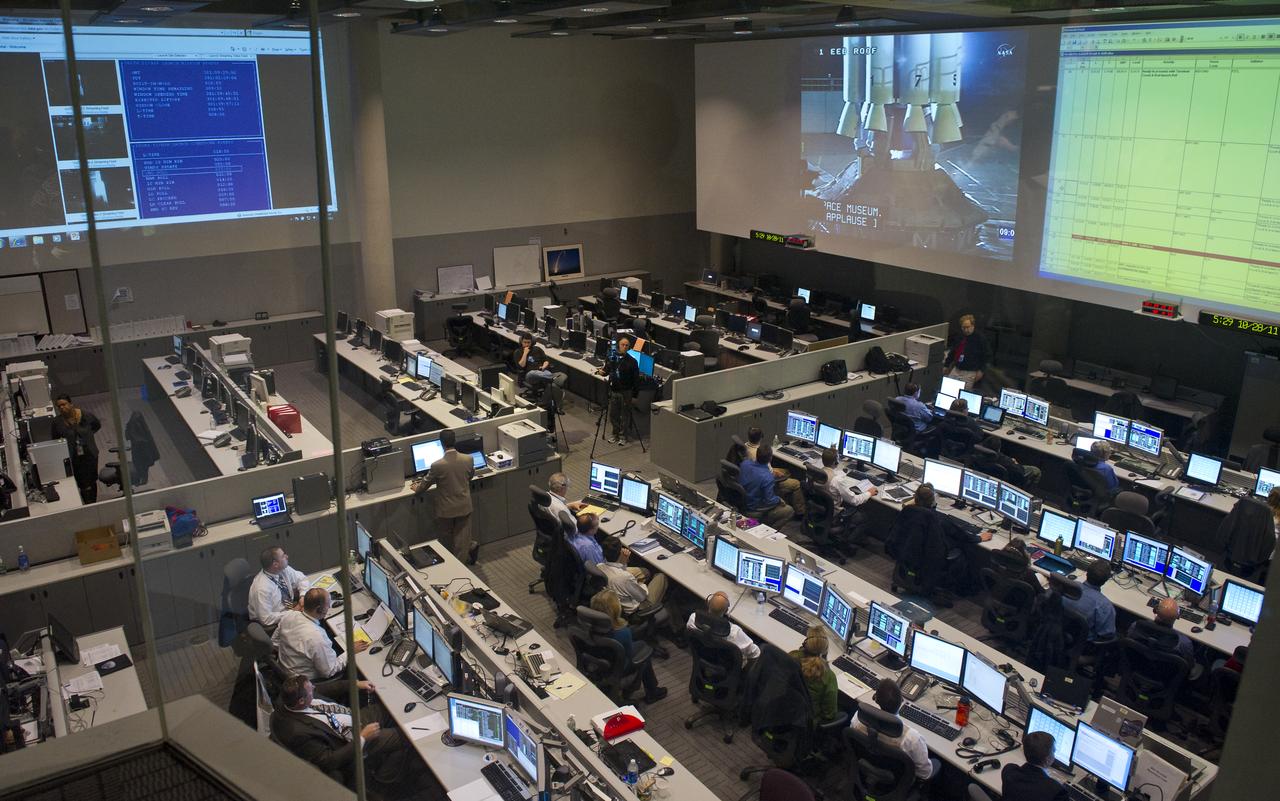

The Satellite Operations Facility of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is seen here minutes before the launch of the National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System Preparatory Project (NPP) on Friday, Oct. 28, 2011 in Suitland, Md. NPP is a joint venture between NASA and NOAA, and is the nation's newest Earth-observing satellite, which will provide data on climate change science, allow for accurate weather forecasts and advance warning for severe weather. NPP was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Dr. Kathy Sullivan, center, Deputy Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and former NASA astronaut is interviewed by a local television network at NOAA's Satellite Operations Facility in Suitland, Md. after the successful launch of the National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System Preparatory Project (NPP) on Friday, Oct. 28, 2011. NPP is a joint venture between NASA and NOAA, and is the nation's newest Earth-observing satellite, which will provide data on climate change science, allow for accurate weather forecasts and advance warning for severe weather. NPP was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
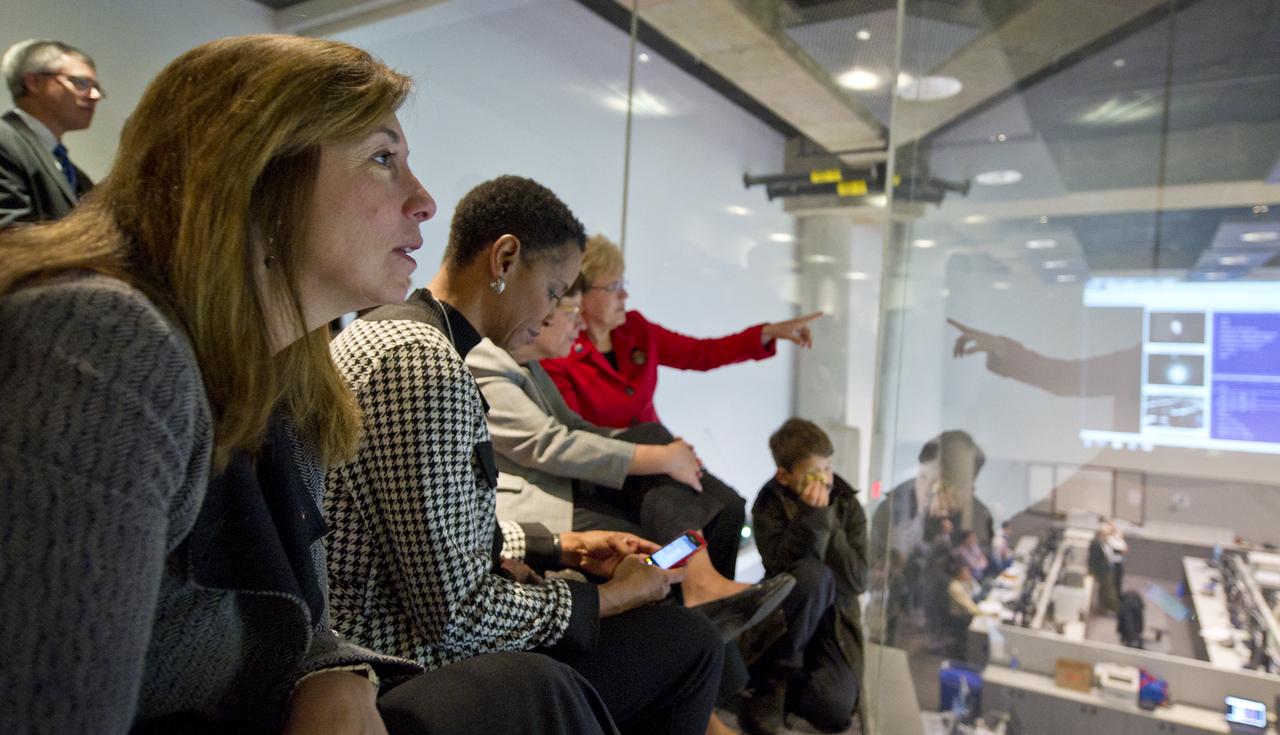

NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver, left, watches the launch of the National Polar-orbiting Operational Environmental Satellite System Preparatory Project (NPP) at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Satellite Operations Center on Friday, Oct. 28, 2011 in Suitland, Md. U.S Congresswoman Donna Edwards, D-Md., is seen next to Garver. NPP is a joint venture between NASA and NOAA, and is the nation's newest Earth-observing satellite, which will provide data on climate change science, allow for accurate weather forecasts and advance warning for severe weather. NPP was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-on (GRACE-FO) mission is a partnership between NASA and the German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ). GRACE-FO is a successor to the original GRACE mission, which began orbiting Earth on March 17, 2002. GRACE-FO will carry on the extremely successful work of its predecessor while testing a new technology designed to dramatically improve the already remarkable precision of its measurement system. The GRACE missions measure variations in gravity over Earth's surface, producing a new map of the gravity field every 30 days. Thus, GRACE shows how the planet's gravity differs not only from one location to another, but also from one period of time to another. Airbus Defence and Space (Friedrichshafen/Germany) is the industrial prime contractor to build the satellites.
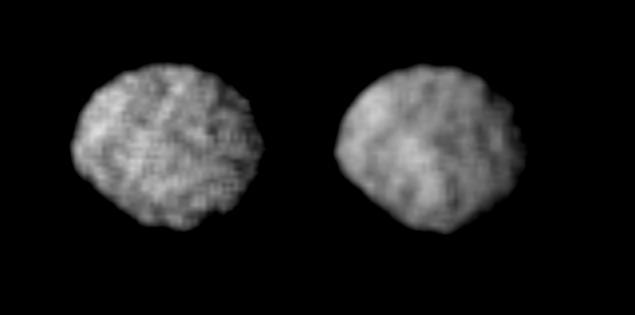
Satellite 1989N2

Satellite Trio
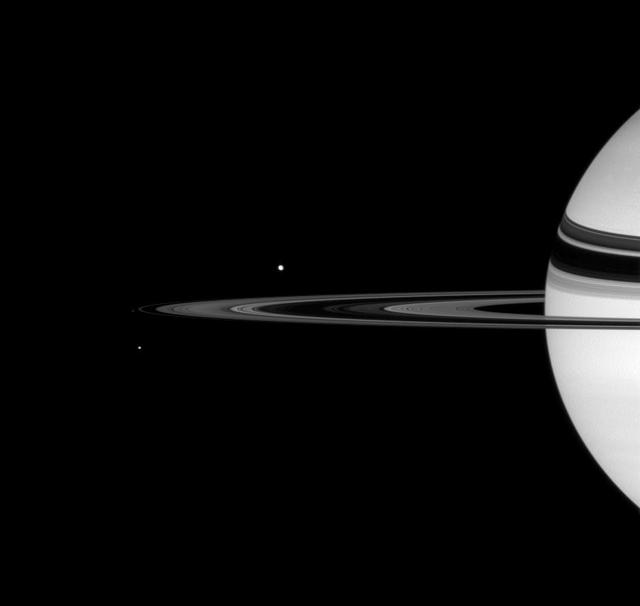

Circling Satellites
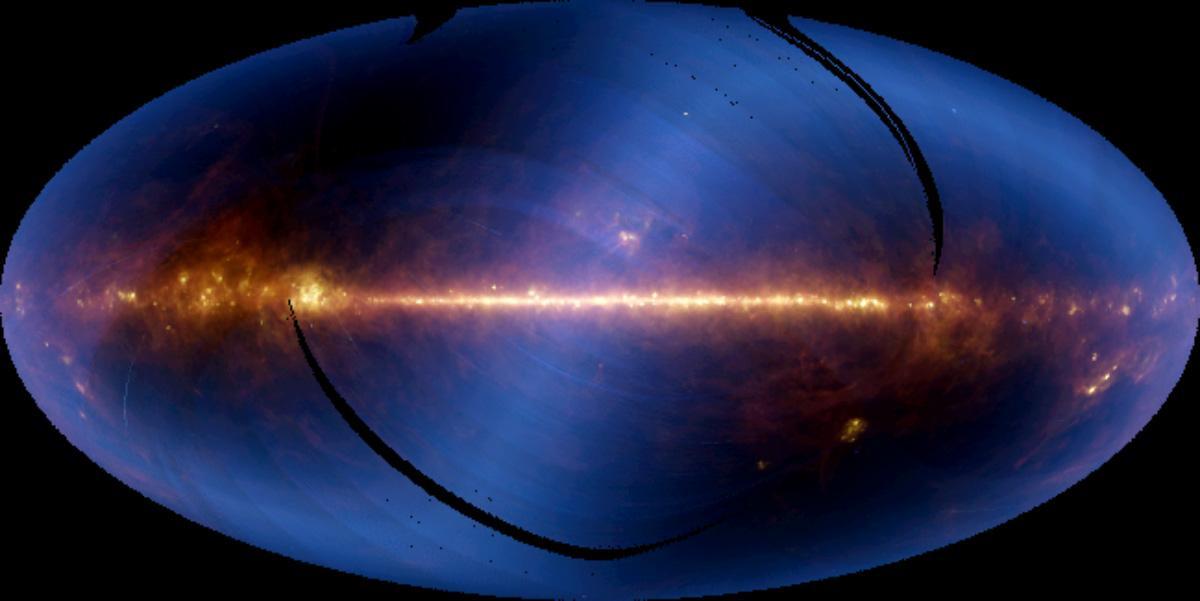
Nearly the entire sky, as seen in infrared wavelengths and projected at one-half degree resolution, is shown in this image, assembled from six months of data from the NASA Infrared Astronomical Satellite, or IRAS.
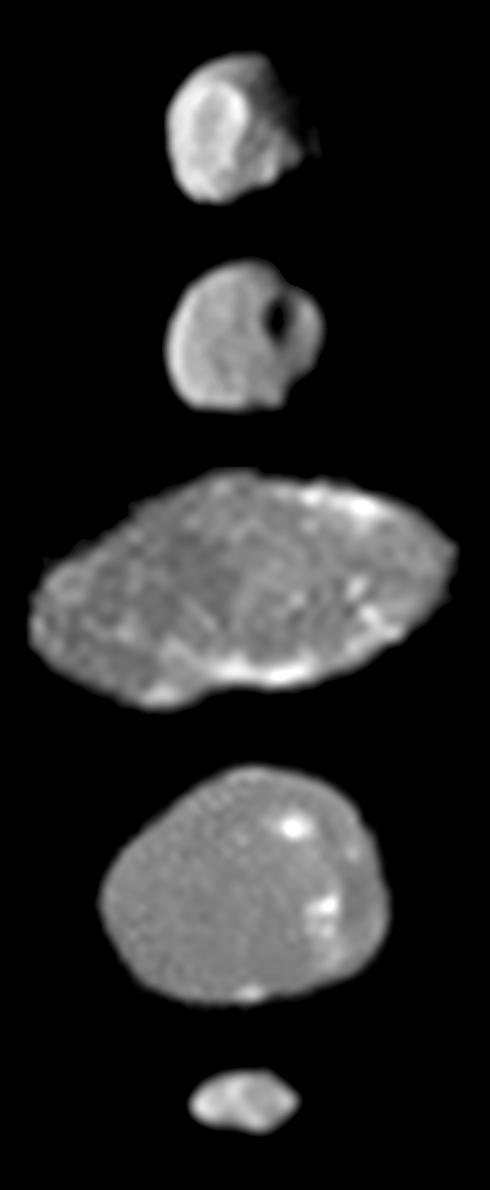

Jupiter Small Satellite Montage

Saturn Outer Satellite, Phoebe

Saturn Satellite Rhea

Collage of Saturn Smaller Satellites
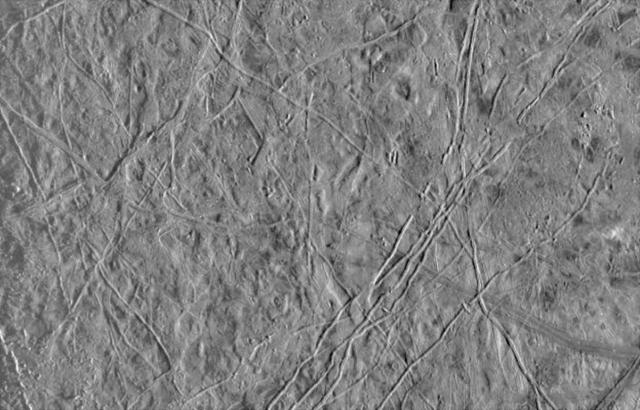
Jupiter Icy Satellite Europa

Saturn Satellite Dione

Saturn outer satellite - Phoebe
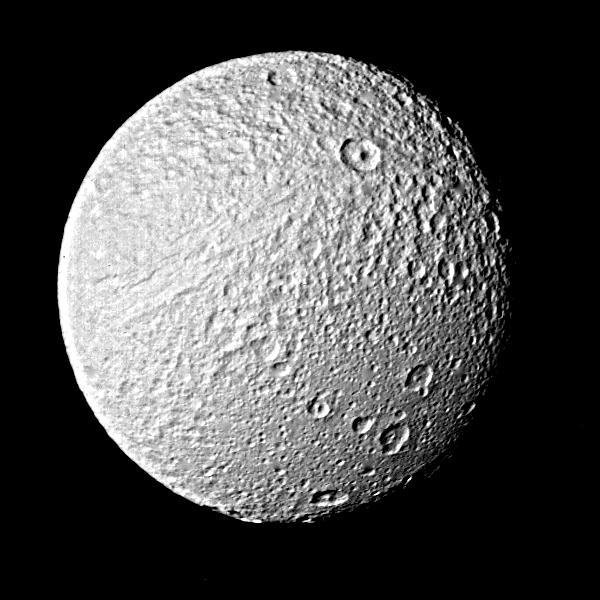

Photograph of Saturns Satellite Tethys
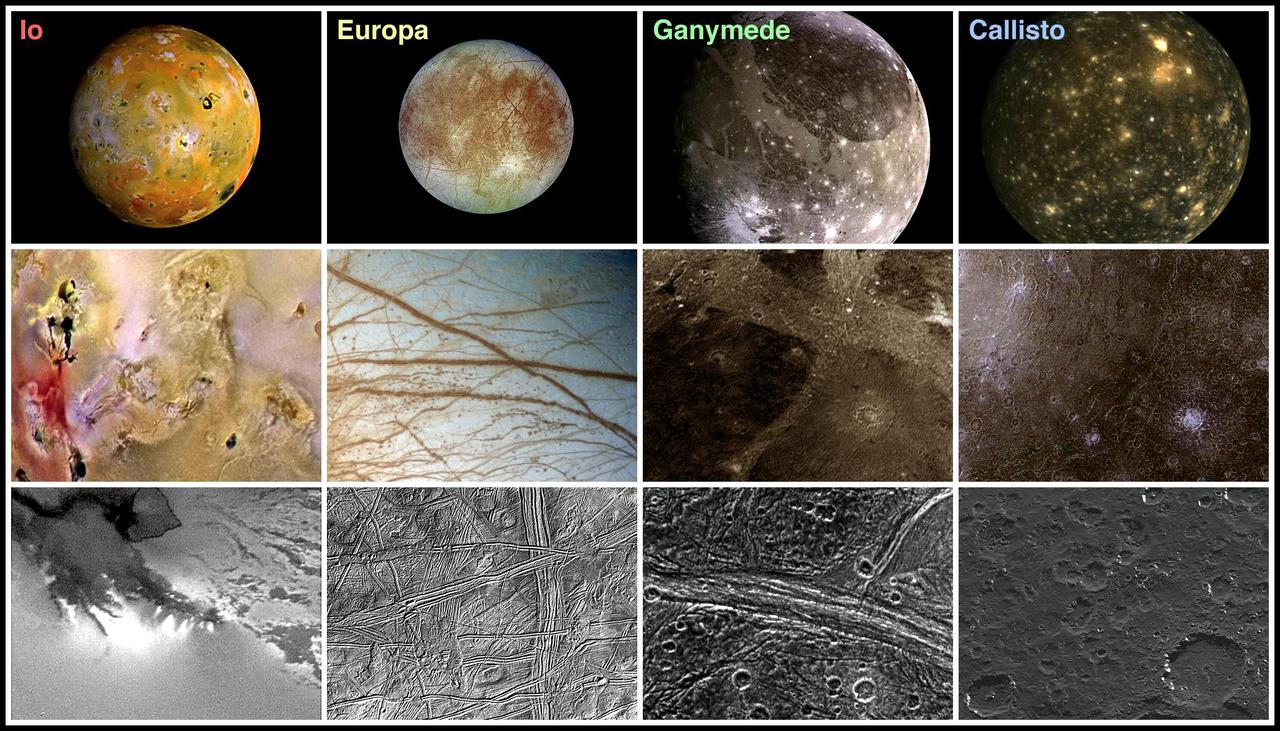
Landscape Comparisons - Galilean Satellites
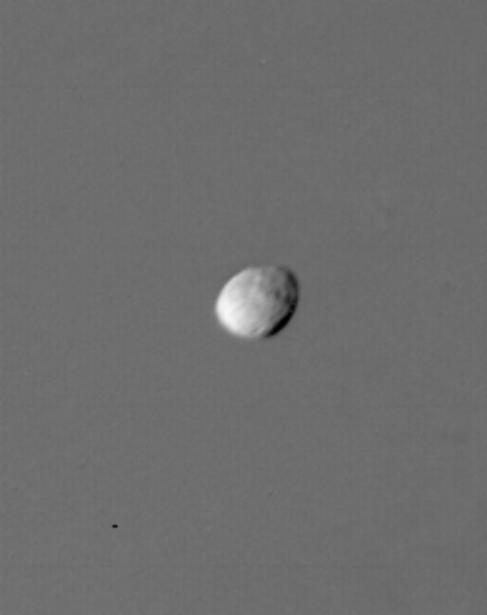
Saturn Satellite 1980S1

51I-32-059 (27 August 1985) --- The American Satellite Company (ASC) communications satellite rises from the cargo bay at 6:54 a.m. August 27, 1985.
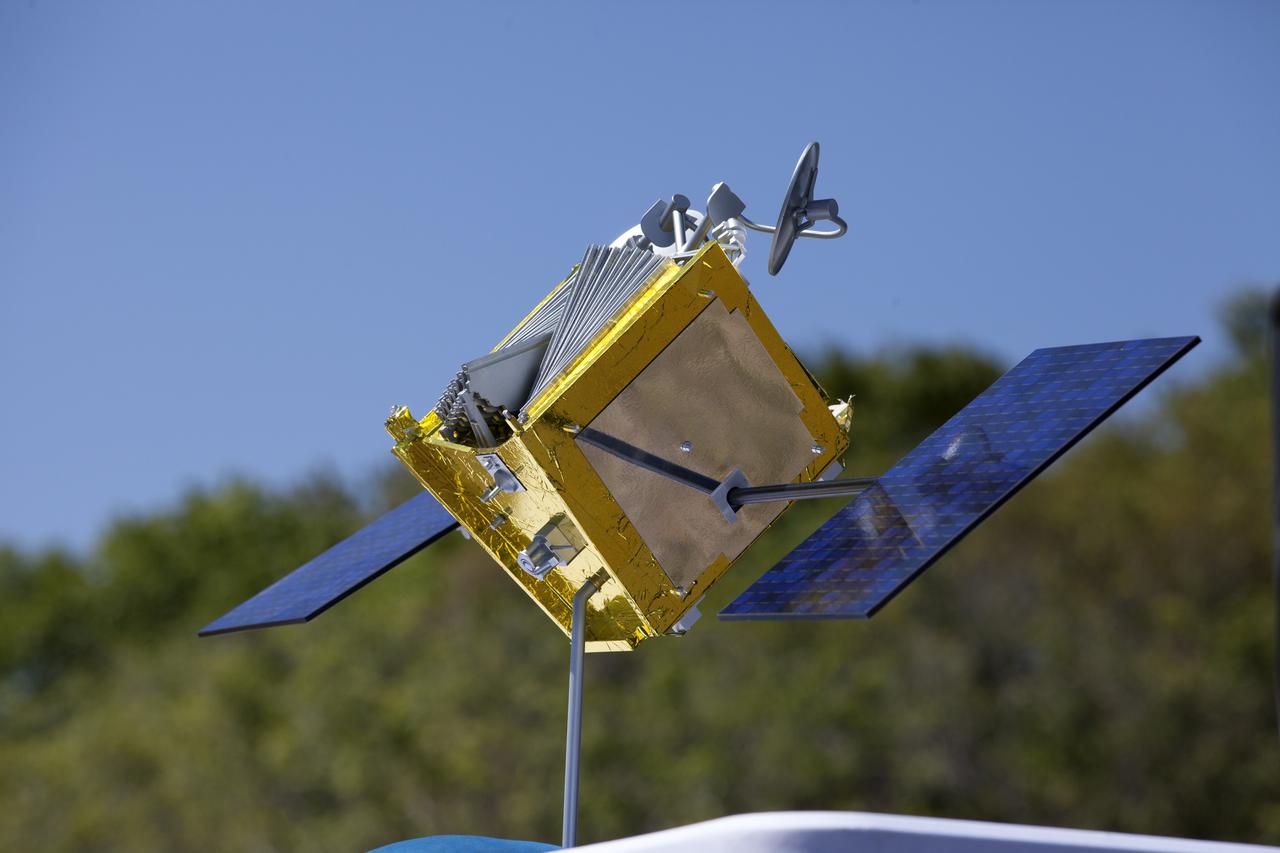

A model of a OneWeb satellite like those the company will build to will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. The company plans to launch 2,000 of the satellites as part of its constellation. The satellites will be built at a new factory at Exploration Park at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The company held a groundbreaking ceremony for the factory. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

A model of a OneWeb satellite like those the company will build to will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. The company plans to launch 2,000 of the satellites as part of its constellation. The satellites will be built at a new factory at Exploration Park at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The company held a groundbreaking ceremony for the factory. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Brian Holz, CEO of OneWeb Satellites, speaks during the groundbreaking ceremony at Kennedy's Exploration Park for OneWeb. The company, in partnership with Airbus, is building a 150,000-square-foot factory to manufacture satellites that will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

A CREW INSTALLS A NEW EARTH SCIENCE RECEIVING SATELLITE ANTENNA OUTSIDE MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER'S ACTIVITIES BUILDING 4316

A CREW INSTALLS A NEW EARTH SCIENCE RECEIVING SATELLITE ANTENNA OUTSIDE MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER'S ACTIVITIES BUILDING 4316

A CREW INSTALLS A NEW EARTH SCIENCE RECEIVING SATELLITE ANTENNA OUTSIDE MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER'S ACTIVITIES BUILDING 4316

A CREW INSTALLS A NEW EARTH SCIENCE RECEIVING SATELLITE ANTENNA OUTSIDE MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER'S ACTIVITIES BUILDING 4316
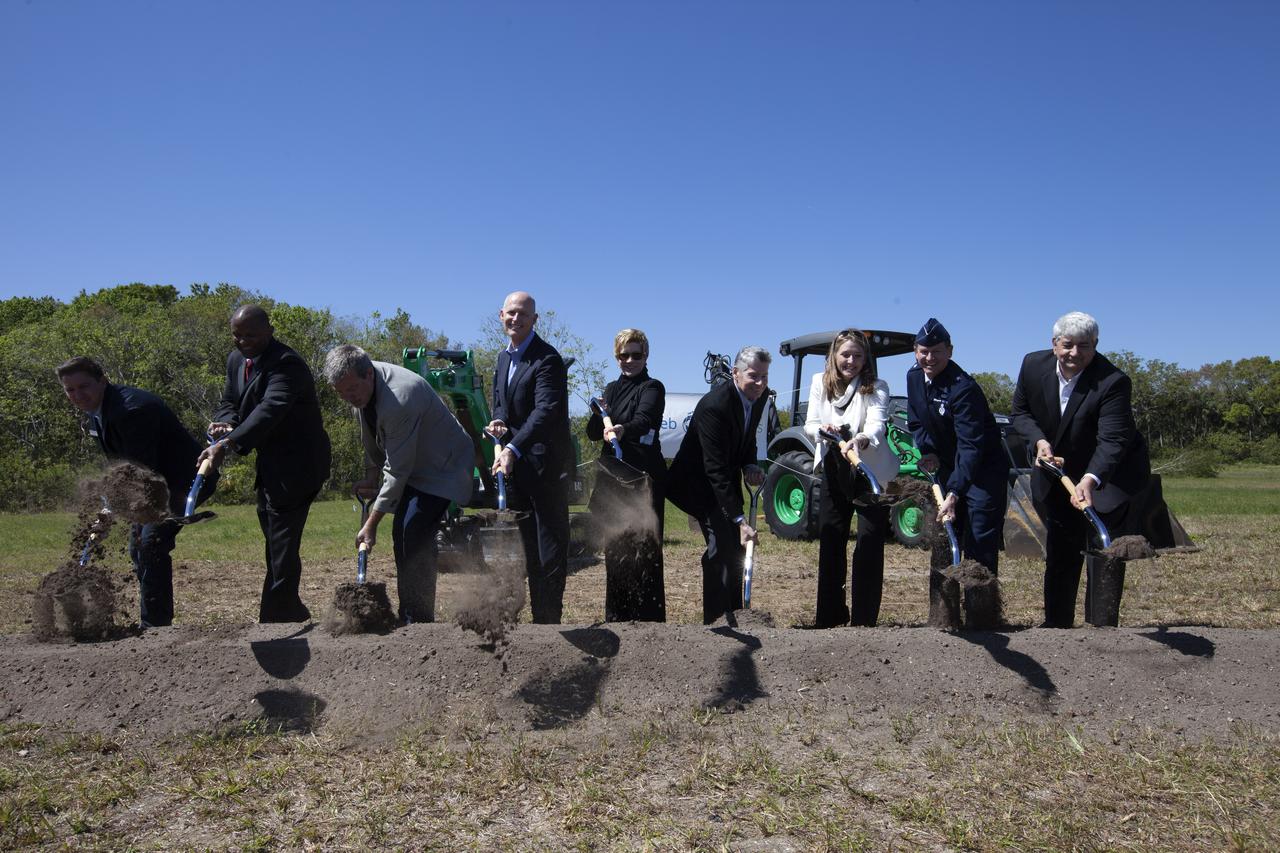

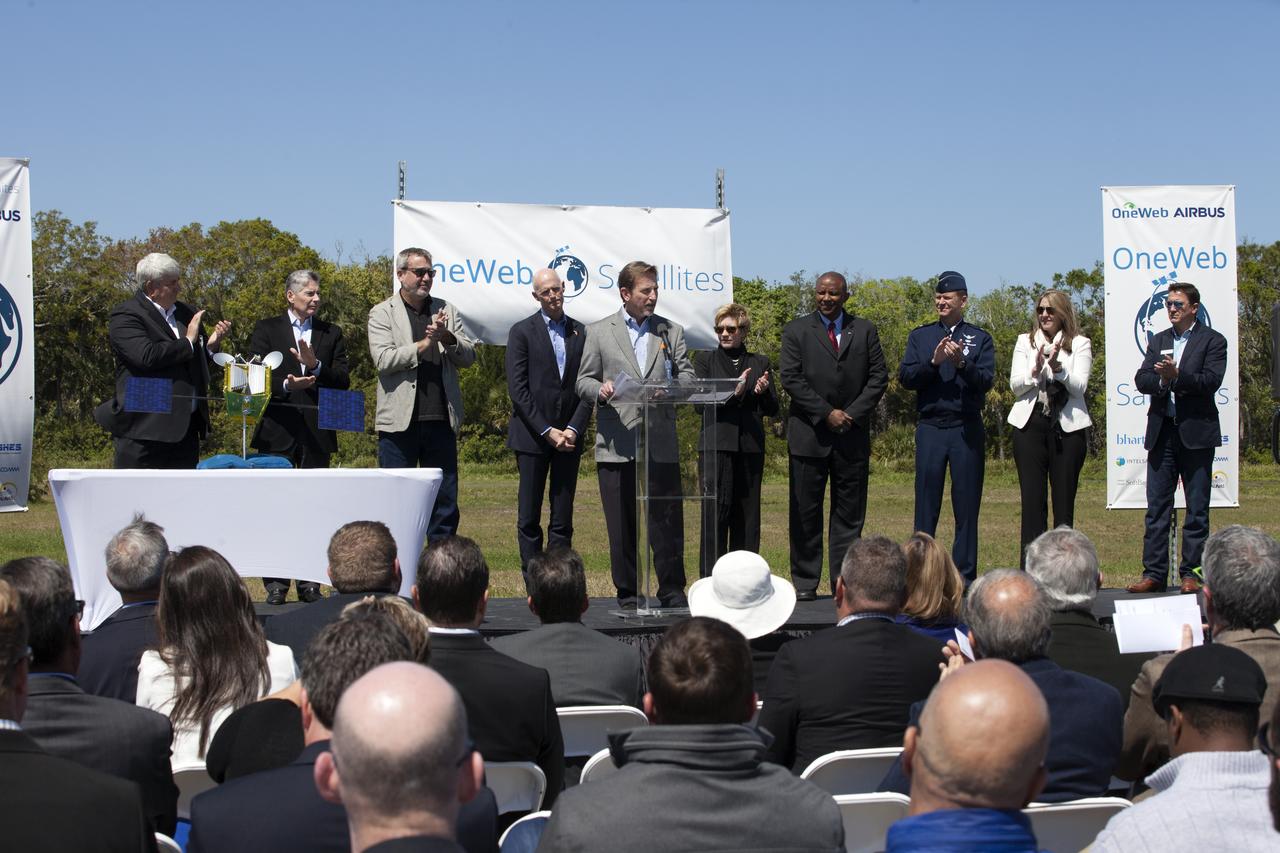
Officials break ground for a 150,000-square-foot manufacturing facility for OneWeb Satellites at Exploration Park at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The company, in partnership with Airbus, is building a 150,000-square-foot factory to manufacture satellites that will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. The officials are, from left, John Saul, operations manager of Hensell-Phelps; Kelvin Manning, associate director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center; Brian Holz, CEO of OneWeb Satellites; Rick Scott, governor of Florida; Lynda Weatherman, president and CEO of the Economic Development Council of the Space Coast; Mike Cosentino, president, Airbus Defense and Space; Cissy Procter, executive director of the Florida Department of Economic Activity; Gen. Wayne Monteith, commander of the 45th Space Wing of the U.S. Air Force; and Jim Kuzma, COO of Space Florida. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Hubble Gallery of Jupiter Galilean Satellites
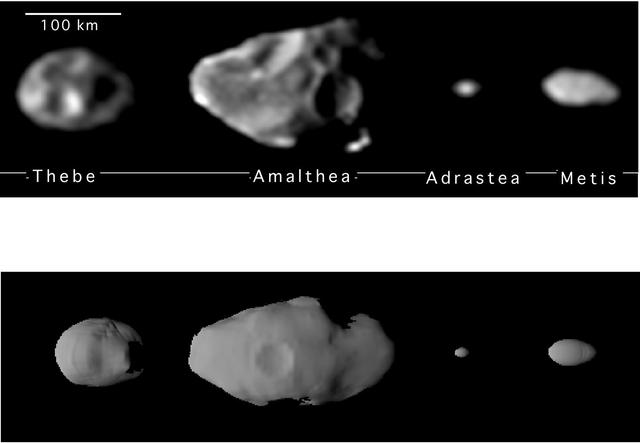
Shapes of the Small Inner Satellites of Jupiter

Saturn F-ring and Inner Satellite

Satellite Footprints Seen in Jupiter Aurora

Jupiter Inner Satellites and Ring Components
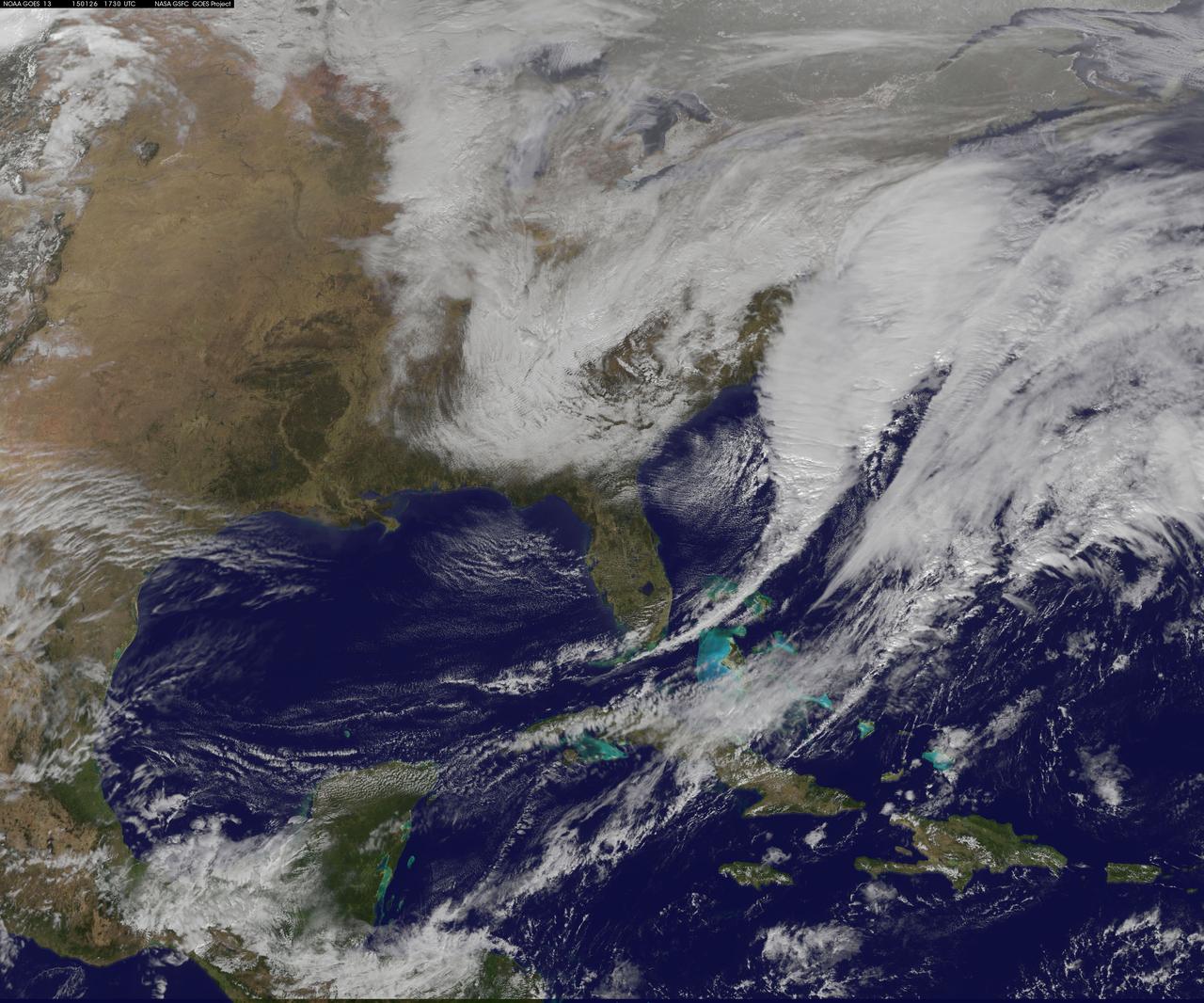
National Weather Service forecasters have been tracking a low pressure area that moved from the Midwest into the Atlantic Ocean today, and is expected to become a strong nor'easter that will bring blizzard conditions to the northeastern U.S. The path of the system was captured in a NASA movie of NOAA's GOES-East satellite imagery. On Monday, January 26, 2015, the National Weather Service noted: A storm system off the East Coast will continue to strengthen as it develops into a major nor'easter on Monday. As the storm moves up the coast, it is expected to bring snowfall of 1-3 feet or more to many parts of the Northeast through Tuesday evening, including New York City and Boston. Strong, gusty winds will combine with the snow to create blizzard conditions along and near the coast. Winter storm warnings are in effect for the panhandles of West Virginia and Maryland, much of interior New England down to the northern Mid-Atlantic as well as for Nantucket Island, Massachusetts. Winter weather advisories are in effect for portions of the Ohio Valley, Mid-Atlantic and the southern Appalachians as well as a narrow area across interior New England. To create the video and imagery, NASA/NOAA's GOES Project located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland overlays the cloud data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite on a true-color image of land and ocean created by data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. Together, these data create the entire animation of the storm and show its movement. GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's NWS website: <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a> For more information about GOES satellites, visit: <a href="http://www.goes.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.goes.noaa.gov/</a> or goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
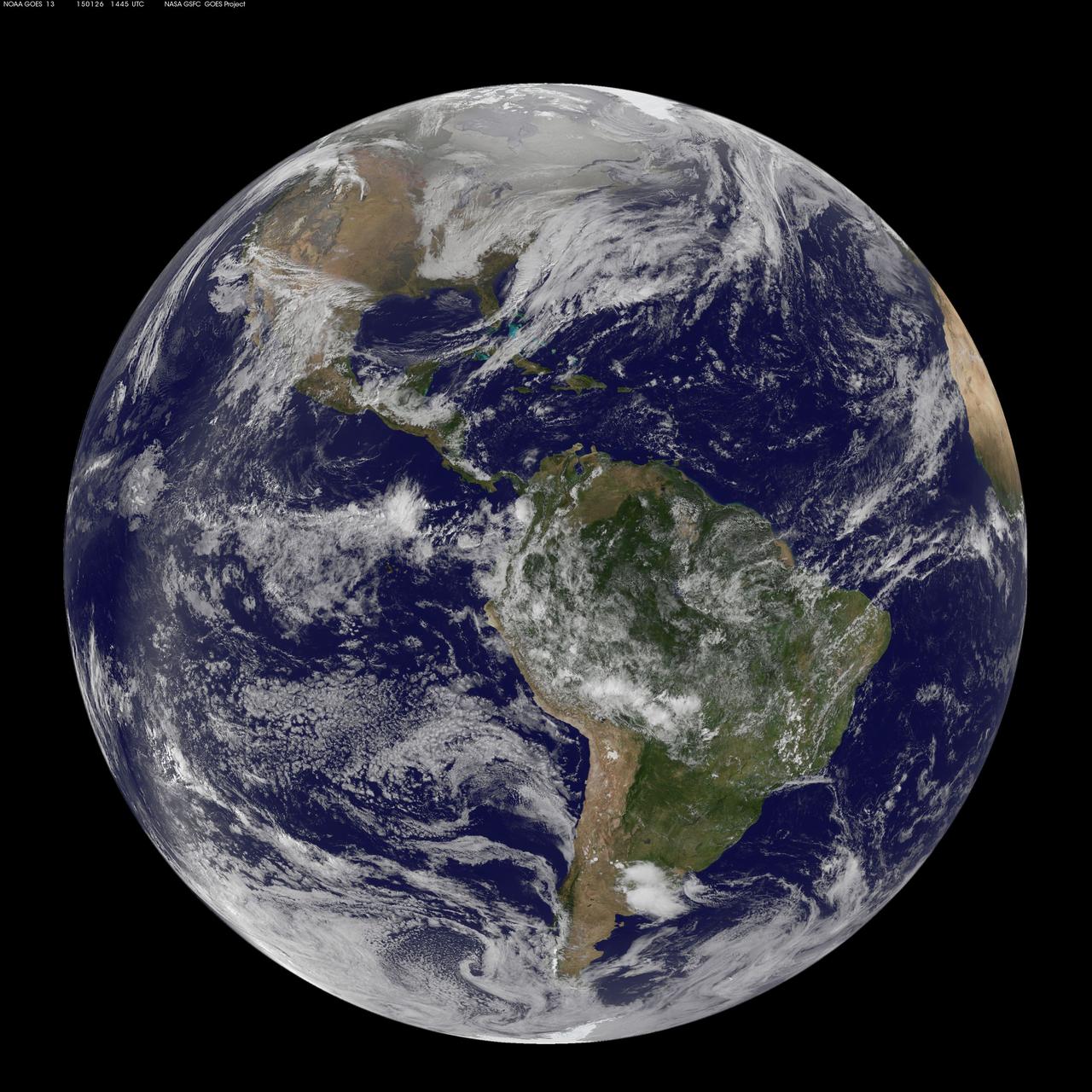
National Weather Service forecasters have been tracking a low pressure area that moved from the Midwest into the Atlantic Ocean today, and is expected to become a strong nor'easter that will bring blizzard conditions to the northeastern U.S. The path of the system was captured in a NASA movie of NOAA's GOES-East satellite imagery. (This GOES 13 image was captured on January 26, 2015 at 1445 UTC.) On Monday, January 26, 2015, the National Weather Service noted: A storm system off the East Coast will continue to strengthen as it develops into a major nor'easter on Monday. As the storm moves up the coast, it is expected to bring snowfall of 1-3 feet or more to many parts of the Northeast through Tuesday evening, including New York City and Boston. Strong, gusty winds will combine with the snow to create blizzard conditions along and near the coast. Winter storm warnings are in effect for the panhandles of West Virginia and Maryland, much of interior New England down to the northern Mid-Atlantic as well as for Nantucket Island, Massachusetts. Winter weather advisories are in effect for portions of the Ohio Valley, Mid-Atlantic and the southern Appalachians as well as a narrow area across interior New England. To create the video and imagery, NASA/NOAA's GOES Project located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland overlays the cloud data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite on a true-color image of land and ocean created by data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. Together, these data create the entire animation of the storm and show its movement. GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's NWS website: <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a> For more information about GOES satellites, visit: <a href="http://www.goes.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.goes.noaa.gov/</a> or goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center

Jim Kuzma, COO of Space Florida, speaks during the groundbreaking ceremony at Kennedy's Exploration Park for OneWeb. The company, in partnership with Airbus, is building a 150,000-square-foot factory to manufacture satellites that will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Cissy Procter, executive director of the Florida Department of Economic Activity, speaks during the groundbreaking ceremony at Kennedy's Exploration Park for OneWeb. The company, in partnership with Airbus, is building a 150,000-square-foot factory to manufacture satellites that will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Florida Governor Rick Scott speaks during the groundbreaking ceremony at Kennedy's Exploration Park for OneWeb. The company, in partnership with Airbus, is building a 150,000-square-foot factory to manufacture satellites that will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Dale Ketchum of Space Florida opens the groundbreaking ceremony at Kennedy's Exploration Park for OneWeb. The company, in partnership with Airbus, is building a 150,000-square-foot factory to manufacture satellites that will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. Behind him are, from left, Jim Kuzma, COO of Space Florida; Mike Cosentino, president, Airbus Defense and Space; Brian Holz, CEO of OneWeb Satellites; Rick Scott, governor of Florida; Lynda Weatherman, president and CEO of the Economic Development Council of the Space Coast; Kelvin Manning, associate director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center; Gen. Wayne Monteith, commander of the 45th Space Wing of the U.S. Air Force; Cissy Procter, executive director of the Florida Department of Economic Activity; and John Saul, operations manager of Hensell-Phelps. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
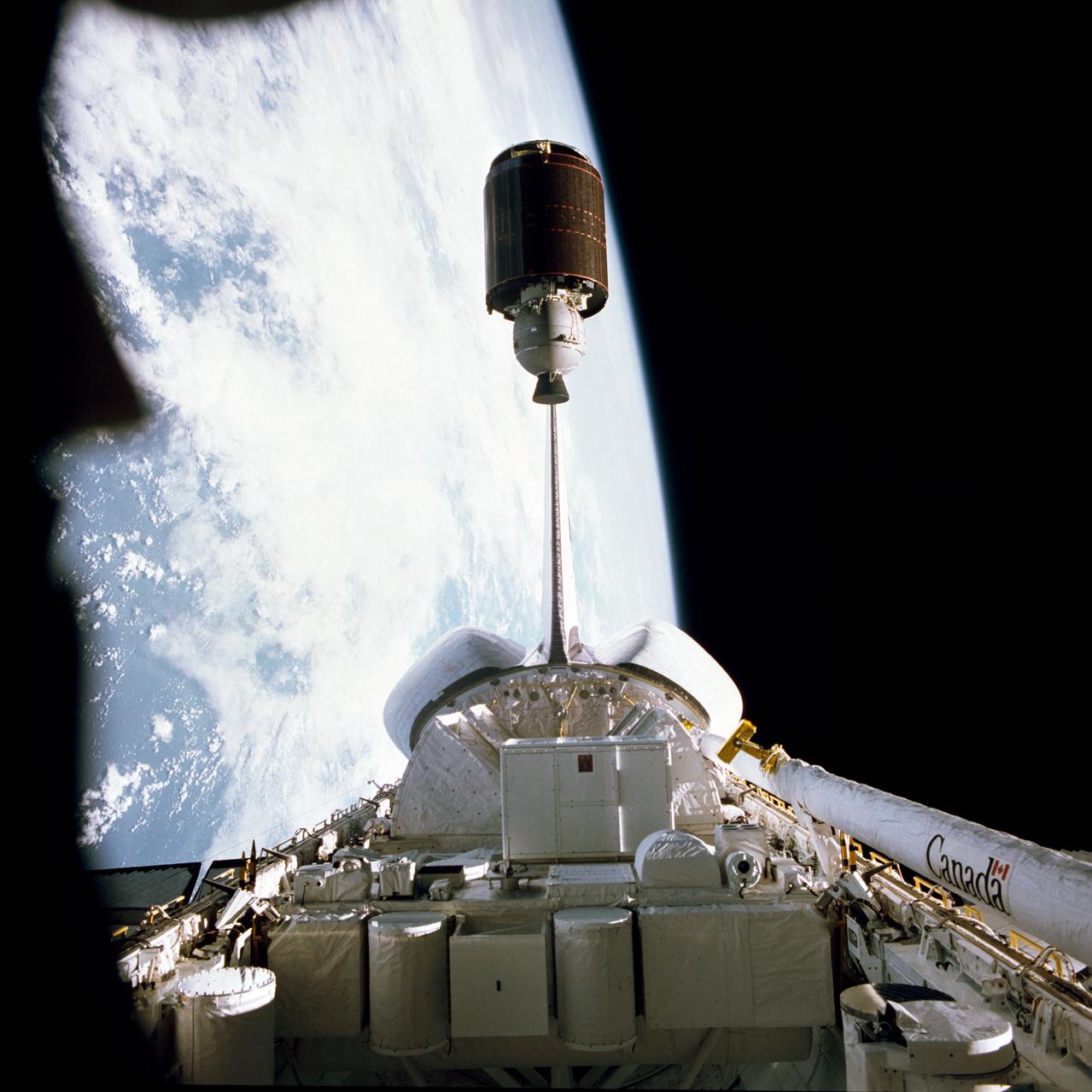

S83-35764 (19 June 1983) --- The Indonesian Palapa B communications satellite is just about to clear the vertical stabilizer of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger to begin its way toward its Earth-orbital destination. Also visible in this 70mm exposure, photographed through the flight deck?s aft windows, are the Shuttle pallet satellite, the experiment package for NASA?s office of space and terrestrial applications (OSTA-2), the now vacated protective cradles for Palapa and Telesat Canada?s Anik C2 satellites, some getaway special (GAS) canisters and the Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS) arm.
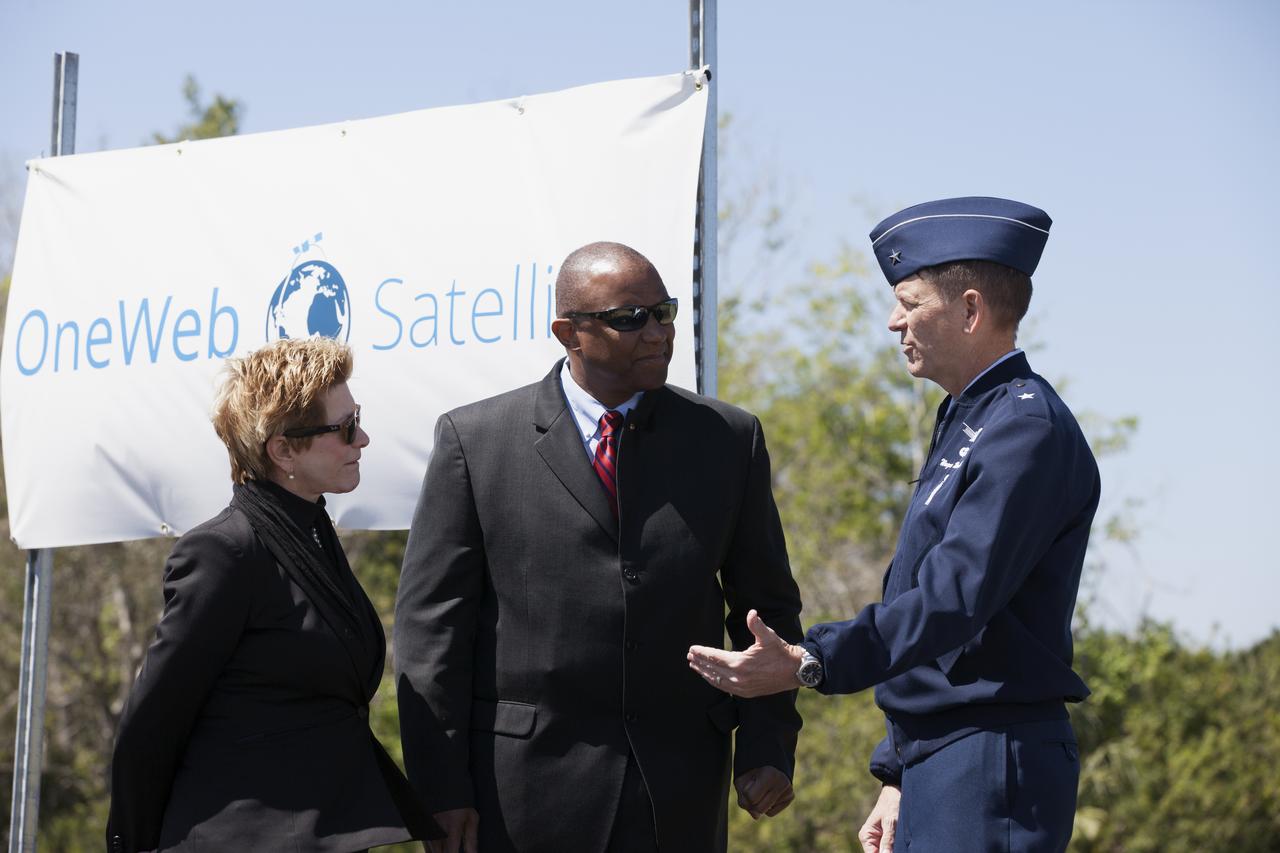

Lynda Weatherman, president and CEO of the Economic Development Council of the Space Coast, talks with Kelvin Manning, associate director of NASA's Kennedy Space Center, and Gen. Wayne Monteith, commander of the 45th Space Wing of the U.S. Air Force, prior to a groundbreaking ceremony at Kennedy's Exploration Park for OneWeb. The company, in partnership with Airbus, is building a 150,000-square-foot factory to manufacture satellites that will connect all areas of the world to the Internet wirelessly. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
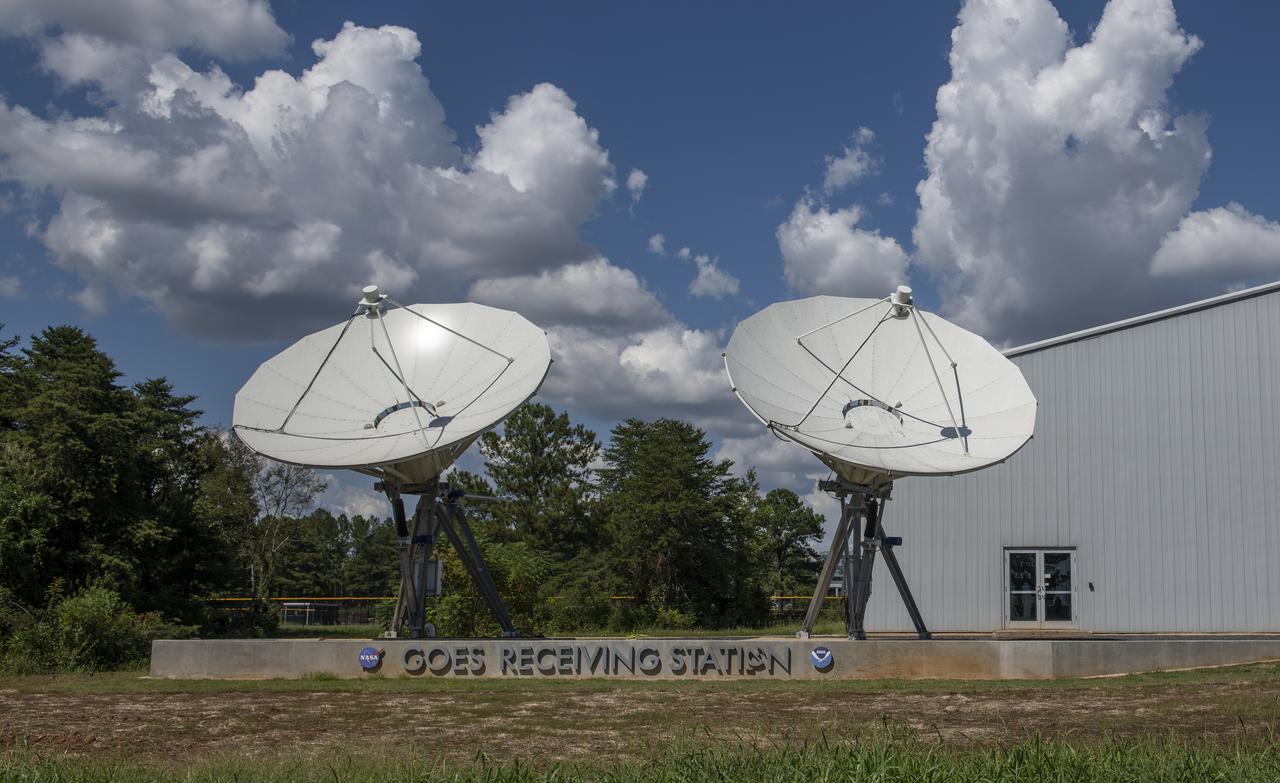

The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) photographed prior to the dedication of the site on September 21, 2018.
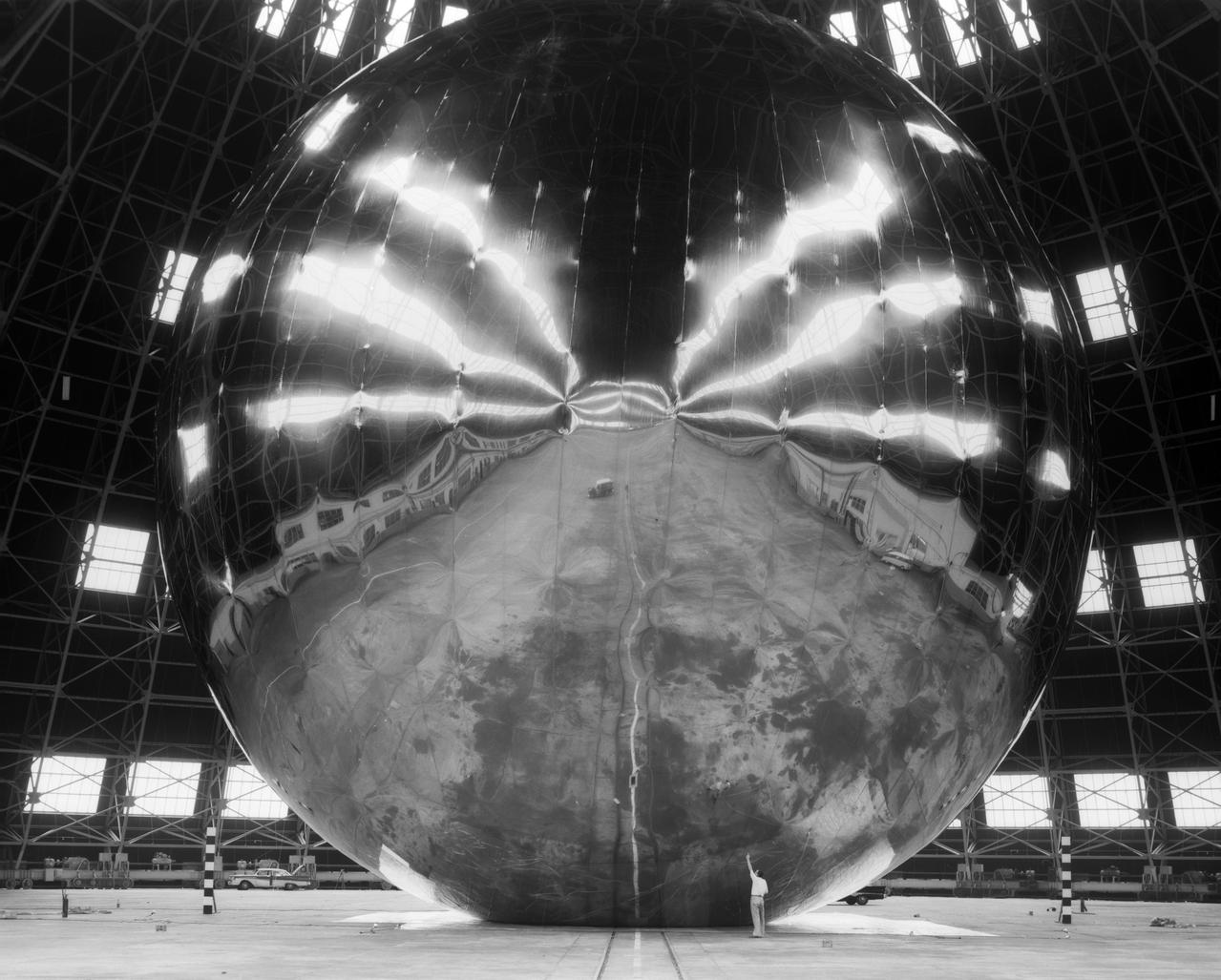

Echo Satellite
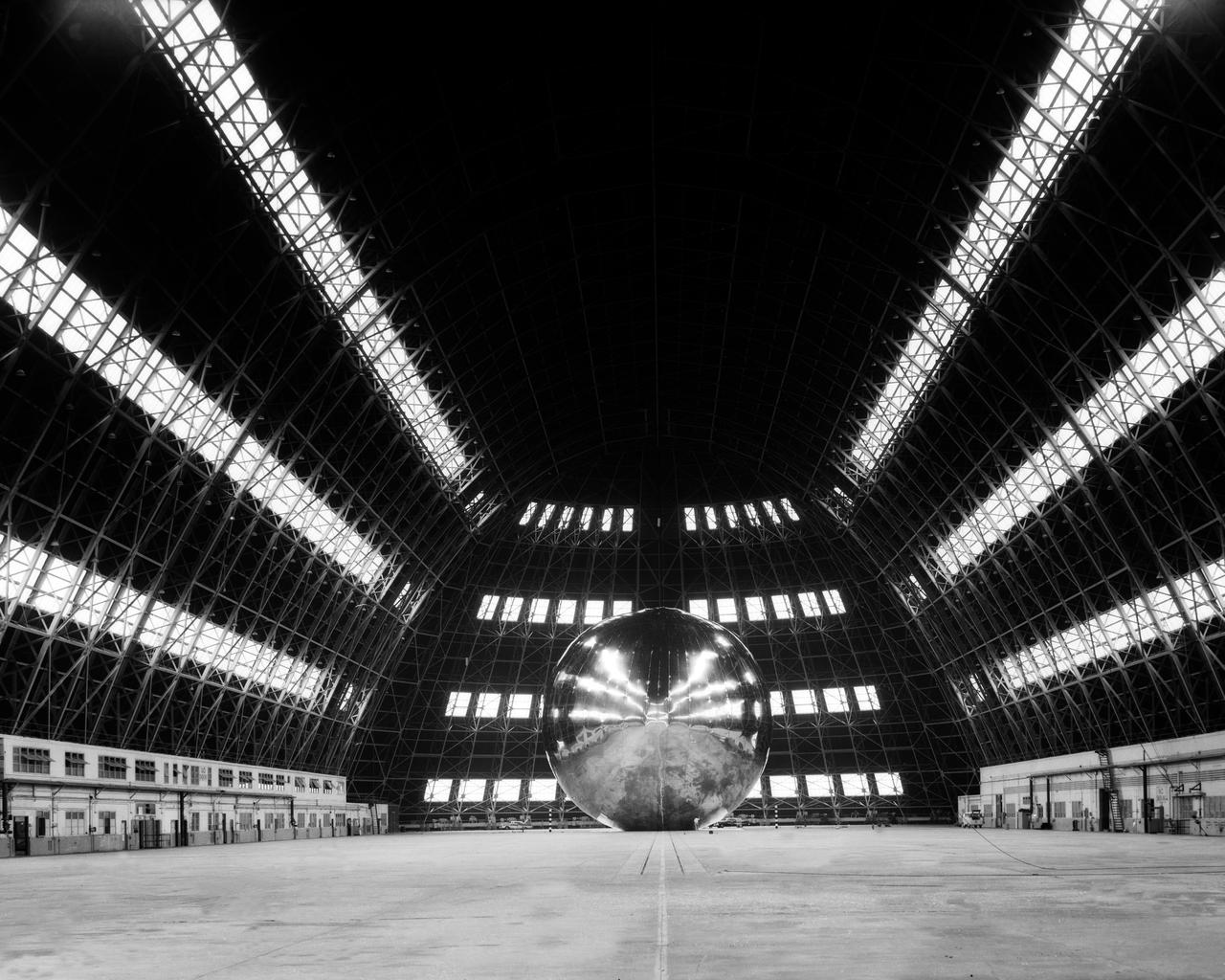

Echo Satellite
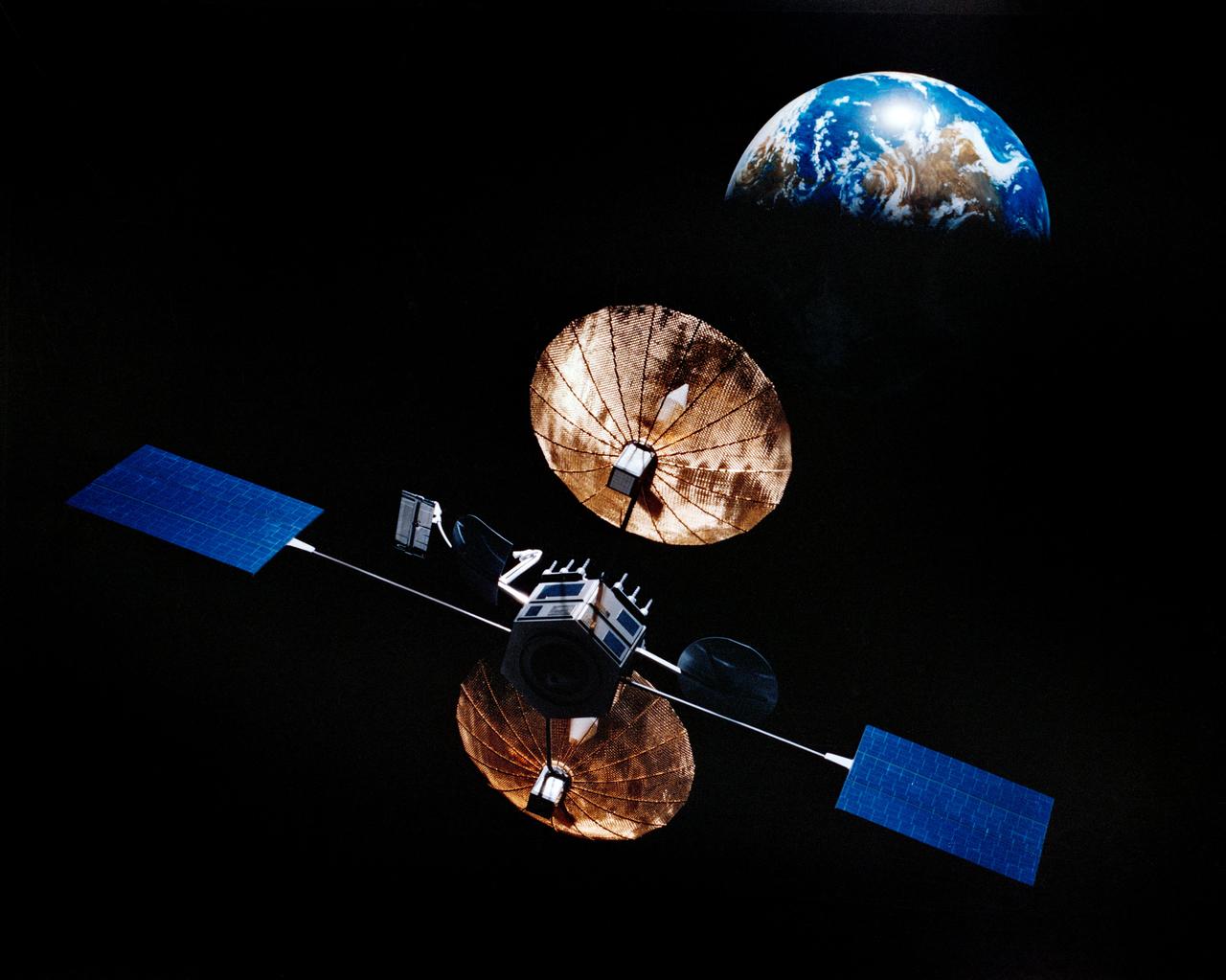

Artist concept of satellite with solar panels deployed in orbit above the earth.
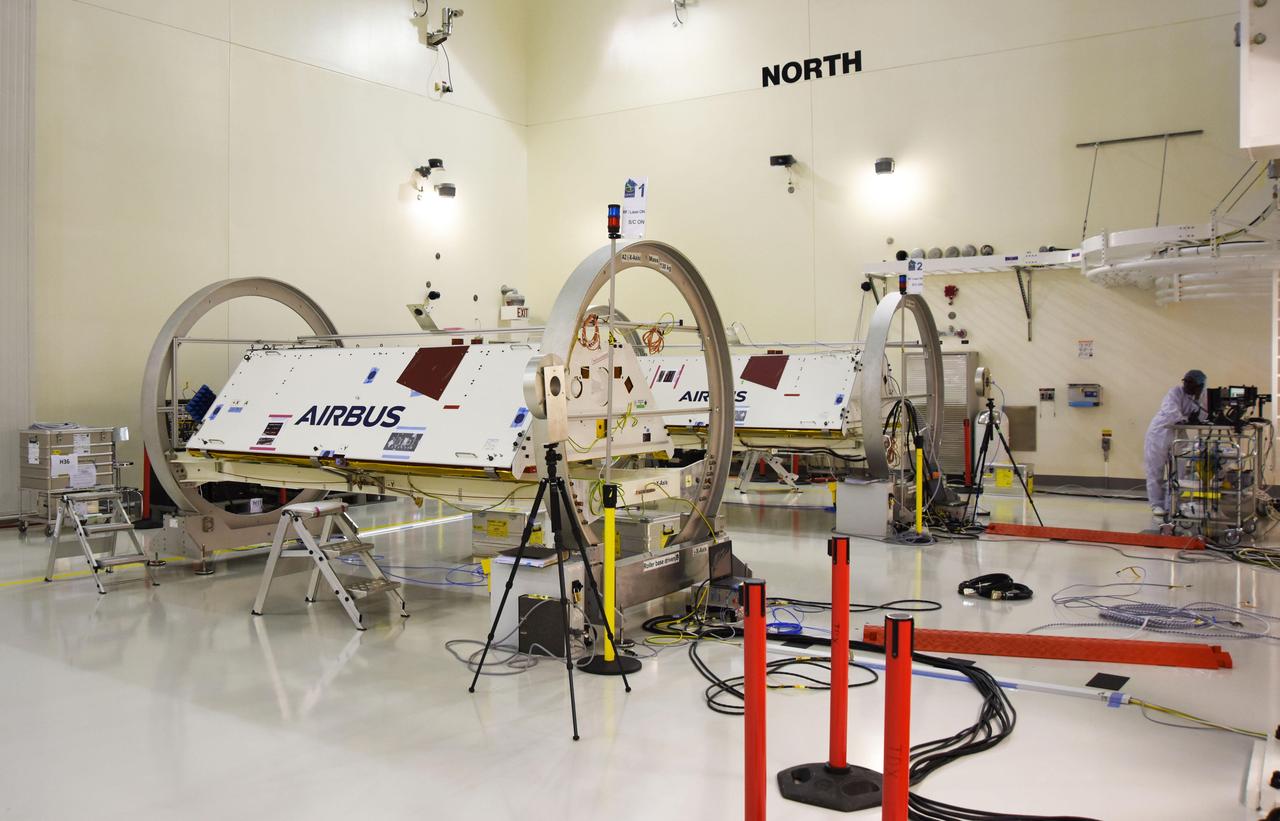

The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) twin satellites, attached to turntable fixtures, at the Astrotech Space Operations processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. GRACE-FO will extend GRACE's legacy of scientific achievements, which range from tracking mass changes of Earth's polar ice sheets and estimating global groundwater changes, to measuring the mass changes of large earthquakes and inferring changes in deep ocean currents, a driving force in climate. To date, GRACE observations have been used in more than 4,300 research publications. Its measurements provide a unique view of the Earth system and have far-reaching benefits to society, such as providing insights into where global groundwater resources may be shrinking or growing and where dry soils are contributing to drought. GRACE-FO is planned to fly at least five years. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22338

The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) twin satellites, attached to turntable fixtures, at the Astrotech Space Operations processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. GRACE-FO will extend GRACE's legacy of scientific achievements, which range from tracking mass changes of Earth's polar ice sheets and estimating global groundwater changes, to measuring the mass changes of large earthquakes and inferring changes in deep ocean currents, a driving force in climate. To date, GRACE observations have been used in more than 4,300 research publications. Its measurements provide a unique view of the Earth system and have far-reaching benefits to society, such as providing insights into where global groundwater resources may be shrinking or growing and where dry soils are contributing to drought. GRACE-FO is planned to fly at least five years. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22340
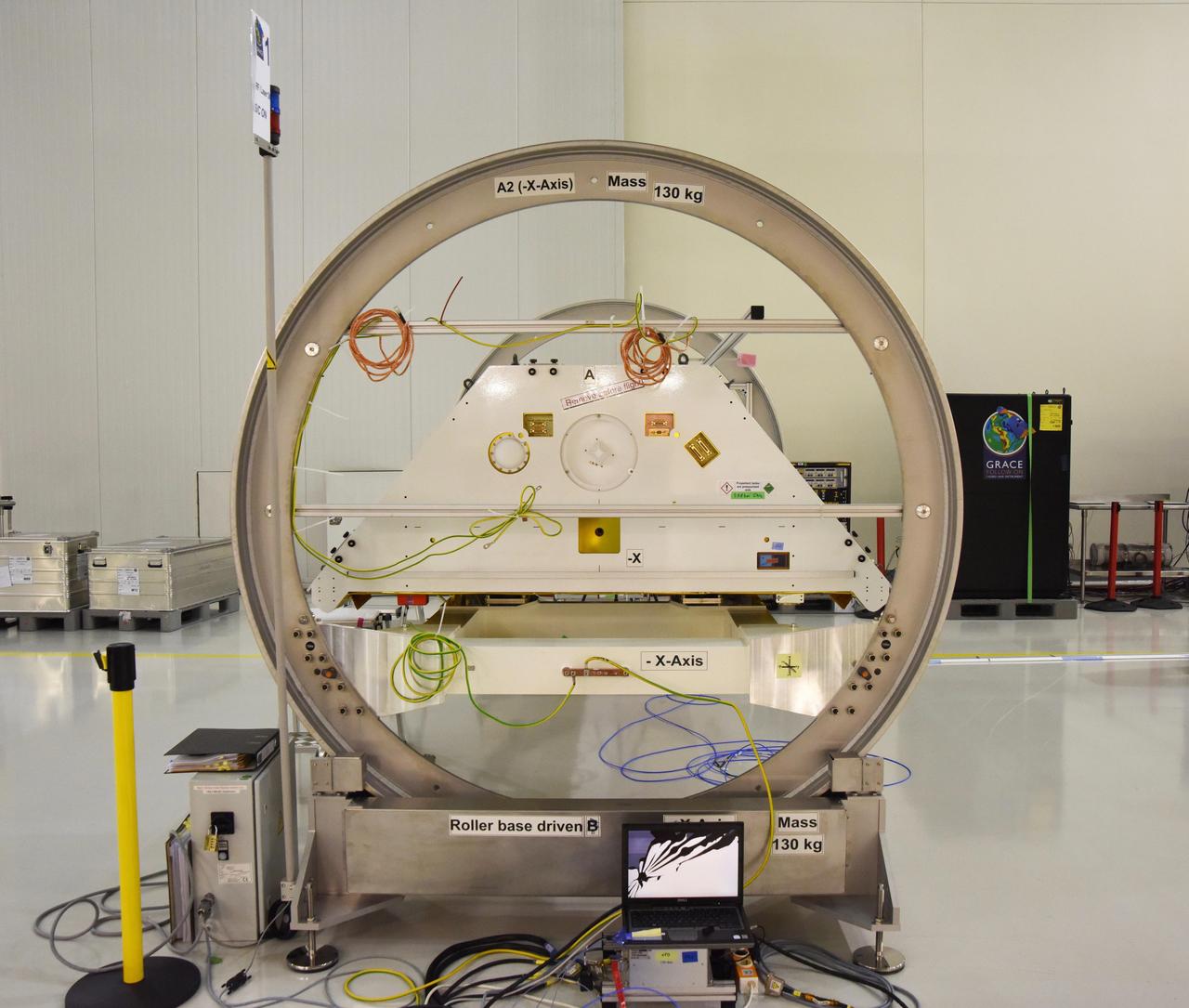

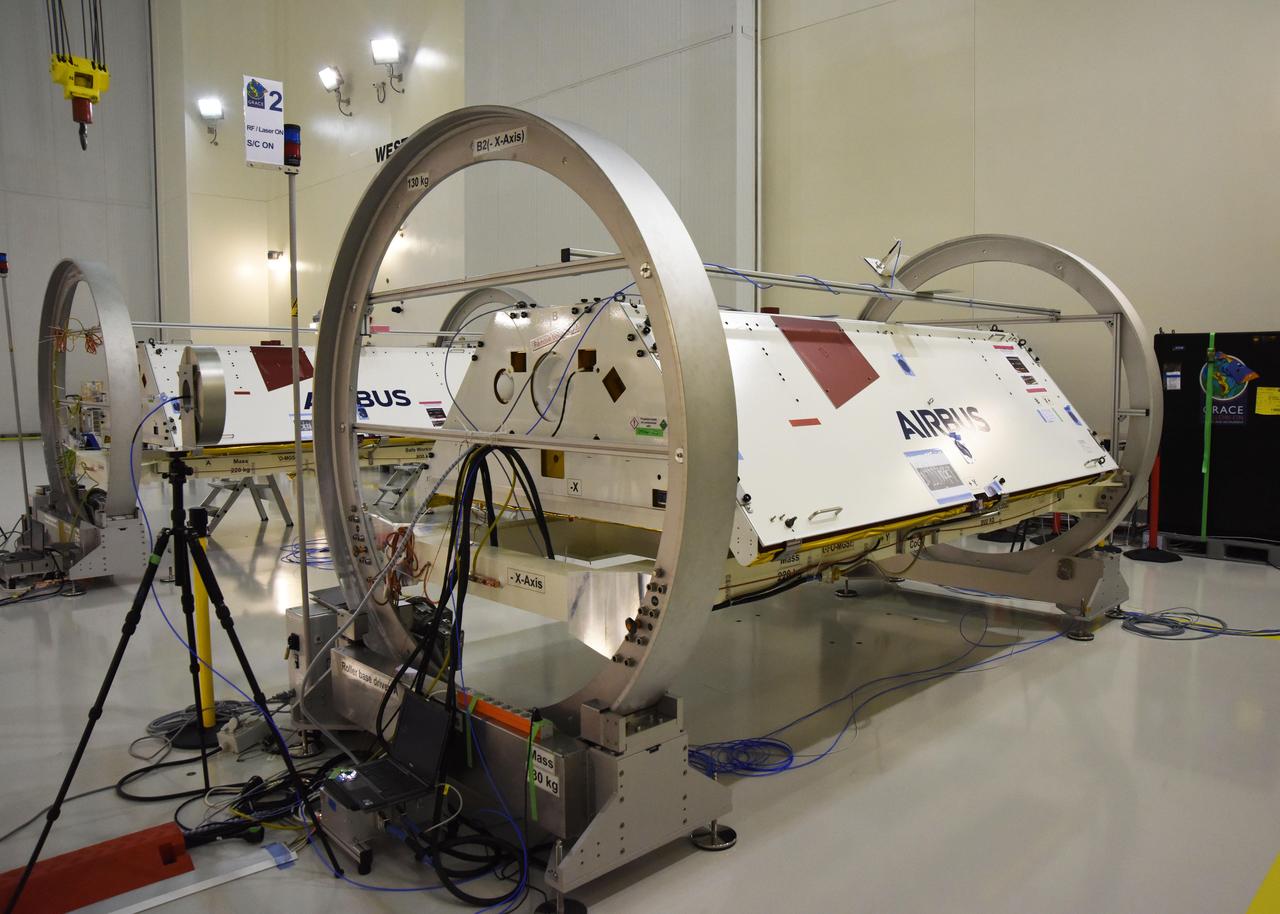
One of the two Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) satellites and its turntable fixture at the Astrotech Space Operations processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. GRACE-FO will extend GRACE's legacy of scientific achievements, which range from tracking mass changes of Earth's polar ice sheets and estimating global groundwater changes, to measuring the mass changes of large earthquakes and inferring changes in deep ocean currents, a driving force in climate. To date, GRACE observations have been used in more than 4,300 research publications. Its measurements provide a unique view of the Earth system and have far-reaching benefits to society, such as providing insights into where global groundwater resources may be shrinking or growing and where dry soils are contributing to drought. GRACE-FO is planned to fly at least five years. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22339
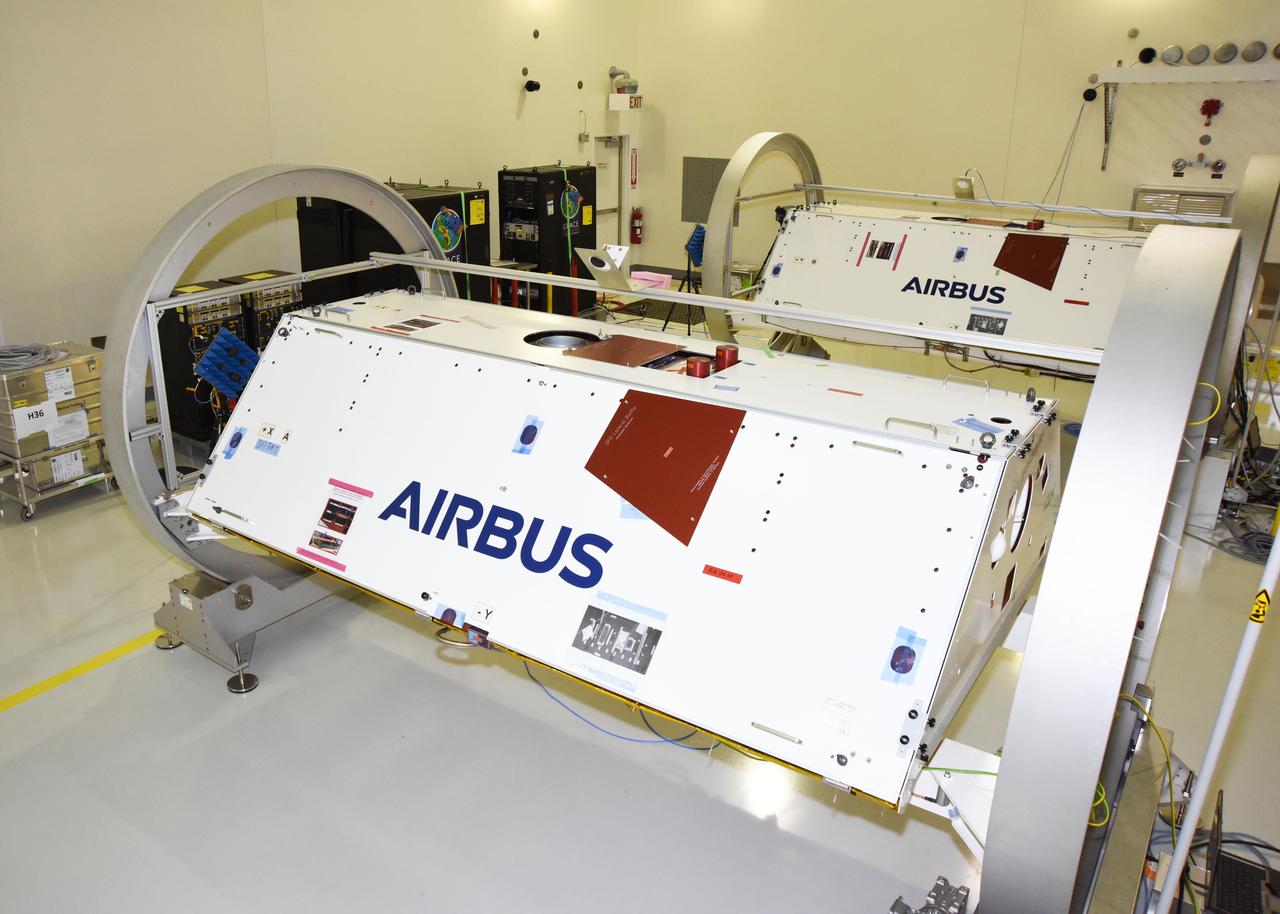
The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) twin satellites, attached to turntable fixtures, at the Astrotech Space Operations processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base, California. GRACE-FO will extend GRACE's legacy of scientific achievements, which range from tracking mass changes of Earth's polar ice sheets and estimating global groundwater changes, to measuring the mass changes of large earthquakes and inferring changes in deep ocean currents, a driving force in climate. To date, GRACE observations have been used in more than 4,300 research publications. Its measurements provide a unique view of the Earth system and have far-reaching benefits to society, such as providing insights into where global groundwater resources may be shrinking or growing and where dry soils are contributing to drought. GRACE-FO is planned to fly at least five years. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22341
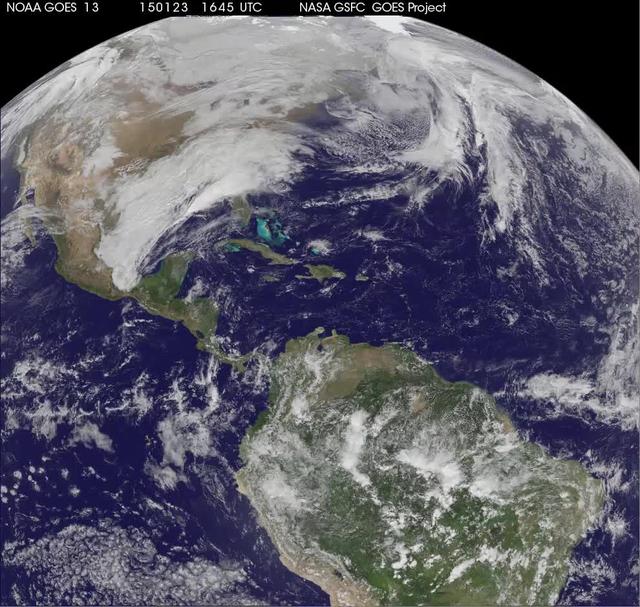

National Weather Service forecasters have been tracking a low pressure area that moved from the Midwest into the Atlantic Ocean today, and is expected to become a strong nor'easter that will bring blizzard conditions to the northeastern U.S. The path of the system was captured in a NASA movie of NOAA's GOES-East satellite imagery. An animation of visible and infrared imagery from NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental or GOES satellite captured over the period of January 24 through 26 showed the progression of the developing nor'easter. The satellite animation began on Jan. 24 when clouds associated with a cold front preceding the low, pushed off the U.S. East coast. The front was followed by a low pressure area that moved from the Midwest to the southeast. That low moved over the Carolinas and exited into the Atlantic Ocean on Jan. 26. NOAA's National Weather Service forecast calls for the low to intensify along the Eastern Seaboard and bring blizzard conditions to the northeastern U.S. on Monday night, January 26 and Tuesday, January 27. On Monday, January 26, 2015, the National Weather Service noted: A storm system off the East Coast will continue to strengthen as it develops into a major nor'easter on Monday. As the storm moves up the coast, it is expected to bring snowfall of 1-3 feet or more to many parts of the Northeast through Tuesday evening, including New York City and Boston. Strong, gusty winds will combine with the snow to create blizzard conditions along and near the coast. Winter storm warnings are in effect for the panhandles of West Virginia and Maryland, much of interior New England down to the northern Mid-Atlantic as well as for Nantucket Island, Massachusetts. Winter weather advisories are in effect for portions of the Ohio Valley, Mid-Atlantic and the southern Appalachians as well as a narrow area across interior New England. To create the video and imagery, NASA/NOAA's GOES Project located at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland overlays the cloud data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite on a true-color image of land and ocean created by data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, or MODIS, instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. Together, these data create the entire animation of the storm and show its movement. GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's NWS website: <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a> For more information about GOES satellites, visit: <a href="http://www.goes.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.goes.noaa.gov/</a> or goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
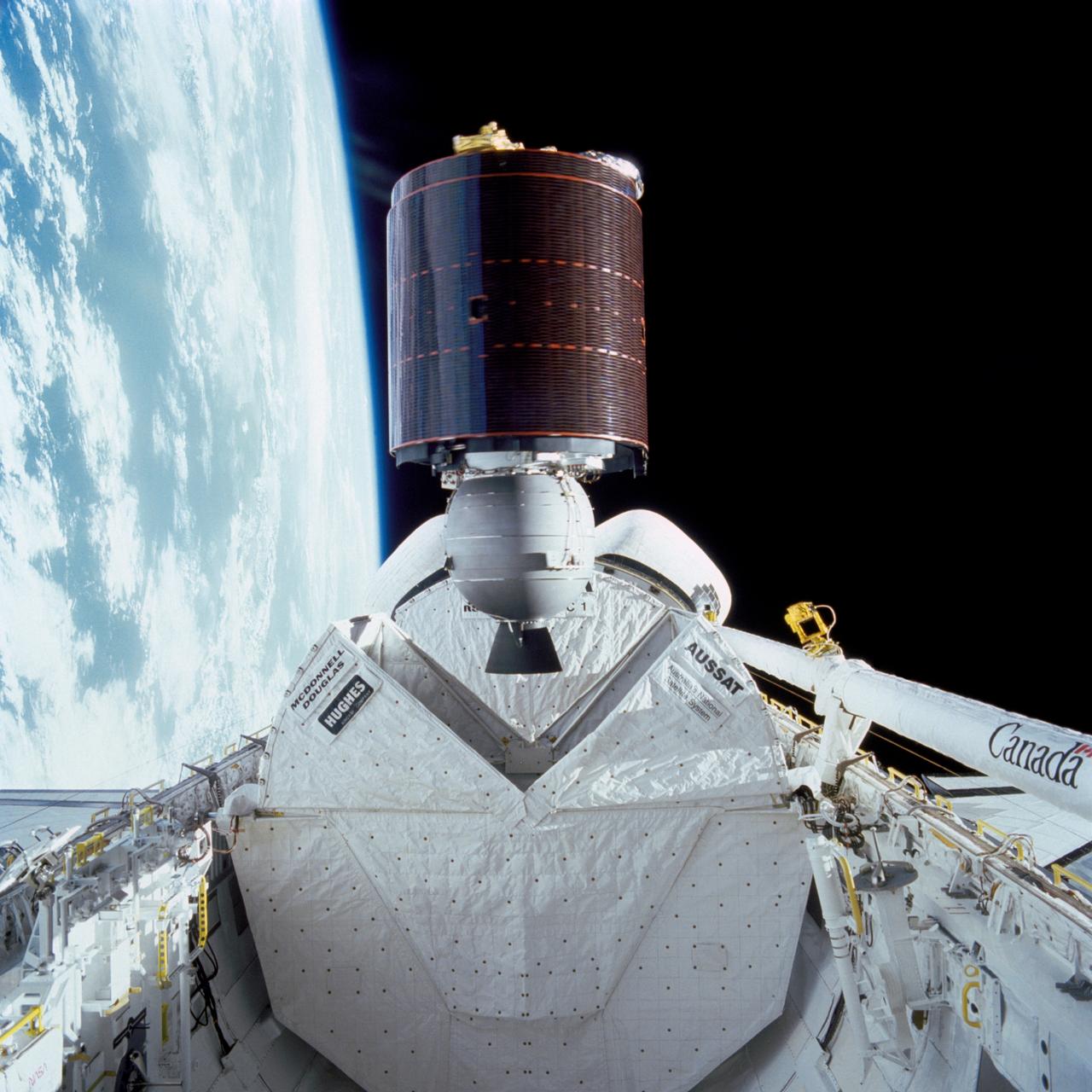

51I-32-023 (27 Aug. 1985) --- Australia's AUSSAT communications satellite is deployed from the payload bay of the space shuttle Discovery on flight day one. A portion of the cloudy surface of Earth can be seen to the left of the frame. Photo credit: NASA
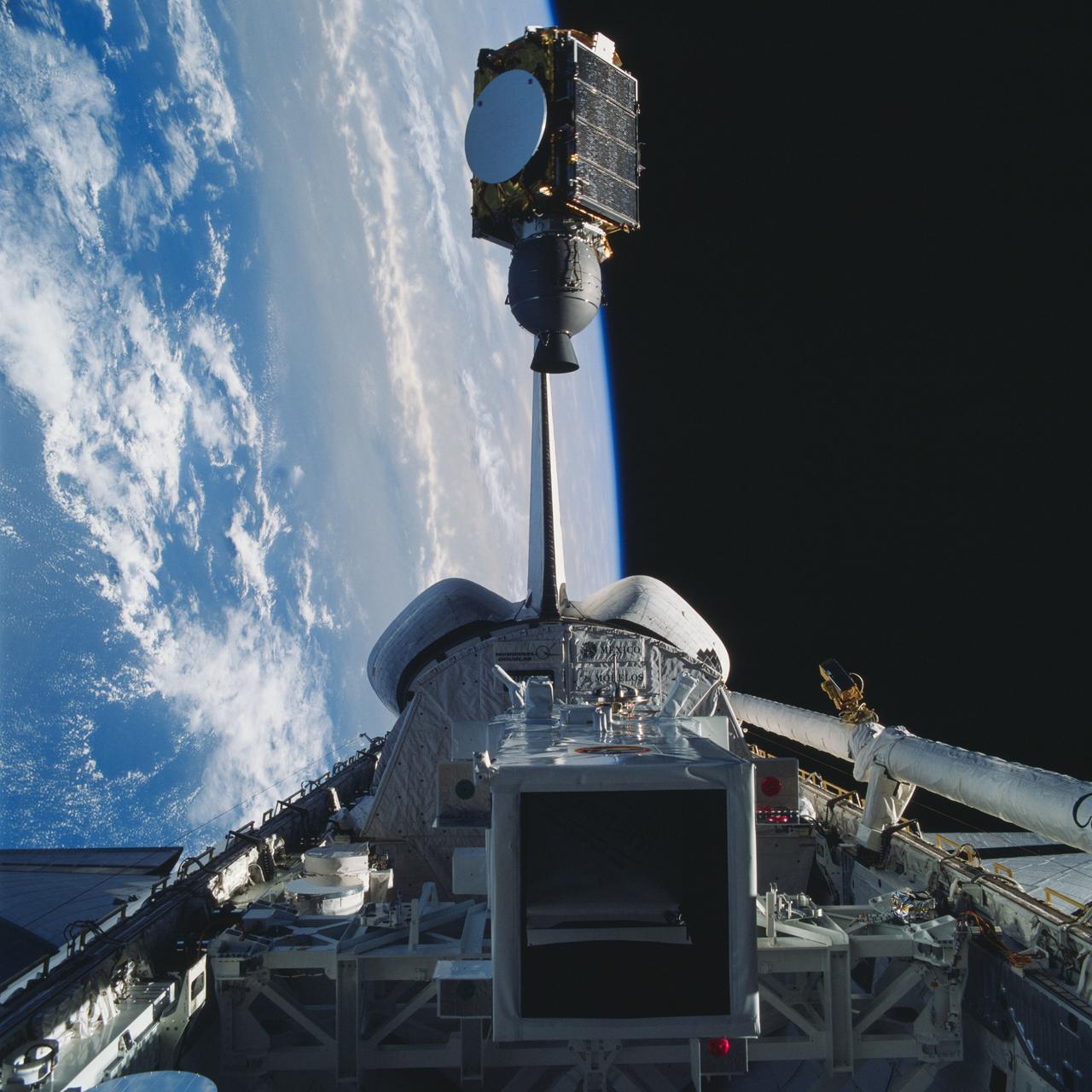

Arabsat communications satellite deploying from Discovery's payload bay. Cloudy Earth's surface can be seen to the left of the frame.

View of the Syncom-IV (LEASAT) satellite from the flight deck window taken by Astronaut S. David Griggs.
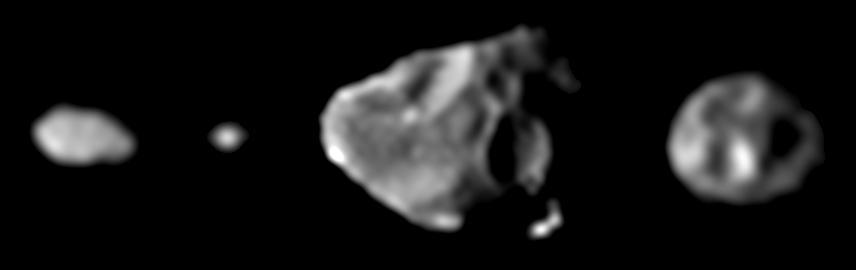
Family Portrait of the Small Inner Satellites of Jupiter
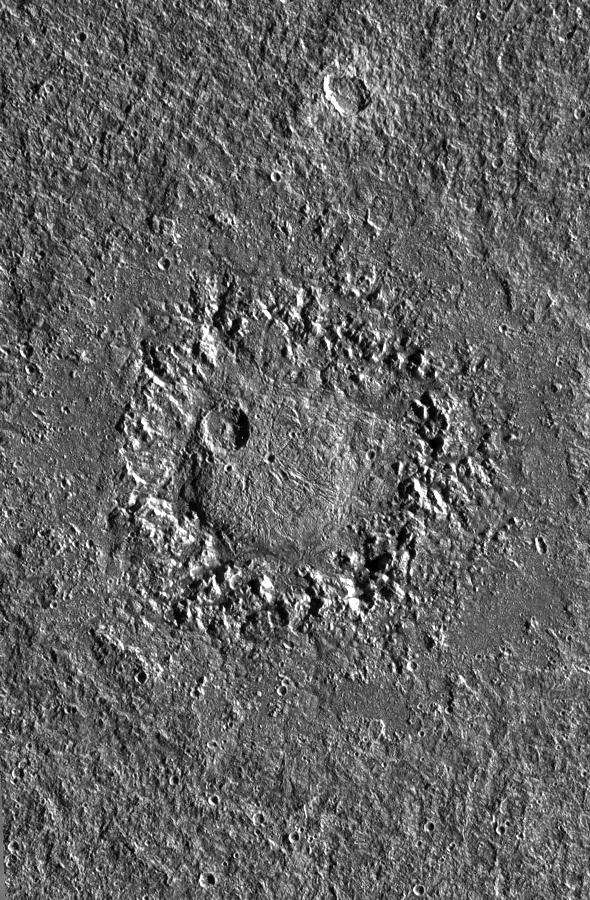

Dome Crater Neith on Jupiter Satellite Ganymede
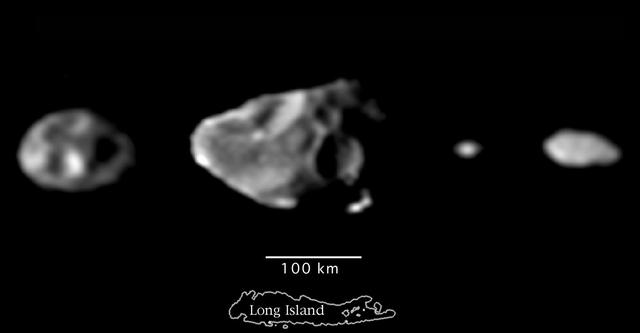
Scale Comparison of the Inner Small Satellites of Jupiter

Jupiter and its Galilean Satellites as viewed from Mars
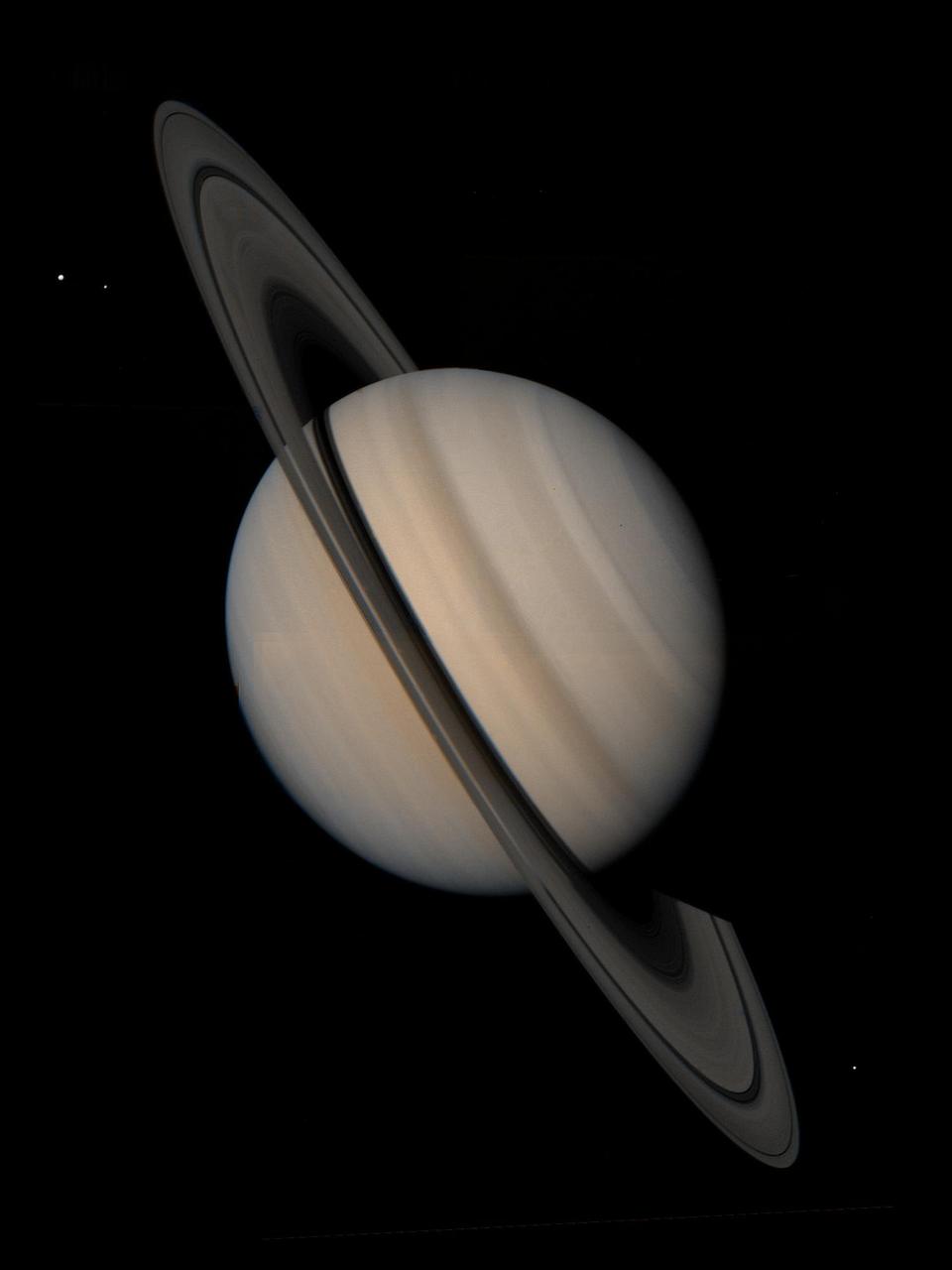

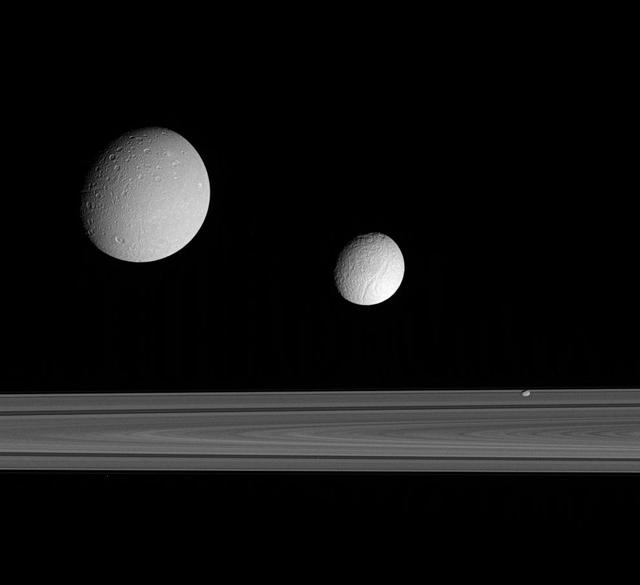
Saturn and its Satellites Tethys, Enceladus and Mimas
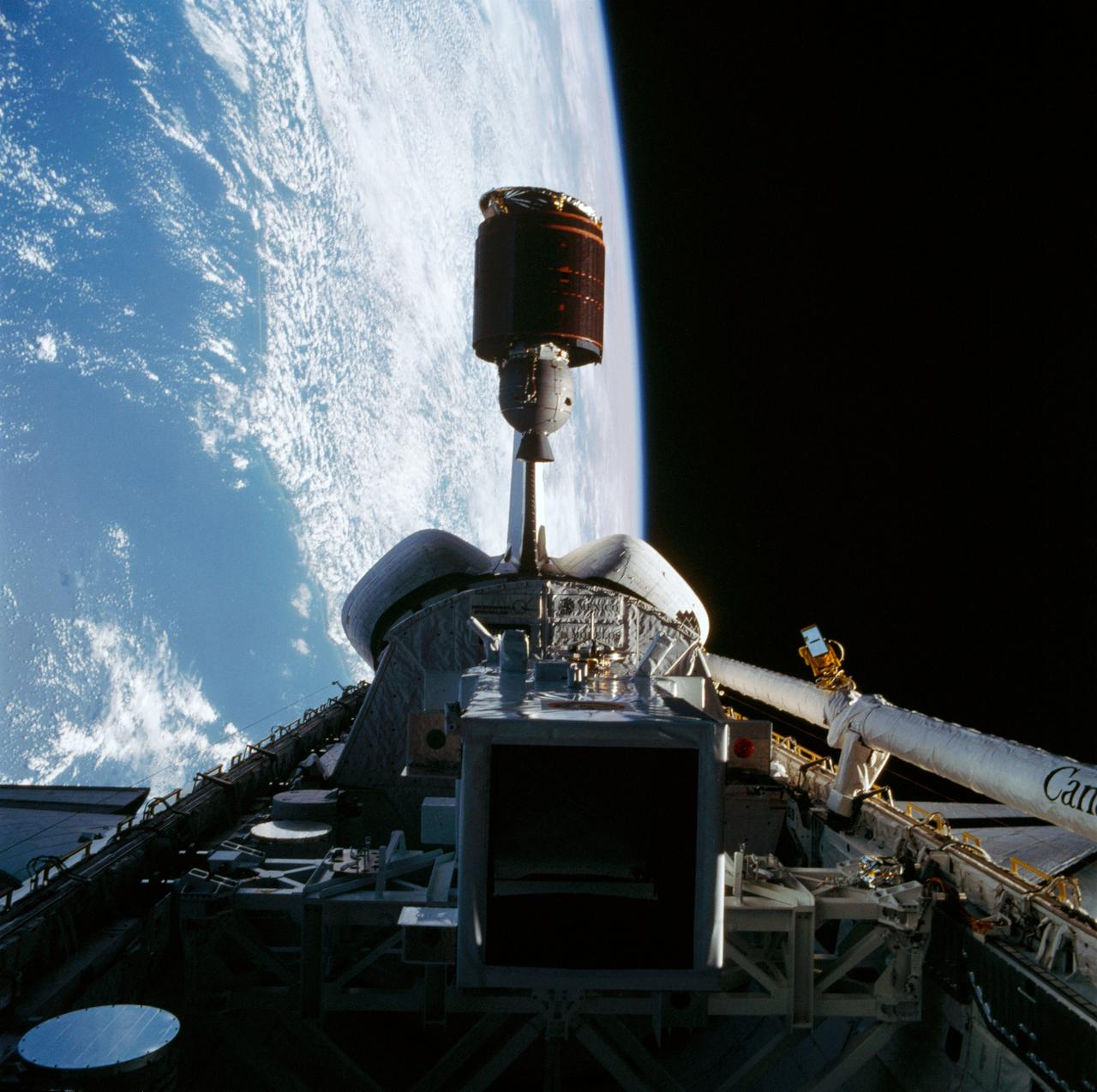

Telstar 3-D communications satellite deploying from Discovery's payload bay. Cloudy Earth's surface can be seen to the left of the frame.
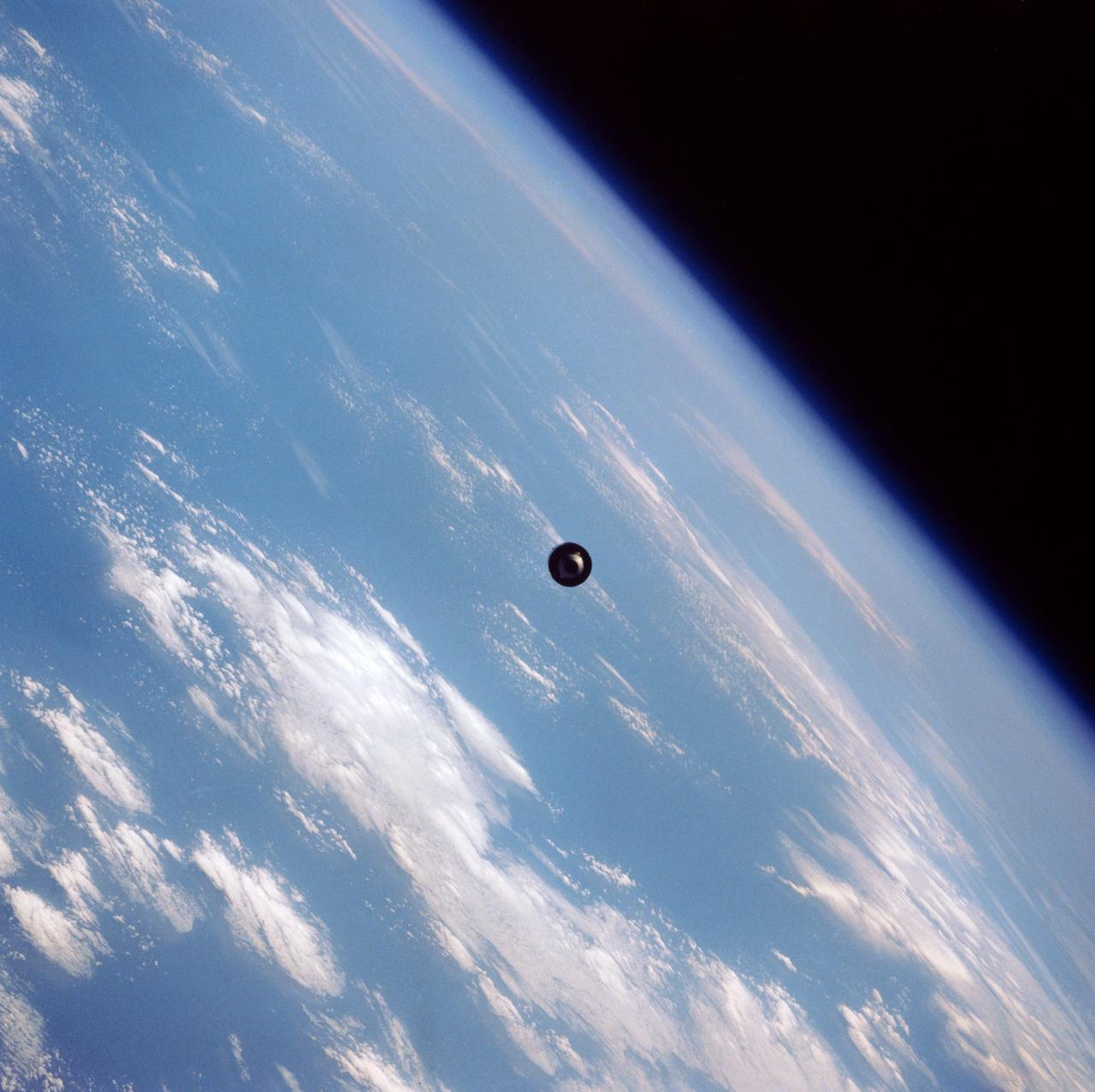

41D-39-068 (1 Sept 1984) --- Quickly moving away from the Space Shuttle Discovery is the Telstar 3 communications satellite, deployed September 1, 1984. The 41-D crew successfully completed three satellite placements, of which this was the last. Telstar was the second 41-D deployed satellite to be equipped with a payload assist module (PAM-D). The frame was exposed with a 70mm camera.
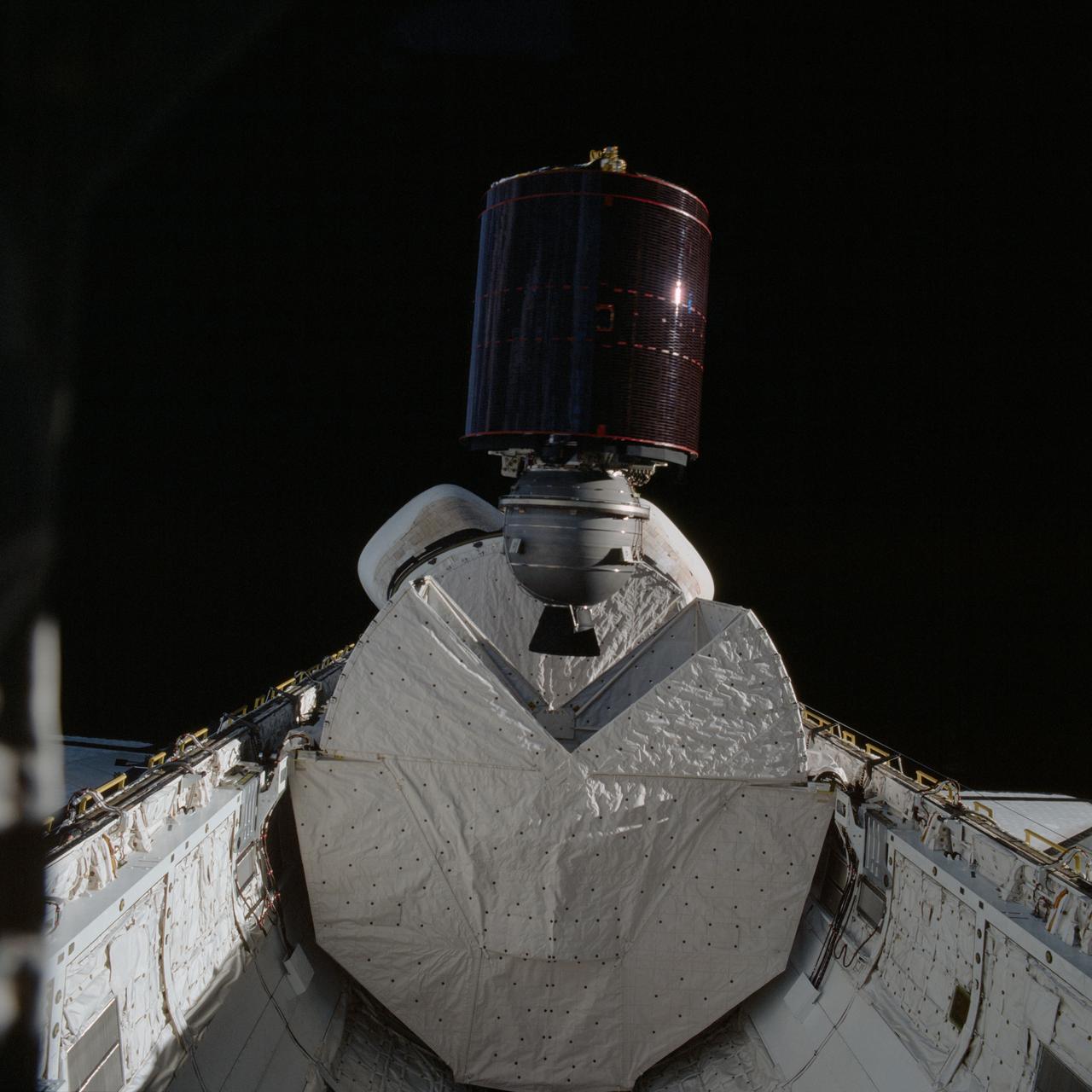

STS005-38-943 (17 Nov. 1982) --- The Satellite Business Systems (SBS-3) satellte is deployed from its protective cradle in the cargo bay of the space shuttle Columbia. Part of Columbia's wings can be seen on both the port and starboard sides. Part of both orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods are seen at center. The vertical stabilizer is obscured by the satellite. Photo credit: NASA
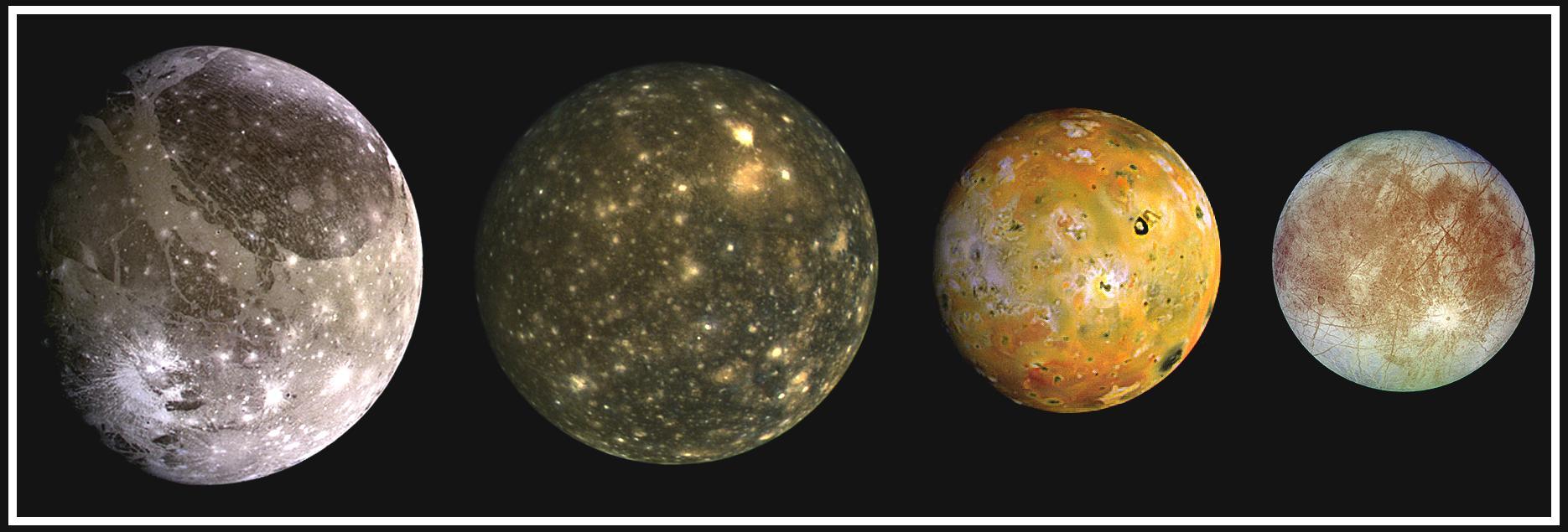
This composite includes the four largest moons of Jupiter which are known as the Galilean satellites. From left to right, the moons shown are Ganymede, Callisto, Io, and Europa. The Galilean satellites were first seen by the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei in 1610. In order of increasing distance from Jupiter, Io is closest, followed by Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. The order of these satellites from the planet Jupiter helps to explain some of the visible differences among the moons. Io is subject to the strongest tidal stresses from the massive planet. These stresses generate internal heating which is released at the surface and makes Io the most volcanically active body in our solar system. Europa appears to be strongly differentiated with a rock/iron core, an ice layer at its surface, and the potential for local or global zones of water between these layers. Tectonic resurfacing brightens terrain on the less active and partially differentiated moon Ganymede. Callisto, furthest from Jupiter, appears heavily cratered at low resolutions and shows no evidence of internal activity. North is to the top of this composite picture in which these satellites have all been scaled to a common factor of 10 kilometers (6 miles) per picture element. The Solid State Imaging (CCD) system aboard NASA's Galileo spacecraft obtained the Io and Ganymede images in June 1996, while the Europa images were obtained in September 1996. Because Galileo focuses on high resolution imaging of regional areas on Callisto rather than global coverage, the portrait of Callisto is from the 1979 flyby of NASA's Voyager spacecraft. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00601
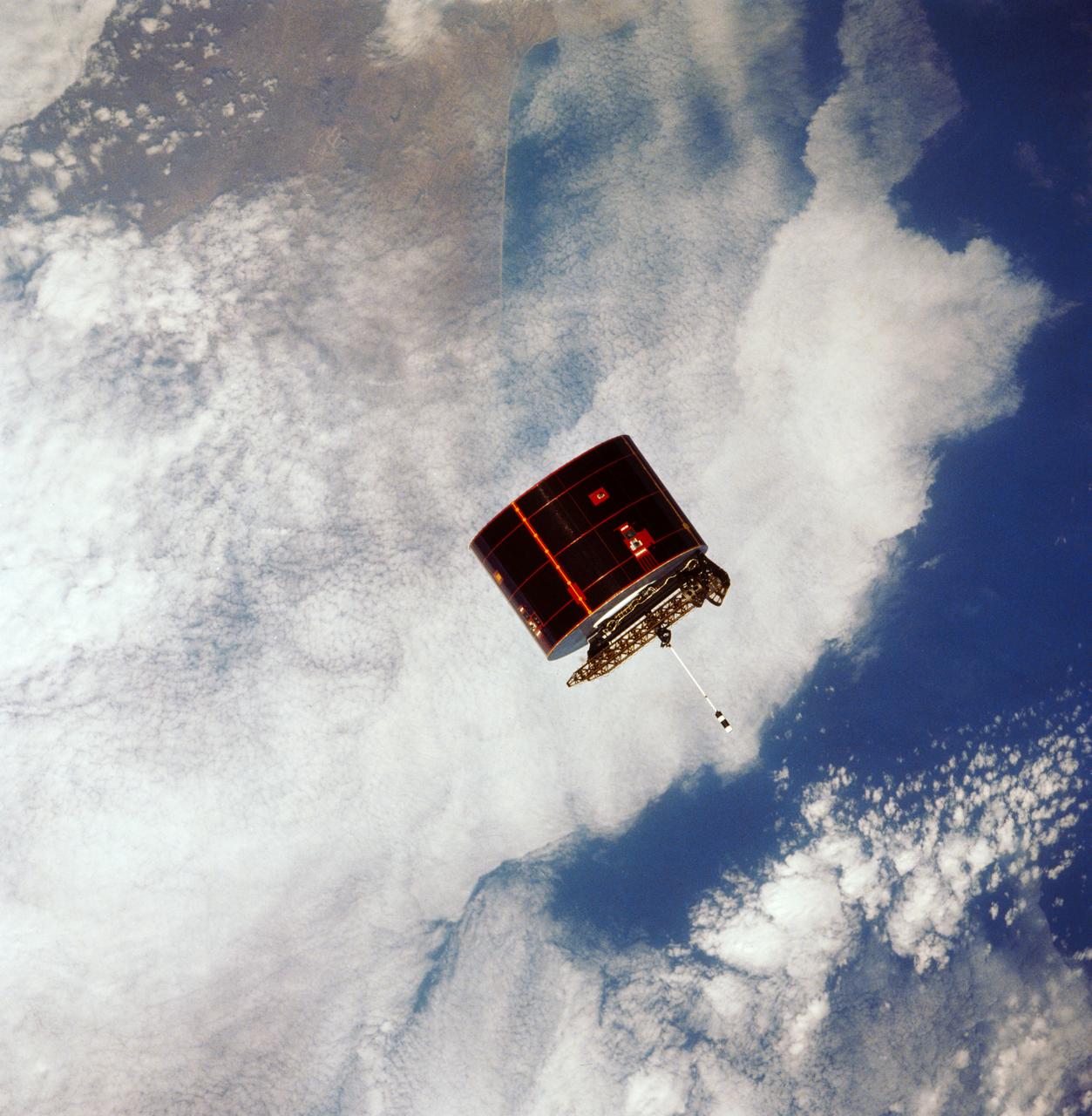

41D-32-067 (31 Aug 1984) --- The Atlantic Oceans coastline of Angola forms the backdrop for this scene of the Syncom IV (Leasat-2) spacecraft as it and the Space Shuttle Discovery begin their relative separation on Day Two of a busy-six-day 41-D mission. Moments, earlier in a Frisbee-like fashion, the spacecraft departed the Discovery’s cargo bay, marking the second of three scheduled satellite placements for the spacecraft’s maiden voyage. The scene was photographed with a 70mm camera aimed through the aft windows on the flight deck.
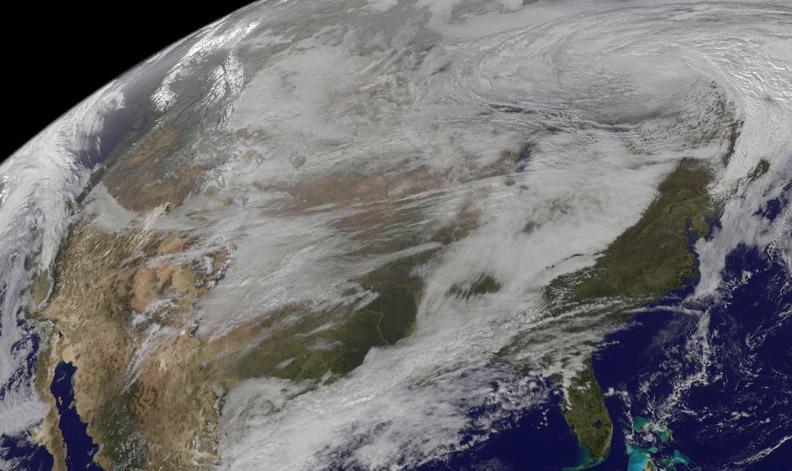

On Nov. 12, NOAA's GOES satellite showed the storm system that brought wintry weather entire U.S. centered near Ontario, Canada. Snow is visible in the U.S. and Canadian Rockies. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/new-satellite-movie-shows-us-pre-winter-wintry-outbreak/#.VGPP8t6FxgP" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/new-satellite-movie-shows-us...</a> Image Credit: NASA/NOAA GOES Project
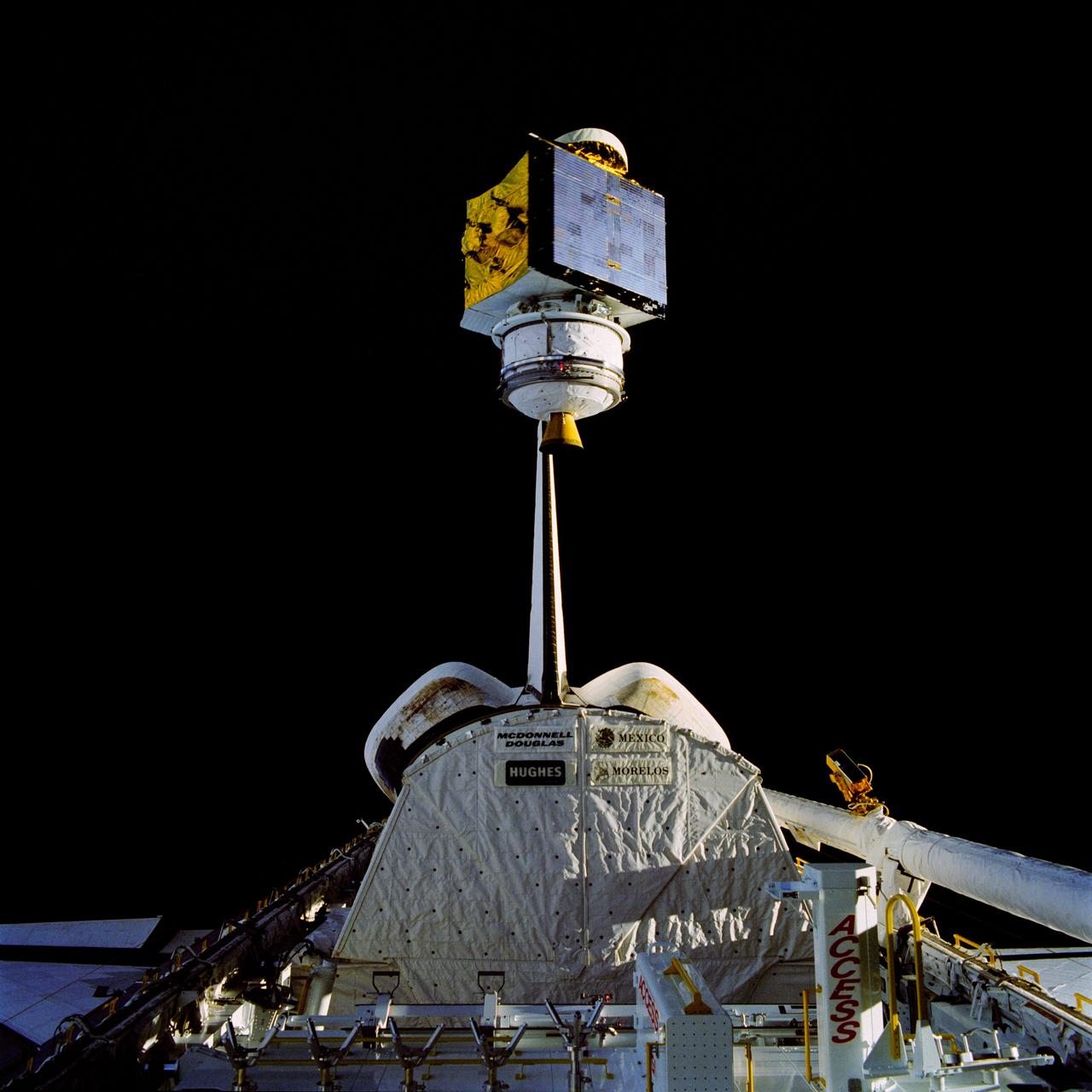

61B-38-36W (28 Nov 1985) --- The 4,144-pound RCA Satcom K-2 communications satellite is photographed as it spins from the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Atlantis. A TV camera at right records the deployment for a later playback to Earth. This frame was photographed with a handheld Hasselblad camera inside the spacecraft.

This image from NOAA's GOES satellite shows the swaths of snow across the Midwest after the weekend storms (December 7 and 8) there. This visible image was captured at 1745 UTC/12:45 p.m. EST on December 10, 2013. The riverine topography is highlighted by the snowfall, and the forested Ozarks appear as a dark patch west of St. Louis, Missouri. The image was created by NASA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. For more information about GOES, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/goes" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/goes</a>. Credit: NASA Goddard/Dennis Chesters <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA's Aqua Satellite Celebrates 10th Anniversary The Aqua satellite mission has proved to be a major component of the Earth Observing System (EOS) for its ability to gather unprecedented amounts of information on Earth’s water cycle, including measurements on water vapor, clouds, precipitation, ice, and snow. Aqua data has helped improve weather prediction, detection of forest fires, volcanic ash, and sandstorms. In addition, Aqua data have been used to detect and monitor such greenhouse gases as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane, and to examine the energy imbalance at the top of the Earth's atmosphere and the various components of it. With these uses of Aqua data, scientists have been able to better understand our Earth over the course of the past ten years. Aqua is a major international Earth Science satellite mission centered at NASA. Launched on May 4, 2002, the satellite has six different Earth-observing instruments on board and is named for the large amount of information being obtained about water in the Earth system from its stream of approximately 89 Gigabytes of data a day. The water variables being measured include almost all elements of the water cycle and involve water in its liquid, solid, and vapor forms. Additional variables being measured include radiative energy fluxes, aerosols, vegetation cover on the land, phytoplankton and dissolved organic matter in the oceans, and air, land, and water temperatures. For more information about NASA's Aqua satellite, visit: aqua.nasa.gov ------------ Caption: Artist rendition of the NASA's Aqua satellite, which carries the MODIS and AIRS instruments. Credit: NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
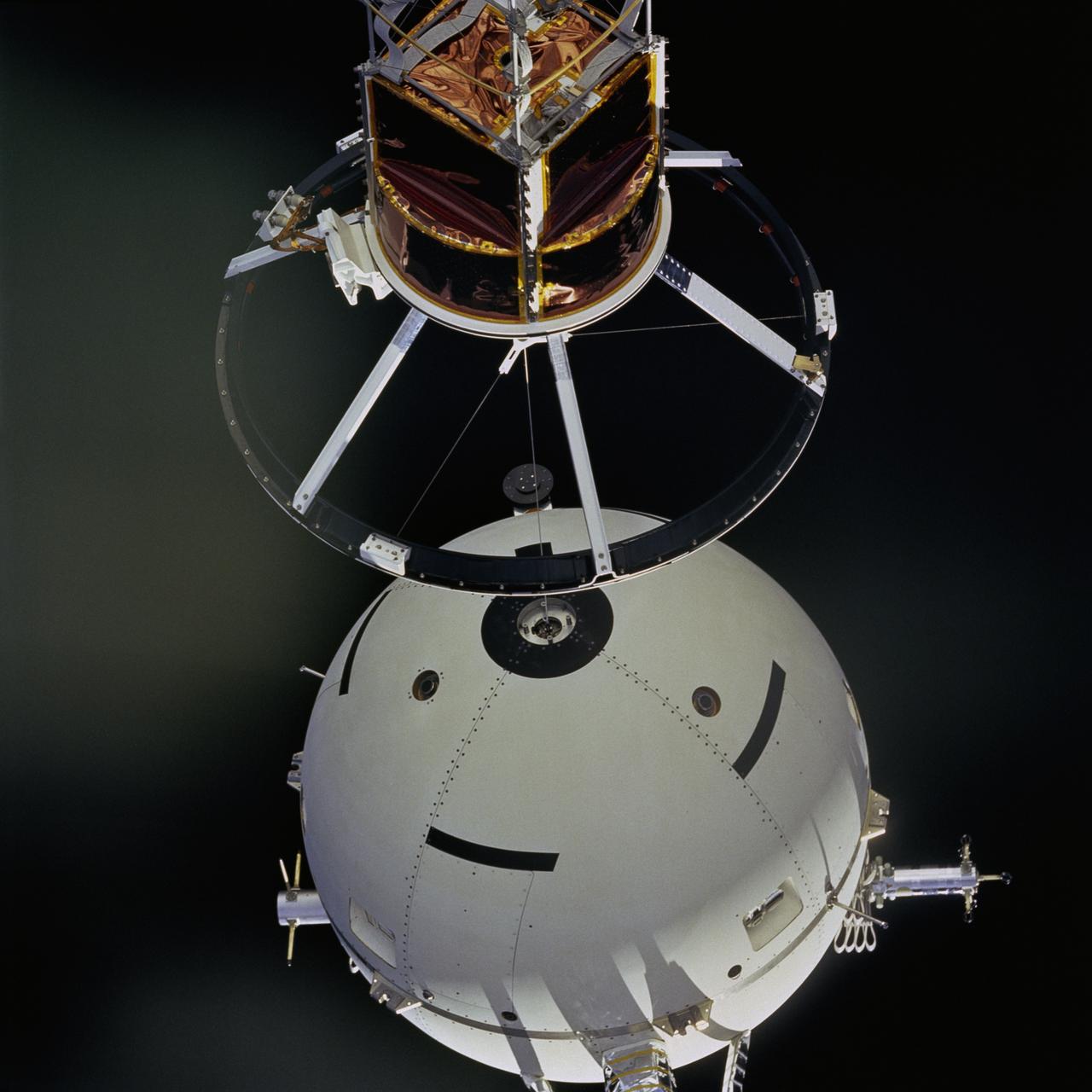

STS046-73-052 (4 Aug 1992) --- A 70mm handheld camera was used by the crew members to capture this medium close-up view of early operations with the Tethered Satellite System (TSS). The sphere can be seen moving away from the ring structure on the boom device in the Space Shuttle Atlantis' cargo bay.
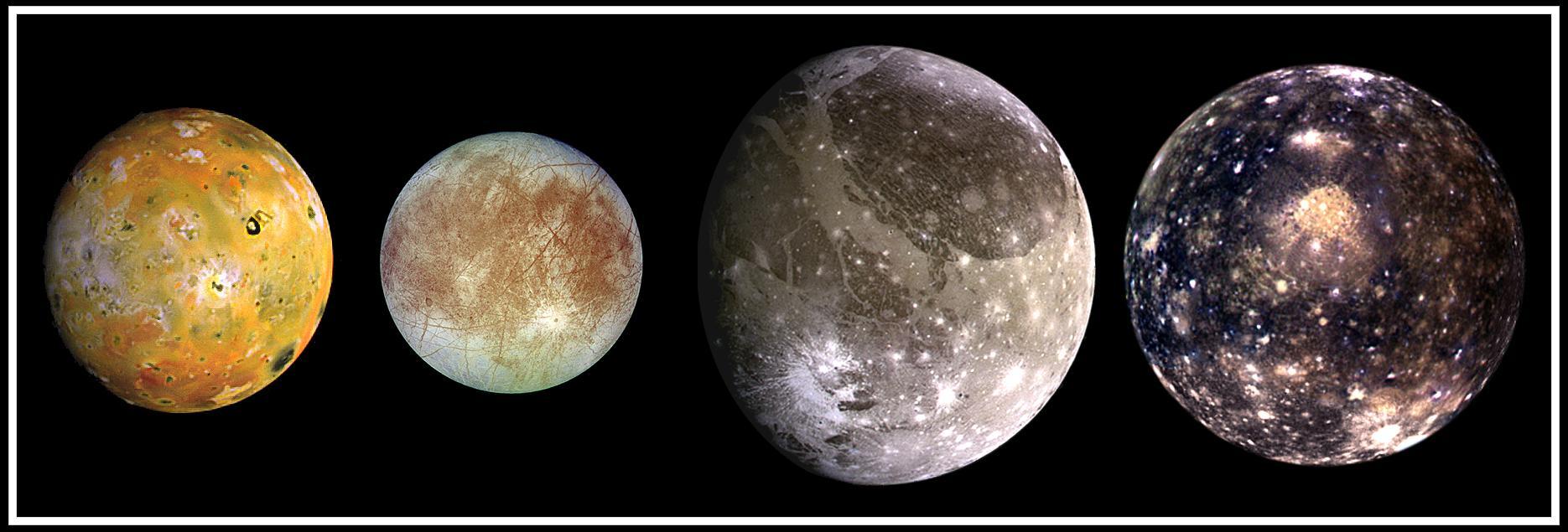

This composite includes the four largest moons of Jupiter which are known as the Galilean satellites. Shown from left to right are Io, closest to Jupiter, followed by Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
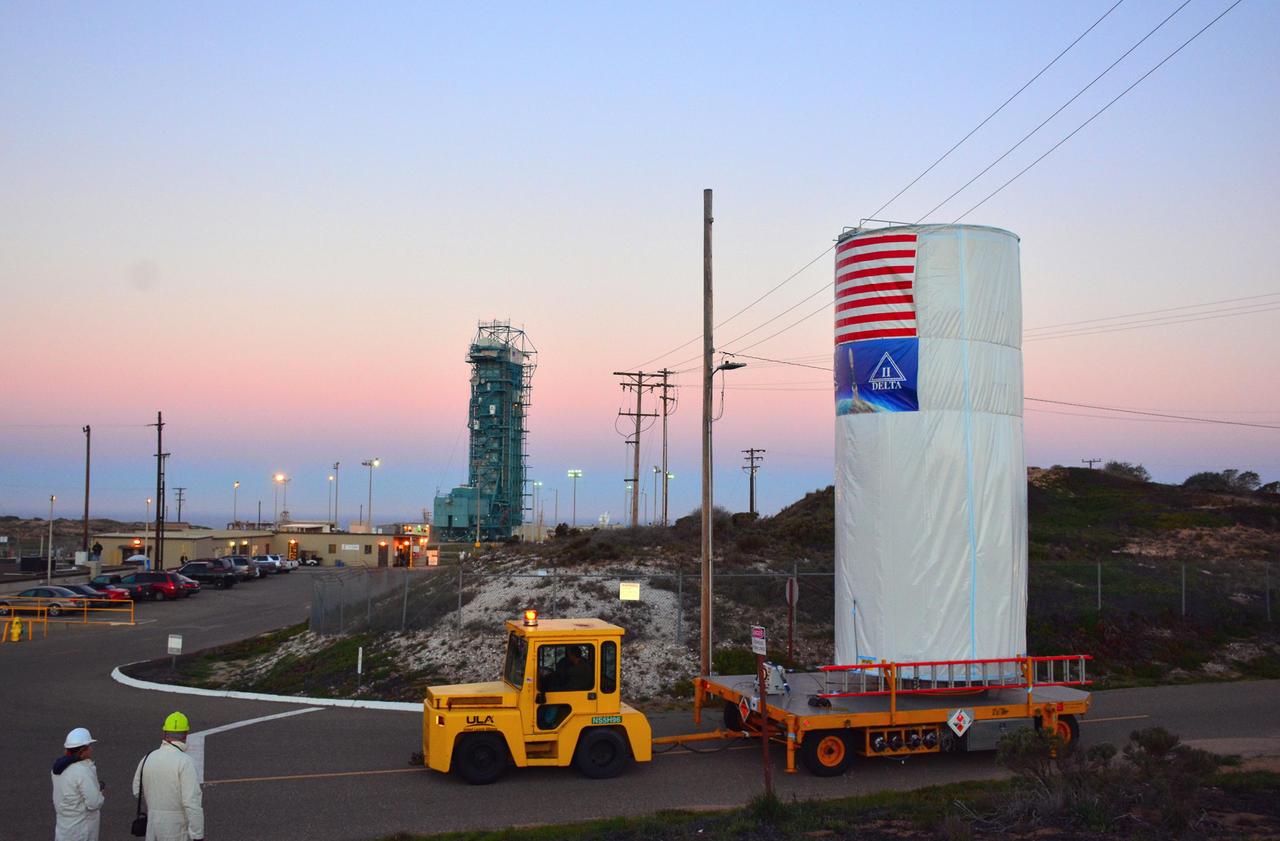

NASA Soil Moisture Active Passive SMAP satellite is transported across Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to Space Launch Complex 2, where it will be mated to a Delta II rocket for launch, targeted for Jan. 29.
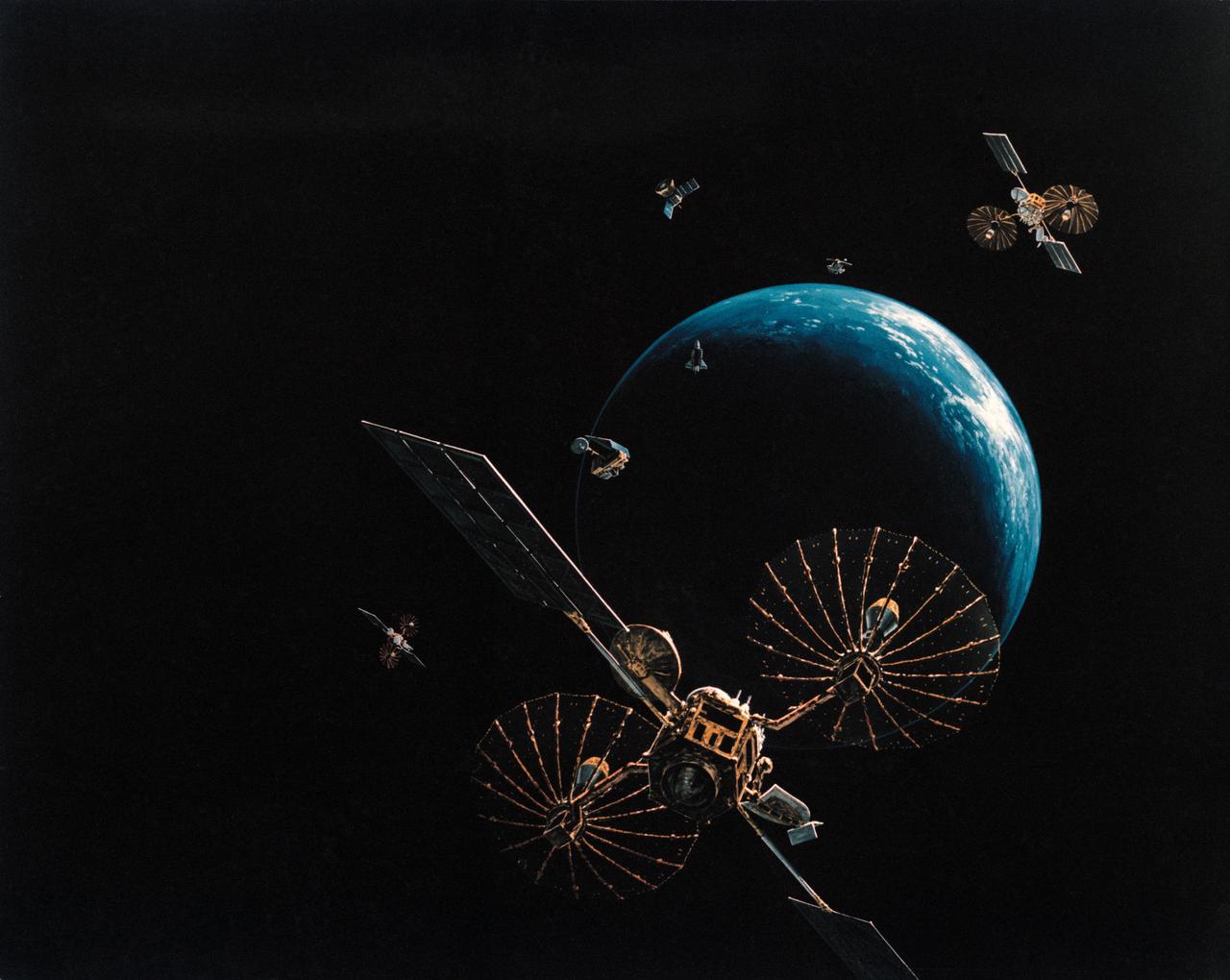

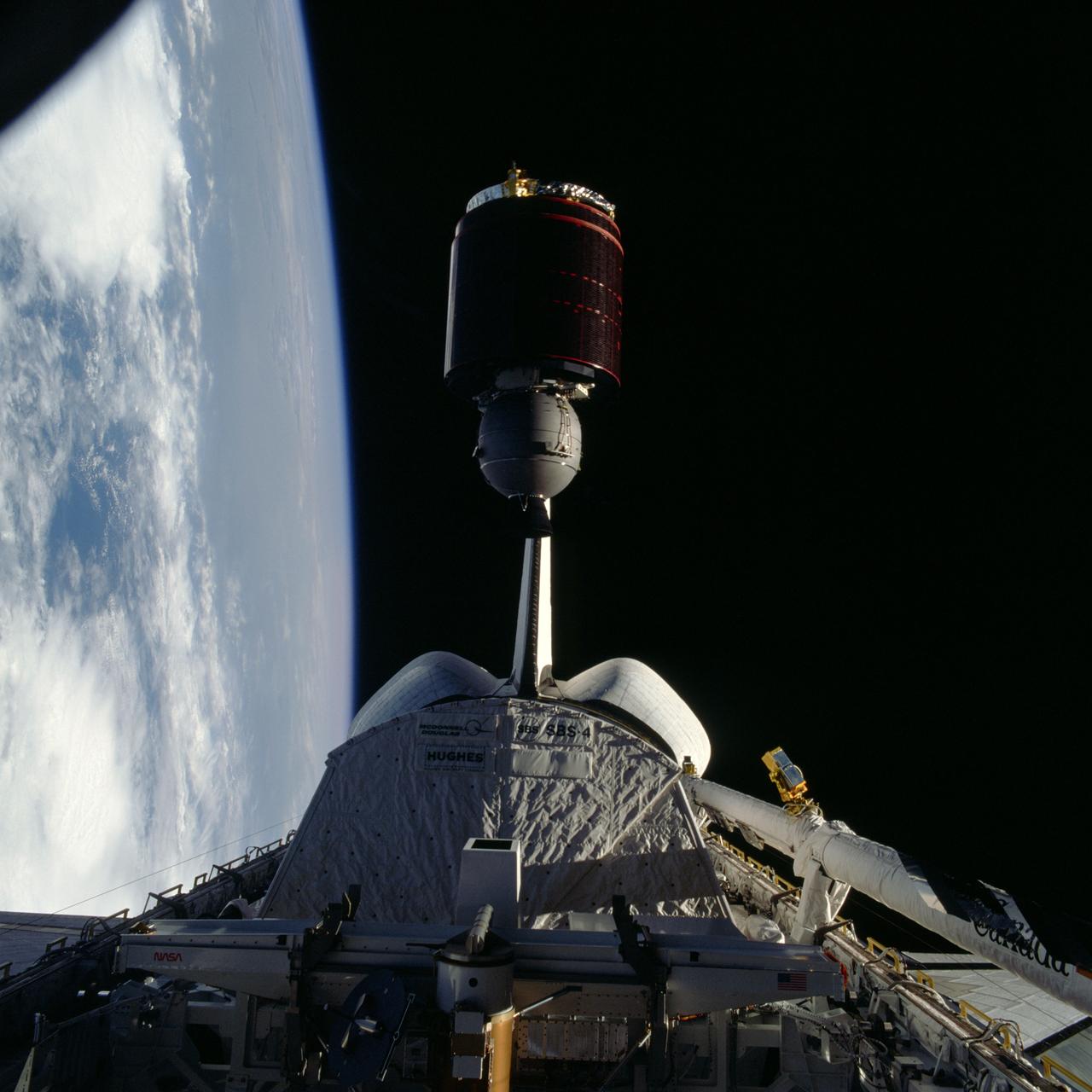
Artist concept shows the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite E (TDRS-E) augmenting a sophisticated TDRS system (TDRSS) communications network after deployment during STS-43 from Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104. TDRS, built by TRW, will be placed in a geosynchronous orbit and after onorbit testing, which requires several weeks, will be designated TDRS-5. The communications satellite will replace TDRS-3 at 174 degrees West longitude. The backbone of NASA's space-to-ground communications, the TDRSs have increased NASA's ability to send and receive data to spacecraft in low-earth orbit to more than 85 percent of the time. Before TDRS, NASA relied solely on a system of ground stations that permitted communications only 15 percent of the time. Increased coverage has allowed onorbit repairs, live television broadcast from space and continuous dialogues between astronaut crews and ground control during critical periods such as Space Shuttle landings.
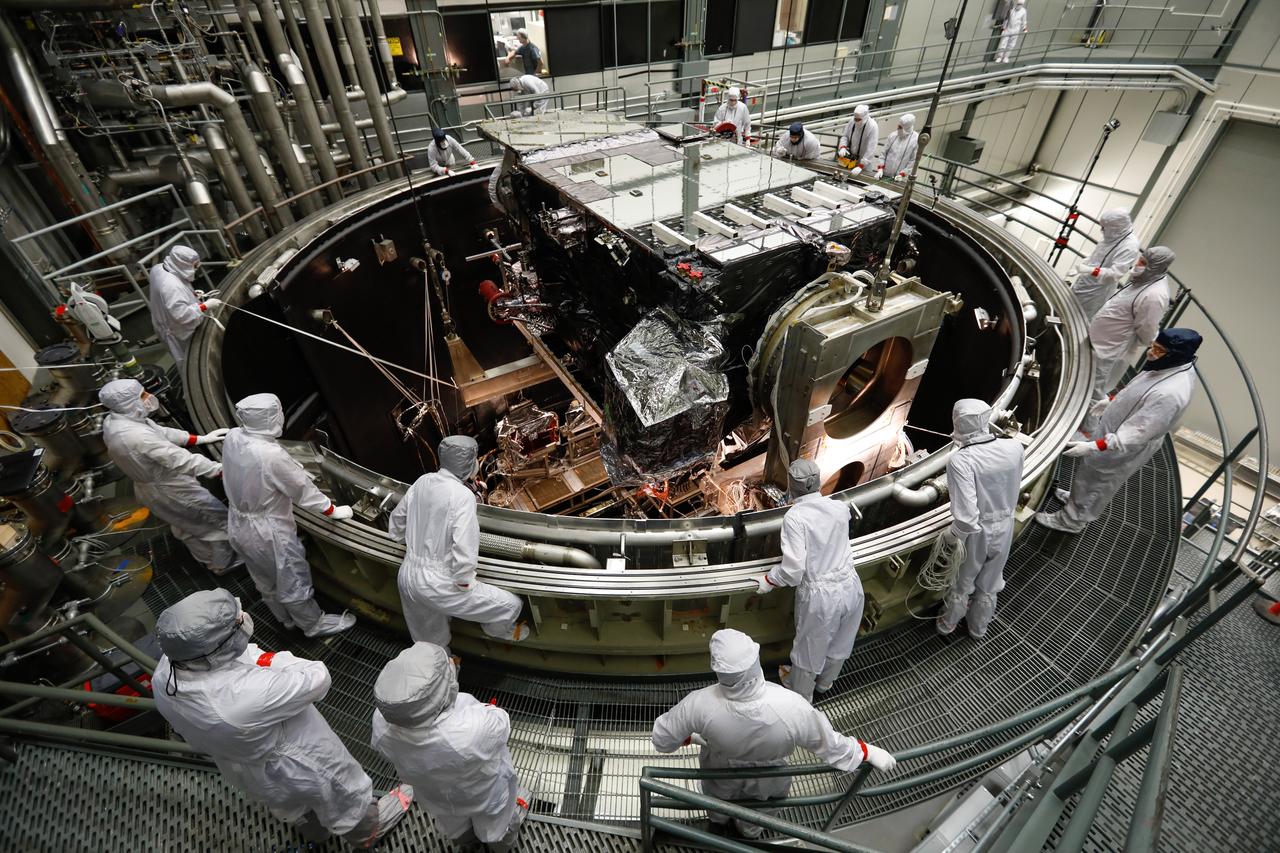

In March, NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S (GOES-S) satellite was lifted into a thermal vacuum chamber to test its ability to function in the cold void of space in its orbit 22,300 miles above the Earth. The most complicated and challenging test is thermal vacuum where a satellite experiences four cycles of extreme cold to extreme heat in a giant vacuum chamber. To simulate the environment of space, the chamber is cooled to below minus 100 degrees Celsius or minus 148 degrees Fahrenheit and air is pumped out. The test simulates the temperature changes GOES-S will encounter in space, as well as worst case scenarios of whether the instruments can come back to life in case of a shut down that exposes them to even colder temperatures. In this photo from March 8, the GOES-S satellite was lowered into the giant vacuum chamber at Lockheed Martin Space Systems, Denver, Colorado. GOES-S will be in the thermal vacuum chamber for 45 days. As of March 30, two of four thermal cycles were complete. GOES-S is the second in the GOES-R series. The GOES-R program is a collaborative development and acquisition effort between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and NASA. The GOES-R series of satellites will help meteorologists observe and predict local weather events, including thunderstorms, tornadoes, fog, flash floods, and other severe weather. In addition, GOES-R will monitor hazards such as aerosols, dust storms, volcanic eruptions, and forest fires and will also be used for space weather, oceanography, climate monitoring, in-situ data collection, and for search and rescue. Credit: Lockheed Martin <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
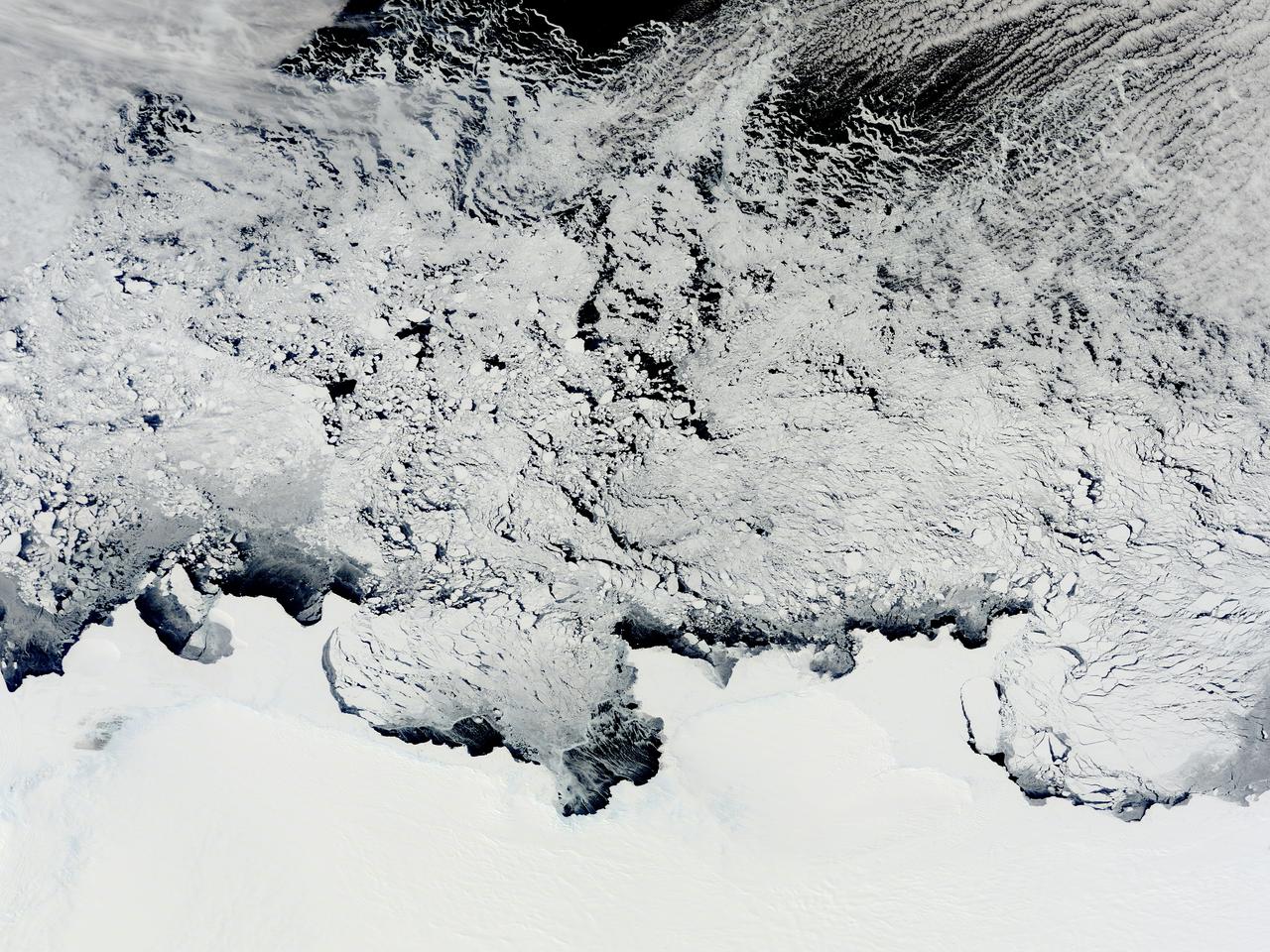

NASA image acquired November 2, 2011 The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured this image of the Knox, Budd Law Dome, and Sabrina Coasts, Antarctica on November 2, 2011 at 01:40 UTC (Nov. 1 at 9:40 p.m. EDT). Operation Ice Bridge is exploring Antarctic ice, and more information can be found at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/icebridge" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/icebridge</a>. Image Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA and NOAA satellites are providing various views of the major winter storm marching toward the U.S. East coast on March 13. The storm is forecast to merge with another system and is expected to bring large snowfall totals from the Mid-Atlantic to New England. NASA's Aqua satellite gathered infrared data from the storm system and the area ahead of the storm for cloud and ground temperatures. NOAA's GOES-East satellite provided visible and infrared imagery that showed the extent and the movement of the system. Forecasters at the National Weather Service's Weather Prediction Center (WPC) noted that the low pressure system crossing the Midwest states and Ohio Valley is expected to merge with another low off the southeast U.S. coast. WPC stated "This will allow for a strong nor'easter to develop near the coast and cause a late-season snowstorm from the central Appalachians to New England, including many of the big cities in the Northeast U.S." Credits: NASA/NOAA GOES Project

This image captured by the NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft on July 30, 1989, was used to confirm the discovery of three new satellites orbiting Neptune.
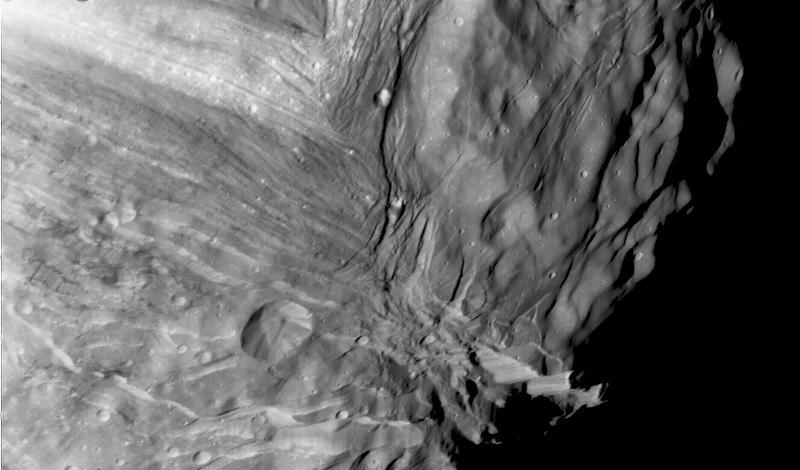
Miranda, innermost of Uranus large satellites, is seen at close range in this Voyager 2 image, taken Jan. 24, 1986, as part of a high-resolution mosaicing sequence.

On Jan. 18, 1986, NASA Voyager 2 discoverd three Uranus satellites. All three lie outside the orbits of Uranus nine known rings, the outermost of which, the epsilon ring, is seen at upper right. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00368
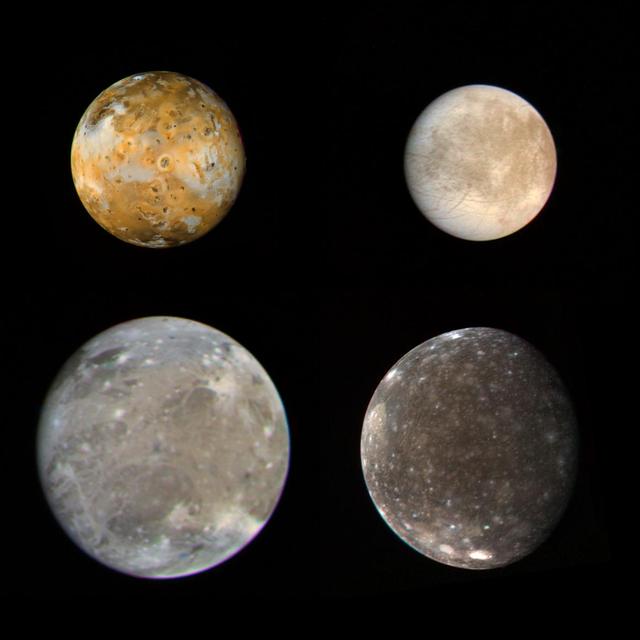

These photos of the four Galilean satellites of Jupiter were taken by NASA Voyager 1 during its approach to the planet in early March 1979. Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto are shown in their correct relative sizes. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00012

A model of the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and a spare camera lens are seen during a media briefing, Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

A model of the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and a spare camera lens are seen during a media briefing, Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Astronat Dale A. Gardner achieves a hard dock with the previously spinning Westar VI satellite. Gardner uses a "stinger" device to stabilize the communications satellite.
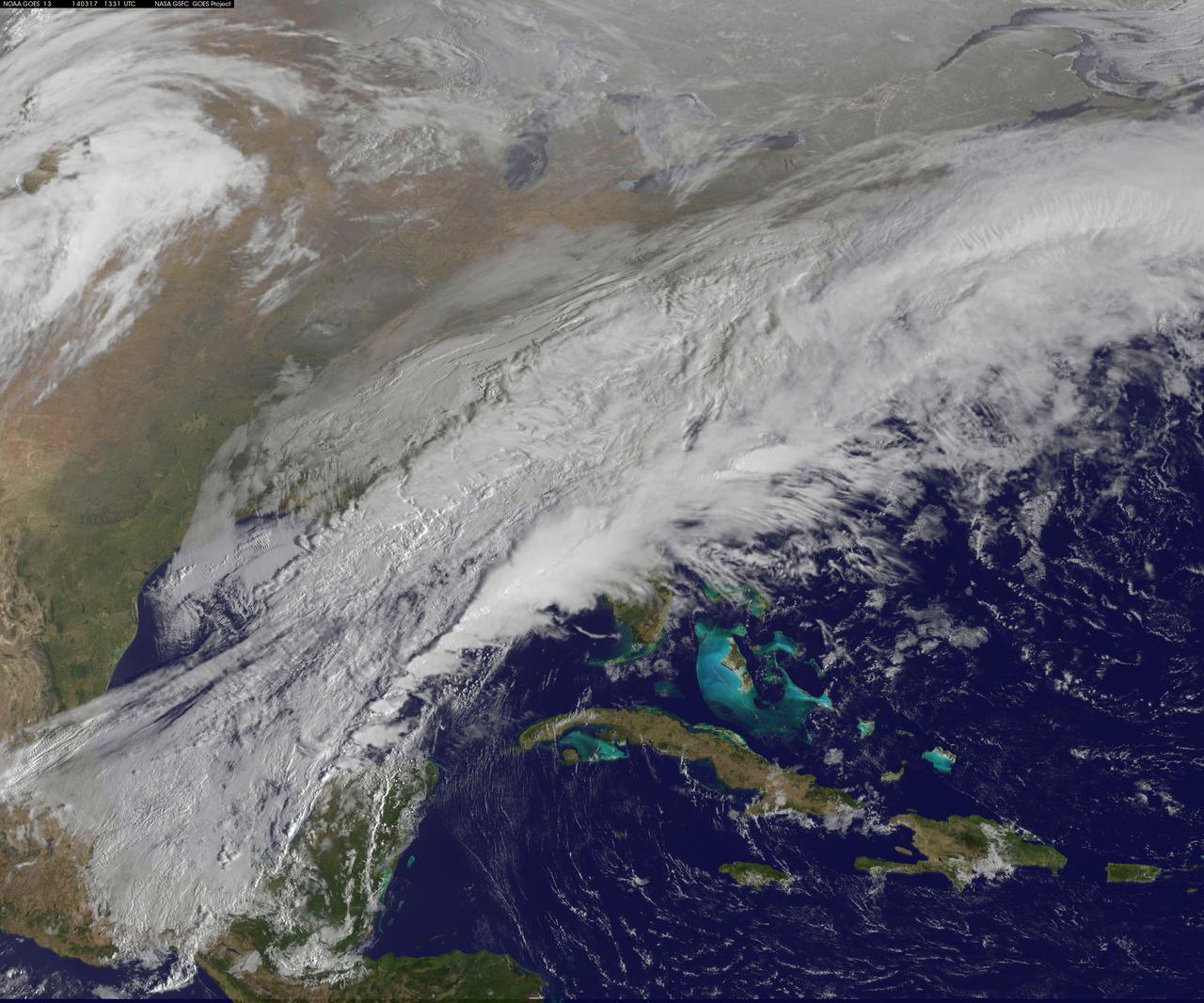

The green of St. Patrick's Day in the Mid-Atlantic was covered by white snow as a result of a late winter snow storm. The covering of the green was captured in a movie made at NASA using NOAA's GOES satellite data. The winter storm dropped snow totals from 6" to 12" of snow from Baltimore, Md. to Richmond, Va. The storm arrived during the evening of March 16 and continued through March 17. As of 1 p.m. EDT, light bands of snow continued to fall throughout the Washington, D.C. area. NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured the path the storm took through the Mid-Atlantic as it moved in from the west on March 15 and dropped snow March 16 and 17. NOAA's GOES-East satellite sits in a fixed orbit in space and captures visible and infrared imagery of all weather over the eastern U.S. and Atlantic Ocean. As of 1 p.m. EDT on March 17, the National Weather Service still maintained a Winter Storm Warning from Cecil County in northeastern Maryland that stretched west to Frederick County. The warning continued in Virginia counties including Clarke, Warren, Rappahannock, Madison and stretched to Albemarle and southwest. Southeastern counties in Virginia south of the city of Fredericksburg remained under a Winter Weather Advisory. GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's NWS website: <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a> For more information about GOES satellites, visit: <a href="http://www.goes.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.goes.noaa.gov/</a> or goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/ Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Sara Seager, TESS deputy director of science, MIT discusses the upcoming launch of NASA’s next planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Sara Seager, TESS deputy director of science, MIT discusses the upcoming launch of NASA’s next planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Jeff Volosin, TESS project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, holds a spare camera lens and a model of the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) during a media briefing, Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Jeff Volosin, TESS project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, holds a model of the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) during a media briefing, Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Astrophysics Division director Paul Hertz is seen during a media briefing where he and other astrophysics experts are discussing the upcoming launch of NASA’s next planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer Felicia Chou moderates a media briefing where astrophysics experts discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s next planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Public Affairs Officer Felicia Chou moderates a media briefing where astrophysics experts discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s next planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

George Ricker, TESS principal investigator, MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research, discusses the upcoming launch of NASA’s next planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Astrophysics Division director Paul Hertz, left, and Sara Seager, TESS deputy director of science, MIT, discuss the upcoming launch of NASA’s next planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Sara Seager, TESS deputy director of science, MIT discusses the upcoming launch of NASA’s next planet hunter, the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
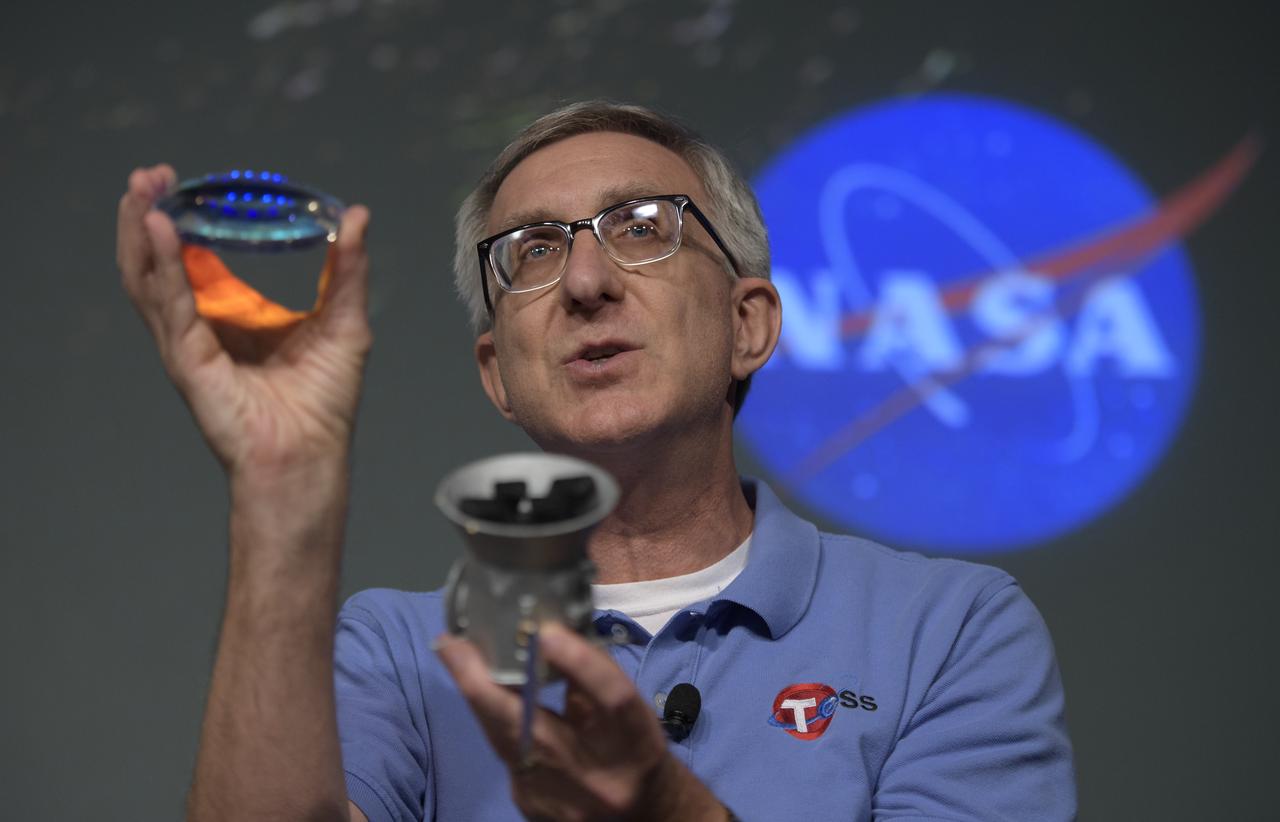

Jeff Volosin, TESS project manager, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, holds a spare camera lens and a model of the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) during a media briefing, Wednesday, March 28, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

STS060-93-043 (9 Feb 1994) --- BREMSAT, a 140 pound (63 kilogram) satellite, quickly leaves the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Discovery. The 480 mm (19 inch) deployable satellite was built by the University of Bremen's Center of Applied Space Technology and Microgravity (ZARM) under sponsorship of the German Space Agency (DARA). A modified ejection system in one of the payload bay's getaway special (GAS) type canisters aided the STS-60 crew members in deploying the satellite toward the end of their eight-day mission in Earth orbit.
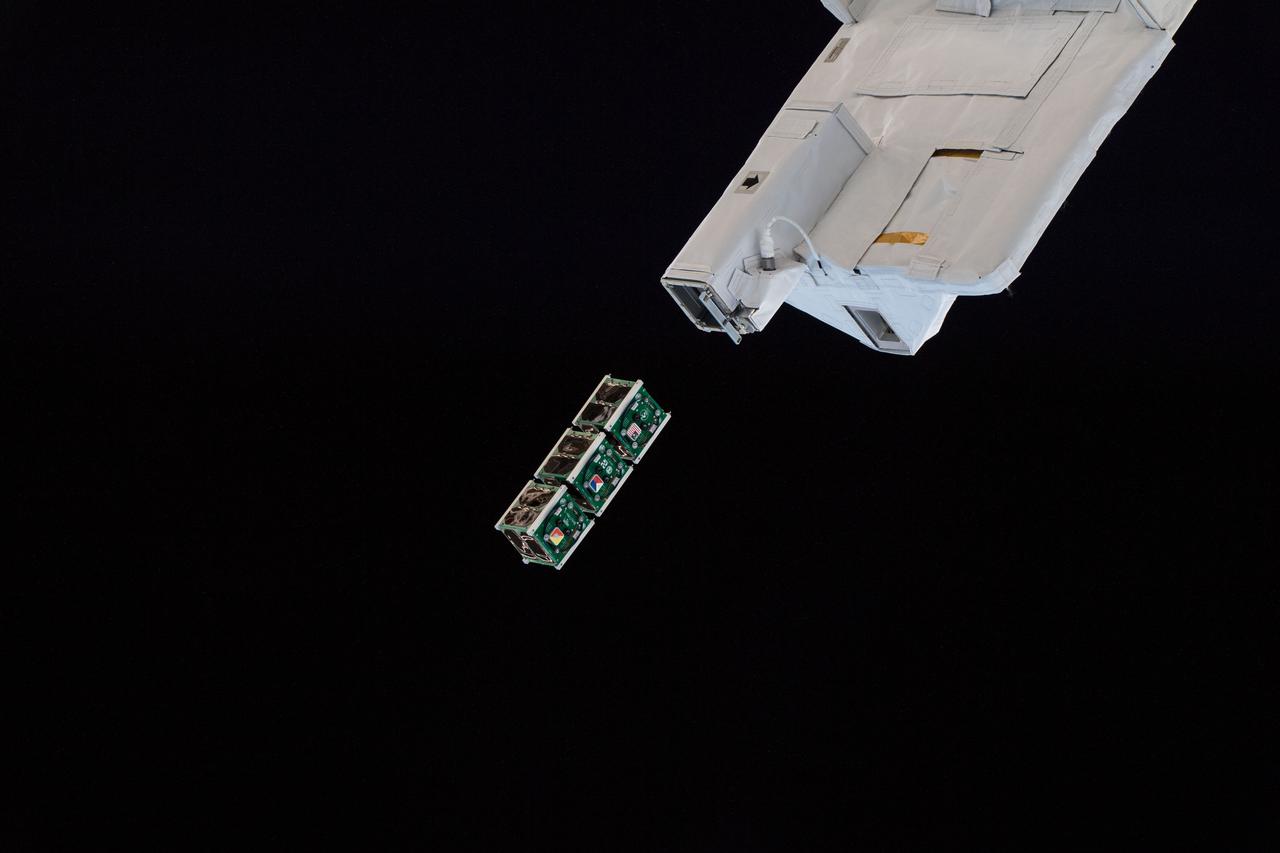
iss056e130478 (8/10/2018) --- A view of the BIRDS-2 Satellite Deployment during JSSOD-9 operations. The JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) provides a novel, safe, small satellite launching capability to the International Space Station (ISS). Once the J-SSOD including satellite install cases with small satellites are installed on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP) by crewmembers, it is passed through the JEM airlock for retrieval, positioning and deployment by the JEMRMS.

41D-37-050 (1 Sept 1984) --- Telstar, the third of three satellites to be placed into space via the Earth-orbiting Discovery, departs from the cargo bay of the manned vehicle during 41-D's third day in space. The scene was photographed at 9:35 a.m. (CDT), Sept. 1, 1984, with a 70mm handheld hasselblad camera aimed through the windows on the flight deck. Heavy clouds cover much of the water and land mass of Earth in the background.
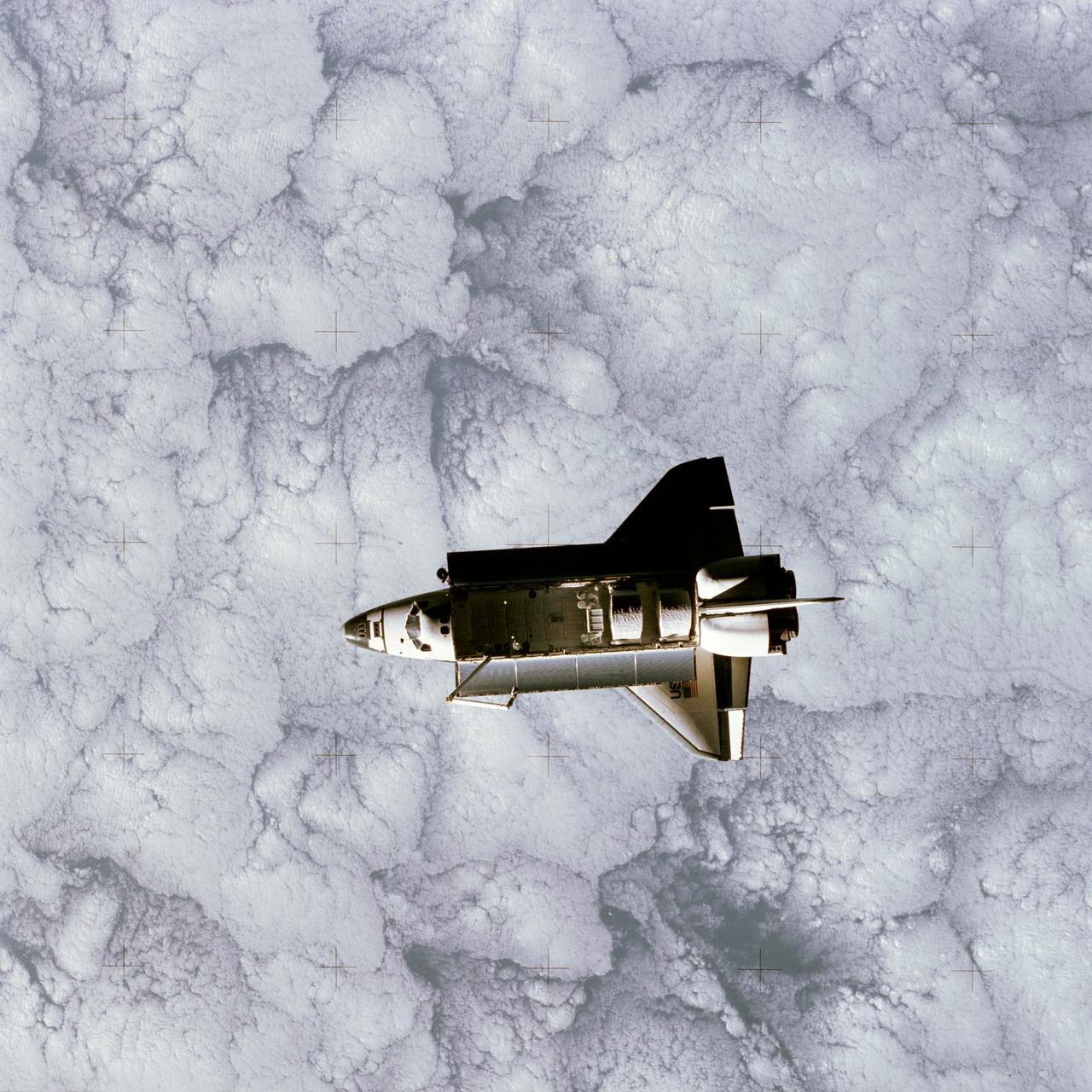

STS007-32-1667 (22 June 1983) --- The Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger over a heavily cloud-covered portion of the Earth was captured by a 70mm camera onboard the temporarily free-flying Shuttle Pallet Satellite (SPAS-01) during a busy Day 5 on the STS-7 mission. Visible in the cargo bay are the protective cradles for the now vacated Telesat Anik C2 and Palapa-B communications satellites, the pallet for the NASA Office of Space and Terrestrial Applications (OSTA-2); the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) and the KU-Band antenna. The STS-7 astronaut crew and the RMS arm later retrieved the SPAS and returned it to a stowed position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Challenger for the return to Earth.
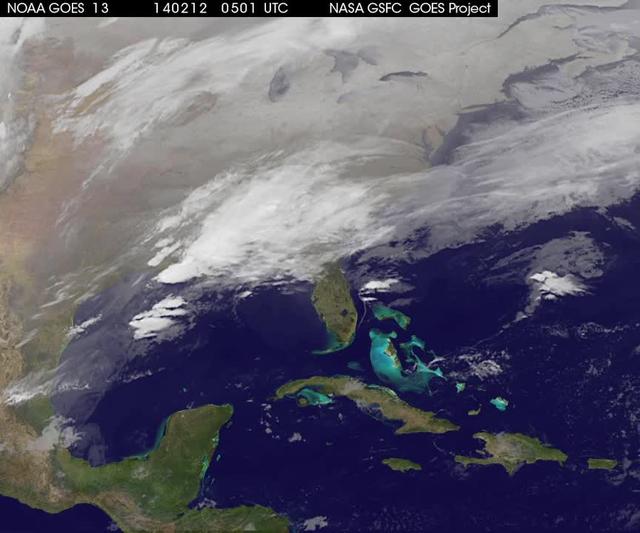

A new NASA video of NOAA's GOES satellite imagery shows three days of movement of the massive winter storm that stretches from the southern U.S. to the northeast. Visible and infrared imagery from NOAA's GOES-East or GOES-13 satellite from Feb. 10 at 1815 UTC/1:15 p.m. EST to Feb. 12 to 1845 UTC/1:45 p.m. EST were compiled into a video made by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. In the video, viewers can see the development and movement of the clouds associated with the progression of the frontal system and related low pressure areas that make up the massive storm. The video also shows the snow covered ground over the Great Lakes region and Ohio Valley that stretches to northern New England. The clouds and fallen snow data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite were overlaid on a true-color image of land and ocean created by data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua and Terra satellites. On February 12 at 10 a.m. EST, NOAA's National Weather Service or NWS continued to issue watches and warnings from Texas to New England. Specifically, NWS cited Winter Storm Warnings and Winter Weather Advisories were in effect from eastern Texas eastward across the interior section of southeastern U.S. states and across much of the eastern seaboard including the Appalachians. Winter storm watches are in effect for portions of northern New England as well as along the western slopes of northern and central Appalachians. For updates on local forecasts, watches and warnings, visit NOAA's <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a> webpage. NOAA's Weather Prediction Center or WPC noted the storm is expected to bring "freezing rain spreading into the Carolinas, significant snow accumulations are expected in the interior Mid-Atlantic states tonight into Thursday and ice storm warnings and freezing rain advisories are in effect across much of central Georgia. GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's WPC website; <a href="http://www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.hpc.ncep.noaa.gov/</a> For more information about GOES satellites, visit: <a href="http://www.goes.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.goes.noaa.gov/</a> or <a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">Credit: NOAA/NASA GOES Project</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Landsat 7 image of Phoenix, Arizona acquired November 28, 2014. Landsat 7 is a U.S. satellite used to acquire remotely sensed images of the Earth's land surface and surrounding coastal regions. It is maintained by the Landsat 7 Project Science Office at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. Landsat satellites have been acquiring images of the Earth’s land surface since 1972. Currently there are more than 2 million Landsat images in the National Satellite Land Remote Sensing Data Archive. For more information visit: <a href="http://landsat.usgs.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.usgs.gov/</a>..To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to:.<a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat 7 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
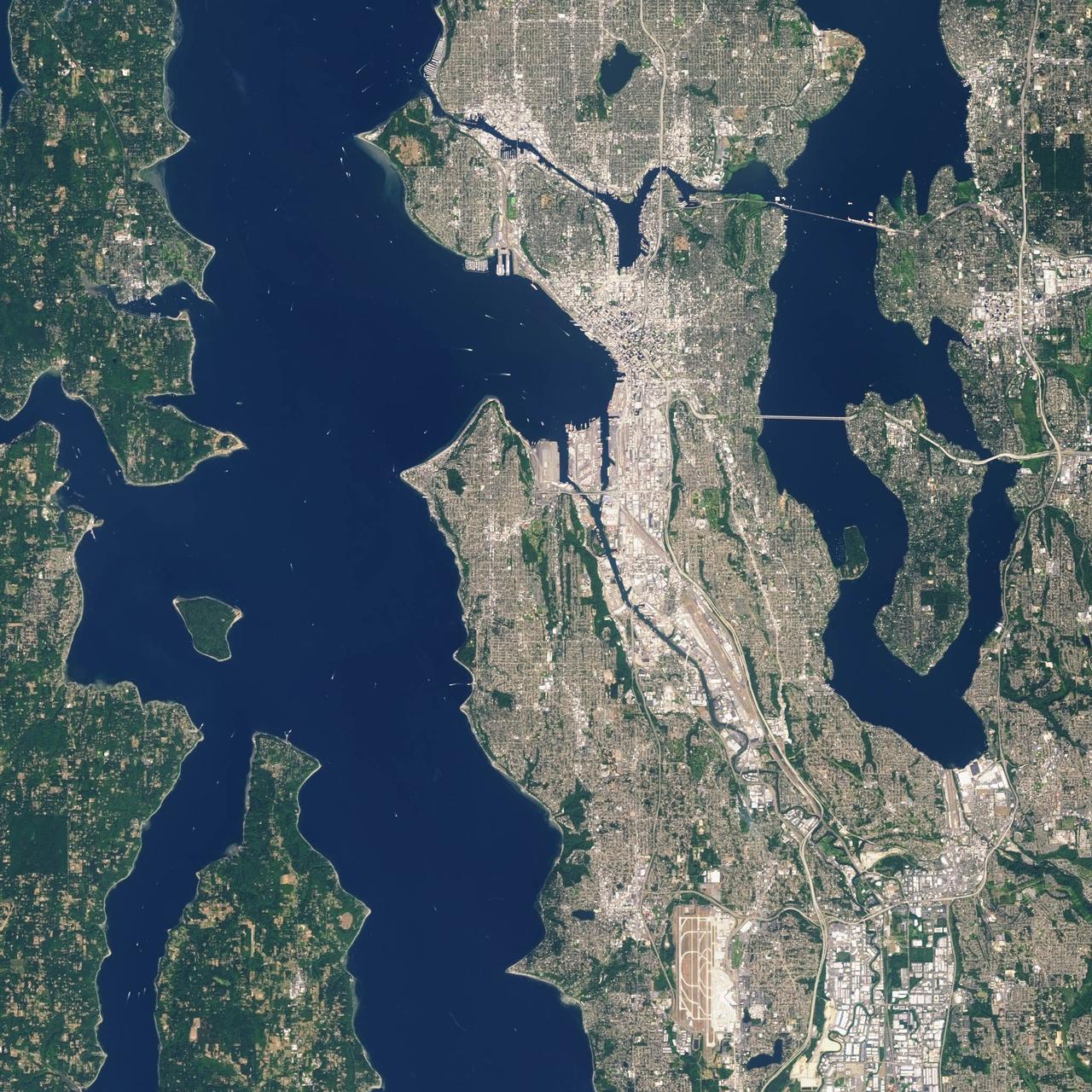
Landsat 7 image of Seattle, Washington acquired August 23, 2014. Landsat 7 is a U.S. satellite used to acquire remotely sensed images of the Earth's land surface and surrounding coastal regions. It is maintained by the Landsat 7 Project Science Office at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD. Landsat satellites have been acquiring images of the Earth’s land surface since 1972. Currently there are more than 2 million Landsat images in the National Satellite Land Remote Sensing Data Archive. For more information visit: <a href="http://landsat.usgs.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.usgs.gov/</a>..To learn more about the Landsat satellite go to:.<a href="http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Landsat 7 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

This Voyager 2 image of Miranda was taken Jan. 23, 1986, as the spacecraft neared Uranus. Miranda is the innermost of the five Uranian satellites known from Earth-based observations.