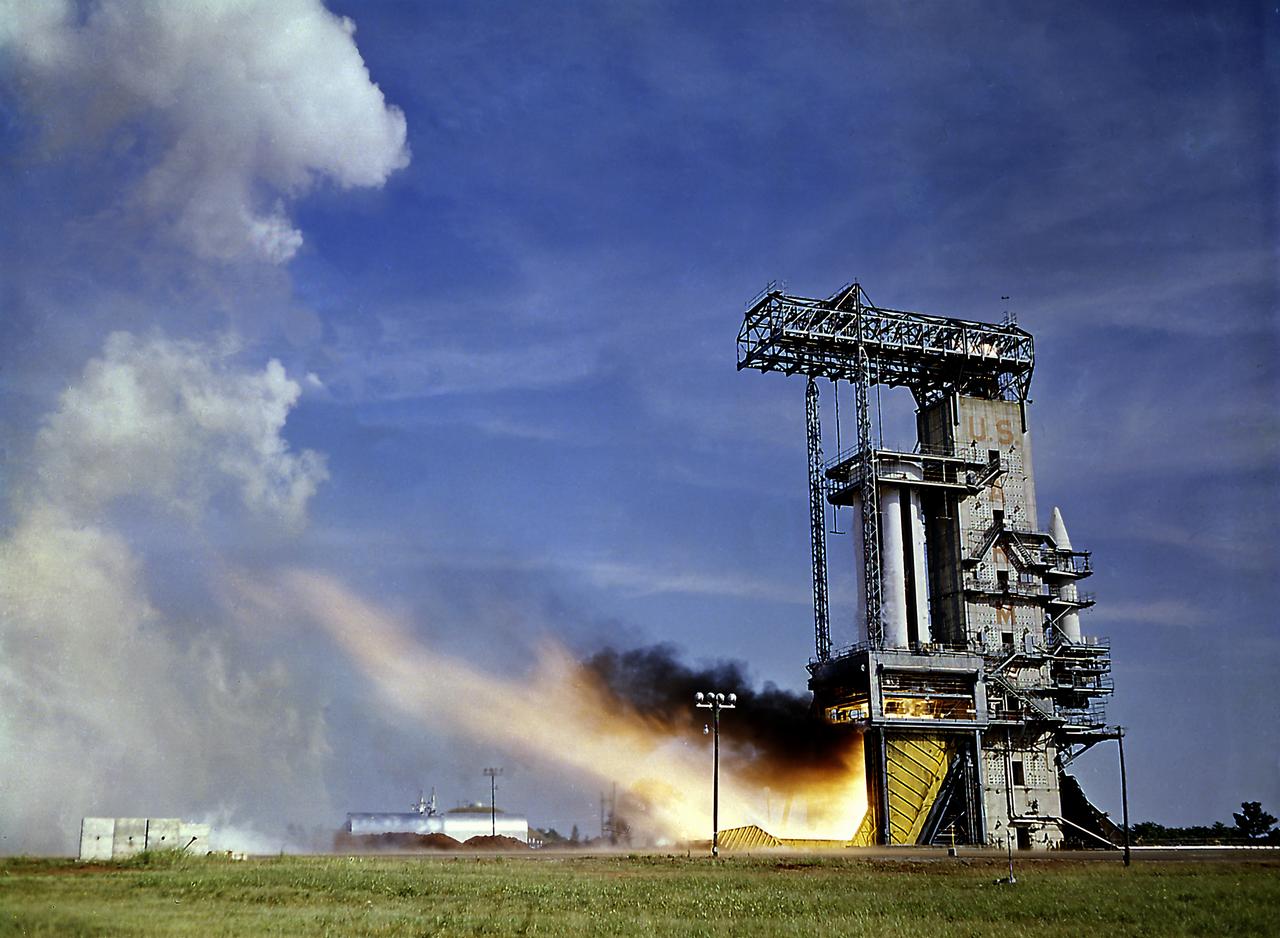

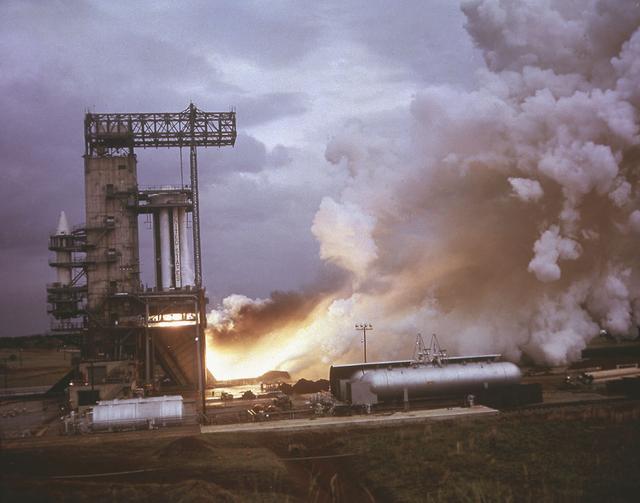
The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway. A series of static tests of the Saturn I booster (S-I stage) began June 3, 1960 at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This photograph depicts the Saturn I S-I stage equipped with eight H-1 engines, being successfully test-fired for the duration of 121 seconds on June 15, 1960.
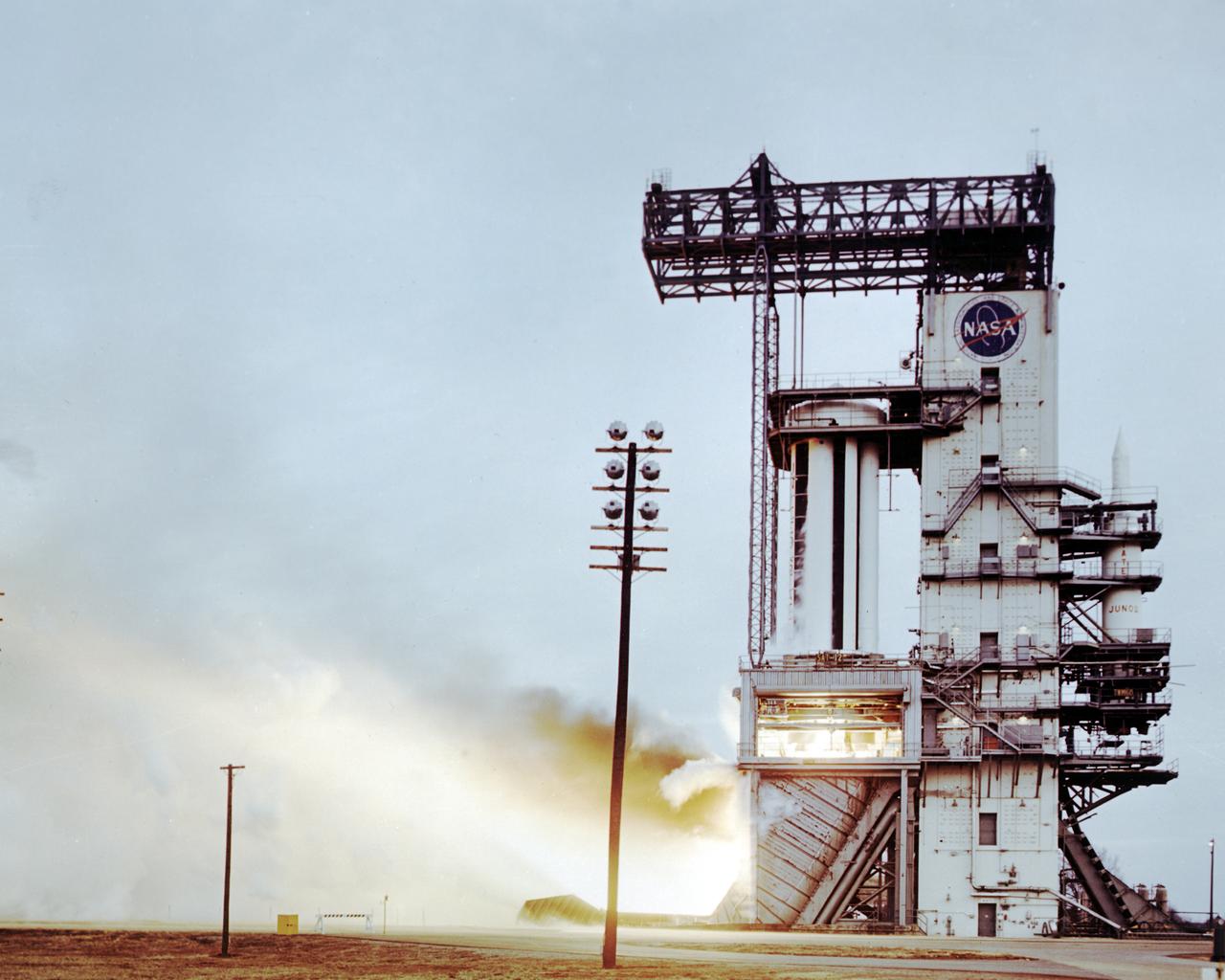

The Saturn project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway. A series of static tests of the Saturn I booster (S-I stage) began June 3, 1960 at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). This photograph depicts the Saturn I S-I stage equipped with eight H-1 engines, being successfully test-fired on February 4, 1961. A Juno rocket is visible on the right side of the test stand.

This montage illustrates the various configurations and missions of the three classes of the Saturn vehicles developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The missions for the Saturn I included atmospheric science investigations and the deployment of the Pegasus meteroid-detection satellite as well as launch vehicle development. The Saturn IB vehicle tested the Apollo spacecraft and launched the three marned Skylab missions as well as the Apollo Soyuz test project. The Saturn V vehicle launched the manned lunar orbital/landing missions, and the Skylab Orbital Workshop in 1973.
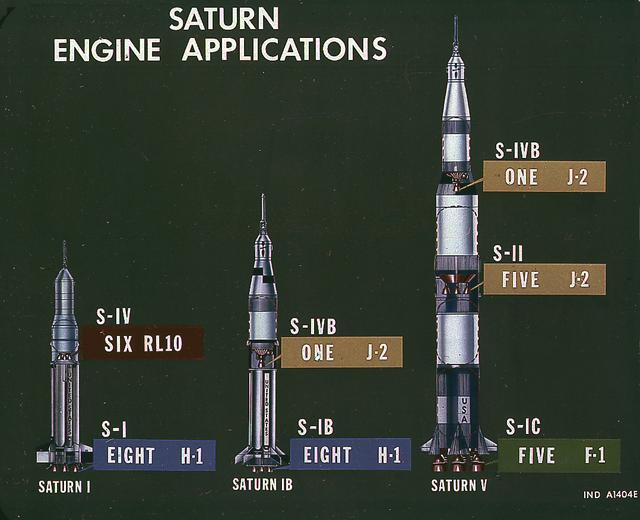
This image illustrates the basic differences between the three Saturn launch vehicles developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The Saturn I, consisted of two stages, the S-I (eight H-1 engines) and the S-IV (six RL-10 engines). The Saturn IB (center) also consisted of two stages, the S-IB (eight H-1 engines) and the S-IVB (one J-2 engine). The Saturn V consisted of three stages, the S-IC (five F-1 engines), the S-II (five J-2 engines), and the S-IVB (one J-2 engine).
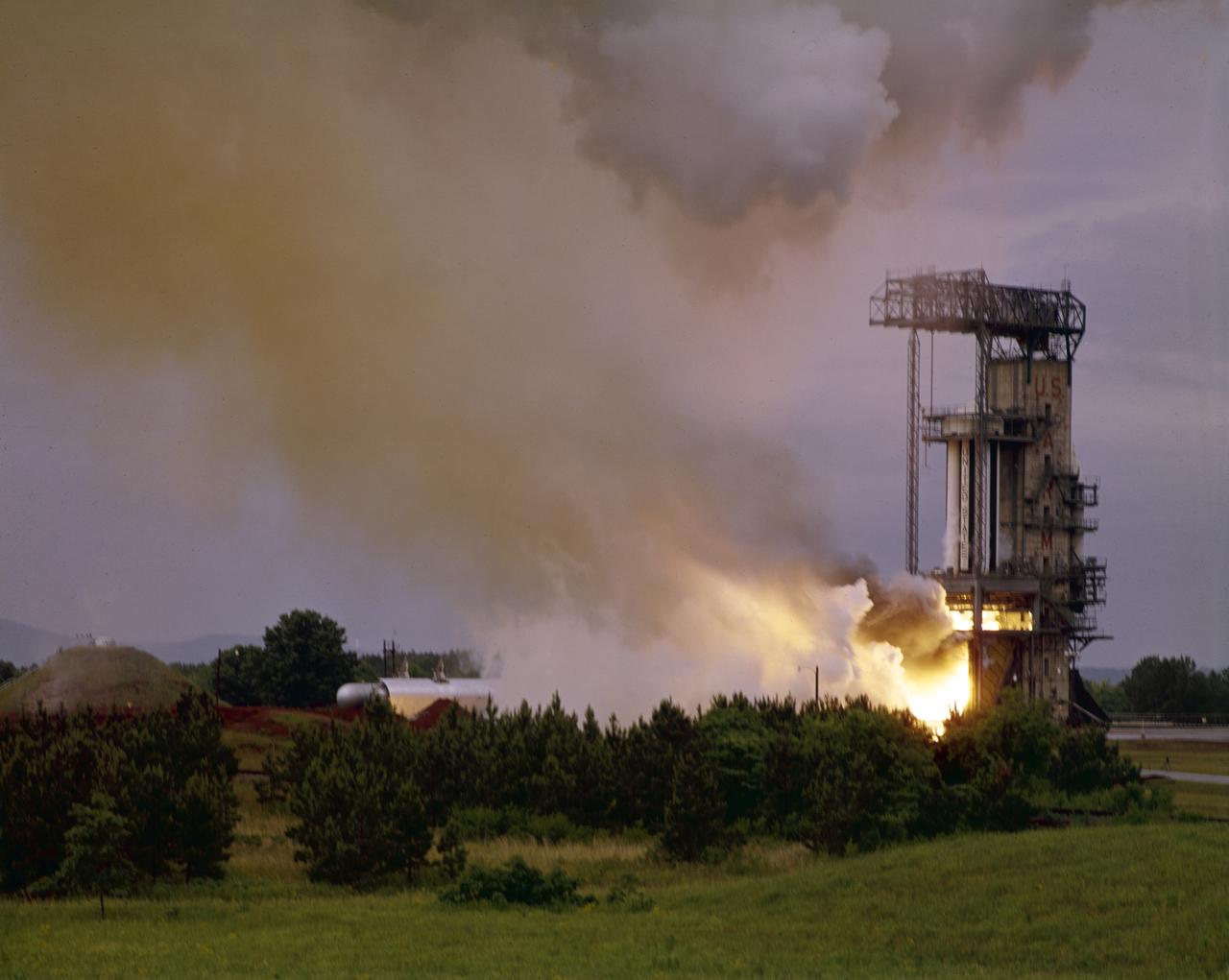

Pictured is one of the earliest testing of the Saturn I S-I (first) stage, with a cluster of eight H-1 engines, at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). It was a part of the test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept. MSFC was responsible for designing and development the Saturn launch vehicles.
A Cluster of eight H-1 engines were used to thrust the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. Each H-1 engine, fueled with liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1), had a thrust of 188,000 pound each for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds. The H-1 engine was developed under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).

The Marshall Space Flight Center's first Saturn I vehicle, SA-1, lifts off from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on October 27, 1961. This early configuration, Saturn I Block I, 162 feet tall and weighing 460 tons, consisted of the eight H-1 engines S-I stage and the dummy second stage (S-IV stage).
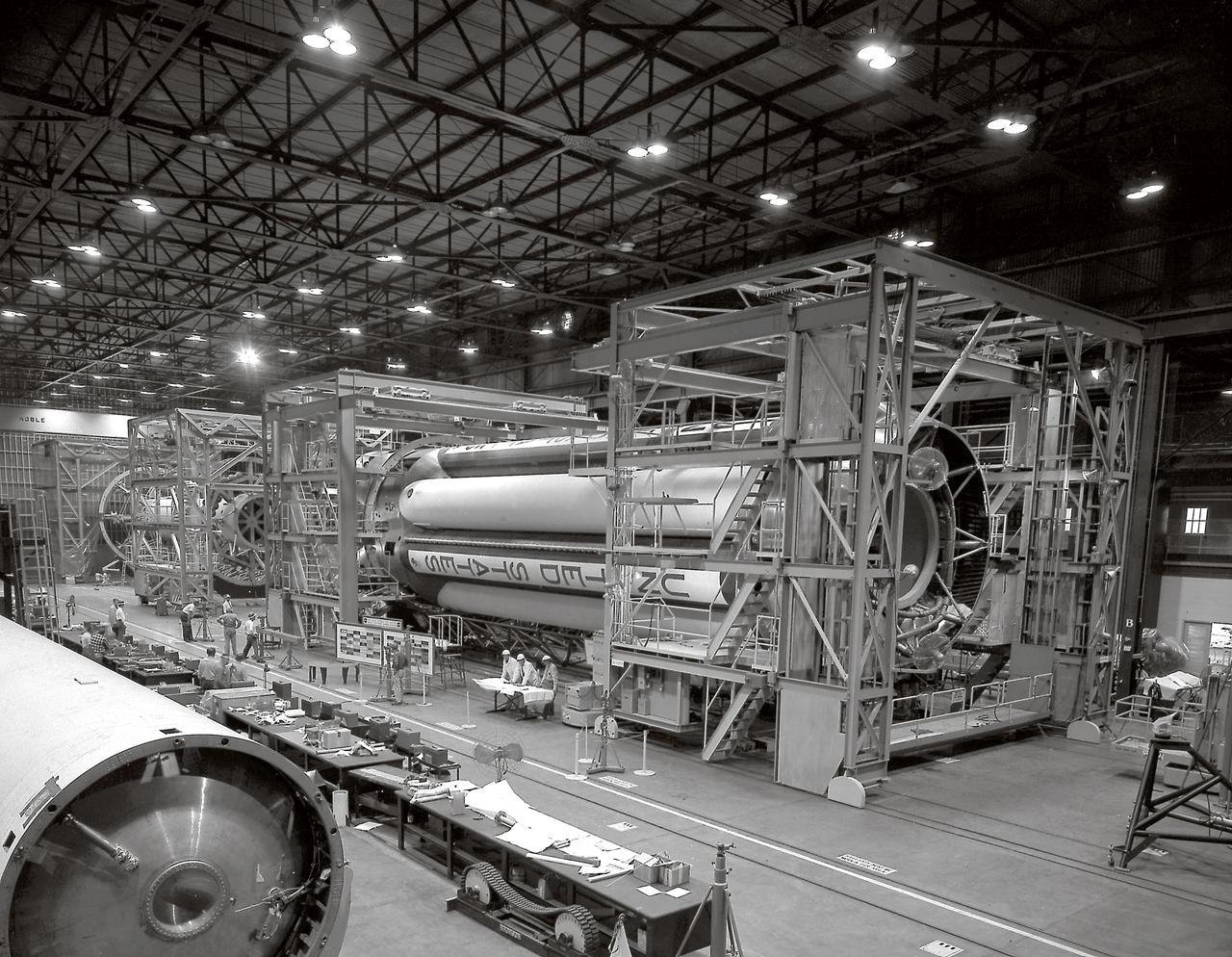

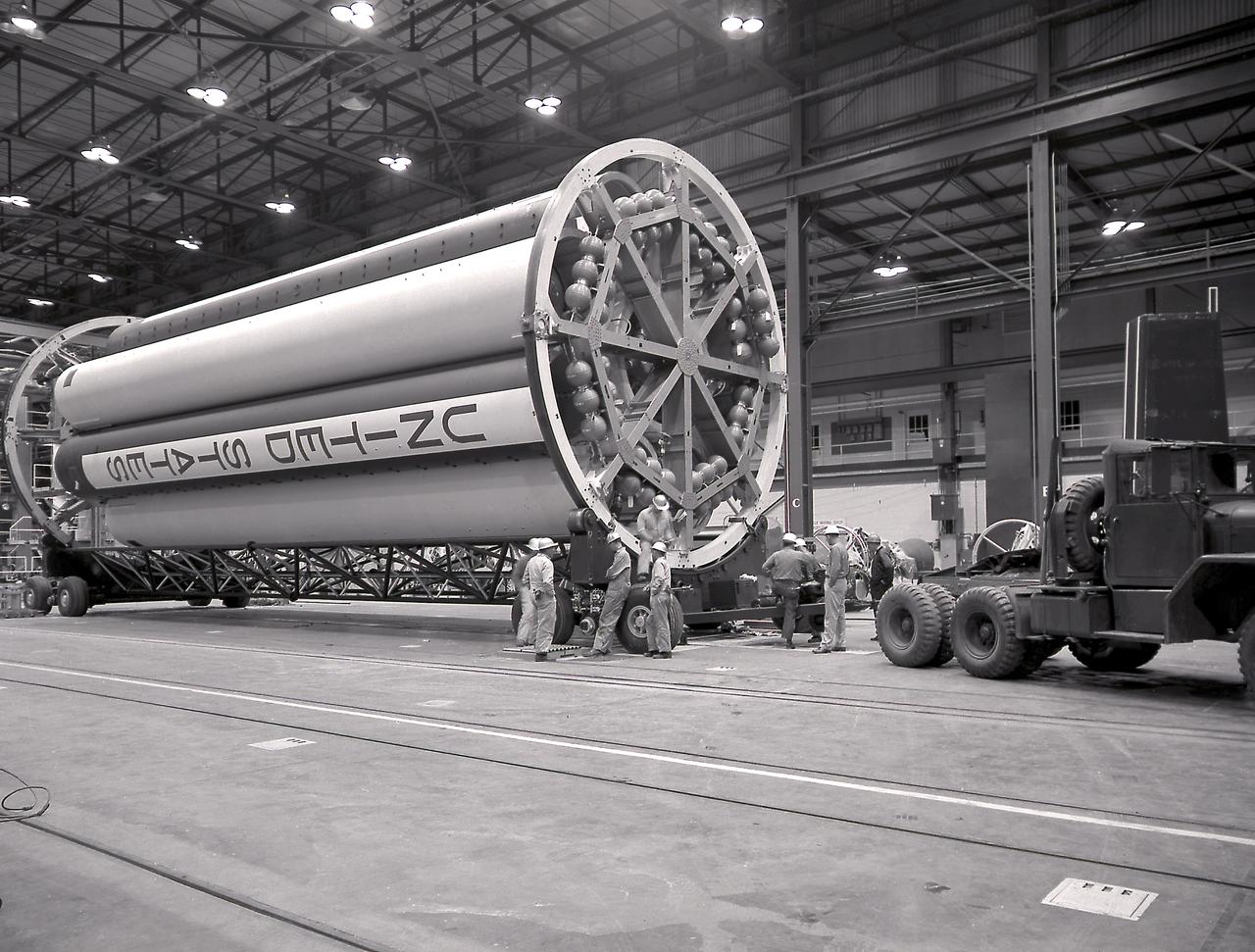
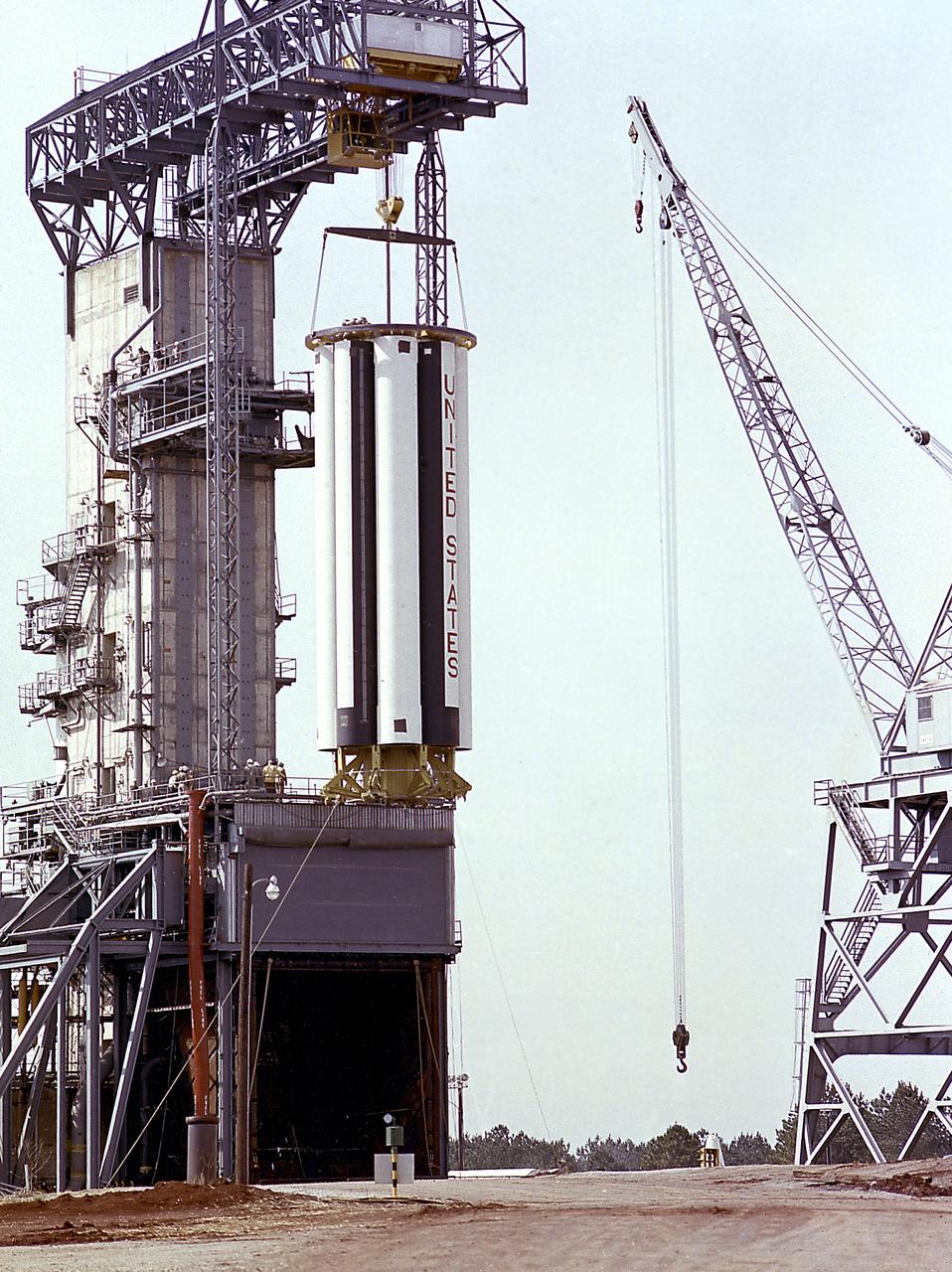
The S-I stages for the Saturn I (SA-1 at right and SA-2 at left) are being assembled at the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705. The Saturn I S-I stage had eight H-1 engines clustered, using liquid oxygen/kerosene-1 (LOX/RP-1) propellants capable of producing a total of 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.
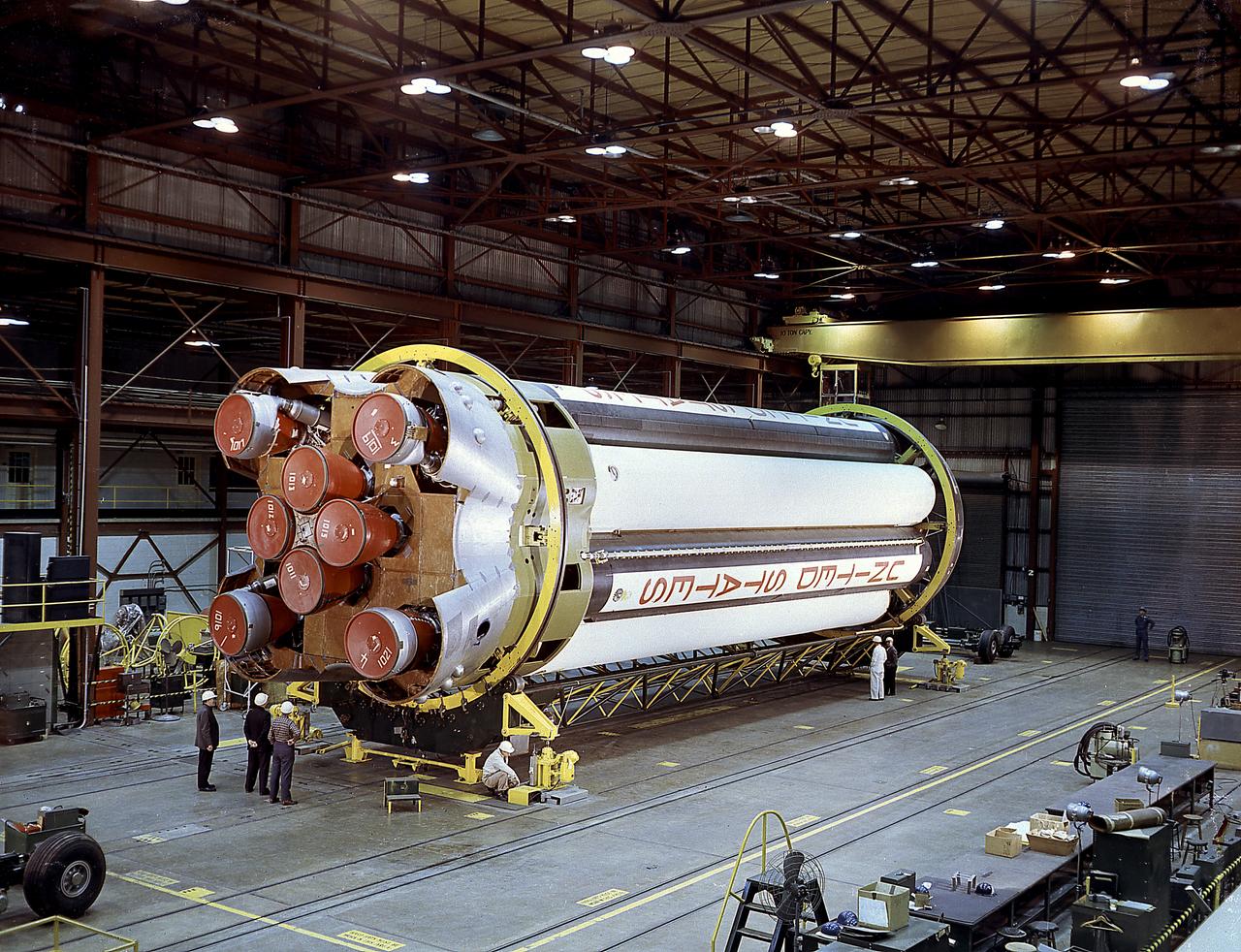

The completely assembled Saturn 1 S-1 stage is being ready for checkout in the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705, January 18, 1961. The Saturn I S-I stage had eight H-1 engines clustered, using liquid oxygen/kerosene-1 (LOX/RP-1) propellants capable of producing a total of 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.
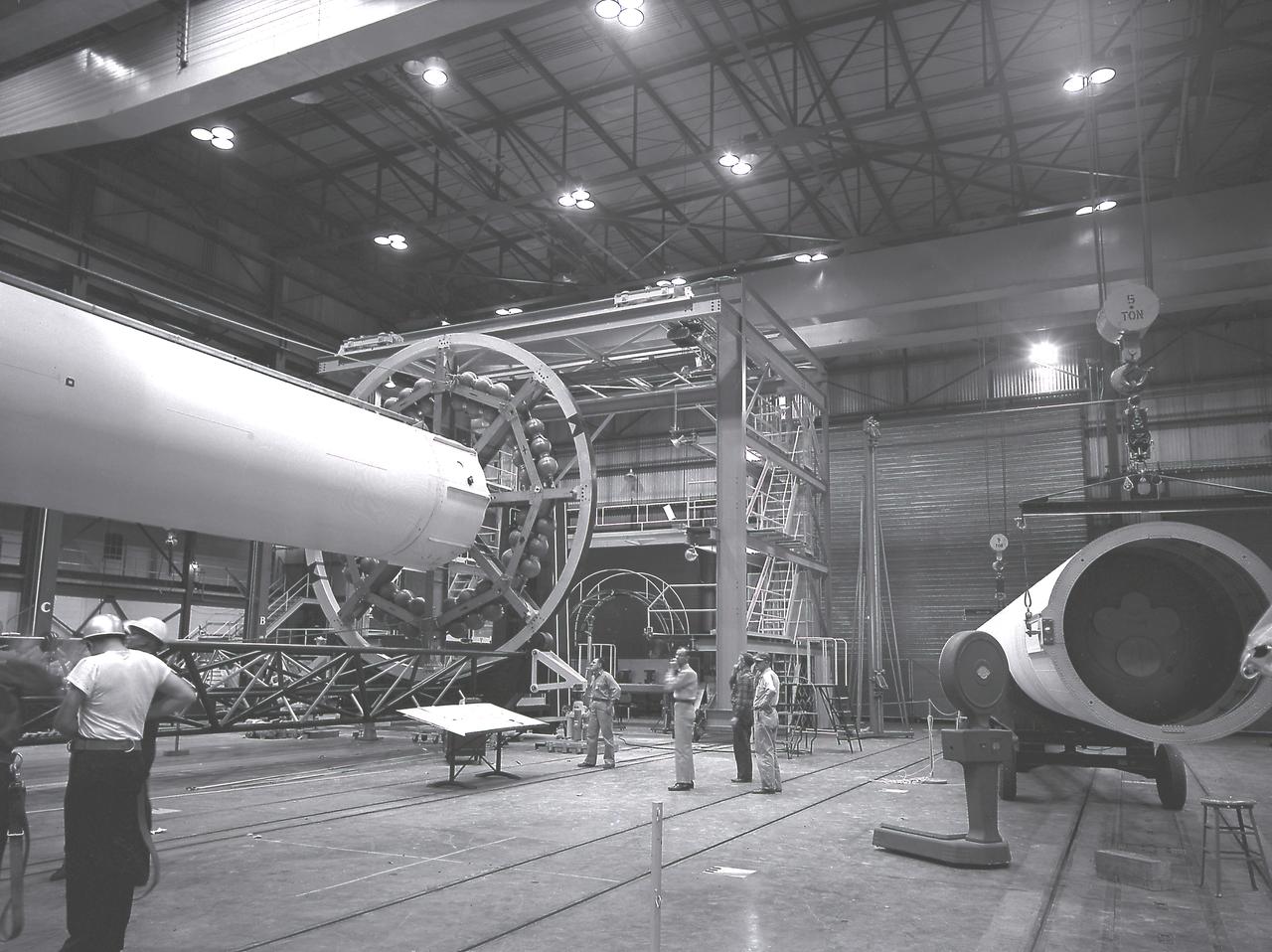

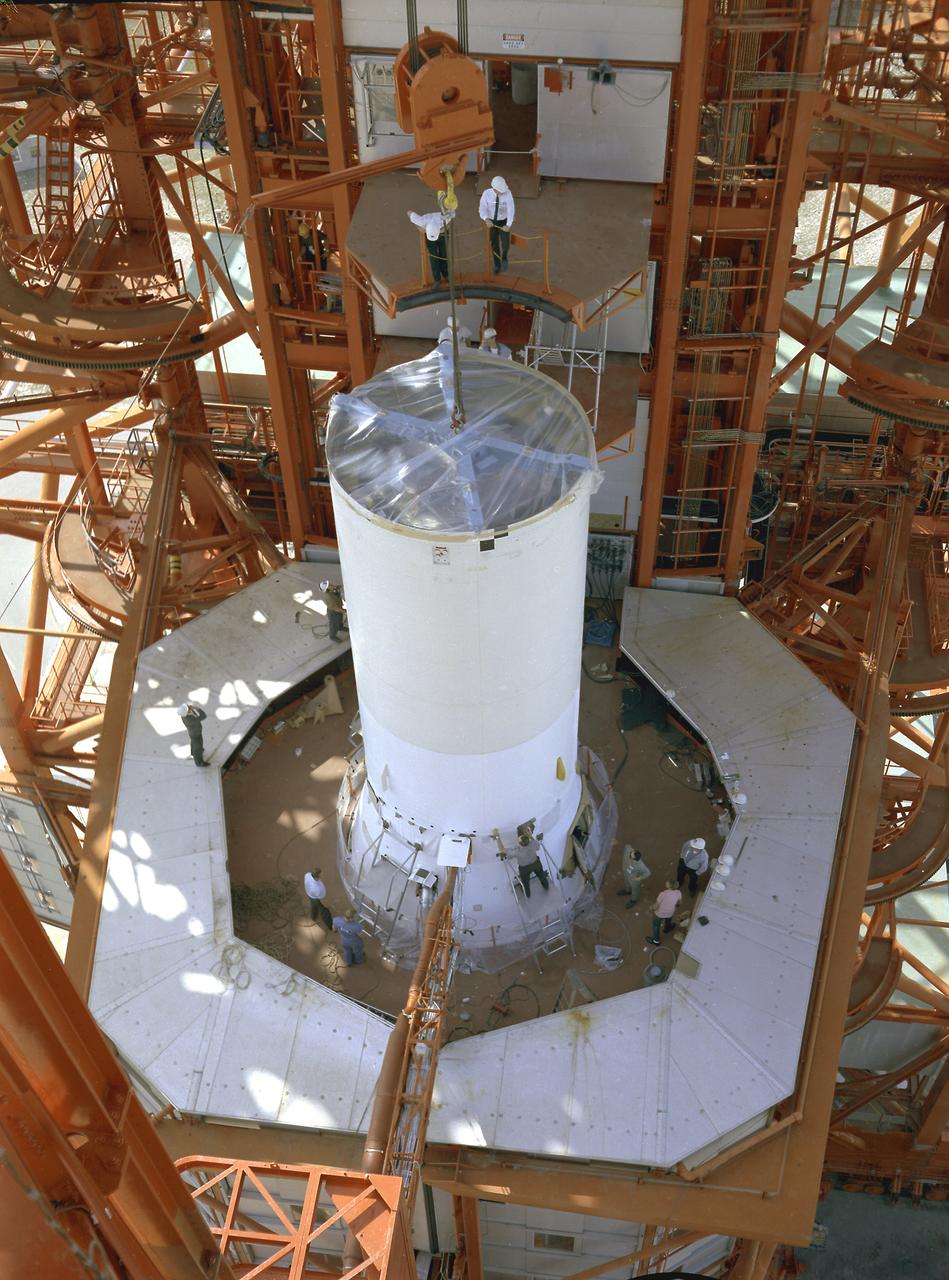
The Saturn I liquid-oxygen (LOX) tank for the Saturn I S-I stage being aligned with the end spider beam in the fabrication and engineering laboratory, building 4705, at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
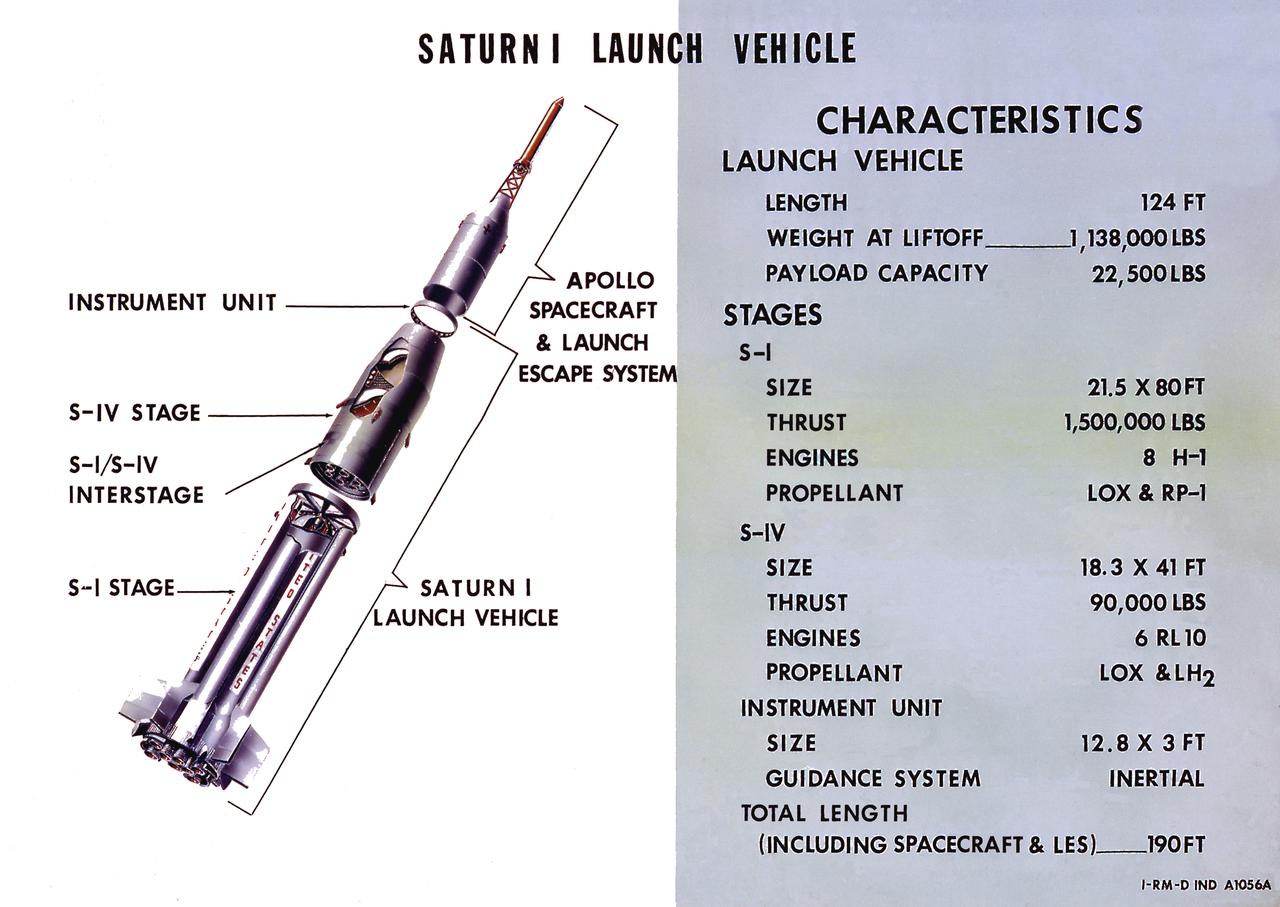
A cutaway illustration of Saturn I launch vehicle characteristics: The Saturn I, first of the Saturn launch vehicles' family, is a two-stage vehicle with a low-earth-orbit payload capability of approximately 25,000 pounds. The research and development program was plarned in two phases or blocks; one for first stage development (Block I) and the second for first and second stage development (Block II). The S-I (first) stage consisted of a cluster of nine propellant tanks and eight H-1 engines built by Rocketdyne, yeilding a total thrust of 1,500,000 pounds. The second stage identified as S-IV, was designed as a single cylinder with a common bulkhead separating the liquid oxygen from the liquid hydrogen. Propulsion was provided by six RL-10 engines built by Pratt Whitney, capable of producing a combined thrust of 90,000 pounds. Of the 10 Saturn I's planned, the first eight were designed and built at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The remaining two were built by the Chrysler Corporation.
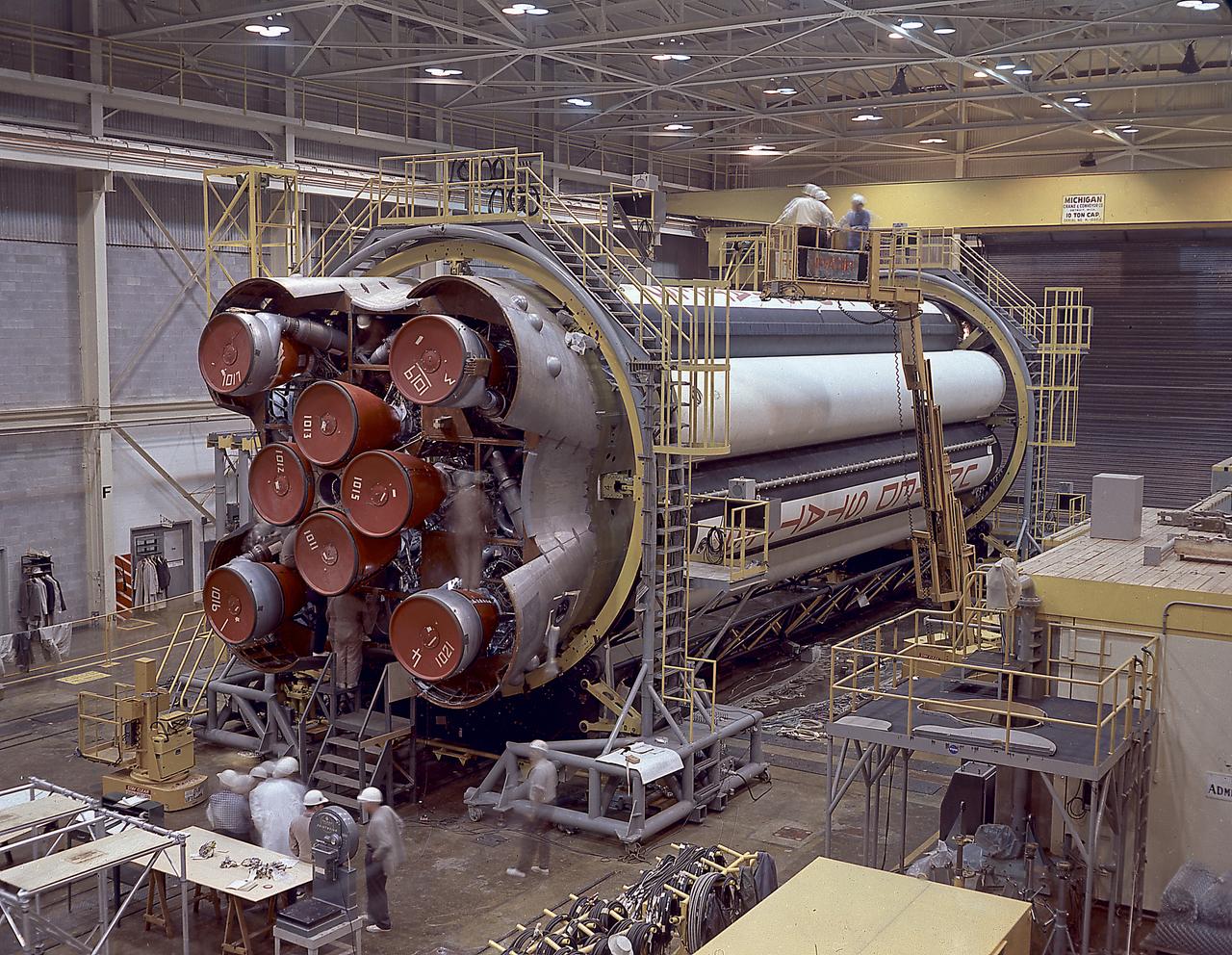
The photograph shows the completed Saturn 1 S-1 stage (booster) during the checkout in the Marshall Space Flight Center, building 4705, January 23, 1961. The Saturn I S-I stage had eight H-1 engines clustered, using liquid oxygen/kerosene-1 (LOX/RP-1) propellants capable of producing a total of 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.
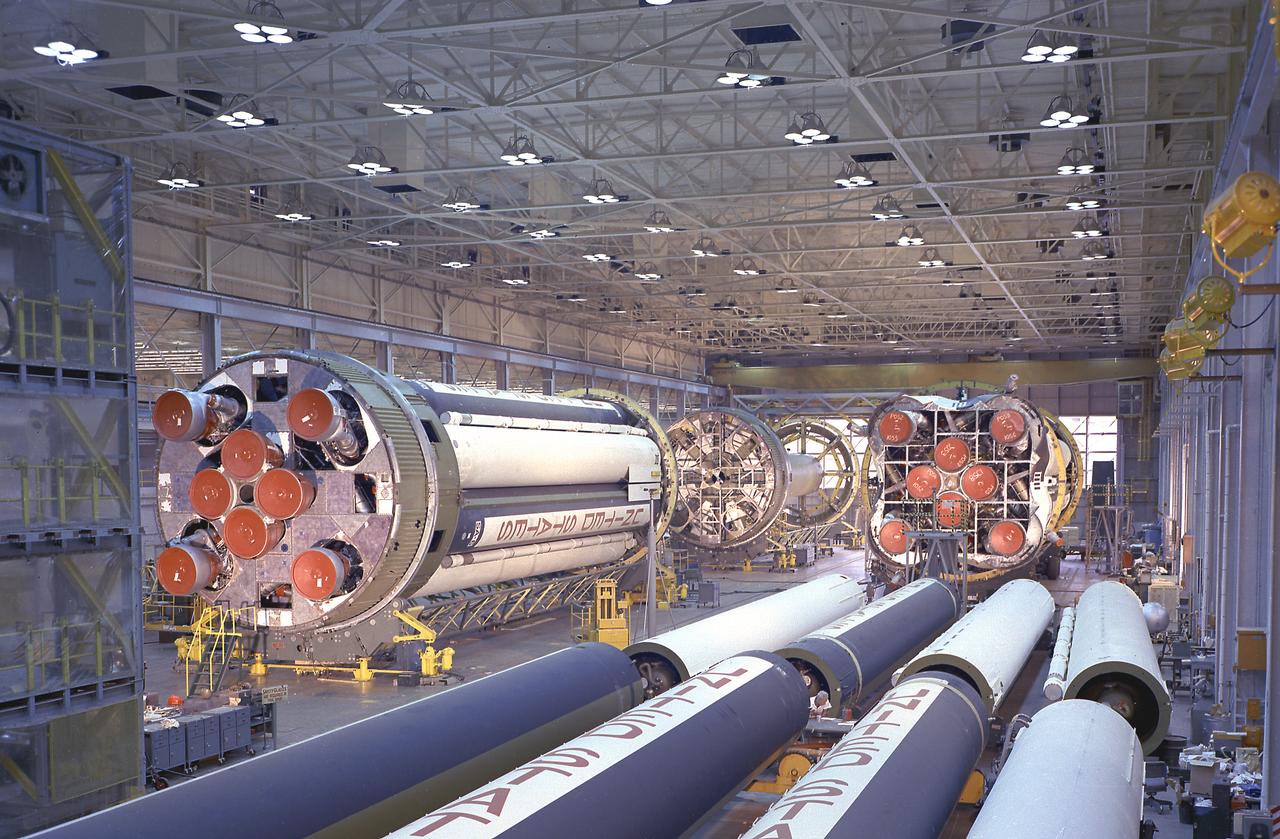

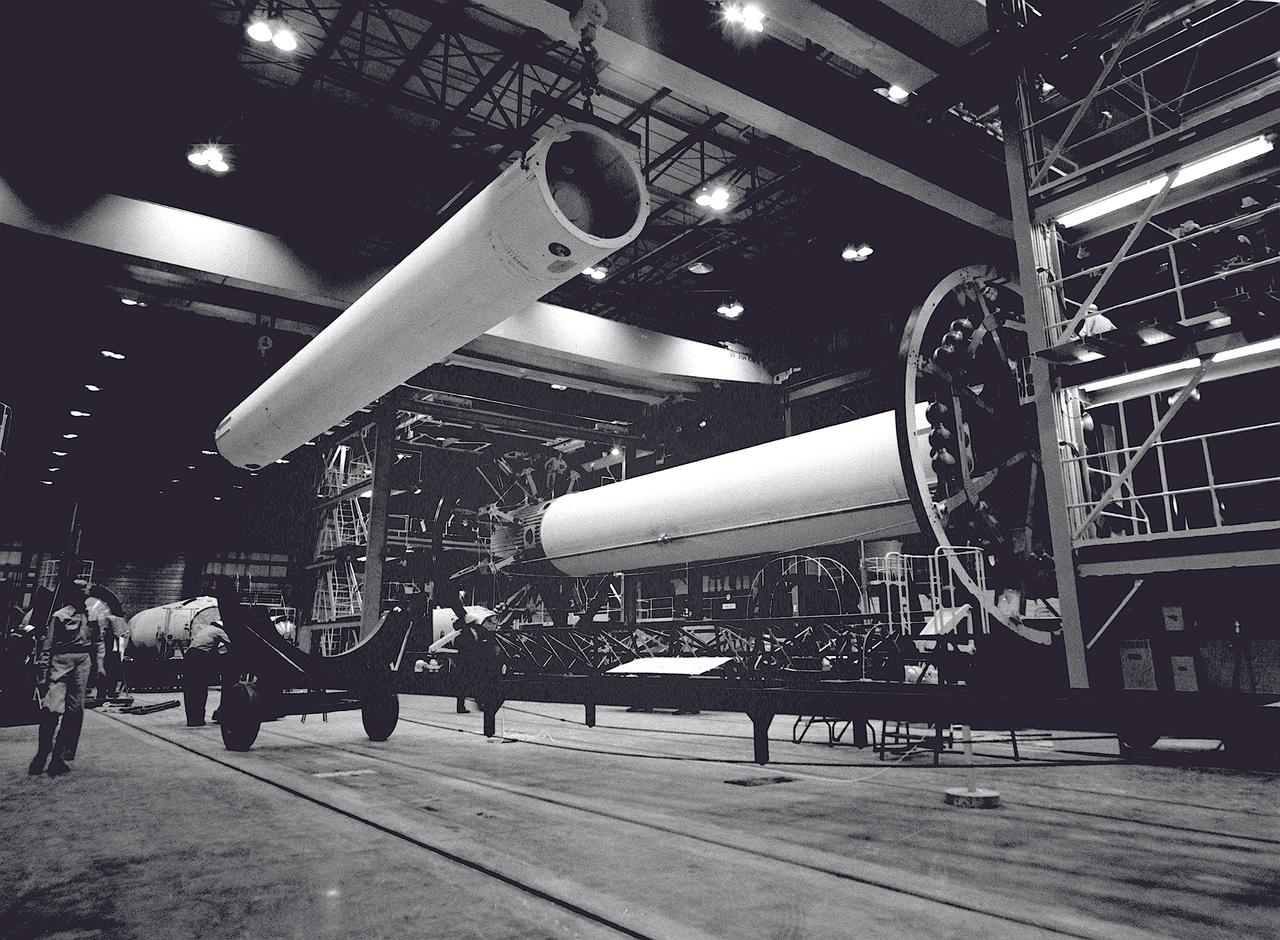
In this photograph, the Saturn I S-I stages for the SA-4, SA-6, and SA-7 missions were being assembled at the Fabrication and Assembly Engineering Division in the Marshall Space Flight Center building 4705, January 13, 1963.
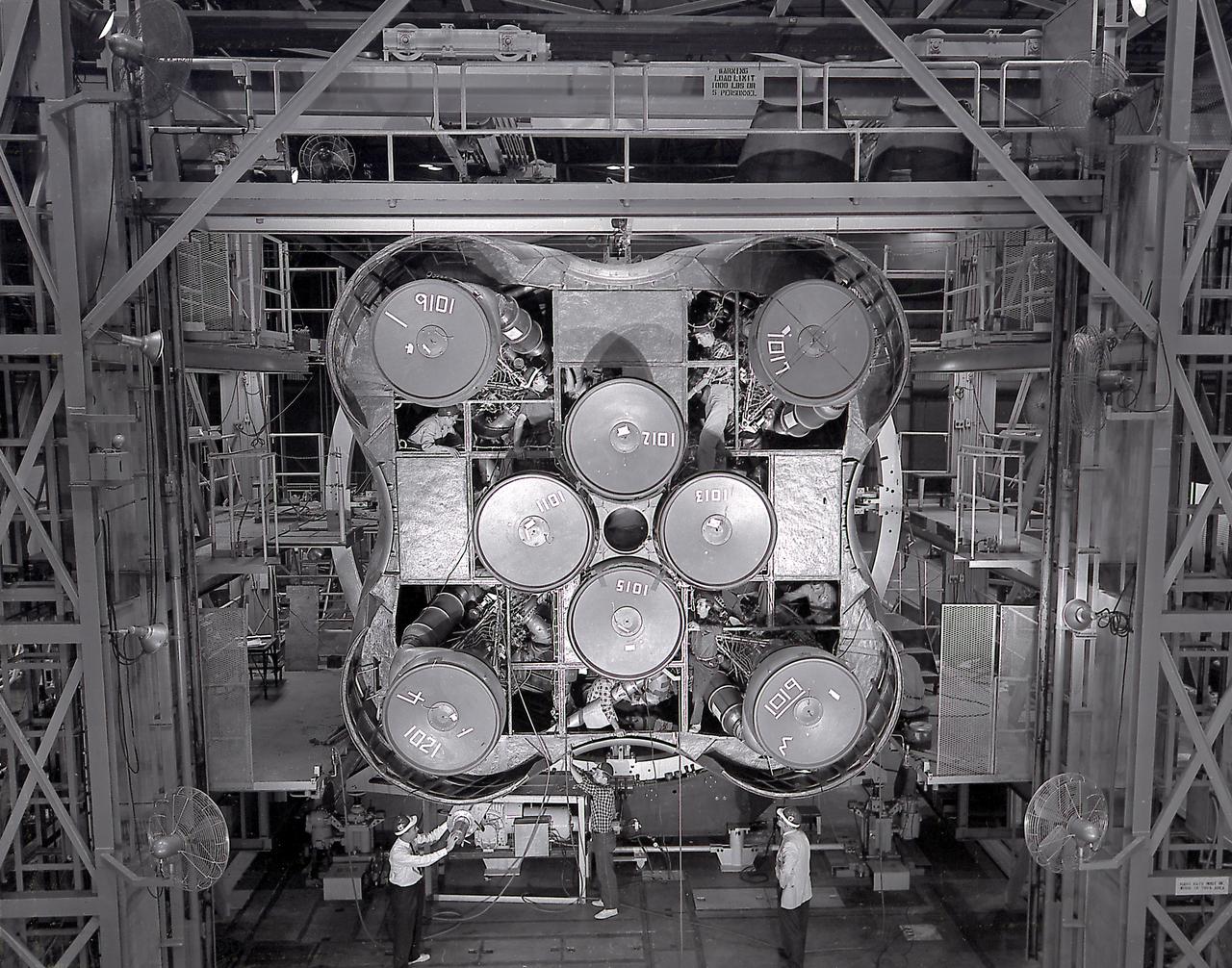
The Saturn I S-I stage with eight H-1 engines, located in Marshall Space Flight Center building 4705, showing the positioning of eight H-1 engines. The Saturn I S-I stage had eight H-1 engines clustered, using liquid oxygen/kerosene-1 (LOX/RP-1) propellants capable of producing a total of 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.

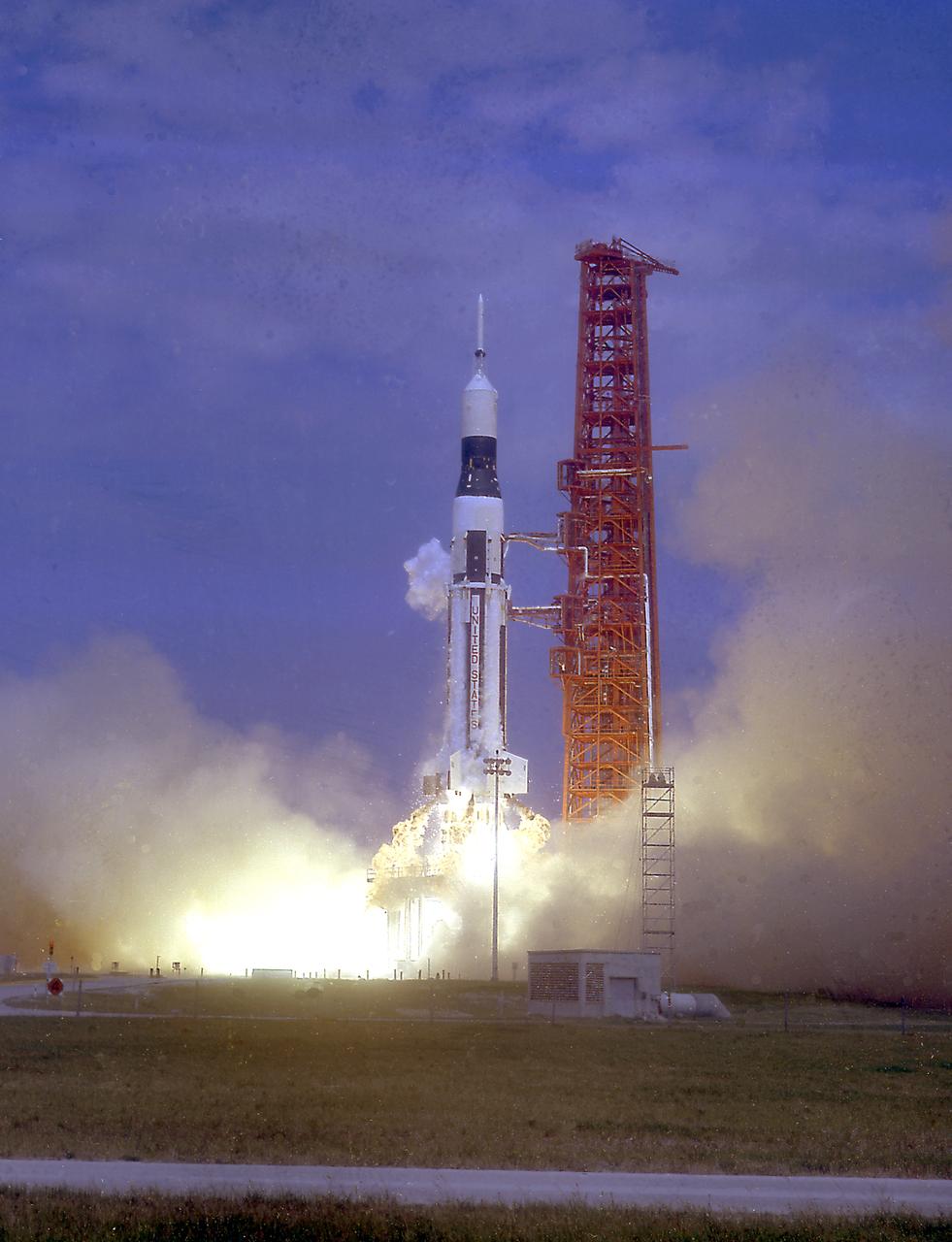
The SA-9 (Saturn I Block II), the eighth Saturn I flight, lifted off on February 16, 1965. This was the first Saturn with an operational payload, the Pegasus I meteoroid detection satellite. SA-9 successfully deployed the Pegasus I, NASA's largest unmarned instrumented satellite, into near Earth orbit.
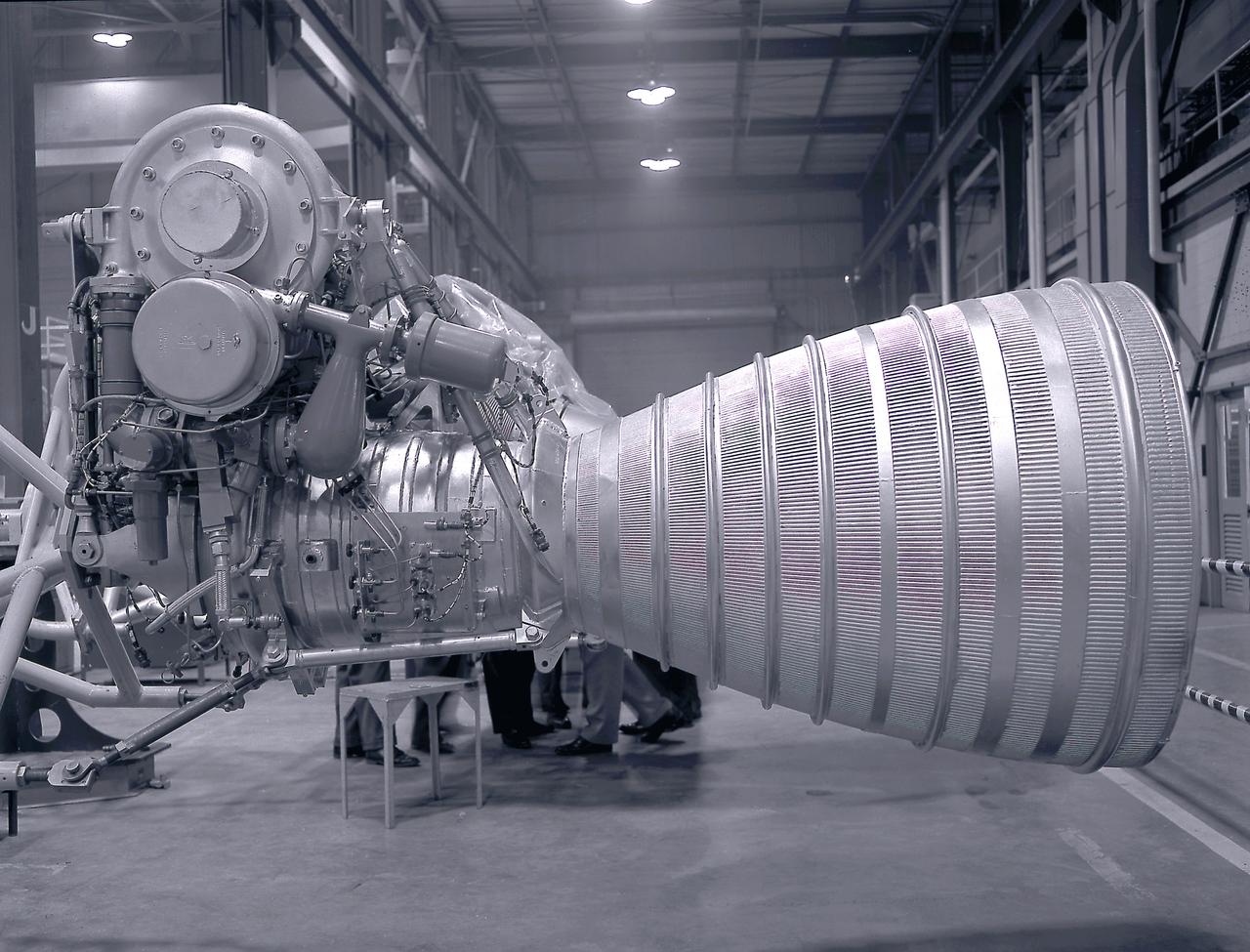
A Cluster of eight H-1 engines were used to thrust the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. The H-1 engine, fueled with liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1), had a thrust of 188,000 pound each for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds. Each H-1 engine was developed under the direction of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
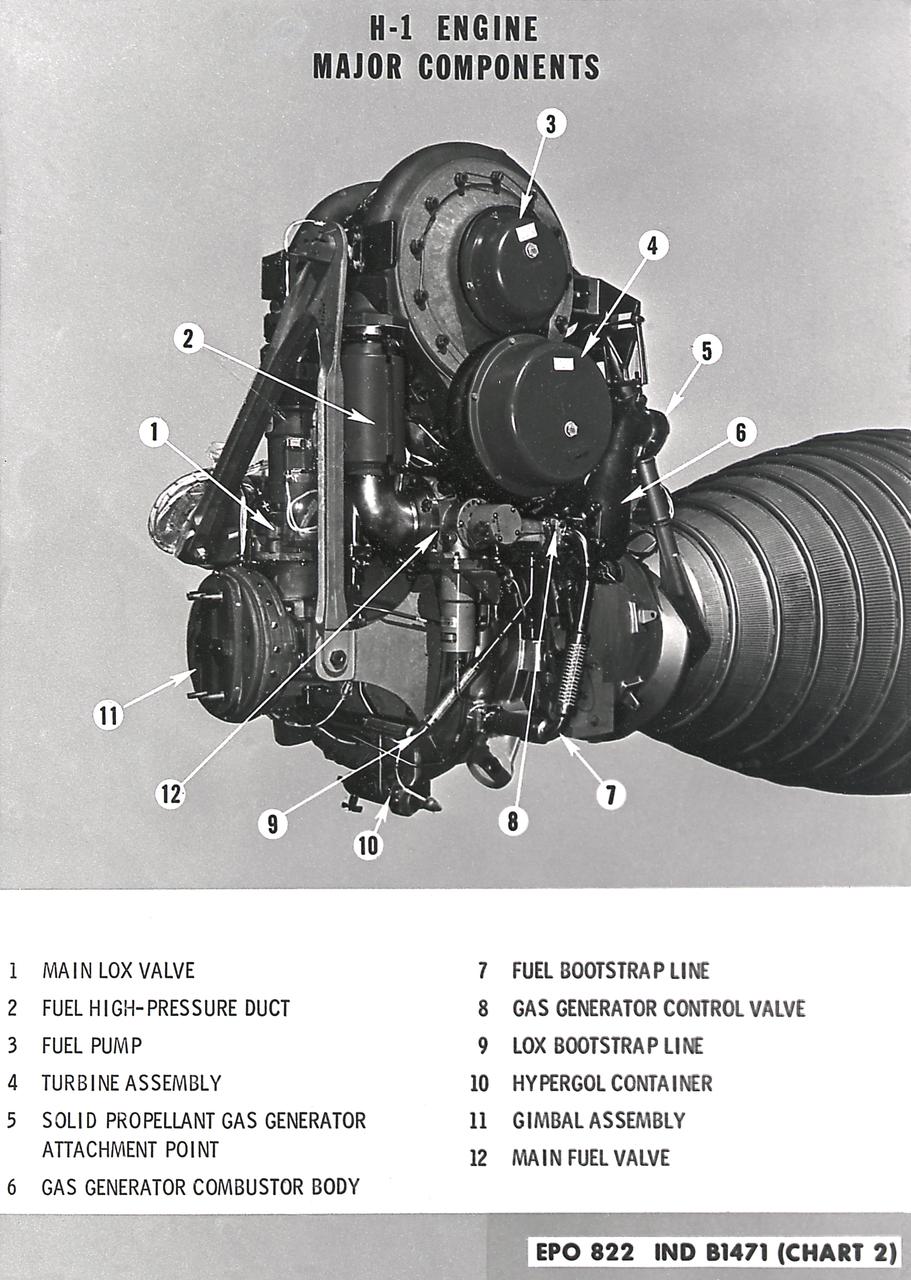
H-1 engine major components with callouts (chart 1). The H-1 engine was used in a cluster of eight on the the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern: four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. Each H-1 engine had a thrust of 188,000 pounds for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds.

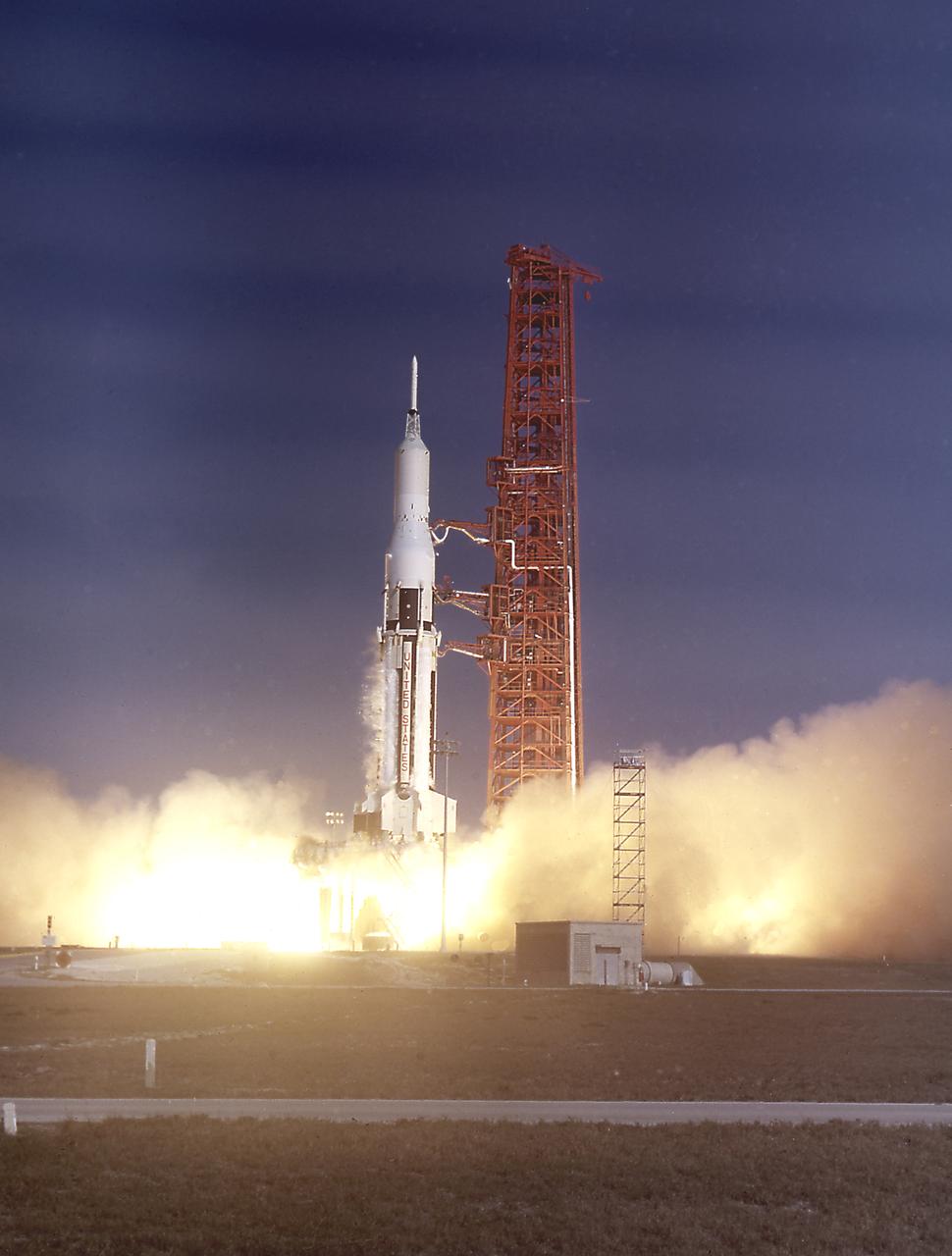
The launch of the SA-7 (Saturn I Block II) was on September 18, 1964. The SA-7 mission was the second orbital flight of the S-IV stage (second stage) with the payload consisting of the Apollo command and service module's instrument unit. The Saturn I Block II vehicle had two live stages, and were basically in the two-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. While the tank arrangement and the engine patterns were the same, there were marked changes between the Block I and II versions. The first stage (S-I stage) was an improved version of the Block I S-I stage. The Block II S-1 stage had eight fins added for greater aerodynamic stability in the lower atmosphere.
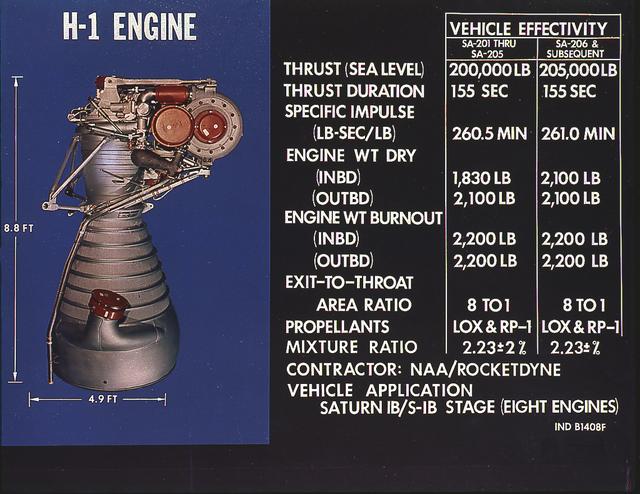
H-1 engine characteristics: The H-1 engine was developed under the management of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The cluster of eight H-1 engines was used to power the first stage of the Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IVB stage) launch vehicles, and produced 188,00 pounds of thrust, a combined thrust of 1,500,000 pounds, later uprated to 205,000 pounds of thrust and a combined total thrust of 1,650,000 pounds for the Saturn IB program.
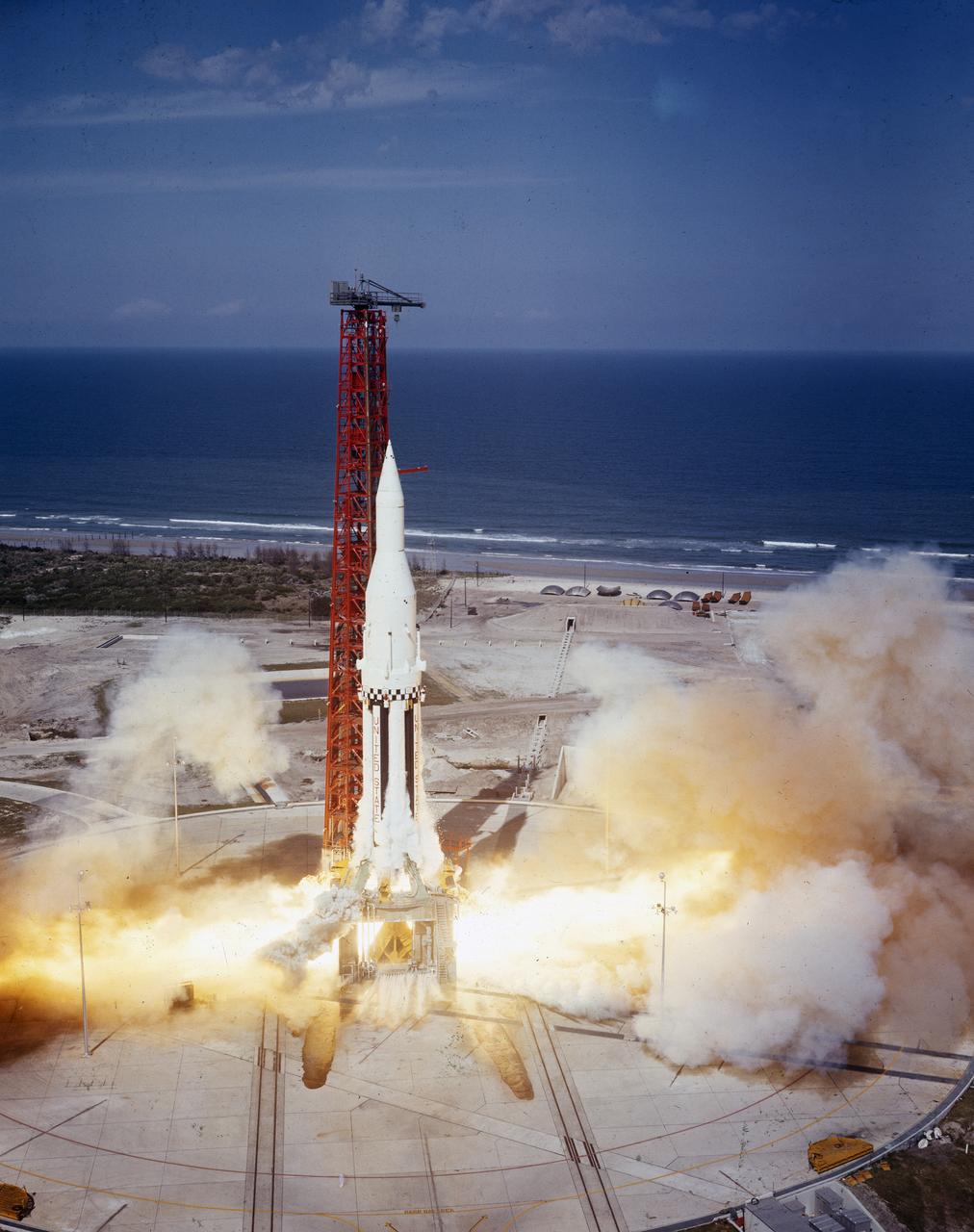

The Saturn I (SA-4) flight lifted off from Kennedy Space Center launch Complex 34, March 28, 1963. The fourth launch of Saturn launch vehicles developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, incorporated a Saturn I, Block I engine. The typical height of a Block I vehicle was approximately 163 feet and had only one live stage. It consisted of eight tanks, each 70 inches in diameter, clustered around a central tank, 105 inches in diameter. Four of the external tanks were fuel tanks for the RP-1 (kerosene) fuel. The other four, spaced alternately with the fuel tanks, were liquid oxygen tanks as was the large center tank. All fuel tanks and liquid oxygen tanks drained at the same rates respectively. The thrust for the stage came from eight H-1 engines, each producing a thrust of 165,000 pounds, for a total thrust of over 1,300,000 pounds. The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis and canted outward slightly, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern offset 40 degrees from the inner pattern. Unlike the inner engines, each outer engine was gimbaled. That is, each could be swung through an arc. They were gimbaled as a means of steering the rocket, by letting the instrumentation of the rocket correct any deviations of its powered trajectory. The block I required engine gimabling as the only method of guiding and stabilizing the rocket through the lower atmosphere. The upper stages of the Block I rocket reflected the three-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. Like SA-3, the SA-4 flight’s upper stage ejected 113,560 liters (30,000 gallons) of ballast water in the upper atmosphere for "Project Highwater" physics experiment. Release of this vast quantity of water in a near-space environment marked the second purely scientific large-scale experiment. The SA-4 was the last Block I rocket launch.
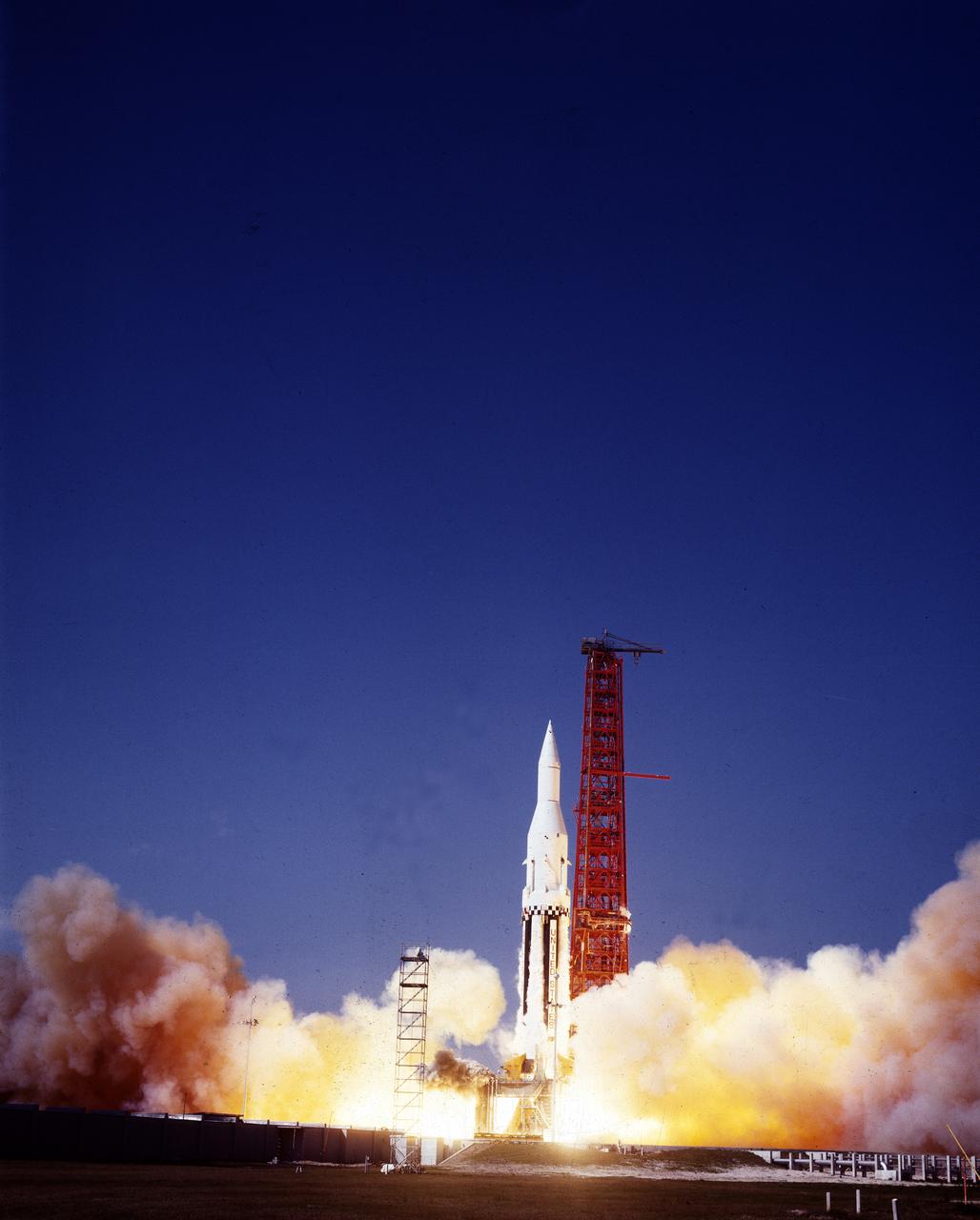

The Saturn I (SA-4) flight lifted off from Kennedy Space Center launch Complex 34, March 28, 1963. The fourth launch of Saturn launch vehicles, developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, incorporated a Saturn I, Block I engine. The typical height of a Block I vehicle was approximately 163 feet and had only one live stage. It consisted of eight tanks, each 70 inches in diameter, clustered around a central tank, 105 inches in diameter. Four of the external tanks were fuel tanks for the RP-1 (kerosene) fuel. The other four, spaced alternately with the fuel tanks, were liquid oxygen tanks as was the large center tank. All fuel tanks and liquid oxygen tanks drained at the same rates respectively. The thrust for the stage came from eight H-1 engines, each producing a thrust of 165,000 pounds, for a total thrust of over 1,300,000 pounds. The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis and canted outward slightly, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern offset 40 degrees from the inner pattern. Unlike the inner engines, each outer engine was gimbaled. That is, each could be swung through an arc. They were gimbaled as a means of steering the rocket, by letting the instrumentation of the rocket correct any deviations of its powered trajectory. The block I required engine gimabling as the only method of guiding and stabilizing the rocket through the lower atmosphere. The upper stages of the Block I rocket reflected the three-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. Like SA-3, the SA-4 flight’s upper stage ejected 113,560 liters (30,000 gallons) of ballast water in the upper atmosphere for "Project Highwater" physics experiment. Release of this vast quantity of water in a near-space environment marked the second purely scientific large-scale experiment. The SA-4 was the last Block I rocket launch.
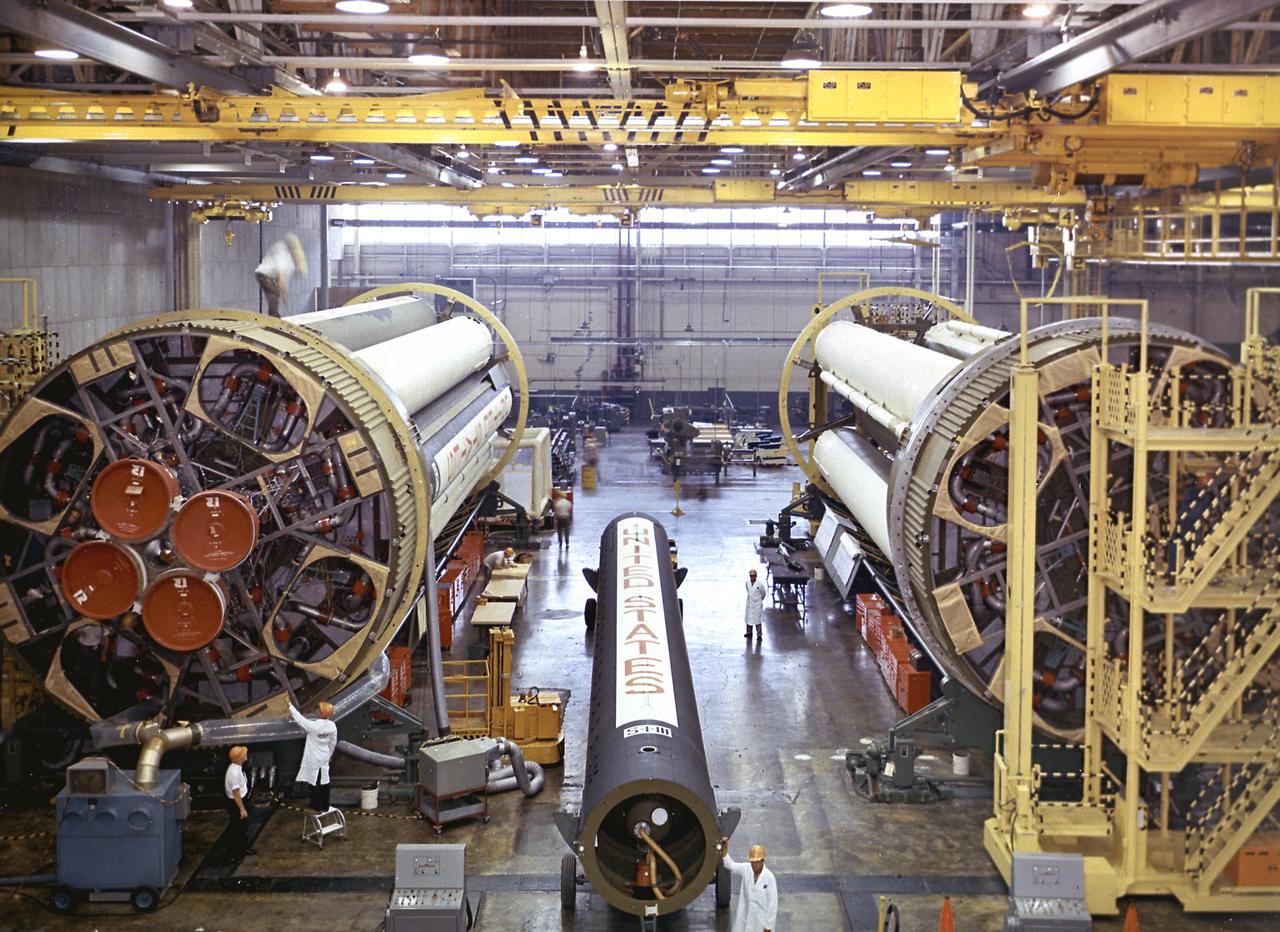

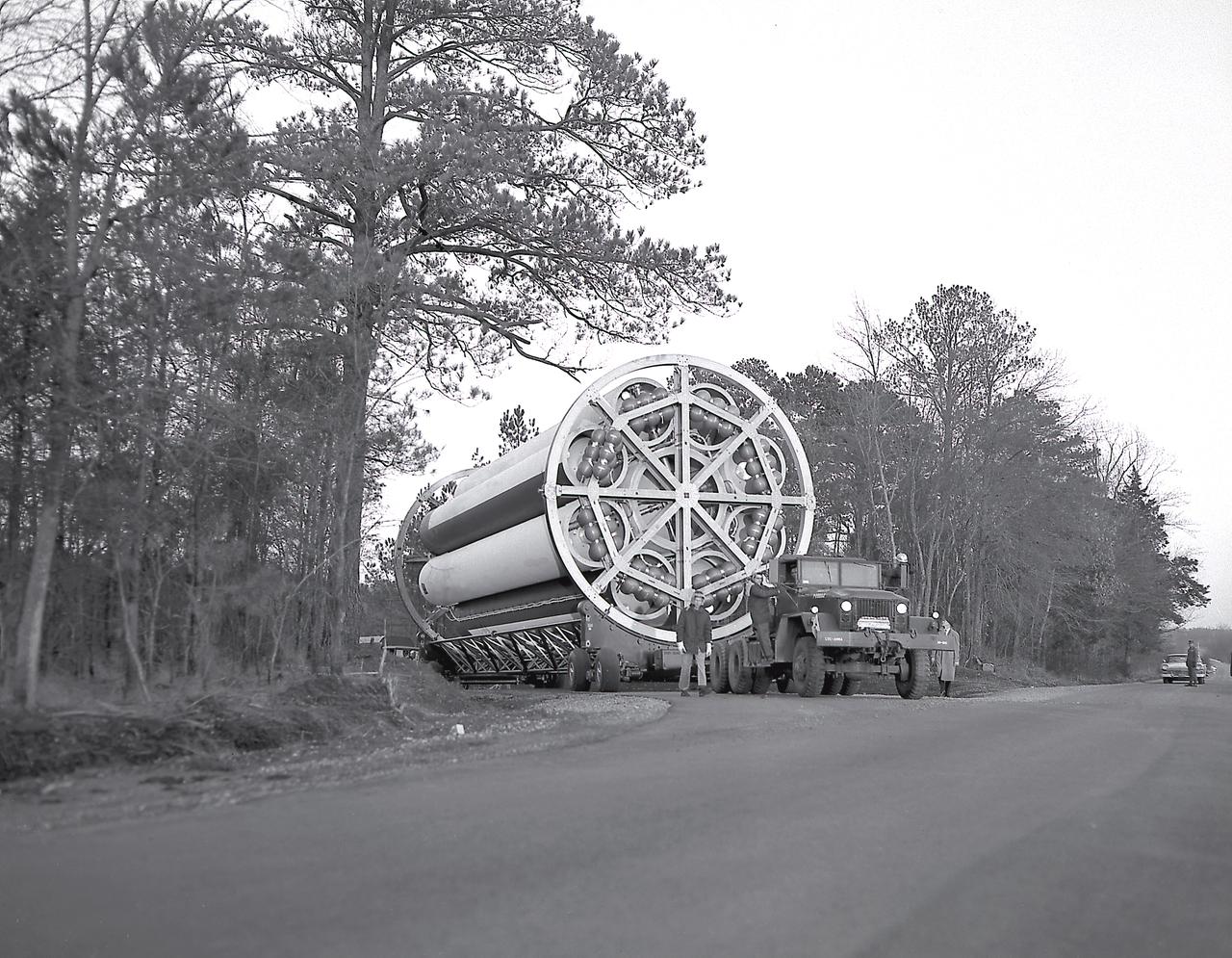
The Saturn I S-I stages for the SA-8 and SA-10 mission in final assembly phase in a manufacturing building at the Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Louisiana. The SA-8 mission was launched on May 25, 1965 with the first industry-built booster, and deployed the Pegasus II Micrometeoroid Detection satellite. The SA-10 mission was the last Saturn I mission, launched on July 30, 1965, and carried the Pegasus III Meteoroid Detection satellite.
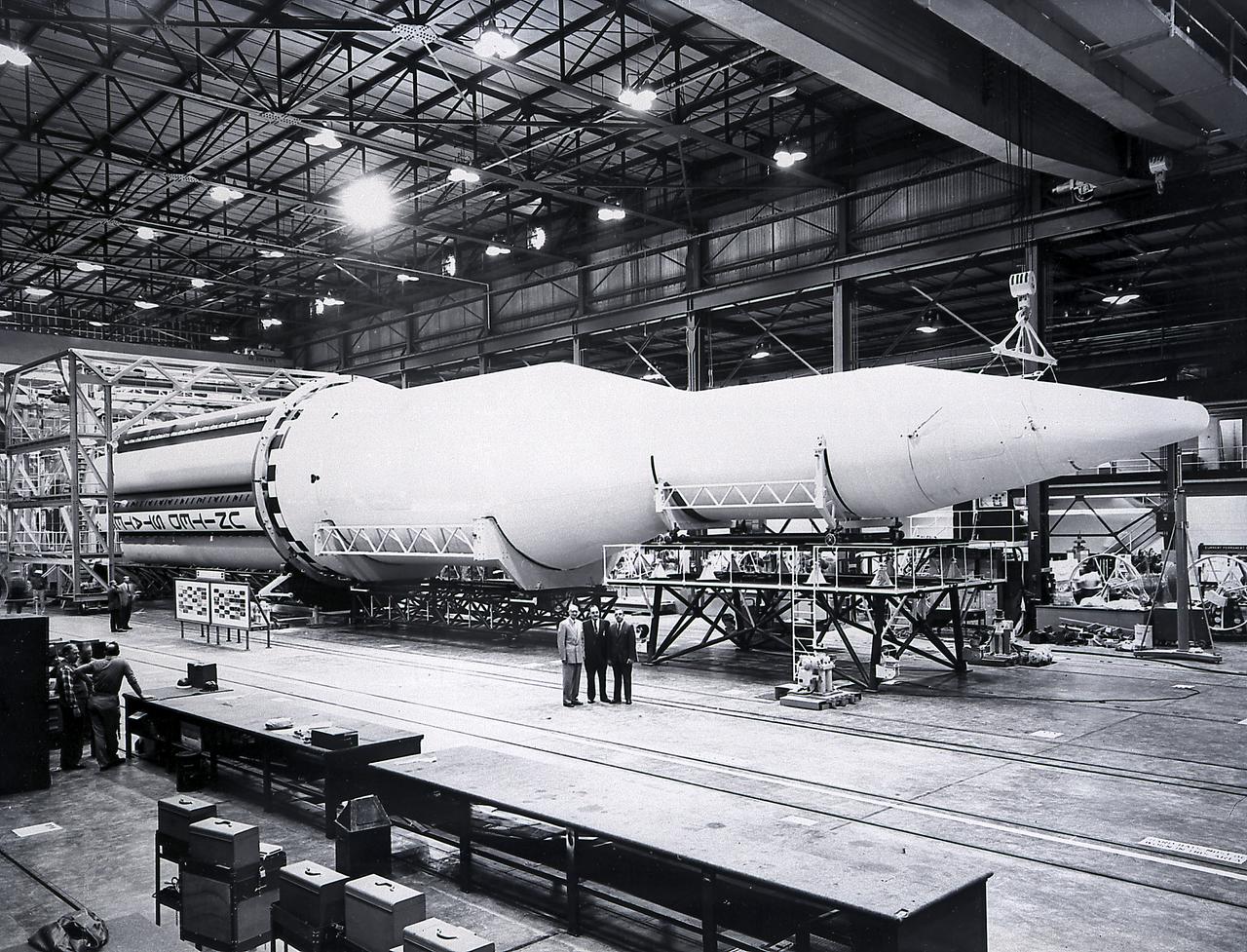

A completed Saturn I launch vehicle in the Fabrication and Assembly Engineering Division at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The Saturn I launch vehicle is composed of an S-I first stage or booster (rear), powered by eight H-1 engines having a thrust of 1,500,000 pounds, followed by a dummy S-IV second stage with six RL-10 engine, with a total thrust of 90,000 pounds.
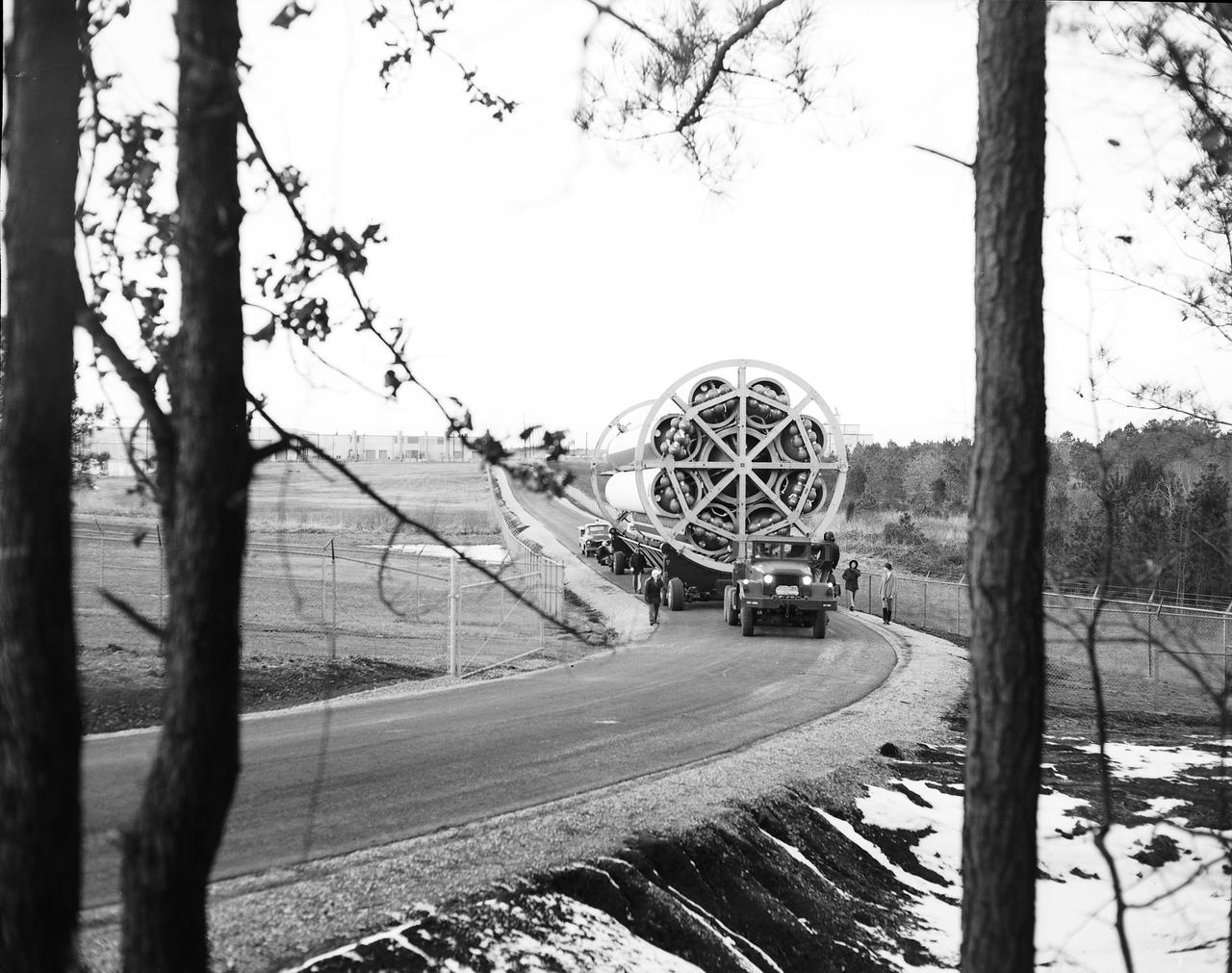

This photograph shows the Saturn-I first stage (S-1 stage) being transported to the test stand for a static test firing at the Marshall Space Flight Center. Soon after NASA began operations in October 1958, it was evident that sending people and substantial equipment beyond the Earth's gravitational field would require launch vehicles with weight-lifting capabilities far beyond any developed to that time. In early 1959, NASA accepted the proposal of Dr. Wernher von Braun for a multistage rocket, with a number of engines clustered in one or more of the stages to provide a large total thrust. The initiation of the Saturn launch vehicle program ultimately led to the study and preliminary plarning of many different configurations and resulted in production of three Saturn launch vehicles, the Saturn-I, Saturn I-B, and Saturn V. The Saturn family of launch vehicles began with the Saturn-I, a two-stage vehicle originally designated C-1. The research and development program was planned in two phases, or blocks: one for first stage development (Block I) and the second for both first and second stage development (Block-II). Saturn I had a low-earth-orbit payload capability of approximately 25,000 pounds. The design of the first stage (S-1 stage) used a cluster of propellant tanks containing liquid oxygen (LOX) and kerosene (RP-1), and eight H-1 engines, yielding a total thrust of 1,500,000 pounds. Of the ten Saturn-Is planned, the first eight were designed and built at the Marshall Space Flight Center, and the remaining two were built by the Chrysler Corporation.
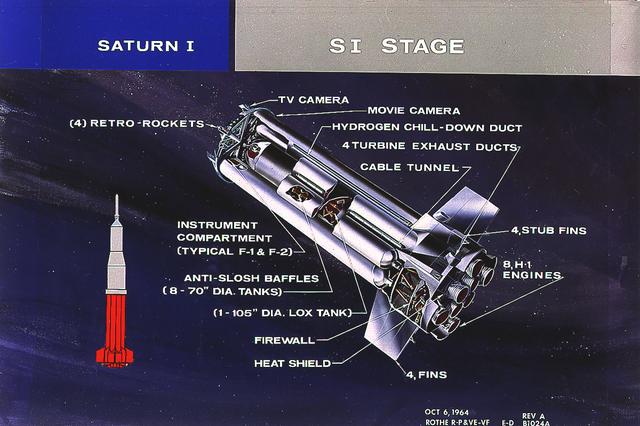
This cutaway illustrates the S-I stage, the first stage of the Saturn I vehicle developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The stage was propelled by a cluster of eight H-1 engines, capable of producing 1,500,000 pounds of thrust.
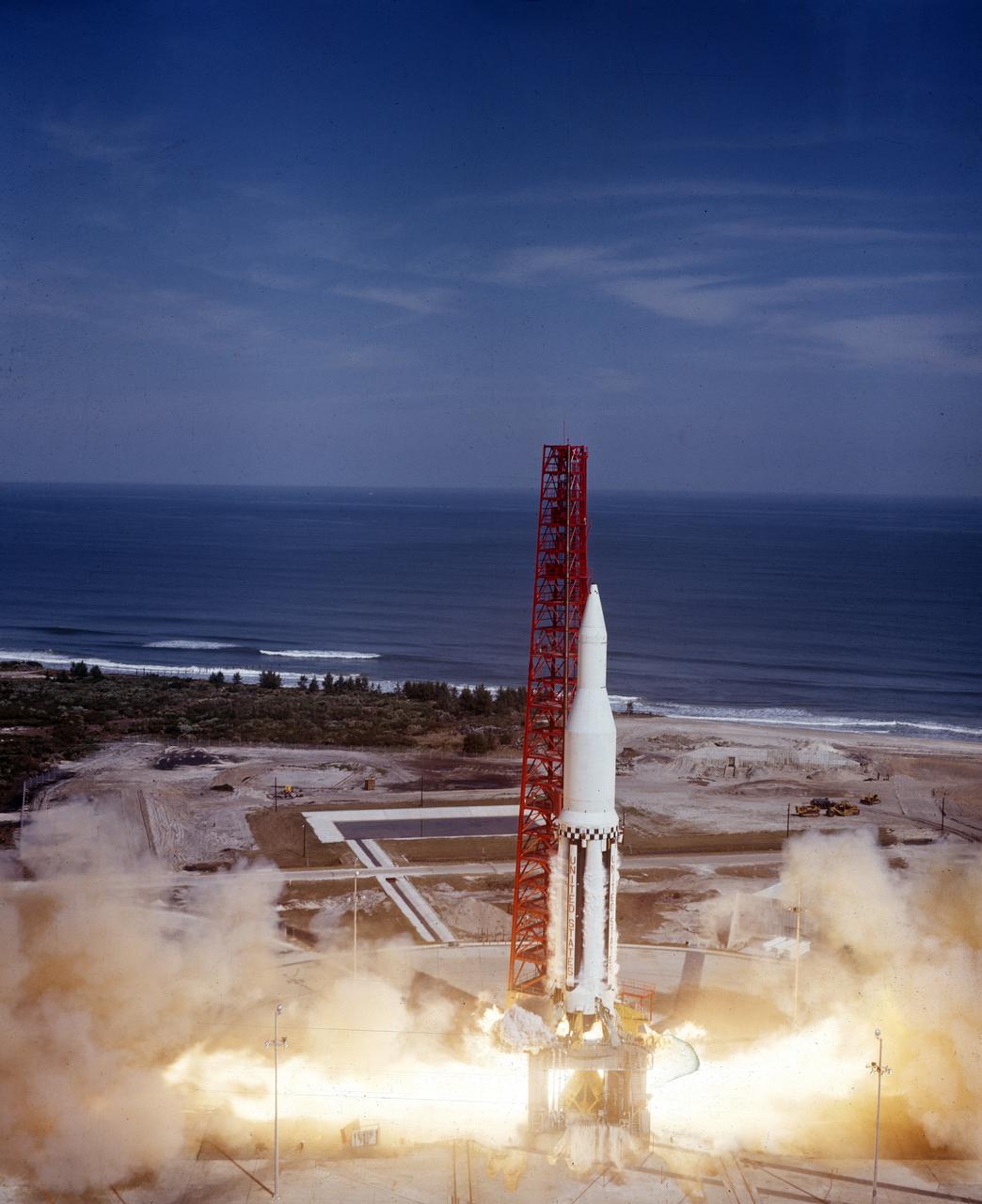

The Saturn I (SA-3) flight lifted off from Kennedy Space Center launch Complex 34, November 16, 1962. The third launch of Saturn launch vehicles, developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, incorporated a Saturn I, Block I engine. The typical height of a Block I vehicle was approximately 163 feet. and had only one live stage. It consisted of eight tanks, each 70 inches in diameter, clustered around a central tank, 105 inches in diameter. Four of the external tanks were fuel tanks for the RP-1 (kerosene) fuel. The other four, spaced alternately with the fuel tanks, were liquid oxygen tanks as was the large center tank. All fuel tanks and liquid oxygen tanks drained at the same rates respectively. The thrust for the stage came from eight H-1 engines, each producing a thrust of 165,000 pounds, for a total thrust of over 1,300,000 pounds. The engines were arranged in a double pattern. Four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis and canted outward slightly, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern offset 40 degrees from the inner pattern. Unlike the inner engines, each outer engine was gimbaled. That is, each could be swung through an arc. They were gimbaled as a means of steering the rocket, by letting the instrumentation of the rocket correct any deviations of its powered trajectory. The block I required engine gimabling as the only method of guiding and stabilizing the rocket through the lower atmosphere. The upper stages of the Block I rocket reflected the three-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. During the SA-3 flight, the upper stage ejected 113,560 liters (30,000 gallons) of ballast water in the upper atmosphere for "Project Highwater" physics experiment. The water was released at an altitude of 65 miles, where within only 5 seconds, it expanded into a massive ice cloud 4.6 miles in diameter. Release of this vast quantity of water in a near-space environment marked the first purely scientific large-scale experiment.
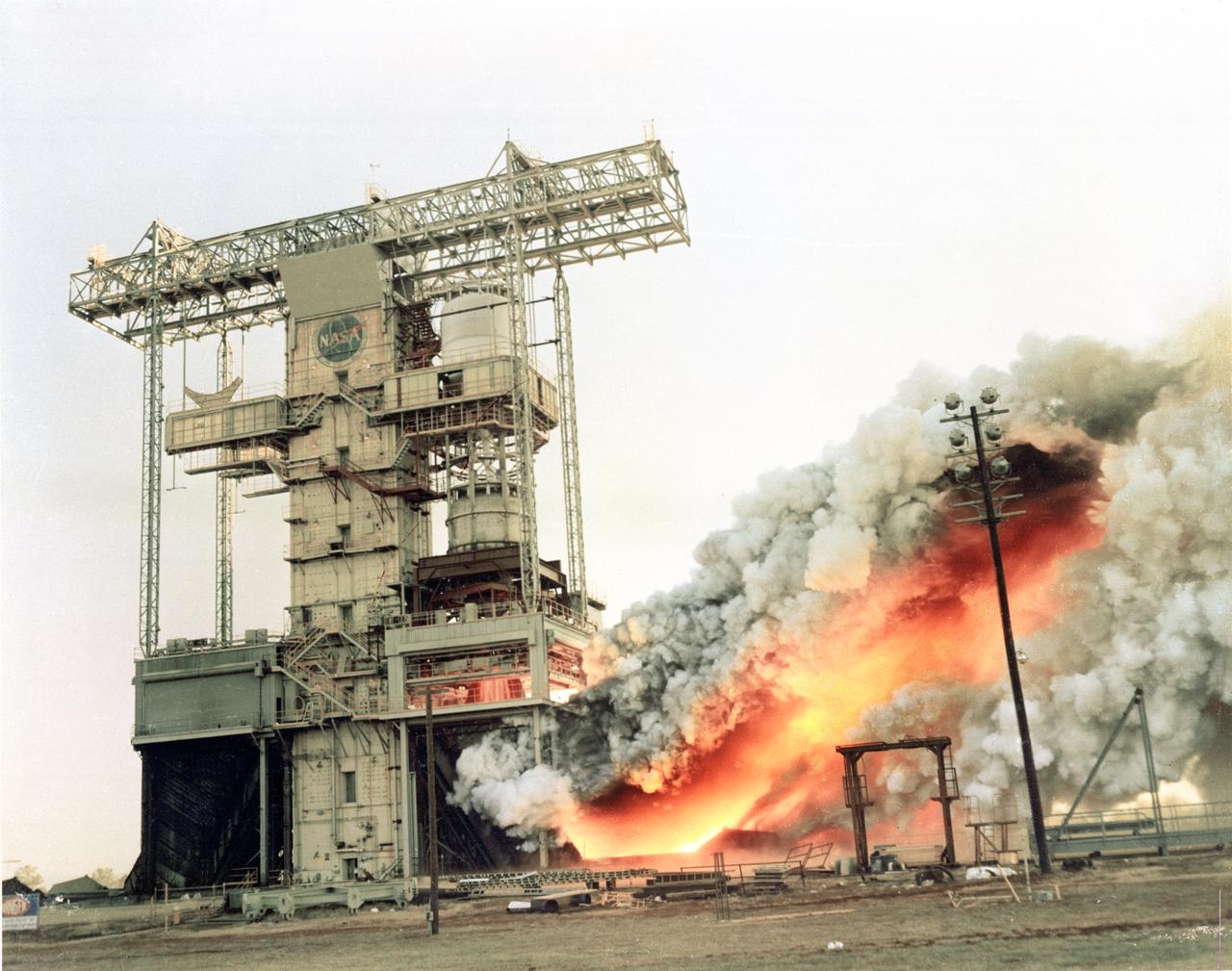

Pictured is a dual position Saturn I/IB test at the T-Stand at Marshall Space Flight Center. This stand was built to test two articles at the same time, thus providing engineers at MSFC with the opportunity to compare identical burns.

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being placed on a transporter and later being installed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, on January 19, 1960, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.

A spider beam for cornecting the Saturn I fuel tanks is being positioned in the fabrication and engineering laboratory of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
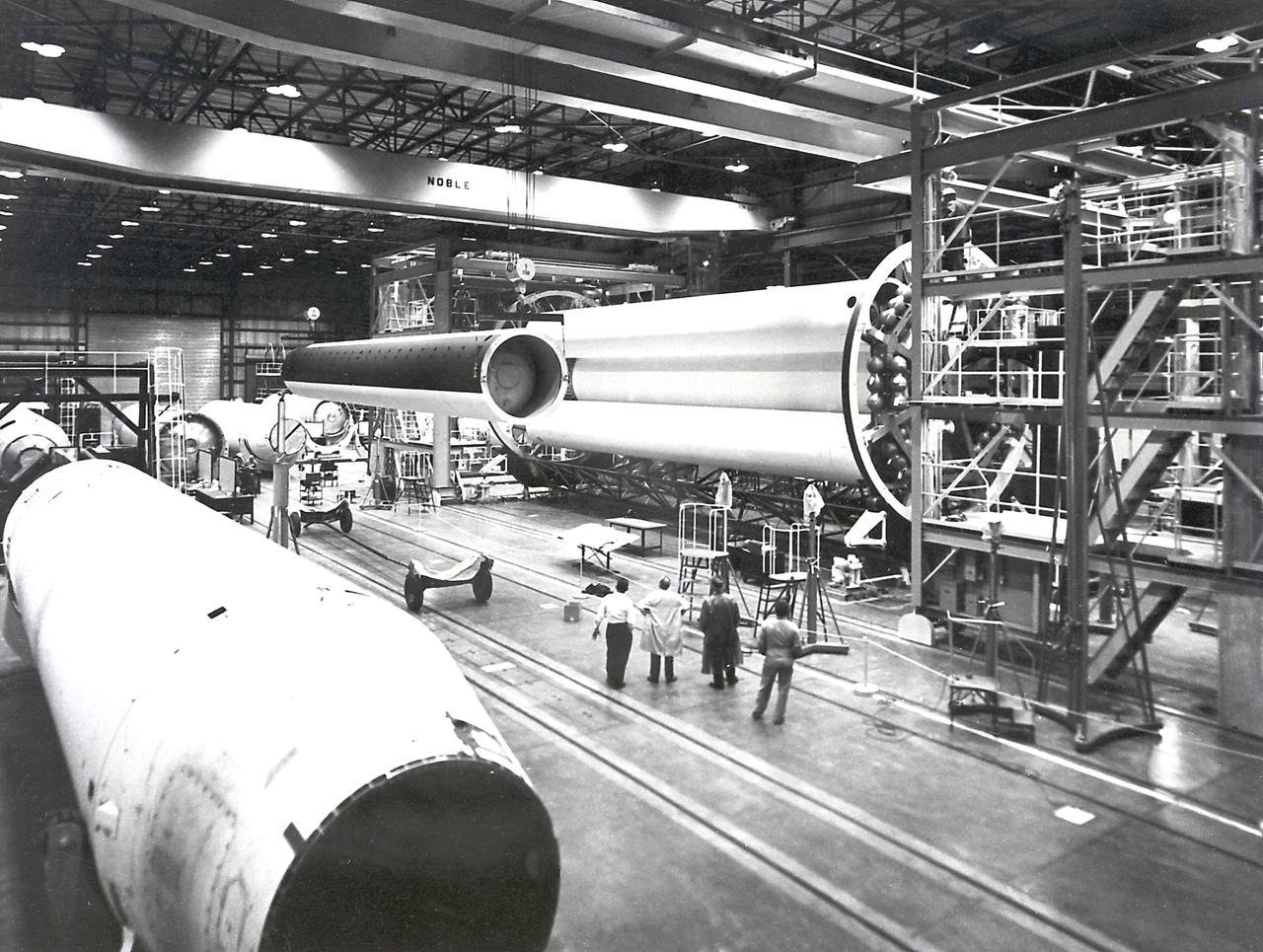
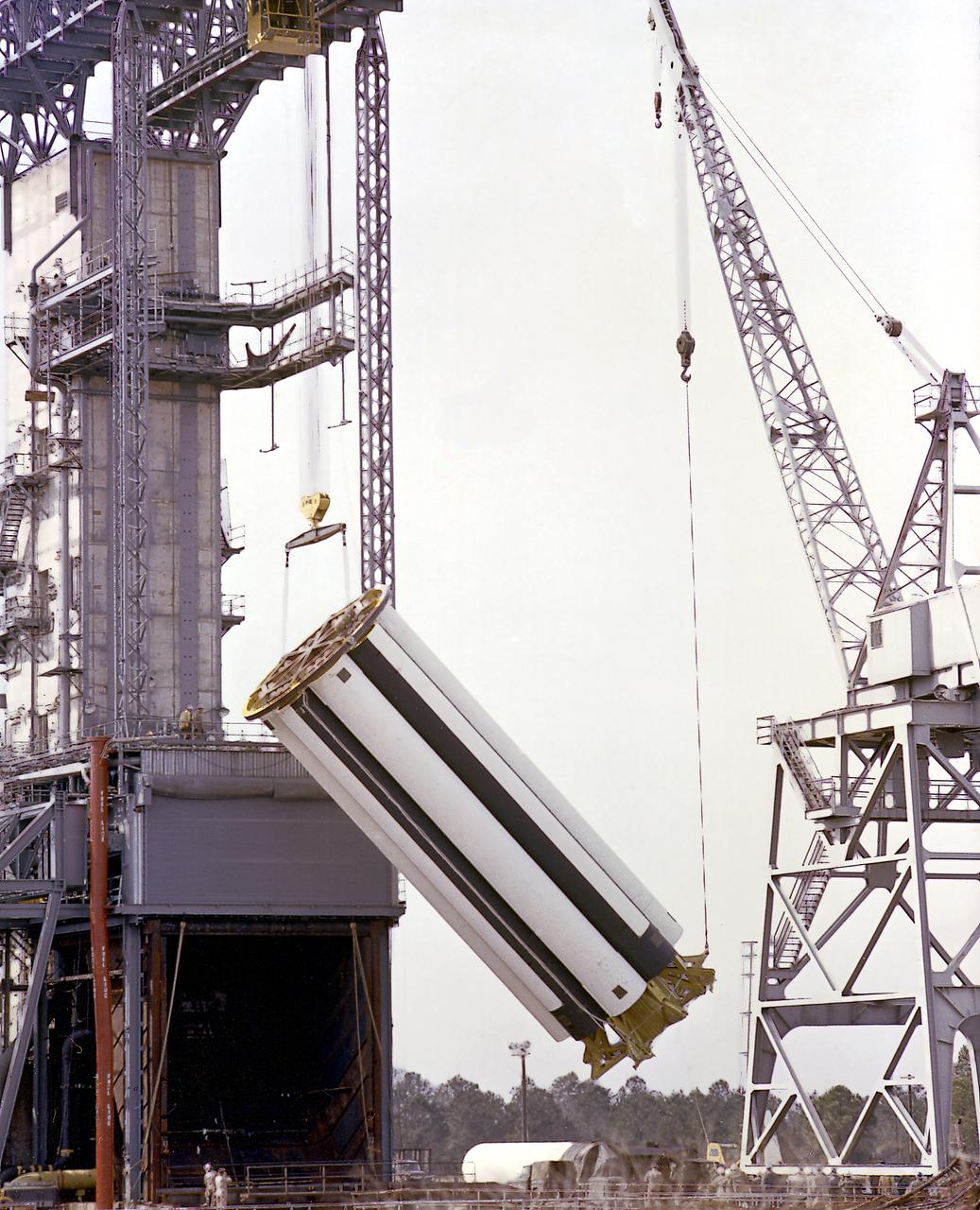
The Saturn I S-I stage is being assembled in the fabrication and engineering laboratory at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The two end spider beams are cornected to the central 267-centimeter diameter liquid-oxygen (LOX) tank. The 178-centimeter outer tank, used alternately for liquid oxygen and kerosene, is being lifted into position.
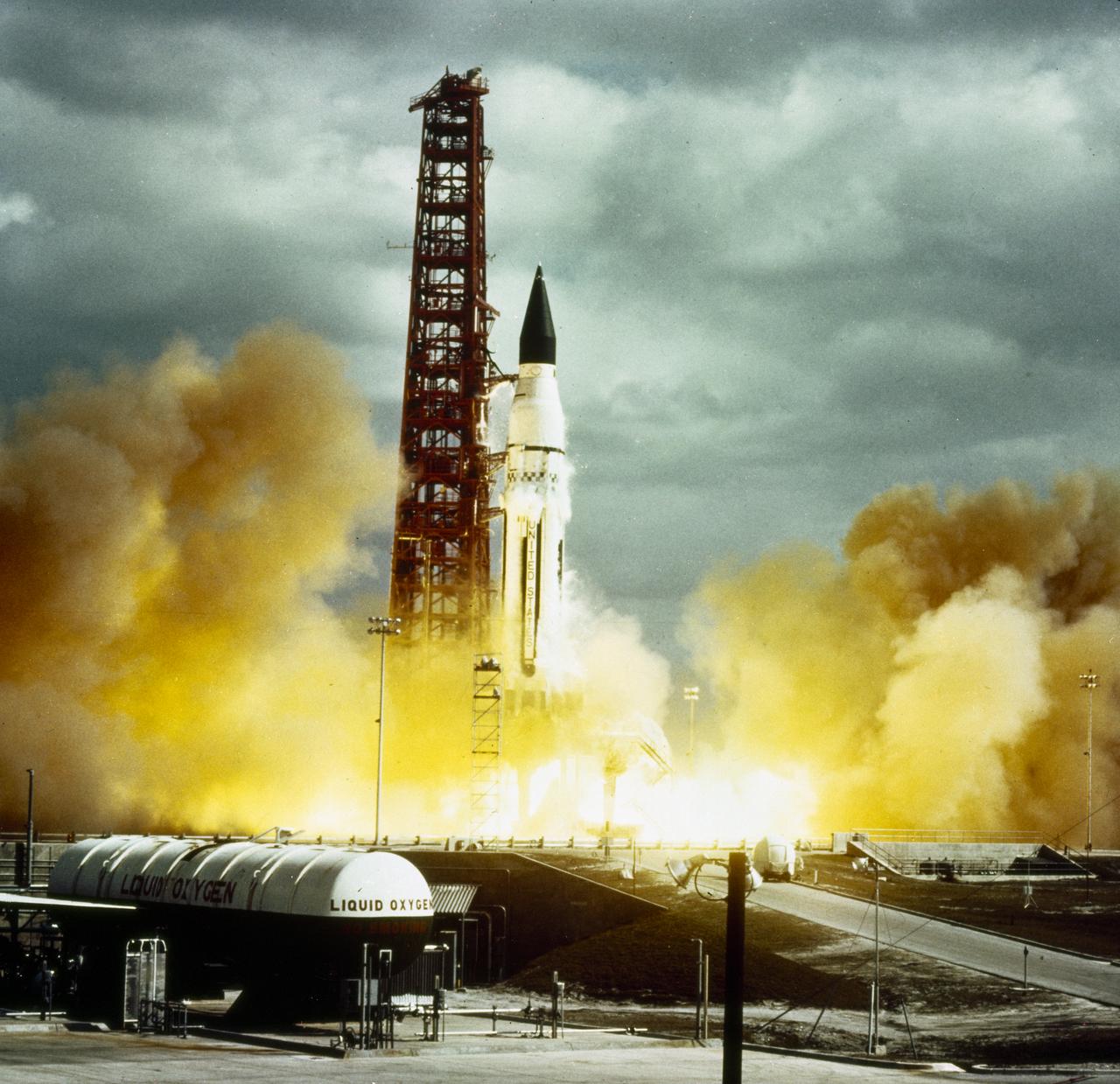

Developed at MSFC under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun, the SA-5 incorporated a Saturn I, Block II engine. Launched on January 29, 1964, SA-5 was the first two stage (Block II) Saturn with orbital capability and performed the first test of Instrument Unit and successful stage separation. Block II vehicles had two live stages, and were basically in the two-stage configuration of the Saturn I vehicle. There were marked changes between the Block I and II versions. The Block II S-I stage had eight fins added for greater aerodynamic stability in the lower atmosphere. All Block II H-1 engines had a thrust of 188,000 pounds each for a combined thrust over 1,500,000 pounds. The Block II second stage (S-IV) had six RL-10 hydrogen-oxygen engines, each producing a thrust of 15,000 pounds for a total combined thrust of 90,000 pounds. A motion picture camera capsule loated on stage I was successful recovered.
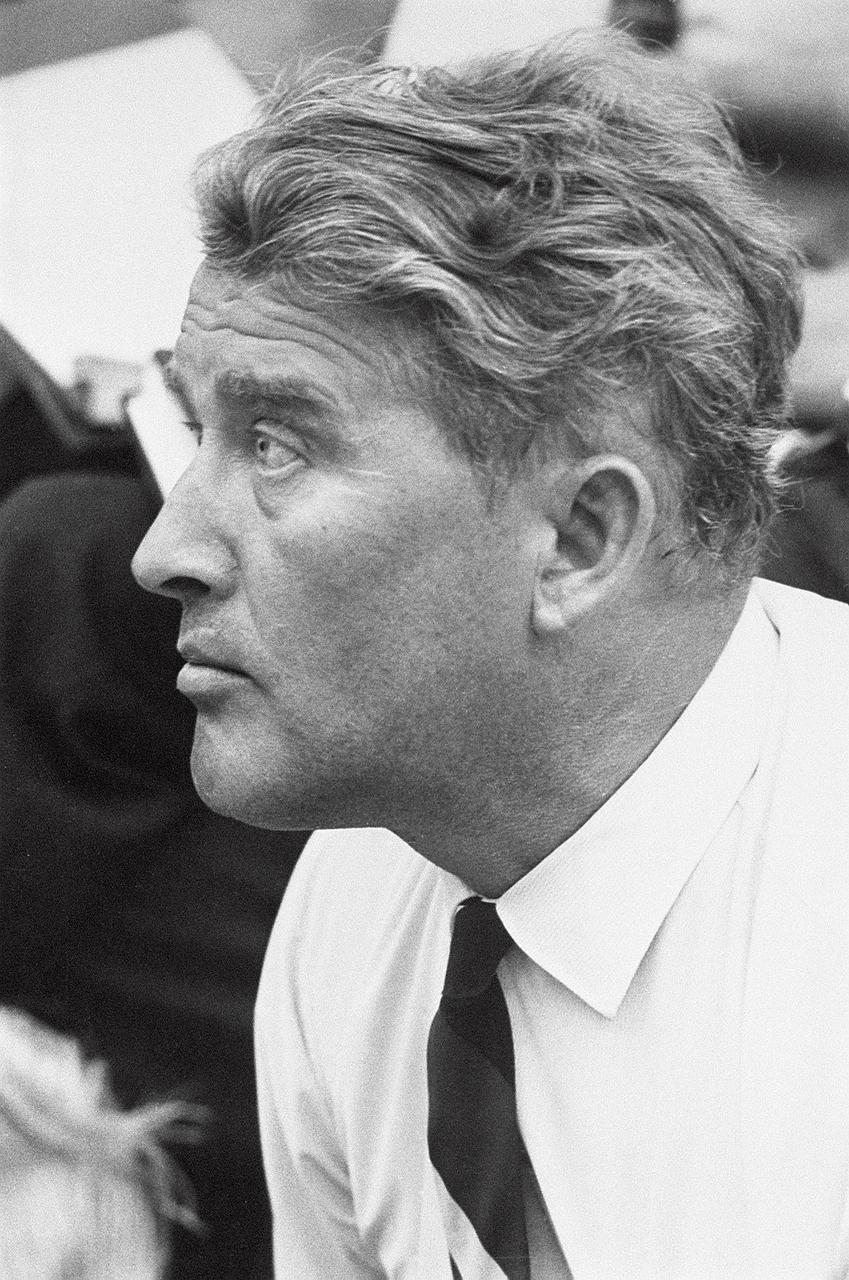

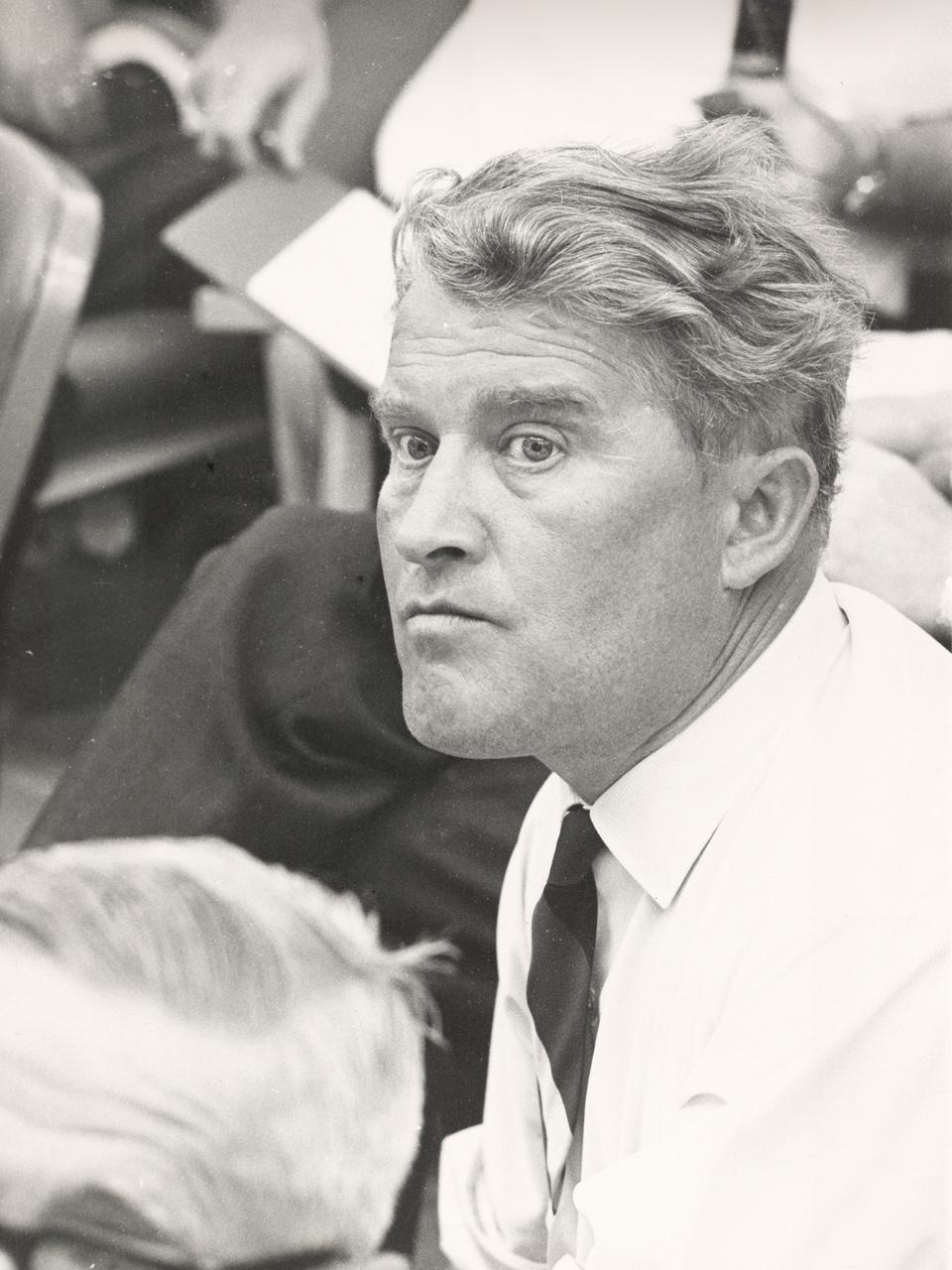
This profile of Dr. von Braun was taken in the Launch Complex Control Center at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida during the launch of Saturn I vehicle (SA-8) on May 25, 1965.

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program, to prove out the clustered-booster concept, was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being installed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, on January 19, 1960, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960 as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being transported to the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.
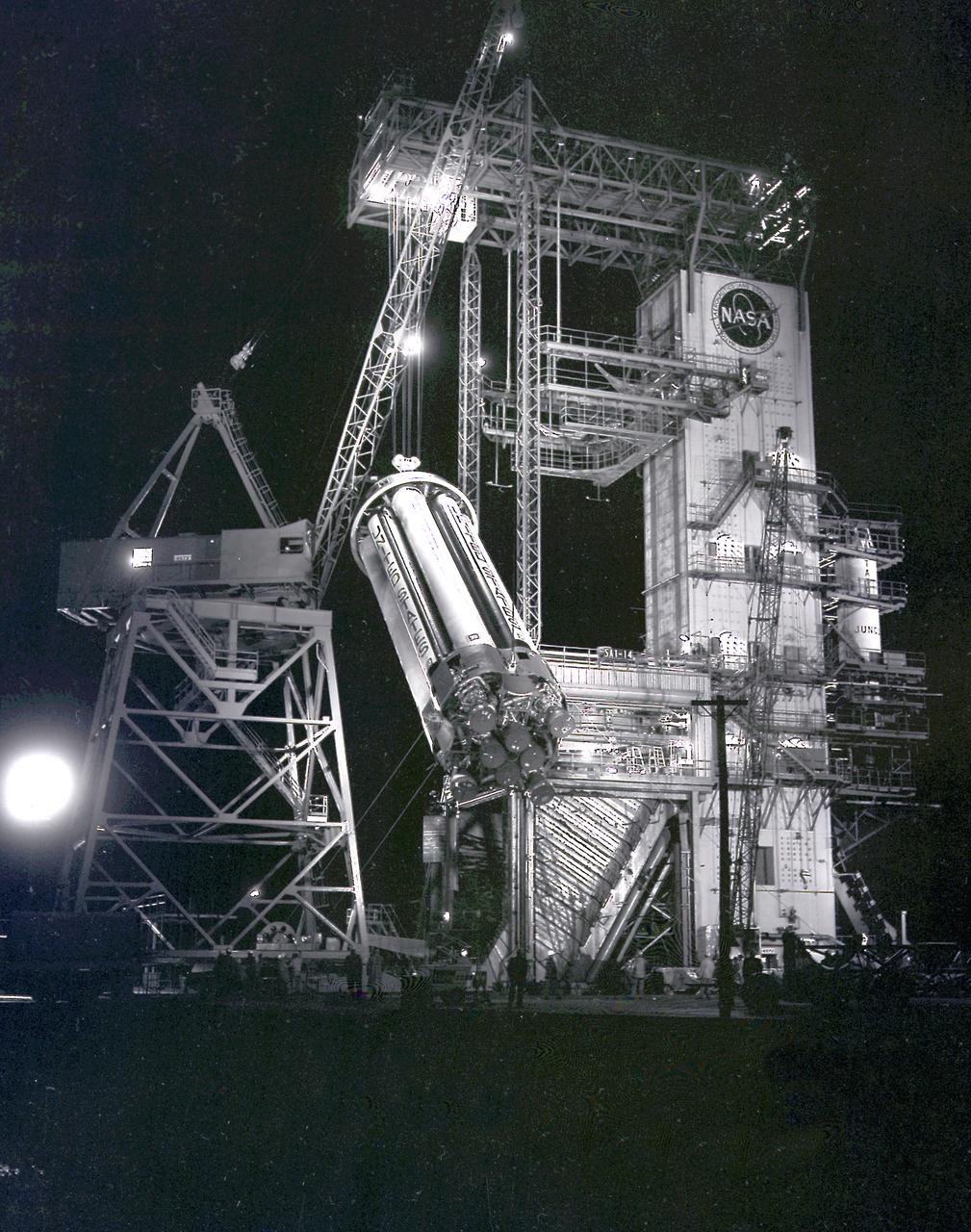
This night photograph depicts the SA-1 booster (Saturn I S-I stage) being removed from the test stand after the first flight qualification testing at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
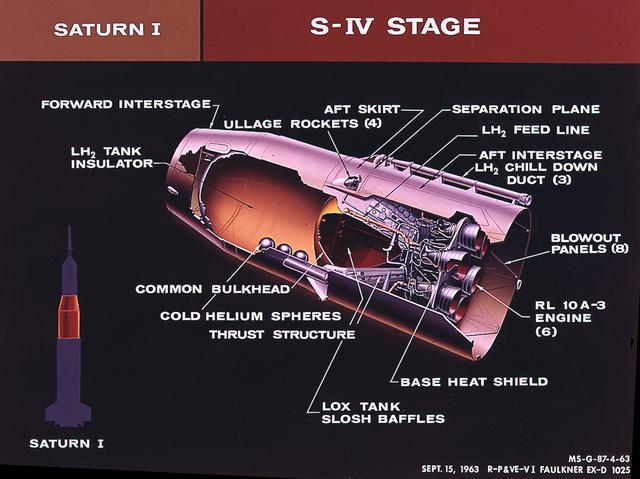
This cutaway of the Saturn I S-IV stage (second stage) illustrates the booster's components. Powered by six RL-10 engines, the S-IV stage was capable of producing 90,000 pounds of thrust. Development of the Saturn S-IV stage by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) contributed many technological breakthroughs vital to the success of the Apollo lunar program, including the use of liquid hydrogen as a propellant.

The Saturn I S-I stage is being assembled in the fabrication and engineering laboratory at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The two end spider beams are cornected to the central 267-centimeter diameter liquid-oxygen (LOX) tank. The first of the eight 178-centimeter outer tanks, used alternately for liquid oxygen and kerosene, is being lifted into position.

Pegasus-1, meteoroid detection satellite, installed on Saturn I (SA-9 mission) S-IV stage, January 13, 1965. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth. SA-9 was launched on February 16, 1965 and the Pegasus-1 satellite was the first operational payload for Saturn I.
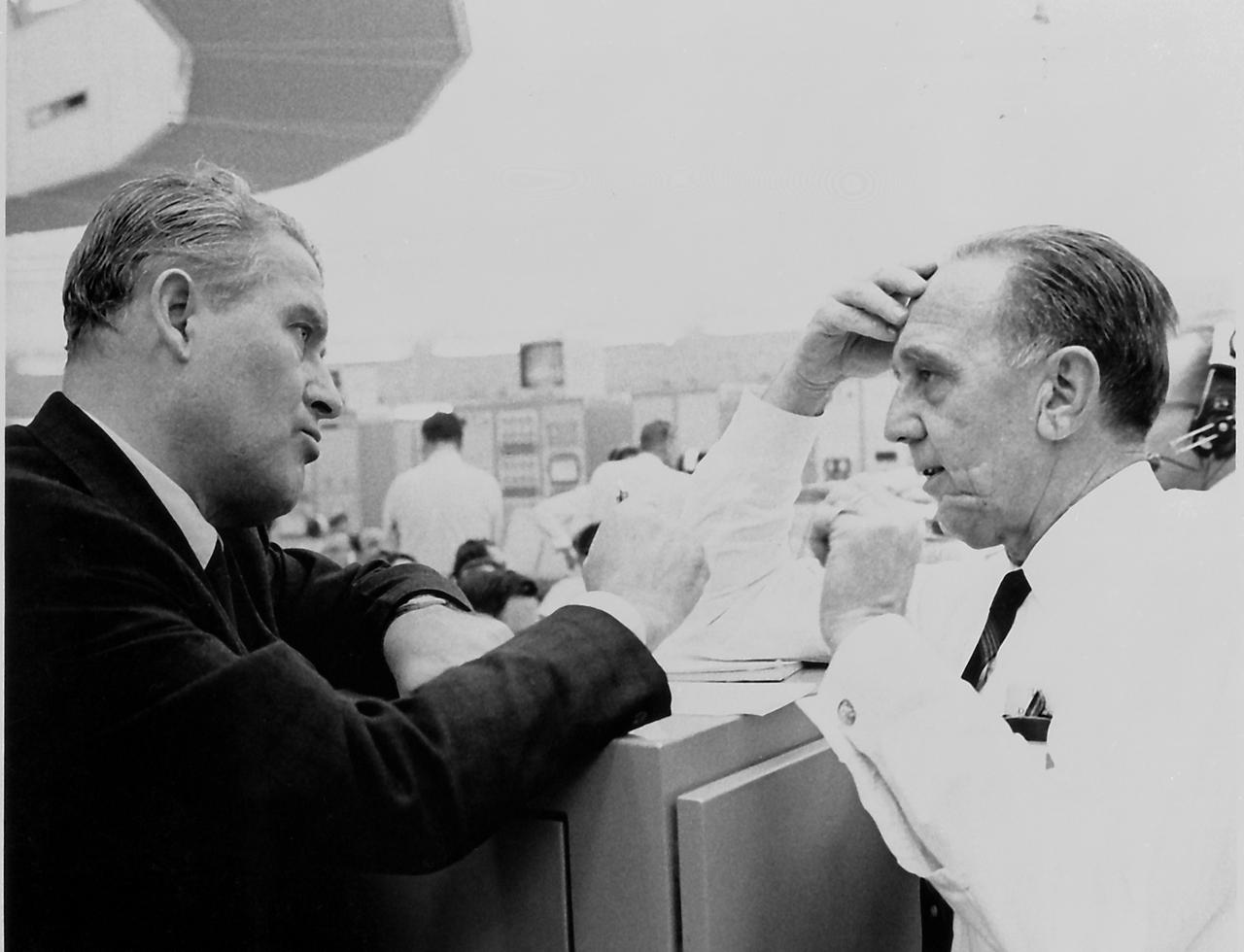

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun (left) confers with the Director of the MSFC Launch Operation Directorate, Dr. Debus, during the countdown for the Saturn/Pegasus (Saturn I, SA-9) launch. The successful launch of the Pegasus satellite marked the largest unmarned instrumented satellite in orbit up to 1965.

In this photo, Dr. von Braun anxiously awaits the launch of the Saturn I vehicle (SA-8) in the Launch Complex Control Center at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 25, 1965. The SA-8 mission made the first night launch and deployed the Pegasus II micro meteoroid detection satellite.
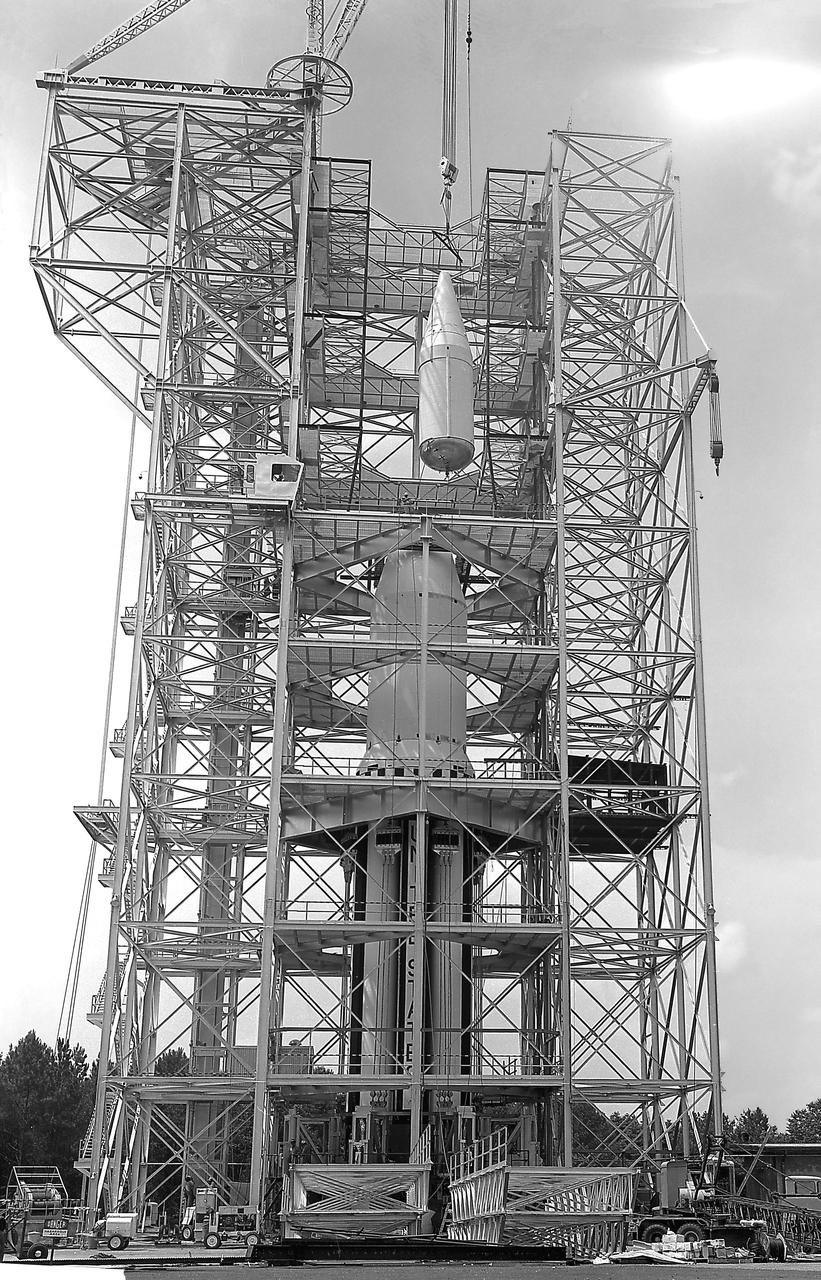

This image depicts the Saturn I launch vehicle placed in the dynamic test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). A dummy booster was moved to the dynamic test stand early in June, and, for the first time, vertically mated with dummy S-I and S-IV stages. The assembled vehicle was readied for dynamic testing to investigate the integrity of the support structure.
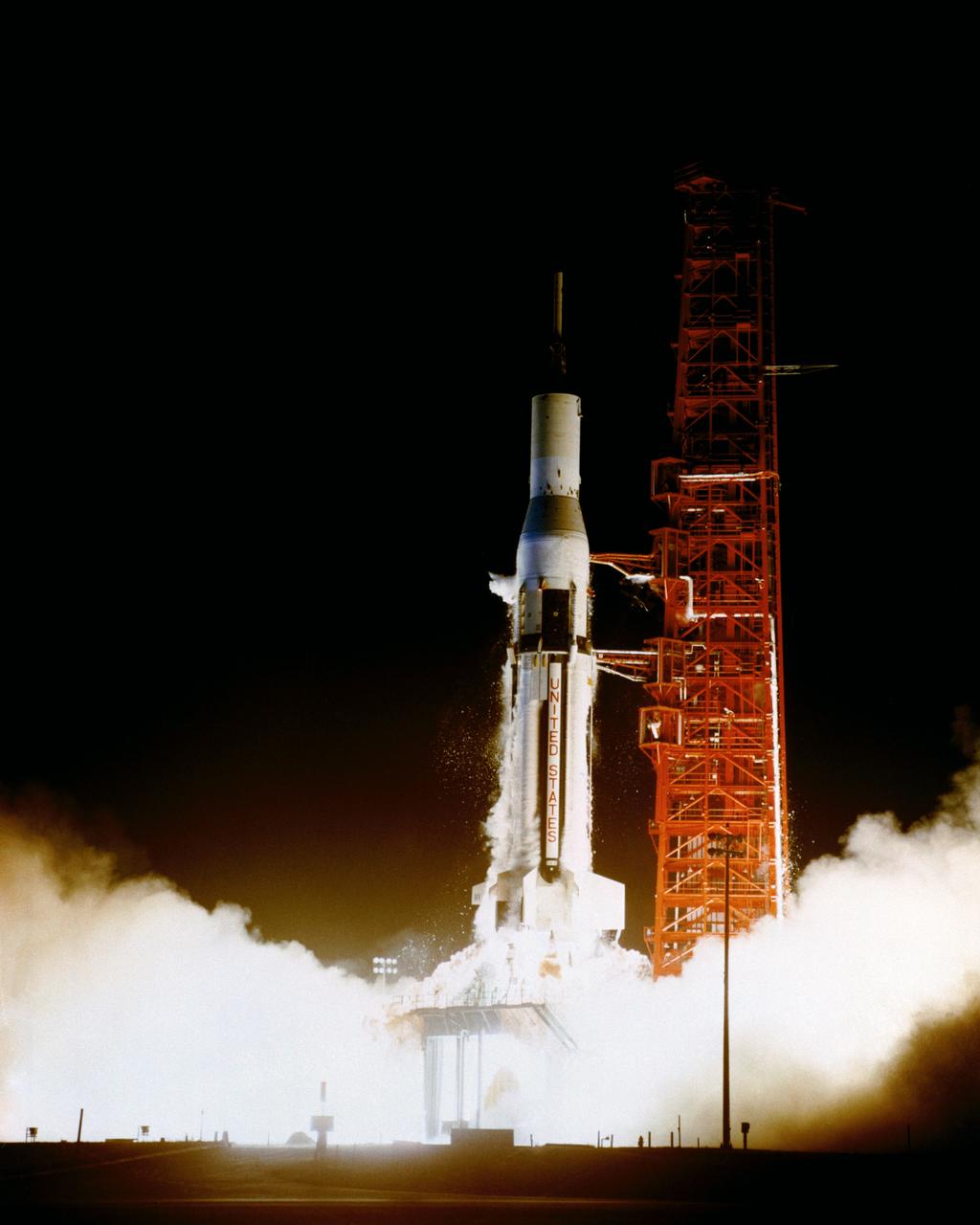

First night time launching of a Saturn I launch vehicle took place at 2:35 a.m., May 25, 1965, with the launch of the second Pegasus meteoroid detection satellite from Complex 37, Cape Kennedy, Florida.
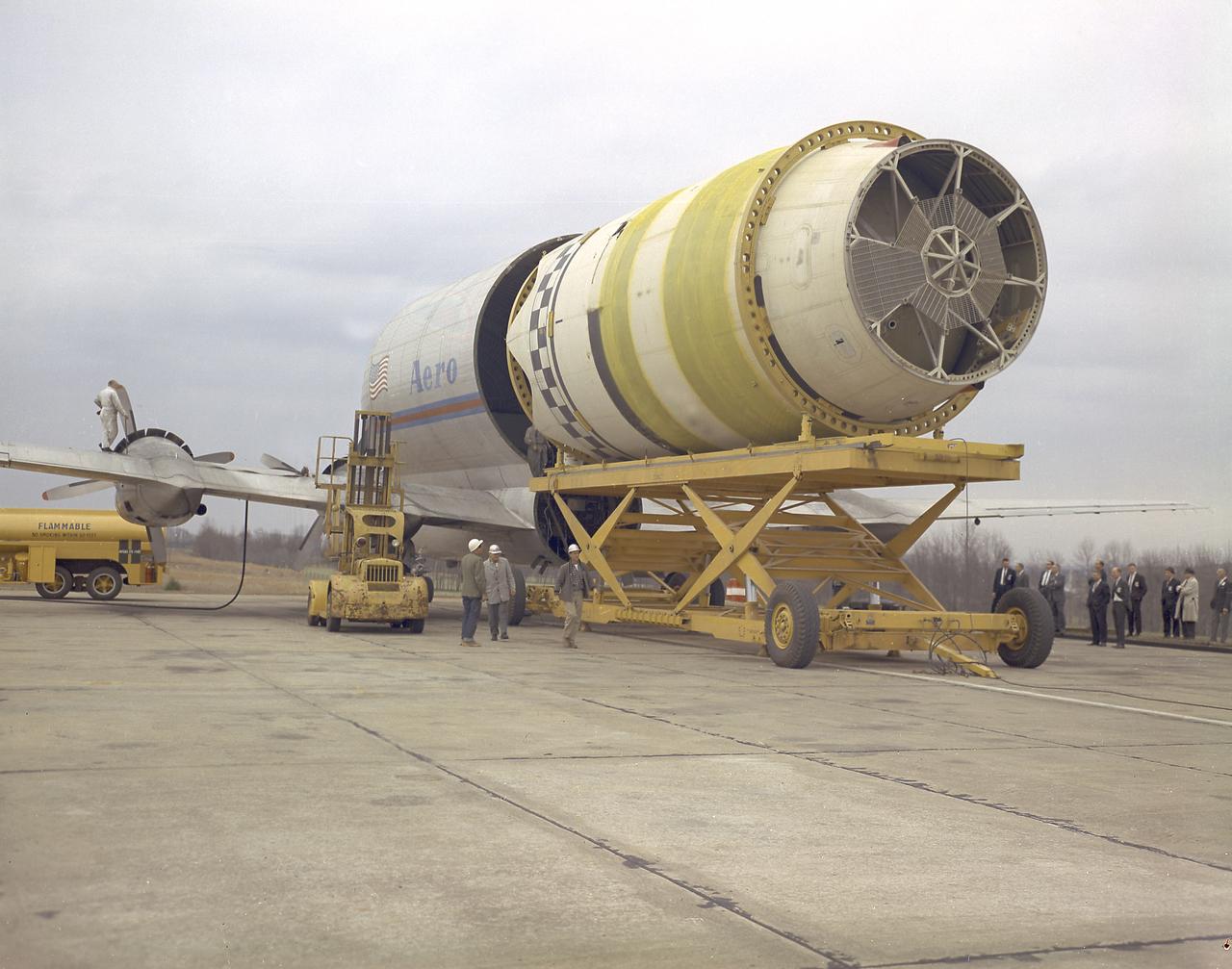

The photograph shows the loading operation of the Saturn I S-IV stage (second stage) into the Pregnant Guppy at the Redstone Airfield, Huntsville, Alabama. The Pregnant Guppy was a Boeing B-377 Stratocruiser modified to transport various stages of Saturn launch vehicles. The modification project called for lengthening the fuselage to accommodate the S-IV stage. After the flight test of that modification, phase two called for the enlargement of the plane's cabin section to approximately double its normal volume. The fuselage separated just aft of the wing's trailing edge to load and unload the S-IV and other cargoes.
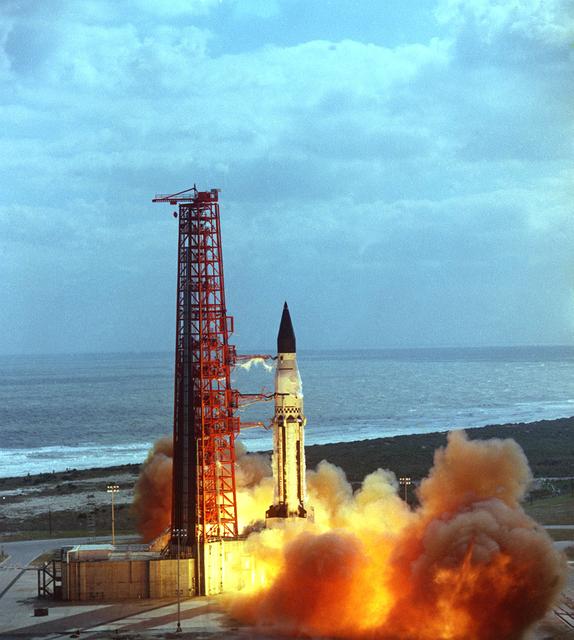

The launch of the SA-5 on January 29, 1964 was the fifth Saturn I launch vehicle. The SA-5 marked a number of firsts in the Marshall Space Flight Center-managed Saturn development program, including the first flight of Saturn I Block II vehicle with eight aerodynamic fins at the bottom of the S-I stage (first stage) for enhanced stability in flight. This also was the first flight of a live S-IV (second or upper) stage with the cluster of six liquid hydrogen-fueled RL-10 engines. the first successful second stage separation, and the first use of the Launch Complex 37.
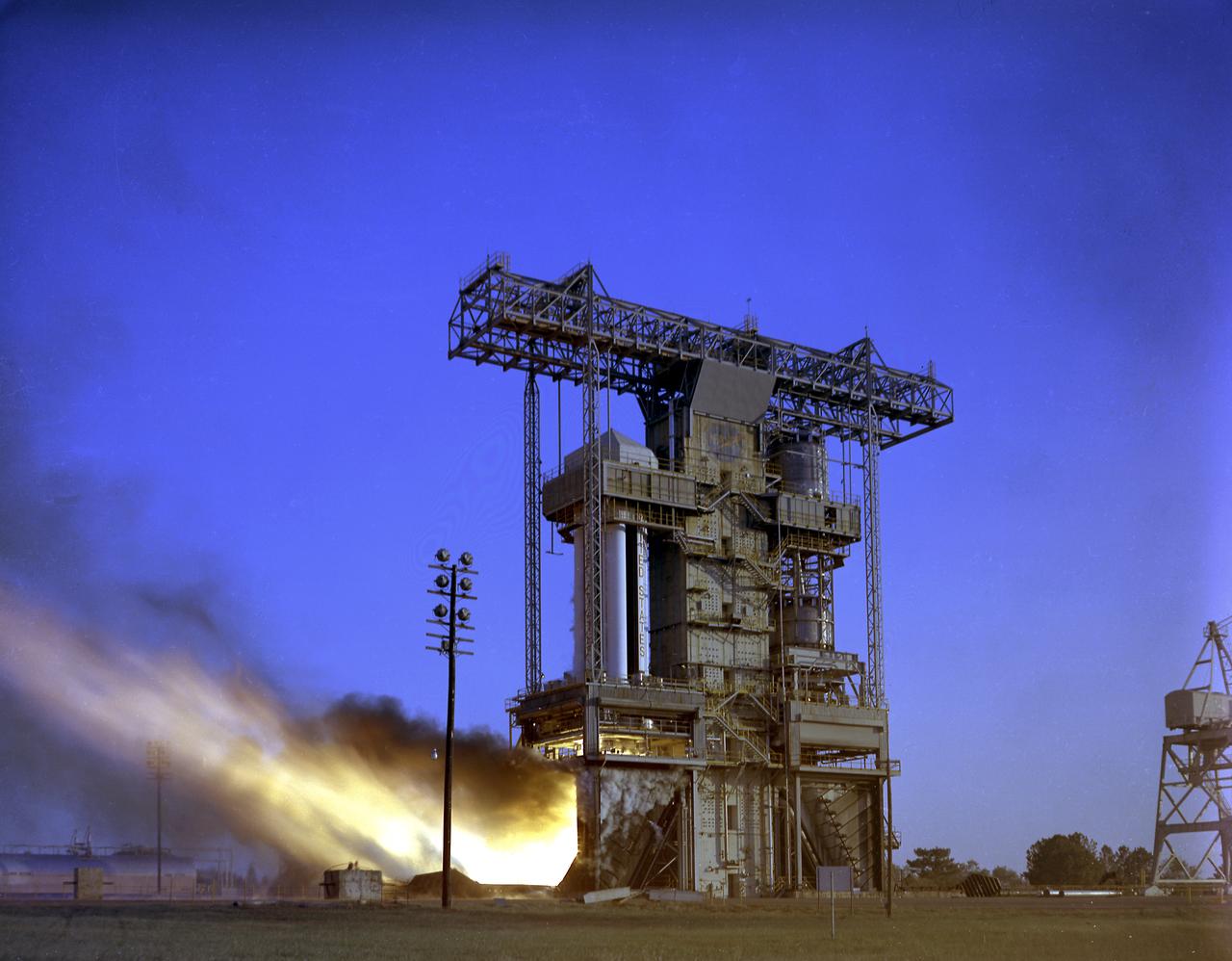

Test firing of the Saturn I S-I Stage (S-1-10) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. This test stand was originally constructed in 1951 and sometimes called the Redstone or T tower. In l961, the test stand was modified to permit static firing of the S-I/S-IB stages, which produced a total thrust of 1,600,000 pounds. The name of the stand was then changed to the S-IB Static Test Stand.
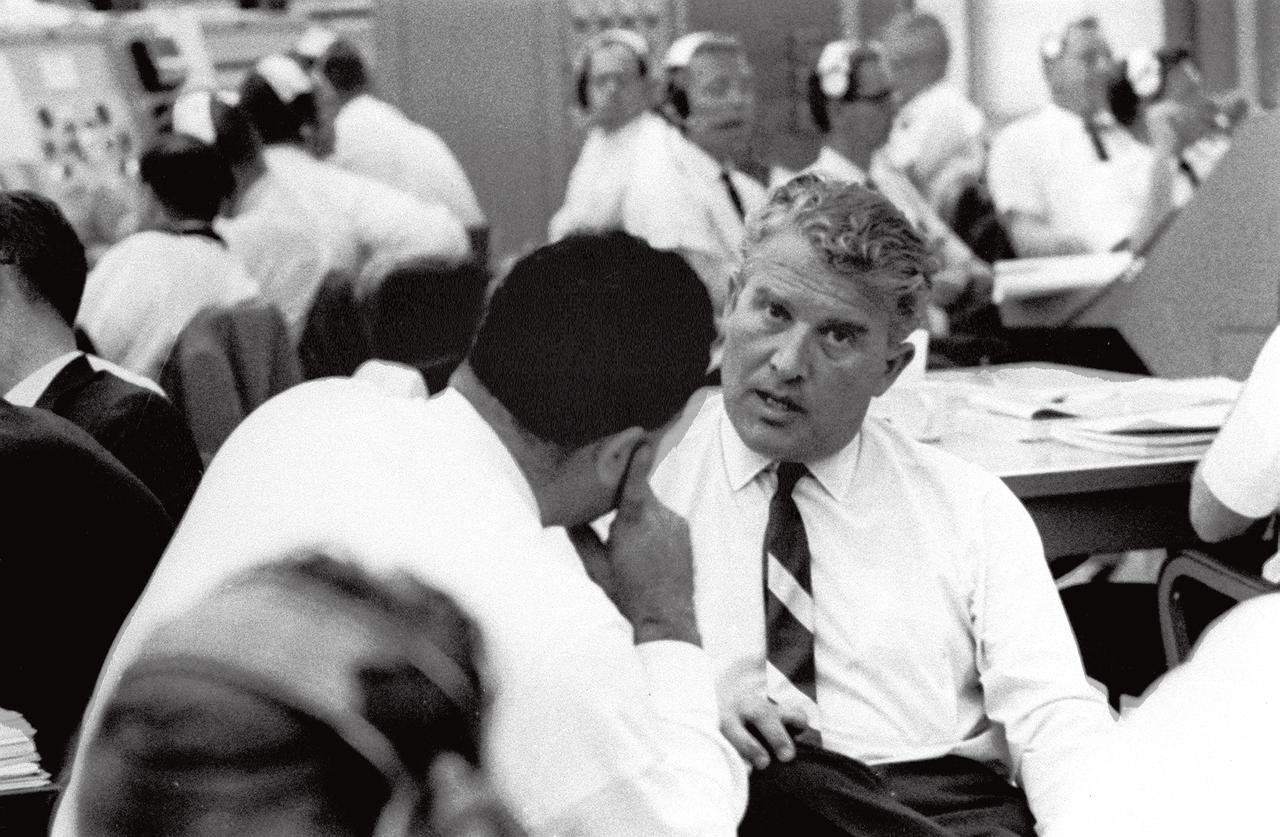

In this photograph at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Complex 37 Control Center, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director Wernher von Braun (right) talks with KSC's Rocco Petrone while awaiting the launch of SA-8 (Saturn I) on May 25, 1965. Petrone played key roles at KSC in the development of Saturn launch facilities before becoming the director of launch operations in 1966.
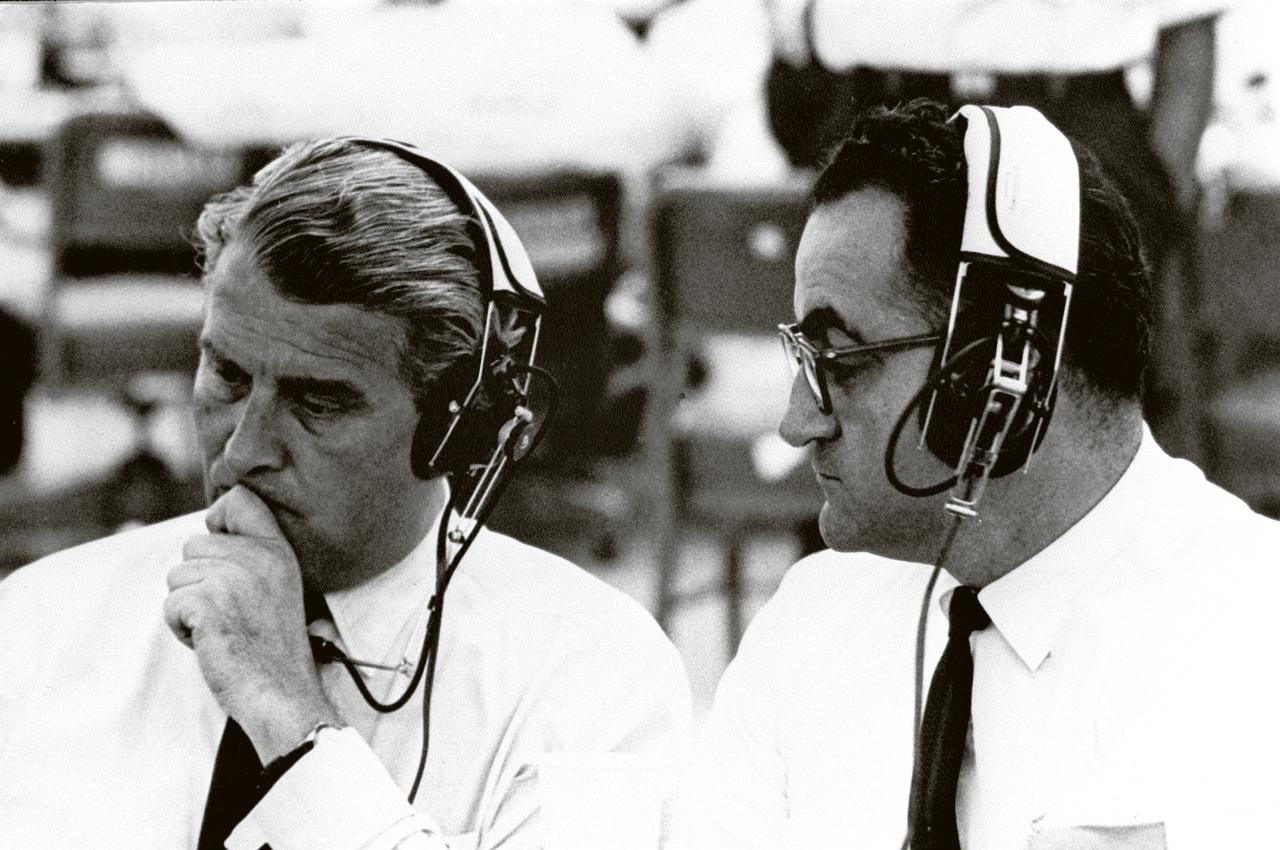

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director Dr. Wernher von Braun (left) with Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Rocco Petrone prior to the January 29, 1964 launch of SA-5, the first Block II configuration of the Saturn I launch vehicle. Petrone played key roles at KSC in the development of Saturn launch facilities before becoming director of launch operations in 1966.

The Saturn Project was approved on January 18, 1960, as a program of the highest national priority. The formal test program to prove out the clustered-booster concept was well underway at Redstone Arsenal. This photograph depicts a mockup of the Saturn booster (S-I stage) being installed in the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) test stand, on January 19, 1960, to check mating of the booster and stand and servicing methods.
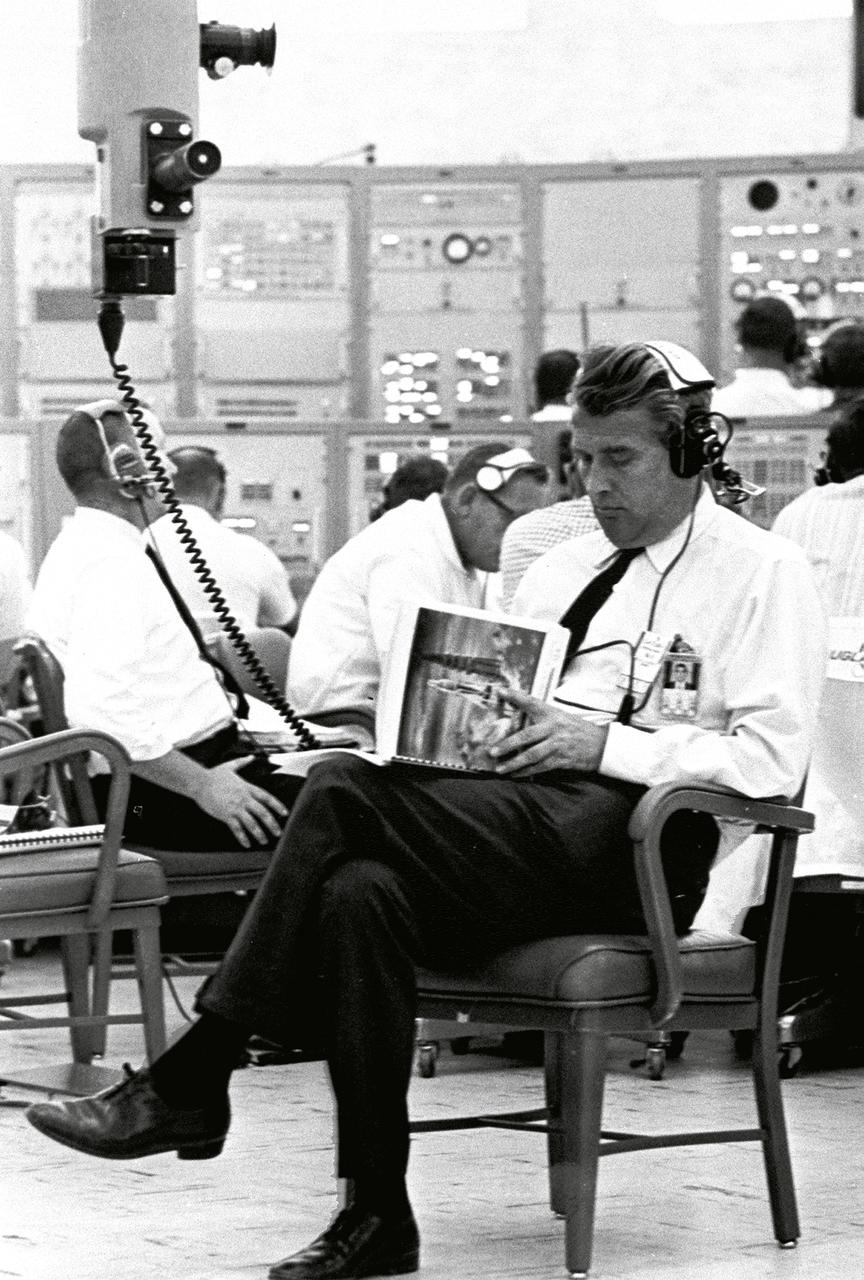

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director Wernher von Braun, seated near a periscope in Kennedy Space Center's Blockhouse 34, on May 28, 1964, looks over a flight manual while awaiting the launch of SA-6, the sixth Saturn I flight. Also known as Apollo Mission A-101, the launch marked the first flight of an Apollo spacecraft with a Saturn launch vehicle.

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the birthplace of the United States' rocket program. In the early 1960s, most of the rocket development and testing were done at the MSFC. Pictured is an example of what the test engineers would have seen from the pillbox as eight H-1 engines for the first stage of the Saturn I rocket were test fired.
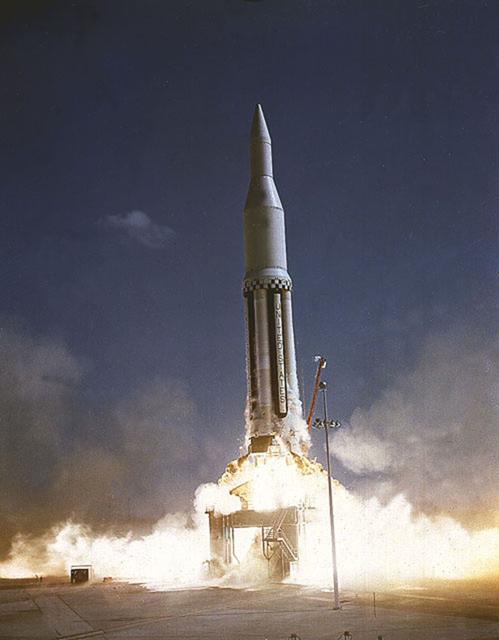
The second flight of the Saturn I vehicle, the SA-2, was successfully launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida on April 15, 1962. This vehicle had a secondary mission. After the first stage shutoff, at a 65-mile altitude, the water-filled upper stage was exploded, dumping 95 tons of water in the upper atmosphere. The resulting massive ice cloud rose to a height of 90 miles. The experiment, called Project Highwater, was intended to investigate the effects on the ionosphere of the sudden release of such a great volume of water.
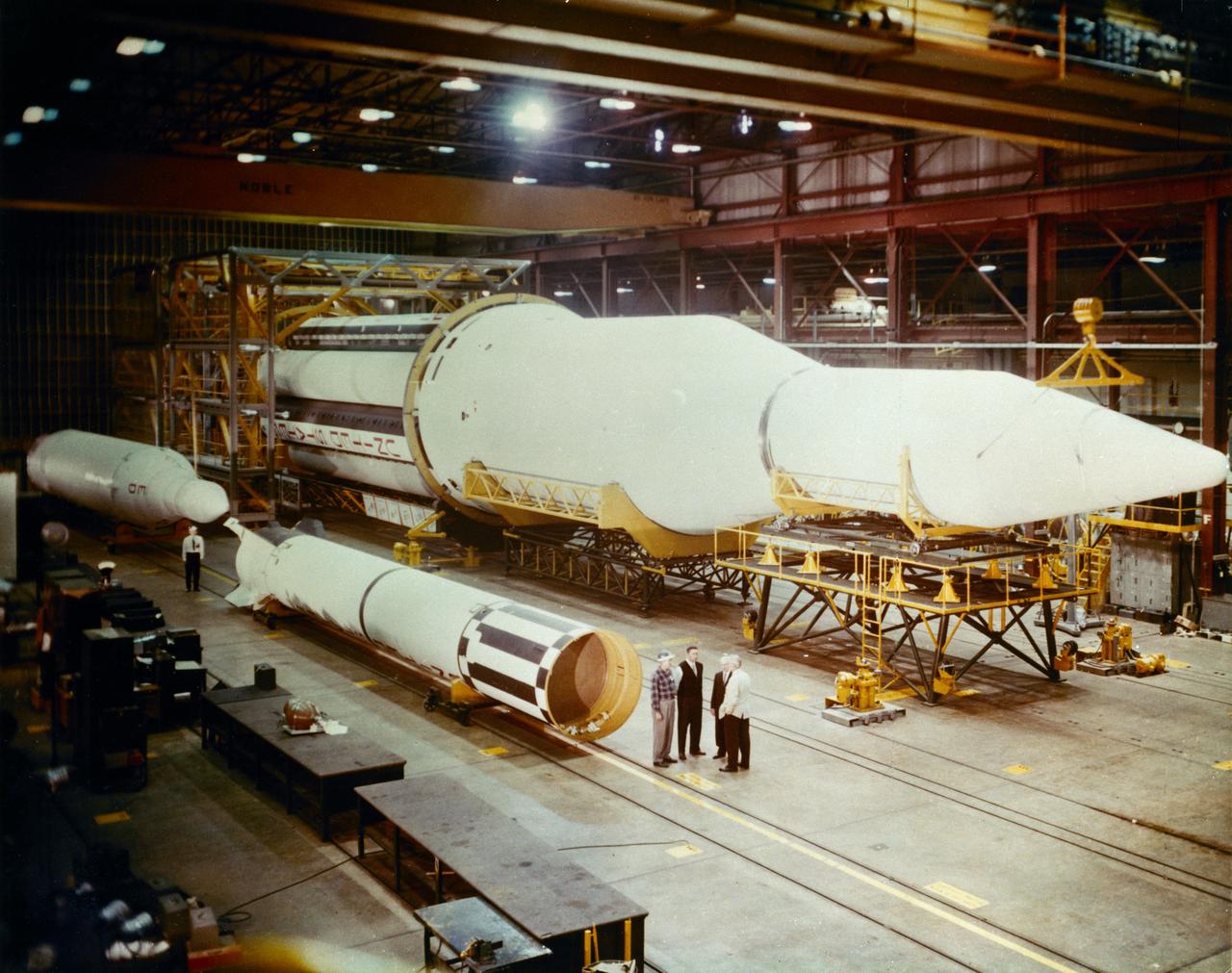

Progress in the Saturn program, depicted below, was described by Dr. Wernher von Braun, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Director, in an appearance before the Senate Committee of Aeronautical and Space Sciences. "The flight configuration of the giant three-stage Saturn C-1 rocket (later called Saturn I Block I) is seen in the Fabrication and Assembly Engineering Division at MSFC. Dwarfed by the 180-foot C-1 are a Juno II rocket (left rear) and a Mercury-Redstone rocket (front foreground). The C-1 (first version of the Saturn rocket) is composed of an S-1 first stage or booster (rear), powered by eight H-1 engines having a thrust of 1,500,000 pounds, followed by a dummy S-IV second stage and a dummy S-V third stage. The "live" S-IV for later flights, under development by Douglas Aircraft Co., will be powered by four Pratt Whitney LR-119 engines having 17,500,000 pounds thrust each. The live S-V, under development by Convair Division of General Dynamics Corp., will use two LR-119 engines. With all three stages live, the C-1 will be capable of placing 19,000 pounds into a 300-mile Earth orbit, sending 5,000 pounds to escape velocity, or lofting 2,500 pounds to Mars or Venus. The second version Saturn C-2 (later called Saturn 1 Block II) would double these capabilities. Early C-1 flights will employ a live S-1 with dummy upper stages. The first such flight is scheduled late this year."
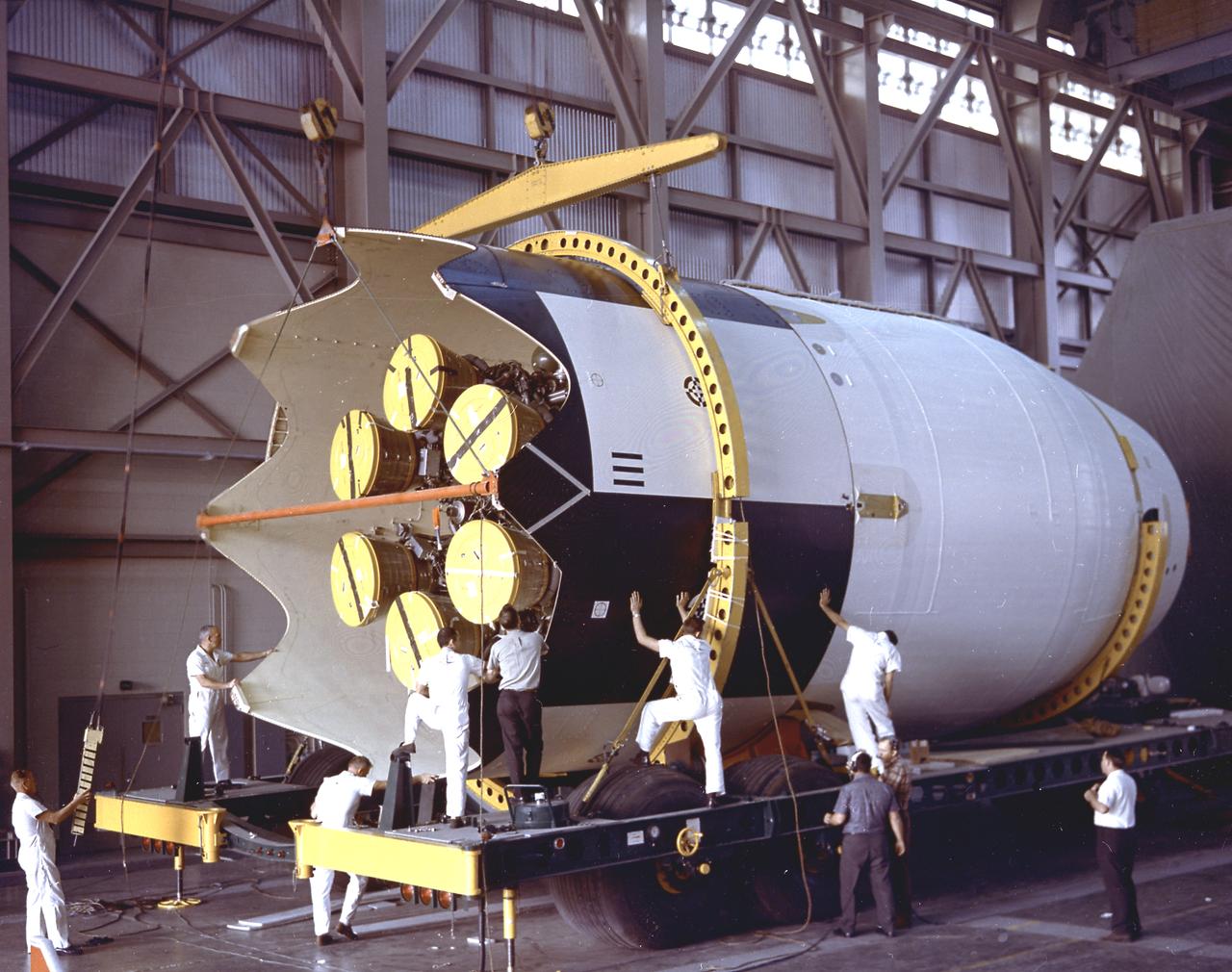

The Saturn I S-IV stage (second stage) assembly for the SA-9 mission underwent the weight and balance test in the hangar building at Cape Canaveral. The S-IV stage had six RL-10 engines which used liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as its propellants arranged in a circle. Each RL-10 engine produced a thrust of 15,000 pounds, a total combined thrust of 90,000 pounds. The SA-9 mission was the first Saturn with operational payload Pegasus I, meteoroid detection satellite, and launched on February 16, 1965.

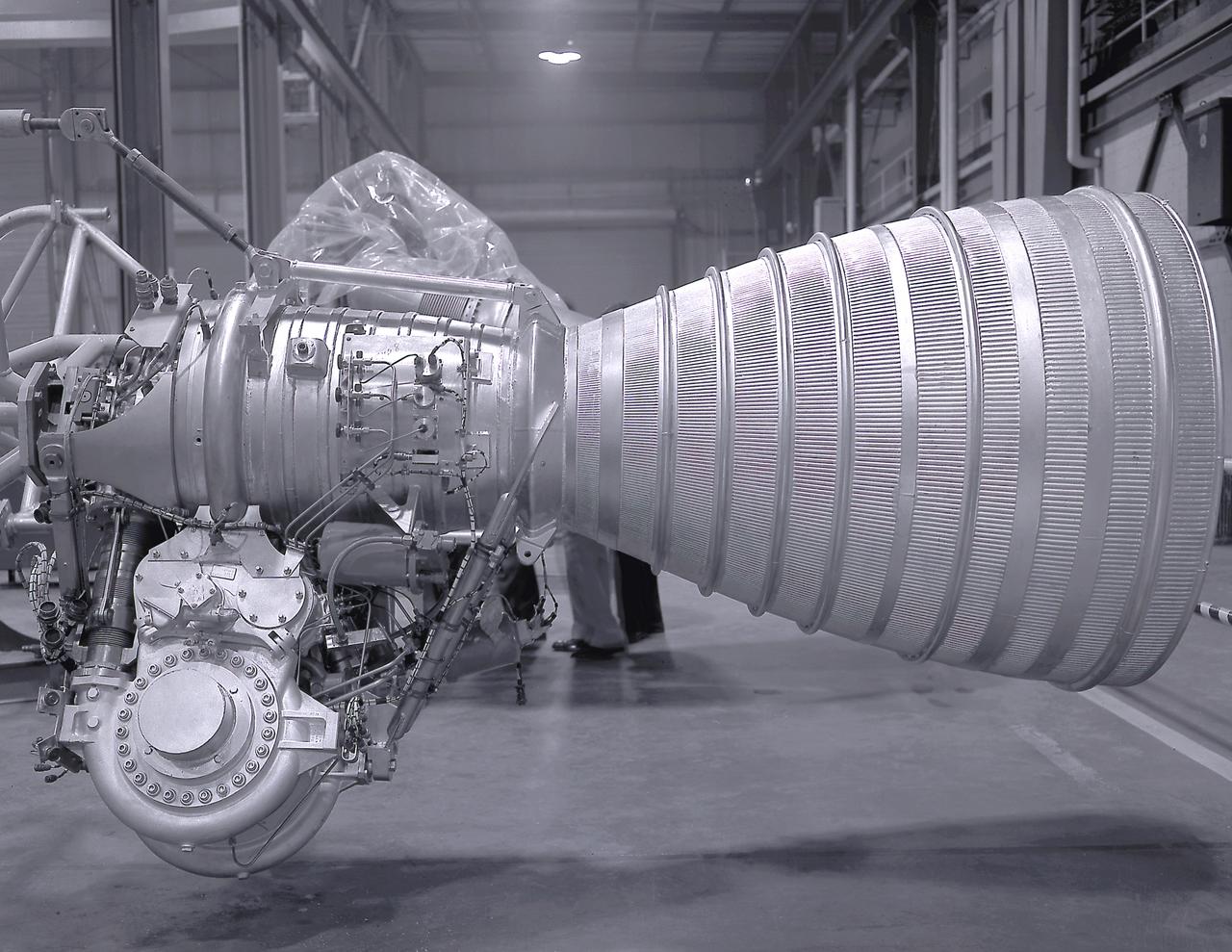
RL-10 engine characteristics. The RL-10 engine was developed under the management of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) to power the Saturn I upper stage (S-IV stage). The six RL-10 engines, which used liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as propellants, were arranged in a circle on the aft end of the S-IV stage.
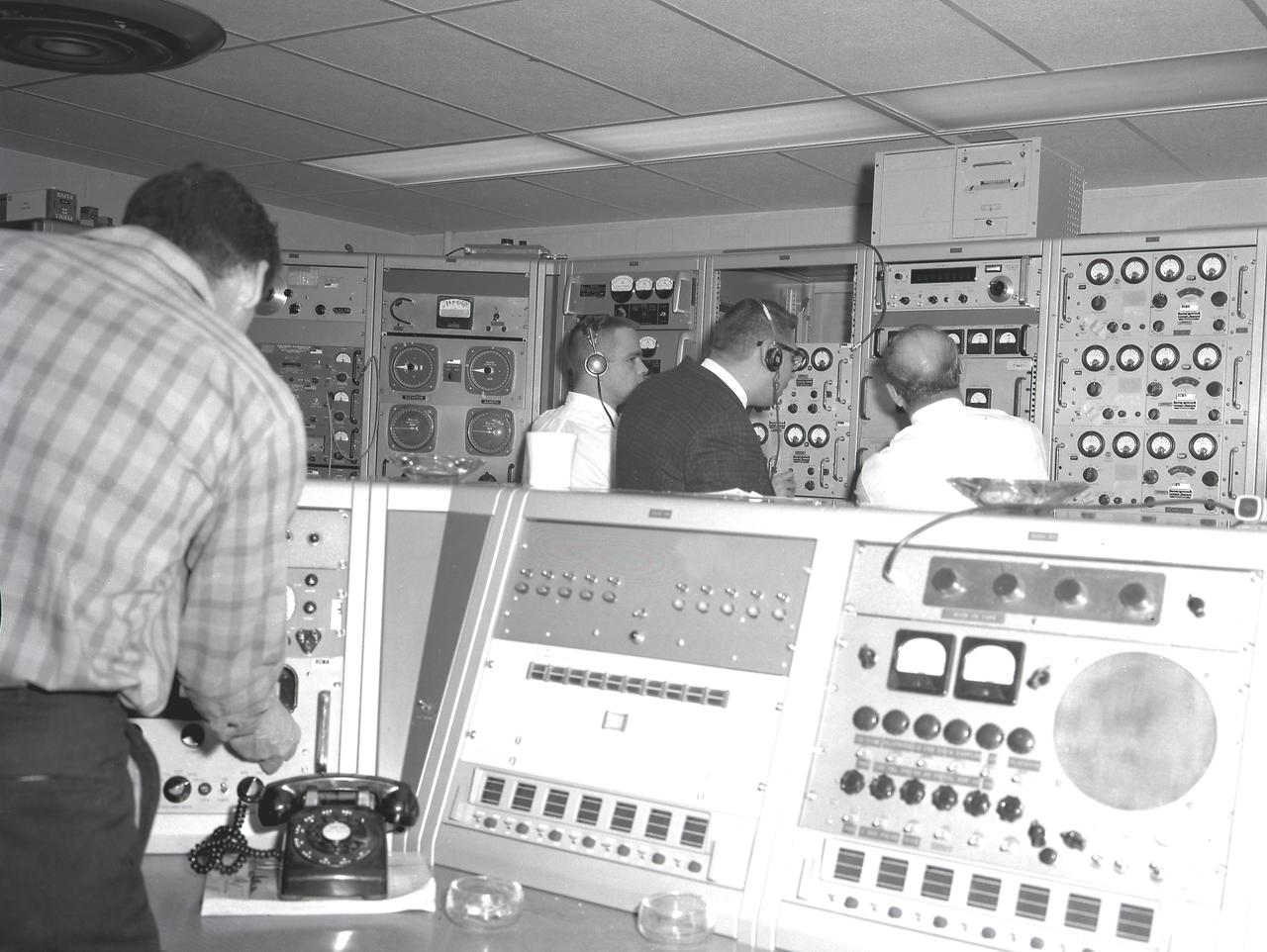

Activities at Green Mountain Tracking Station, Alabama, during lift-off of the Saturn I, SA-9 mission, showing the overall view of instrument panels used in tracking the Pegasus, meteoroid-detection satellite. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth.
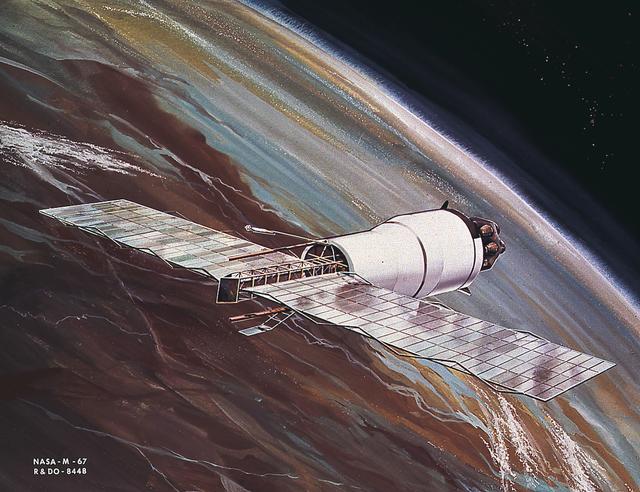

This image is an artist's conception of the Pegasus, meteoroid detection satellite, in orbit with meteoroid detector extended. The satellite, a payload for Saturn I SA-8, SA-9, and SA-10 missions, was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth.
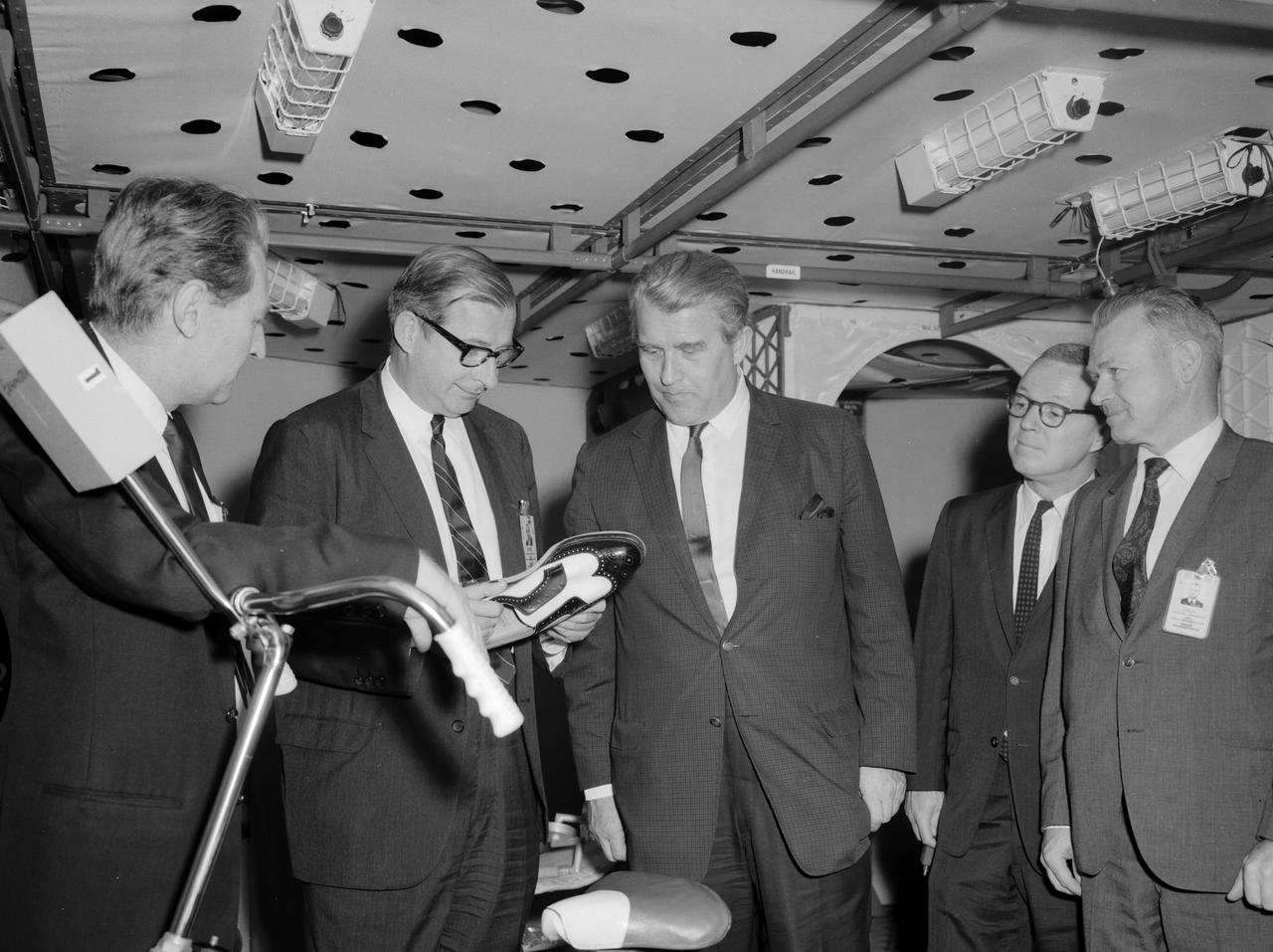

Pictured from the left, in the Saturn I mockup, are: William Brooksbank, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Propulsion and Vehicle Engineering Laboratory; Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Deputy Administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA); Dr. Wernher von Braun, MSFC director; Colonel Clare F. Farley, executive officer of the Office of the Administrator; and Charles J. Donlan, newly appointed deputy associate administrator for Manned Space Flight, technical. The party examined an ordinary man’s shoe (held by Paine) outfitted for use in the Saturn I Workshop. The shoe had a unique fastener built into the sole to allow an astronaut to move about the workshop floor and to remain in one position if he desired. Dr. Paine and his party indulged in a two-day tour at the Marshall Space Flight Center getting acquainted with Marshall personnel and programs. It was Paine’s first visit to the center since assuming the NASA post on February 1, 1968.
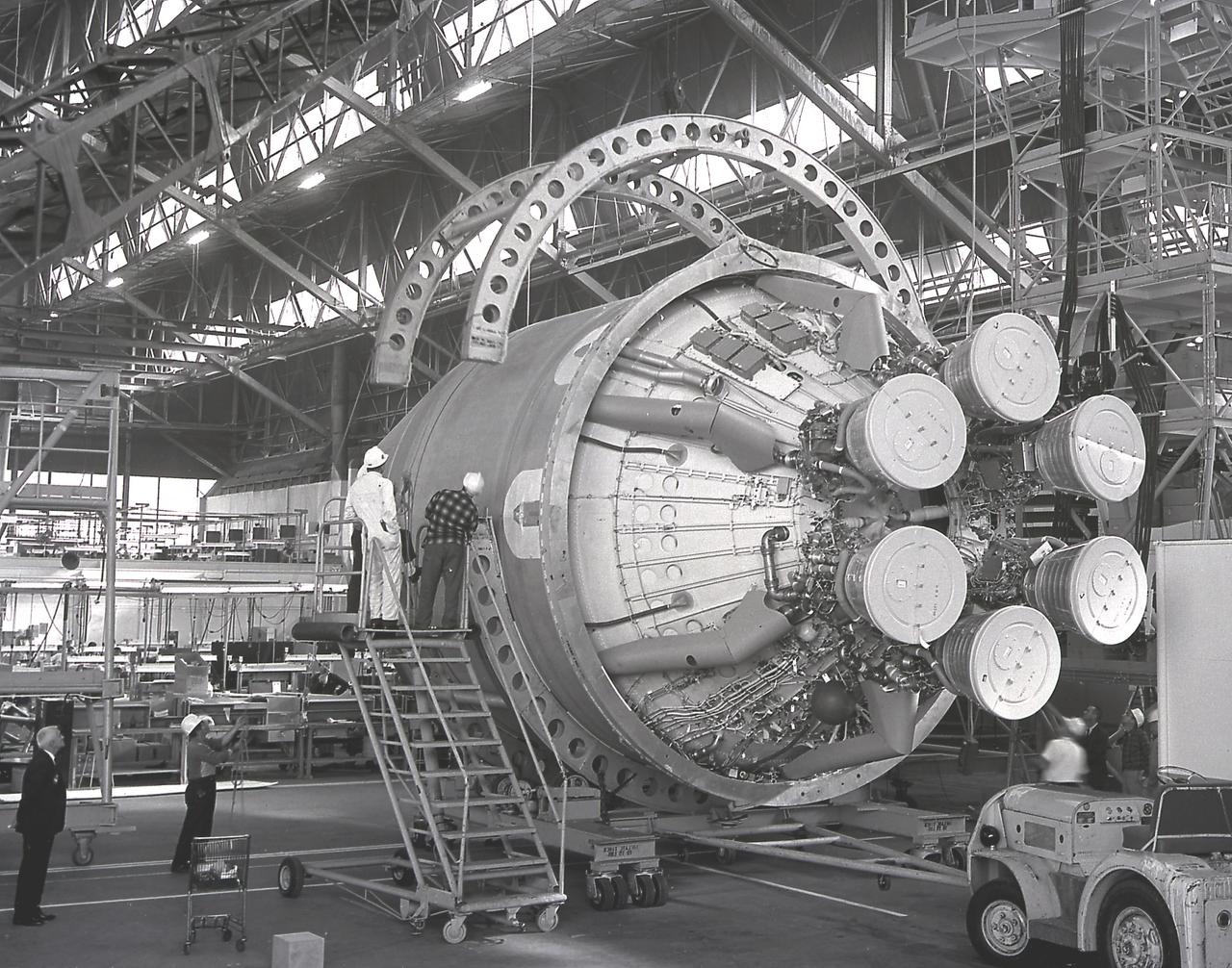
The Saturn I S-IV stage (second stage) for the SA-7 mission being prepared for shipment to Cape Canaveral, Florida. The S-IV stage had six RL-10 engines, which used liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen as its propellants, arranged in a circle. Each RL-10 engine produced a thrust of 15,000 pounds for a total combined thrust of 90,000 pounds. The SA-7 mission was launched on September 18, 1964 from Cape Canaveral, Florida, and its S-IV stage made the second orbital flight.
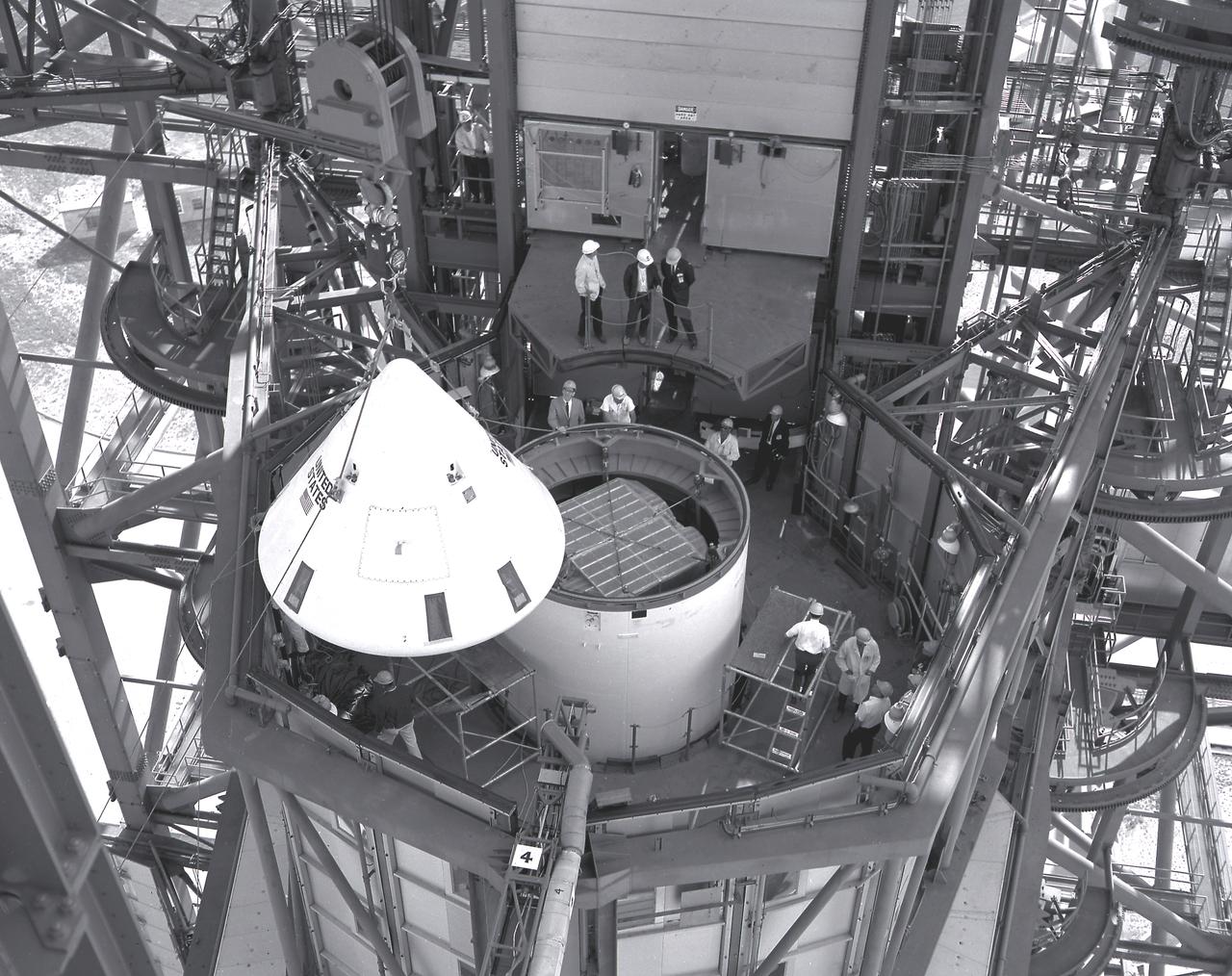
In this photograph, the Pegasus, meteoroid detection satellite is installed in its specially modified Apollo service module atop the S-IV stage (second stage) of a Saturn I vehicle for the SA-9 mission at Cape Kennedy. Personnel in the service structure moved the boilerplate Apollo command module into place to cap the vehicle. The command and service modules, visible here, were jettisoned into orbit to free the Pegasus for wing deployment. The satellite was used to obtain data on frequency and penetration of the potentially hazardous micrometeoroids in low Earth orbits and to relay the information back to Earth. The SA-9 was launched on February 16, 1965.
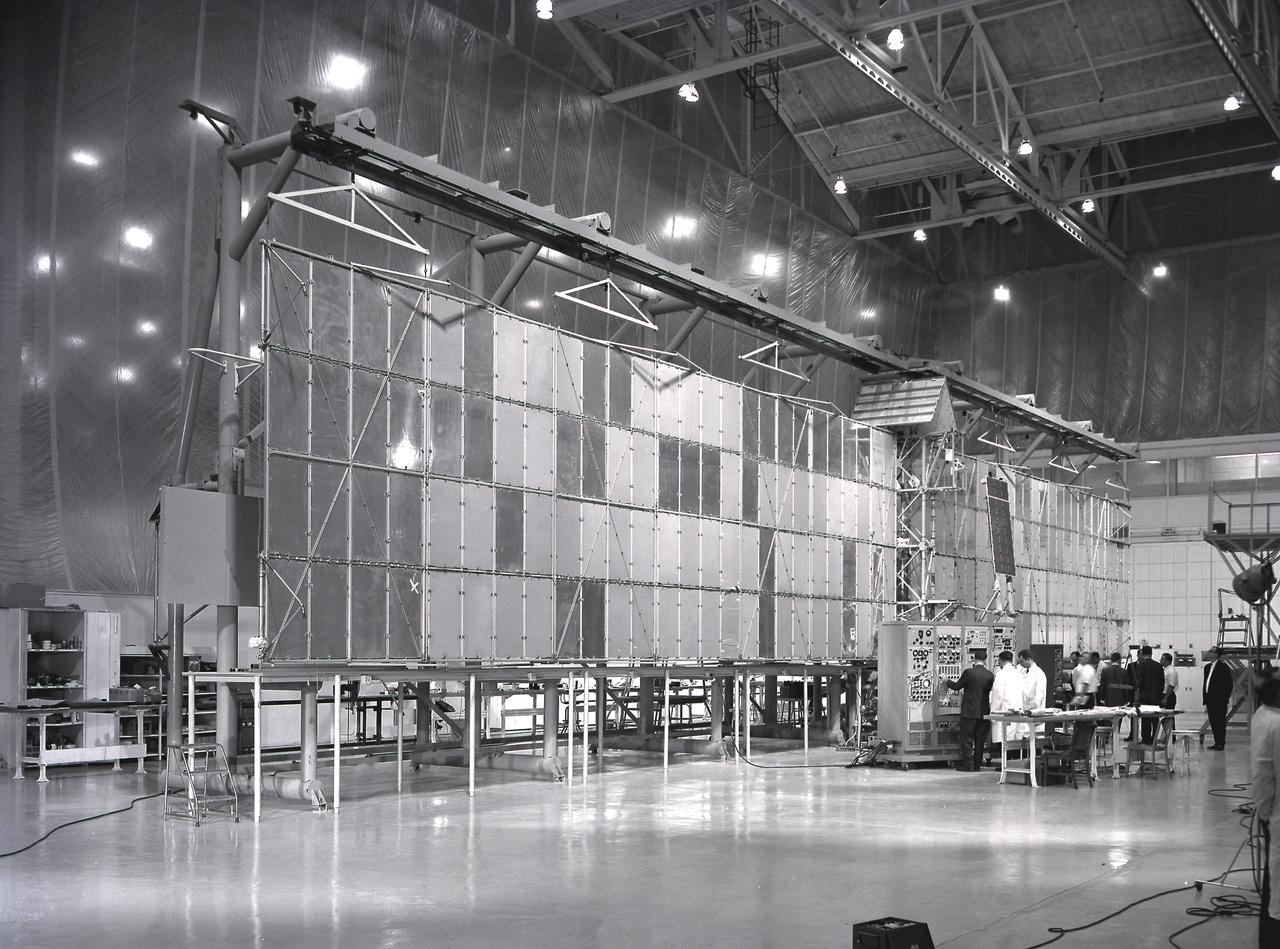

Fairchild technicians check out the extended Pegasus meteoroid detection surface. The Pegasus was developed by Fairchild Stratos Corporation, Hagerstown, Maryland, for NASA through the Marshall Space Flight Center. Three Pegasus satellites were flown aboard Saturn I SA-8, SA-9, and SA-10 missions. After being placed into orbit around the Earth, the satellite unfolded a series of giant panels to form a pair of wings measuring 96 feet across. The purpose of the satellite was to electronically record the size and frequency of particles in space, and compare the performance of protected and unprotected solar cells as important new preliminaries to a marned flight to the Moon.
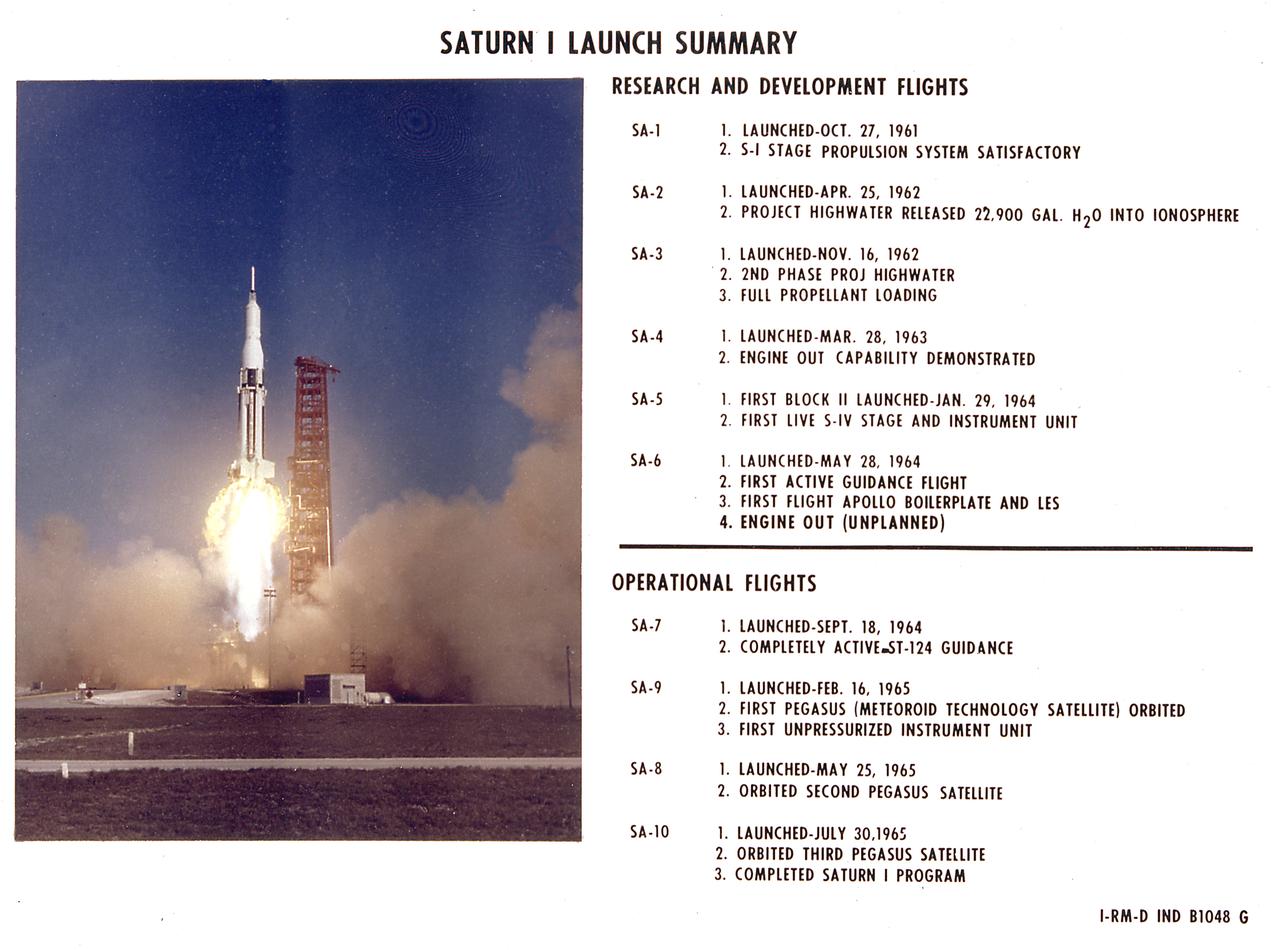
Saturn 1 Launch summary of research and development flights and operational flights. NASA's initial development plan for the Saturn program had called for the Saturn I to serve as a stepping stone to the development of larger Saturn vehicles ultimately known as the Saturn IB and Saturn V. The Saturn I launch vehicle proved the feasibility of the clustered engines and provided significant new payload lifting capabilities.
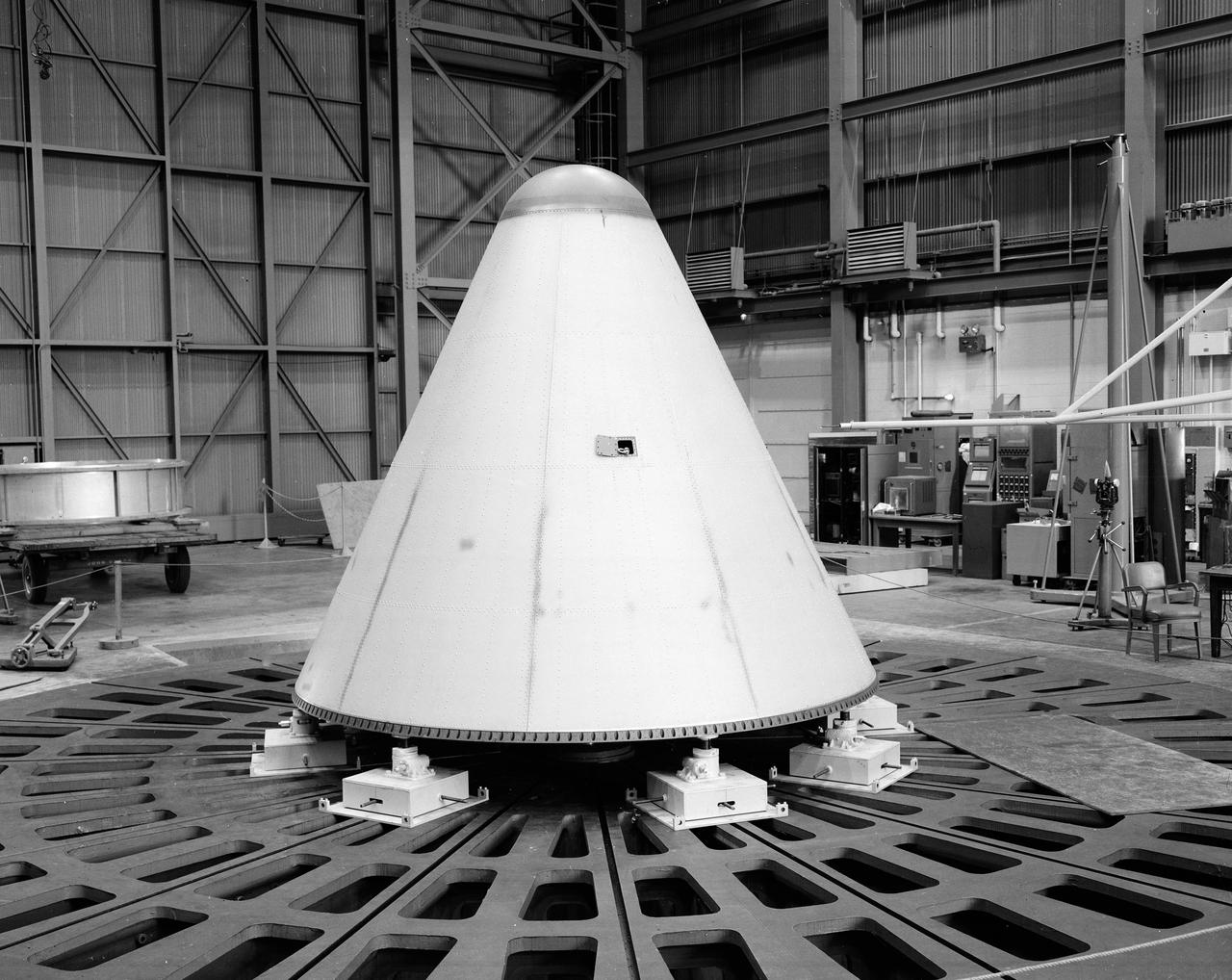

Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC’s “building block” approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions. The Saturn IB vehicle was a two-stage rocket and had a payload capability about 50 percent greater than the Saturn I vehicle. The first stage, S-IB stage, was a redesigned first stage of the Saturn I. This photograph is of the S-IB nose cone #3 during assembly in building 4752.
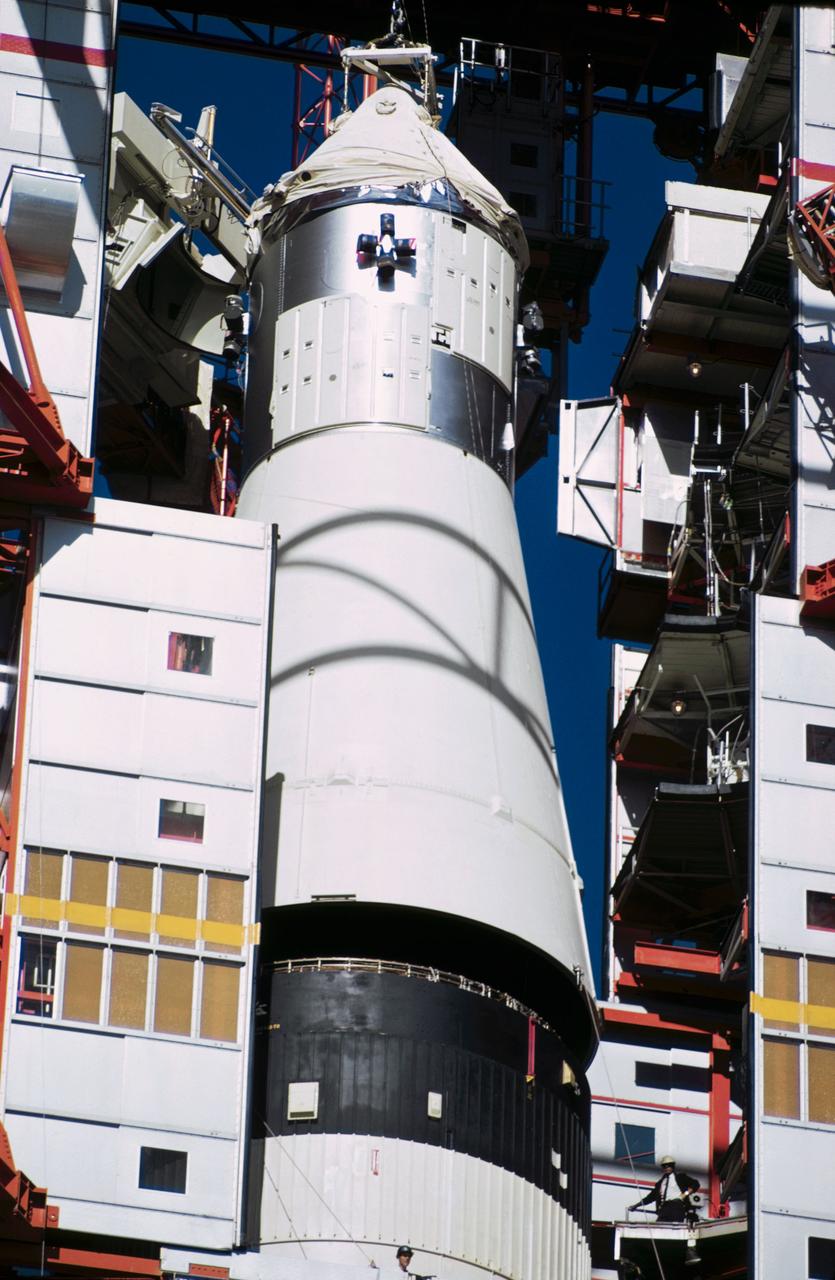

S67-17042 (1967) --- Apollo Spacecraft 012 is hoisted to the top of the gantry at Pad 34 during the Apollo/Saturn Mission 204 erection. S/C 012 will be mated with the uprated Saturn I launch vehicle.
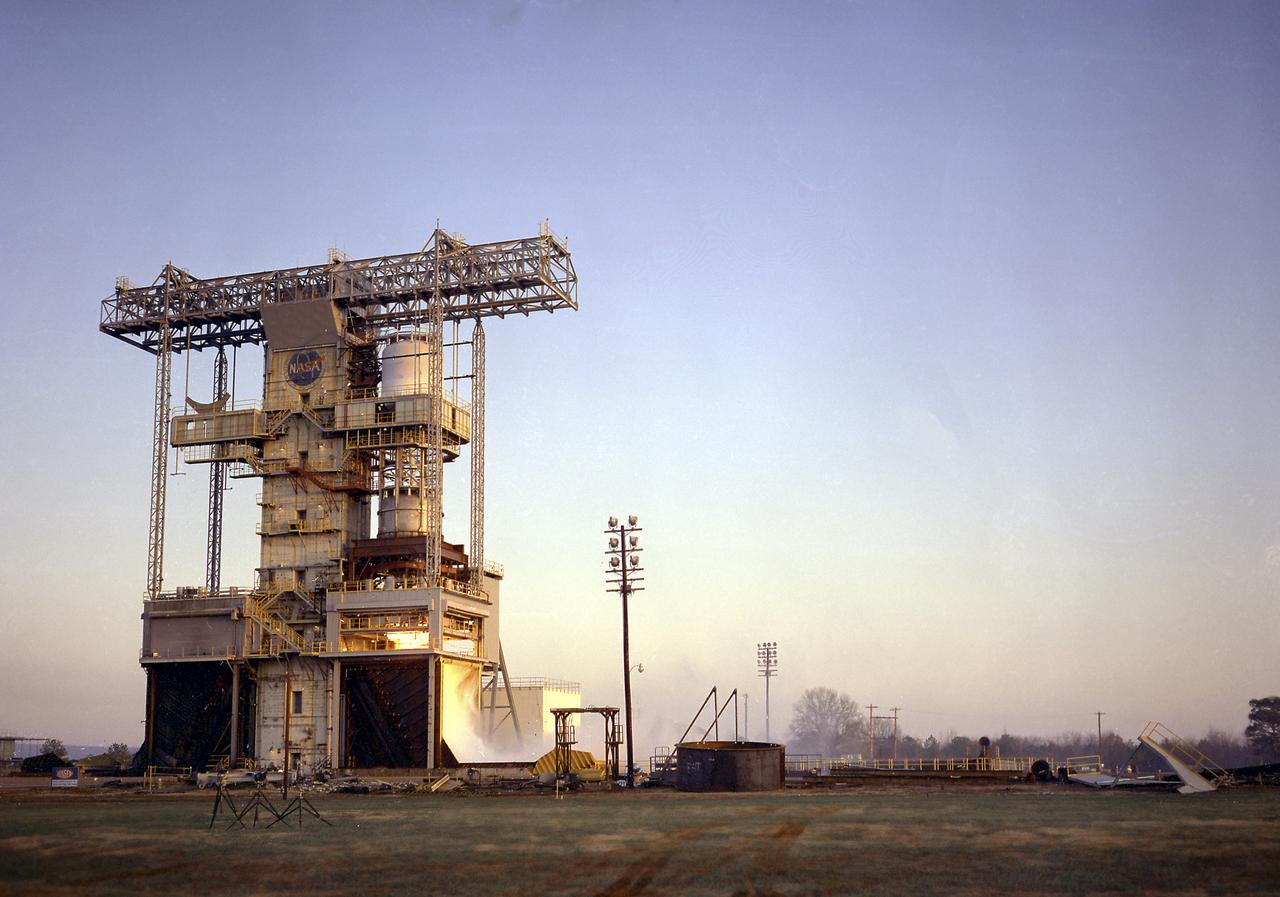

The test laboratory of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) tested the F-1 engine, the most powerful rocket engine ever fired at MSFC. The engine was tested on the newly modified Saturn IB static test stand that had been used for three years to test the Saturn I eight-engine booster, S-I (first) stage. In 1961, the test stand was modified to permit static firing of the S-I/S-IB stage and the name of the stand was then changed to the S-IB Static Test Stand. Producing a combined thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, five F-1 engines powered the S-IC (first) stage of the Saturn V vehicle for the marned lunar mission.
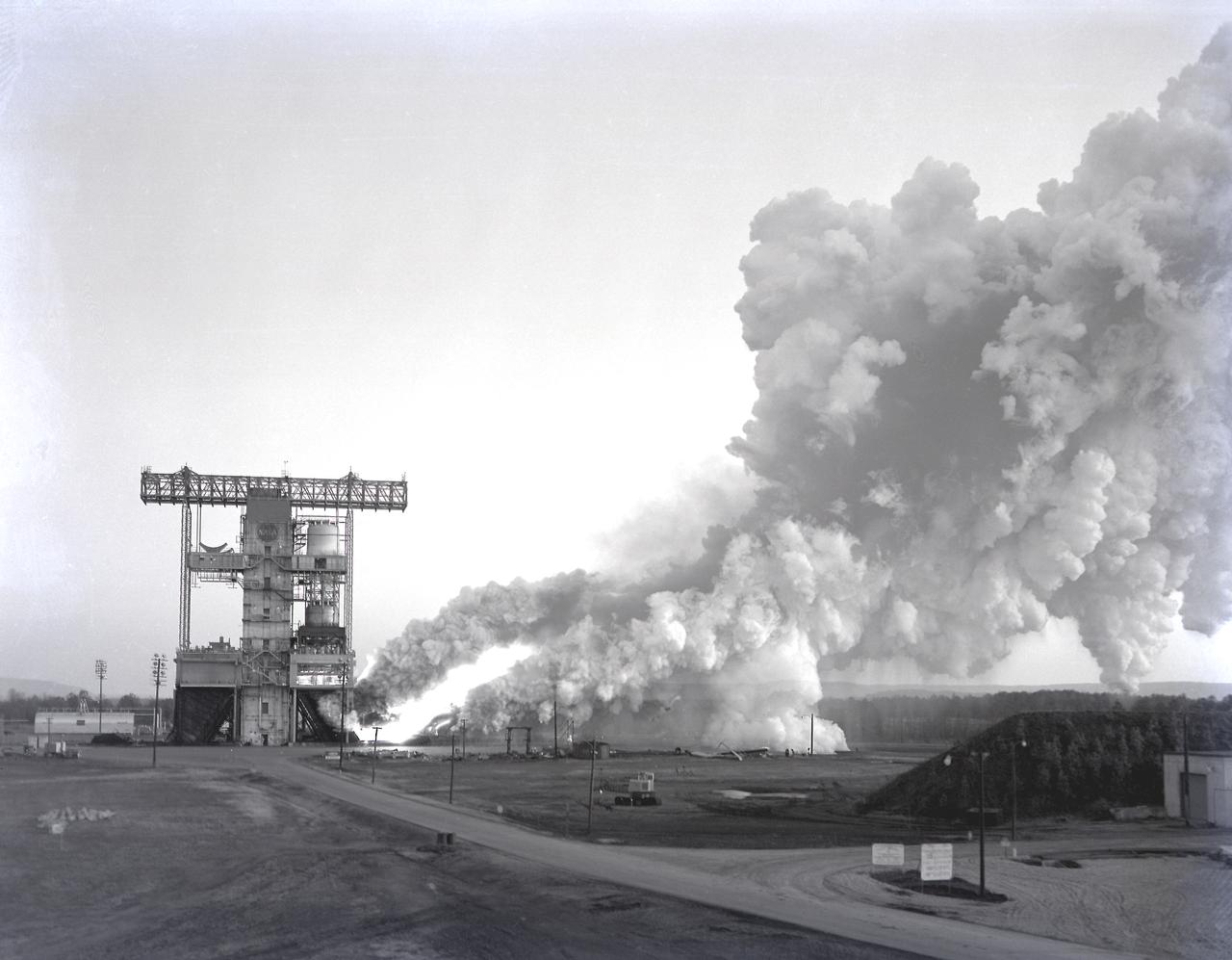

The test laboratory of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) tested the F-1 engine, the most powerful rocket engine ever fired at MSFC. The engine was tested on the newly modified Saturn IB Static Test Stand which had been used for three years to test the Saturn I eight-engine booster, S-I (first) stage. In 1961 the test stand was modified to permit static firing of the S-I/S-IB stage and the name of the stand was then changed to the S-IB Static Test Stand. Producing a combined thrust of 7,500,000 pounds, five F-1 engines powered the S-IC (first) stage of the Saturn V vehicle for the marned lunar mission.
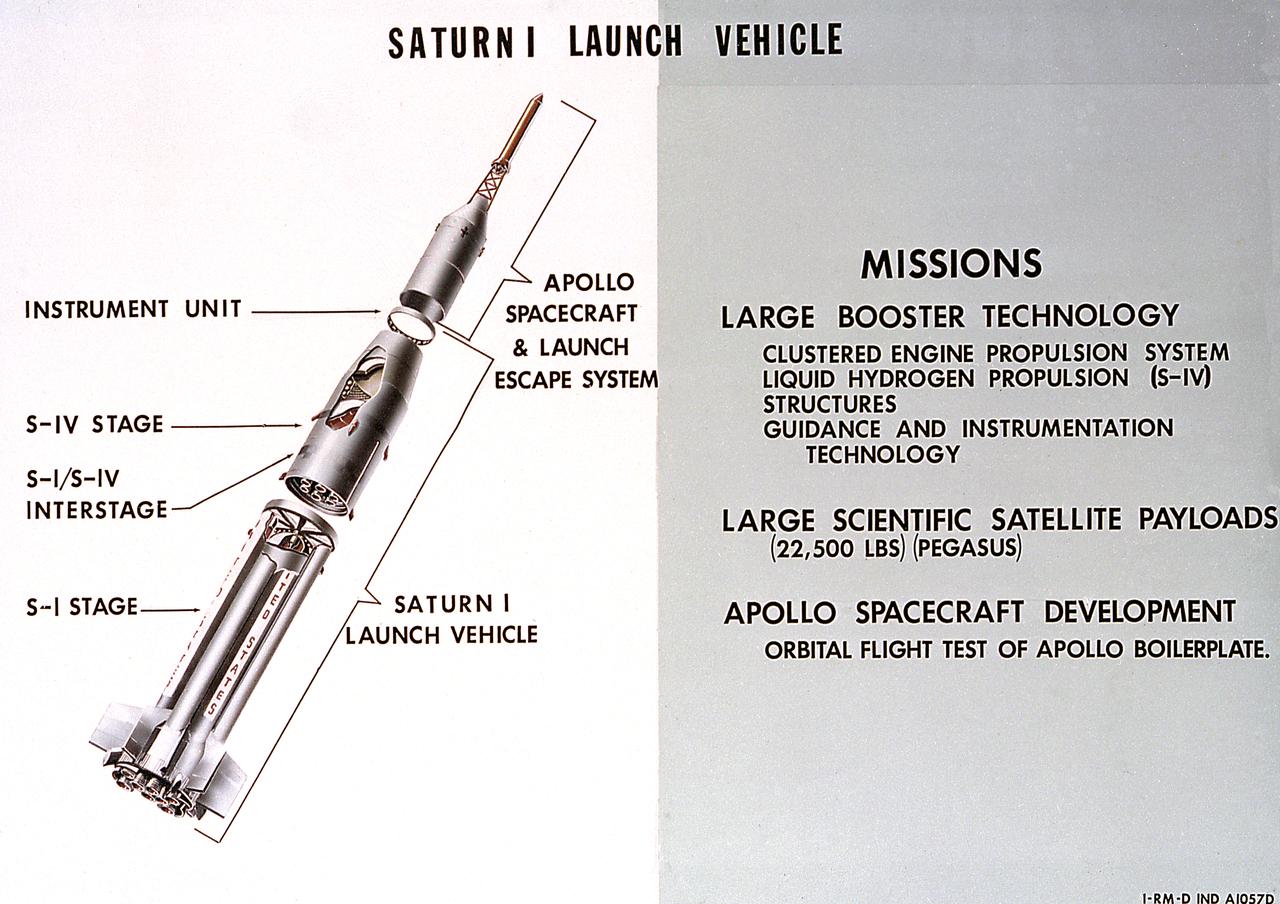
A cutaway illustration of Saturn 1 launch vehicle mission. The Saturn I, first of the Saturn launch vehicles' family, is a two-stage vehicle with a low-earth-orbit payload capability of approximately 25,000 pounds. The research and development program was plarned in two phases or blocks; one for first stage development (Block I) and the second for first and second stage development (Block II). The S-I (first) stage consisted of a cluster of nine propellant tanks and eight H-1 engines built by Rocketdyne, yeilding a total thrust of 1,500,000 pounds. The second stage of Saturn I, identified as S-IV, was designed as a single cylinder with a common bulkhead separating the liquid oxygen from the liquid hydrogen. Propulsion was provided by six RL-10 engines built by Pratt Whitney, capable of producing a combined thrust of 90,000 pounds. Of the 10 Saturn I's planned, the first eight were designed and built at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The remaining two were built by the Chrysler Corporation.

This drawing clearly shows the comparative sizes of the rocket engines used to launch the Saturn vehicles. The RL-10 and the H-1 engines were used to launch the Saturn I rockets. The J-2 engine was used on the second stage of Saturn IB and the second and third stages of Saturn V. The F-1 engine was used on the first stage of the Saturn V.
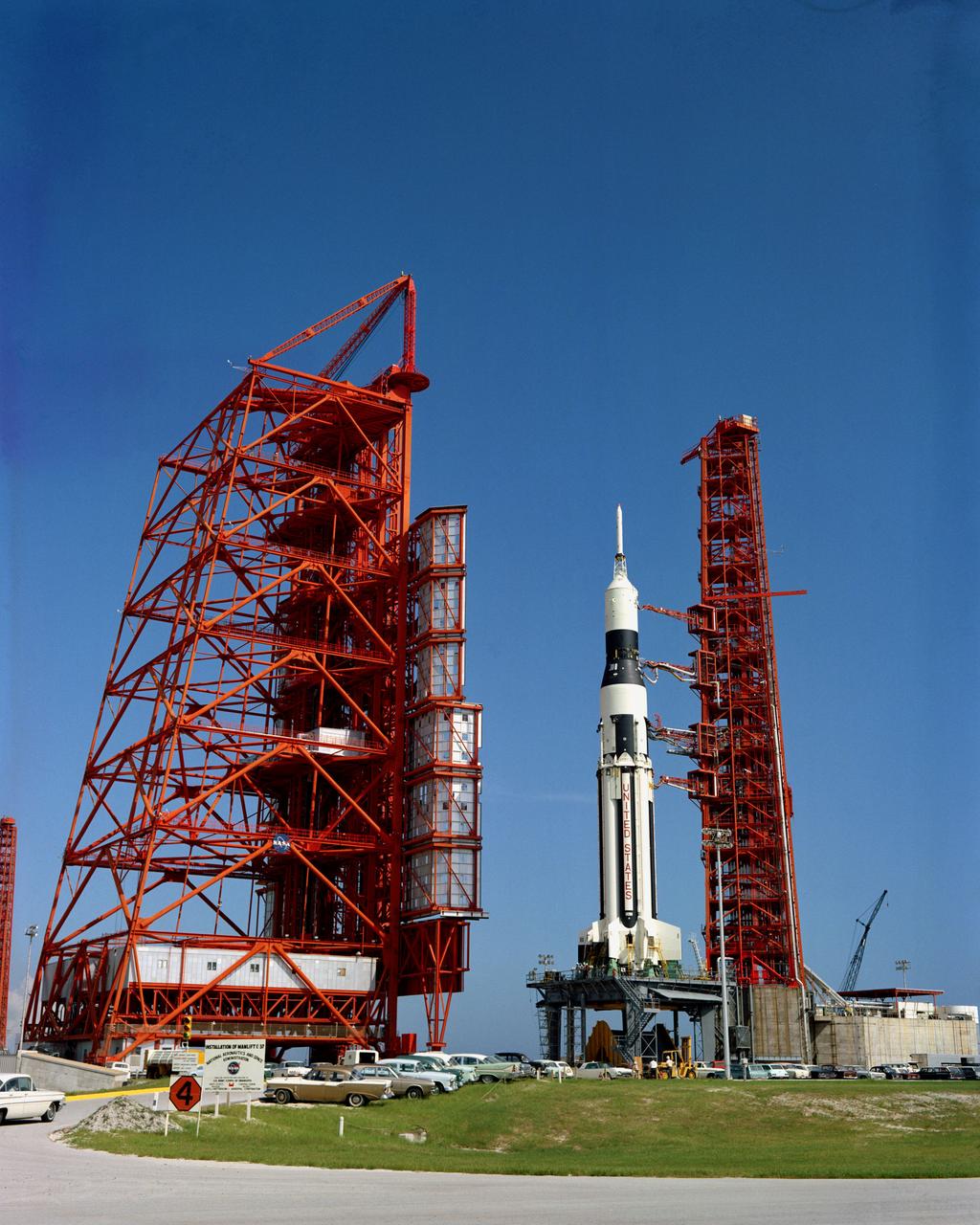

View of a Saturn I on the launch pad for a Radio Frequency Interference Test, to be conducted at LC-37A. Cape Kennedy Missile Test Center
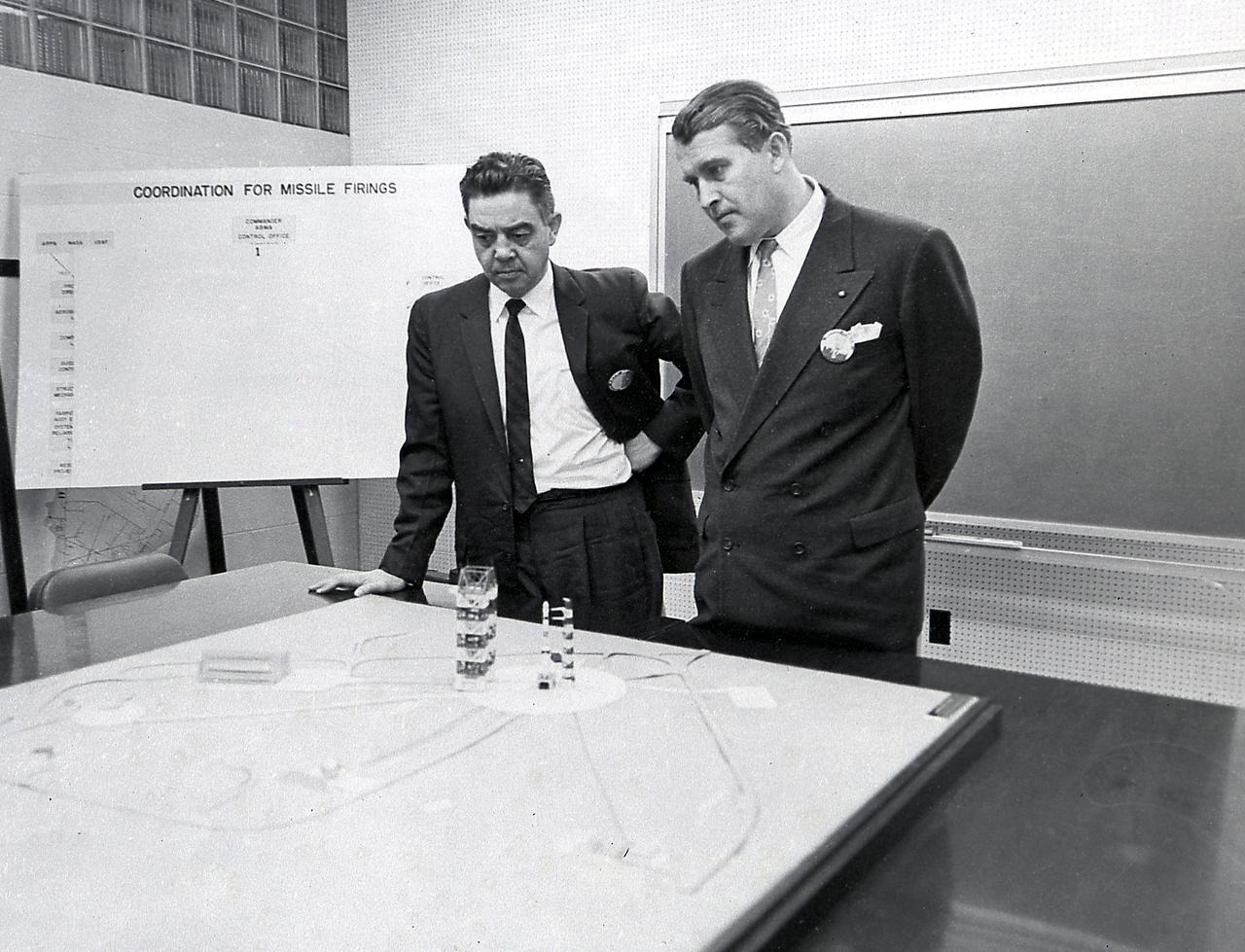

Dr. von Braun and Don Ostrander, head of the Launch Vehicle Program of the NASA Headquarters look at a model of the Saturn I launch complex 34.

This 1968 cutaway drawing illustrates the Saturn IB launch vehicle with its two booster stages, the S-IB and S-IVB. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the marned lunar mission.

Workmen at the Kennedy Space Center position the nose cone for the 204LM-1, an unmanned Apollo mission that tested the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) in Earth orbit. Also known as Apollo 5, the spacecraft was launched on the fourth Saturn IBC launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IBC utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.

Workmen at the Kennedy Space Center position the nose cone for the 204LM-1, an unmanned Apollo mission that tested the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) in Earth orbit. Also known as Apollo 5, the spacecraft was launched on the fourth Saturn IBC launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IBC utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.

This chart provides a launch summary of the Saturn IB launch vehicle as of 1973. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the marned lunar missions.
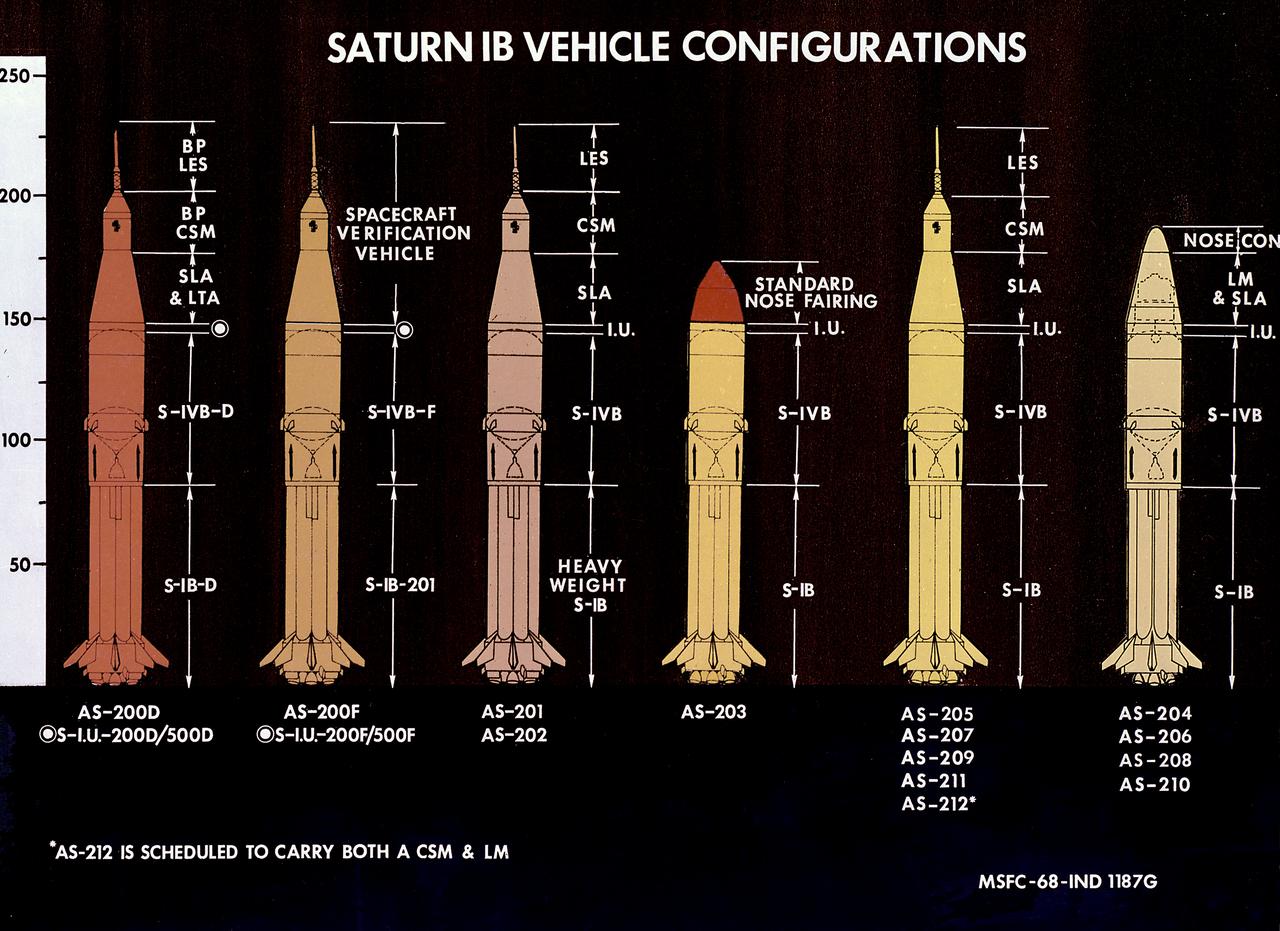
This 1968 chart depicts the various mission configurations for the Saturn IB launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the marned lunar missions.

This undated cutaway drawing illustrates the Saturn IB launch vehicle with its two booster stages, the S-IB and S-IVB. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the marned lunar missions.
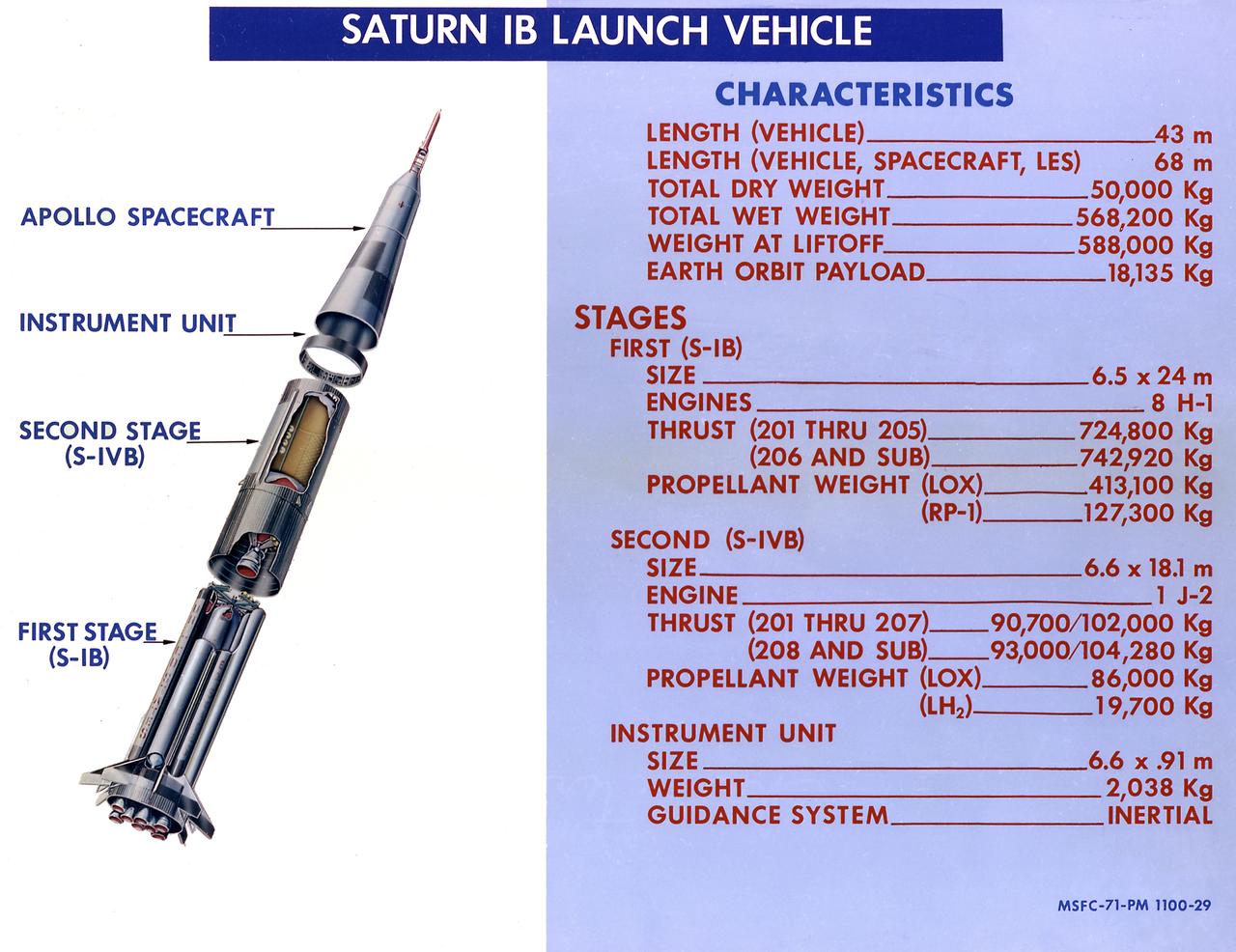
This 1968 cutaway drawing illustrates the Saturn IB launch vehicle with its two booster stages, the S-IB (first stage) and S-IVB (second stage), and provides the vital statistics in metric units. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the marned lunar missions.

This 1968 chart illustrates the characteristics and proposed missions for the Saturn IB launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the marned lunar missions.
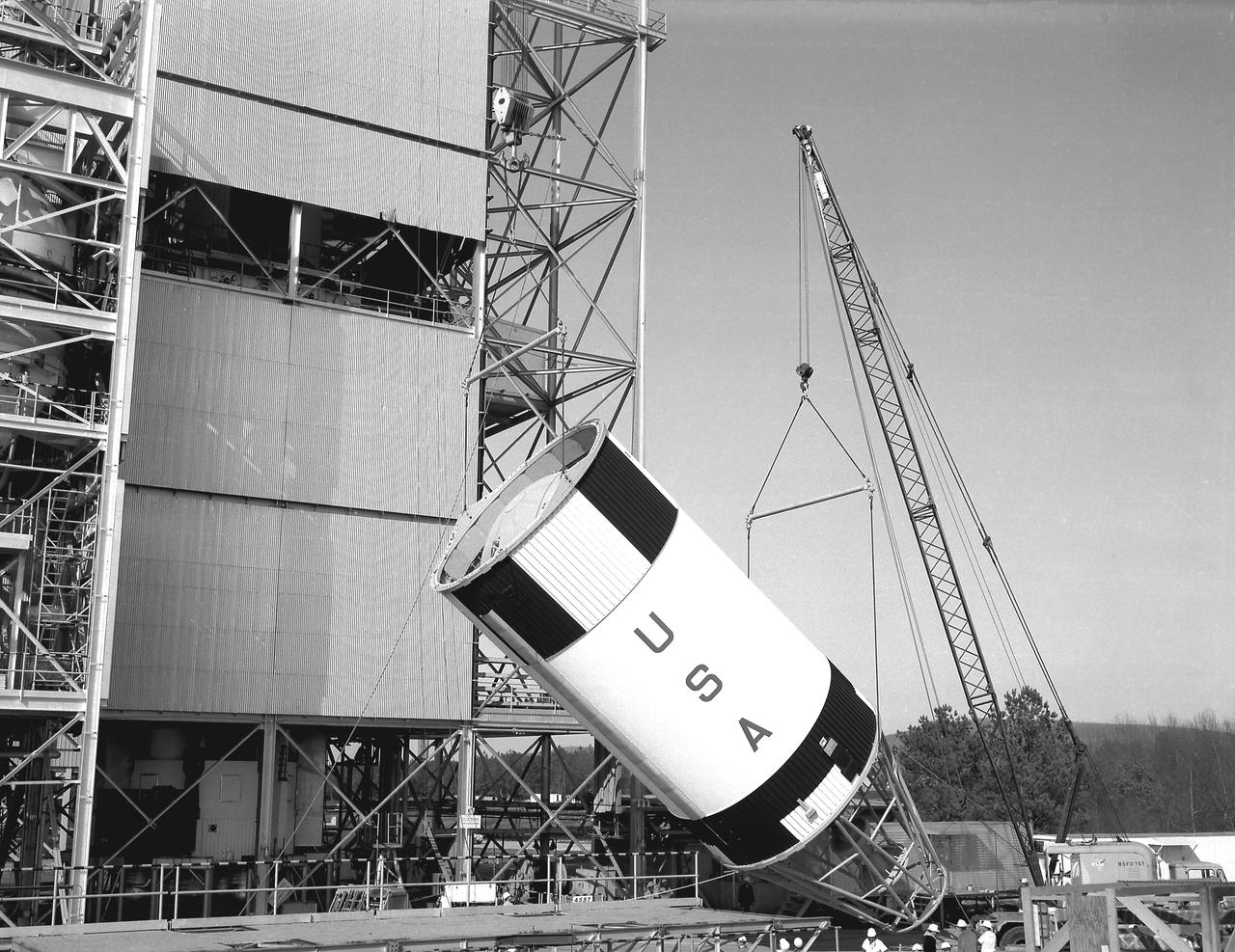

Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) workers hoist a dynamic test version of the S-IVB stage, the Saturn IB launch vehicle's second stage, into the Center's Dynamic Test Stand on January 18, 1965. MSFC Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the launch vehicle's structural soundness. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
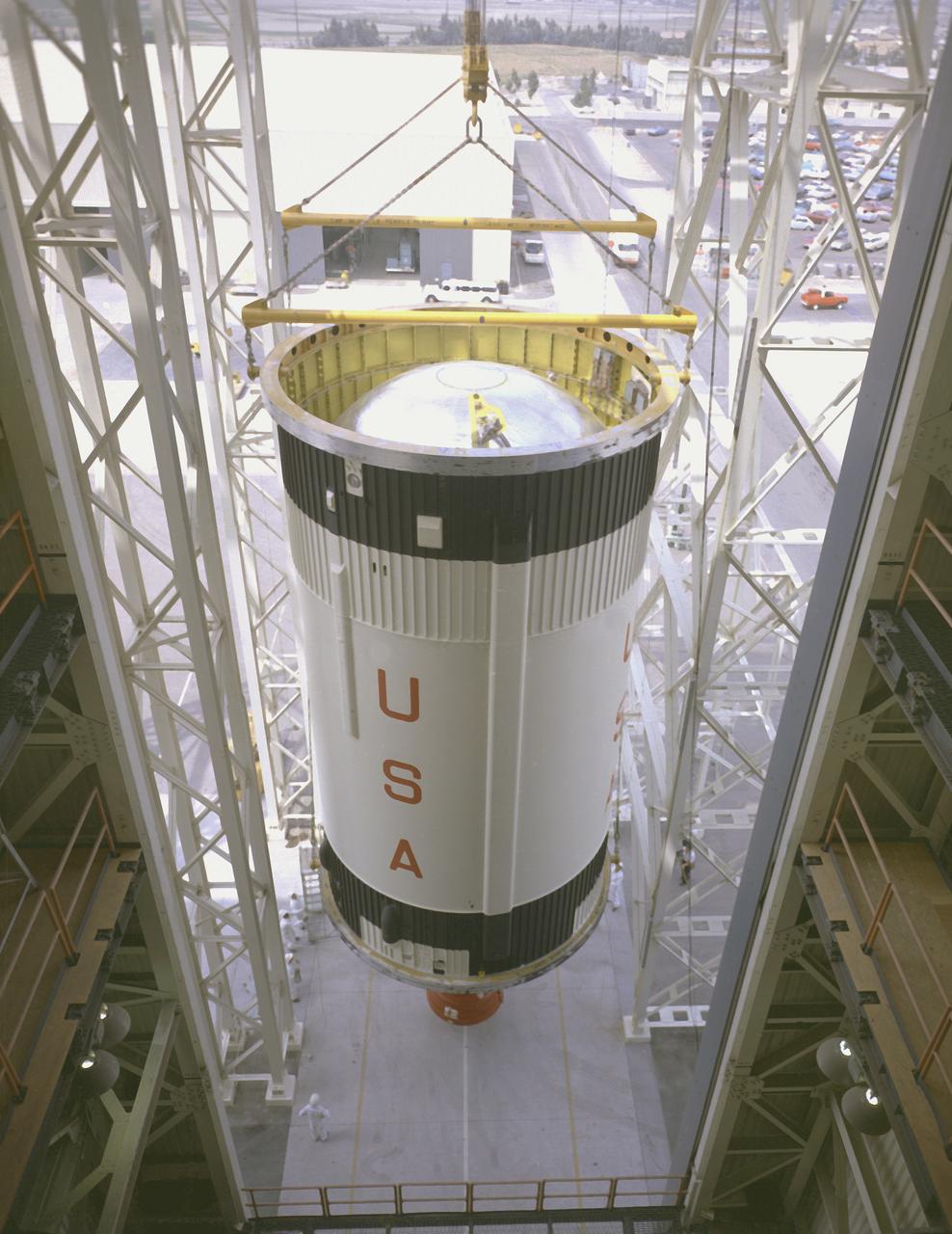

Workers at McDornel-Douglas install the Saturn IB S-IVB (second) stage for the Apollo-Soyuz mission into the company's S-IVB assembly and checkout tower in Huntington Beach, California. The Saturn IB launch vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in its "building block" approach to Saturn rocket development. This vehicle utilized the Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the capabilities of a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft required for the manned lunar missions. The S-IVB stage, later used as the third stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle, was powered by a single J-2 engine initially capable of 200,000 pounds of thrust.
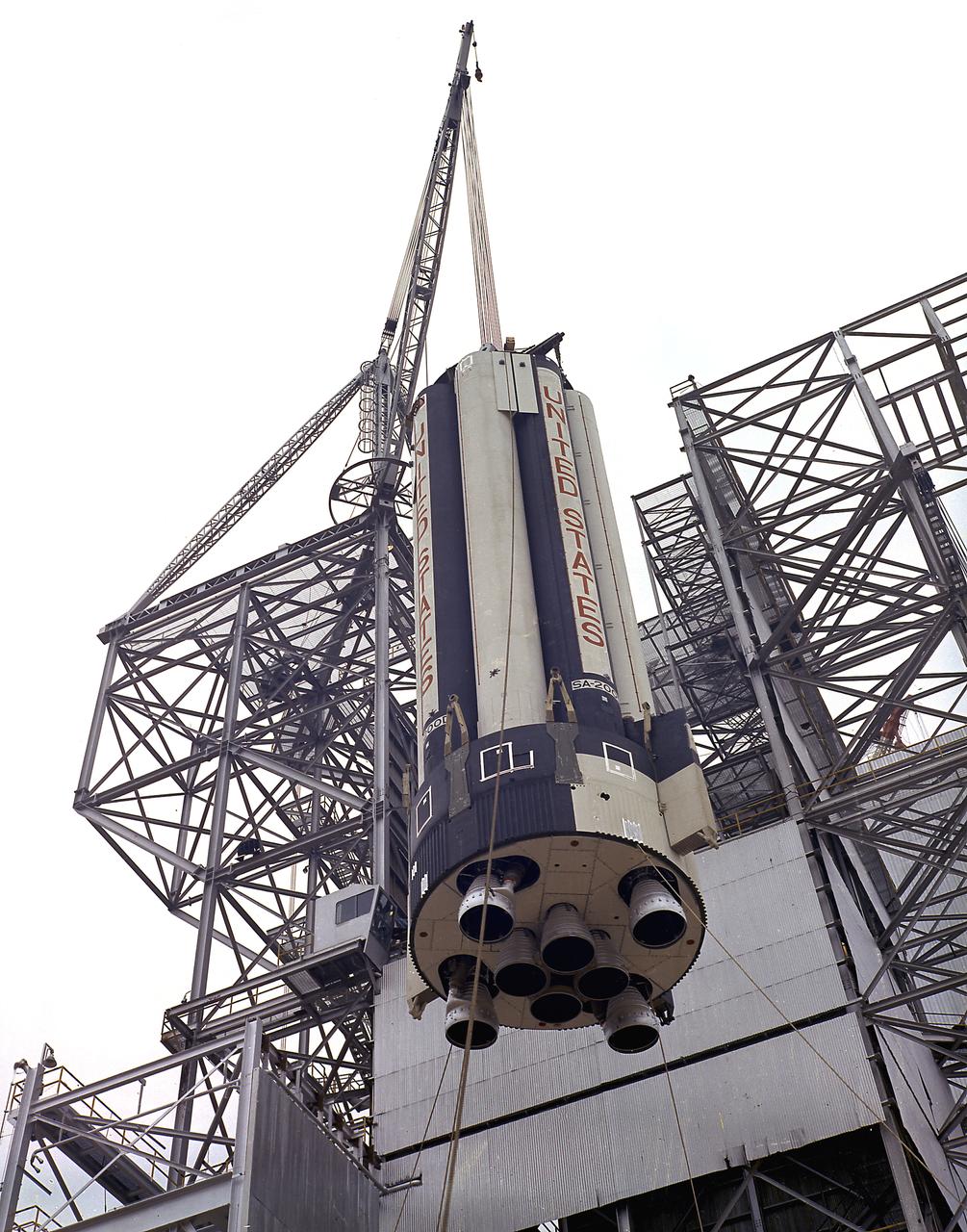

Workers at the Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) Dynamic Test Stand install S-IB-200D, a dynamic test version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage, on January 11, 1965. MSFC Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the launch vehicle's structural soundness. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
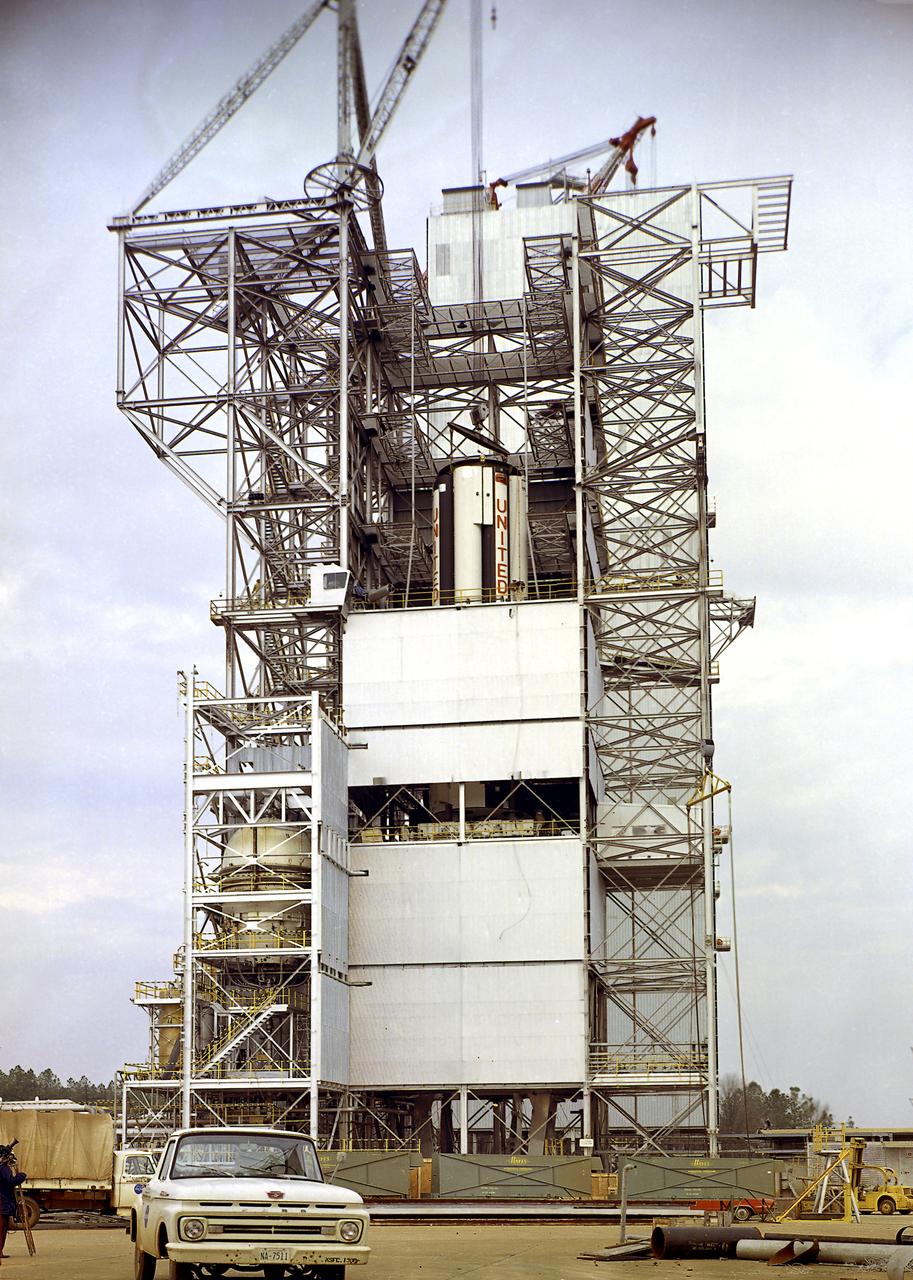
Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) workers lower S-IB-200D, a dynamic test version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB stage), into the Center's Dynamic Test Stand on January 12, 1965. Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the structural soundness of the launch vehicle. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine large boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.

Workmen at the Kennedy Space Center hoist the Saturn Lunar Module (LM) Adapter into position during assembly of the 204LM-1, an unmanned Apollo mission that tested the Apollo Lunar Module in Earth orbit. Also known as Apollo 5, the spacecraft was launched on the fourth Saturn IB launch vehicle. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine a larger booster and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
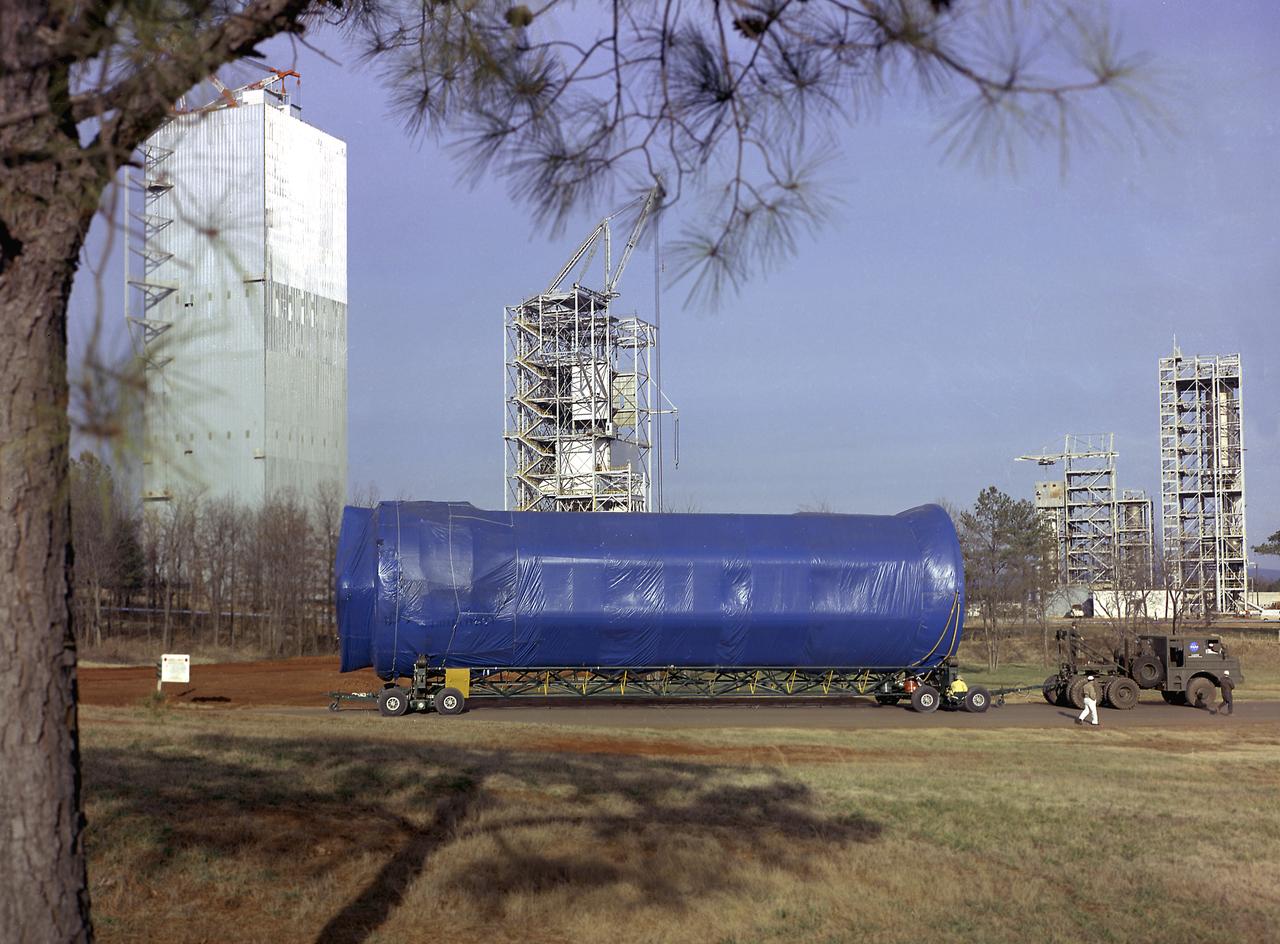

S-IB-200D, a dynamic test version of the Saturn IB launch vehicle's first stage (S-IB), makes its way to the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) East Test Area on January 4, 1965. Test Laboratory persornel assembled a complete Saturn IB to test the structural soundness of the launch vehicle in the Dynamic Test Stand. Developed by the MSFC as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the manned lunar missions.
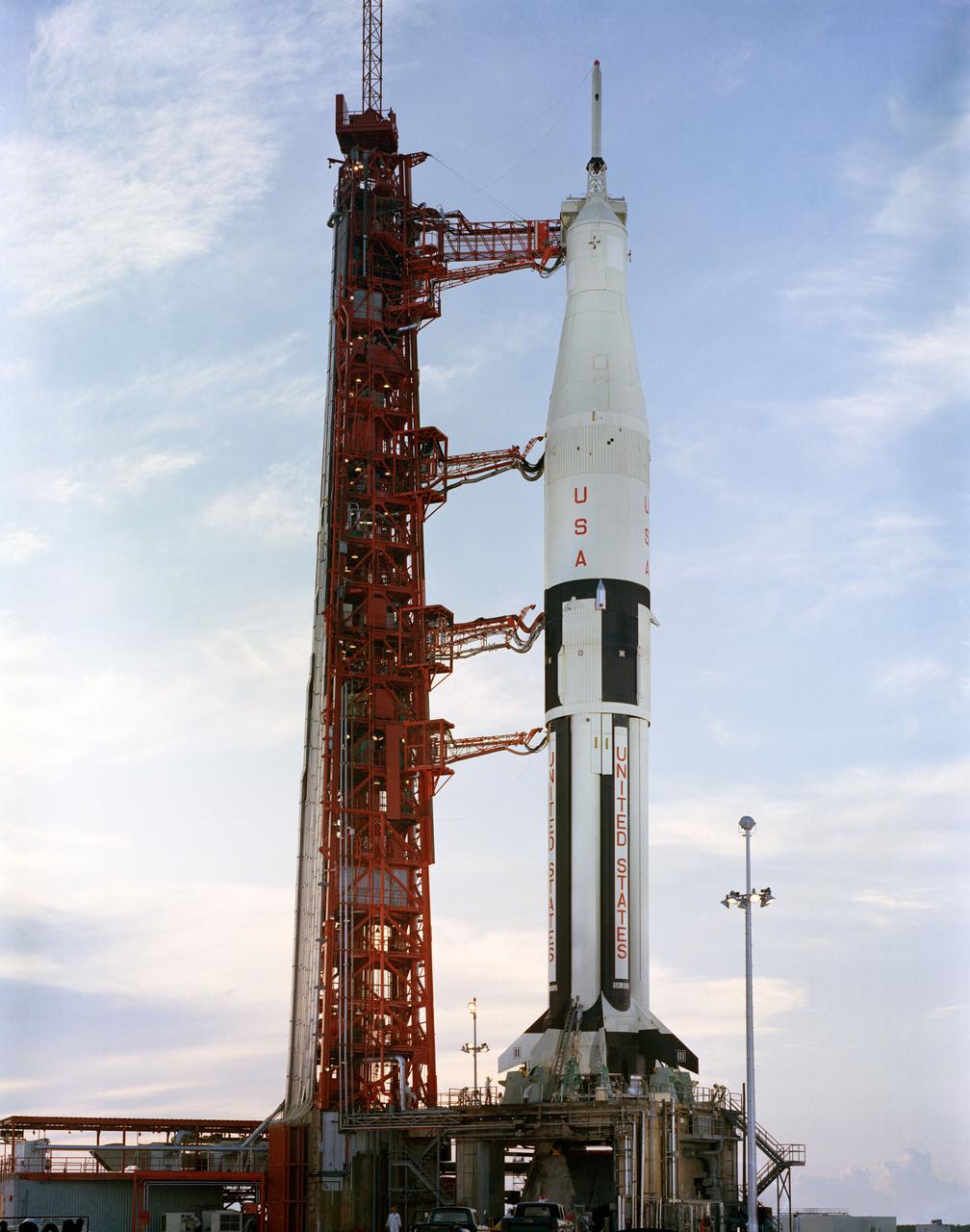

Scene at the LC-34 during an A/S 202 Prelaunch Alert. The mission was a step toward qualifying the Apollo Command and Service Modules (CSM) and the uprated Saturn I Launch Vehicle for manned flight. KSC, FL
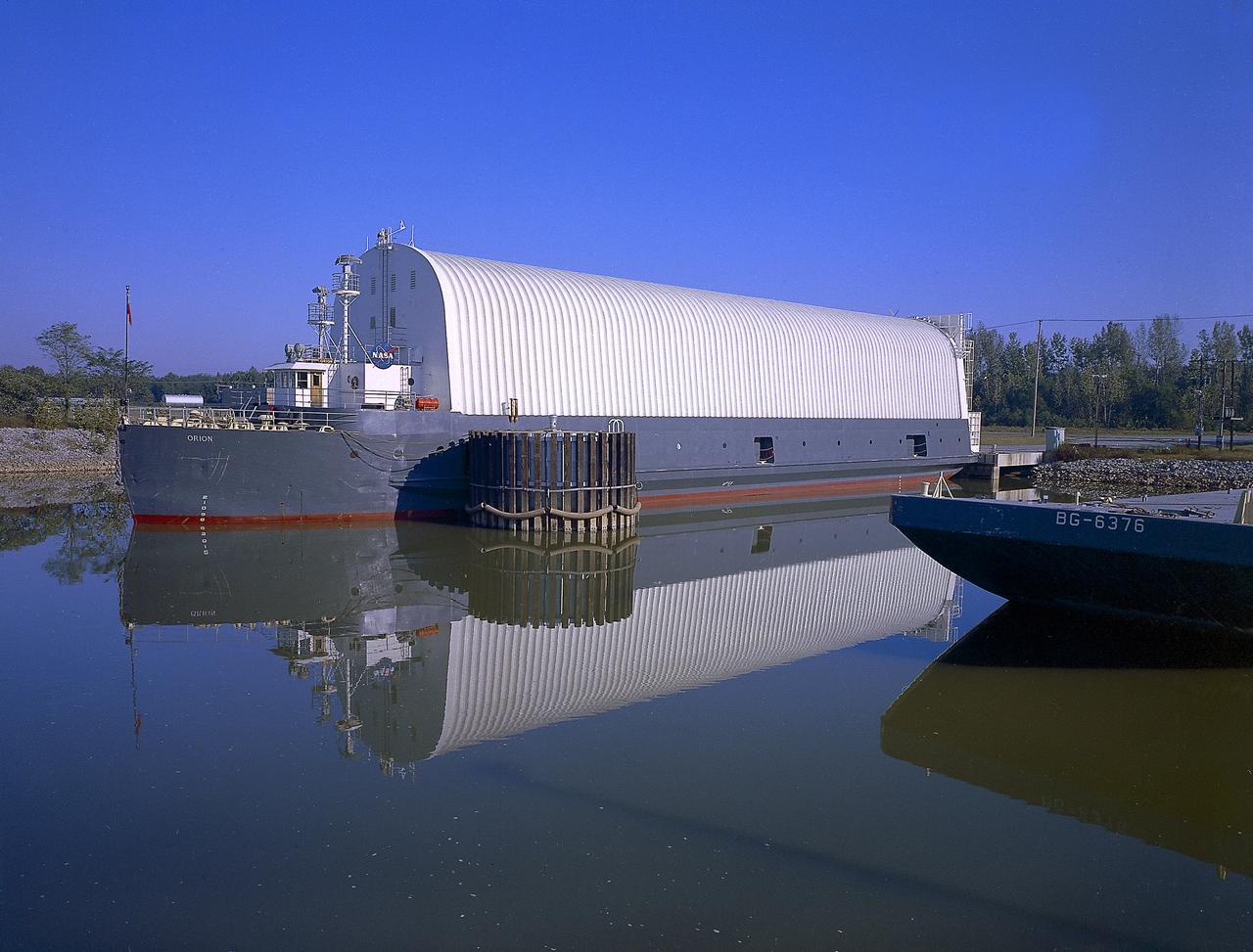

NASA used barges for transporting full-sized stages for the Saturn I, Saturn IB, and Saturn V vehicles between the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the manufacturing plant at the Michoud Assembly Facility (MAF), the Mississippi Test Facility for testing, and the Kennedy Space Center. The barges traveled from the MSFC dock to the MAF, a total of 1,086.7 miles up the Tennessee River and down the Mississippi River. The barges also transported the assembled stages of the Saturn vehicle from the MAF to the Kennedy Space Center, a total of 932.4 miles along the Gulf of Mexico and up along the Atlantic Ocean, for the final assembly and the launch. This photograph shows the barge Orion at the MSFC dock.
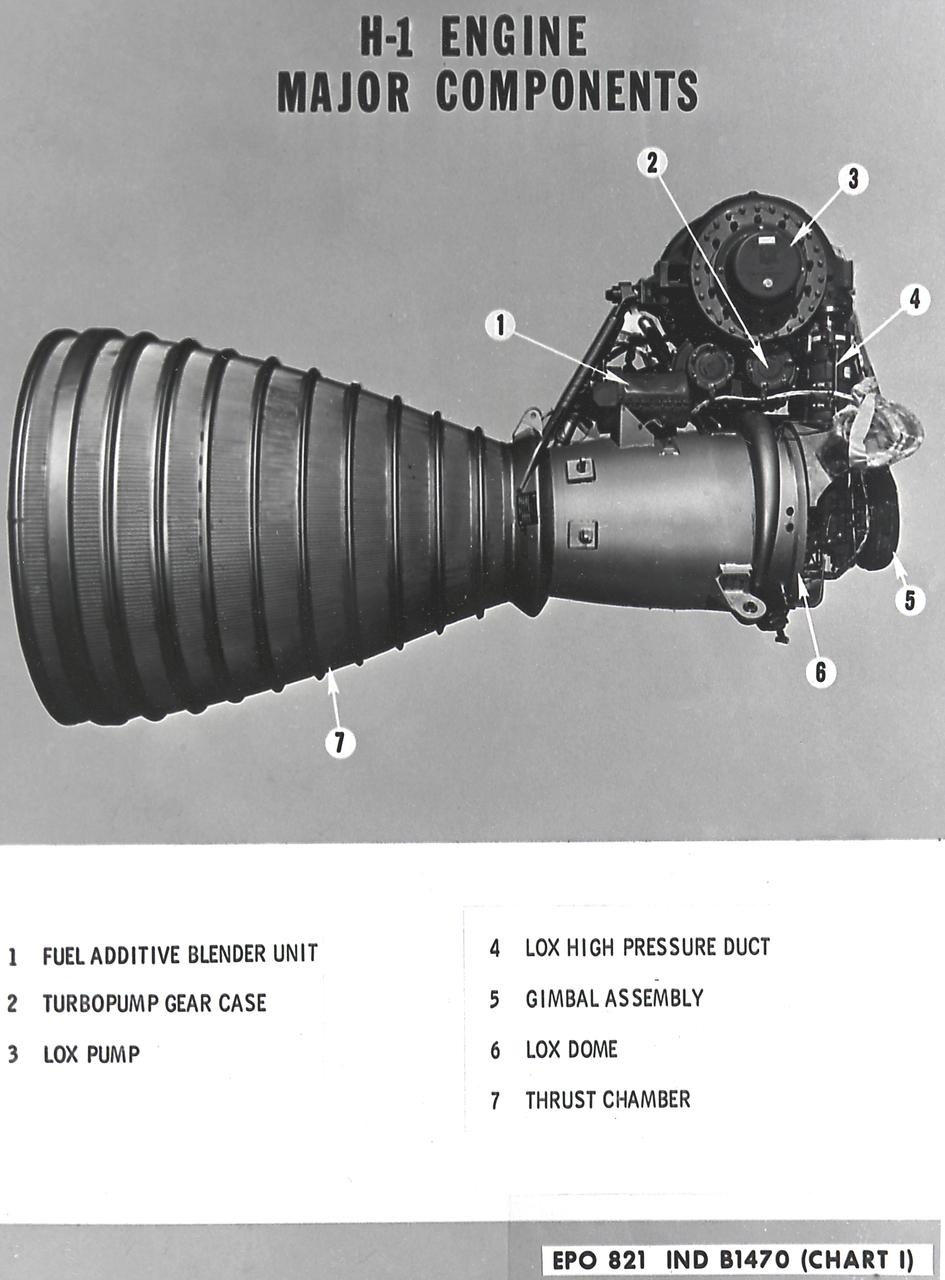
H-1 Engine major components with callouts (chart 1): The H-1 engine was used in a cluster of eight on the the first stage of Saturn I (S-I stage) and Saturn IB (S-IB stage). The engines were arranged in a double pattern: four engines, located inboard, were fixed in a square pattern around the stage axis, while the remaining four engines were located outboard in a larger square pattern and each outer engine was gimbaled. Each H-1 engine had a thrust of 188,000 pounds for a combined thrust of over 1,500,000 pounds.
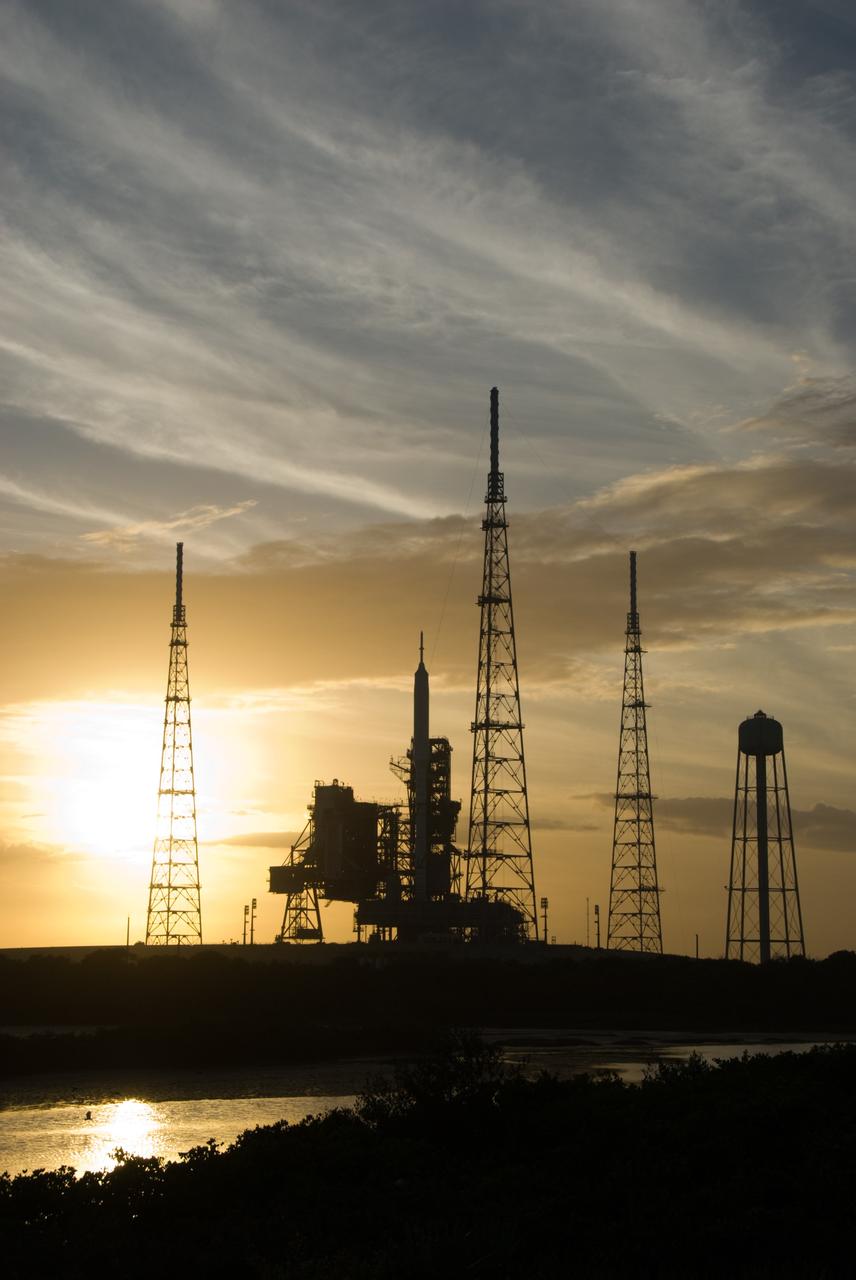

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As the sun sets behind Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X rocket awaits the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As the sun sets behind Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X rocket awaits the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
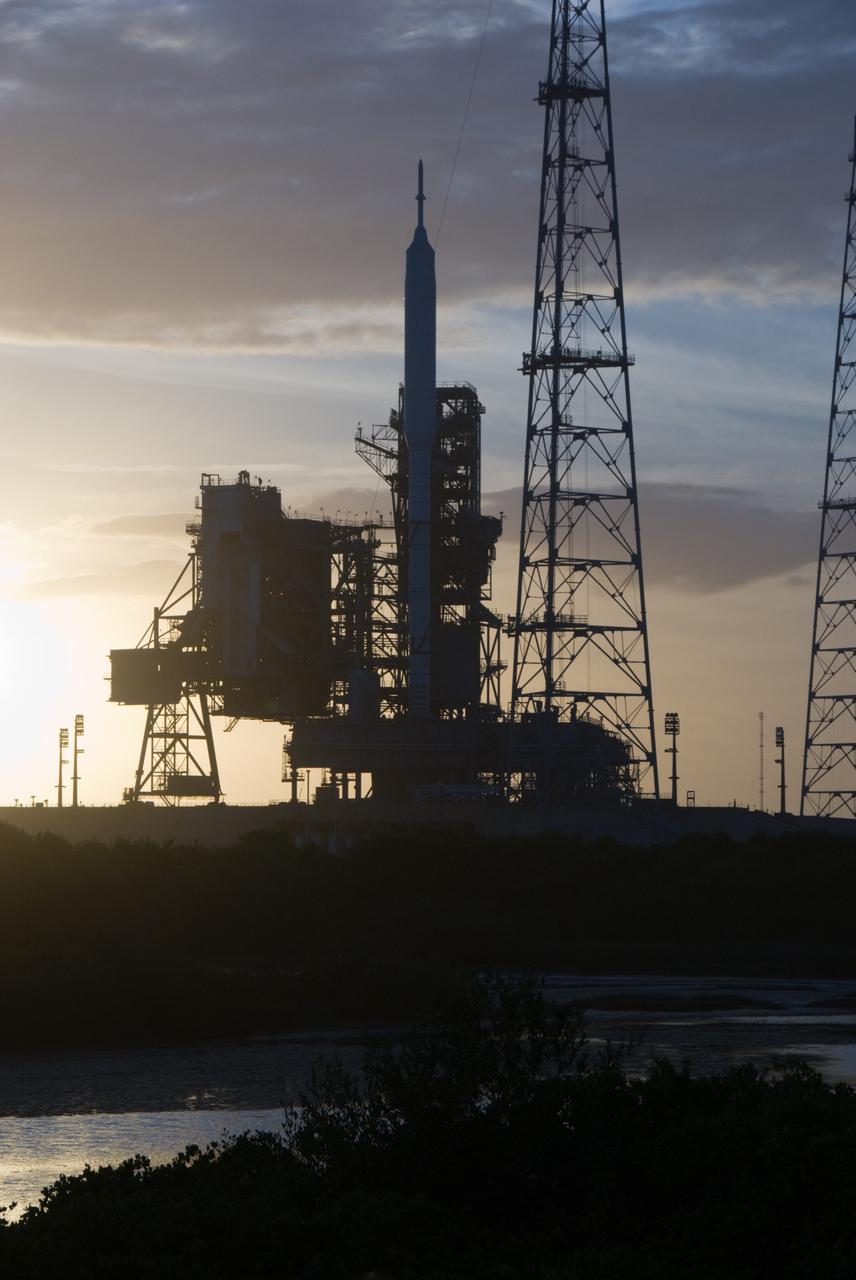

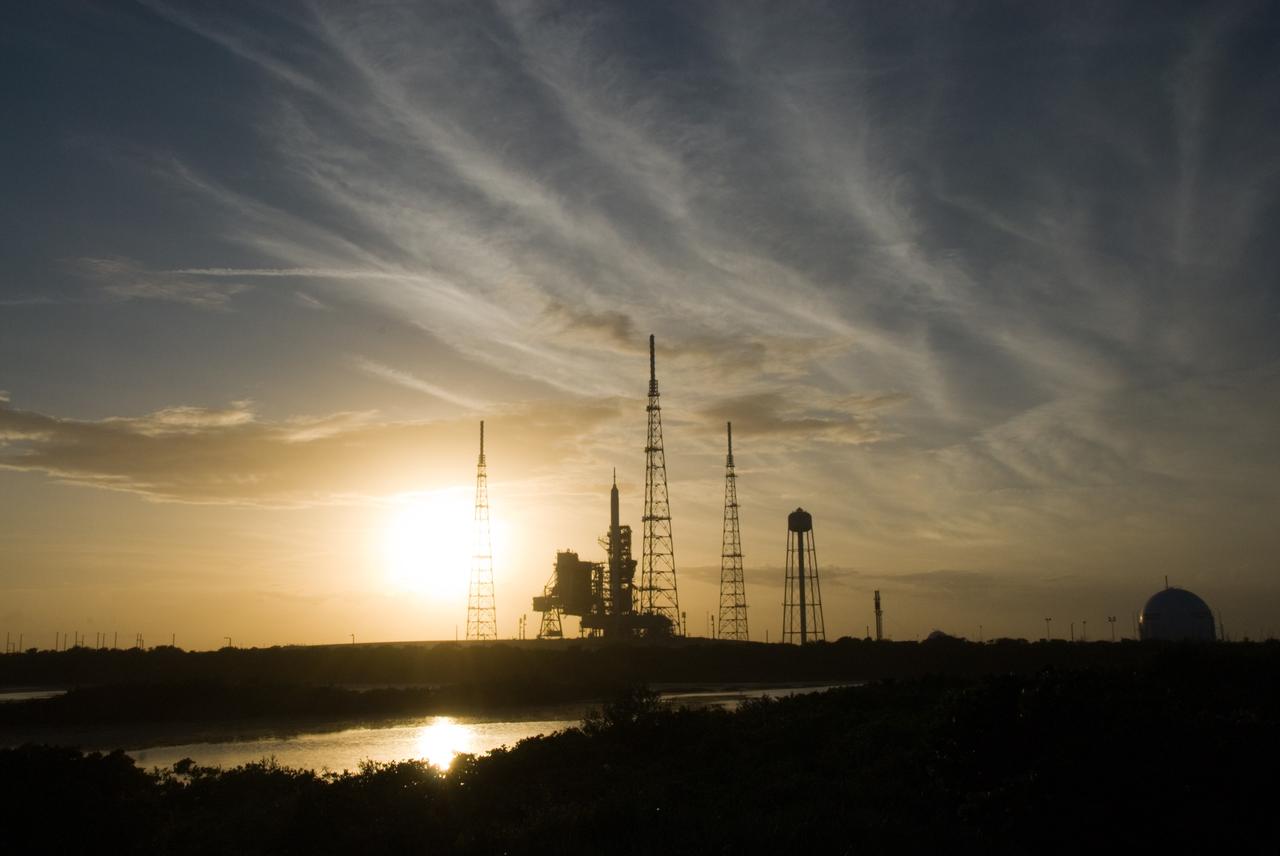
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Sunset at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida finds the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
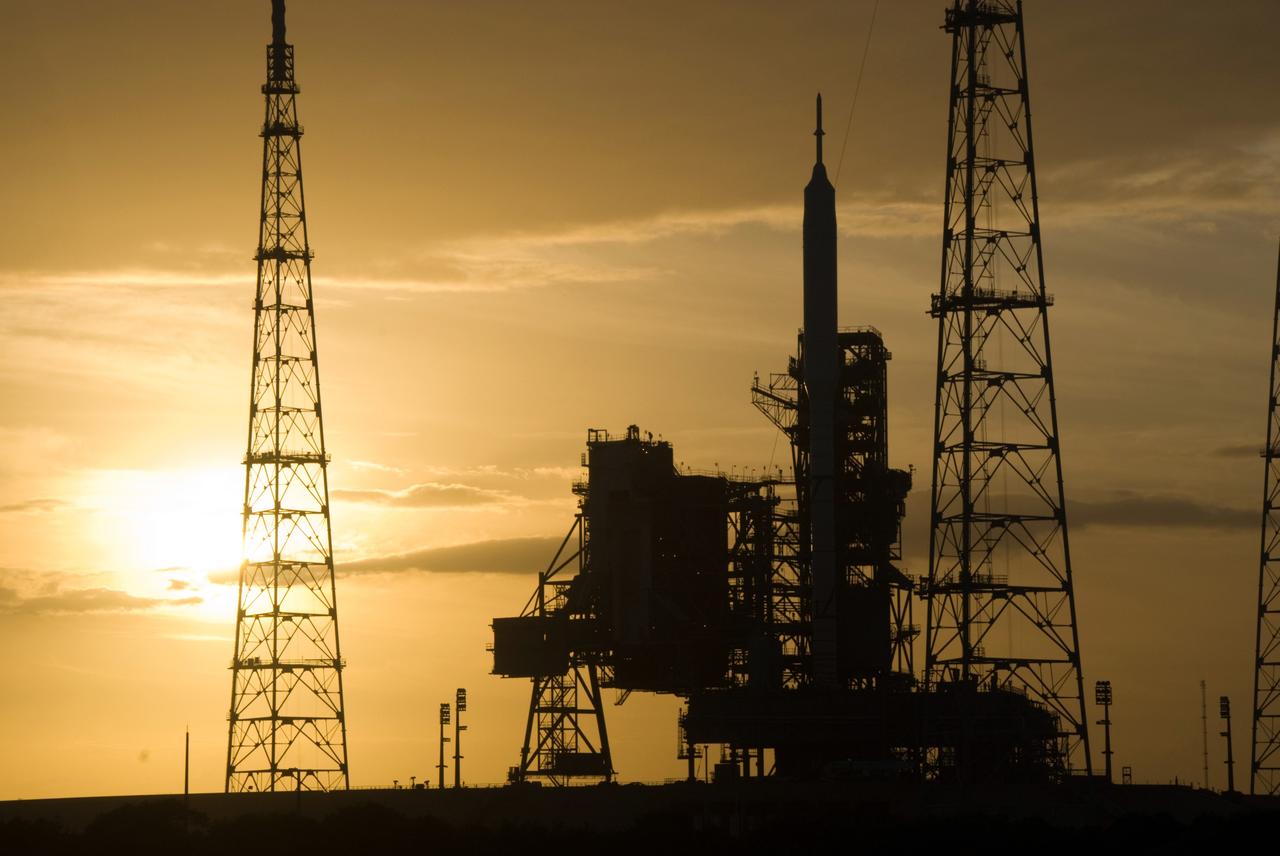

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As the sun sets behind Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X rocket awaits the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
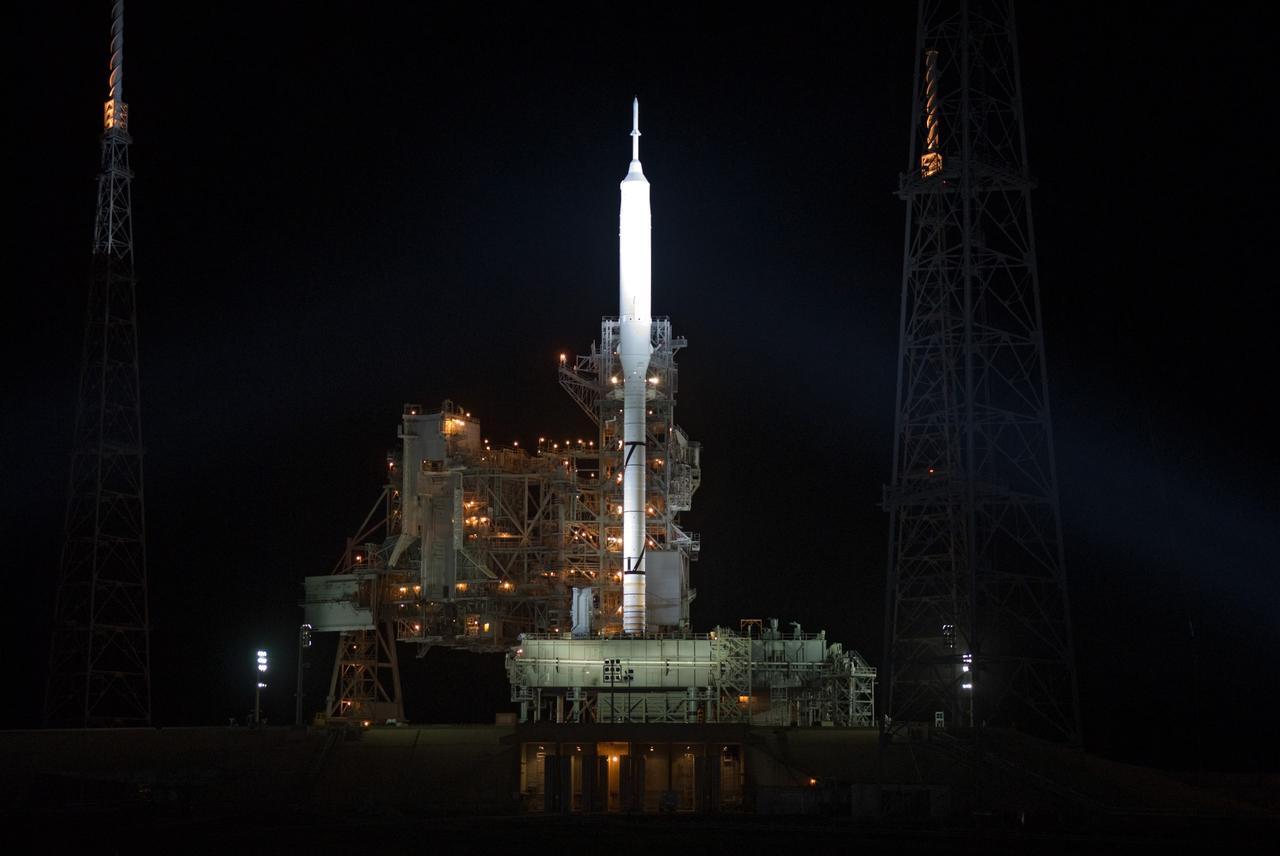

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As nightfall comes to Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, xenon lights reveal the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
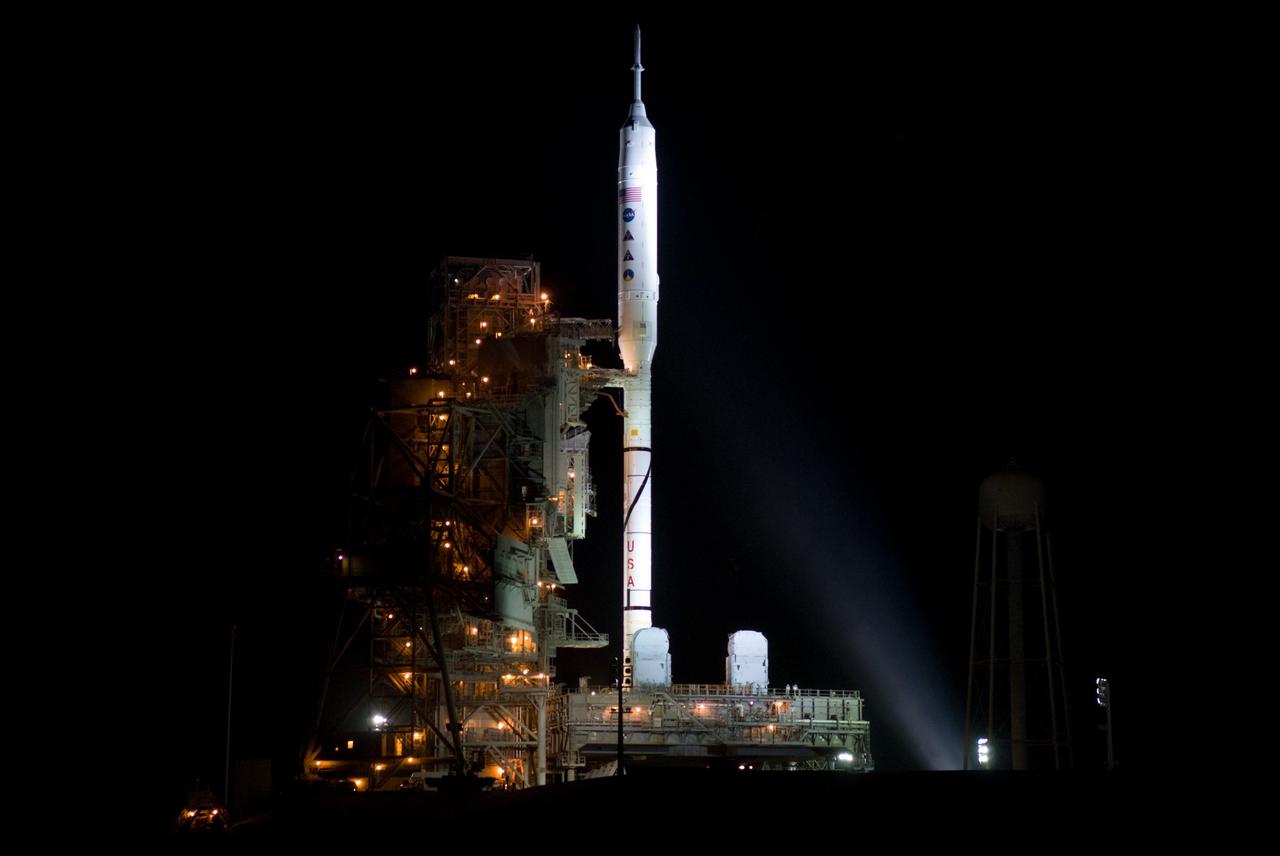

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As night settles over Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, xenon lights reveal the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
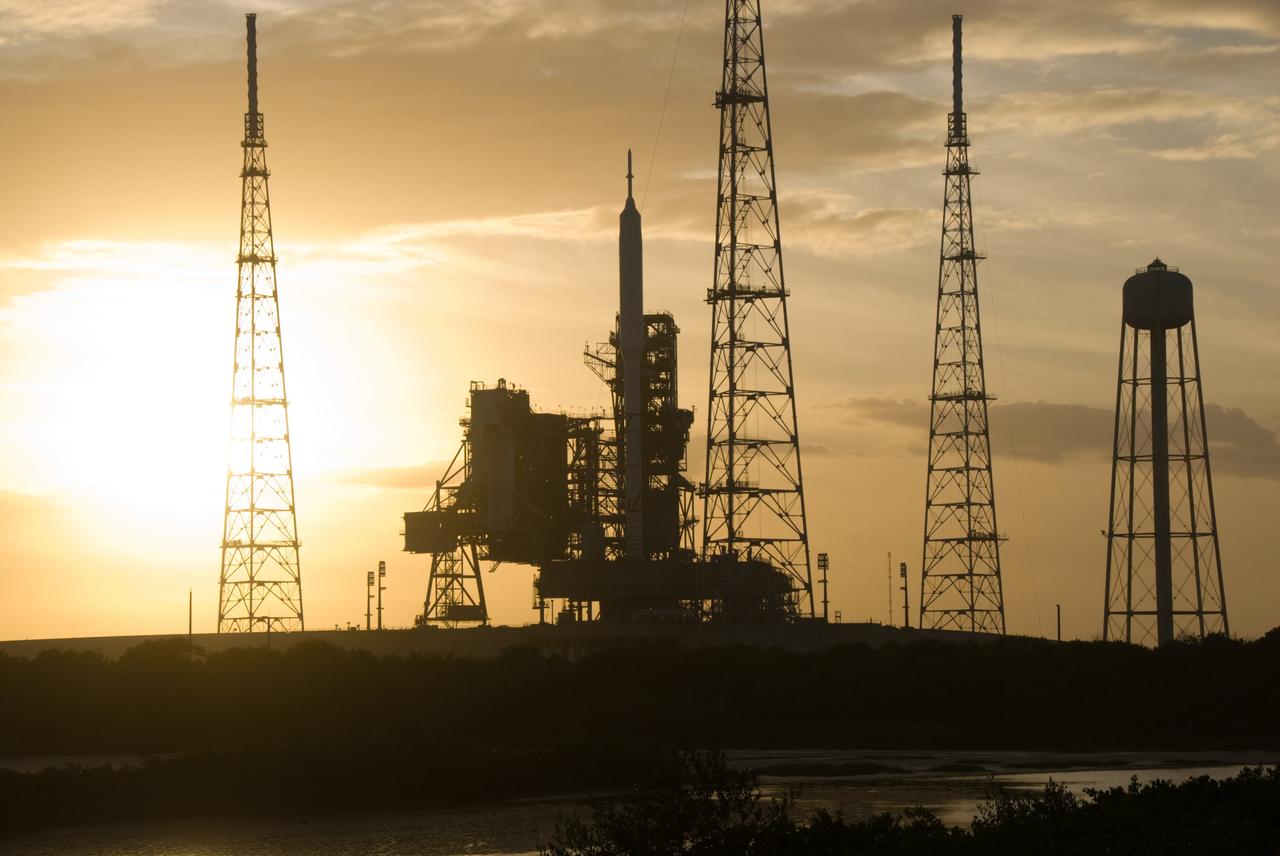

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As the sun sets behind Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X rocket awaits the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
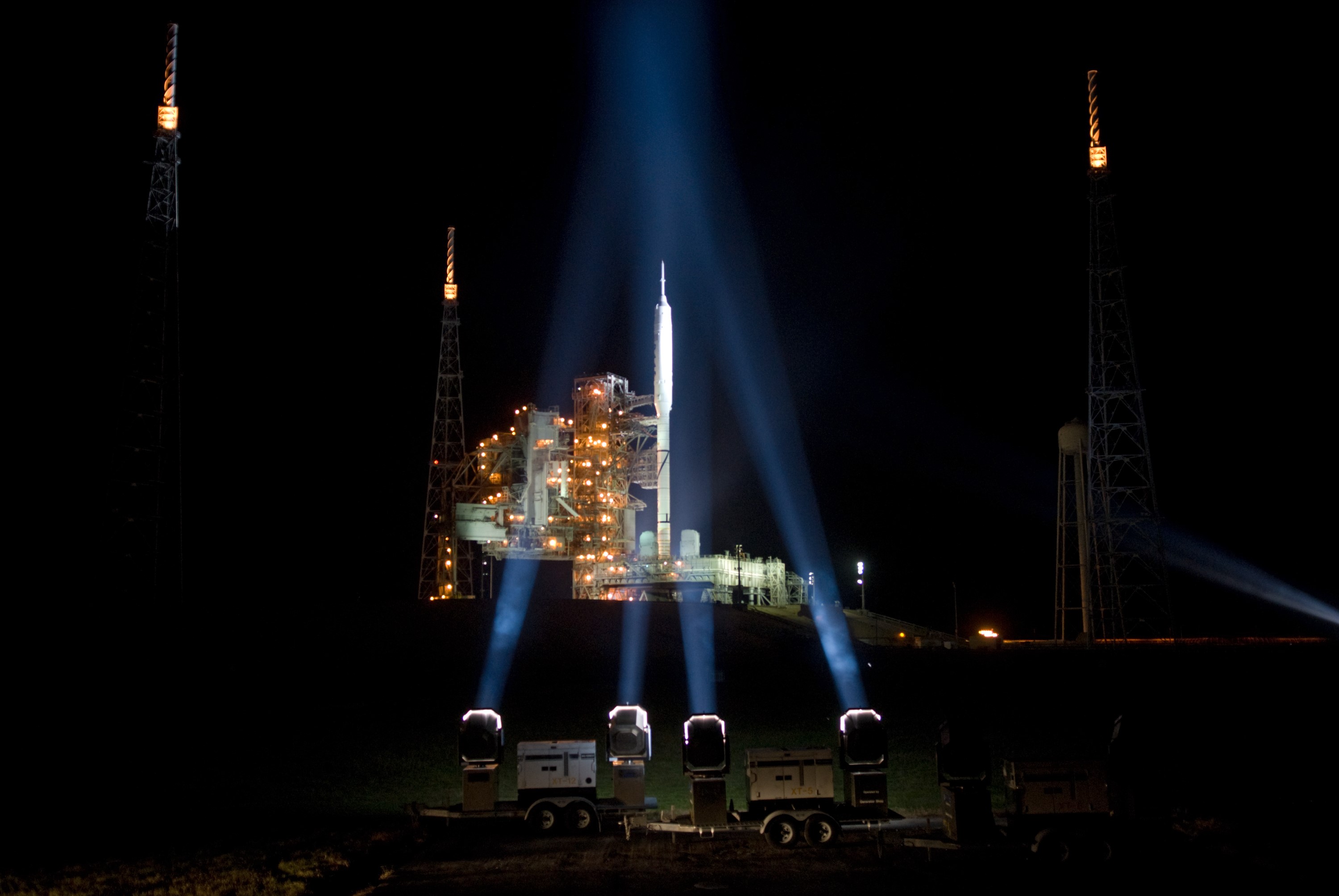

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As nightfall comes to Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, xenon lights reveal the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
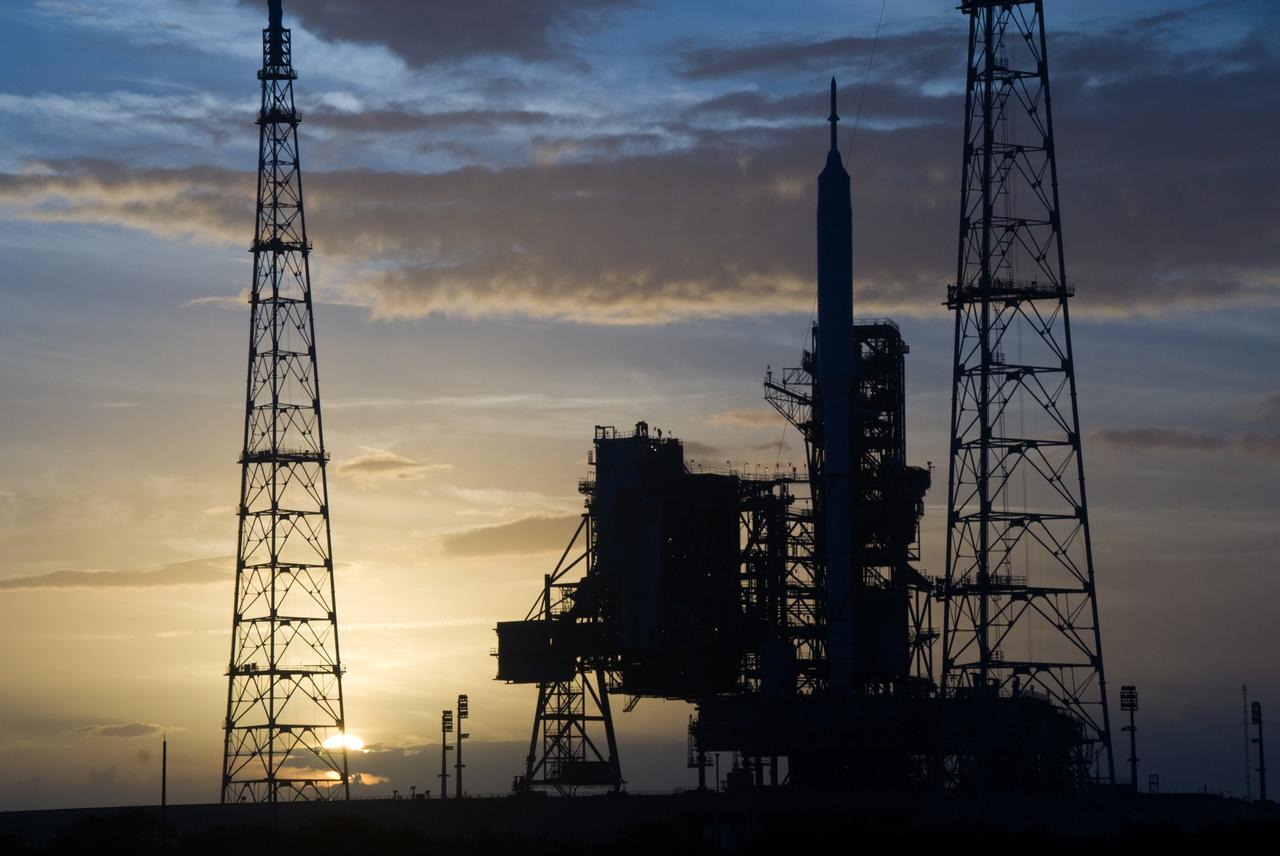

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Sunset at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida finds the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
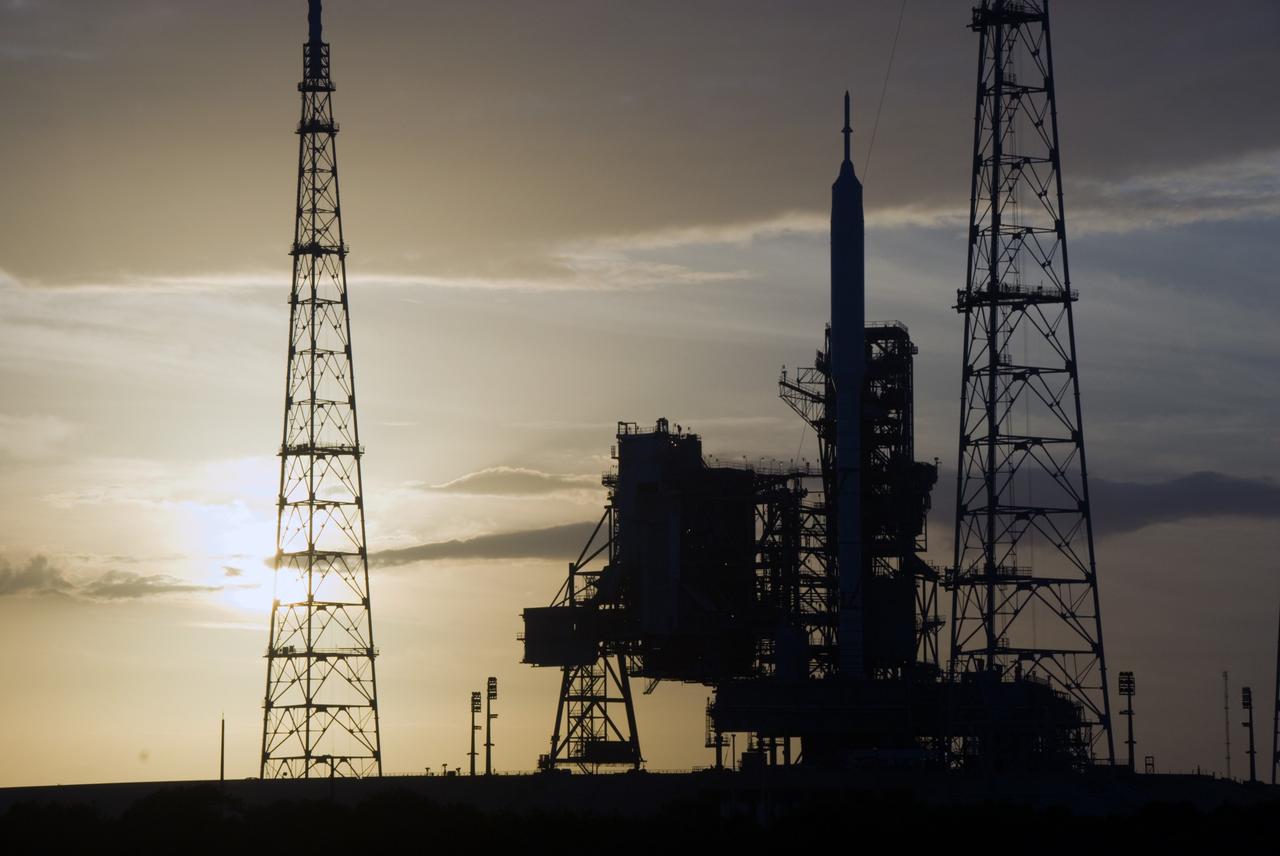

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As the sun sets behind Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X rocket awaits the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
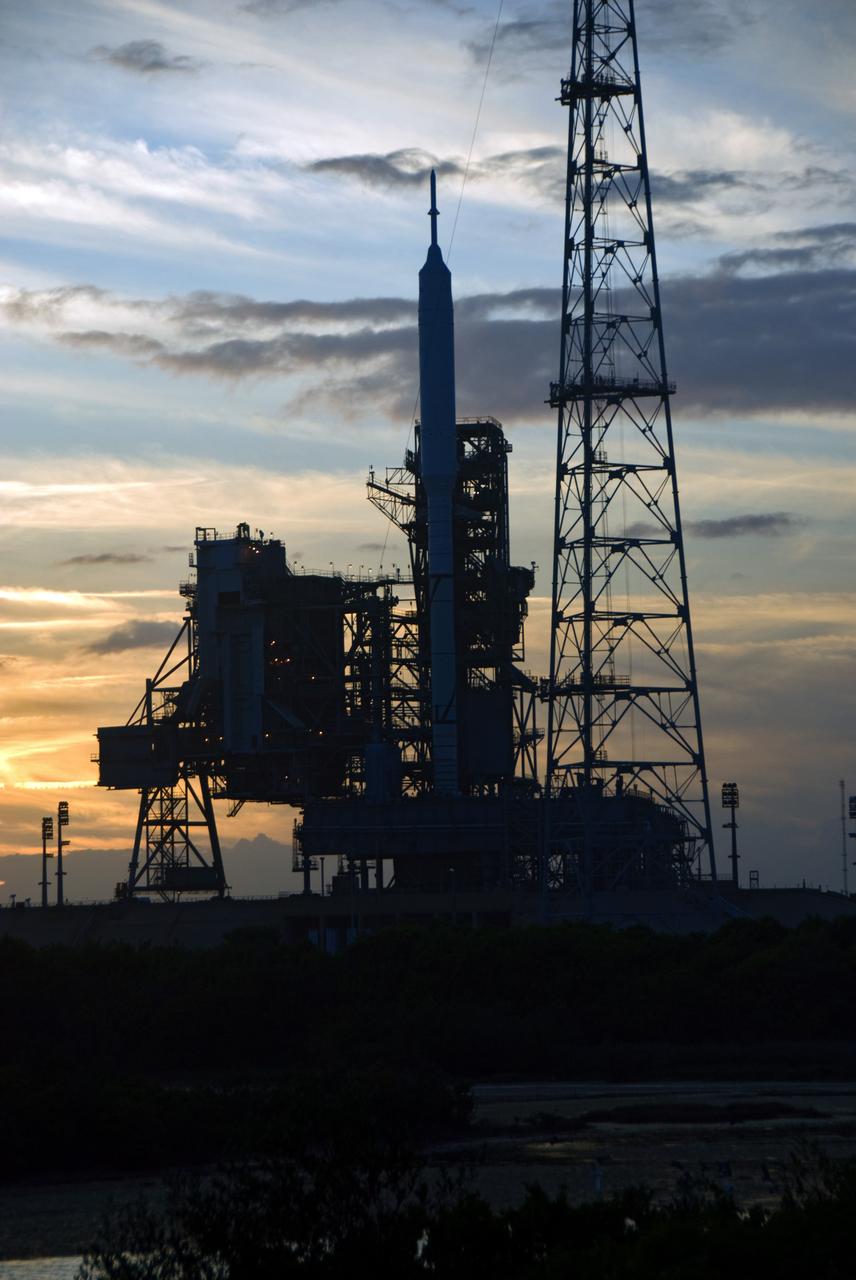

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Sunset at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida finds the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
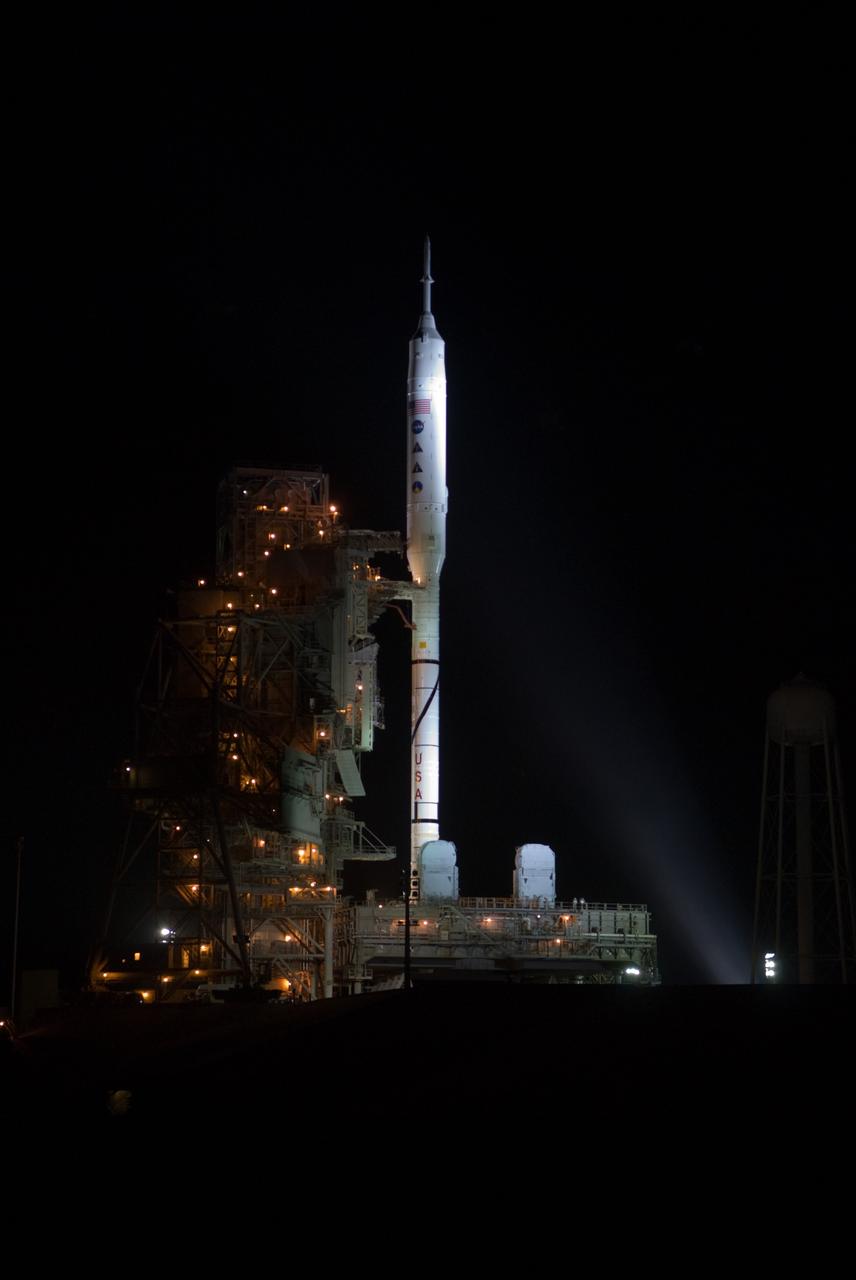

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As night settles over Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, xenon lights reveal the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
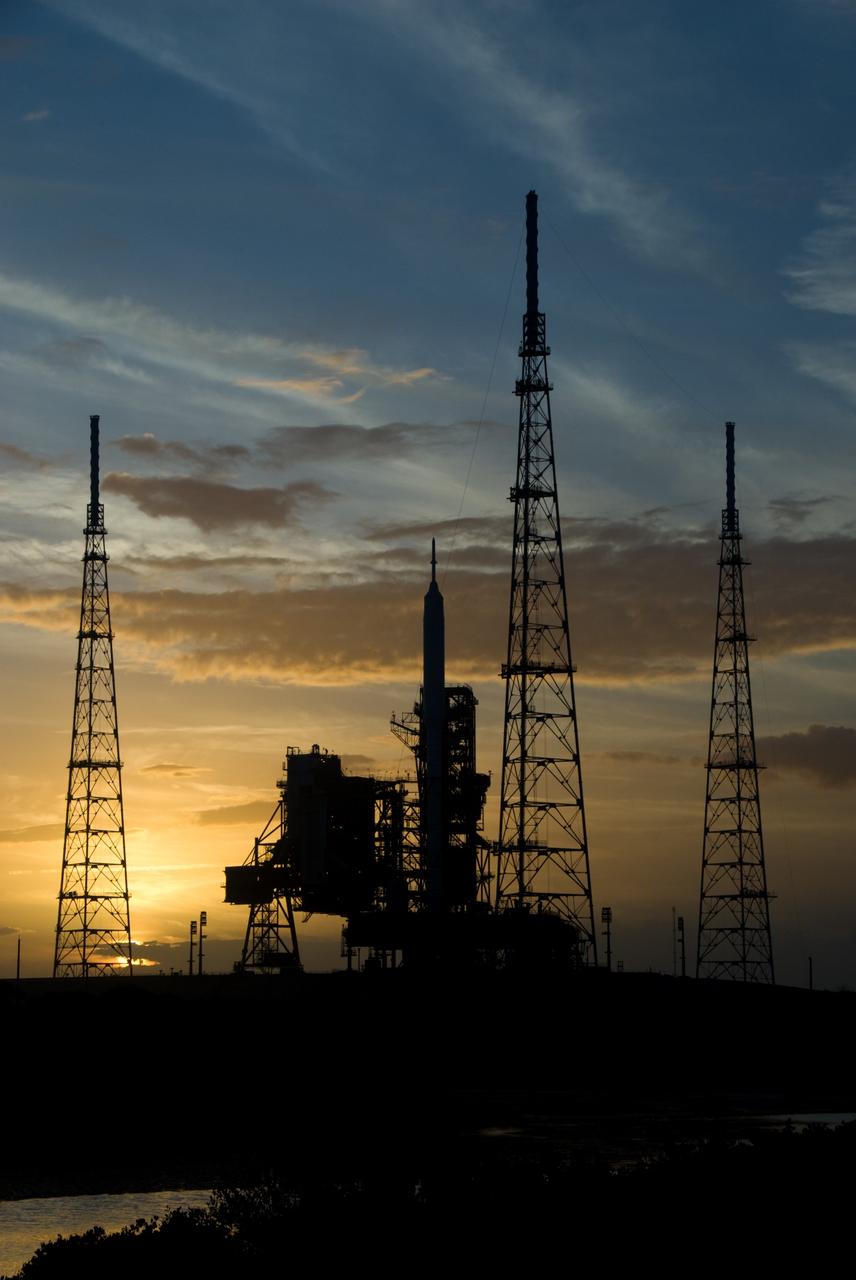

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Sunset at Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida finds the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
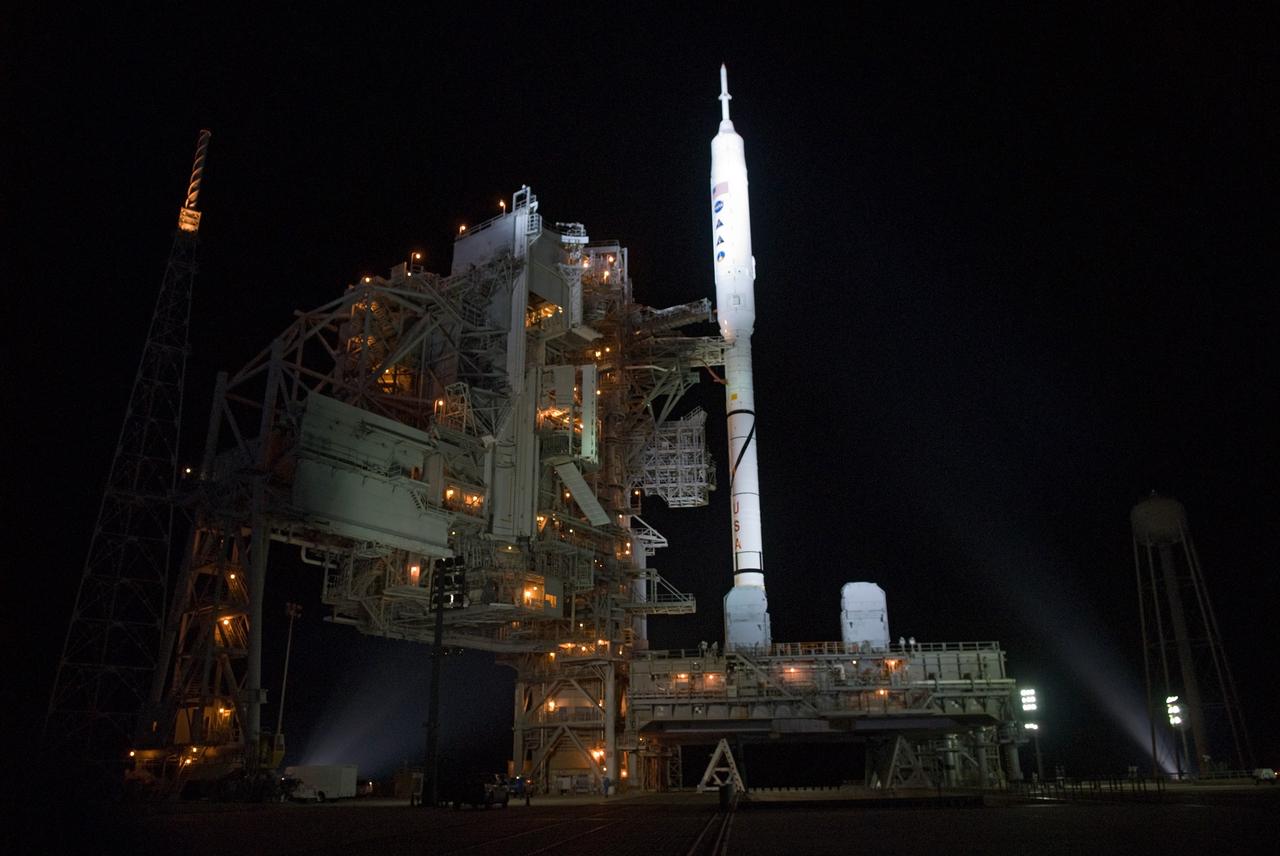

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - As night settles over Launch Complex 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, xenon lights reveal the Ares I-X rocket awaiting the approaching liftoff of its flight test. This is the first time since the Apollo Program's Saturn rockets were retired that a vehicle other than the space shuttle has occupied the pad. Part of the Constellation Program, the Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I. The Ares I-X flight test is set for Oct. 27. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett