
A model Sample Recovery Helicopter drives and positions itself over a sample tube during a test in the Mars Yard at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Two Sample Recovery Helicopters are slated to fly to Mars as part of the Mars Sample Return campaign. NASA is developing the Sample Recovery Helicopters to serve as backups to the agency's Perseverance rover in transporting sample tubes to the Sample Retrieval Lander. These helicopters are follow-ons to NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, which arrived at the Red Planet in the belly of Perseverance in February 2021. The Sample Recovery Helicopters have wheels instead of feet, as well as a small manipulator arm with a two-fingered gripper capable of carrying precious sample tubes. Testing of the Sample Recovery Helicopters is ongoing. The testbed was made by AeroVironment Inc. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25320
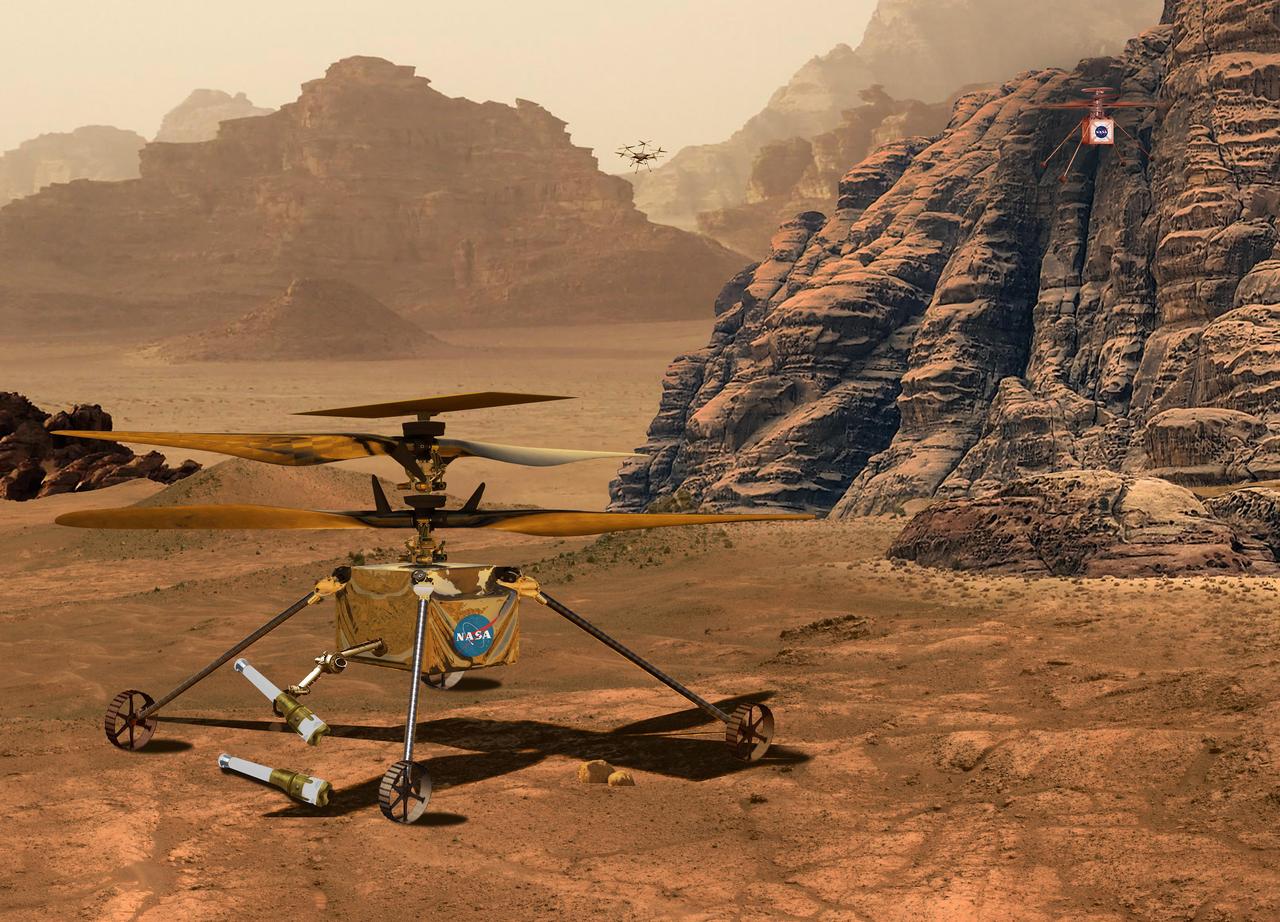

This illustration depicts three different of models of NASA's solar-powered Mars helicopter. In the upper right is the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, currently operating at Jezero Crater. Depicted in the foreground is one of two Sample Recovery Helicopters slated to fly to Mars as part of the Mars Sample Return Campaign. NASA is developing the Sample Recovery Helicopters to serve as backups to the agency's Perseverance rover in transporting sample tubes to the Sample Return Lander. In the upper center of image is the Mars Science Helicopter concept. A proposed follow-on to Ingenuity, the six-rotor Mars Science Helicopter could be used during future Mars missions to serve as an aerial scout and carry between 4.5 and 11 pounds (2 to 5 kilograms) of payload, including science instruments, to study terrain that rovers can't reach. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25338
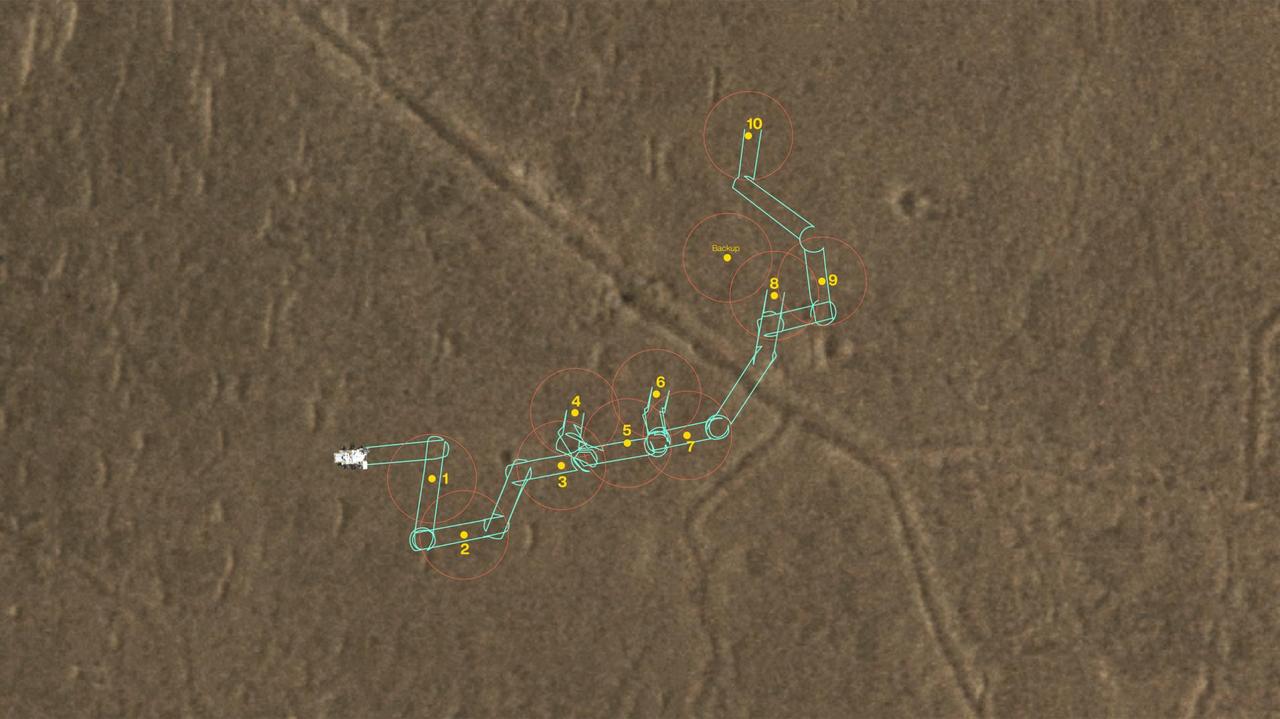
This map shows where NASA's Perseverance Mars rover will be dropping 10 samples that a future mission could pick up. The orange circles represent areas where a Sample Recovery Helicopter could safely operate to acquire the sample tubes. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25678
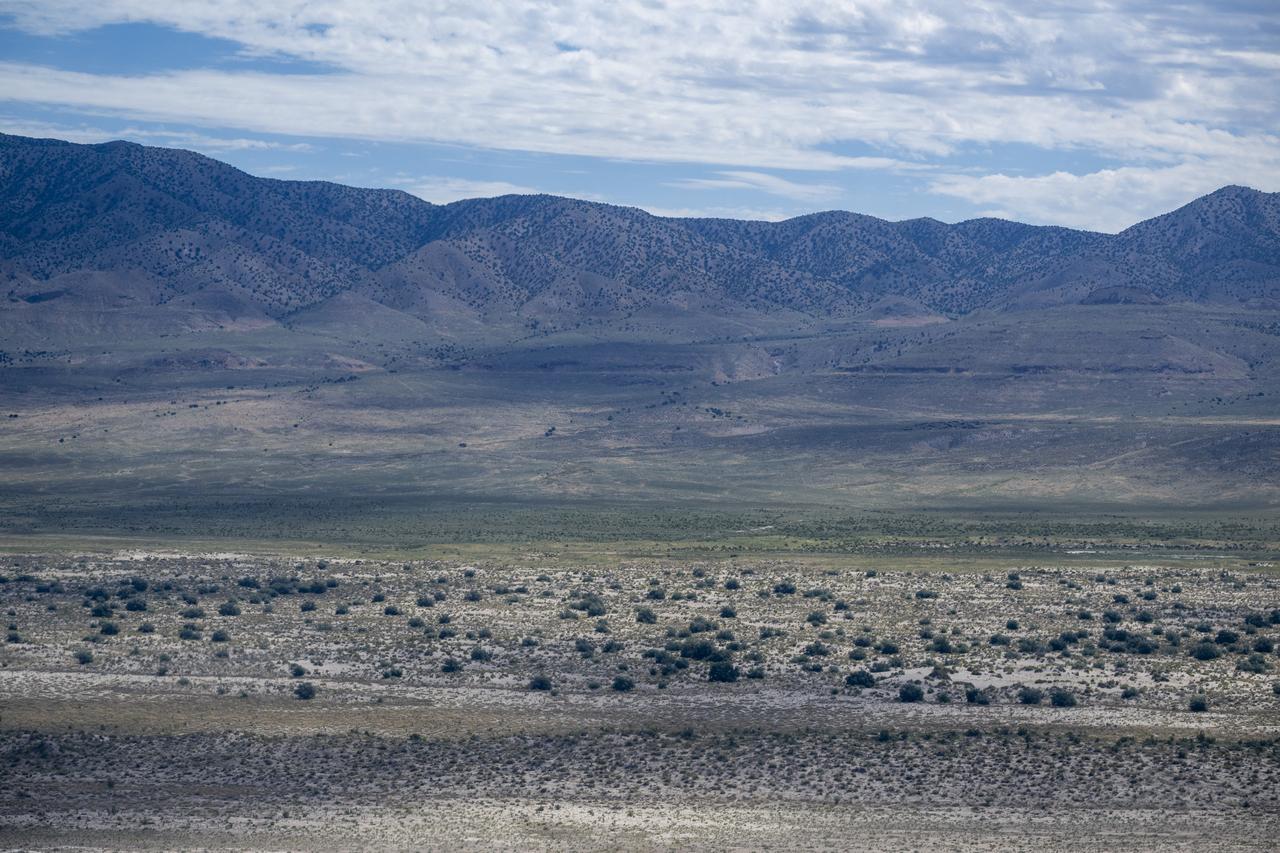

The Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range is seen from the cockpit of a helicopter, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, as recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

The Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range is seen from the cockpit of a helicopter, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, as recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

A training model of the sample return capsule is seen from the cockpit of a helicopter as recovery teams participate training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
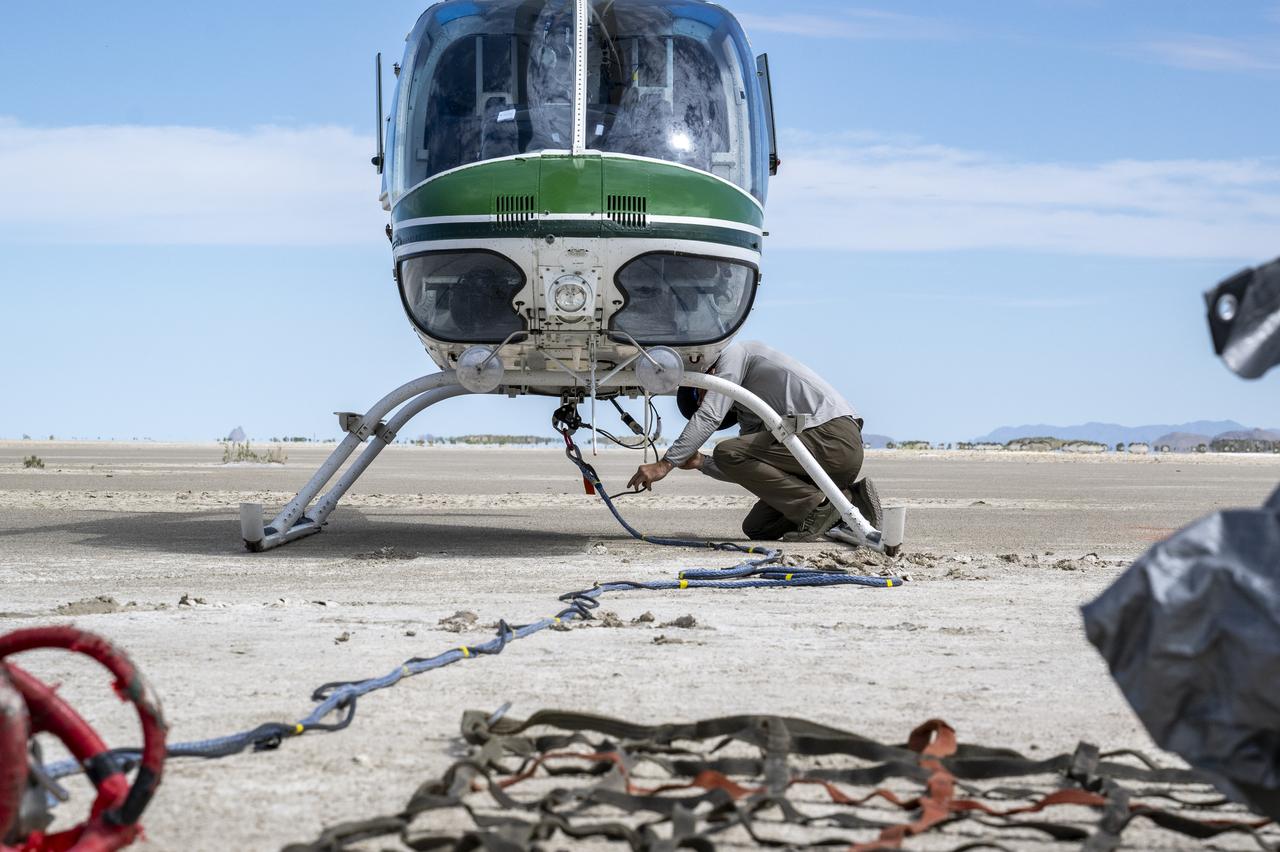

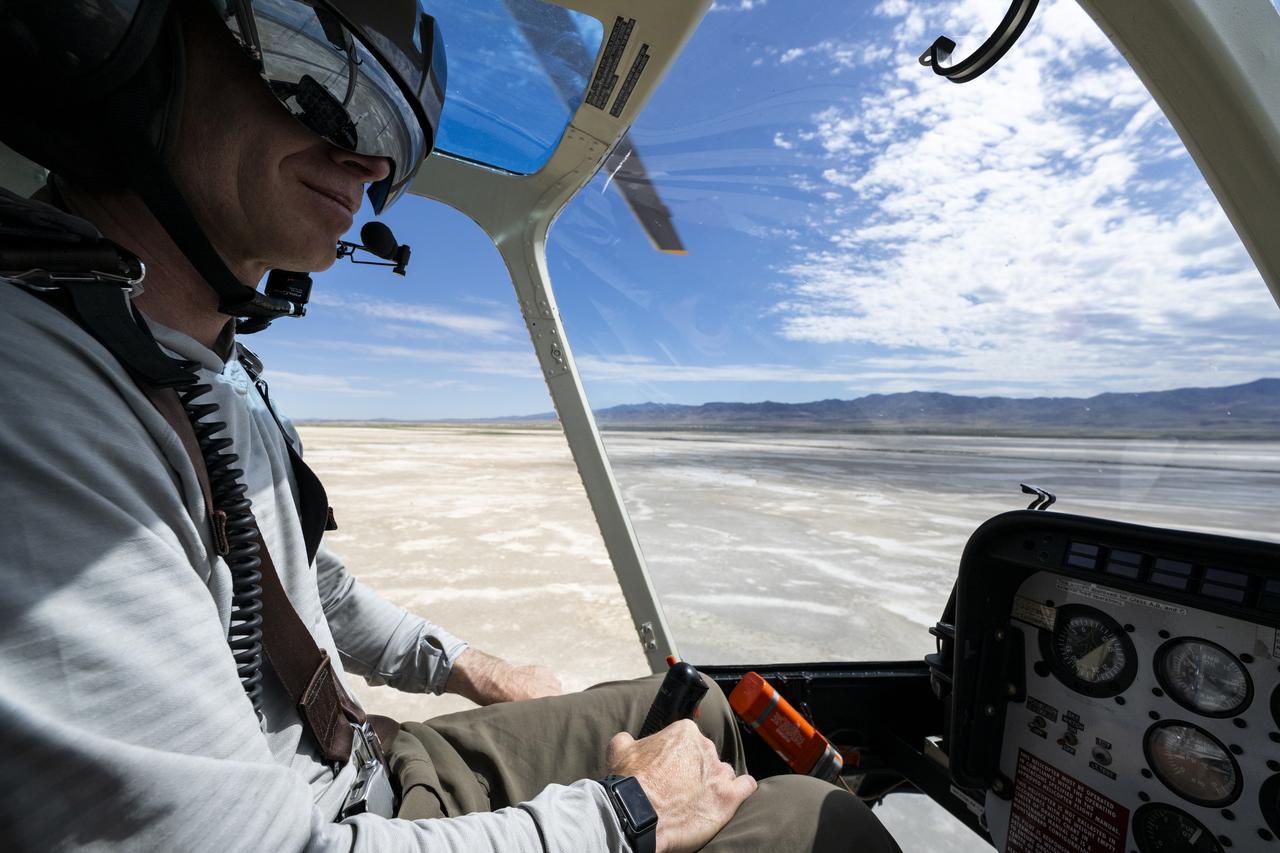
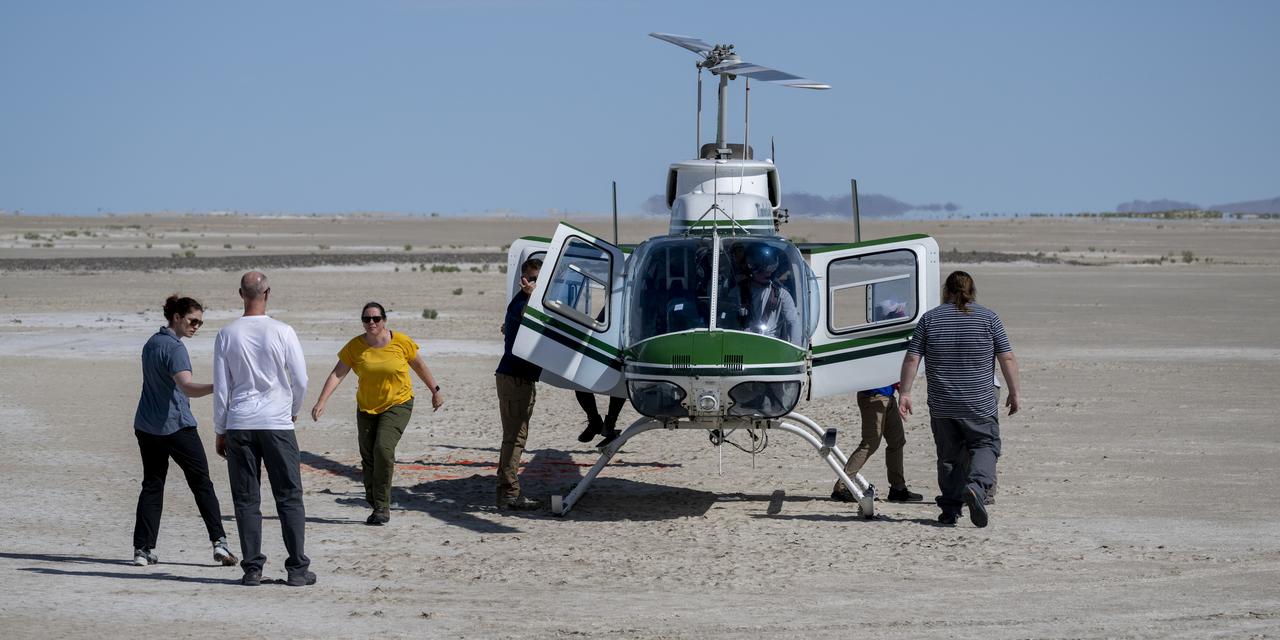
Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
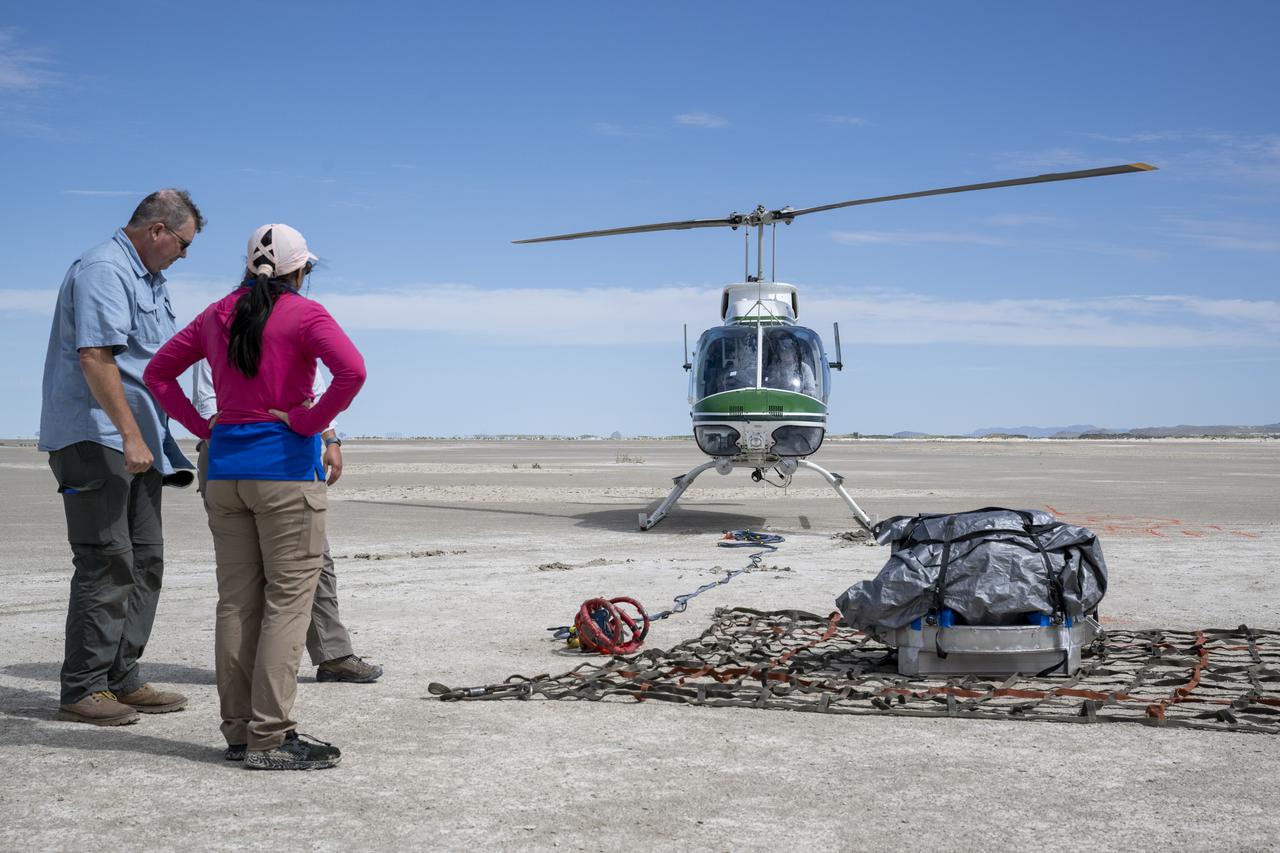

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
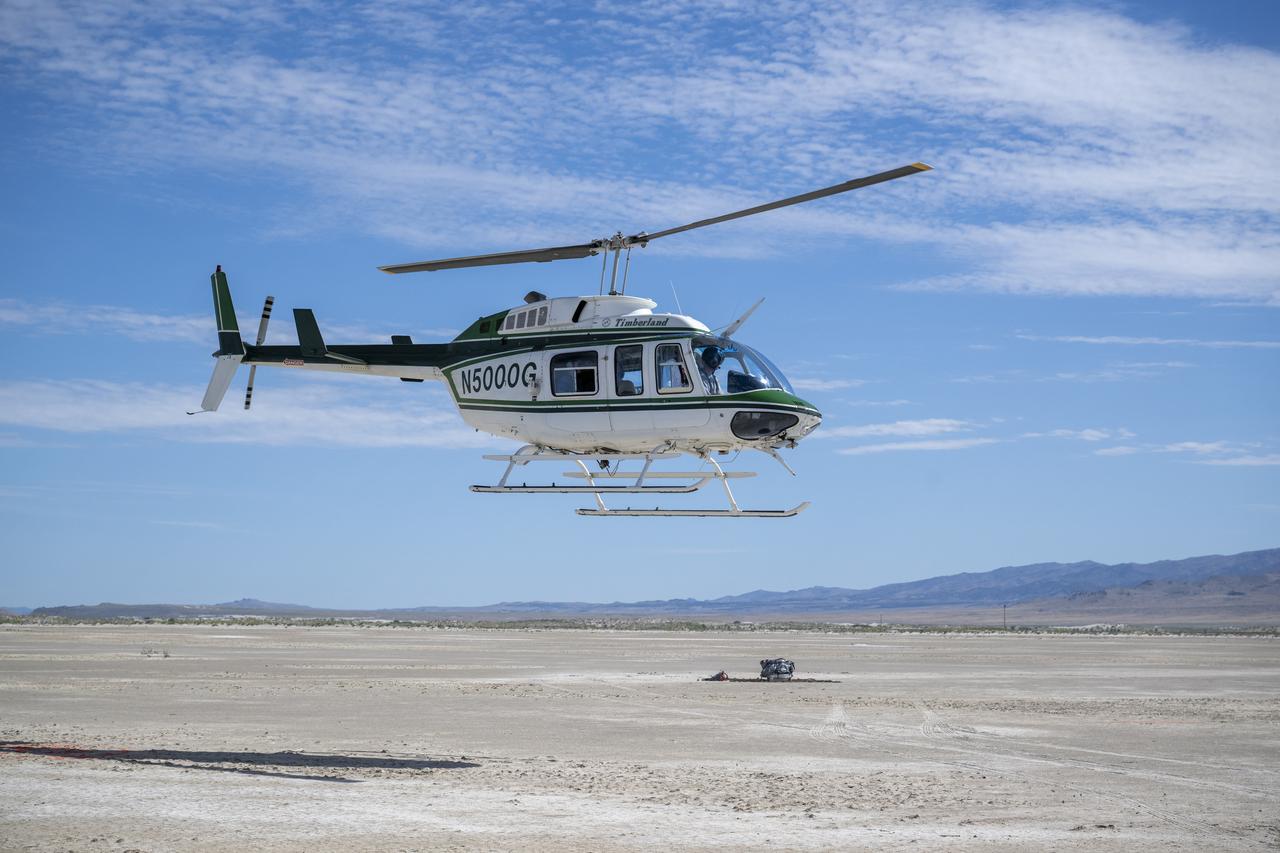

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
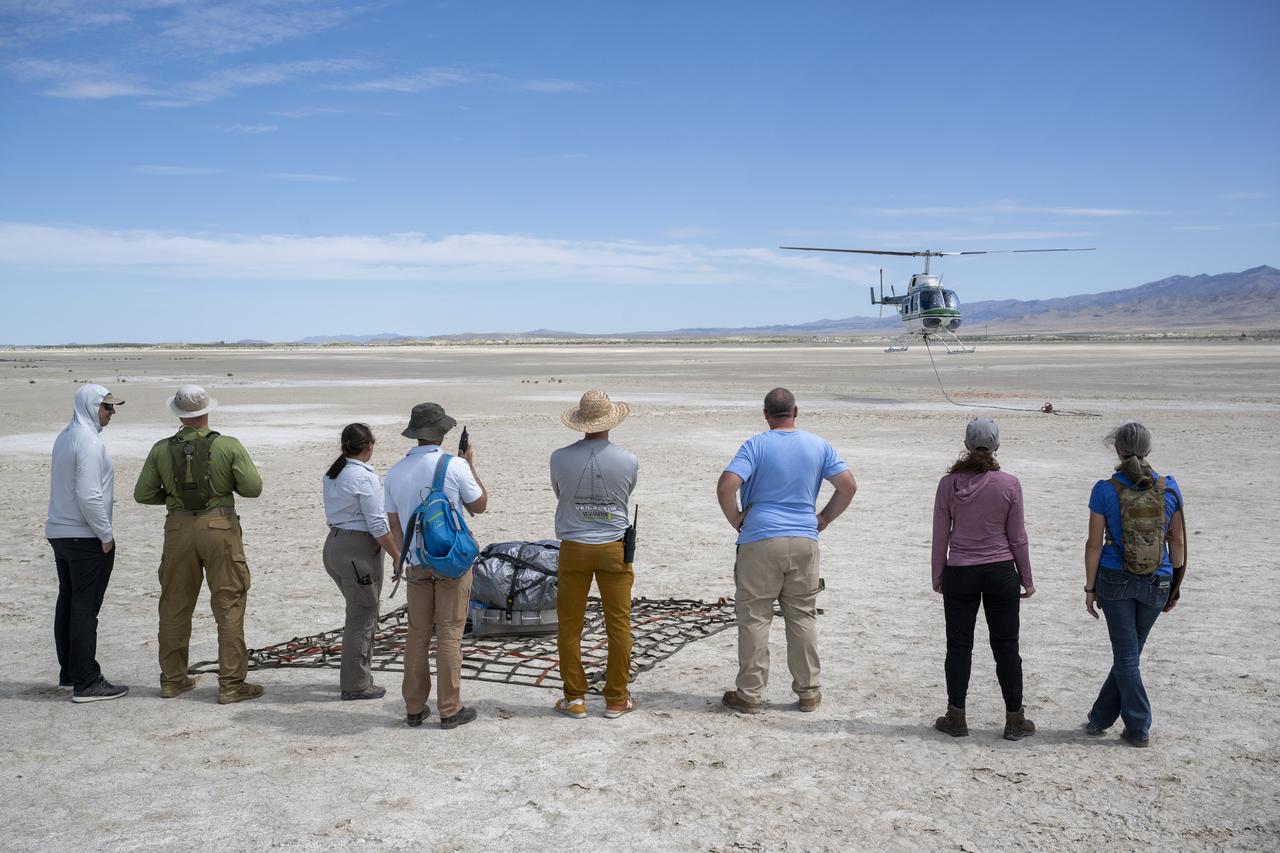

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
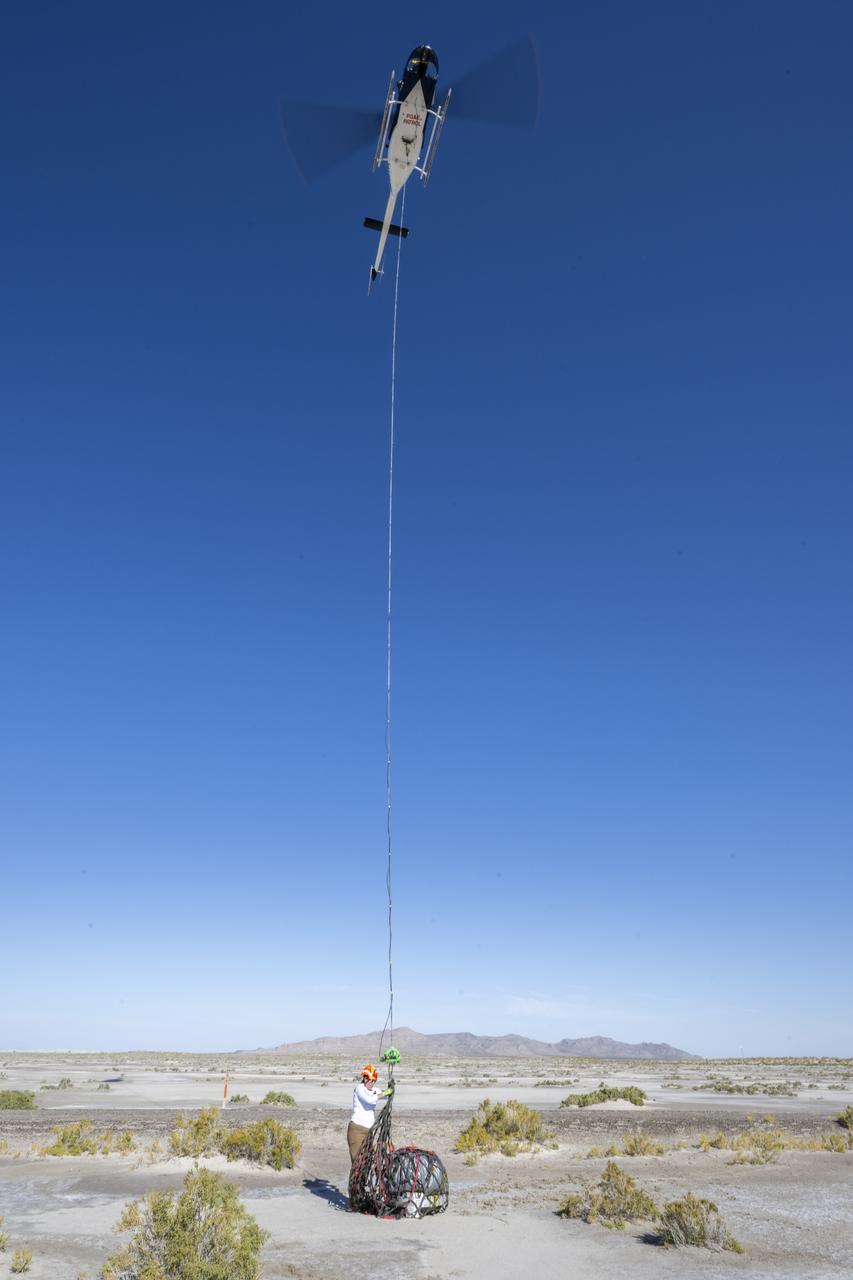

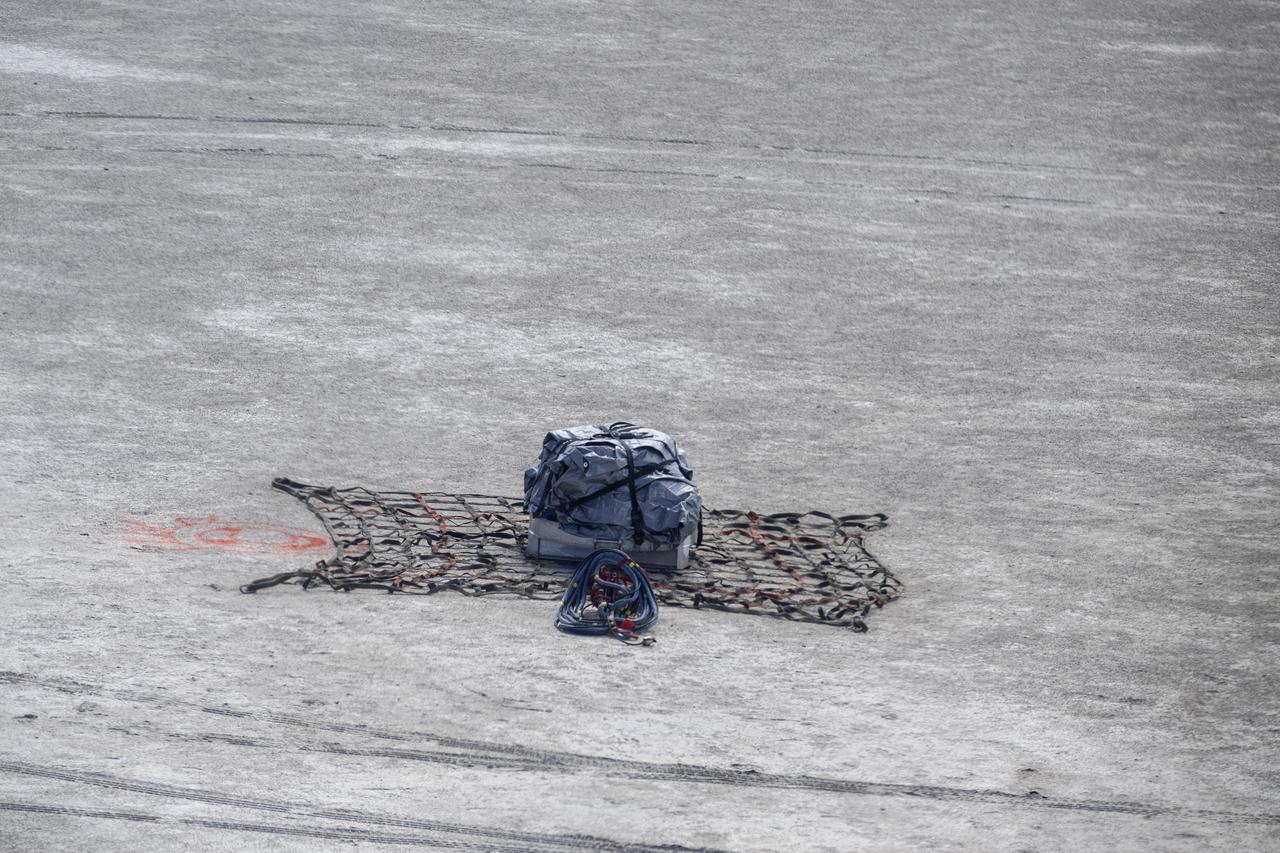
On Scene Commander of Recovery Jasmine Nakayama attaches the sample return capsule from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission to a helicopter for transport to the cleanroom, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, shortly after the capsule landed at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber
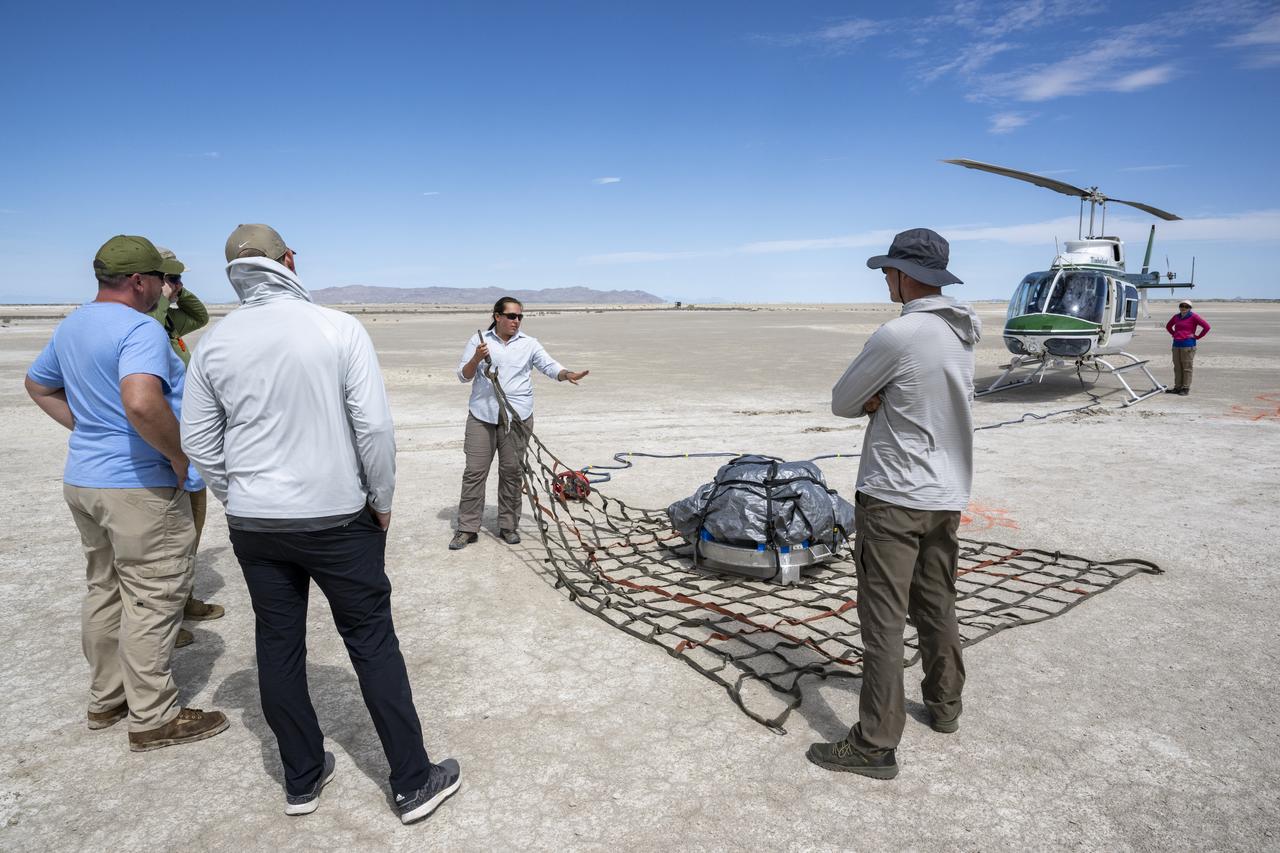

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
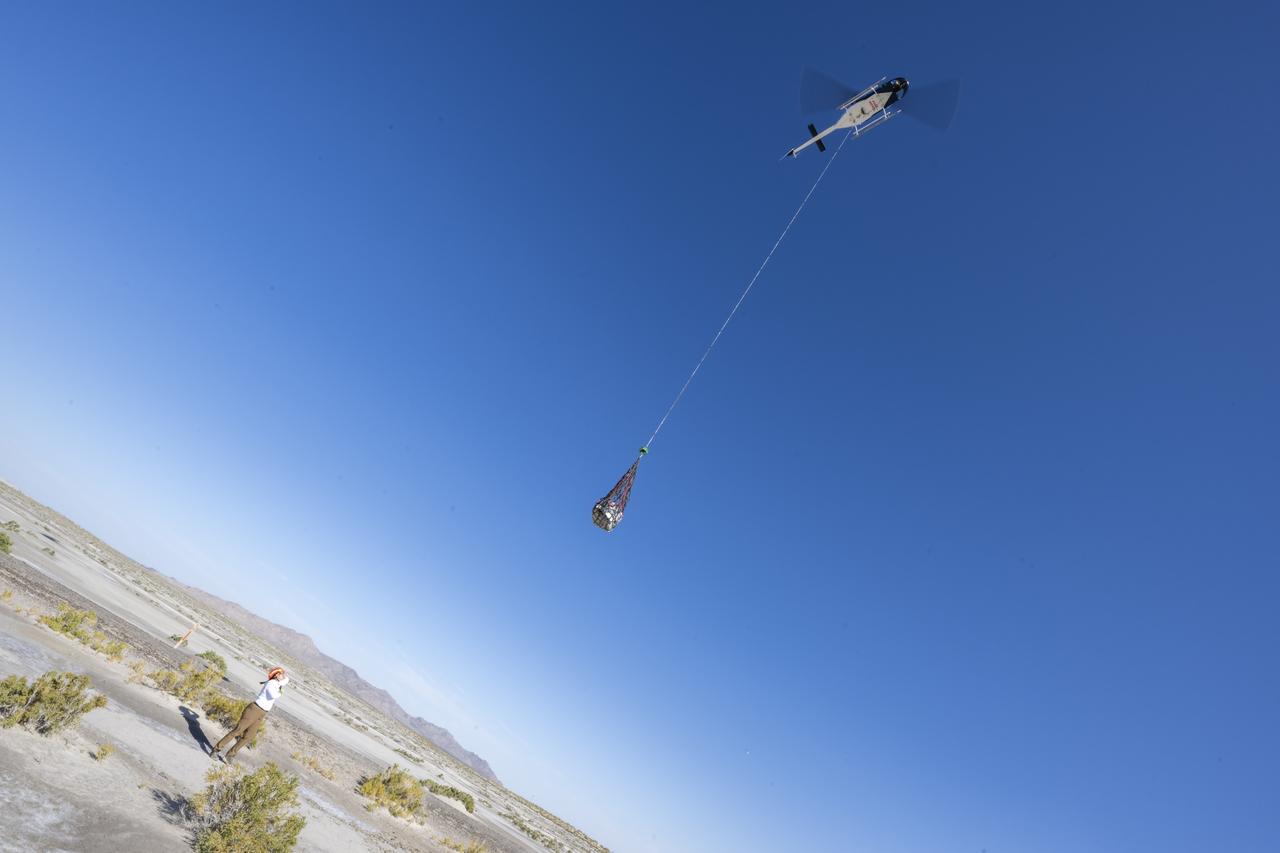

On Scene Commander of Recovery Jasmine Nakayama attaches the sample return capsule from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission to a helicopter for transport to the cleanroom, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, shortly after the capsule landed at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber
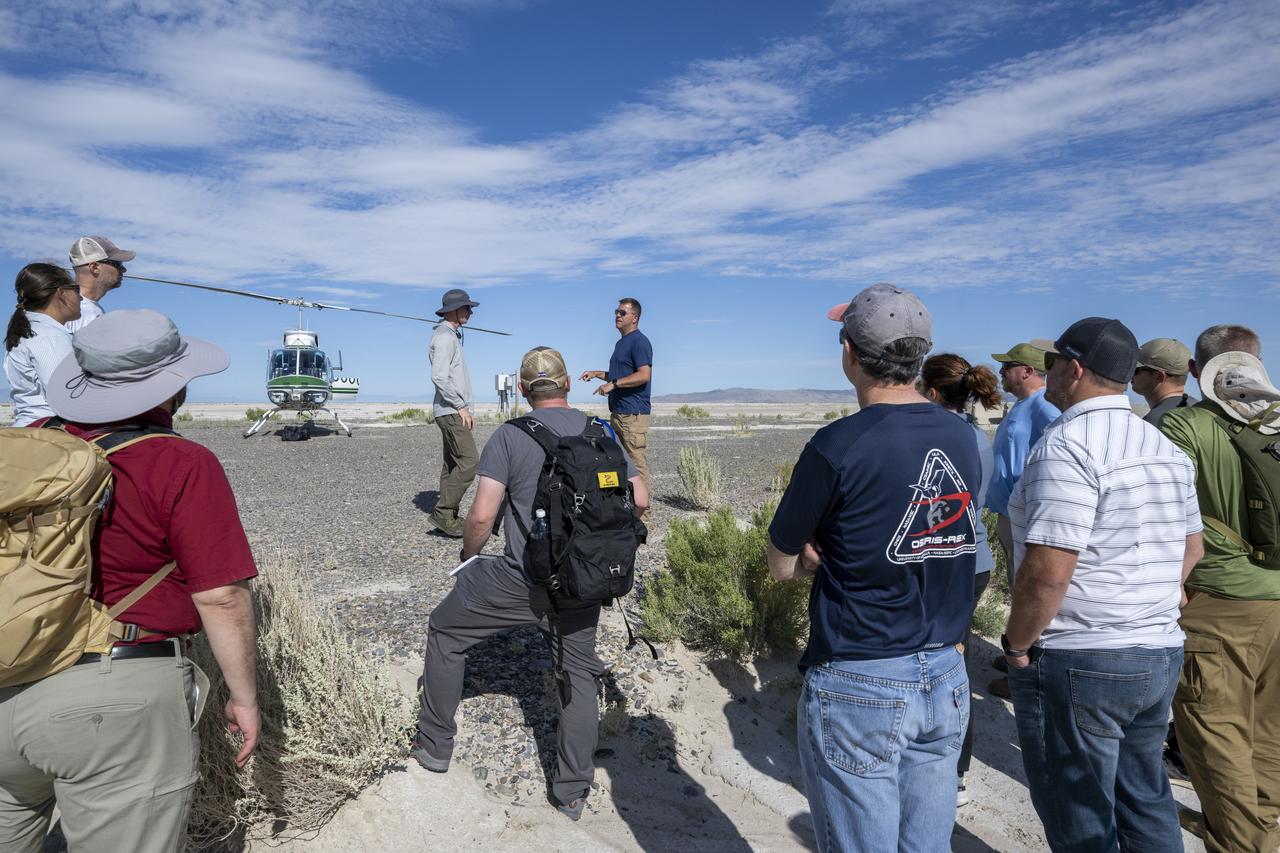

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
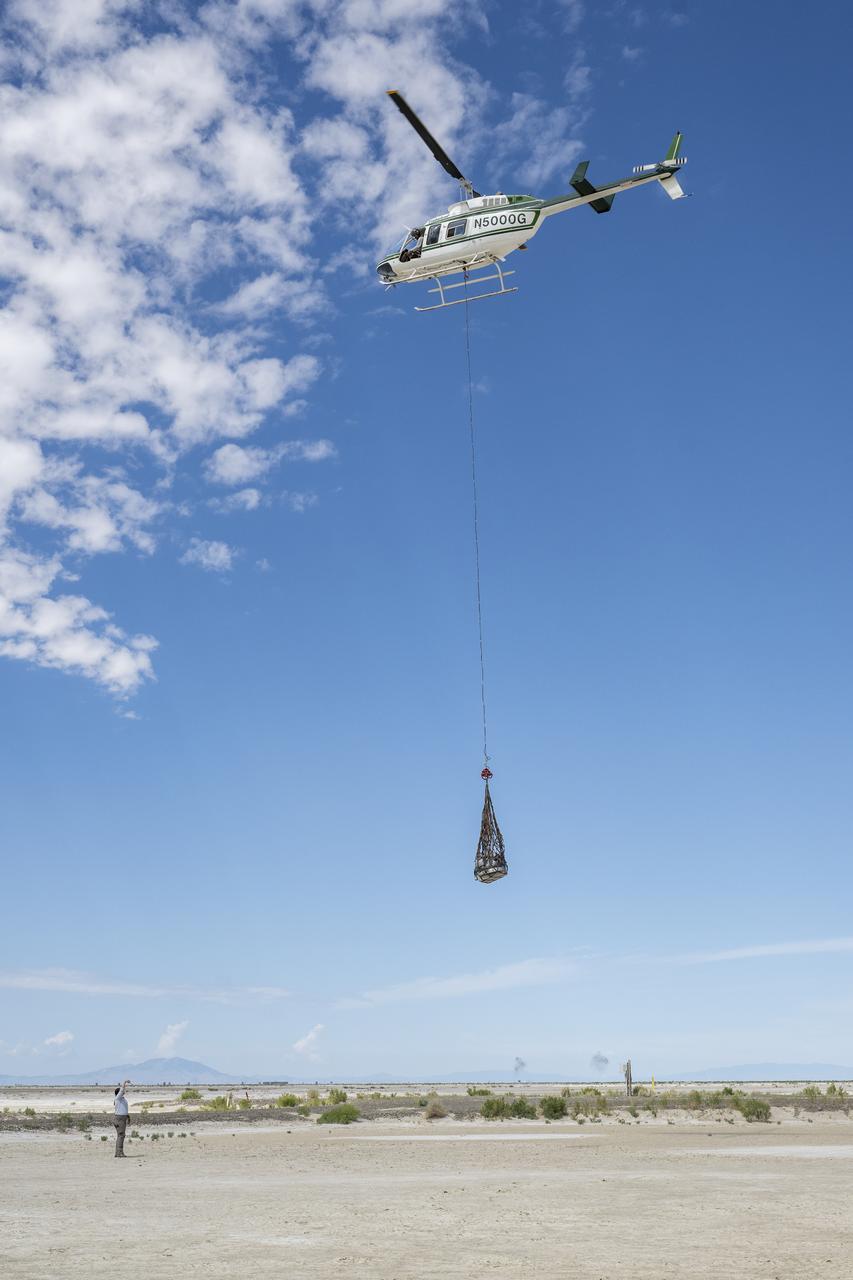

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
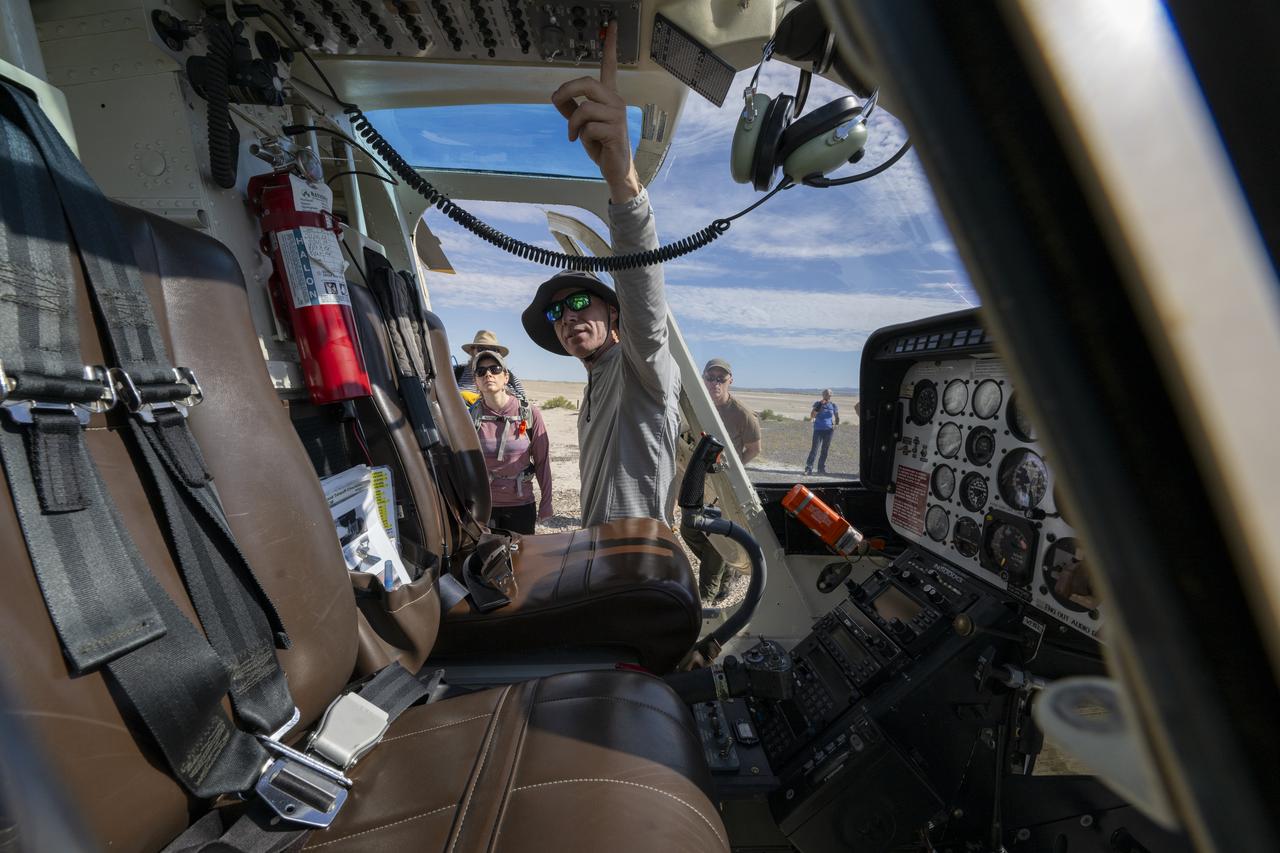

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
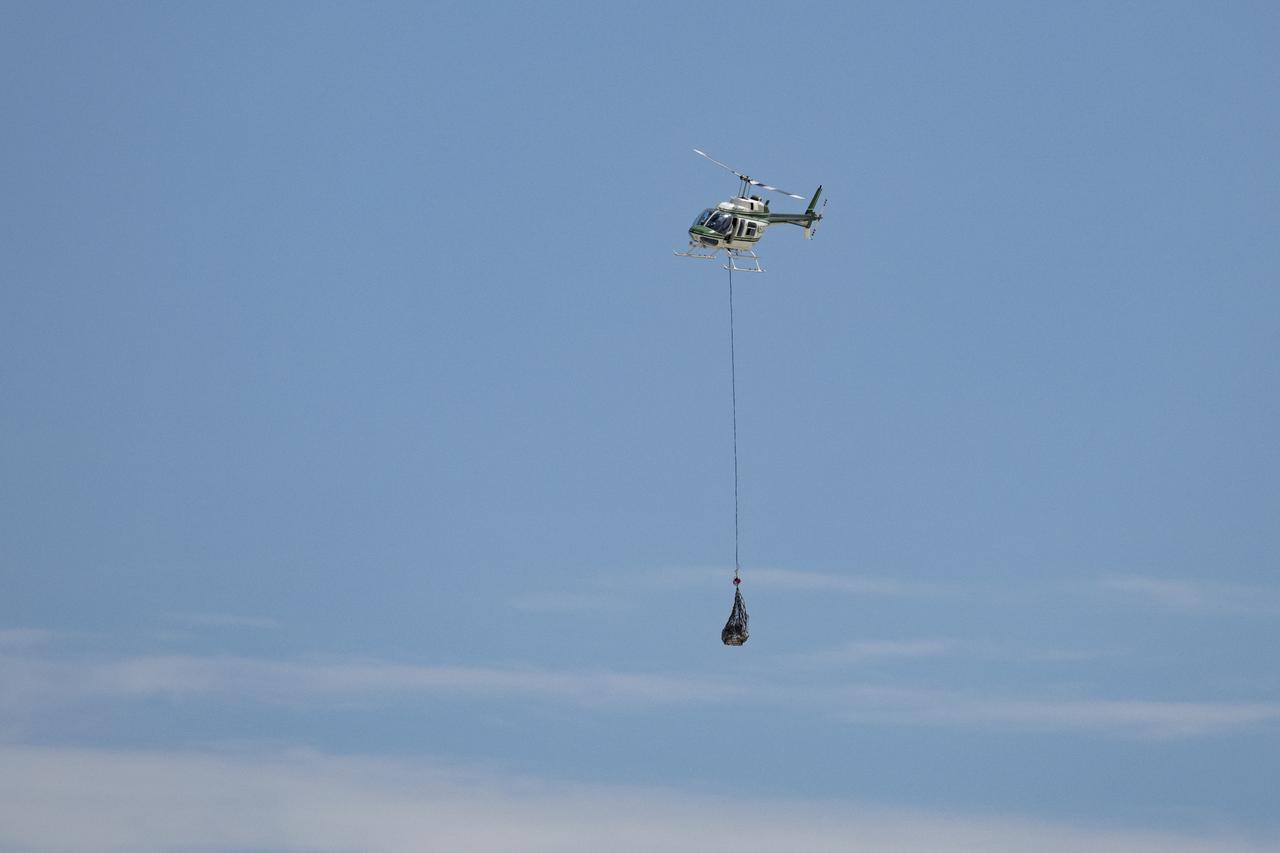

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
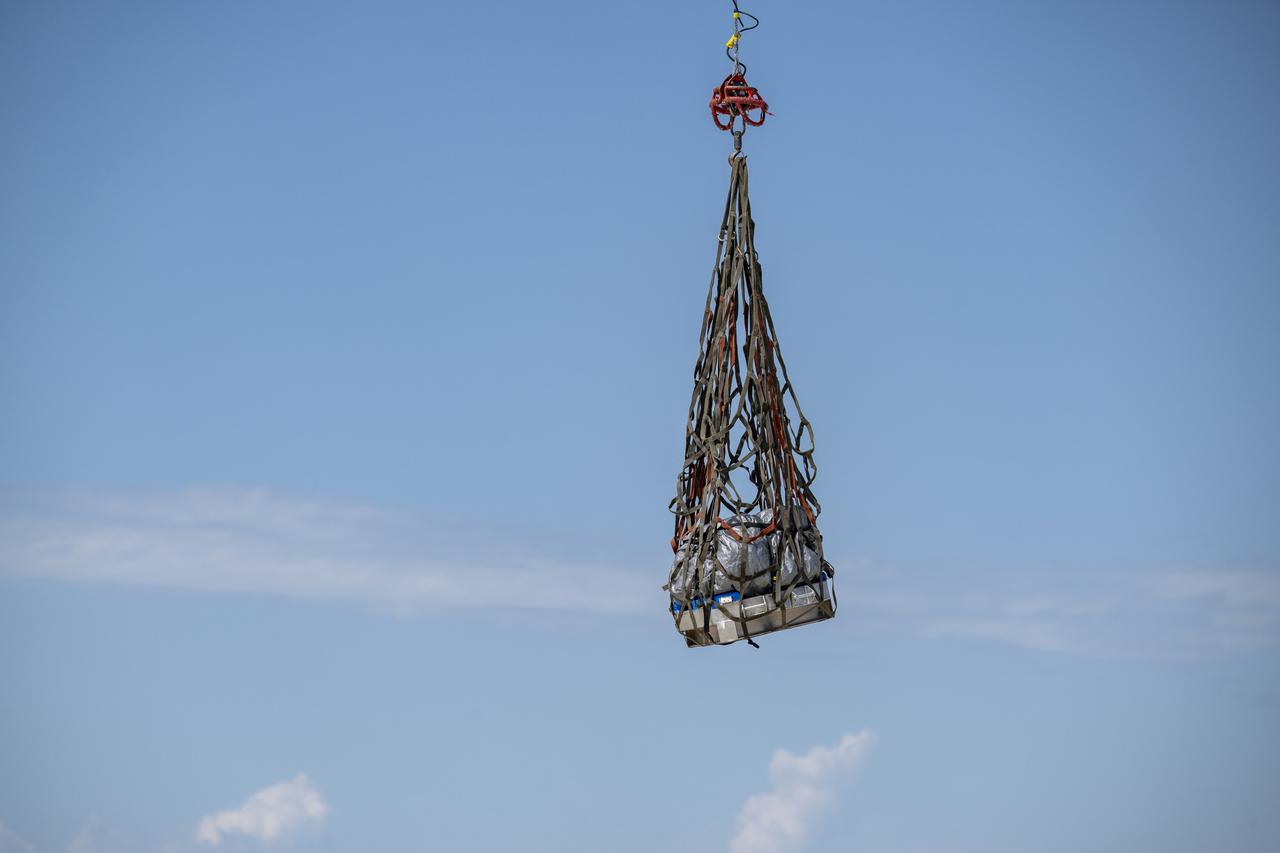

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
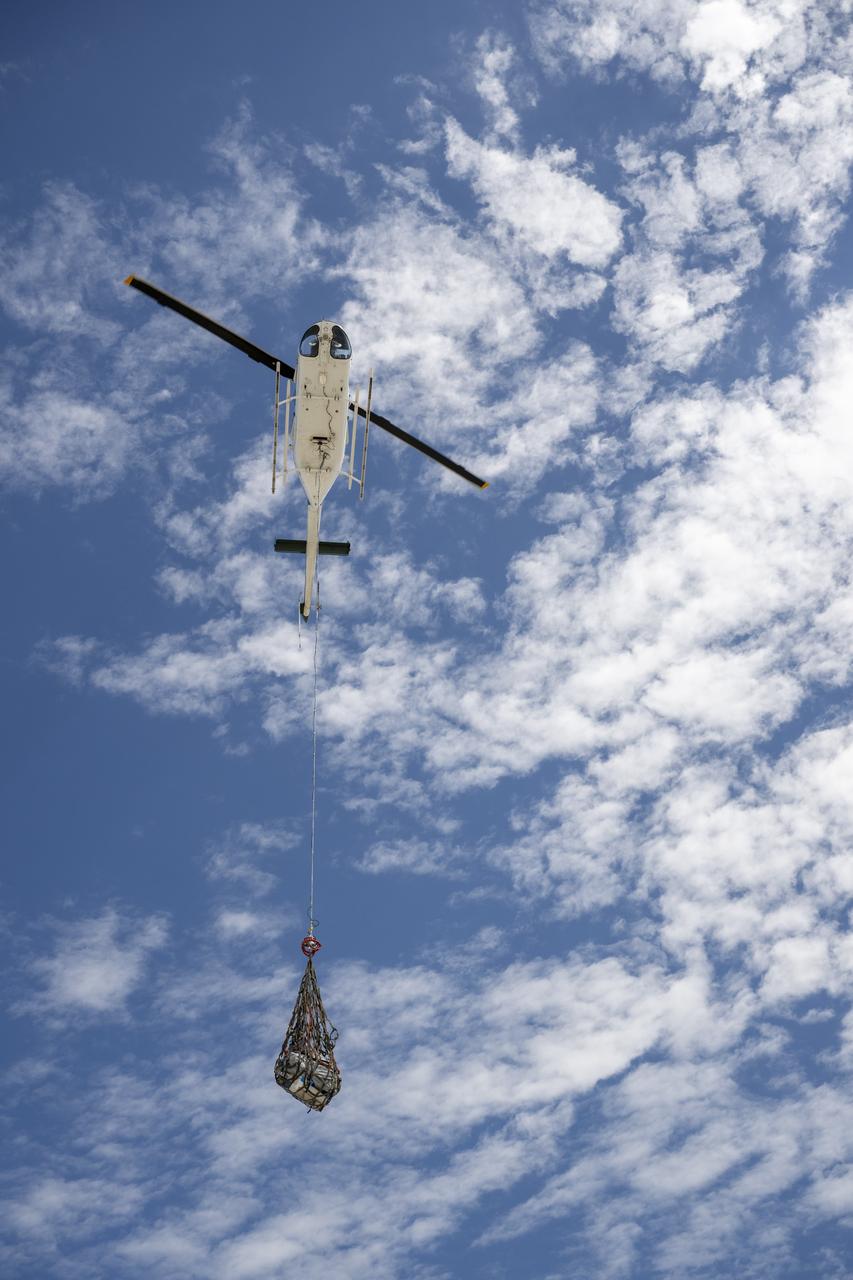

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

On Scene Commander of Recovery Jasmine Nakayama attaches the sample return capsule from NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission to a helicopter for transport to the cleanroom, Sunday, Sept. 24, 2023, shortly after the capsule landed at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber
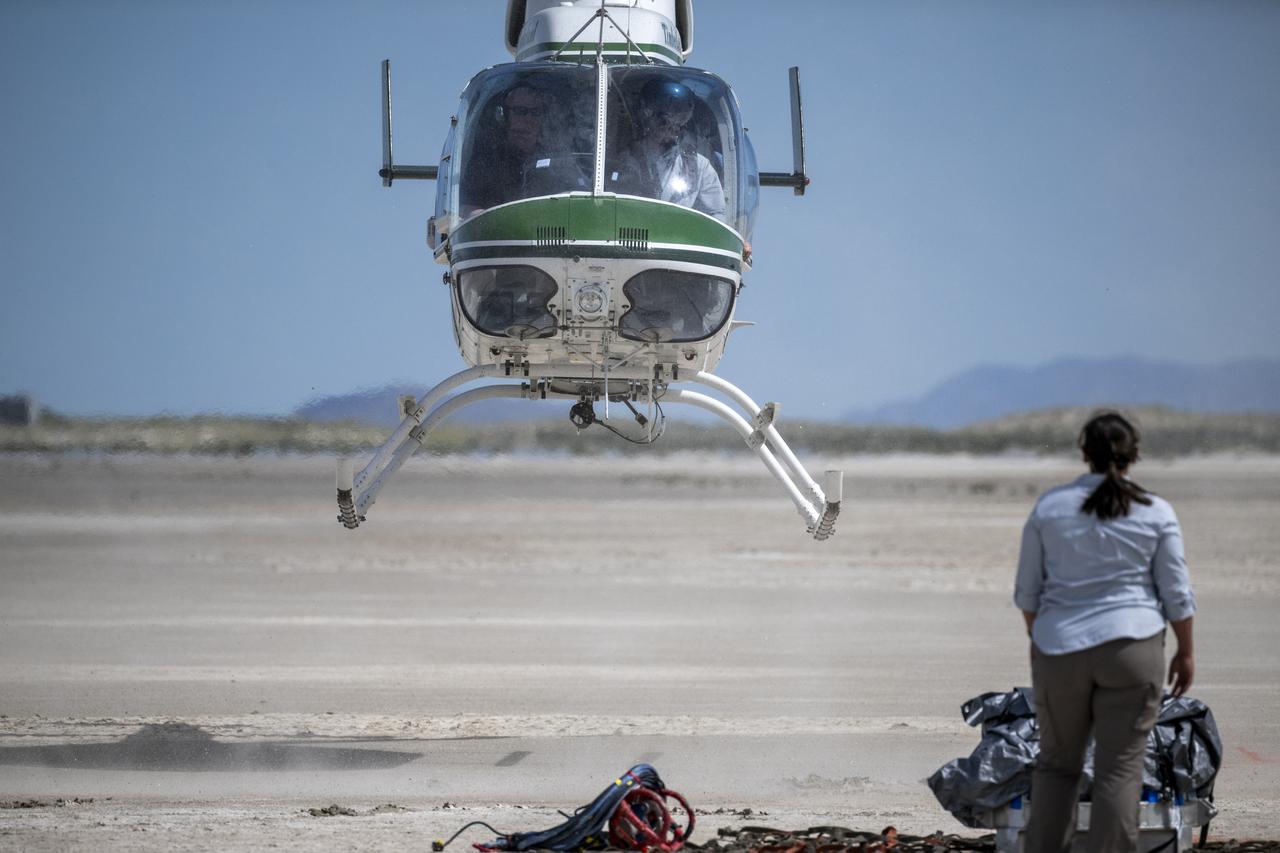

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
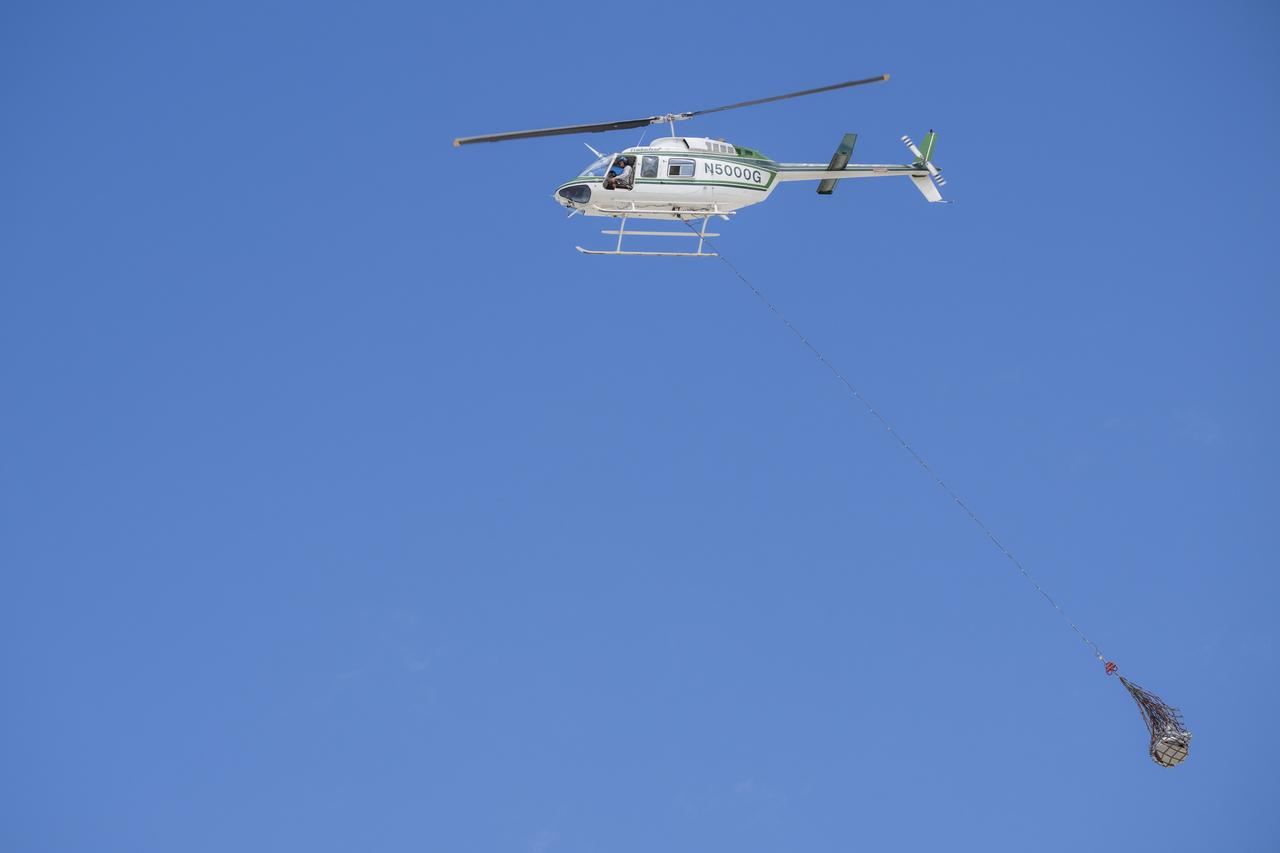

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
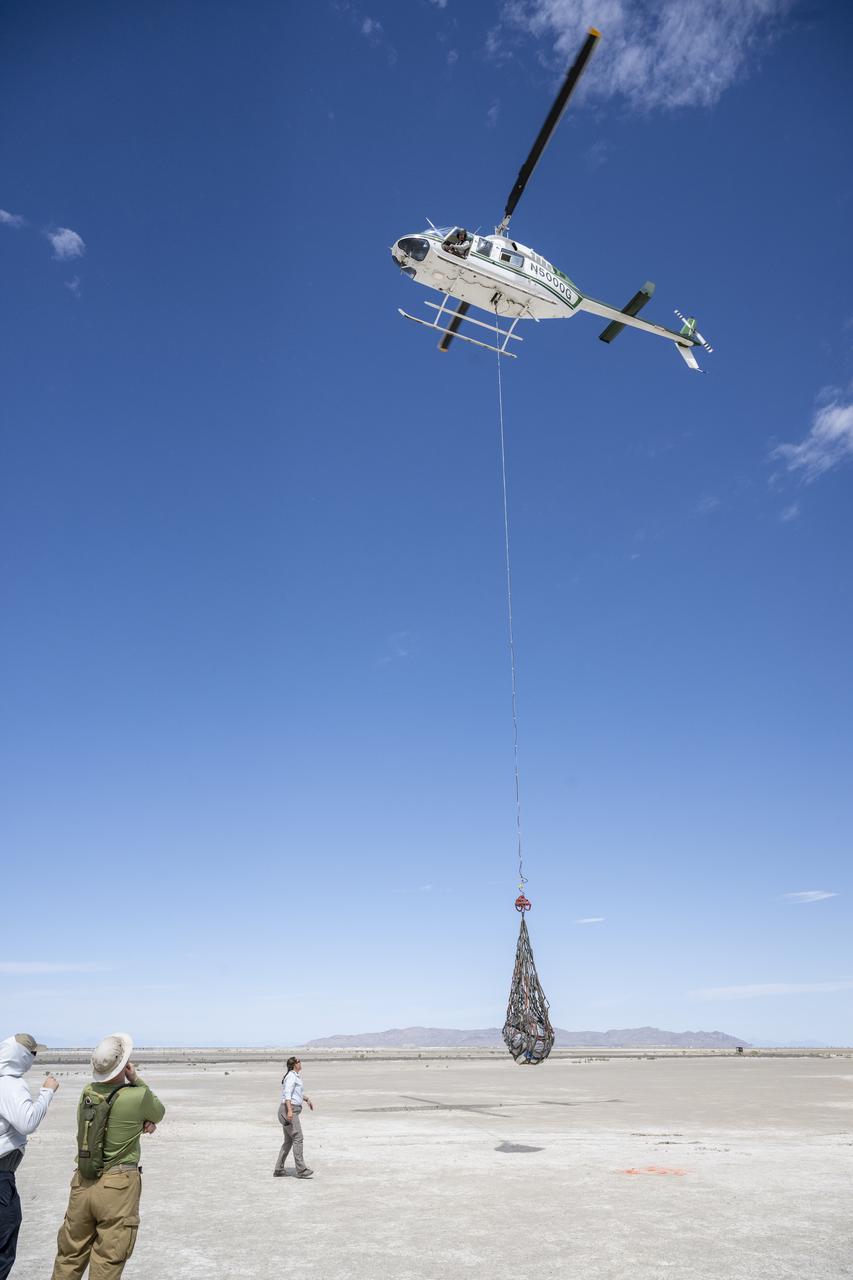

Recovery teams participate in helicopter training in preparation for the retrieval of the sample return capsule from NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission, Wednesday, July 19, 2023, at the Department of Defense's Utah Test and Training Range. The sample was collected from the asteroid Bennu in October 2020 by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft and will return to Earth on September 24th, landing under parachute at the Utah Test and Training Range. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
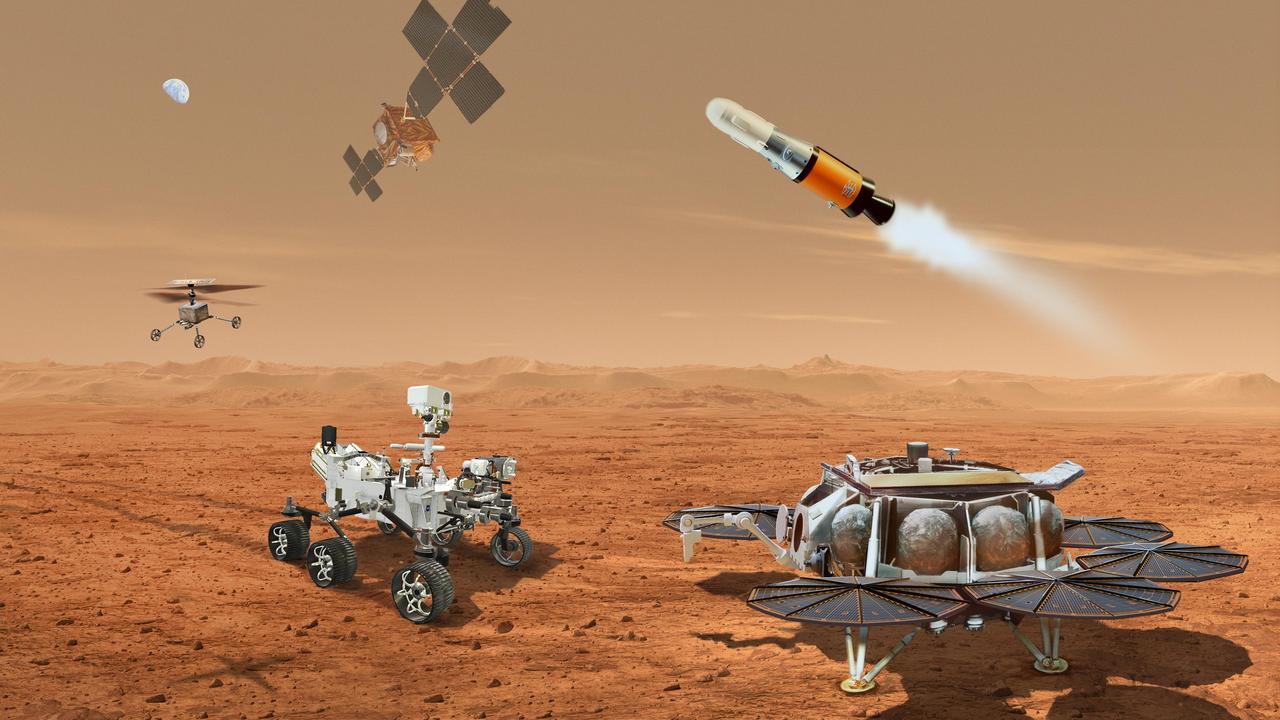
This illustration shows a concept for multiple robots that would team up to ferry to Earth samples of rocks and soil being collected from the Martian surface by NASA's Mars Perseverance rover. NASA and ESA (European Space Agency) are developing concepts for the Mars Sample Return program, designed to retrieve the rock and soil samples Perseverance has collected and stored in sealed tubes. In the future, the samples would be returned to Earth for detailed laboratory analysis. The current concept envisions delivering a Mars lander near Jezero Crater, where Perseverance (far left) collects samples. A NASA-provided Sample Retrieval Lander (far right) would carry a NASA rocket (the Mars Ascent Vehicle). Perseverance would gather sample tubes it has cached on the Mars surface and transport them to the Sample Retrieval Lander, where they would then be transferred by a Sample Transfer Arm provided by ESA onto the Mars Ascent Vehicle. The arm is based on a human arm, with an elbow, shoulder, and wrist. The Mars Ascent Vehicle would launch a container with the sample tubes inside into orbit. Waiting in Mars orbit would be an ESA-provided Earth Return Obiter, which would rendezvous with and capture the Orbiting Sample Container using a NASA-provided Capture, Containment, and Return System. This system would capture and orient the container, then prepare it for return to Earth inside the Earth Entry System. Also depicted is one of two Sample Recovery Helicopters NASA will develop to be transported to Mars on the Sample Retrieval Lander, just as the Ingenuity helicopter was carried on the Perseverance rover. The helicopters would serve as backups to Perseverance in transporting sample tubes to the Lander. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25326

NASA's Perseverance rover deposited the first of several sample tubes onto the Martian surface on Dec. 21, 2022, the 653rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This composite image of the tube, filled with a sample of igneous rock, is made up of a series of stitched-together images taken by a camera called WATSON (Wide Angle Topographic Sensor for Operations and eNgineering) on the end of the rover's 7-foot-long (2-meter-long) robotic arm. Perseverance has been taking duplicate samples from each rock target the mission selects. After having dropped its first sample on the surface, the rover now has 17 samples in its belly, including one atmospheric sample. Based on the architecture of the Mars Sample Return campaign, the rover would deliver samples to a robotic lander carrying a small rocket that would blast them off to space. The depot will serve as a backup if Perseverance can't deliver its samples. In that case, a pair of Sample Recovery Helicopters would be called upon to pick up the sample tubes and deliver them to the lander. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25663
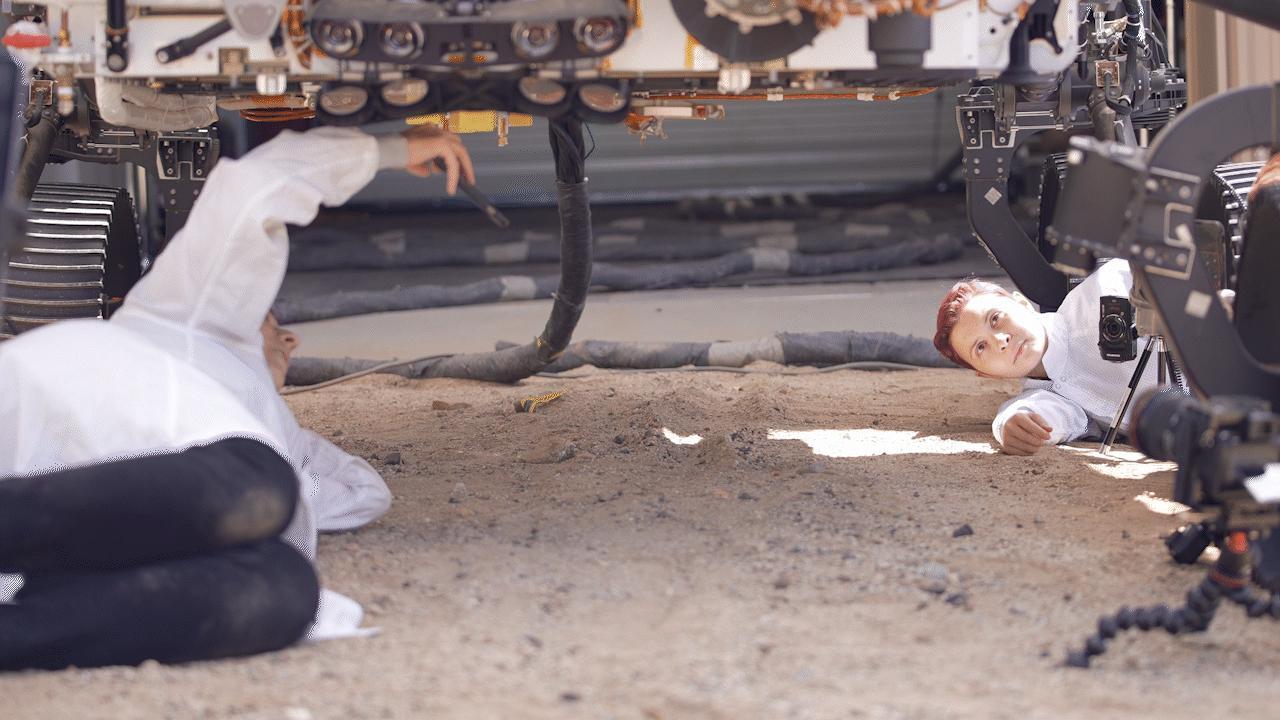

Engineers react with surprise while testing how NASA's Perseverance rover will deposit its sample tubes on the Martian surface. Less than 5% of the time, a flat end on the sample tube caused it to land straight up after dropping. This test was conducted using OPTIMISM, a full-scale replica of Perseverance, in the Mars Yard at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Perseverance has been taking duplicate samples from each rock target the mission selects. After depositing one sample on the surface Dec. 21, 2022, the rover has 17 samples in its belly, including one atmospheric sample. Based on the architecture of the Mars Sample Return campaign, the rover would deliver samples to a robotic lander carrying a small rocket that would blast them off to space. The depot will serve as a backup if Perseverance can't deliver its samples. In that case, a pair of Sample Recovery Helicopters would be called upon to pick up the sample tubes and deliver them to the lander. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25677
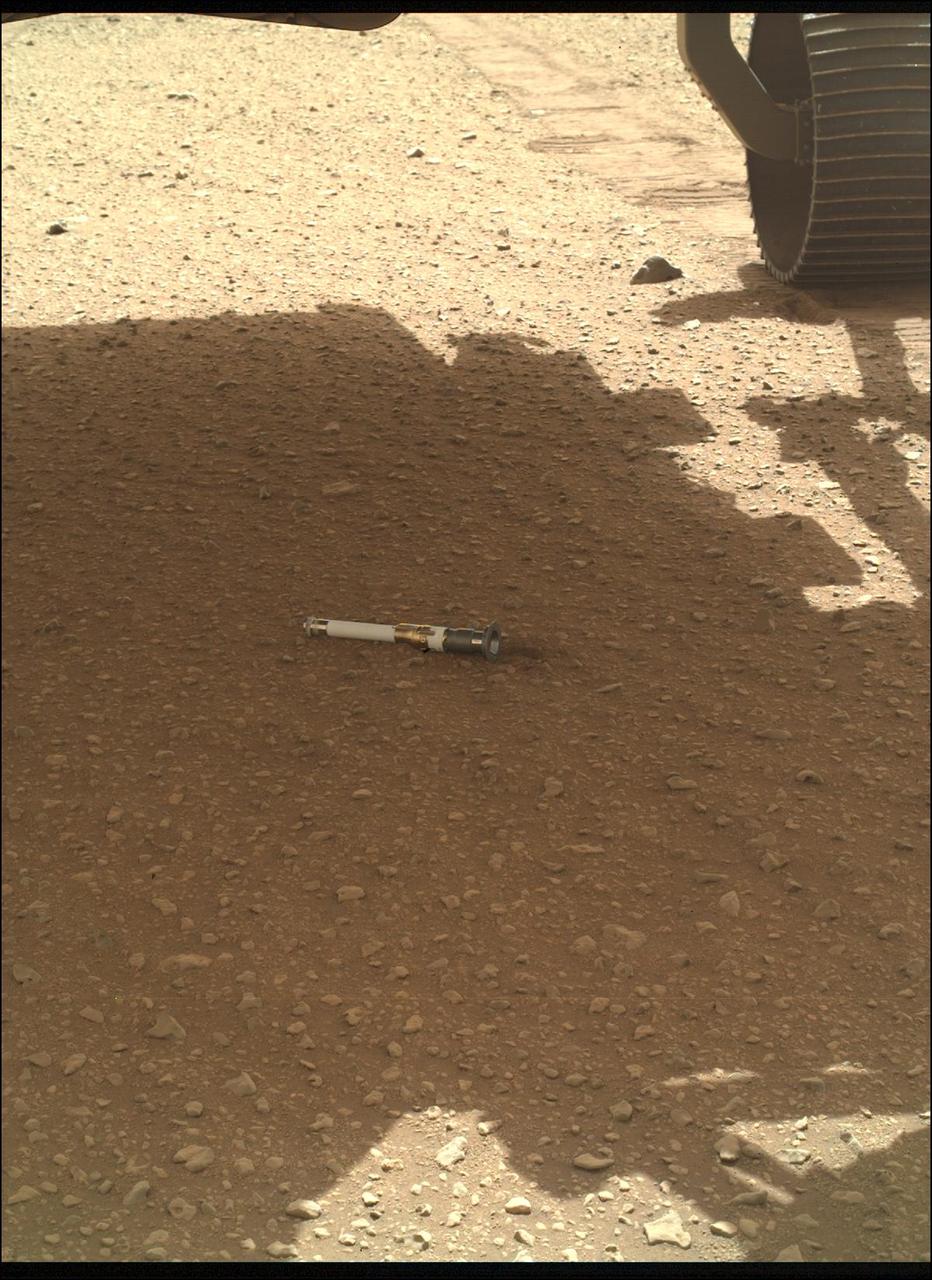

NASA's Perseverance rover deposited the first of several samples onto the Martian surface on Dec. 21, 2022, the 653rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Perseverance has been taking duplicate samples from each rock target the mission selects. The rover currently has 17 samples in its belly, including one atmospheric sample. Based on the architecture of the Mars Sample Return campaign, the rover would deliver samples to a robotic lander carrying a small rocket that would blast them off to space. The depot will serve as a backup if Perseverance can't deliver its samples. In that case, a pair of Sample Recovery Helicopters would be called upon to pick up the sample tubes and deliver them to the lander. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25652
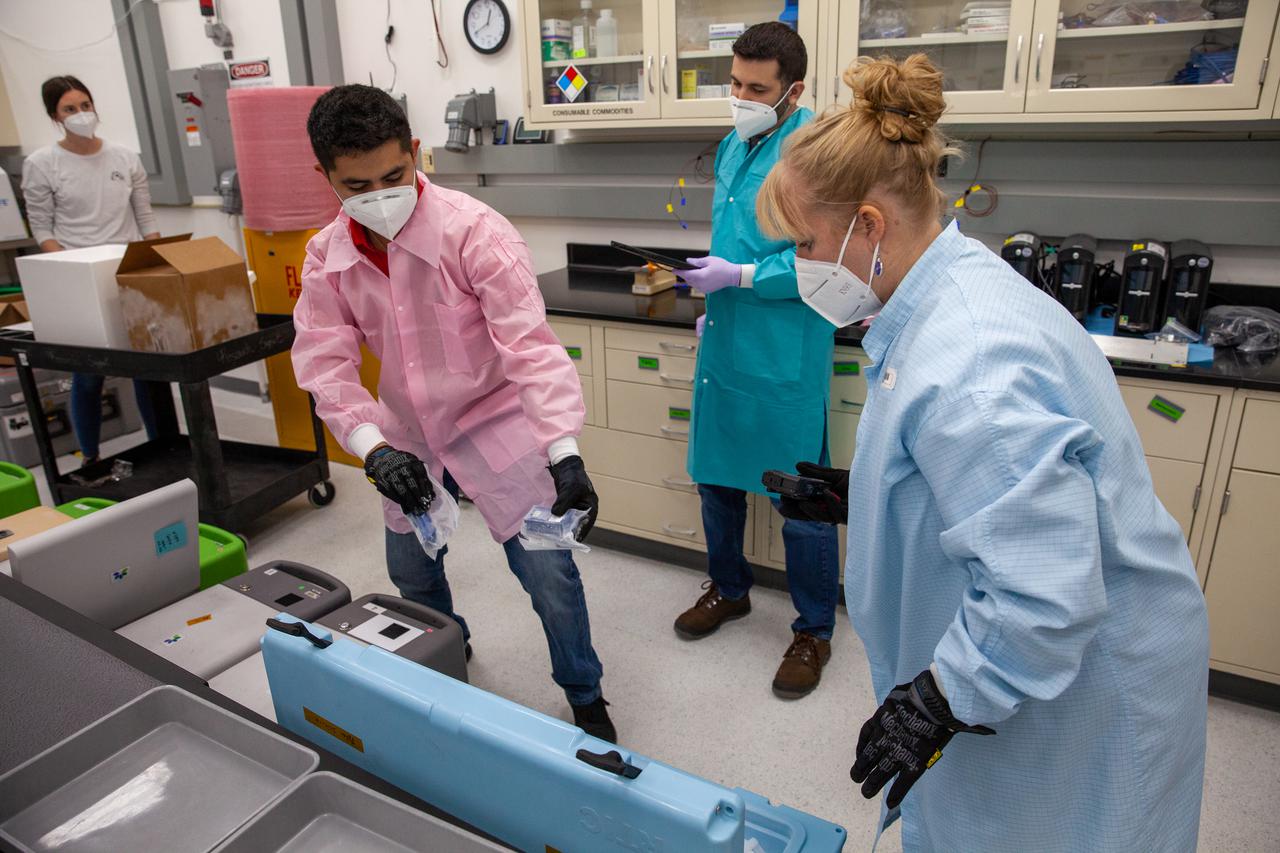

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
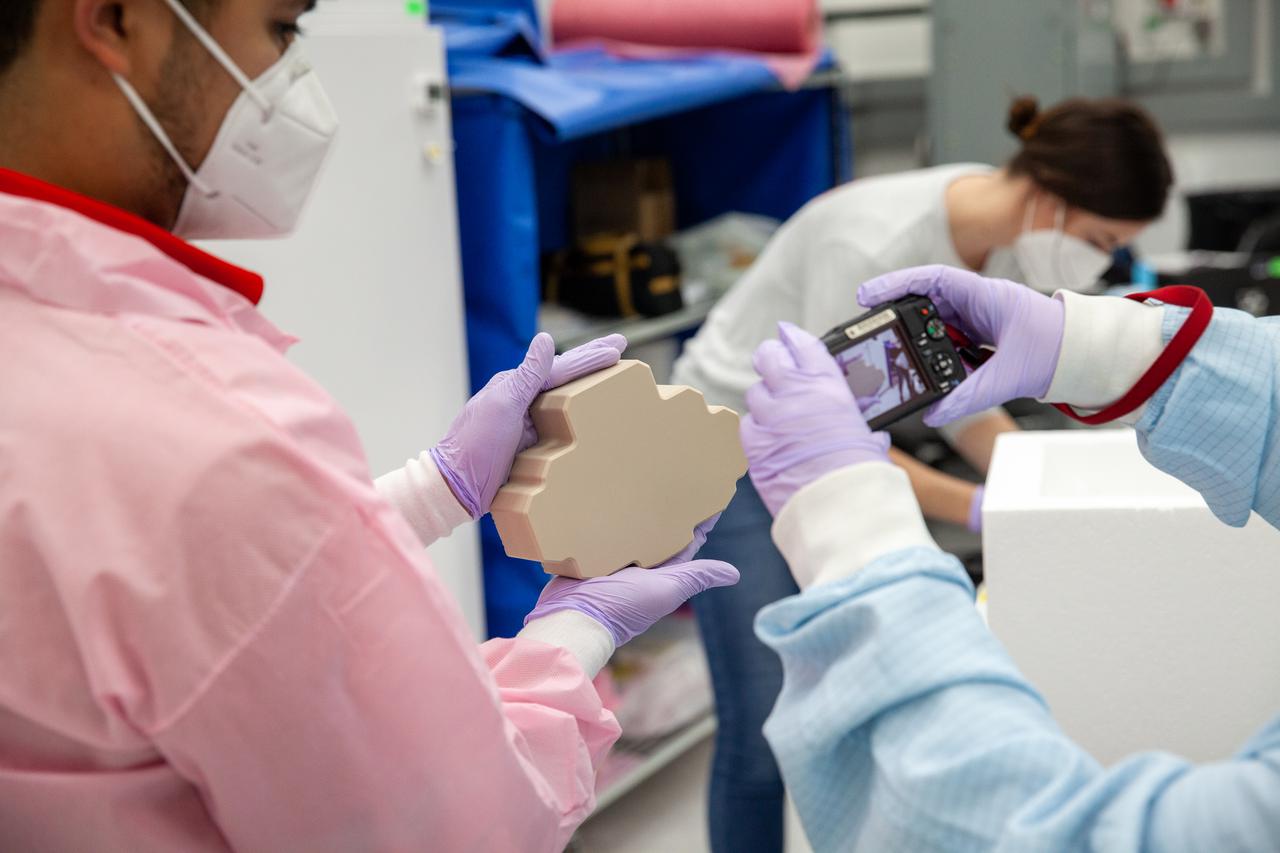

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
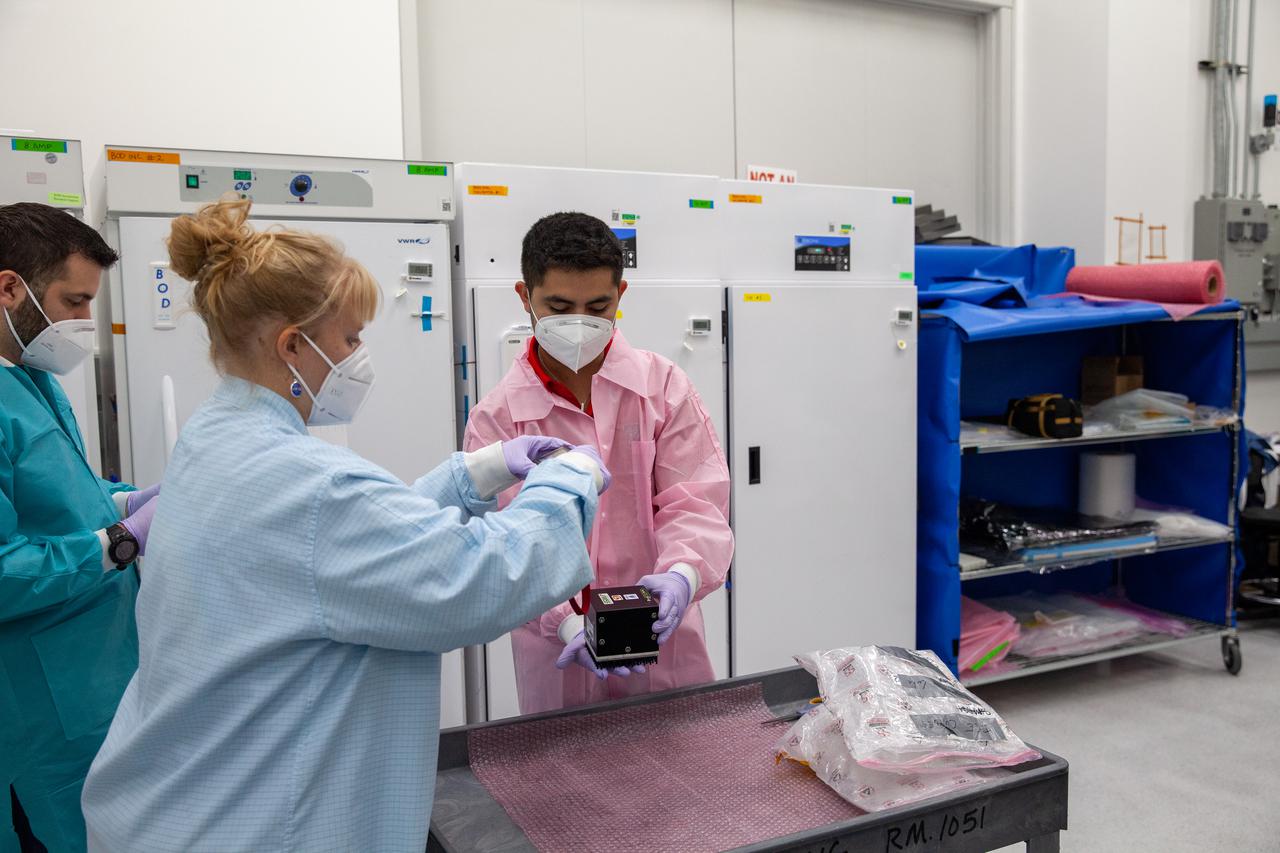

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
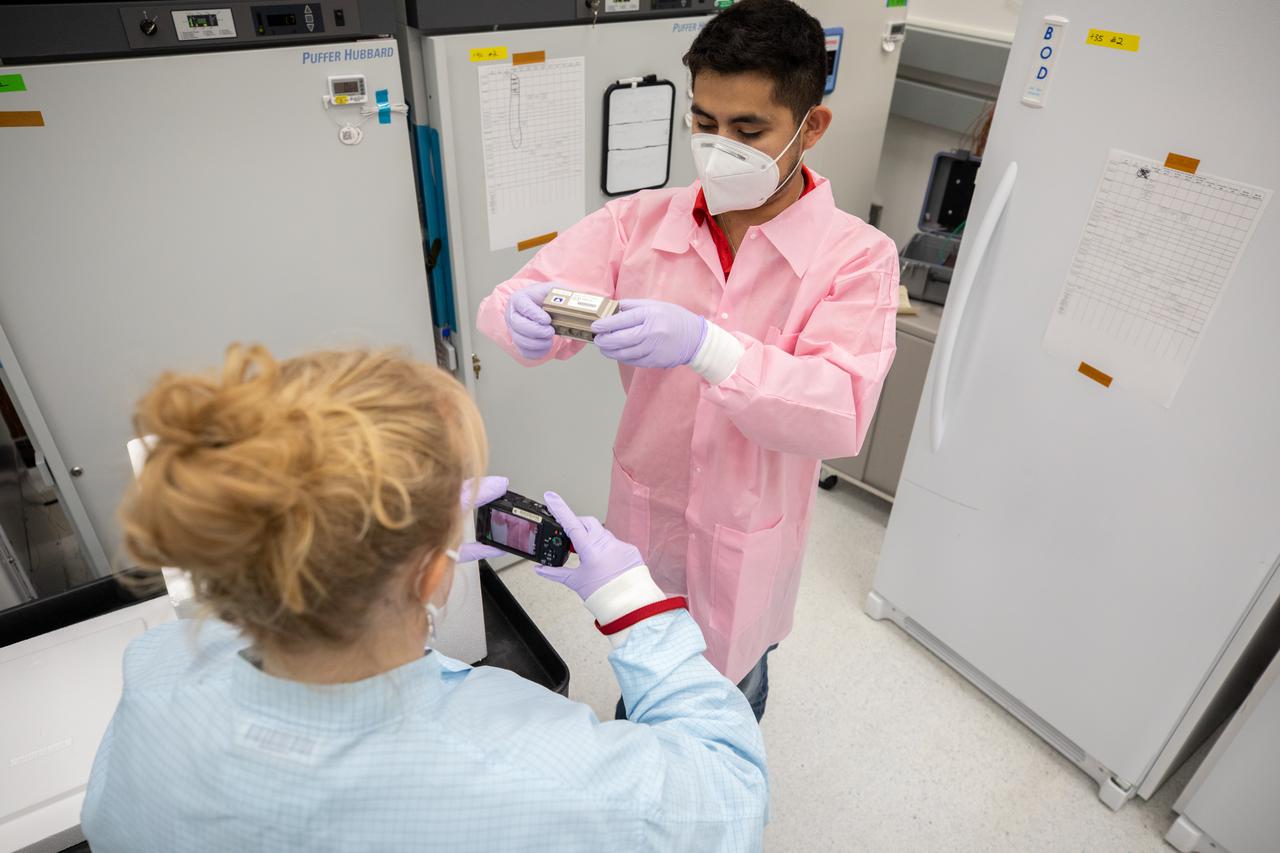
Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
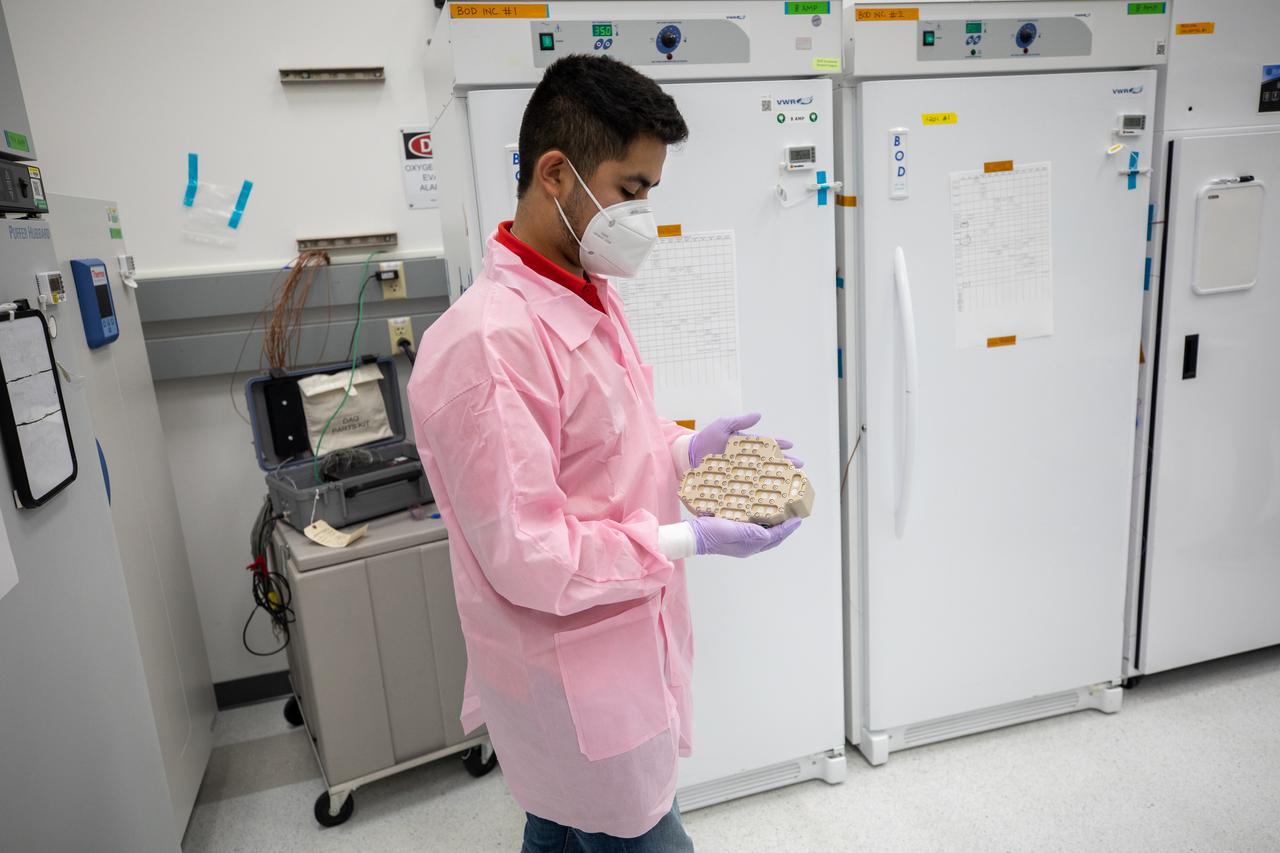

A member of the cold stowage team unpacks science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
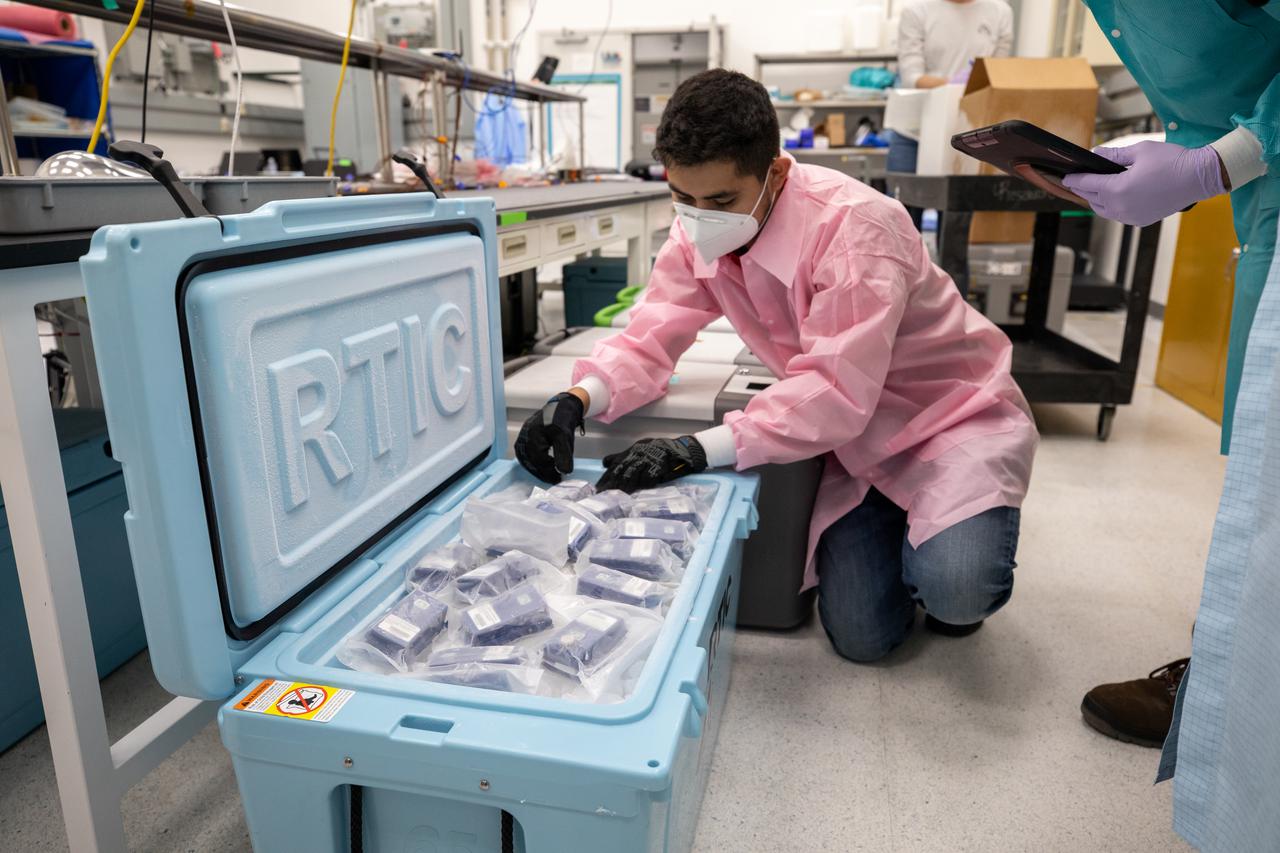

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
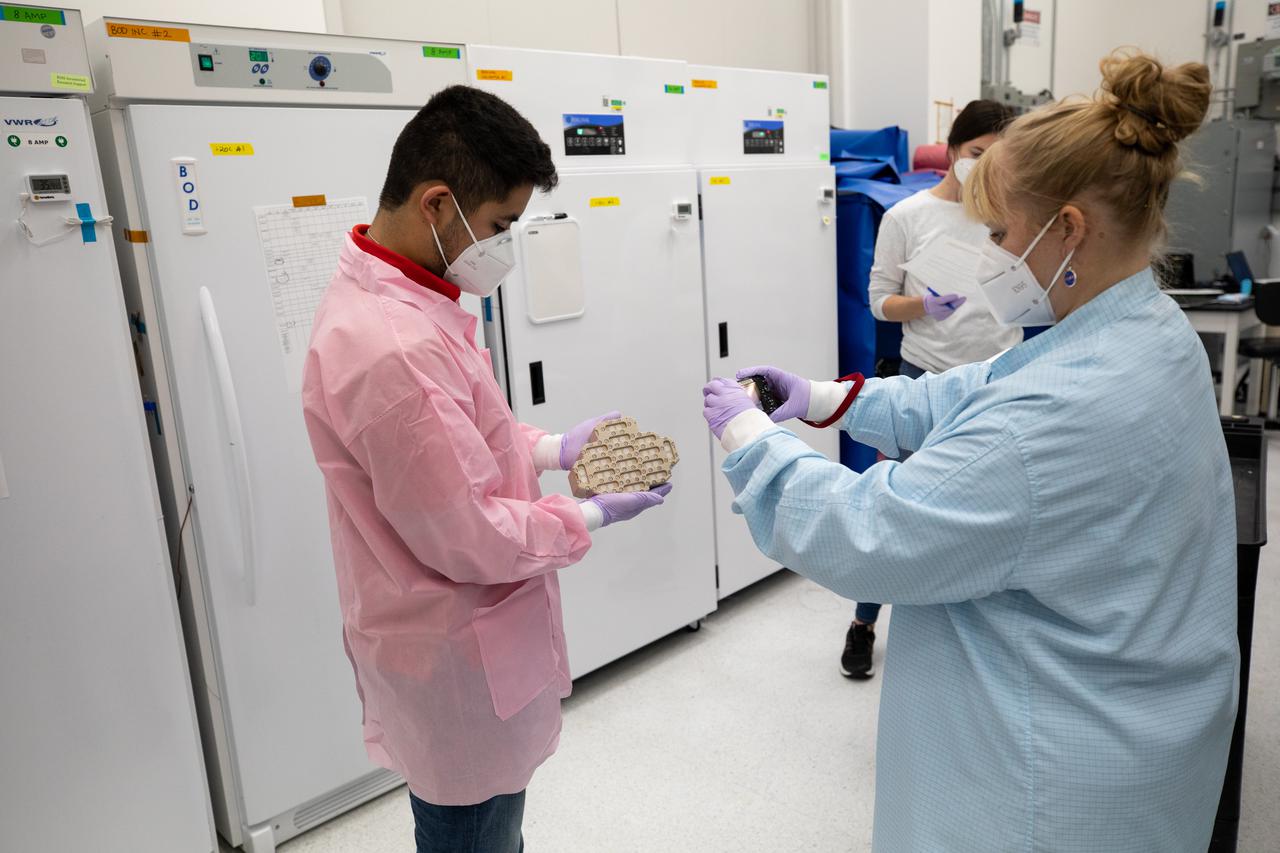

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
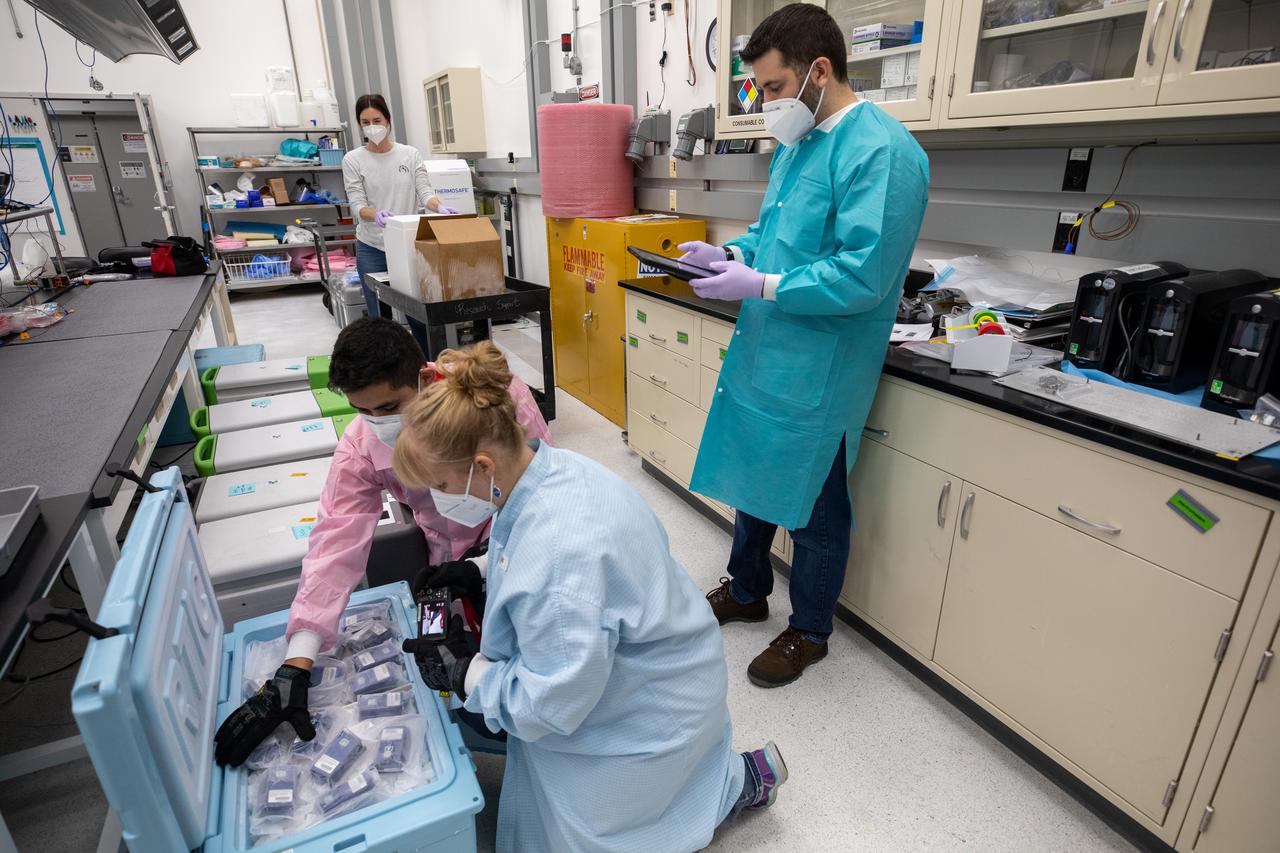

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.

Shown here is the SpaceX Cargo Dragon spacecraft on board the company's Go Navigator recovery ship after making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast on Jan. 13, 2020, at 8:26 p.m. EST. Just after loading Dragon onto Go Navigator, SpaceX packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth. Photo credit: SpaceX
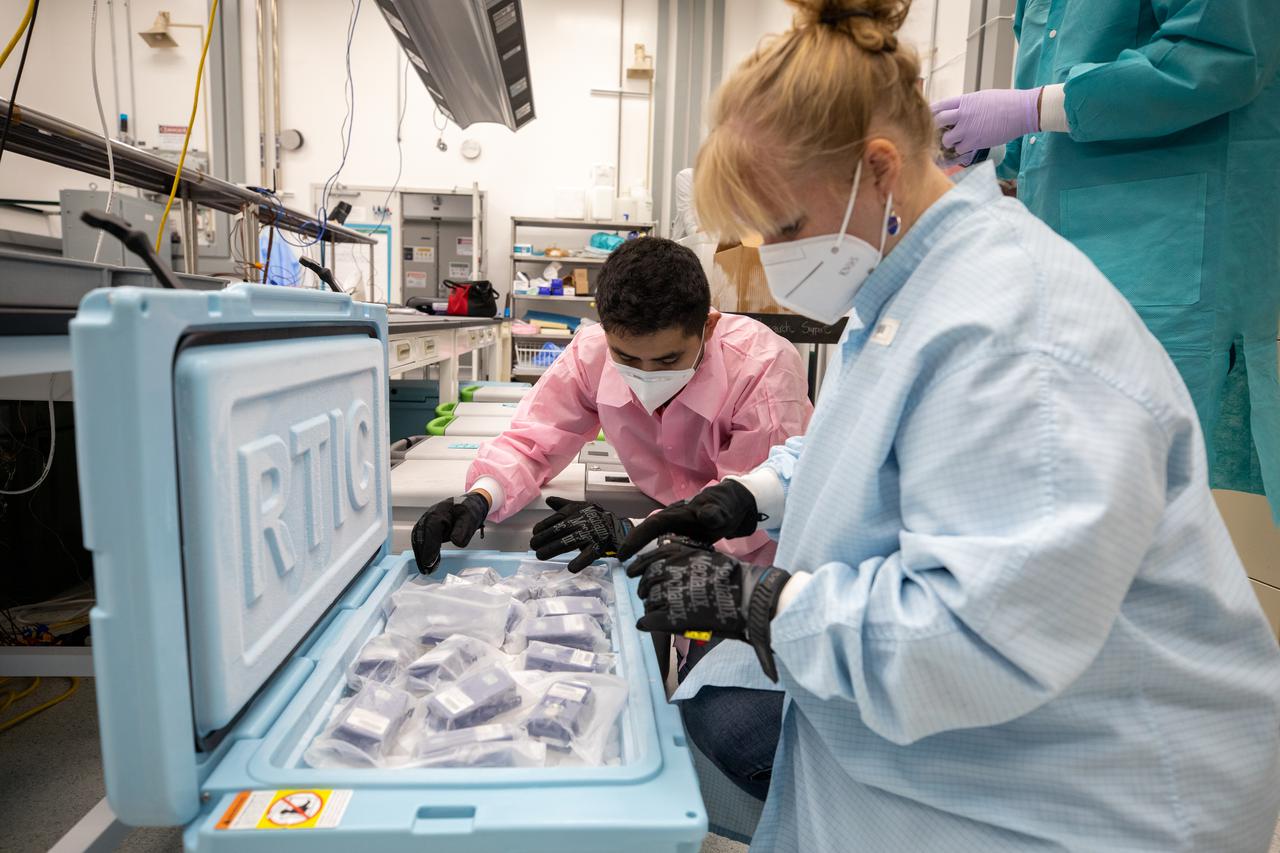

Members of the cold stowage team unpack science experiments inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 14, 2021. The experiments returned to Earth on SpaceX’s 21st commercial resupply services mission (CRS-21). Making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast, at 8:26 p.m. EST on Jan. 13, the SpaceX cargo Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. After splashdown, SpaceX loaded Dragon aboard their Go Navigator recovery ship and packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to Kennedy. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule also boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth.
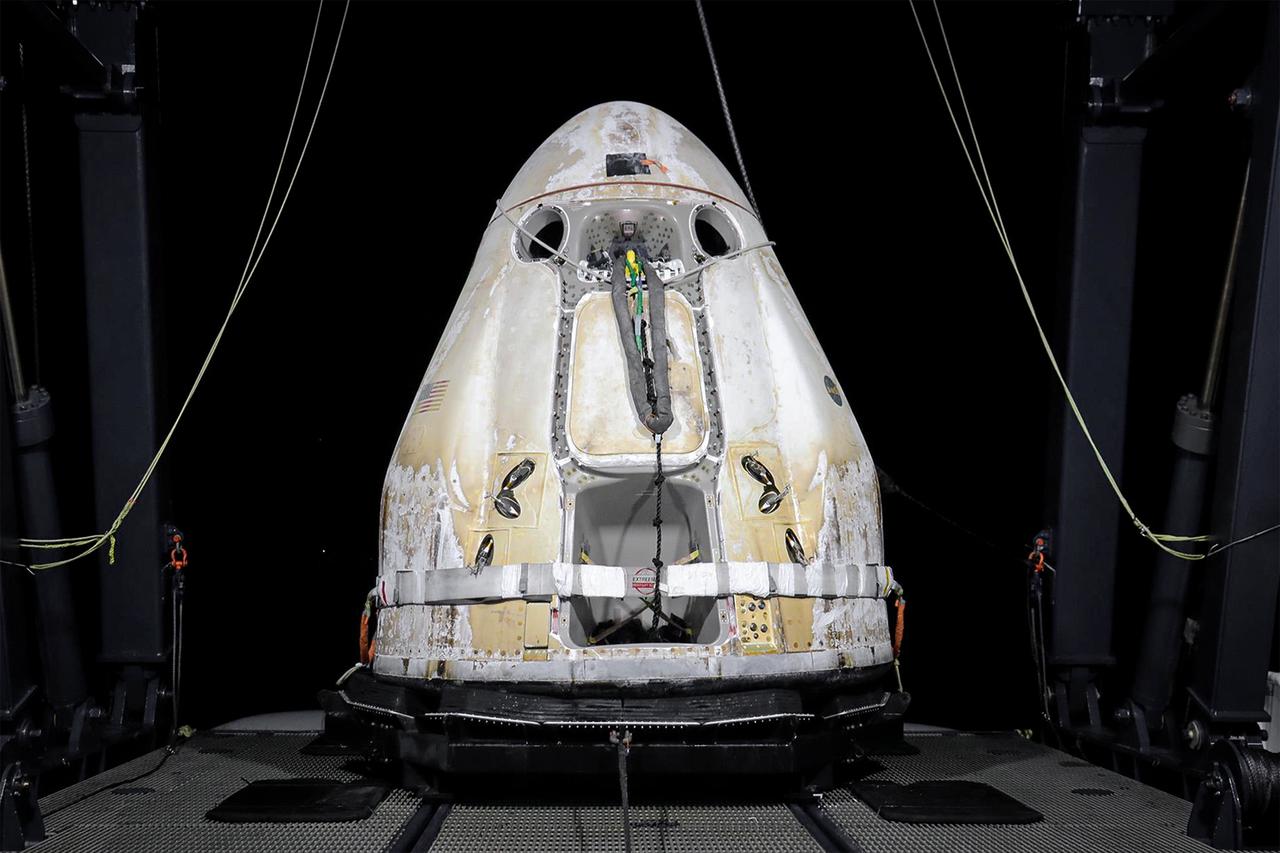

Shown here is the SpaceX Cargo Dragon spacecraft on board the company's Go Navigator recovery ship after making its successful parachute-assisted splashdown west of Tampa off the Florida coast on Jan. 13, 2020, at 8:26 p.m. EST. Just after loading Dragon onto Go Navigator, SpaceX packed an Airbus H225 helicopter with the time-sensitive research cargo for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Dragon returned more than 4,400 pounds of scientific experiments and other cargo from the International Space Station. The upgraded cargo Dragon capsule boasts double the powered locker capacity to preserve science samples, allowing for a significant increase in the research that can be carried back to Earth. Photo credit: SpaceX