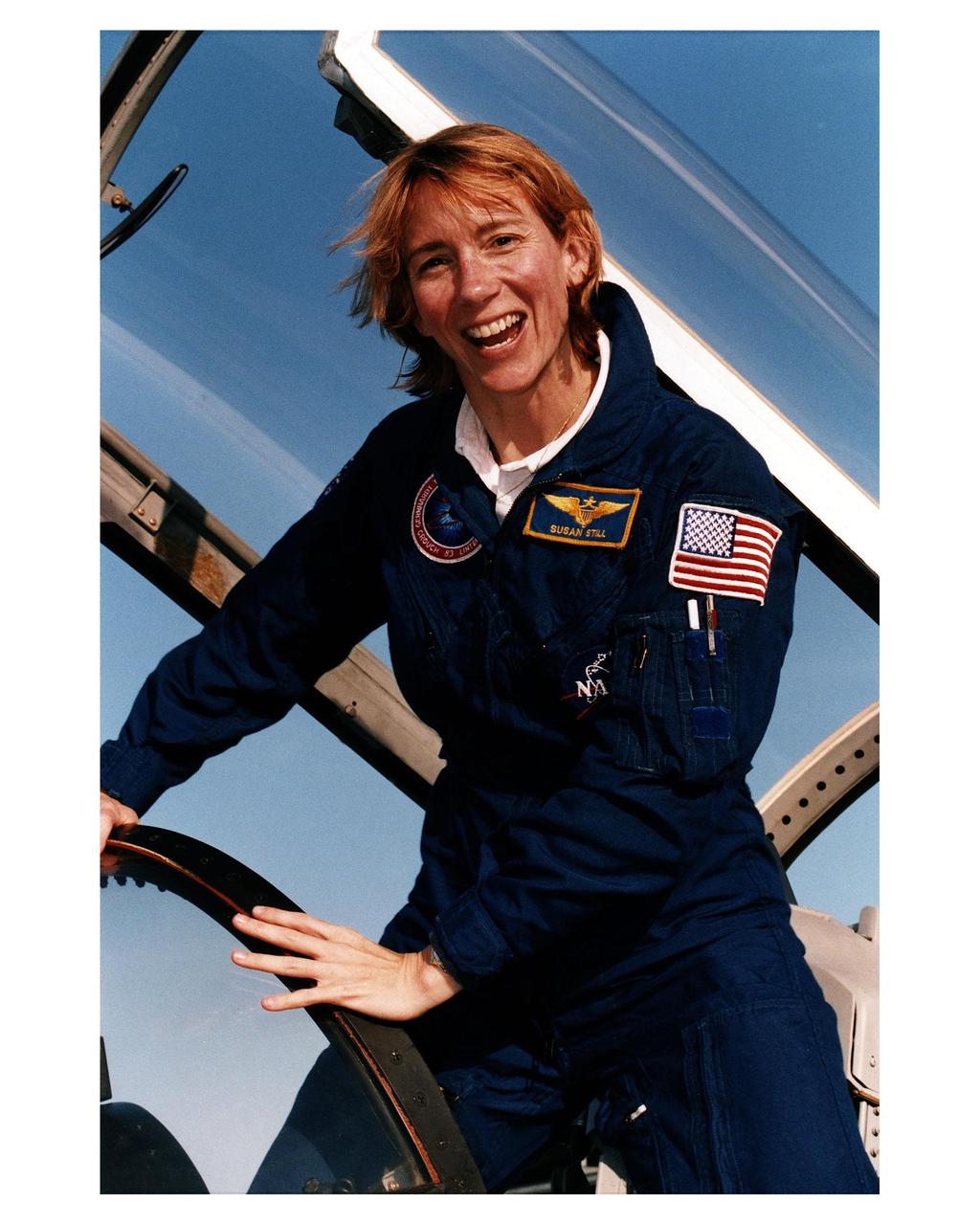

STS-83 Pilot Susan Still (emerging from T-38 cockpit) and other members of the STS-83 crew arrive at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility in preparation for their <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test.</a

STS-83 Crew Commander James Halsell (in T-38 cockpit) and other members of the STS-83 crew arrive at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility in preparation for their <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test.</a
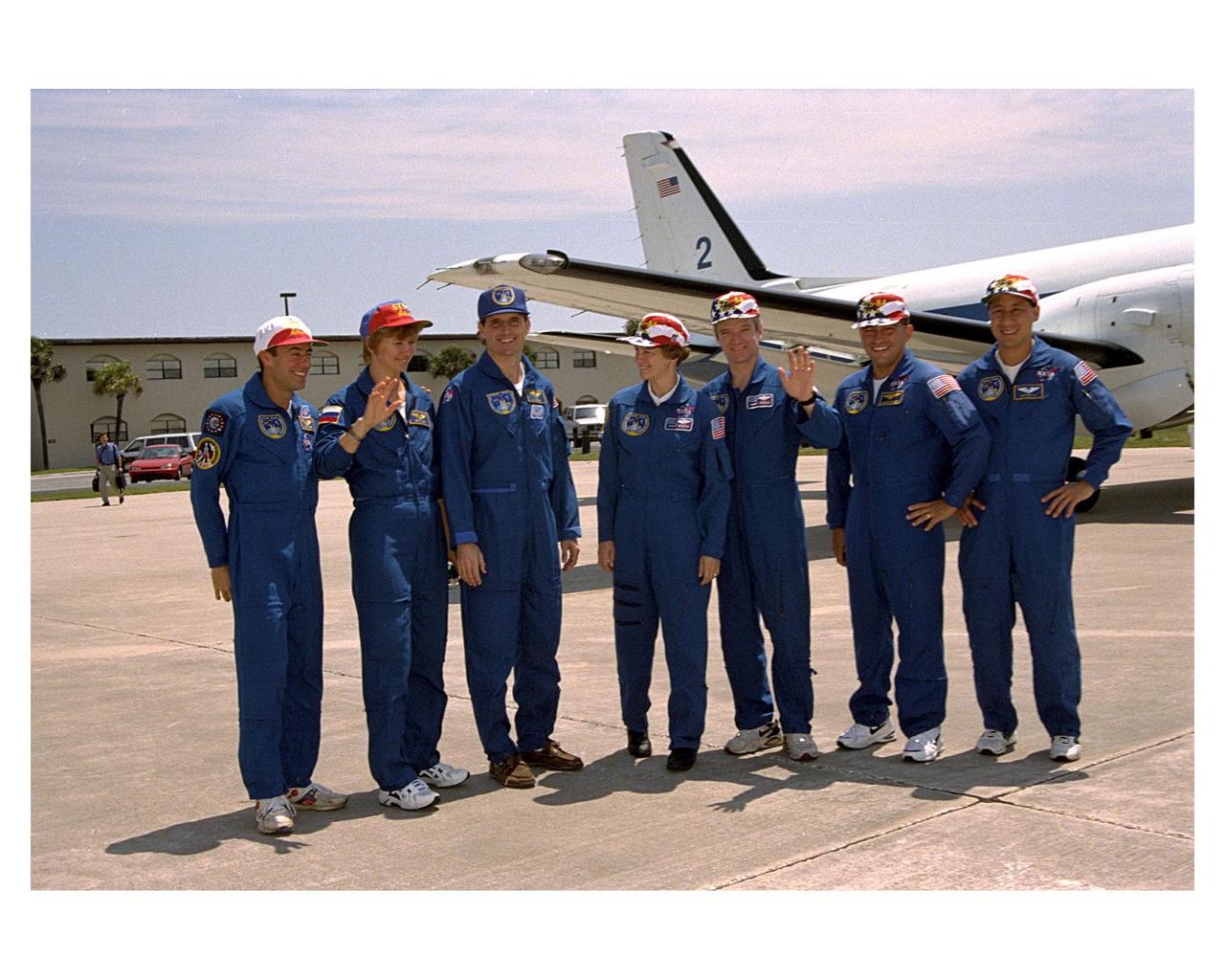

STS-83 crew departure from Patrick Air Force Base

STS-83 crew departure from Patrick Air Force Base

CAPILLARY DRIVEN HEAT TRANSFER EXPERIMENT MSL-1 MICROGRAVITY SCIENCE LABORATORY SHUTTLE FLIGHT STS-83 CREW TRAINING

CAPILLARY DRIVEN HEAT TRANSFER EXPERIMENT MSL-1 MICROGRAVITY SCIENCE LABORATORY SHUTTLE FLIGHT STS-83 CREW TRAINING
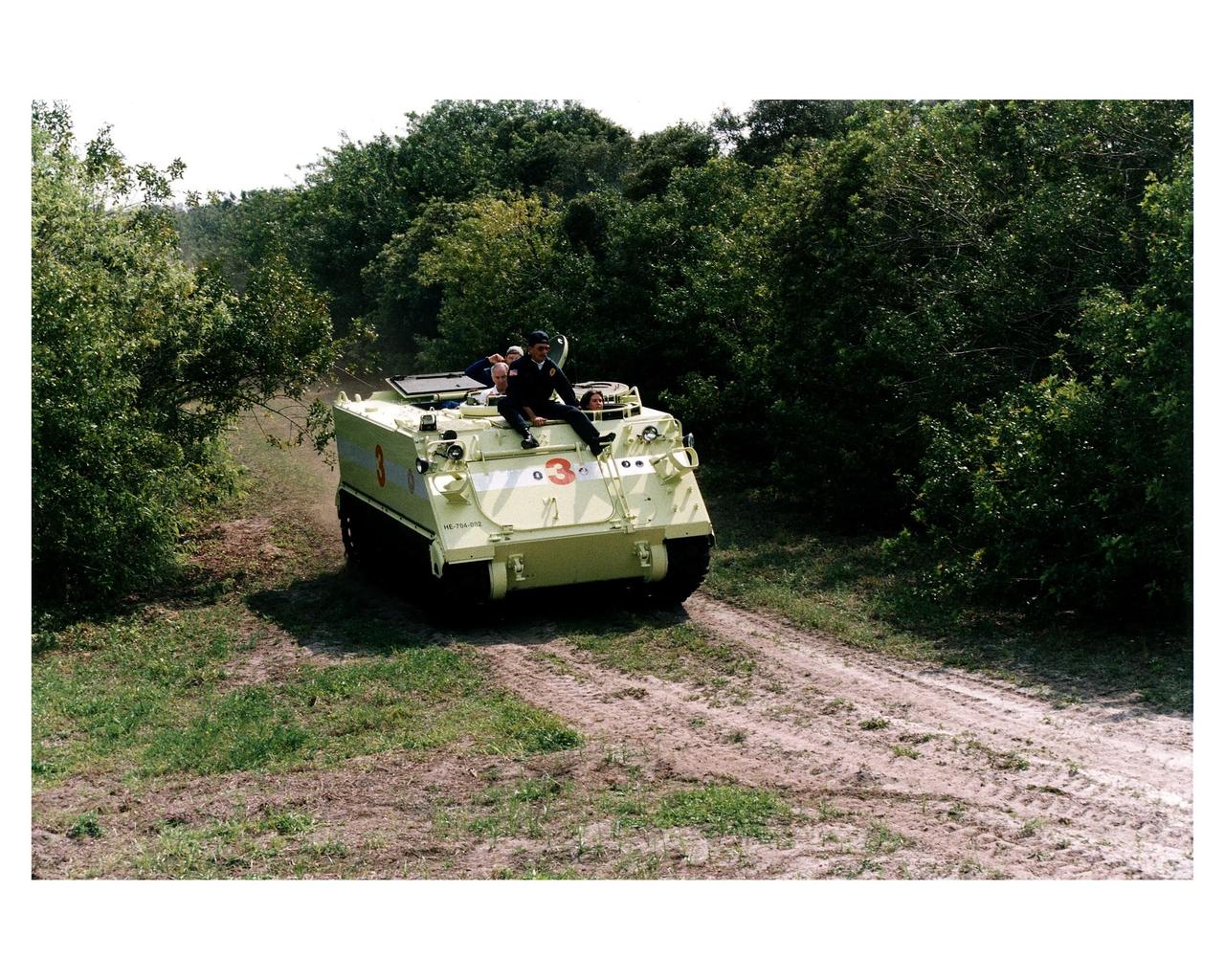

STS-83 crew M113 driver training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT
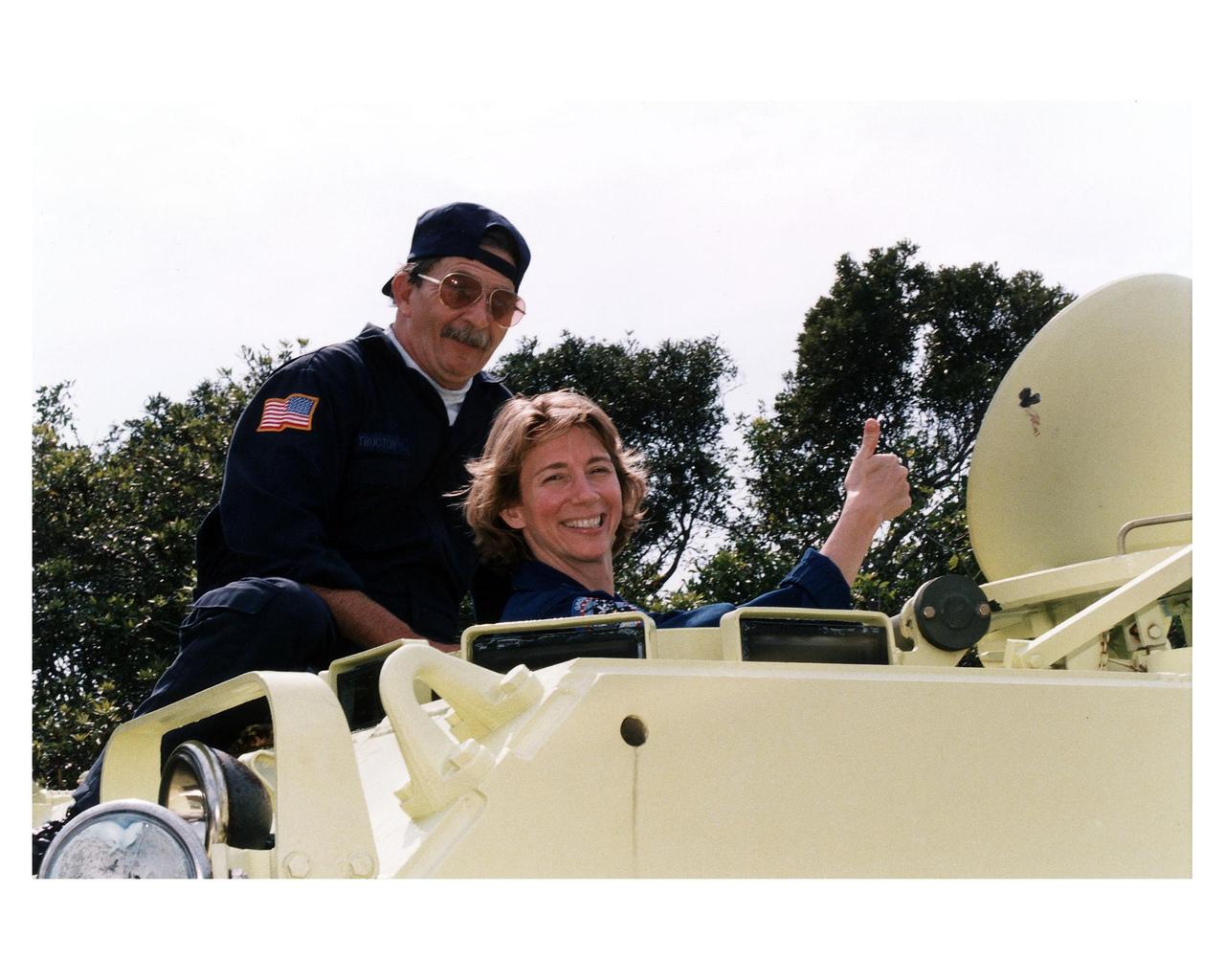

STS-83 crew M113 driver training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT

STS-83 SOFBALL AND LSP STRUCTURES OF FLAMEBALLS AT LOW LEWIS NUMBER AND LAMINATOR SOOT PROCESSING

STS-83 crew member in the white room at Launch Pad 39A prior to entering the crew compartment of Columbia for launc

CAPILLARY DRIVEN HEAT TRANSFER EXPERIMENT MSL-1 MICROGRAVITY SCIENCE LABORATORY SHUTTLE FLIGHT STS-83 CREW TRAINING

STS-83 SOFBALL AND LSP STRUCTURES OF FLAMEBALLS AT LOW LEWIS NUMBER AND LAMINATOR SOOT PROCESSING

STS-83 crew M113 driver training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT

STS-83 crew member in the white room at Launch Pad 39A prior to entering the crew compartment of Columbia for launc

STS-83 crew M113 driver training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT

STS-83 SOFBALL AND LSP STRUCTURES OF FLAMEBALLS AT LOW LEWIS NUMBER AND LAMINATOR SOOT PROCESSING

CAPILLARY DRIVEN HEAT TRANSFER EXPERIMENT MSL-1 MICROGRAVITY SCIENCE LABORATORY SHUTTLE FLIGHT STS-83 CREW TRAINING

CAPILLARY DRIVEN HEAT TRANSFER EXPERIMENT MSL-1 MICROGRAVITY SCIENCE LABORATORY SHUTTLE FLIGHT STS-83 CREW TRAINING

STS-83 crew M113 driver training during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT

CAPILLARY DRIVEN HEAT TRANSFER EXPERIMENT MSL-1 MICROGRAVITY SCIENCE LABORATORY SHUTTLE FLIGHT STS-83 CREW TRAINING
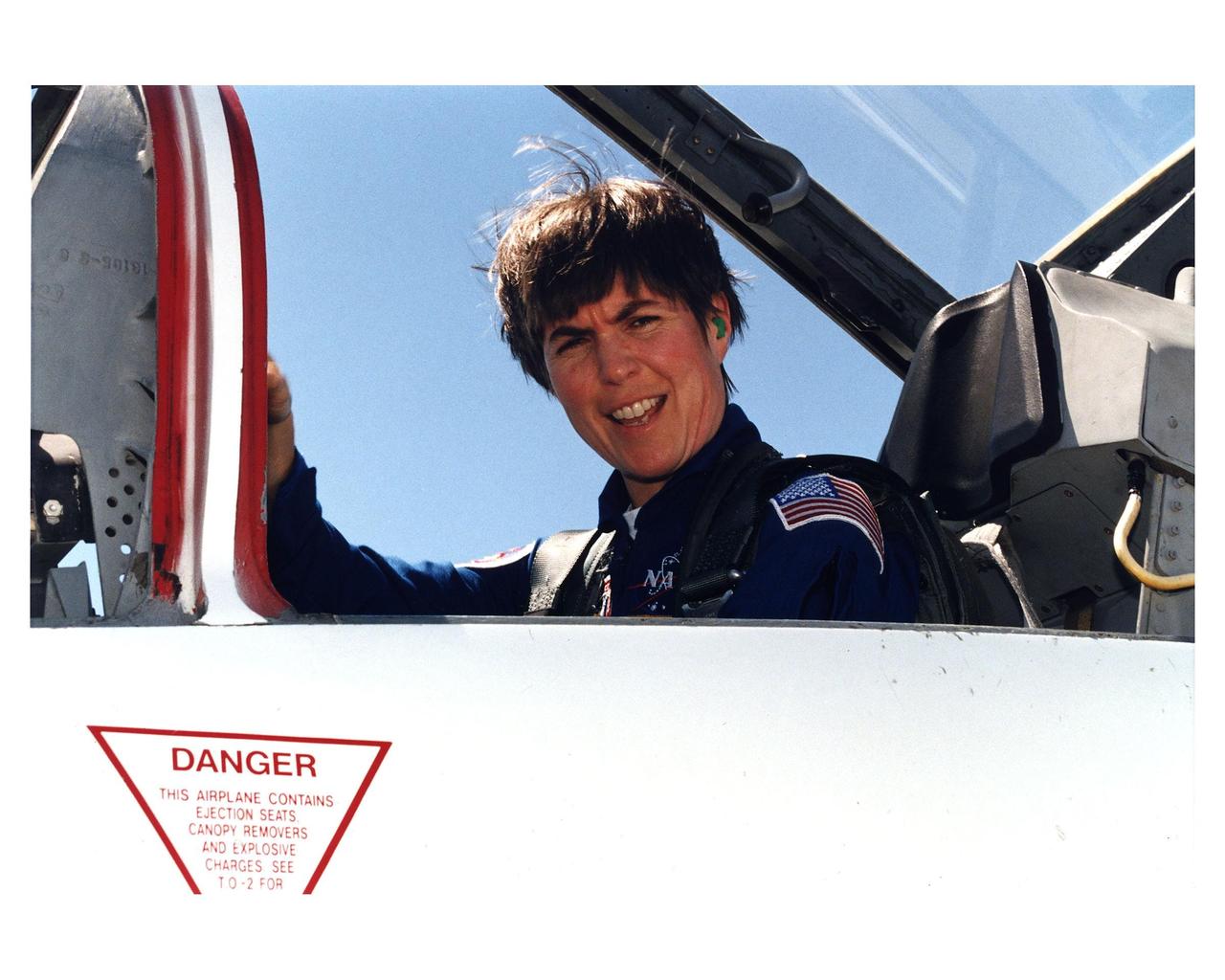

STS-83 Payload Commander Janice E. Voss arrives at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 prior to Columbia's launch

The STS-83 crew departs the Operations and Checkout Building on their way to Launch Complex 39A during the crew's <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT).</a
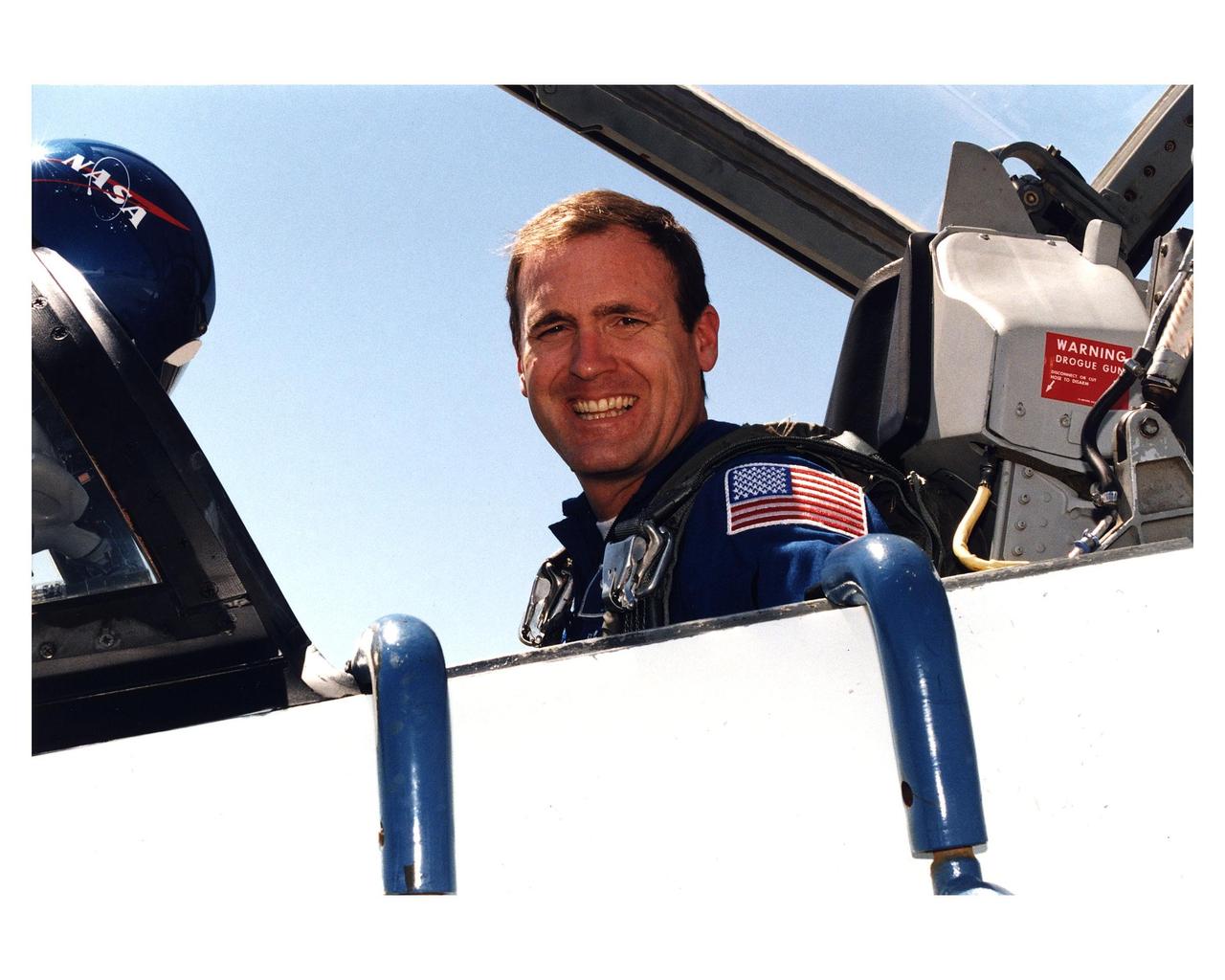

STS-83 Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr. arrives at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 prior to Columbia's launch
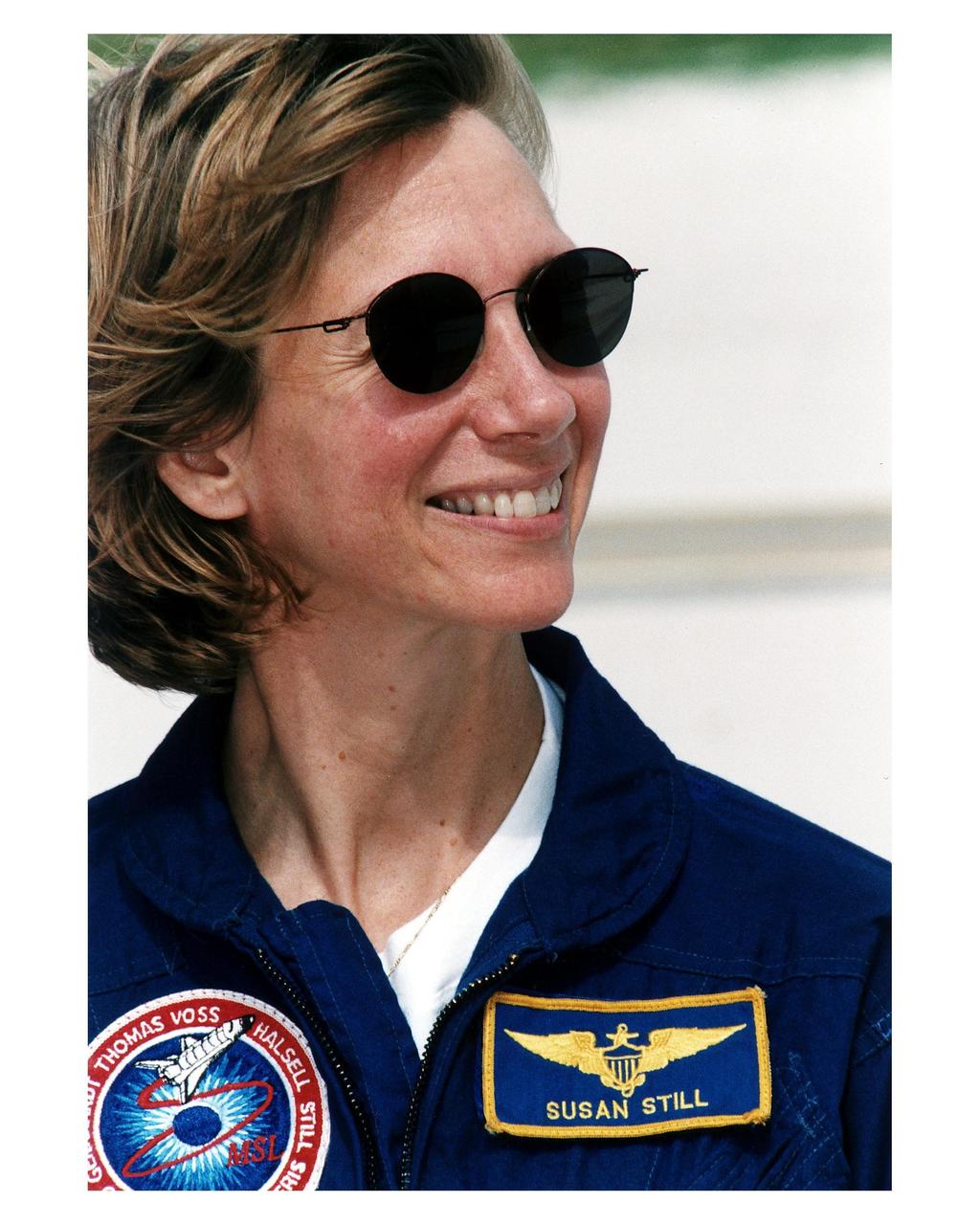

STS-83 Pilot Susan L. Still talks to the media at Launch Complex 39A during the crew's <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT).</a
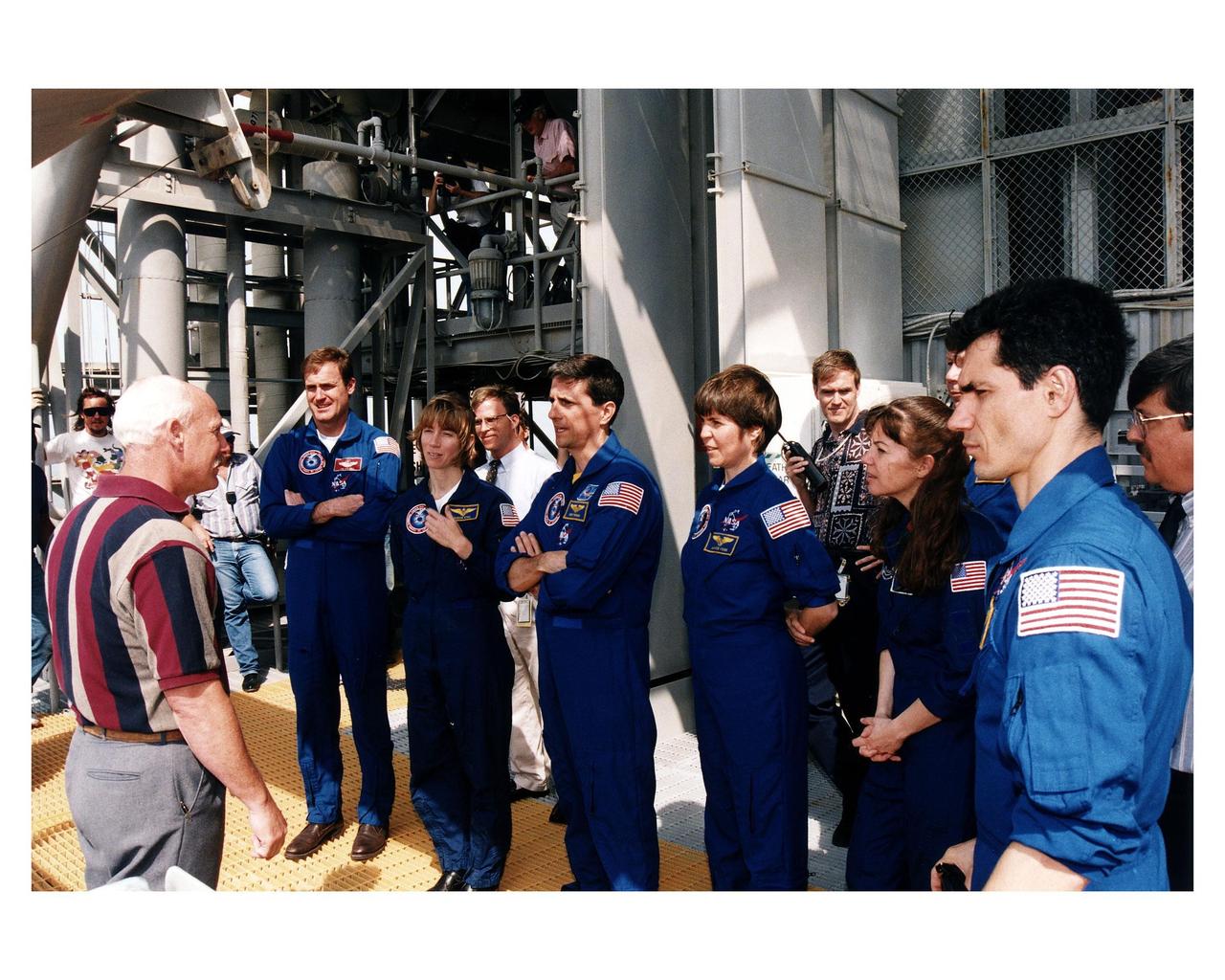

Members of the STS-83 crew receive instruction at Launch Complex 39A during the crew's <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT).</a

STS-83 Payload Specialist Roger K. Crouch and Pilot Susan Leigh Still arrive at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility prior to Columbia's launch

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-83 crew member in the white room at Launch Pad 39A prior to entering the crew compartment of Space Shuttle Columbia for launch.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-83 crew member in the white room at Launch Pad 39A prior to entering the crew compartment of Space Shuttle Columbia for launch.
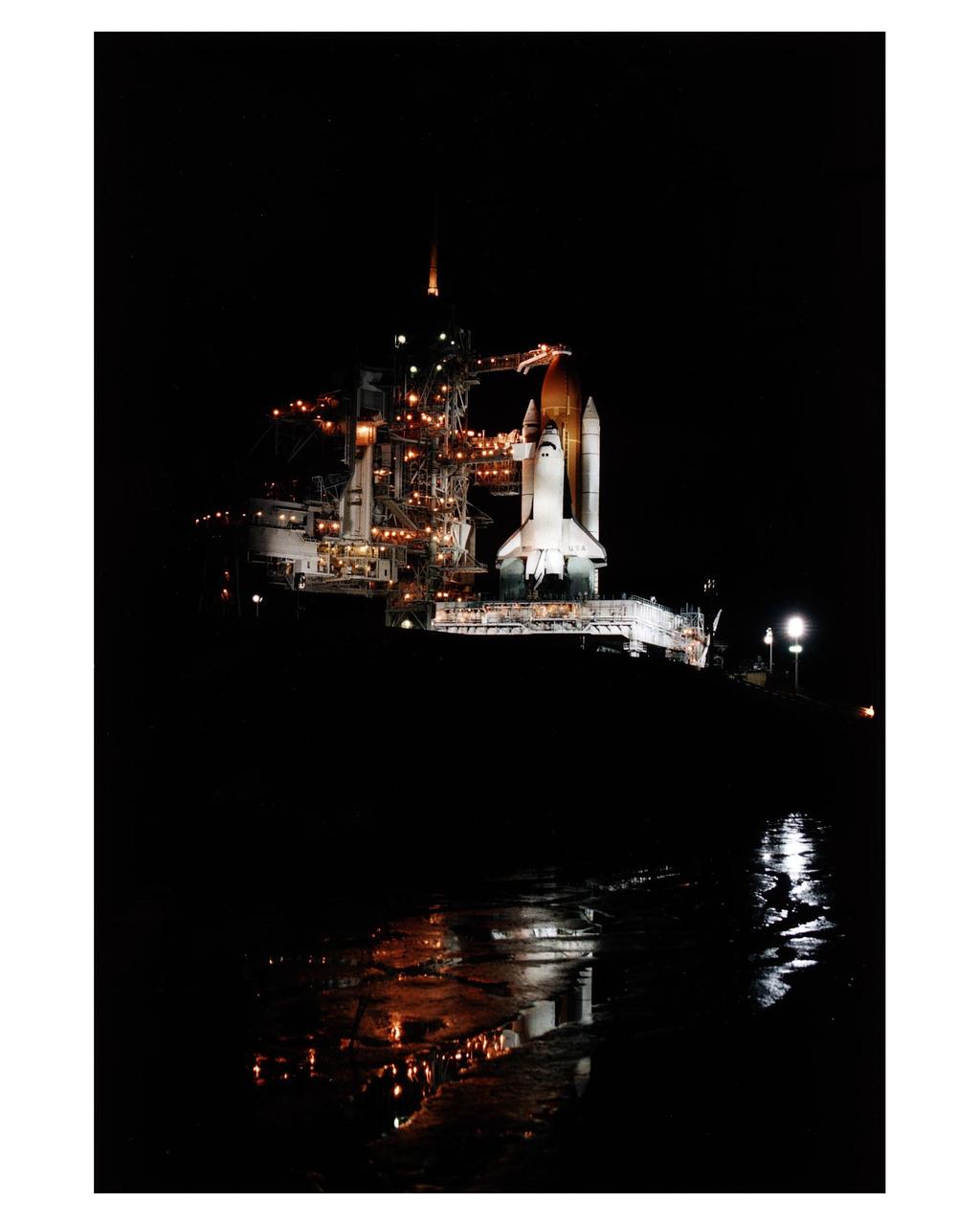

The Space Shuttle Columbia stands poised in the night for the STS-83 Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission after the Rotating Service Structure of Launch Pad 39A has been moved back prior to the start of fueling operations that take place about 12 hours before liftoff. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station as well as research in combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
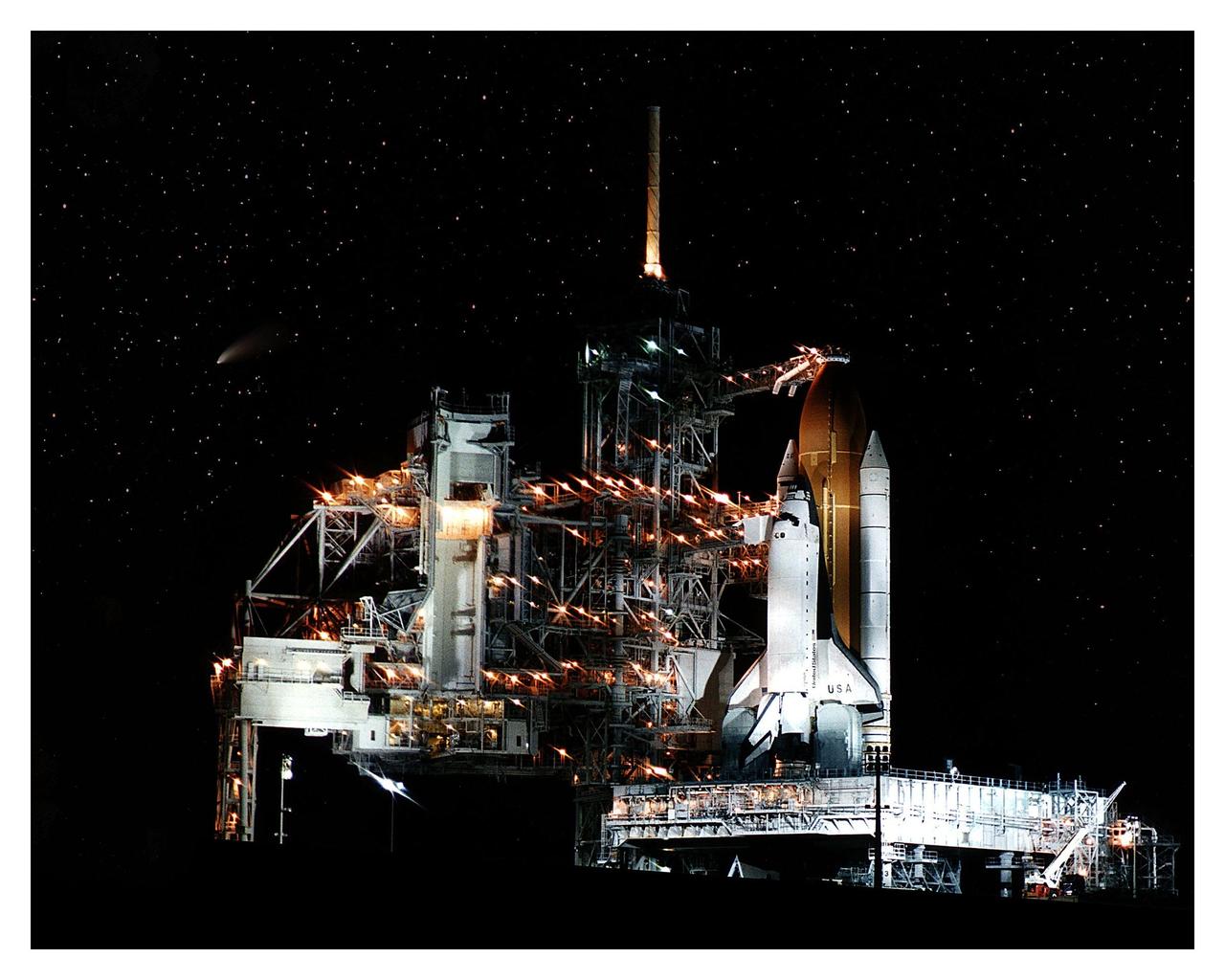

The soon-to-be-spaceborne Space Shuttle Columbia gets a flyby visit from the Comet Hale-Bopp (shown as the streak at left center) while awaiting launch on the STS-83 mission. This photo was taken the night before the planned liftoff on April 4, 1997. The Rotating Service Structure at Launch Pad 39A has been moved back prior to the start of operations to fuel the external tank. The primary objective of the STS-83 flight is to operate the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1), which will test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that will be used on the International Space Station. Columbia will have a crew of seven
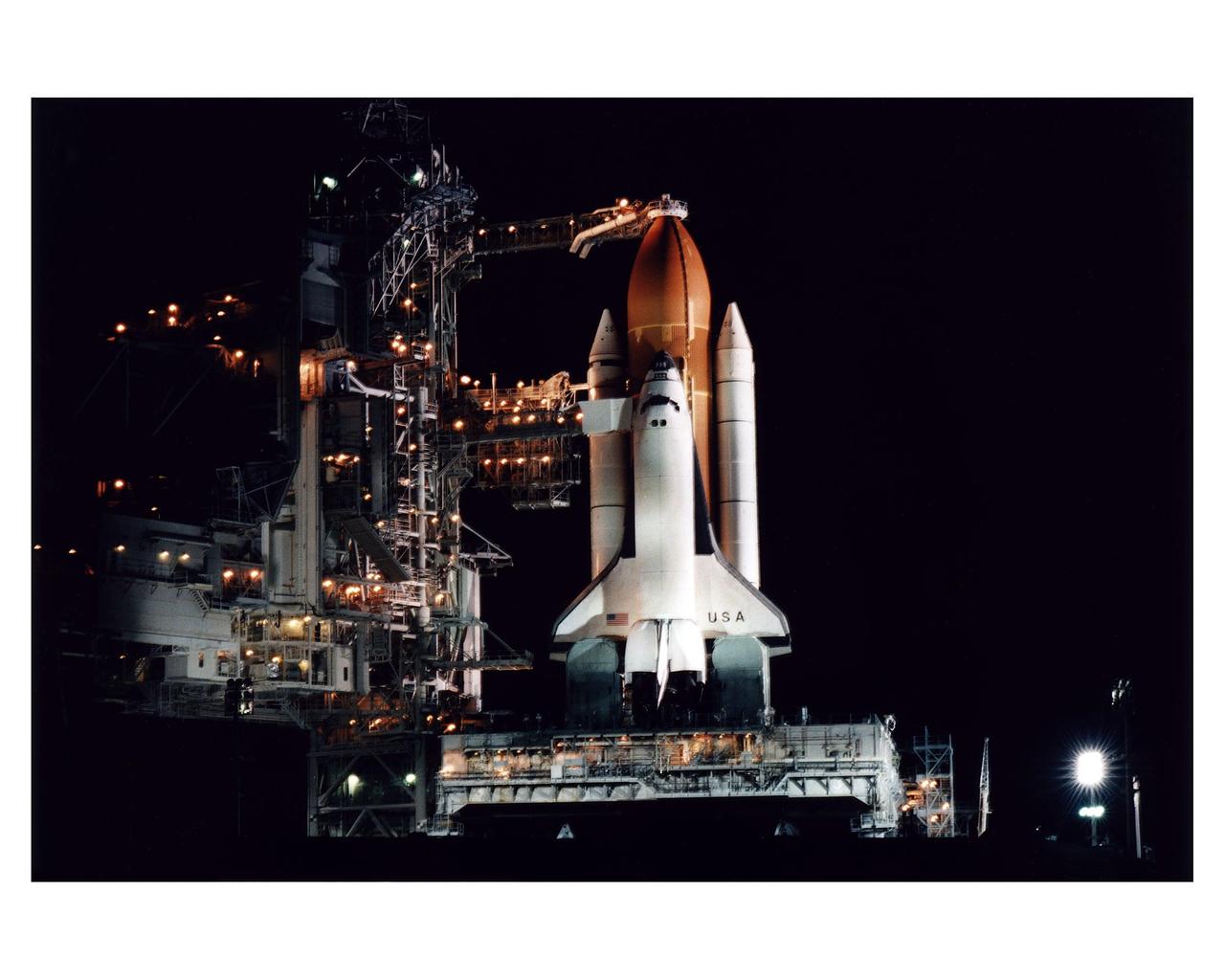

The Space Shuttle Columbia stands poised in the night for the STS-83 Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission after the Rotating Service Structure of Launch Pad 39A has been moved back prior to the start of fueling operations that take place about 12 hours before liftoff. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station as well as research in combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments

The Space Shuttle Columbia stands poised in the night for the STS-83 Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission after the Rotating Service Structure of Launch Pad 39A has been moved back prior to the start of fueling operations that take place about 12 hours before liftoff. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station as well as research in combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
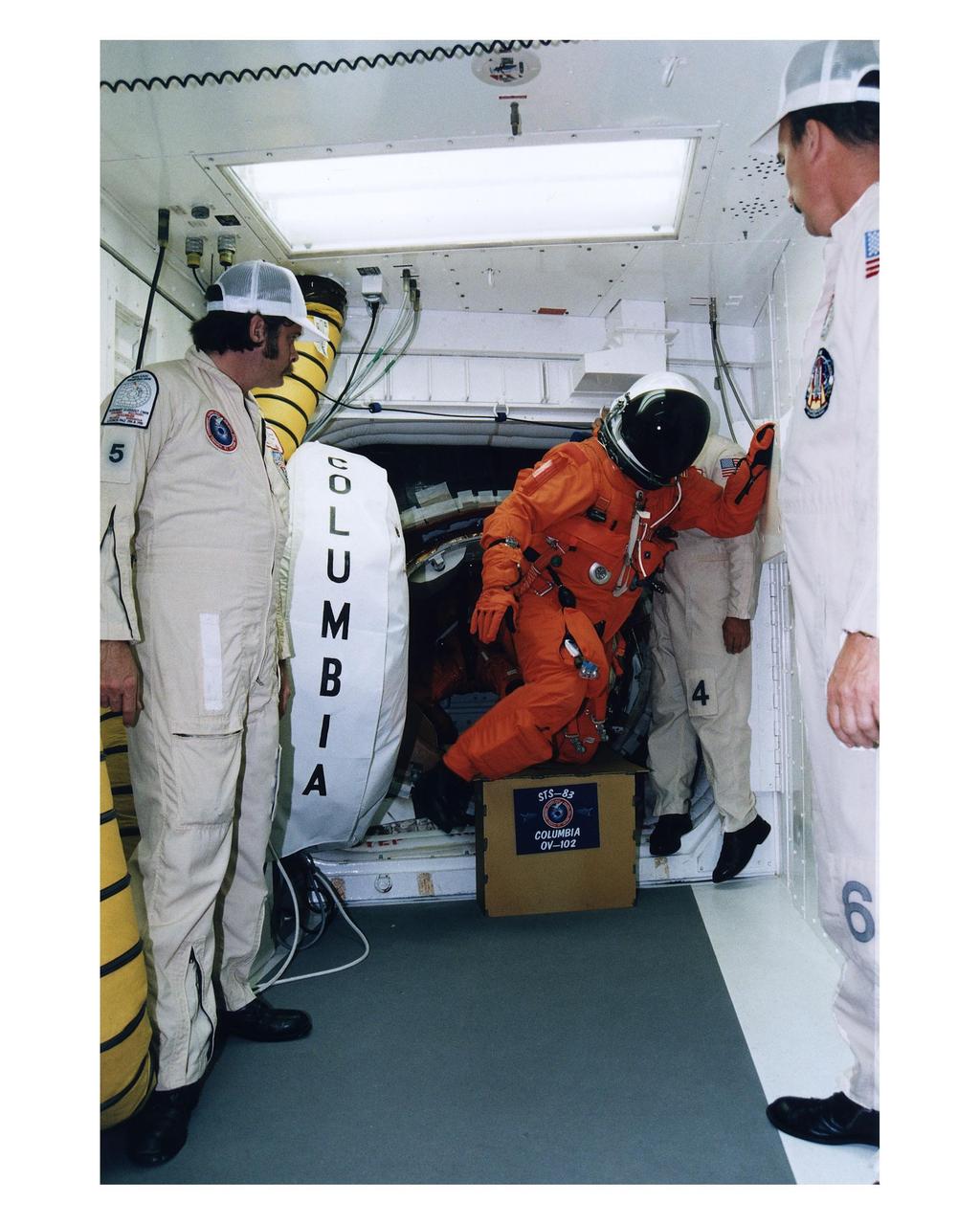

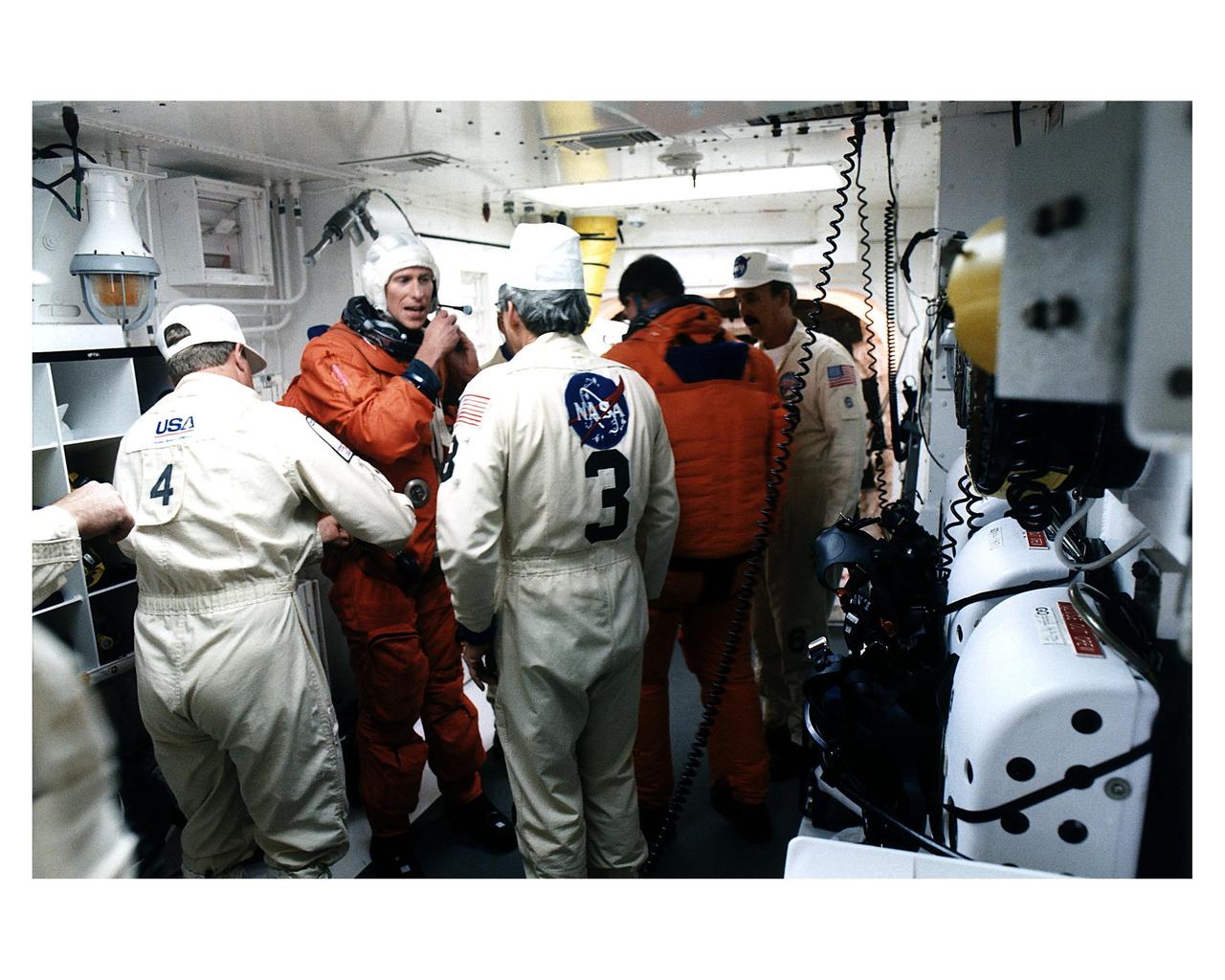
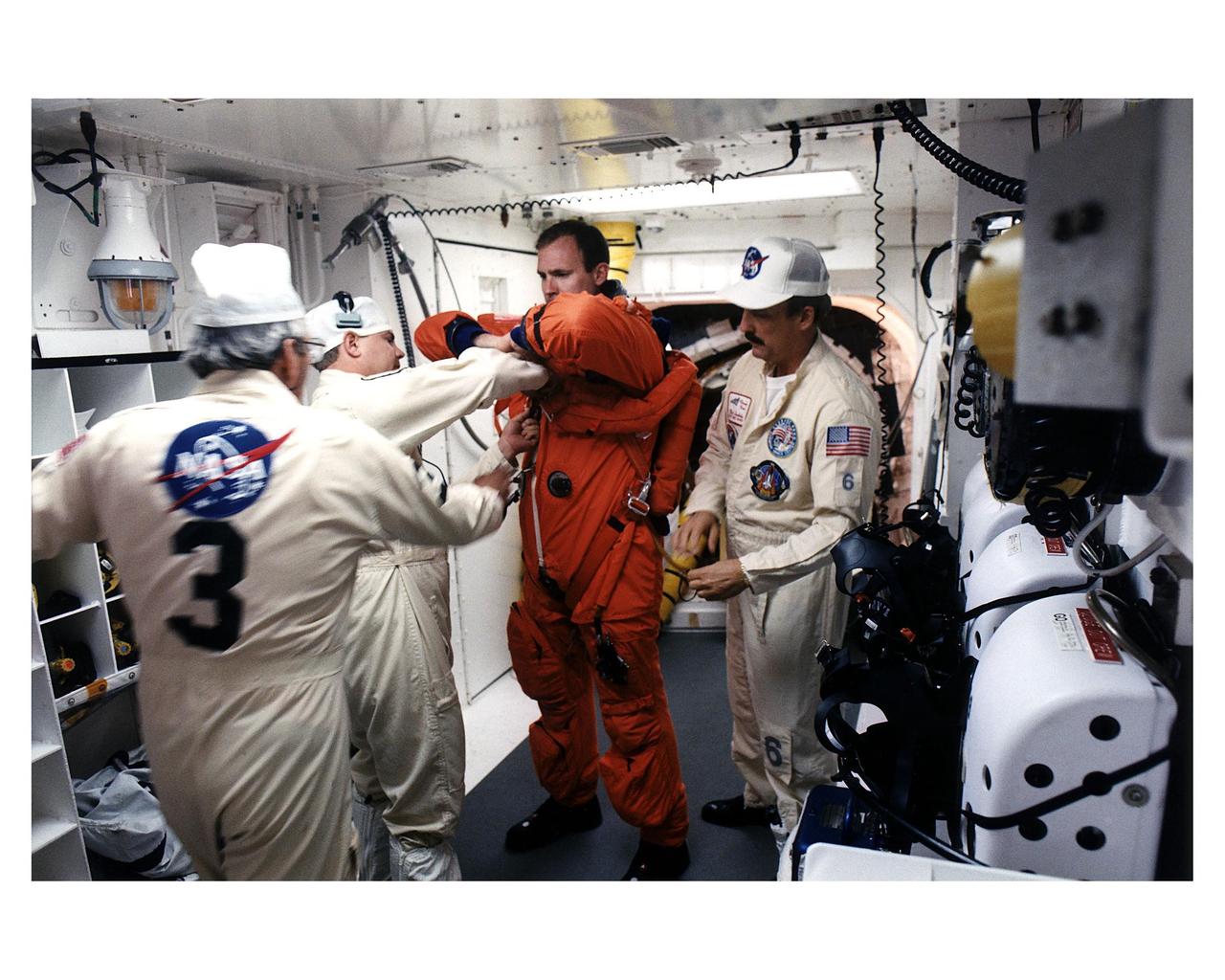
A member of the STS-83 flight crew enters the crew hatch of the Space Shuttle Columbia with the help of the white room crew during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) exercises for that mission. Members of the white room crew are (from left): Steve Crosbie, Rene Arriens and Bob Saulnier. The STS-83 crew members for the 16-day Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission are: Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr.; Pilot Susan L. Still; Payload Commander Janice Voss; Mission Specialists Michael L. Gernhardt and Donald A. Thomas; and Payload Specialists Gregory T. Linteris and Roger K. Crouch
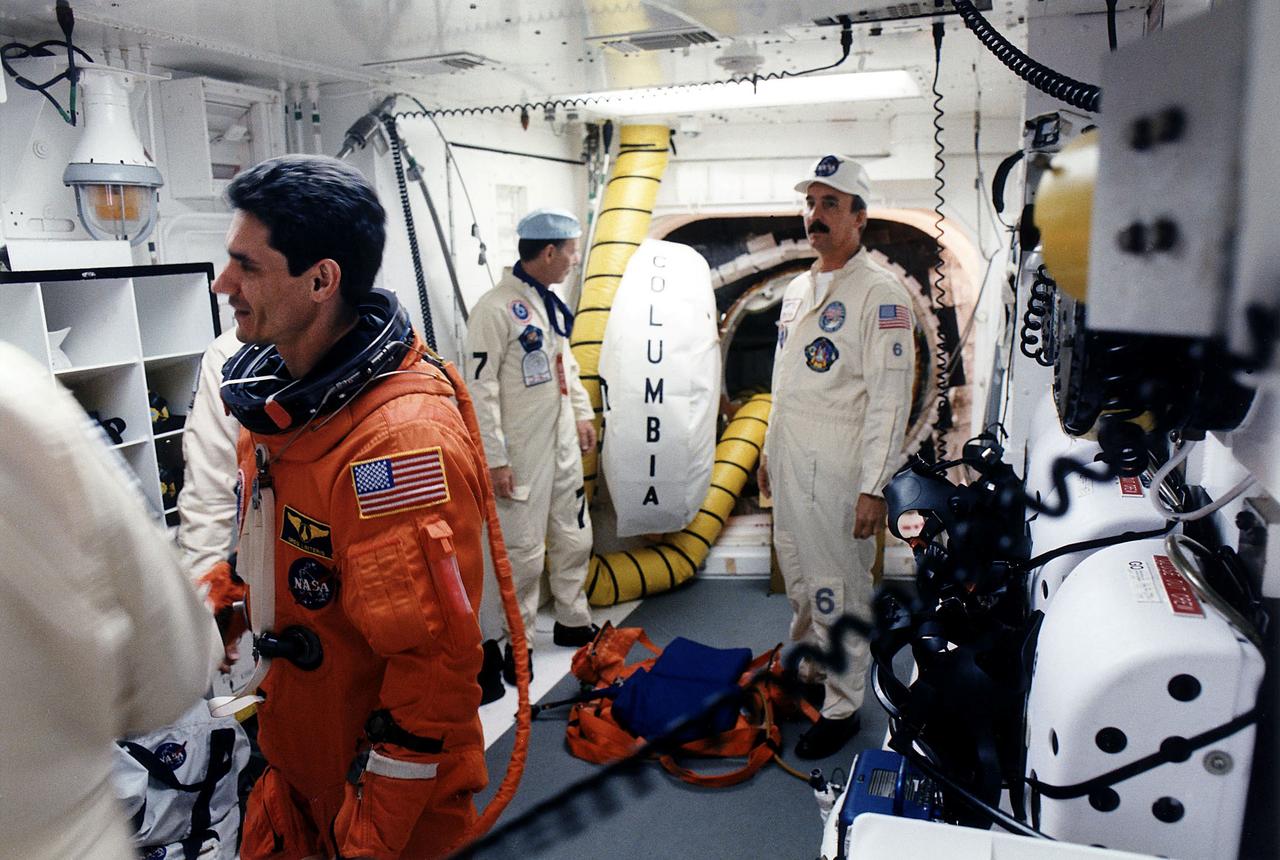

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-83 Payload Specialist Gregory T. Linteris chats with White Room closeout crew members as he prepares to enter the Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Pad 39A. Closeout crew workers Max Kandler (second from right) and Bob Saulnier wait to assist Linteris with his ascent/reentry suit.
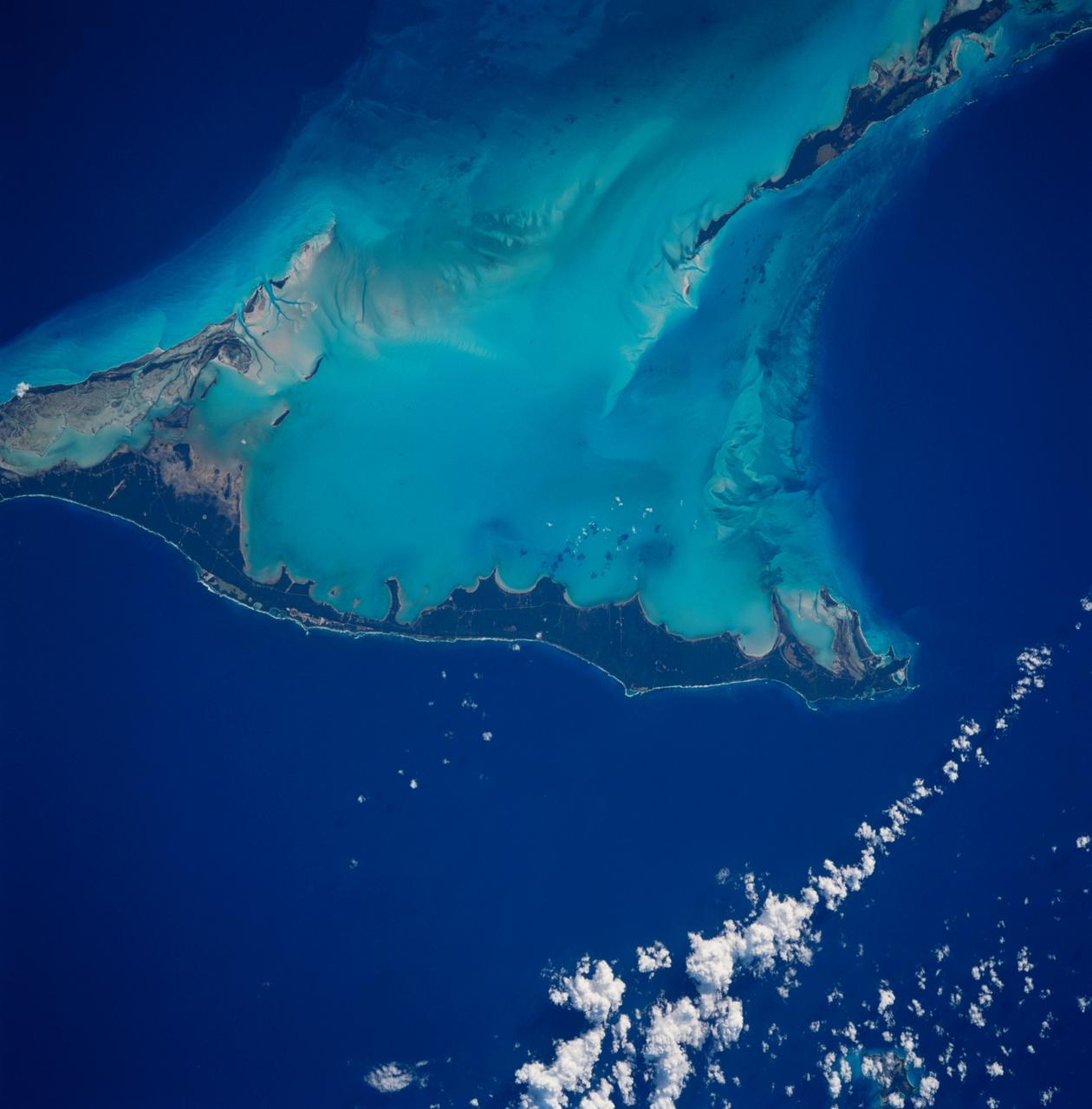

STS083-712-063 (4-8 April 1997) --- Northern half of Long Island, Bahamas. The vivid blues of the Bahamas stand out from space. Long Island and Great Exuma Island, which extends from the west north west into the photo, is on the eastern side of the Great Bahama Bank and form the borders of Exuma Sound. This photograph provides a rare opportunity to observe a natural chemical laboratory at work. Limestone of quite a different sort from that forming the Great Barrier Reef is actually in the process of formation. Long Island itself is little more than a sandbar rising just a few meters (about 30 to 50 meters) above sea level but it separates the deep, dark blue waters of the Atlantic on the right from the 10-meter (33 feet) shallows of the Great Bahama Bank (left). Details of the topography of the bank are visible through the clear waters. The shallow waters are warm and become extremely salty. Crystals of aragonite, a calcium carbonate mineral, are precipitated and formed into spherical sand-sized oolites as the tidal currents swirl back and forth. Lithification of the carbonate sands produces an oolithic limestone. Although the water is warm and clear, corals do not live in the shallows, probably because of the elevated salt content. Although chemically similar, the oolithic limestone forming Long Island is very different from coral reef limestone. An airfield is visible at the northern and central (bottom of photo) part of the island.
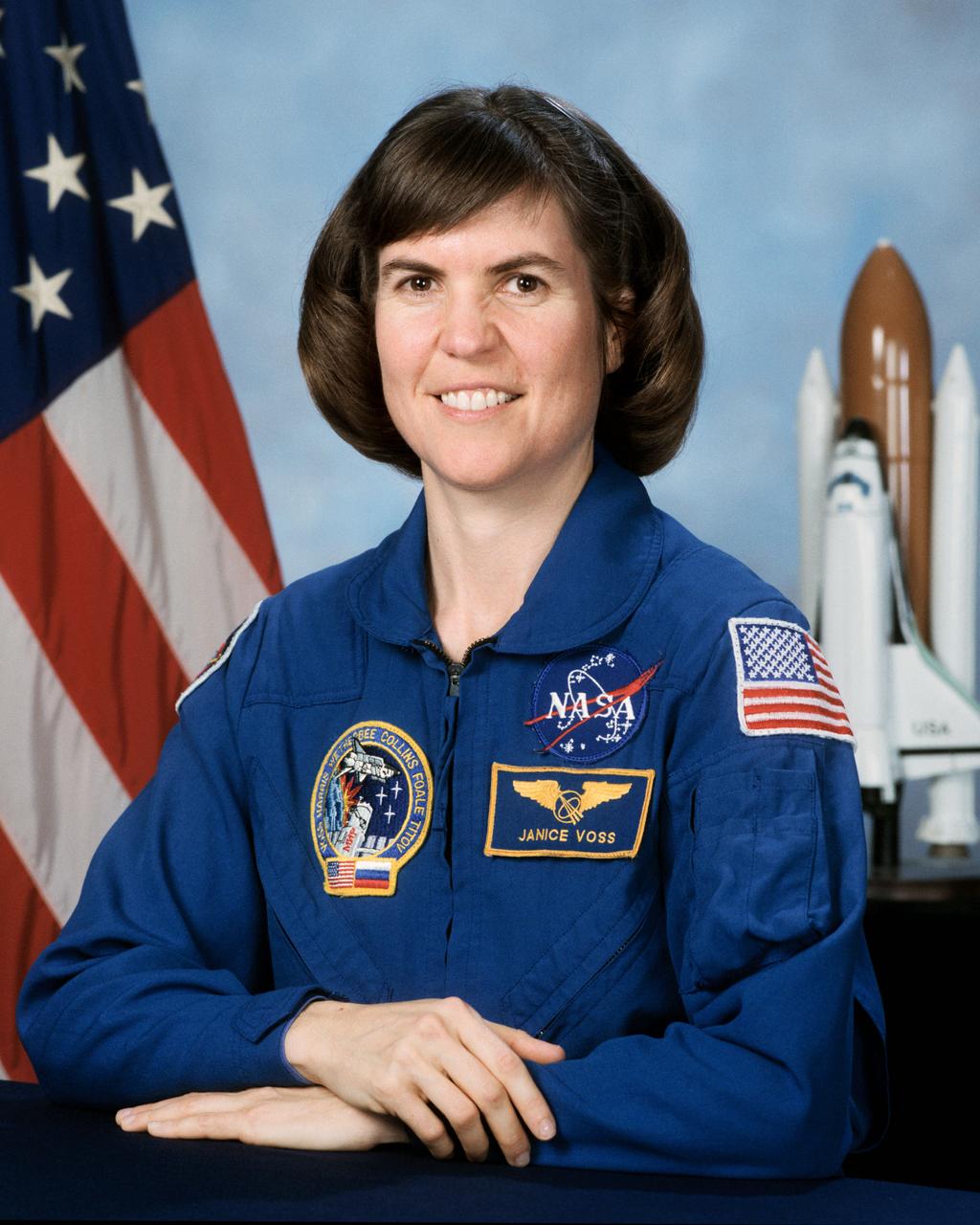

S97-02820 (17 Dec. 1996) --- Astronaut Janice Voss, mission specialist.
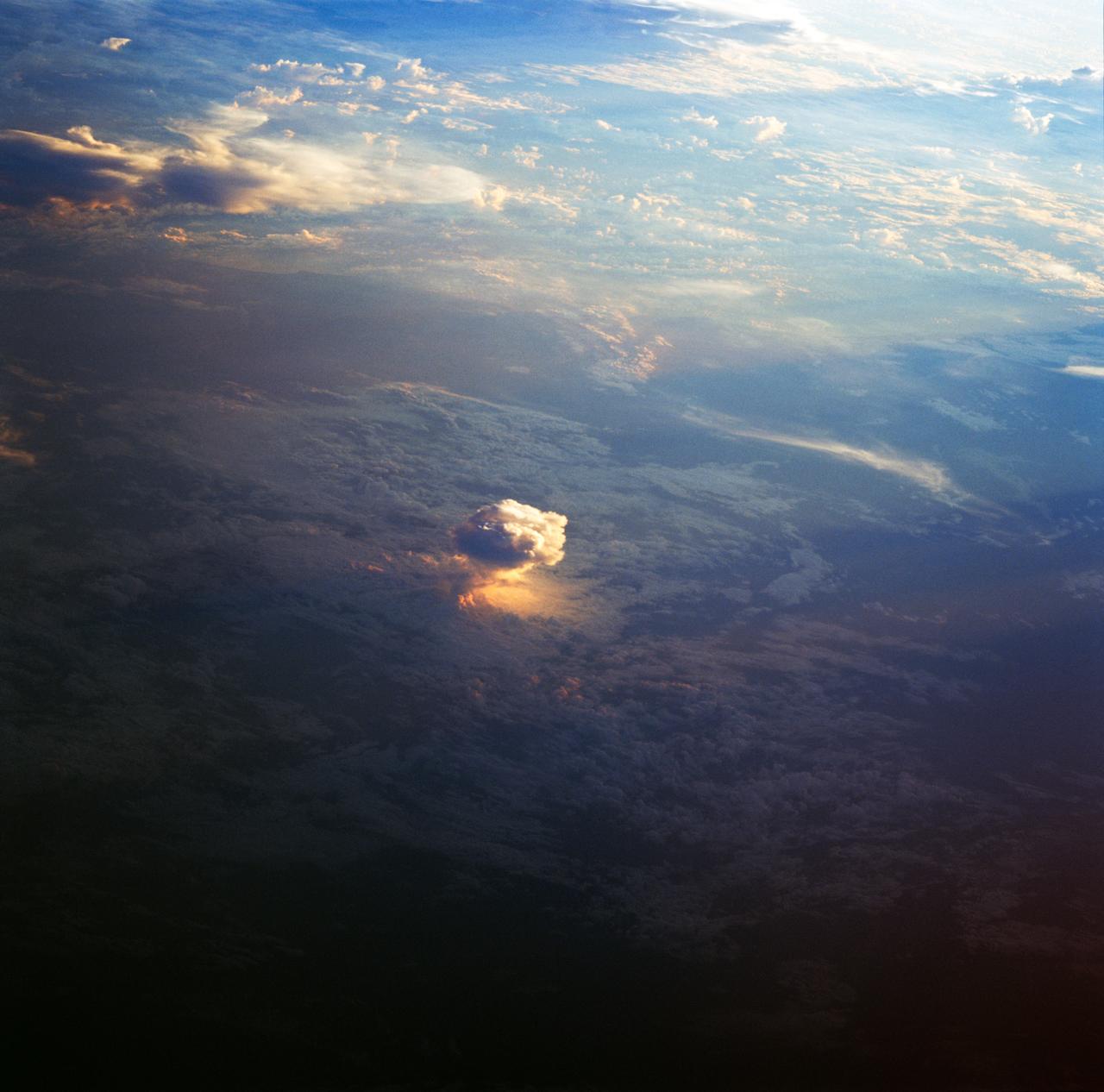

STS083-712-068 (4-8 April 1997)--- This is a thunderstorm cell that towers above the surrounding cloud deck and is illuminated by the last rays of the setting sun.
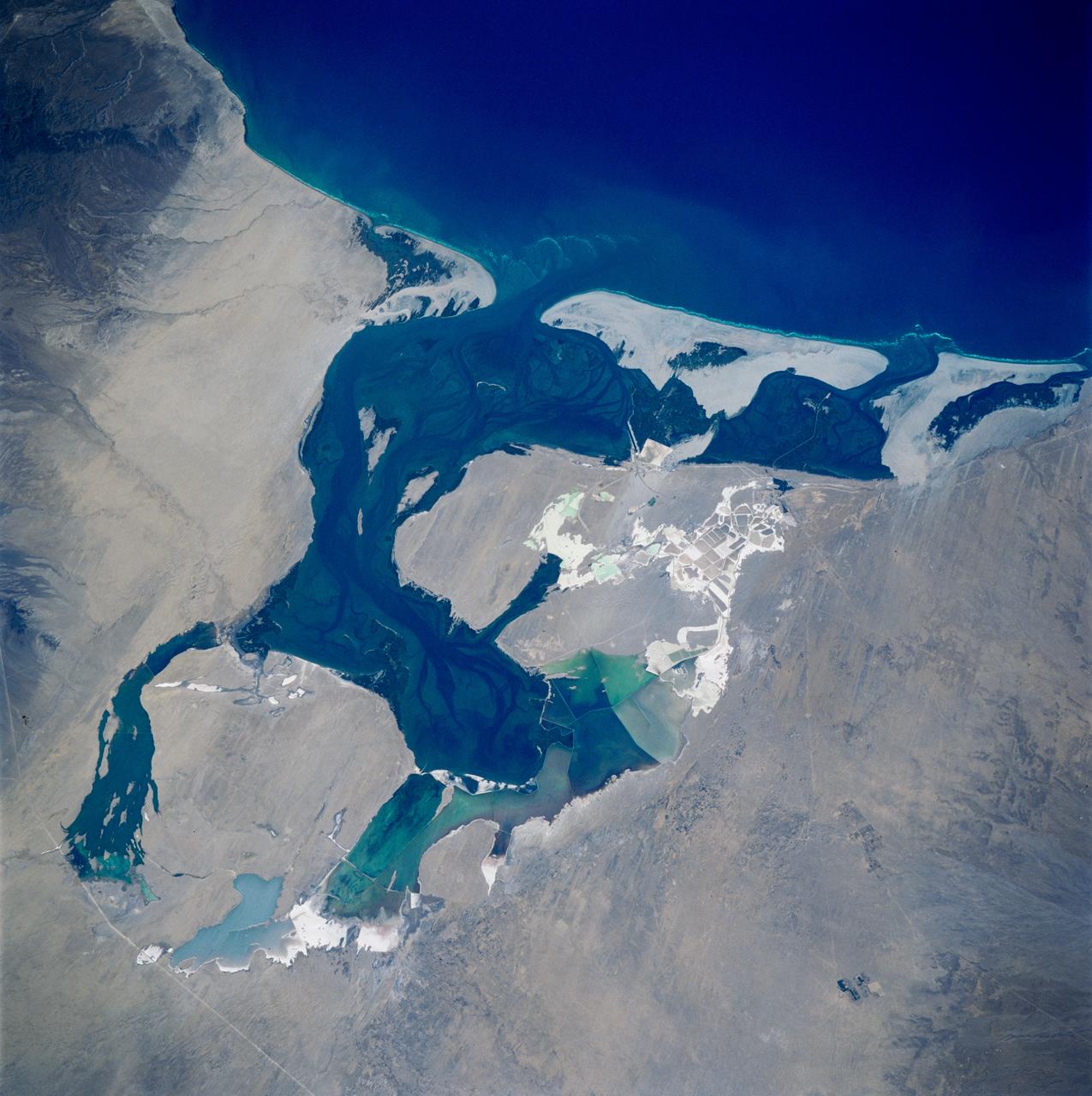

STS083-749-084 (4-8 April 1997) --- Laguna Oja De Liebre, Baja, gray whale breeding ground Laguna Oja De Liebre, Baja (Scammons Lagoon) is located on the west coast in the plains of the central Baja. This lagoon and others like it along the Baja coast are used for breeding grounds for the gray whale. One group of gray whales inhabits the Sea of Okhotsk in summer, migrating south in winter then breed off southern Korea. The other summers in the Bering and Chukchi seas and travels south to winter breeding grounds along the coast of Baja California. The gray whale was hunted almost to extinction by 1925 but was placed under complete international protection and since the 1940s has increased in numbers. The white grids seen in the photo are commercial salt ponds.
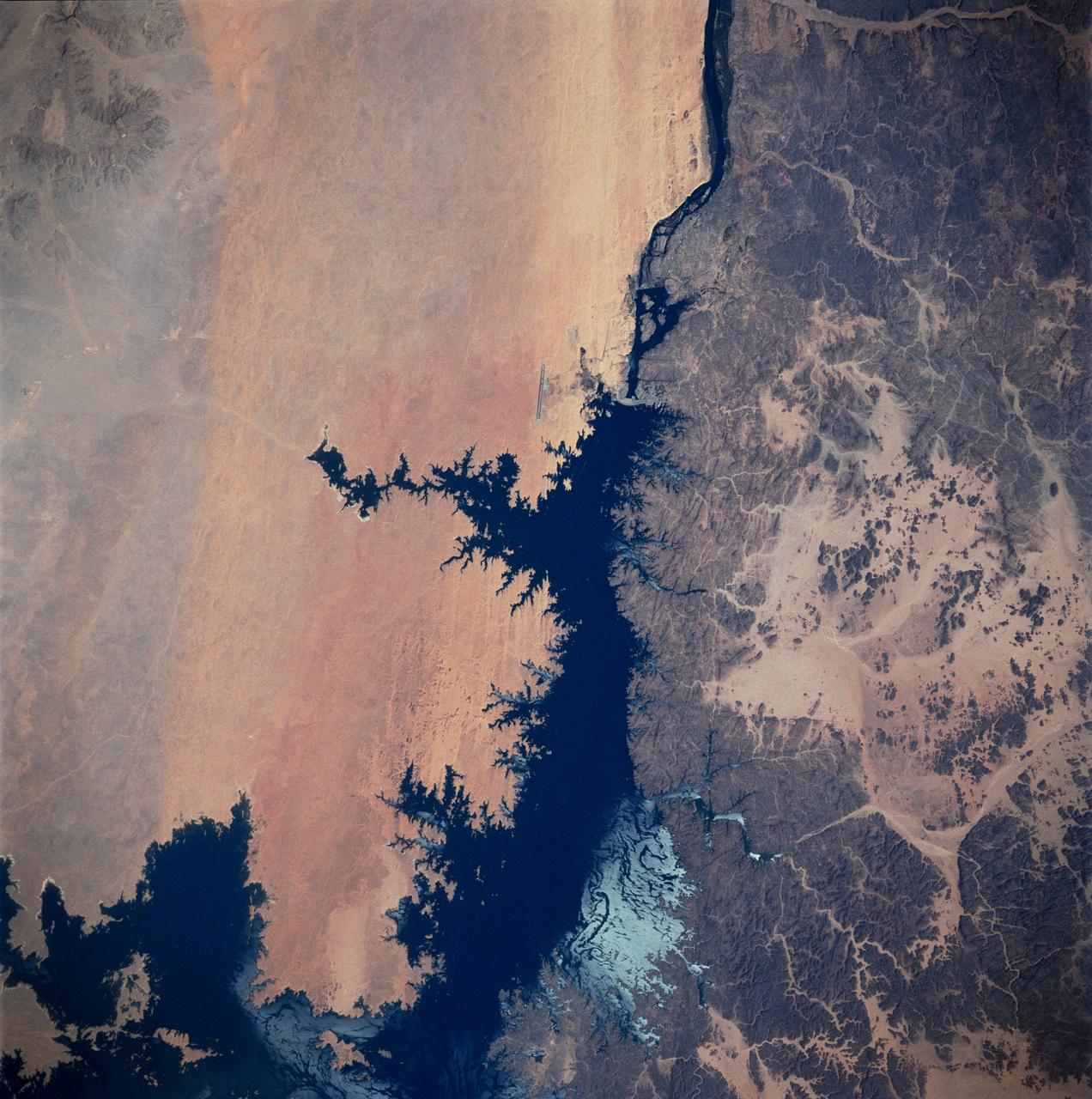

STS083-747-026 (4-8 April 1997) --- Aswan Dam and Lake Nasser along the Nile River, Egypt. The Aswan Dam controls the flow of the Nile River forming Lake Nasser. Lake Nasser is reaching relatively high water levels due to the plentiful rains since December 1996 in Kenya, near the headwaters of the Nile river. The light colored areas in the Lake are where the sun is reflecting off the surface of the water. These areas are fairly calm and not disturbed by wind gusts enabling the sunglint to show water current patterns on the surface. The Aswan runway is seen as a dark set of lines west of the Aswan Dam.
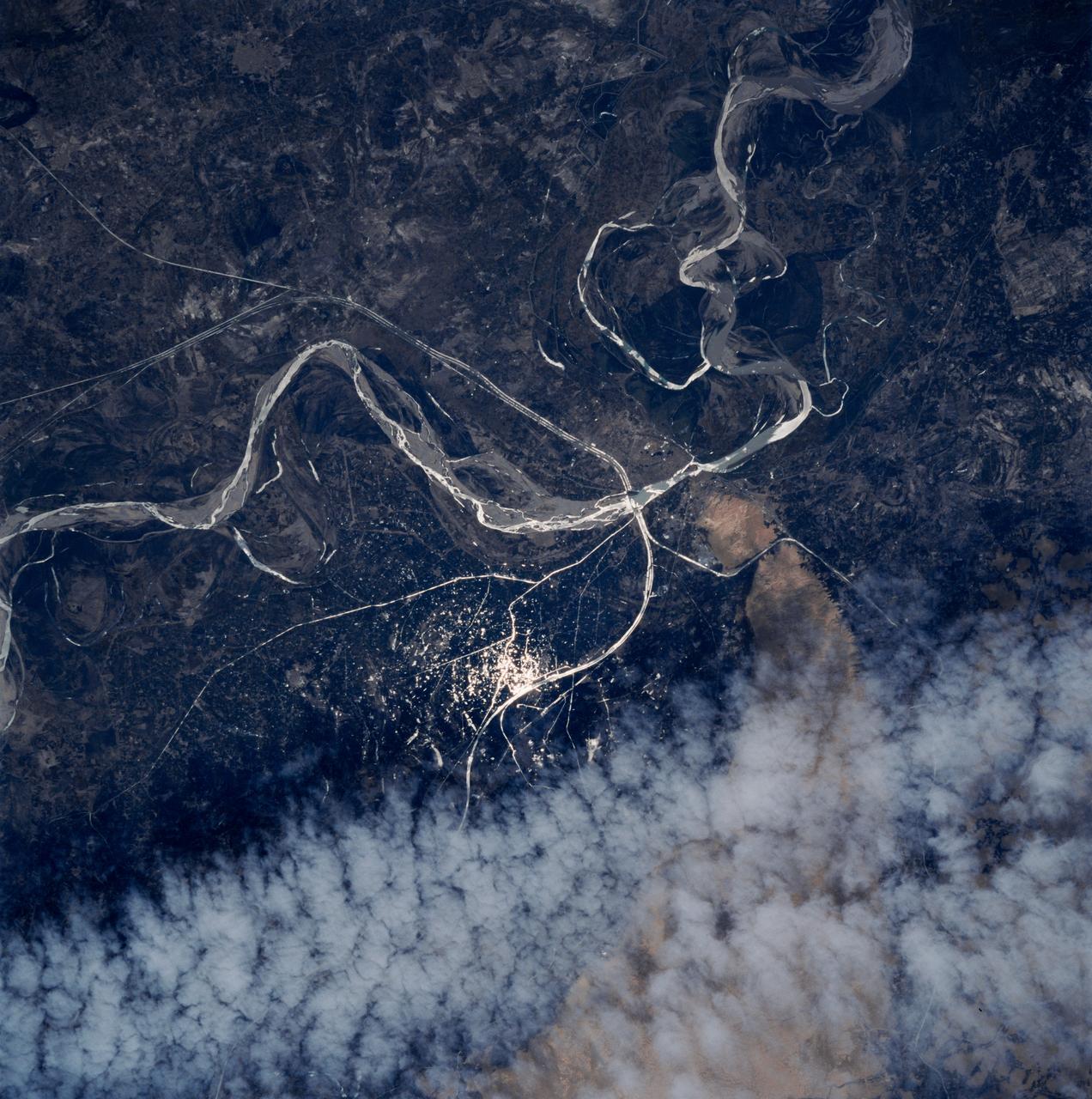

STS083-747-052 (4-8 April 1997) --- Sunglint on the Indus River, Sukkar, and Rohri, Pakistan. Sukkar city (27.42 north 68.52 east), Sindh province, southeastern Pakistan lies on the west bank of the Indus River, connected with Rohri on the opposite bank by a cantilever bridge. Midstream between the two cities is the strategic island fortress of Bukkur. The old town contains many historic tombs and mosques, including the Mir Ma'sum Shah Minaret (c. AD 1607). An industrial and trade center, it has biscuit, cigarette, oil, lime, and cement factories, and cotton, silk, thread, and flour mills; boat building is also significant. The surrounding region is a vast alluvial plain broken only occasionally by low limestone hills. A portion of the Thar Desert is reaching from the south to Rohri. The Sukkur Barrage, highlighted by the sunglint, was completed in 1932. Nearly 1 mile (1.6 kilometers) long it crosses the Indus River 3 miles (4.8 kilometers) below Sukkur Gorge and feeds irrigation canals. The canals originating from it serve a cultivable area of about five million acres of land producing both food and cash crops, such as wheat, cotton, rice, oilseed, and fruit cultivation.
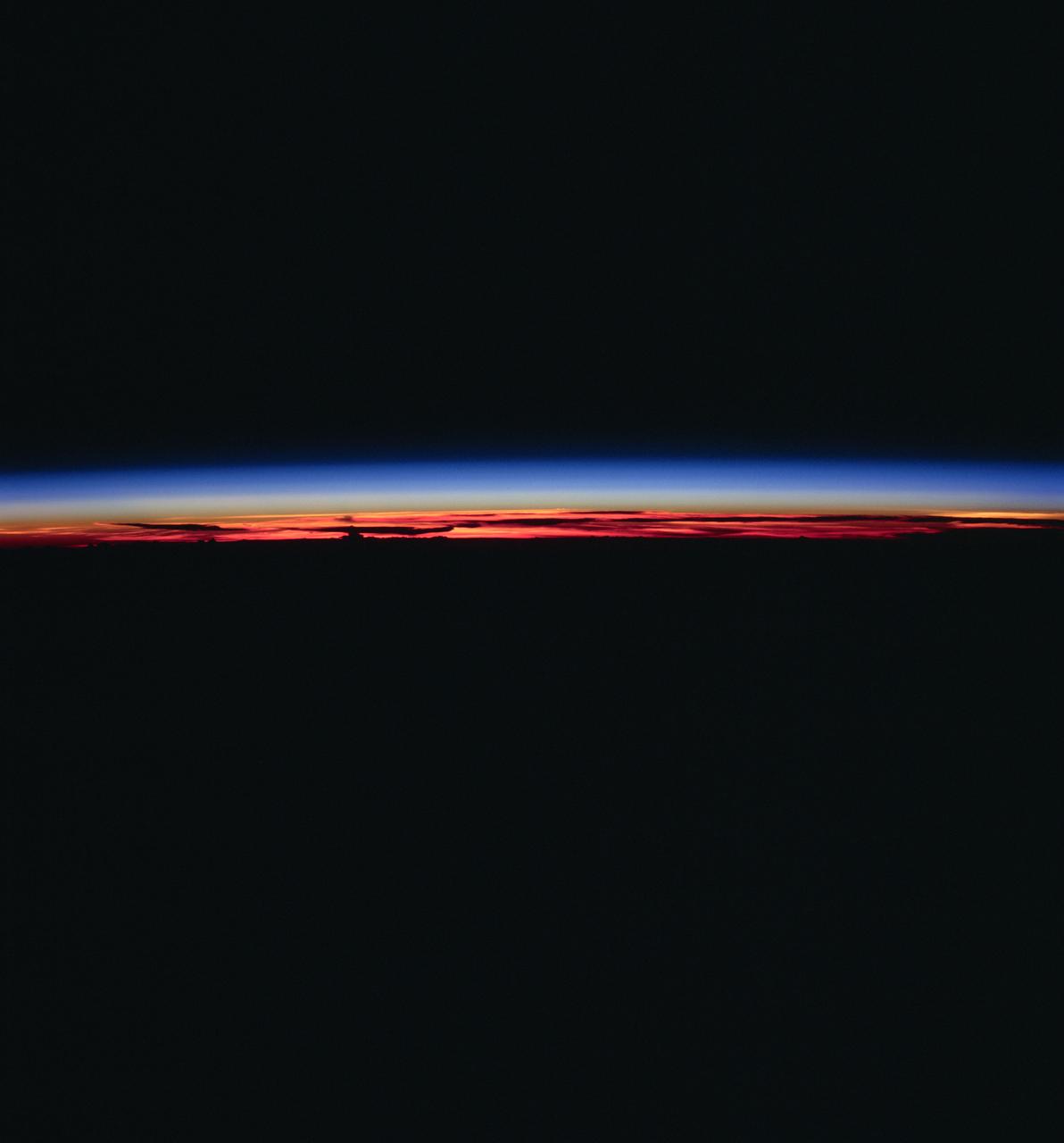

STS083-748-006 (4-8 April 1997) --- This type of scene is seen about every 45 minutes as the astronauts travel around the world. Sunrises and sunsets differ in structure, since the tropopause altitude and atmospheric lamina temperatures vary with time of day, season, and latitude. Close analysis of these terminator photographs provide counts of the number and spacing of atmospheric laminae. In the photographs, as many as 4 laminae have been noted in the normally red-to-orange troposphere, and up to 12 laminae have been counted in the blue upper atmosphere. However, true replication of human vision is not possible using present films. For instance, while on orbit, one astronaut counted 22 layers. The photograph of that event recorded only 8 such layers.
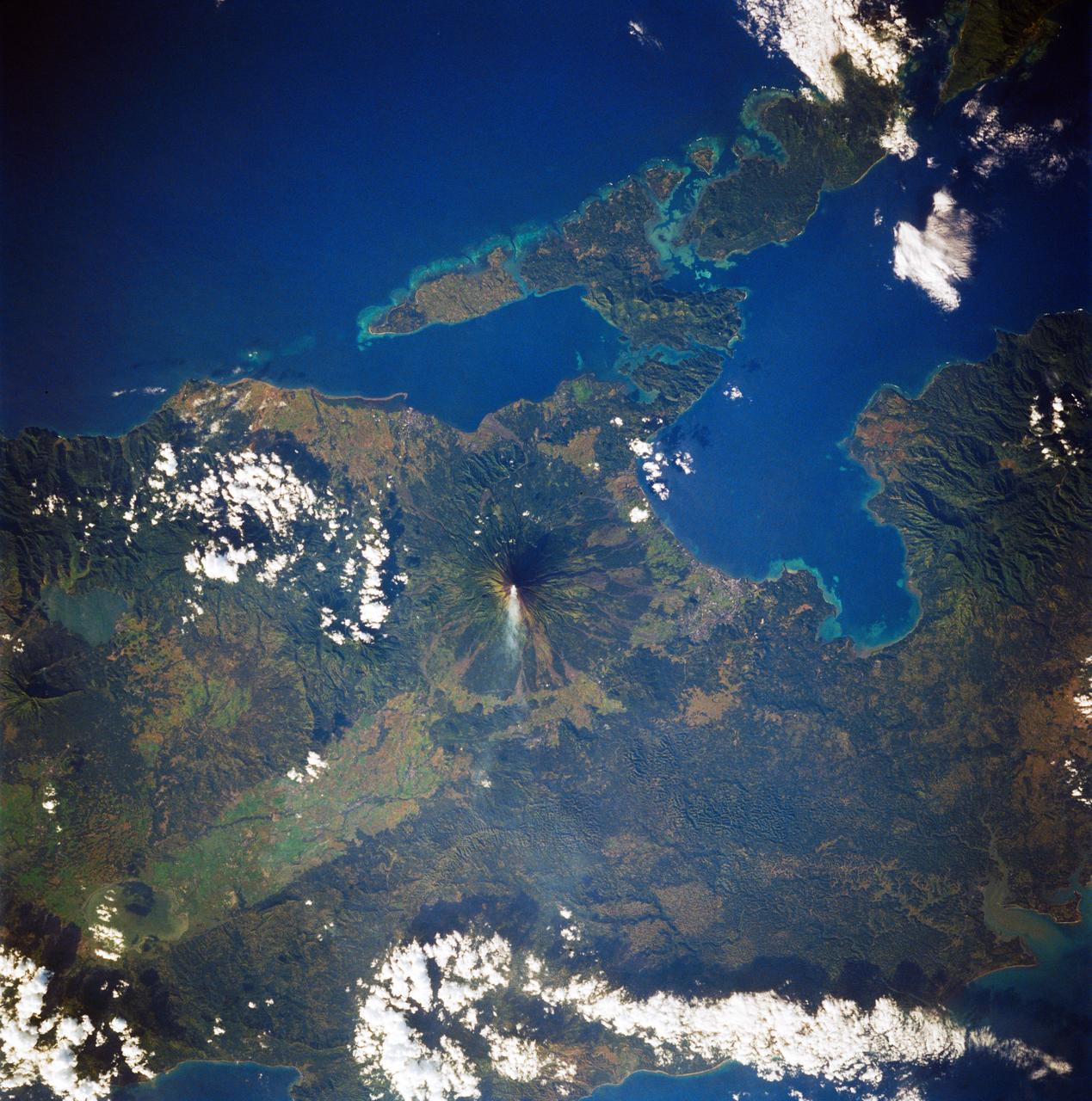

STS083-747-088 (4-8 April 1997)--- Mayon Volcano with a Plume, Luzon, the Philippines Mayon has the classic conical shape of a strato volcano. It is the most active volcano in the Philippines and continues to be active as demonstrated by the plume in the photo. Since 1616, Mayon has erupted 47 times. The most recent major eruption, in 1993, began unexpectedly with an explosion. The initial eruption lasted only 30 minutes but it generated pyroclastic flows that killed 68 people and prompted the evacuation of 60,000 others.
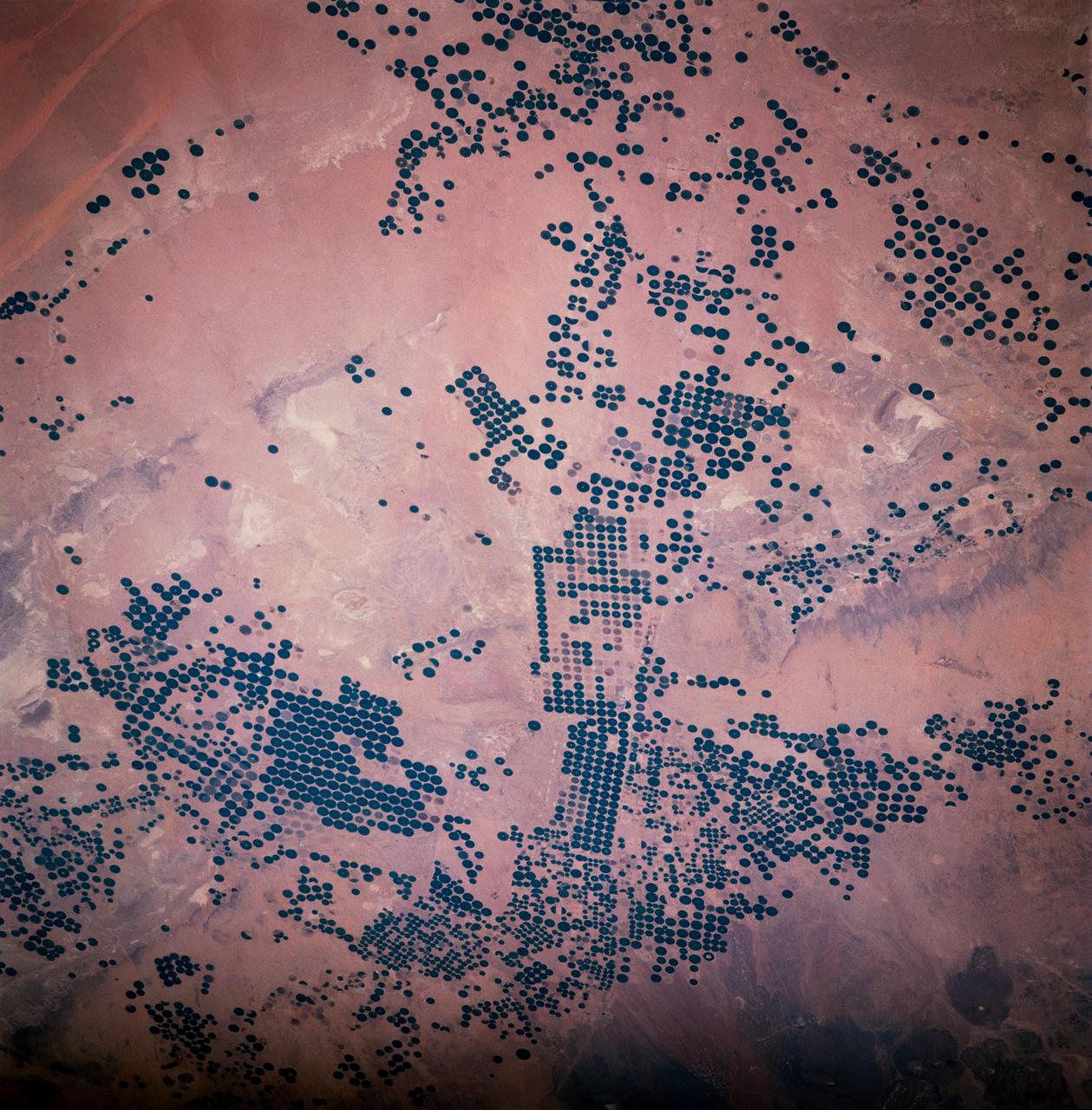

STS083-747-033 (4-8 April 1997) --- Center Pivot Irrigation, in Saudi Arabia. This irrigation project in Saudi Arabia is typical of many isolated irrigation projects scattered throughout the arid and hyper-arid regions of the Earth. Fossil water is mined from depths as great as 3,000 feet, pumped to the surface, and distributed via large center pivot irrigation feeds. The circles of green irrigated vegetation may comprise a variety of agricultural commodities from alfalfa to wheat. Diameters of the normally circular fields range from a few hundred meters to as much as 2 miles. The projects often trace out a narrow, sinuous, and seemingly random path. Actually, engineers generally seek ancient river channels now buried by the sand seas. The fossil waters mined in these projects accumulated during periods of wetter climate in the Pleistocene glacial epochs, between 10,000 to 2 million years ago, and are not being replenished under current climatic conditions. The projects, therefore, will have limited production as the reservoirs are drained. Water, of course, is the key to agriculture in Saudi Arabia. The Kingdom has implemented a multifaceted program to provide the vast supplies of water necessary to achieve the spectacular growth of the agricultural sector. A network of dams has been built to trap and utilize precious seasonal floods. Vast underground water reservoirs have been tapped through deep wells. Desalination plants have been built to produce fresh water from the sea for urban and industrial use, thereby freeing other sources for agriculture. Facilities have also been put into place to treat urban and industrial run-off for agricultural irrigation. These efforts collectively have helped transform vast tracts of the desert into fertile farmland. Land under cultivation has grown from under 400,000 acres in 1976 to more than 8 million acres in 1993.

STS083-749-079 (4-8 April 1997) --- Cloud wake covers the Leeward Islands. Like a ship making a wake in the water, Guadeloupe Island is making a wake in the clouds. Seeing certain weather features tells us information as to what the conditions were at the time the photo was taken. For instance, a solid cloud area is formed behind the island in this photo so the winds are under or at 5 meters per second (mps). If the winds were greater Von Karman Vortices would develop. Formation of Von Karman Vortices requires wind speeds of 5 and 13 mps and a strong low level temperature inversion below the highest peak of the island.
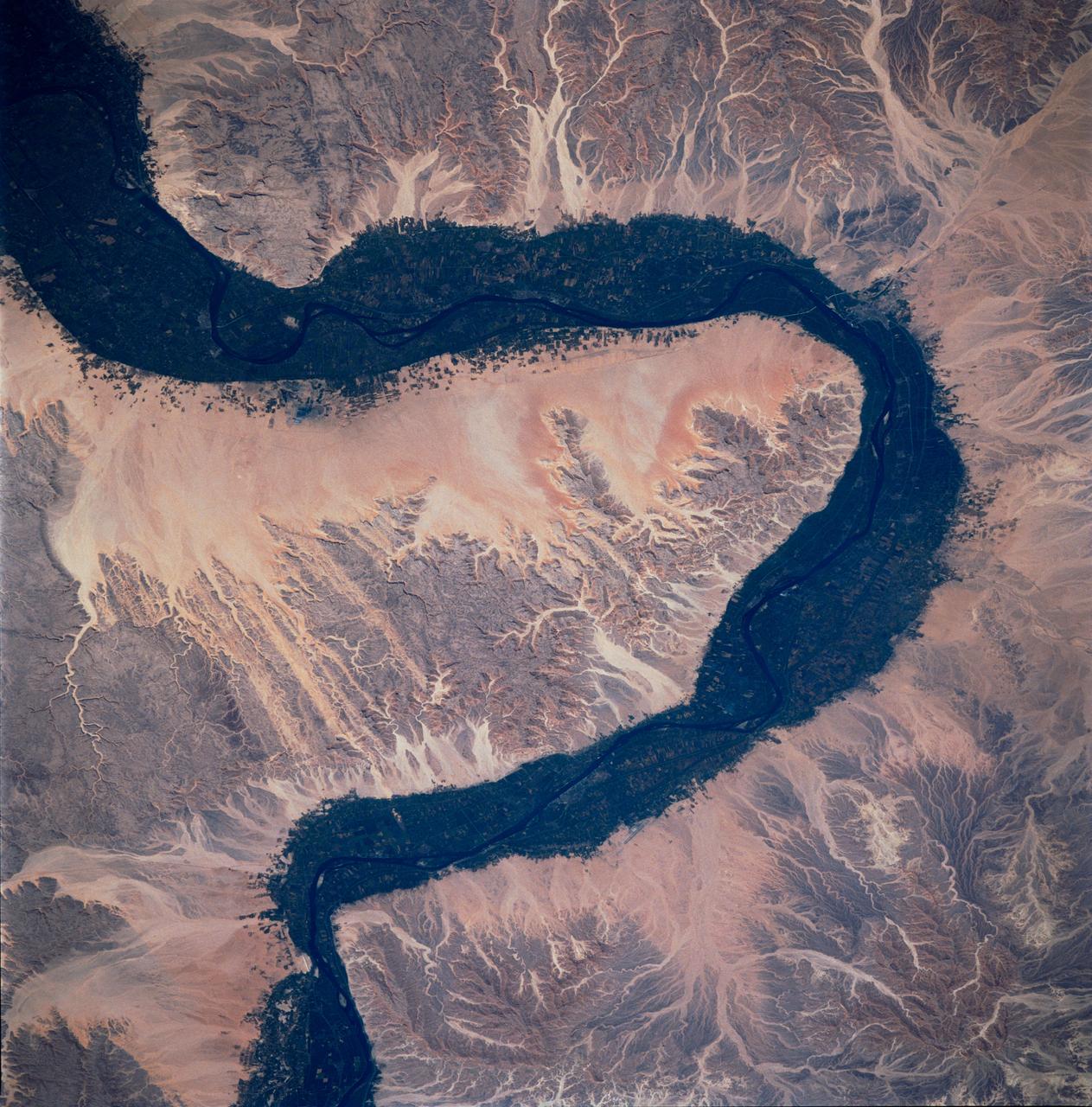

STS083-748-066 (4-8 April 1997) --- Luxor, Qus, and Qina, Egypt on the Nile. The Nile, which is about 4,132 miles long, is the longest river in the world. This photo demonstrates the dependency of the local agriculture on the River. This area is the historic area of ancient Thebes. Luxor, also called EL-AKSUR, or AL-UQSUR, a market town along the southern part of the Nile's curve, is located on the southern half of the ruins of Thebes. Ancient Thebes was about six miles square; the main part of the city was situated along the Nile's east bank; along the west bank was "the city of the dead" -- an area containing the Egyptian kings' mortuary temples and the houses of those priests, soldiers, craftsmen, and laborers who were devoted to their service. Qina, extending 3 - 4 miles (5 - 6 kilometers) on each side of the Nile River between the Arabian and Libyan deserts, is seen on the northeast part of the rivers curve. Occupying the great bend in the Nile Valley, it has an area of 715 square miles (1,851 square kilometers) and contains the celebrated ruins of Thebes and the Valley of the Tombs of the Kings. Qina has a dense agricultural population (more than 3,000 persons per square mile), and most of its land is under basin irrigation, yielding only one crop annually. Main crops are sugar (about three-fifths of the nation's production), lentils, and grains.
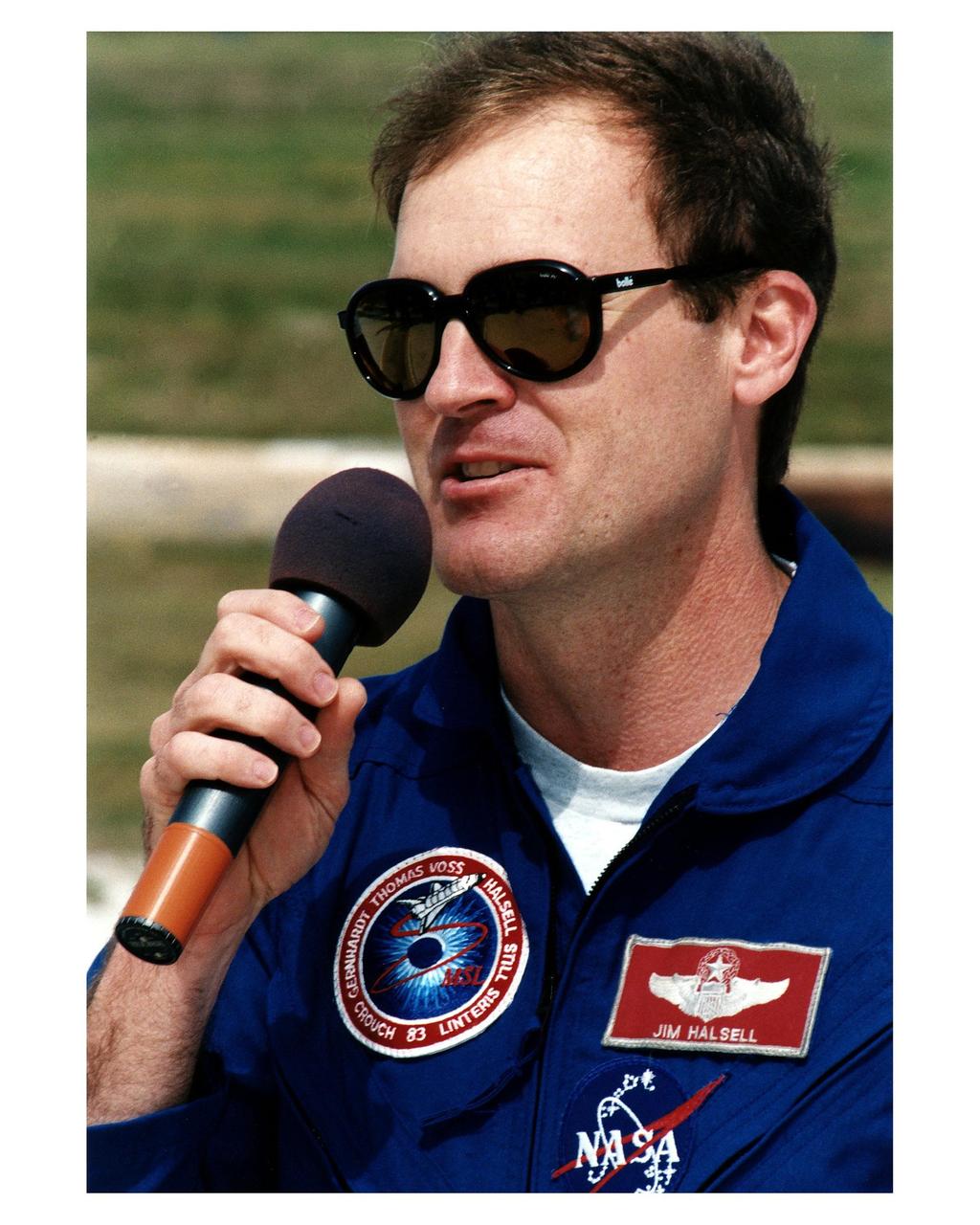

STS-83 Mission Commander James D. Halsell talks to the media at Launch Complex 39A during the crew's <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT).</a

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Greeted by cheers from wellwishers at KSC and eager for their ventur into space on the Microgrvity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the STS-83 astronauts depart the Operations and Checkout Building on their way to Launch Pad 39A. Leading the seven-member crew is Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. Behind Halsell and to his right is Pilot Susan L. Still. Behind Still is Payload Commander Janice Voss, with Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas to her left. Behind Thomas, in order, are Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. Also onboard is the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attched to the right side of Columbia's payload bay.
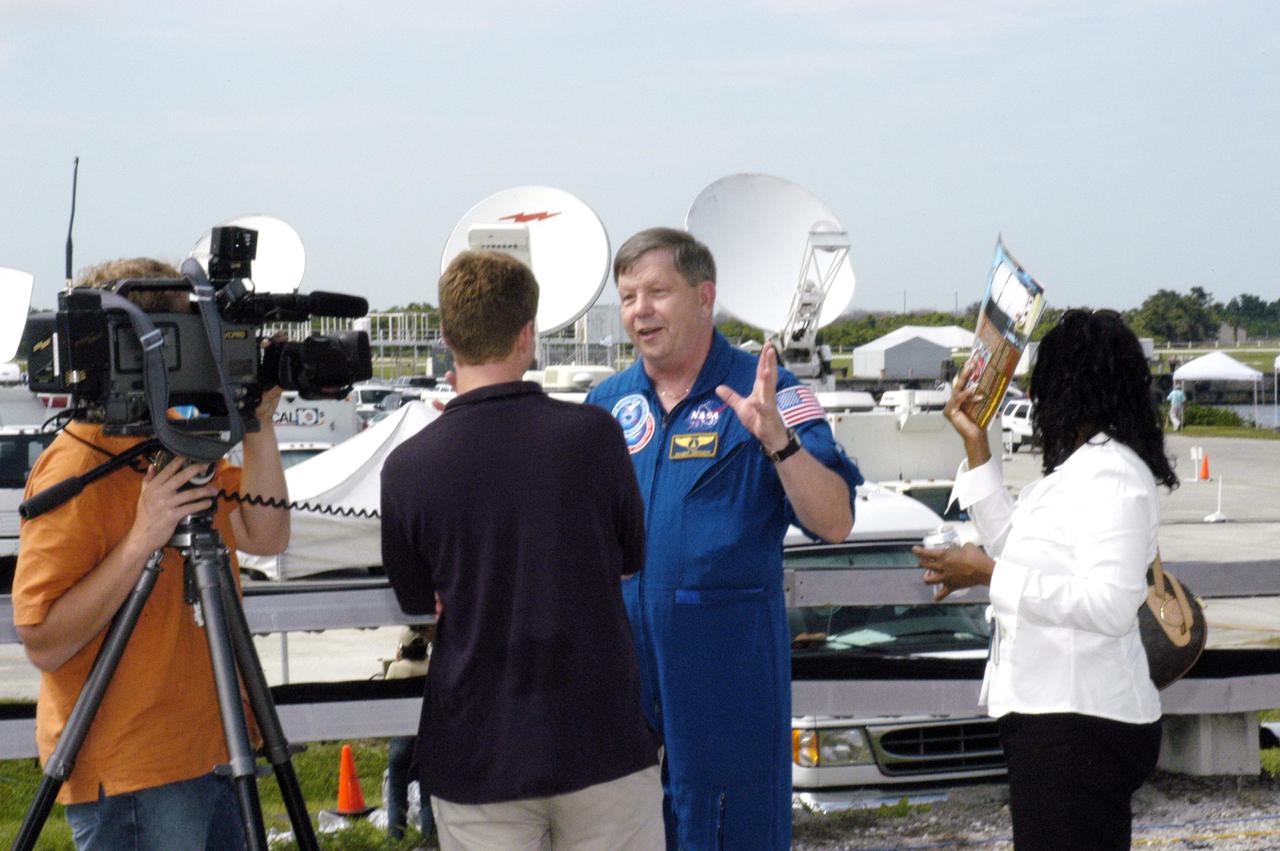

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Roger Crouch (center), a payload specialist, talks to the media prior to the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. He has flown on two Shuttle missions, STS-83 and STS-94. STS-114 is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. More than a thousand media representatives from 36 states, the District of Columbia and 32 countries converged on the News Center for the historic launch.
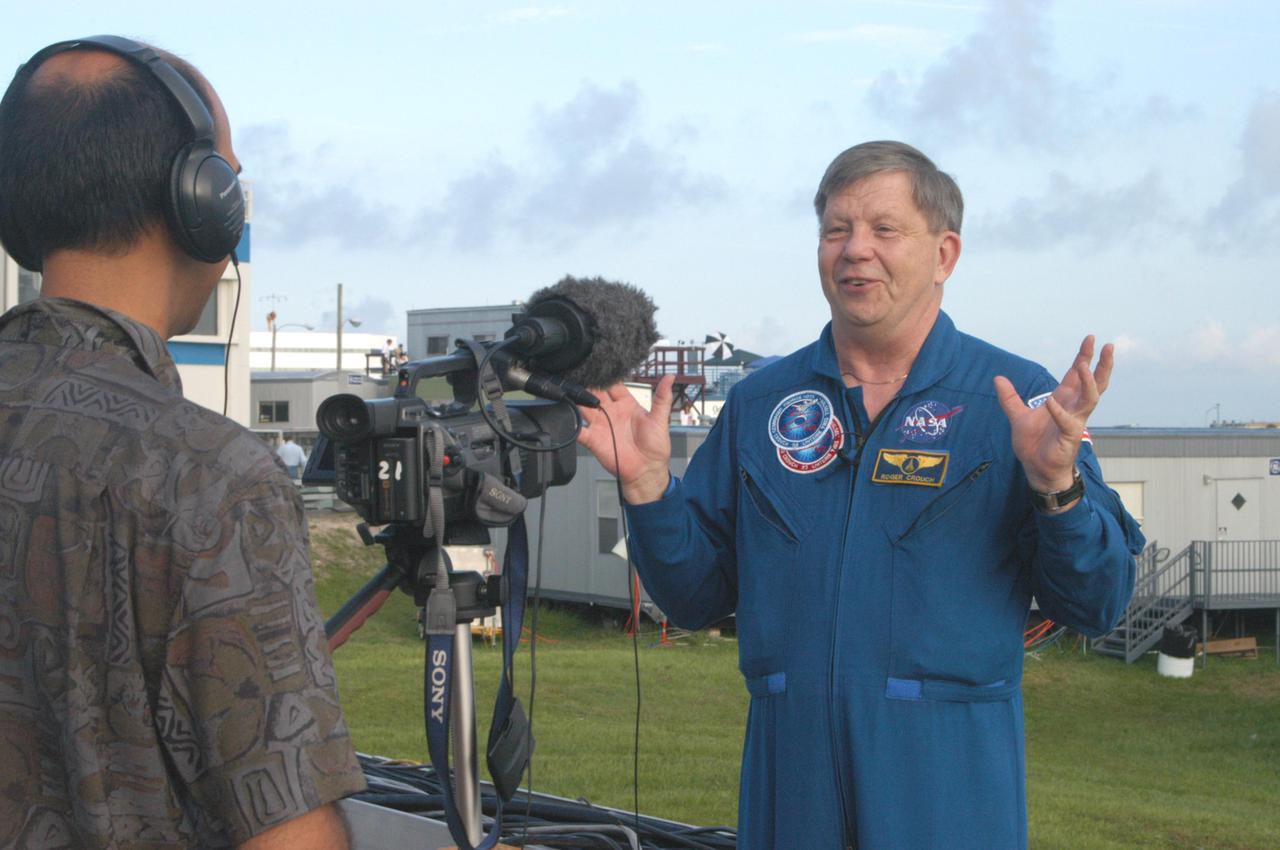

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Roger Crouch, a payload specialist, talks to the media prior to the launch at 3:51 p.m. of Space Shuttle Discovery on the historic Return to Flight mission STS-114. He has flown on two Shuttle missions, STS-83 and STS-94. STS-114 is the 114th Space Shuttle flight and the 31st for Discovery. The 12-day mission is expected to end with touchdown at the Shuttle Landing Facility at 11:06 a.m. July 25.
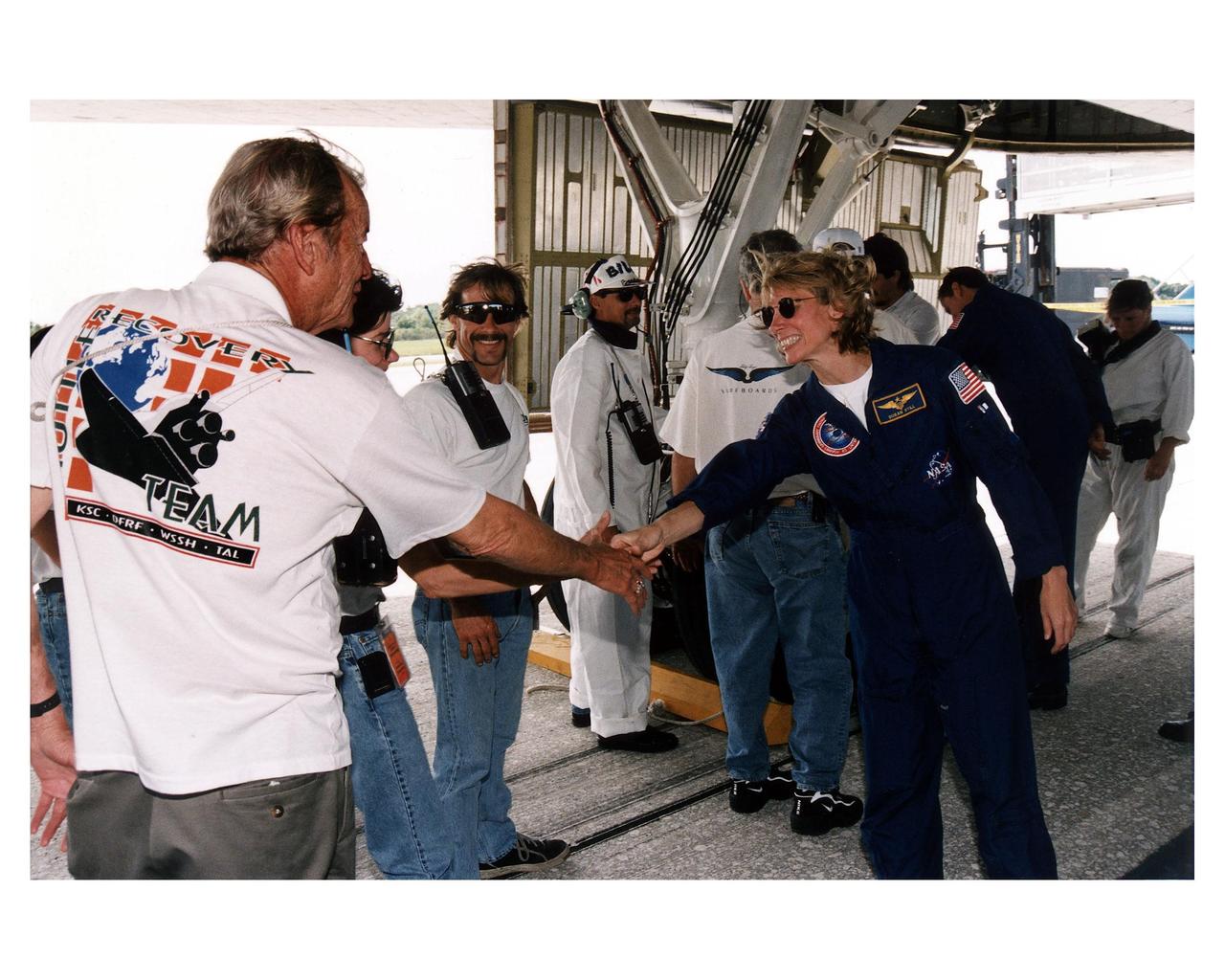

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-83 Pilot Susan L. Still greets KSC postlanding operations workers on Runway 33 at the Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility after the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia landed at 2:33:11 p. m. EDT, April 8, to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. At main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981
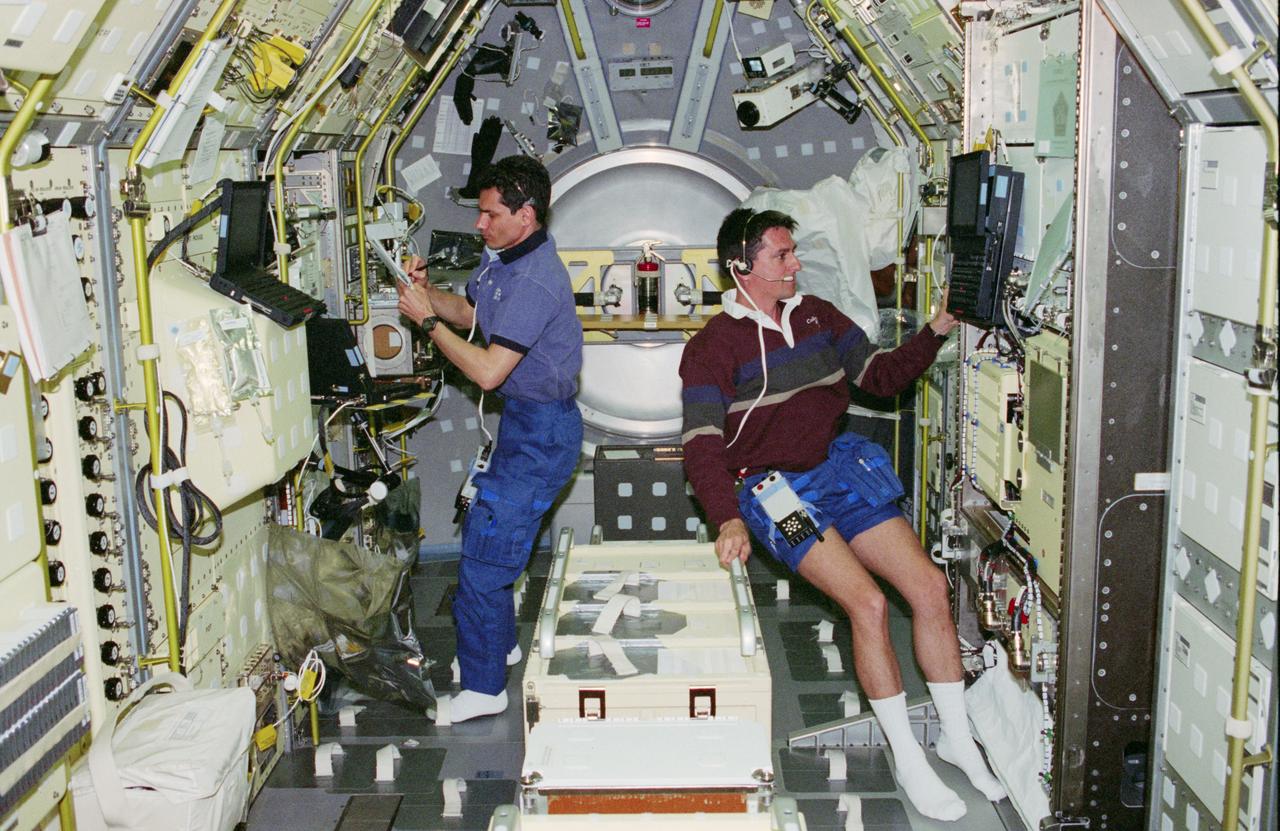

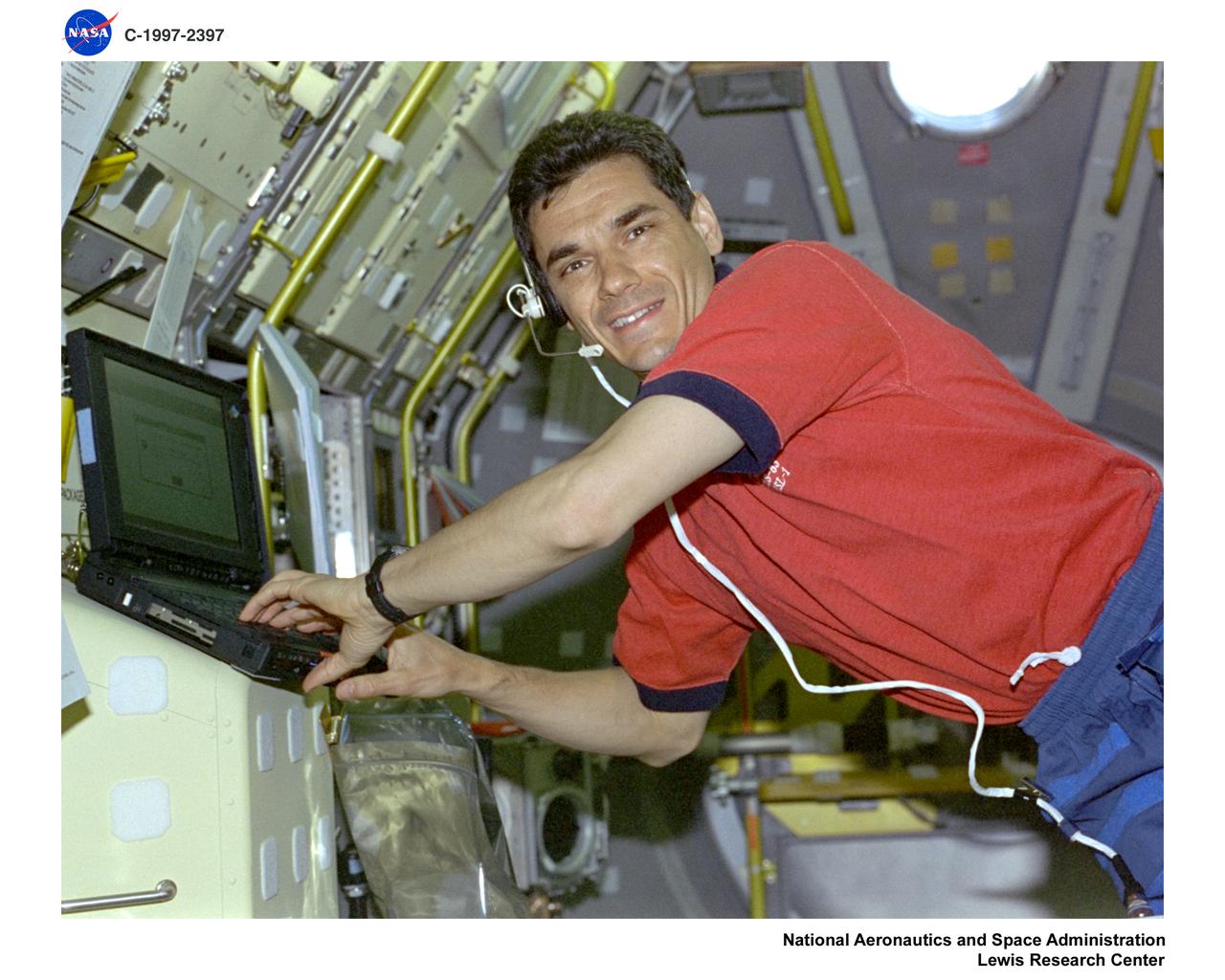
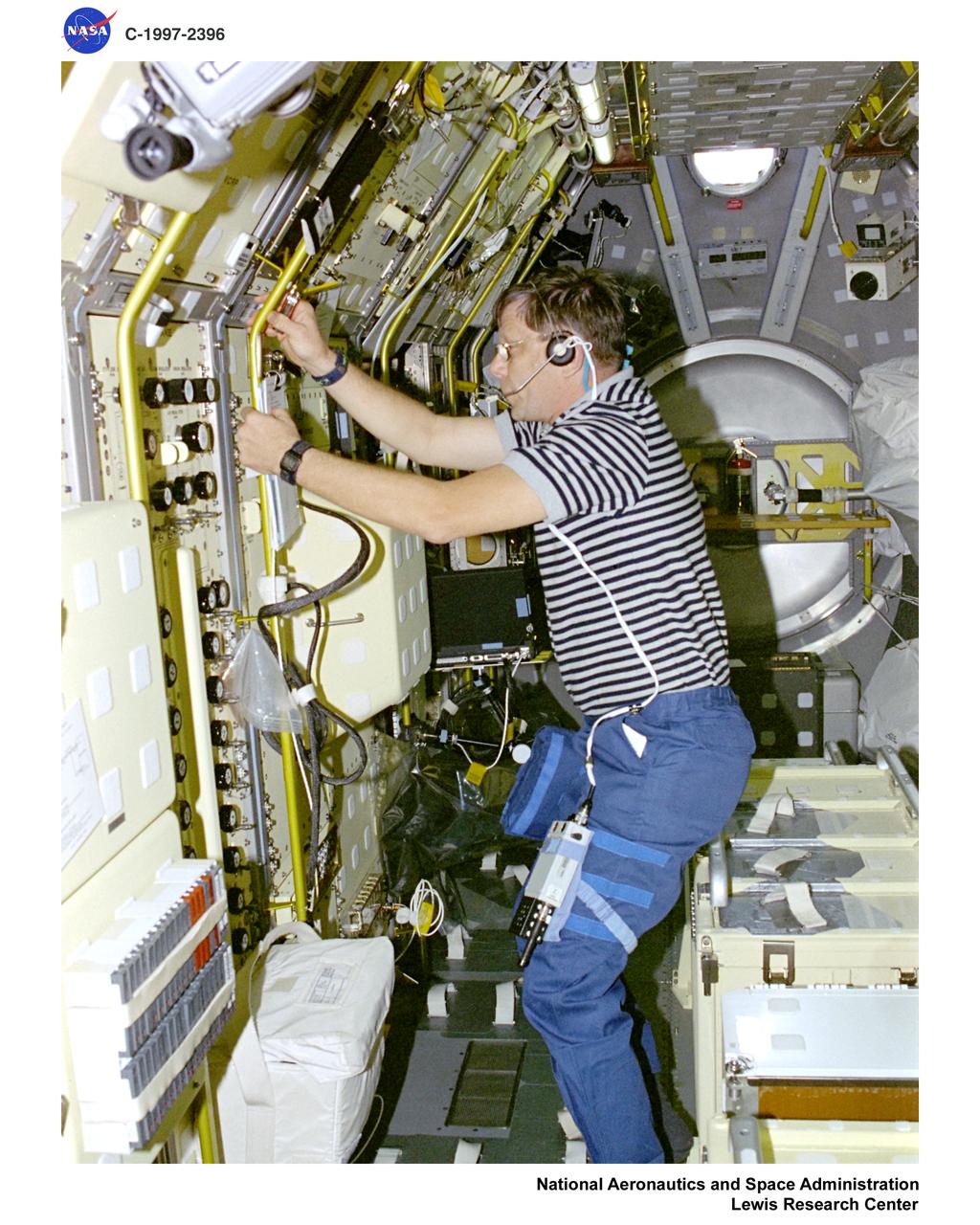
STS083-312-031 (4-8 April 1997) --- Payload specialist Gregory T. Linteris (left) is seen at the Mid Deck Glove Box (MGBX), while astronaut Donald A. Thomas, mission specialist, works at the Expedite the Processing of Experiments to Space Station (EXPRESS) rack. MGBX is a facility that allows scientists the capability of doing tests on hardware and materials that are not approved to be handled in the open Spacelab. It is equipped with photographic, video and data recording capability, allowing a complete record of experiment operations. Experiments performed on STS-83 were Bubble Drop Nonlinear Dynamics and Fiber Supported Droplet Combustion. EXPRESS is designed to provide accommodations for Sub-rack payloads on Space Station. For STS-83, it held two payloads. The Physics of Hard Colloidal Spheres (PHaSE) and ASTRO-Plant Generic Bioprocessing Apparatus (ASTRO-PGBA), a facility with light and atmospheric controls which supports plant growth for commercial research.
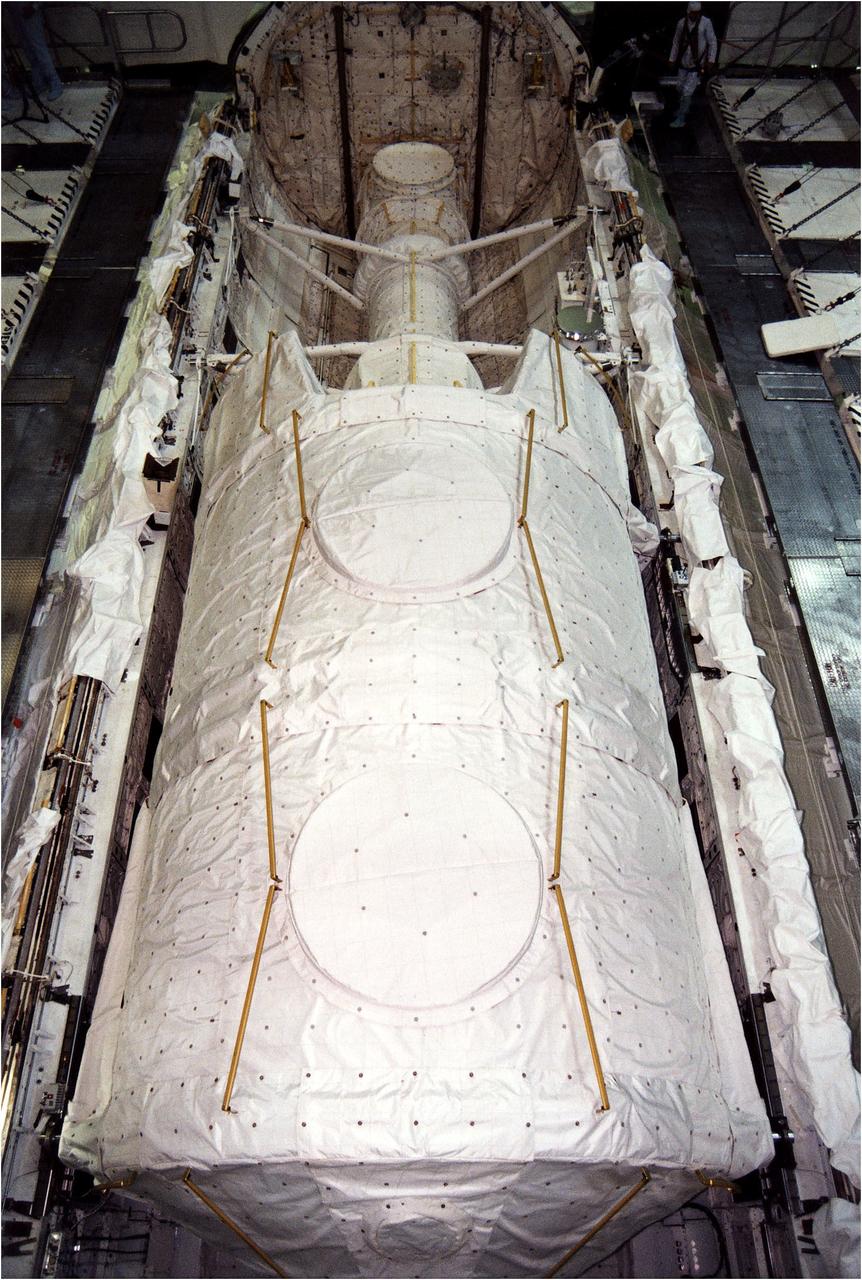
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. The Spacelab long crew transfer tunnel that leads from the orbiter's crew airlock to the module is also aboard, as well as the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attached to the right side of Columbia's payload bay. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments.
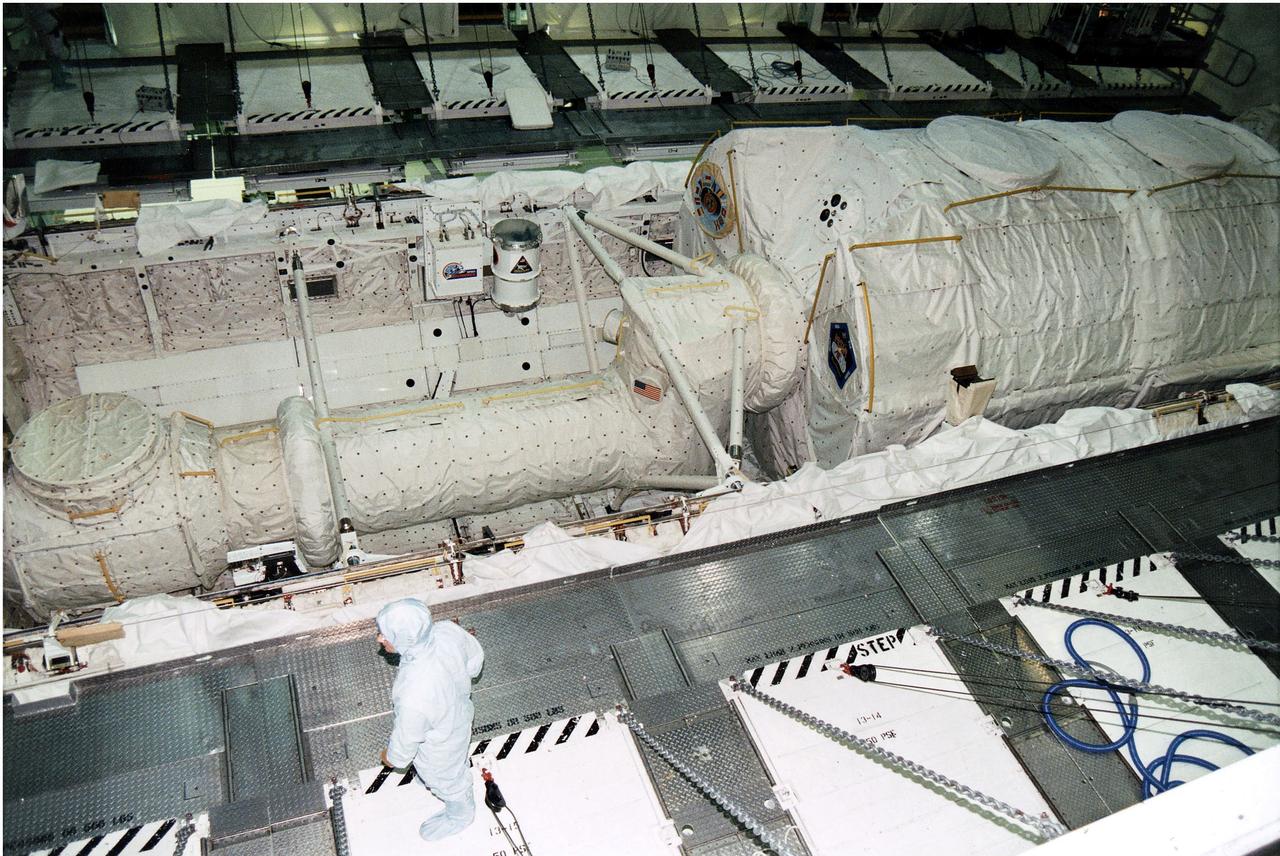
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. The Spacelab long crew transfer tunnel that leads from the orbiter's crew airlock to the module is also aboard, as well as the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attached to the right side of Columbia's payload bay. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments.
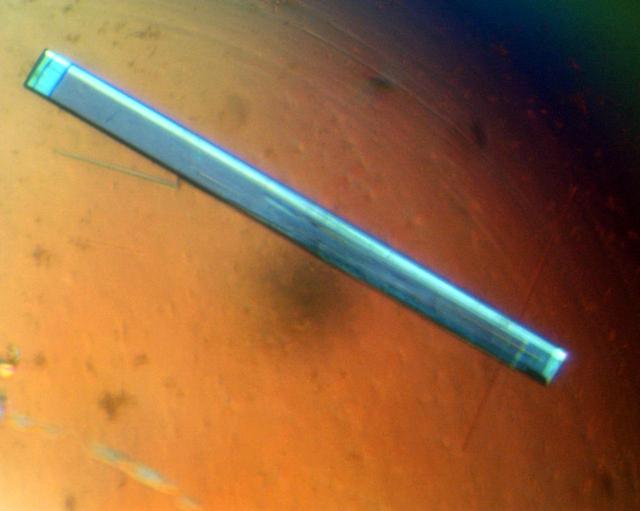
Parvalbumins are found in the muscles, endocrine glands, skin cells, and some neurons of vertebrates, but the role they play for musculature is not yet understood. Researchers are exploring theories of a correlation between parvalbumin concentration levels and the relaxation speed of mammalian muscles after contraction. An ultra-high resolution structure was achieved from samples grown on STS-83 and in July 1997, during STS-94, PCAM produced the largest crystals of pike parvalbumin grown to date. Principal Investigator: Dan Carter of New Century Pharmaceuticals.
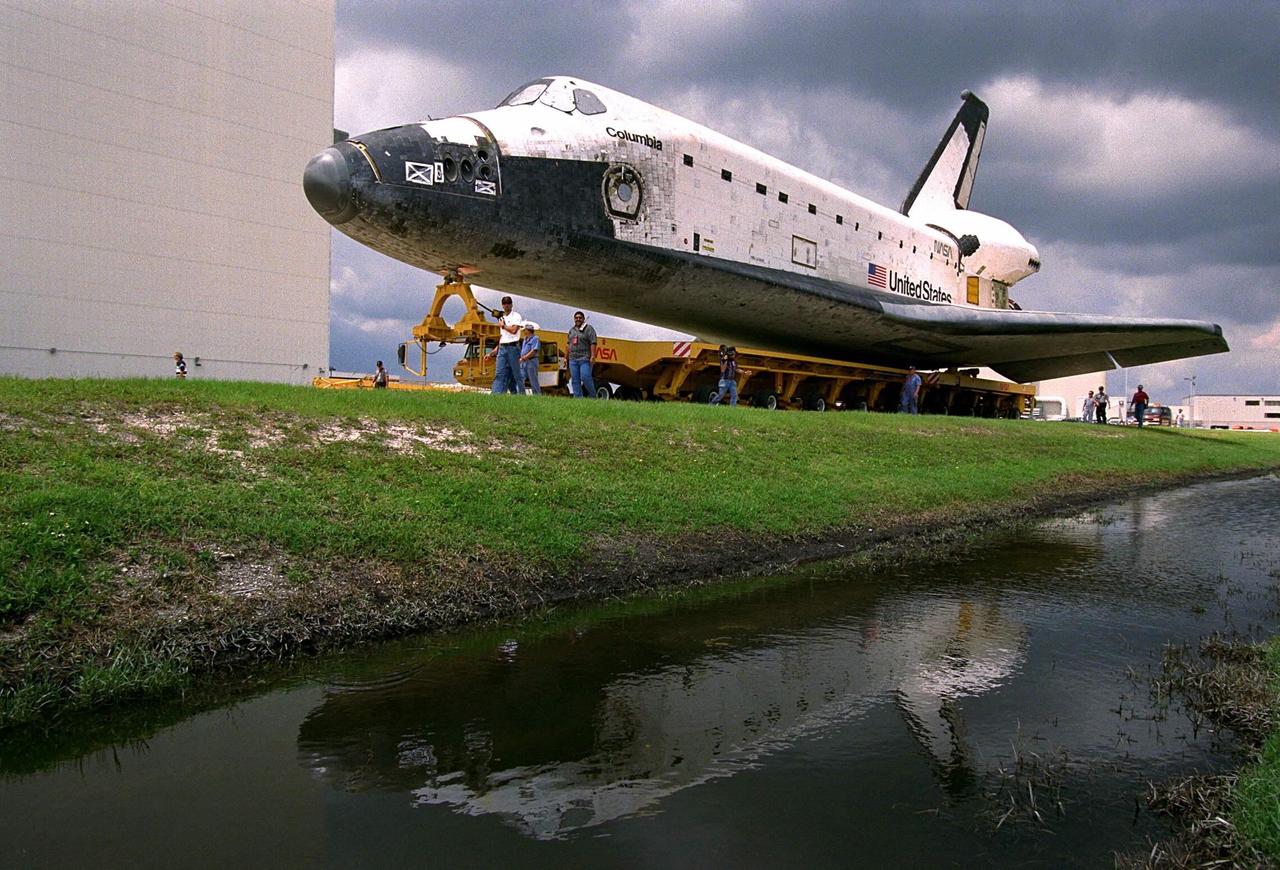

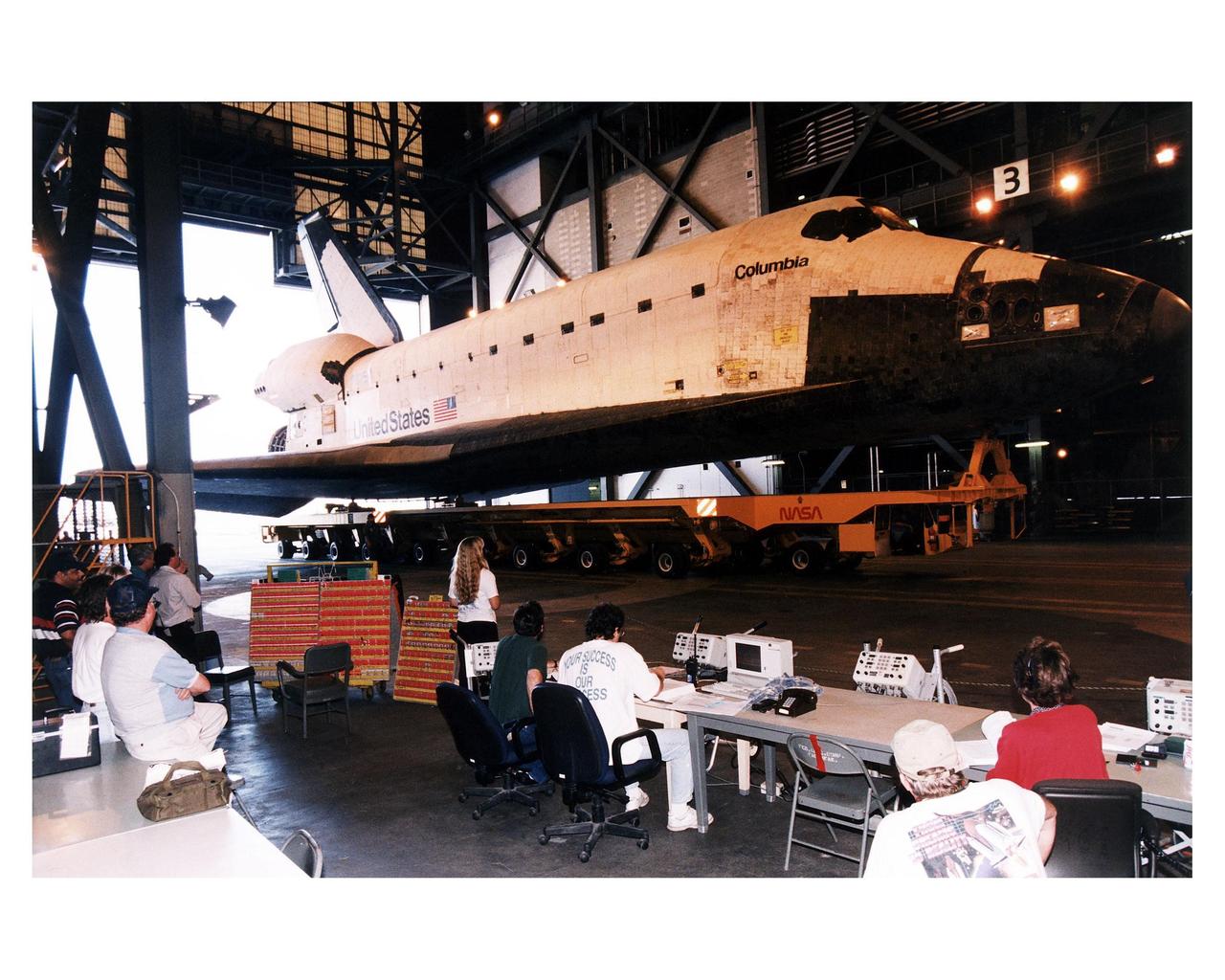
The Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia is reflected in a nearby pond as it rolls over to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) June 4 from Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) 1 atop its transporter in preparation for the STS-94 mission. Once inside the VAB, Columbia will be hoisted to be mated with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Columbia was moved to the OPF April 8 after the completion of the STS-83 mission. KSC payloads processing employees then began work to reservice the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module in the orbiter’s payload bay for the STS-94 mission. This was the first time that this type of payload was reserviced without removing it from the payload bay. This new procedure pioneers processing efforts for possible quick relaunch turnaround times for future payloads. The MSL-1 module will fly again with the full complement of STS-83 experiments after that mission was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. During the scheduled 16-day STS-94 mission, the experiments will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
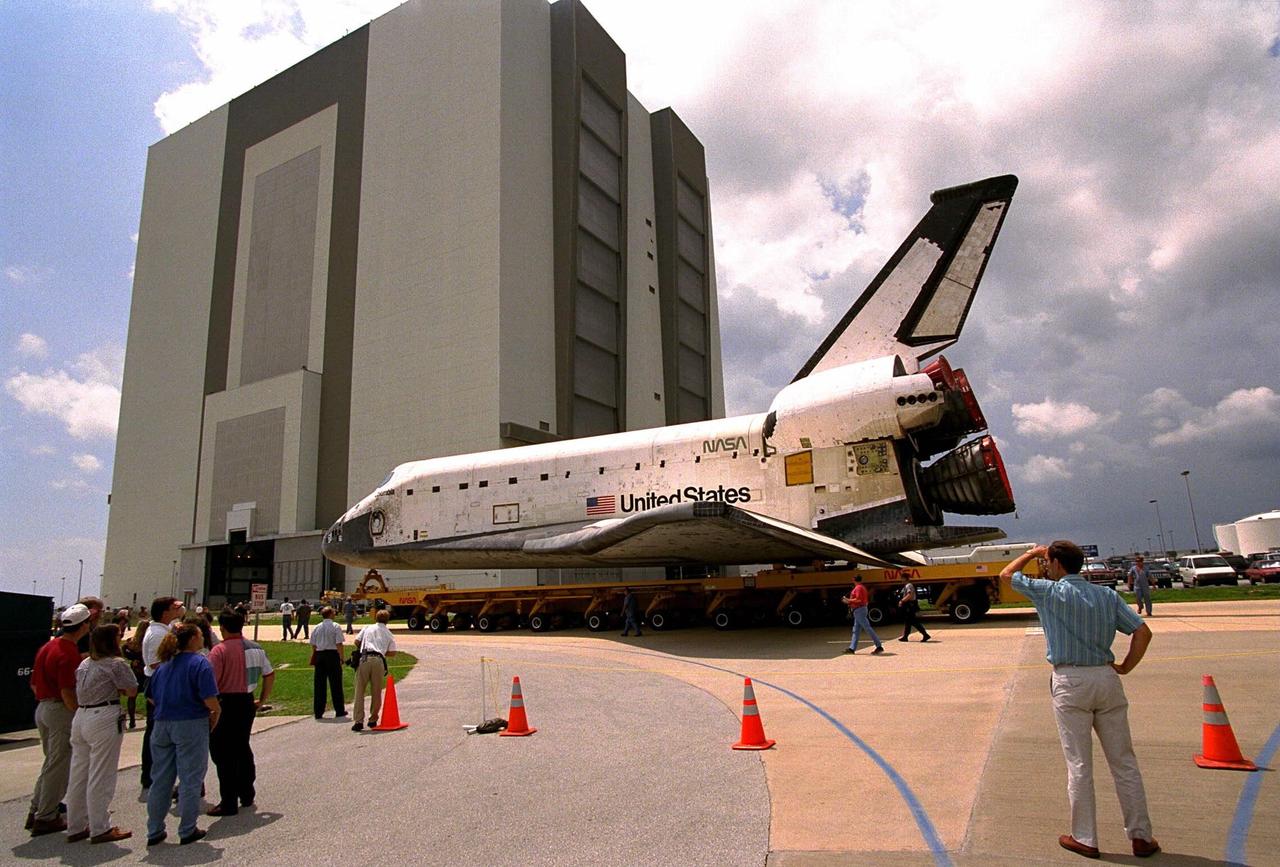

While KSC workers in the Launch Complex 39 Area watch, The Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia rolls over to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) June 4 from Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF)1 atop its transporter in preparation for the STS-94 mission. Once inside the VAB, Columbia will be hoisted to be mated with its solid rocket boosters and external tank. Columbia was moved to the OPF April 8 after the completion of the STS-83 mission. KSC payloads processing employees then began work to reservice the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module in the orbiter’s payload bay for the STS-94 mission. This was the first time that this type of payload was reserviced without removing it from the payload bay. This new procedure pioneers processing efforts for possible quick relaunch turnaround times for future payloads. The MSL-1 module will fly again with the full complement of STS-83 experiments after that mission was cut short due to indications of a faulty fuel cell. During the scheduled 16-day STS-94 mission, the experiments will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
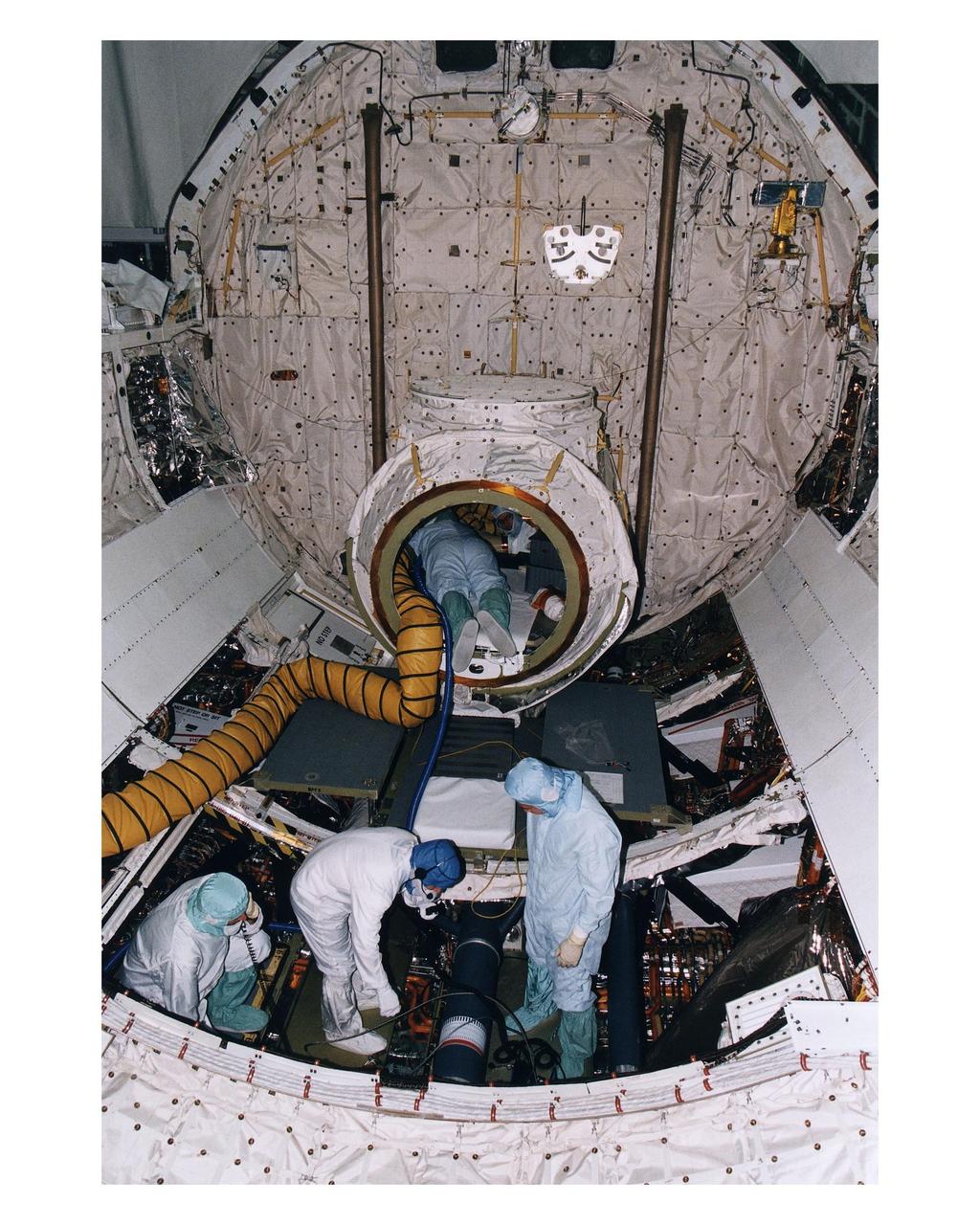

KSC payload processing employees in Orbiter Processing Facility 1 prepare the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia’s crew airlock and payload bay for the reinstallation of the Spacelab long transfer tunnel that leads from the airlock to the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module. The tunnel was taken out after the STS-83 mission to allow better access to the MSL-1 module during reservicing operations to prepare it for for the STS-94 mission. That space flight is now scheduled to lift off in early July. This was the first time that this type of payload was reserviced without removing it from the payload bay. This new procedure pioneers processing efforts for quick relaunch turnaround times for future payloads. The Spacelab module was scheduled to fly again with the full complement of STS-83 experiments after that mission was cut short due to a faulty fuel cell. During the scheduled 16-day STS-94 mission, the experiments will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
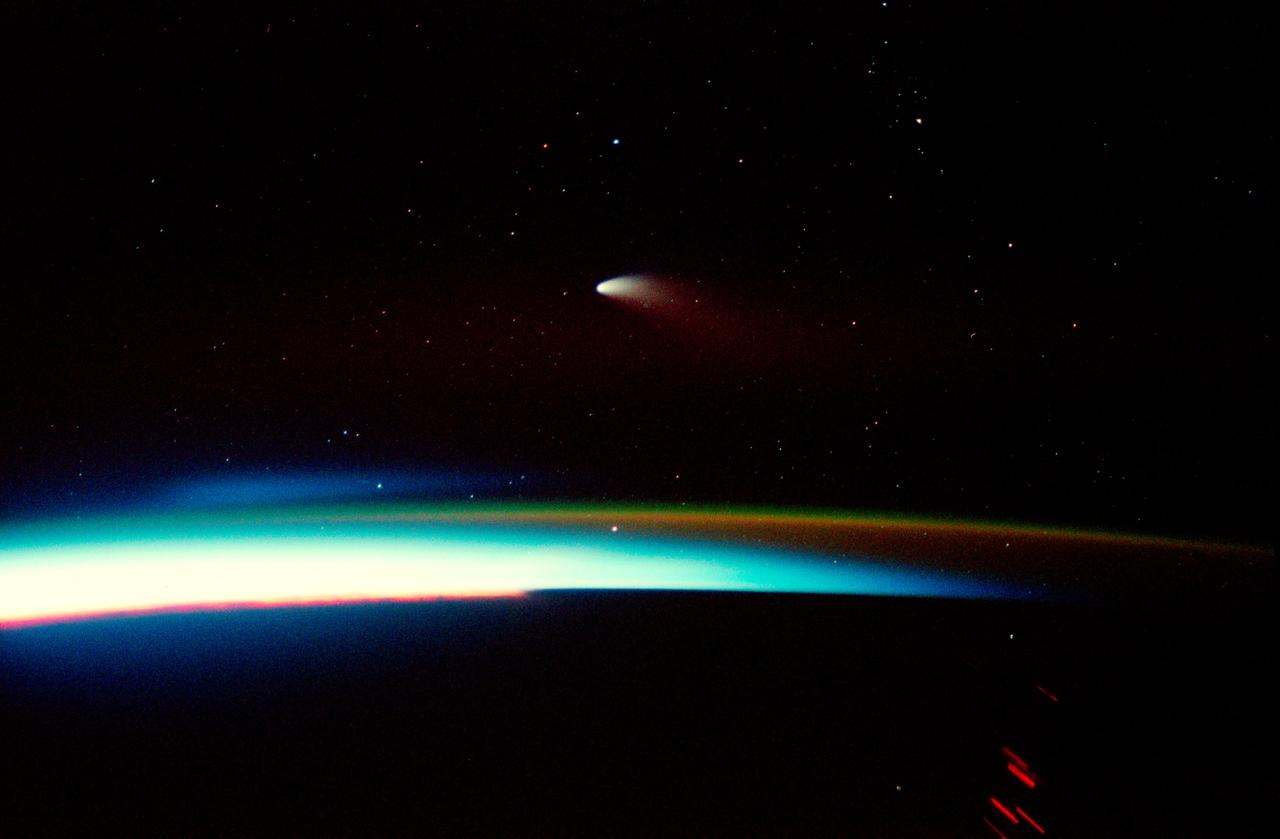

STS083-507-023 (4-8 April 1997)--- A 35mm camera was used to record this time-exposed image of Comet Hale-Bopp at sunset. As a spin-off of the more lengthy time exposure, city lights and petroleum fires are seen as distorted streaks.

S88-44517 (13 Aug 1988) --- Student experimenter John C. Vellinger, right, explains operation of an incubator used in his experiment to be carried onboard the Discovery for NASA's STS-29 mission next year. His primary audience is made up of STS-29's five-man crew, who will monitor in-space operation of the experiment, titled "Chicken Embryo Development in Space." Kentucky Fried Chicken.
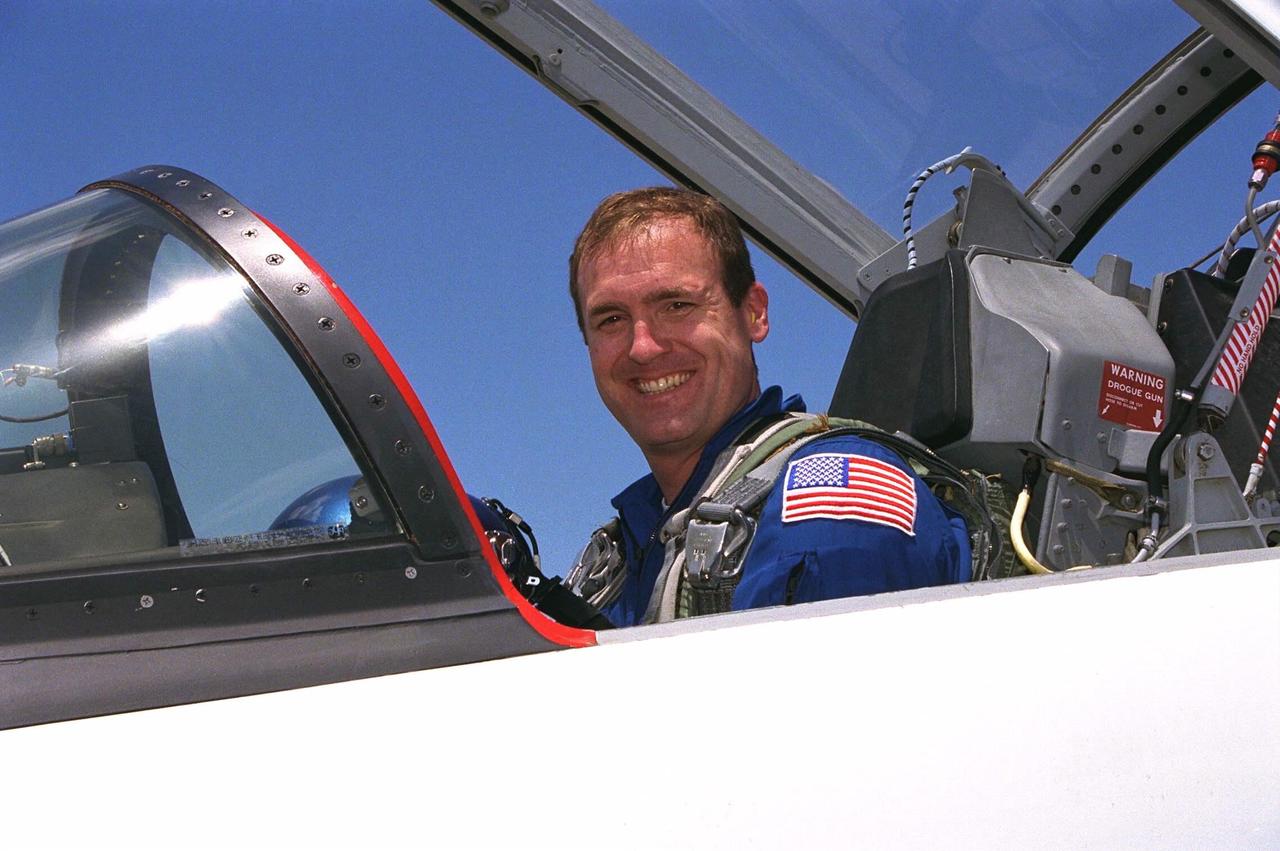

STS-94 Commander James D. Halsell, Jr., arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 jet in preparation for the reflight of the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 mission. Launch is scheduled for July 1, 1997, at 2:37 p.m. EDT. The laboratory was scheduled to fly again with the full complement of STS-83 experiments after that mission was cut short due to a faulty fuel cell. During the scheduled 16-day STS-94 mission, the experiments will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
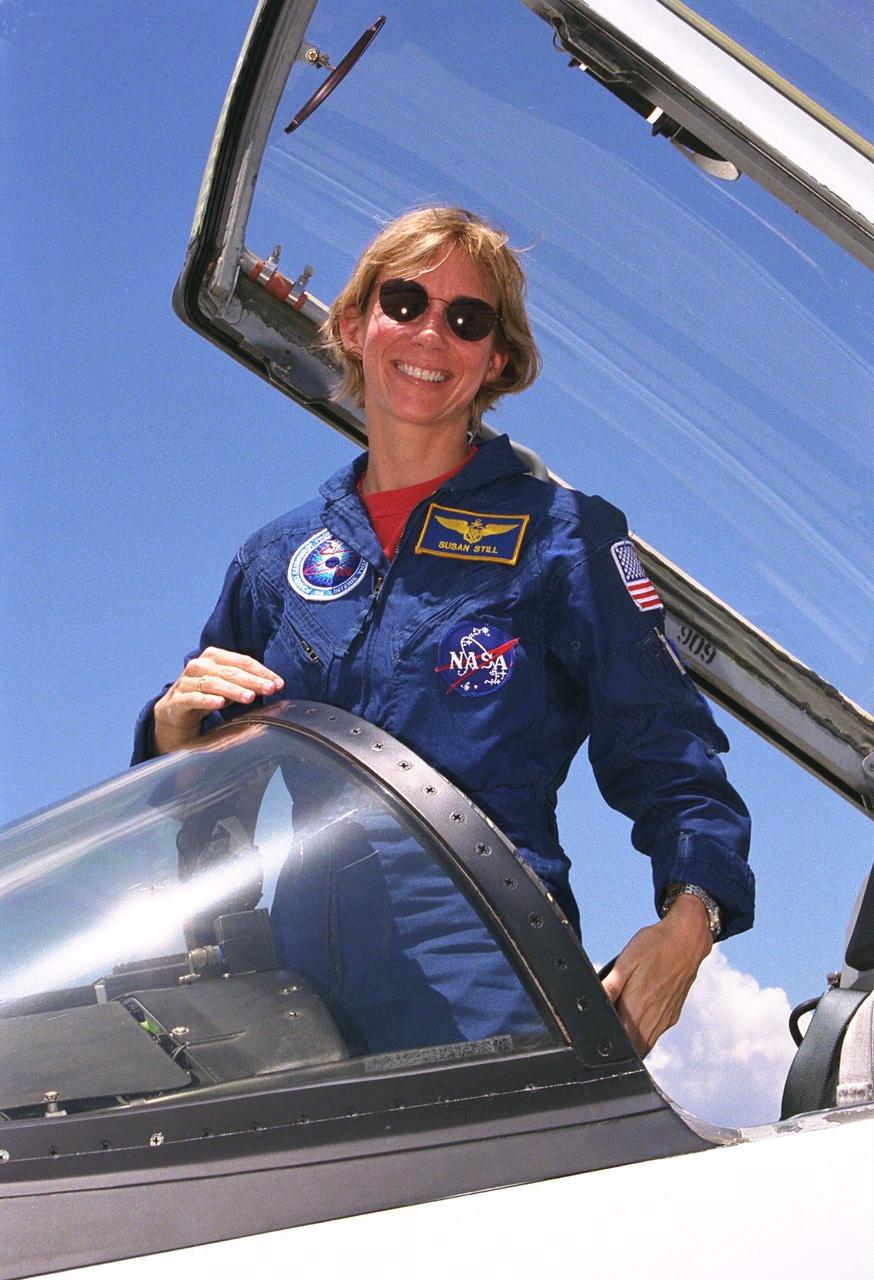

STS-94 Pilot Susan Leigh Still arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 jet in preparation for the reflight of the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 mission. Launch is scheduled for July 1, 1997, at 2:37 p.m. EDT. The laboratory was scheduled to fly again with the full complement of STS-83 experiments after that mission was cut short due to a faulty fuel cell. During the scheduled 16-day STS-94 mission, the experiments will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
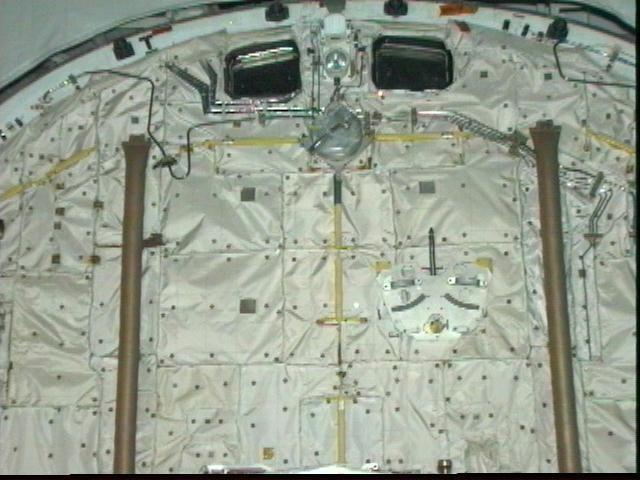

Yesterday, NASA decided to postpone for 24-hours the launch of Columbia on mission STS-83 due to a requirement to add additional thermal insulation to water coolant lines in the orbiter's payload bay. The water coolant lines are seen here winding their way around the window on the left. Managers determined that the lines, which cool various electronics on the orbiter, were not properly insulated and could possibly freeze during Columbia's 16-days in space. Columbia's launch is now set for 2:00 p.m. EST on Friday, April 4, 1997
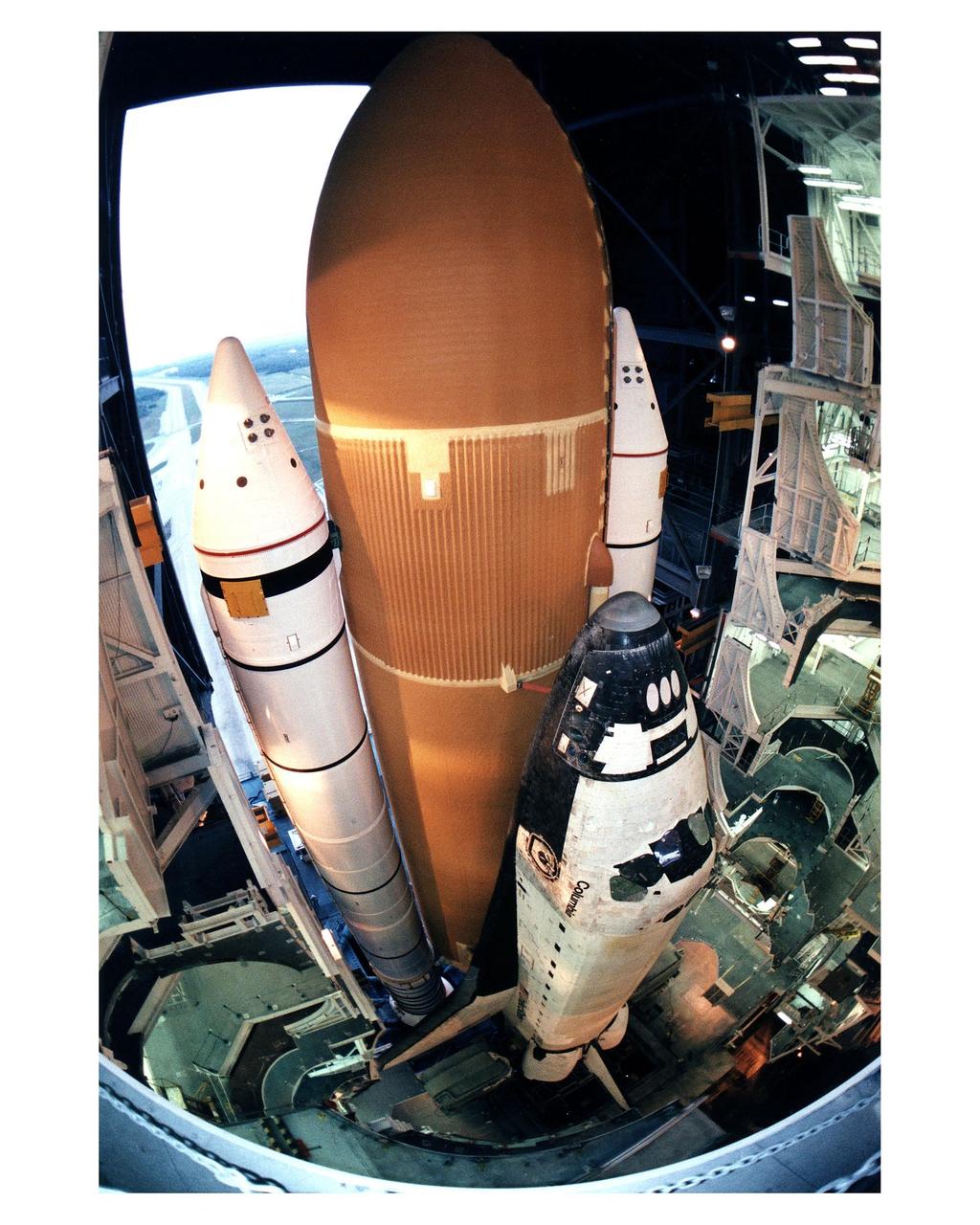

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia begins its rollout from the Vehicle Assembly Building to Launch Pad 39A in preparation for the STS-83 mission. The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is the primary payload on this 16-day spaceflight. The MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station, while the seven-member flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments

Apollo 7 Commander Walter M. "Wally" Schirra and his wife, Josephine, were among the many special NASA STS-83 launch guests who witnessed the liftoff of the Space Shuttle Columbia April 4 at the Banana Creek VIP Viewing Site at KSC. Columbia took off from Launch Pad 39A at 2:20:32 p.m. EST to begin the 16-day Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission

Apollo 11 Commander Neil A. Armstrong and his wife, Carol, were among the many special NASA STS-83 launch guests who witnessed the liftoff of the Space Shuttle Columbia April 4 at the Banana Creek VIP Viewing Site at KSC. Columbia took off from Launch Pad 39A at 2:20:32 p.m. EST to begin the 16-day Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission
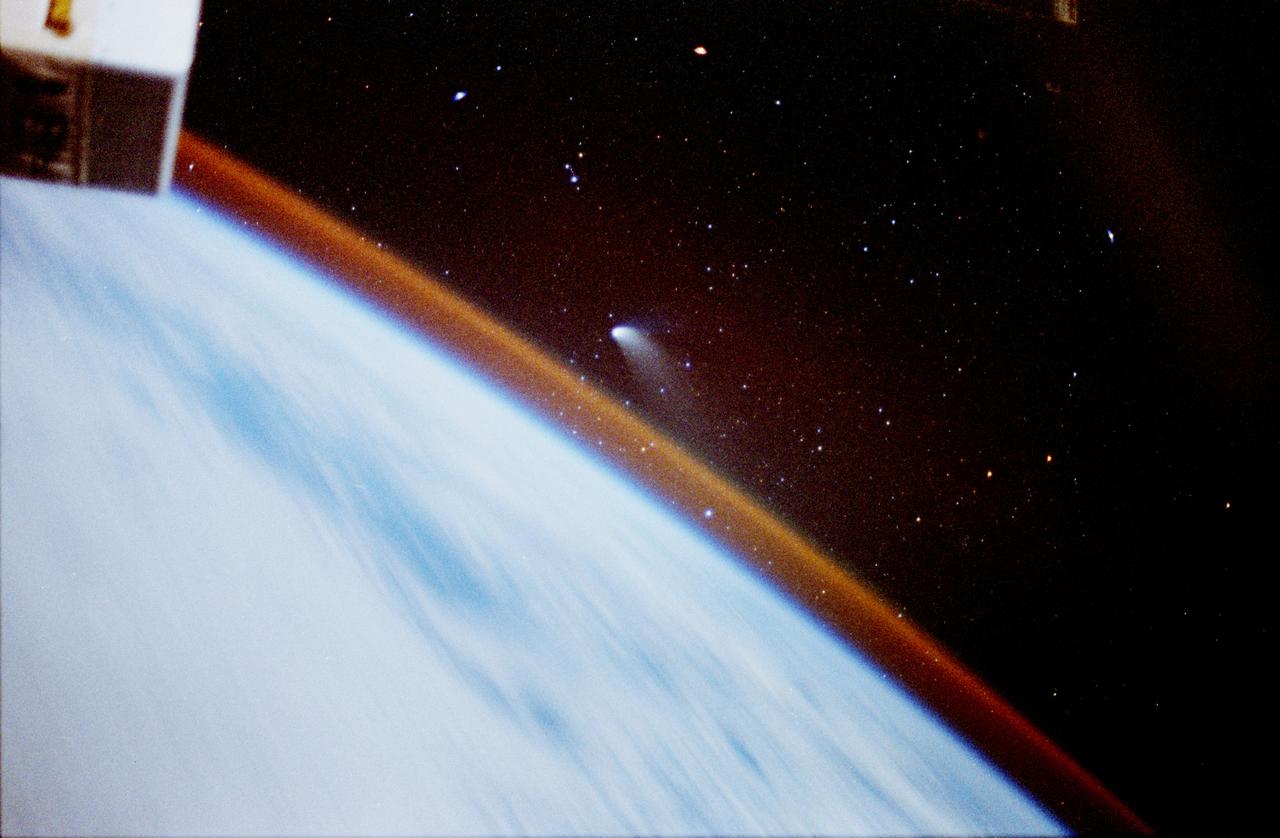

STS084-389-024 (15-24 May 1997) --- Comet Hale Bopp, seen and photographed a month and a half ago by the STS-83 crew aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia, was also visible on this mission and the crew took advantage of several photo opportunities. A crewmember used an eight-second time exposure on a 35mm camera to expose this frame of the comet over Earth's horizon. Streaking of the stars, usually associated with time exposures, was avoided due to Space Shuttle Atlantis' inertial attitude with the stars.

The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is lowered into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
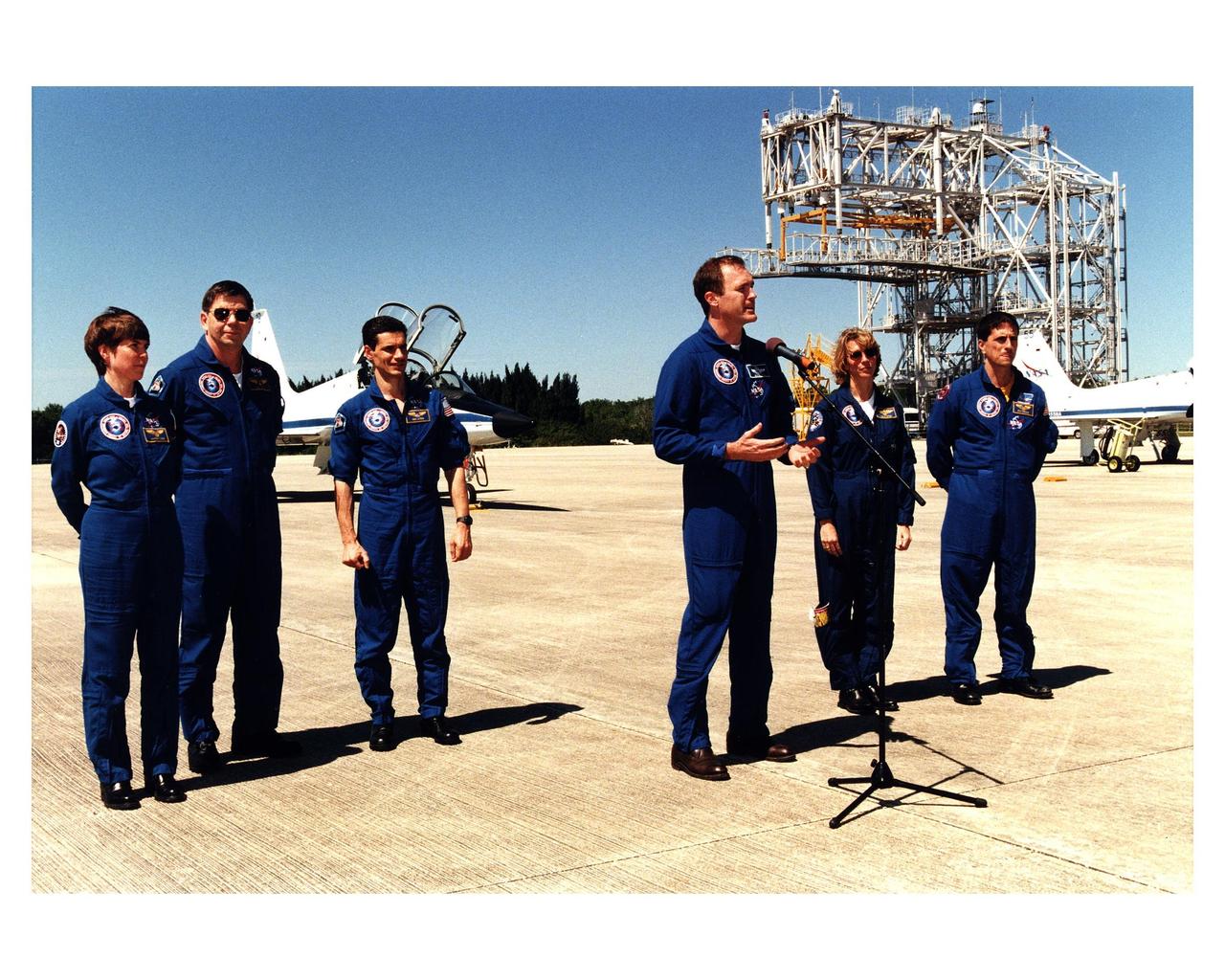

With the mate-demate device as backdrop, six of the seven STS-83 crew members speak to the media after arriving at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility prior to Space Shuttle Columbia's launch. From left to right, they are Payload Commander Janice E. Voss; Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris; Commander James D. Halsell, Jr.; Pilot Susan Leigh Still; and Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas. Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt arrived separately later in the afternoon
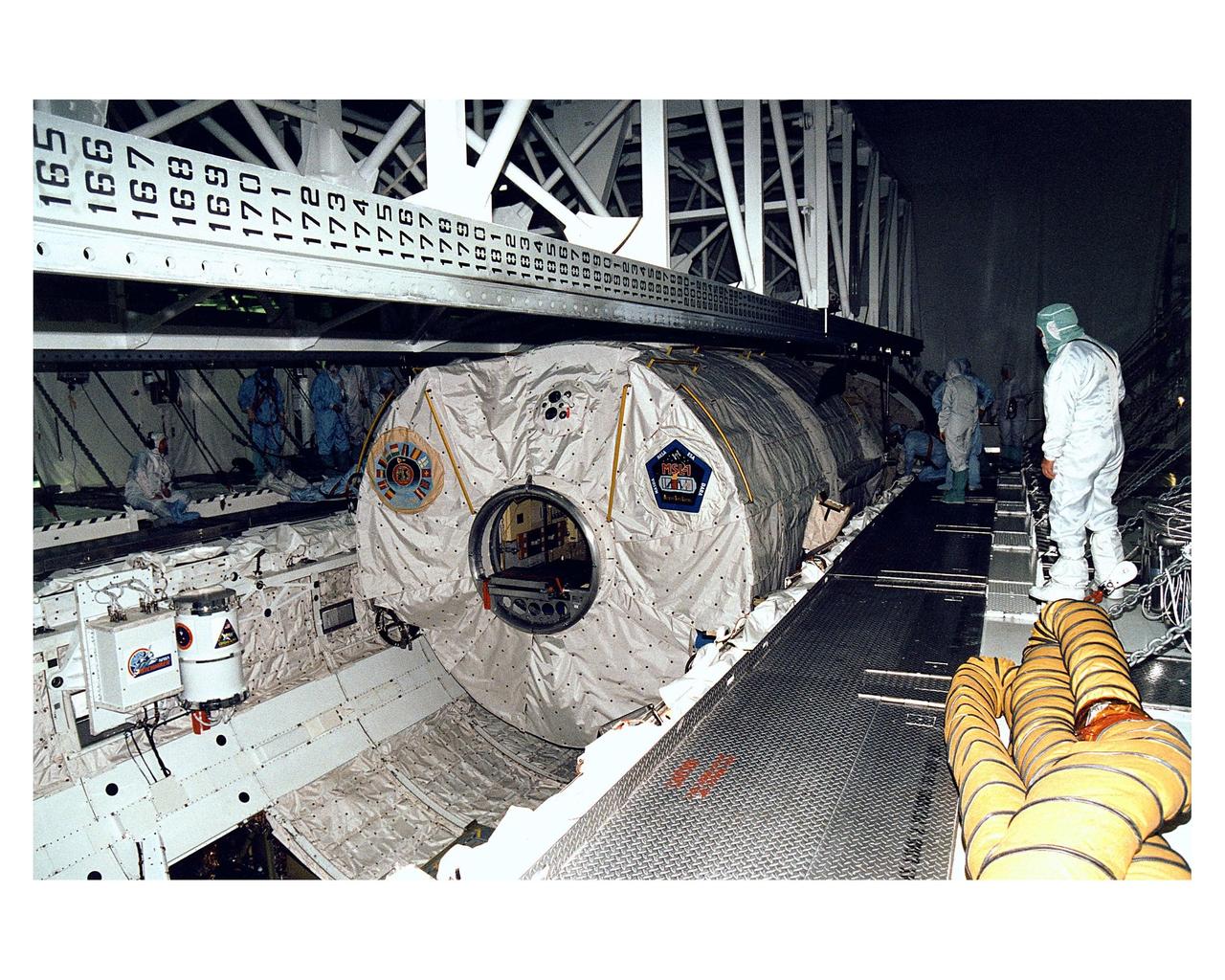

The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is lowered into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments

STS-83 Payload Specialist Gregory T. Linteris, Mission Specialist Janice E. Voss, and Payload Specialist Roger K. Crouch participate in emergency egress training at Launch Complex 39A during the crew's <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT).</a> They are seen here in one of the pads' seven <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/pads.htm#emergenc">slidewire baskets.</a
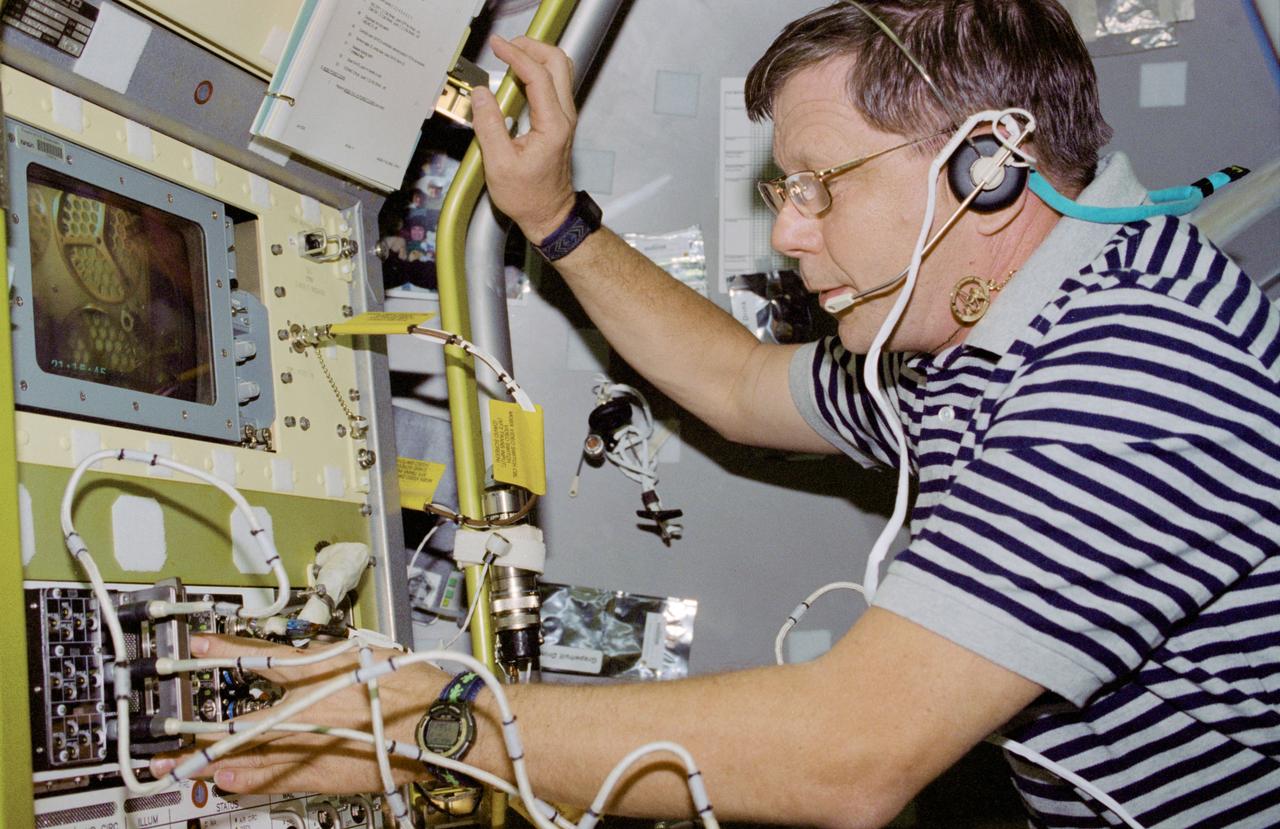

STS083-346-024 (4-8 April 1997) --- Payload specialist Roger K. Crouch performs the activation for the Mid Deck Glove Box (MGBX). Made to accommodate a variety of hardware and materials testing, the facility offers physical isolation and a negative air pressure environment so that items that are not suitable for handling in the open Spacelab can be protected. One experiment that was performed on STS-83 is the Internal Flows in a Free Drop (IFFD), an experiment that investigates rotation and position control of drops by varying acoustic pressures.
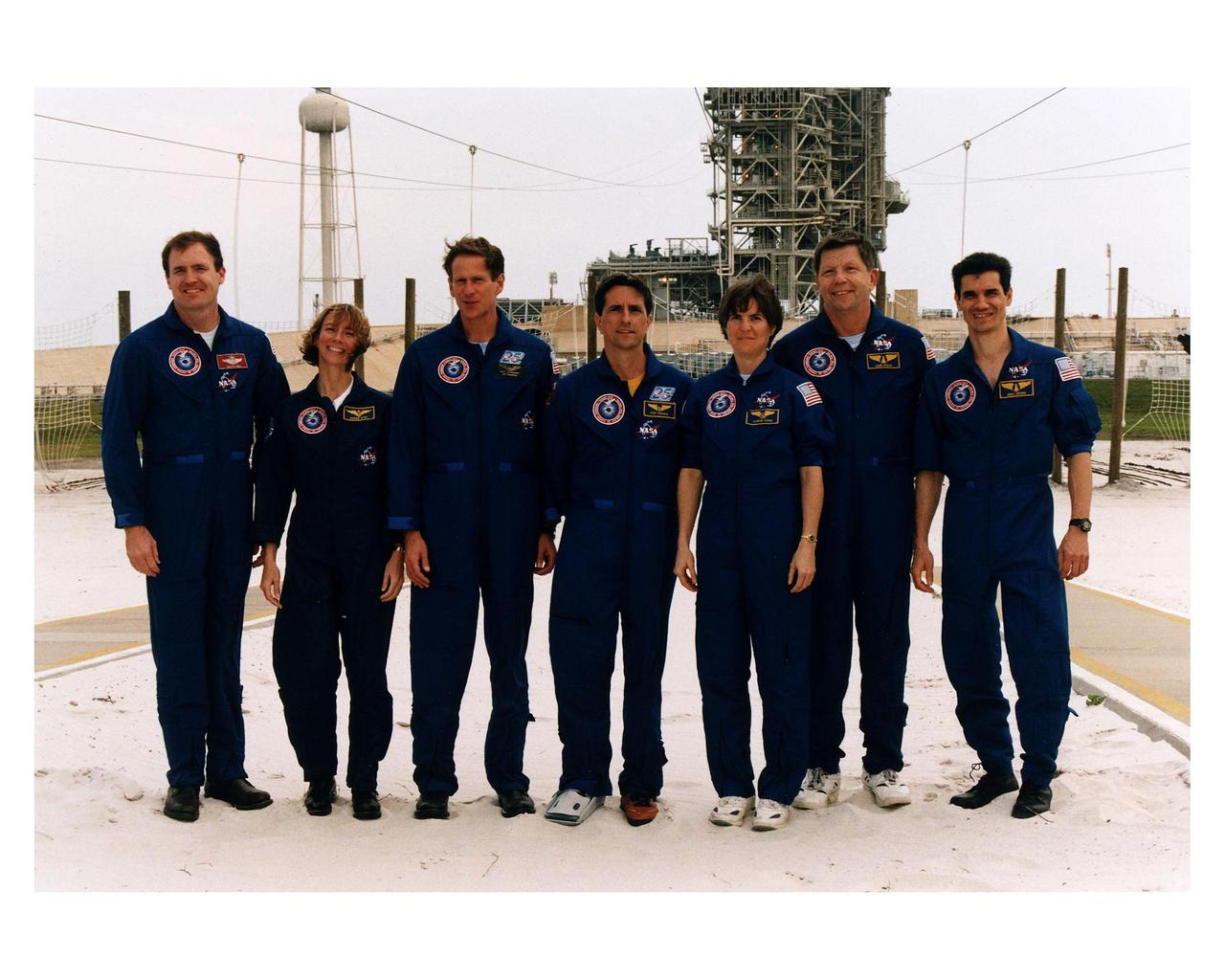

The STS-83 crew poses for the media at Launch Complex 39A during the crew's <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT).</a> From left to right, they are Mission Commander James D. Halsell; Pilot Susan L. Still; Mission Specialists Michael L. Gernhardt, Donald Thomas, and Janice E. Voss; and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris
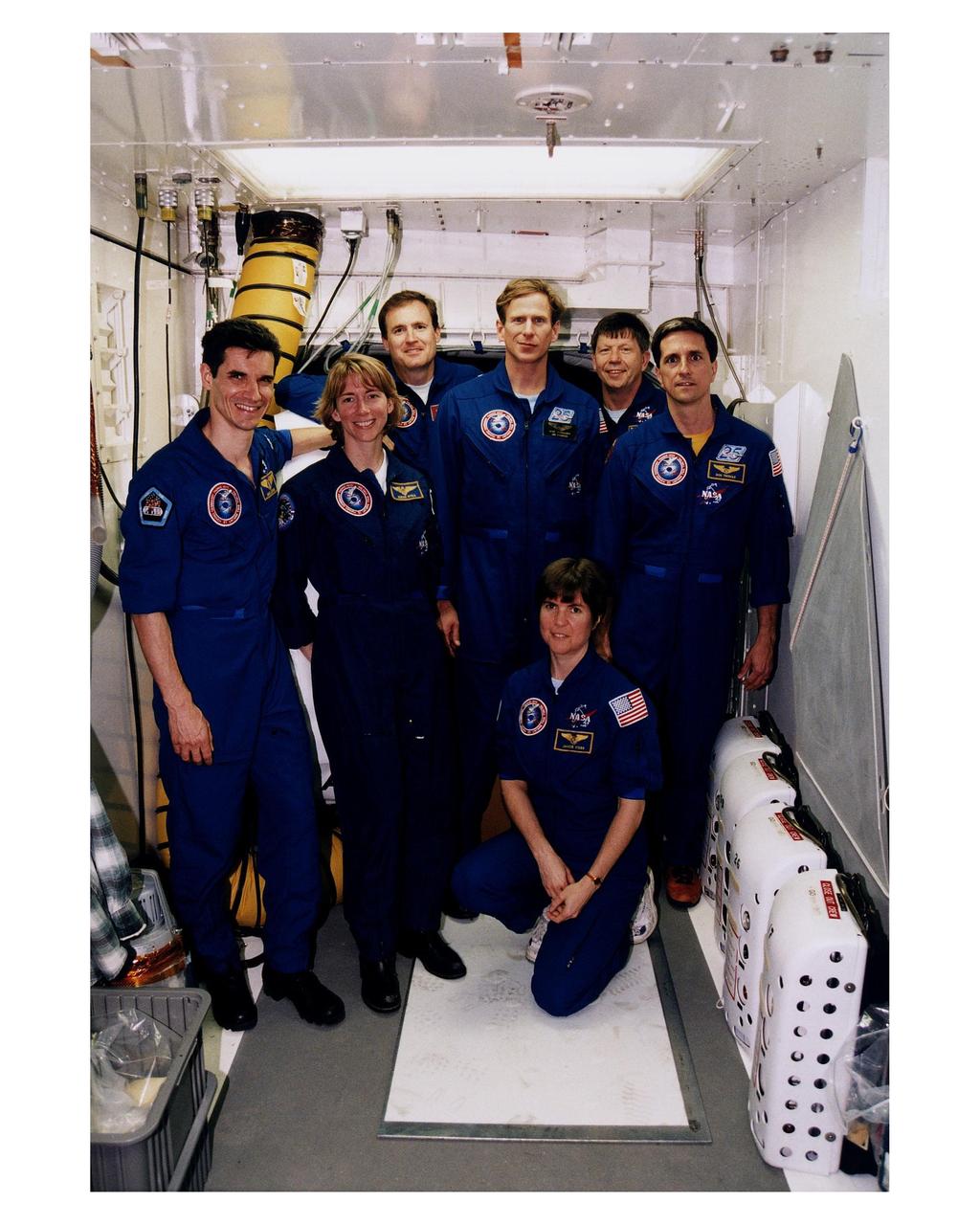

The STS-83 crew poses in the White Room at Launch Complex 39A during the crew's <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT).</a> From left to right, standing, they are Payload Specialist Gregory T. Linteris, Pilot Susan L. Still, Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Payload Specialist Roger K. Crouch, and Mission Specialist Donald Thomas. Mission Specialist Janice E. Voss is kneeling
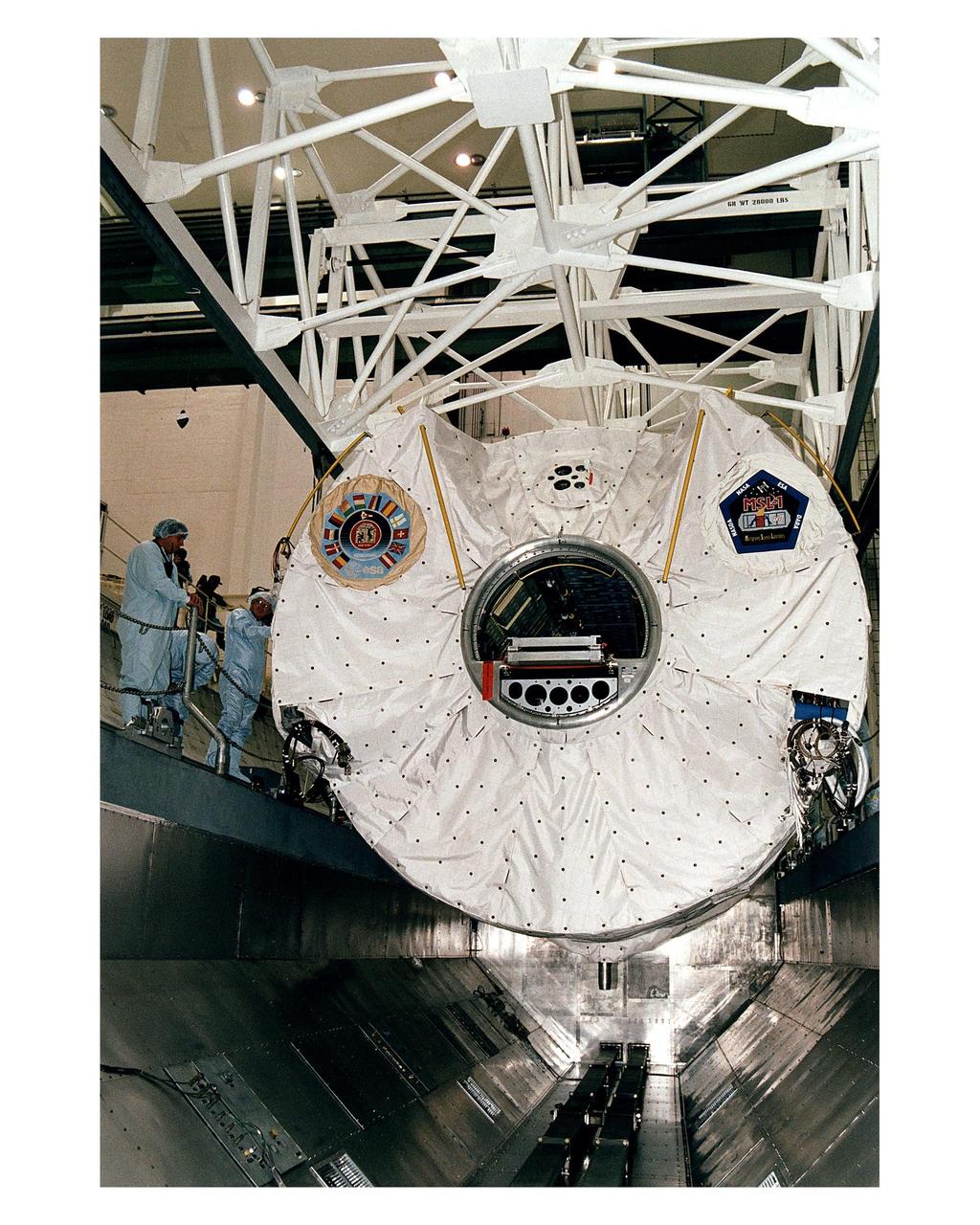

The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is moved to be installed into a payload canister in the Operations and Checkout Building. Once in the canister, the MSL-1 will be transported to Orbiter Processing Bay 1 where it will be integrated into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
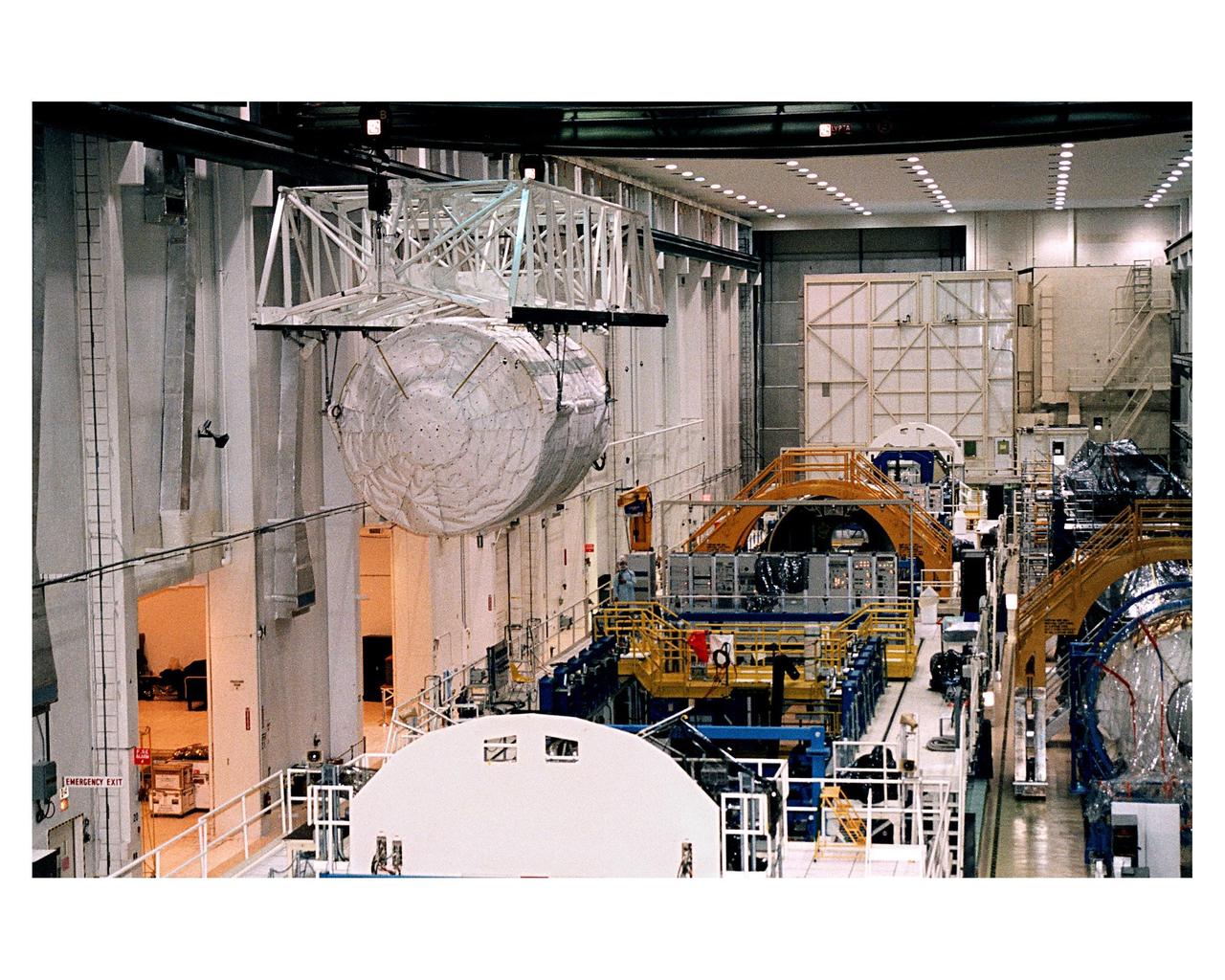
The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is moved to be installed into a payload canister in the Operations and Checkout Building. Once in the canister, the MSL-1 will be transported to Orbiter Processing Bay 1 where it will be integrated into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments
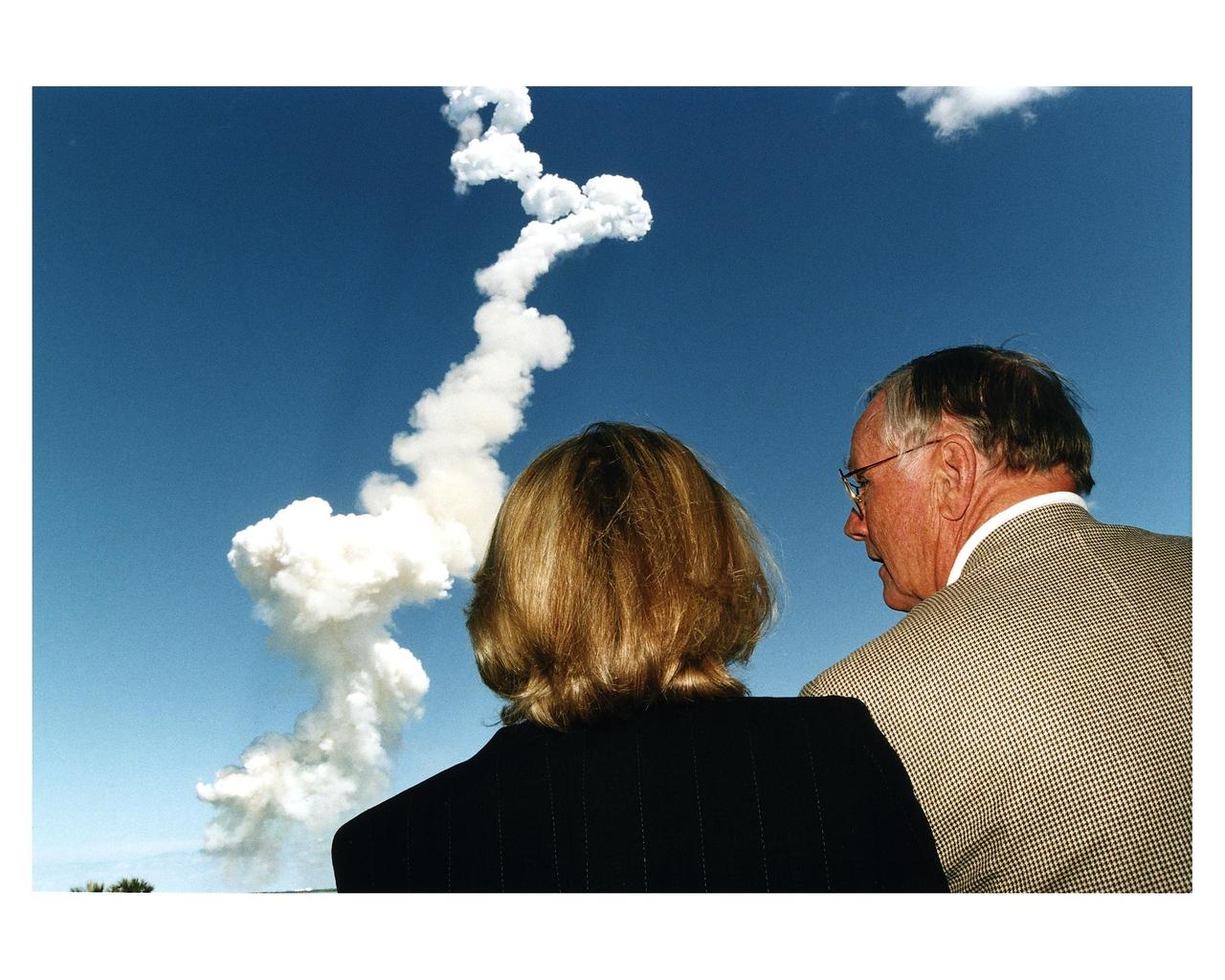

Apollo l1 Commander Neil A. Armstrong and his wife, Carol, were among the many special NASA STS-83 launch guests who witnessed the liftoff of the Space Shuttle Columbia April 4 at the Banana Creek VIP Viewing Site at KSC. Columbia took off from Launch Pad 39A at 2:20:32 p.m. EST to begin the 16-day Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission
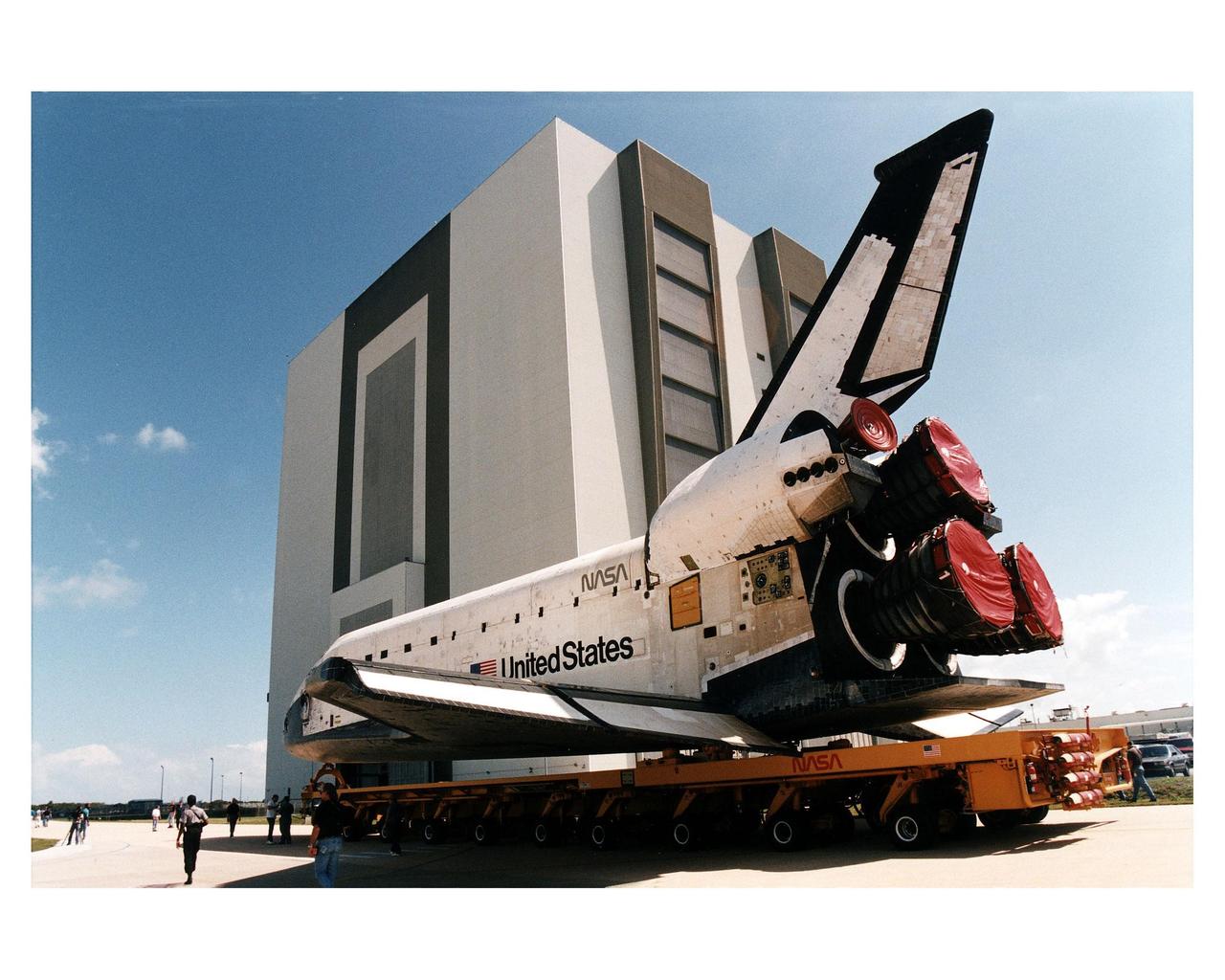

Space Shuttle Columbia rolls over from Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1 to the Vehicle Assembly Building to be mated to its external tank/solid rocket booster stack. Roll out to Pad 39A in preparation for mission STS-83 is set for first motion at 7 a.m. on Tuesday. Launch is currently targeted for April 3 at 2:01 p.m. EST

The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is moved to be installed into a payload canister in the Operations and Checkout Building. Once in the canister, the MSL-1 will be transported to Orbiter Processing Bay 1 where it will be integrated into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments

Space Shuttle Columbia rolls over from Orbiter Processing Facility bay 1 to the Vehicle Assembly Building to be mated to its external tank/solid rocket booster stack. Roll out to Pad 39A in preparation for mission STS-83 is set for first motion at 7 a.m. on Tuesday. Launch is currently targeted for April 3 at 2:01 p.m. EST
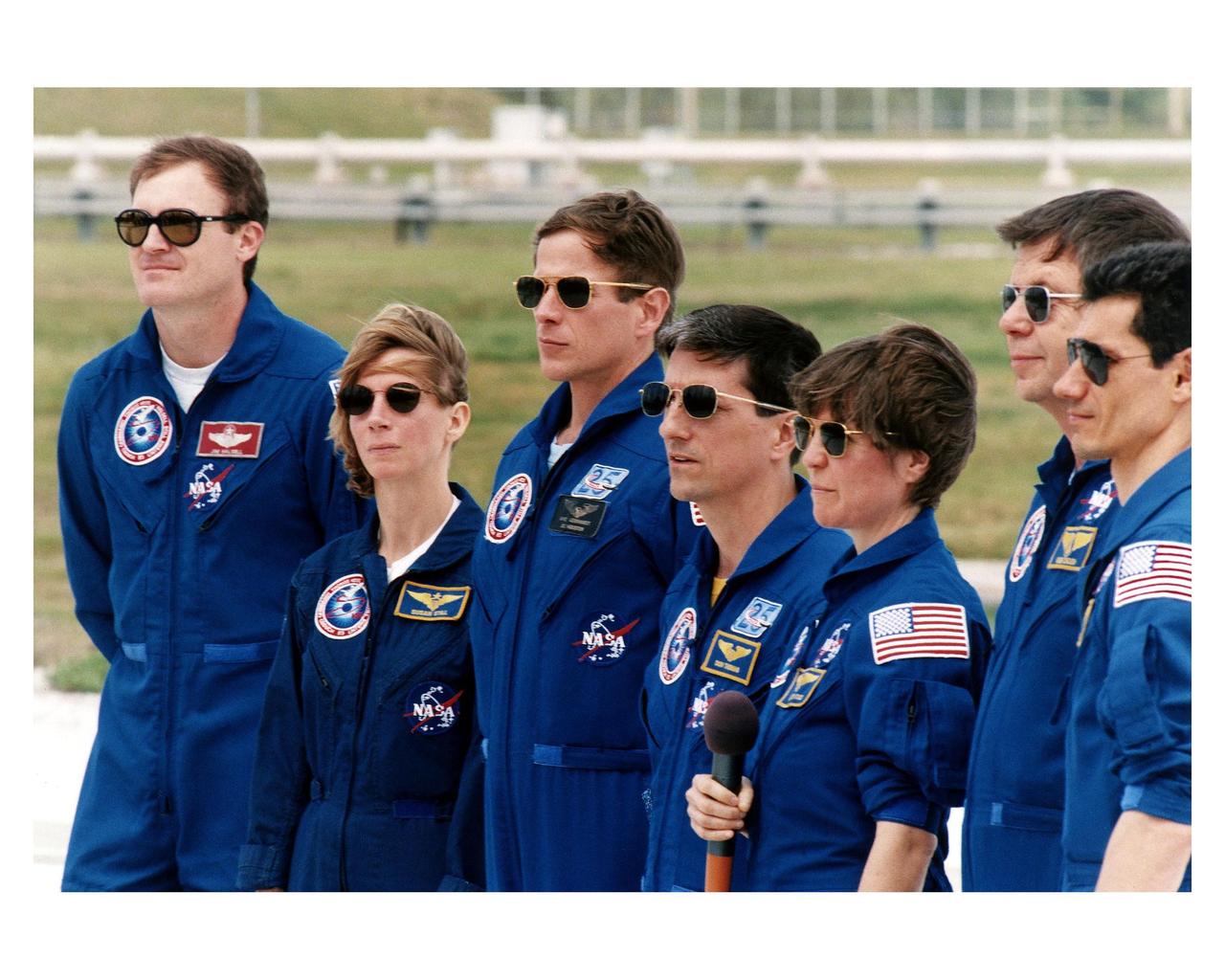

The Space Shuttle Mission STS-83 crew talks to the media at Launch Complex 39A during the crew's <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT).</a> From left to right, they are Mission Commander James D. Halsell; Pilot Susan L. Still; Mission Specialists Michael L. Gernhardt, Donald Thomas, and Janice E. Voss (holding microphone); and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris
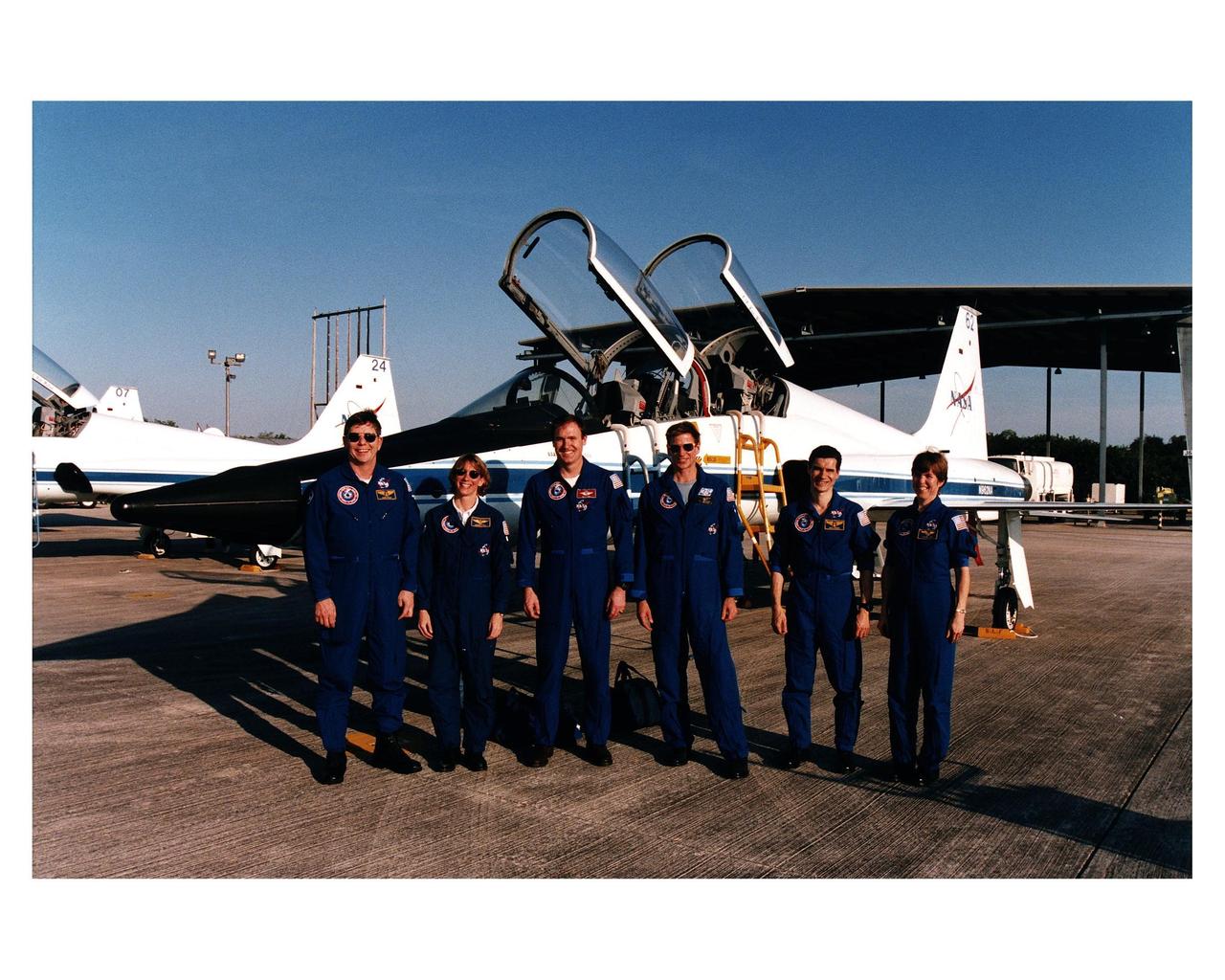

Six of the seven astronauts assigned to the STS-83 crew arrive at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility in preparation for their <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/release/1997/40-97.htm">Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test.</a> From left to right, they are Payload Specialist Roger K. Crouch, Pilot Susan L. Still, Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt, Payload Specialist Gregory T. Linteris, and Mission Specialist Janice E. Voss
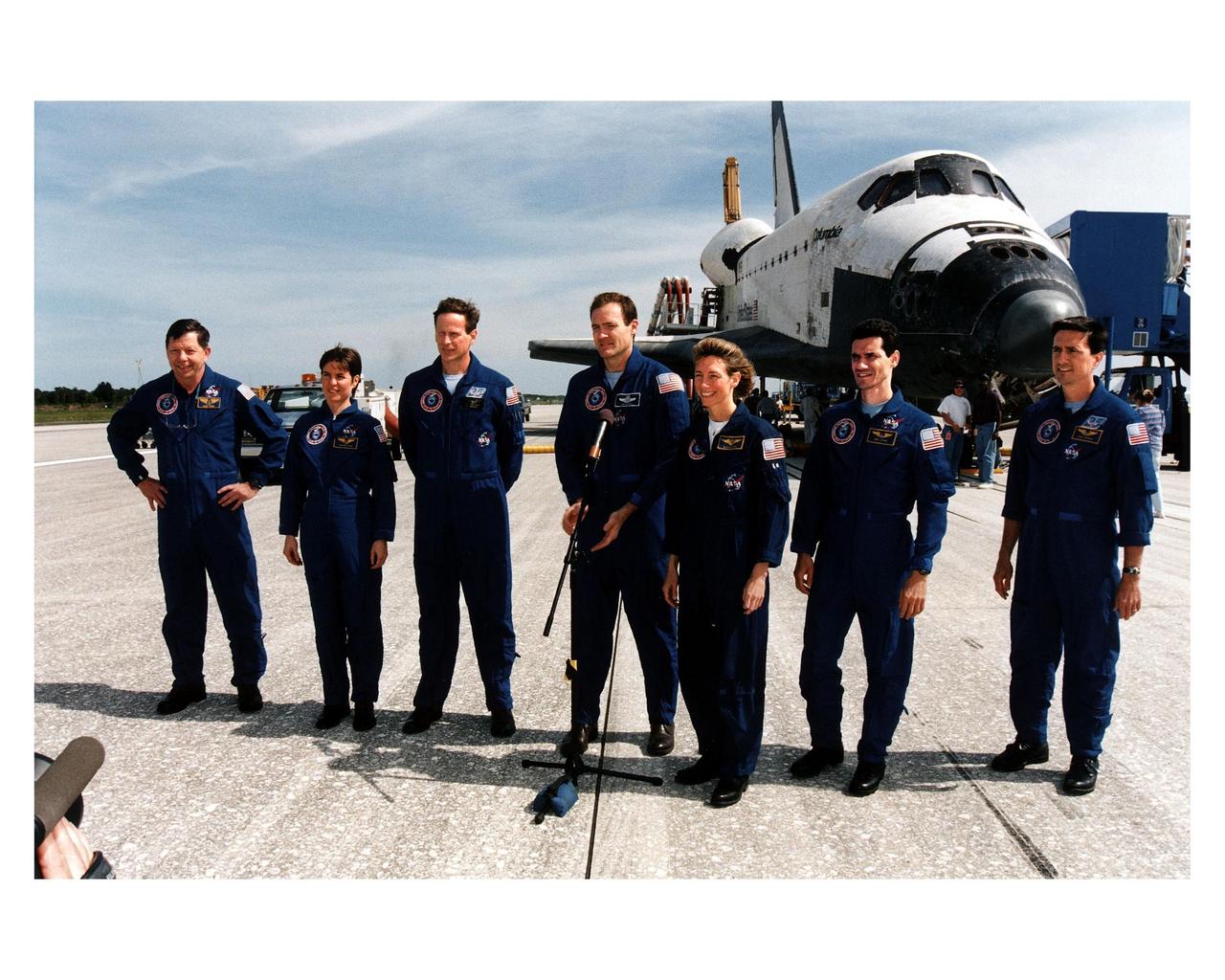

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- With the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in the background, STS-83 Mission Commander James D. Halsell (center) gives a post-landing briefing on Runway 33 at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility. Columbia landed at 2:33:11 p. m. EDT, April 8, to conclude the Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission. The other flight crew members (from left) are: Payload Specialist Roger K. Crouch; Payload Commander Janice Voss; Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt; Pilot Susan L. Still; Payload Specialist Gregory T. Linteris; and Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas. At main gear touchdown, the STS-83 mission duration was 3 days, 23 hours, 12 minutes. The planned 16-day mission was cut short by a faulty fuel cell. This is only the third time in Shuttle program history that an orbiter was brought home early due to mechanical problems. This was also the 36th KSC landing since the program began in 1981

STS-94 Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas prepares to enter the Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Pad 39A in preparation for launch. He has flown on STS-83, STS-70 and STS-65. He holds a doctorate in materials science and has been the Principal Investigator for a Space Shuttle crystal growth experiment. Because of his background in materials science, Thomas will be concentrating his efforts during the Red shift on the five experiments in this discipline in the Large Isothermal Furnace. He also will work on the ten materials science investigations in the Electromagnetic Containerless Processing Facility and four that will be measuring the effects of microgravity and motion in the orbiter on the experiments. Thomas and six fellow crew members will lift off during a launch window that opens at 1:50 p.m. EDT, July 1. The launch window will open 47 minutes early to improve the opportunity to lift off before Florida summer rain showers reach the space center
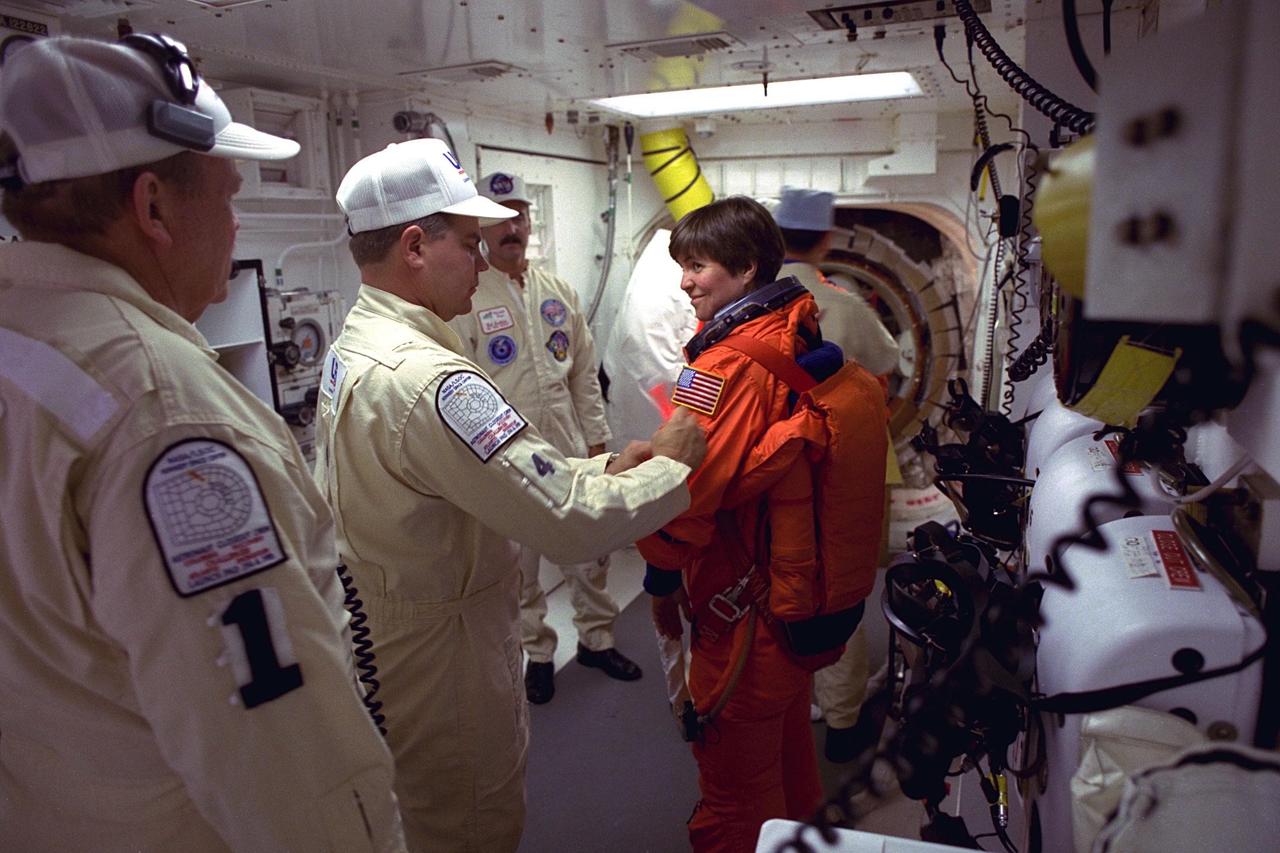

STS-94 Payload Commander Janice Voss prepares to enter the Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Pad 39A in preparation for launch. She has flown on STS-83, STS-63 and STS-57. Voss holds a doctorate degree in aeronautics/astronautics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and has earned two NASA Space Flight Medals. As Payload Commander and a member of the Blue team, Voss will have overall responsibility for the operation of all of the MSL-1 experiments. During the experimentation phase of the mission, she be working primarily with three combustion experiments. She and six fellow crew members will lift off during a launch window that opens at 1:50 p.m. EDT, July 1. The launch window will open 47 minutes early to improve the opportunity to lift off before Florida summer rain showers reach the space center
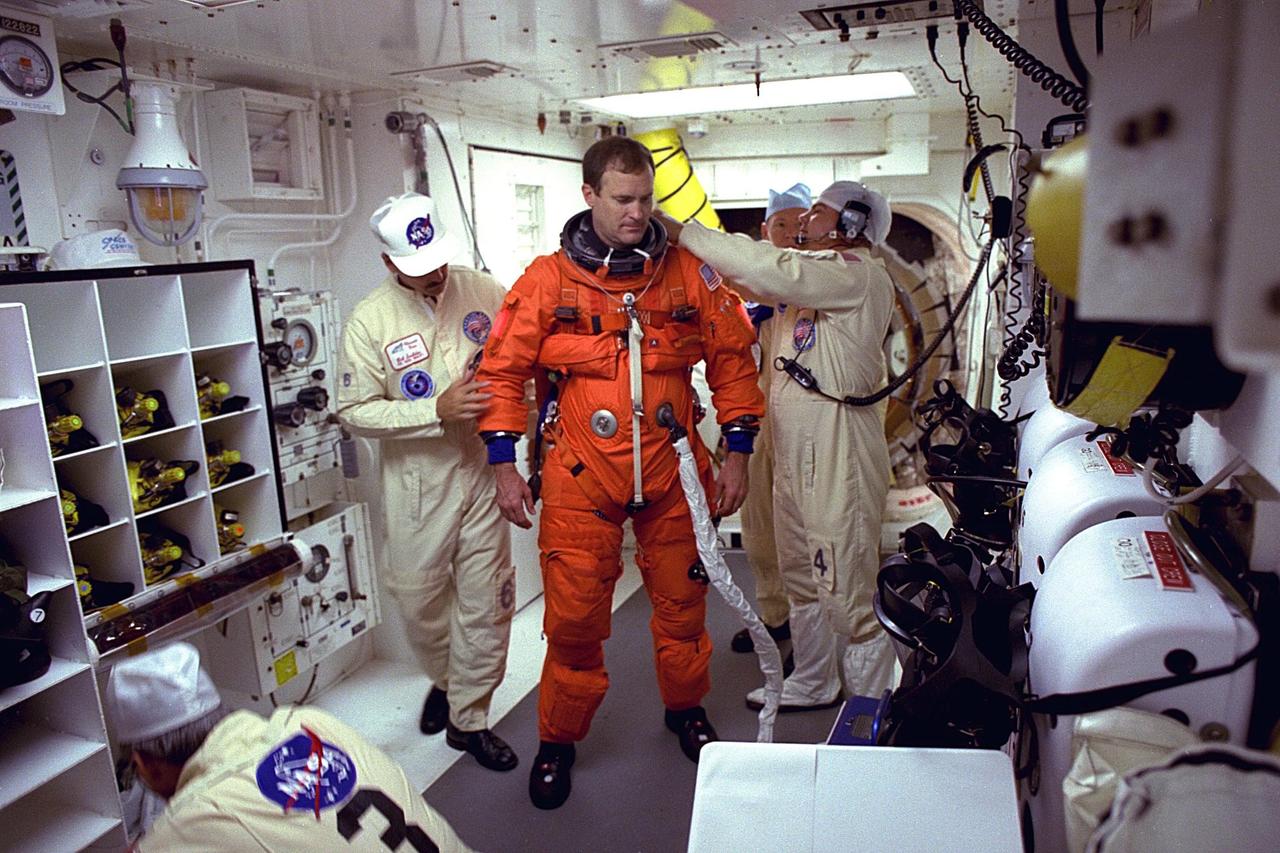

STS-94 Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr., prepares to enter the Space Shuttle Columbia at Launch Pad 39A in preparation for launch. Halsell is on his fourth space flight, having served as commander of STS-83 and pilot of both STS-74 and STS-65. He is a lieutenant colonel in the Air Force and a former SR-71 Blackbird test pilot and holds master’s degrees in management and space operations. Halsell will have responsibility for the success of the mission and will operate and maintain Columbia during the Red, or second shift. He will also assist with a materials science experiment and a protein crystal growth payload during the 16-day mission. Halsell and six fellow crew members will lift off during a launch window that opens at 1:50 p.m. EDT, July 1. The launch window will open 47 minutes early to improve the opportunity to lift off before Florida summer rain showers reach the space center
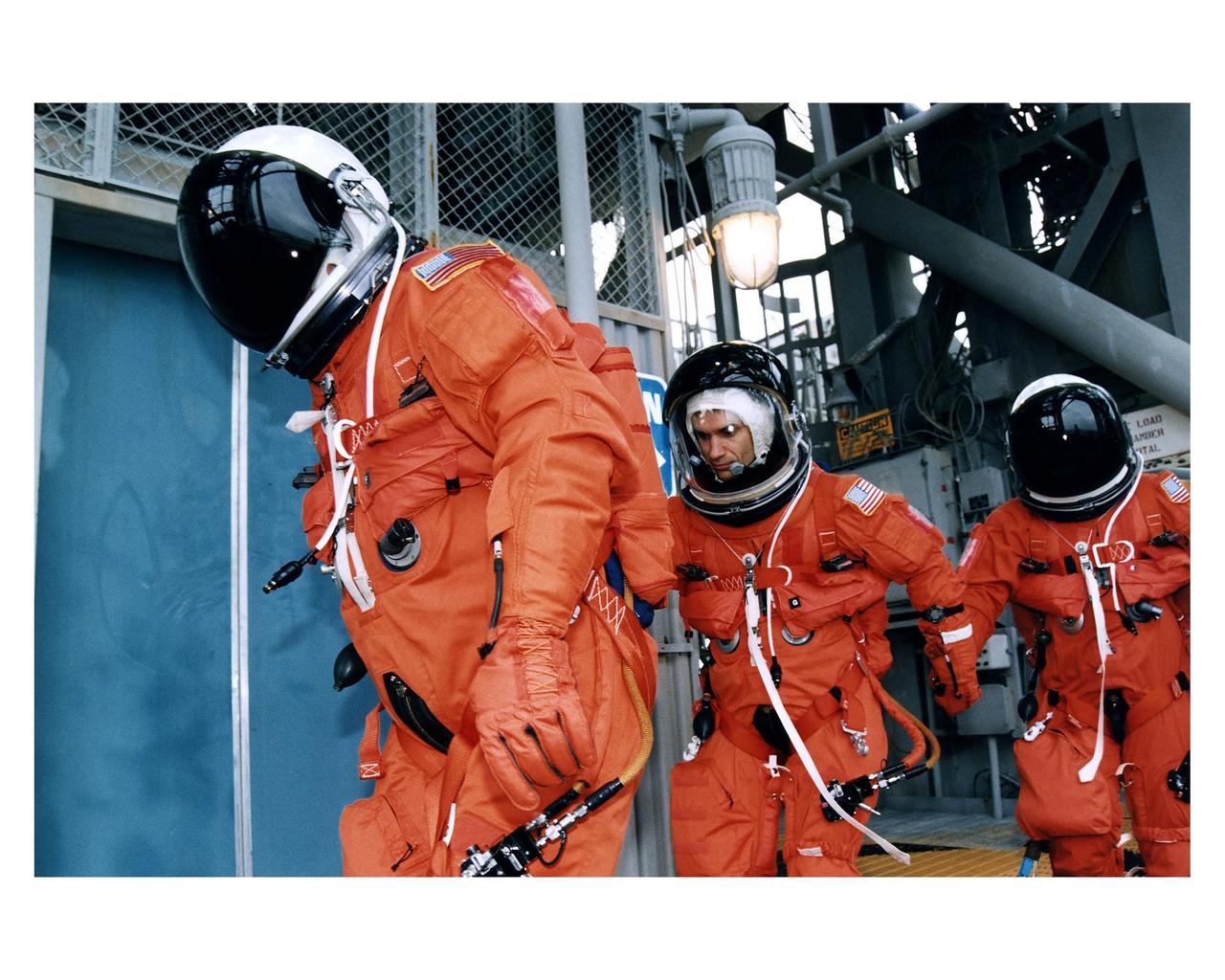

Three members of the STS-83 flight crew head toward the orbiter access arm on the 195-foot level Launch of Pad 39A that will take them to the crew hatch of the Space Shuttle Columbia during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) exercises for that mission. Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas is in the center of the group. Other crew members on the 16-day Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission are: Mission Commander James D. Halsell, Jr.; Pilot Susan L. Still; Payload Commander Janice Voss; Mission Specialist Michael L.Gernhardt; and Payload Specialists Gregory T. Linteris and Roger K. Crouch
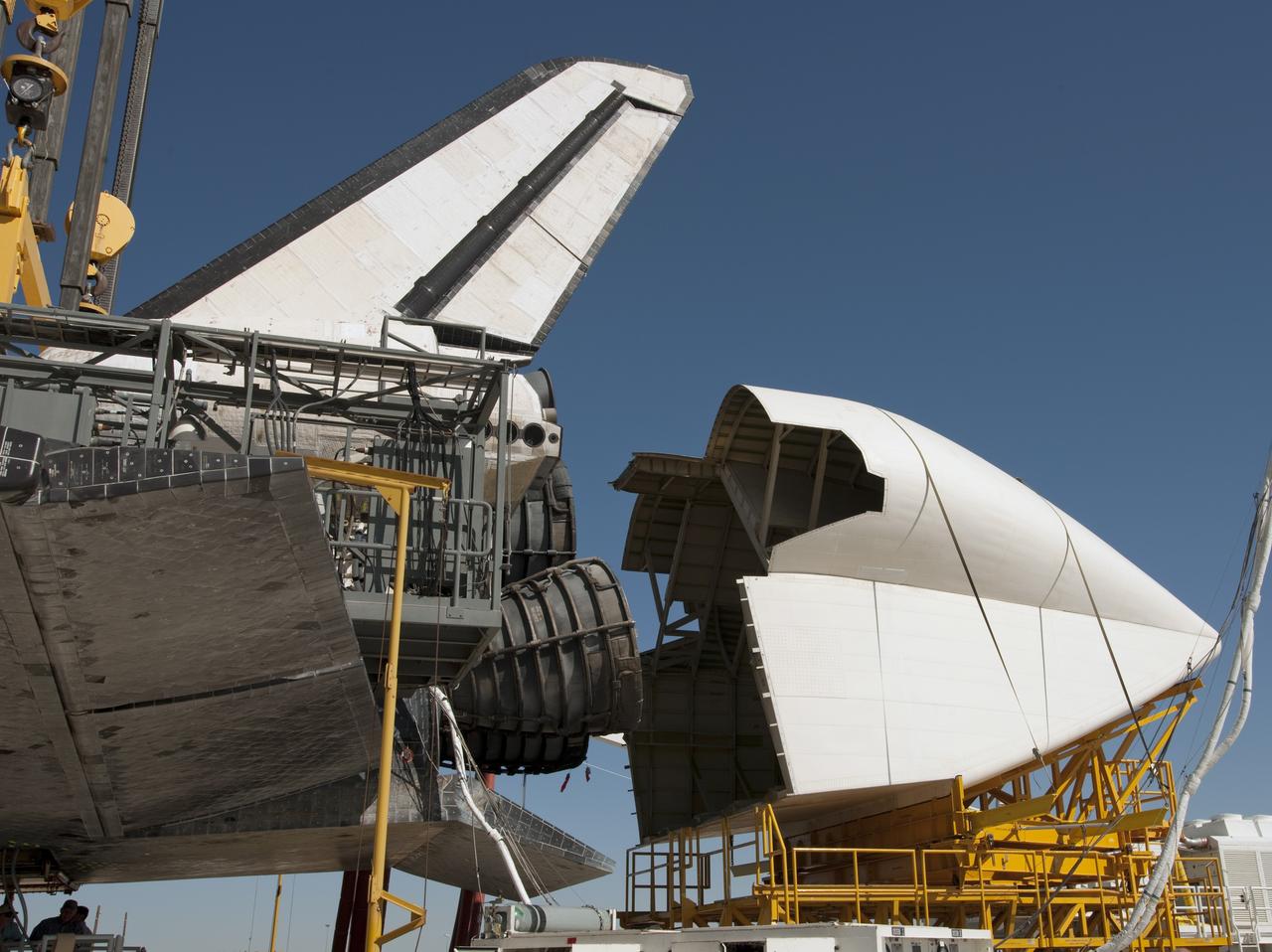

EDWARDS AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – ((ED09-0253-83) The tail cone that improves the aerodynamics of the space shuttle for its cross-country ferry flight is positioned aft of shuttle Discovery’s rocket nozzles prior to installation at NASA’s Dryden Flight Research Center. Discovery returned to Earth Sept. 11 on the STS-128 mission, landing at Edwards Air Force Base in California. The shuttle delivered more than 7 tons of supplies, science racks and equipment, as well as additional environmental hardware to sustain six crew members on the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Landis