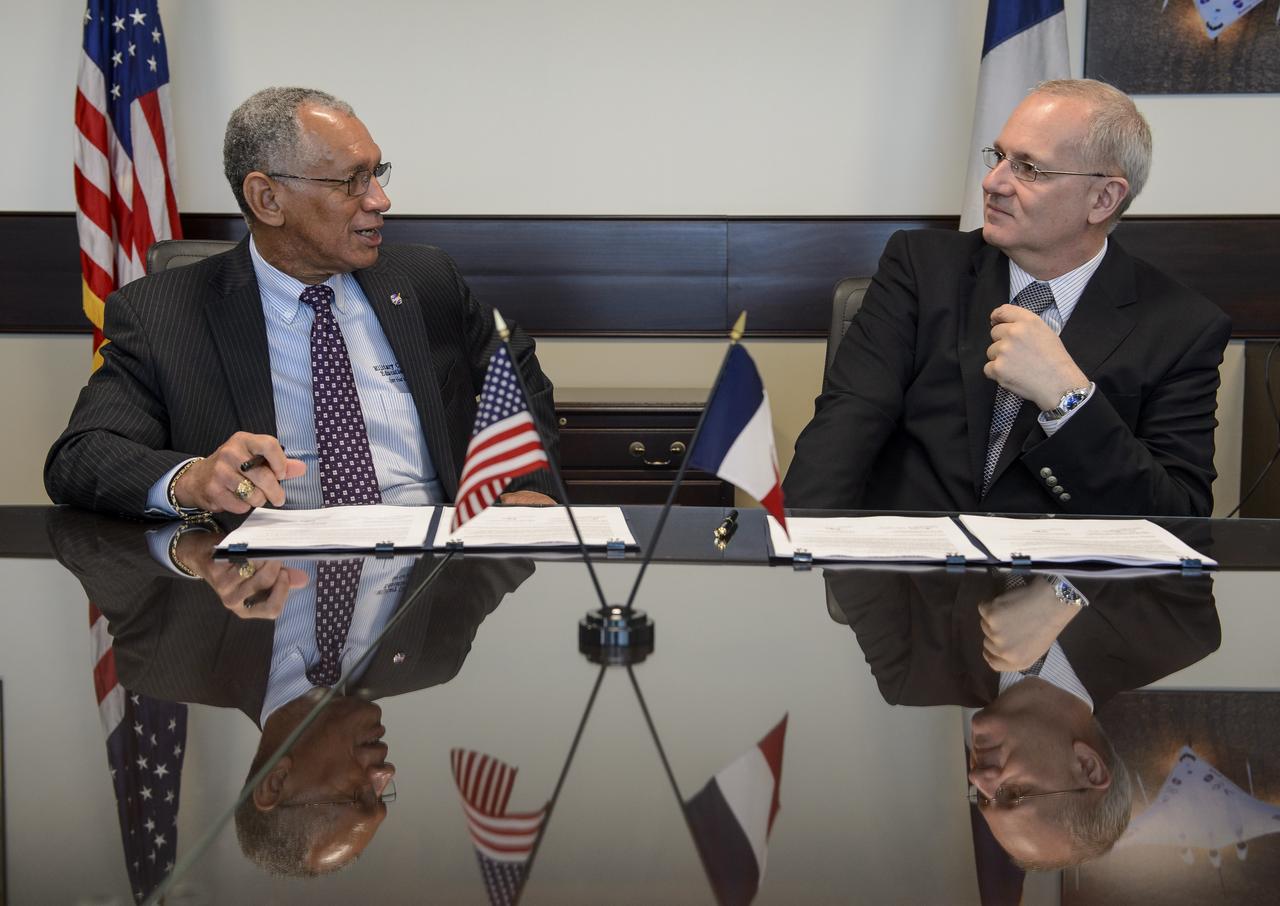

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES) President Jean-Yves Le Gall talk after signing an agreement to move from feasibility studies to implementation of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission, Friday, May 2, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The SWOT mission will use wide swath altimetry technology to produce high-resolution elevation measurements of the surface of lakes, reservoirs, and wetlands and of the ocean surface. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
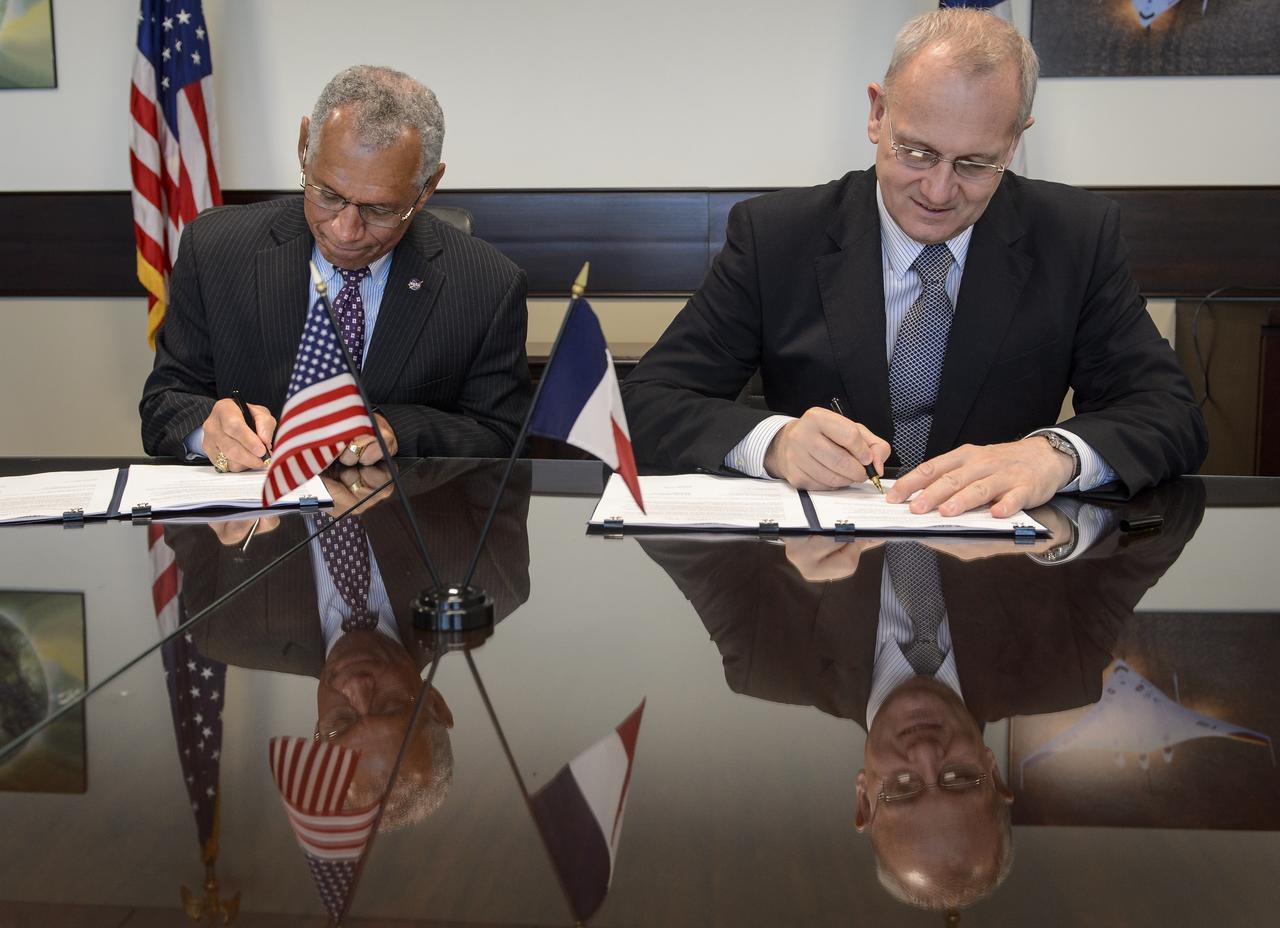

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, and Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES) President Jean-Yves Le Gall sign an agreement to move from feasibility studies to implementation of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission, Friday, May 2, 2014 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The SWOT mission will use wide swath altimetry technology to produce high-resolution elevation measurements of the surface of lakes, reservoirs, and wetlands and of the ocean surface. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
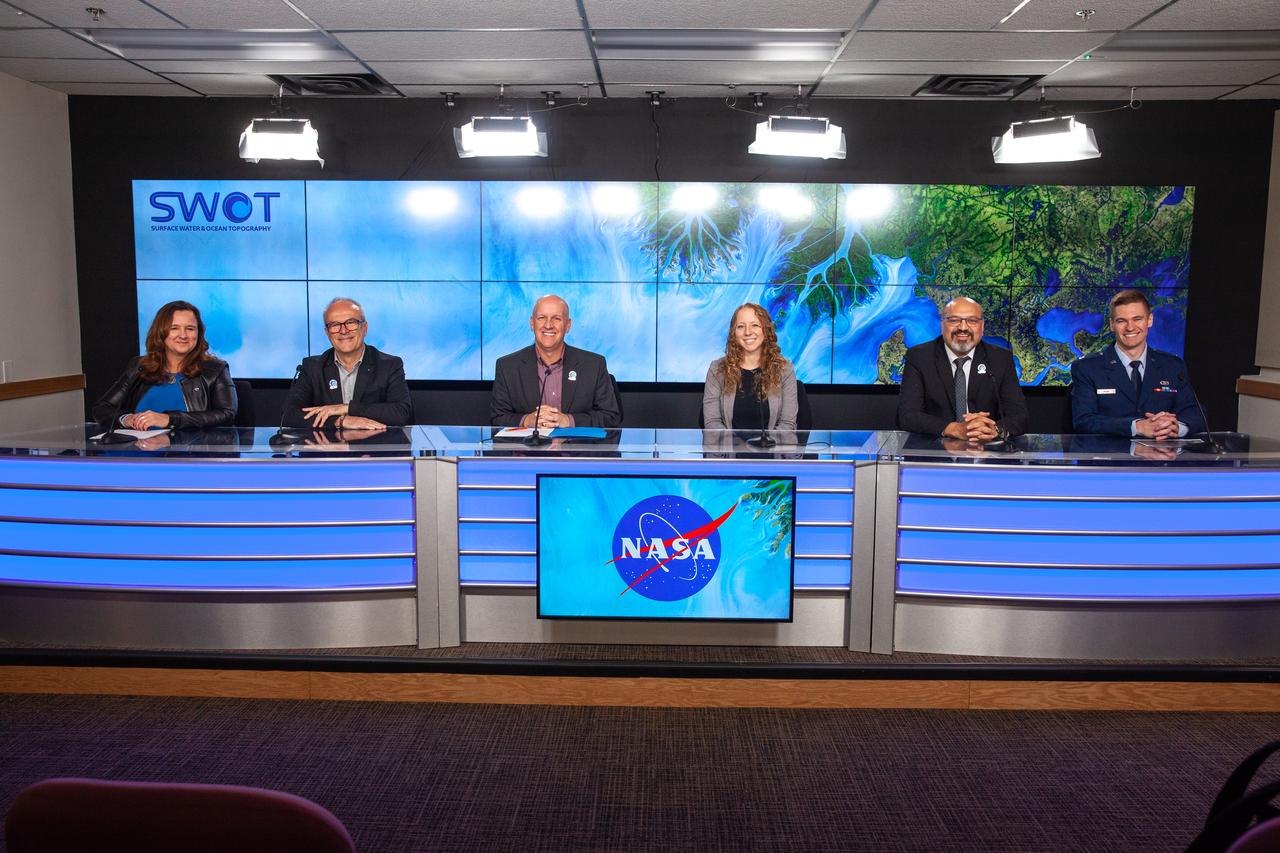

NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) hold a prelaunch news conference for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Participating from left are Karen St. Germain, Earth Science Division director, NASA; Thierry Lafon, SWOT project manager, CNES; Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program; Julianna Scheiman, civil satellite missions director, SpaceX; Parag Vaze, SWOT project manager, Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Capt. Max Rush, launch weather officer, U.S. Air Force. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
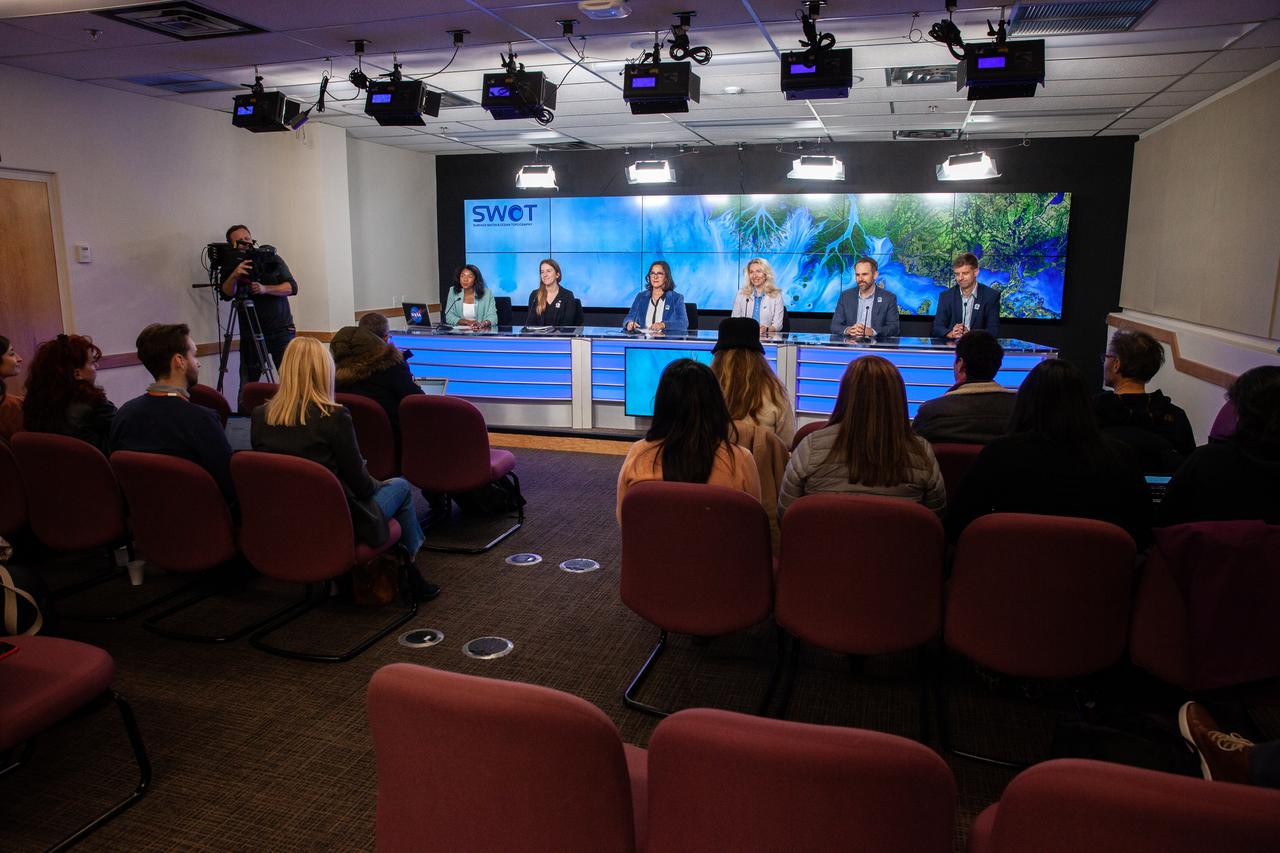

NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) hold a science briefing on the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 13, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Participating from left are Katherine Calvin, chief scientist and senior climate advisor, NASA; Selma Cherchali, Earth observation program head, CNES; Nadya Vinogradova Shiffer, SWOT program scientist, NASA; Tamlin Pavelsky, SWOT hydrology science lead, University of North Carolina; Benjamin Hamlington, research scientist, Sea Level and Ice Group, Jet Propulsion Laboratory. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
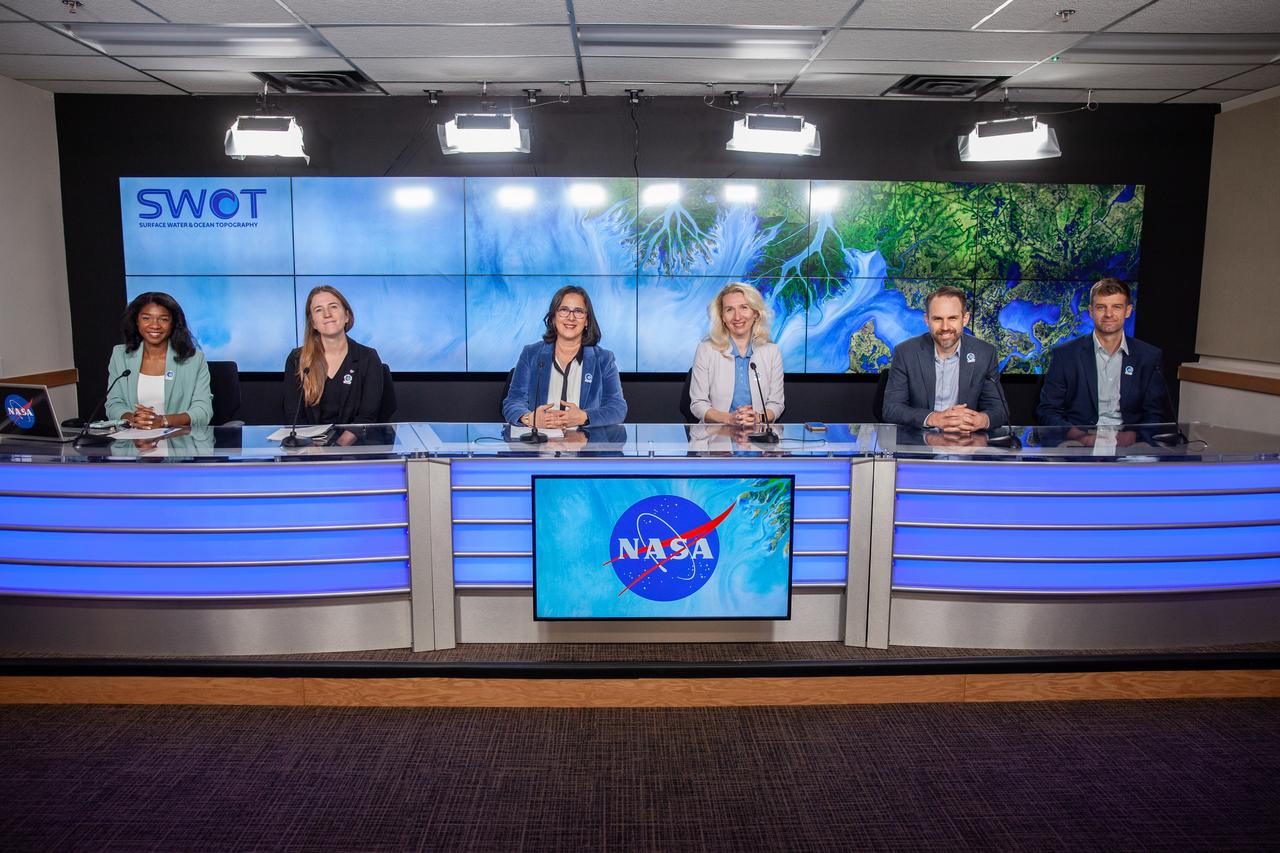

NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) hold a science briefing on the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 13, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Participating from left are Katherine Calvin, chief scientist and senior climate advisor, NASA; Selma Cherchali, Earth observation program head, CNES; Nadya Vinogradova Shiffer, SWOT program scientist, NASA; Tamlin Pavelsky, SWOT hydrology science lead, University of North Carolina; Benjamin Hamlington, research scientist, Sea Level and Ice Group, Jet Propulsion Laboratory. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

Jasmine Hopkins, NASA Communications, moderates a science briefing held by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 13, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
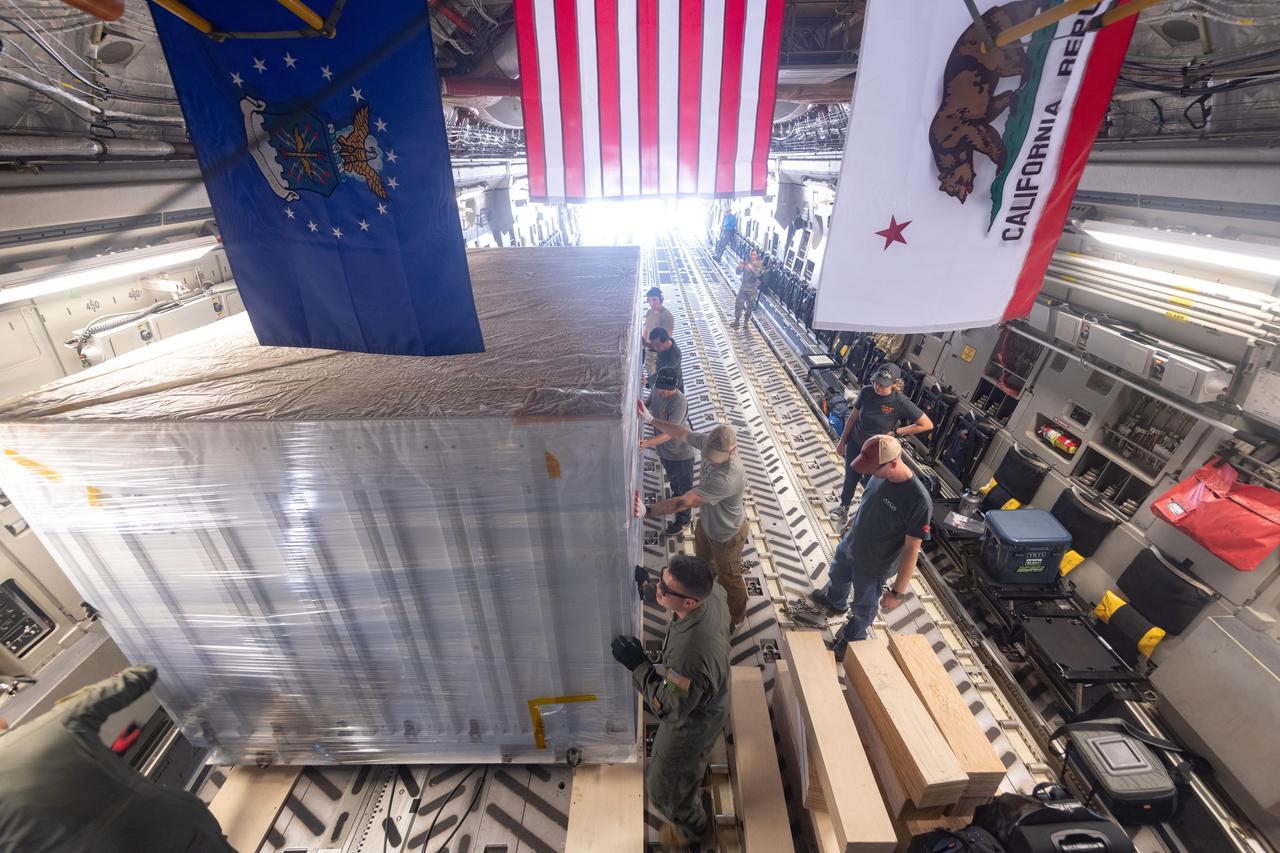

On June 27, 2021, teams from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and the March Air Reserve Base in Riverside County, California, loaded the scientific heart of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission into a C-17 airplane. The hardware – which includes research instruments – was headed to a clean room facility near Cannes, France, where engineers and technicians completed assembly of the satellite over the next year. The satellite was subsequently shipped back to California for its December 2022 launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base. SWOT will make global surveys of the water on Earth's surface. By measuring its height, researchers can track the volume and location of the finite resource around the world. The data will help with monitoring changes in floodplains and wetlands, measure how much fresh water flows into and out of lakes and rivers and back to the ocean, and track regional shifts in sea level. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25624
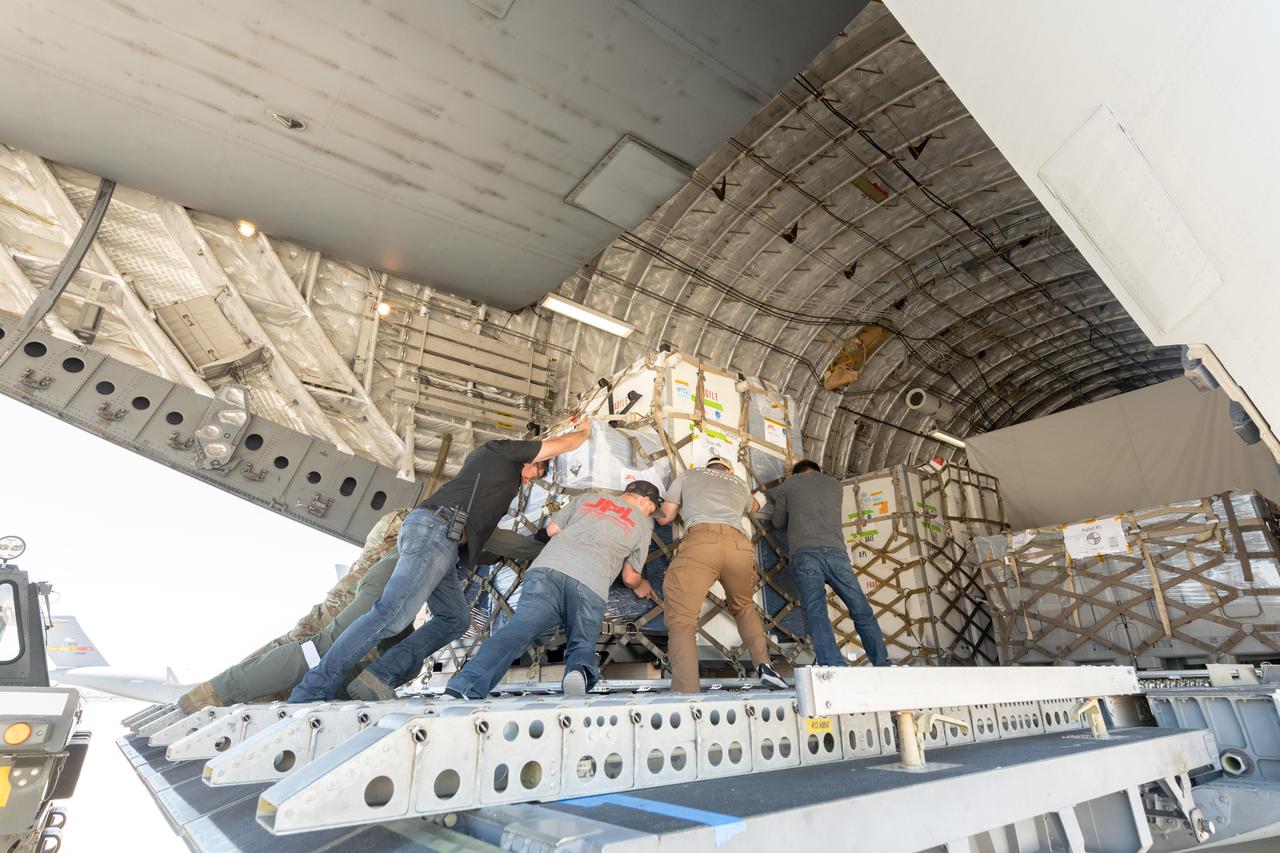

On June 27, 2021, teams from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and the March Air Reserve Base in Riverside County, California, loaded the scientific heart of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission into a C-17 airplane. The hardware – which includes research instruments – was headed to a clean room facility near Cannes, France, where engineers and technicians completed assembly of the satellite over the next year. The satellite was subsequently shipped back to California for its December 2022 launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base. SWOT will make global surveys of the water on Earth's surface. By measuring its height, researchers can track the volume and location of the finite resource around the world. The data will help with monitoring changes in floodplains and wetlands, measure how much fresh water flows into and out of lakes and rivers and back to the ocean, and track regional shifts in sea level. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25625

The mighty Yukon River and nearby lakes appear in red in this image produced using data recorded on June 18, 2023, by the international Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite as it passed over Alaska. The satellite measures the height of nearly all the water on Earth's surface, providing one of the most detailed, comprehensive views yet of the planet's ocean and fresh water. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and the French space agency, CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales). SWOT will address some of the most pressing climate change questions of our time, offering insights into areas including how a warming world is accelerating Earth's water cycle, leading to more volatile precipitation patterns. SWOT will also help researchers better understand how climate change affects water storage in lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, and how communities can better manage water resources and prepare for floods and other disasters. SWOT passed over the Yukon River and recorded this data during a period called calibration and validation, when the mission confirms the accuracy of its data. Calibration involved ensuring SWOT's software and hardware – including its main scientific instrument, the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) and its antenna – operate as designed. During validation activities, dozens of research teams headed into the field to measure water levels and the slope of rivers, including the Yukon. Mission scientists then compared field measurements to the data taken by the satellite to ensure SWOT's accuracy. In mid-June, the team of freshwater researchers tasked with gathering data on the Yukon drifted down the waterway around midnight – the same time as SWOT passed overhead, collecting its own data on the river. Launched on Dec. 16, 2022, from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT is now in its operations phase, collecting data that will be used for research and other purposes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25780
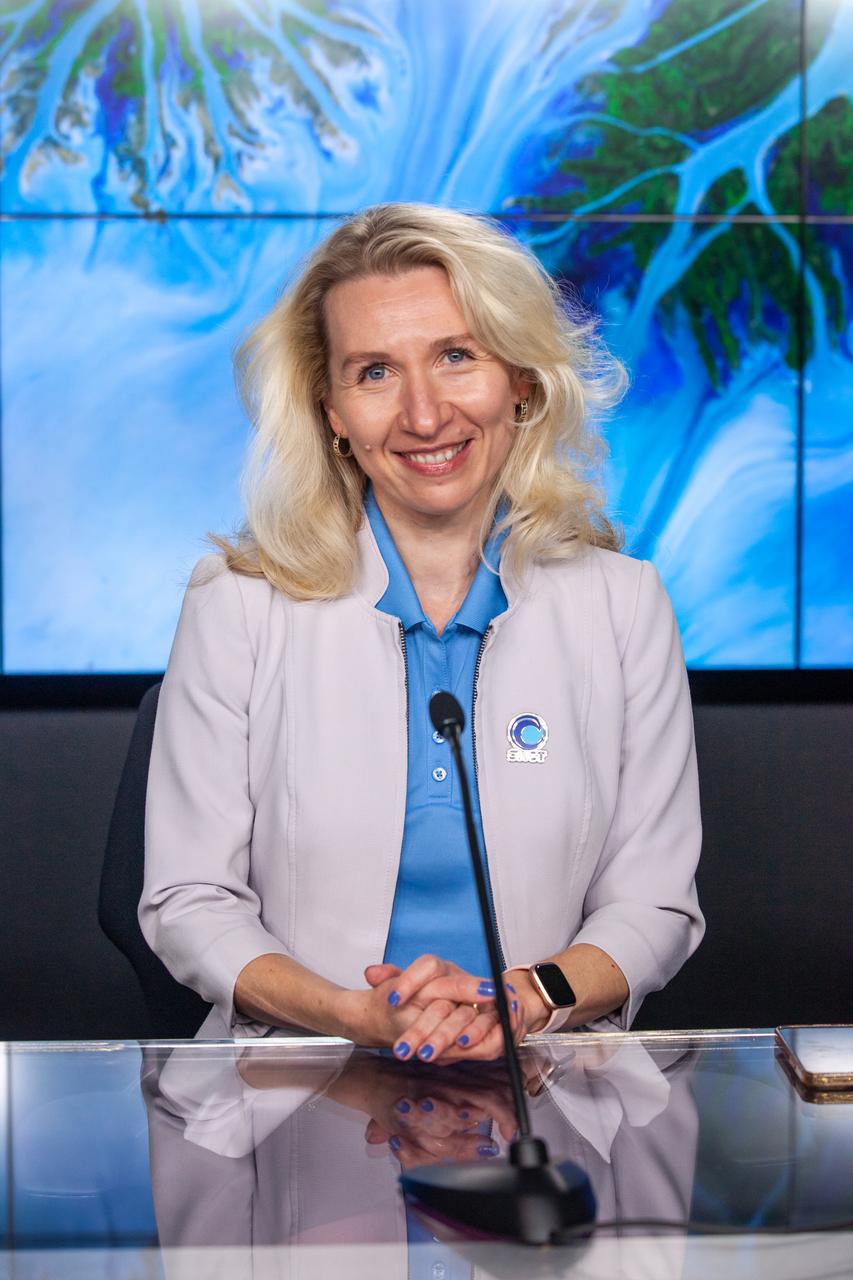

Nadya Vinogradova Shiffer, SWOT program scientist, NASA, participates in a science briefing held by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 13, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

Parag Vaze, SWOT project manager, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, participates in a prelaunch news conference held by NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

Tamlin Pavelsky, SWOT hydrology science lead, University of North Carolina, participates in a science briefing held by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 13, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

Thierry Lafon, SWOT project manager, CNES, participates in a prelaunch news conference held by NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
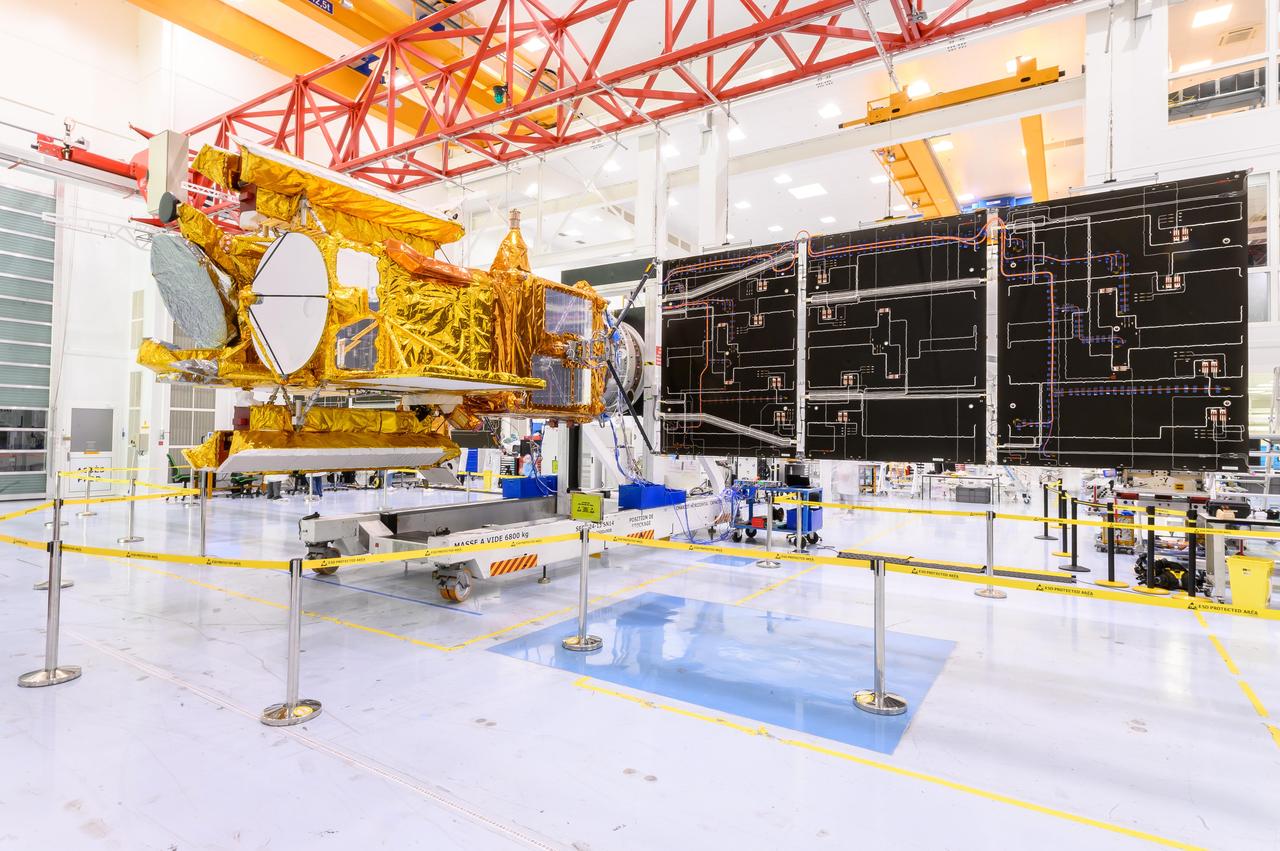

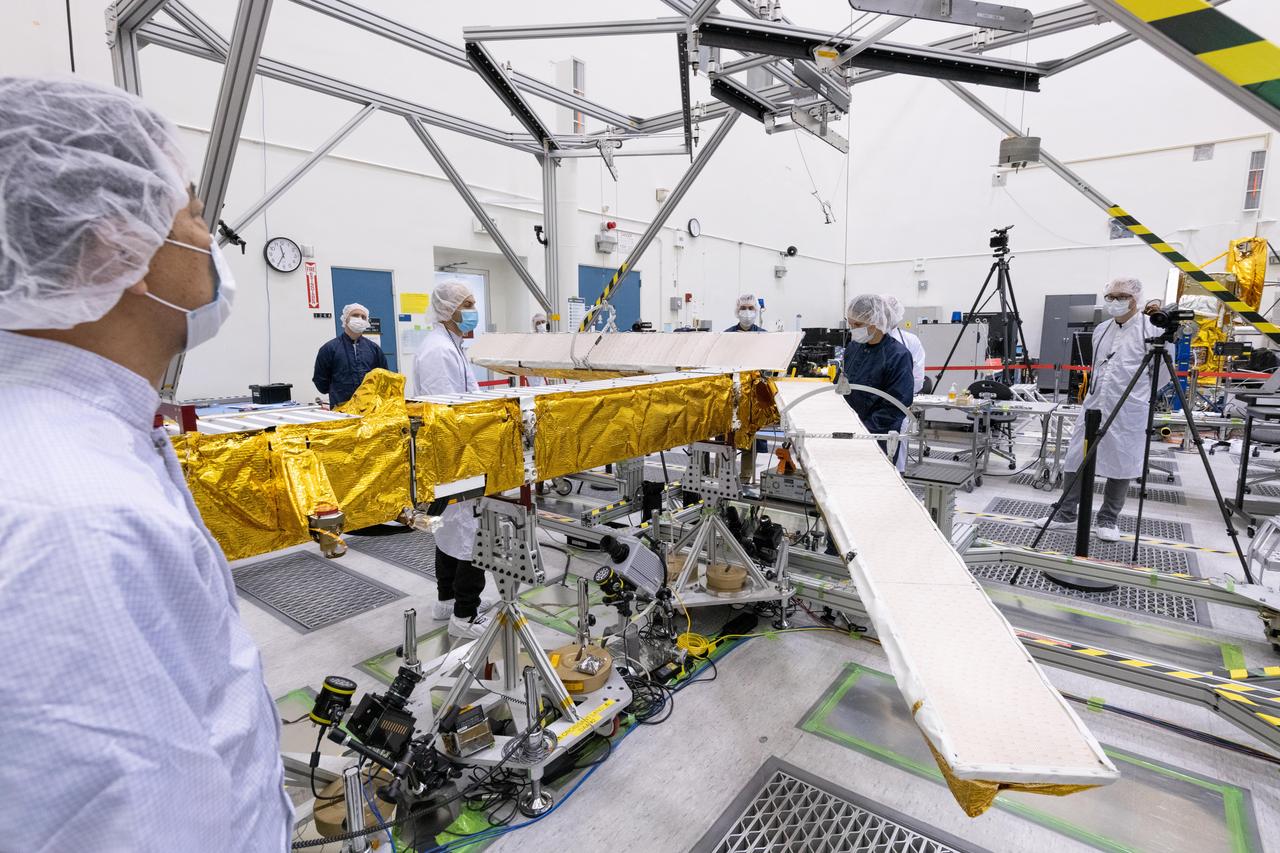
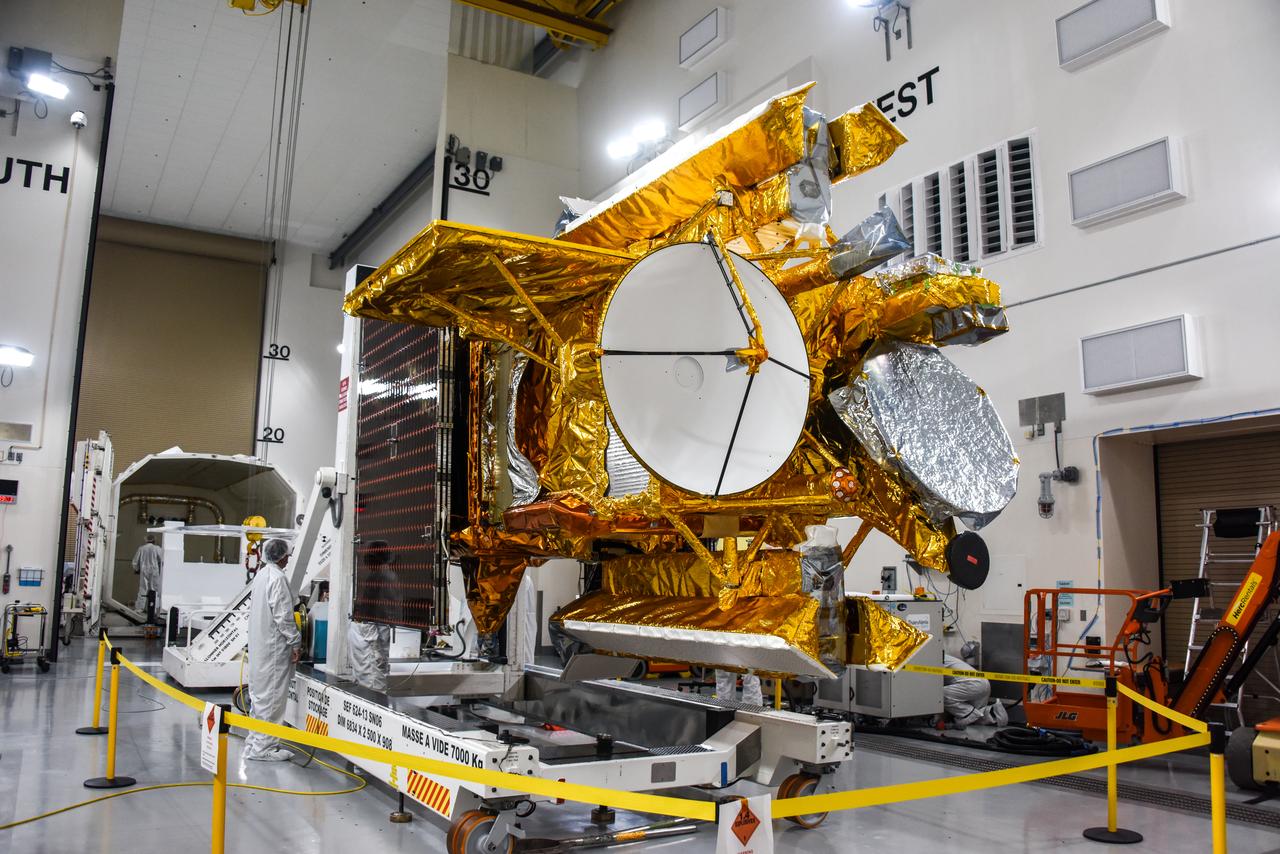
The solar panels on the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite unfold as part of a test in January 2022 at a Thales Alenia Space manufacturing facility near Cannes, France. The SWOT mission is being jointly led by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the United Kingdom Space Agency. Many of SWOT's radar instruments were built at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California before being transported to France, where Thales Alenia is assembling the full satellite. Following a series of tests, SWOT will be transported to Vandenberg Space Force Base in Southern California for launch in November 2022. In orbit, SWOT will collect information of unprecedented detail on sea-level height, which will help scientists study the role of ocean currents in moderating climate change, as well as the elevations of fresh water bodies, which will enable researchers for the first time to take inventory of the planet's rivers, lakes, reservoirs, and other surface water. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25147

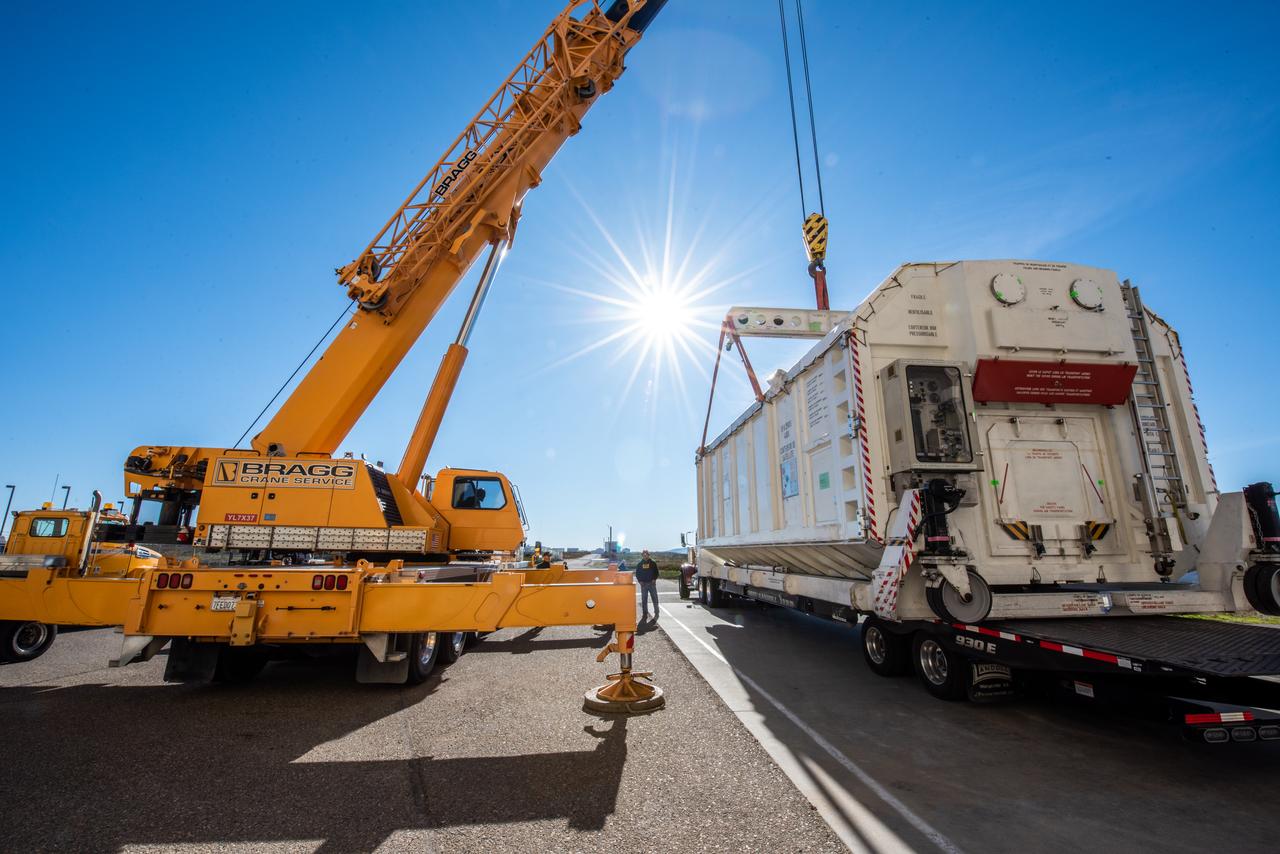
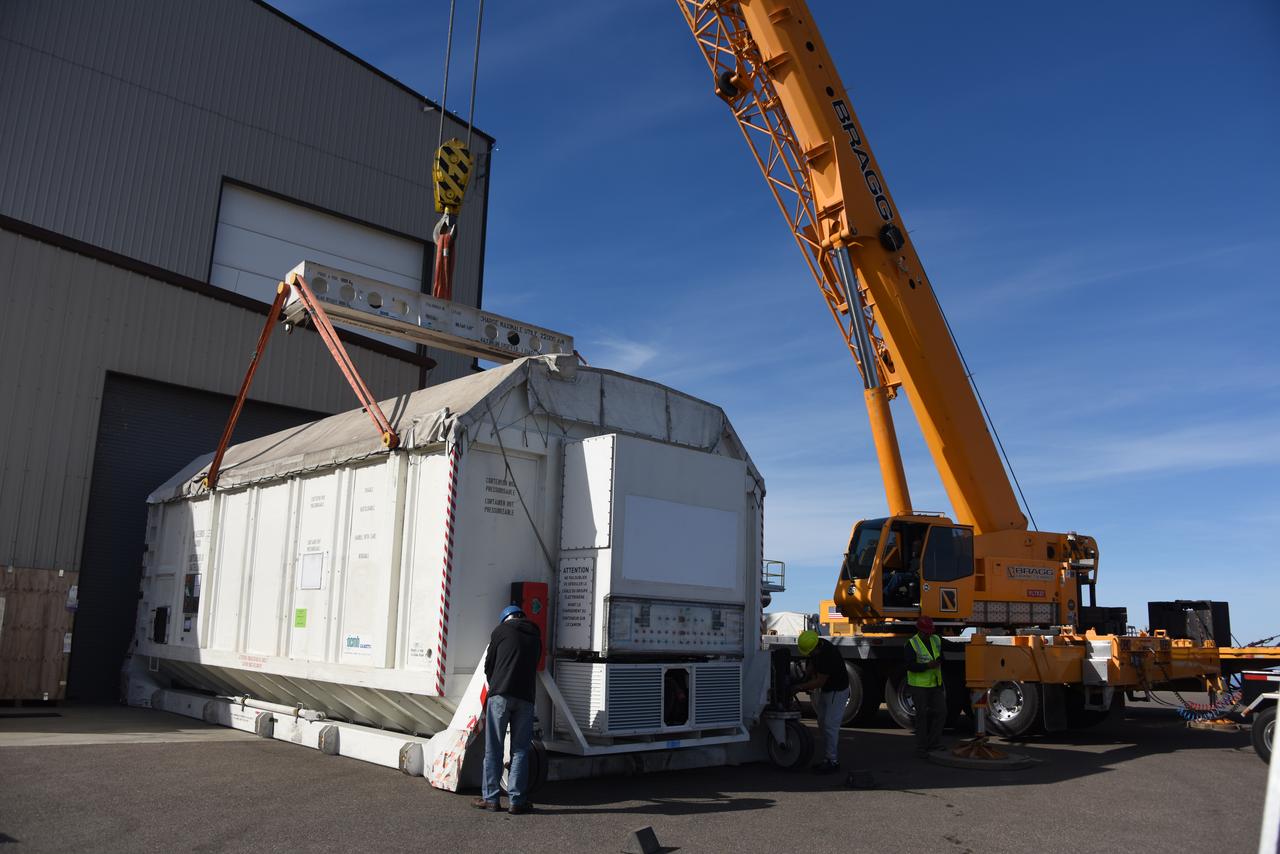
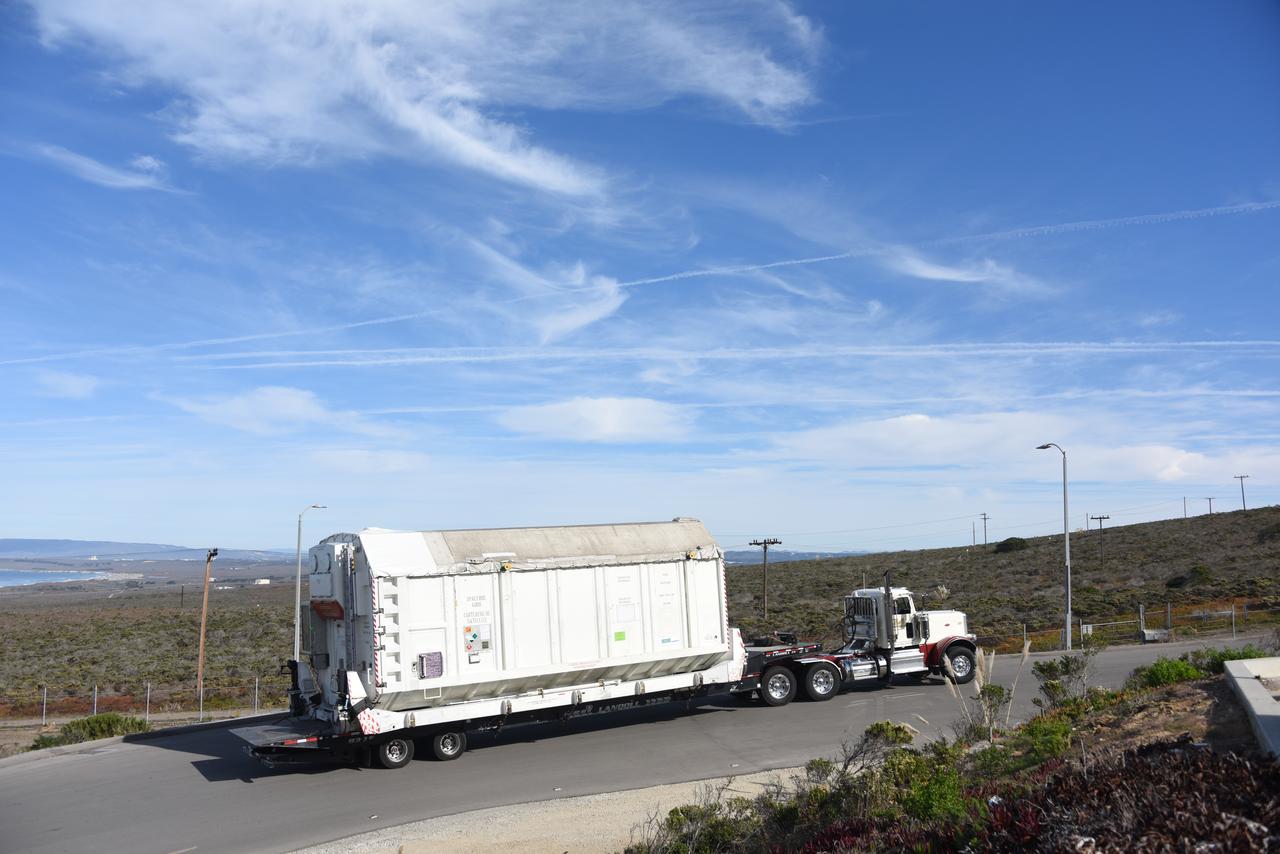
The ground service equipment for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 13, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
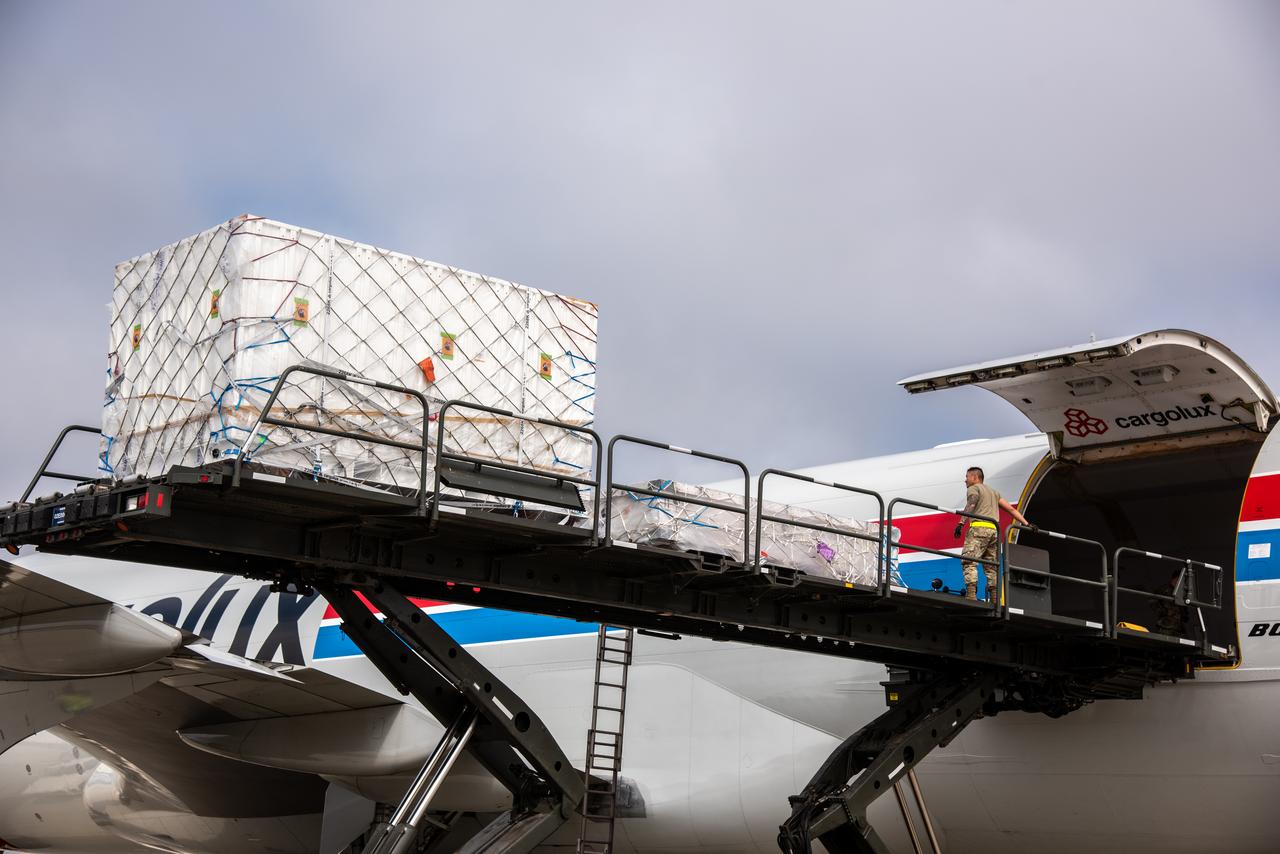

The ground service equipment for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 13, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 16, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 16, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
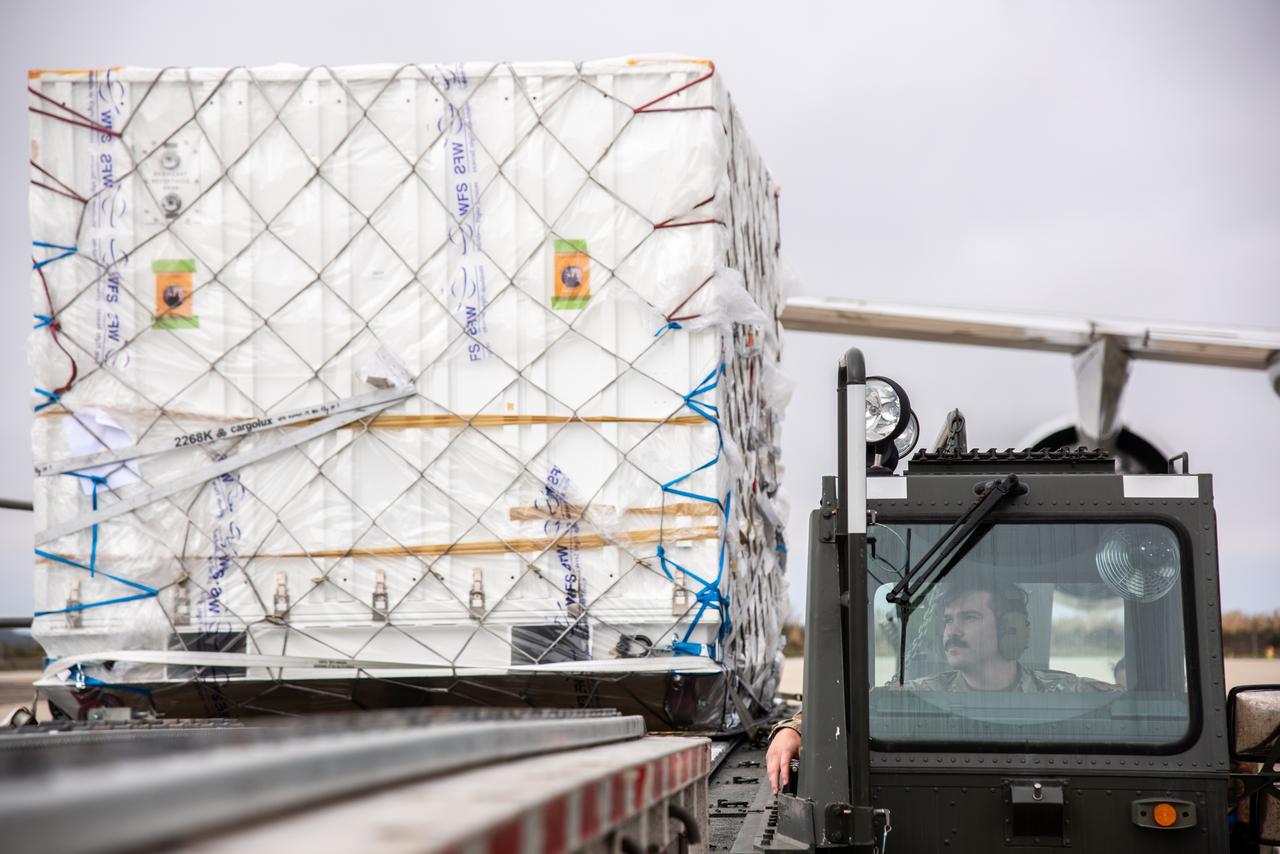

The ground service equipment for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 13, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 16, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

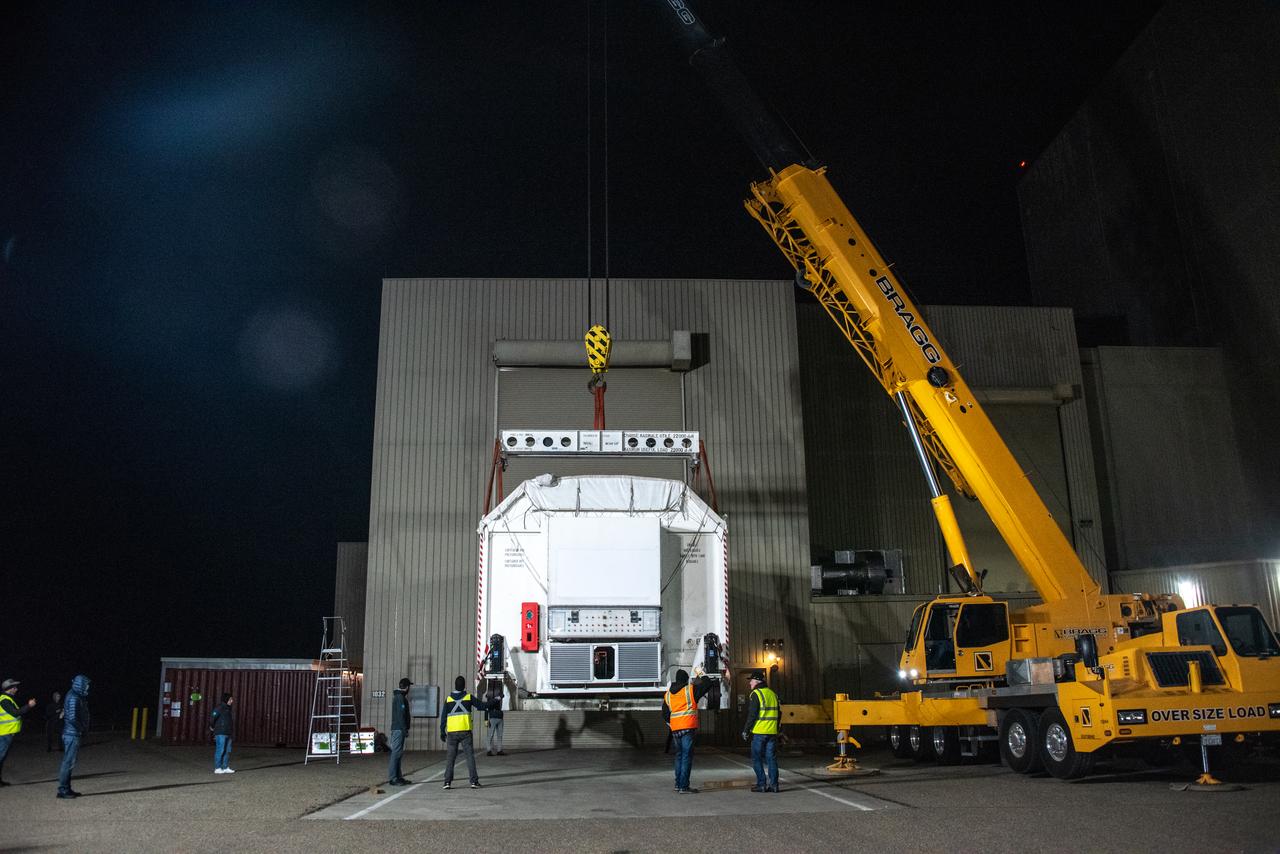
The ground service equipment for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 13, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

The ground service equipment for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 13, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Oct. 16, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

Julianna Scheiman, civil satellite missions director, SpaceX, participates in a prelaunch news conference held by NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

Members of the international Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission test one of the antennas for the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES) – with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the UK Space Agency. KaRIn is the scientific heart of the SWOT satellite, which will survey the water on more than 90% of Earth's surface, measuring the height of water in lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. To do that, KaRIn will transmit radar pulses to Earth's surface and use its two antennas to triangulate the return signals that bounce back. Mounted at the ends of a boom 33 feet (10 meters) long, the antennas will collect data along a swath 30 miles (50 kilometers) wide on either side of the satellite. KaRIn will operate in two modes: A lower-resolution mode over the ocean will involve significant onboard processing of the data to reduce the volume of information sent during downlinks to Earth; a higher-resolution mode will be used mainly over land. Scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Dec. 15, 2022, SWOT is being jointly developed by NASA and CNES, with contributions from the CSA and the UK Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, leads the U.S. component of the project. For the flight system payload, NASA is providing the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument, a GPS science receiver, a laser retroreflector, a two-beam microwave radiometer, and NASA instrument operations. CNES is providing the Doppler Orbitography and Radioposition Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) system, the dual frequency Poseidon altimeter (developed by Thales Alenia Space), the KaRIn radio-frequency subsystem (together with Thales Alenia Space and with support from the UK Space Agency), the satellite platform, and ground control segment. CSA is providing the KaRIn high-power transmitter assembly. NASA is providing the launch vehicle and associated launch services. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25594

Katherine Calvin, chief scientist and senior climate advisor, NASA, participates in a science briefing held by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 13, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

Benjamin Hamlington, research scientist, Sea Level and Ice Group, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, participates in a science briefing held by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 13, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
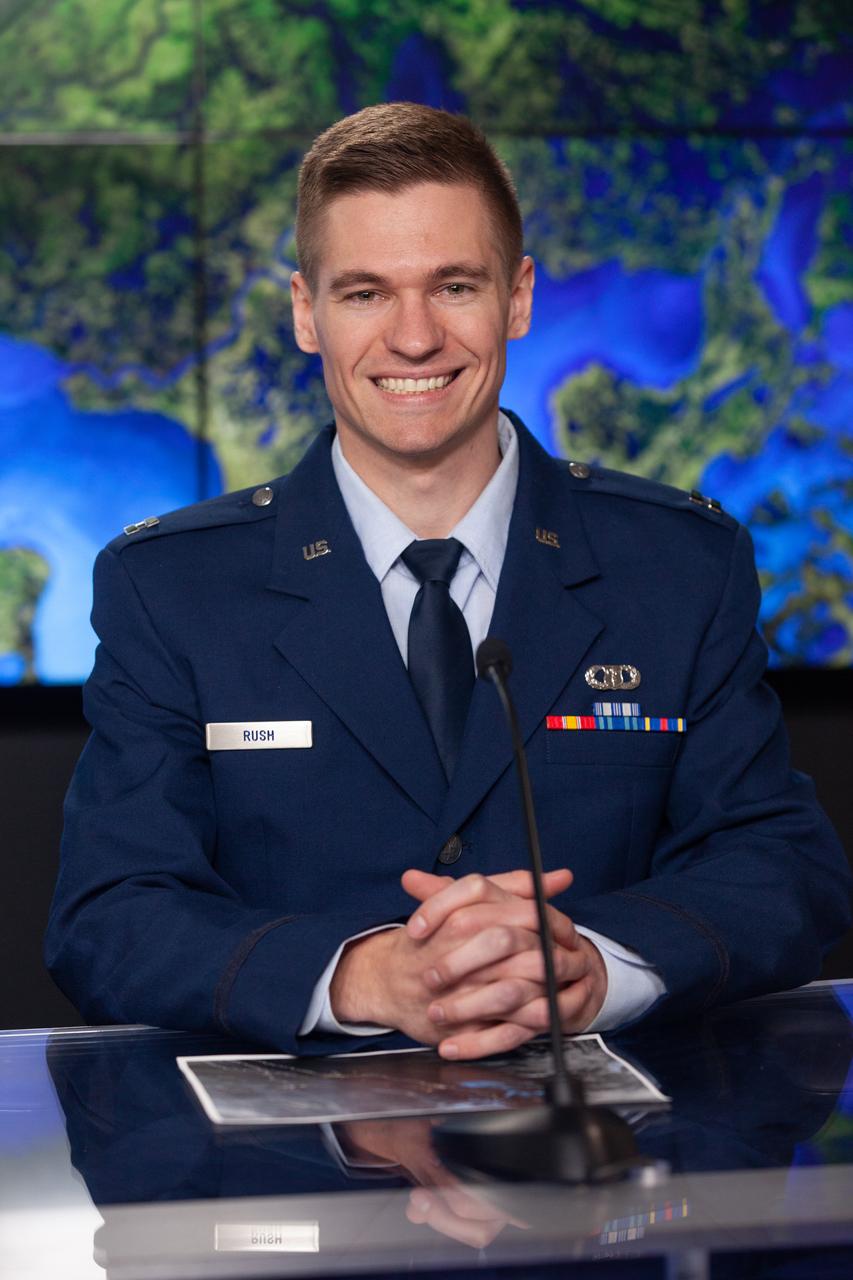

Capt. Max Rush, launch weather officer, U.S. Air Force, participates in a prelaunch news conference held by NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
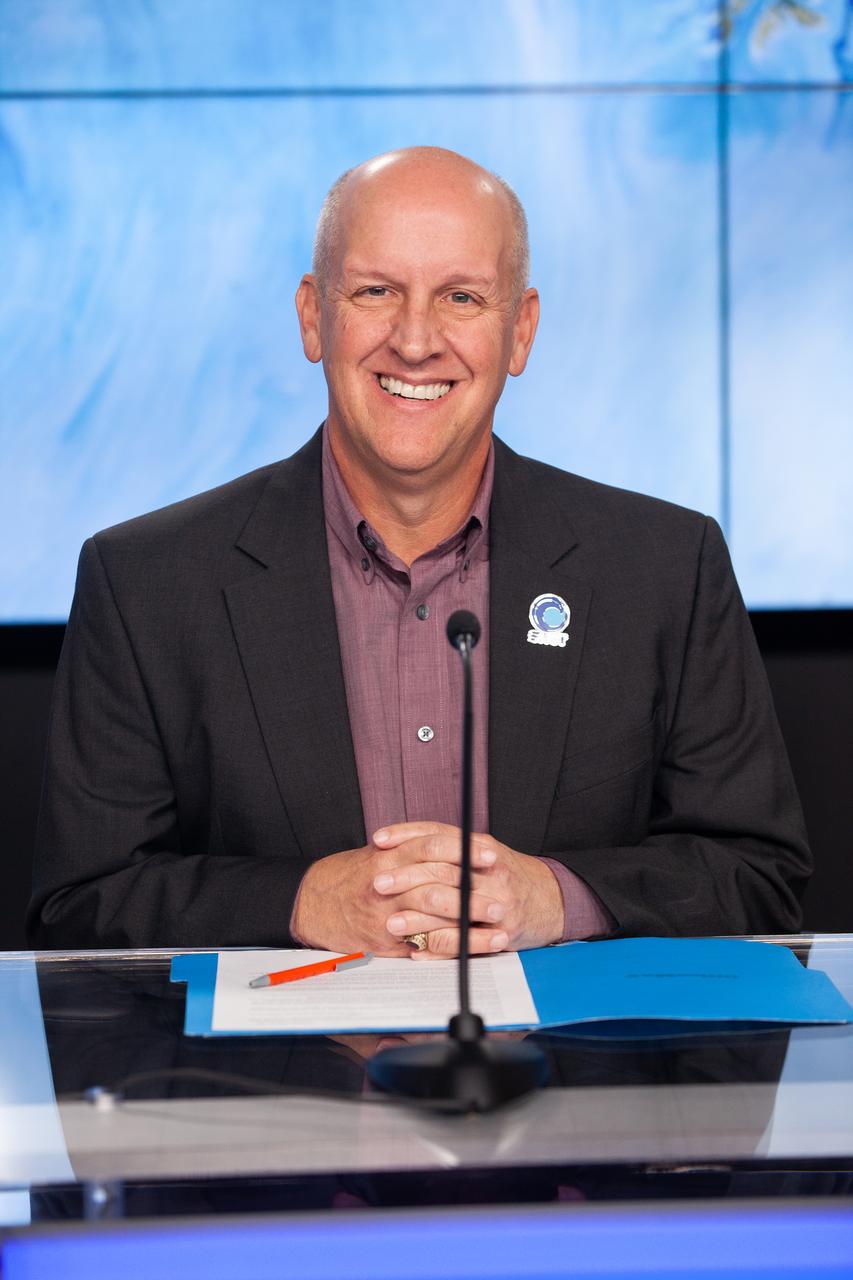

Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program, participates in a prelaunch news conference held by NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
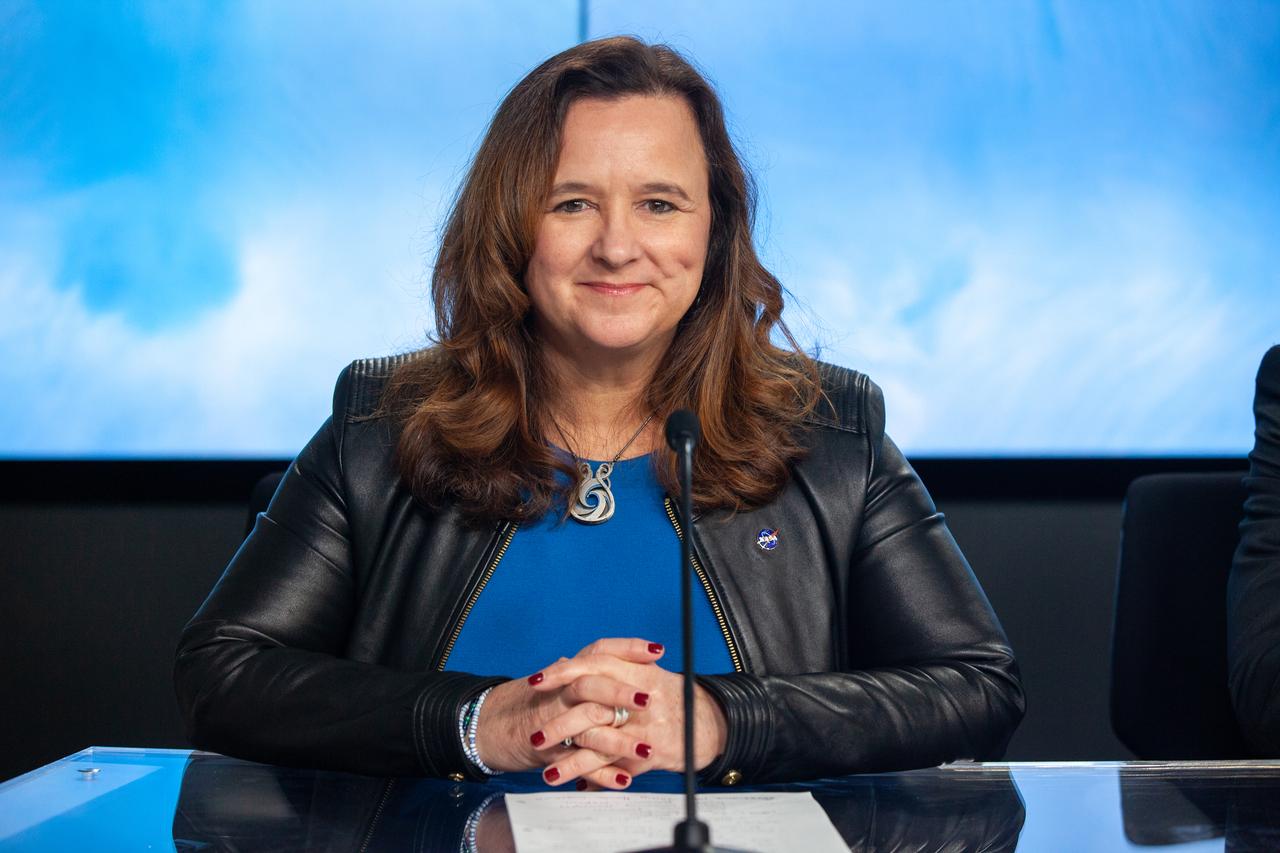

Karen St. Germain, Earth Science Division director, NASA, participates in a prelaunch news conference held by NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
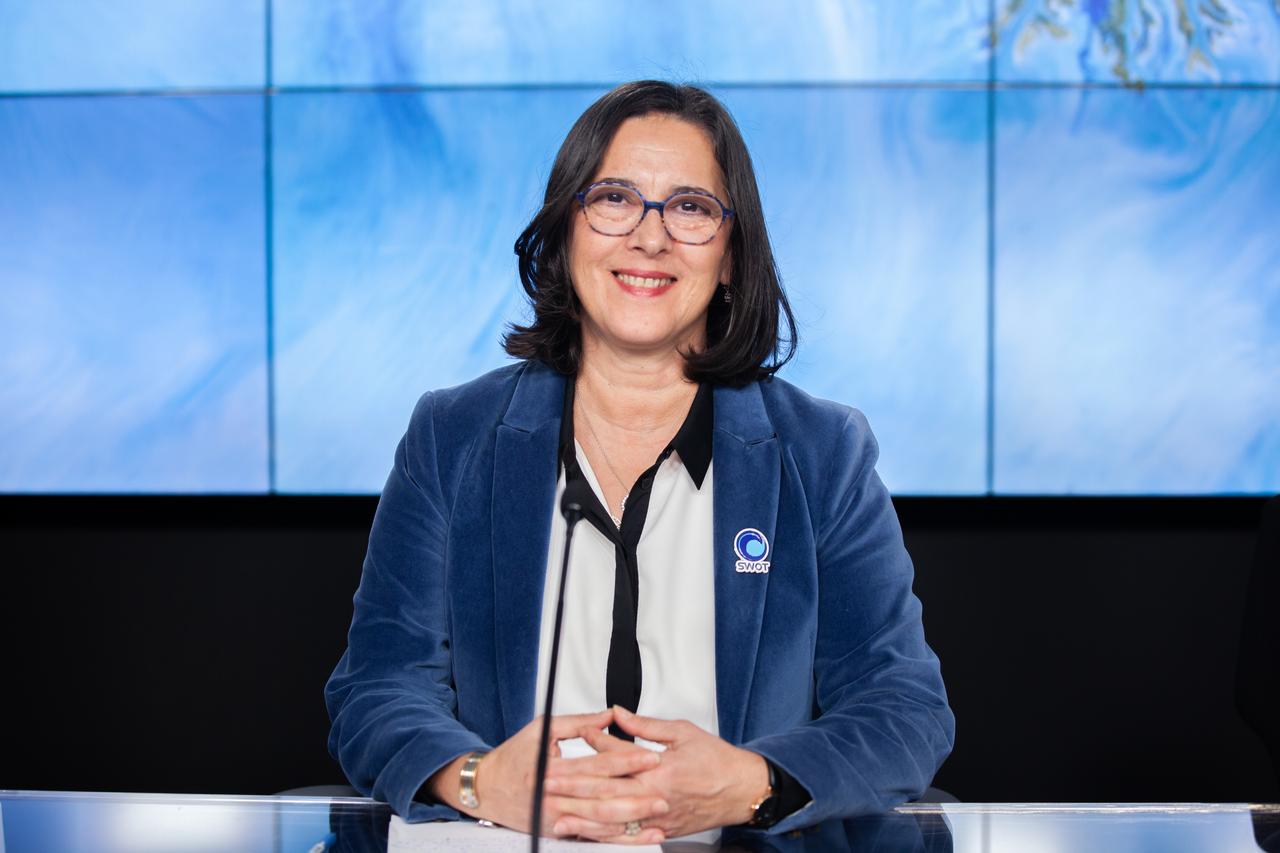

Selma Cherchali, Earth observation program head, CNES, participates in a science briefing held by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 13, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

Megan Cruz, NASA Communications, moderates a prelaunch news conference held by NASA, SpaceX, and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES) for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission on Dec. 14, 2022, at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. SWOT is scheduled to launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex-4 East at Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST. SWOT will be NASA’s first global survey of nearly all water on Earth’s surface. Scientists plan to use its observations to better understand the global water cycle, furnish insight into the ocean’s role in how climate change unfolds, and provide a global inventory of water resources. The SWOT mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and CNES with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
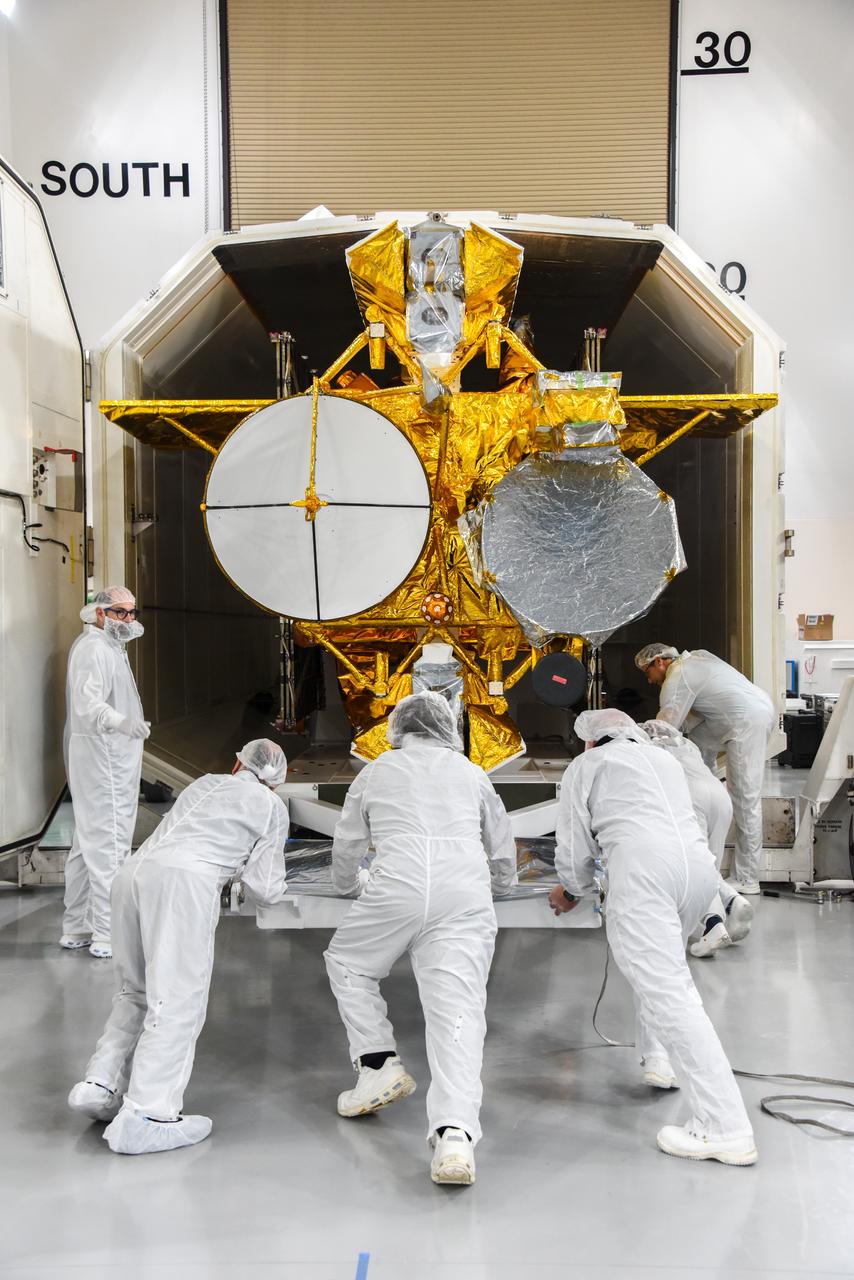

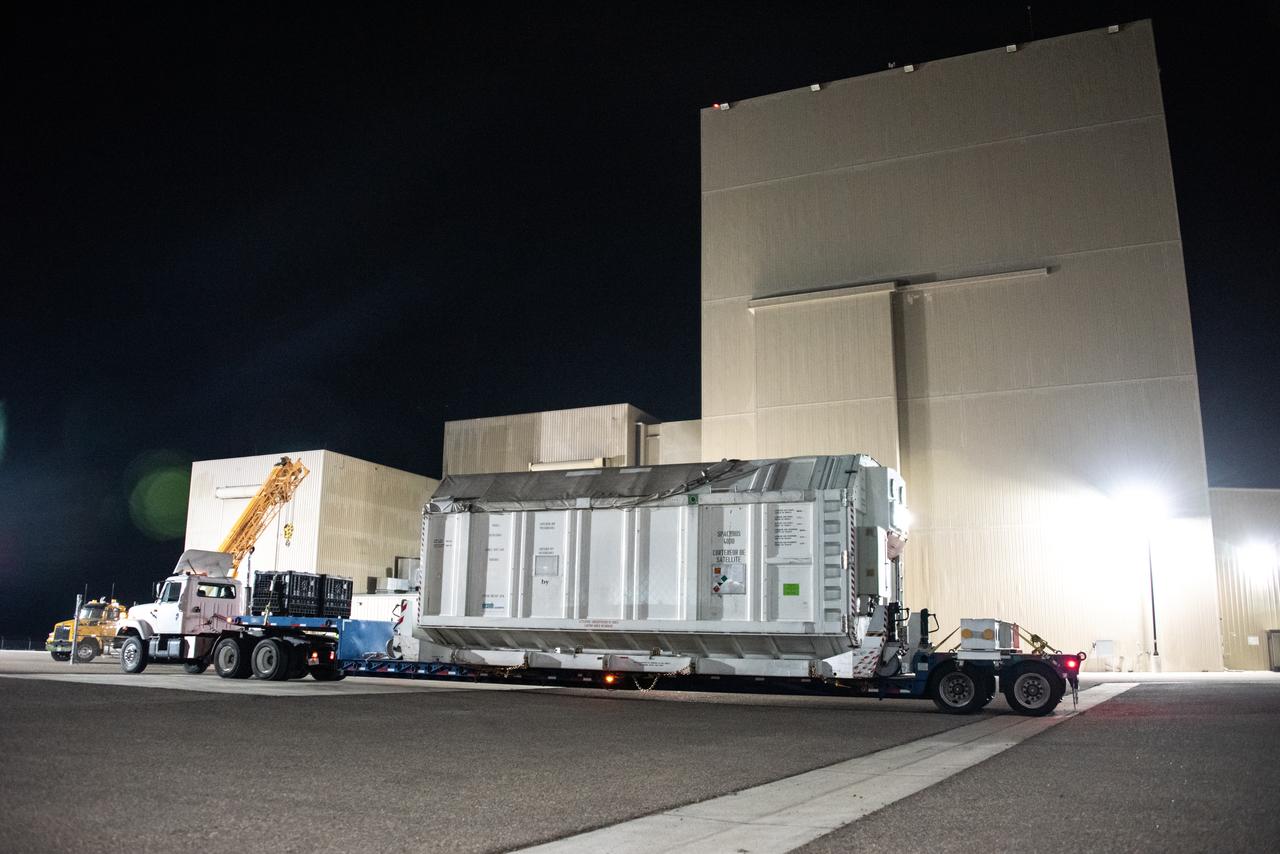
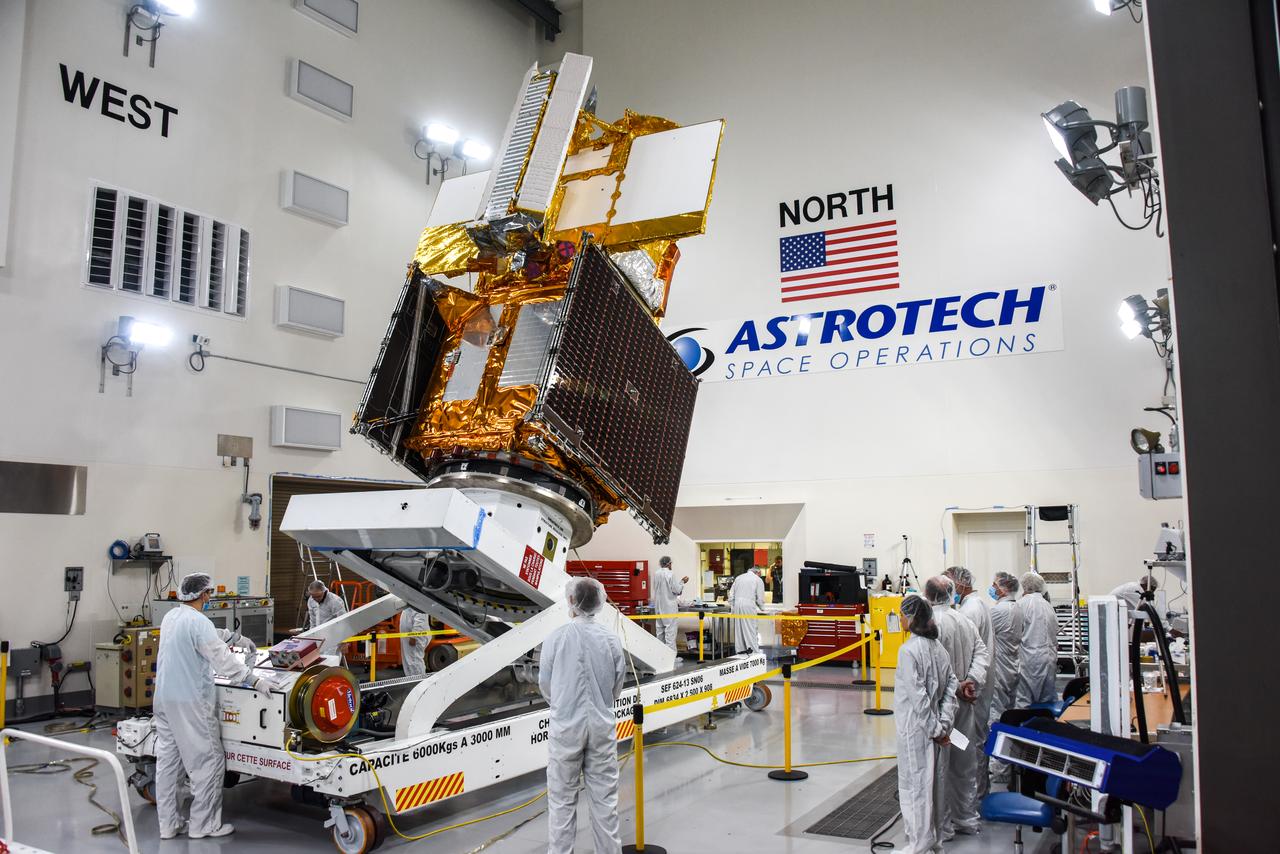
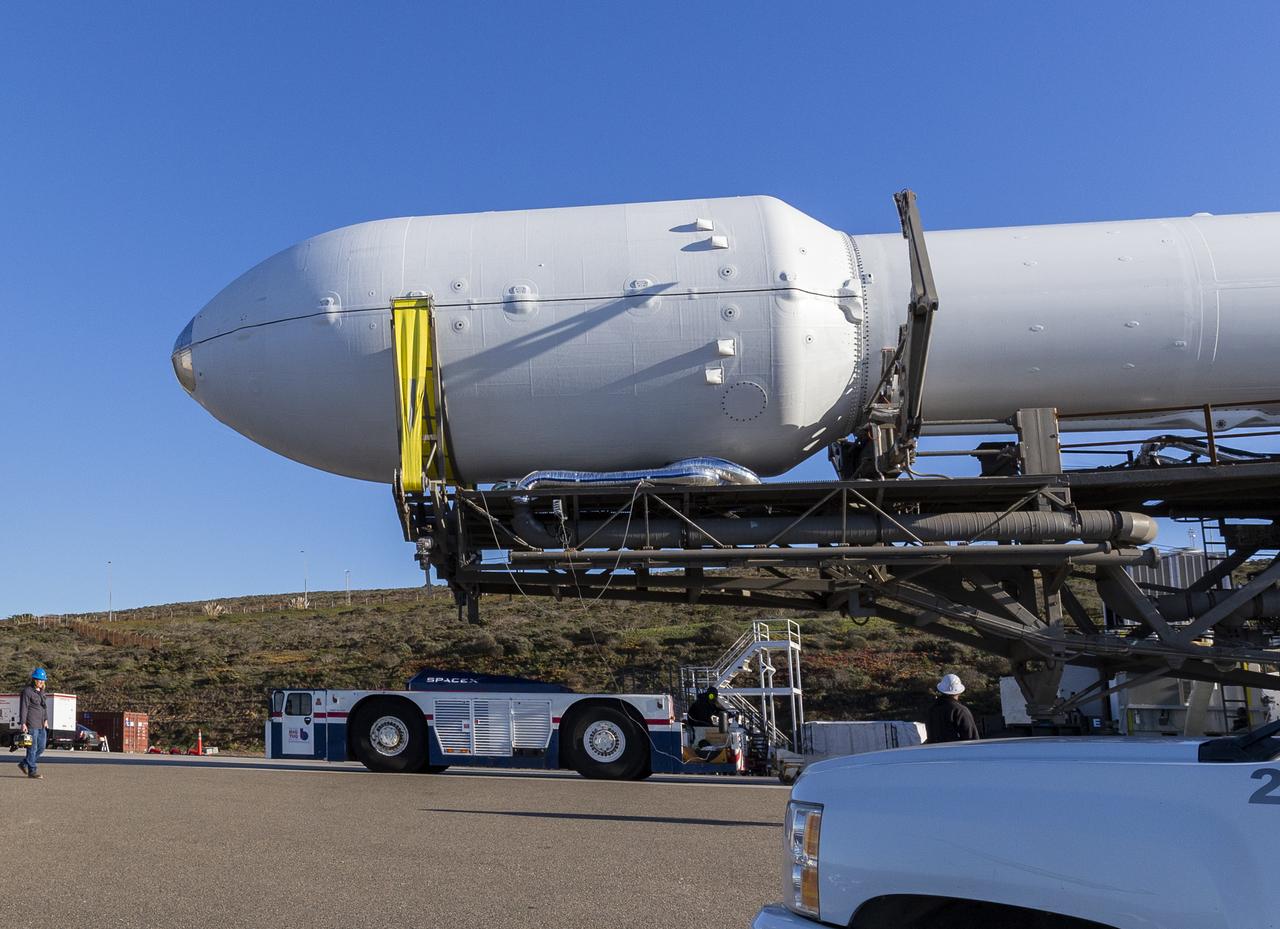
The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is moved into a transport container inside the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 18, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

A container, with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft inside, is moved to a trailer at the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 19, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

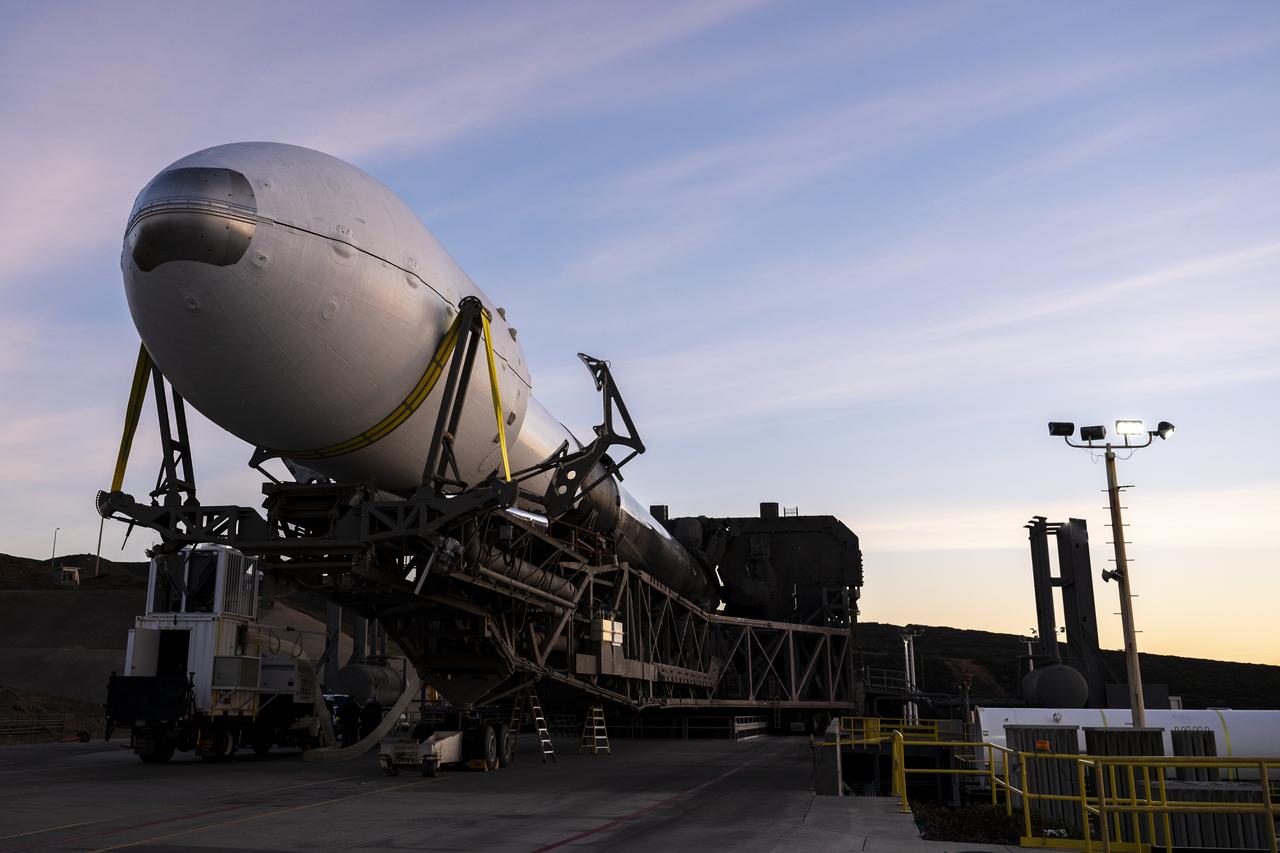
The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is transported from Astrotech to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 21, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is moved into a transport container inside the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 18, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
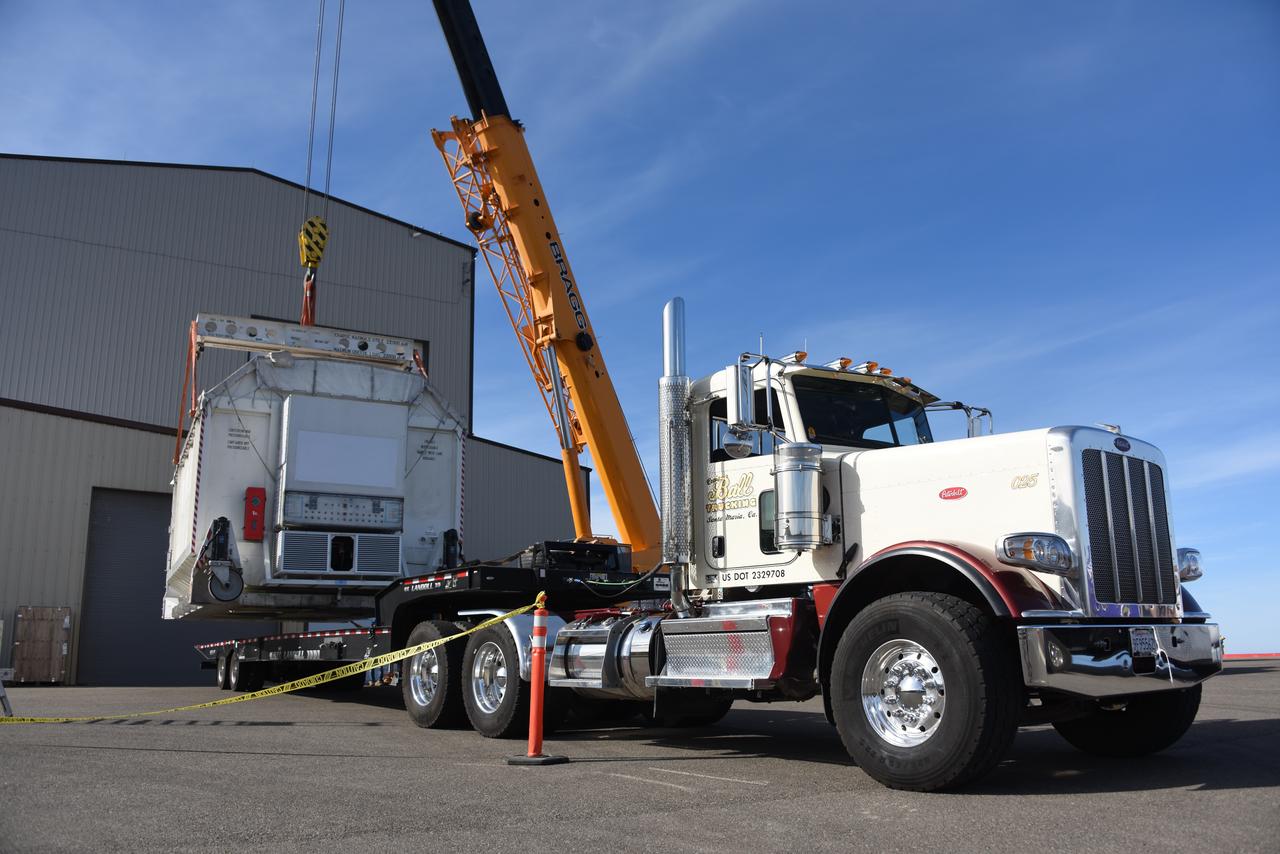

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is transported from Astrotech to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 21, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

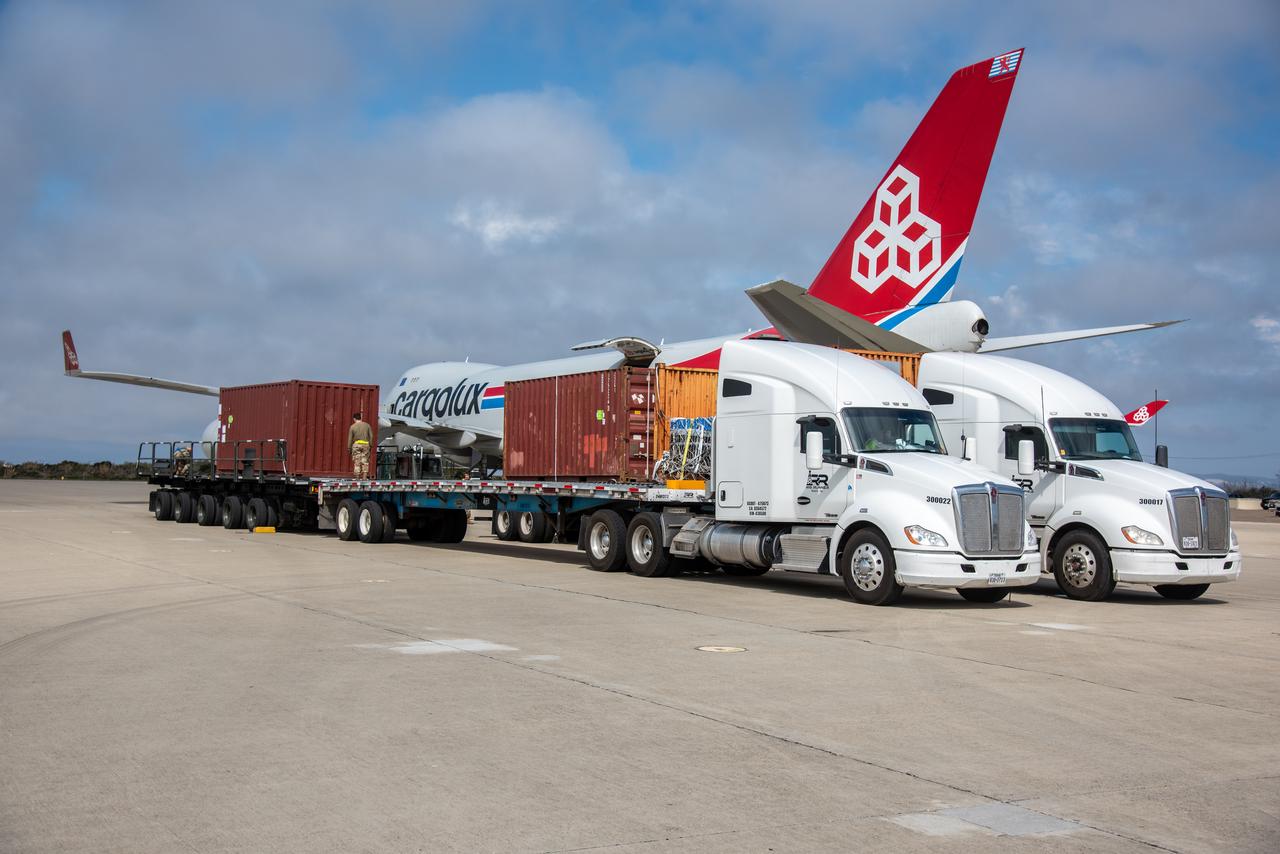
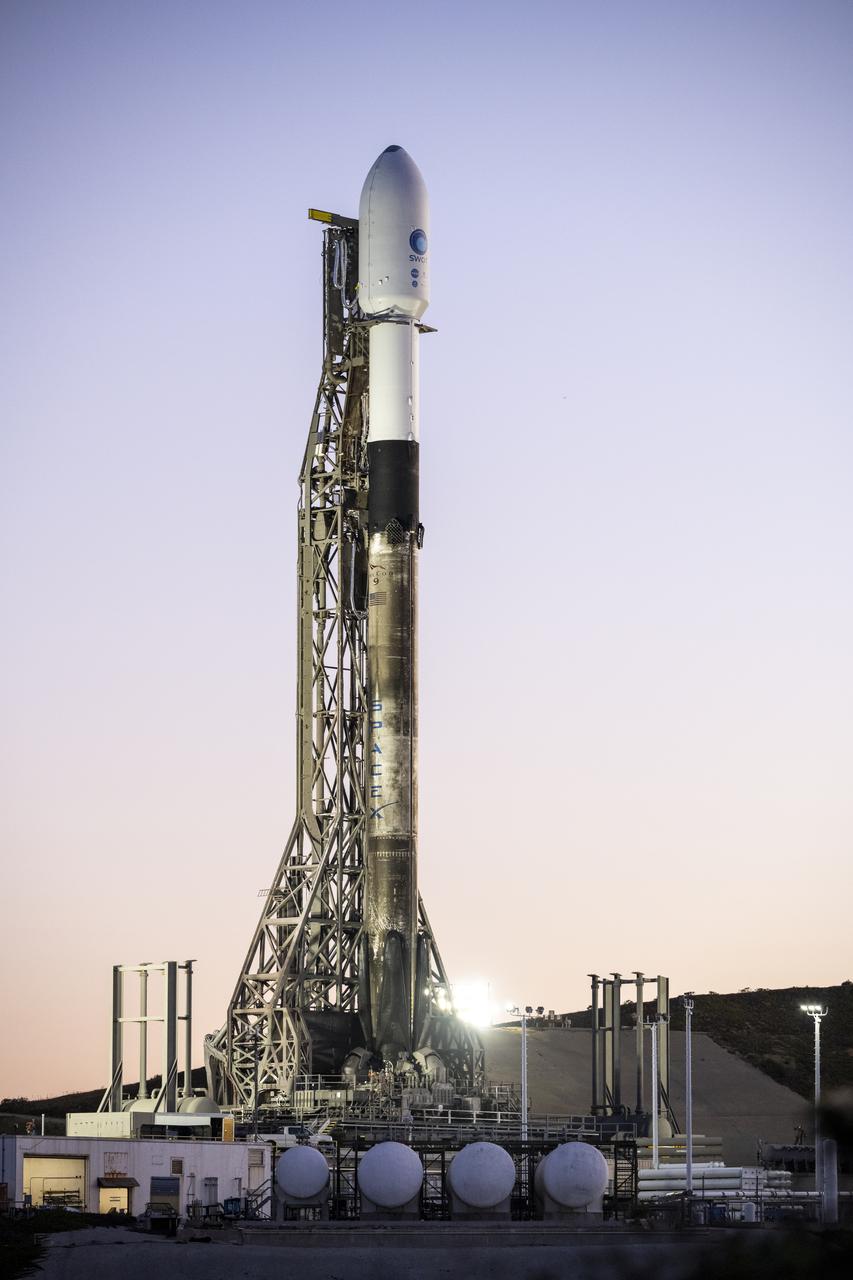
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is transported from Astrotech to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 21, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
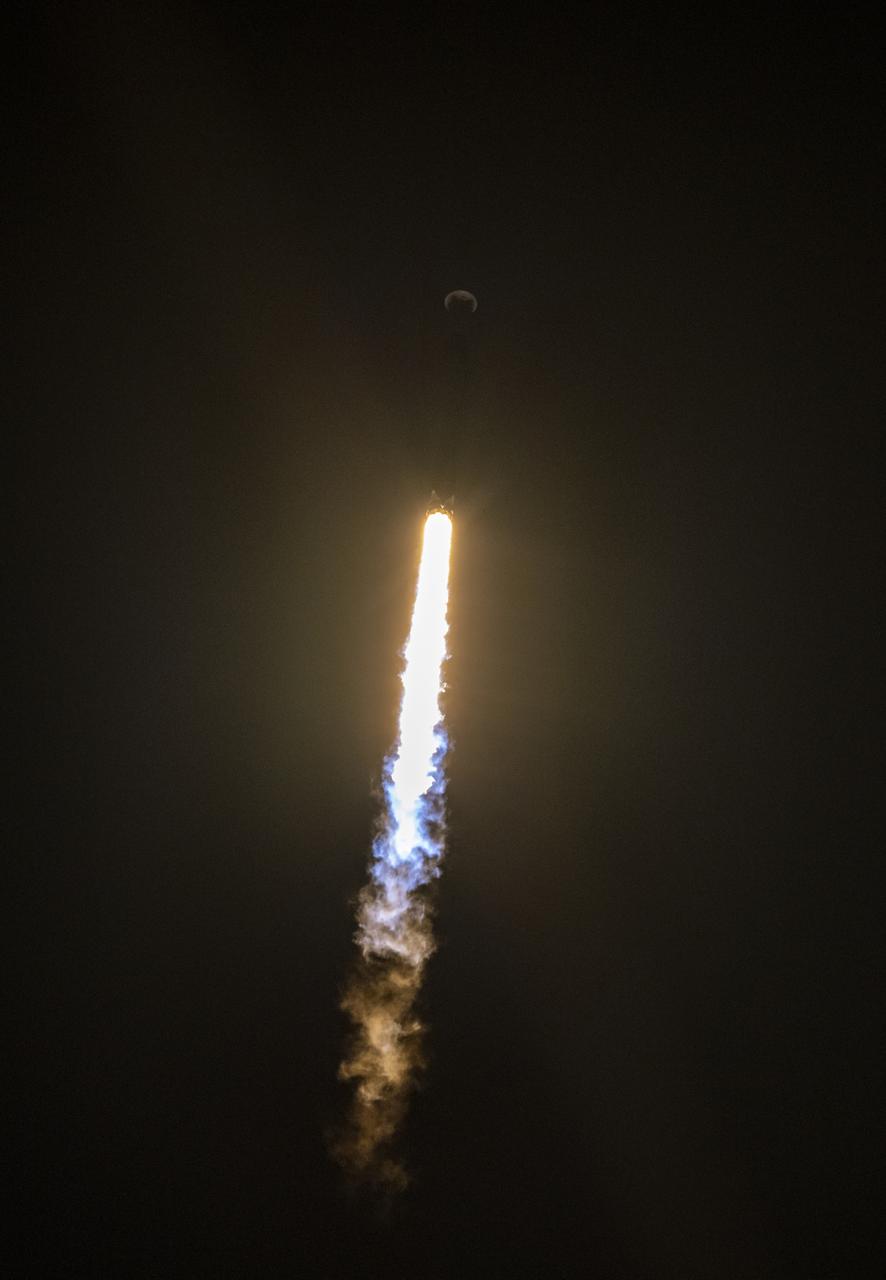

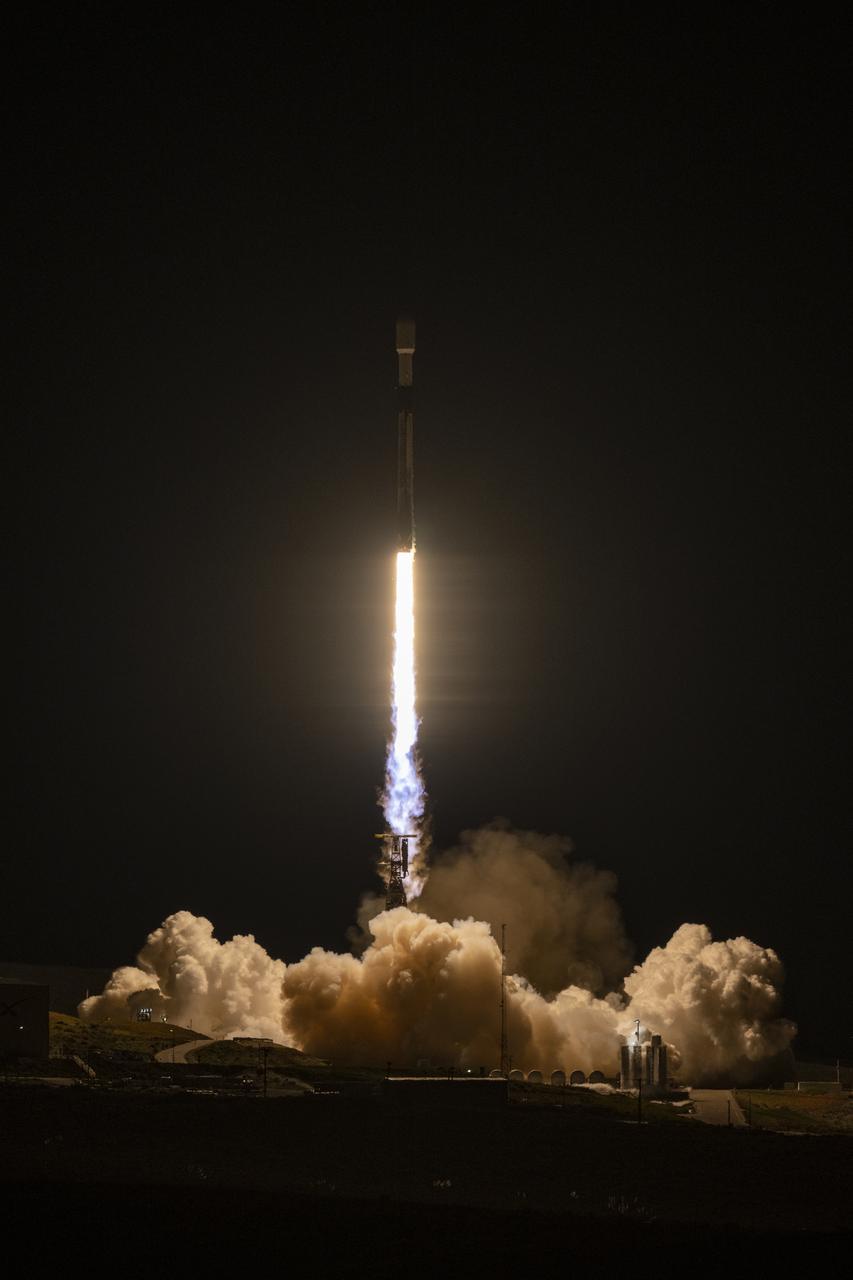
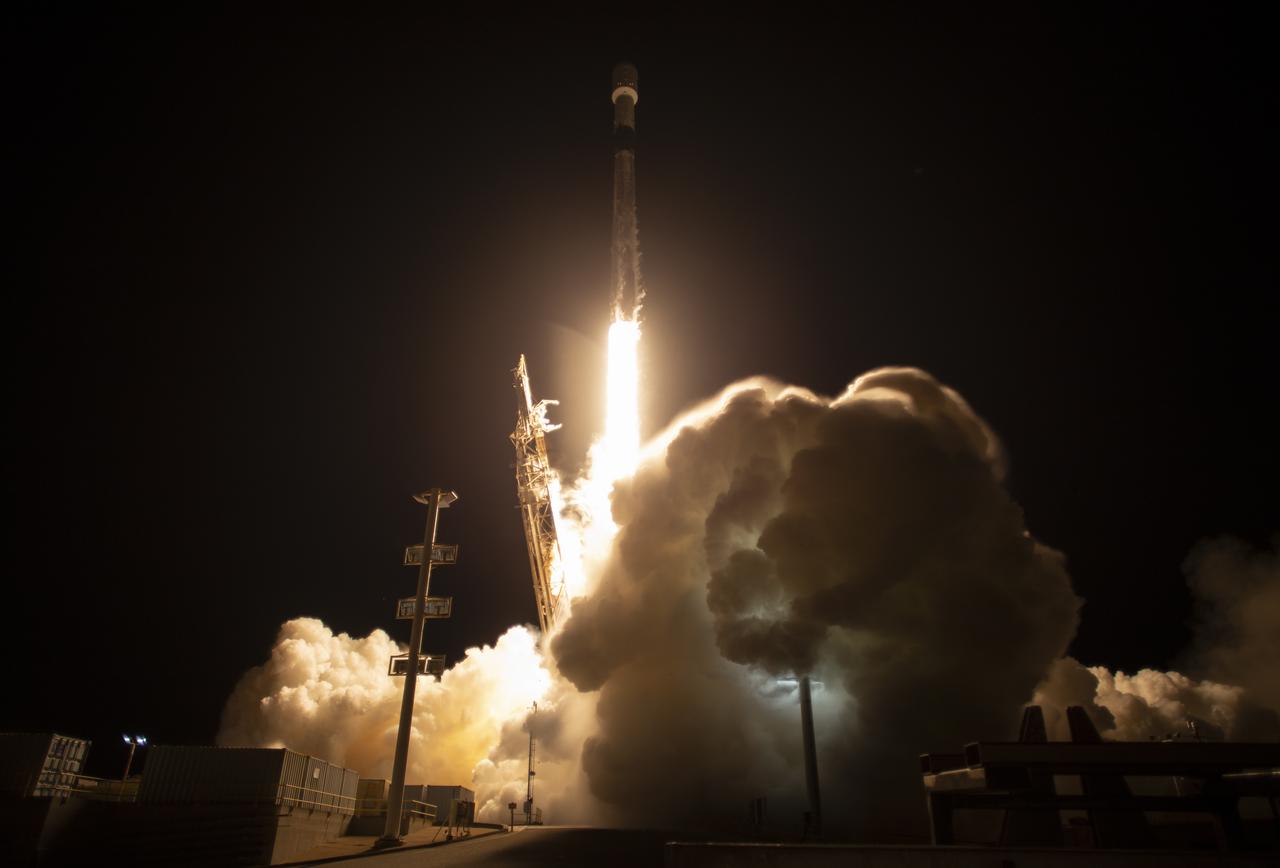
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
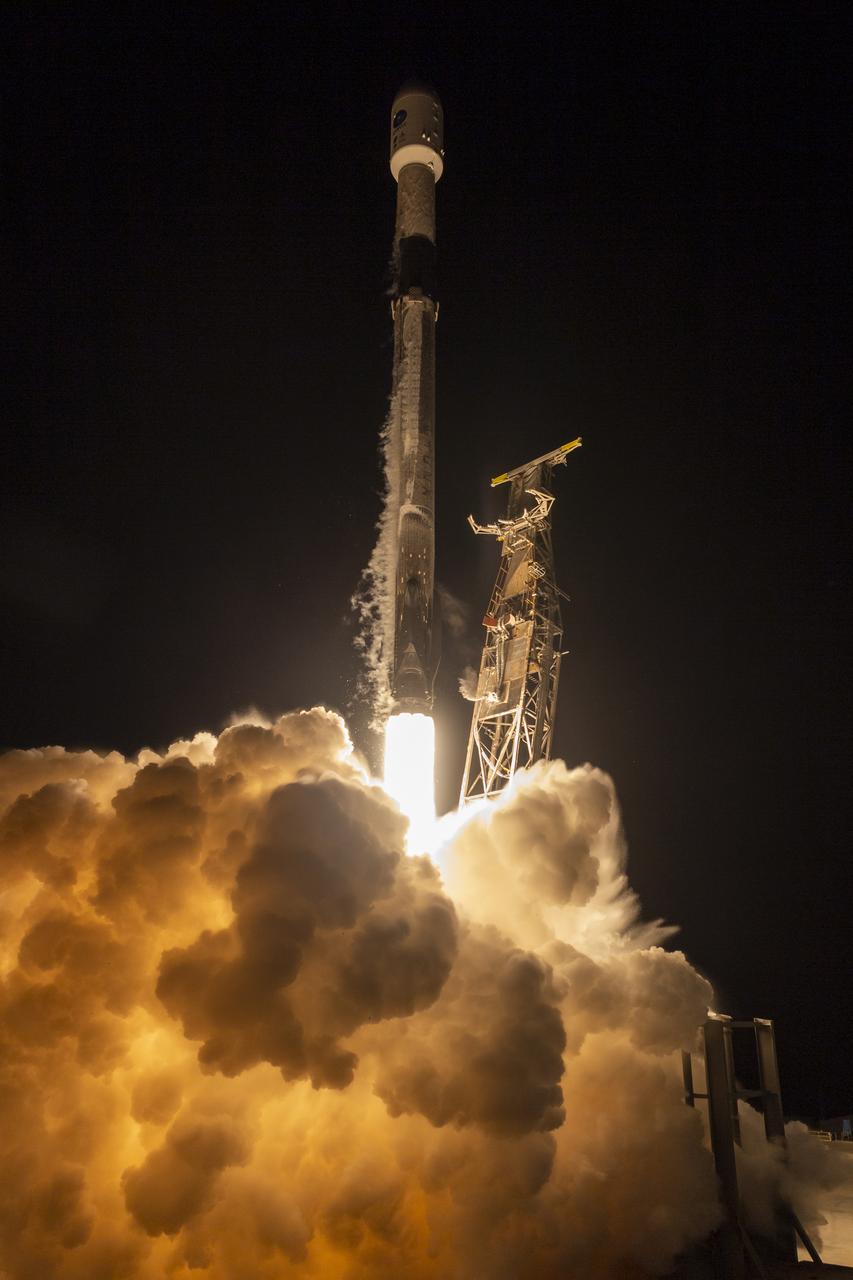

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
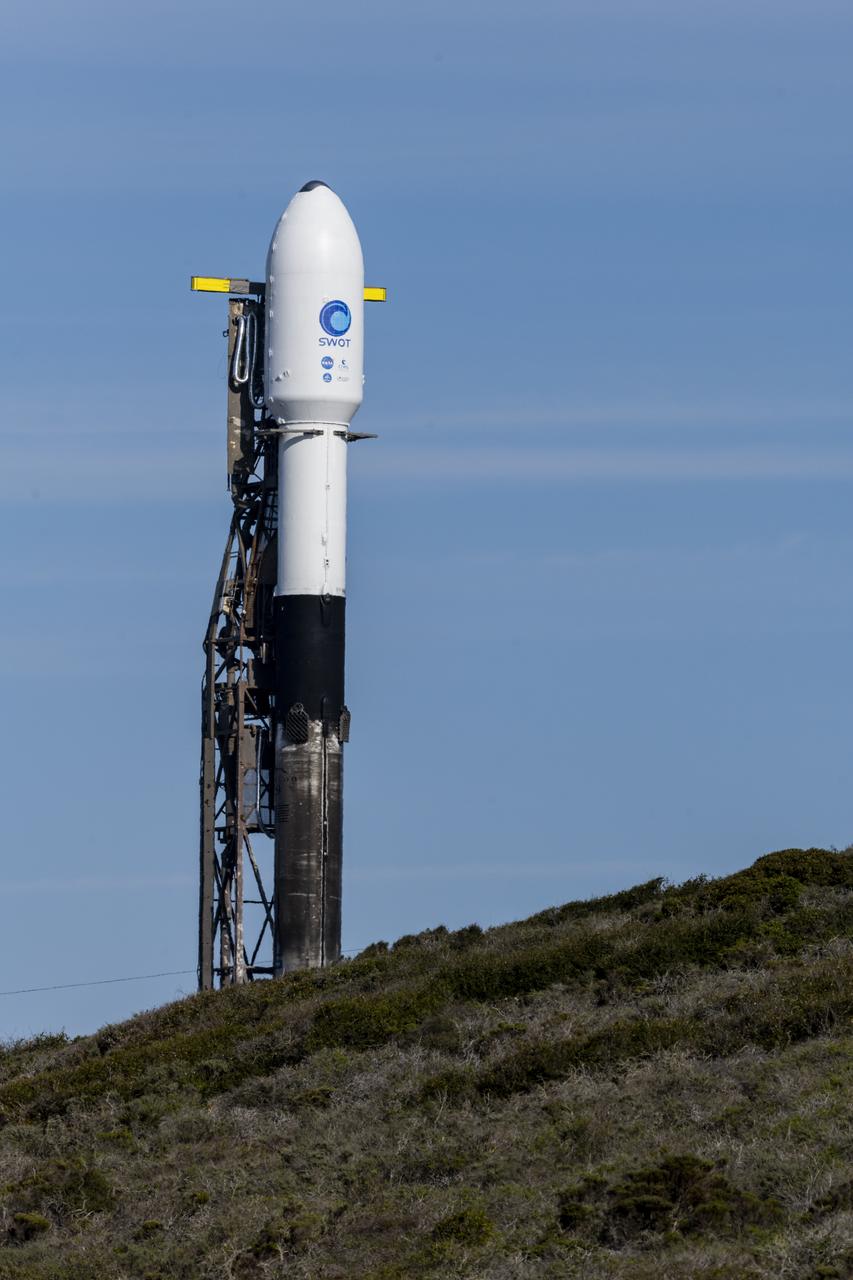

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
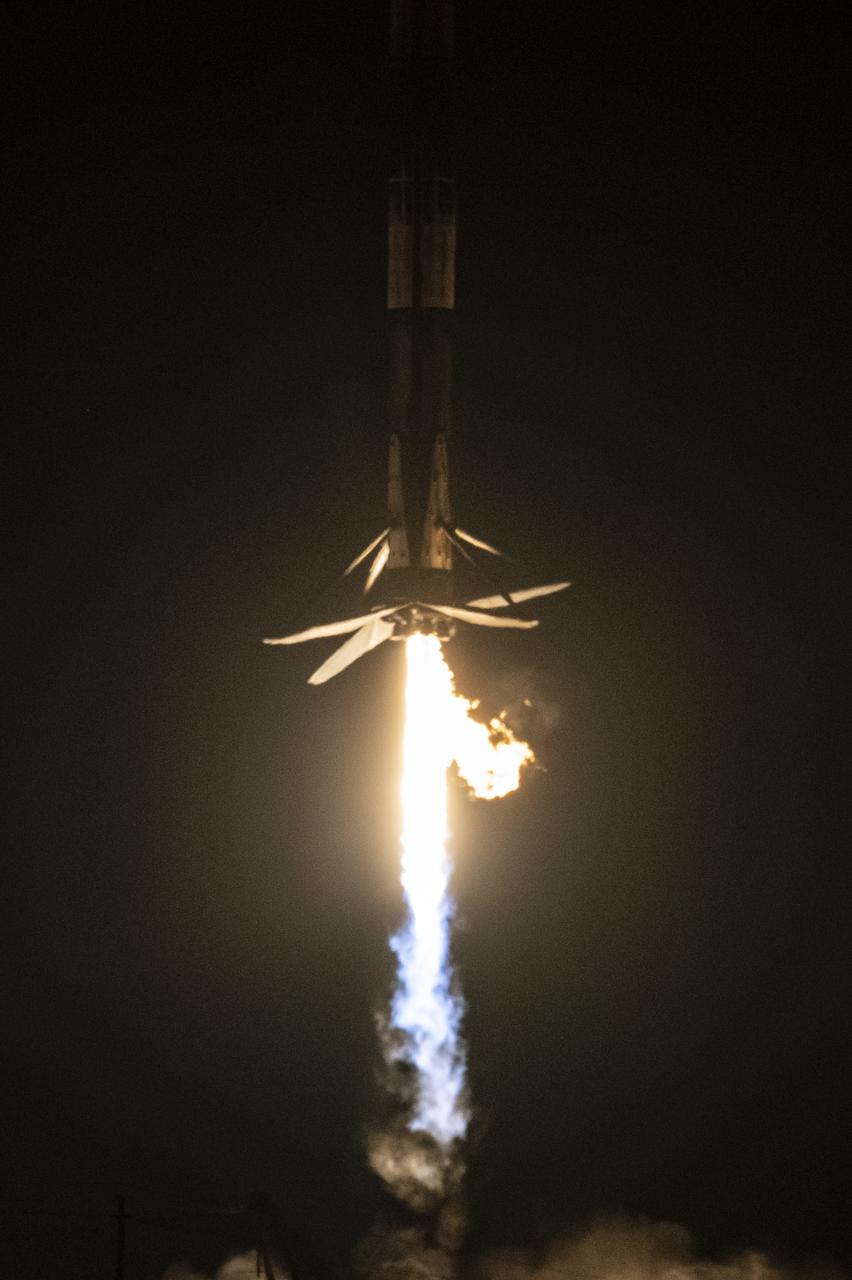

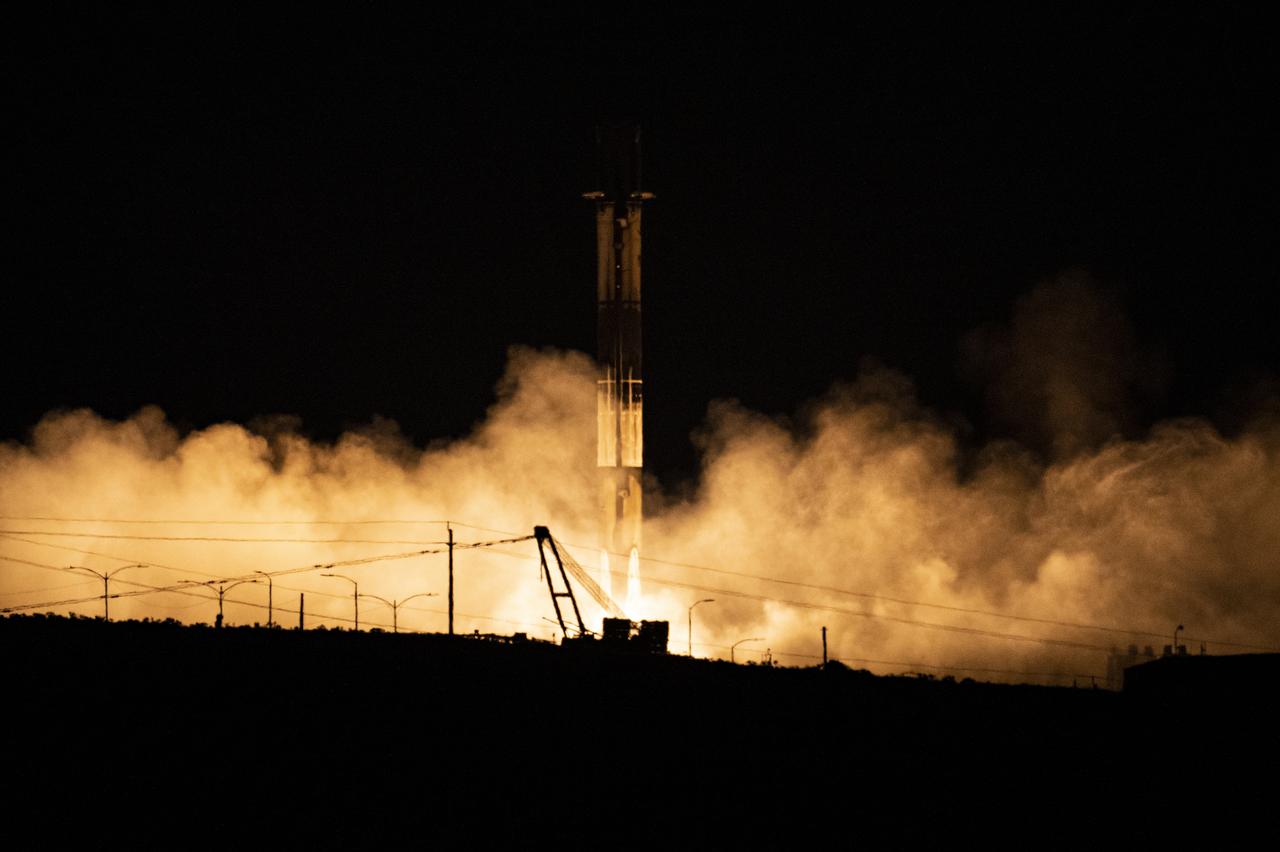
A SpaceX Falcon 9 first-stage booster returns to the landing pad following the launch of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
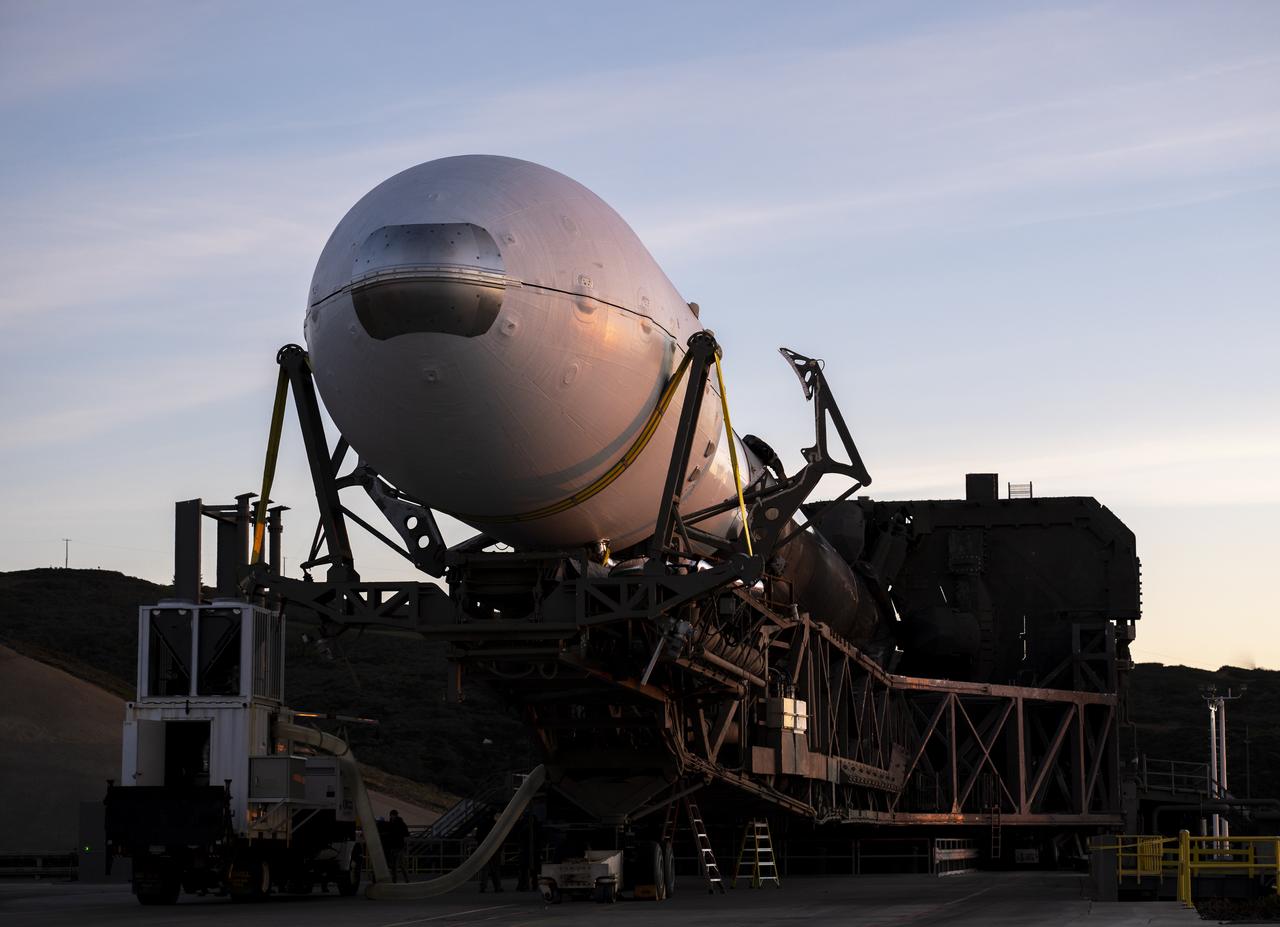

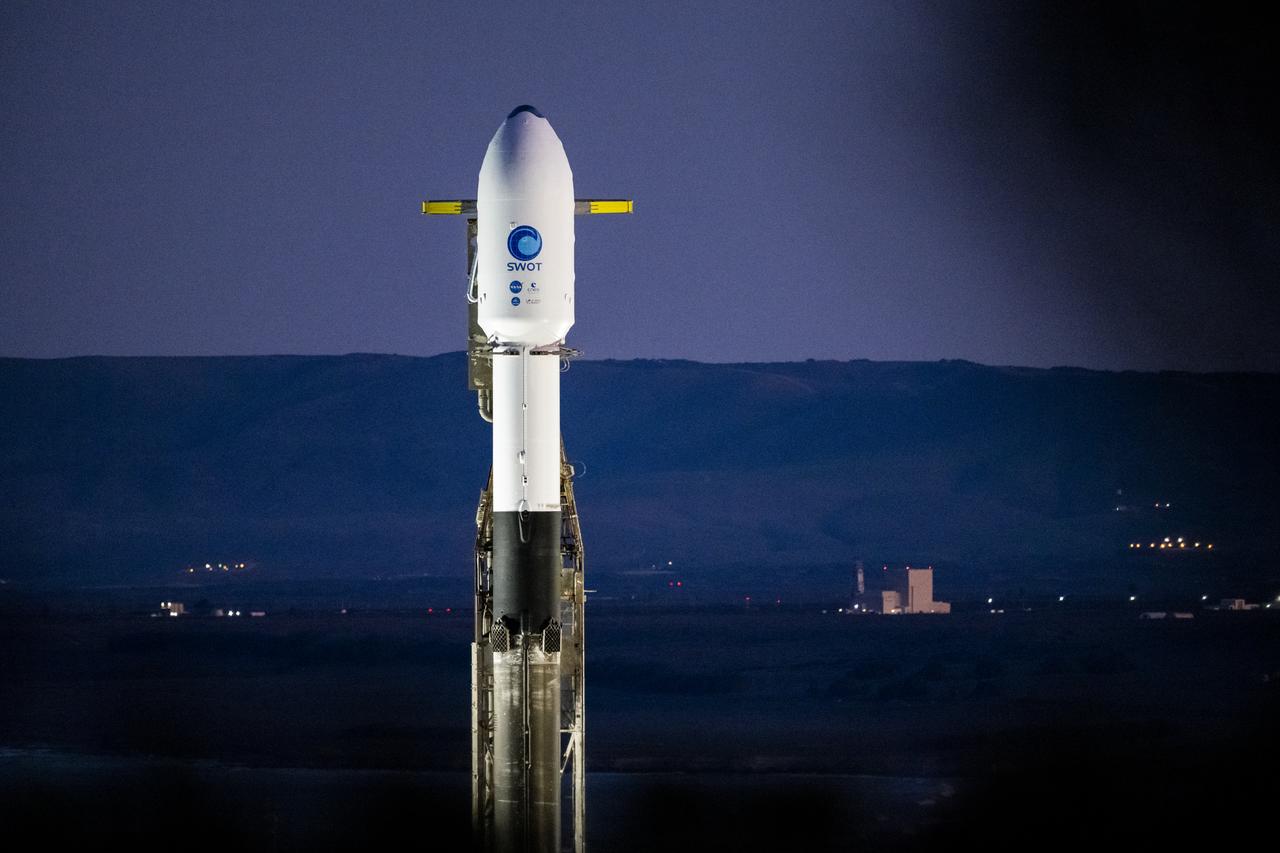
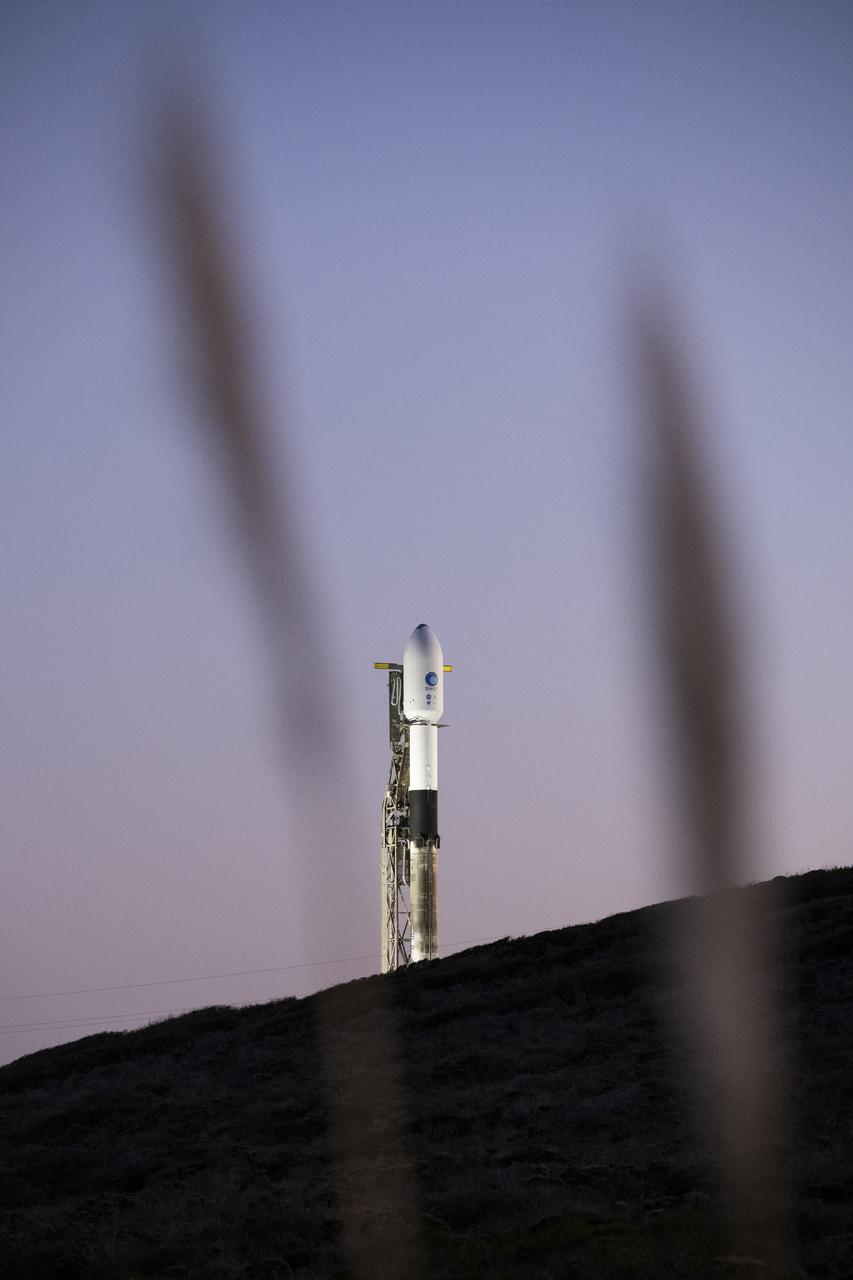
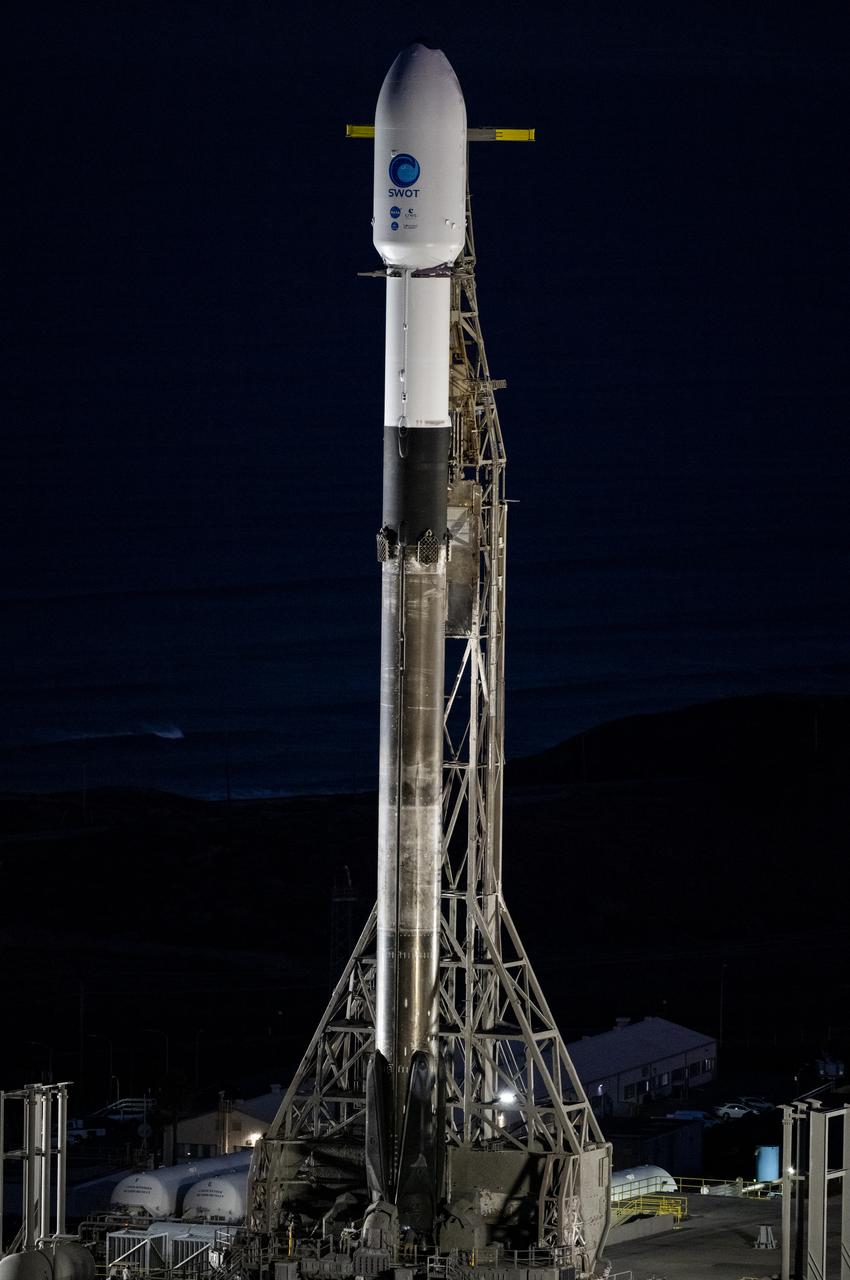
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as it rolls out to the pad, Tuesday, Dec. 13, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
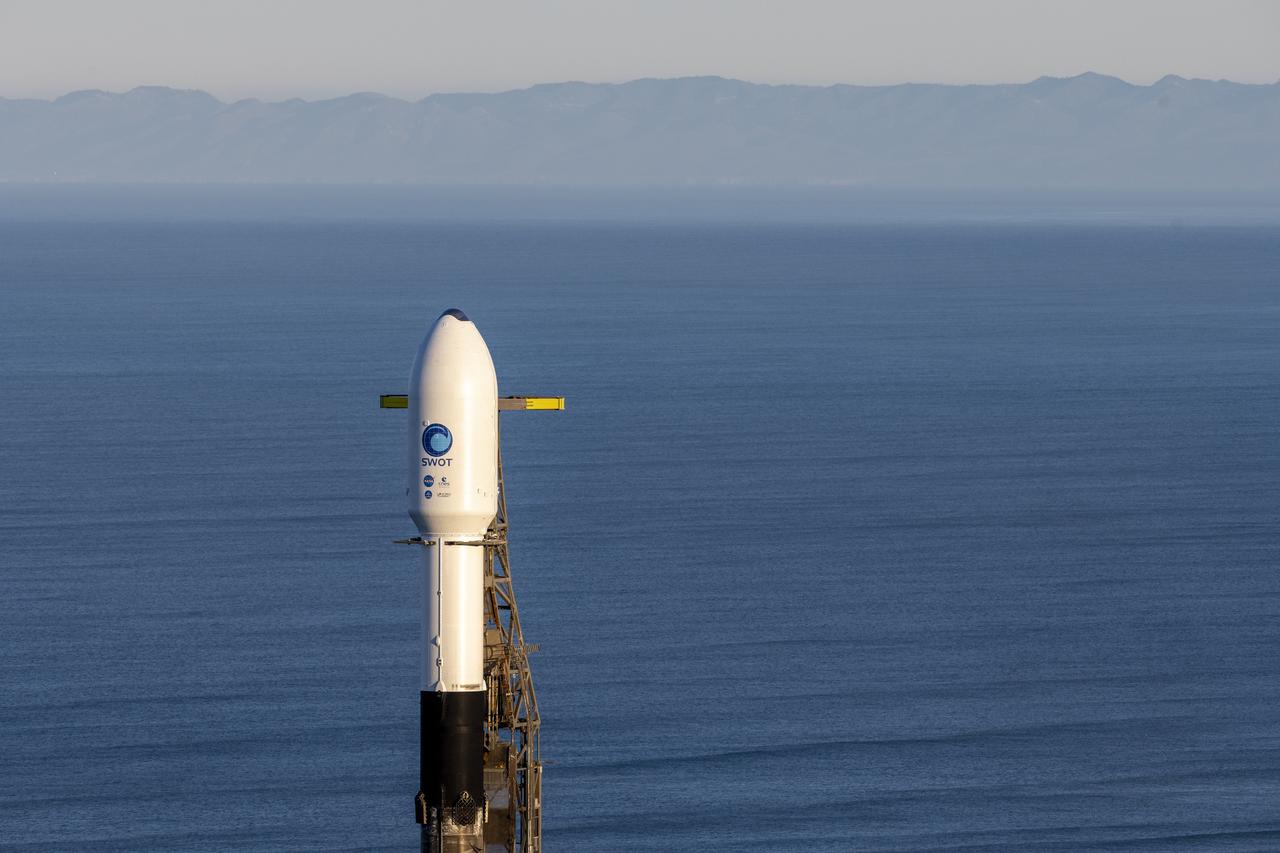

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
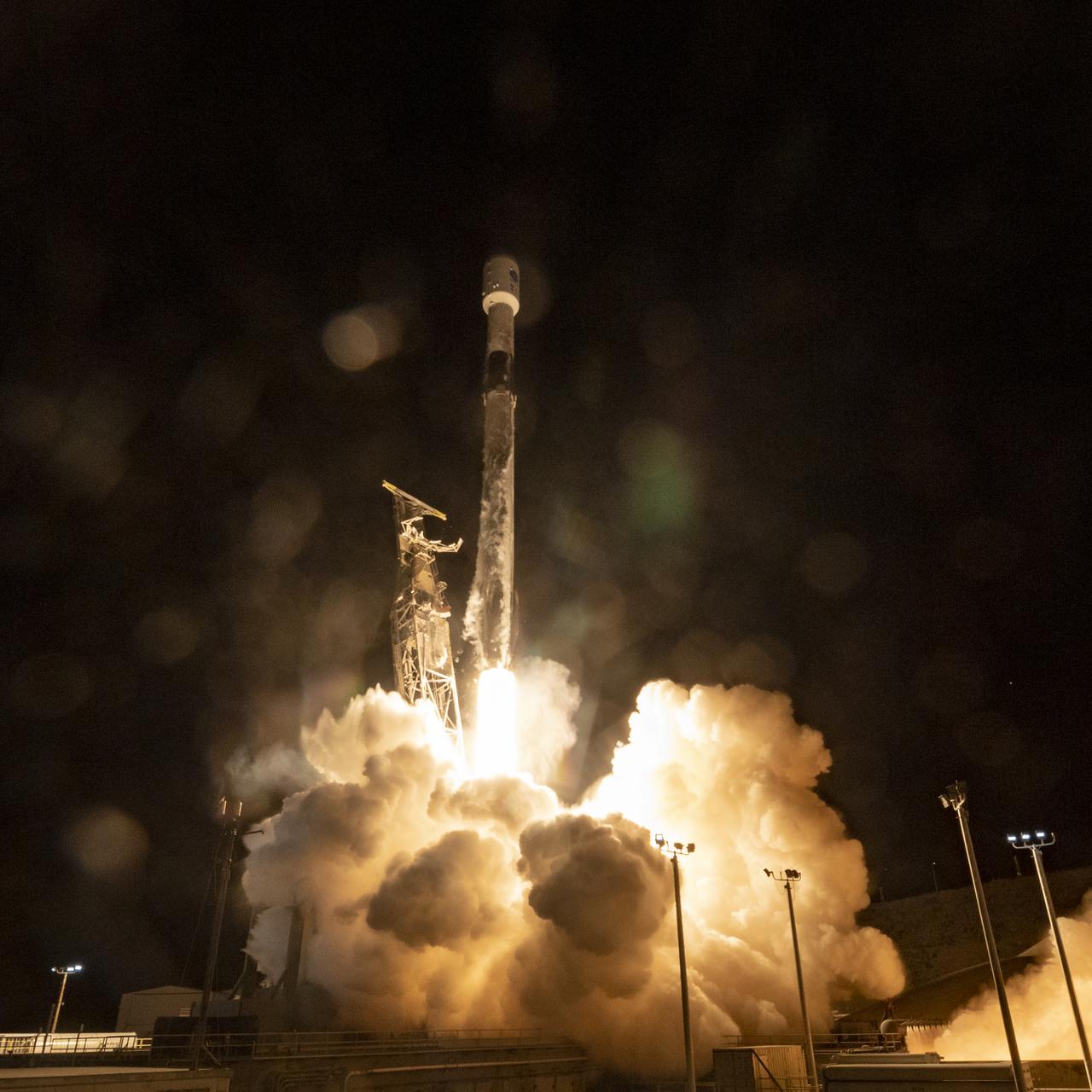

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
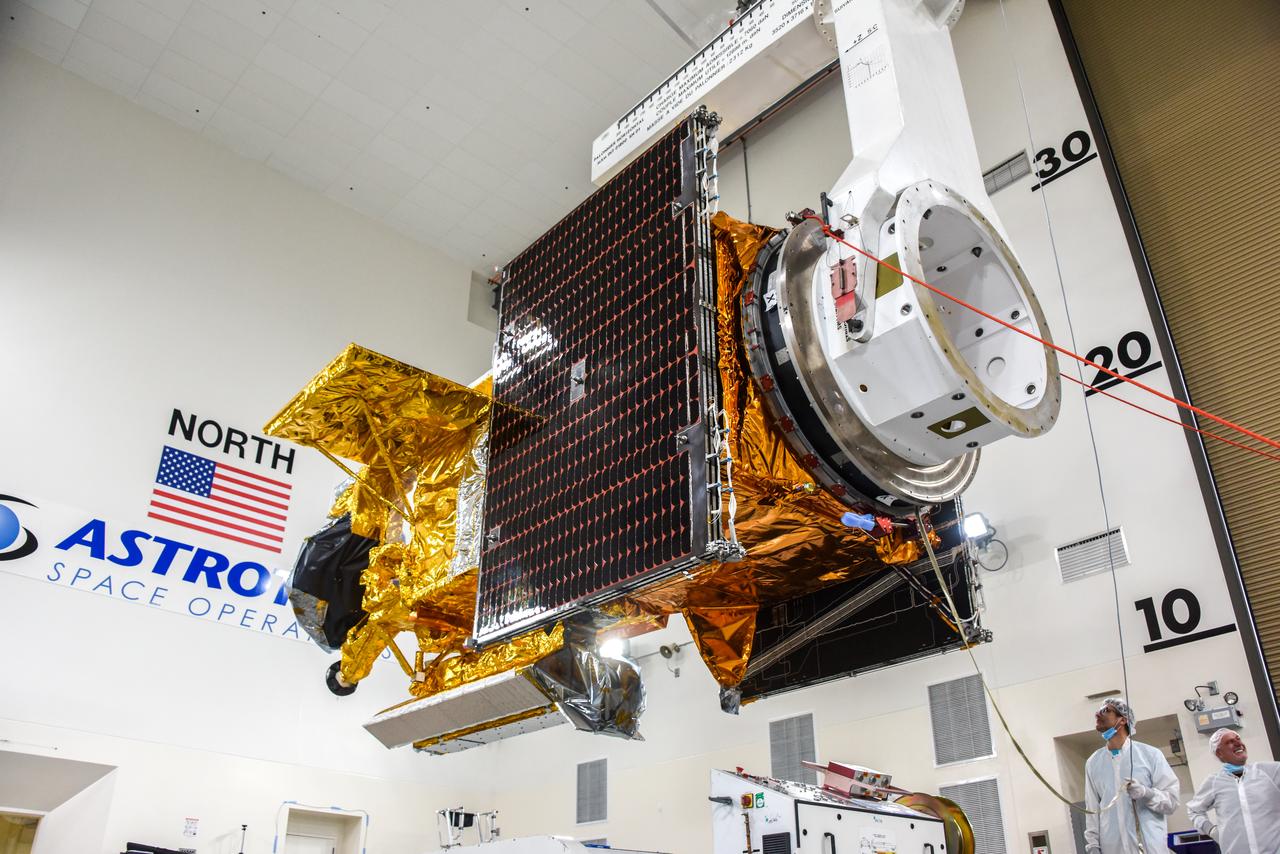

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is moved into a transport container inside the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 18, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
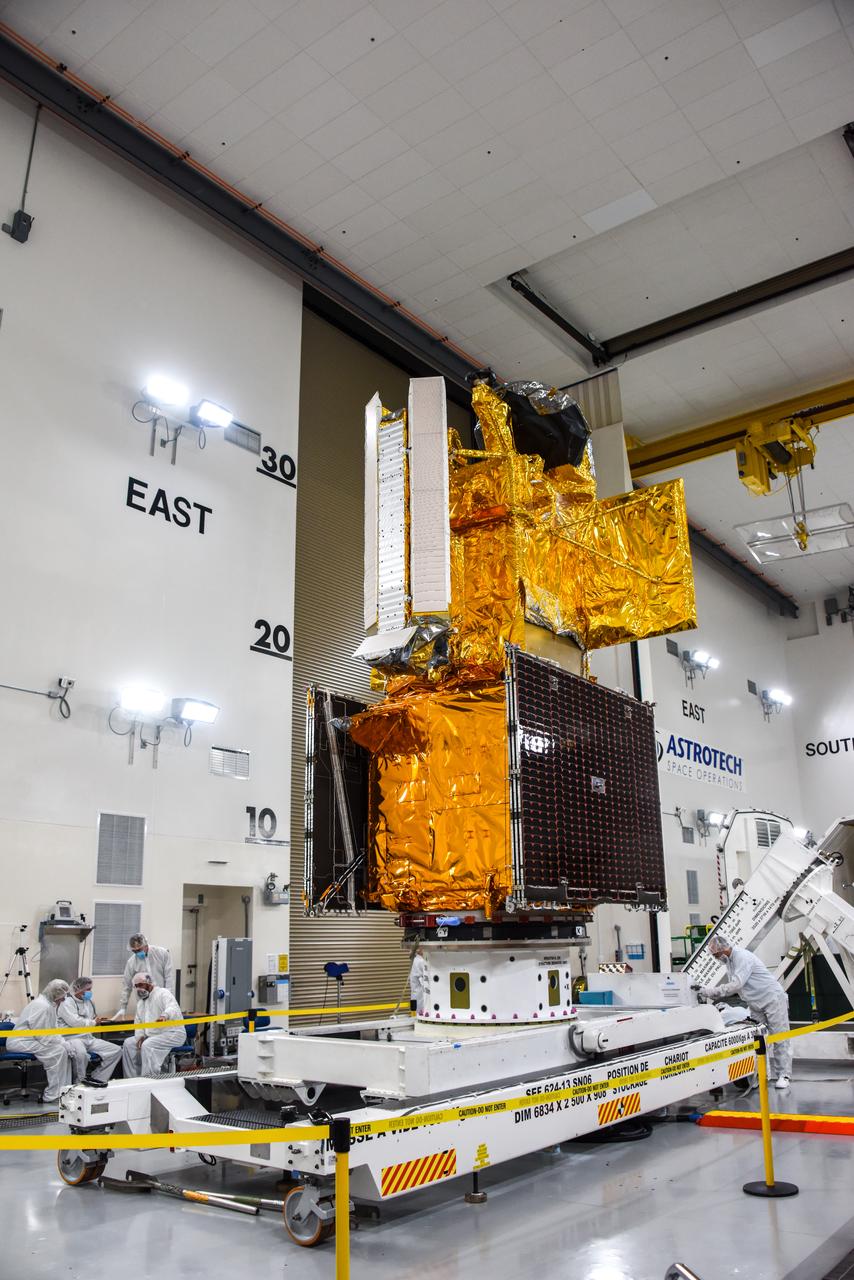

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is moved into a transport container inside the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 18, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as it rolls out to the pad, Tuesday, Dec. 13, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
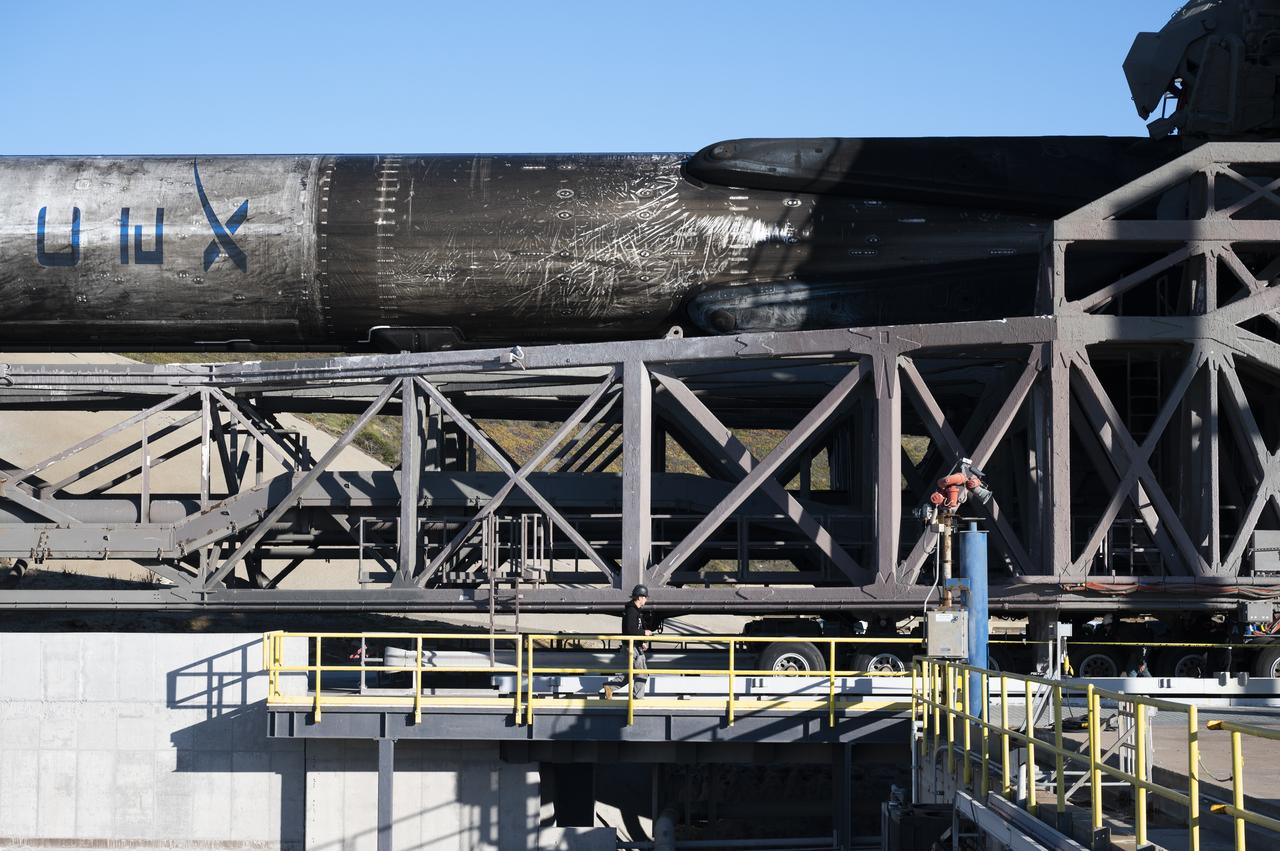

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as it rolls out to the pad, Tuesday, Dec. 13, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
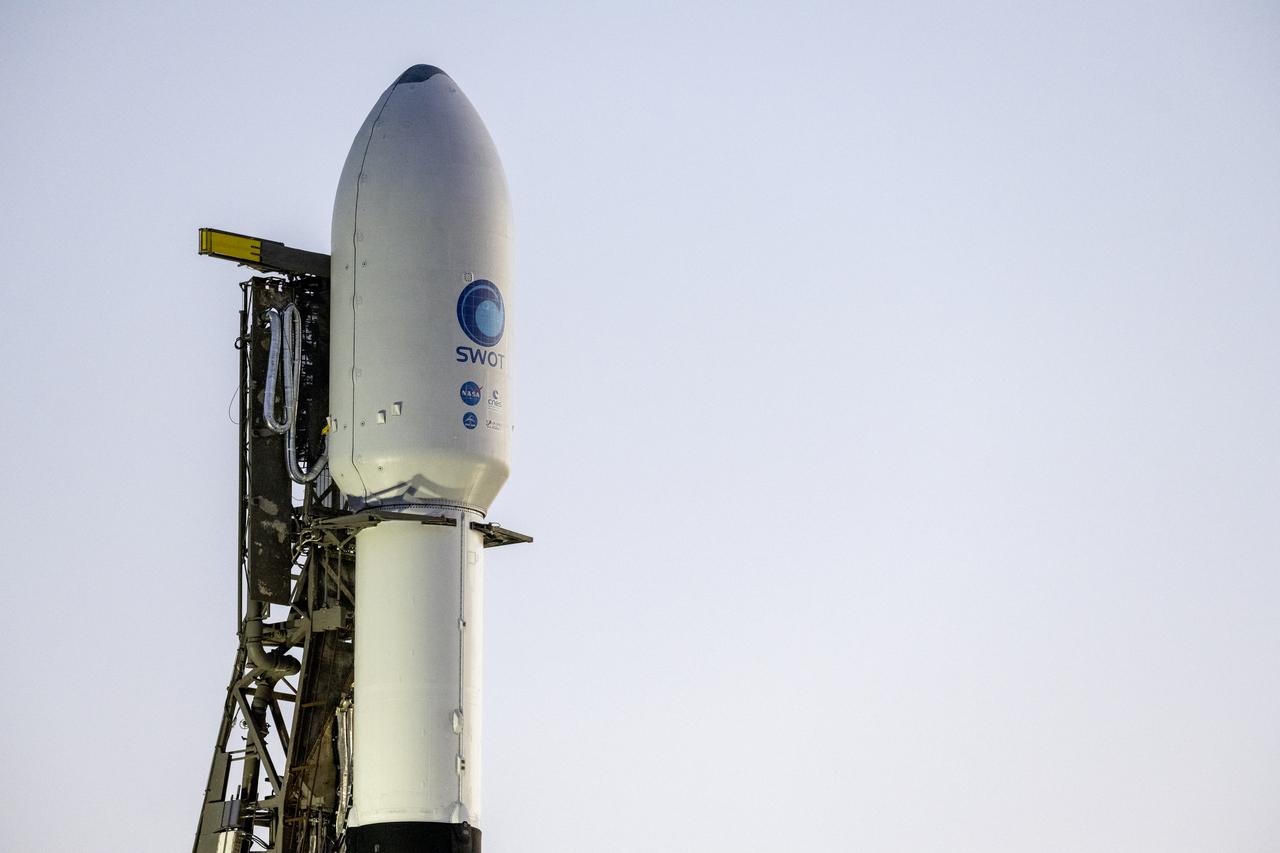

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A container, with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft inside, is moved to a trailer at the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 19, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A SpaceX Falcon 9 first-stage booster returns to the landing pad following the launch of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as it rolls out to the pad, Tuesday, Dec. 13, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is transported from Astrotech to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 21, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is moved into a transport container inside the Astrotech facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 18, 2022. The satellite will be transported to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. It is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
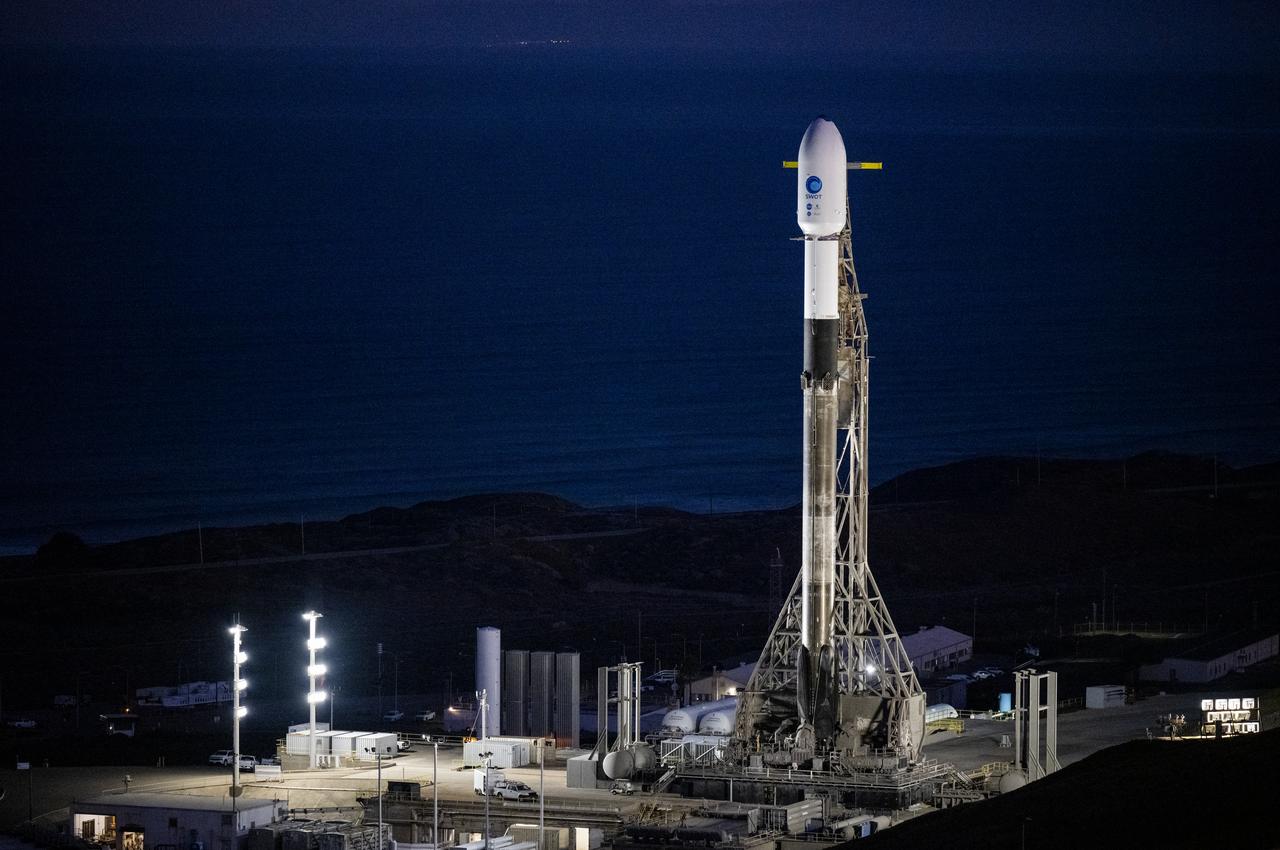

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
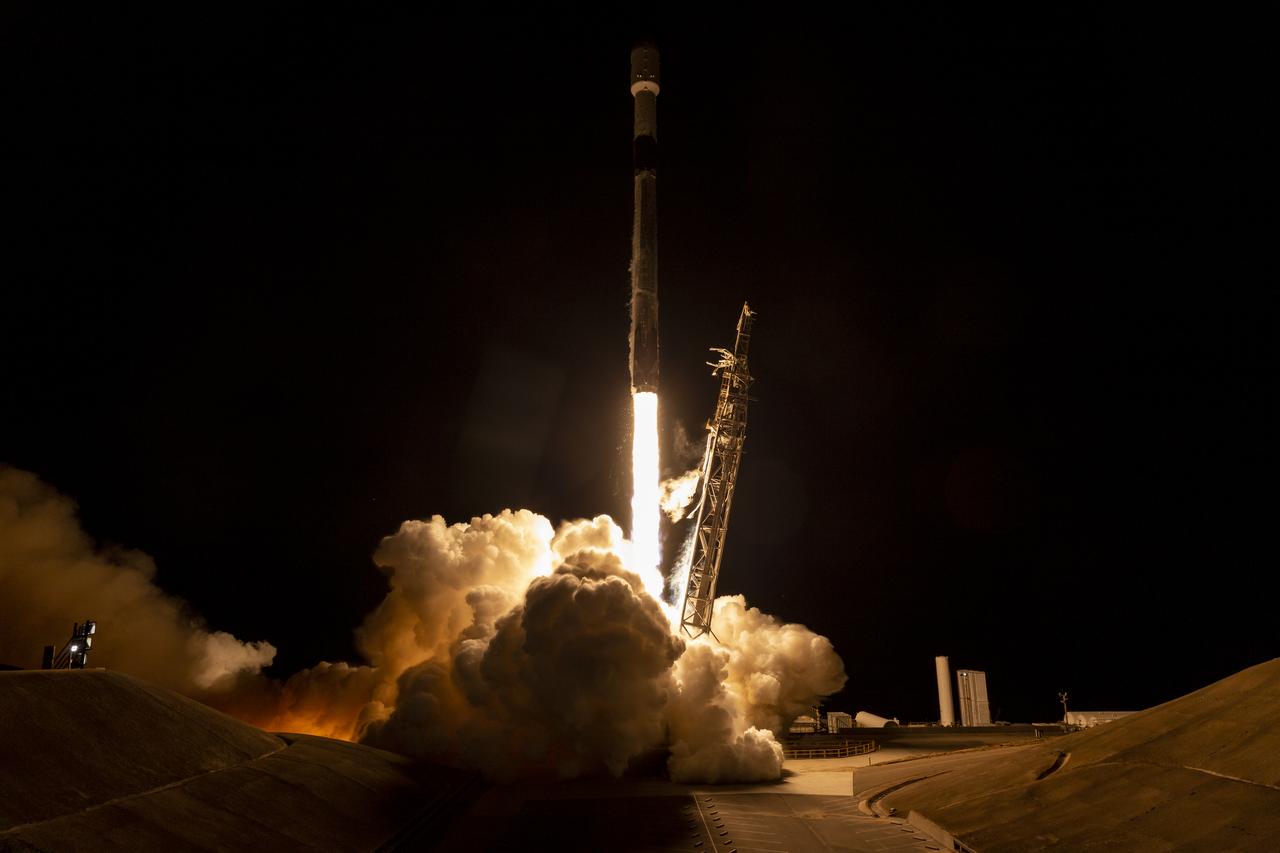

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
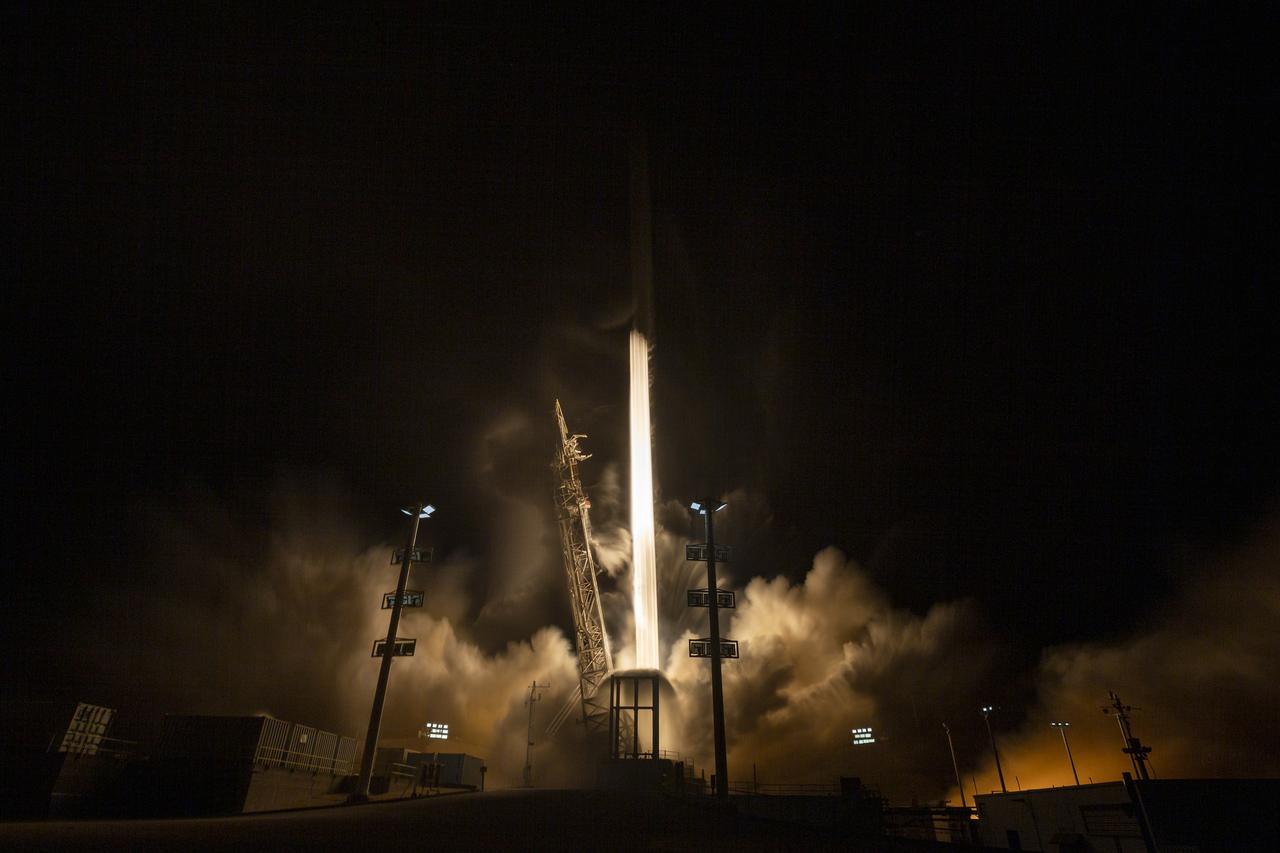

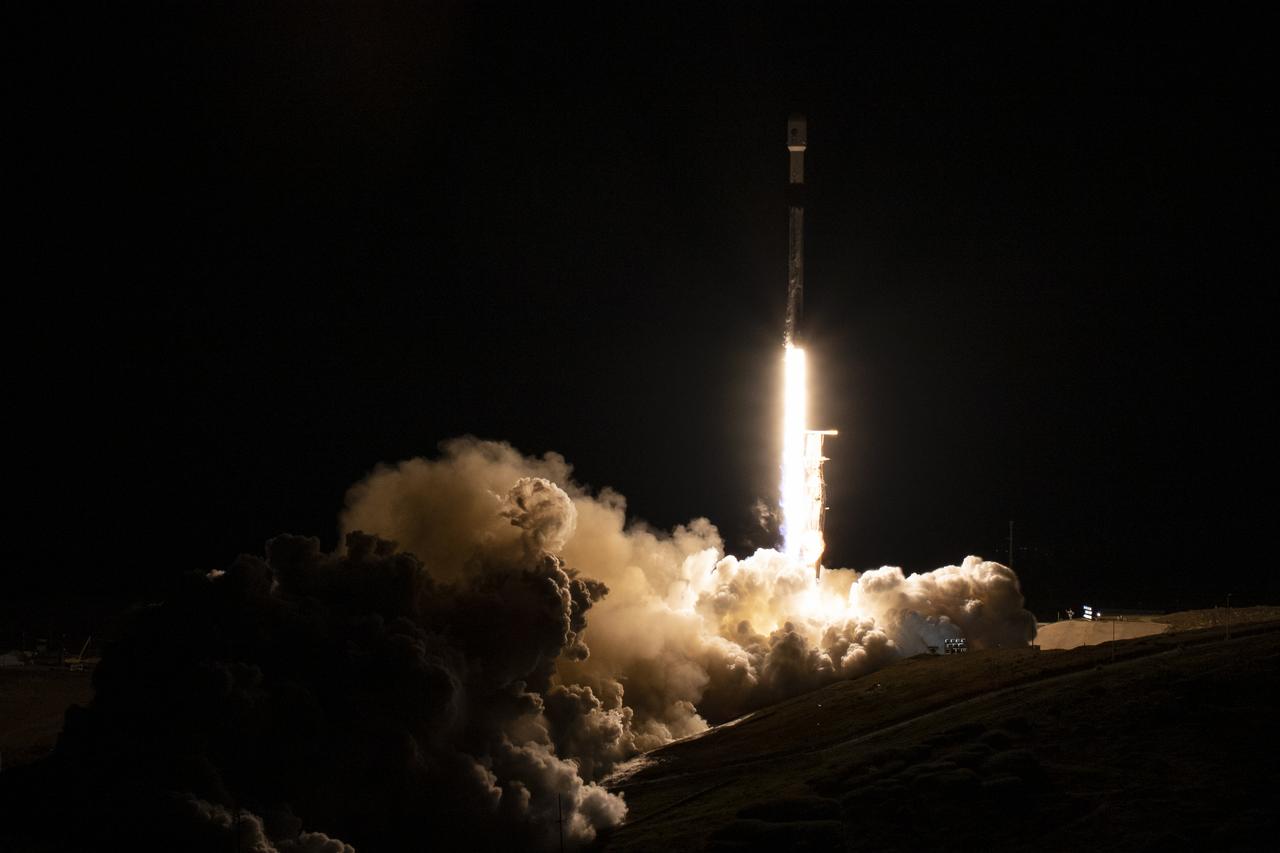
In this 30 second exposure, A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
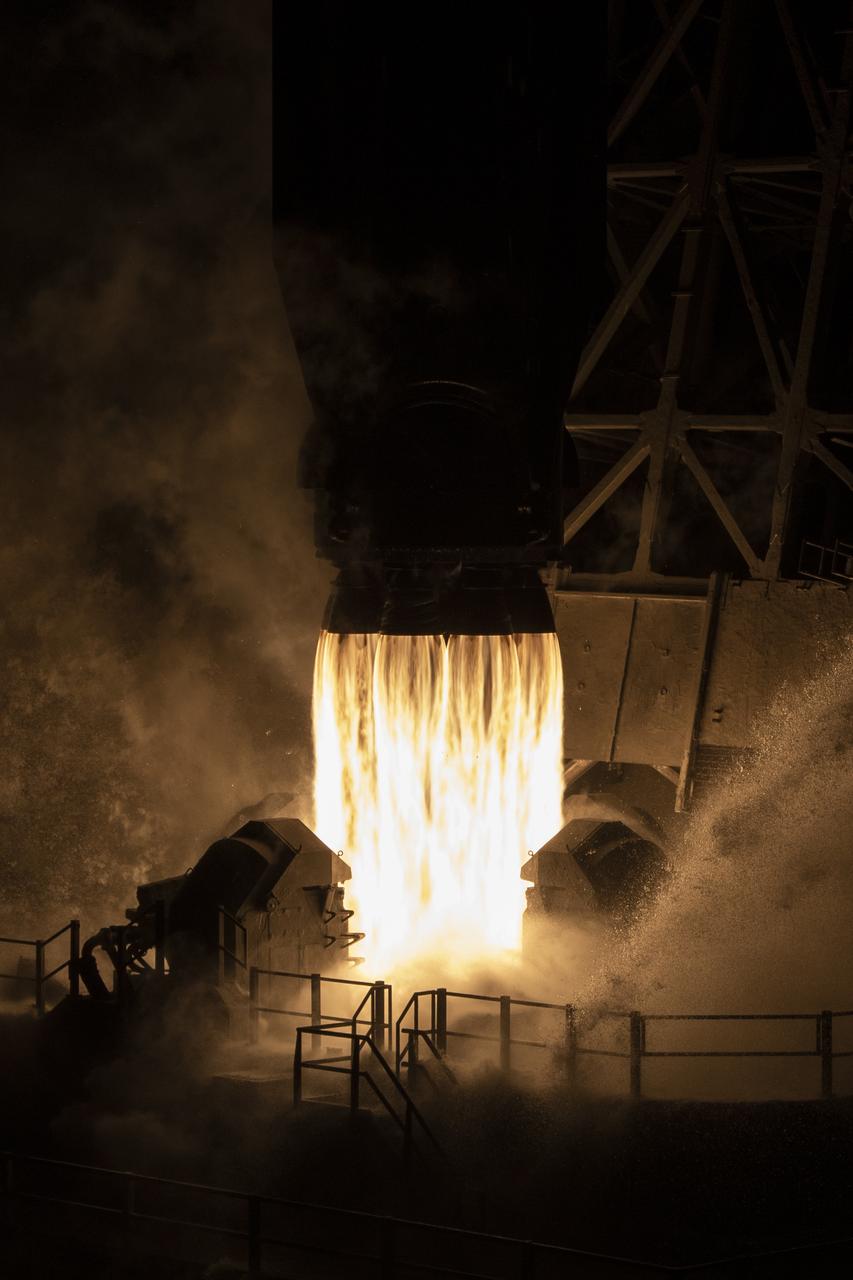

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
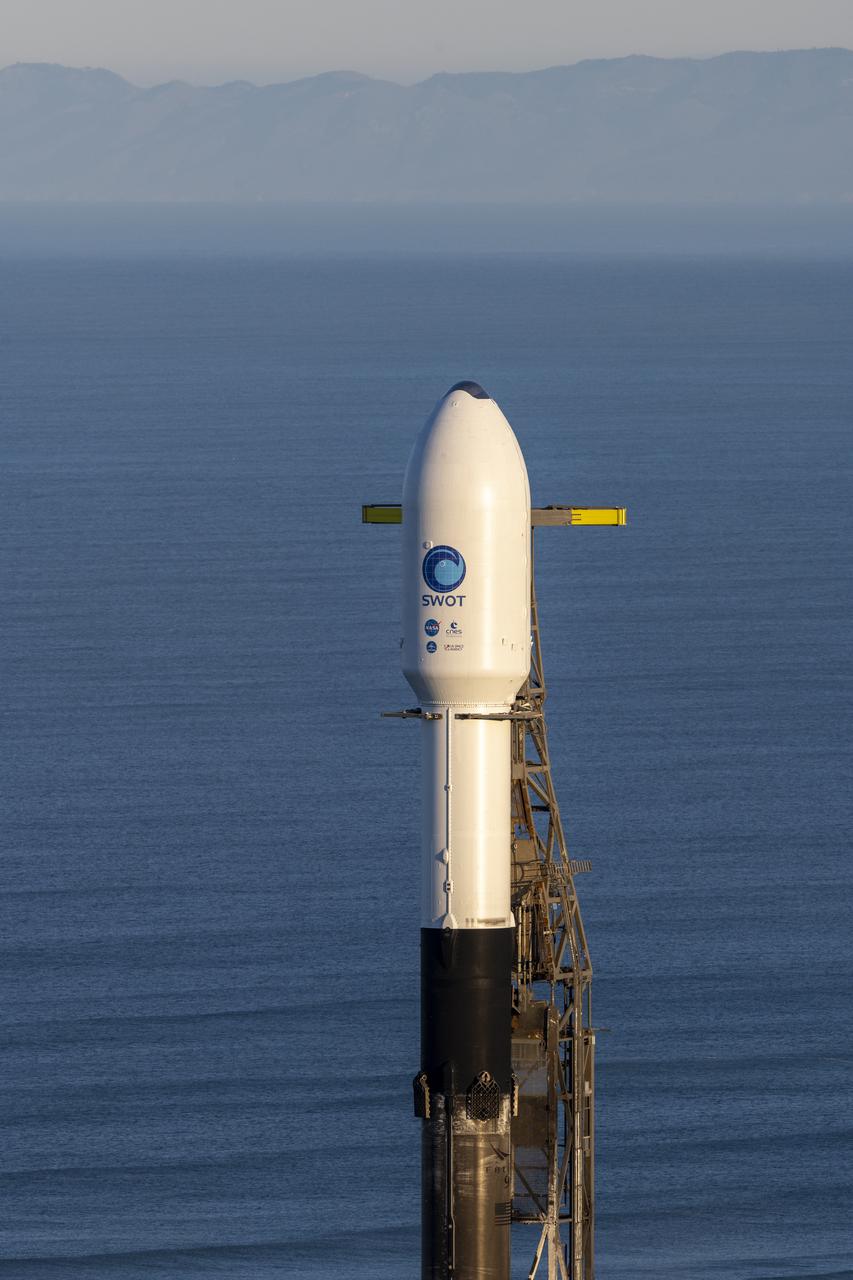

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as preparations for launch continue, Wednesday, Dec. 14, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
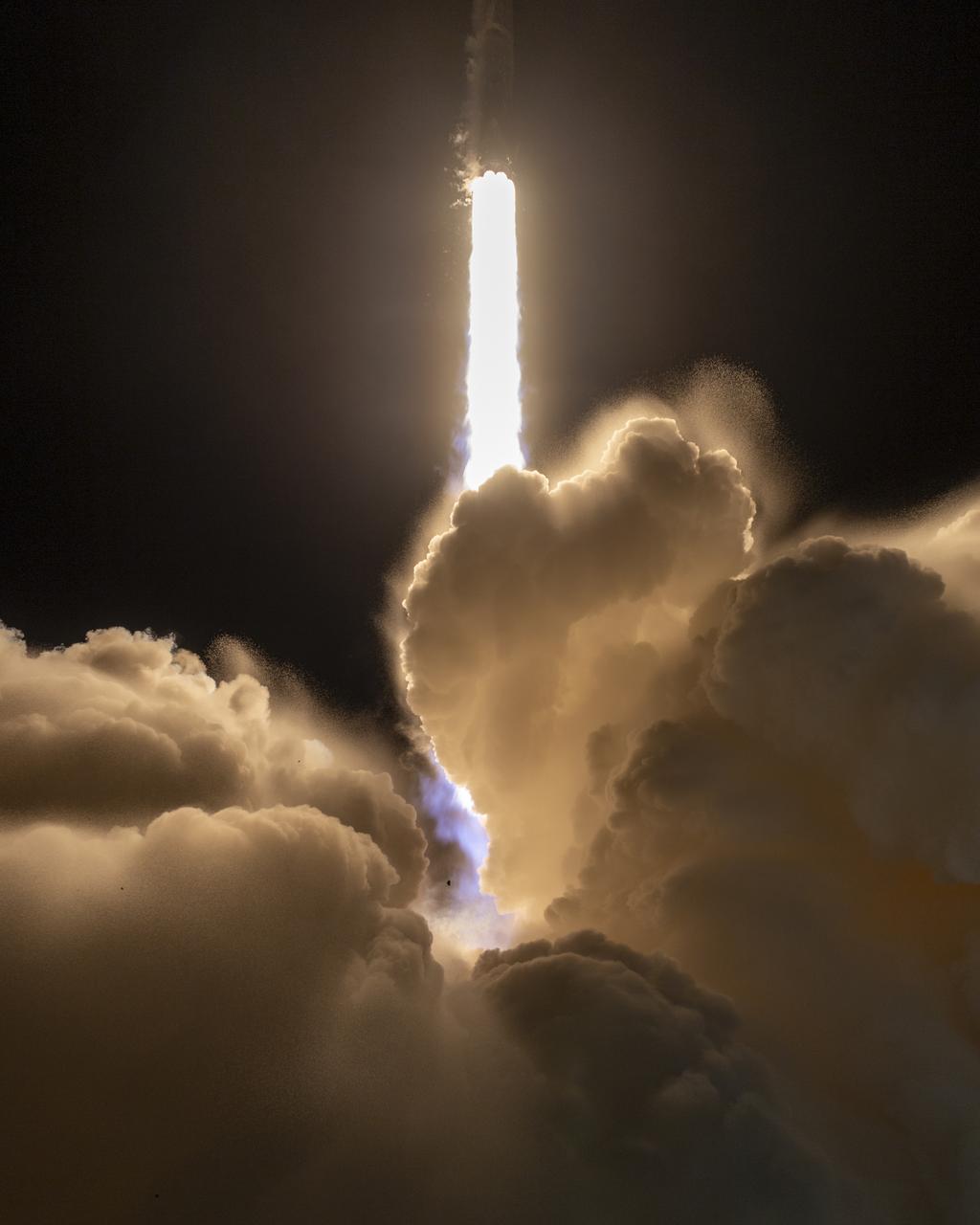

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
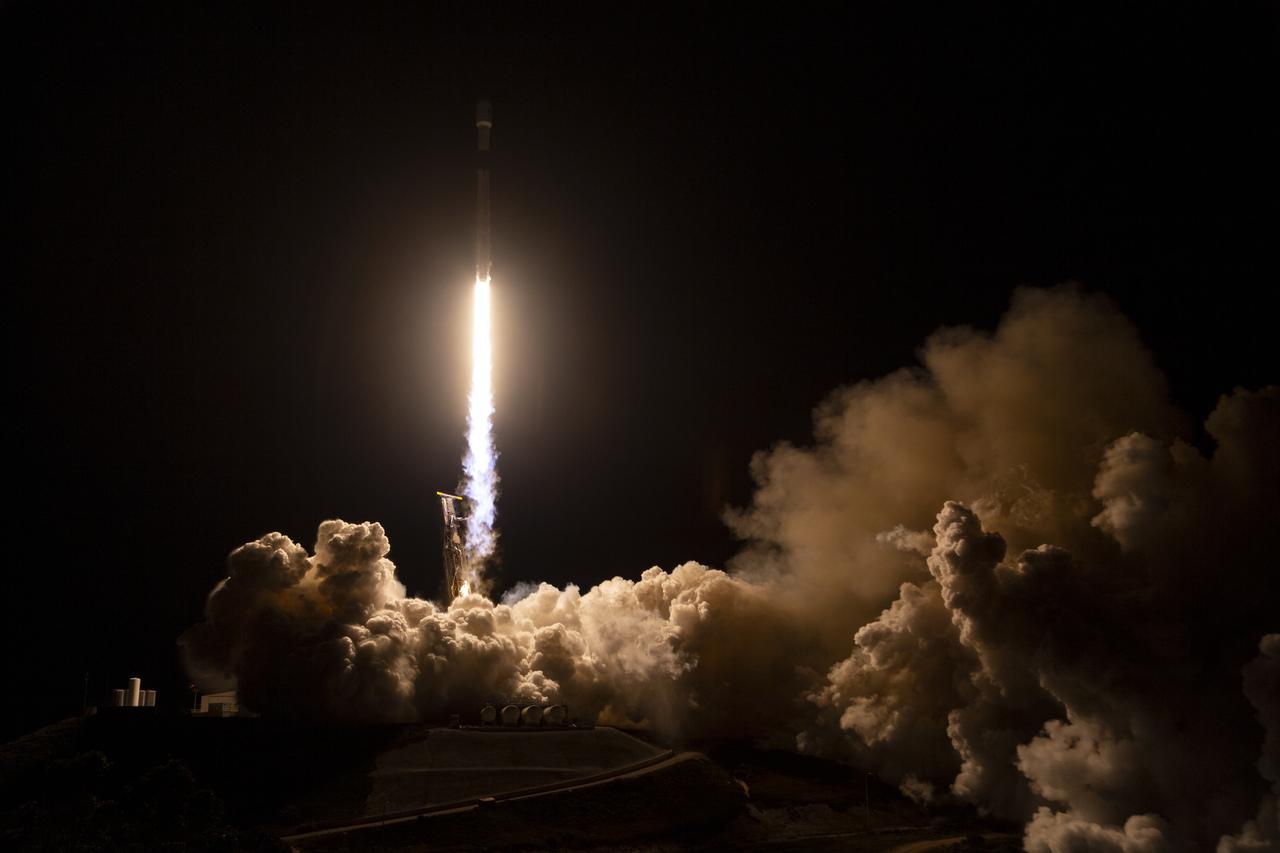

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
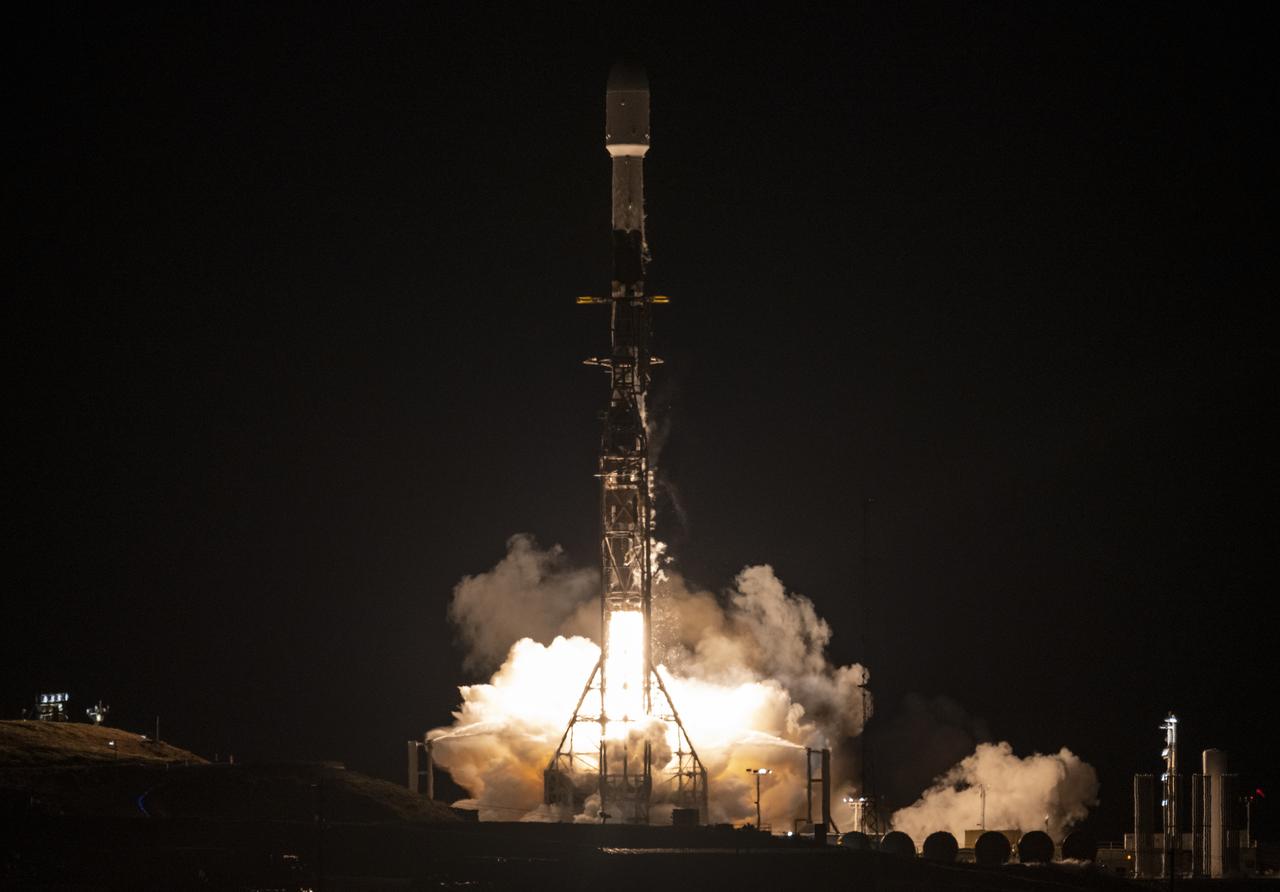

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft is transported from Astrotech to the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Nov. 21, 2022. SWOT is the first mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite is set to launch aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket in December from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.

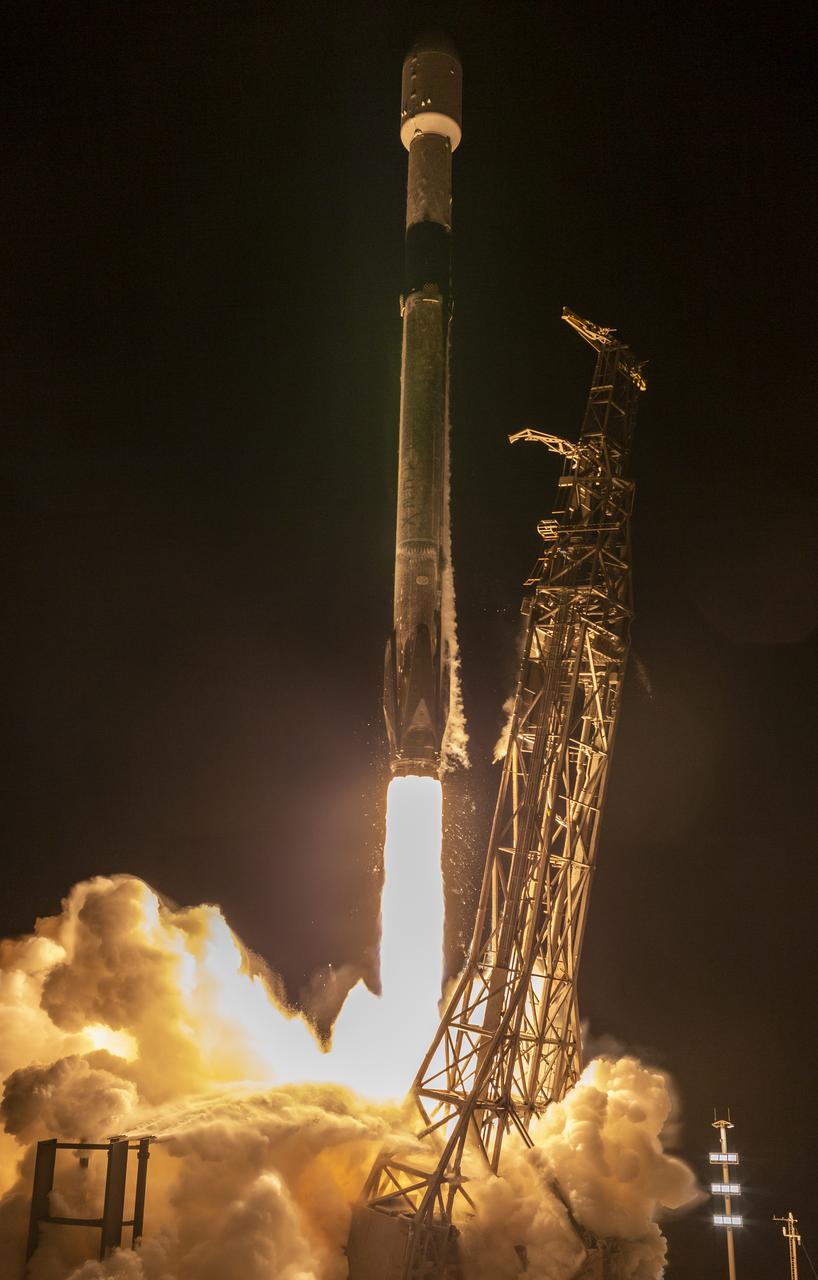
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard is seen as it rolls out to the pad, Tuesday, Dec. 13, 2022, at Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
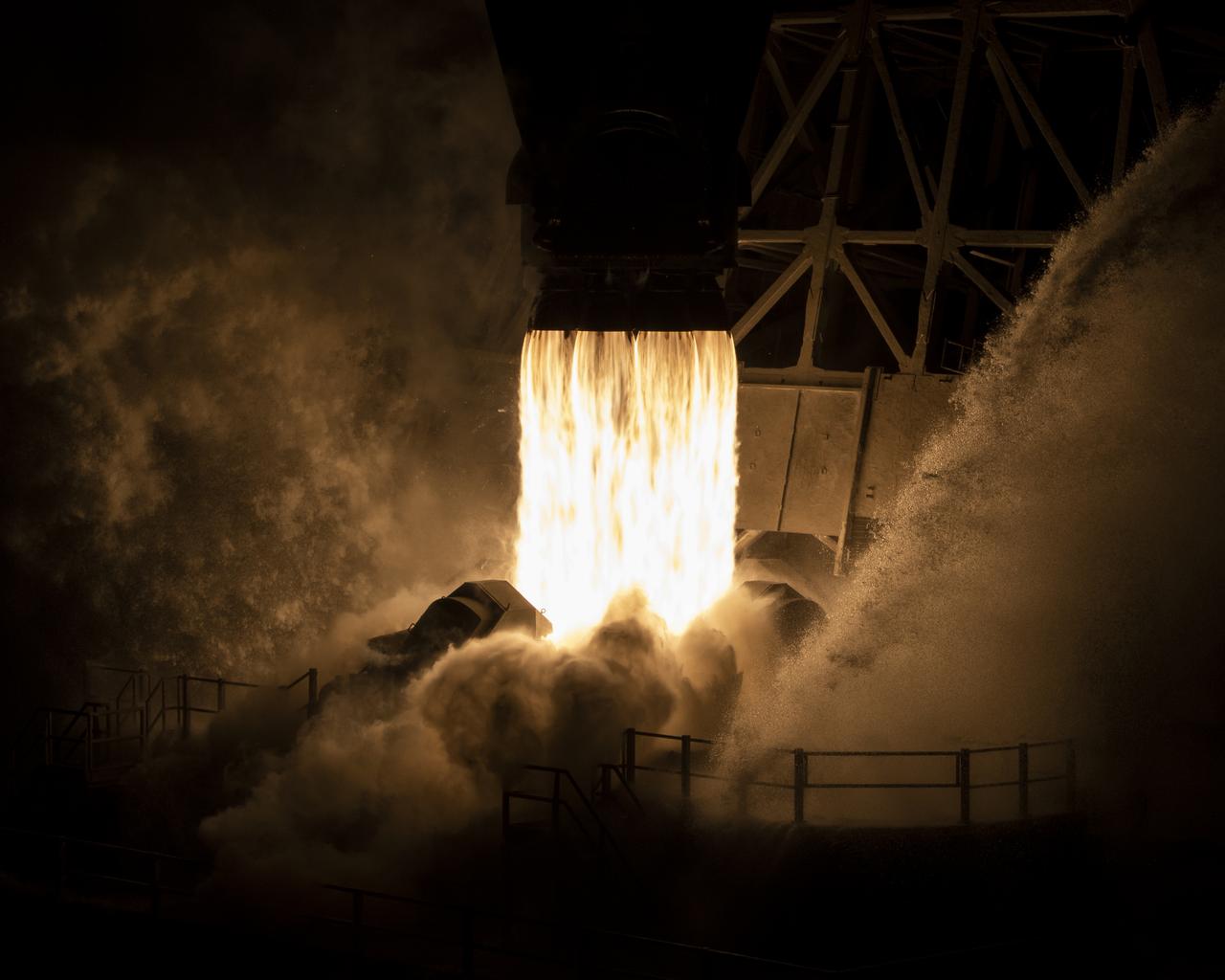

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
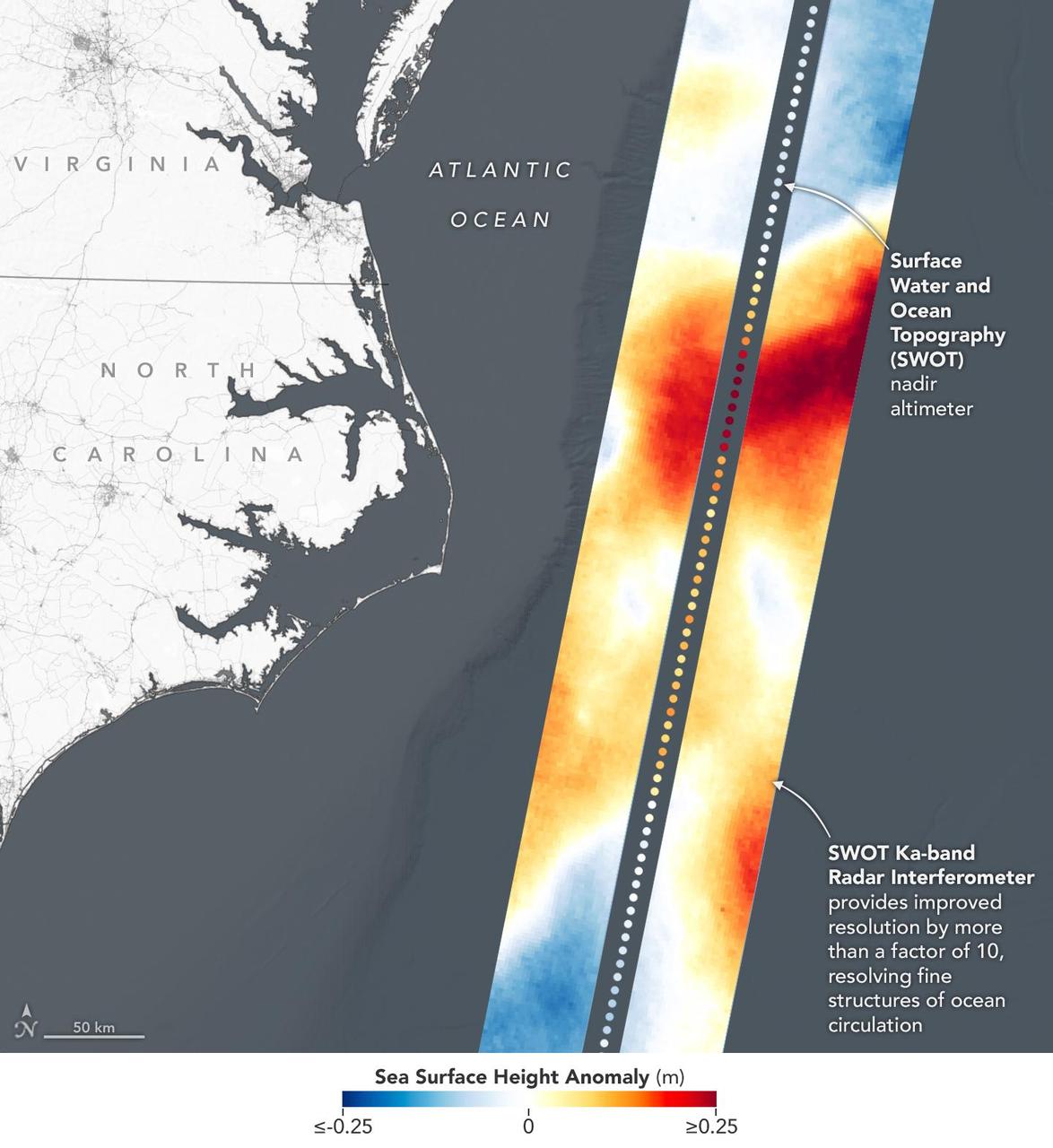
This visualization shows sea surface height measurements in the Gulf Stream off the coast of North Carolina and Virginia. The data was collected on Jan. 21, 2023, by an instrument on the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite called the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn). KaRIn's two antennas acquired data that was mapped as two wide, colored strips spanning a total of 75 miles (120 kilometers) across. In the visualization, red and orange areas represent sea levels that are higher than the global average, while shades of blue represent sea levels that are lower than average. The spatial resolution of SWOT ocean measurements is 10 times greater than the composite of sea surface height data gathered over the same area by seven other satellites that same day. KaRIn is the scientific heart of the SWOT mission. It's a radar instrument with one antenna at each end of a boom that's 33 feet (10 meters) long. This enables KaRIn to look off to either side of a center line directly below the satellite as the instrument bounces microwave signals off of Earth's surface. The returning radar signals arrive at each antenna slightly out of step, or phase, from one another. When these signals are combined with other information about the antennas and the satellite's altitude, scientists will be able to map the height of water on Earth's surface with never-before-seen clarity. Led by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES), SWOT will measure the height of water on over 90% of Earth's surface, providing a high-definition survey of our planet's water for the first time. The satellite's measurements of freshwater bodies and the ocean will provide insights into how the ocean influences climate change; how a warming world affects lakes, rivers, and reservoirs; and how communities can better prepare for disasters like floods. Launched on Dec. 16, 2022, from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT is now in a six-month period called commissioning, calibration and validation. This is when engineers on the mission check out the satellite's systems and science instruments to ensure data accuracy before the start of science operations in July. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25772
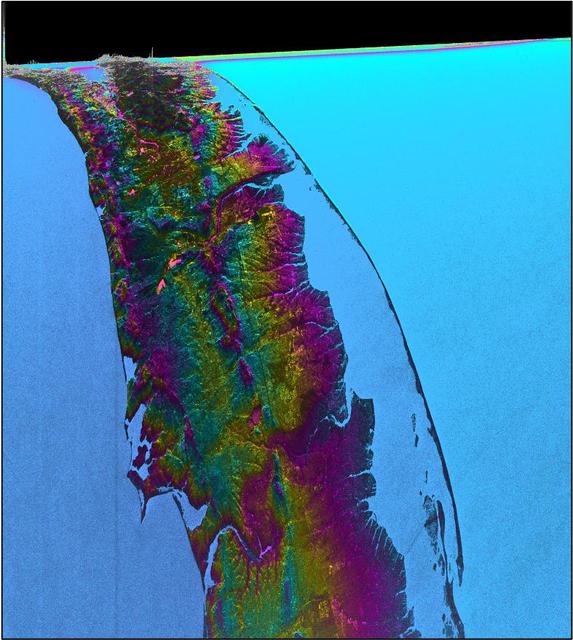
This visualization shows water features on New York's Long Island – shown as bright pink splotches nestled within the landscape. Purple, yellow, green, and dark blue shades represent different land elevations, while the surrounding ocean is a lighter blue. The data was collected on Jan. 21, 2023, by an instrument on the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite called the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn). KaRIn is the scientific heart of the SWOT mission. It's a radar instrument with one antenna at each end of a boom that’s 33 feet (10 meters) long. This enables KaRIn to look off to either side of a center line directly below the satellite as the instrument bounces microwave signals off of Earth's surface. The returning radar signals arrive at each antenna slightly out of step, or phase, from one another. When these signals are combined with other information about the antennas and the satellite's altitude, scientists will be able to map the height of water on Earth's surface with never-before-seen clarity. This initial inland image is a tantalizing indication of how SWOT can measure details of smaller lakes, ponds, and rivers in ways that satellites could not before. Such data will be used to produce an extraordinary accounting of the freshwater on Earth's surface in ways useful to researchers, policymakers, and water resource managers. Led by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES), SWOT will measure the height of water on over 90% of Earth's surface, providing a high-definition survey of our planet's water for the first time. The satellite's measurements of freshwater bodies and the ocean will provide insights into how the ocean influences climate change; how a warming world affects lakes, rivers, and reservoirs; and how communities can better prepare for floods and other disasters. Launched on Dec. 16, 2022, from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT is now in a six-month period called commissioning, calibration and validation. This is when engineers on the mission check out the satellite's systems and science instruments to ensure data accuracy before the start of science operations in July. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25774
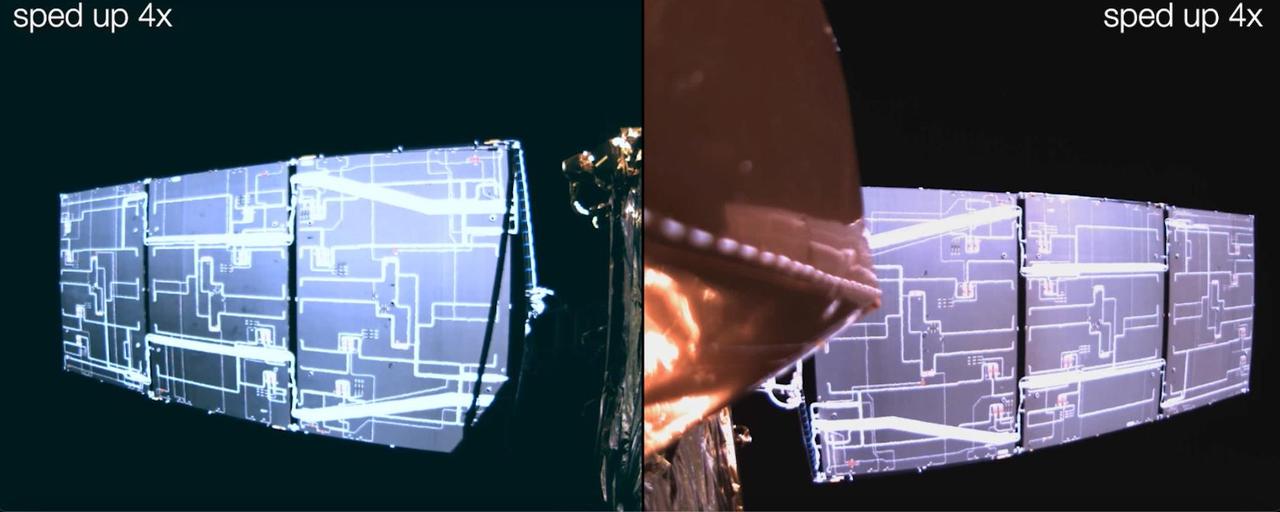

This video is a series of images showing the deployment of the solar arrays that power the international Surface Water and Ocean Topography satellite (SWOT). The mission captured the roughly 10-minute process with two of the four commercial cameras aboard the satellite (the same type used to capture NASA's Perseverance rover landing on Mars). The satellite launched Dec. 16, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, and the arrays started their deployment at 5:01 a.m. PST. SWOT's two solar arrays measure 48.8 feet (14.9 meters) from end to end, with a total surface area of 335 square feet (31 square meters). Extending from opposite sides of the spacecraft bus, the arrays remain pointed at the Sun via small motors. They provide 8 kilowatts of power to the satellite, which has a 1.5-kilowatt total power demand. SWOT will survey the height of water in Earth's lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite will cover the planet's surface at least once every 21 days and has a prime mission of three years. It was jointly developed by NASA and France's Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the UK Space Agency. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25563
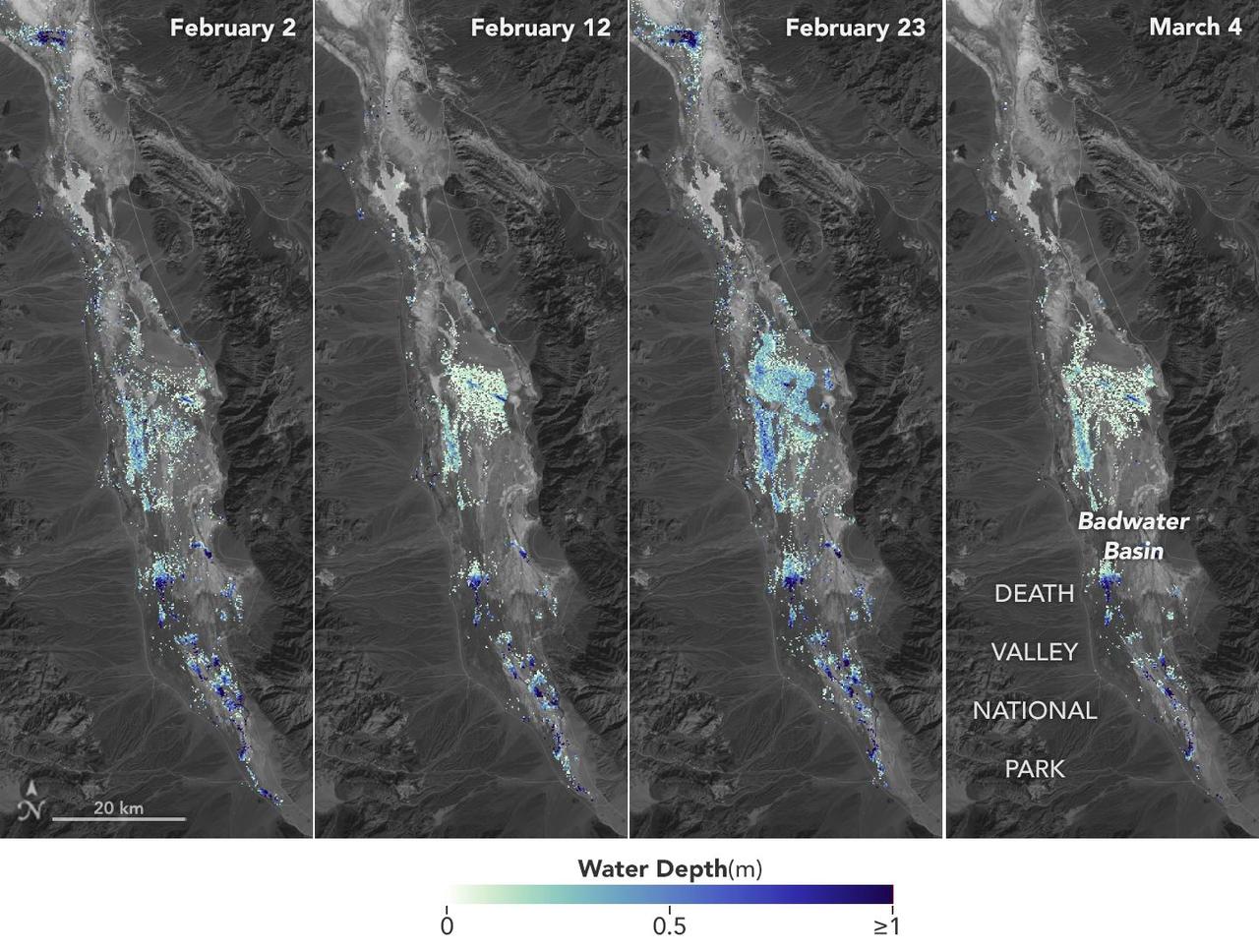
California's Death Valley, the driest place in North America, has hosted an ephemeral lake since late 2023. In March 2024, a NASA-led analysis calculated water depths in the temporary lake over several weeks in February and March 2024, demonstrating the possibilities of the latest water-observing mission, the U.S.-French Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite. The analysis found that water depths in the lake ranged between about 3 feet (1 meter) to less than 1.5 feet (0.5 meters) over the course of several weeks. This period included a series of storms that swept across California, bringing record amounts of rainfall. To estimate the depth of the lake, known informally as Lake Manly, researchers used water level data collected by SWOT and subtracted corresponding U.S. Geological Survey land elevation information for Badwater Basin. The researchers found that the water levels varied across space and time in the roughly 10-day period between SWOT observations. In the visualization above, water depths of about 3 feet (1 meter) appear dark blue; those of less than 1.5 feet (0.5 meters) appear light yellow. Right after a series of storms in early February, the temporary lake was about 6 miles (10 kilometers) long and 3 miles (5 kilometers) wide. Each pixel in the image represents an area that is about 330 feet by 330 feet (100 meters by 100 meters). Unlike many lakes around the world, Death Valley's lake is temporary, relatively shallow, and strong winds are enough to move the freshwater body a couple of miles, as happened from Feb. 29 to March 2. Since there isn't typically water in Badwater Basin, researchers don't have permanent instruments in place for studying water in this area. SWOT can fill the data gap for when places like this, and others around the world, become inundated. Since shortly after launch in December 2022, SWOT has been measuring the height of nearly all water on Earth's surface, developing one of the most detailed and comprehensive views of the planet's oceans and freshwater lakes and rivers. Not only can the satellite detect the extent of water, as other satellites can, but SWOT can also measure water surface levels. Combined with other types of information, SWOT measurements can yield water depth data for inland features like lakes and rivers. The SWOT science team makes its measurements using the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument. With two antennas spread 33 feet (10 meters) apart on a boom, KaRIn produces a pair of data swaths as it circles the globe, bouncing radar pulses off water surfaces to collect surface-height information. Launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT is now in its operations phase, collecting data that will be used for research and other purposes. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26184
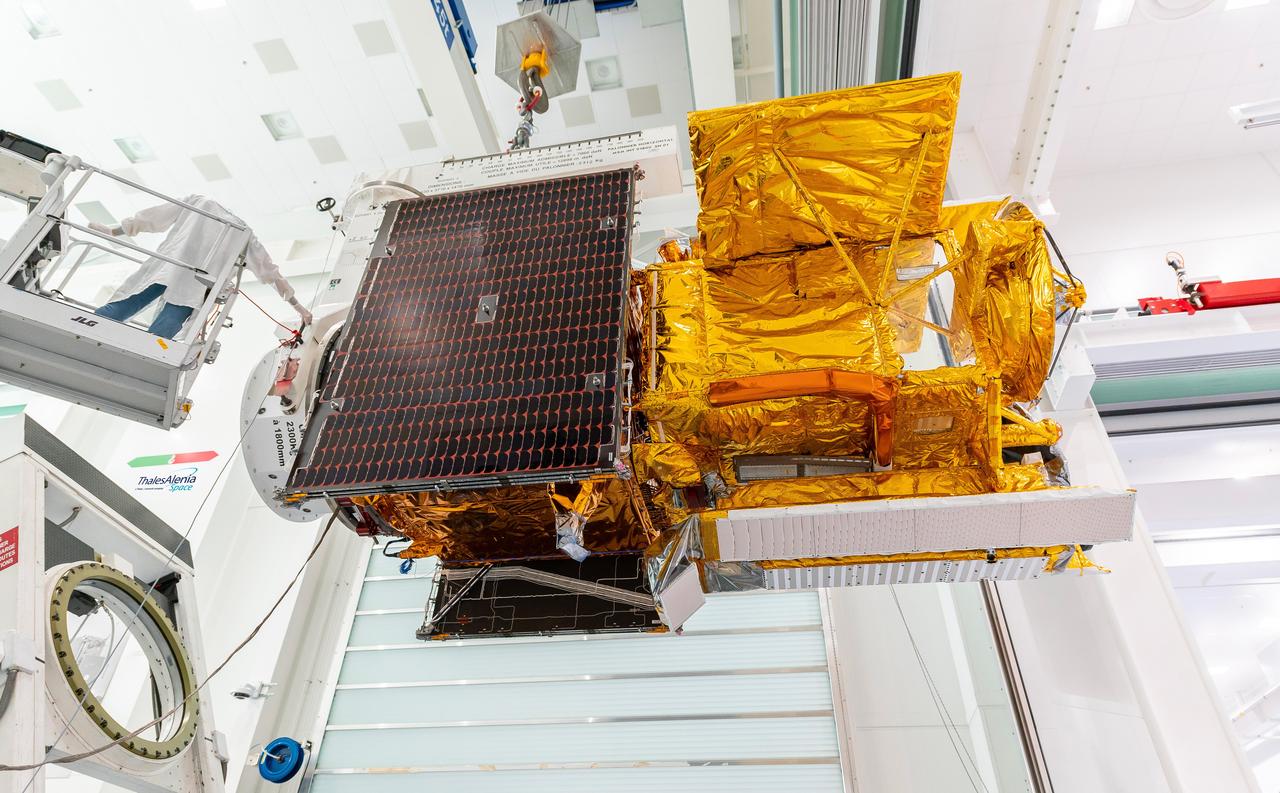

Workers in a clean room in Cannes, France, load the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite into a container in preparation for shipping the spacecraft to the U.S. SWOT is an international mission led by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES) that will survey water on more than 90% of Earth's surface. The spacecraft will view water in Earth's lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean in higher definition than ever before. The information that SWOT gathers will help inform water management decisions and prepare communities for rising seas and changing coastlines. It will also help researchers better understand the exchange of heat and carbon between the ocean and atmosphere, an important component of the role that Earth's ocean plays in the planet's climate. SWOT will launch out of the Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California no earlier than Dec. 5, 2022. SWOT is being jointly developed by NASA and CNES, with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the United Kingdom Space Agency. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, leads the U.S. component of the project. For the flight system payload, NASA is providing the KaRIn instrument, a GPS science receiver, a laser retroreflector, a two-beam microwave radiometer, and NASA instrument operations. CNES is providing the Doppler Orbitography and Radioposition Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) system, the dual frequency Poseidon altimeter (developed by Thales Alenia Space), the KaRIn radio-frequency subsystem (together with Thales Alenia Space and with support from the UK Space Agency), the platform, and ground control segment. CSA is providing the KaRIn high-power transmitter assembly. NASA is providing the launch vehicle and associated launch services. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24910
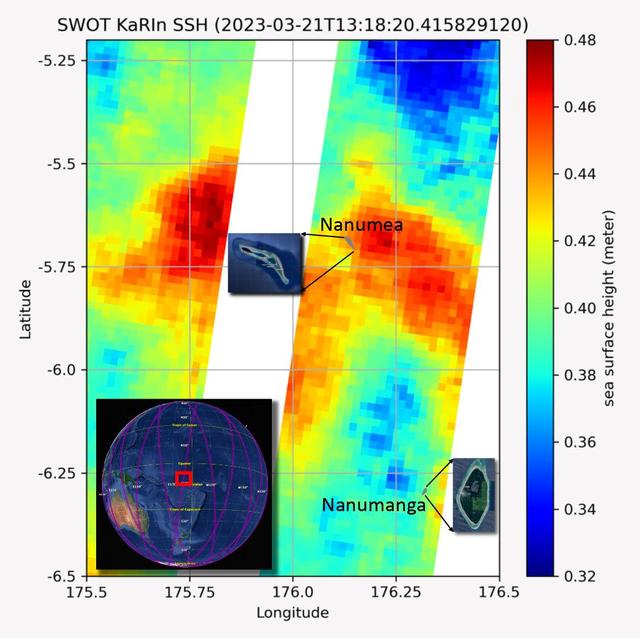
The recently launched Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission collected data on sea levels around two of the inhabited islands of Tuvalu, a nation in the South Pacific Ocean that has been threatened with sea level rise that substantially exceeds the global average. The image shows two areas of red that indicate higher than normal sea levels around two of Tuvalu's inhabited islands, Nanumanga and Nanumea. The higher sea levels were likely caused by internal tides or circular currents called eddies. The SWOT data illuminates for the first time these small ocean features that, when they occur on top of rising sea levels, can lead to episodic flooding along coastlines. The Tuvalu data was collected March 21, 2023. Rising seas are a direct consequence of climate change. On a global scale, the combination of warming ocean waters and ice melt from glaciers and ice sheets is leading to sea level rise that is occurring at an ever-increasing rate. The current rate of rise is more than 0.15 inches (4 millimeters) per year, an increase from 0.08 inches (2 millimeters) per year in 1993. This seemingly small increase holds great significance for coastal communities that have seen more than a century of persistent sea level rise. The gap between the average high tide and flooding conditions has narrowed, and coastal impacts driven by sea level rise have increased in frequency and severity in recent years. This is particularly true for low-lying island nations like Tuvalu, located about 620 miles (1,000 kilometers) north of Fiji. Sea level rise does not occur at the same rate everywhere across the globe, and can be exacerbated by natural ocean fluctuations that occur over time periods from years to decades. For Tuvalu, the amount of sea level rise has been substantially higher than the global average over the past three decades. The amount of rise, when coupled with Tuvalu's low land elevations, places the country increasingly under threat. In the near term, sea level rise will combine with naturally occurring ocean variability and storms to exacerbate events like coastal flooding. Monitoring and understanding sea level change is critical for Tuvalu and other low-lying island nations. Launched on Dec. 16, 2022, from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT collected the Tuvalu sea level data during a period of commissioning, calibration, and validation. Engineers are checking out the performance of the satellite's systems and science instruments before the planned start of science operations in summer 2023. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25777
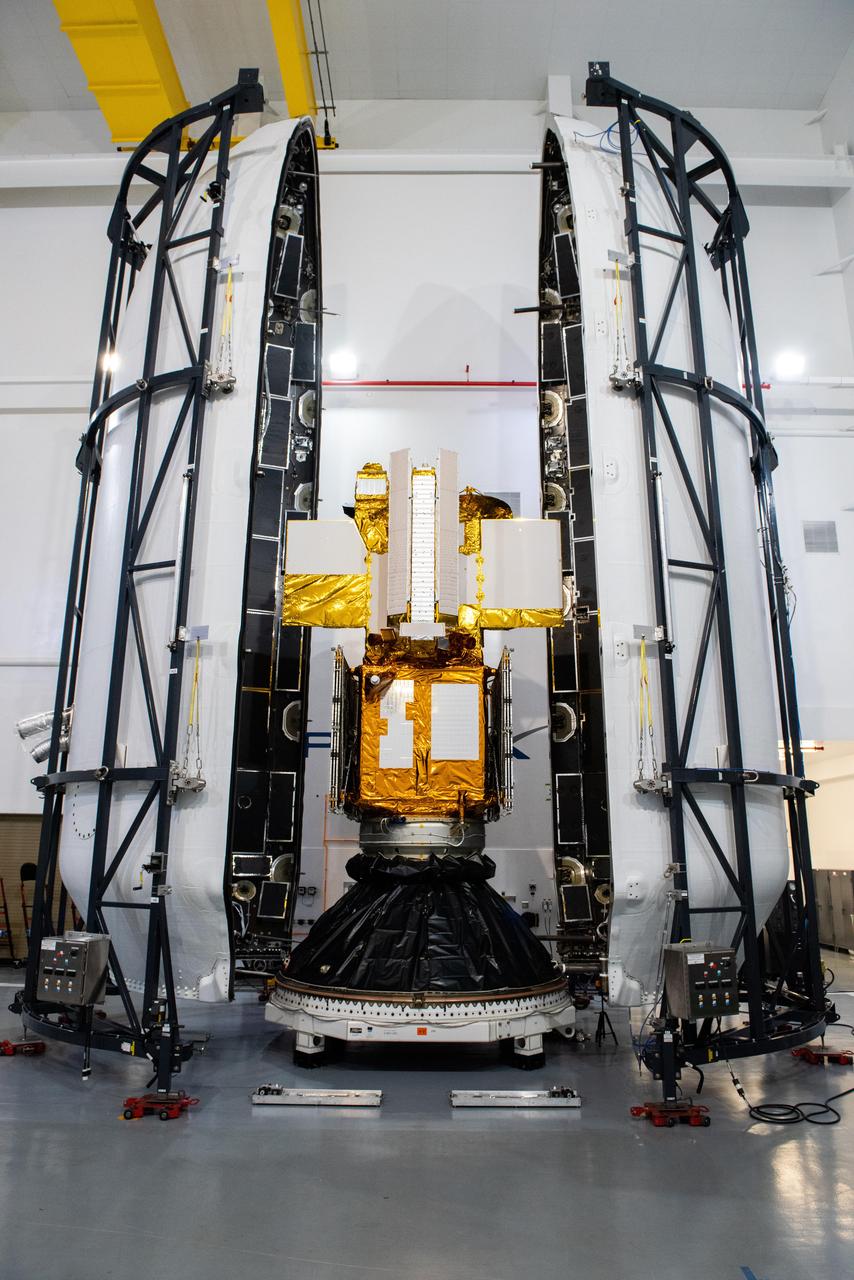

Technicians encapsulated the SWOT satellite, or the Surface Water and Ocean Topography mission, in its payload fairing on Dec. 8, 2022, in preparation for launch. At the SpaceX processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, technicians completed the operation and will soon mate the fairing to the top of a Falcon 9 rocket. The fairing protects the satellite from aerodynamic pressure and heating during ascent. After the rocket escapes Earth's atmosphere, the fairing separates into two halves, which are jettisoned back to Earth. Once in orbit, SWOT will measure the height of water in freshwater bodies and the ocean on more than 90% of Earth's surface. This information will provide insights into how the ocean influences climate change; how a warming world affects lakes, rivers, and reservoirs; and how communities can better prepare for disasters, such as floods. SWOT is a collaborative effort by NASA and France's Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES) with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and UK Space Agency. Launch is targeted for Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25627
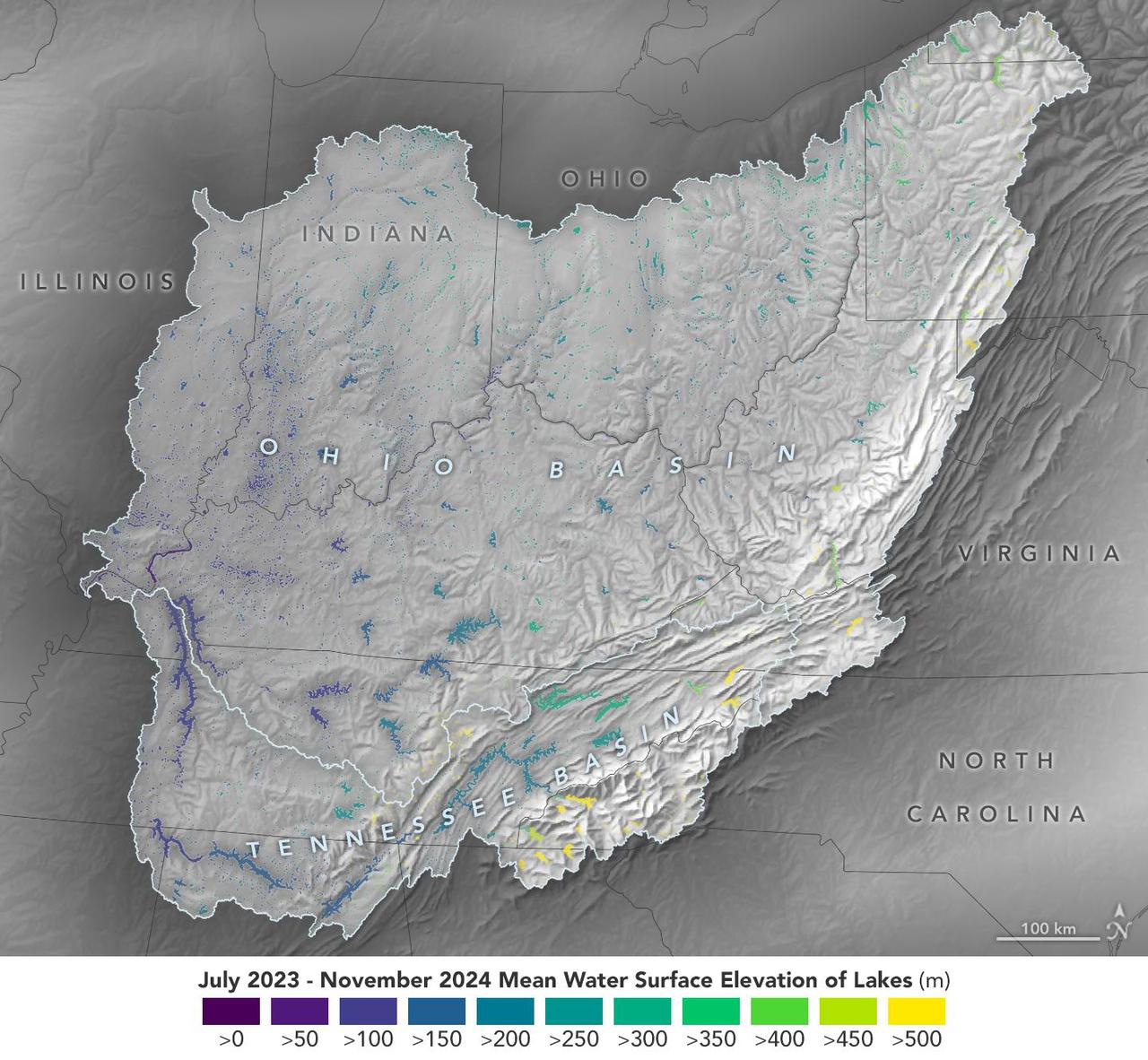
This visualization based on data from the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite shows the average water level for lakes and reservoirs in the Ohio River Basin from July 2023 to November 2024. Yellow indicates values greater than 1,600 feet (500 meters) above sea level, and dark purple represents water levels less than 330 feet (100 meters). Comparing how such levels change can help hydrologists measure water availability over time in a local area or across a watershed. Since early 2023, SWOT has been measuring the height of nearly all water on Earth's surface – including oceans, lakes, reservoirs, and rivers – covering nearly the entire globe at least once every 21 days. The satellite also measures the horizontal extent of water in freshwater bodies. Earlier this year, the SWOT mission started making validated data (processed measurements that have been checked for accuracy) publicly available. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26188

This animation, created in 2012, shows the increasing clarity and detail of measurements of sea height made by successive satellite altimeters launched by NASA and other agencies over the past four decades, concluding with data at the resolution possible with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite, expected to launch in December 2022. Each new spacecraft has been able to obtain higher-resolution observations than its predecessors. Sea height is key to understanding how much, and how fast, the oceans are rising in a warming climate. The animation starts with Seasat, launched in 1978 as one of the NASA's earliest Earth-observing satellites, then moves to Geosat, a U.S. Navy spacecraft launched in 1985, and on to ERS-1, TOPEX/Poseidon, ERS-2, Jason-1, Envisat, and Jason-2. Since the end of the time period shown in the animation, subsequent satellites have continued measuring sea height, creating an ongoing, decadeslong record. In March 2022, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, a joint U.S.-European mission, became the official reference satellite for global sea level measurements. SWOT will be latest spacecraft to observe ocean heights from Earth orbit. Its measurements will provide unprecedented insights into the activity of small-scale currents and their impact on climate change. Researchers believe small-scale currents, which are less than 60 miles (100 kilometers) in size, have a significant influence on the ocean's ability to absorb atmospheric heat and carbon and thereby moderate global temperature change. To measure these currents, SWOT will employ the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn), a new technology developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California that will offer even greater spatial resolution than previous instruments that studied the ocean. SWOT will survey the water in Earth's lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. The satellite will cover the planet's surface twice every 21 days and has a prime mission of three years. It was jointly developed by NASA and France's Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the UK Space Agency. JPL, a division of Caltech in Southern California, manages the U.S. portion of the mission for NASA. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25561
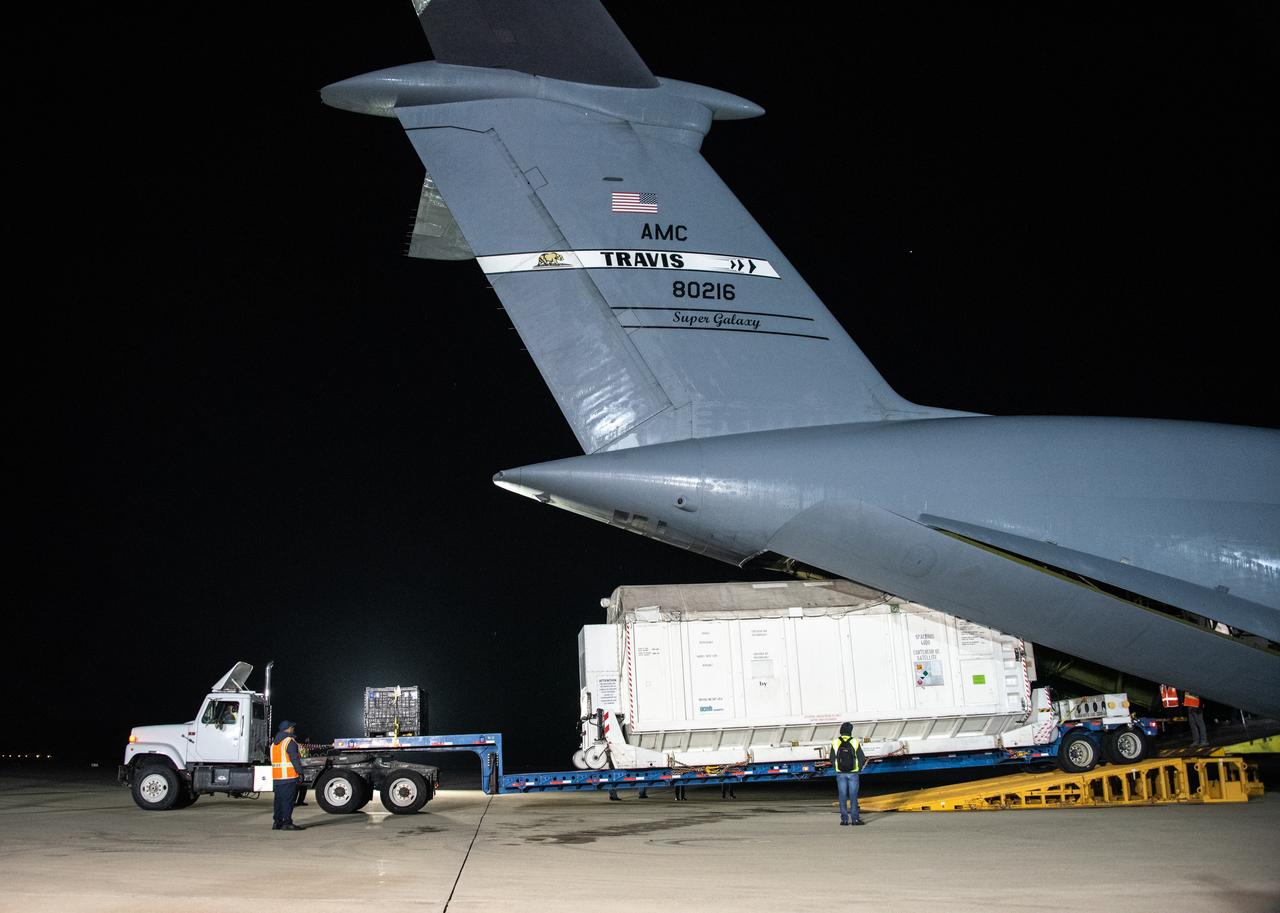

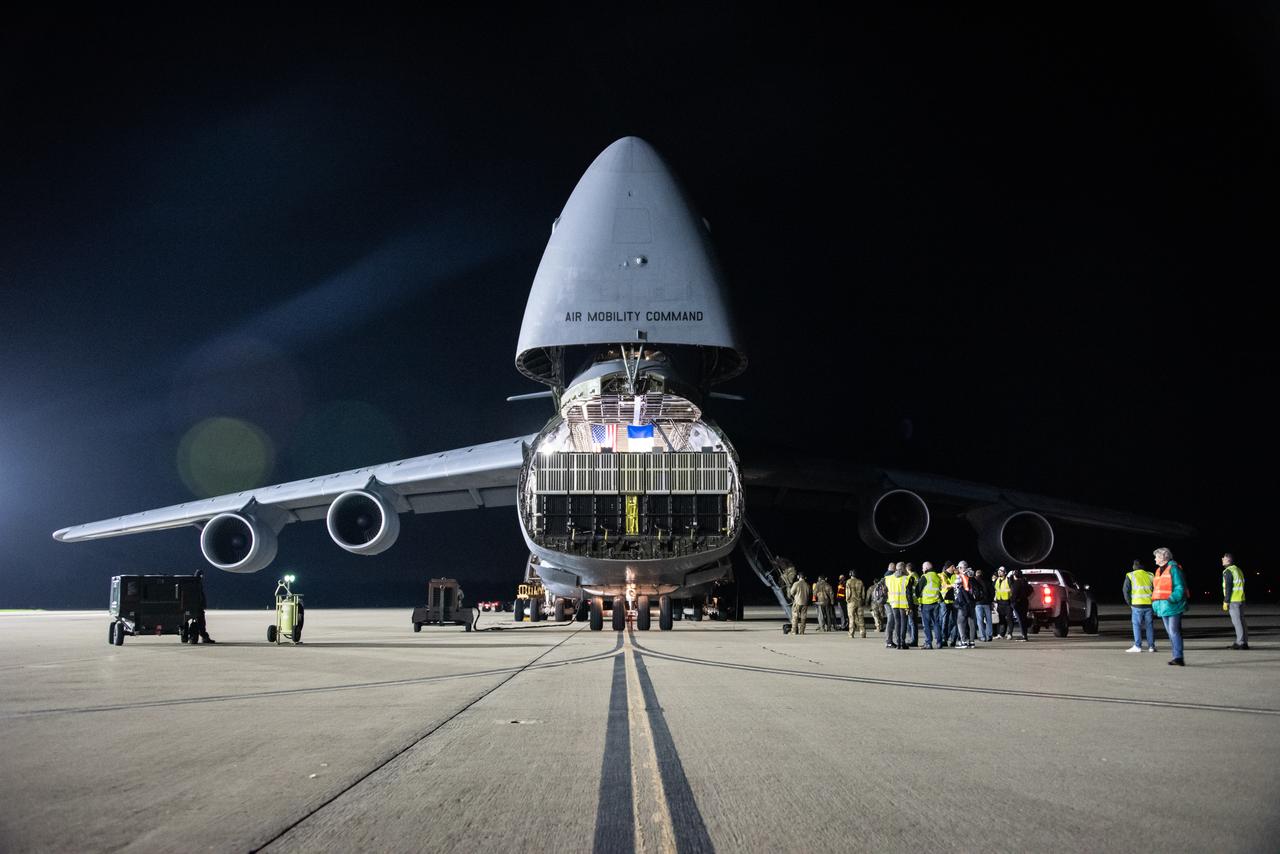
NASA’s Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite arrives from France aboard a U.S. Air Force C-5 Galaxy aircraft at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on Oct. 16, 2022. Teams will transport the satellite to Astrotech Space Operations facility to begin final preparations for the spacecraft’s December launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Center-4 East. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales, with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean.
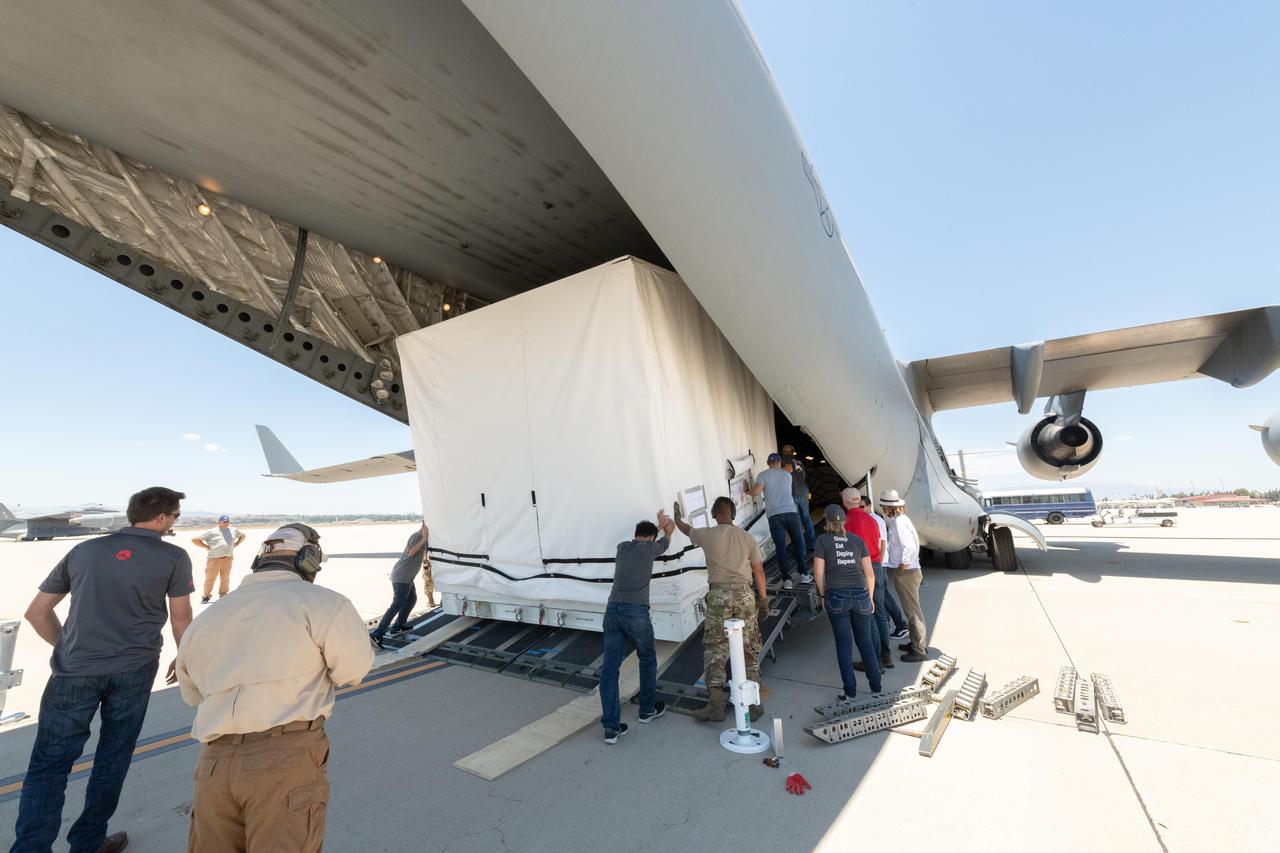

On June 27, 2021, teams from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and the March Air Reserve Base in Riverside County, California, loaded the scientific heart of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission into a C-17 airplane. The hardware – which includes research instruments – is headed to a clean room facility near Cannes, France, where engineers and technicians will complete assembly of the satellite over the next year. SWOT will make global surveys of Earth's surface water. By measuring its height, researchers can track the volume and location of the finite resource around the world. The data will help with monitoring changes in floodplains and wetlands, measure how much fresh water flows into and out of lakes and rivers and back to the ocean, and track regional shifts in sea level. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24534
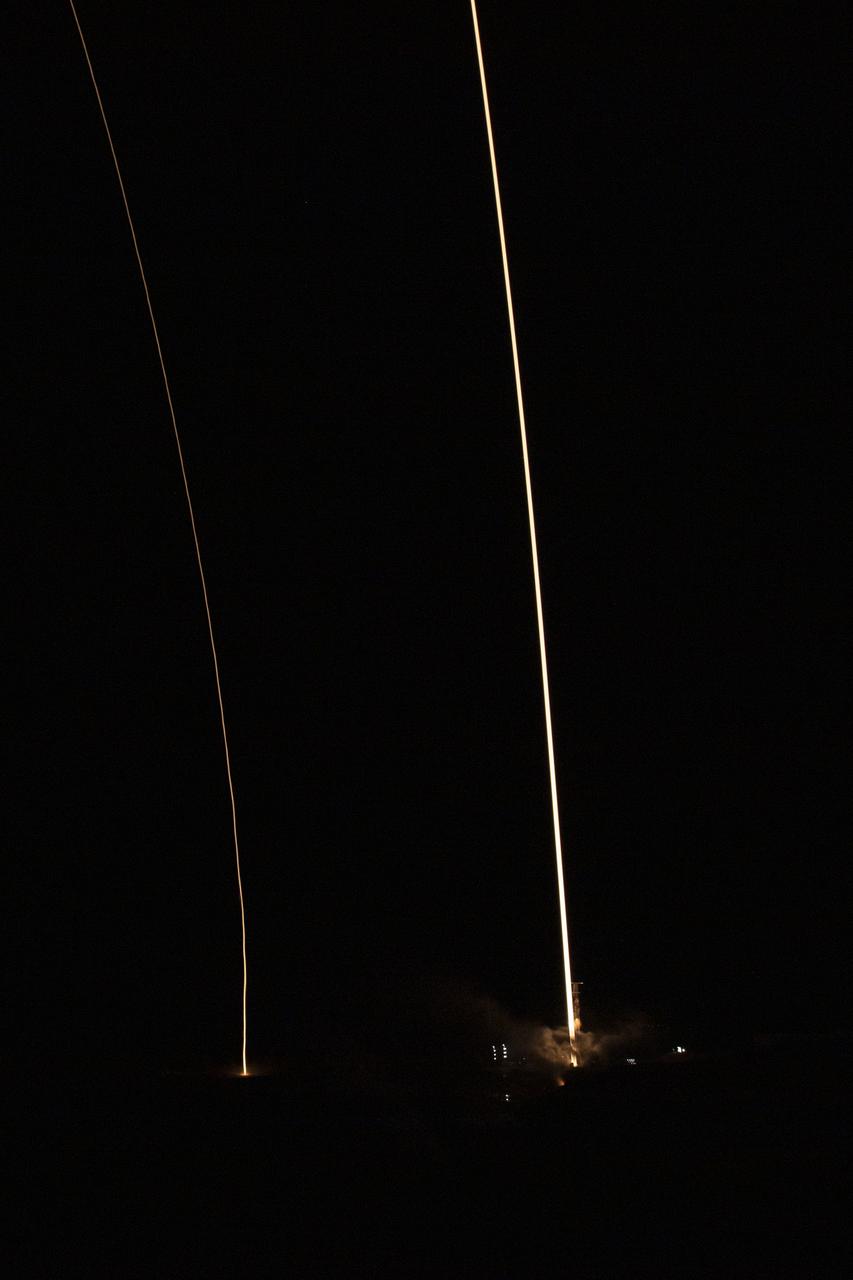

In this 8 minute exposure, A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launches with the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) spacecraft onboard, right, Friday, Dec. 16, 2022, from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The SpaceX Falcon 9 first-stage booster is also seen, left, as it returns to the landing pad following the launch. Jointly developed by NASA and Centre National D'Etudes Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency, SWOT is the first satellite mission that will observe nearly all water on Earth’s surface, measuring the height of water in the planet’s lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
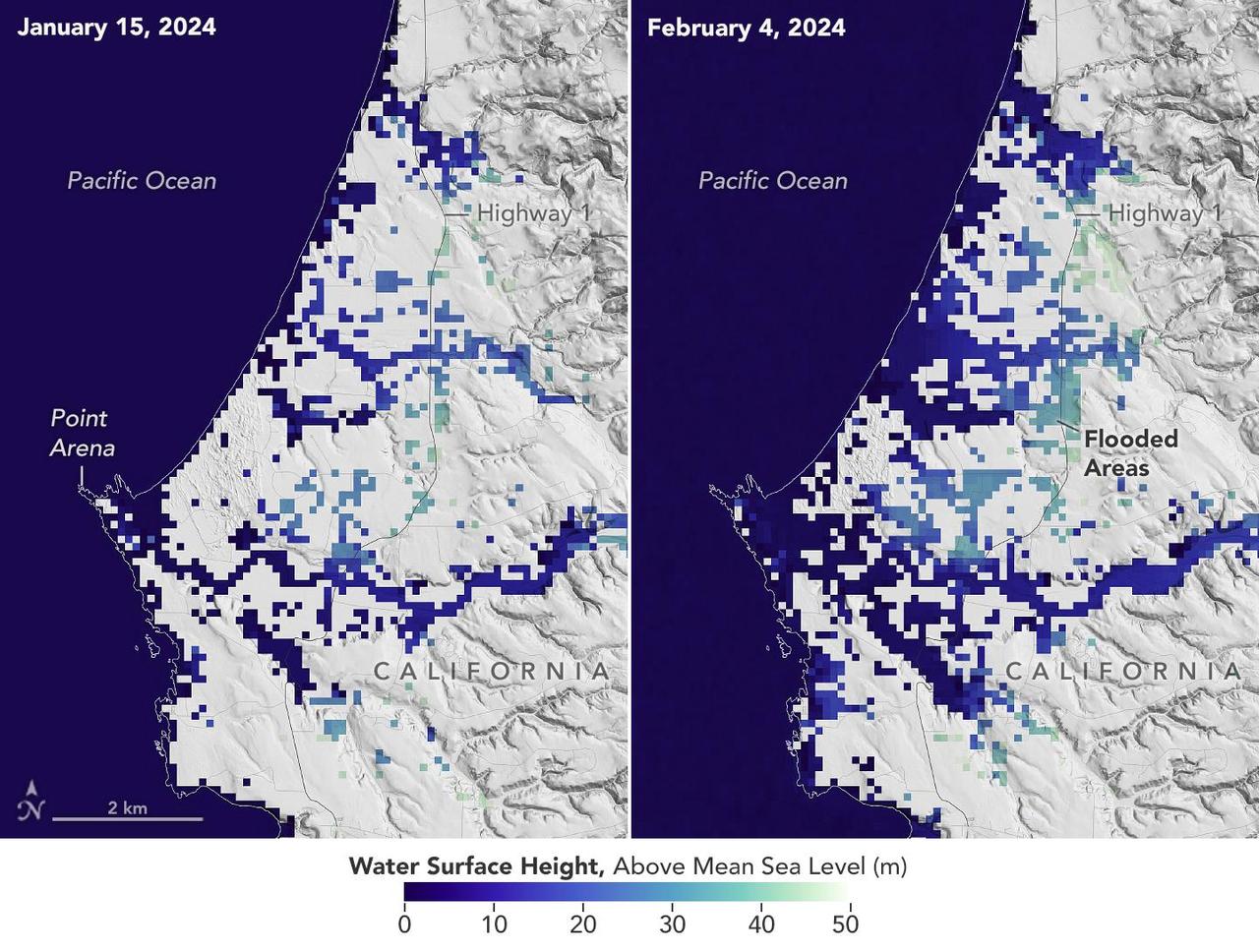
A series of atmospheric rivers drenched California in February 2024, with record amounts of rainfall and hurricane-force winds sweeping across parts of the state. The Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) mission captured data on coastal flooding near the community of Manchester, roughly 105 miles (169 kilometers) north of San Francisco. The satellite is a collaboration between NASA and the French space agency, CNES (Centre National d'Études Spatiales). The image shows the area on Jan. 15, 2024, before the rain and snow from atmospheric rivers hit California, and then again on Feb. 4, 2024, after the first in a series of storms soaked the state. Water heights are shown in shades of green and blue, with lighter hues indicating the highest levels relative to mean sea level. (Data for inland areas includes the height of the floodwaters plus the ground elevation beneath it.) Each pixel in the image represents an area that is 330 feet by 330 feet (100 meters by 100 meters). Since December 2022, SWOT has been measuring the height of nearly all water on Earth's surface, developing one of the most detailed, comprehensive views yet of the planet's oceans and freshwater lakes and rivers. Not only can the satellite detect the extent of the water on Earth's surface, as other satellites can, but SWOT can also provide water level data. The mission science team made the measurements using the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument. With two antennas spread 33 feet (10 meters) apart on a boom, KaRIn produces a pair of data swaths as it circles the globe, bouncing radar pulses off water surfaces to collect surface-height measurements. Launched from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT is now in its operations phase, collecting data that will be used for research and other purposes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26182
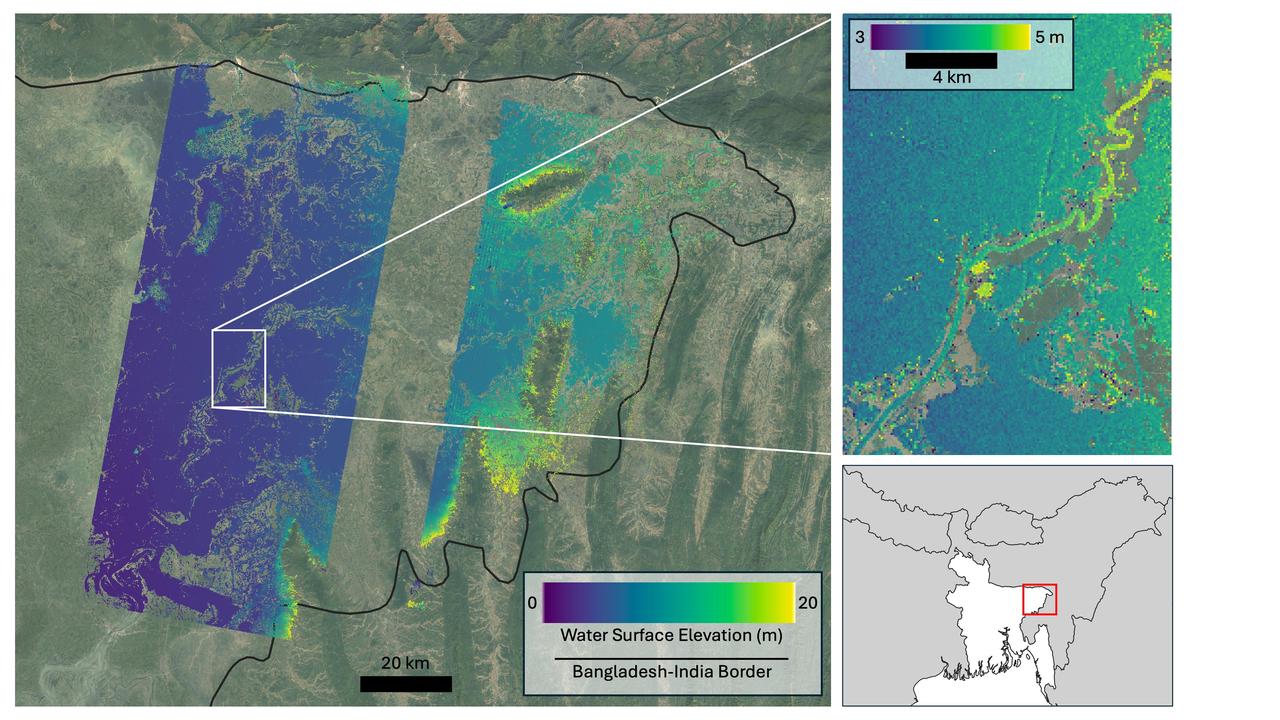
Flooding from monsoon rains covers a wide region of northeast Bangladesh near the India border in this Oct. 8, 2023, image showing data from the U.S.-French Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite. Around that time, heavy monsoon rains affected various parts of Bangladesh, including the region depicted here, home to Sylhet, the country's fifth-largest city (population approximately 700,000). Sylhet and surrounding areas experienced substantial flooding. The SWOT data, overlaid on a standard Google Earth image, shows the precise surface elevation of the floodwaters. The vast majority of the land area within the region imaged by SWOT is flooded. In the main image at left, dark blue indicates waters just above sea level, while yellow represents 65 feet (20 meters) above sea level. The inset at top right zooms in on a section of the Kalni River, a tributary of one of Bangladesh's three major rivers, the Meghna. The main channel of the Kalni is about 650 feet (200 meters) wide. In the inset at top right, dark blue indicates water about 10 feet (3 meters) above sea level and yellow is used for waters about 16 feet (5 meters) above sea level. The zoomed-in data can be used to determine the slope of the river, which tells hydrologists how fast water flows through it and off a landscape. The water surface elevations depicted are higher in the top right of the inset than they are in the bottom left. The data also shows the elevation of the river is generally greater than that of water in the floodplain around it, telling hydrologists that water is likely flowing from the river into the floodplain. Each pixel in the image represents an area that is about 330 feet by 330 feet (100 meters by 100 meters). The image shows data from SWOT's Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument antennas, which don't cover a 12-mile-wide (20-kilometer-wide) strip right underneath the satellite. For that gap, a separate instrument collects water surface elevation data that isn't shown here. Bangladesh is a low-lying, generally flat country that chronically suffers from two types of flooding. Monsoon rains cause rivers that flow into Bangladesh from neighboring countries, especially India, to flood. And flash flooding occurs during the pre-monsoon season and can damage agricultural crops if not forecast with sufficient warning. While the use of satellite altimetry and precipitation in models has shown some promise for flood forecasting in Bangladesh, forecasting both types of flooding with sufficient lead time has remained challenging due to a lack of timely, high-spatial-resolution information on water elevation. SWOT is the first satellite to provide this information over entire regions, enabling improved forecasts and filling the data gap when places like Bangladesh become inundated. The Bangladesh Water Development Board, which is in charge of national flood forecasting and management, is now exploring how to incorporate SWOT water elevation information into its flood inundation forecasting system. Since shortly after launch in December 2022, SWOT has been measuring the height of nearly all water on Earth's surface, developing one of the most detailed, comprehensive views yet of the planet's oceans and freshwater lakes and rivers. The mission science team makes measurements using the KaRIn instrument. With two antennas spread 33 feet (10 meters) apart on a boom, KaRIn produces a pair of data swaths as it circles the globe, bouncing radar pulses off water surfaces to collect surface-height information. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26343

This illustration depicts the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite, a mission led by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES). The scientific heart of the SWOT satellite is the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument, which will measure the height of water in Earth's lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and ocean. To do that, KaRIn will transmit radar pulses to Earth's surface and use two antennas – seen to the left and right of the spacecraft bus – to triangulate the return signals that bounce back. Mounted at the ends of a boom 33 feet (10 meters) long, the antennas will collect data over two swaths of Earth's surface at a time, each of them 30 miles (50 kilometers) wide and located on either side of the satellite. KaRIn will operate in two modes: A lower-resolution mode over the ocean will involve significant onboard processing of the data to reduce the volume of information sent during downlinks to Earth; a higher-resolution mode will be used mainly over land. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25621
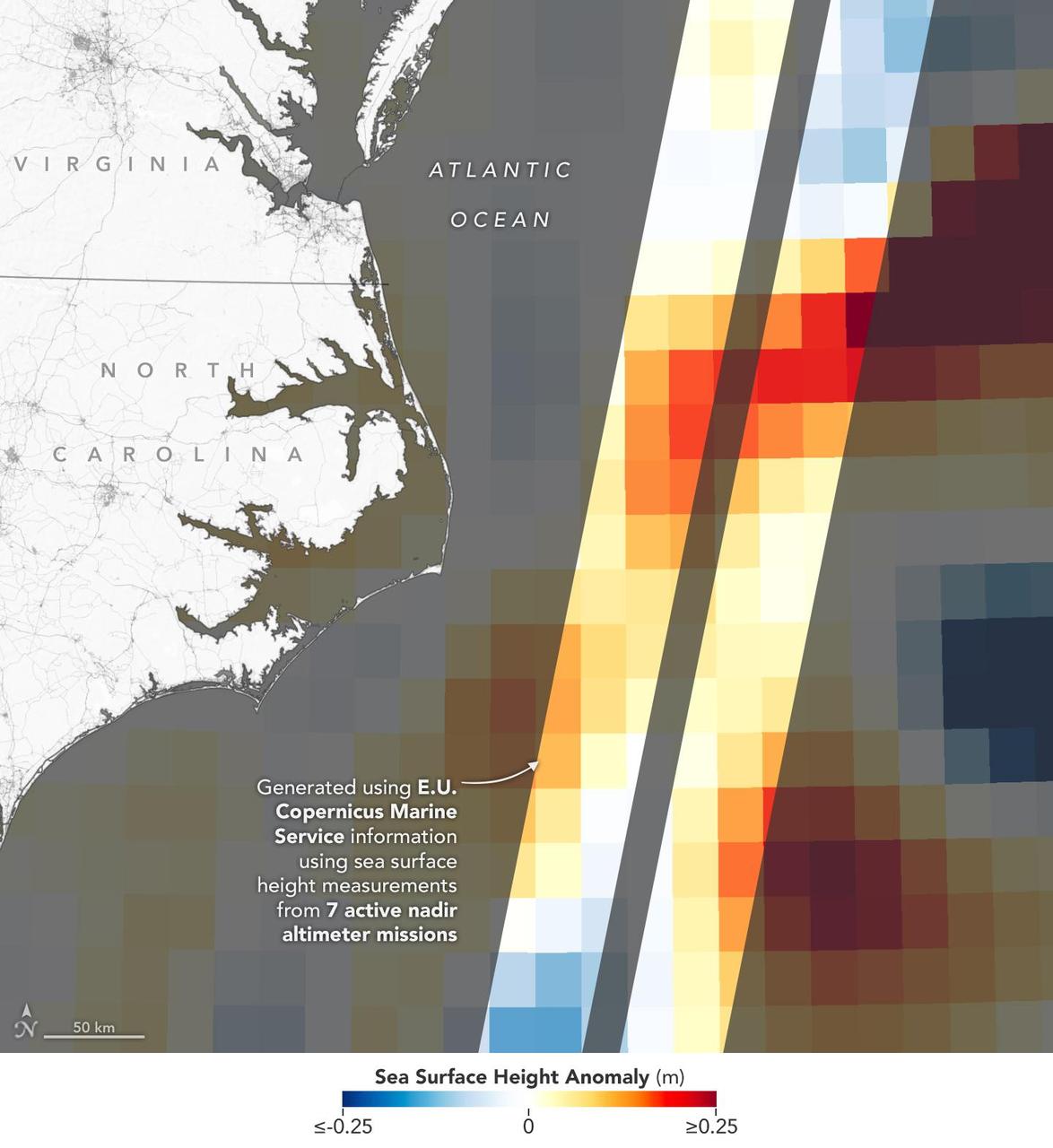
This visualization shows sea surface height measurements of the Gulf Stream off the coast of North Carolina and Virginia. The data was collected on Jan. 21, 2023, by seven satellites currently in operation. The information, provided by the Copernicus Marine Service of ESA (European Space Agency), comes from radar instruments called Earth-facing altimeters. In the visualization, red and orange areas represent sea levels that are higher than the global average, while shades of blue represent sea levels that are lower than average. An altimeter – widely used to measure sea level from space – works by bouncing radar signals off the ocean's surface directly beneath the instrument. It records both the time the signal takes to travel from a satellite to Earth and back, as well as the strength of the return signal. The spatial resolution offered by these instruments – shown in the composite image that's been modified so that different sea levels appear as different colors – is in contrast to the spatial resolution offered by a new instrument called the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn), which is 10 times greater. KaRIn launched on board the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite on Dec. 16, 2022. SWOT is now in a six-month period called commissioning, calibration and validation. This is when engineers on the mission check out the performance of the satellite's systems and science instruments before the planned start of science operations in July 2023. Led by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES), SWOT will measure the height of water on over 90% of Earth's surface, providing a high-definition survey of our planet's water for the first time. The satellite's measurements of freshwater bodies and the ocean will provide insights into how the ocean influences climate change; how a warming world affects lakes, rivers, and reservoirs; and how communities can better prepare for floods and other disasters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25773
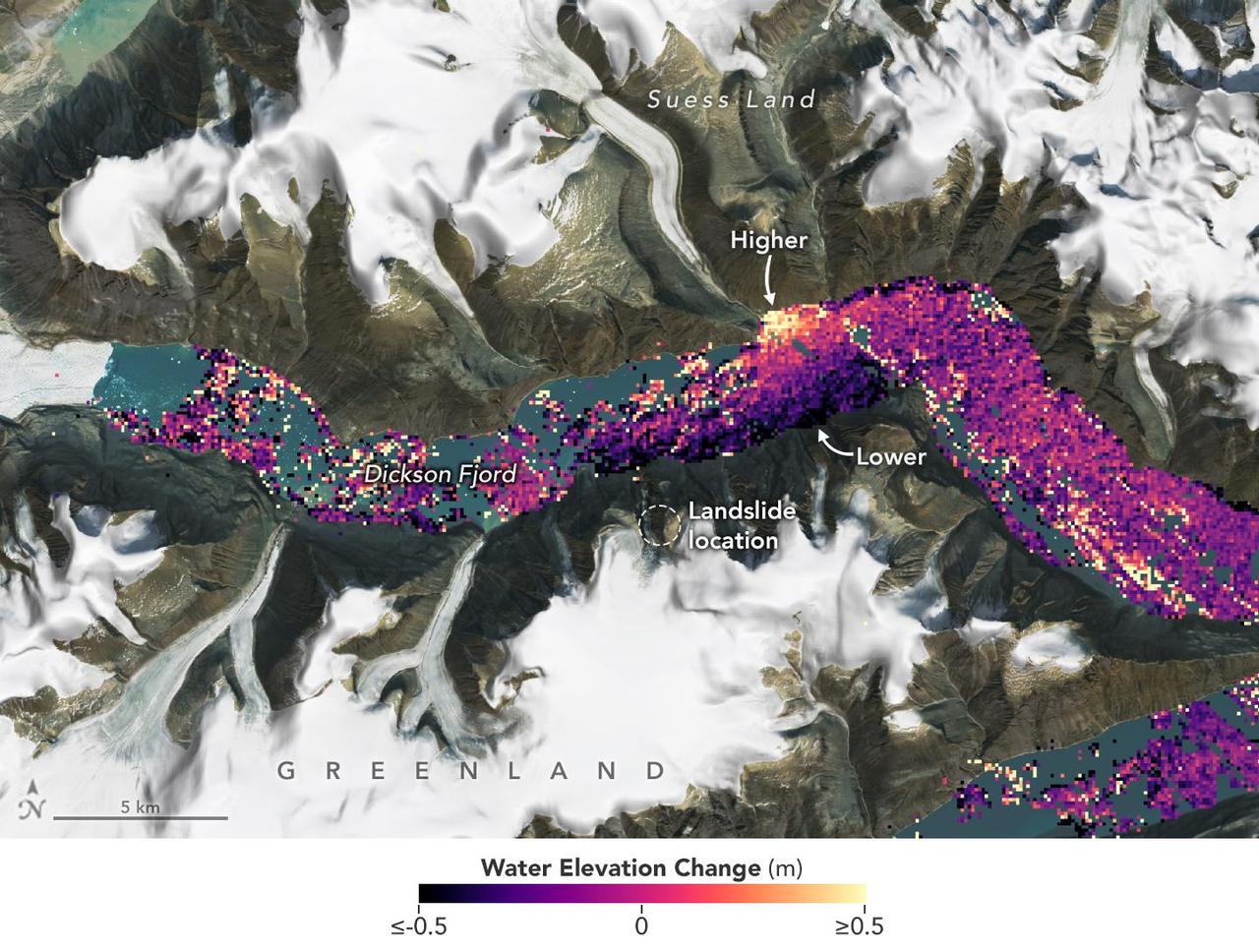
A visualization based on data from the international SWOT satellite mission shows the unique contours of a tsunami that sloshed within the steep walls of a fjord in Greenland in September 2023. Triggered by a massive landslide, the tsunami generated a seismic rumble that reverberated around the world for nine days. Short for Surface Water and Ocean Topography, SWOT collected water elevation measurements in the Dickson Fjord on Sept. 17, 2023, the day after the initial landslide and tsunami. The data was compared with measurements made under normal conditions a few weeks prior, on Aug. 6, 2023. Colors toward the lighter end of the scale indicate higher water levels, and darker colors indicate lower-than-normal levels. The data suggest that water levels at some points along the north side of the fjord were as much as 4 feet (1.2 meters) higher than on the south. In a September 2024 paper in Science, researchers traced a seismic signal back to the tsunami, which began when more than 880 million cubic feet of rock and ice (25 million cubic meters) fell into the Dickson Fjord. Part of a network of channels on Greenland's eastern coast, the fjord is about 1,772 feet (540 meters) deep and 1.7 miles (2.7 kilometers) wide, with walls taller than 6,000 feet (1,830 meters). Far from the open ocean, in a confined space, the energy of the tsunami's motion had limited opportunity to dissipate, so the wave moved back and forth about every 90 seconds for nine days. It caused tremors recorded on seismic instruments thousands of miles away. Launched in December 2022 from Vandenberg Space Force Base in central California, SWOT is now in its operations phase, collecting data that will be used for research and other purposes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26420

The international Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite is shown in orbit over Earth in this illustration, with sunlight glinting off one of its solar arrays and both antennas of its Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument extended. The mission is a collaborative effort between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES) – with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the UK Space Agency. KaRIn is the scientific heart of the SWOT satellite, which will survey the water on more than 90% of Earth's surface, measuring the height of water in lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean. To do that, KaRIn will transmit radar pulses to Earth's surface and use its two antennas to triangulate the return signals that bounce back. Mounted at the ends of a boom 33 feet (10 meters) long, the antennas will collect data along a swath 30 miles (50 kilometers) wide on either side of the satellite. KaRIn will operate in two modes: A lower-resolution mode over the ocean will involve significant onboard processing of the data to reduce the volume of information sent during downlinks to Earth; a higher-resolution mode will be used mainly over land. Scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base in Central California on Dec. 15, 2022, SWOT is being jointly developed by NASA and CNES, with contributions from the CSA and the UK Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, leads the U.S. component of the project. For the flight system payload, NASA is providing the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument, a GPS science receiver, a laser retroreflector, a two-beam microwave radiometer, and NASA instrument operations. CNES is providing the Doppler Orbitography and Radioposition Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) system, the dual frequency Poseidon altimeter (developed by Thales Alenia Space), the KaRIn radio-frequency subsystem (together with Thales Alenia Space and with support from the UK Space Agency), the satellite platform, and ground control segment. CSA is providing the KaRIn high-power transmitter assembly. NASA is providing the launch vehicle and associated launch services. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25595

The new international satellite mission called Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) — slated for launch in late 2022 — will measure the height of Earth's surface water. The data the spacecraft will collect will help researchers understand and track the volume and location of water around the world. The satellite will assist with monitoring changes in floodplains and wetlands, measuring how much fresh water flows into and out of lakes and rivers and back to the ocean, and tracking regional shifts in sea level at scales never seen before. The satellite will also provide information on small-scale ocean currents that will support real-time marine operations affected by tides, currents, storm surge, sediment transport, and water quality issues. The payload is taking shape in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California before being shipped to France. There, technicians and engineers from the French space agency Centre National d'Etudes Spatial (CNES), their prime contractor Thales Alenia Space, and JPL will complete the build and prepare the satellite for shipment to its California launch site at Vandenberg Air Force Base. JPL project manager Parag Vaze (pronounced vah-zay) is central to ensuring the handoff to his CNES counterpart Thierry Lafon goes smoothly. SWOT is being jointly developed by NASA and CNES, with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency (UKSA). JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California, leads the U.S. component of the project. For the flight system, NASA is providing the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument, a GPS science receiver, a laser retroreflector, and a two-beam microwave radiometer. CNES is providing the Doppler Orbitography and Radioposition Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) system, nadir altimeter, and the KaRIn RF subsystem (with support from the UKSA). CSA is providing the KaRIn high-power transmitter assembly. NASA is providing associated launch services. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24531

This illustration depicts the Surface Water and Ocean Topography satellite, a mission led by NASA and the French space agency Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES). The scientific heart of the SWOT satellite is the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn) instrument, which will measure the height of water in Earth's lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and ocean. To do that, KaRIn will transmit radar pulses to Earth's surface and use two antennas – seen to the left and right of the spacecraft bus – to triangulate the return signals that bounce back. Mounted at the ends of a boom 33 feet (10 meters) long, the antennas will collect data over two swaths of Earth's surface at a time, each of them 30 miles (50 kilometers) wide and located on either side of the satellite. KaRIn will operate in two modes: A lower-resolution mode over the ocean will involve significant onboard processing of the data to reduce the volume of information sent during downlinks to Earth; a higher-resolution mode will be used mainly over land. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24530