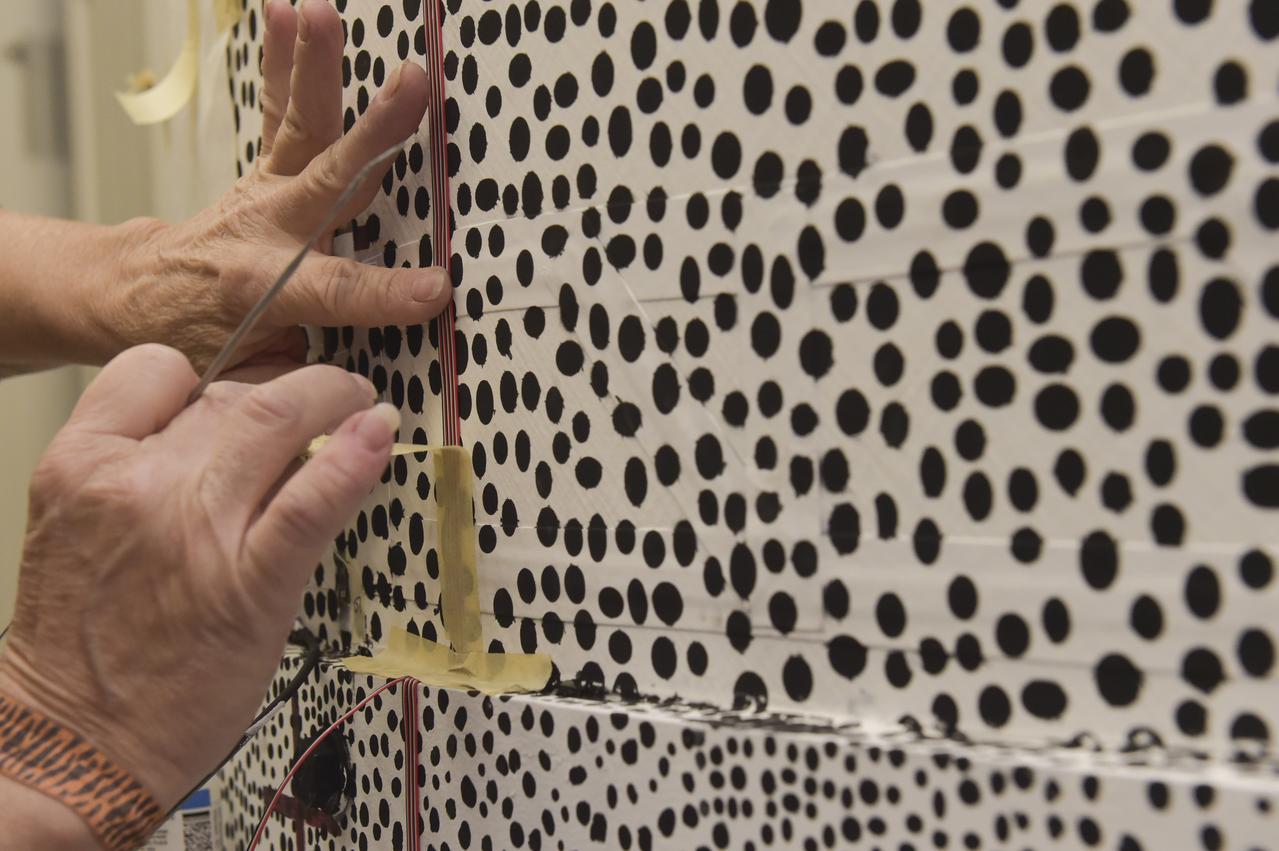

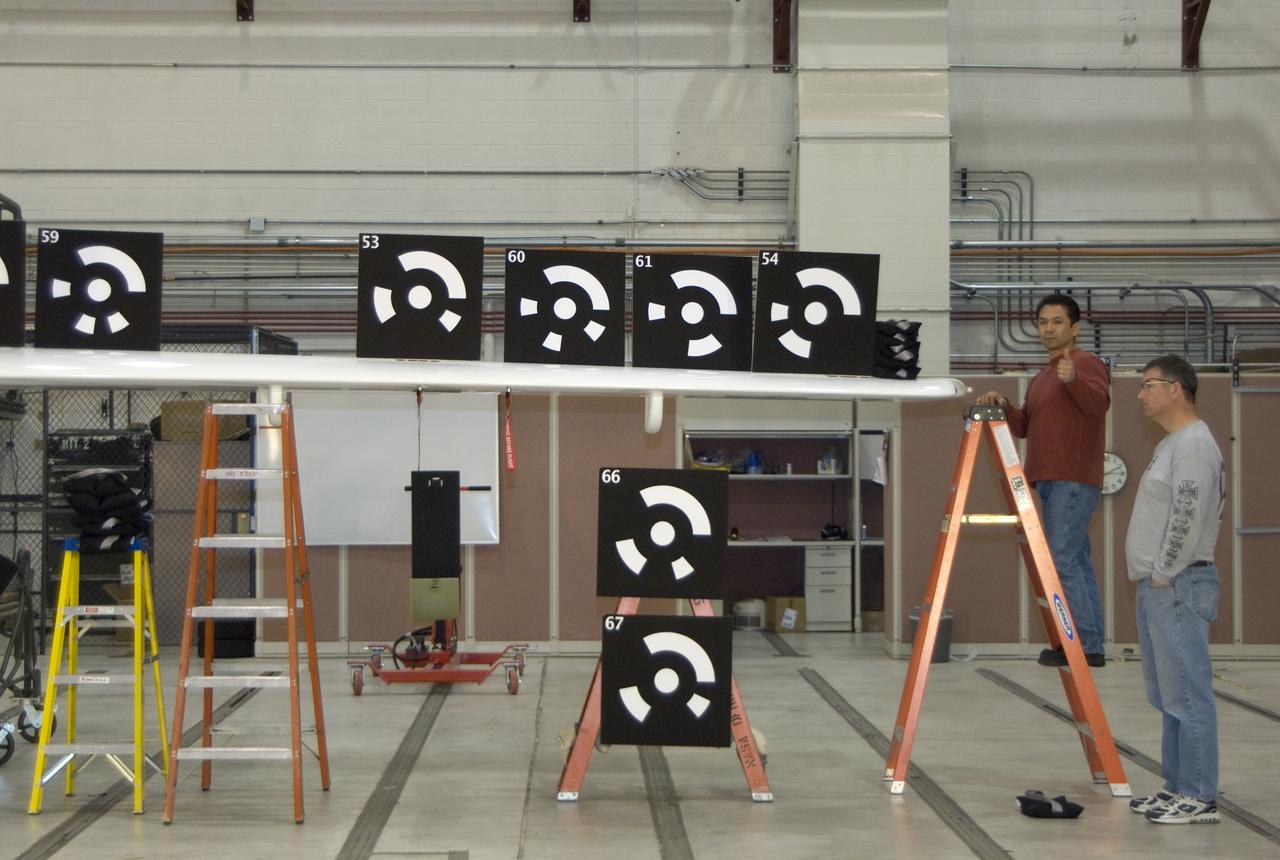
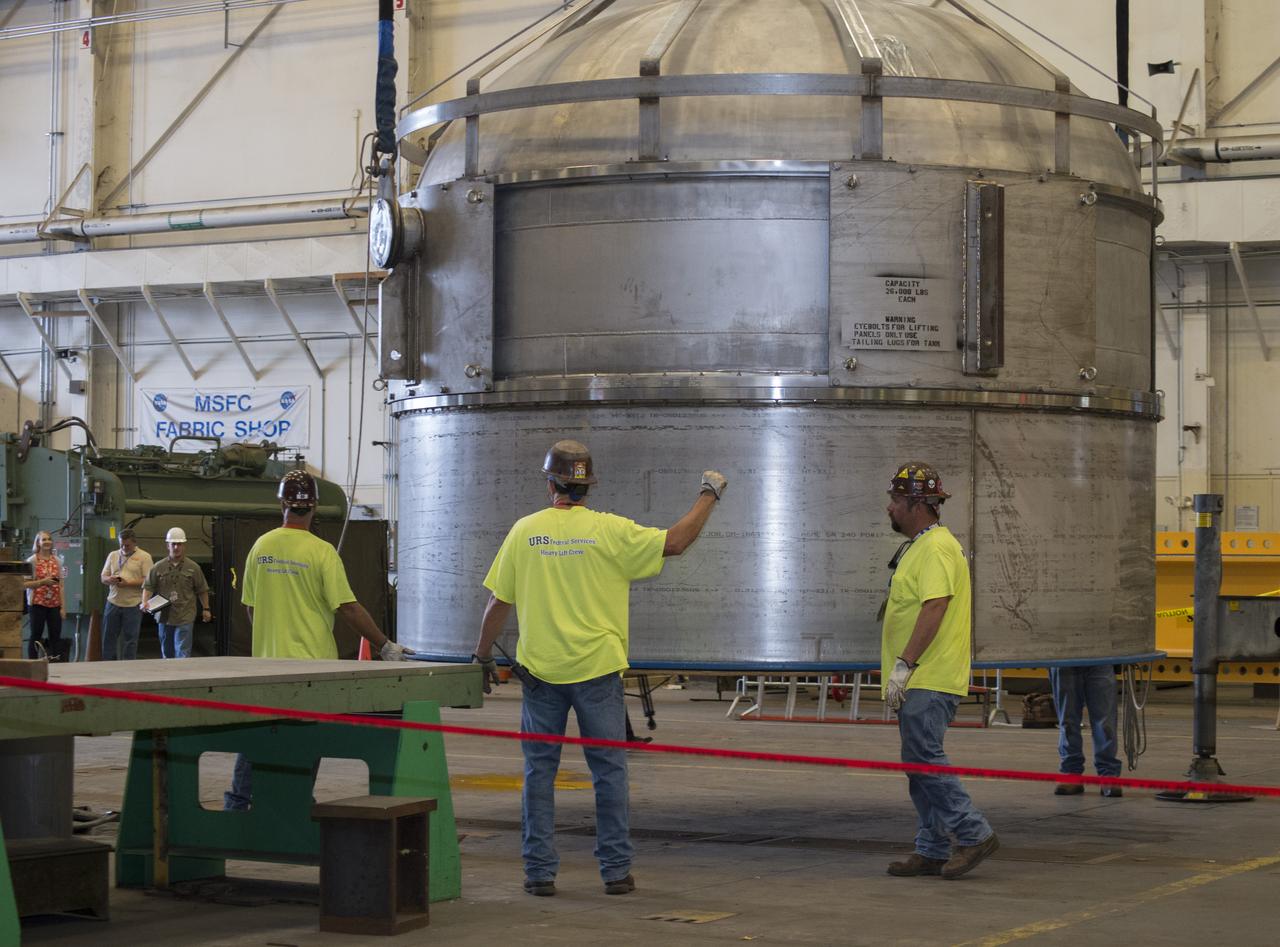
INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
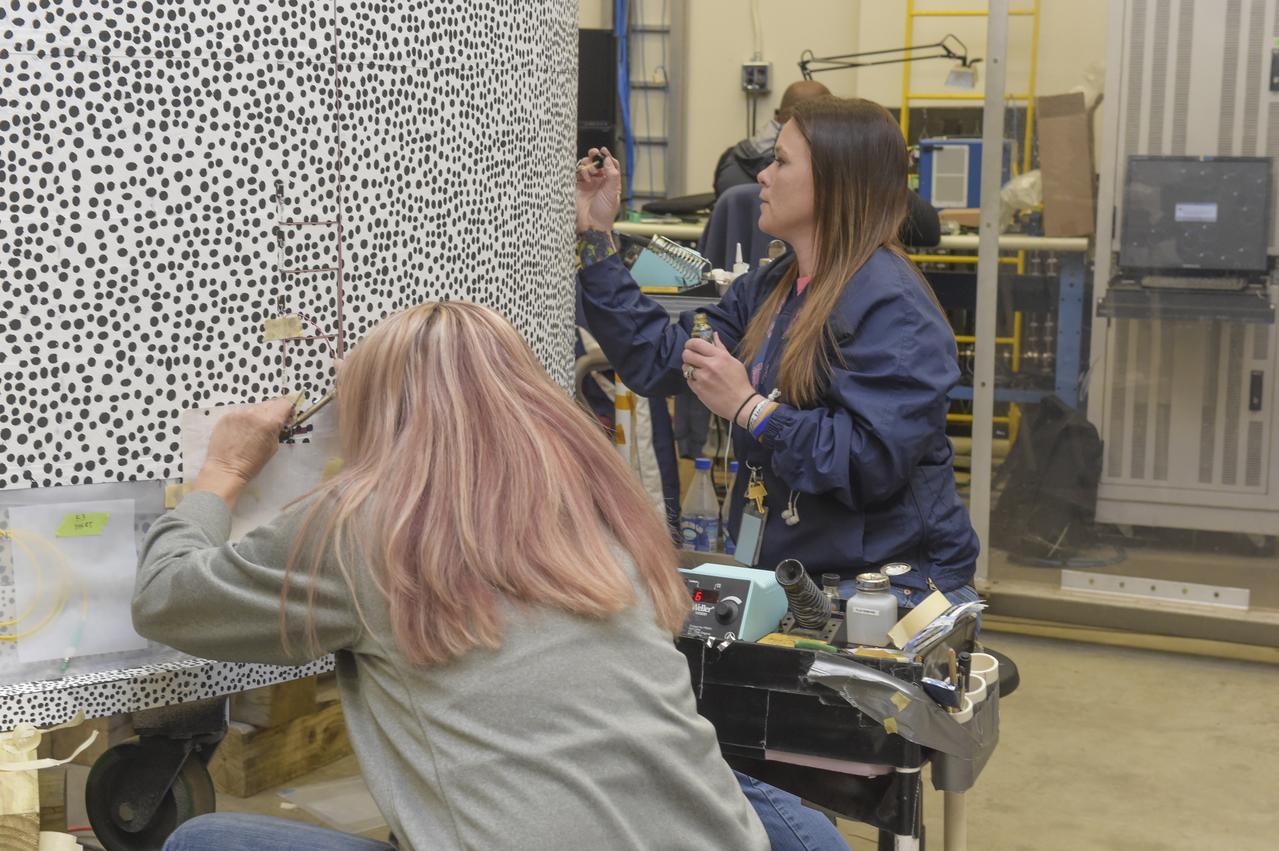

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
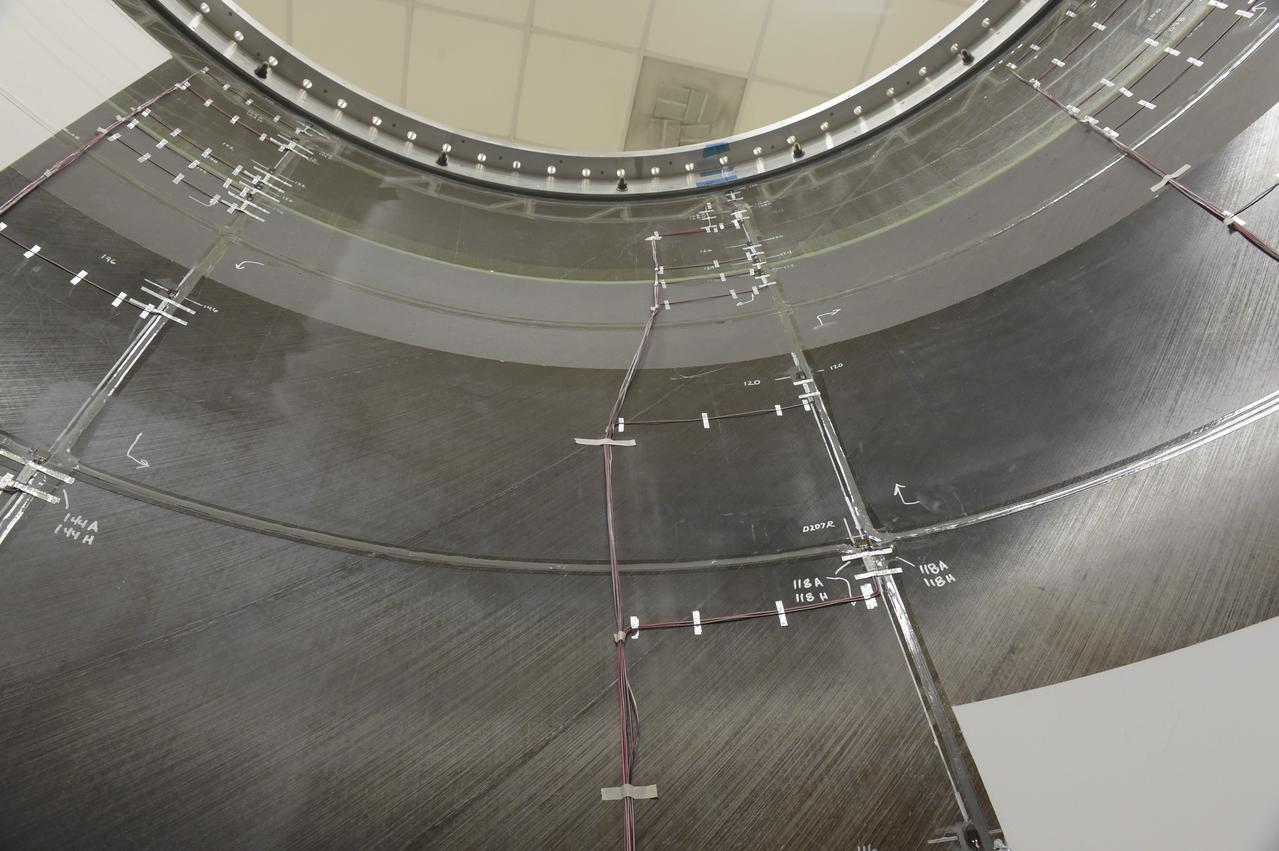

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
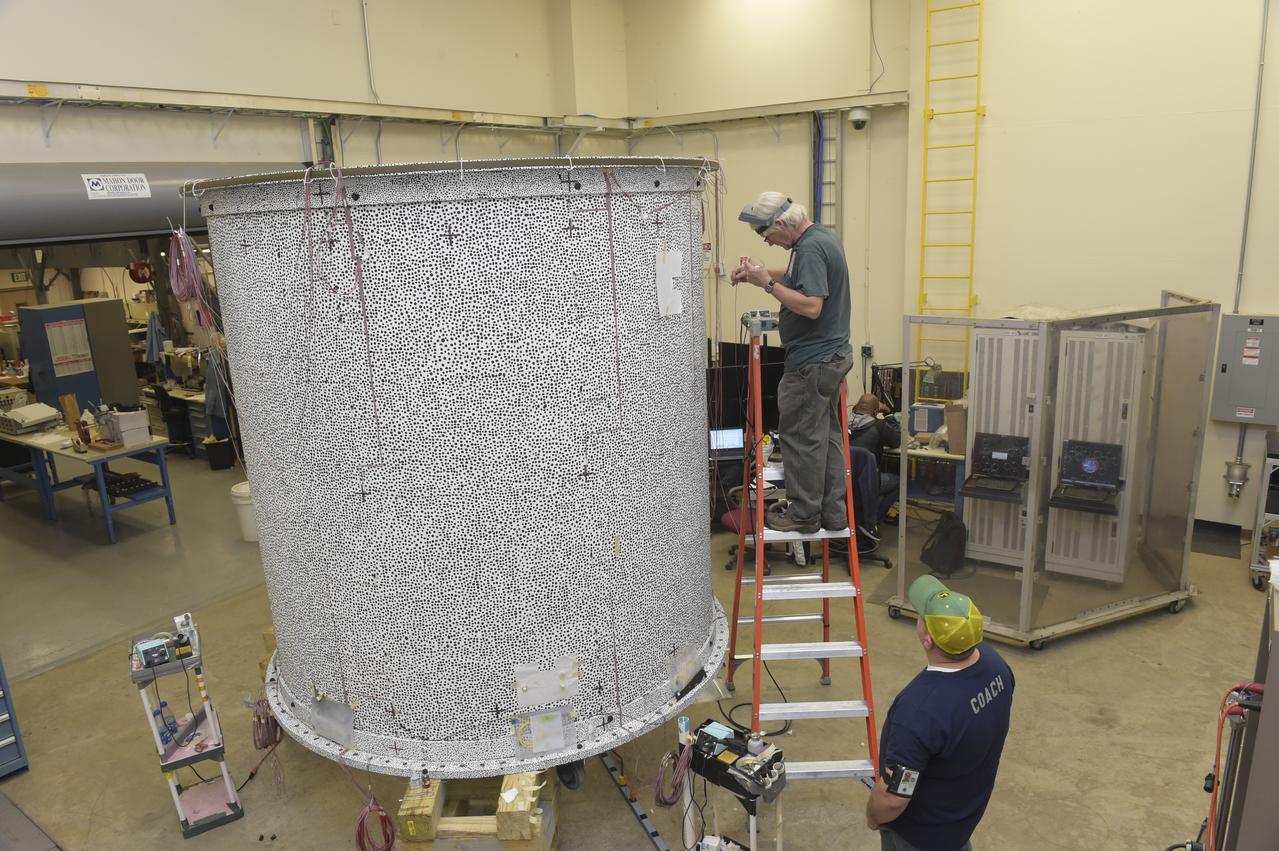

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.

INSTALLATION OF STRESS SENSORS TO SHELL BUCKLE KNOCKDOWN FACTOR COMPOSITE TANK.
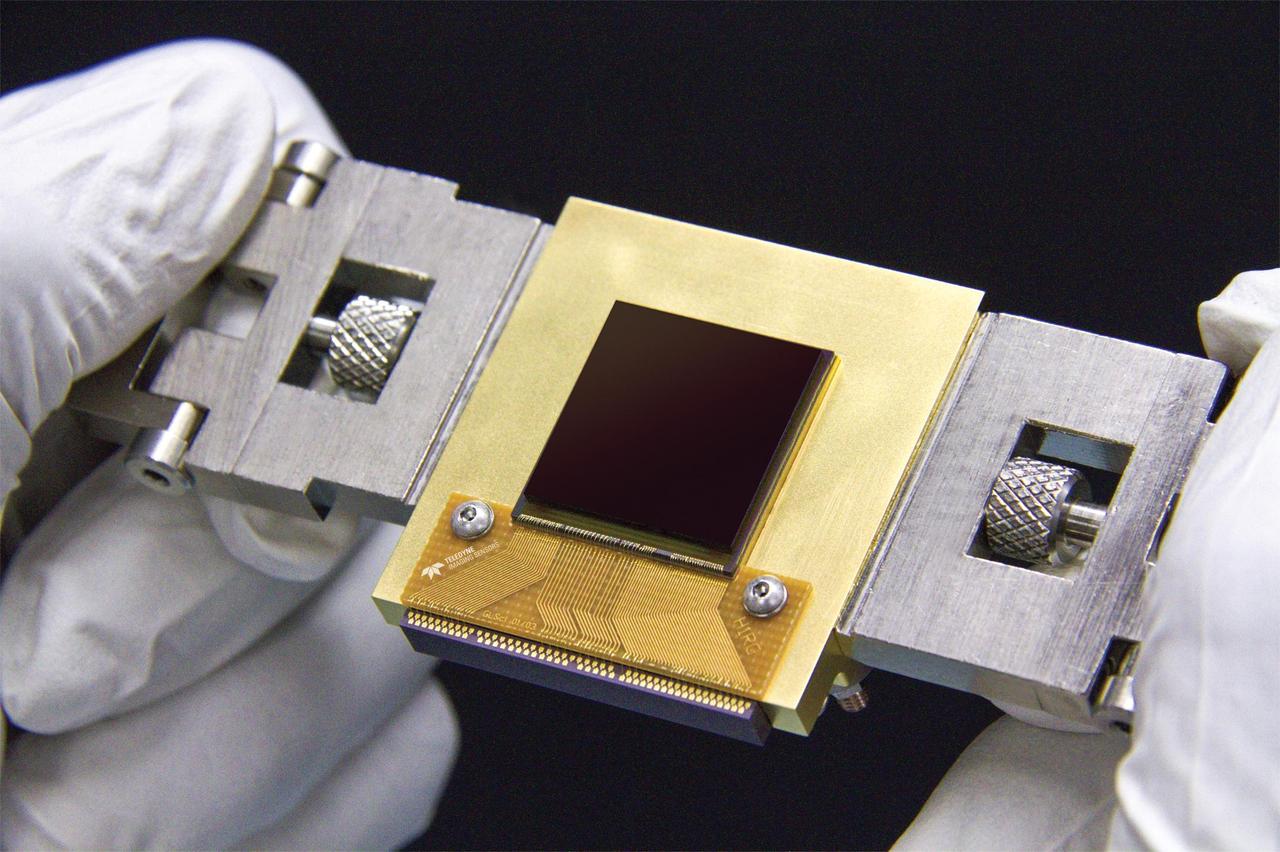
The NEOCam chip is the first megapixel sensor capable of detecting infrared wavelengths at temperatures achievable in deep space without refrigerators or cryogens.
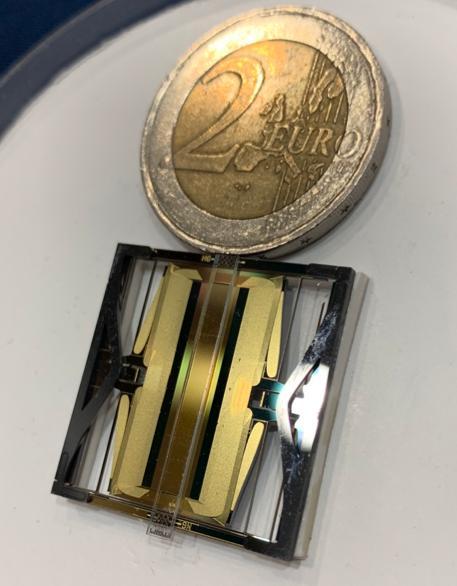
A copy of one of the sensors on NASA InSight's seismometer, compared to a 2-euro coin (about 1 inch wide). The short-period seismometer has three of these sensors. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22926

Mini Impactor Sensors for Lunar Geotechnical Arrays

PATRICK CHAMPEY, (LEFT), DICK GATES, (RIGHT), AND BILL PODGORSKI, (SEATED), ALIGN SUN SENSOR TO HI-C TELESCOPE USING THEODOLITE

One of two wind sensors springs out of the mast on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. These sensors are part of the Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA), the rover's set of weather instrumentation. MEDA was provided to NASA by the Centro de Astrobiología (CAB) at the Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aeroespacial in Madrid, Spain. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent missions, currently under consideration by NASA in cooperation with ESA (the European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these cached samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 mission is part of a larger program that includes missions to the Moon as a way to prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Charged with returning astronauts to the Moon by 2024, NASA will establish a sustained human presence on and around the Moon by 2028 through NASA's Artemis lunar exploration plans. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24175
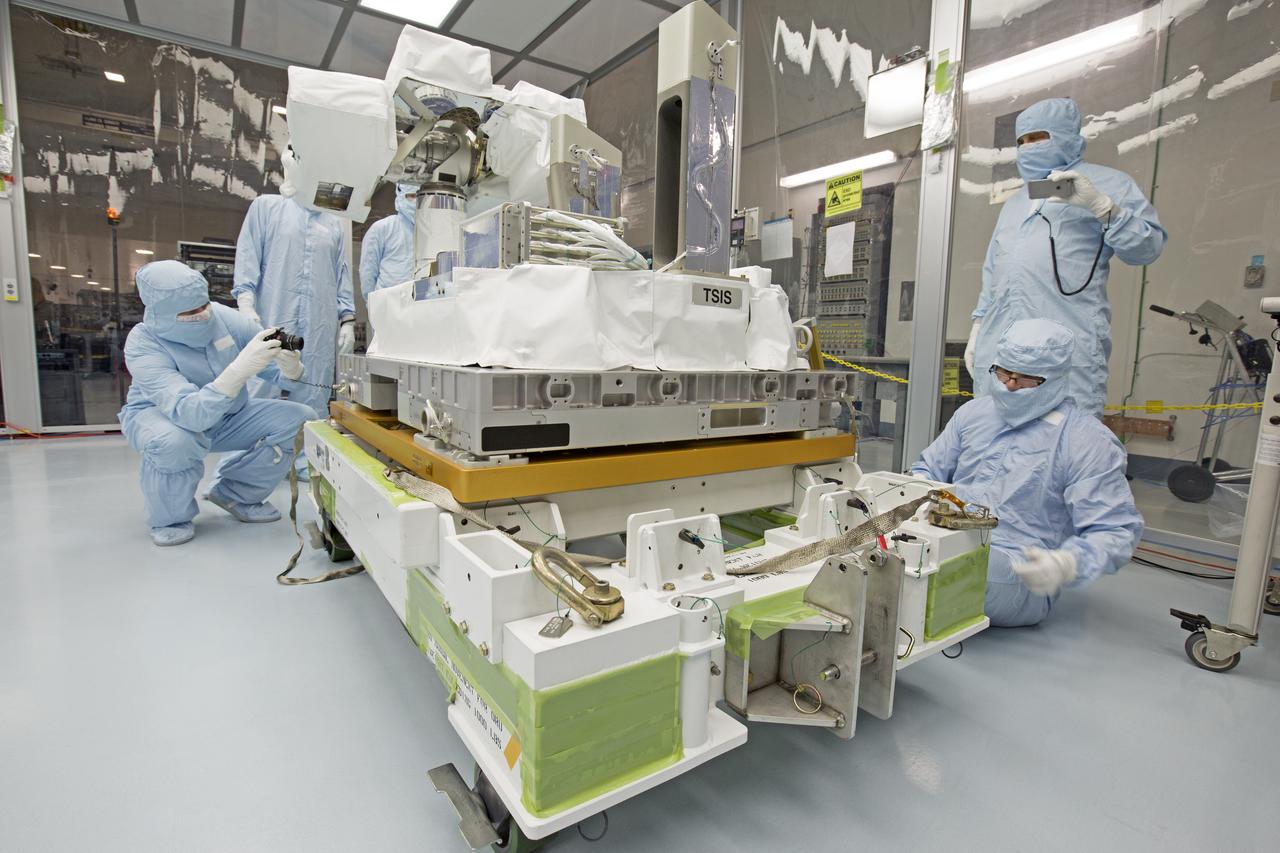

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies, and other payload team members performs spacewalk tool fit-checks of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
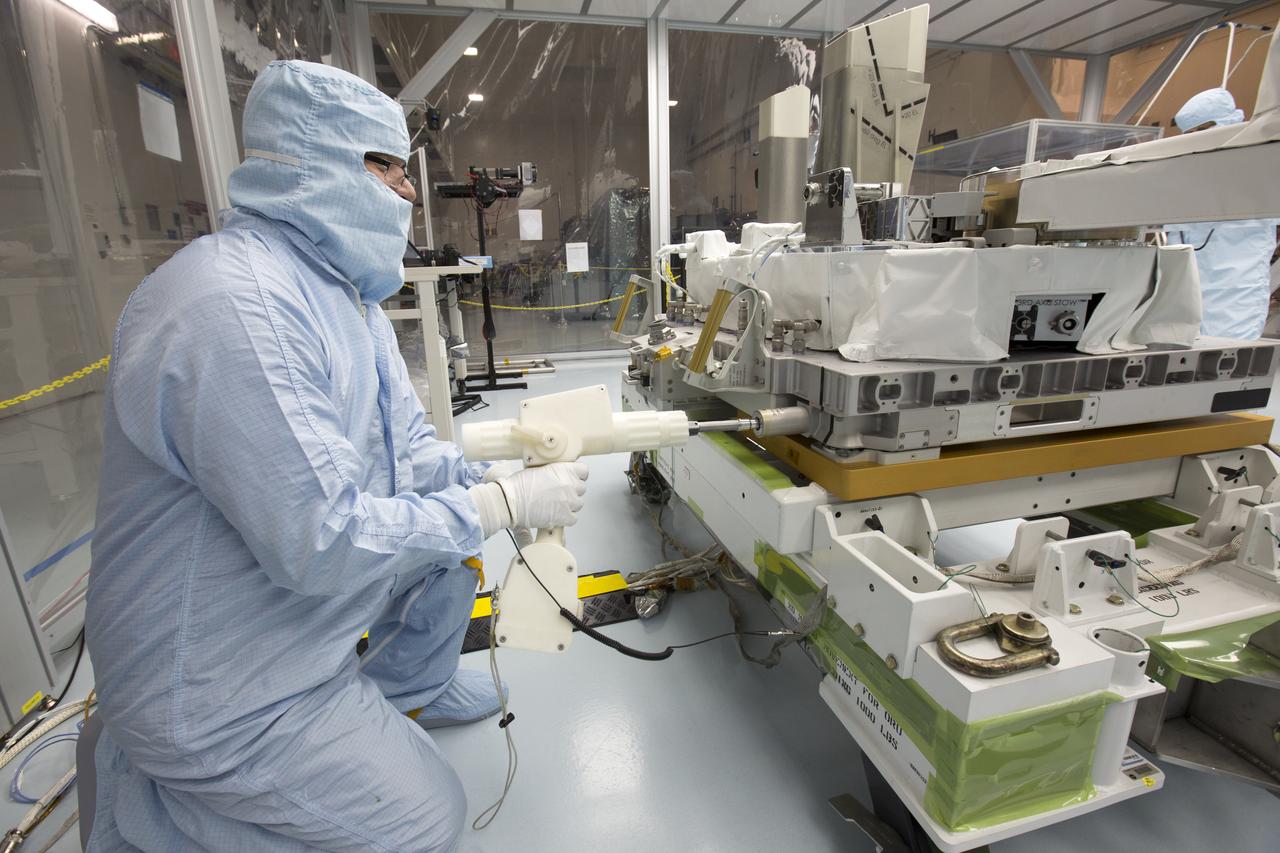

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs spacewalk tool fit-checks of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
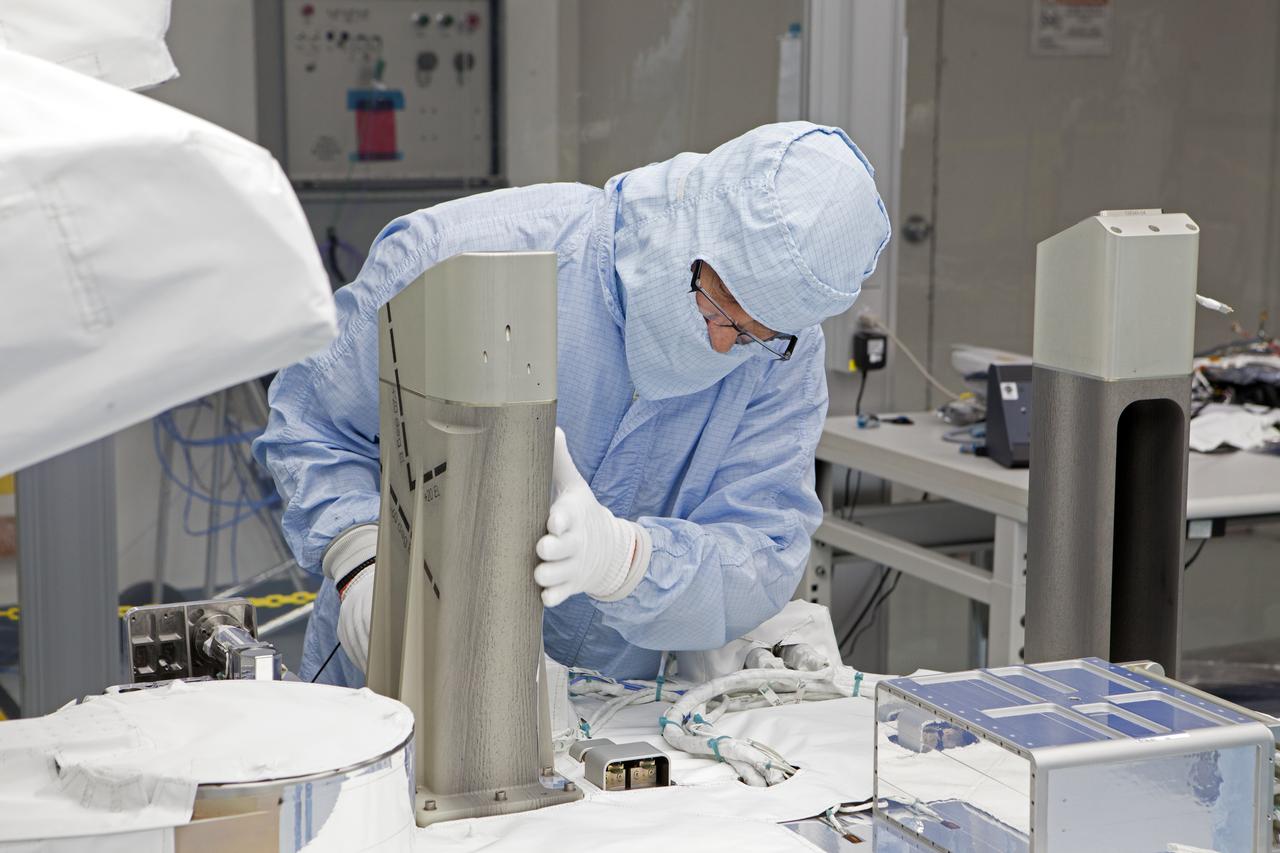

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.

This set of images shows part of the deployment of the Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA) wind sensors on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. MEDA is a set of weather sensors, with the wind sensor components on the rover's remote sensing mast. These images were taken by Perseverance's Navigation Cameras on Feb. 28, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24339
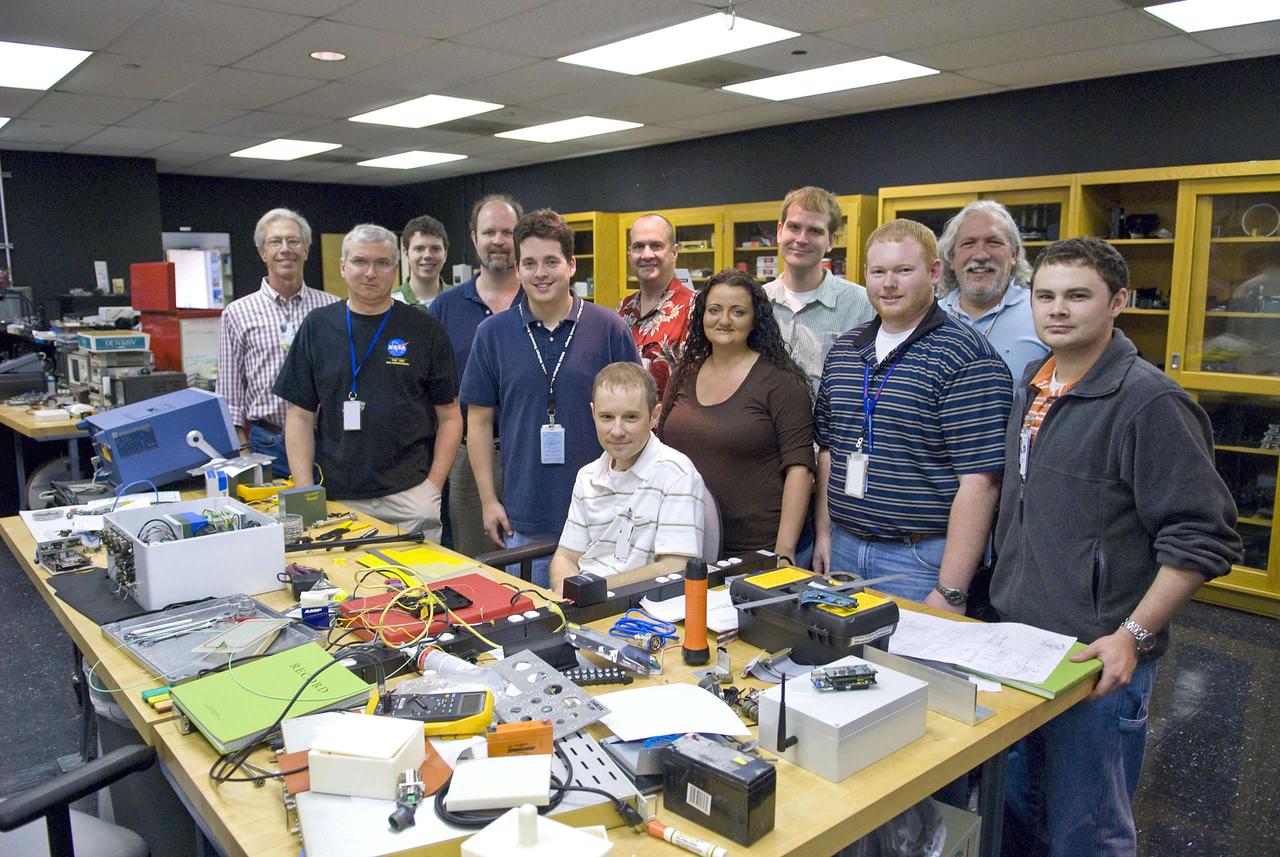

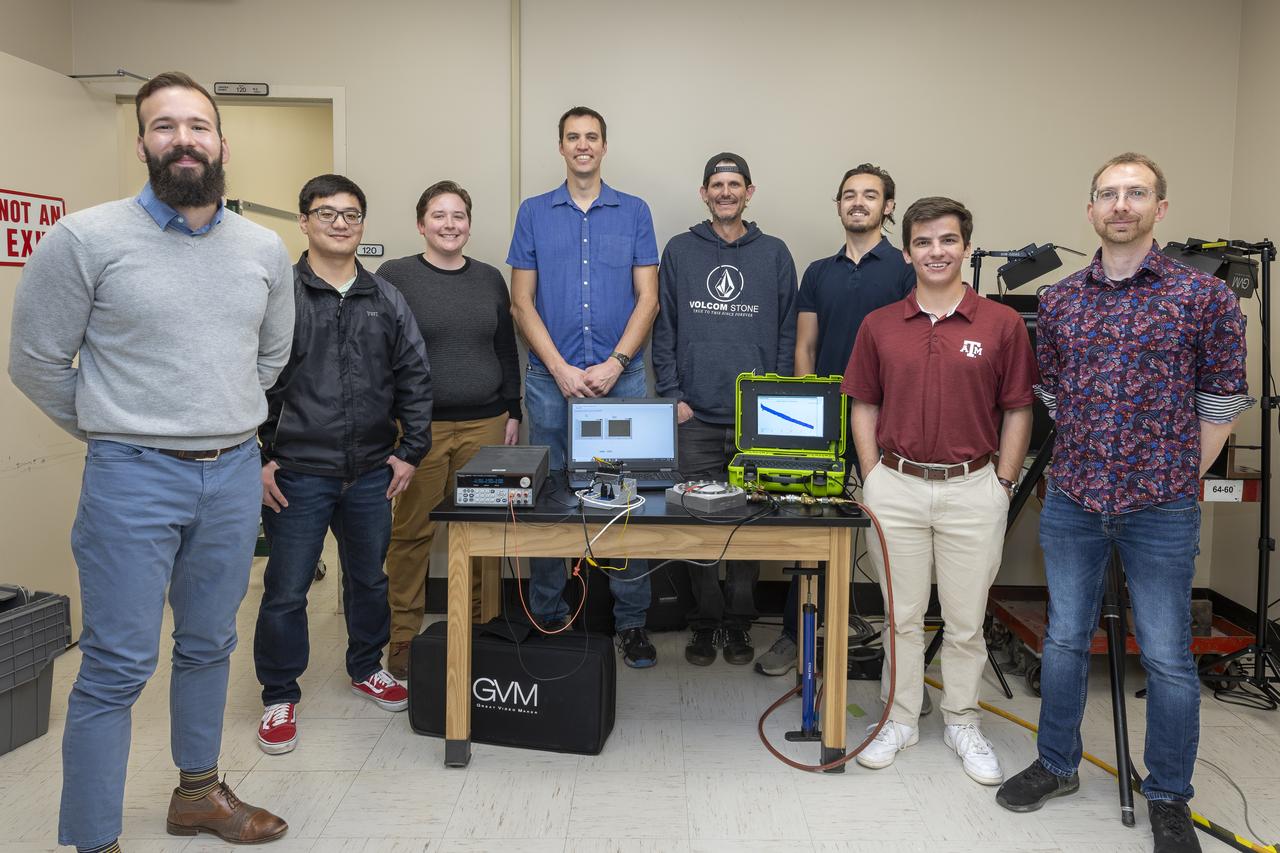
Engineers working on the smart and intelligent sensor payload project include (l to r): Ed Conley (NASA), Mark Mitchell (Jacobs Technology), Luke Richards (NASA), Robert Drackett (Jacobs Technology), Mark Turowski (Jacobs Technology) , Richard Franzl (seated, Jacobs Technology), Greg McVay (Jacobs Technology), Brianne Guillot (Jacobs Technology), Jon Morris (Jacobs Technology), Stephen Rawls (NASA), John Schmalzel (NASA) and Andrew Bracey (NASA).
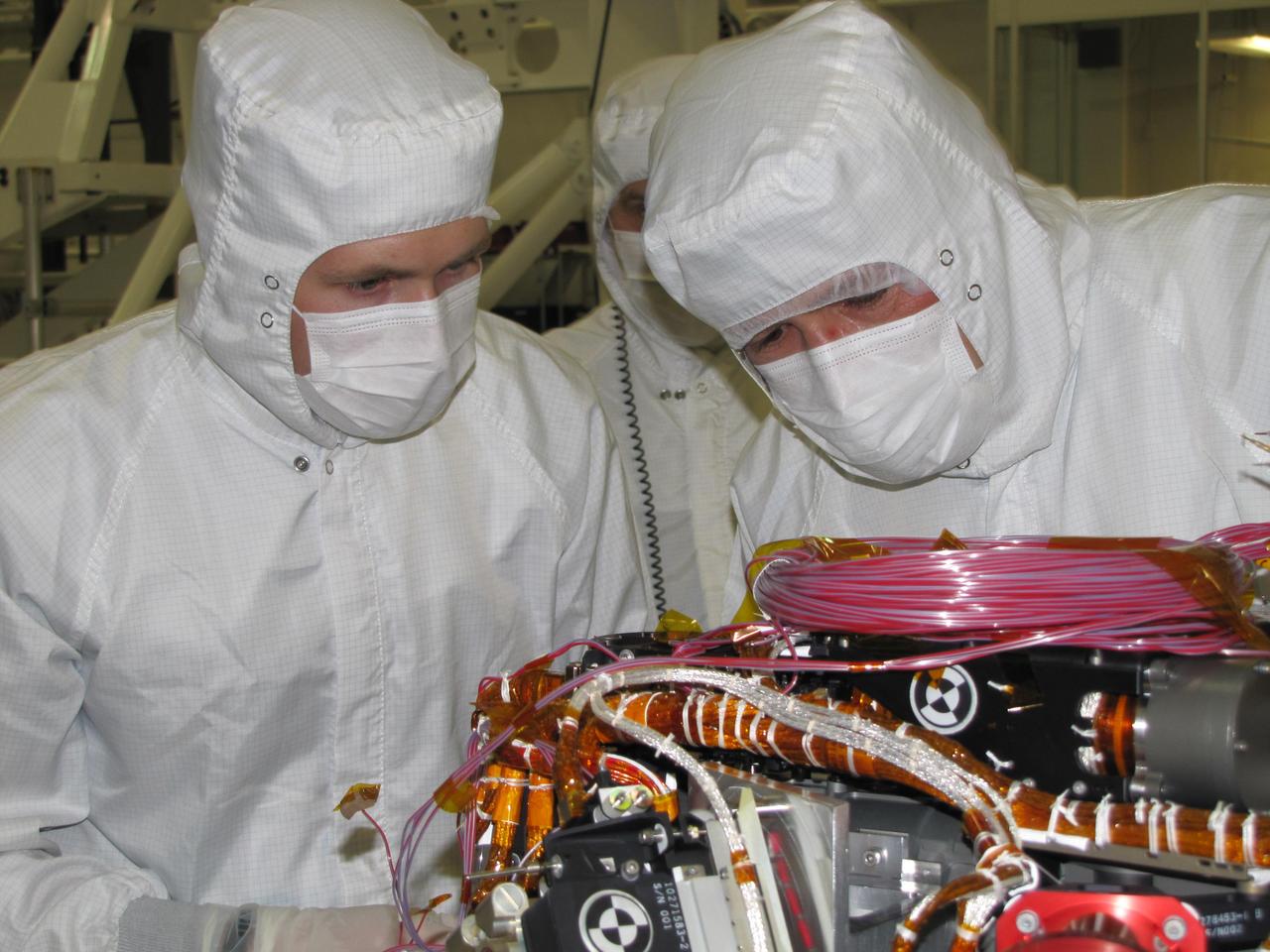

Grad student Nicholas Boyd left and Principal Investigator Ralf Gellert, both of the University of Guelph, Ontario, Canada, prepare for the installation of the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer sensor head during testing at NASA JPL.
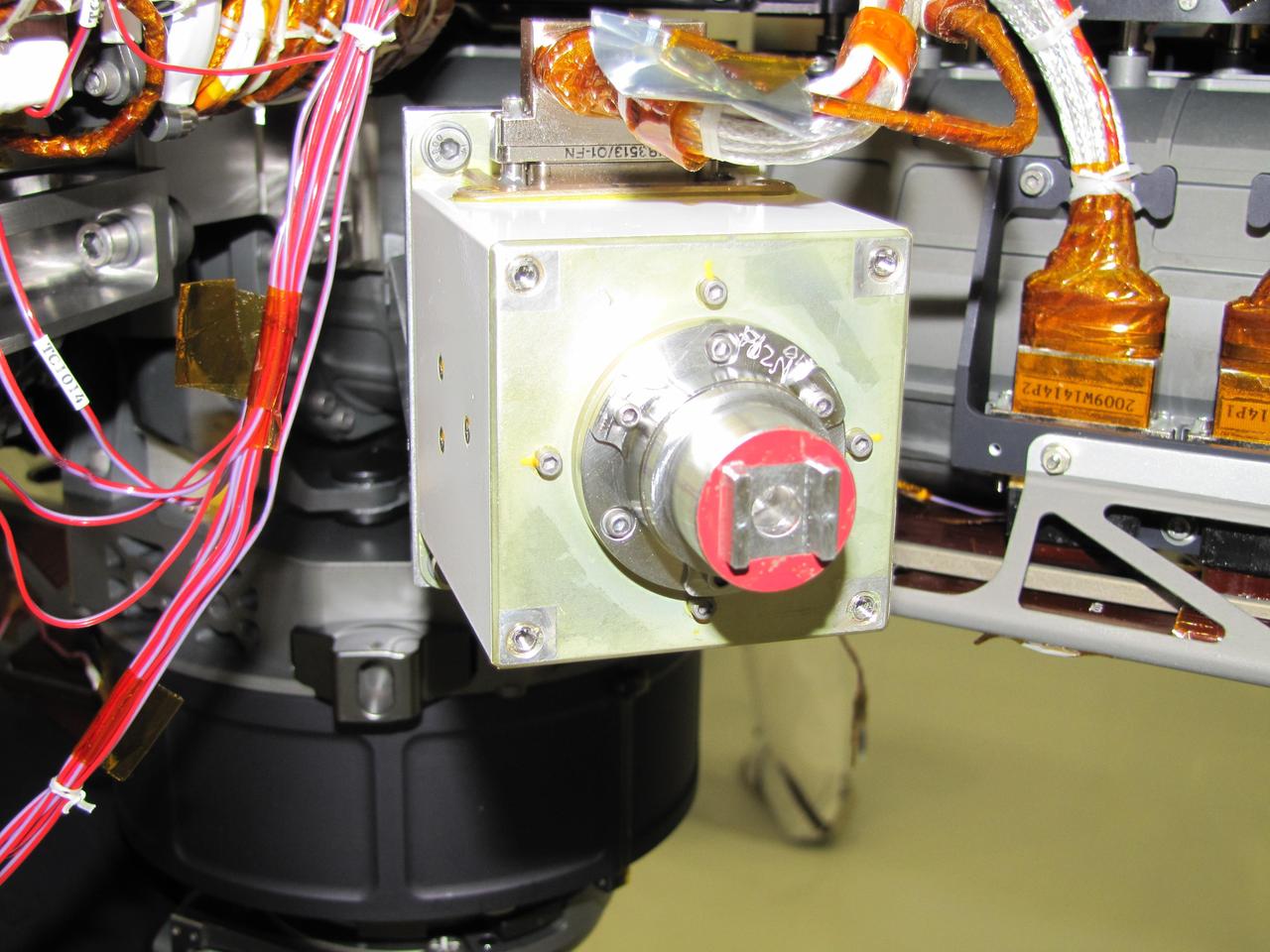

The sensor head on the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer instrument was installed during testing at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The instrument is part of NASA Curiosity rover.

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, center, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by Dwayne Swieter, left, and Norm Perish, right, TSIS-1 payload team members from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
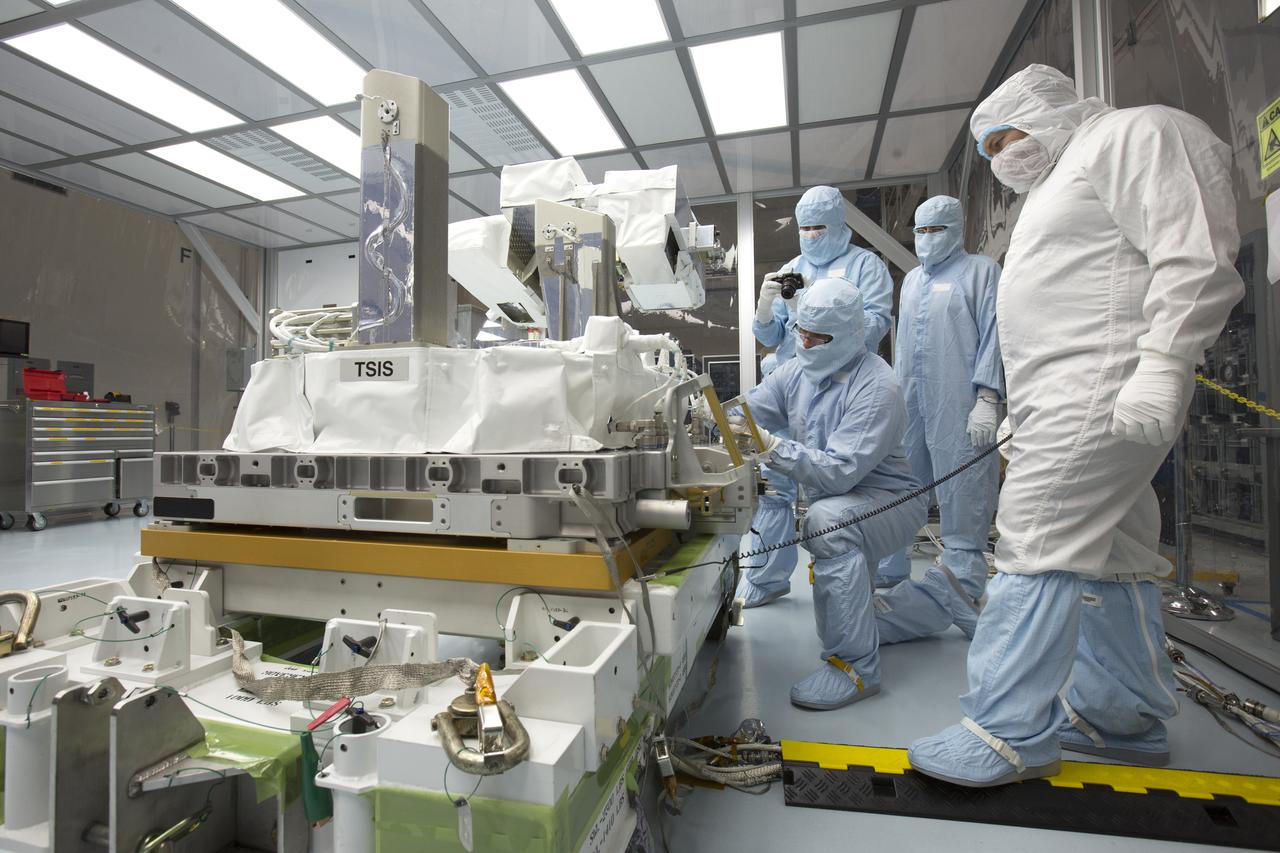

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies applies crew preference tape to the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by TSIS-1 payload team members from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). Standing from left to right are Tom Patton, Greg Ucker and Norm Perish. TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, right, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by Norm Perish, left, a TSIS-1 payload team member from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by Dwayne Swieter, right, a TSIS-1 payload team member from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.

In the high bay of Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility, Chris Hardcastle, left, of Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies performs a sharp edge inspection of the integrated Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 (TSIS-1) payload and the EXPRESS Pallet Adapter. Hardcastle is joined by Dwayne Swieter, right, a TSIS-1 payload team member from the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, a Research Institute at the University of Colorado (Boulder). TSIS-1 is designed to measure the Sun's energy input into Earth by seeing how it is distributed across different wavelengths of light. These measurements help scientists establish Earth's total energy and how our planet's atmosphere responds to changes in the Sun's energy output. TSIS-1 will launch on SpaceX's 13th commercial resupply mission to the International Space Station.
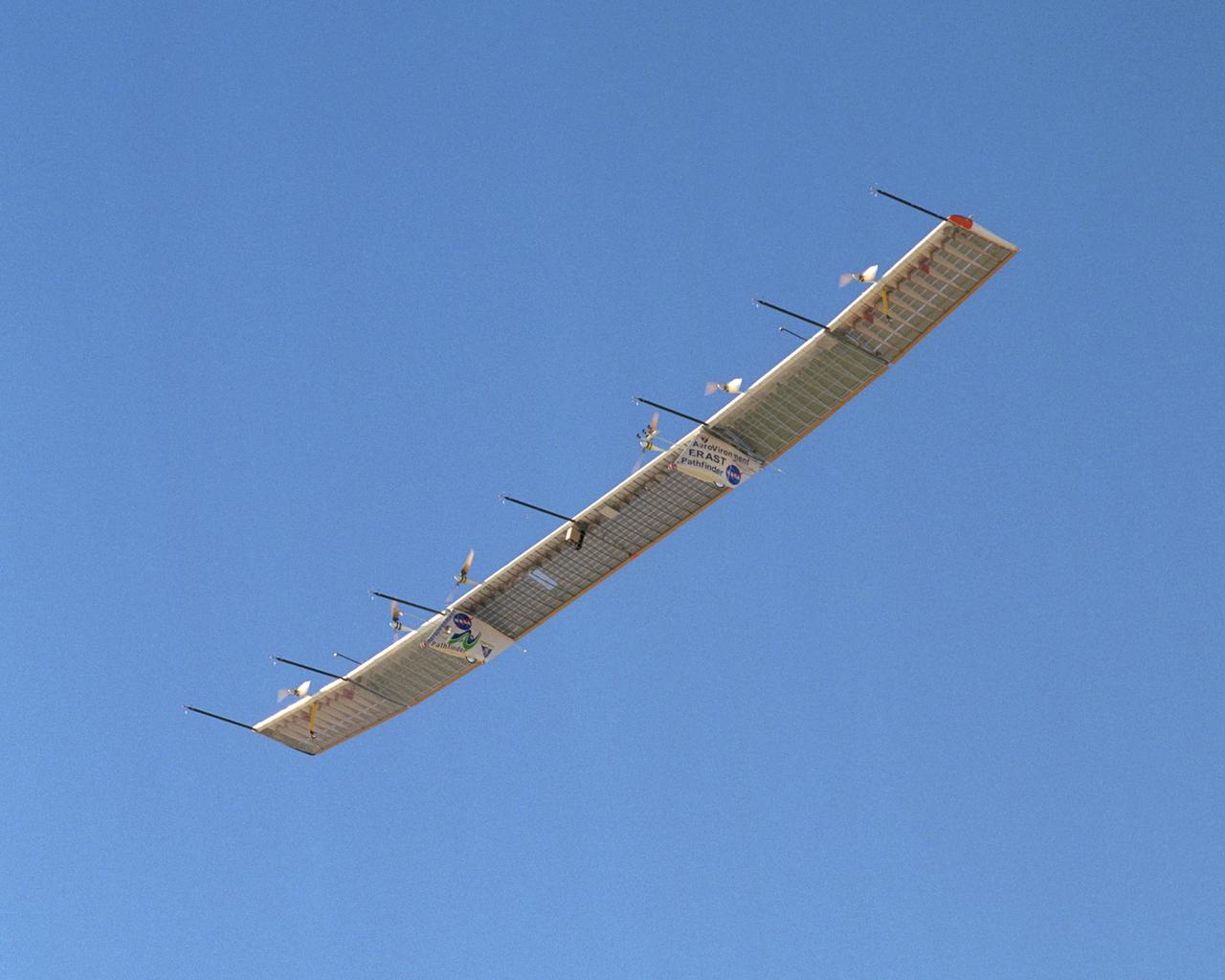

With its sensor booms projecting ahead of the wing, the Pathfinder-Plus solar-electric aircraft soars under a blue sky on a turbulence measurement research flight.

Laboratory Researcher suits up for work in a research clean room. Personal Protective Equipment, PPE, Portait Series

A rugged, highly accurate, low-temperature sensor is developed by NASA researchers. A new sensor allows accurate, quick low-temperature measurements in rugged environments. This is especially useful in piping with very cold liquids under high pressure, and high flow rate conditions.
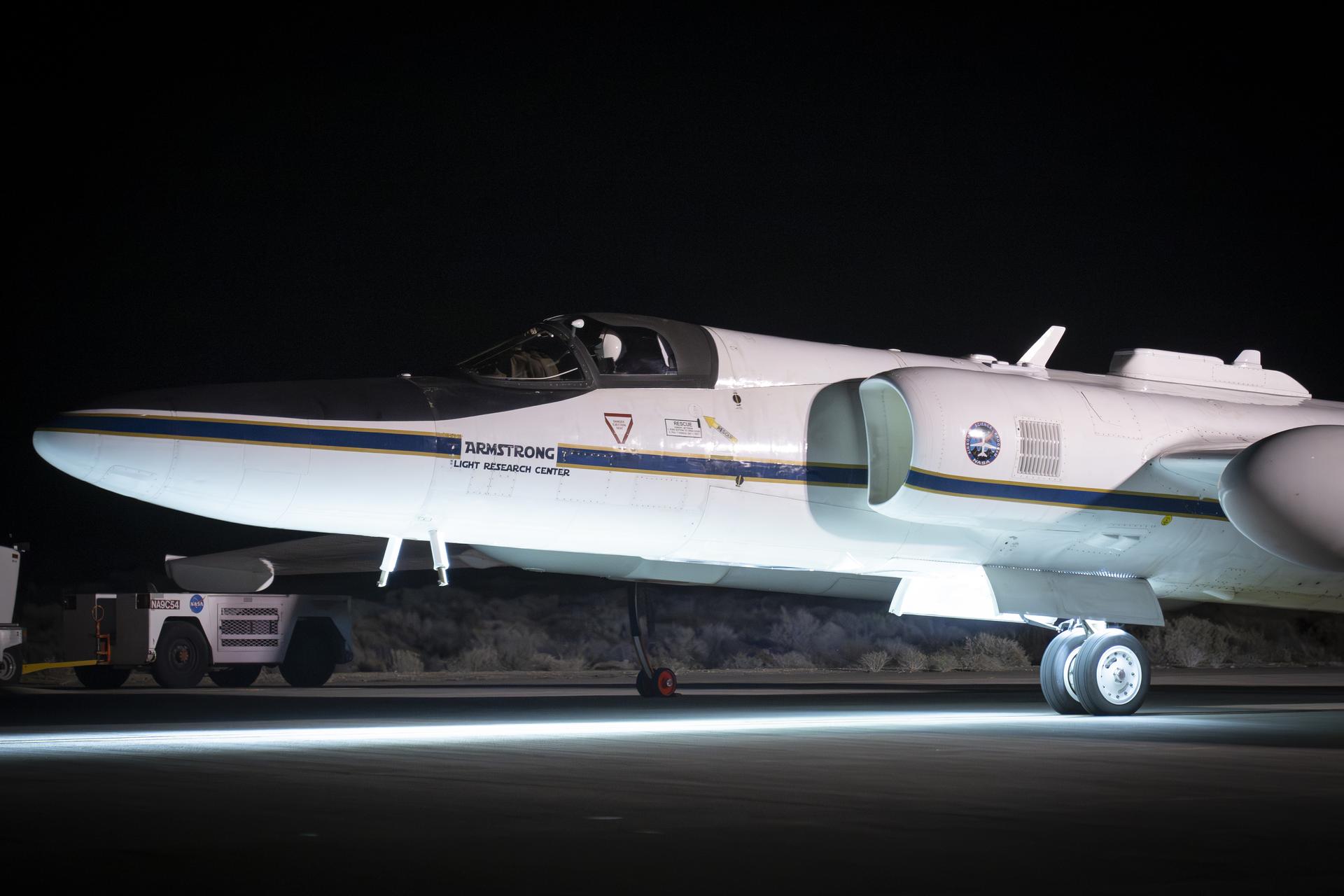

NASA’s ER-2 high-altitude aircraft prepares for a night flight with the Airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (air-LUSI) instrument on Monday, Feb. 2, 2026. The instrument measures Moonlight to improve accuracy of space-based sensors that forecast the weather, monitor agriculture, and study Earth’s ecosystem.
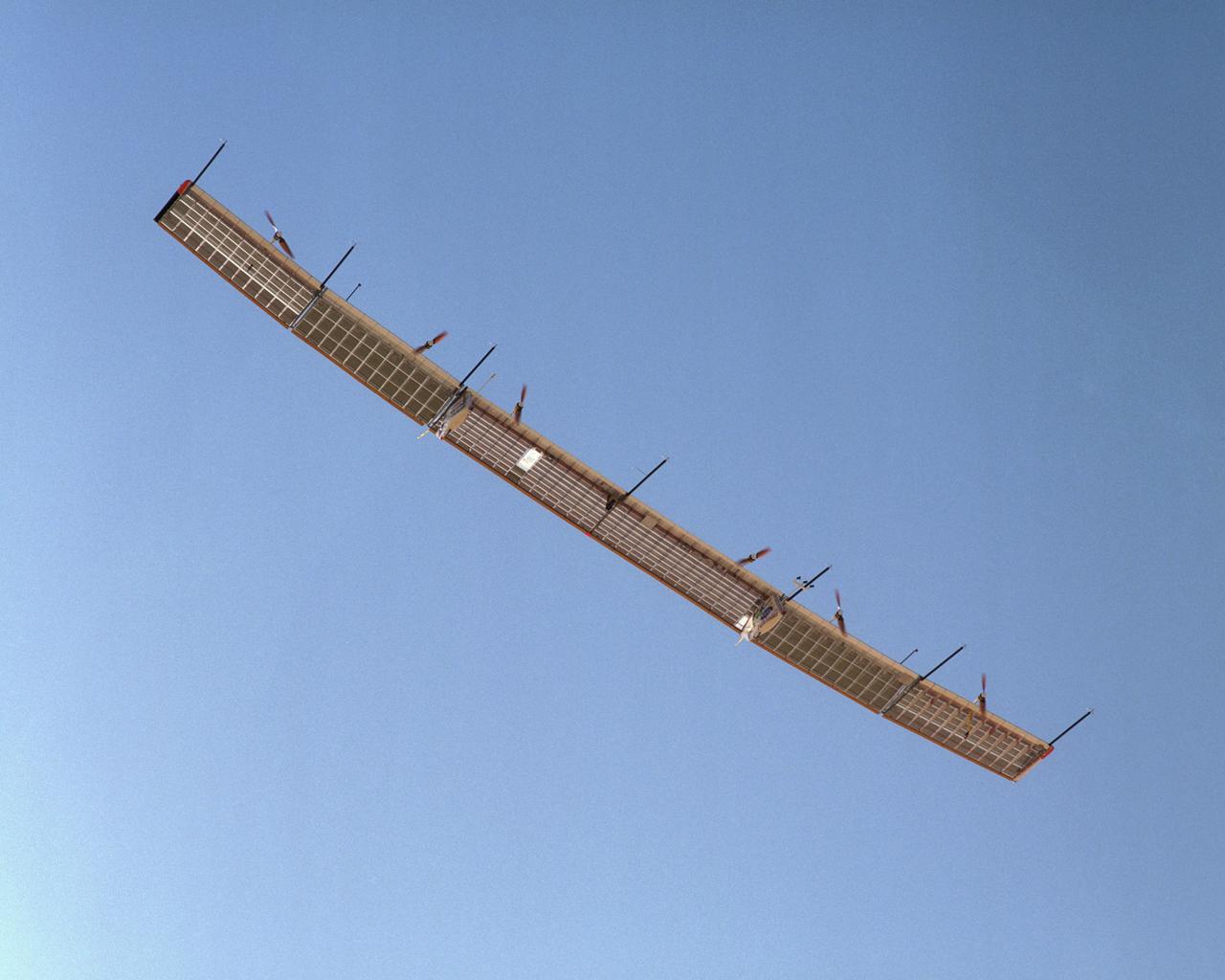
With its sensor booms projecting ahead of the wing, the Pathfinder-Plus solar wing soars under a blue sky on its final turbulence measurement research flight.

Boeing technicians that installed sensors inside of the Intertank STA.
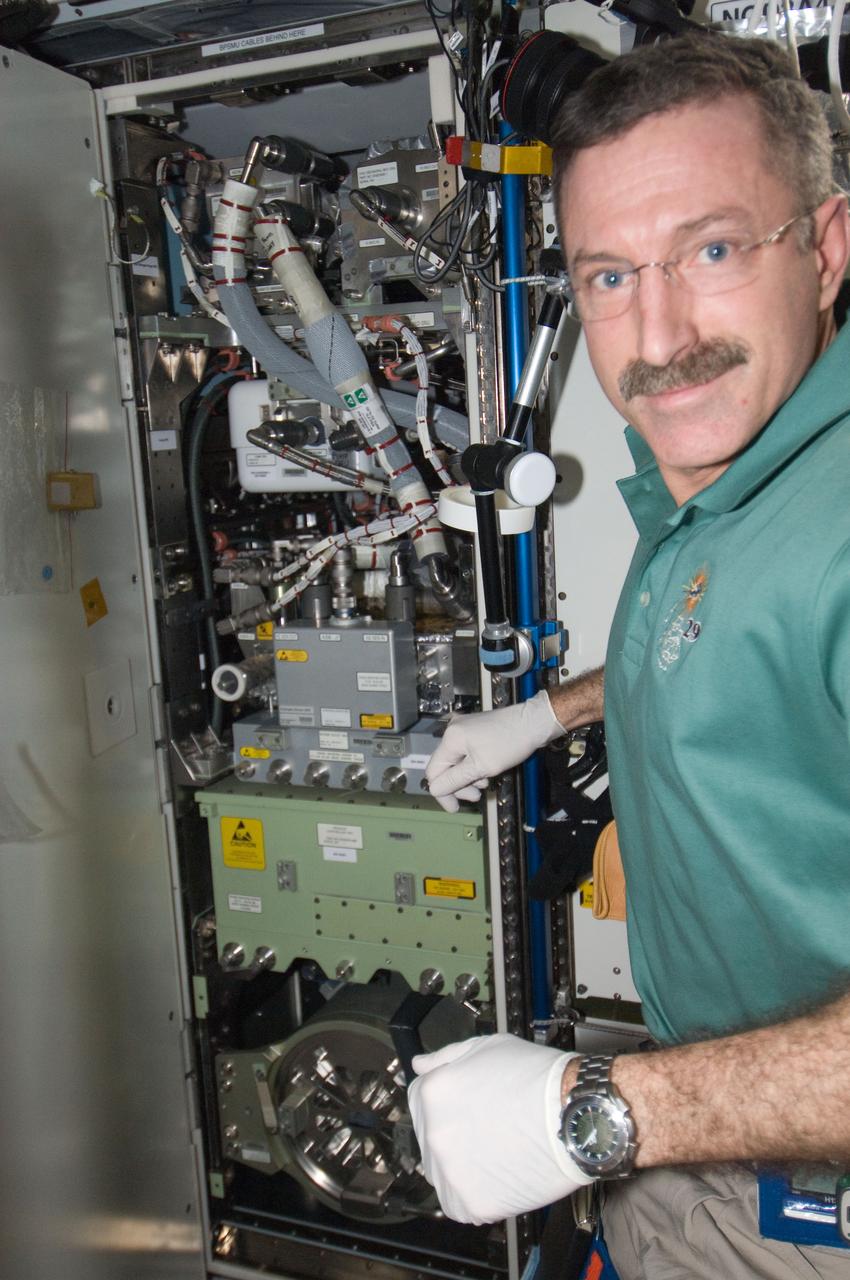

ISS030-E-236919 (18 April 2012) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, works with the Oxygen Generator System (OGS) rack in the Tranquility node of the International Space Station. Burbank unpowered the OGS, purged the hydrogen sensor Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) with the Hydrogen Sensor ORU Purge Adapter (HOPA) for return to Earth, and replaced the hydrogen sensor with a new spare, then cleaned the rack Avionics Air Assembly (AAA).
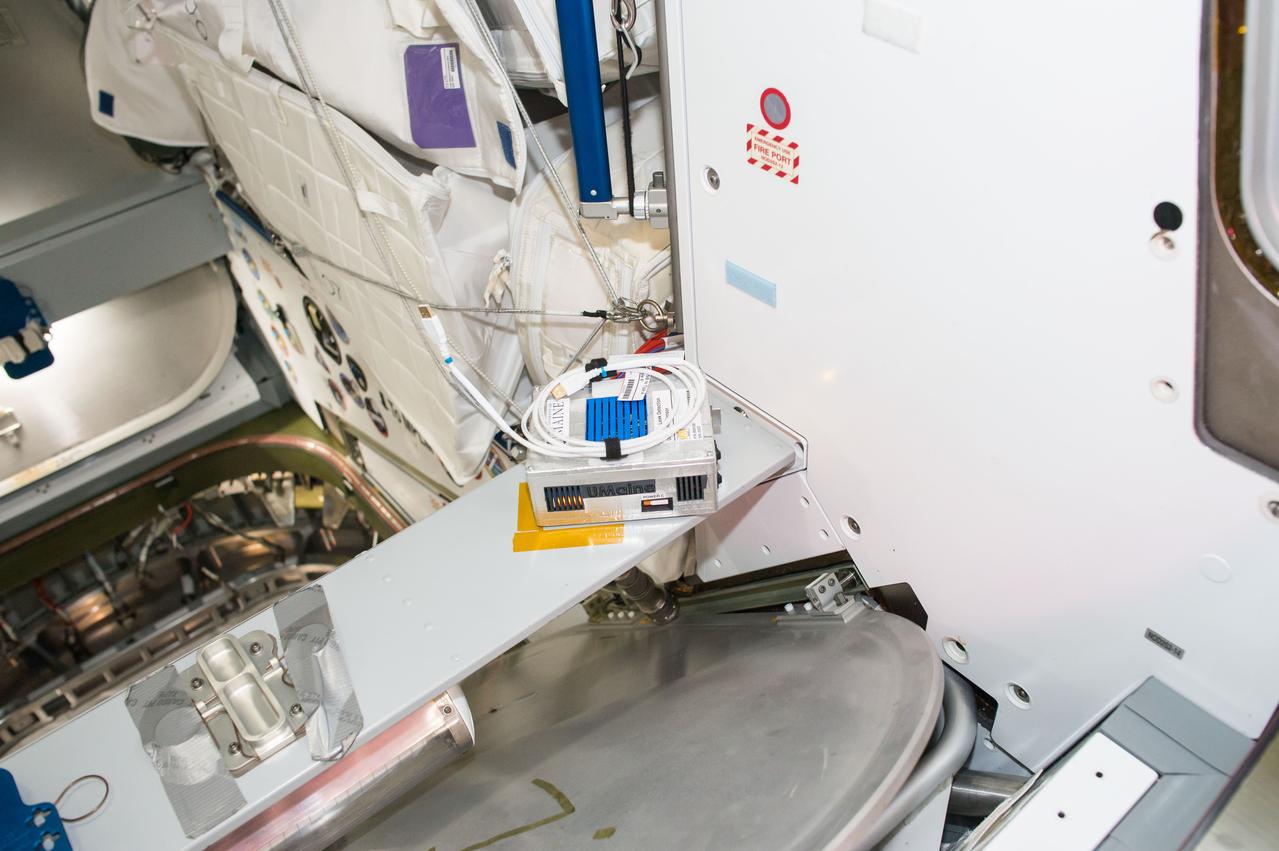

iss050e035315 (1/26/2017) --- A view of the Wireless Leak Detector Ultrasonic Sensor aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Joint Leak Detection and Localization Based on Fast Bayesian Inference from Network of Ultrasonic Sensor Arrays in Microgravity Environment (Wireless Leak Detection) investigation compares signals received at various ultrasonic sensors to reveal the location of air leaks, which can then be repaired.
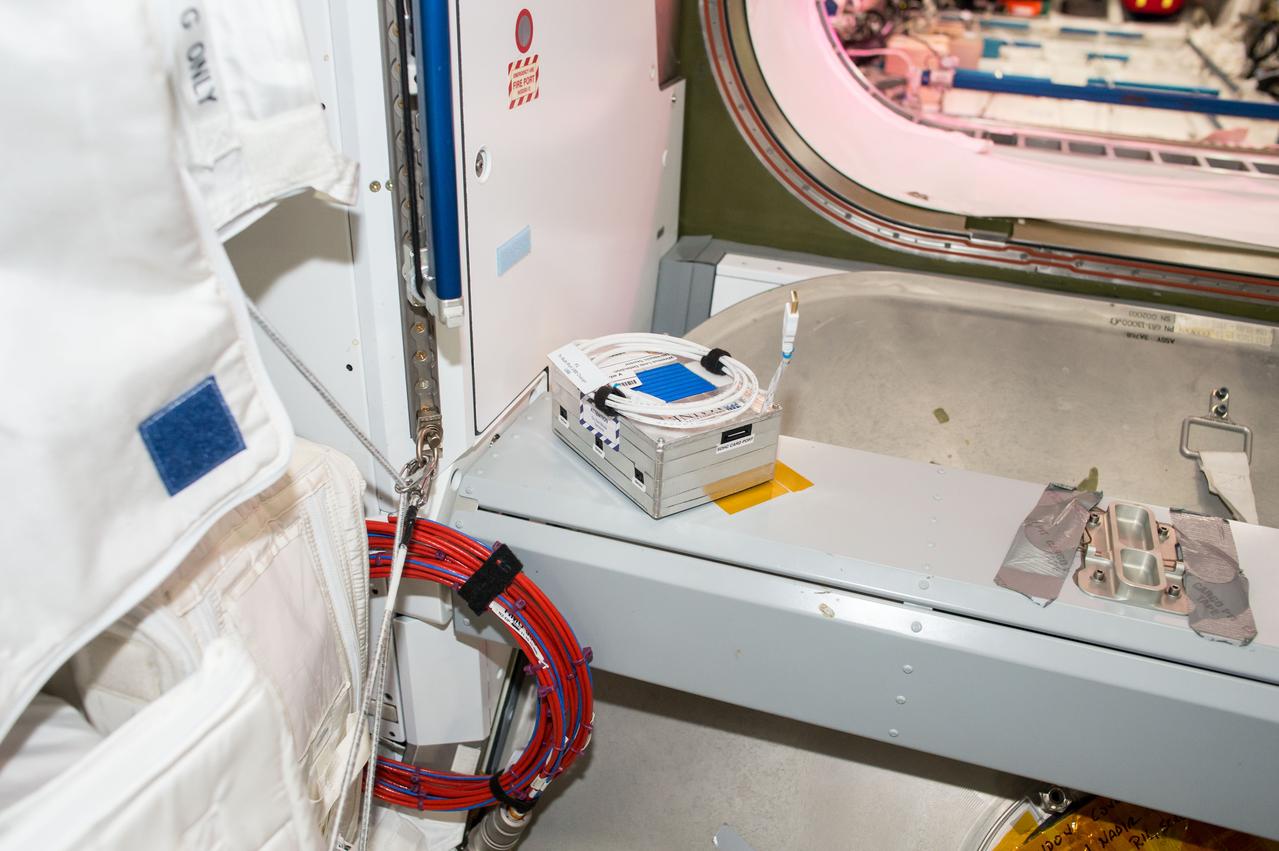

iss050e035314 (1/26/2017) --- A view of the Wireless Leak Detector Ultrasonic Sensor aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Joint Leak Detection and Localization Based on Fast Bayesian Inference from Network of Ultrasonic Sensor Arrays in Microgravity Environment (Wireless Leak Detection) investigation compares signals received at various ultrasonic sensors to reveal the location of air leaks, which can then be repaired.
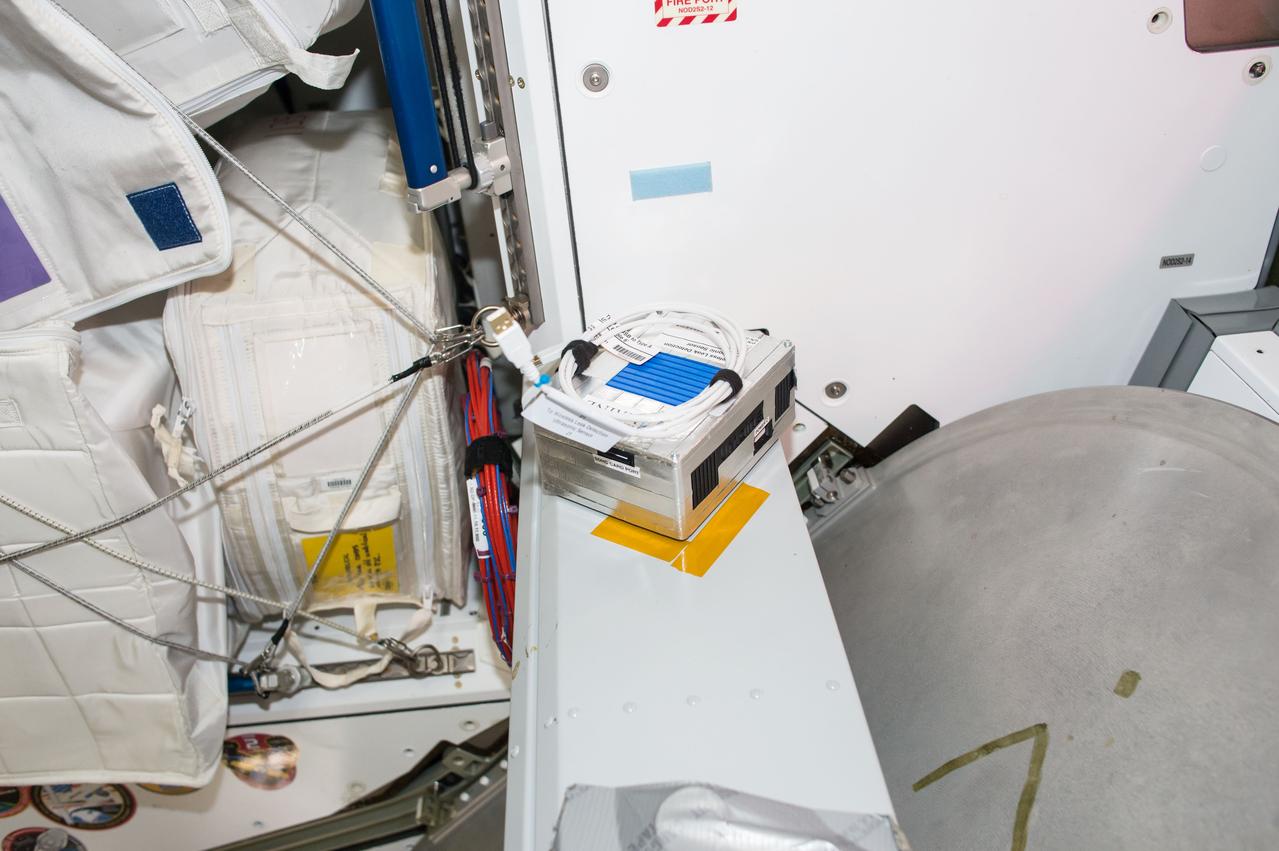

iss050e035313 (1/26/2017) --- A view of the Wireless Leak Detector Ultrasonic Sensor aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Joint Leak Detection and Localization Based on Fast Bayesian Inference from Network of Ultrasonic Sensor Arrays in Microgravity Environment (Wireless Leak Detection) investigation compares signals received at various ultrasonic sensors to reveal the location of air leaks, which can then be repaired.
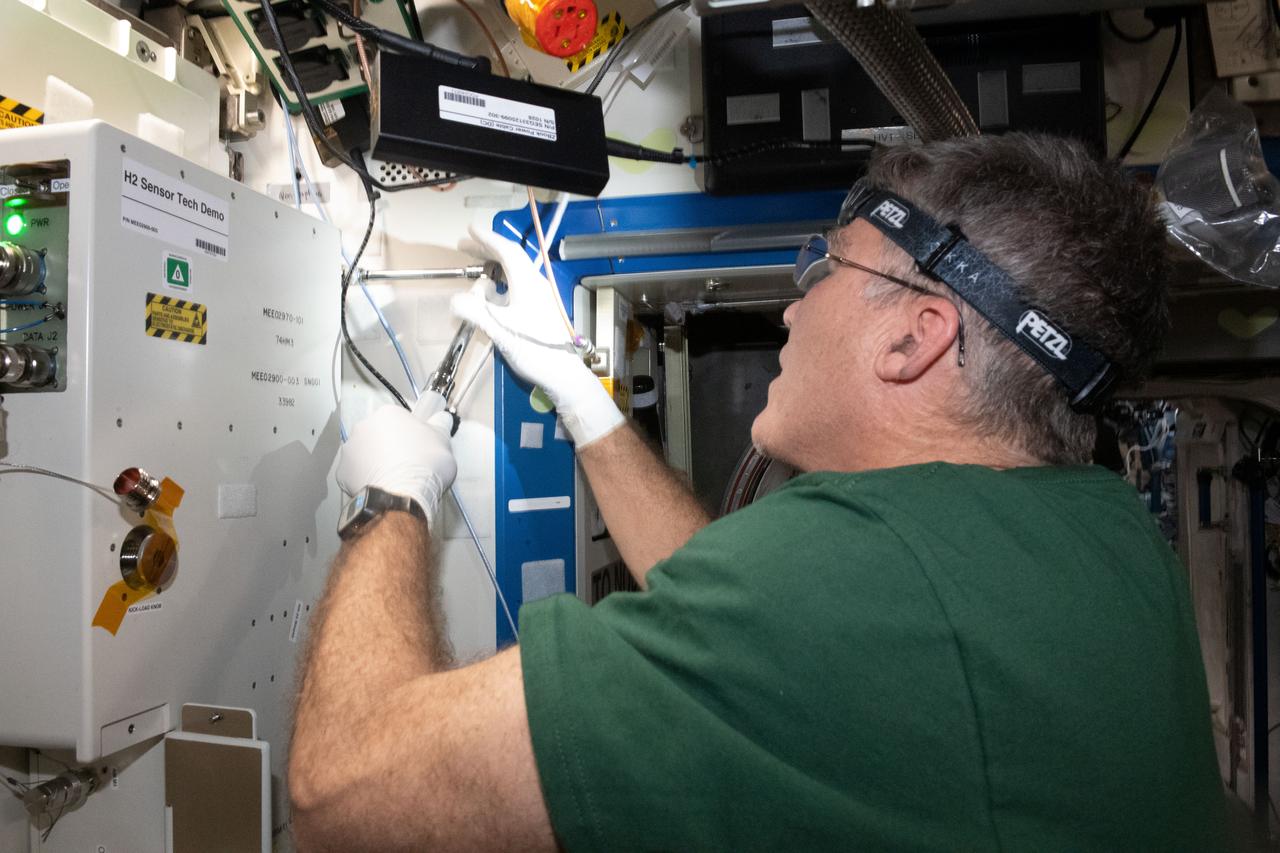

iss069e008416 (May 2, 2023) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Stephen Bowen installs the Advanced Hydrogen Sensor Technology Demonstration (OGA H2 Sensor Demo) on the Destiny laboratory module's Oxygen Generation System rack aboard the International Space Station. The device is testing new sensors to promote a longer operational life inside advanced oxygen generation systems for future space exploration missions.
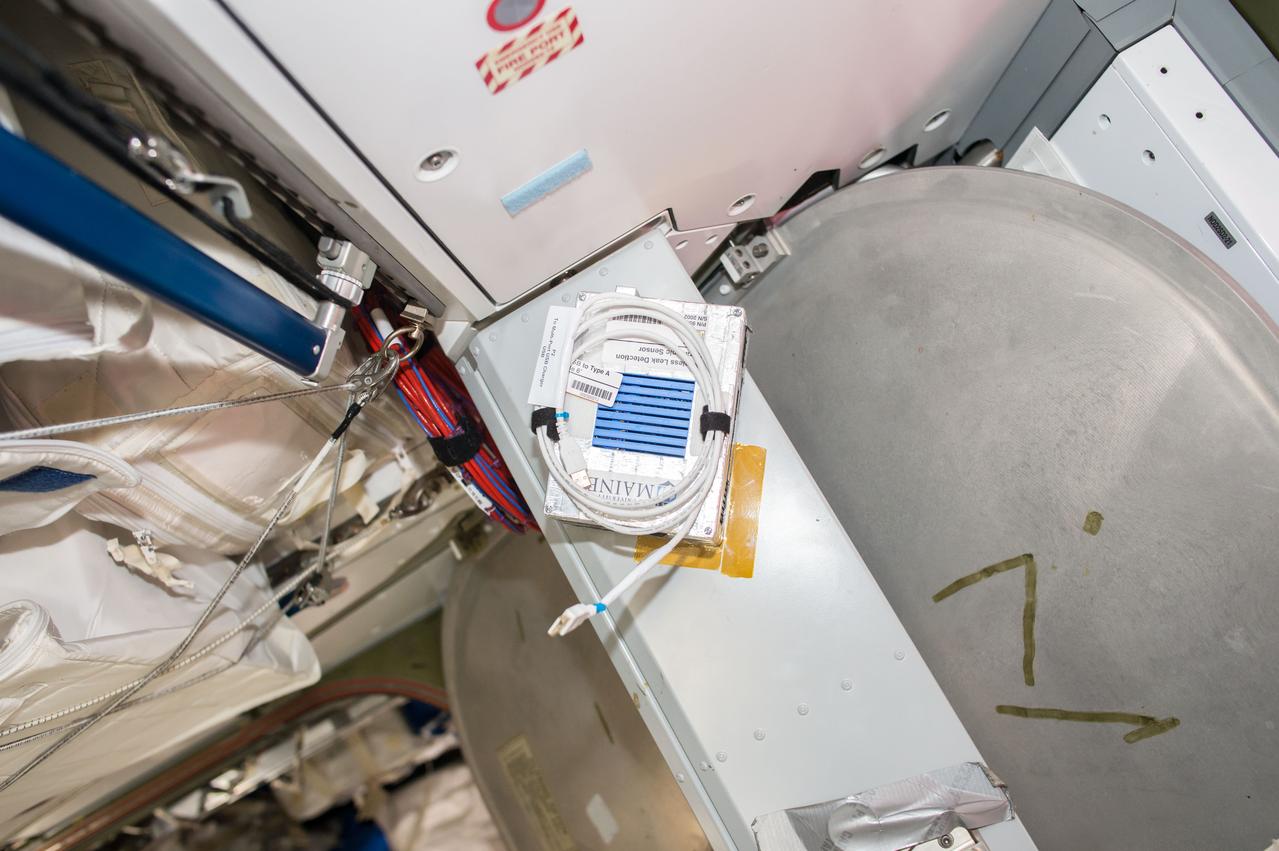

iss050e035316 (1/26/2017) --- A view of the Wireless Leak Detector Ultrasonic Sensor aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Joint Leak Detection and Localization Based on Fast Bayesian Inference from Network of Ultrasonic Sensor Arrays in Microgravity Environment (Wireless Leak Detection) investigation compares signals received at various ultrasonic sensors to reveal the location of air leaks, which can then be repaired.

Sensors on two finger-like mini-booms extending horizontally from the mast of NASA Mars rover Curiosity will monitor wind speed, wind direction and air temperature; image taken during installation of the instrument inside a clean room at NASA JPL.
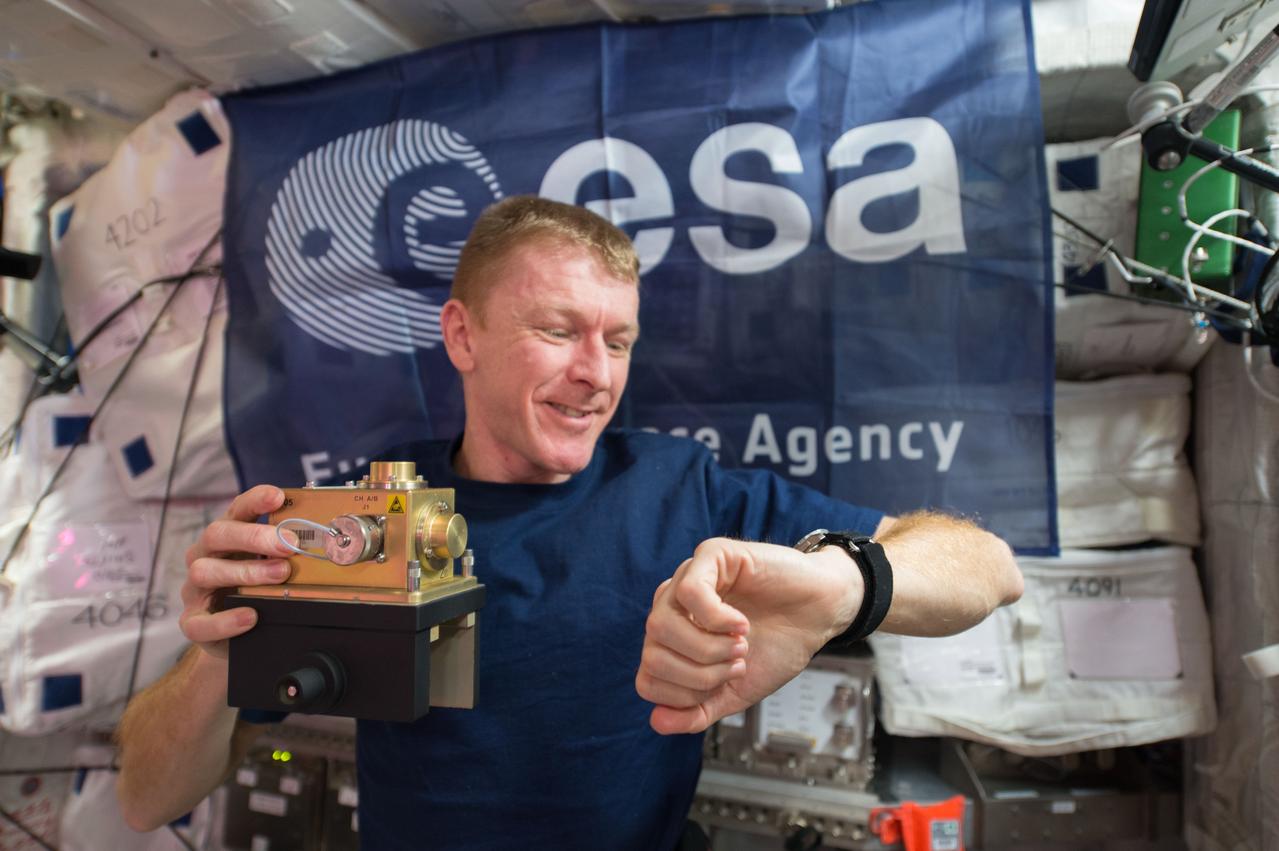

ISS046e024411 (01/26/2016) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Timothy Peake prepares to install a space acceleration measurement system sensor inside the European Columbus module aboard the International Space Station. The device is used in an ongoing study of the small forces (vibrations and accelerations) on the International Space Station resulting from the operation of hardware, crew activities, dockings and maneuvering. Results generalize the types of vibrations affecting vibration-sensitive experiments.
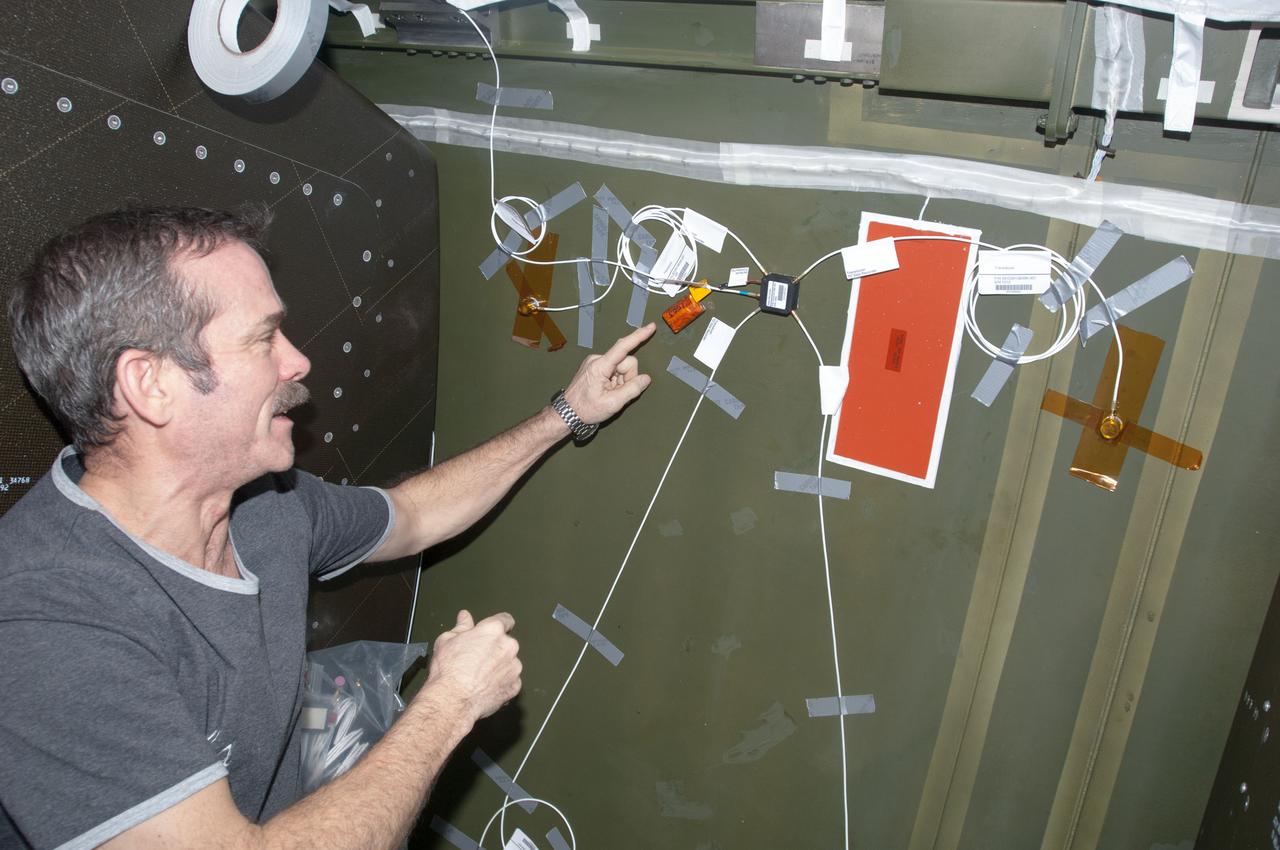

ISS034-E-038211 (1 Feb. 2013) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Chris Hadfield, Expedition 34 flight engineer, installs Ultra-Sonic Background Noise Tests (UBNT) sensors behind a rack in the Destiny laboratory, using the International Space Station (ISS) as Testbed for Analog Research (ISTAR) procedures. These sensors detect high frequency noise levels generated by ISS hardware and equipment operating within Destiny.

View of Canadian Space Agency (CSA) Chris Hadfield,Expedition 34 Flight Engineer (FE),installing Ultra-Sonic Background Noise Tests (UBNT) sensors behind rack in the U.S. Laboratory using the International Space Station (ISS) as Testbed for Analog Research (ISTAR) procedures. These sensors detect high frequency noise levels generated by ISS hardware and equipment operating within the U.S. Laboratory. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.

ISS034-E-030216 (16 Jan. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Kevin Ford, Expedition 34 commander, installs a Ultra-Sonic Background Noise Tests (UBNT) sensor kit behind a rack in the Destiny of the International Space Station.

ISS034-E-030218 (16 Jan. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Kevin Ford, Expedition 34 commander, installs a Ultra-Sonic Background Noise Tests (UBNT) sensor kit behind a rack in the Destiny of the International Space Station.
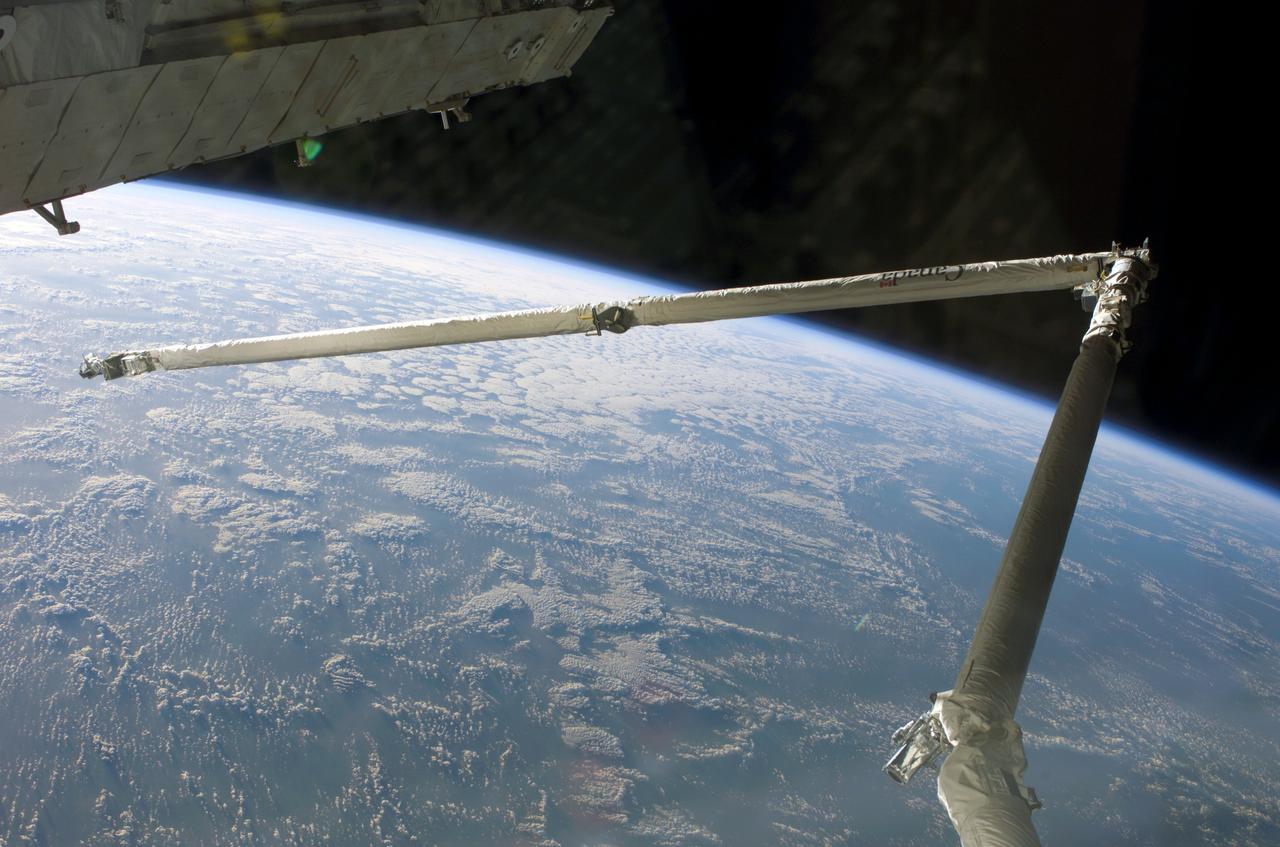

S114-E-5712 (28 July 2005) --- This view of the Orbital Boom Sensor System, backdropped by clouds and Earth’s limb, was taken by the STS-114 crew during approach and docking operations with the international space station.
The test team prepares a test fixture with a nylon fabric sample at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The fabric in the test fixture forms a bubble when pressure is applied to the silicone bladder underneath. A similar test can be performed with a sensor on the fabric to verify the sensor will work when stretched in three dimensions.
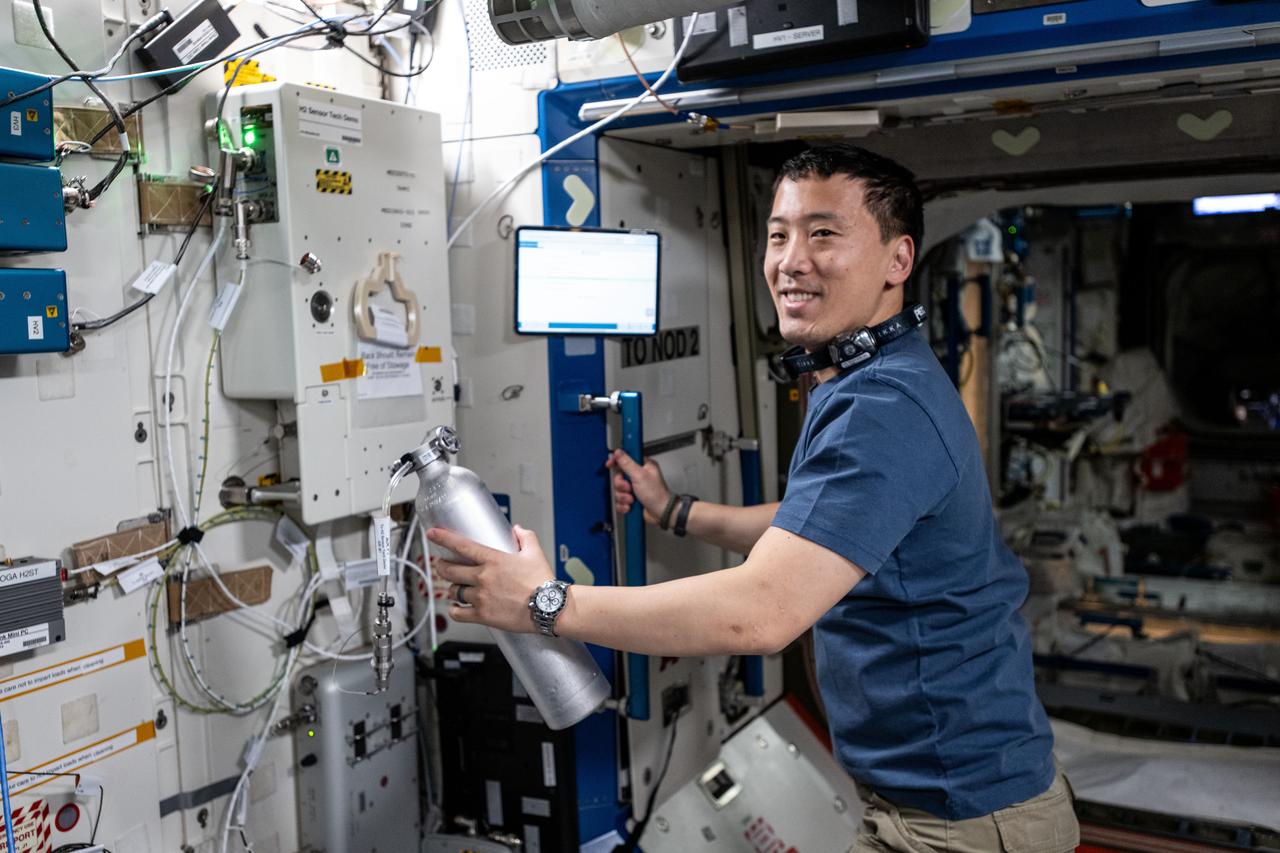

iss072e941773 (April 9, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim installs experimental hydrogen sensors to test the advanced life support gear for longer calibration life and improved reliability aboard the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module.
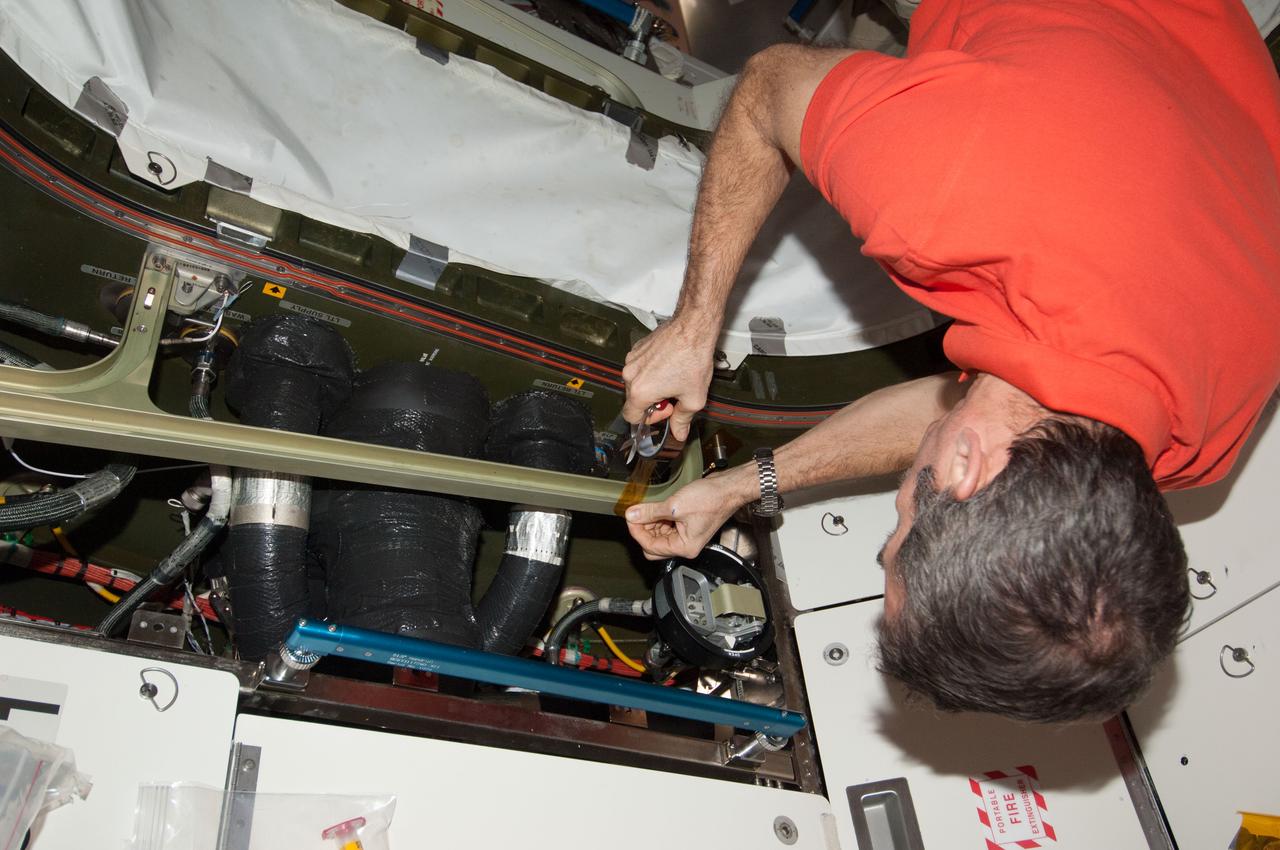

ISS034-E-037330 (31 Jan. 2013) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Chris Hadfield, Expedition 34 flight engineer, installs a Ultra-Sonic Background Noise Tests (UBNT) sensor kit behind a rack in the Destiny of the International Space Station.
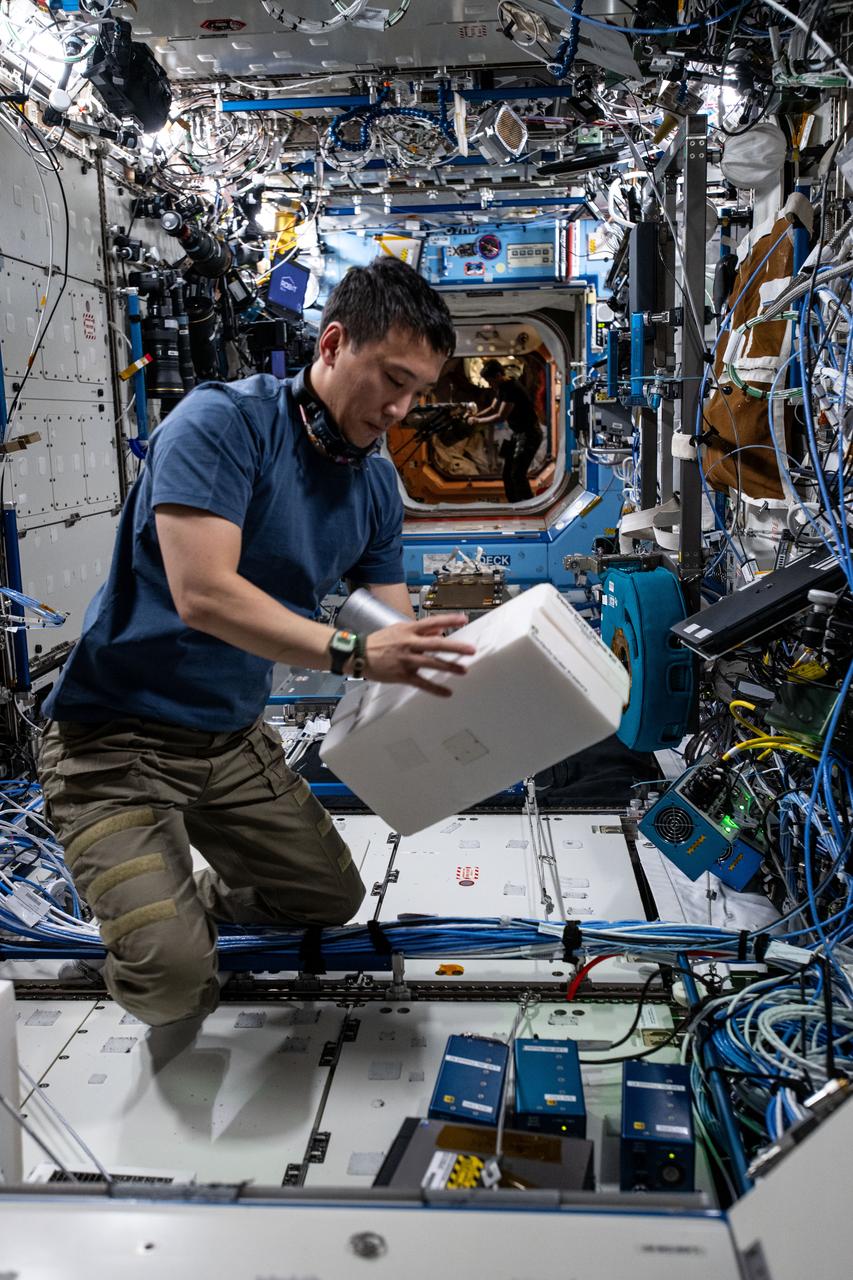

iss072e941778 (April 9, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim installs experimental hydrogen sensors to test the advanced life support gear for longer calibration life and improved reliability aboard the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module.
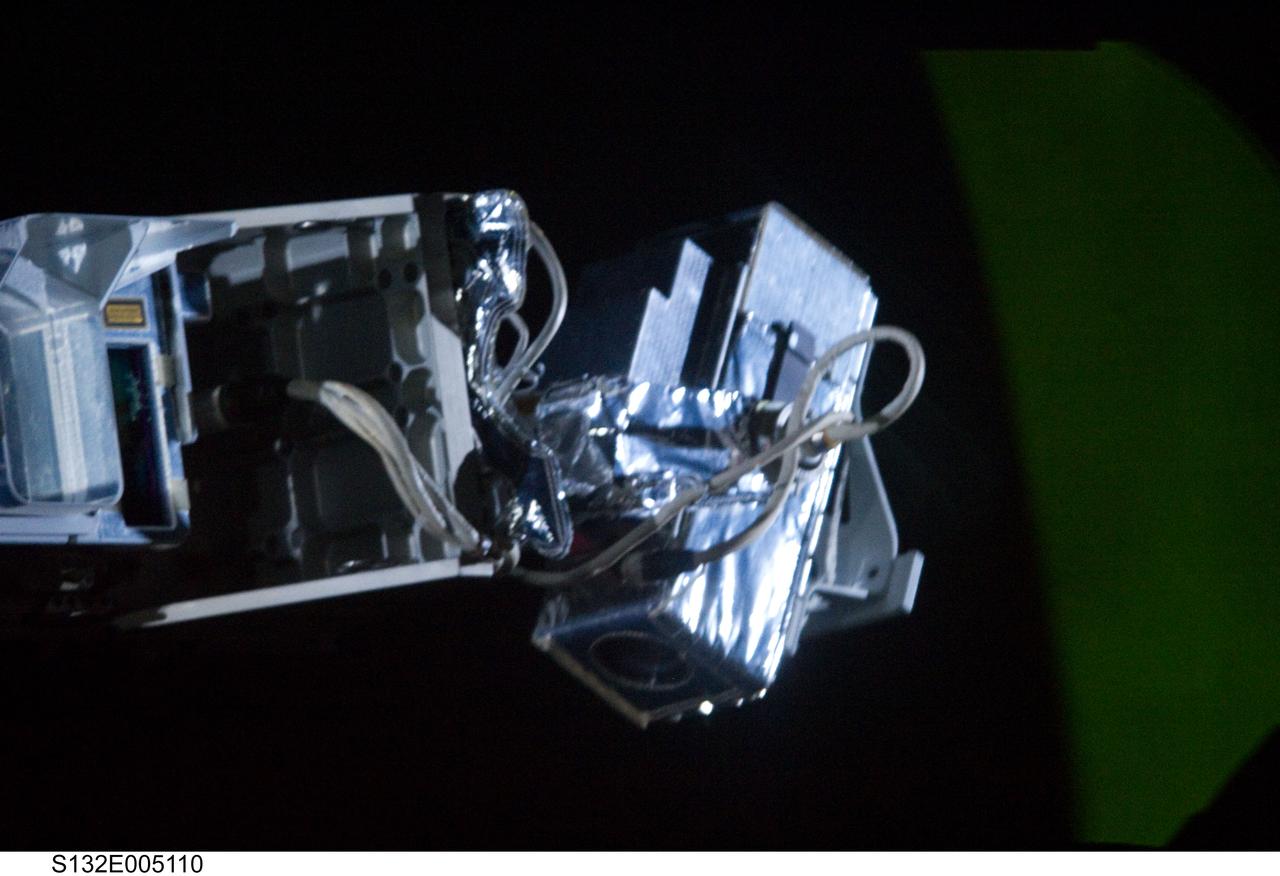

S132-E-005110 (15 May 2010) --- While preparing for the routine inspection of Atlantis’ thermal protection system on Flight Day 2, the STS-132 crew discovered a cable was being pinched and preventing the sensor package pan and tilt unit from moving properly. There are alternate sensor packages that do not require the pan and tilt function; and personnel in the Johnson Space Center’s Mission Control Center are evaluating those procedures. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Pressure is applied to a test fixture with a nylon fabric sample until it fails at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The fabric in the test fixture forms a bubble when pressure is applied to the silicone bladder underneath. In this frame, the silicone bladder is visible underneath the torn fabric after it was inflated to failure. A similar test can be performed with a sensor on the fabric to verify the sensor will work when stretched in three dimensions.

Erick Rossi De La Fuente, from left, John Rudy, L. J. Hantsche, Adam Curry, Jeff Howell, Coby Asselin, Benjamin Mayeux, and Paul Bean pose with a test fixture, material, sensor, and data acquisition systems at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The sensor tests seek to quantify the limits of the material to improve computer models and make more reliable supersonic parachutes.

NASA researchers James Cowart and Elizabeth Nail add sensors, wiring and cameras, to the NASA Airborne Instrumentation for Real-world Video of Urban Environments (AIRVUE) sensor pod at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in late February 2024. The AIRVUE pod was flown on a helicopter at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida and is used to collect data for future autonomous aircraft.

Although the new fiber optic sensors on the Ikhana, which are located on fibers that are the diameter of a human hair, are not visible, the sealant used to cover them can be seen in this view from above the left wing. NASA Dryden Flight Research Center is evaluating an advanced fiber optic-based sensing technology installed on the wings of NASA's Ikhana aircraft. The fiber optic system measures and displays the shape of the aircraft's wings in flight. There are other potential safety applications for the technology, such as vehicle structural health monitoring. If an aircraft structure can be monitored with sensors and a computer can manipulate flight control surfaces to compensate for stresses on the wings, structural control can be established to prevent situations that might otherwise result in a loss of control.

iss056e014487 (June 18, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Ricky Arnold of NASA is pictured in the Unity module during life support maintenance work to remove and replace an Oxygen Generation System Hydrogen Sensor.
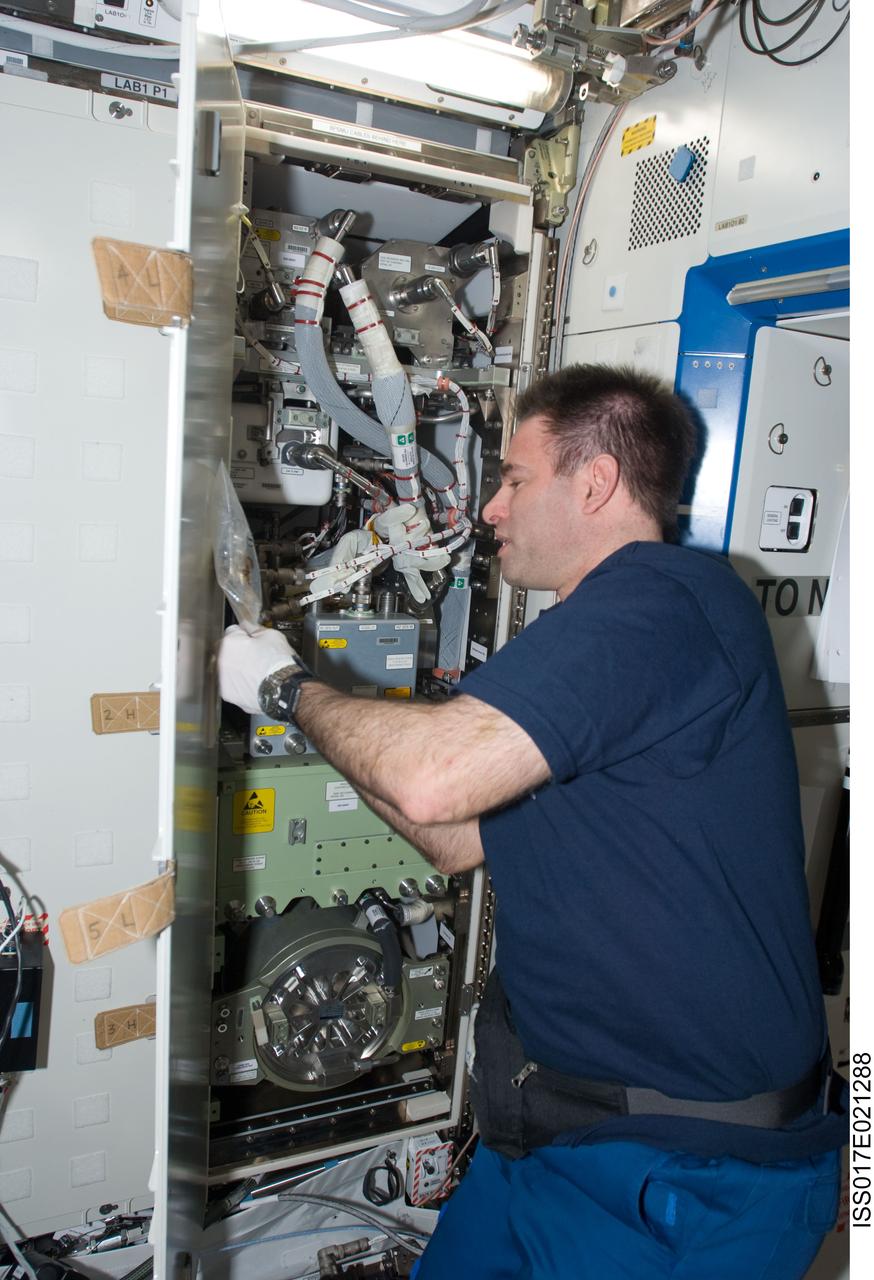

ISS017-E-021288 (15 Oct. 2008) --- Astronaut Greg Chamitoff, Expedition 17/18 flight engineer, works with the hydrogen (H2) sensor in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
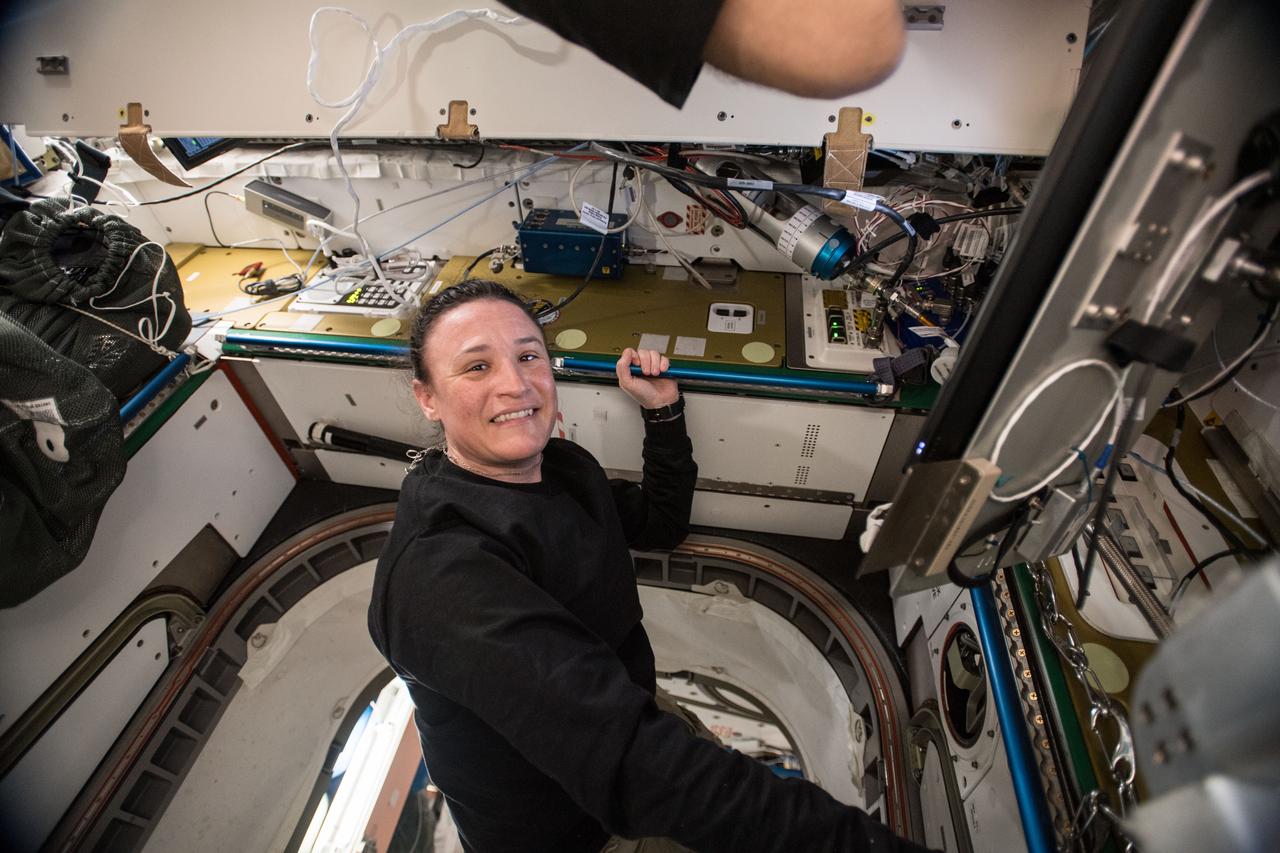

iss056e014502 (June 18, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineer Serena Auñón-Chancellor of NASA is pictured in the Unity module during life support maintenance work to remove and replace an Oxygen Generation System Hydrogen Sensor.
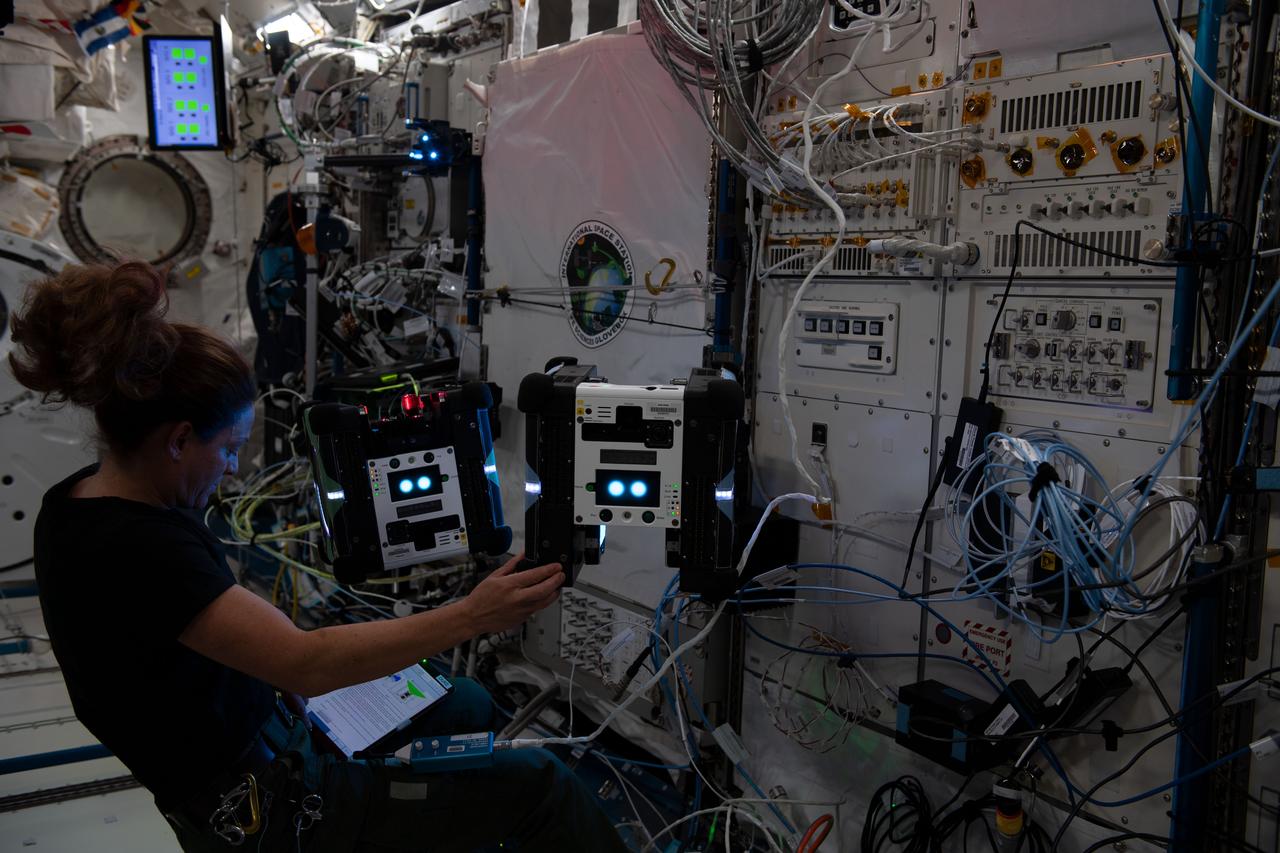

iss068e020703 (Nov. 7, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Nicole Mann works with a pair of free-flying, cube-shaped Astrobee robotic helpers inside the Kibo laboratory module. The toaster-sized, autonomous robots were demonstrating the use of a photogrammetric vision-based technology for guidance, navigation, and control as part of the Smartphone Vision Guidance Sensor experiment.
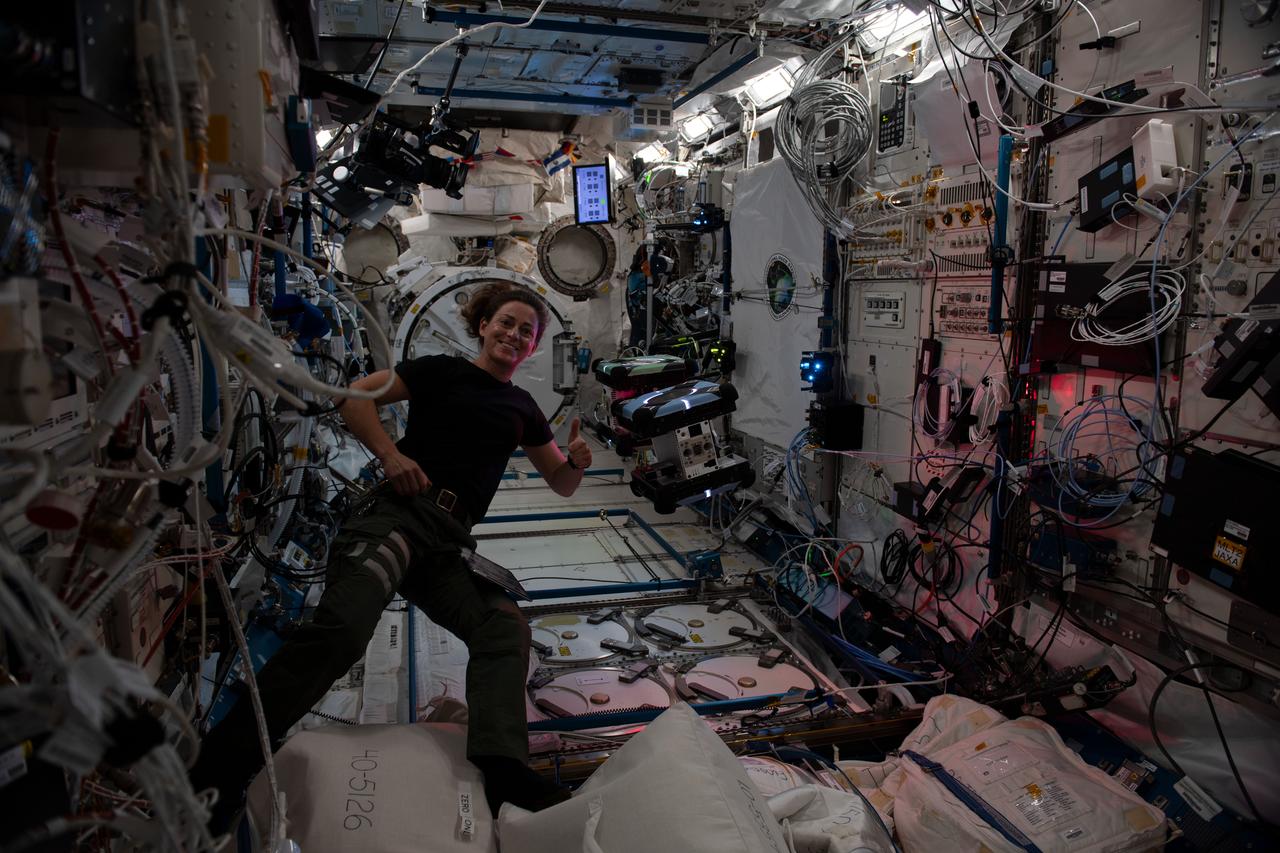

iss068e020734 (Nov. 7, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Nicole Mann poses with a pair of free-flying, cube-shaped Astrobee robotic helpers inside the Kibo laboratory module. The toaster-sized, autonomous robots were demonstrating the use of a photogrammetric vision-based technology for guidance, navigation, and control as part of the Smartphone Vision Guidance Sensor experiment.

S66-09379 (1 Oct. 1966) --- Tri-Axis Magnetometer-Sensor Unit mounted on telescoping boom. Cable connects Sensor Unit with Electronics Unit mounted on retrograde beam in retrograde adapter section. Objective of experiment is to monitor the direction and amplitude of Earth's magnetic field (Gemini-12). Photo credit: NASA
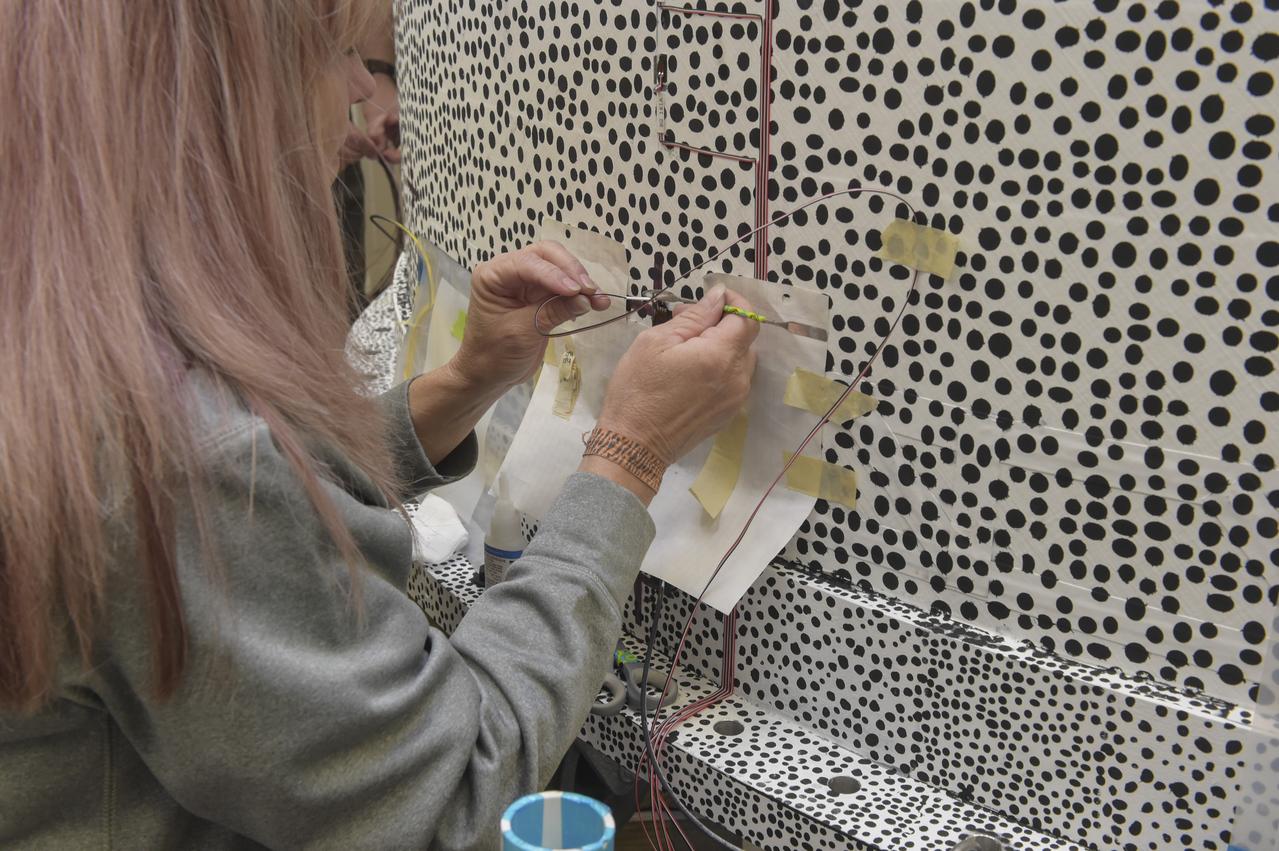
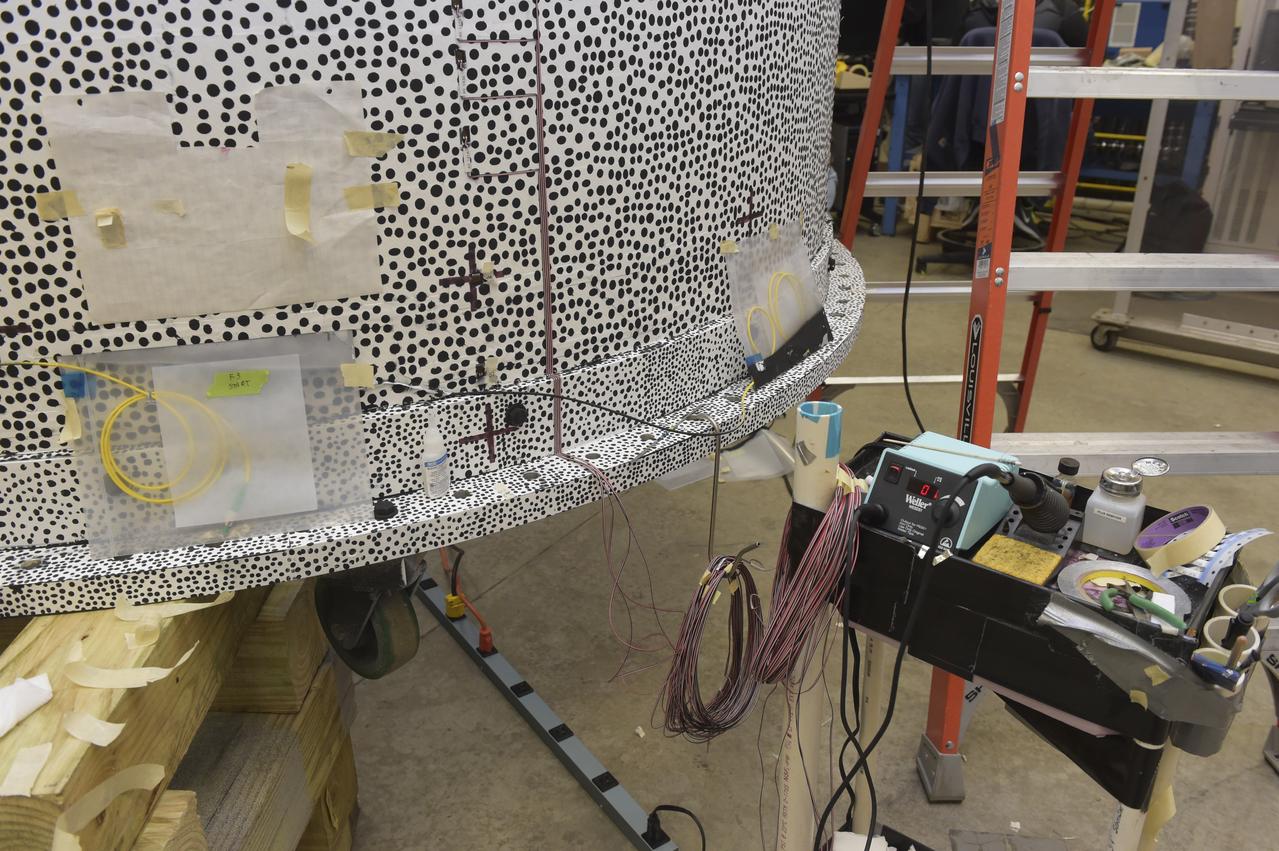
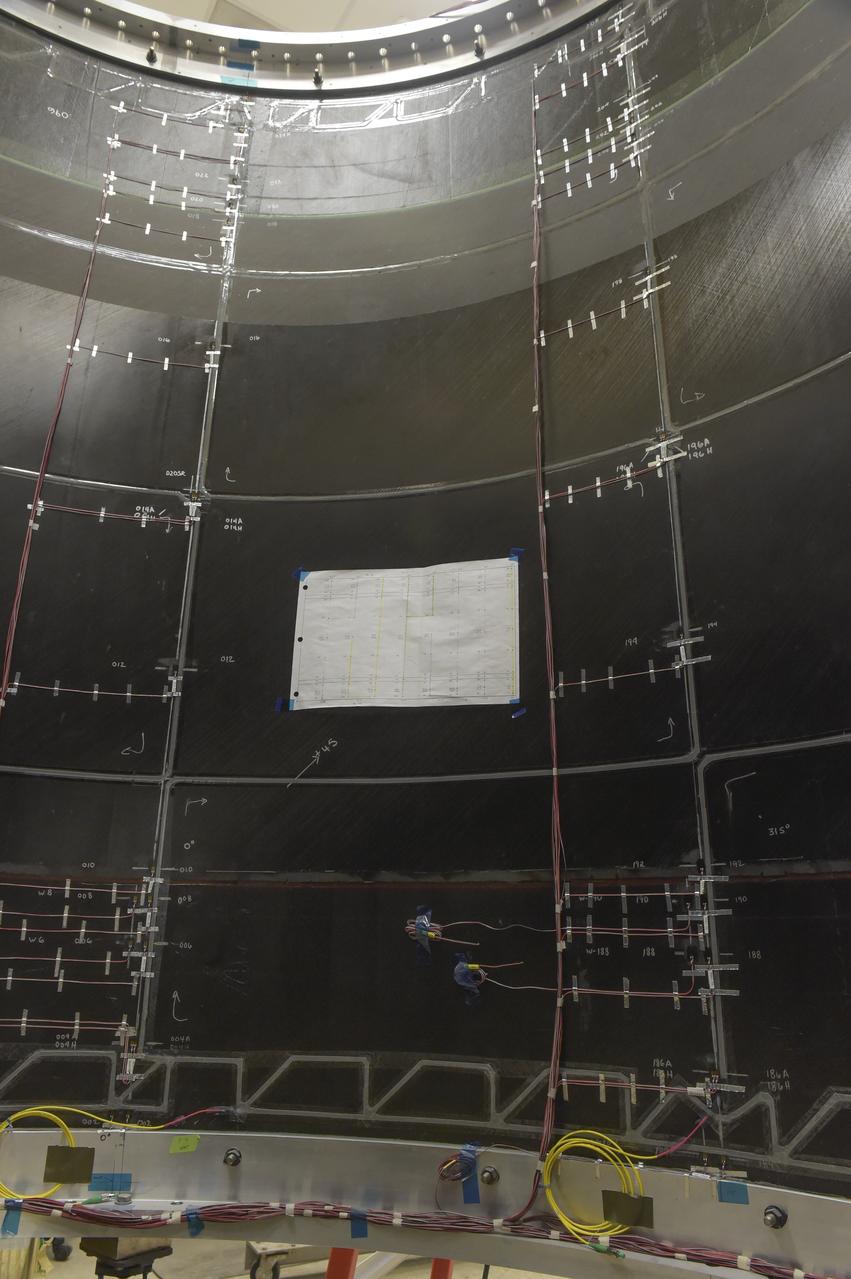
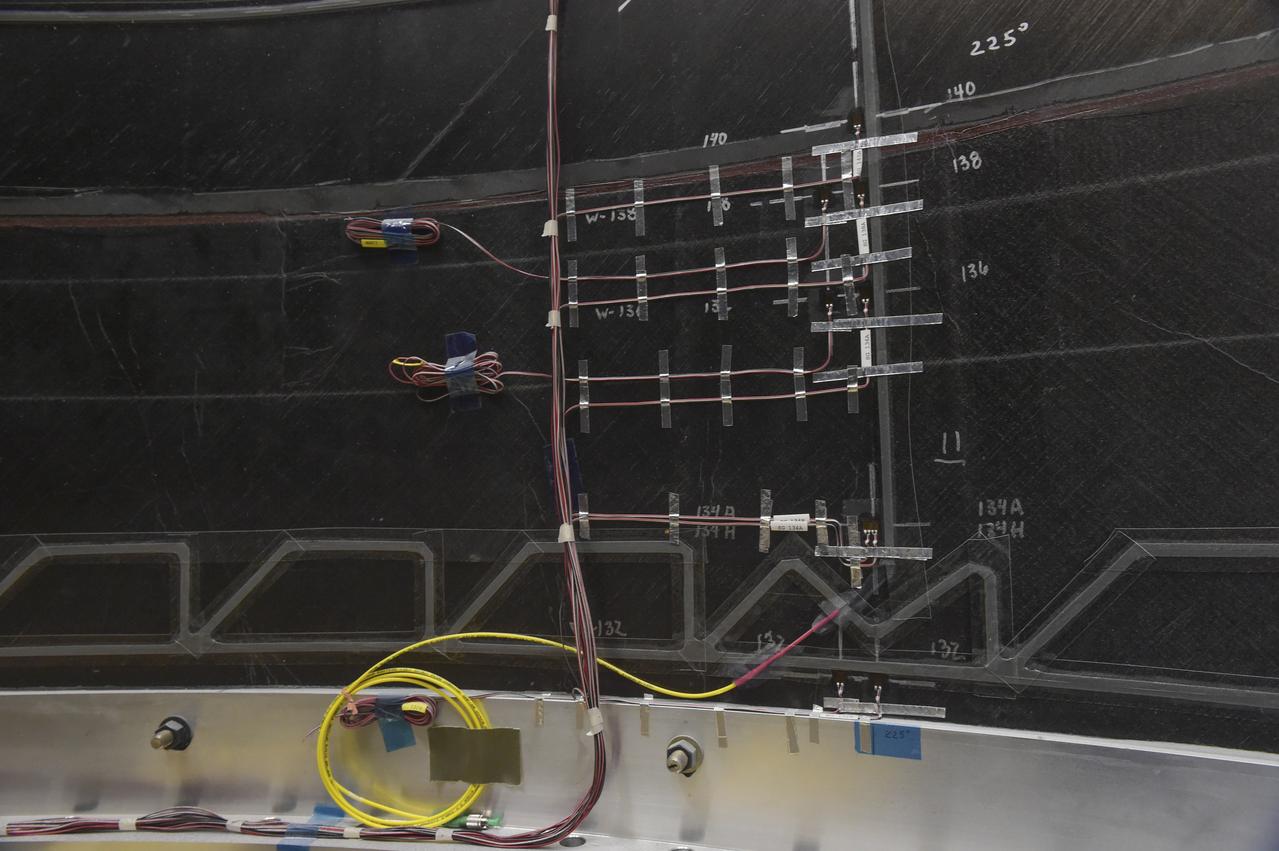
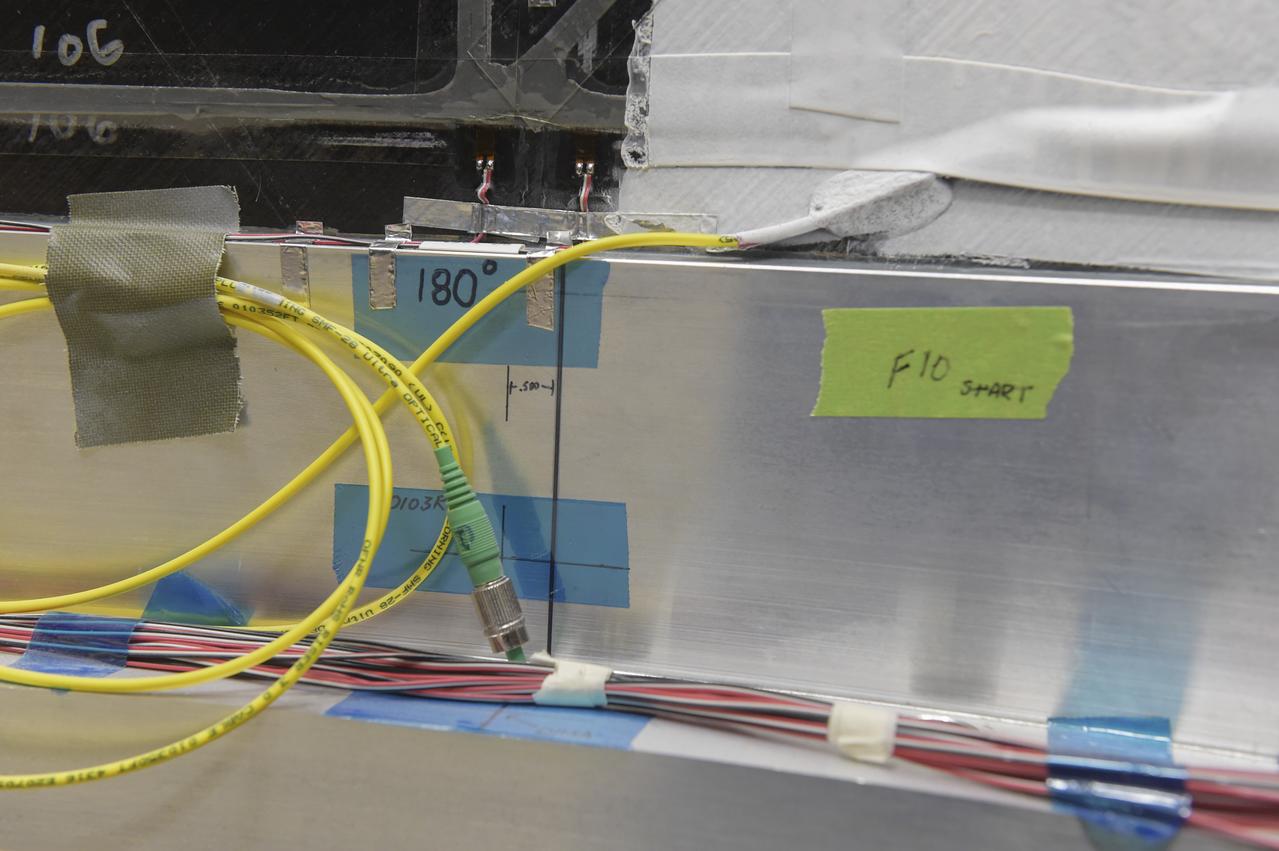
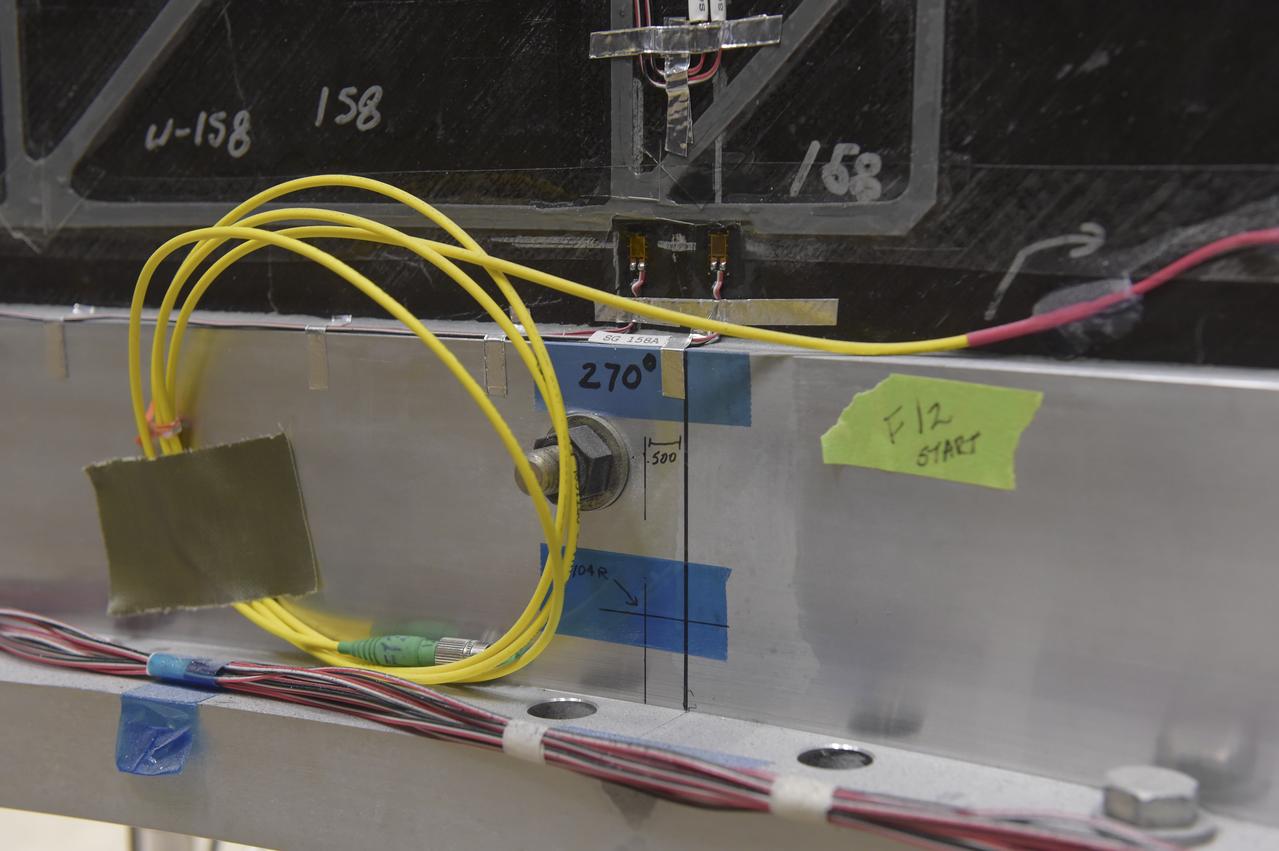
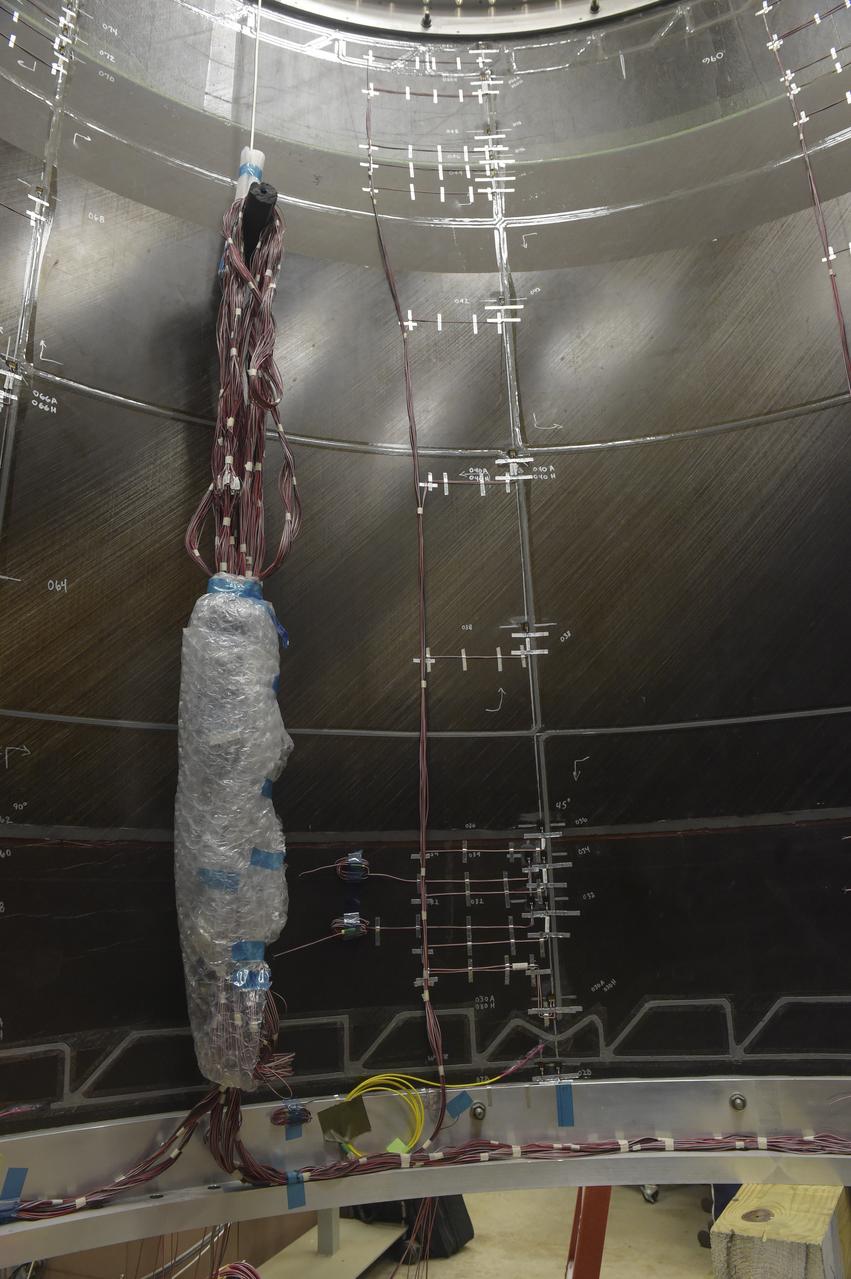
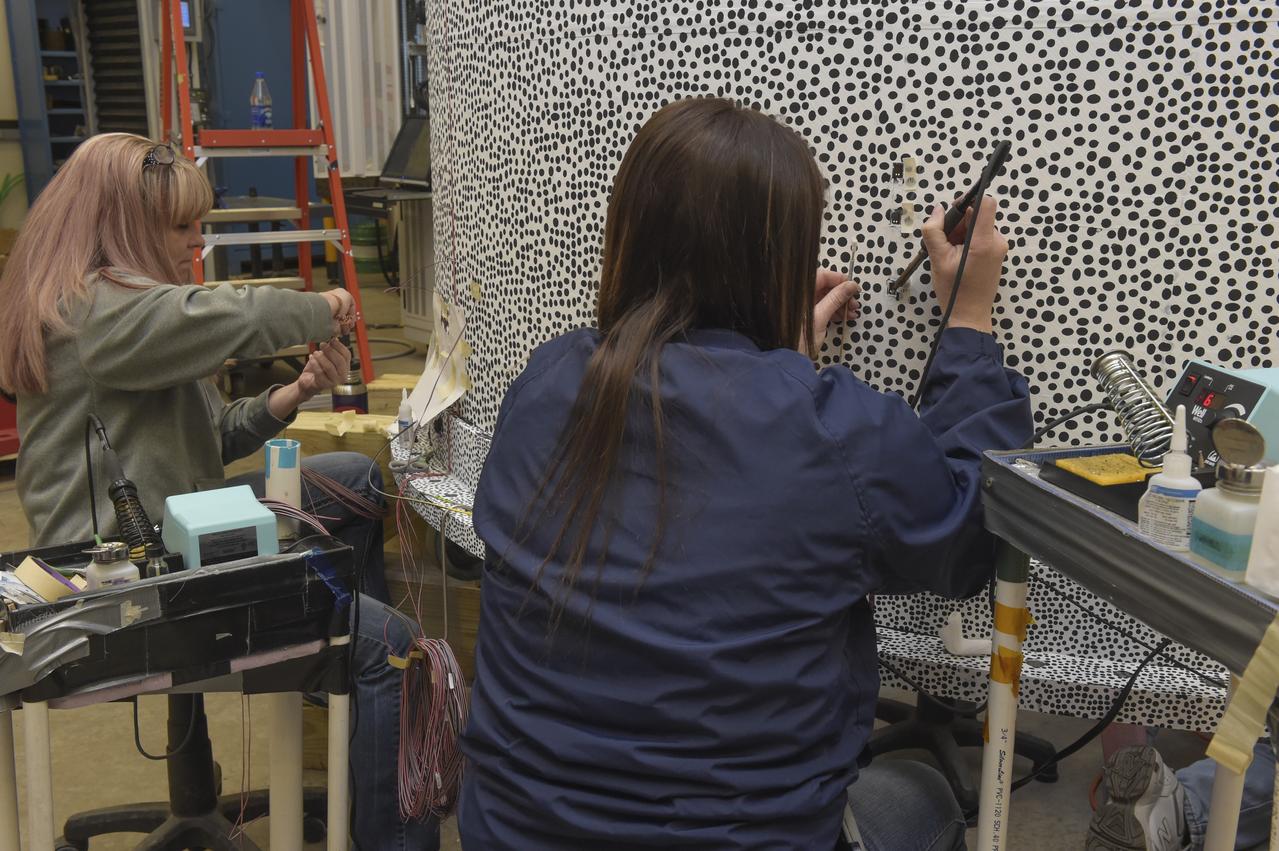
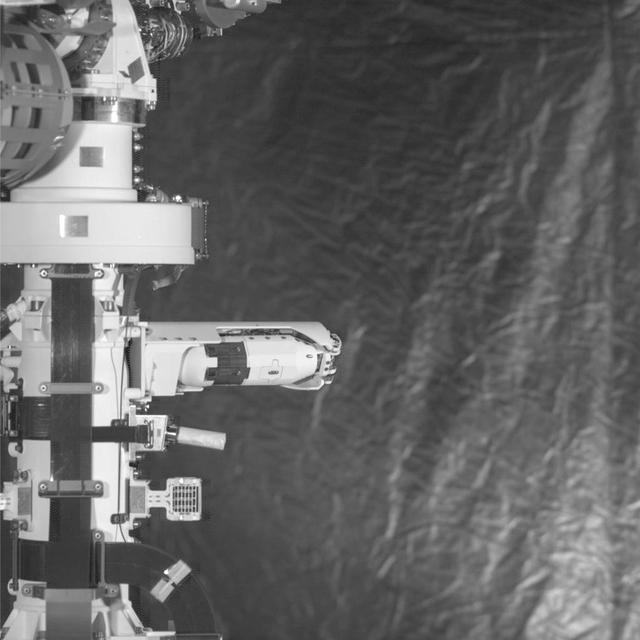
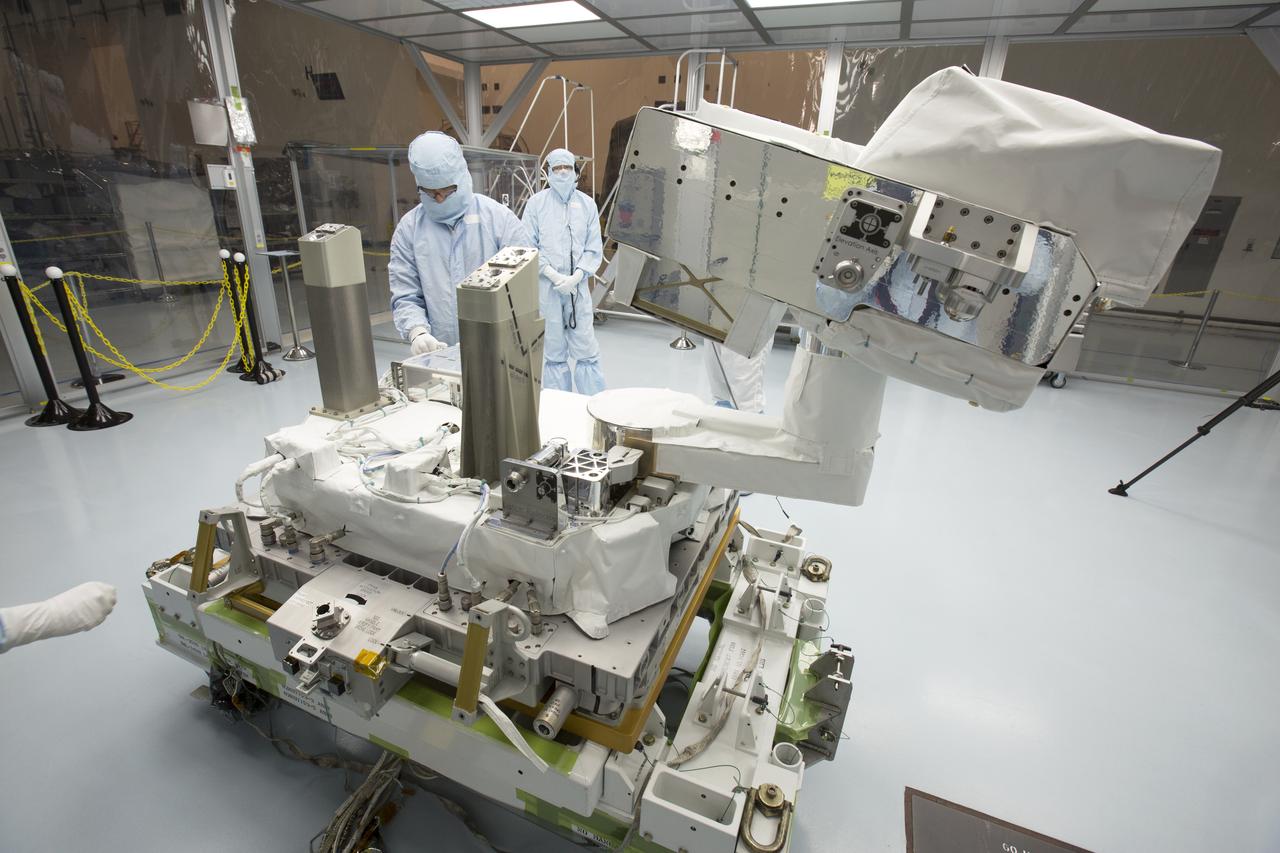
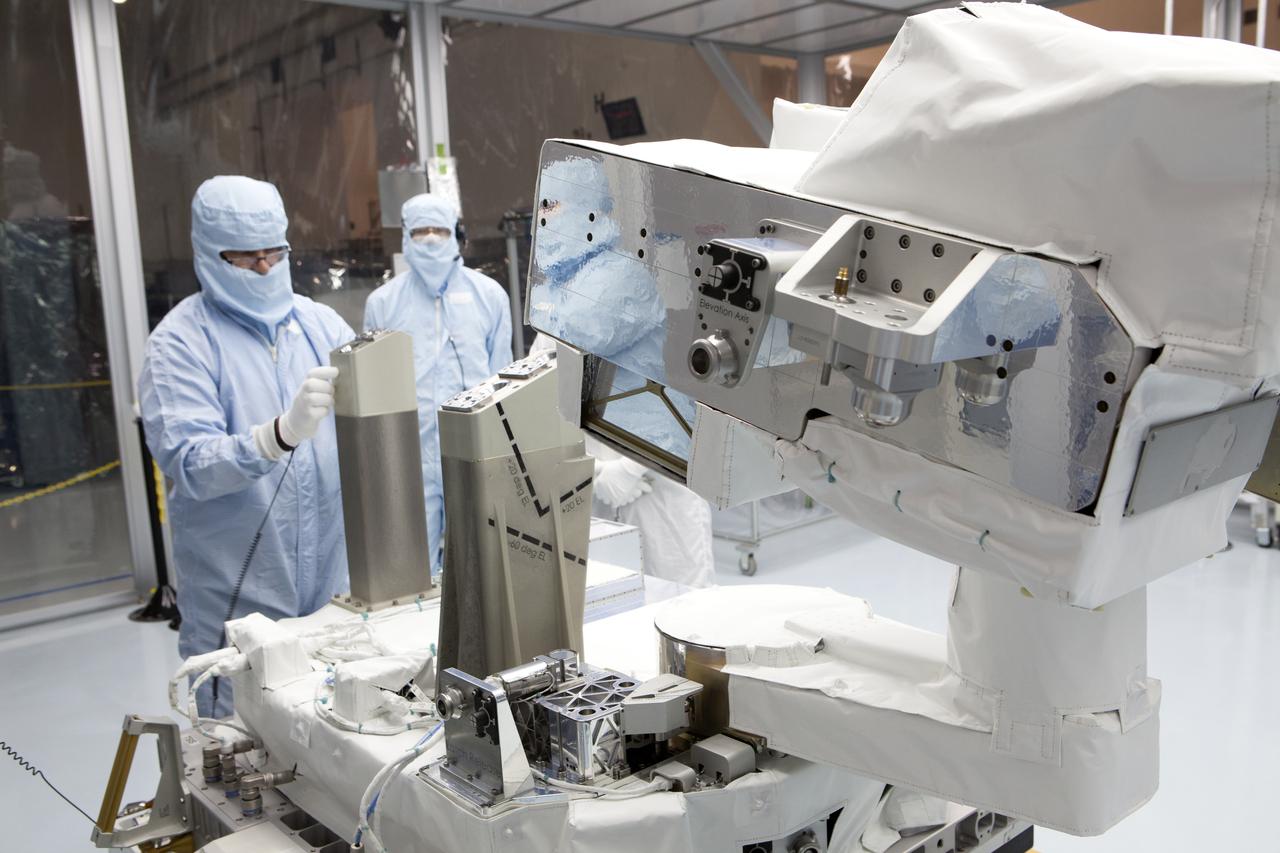
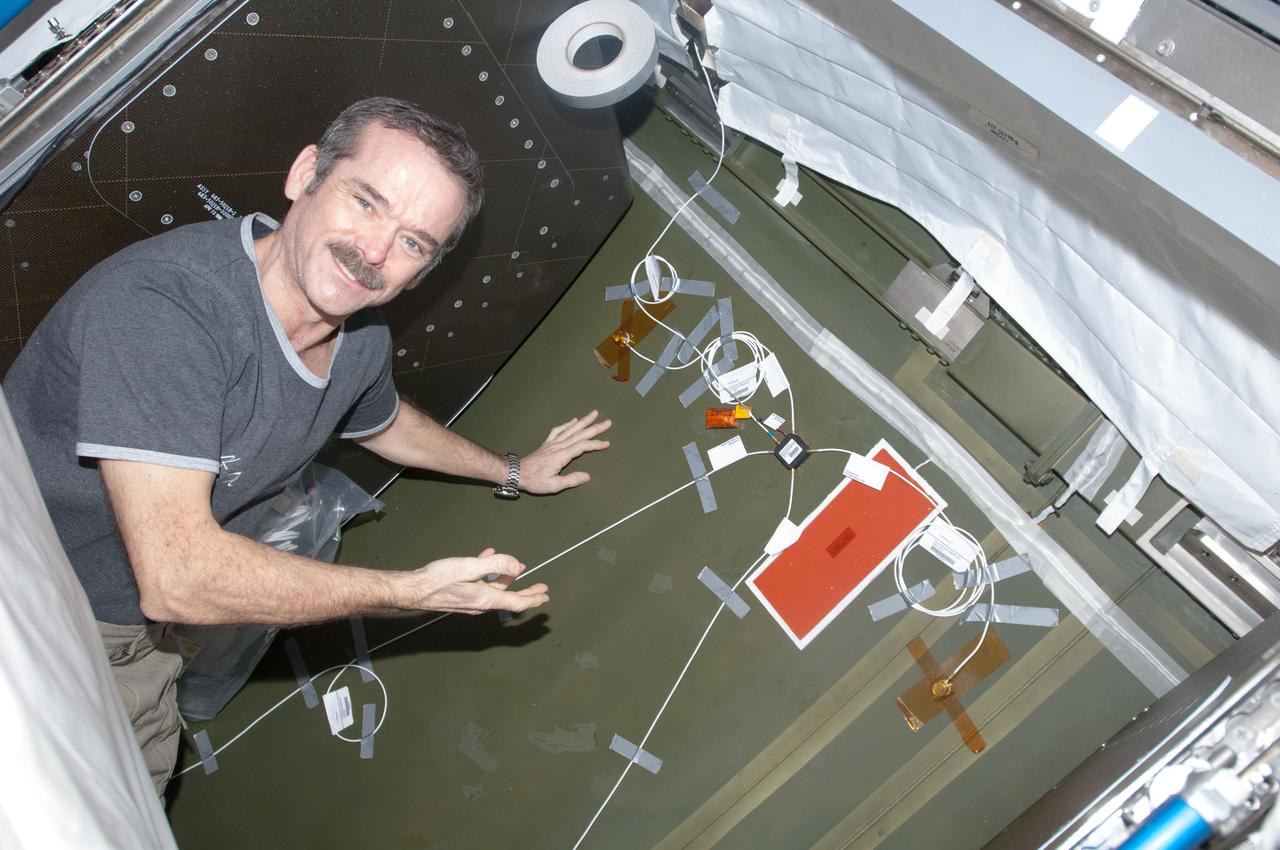
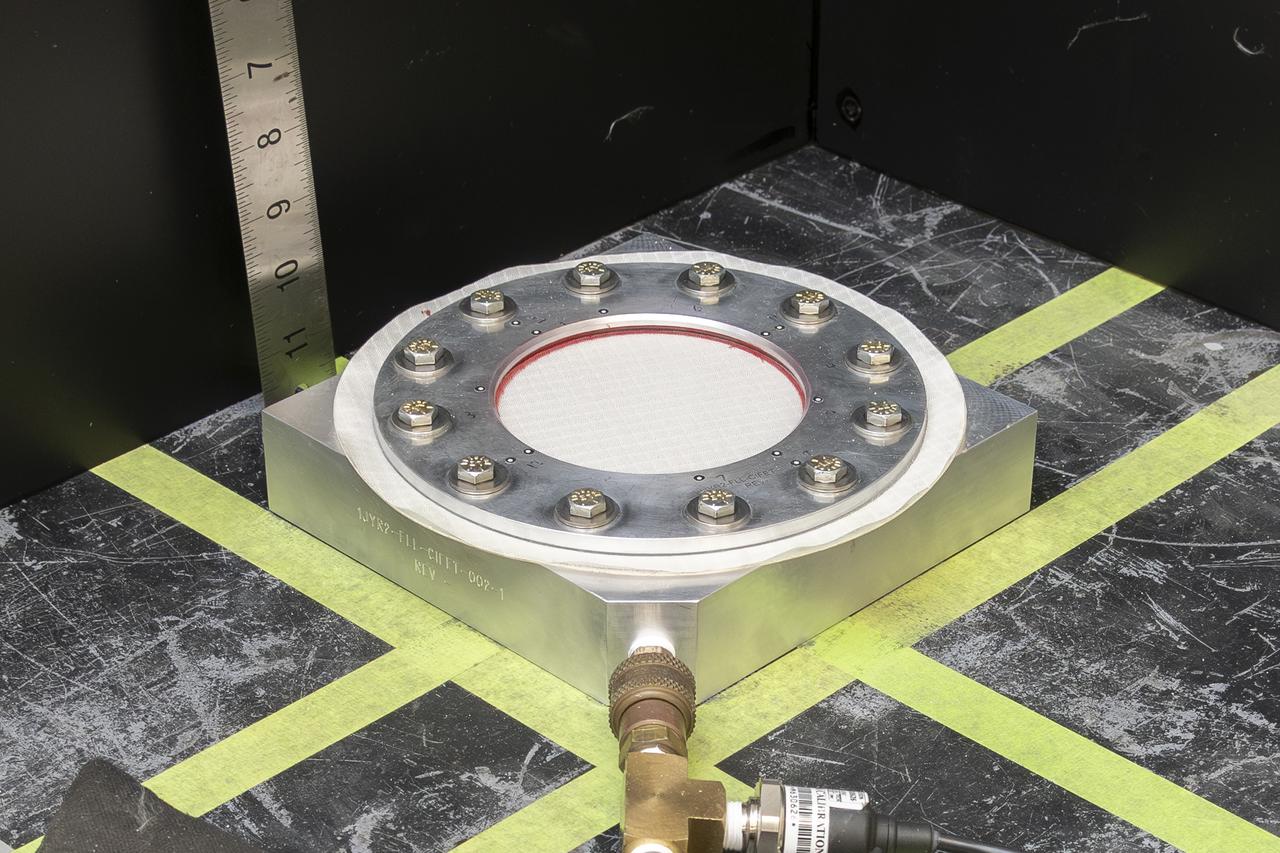
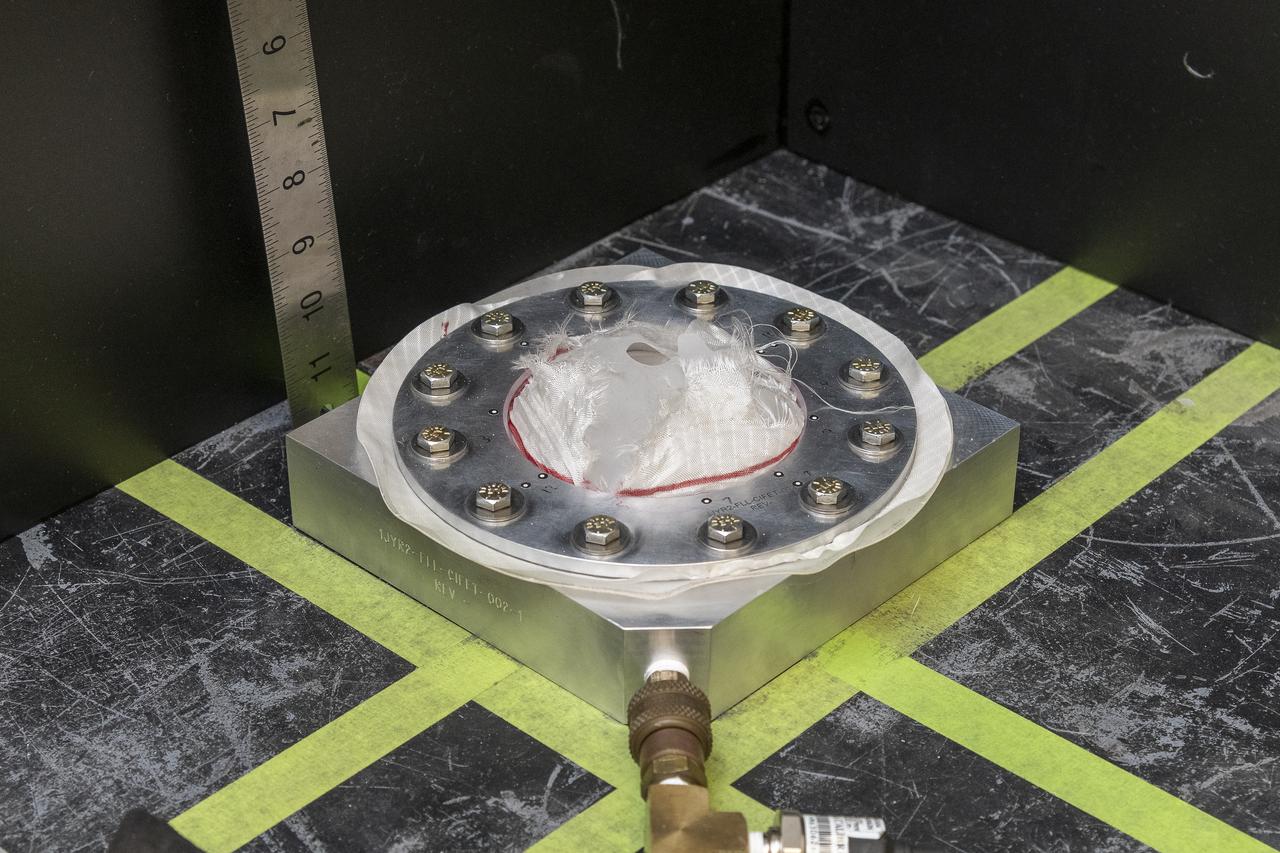
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Several Lead Zirconate Titanate, or PZT, mass gaging sensors have been attached to a composite tank during a test inside a laboratory at the Cryogenics Testbed Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PZT-based system was developed at Kennedy as a way to measure the mass of a fluid and the structural health of a tank using vibration signatures on Earth or in reduced/zero g gravity. The mass gaging technology has received approval to be on the first sub-orbital flight on the Virgin Galactic Space Plane in 2015. NASA experiments using the PZT technology will be used by Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in conjunction with Carthage College on a fluid transfer experiment. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Several Lead Zirconate Titanate, or PZT, mass gaging sensors have been attached to a composite tank during a test inside a laboratory at the Cryogenics Testbed Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The PZT-based system was developed at Kennedy as a way to measure the mass of a fluid and the structural health of a tank using vibration signatures on Earth or in reduced/zero g gravity. The mass gaging technology has received approval to be on the first sub-orbital flight on the Virgin Galactic Space Plane in 2015. NASA experiments using the PZT technology will be used by Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in conjunction with Carthage College on a fluid transfer experiment. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

jsc2021e033556 (8/4/2021) --- Thermo-Mini device with integrated sensor system and data storage - Placed on the head, Thermo-Mini monitors continuously the core body temperature of the astronaut (36 hrs measurement) before, during and after the ISS-mission.
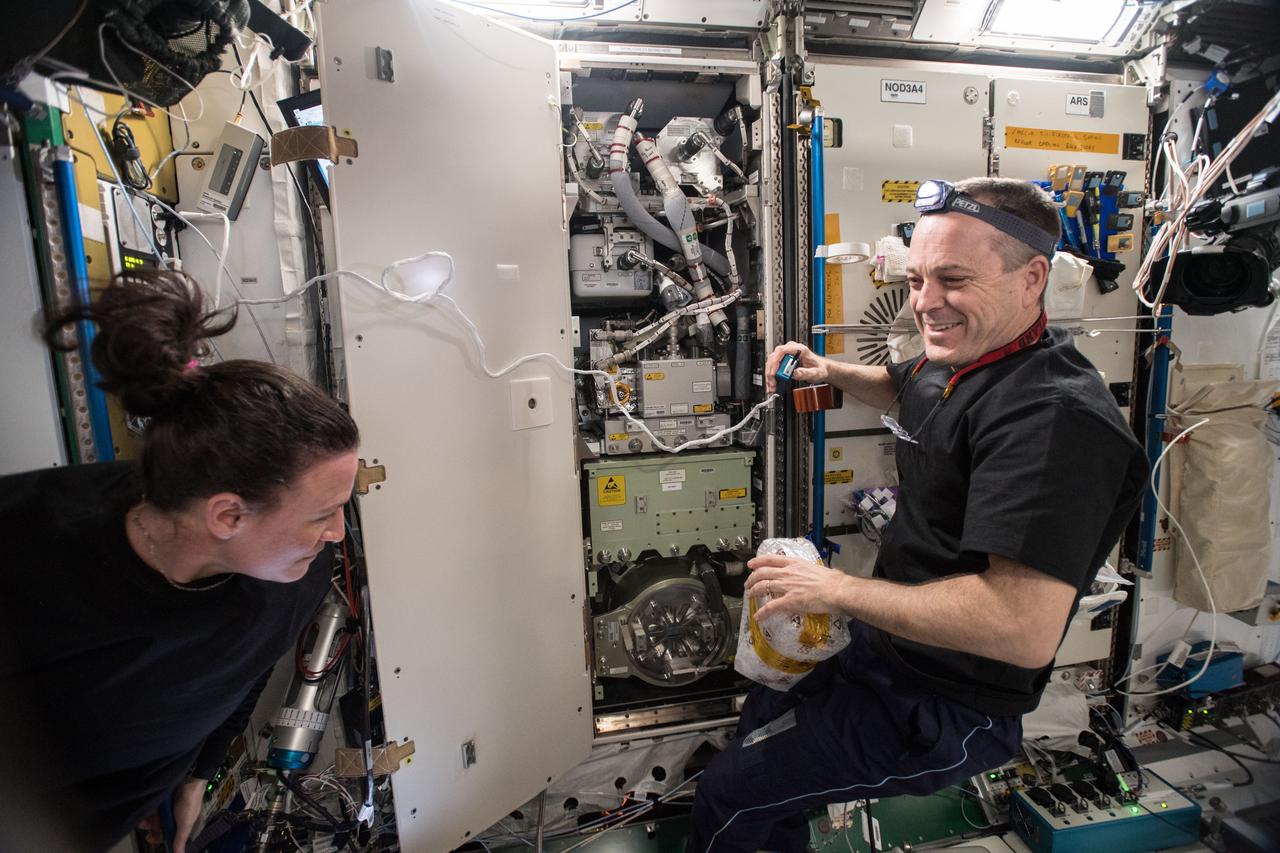

iss056e014488 (June 18, 2018) --- Expedition 56 Flight Engineers Serena Auñón-Chancellor (right) and Ricky Arnold of NASA are pictured in the Unity module during life support maintenance work to remove and replace an Oxygen Generation System Hydrogen Sensor.

This overhead view of the X-59 shows the aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. During the assembly of this experimental aircraft, the team often has to remove components to effectively and safely assemble other sections of the aircraft. In this image, the nose is not attached and the horizontal stabilators are shown behind the tail. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to produce data that will help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.

This overhead view of the X-59 shows the aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. During the assembly of this experimental aircraft, the team often has to remove components to effectively and safely assemble other sections of the aircraft. In this image, the nose is not attached and the horizontal stabilators are shown behind the tail. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to produce data that will help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
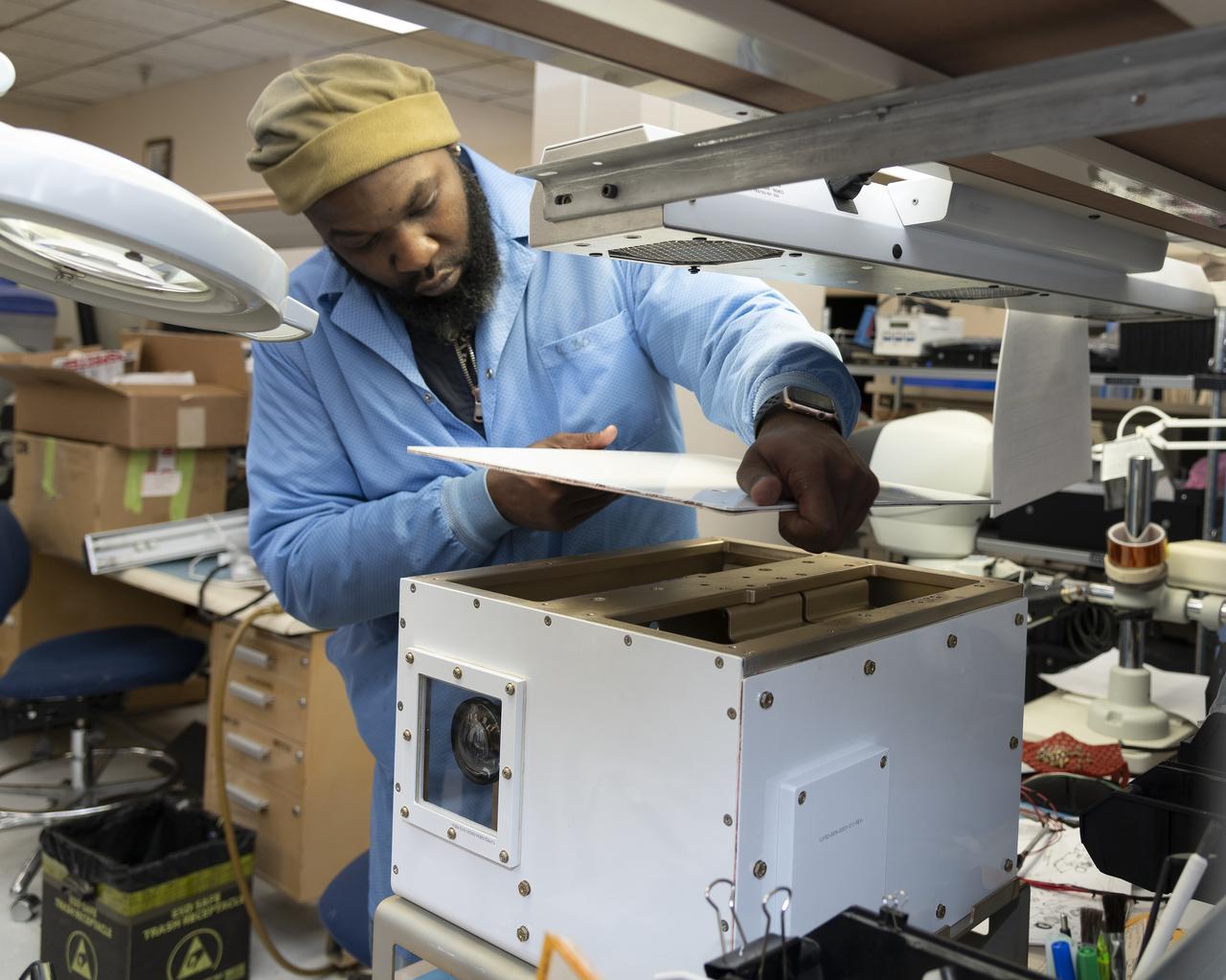

NASA researcher James Cowart adds the top back onto the NASA Airborne Instrumentation for Real-world Video of Urban Environments (AIRVUE) sensor pod at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in late February 2024. The pod houses sensors, wiring and cameras. The AIRVUE pod was flown on a helicopter at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida and is used to collect data for future autonomous aircraft.
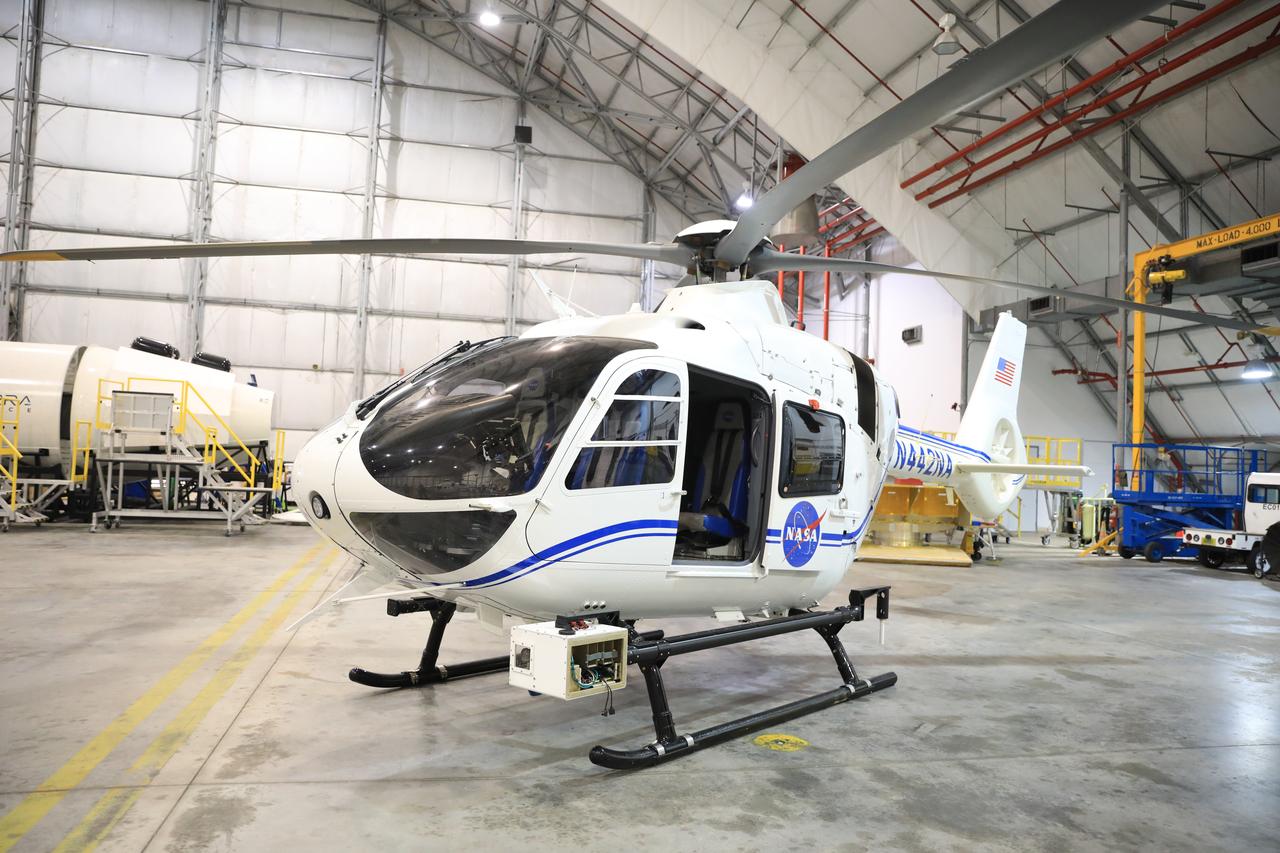

The NASA Airborne Instrumentation for Real-world Video of Urban Environments (AIRVUE) sensor pod is attached to the base of a NASA helicopter at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida in April 2024 before a flight to test the pod’s cameras and sensors. The AIRVUE pod will be used to collect data for autonomous aircraft like air taxis, drones, or other Advanced Air Mobility aircraft.

Ikhana fiber optic wing shape sensor team: clockwise from left, Anthony "Nino" Piazza, Allen Parker, William Ko and Lance Richards. The sensors, located along a fiber the thickness of a human hair, aren't visible in the center of the Ikhana aircraft's left wing. NASA Dryden Flight Research Center is evaluating an advanced fiber optic-based sensing technology installed on the wings of NASA's Ikhana aircraft. The fiber optic system measures and displays the shape of the aircraft's wings in flight. There are other potential safety applications for the technology, such as vehicle structural health monitoring. If an aircraft structure can be monitored with sensors and a computer can manipulate flight control surfaces to compensate for stresses on the wings, structural control can be established to prevent situations that might otherwise result in a loss of control.
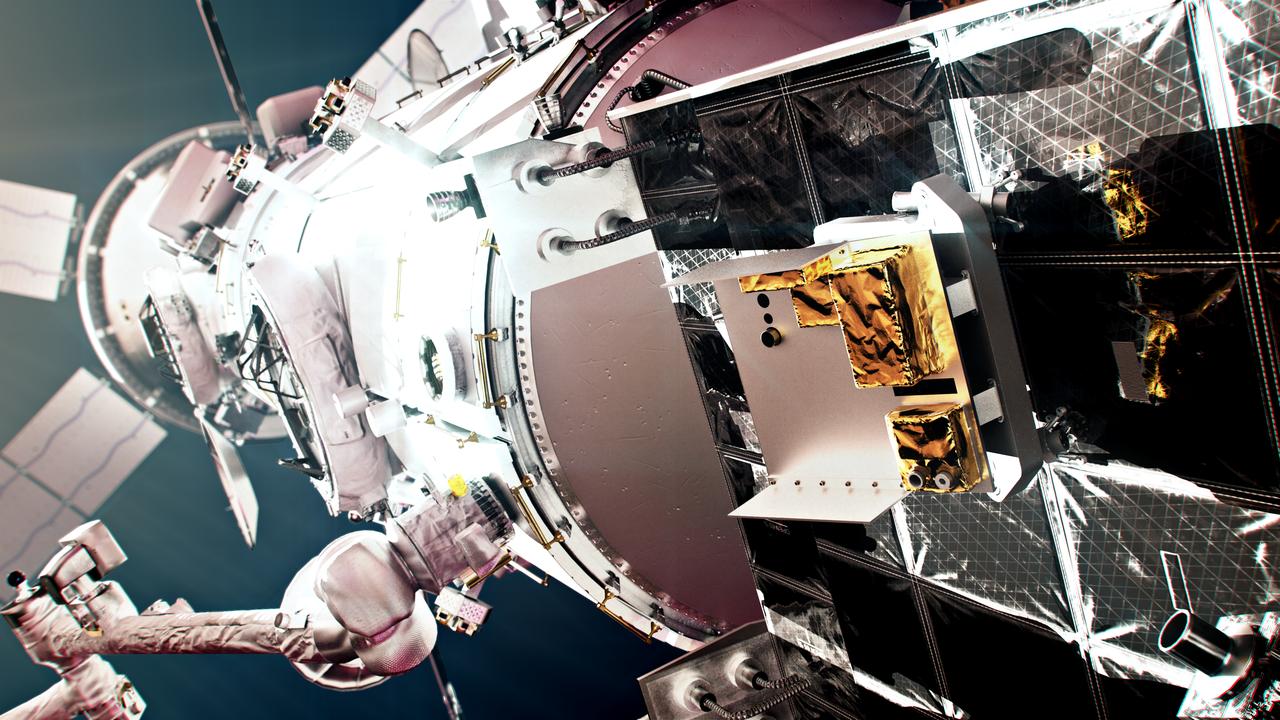

The European Radiation Sensors Array is one of the first three science payloads selected to fly on the Gateway space station. ERSA will study solar and cosmic radiation to help the science community better understand this primary concern for people and hardware during deep space travels.
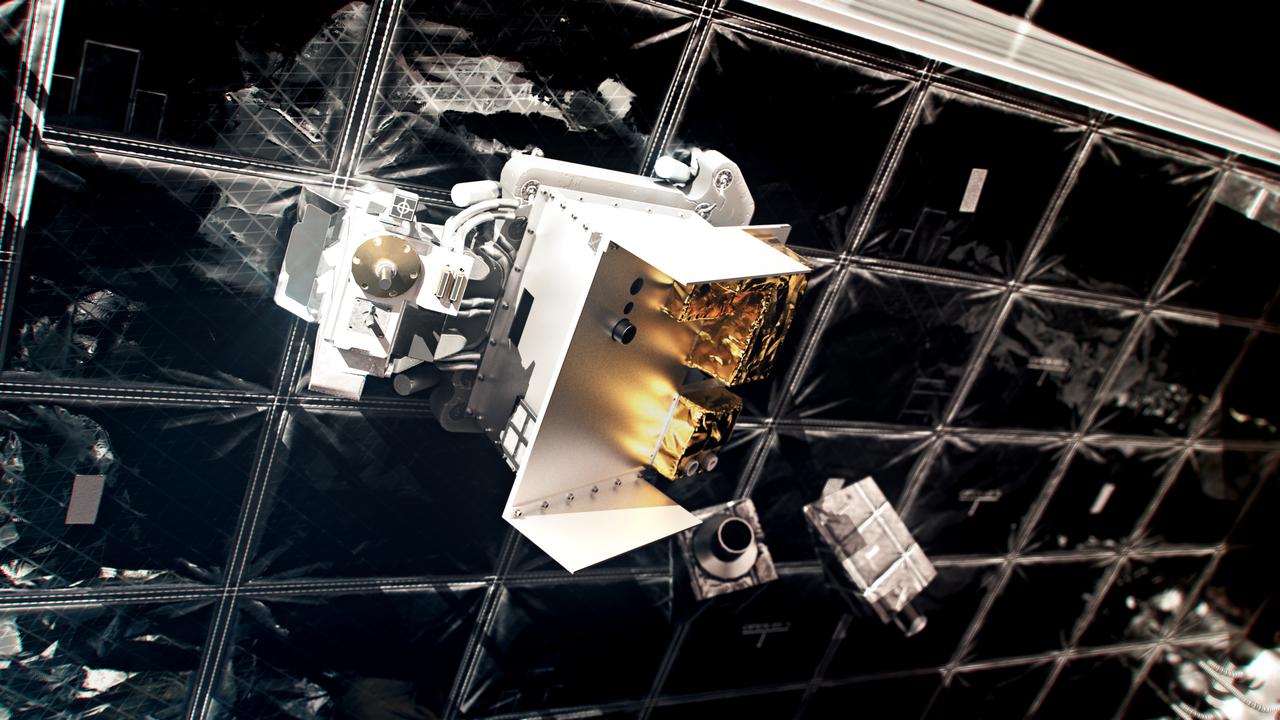

The European Radiation Sensors Array is one of the first three science payloads selected to fly on the Gateway space station. ERSA will study solar and cosmic radiation to help the science community better understand this primary concern for people and hardware during deep space travels.

NASA's AVIRIS-3 sensor, an airborne imaging spectrometer built and operated by the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, captured infrared data of a wildfire 4 miles (2.5 kilometers) southwest of the unincorporated community of Perdido, Alabama, on March 21, 2025. Within minutes of flying over, real-time maps of the fire were sent via satellite internet to firefighters with the Alabama Forestry Commission, who used it to contain the fire, preventing it from reaching six buildings. The first image in the series combines reflection data from AVIRIS-3 (Airborne Visible Infrared Imaging Spectrometer 3) at three infrared wavelengths that are invisible to the human eye – 2,350 nanometers, 1,200 nanometers, and 1,000 nanometers. In the resulting composite image, the colors indicate where the fire was burning most intensely. Orange and red areas show cooler-burning areas, while yellow indicates the most intense flames. Burned areas show up as dark red or brown. The second image in the series looks solely at the 2,400 nanometers wavelength. The images are particularly useful for seeing hot spots and the perimeters of fires, which show brightly against a red background. The third image in the series combines light at 1,610 nanometers, 850 nanometers, and 550 nanometers. This view shows burn areas and smoke. The AVIRIS-3 sensor belongs to a line of imaging spectrometers built at JPL since 1986. The instruments have been used to study a wide range of phenomena – including fire – by measuring sunlight reflecting from the planet's surface. Data from imaging spectrometers like AVIRIS-3 typically takes days or weeks to be processed into highly detailed, multilayer image products used for research. By simplifying the calibration algorithms, researchers were able to process data on a computer aboard the plane in a sliver of the time it otherwise would have taken, and airborne satellite internet connectivity enabled the images to be distributed almost immediately, while the plane was still in flight, rather than after it landed. Flying about 9,000 feet (3,000 meters) in altitude aboard a NASA King Air B200 research plane, AVIRIS-3 collected data on the Castleberry Fire while preparing for prescribed burn experiments that took place in the Geneva State Forest in Alabama on March 28 and at Fort Stewart-Hunter Army Airfield in Georgia from April 14 to 20. The burns were part of a NASA 2025 FireSense Airborne Campaign. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26498
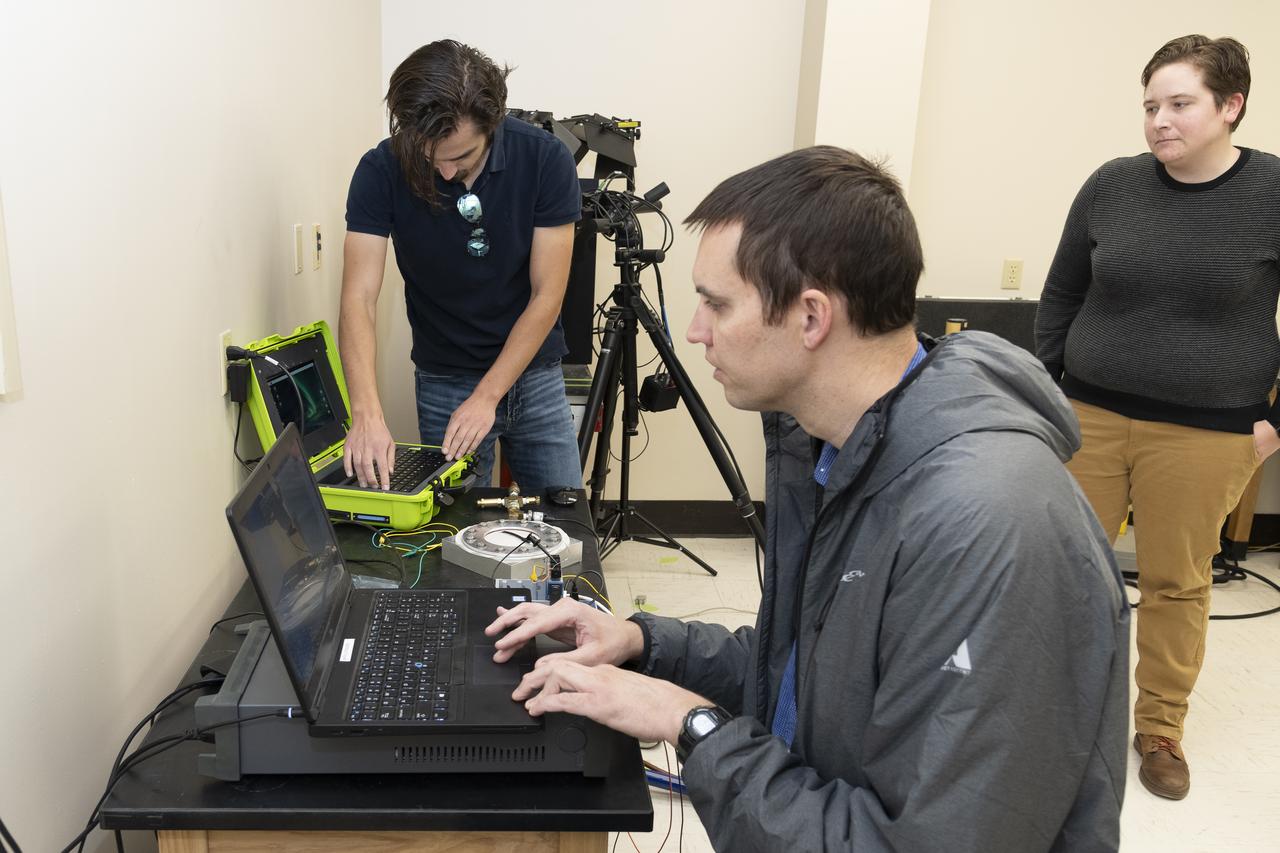

Coby Asselin, from left, Adam Curry, and L. J. Hantsche set up the data acquisition systems used during testing of a senor to determine parachute canopy material strength at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The sensor tests seek to quantify the limits of the material to improve computer models and make more reliable supersonic parachutes.
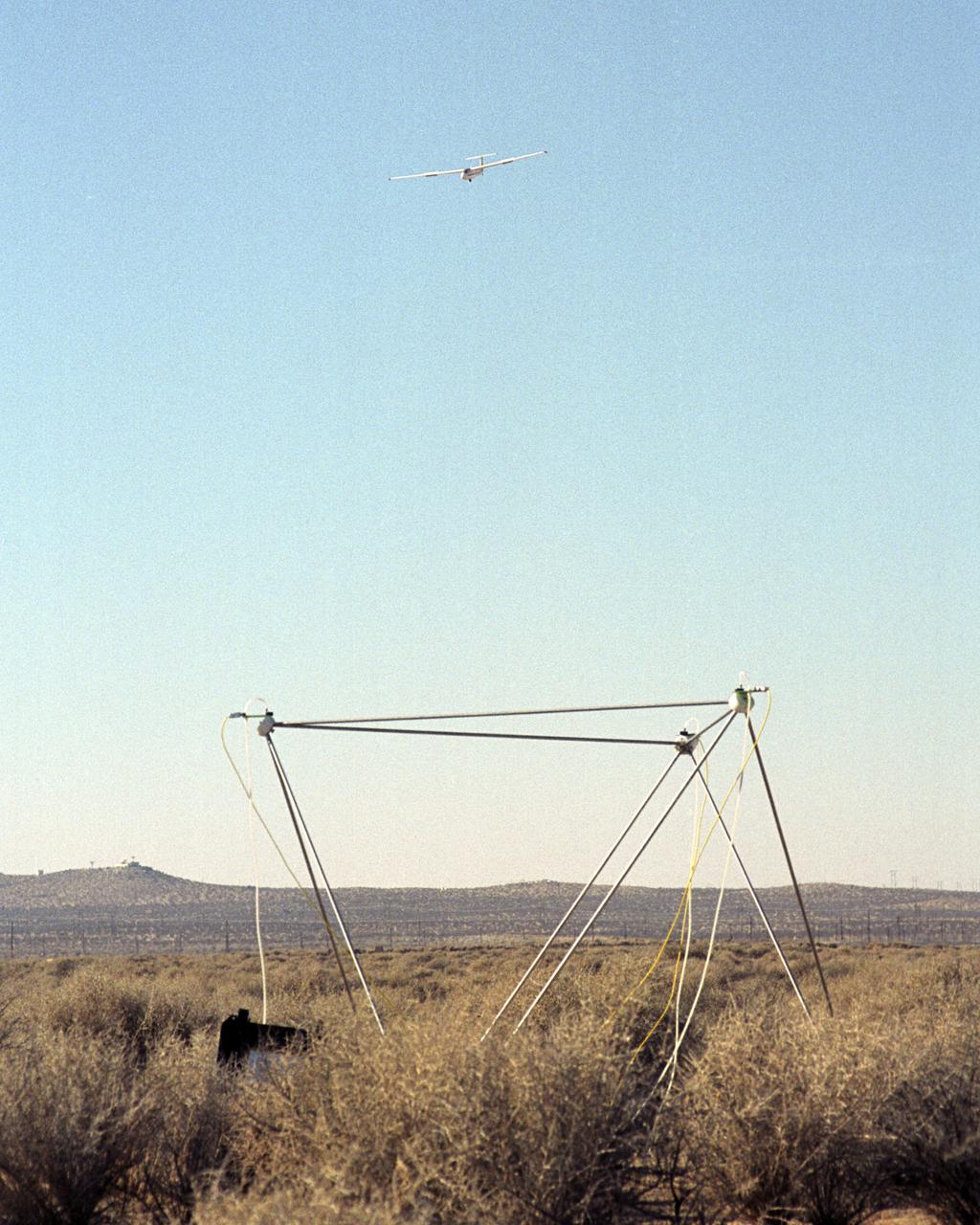

A United States Air Force Test Pilot School Blanik L-23 glider carrying a microphone and a pressure transducer flies near a BADS (Boom Amplitudes Direction System) sensor following flight at an altitude of 10 thousand feet under the path of the F-5E SSBE aircraft. The SSBE (Shaped Sonic Boom Experiment) was formerly known as the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration, or SSBD, and is part of DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. On August 27, 2003, the F-5E SSBD aircraft demonstrated a method to reduce the intensity of sonic booms.
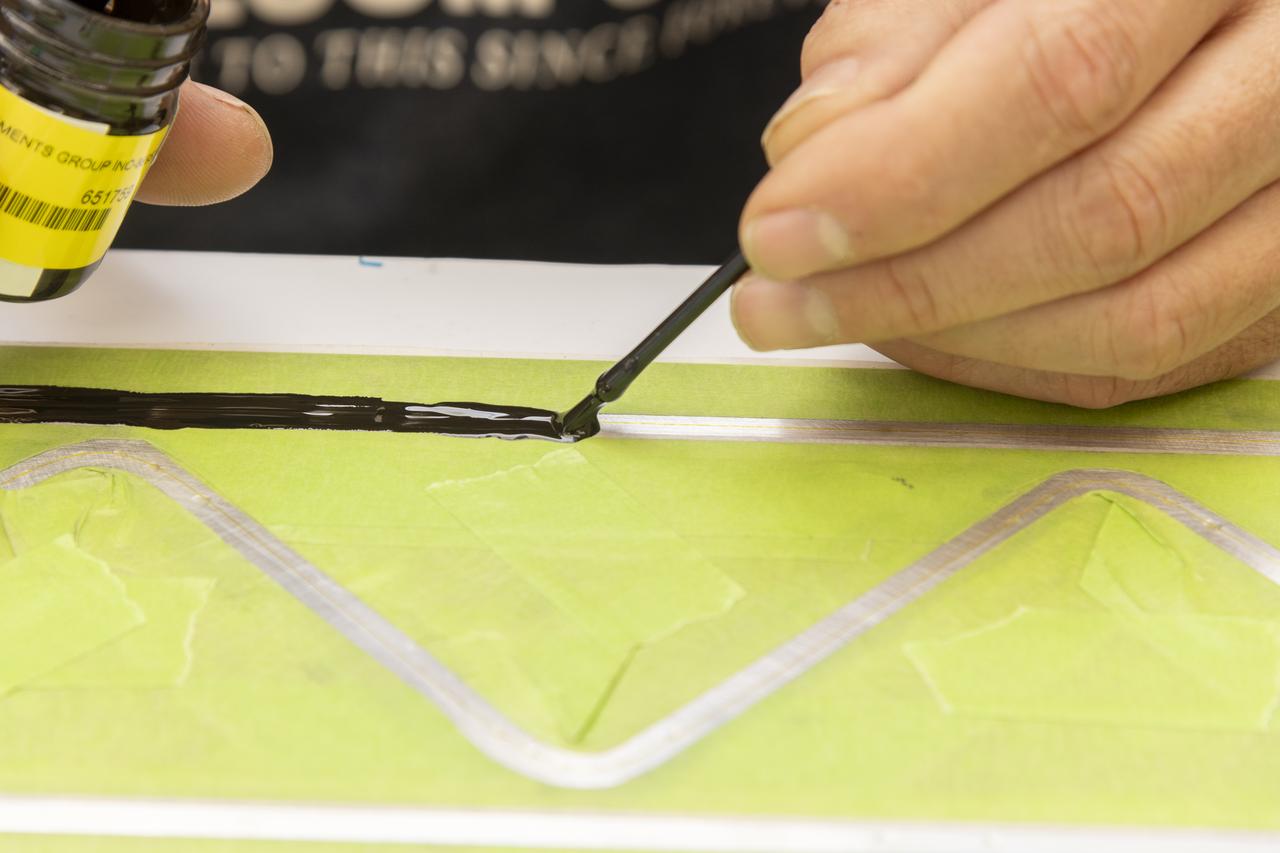
An epoxy is applied to adhere the fiber optic sensor installation on the Mock Truss-Braced Wing 10-foot model at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.

NASA engineer Larry Hudson and Ikhana ground crew member James Smith work on a ground validation test with new fiber optic sensors that led to validation flights on the Ikhana aircraft. NASA Dryden Flight Research Center is evaluating an advanced fiber optic-based sensing technology installed on the wings of NASA's Ikhana aircraft. The fiber optic system measures and displays the shape of the aircraft's wings in flight. There are other potential safety applications for the technology, such as vehicle structural health monitoring. If an aircraft structure can be monitored with sensors and a computer can manipulate flight control surfaces to compensate for stresses on the wings, structural control can be established to prevent situations that might otherwise result in a loss of control.

The NEOCam sensor right is the lynchpin for the proposed Near Earth Object Camera, or NEOCam, space mission left.
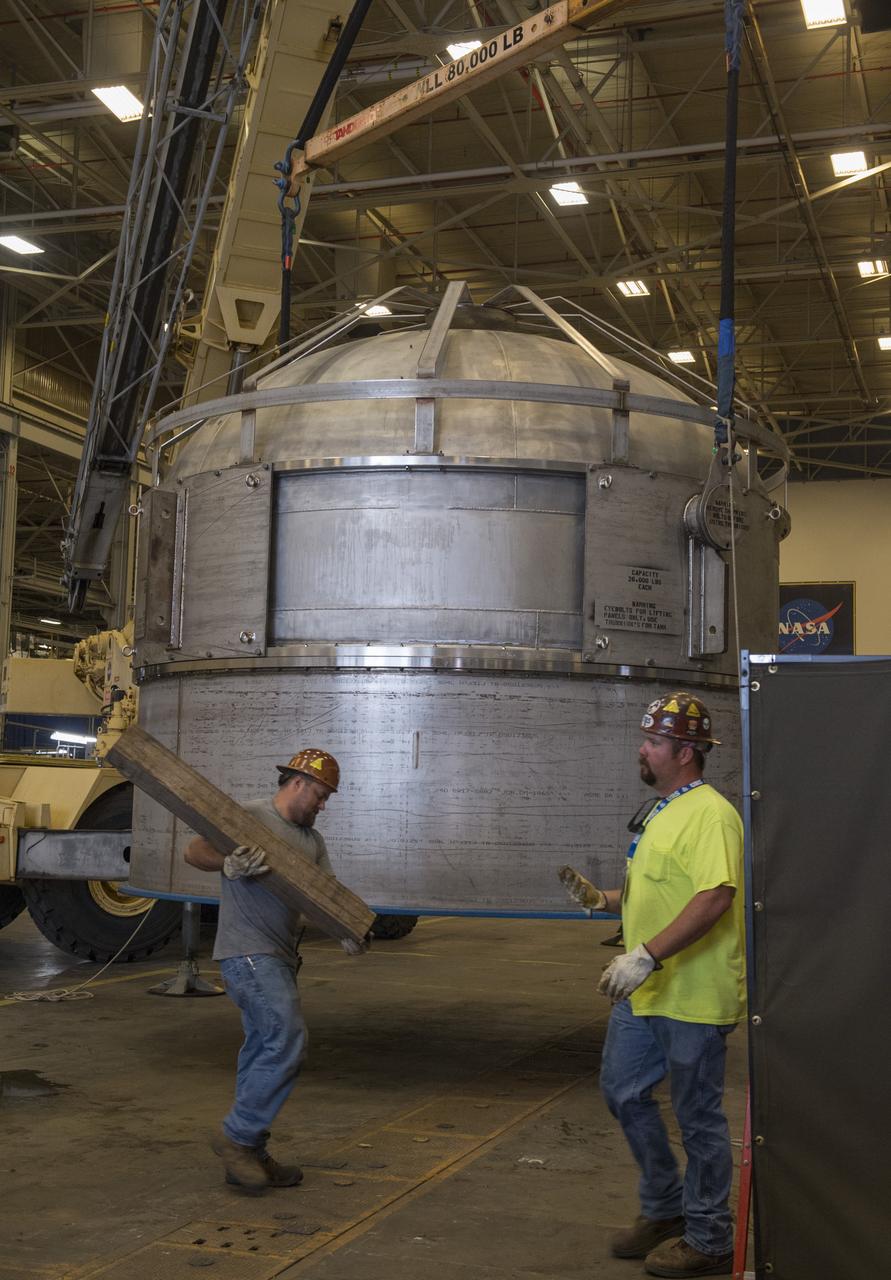

SHIIVER (Structural Heat Intercept Insulation Vibration Evaluation Rig) is a cryogenic test tank developed to evaluate heat intercept concepts. It arrived at Marshall Space Flight Center on August 10, 2017. The tank will receive heat sensors and spray-on foam insulation before making its way to Plum Brook station for further insulation and testing.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Lockheed Martin technicians in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center begin to apply new foam over the manhole cover on the lower end of external tank No. 119. The manhole was removed to access the area where the tank's four liquid hydrogen engine cutoff sensors were replaced. Once reinstalled, the manhole required new foam to be applied. The tank is being prepared to launch Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-121 in July. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
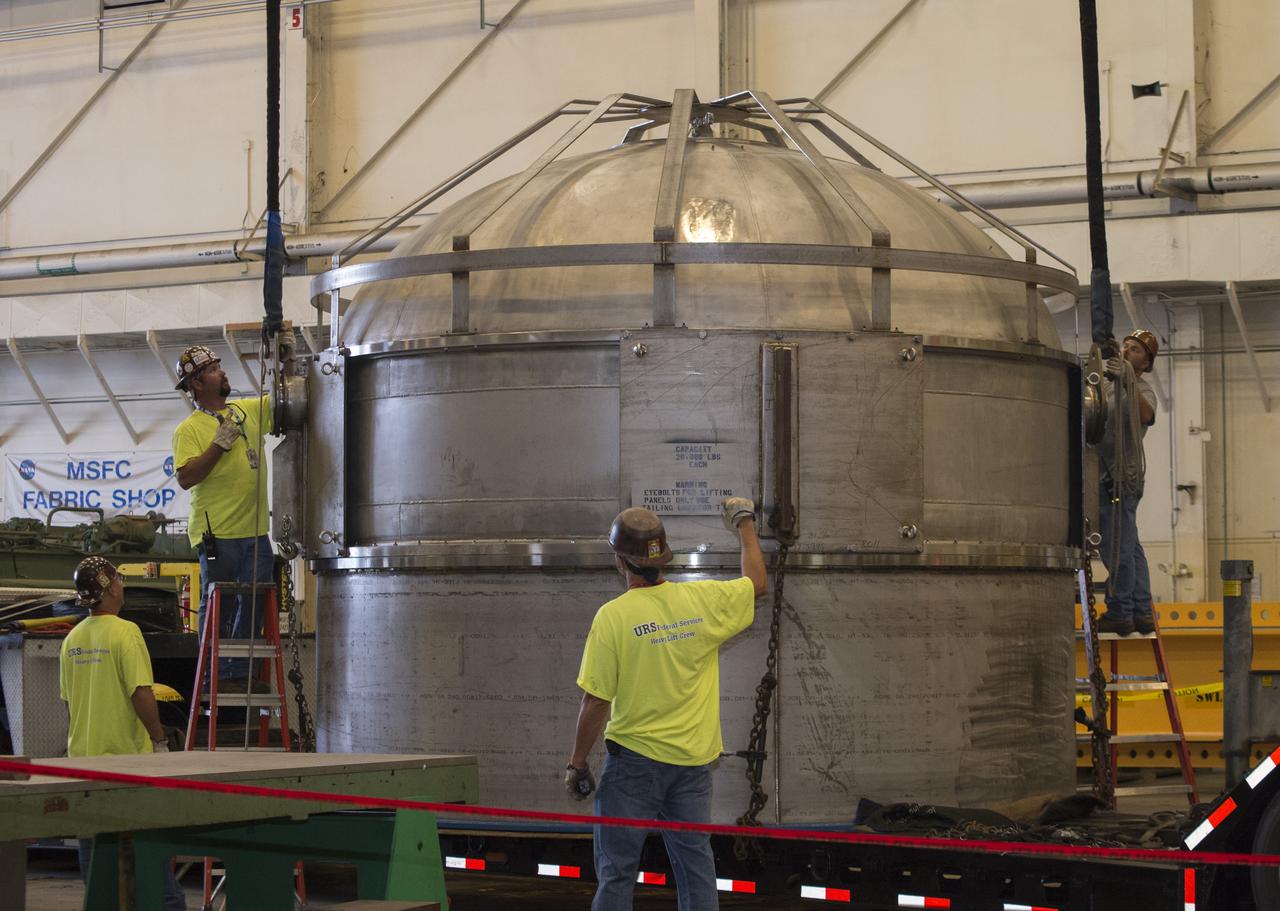

SHIIVER (Structural Heat Intercept Insulation Vibration Evaluation Rig) is a cryogenic test tank developed to evaluate heat intercept concepts. It arrived at Marshall Space Flight Center on August 10, 2017. The tank will receive heat sensors and spray-on foam insulation before making its way to Plum Brook station for further insulation and testing.
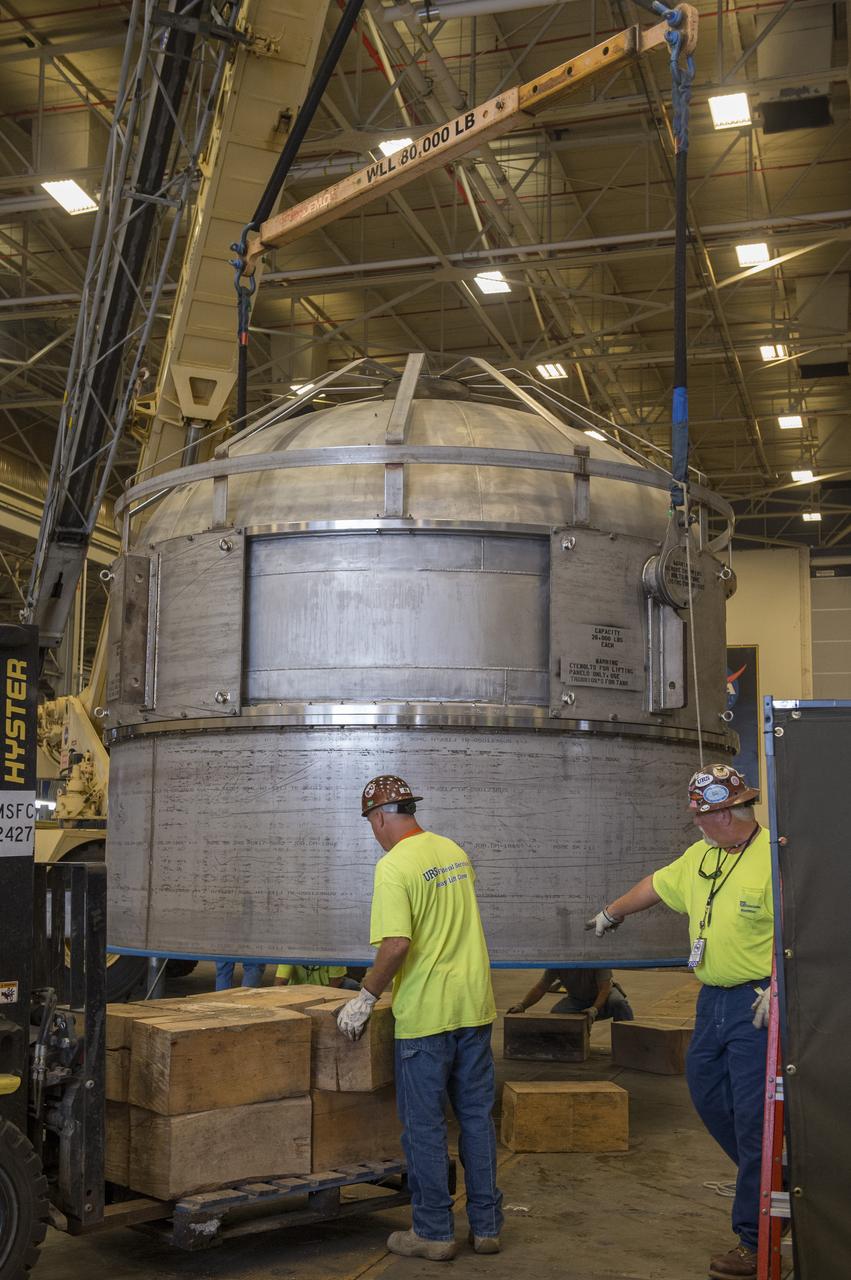

SHIIVER (Structural Heat Intercept Insulation Vibration Evaluation Rig) is a cryogenic test tank developed to evaluate heat intercept concepts. It arrived at Marshall Space Flight Center on August 10, 2017. The tank will receive heat sensors and spray-on foam insulation before making its way to Plum Brook station for further insulation and testing.

SHIIVER (Structural Heat Intercept Insulation Vibration Evaluation Rig) is a cryogenic test tank developed to evaluate heat intercept concepts. It arrived at Marshall Space Flight Center on August 10, 2017. The tank will receive heat sensors and spray-on foam insulation before making its way to Plum Brook station for further insulation and testing.SHIIVER Tank Arrives at NASA’s Marshall Center for Spray-On Foam Insulation

SHIIVER (Structural Heat Intercept Insulation Vibration Evaluation Rig) is a cryogenic test tank developed to evaluate heat intercept concepts. It arrived at Marshall Space Flight Center on August 10, 2017. The tank will receive heat sensors and spray-on foam insulation before making its way to Plum Brook station for further insulation and testing.
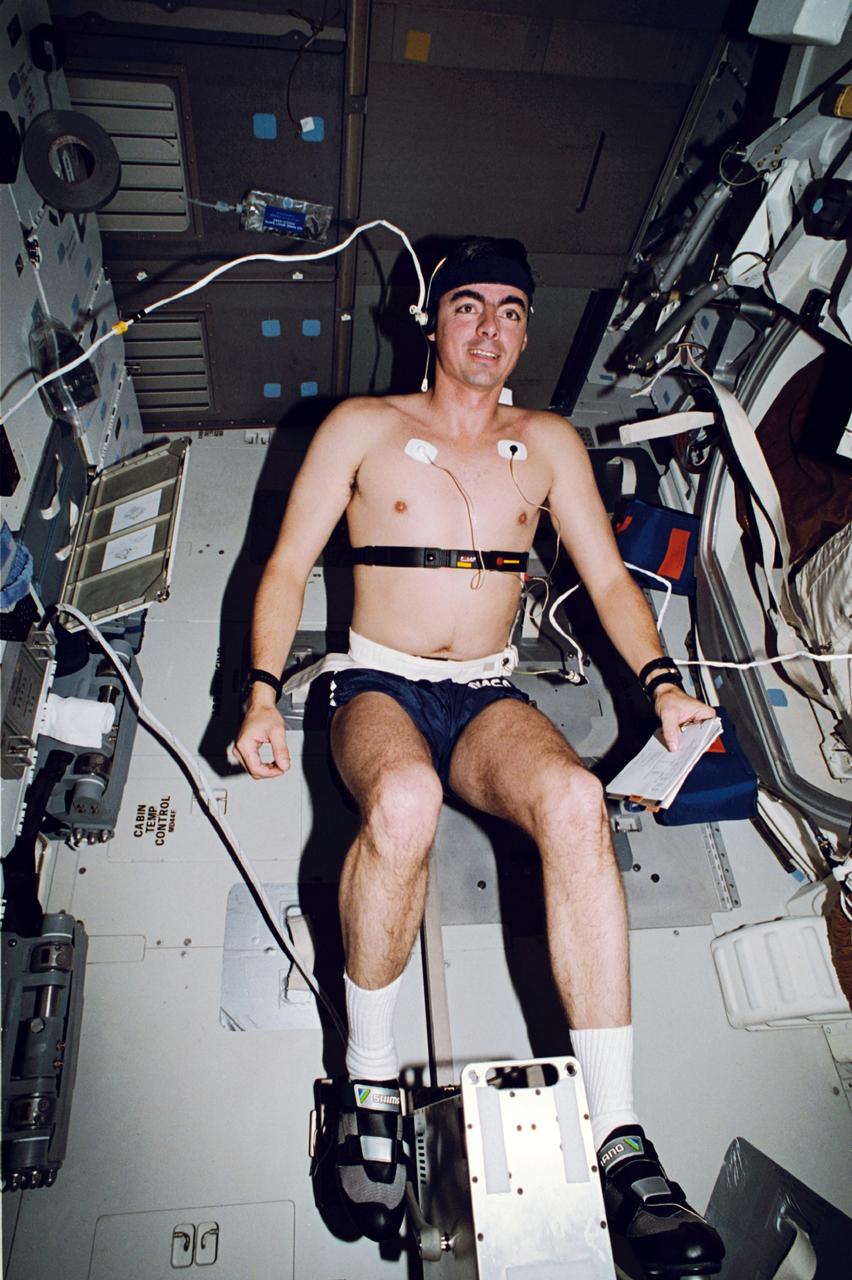
STS046-24-025 (31 July-8 Aug. 1992) --- Astronaut Andrew M. Allen, STS-46 pilot, exercises on the bicycle ergometer device on the flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis as it makes one of its 127 total orbits for the eight-day mission. Allen, equipped with sensors for monitoring his biological systems during the run, was joined by four other NASA astronauts and two European scientists on the mission.

SHIIVER (Structural Heat Intercept Insulation Vibration Evaluation Rig) is a cryogenic test tank developed to evaluate heat intercept concepts. It arrived at Marshall Space Flight Center on August 10, 2017. The tank will receive heat sensors and spray-on foam insulation before making its way to Plum Brook station for further insulation and testing.
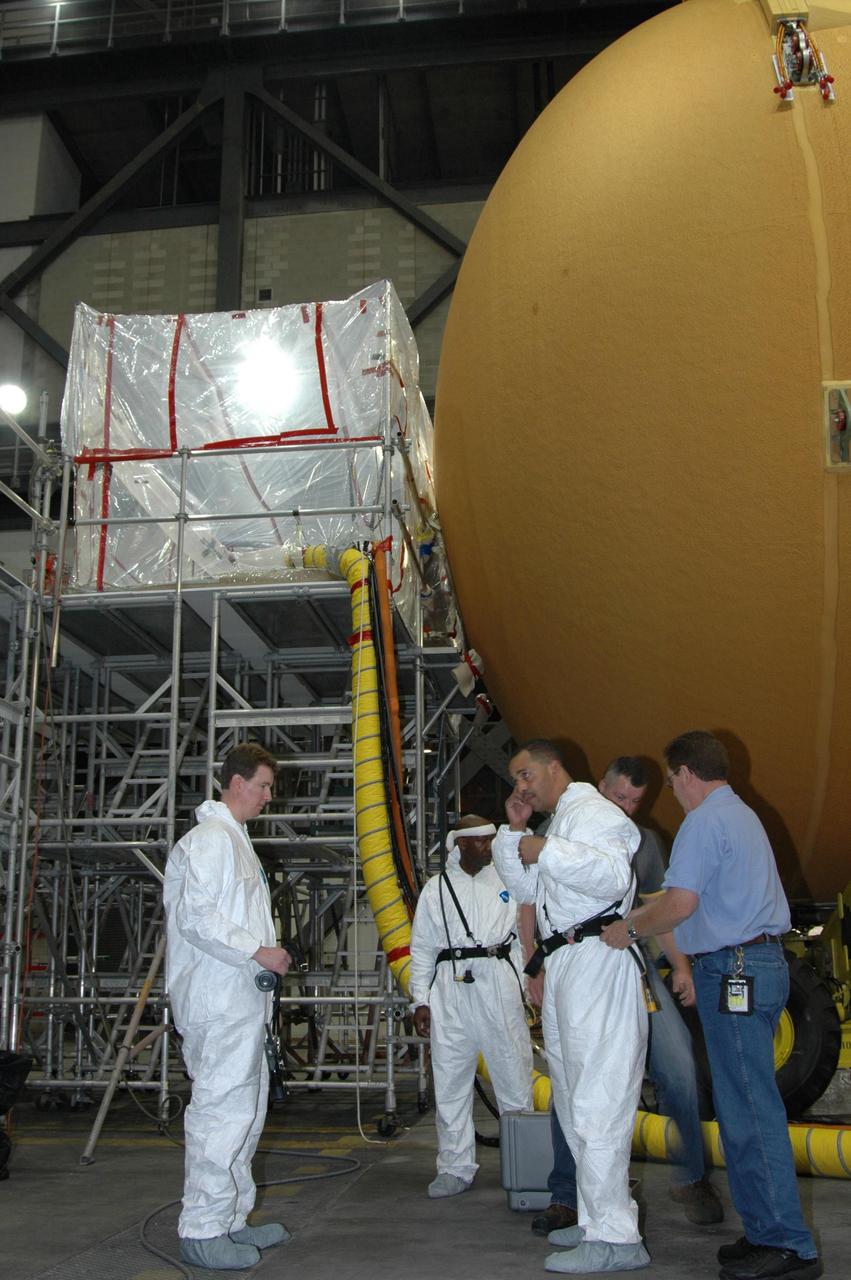

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Lockheed Martin technicians in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center prepare for the application of new foam over the manhole cover on the lower end of external tank No. 119. The manhole was removed to access the area where the tank's four liquid hydrogen engine cutoff sensors were replaced. Once reinstalled, the manhole required new foam to be applied. The tank is being prepared to launch Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-121 in July. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Lockheed Martin technicians in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center apply new foam over the manhole cover on the lower end of external tank No. 119. The manhole was removed to access the area where the tank's four liquid hydrogen engine cutoff sensors were replaced. Once reinstalled, the manhole required new foam to be applied. The tank is being prepared to launch Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-121 in July. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
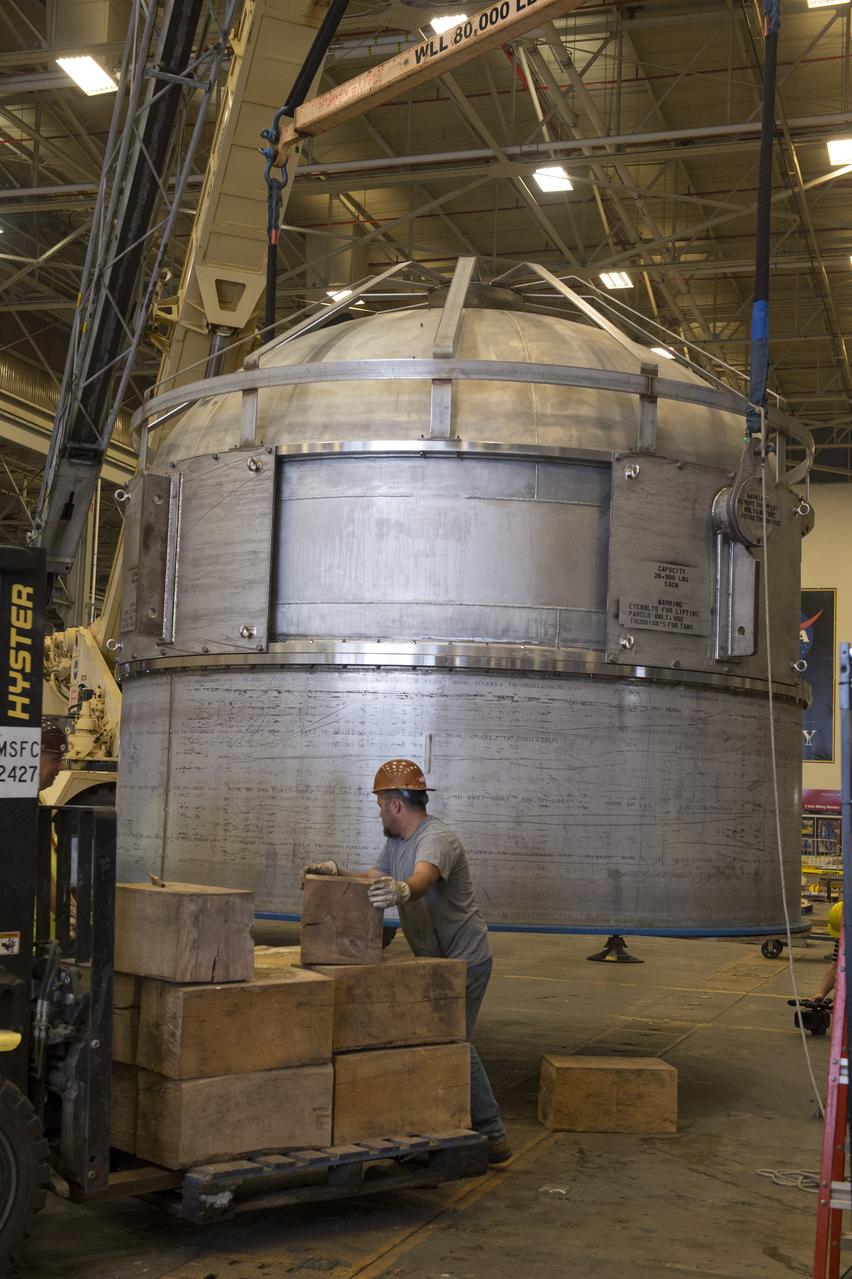

SHIIVER (Structural Heat Intercept Insulation Vibration Evaluation Rig) is a cryogenic test tank developed to evaluate heat intercept concepts. It arrived at Marshall Space Flight Center on August 10, 2017. The tank will receive heat sensors and spray-on foam insulation before making its way to Plum Brook station for further insulation and testing.

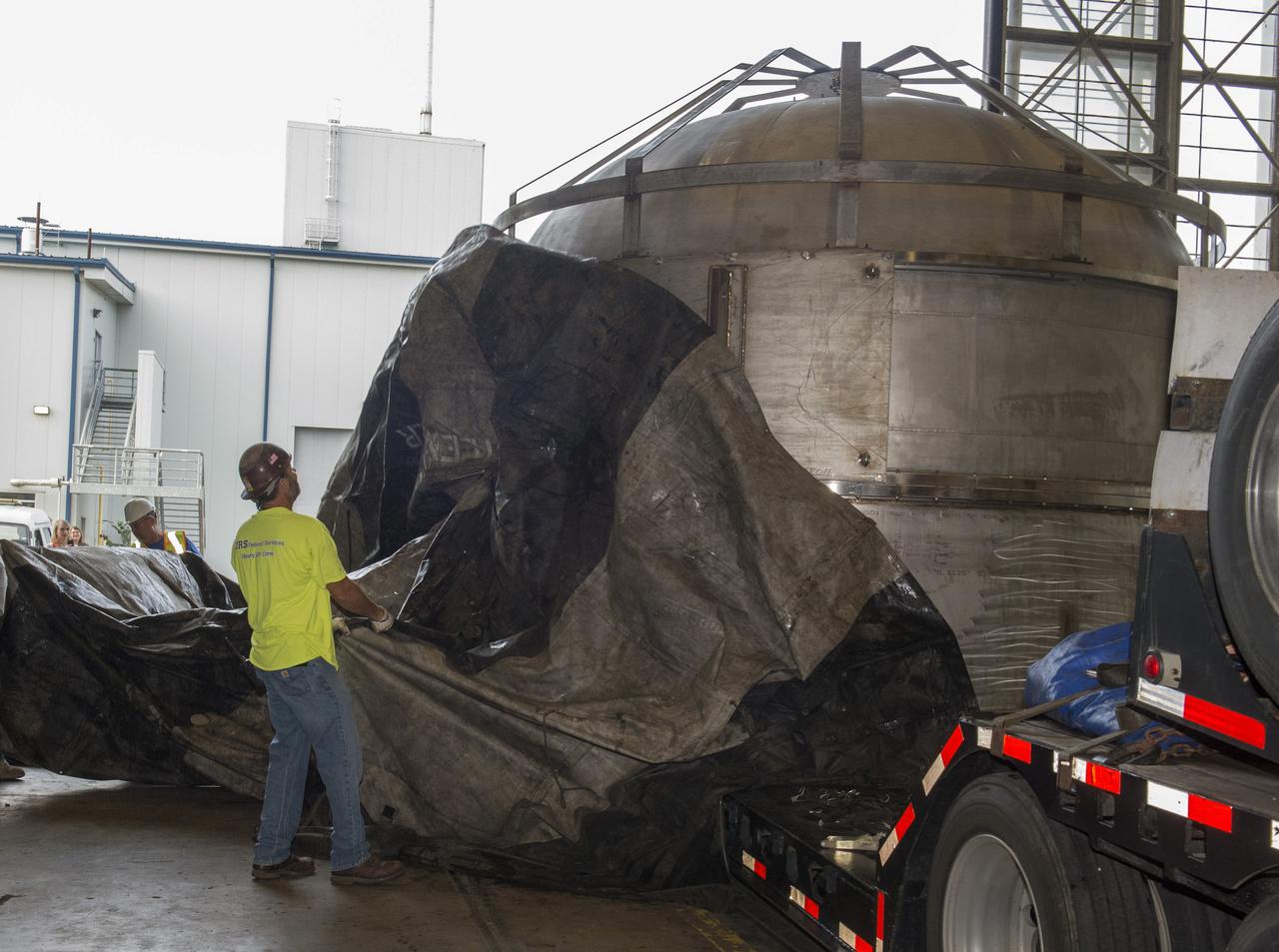
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Lockheed Martin technicians in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center prepare for the application of new foam over the manhole cover on the lower end of external tank No. 119. The manhole was removed to access the area where the tank's four liquid hydrogen engine cutoff sensors were replaced. Once reinstalled, the manhole required new foam to be applied. The tank is being prepared to launch Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-121 in July. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

SHIIVER Tank Arrives at NASA’s Marshall Center for Spray-On Foam InsulationSHIIVER (Structural Heat Intercept Insulation Vibration Evaluation Rig) is a cryogenic test tank developed to evaluate heat intercept concepts. It arrived at Marshall Space Flight Center on August 10, 2017. The tank will receive heat sensors and spray-on foam insulation before making its way to Plum Brook station for further insulation and testing.
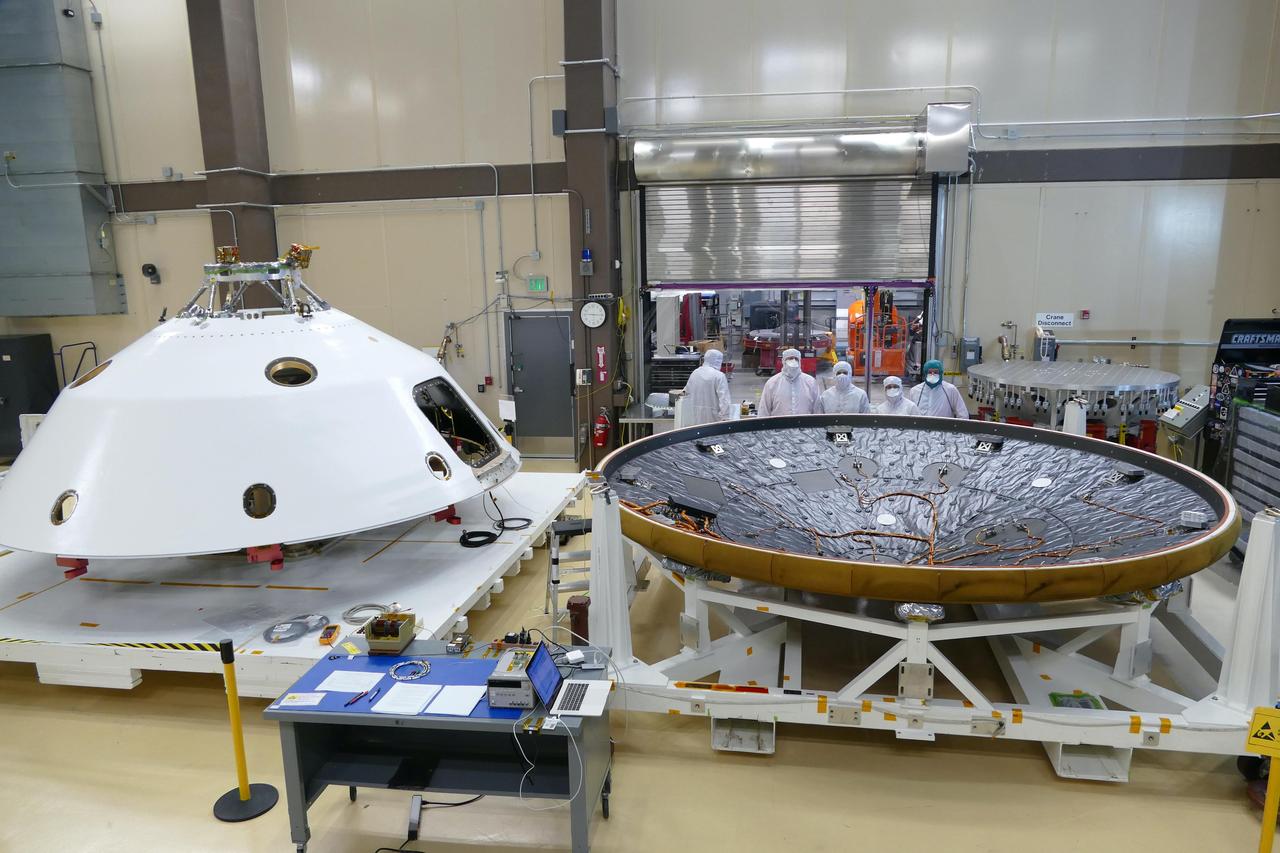

MEDLI2 sensors are installed on the Mars 2020 heat shield and back shell prior to launch. The sensors will measure the environment surrounding the spacecraft and the performance of thermal protection system material during the atmospheric entry phase of NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23989
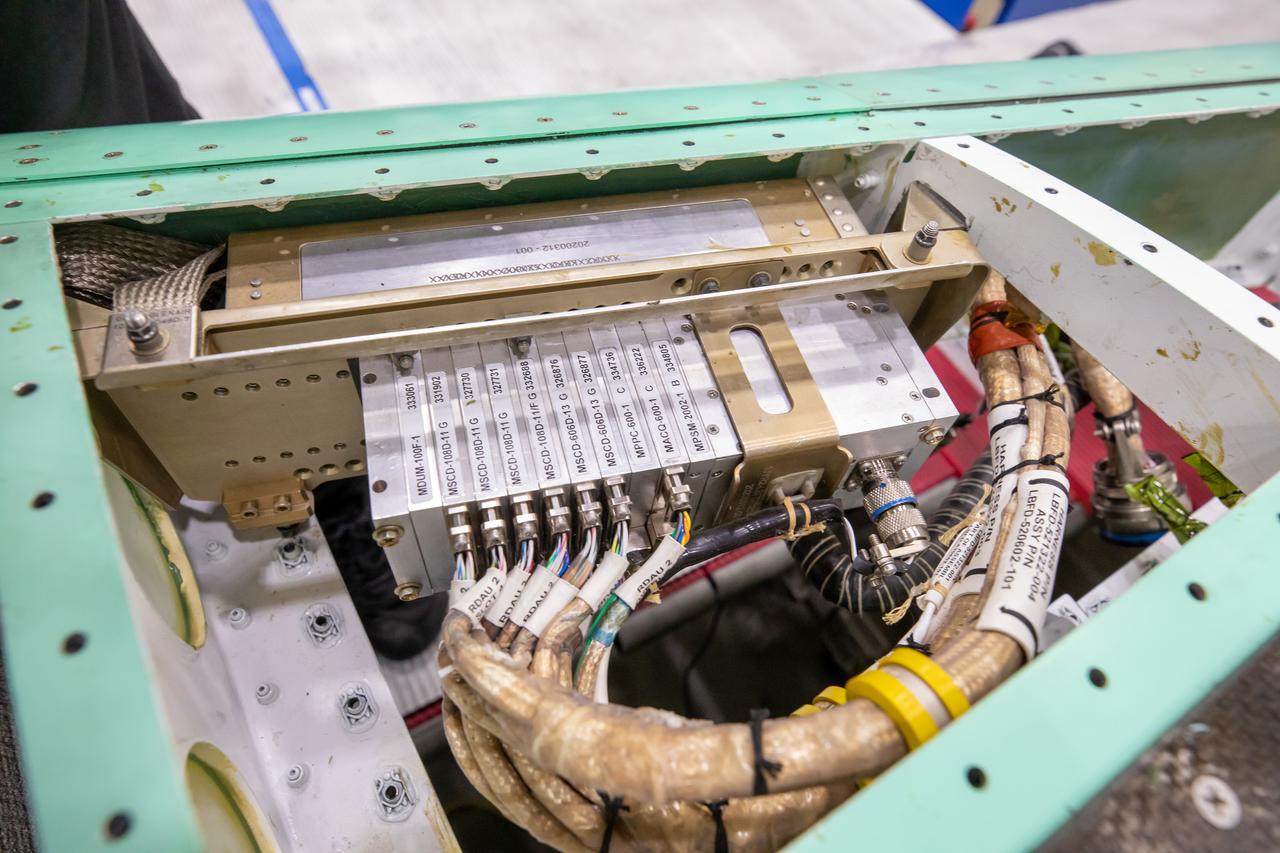
Here is a closeup of some of the X-59’s wiring and instrumentation system. Displayed here is the remote instrumentation encoder, which can be found in the wing of the aircraft. This encoder communicates with the plane’s other instrumentation systems like pressure and temperature sensors within the X-59.

This artist's concept shows NASA's InSight lander with its instruments deployed on the Martian surface. InSight's package of weather sensors, called the Auxiliary Payload Subsystem (APSS), includes an air pressure sensor inside the lander -- its inlet is visible on InSight's deck -- and two air temperature and wind sensors on the deck. Under the deck's edge is a magnetometer, provided by UCLA, to measure changes in the local magnetic field that could also influence SEIS. InSight's air temperature and wind sensors are actually refurbished spares built for Curiosity's Rover Environmental Monitoring Station (REMS). Called Temperature and Wind for InSight, or TWINS, these two east- and west-facing booms sit on the lander's deck and were provided by Spain's Centro de Astrobiología (CAB). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22957
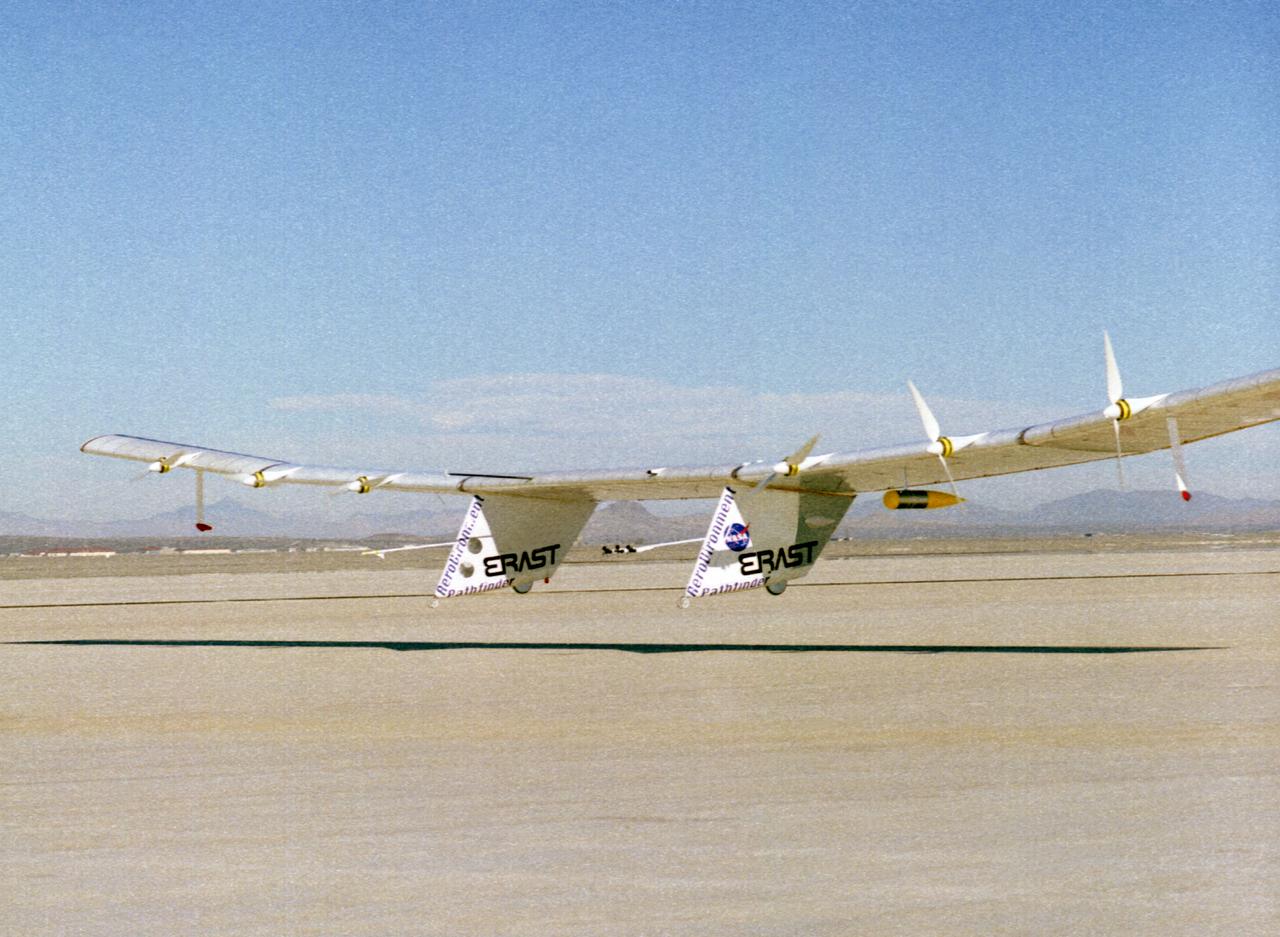

The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft settles in for landing on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, after a successful test flight Nov. 19, 1996. The ultra-light craft flew a racetrack pattern at low altitudes over the flight test area for two hours while project engineers checked out various systems and sensors on the uninhabited aircraft. The Pathfinder was controlled by two pilots, one in a mobile control unit which followed the craft, the other in a stationary control station. Pathfinder, developed by AeroVironment, Inc., is one of several designs being evaluated under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.
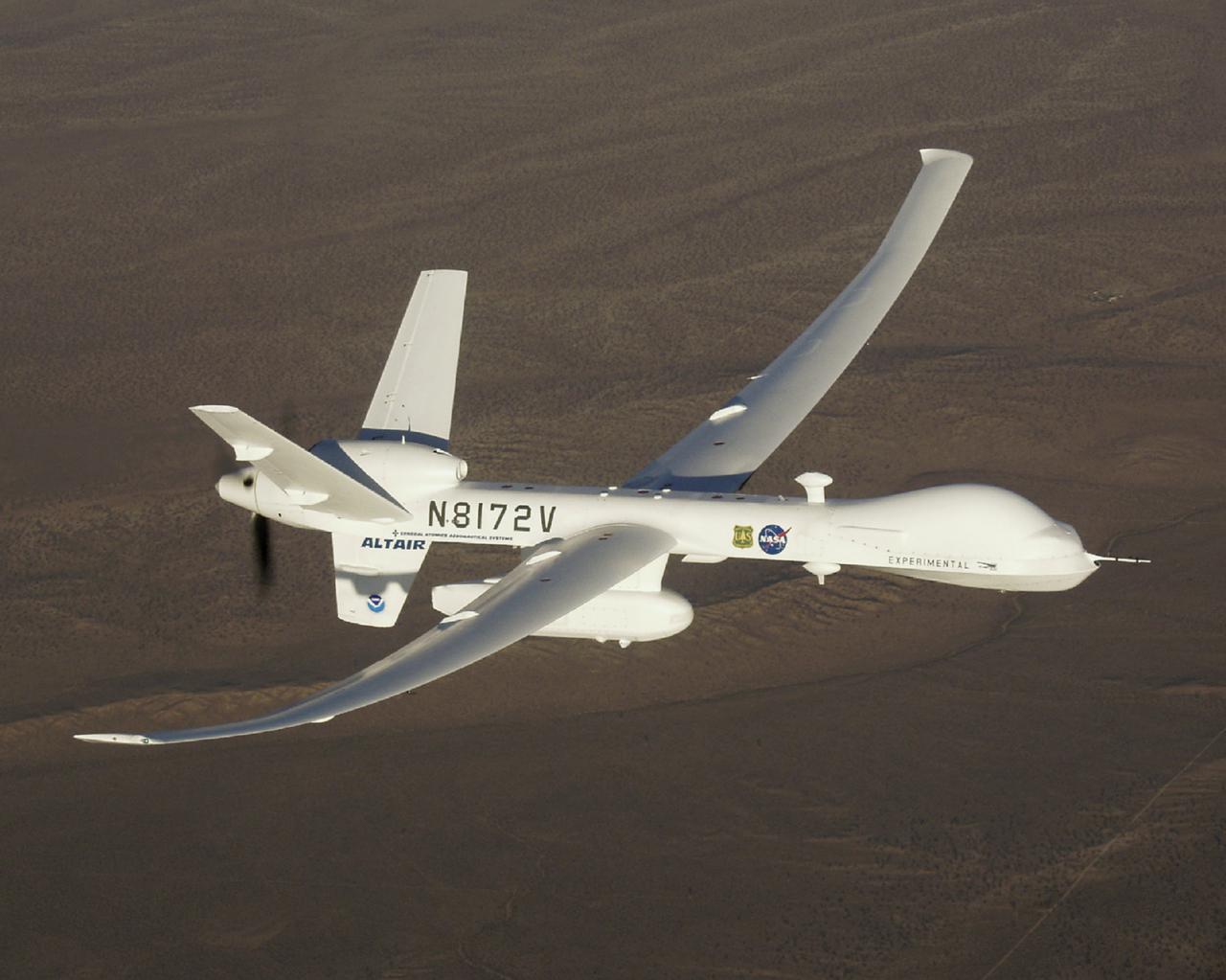

Equipped with a pod-mounted infrared imaging sensor, the Altair UAS aided fire mapping efforts over wildfires in central and southern California in late 2006.
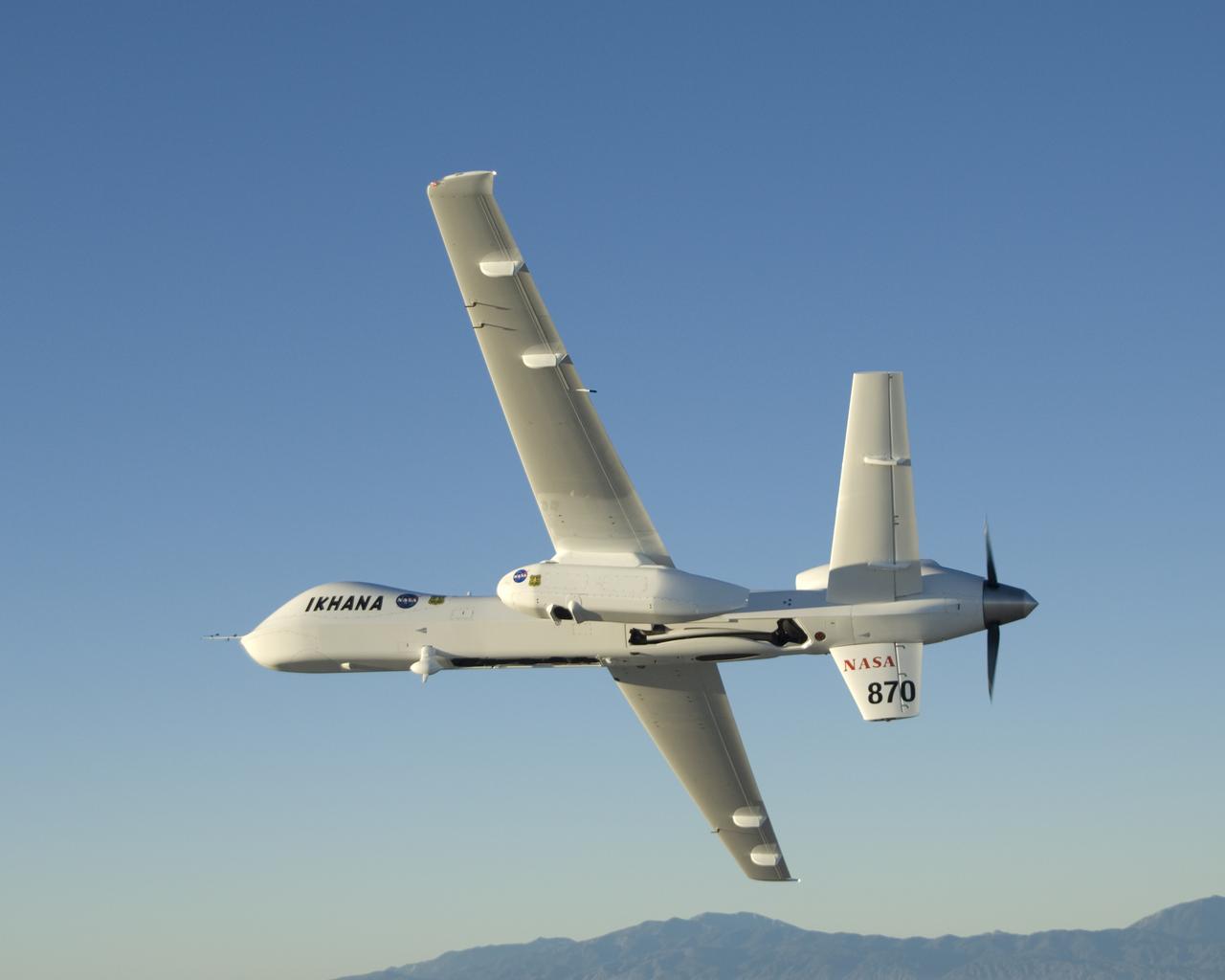

Carrying its sensor pod, NASA's remotely piloted Ikhana unmanned aircraft banks away during a checkout flight in the Western States Fire Mission.
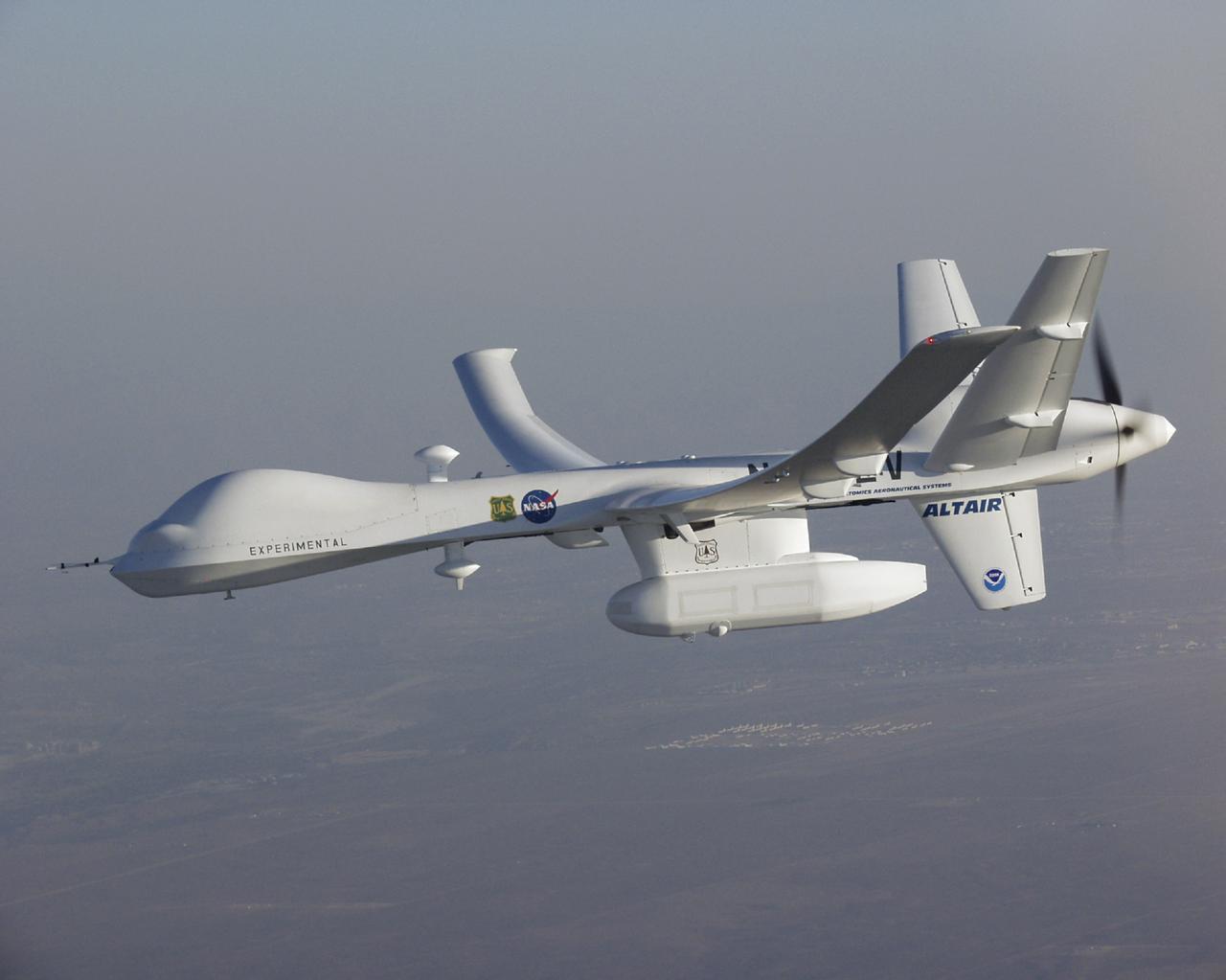

A high-tech infrared imaging sensor in its underbelly pod, the Altair UAS flew repeated passes over the Esperanza fire to aid firefighting efforts.