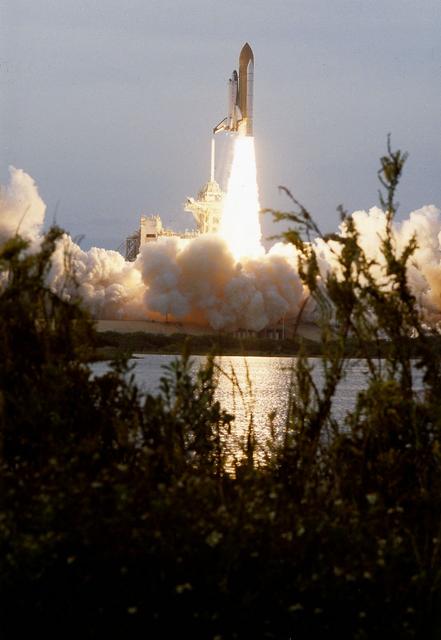

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-87) soared from Launch Pad 39B on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload (USMP-4) and Spartan-201 satellite which were managed by scientists and engineers from the Marshall Space Flight Center. During the 16-day mission, the crew oversaw experiments in microgravity; deployed and retrieved a solar satellite; and tested a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Two crew members, Dr. Takao Doi and Winston Scott also performed a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers.

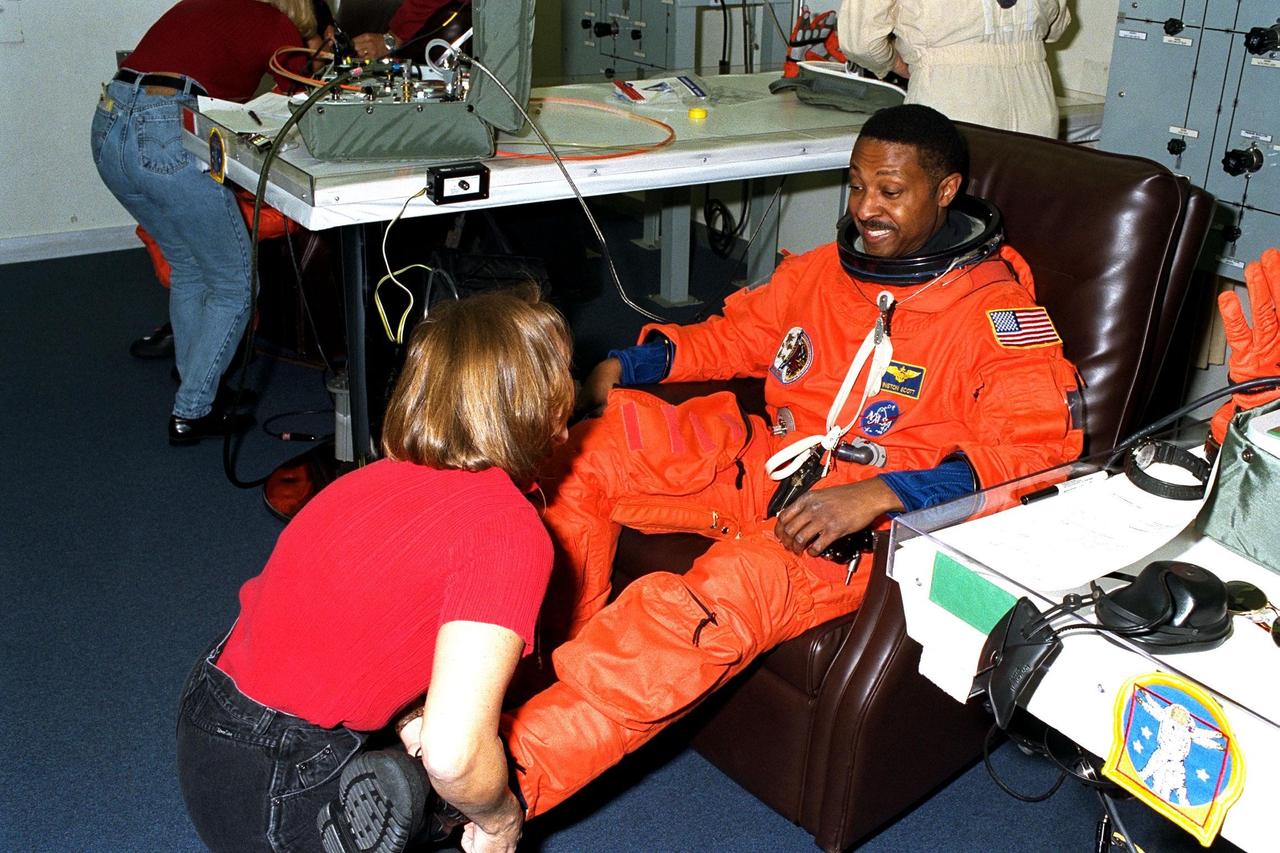
STS-87 Mission Specialist Winston Scott is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. Scott is scheduled to perform an extravehicular activity spacewalk with Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, during STS-87. Scott also performed a spacewalk on the STS-72 mission

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, Columbia rolls out to Launch Complex 39B atop the crawler-transporter. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is tentatively scheduled for Nov. 19

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, Columbia rolls out to Launch Complex 39B atop the crawler-transporter. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is tentatively scheduled for Nov. 19
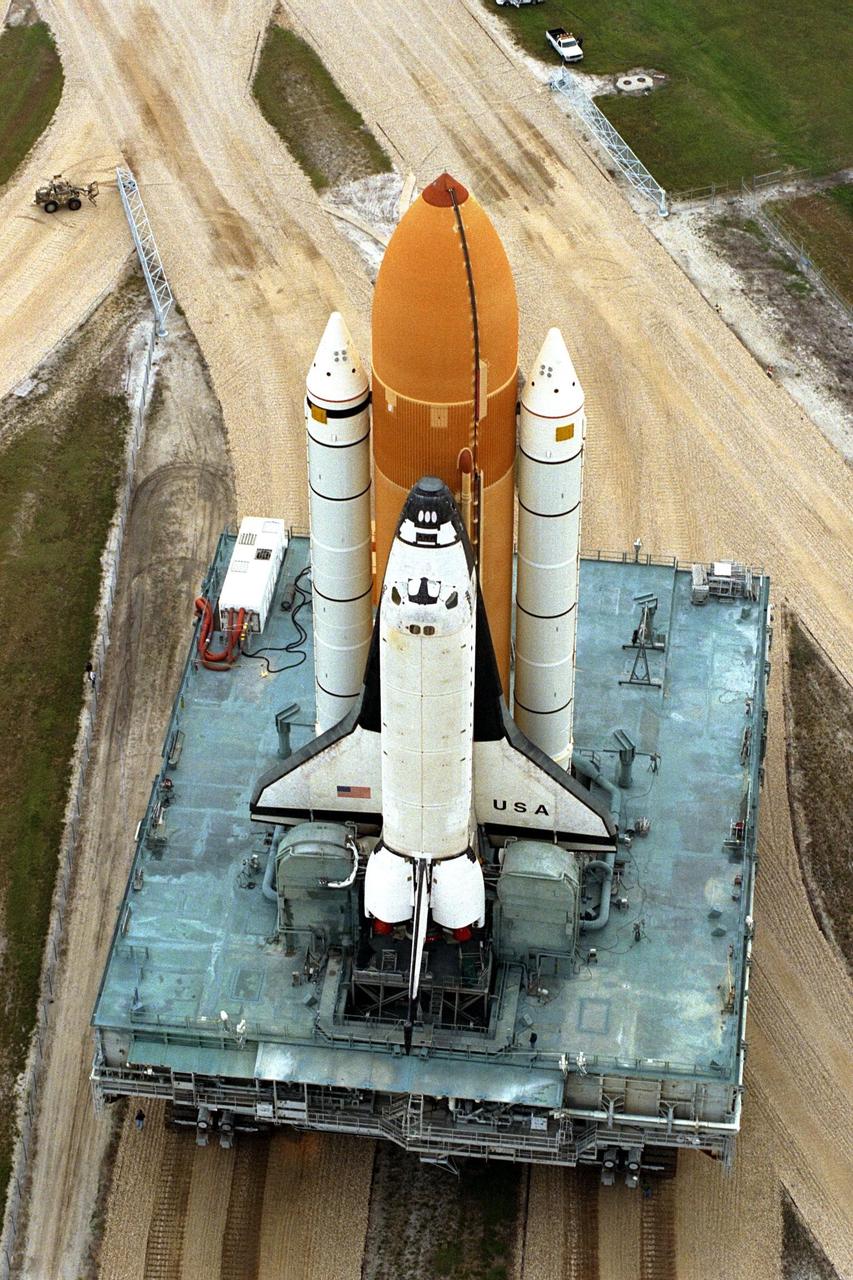

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, Columbia rolls out to Launch Complex 39B atop the crawler-transporter. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is tentatively scheduled for Nov. 19
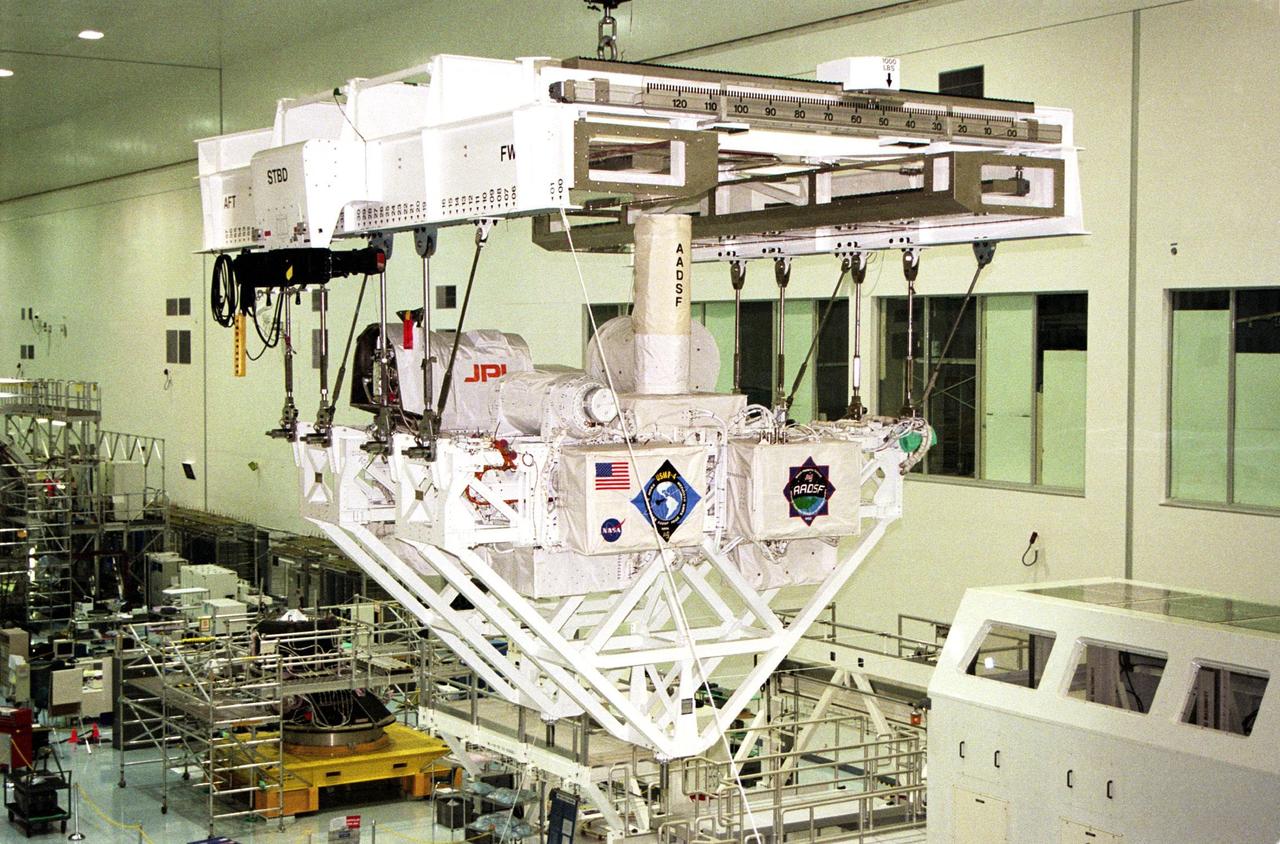
In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the United States Microgravity Payload-4 undergoes final processing in the Space Station Processing Facility before its move to Launch Complex 39B. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the United States Microgravity Payload-4 undergoes final processing in the Space Station Processing Facility before its move to Launch Complex 39B. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the United States Microgravity Payload-4 undergoes final processing in the Space Station Processing Facility before its move to Launch Complex 39B. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
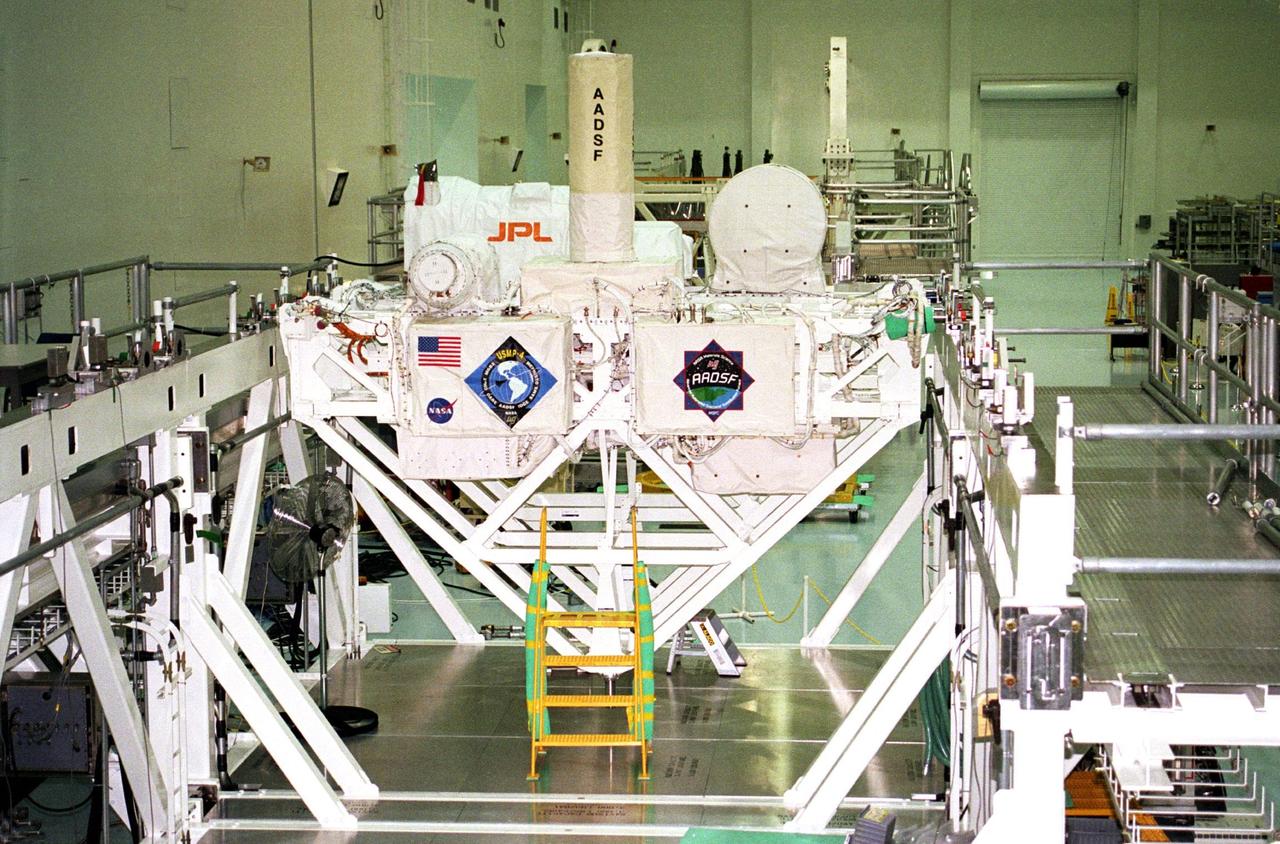

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the United States Microgravity Payload-4 undergoes final processing in the Space Station Processing Facility before its move to Launch Complex 39B. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
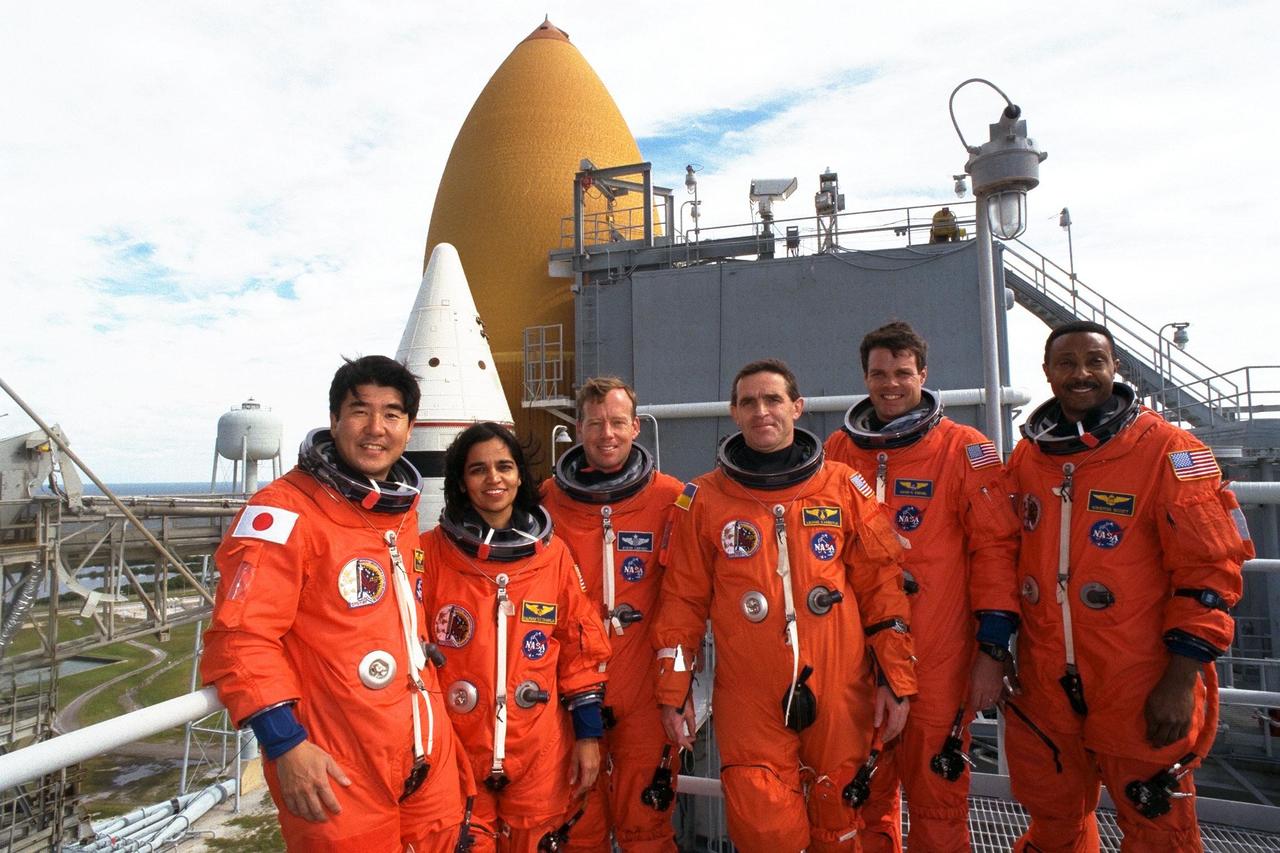

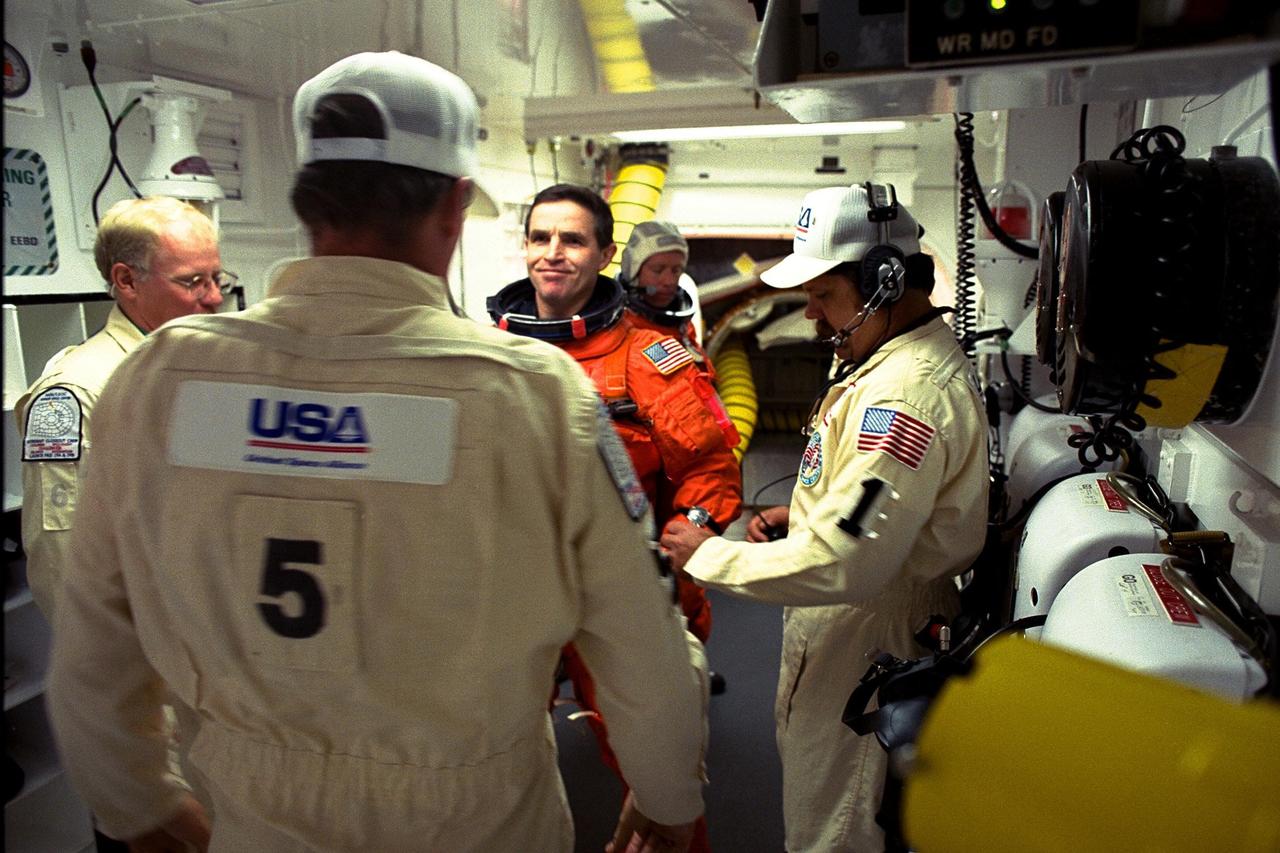
The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
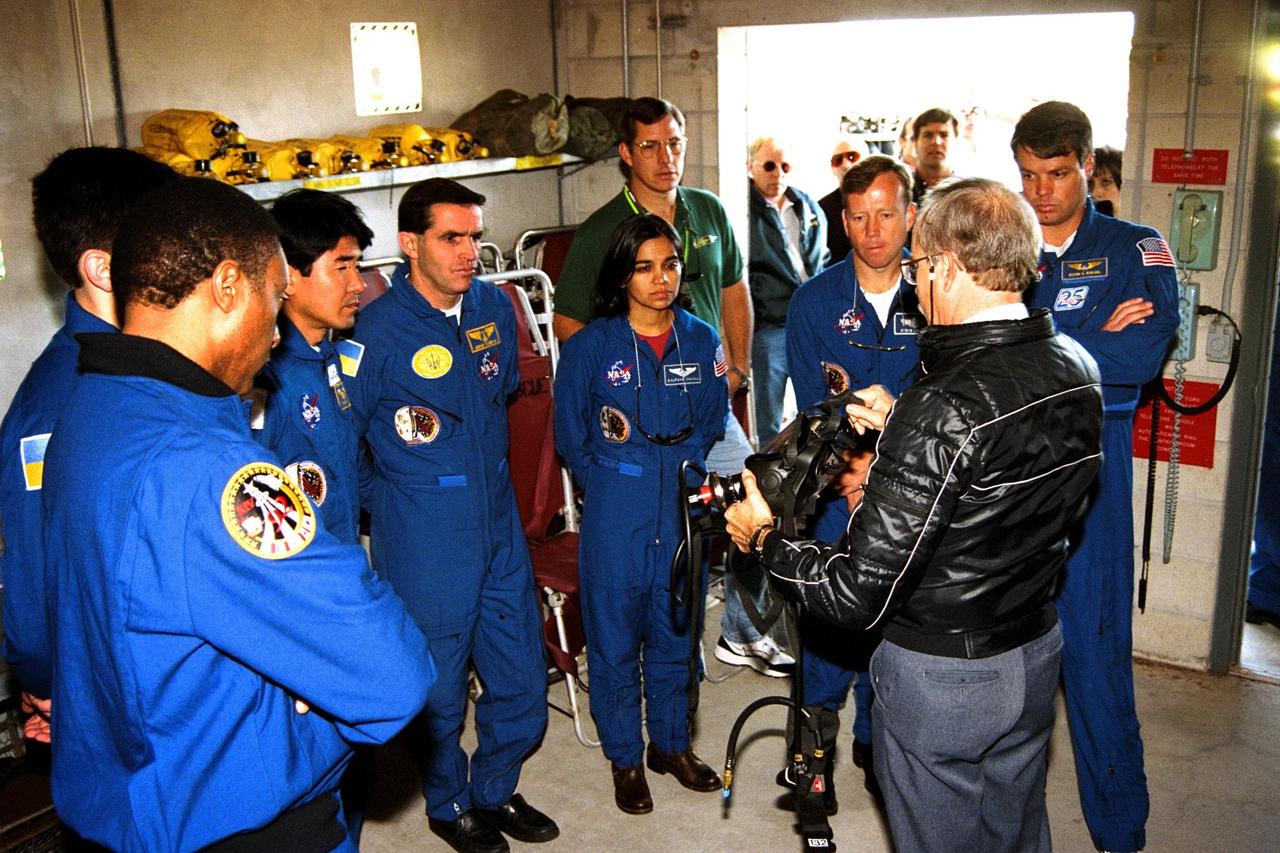

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
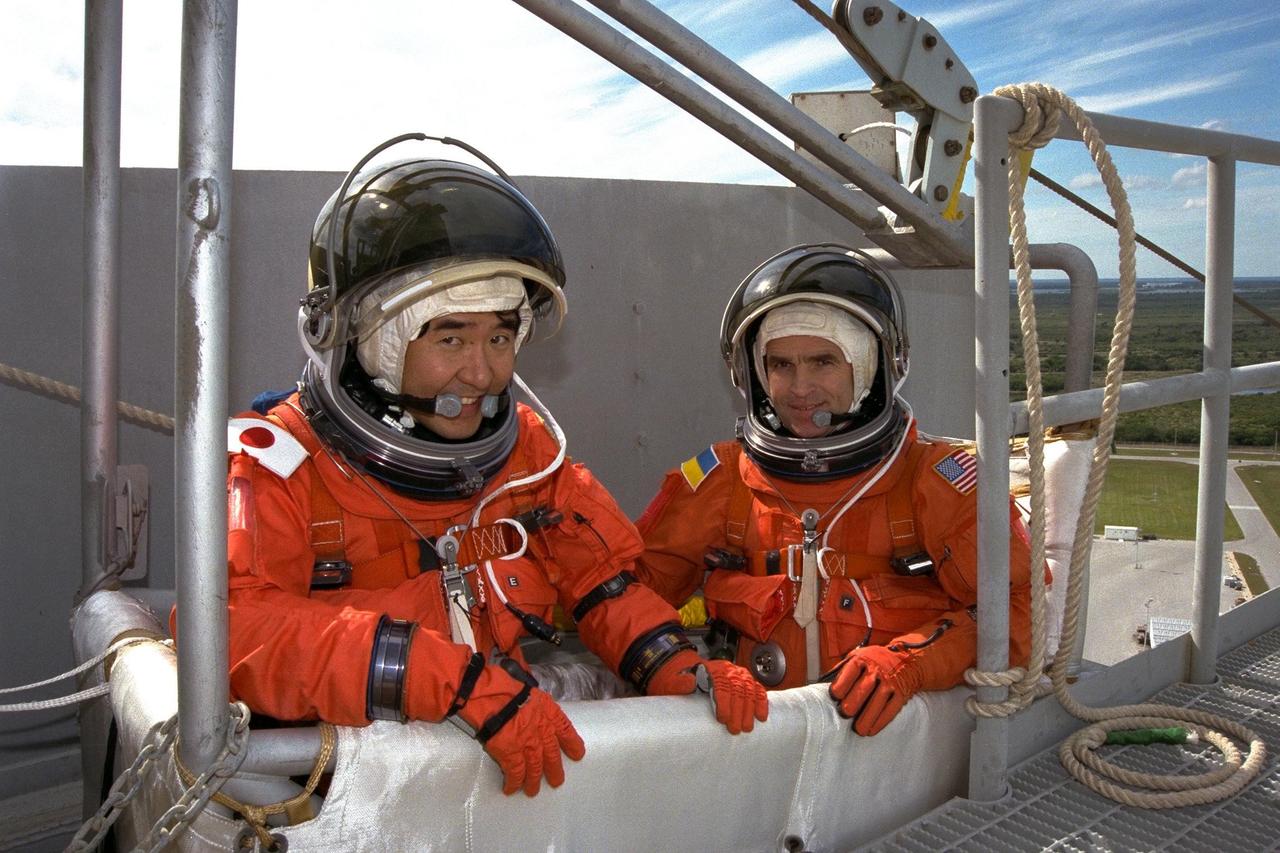

The STS-87 crew participates in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities at Launch Complex 39B
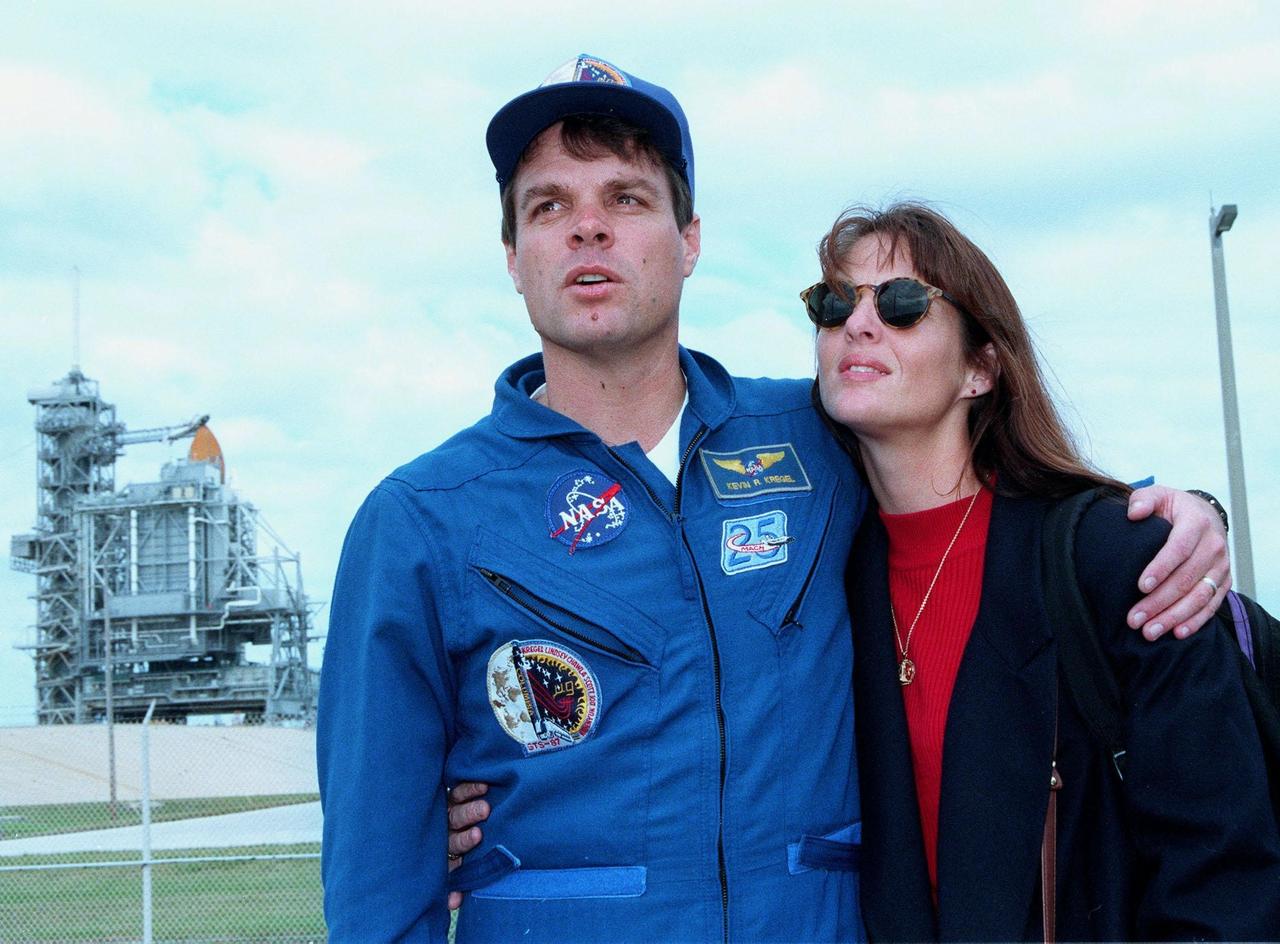

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel poses with his wife, Jeannie Kregel, in front of Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
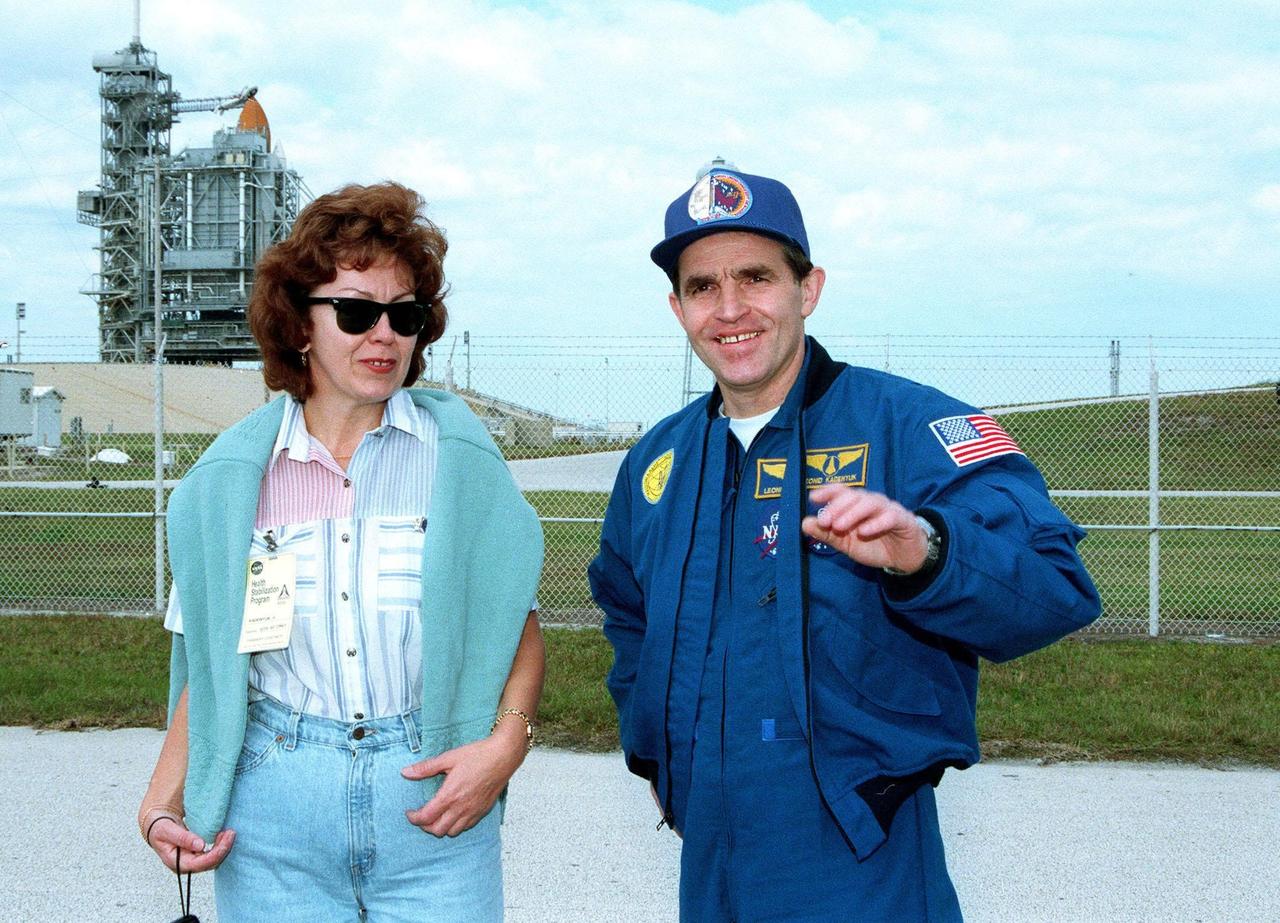

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine poses with his wife, Vera Kadenyuk, in front of Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; and Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Winston Scott; and Takao Doi, Ph.D., National Space Development Agency of Japan. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
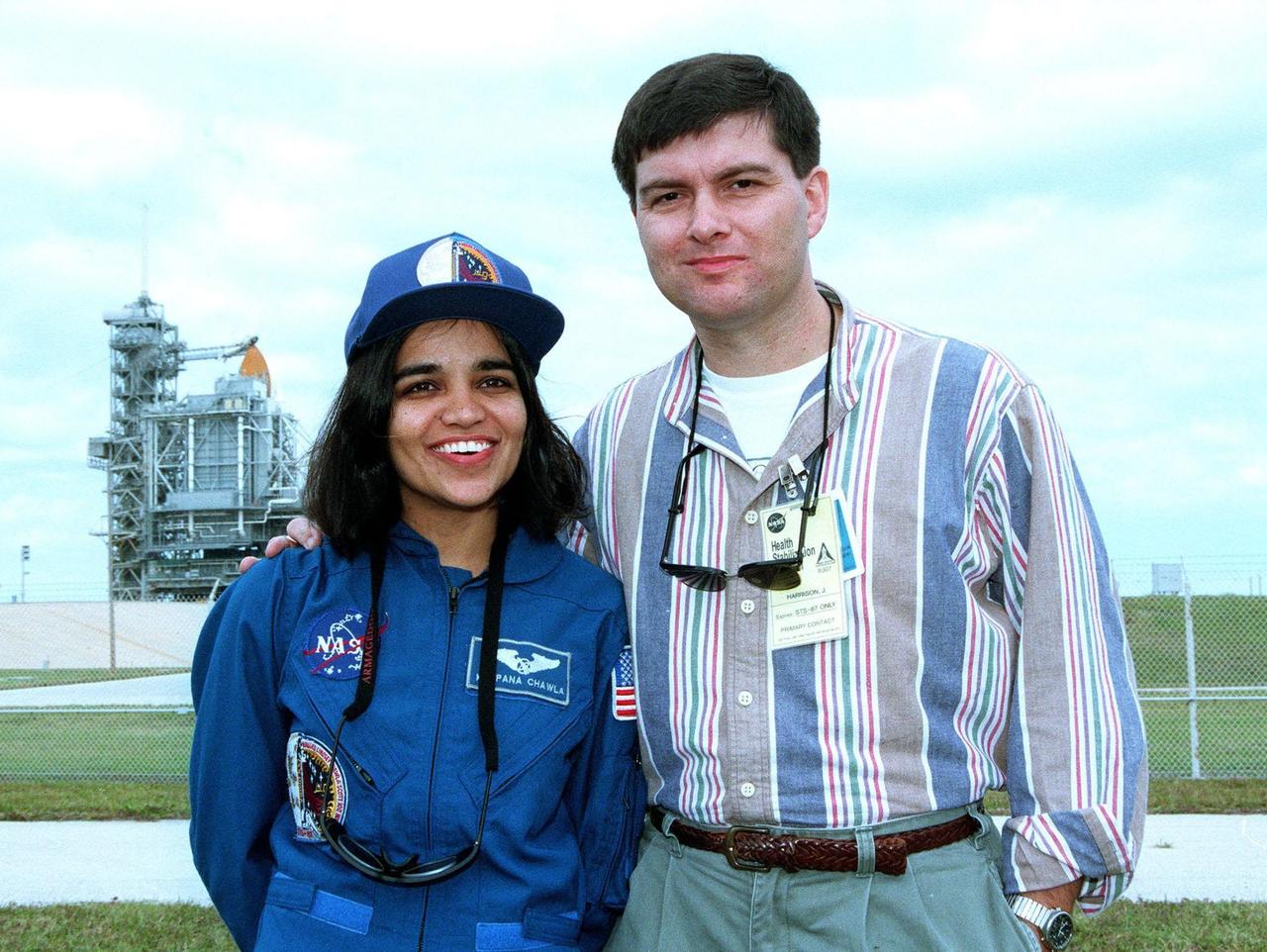

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., poses with her husband, Jean-Pierre Harrison, in front of Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Winston Scott and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
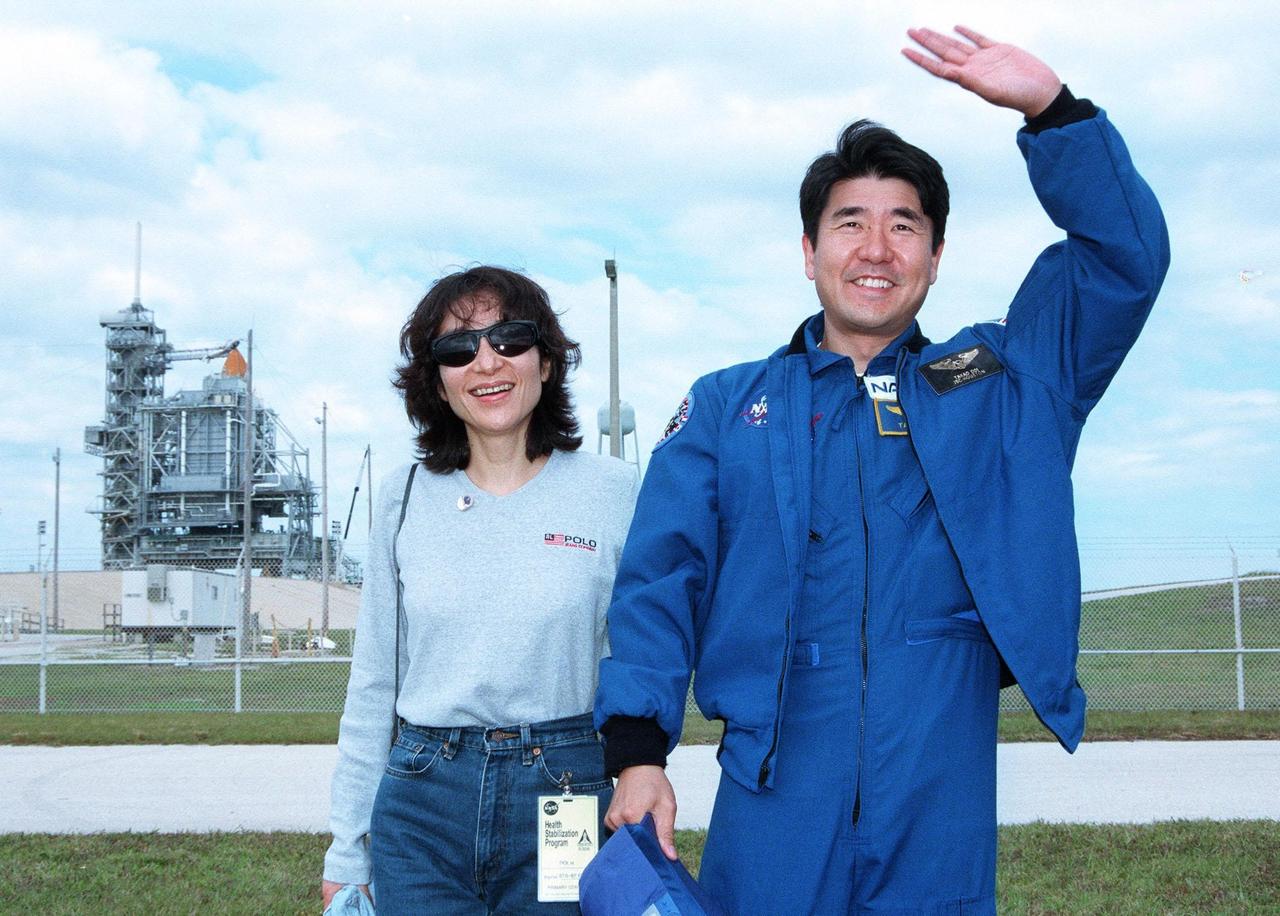

STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan poses with his wife, Hitomi Doi, in front of Kennedy Space Center's Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. The other STS-87 crew members are Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., and Winston Scott; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
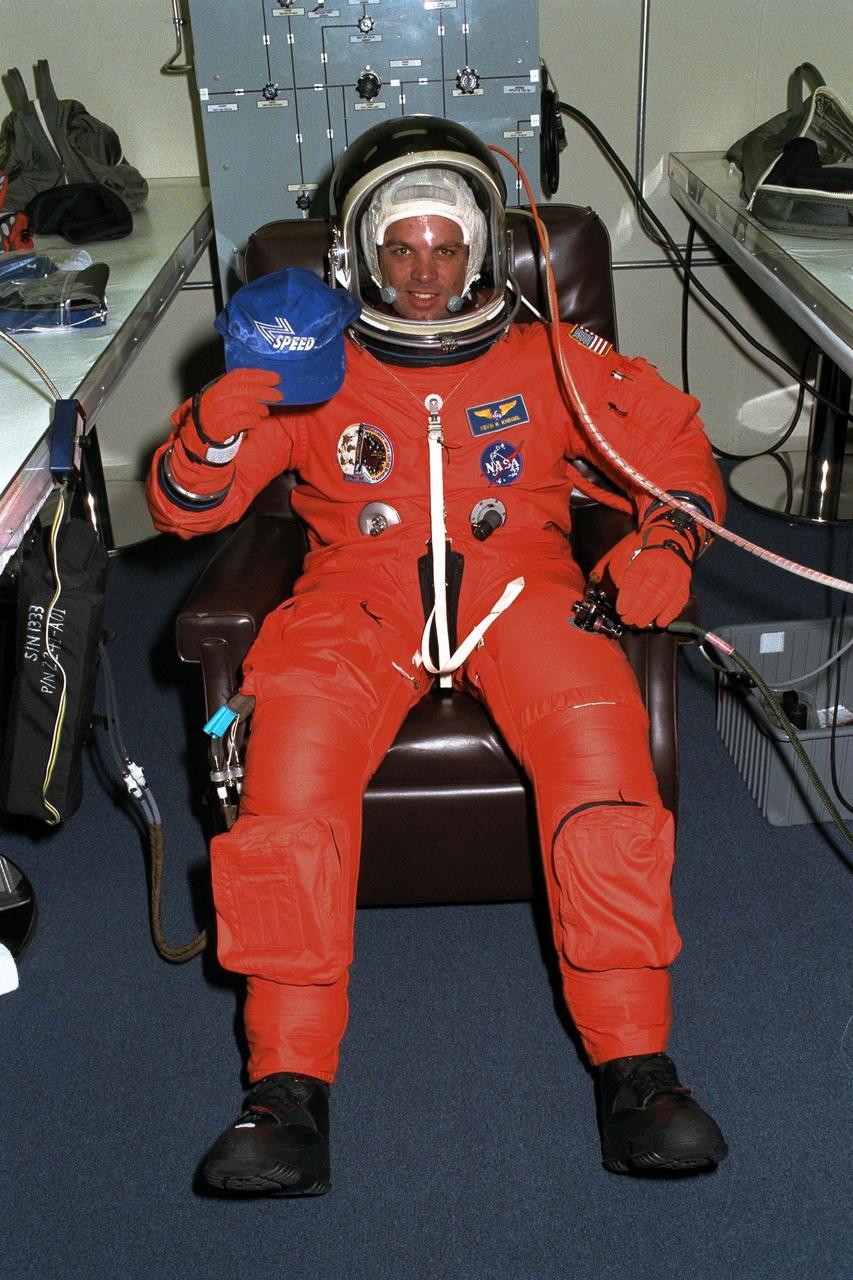

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel sits in his launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building holding a cap of his son’s soccer team of which Kregel is the coach. Shortly, he and the five other crew members of STS-87 will depart for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. A veteran of two space flights (STS-70 and -78), Kregel has logged more than 618 hours in space
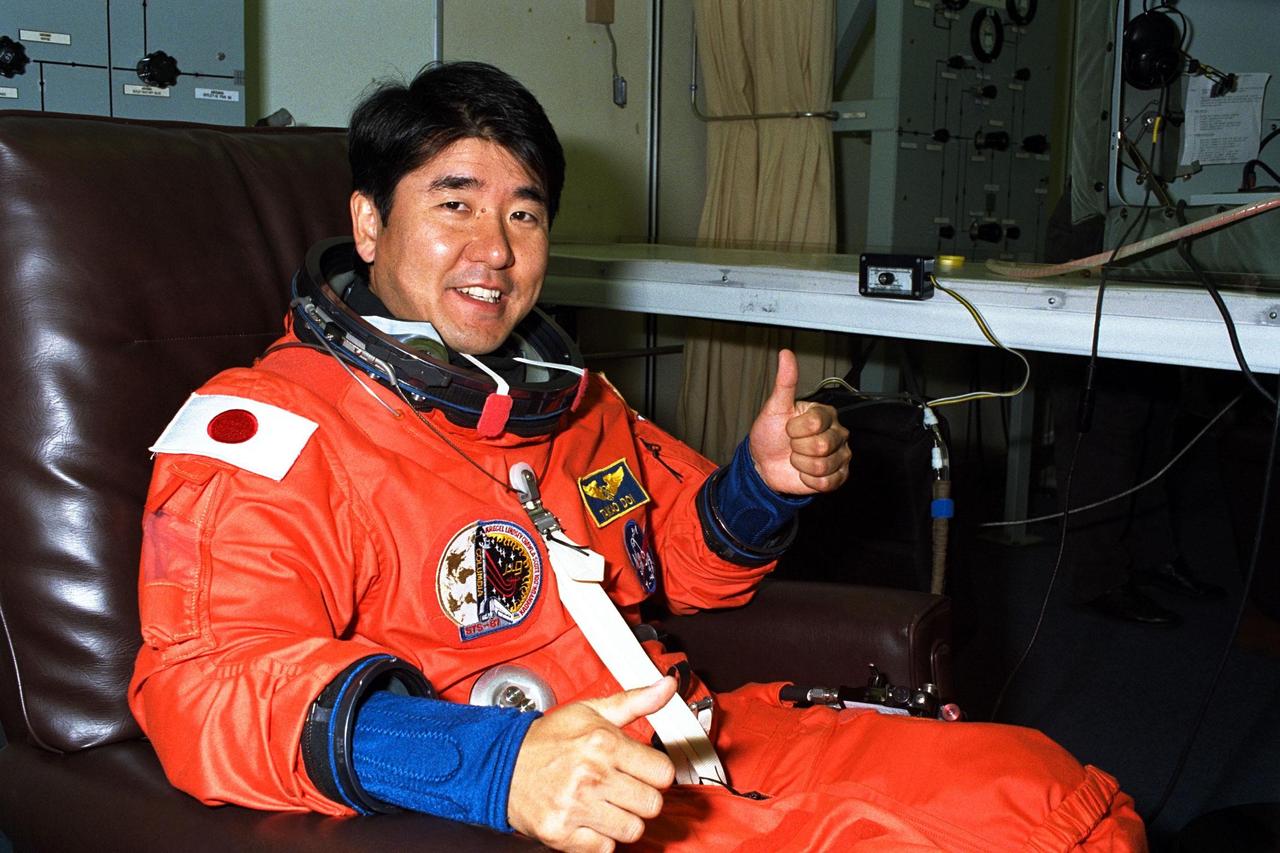

STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, gives a ‘thumbs up’ in his launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building. He and the five other crew members will depart shortly for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Dr. Doi is scheduled to perform an extravehicular activity spacewalk with Mission Specialist Winston Scott during STS-87
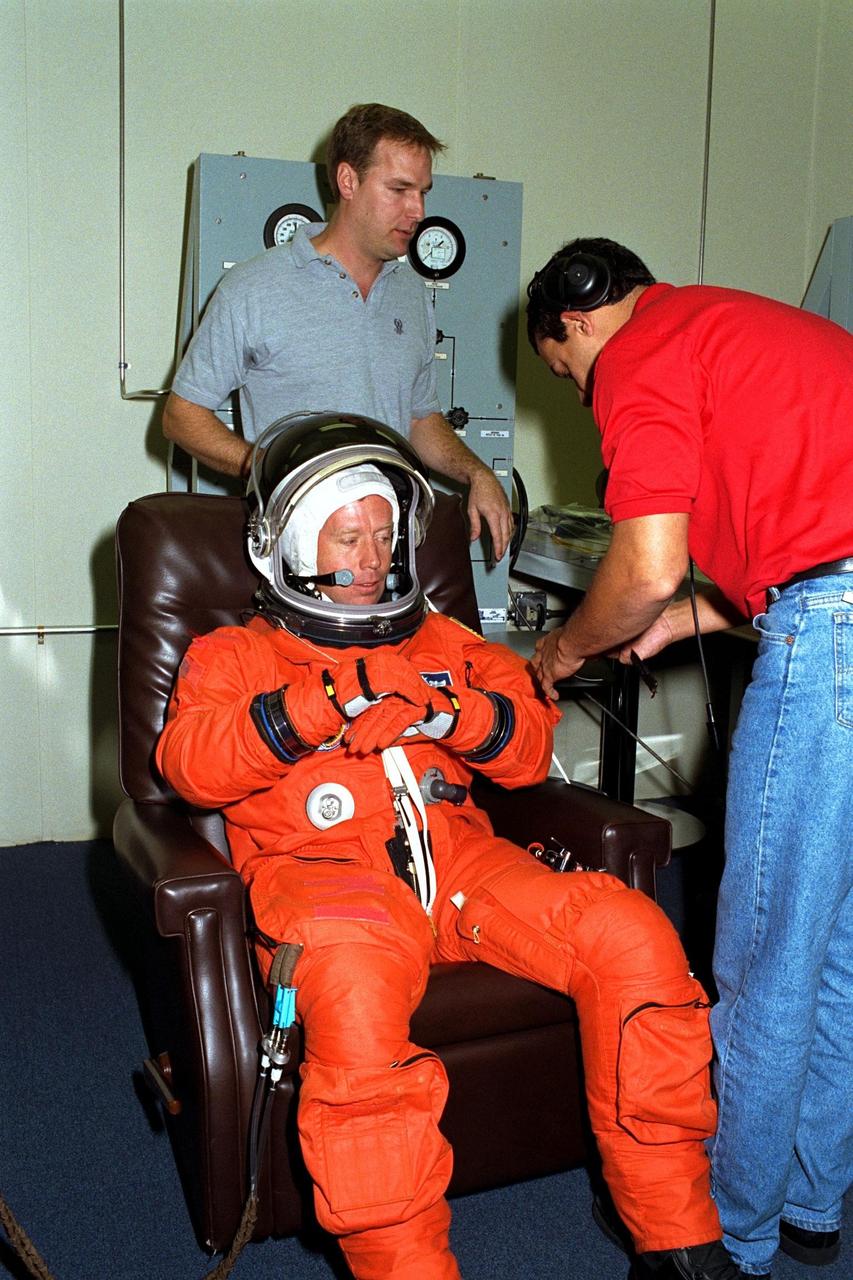

STS-87 Pilot Steven Lindsey dons his launch and entry suit with the help of two assistants in the Operations and Checkout Building. Shortly, he and the five other crew members of STS-87 will depart for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Although this is his first Shuttle flight, Lindsey has logged more than 2,700 hours of flying time in 49 different types of aircraft
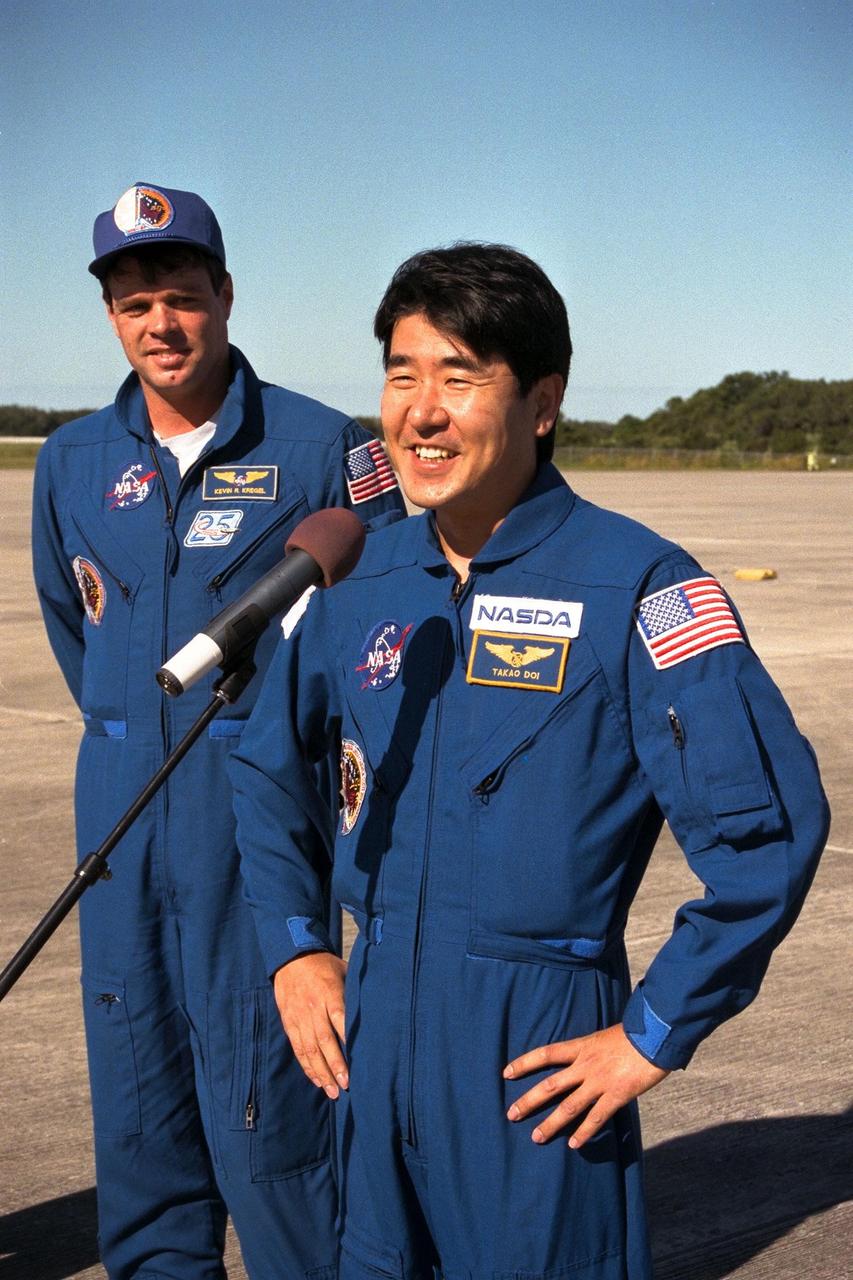

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the crew arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) for their mission. The TCDT is a dress rehearsal for launch. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is targeted for Nov. 19

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., sits in her launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building before she and the five other crew members of STS-87 depart for Launch Pad 39B. There, the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Born in Karnal, India, Dr. Chawla received her doctorate of philosophy in aerospace engineering from the University of Colorado in 1988. This is Chawla’s first mission for NASA

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., is assisted with her ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist. Kneeing before Dr. Chawla to assist her is George Schram, USA mechanical technician, as Dr. Chawla prepares to enter the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia on launch day. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201
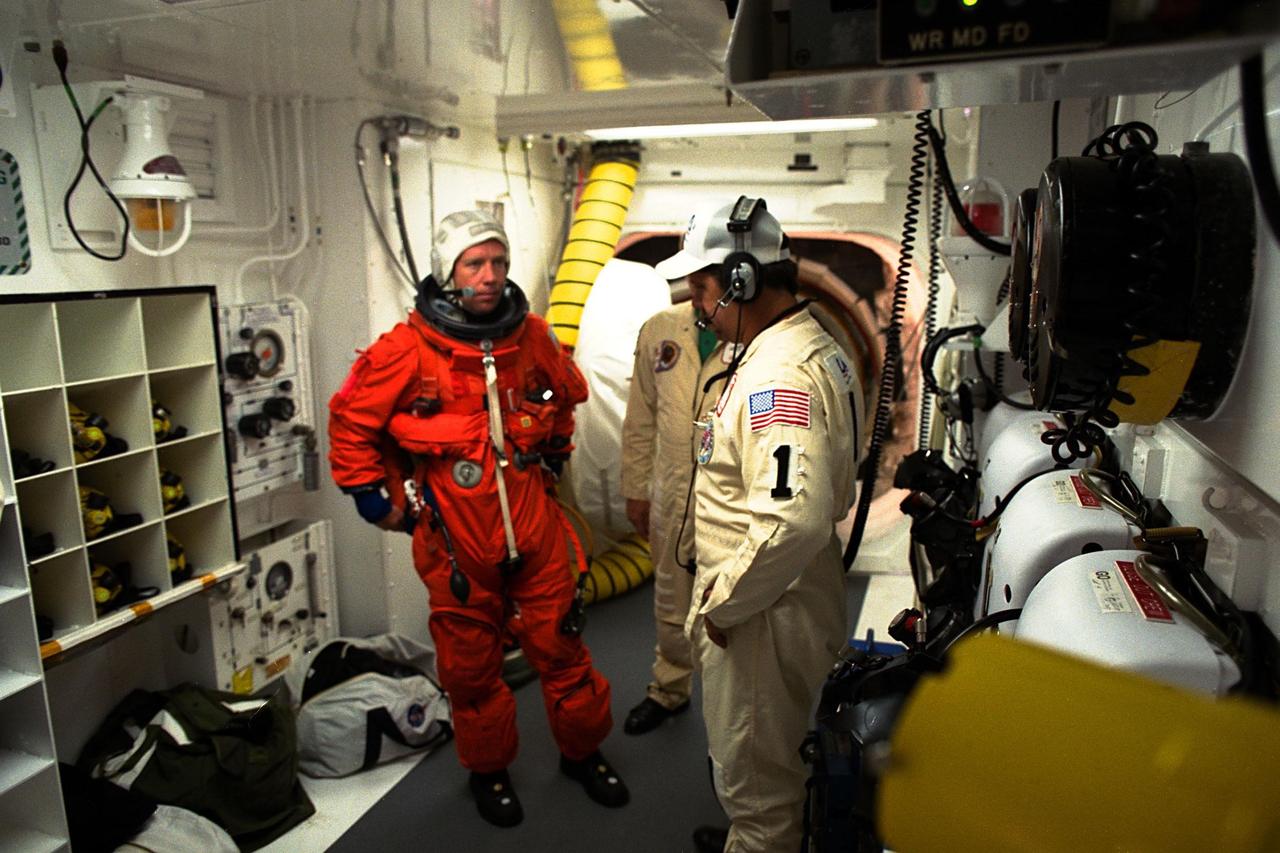

STS-87 Pilot Steven Lindsey is inspected before launch in his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Travis Thompson, USA orbiter vehicle closeout chief. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. Although this is his first Shuttle flight, Lindsey has logged more than 2,700 hours of flying time in 49 different types of aircraft
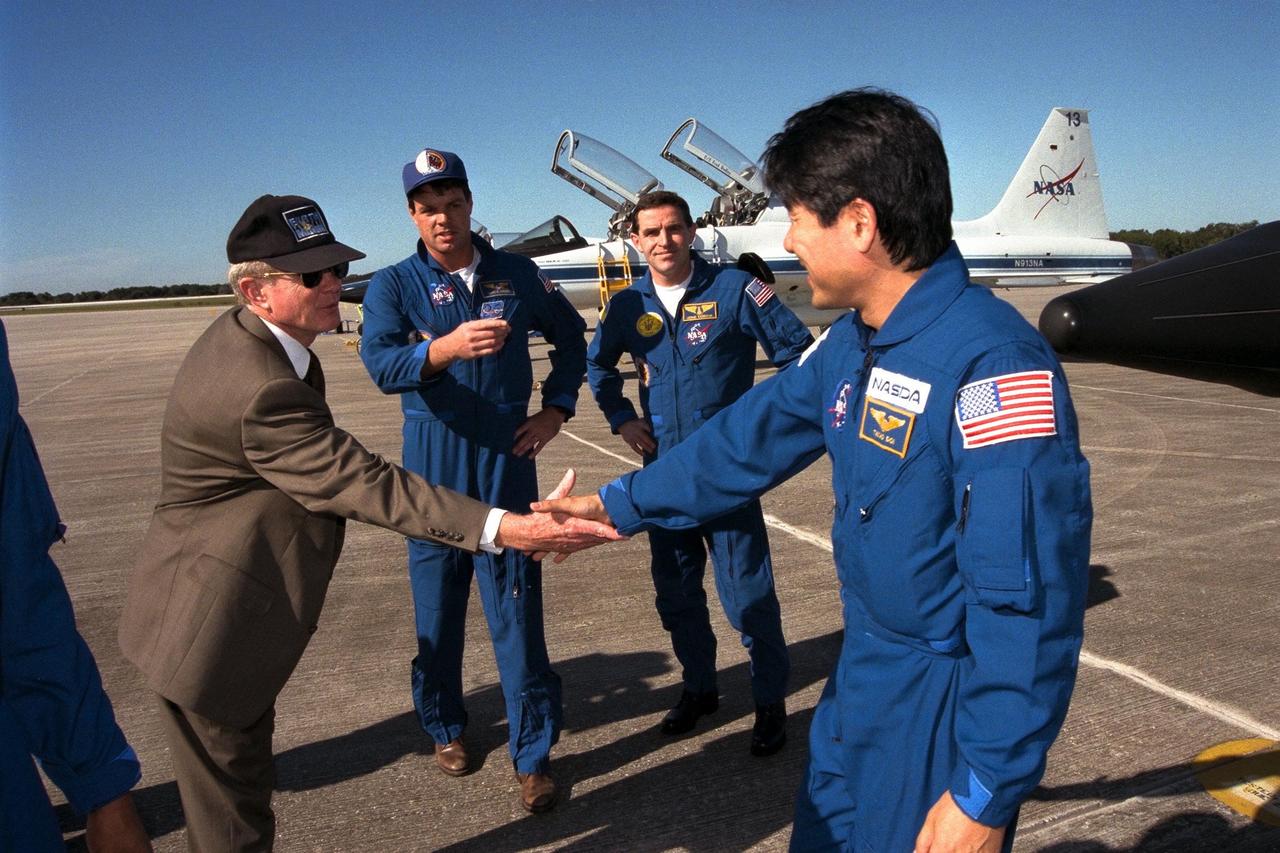

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the crew arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) for their mission. The TCDT is a dress rehearsal for launch. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is targeted for Nov. 19
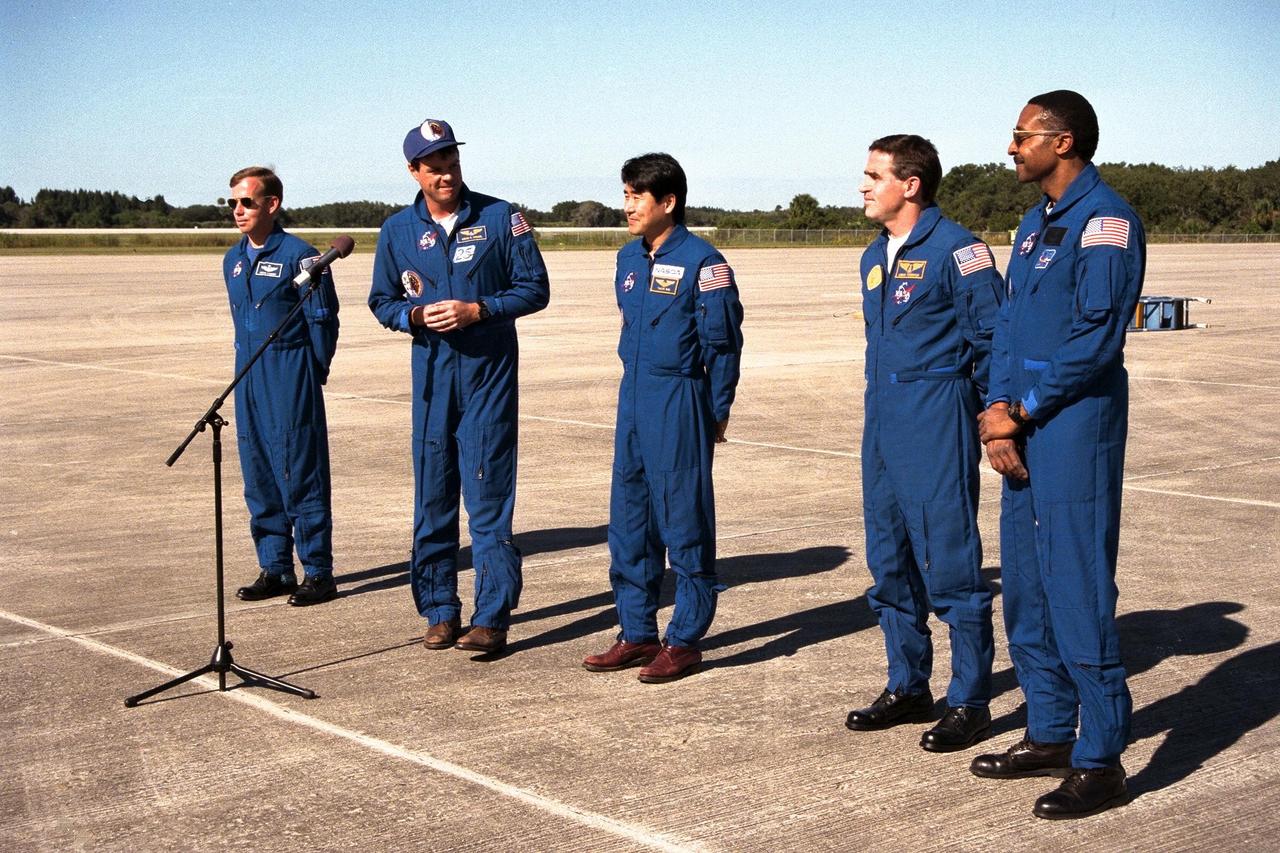

In preparation for Space Shuttle Mission STS-87, the crew arrives at the Kennedy Space Center Shuttle Landing Facility to participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) for their mission. The TCDT is a dress rehearsal for launch. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Launch is targeted for Nov. 19
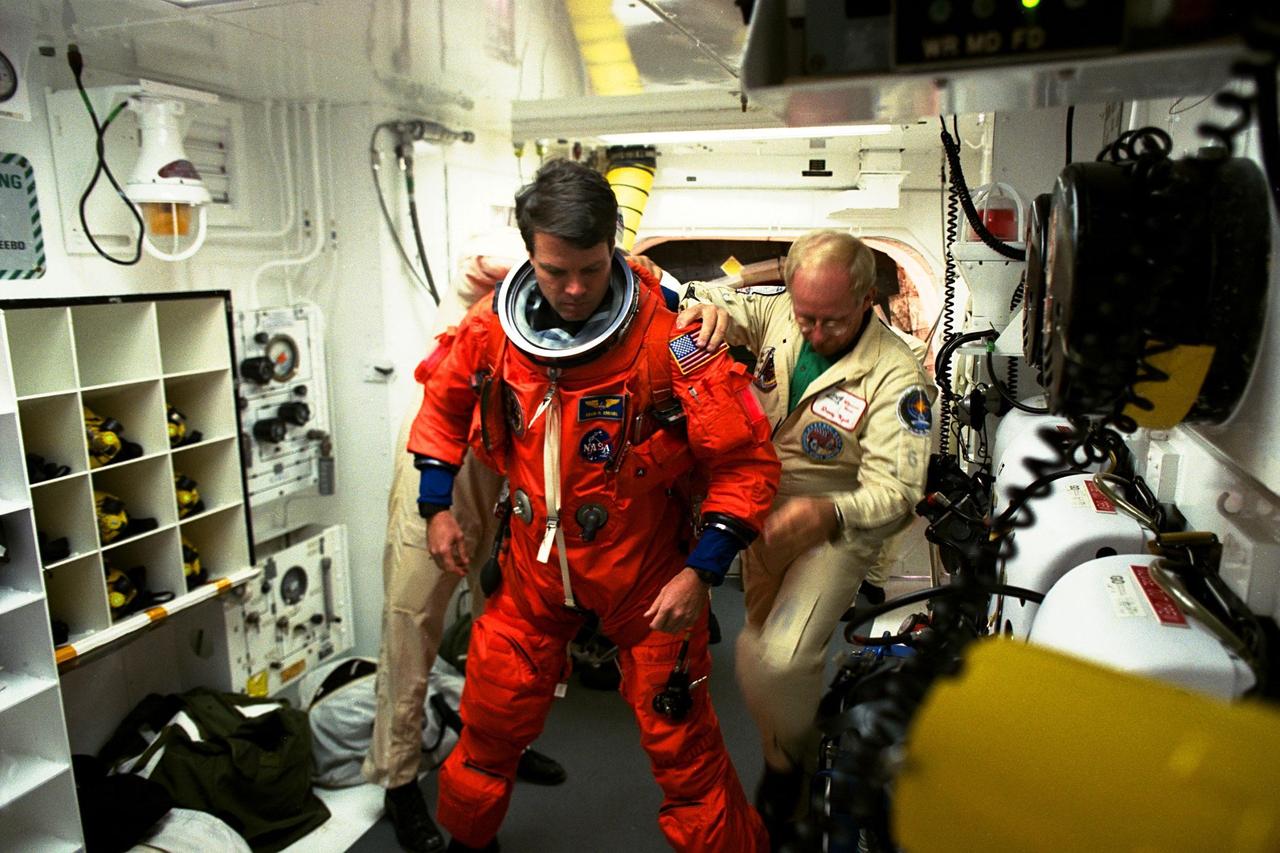

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. A veteran of two space flights (STS-70 and -78), Kregel has logged more than 618 hours in space
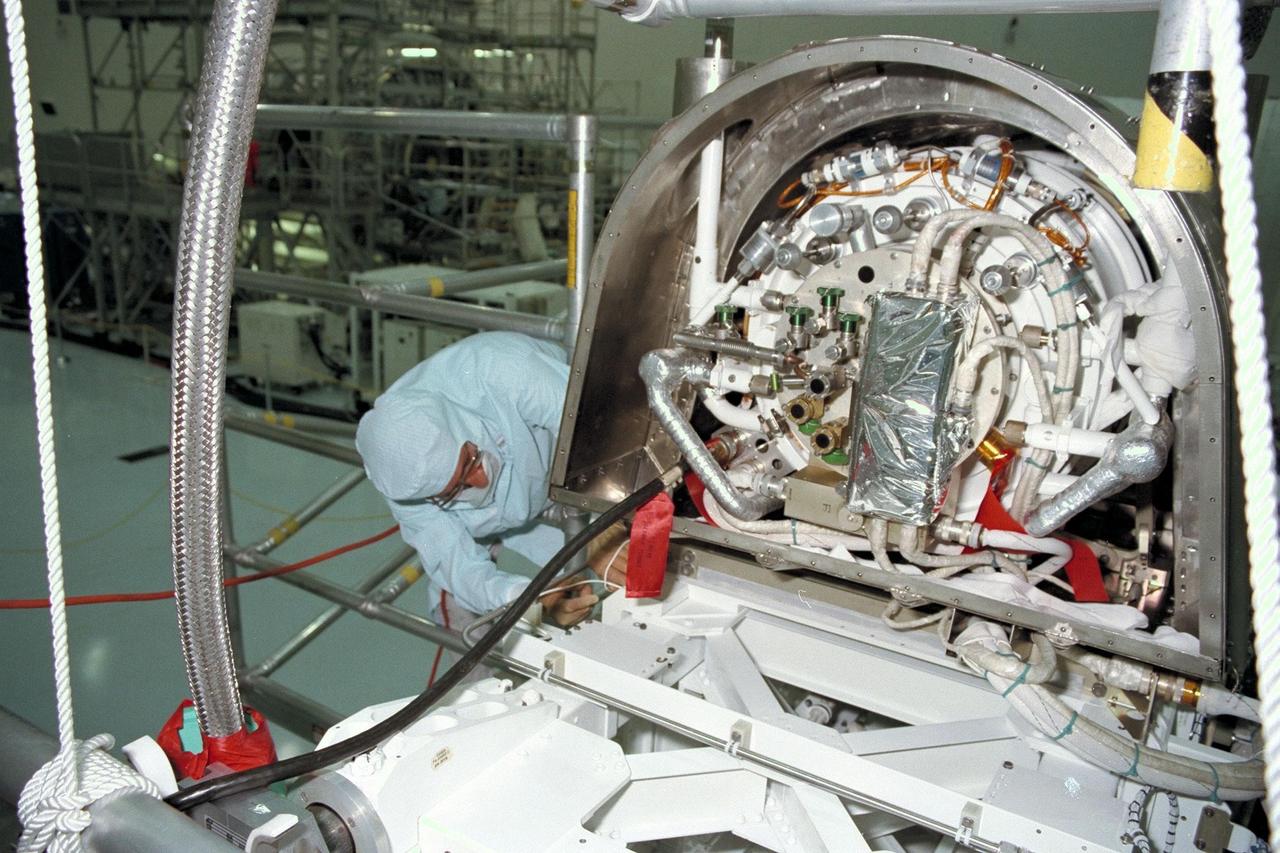

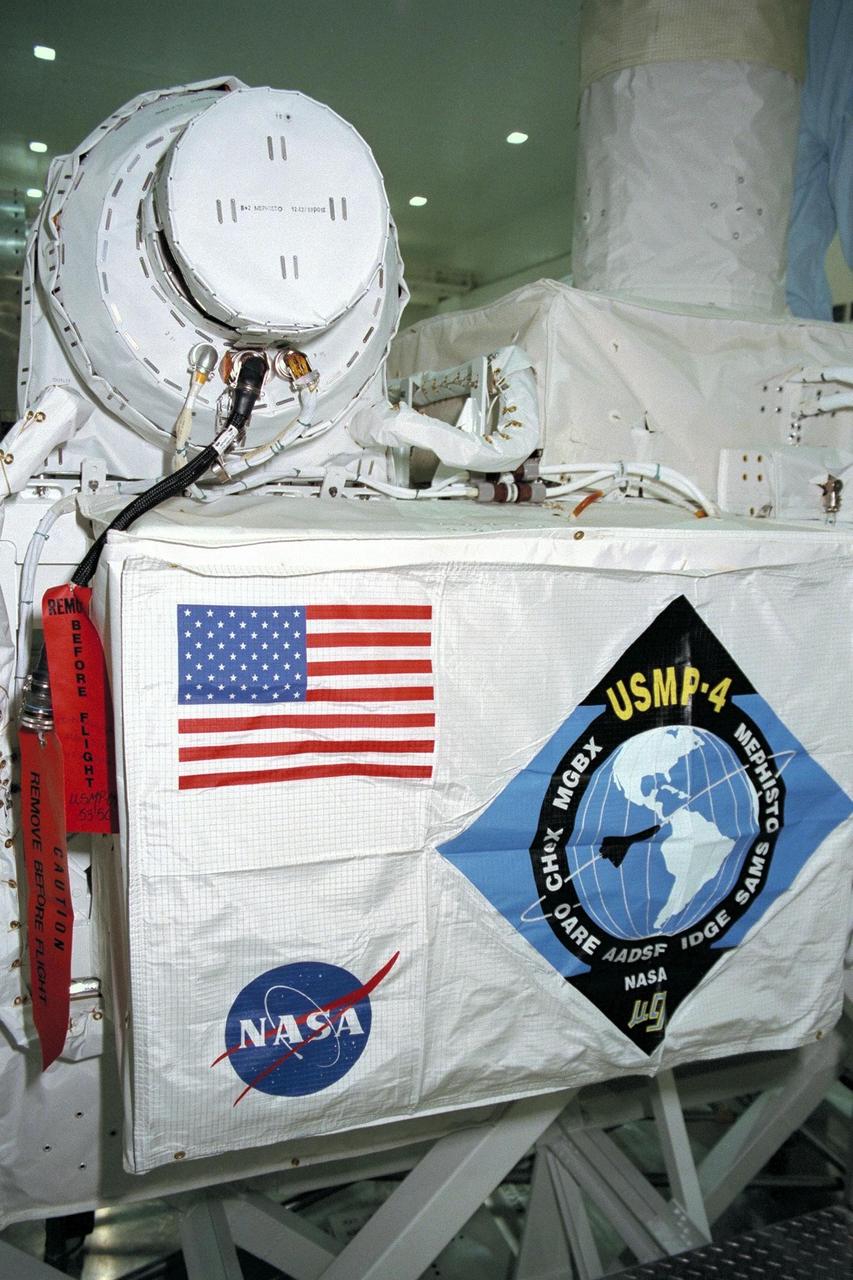
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Here, a technician is monitoring the Confined Helium Experiment, or CHeX, that will use microgravity to study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between silicon disks. CHeX and several other experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
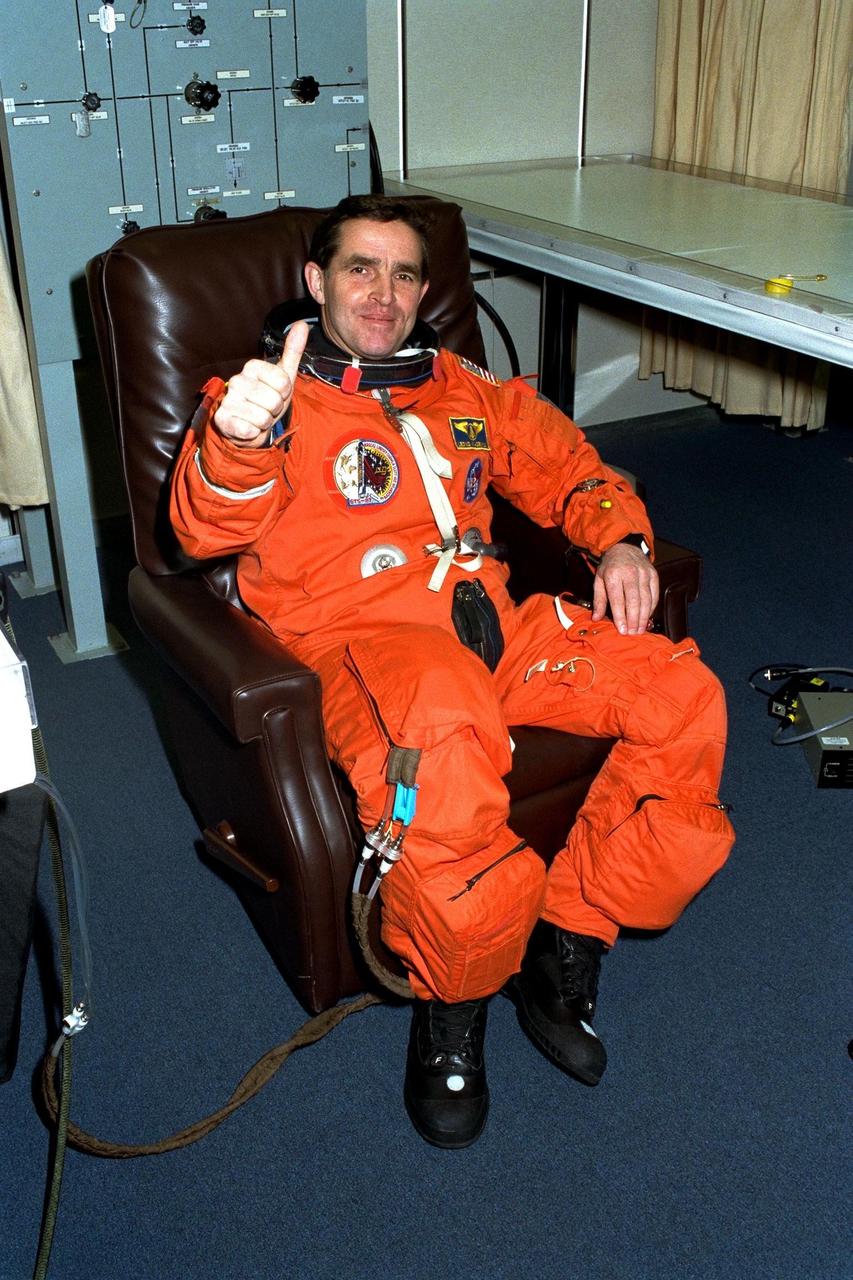

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine gives a ‘thumbs up’ in his launch and entry suit in the Operations and Checkout Building. He and the five other crew members of STS-87 will depart shortly for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Kadenyuk will be flying his first mission on STS-87. During the mission, Kadenyuk will pollinate Brassica rapa plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia’s middeck and features an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on Brassica rapa seedlings

STS-87 Mission Specialist Winston Scott dons his launch and entry suit with the assistance of a suit technician in the Operations and Checkout Building. This is Scott’s second space flight. He and the five other crew members will depart shortly for Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on a 16-day mission to perform microgravity and solar research. Scott is scheduled to perform an extravehicular activity spacewalk with Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, during STS-87. He also performed a spacewalk on STS-72
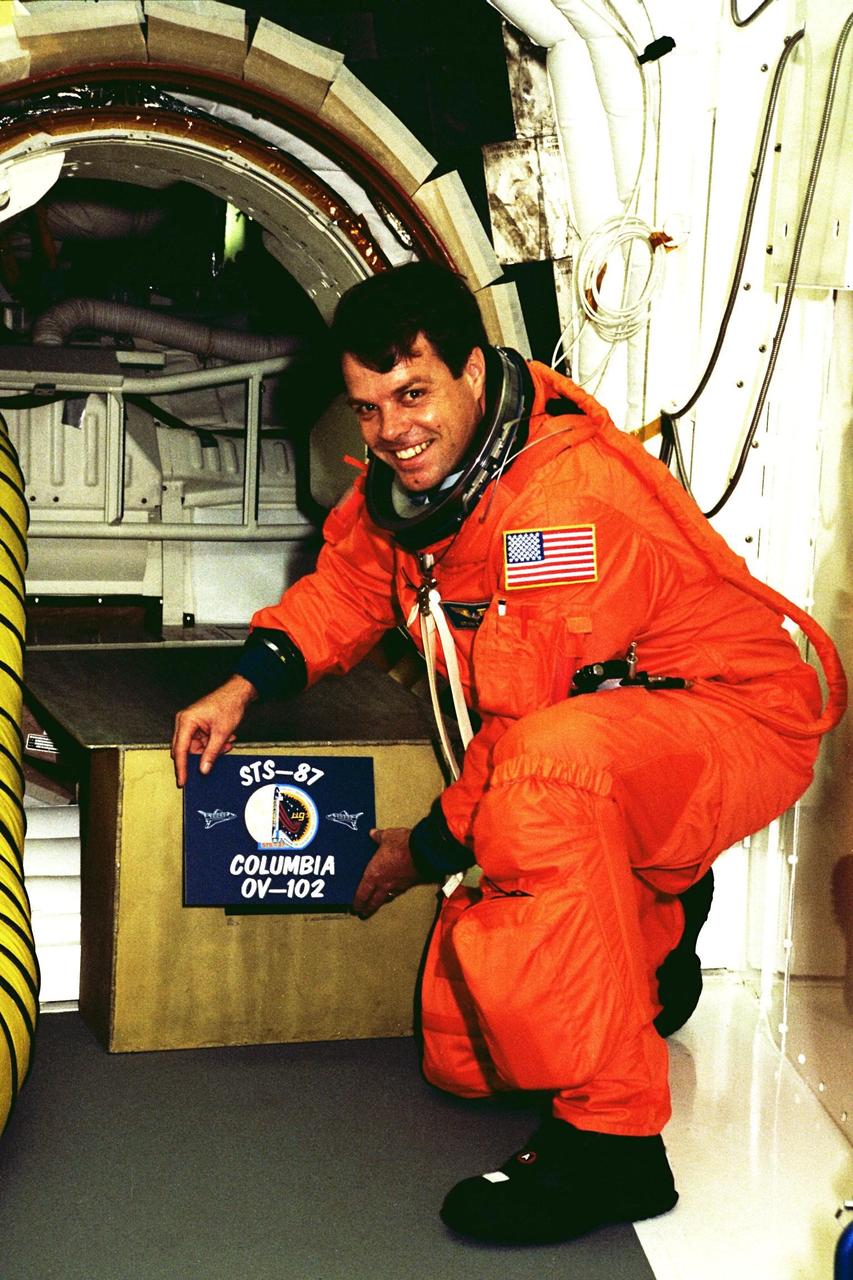

STS-87 Commander Kevin Kregel holds the crew patch in front of Columbia’s entry hatch at Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
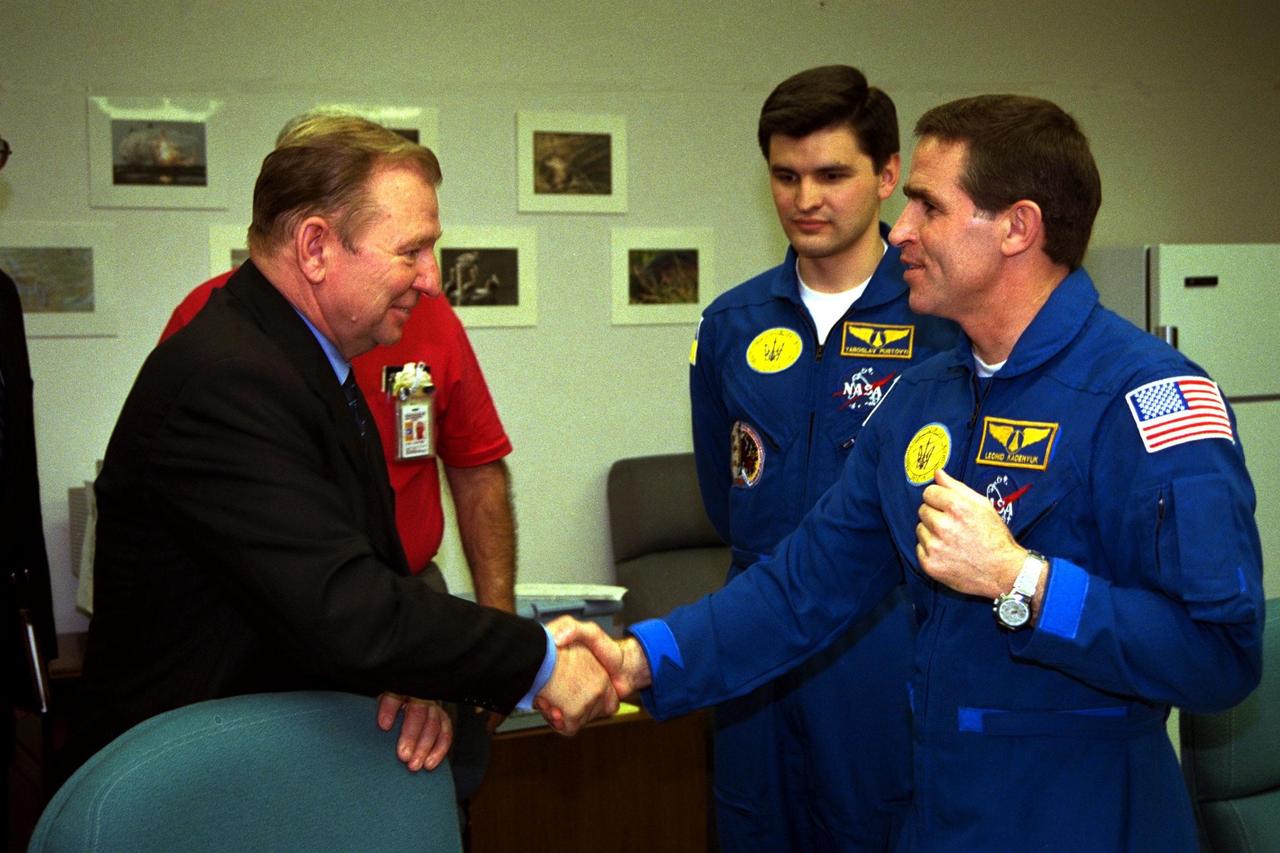

The president of the Ukraine, Leonid Kuchma, shakes hands with Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk, at right, as backup Payload Specialist Yaroslav Pustovyi, both of the National Space Agency of Ukraine, looks on during prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 launch of STS-87. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, Kadenyuk will pollinate Brassica rapa plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia during its 16-day mission. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia's middeck and will feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on Brassica rapa seedlings. Students in Ukrainian and American schools will participate in the same experiment with Kadenyuk in space. Kadenyuk will be flying his first Shuttle mission on STS-87
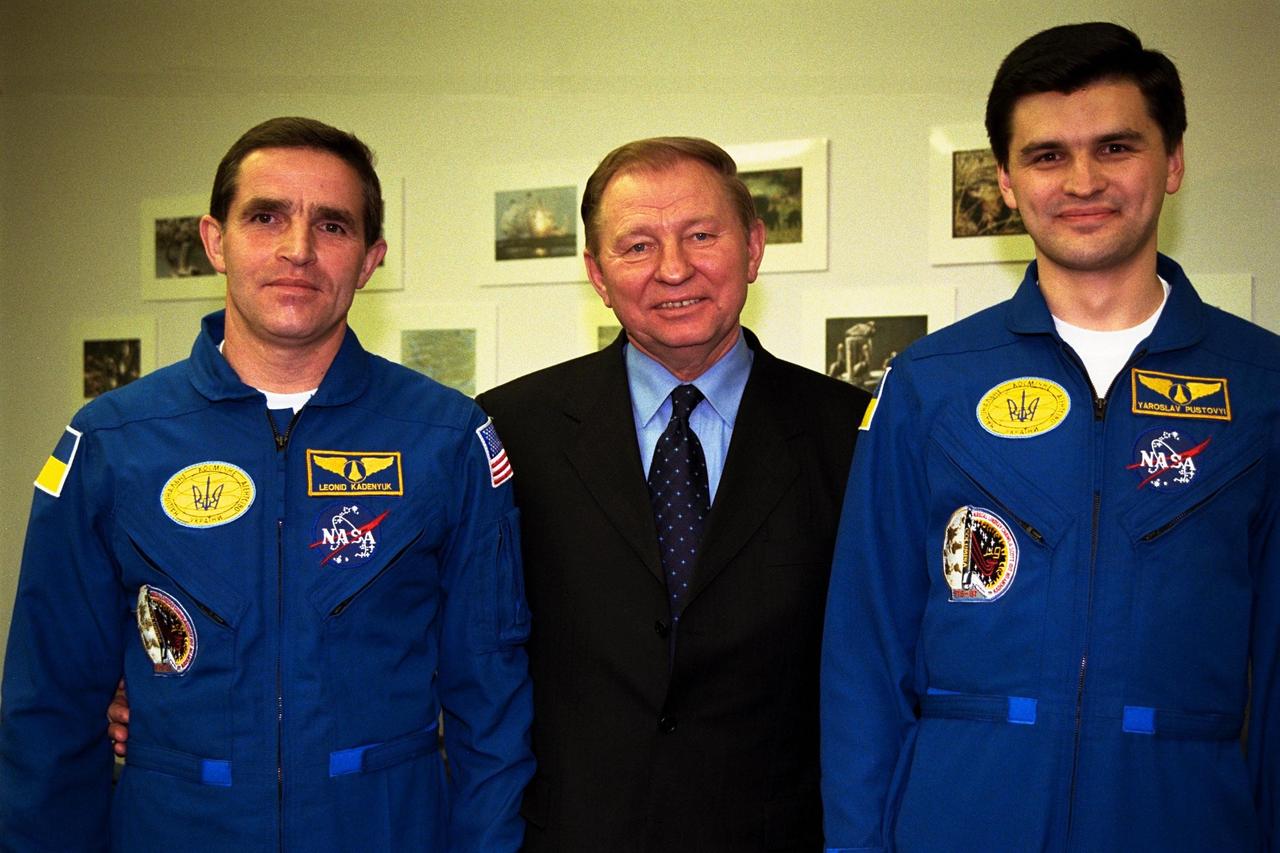

The president of the Ukraine, Leonid Kuchma, is flanked by Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk, at left, and backup Payload Specialist Yaroslav Pustovyi, at right, both of the National Space Agency of Ukraine, during prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 launch of STS-87. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. During the mission, Kadenyuk will pollinate Brassica rapa plants as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia during its 16-day mission. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia's middeck and will feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on Brassica rapa seedlings. Students in Ukrainian and American schools will participate in the same experiment with Kadenyuk in space. Kadenyuk will be flying his first Shuttle mission on STS-87
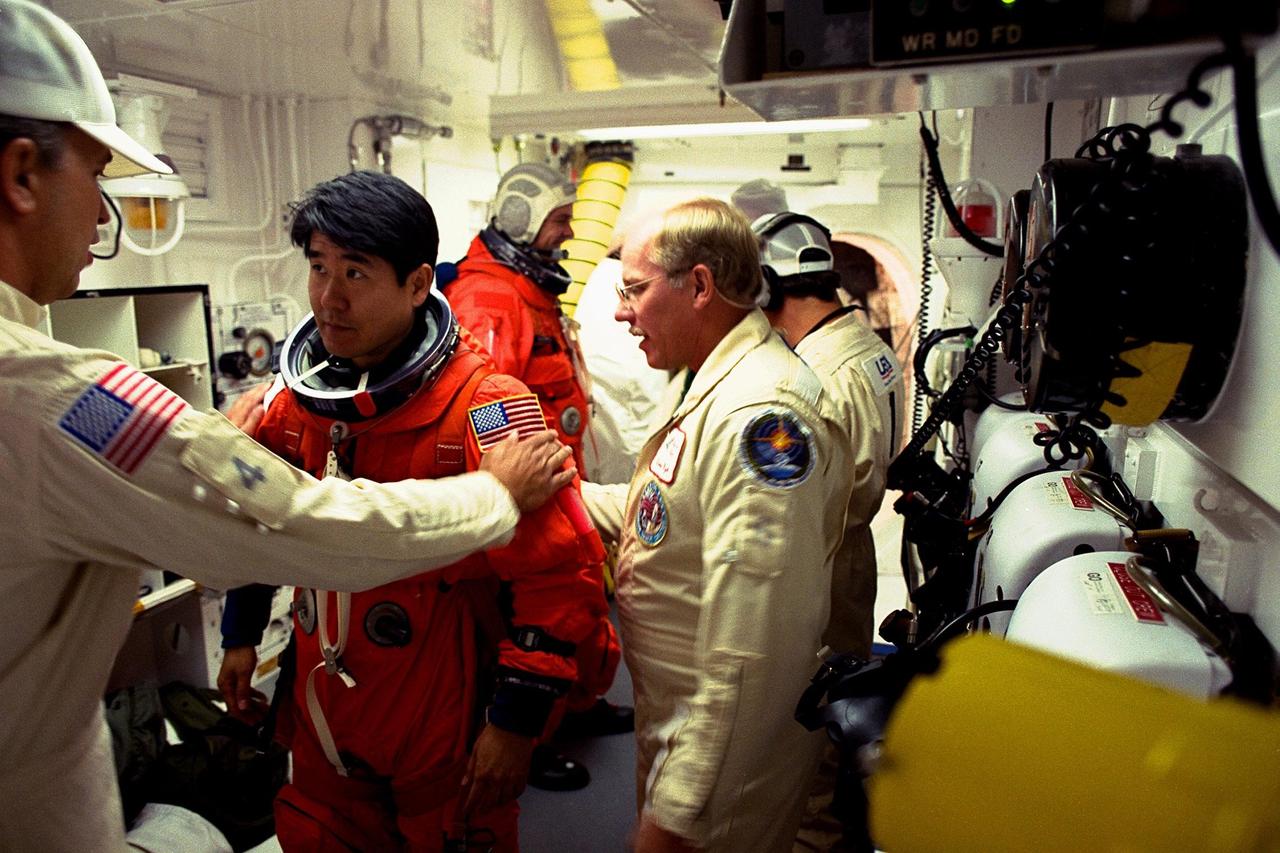

STS-87 Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, is assisted with his ascent and re-entry flight suit by Dave Law, USA mechanical technician, in the white room at Launch Pad 39B as Dr. Doi prepares to enter the Space Shuttle orbiter Columbia on launch day. At right wearing glasses is Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. The 16-day mission will include a spacewalk by Dr. Doi and Mission Specialist Winston Scott

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine is assisted with final preparations before launch in the white room at Launch Pad 39B by Danny Wyatt, NASA quality assurance specialist, at left; George Schram, USA mechanical technician, facing Kadenyuk; and Travis Thompson, USA orbiter vehicle closeout chief, at right. STS-87 is the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201. The 16-day mission will include the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment (CUE), a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia’s middeck and will feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on Brassica rapa seedlings
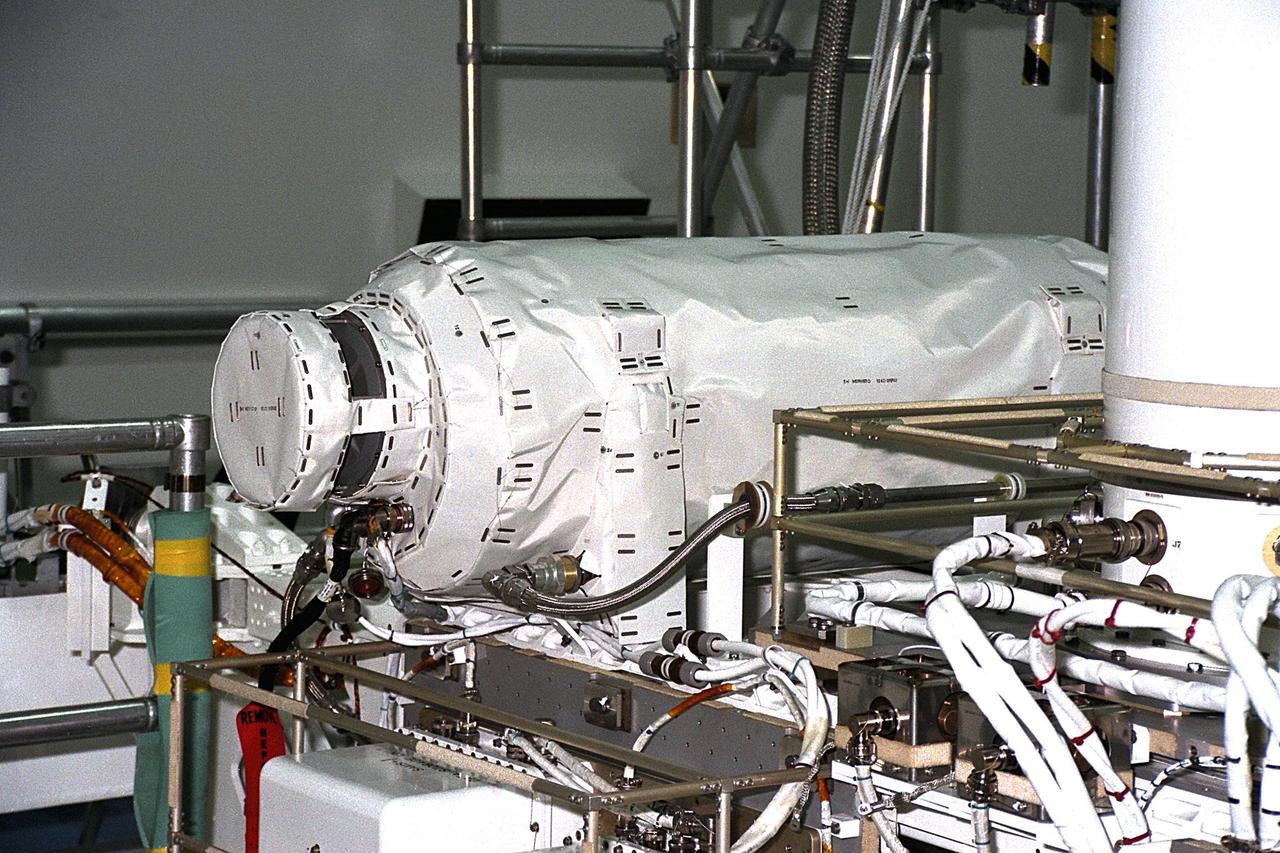
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). This horizontal tube is known as MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. This experiment, designed for the study of solidification (or freezing) during the growth cycle of liquid materials used for semiconductor crystals, aims to aid in the development of techniques for growing higher quality crystals on Earth. All STS-87 experiments are scheduled for launch on Nov. 19 from KSC
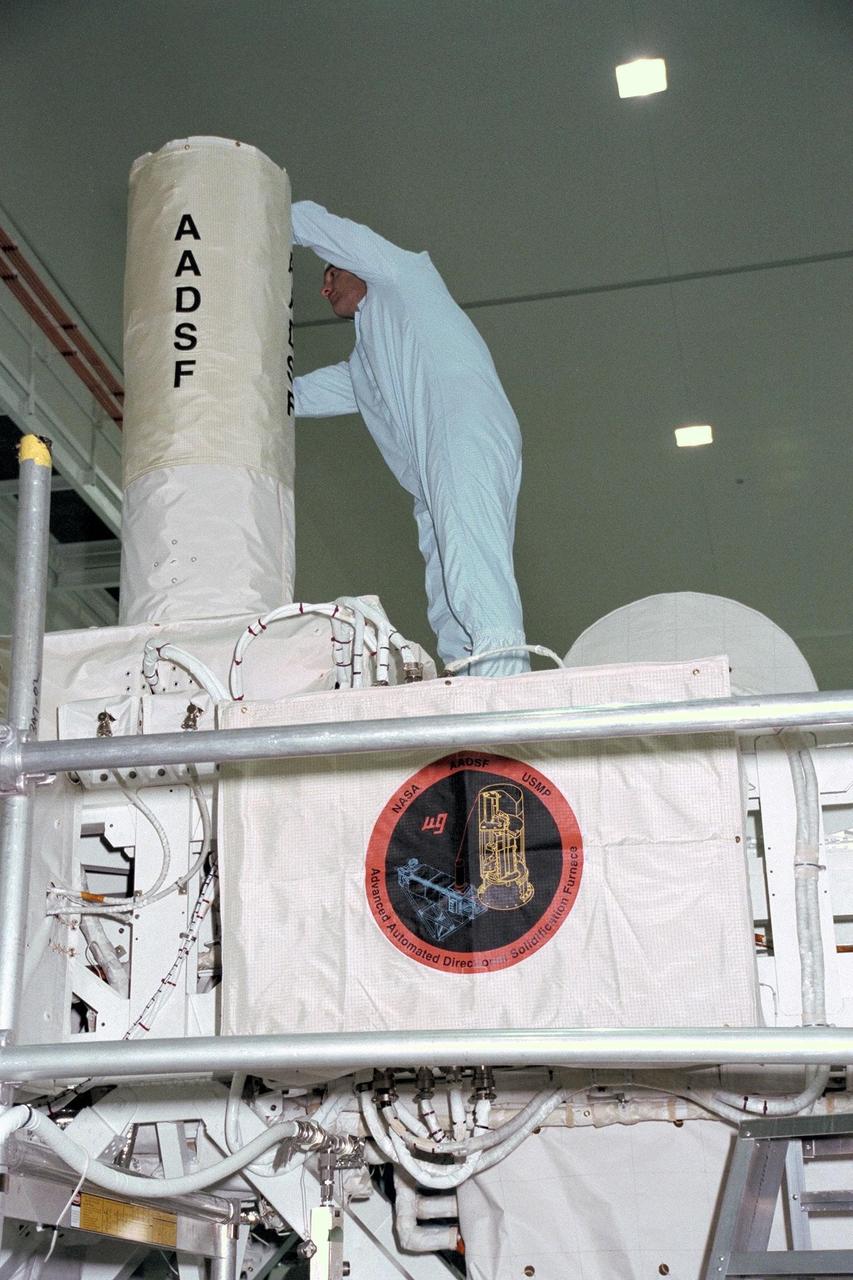

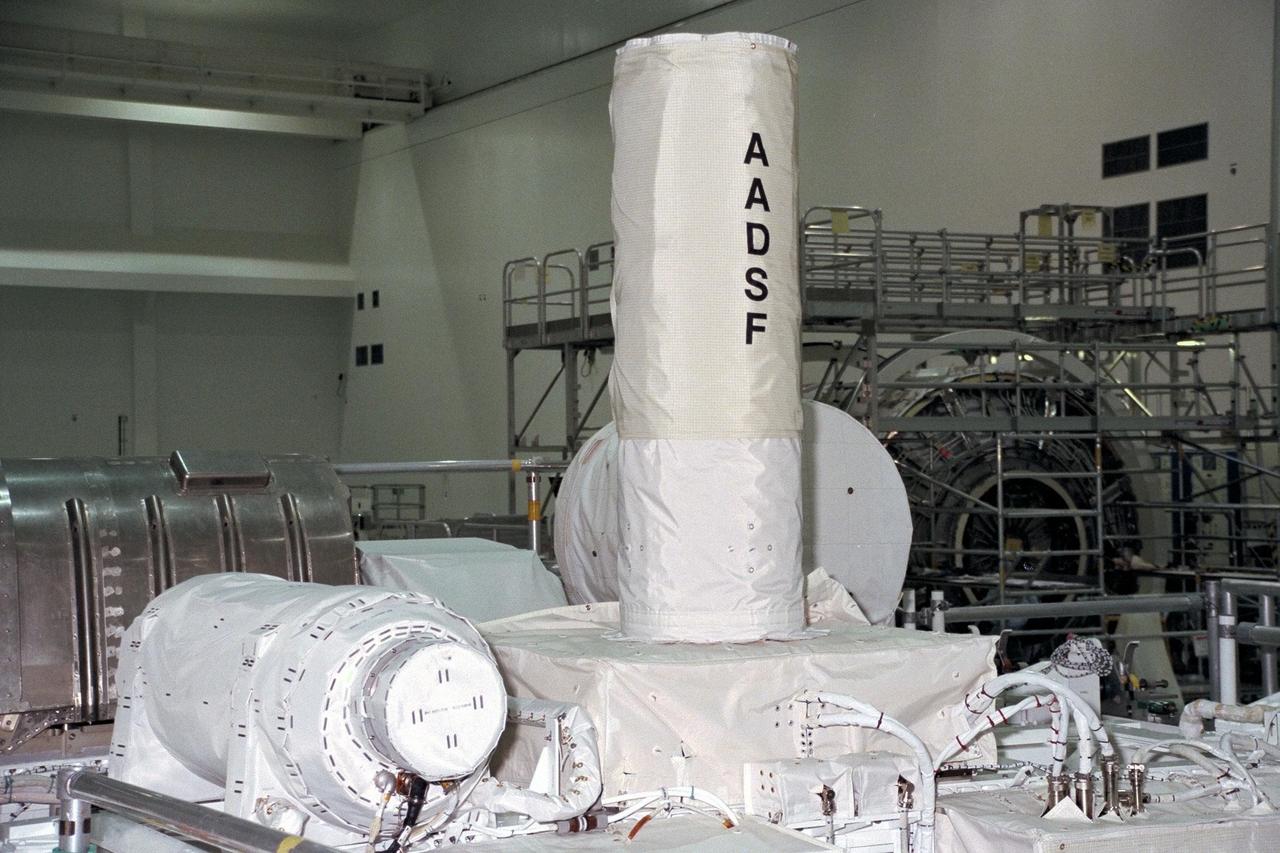
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). A technician is working on the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which will be used by researchers to study the solidification of semiconductor materials in microgravity. Scientists will be able to better understand how microgravity influences the solidification process of these materials and develop better methods for controlling that process during future Space flights and Earth-based production. All STS-87 experiments are scheduled for launch on Nov. 19 from KSC
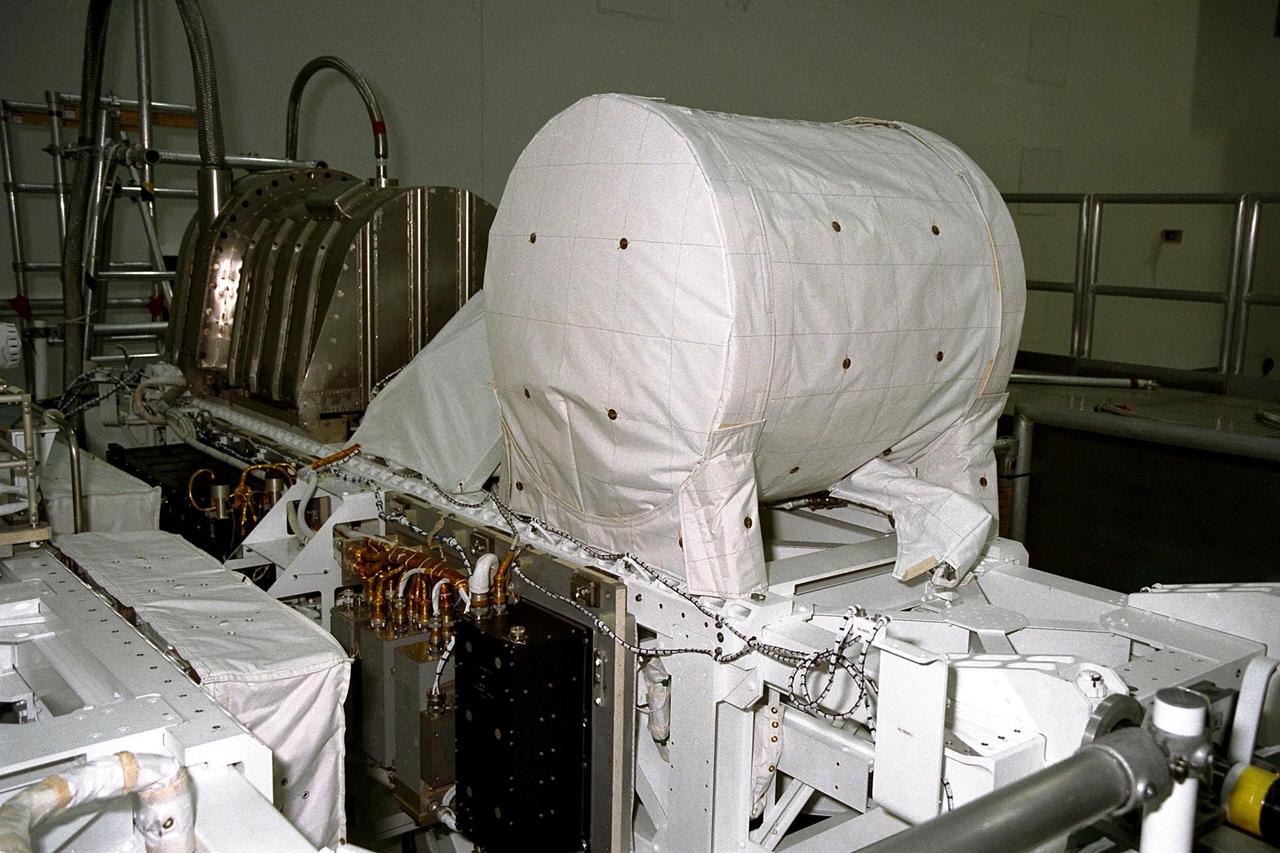

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. The metallic breadbox-like structure behind the IDGE is the Confined Helium Experiment (CHeX) that will study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between solid surface, and microgravity. These experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
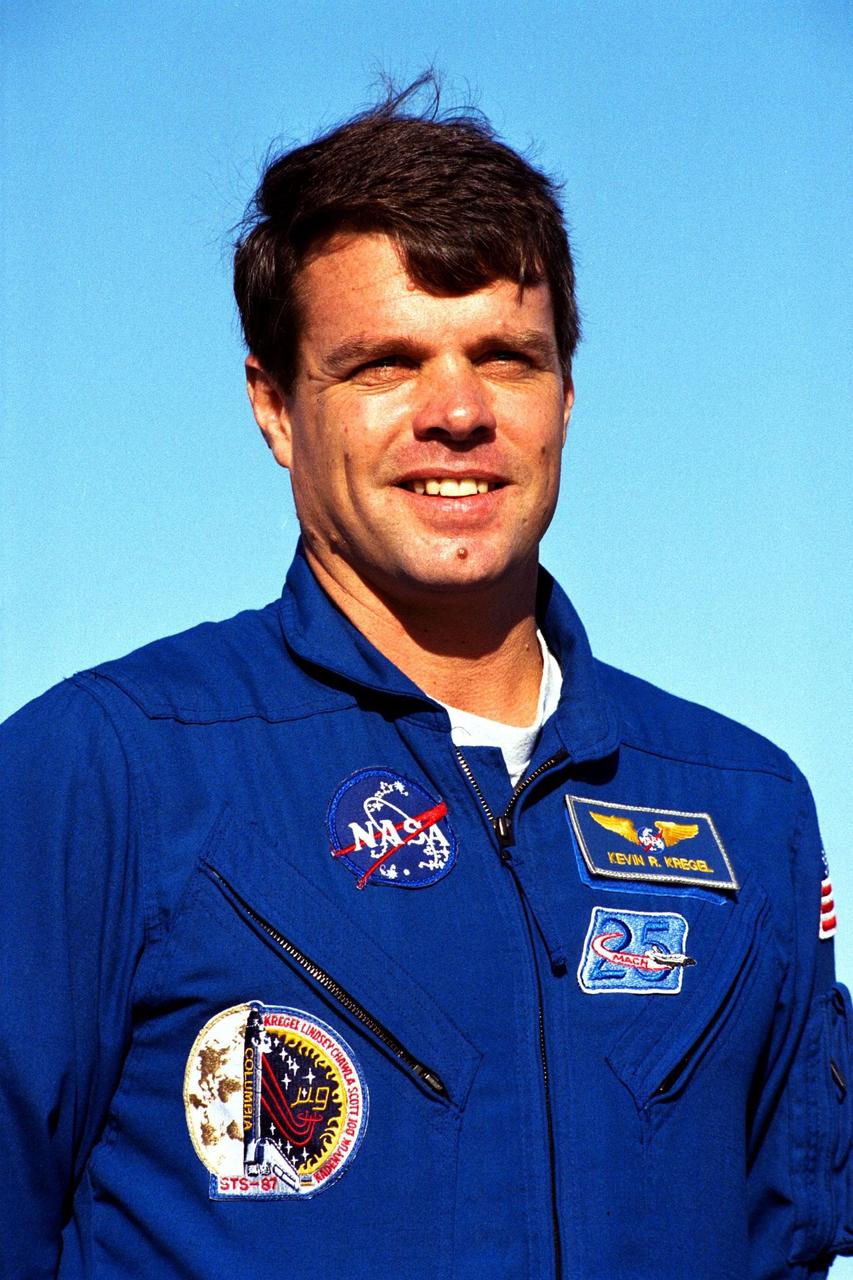

Kevin Kregel, commander of the STS-87 crew, participates in a news briefing at Launch Pad 39B during the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Selected by NASA in 1992, Kregel is a veteran of two space flights (STS-70 and 78) and has logged over 618 hours in space. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-87 is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from pad 39B at KSC

STS-87 Mission Specialist Winston Scott poses in his orange launch and entry spacesuit with NASA suit technicians at Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. Scott will be performing an extravehicular activity (EVA) spacewalk during the mission. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
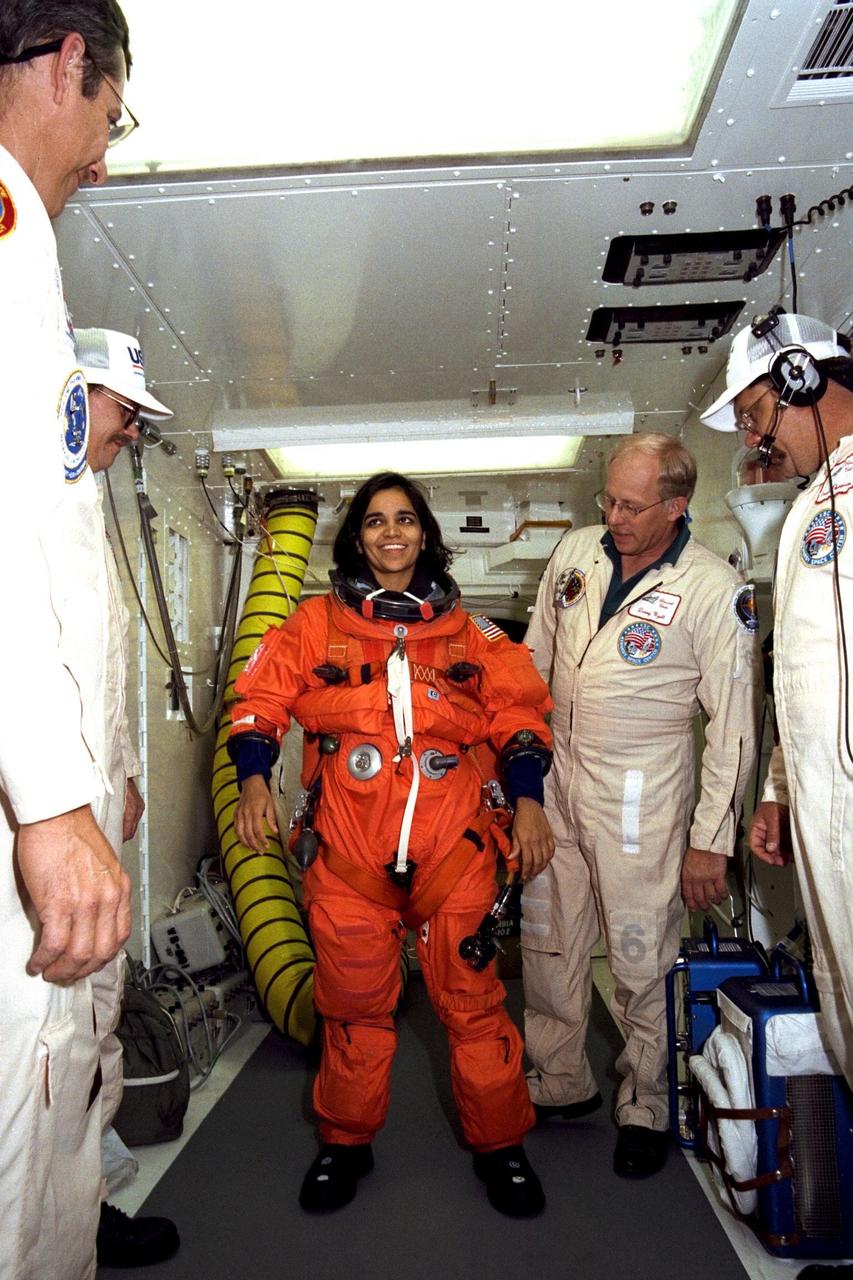

STS-87 Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., is assisted with her orange launch and entry spacesuit by NASA suit technicians at Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU) is assisted with his orange launch and entry spacesuit by NASA suit technicians at Launch Pad 39B during Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
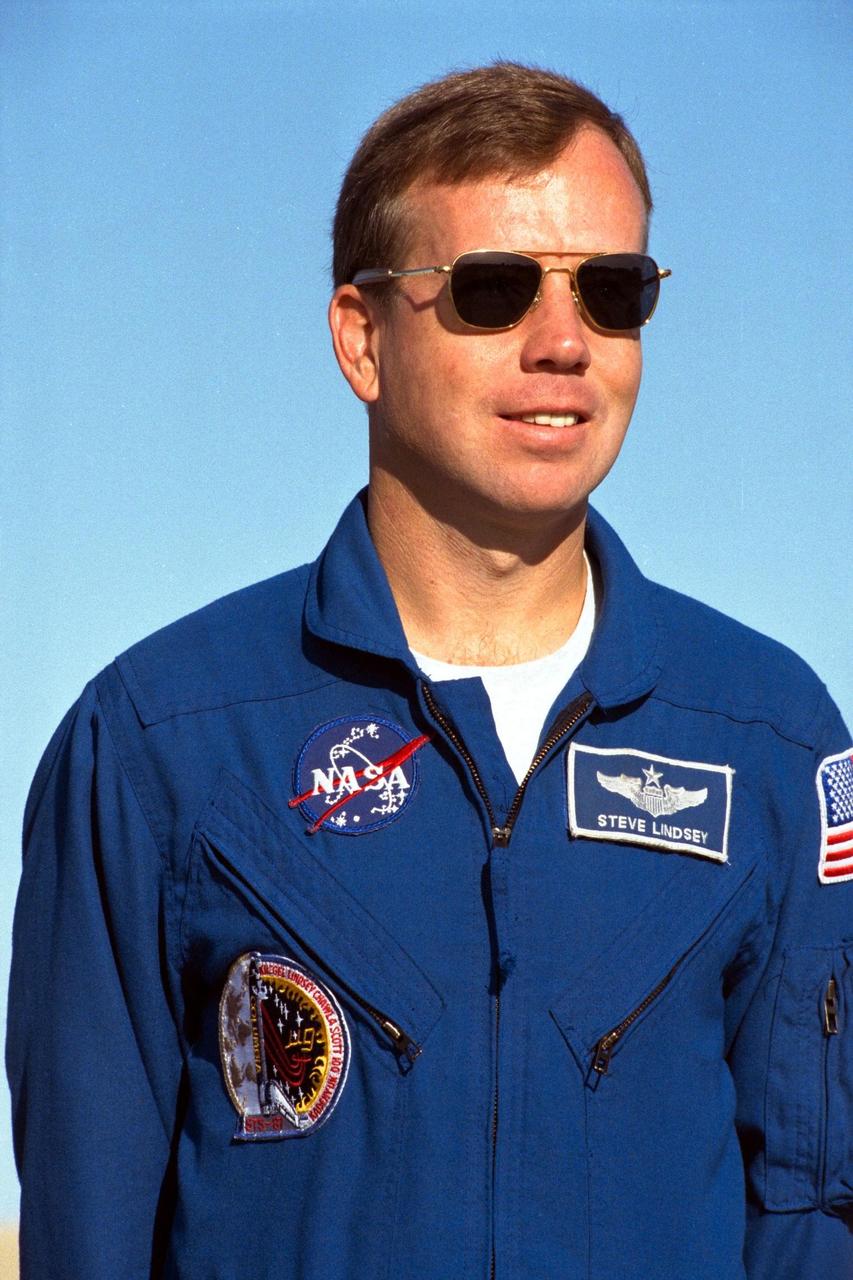

Steven Lindsey, the pilot of the STS-87 crew, participates in a news briefing at Launch Pad 39B during the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). A major in the U.S. Air Force, Lindsey became an astronaut in May 1996. This is his first flight on the Space Shuttle, but he previously has logged more than 2,700 hours of flying time in 49 different types of aircraft. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-87 is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from pad 39B at KSC
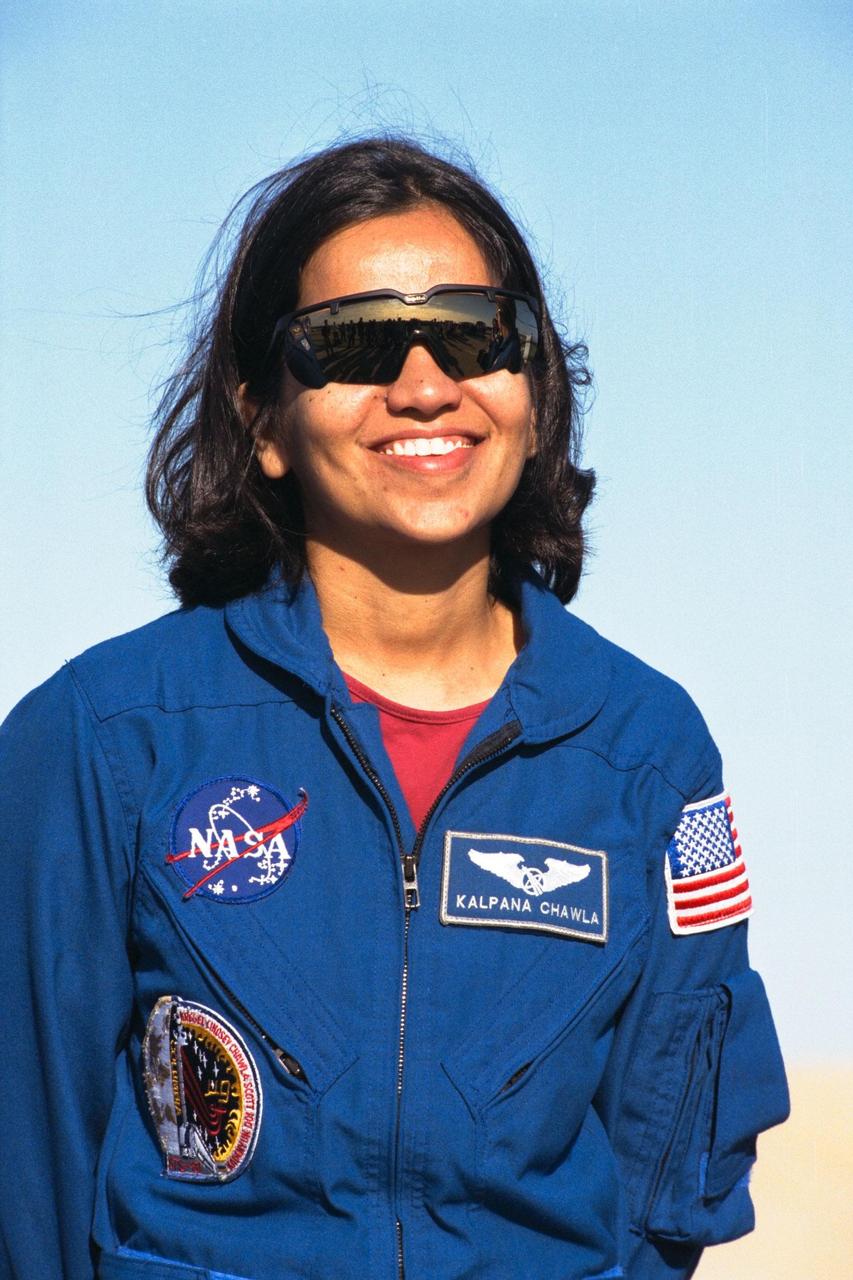

Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., a mission specialist of the STS-87 crew, participates in a news briefing at Launch Pad 39B during the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). First-time Shuttle flier Dr. Chawla reported for training as an astronaut at Johnson Space Center in 1995. She has a doctorate in aerospace engineering from the University of Colorado. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-87 is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from pad 39B at KSC
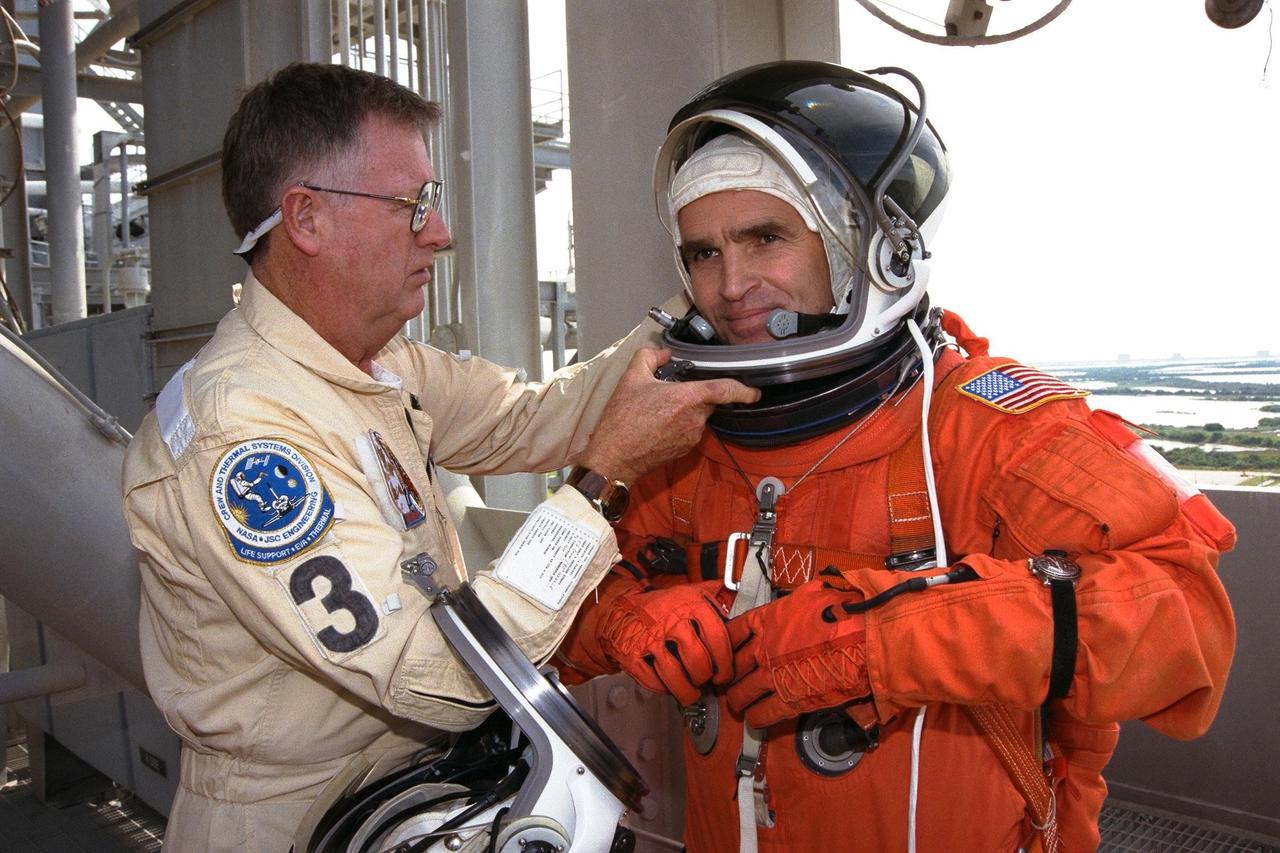

STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk, at right, of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU) is assisted into his orange launch and entry spacesuit ensemble by NASA Suit Technician Al Rochford, at left, before participating in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The crew of the STS-87 mission is scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
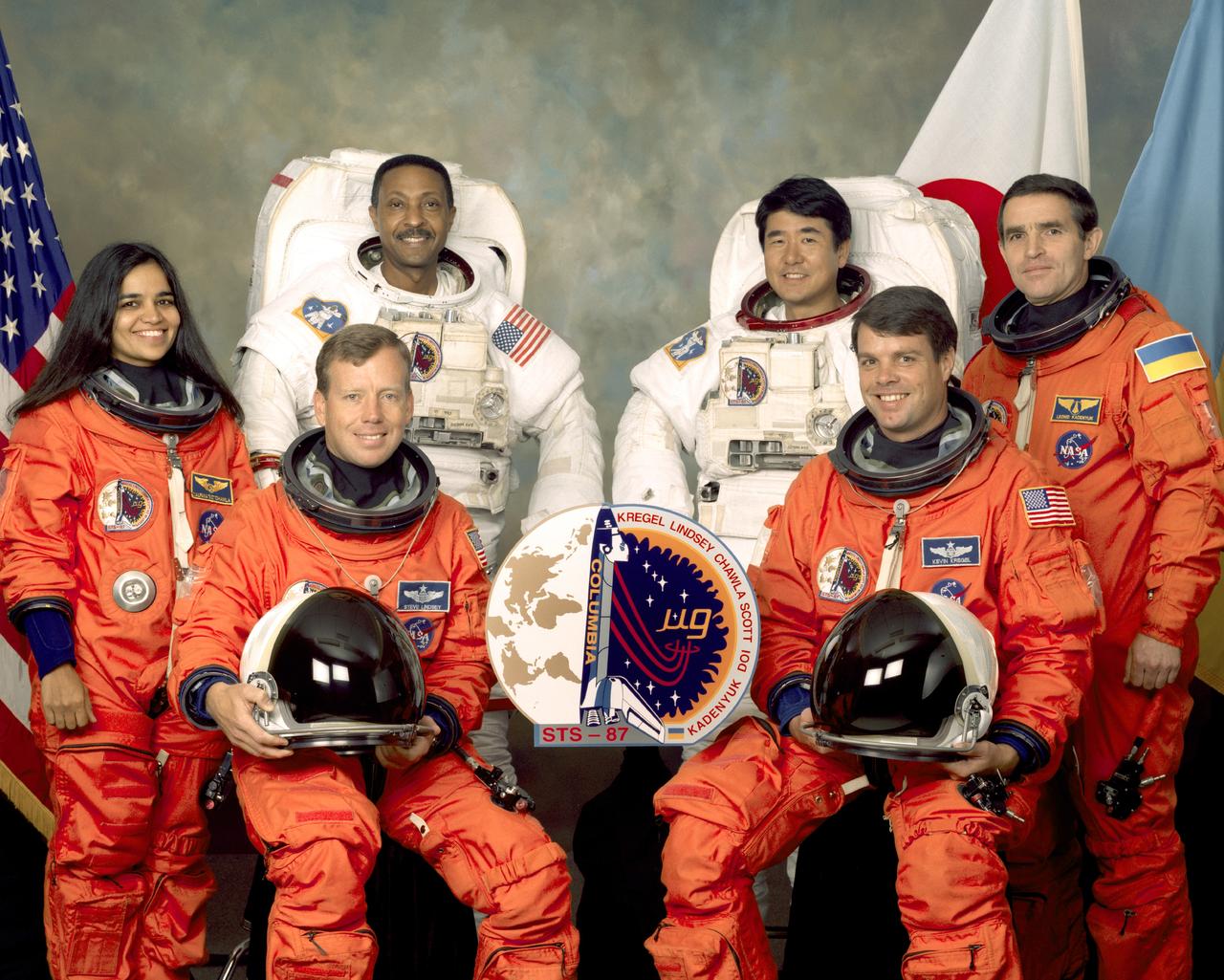

Five astronauts and a payload specialist take a break from training at the Johnson Space Center (JSC) to pose for the STS-87 crew portrait. Wearing the orange partial pressure launch and entry suits, from the left, are Kalpana Chawla, mission specialist; Steven W. Lindsey, pilot; Kevin R. Kregel, mission commander; and Leonid K. Kadenyuk, Ukrainian payload specialist. Wearing the white Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) space suits are mission specialists Winston E. Scott (left) and Takao Doi (right). Doi represents Japan’s National Space Development Agency (NASDA). The STS-87 mission launched aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia on November 19, 1997. The primary payload for the mission was the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4).

The crew of STS-87 pose with their spouses in front of Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Pad 39B during final prelaunch activities leading up to the scheduled Nov. 19 liftoff. From left to right are: Vera Kadenyuk, wife of Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine who is next to Vera; Mission Specialist Winston Scott and his wife, Marilyn; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan, and his wife, Hitomi; Jeannie Kregel, who is married to Commander Kevin Kregel standing next to her; Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., and her husband, Jean-Pierre Harrison; and Pilot Steven Lindsey and his wife Diane. STS-87 will be the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite
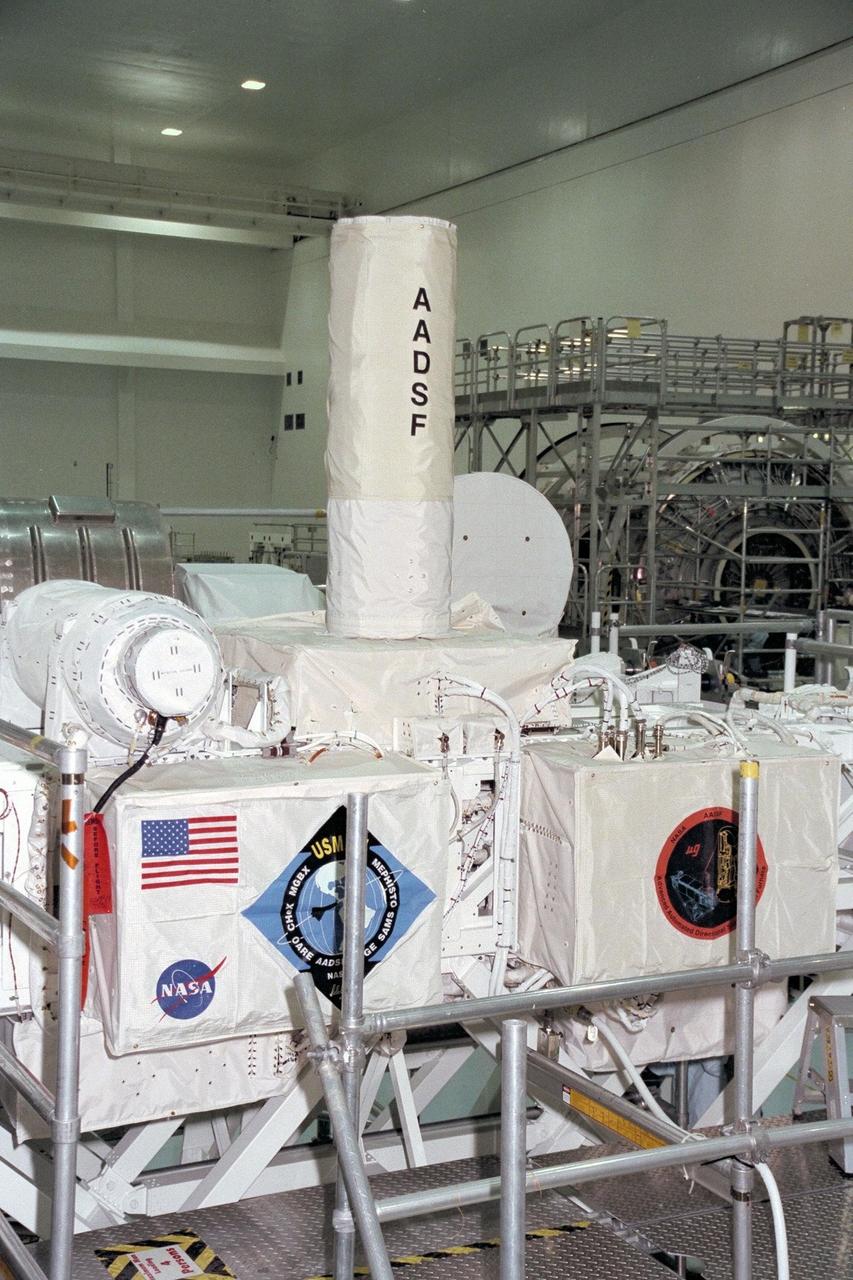
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube to the left of it is MEPHISTO, a French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Seen at right behind the AADSF in the circular white cover is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
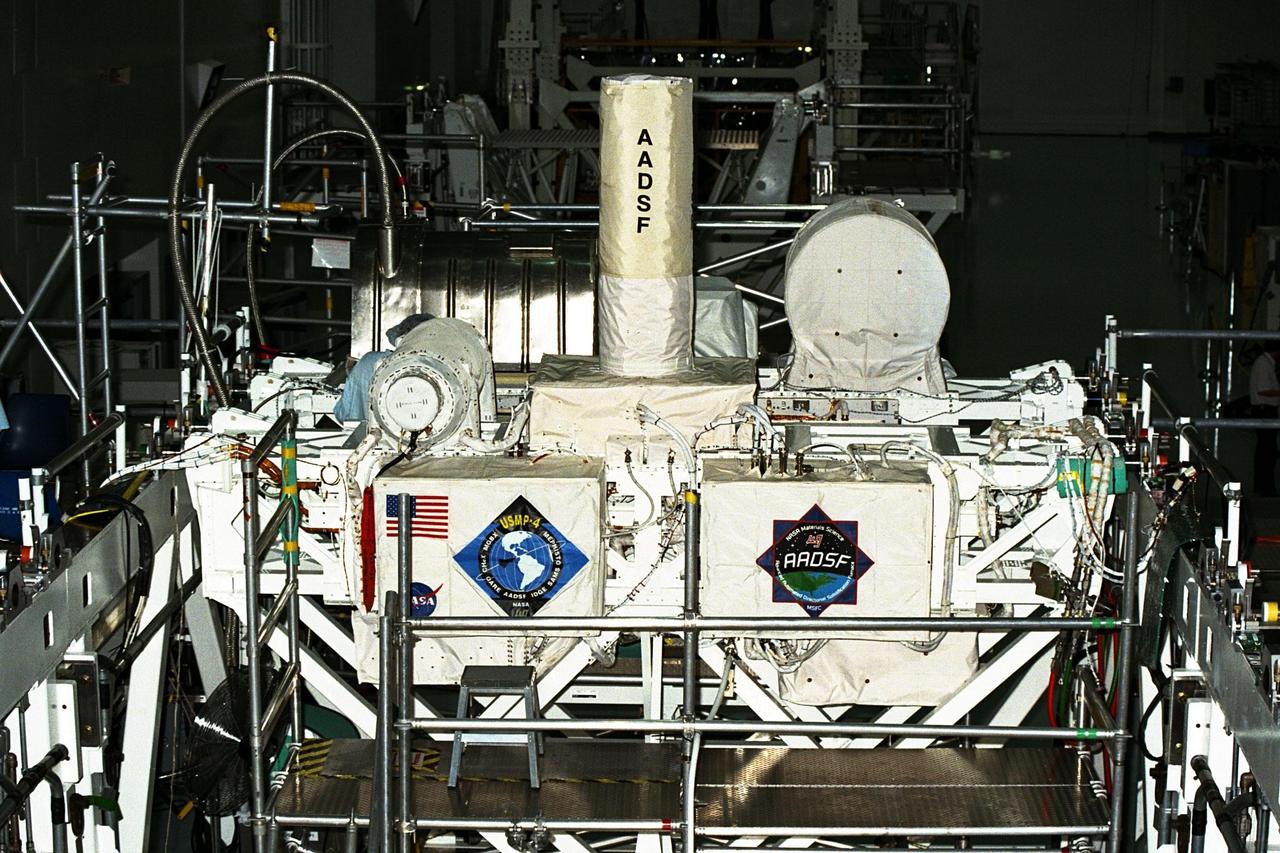
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at left is the USMP-4 logo with the acronyms of its experiments. Above the American flag at left is the MEPHISTO experiment, a cooperative American and French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which is a sophisticated materials science facility used for studying a common method of processing semiconductor crystals called directional solidification. The white horizontal tube to the right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. All USMP-4 experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The large white vertical cylinder in the middle of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube to its left is MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Seen to the right of the AADSF is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The vertical tube in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which will be used by researchers to study the solidification of semiconductor materials in microgravity. Scientists will be able to better understand how microgravity influences the solidification process of these materials and develop better methods for controlling that process during future Space flights and Earth-based production. To its left is MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. All STS-87 experiments are scheduled for launch on Nov. 19 from KSC
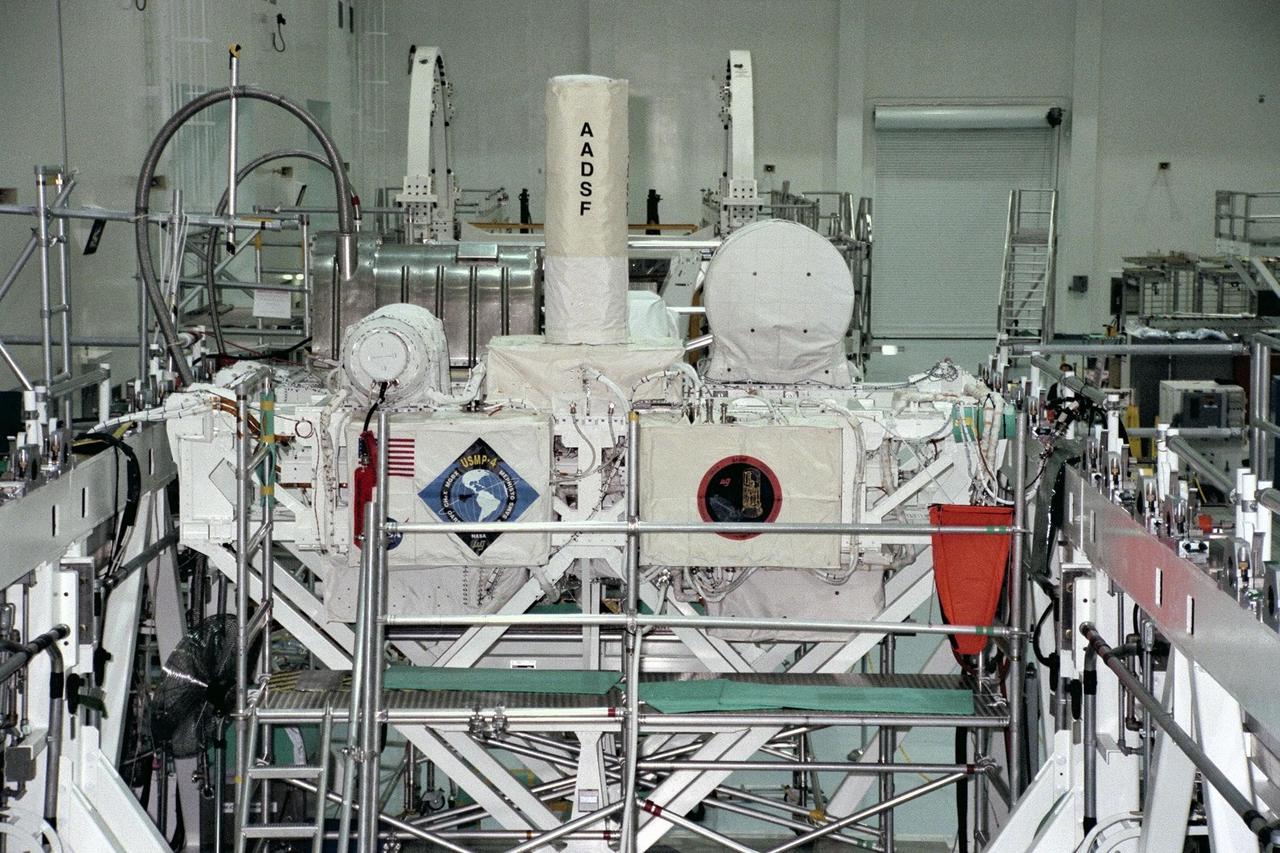
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at right is the USMP-4 logo with the acronyms of its experiments. Above the American flag at left is the MEPHISTO experiment, a cooperative American and French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Scientists will study changes in solidification rates, temperature, and interface shape of an alloy to understand how these changes affect composition and properties of the metal produced. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All USMP-4 experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
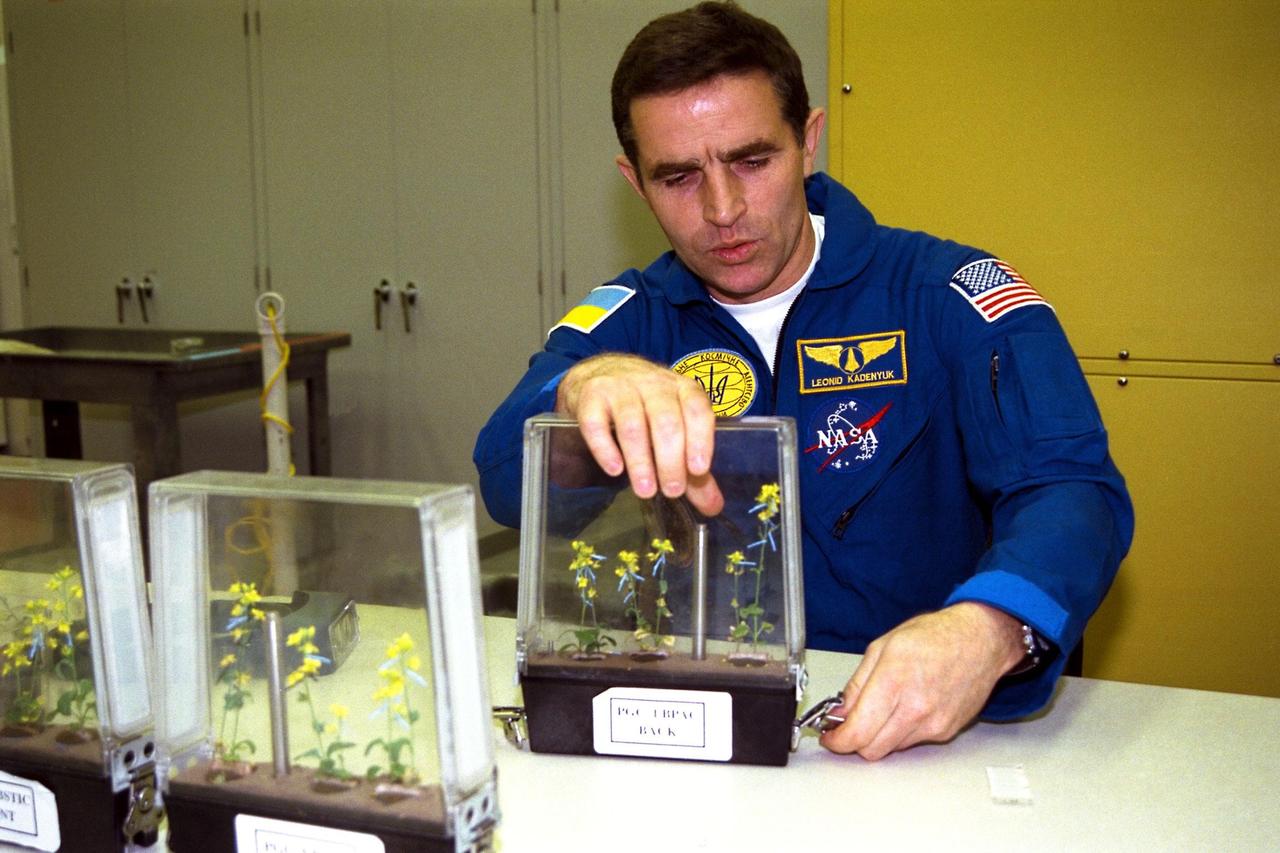

Participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center is STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU). Here, Cosmonaut Kadenyuk is inspecting flowers for pollination and fertilization, which will occur as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia during its 16-day mission, scheduled to take off from KSC’s Launch Pad 39-B on Nov. 19. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia’s middeck and feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on the pollinating Brassica rapa seedlings. Students in Ukrainian and American schools will participate in the same experiment on the ground and have several live opportunities to discuss the experiment with Kadenyuk in Space. Kadenyuk of the Ukraine will be flying his first Shuttle mission on STS-87
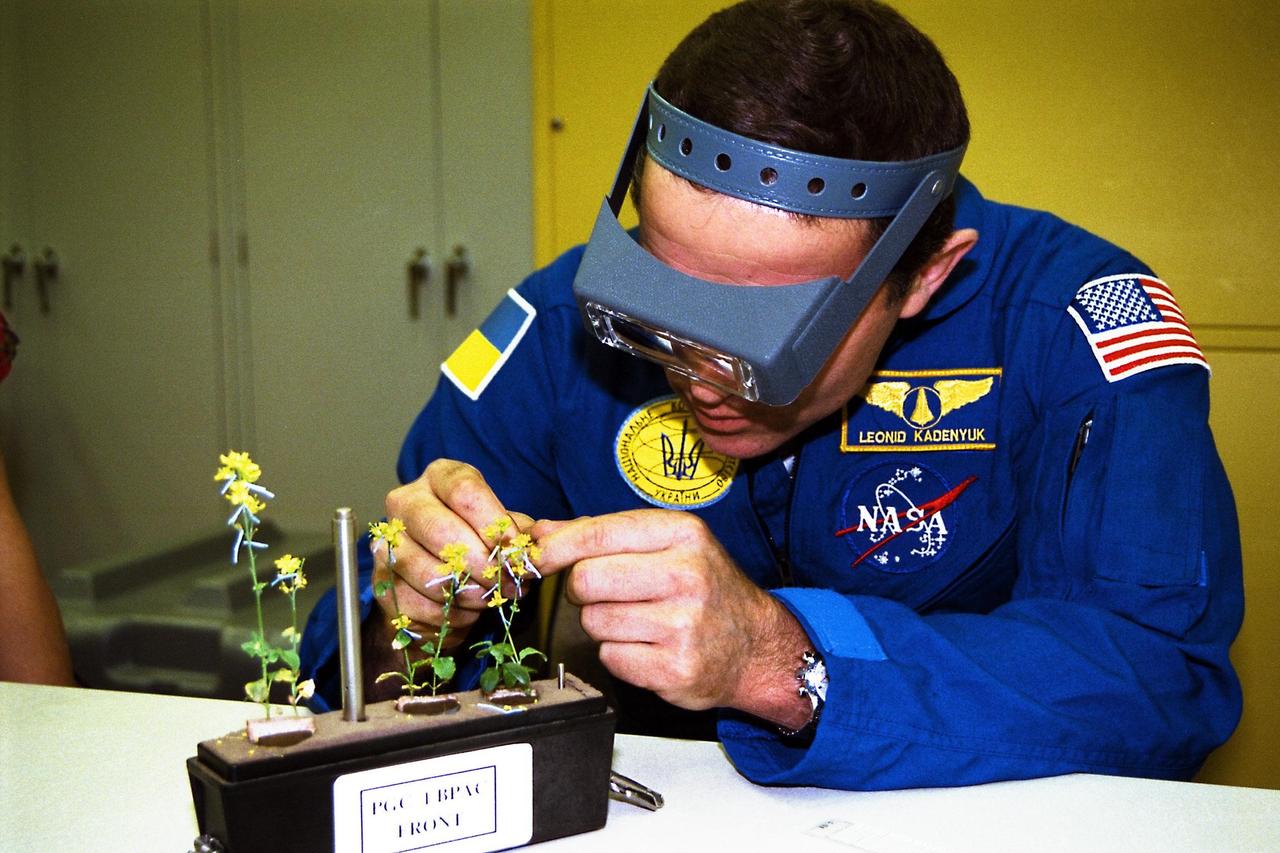

Participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT) at Kennedy Space Center is STS-87 Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU). Here, Cosmonaut Kadenyuk is inspecting flowers for pollination and fertilization, which will occur as part of the Collaborative Ukrainian Experiment, or CUE, aboard Columbia during its 16-day mission, scheduled to take off from KSC’s Launch Pad 39-B on Nov. 19. The CUE experiment is a collection of 10 plant space biology experiments that will fly in Columbia’s middeck and feature an educational component that involves evaluating the effects of microgravity on the pollinating Brassica rapa seedlings. Students in Ukrainian and American schools will participate in the same experiment on the ground and have several live opportunities to discuss the experiment with Kadenyuk in Space. Kadenyuk of the Ukraine will be flying his first Shuttle mission on STS-87
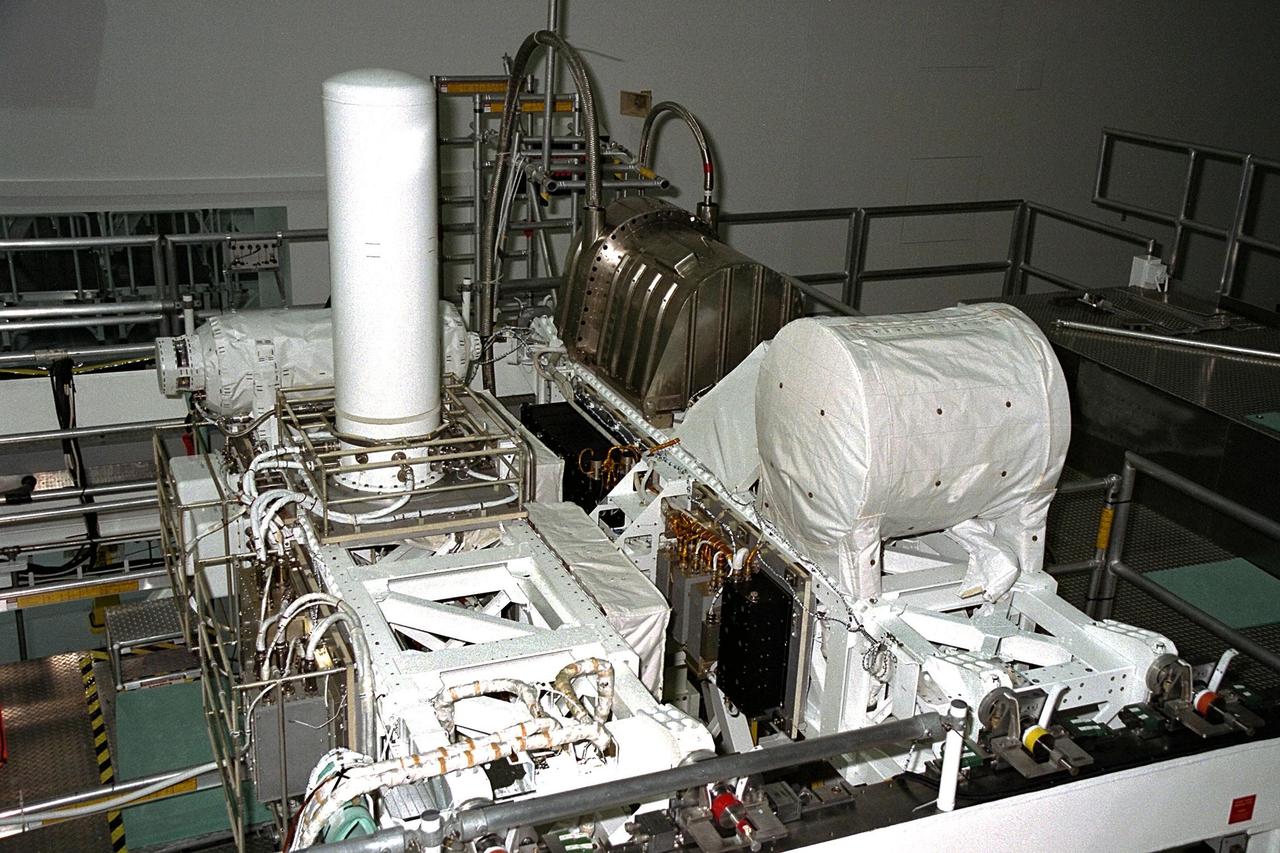

United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. The metallic breadbox-like structure behind the IDGE is the Confined Helium Experiment (CHeX) that will study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between solid surfaces and microgravity. The large white vertical cylinder at left is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube behind it is MEPHISTO, the French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Just below the left end of MEPHISTO is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
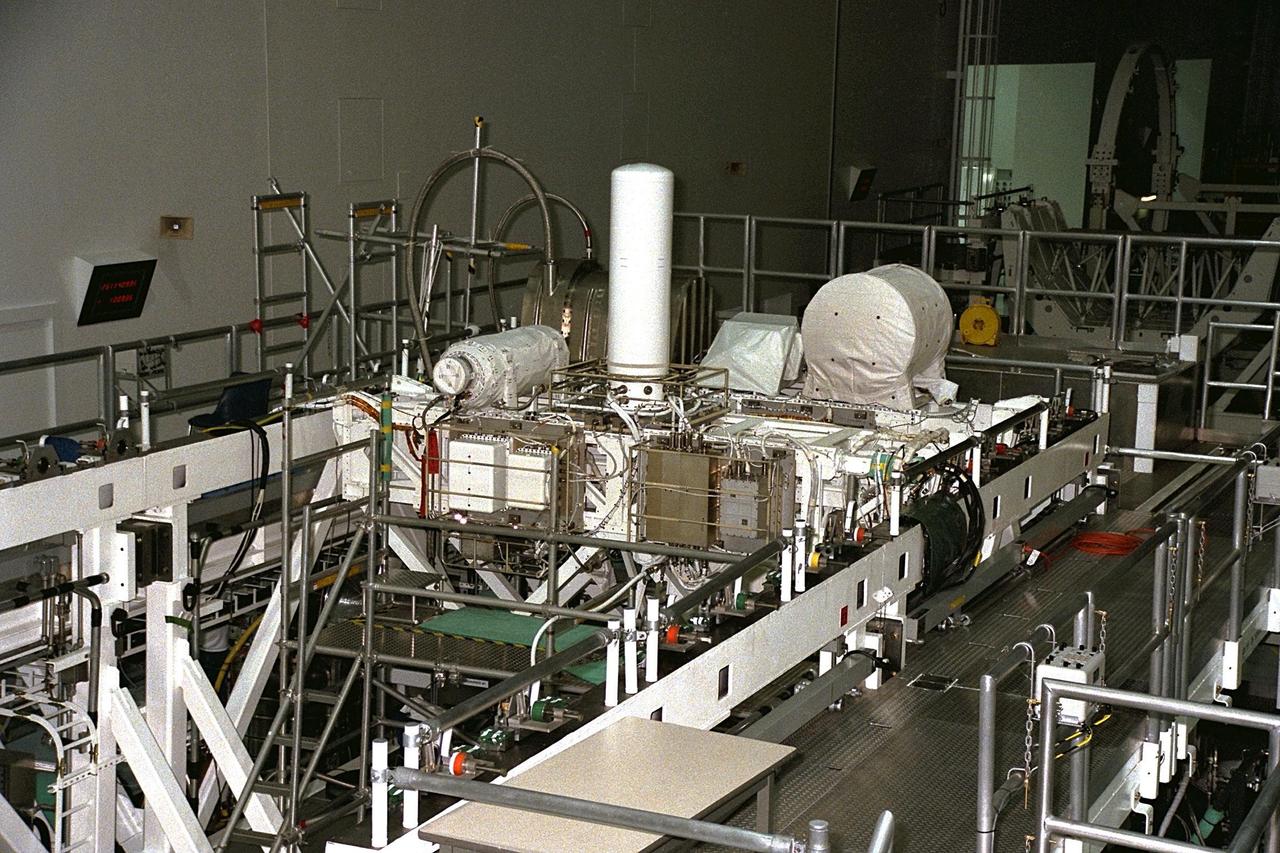
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen at right in the circular white cover is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment. The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) and the horizontal tube to the left of it is MEPHISTO, a French acronym for a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Just below MEPHISTO is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. The The metallic breadbox-like structure behind the AADSF is the Confined Helium Experiment (CHeX) that will study one of the basic influences on the behavior and properties of materials by using liquid helium confined between solid surfaces and microgravity. All of these experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
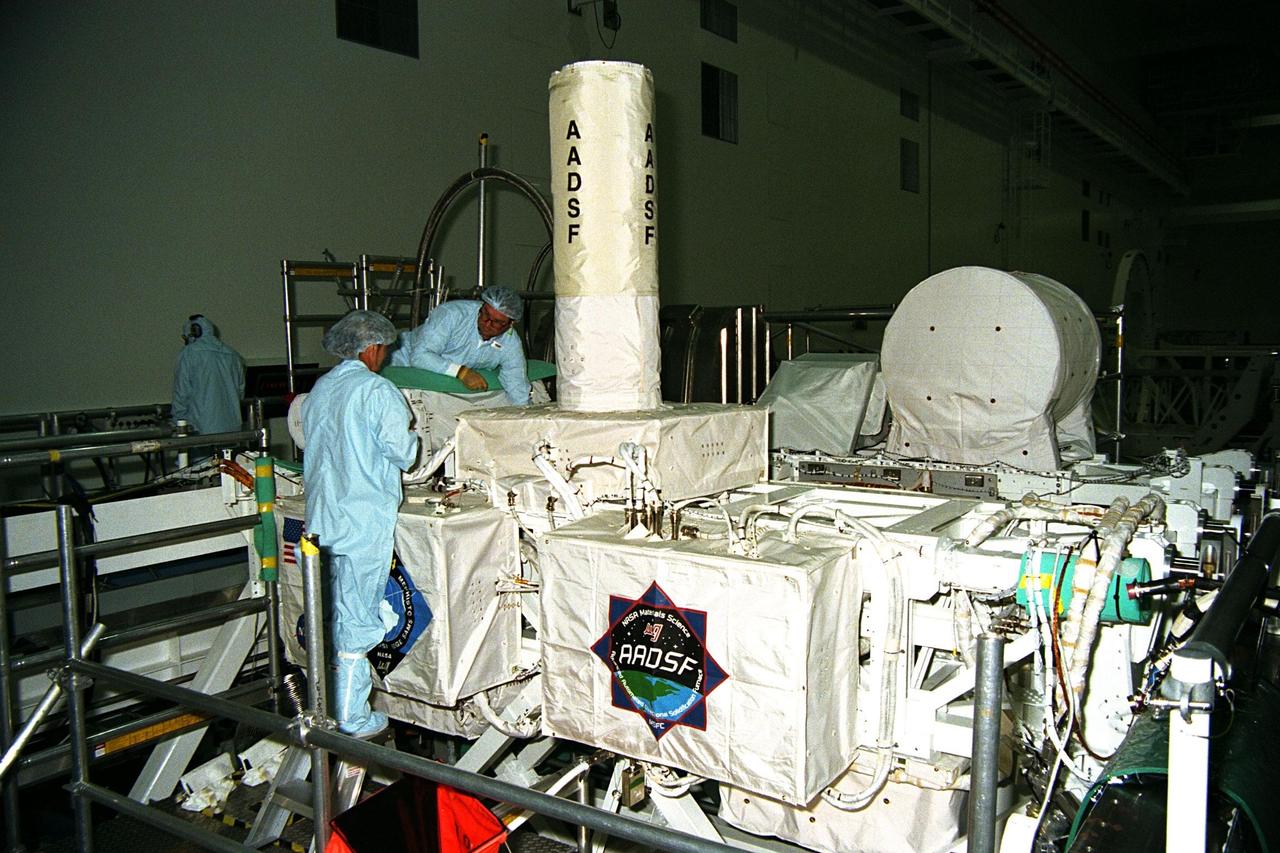

Technicians are monitoring experiments on the United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) in preparation for its scheduled launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from Kennedy Space Center (KSC). USMP-4 experiments are prepared in the Space Station Processing Facility at KSC. The large white vertical cylinder in the center of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF), which is a sophisticated materials science facility used for studying a common method of processing semiconductor crystals called directional solidification. The white horizontal tube to the right is the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), which will be used to study the dendritic solidification of molten materials in the microgravity environment
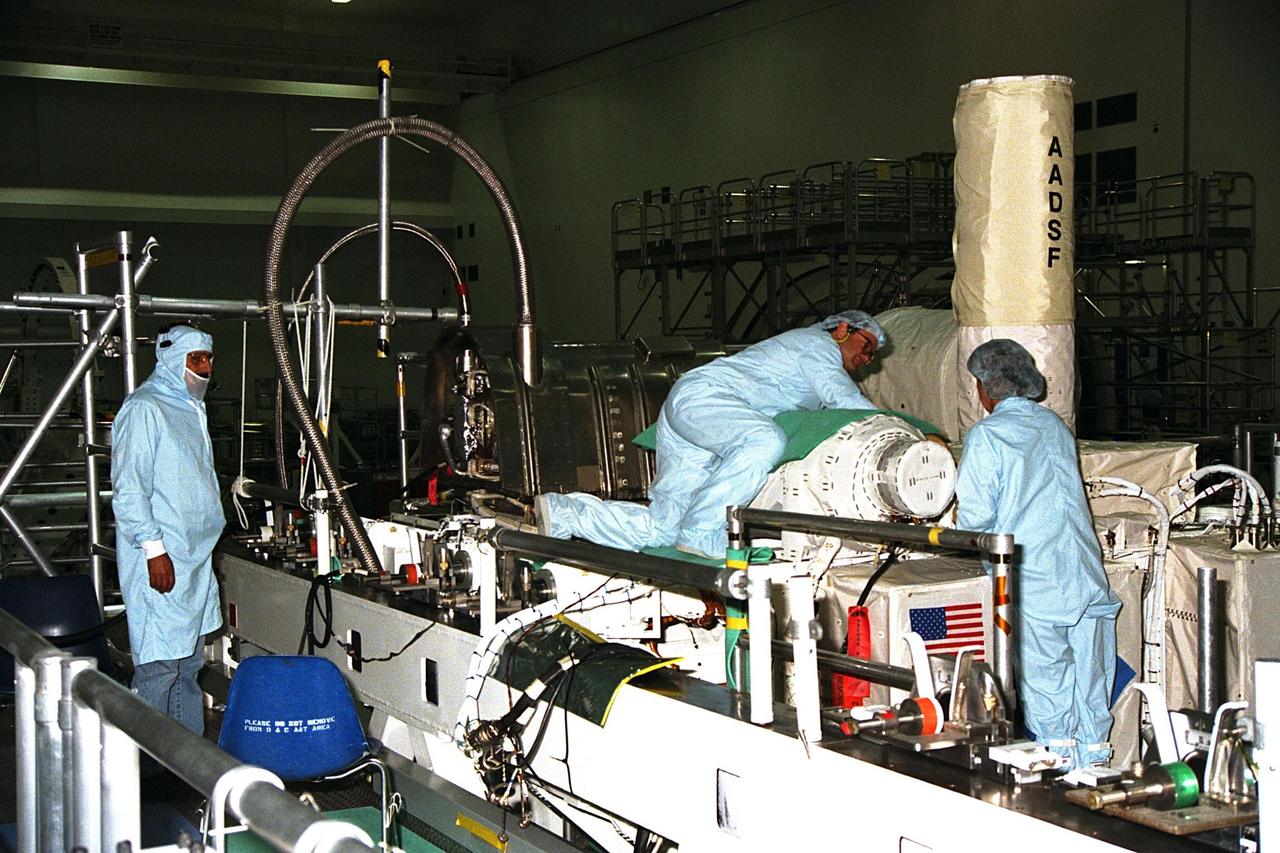

Technicians are monitoring experiments on the United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) in preparation for its scheduled launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from Kennedy Space Center (KSC). USMP-4 experiments are prepared in the Space Station Processing Facility at KSC. The large white vertical cylinder at the right of the photo is the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF ), which is a sophisticated materials science facility used for studying a common method of processing semiconductor crystals called directional solidification. The technician in the middle of the photo is leaning over MEPHISTO, a cooperative American-French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth

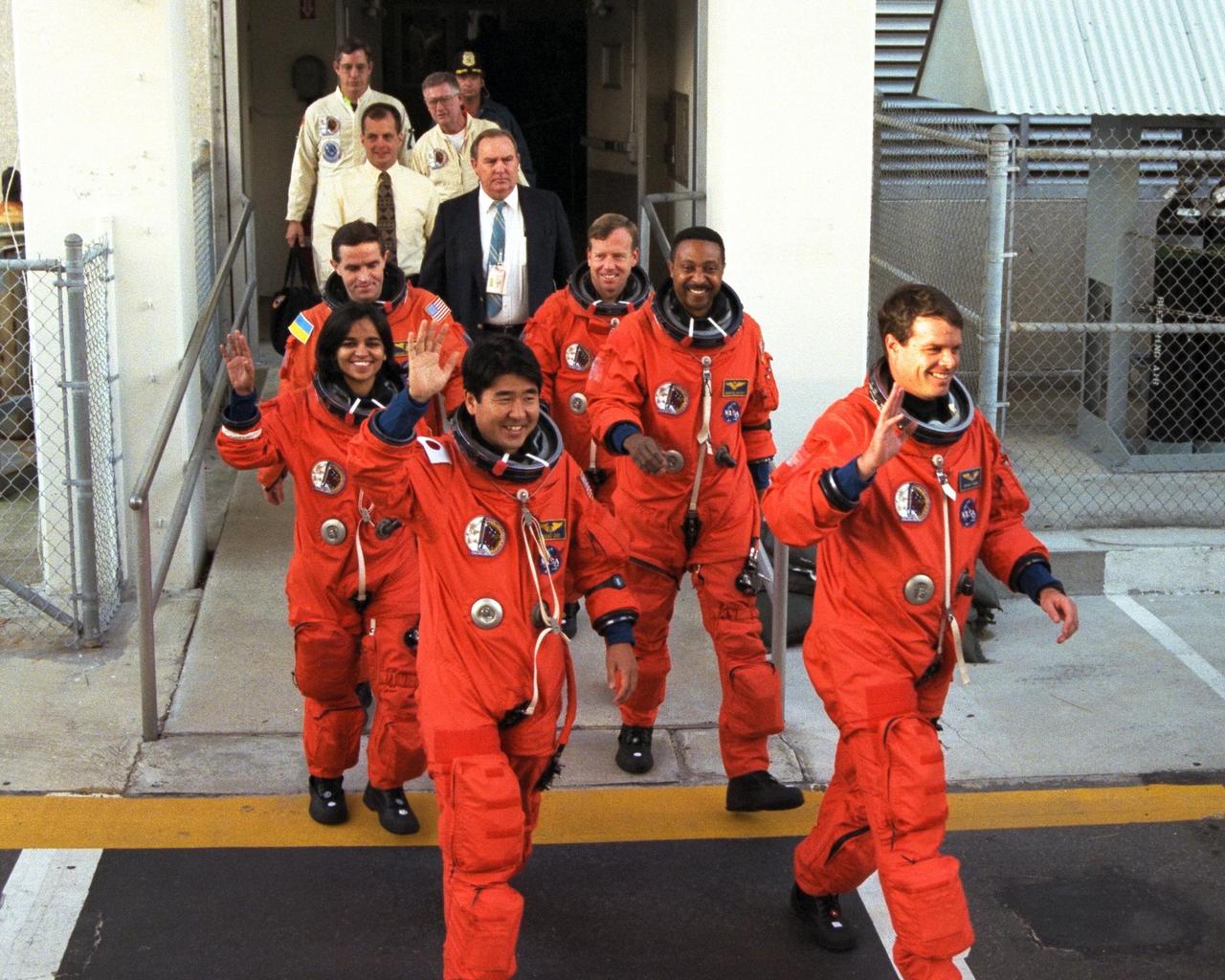
The crew of Mission STS-87 depart from the Operations and Checkout Building en route to Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. They are, from left to right, front to back: Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Mission Specialist Winston Scott (near van); Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine; and Pilot Steven Lindsey (near van). Missing from this photo are Commander Kevin Kregel and Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D. The Space Shuttle Columbia and its crew of six members are scheduled to lift off during a two-and-a-half hour launch window, which opens at 2:46 p.m
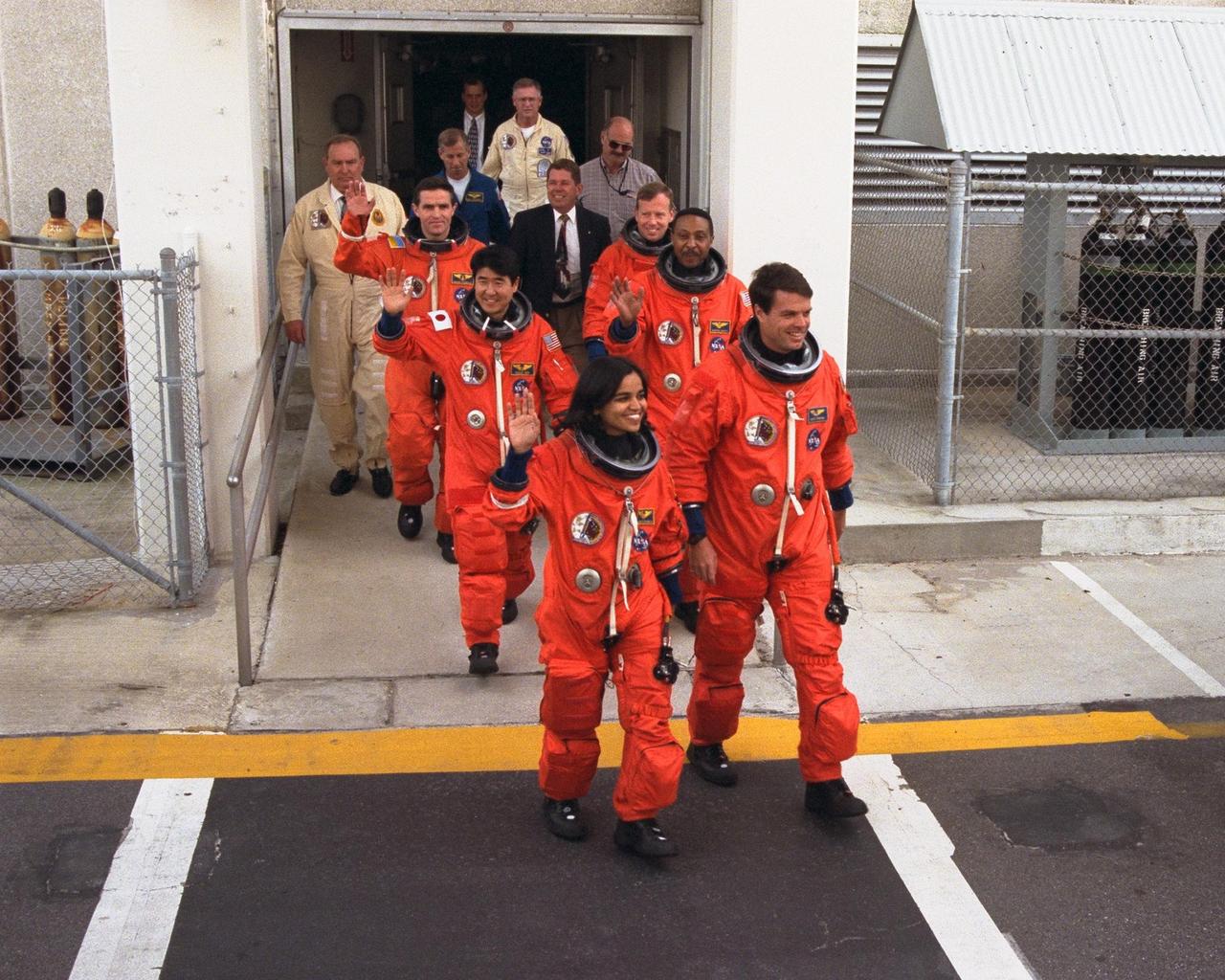

The crew of Mission STS-87 depart from the Operations and Checkout Building en route to Launch Pad 39B, where the Space Shuttle Columbia awaits liftoff on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and the Spartan-201 deployable satellite. Leading the way are, from left to right, front to back: Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Commander Kevin Kregel; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Mission Specialist Winston Scott; Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine; and Pilot Steven Lindsey. The Space Shuttle Columbia and its crew of six members are scheduled to lift off during a two-and-a-half hour launch window, which opens at 2:46 p.m
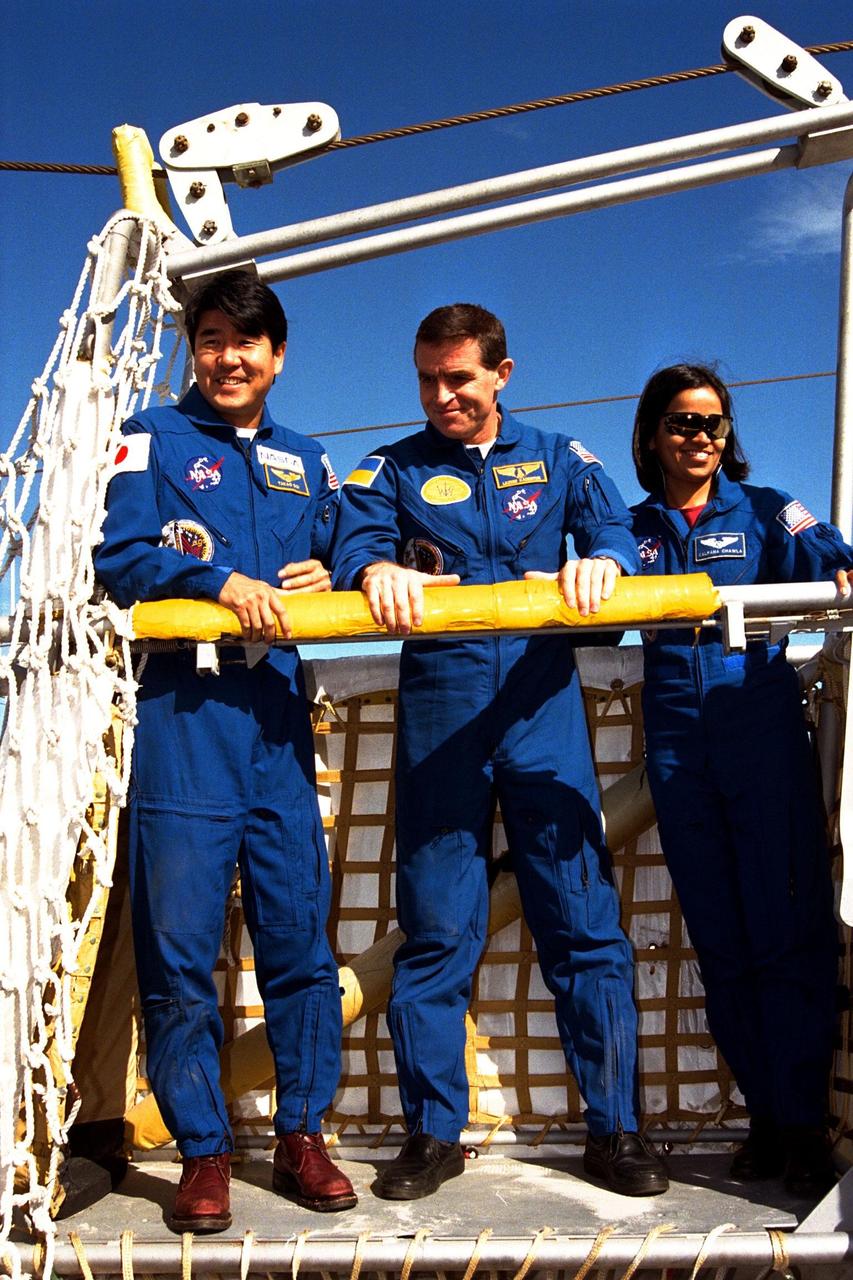

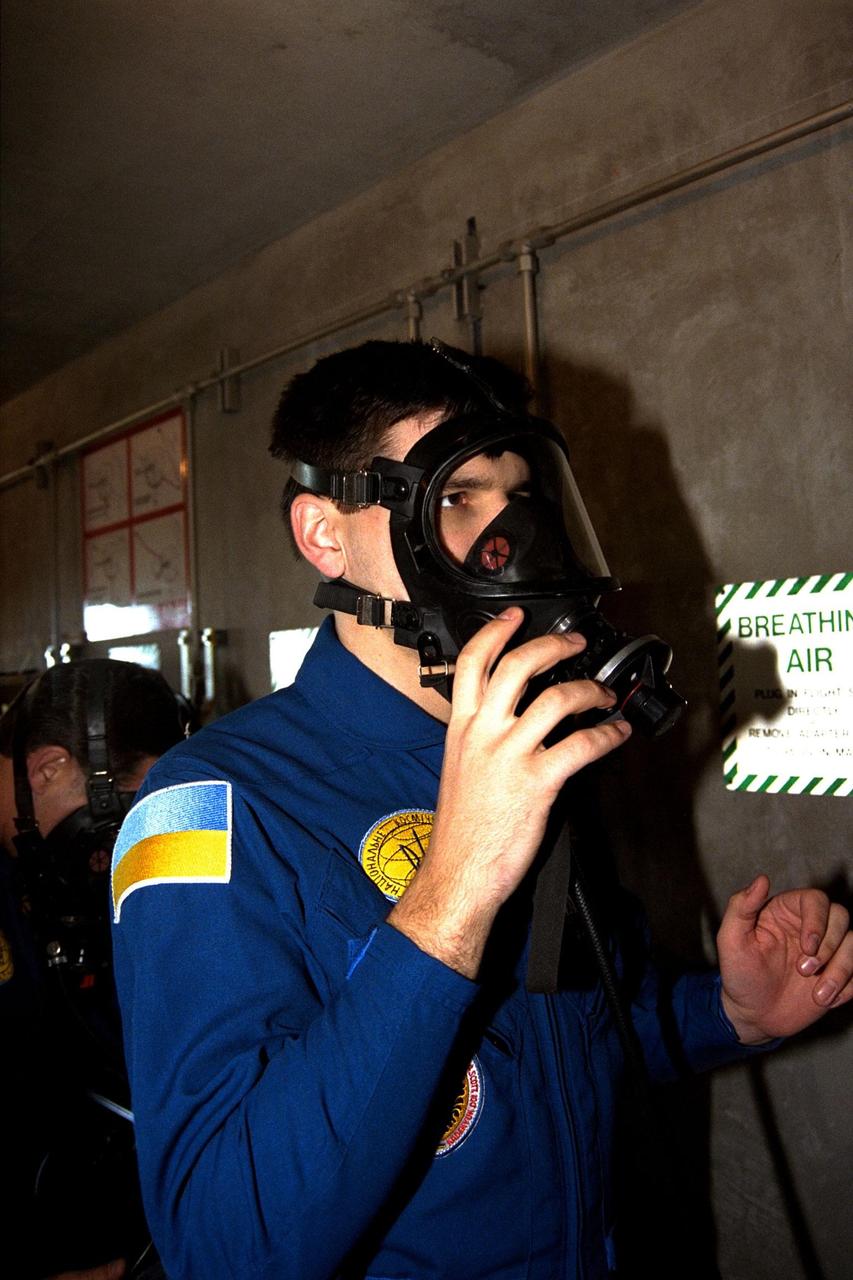
The crew of the STS-87 mission, scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center (KSC), participates in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at KSC. Testing a slidewire basket that is part of the pad’s emergency egress system are, from left, Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU); and Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
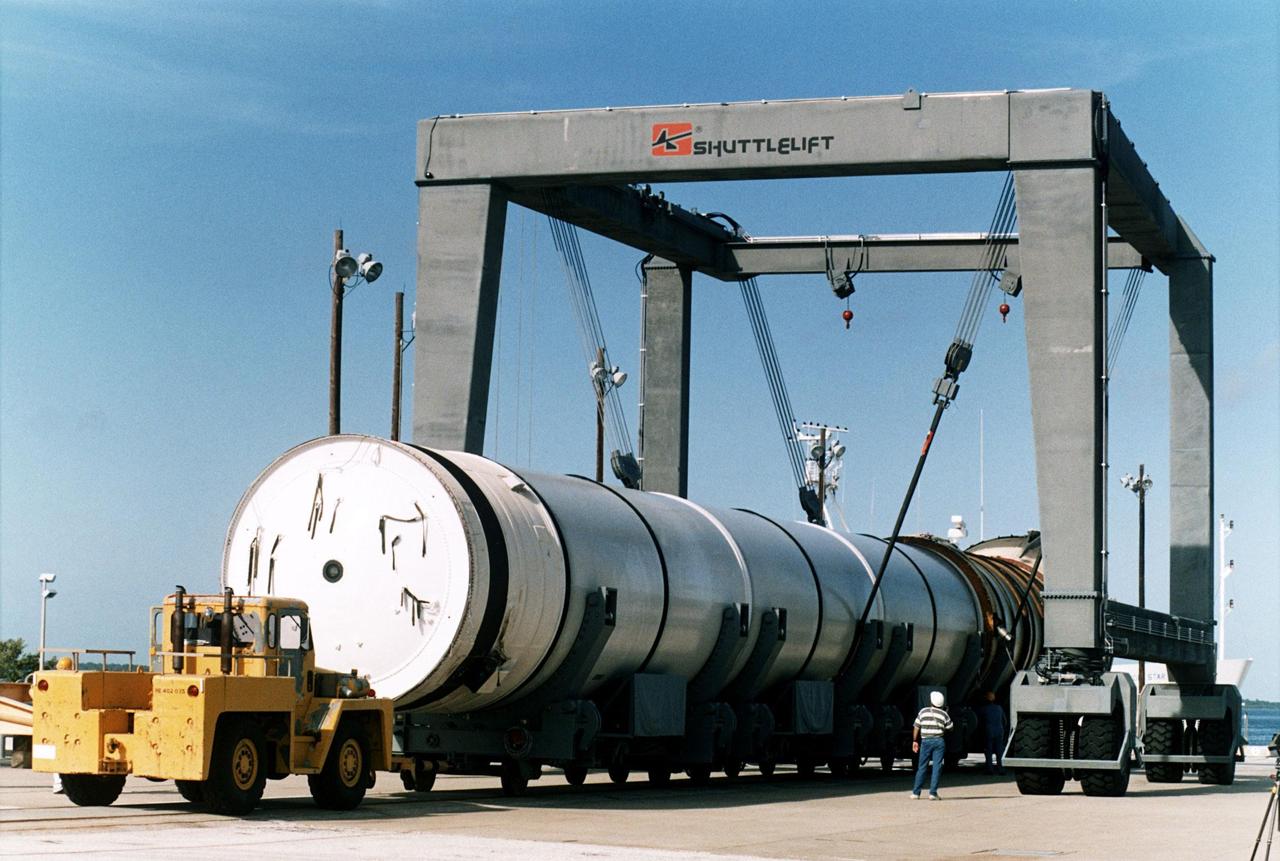

A spent solid rocket booster (SRB) from the STS-87 launch on Nov. 19 is lifted in a hoisting slip in the Hangar AF area at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Hangar AF is a building originally used for Project Mercury, the first U.S. manned space program. The SRBs are the largest solid propellant motors ever flown and the first designed for reuse. After a Shuttle is launched, the SRBs are jettisoned at two minutes, seven seconds into the flight. At six minutes and 44 seconds after liftoff, the spent SRBs, weighing about 165,000 lb., have slowed their descent speed to about 62 mph and splashdown takes place in a predetermined area. They are retrieved from the Atlantic Ocean by special recovery vessels and returned for refurbishment and eventual reuse on future Shuttle flights. Once at Hangar AF, the SRBs are unloaded onto a hoisting slip and mobile gantry cranes lift them onto tracked dollies where they are safed and undergo their first washing
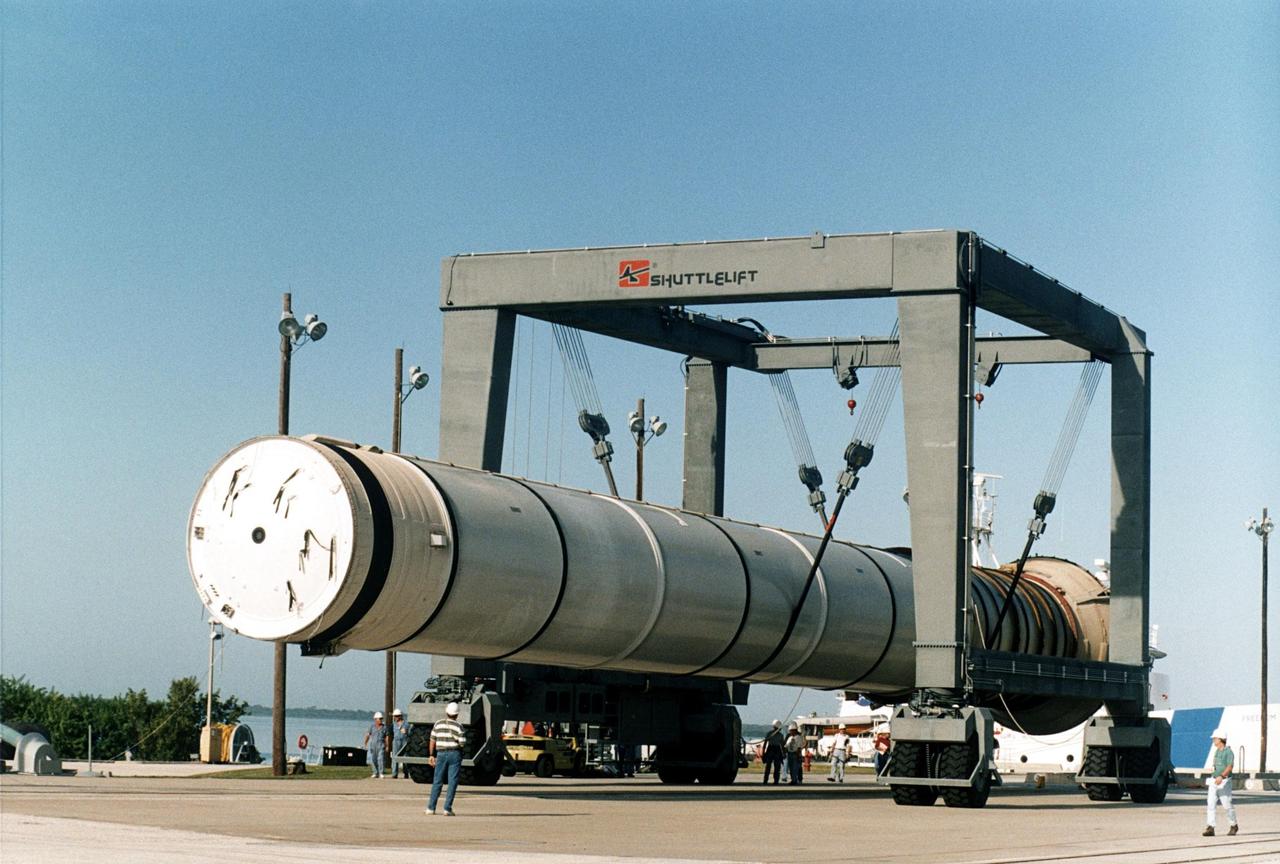

A spent solid rocket booster (SRB) from the STS-87 launch on Nov. 19 is lifted in a hoisting slip in the Hangar AF area at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Hangar AF is a building originally used for Project Mercury, the first U.S. manned space program. The SRBs are the largest solid propellant motors ever flown and the first designed for reuse. After a Shuttle is launched, the SRBs are jettisoned at two minutes, seven seconds into the flight. At six minutes and 44 seconds after liftoff, the spent SRBs, weighing about 165,000 lb., have slowed their descent speed to about 62 mph and splashdown takes place in a predetermined area. They are retrieved from the Atlantic Ocean by special recovery vessels and returned for refurbishment and eventual reuse on future Shuttle flights. Once at Hangar AF, the SRBs are unloaded onto a hoisting slip and mobile gantry cranes lift them onto tracked dollies where they are safed and undergo their first washing
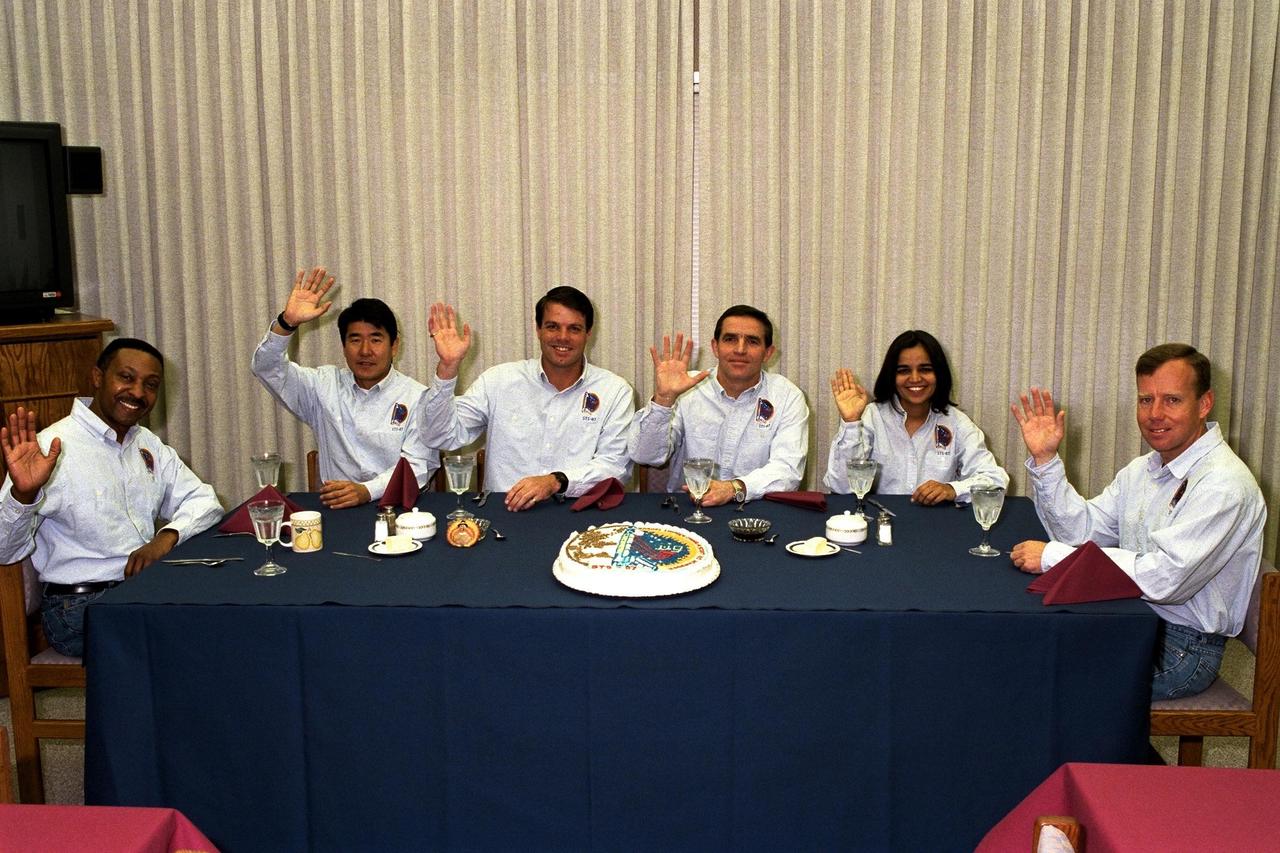

The STS-87 flight crew enjoy the traditional pre-liftoff breakfast in the crew quarters of the Operations and Checkout Building. They are, from left, Mission Specialist Winston Scott; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Commander Kevin Kregel; Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine; Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; and Pilot Steven Lindsey. After a weather briefing, the flight crew will be fitted with their launch and entry suits and depart for Launch Pad 39B. Once there, they will take their positions in the crew cabin of the Space Shuttle Columbia to await liftoff during a two-and-a-half-hour window that will open at 2:46 p.m. EDT, Nov. 19
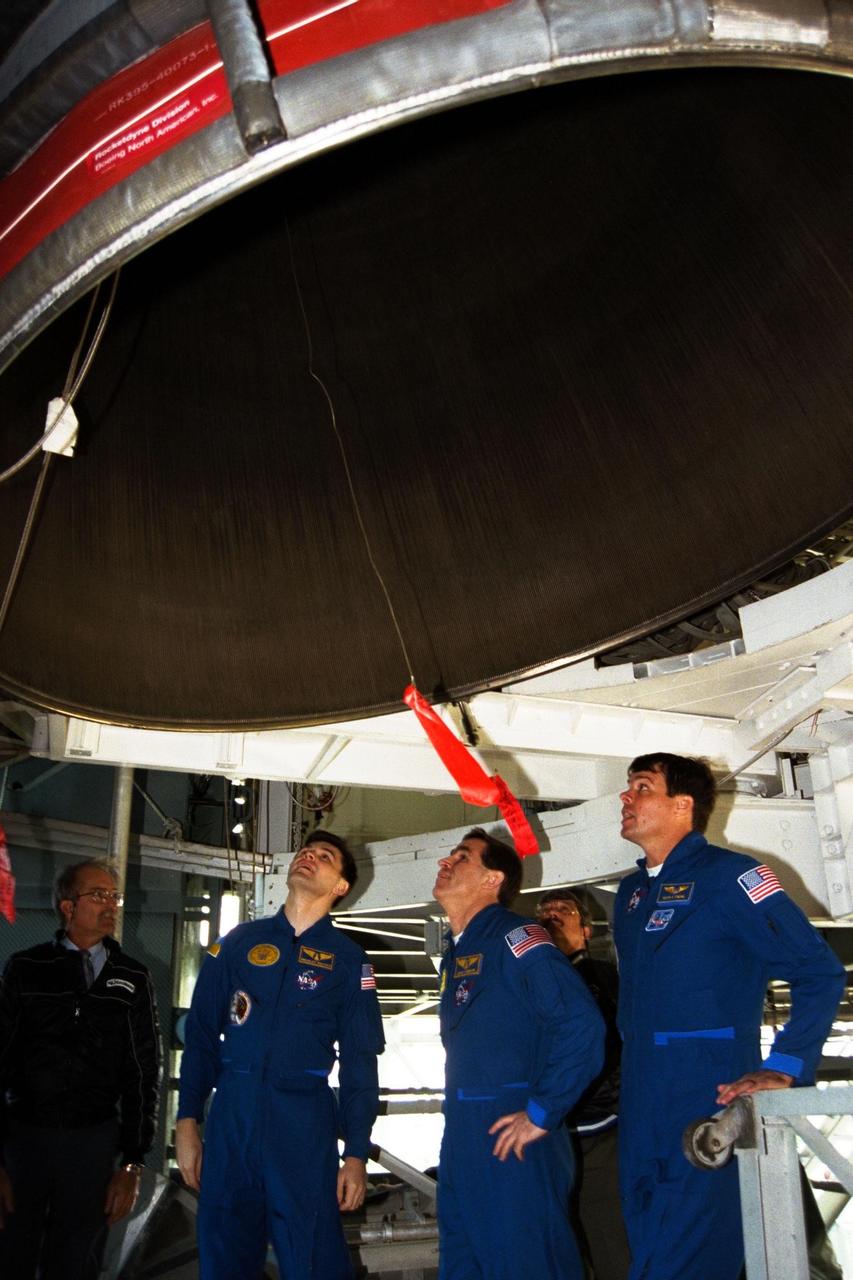

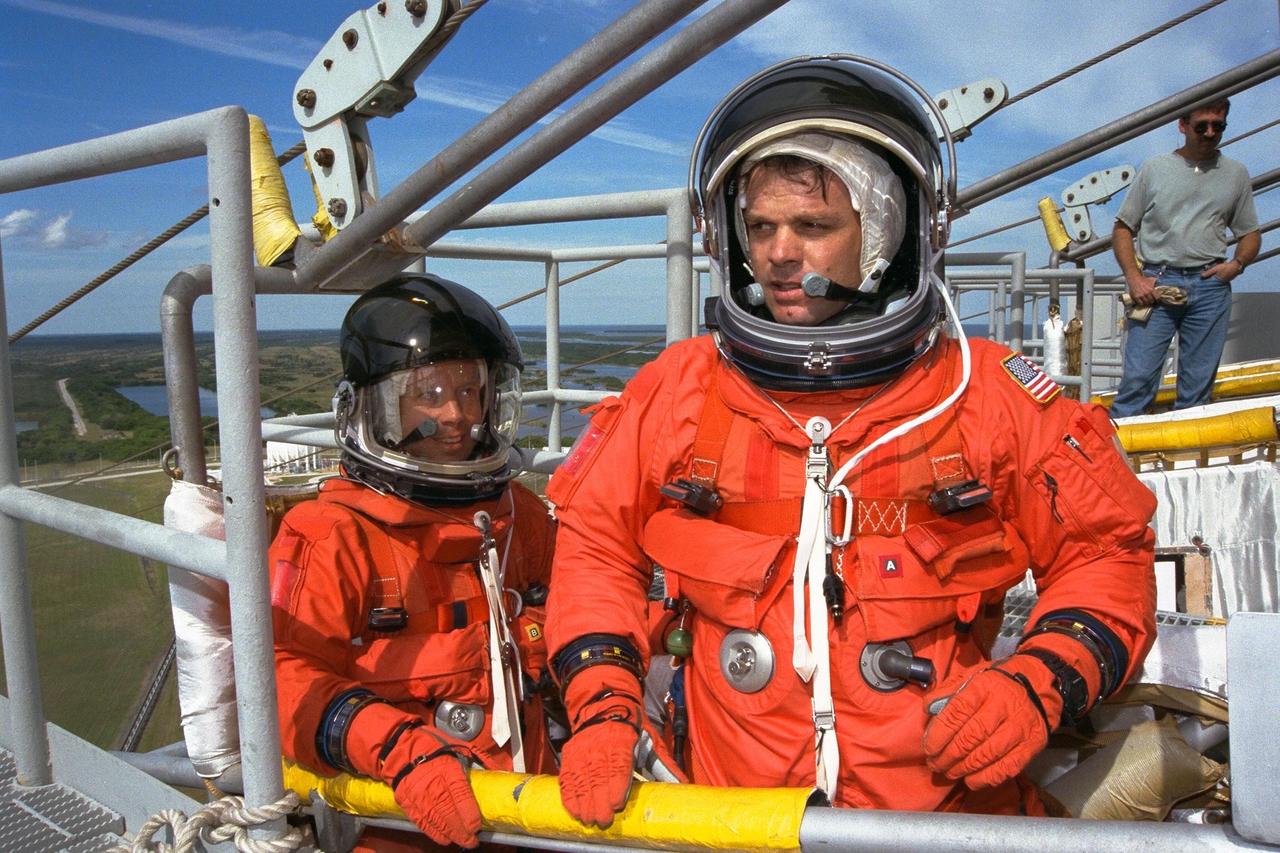
The crew of the STS-87 mission, scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center (KSC), participates in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at KSC. Getting a close look at one of the Space Shuttle’s main engines are, from right, Commander Kevin Kregel, Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU), and Kadenyuk’s back-up, Yaroslav Pustovyi, Ph.D., also of NSAU. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight, providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
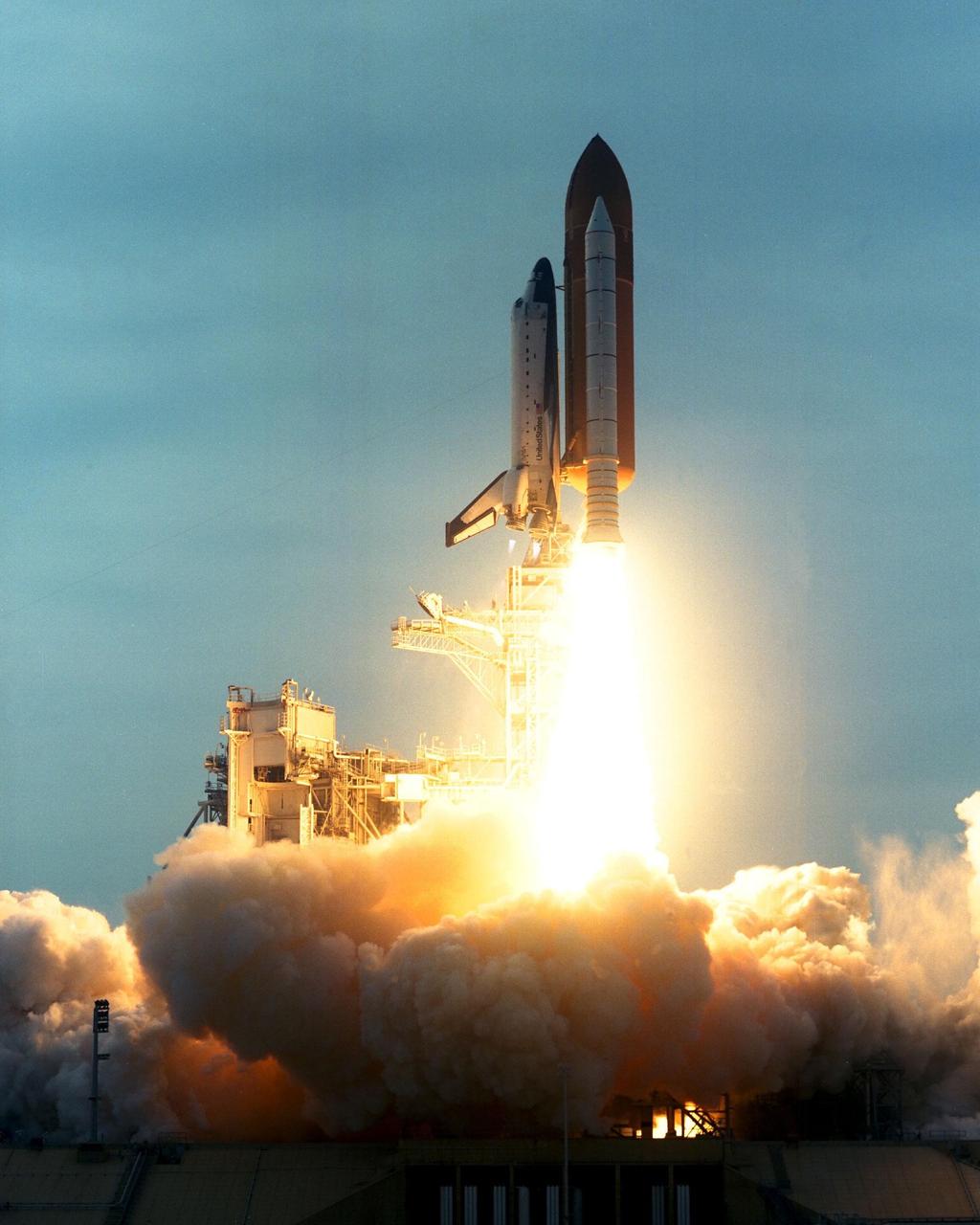

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers
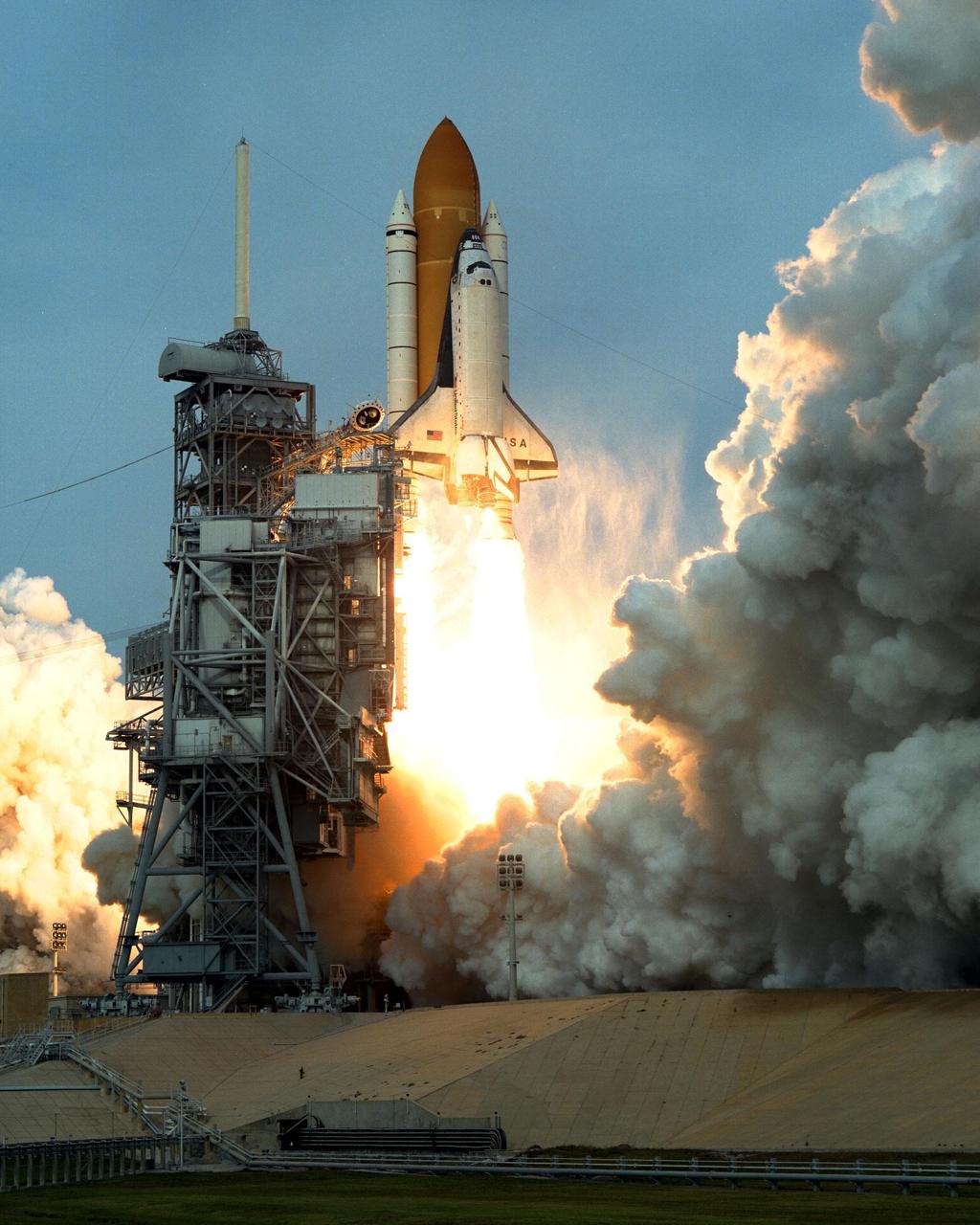

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers
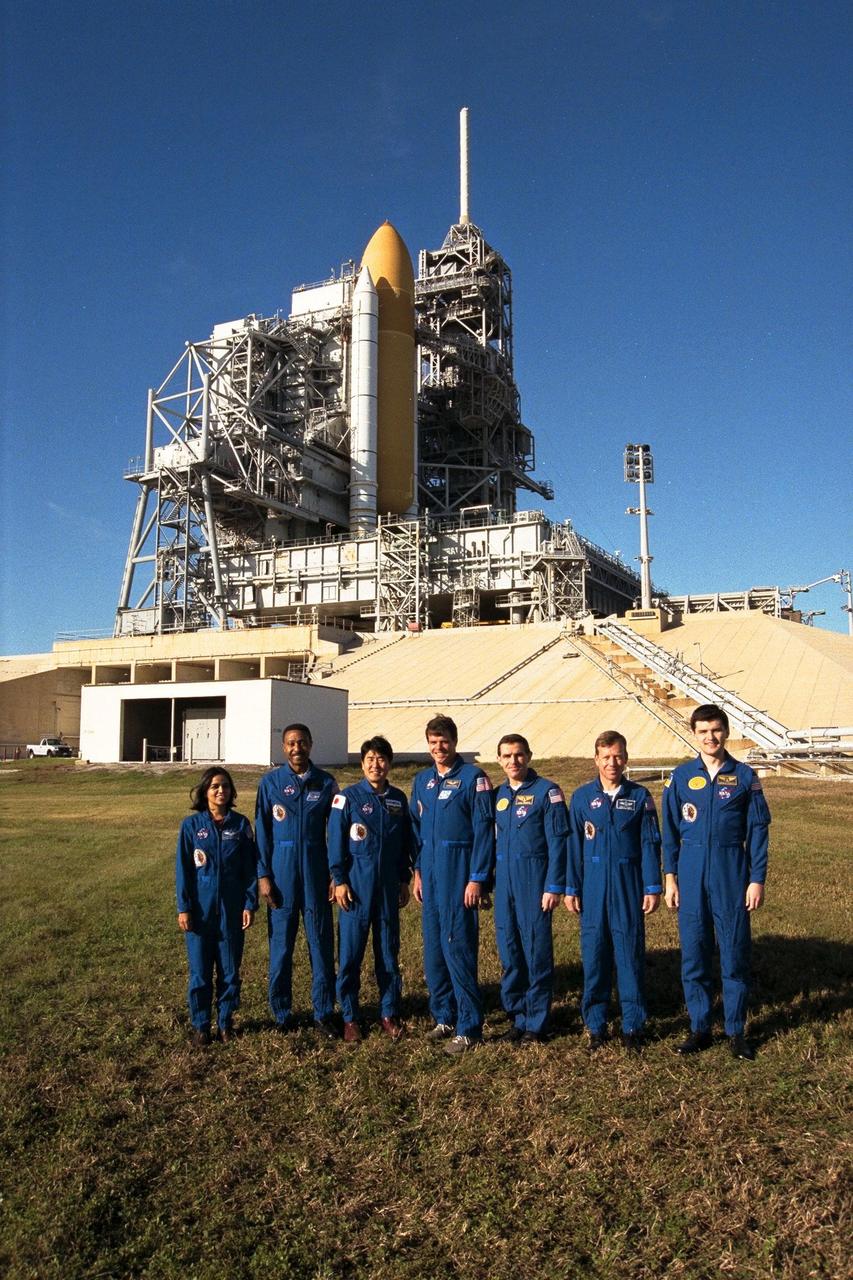

The crew of the STS-87 mission, scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center (KSC), participate in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at KSC. Posing for a group shot by Pad 39B are, from left to right, Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Mission Specialist Winston Scott; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Commander Kevin Kregel; Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU); Pilot Steven Lindsey; and Kadenyuk’s back-up, Yaroslav Pustovyi, Ph.D., also of NSAU. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight, providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
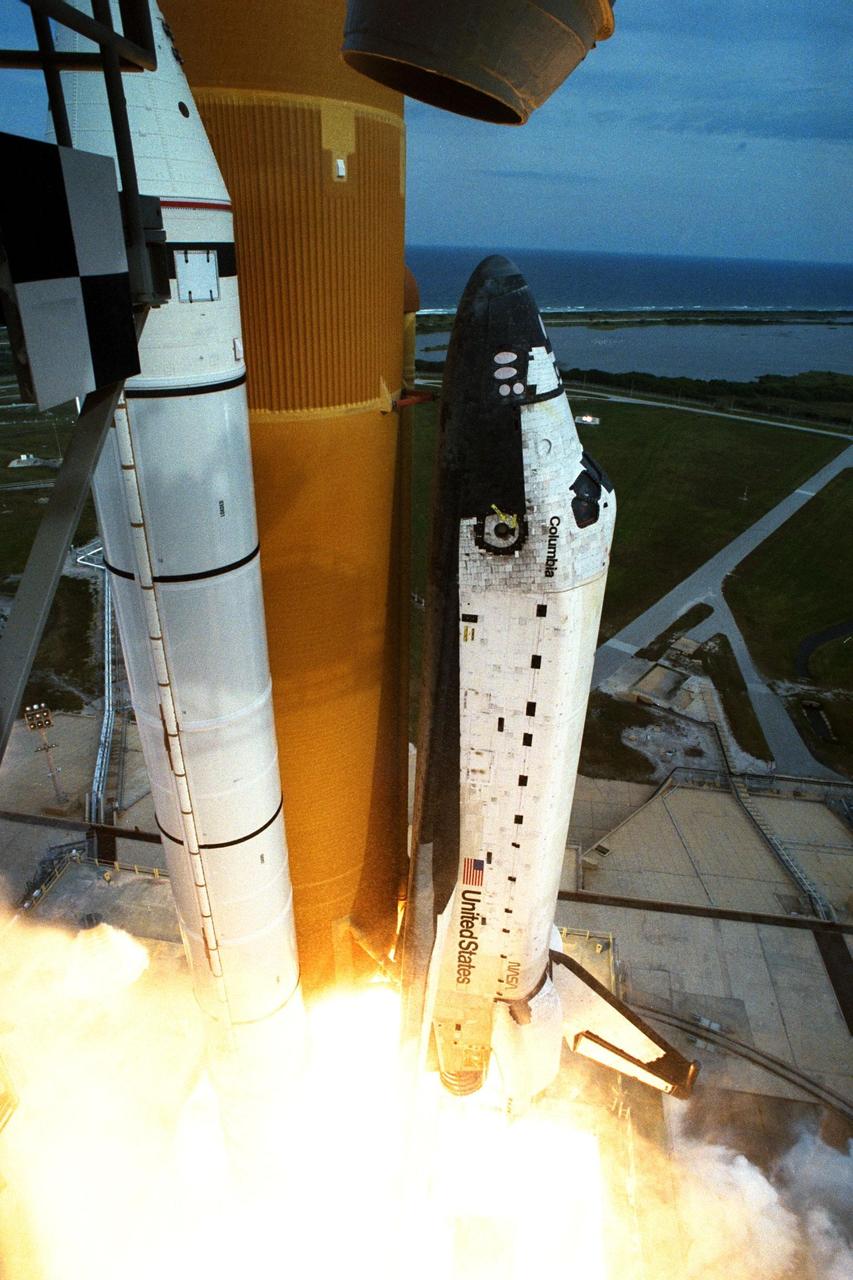

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers
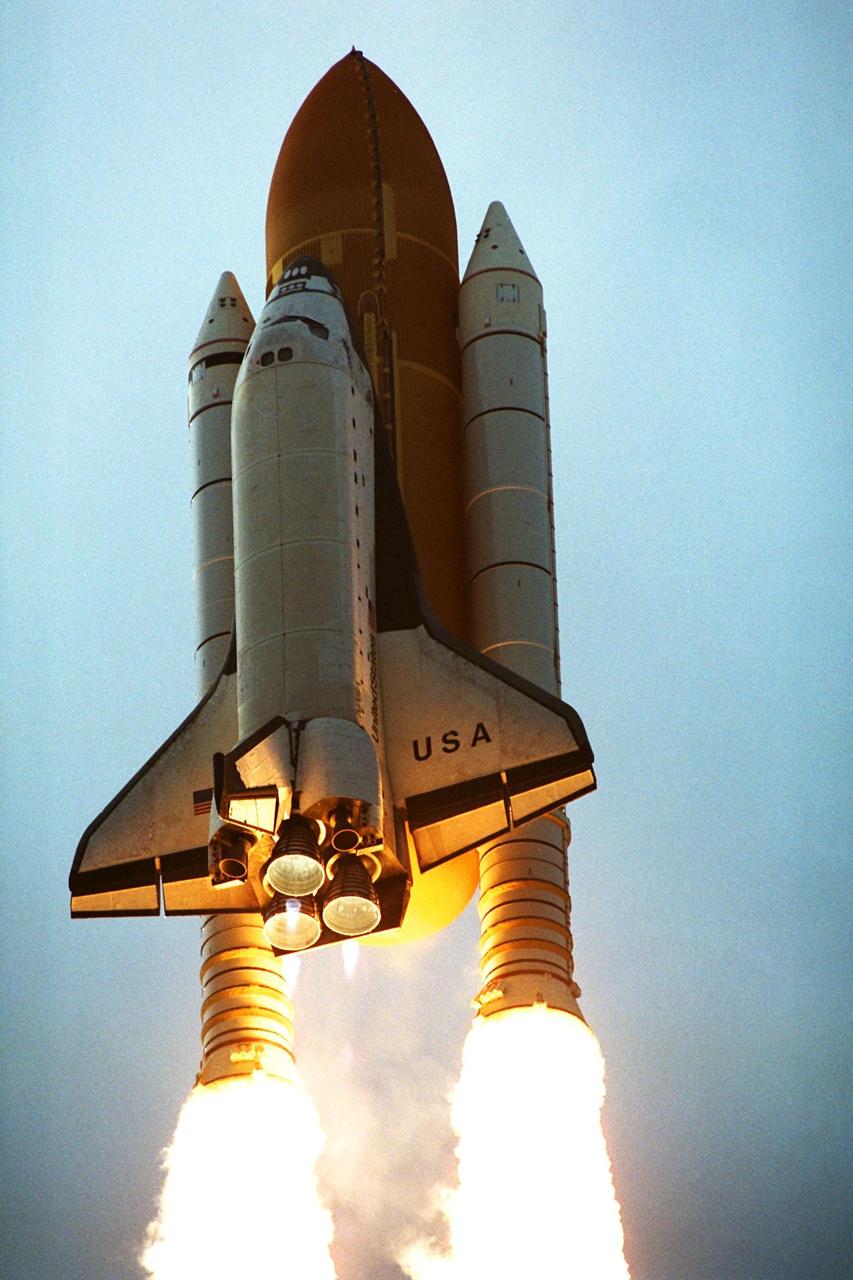

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers
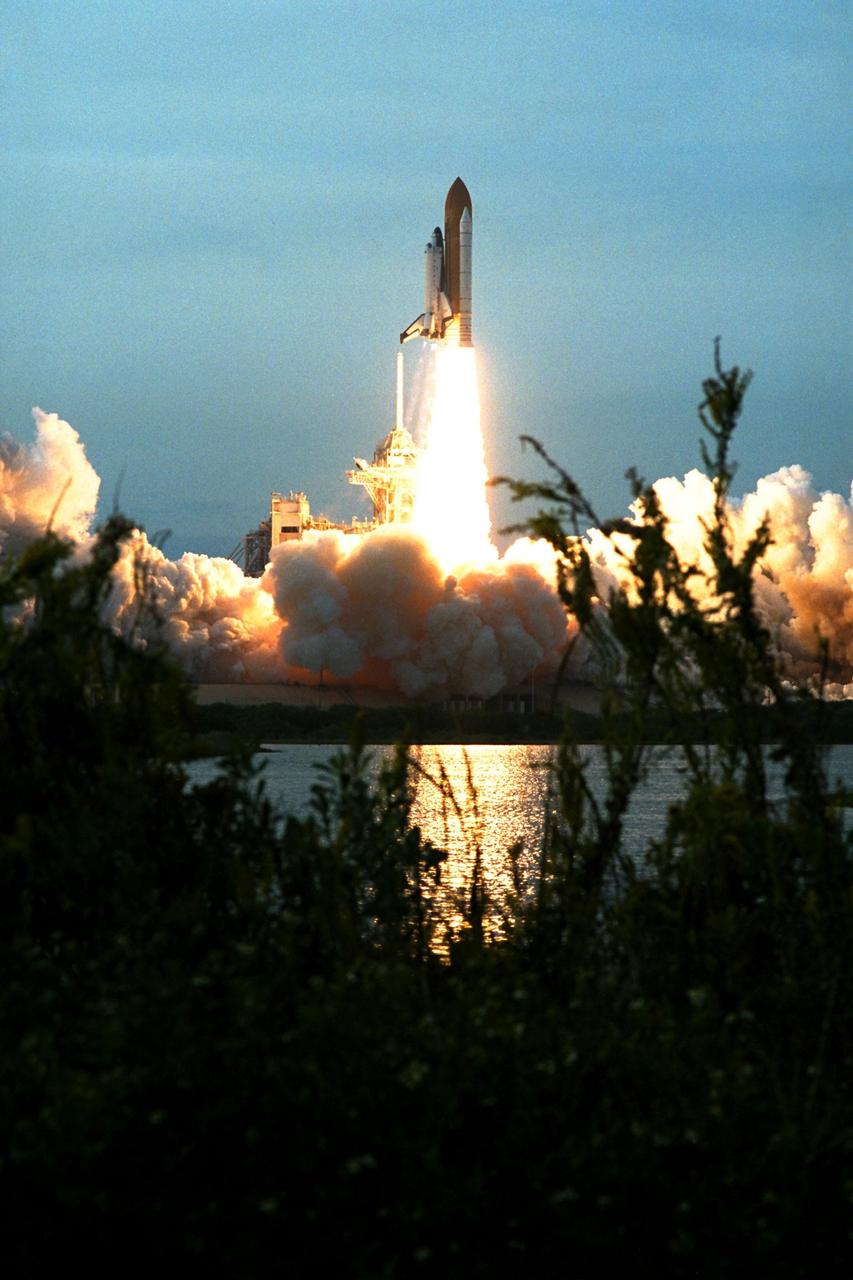

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers
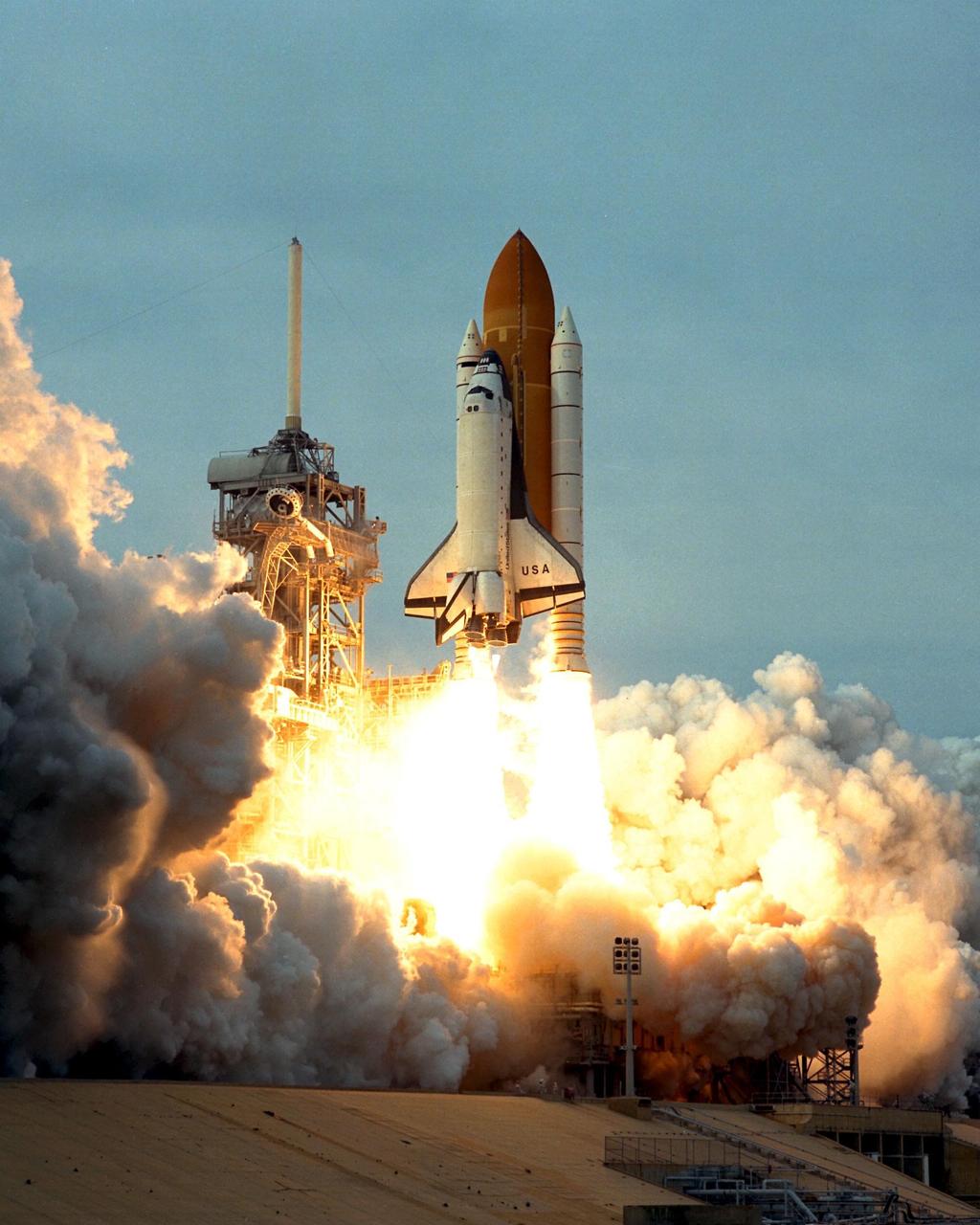

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers
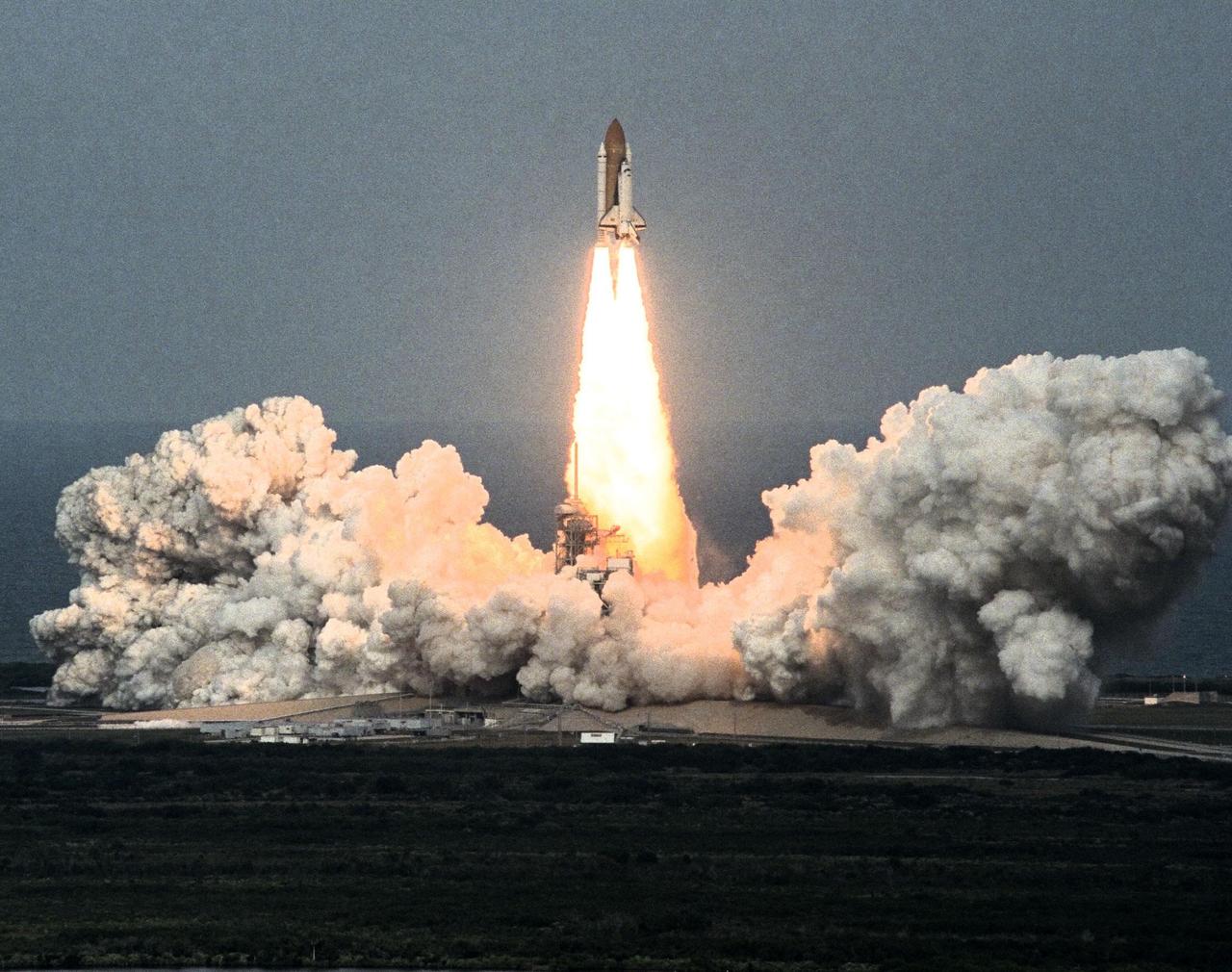

Like a rising sun lighting up the afternoon sky, the Space Shuttle Columbia soars from Launch Pad 39B at 2:46:00 p.m. EST, November 19, on the fourth flight of the United States Microgravity Payload and Spartan-201 satellite. The crew members include Mission Commander Kevin Kregel.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialists Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D., Winston Scott, and Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine. During the 16-day STS-87 mission, the crew will oversee experiments in microgravity; deploy and retrieve a solar satellite; and test a new experimental camera, the AERCam Sprint. Dr. Doi and Scott also will perform a spacewalk to practice International Space Station maneuvers
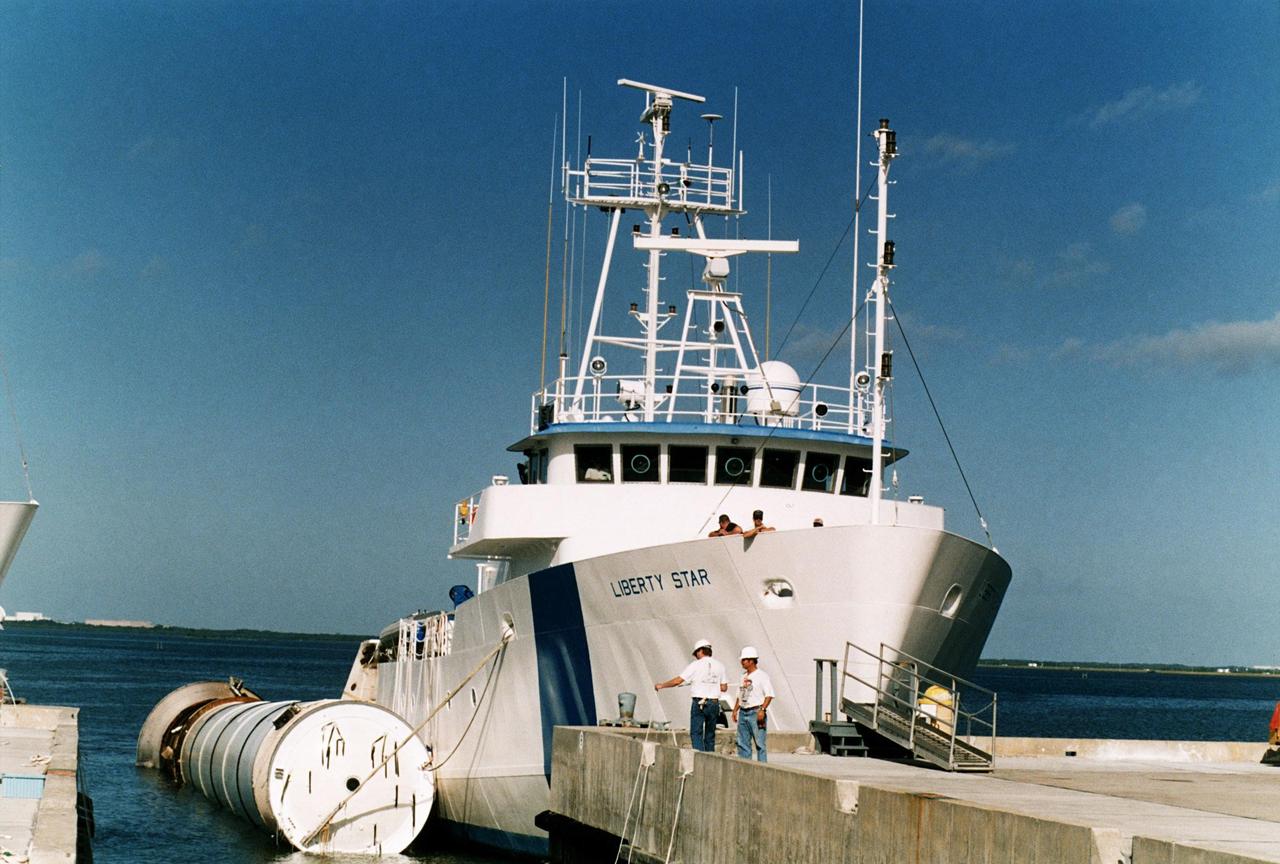

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seen carrying a spent solid rocket booster (SRB) from the STS-87 launch on Nov. 19 is the solid rocket booster recovery ship Liberty Star as it reenters the Hangar AF area at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Hangar AF is a building originally used for Project Mercury, the first U.S. manned space program. The SRBs are the largest solid propellant motors ever flown and the first designed for reuse. After a Shuttle is launched, the SRBs are jettisoned at two minutes, seven seconds into the flight. At six minutes and 44 seconds after liftoff, the spent SRBs, weighing about 165,000 lb., have slowed their descent speed to about 62 mph and splashdown takes place in a predetermined area. They are retrieved from the Atlantic Ocean by special recovery vessels and returned for refurbishment and eventual reuse on future Shuttle flights. Once at Hangar AF, the SRBs are unloaded onto a hoisting slip and mobile gantry cranes lift them onto tracked dollies where they are safed and undergo their first washing
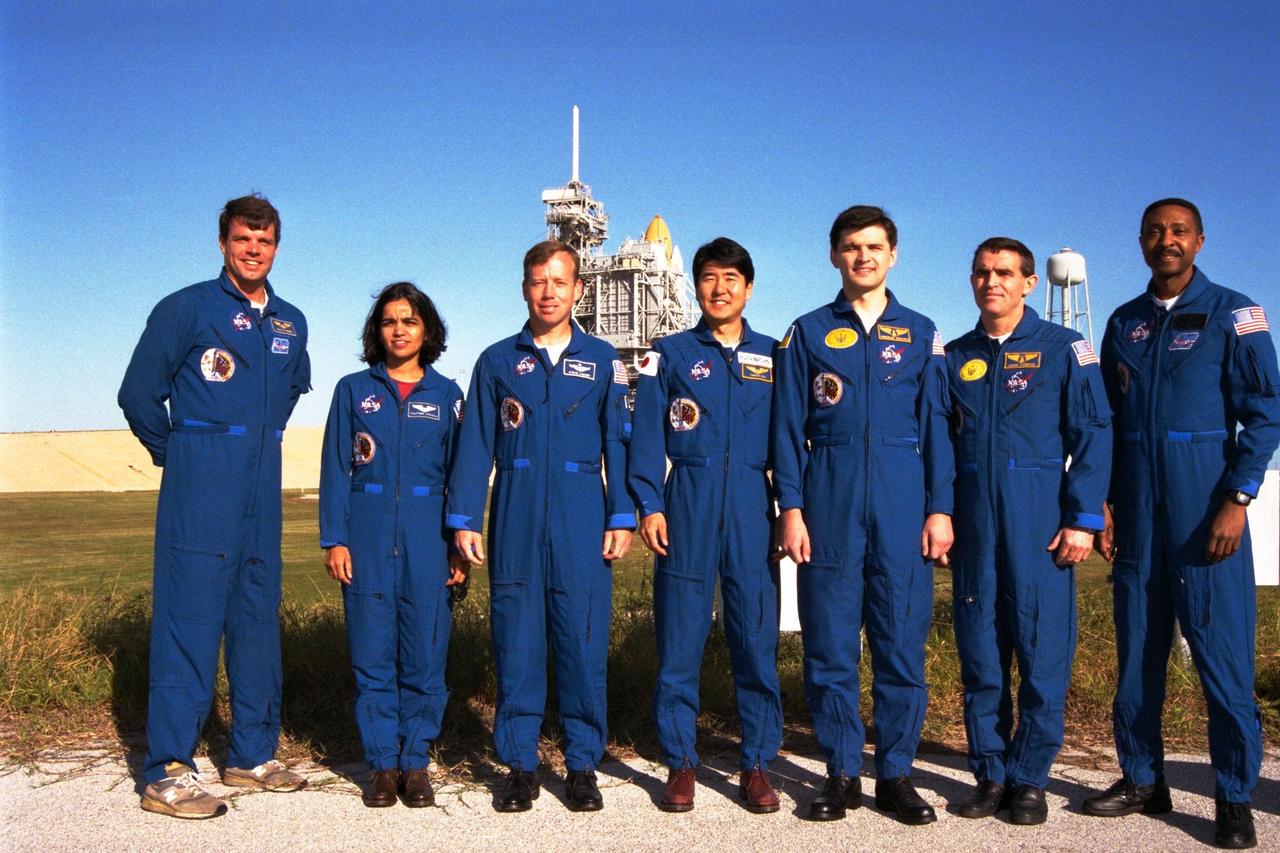

The crew of the STS-87 mission, scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center (KSC), poses at the pad during a break in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at KSC. Standing in front of the Shuttle Columbia are, from left, Commander Kevin Kregel; Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; backup Payload Specialist Yaroslav Pustovyi, Ph.D., of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU); Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of NSAU; and Mission Specialist Winston Scott. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cutoff. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay
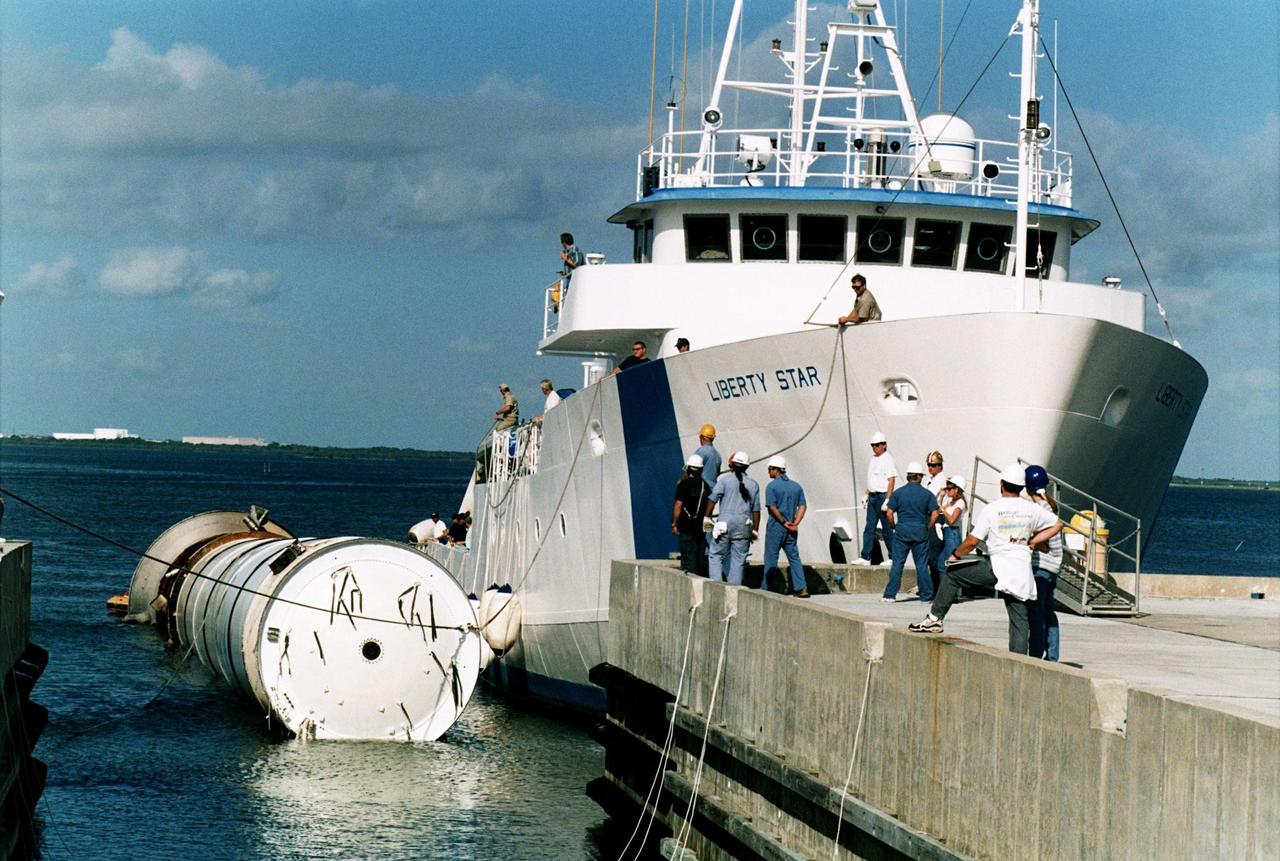

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Seen carrying a spent solid rocket booster (SRB) from the STS-87 launch on Nov. 19 is the solid rocket booster recovery ship Liberty Star as it reenters the Hangar AF area at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Hangar AF is a building originally used for Project Mercury, the first U.S. manned space program. The SRBs are the largest solid propellant motors ever flown and the first designed for reuse. After a Shuttle is launched, the SRBs are jettisoned at two minutes, seven seconds into the flight. At six minutes and 44 seconds after liftoff, the spent SRBs, weighing about 165,000 lb., have slowed their descent speed to about 62 mph and splashdown takes place in a predetermined area. They are retrieved from the Atlantic Ocean by special recovery vessels and returned for refurbishment and eventual reuse on future Shuttle flights. Once at Hangar AF, the SRBs are unloaded onto a hoisting slip and mobile gantry cranes lift them onto tracked dollies where they are safed and undergo their first washing
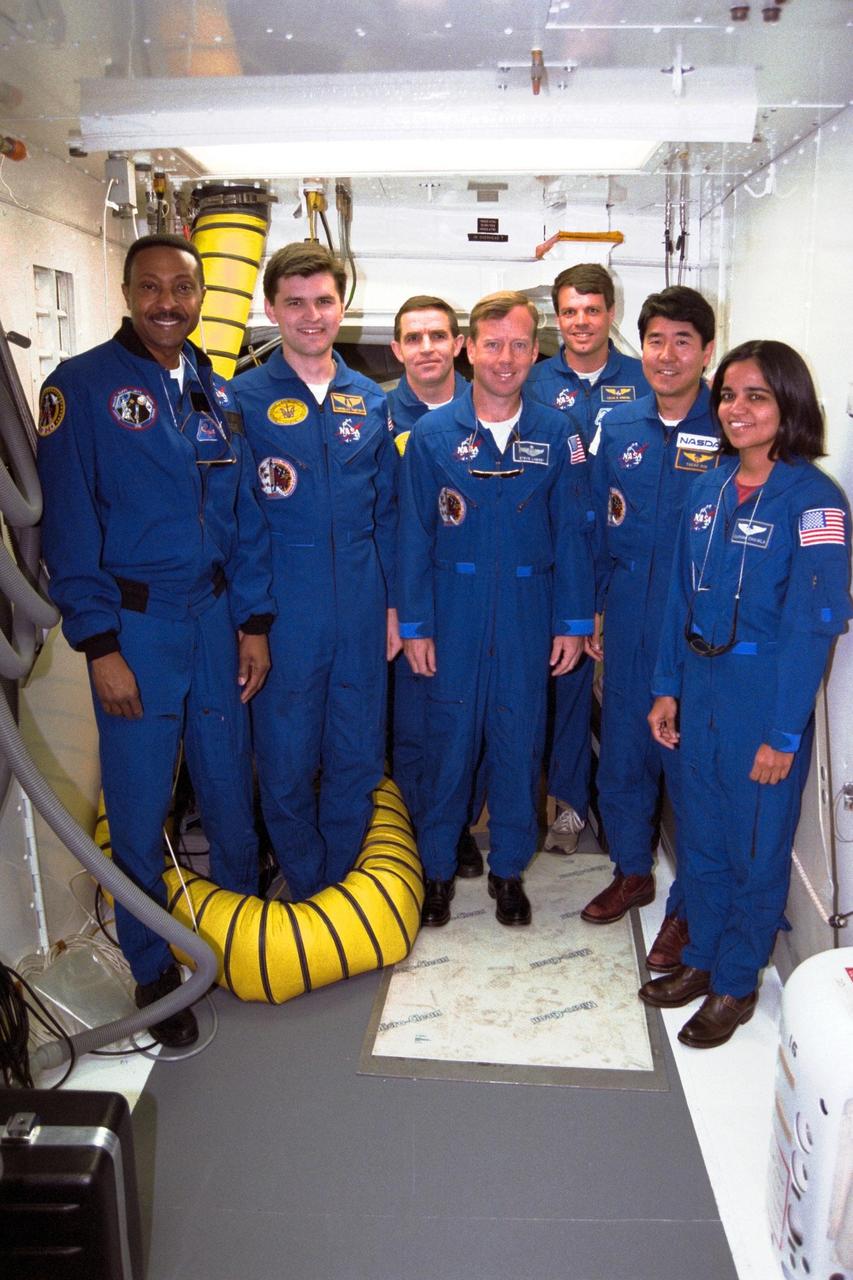

The crew of the STS-87 mission, scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center (KSC), participates in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at KSC. Standing, from left, are Mission Specialist Winston Scott; backup Payload Specialist Yaroslav Pustovyi, Ph.D., of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU); Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of NSAU; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Commander Kevin Kregel; Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; and Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The frustum of a forward skirt assembly of a spent solid rocket booster (SRB) from the STS-87 launch on Nov. 19 is transported into the Hangar AF area at Cape Canaveral Air Station. Hangar AF is a building originally used for Project Mercury, the first U.S. manned space program. The SRBs are the largest solid propellant motors ever flown and the first designed for reuse. After a Shuttle is launched, the SRBs are jettisoned at two minutes, seven seconds into the flight. At six minutes and 44 seconds after liftoff, the spent SRBs, weighing about 165,000 lb., have slowed their descent speed to about 62 mph and splashdown takes place in a predetermined area. They are retrieved from the Atlantic Ocean by special recovery vessels and returned for refurbishment and eventual reuse on future Shuttle flights. Once at Hangar AF, the SRBs are unloaded onto a hoisting slip and mobile gantry cranes lift them onto tracked dollies where they are safed and undergo their first washing
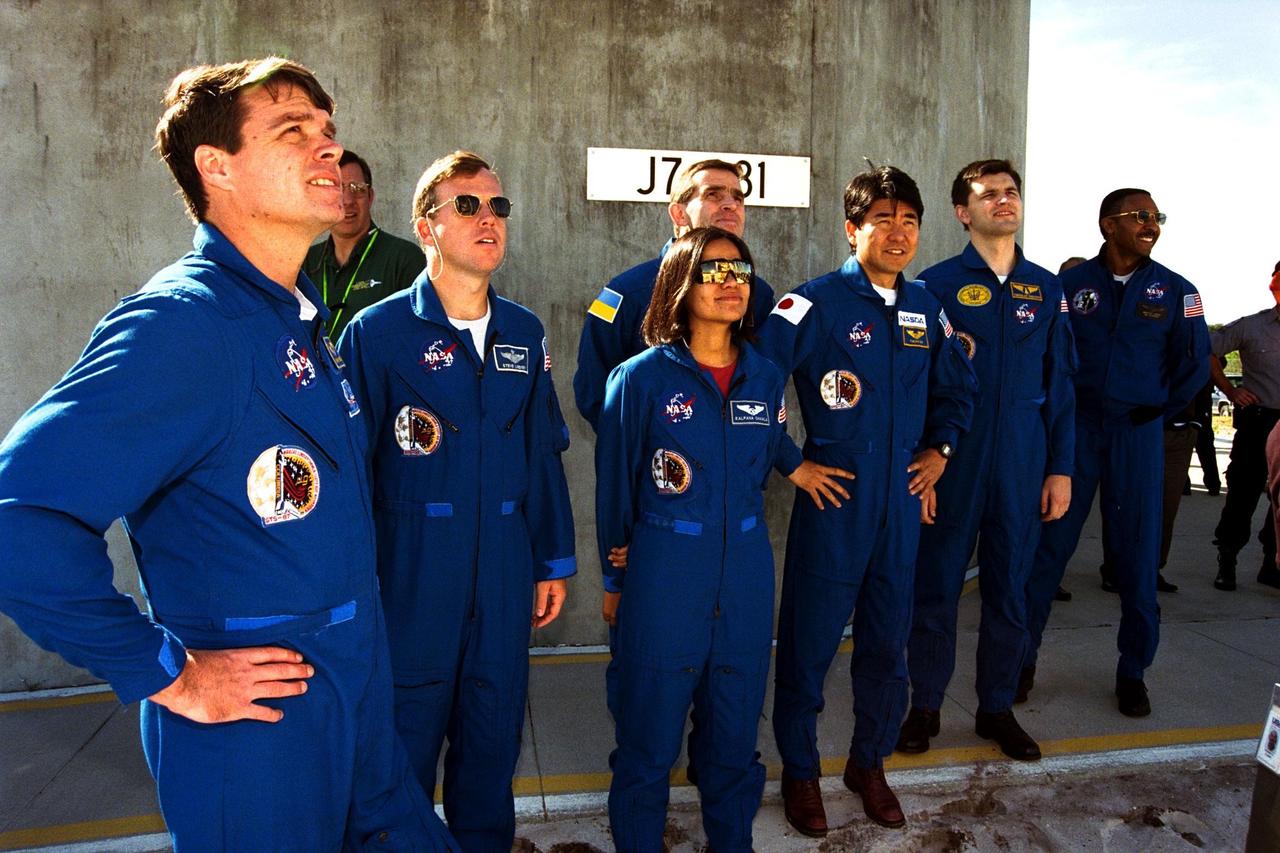

The crew of the STS-87 mission, scheduled for launch Nov. 19 aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia from Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center (KSC), participates in the Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) at KSC. Getting a look at the Space Shuttle Columbia are, from left, Commander Kevin Kregel; Pilot Steven Lindsey; Mission Specialist Kalpana Chawla, Ph.D.; Payload Specialist Leonid Kadenyuk of the National Space Agency of Ukraine (NSAU); Mission Specialist Takao Doi, Ph.D., of the National Space Development Agency of Japan; Kadenyuk’s back-up, Yaroslav Pustovyi, Ph.D., also of NSAU; and Mission Specialist Winston Scott. The TCDT is held at KSC prior to each Space Shuttle flight providing the crew of each mission opportunities to participate in simulated countdown activities. The TCDT ends with a mock launch countdown culminating in a simulated main engine cut-off. The crew also spends time undergoing emergency egress training exercises at the pad and has an opportunity to view and inspect the payloads in the orbiter's payload bay

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A post-landing news conference is held in the NASA Press Site auditorium at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida after the picture-perfect landing of space shuttle Atlantis concluding the STS-129 mission. From left are NASA Public Affairs moderator Allard Beutel; Bill Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for Space Operations; Mike Moses, chair, Mission Management Team; and Mike Leinbach, space shuttle launch director. Main gear touchdown at Kennedy's Shuttle Landing Facility was at 9:44:23 a.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown was at 9:44:36 a.m., and wheels stop was at 9:45:05 a.m. Returning aboard Atlantis were STS-129 Commander Charles O. Hobaugh; Pilot Barry E. Wilmore; Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Randy Bresnik, Mike Foreman and Robert L. Satcher Jr.; and Expedition 20 and 21 Flight Engineer Nicole Stott who spent 87 days aboard the International Space Station. STS-129 is the final space shuttle Expedition crew rotation flight on the manifest. On STS-129, the crew delivered 14 tons of cargo to the orbiting laboratory, including two ExPRESS Logistics Carriers containing spare parts to sustain station operations after the shuttles are retired next year. For information on the STS-129 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts129/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann