
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, Columbia rolls out to Launch Complex 39B atop the crawler-transporter. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is tentatively scheduled for Nov. 19
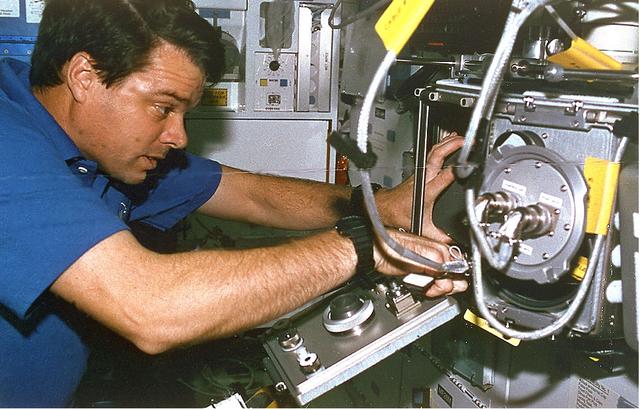
Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-87) Mission Commander Kevin R. Kregel sets up the mid-deck glove box during early hours of the 16-day United States Microgravity Payload 4 (USMP-4) mission. Kregel was joined by four other astronauts and a Ukrainian payload specialist for the mission.
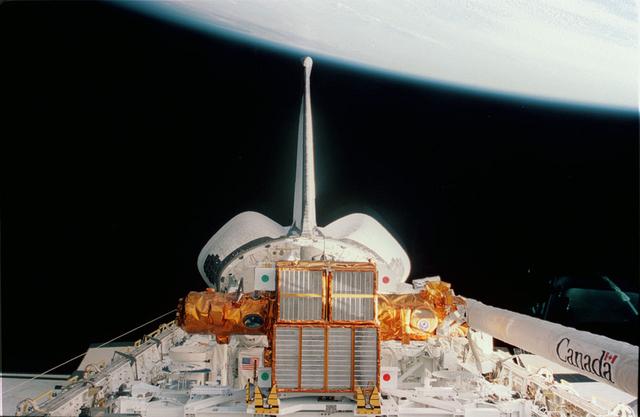

STS-87 Onboard Photo: The U. S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) is carried aboard multi-purpose experiment support structures mounted in the shuttle payload bay and sparning the width of the orbiter.
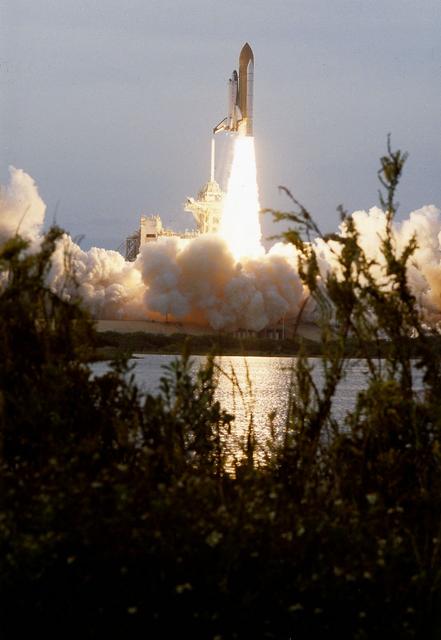

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-87) soared from Launch Pad 39B on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload (USMP-4) and Spartan-201 satellite which were managed by scientists and engineers from the Marshall Space Flight Center. During the 16-day mission, the crew oversaw experiments in microgravity; deployed and retrieved a solar satellite; and tested a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Two crew members, Dr. Takao Doi and Winston Scott also performed a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers.
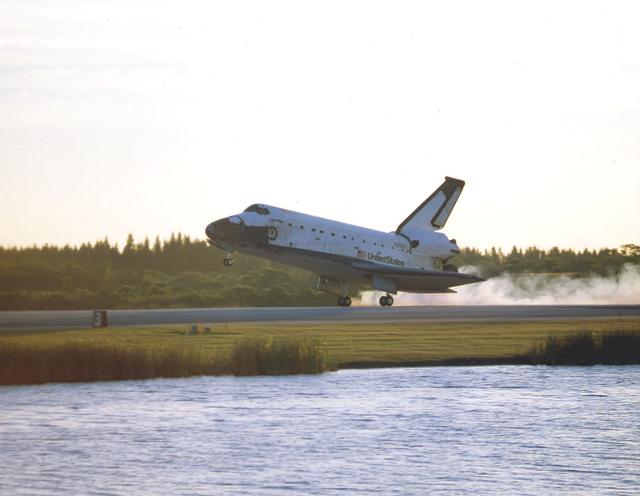

With Commander Kevin R. Kregel and Pilot Steven W. Lindsey at the controls, the orbiter Columbia (STS-87) touched down its main gear on Runway 33 at Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Shuttle Landing Facility to complete a 15-day, 16-hour and 34-minute-long mission of 6.5 million miles. During the 88th Space Shuttle mission, the crew performed experiments on the United States Microgravity Payload-4 and pollinated plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment. This was the 12th landing for Columbia at KSC and the 41st KSC landing in the history of the Space Shuttle program.
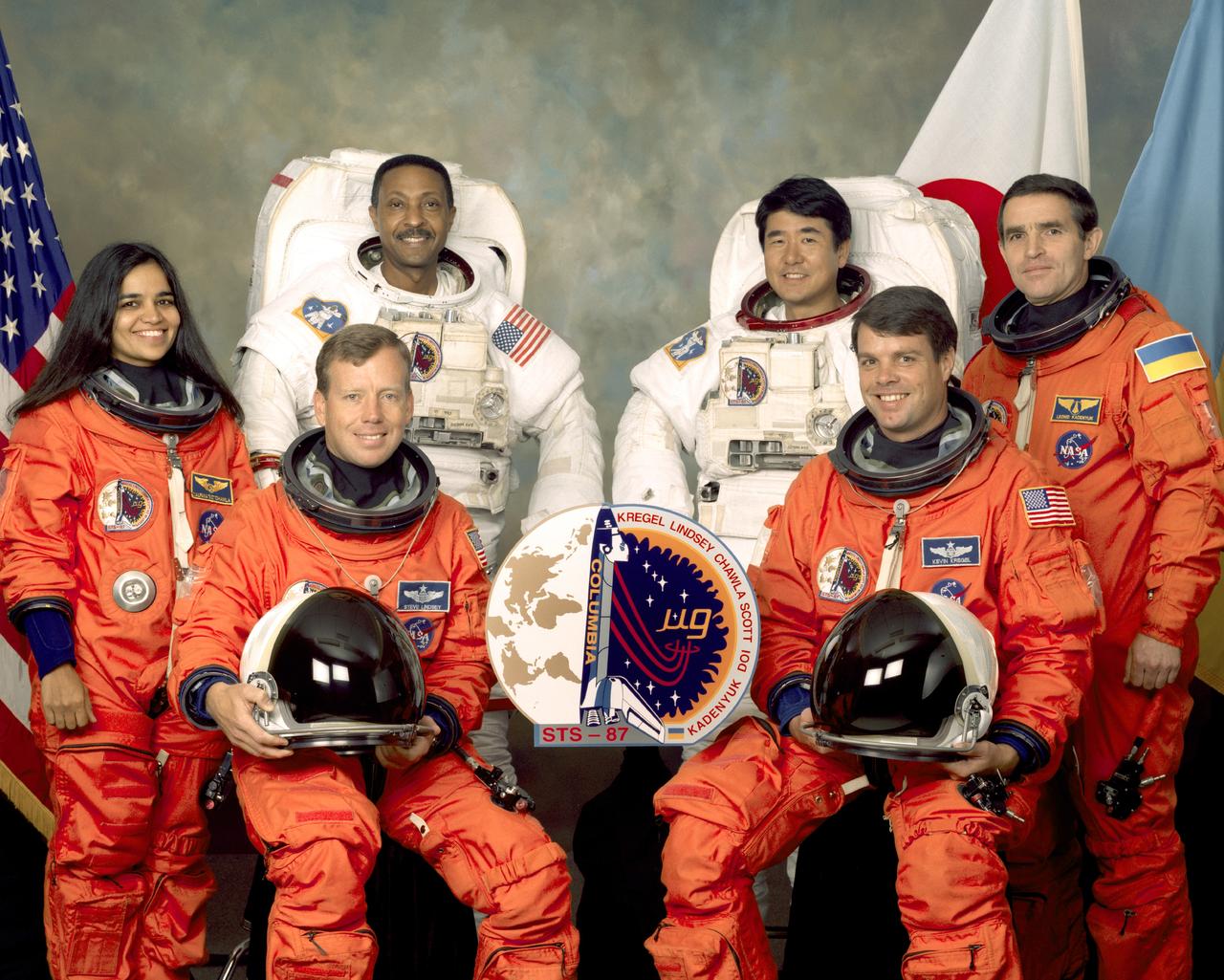

Five astronauts and a payload specialist take a break from training at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) to pose for the STS-87 crew portrait. Wearing the orange partial pressure launch and entry suits, from the left, are Kalpana Chawla, mission specialist; Steven W. Lindsey, pilot; Kevin R. Kregel, mission commander; and Leonid K. Kadenyuk, Ukrainian payload specialist. Wearing the white Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suits are mission specialists Winston E. Scott (left) and Takao Doi (right). Doi represents Japan’s National Space Development Agency (NASDA). The STS-87 mission launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on November 19, 1997. The primary payload for the mission was the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4).
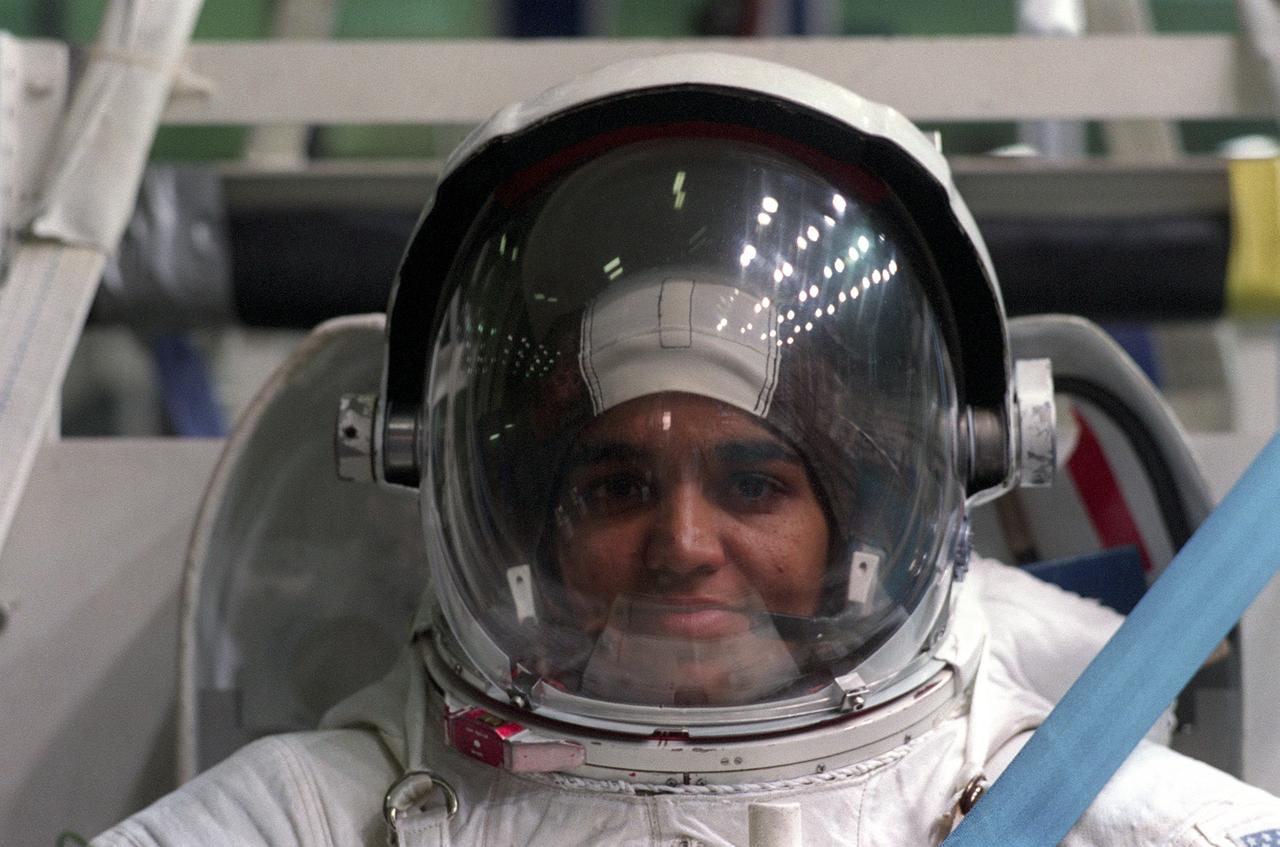

Attired in a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suit, astronaut and mission specialist Kalpana Chawla, prepares to go underwater in the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (NBL) near Johnson Space Center. This particular training was in preparation for the STS-87 mission. The Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-87) was the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload (USMP-4) and Spartan-201 satellite, both managed by scientists and engineers from the Marshall Space Flight Center.
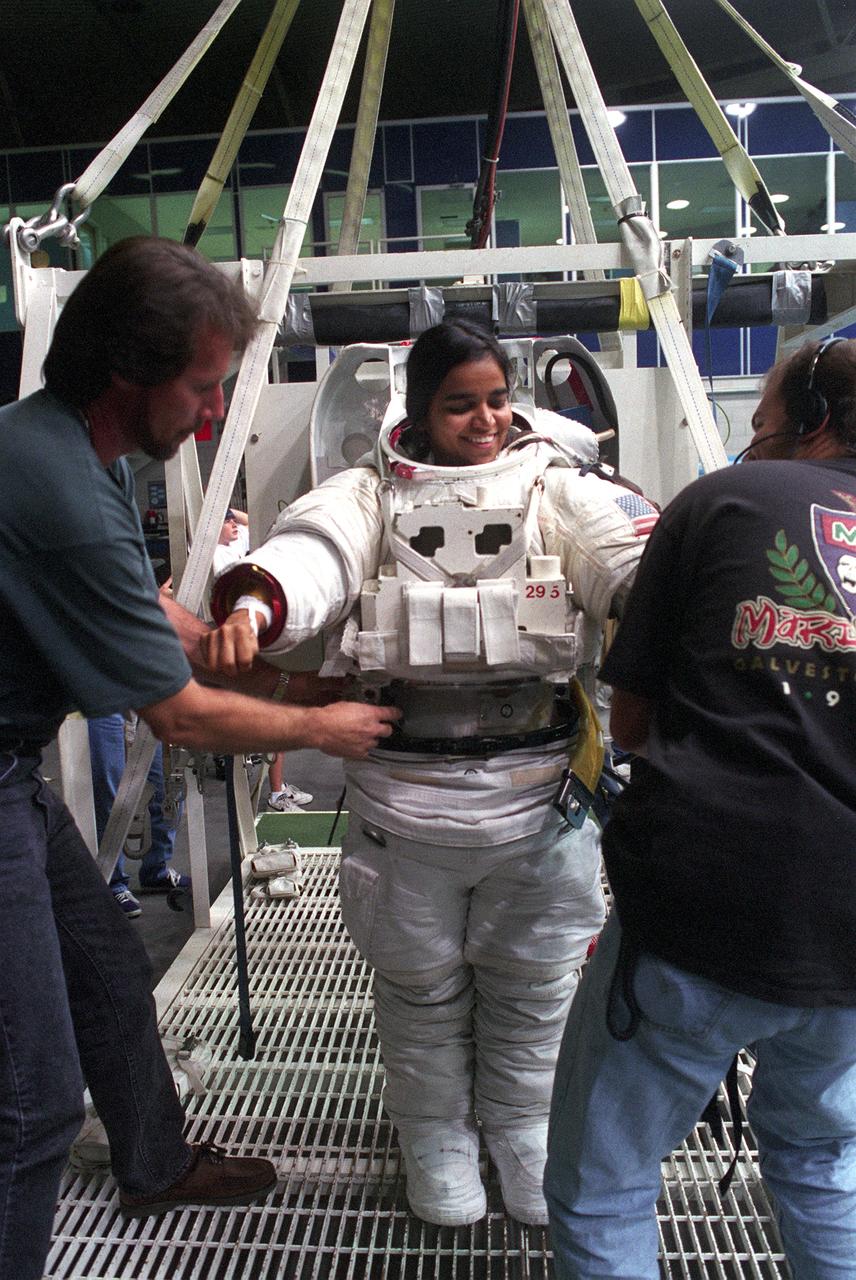

Astronaut and mission specialist Kalpana Chawla, receives assistance in donning a training version of the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suit, prior to an underwater training session in the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (NBL) near Johnson Space Center. This particular training was in preparation for the STS-87 mission. The Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-87) was the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload (USMP-4) and Spartan-201 satellite, both managed by scientists and engineers from the Marshall Space Flight Center.
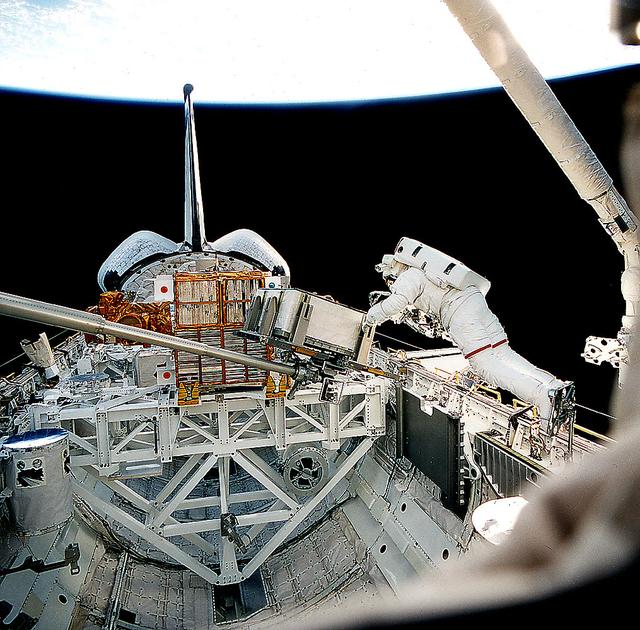

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia's (STS-87) first ever Extravehicular Activity (EVA), astronaut Takao Doi works with a 156-pound crane carried onboard for the first time. The crane's inclusion and the work with it are part of a continuing preparation effort for future work on the International Space Station (ISS). The ongoing project allows for evaluation of tools and operating methods to be applied to the construction of the Space Station. This crane device is designed to aid future space walkers in transporting Orbital Replacement Units (ORU), with a mass up to 600 pounds (like the simulated battery pictured here), from translating carts on the exterior of ISS to various worksites on the truss structure. Earlier Doi, an international mission specialist representing Japan, and astronaut Winston E. Scott, mission specialist, had installed the crane in a socket along the middle port side of Columbia's cargo bay for the evaluation. The two began the crane operations after completing a contingency EVA to snag the free-flying Spartan 201 and berth it in the payload bay (visible in the background).
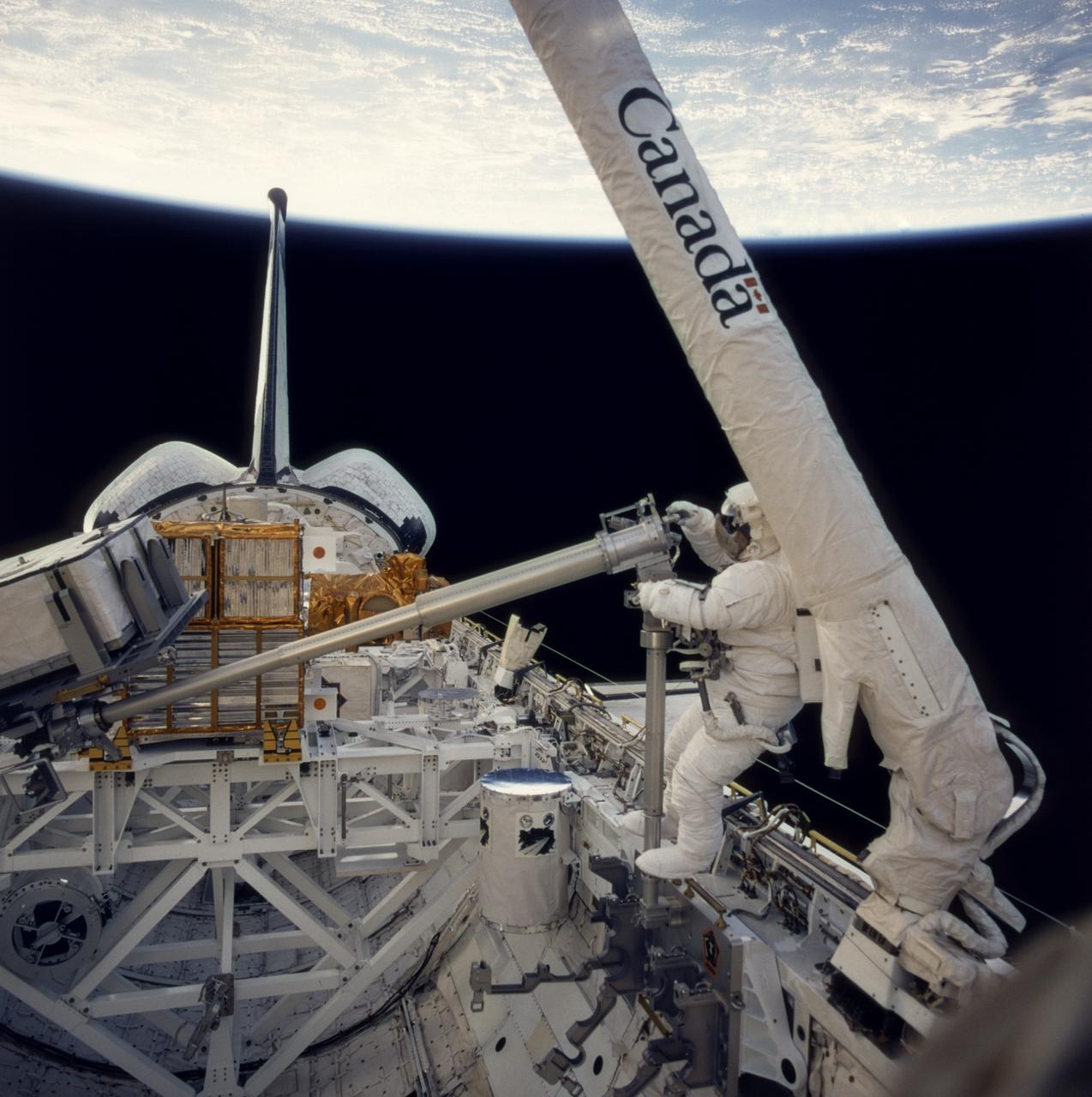

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia's (STS-87) first ever Extravehicular Activity (EVA), astronaut Takao Doi works with a 156-pound crane carried onboard for the first time. The crane's inclusion and the work with it are part of a continuing preparation effort for future work on the International Space Station (ISS). The ongoing project allows for evaluation of tools and operating methods to be applied to the construction of the Space Station. This crane device is designed to aid future space walkers in transporting Orbital Replacement Units (ORU), with a mass up to 600 pounds (like the simulated battery pictured here), from translating carts on the exterior of ISS to various worksites on the truss structure. Earlier Doi, an international mission specialist representing Japan, and astronaut Winston E. Scott, mission specialist, had installed the crane in a socket along the middle port side of Columbia's cargo bay for the evaluation. The two began the crane operations after completing a contingency EVA to snag the free-flying Spartan 201 and berth it in the payload bay (visible in the background).
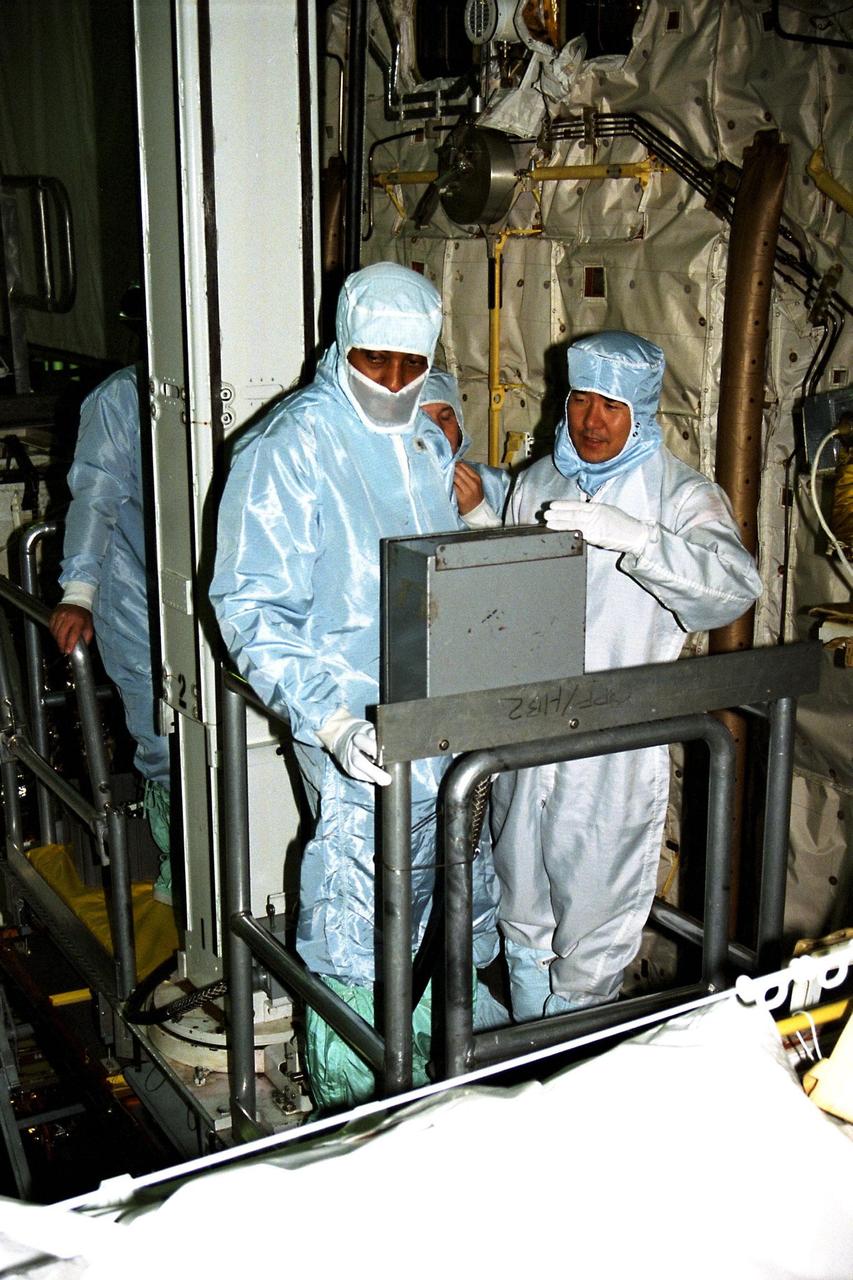

Participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center are STS-87 crew members Winston Scott, at left, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, both mission specialists on STS-87. The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working on-orbit. STS-87 will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the STS-87 mission, scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC, Dr. Doi and Scott will both perform spacewalks. STS-87 is scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC

STS-87 Mission Specialist Winston Scott is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. Scott is scheduled to perform an extravehicular activity spacewalk with Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, during STS-87. Scott also performed a spacewalk on the STS-72 mission
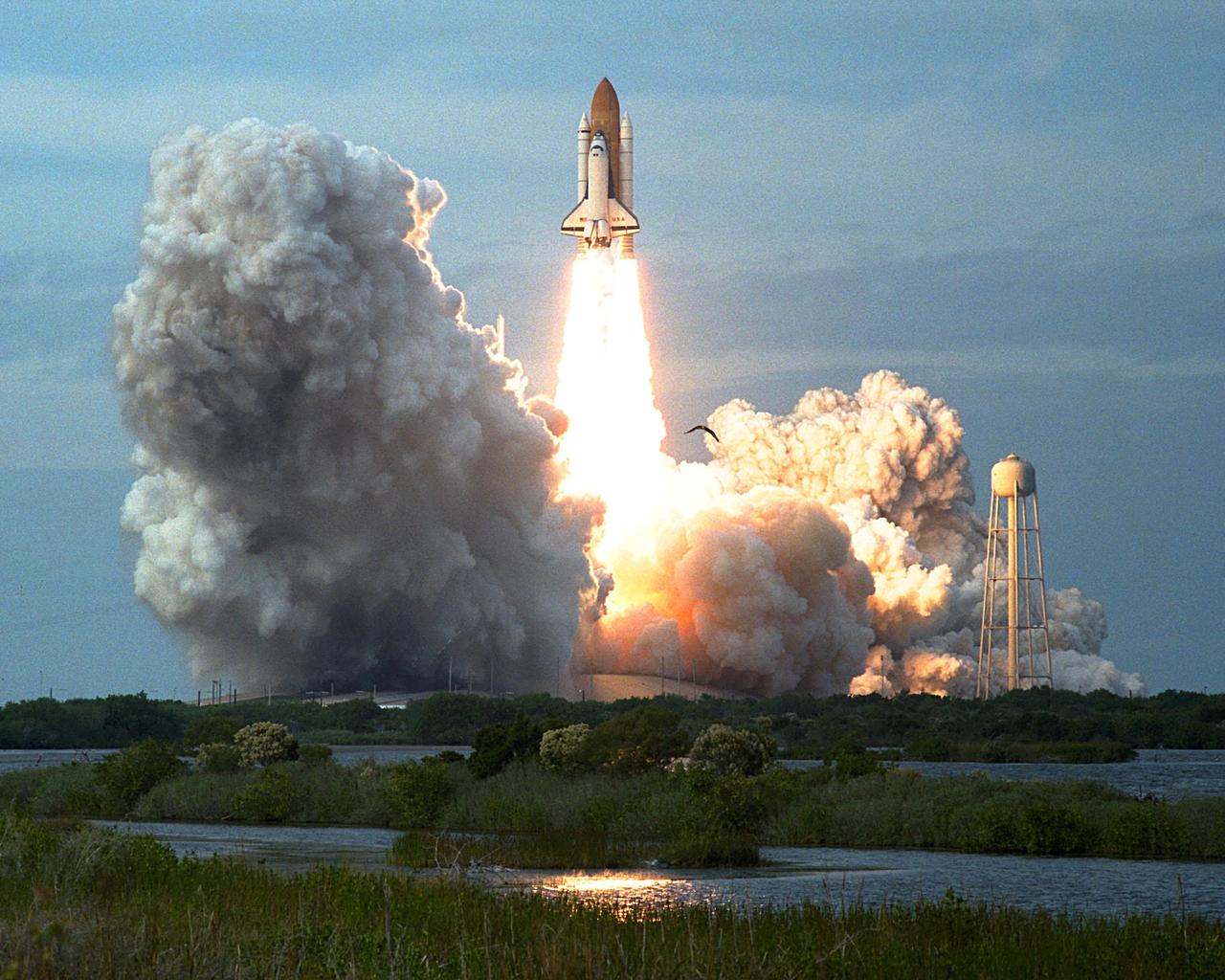

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-87: Columbia
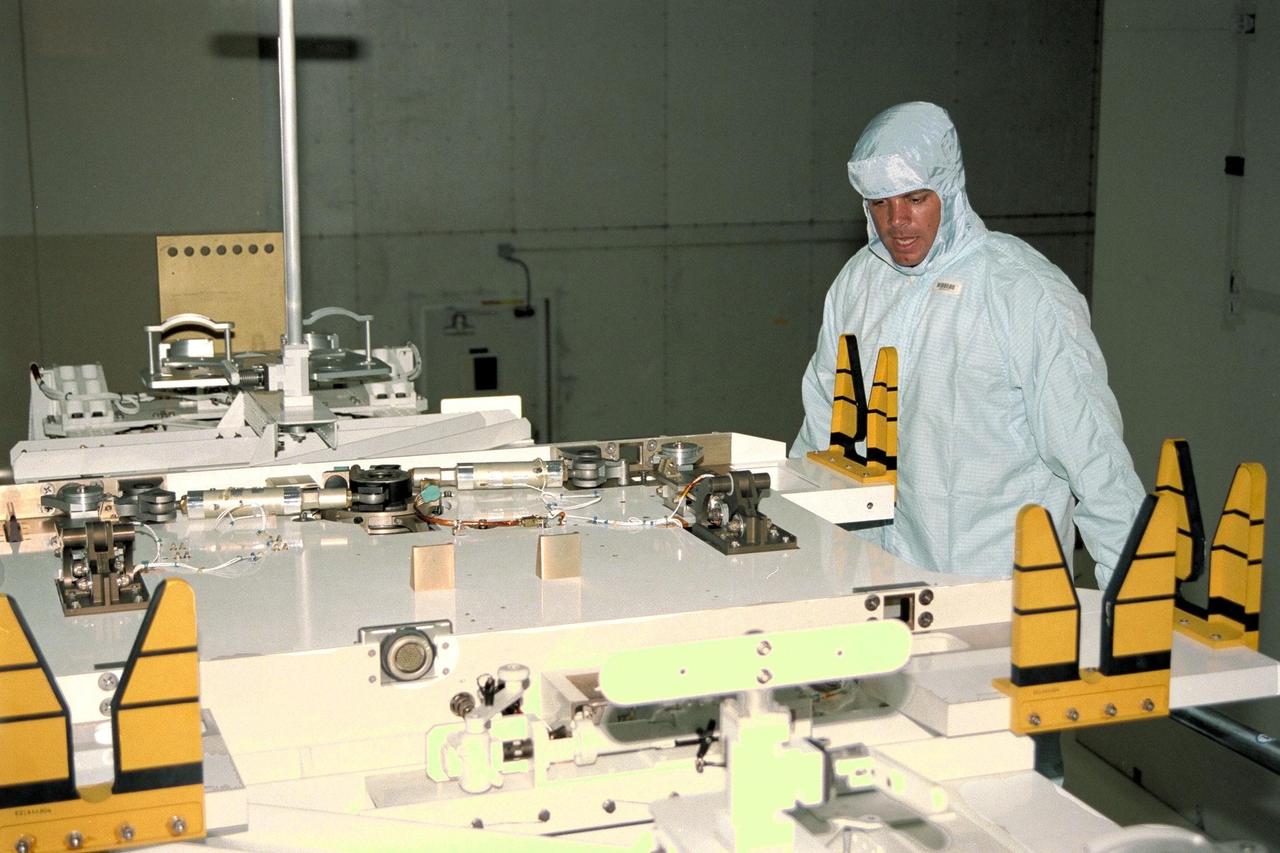

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel participates in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) in Kennedy Space Center’s (KSC's) Vertical Processing Facility. The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working on-orbit. STS-87 will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. STS-87 is scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC
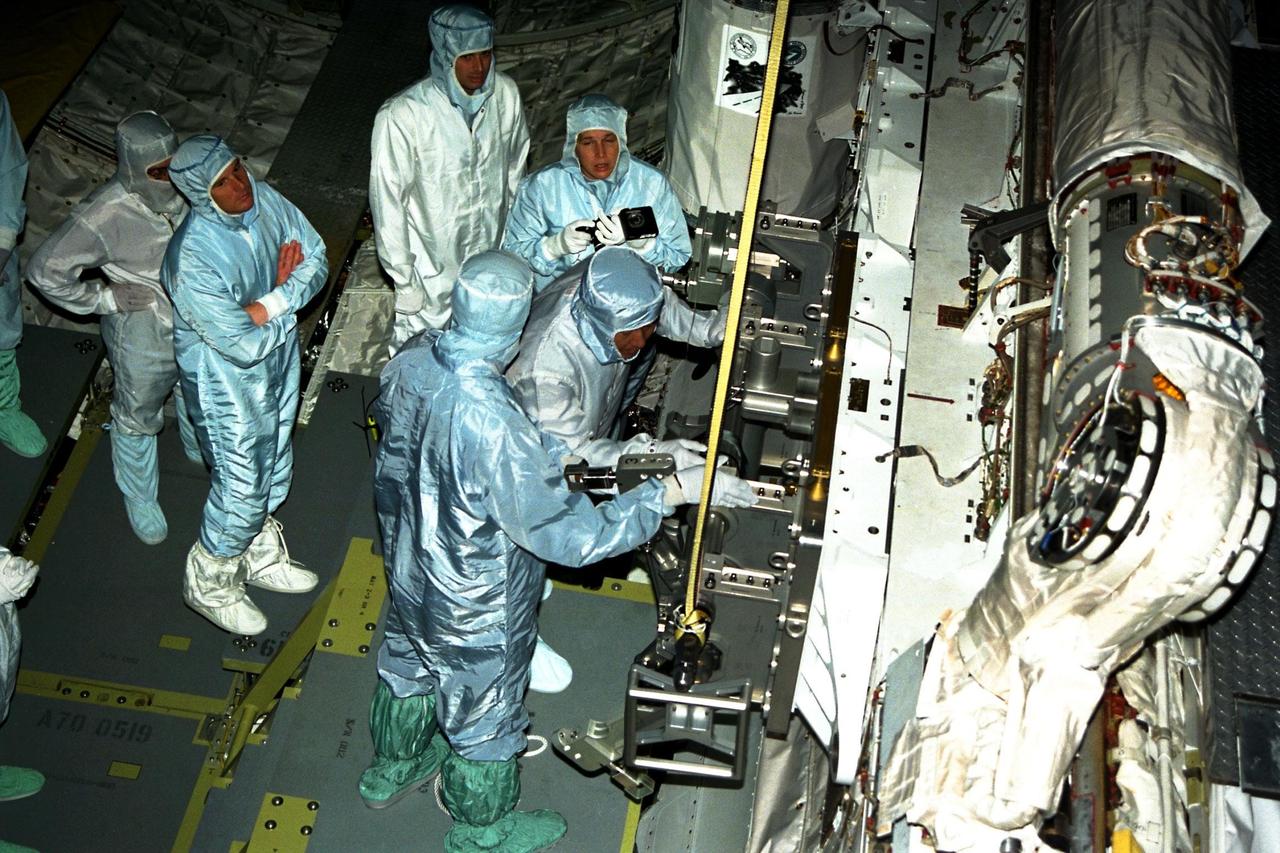

STS-87 astronaut crew members participate in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working on-orbit. STS-87 will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. STS-87 is scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC
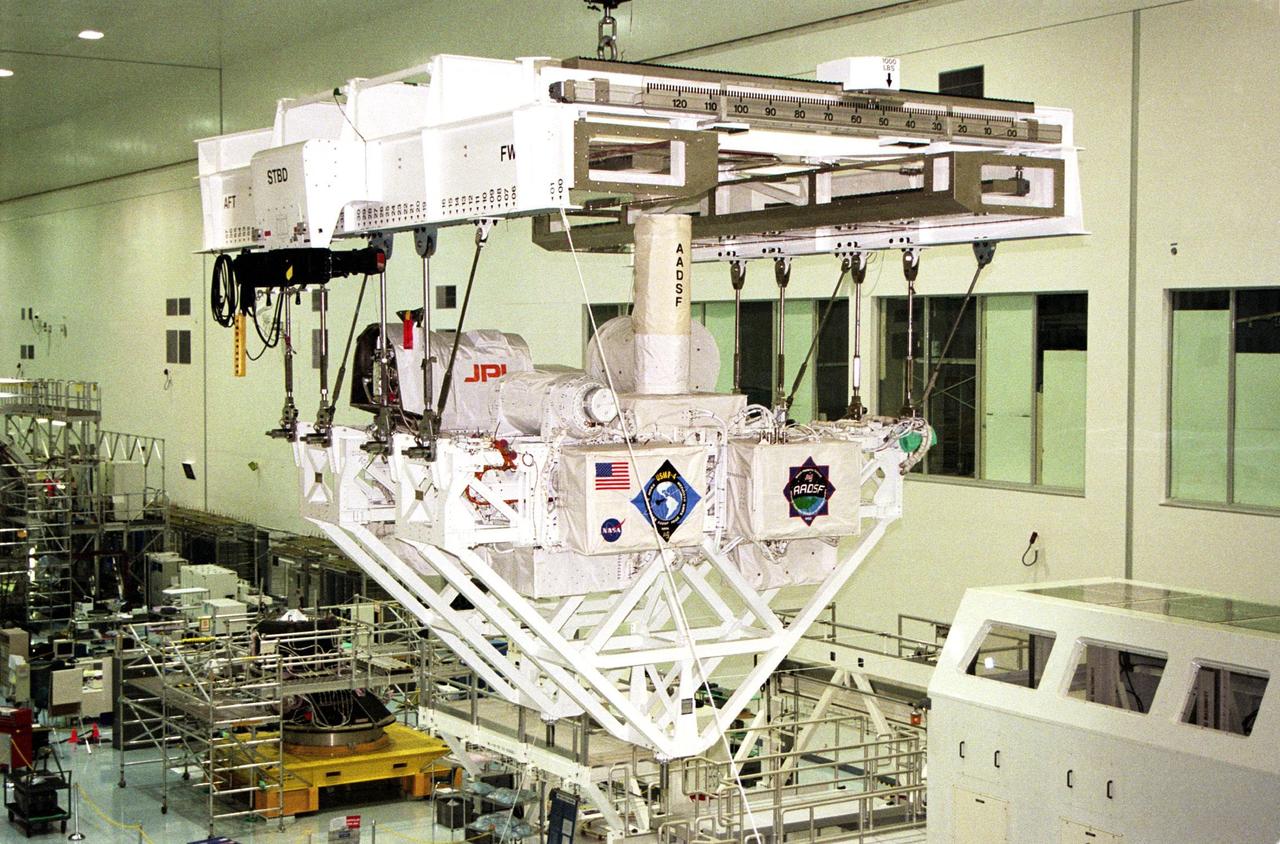
In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the United States Microgravity Payload-4 undergoes final processing in the Space Station Processing Facility before its move to Launch Complex 39B. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, Columbia rolls out to Launch Complex 39B atop the crawler-transporter. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is tentatively scheduled for Nov. 19

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the United States Microgravity Payload-4 undergoes final processing in the Space Station Processing Facility before its move to Launch Complex 39B. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the United States Microgravity Payload-4 undergoes final processing in the Space Station Processing Facility before its move to Launch Complex 39B. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
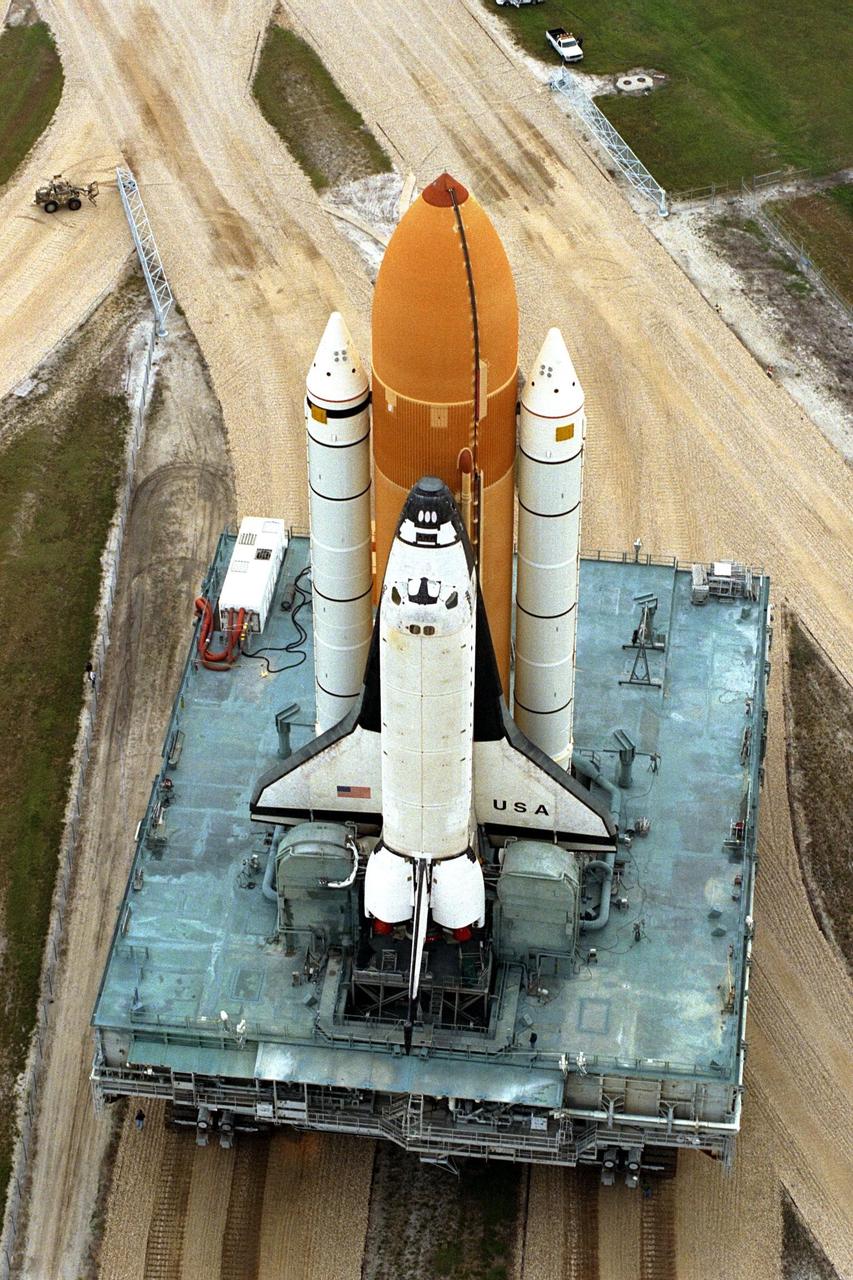

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, Columbia rolls out to Launch Complex 39B atop the crawler-transporter. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is tentatively scheduled for Nov. 19
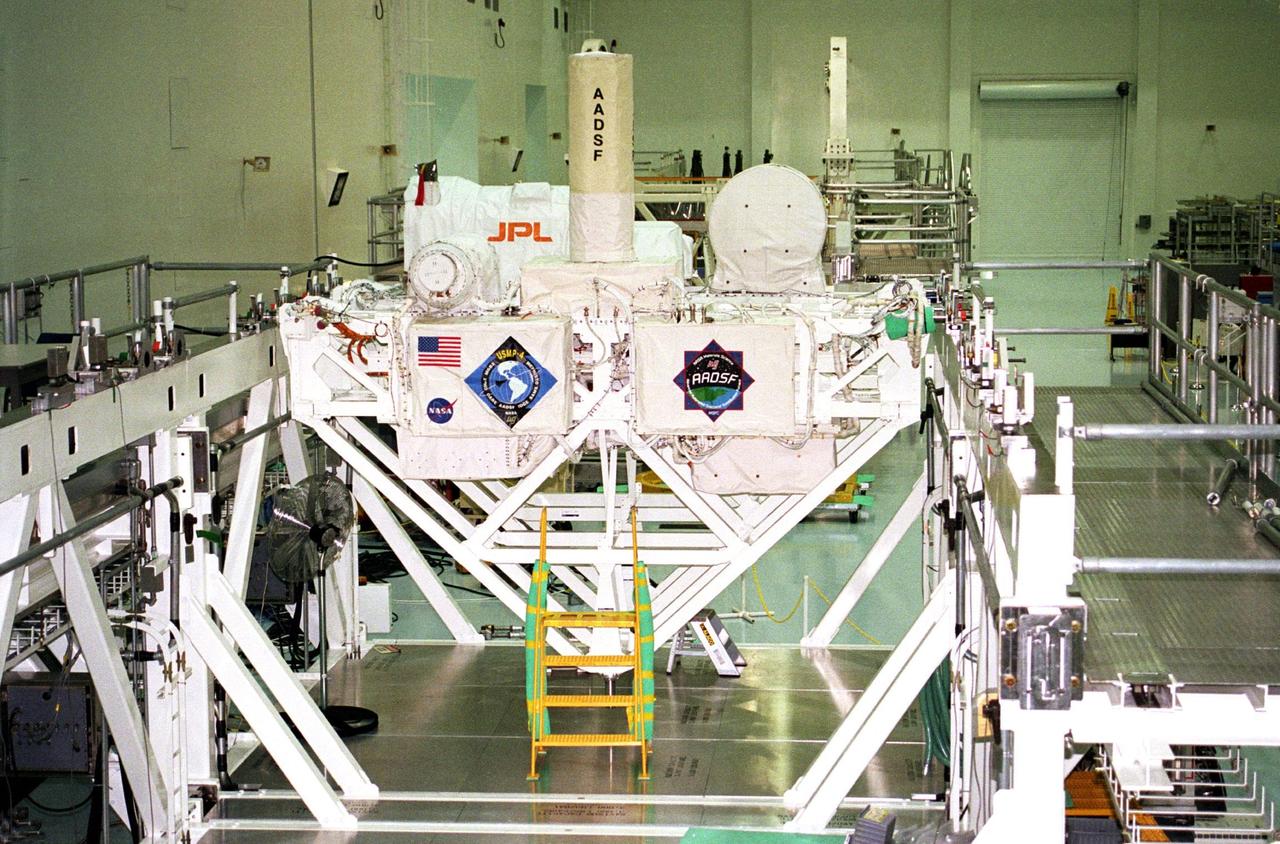

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the United States Microgravity Payload-4 undergoes final processing in the Space Station Processing Facility before its move to Launch Complex 39B. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
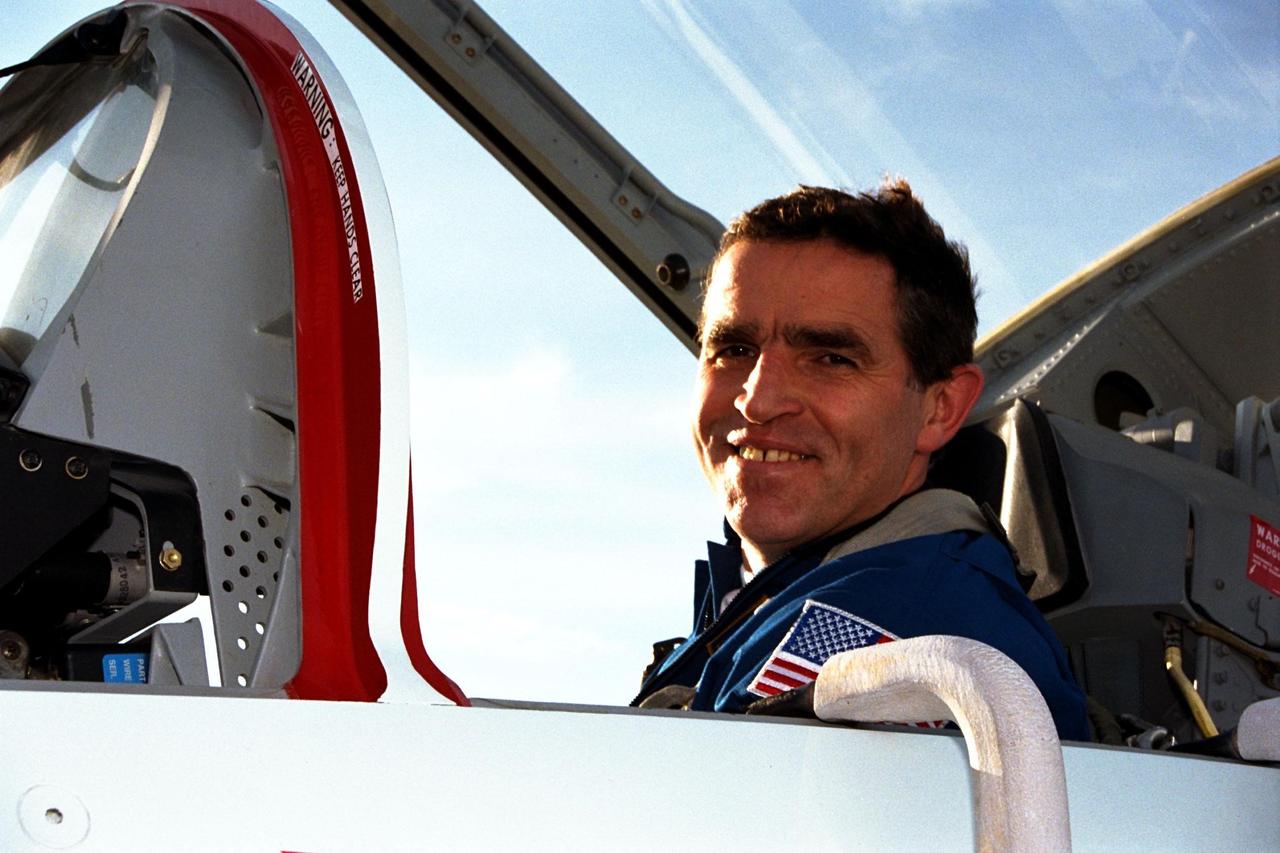

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine arrives at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 jet for the final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; and Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Winston Scott. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
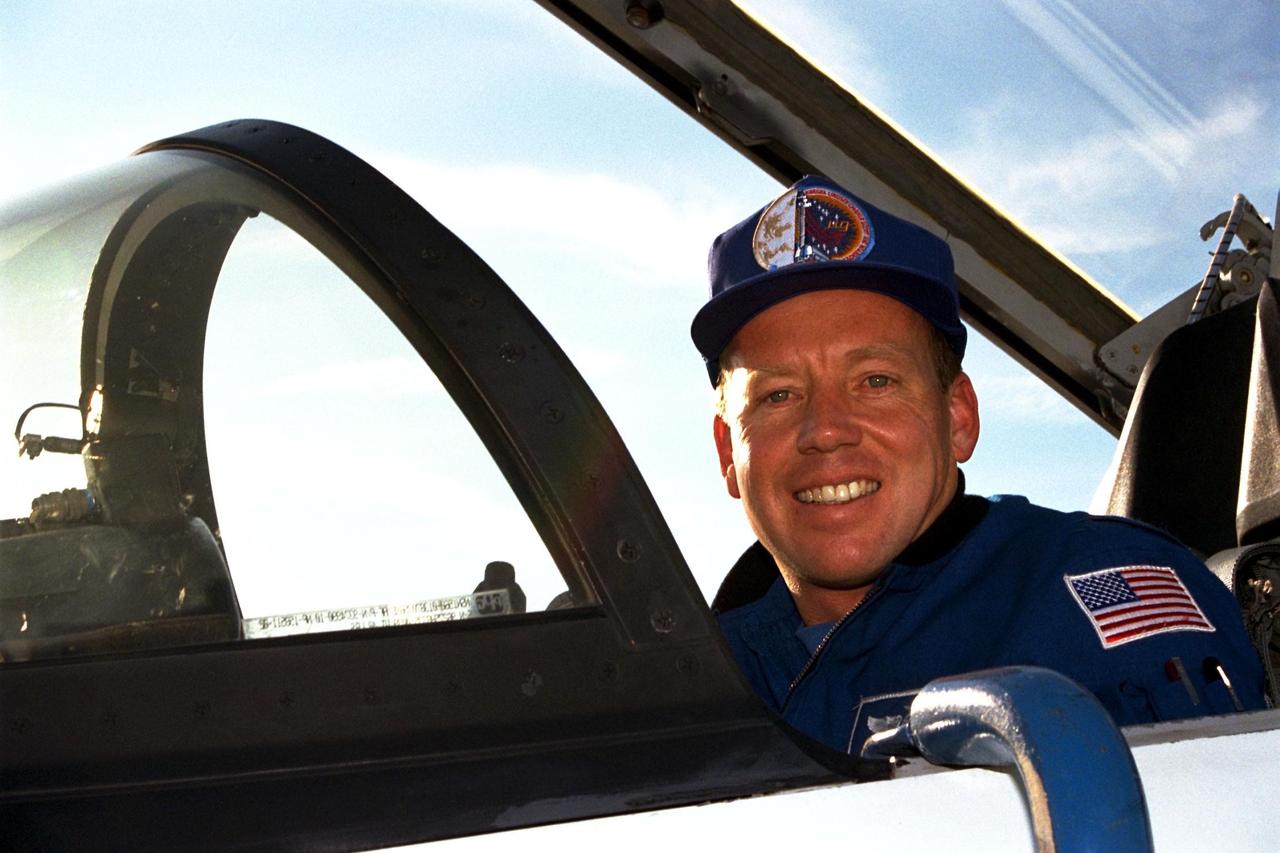

STS-87 Pilot Steven Lindsey arrives at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 jet for the final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Commander Kevin Kregel; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Winston Scott; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
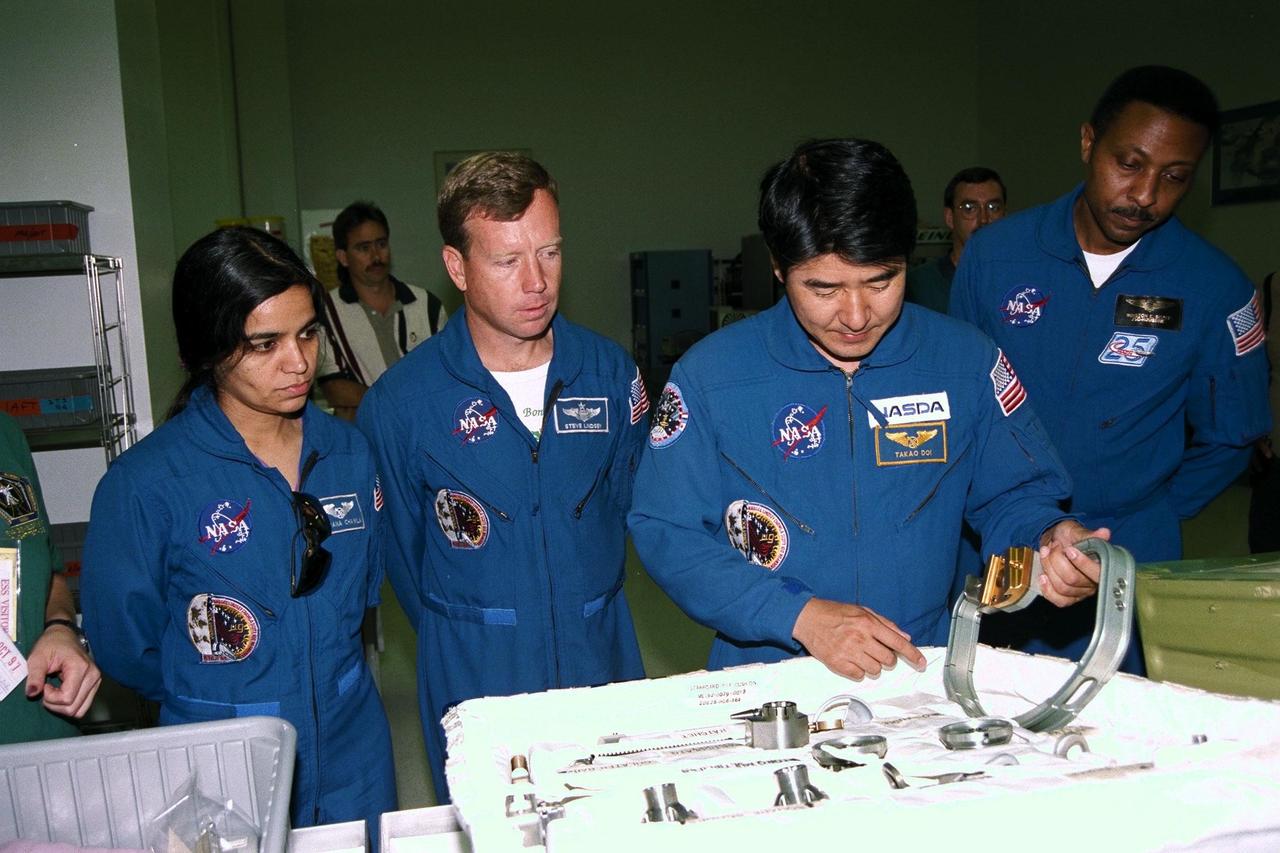

STS-87 astronaut crew members participate in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) in Kennedy Space Center’s (KSC's) Vertical Processing Facility. From left are Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialist Takao Doi , Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Mission Specialist Winston Scott. The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working onorbit. STS-87 will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the STS-87 mission, scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC, Dr. Doi and Scott will both perform spacewalks
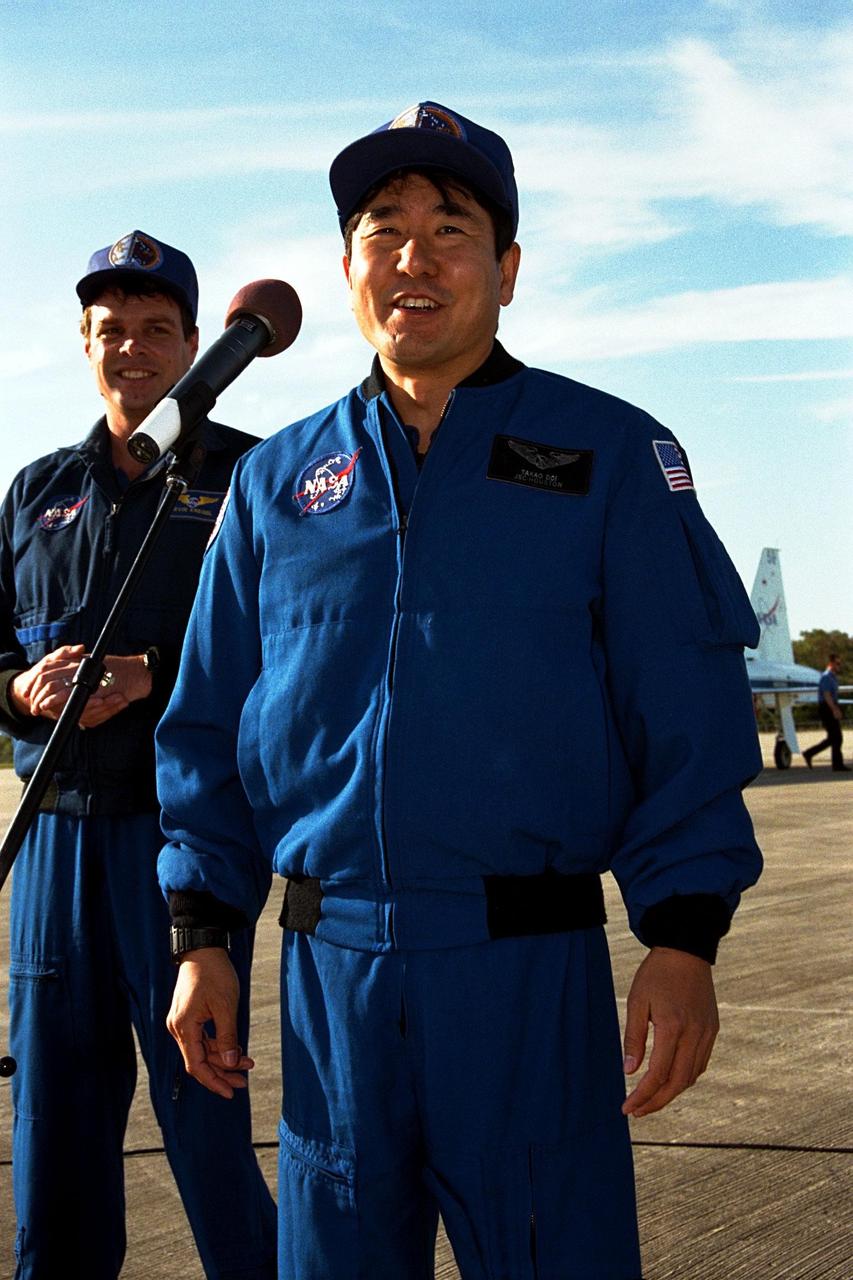

As STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel looks on, Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan addresses members of the press and media at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility after arriving for the final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. Other STS-87 crew members not pictured are Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., and Winston Scott; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
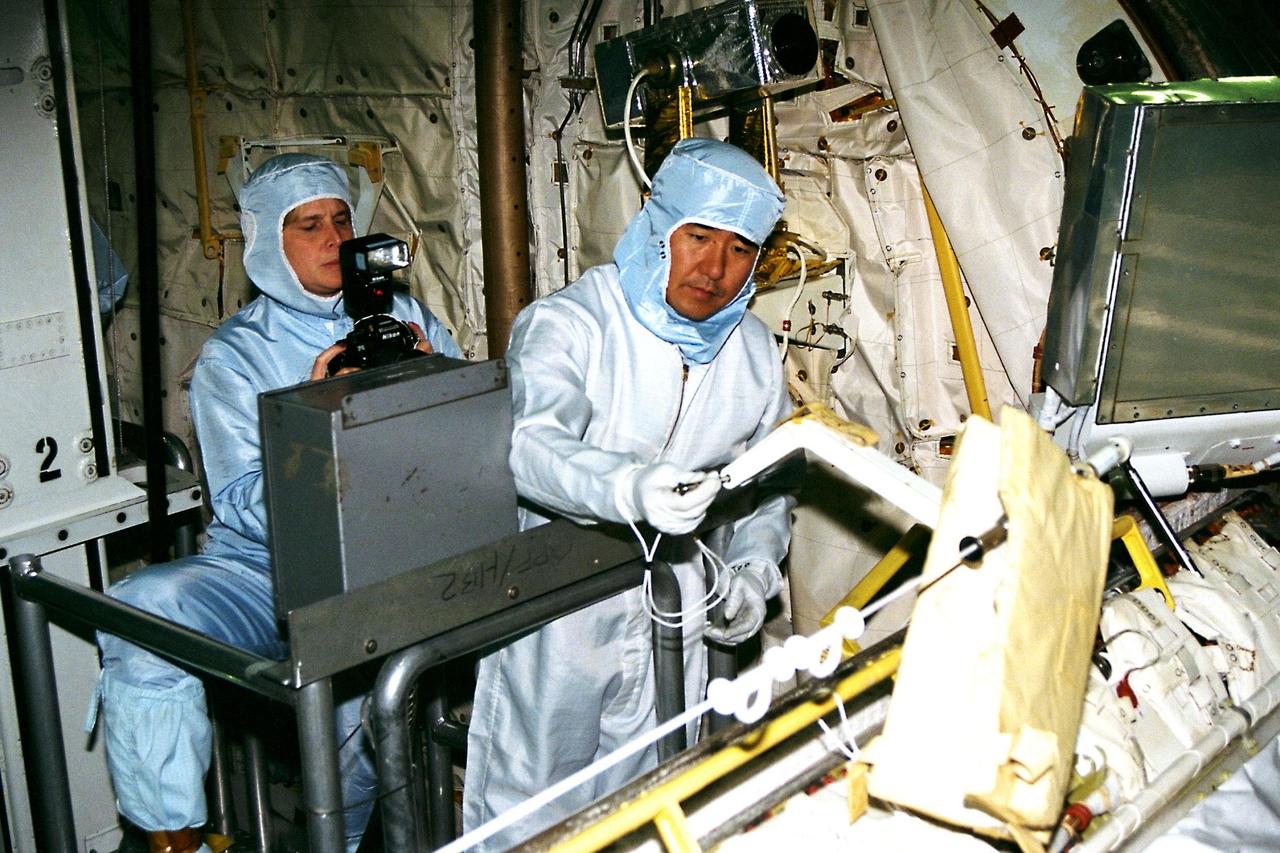

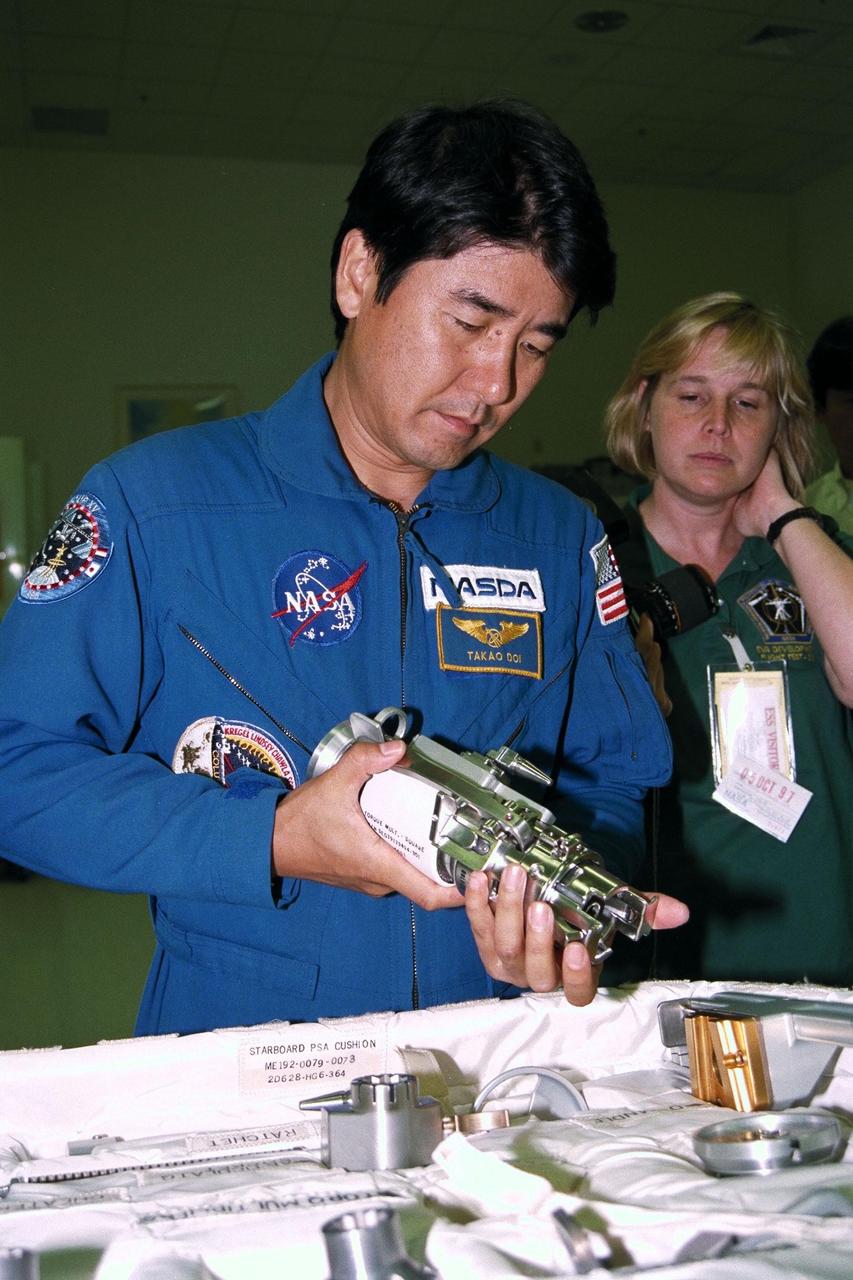
STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi , Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, participates in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Glenda Laws, the extravehicular activity (EVA) coordinator, Johnson Space Center, stands behind Dr. Doi. The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working on-orbit. STS-87 will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, Dr. Doi will be the first Japanese astronaut to perform a spacewalk. STS-87 is scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel addresses members of the press and media at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility after arriving for the final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The STS-87 crew members are, from left to right, Mission Specialists Winston Scott and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Commander Kevin Kregel; Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine; Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; and Pilot Steven Lindsey. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
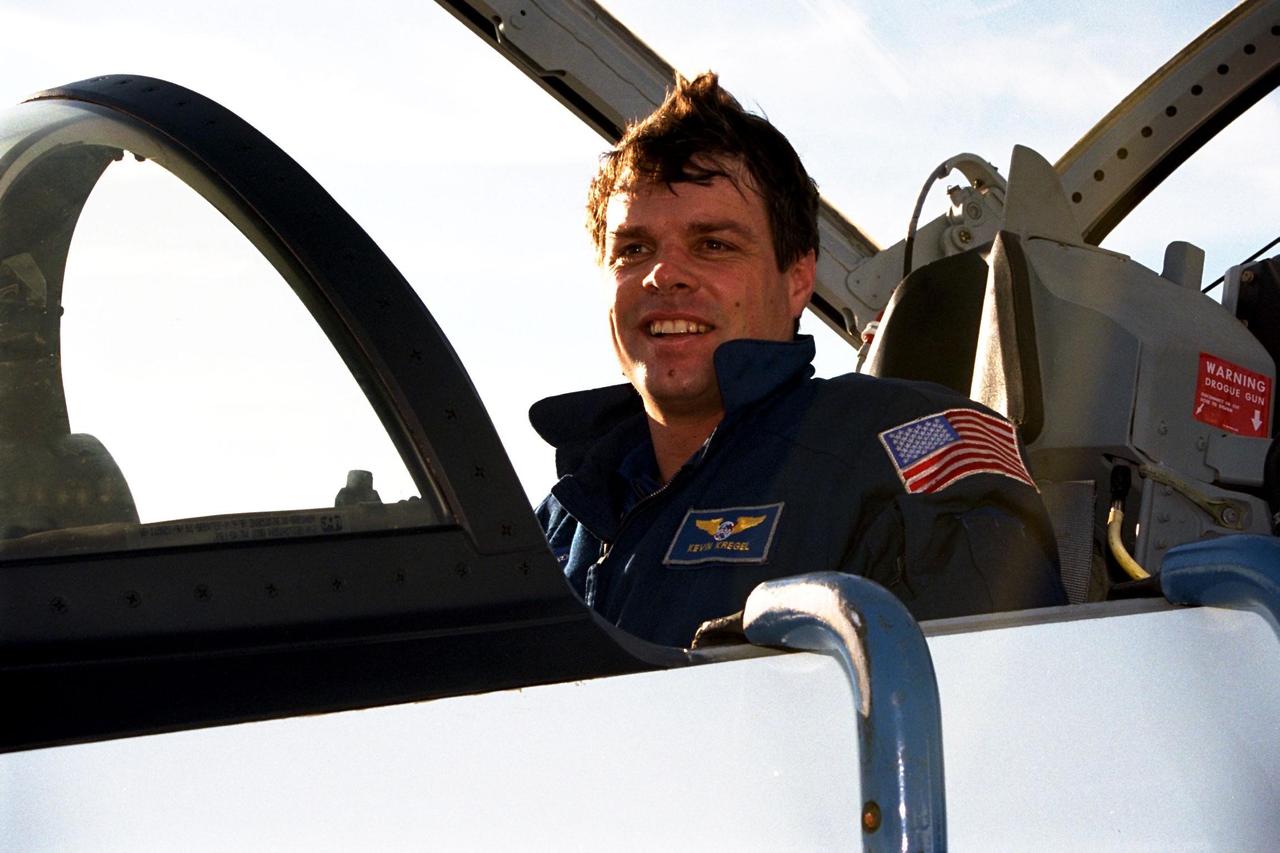

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel arrives at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 jet for the final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Winston Scott; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
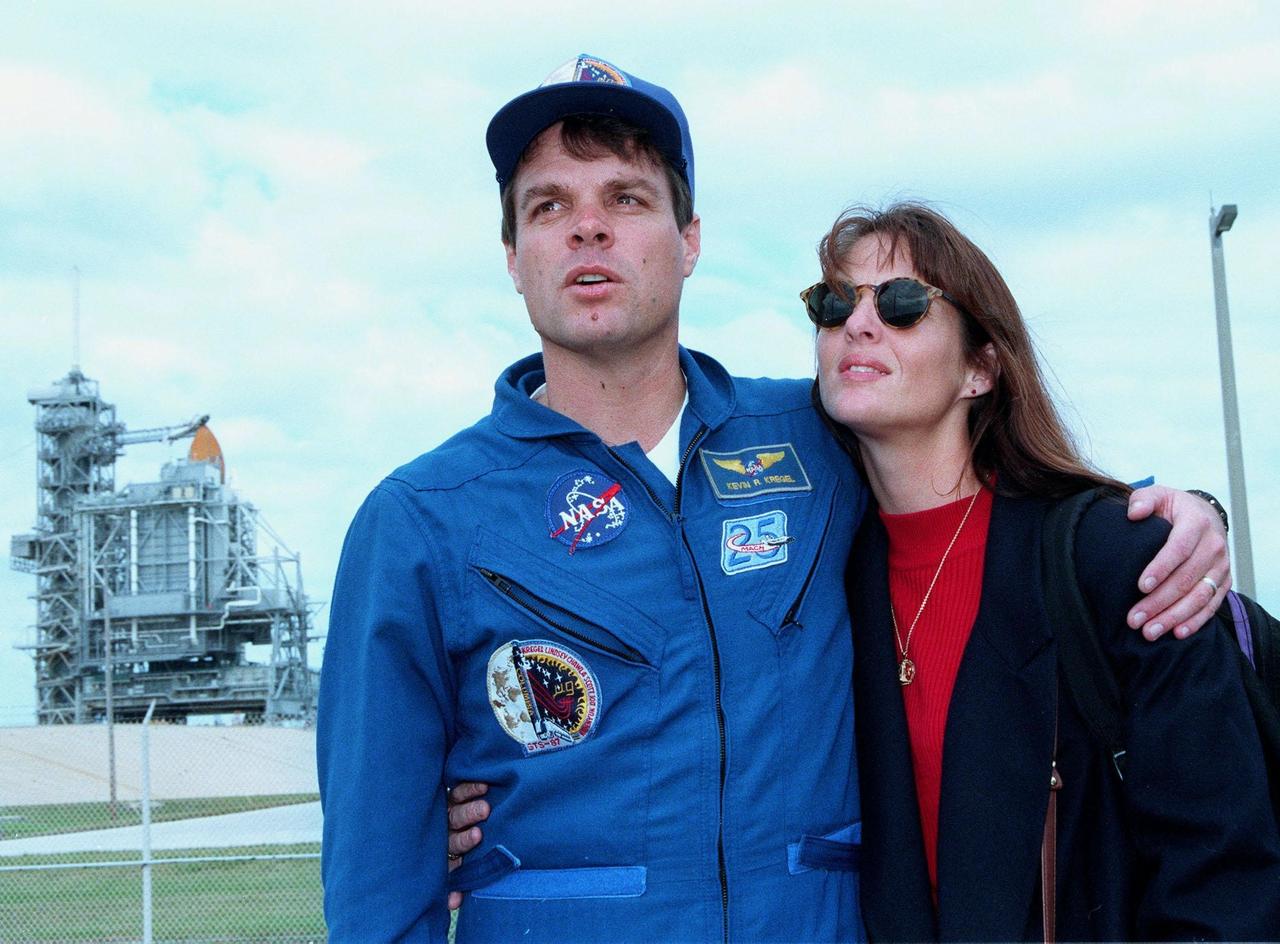

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel poses with his wife, Jeannie Kregel, in front of Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
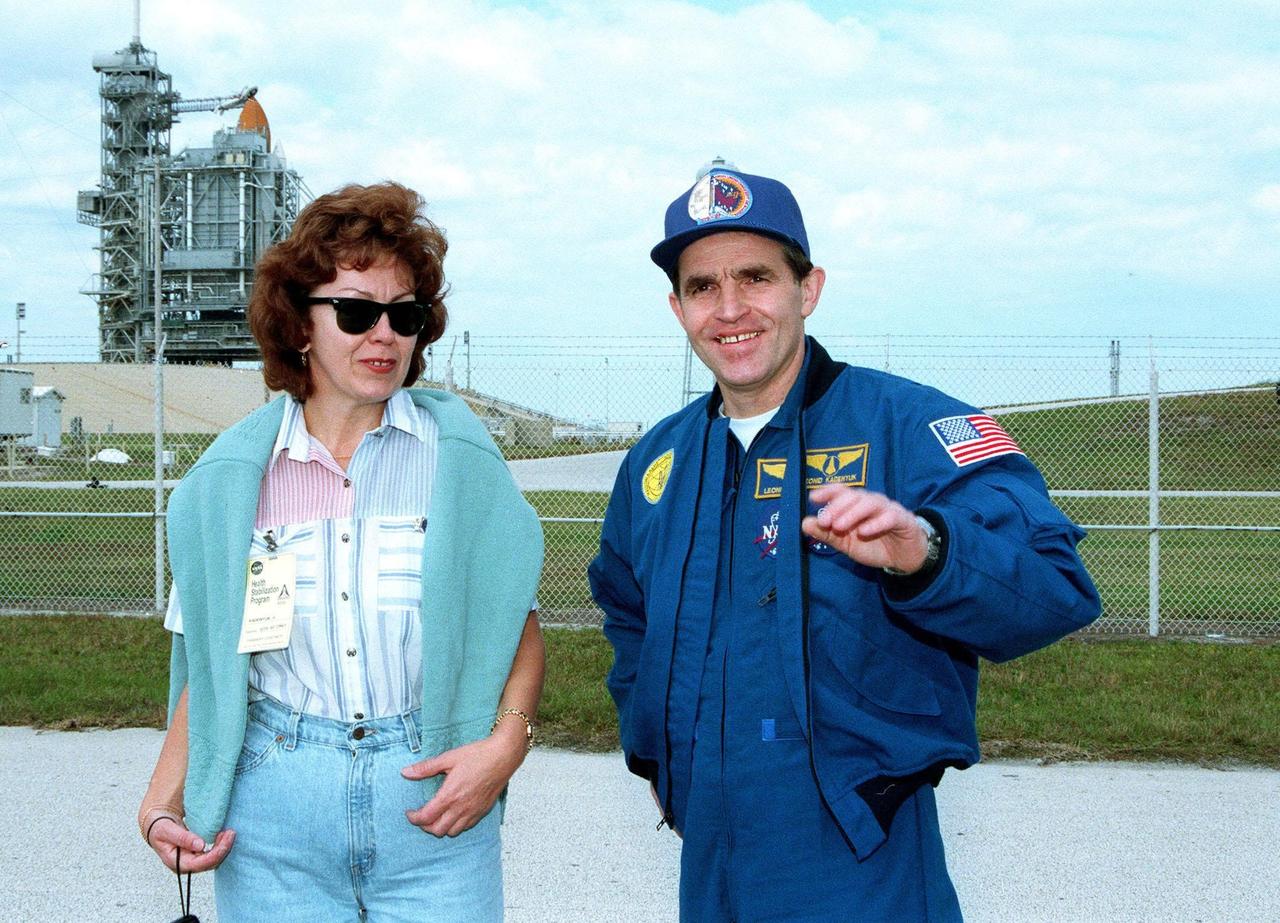

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine poses with his wife, Vera Kadenyuk, in front of Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; and Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Winston Scott; and Takao Doi, Ph.D., National Space Development Agency of Japan. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
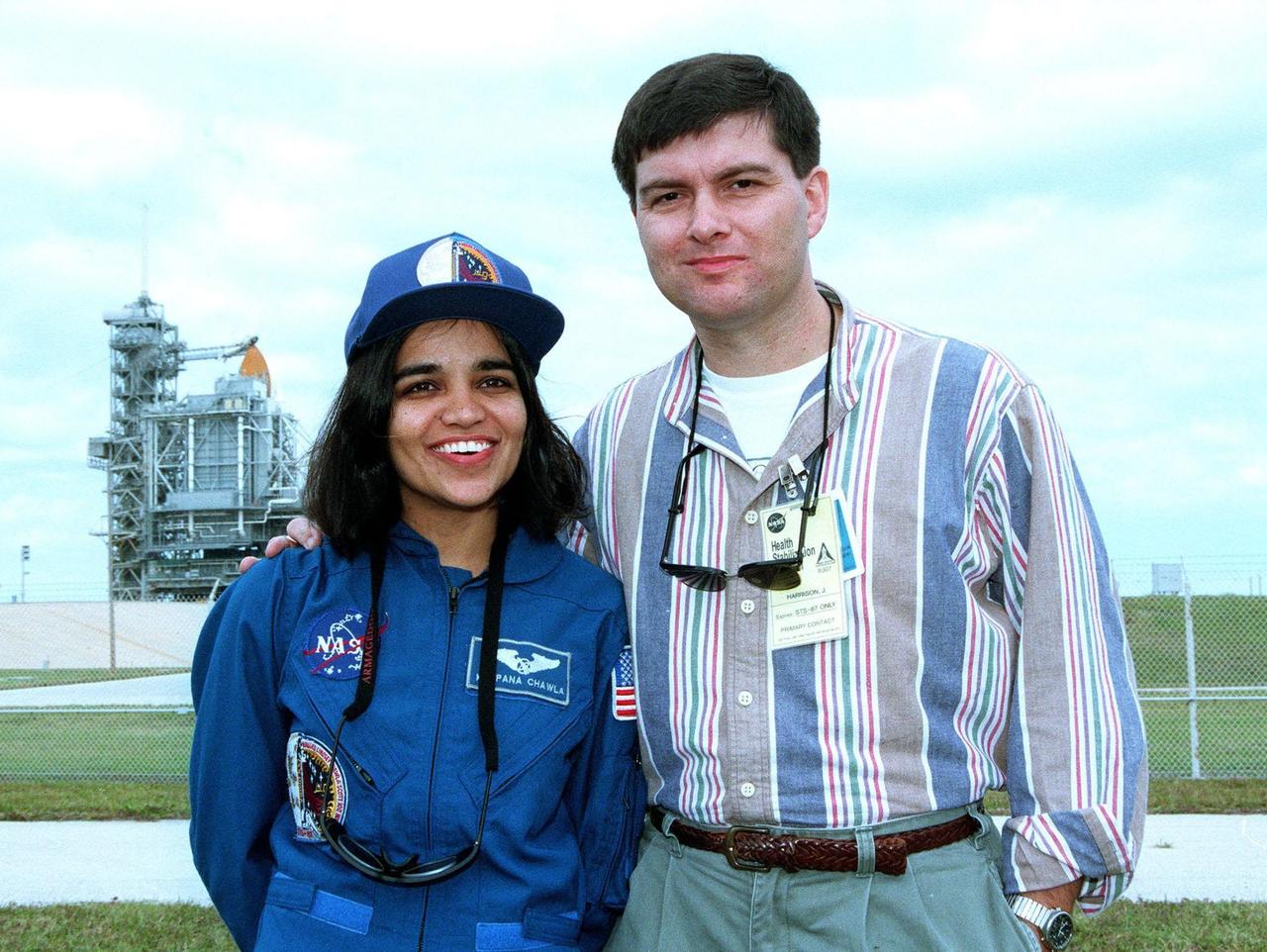

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., poses with her husband, Jean-Pierre Harrison, in front of Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Winston Scott and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite

STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi , Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, participates in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) in Kennedy Space Center’s (KSC's) Vertical Processing Facility. Glenda Laws, the extravehicular activity (EVA) coordinator, Johnson Space Center, stands behind Dr. Doi. The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working on-orbit. STS-87 will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, Dr. Doi will be the first Japanese astronaut to perform a spacewalk. STS-87 is scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC
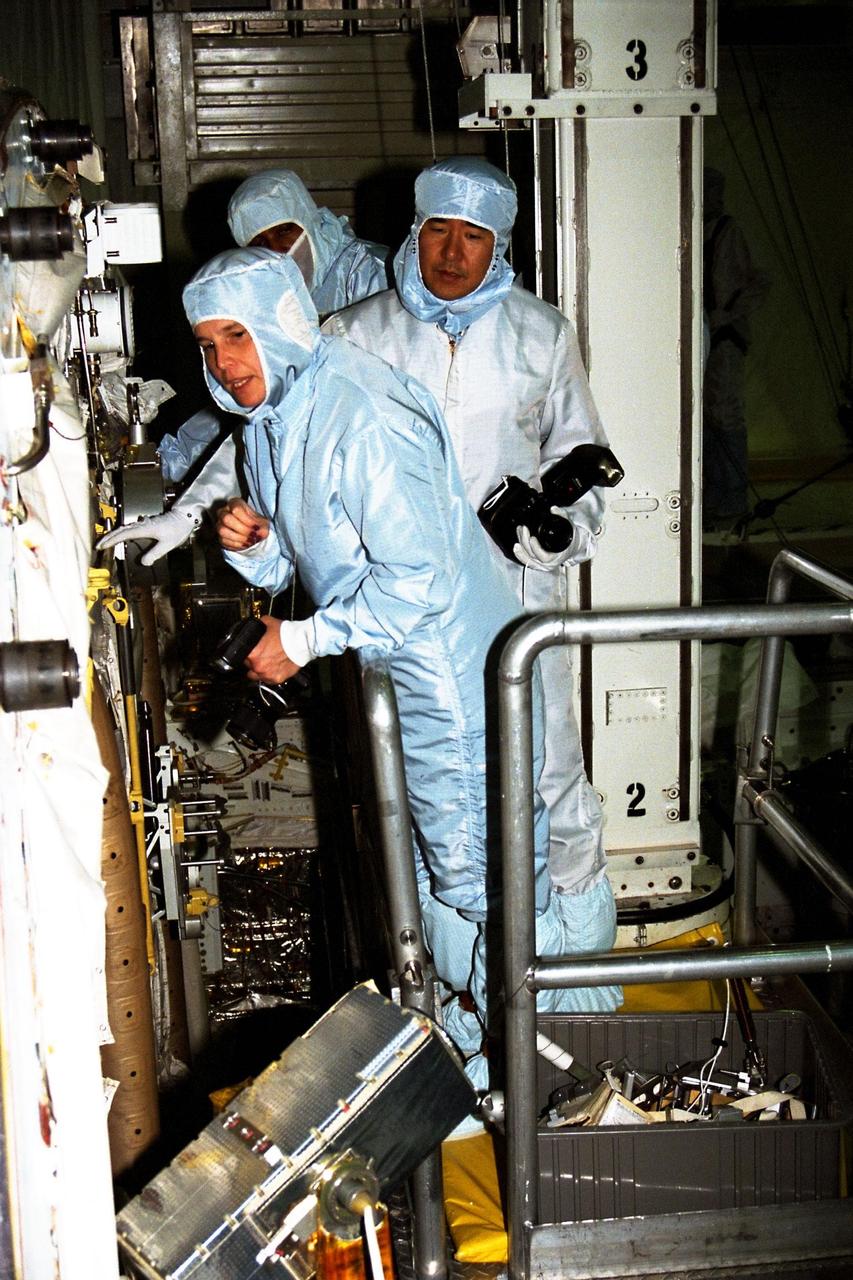

Participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center are STS-87 crew members, assisted by Glenda Laws, extravehicular activity (EVA) coordinator, Johnson Space Center. Standing behind Laws are Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, and Winston Scott, both mission specialists on STS-87. The STS-87 mission will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC, Dr. Doi and Scott will both perform spacewalks
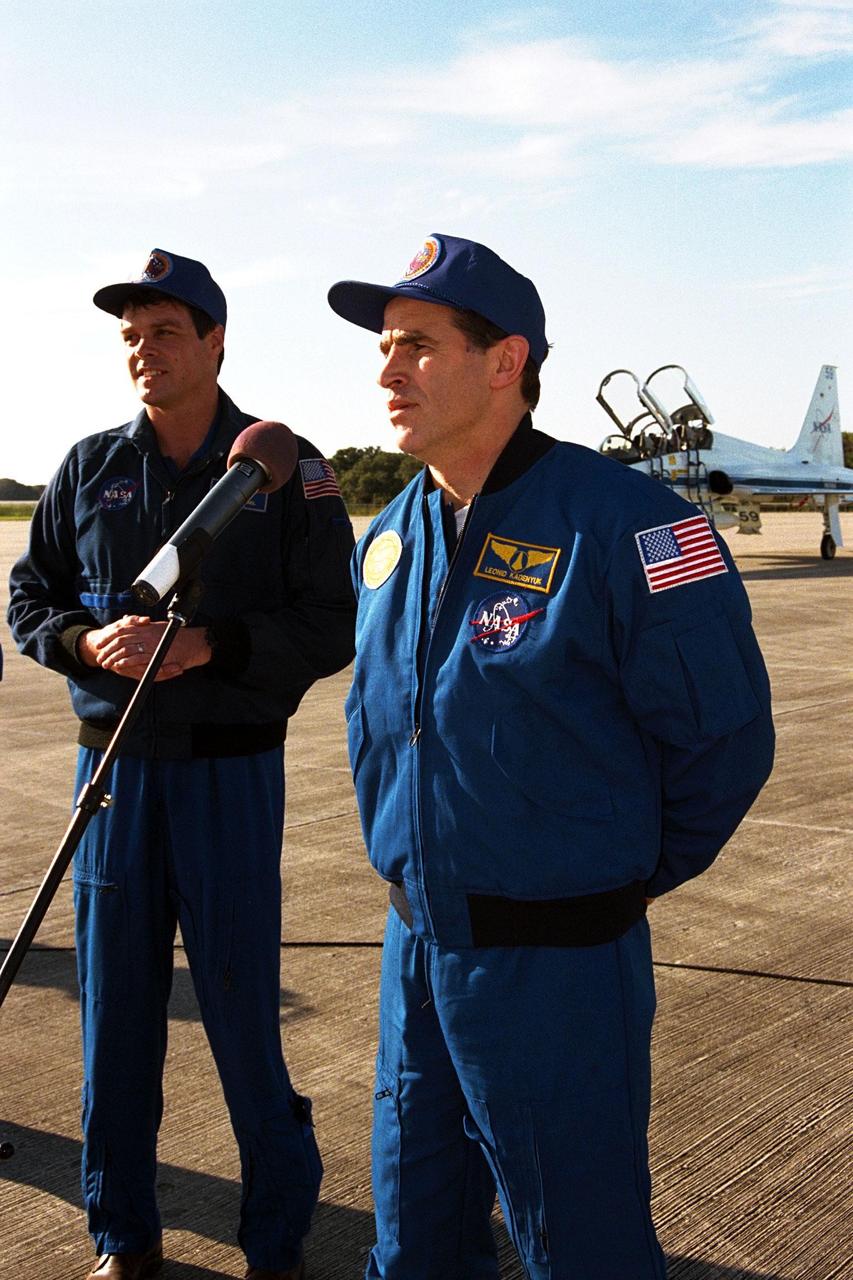

As STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel looks on, Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine addresses members of the press and media at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility after arriving for the final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. Other STS-87 crew members not pictured are Pilot Steven Lindsey; and Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Winston Scott. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
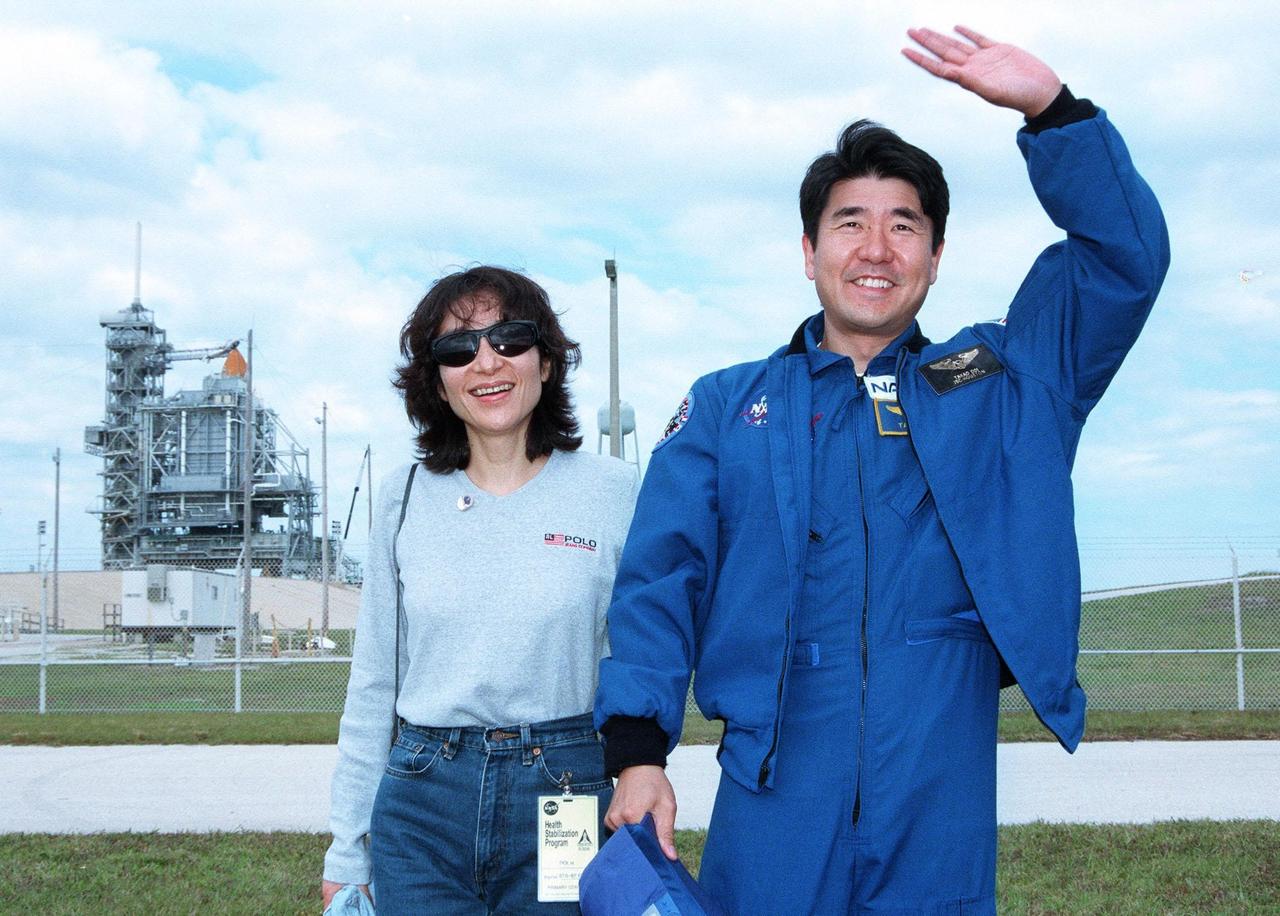

STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan poses with his wife, Hitomi Doi, in front of Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., and Winston Scott; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
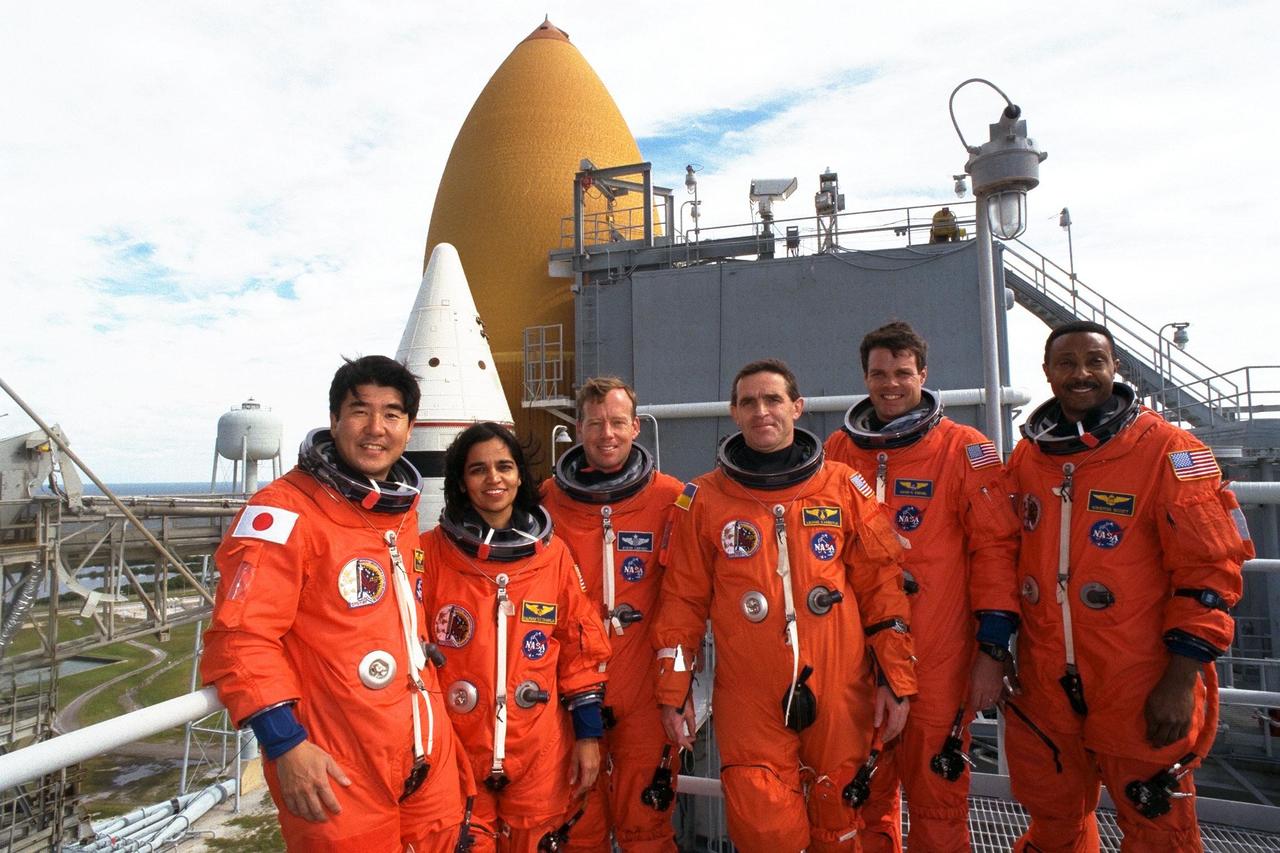

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
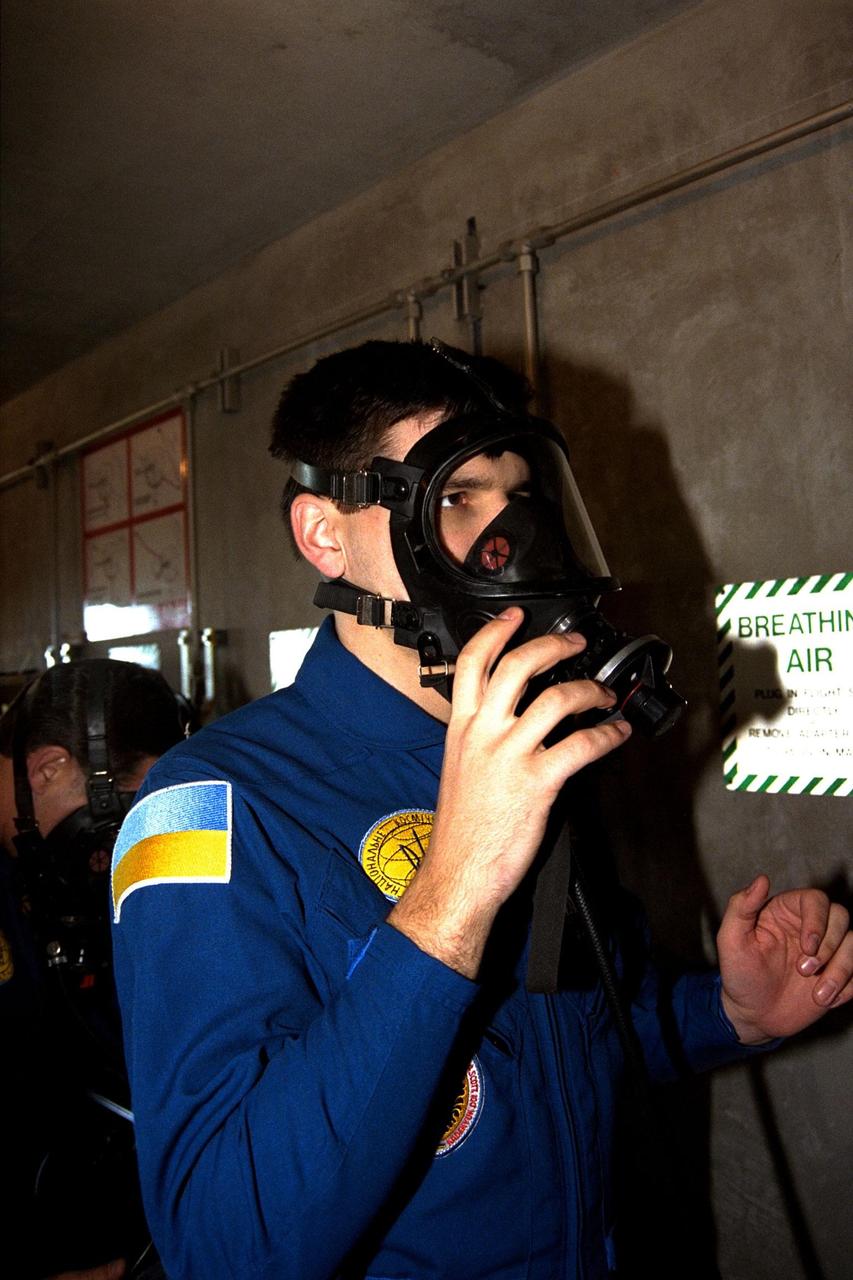

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
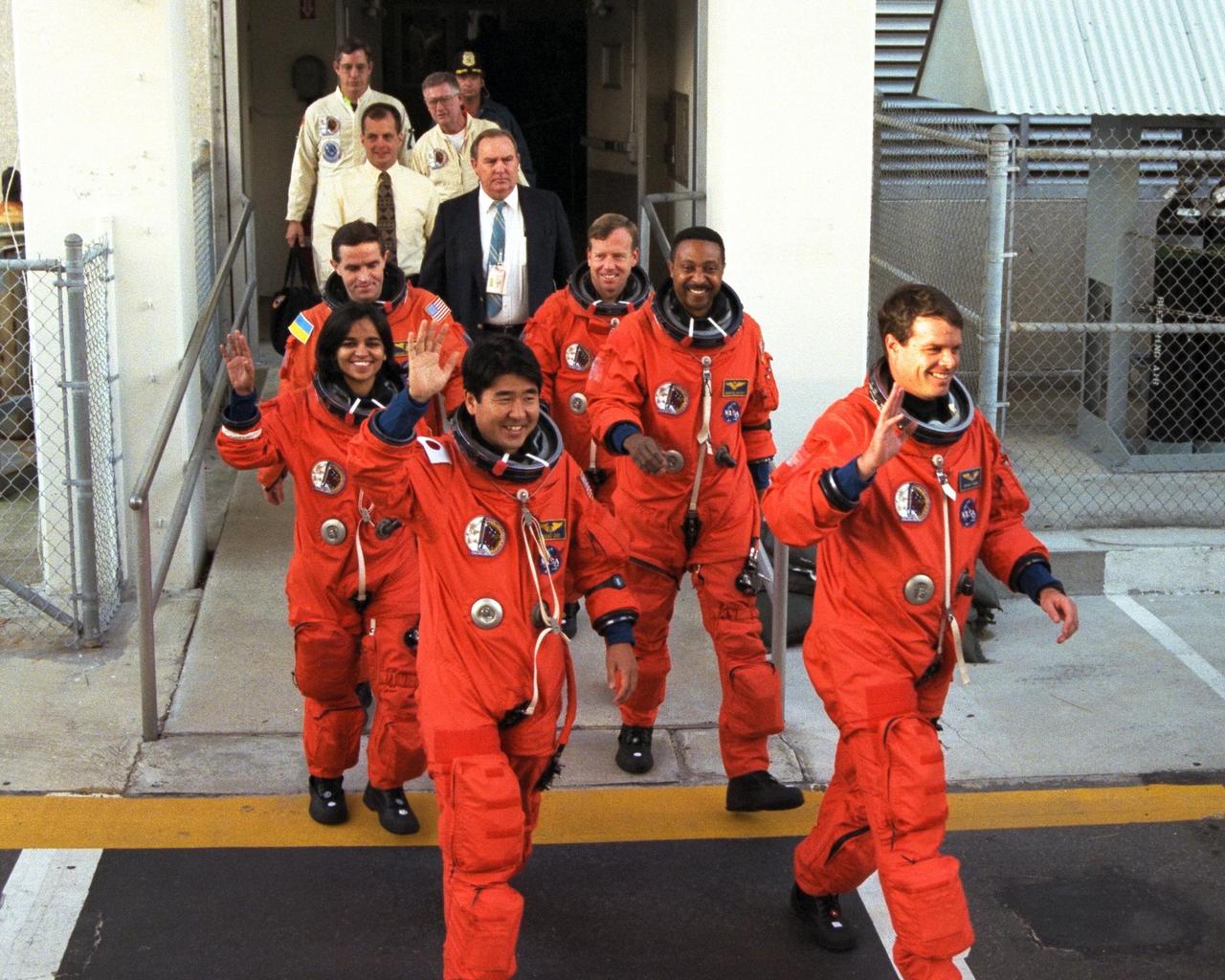

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
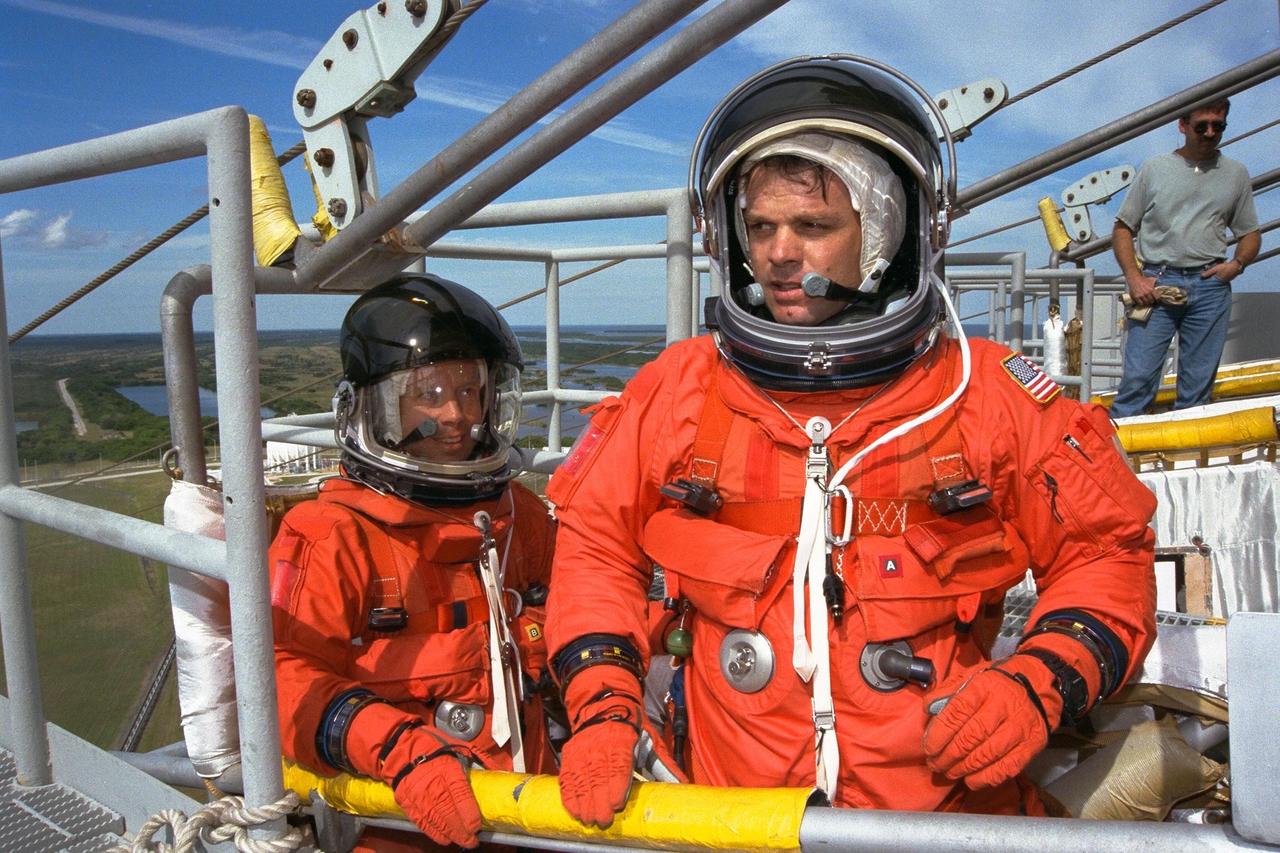

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
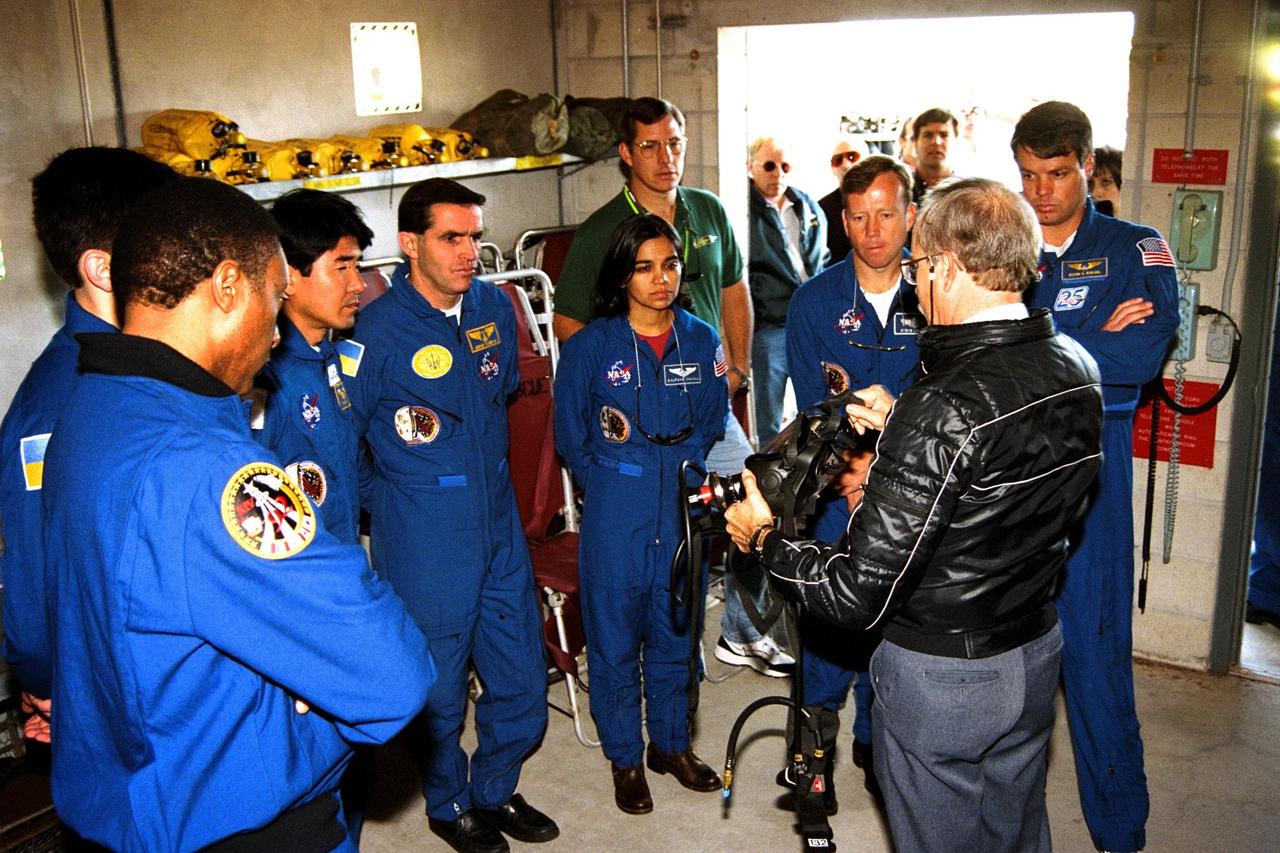

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
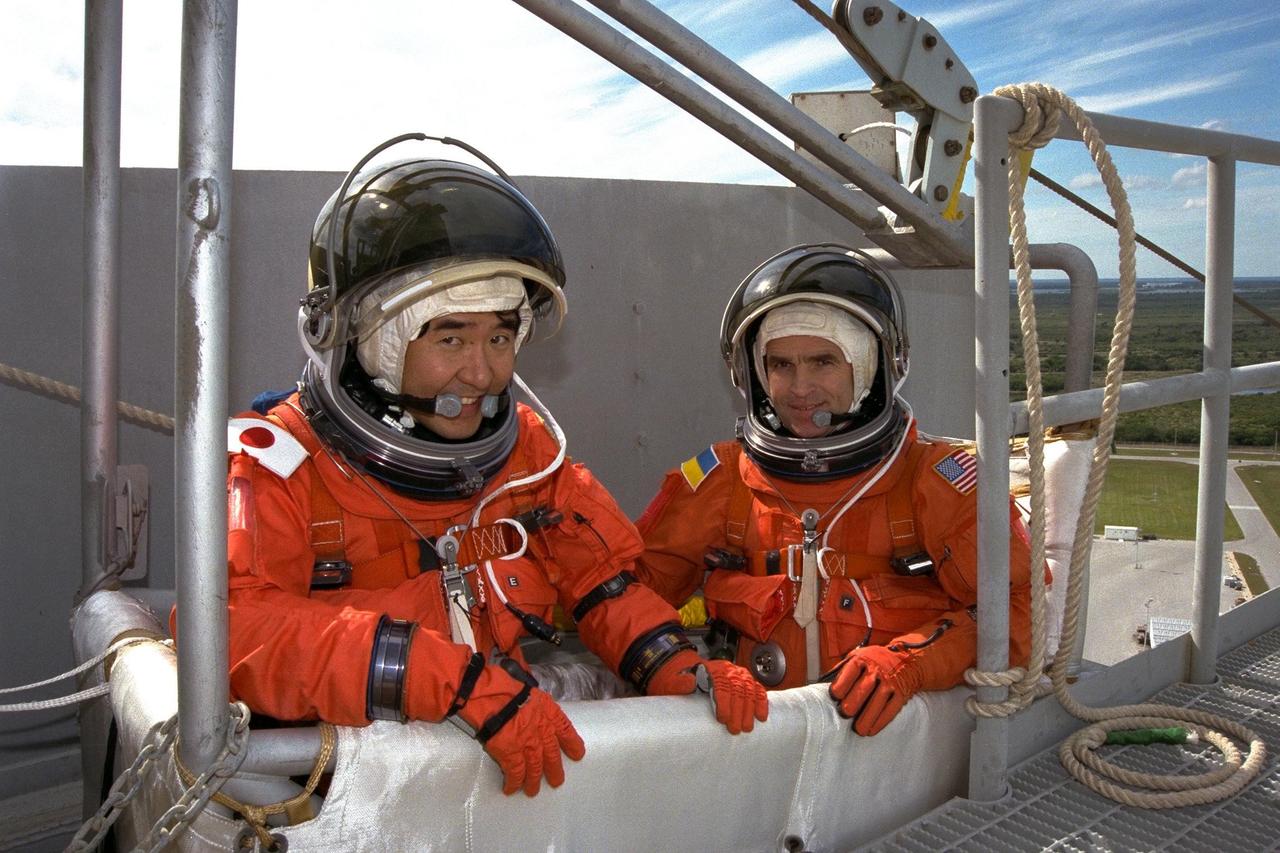

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
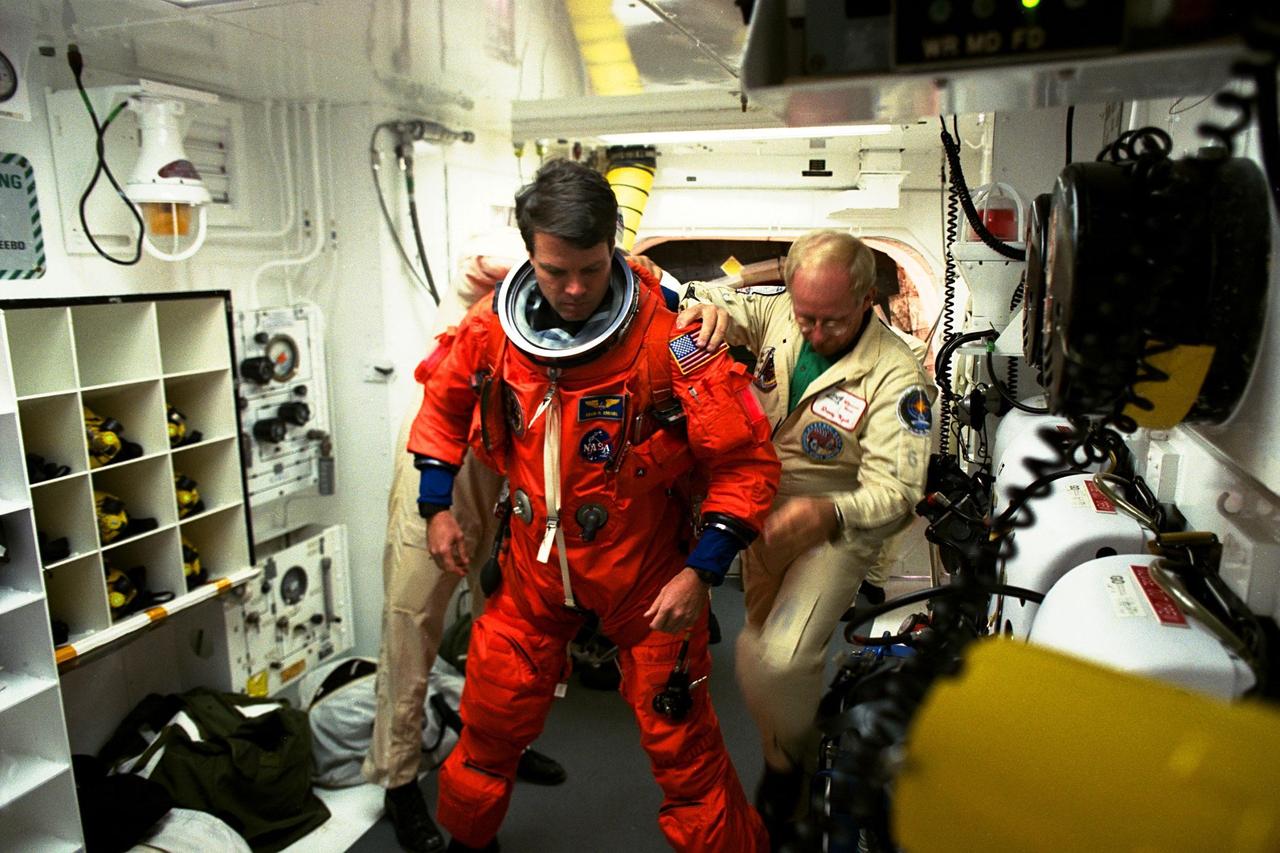

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. A veteran of two space flights (STS-70 and -78), Kregel has logged more than 618 hours in space
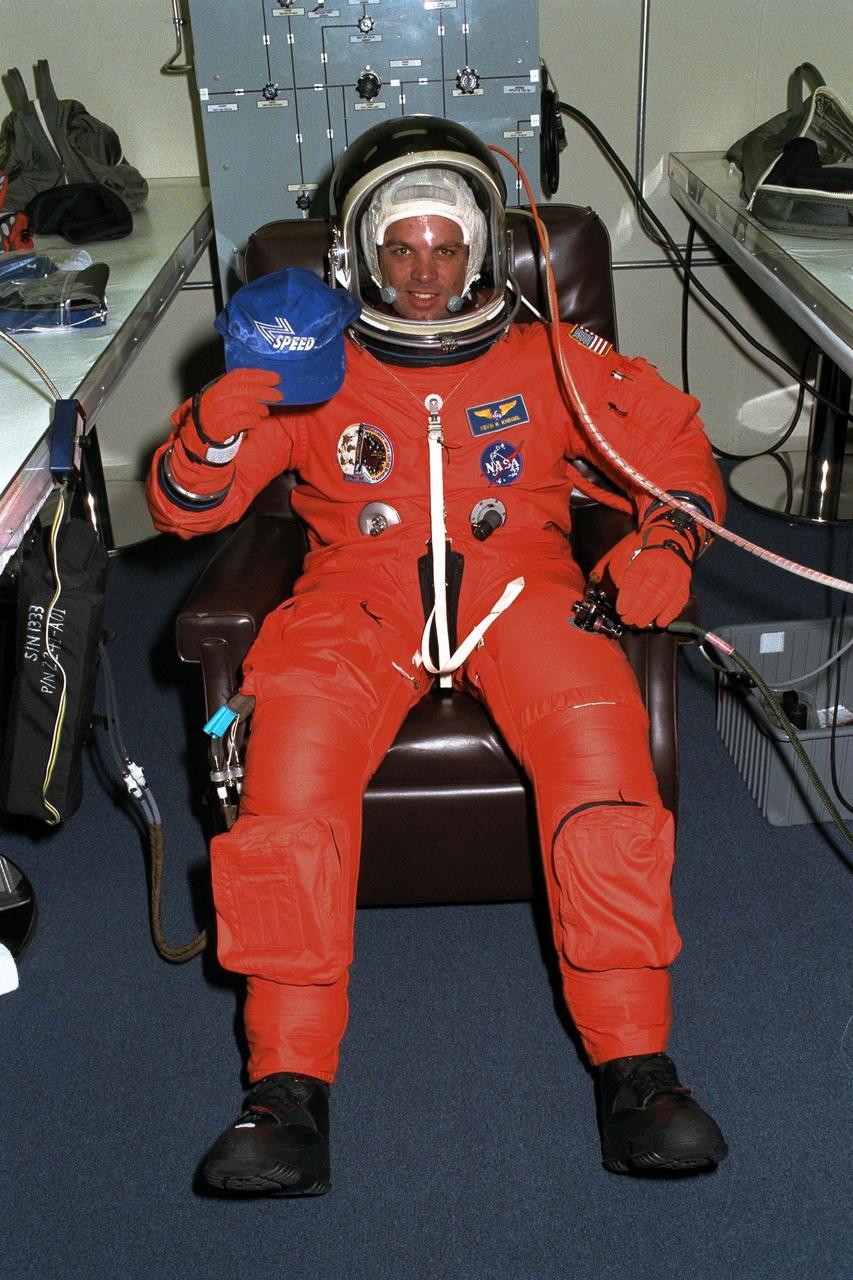

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel sits in his launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building holding a cap of his son’s soccer team of which Kregel is the coach. Shortly, he and the five other crew members of STS-87 will depart for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. A veteran of two space flights (STS-70 and -78), Kregel has logged more than 618 hours in space
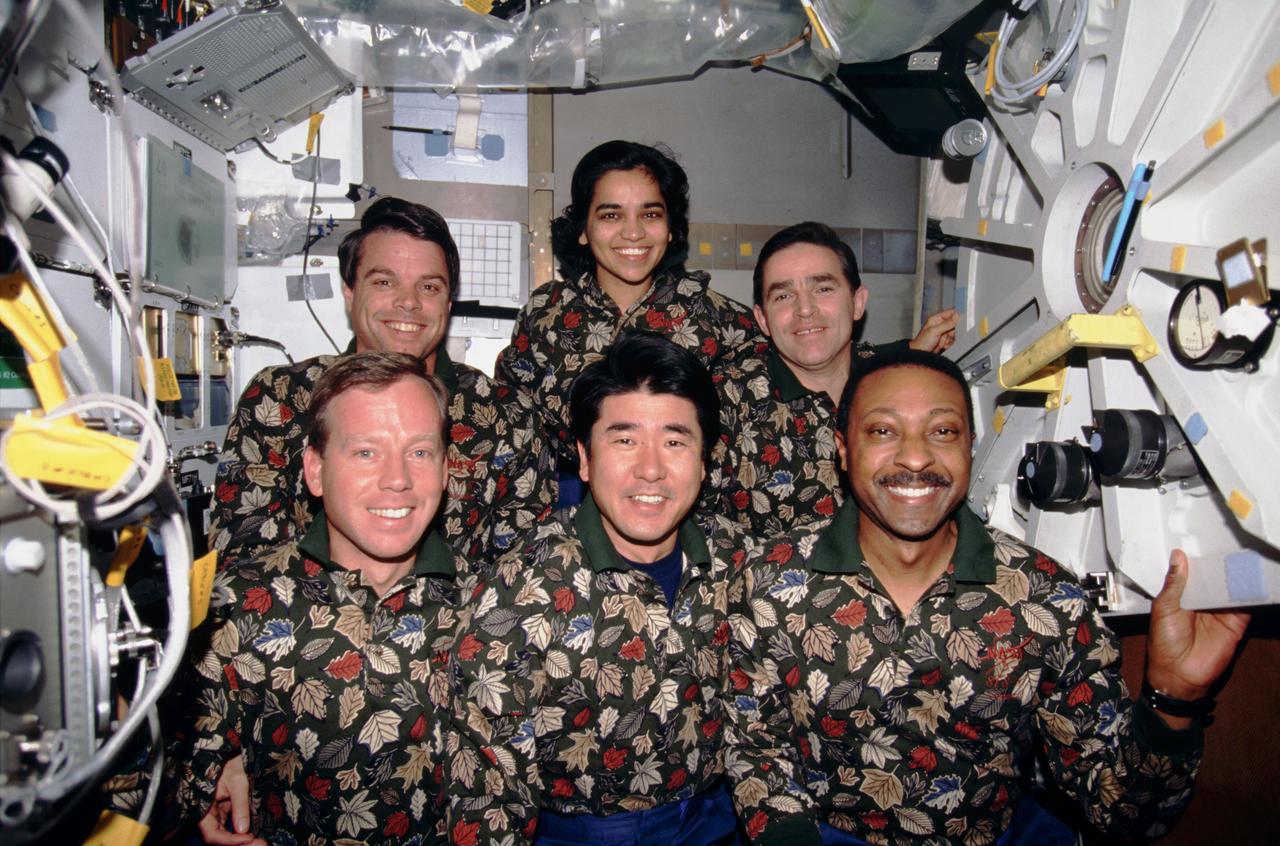

STS087-307-006 (19 November – 5 December 1997) --- One of the crew members' traditional in-flight crew portraits has them posed in other-than traditional attire on the Space Shuttle Columbia's mid-deck. On the front row, from the left, are astronauts Steven W. Lindsey, pilot; Takao Doi, an international mission specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA); and Winston E. Scott, mission specialist. In the back are astronauts Kevin R. Kregel, mission commander; and Kalpana Chawla, mission specialist, along with Ukrainian payload specialist Leonid K. Kadenyuk.

STS087-307-002 (19 November - 5 December 1997) --- On the Space Shuttle Columbia's middeck, the crewmembers for the mission pose for the traditional in-flight portrait. In front, left to right, are astronauts Steven W. Lindsey, pilot; Takao Doi, mission specialist representing Japan's National Space Development Agency (NASDA); and Winston E. Scott, mission specialist. In back are, from the left, astronauts Kevin R. Kregel, commander; and Kalpana Chawla, mission specialist; along with payload specialist Leonid Kadenyuk.
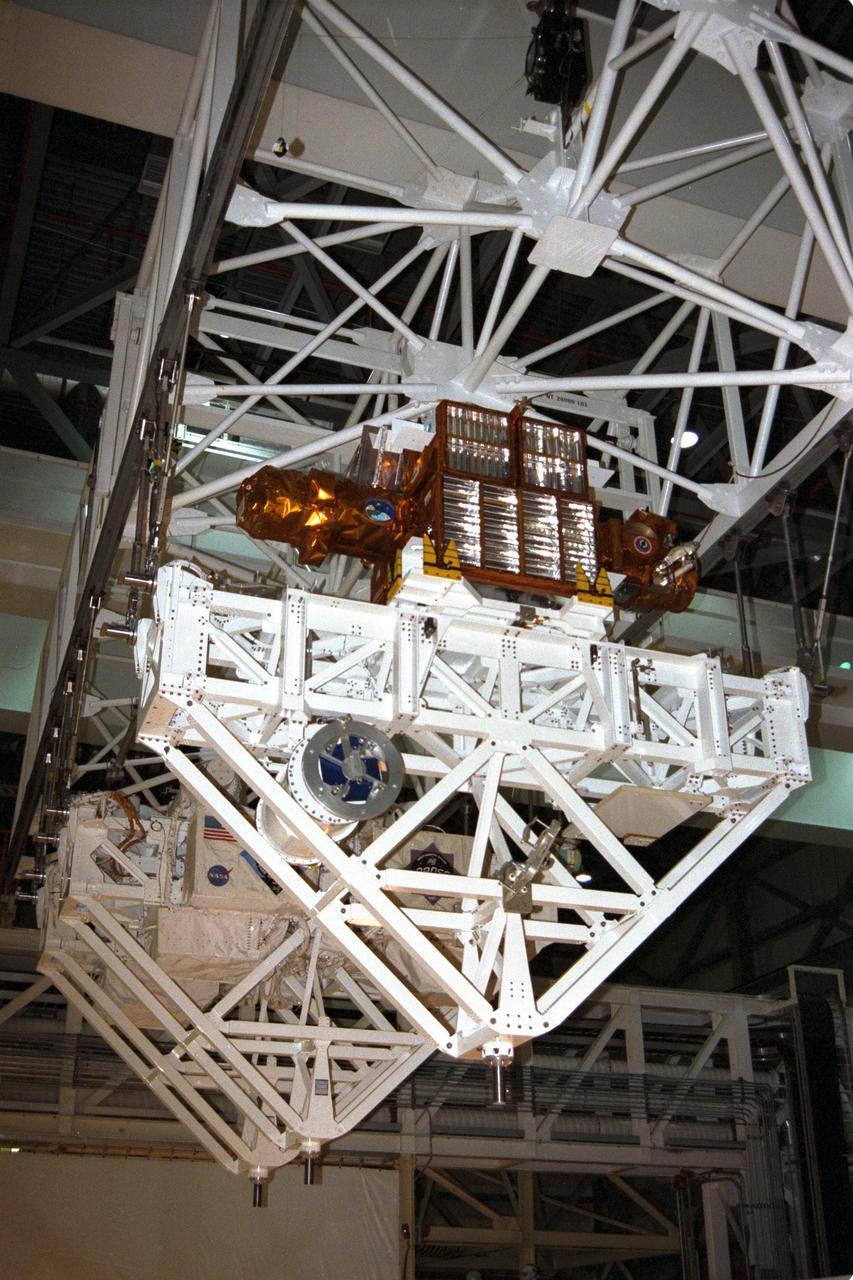
The Spartan payload, which flew on STS-87, is removed from Columbia's cargo bay in Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3 and will be transported to the Vertical Processing Facility
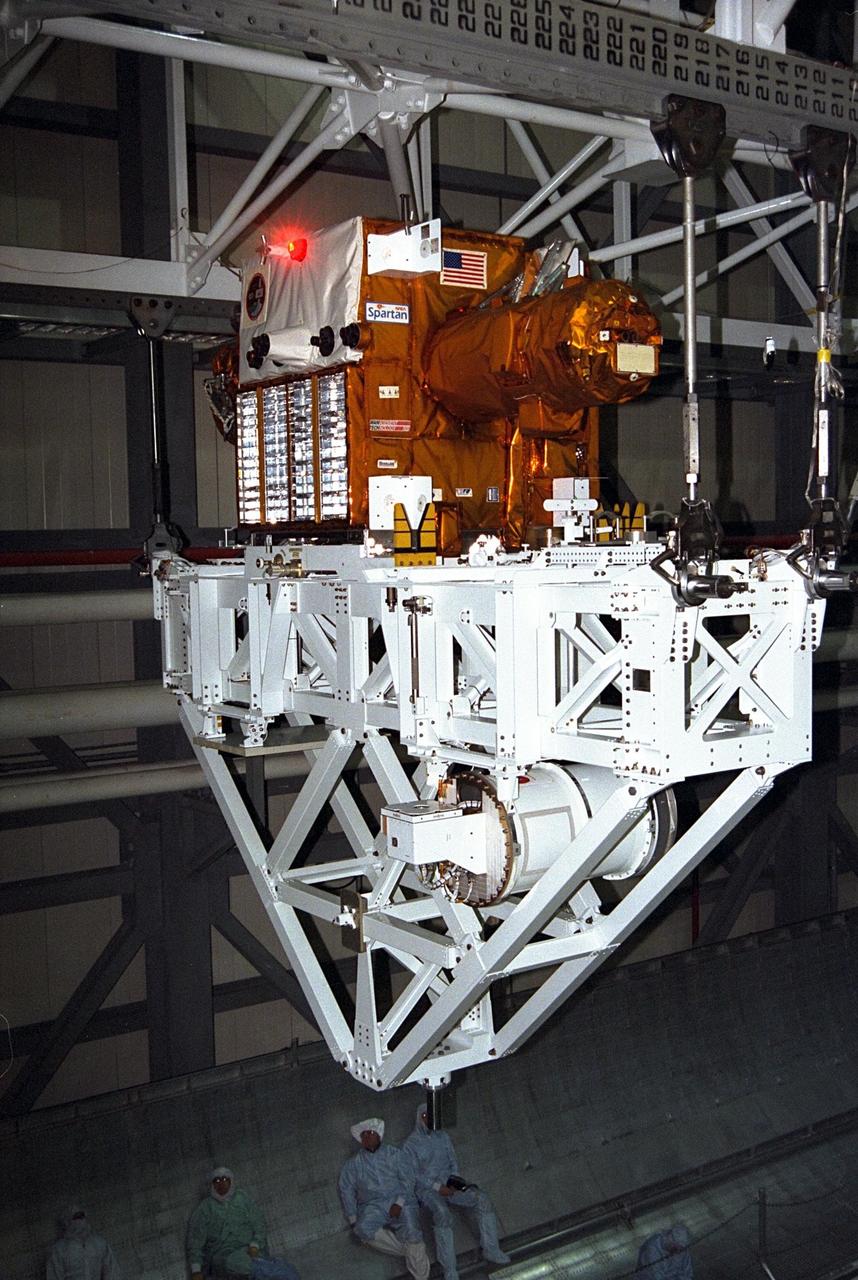
The Spartan payload, which flew on STS-87, is removed from Columbia's cargo bay in Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3 and will be transported to the Vertical Processing Facility
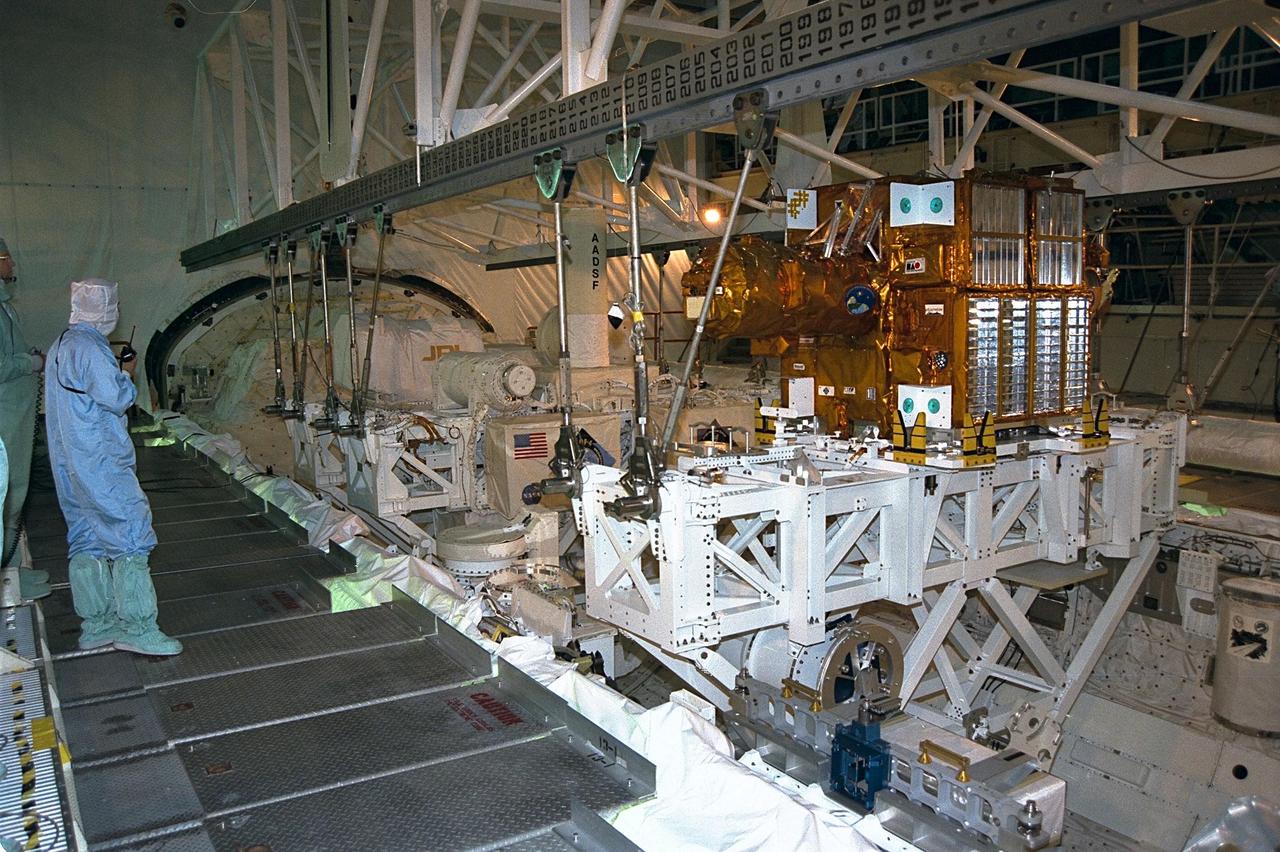

The Spartan payload, which flew on STS-87, is removed from Columbia's cargo bay in Orbiter Processing Facility Bay 3 and will be transported to the Vertical Processing Facility
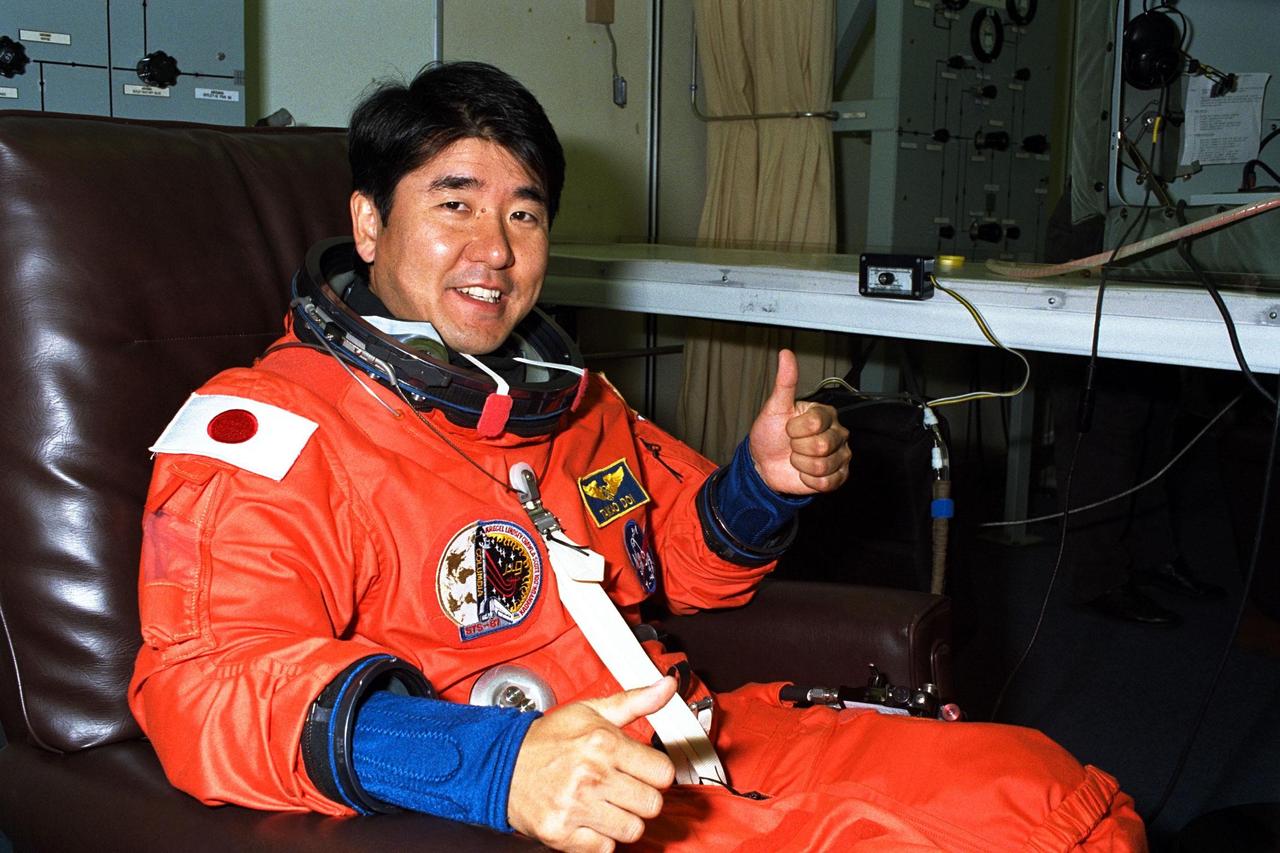

STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, gives a ‘thumbs up’ in his launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building. He and the five other crew members will depart shortly for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Dr. Doi is scheduled to perform an extravehicular activity spacewalk with Mission Specialist Winston Scott during STS-87
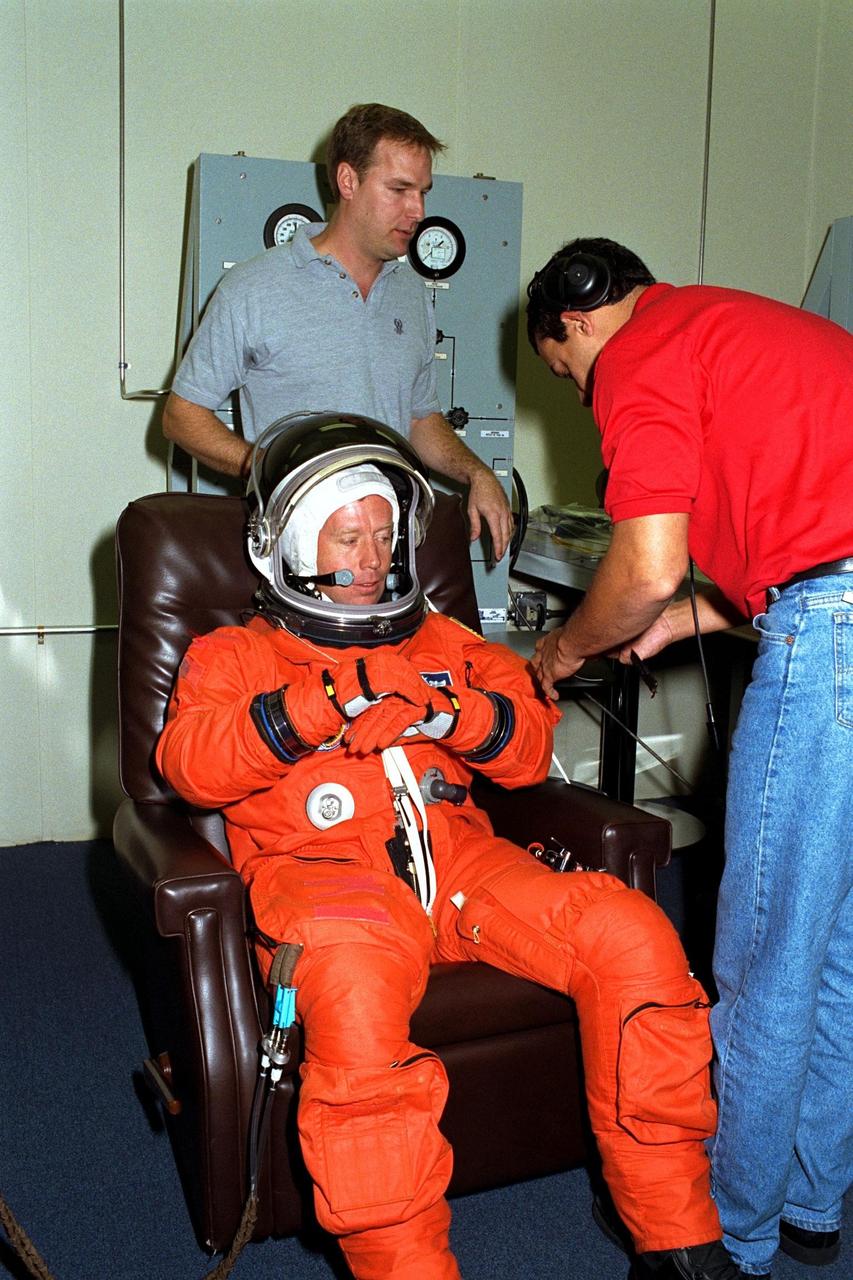

STS-87 Pilot Steven Lindsey dons his launch and entry suit with the help of two assistants in the Operations and Checkout Building. Shortly, he and the five other crew members of STS-87 will depart for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Although this is his first Shuttle flight, Lindsey has logged more than 2,700 hours of flying time in 49 different types of aircraft
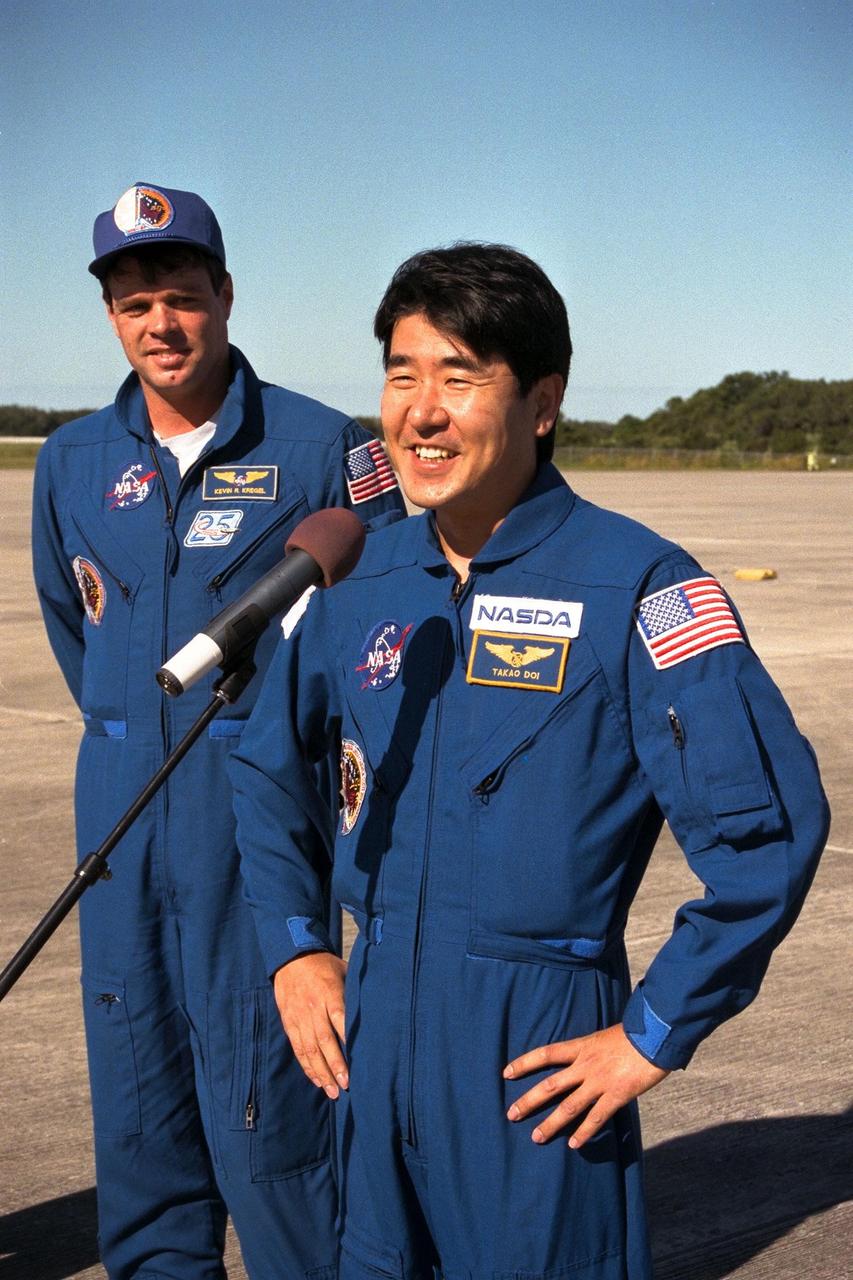

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the crew arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) for their mission. The TCDT is a dress rehearsal for launch. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is targeted for Nov. 19

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the orbiter Columbia is lifted into high bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The orbiter will be mated to the <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/count3.htm#et">external tank</a> and <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/ships.htm#srbs">solid rocket boosters</a> over the weekend and is slated to roll out to Pad 39B on Wednesday. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., sits in her launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building before she and the five other crew members of STS-87 depart for Launch Pad 39B. There, the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Born in Karnal, India, Dr. Chawla received her doctorate of philosophy in aerospace engineering from the University of Colorado in 1988. This is Chawla’s first mission for NASA

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., is assisted with her ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist. Kneeing before Dr. Chawla to assist her is George Schram, USA mechanical technician, as Dr. Chawla prepares to enter the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia on launch day. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201
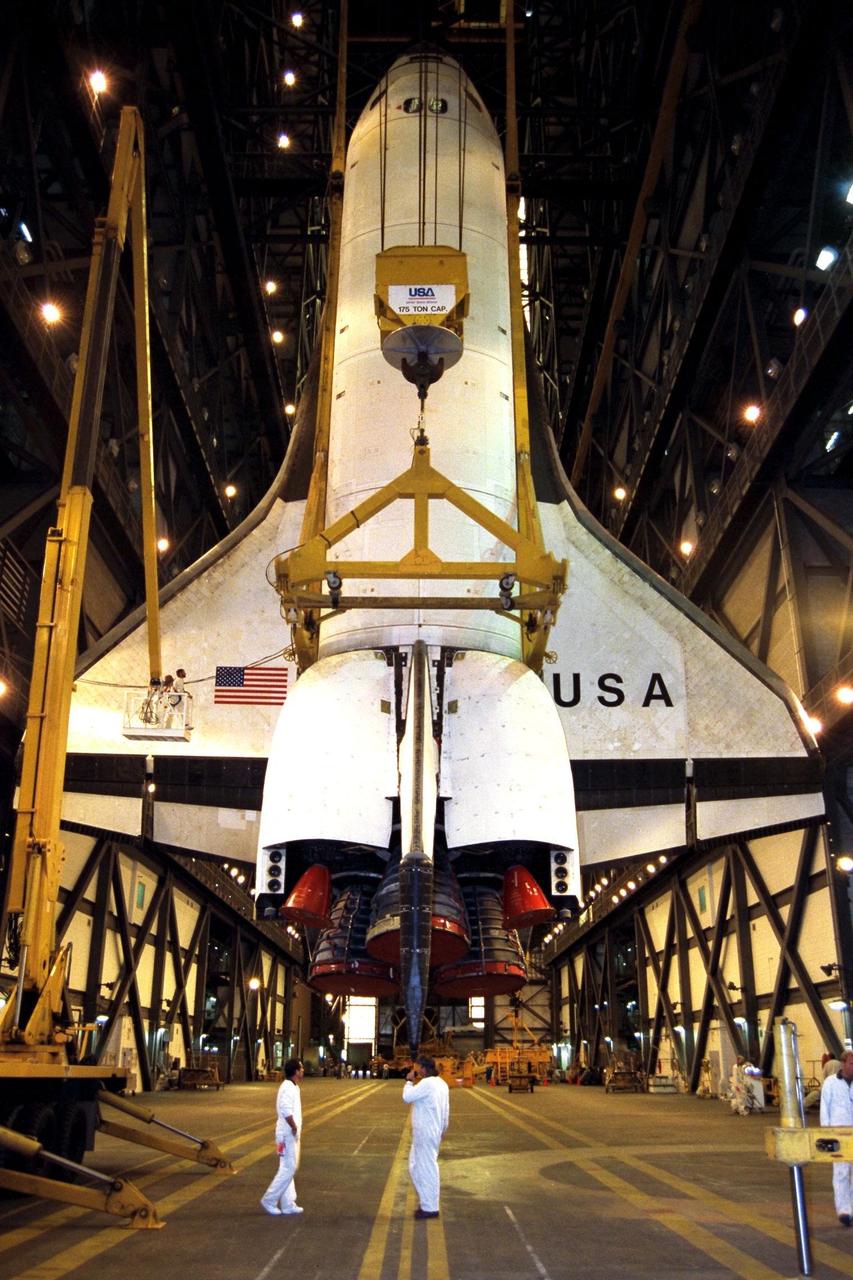

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the orbiter Columbia is lifted into high bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The orbiter will be mated to the <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/count3.htm#et">external tank</a> and <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/ships.htm#srbs">solid rocket boosters</a> over the weekend and is slated to roll out to Pad 39B on Wednesday. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
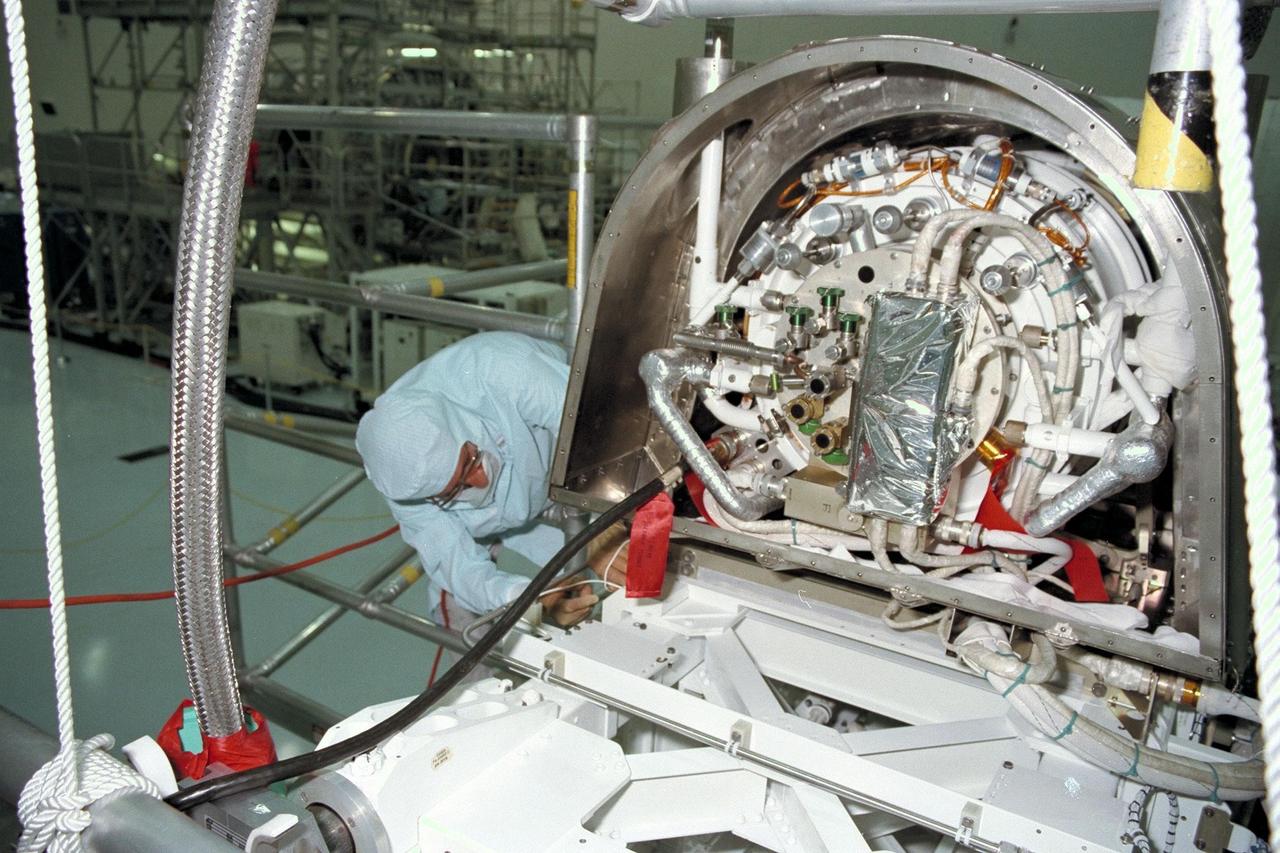

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Here, a technician is monitoring the Confined Helium Experiment, or CHeX, that will use microgravity to study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between silicon disks. CHeX and several other experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
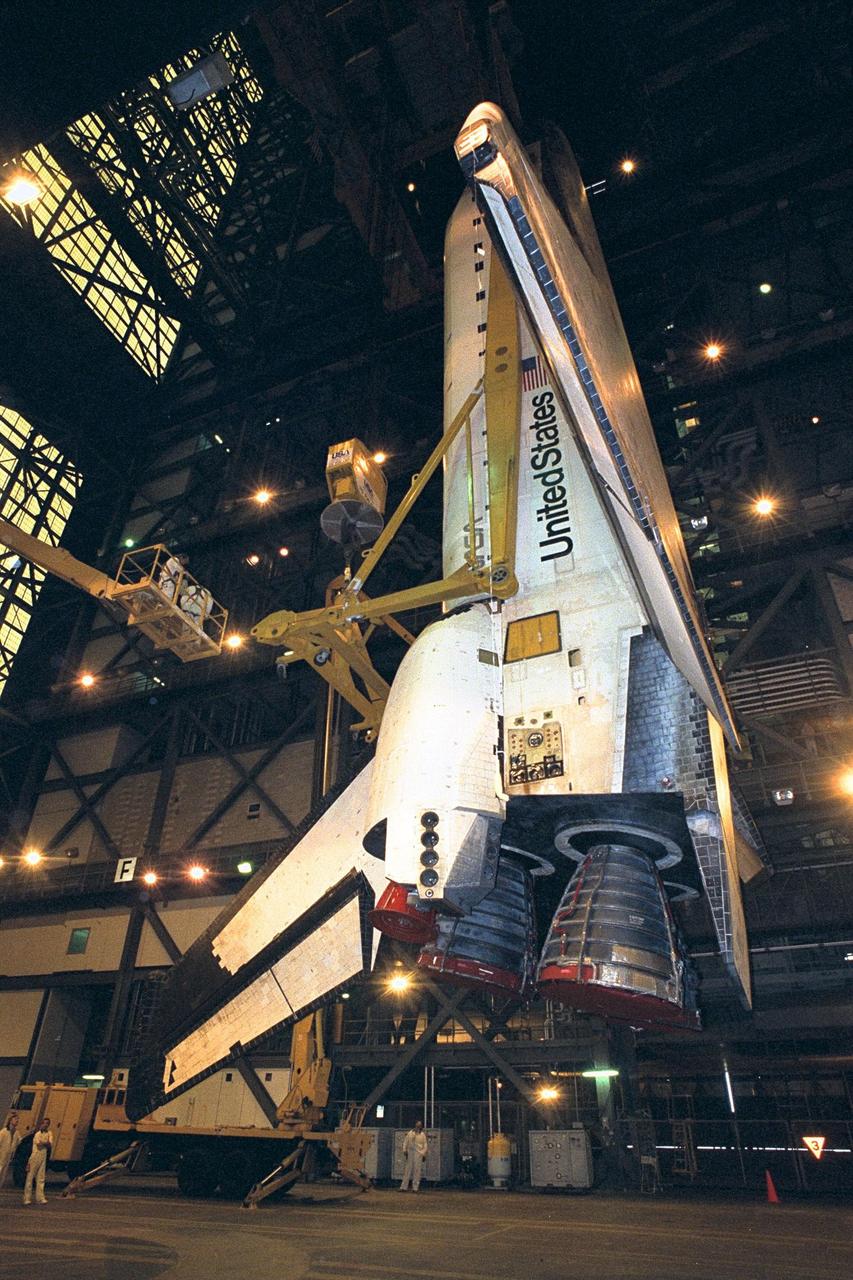

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the orbiter Columbia is lifted into high bay 3 in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The orbiter will be mated to the <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/count3.htm#et">external tank</a> and <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/ships.htm#srbs">solid rocket boosters</a> over the weekend and is slated to roll out to Pad 39B on Wednesday. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
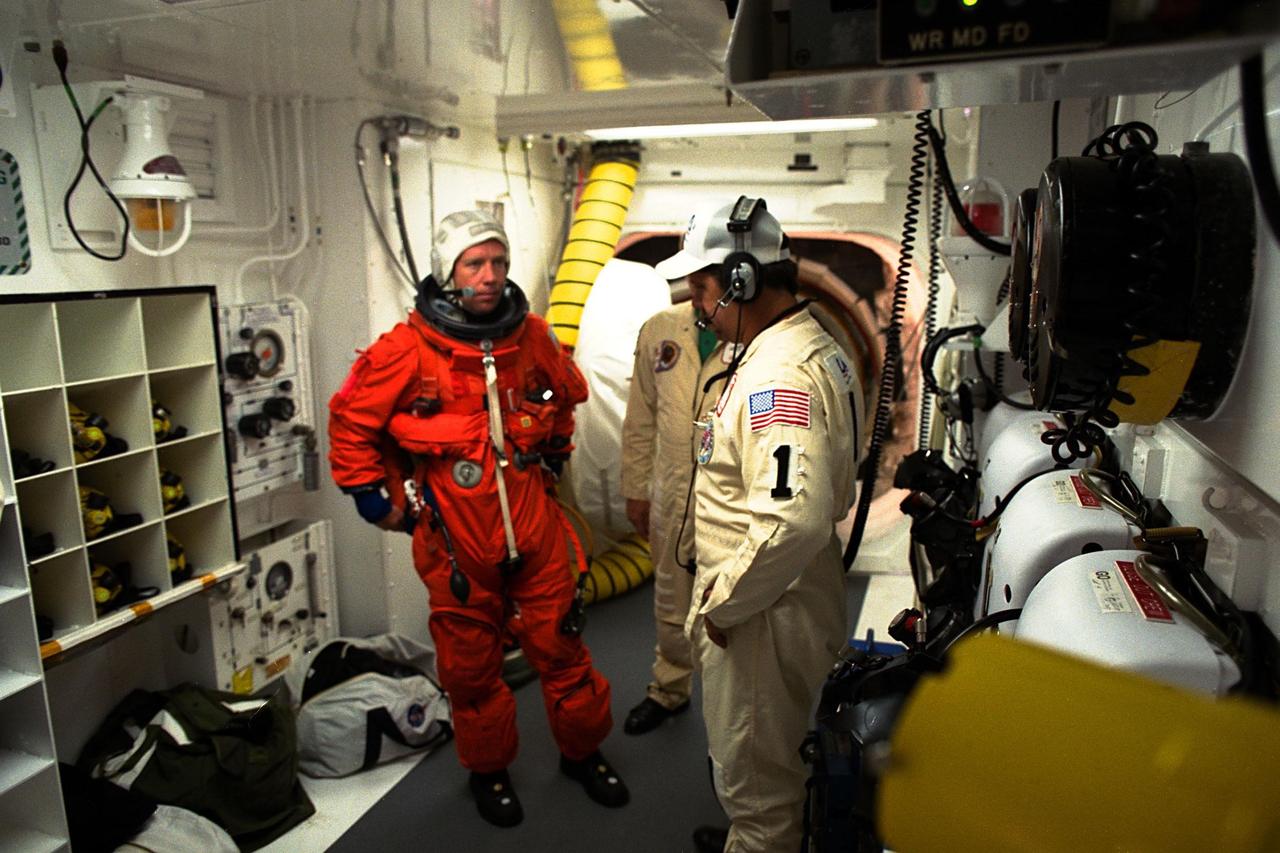

STS-87 Pilot Steven Lindsey is inspected before launch in his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Travis Thompson, USA orbiter vehicle closeout chief. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. Although this is his first Shuttle flight, Lindsey has logged more than 2,700 hours of flying time in 49 different types of aircraft
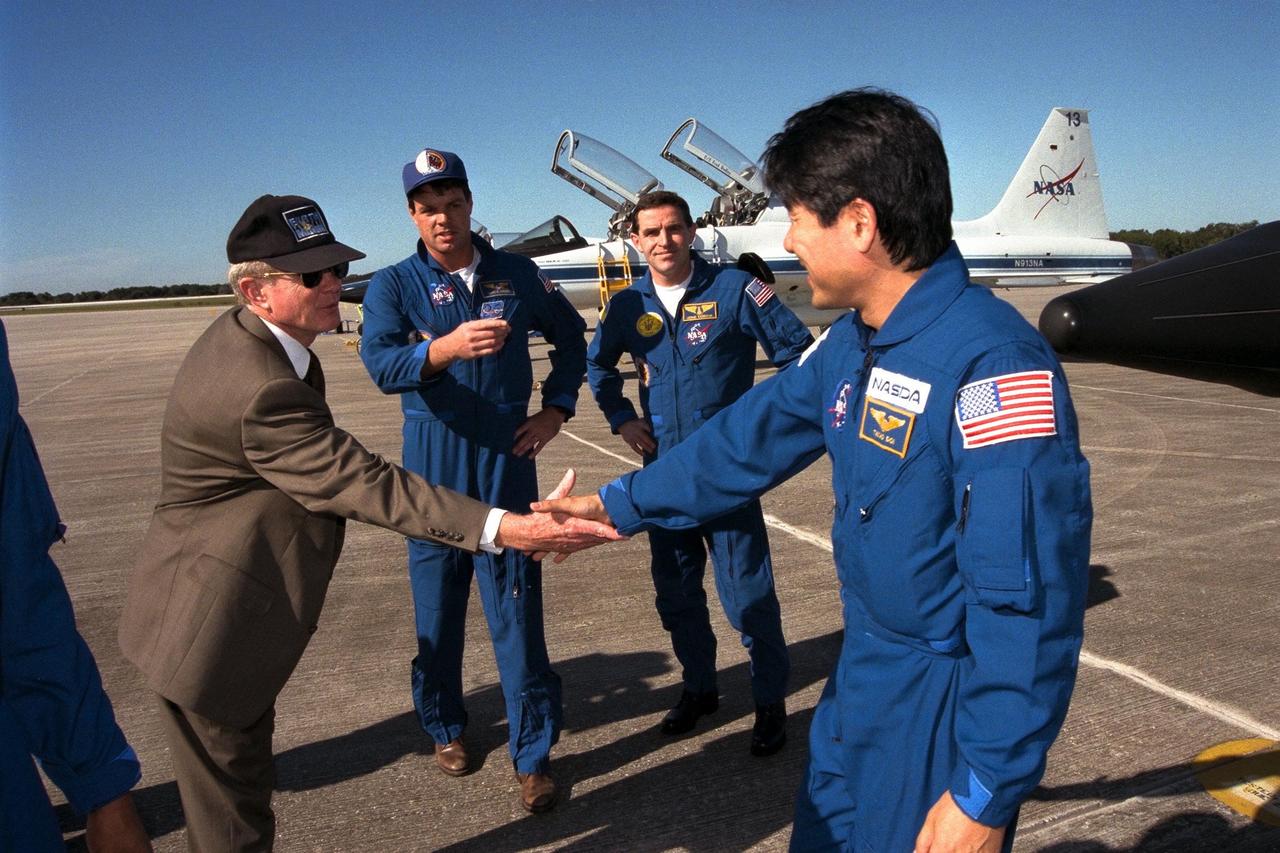

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the crew arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) for their mission. The TCDT is a dress rehearsal for launch. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is targeted for Nov. 19
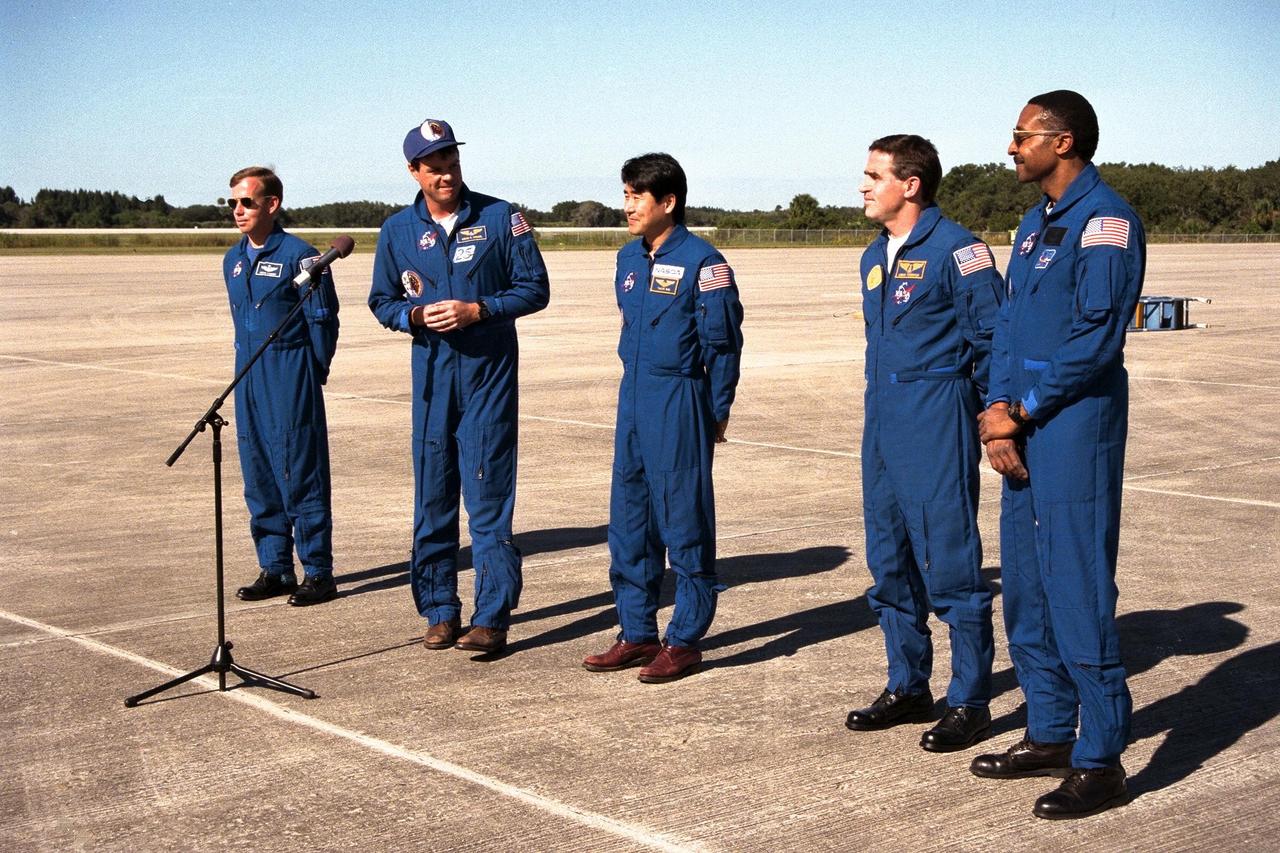

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the crew arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) for their mission. The TCDT is a dress rehearsal for launch. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is targeted for Nov. 19
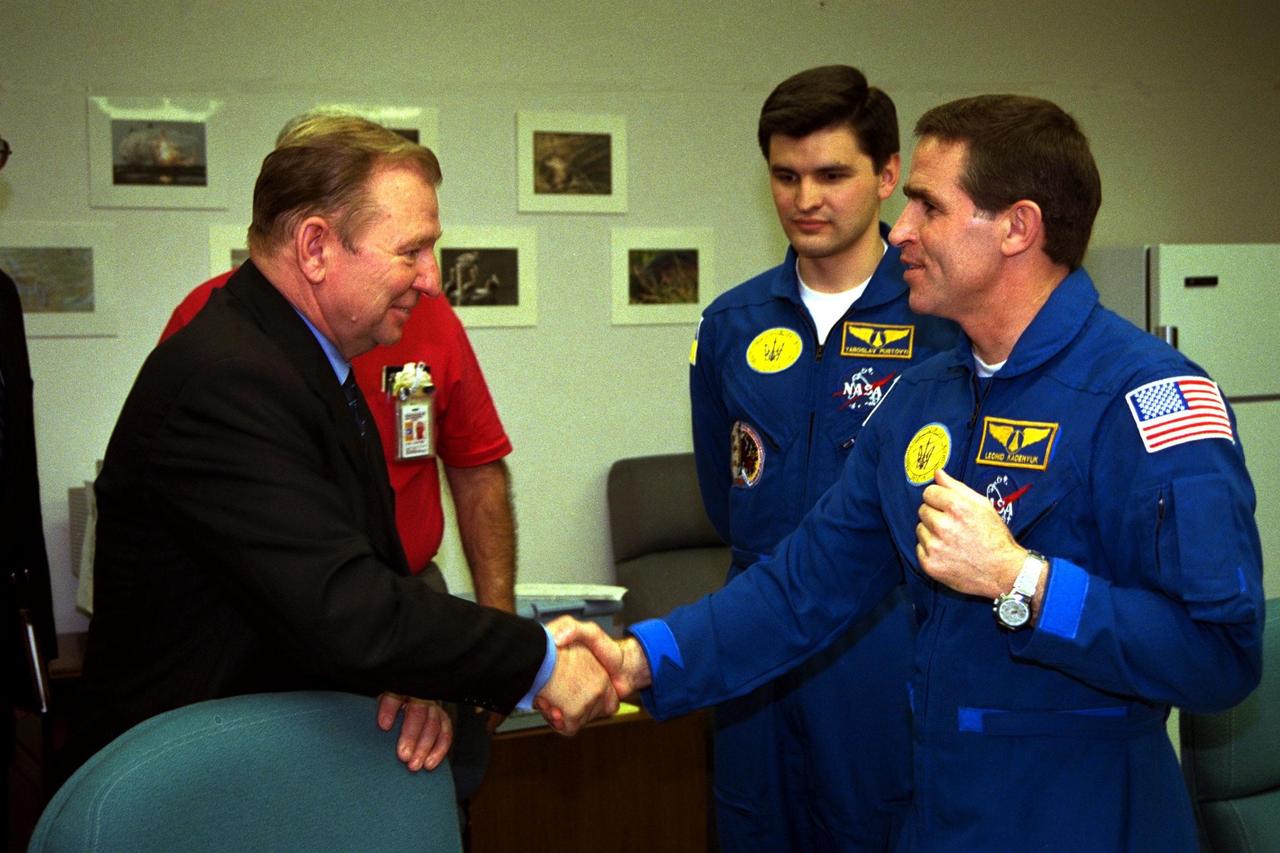

The president of the Ukraine, Leonid Kuchma, shakes hands with Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk, at right, as backup Payload Specialist Yaroslav Pustovyi, both of the National Space Agency of Ukraine, looks on during prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 launch of STS-87. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, Kadenyuk will pollinate Brassica rapa plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia during its 16-day mission. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia's middeck and will feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on Brassica rapa seedlings. Students in Ukrainian and American schools will participate in the same experiment with Kadenyuk in space. Kadenyuk will be flying his first Shuttle mission on STS-87
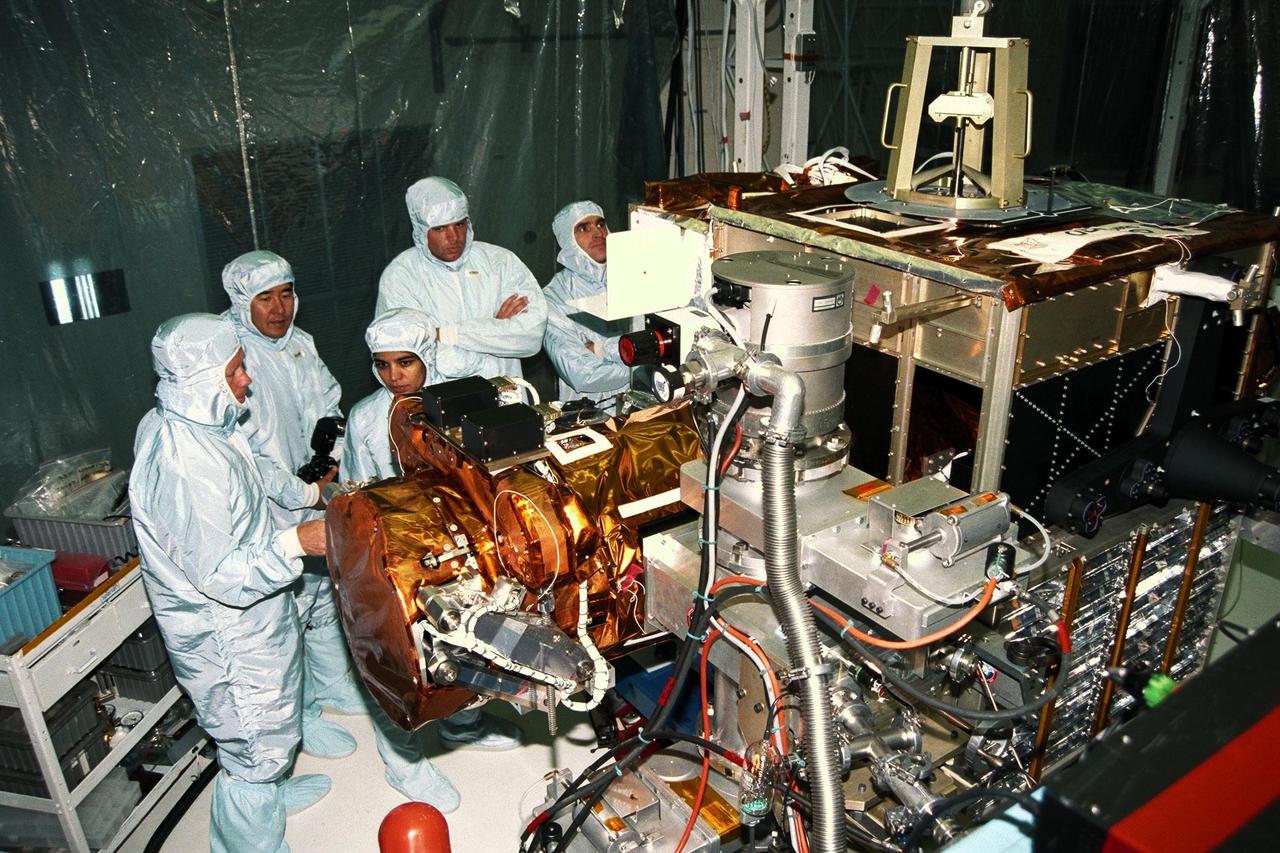
STS-87 astronaut crew members participate in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) with the Spartan-201 payload in Kennedy Space Center’s (KSC's) Vertical Processing Facility. From left are Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Commander Kevin Kregel; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working on-orbit. STS-87 will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, Dr. Doi will be the first Japanese astronaut to perform a spacewalk. STS-87 is scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC
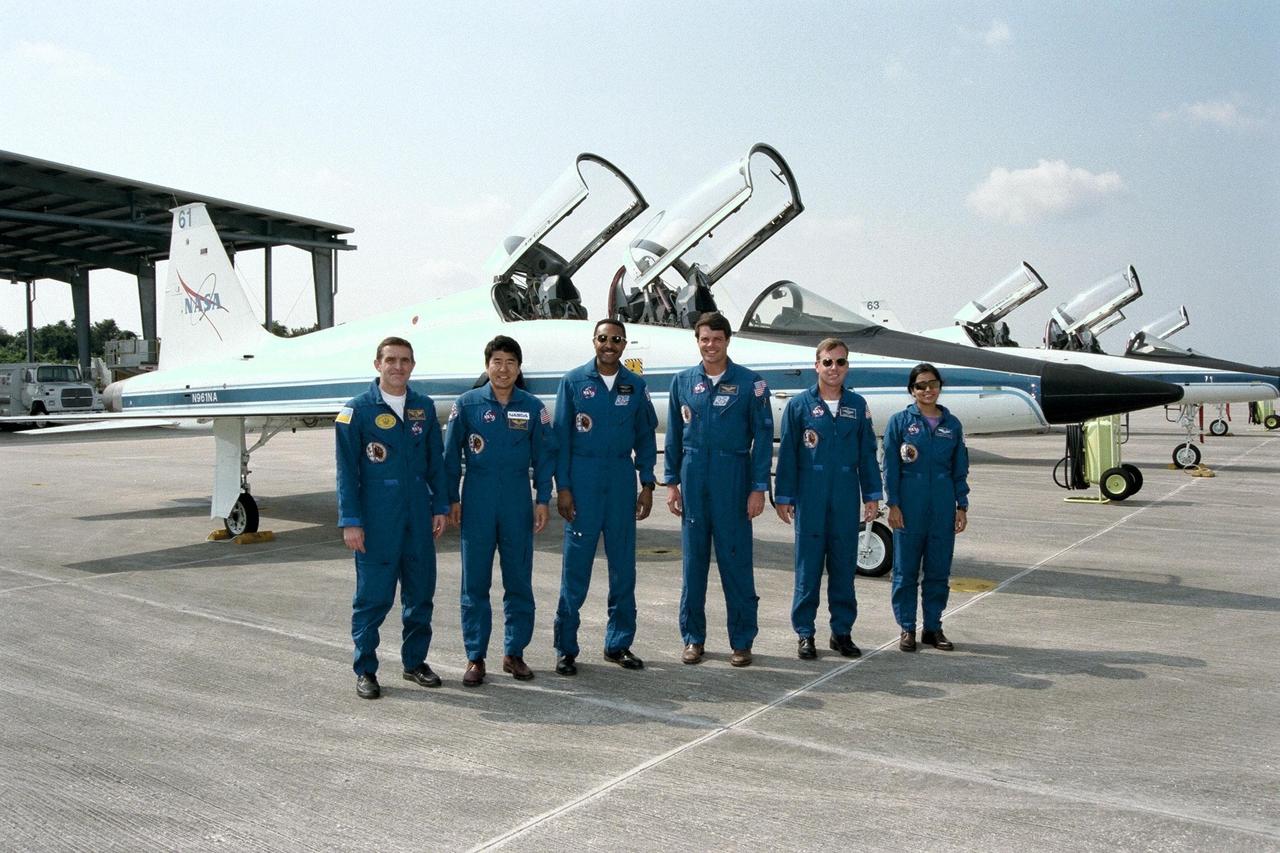

STS-87 astronaut crew members prepare to fly back to Johnson Space Center in Houston after participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in early October. From left are Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Mission Specialist Winston Scott; Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; and Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D. The CEIT gives astronauts an opportunity to get a hands-on look at the payloads with which they will be working on-orbit. STS-87 will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the STS-87 mission, scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC, Dr. Doi and Scott will both perform spacewalks
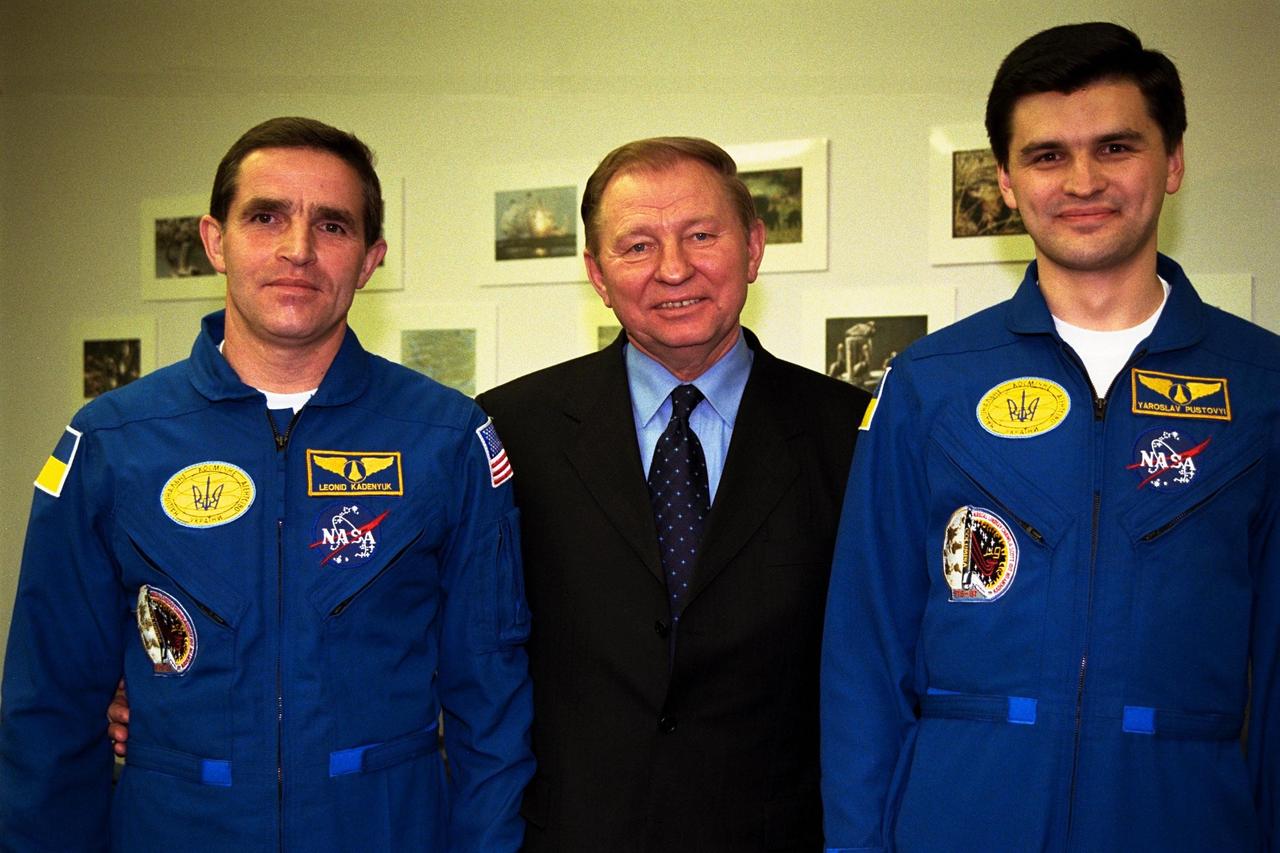

The president of the Ukraine, Leonid Kuchma, is flanked by Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk, at left, and backup Payload Specialist Yaroslav Pustovyi, at right, both of the National Space Agency of Ukraine, during prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 launch of STS-87. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, Kadenyuk will pollinate Brassica rapa plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia during its 16-day mission. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia's middeck and will feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on Brassica rapa seedlings. Students in Ukrainian and American schools will participate in the same experiment with Kadenyuk in space. Kadenyuk will be flying his first Shuttle mission on STS-87
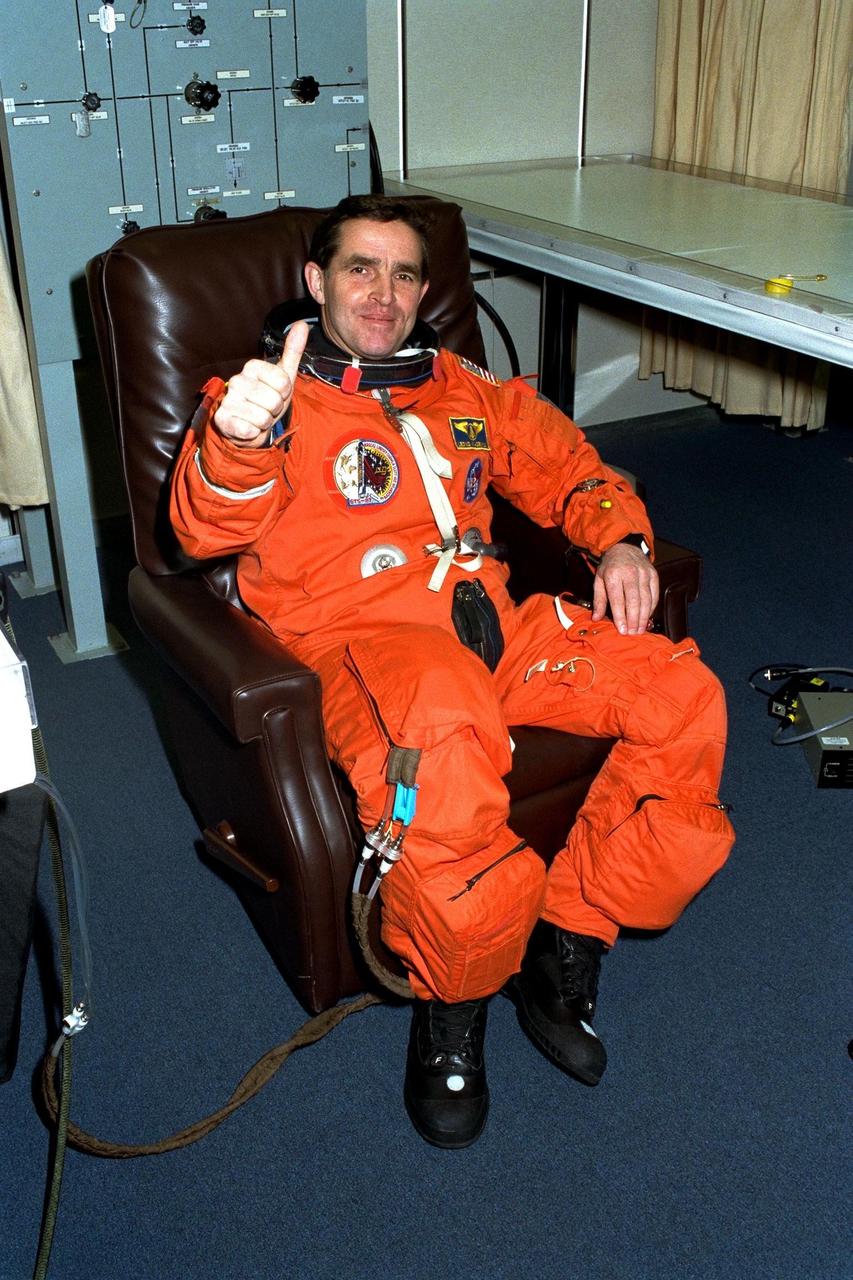

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine gives a ‘thumbs up’ in his launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building. He and the five other crew members of STS-87 will depart shortly for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Kadenyuk will be flying his first mission on STS-87. During the mission, Kadenyuk will pollinate Brassica rapa plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia’s middeck and features an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on Brassica rapa seedlings
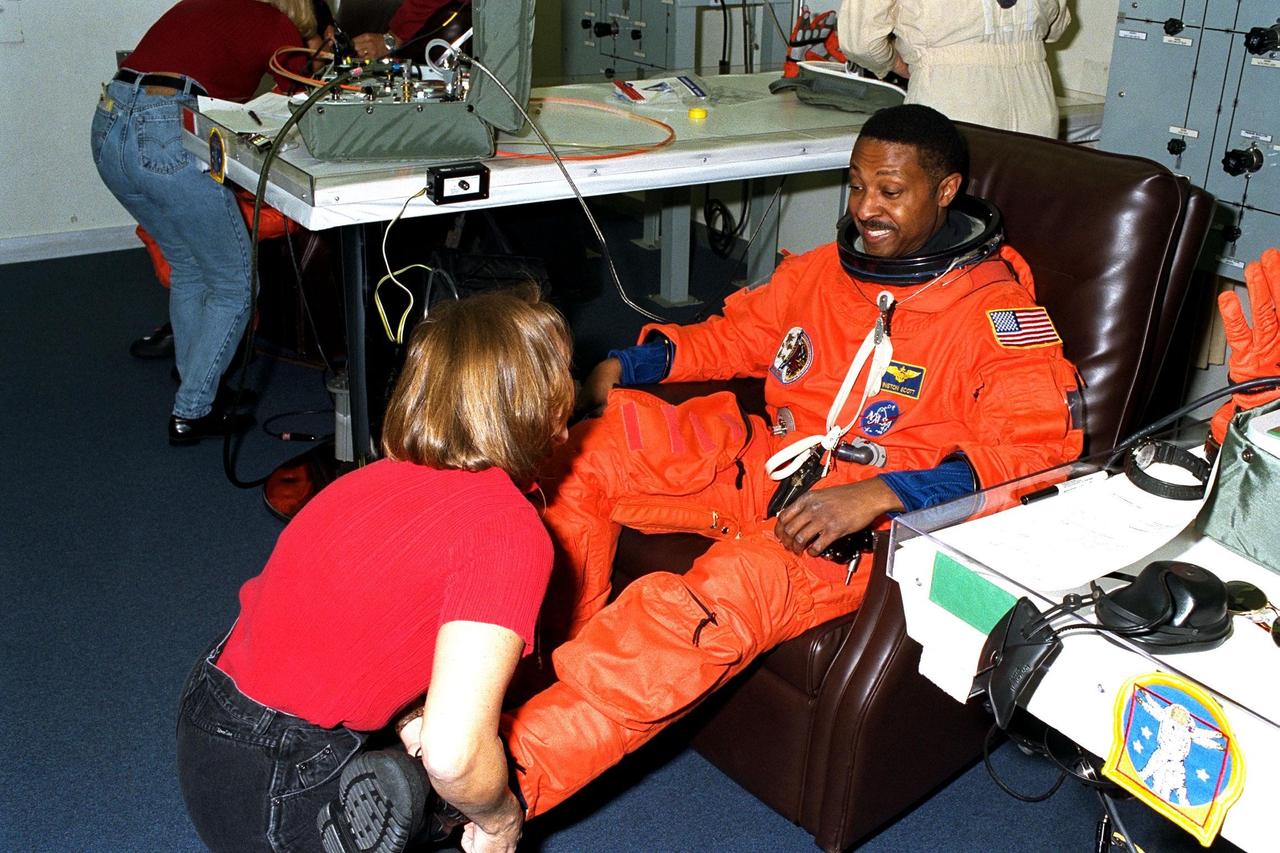

STS-87 Mission Specialist Winston Scott dons his launch and entry suit with the assistance of a suit technician in the Operations and Checkout Building. This is Scott’s second space flight. He and the five other crew members will depart shortly for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Scott is scheduled to perform an extravehicular activity spacewalk with Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, during STS-87. He also performed a spacewalk on STS-72
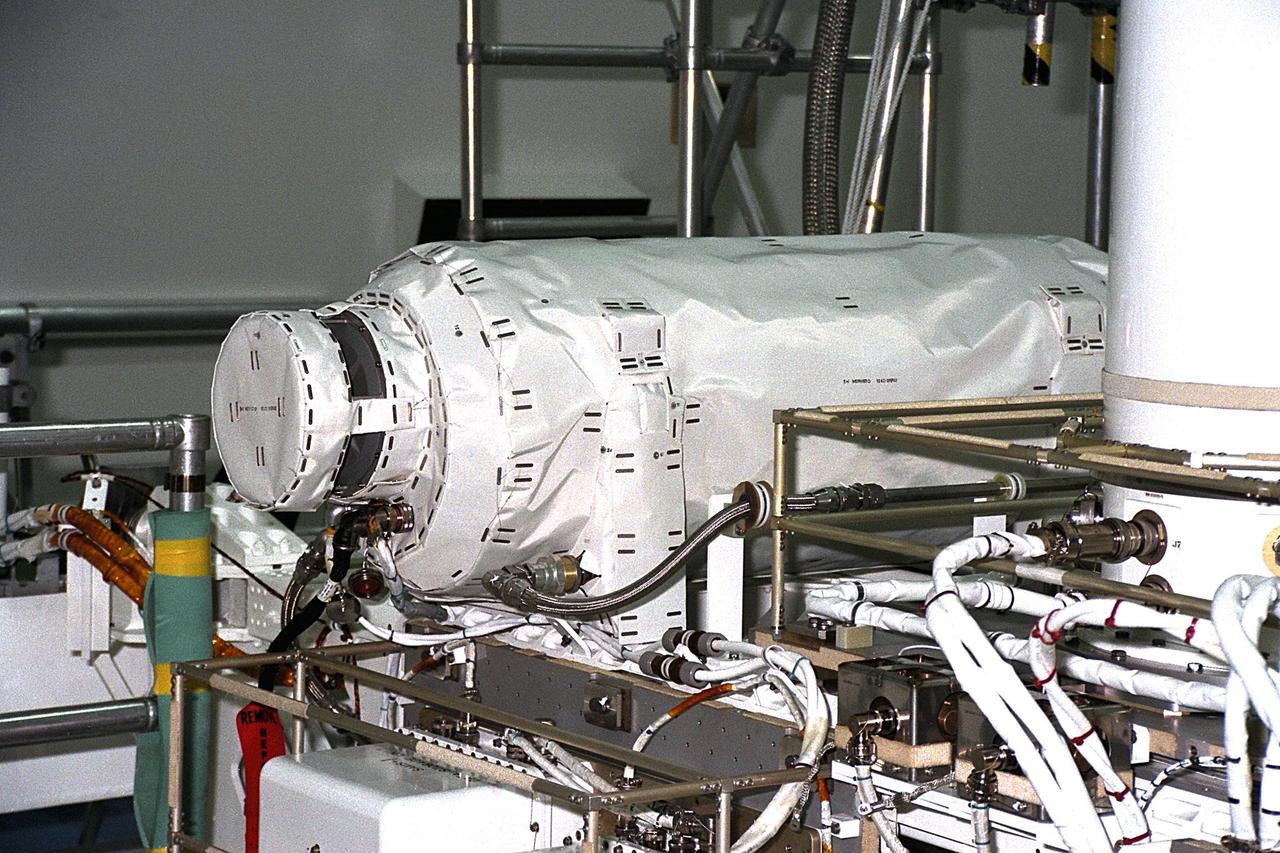
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). This horizontal tube is known as MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. This experiment, designed for the study of solidification (or freezing) during the growth cycle of liquid materials used for semiconductor crystals, aims to aid in the development of techniques for growing higher quality crystals on Earth. All STS-87 experiments are scheduled for launch on Nov. 19 from KSC
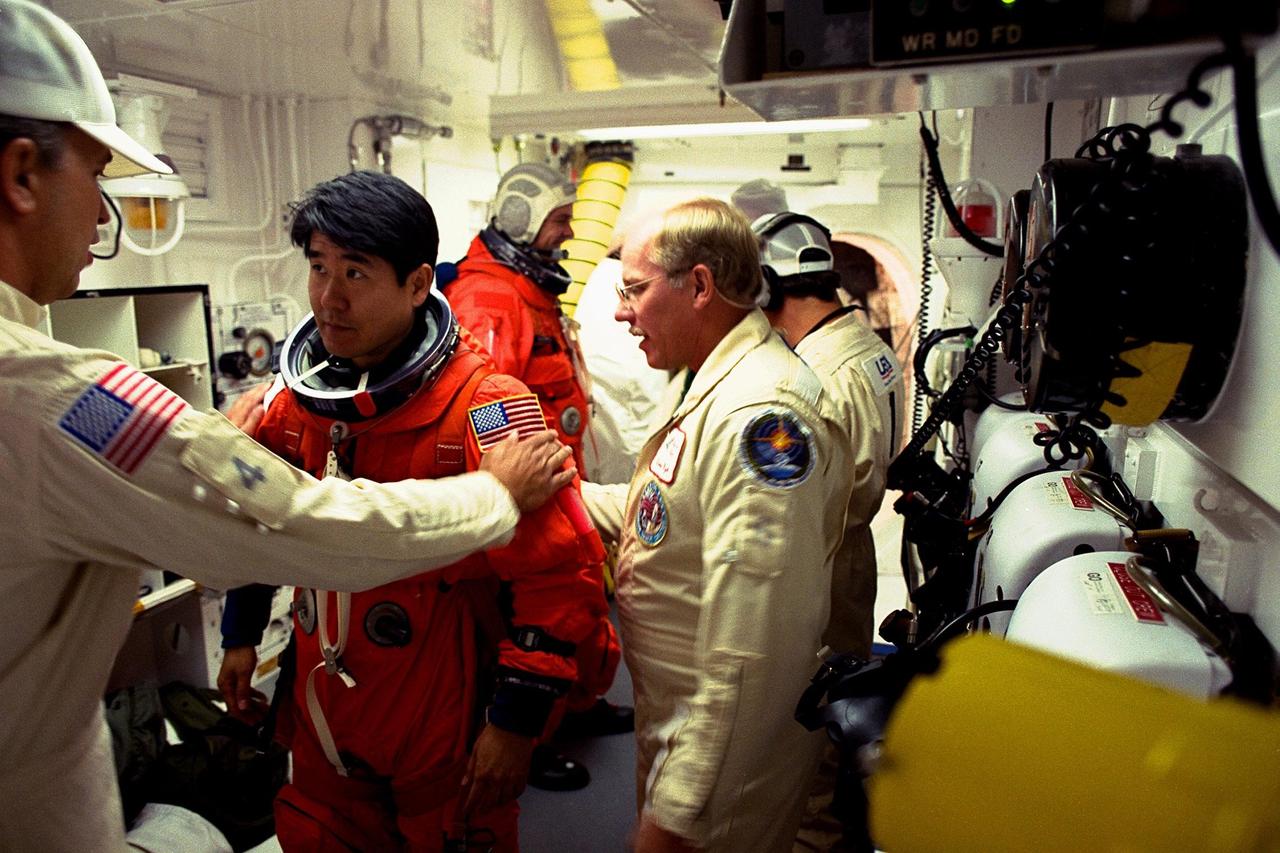

STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit by Dave Law, USA mechanical technician, in the white room at Launch Pad 39B as Dr. Doi prepares to enter the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia on launch day. At right wearing glasses is Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. The 16-day mission will include a spacewalk by Dr. Doi and Mission Specialist Winston Scott
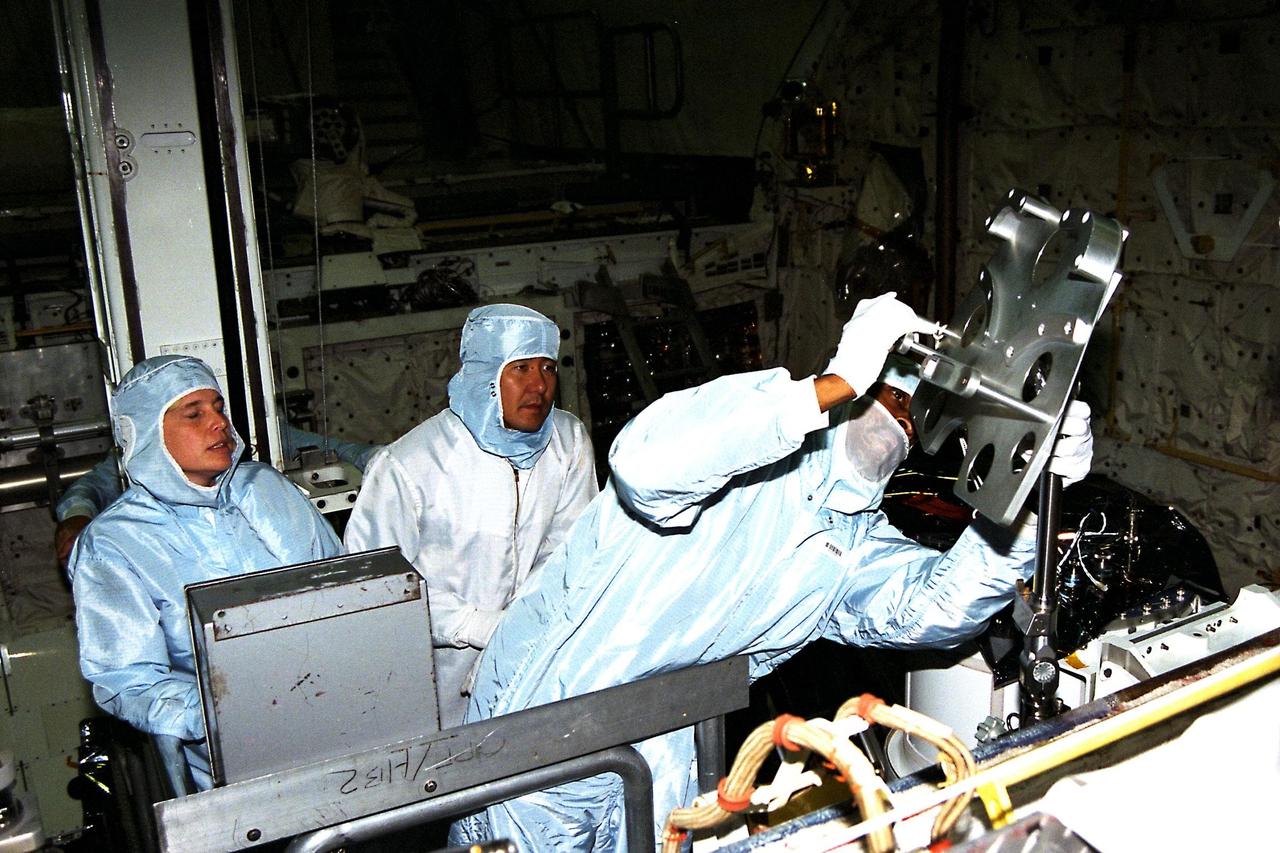

Participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center are STS-87 crew members, assisted by Glenda Laws, extravehicular activity (EVA) coordinator, Johnson Space Center, at left. Next to Laws is Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, who is looking on as Mission Specialist Winston Scott gets a hands-on look at some of the equipment. The STS-87 mission will be the fourth United States Microgravity Payload and flight of the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, scheduled for a Nov. 19 liftoff from KSC, Dr. Doi and Scott will both perform spacewalks
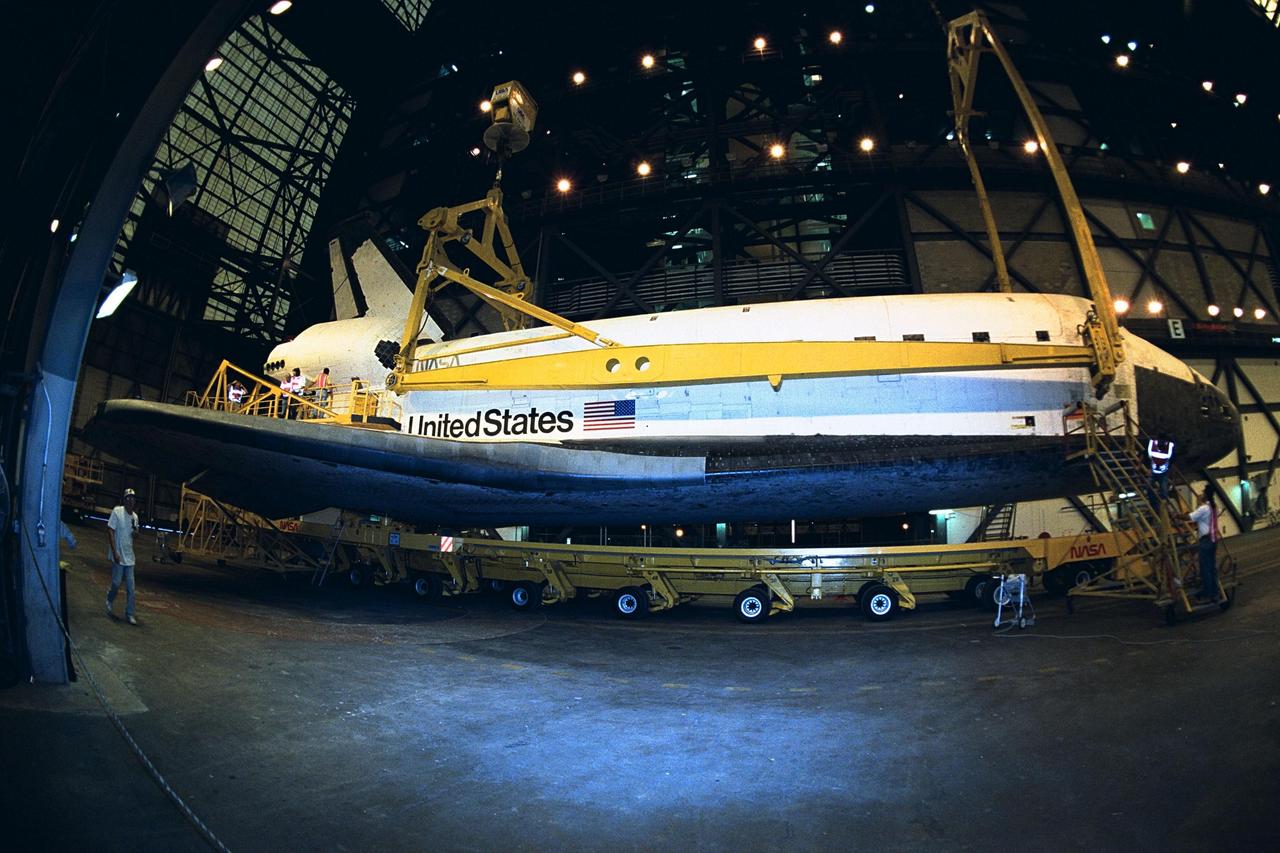

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the orbiter Columbia rolled into the Vehicle Assembly Building transfer aisle at about 6 a.m. today. The orbiter will be mated to the <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/count3.htm#et">external tank</a> and <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/ships.htm#srbs">solid rocket boosters</a> in high bay 3 over the weekend and is slated to roll out to Pad 39B on Wednesday. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
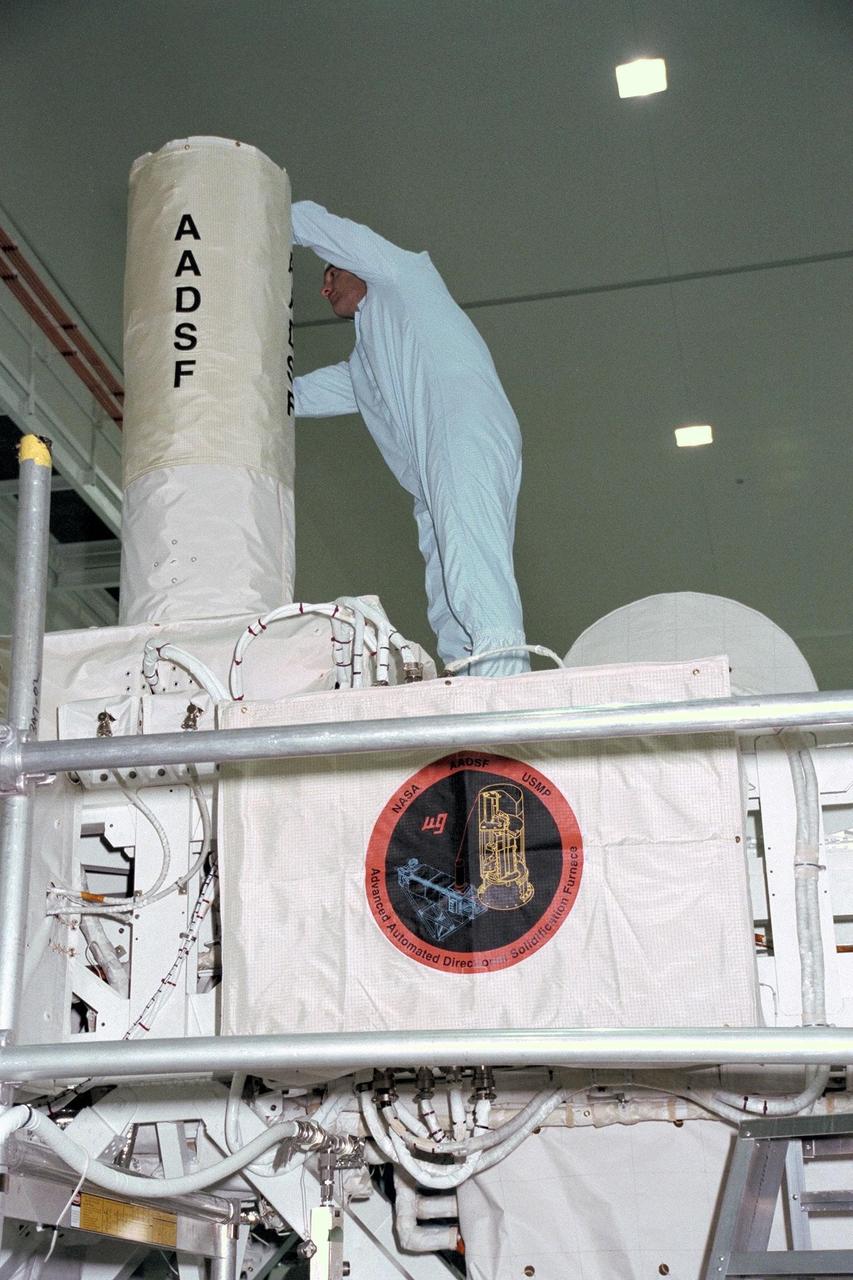

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). A technician is working on the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which will be used by researchers to study the solidification of semiconductor materials in microgravity. Scientists will be able to better understand how microgravity influences the solidification process of these materials and develop better methods for controlling that process during future Space flights and Earth-based production. All STS-87 experiments are scheduled for launch on Nov. 19 from KSC
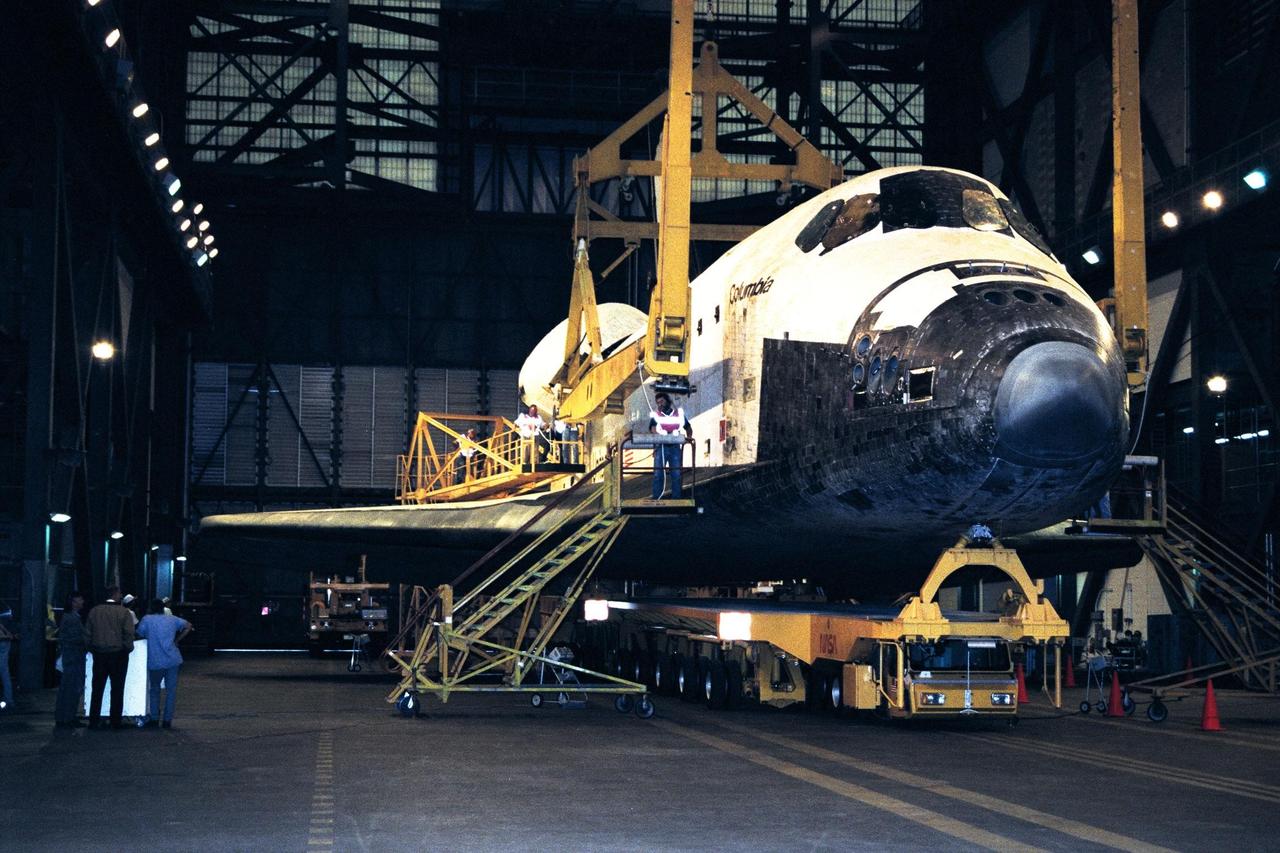

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the orbiter Columbia rolled into the Vehicle Assembly Building transfer aisle at about 6 a.m. today. The orbiter will be mated to the <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/count3.htm#et">external tank</a> and <a href="http://www-pao.ksc.nasa.gov/kscpao/nasafact/ships.htm#srbs">solid rocket boosters</a> in high bay 3 over the weekend and is slated to roll out to Pad 39B on Wednesday. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
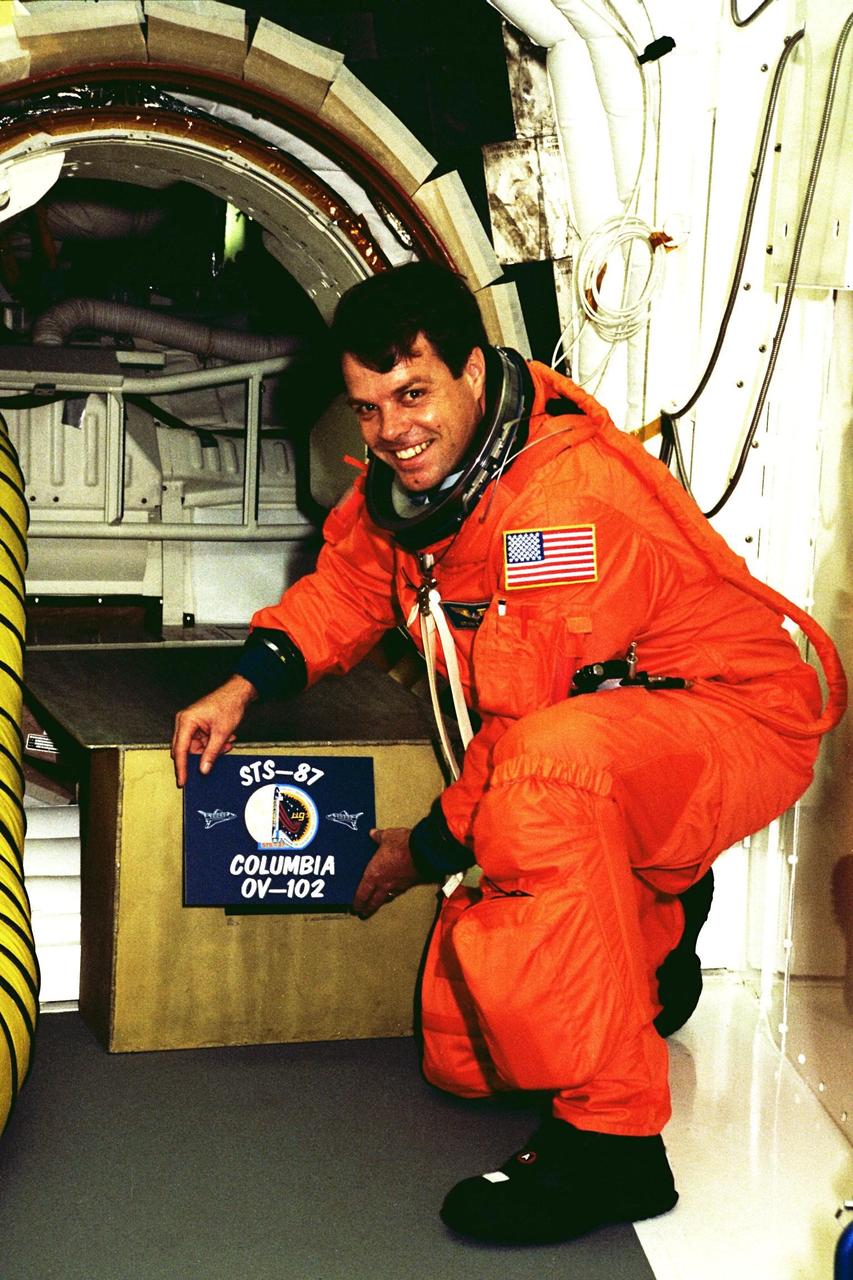

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel holds the crew patch in front of Columbia’s entry hatch at Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
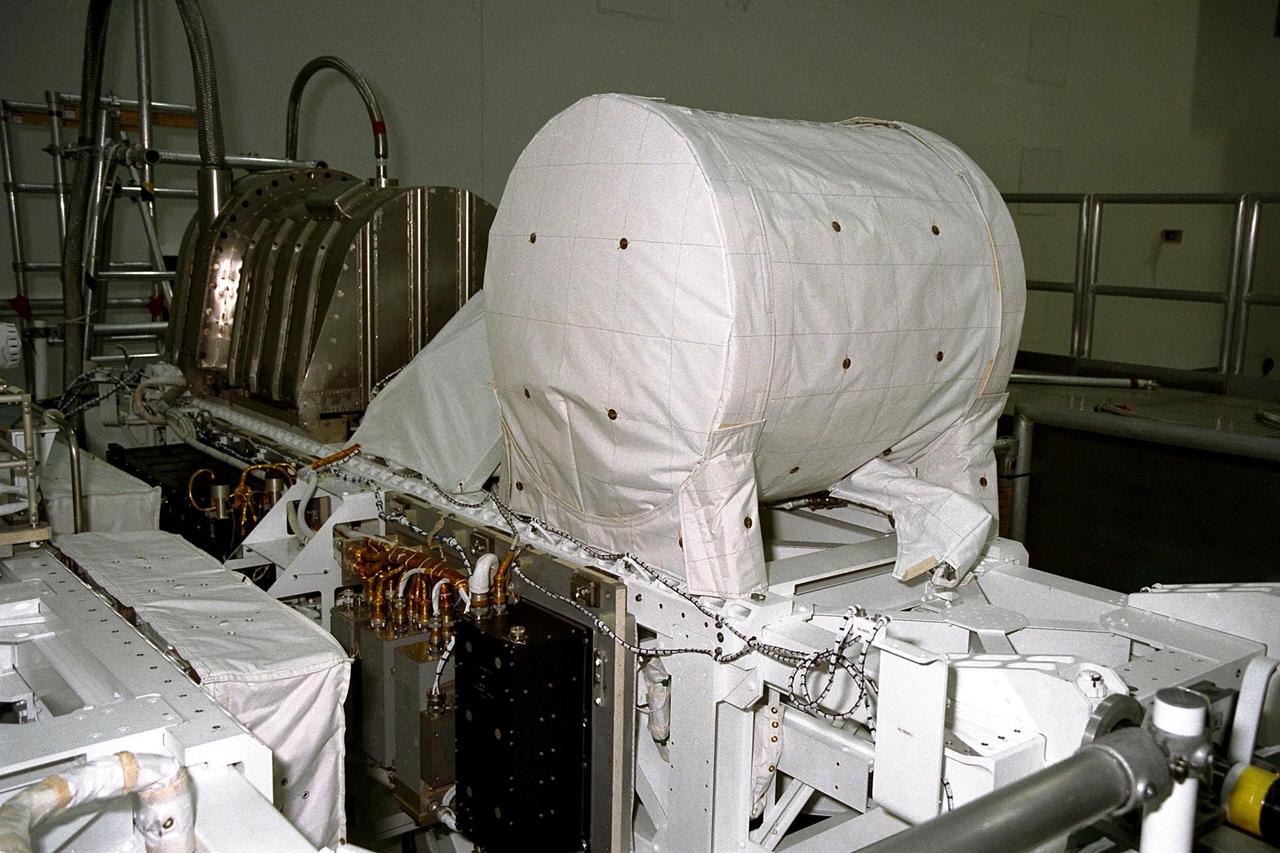

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. The metallic breadbox-like structure behind the IDGE is the Confined Helium Experiment (CHeX) that will study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between solid surface, and microgravity. These experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
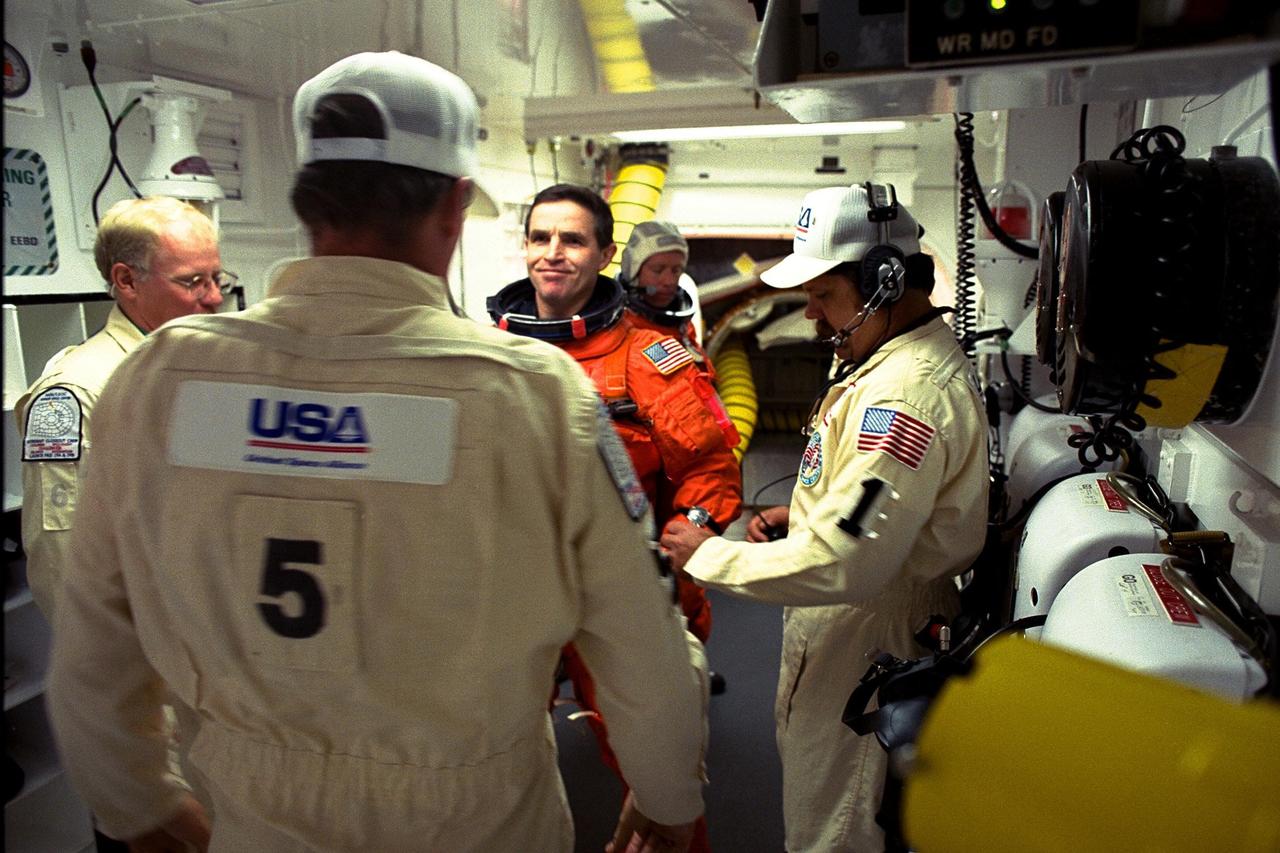

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine is assisted with final preparations before launch in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist, at left; George Schram, USA mechanical technician, facing Kadenyuk; and Travis Thompson, USA orbiter vehicle closeout chief, at right. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. The 16-day mission will include the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment (CUE), a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia’s middeck and will feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on Brassica rapa seedlings
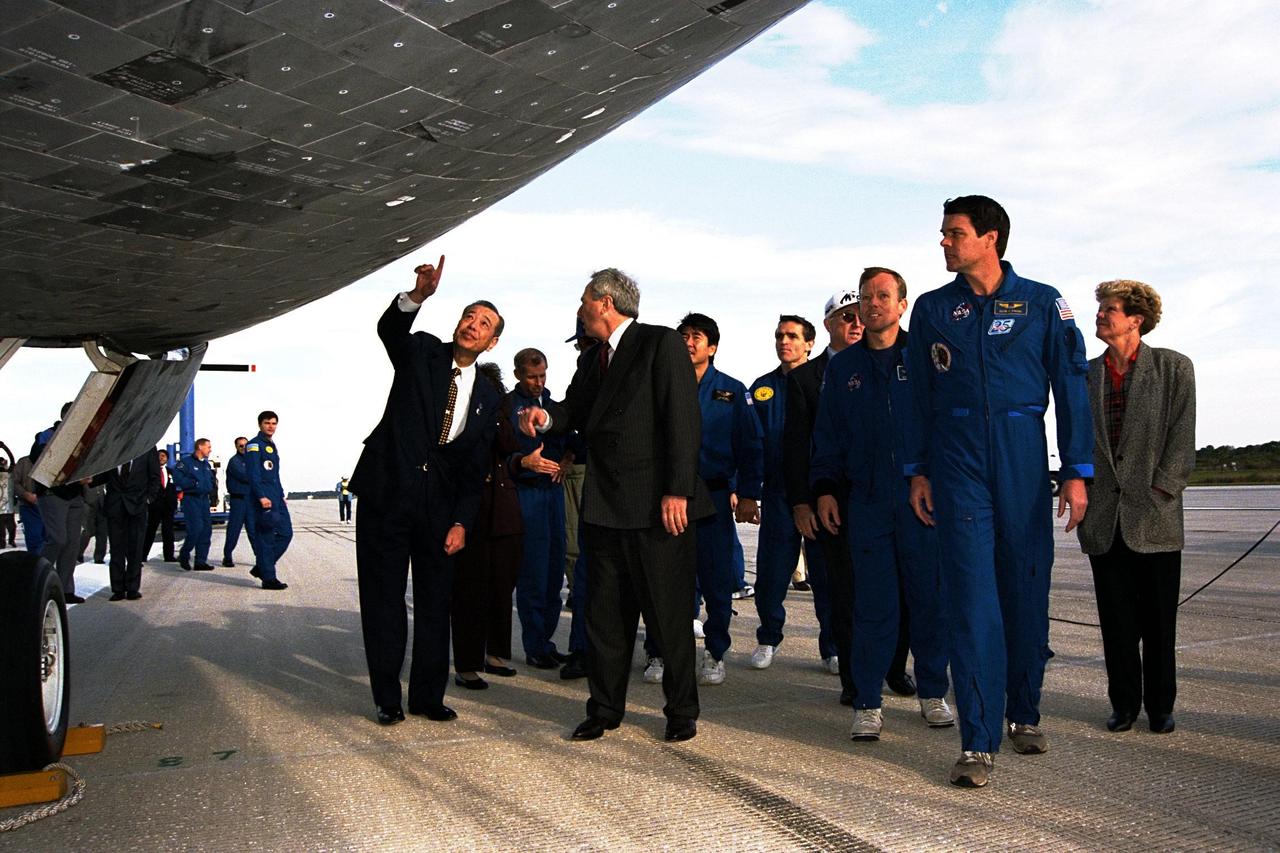

STS-87 crew members regard the tiles underneath the orbiter Columbia shortly after its return to Runway 33 at Kennedy Space Center's Shuttle Landing Facility. Pointing to the tiles is the president of the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan, Isao Uchida, who is standing next to NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin. STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel, at right, looks on as Pilot Steve Lindsey follows behind him to continue inspecting the orbiter. STS-87 concluded its mission with a main gear touchdown at 7:20:04 a.m. EST Dec. 5, drawing the 15-day, 16-hour and 34-minute-long mission of 6.5 million miles to a close. Also onboard the orbiter were Mission Specialists Winston Scott; Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of NASDA; along with Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 88th Space Shuttle mission, the crew performed experiments on the United States Microgravity Payload-4 and pollinated plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment. This was the 12th landing for Columbia at KSC and the 41st KSC landing in the history of the Space Shuttle program
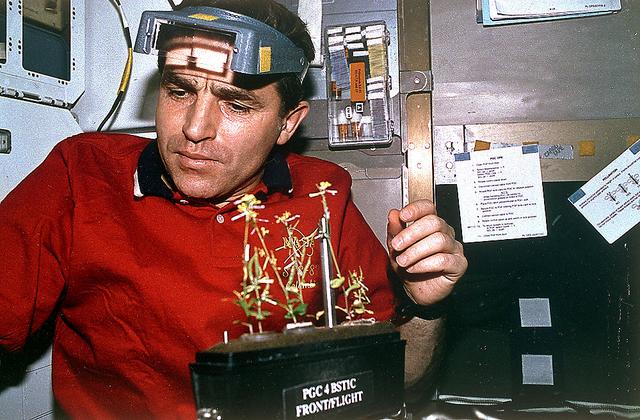

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-87) mid-deck, Leonid Kadenyuk, Ukrainian payload specialist, works with the Brassica rapa plants being grown for the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment (CUE). Kadenyuk joined five astronauts for 16-days in Earth-orbit in support of the United States Microgravity Payload 4 (USMP-4) mission.

Kevin Kregel, commander of the STS-87 crew, participates in a news briefing at Launch Pad 39B during the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Selected by NASA in 1992, Kregel is a veteran of two space flights (STS-70 and 78) and has logged over 618 hours in space. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-87 is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from pad 39B at KSC

The crew of STS-87 pose with their spouses in front of Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. From left to right are: Vera Kadenyuk, wife of Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine who is next to Vera; Mission Specialist Winston Scott and his wife, Marilyn; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, and his wife, Hitomi; Jeannie Kregel, who is married to Commander Kevin Kregel standing next to her; Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., and her husband, Jean-Pierre Harrison; and Pilot Steven Lindsey and his wife Diane. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
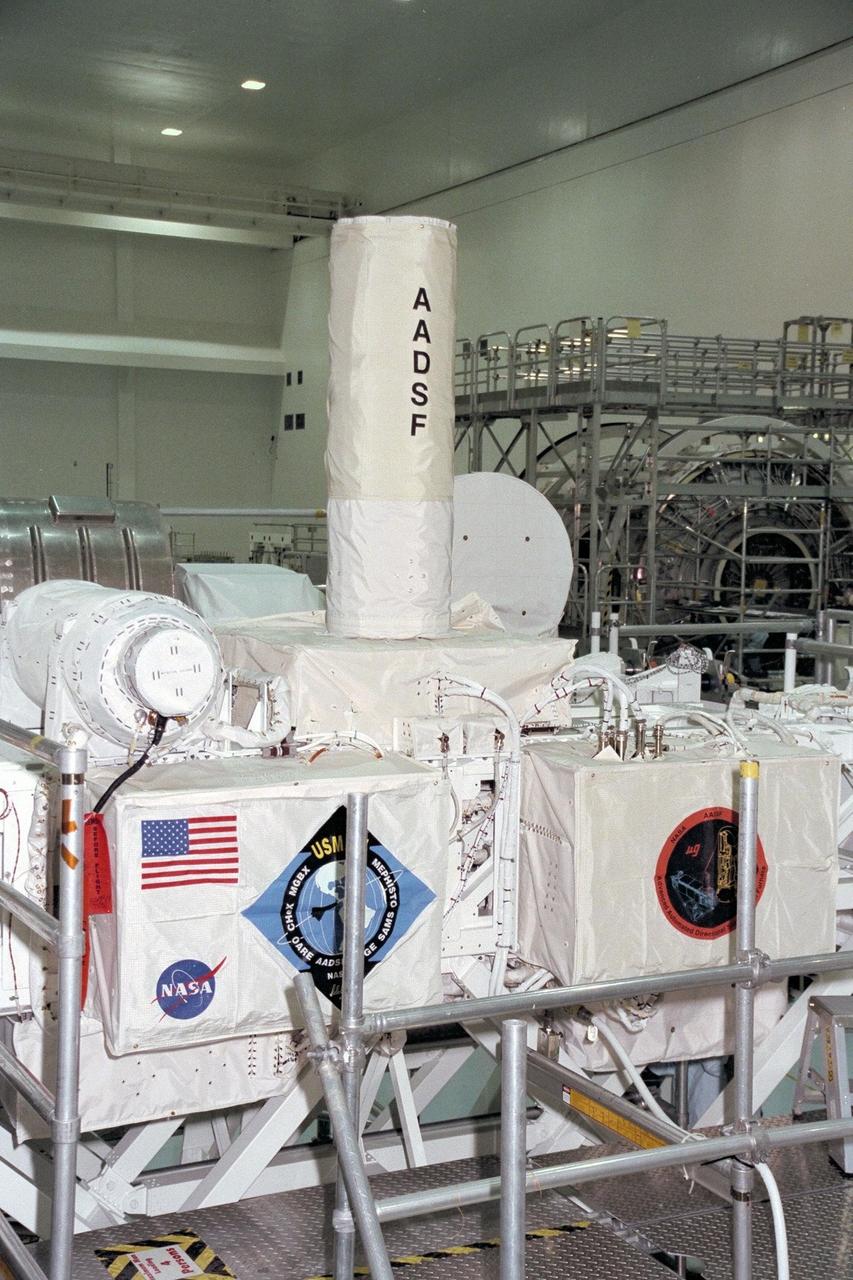
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube to the left of it is MEPHISTO, a French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Seen at right behind the AADSF in the circular white cover is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
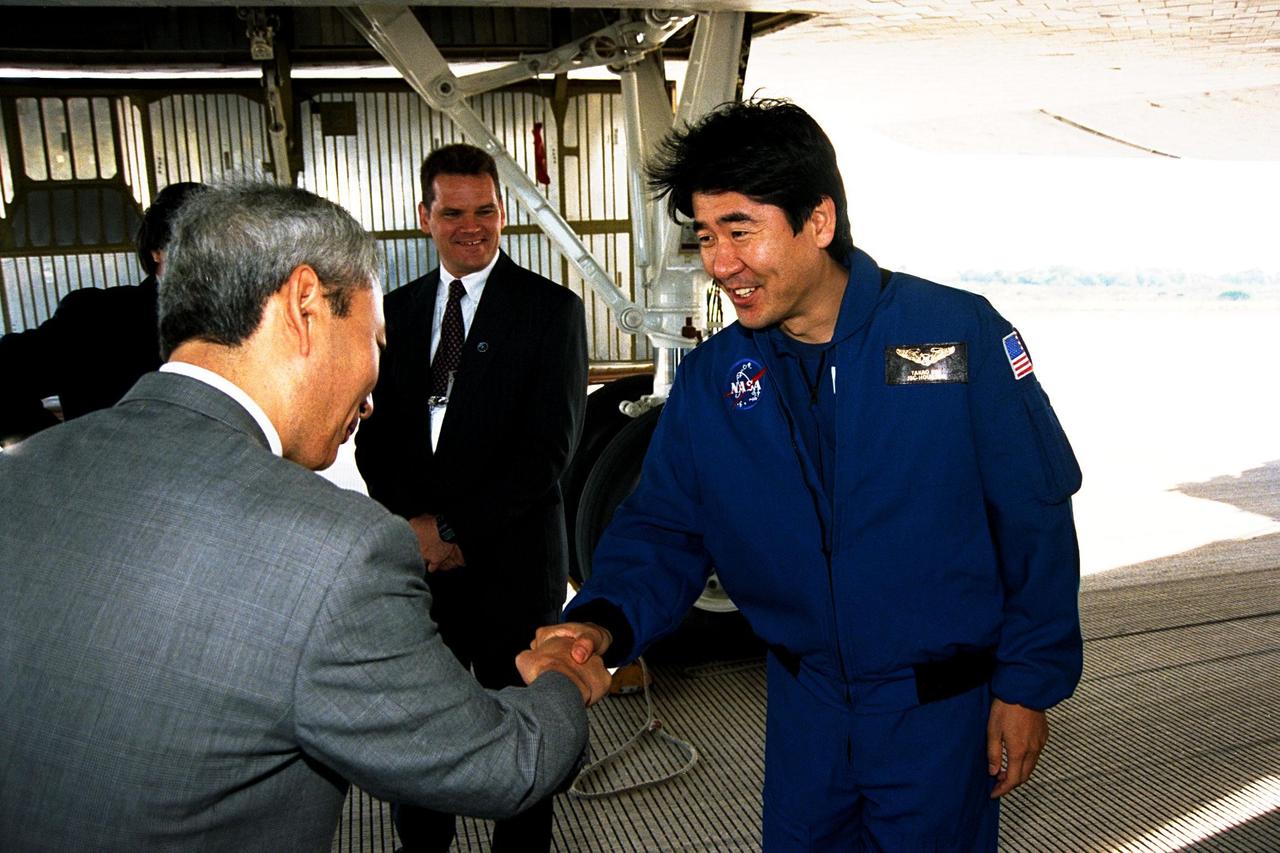

STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan greets a NASDA official shortly after the orbiter Columbia returned to KSC, touching down on Runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility. STS-87 concluded its mission with a main gear touchdown at 7:20:04 a.m. EST Dec. 5, drawing the 15-day, 16-hour and 34-minute-long mission of 6.5 million miles to a close. Also onboard the orbiter were Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Winston Scott and Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 88th Space Shuttle mission, the crew performed experiments on the United States Microgravity Payload-4 and pollinated plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment. This was the 12th landing for Columbia at KSC and the 41st KSC landing in the history of the Space Shuttle program
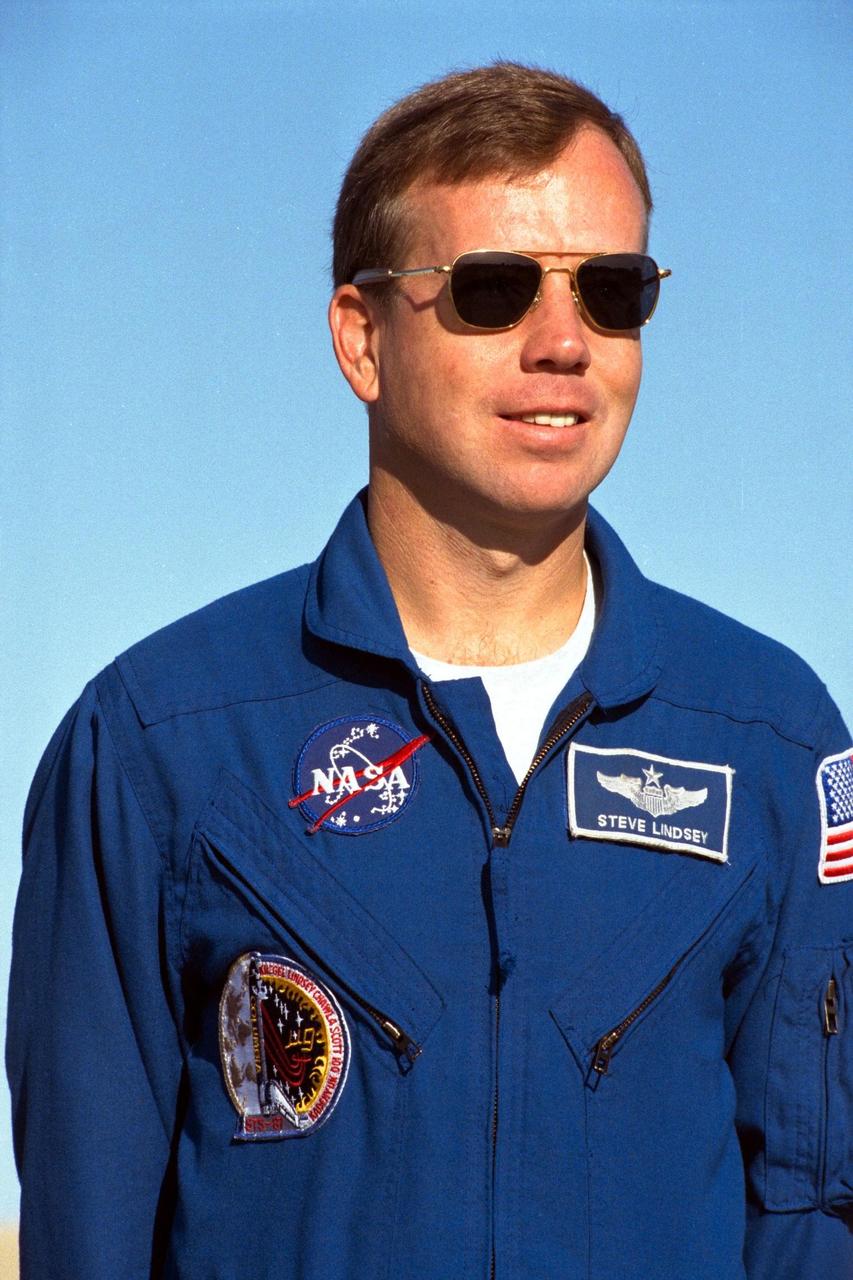

Steven Lindsey, the pilot of the STS-87 crew, participates in a news briefing at Launch Pad 39B during the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). A major in the U.S. Air Force, Lindsey became an astronaut in May 1996. This is his first flight on the Space Shuttle, but he previously has logged more than 2,700 hours of flying time in 49 different types of aircraft. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-87 is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from pad 39B at KSC

STS-87 Mission Specialist Winston Scott poses in his orange launch and entry spacesuit with NASA suit technicians at Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. Scott will be performing an extravehicular activity (EVA) spacewalk during the mission. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
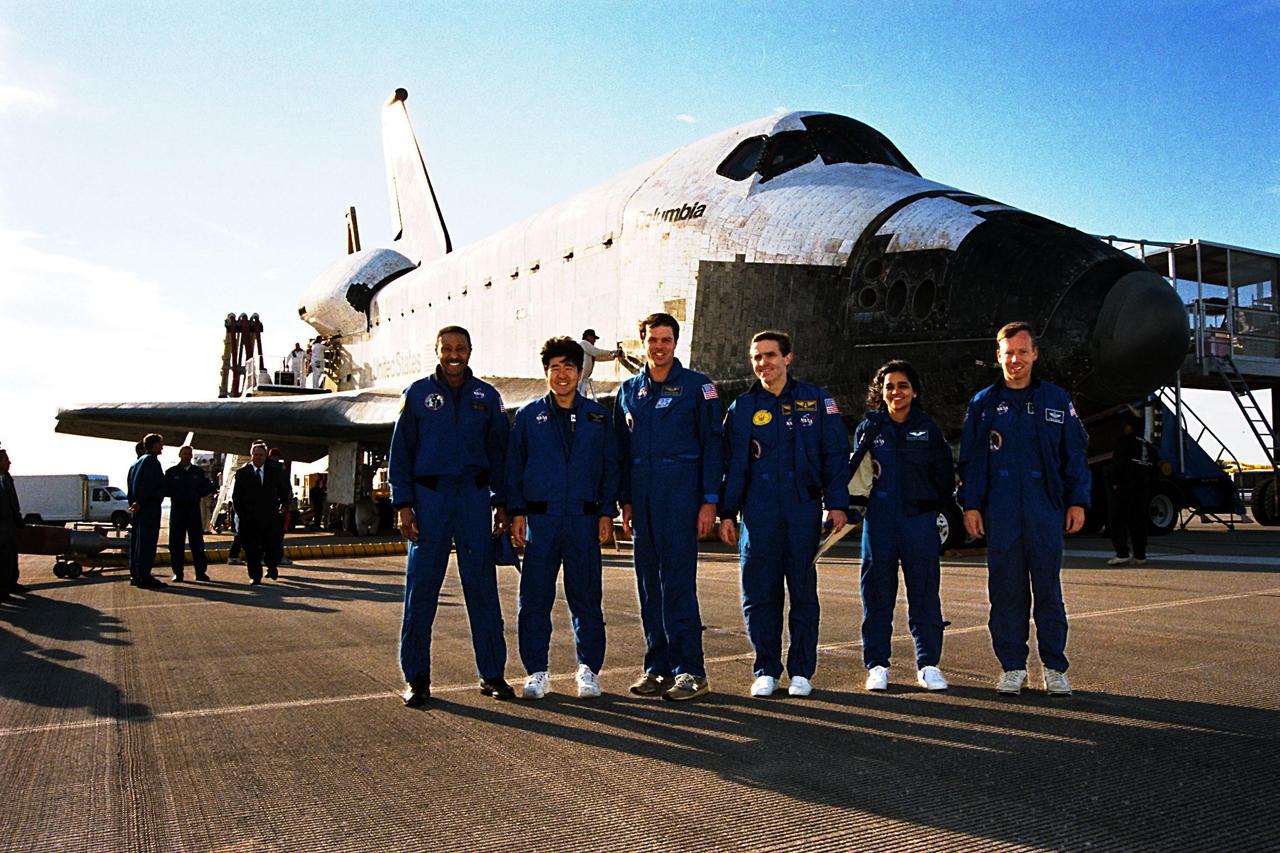

The STS-87 crew pose in front of the orbiter Columbia shortly after landing on Runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility. STS-87 concluded its mission with a main gear touchdown at 7:20:04 a.m. EST Dec. 5, drawing the 15-day, 16-hour and 34-minute-long mission of 6.5 million miles to a close. From left to right are Mission Specialists Winston Scott and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Commander Kevin Kregel; Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine; Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; and Pilot Steven Lindsey. During the 88th Space Shuttle mission, the crew performed experiments on the United States Microgravity Payload-4 and pollinated plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment. This was the 12th landing for Columbia at KSC and the 41st KSC landing in the history of the Space Shuttle program
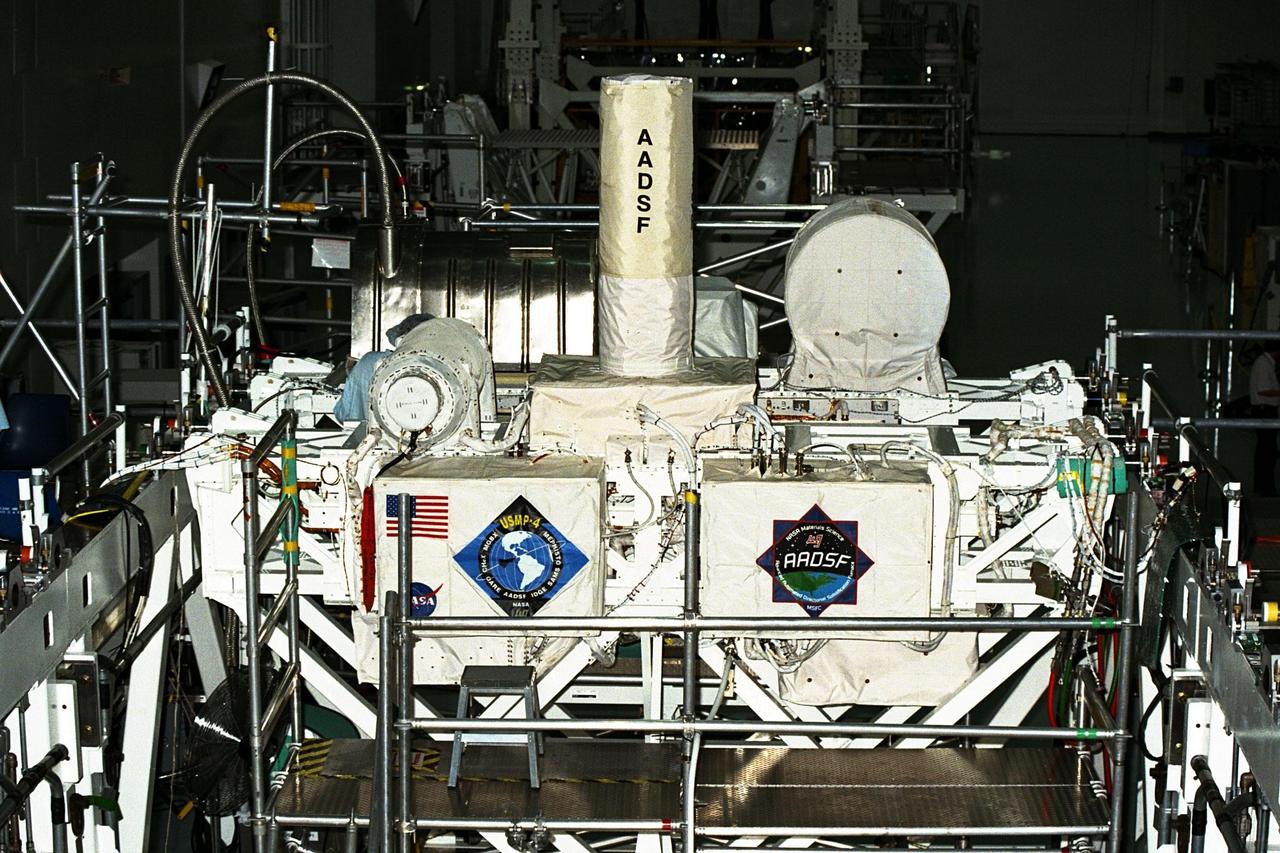
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at left is the USMP-4 logo with the acronyms of its experiments. Above the American flag at left is the MEPHISTO experiment, a cooperative American and French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which is a sophisticated materials science facility used for studying a common method of processing semiconductor crystals called directional solidification. The white horizontal tube to the right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. All USMP-4 experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
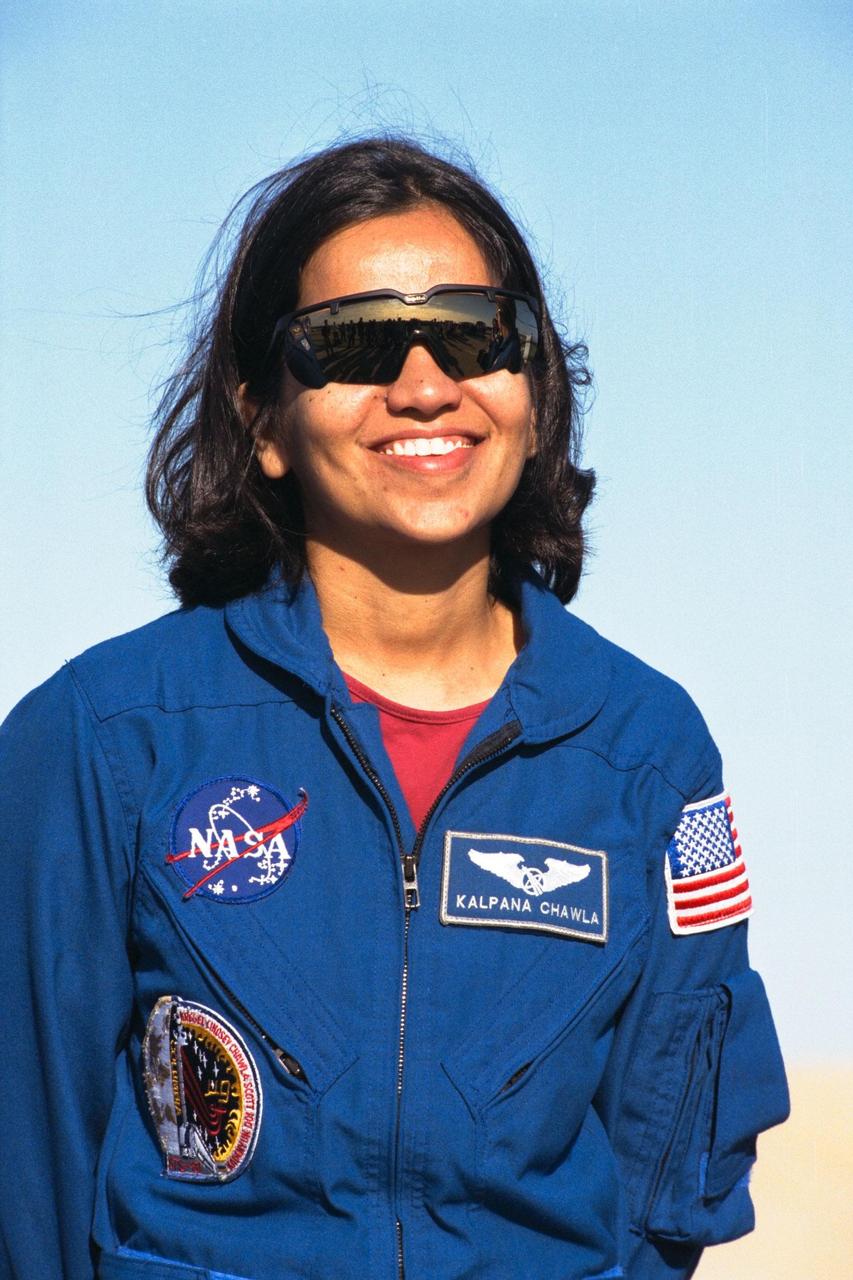

Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., a mission specialist of the STS-87 crew, participates in a news briefing at Launch Pad 39B during the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). First-time Shuttle flier Dr. Chawla reported for training as an astronaut at Johnson Space Center in 1995. She has a doctorate in aerospace engineering from the University of Colorado. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-87 is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from pad 39B at KSC
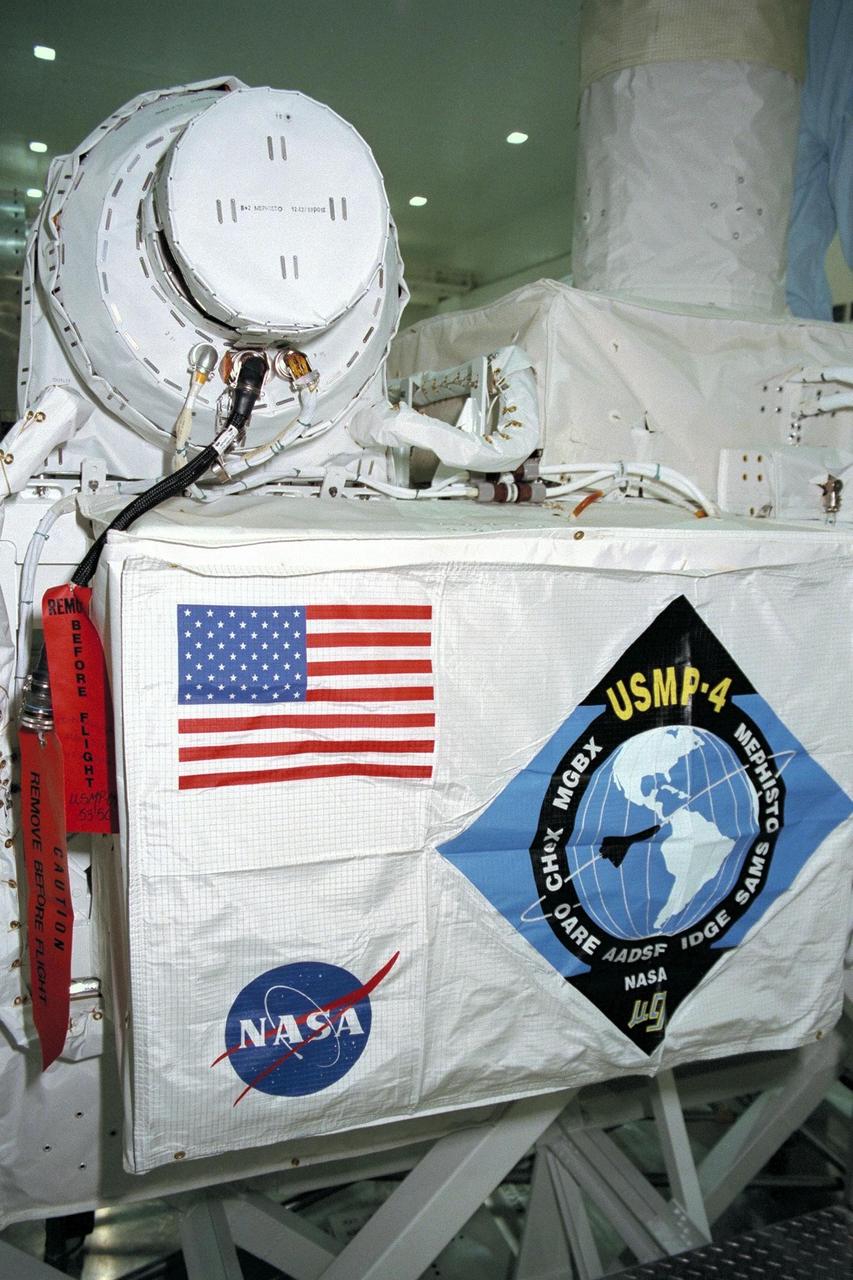

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The large white vertical cylinder in the middle of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube to its left is MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Seen to the right of the AADSF is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
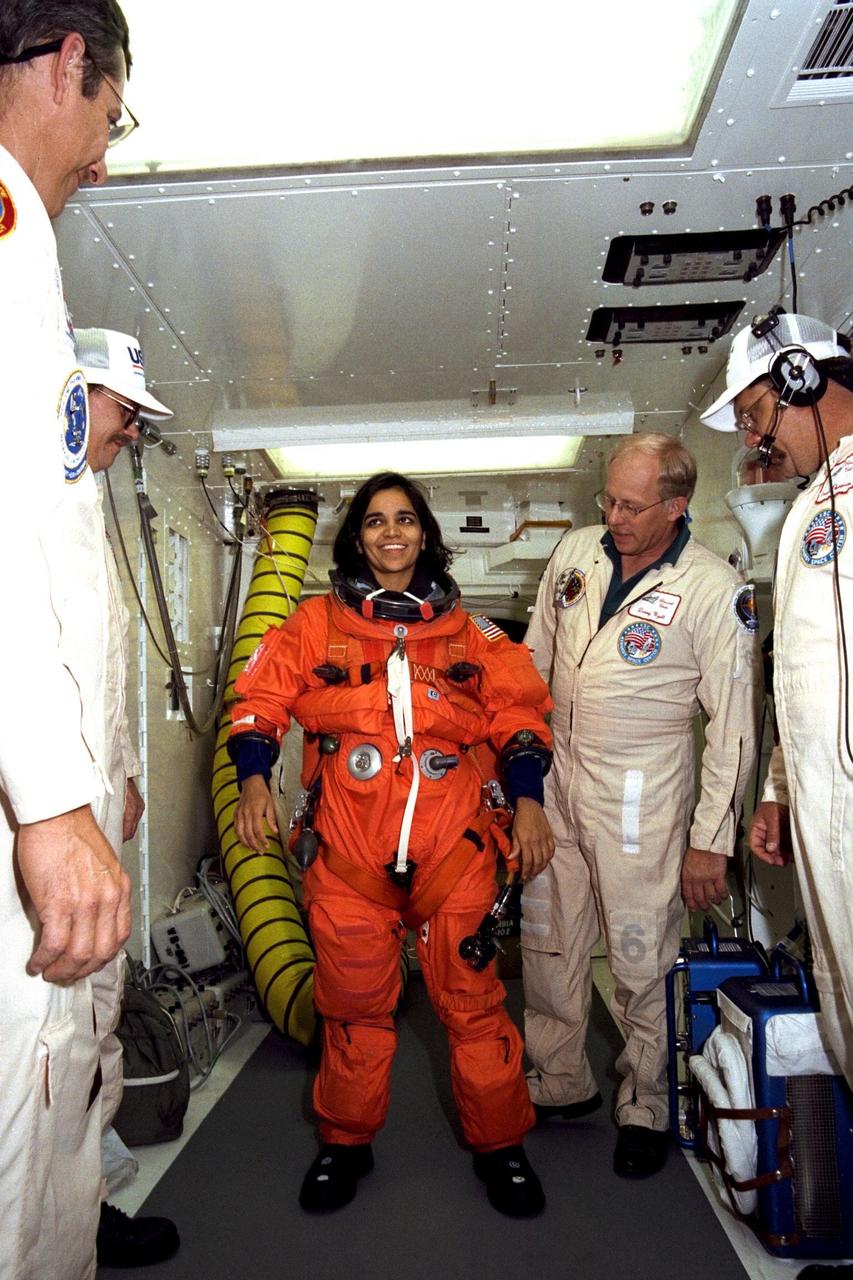

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., is assisted with her orange launch and entry spacesuit by NASA suit technicians at Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
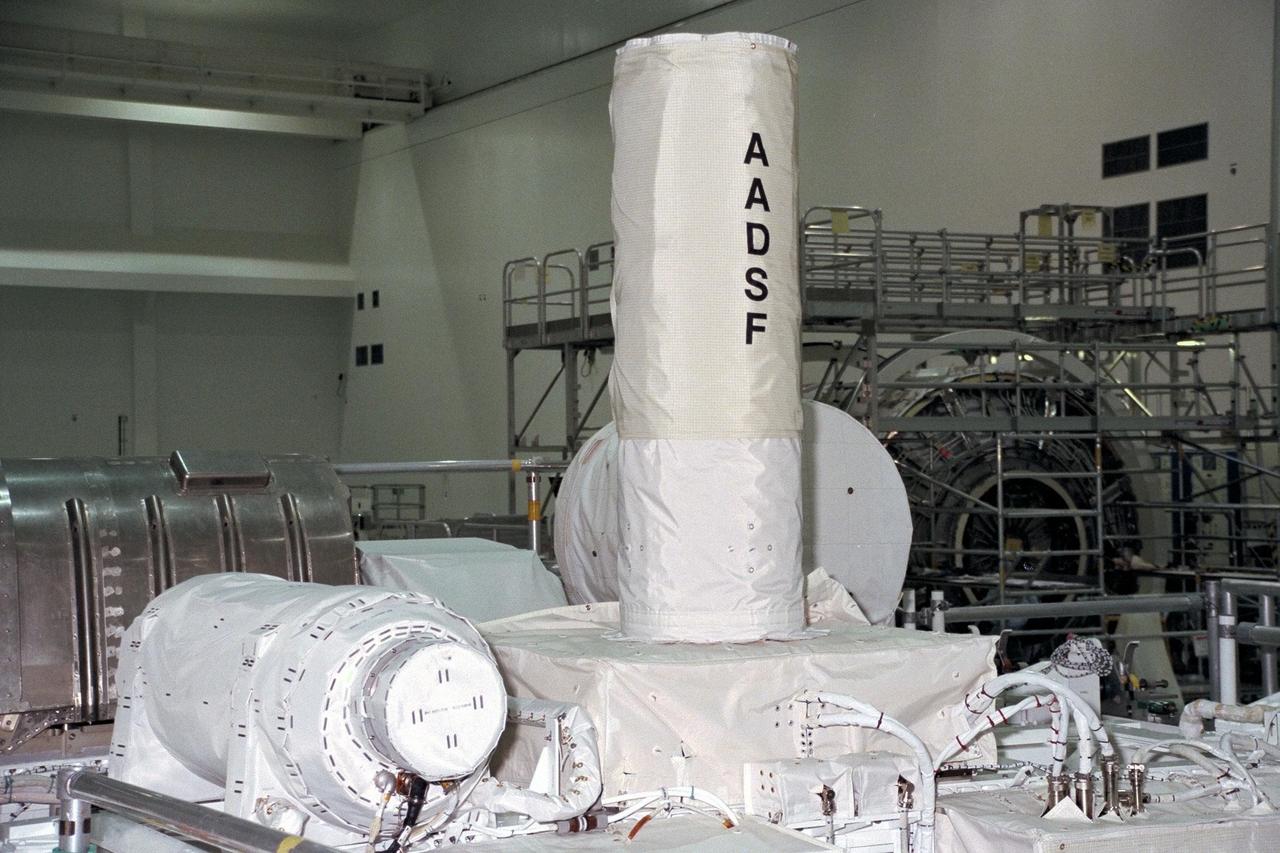

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The vertical tube in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which will be used by researchers to study the solidification of semiconductor materials in microgravity. Scientists will be able to better understand how microgravity influences the solidification process of these materials and develop better methods for controlling that process during future Space flights and Earth-based production. To its left is MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. All STS-87 experiments are scheduled for launch on Nov. 19 from KSC

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU) is assisted with his orange launch and entry spacesuit by NASA suit technicians at Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
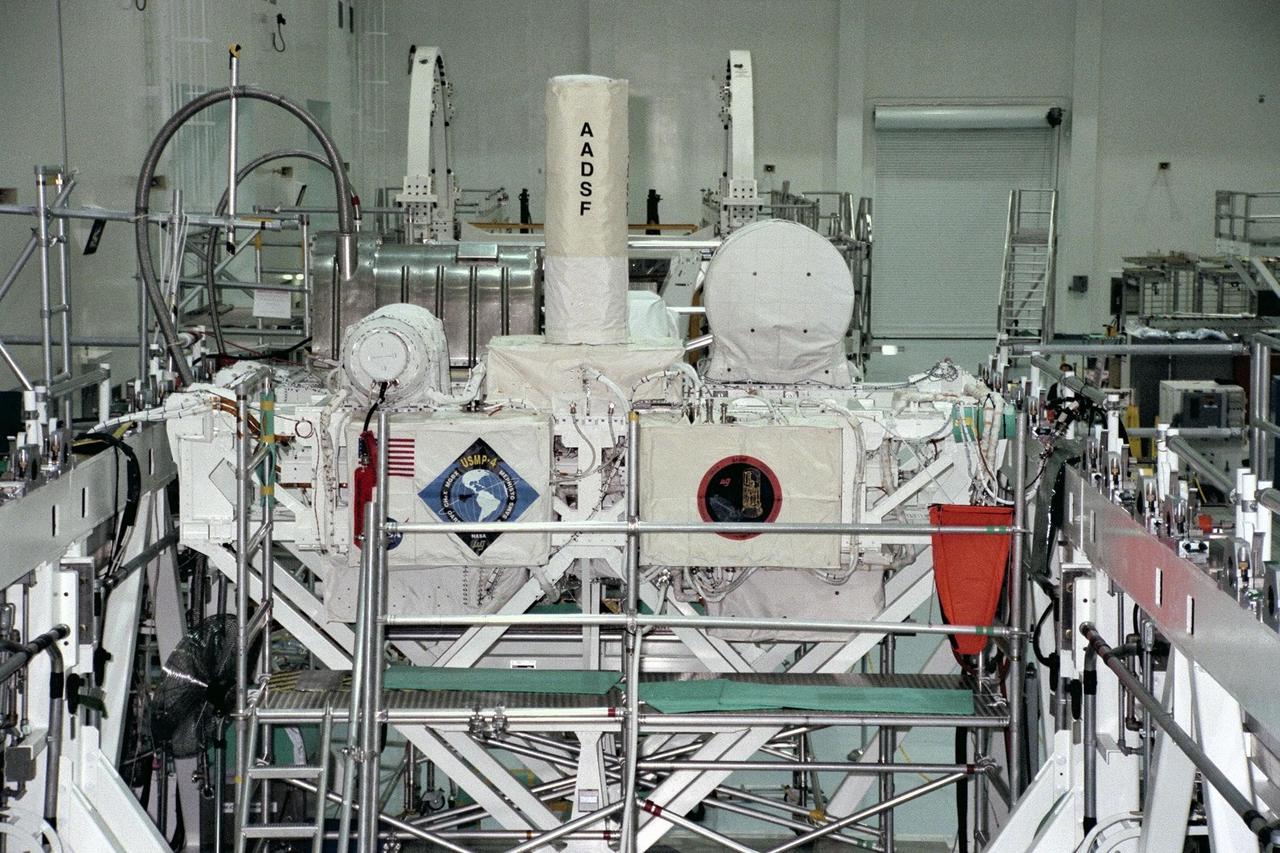
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at right is the USMP-4 logo with the acronyms of its experiments. Above the American flag at left is the MEPHISTO experiment, a cooperative American and French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Scientists will study changes in solidification rates, temperature, and interface shape of an alloy to understand how these changes affect composition and properties of the metal produced. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All USMP-4 experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
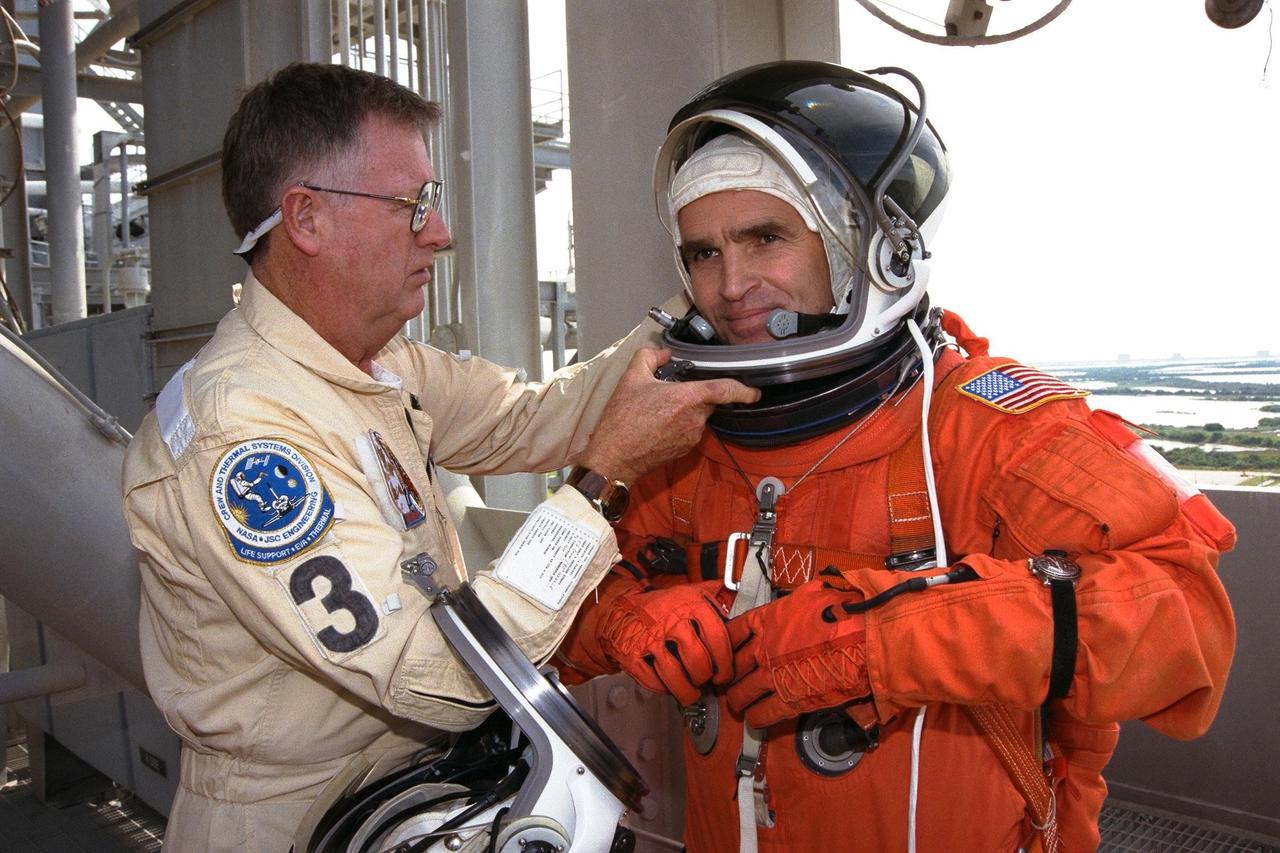

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk, at right, of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU) is assisted into his orange launch and entry spacesuit ensemble by NASA Suit Technician Al Rochford, at left, before participating in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
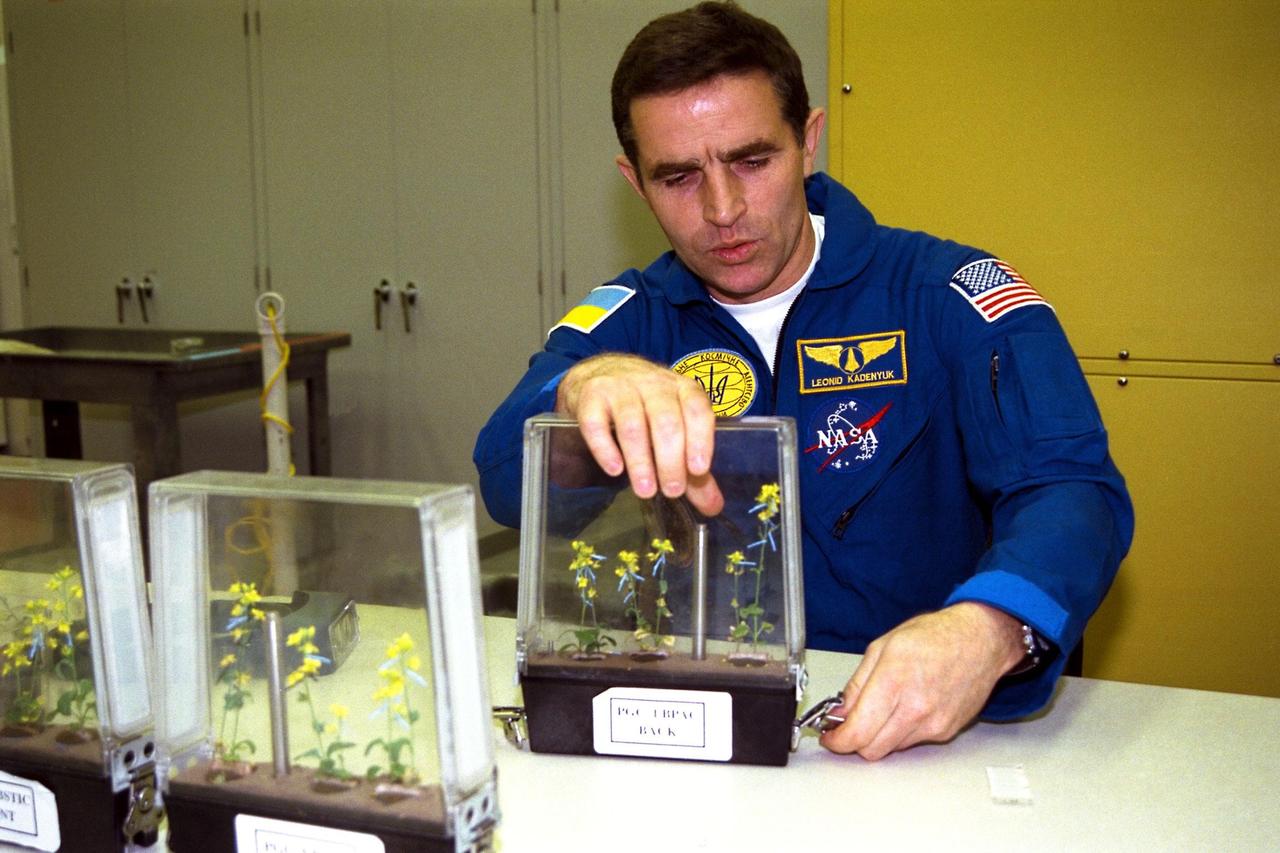

Participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center is STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU). Here, Cosmonaut Kadenyuk is inspecting flowers for pollination and fertilization, which will occur as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia during its 16-day mission, scheduled to take off from KSC’s Launch Pad 39-B on Nov. 19. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia’s middeck and feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on the pollinating Brassica rapa seedlings. Students in Ukrainian and American schools will participate in the same experiment on the ground and have several live opportunities to discuss the experiment with Kadenyuk in Space. Kadenyuk of the Ukraine will be flying his first Shuttle mission on STS-87
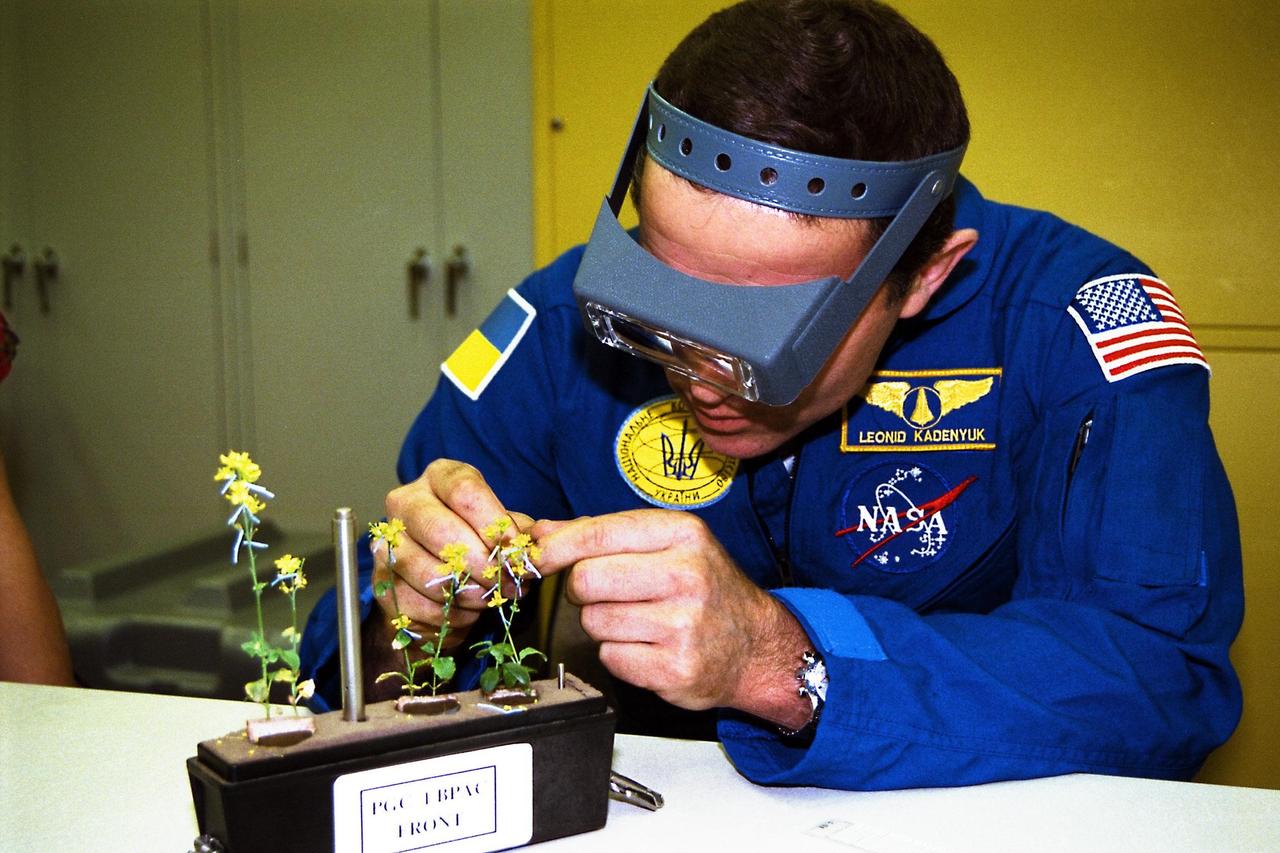

Participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center is STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU). Here, Cosmonaut Kadenyuk is inspecting flowers for pollination and fertilization, which will occur as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia during its 16-day mission, scheduled to take off from KSC’s Launch Pad 39-B on Nov. 19. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia’s middeck and feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on the pollinating Brassica rapa seedlings. Students in Ukrainian and American schools will participate in the same experiment on the ground and have several live opportunities to discuss the experiment with Kadenyuk in Space. Kadenyuk of the Ukraine will be flying his first Shuttle mission on STS-87
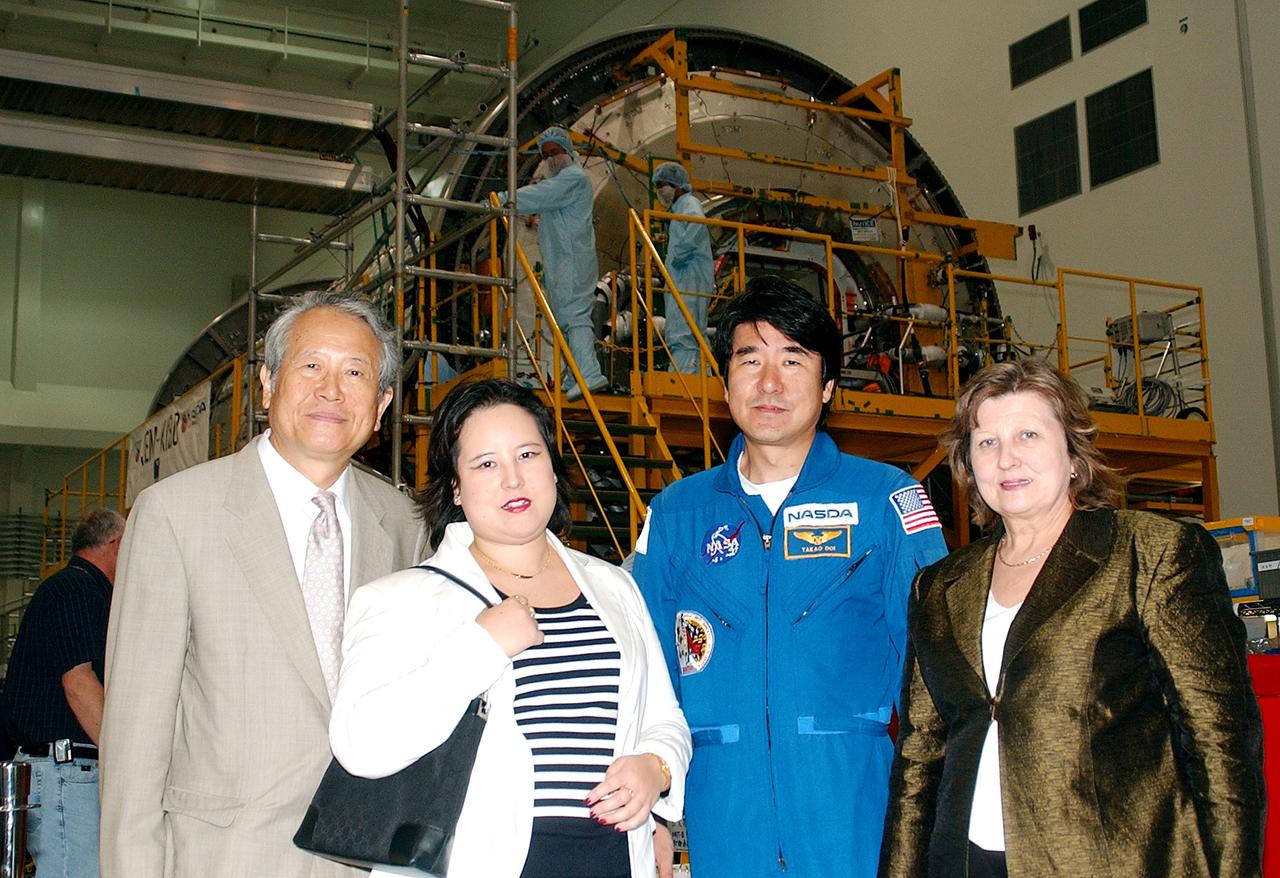

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - From left, the Consul General of Japan Ko Kodaira, his daughter Reiko, astronaut Dr. Takao Doi, and Kodaira's wife Marie pause for a photograph in the Space Station Processing Facility during their visit to Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Doi represented Japan on Space Shuttle mission STS-87, the fourth U.S Microgravity Payload flight. Kodaira is touring the facilities at KSC at the invitation of the local office of the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) to acquaint him with KSC's unique processing capabilities.
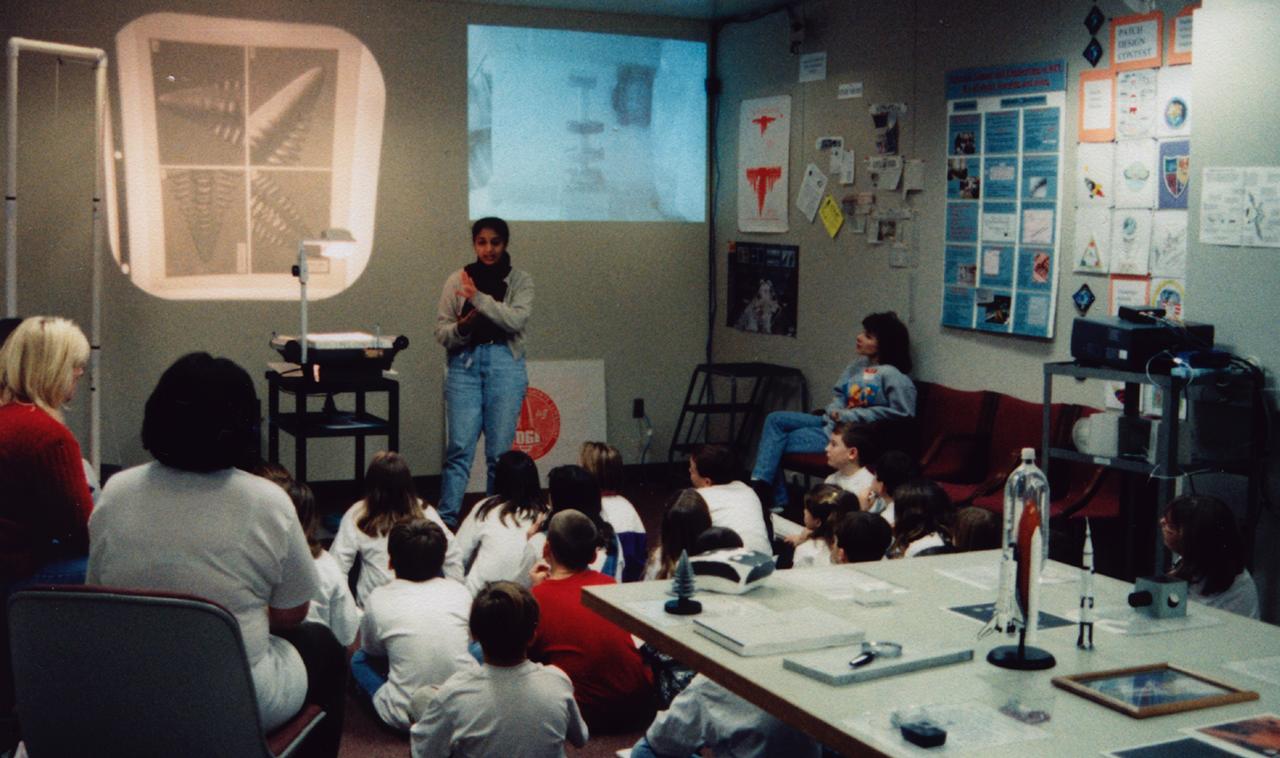

Pratima Rao lectures students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI
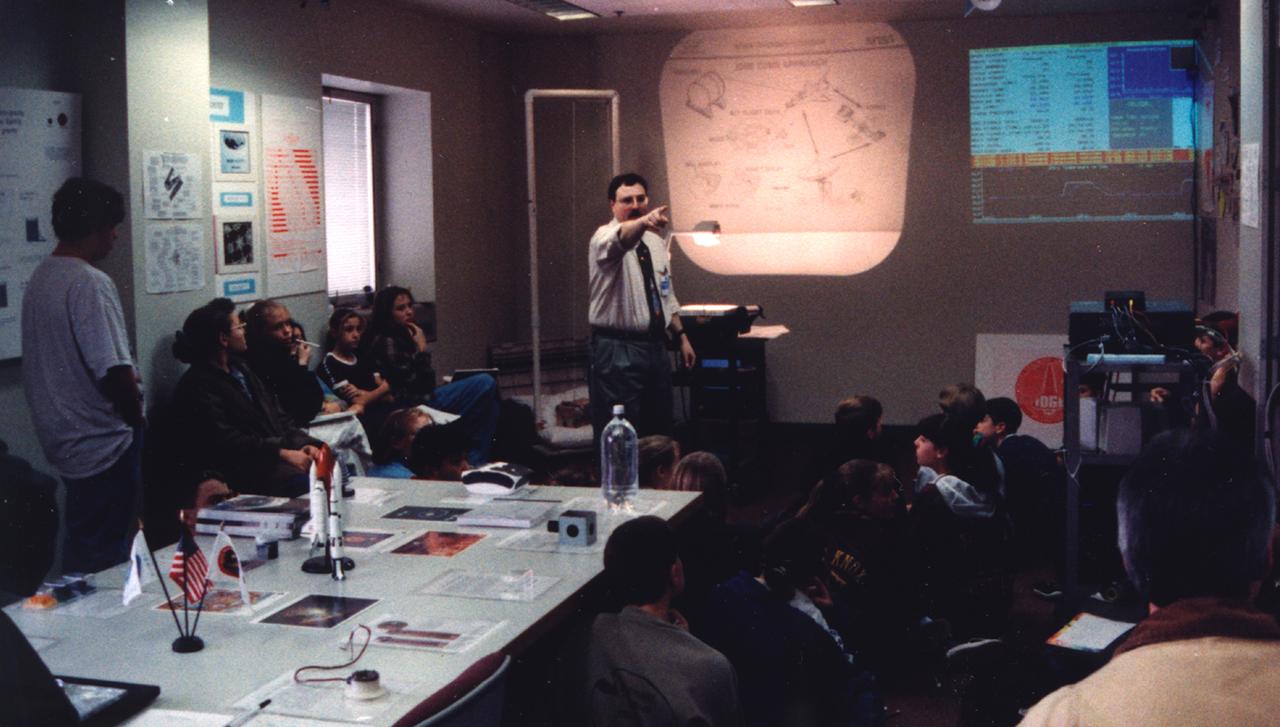

Matthew Koss lectures middle-school students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI