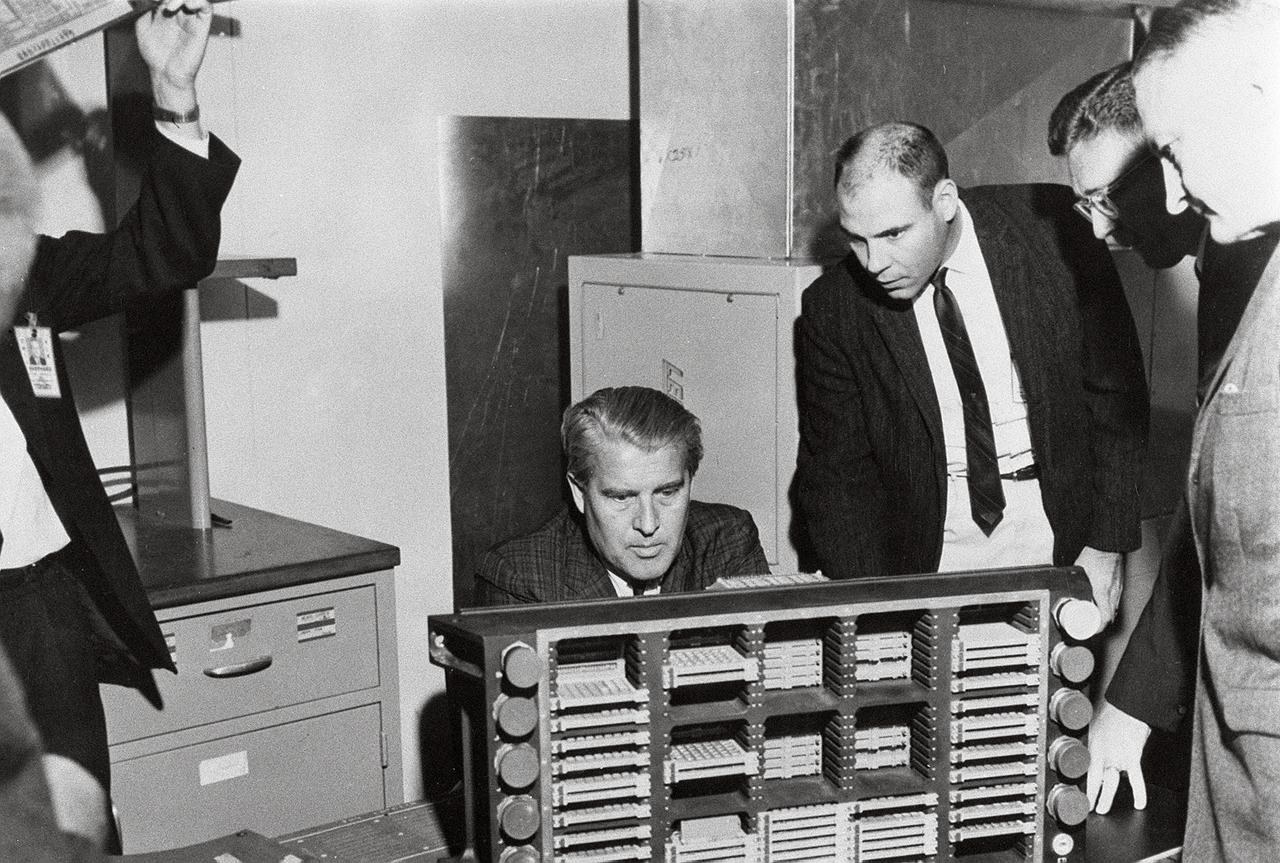

This photograph is dated March 10, 1966, and shows Dr. von Braun (seated) examining a Saturn computer in the Astrionics Laboratory at the Marshall Space Flight Center. Standing left to right are J.B. White, Brooks Moore, and Herman K. Weidner.
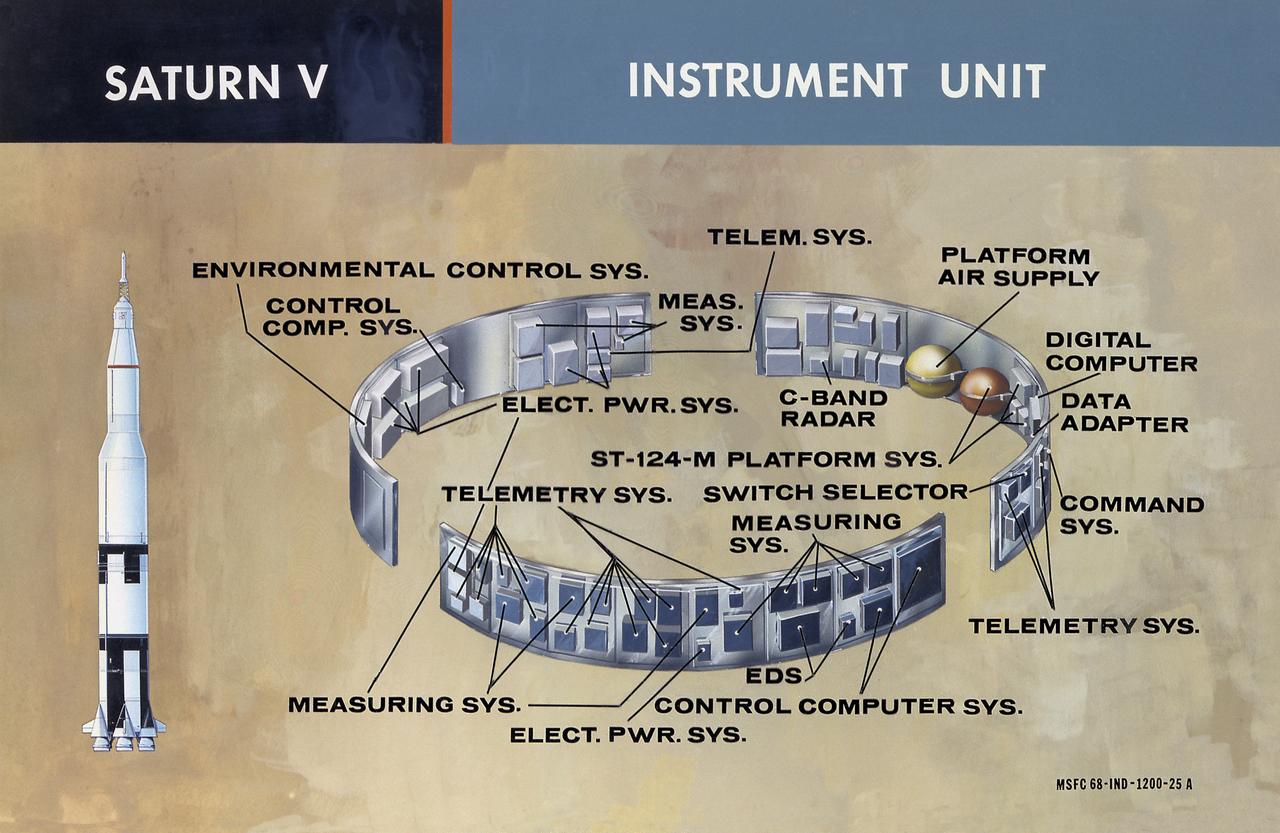
This illustration shows the major components of the instrument unit (IU). Developed and manufactured by International Business Machines, the IU is 3 feet high and 21 feet in diameter and mounted atop an S-IVB, between the third stage and the Apollo spacecraft. It contained the computers, all guidance, control, and sequencing equipment to keep the the launch vehicle properly functioning and on its course. The IU was essentially the same in both the Saturn IB and the Saturn V.
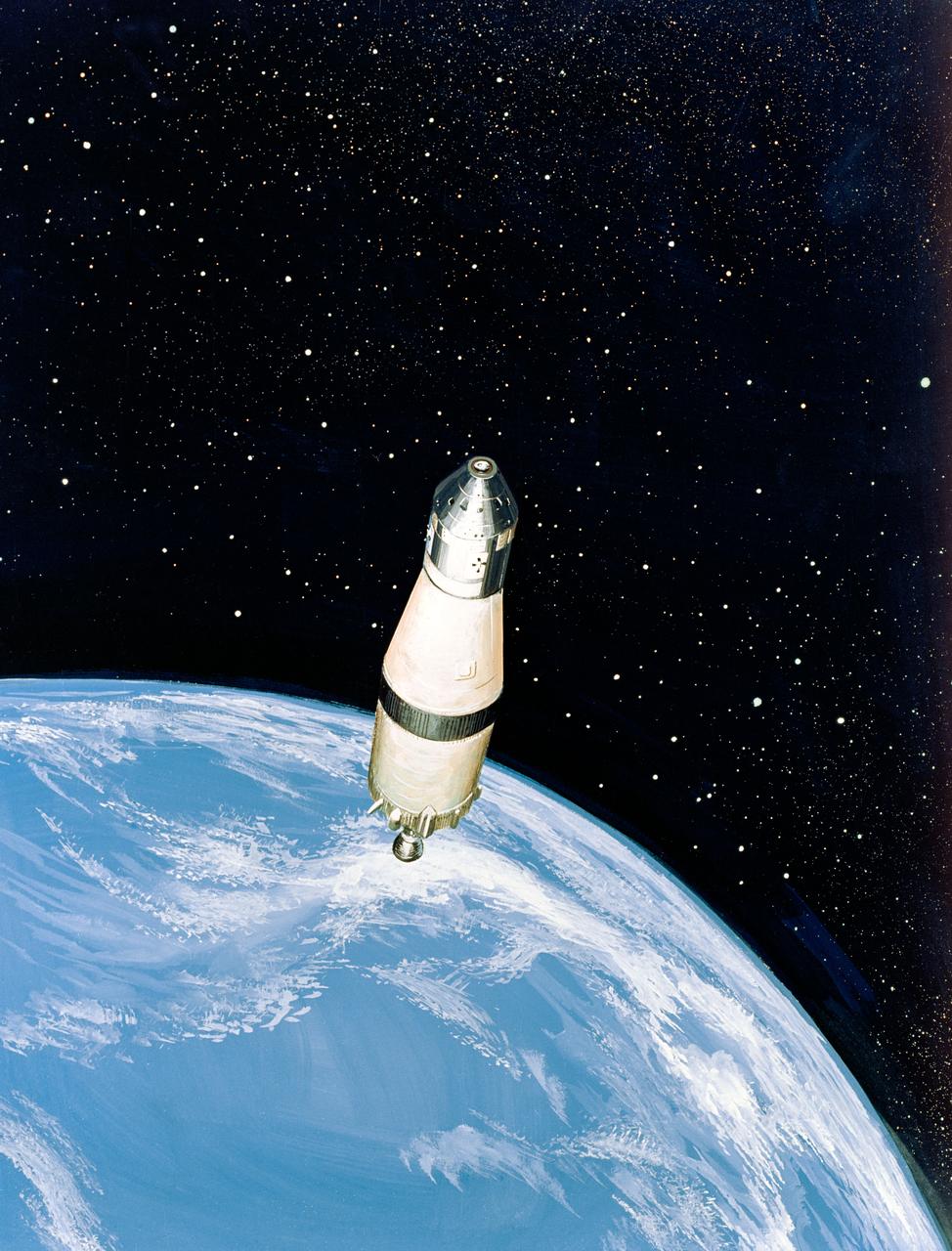

S68-51304 (December 1968) --- North American Rockwell artist's concept illustrating a phase of the scheduled Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. Here, the Apollo 8 spacecraft Command and Service Modules (CSM), still attached to the Saturn V (S-IVB) third stage, heads for the moon at a speed of about 24,300 miles per hour. The trajectory, computed from the Saturn V's third stage instrumentation unit, provides a "free return" to Earth around the moon.
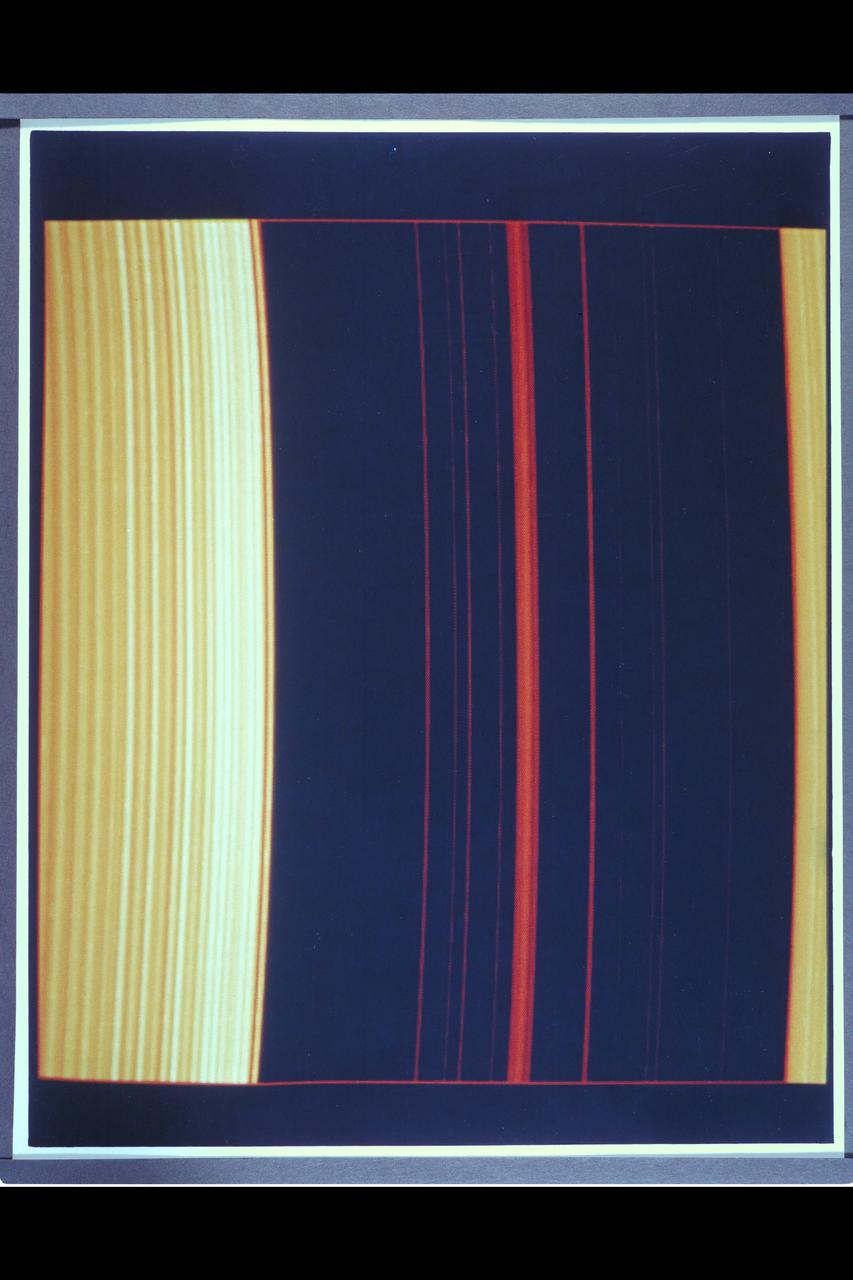

Resolution : 2 km. ( 1.2 miles ) P-24069C In this computer generated photograph, created from a cross section of Saturn's rings by Voyager 2 photopolarimeter's star occulation, the Encke Division in the outer A-ring. Clearly shown is the central ringlet, also observed by the imaging cameras.

A computer screen in mission control displays mission elapsed time for Cassini minutes after the spacecraft plunged into Saturn's atmosphere, Friday, Sept. 15, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. Loss of contact with the Cassini spacecraft occurred at 7:55 a.m. EDT (4:55 a.m. PDT). The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Resolution : 1 km. ( .6 miles ) Region Shown : 100 km. ( 60 miles ) P-24068C This computer generated photograph was created from a cross-section of Saturn's rings as measured by Voyager 2 photopolarimeter's occulation of the star Delta Scorpii. The region shown is near the inner edge of the Encke Division in the outer part of A-ring. The waves seen at left become successively closer together nearer to the Encke Division. At right are four strands of the ringlet that lies within the Encke Division. Voyager 2's imaging system saw this structure as a single ringlet.
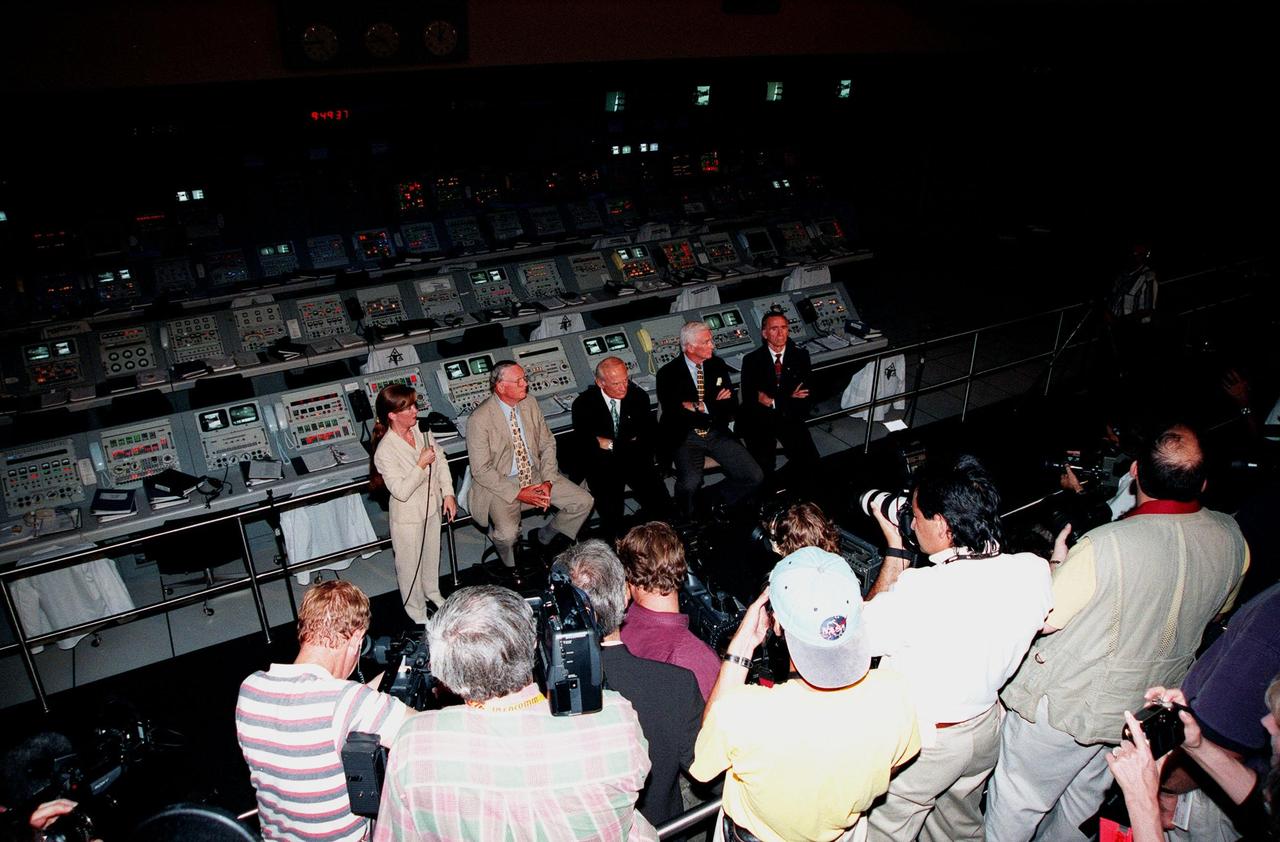

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Viewed from above, former Apollo astronauts (seated, left to right) Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin who flew on Apollo 11, the launch to the moon; Gene Cernan, who flew on Apollo 10 and 17; and Walt Cunningham, who flew on Apollo 7, answer questions from the media during a press conference in the Apollo/Saturn V Center. At left is Lisa Malone, chief of KSC's Media Services branch, who monitored the session. In the background are the original computer consoles used in the firing room during the Apollo program. They are now part of the reenactment of the Apollo launches in the exhibit at the center. The four astronauts were at KSC for the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969
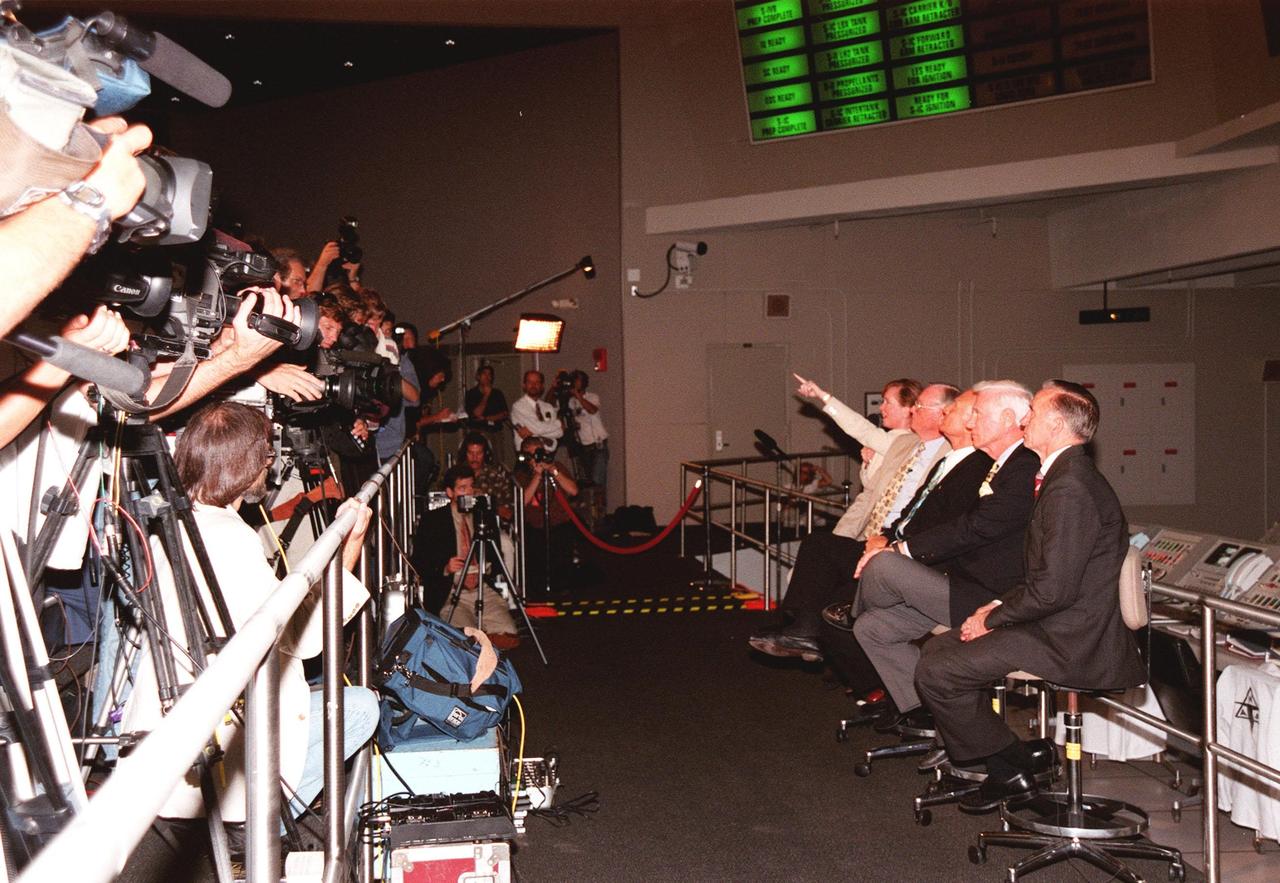

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Apollo/Saturn V Center, Lisa Malone, chief of KSC's Media Services branch, identifies a reporter in the stands to pose a question to one of the former Apollo astronauts seated next to her. From left to right, they are Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin who flew on Apollo 11, the launch to the moon; Gene Cernan, who flew on Apollo 10 and 17; and Walt Cunningham, who flew on Apollo 7. Behind them on the lower floor are the original computer consoles used in the firing room during the Apollo program. They are now part of the reenactment of the Apollo launches in the exhibit at the center. This is the 30th anniversary of the launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Neil Armstrong was the first man to set foot on the moon

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In this closeup viewed from above, former Apollo astronauts (seated, left to right) Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin who flew on Apollo 11, the launch to the moon; Gene Cernan, who flew on Apollo 10 and 17; and Walt Cunningham, who flew on Apollo 7, answer questions from the media during a press conference in the Apollo/Saturn V Center. At left is Lisa Malone, chief of KSC's Media Services branch, who monitored the session. In the background are the original computer consoles used in the firing room during the Apollo program. They are now part of the reenactment of the Apollo launches in the exhibit at the center. The four astronauts were at KSC for the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969
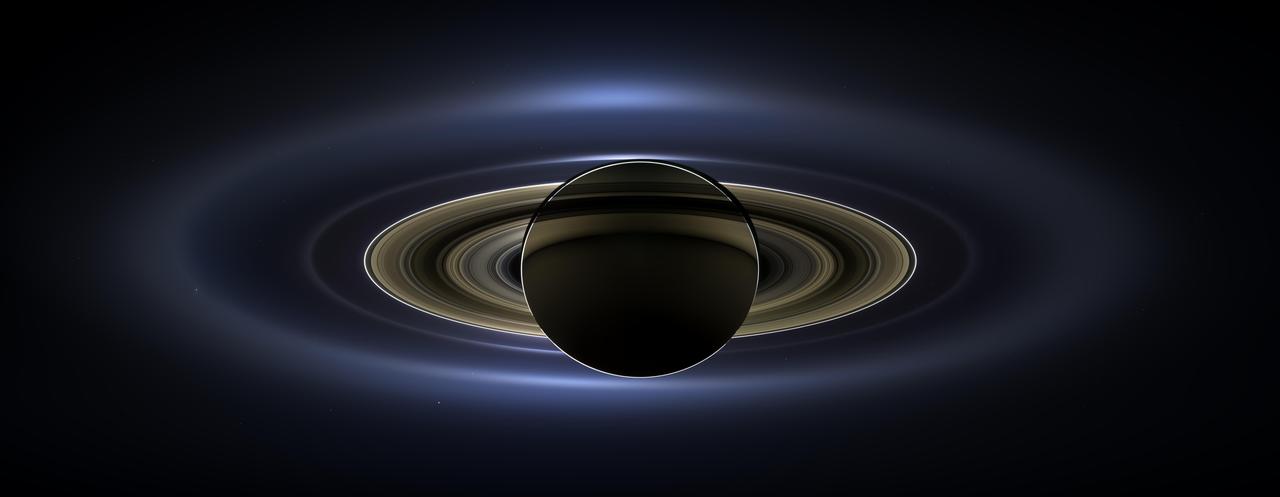

On July 19, 2013, in an event celebrated the world over, NASA's Cassini spacecraft slipped into Saturn's shadow and turned to image the planet, seven of its moons, its inner rings -- and, in the background, our home planet, Earth. With the sun's powerful and potentially damaging rays eclipsed by Saturn itself, Cassini's onboard cameras were able to take advantage of this unique viewing geometry. They acquired a panoramic mosaic of the Saturn system that allows scientists to see details in the rings and throughout the system as they are backlit by the sun. This mosaic is special as it marks the third time our home planet was imaged from the outer solar system; the second time it was imaged by Cassini from Saturn's orbit; and the first time ever that inhabitants of Earth were made aware in advance that their photo would be taken from such a great distance. With both Cassini's wide-angle and narrow-angle cameras aimed at Saturn, Cassini was able to capture 323 images in just over four hours. This final mosaic uses 141 of those wide-angle images. Images taken using the red, green and blue spectral filters of the wide-angle camera were combined and mosaicked together to create this natural-color view. A brightened version with contrast and color enhanced (Figure 1), a version with just the planets annotated (Figure 2), and an annotated version (Figure 3) are shown above. This image spans about 404,880 miles (651,591 kilometers) across. The outermost ring shown here is Saturn's E ring, the core of which is situated about 149,000 miles (240,000 kilometers) from Saturn. The geysers erupting from the south polar terrain of the moon Enceladus supply the fine icy particles that comprise the E ring; diffraction by sunlight gives the ring its blue color. Enceladus (313 miles, or 504 kilometers, across) and the extended plume formed by its jets are visible, embedded in the E ring on the left side of the mosaic. At the 12 o'clock position and a bit inward from the E ring lies the barely discernible ring created by the tiny, Cassini-discovered moon, Pallene (3 miles, or 4 kilometers, across). (For more on structures like Pallene's ring, see PIA08328). The next narrow and easily seen ring inward is the G ring. Interior to the G ring, near the 11 o'clock position, one can barely see the more diffuse ring created by the co-orbital moons, Janus (111 miles, or 179 kilometers, across) and Epimetheus (70 miles, or 113 kilometers, across). Farther inward, we see the very bright F ring closely encircling the main rings of Saturn. Following the outermost E ring counter-clockwise from Enceladus, the moon Tethys (662 miles, or 1,066 kilometers, across) appears as a large yellow orb just outside of the E ring. Tethys is positioned on the illuminated side of Saturn; its icy surface is shining brightly from yellow sunlight reflected by Saturn. Continuing to about the 2 o'clock position is a dark pixel just outside of the G ring; this dark pixel is Saturn's Death Star moon, Mimas (246 miles, or 396 kilometers, across). Mimas appears, upon close inspection, as a very thin crescent because Cassini is looking mostly at its non-illuminated face. The moons Prometheus, Pandora, Janus and Epimetheus are also visible in the mosaic near Saturn's bright narrow F ring. Prometheus (53 miles, or 86 kilometers, across) is visible as a faint black dot just inside the F ring and at the 9 o'clock position. On the opposite side of the rings, just outside the F ring, Pandora (50 miles, or 81 kilometers, across) can be seen as a bright white dot. Pandora and Prometheus are shepherd moons and gravitational interactions between the ring and the moons keep the F ring narrowly confined. At the 11 o'clock position in between the F ring and the G ring, Janus (111 miles, or 179 kilometers, across) appears as a faint black dot. Janus and Prometheus are dark for the same reason Mimas is mostly dark: we are looking at their non-illuminated sides in this mosaic. Midway between the F ring and the G ring, at about the 8 o'clock position, is a single bright pixel, Epimetheus. Looking more closely at Enceladus, Mimas and Tethys, especially in the brightened version of the mosaic, one can see these moons casting shadows through the E ring like a telephone pole might cast a shadow through a fog. In the non-brightened version of the mosaic, one can see bright clumps of ring material orbiting within the Encke gap near the outer edge of the main rings and immediately to the lower left of the globe of Saturn. Also, in the dark B ring within the main rings, at the 9 o'clock position, one can see the faint outlines of two spoke features, first sighted by NASA's Voyager spacecraft in the early 1980s and extensively studied by Cassini. Finally, in the lower right of the mosaic, in between the bright blue E ring and the faint but defined G ring, is the pale blue dot of our planet, Earth. Look closely and you can see the moon protruding from the Earth's lower right. (For a higher resolution view of the Earth and moon taken during this campaign, see PIA14949.) Earth's twin, Venus, appears as a bright white dot in the upper left quadrant of the mosaic, also between the G and E rings. Mars also appears as a faint red dot embedded in the outer edge of the E ring, above and to the left of Venus. For ease of visibility, Earth, Venus, Mars, Enceladus, Epimetheus and Pandora were all brightened by a factor of eight and a half relative to Saturn. Tethys was brightened by a factor of four. In total, 809 background stars are visible and were brightened by a factor ranging from six, for the brightest stars, to 16, for the faintest. The faint outer rings (from the G ring to the E ring) were also brightened relative to the already bright main rings by factors ranging from two to eight, with the lower-phase-angle (and therefore fainter) regions of these rings brightened the most. The brightened version of the mosaic was further brightened and contrast-enhanced all over to accommodate print applications and a wide range of computer-screen viewing conditions. Some ring features -- such as full rings traced out by tiny moons -- do not appear in this version of the mosaic because they require extreme computer enhancement, which would adversely affect the rest of the mosaic. This version was processed for balance and beauty. This view looks toward the unlit side of the rings from about 17 degrees below the ring plane. Cassini was approximately 746,000 miles (1.2 million kilometers) from Saturn when the images in this mosaic were taken. Image scale on Saturn is about 45 miles (72 kilometers) per pixel. This mosaic was made from pictures taken over a span of more than four hours while the planets, moons and stars were all moving relative to Cassini. Thus, due to spacecraft motion, these objects in the locations shown here were not in these specific places over the entire duration of the imaging campaign. Note also that Venus appears far from Earth, as does Mars, because they were on the opposite side of the sun from Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA17172
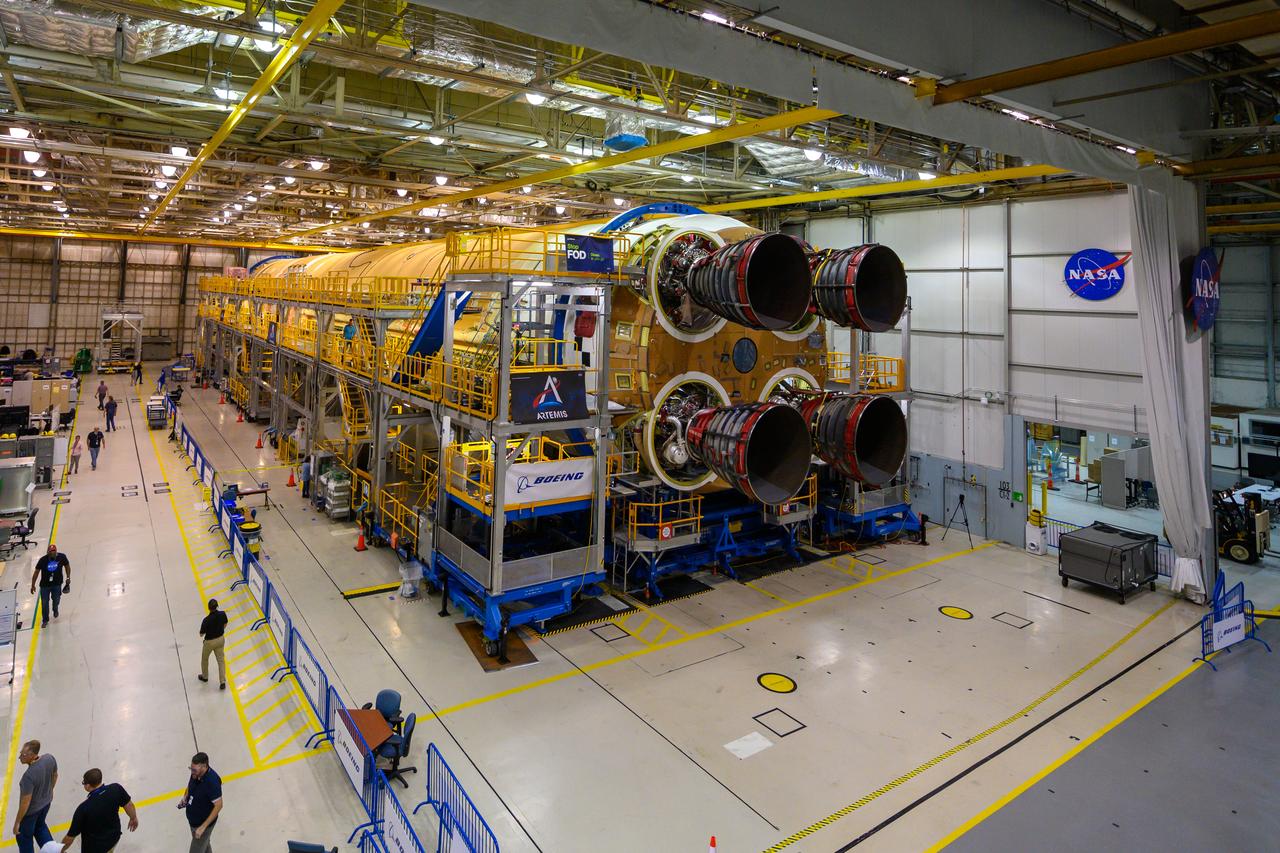

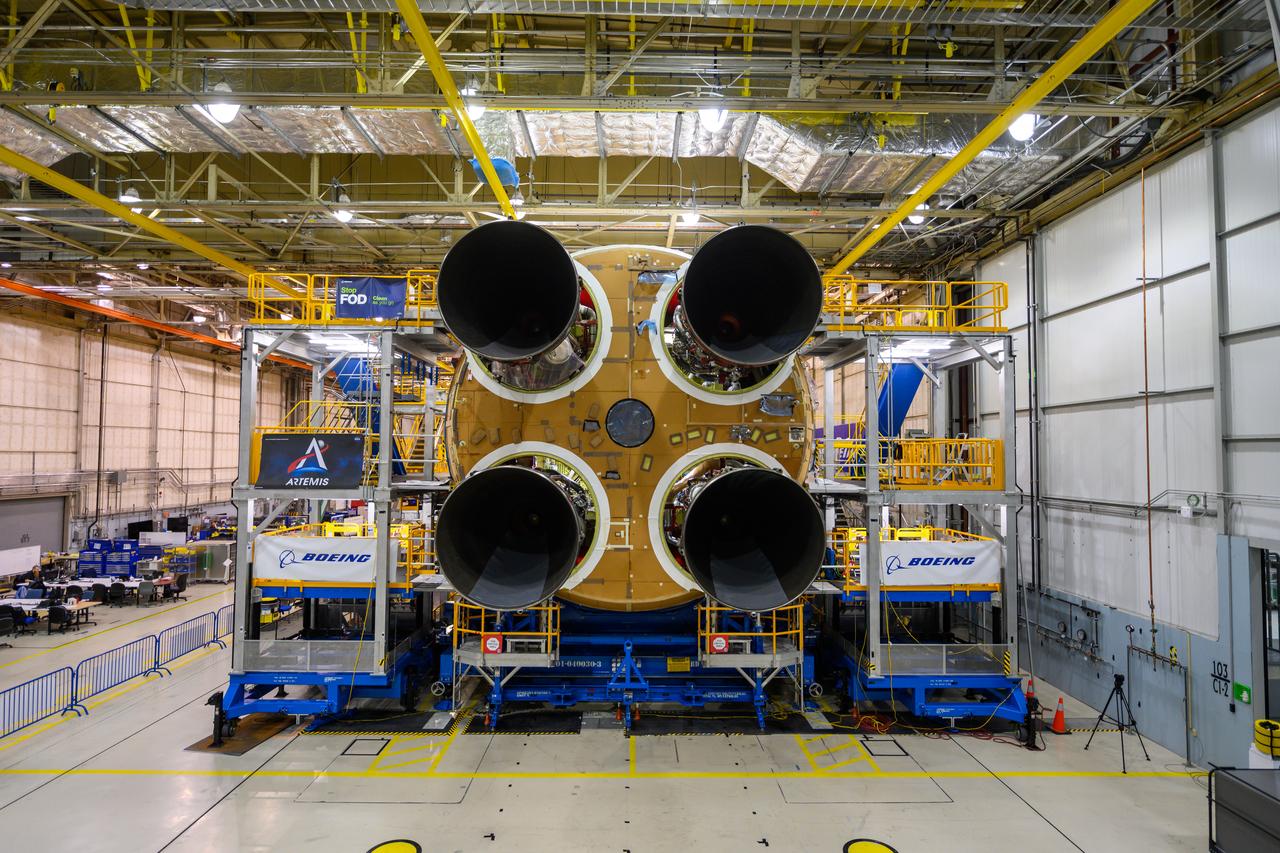
This photo shows all four RS-25 engines attached to the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission to the Moon. To complete assembly of the rocket stage, engineers and technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are now integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. The completed core stage with all four RS-25 engines attached is the largest rocket stage NASA has built since the Saturn V stages for the Apollo Program that first sent Americans to the Moon. The stage, which includes two propellant tanks, provides more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I to the Moon. Engineers and technicians attached the fourth RS-25 engine to the rocket stage Nov. 6 just one day after structurally mating the third engine. The first two RS-25 engines were structurally mated to the stage in October. After assembly is complete, crews will conduct an integrated functional test of flight computers, avionics and electrical systems that run throughout the 212-foot-tall core stage in preparation for its completion later this year. This testing is the first time all the flight avionics systems will be tested together to ensure the systems communicate with each other and will perform properly to control the rocket’s flight. Integration of the RS-25 engines to the recently completed core stage structure is a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
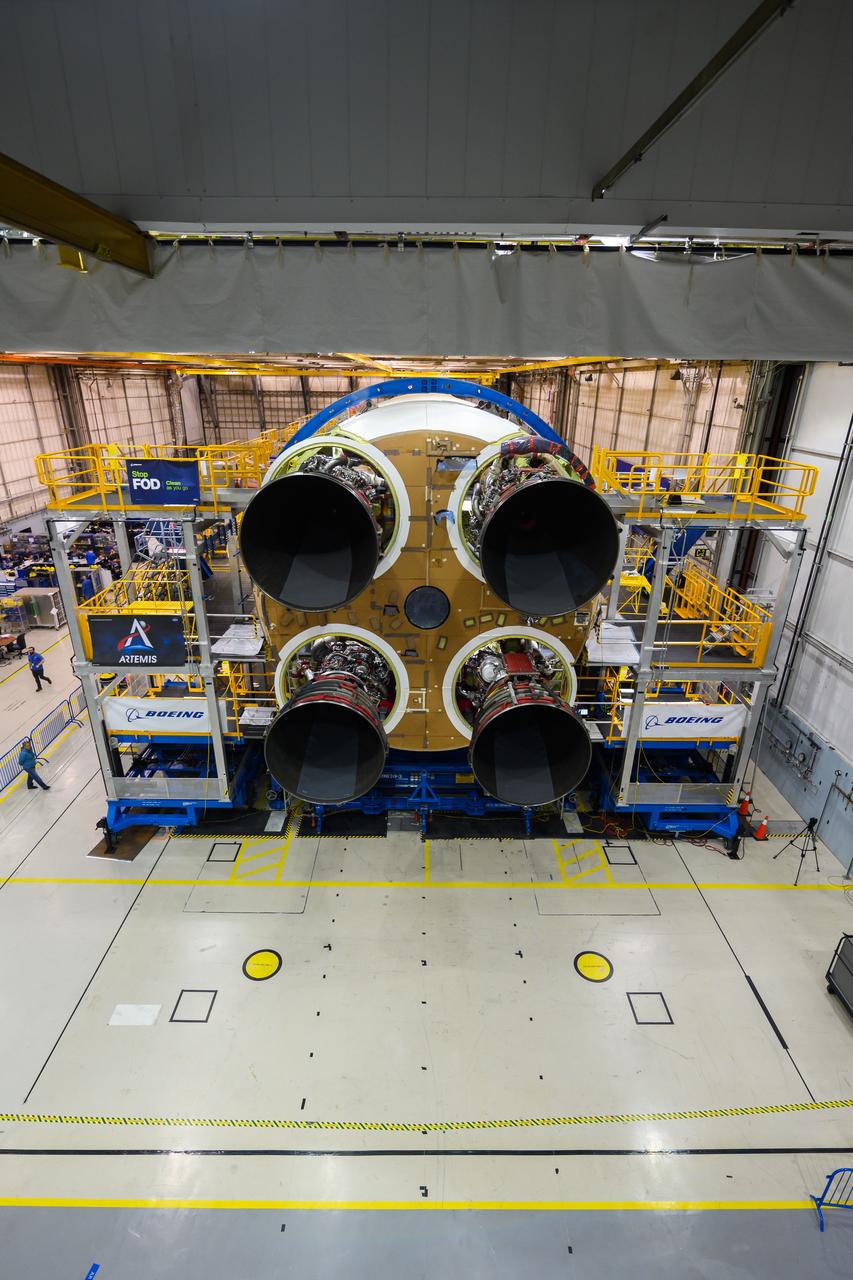

This photo shows all four RS-25 engines attached to the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission to the Moon. To complete assembly of the rocket stage, engineers and technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are now integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. The completed core stage with all four RS-25 engines attached is the largest rocket stage NASA has built since the Saturn V stages for the Apollo Program that first sent Americans to the Moon. The stage, which includes two propellant tanks, provides more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I to the Moon. Engineers and technicians attached the fourth RS-25 engine to the rocket stage Nov. 6 just one day after structurally mating the third engine. The first two RS-25 engines were structurally mated to the stage in October. After assembly is complete, crews will conduct an integrated functional test of flight computers, avionics and electrical systems that run throughout the 212-foot-tall core stage in preparation for its completion later this year. This testing is the first time all the flight avionics systems will be tested together to ensure the systems communicate with each other and will perform properly to control the rocket’s flight. Integration of the RS-25 engines to the recently completed core stage structure is a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
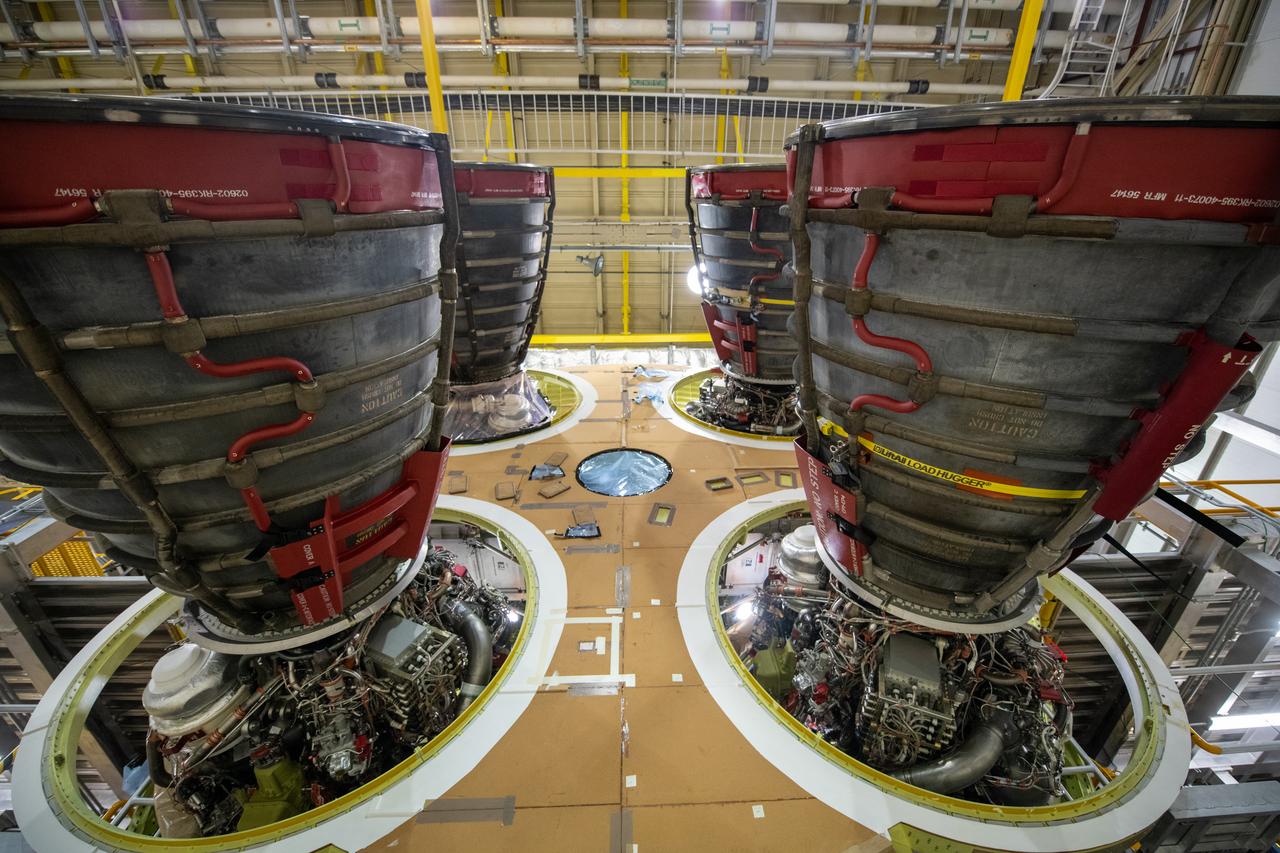

This photo shows all four RS-25 engines attached to the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission to the Moon. To complete assembly of the rocket stage, engineers and technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are now integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. The completed core stage with all four RS-25 engines attached is the largest rocket stage NASA has built since the Saturn V stages for the Apollo Program that first sent Americans to the Moon. The stage, which includes two propellant tanks, provides more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I to the Moon. Engineers and technicians attached the fourth RS-25 engine to the rocket stage Nov. 6 just one day after structurally mating the third engine. The first two RS-25 engines were structurally mated to the stage in October. After assembly is complete, crews will conduct an integrated functional test of flight computers, avionics and electrical systems that run throughout the 212-foot-tall core stage in preparation for its completion later this year. This testing is the first time all the flight avionics systems will be tested together to ensure the systems communicate with each other and will perform properly to control the rocket’s flight. Integration of the RS-25 engines to the recently completed core stage structure is a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
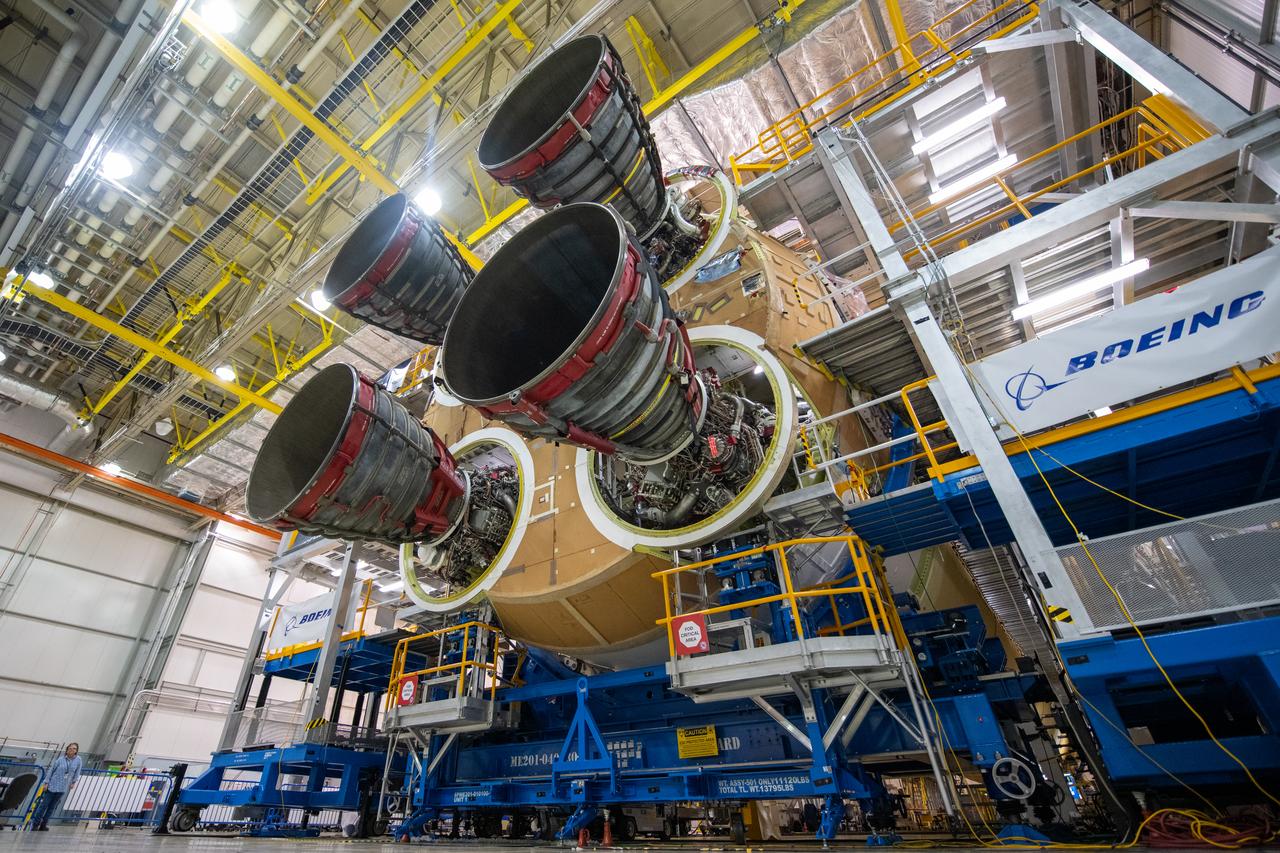

This photo shows all four RS-25 engines attached to the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission to the Moon. To complete assembly of the rocket stage, engineers and technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are now integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. The completed core stage with all four RS-25 engines attached is the largest rocket stage NASA has built since the Saturn V stages for the Apollo Program that first sent Americans to the Moon. The stage, which includes two propellant tanks, provides more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I to the Moon. Engineers and technicians attached the fourth RS-25 engine to the rocket stage Nov. 6 just one day after structurally mating the third engine. The first two RS-25 engines were structurally mated to the stage in October. After assembly is complete, crews will conduct an integrated functional test of flight computers, avionics and electrical systems that run throughout the 212-foot-tall core stage in preparation for its completion later this year. This testing is the first time all the flight avionics systems will be tested together to ensure the systems communicate with each other and will perform properly to control the rocket’s flight. Integration of the RS-25 engines to the recently completed core stage structure is a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
This photo shows all four RS-25 engines attached to the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission to the Moon. To complete assembly of the rocket stage, engineers and technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are now integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. The completed core stage with all four RS-25 engines attached is the largest rocket stage NASA has built since the Saturn V stages for the Apollo Program that first sent Americans to the Moon. The stage, which includes two propellant tanks, provides more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send Artemis I to the Moon. Engineers and technicians attached the fourth RS-25 engine to the rocket stage Nov. 6 just one day after structurally mating the third engine. The first two RS-25 engines were structurally mated to the stage in October. After assembly is complete, crews will conduct an integrated functional test of flight computers, avionics and electrical systems that run throughout the 212-foot-tall core stage in preparation for its completion later this year. This testing is the first time all the flight avionics systems will be tested together to ensure the systems communicate with each other and will perform properly to control the rocket’s flight. Integration of the RS-25 engines to the recently completed core stage structure is a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Range: 72.3 million km. ( 44.9 million miles ) P-29314B/W This Voyager 2 photograph of Uranus shows the planets outermost, or epsilon, ring. This is a computerized summation of six images shot by the narrow angle camera. It is the first photo to show the epsilon ring unblurred by Earth's atmosphere. The Epsilon ring, some 51,200 km. ( 31,800 miles ) from the planets center, is the most prominent of Uranus' nine known rings. Ground based observations of stellar occulations by the rings have determined that the Epsilon ring is eccentric, or elliptical, with its widest portion about 100 km. ( 60 miles ) wide and its narrowest portion about 20 km. (12 miles ). Estimates of the rings brightness suggest that it is also very dark, with a reflectance of only 1 or 2 percent and a probable composition of carbonaceous material similiar to that on dark asteroids and the dark side of Saturn's moon Lapetus. Because the ring is so narrow and dark, at this range, the Voyager camera could not resolve even the widest part, resulting in long exposure times so obtain a good image. six exposures of 11 or 15 second duration were added together by computer to produce this image. In this image, the central portion is greatly overexposed. Various artifacts due to electronic effects and image proccessing can be seen in the central portion of the frame, including the dark image just above the planets image, the diffuse brightening below it and the small, bright projection from the edge of the planet in the upper left. The ring is distinctly less prominent in the lower left portion and more prominent in the upper right. This is in agreement with the predicted locations of the narrow and wide portions of the ring, respectively.