
The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite undergoes final preparations in a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California for an early November launch. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). Other partners include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the intergovernmental European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), and France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24131
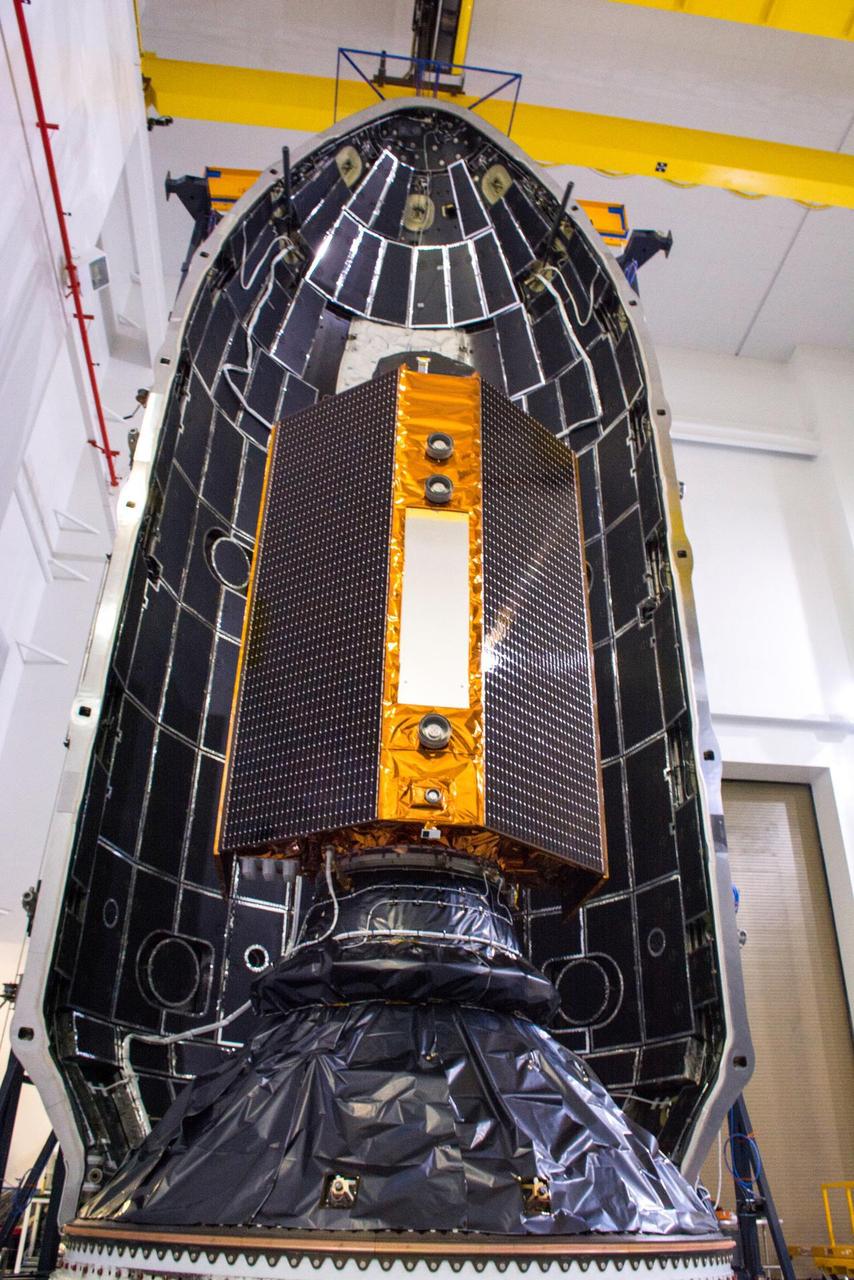

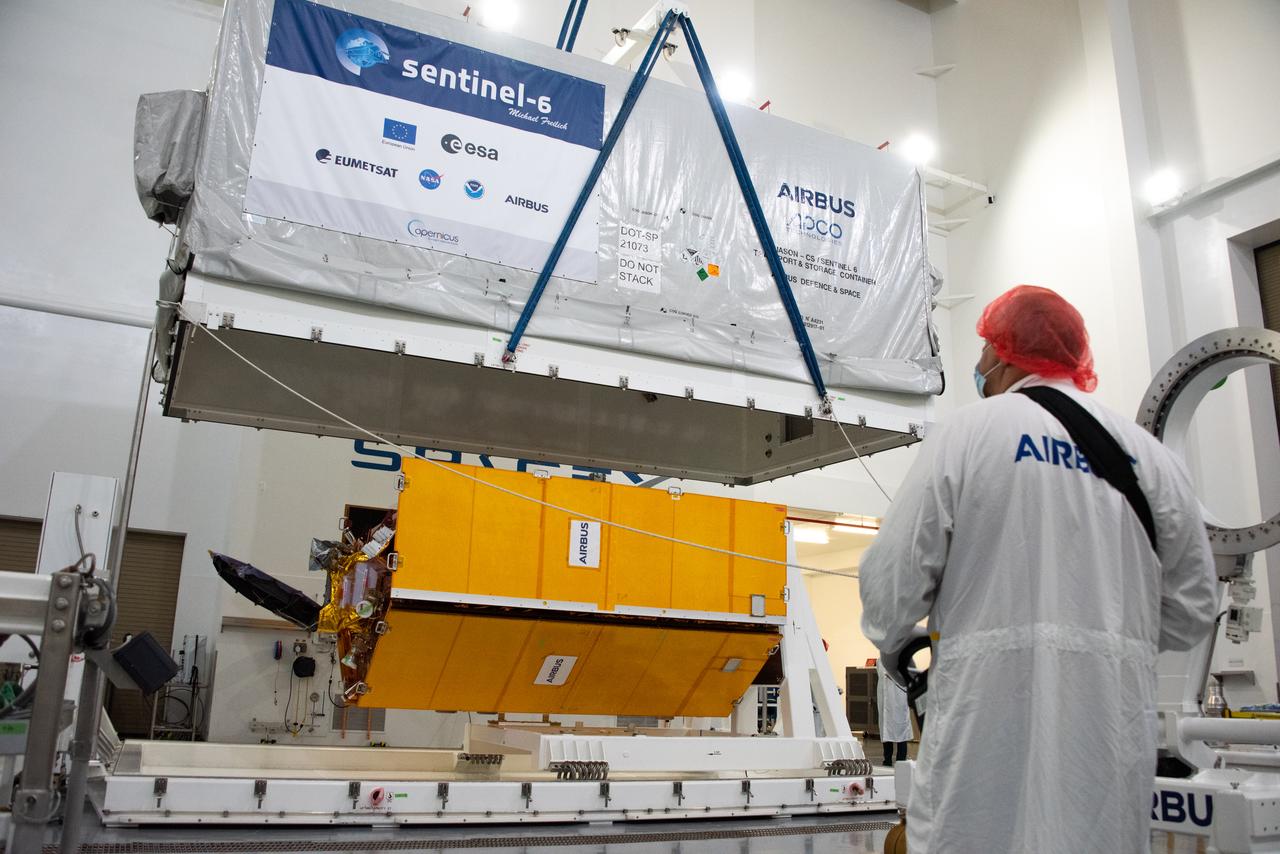
The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is encapsulated in a protective nosecone, or payload fairing, in the SpaceX Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will sit atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket during the late-November 2020 launch that will place the satellite in Earth orbit. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical satellites that are a part of the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, a U.S.-European collaboration. The mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world's oceans, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich's twin, Sentinel-6B, is scheduled to launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24133

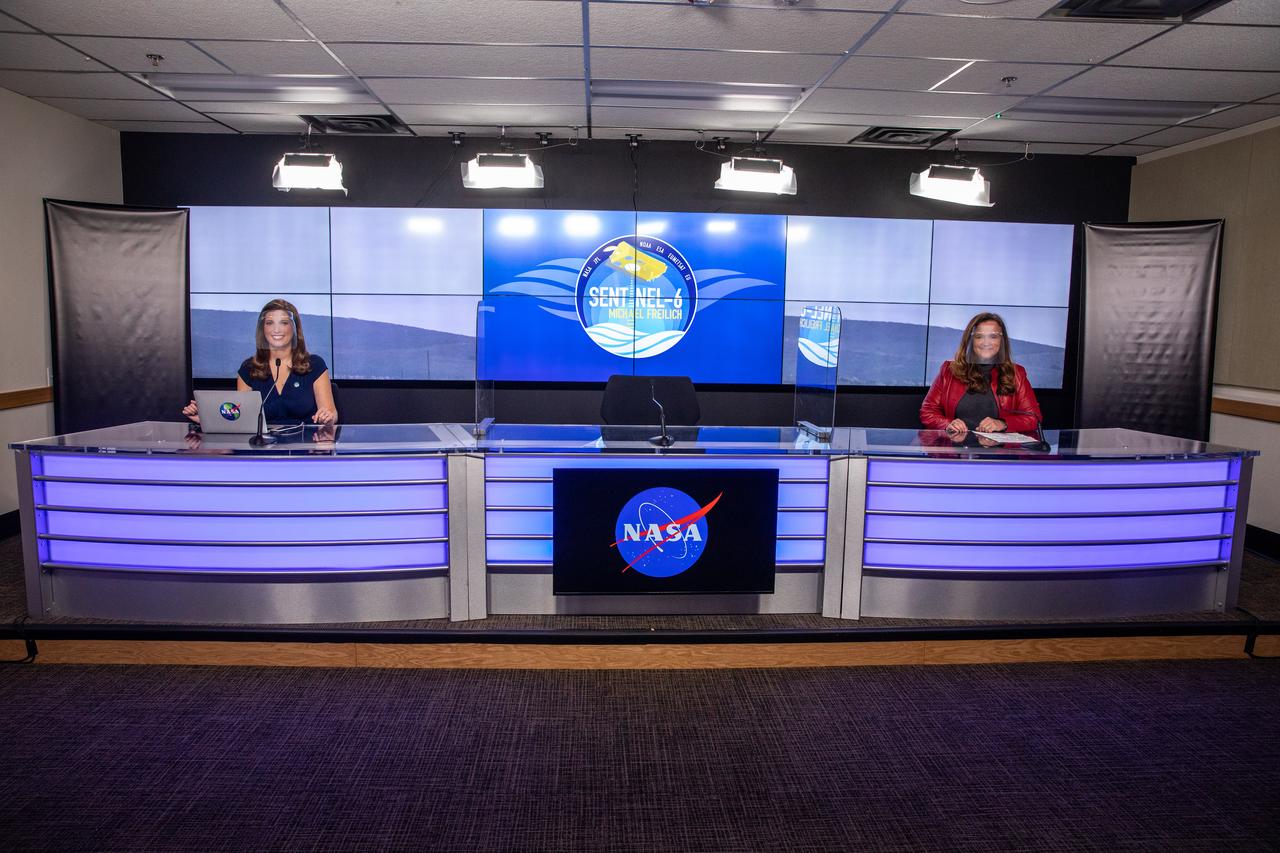
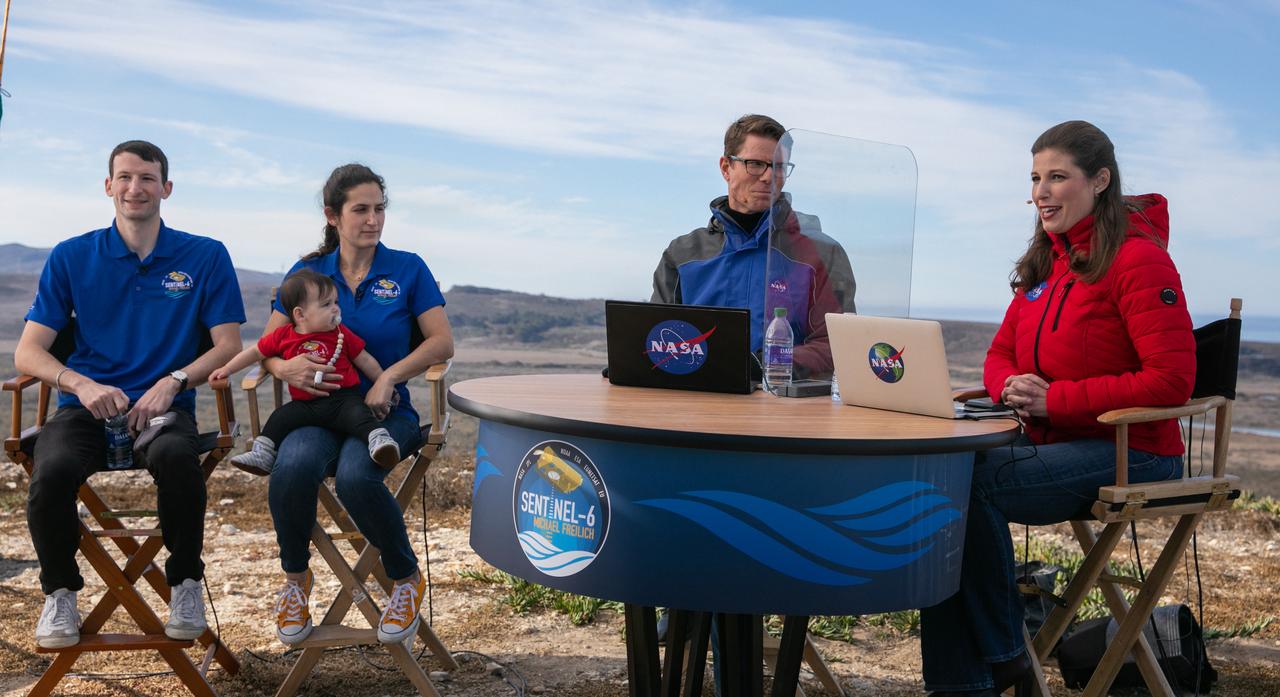
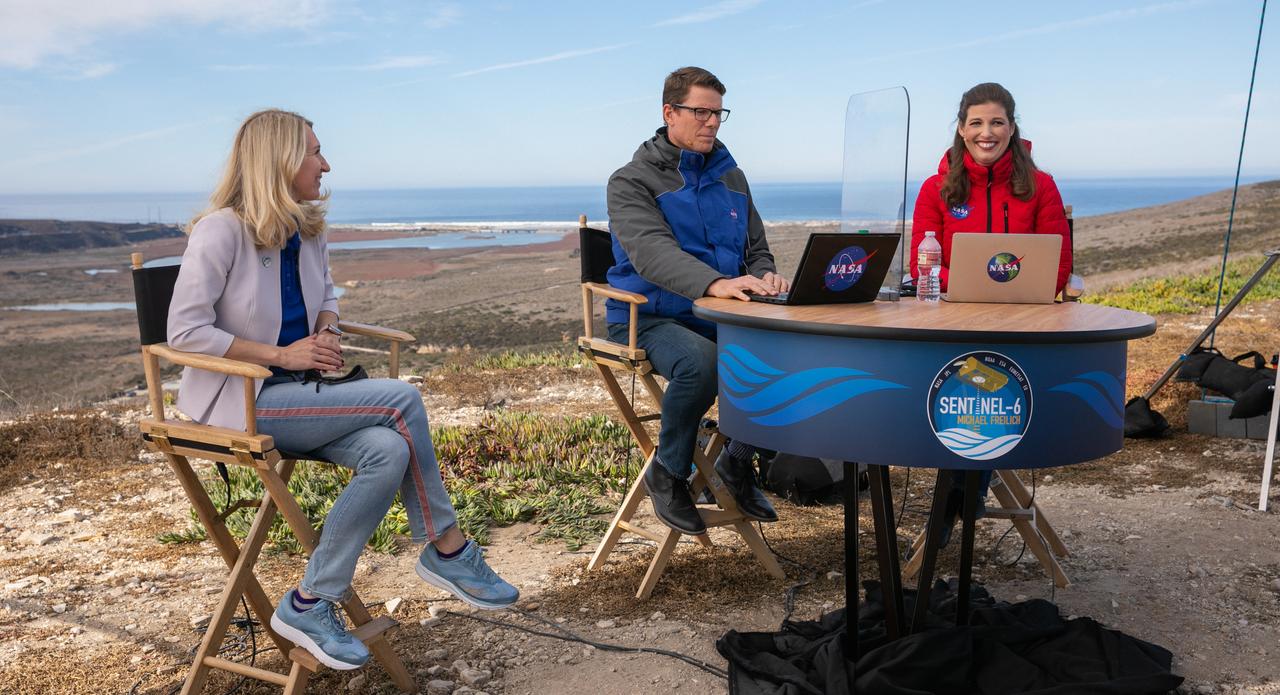
Marina Jurica of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena moderates a science briefing for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Marina Jurica of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena moderates a science briefing for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Parag Vaze, project manager, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, participates in a prelaunch news conference for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
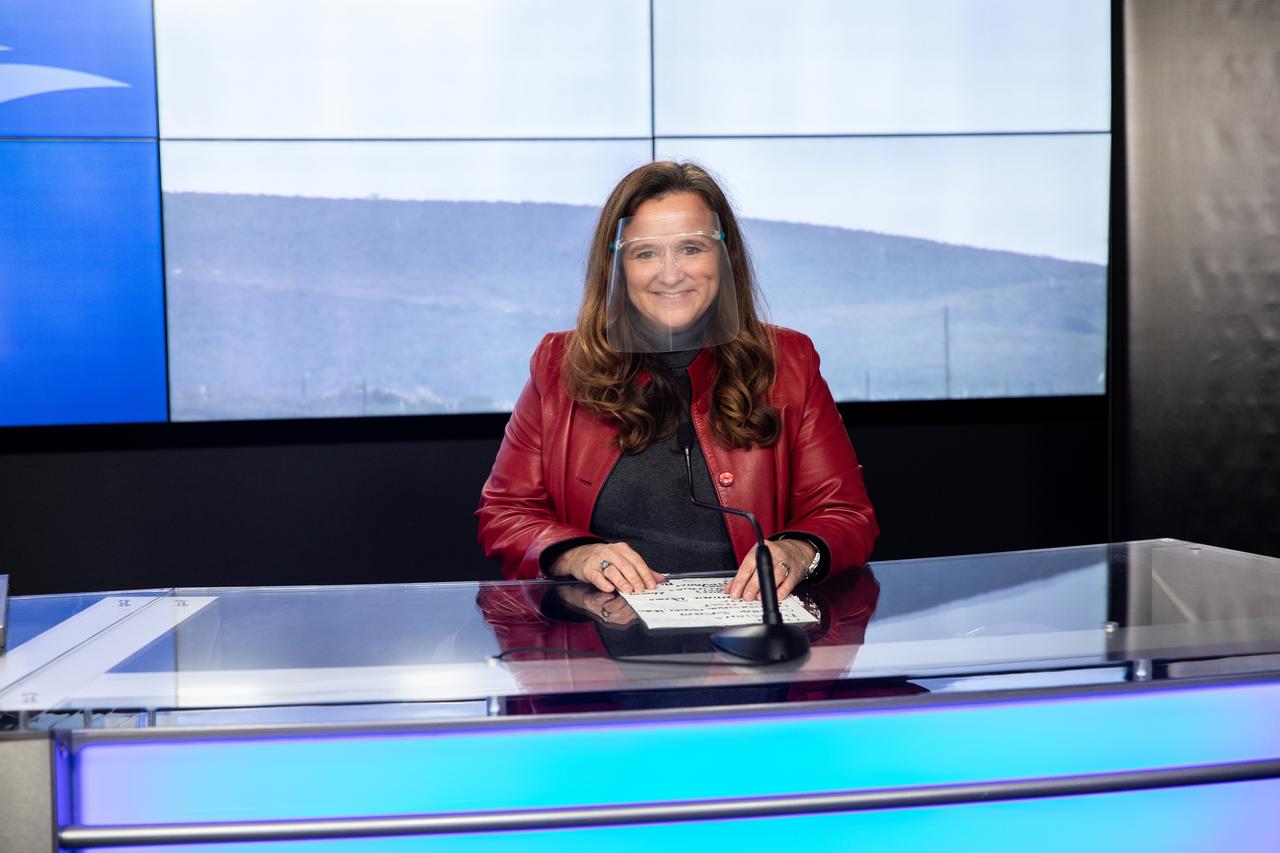

Karen St. Germain, director of NASA’s Earth Science Division, participates in a science briefing for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Marina Jurica of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena moderates a science briefing for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
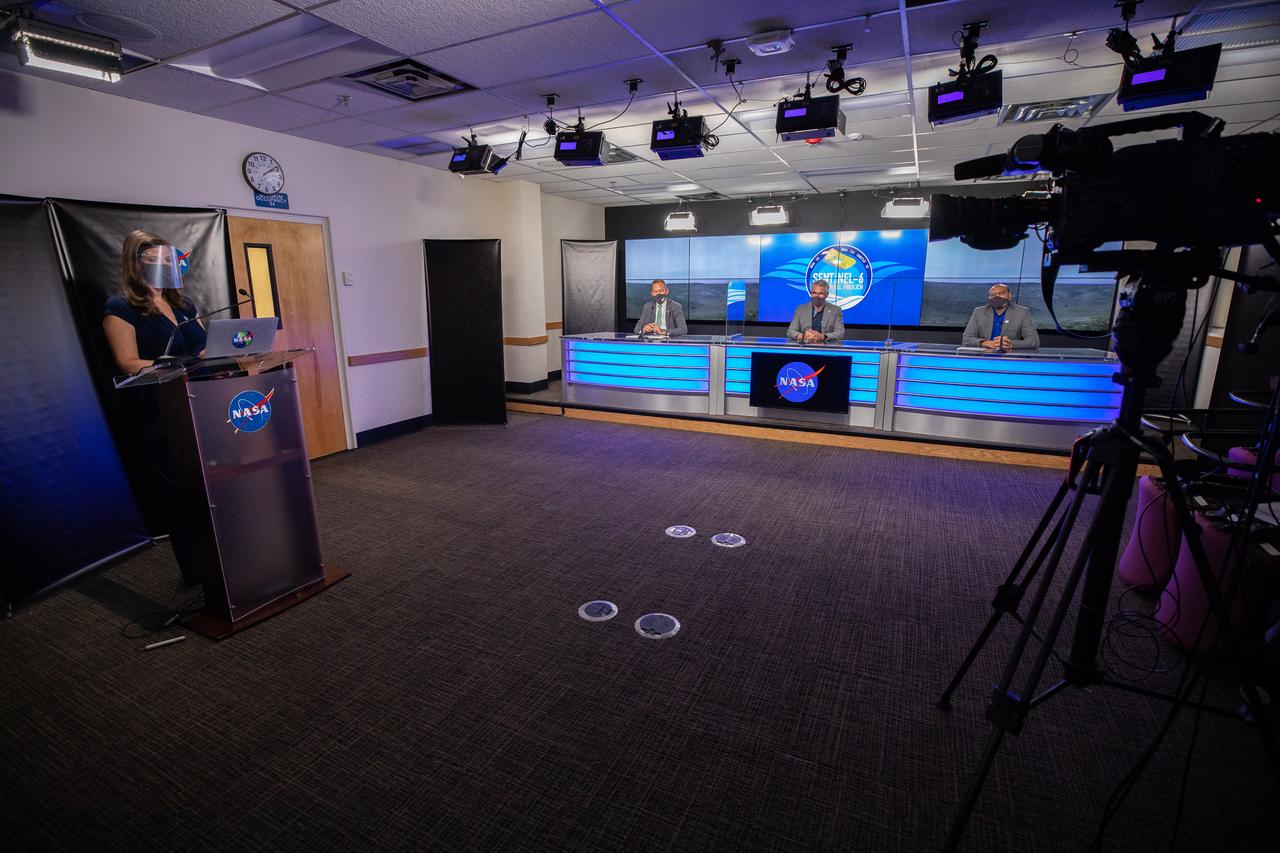

Mission and launch officials participate in a prelaunch news conference for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. From left are Marina Jurica of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena; Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters; Pierrik Vuilleumier, project manager, European Space Agency (ESA); and Parag Vaze, project manager, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

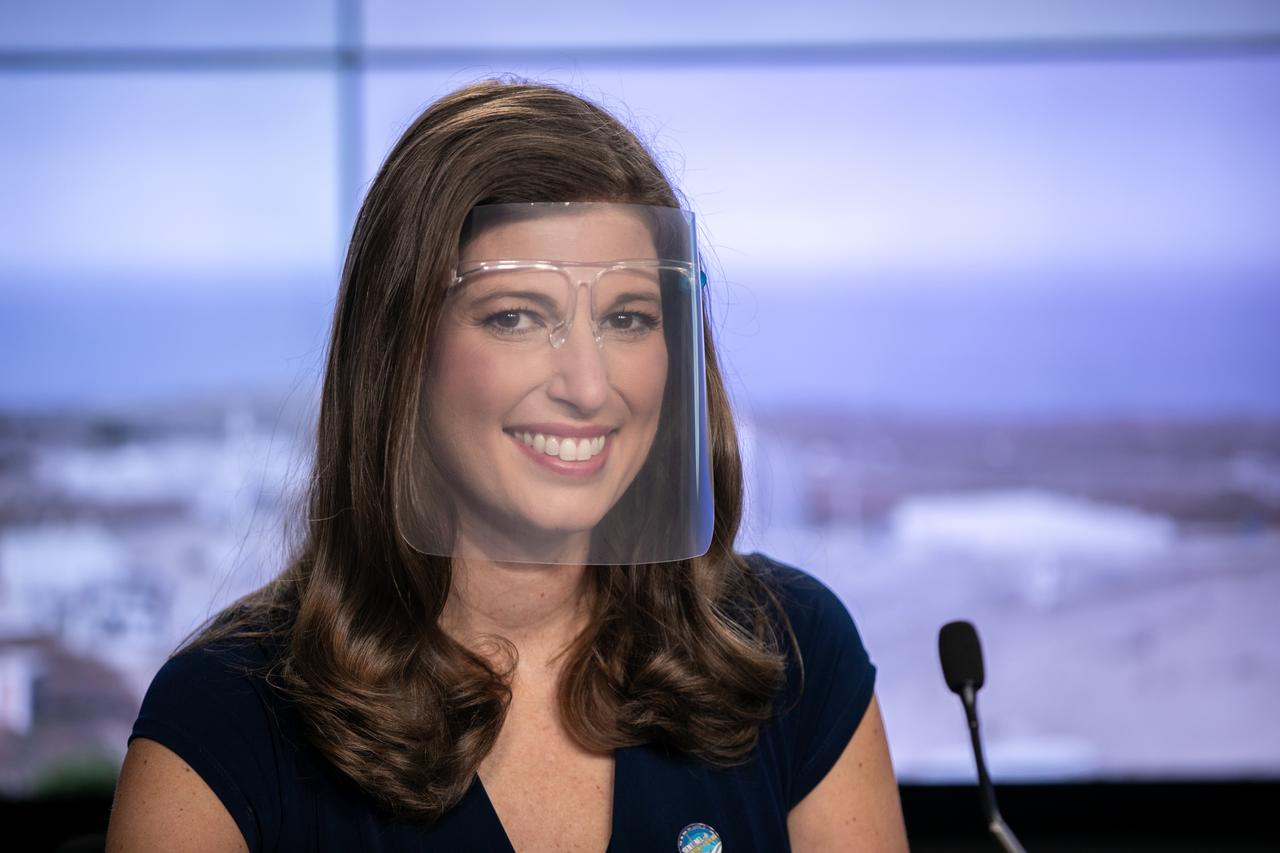
Karen St. Germain, director of NASA’s Earth Science Division, participates in a science briefing for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
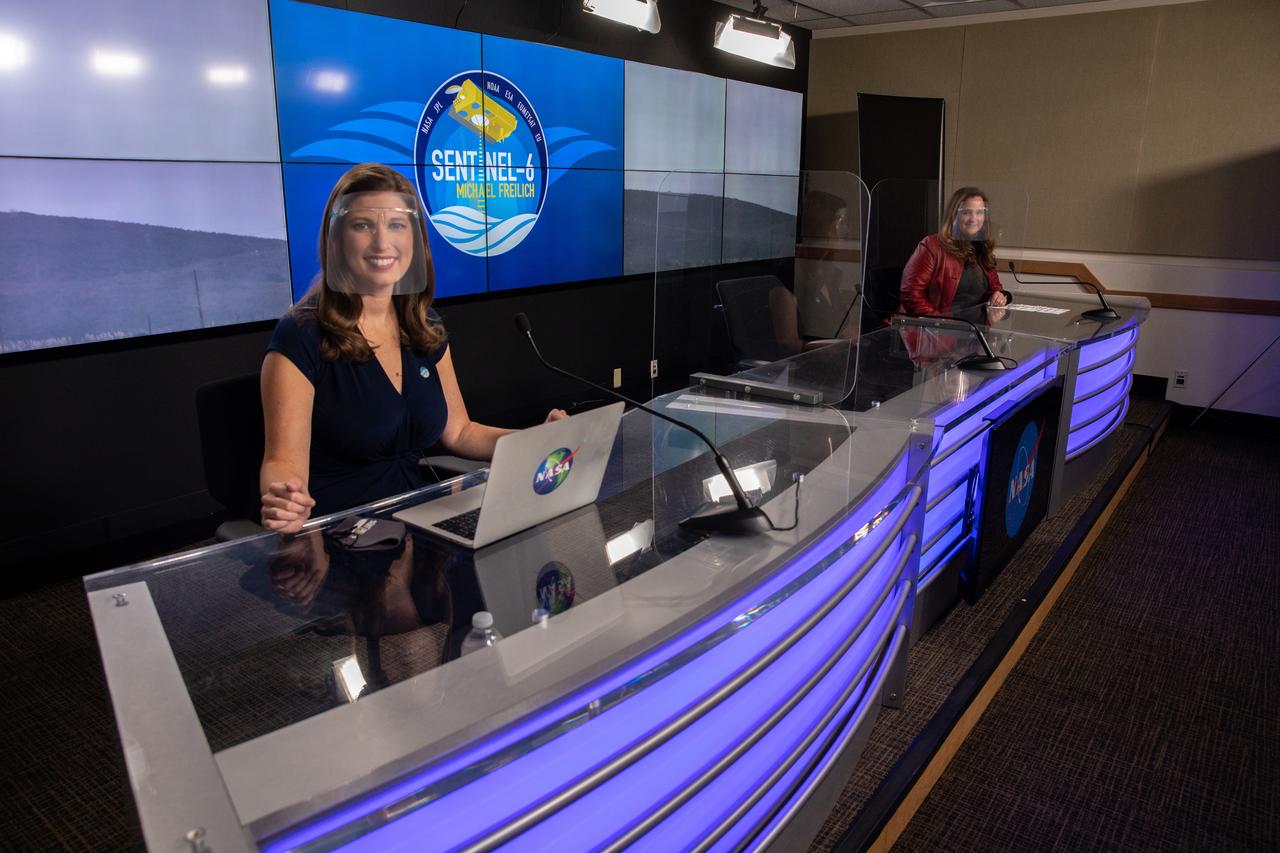

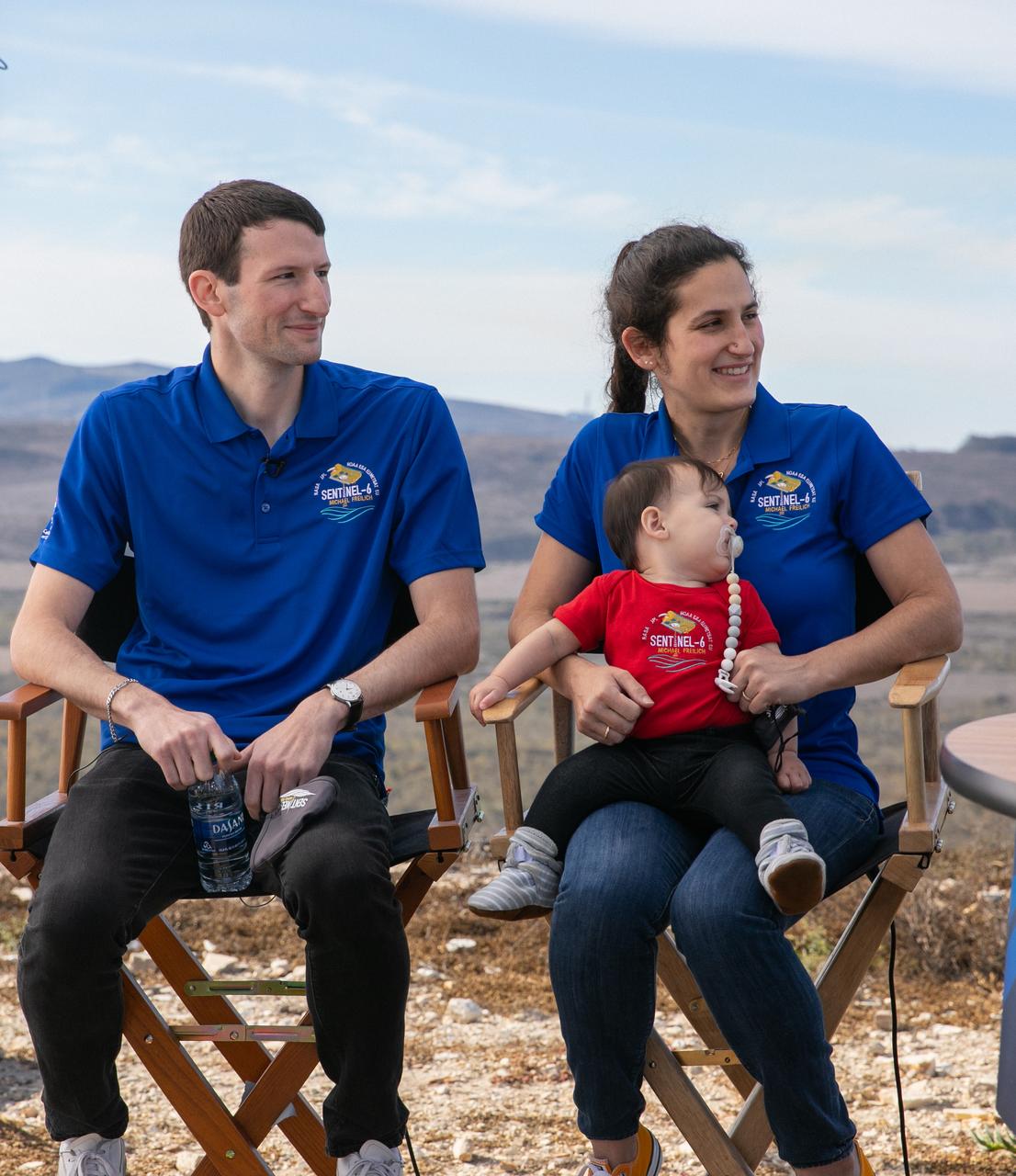
Marina Jurica of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, foreground, and Karen St. Germain, director of the agency’s Earth Science Division, participate in a science briefing for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Marina Jurica of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, left, and Karen St. Germain, director of the agency’s Earth Science Division, participate in a science briefing for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
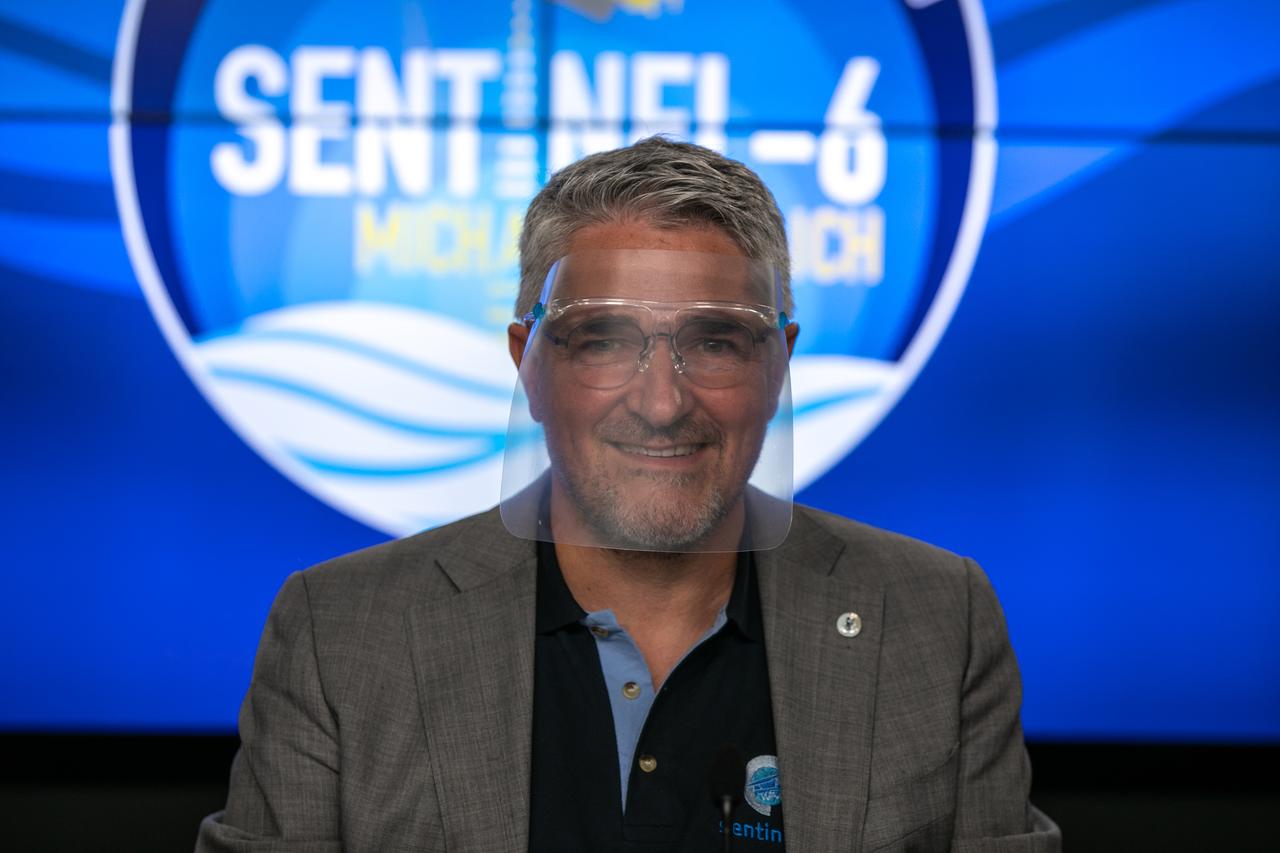

Pierrik Vuilleumier, project manager, European Space Agency (ESA), participates in a prelaunch news conference for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
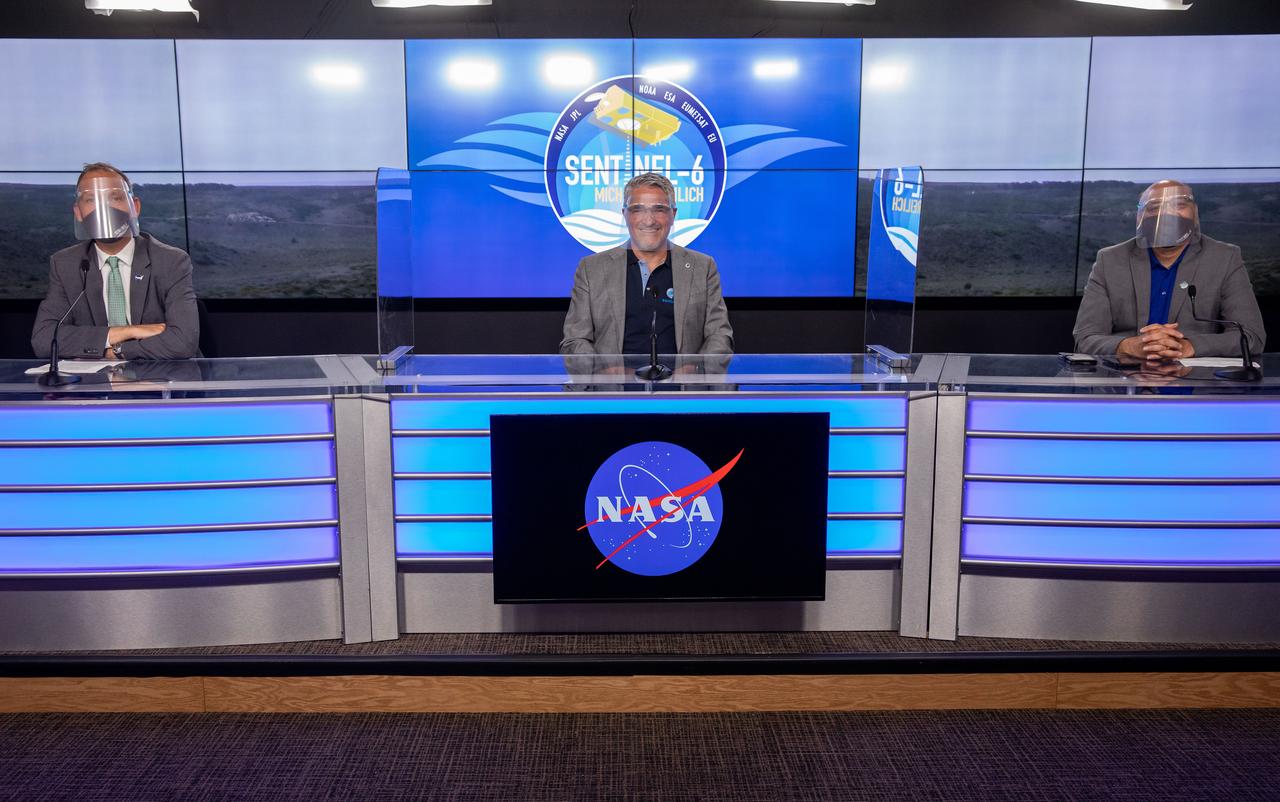

Mission and launch officials participate in a prelaunch news conference for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. From left are Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters; Pierrik Vuilleumier, project manager, European Space Agency (ESA); and Parag Vaze, project manager, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, participates in a prelaunch news conference for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Marina Jurica of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena moderates a prelaunch news conference for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

European Space Agency’s Copernicus Space Segment Programme Manager Guido Levrini, left, greets Dr. Michael Freilich’s wife, Shoshannah, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Seen in the background between them is Freilich’s son, Daniel, and to his right is Freilich’s daughter, Sarah. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
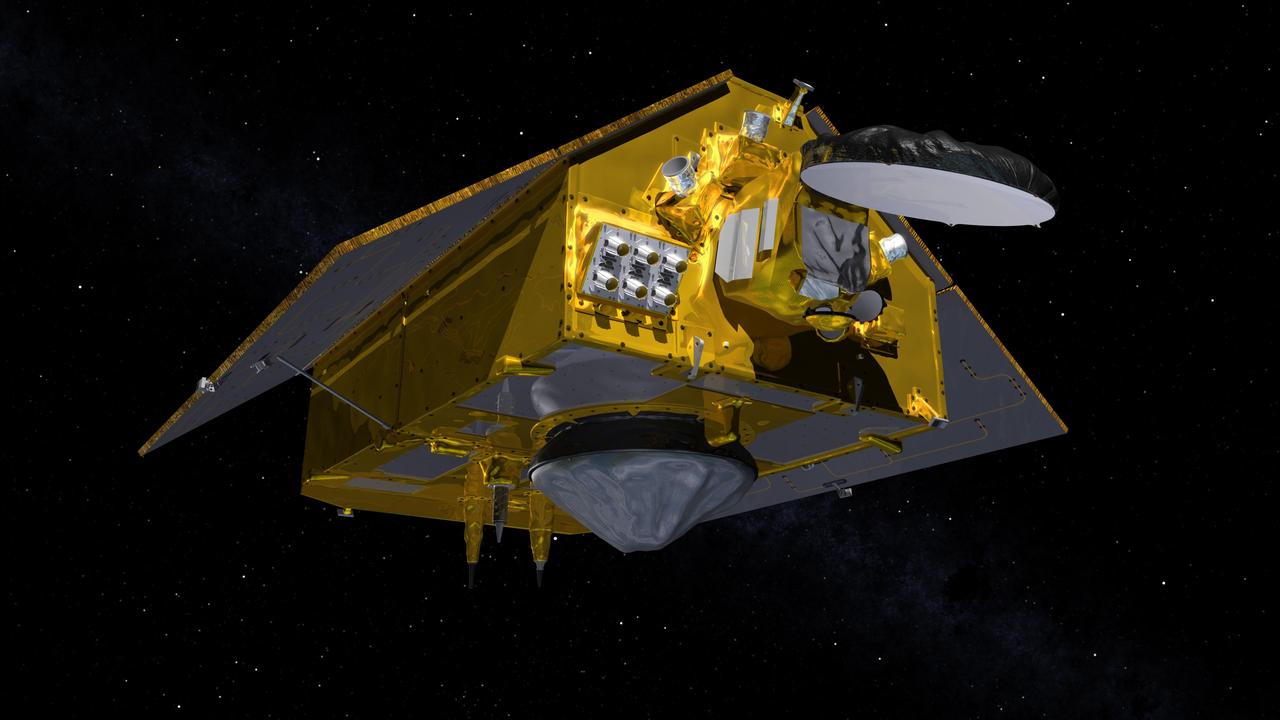

This illustration shows the front of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft in orbit above Earth with its deployable solar panels extended. As the world's latest ocean-monitoring satellite, it is launching on Nov. 10, 2020, to collect the most accurate data yet on global sea level and how our oceans are rising in response to climate change. The mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity that will help improve weather forecasts and climate models. The conelike instrument on the bottom (Earth-facing side) of the spacecraft is the satellite's Poseidon-4 radar altimeter. The disklike instrument at the front of the spacecraft is the Advanced Microwave Radiometer (AMR-C). Both instruments will be used together to measure ocean surface height. The gray rectangle with six cones attached at the front-left of the spacecraft is part of the Global Navigation Satellite System - Radio Occultation (GNSS-RO) instrument. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich extends the near-30-year record of satellite measurements of sea level initiated by the U.S.-European TOPEX/Poseidon mission in 1992 and that continued with the Jason-1, 2, and 3 series of sea level observation satellites. Launched in 2016, Jason-3 is currently providing data. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). Other partners include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the intergovernmental European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), and France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24106
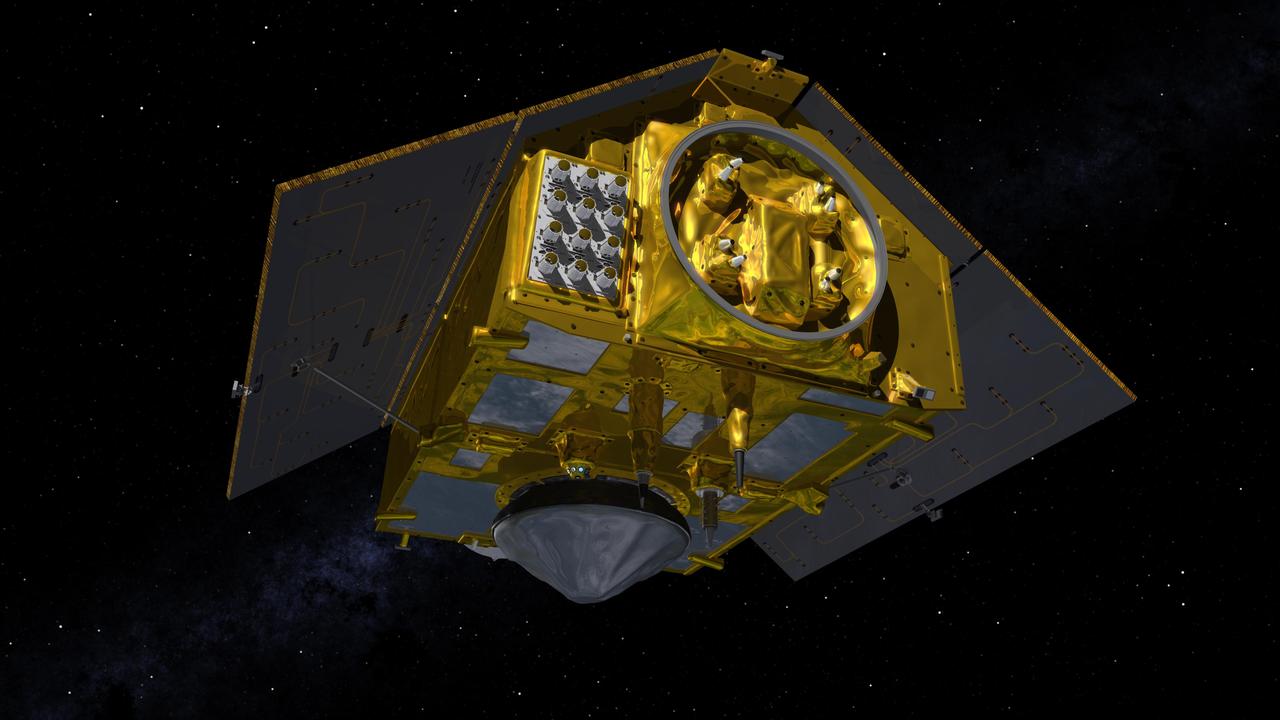

This illustration shows the rear of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft in orbit above Earth with its deployable solar panels extended. As the world's latest ocean-monitoring satellite, it is launching on Nov. 10, 2020, to collect the most accurate data yet on global sea level and how our oceans are rising in response to climate change. The mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity that will help improve weather forecasts and climate models. The conelike instrument on the bottom (Earth-facing side) of the spacecraft is the satellite's Poseidon-4 radar altimeter. When used with the Advanced Microwave Radiometer (AMR-C) attached to the front of the spacecraft, both instruments will be used to make precise measurements of sea surface height. The gray rectangle with 12 cones attached at the rear-left of the spacecraft is part of the Global Navigation Satellite System - Radio Occultation (GNSS-RO) instrument. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich extends the near-30-year record of satellite measurements of sea level initiated by the U.S.-European TOPEX/Poseidon mission in 1992 and that continued with the Jason-1, 2, and 3 series of sea level observation satellites. Launched in 2016, Jason-3 is currently providing data. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). Other partners include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the intergovernmental European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), and France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24107
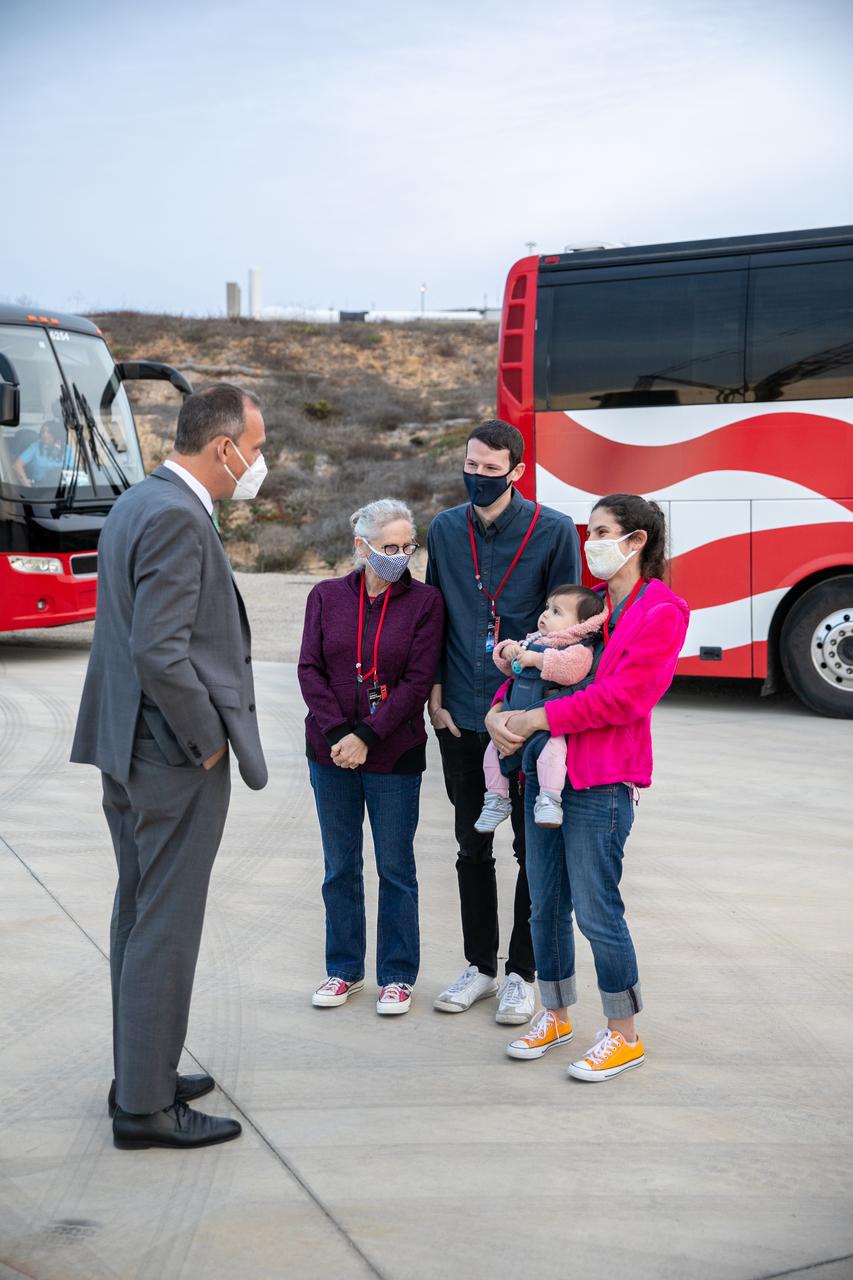

Associate Administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen, far left, greets family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. From left are Freilich’s wife, Shoshannah, and their children, Daniel and Sarah. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
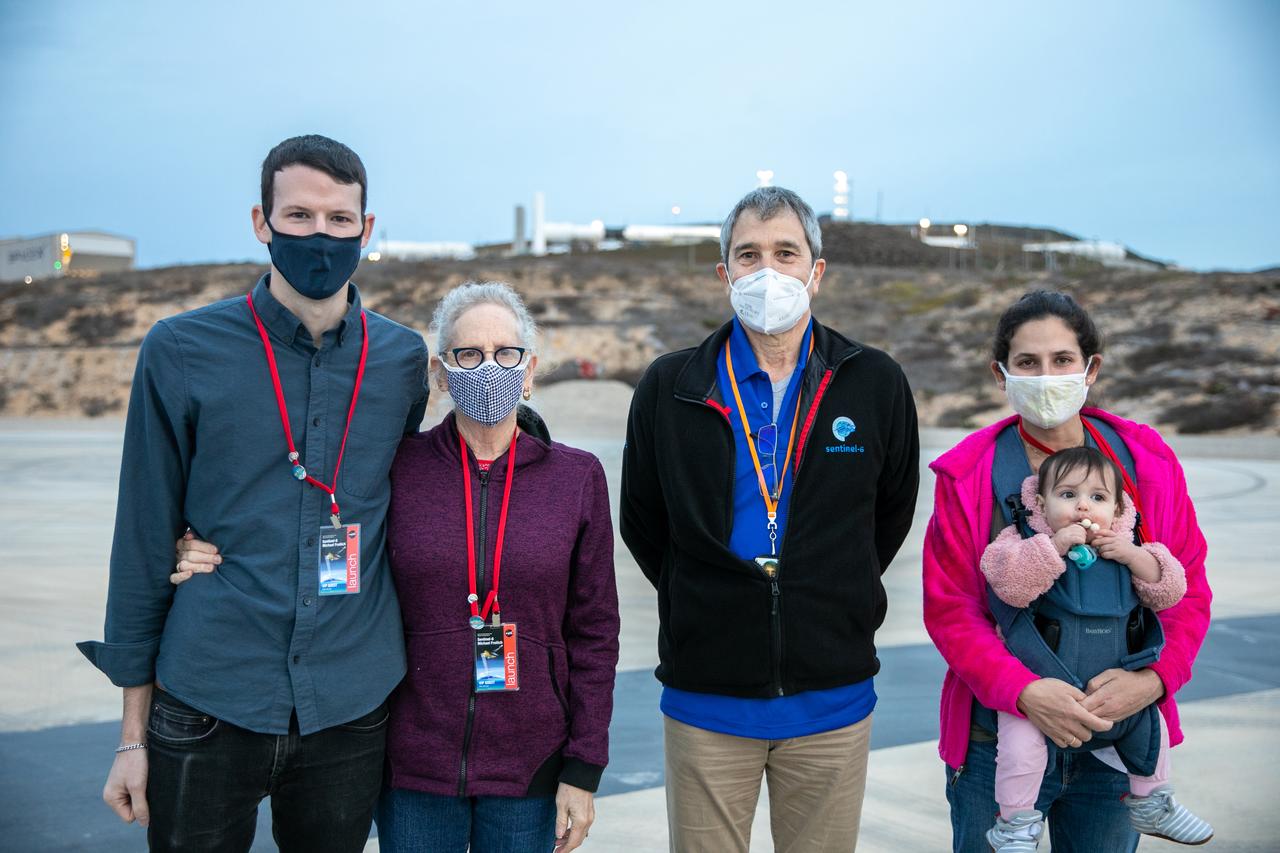

Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, pause for a photograph with European Space Agency’s Copernicus Space Segment Programme Manager Guido Levrini, second from right, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. From left are Freilich’s son and wife, Daniel and Shoshannah, and at far right is his daughter, Sarah. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

European Space Agency’s Copernicus Space Segment Programme Manager Guido Levrini, left, greets Dr. Michael Freilich’s daughter, Sarah, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Standing next to her is her mother, Shoshannah, and brother, Daniel. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
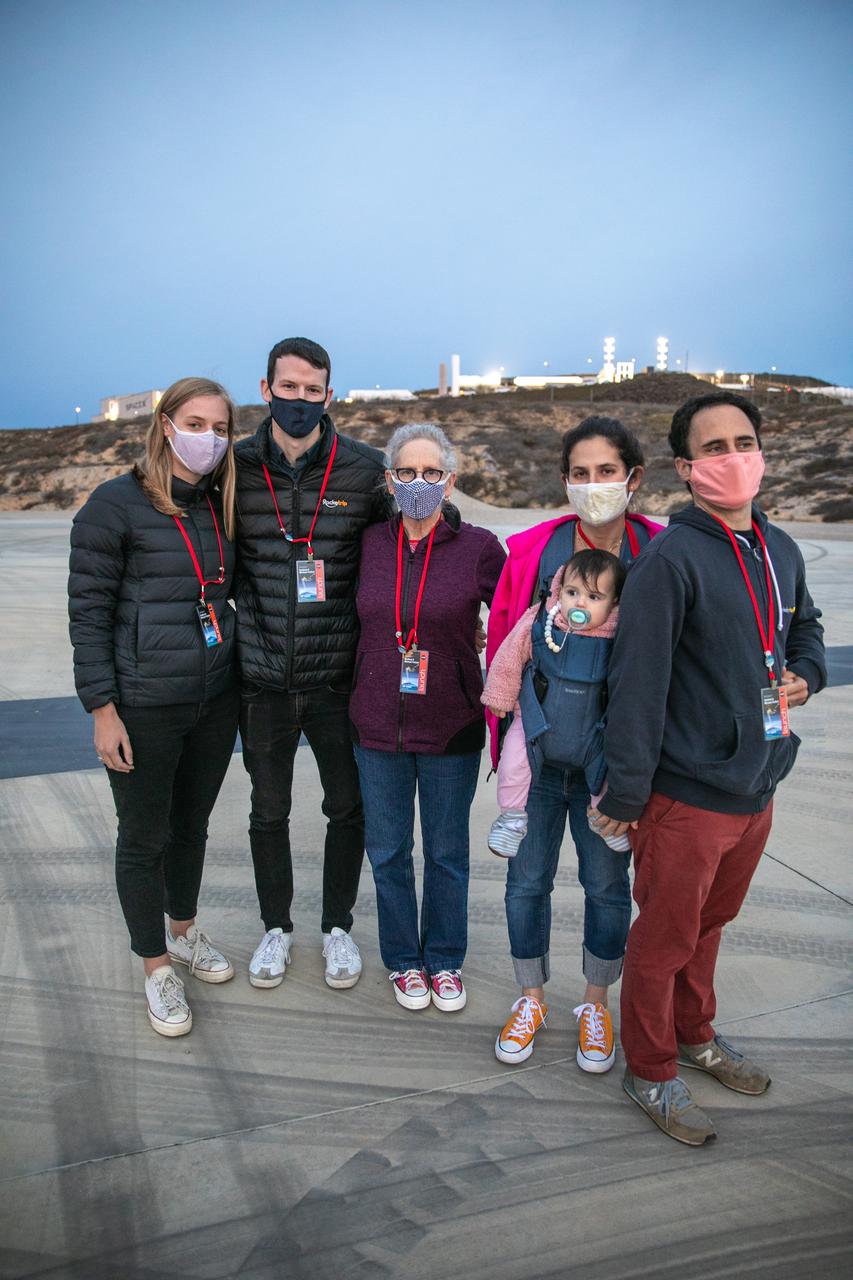

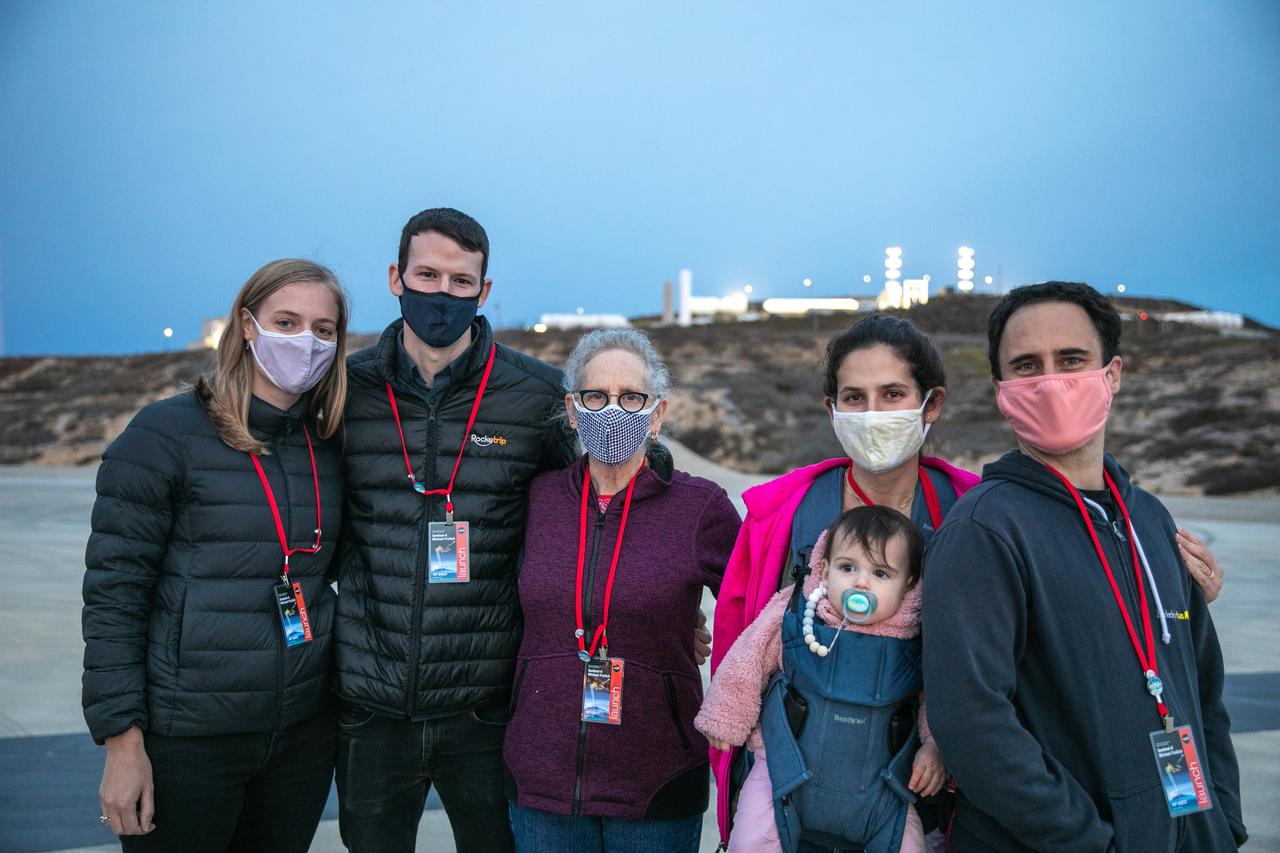
Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

European Space Agency’s Copernicus Space Segment Programme Manager Guido Levrini, far left, greets family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. From left are his children, Daniel and Sarah, and his wife, Shoshannah. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

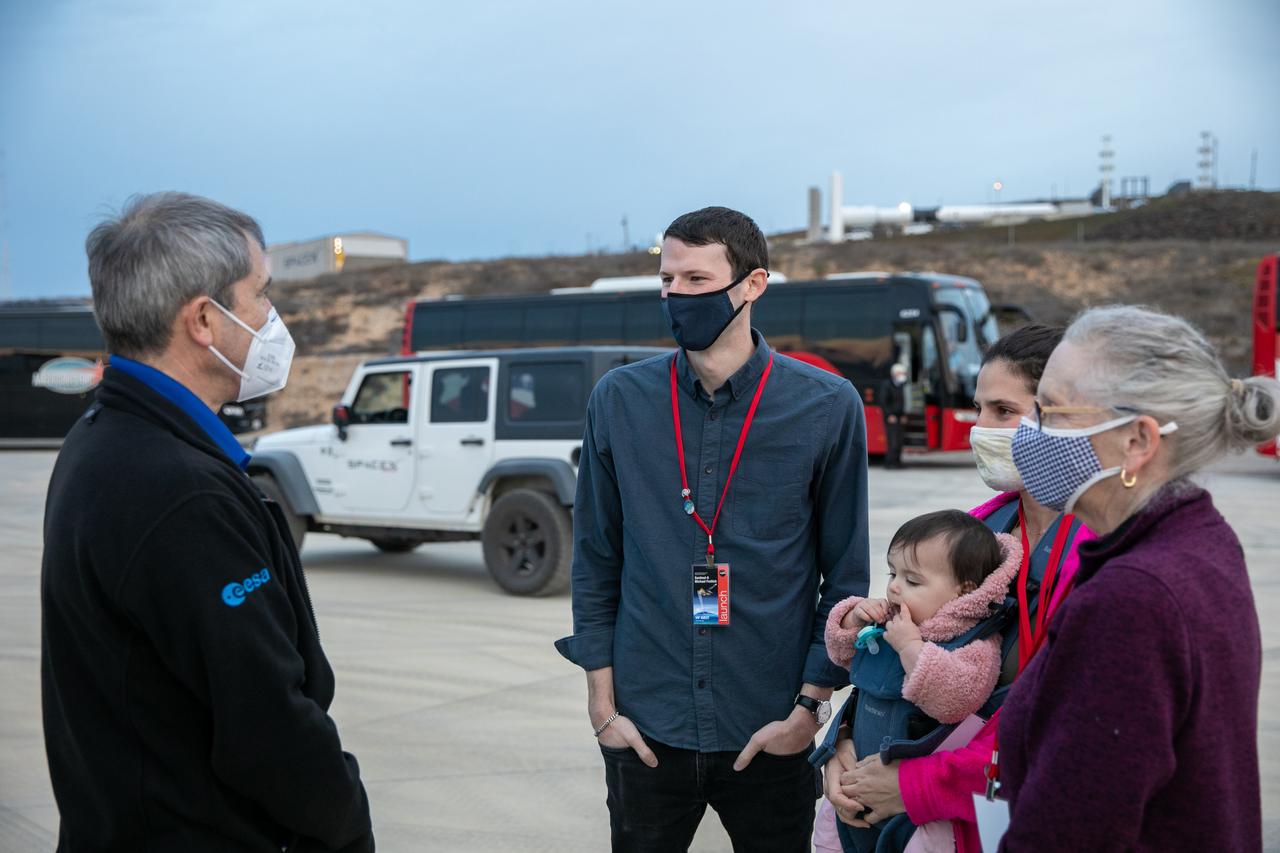
Associate Administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen speaks to family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
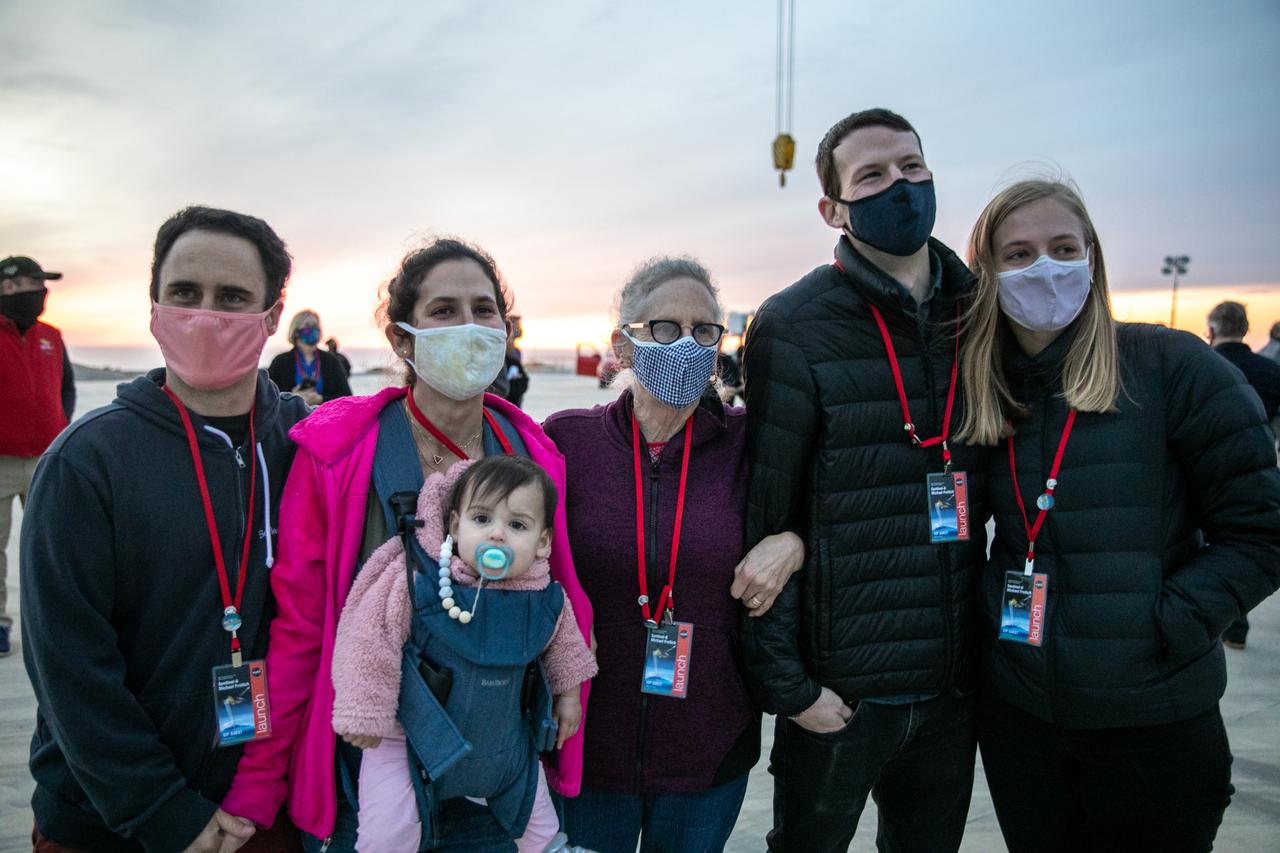

Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
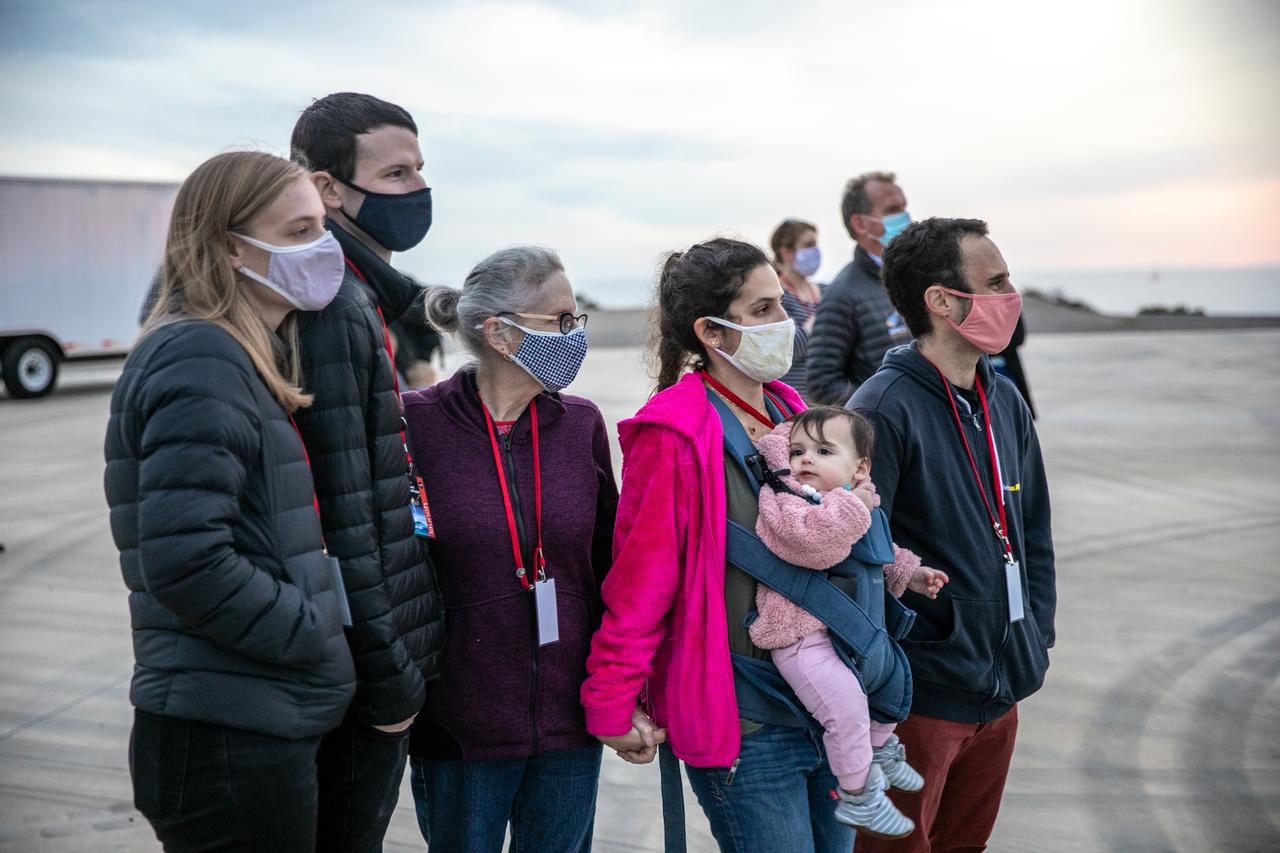

Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
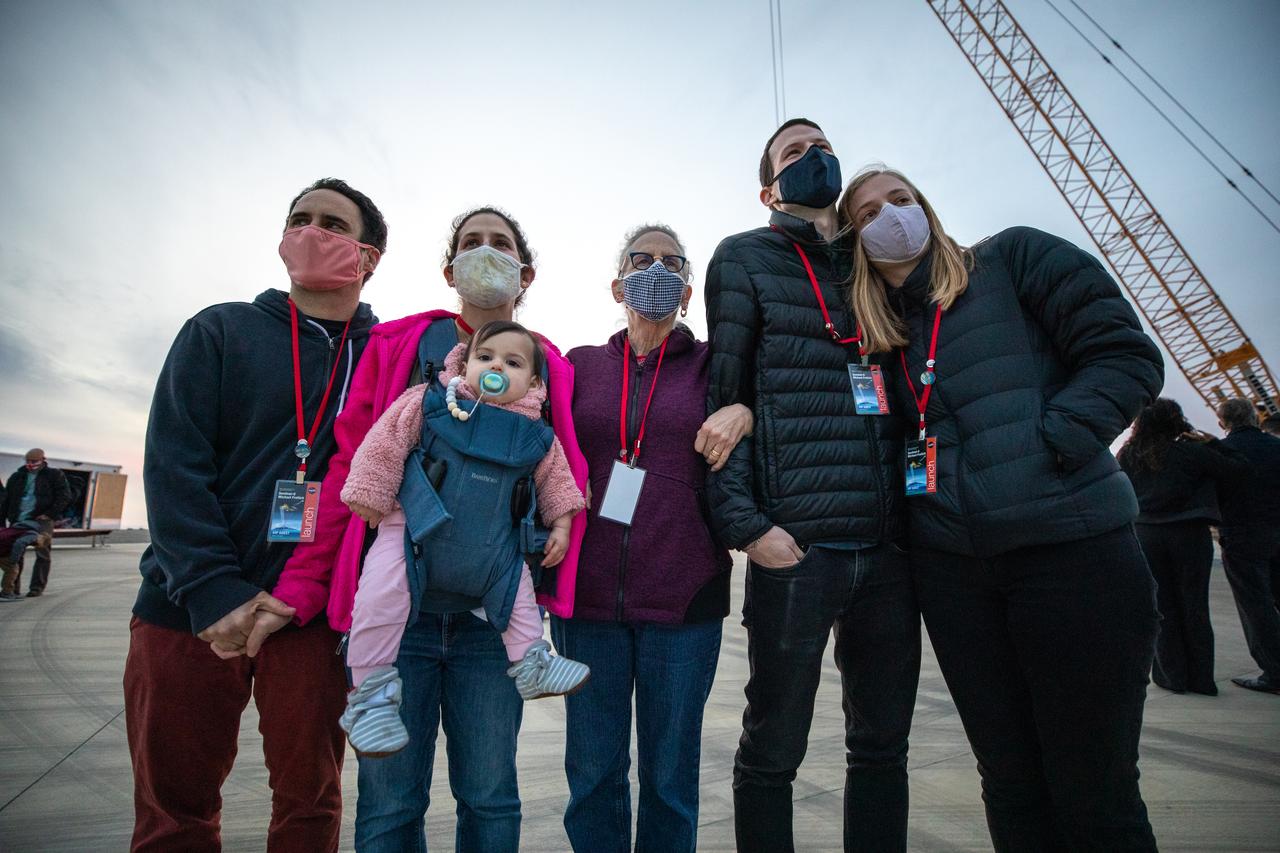

Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
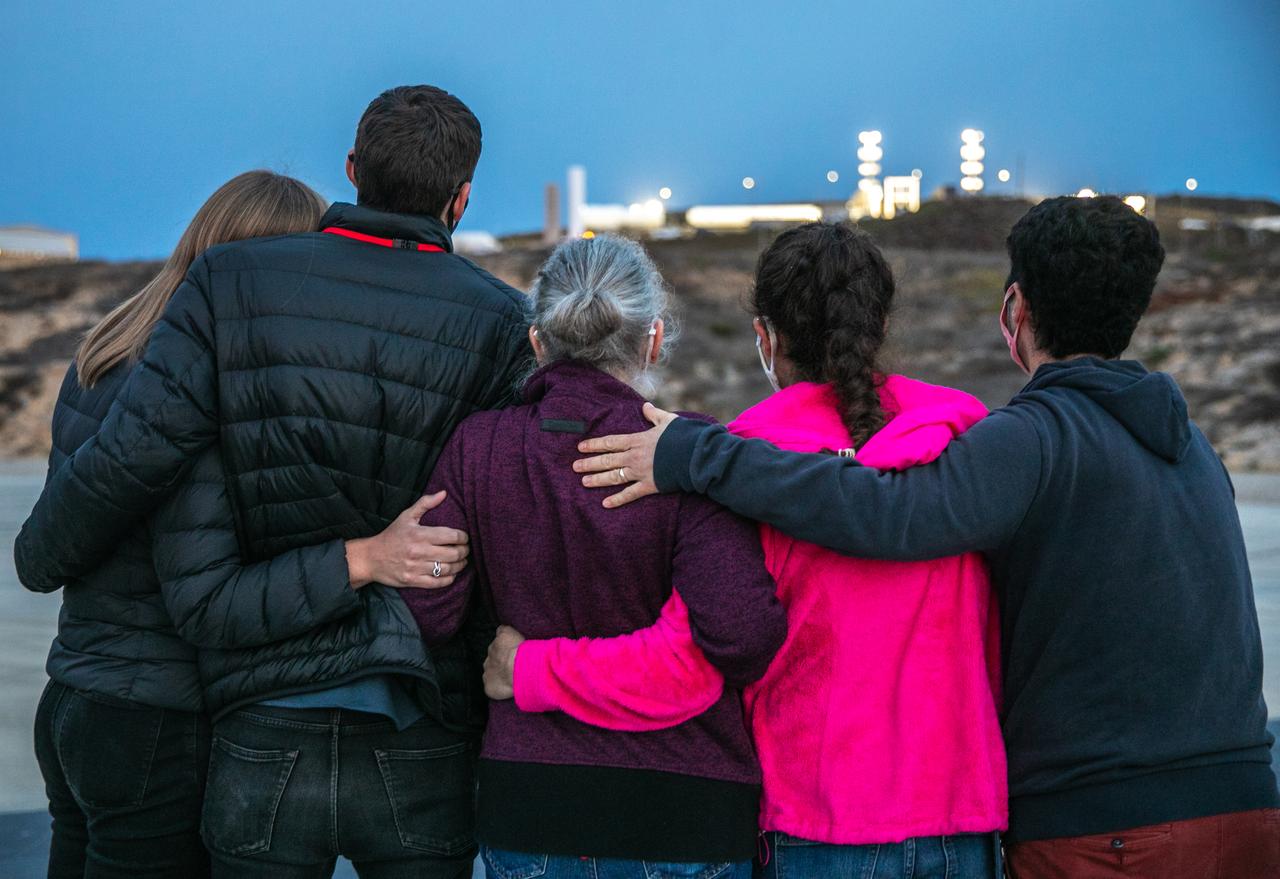

Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

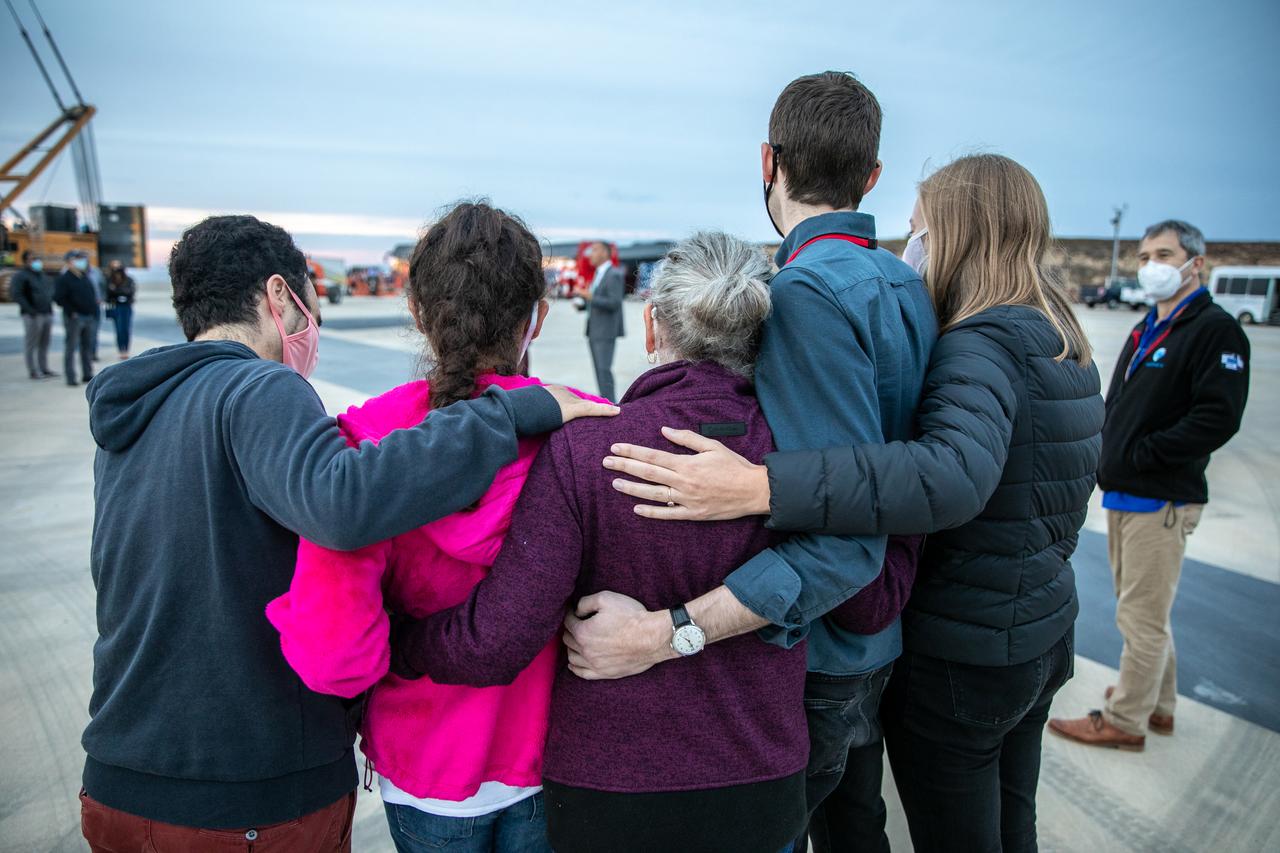
Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

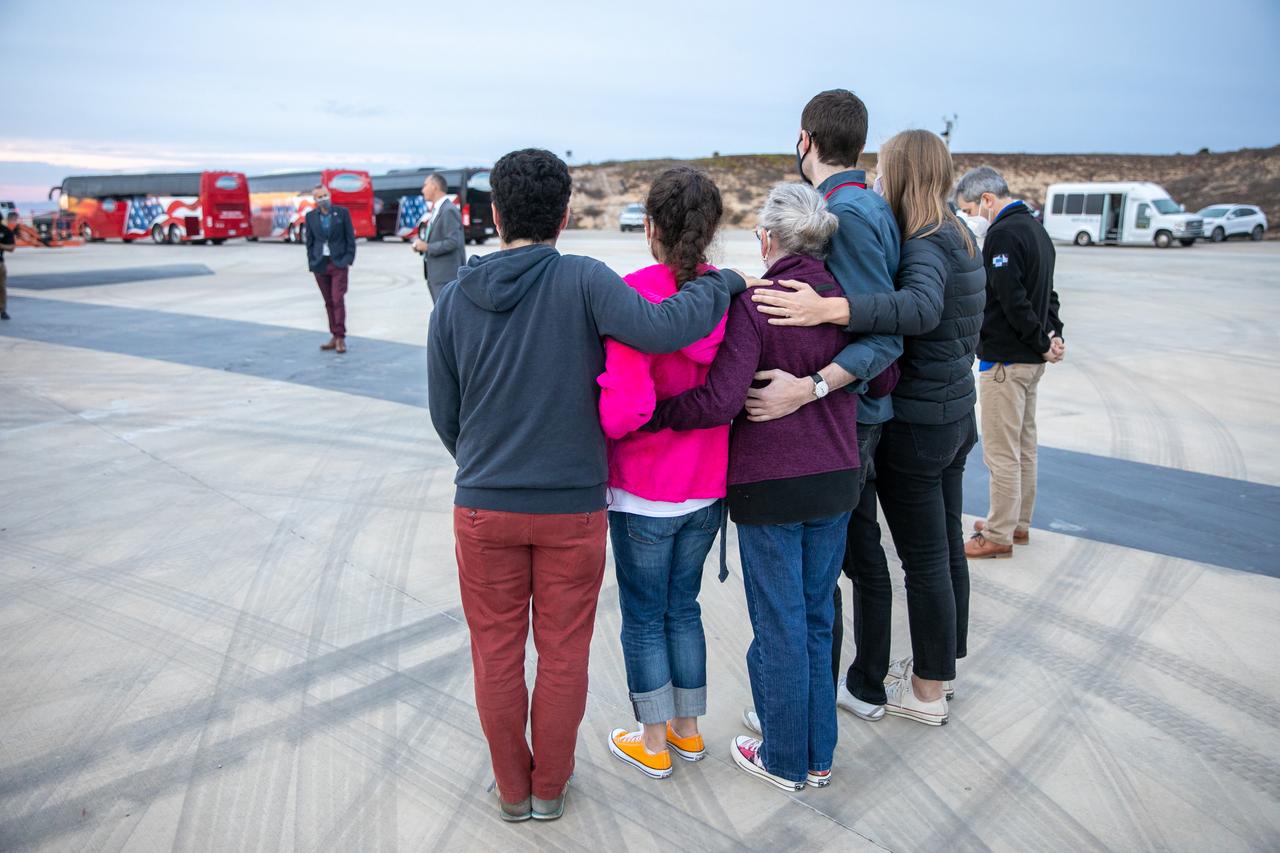
Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Family members of Dr. Michael Freilich, for whom the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is named, gather at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, the day before the spacecraft’s planned launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket. Freilich served as director of NASA’s Earth Science Division in the Science Mission Directorate at the agency’s Headquarters from 2006 until his retirement in 2019. A tireless advocate for advancing satellite measurements of the ocean, he was instrumental in advancing ocean altimetry and helped drive the evolution of NASA Earth science from a program that launched an Earth-observing space mission every few years to one that launches several missions each year. Freilich died Aug. 5, 2020, of pancreatic cancer. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

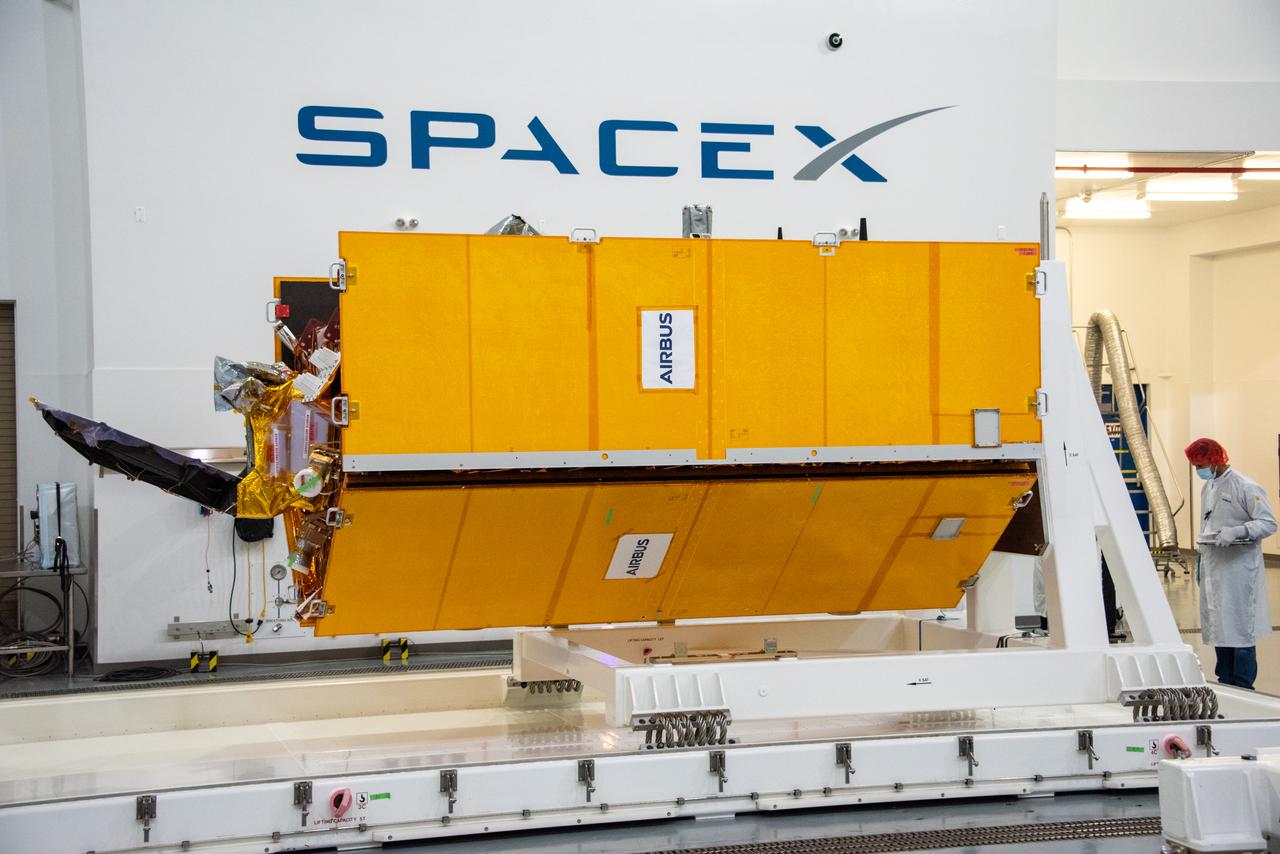
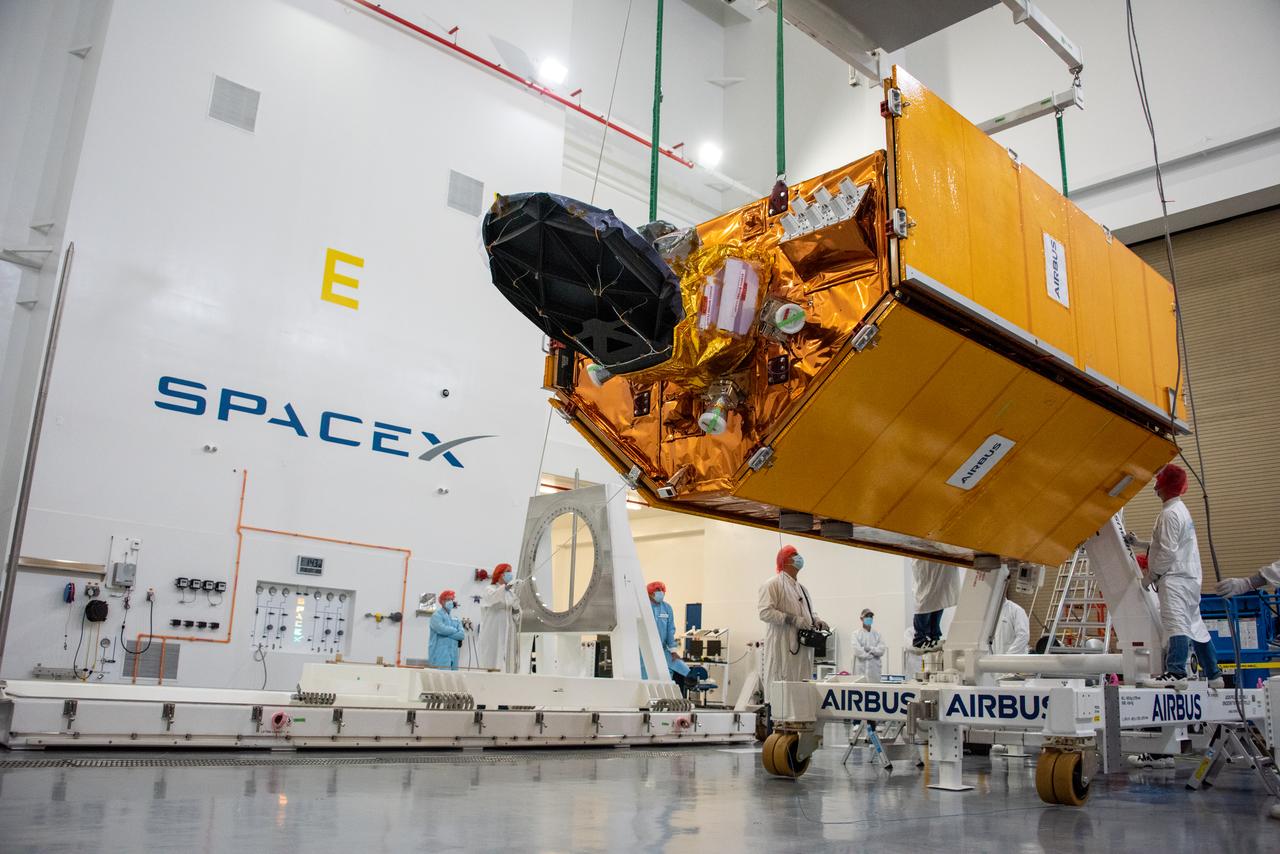
Technicians and engineers working on the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite pose in front of the spacecraft as it sits in a protective nosecone, or payload fairing, in the SpaceX Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Once it's closed up, the fairing will sit atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket when it launches from Vandenburg Air Force Base in central California in late November 2020. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical satellites that are a part of the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission, a U.S.-European collaboration. The mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world's oceans, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich's twin, Sentinel-6B, is scheduled to launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24134
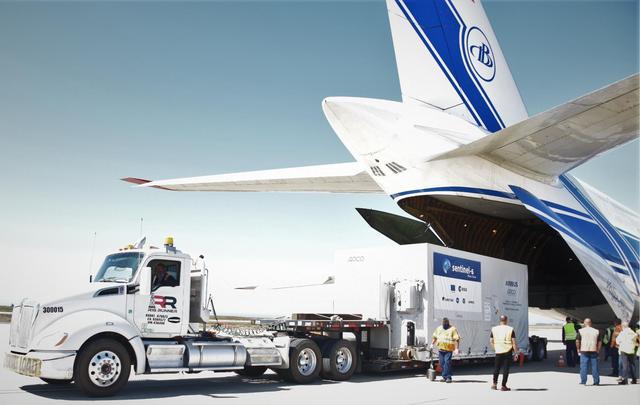

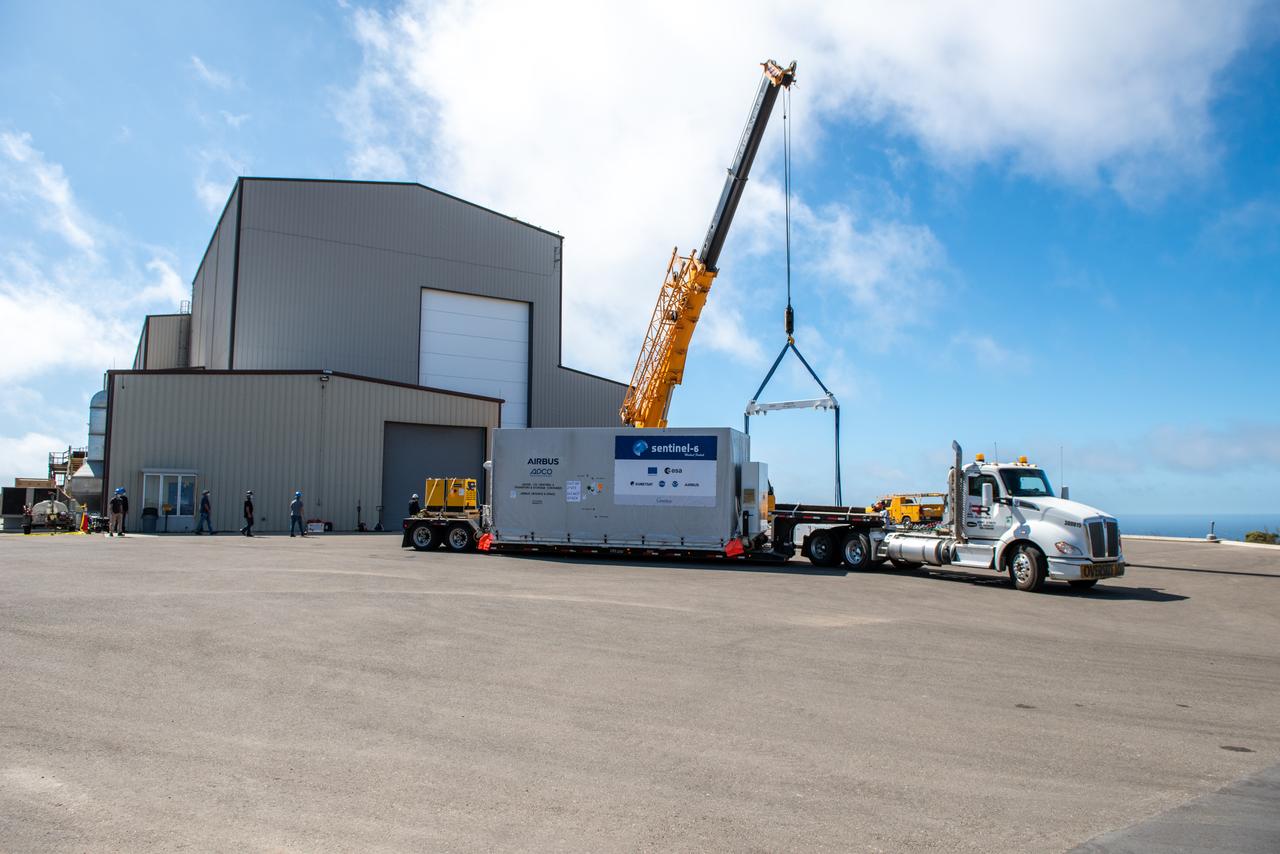
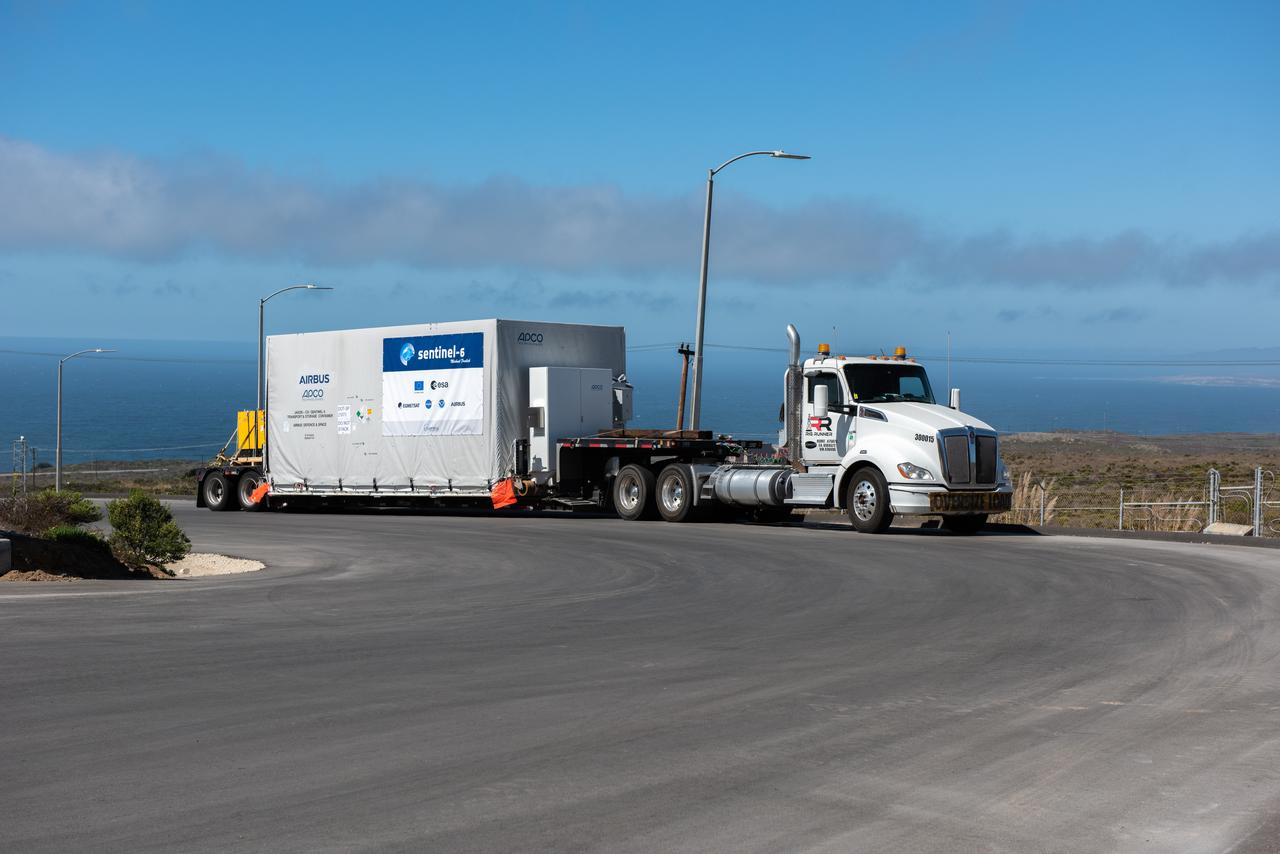
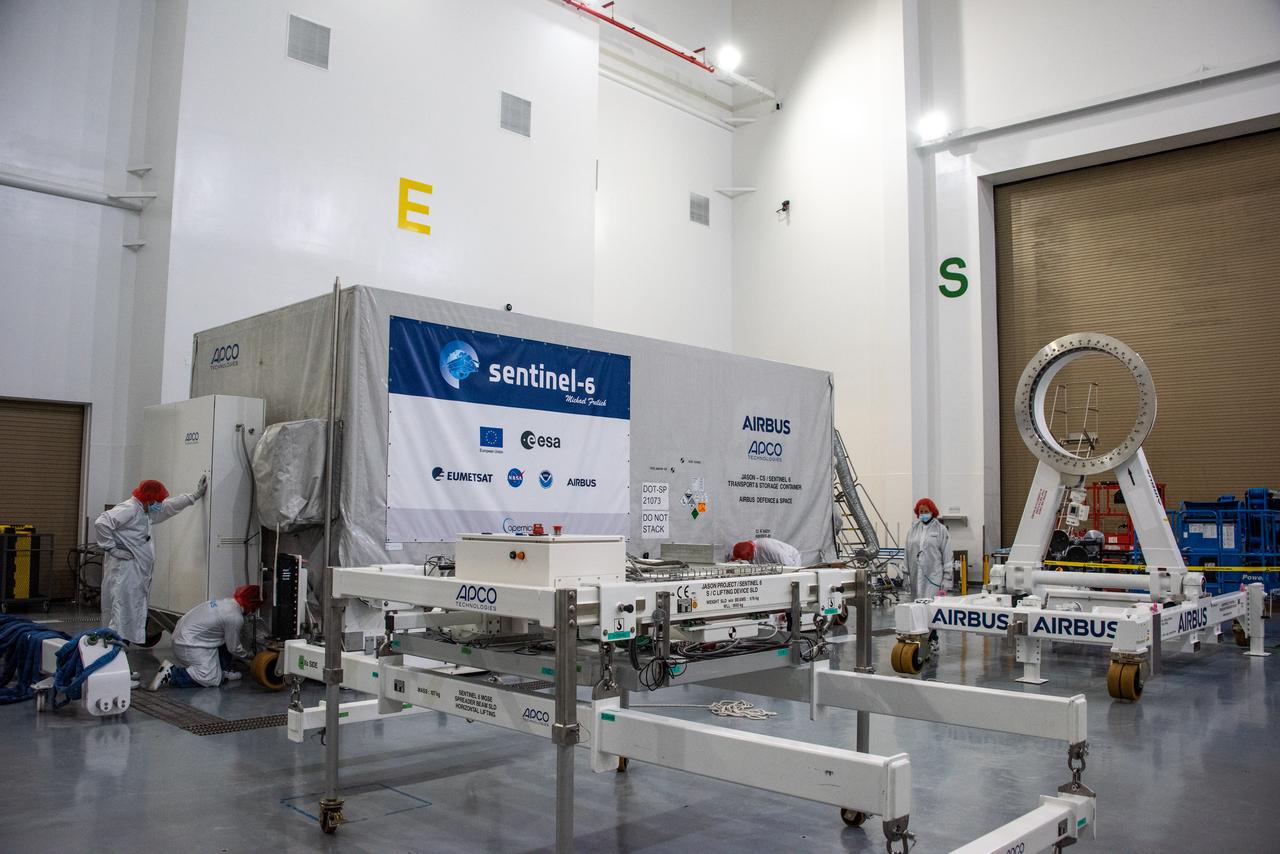
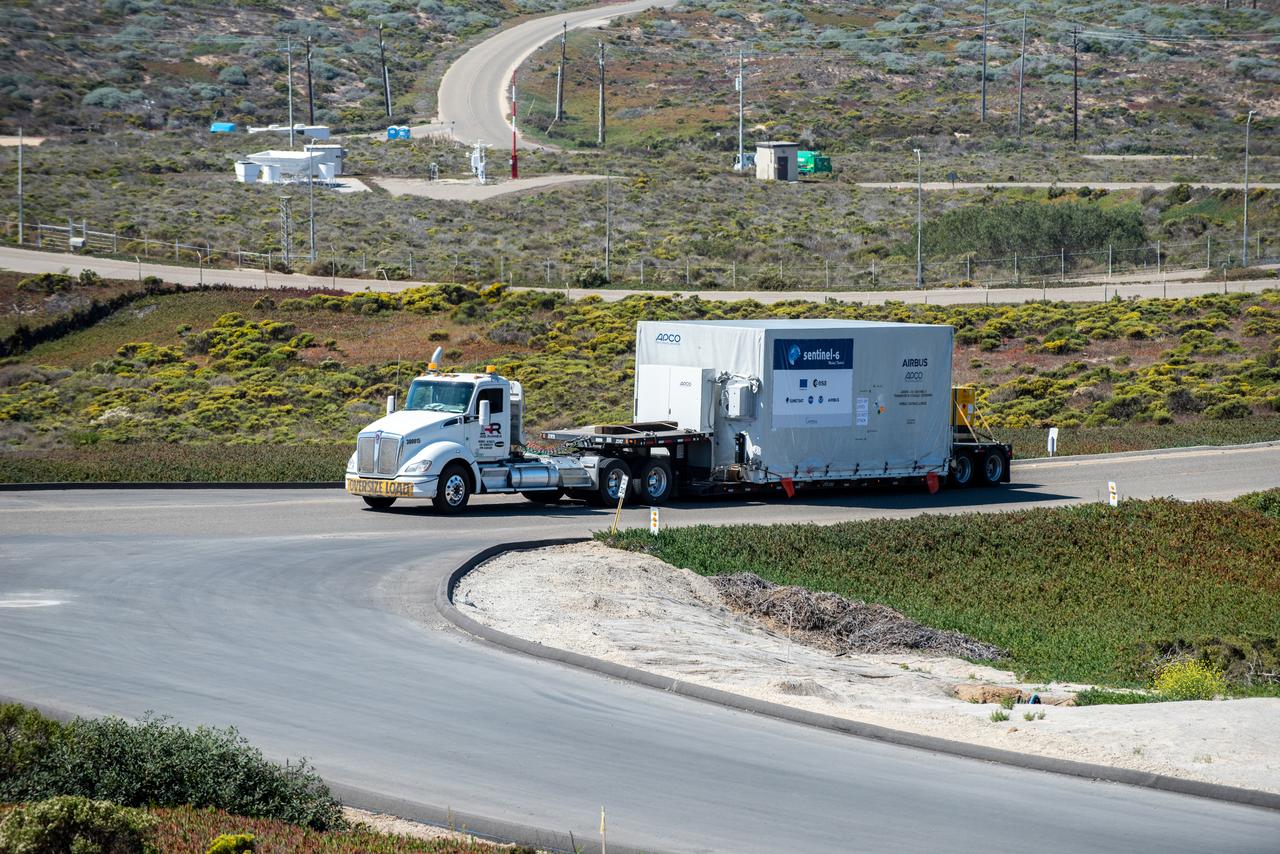
A shipping container containing the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is transported on a truck to the SpaceX payload processing facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base after arriving in California on Sept. 24, 2020. An Antonov aircraft carrying the spacecraft arrived at around 10:40 a.m. PDT (1:40 p.m. EDT) after a two-day journey from an IABG engineering facility near Munich, Germany. The ocean-monitoring satellite will undergo prelaunch tests before its scheduled launch on Nov. 10, 2020. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich will begin a five-and-a-half-year mission to collect sea surface height measurements down to the centimeter for 90% of the world's oceans. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. Sentinel-6/Jason-CS is being jointly developed by ESA, the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), NASA, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, with funding support from the European Commission and technical support from France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). JPL, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, is contributing three science instruments for each Sentinel-6 satellite: the Advanced Microwave Radiometer, the Global Navigation Satellite System - Radio Occultation, and the Laser Retroreflector Array. NASA is also contributing launch services, ground systems supporting operation of the NASA science instruments, the science data processors for two of these instruments, and support for the international Ocean Surface Topography Science Team. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24104
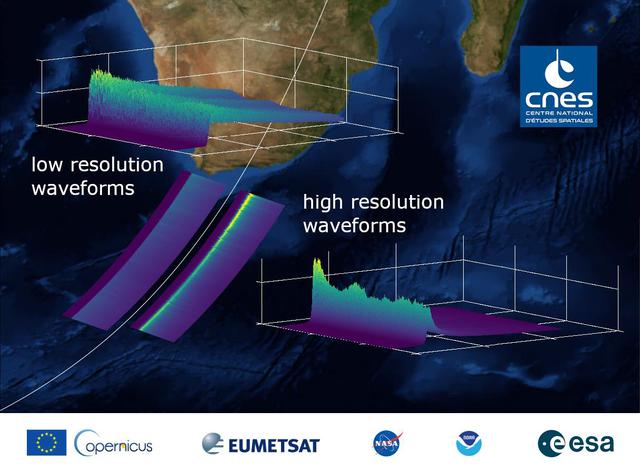
This graphic, released on Dec. 10, 2020, shows the basic radar measurements, called waveforms, collected by the instrument that monitors sea level on the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which launched Nov. 21, 2020. The instrument, called an altimeter, works by bouncing a radar signal off the ocean surface and measuring how long it takes to go out and return. The higher-resolution waveforms focus on a smaller area of the ocean than the lower-resolution waveforms, allowing researchers to resolve smaller ocean features such as currents closer to the coast. The waveform provides information not only on sea level, but also on wave height and wind speed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24136
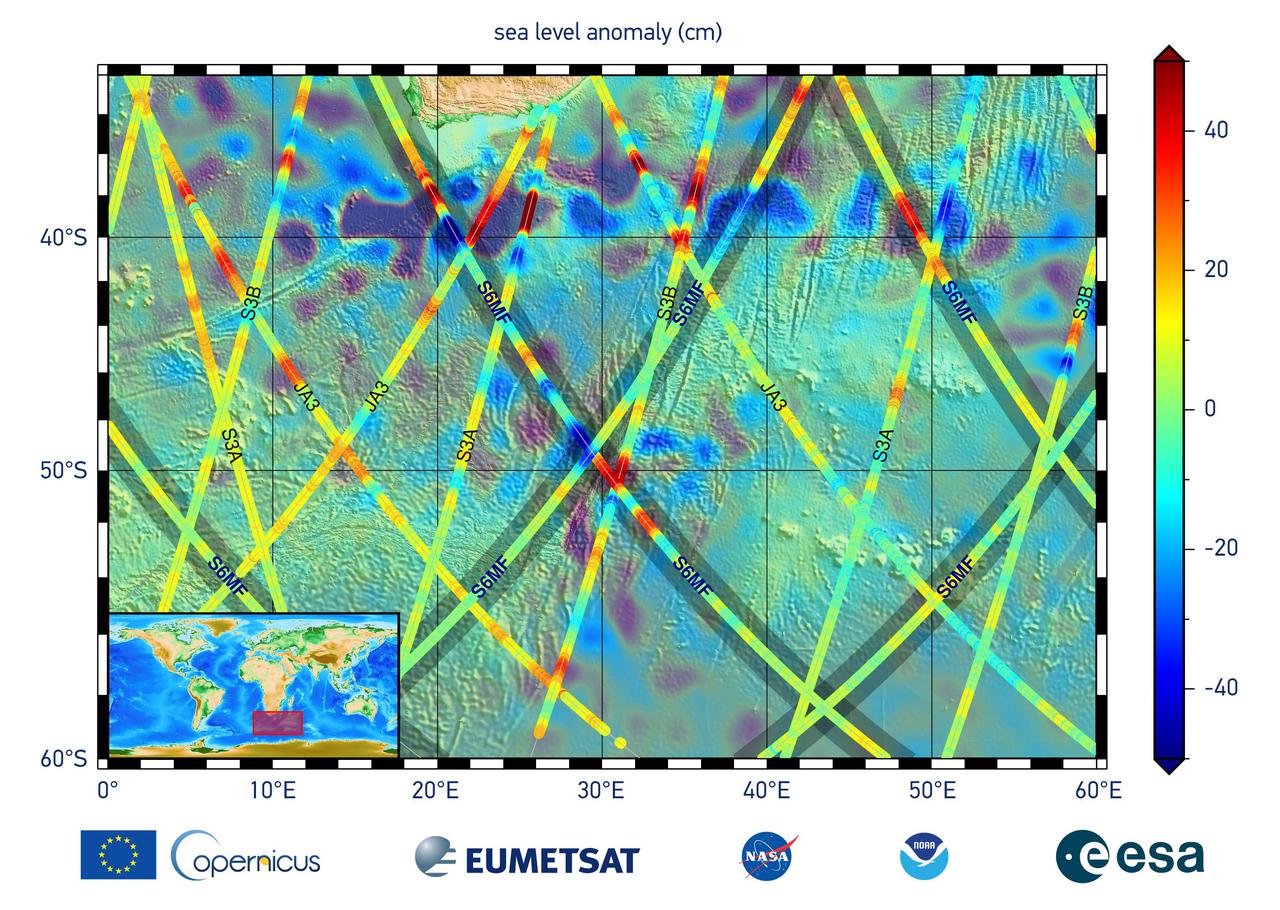
This graphic, released on Dec. 10, 2020, shows the first sea level measurements taken by Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich (S6MF), which launched Nov. 21, 2020. It focuses on the ocean off the southern tip of Africa, where red colors indicate higher sea level relative to blue areas, which are lower. Also included are sea surface height measurements from three other satellites for comparison: Jason-3 (JA3), Sentinel-3A (S3A), and Sentinel-3B (S3B). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24135

This illustration shows the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft in orbit above Earth with its deployable solar panels extended. As the world's latest ocean-monitoring satellite, it will collect the most accurate data yet on global sea level and how our oceans are rising in response to climate change. The mission will also collect precise data of atmospheric temperature and humidity that will help improve weather forecasts and climate models. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich extends the near-30-year record of satellite measurements of sea level that was initiated by the U.S.-European TOPEX/Poseidon mission in 1992 and continued with the Jason-1, 2, and 3 series of sea level observation satellites. Launched in 2016, Jason-3 is currently providing data. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). Other partners include the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the intergovernmental European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), and France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24105
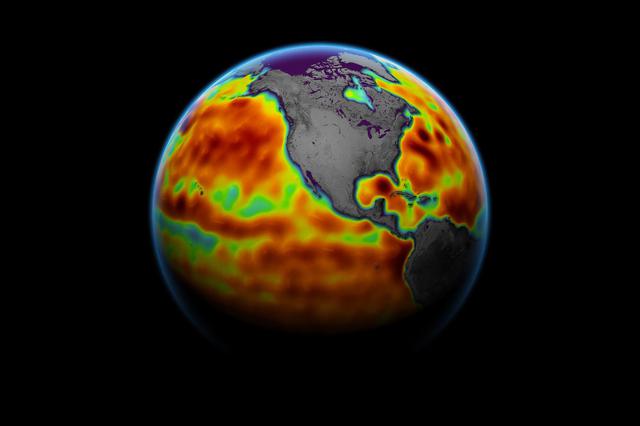
This map shows sea level measured by the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite from June 5 to15. Red areas are regions where sea level is higher than normal, and blue areas indicate areas where it's lower than normal. The measurements are part of a set of data streams that become available to the public hours to a couple of days after the satellite collects them. The difference in when the products become available balances accuracy with delivery timeliness for tasks like forecasting the weather or helping to monitor the formation of hurricanes. The satellite, named after former NASA Earth Science Division Director Michael Freilich, collects its measurements for about 90% of the world's oceans. The spacecraft is one of two satellites that compose the Copernicus Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission. The second satellite, Sentinel-6B, is slated for launch in 2025. Together, they are the latest in a series of spacecraft starting with TOPEX/Poseidon in 1992 and continuing with the Jason series of satellites that have been gathering precise ocean height measurements for nearly 30 years. Shortly after launch in Nov. 2020, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich moved into position, trailing the current reference sea level satellite Jason-3 by 30 seconds. Scientists and engineers then spent time cross-calibrating the data collected by both satellites to ensure the continuity of measurements between the two. Once assured of the data quality, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich will then become the primary sea level satellite. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24533

A shipping container containing the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is removed from an Antonov 124 aircraft at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The flight arrived at around 10:40 a.m. PDT (1:40 p.m. EDT) after a two-day journey from an IABG engineering facility near Munich, Germany. The ocean-monitoring satellite will undergo prelaunch tests before its scheduled launch on Nov. 10, 2020. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich will begin a five-and-a-half-year mission to collect sea surface height measurements down to the centimeter for 90% of the world's oceans. The satellite is named after Dr. Michael Freilich, the former director of NASA's Earth Science Division and an instrumental figure in advancing ocean observations from space. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is one of two identical spacecraft that compose the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission developed in partnership with ESA (the European Space Agency). ESA is developing the new Sentinel family of missions specifically to support the operational needs of the European Union's Copernicus program, the EU's Earth observation program managed by the European Commission. The spacecraft's twin, Sentinel-6B, will launch in 2025. Sentinel-6/Jason-CS is being jointly developed by ESA, the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), NASA, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, with funding support from the European Commission and technical support from France's National Centre for Space Studies (CNES). NASA JPL is contributing three science instruments for each Sentinel-6 satellite: the Advanced Microwave Radiometer, the Global Navigation Satellite System - Radio Occultation, and the Laser Retroreflector Array. NASA is also contributing launch services, ground systems supporting operation of the NASA science instruments, the science data processors for two of these instruments, and support for the international Ocean Surface Topography Science Team. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24103

Daniel Freilich, left, and Sarah Freilich, children of Dr. Michael Freilich, speak with NASA Commentators Derrol Nail and Marina Jurica during the launch broadcast for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission on Nov. 21, 2020, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Daniel Freilich, left, and Sarah Freilich, children of Dr. Michael Freilich, participate in the launch broadcast for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission on Nov. 21, 2020, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

Tim Dunn, launch director for NASA’s Launch Services Program, participates in a Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich virtual media briefing from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 16, 2020. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is scheduled to launch on Nov. 10, 2020, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Station. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida is responsible for launch management.
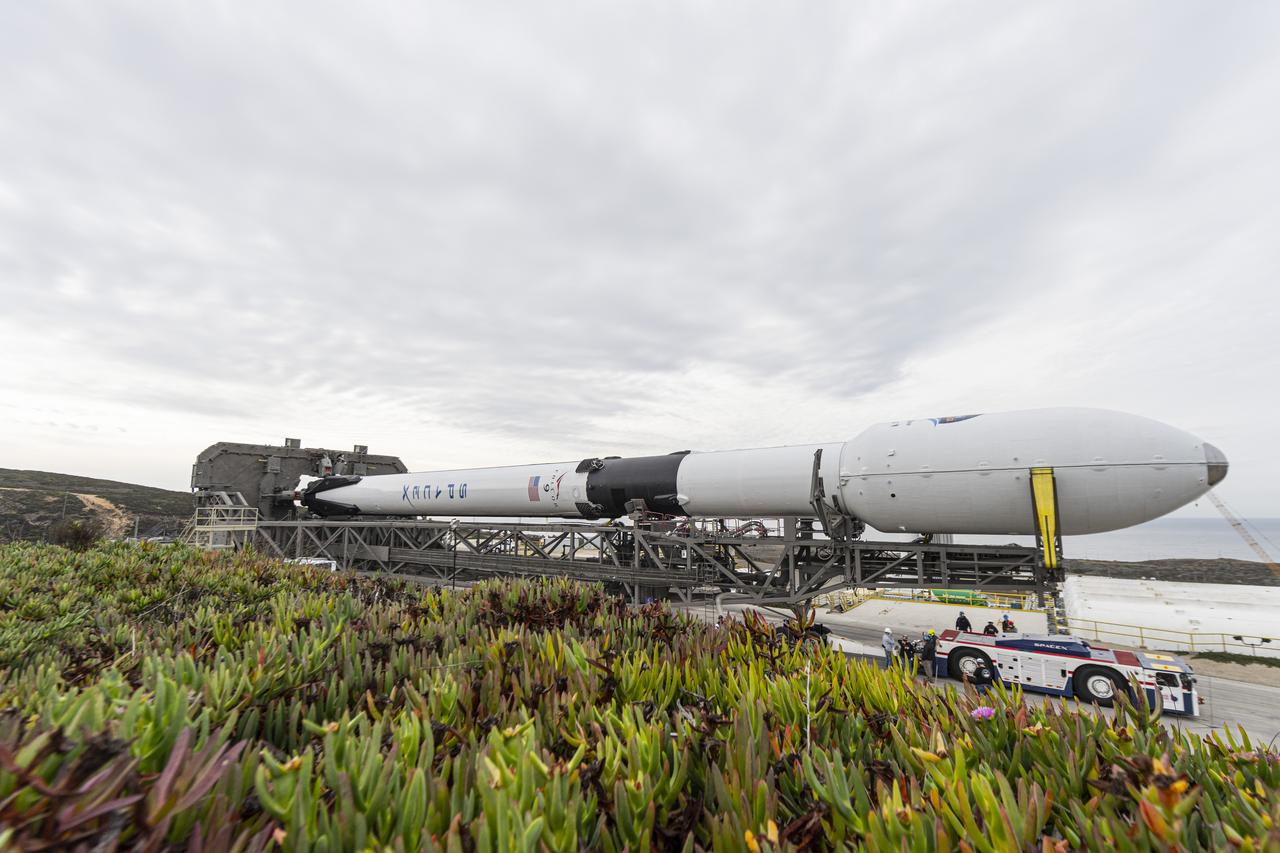

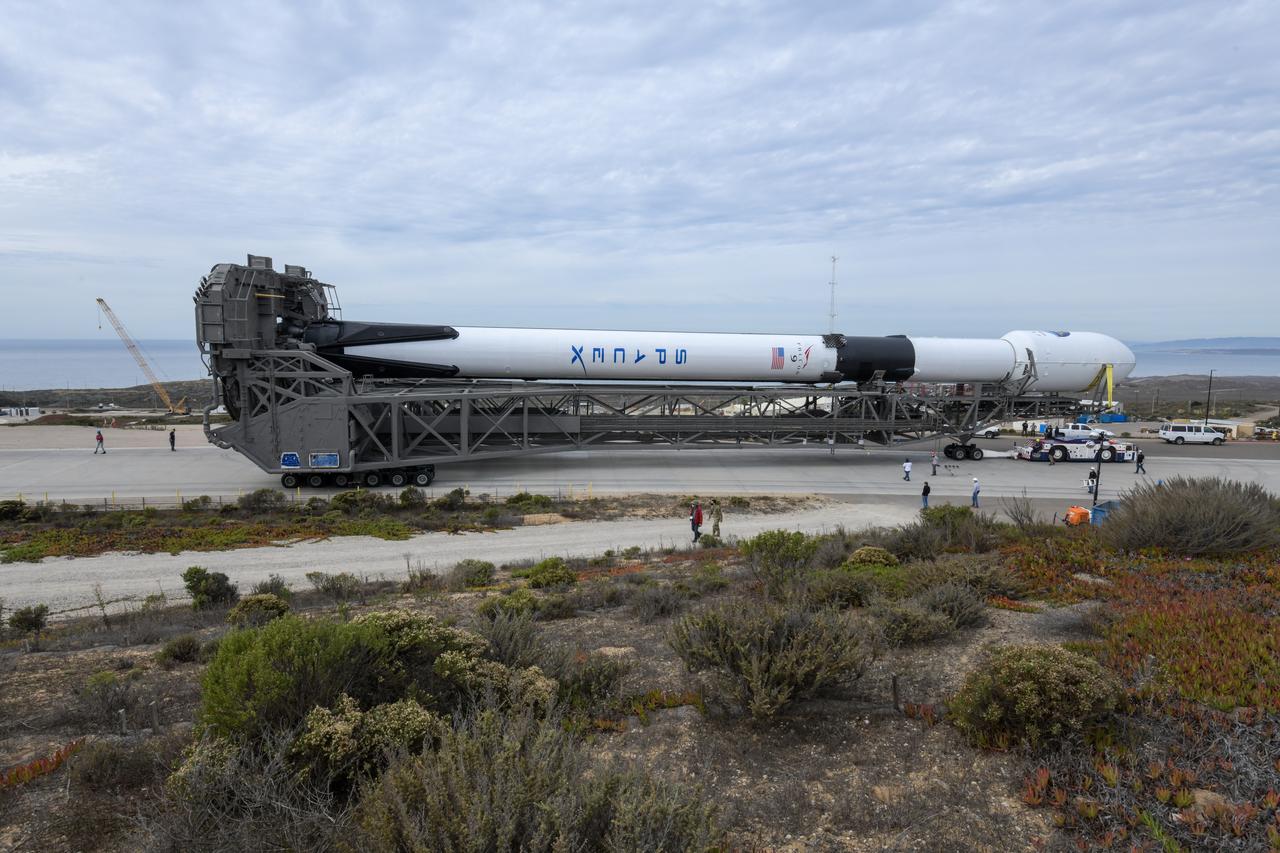
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, is rolled to Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, in preparation for launch. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
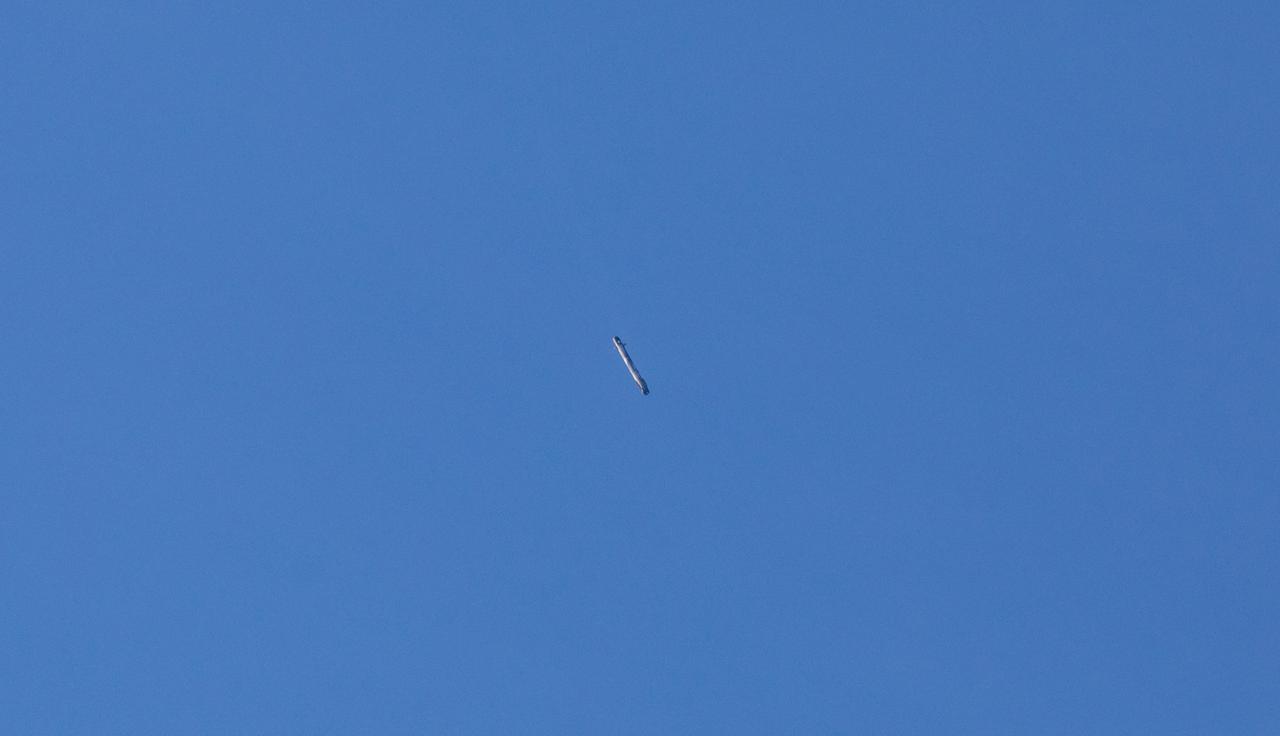

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down toward a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
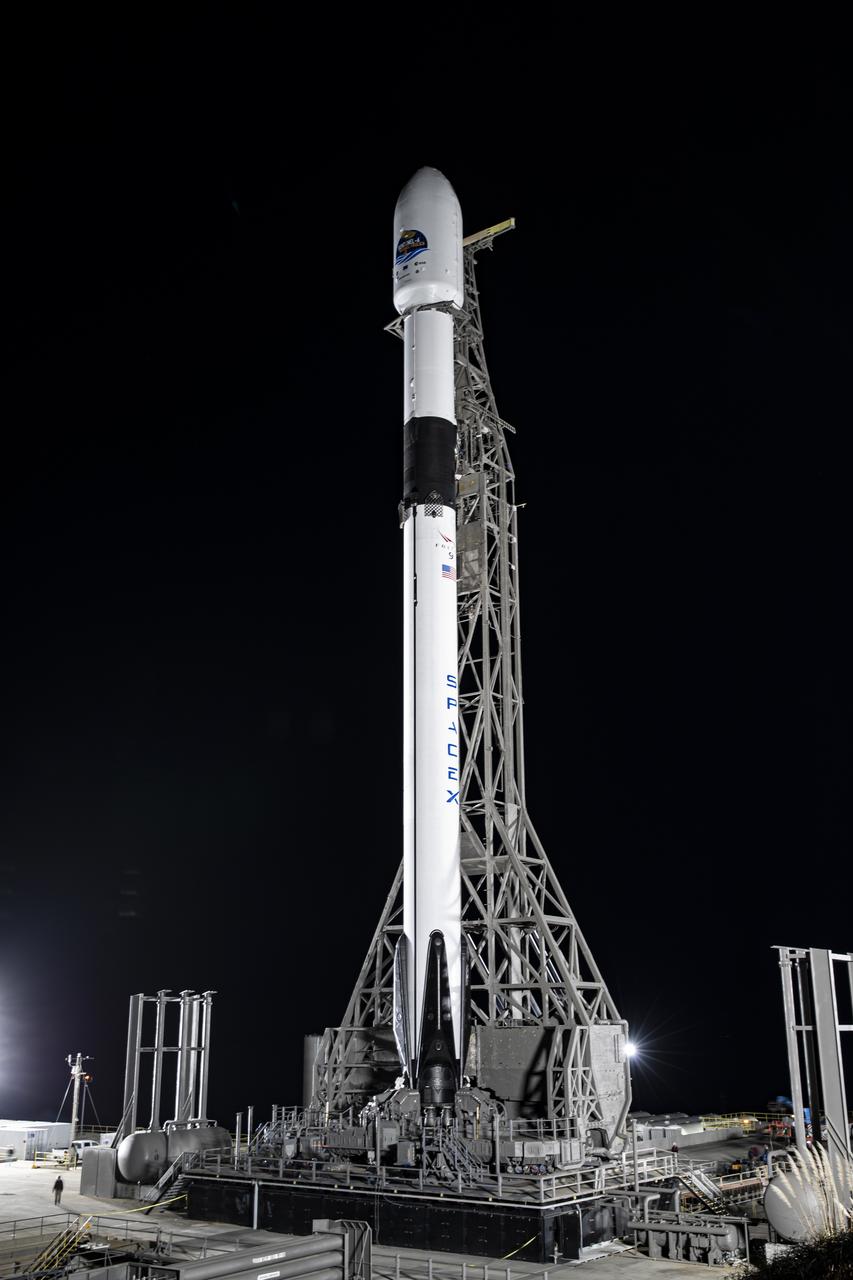

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
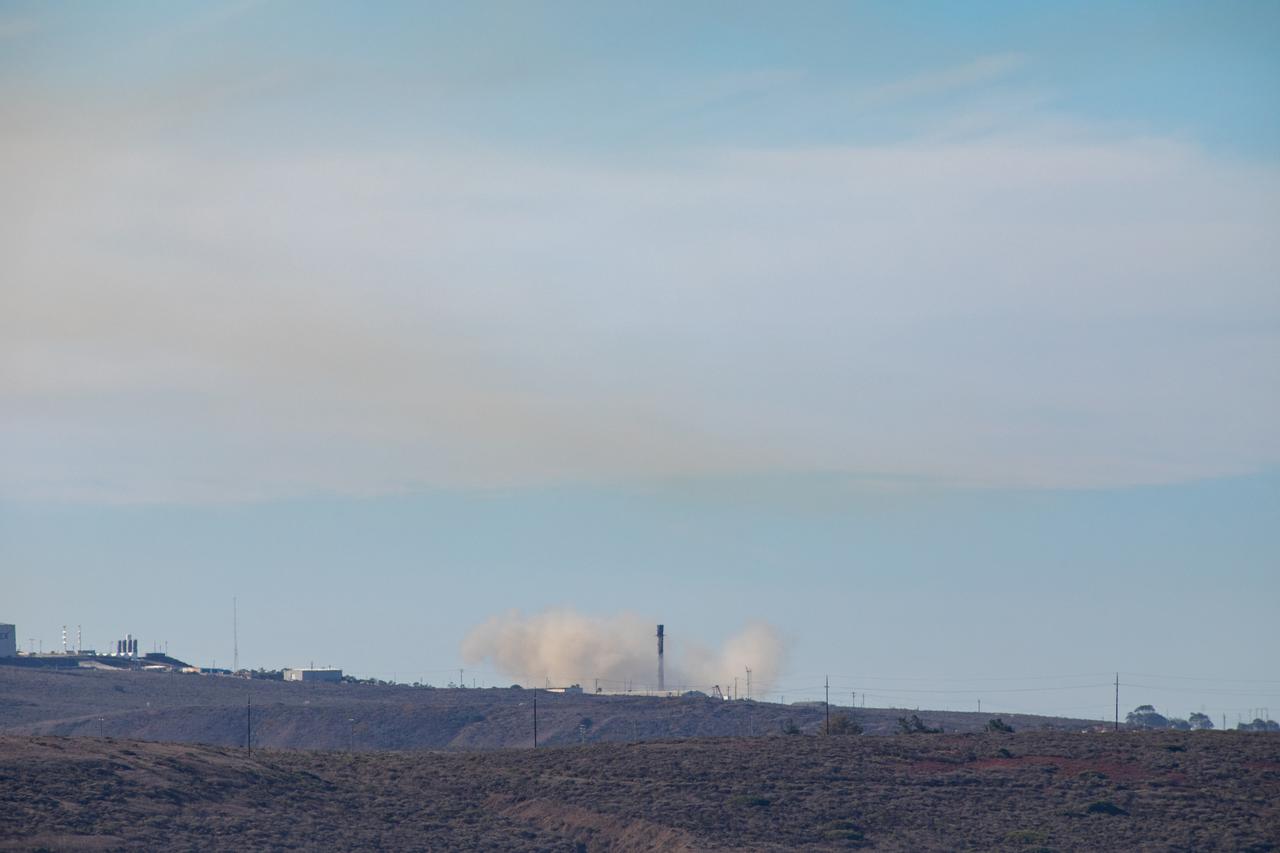

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Phillip Hargrove, a NASA launch trajectory analyst with the agency’s Launch Services Program, left, and NASA Launch Commentator Joshua Santora participate in the launch broadcast for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission on Nov. 21, 2020, in the Press Site auditorium at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft launched from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Phillip Hargrove, a NASA launch trajectory analyst with the agency’s Launch Services Program, participates in the launch broadcast for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission on Nov. 21, 2020, in the Press Site auditorium at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft launched from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, rolls from SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

NASA Program Scientist Nadya Vinogradova Shiffer, left, of the agency’s Science Mission Directorate, speaks with NASA Commentators Derrol Nail and Marina Jurica during the launch broadcast for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission on Nov. 21, 2020, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

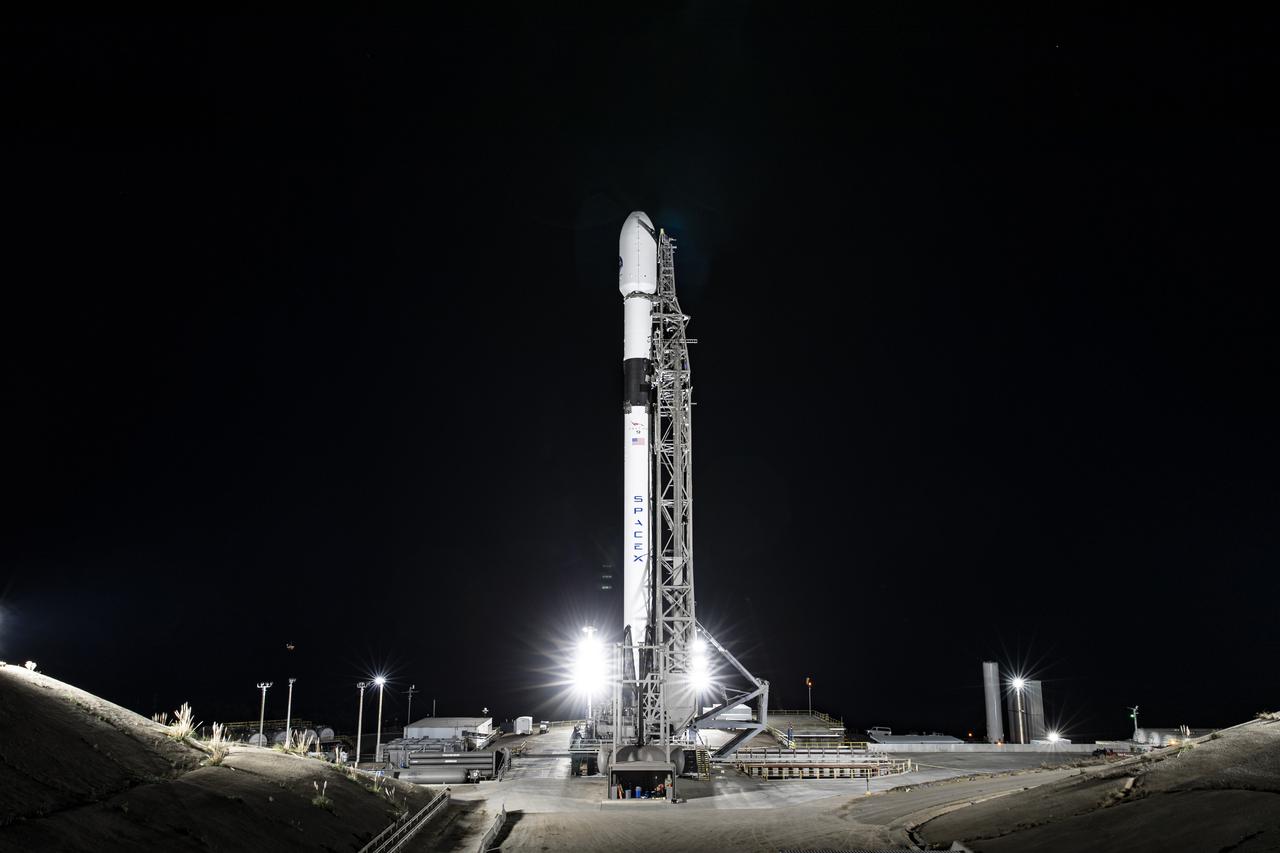
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft awaits liftoff from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
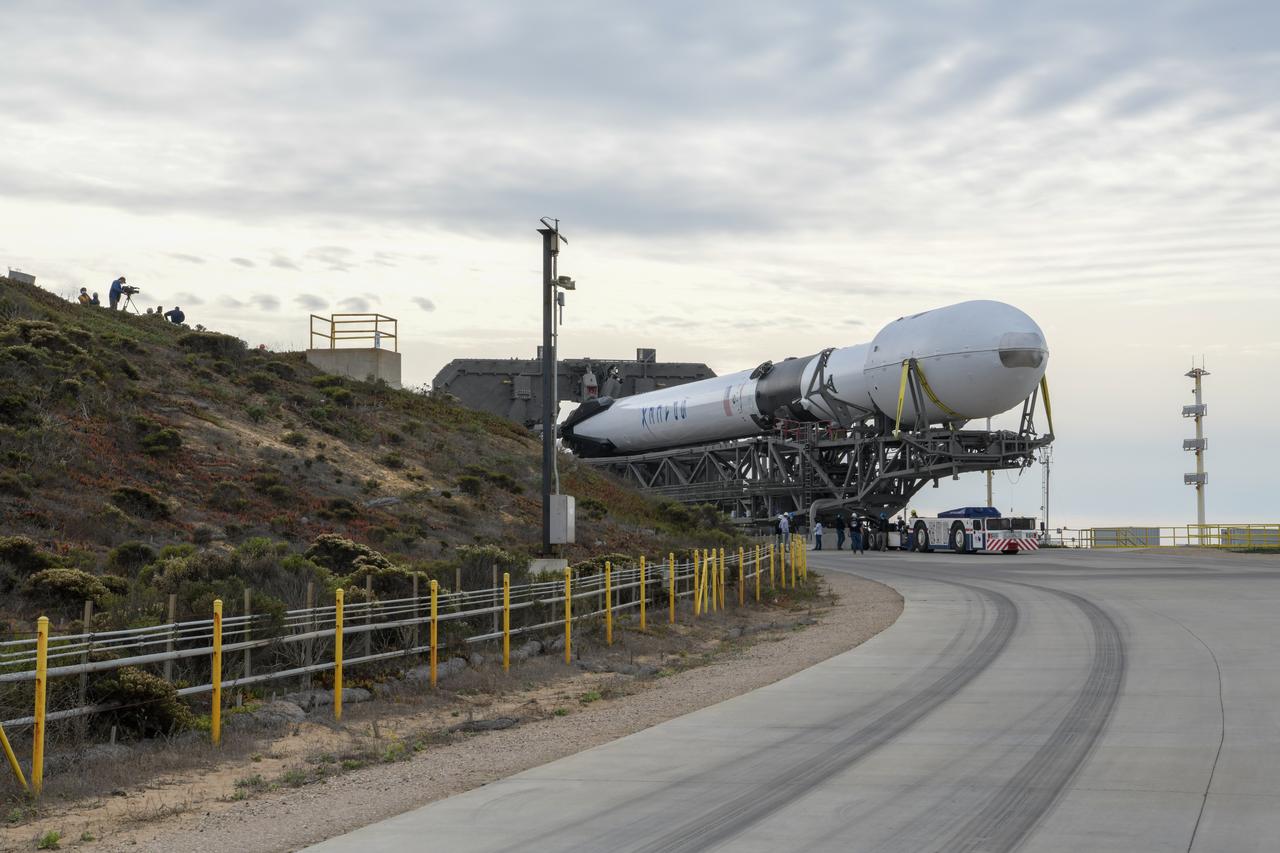

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, rolls from SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

NASA Launch Commentator Derrol Nail participates in the launch broadcast for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission on Nov. 21, 2020, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft launched from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, rolls from SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Clear, sunny skies provide a backdrop for California’s Vandenberg Air Force Base, where the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft awaits liftoff from Space Launch Complex 4, Nov. 21, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
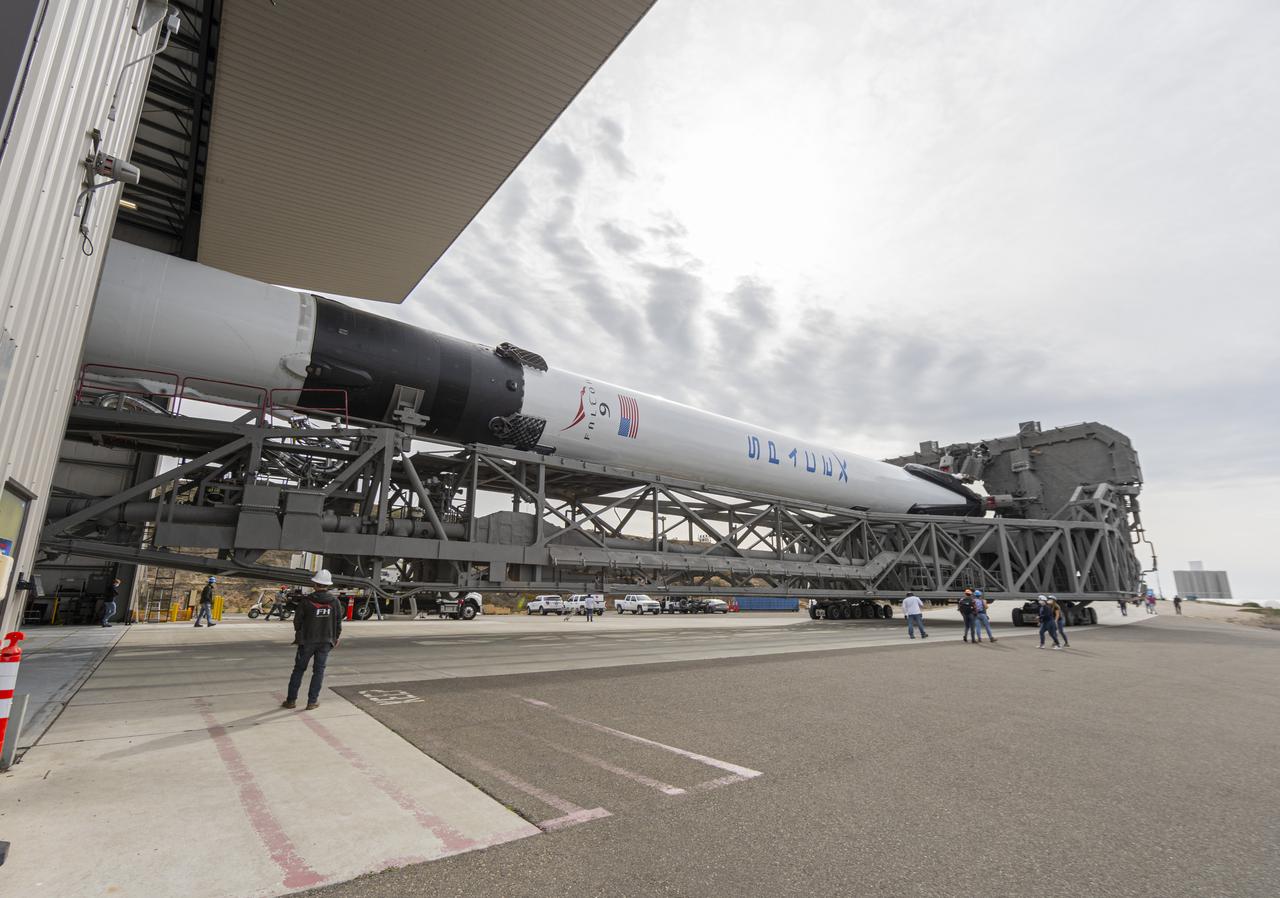

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, departs SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California for its journey to Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
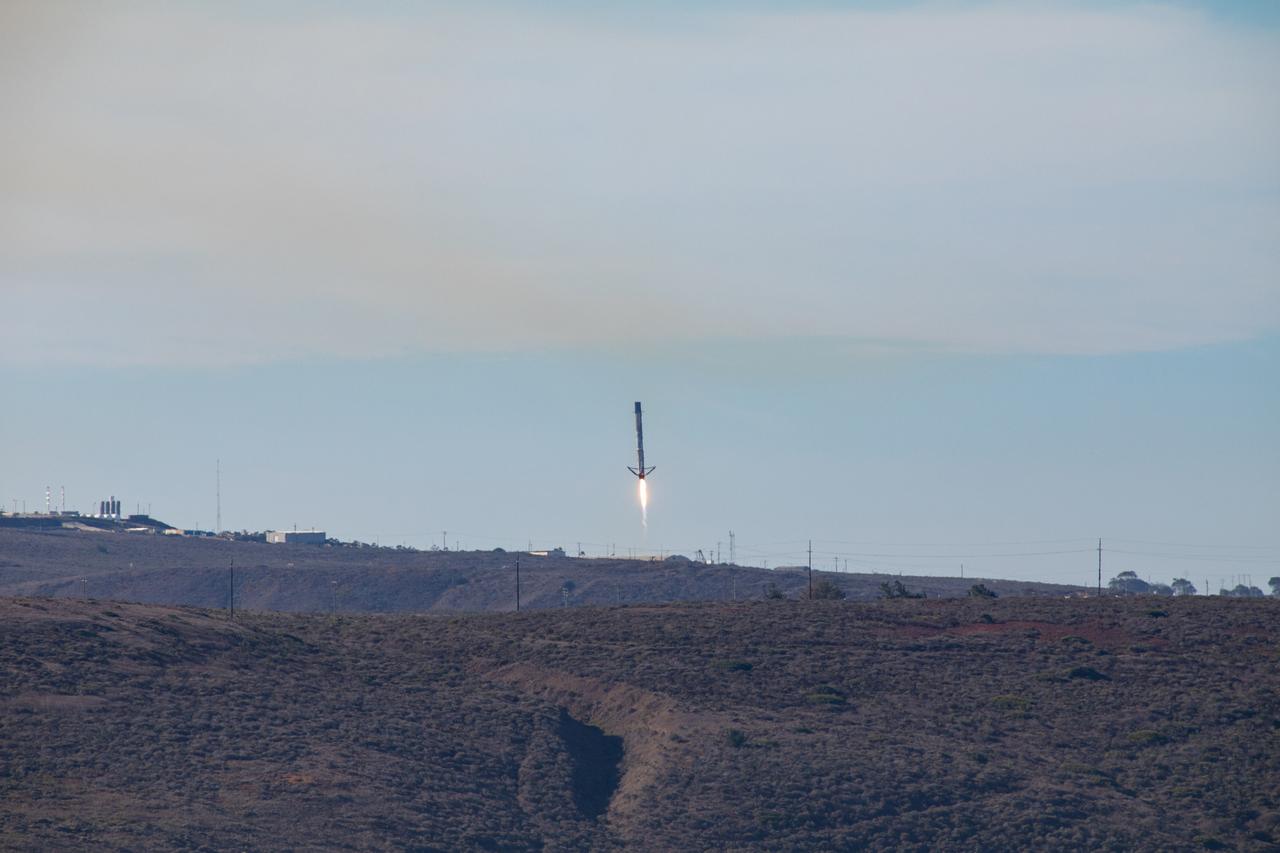

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
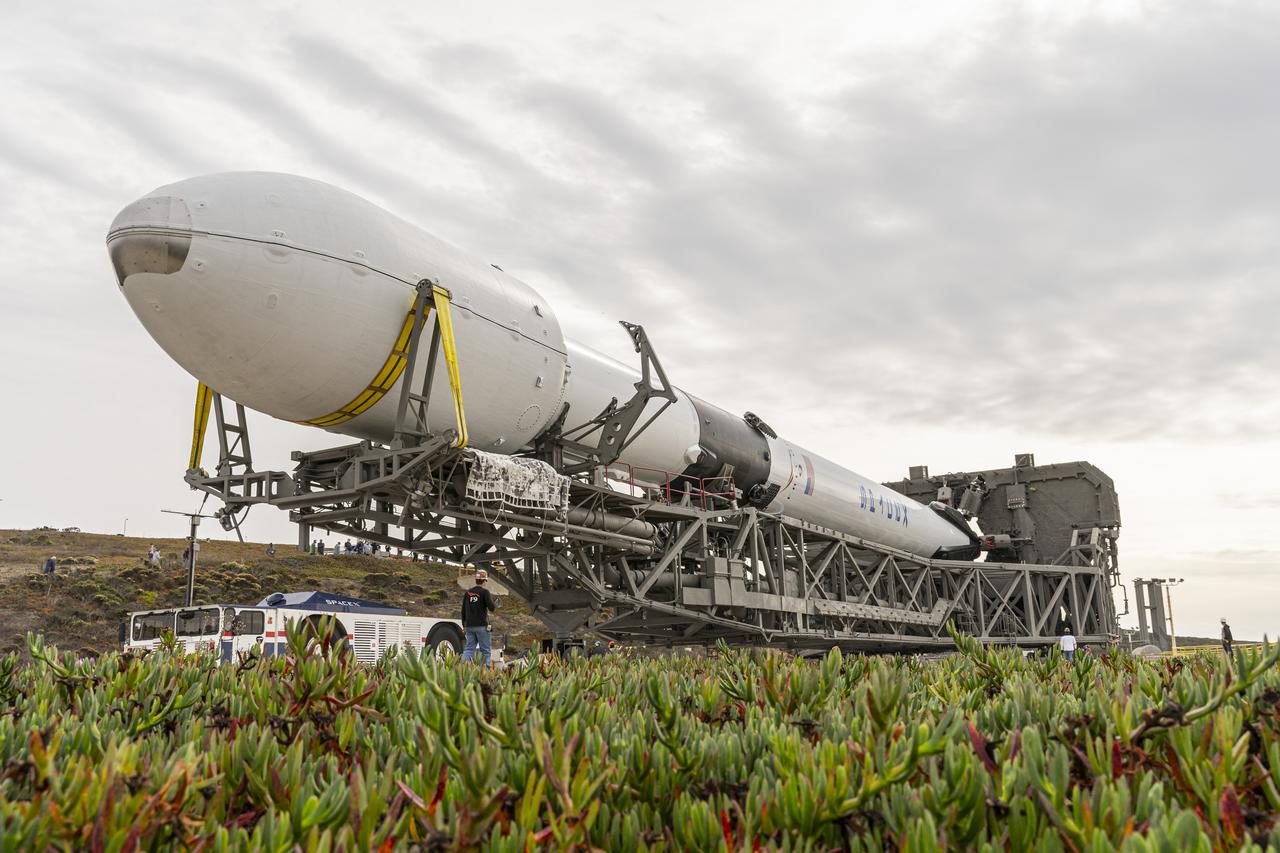

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, is rolled to Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020, in preparation for launch. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
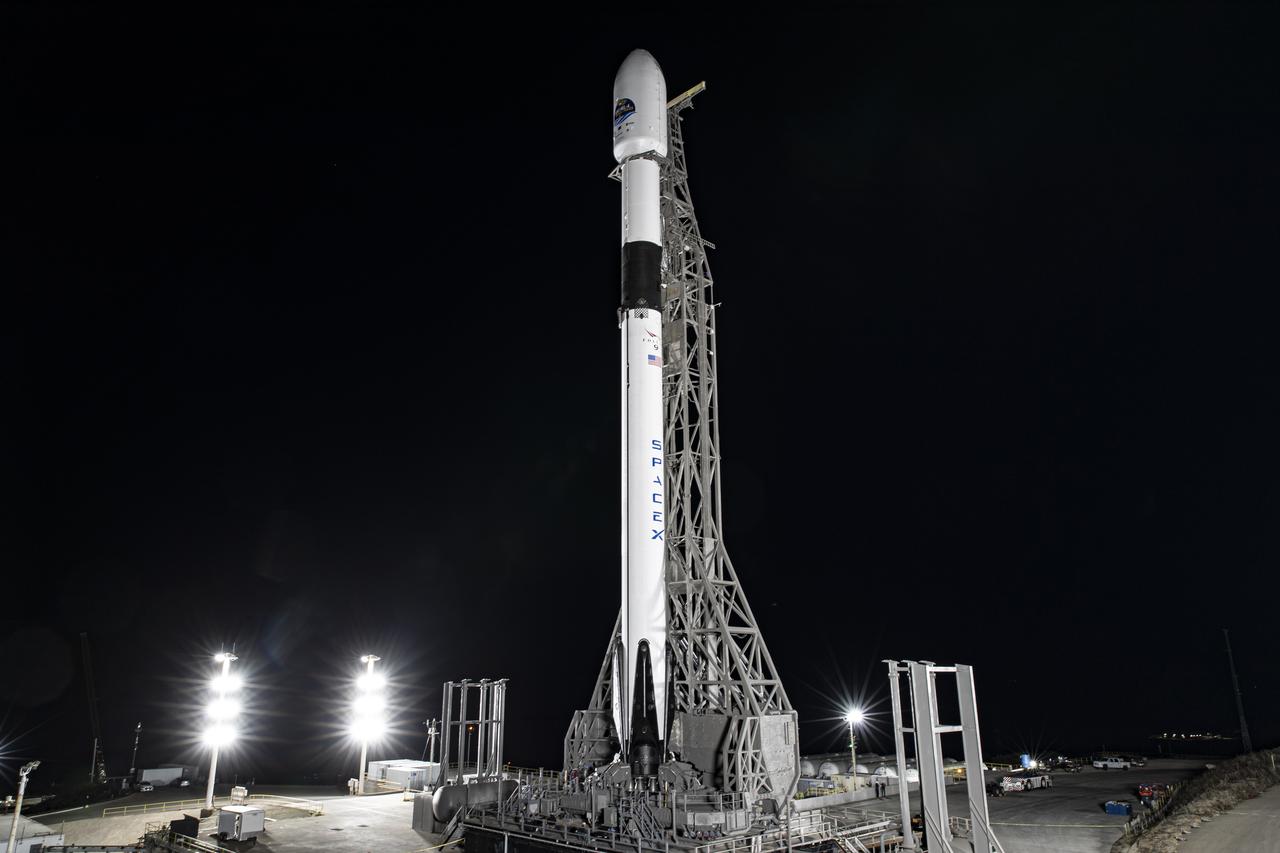

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

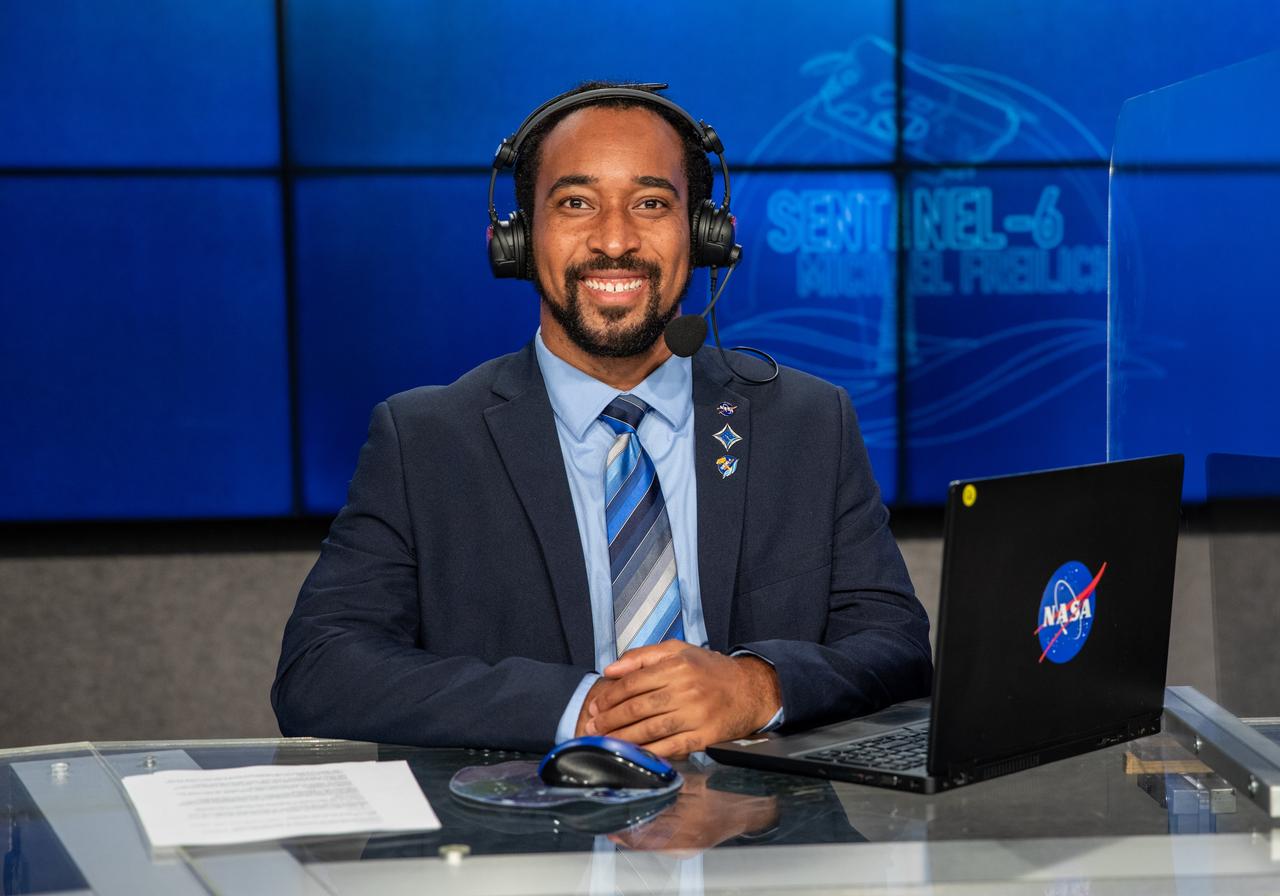
NASA Launch Commentator Joshua Santora participates in the launch broadcast for the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission on Nov. 21, 2020, in the Press Site auditorium at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft launched from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The protective payload fairing containing the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite is seen atop the SpaceX Falcon 9 after the rocket was lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down toward a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, topped with the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite secured inside its payload fairing, rolls from SpaceX’s Payload Processing Facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 20, 2020. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich team members from European Space Agency pose with the spacecraft during processing. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 10, 2020 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is responsible for launch management.

Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich team members from European Space Agency pose with the spacecraft during processing. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 10, 2020 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is responsible for launch management.

Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich team members from European Space Agency pose with the spacecraft during processing. Launch is scheduled for Nov. 10, 2020 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center is responsible for launch management.

This graph shows the rise in global mean sea level from 1993 to 2023 based on data from a series of five international satellites. The solid red line indicates the trajectory of this increase, which has more than doubled over the three decades. The dotted red line projects future sea level rise. The relatively large jump in sea level from 2022 to 2023, a rise of about 0.3 inches (0.76 centimeters), is due mostly to a warming climate and the development of a strong El Niño. The 2022-2023 rise is equivalent to draining a quarter of Lake Superior into the ocean over the course of a year. This NASA-led analysis is based on a sea level data set featuring more than 30 years of satellite observations, starting with the U.S.-French TOPEX/Poseidon mission, which launched in 1992. The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission, which launched in November 2020, is the latest in the series of satellites that have contributed to this sea level record. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26183
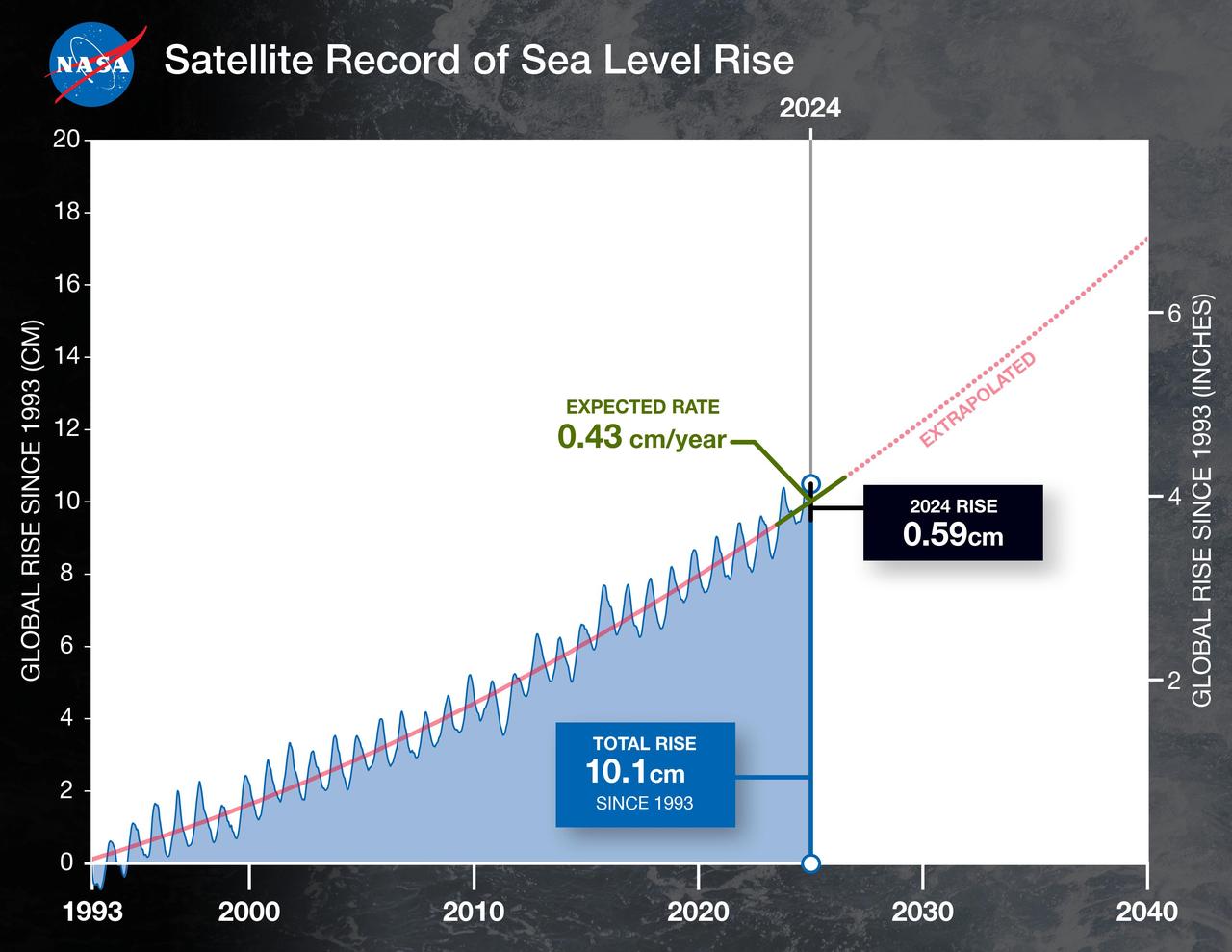
This graph shows the rise in global mean sea level from 1993 to 2024 based on data from a series of five international satellites. The solid red line indicates the trajectory of this increase, which has more than doubled over the three decades. The dotted red line projects future sea level rise. Global sea level rose faster than expected in 2024 due mostly to ocean water expanding as it warms, or thermal expansion. According to a NASA-led analysis, last year's rate of rise was 0.23 inches (0.59 centimeters) per year, compared to the expected rate of 0.17 inches (0.43 centimeters) per year. In recent years, about two-thirds of sea level rise was due to the addition of water from land into the ocean by melting ice sheets and glaciers. About a third came from thermal expansion of seawater. But in 2024, those contributions flipped, with two-thirds of sea level rise coming from thermal expansion. This NASA-led analysis is based on a sea level dataset featuring more than 30 years of satellite observations, starting with the U.S.-French TOPEX/Poseidon mission, which launched in 1992. The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission, which launched in November 2020, is the latest in the series of satellites that have contributed to this sea level record. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26189

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, arrives at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020, aboard an Antonov cargo aircraft. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
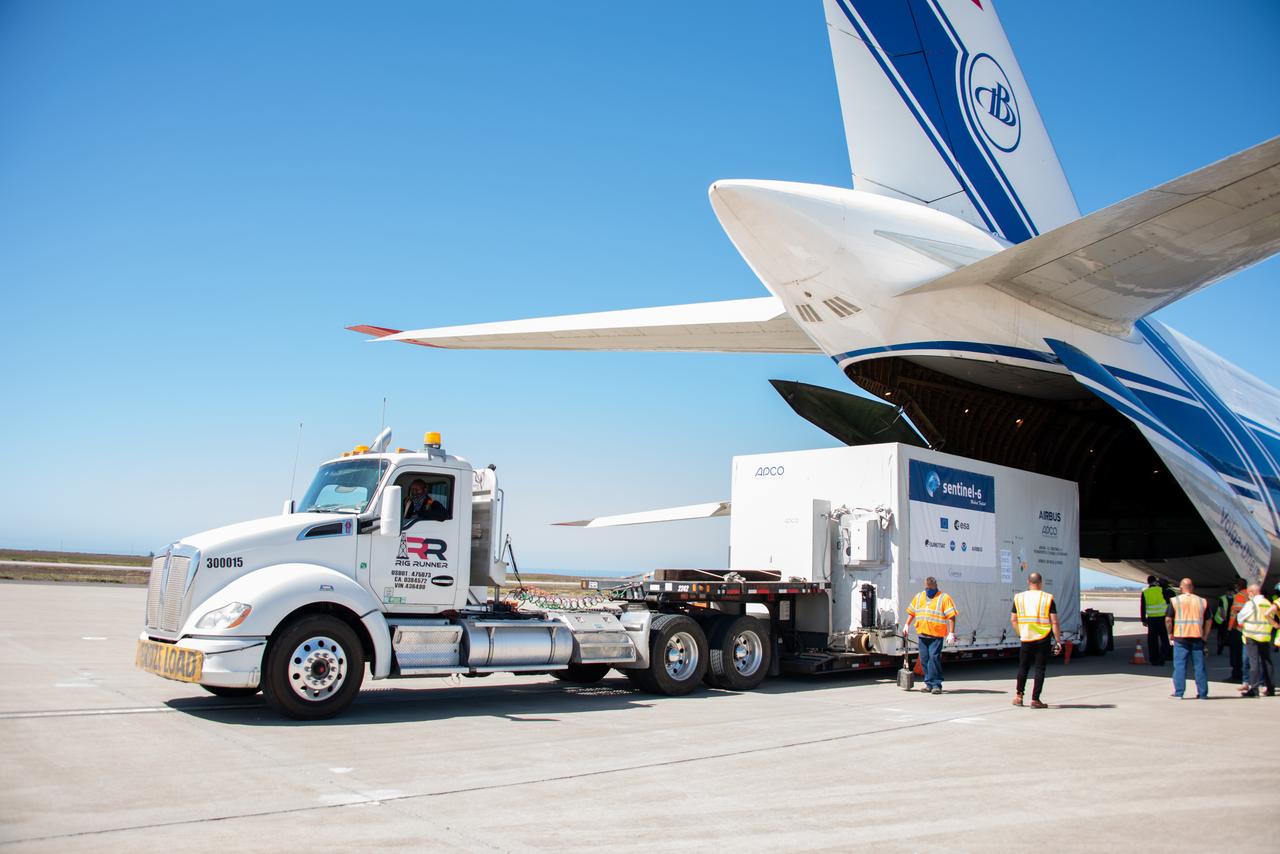

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, is placed on a transport vehicle after the spacecraft’s arrival at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California aboard a Antonov cargo aircraft, Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
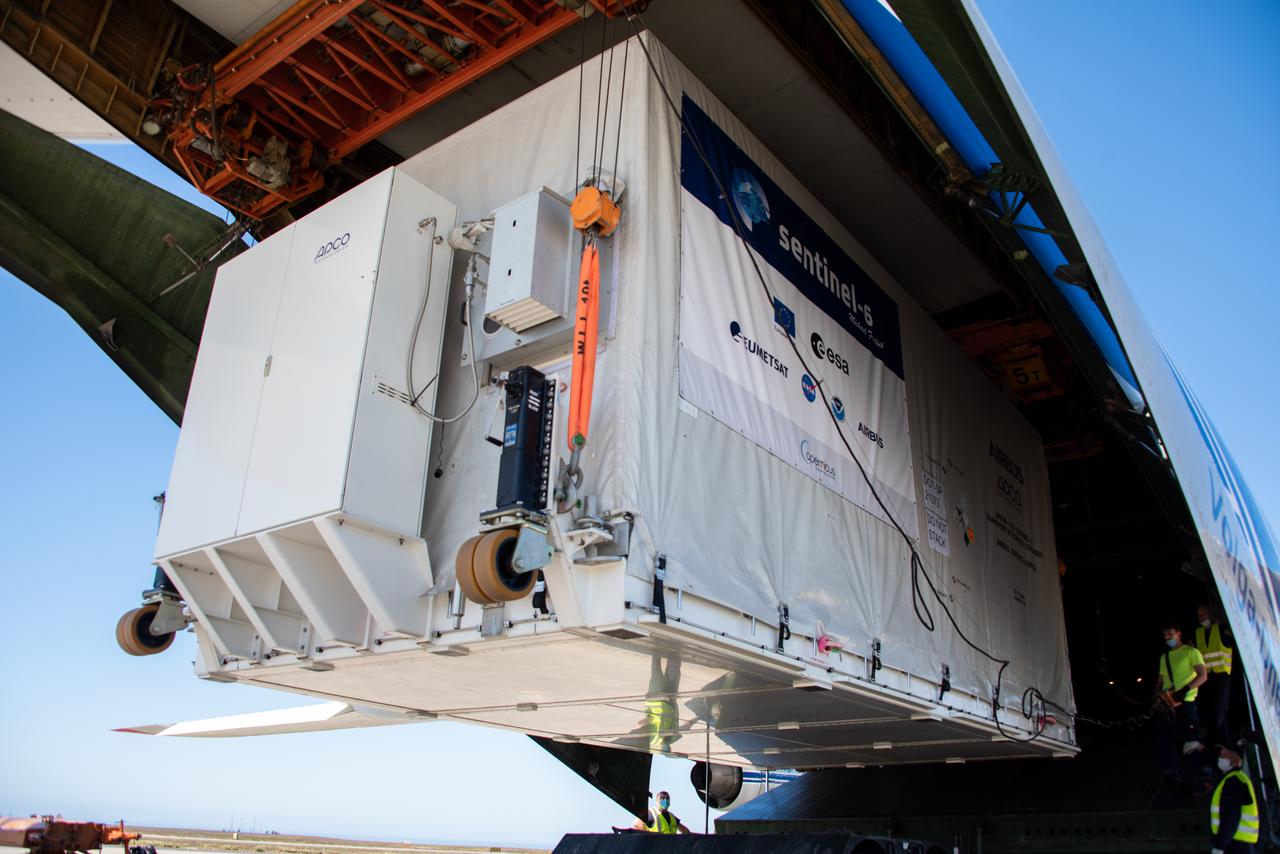

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, is offloaded from the Antonov cargo aircraft that delivered it to Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, is offloaded from the Antonov cargo aircraft that delivered it to Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
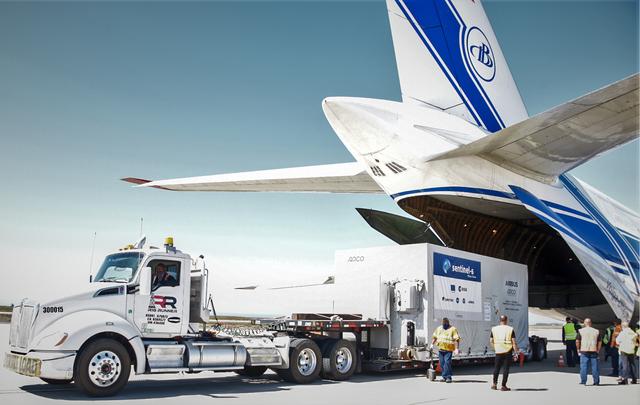

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, arrives at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020, aboard an Antonov cargo aircraft. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
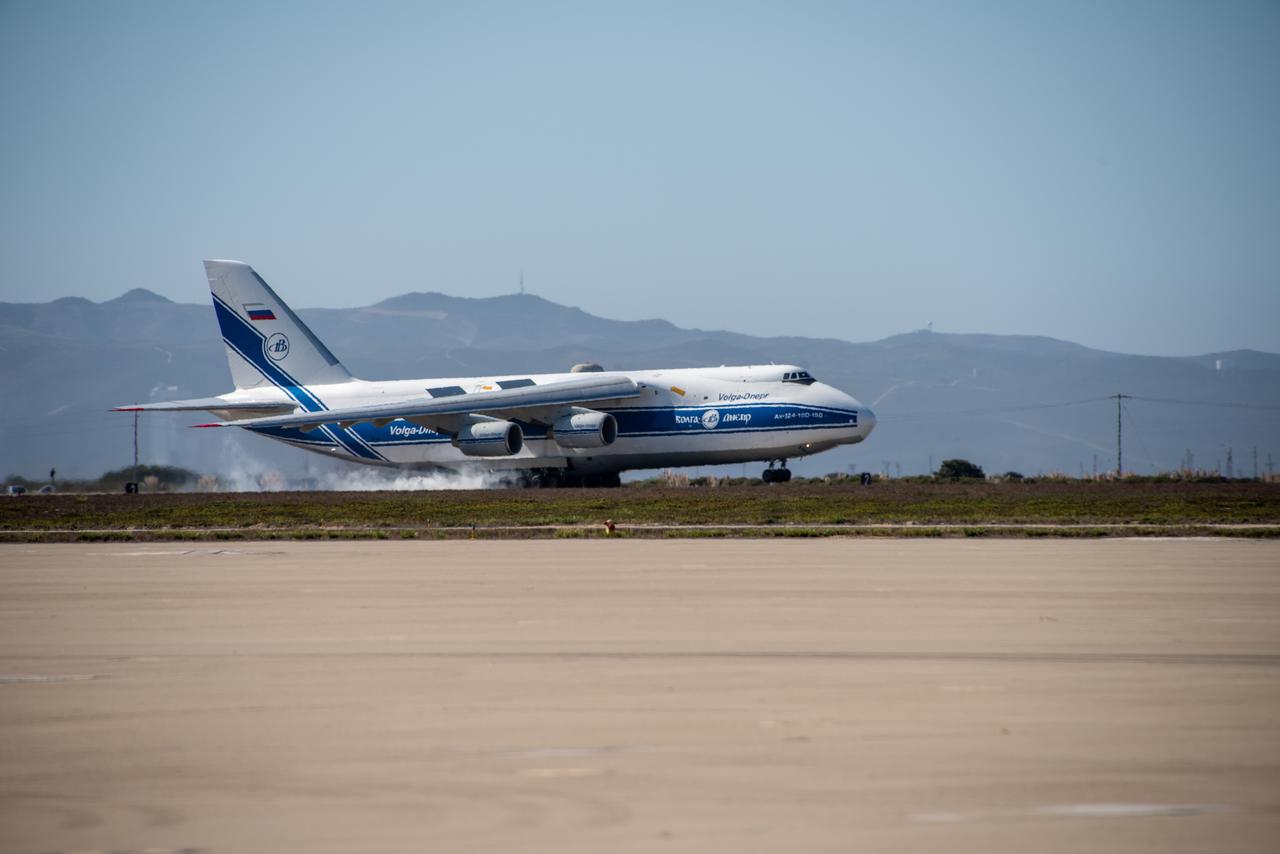

The Antonov cargo aircraft carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite touches down on the runway at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
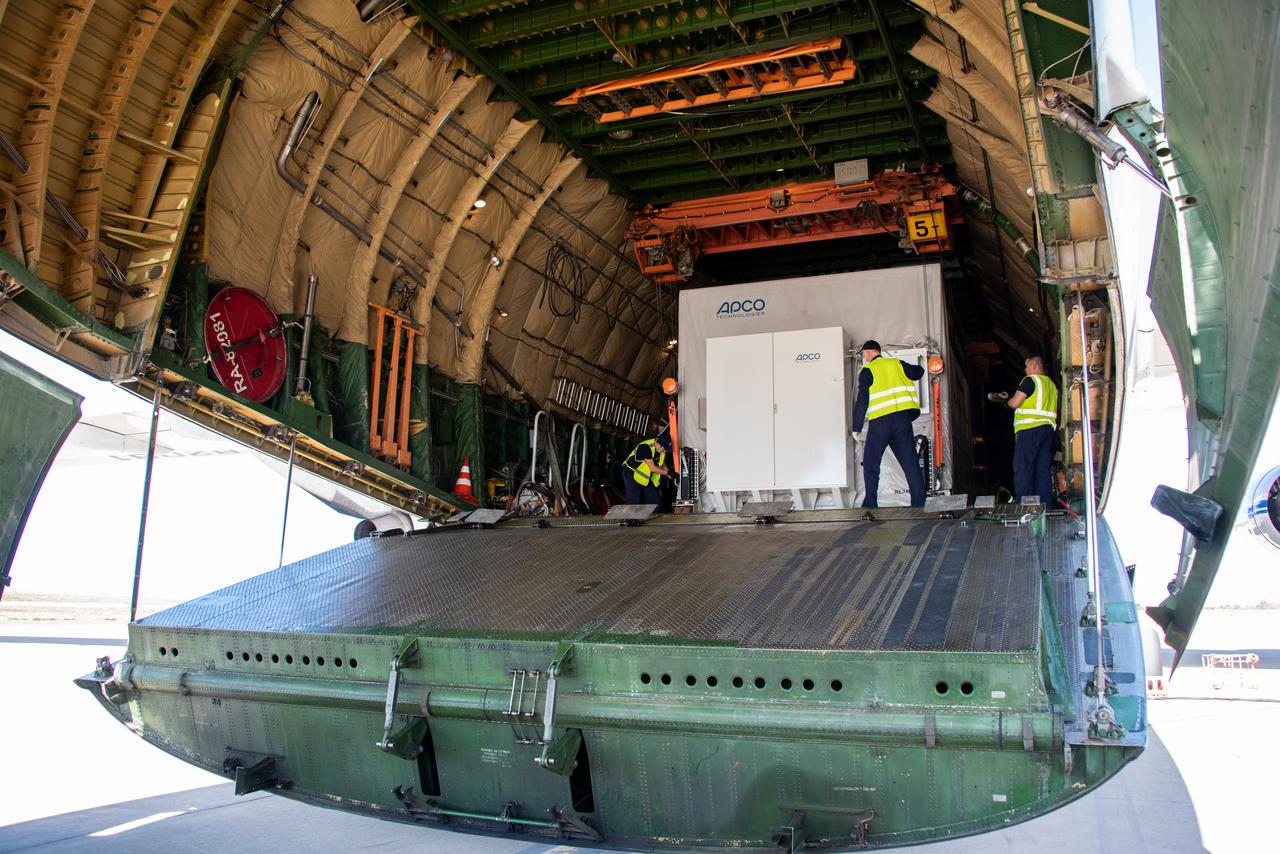

The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, secured inside a shipping container, is visible inside the Antonov cargo aircraft that delivered it to Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 24, 2020. The mission is an international partnership and the first launch of a constellation of two satellites that will observe changes in Earth’s sea levels for at least the next decade. Launching atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich is targeted to lift off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 10, 2020. The Launch Services Program at Kennedy is responsible for launch management.
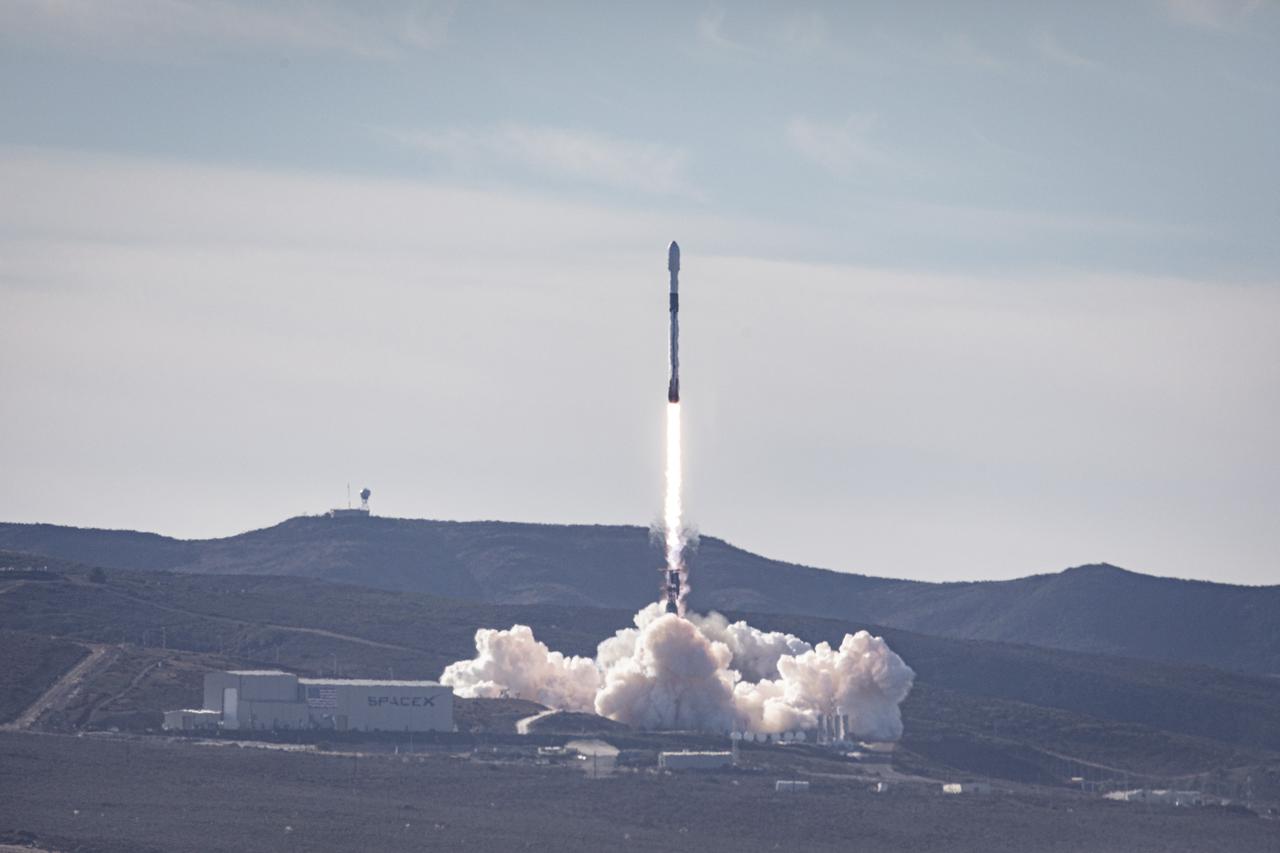

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
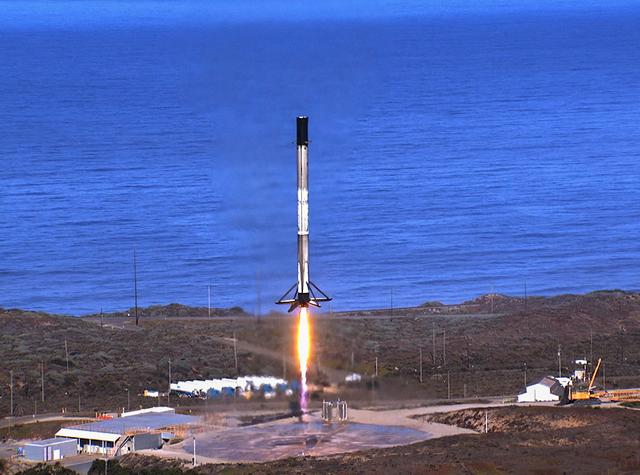

The SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage booster lands at Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California after launching the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft on Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
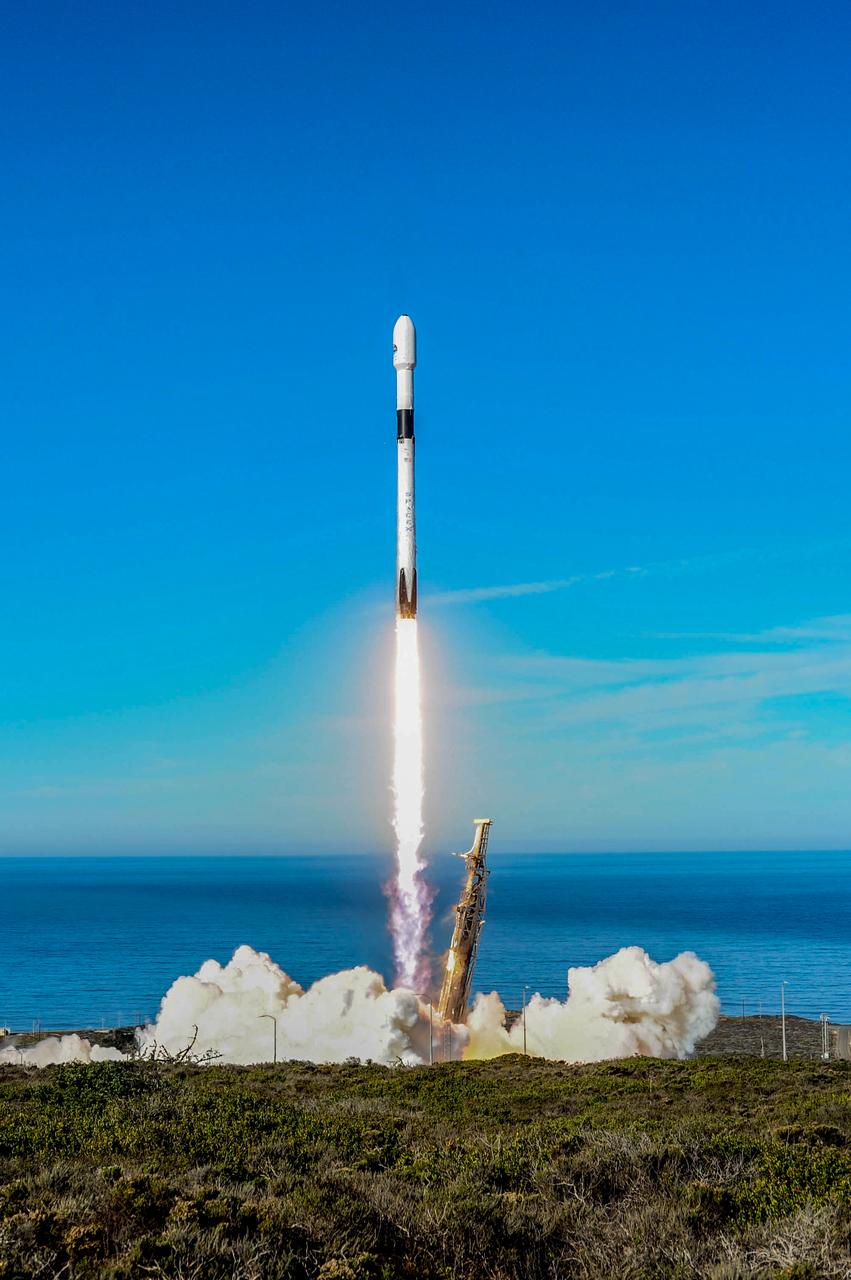

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
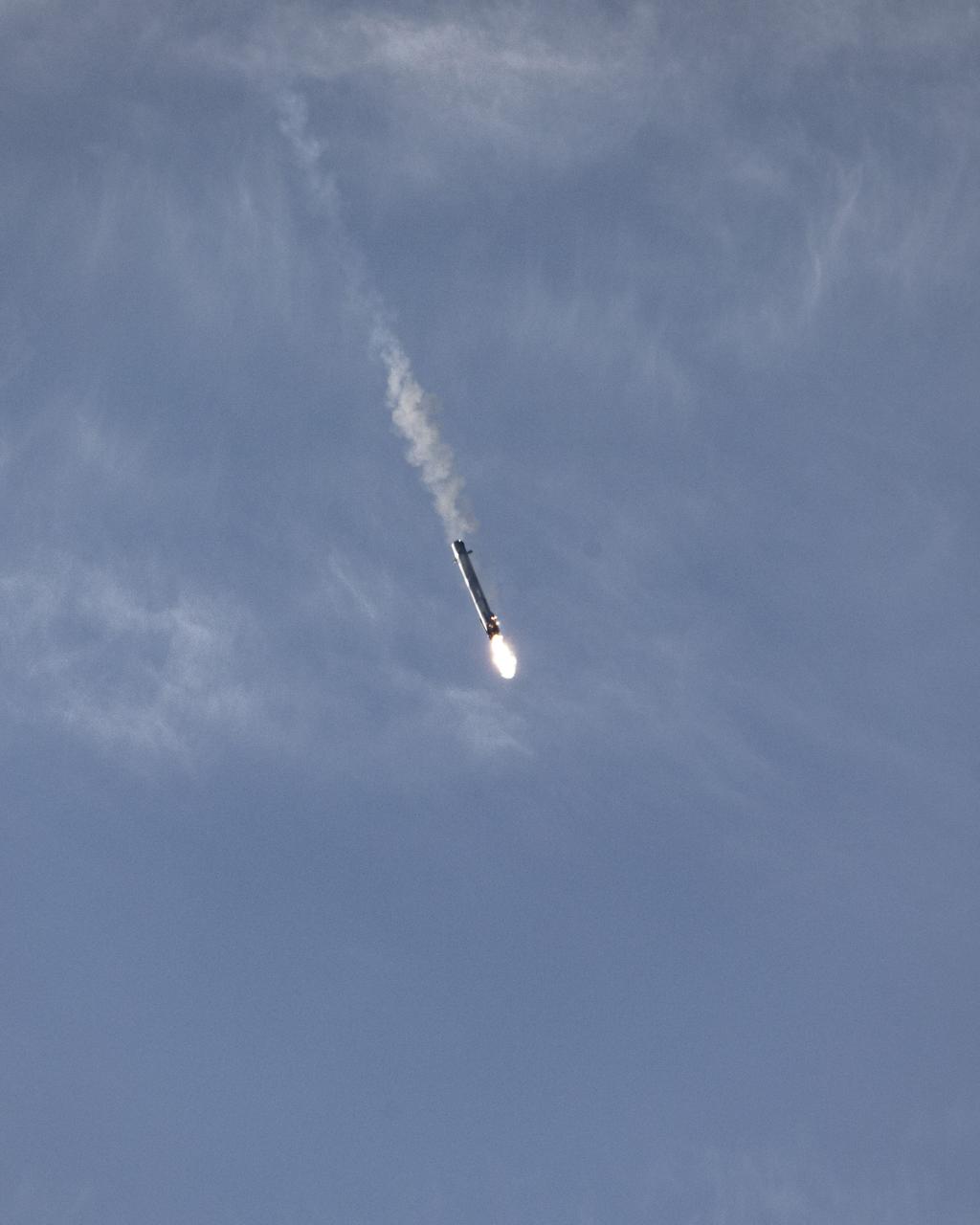

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Falcon 9 carrying the satellite lifted off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
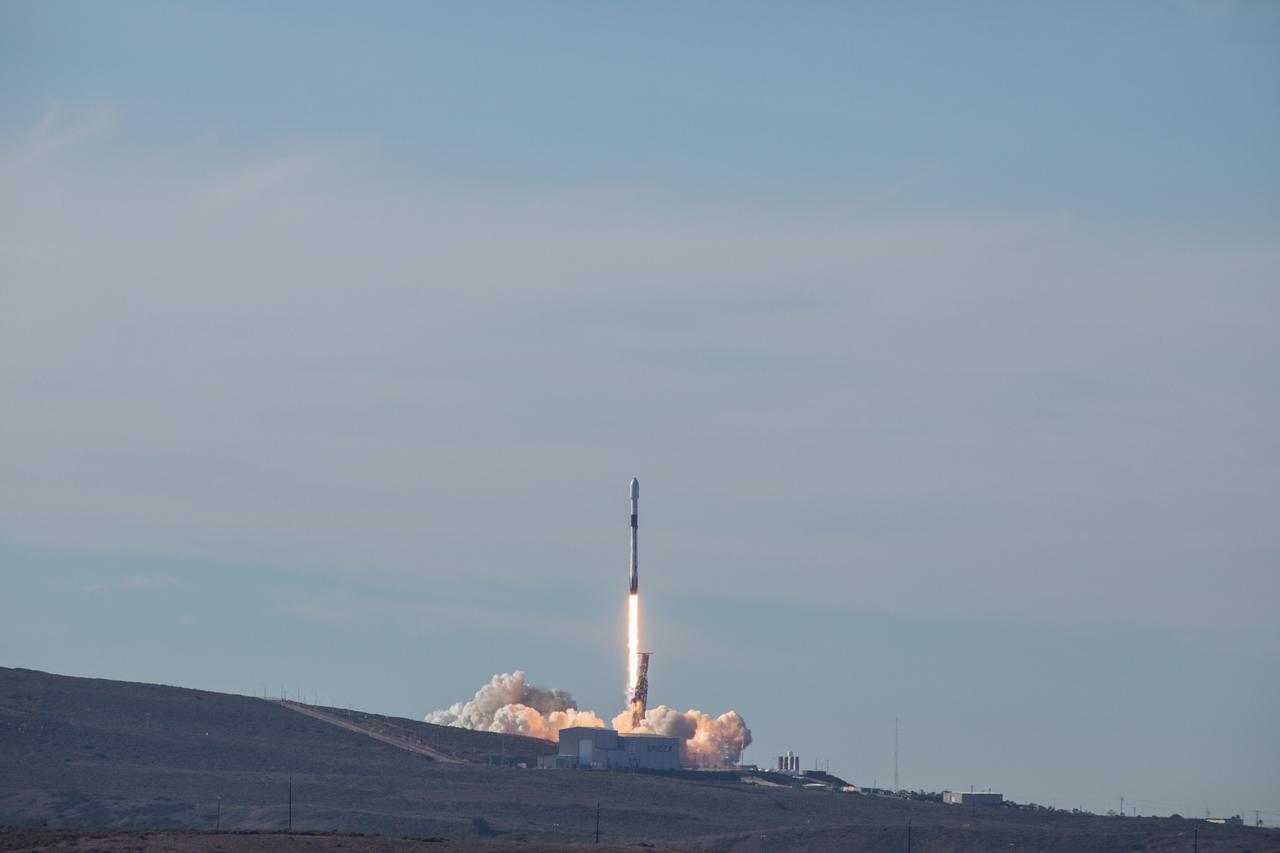

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
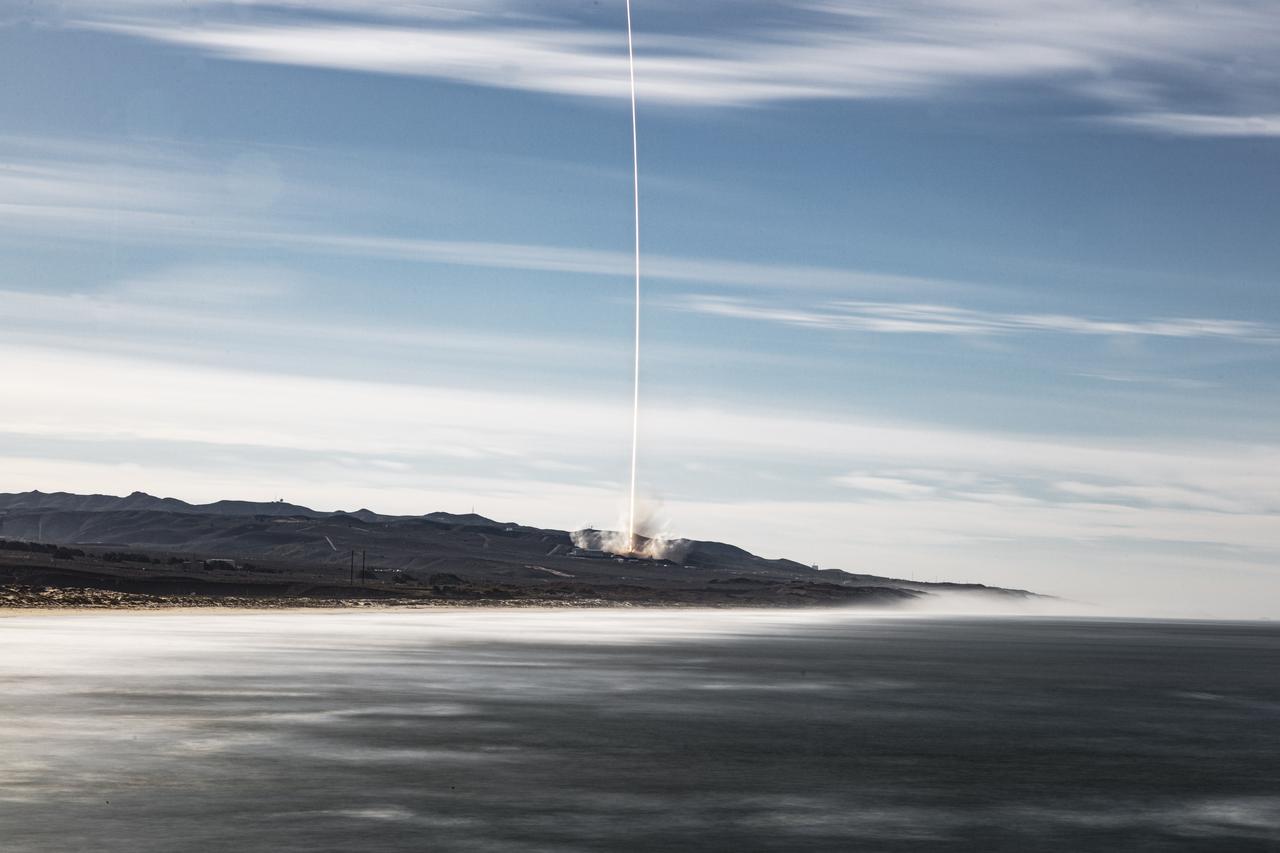

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Falcon 9 carrying the satellite lifted off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
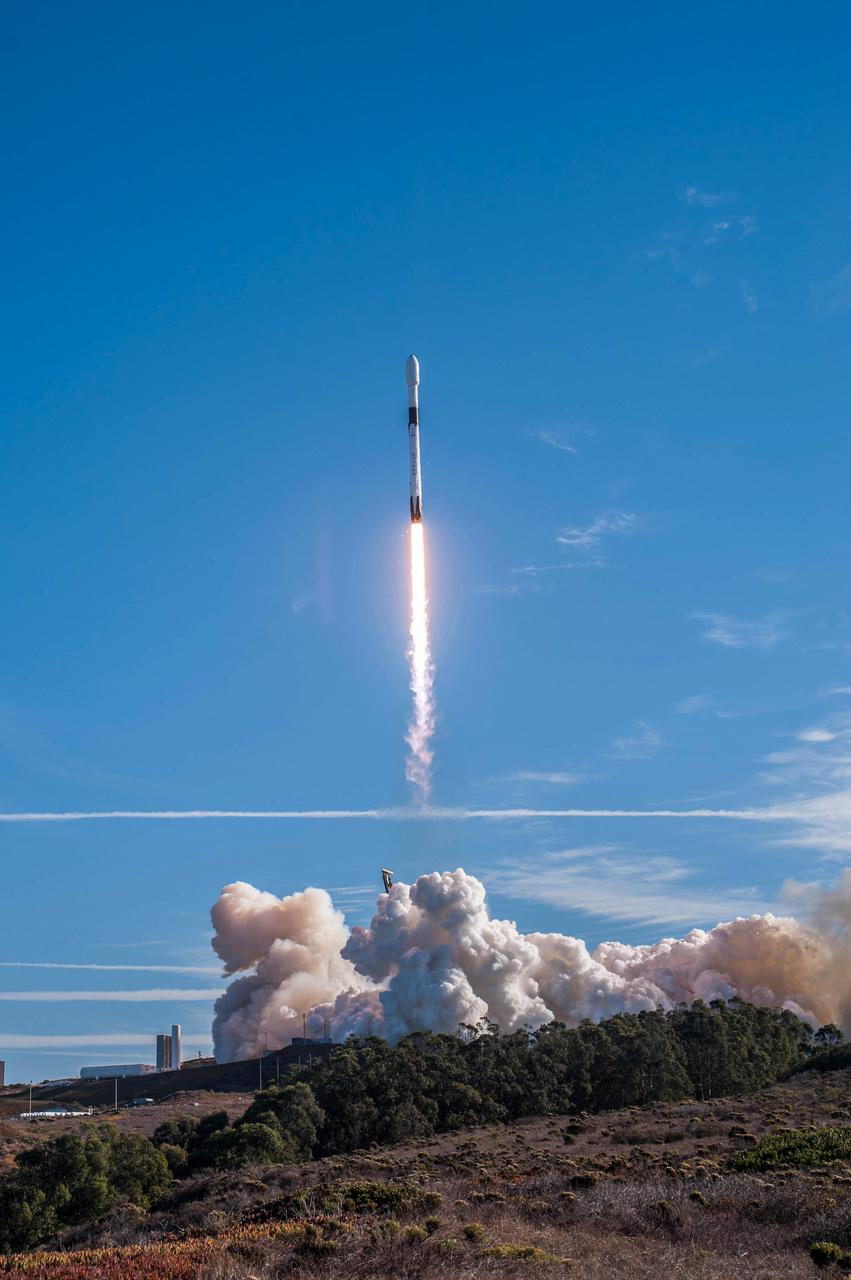

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
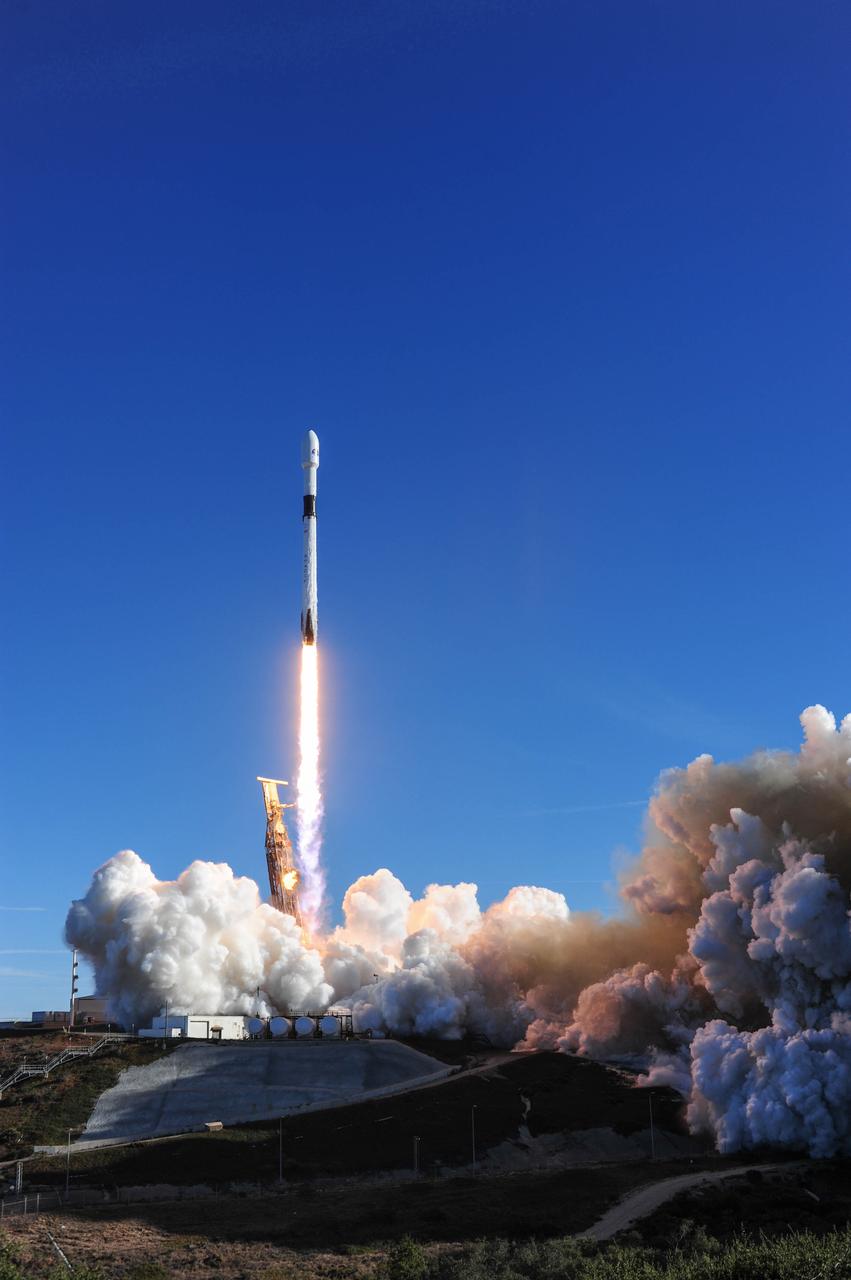

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
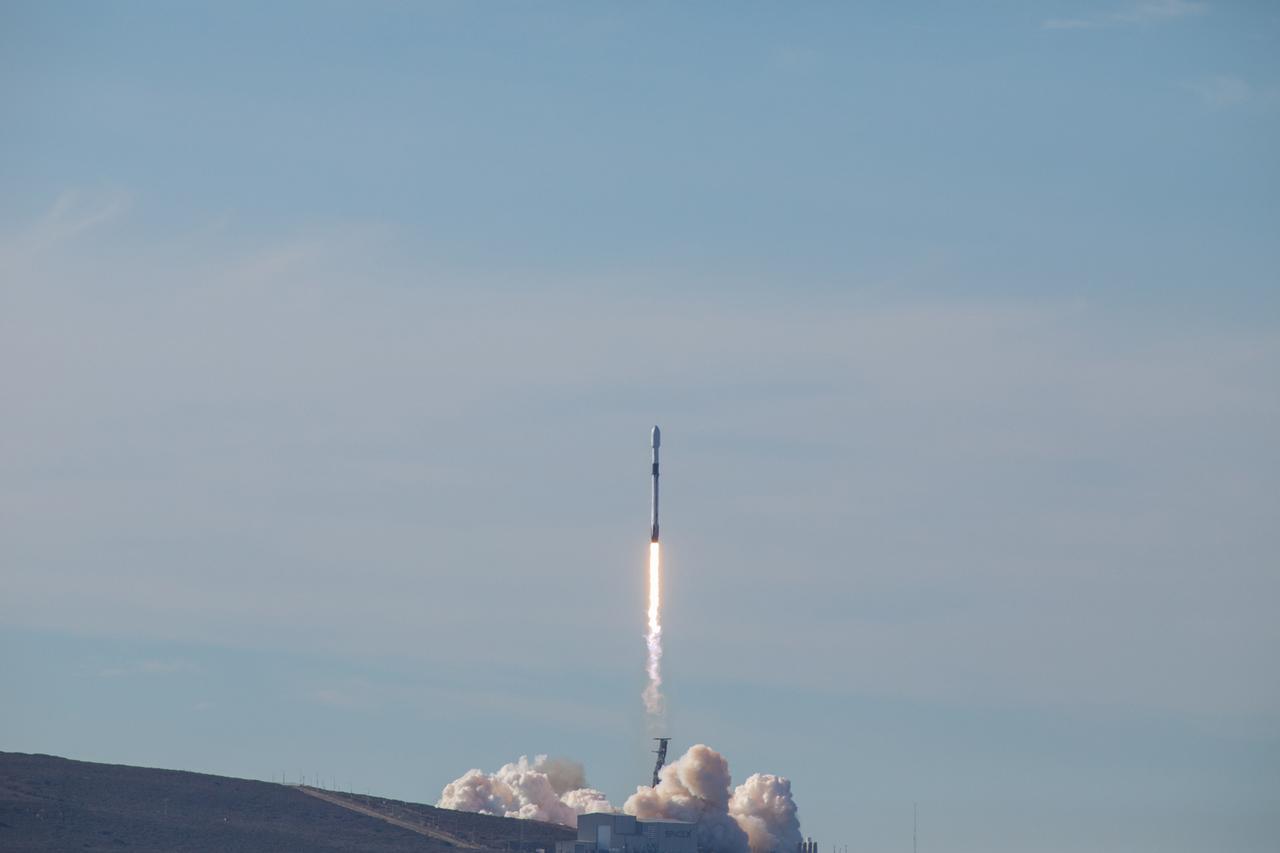

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
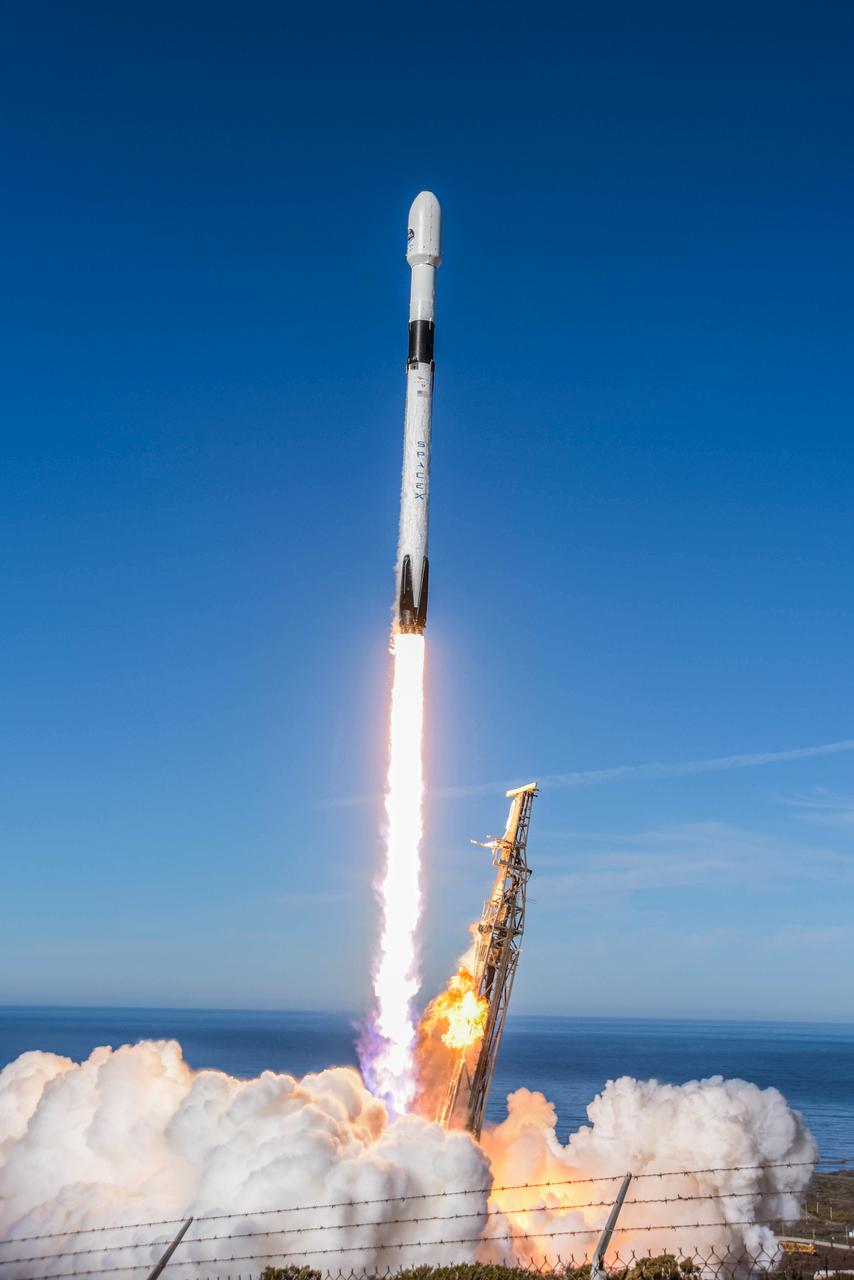

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
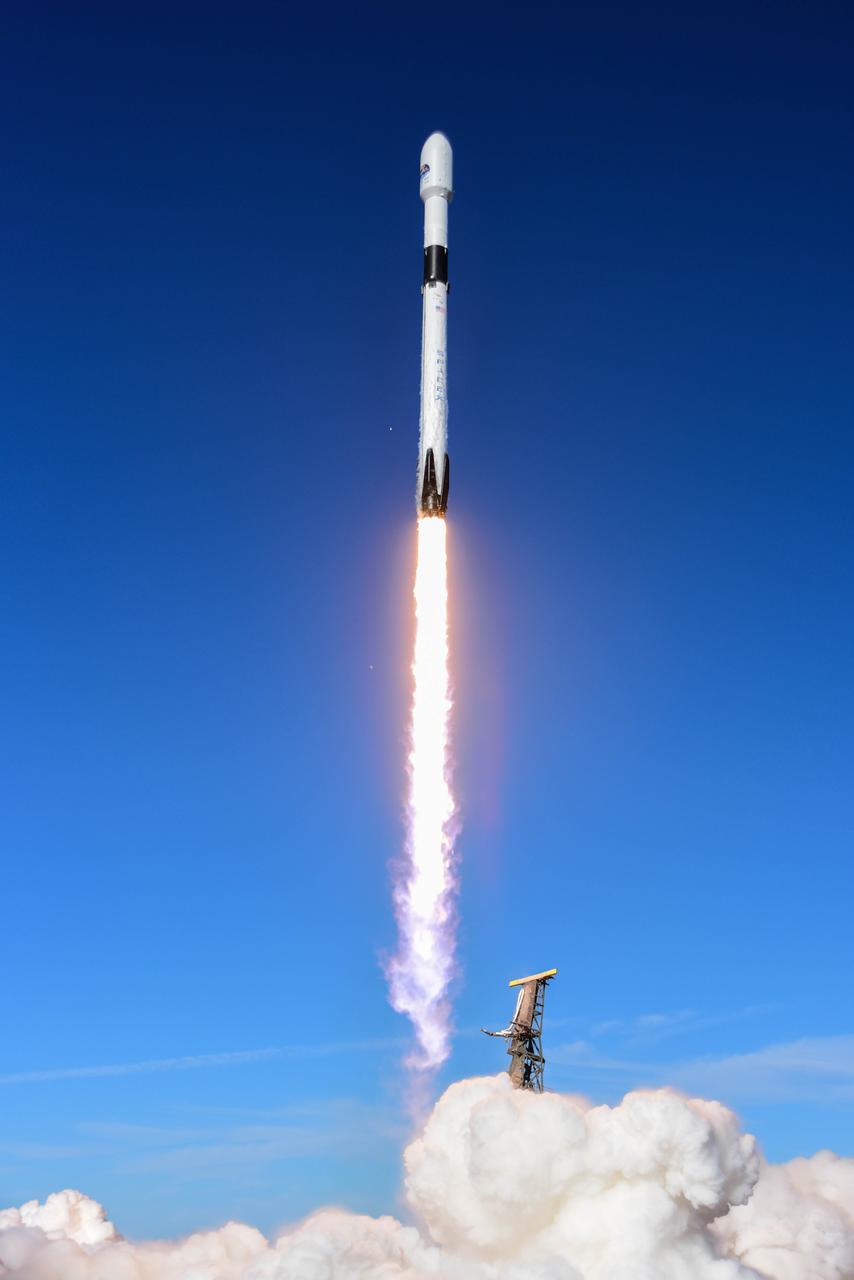

The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich spacecraft lifts off from Space Launch Complex 4 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.