A Suite of Features
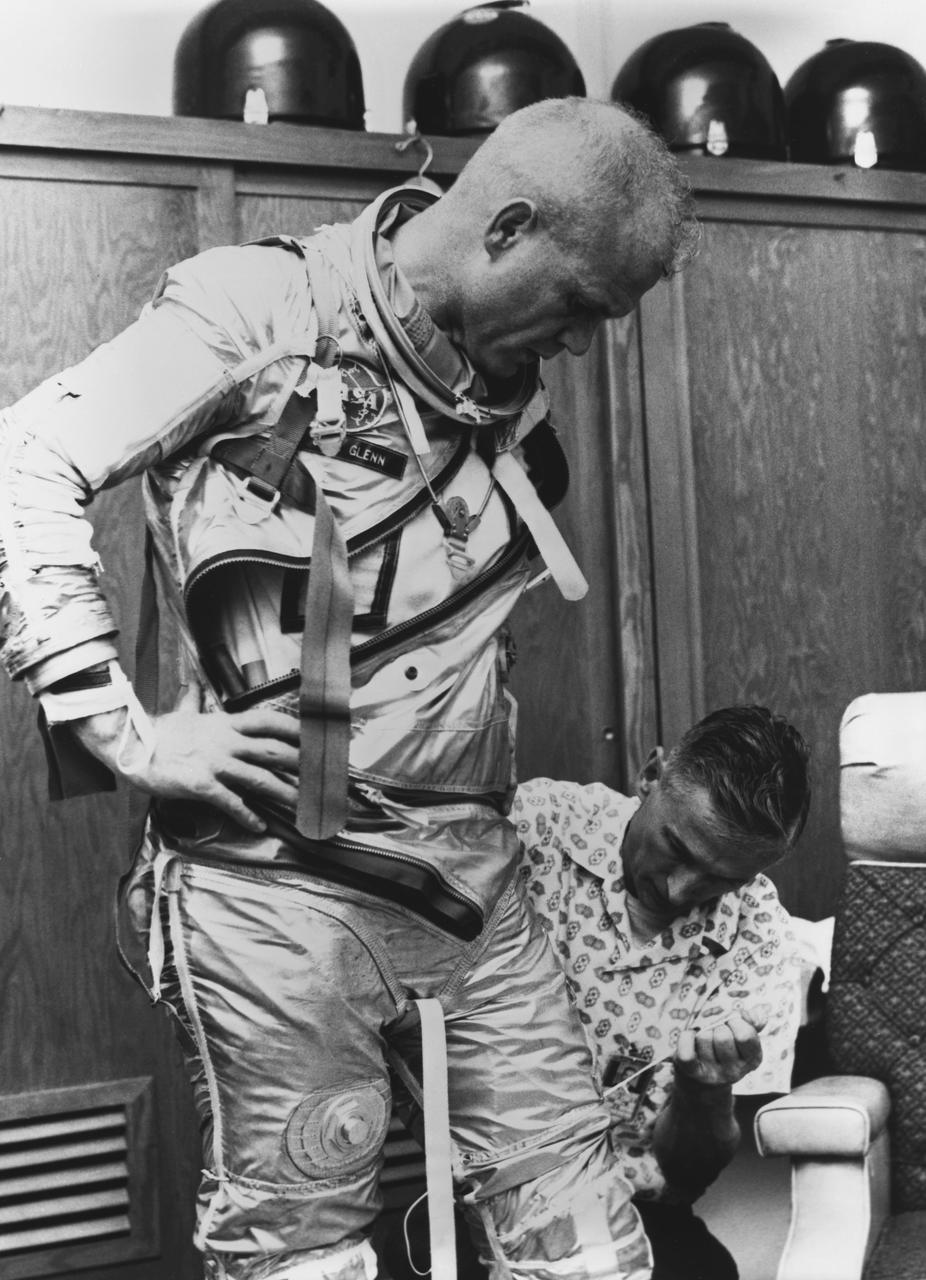

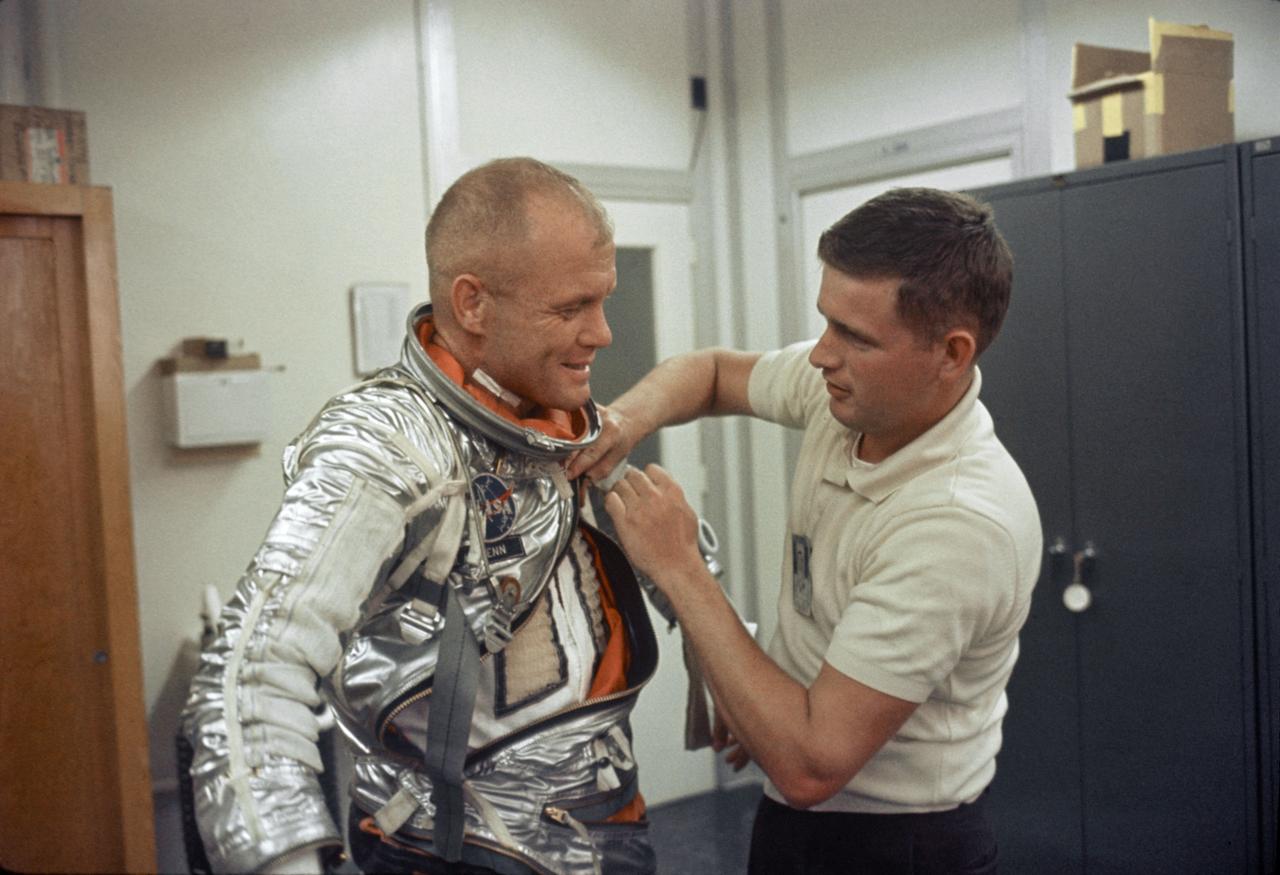
S62-00246 (5 Feb. 1962) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. is assisted by Joe W. Schmitt as he suits up in practice for the preparation of Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) mission. Photo credit: NASA
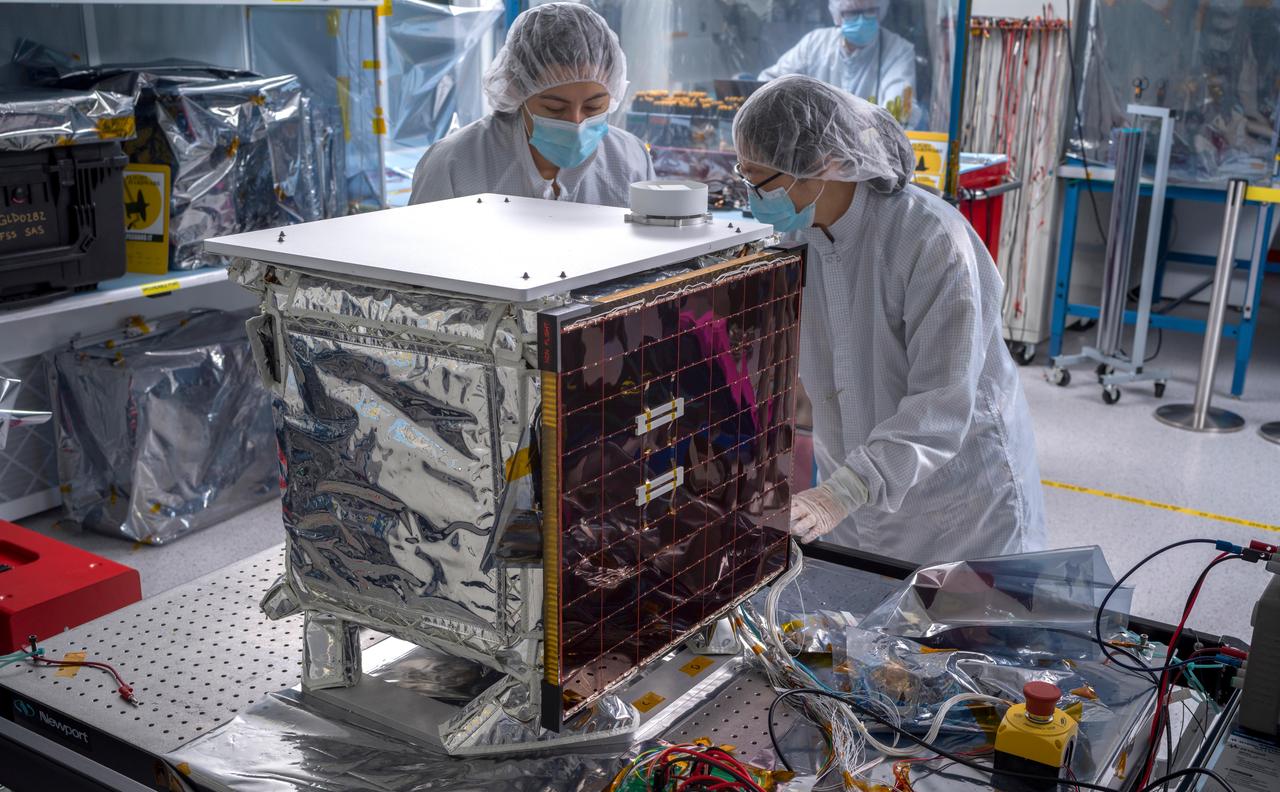

In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in March 2024, engineers and technicians work to prepare the agency's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) for environmental testing to simulate conditions it will encounter in space. Along with being placed in a vacuum chamber and subjected to extreme temperatures, the instrument suite will undergo severe shaking that mimics the rocket's motion during launch. The cube-shaped payload contains two instruments that will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. The two seismometers are packaged together with a large battery, a computer, and electronics inside a cube structure that's surrounded by several layers of insulation and suspended within an outer protective cube, which is in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. The suite's single solar panel can be seen at center. On top is a white radiator that will allow the suite to shed heat generated by its electronics during the hot lunar daytime hours. The puck-like object atop the radiator is the suite's antenna, for communicating with two small relay satellites that will orbit the Moon and send data to Earth. Pictured (from left): Joanna Farias, and Bert Turney, and Hsin-Yi Hao. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26299
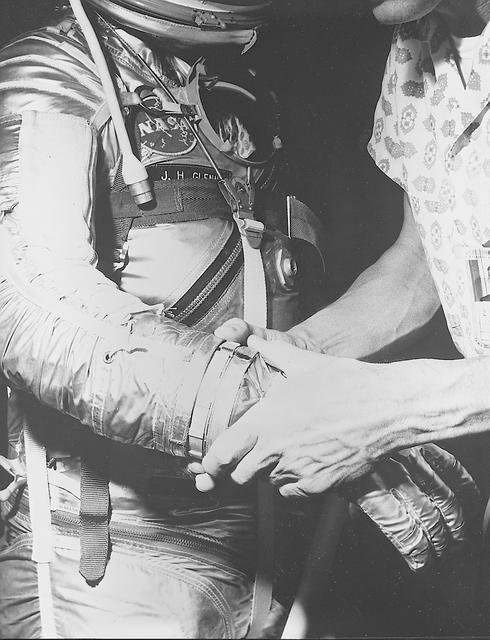

S62-00249 (1962) --- View of astronaut John H. Glenn Jr. being fitted with gloves for his spacesuit during preflight training activities at Cape Canaveral, Florida. Glenn is assisted by suit technician Joe Schmitt. Photo credit: NASA
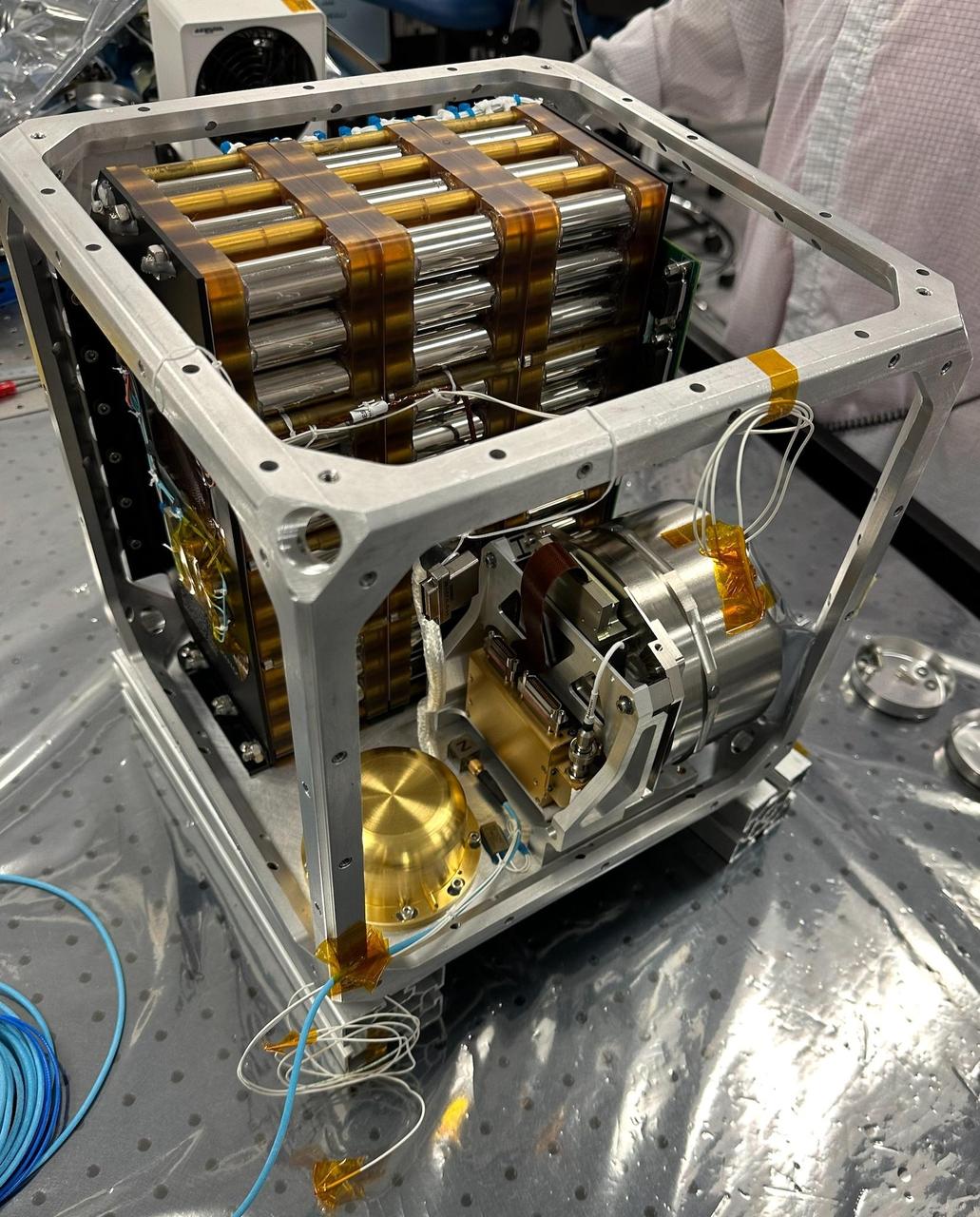
NASA's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) is assembled in a clean room at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in November 2023. Two sensitive seismometers packaged in the suite's cube-within-a-cube structure will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. Seen here is the inner cube structure, with the suite's large battery at rear. The gold, puck-shaped device at left is the Short Period sensor, or SP, which measures motion in three directions using sensors etched into a trio of square silicon chips, each about 1 inch (25 millimeters) wide. At right, within the silver cylindrical enclosure, is the Very Broadband seismometer, or VBB, the most sensitive seismometer ever built for use in space exploration. It can detect ground motions smaller than the size of a single hydrogen atom, measuring up-and-down movement using a pendulum held in place by a spring. Constructed as a backup instrument (a "flight spare") for NASA's InSight Mars lander by the French space agency, CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales), the VBB was slightly modified and packaged in a new enclosure for lunar use. The suite's computer and electronics are packed alongside the battery and seismometers. After being encased in insulation, this inner cube was suspended within a protective outer cube, which was in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26300
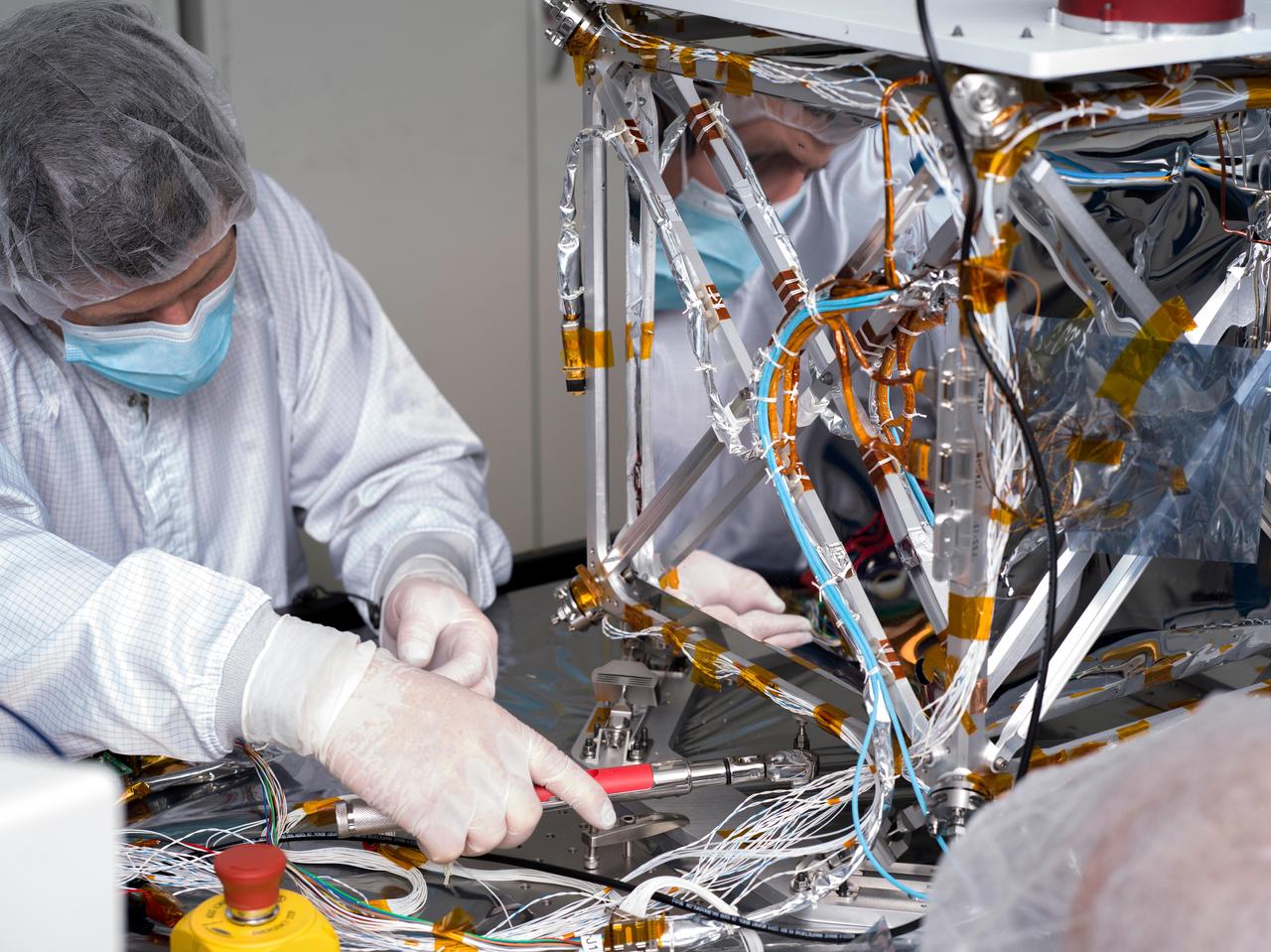
In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in March 2024, technician Nik Schwarz prepares the agency's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) for testing. The cube-shaped payload contains two instruments that will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. The two seismometers are packaged together with a large battery, a computer, and electronics inside a cube structure that's surrounded by several layers of insulation (the shiny, reflective material seen here) and suspended within an outer protective cube, which is in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. A technician is here attaching a stiffening brace to the bottom of the FSS outer cube structure. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26341
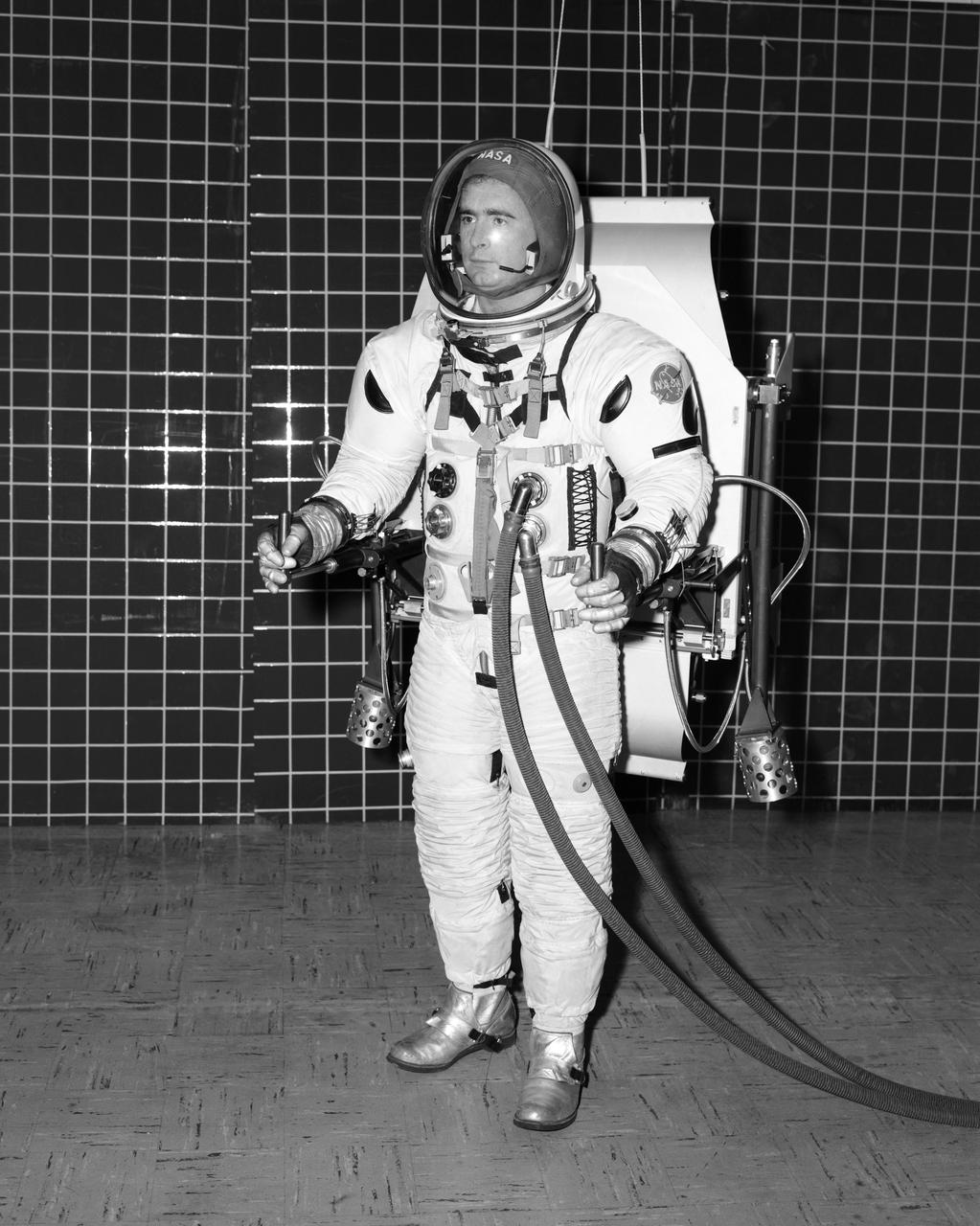

Space Suit: NASA Langley researcher (Kenneth R. Yenni) tries out a proposal for an Apollo space suit.
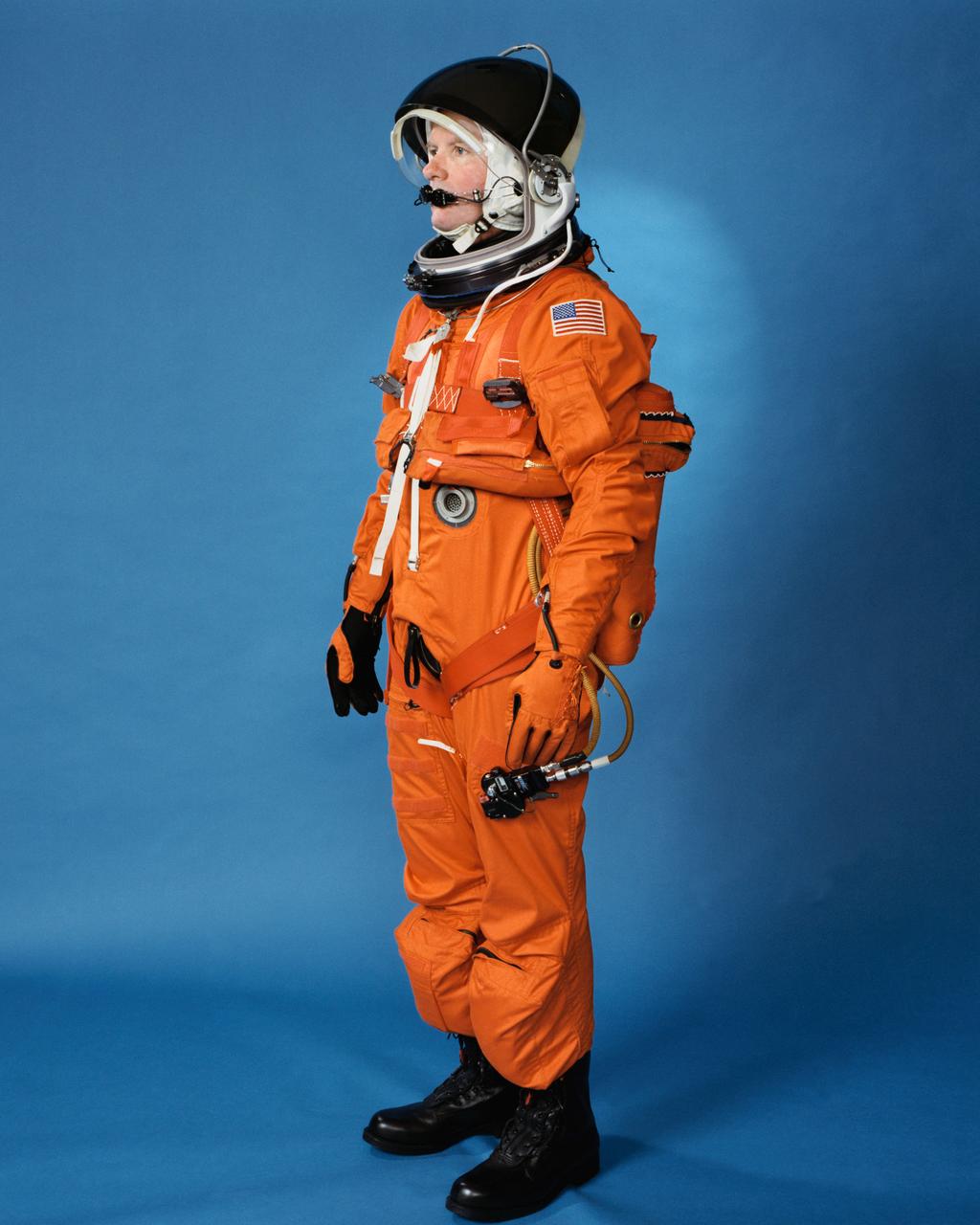

Space shuttle orange launch and entry suit (LES), a partial pressure suit, is modeled by a technician. LES was designed for STS-26, the return to flight mission, and subsequent missions. Included in the crew escape system (CES) package are launch and entry helmet (LEH) with communications carrier (COMM CAP), parachute pack and harness, life raft, life preserver unit (LPU), LES gloves, suit oxygen manifold and valves, boots, and survival gear.
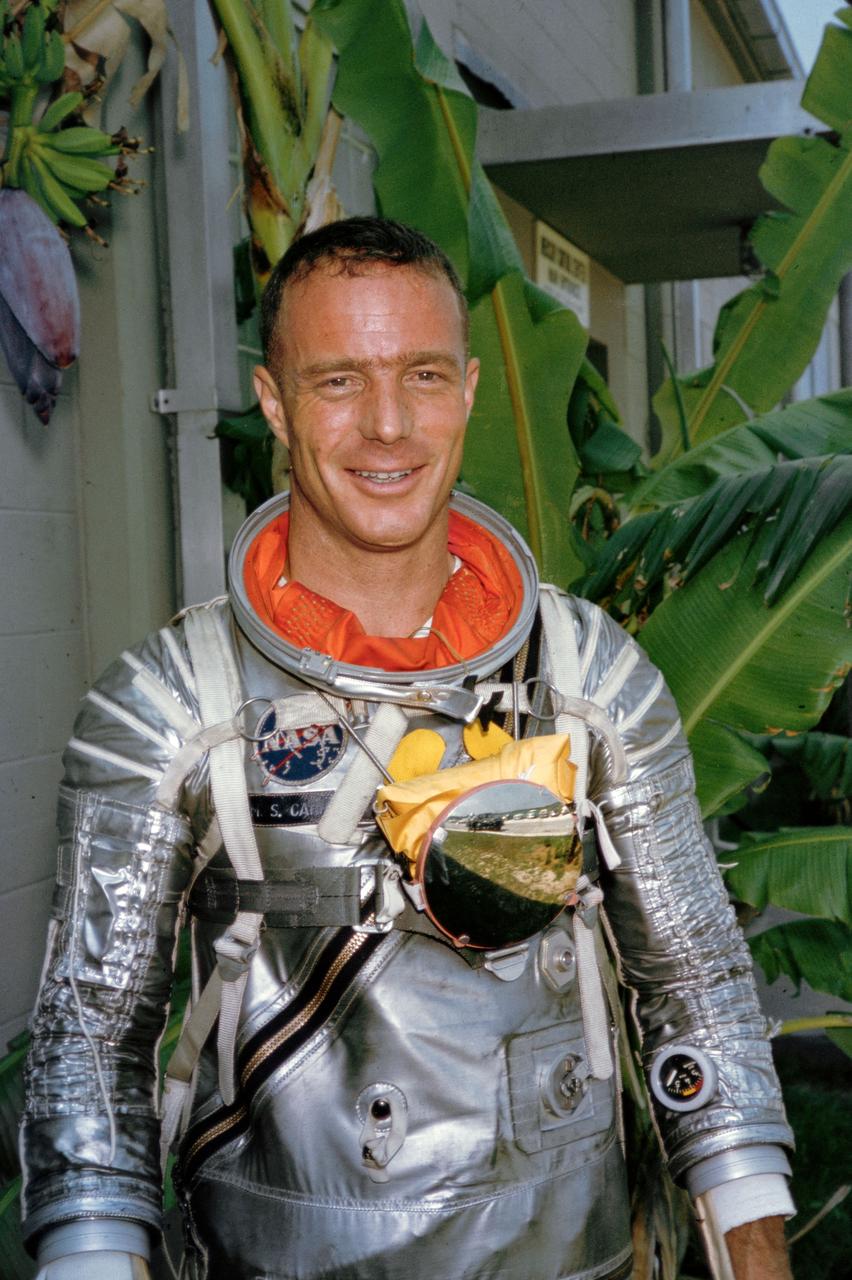

S64-36908 (1962) --- Portrait view of astronaut M. Scott Carpenter, wearing Mercury pressure suit, posing for pictures during astronaut training at the Cape Canaveral, Florida. Photo credit: NASA

Child in Astronaut suit
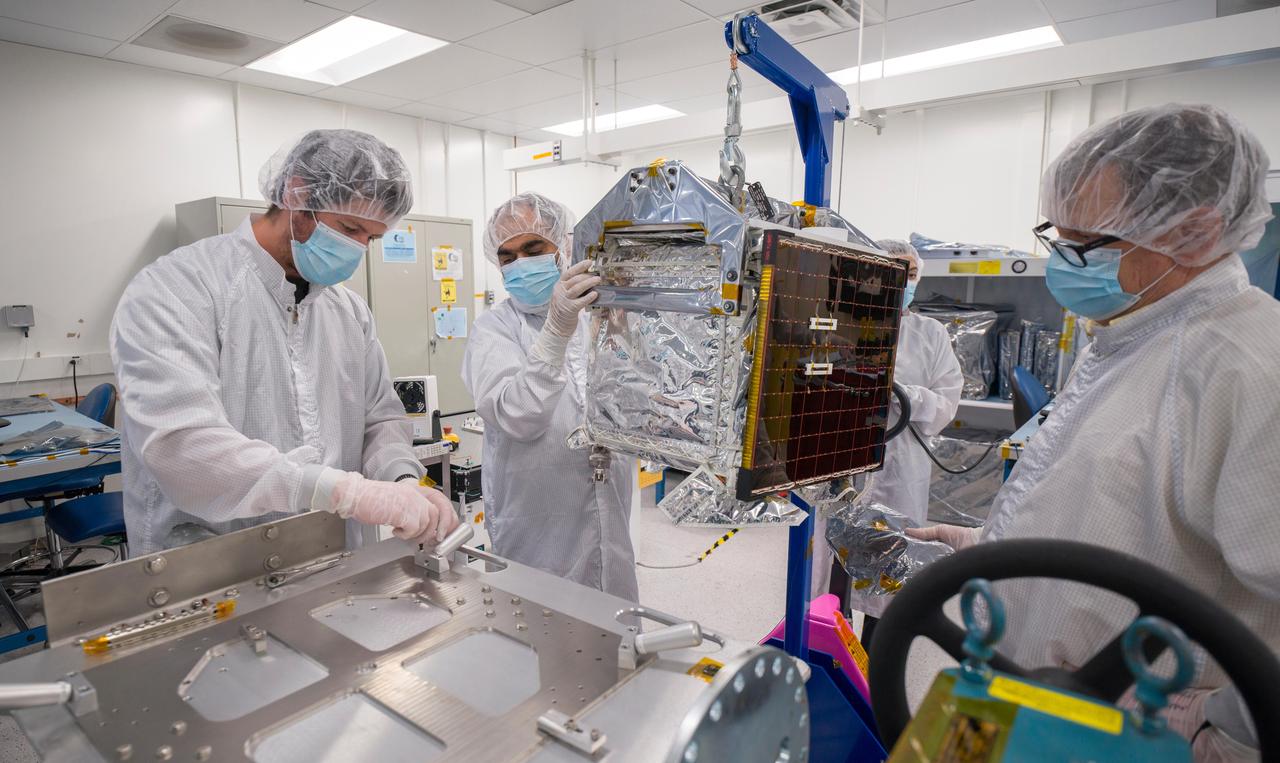

In a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in March 2024, engineers and technicians prepare the agency's Farside Seismic Suite (FSS) for testing. The cube-shaped payload contains two instruments that will gather NASA's first seismic data from the Moon in nearly 50 years and take the first-ever seismic measurements from the Moon's far side. FSS will operate continuously for at least 4½ months, working through the long, cold lunar nights. Here, engineers move FSS onto a fixture that will allow them to tilt the payload, simulating the pull of lunar gravity in the direction at which one of the instrument's two seismometers is sensitive to motion. (The Moon's gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's.) Called an ambient tilt test, this activity allows engineers to check the seismometers' performance. The two seismometers are packaged together with a large battery, a computer, and electronics inside a cube structure that's surrounded by several layers of insulation and suspended within an outer protective cube, which is in turn covered with a shiny insulating blanket. The suite's single solar panel can be seen right of center. Surrounding the instrument are (from left): Nik Schwarz, Vik Singh, Joanna Farias, and Bert Turney. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26298
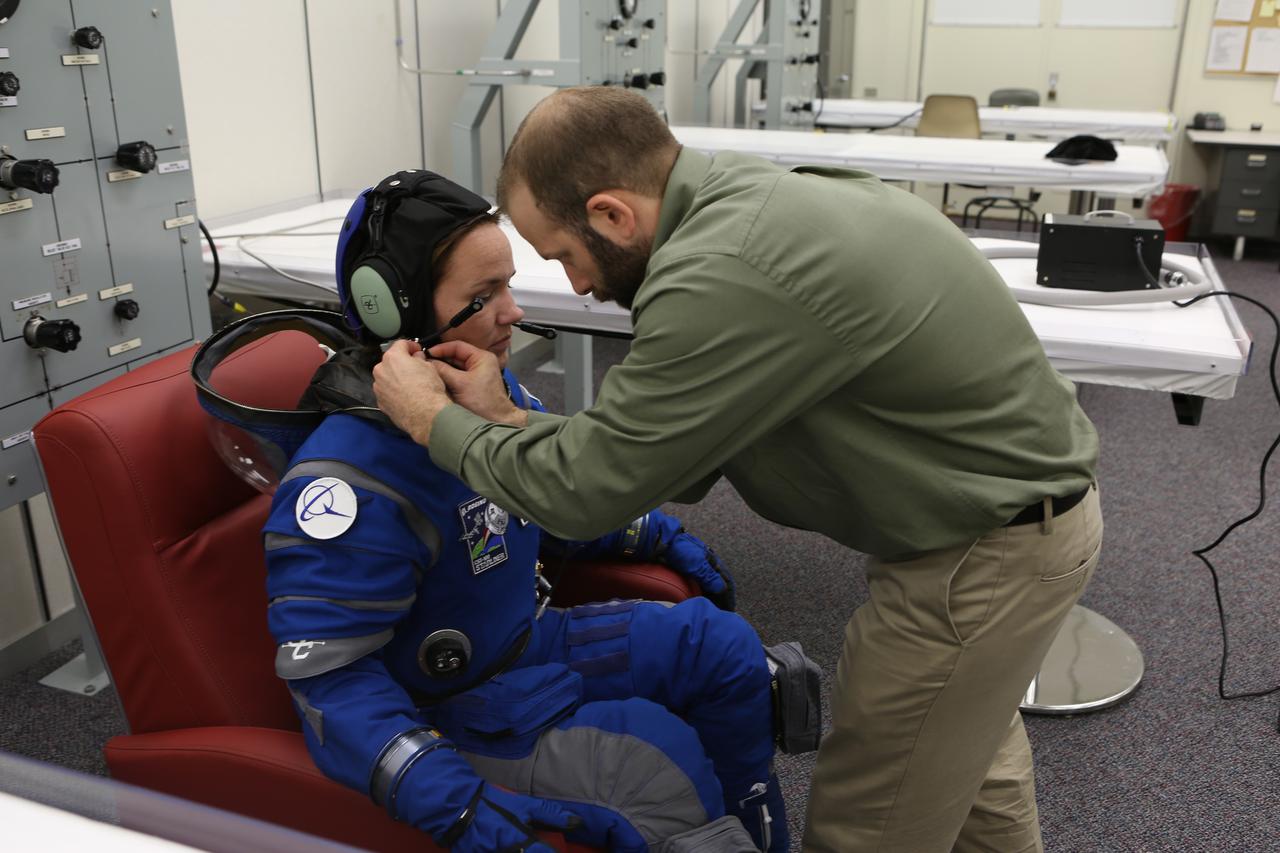

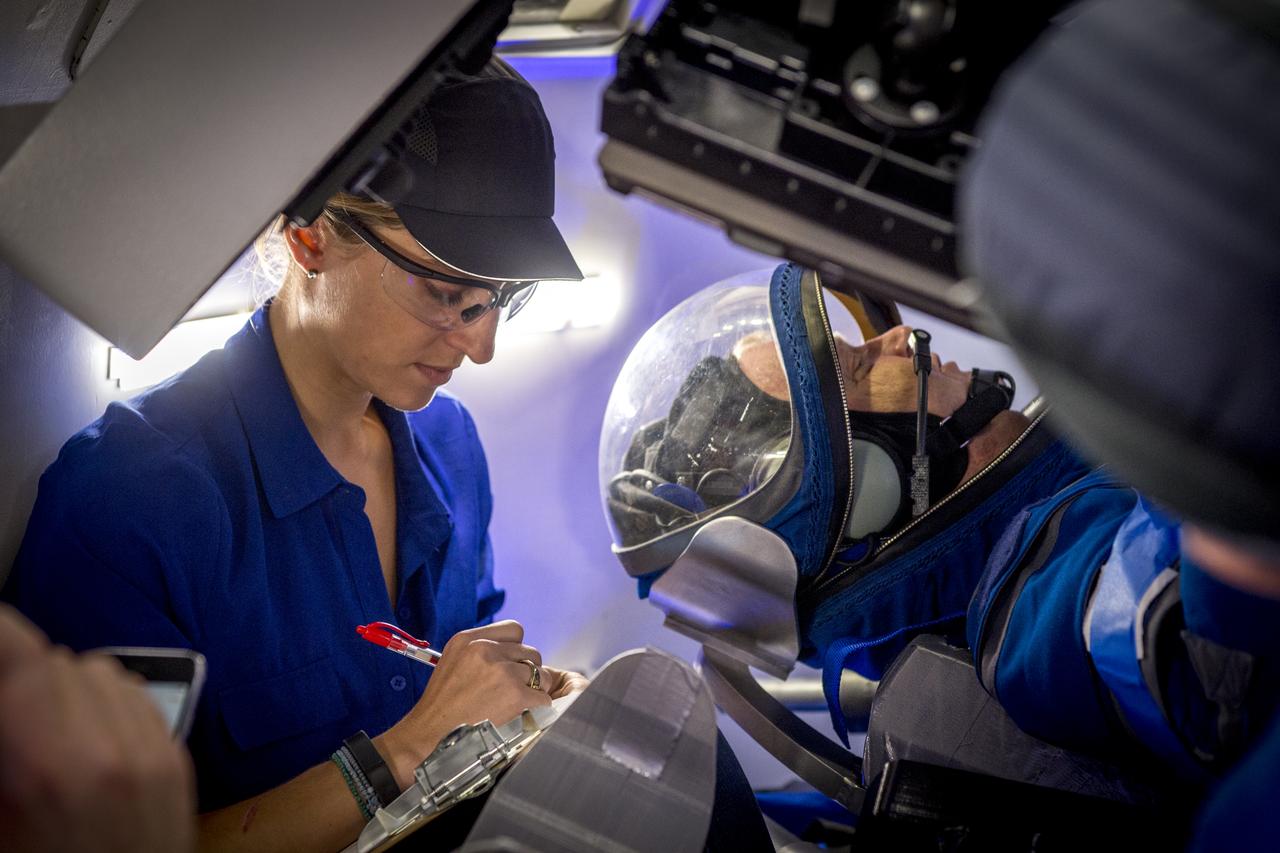
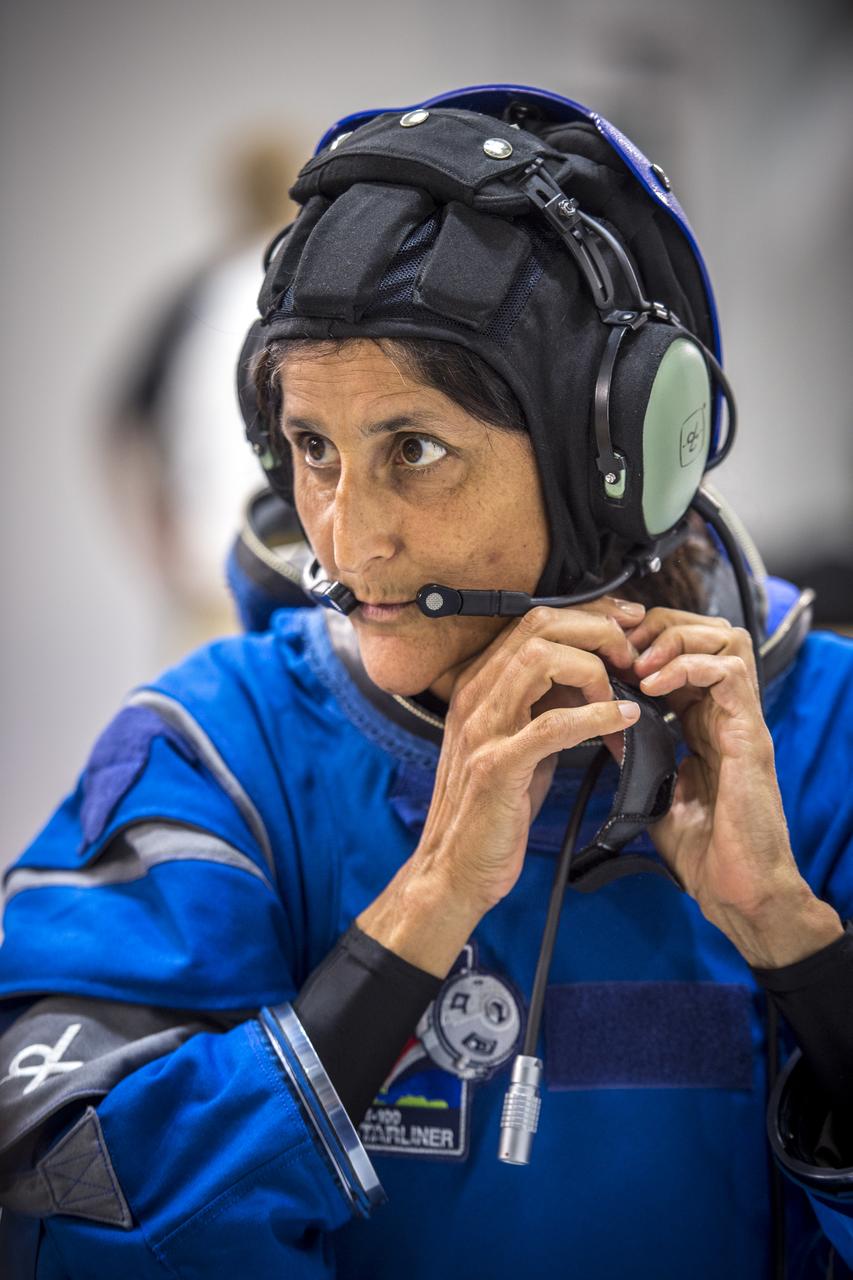
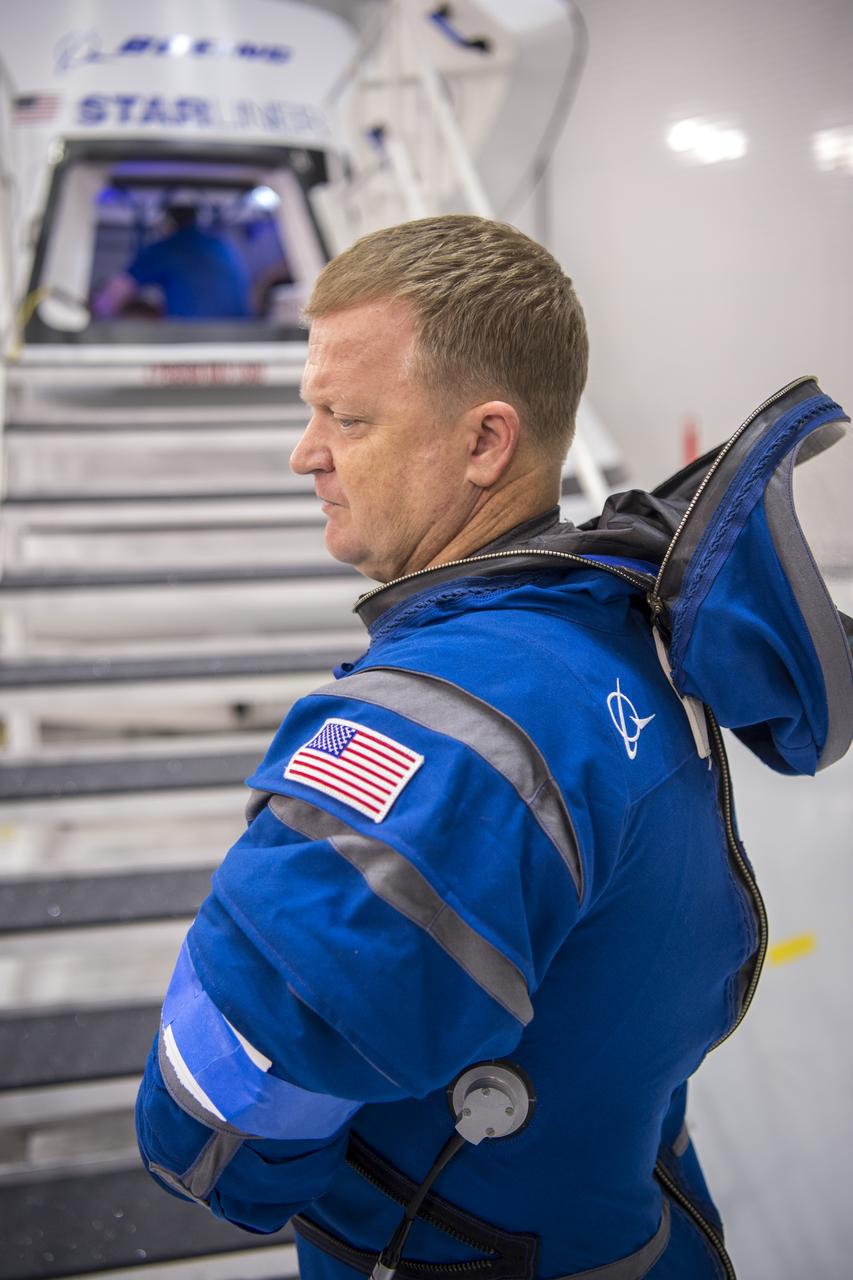
A suit technician prepares for a pressure test of Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day inside Crew Quarters at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
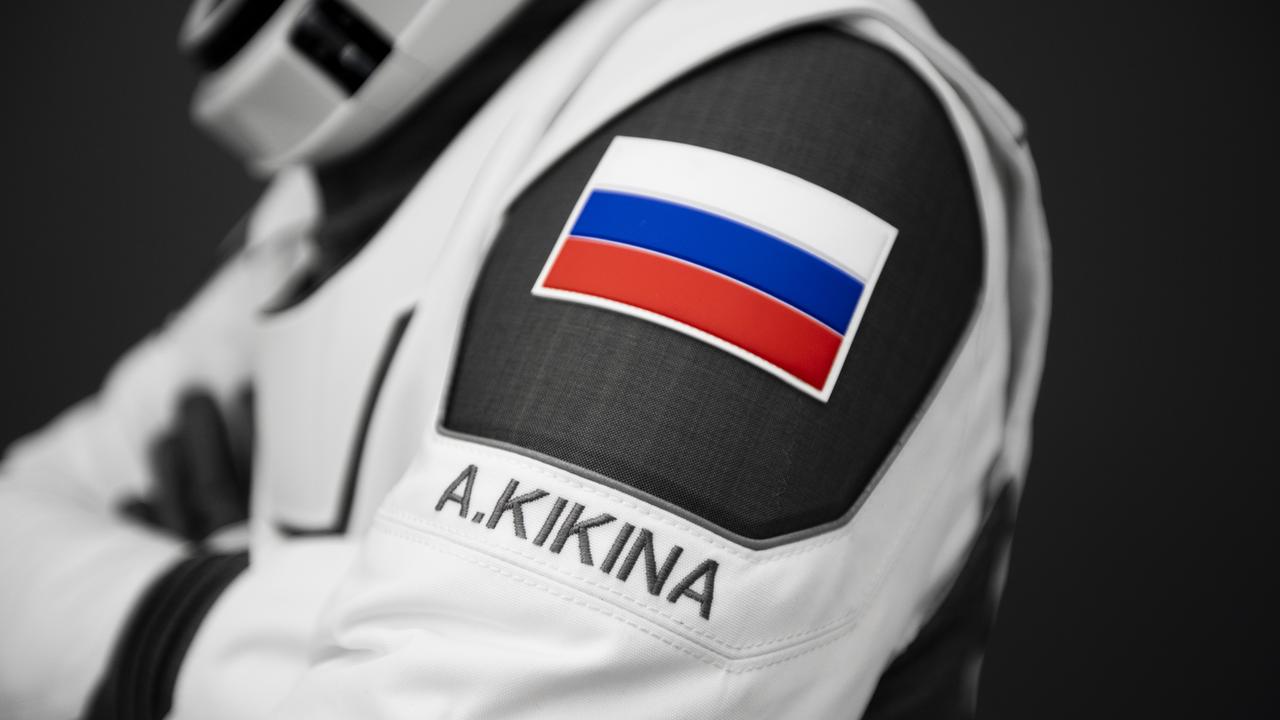

A SpaceX suit bears the name of cosmonaut Anna Kikina and a Russian flag. Kikina is a crewmember of NASA's SpaceX Crew-5 mission to the International Space Station.

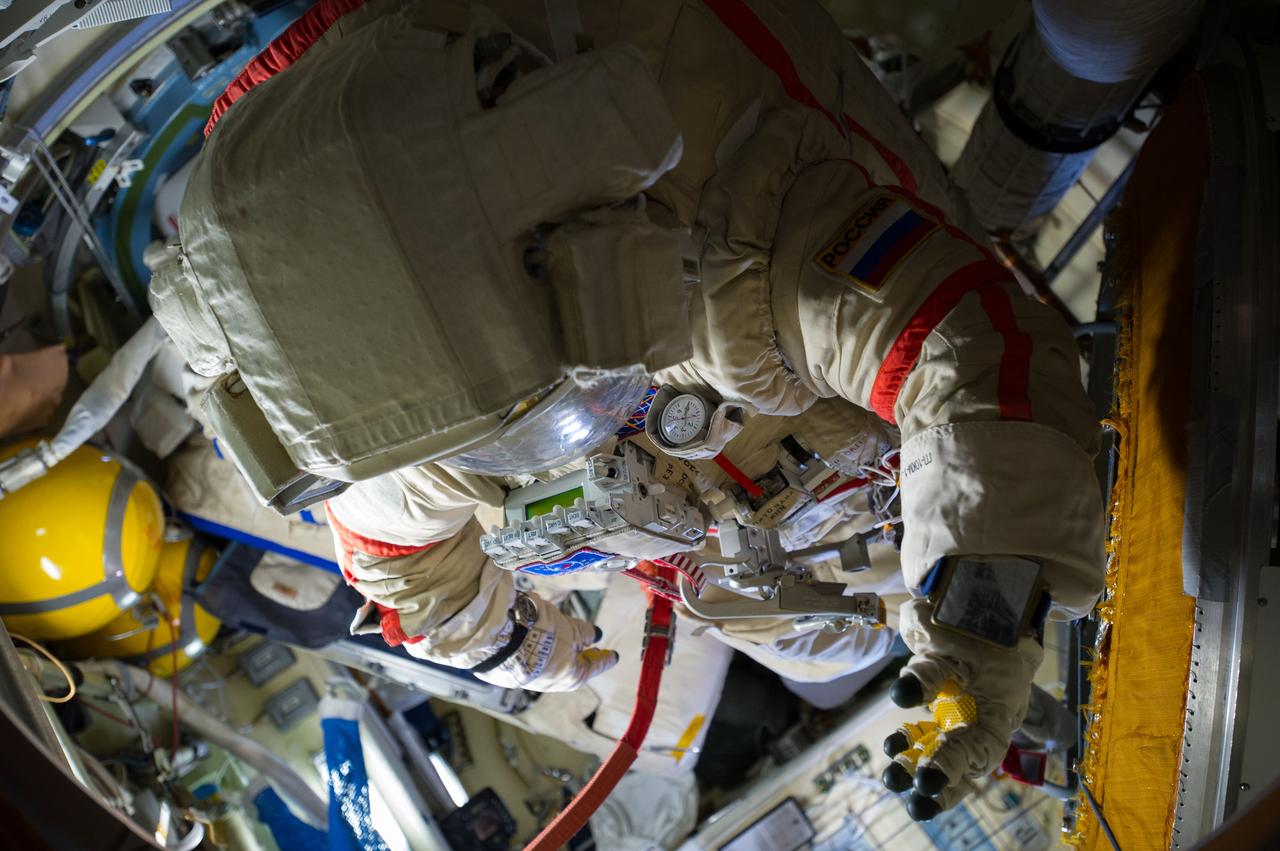
ISS040-E-013842 (17 June 2014) --- Russian cosmonaut Oleg Artemyev, Expedition 40 flight engineer, is pictured with Russian Orlan spacesuits in the International Space Station's Pirs Docking Compartment. Artemyev and Russian cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov donned their Orlan suits for a suited "dry run" dress rehearsal and to check out the suits' various components in advance of a spacewalk scheduled for June 19.
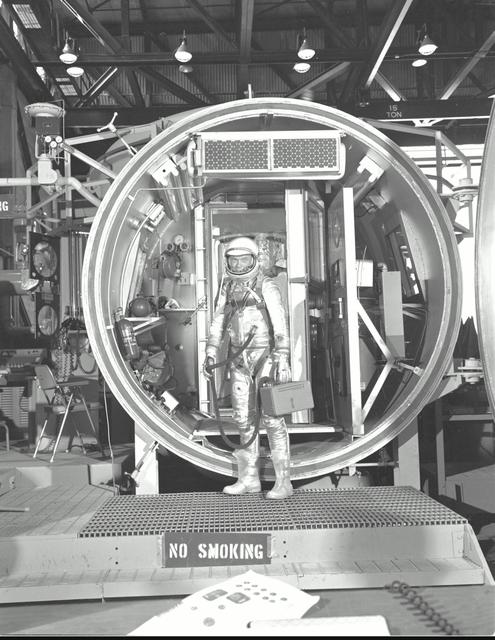
M61-00150 (1961) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., suited with hose to suit ventilation unit attached, during altitude chamber test. He is standing in the entrance to the test chamber with his helmet visor down. Photo credit: NASA
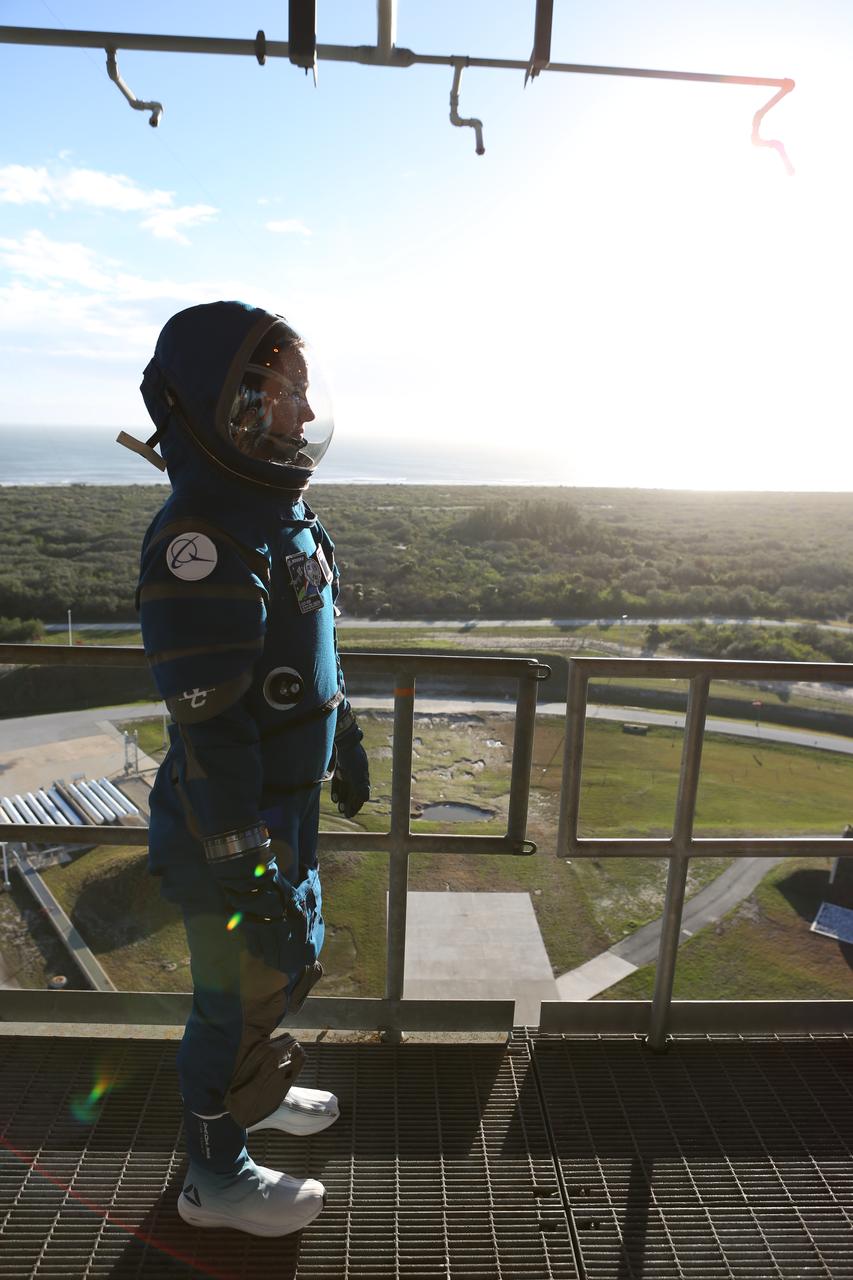

Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
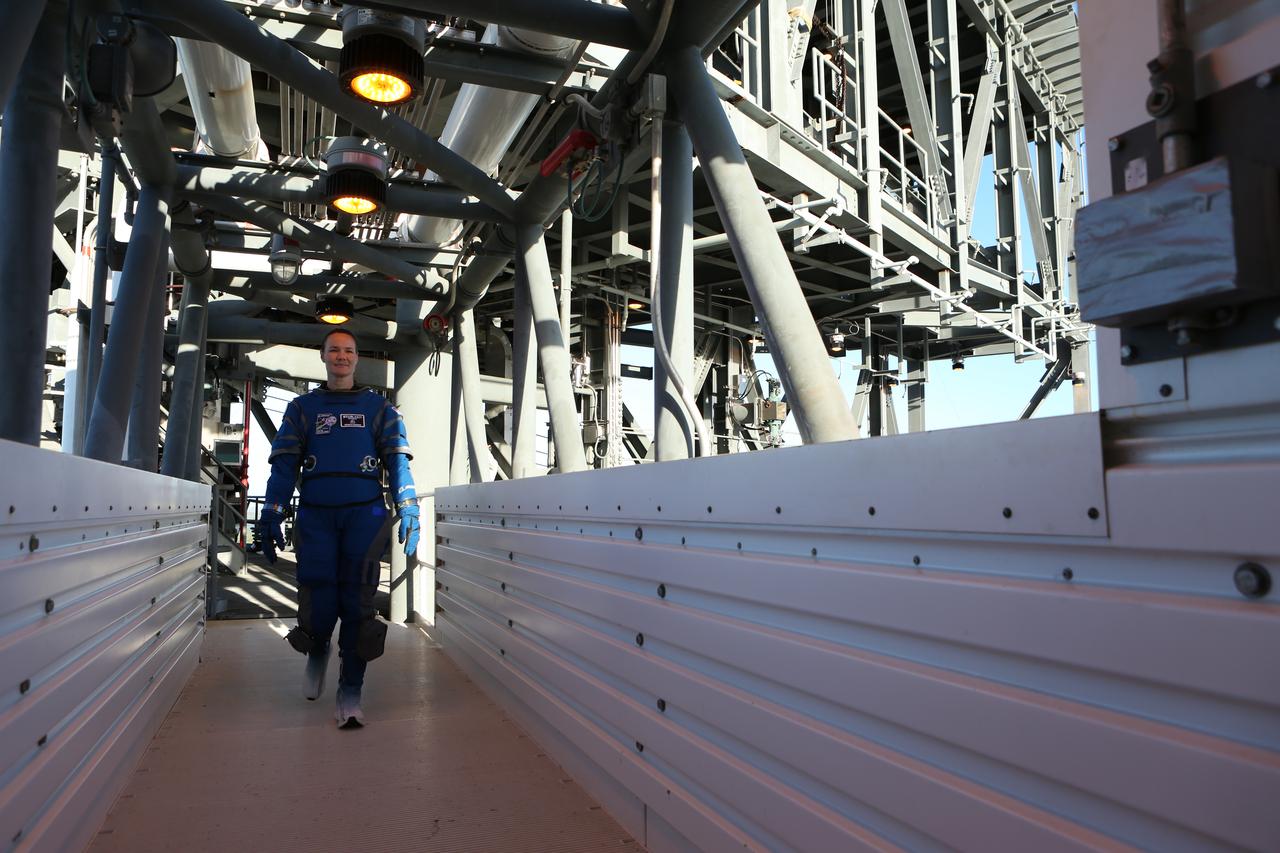

Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
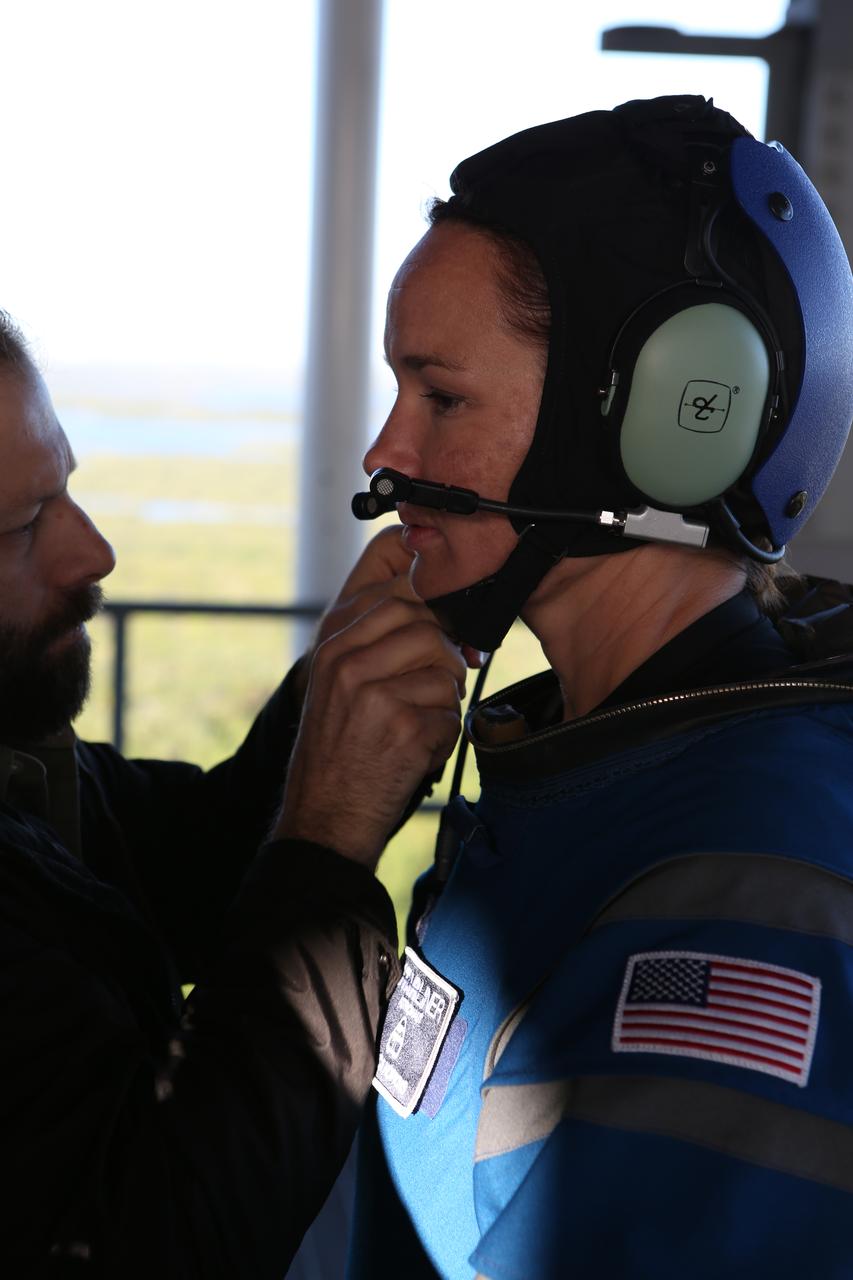

The communications carrier is placed as part of Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
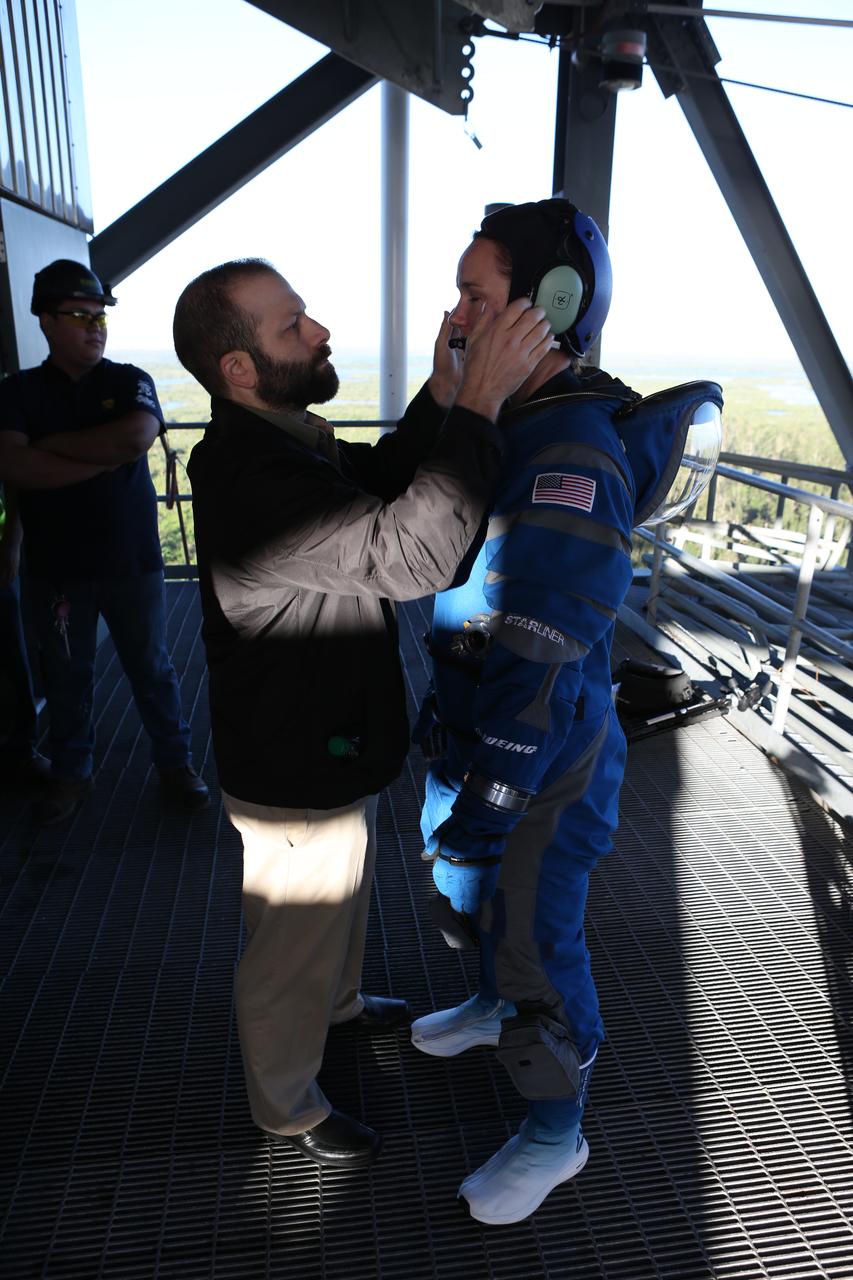

The communications carrier is placed as part of Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
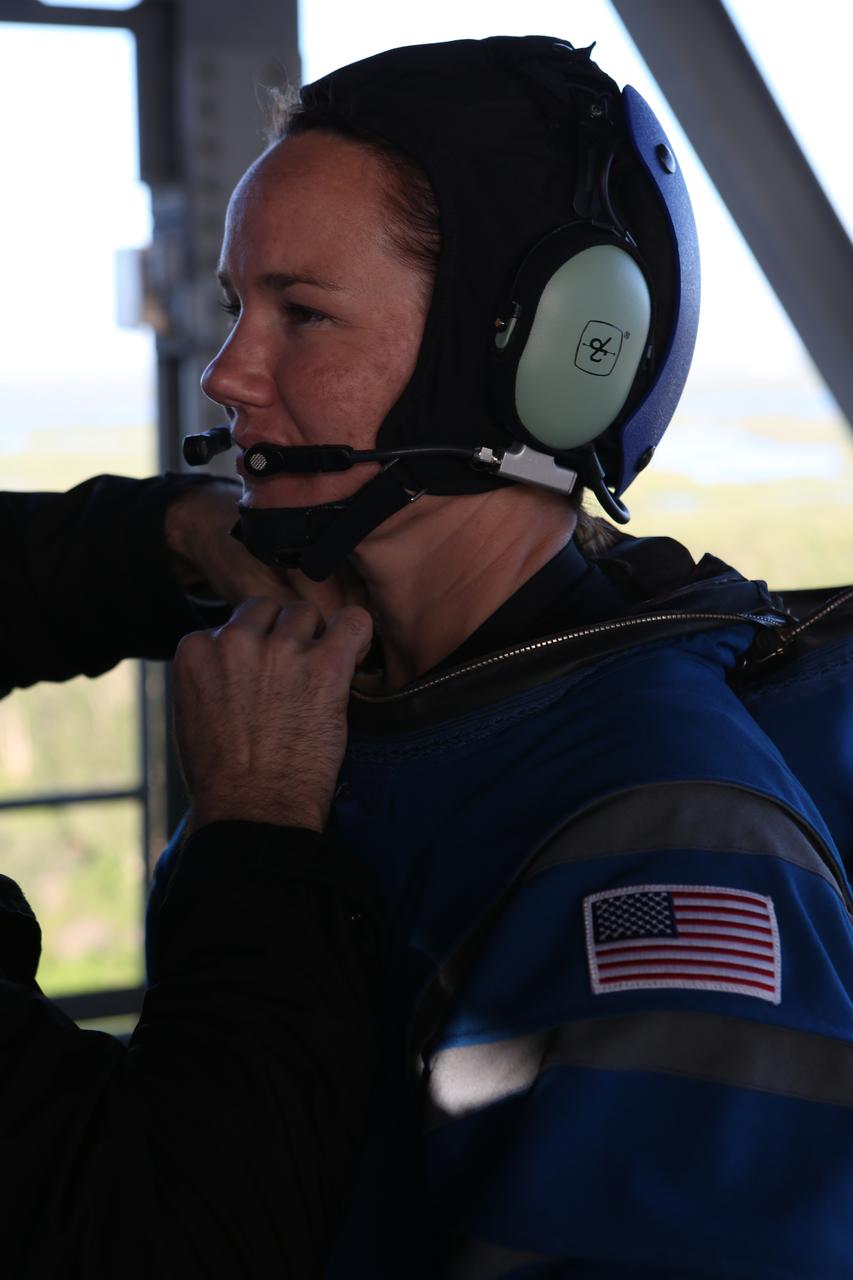

The communications carrier is placed as part of Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. Seen here being worn in the same manner as it will on launch day for the walk to the spacecraft at Space Launch Complex 41, the suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

Photographic documentation of Russian ORLAN space suits in the Pirs Docking Compartment (DC1) ready for EVA 38 as photographed by the Expedition 40 crew.
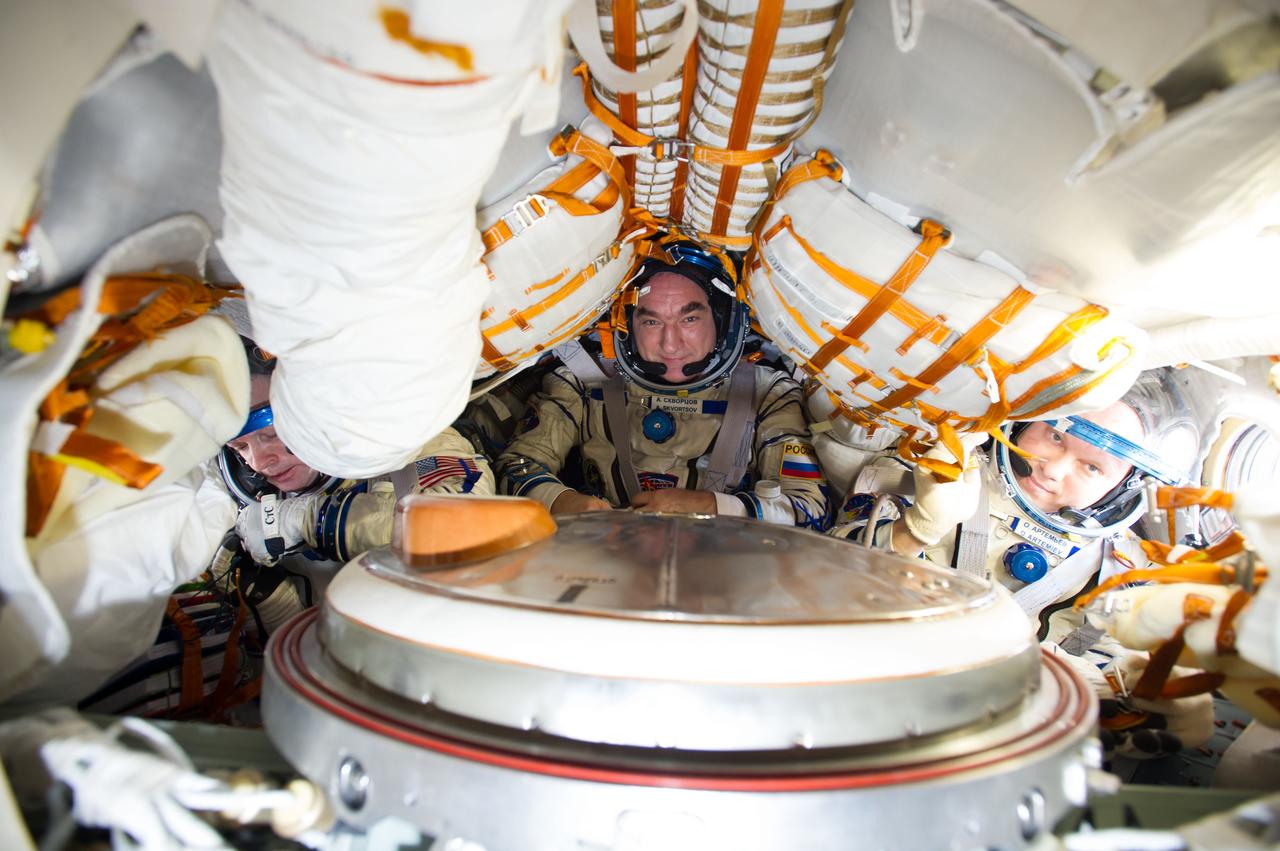

ISS040-E-123151 (2 Sept. 2014) --- Russian cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov (center), Expedition 40 flight engineer and Soyuz commander; along with NASA astronaut Steve Swanson (left), Expedition 40 commander; and Russian cosmonaut Oleg Artemyev, flight engineer, attired in Russian Sokol launch and entry suits, conduct a standard suit leak check in the Soyuz TMA-12M spacecraft in preparation for their return to Earth scheduled for Sept. 10, 2014.
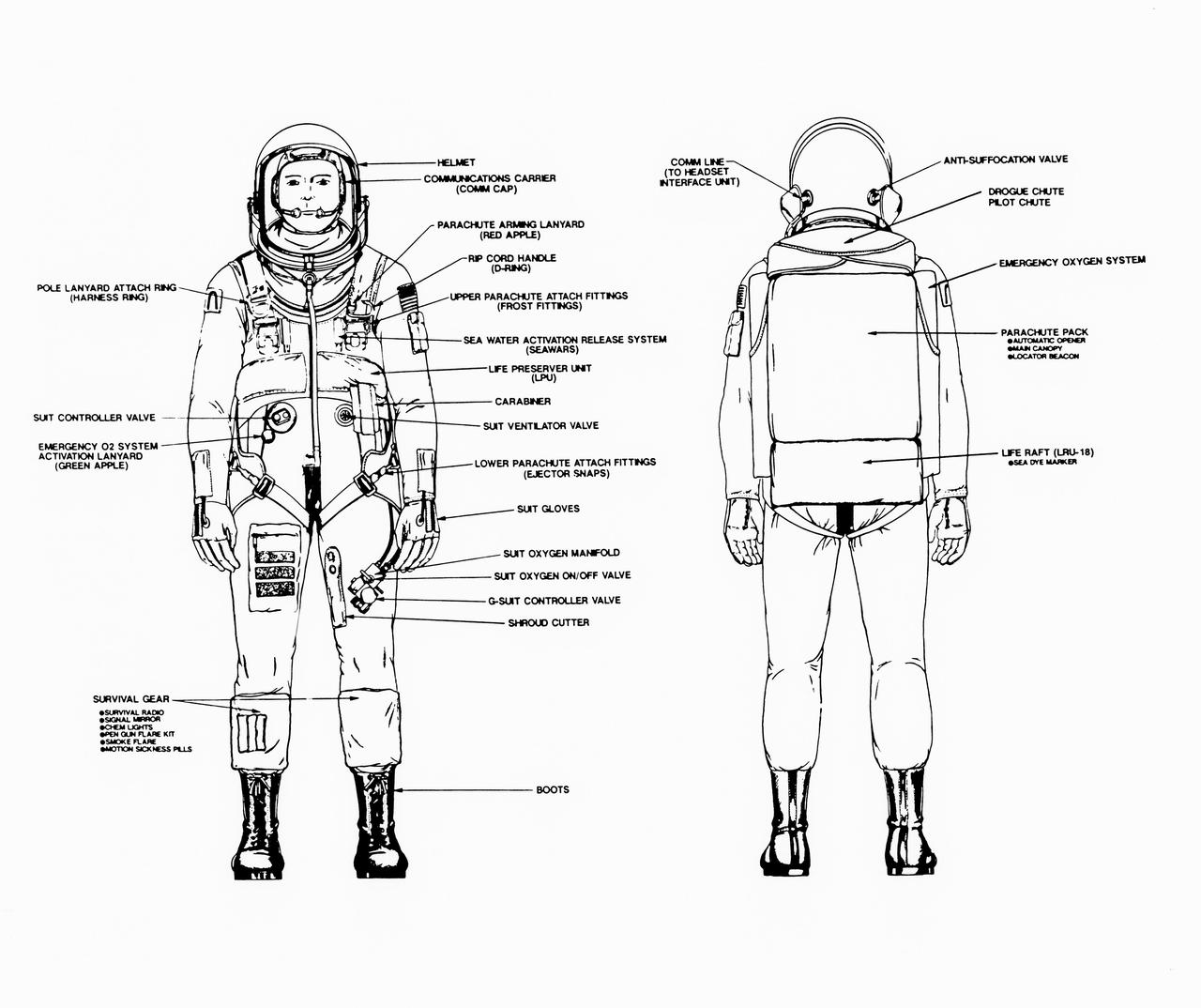
Line drawings illustrate the front and back of the space shuttle launch and entry suit (LES) and labels identify various components. LES was designed for STS-26, the return to flight mission, and subsequent missions. Included in the crew escape system (CES) package are launch and entry helmet (LEH) with communications carrier (COMM CAP), parachute pack and harness, life preserver unit (LPU), life raft unit (LRU), LES gloves, suit oxygen manifold and valves, boots, and survival gear. Details of larger components are also identified.

An operator dons a Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suit inside a room in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 31, 2018. SCAPE operators, wearing the suits, will participate in a hypergolic systems hot flow test at the MPPF. The test will serve as operational validation of the hypergol subsystem and demonstrate that the hypergols subsystem can service the Orion spacecraft, flow fuel at the required rates, drain and de-service the system, and meet the intended timeline. SCAPE suite are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.

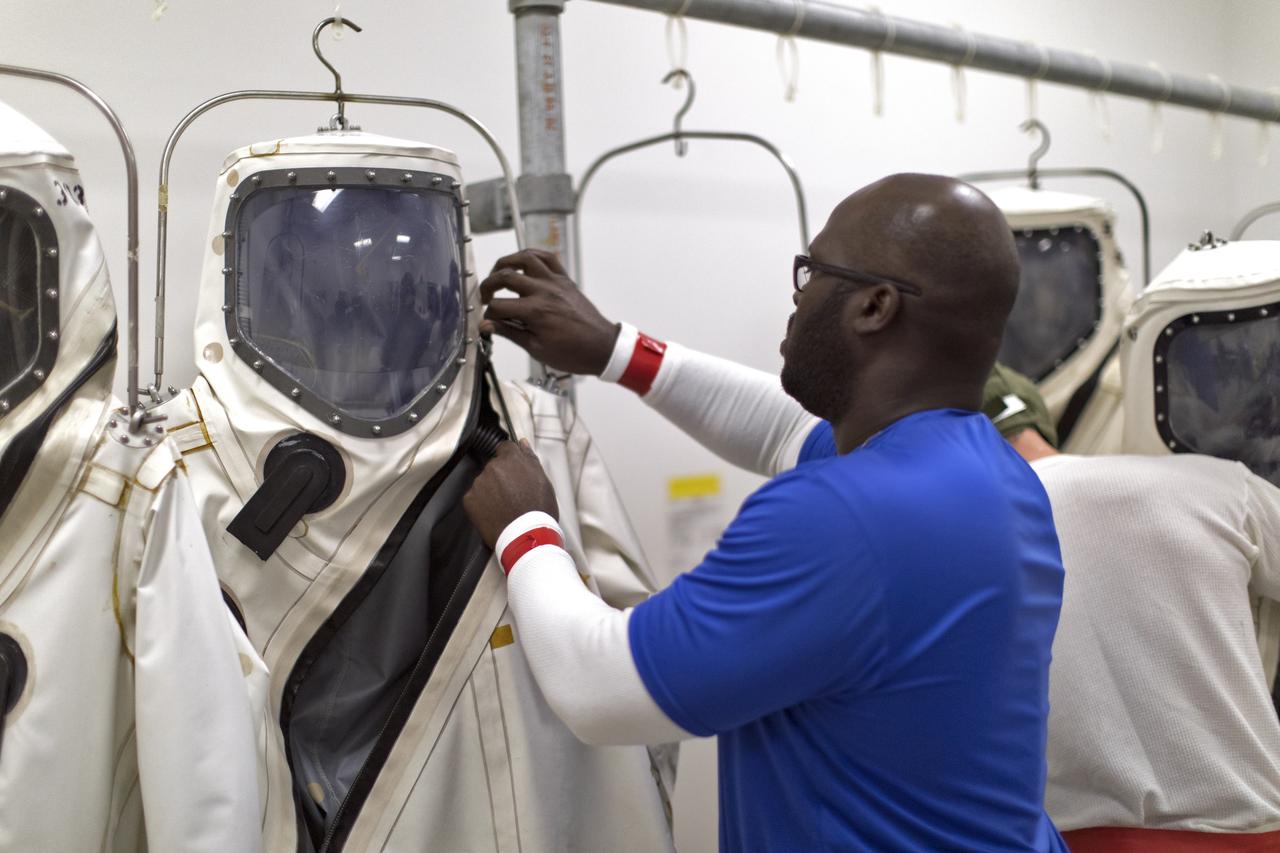
Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits are hanging in a row inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 31, 2018. SCAPE operators will don the suits and then participate in a hypergolic systems hot flow test at the MPPF. The test will serve as operational validation of the hypergol subsystem and demonstrate that the hypergols subsystem can service the Orion spacecraft, flow fuel at the required rates, drain and de-service the system, and meet the intended timeline. SCAPE suite are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
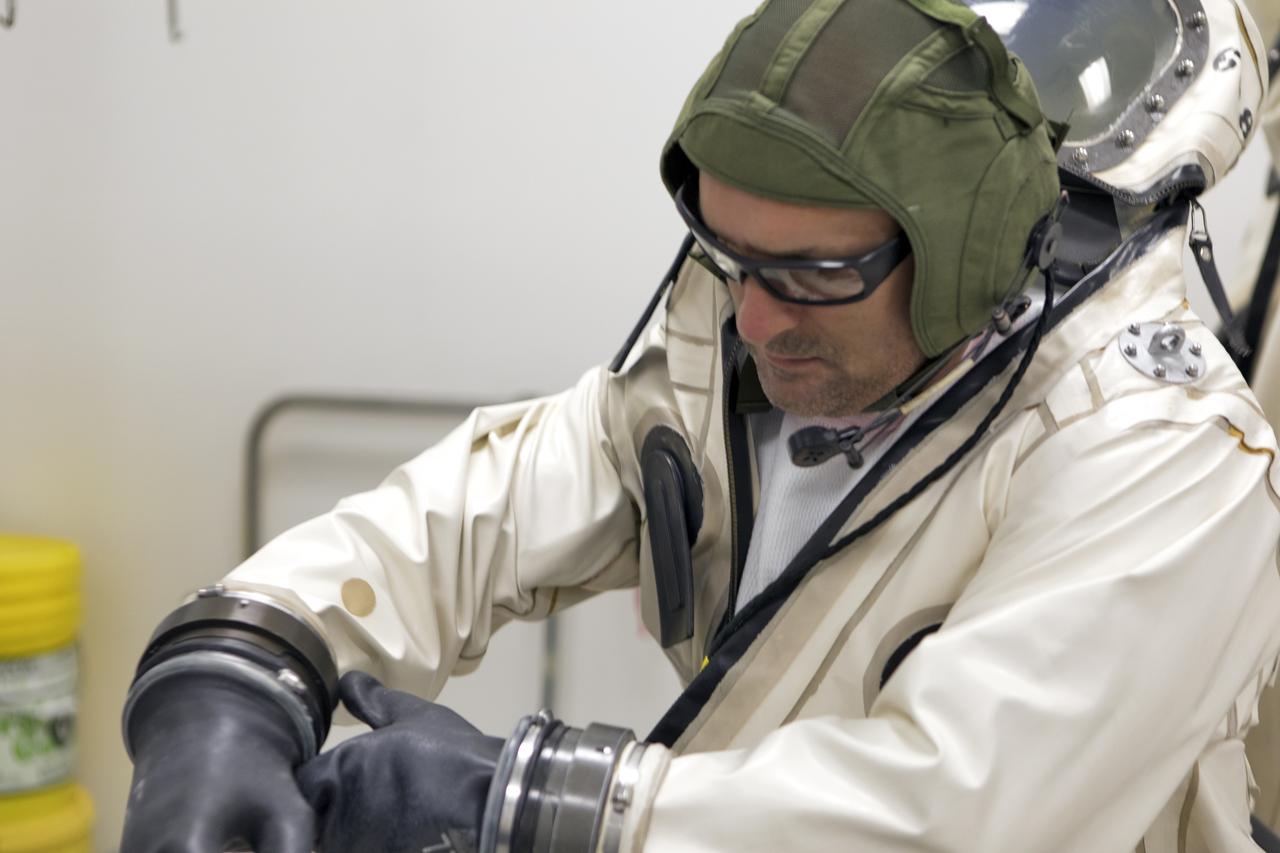

An operator dons a Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suit inside a room in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 31, 2018. SCAPE operators, wearing the suits, will participate in a hypergolic systems hot flow test at the MPPF. The test will serve as operational validation of the hypergol subsystem and demonstrate that the hypergols subsystem can service the Orion spacecraft, flow fuel at the required rates, drain and de-service the system, and meet the intended timeline. SCAPE suite are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.

An operator dons a Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suit inside a room in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 31, 2018. SCAPE operators, wearing the suits, will participate in a hypergolic systems hot flow test at the MPPF. The test will serve as operational validation of the hypergol subsystem and demonstrate that the hypergols subsystem can service the Orion spacecraft, flow fuel at the required rates, drain and de-service the system, and meet the intended timeline. SCAPE suite are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.

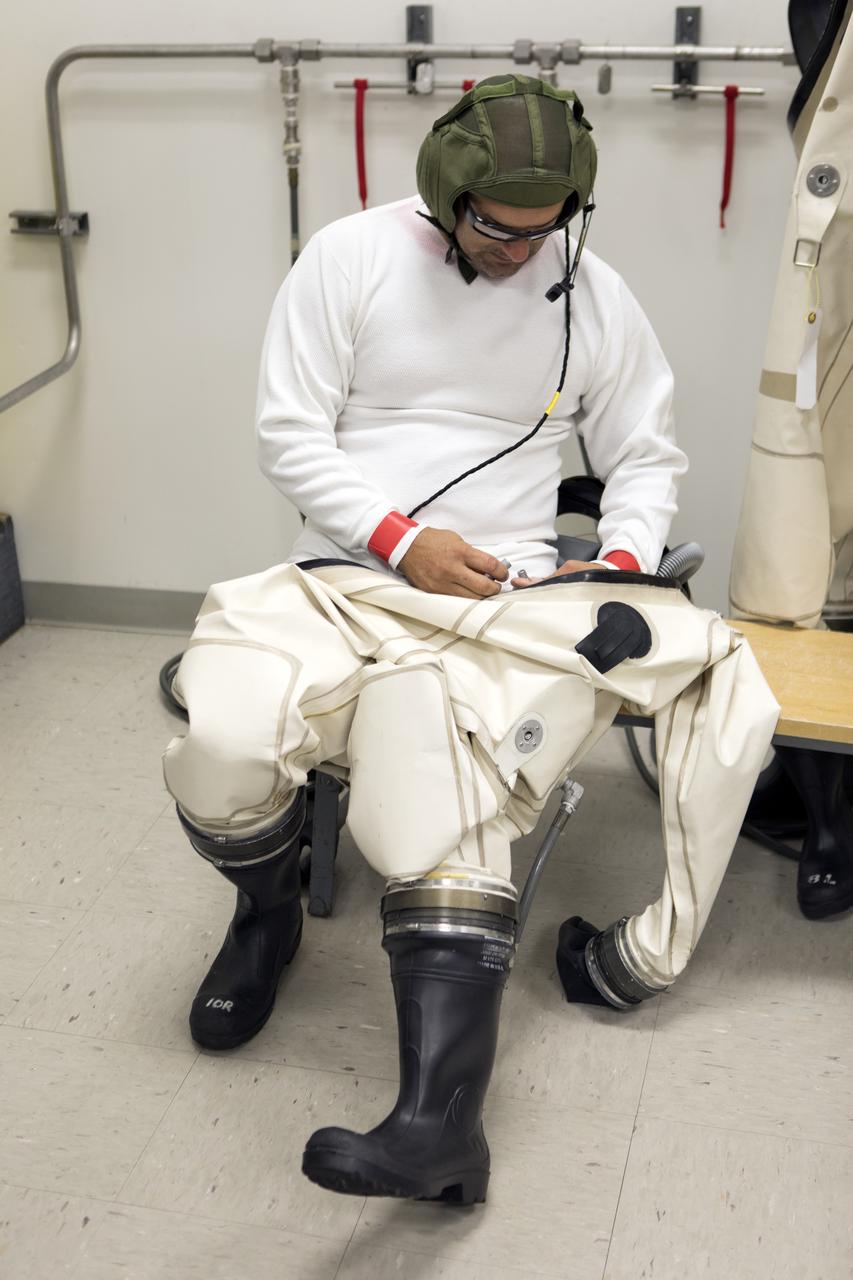
An operator prepares to don a Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suit inside a room in the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 31, 2018. SCAPE operators, wearing the suits, will participate in a hypergolic systems hot flow test at the MPPF. The test will serve as operational validation of the hypergol subsystem and demonstrate that the hypergols subsystem can service the Orion spacecraft, flow fuel at the required rates, drain and de-service the system, and meet the intended timeline. SCAPE suite are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
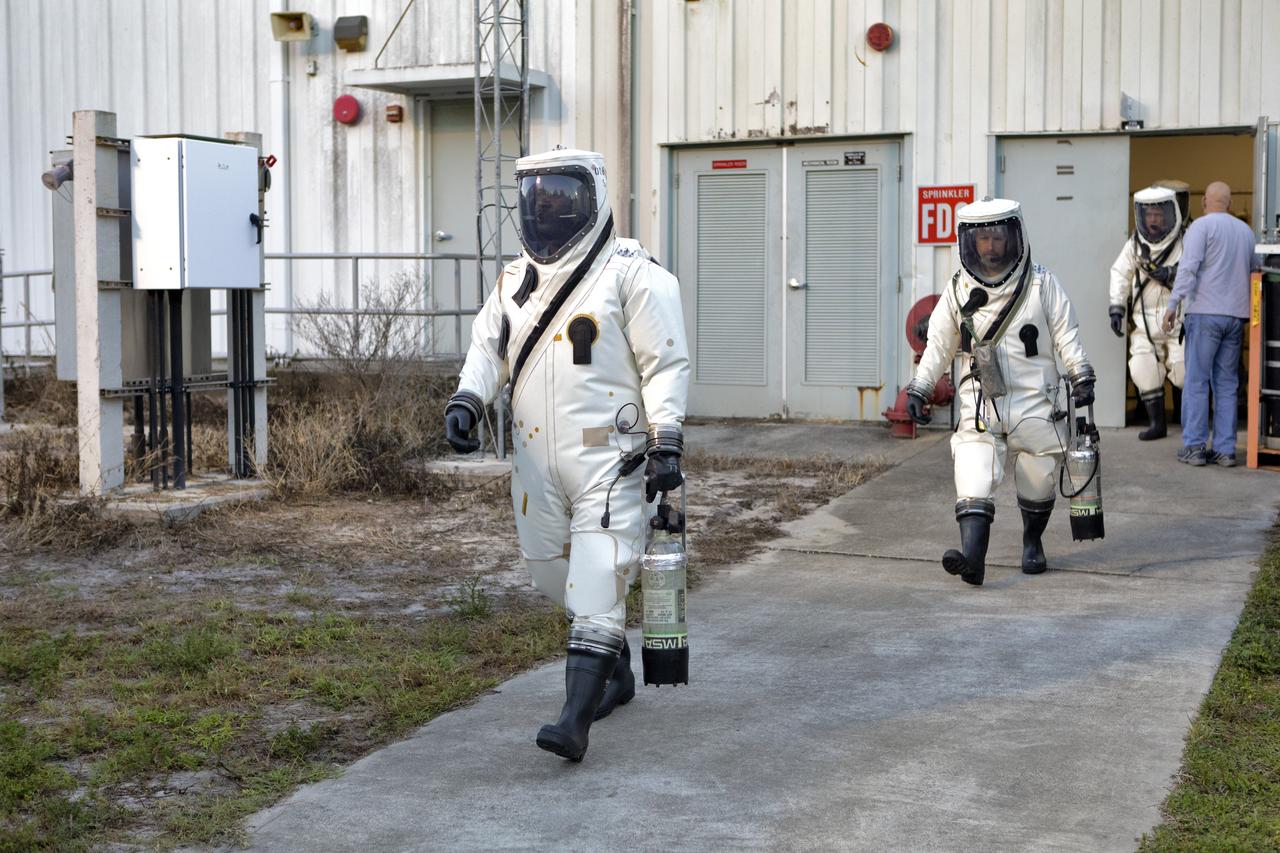

Operators wearing Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits depart the suit-up room at the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 31, 2018. SCAPE operators are preparing to participate in a hypergolic systems hot flow test at the MPPF. The test will serve as operational validation of the hypergol subsystem and demonstrate that the hypergols subsystem can service the Orion spacecraft, flow fuel at the required rates, drain and de-service the system, and meet the intended timeline. SCAPE suite are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
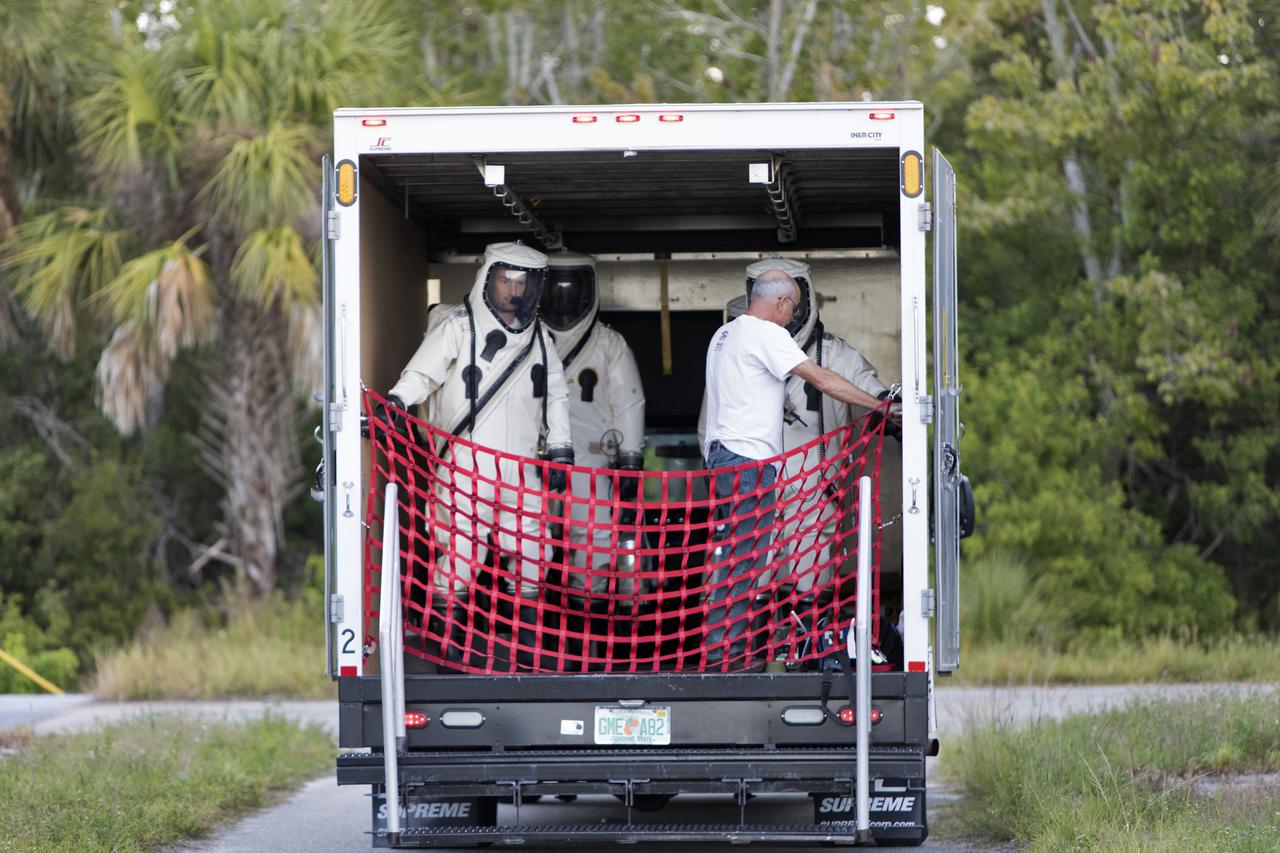

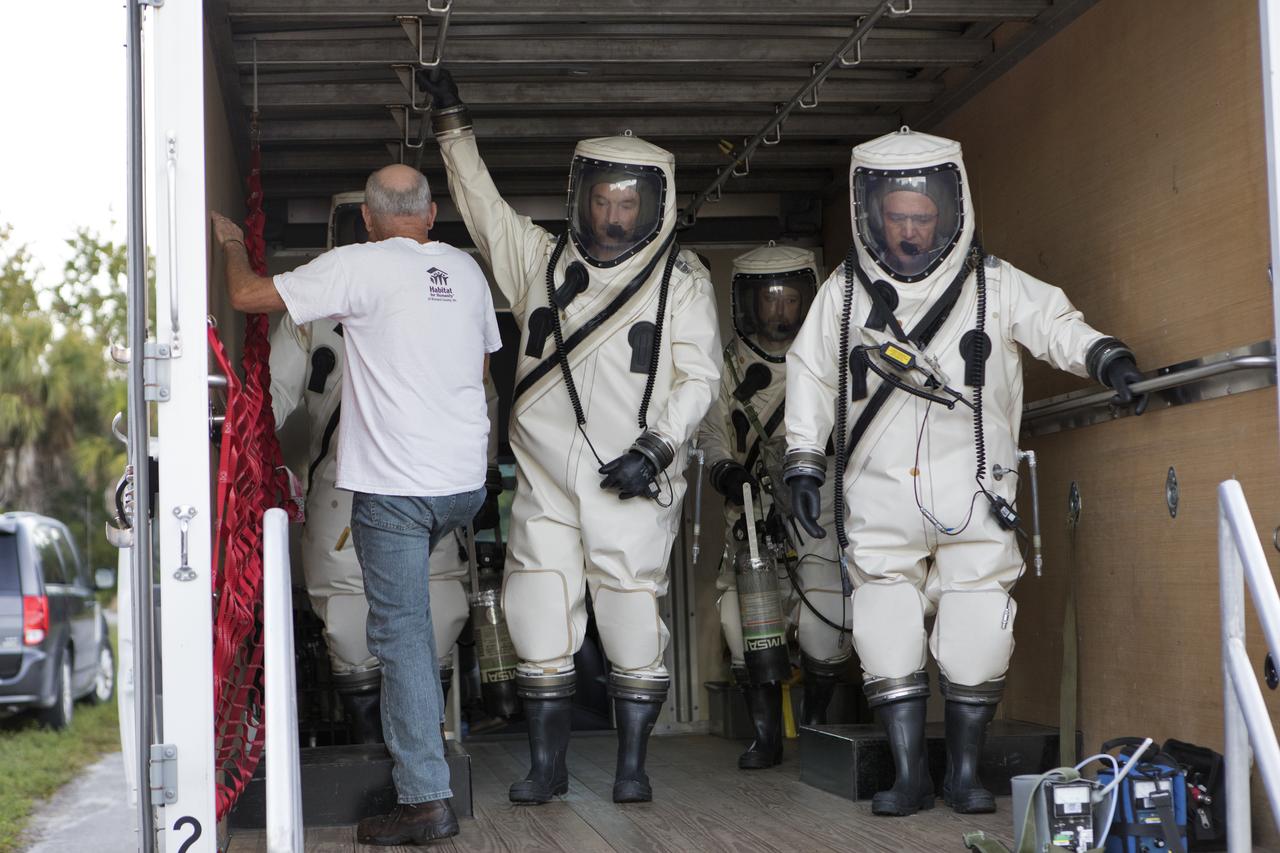
Operators wearing Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble (SCAPE) suits are inside a transport vehicle near the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 31, 2018. SCAPE operators, wearing the suits, will participate in a hypergolic systems hot flow test at the MPPF. The test will serve as operational validation of the hypergol subsystem and demonstrate that the hypergols subsystem can service the Orion spacecraft, flow fuel at the required rates, drain and de-service the system, and meet the intended timeline. SCAPE suite are used in operations involving toxic propellants and are supplied with air either through a hardline or through a self-contained environmental control unit.
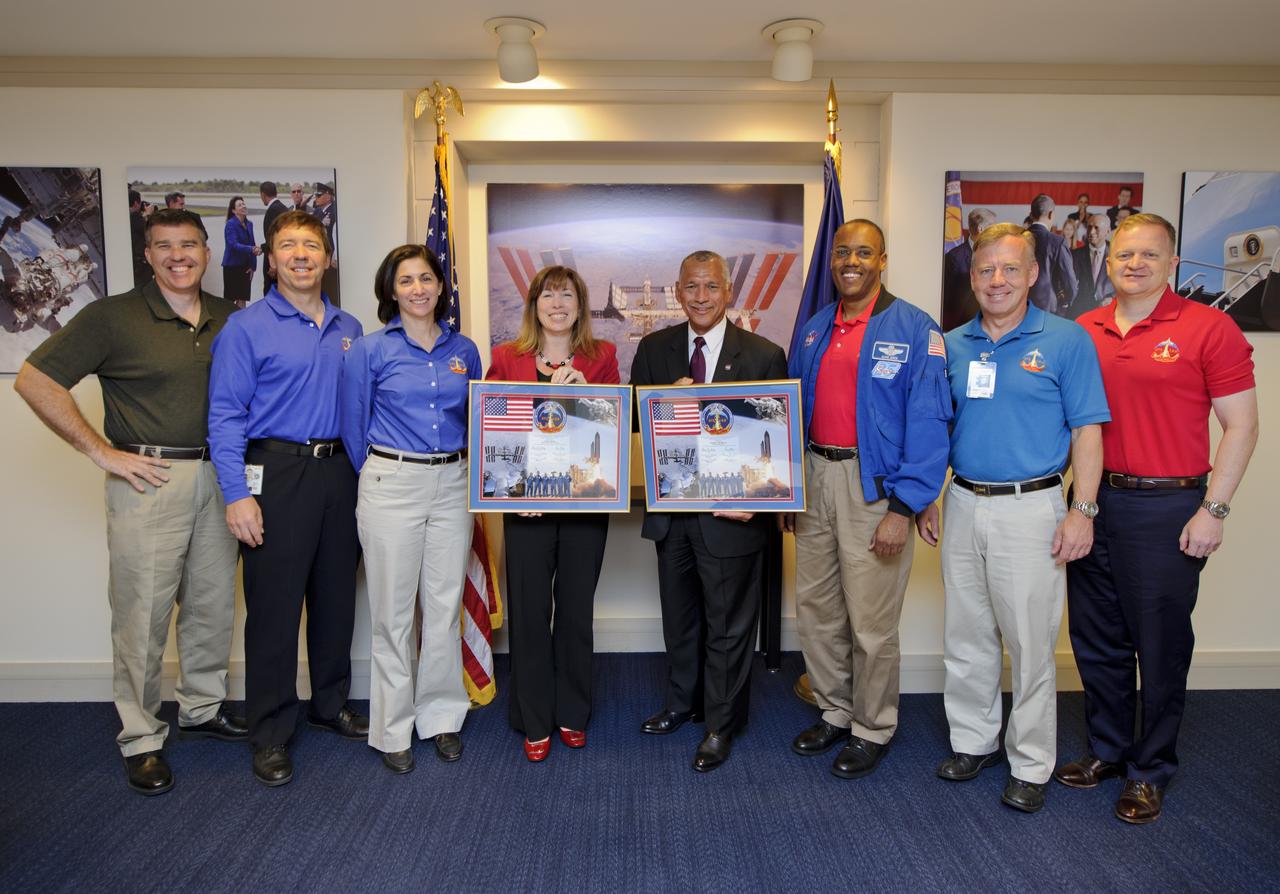

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden along with Deputy Administrator Lori Garver, center, stands with STS-133 crew members from left, Mission Specialists Stephen Bowen, Michael Barratt, Nicole Slott, Alvin Drew, Commander Steve Lindsey, and Pilot Eric Boe after being presented montages, Monday, May 9, 2011, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
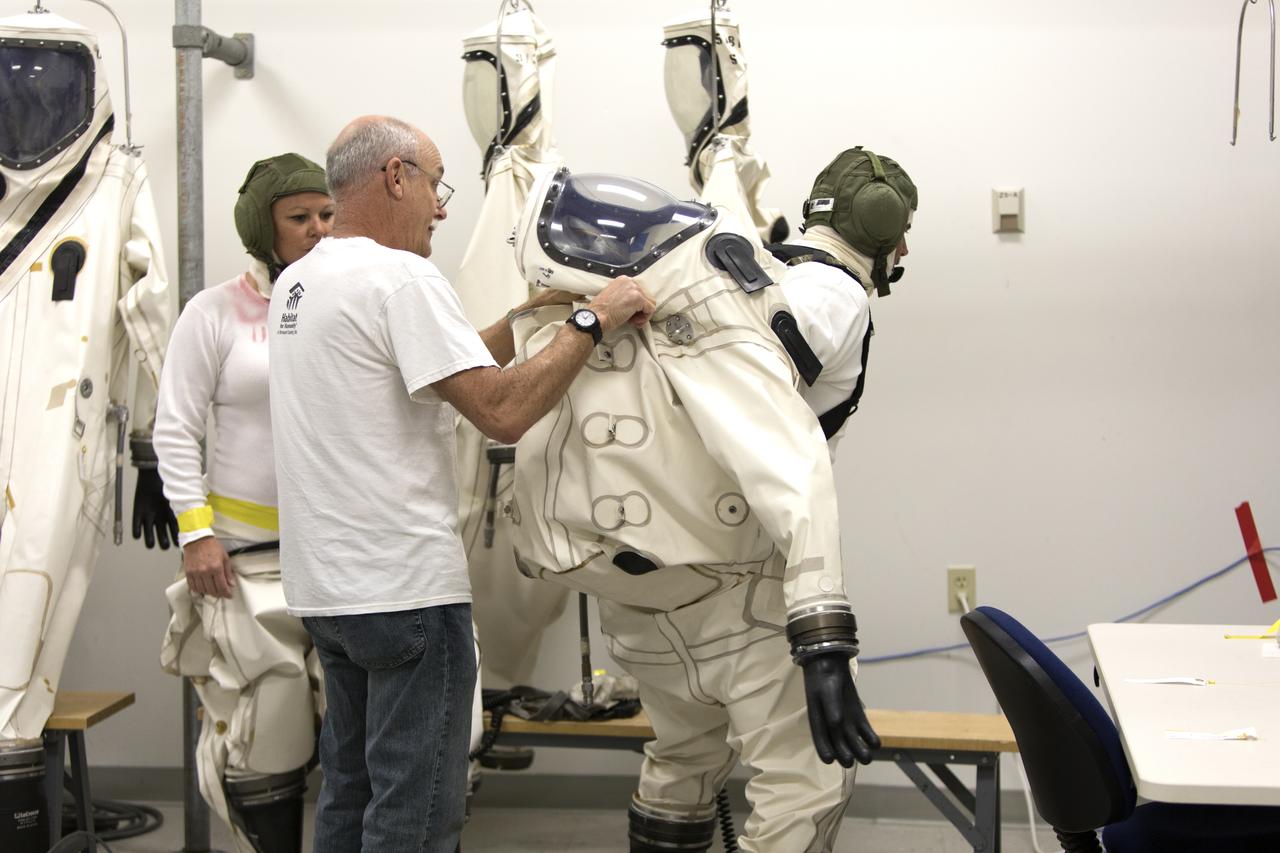

Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.

Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.
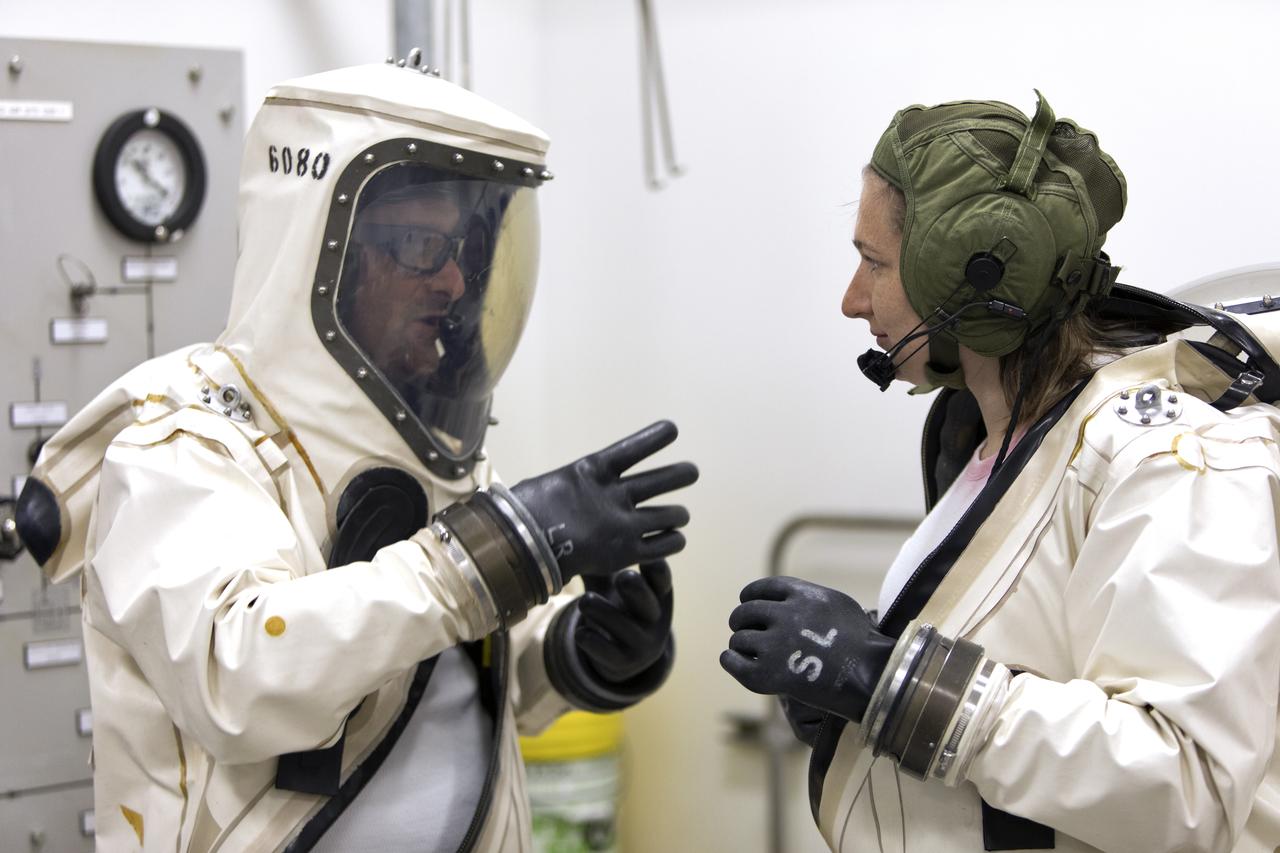

Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.
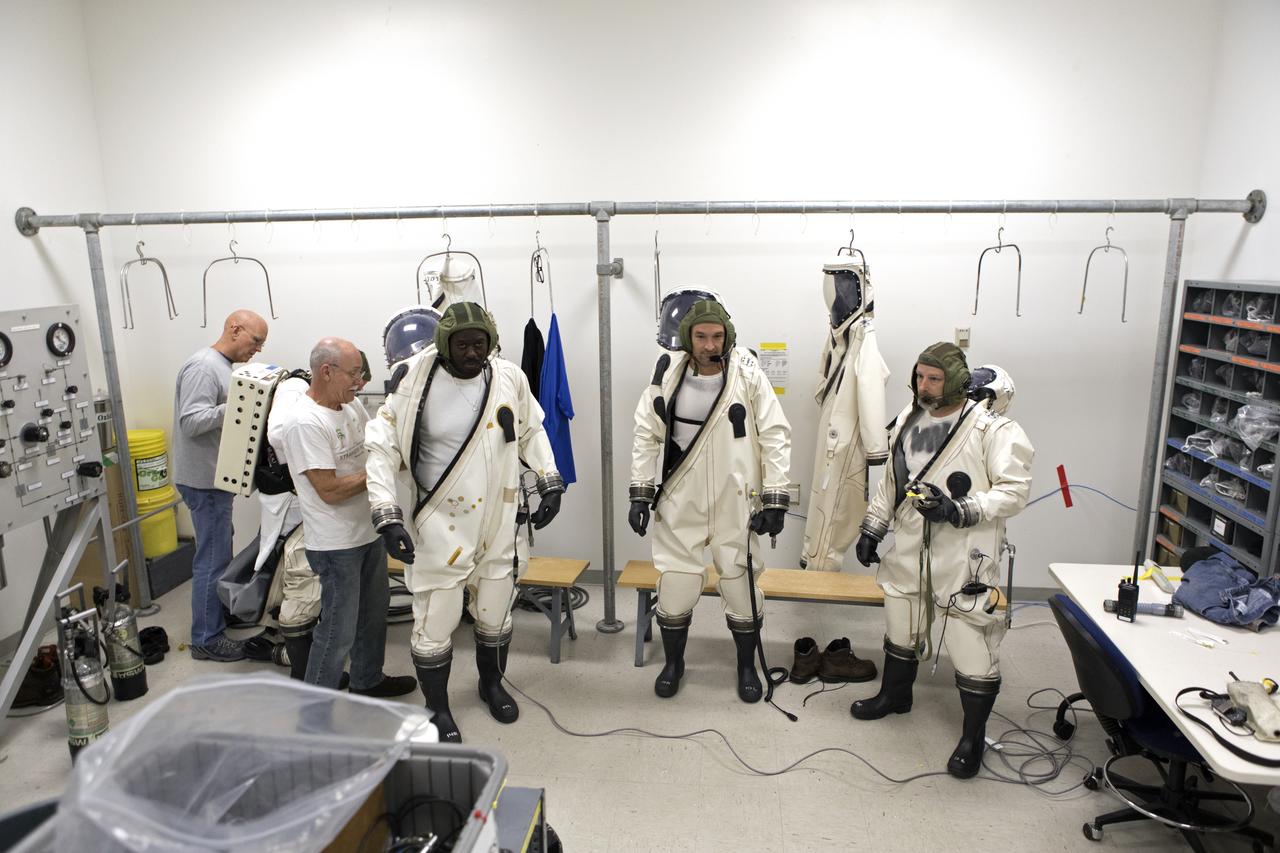

Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.

Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.

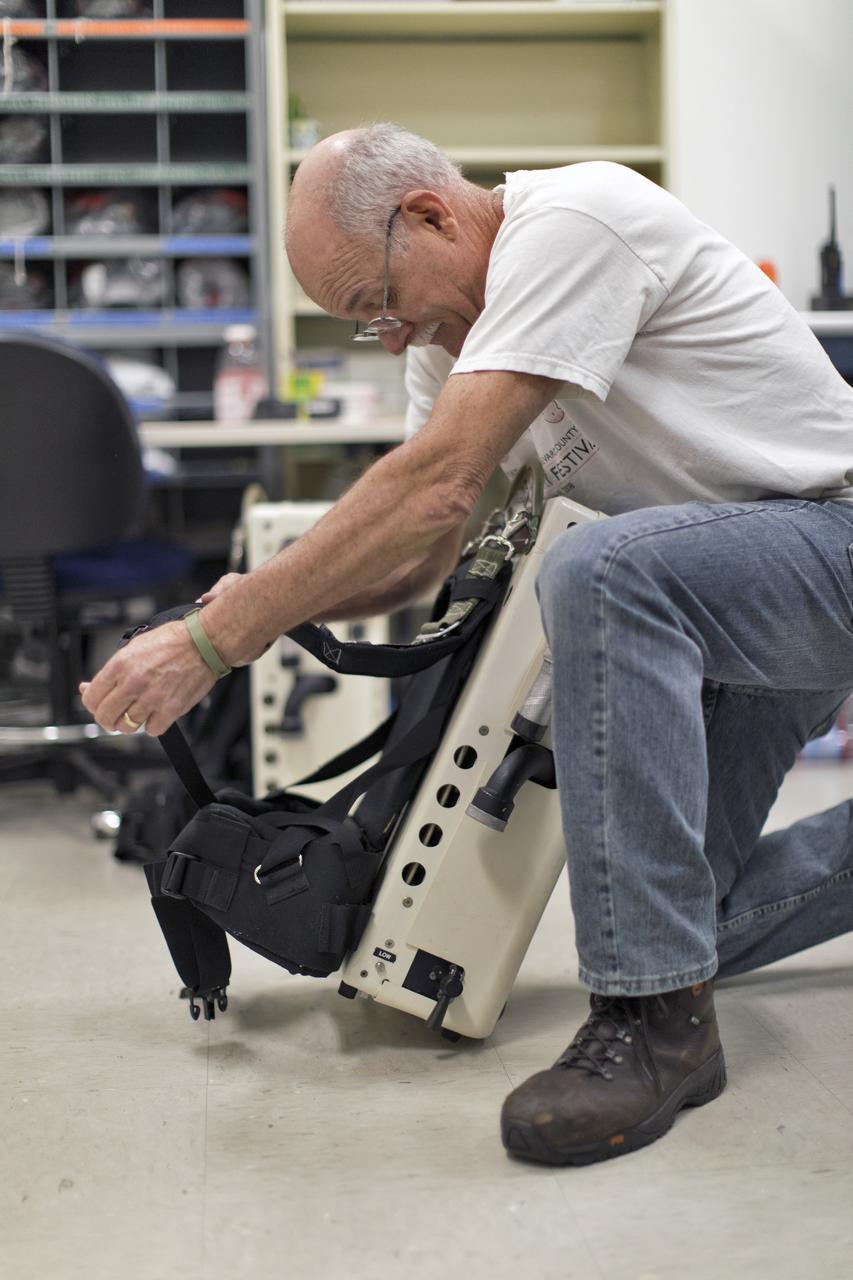
Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.

Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.

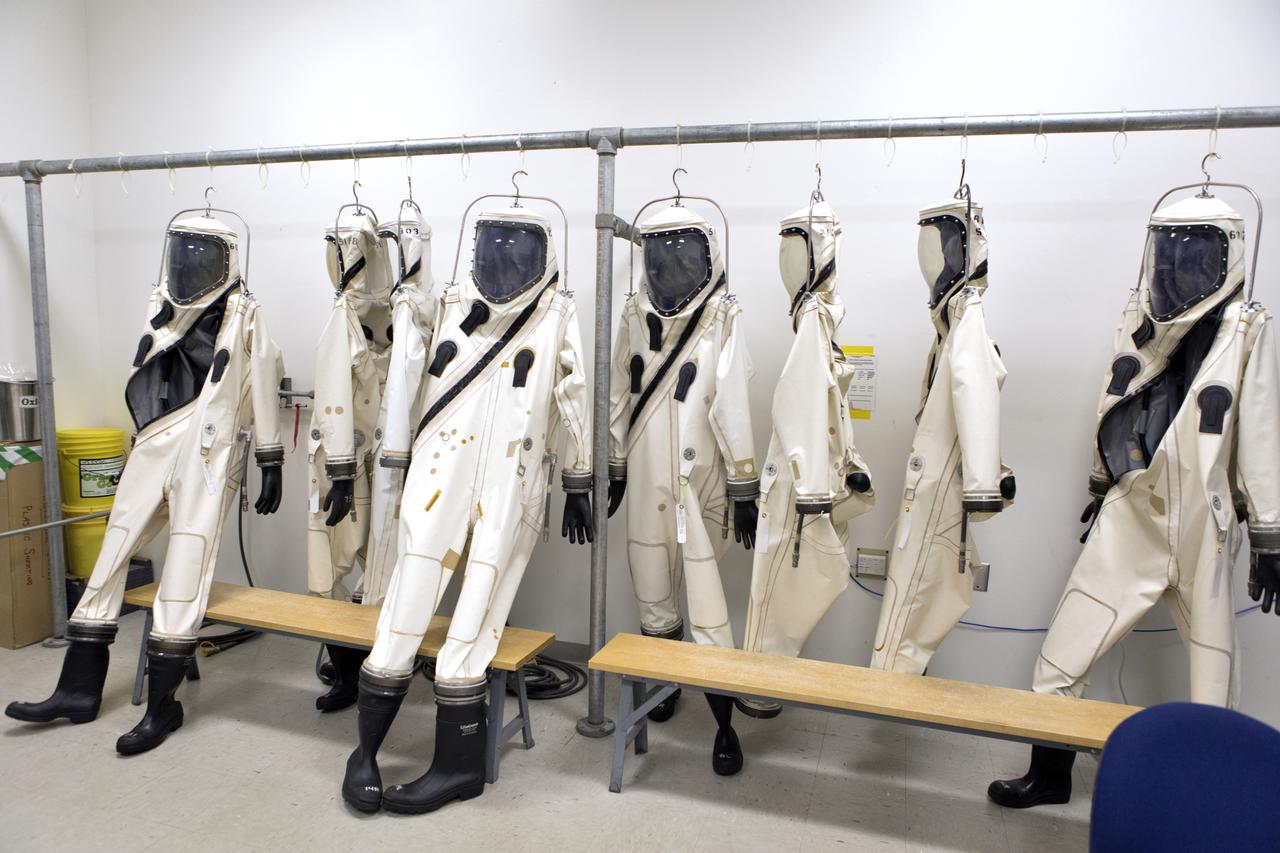
Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.

Technicans inside Kennedy's Multi-Payload Processing Facility do testing in SCAPE (Self-Contained Atmospheric Protective Ensemble) suits.

S64-14843 (1962) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., pilot of the Mercury-Atlas 6 Earth-orbital space mission, is suited up at Cape Canaveral, Florida, during MA-6 preflight activities. Assisting Glenn is suit technician Al Rochford. Photo credit: NASA

A Russian Sokol suit technician prepares to help American spaceflight participant Richard Garriott don his flight suit prior to the Soyuz TMA-13 launch with Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke and Flight Engineer Yuri V. Lonchakov, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24 with two of the Expedition 17 crew members currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A SpaceX launch and entry suit bears a Japanese flag, and the name of JAXA astronaut Koichi Wakata – a crewmember of NASA's SpaceX Crew-5 mission to the International Space Station.
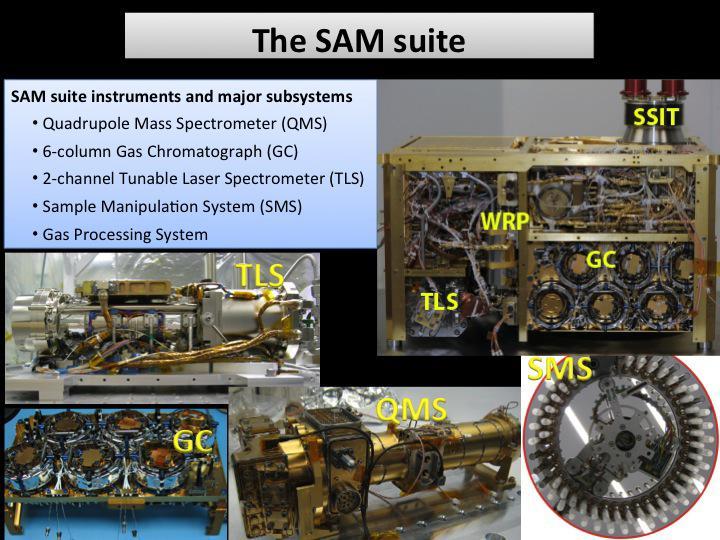
This illustration shows the instruments and subsystems of the Sample Analysis at Mars SAM suite on the Curiosity Rover of NASA Mars Science Laboratory Project. SAM analyzes the gases in the Martian atmosphere.
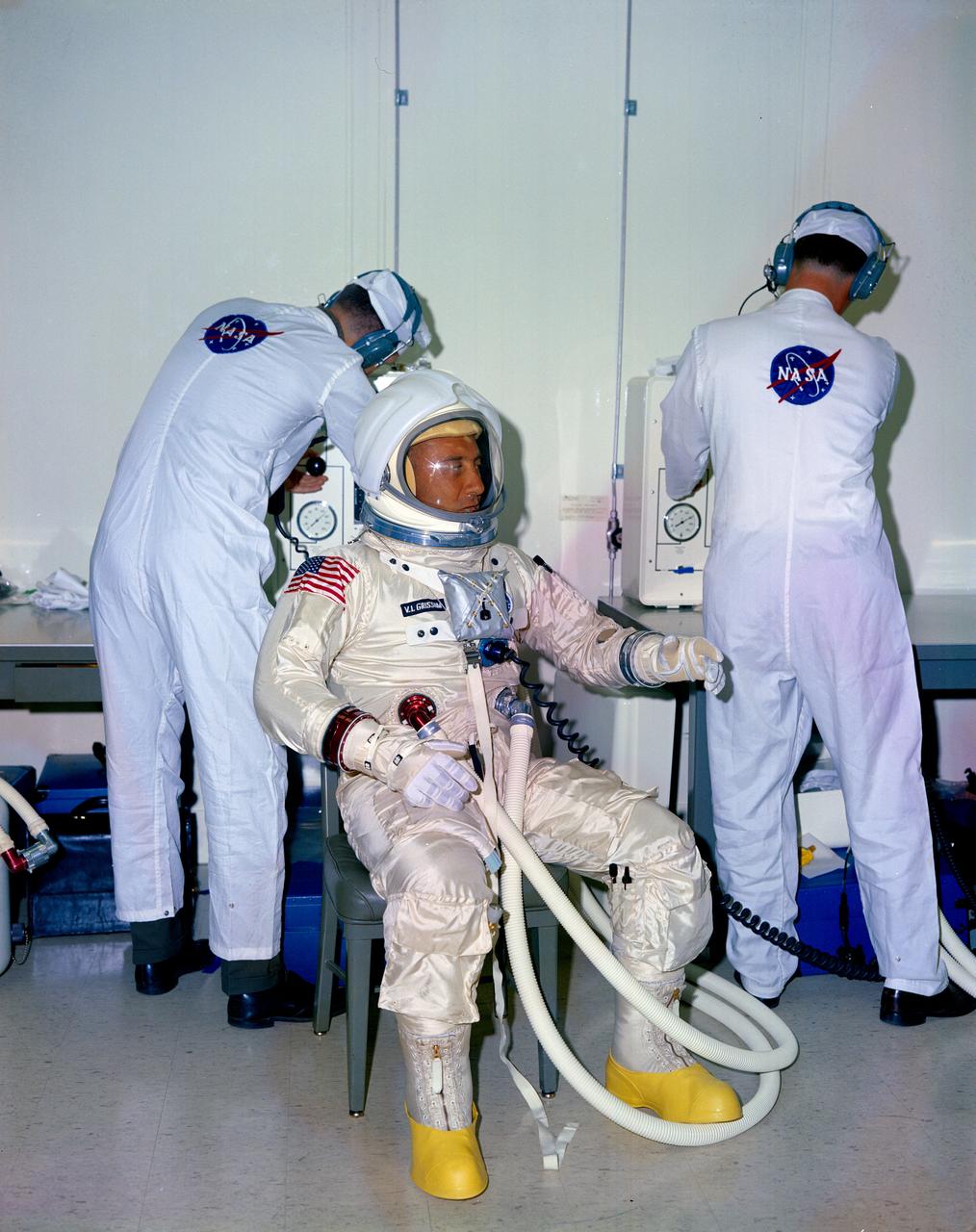

S66-58023 (1966) --- NASA suit technicians assist astronaut Virgil I. Grissom during suiting operations prior to tests at the Kennedy Space Center.
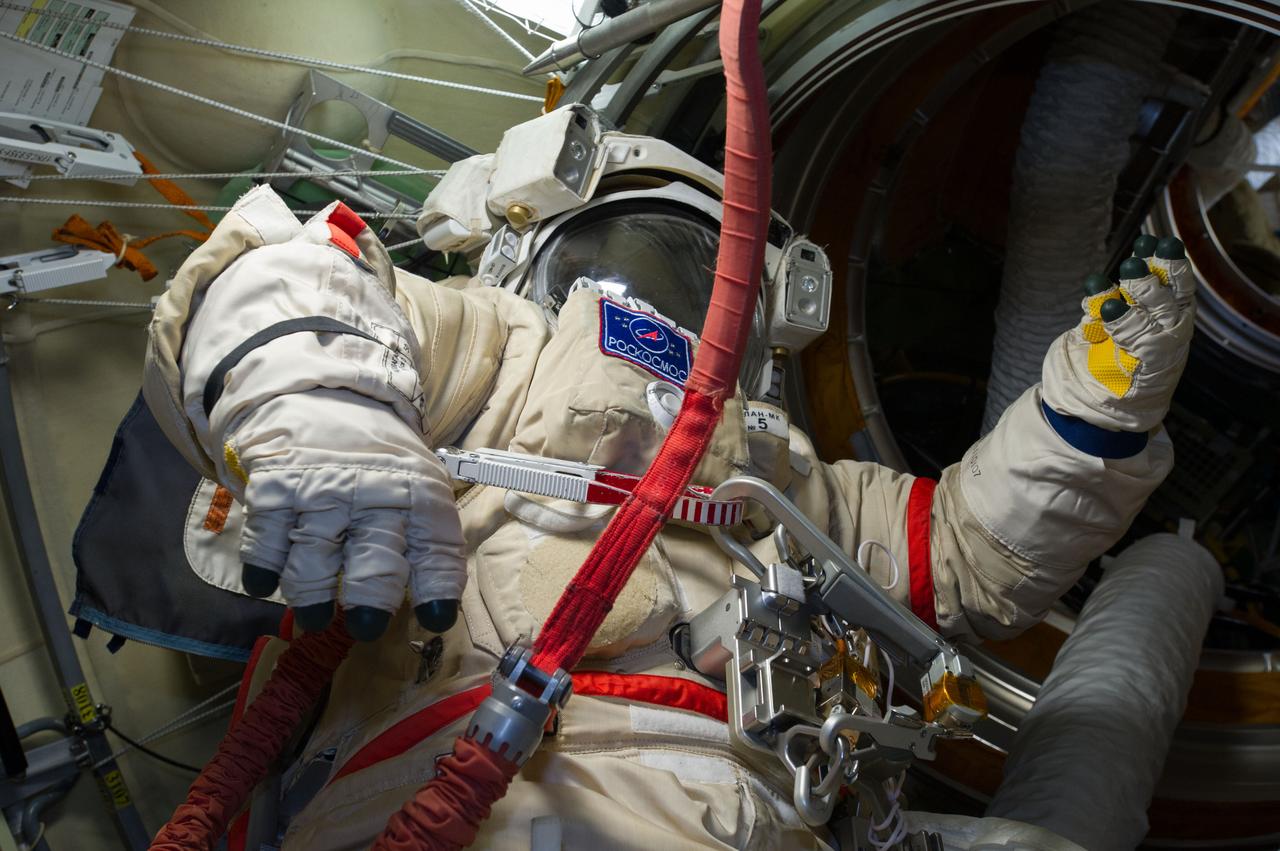

ISS040-E-013827 (17 June 2014) --- This is the Orlan spacesuit of Russian cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov, Expedition 40 flight engineer. Skvortsov and fellow cosmonaut Oleg Artemyev readied their Russian Orlan suits early on June 17 in preparation for a scheduled spacewalk on June 19.
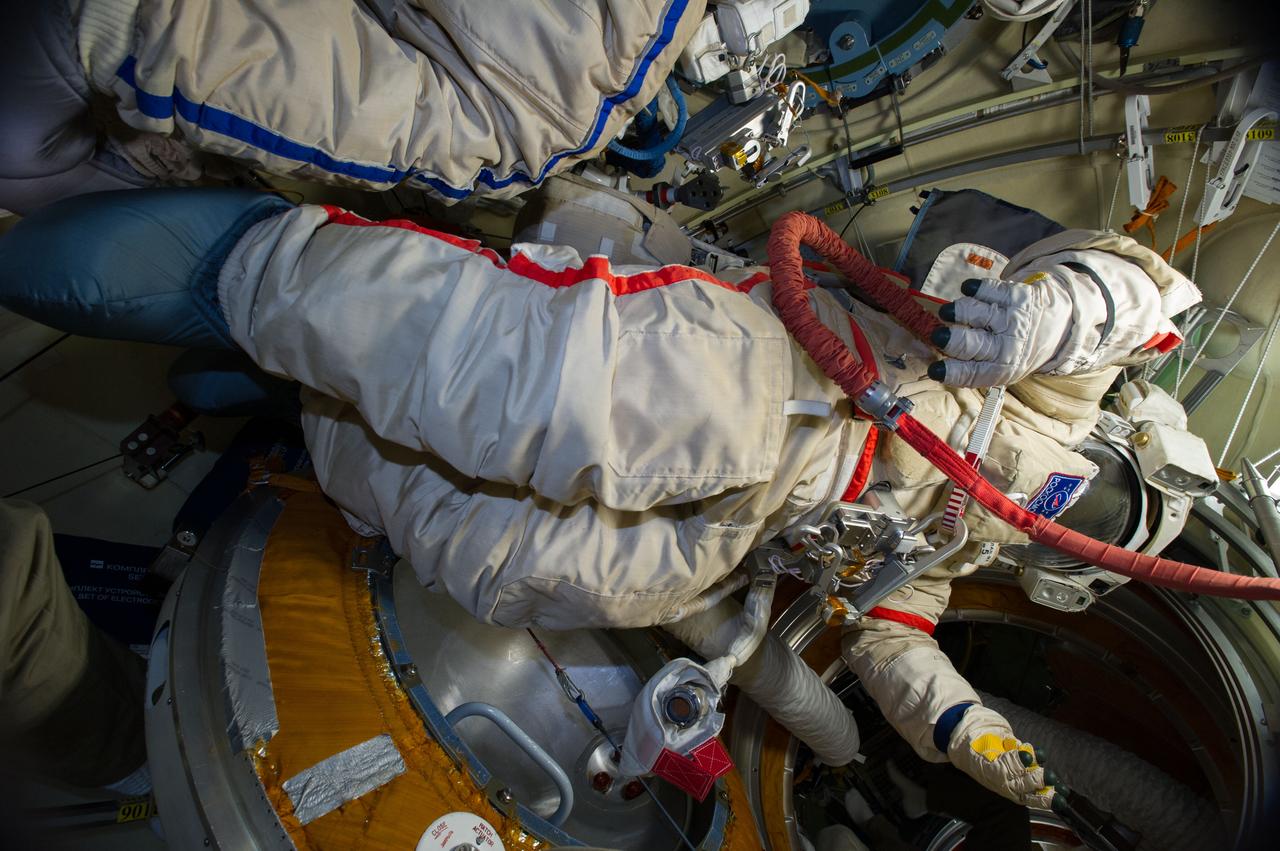

ISS040-E-013826 (17 June 2014) --- This is the Orlan spacesuit of Russian cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov, Expedition 40 flight engineer. Skvortsov and fellow cosmonaut Oleg Artemyev readied their Russian Orlan suits early on June 17 in preparation for a scheduled spacewalk on June 19.

NASA astronaut Eric Boe wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Boe and Suni Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing

NASA astronaut Suni Williams wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Eric Boe and Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing

NASA astronaut Eric Boe wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Boe and Suni Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing
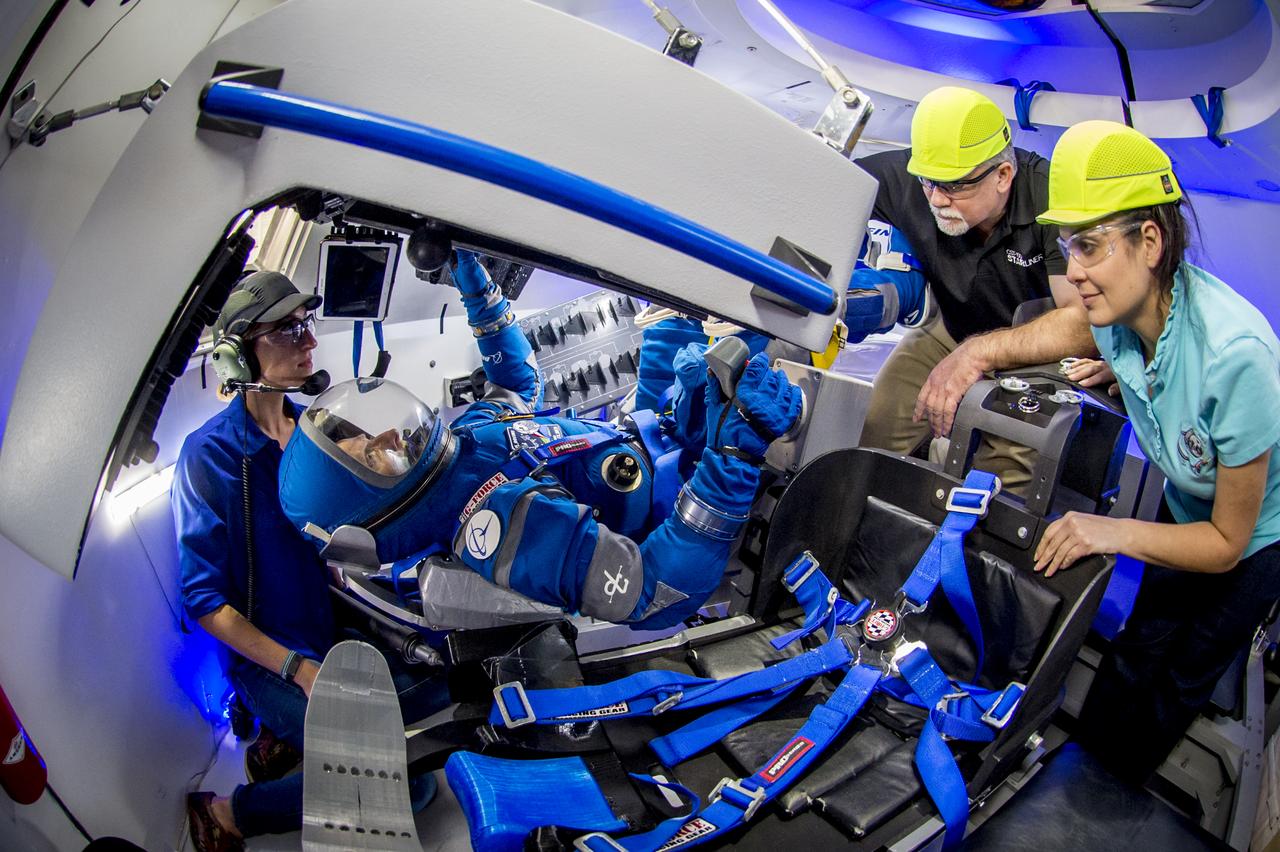

Boeing's Chris Ferguson wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Eric Boe and Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing
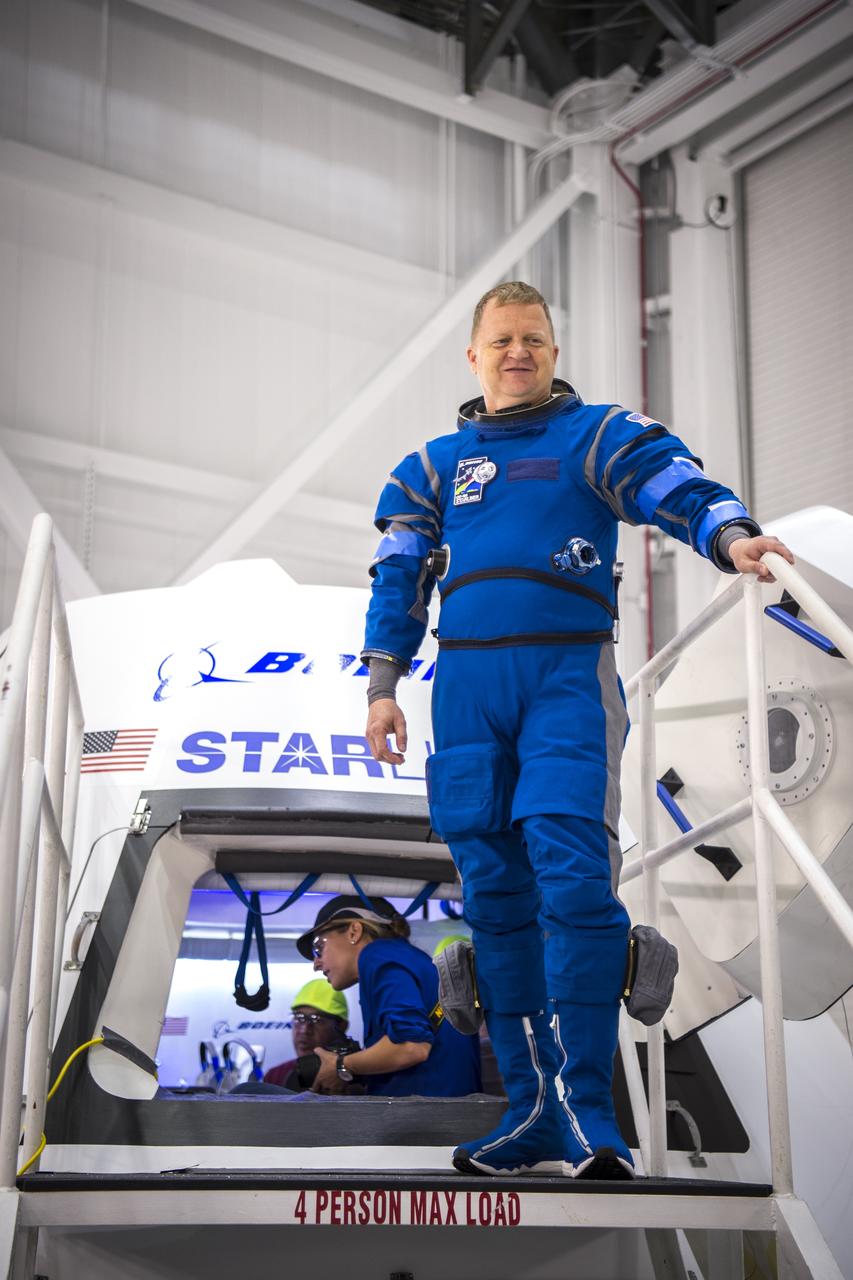

NASA astronaut Eric Boe wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Boe and Suni Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing

NASA astronaut Eric Boe wears Boeing's new spacesuit designed to be worn by astronauts flying on the CST-100 Starliner. The suit is lighter and more flexible than previous spacesuits but retains the ability to pressurize in an emergency. Astronauts will wear the suit throughout the launch and ascent into orbit as well as on the way back to Earth. Starliners will launch atop Atlas V rockets from United Launch Alliance on missions including flights to the International Space Station for NASA's Commercial Crew Program. NASA's commercial crew astronauts Boe and Suni Williams tried on the suits at Boeing’s Commercial Crew and Cargo Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Boe, Williams, Bob Behnken, and Doug Hurley were selected by NASA in July 2015 to train for commercial crew test flights aboard the Starliner and SpaceX’s Crew Dragon spacecraft. The flight assignments have not been set, so all four of the astronauts are rehearsing heavily for flights aboard both vehicles. Photo credit: Boeing
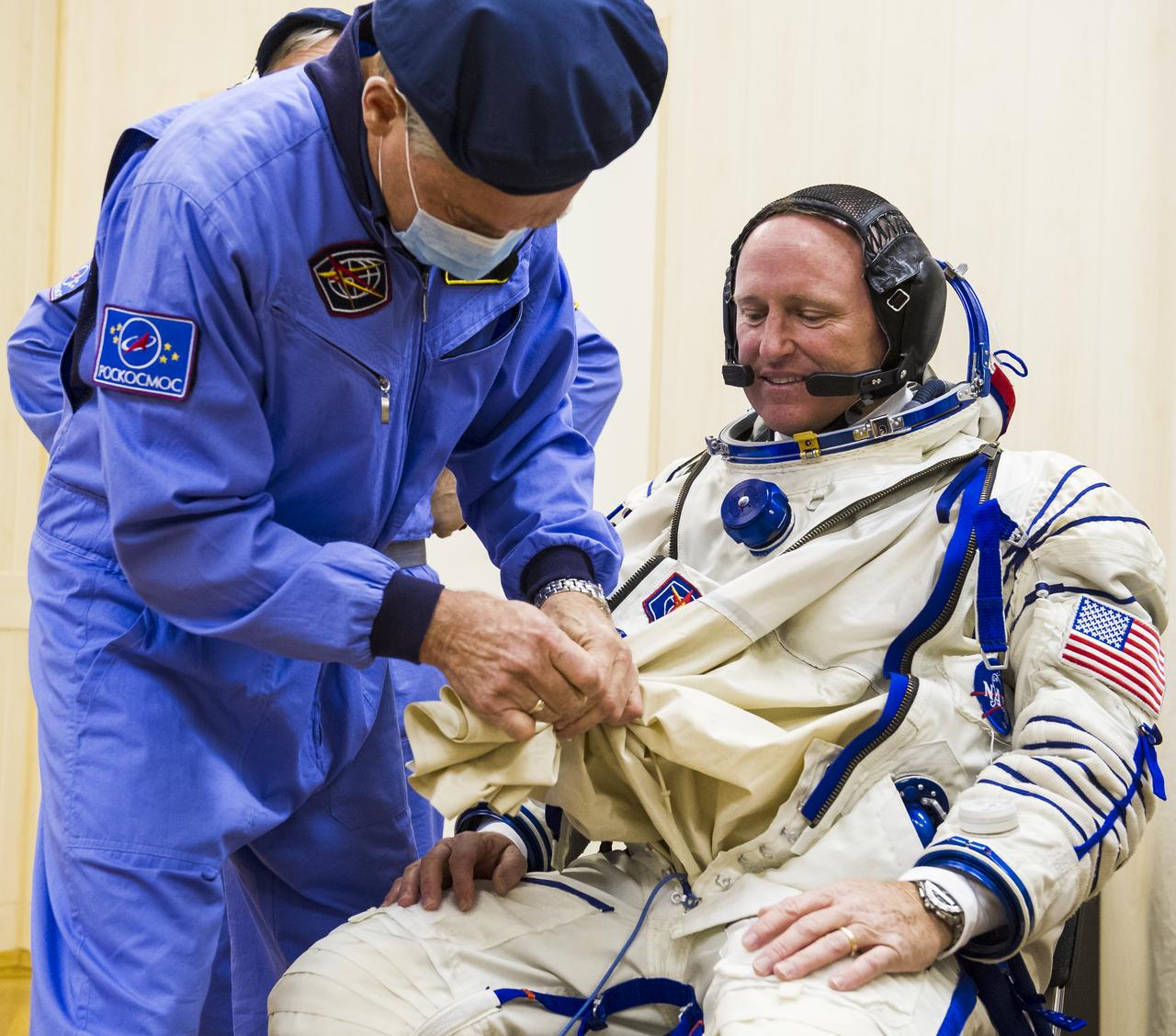

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Elena Serova and Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 and will carry Wilmore, Serova, and Samokutyaev into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
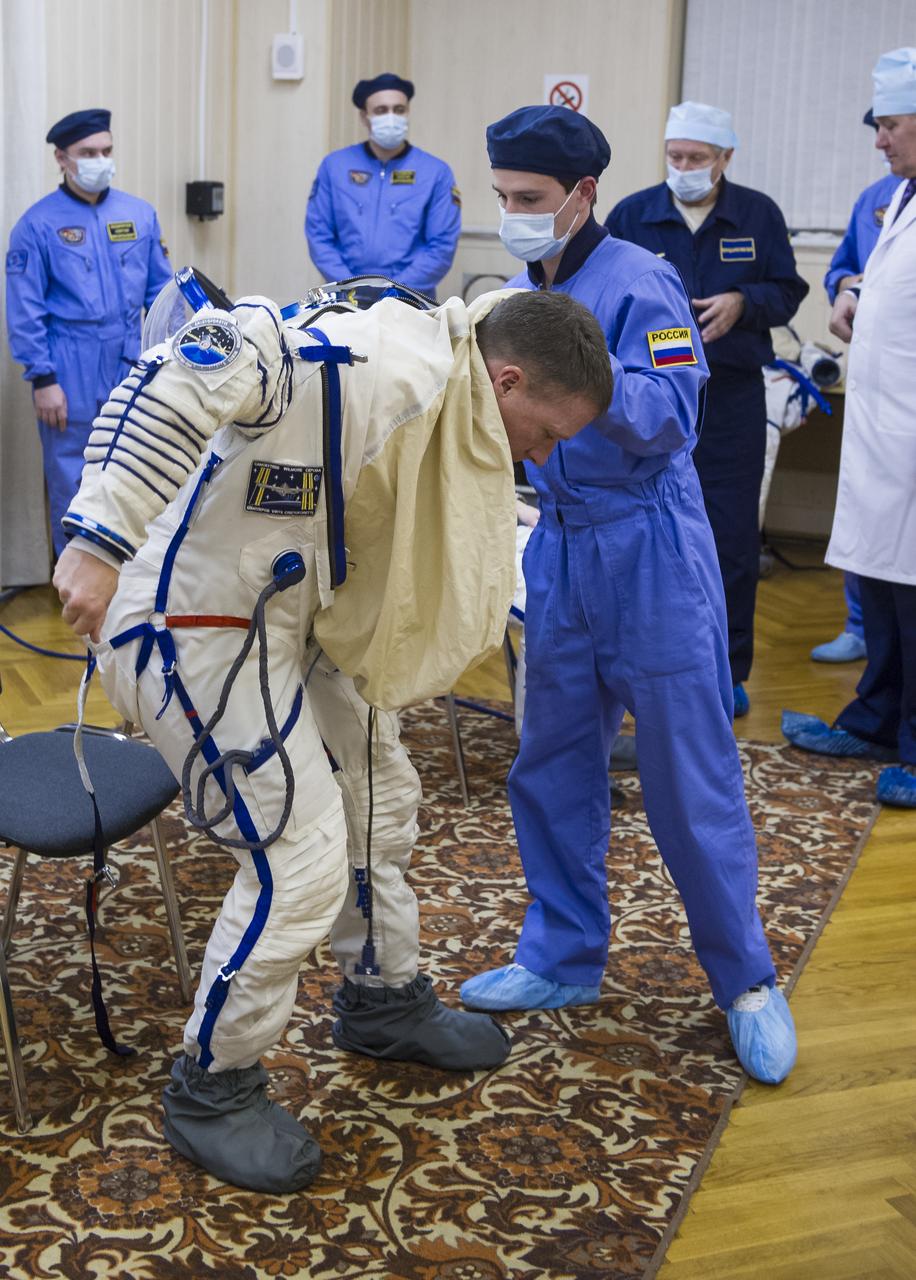

Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA), and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts, Cristoforetti, and Shkaplerov into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
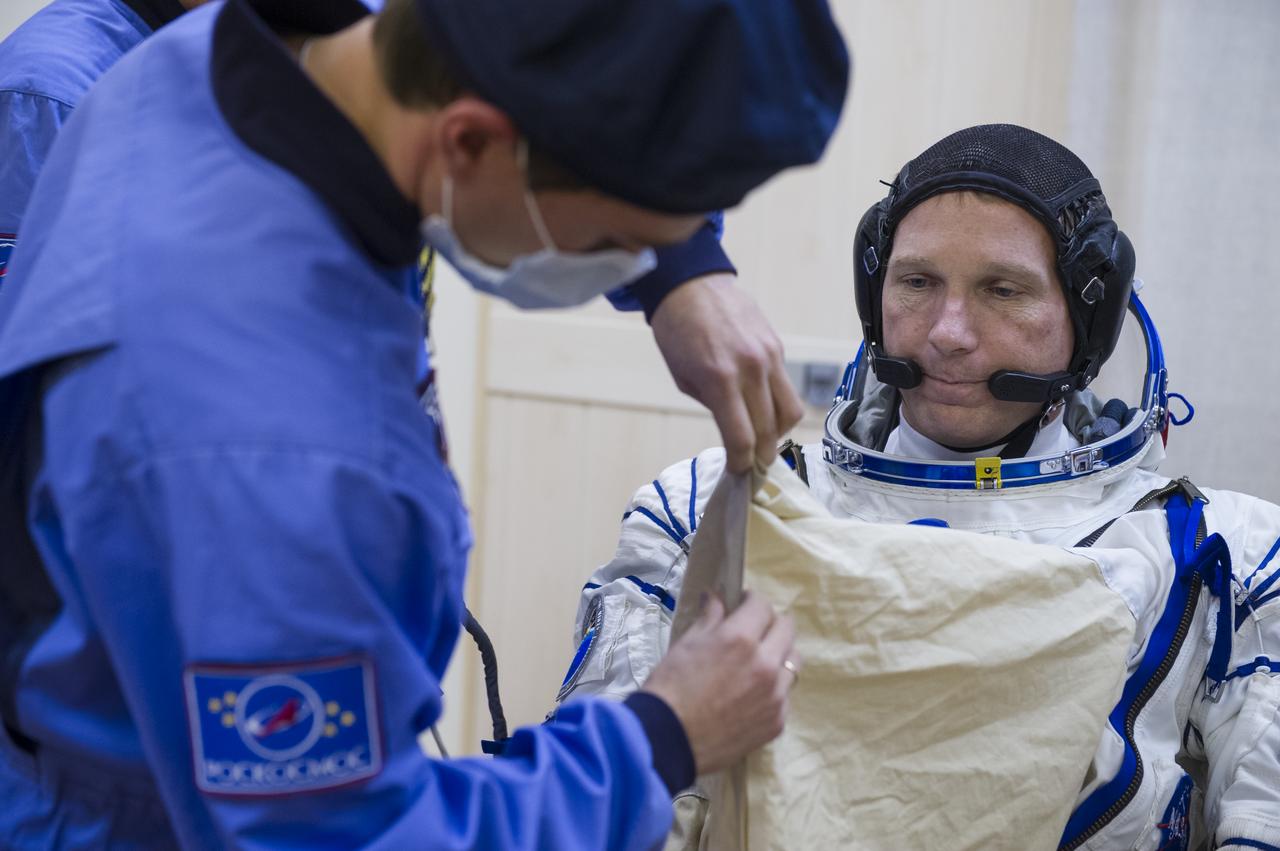

Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA), and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts, Cristoforetti, and Shkaplerov into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
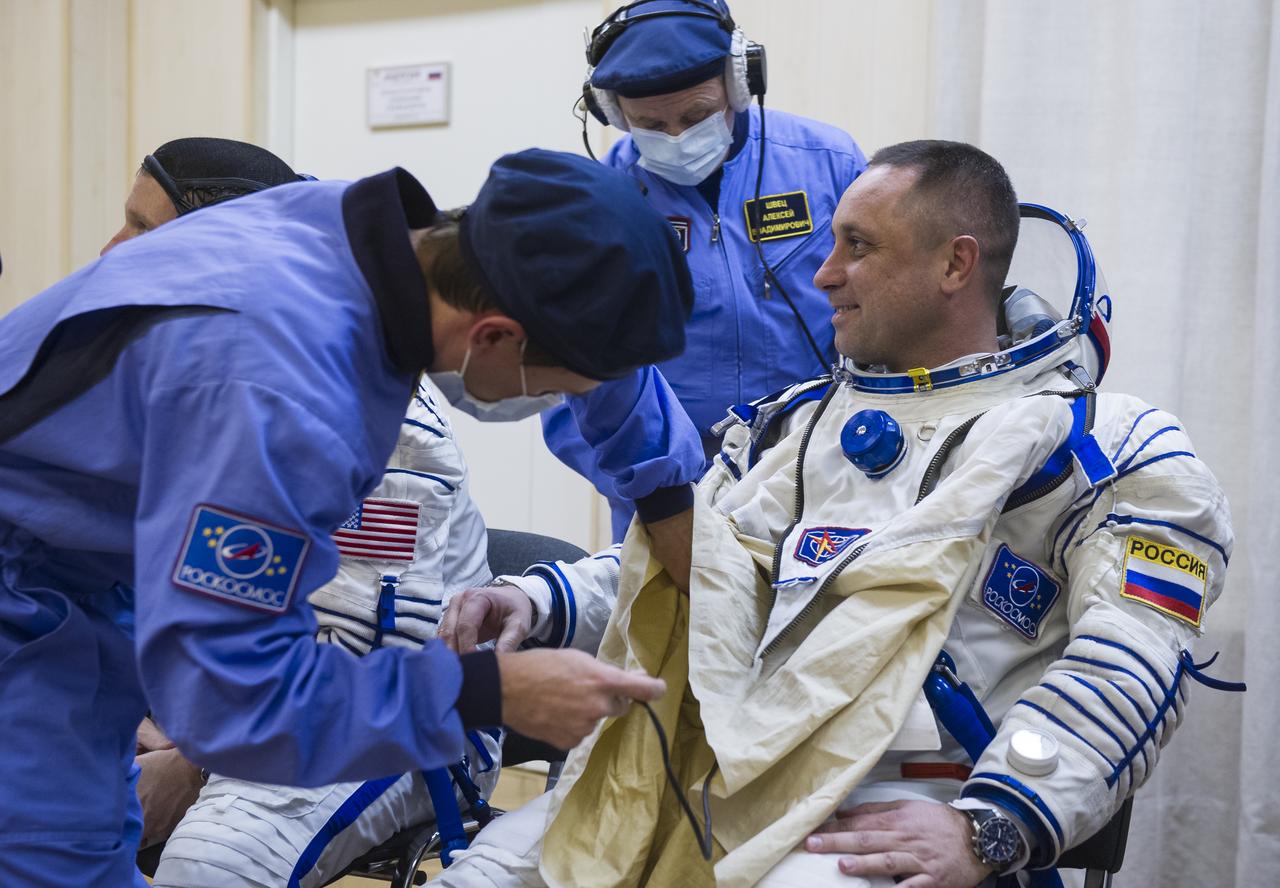

Expedition 42 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA), and Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Shkaplerov, Virts, and Cristoforetti into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
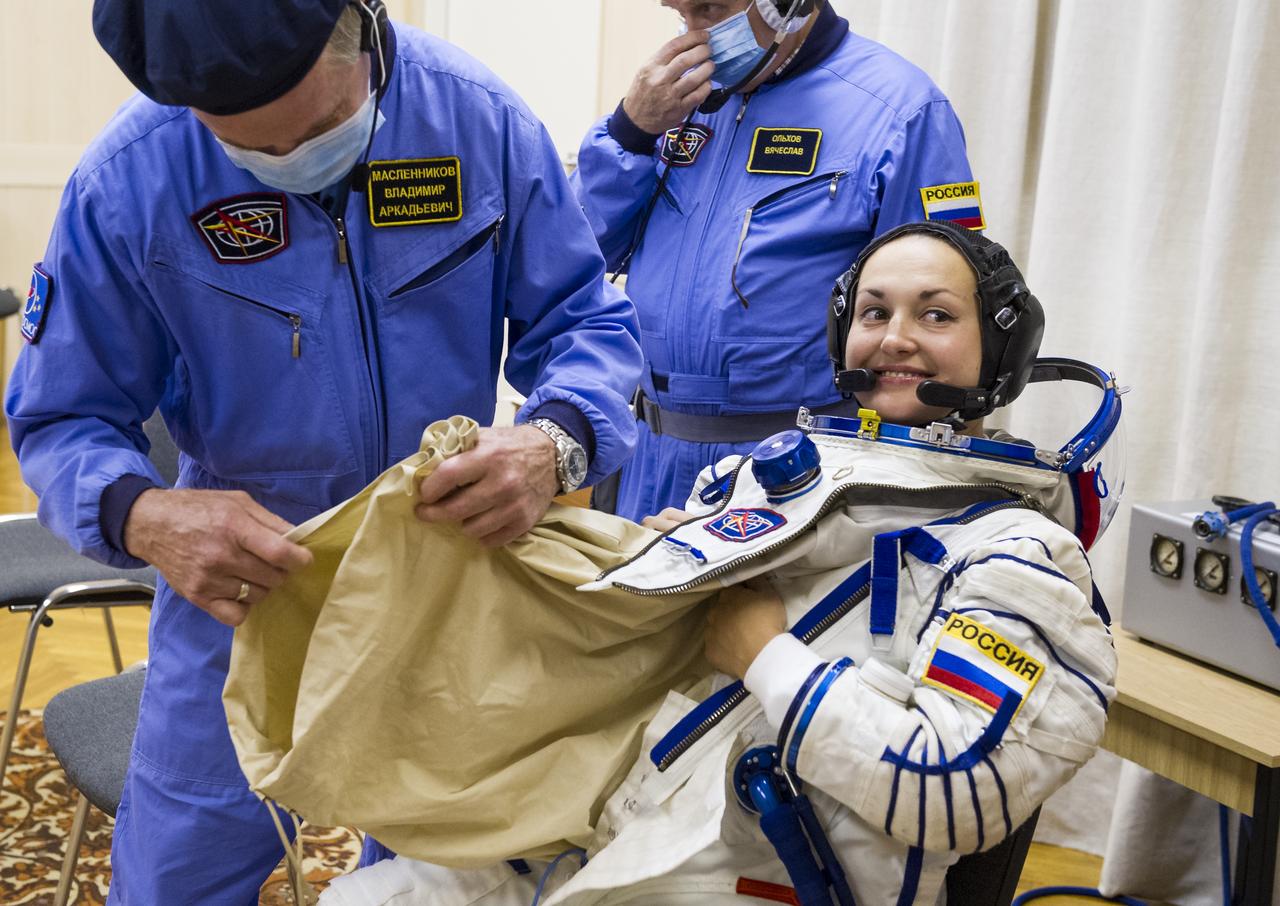

Expedition 41 Flight Engineer Elena Serova of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) is helped into her Russian Sokol suit as she and fellow crewmates, Soyuz Commander Alexander Samokutyaev of Roscosmos, and Flight Engineer Barry Wilmore of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, Sept. 25, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Sept. 26 and will carry Serova, Wilmore, and Samokutyaev into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Serova will become the fourth Russian woman to fly in space and the first Russian woman to live and work on the station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
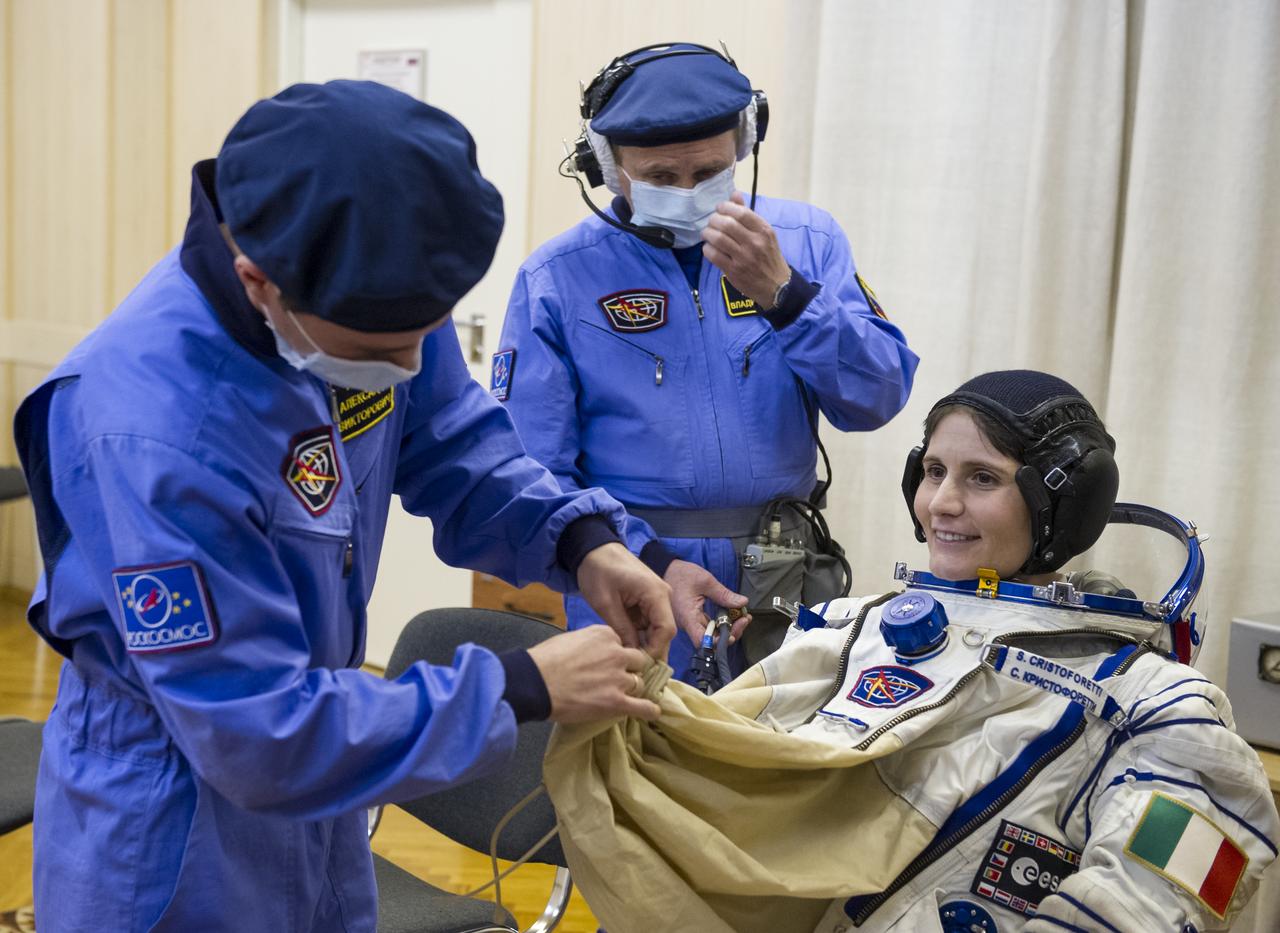

Expedition 42 Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA) is helped into her Russian Sokol suit as she and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA and Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Virts, Cristoforetti, and Shkaplerov into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
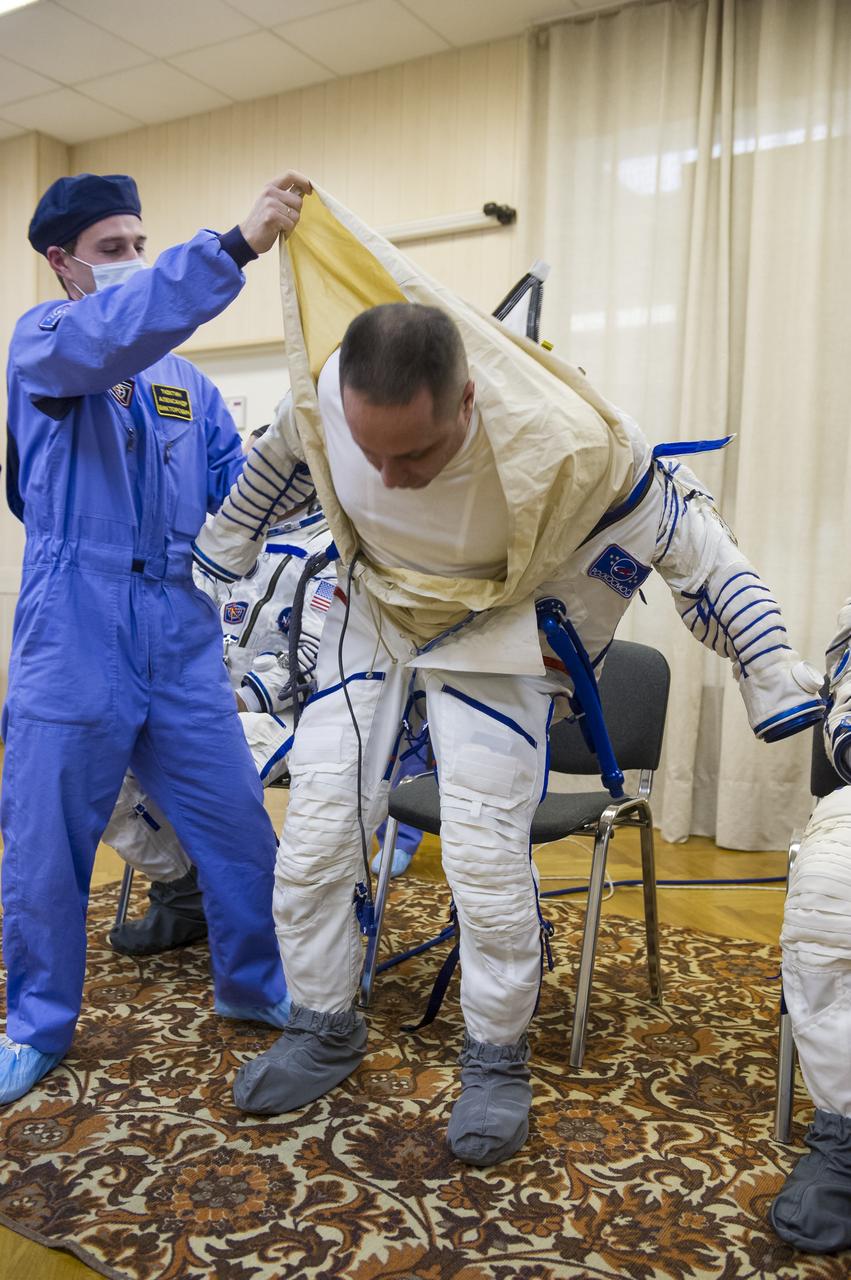

Expedition 42 Soyuz Commander Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos) is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency (ESA), and Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Sunday, Nov. 23, 2014, at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Baikonur, Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the early hours of Nov. 24 and will carry Shkaplerov, Virts, and Cristoforetti into orbit to begin their five and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASAGCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
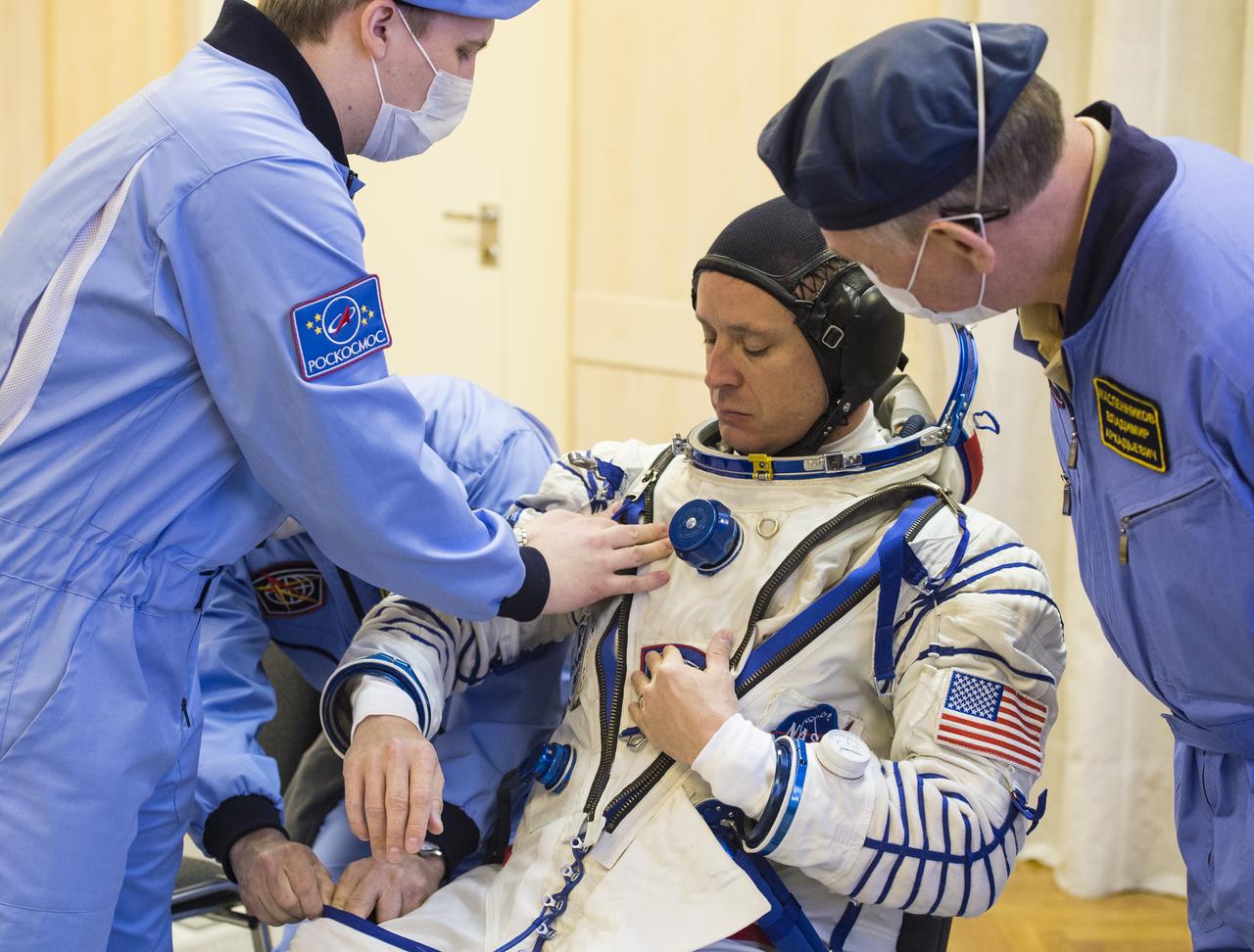

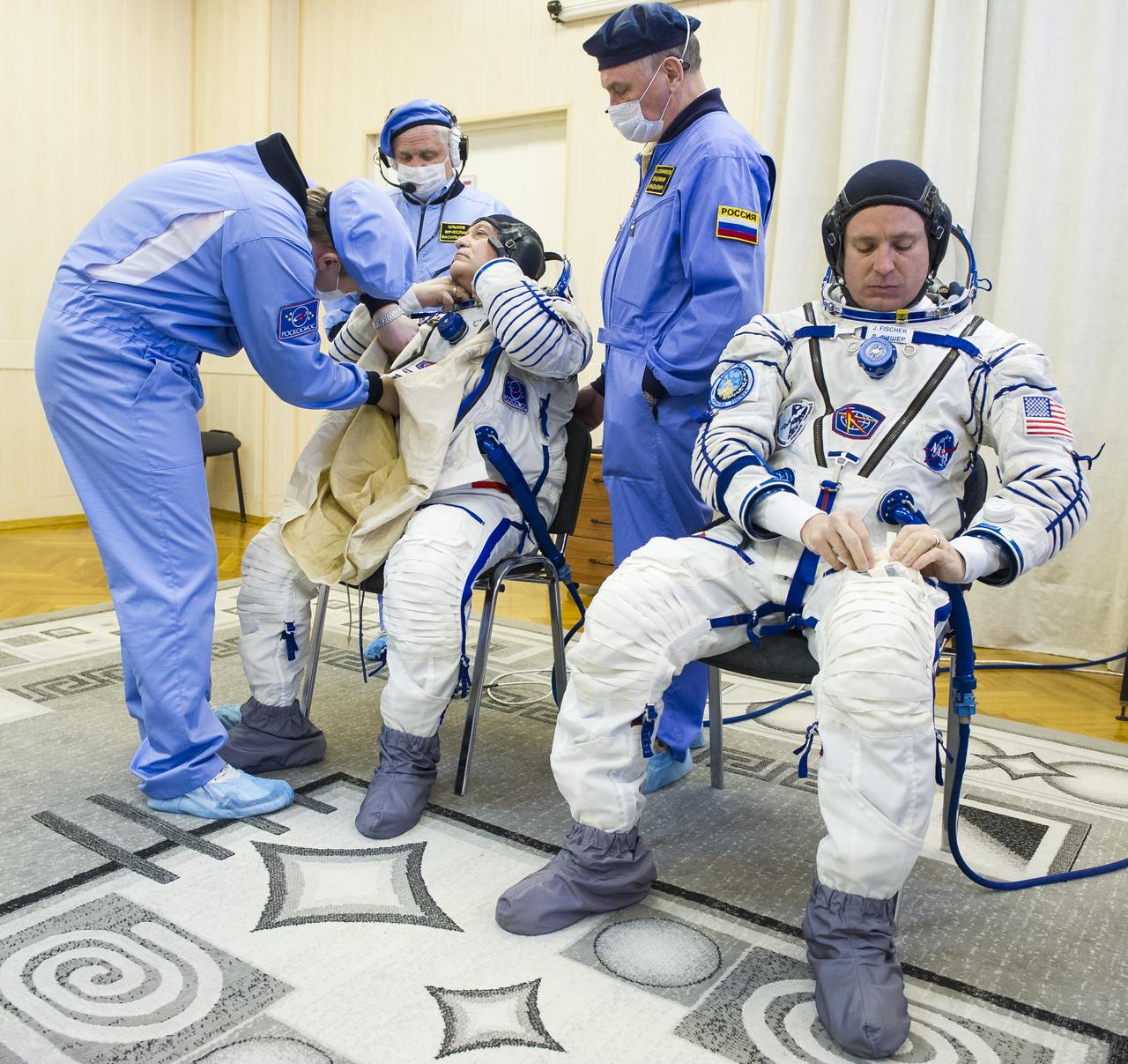
Expedition 51 Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13pm April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Fischer and Yurchikhin into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
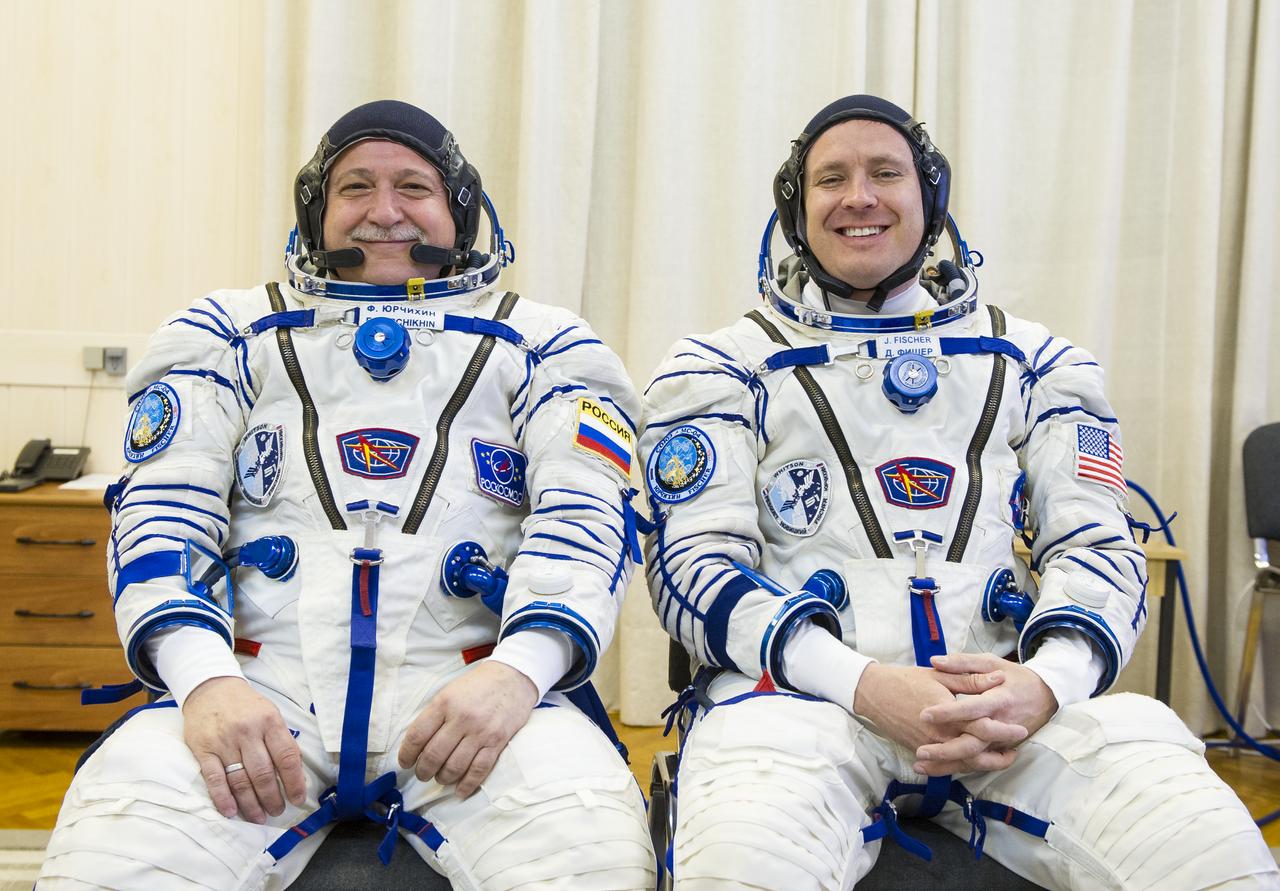

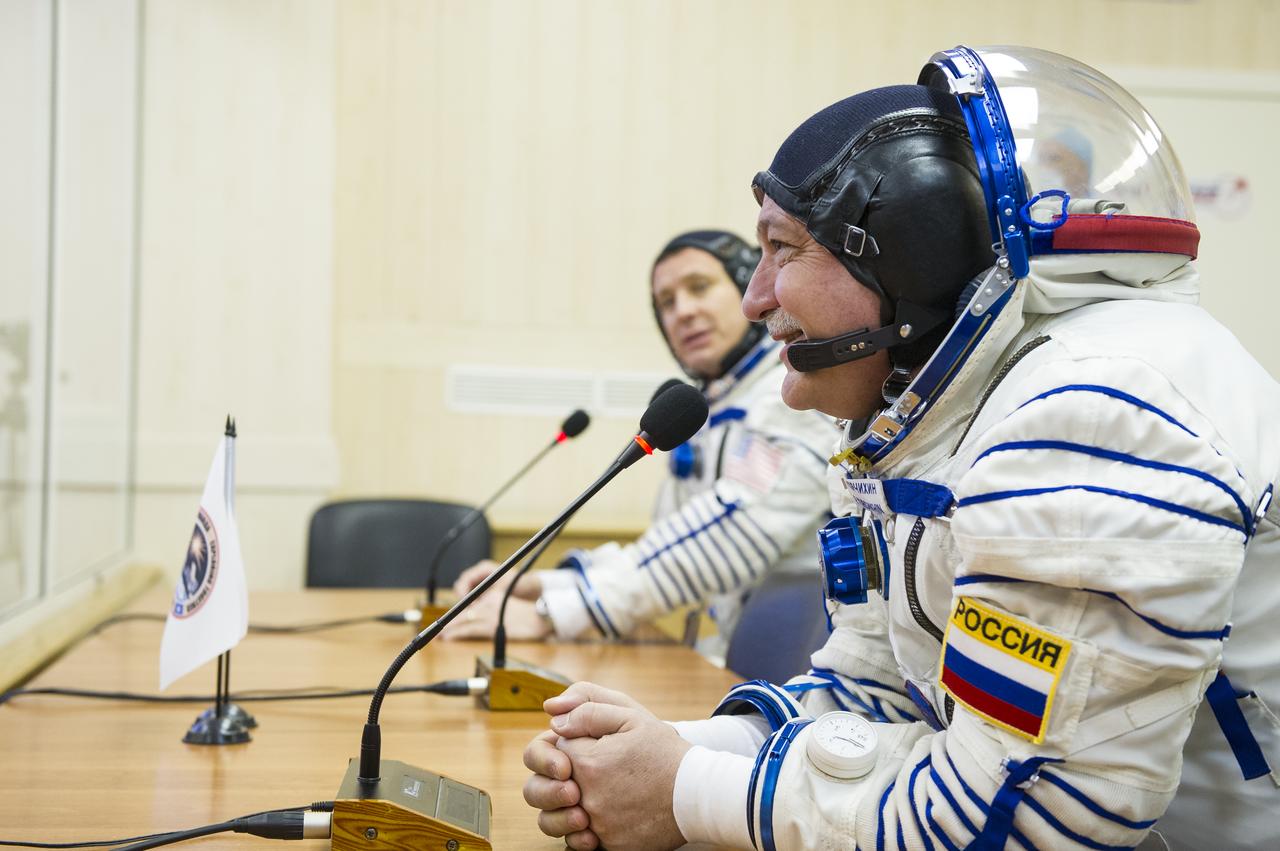
Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos, left, and Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA, right, pose for a photo after being helped into their Russian Sokol suits in preparation for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13 p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Yurchikhin and Fischer into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

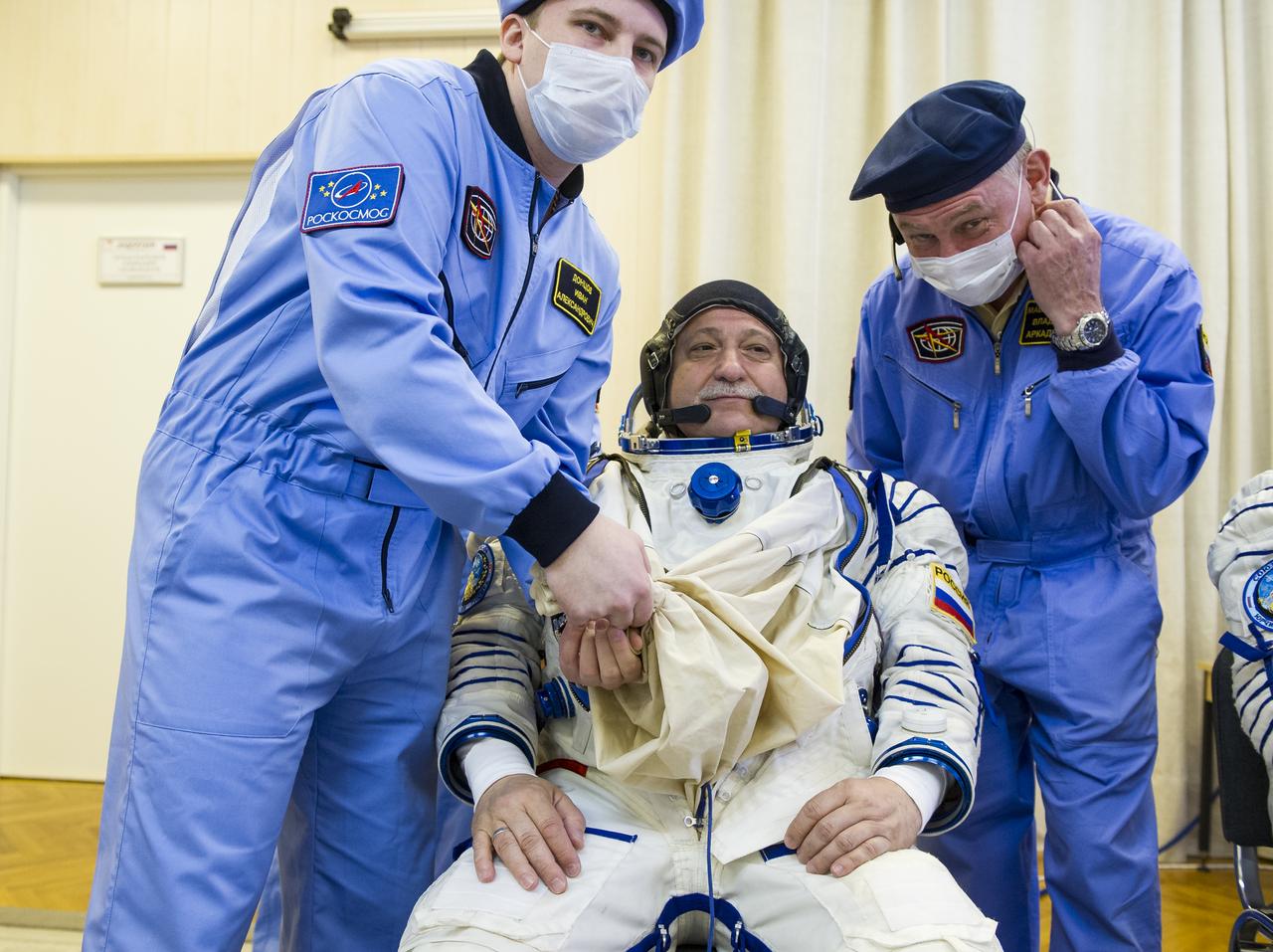
Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13 p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Yurchikhin and Fischer into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13 p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Yurchikhin and Fischer into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13 p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Yurchikhin and Fischer into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos, left, is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA, right, prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13 p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Yurchikhin and Fischer into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)

Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos speaks with his family after having his Russian Sokol suit pressure checked in preparation for launch onboard the Soyuz MS-04 spacecraft on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz spacecraft with Yurchikhin and Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA is scheduled to launch at 1:13 p.m. Baikonur time on April 20. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
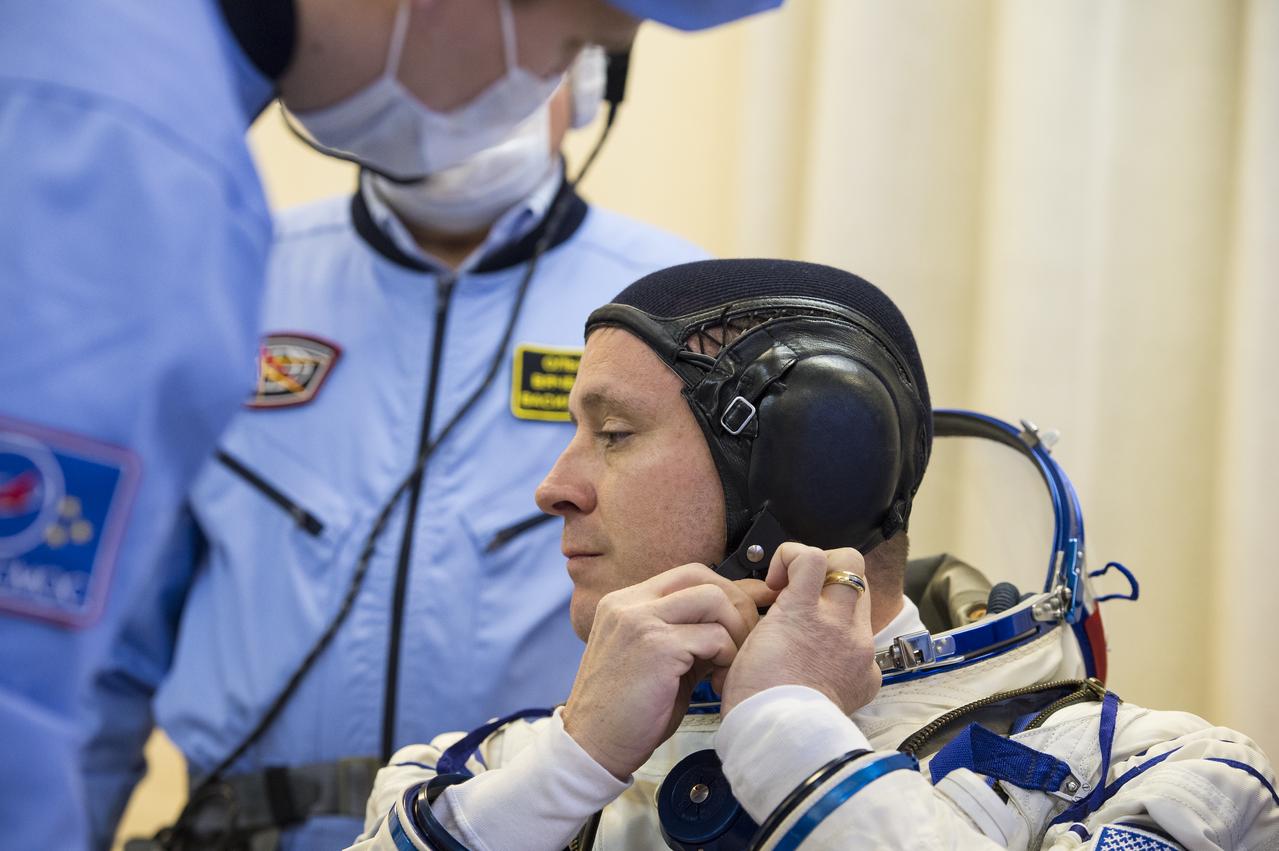

Expedition 51 Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13pm April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Fischer and Yurchikhin into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
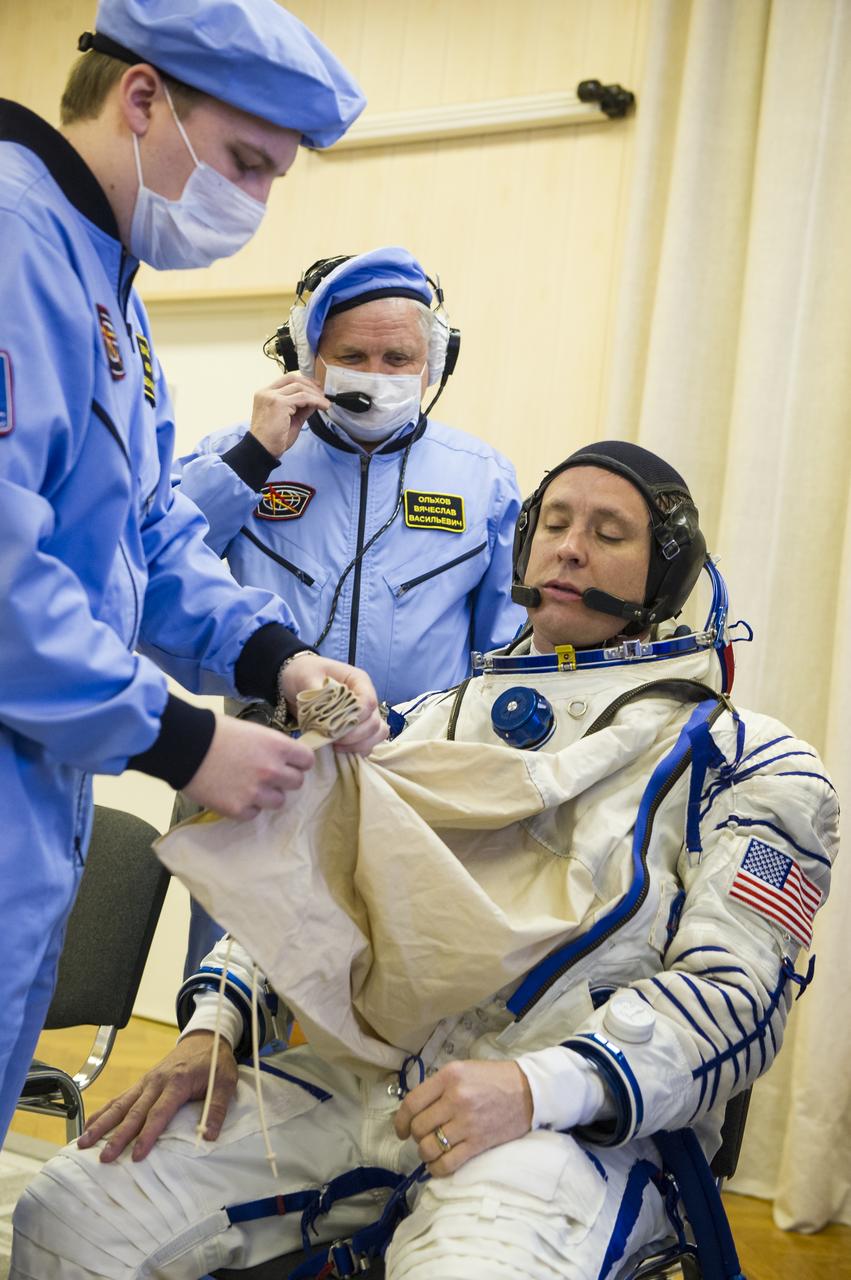

Expedition 51 Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Fischer and Yurchikhin into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
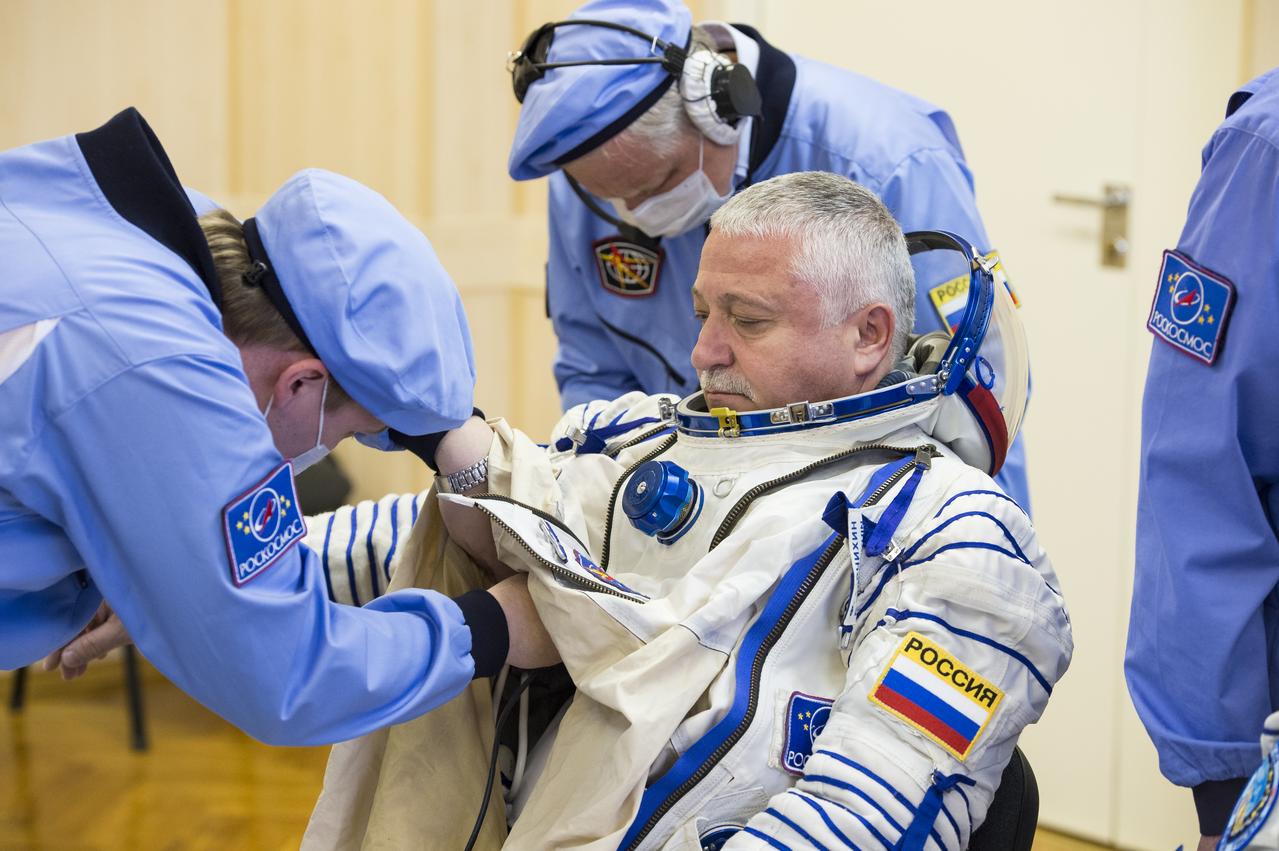

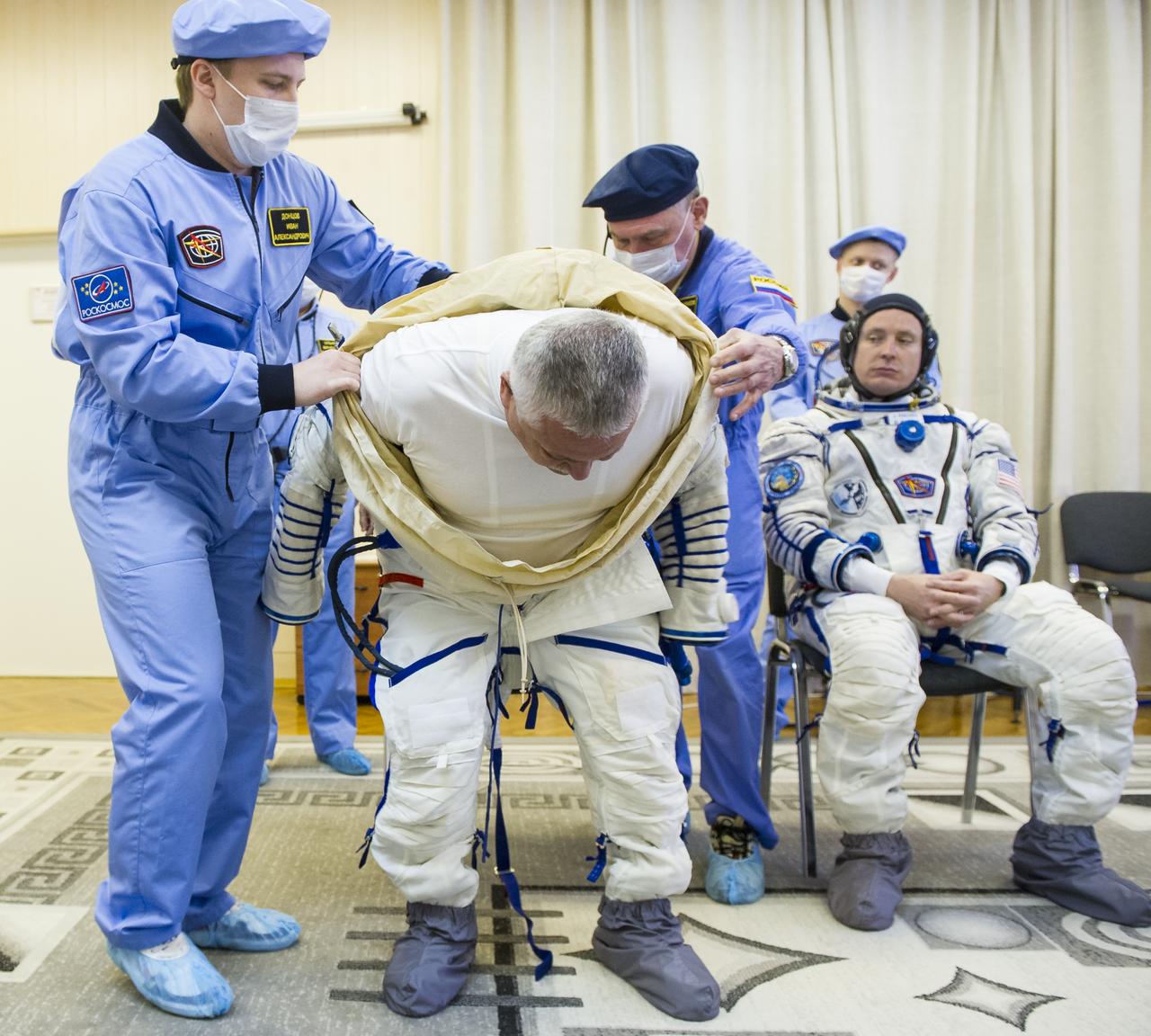
Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13 p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Yurchikhin and Fischer into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
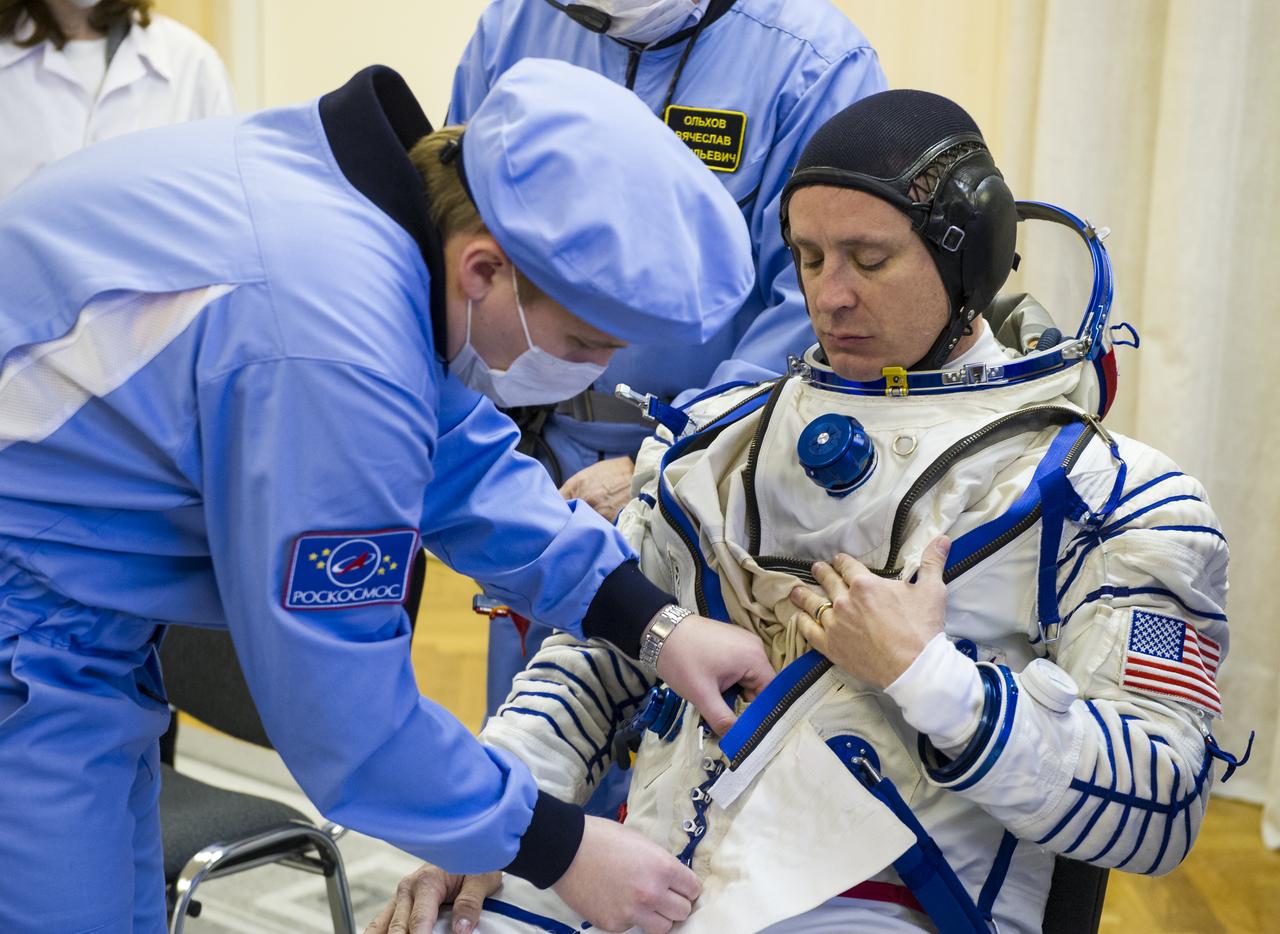

Expedition 51 Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Fischer and Yurchikhin into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
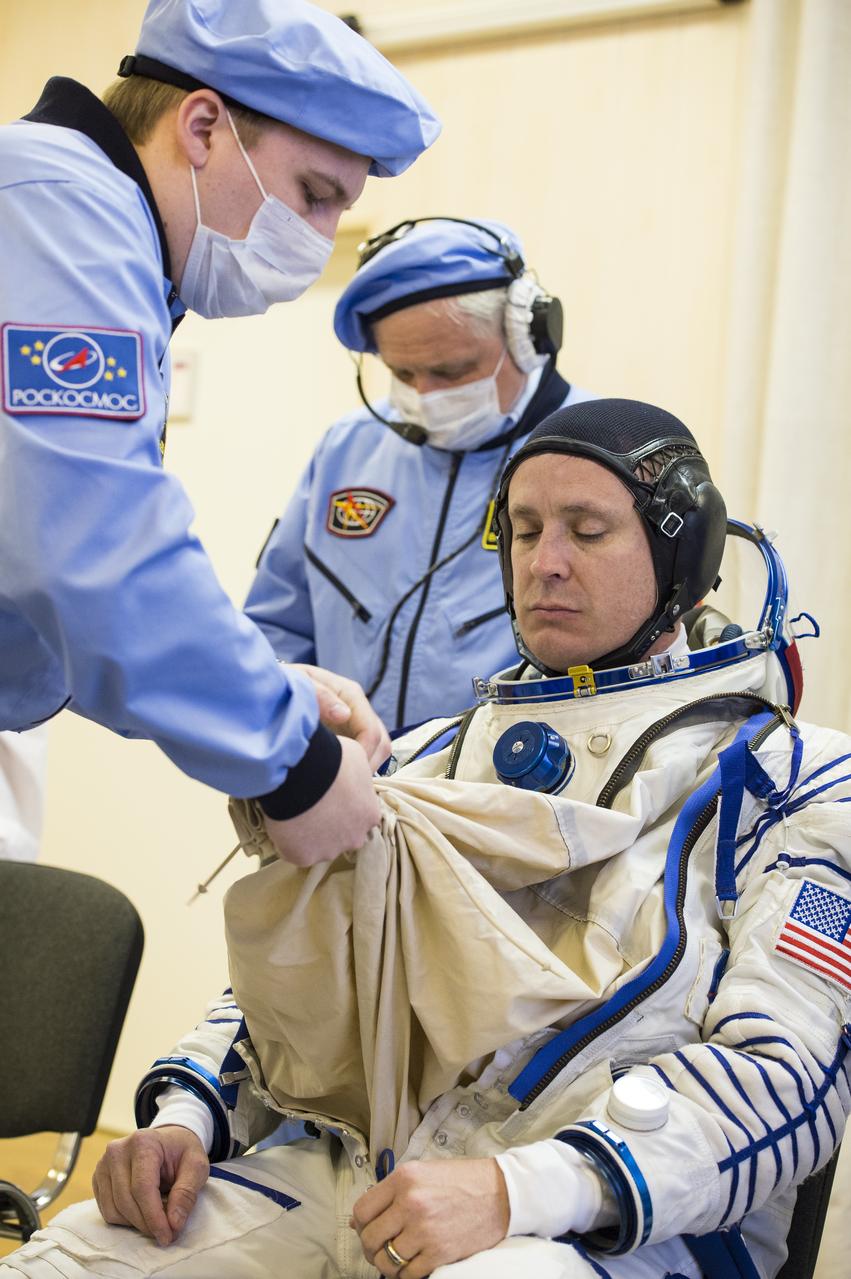

Expedition 51 Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13pm April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Fischer and Yurchikhin into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
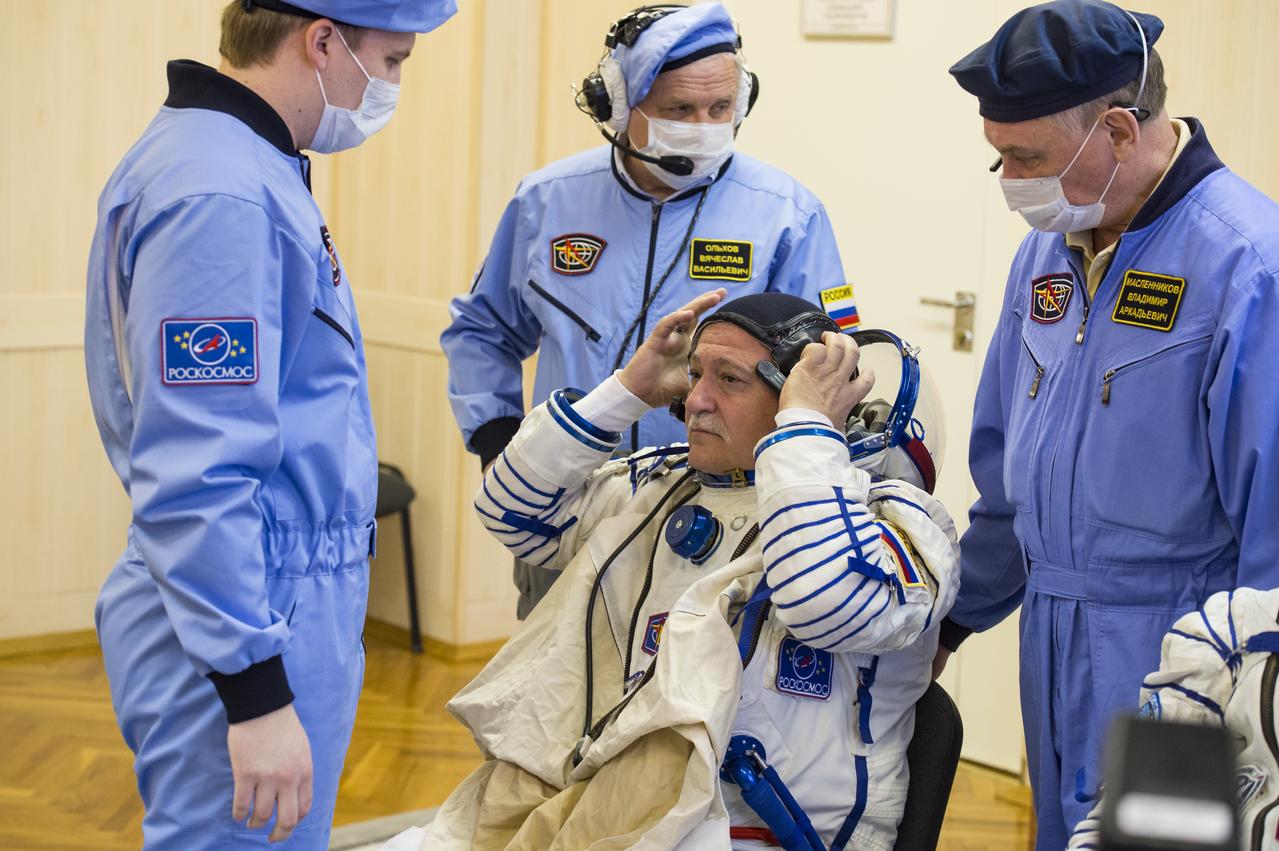

Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13 p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Yurchikhin and Fischer into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
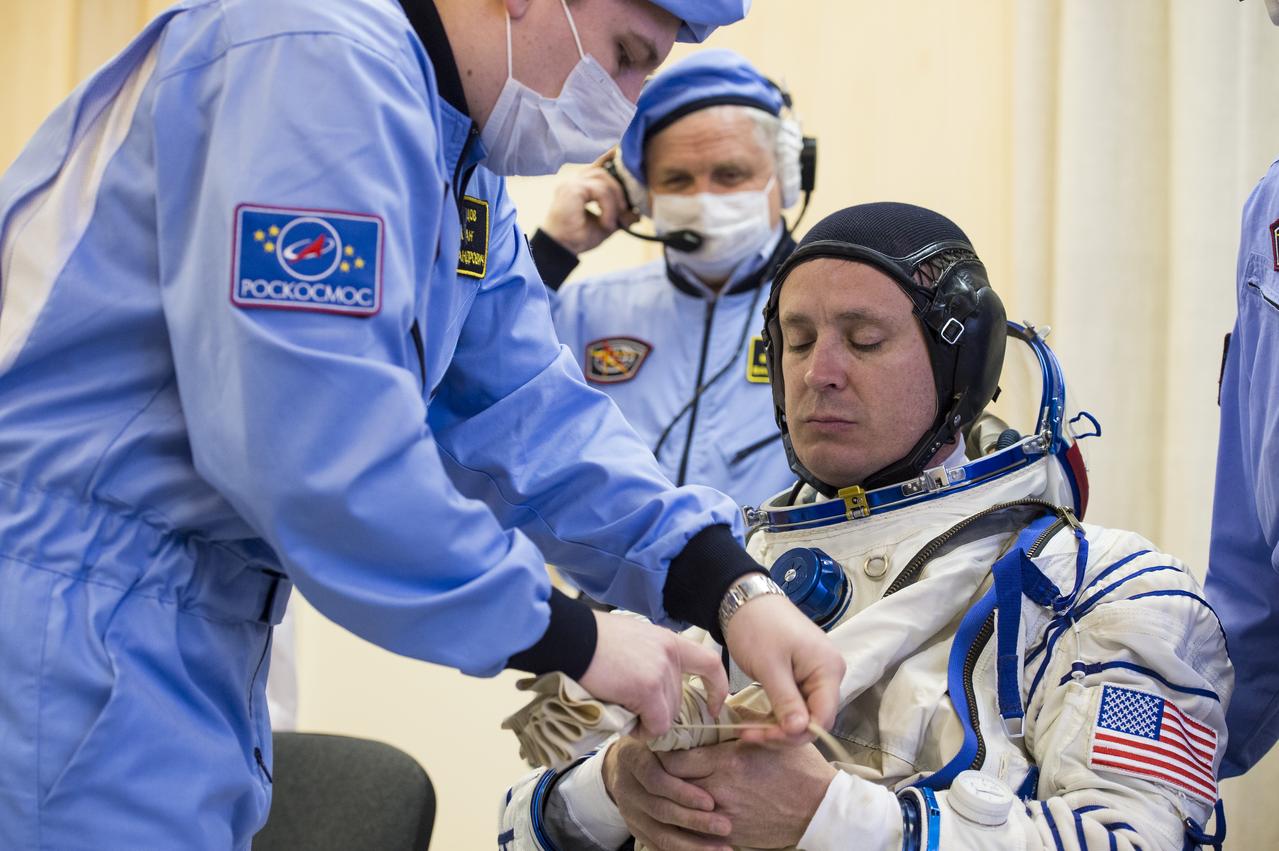

Expedition 51 Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate, Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13pm April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Fischer and Yurchikhin into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
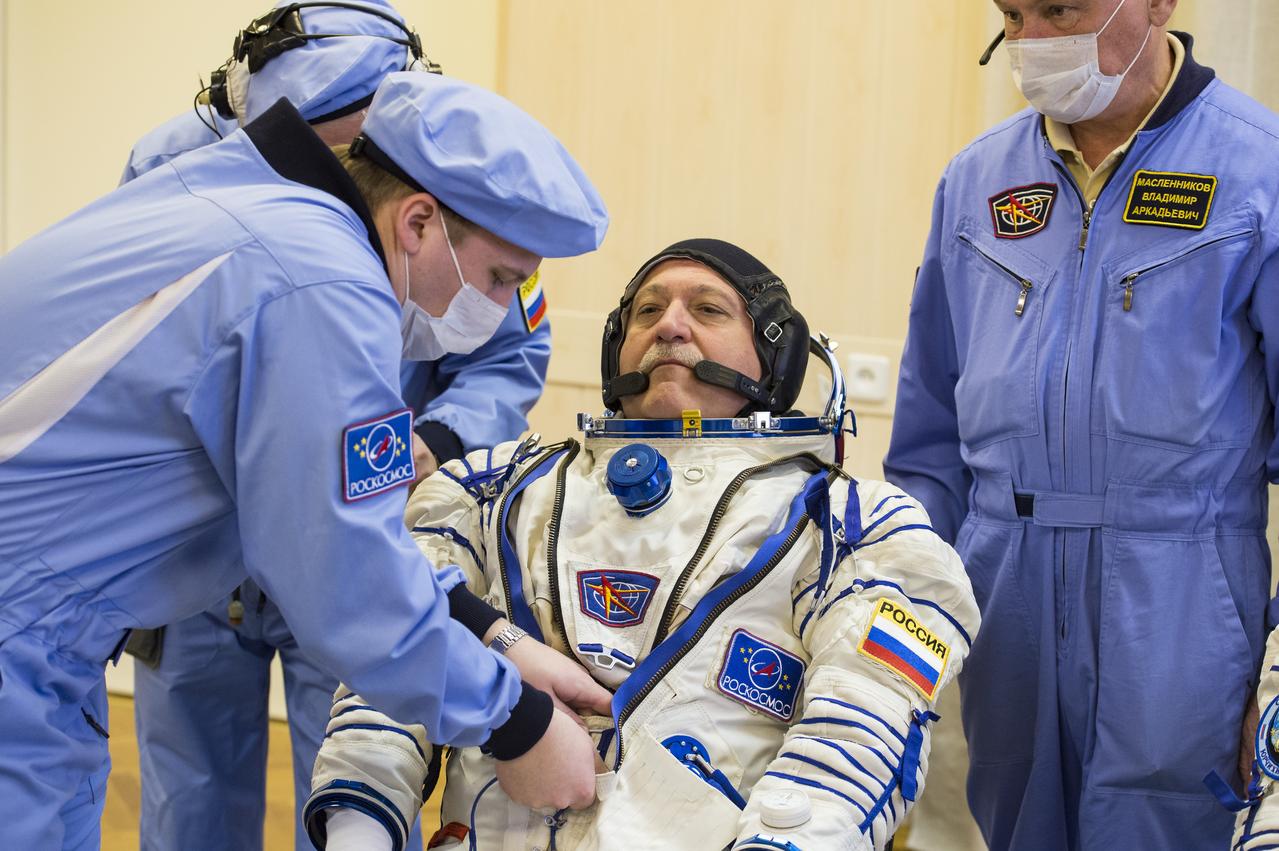

Expedition 51 Soyuz Commander Fyodor Yurchikhin of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmate Flight Engineer Jack Fischer of NASA prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Thursday, April 20, 2017 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for 1:13 p.m. April 20 Baikonur time, and will carry Yurchikhin and Fischer into orbit to begin their four and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/Andrey Shelepin)
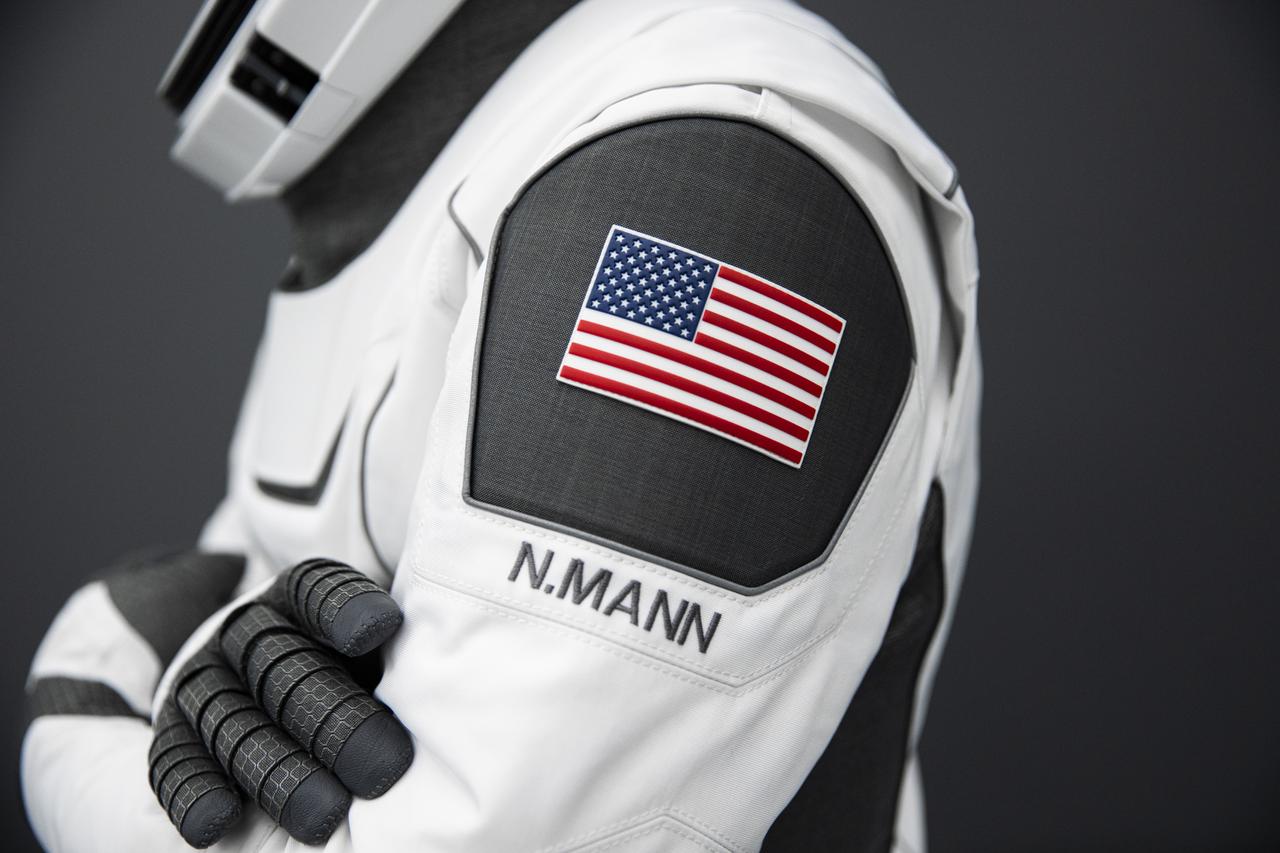

A SpaceX launch and entry suit bears an American flag, and the name of NASA Astronaut Nicole Mann, who will serve as the commander of NASA's SpaceX Crew-5 mission to the International Space Station.
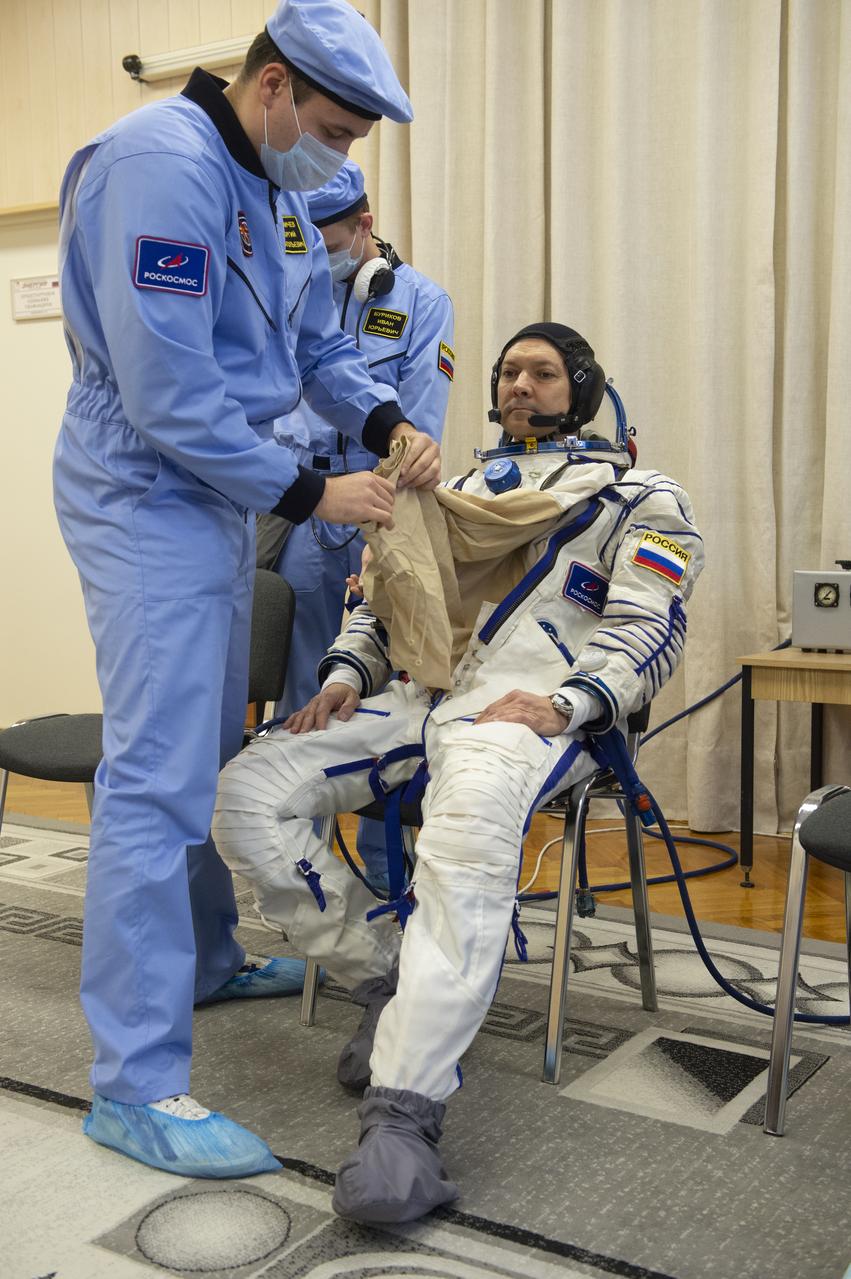

Expedition 58 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Anne McClain of NASA and Flight Engineer David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Monday, Dec. 3, 2018 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the same day and will carry Kononenko, McClain, and Saint-Jacques into orbit to begin their six and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/NASA/Andrey Shelepin)
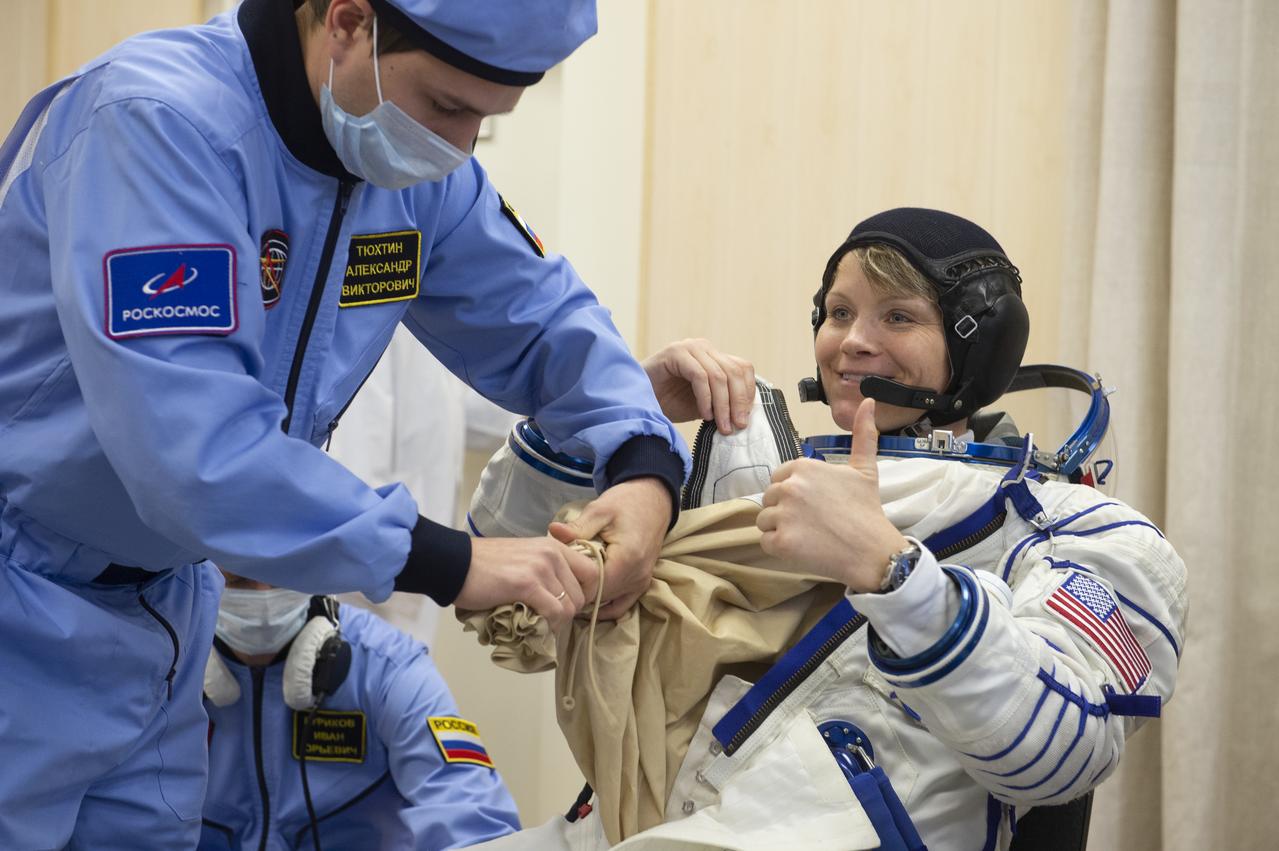

Flight Engineer Anne McClain of NASA is helped into her Russian Sokol suit as she and fellow crewmates, Expedition 58 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos and Flight Engineer David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Monday, Dec. 3, 2018 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the same day and will carry McClain, Kononenko, and Saint-Jacques into orbit to begin their six and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/NASA/Andrey Shelepin)
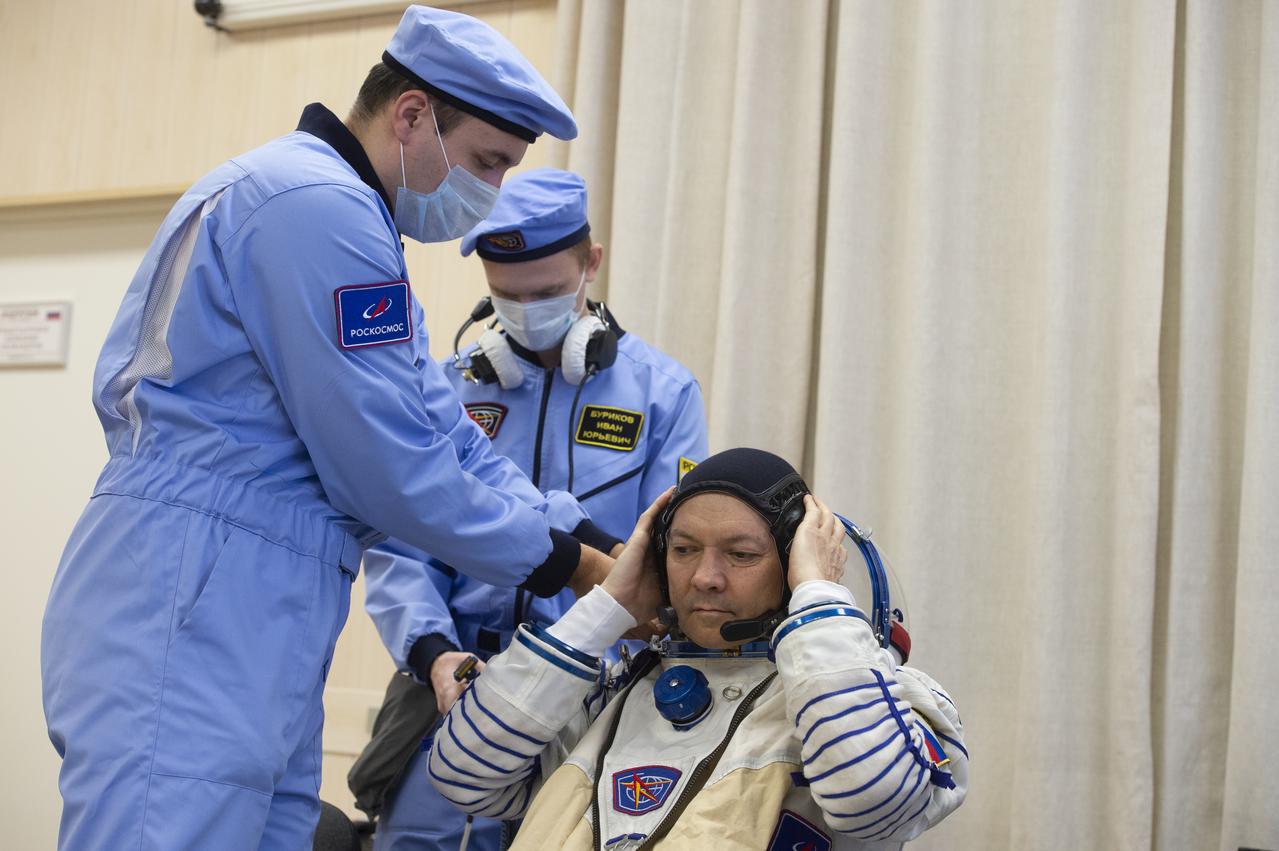

Expedition 58 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Anne McClain of NASA and Flight Engineer David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Monday, Dec. 3, 2018 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the same day and will carry Kononenko, McClain, and Saint-Jacques into orbit to begin their six and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/NASA/Andrey Shelepin)
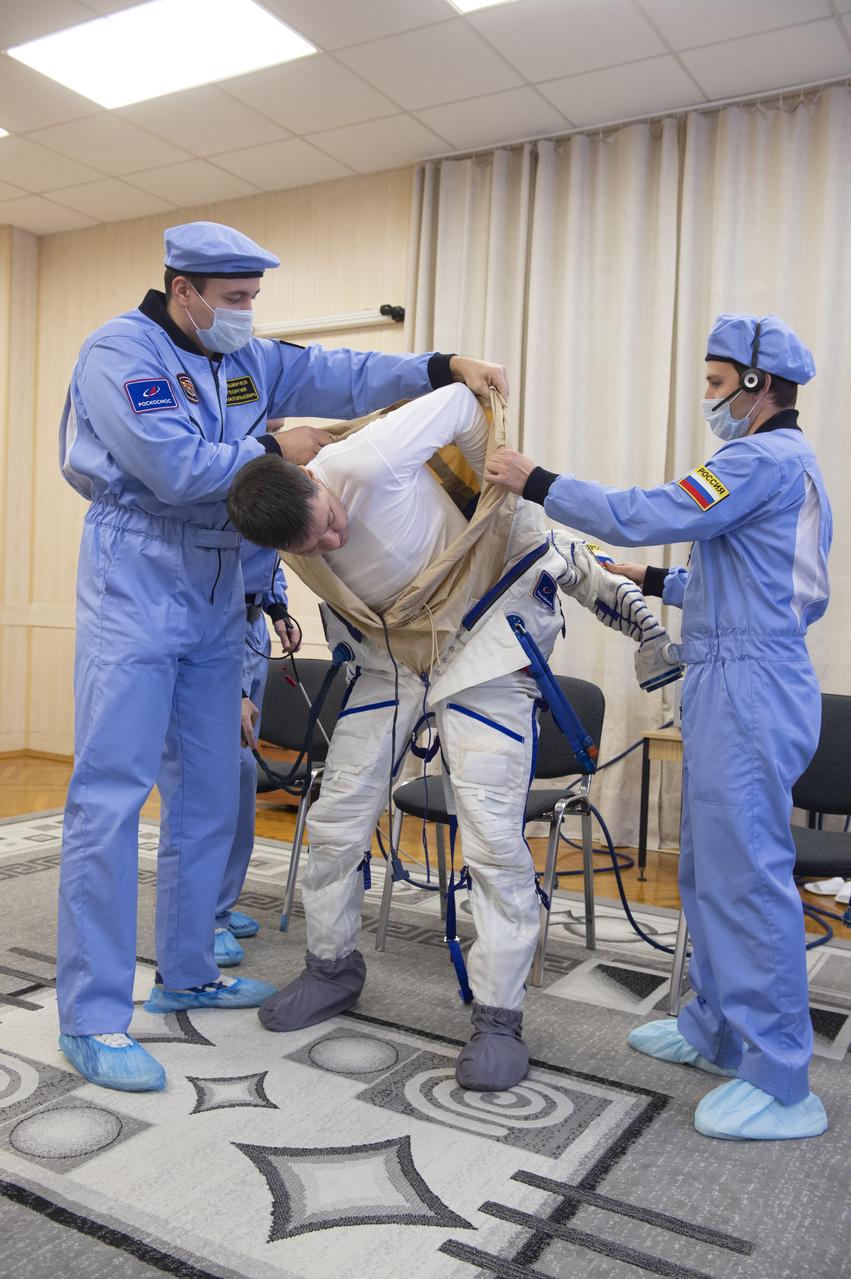
Expedition 58 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Anne McClain of NASA and Flight Engineer David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Monday, Dec. 3, 2018 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the same day and will carry Kononenko, McClain, and Saint-Jacques into orbit to begin their six and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/NASA/Andrey Shelepin)
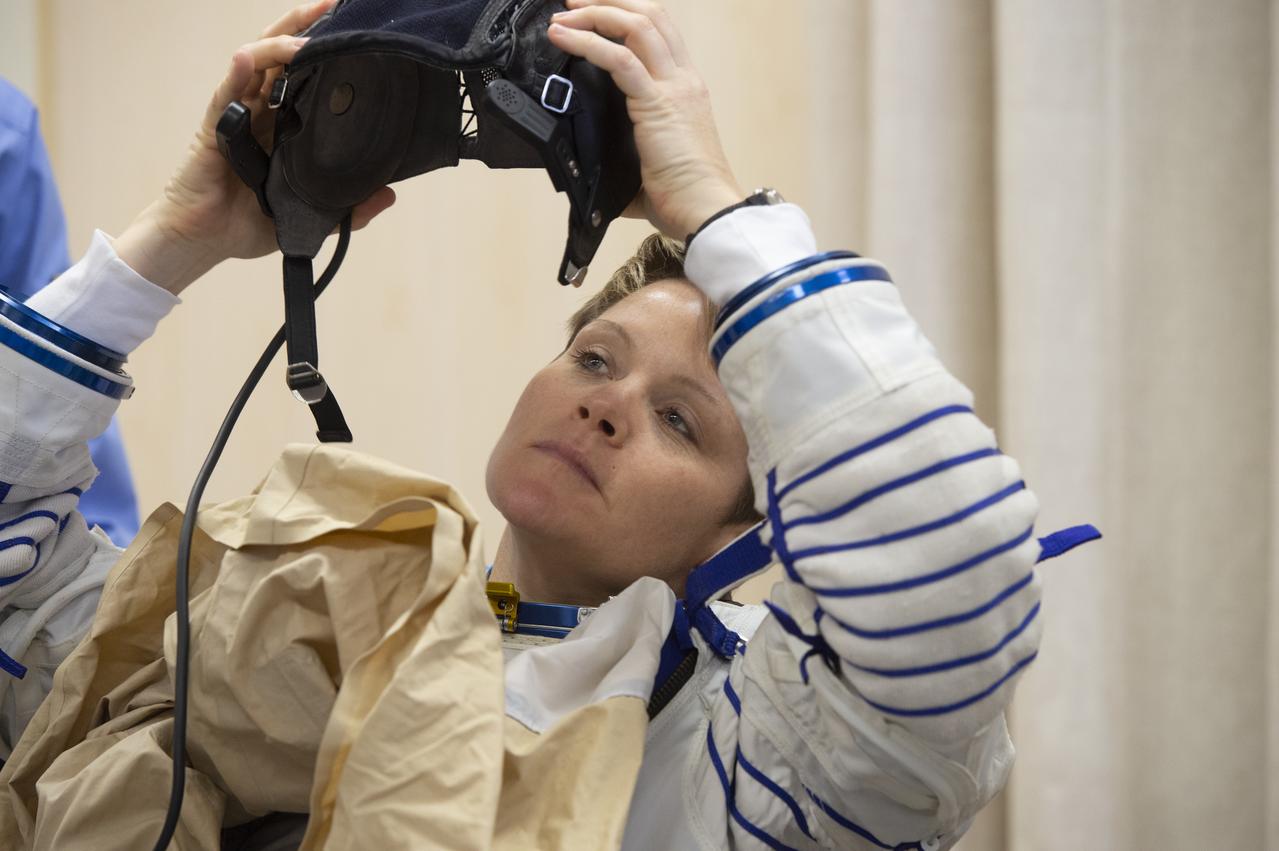

Flight Engineer Anne McClain of NASA is helped into her Russian Sokol suit as she and fellow crewmates, Expedition 58 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos and Flight Engineer David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Monday, Dec. 3, 2018 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the same day and will carry McClain, Kononenko, and Saint-Jacques into orbit to begin their six and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/NASA/Andrey Shelepin)
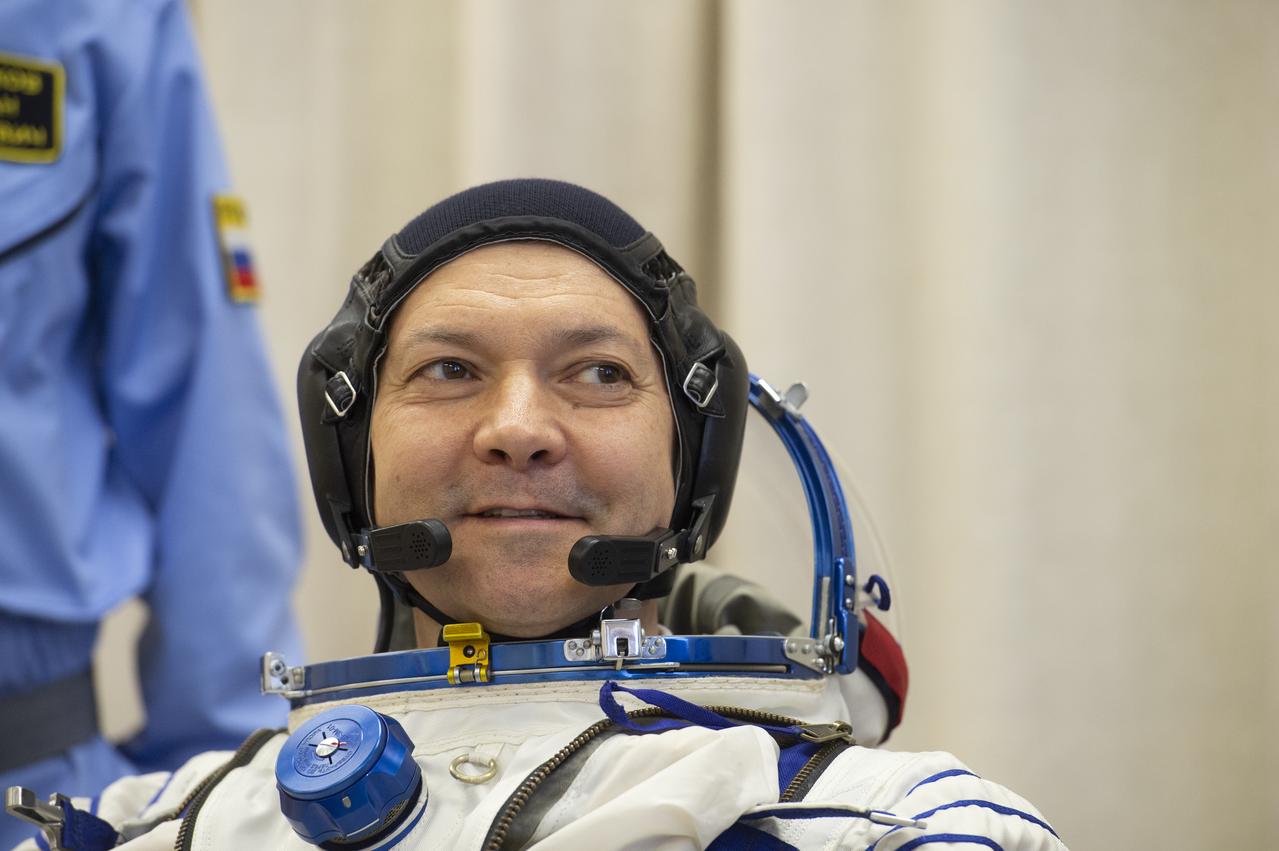

Expedition 58 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos is helped into his Russian Sokol suit as he and fellow crewmates, Flight Engineer Anne McClain of NASA and Flight Engineer David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Monday, Dec. 3, 2018 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the same day and will carry Kononenko, McClain, and Saint-Jacques into orbit to begin their six and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/NASA/Andrey Shelepin)
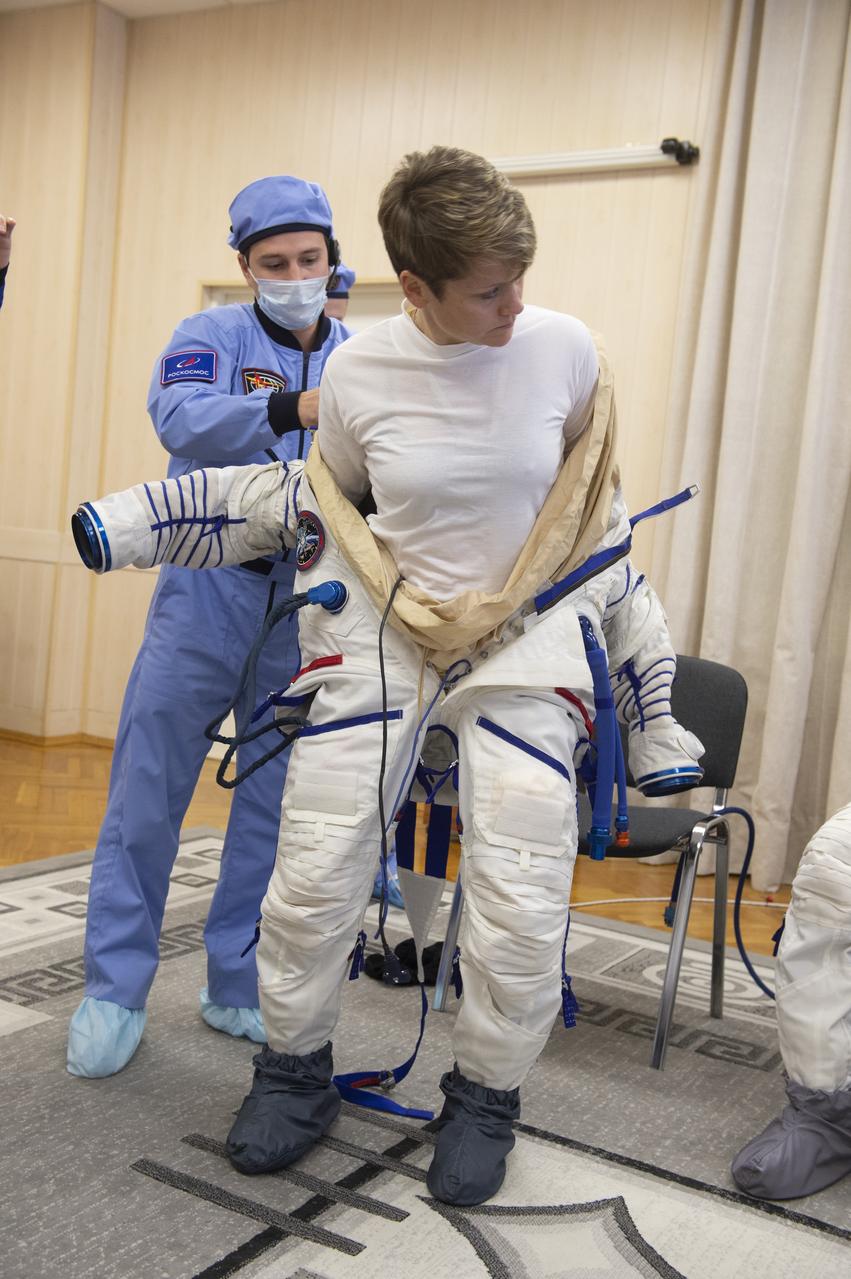

Flight Engineer Anne McClain of NASA is helped into her Russian Sokol suit as she and fellow crewmates, Expedition 58 Soyuz Commander Oleg Kononenko of Roscosmos and Flight Engineer David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) prepare for their Soyuz launch to the International Space Station, on Monday, Dec. 3, 2018 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Launch of the Soyuz rocket is scheduled for the same day and will carry McClain, Kononenko, and Saint-Jacques into orbit to begin their six and a half month mission on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (GCTC/NASA/Andrey Shelepin)
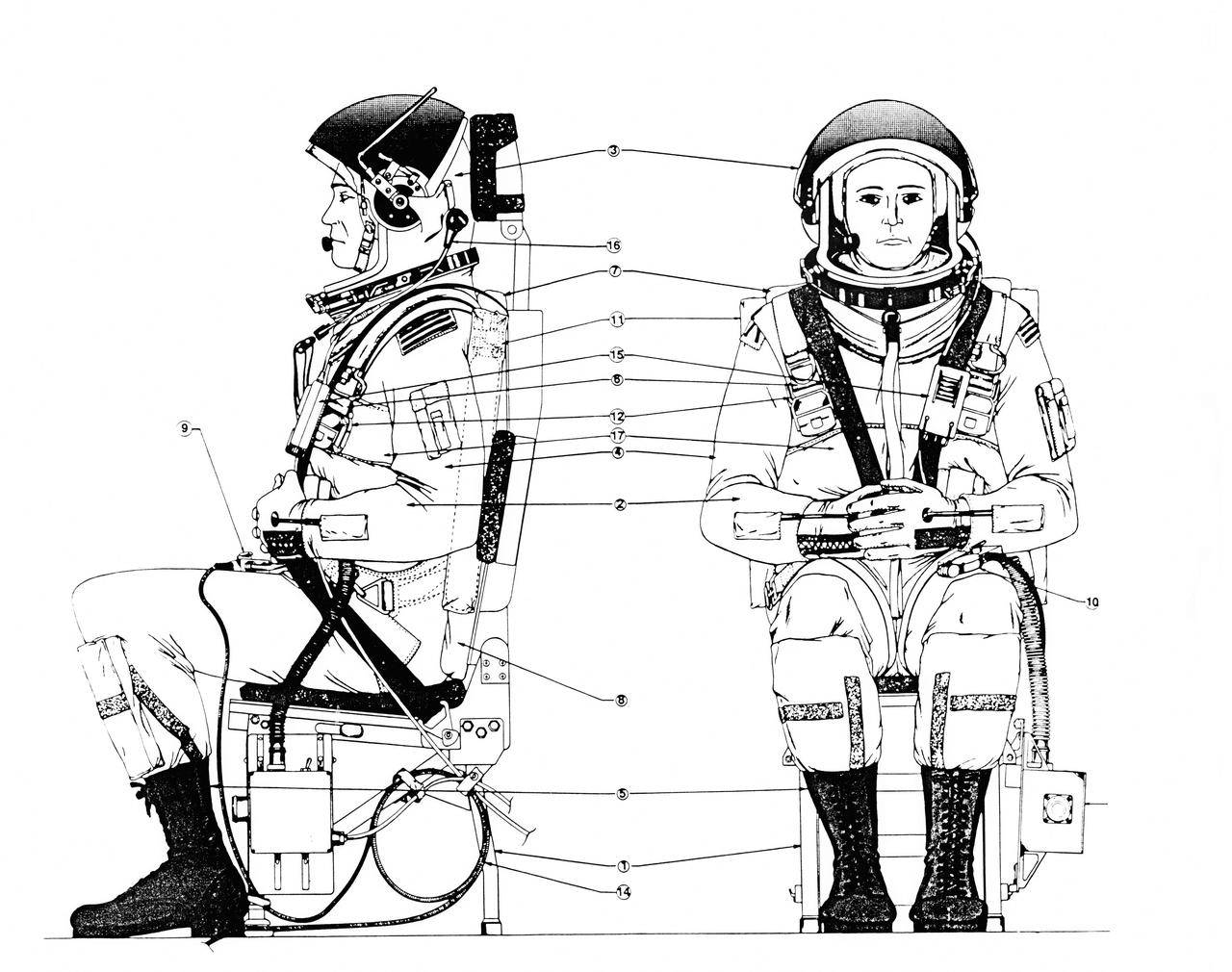
Diagrams of Crew Escape System Partial Pressure Suits, dated July, 1988.
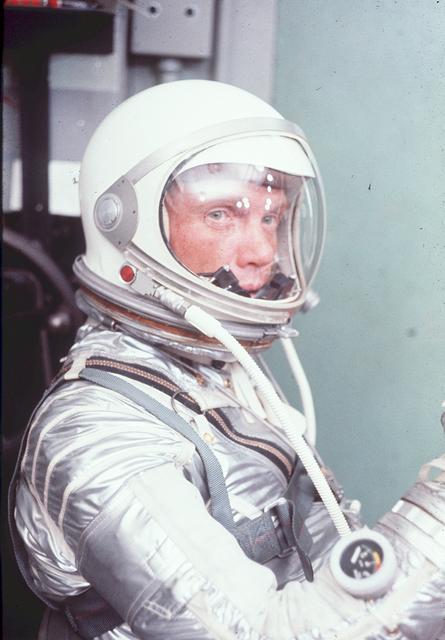

S64-36910 (February 1962) --- Astronaut John H. Glenn Jr., wearing a Mercury pressure suit, was the pilot of the Mercury-Atlas 6 (MA-6) mission. Glenn made America's first manned Earth-orbiting spaceflight on Feb. 20, 1962. This photograph was taken at Cape Canaveral, Florida, during MA-6 preflight training activities. Photo credit: NASA
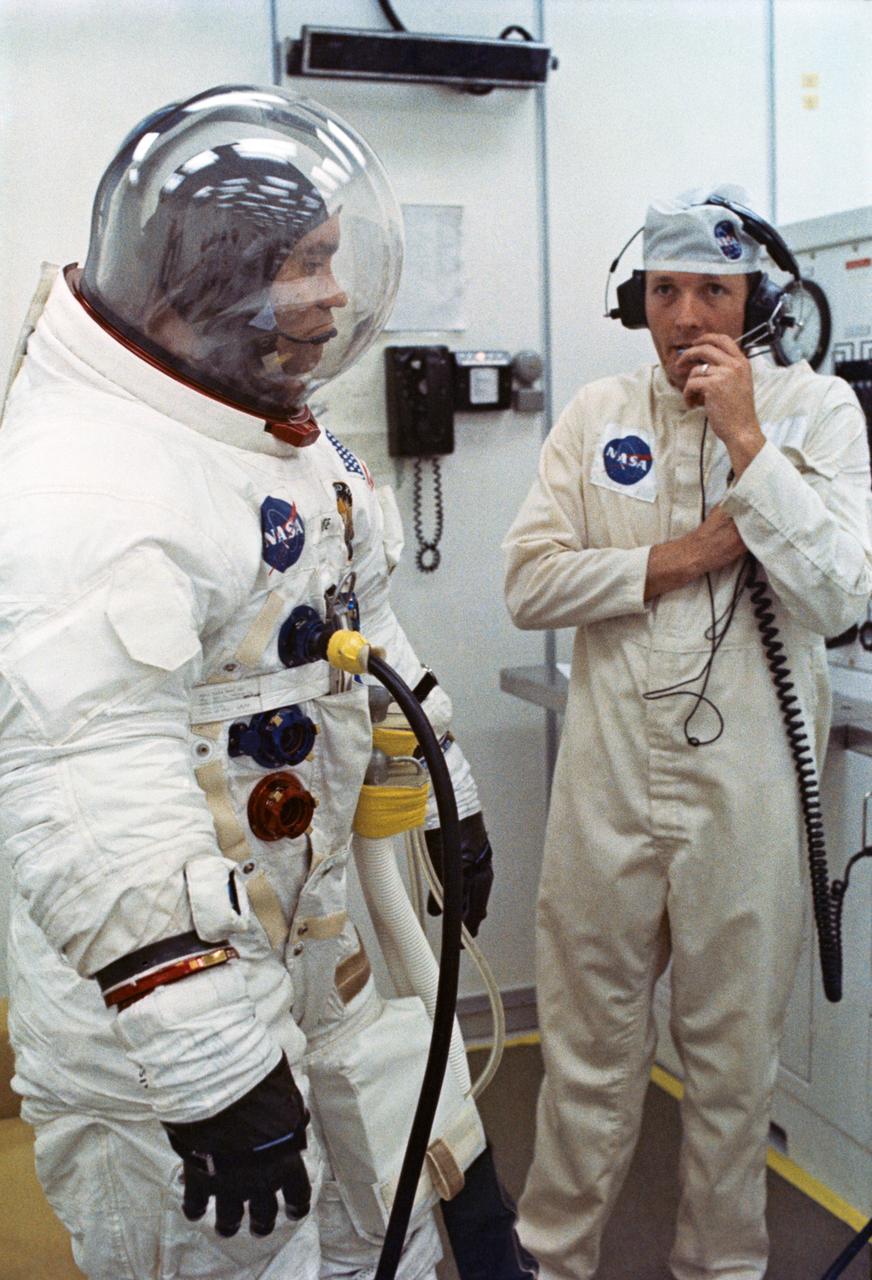

S70-34851 (11 April 1970) --- A space suit technician talks with astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot for NASA's Apollo 13 mission, during suiting up procedures at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Other members of the crew are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot. Swigert replaced astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II as a member of the crew when it was learned he had been exposed to measles.
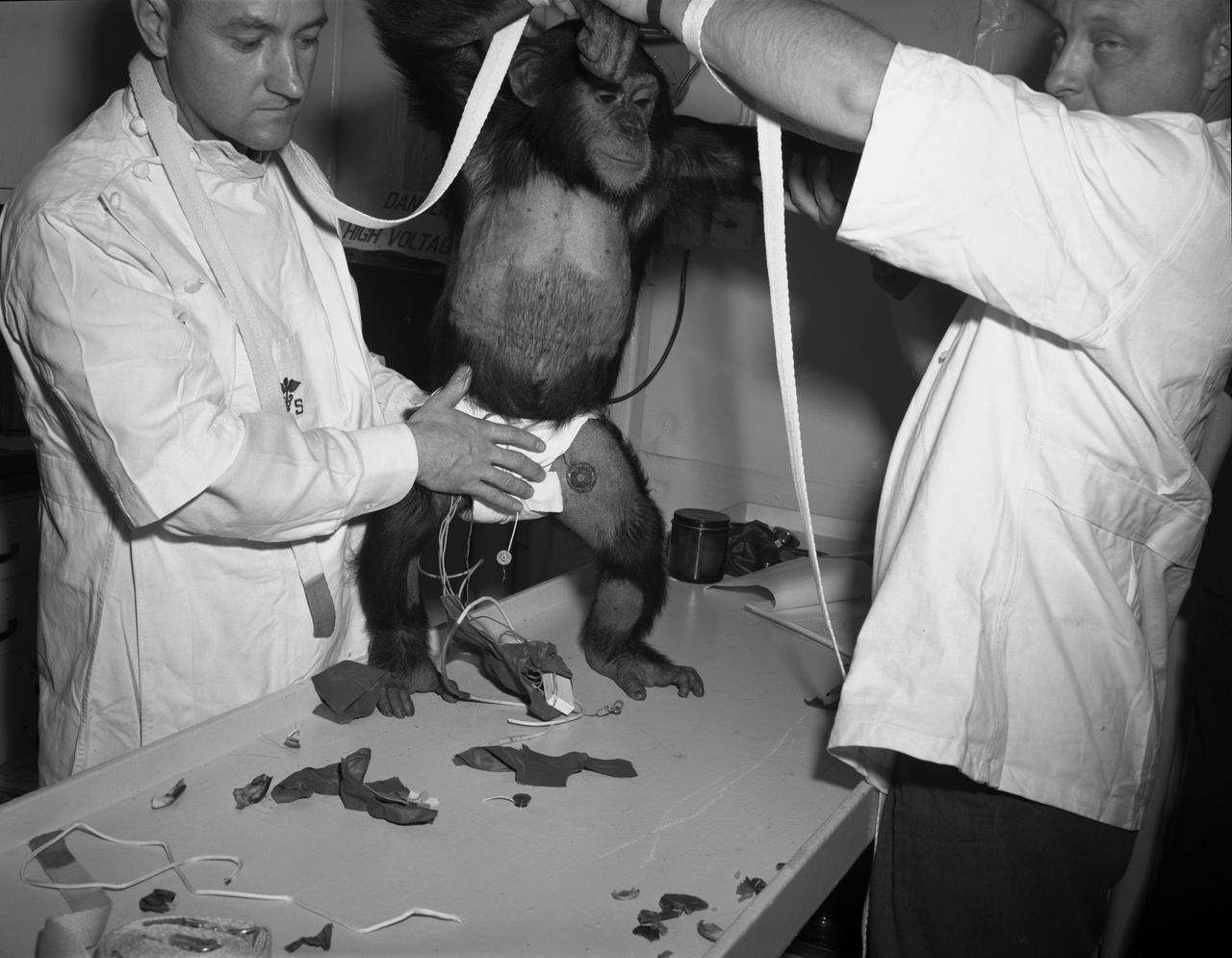

S63-20800 (31 Jan. 1961) --- Chimpanzee "Ham" being assisted into "spacesuit" prior to the Mercury-Redstone 2 (MR-2) test flight which was conducted on Jan. 31, 1961. Photo credit: NASA
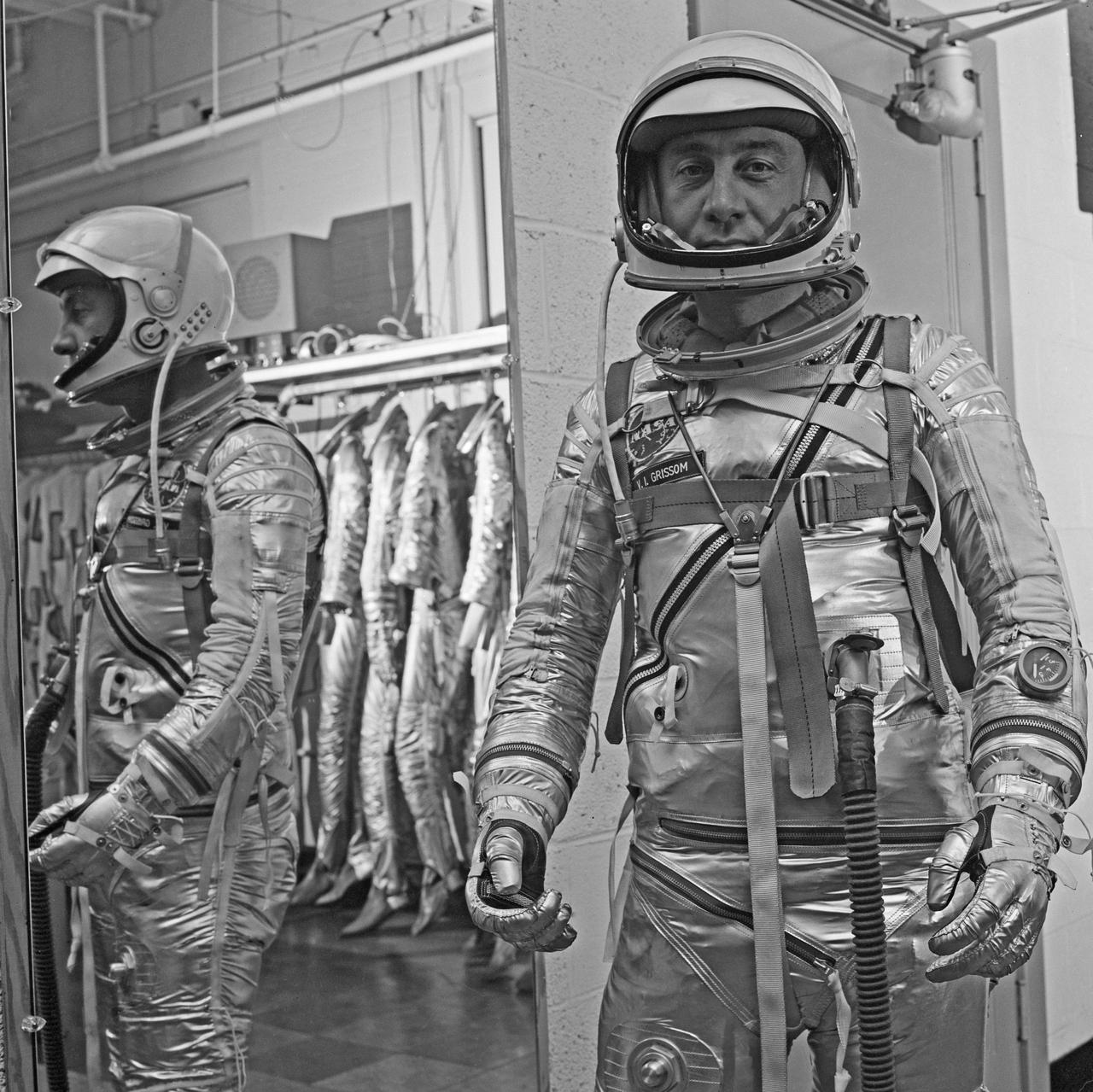

Gus Grissom trying on a Spacesuit; Seated with assistant; Seated with assistant putting on boots; Standing by mirror, name tag visible; Outside in suit, name tag visible. Mercury Project photo, 1961. Original negatives sent to Johnson Space Center when astronauts moved to that center. Photograph take on 03/27/1961.
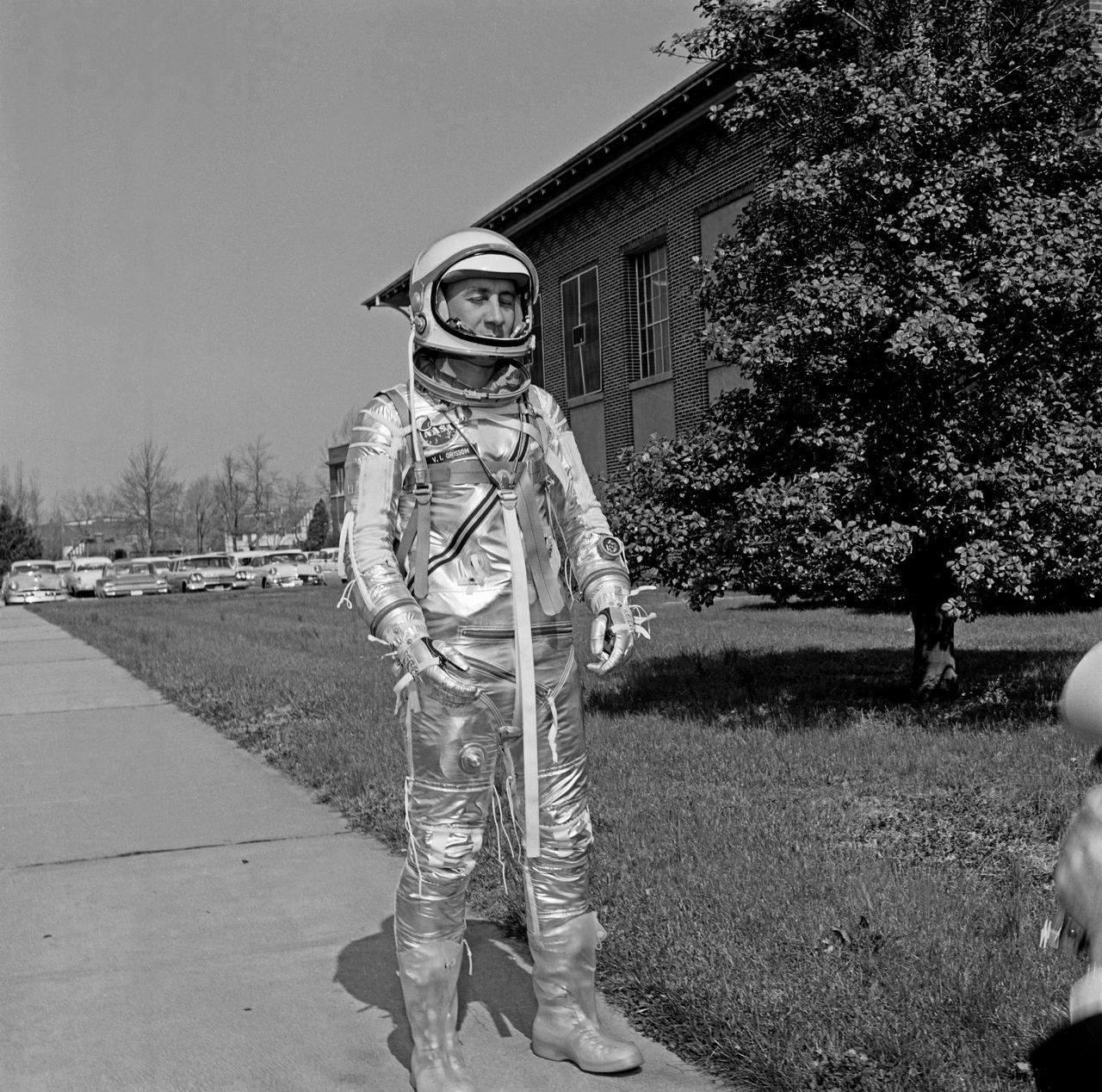

Gus Grissom trying on a Spacesuit; Seated with assistant; Seated with assistant putting on boots; Standing by mirror, name tag visible; Outside in suit, name tag visible. Mercury Project photo, 1961. Original negatives sent to Johnson Space Center when astronauts moved to that center. Photograph take on 03/27/1961.
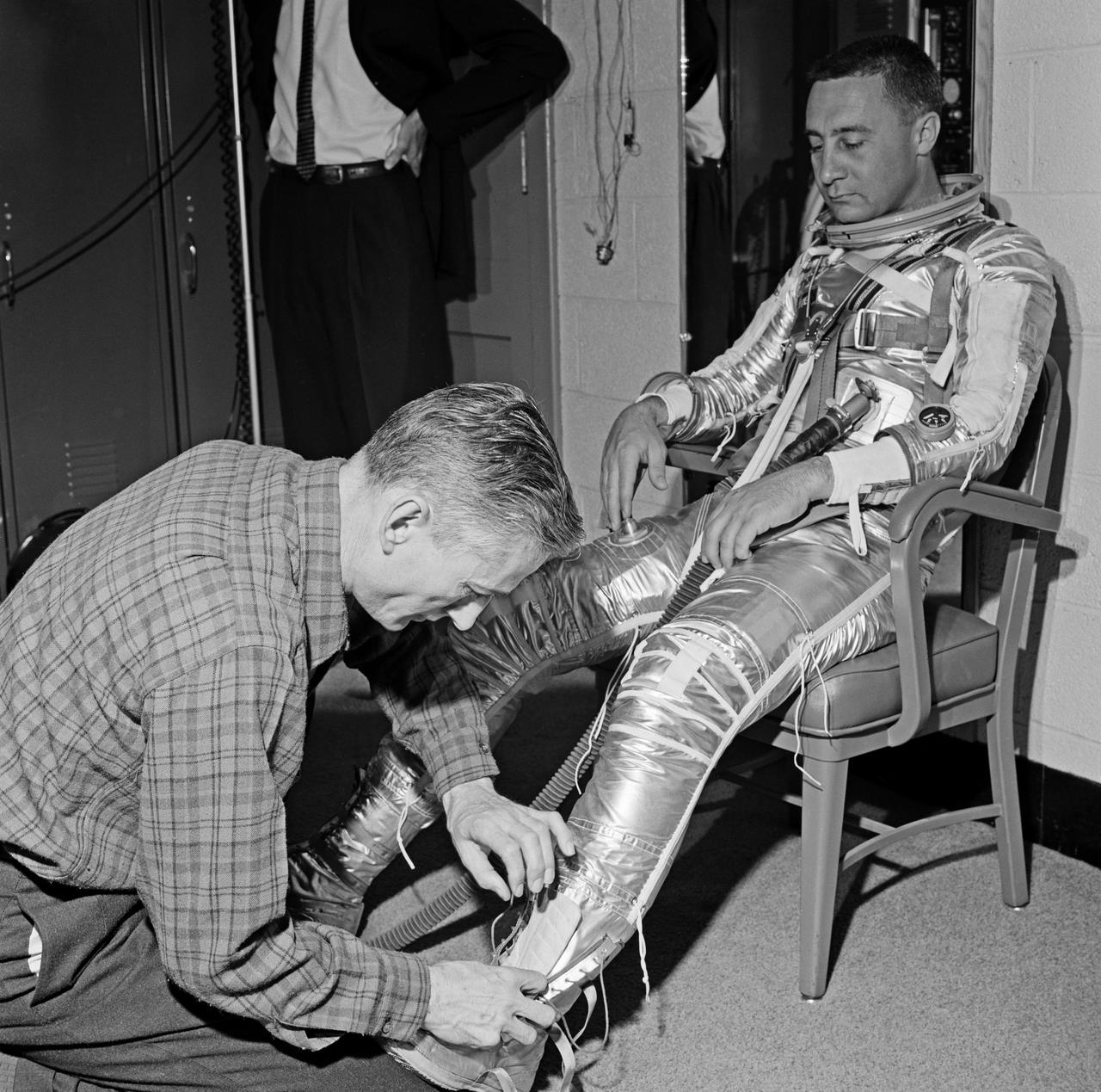
Gus Grissom trying on a Spacesuit; Seated with assistant; Seated with assistant putting on boots; Standing by mirror, name tag visible; Outside in suit, name tag visible. Mercury Project photo, 1961. Original negatives sent to Johnson Space Center when astronauts moved to that center. Photograph take on 03/27/1961.
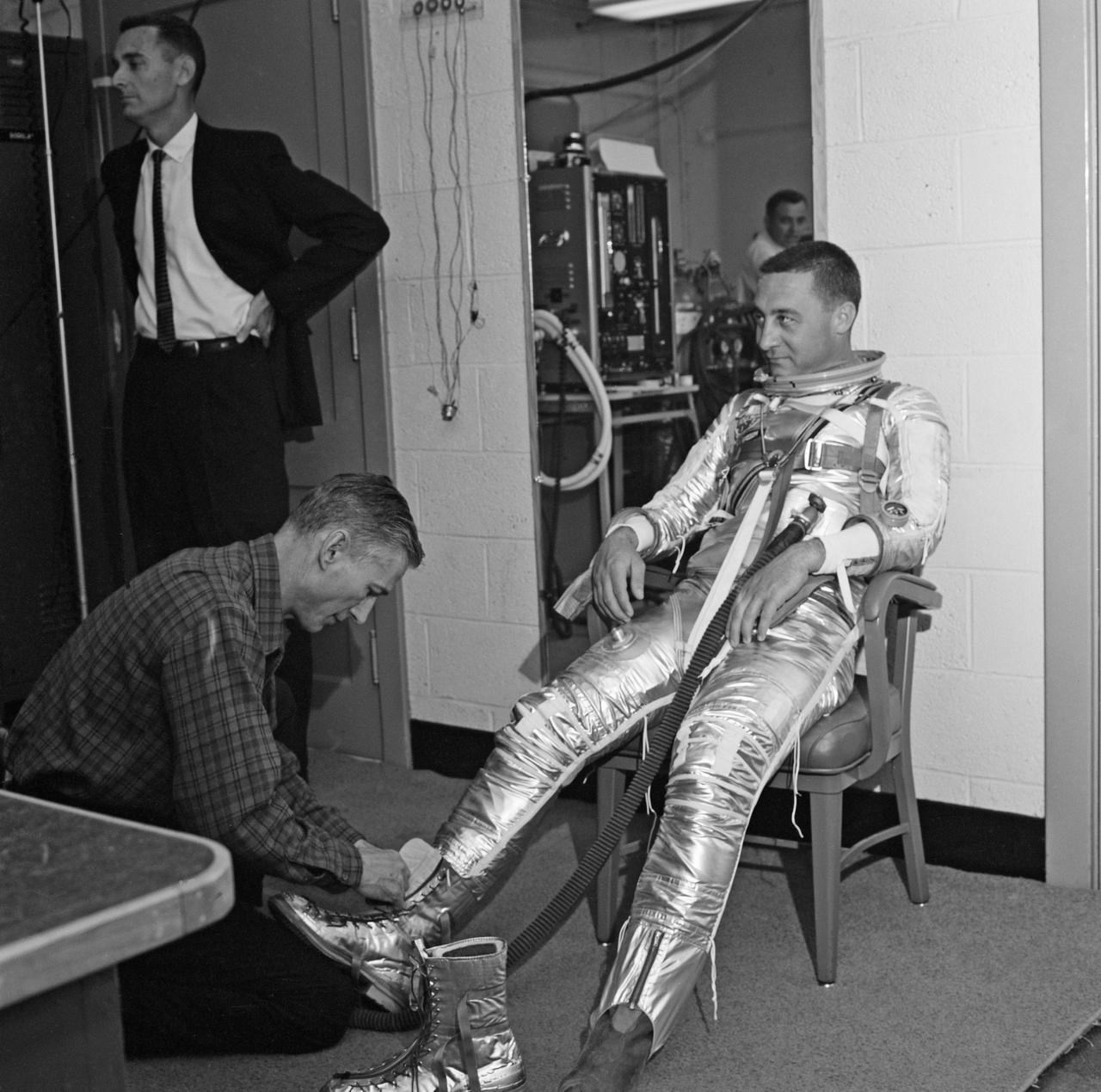
Gus Grissom trying on a Spacesuit; Seated with assistant; Seated with assistant putting on boots; Standing by mirror, name tag visible; Outside in suit, name tag visible. Mercury Project photo, 1961. Original negatives sent to Johnson Space Center when astronauts moved to that center. Photograph take on 03/27/1961.
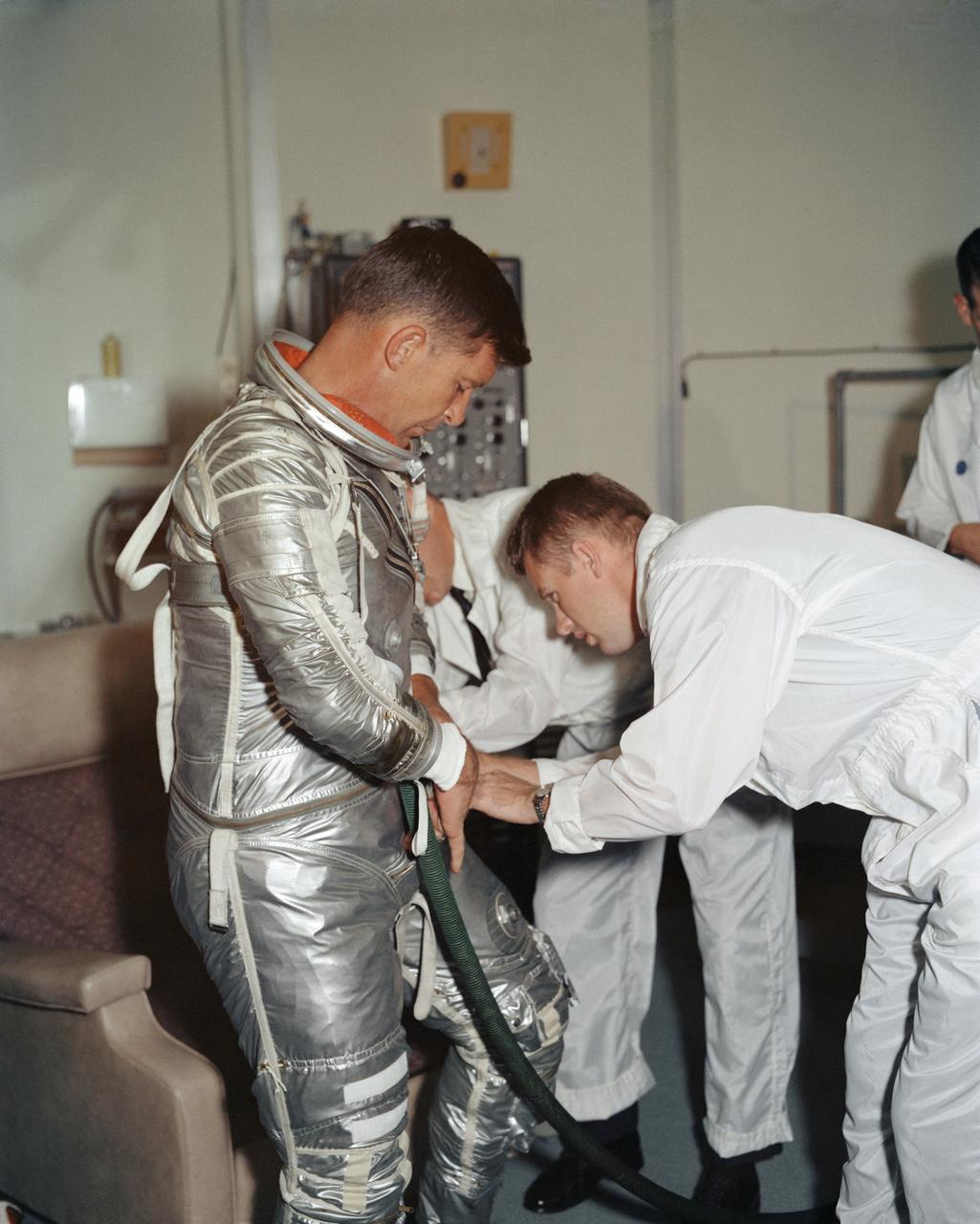

S62-08895 (1962) --- Astronaut Walter M. Schirra Jr., pilot of the Mercury-Atlas 8 (MA-8) Earth-orbital spaceflight, goes through a suiting-up exercise in Hangar "S" at Cape Canaveral several weeks prior to his scheduled Oct. 3, 1962 flight. Photo credit: NASA
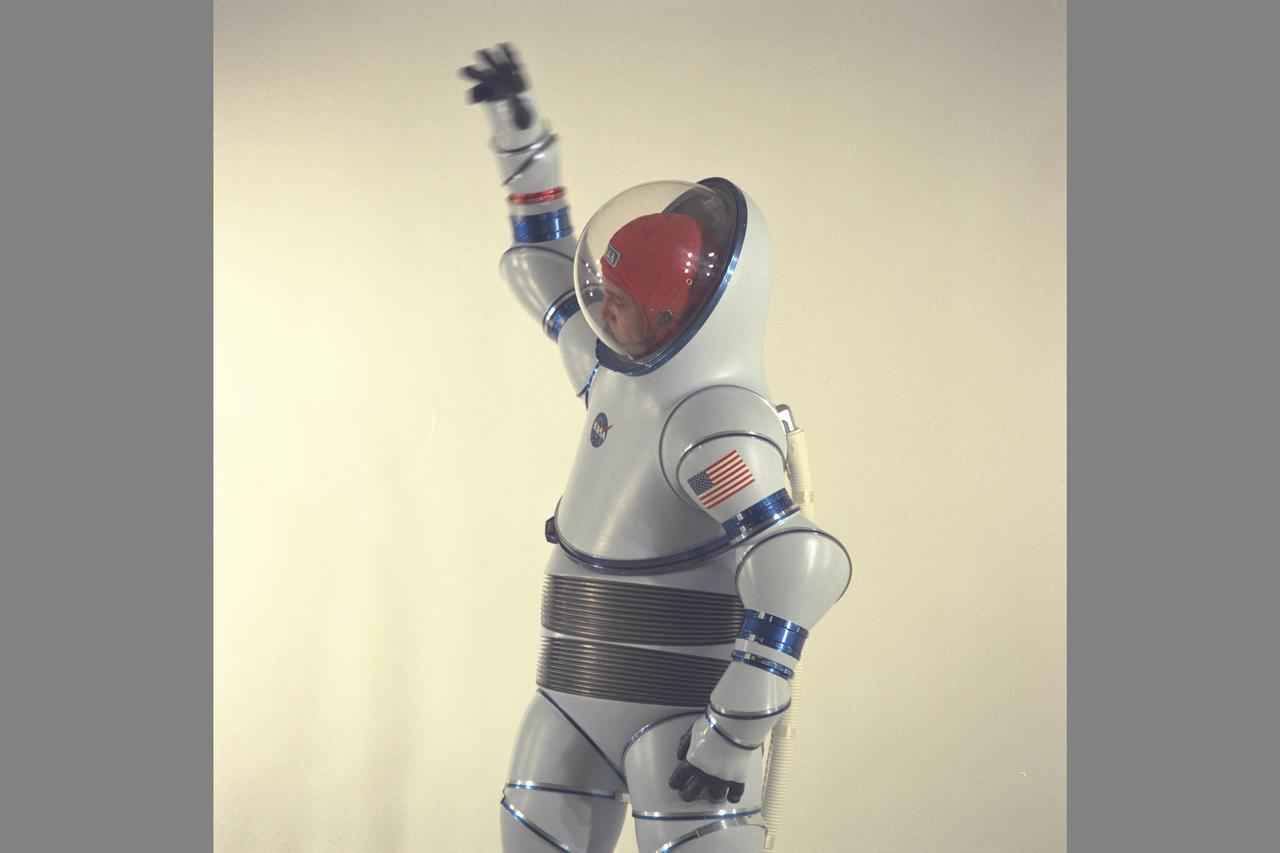

AX-2 Hard Space Suit with Vic Vykukal. Vykukal is the principal investigator of the AX space suit series.
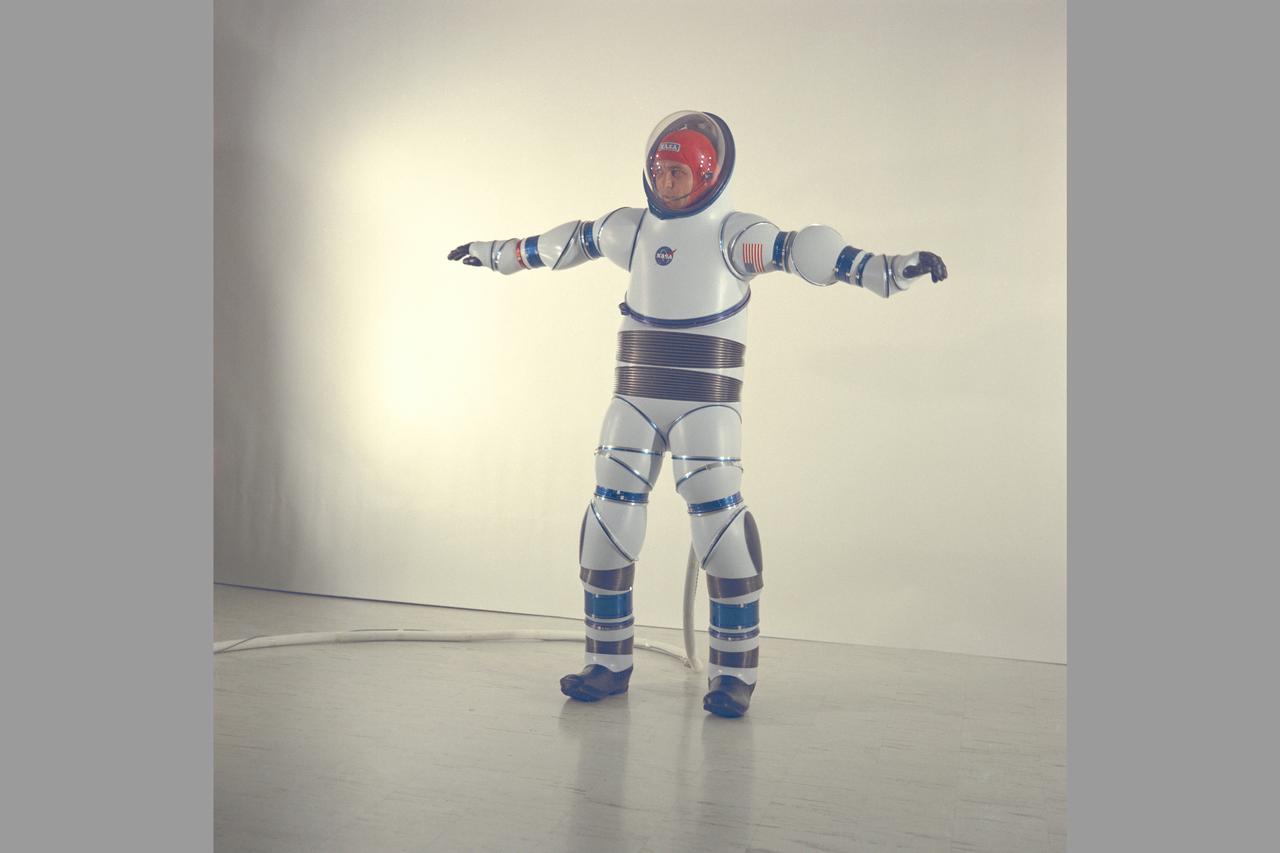

AX-2 Hard Space Suit with Vic Vykukal. Vykukal is the principal investigator of the AX space suit series.

AX-2 Hard Space Suit with Vic Vykukal. Vykukal is the principal investigator of the AX space suit series.
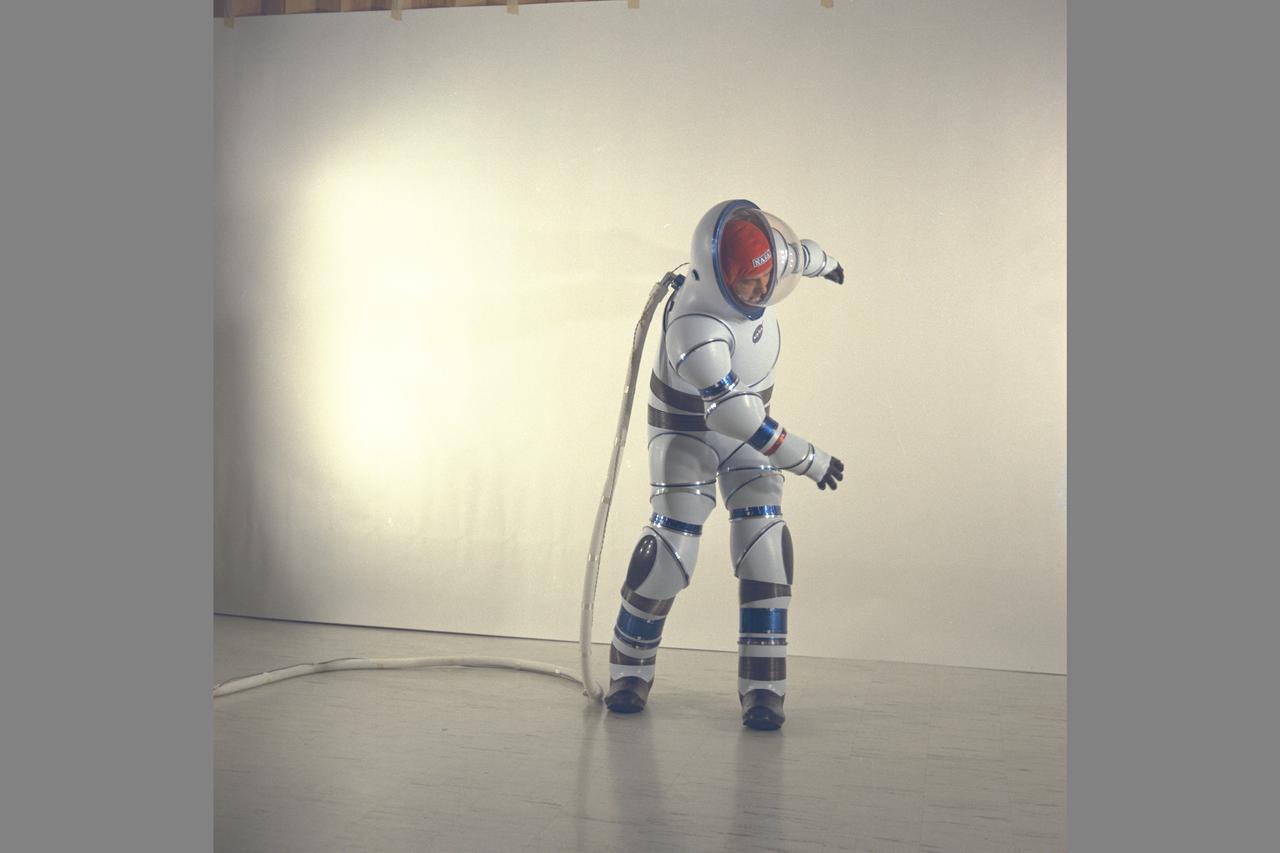

AX-2 Hard Space Suit with Vic Vykukal. Vykukal is the principal investigator of the AX space suit series.
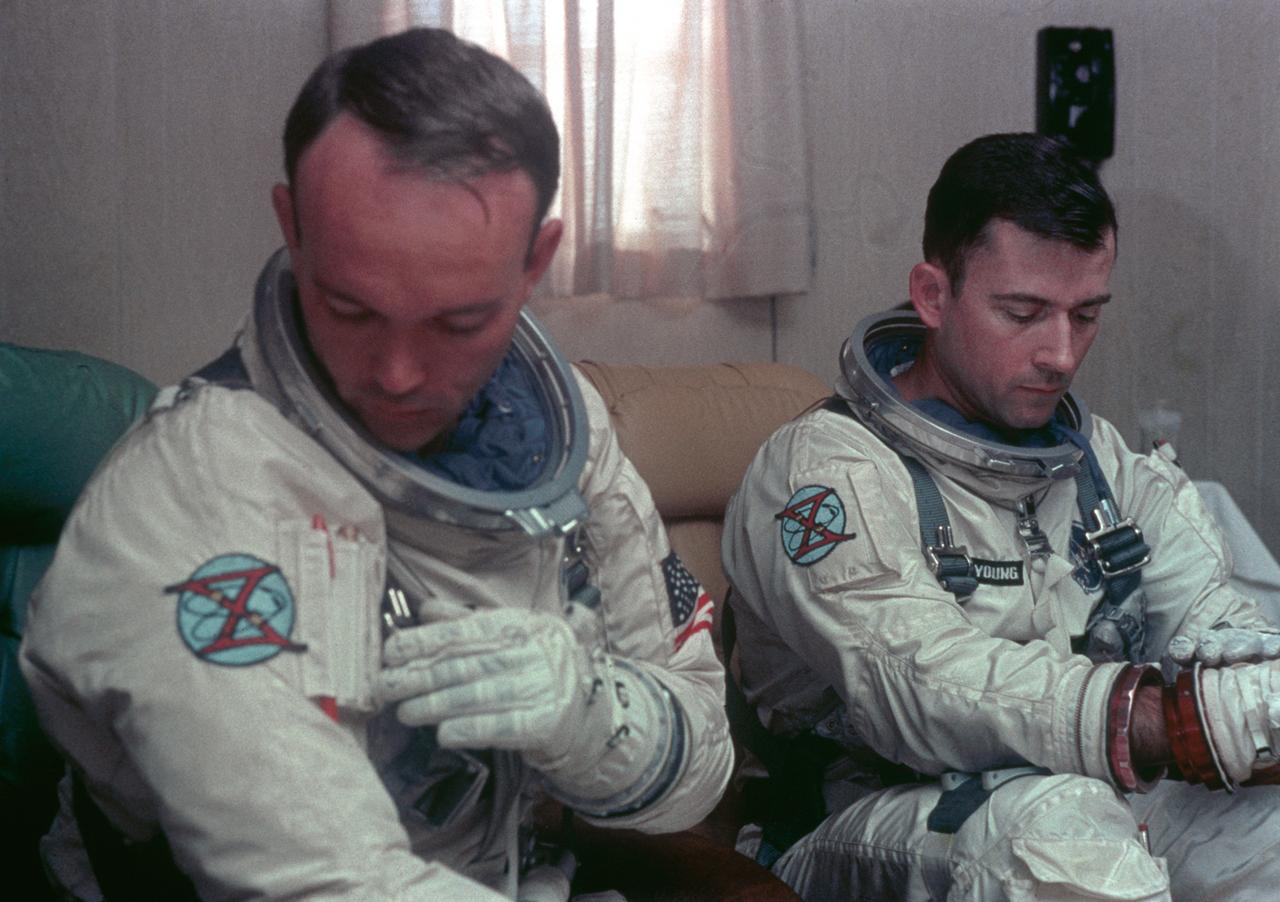

S66-42424 (18 July 1966) --- Astronauts John W. Young (right), command pilot, and Michael Collins (left), pilot, prime crew for the Gemini-10 spaceflight, undergo suiting up operations in the Launch Complex 16 suiting trailer. Photo credit: NASA
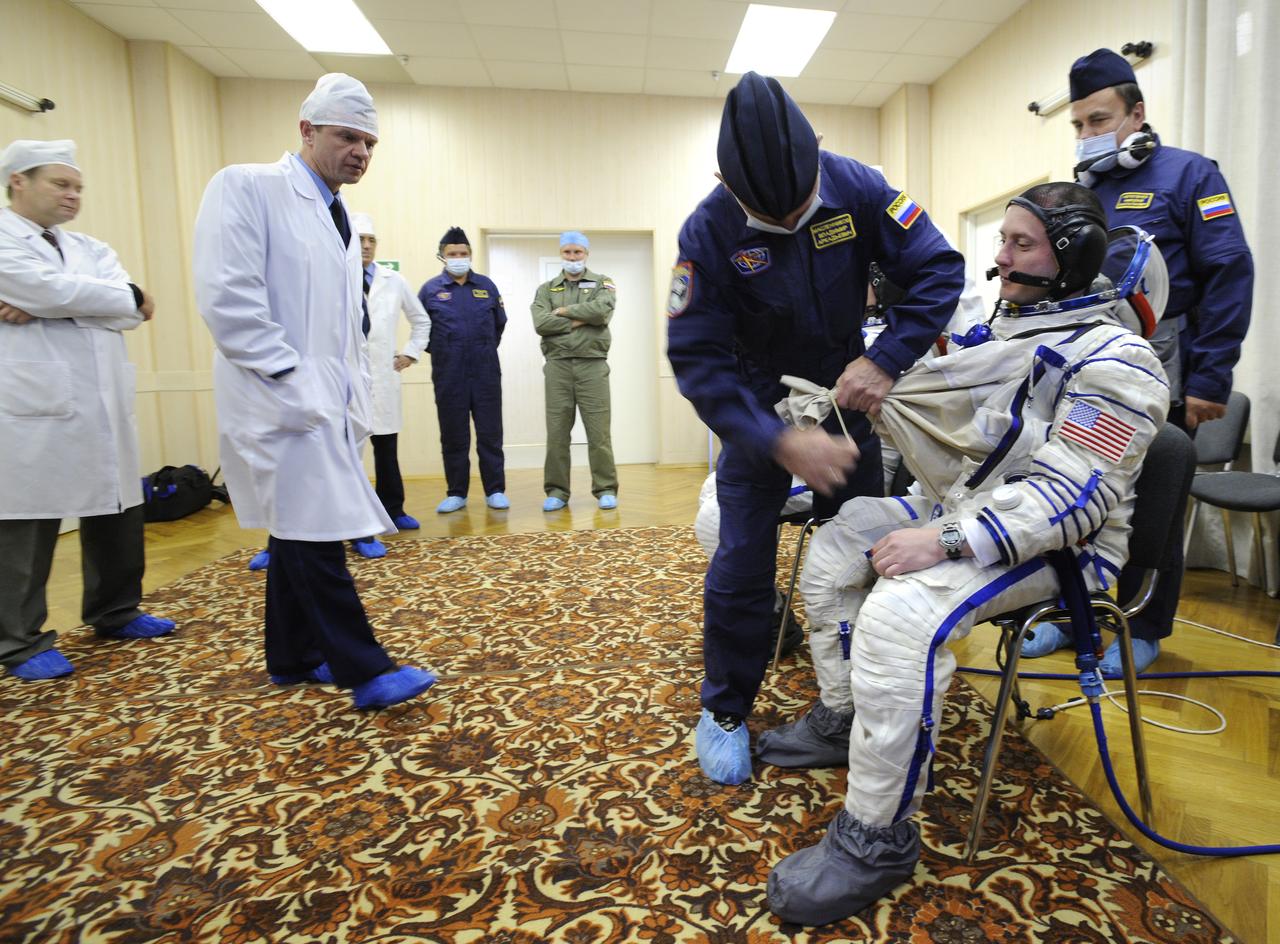

Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke dons his Russian Sokol suit hours before he and Expedition 18 Flight Engineer Yuri V. Lonchakov and American spaceflight participant Richard Garriott launch in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24 with two of the Expedition 17 crew members currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
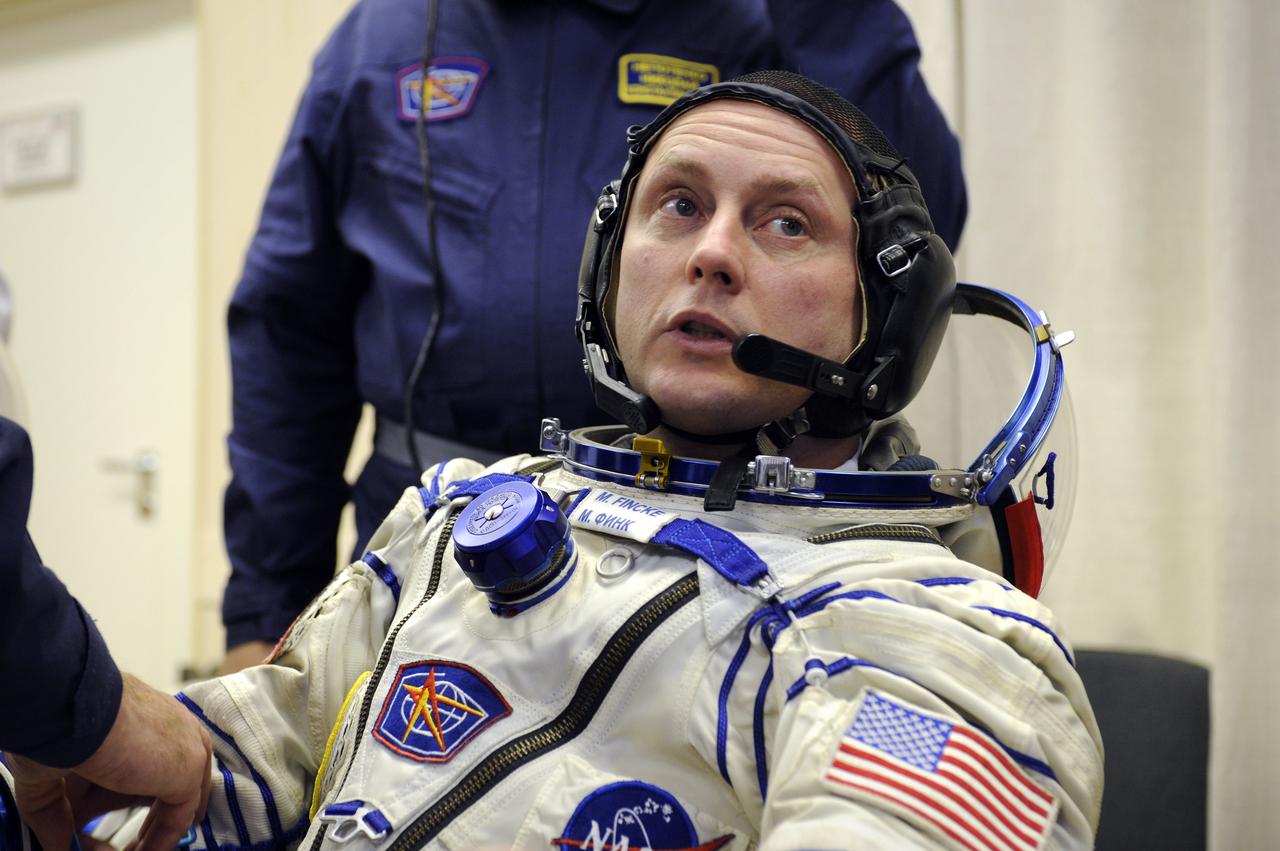

Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke dons his Russian Sokol suit hours before he and Expedition 18 Flight Engineer Yuri V. Lonchakov and American spaceflight participant Richard Garriott launch in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24 with two of the Expedition 17 crew members currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
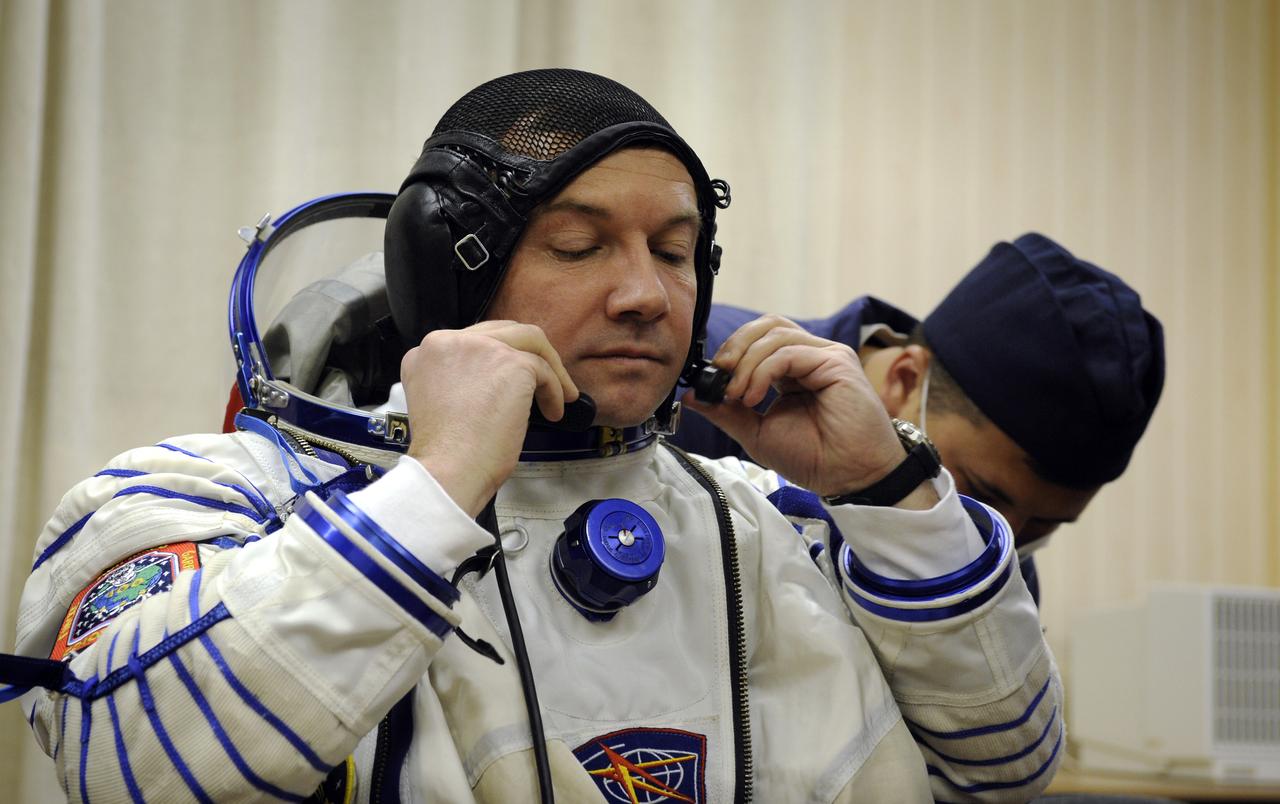

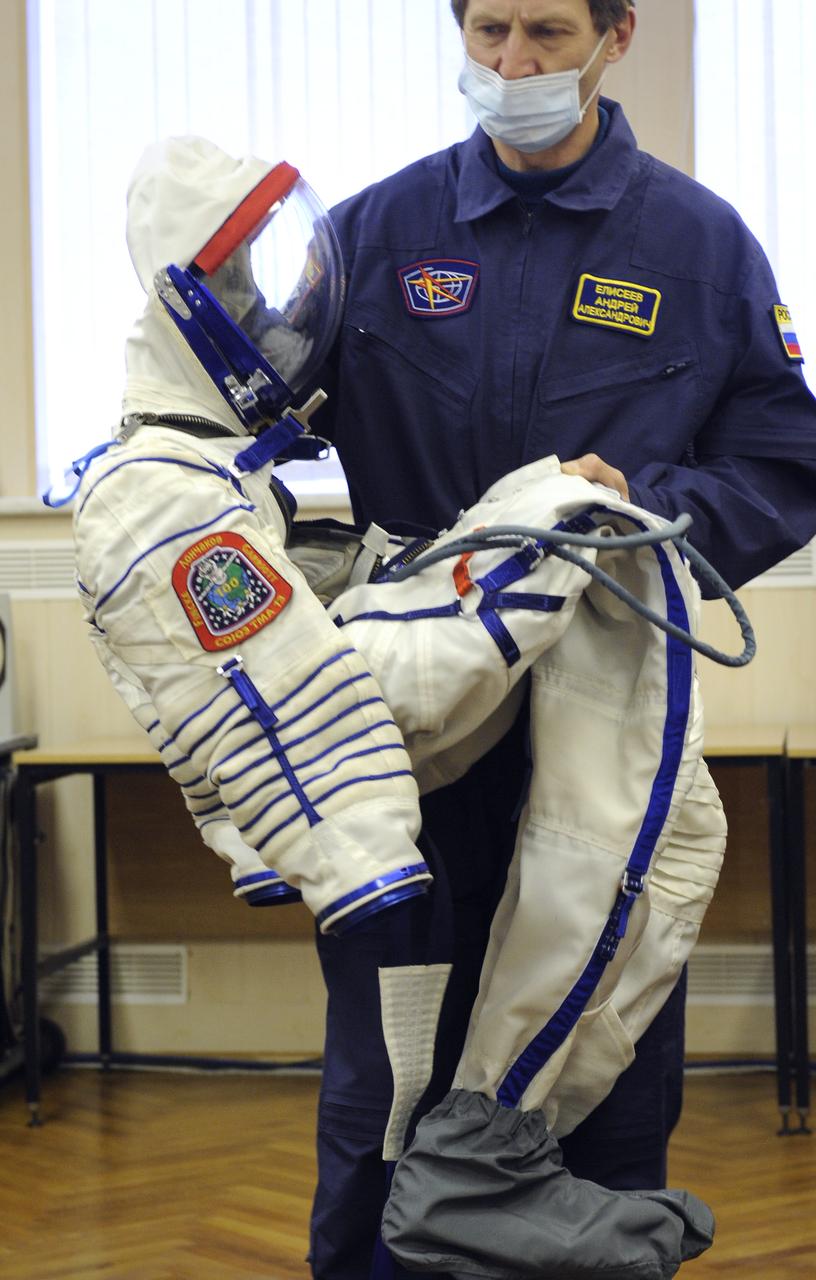
Expedition 18 Flight Engineer Yuri V. Lonchakov dons his Russian Sokol suit hours before he and Expedition 18 Commander Michael Fincke and American spaceflight participant Richard Garriott launch in the Soyuz TMA-13 spacecraft, Sunday, Oct. 12, 2008 from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The three crew members are scheduled to dock with the International Space Station on Oct. 14. Fincke and Lonchakov will spend six months on the station, while Garriott will return to Earth Oct. 24 with two of the Expedition 17 crew members currently on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)