
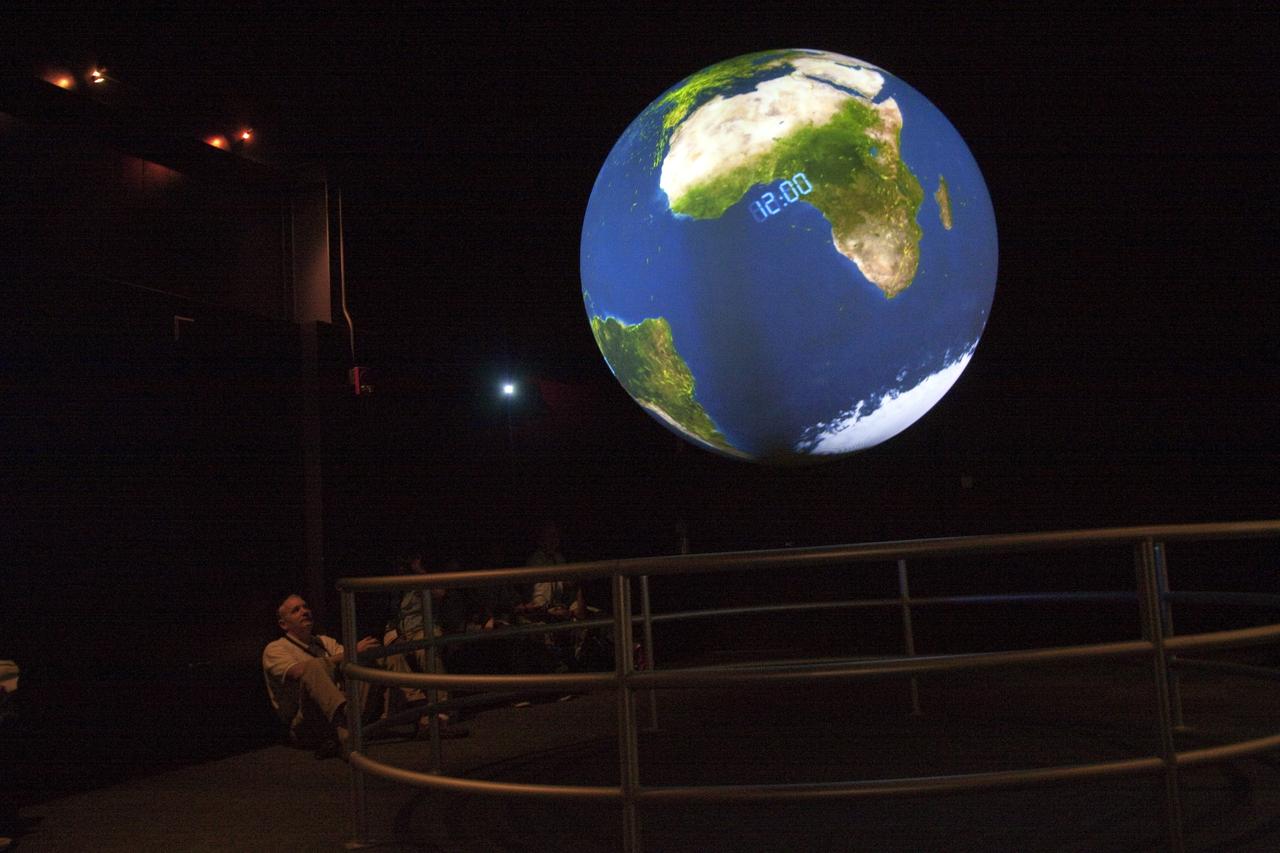
Students from Xavier University Preparatory School in New Orleans view the newest exhibit at StenniSphere, the visitor center at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center - Science on a Sphere, a 68-inch global presentation of planetary data. StenniSphere is only the third NASA visitor center to offer the computer system, which uses four projectors to display data on a globe and present a dynamic, revolving, animated view of Earth and other planets.
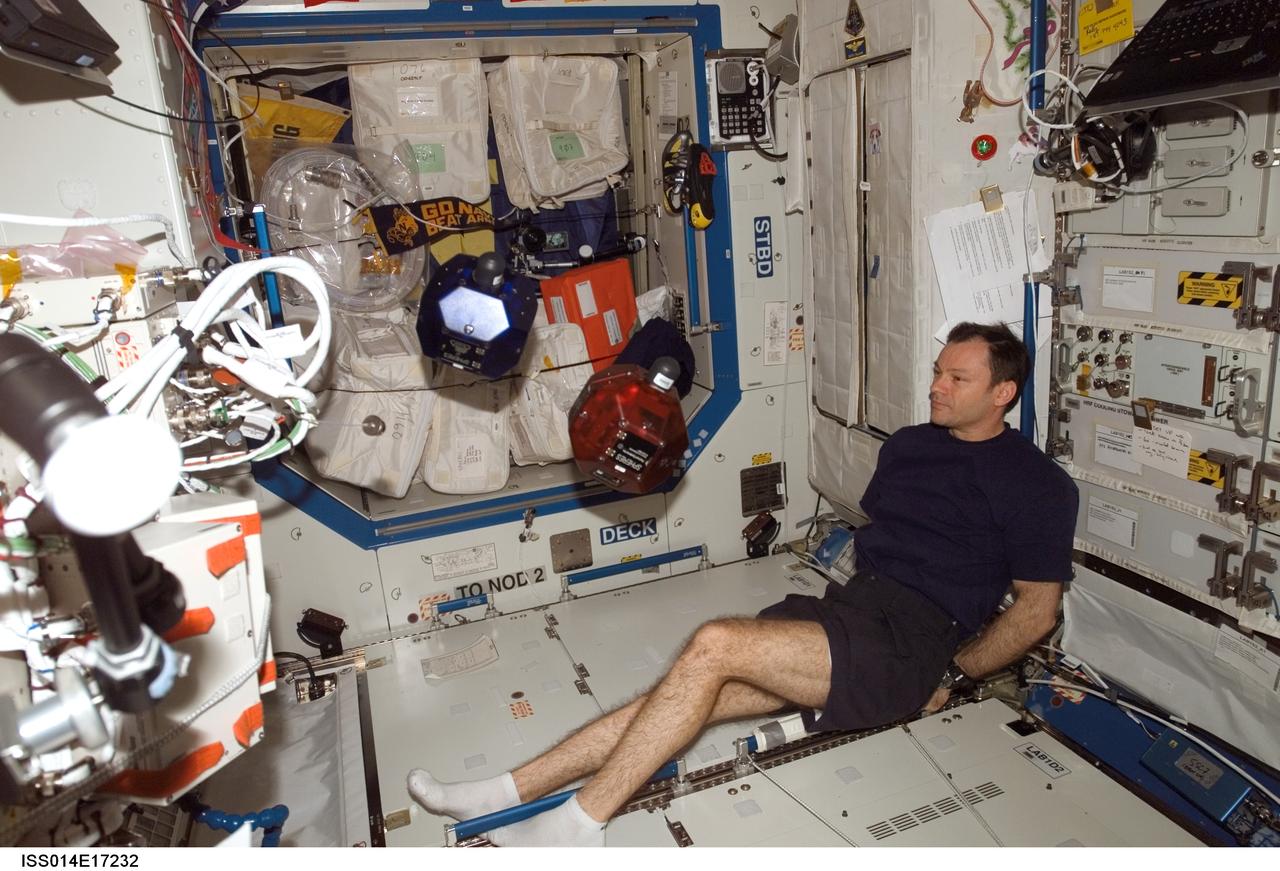

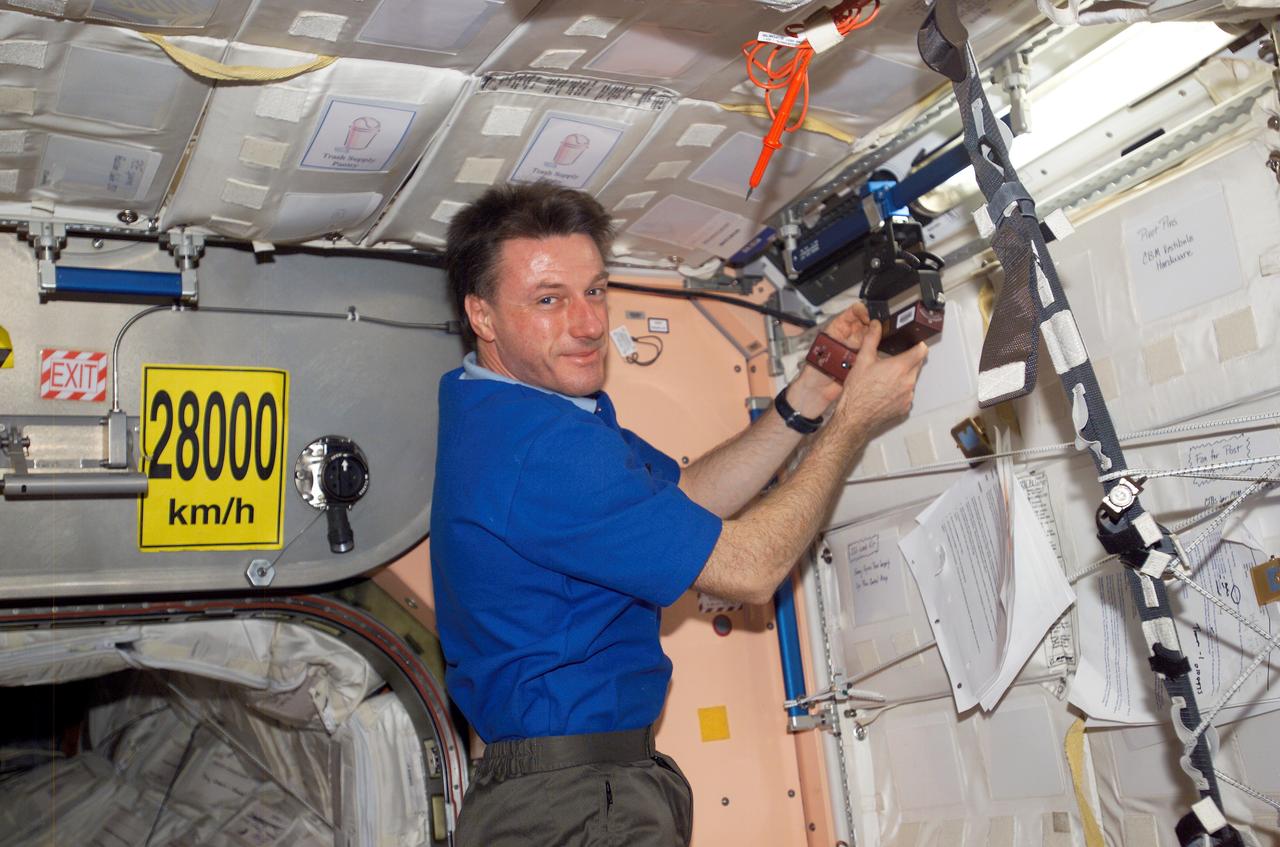
ISS014-E-17232 (17 March 2007) --- Astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, Expedition 14 commander and NASA space station science officer, does a check of the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Beacon / Beacon Tester in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.

Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, The Duke of Edinburgh look on as Goddard employees demonstrate “Science on a Sphere.” This system, developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), uses computers and four video projectors to display animated images on the outside of a 6-foot diameter sphere. Photo Credit: (NASA/Pat Izzo)
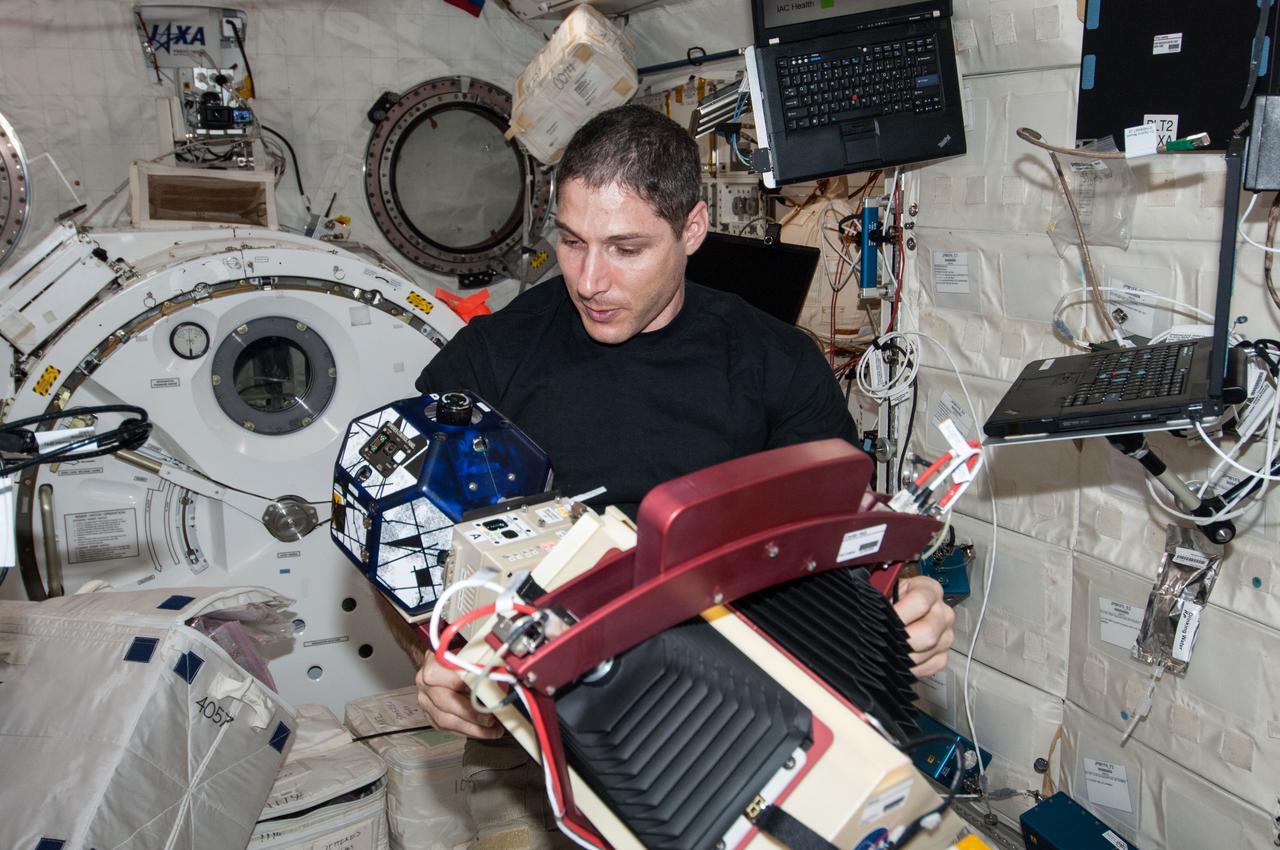

ISS038-E-033890 (22 Jan. 2014) --- In the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory, NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, works with a new experiment using the soccer-ball-sized, free-flying satellites known as Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, which are already on the station. For the SPHERES-Slosh experiment, two SPHERES robots are attached to opposite ends of a metal frame holding the plastic tank with the green-colored water. The new hardware for the SPHERES-Slosh study was delivered to the station aboard Orbital Sciences' Cygnus cargo craft on Jan. 12.
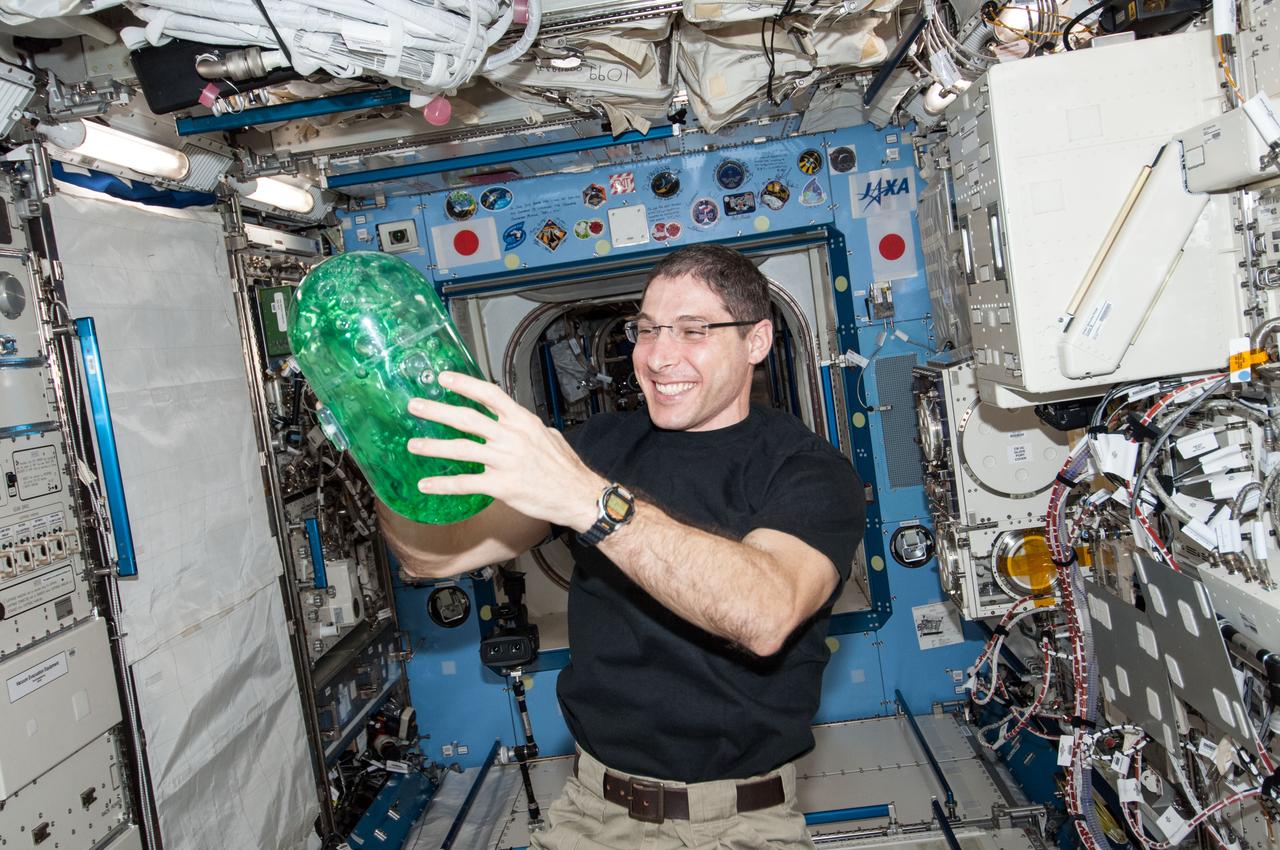

ISS038-E-033884 (22 Jan. 2014) --- In the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory, NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, holds a plastic container partially filled with green-colored water which will be used in a new experiment using the soccer-ball-sized, free-flying satellites known as Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, which are already on the station. For the SPHERES-Slosh experiment, two SPHERES robots are attached to opposite ends of a metal frame holding the plastic tank with the green-colored water. The new hardware for the SPHERES-Slosh study was delivered to the station aboard Orbital Sciences' Cygnus cargo craft on Jan. 12.
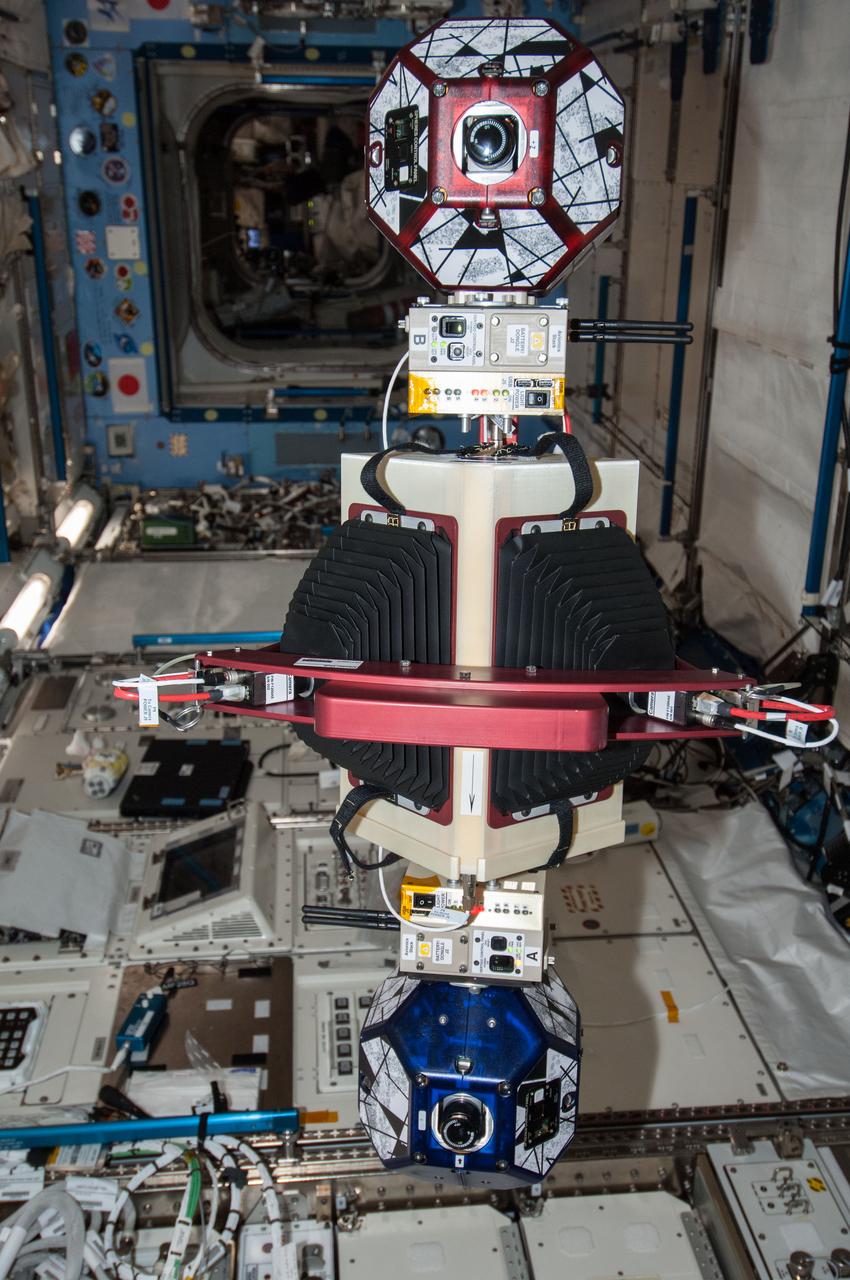
ISS038-E-033888 (22 Jan. 2014) --- A new experiment using the soccer-ball-sized, free-flying satellites known as Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, already on the station, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 38 crew member in the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory. For the SPHERES-Slosh experiment, two SPHERES robots are attached to opposite ends of a metal frame holding a plastic tank with green-colored water. The new hardware for the SPHERES-Slosh study was delivered to the station aboard Orbital Sciences' Cygnus cargo craft on Jan. 12.
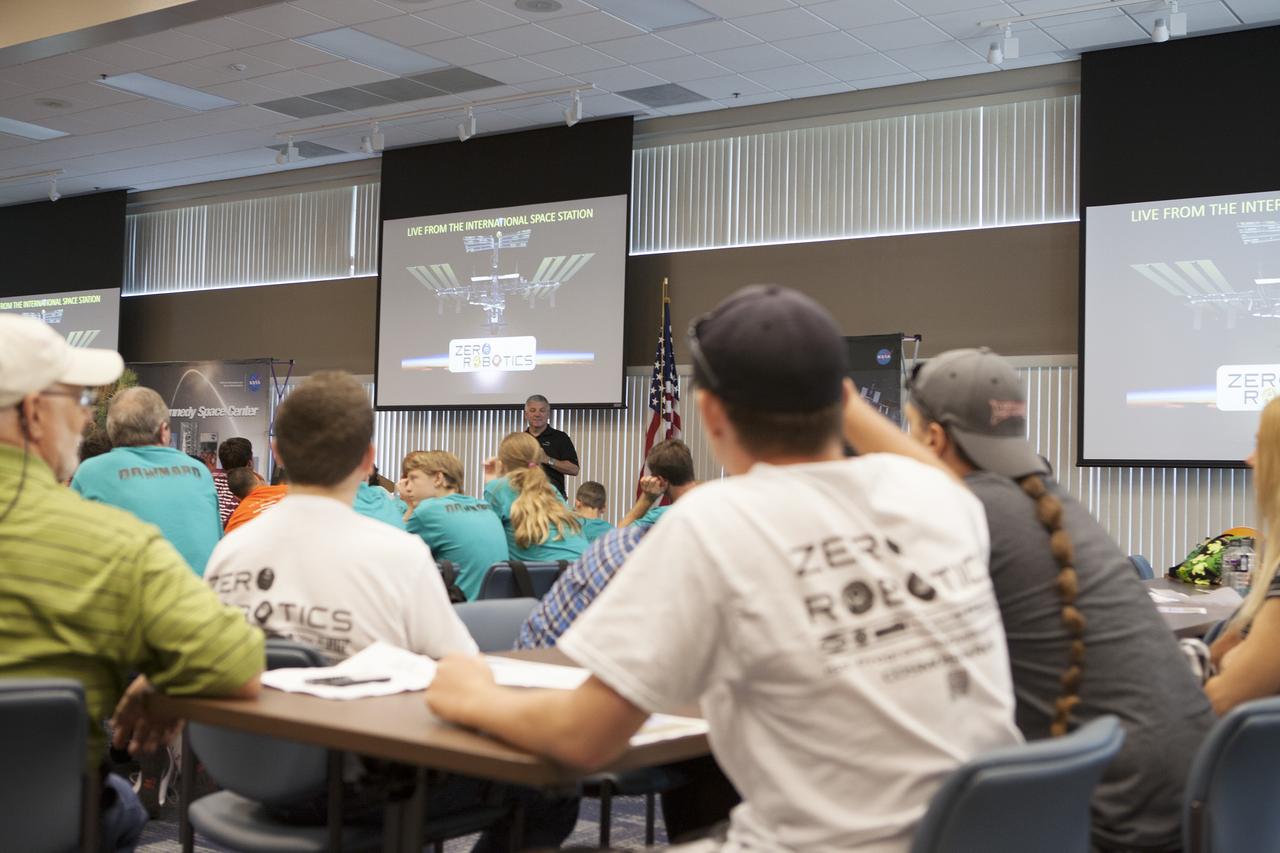

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former astronaut Greg Johnson, executive director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
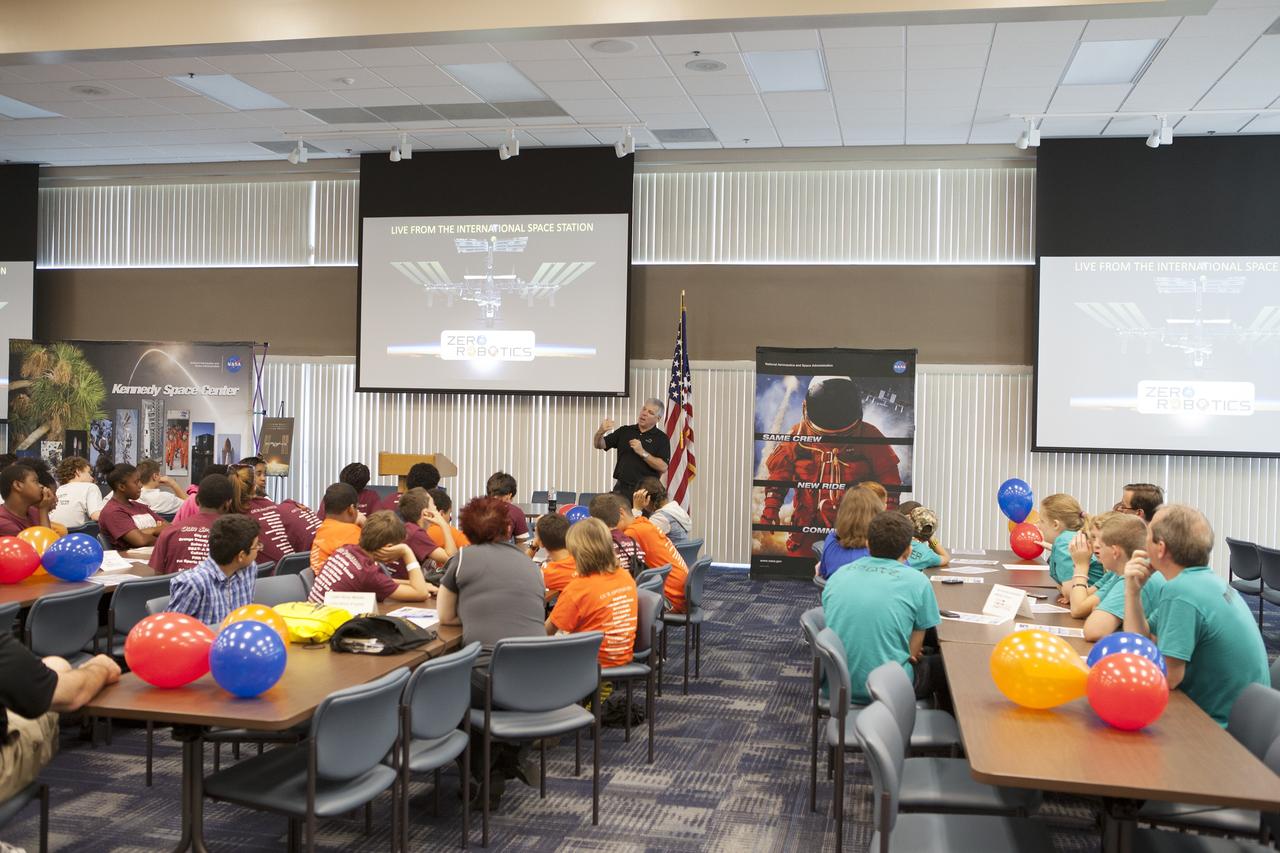

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former astronaut Greg Johnson, executive director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
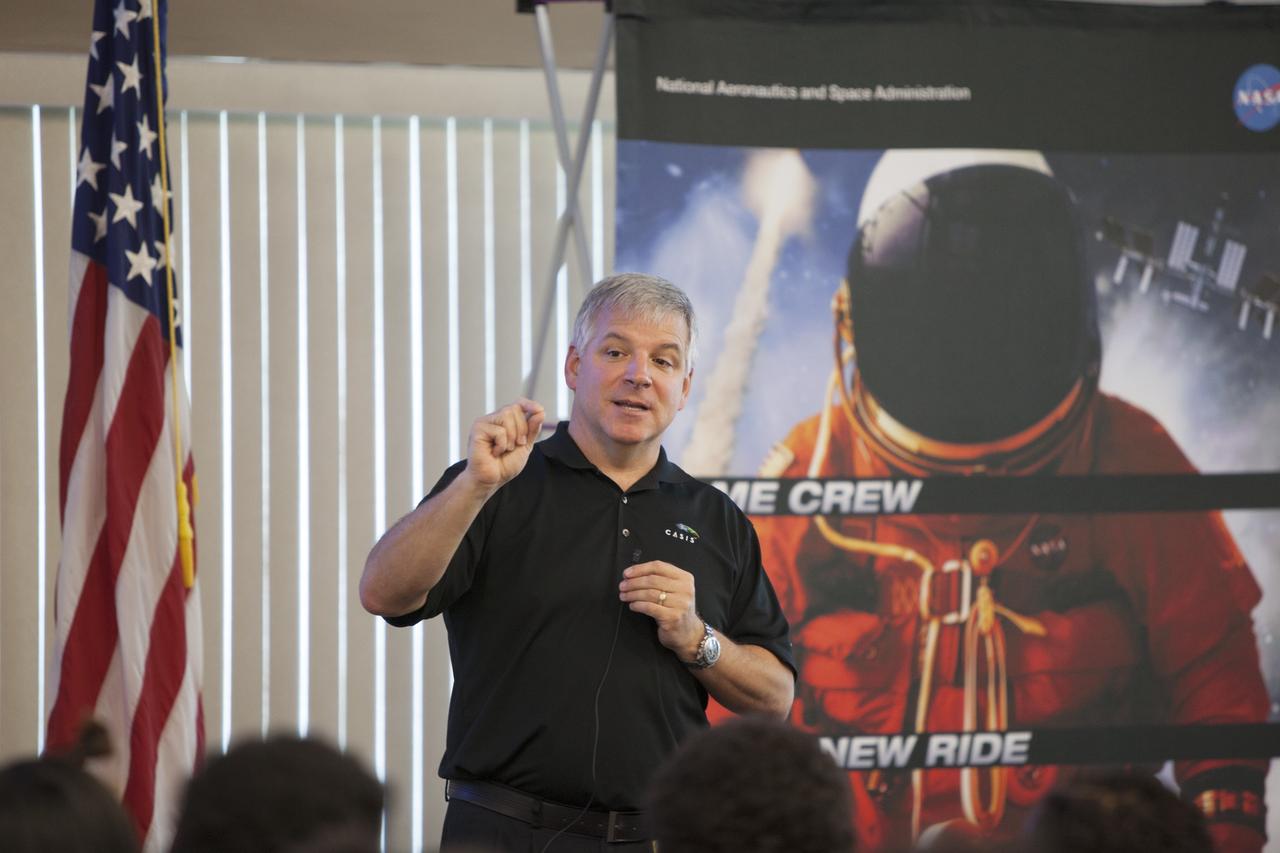

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former astronaut Greg Johnson, executive director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, talks to Florida middle school students and their teachers before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
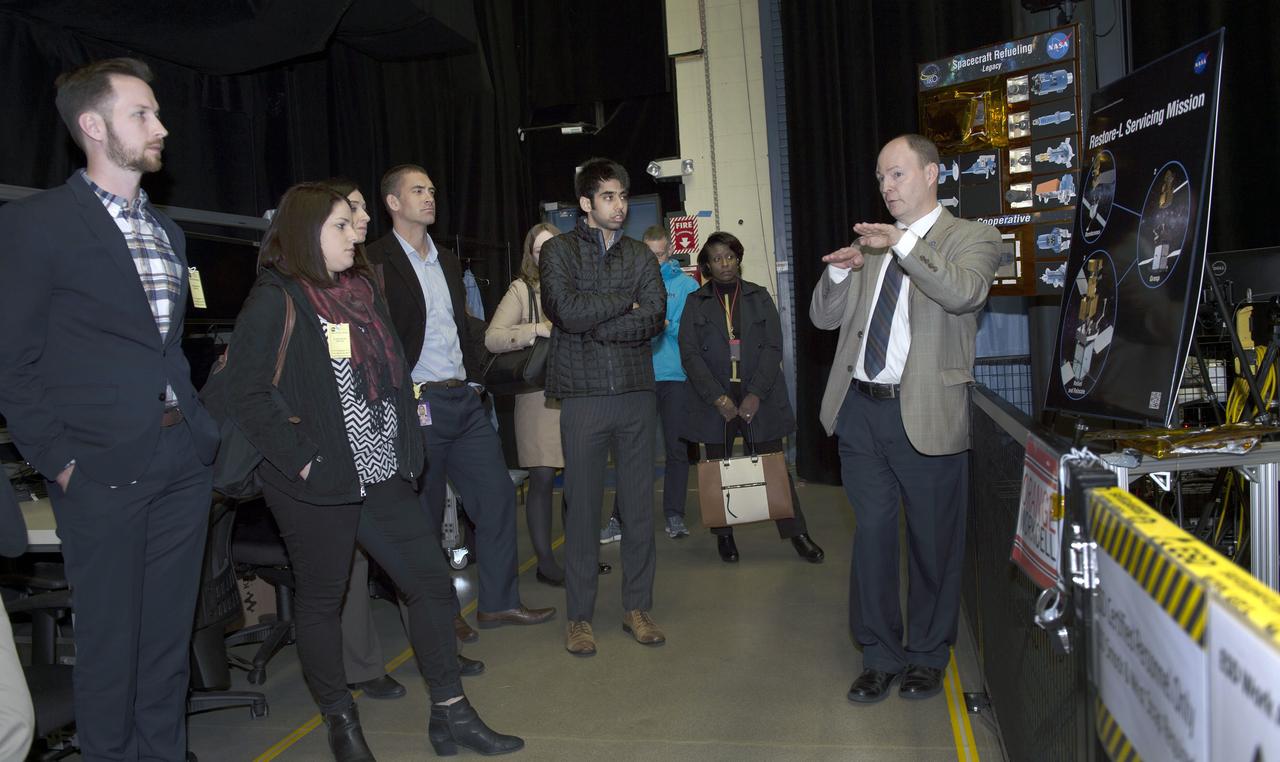

Congressional staff visited Goddard on March 10, 2017. They toured Science on a Sphere J. Garvin, B33 talk on ICESat-2 Dr. Kelly Brunt, Robotic Operations Center - Ben Reed, and JWST-Bill Ochs
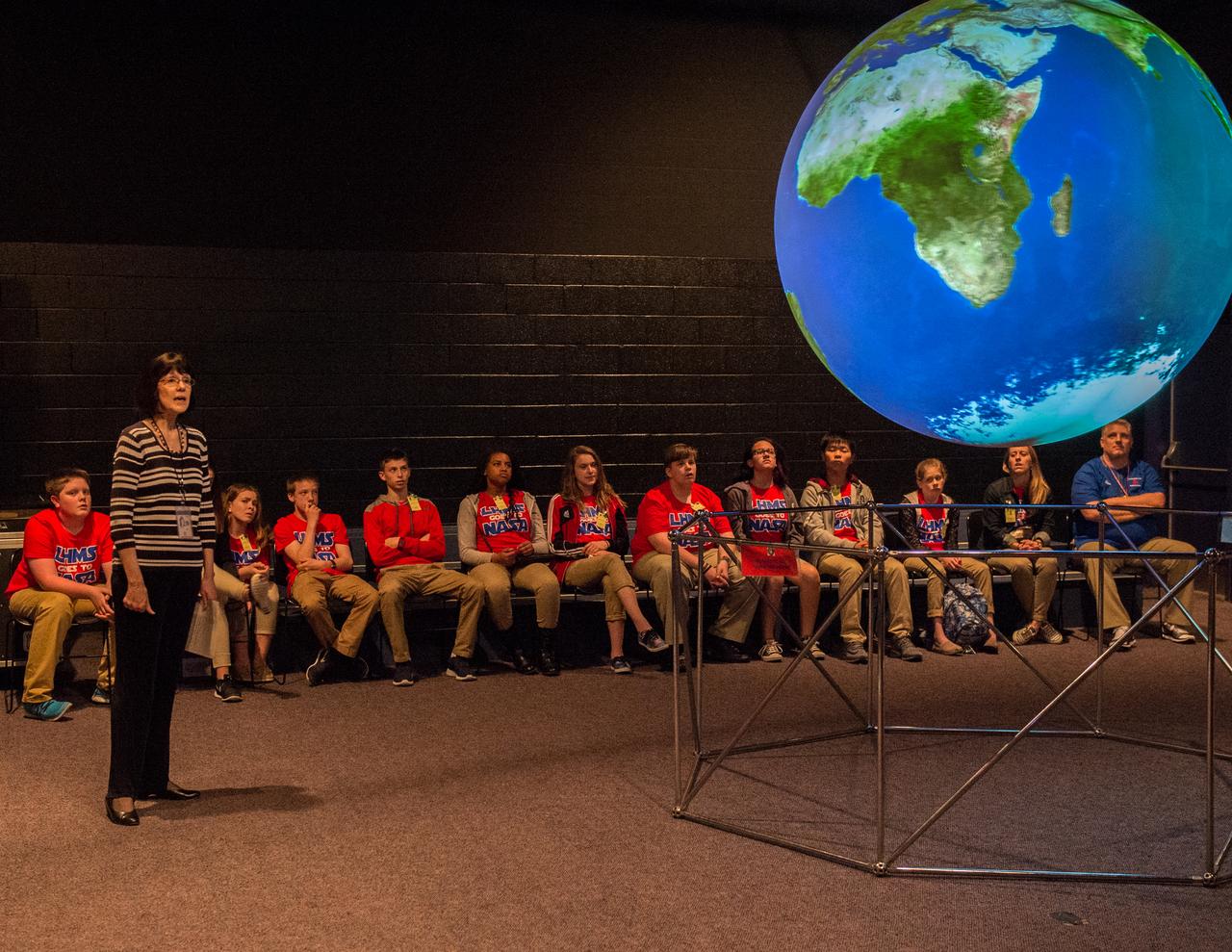

Beating the Odds Student Success/ Leadership Program tours the Goddard Space Flight Center. Judy Bruner, Director of Safety and Mission Assurance Directorate gives a Science on a Sphere Presentation.
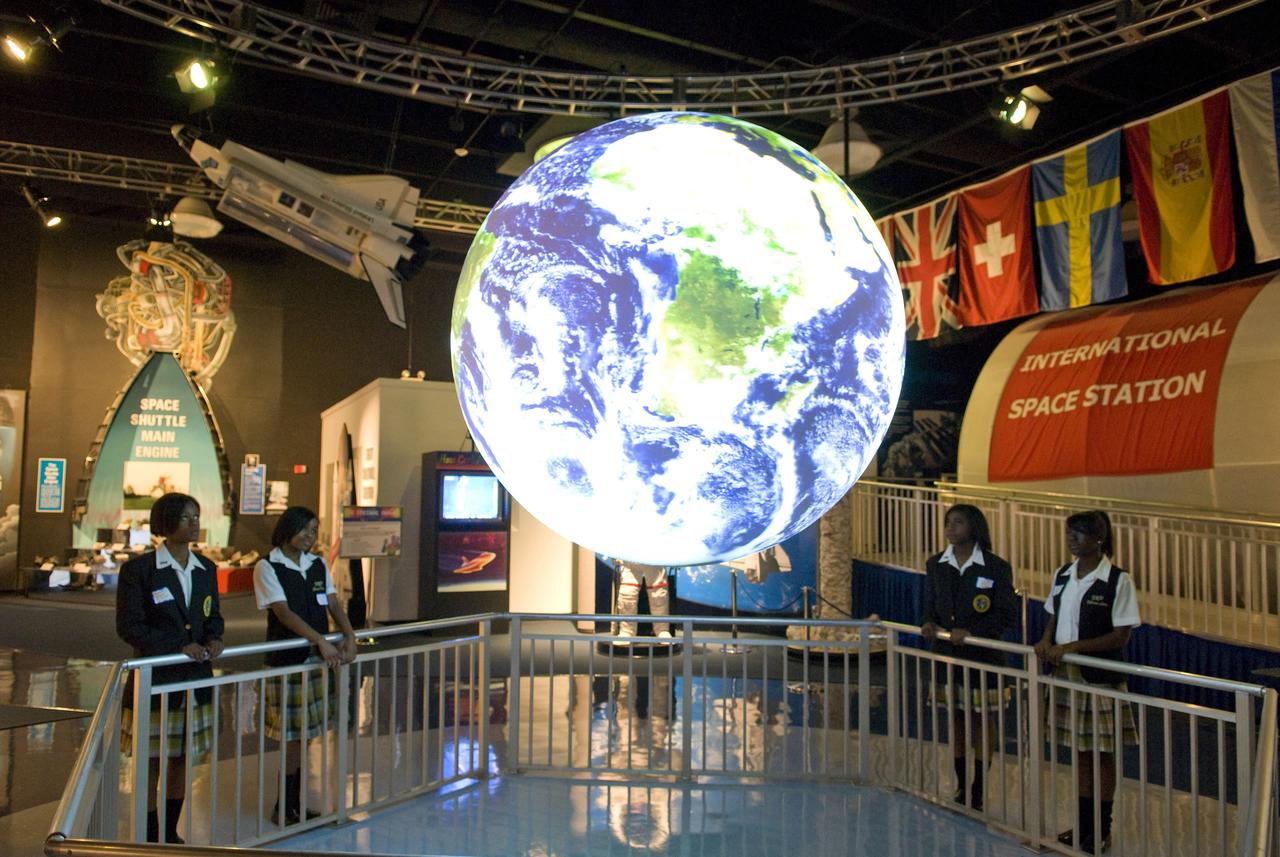

Students of Xavier University Preparatory School in New Orleans watch clouds shift across the globe in near-real time on 'Science on a Sphere' during a recent visit to StenniSphere, the visitor center at NASA's John C. Stennis Space Center. Four projectors work in sync with the suspended sphere to create a revolving display of a planet's atmosphere, oceans and land; to show documentary movies; or to project models of climate change using satellite data. Pictured are students (l to r) Ashante Snowton, Robriane Larry, Zhane Farbe and Ebony Johnson.
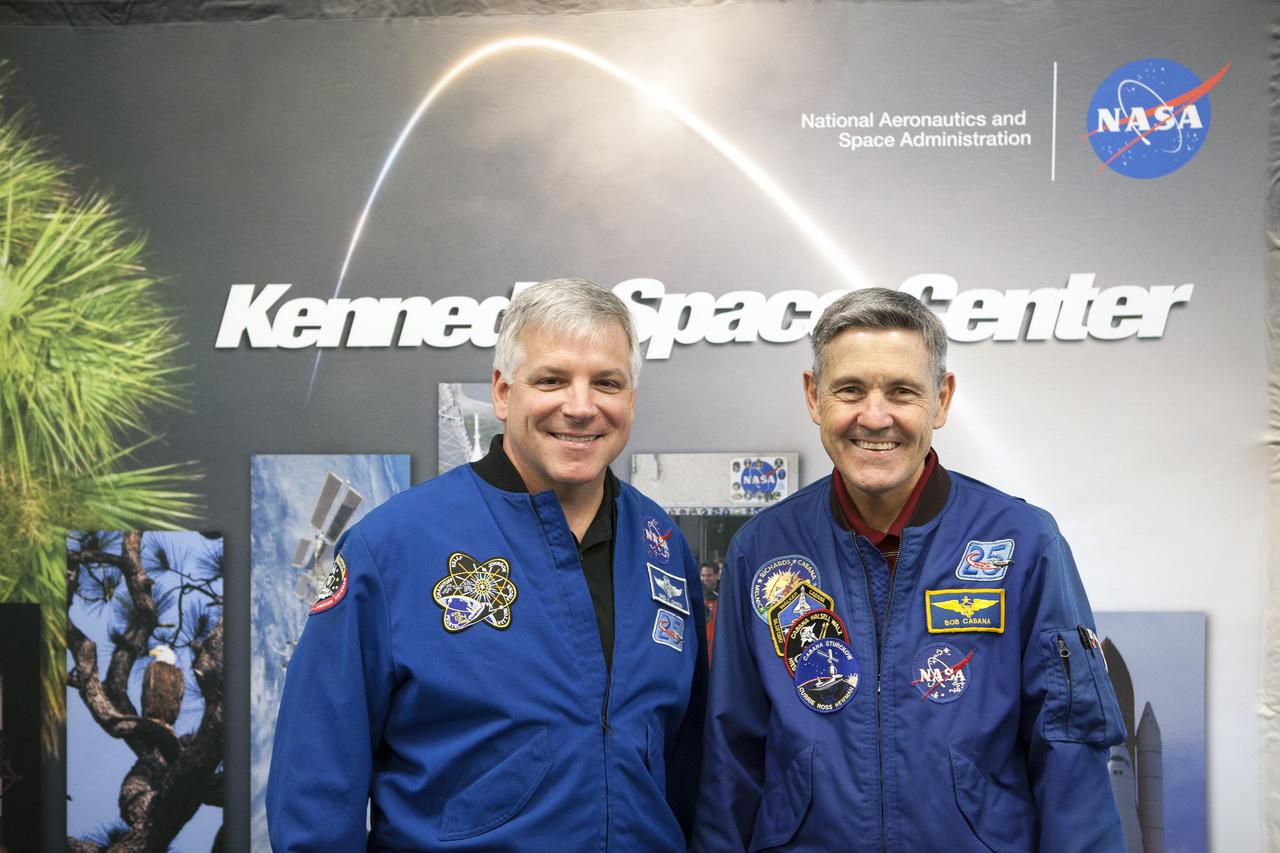

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former astronaut Greg Johnson, at left, executive director of the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space, and NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, visit with Florida middle school students and their teachers before the start of the Zero Robotics finals competition at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility in Florida. Students designed software to control Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites, or SPHERES, and competed with other teams locally. The Zero Robotics is a robotics programming competition where the robots are SPHERES. The competition starts online, where teams program the SPHERES to solve an annual challenge. After several phases of virtual competition in a simulation environment that mimics the real SPHERES, finalists are selected to compete in a live championship aboard the space station. Students compete to win a technically challenging game by programming their strategies into the SPHERES satellites. The programs are autonomous and the students cannot control the satellites during the test. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

ISS008-E-19136 (24 March 2004) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, Expedition 8 commander and NASA ISS science officer, does a check of the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Beacon / Beacon Tester in the Unity node of the International Space Station.
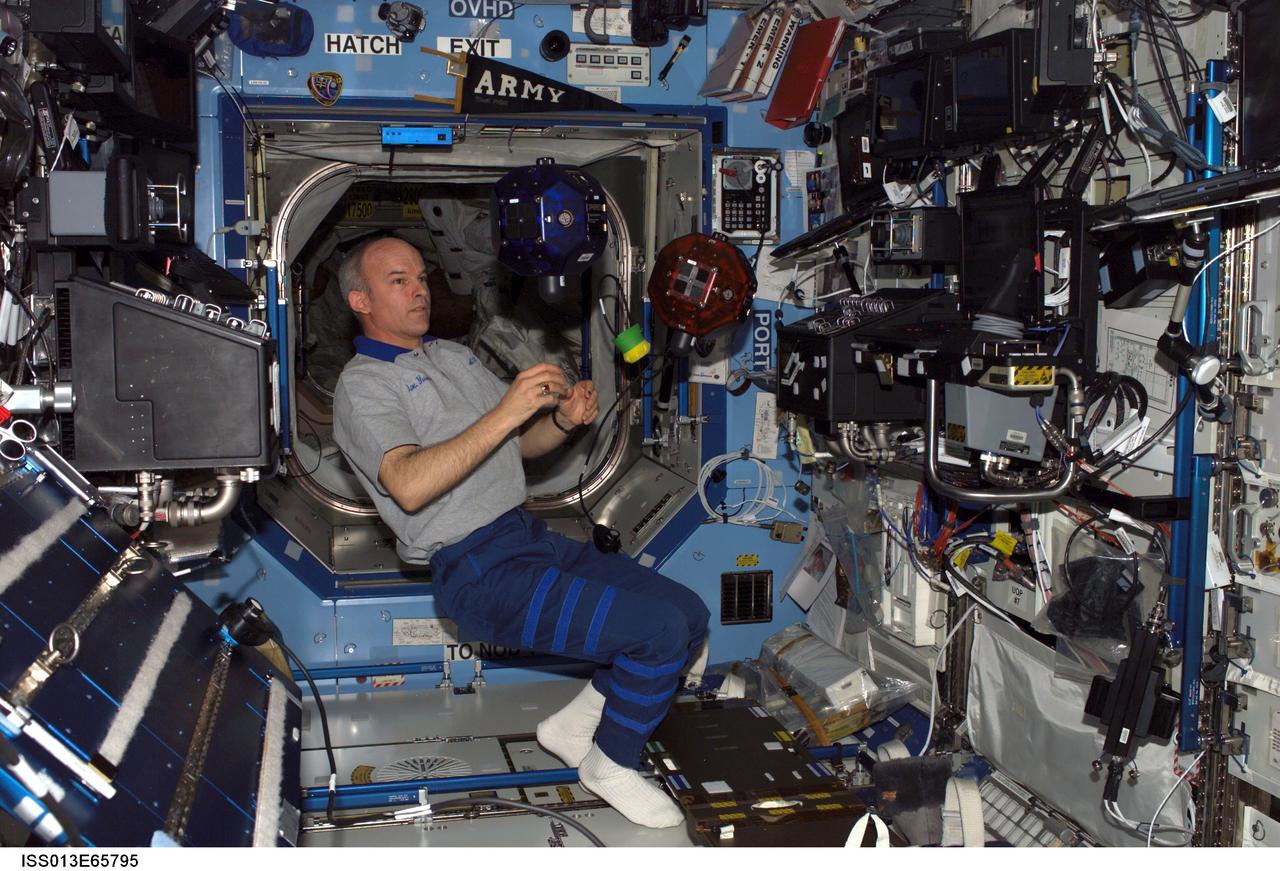

ISS013-E-65795 (12 Aug. 2006) --- Astronaut Jeffrey N. Williams, Expedition 13 NASA space station science officer and flight engineer, does a check of the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Beacon / Beacon Tester in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
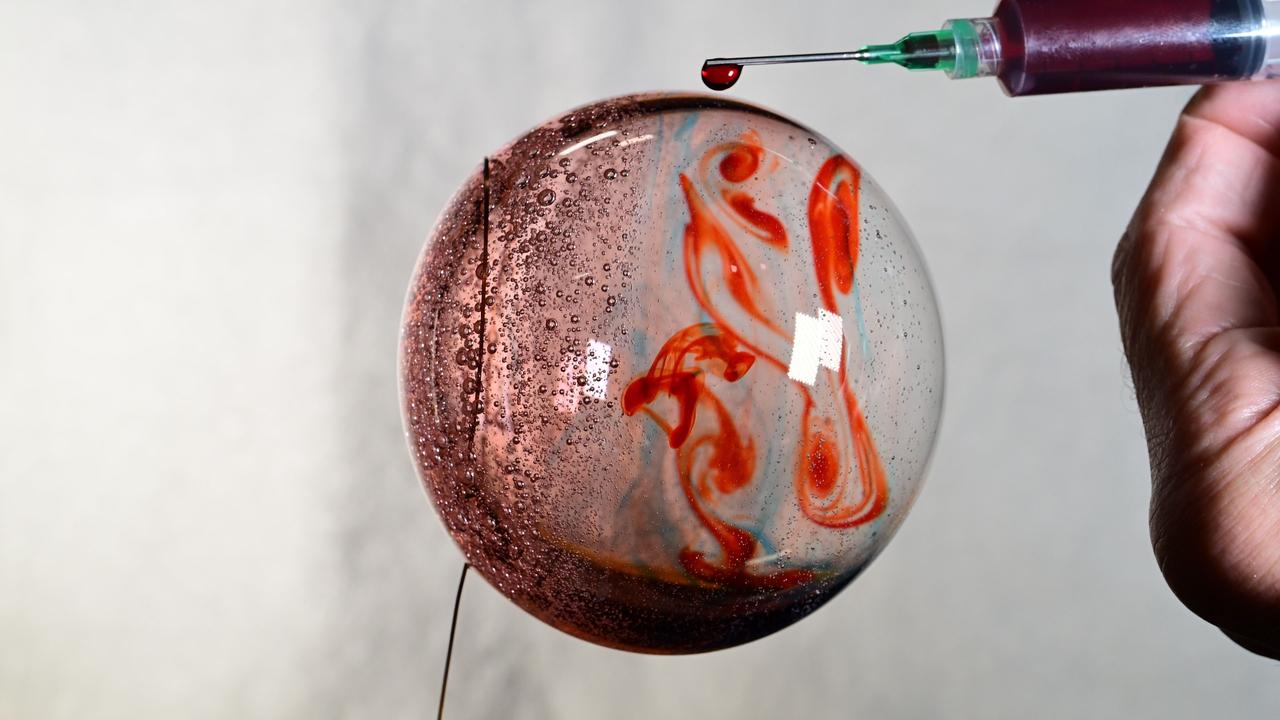
iss072e069543 (Oct. 19, 2024) --- Space science is fun! NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Don Pettit fills this sphere of water with food coloring creating a Jupiter-like effect in the microgravity environment of the International Space Station.
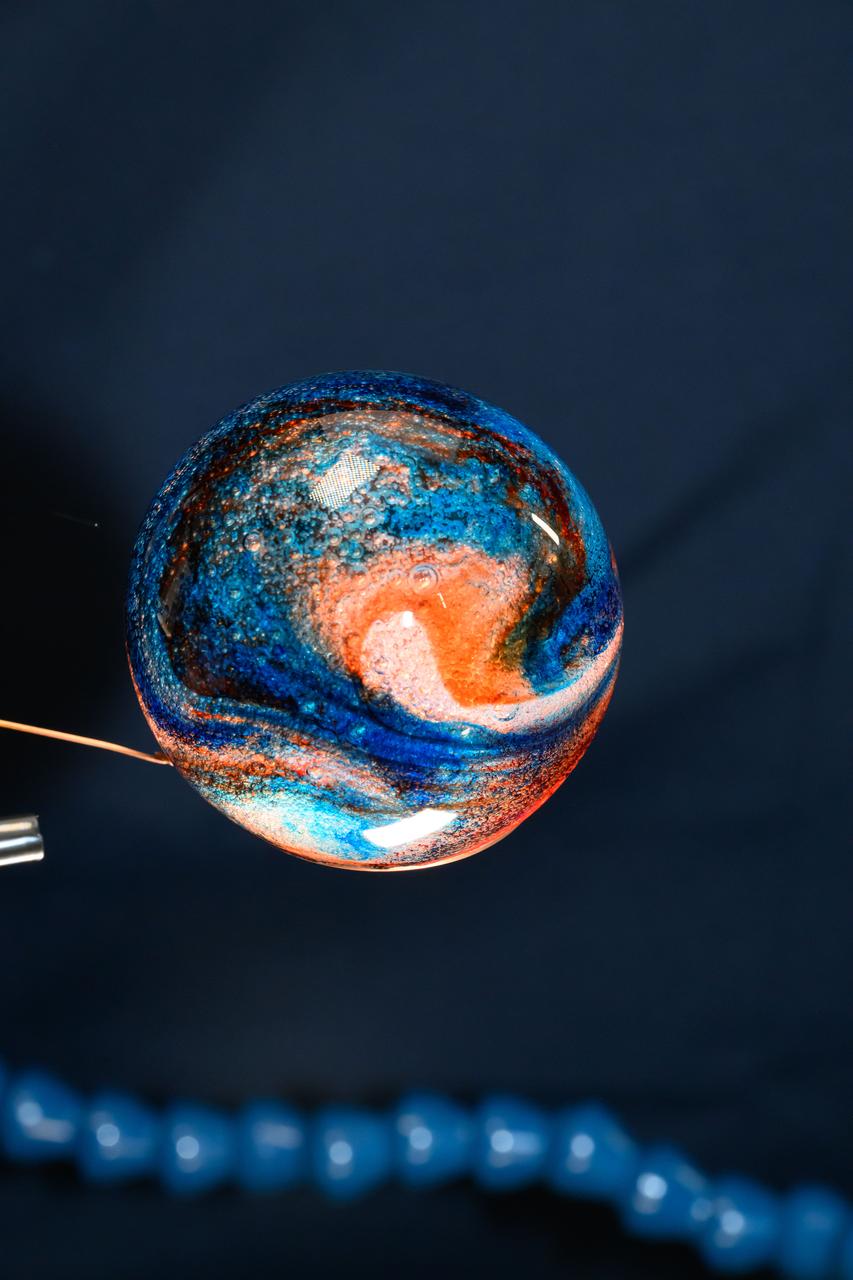

iss072e069592 (Oct. 19, 2024) --- Space science is fun! NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Don Pettit filled this sphere of water with food coloring creating a Jupiter-like effect in the microgravity environment of the International Space Station.
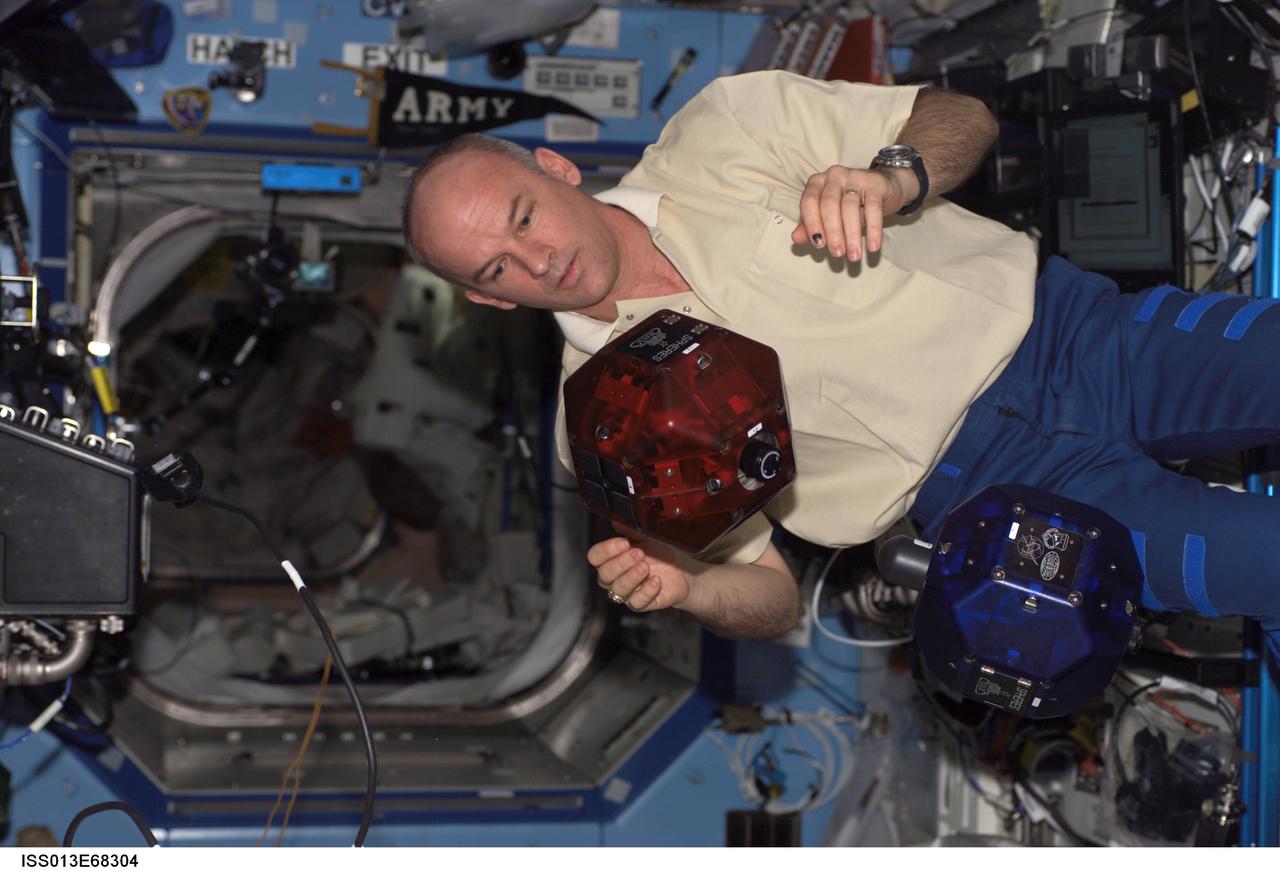

ISS013-E-68304 (19 Aug. 2006) --- Astronaut Jeffrey N. Williams, Expedition 13 NASA space station science officer and flight engineer, does a check of the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Beacon / Beacon Tester in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
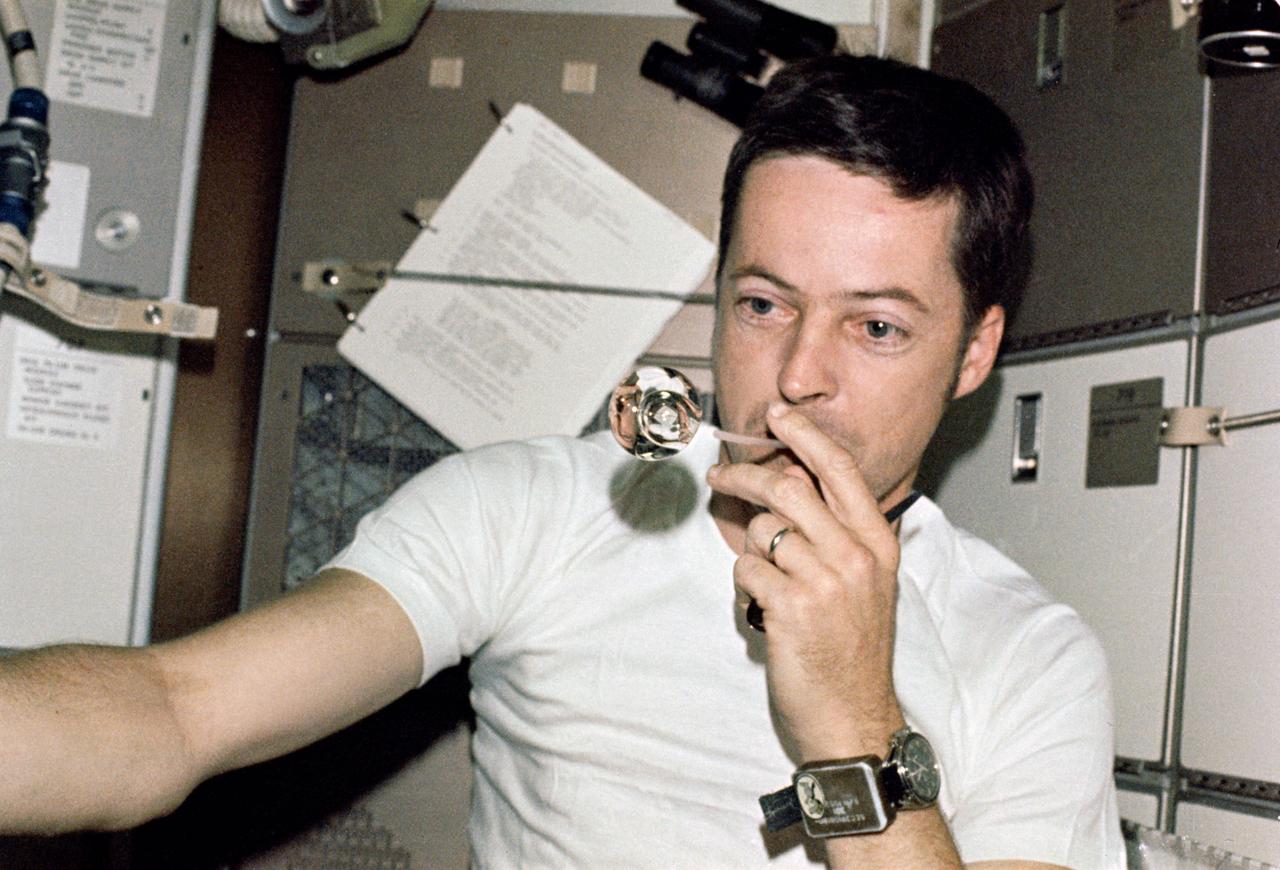

SL2-X9-730 (1 June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, forms a perfect sphere by blowing water droplets from a straw in zero-gravity. He is in the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA
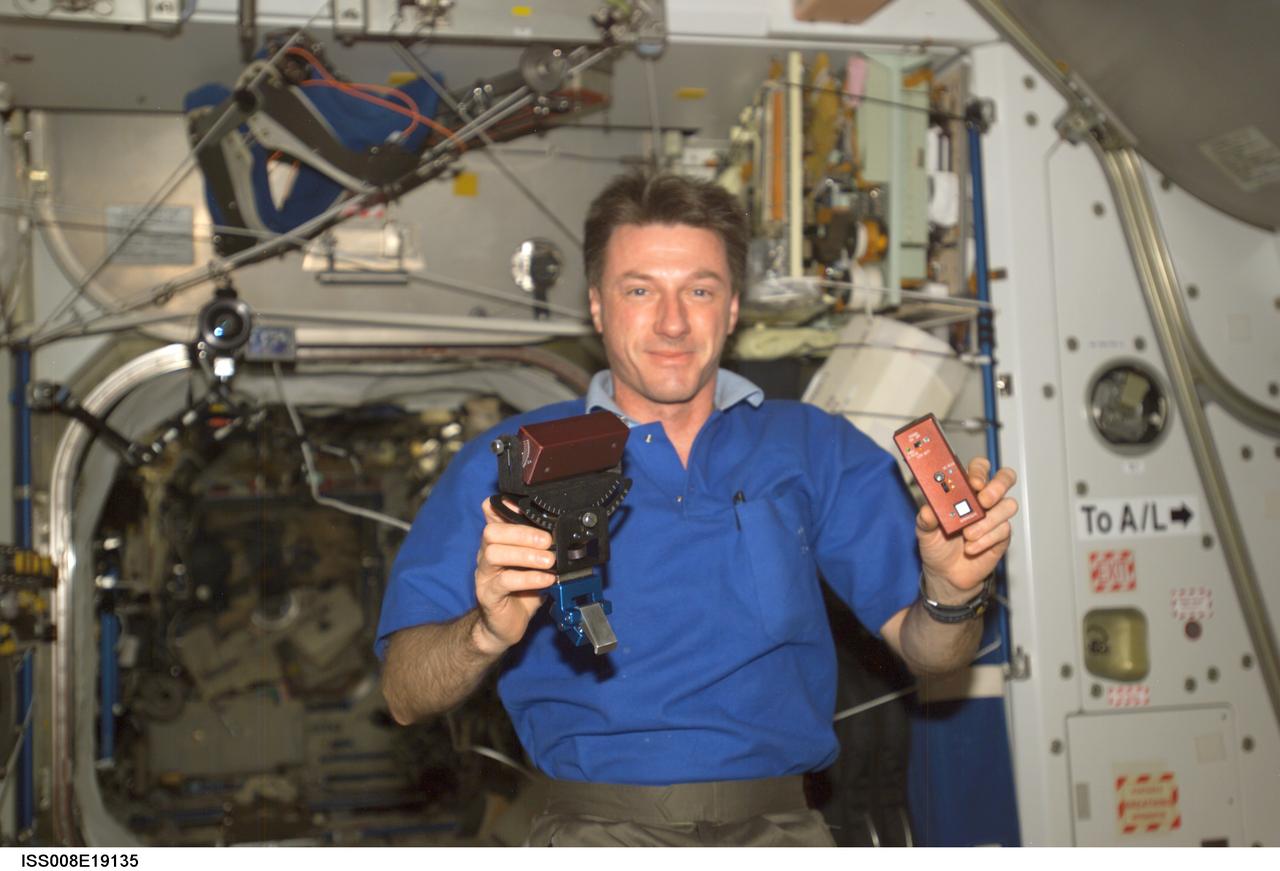

ISS008-E-19135 (24 March 2004) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, Expedition 8 commander and NASA ISS science officer, holds the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Beacon / Beacon Tester in the Unity node of the International Space Station.
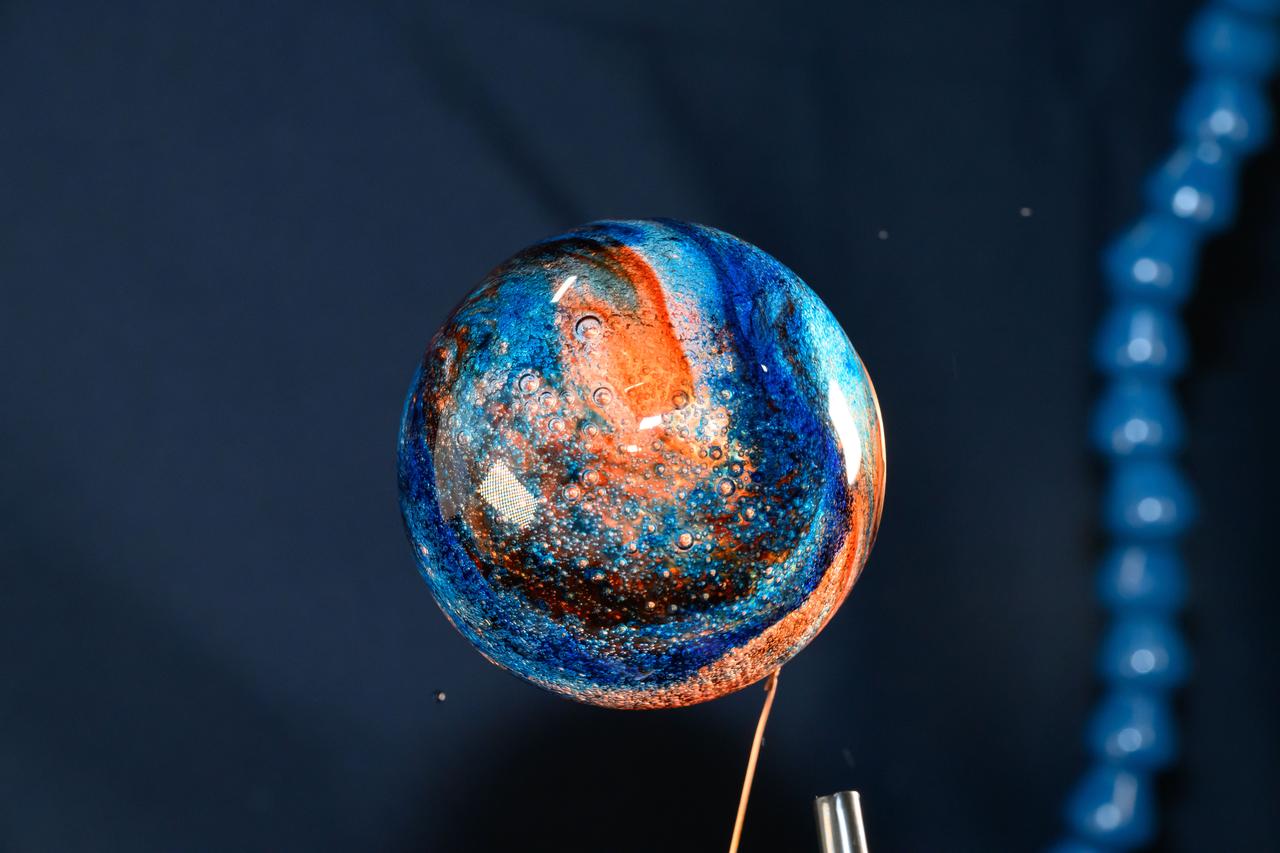

iss072e069593 (Oct. 19, 2024) --- Space science is fun! NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Don Pettit filled this sphere of water with food coloring creating a Jupiter-like effect in the microgravity environment of the International Space Station.
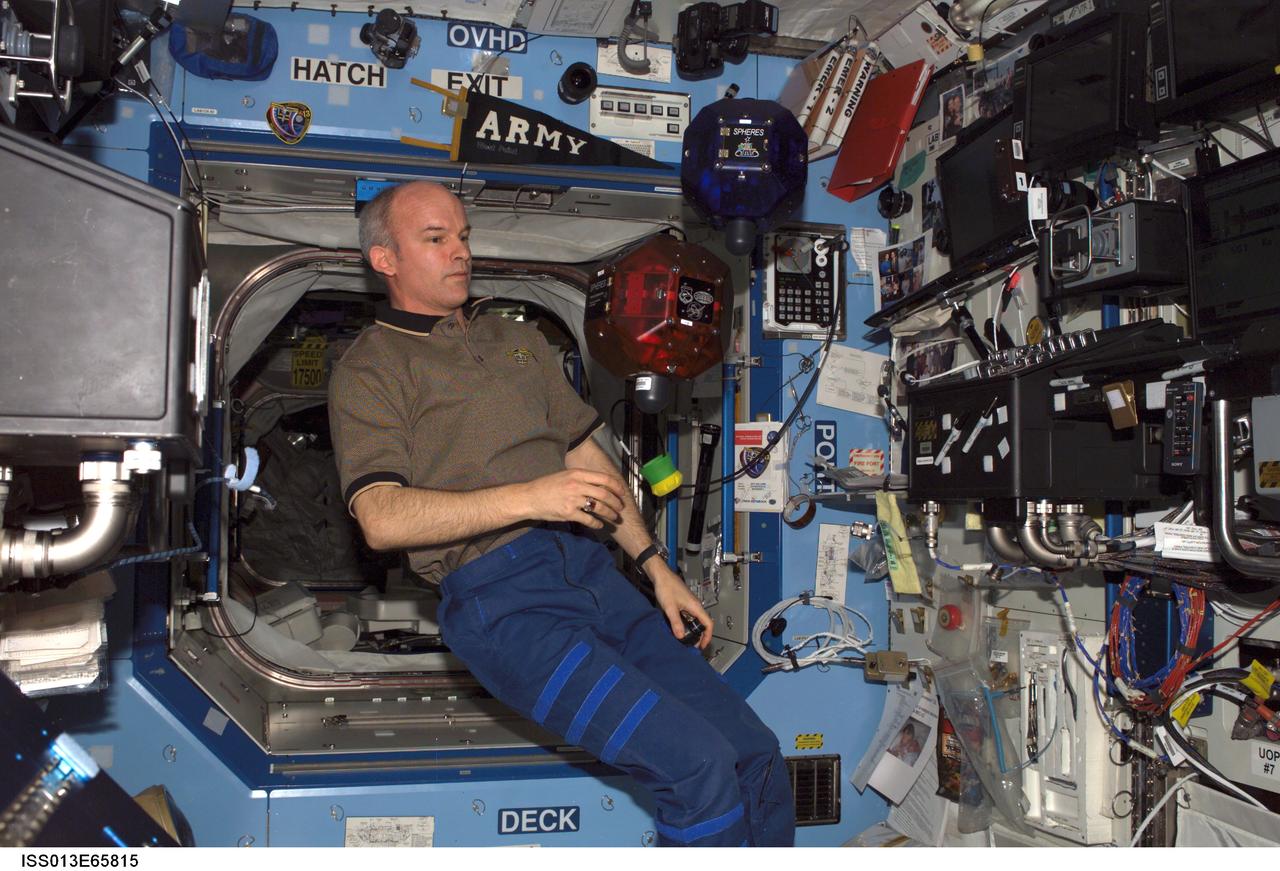

ISS013-E-65815 (12 Aug. 2006) --- Astronaut Jeffrey N. Williams, Expedition 13 NASA space station science officer and flight engineer, does a check of the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Beacon / Beacon Tester in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
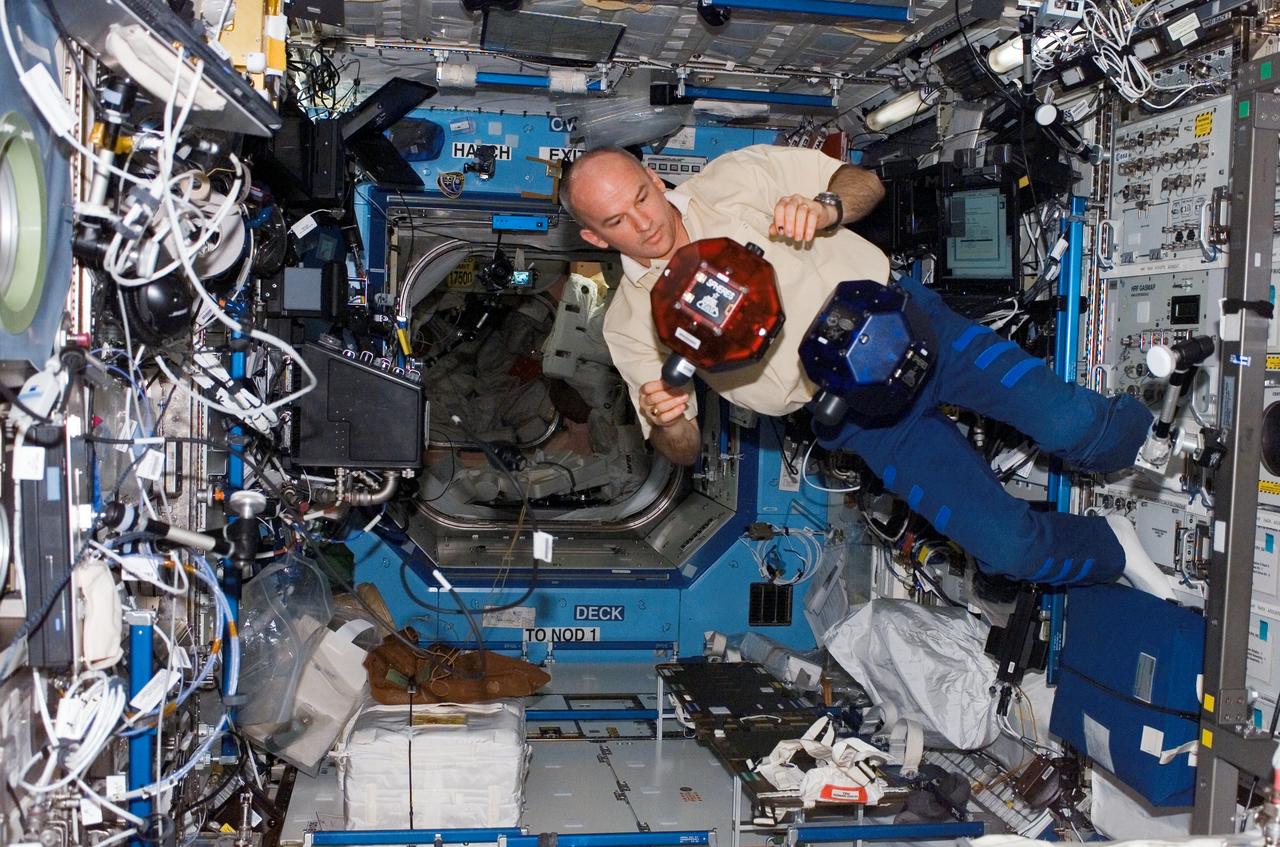

ISS013-E-68303 (19 Aug. 2006) --- Astronaut Jeffrey N. Williams, Expedition 13 NASA space station science officer and flight engineer, does a check of the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Beacon / Beacon Tester in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
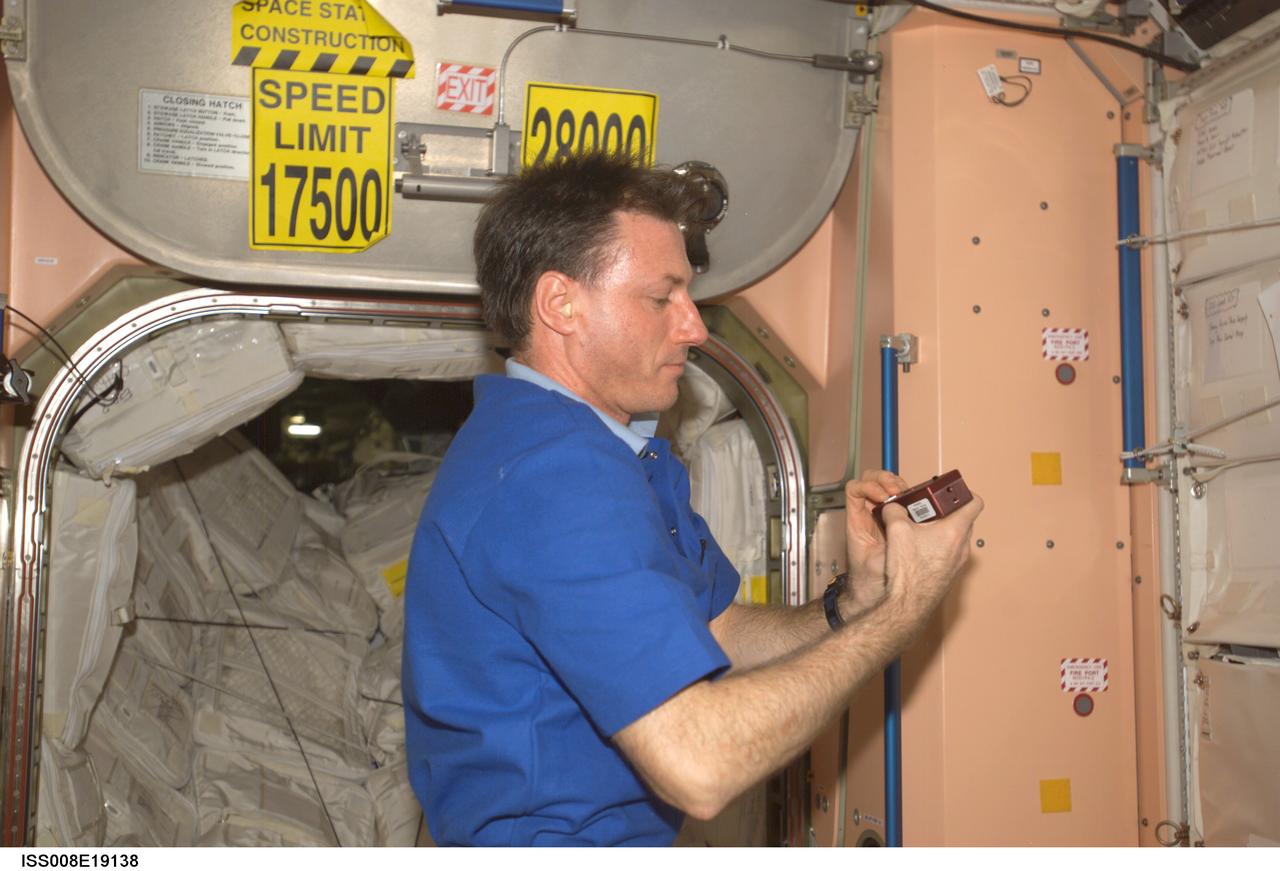

ISS008-E-19138 (24 March 2004) --- Astronaut C. Michael Foale, Expedition 8 commander and NASA ISS science officer, does a check of the Synchronized Position Hold, Engage, Reorient, Experimental Satellites (SPHERES) Beacon / Beacon Tester in the Unity node of the International Space Station.
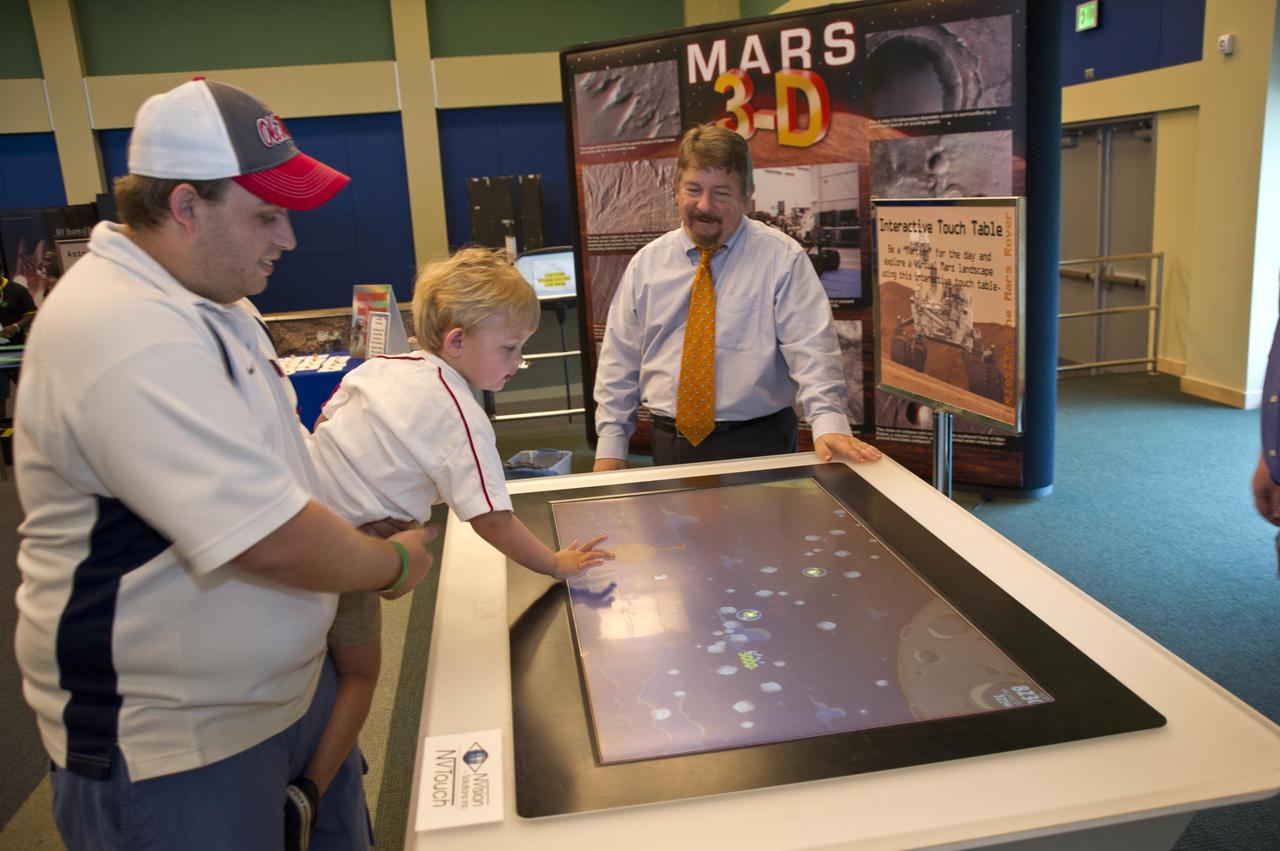

NASA welcomed hundreds of children and accompanying adults to its INFINITY visitor center on Aug. 4, offering Mars-related activities that focused attention on the space agency's Curiosity mission to the Red Planet. Parents and children, such as Myron and Trey (age 3) Cummings, enjoyed exploring Mars using an interactive touch table (top right photo). Midway through the day of activities, visitors in the Science on a Sphere auditorium also enjoyed a presentation on Mars and the Curiosity mission by Dr. Steven Williams, a NASA expert on Mars.
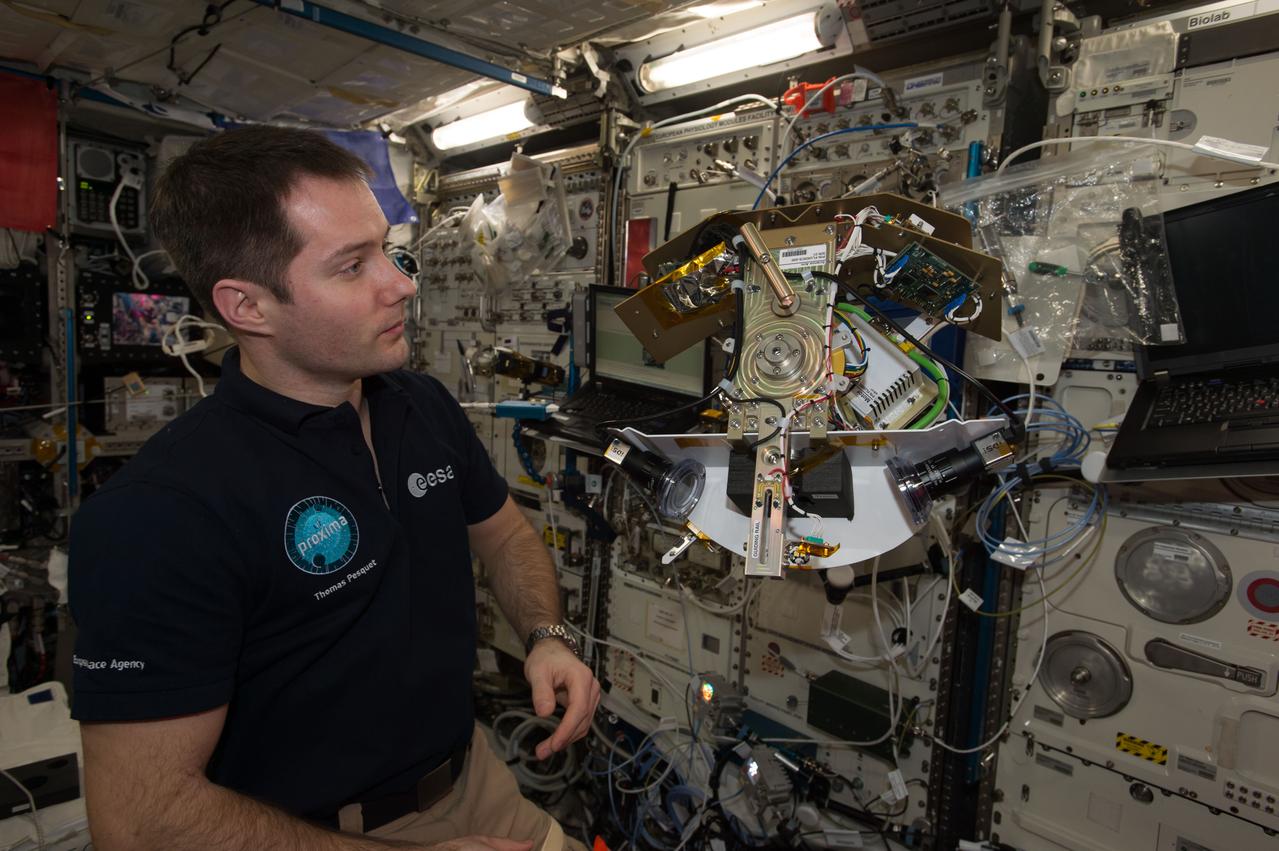

iss051e033986 (5/2/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet is photographed with the assembled Science Arm and Motor for the Fluid Dynamics in Space (FLUIDICS) experiment. Image was taken in the Columbus European Laboratory during preparations for the first run of the experiment. The FLUIDICS investigation evaluates the Center of Mass (CoM) position regarding a temperature gradient on a representation of a fuel tank. The observation of capillary wave turbulence on the surface of a fluid layer in a low-gravity environment can provide insights into measuring the existing volume in a sphere.
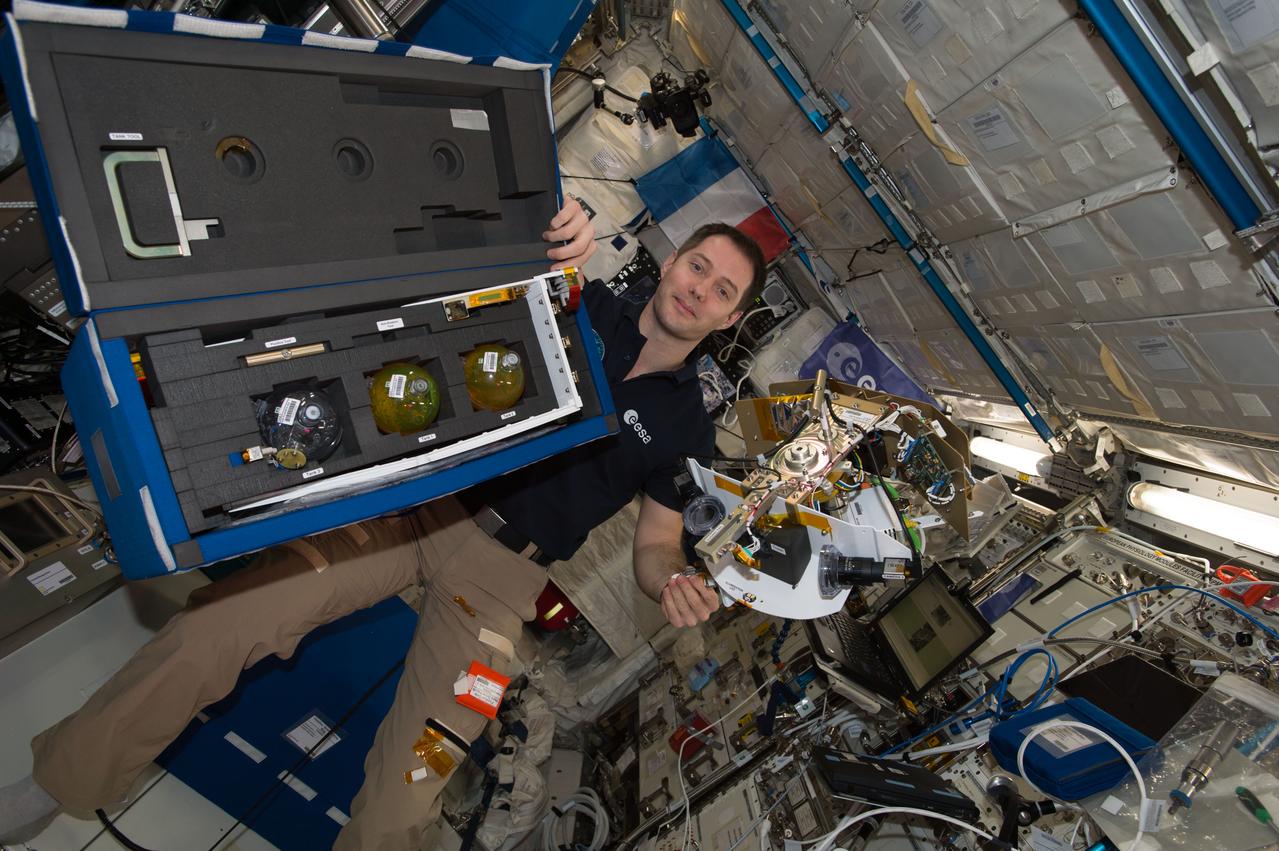

iss051e033988 (5/2/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet is photographed with the Tanks Bag and Science Arm for the Fluid Dynamics in Space (FLUIDICS) experiment. Image was taken in the Columbus European Laboratory during preparations for the first run of the experiment. The FLUIDICS investigation evaluates the Center of Mass (CoM) position regarding a temperature gradient on a representation of a fuel tank. The observation of capillary wave turbulence on the surface of a fluid layer in a low-gravity environment can provide insights into measuring the existing volume in a sphere.
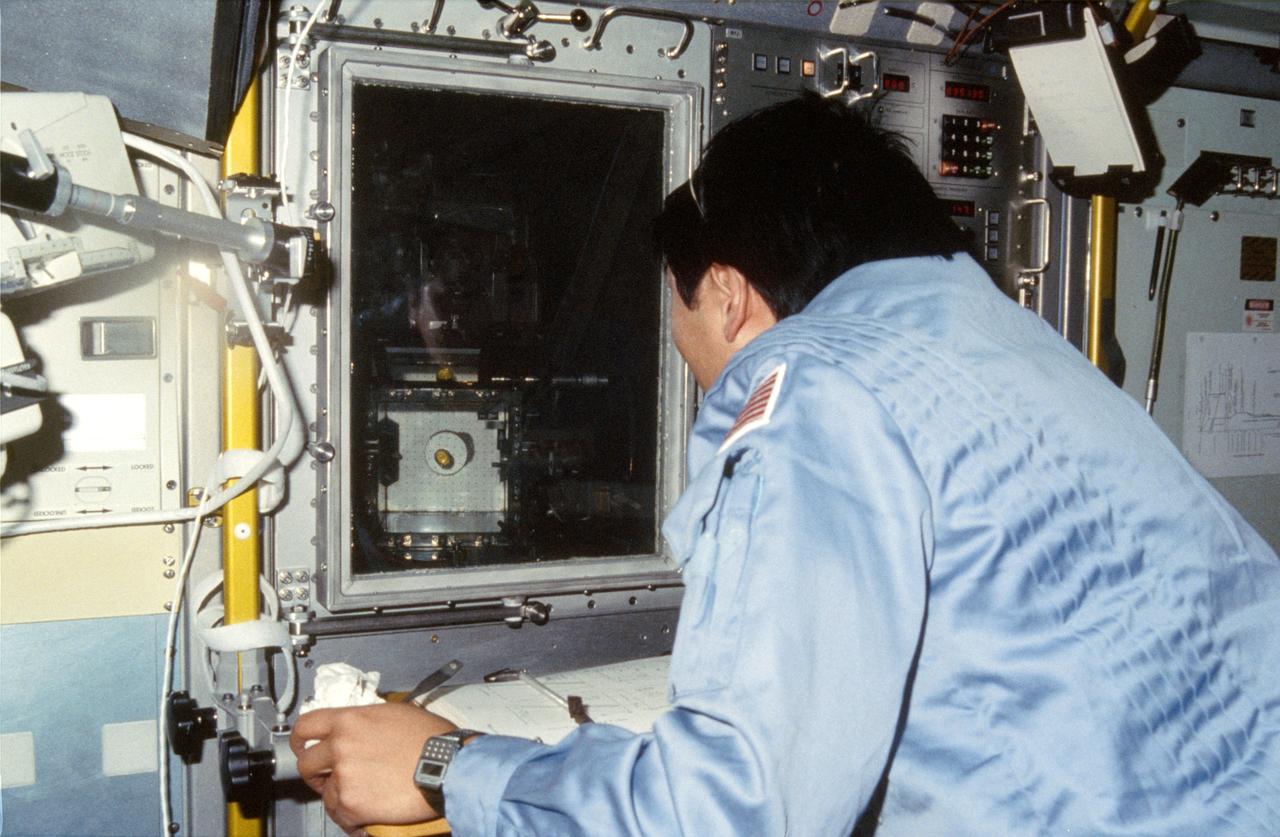
51B-14-038 (29 April-6 May 1985) --- Payload specialist Taylor G. Wang manipulates a 1.5 centimeter diameter sphere in the Drop Dynamics Module (DDM) in the science module aboard the earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Challenger. The photo was taken with a 35mm camera. Dr. Wang is principal investigator for the first-time-to-fly experiment, developed by his team at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California. This photo was one of the first released by NASA upon return to earth of the Spacelab 3 crewmembers.
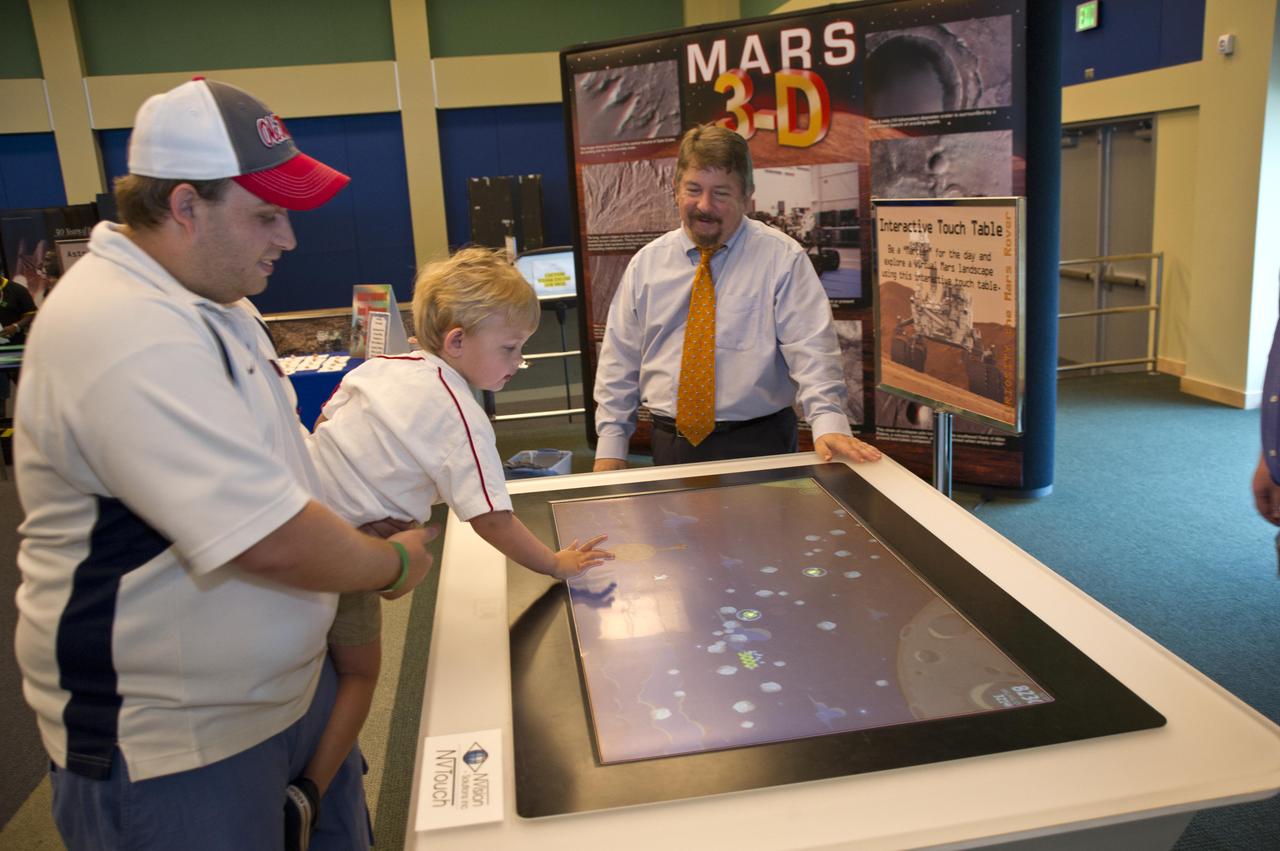

NASA welcomed hundreds of children and accompanying adults to its INFINITY visitor center on Aug. 4, offering Mars-related activities that focused attention on the space agency's Curiosity mission to the Red Planet. Parents and children, such as Myron and Trey (age 3) Cummings, enjoyed exploring Mars using an interactive touch table. Midway through the day of activities, visitors in the Science on a Sphere auditorium also enjoyed a presentation on Mars and the Curiosity mission by Dr. Steven Williams, a NASA expert on Mars.

An R2-D2 model in front of the Science on a Sphere exhibit at the Visitor Center at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Star Wars cosplayers attended a "Yuri's Night" celebration at the visitor center to commemorate the first flight of cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin (April 12, 1961) and the first orbital flight of a space shuttle (April 12, 1981).
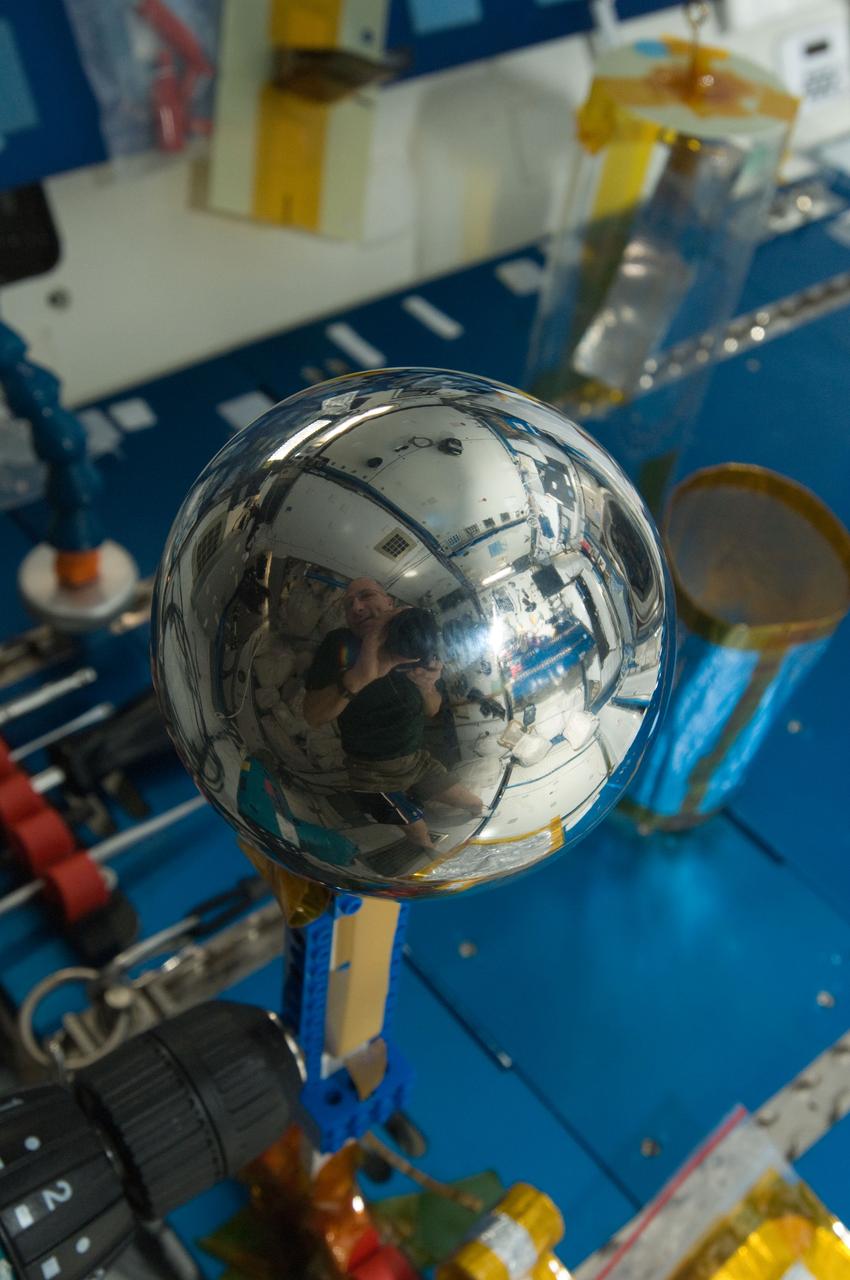
ISS031-E-035391 (12 May 2012) --- NASA astronaut Don Pettit, Expedition 31 flight engineer, took this picture of a four-inch polished metal sphere in the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory on May 12, 2012 using a 28mm lens. A close look of the sphere reveals a mirrored Pettit.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- During the NASA Explorer Schools Symposium at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, students and teachers check out the Science on a Sphere system at the U.S. Astronaut Hall of Fame. About 60 fourth- through 12-grade students from across the nation are at the center May 4-7 participating in tours of processing and launch facilities, as well as several educational activities and a career panel question-and-answer session. About 30 teachers will receive professional development opportunities during the symposium. The participants were competitively selected after they completed an original investigation focused on existing NASA missions or research interests. Photo Credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
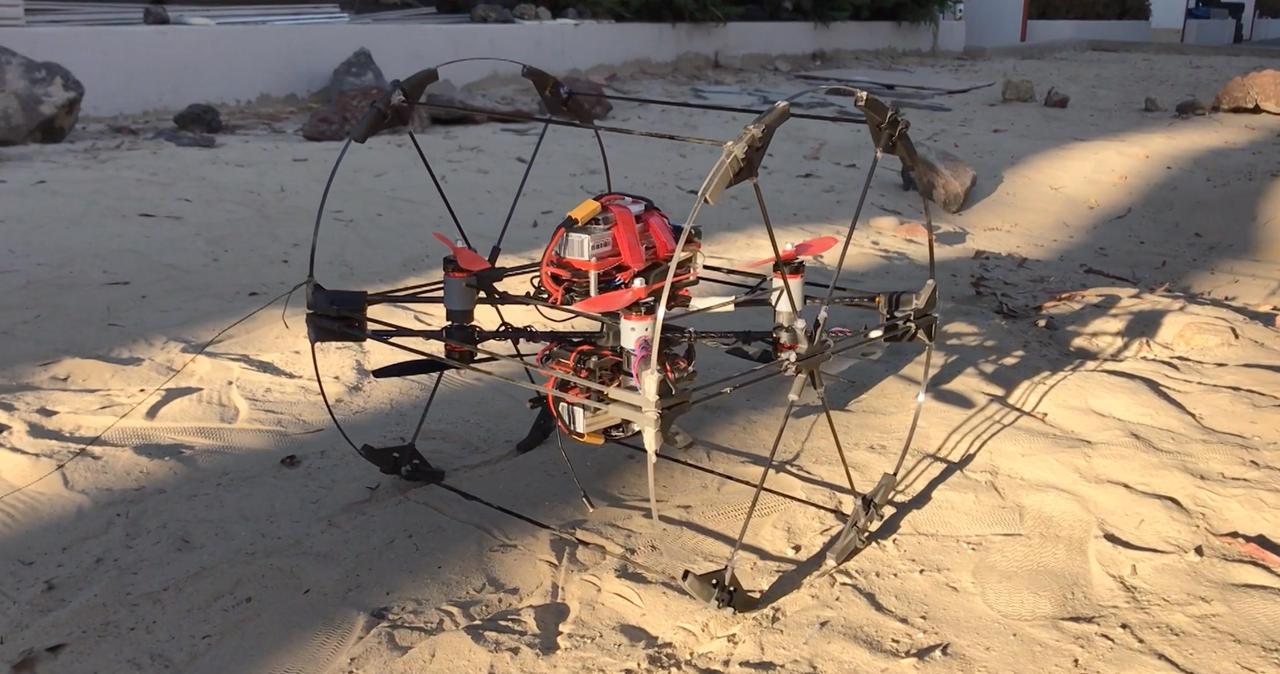

A prototype of the transforming robot Shapeshifter is tested in the robotics yard at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Shapeshifter is made of smaller robots that can morph into rolling spheres, flying drones, swimming submersibles and more. Shapeshifter is a developing concept for a transformational vehicle to explore treacherous, distant worlds. The flying amphibious robot is part of the early-stage research program NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC), which offers several phases of funding to visionary concepts, helping turn ideas that sound like science fiction into science fact. JPL Principle Investigator Ali Agha envisions Shapeshifter as a mission to Saturn's moon Titan, the only other world in the solar system known to have liquid in the form of methane lakes, rivers and seas on its surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23433

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Pictured is Jack Jones in the Mission Manager Area.
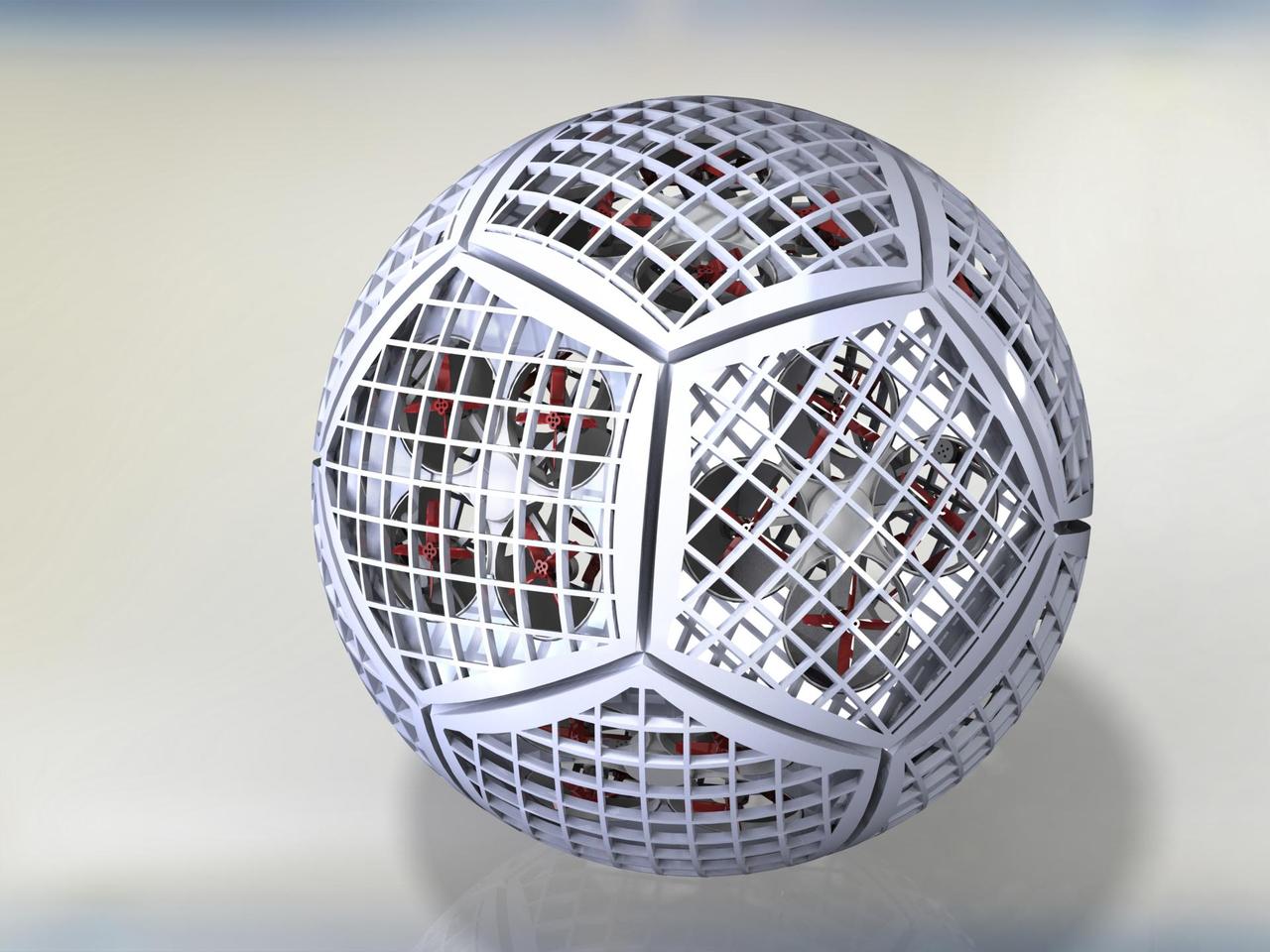
An illustration of the small robots that form Shapeshifter. Dubbed "cobots," they each have a propeller for flying and can combine to form a sphere, rolling on the ground to save energy. Shapeshifter is a developing concept for a transformational vehicle to explore treacherous, distant worlds. The flying amphibious robot is part of the early-stage research program NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC), which offers several phases of funding to visionary concepts, helping turn ideas that sound like science fiction into science fact. JPL Principle Investigator Ali Agha envisions Shapeshifter as a mission to Saturn's moon Titan, the only other world in the solar system known to have liquid in the form of methane lakes, rivers and seas on its surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23435

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Pictured is the TV OPS area of the SL POCC.
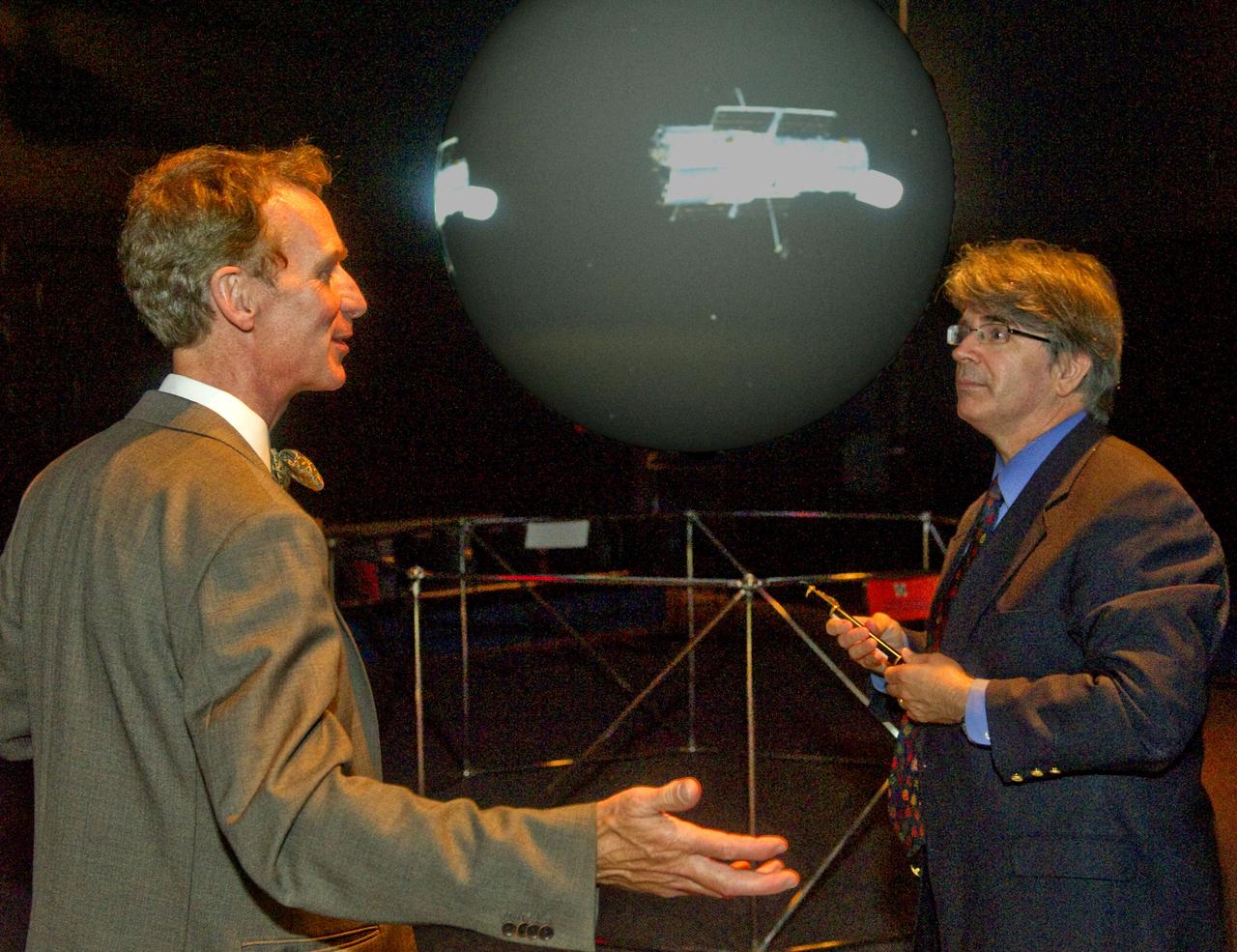

Bill Nye and Dr. Jim Garvin at the Science on a Sphere during a tour of Goddard Space Flight Center on September 8, 2011 Credit: NASA/GSFC/Bill Hrybyk <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
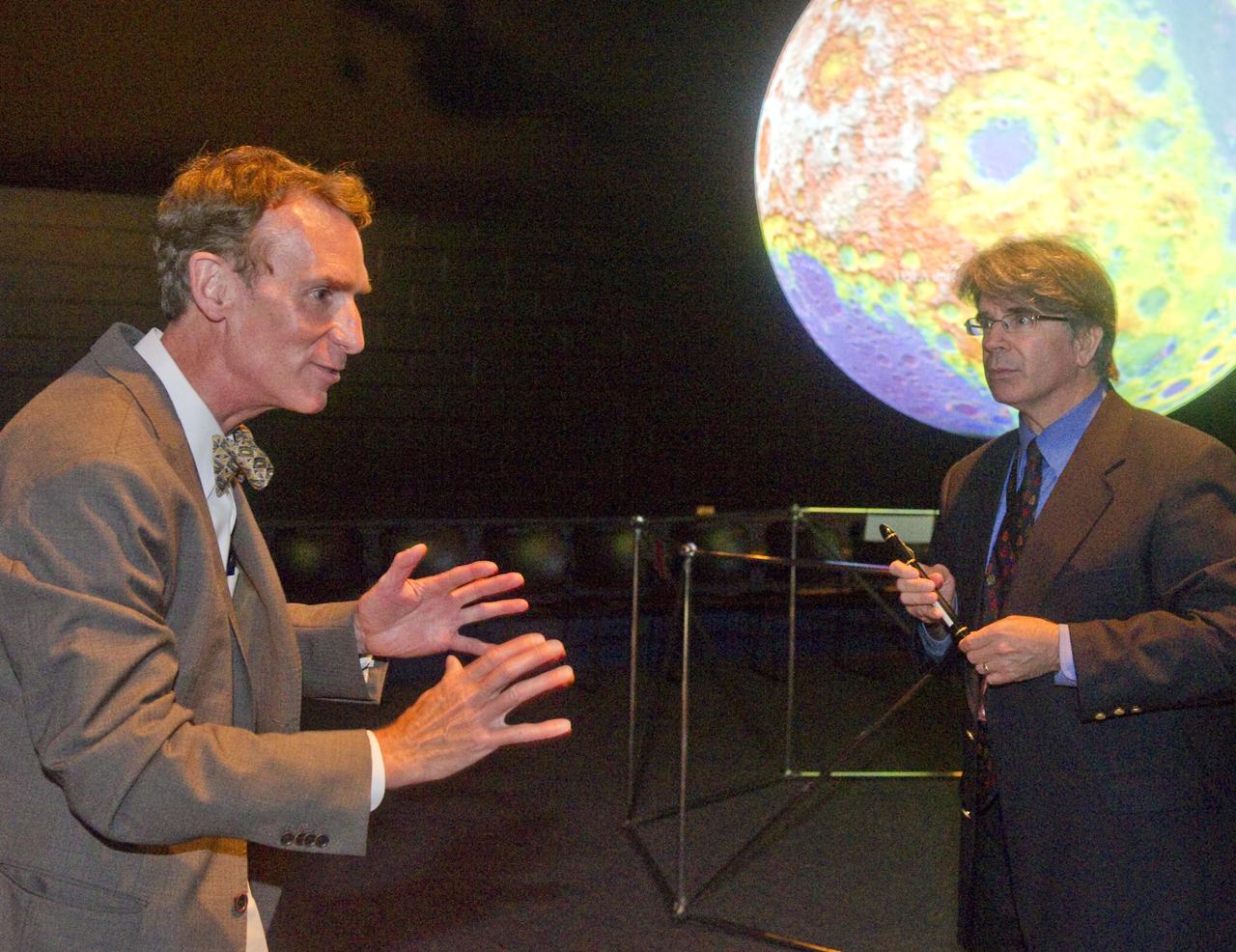

Bill Nye and Dr. Jim Garvin at the Science on a Sphere during a tour of Goddard Space Flight Center on September 8, 2011 Credit: NASA/GSFC/Bill Hrybyk <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo captures the activity of WUPPE (Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment) data review at the Science Operations Area during the mission. This image shows mission activities at the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT) Work Station in the Science Operations Area (SOA).
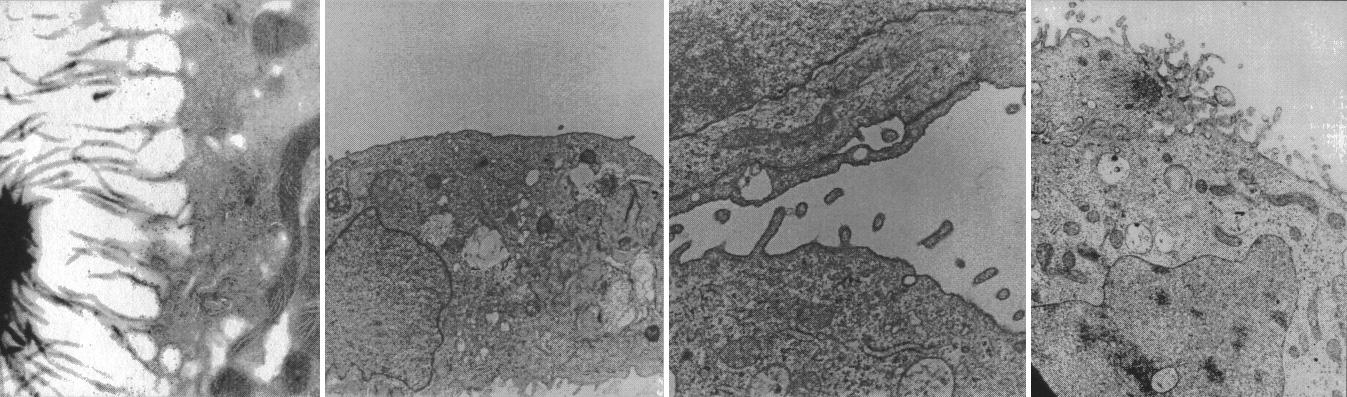
Cells from kidneys lose some of their special features in conventional culture but form spheres replete with specialized cell microvilli (hair) and synthesize hormones that may be clinically useful. Ground-based research studies have demonstrated that both normal and neoplastic cells and tissues recreate many of the characteristics in the NASA bioreactor that they display in vivo. Proximal kidney tubule cells that normally have rich apically oriented microvilli with intercellular clefts in the kidney do not form any of these structures in conventional two-dimensional monolayer culture. However, when normal proximal renal tubule cells are cultured in three-dimensions in the bioreactor, both the microvilli and the intercellular clefts form. This is important because, when the morphology is recreated, the function is more likely also to be rejuvenated. The work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research. The bioreactor is managed by the Biotechnology Cell Science Program at NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC).
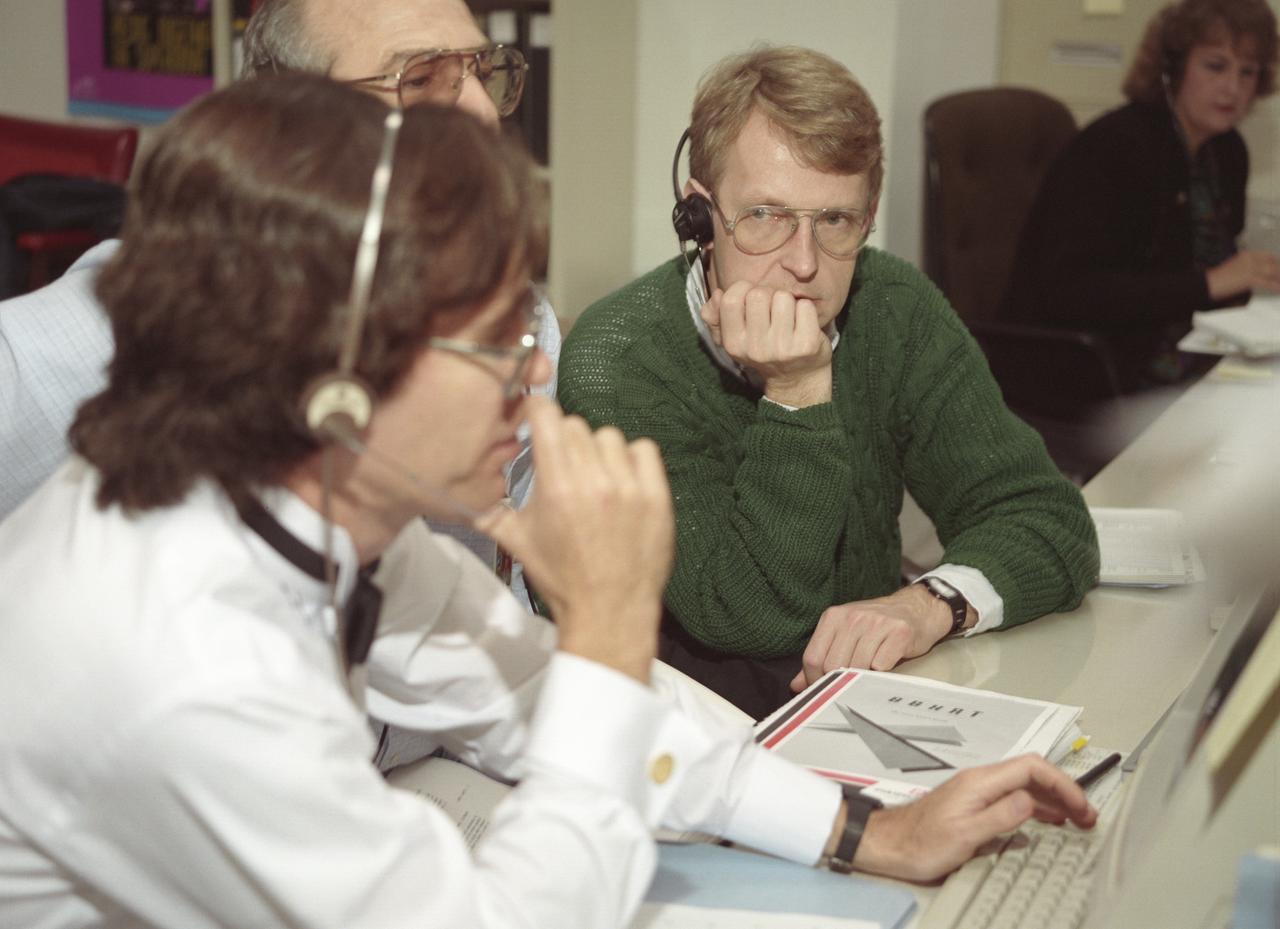

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo captures the activity of BBKRT data review in the Science Operations Area during the mission.
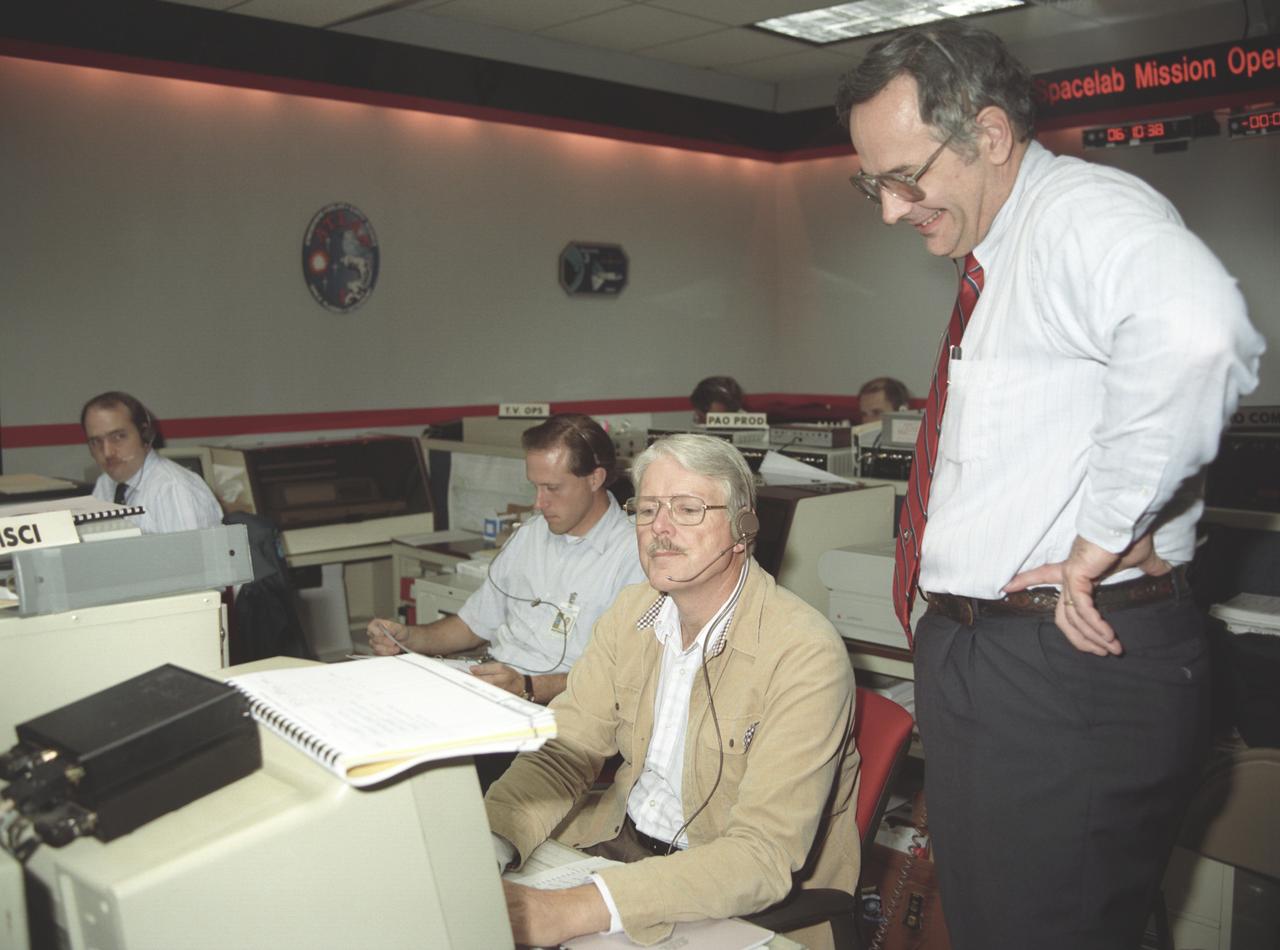

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo captures the activity of WUPPE data review at the Science Operations Area during the mission.
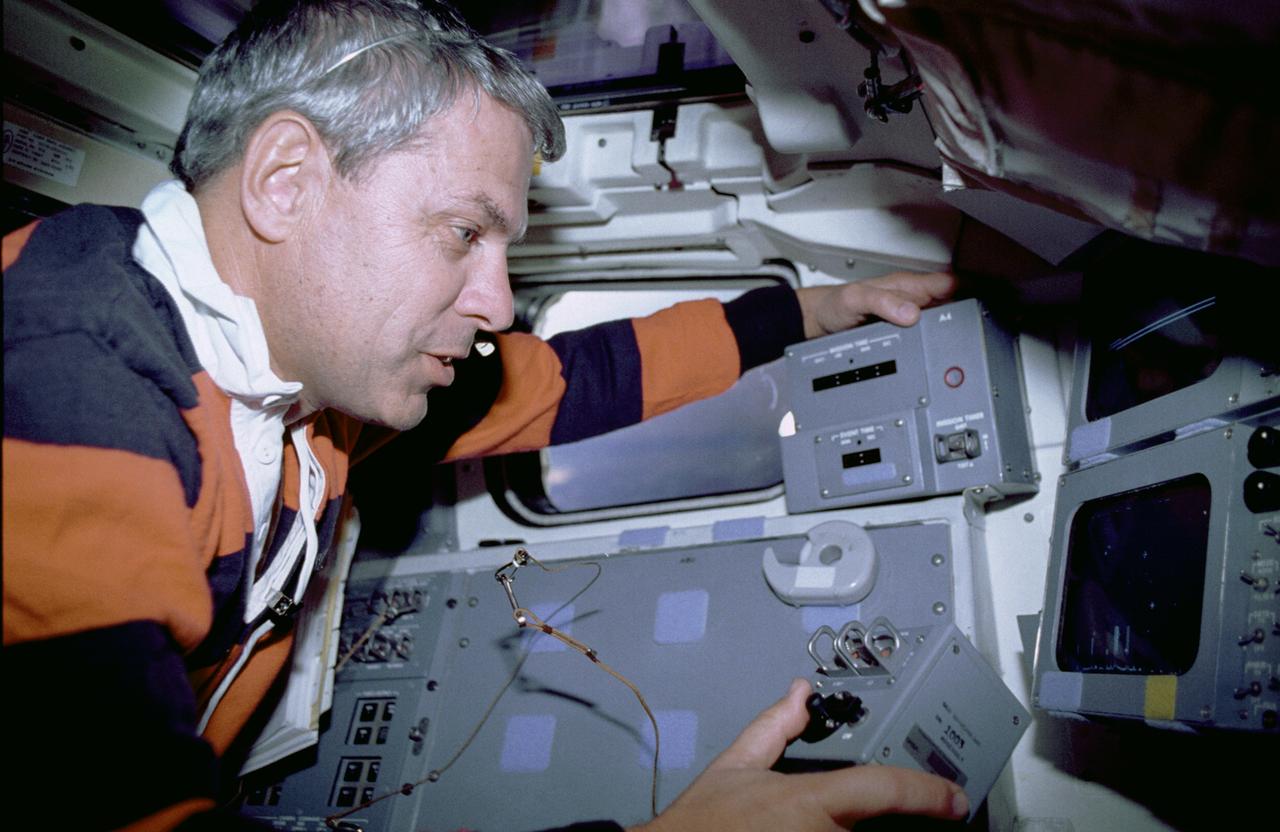

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. Pictured onboard the shuttle is astronaut Robert Parker using a Manual Pointing Controller (MPC) for the ASTRO-1 mission Instrument Pointing System (IPS).
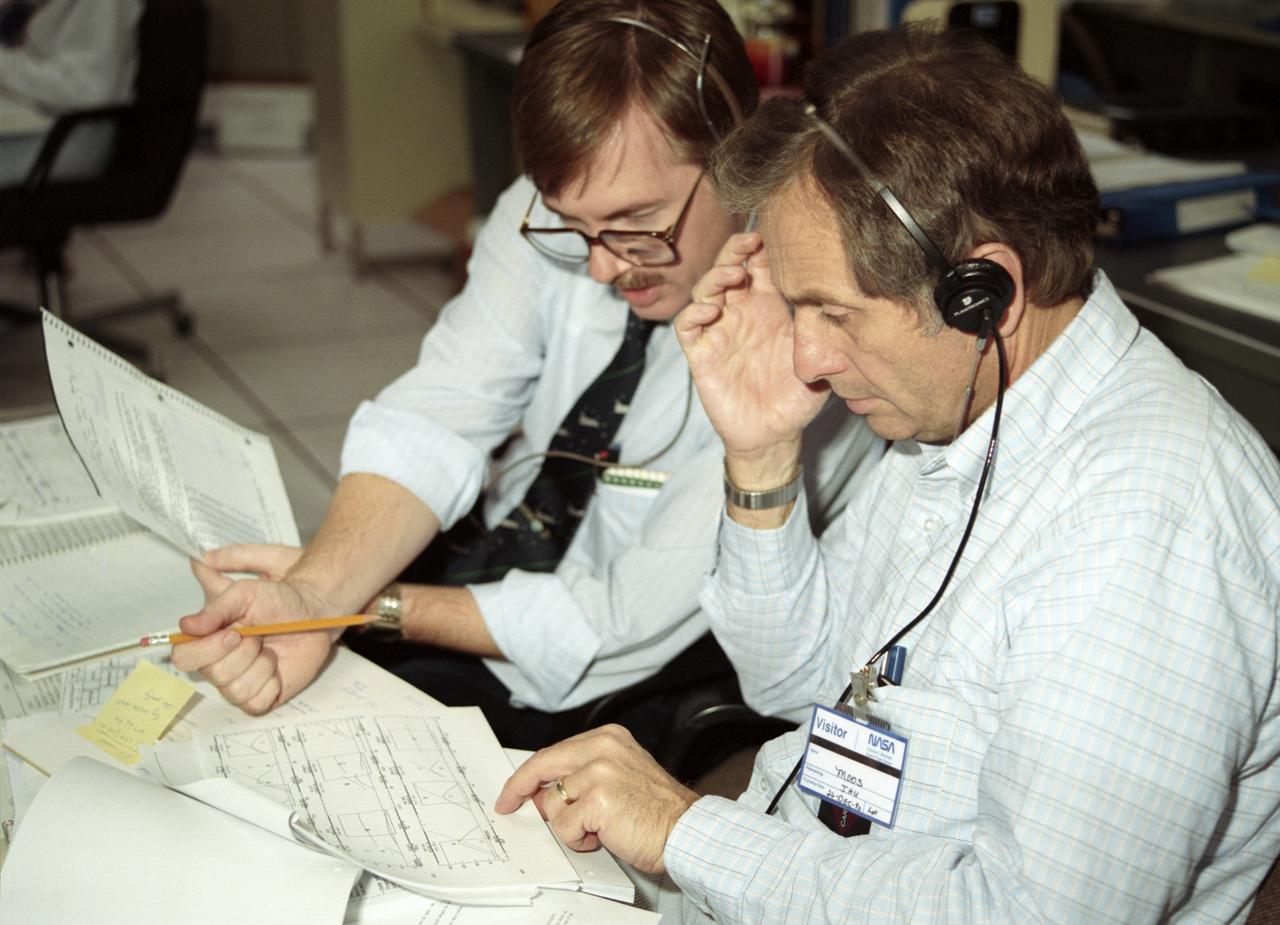

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo captures the activity of viewing HUT data in the Mission Manager Actions Room during the mission.
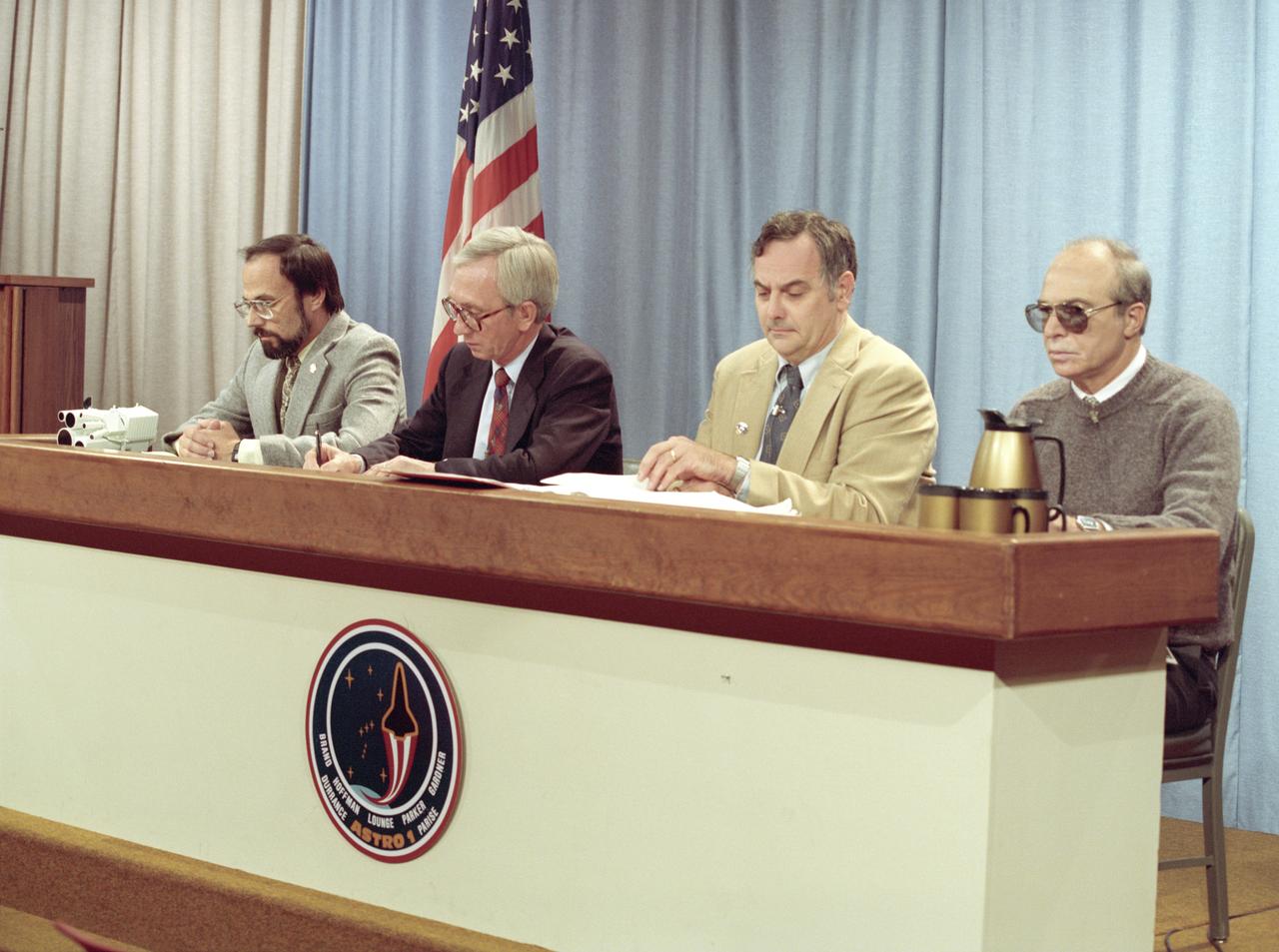

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo captures a press briefing at MSFC during STS-35, ASTRO-1 Mission.
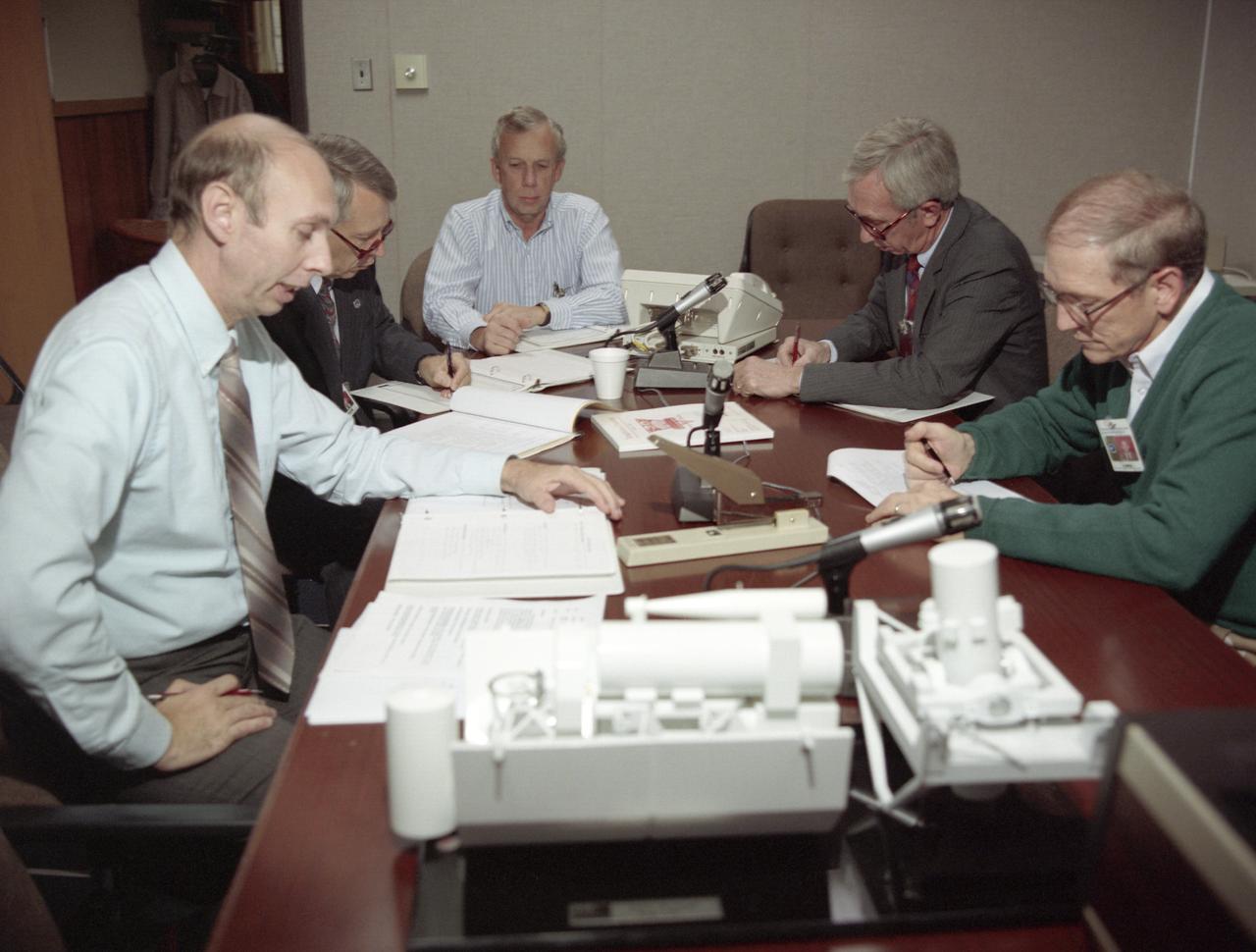

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo captures the activities at the Mission Manager Actions Room during the mission.
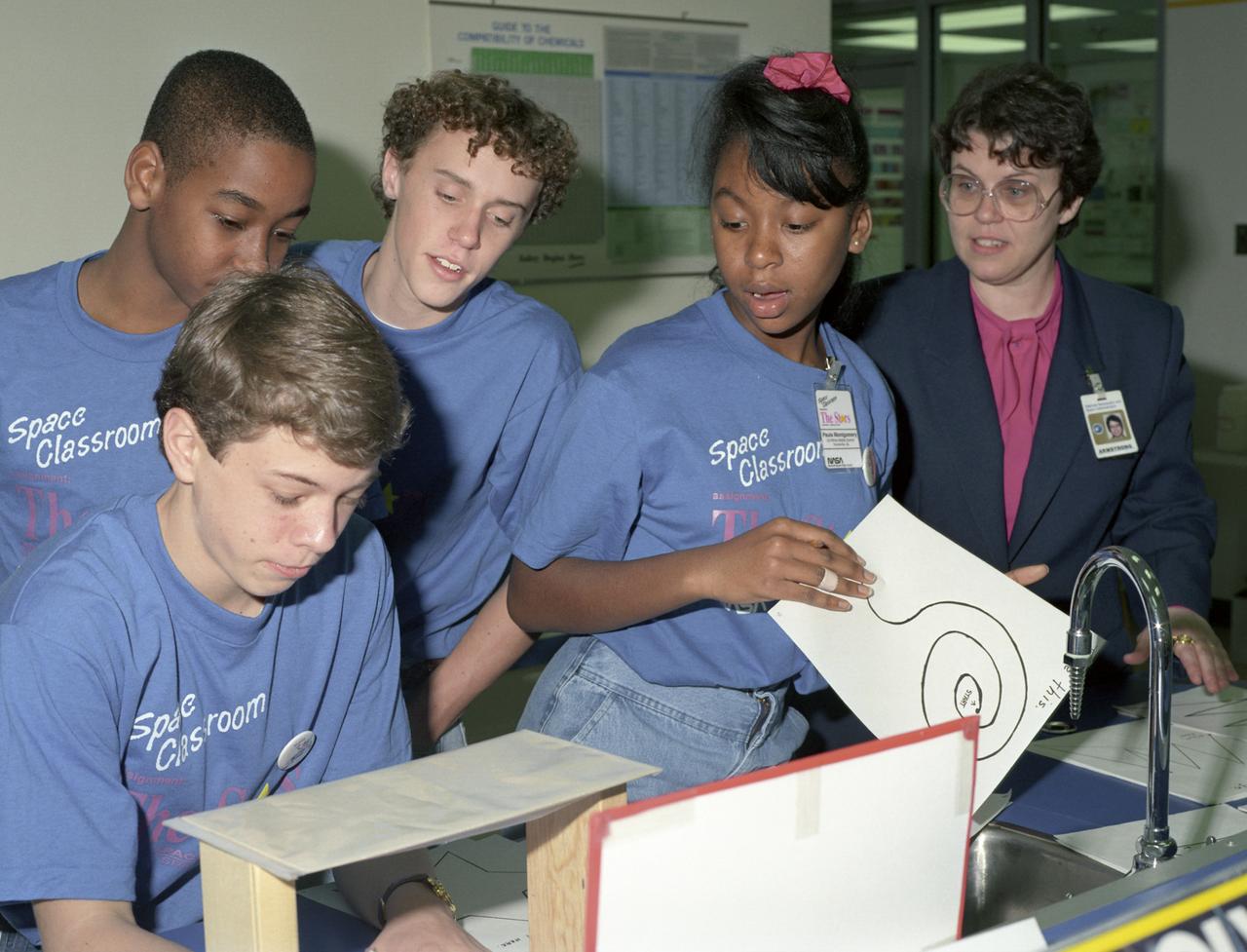

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. This photo is of Space classroom students in the Discovery Optics Lab at MSFC during STS-35, ASTRO-1 mission payload operations.
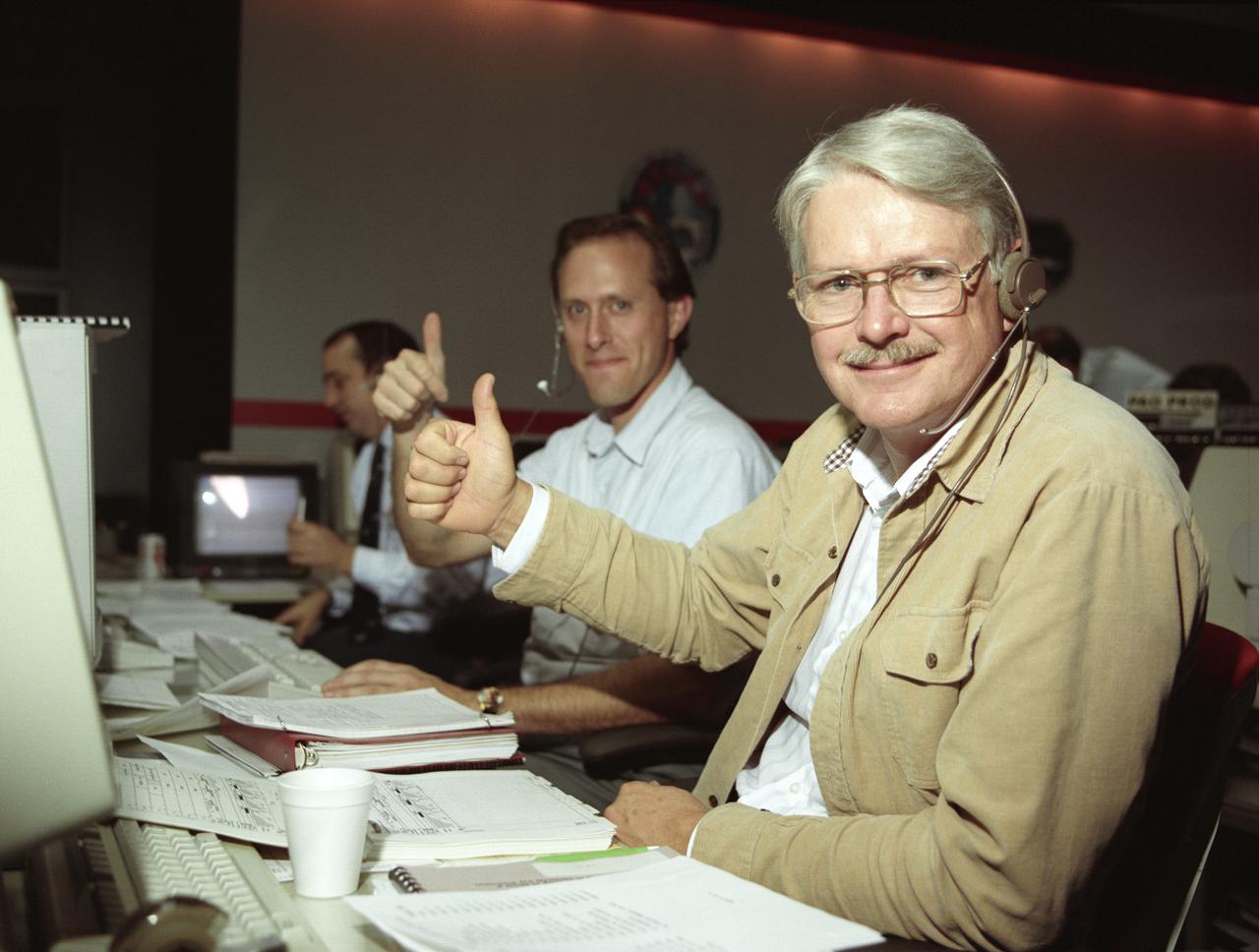

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo captures the activity at the Operations Control Facility during the mission as Dr. Urban and Paul Whitehouse give a “thumbs up”.
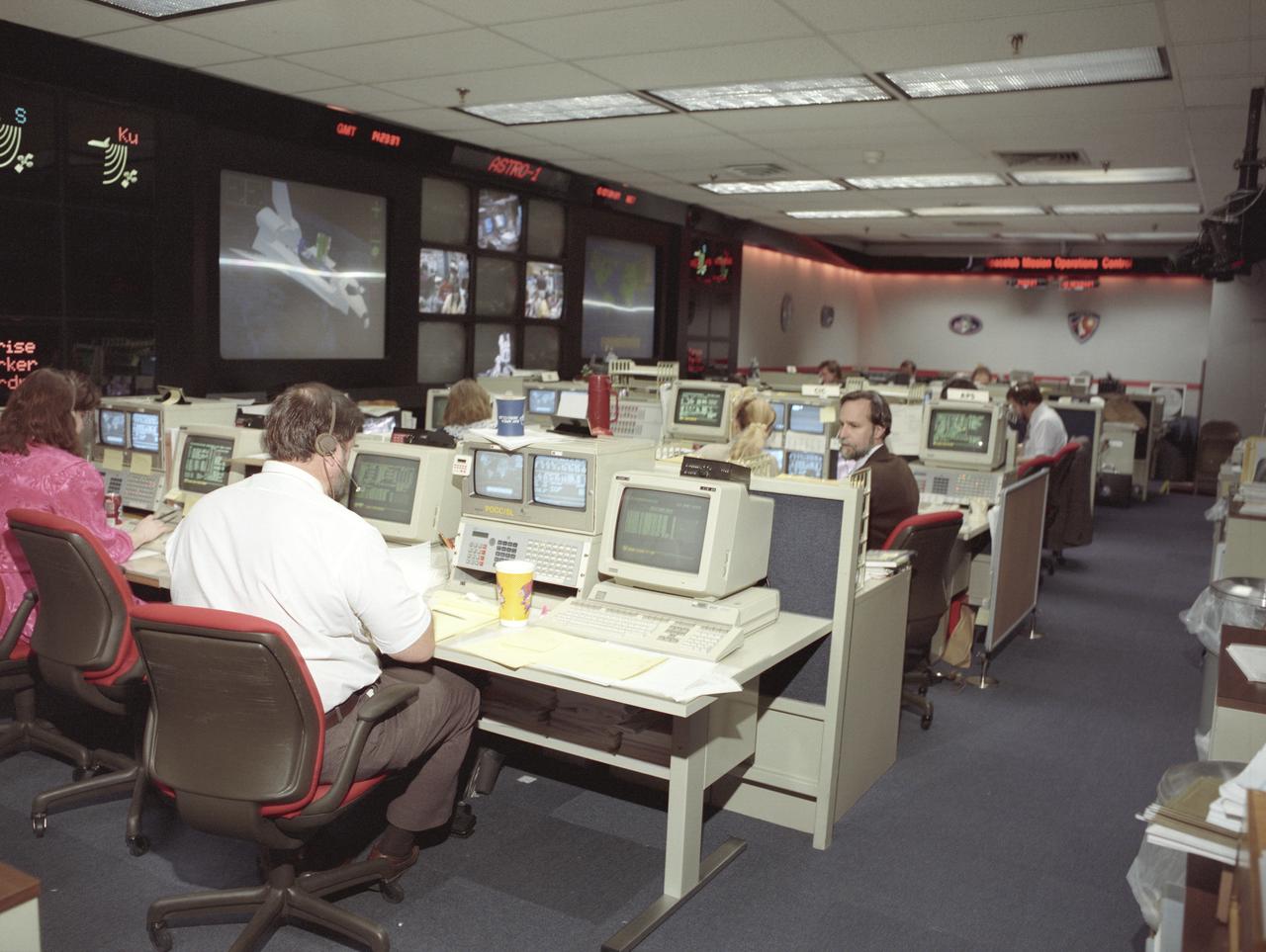

The primary objective of the STS-35 mission was round the clock observation of the celestial sphere in ultraviolet and X-Ray astronomy with the Astro-1 observatory which consisted of four telescopes: the Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT); the Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE); the Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT); and the Broad Band X-Ray Telescope (BBXRT). The Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) was the air/ground communication channel used between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. Teams of controllers and researchers directed on-orbit science operations, sent commands to the spacecraft, received data from experiments aboard the Space Shuttle, adjusted mission schedules to take advantage of unexpected science opportunities or unexpected results, and worked with crew members to resolve problems with their experiments. Due to loss of data used for pointing and operating the ultraviolet telescopes, MSFC ground teams were forced to aim the telescopes with fine tuning by the flight crew. This photo is an overview of the MSFC Payload Control Room (PCR).
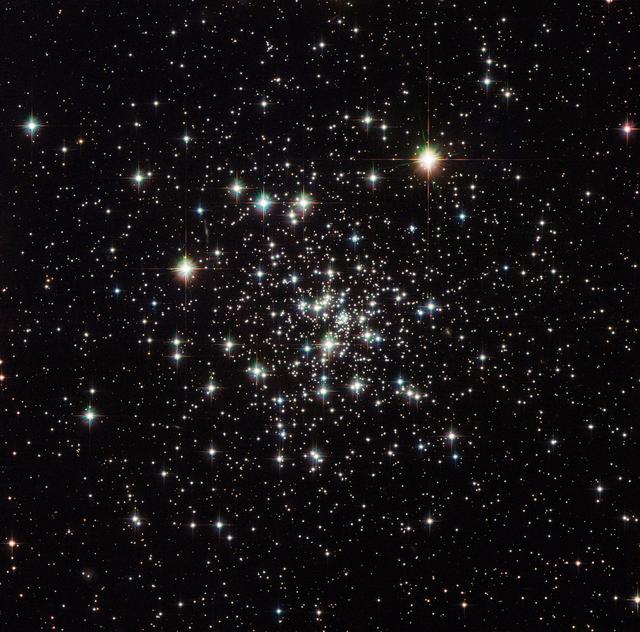

This image captures the stunning NGC 6535, a globular cluster 22,000 light-years away in the constellation of Serpens (The Serpent) that measures one light-year across. Globular clusters are tightly bound groups of stars which orbit galaxies. The large mass in the rich stellar centre of the globular cluster pulls the stars inward to form a ball of stars. The word globulus, from which these clusters take their name, is Latin for small sphere. Globular clusters are generally very ancient objects formed around the same time as their host galaxy. To date, no new star formation has been observed within a globular cluster, which explains the abundance of aging yellow stars in this image, most of them containing very few heavy elements. NGC 6535 was first discovered in 1852 by English astronomer John Russell Hind. The cluster would have appeared to Hind as a small, faint smudge through his telescope. Now, over 160 years later, instruments like the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) and Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) on the NASA/ European Space Agency (ESA) Hubble Space Telescope allow us to marvel at the cluster and its contents in greater detail. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Gilles Chapdelaine <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
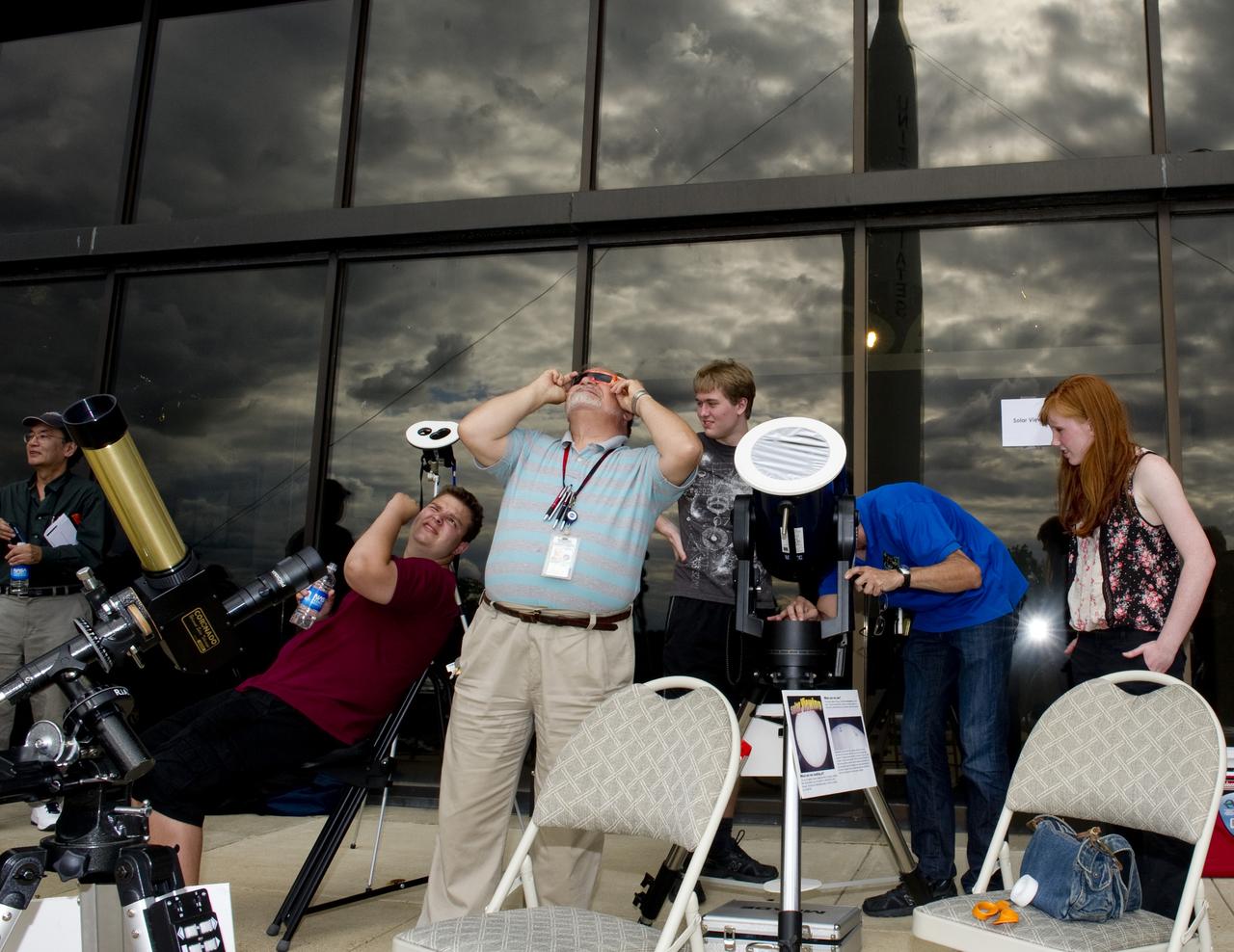

A "transit of Venus" occurs when the planet Venus passes directly between the sun and the Earth. During the event, Venus will be seen from Earth as a small black sphere moving across the face of the sun. Such an event won’t occur again until the year 2117. The Goddard Visitor Center hosted a watch party that included near real-time images from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory mission, coverage of the event from several locations via NASA TV, in-person presentations by NASA experts, hands-on activities for children of all ages. Heavy cloud cover did not allow viewing opportunities of the transit via solar telescopes. Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/Bill Hrybyk <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA image release December 14, 2010 A delicate sphere of gas, photographed by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope, floats serenely in the depths of space. The pristine shell, or bubble, is the result of gas that is being shocked by the expanding blast wave from a supernova. Called SNR 0509-67.5 (or SNR 0509 for short), the bubble is the visible remnant of a powerful stellar explosion in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a small galaxy about 160,000 light-years from Earth. Ripples in the shell's surface may be caused by either subtle variations in the density of the ambient interstellar gas, or possibly driven from the interior by pieces of the ejecta. The bubble-shaped shroud of gas is 23 light-years across and is expanding at more than 11 million miles per hour (5,000 kilometers per second). Astronomers have concluded that the explosion was one of an especially energetic and bright variety of supernovae. Known as Type Ia, such supernova events are thought to result from a white dwarf star in a binary system that robs its partner of material, takes on much more mass than it is able to handle, and eventually explodes. Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys observed the supernova remnant on Oct. 28, 2006 with a filter that isolates light from glowing hydrogen seen in the expanding shell. These observations were then combined with visible-light images of the surrounding star field that were imaged with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 on Nov. 4, 2010. With an age of about 400 years as seen from Earth, the supernova might have been visible to southern hemisphere observers around the year 1600, however, there are no known records of a "new star" in the direction of the LMC near that time. A more recent supernova in the LMC, SN 1987A, did catch the eye of Earth viewers and continues to be studied with ground- and space-based telescopes, including Hubble. For images and more information about SNR 0509, visit: <a href="http://hubblesite.org/news/2010/27" rel="nofollow">hubblesite.org/news/2010/27</a> <a href="http://heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27" rel="nofollow">heritage.stsci.edu/2010/27</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. <b>Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Acknowledgment: J. Hughes (Rutgers University)</b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
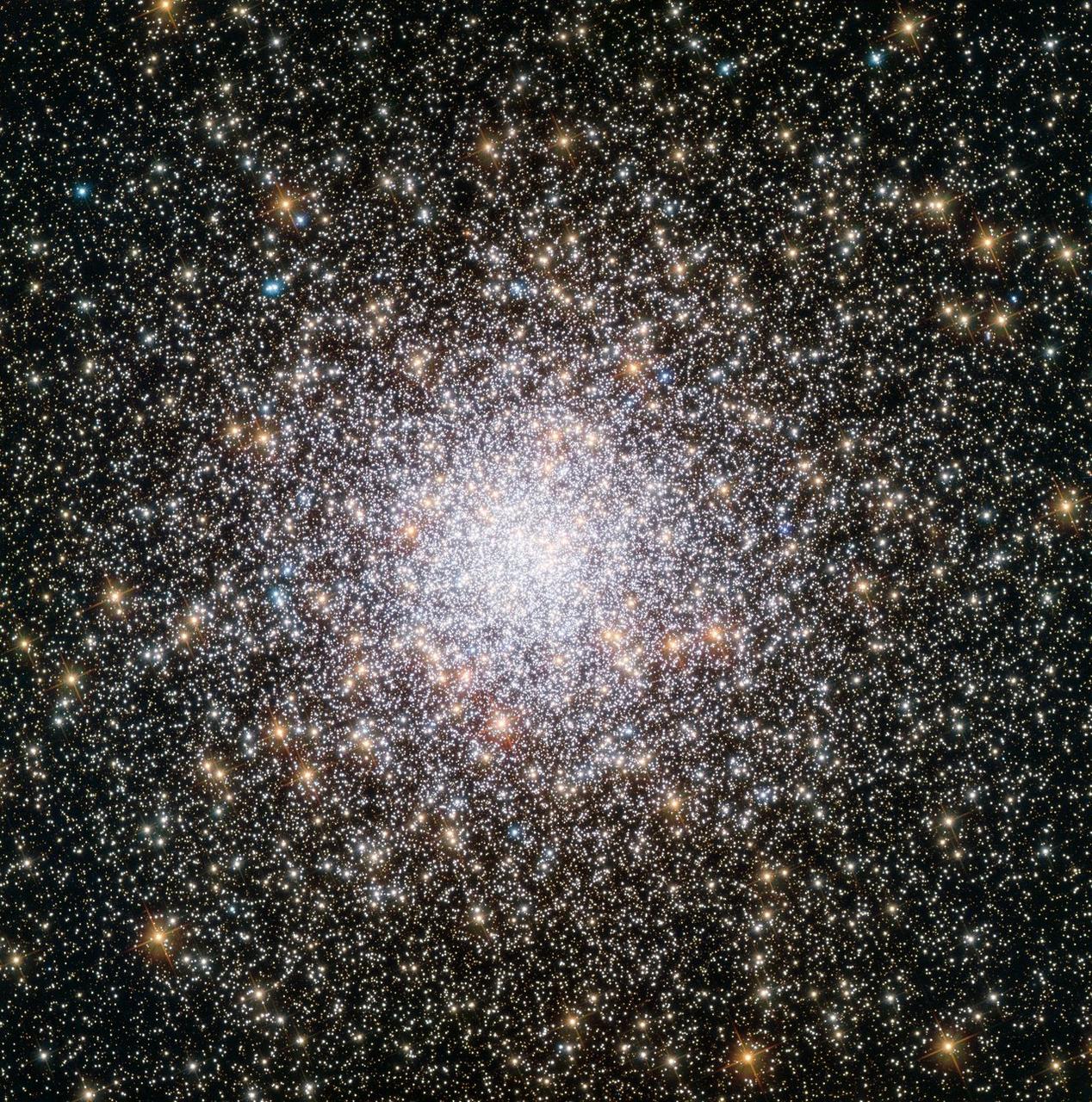

Hubble sees an unusal global cluster that is enriching the interstellar medium with metals Globular clusters offer some of the most spectacular sights in the night sky. These ornate spheres contain hundreds of thousands of stars, and reside in the outskirts of galaxies. The Milky Way contains over 150 such clusters — and the one shown in this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image, named NGC 362, is one of the more unusual ones. As stars make their way through life they fuse elements together in their cores, creating heavier and heavier elements — known in astronomy as metals — in the process. When these stars die, they flood their surroundings with the material they have formed during their lifetimes, enriching the interstellar medium with metals. Stars that form later therefore contain higher proportions of metals than their older relatives. By studying the different elements present within individual stars in NGC 362, astronomers discovered that the cluster boasts a surprisingly high metal content, indicating that it is younger than expected. Although most globular clusters are much older than the majority of stars in their host galaxy, NGC 362 bucks the trend, with an age lying between 10 and 11 billion years old. For reference, the age of the Milky Way is estimated to be above 13 billion years. This image, in which you can view NGC 362’s individual stars, was taken by Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). Credit: ESA/Hubble& NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
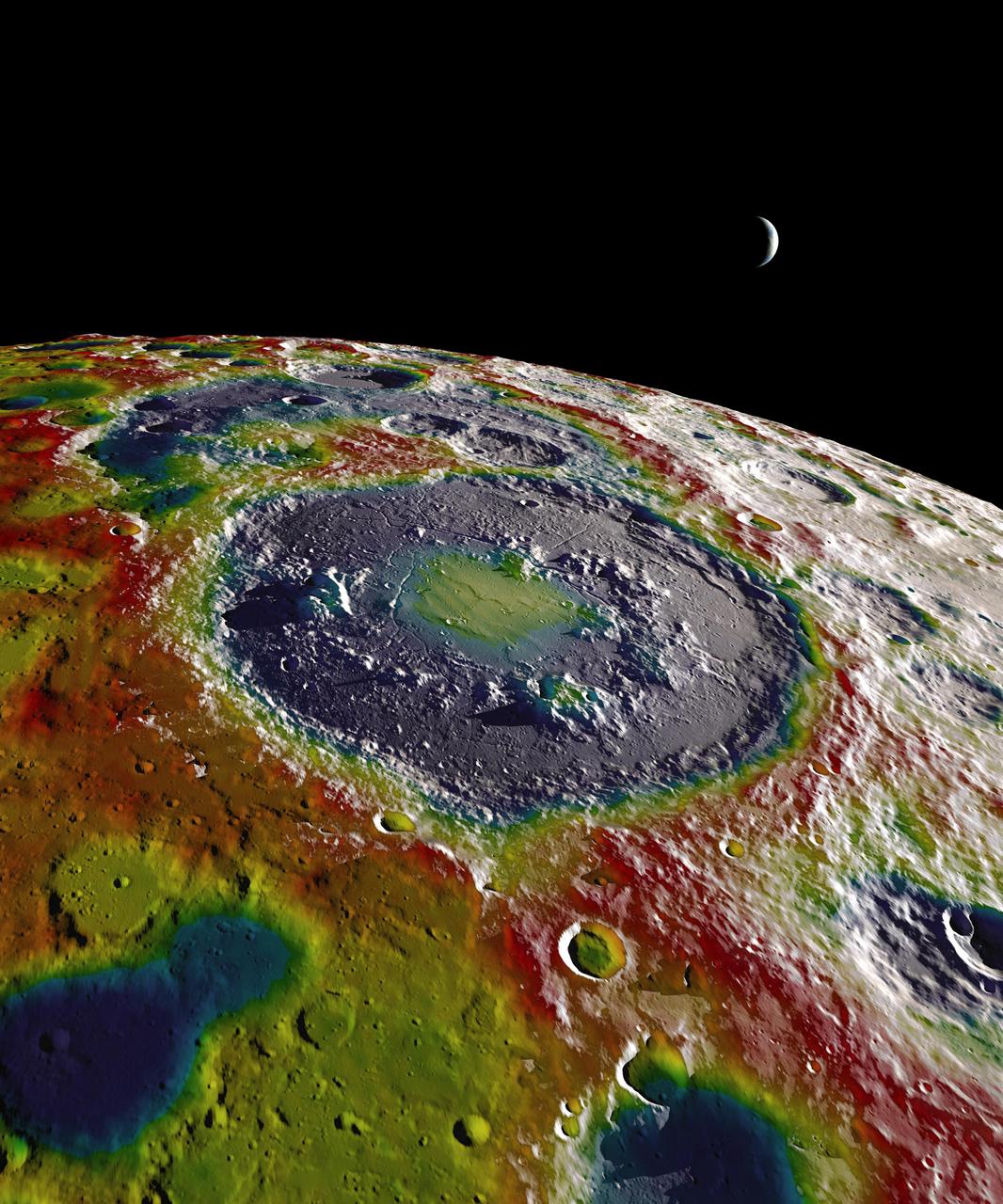

This still image features a free-air gravity map of the Moon's southern latitudes developed by S. Goossens et al. from data returned by the Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory (GRAIL) mission. If the Moon were a perfectly smooth sphere of uniform density, the gravity map would be a single, featureless color, indicating that the force of gravity at a given elevation was the same everywhere. But like other rocky bodies in the solar system, including Earth, the Moon has both a bumpy surface and a lumpy interior. Spacecraft in orbit around the Moon experience slight variations in gravity caused by both of these irregularities. The free-air gravity map shows deviations from the mean gravity that a cueball Moon would have. The deviations are measured in milliGals, a unit of acceleration. On the map, purple is at the low end of the range, at around -400 mGals, and red is at the high end near +400 mGals. Yellow denotes the mean. The map shown here extends from the south pole of the Moon up to 50°S and reveals the gravity for that region in even finer detail than the global gravity maps published previously. The image illustrates the very good correlation between the gravity map and topographic features such as peaks and craters, as well as the mass concentration lying beneath the large Schrödinger basin in the center of the frame. The terrain in the image is based on Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) altimeter and camera data. Credit: NASA's Scientific Visualization Studio <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
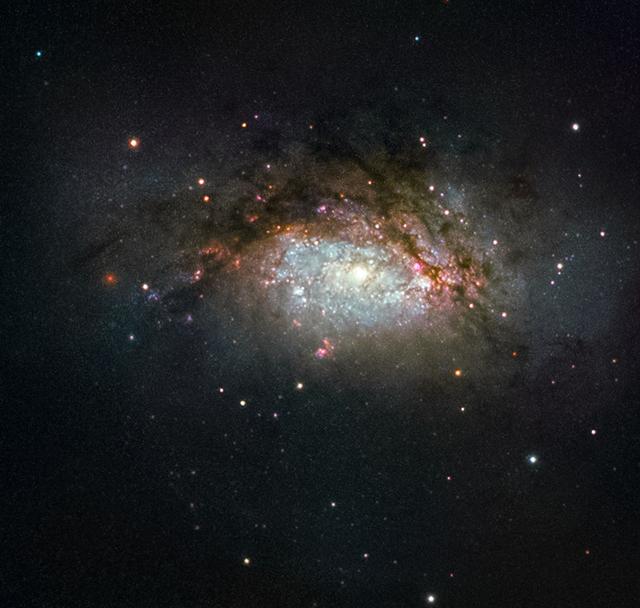

The subject of this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image is known as NGC 3597. It is the product of a collision between two good-sized galaxies, and is slowly evolving to become a giant elliptical galaxy. This type of galaxy has grown more and more common as the universe has evolved, with initially small galaxies merging and progressively building up into larger galactic structures over time. NGC 3597 is located approximately 150 million light-years away in the constellation of Crater (The Cup). Astronomers study NGC 3597 to learn more about how elliptical galaxies form — many ellipticals began their lives far earlier in the history of the universe. Older ellipticals are nicknamed “red and dead” by astronomers because these bloated galaxies are not anymore producing new, bluer stars, and are thus packed full of old and redder stellar populations. Before infirmity sets in, some freshly formed elliptical galaxies experience a final flush of youth, as is the case with NGC 3597. Galaxies smashing together pool their available gas and dust, triggering new rounds of star birth. Some of this material ends up in dense pockets initially called proto-globular clusters, dozens of which festoon NGC 3597. These pockets will go on to collapse and form fully-fledged globular clusters, large spheres that orbit the centers of galaxies like satellites, packed tightly full of millions of stars. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
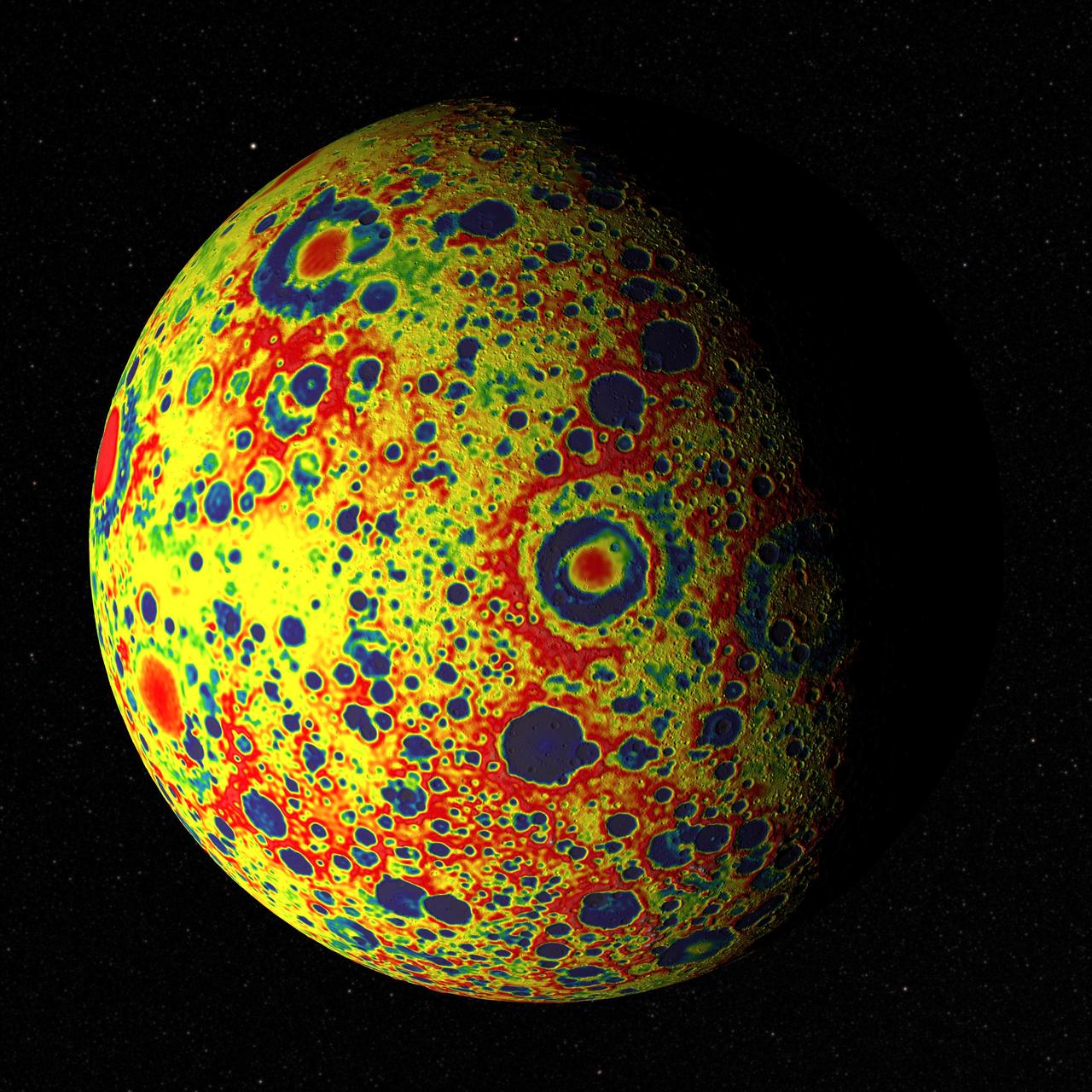
If the Moon were a perfectly smooth sphere of uniform density, the gravity map would be a single, featureless color, indicating that the force of gravity at a given elevation was the same everywhere. But like other rocky bodies in the solar system, including Earth, the Moon has both a bumpy surface and a lumpy interior. Spacecraft in orbit around the Moon experience slight variations in gravity caused by both of these irregularities. The free-air gravity map shows deviations from the mean, the gravity that a cueball Moon would have. The deviations are measured in milliGals, a unit of acceleration. On the map, dark purple is at the low end of the range, at around -400 mGals, and red is at the high end near +400 mGals. Yellow denotes the mean. These views show a part of the Moon's surface that's never visible from Earth. They are centered on lunar coordinates 29°N 142°E. The large, multi-ringed impact feature near the center is Mare Moscoviense. The crater Mendeleev is south of this. The digital elevation model for the terrain is from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter laser altimeter (LOLA). Merely for plausibility, the sun angle and starry background are accurate for specific dates (December 21, 2012, 0:00 UT and January 8, 2013, 14:00 UT, respectively). To see or download more views go to: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?4041" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?4041</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Peering deep into the core of the Crab Nebula, this close-up image reveals the beating heart of one of the most historic and intensively studied remnants of a supernova, an exploding star. The inner region sends out clock-like pulses of radiation and tsunamis of charged particles embedded in magnetic fields. The neutron star at the very center of the Crab Nebula has about the same mass as the sun but compressed into an incredibly dense sphere that is only a few miles across. Spinning 30 times a second, the neutron star shoots out detectable beams of energy that make it look like it's pulsating. The NASA Hubble Space Telescope snapshot is centered on the region around the neutron star (the rightmost of the two bright stars near the center of this image) and the expanding, tattered, filamentary debris surrounding it. Hubble's sharp view captures the intricate details of glowing gas, shown in red, that forms a swirling medley of cavities and filaments. Inside this shell is a ghostly blue glow that is radiation given off by electrons spiraling at nearly the speed of light in the powerful magnetic field around the crushed stellar core. The neutron star is a showcase for extreme physical processes and unimaginable cosmic violence. Bright wisps are moving outward from the neutron star at half the speed of light to form an expanding ring. It is thought that these wisps originate from a shock wave that turns the high-speed wind from the neutron star into extremely energetic particles. When this "heartbeat" radiation signature was first discovered in 1968, astronomers realized they had discovered a new type of astronomical object. Now astronomers know it's the archetype of a class of supernova remnants called pulsars - or rapidly spinning neutron stars. These interstellar "lighthouse beacons" are invaluable for doing observational experiments on a variety of astronomical phenomena, including measuring gravity waves. Observations of the Crab supernova were recorded by Chinese astronomers in 1054 A.D. The nebula, bright enough to be visible in amateur telescopes, is located 6,500 light-years away in the constellation Taurus. Credits: NASA and ESA, Acknowledgment: J. Hester (ASU) and M. Weisskopf (NASA/MSFC) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Simulation frames from this NASA Goddard neutron star merger animation: <a href="http://bit.ly/1jolBYY" rel="nofollow">bit.ly/1jolBYY</a> Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center This supercomputer simulation shows one of the most violent events in the universe: a pair of neutron stars colliding, merging and forming a black hole. A neutron star is the compressed core left behind when a star born with between eight and 30 times the sun's mass explodes as a supernova. Neutron stars pack about 1.5 times the mass of the sun — equivalent to about half a million Earths — into a ball just 12 miles (20 km) across. As the simulation begins, we view an unequally matched pair of neutron stars weighing 1.4 and 1.7 solar masses. They are separated by only about 11 miles, slightly less distance than their own diameters. Redder colors show regions of progressively lower density. As the stars spiral toward each other, intense tides begin to deform them, possibly cracking their crusts. Neutron stars possess incredible density, but their surfaces are comparatively thin, with densities about a million times greater than gold. Their interiors crush matter to a much greater degree densities rise by 100 million times in their centers. To begin to imagine such mind-boggling densities, consider that a cubic centimeter of neutron star matter outweighs Mount Everest. By 7 milliseconds, tidal forces overwhelm and shatter the lesser star. Its superdense contents erupt into the system and curl a spiral arm of incredibly hot material. At 13 milliseconds, the more massive star has accumulated too much mass to support it against gravity and collapses, and a new black hole is born. The black hole's event horizon — its point of no return — is shown by the gray sphere. While most of the matter from both neutron stars will fall into the black hole, some of the less dense, faster moving matter manages to orbit around it, quickly forming a large and rapidly rotating torus. This torus extends for about 124 miles (200 km) and contains the equivalent of 1/5th the mass of our sun. Scientists think neutron star mergers like this produce short gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Short GRBs last less than two seconds yet unleash as much energy as all the stars in our galaxy produce over one year. The rapidly fading afterglow of these explosions presents a challenge to astronomers. A key element in understanding GRBs is getting instruments on large ground-based telescopes to capture afterglows as soon as possible after the burst. The rapid notification and accurate positions provided by NASA's Swift mission creates a vibrant synergy with ground-based observatories that has led to dramatically improved understanding of GRBs, especially for short bursts. This video is public domain and can be downloaded at: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/vis/a010000/a011500/a011530/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>