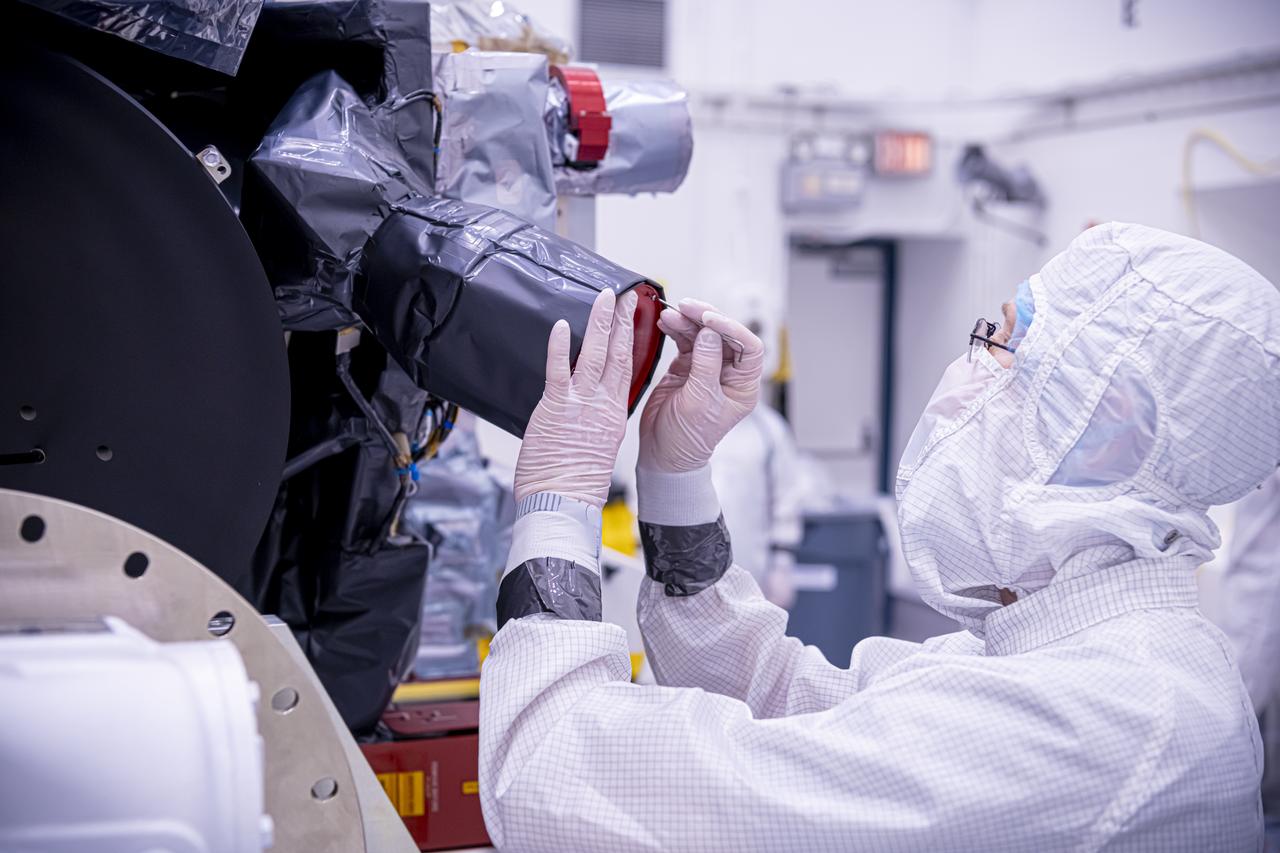

Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

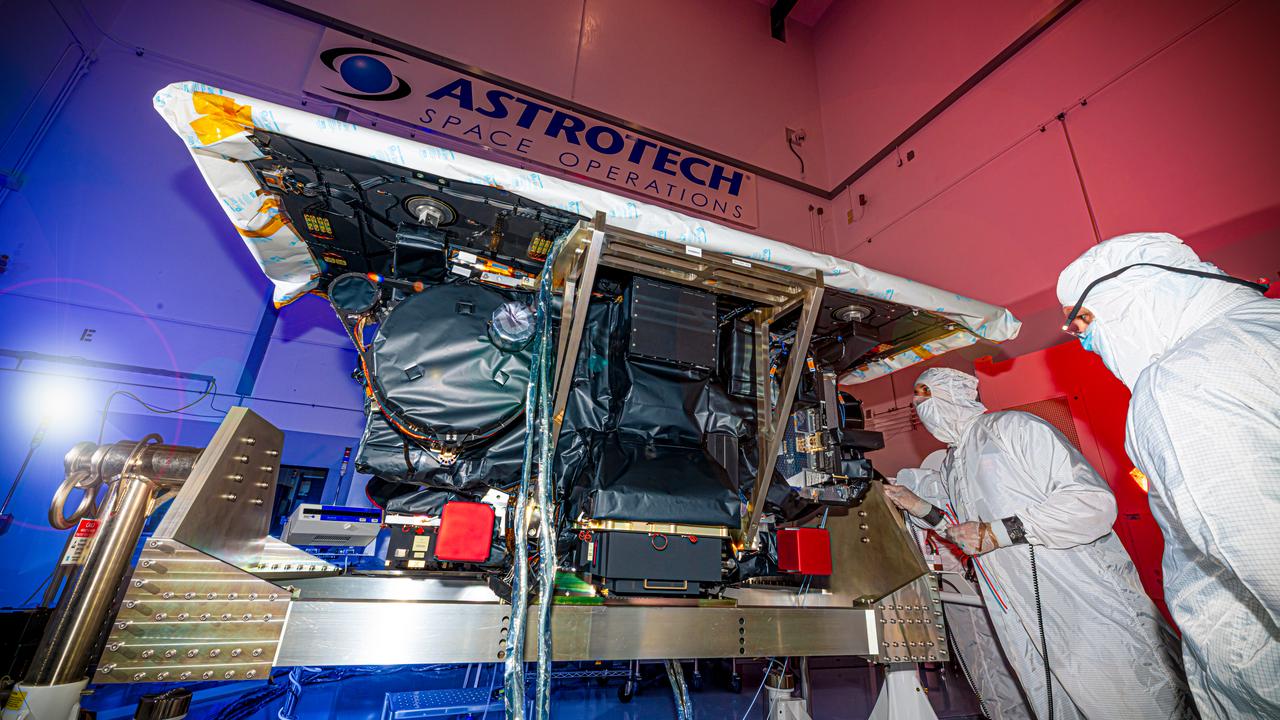
Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

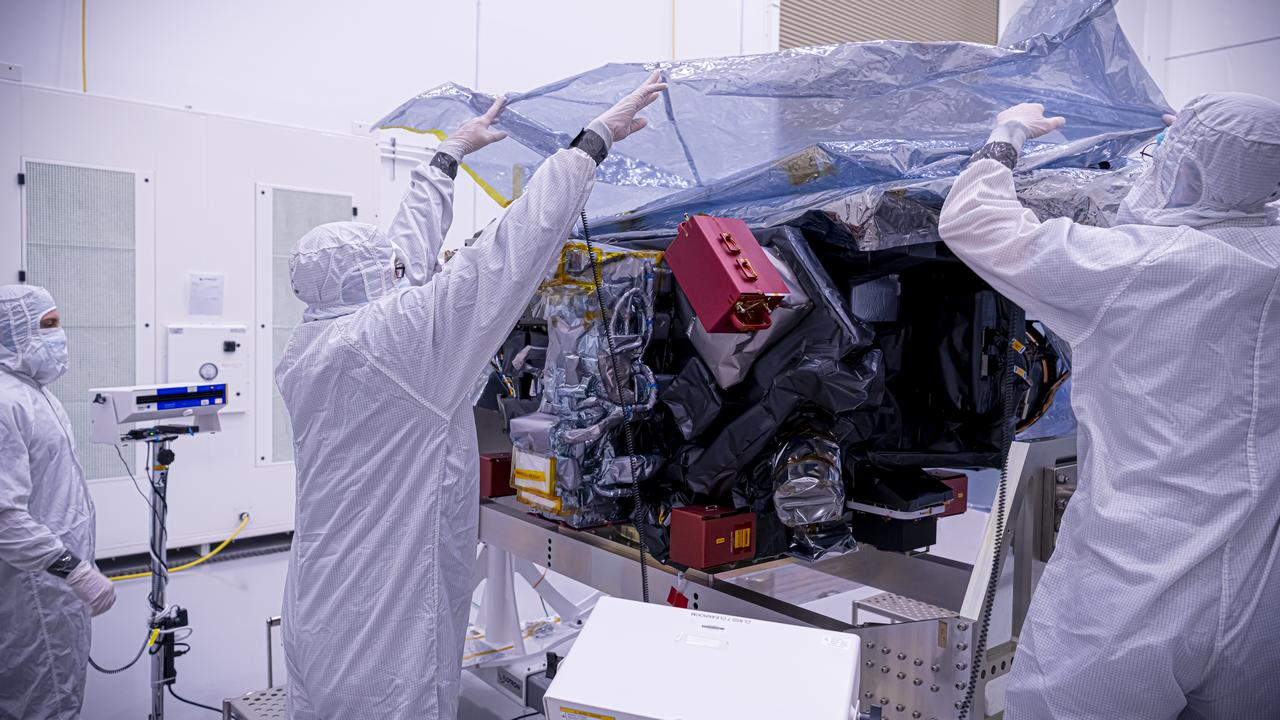
Technicians inspect the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory on Thursday, July 24, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
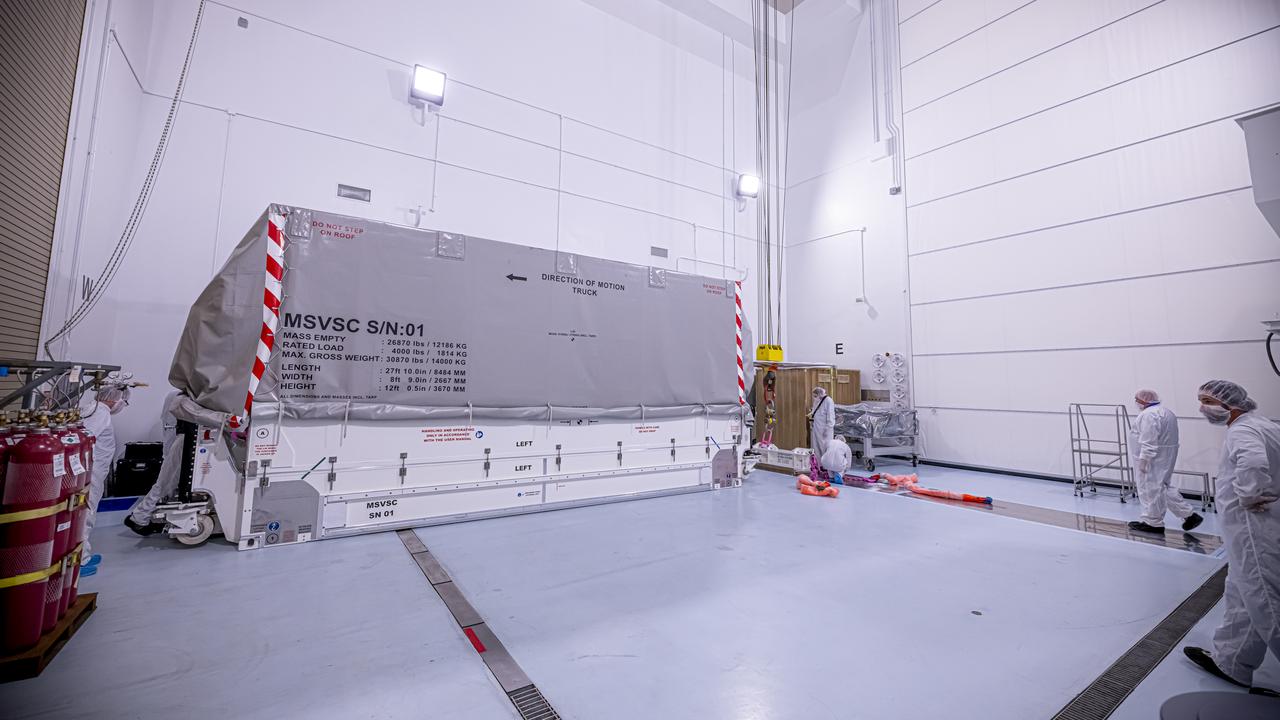

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory, set to provide quicker and more accurate space weather forecasts, arrived Sunday, July 20, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
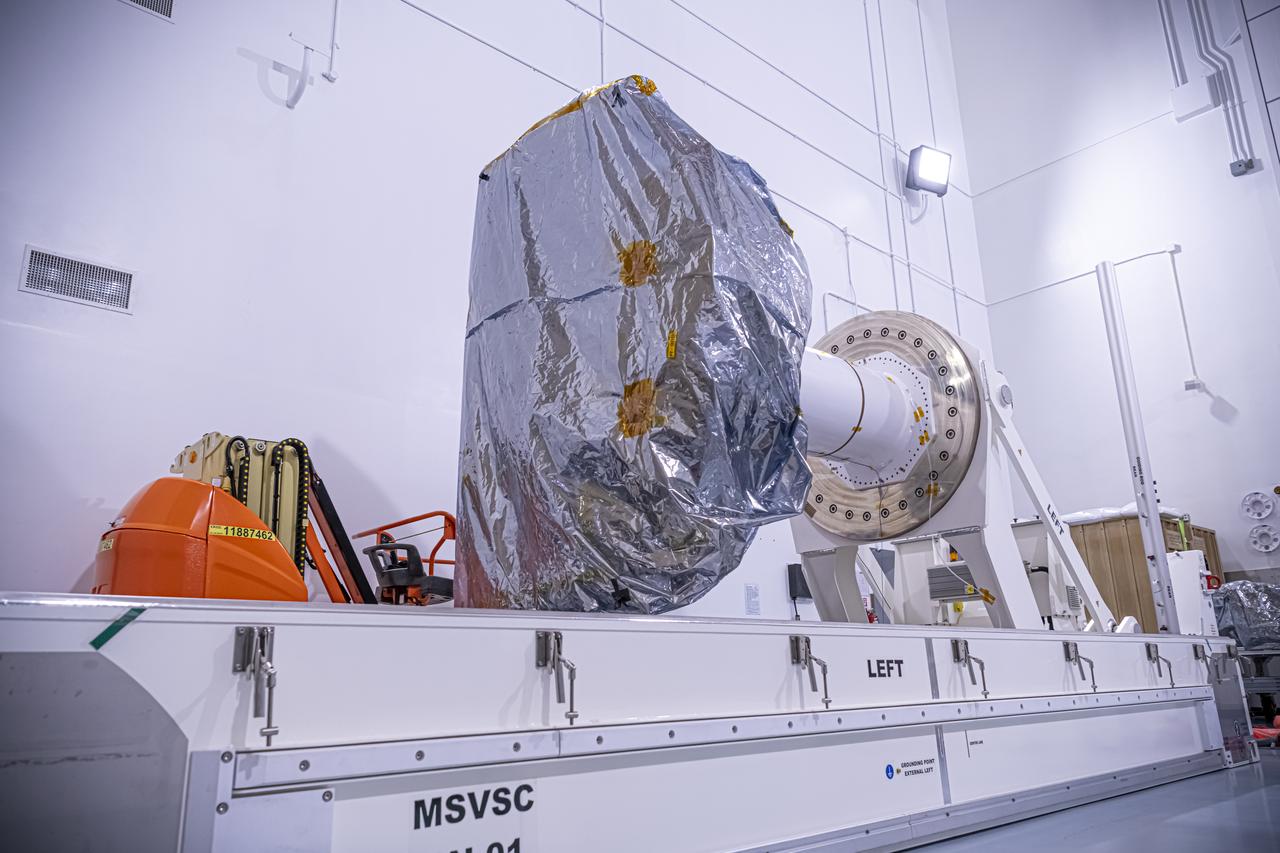

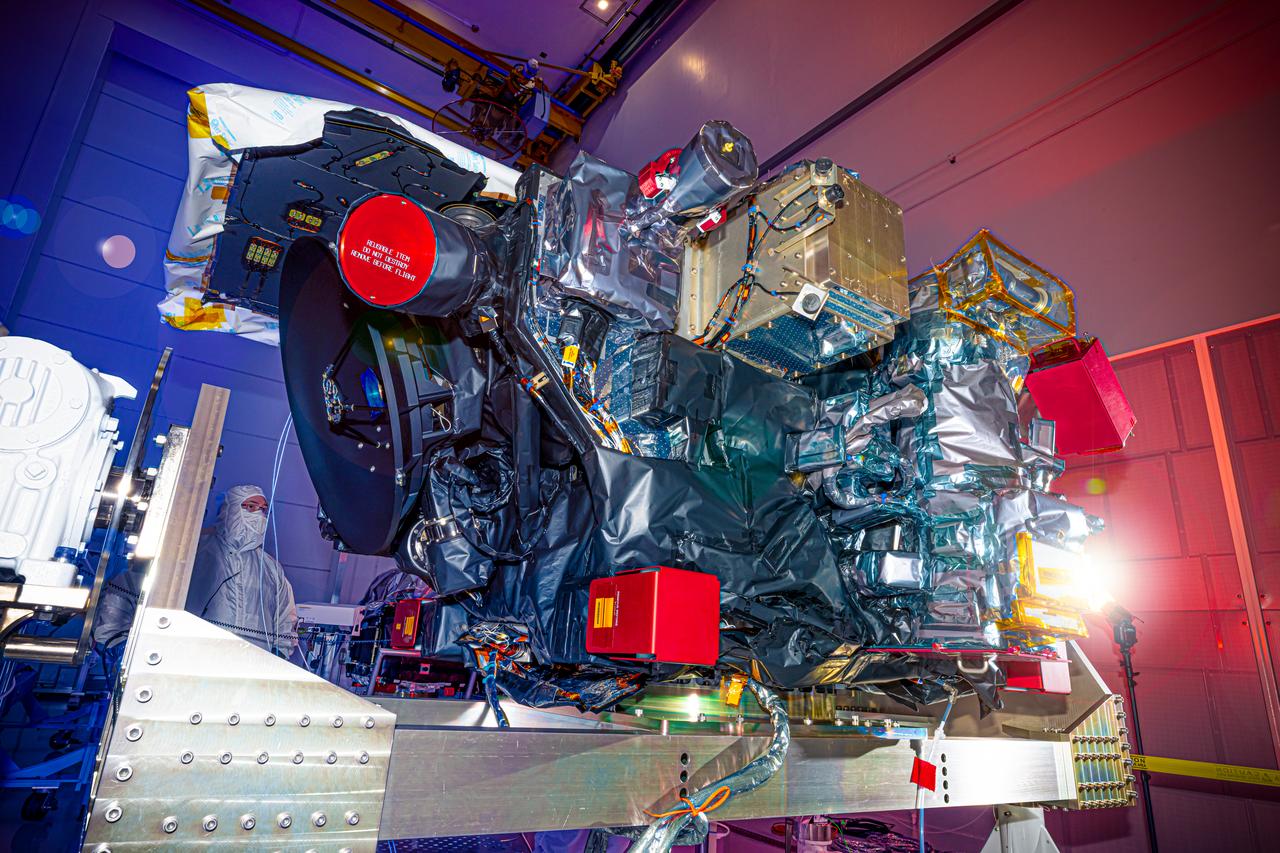
A photographer captures the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory laying horizontal on Tuesday, July 22, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
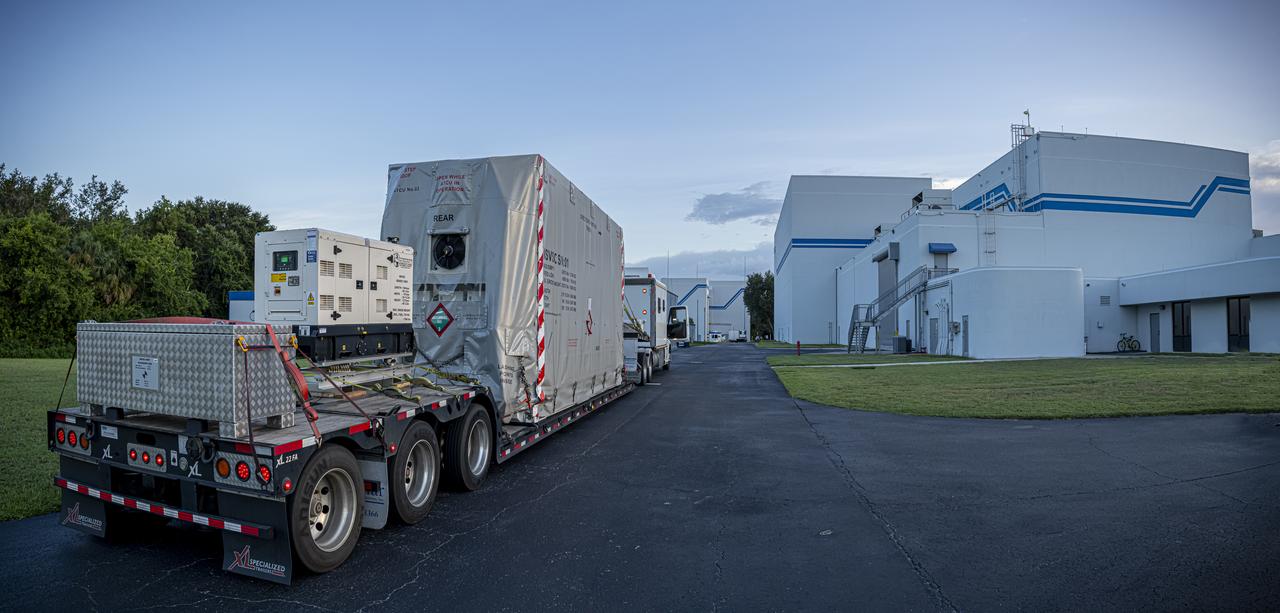

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory, set to provide quicker and more accurate space weather forecasts, arrived Sunday, July 20, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
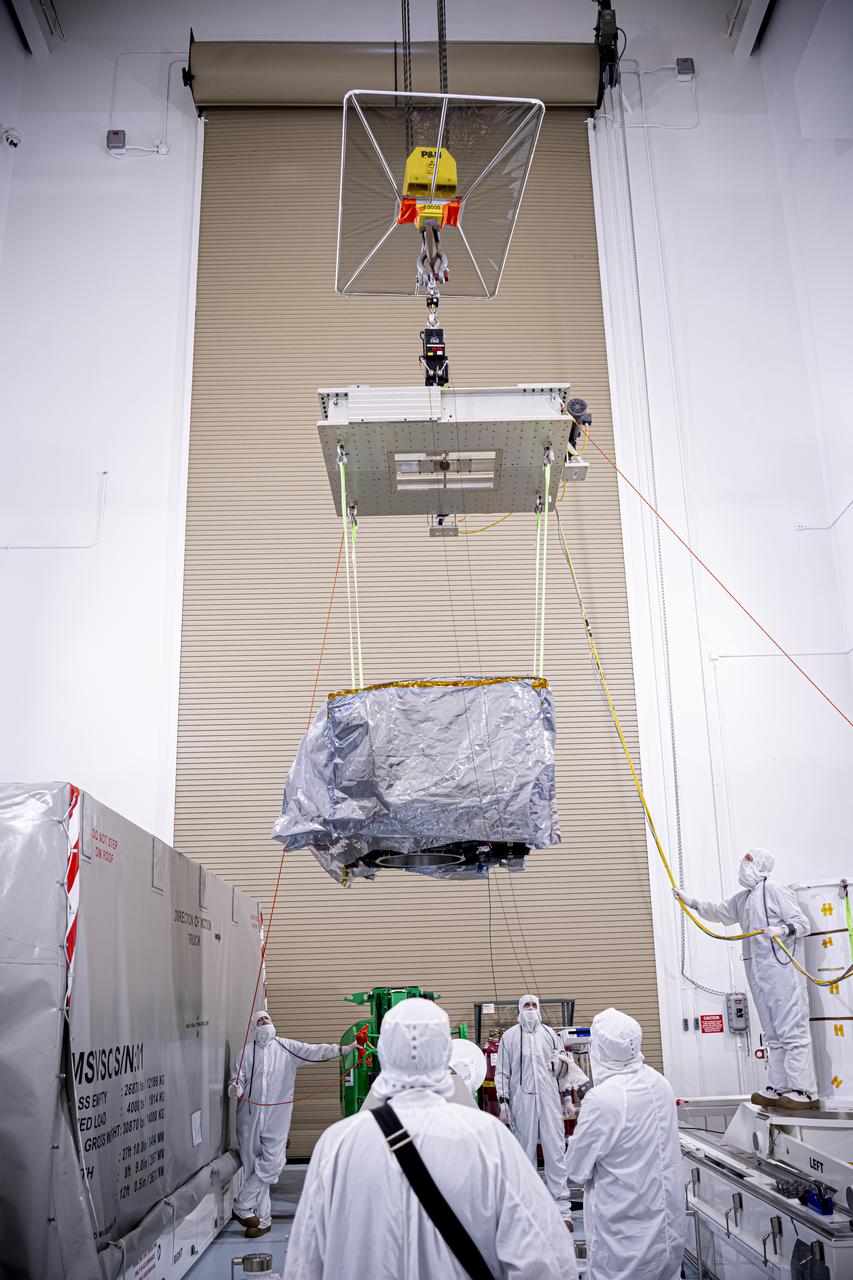

Technicians rotate the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory vertically and use a crane to lift it from its transport container on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
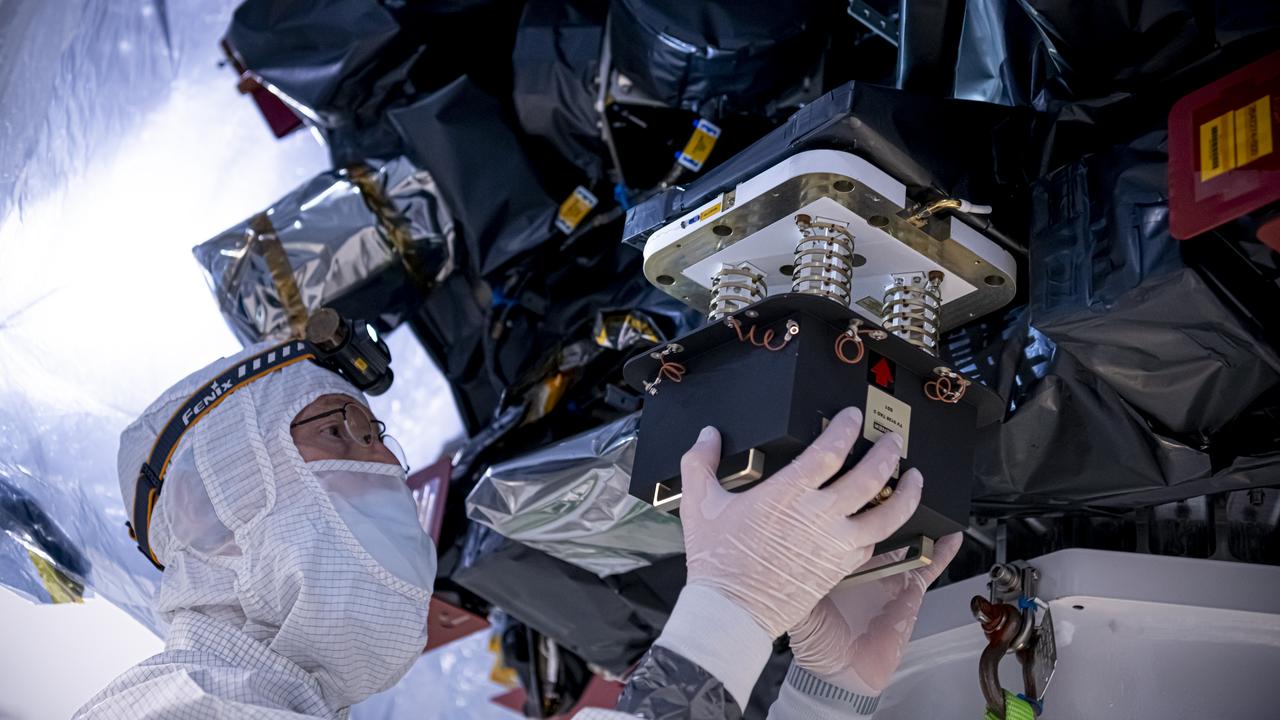

Technicians rotate the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory vertically and use a crane to lift it from its transport container on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians rotate the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory vertically and use a crane to lift it from its transport container on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, following the arrival and unboxing of the observatory at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
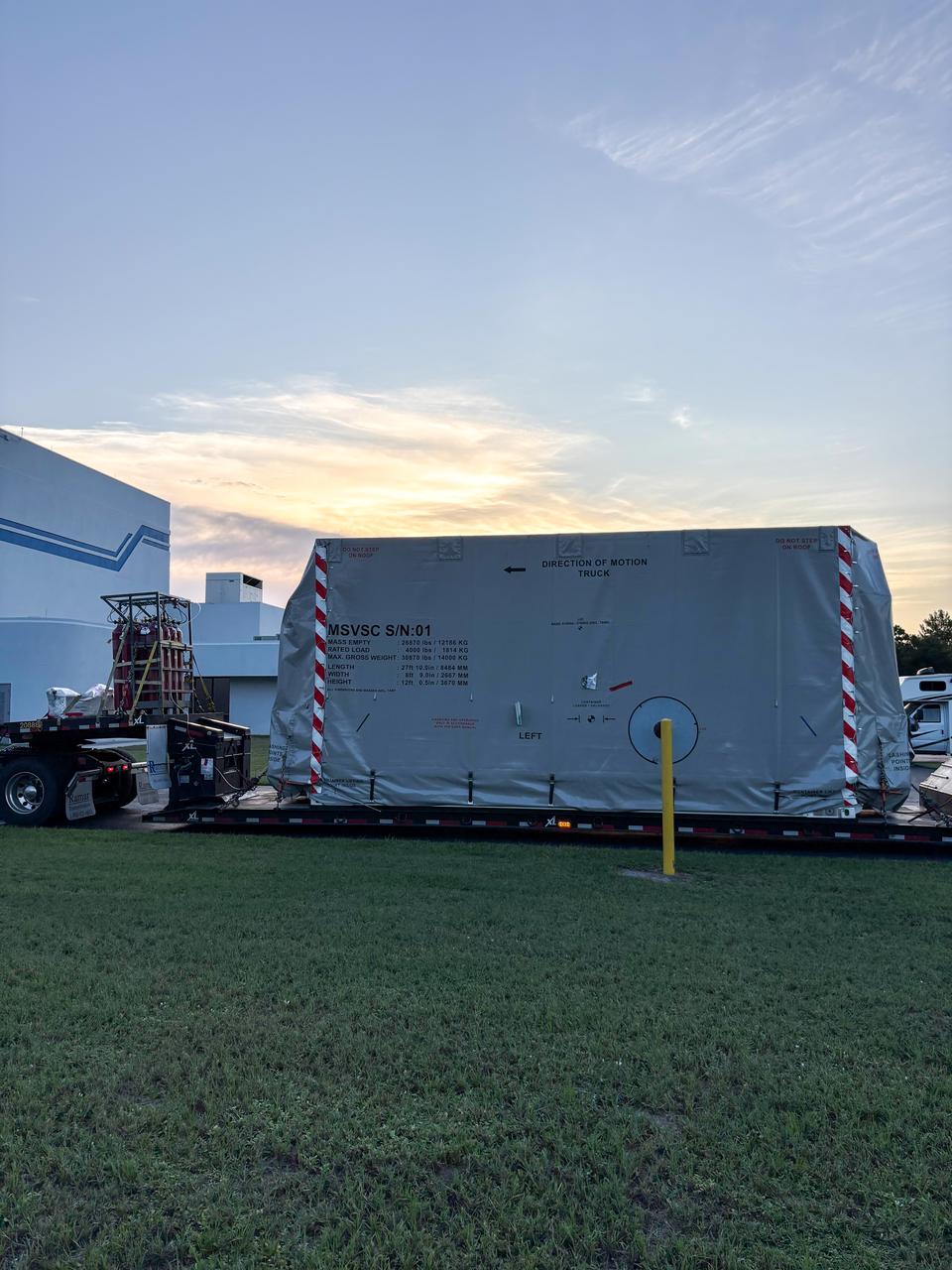

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory, set to provide quicker and more accurate space weather forecasts, arrived Sunday, July 20, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity.
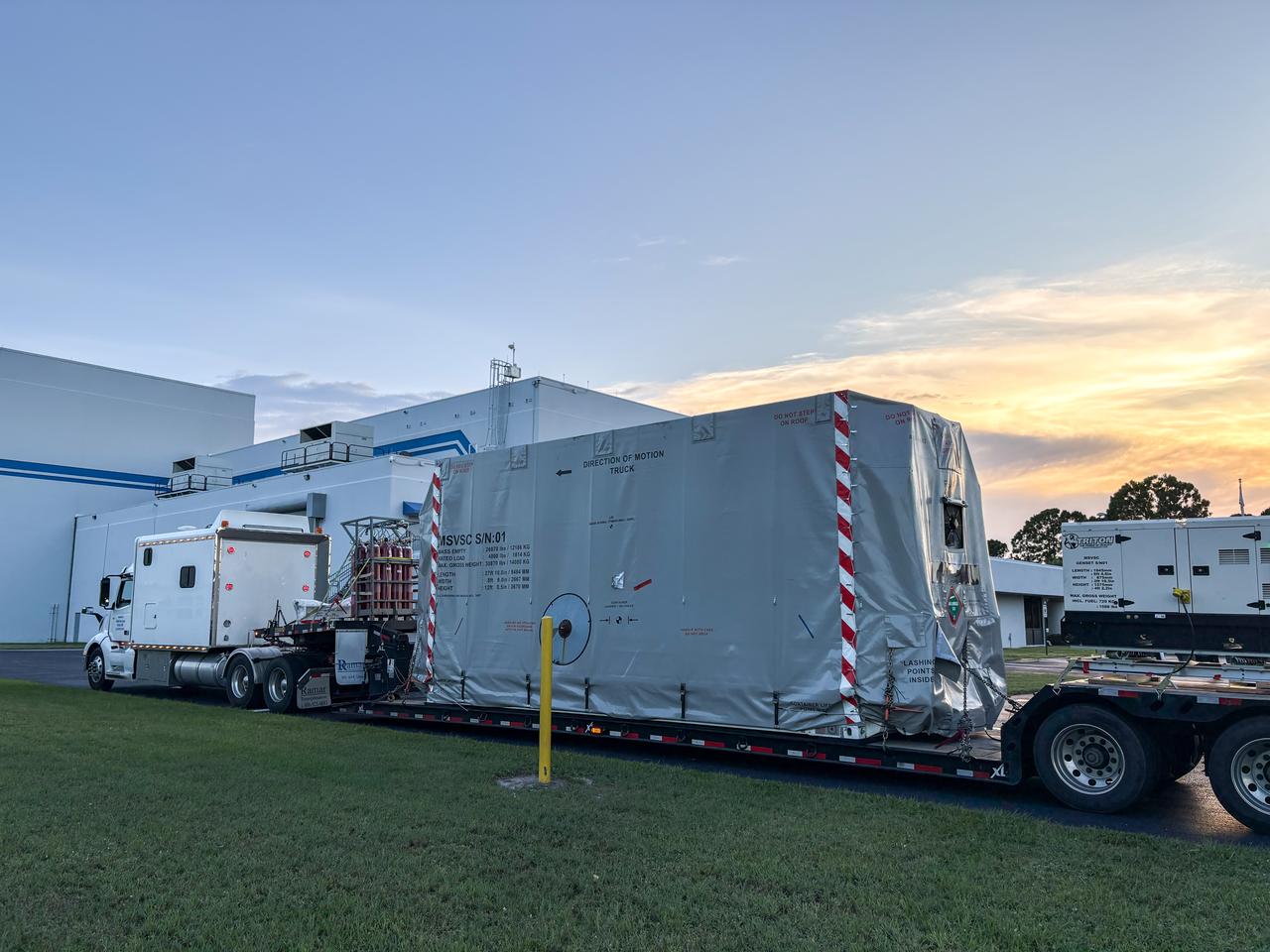

The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory, set to provide quicker and more accurate space weather forecasts, arrived Sunday, July 20, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity.
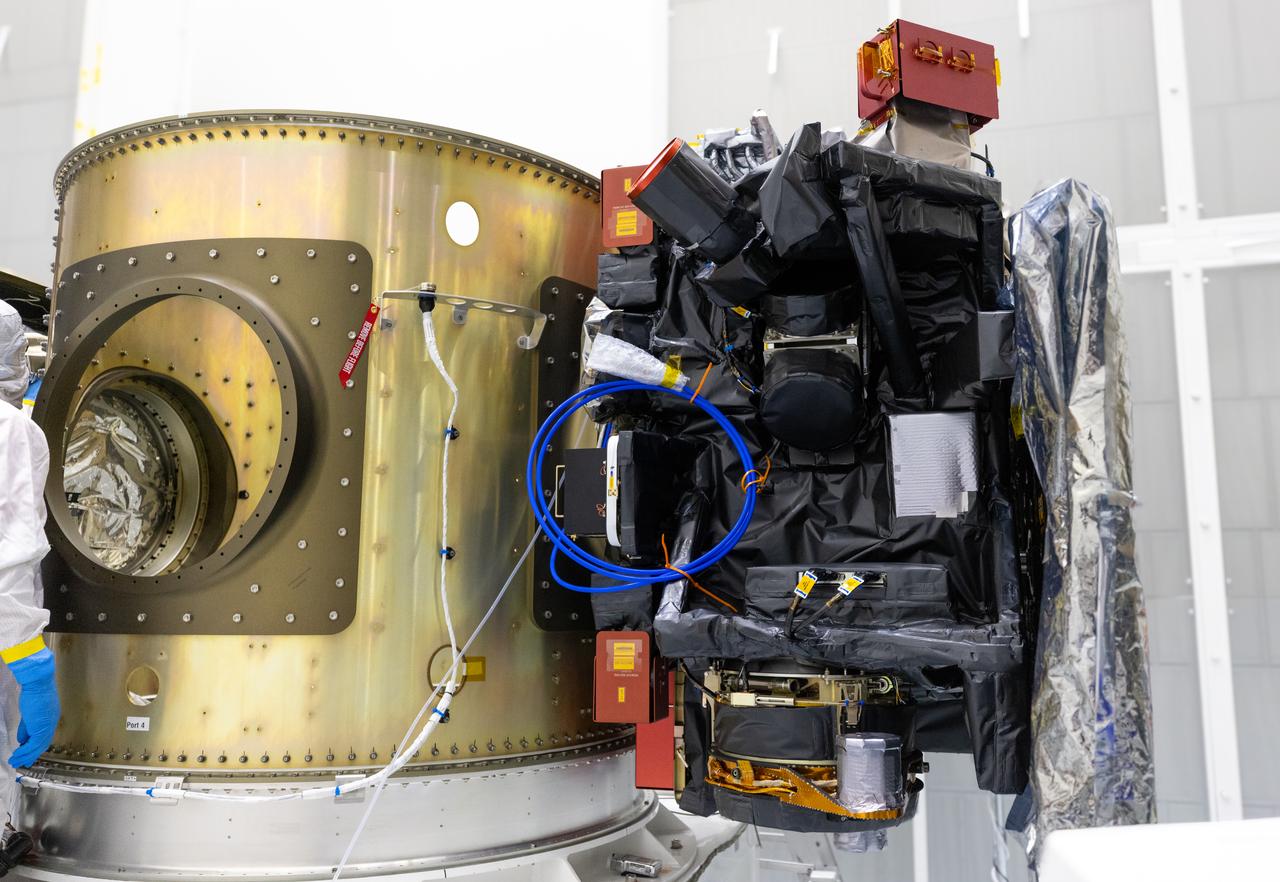
Technicians integrate NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On Lagrange - 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite to the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter Array Ring (ESPA) inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 5, 2025. The integration of the rideshares prepares for the next milestone of attaching NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) Sun mapping observatory to a payload adapter and stacking all three observatories together to prepare them for encapsulation in the payload fairing.
Technicians integrate NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On Lagrange - 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite to the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter Array Ring (ESPA) inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 5, 2025. The integration of the rideshares prepares for the next milestone of attaching NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) Sun mapping observatory to a payload adapter and stacking all three observatories together to prepare them for encapsulation in the payload fairing.
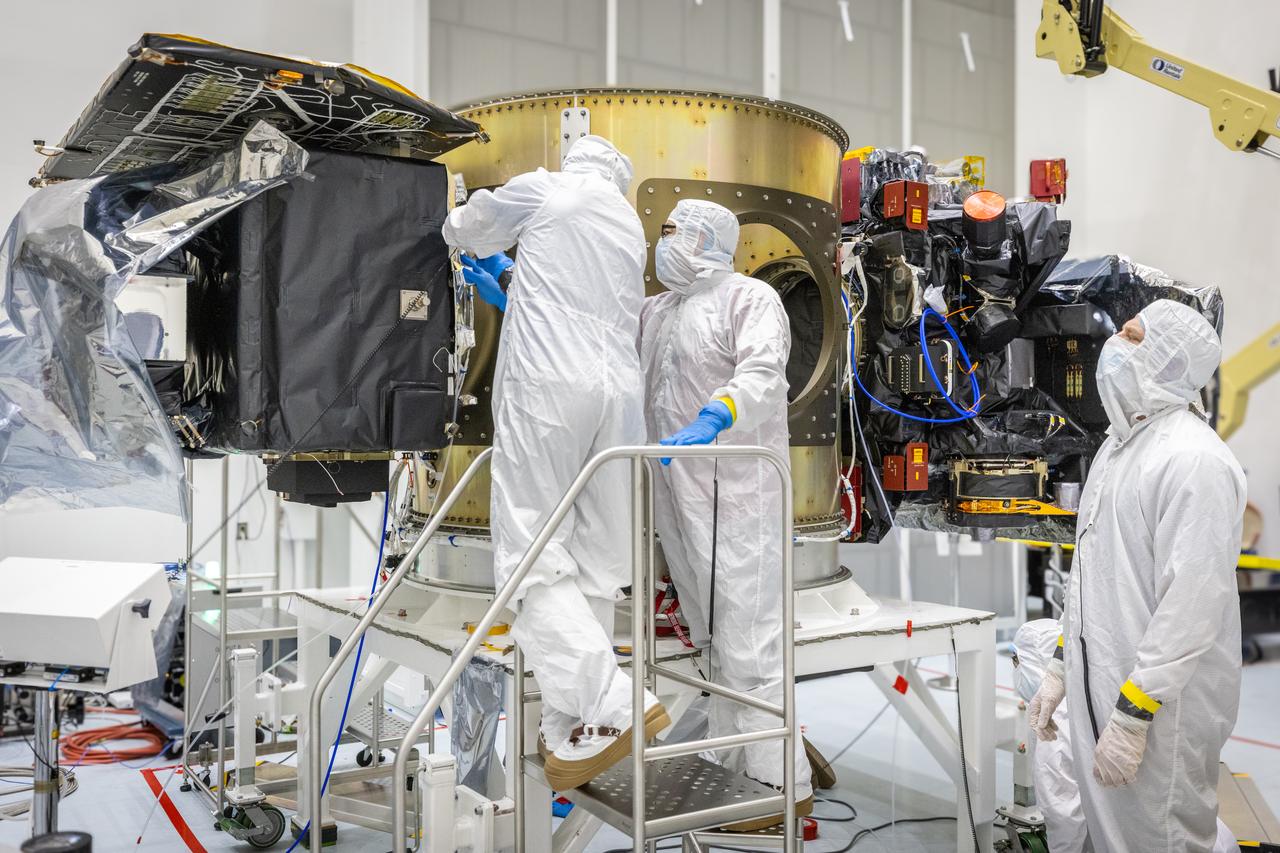

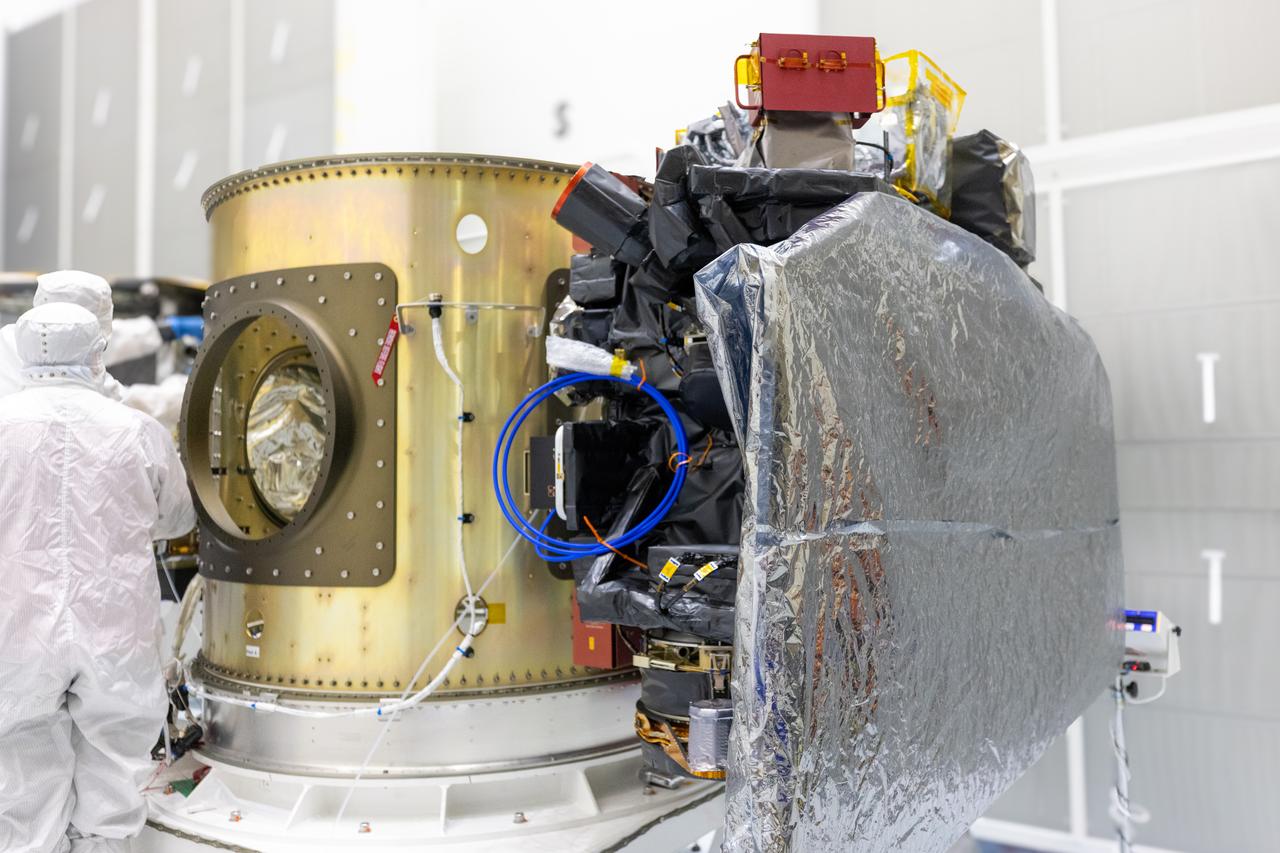
Technicians integrate NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On Lagrange - 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite to the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter Array Ring (ESPA) inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 5, 2025. The integration of the rideshares prepares for the next milestone of attaching NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) Sun mapping observatory to a payload adapter and stacking all three observatories together to prepare them for encapsulation in the payload fairing.
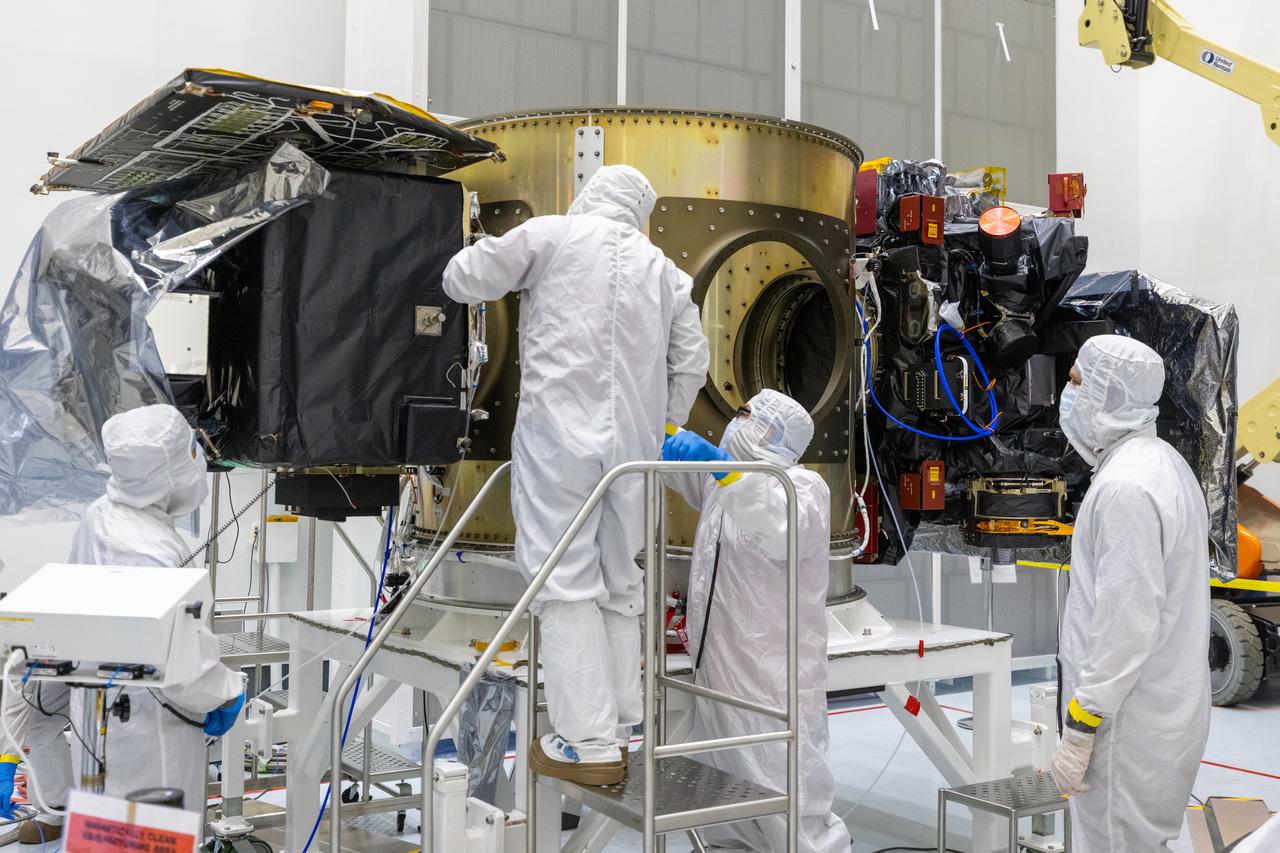

Technicians integrate NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On Lagrange - 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite to the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter Array Ring (ESPA) inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 5, 2025. The integration of the rideshares prepares for the next milestone of attaching NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) Sun mapping observatory to a payload adapter and stacking all three observatories together to prepare them for encapsulation in the payload fairing.
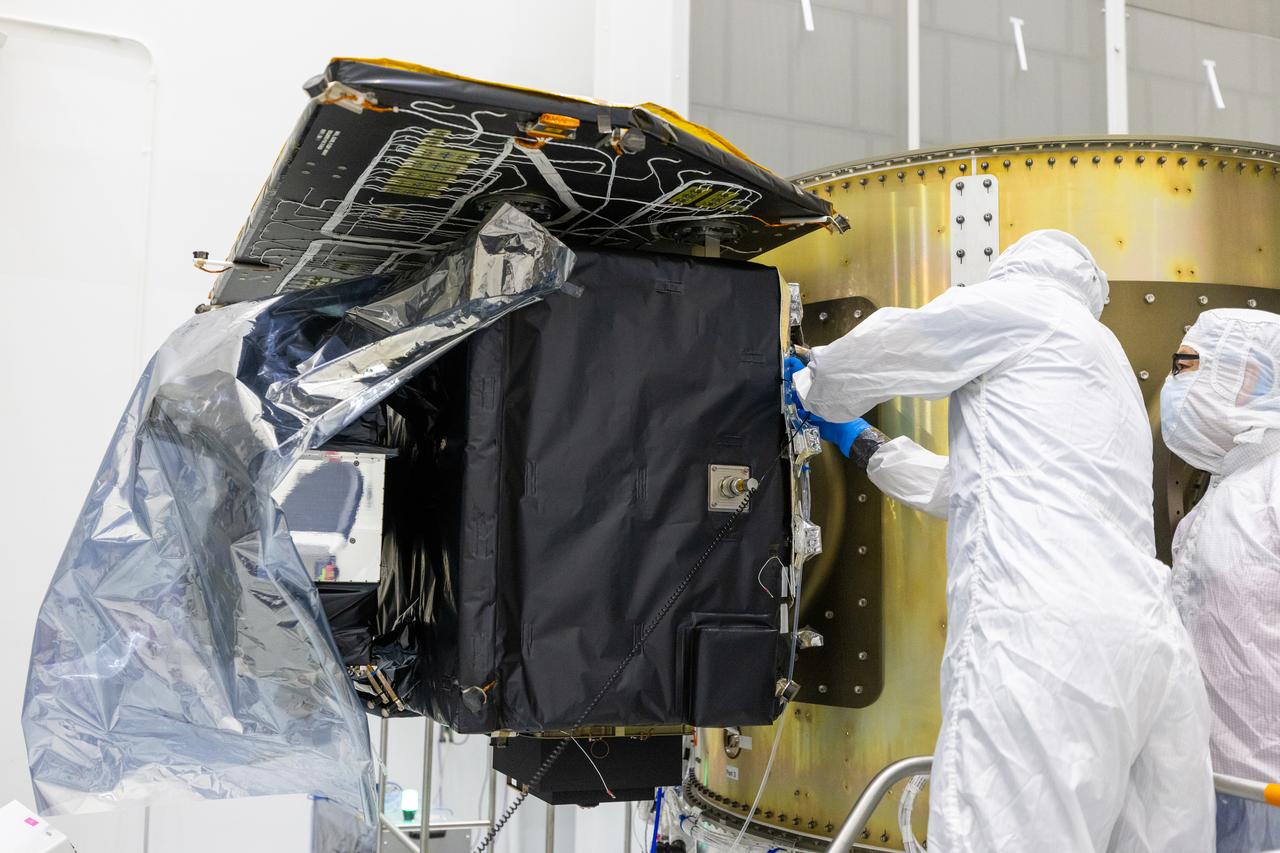

Technicians integrate NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On Lagrange - 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite to the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter Array Ring (ESPA) inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 5, 2025. The integration of the rideshares prepares for the next milestone of attaching NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) Sun mapping observatory to a payload adapter and stacking all three observatories together to prepare them for encapsulation in the payload fairing.

Technicians integrate NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On Lagrange - 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite to the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Secondary Payload Adapter Array Ring (ESPA) inside the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 5, 2025. The integration of the rideshares prepares for the next milestone of attaching NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) Sun mapping observatory to a payload adapter and stacking all three observatories together to prepare them for encapsulation in the payload fairing.

Flags for NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission and its two rideshares, NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft fly outside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of the three missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for no earlier than Tuesday, Sept. 23, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
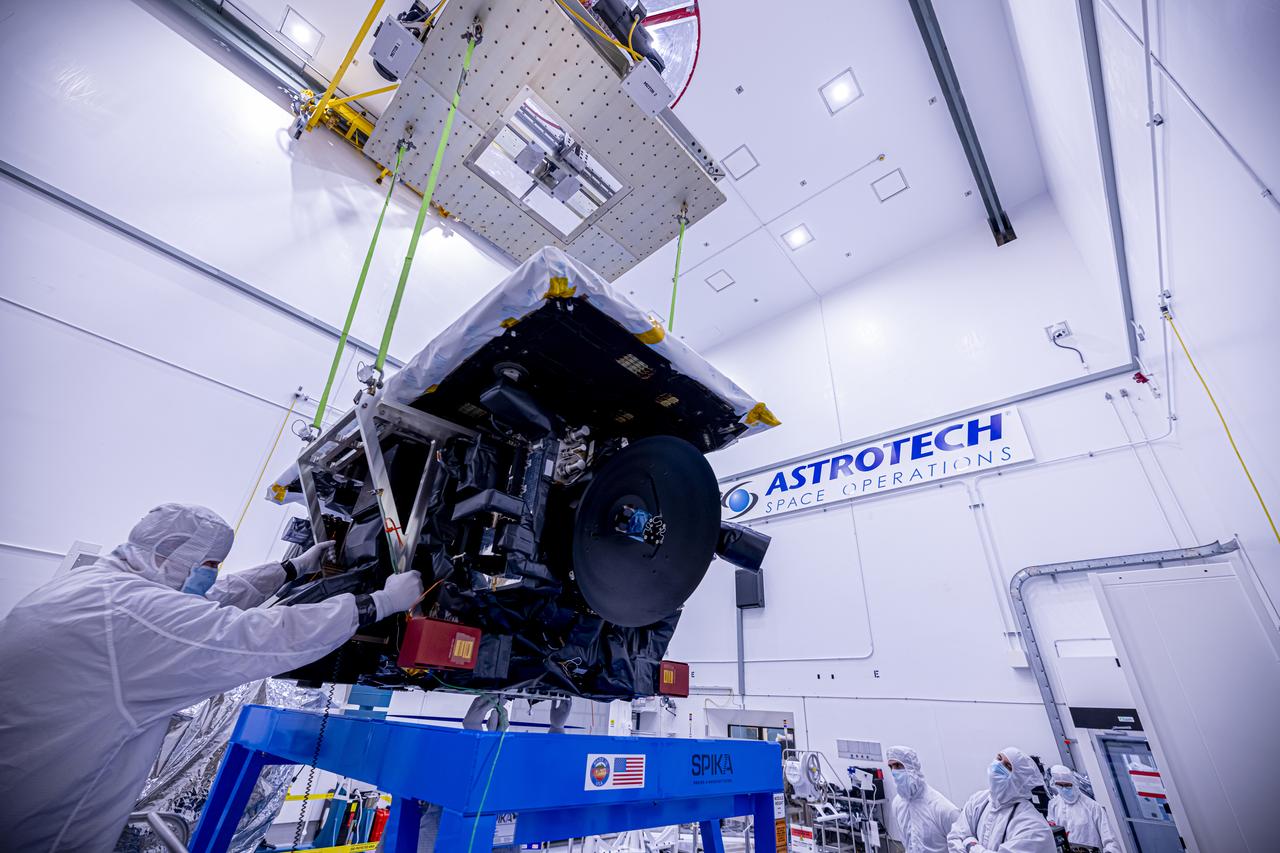

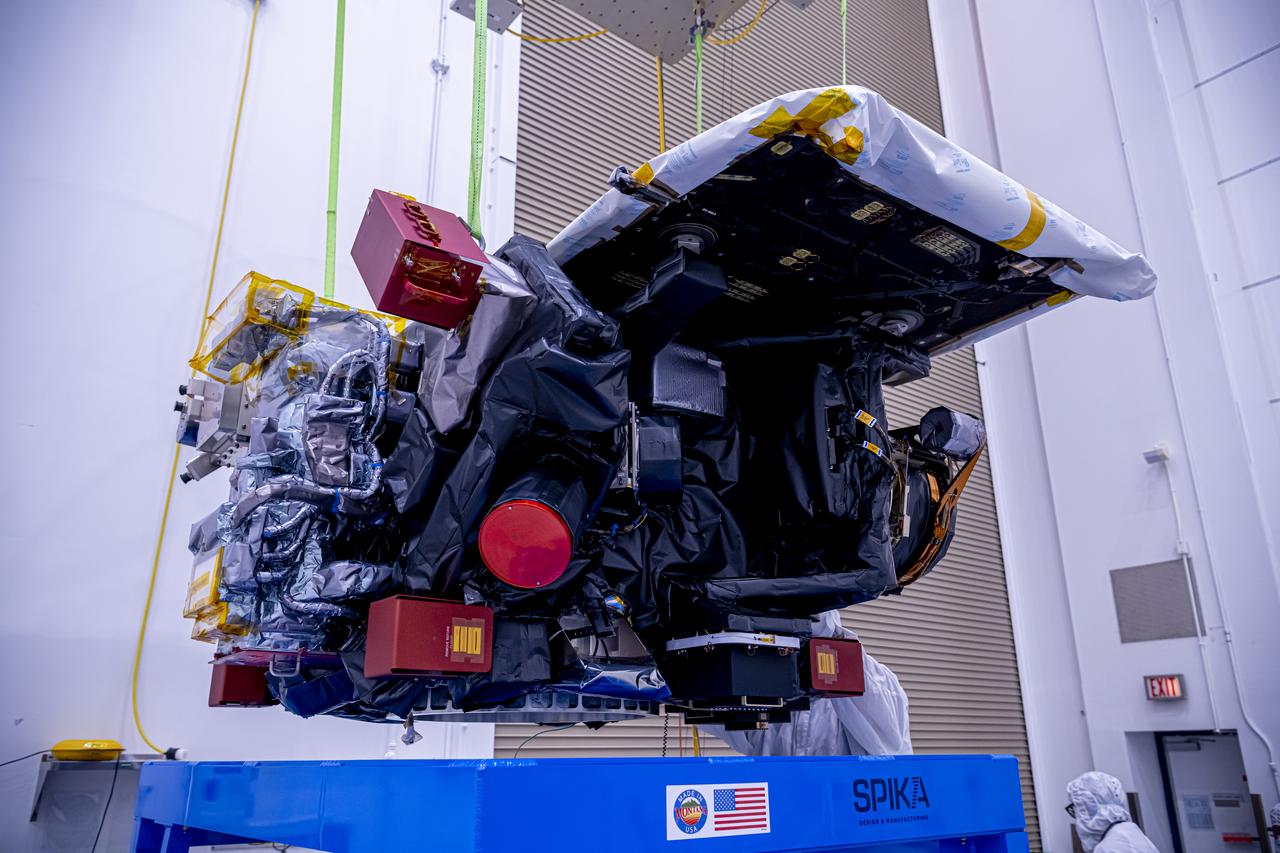
Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

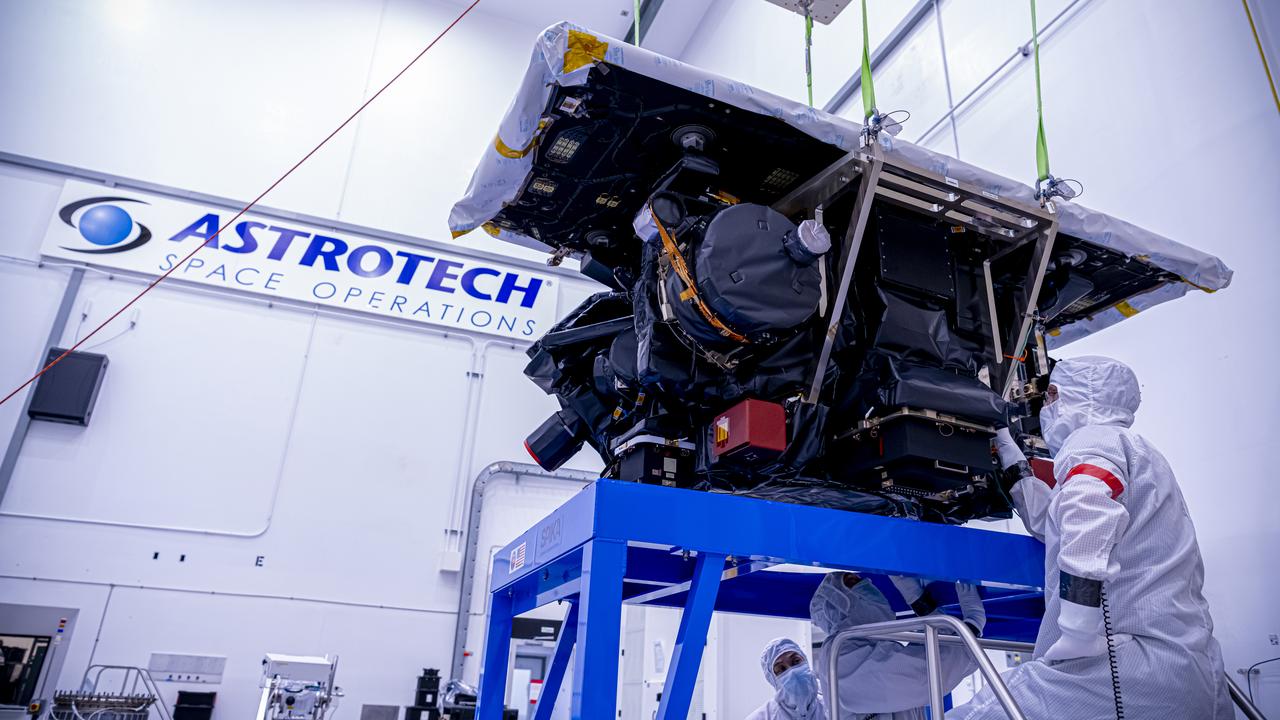
With hardware in the foreground, technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.

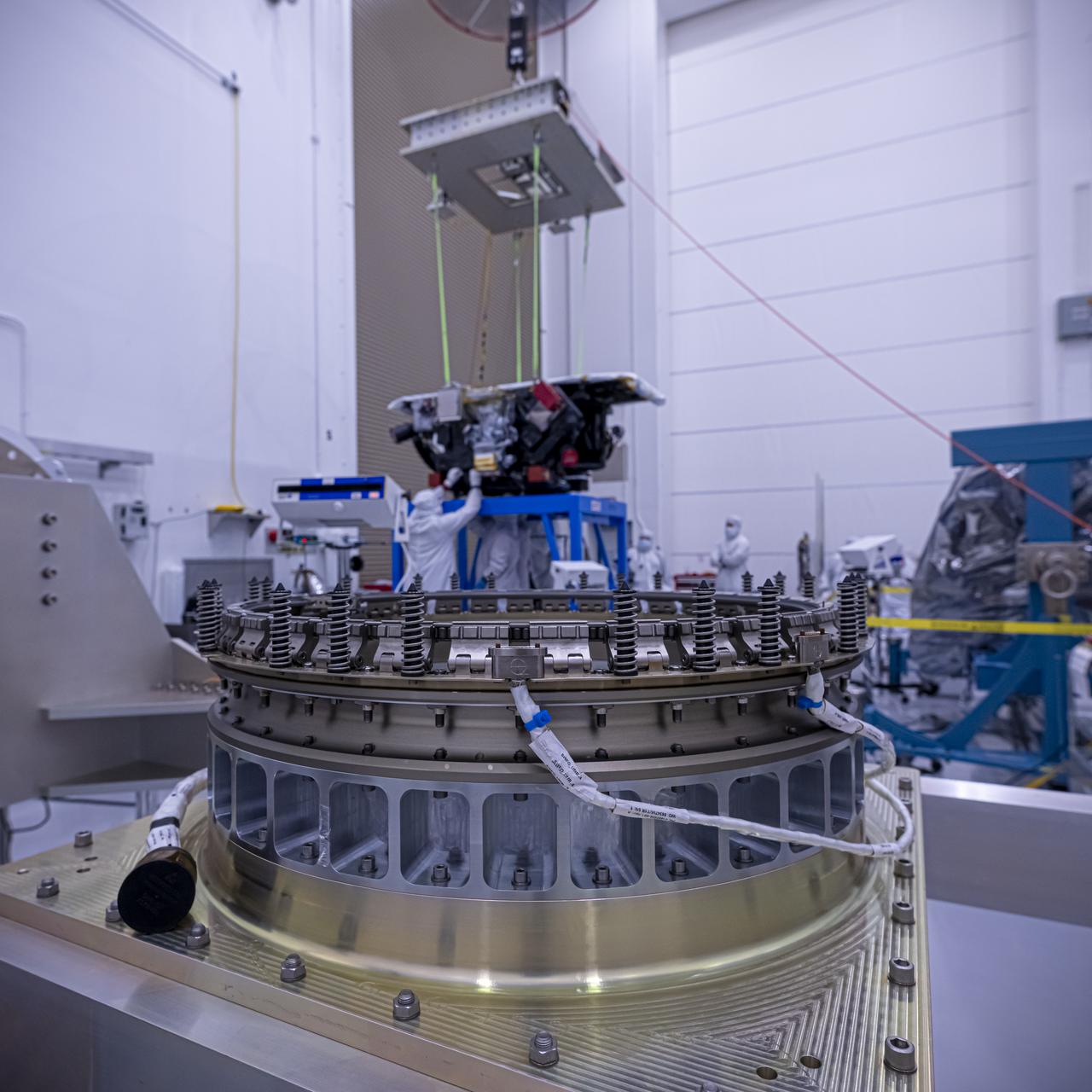
Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
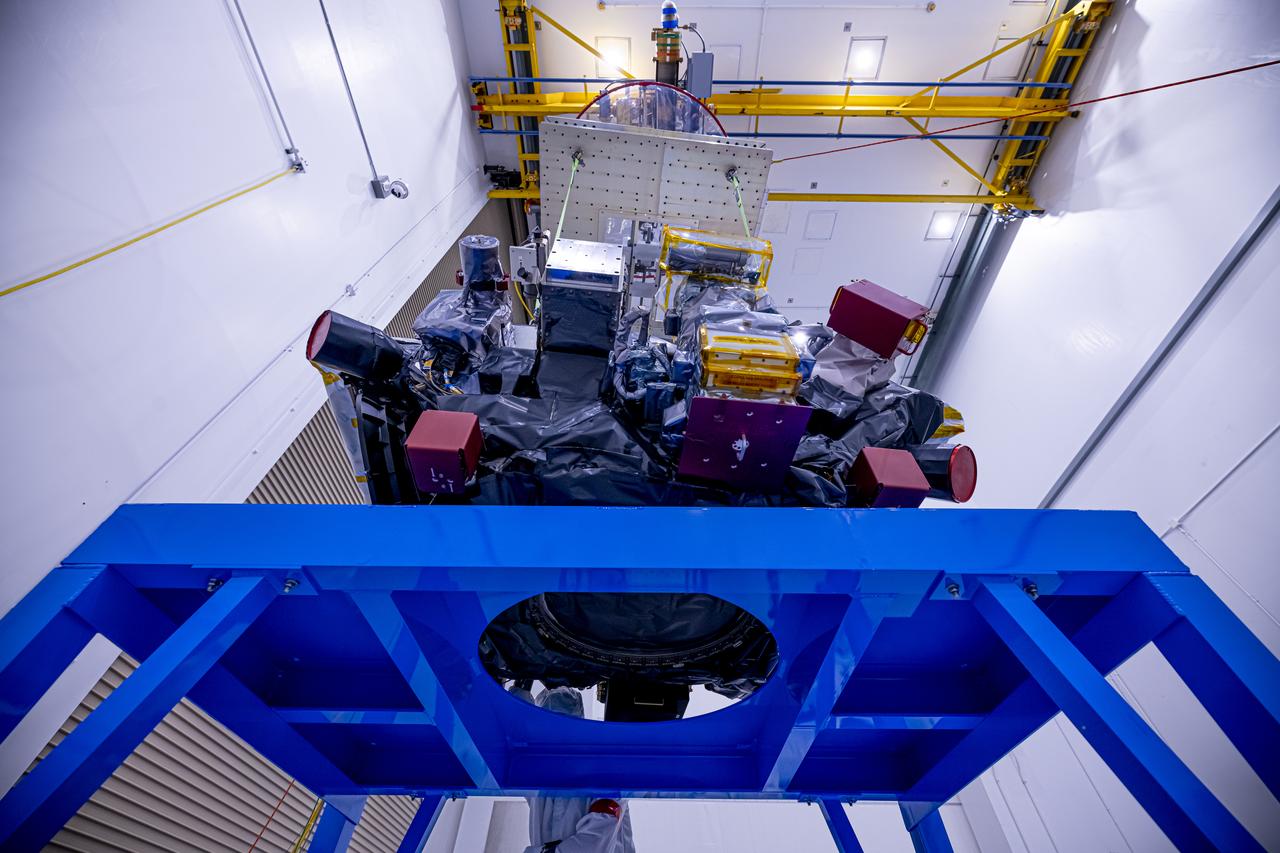

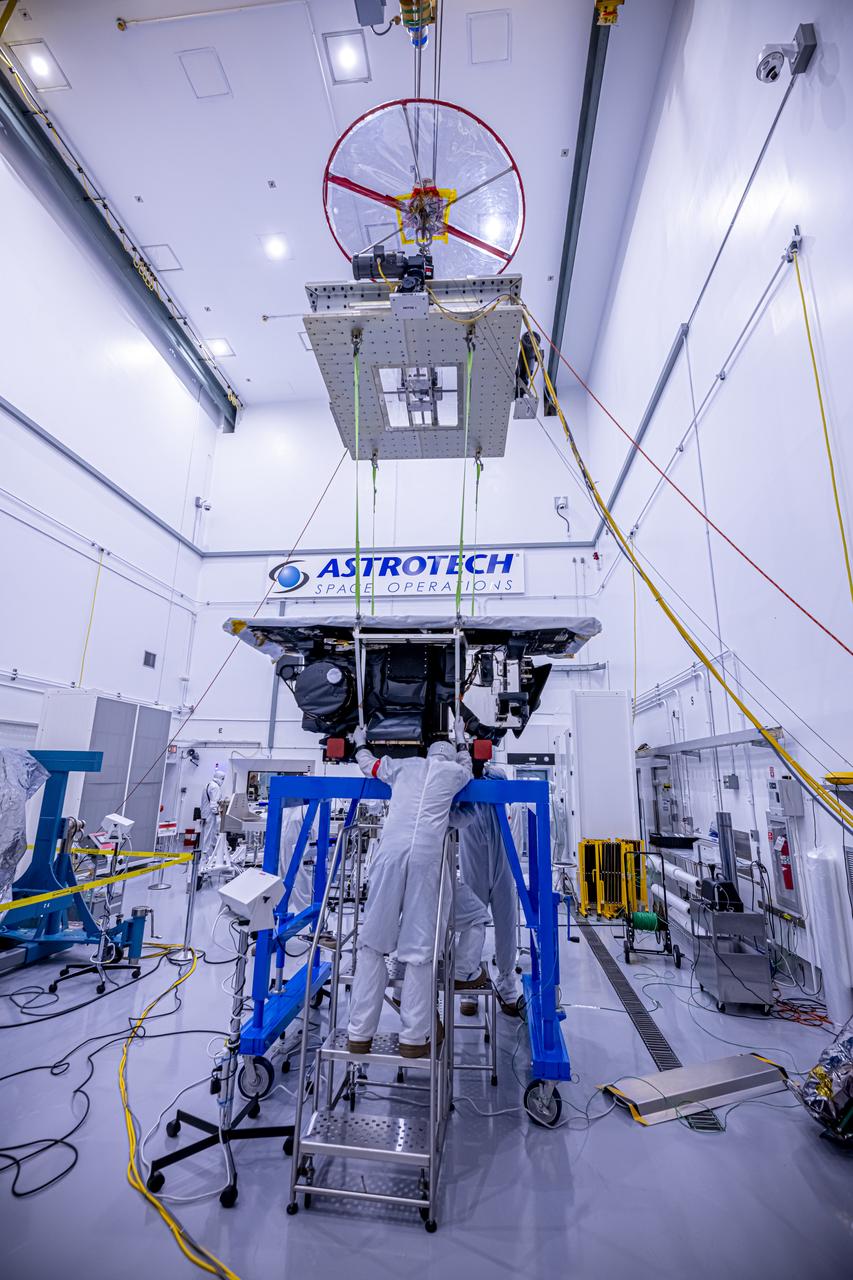
Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
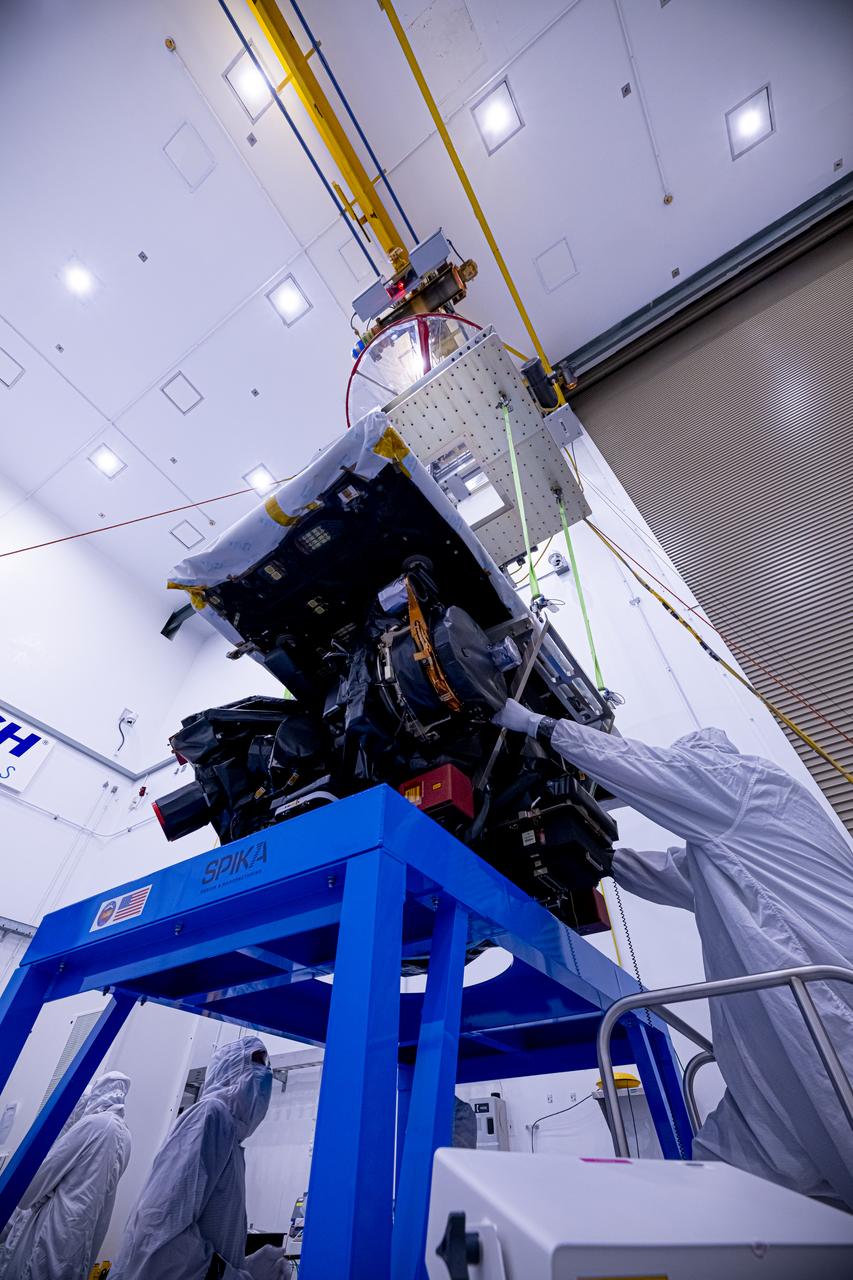

Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
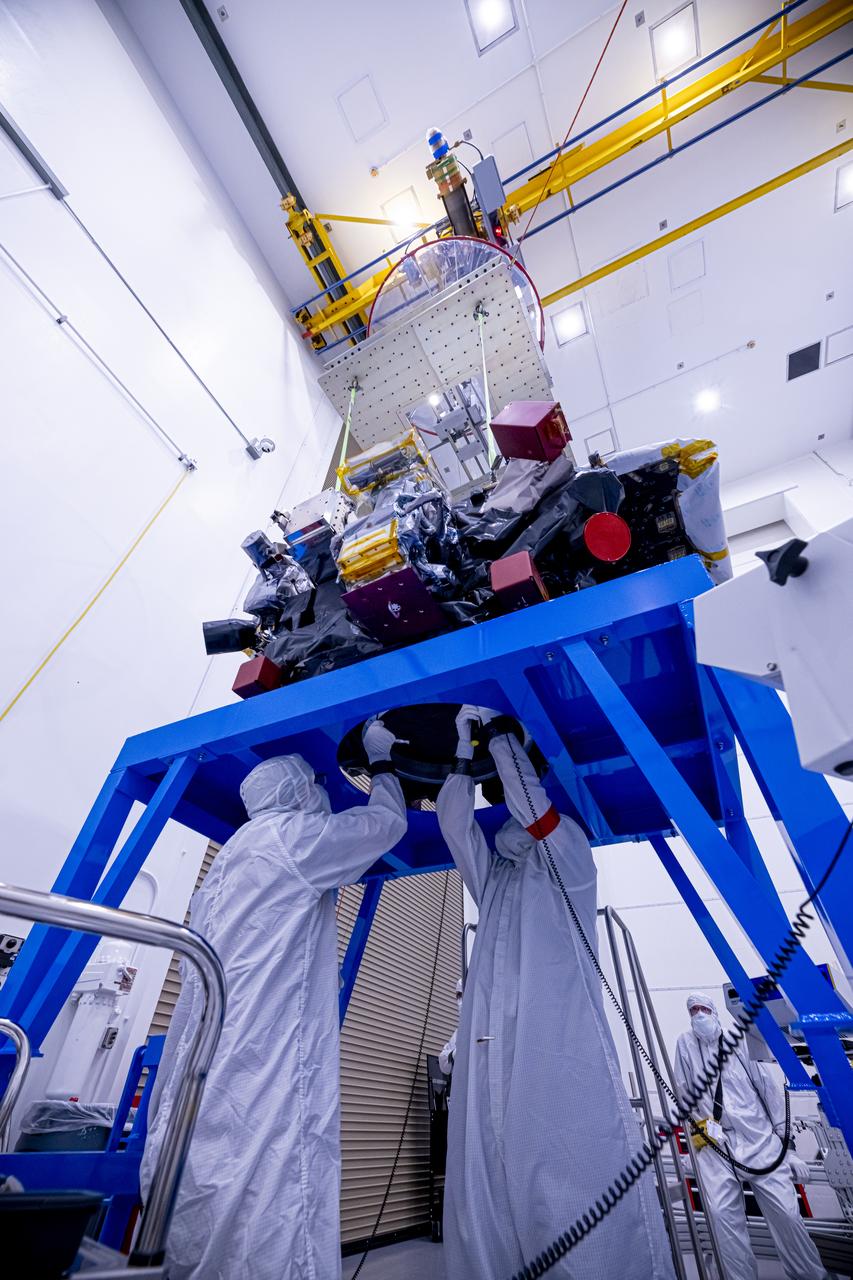

Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
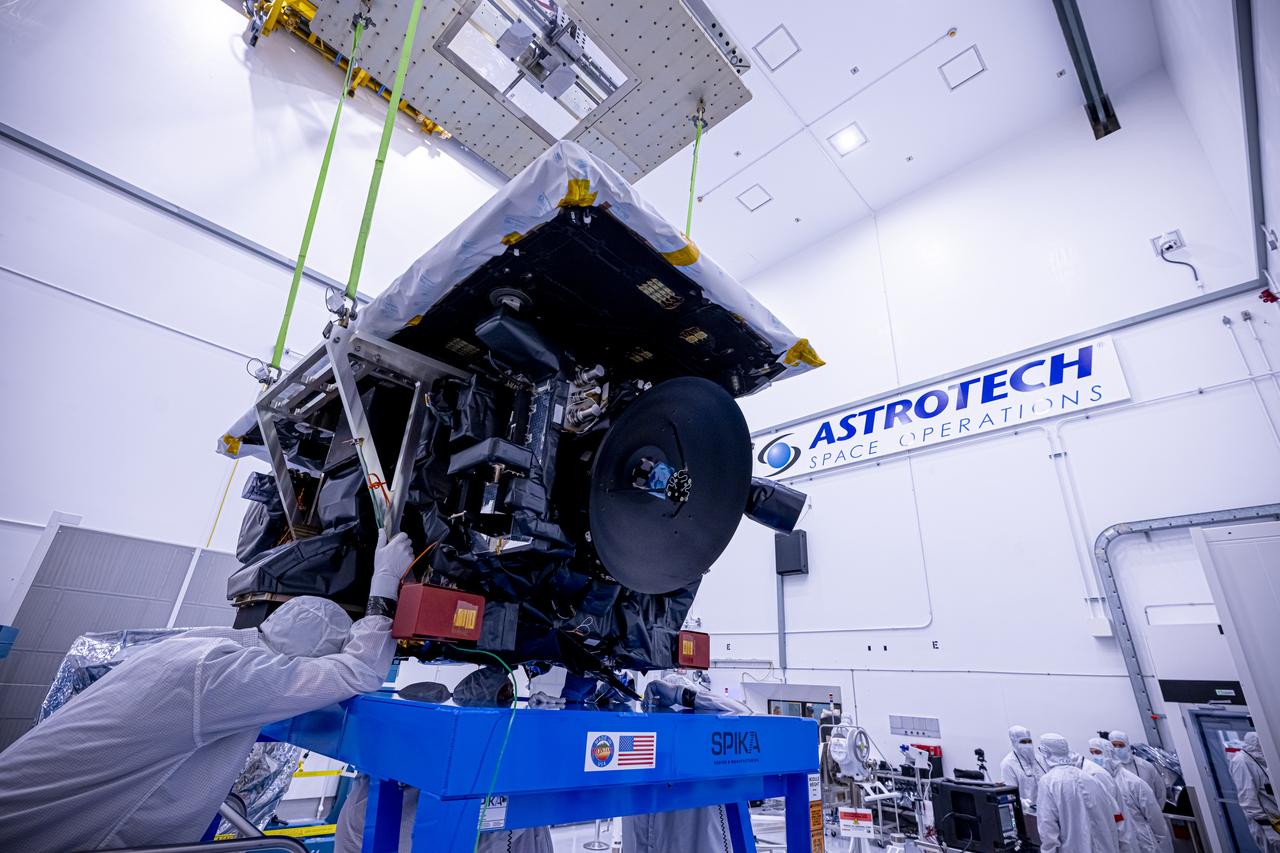

Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
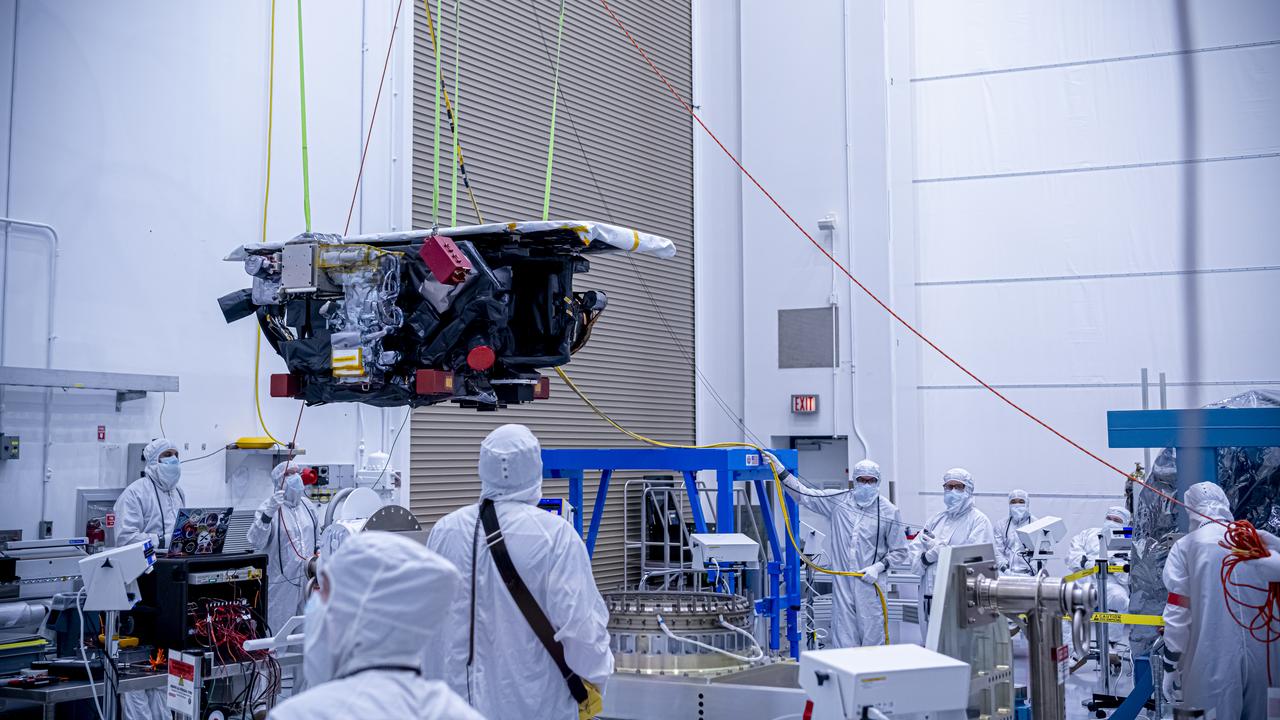

Technicians use a crane to lift the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) Observatory onto a work stand on Friday, July 25, 2025, during prelaunch processing at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SWFO-L1 mission will observe solar eruptions, and monitor incoming space weather 24/7, providing early warnings and validating forecasts that protect vital communication and navigation infrastructure, economic interests, and national security, both on Earth and in space. The observatory will launch as a rideshare with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) no earlier than September 2025.
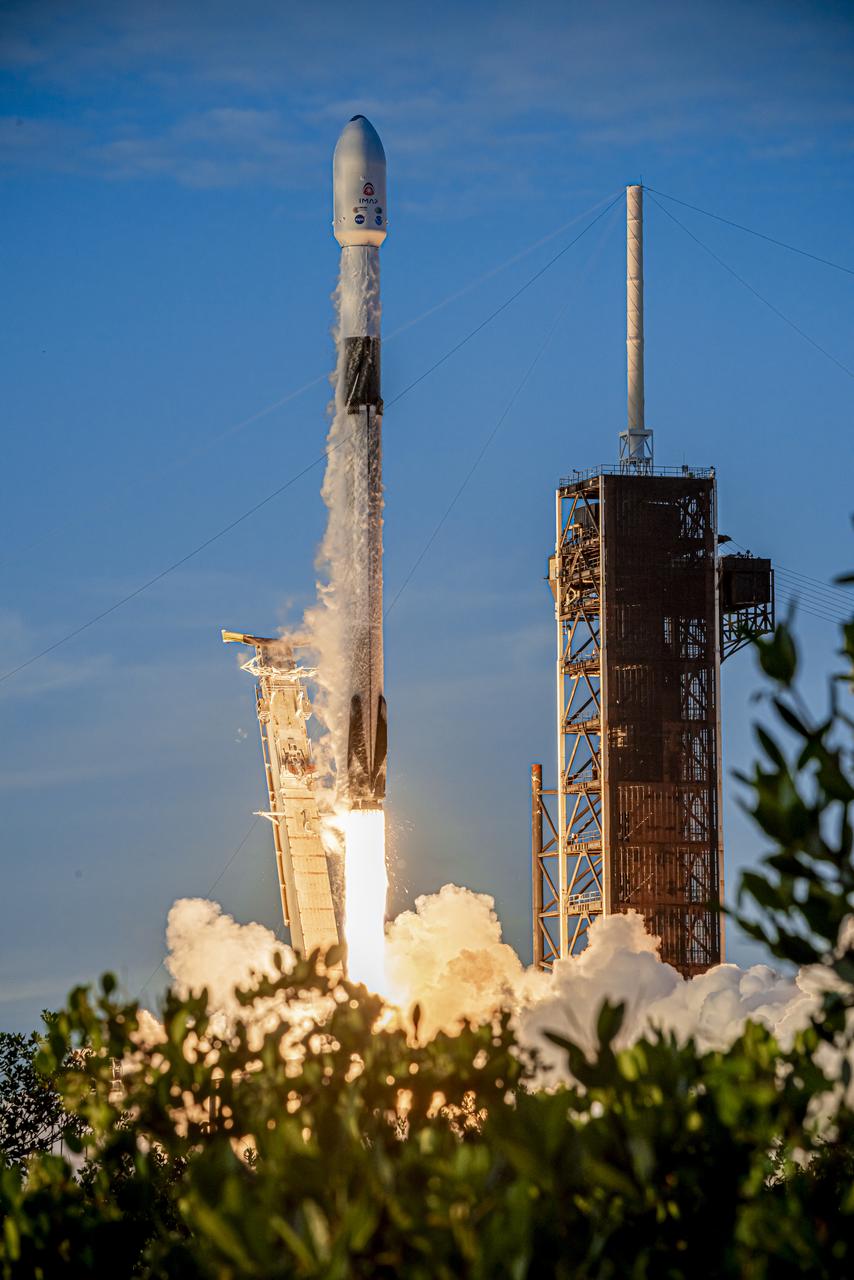

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
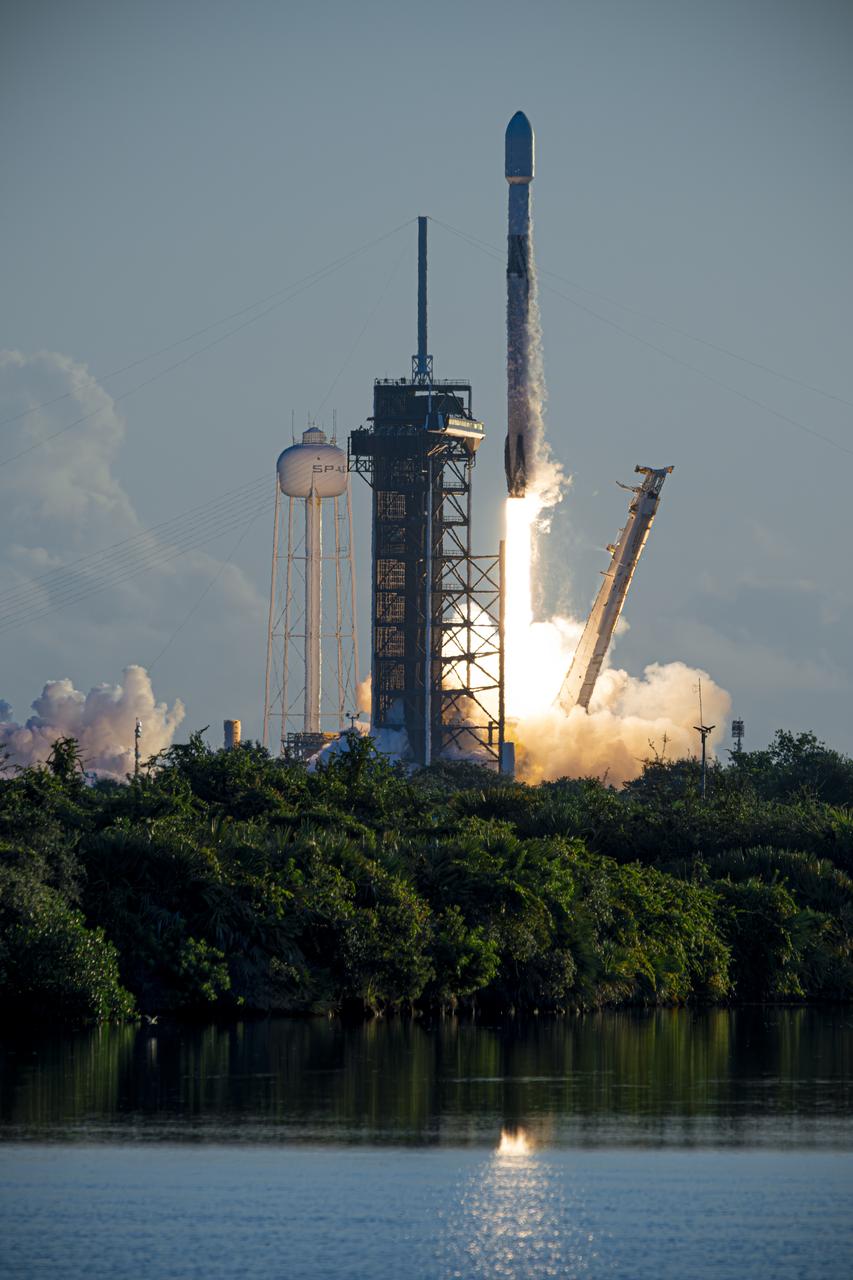

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
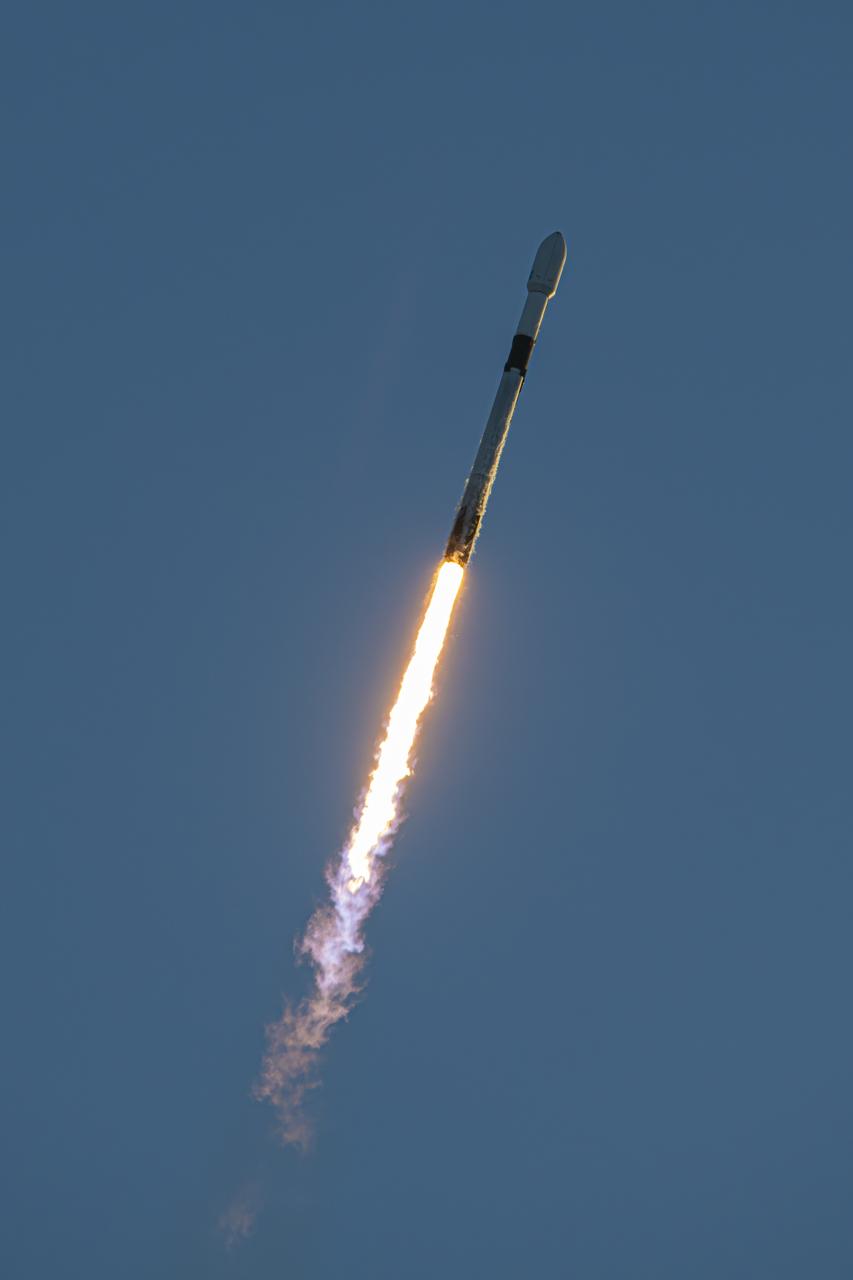

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.

Technicians offloaded NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory following the spacecraft’s arrival on Sunday, July 20, 2025, at the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory is a small satellite set to operate at Lagrange Point 1 (L1), an orbit point between the Earth and Sun about one million miles away, to study the Earth’s exosphere, the outermost part of the atmosphere. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere.
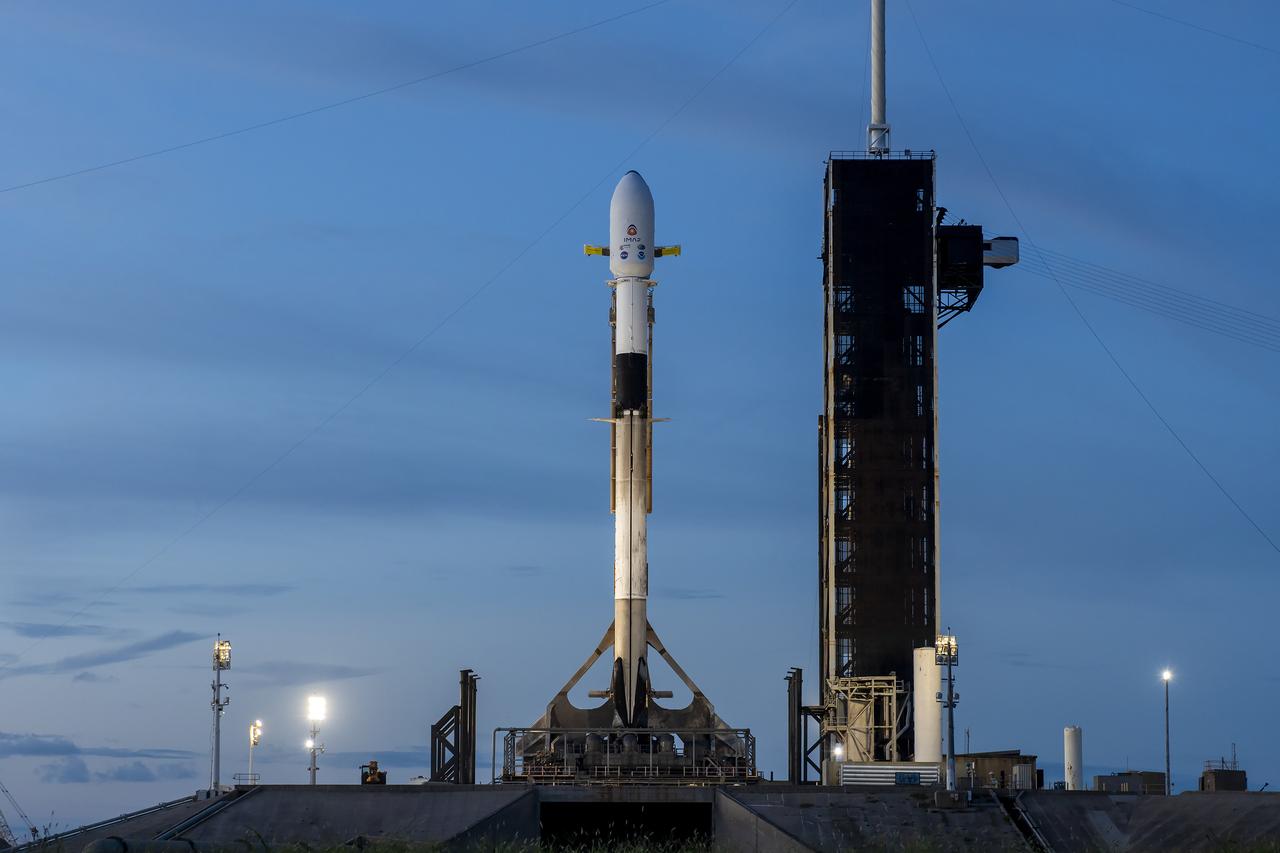

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun rises on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
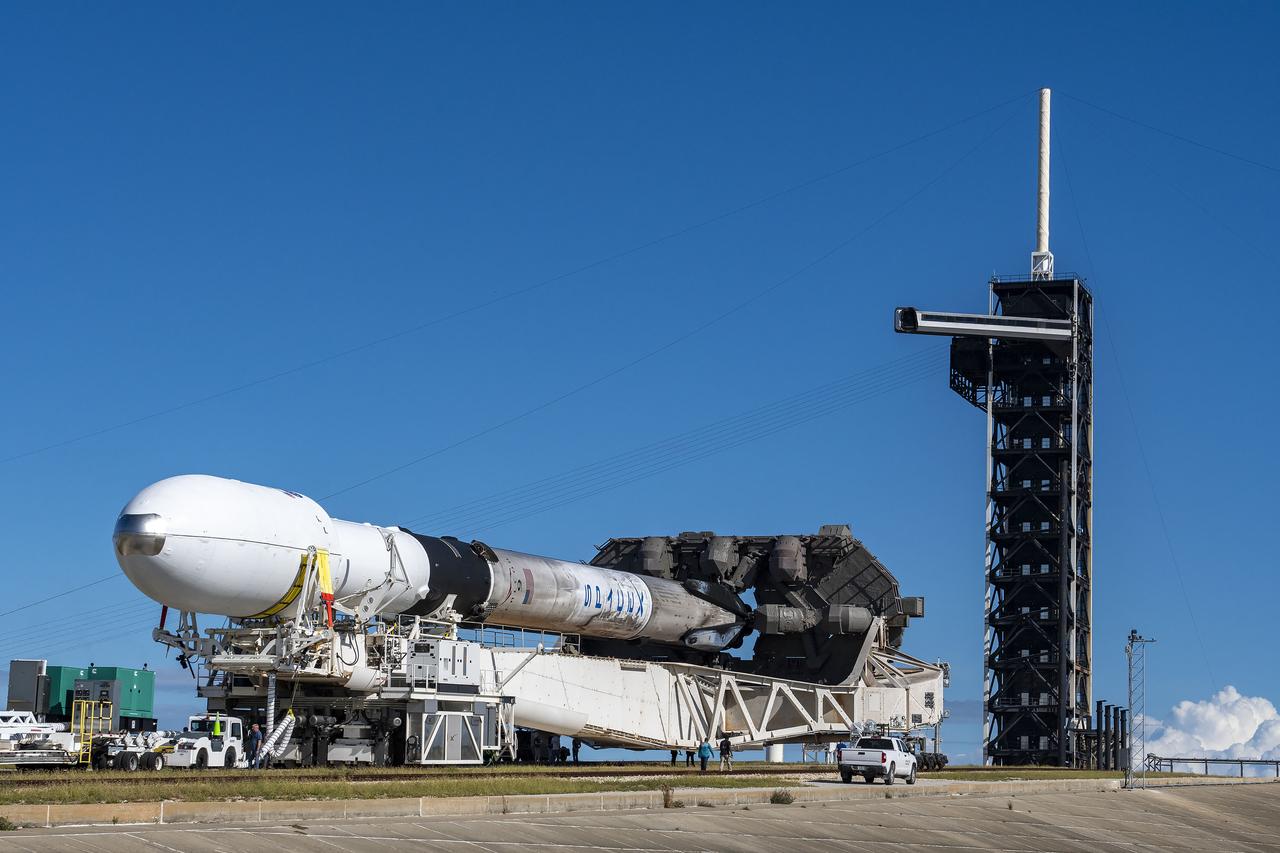

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft attached, rolls to Launch Pad 39A on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
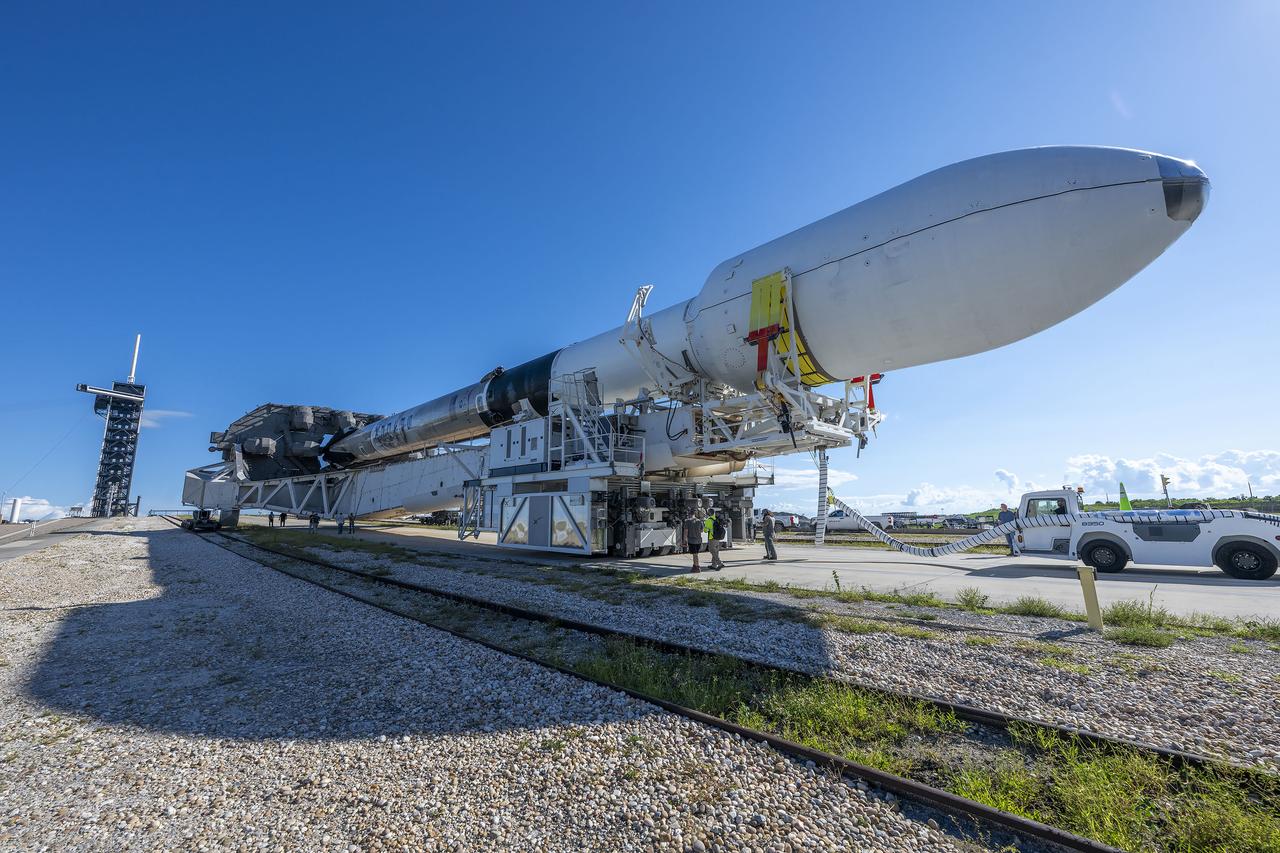

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft attached, rolls to Launch Pad 39A on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
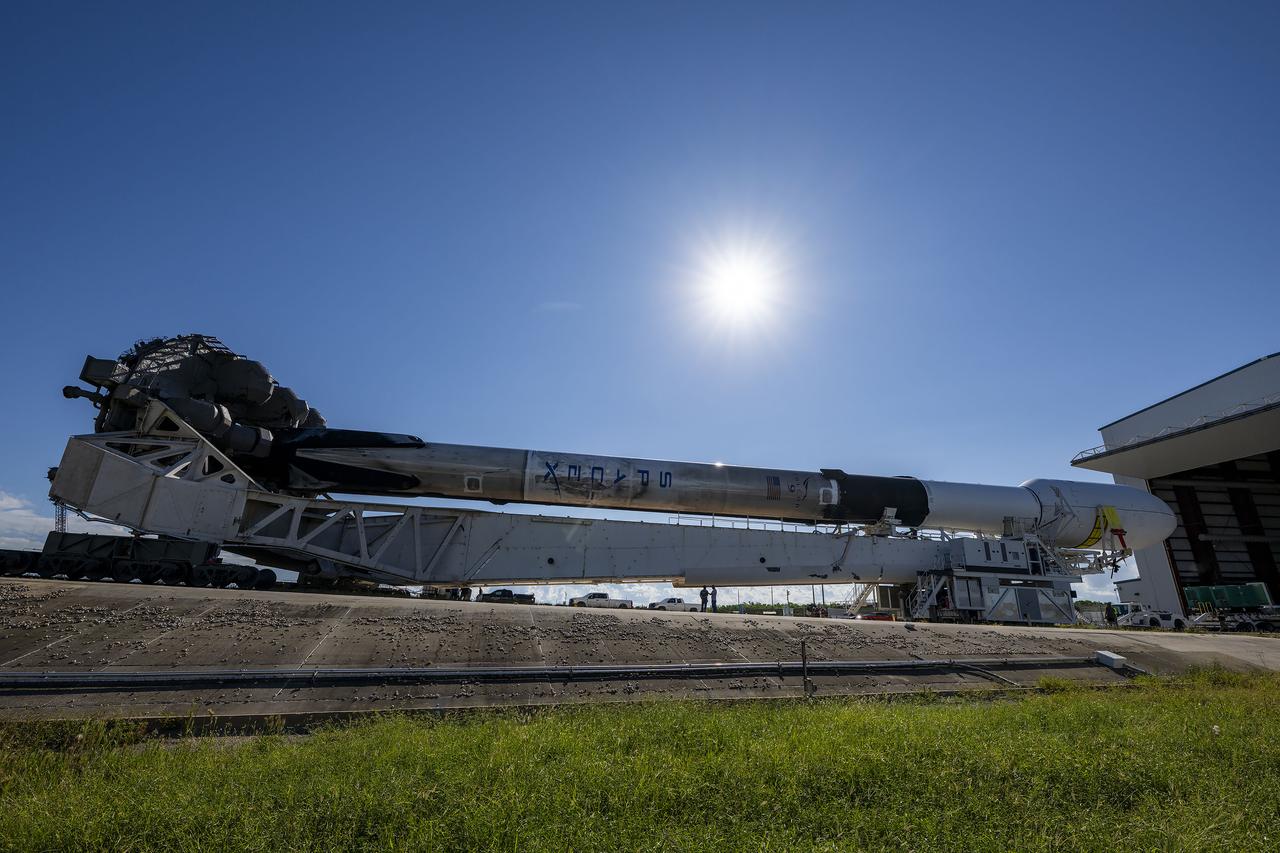

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft attached, rolls to Launch Pad 39A on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
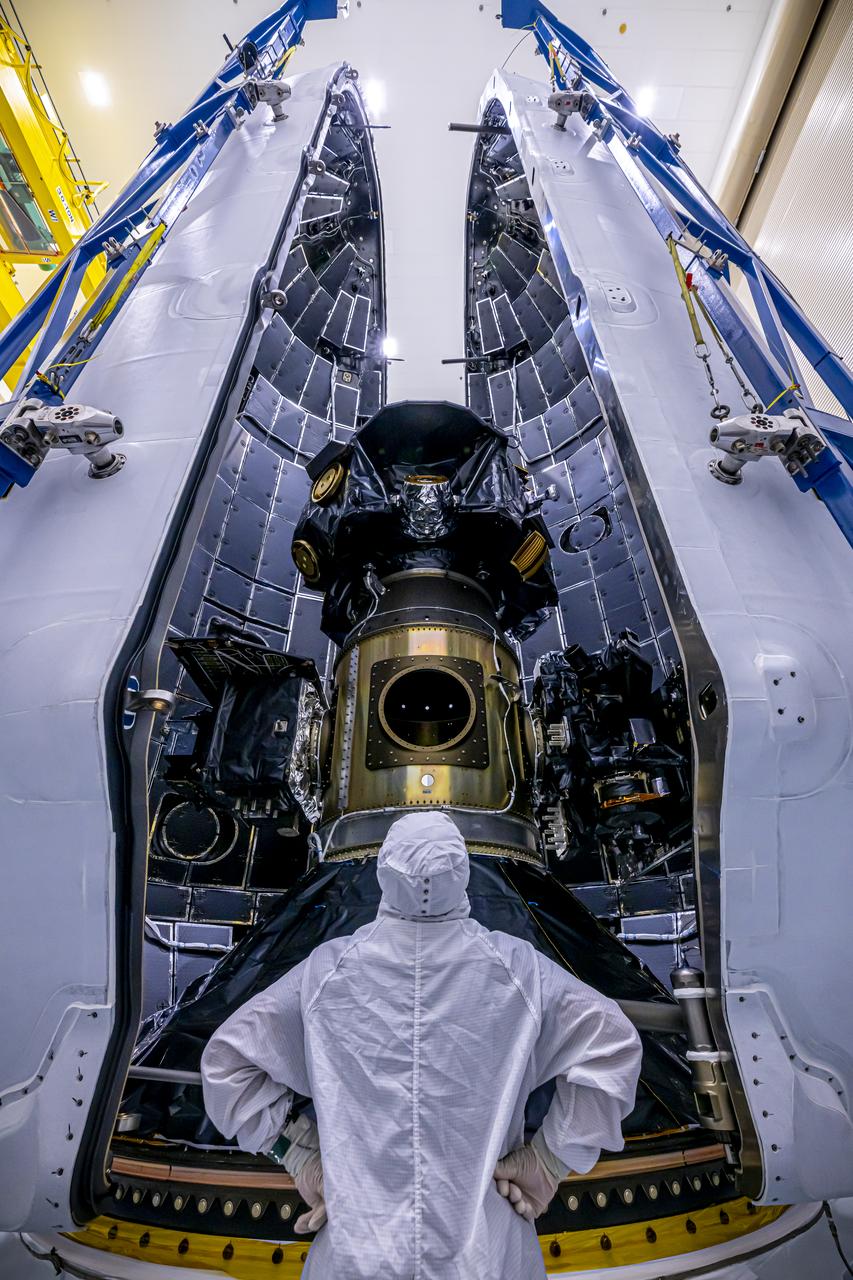

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
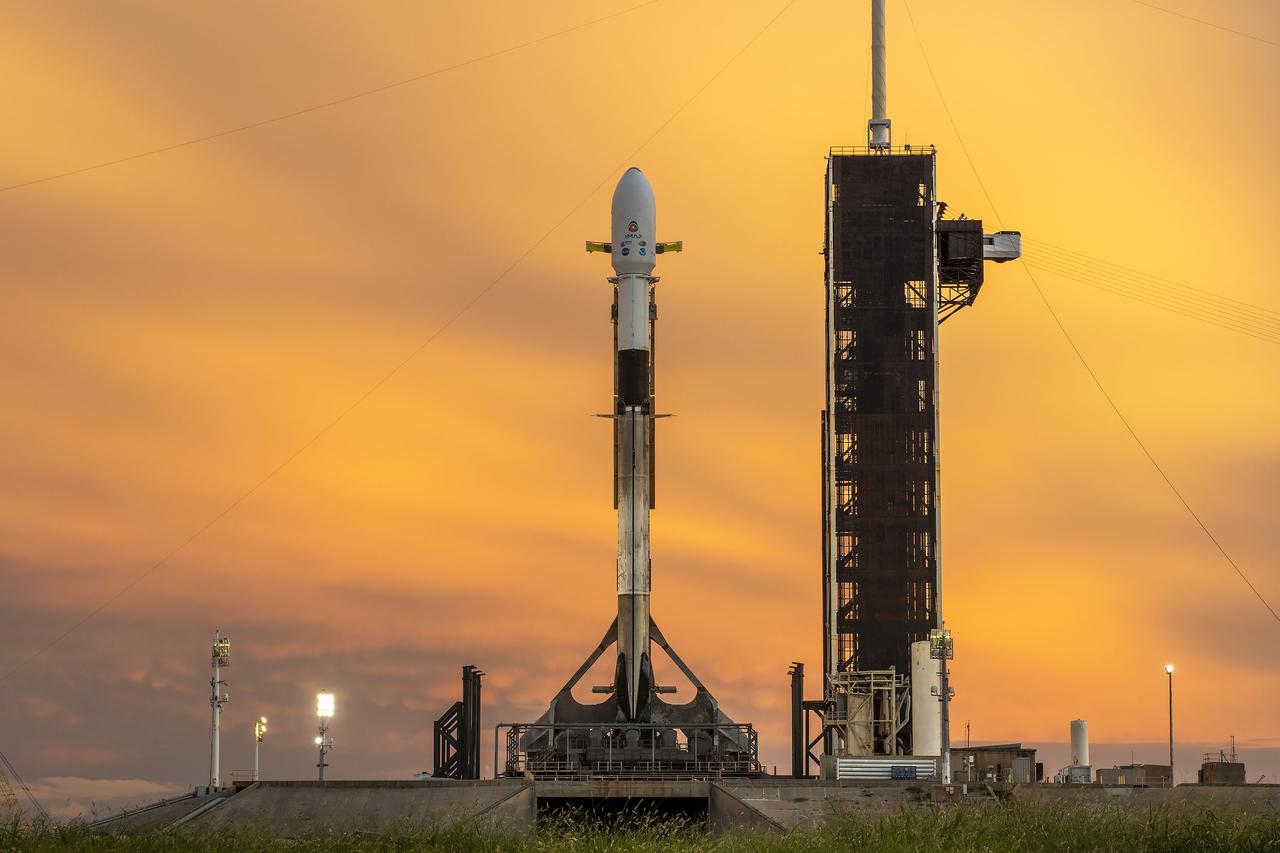

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
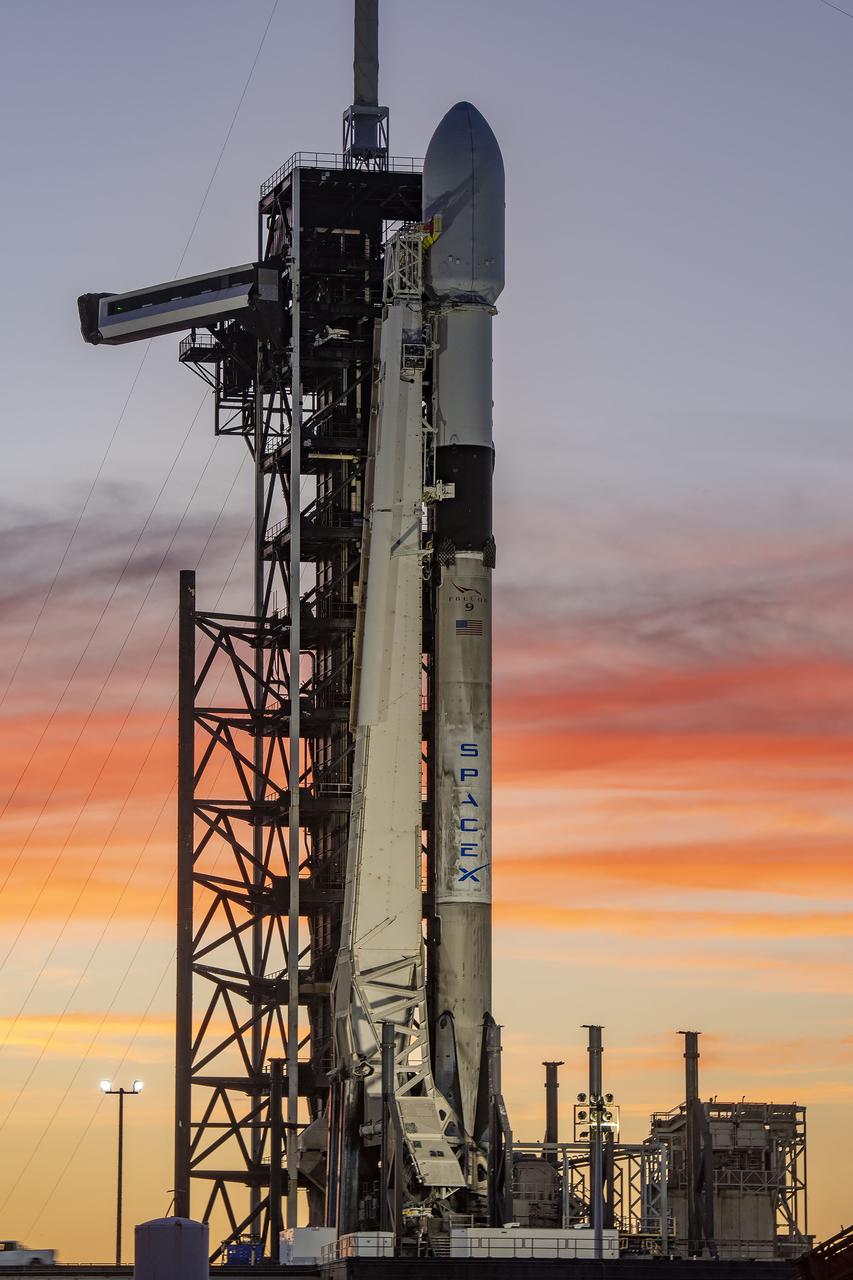

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
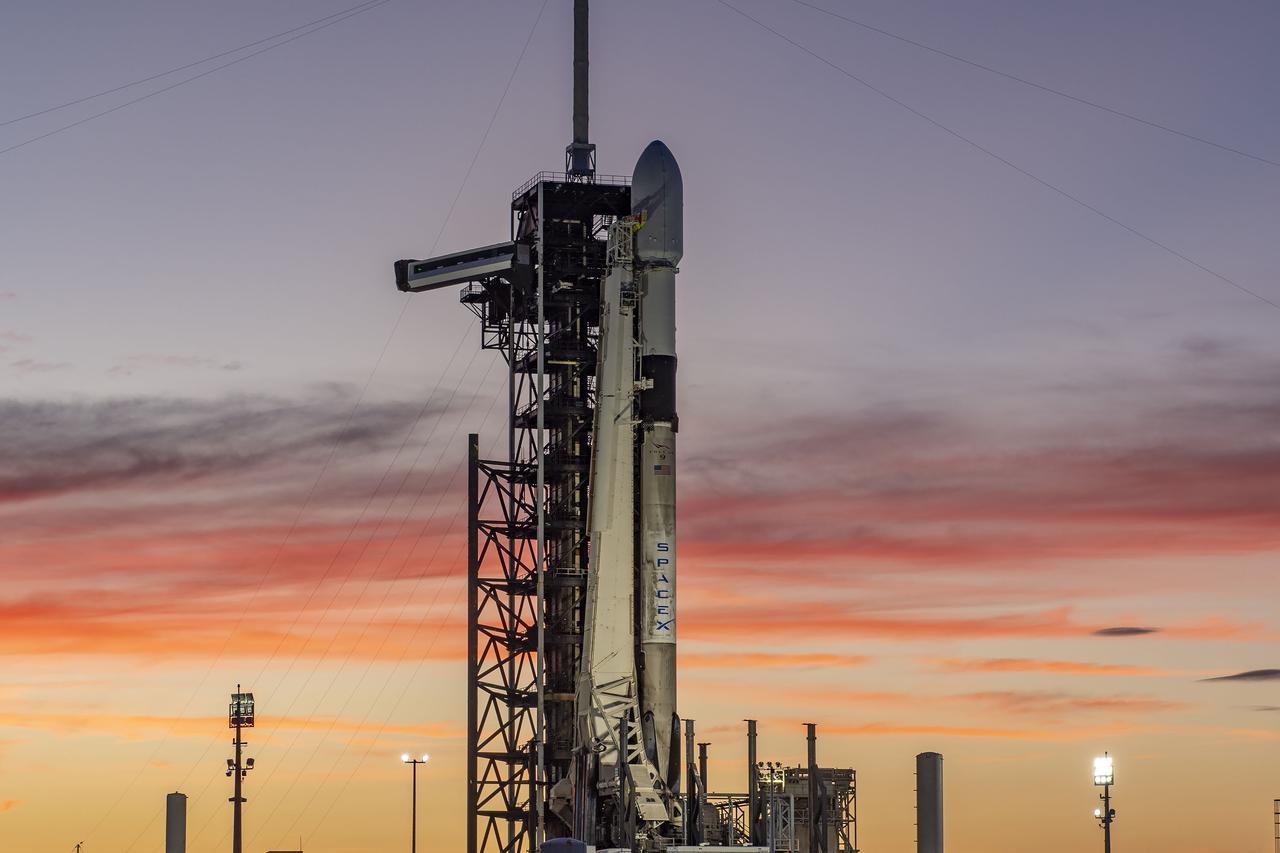

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
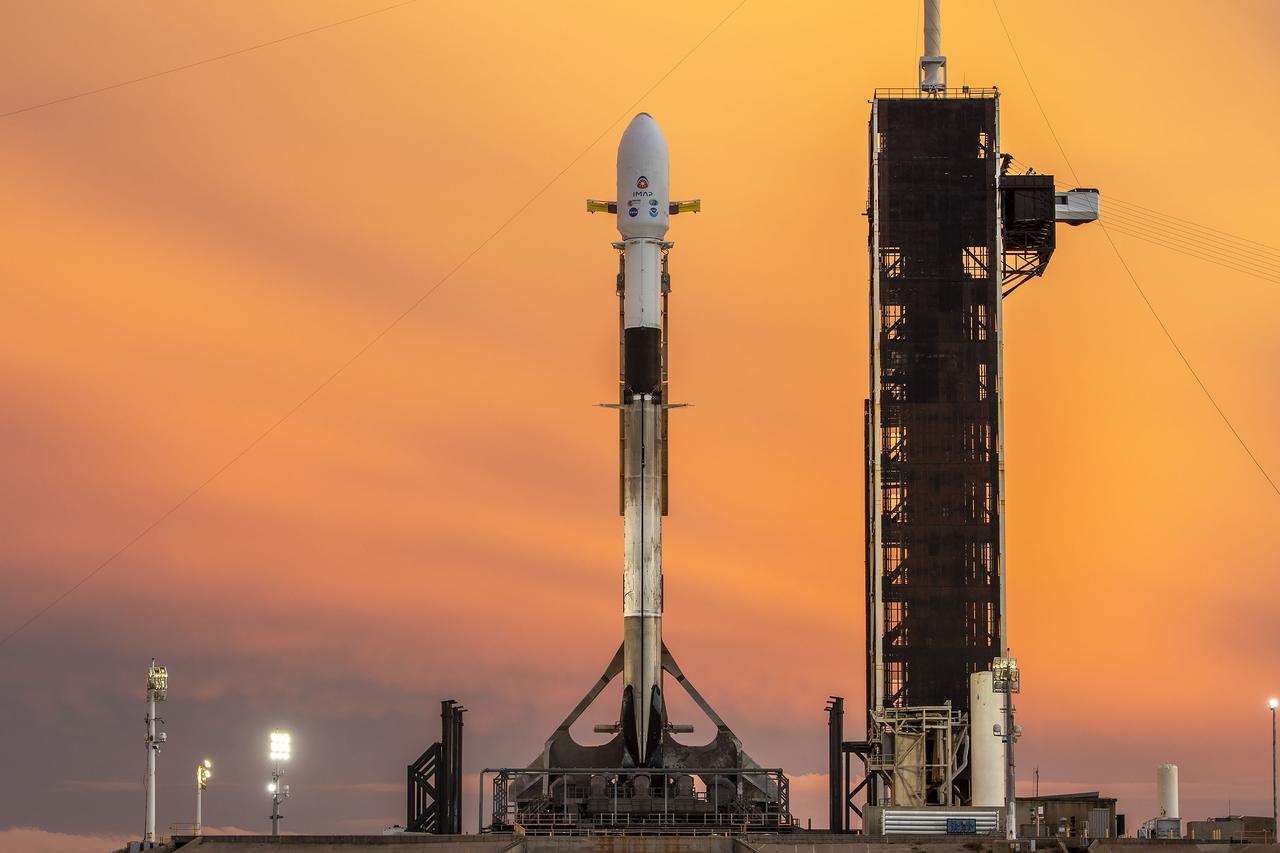

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
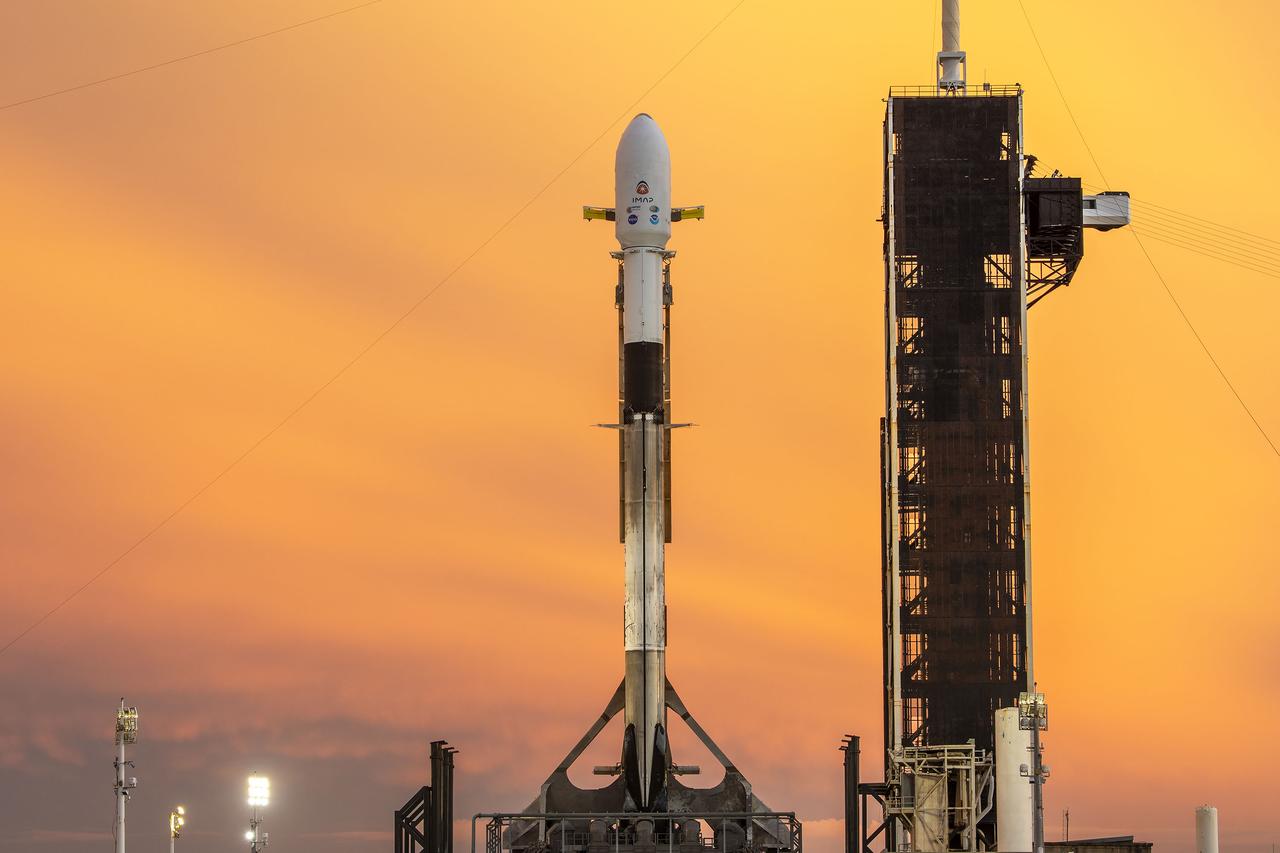

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
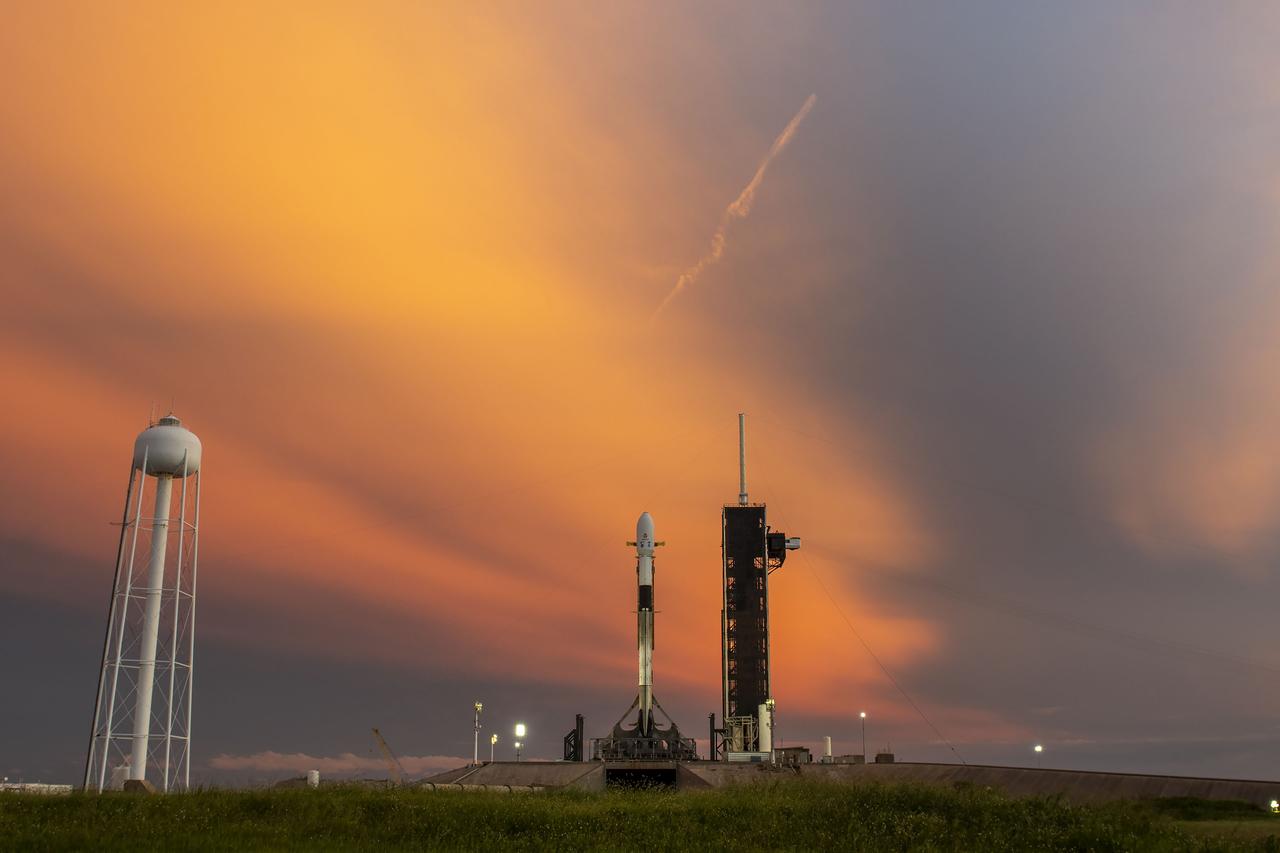

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
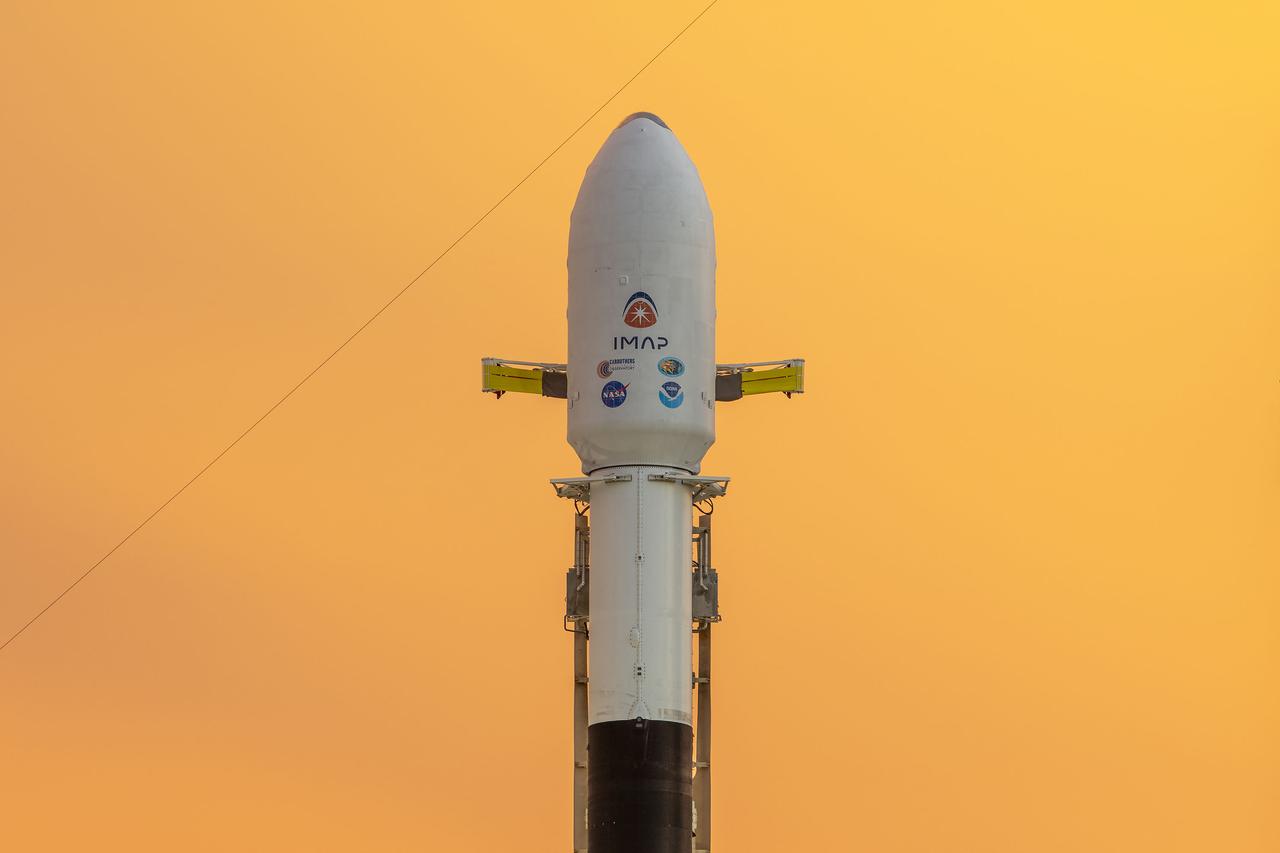

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
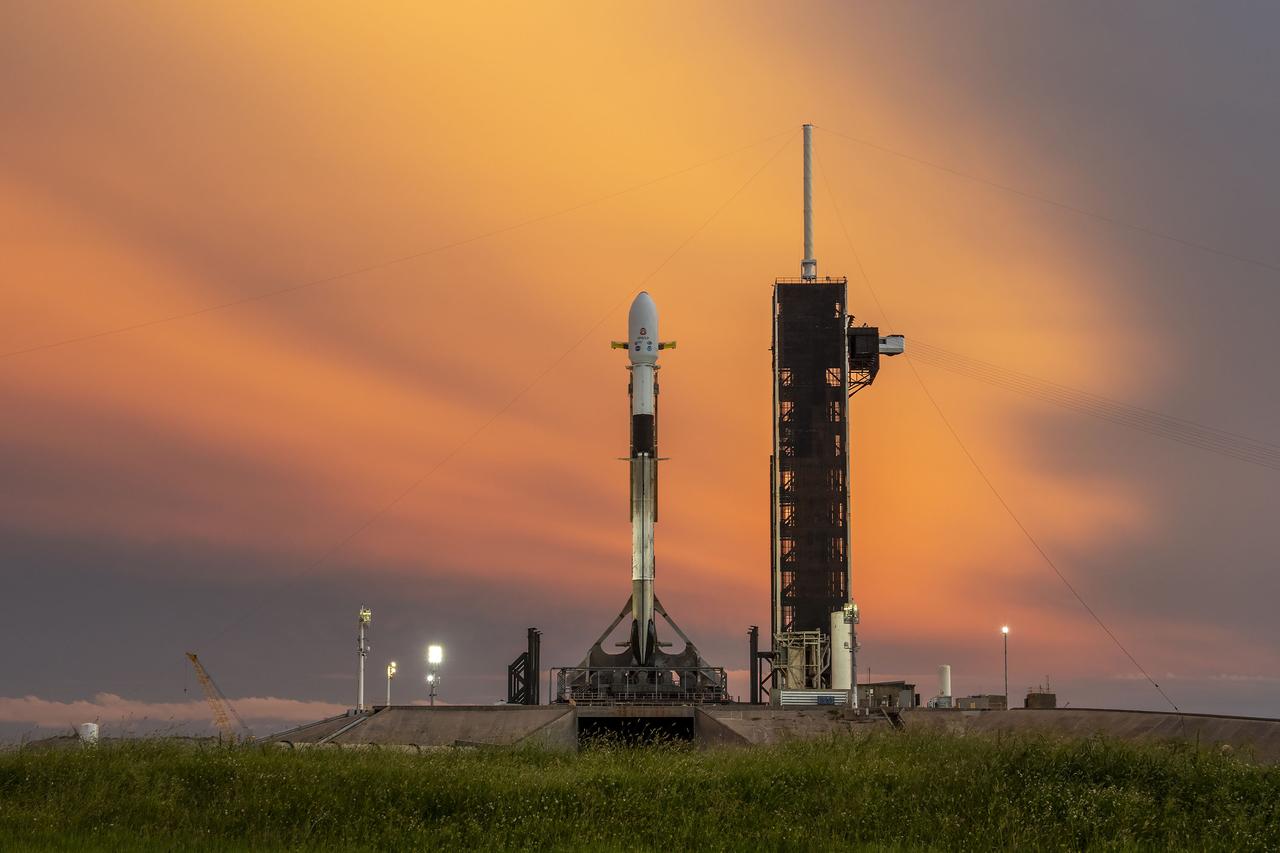

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
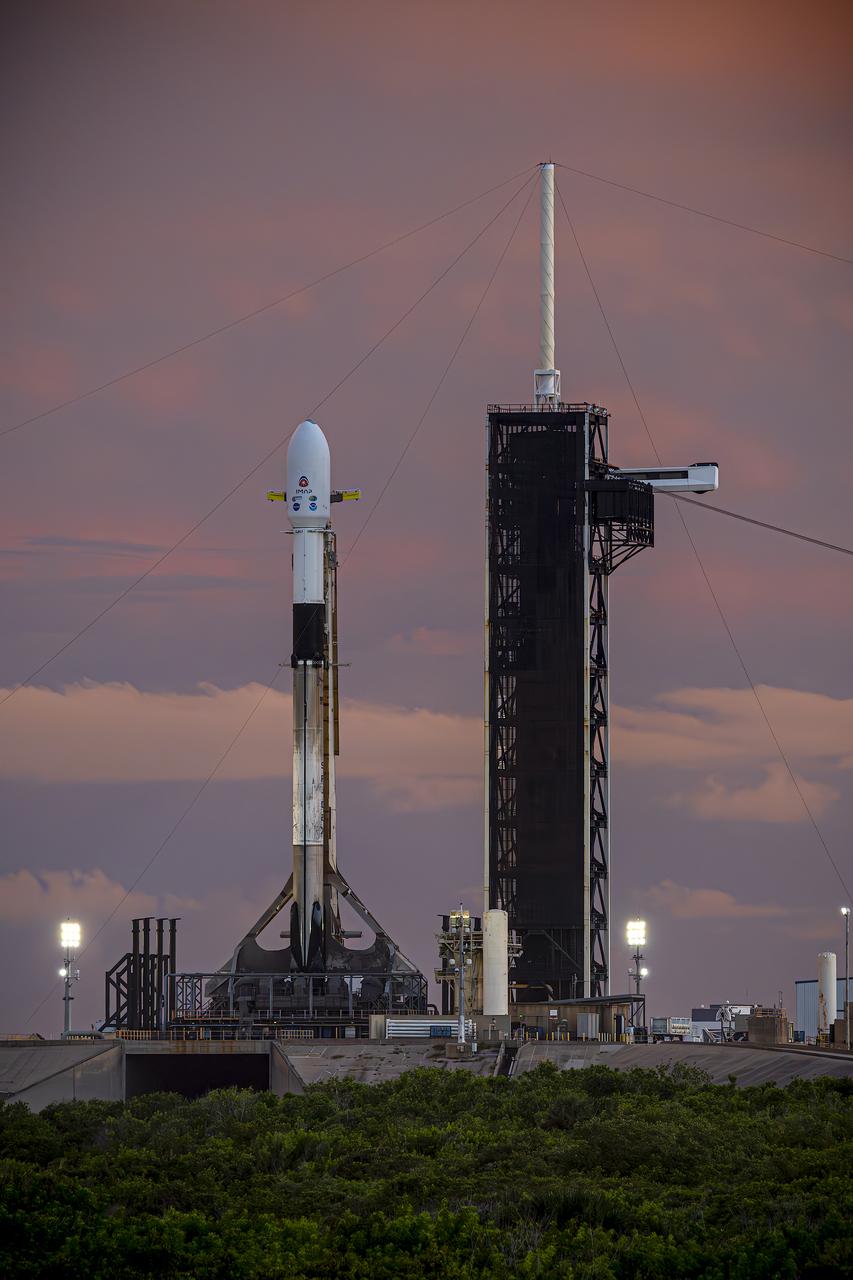

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
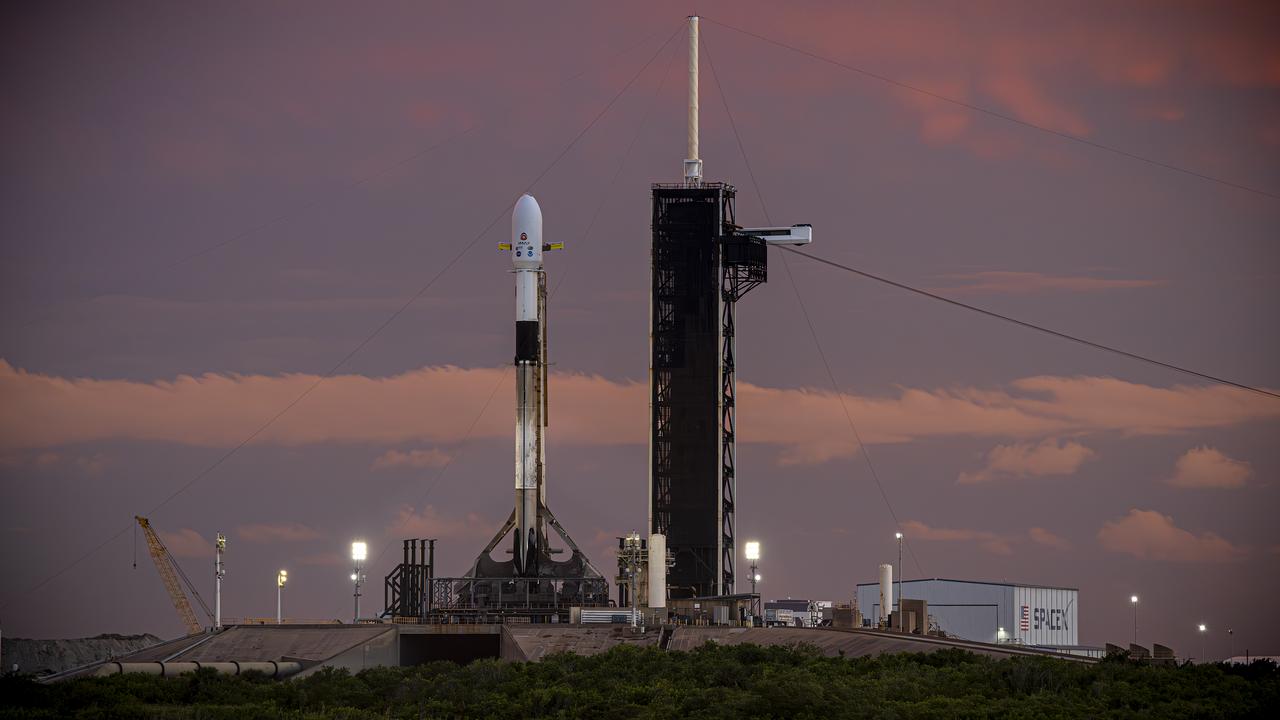

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
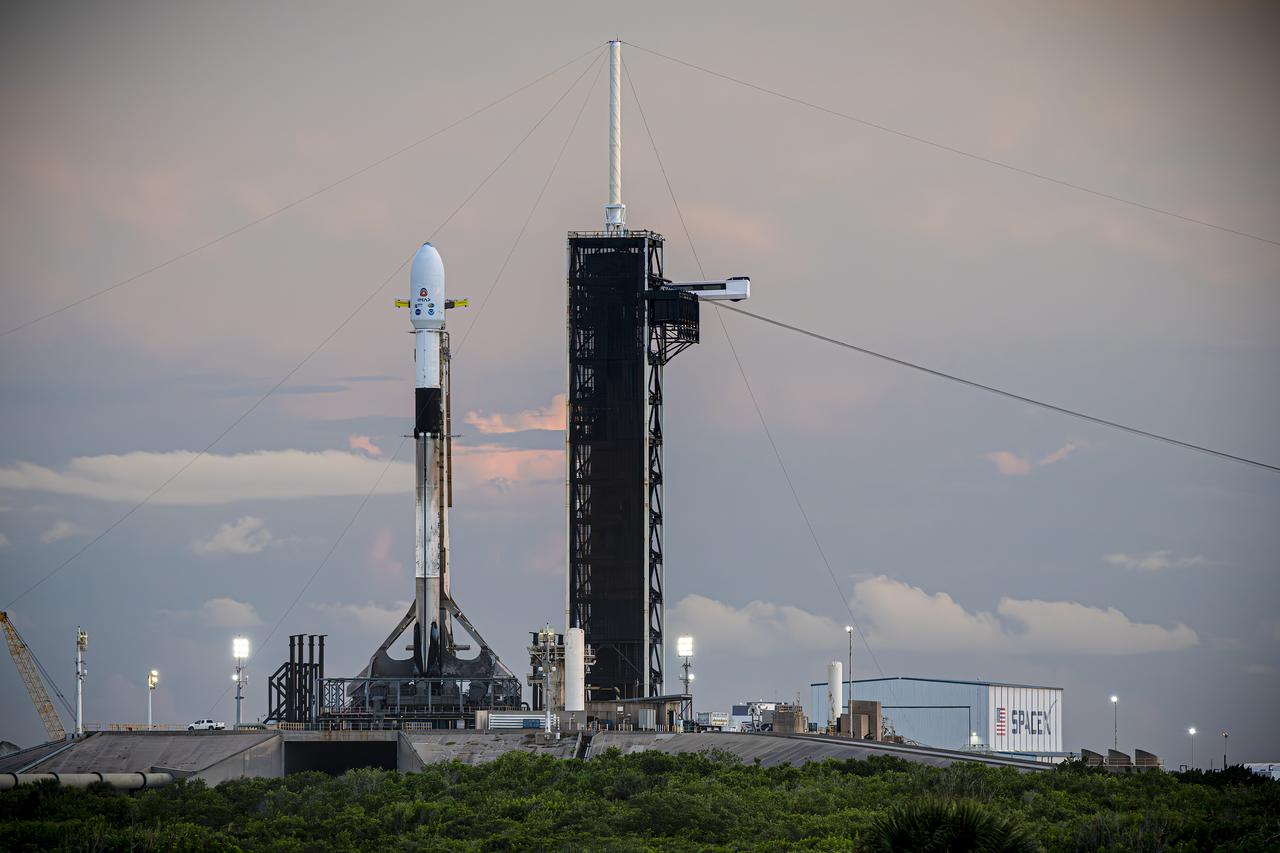

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun sets on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
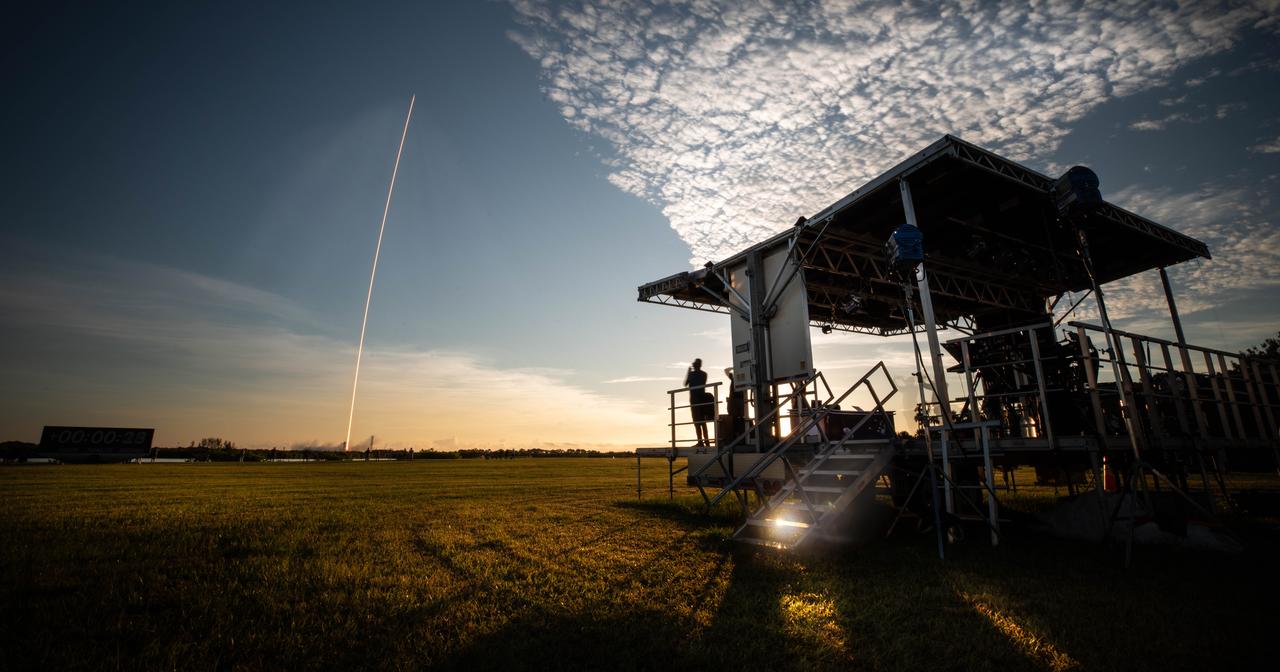

A long exposure photo shows the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lift off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
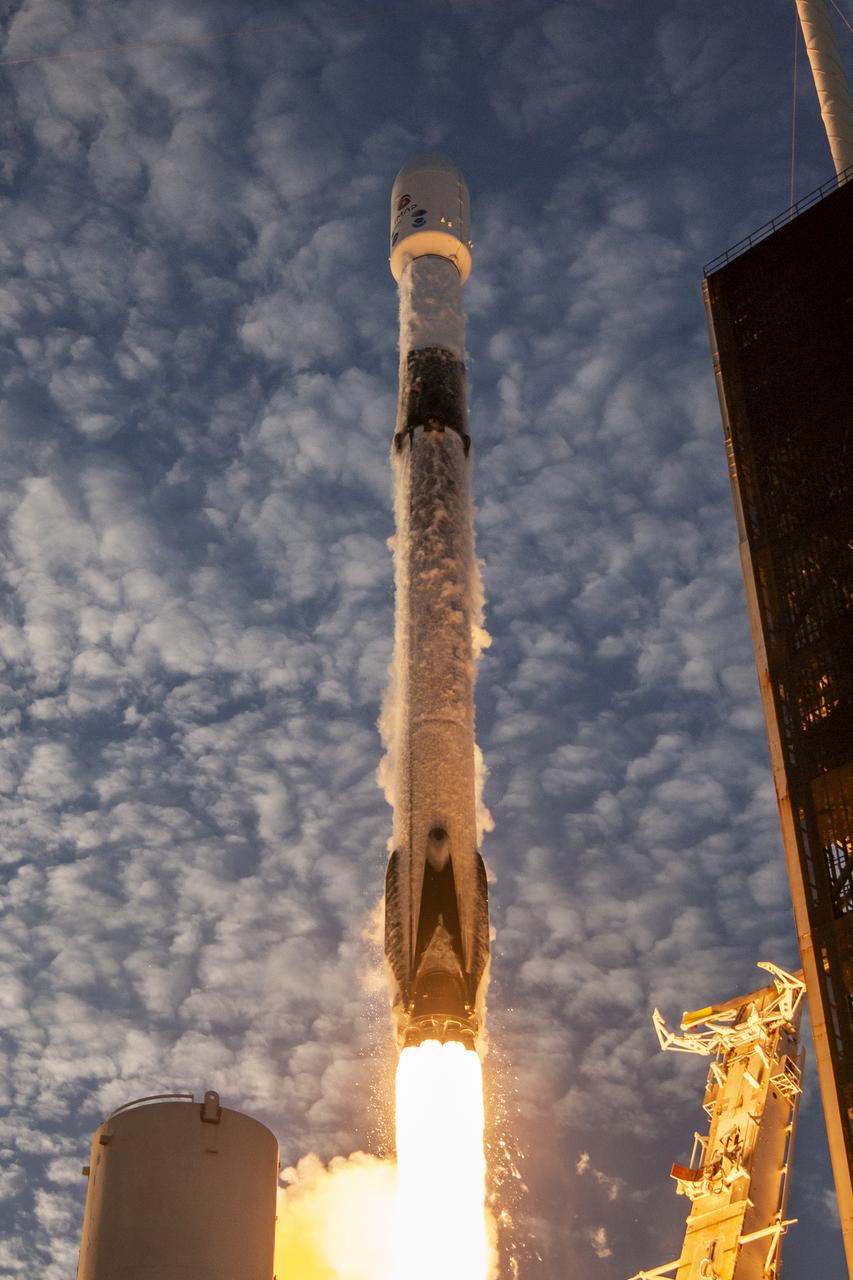

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
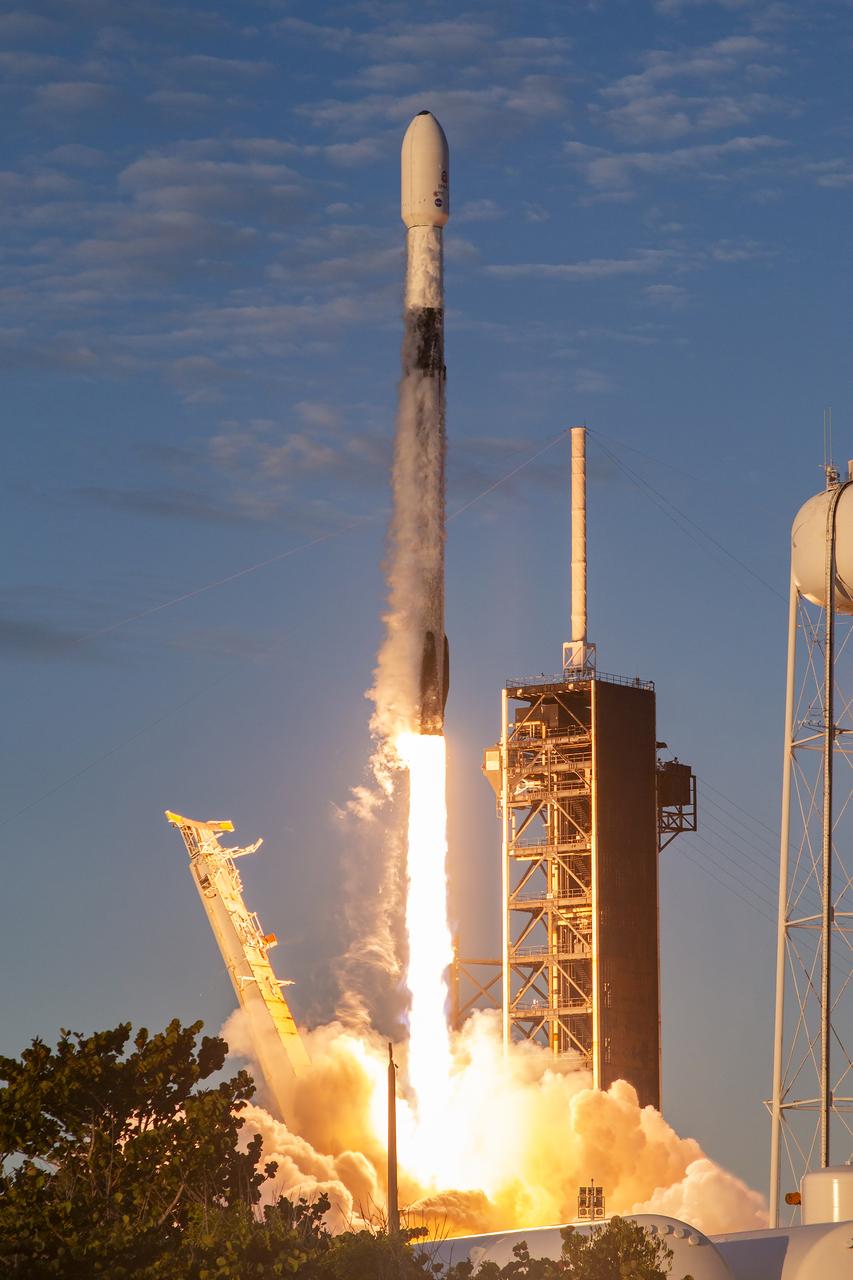

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
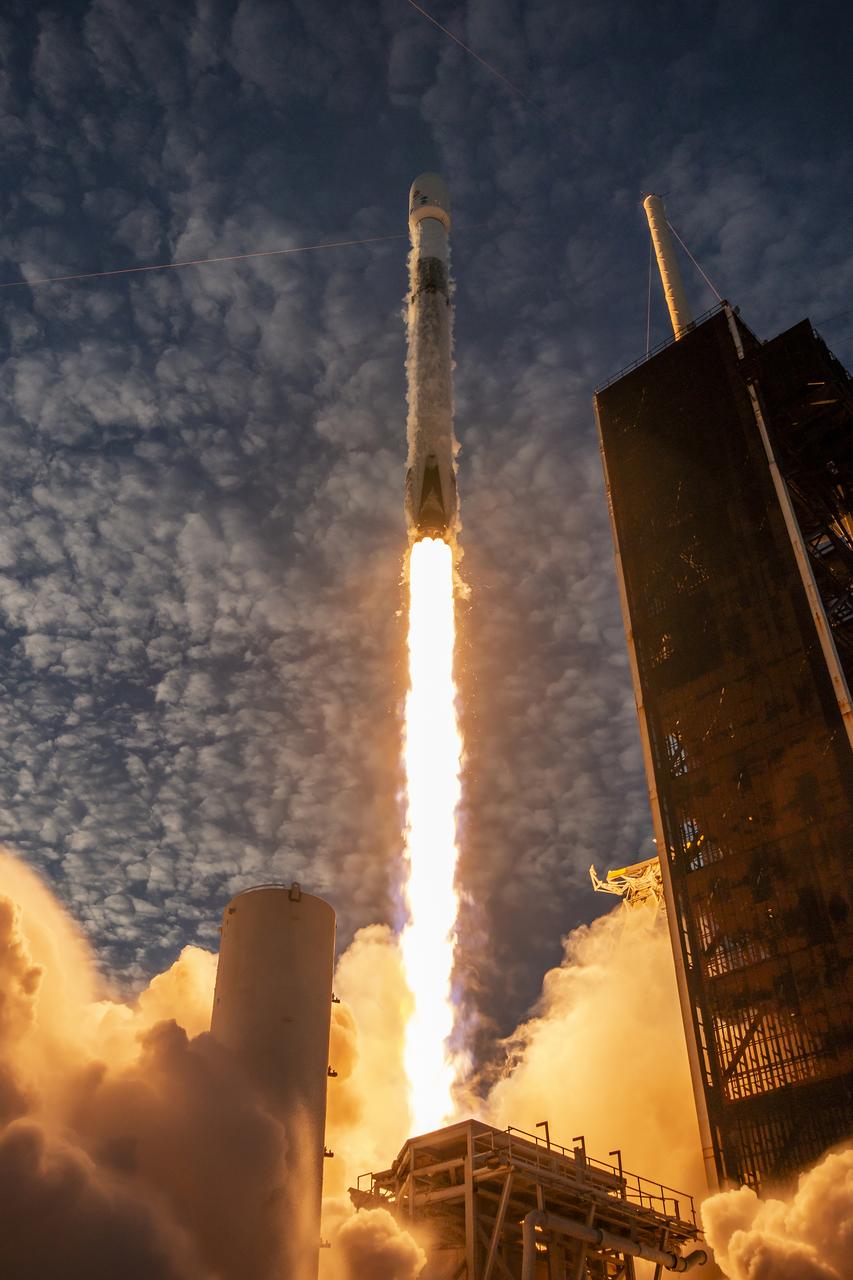

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
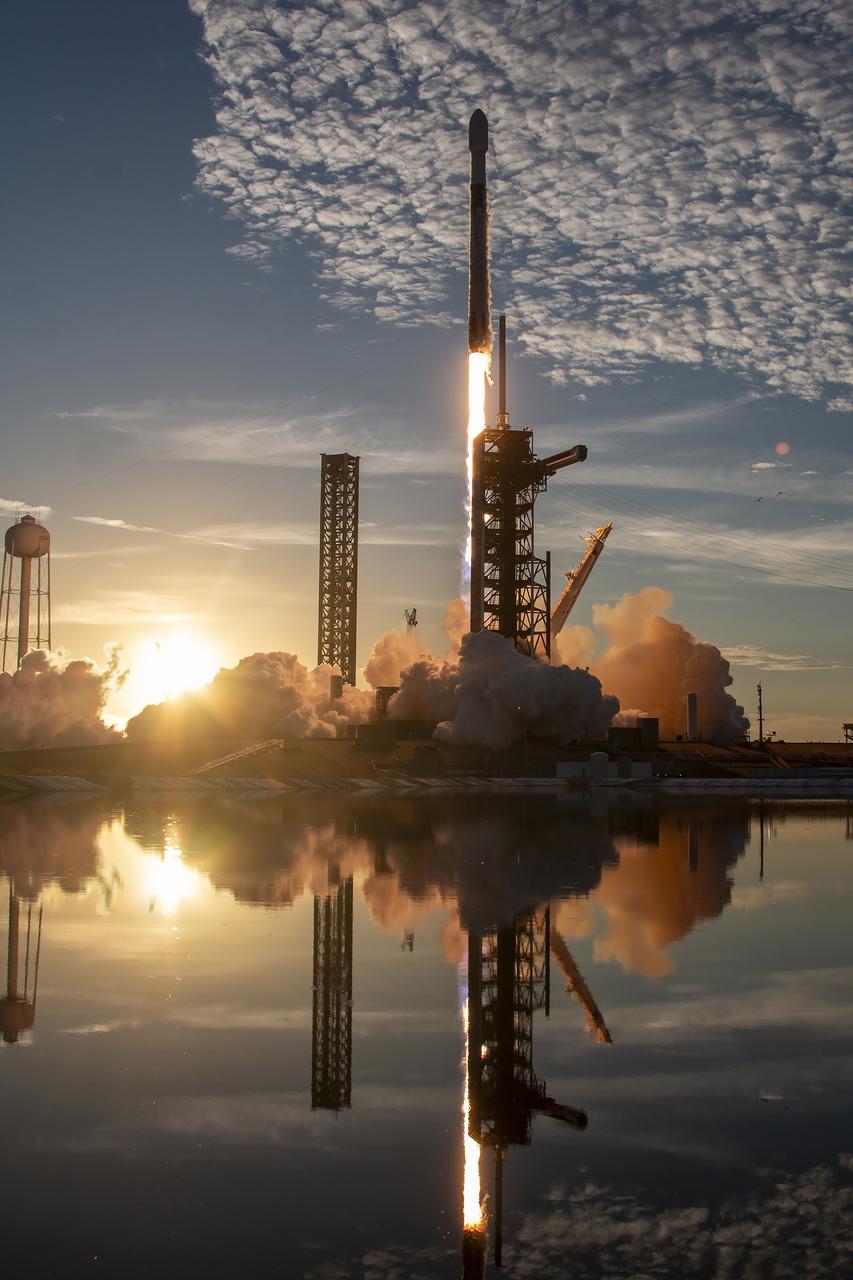

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
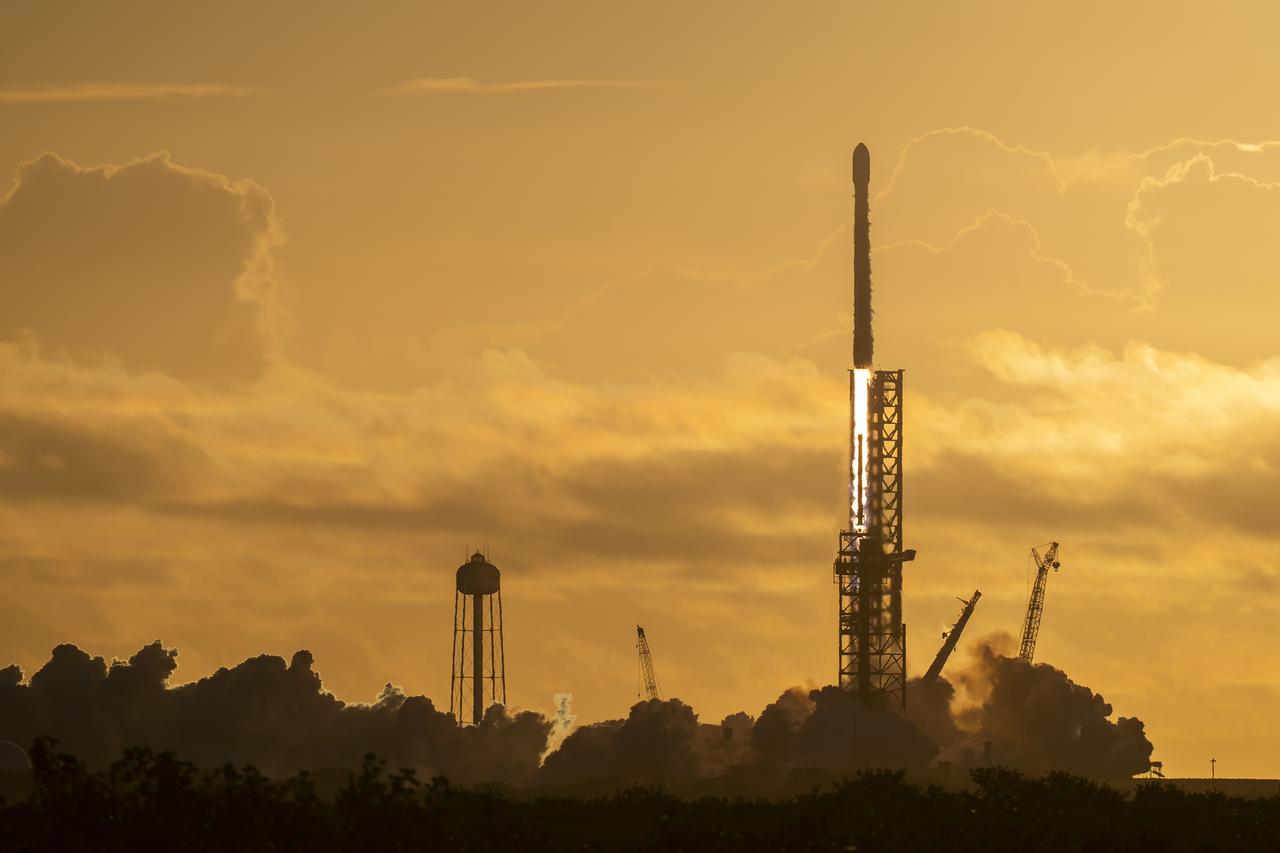

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
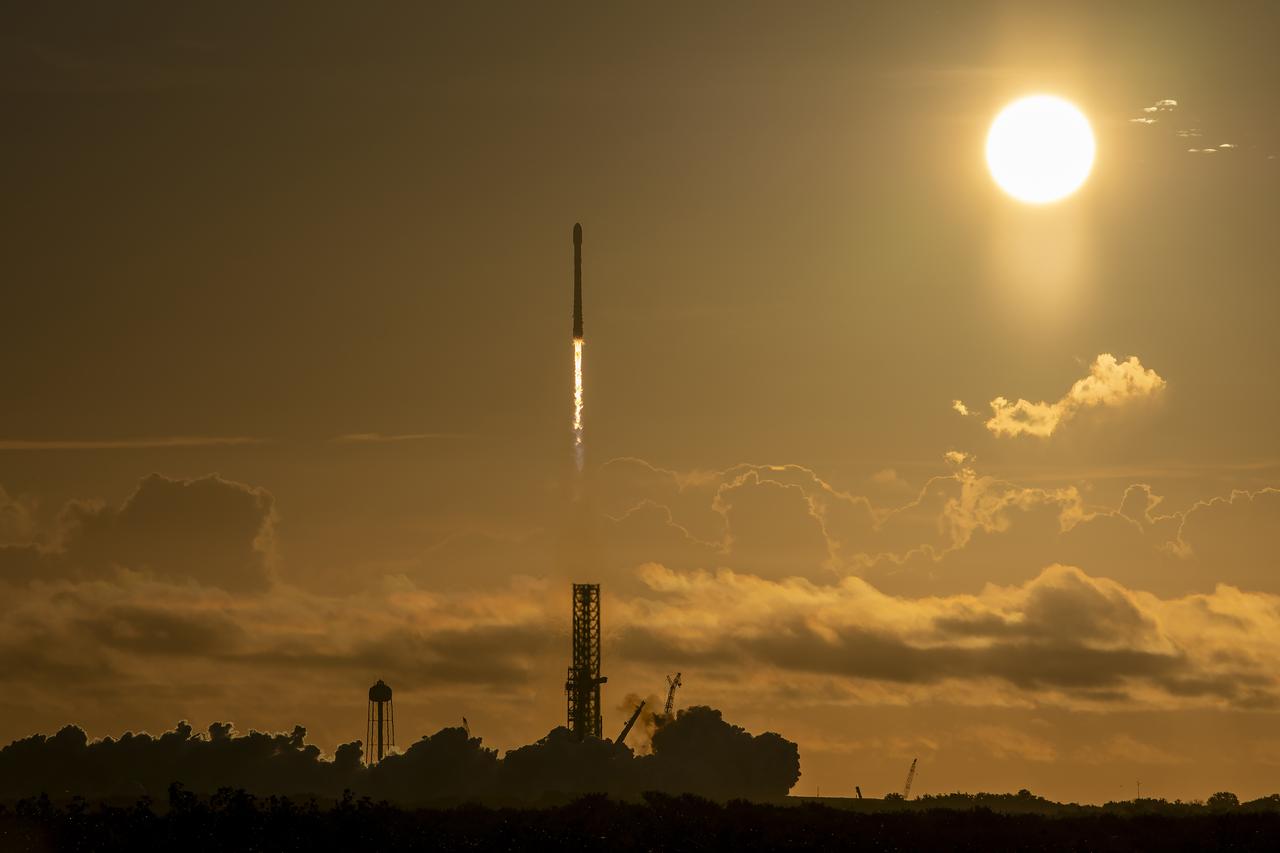

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
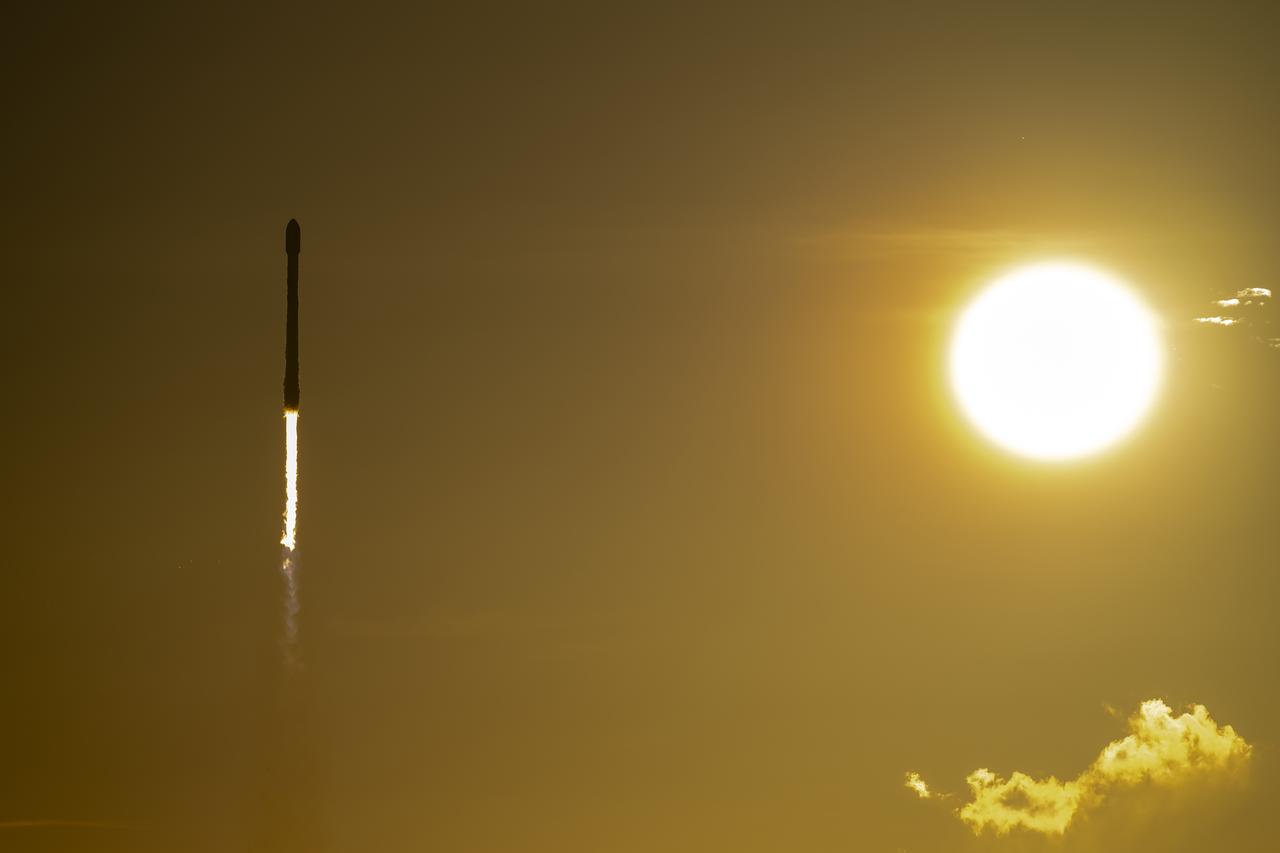

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
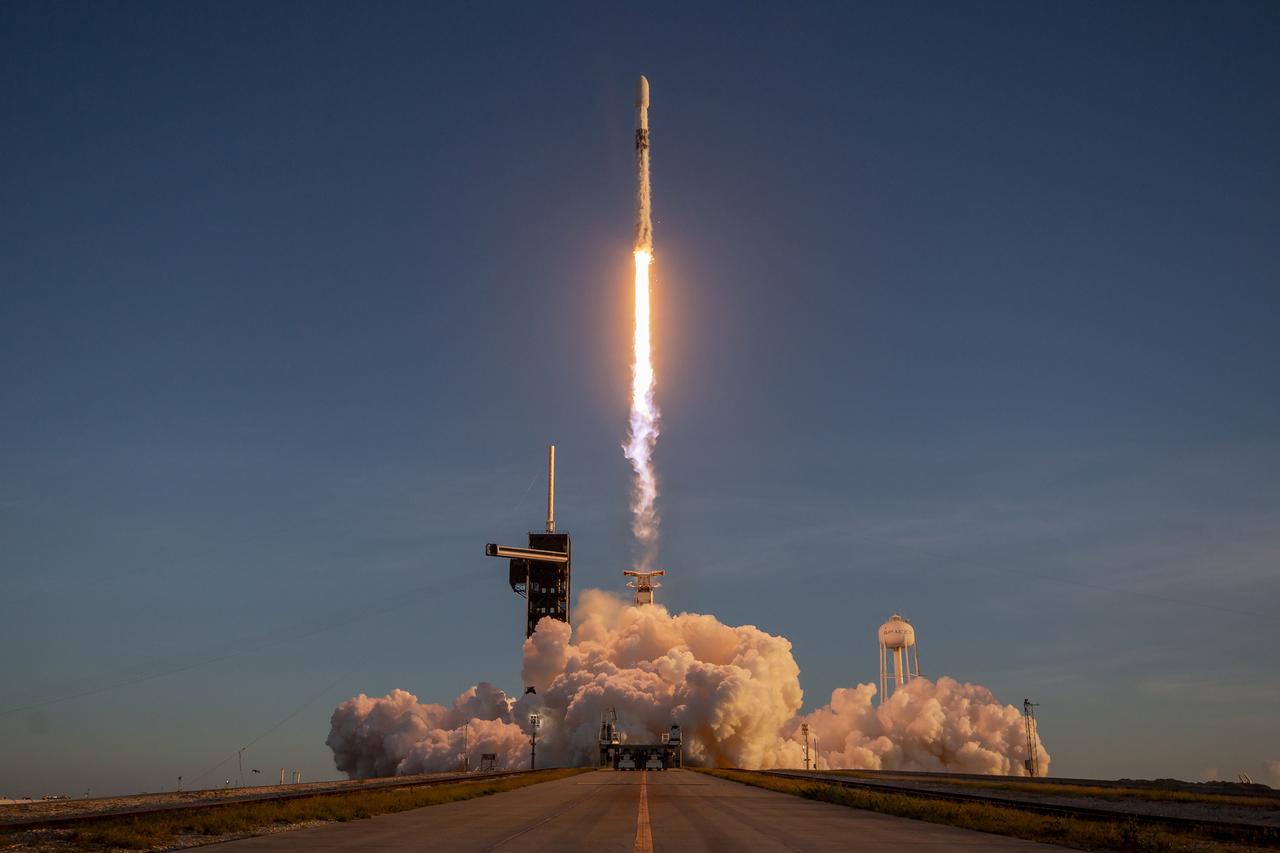

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
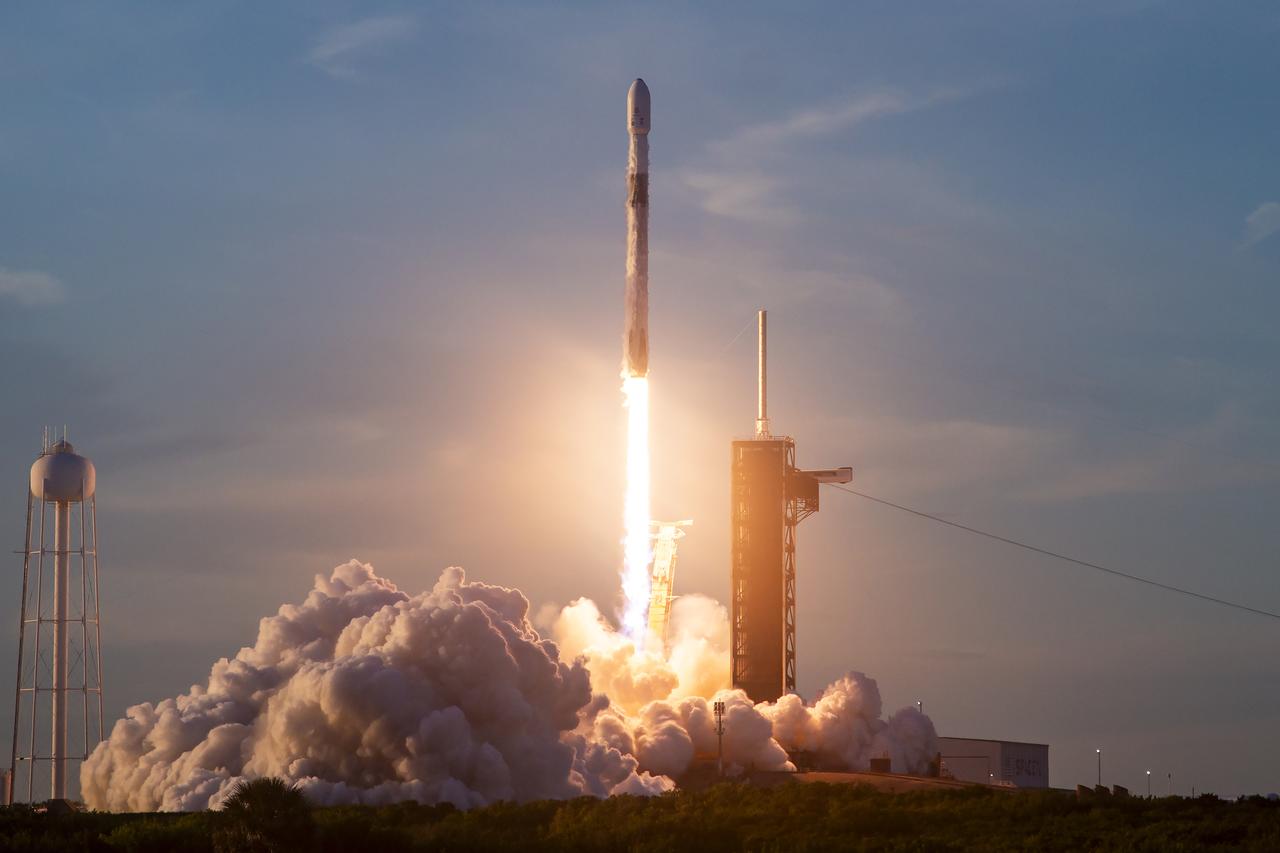

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
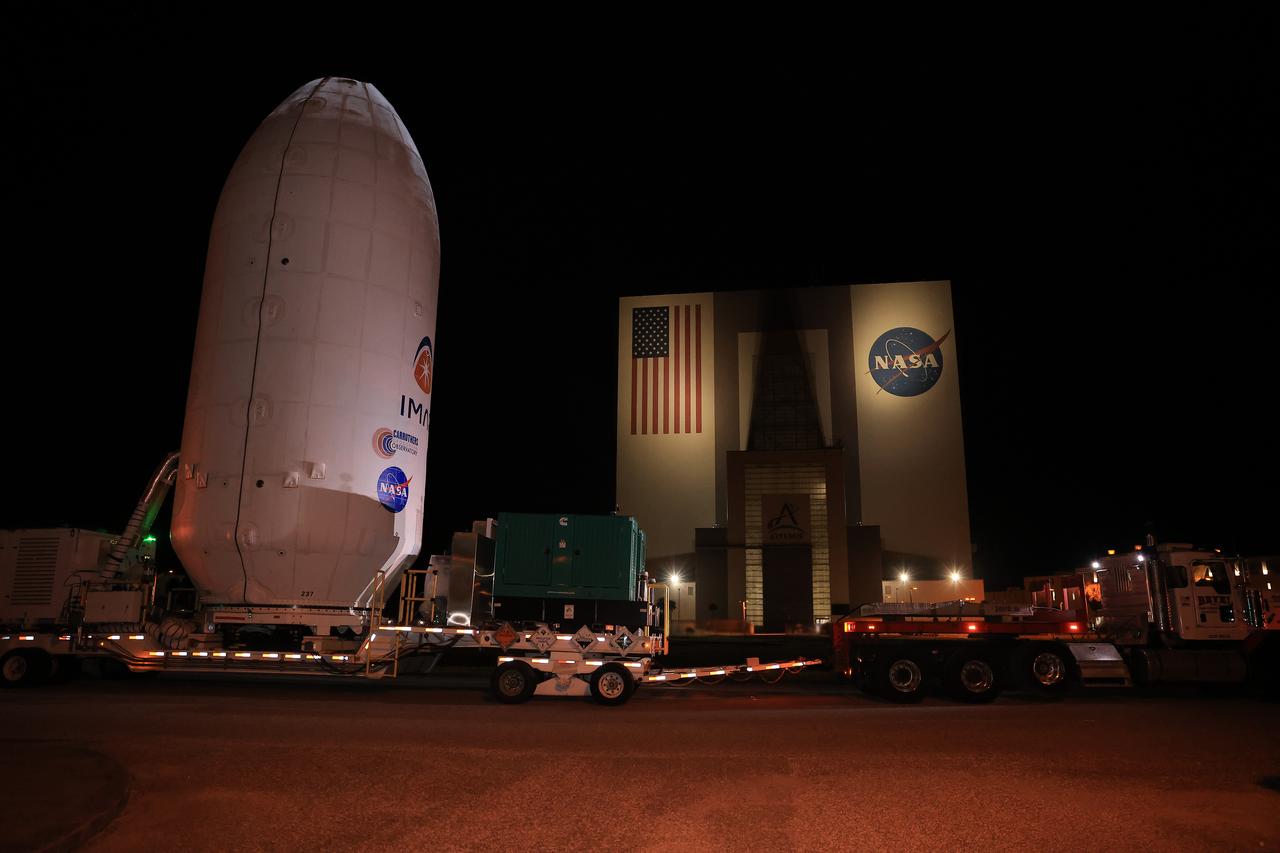

Workers transport NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite late on Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2025, through early Thursday, Sept. 18, 2025, from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville Florida, to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians will soon mate the three spacecraft to a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in preparation for launch. Liftoff is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
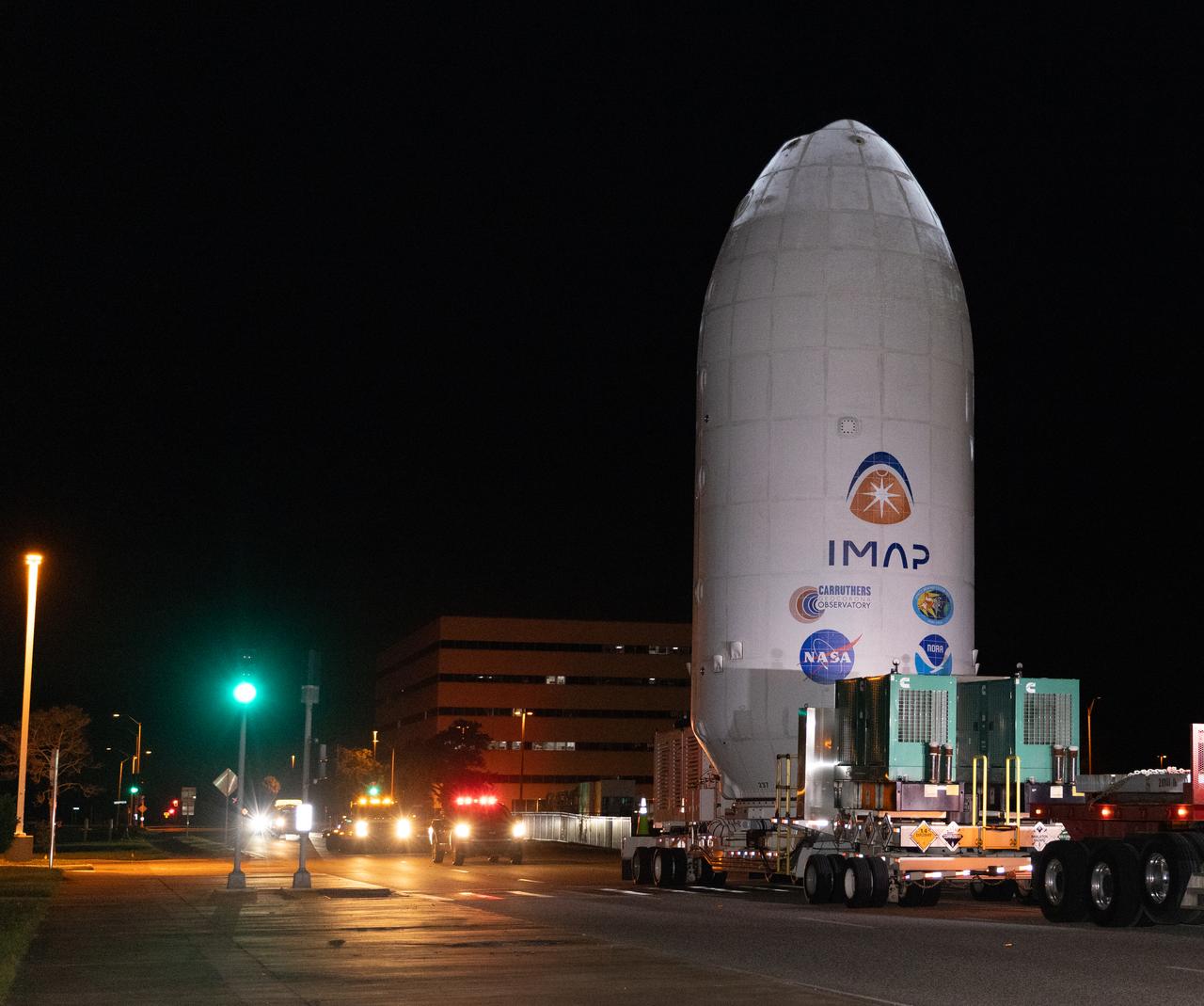

Workers transport NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite late on Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2025, through early Thursday, Sept. 18, 2025, from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville Florida, to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians will soon mate the three spacecraft to a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in preparation for launch. Liftoff is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
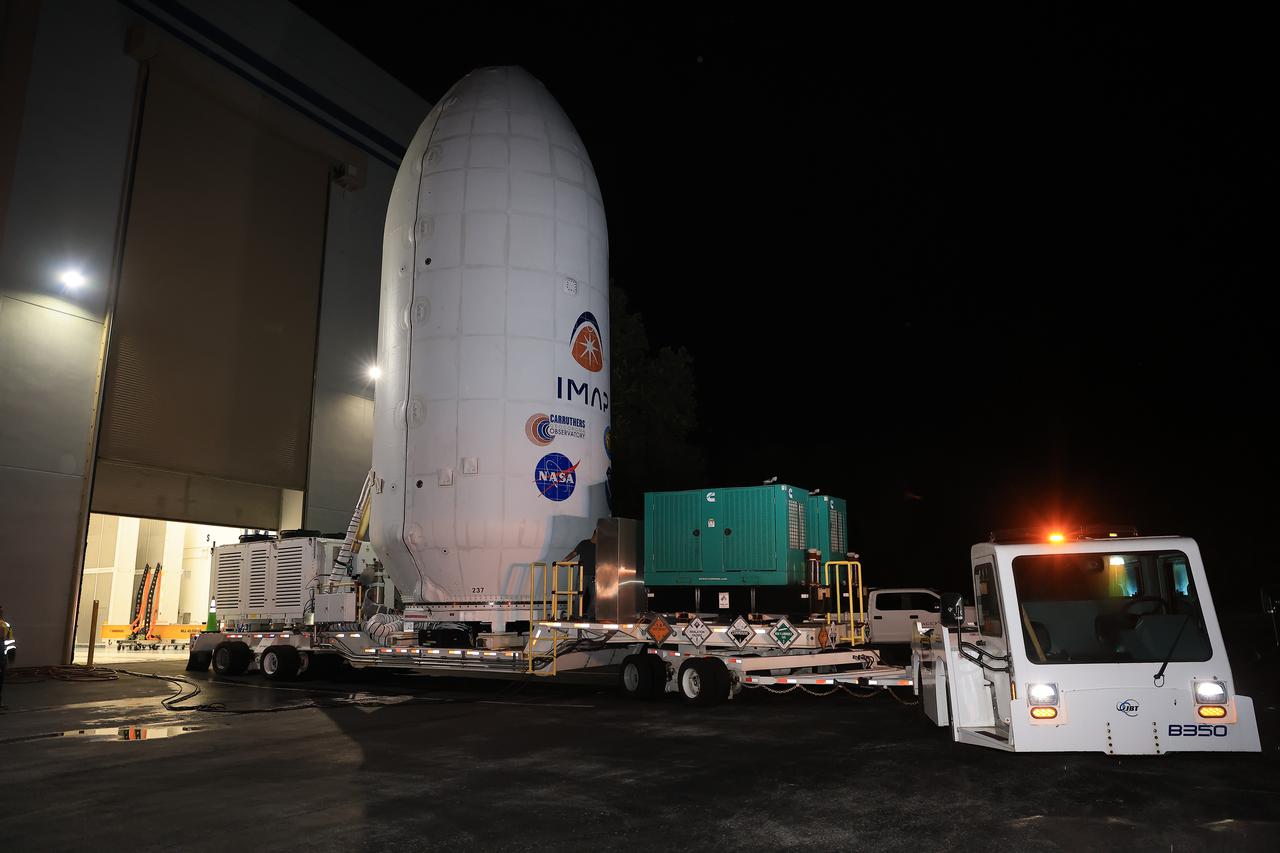

Workers transport NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite late on Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2025, through early Thursday, Sept. 18, 2025, from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville Florida, to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians will soon mate the three spacecraft to a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in preparation for launch. Liftoff is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
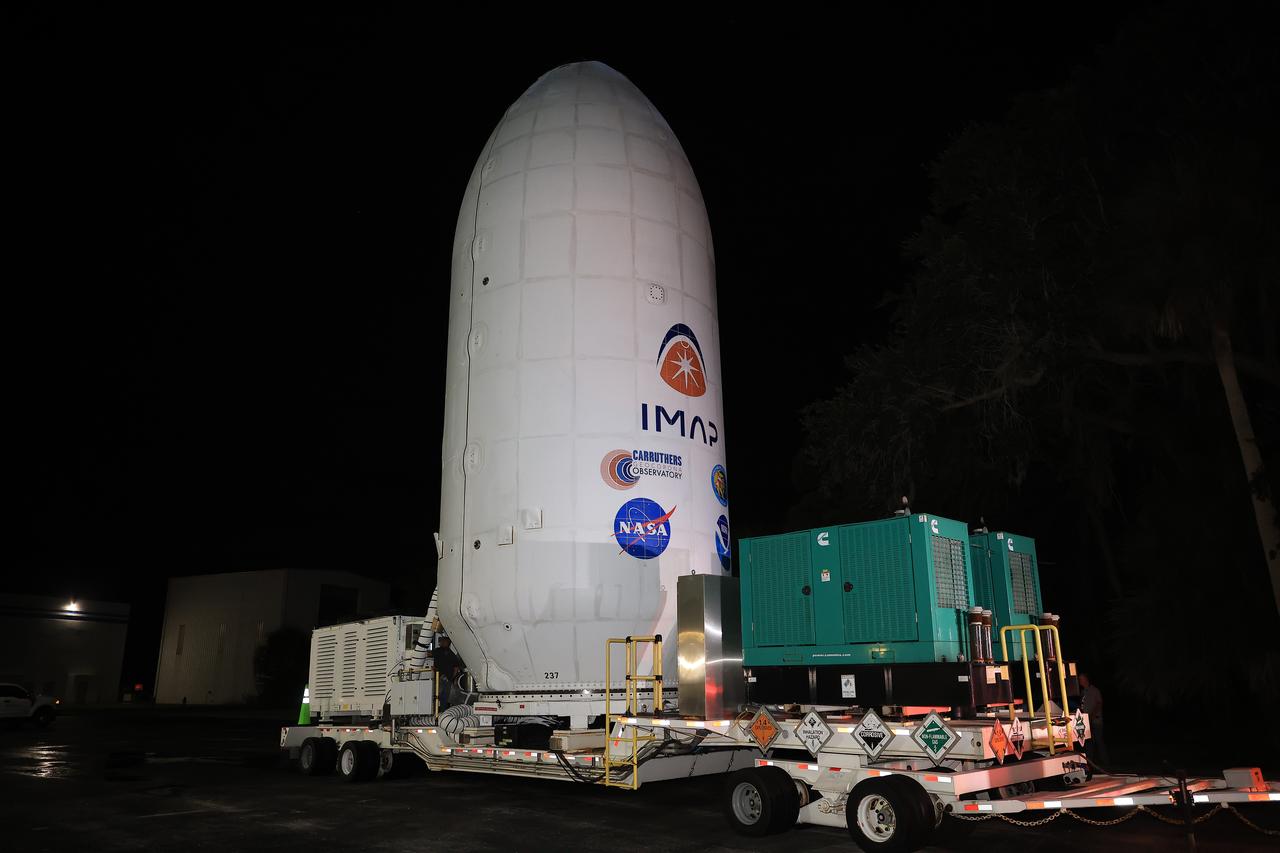

Workers transport NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) satellite late on Wednesday, Sept. 17, 2025, through early Thursday, Sept. 18, 2025, from the Astrotech Space Operations Facility in Titusville Florida, to the SpaceX hangar at Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Technicians will soon mate the three spacecraft to a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in preparation for launch. Liftoff is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
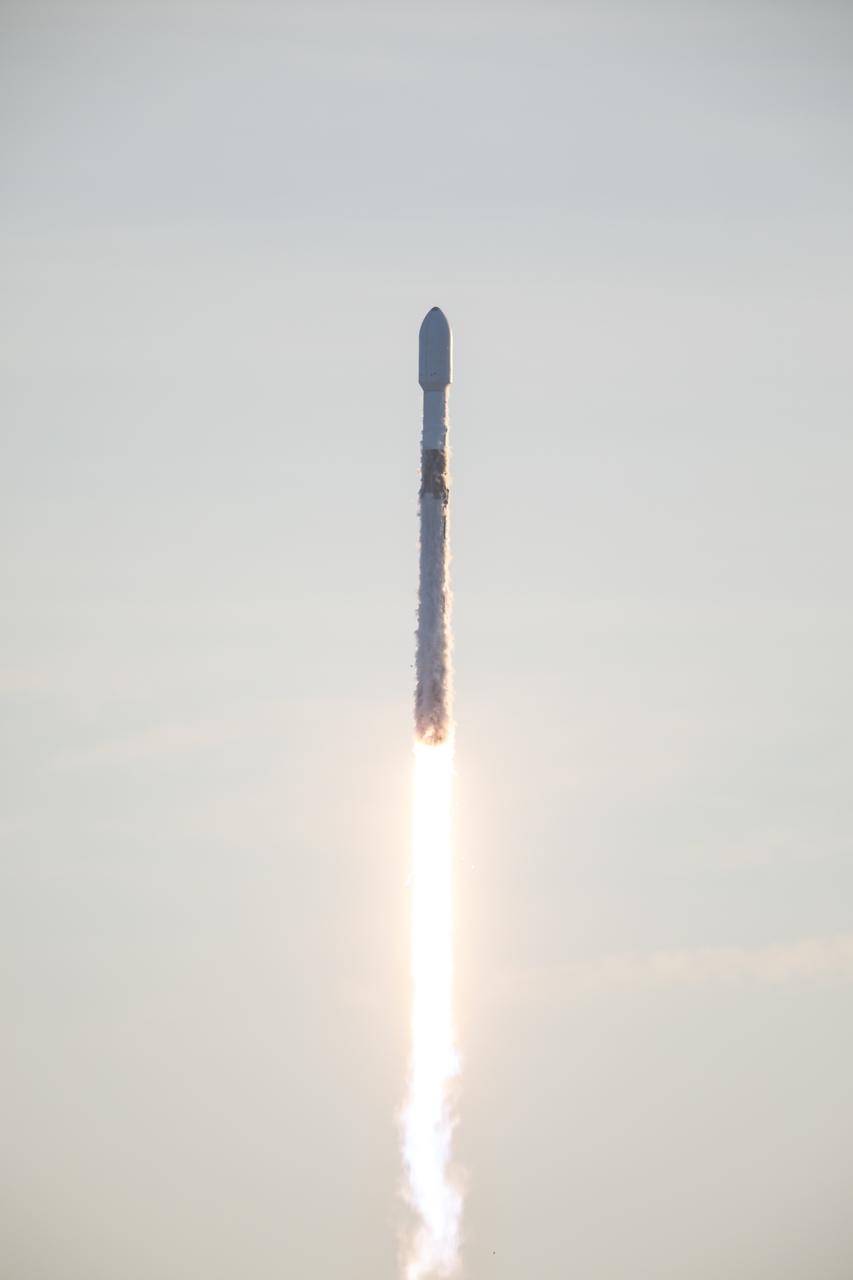

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
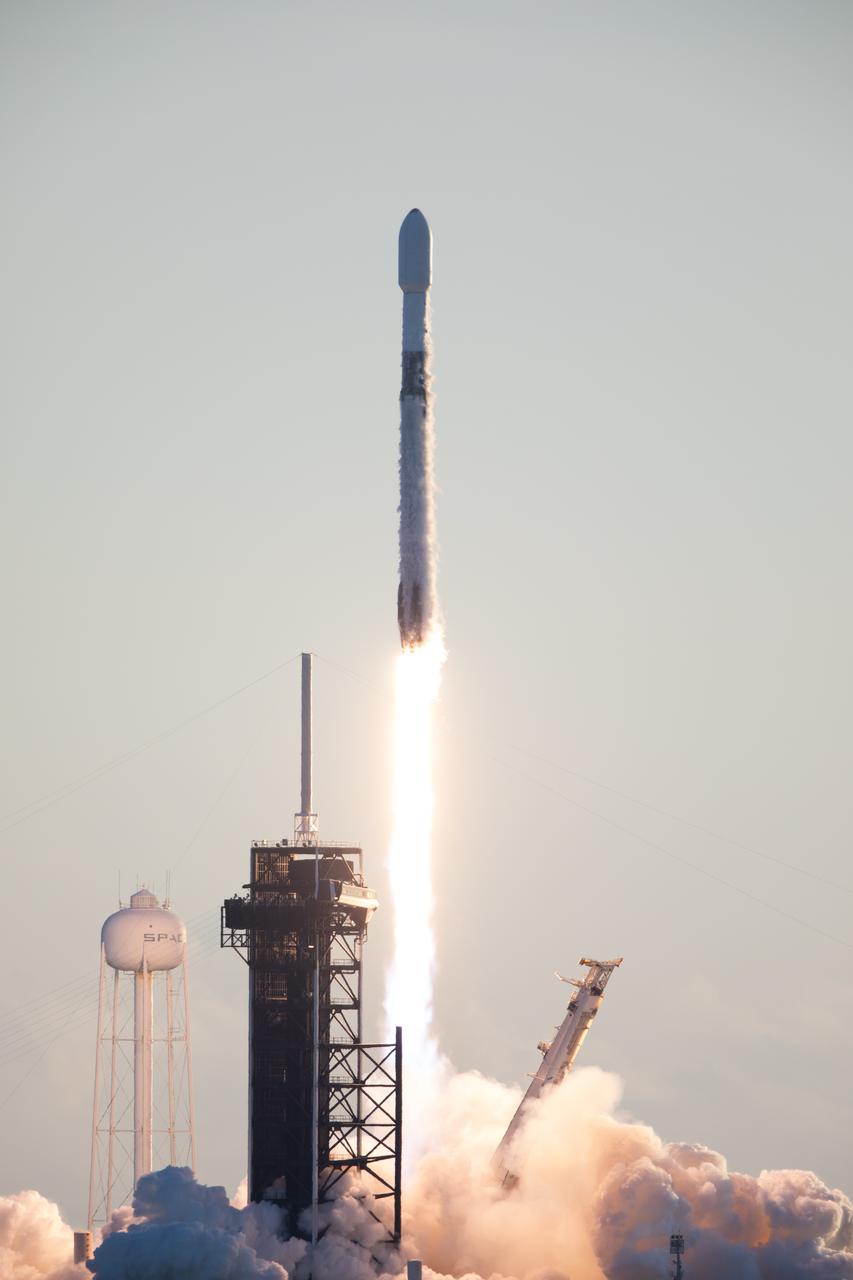

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
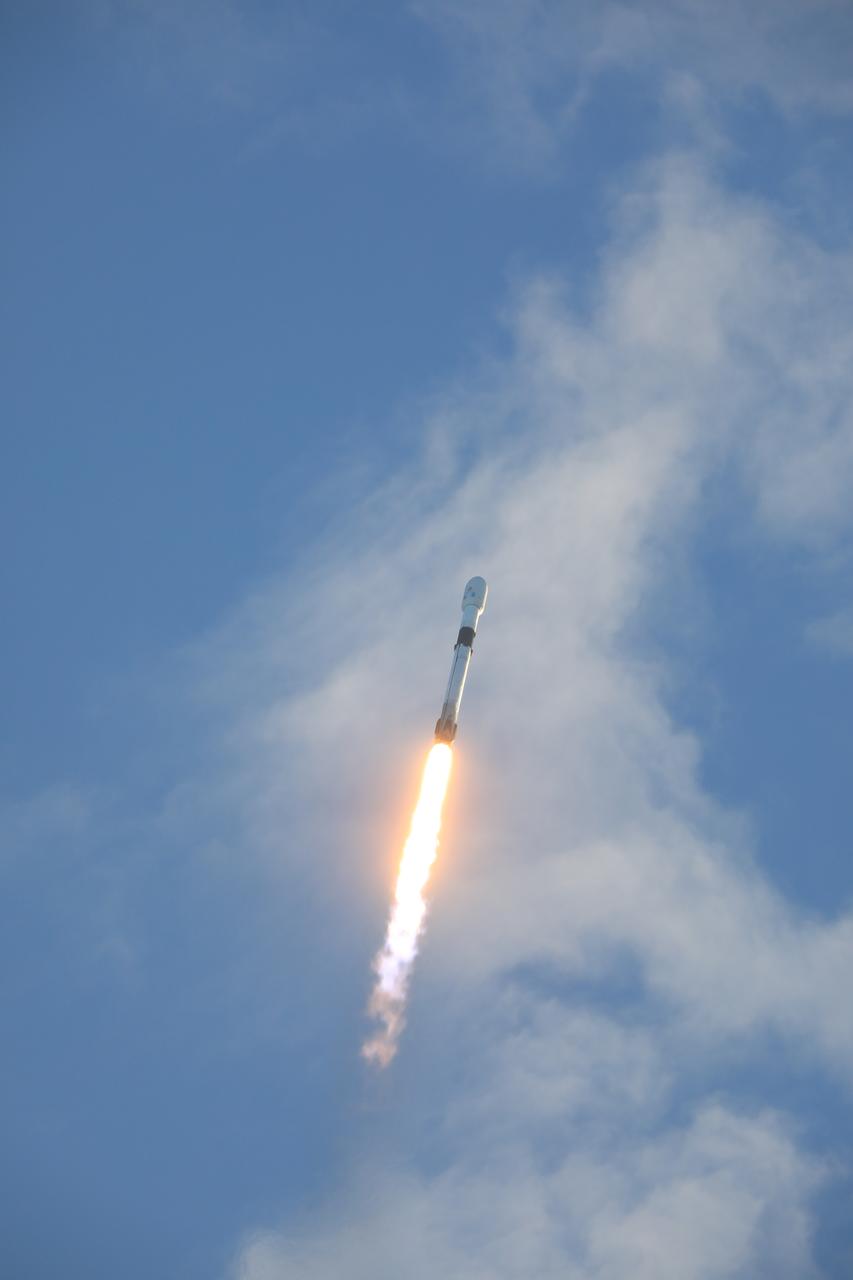

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
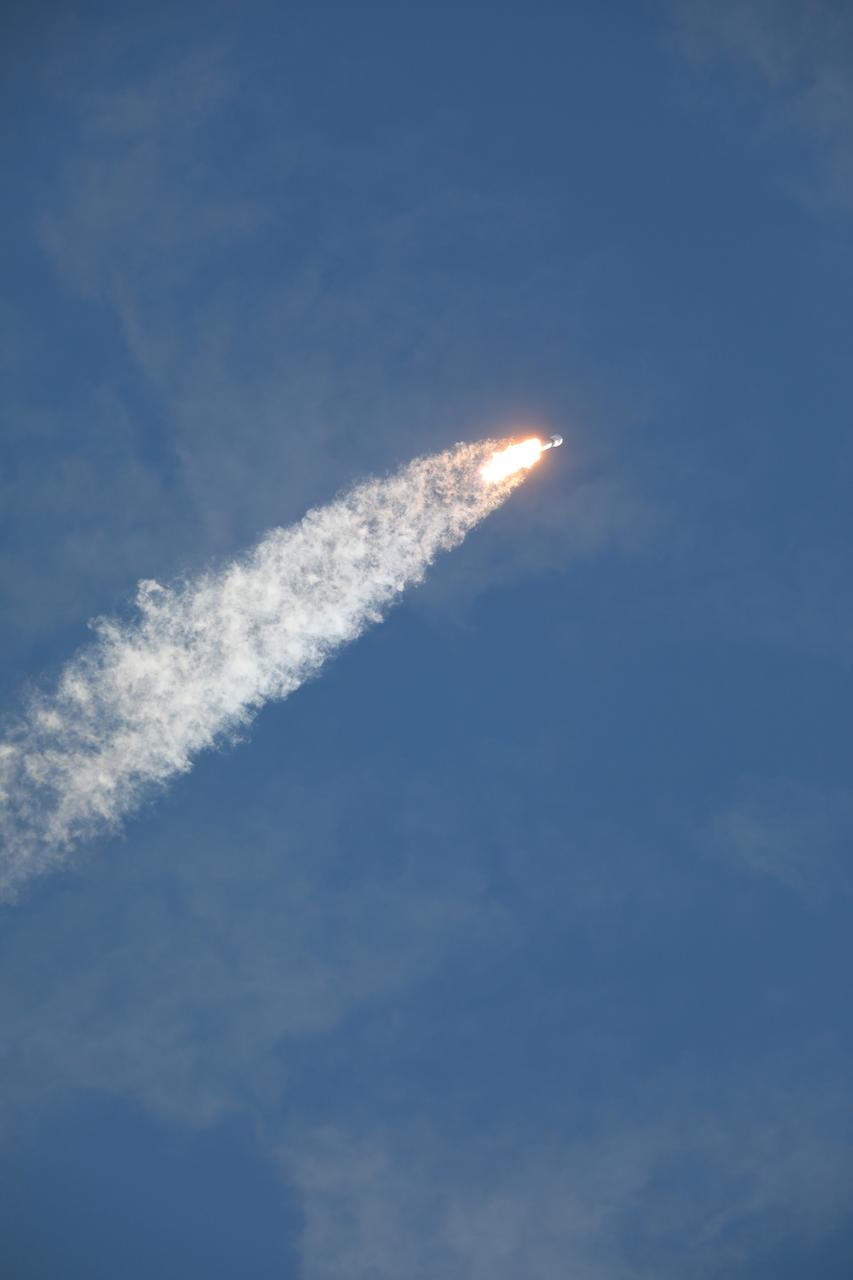

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
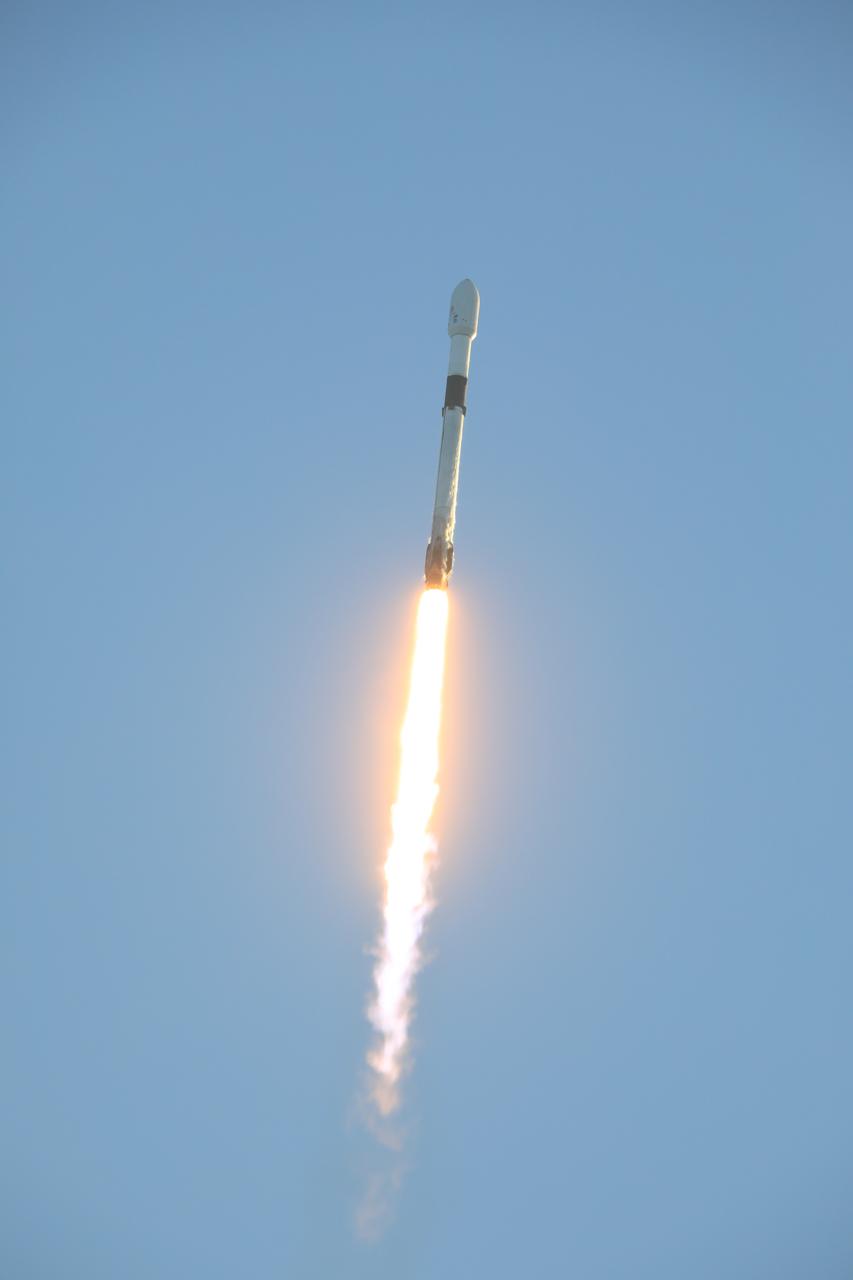

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
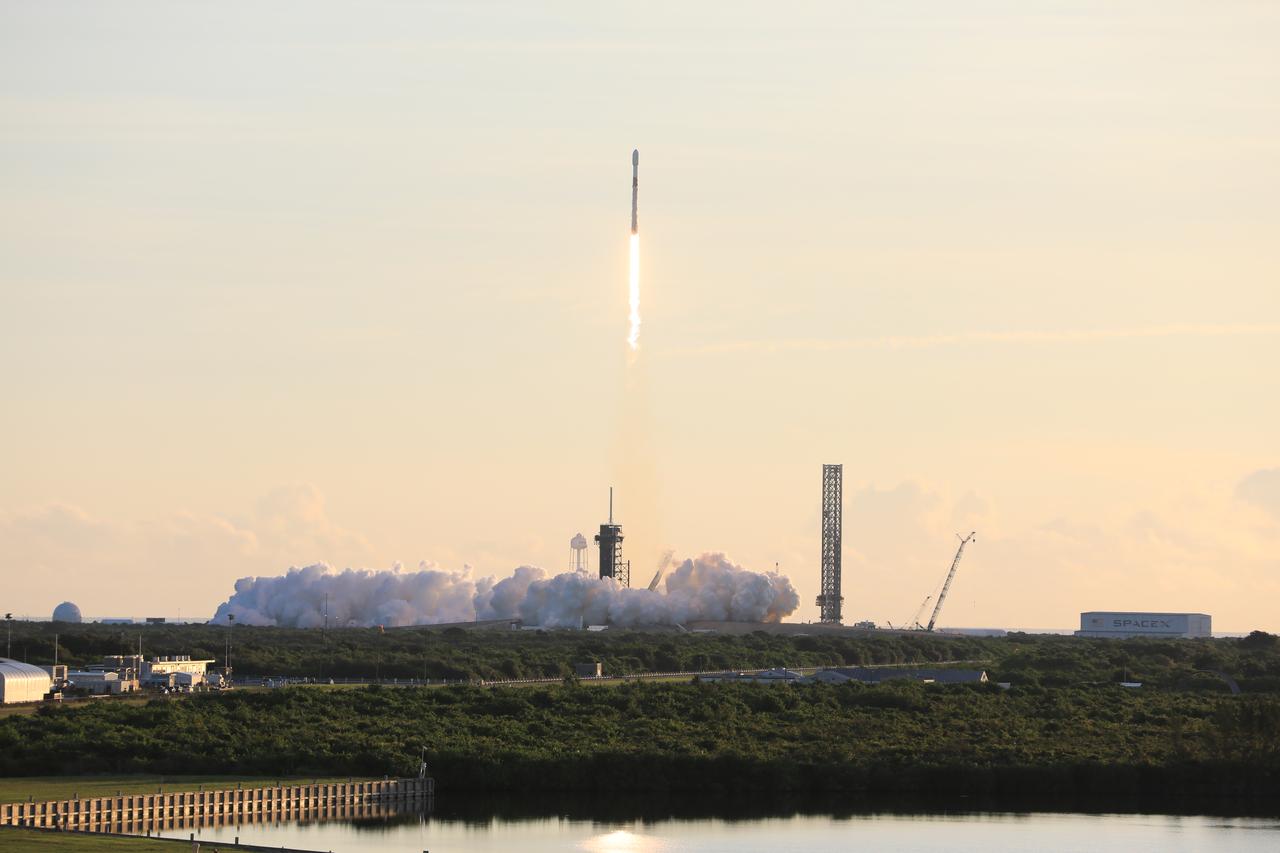

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
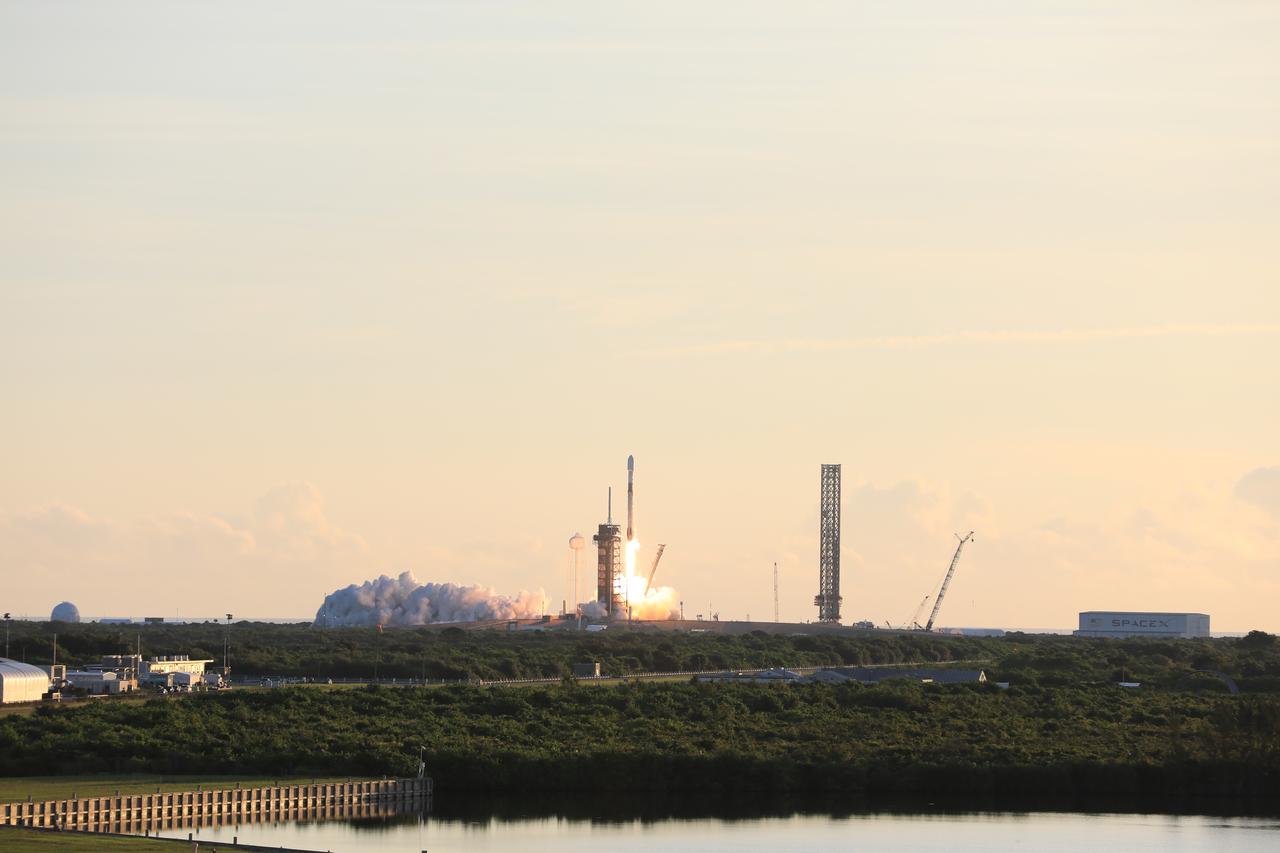

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
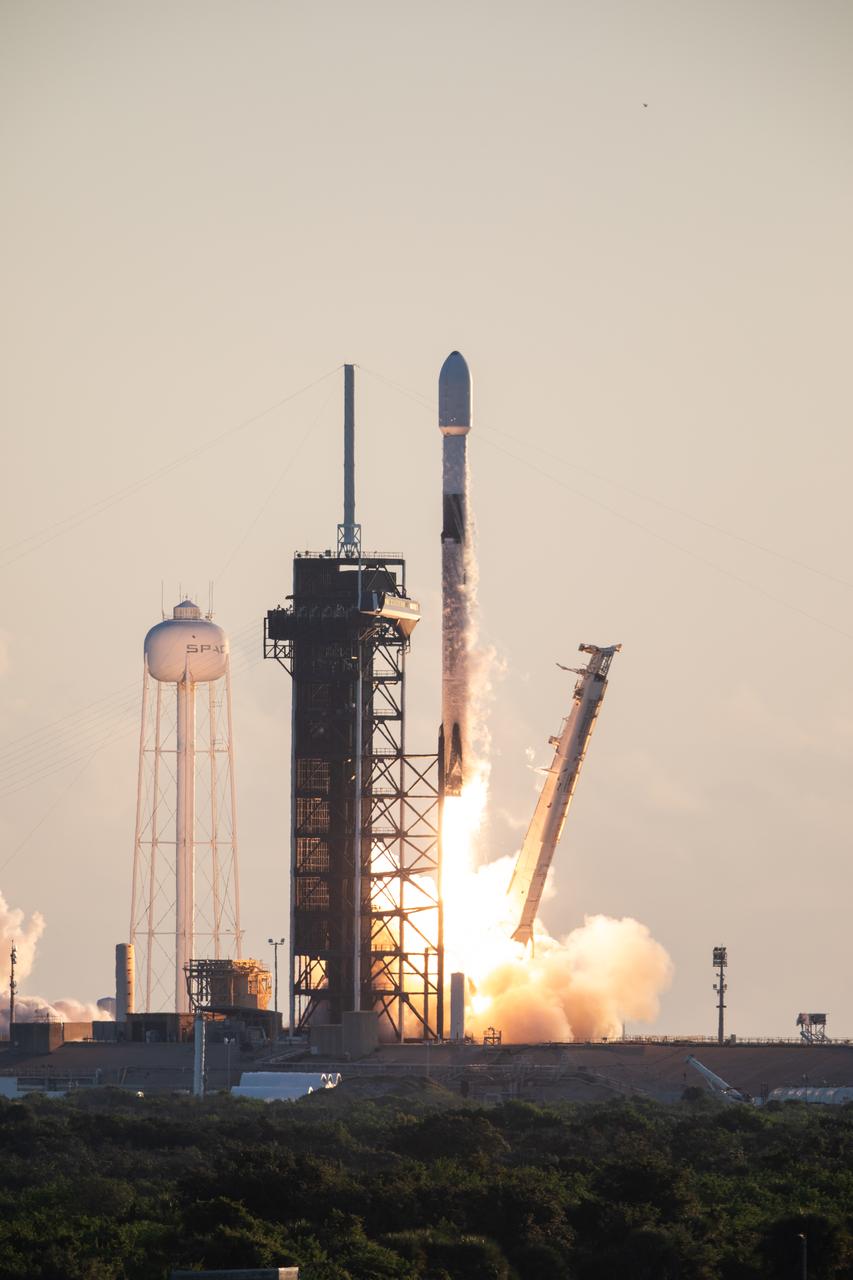

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.

One of two rideshare spacecraft on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory sits on a spacecraft dolly in a high bay inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. The missions, along with NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where SWFO-L1 will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity.

One of two rideshare spacecraft on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory sits on a spacecraft dolly in a high bay inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. The missions, along with NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where SWFO-L1 will monitor the Sun and near-Earth environment using a suite of instruments that provide real-time measurements of solar activity.
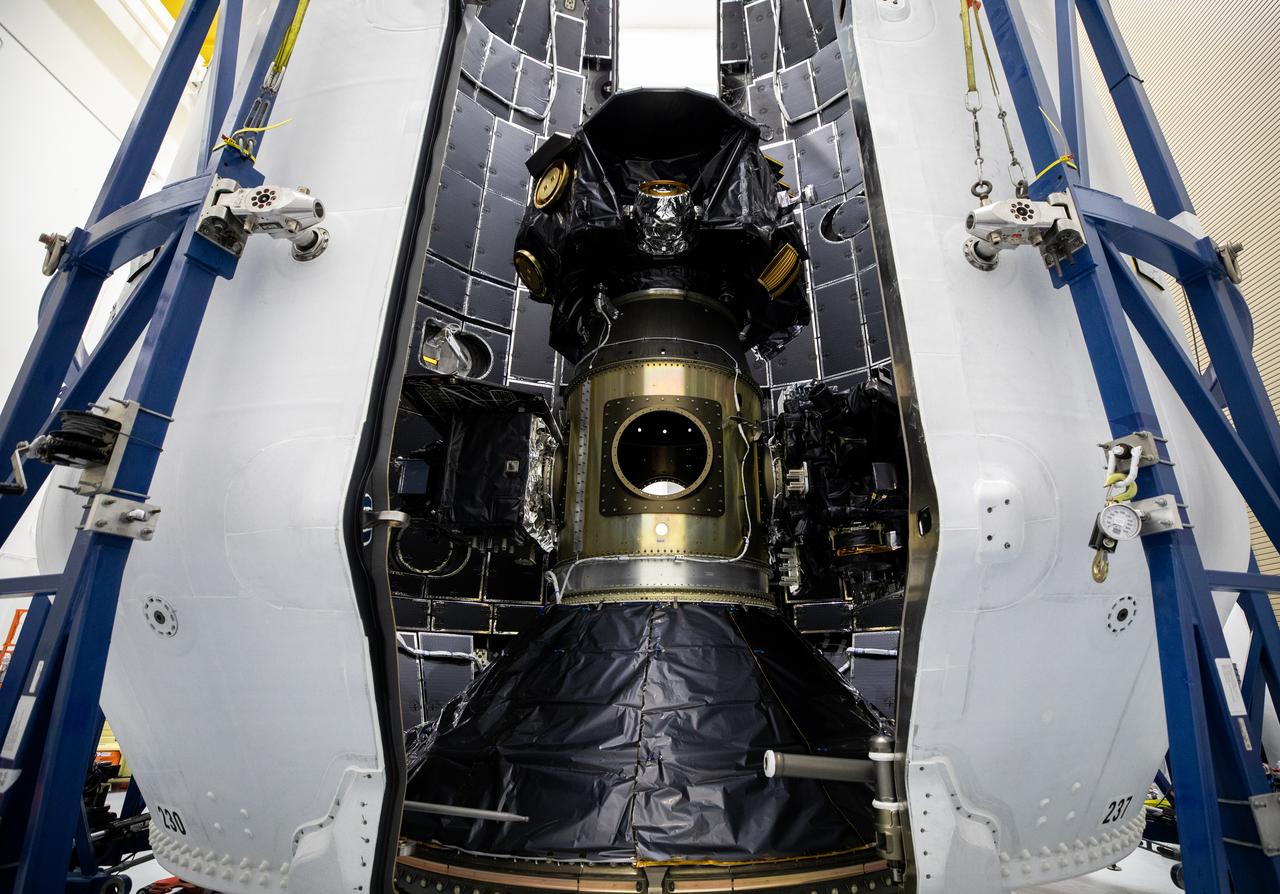

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system. Liftoff of the missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
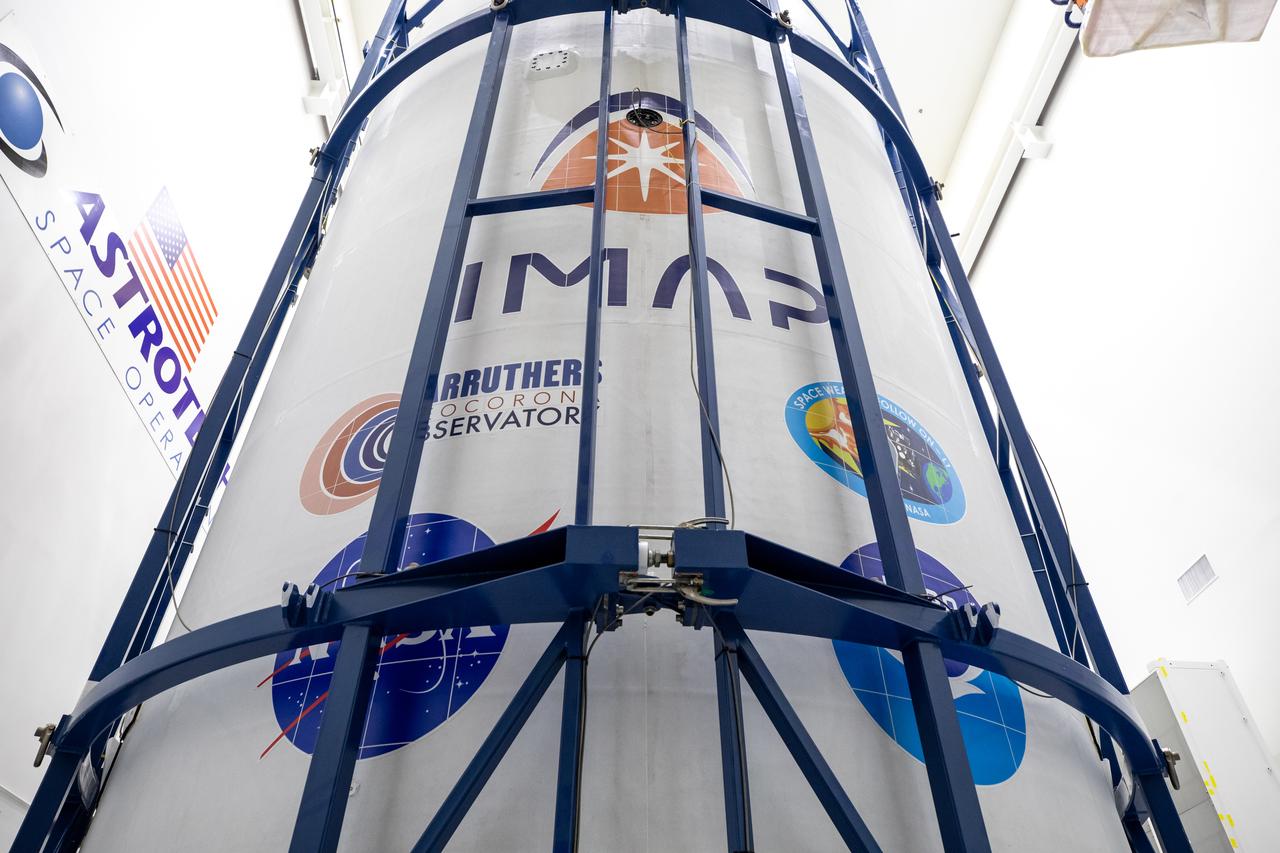

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system. Liftoff of the missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
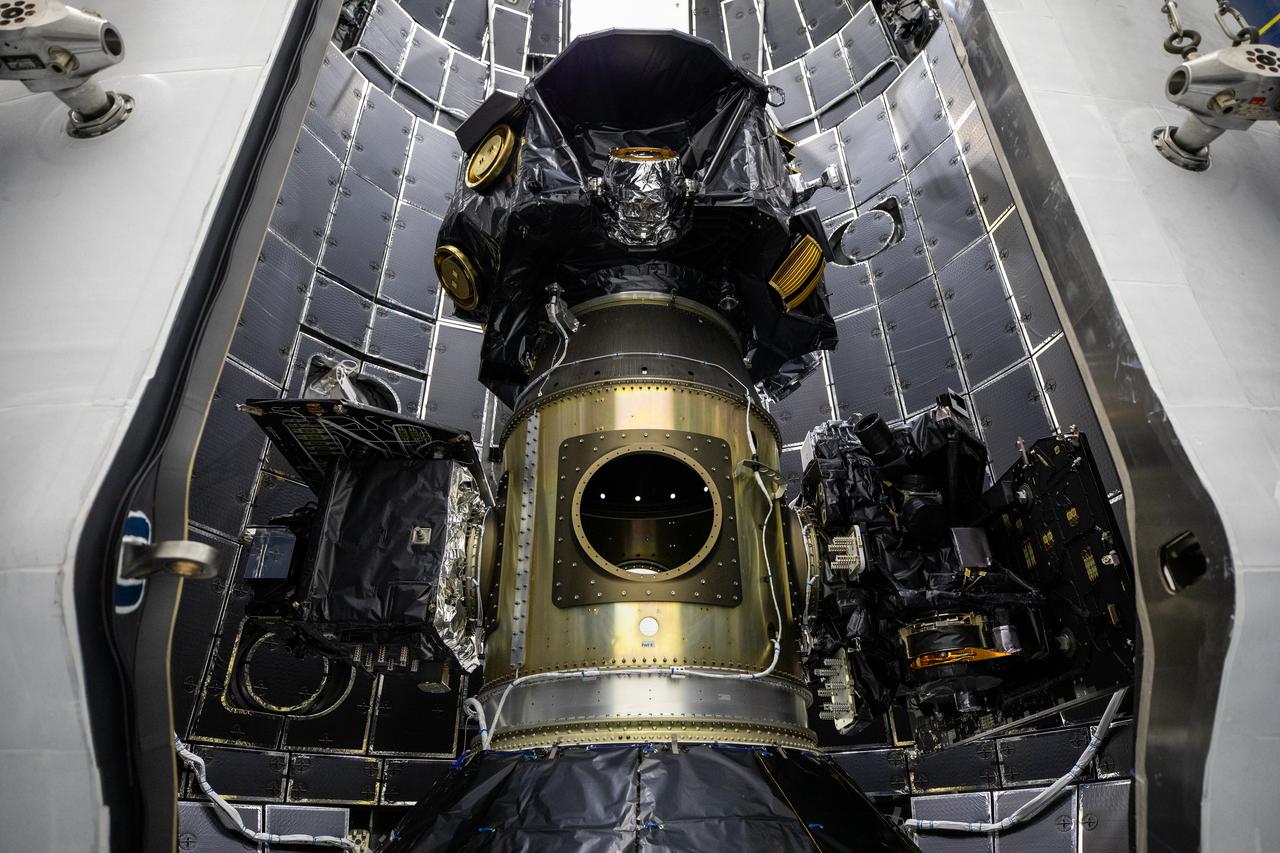

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system. Liftoff of the missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
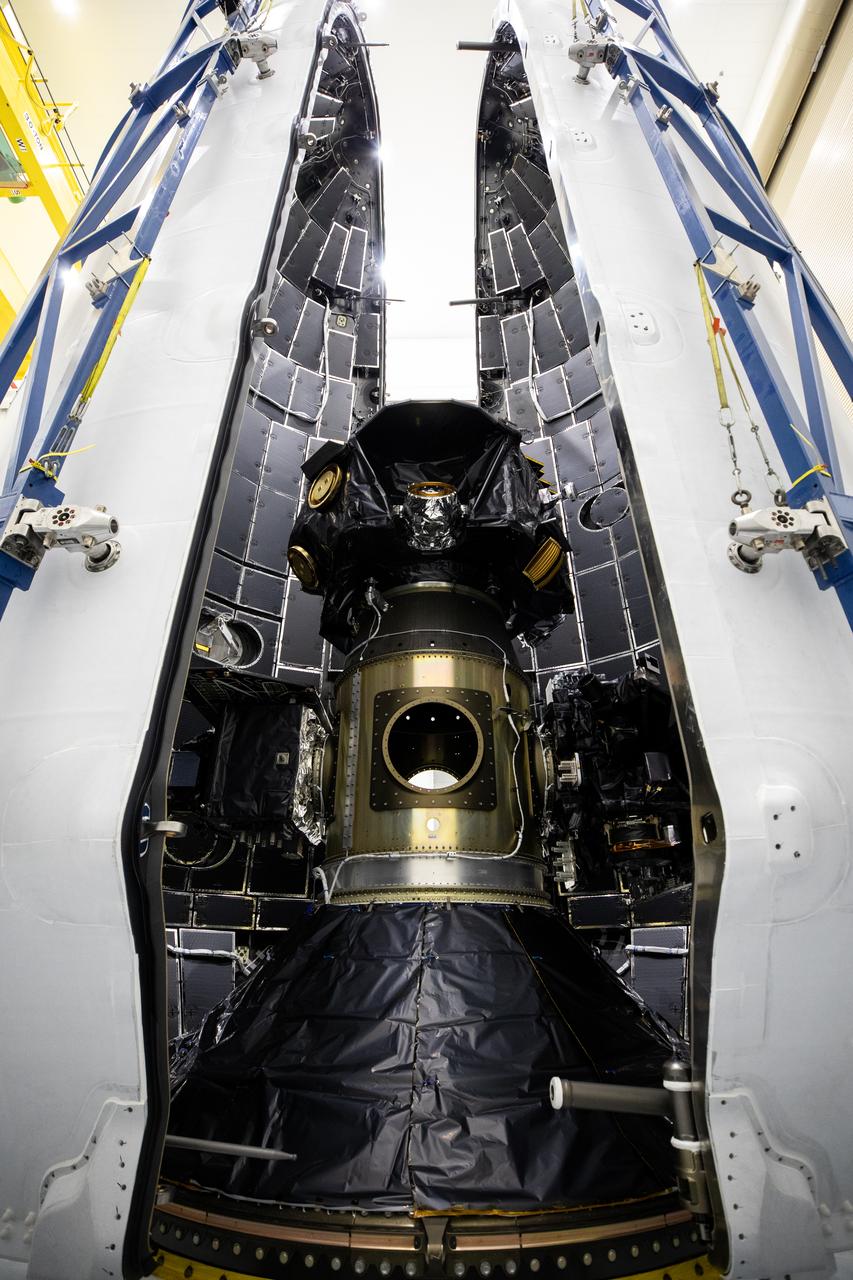

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), along with the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside a SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system. Liftoff of the missions on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
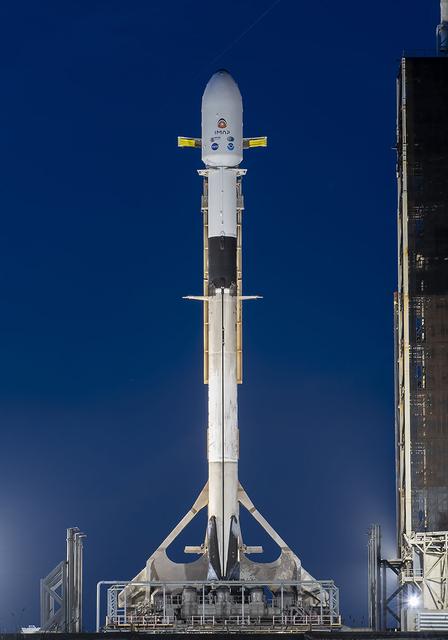

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A during early morning on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A during early morning on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
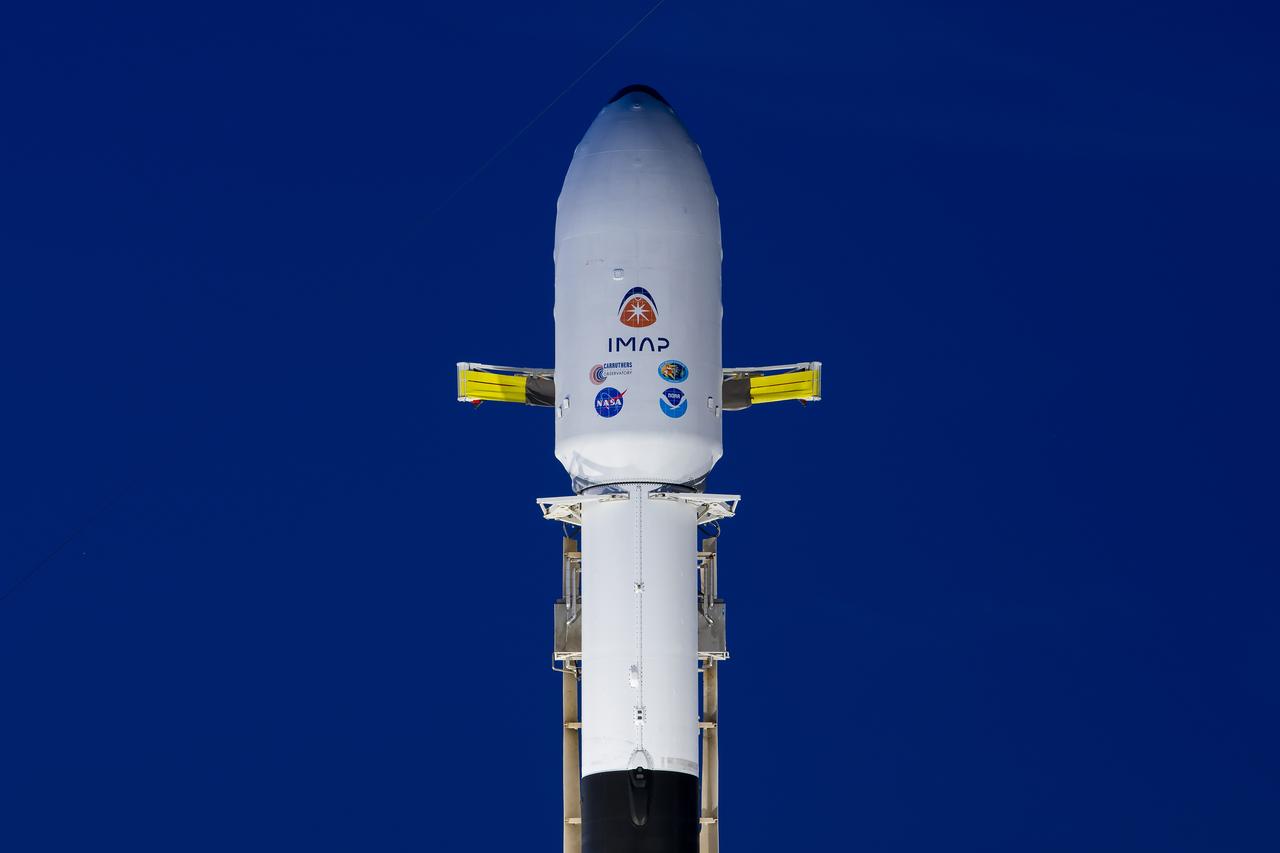

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A during early morning on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
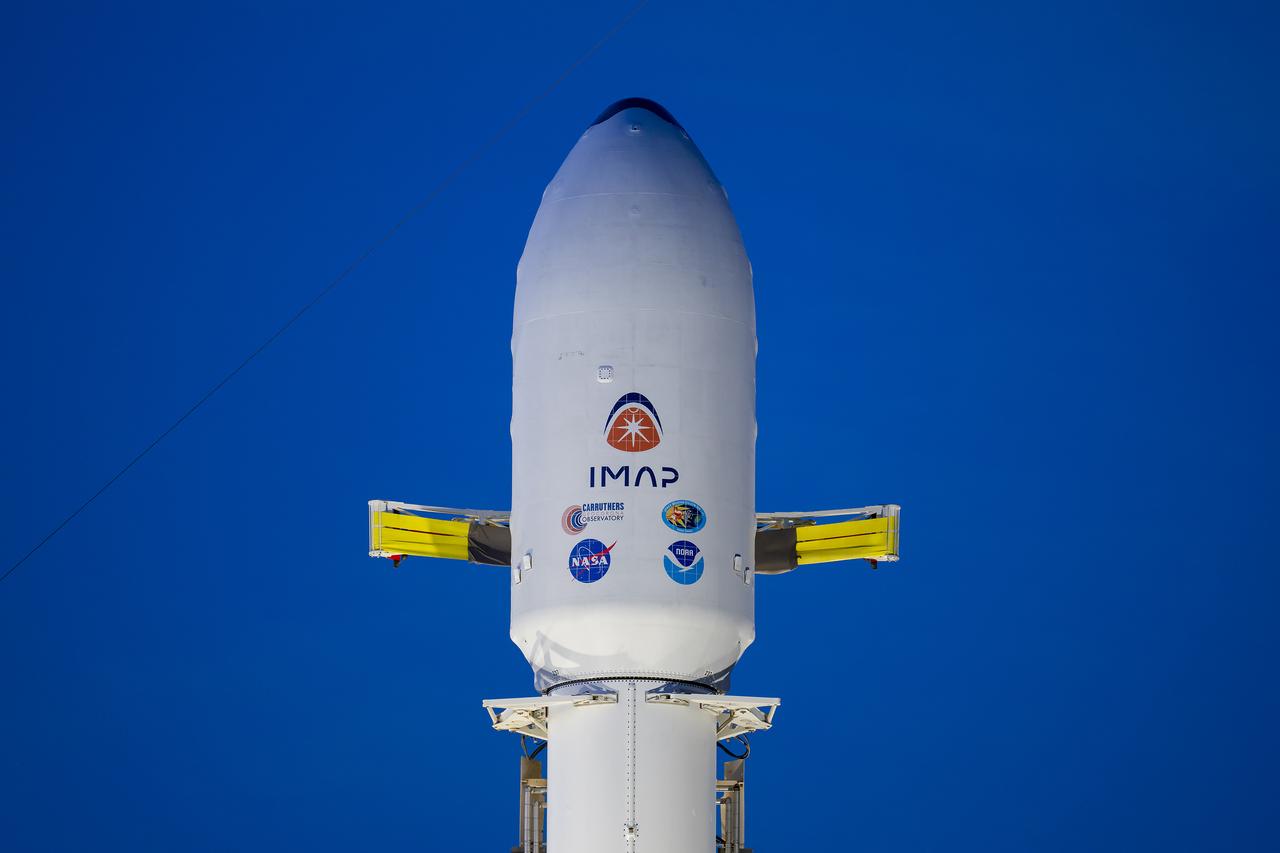

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A during early morning on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
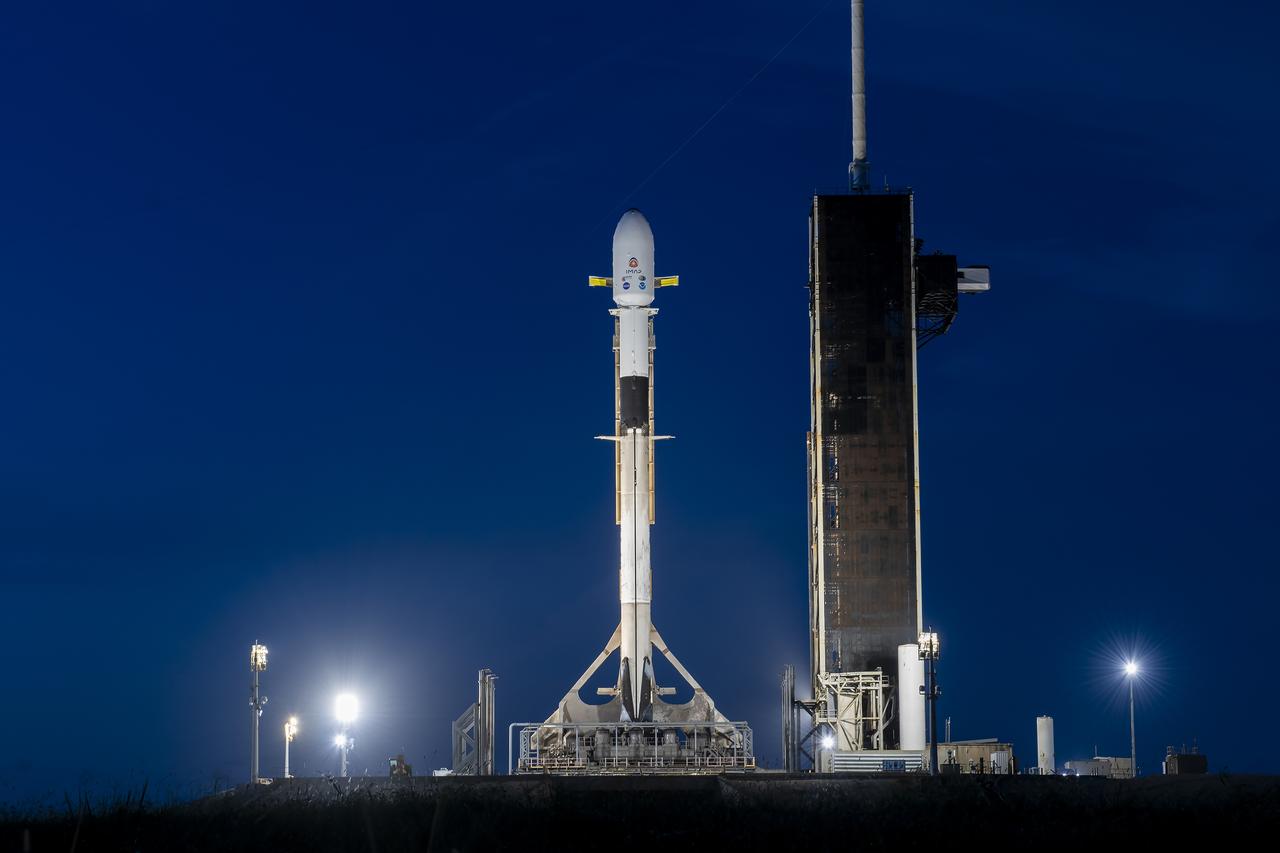

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A during early morning on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
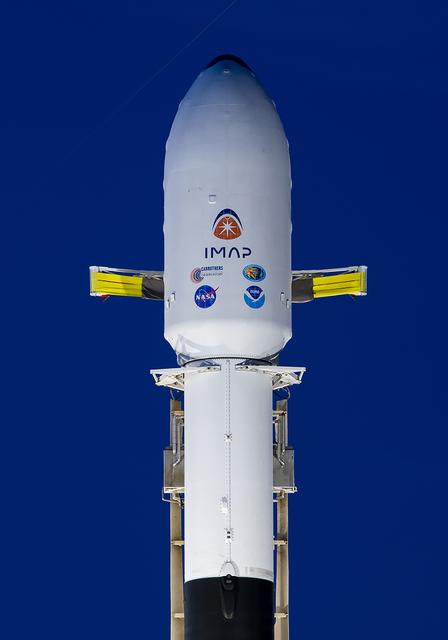

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A during early morning on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.
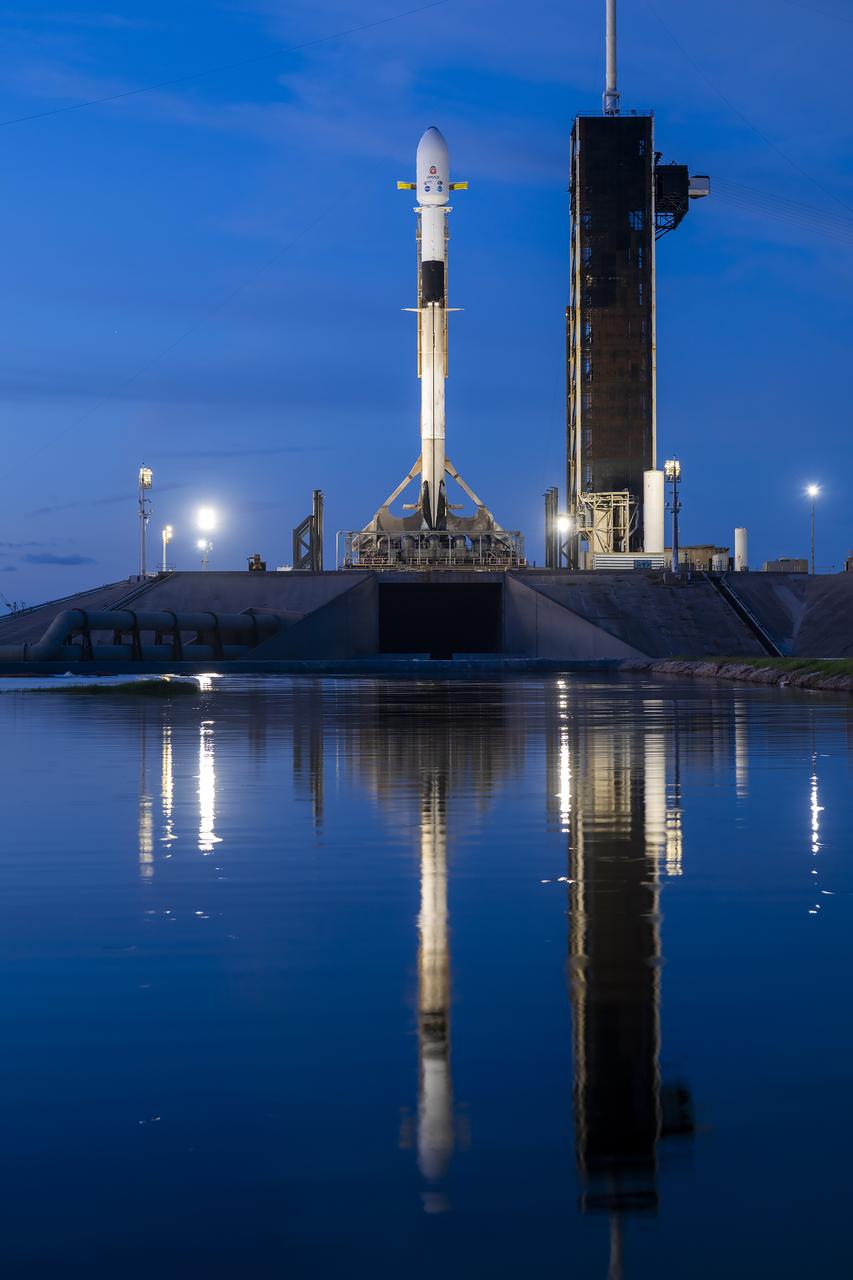

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft atop stands vertical at Launch Complex 39A as the sun rises on Monday, Sept. 22, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. NASA’s IMAP will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings to protect the spacecraft during launch. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. This mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where it will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Tuesday, Sept. 23, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
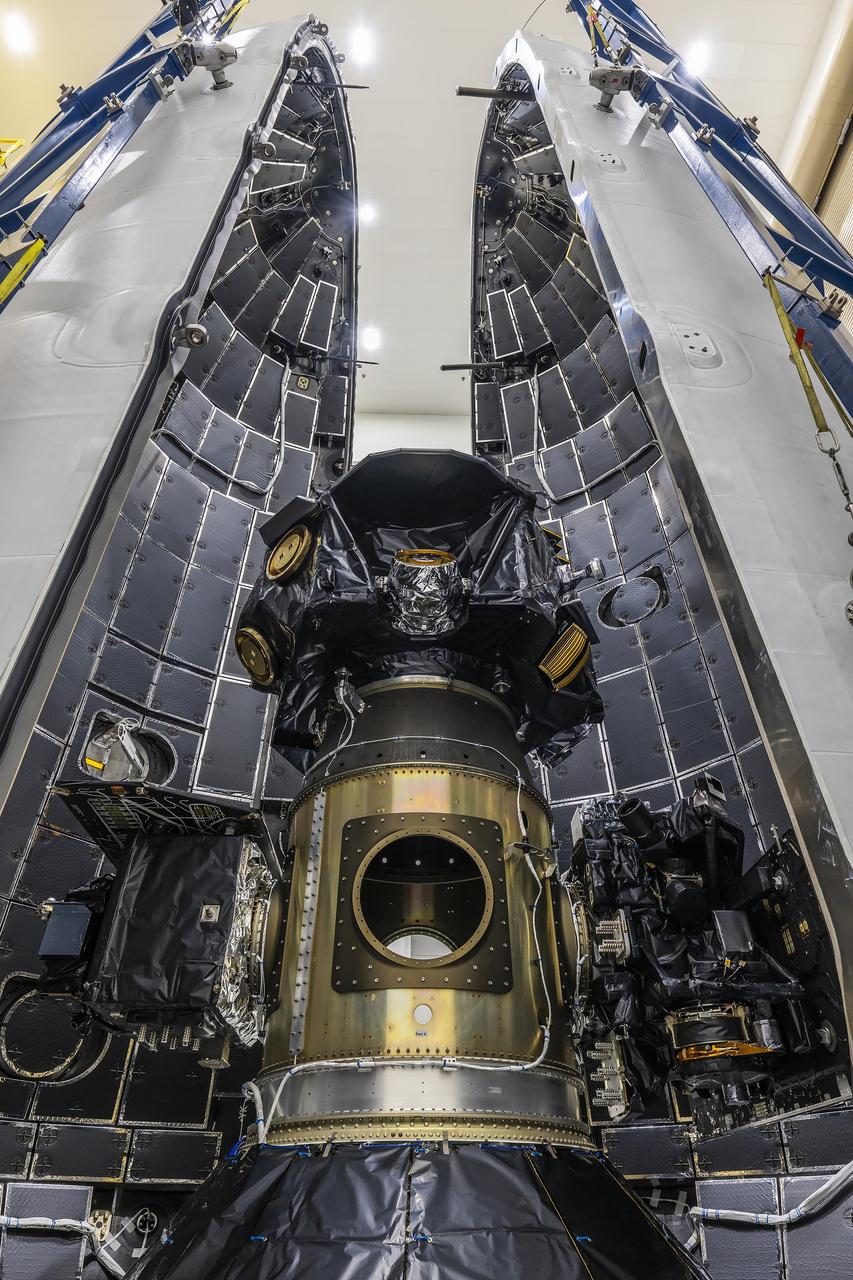

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings to protect the spacecraft during launch. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. This mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where it will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Tuesday, Sept. 23, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
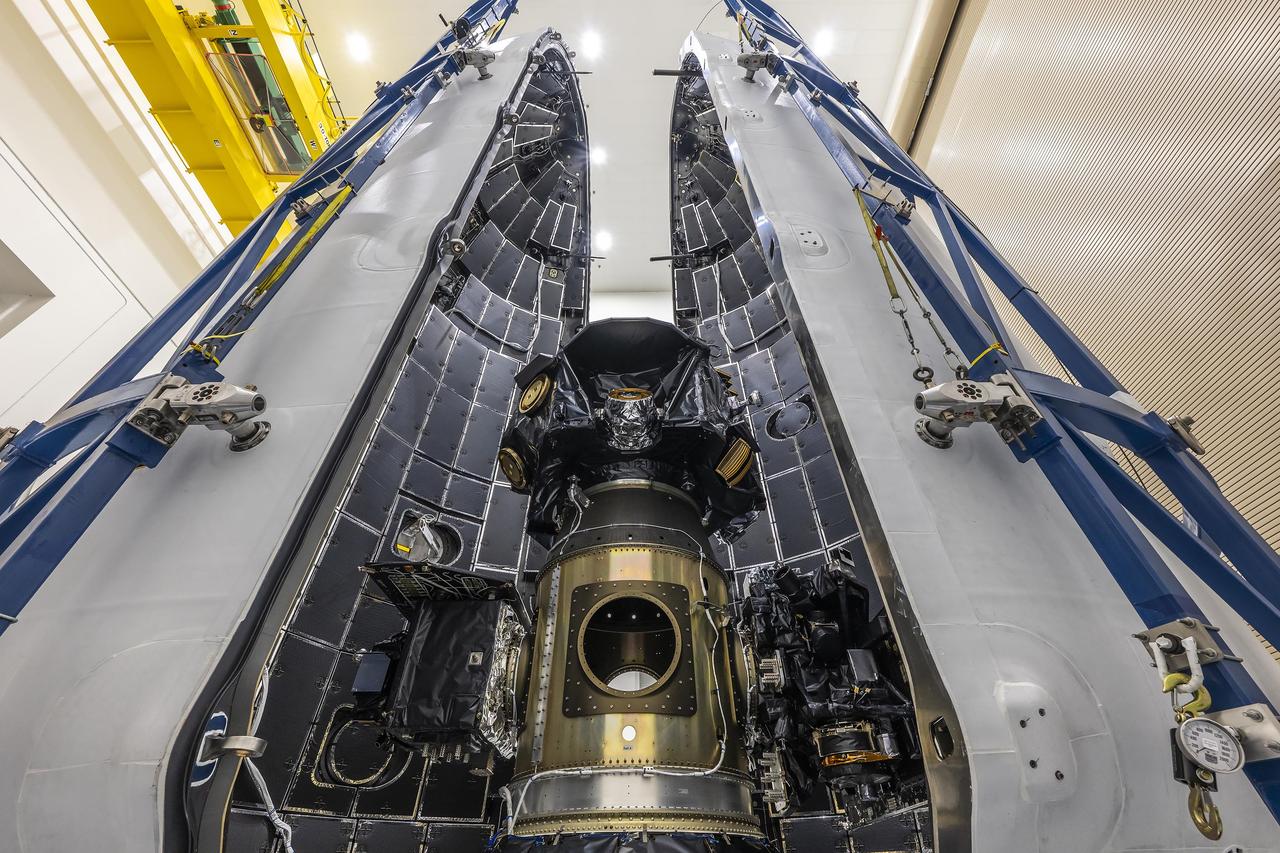

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings to protect the spacecraft during launch. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. This mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where it will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Tuesday, Sept. 23, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
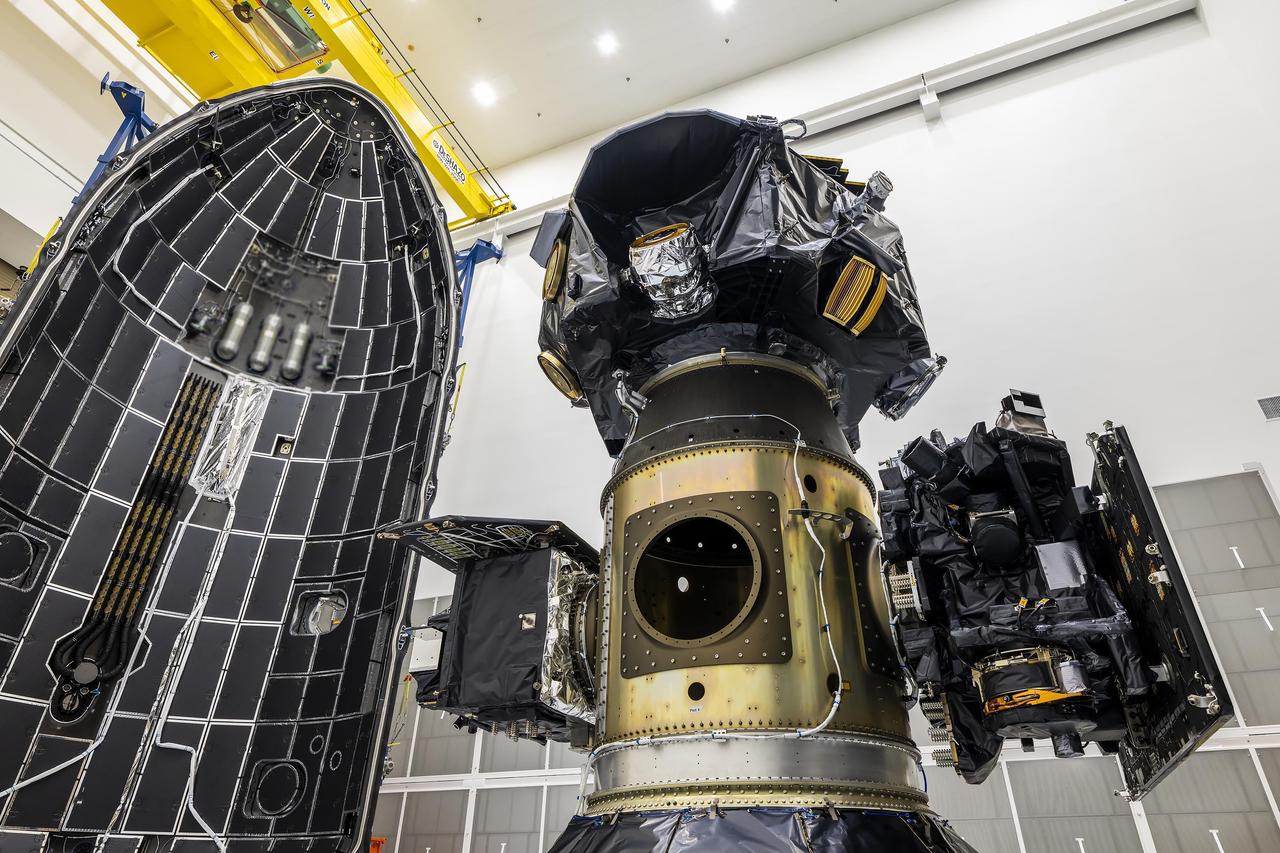

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings to protect the spacecraft during launch. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. This mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where it will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Tuesday, Sept. 23, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.
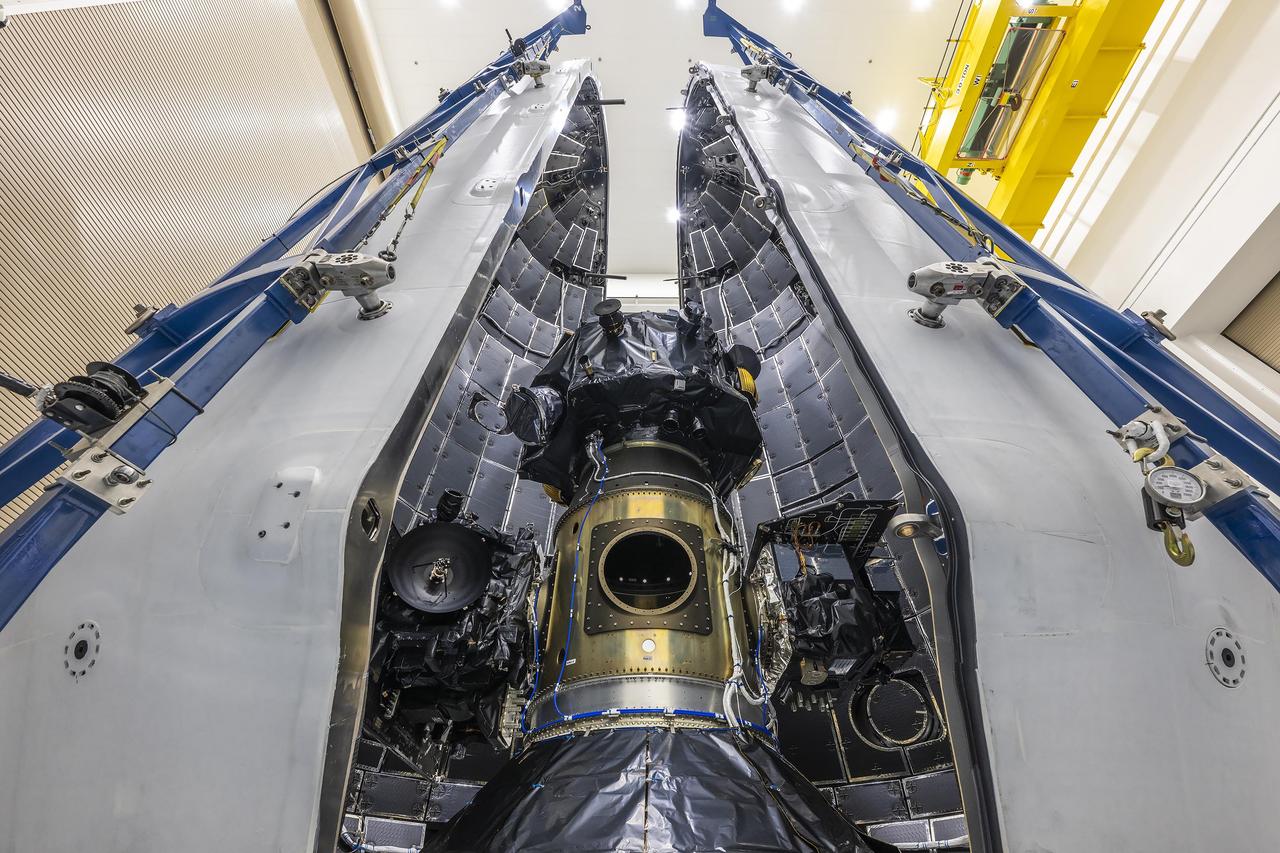

Technicians at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida encapsulate NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, inside SpaceX’s Falcon 9 payload fairings to protect the spacecraft during launch. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. This mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where it will scan the heliosphere, analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system. Launch is targeted for no earlier than Tuesday, Sept. 23, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.

The two rideshare spacecraft on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – sit on spacecraft dollies in a high bay inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. The missions will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth.
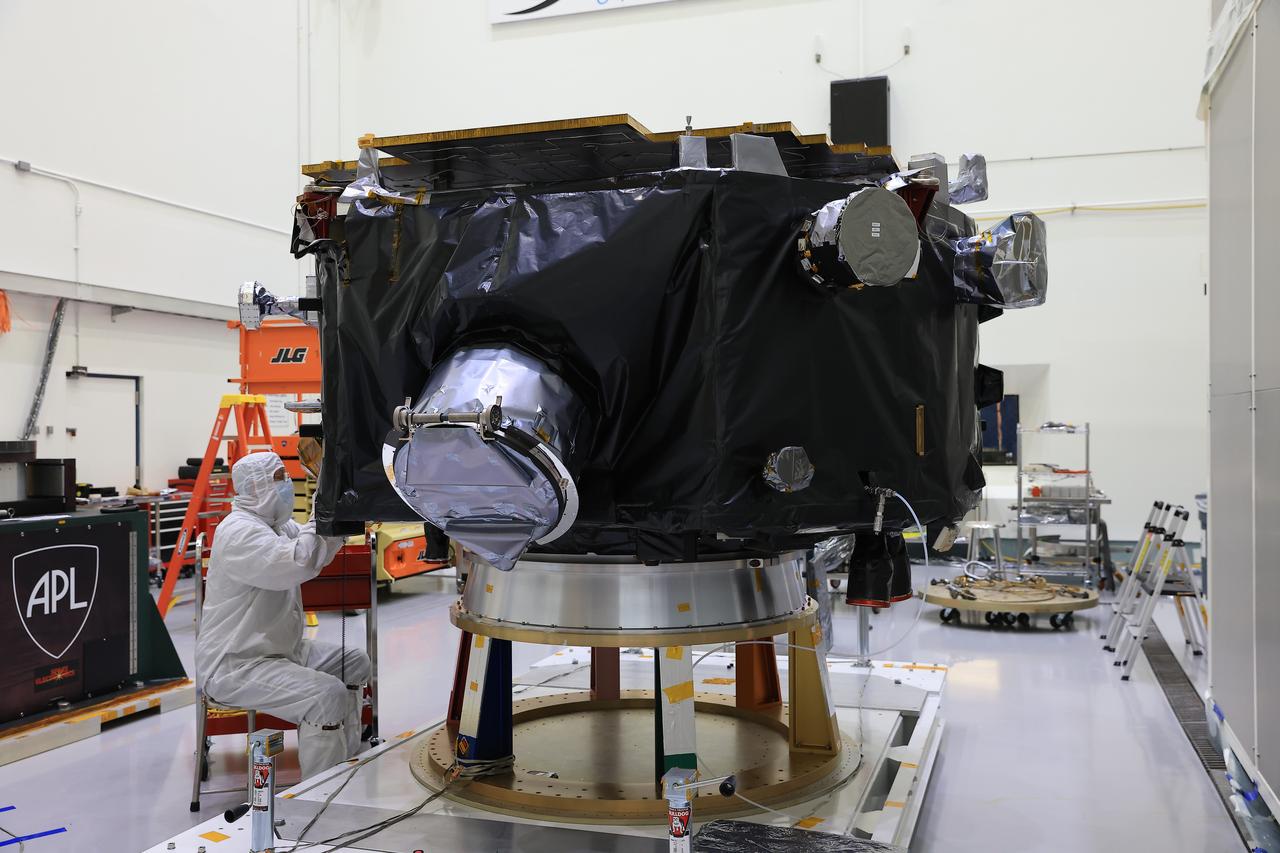

Technicians inspect NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on a spacecraft dolly inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. IMAP and its two rideshares – NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where IMAP will scan the heliosphere, a huge bubble created by the Sun’s wind that encapsulates our entire solar system, and analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.

One of two rideshare spacecraft on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission, NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory sits on a spacecraft dolly in a high bay inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. The missions, along with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory, will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere.

Technicians inspect NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on a spacecraft dolly inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. IMAP and its two rideshares – NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where IMAP will scan the heliosphere, a huge bubble created by the Sun’s wind that encapsulates our entire solar system, and analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.

Technicians inspect NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on a spacecraft dolly inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. IMAP and its two rideshares – NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where IMAP will scan the heliosphere, a huge bubble created by the Sun’s wind that encapsulates our entire solar system, and analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.

Technicians inspect NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) spacecraft on a spacecraft dolly inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. IMAP and its two rideshares – NASA’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth, where IMAP will scan the heliosphere, a huge bubble created by the Sun’s wind that encapsulates our entire solar system, and analyze the composition of charged particles, and investigate how those particles move through the solar system.

One of two rideshare spacecraft on NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission, NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory sits on a spacecraft dolly in a high bay inside Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a NASA-hosted media day on Thursday, Aug. 28, 2025. The missions, along with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory, will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Carruthers will use its ultraviolet cameras to monitor how space weather from the Sun impacts the exosphere, the outermost part of Earth’s atmosphere.

Arlena Moses, launch weather officer, 45th Weather Squadron, U.S. Space Force, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for NASA's IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. This mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeting 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.

Dr. Denton Gibson, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program, participates in a prelaunch news conference on Sunday, Sept. 21, 2025, at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida for NASA's IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe) mission. NASA’s IMAP will use 10 science instruments to study and map the heliosphere, a vast magnetic bubble surrounding the Sun protecting our solar system from radiation incoming from interstellar space. This mission and its two rideshares – NASA’s exosphere-studying Carruthers Geocorona Observatory and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) observatory – will orbit the Sun near Lagrange point 1, about one million miles from Earth. Launch is targeting 7:32 a.m. EDT, Tuesday, Sept. 23, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA Kennedy.