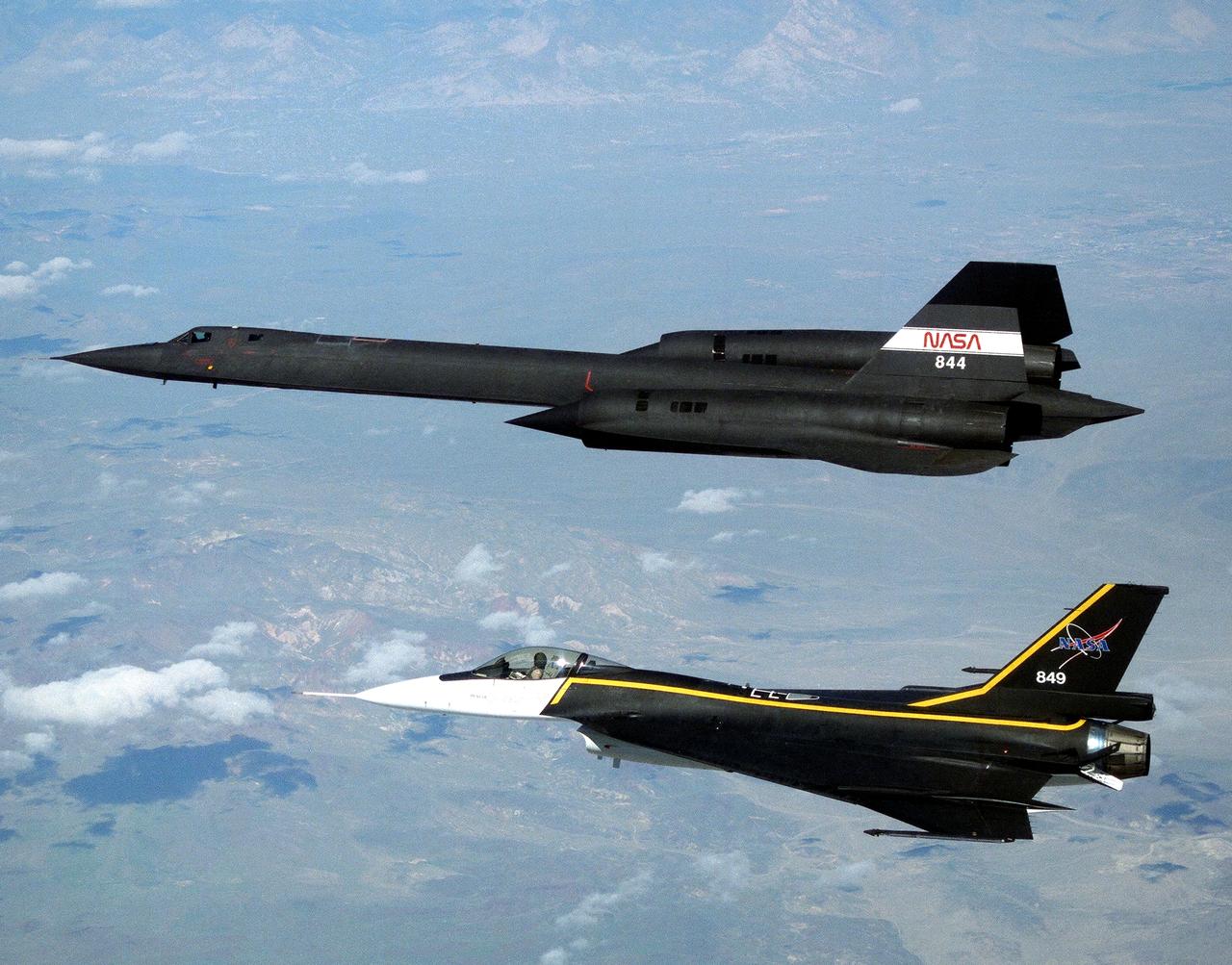

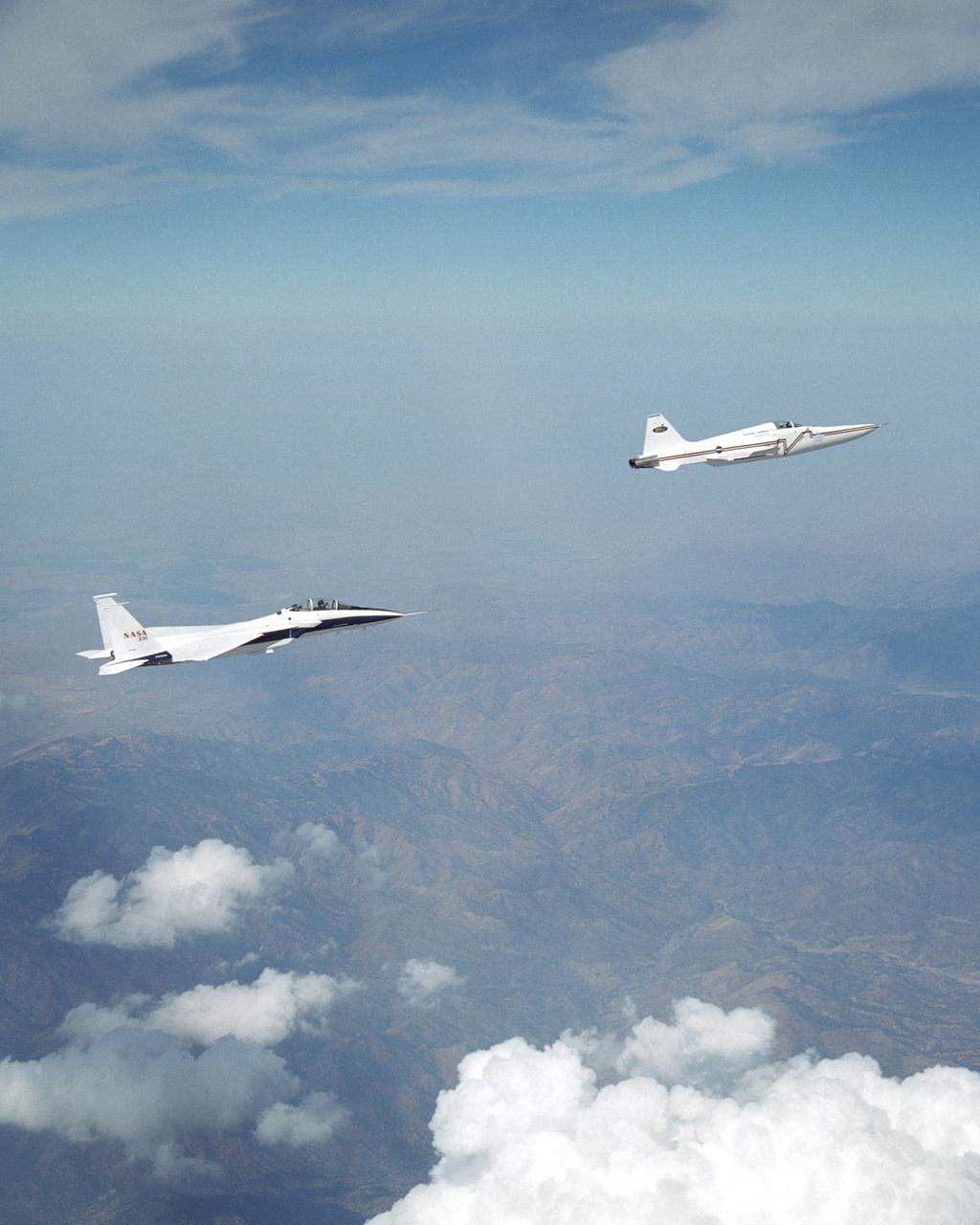
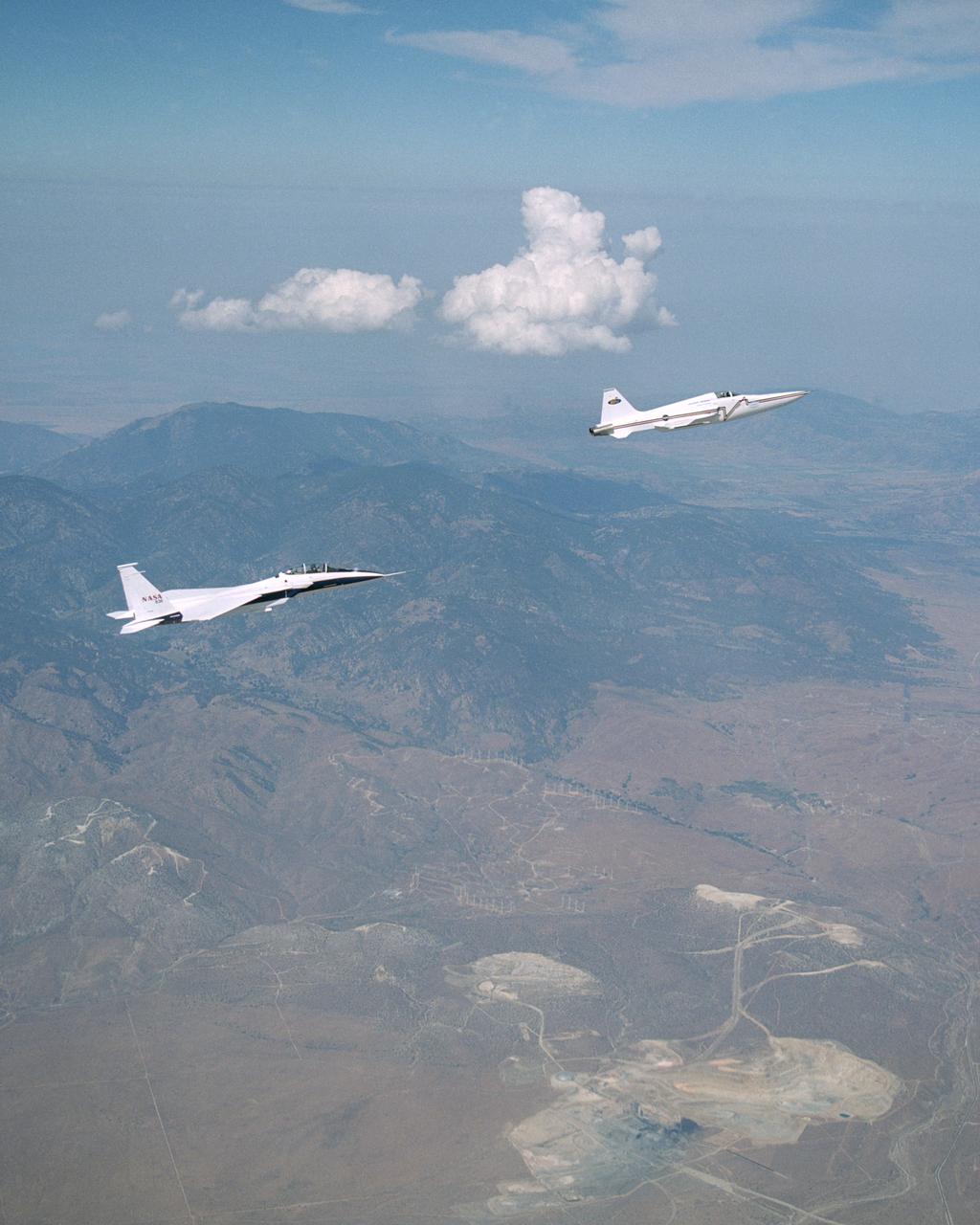
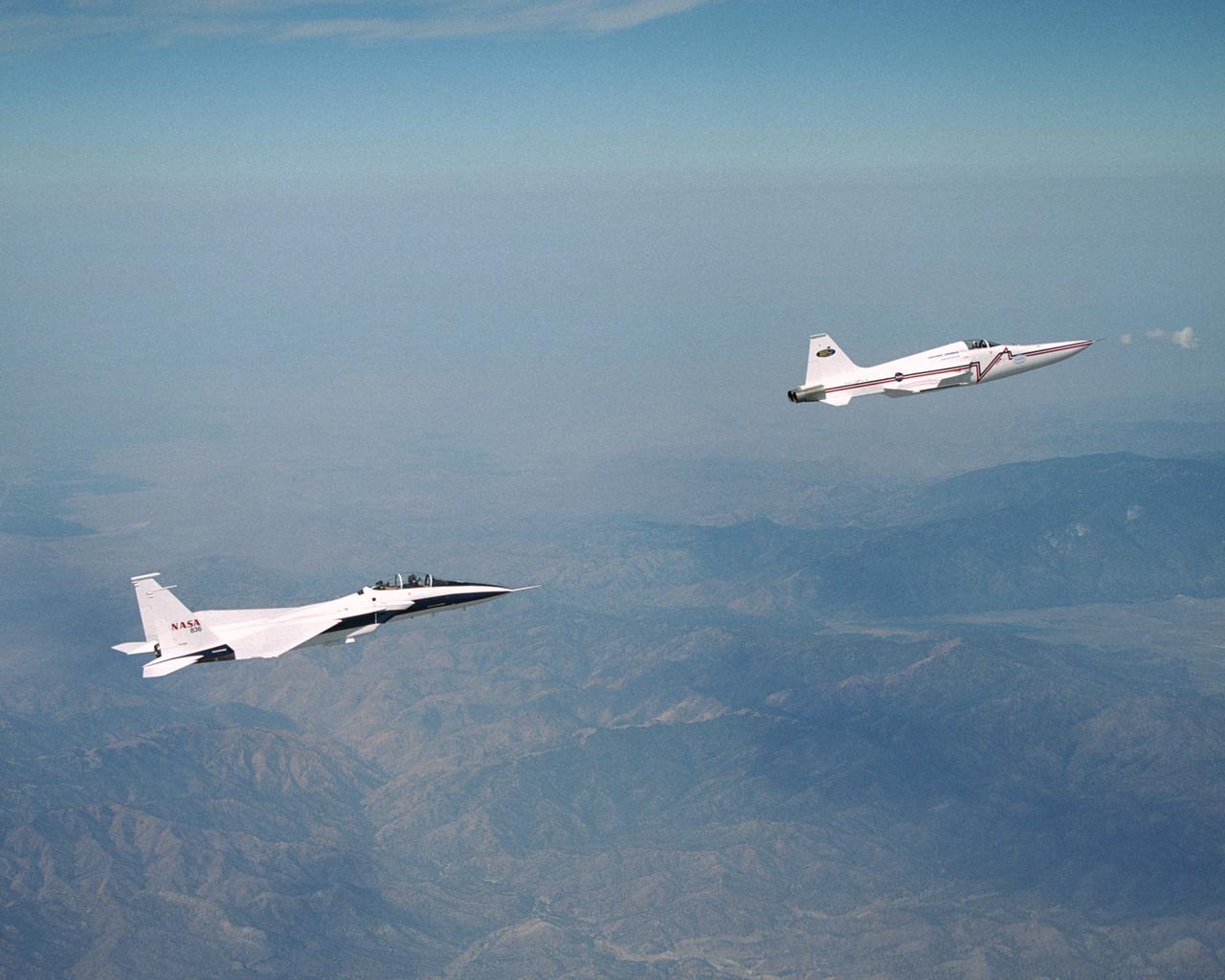
The single-seat F-16XL, NASA 849, joins up with an SR-71A, NASA 844, as crews set up for one of the flights in the recent sonic boom research program conducted by the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. During the missions, the F-16XL probed the shockwaves generated by the SR-71, while at lower altitudes sensors on an F-18 and on a YO-3A, and also on the ground, recorded data from the same shockwave.
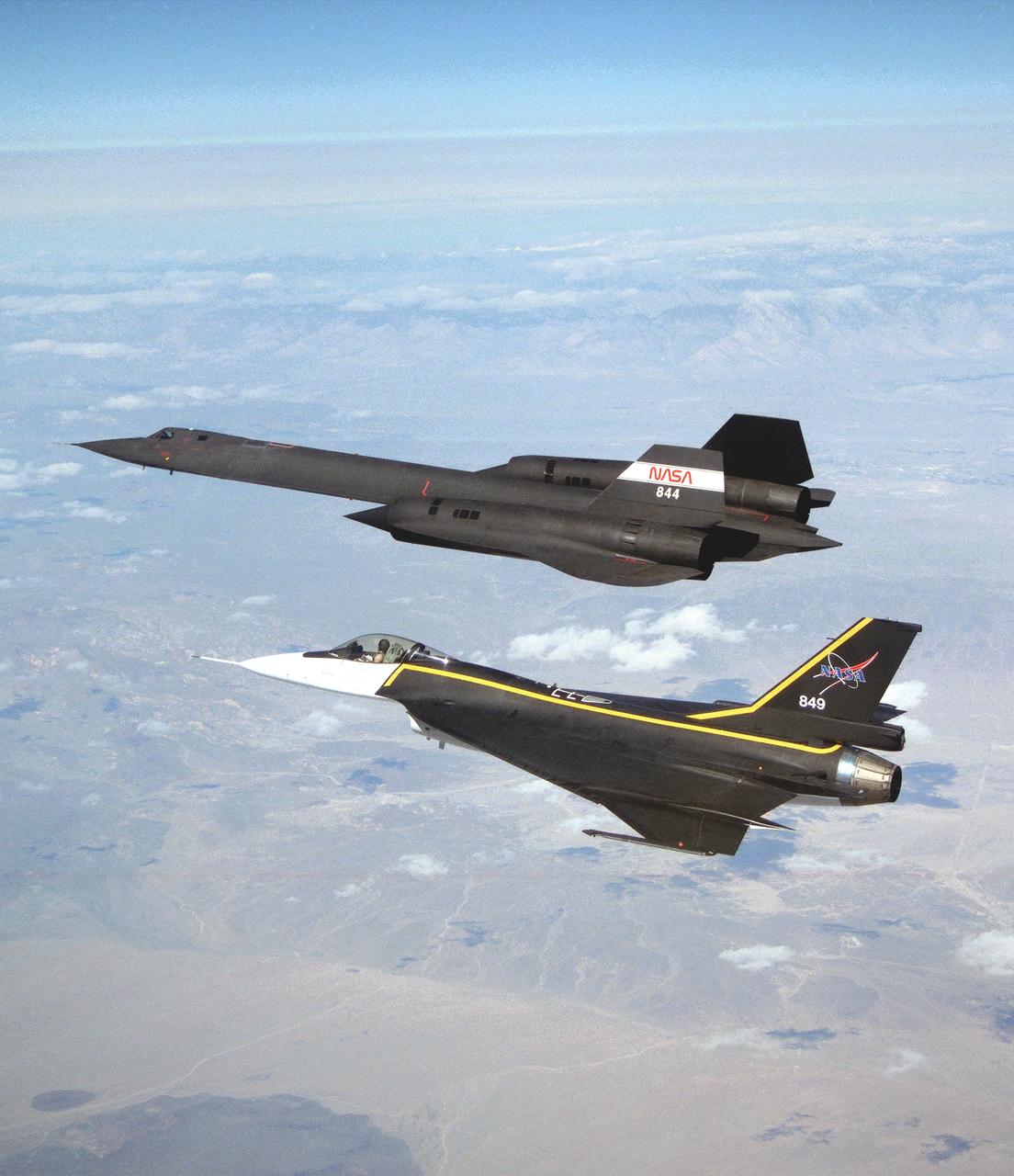

The single-seat F-16XL, NASA 849, joins up with an SR-71A, NASA 844, as crews set up for one of the flights in the recent sonic boom research program conducted by the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. During the missions, the F-16XL probed the shockwaves generated by the SR-71, while at lower altitudes sensors on an F-18 and on a YO-3A, and also on the ground, recorded data from the same shockwave.
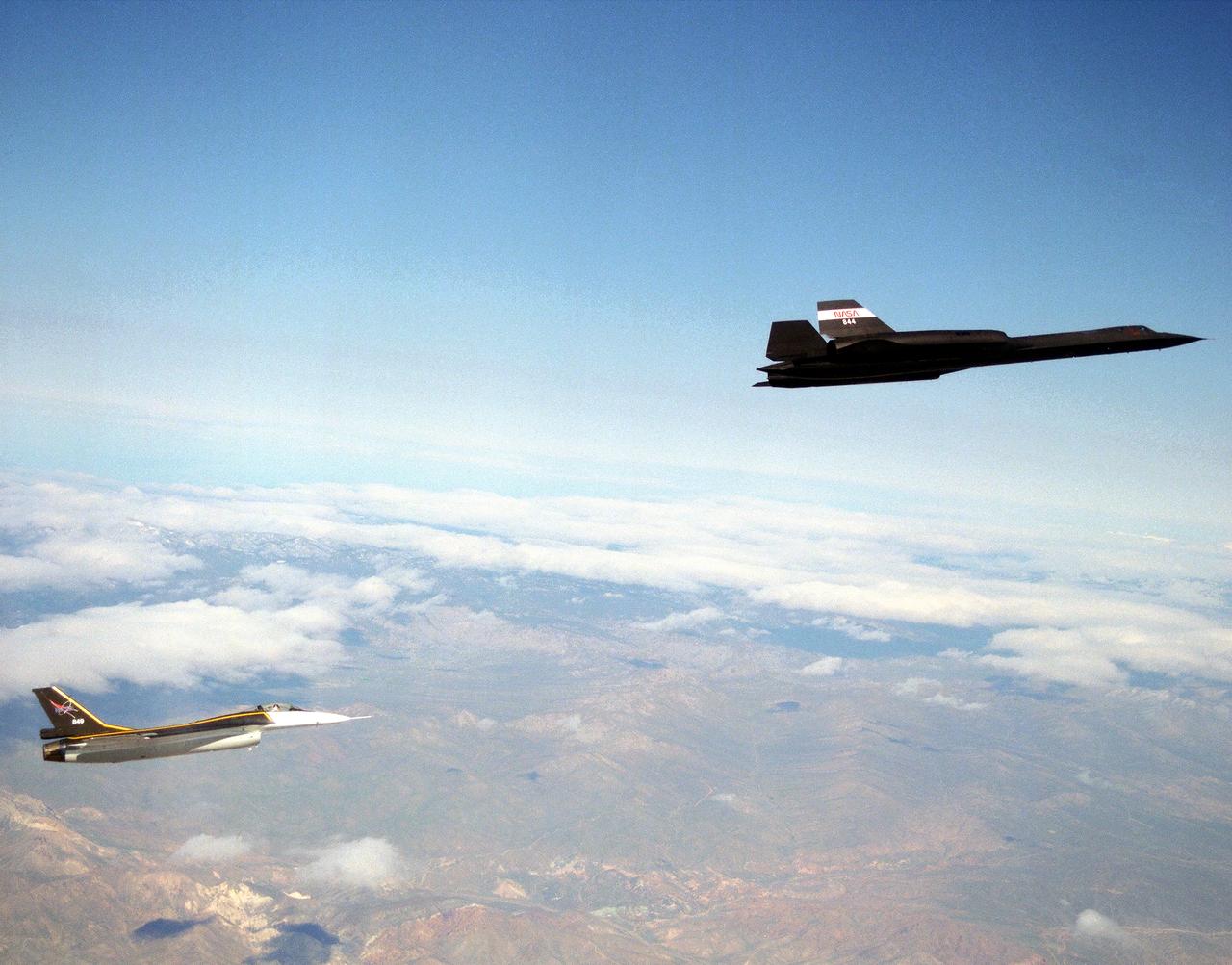

The single-seat F-16XL, NASA 849, joins up with an SR-71A, NASA 844, as crews set up for one of the flights in the recent sonic boom research program conducted by the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. During the missions, the F-16XL probed the shockwaves generated by the SR-71, while at lower altitudes sensors on an F-18 and on a YO-3A, and also on the ground, recorded data from the same shockwave.

The brilliant flash of an exploding star shockwave -- what astronomers call the hock breakout -- is illustrated in artist concept based on NASA Kepler.
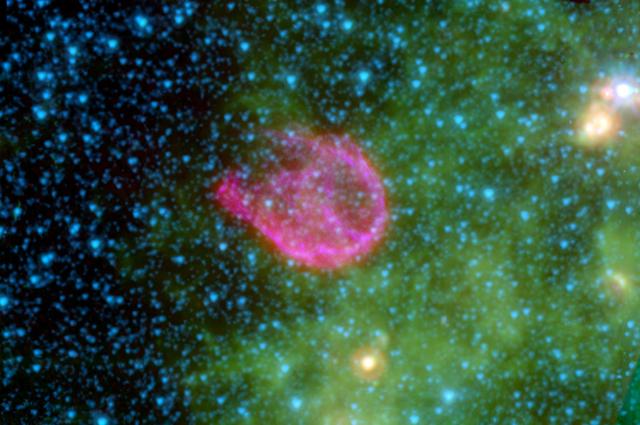

Supernovae are the explosive deaths of the universe most massive stars. This false-color composite from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope and NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory shows the remnant of N132D, the wispy pink shell of gas at center.
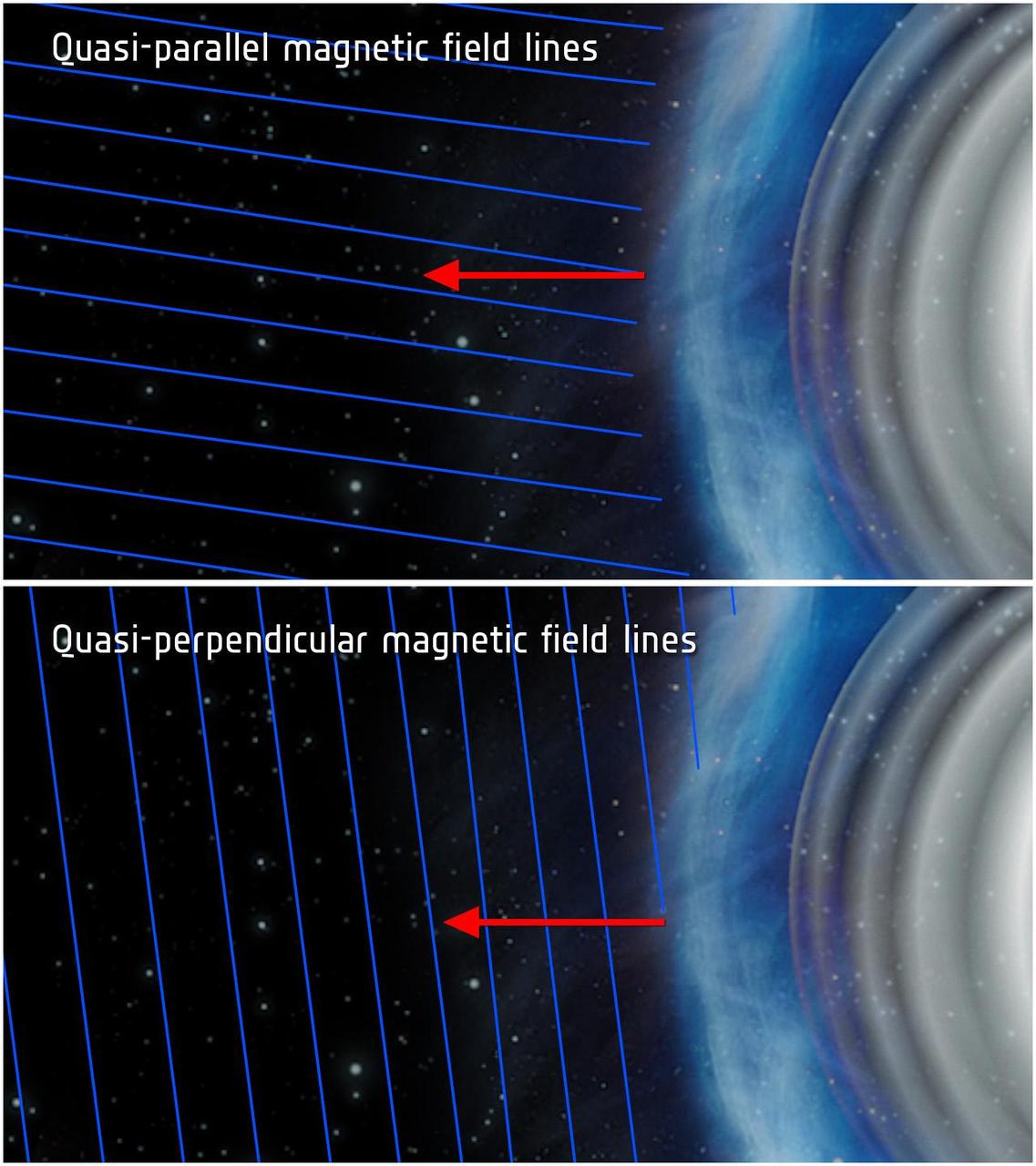

This illustration shows quasi-parallel top and quasi-perpendicular bottom magnetic field conditions at a planetary bow shock. Bow shocks are shockwaves created when the solar wind blows on a planet magnetic field.

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified U.S. Navy F-5E jet in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The project is an effort to lessen sonic booms. During the recent demonstration, the F-15B flew behind the modified F-5E sonic boom demonstrator aircraft in order to measure the aircraft's sonic boom characteristics. Flying behind and below the F-5E, and using its specially-instrumented nose boom, the F-15B recorded many shockwave patterns from the F-5E at various distances and orientations from the aircraft.

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified U.S. Navy F-5E jet in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The project is an effort to lessen sonic booms. During the recent demonstration, the F-15B flew behind the modified F-5E sonic boom demonstrator aircraft in order to measure the aircraft's sonic boom characteristics. Flying behind and below the F-5E, and using its specially-instrumented nose boom, the F-15B recorded many shockwave patterns from the F-5E at various distances and orientations from the aircraft.

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified F-5E in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program.
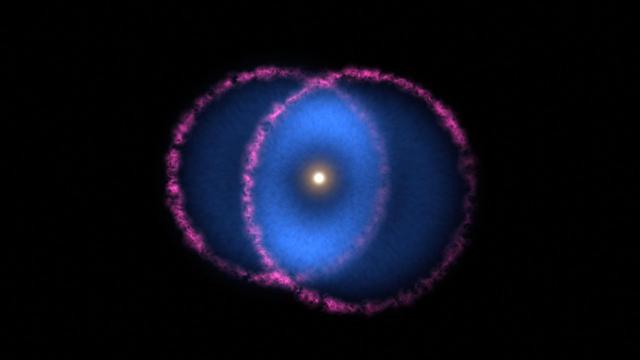
The Blue Ring Nebula is thought to be the product of two stars merging into one. The collision of the bodies ejected a cloud of hot debris into space. A disk of gas orbiting the larger star cut the cloud in half, creating two cones that are moving away from the star in opposite directions. The base of one cone is moving almost directly toward Earth, while the other is moving almost directly away. Magenta represents optical light from the shockwave at the front of the expanding debris cones, outlining the two cone bases at their widest points. Blue represents far-ultraviolet light (not visible to the human eye) and comes from gas behind the shockwave. As the gas expands and cools, it forms hydrogen molecules that interact with the interstellar medium and emit only far-ultraviolet light. These emissions are visible only where the cones overlap (as seen from Earth), forming the blue ring around the central star. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23868
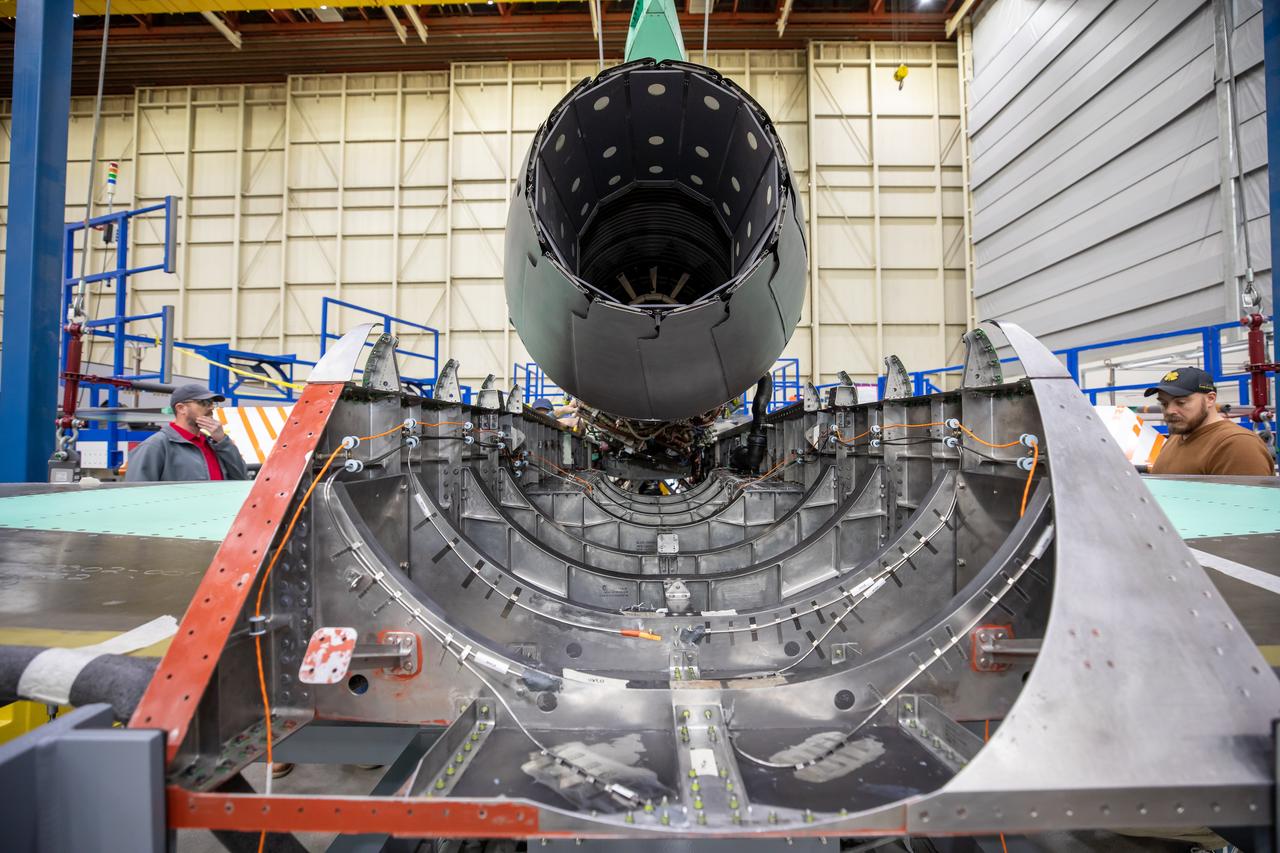

Here is a close-up of the GE F414 engine, from the aft deck or rear, before the tail section of the X-59 is lifted into place and attached to the aircraft. The aft deck helps control the shockwaves at the end of the aircraft and reduce the noise of a sonic boom to more of a sonic thump.

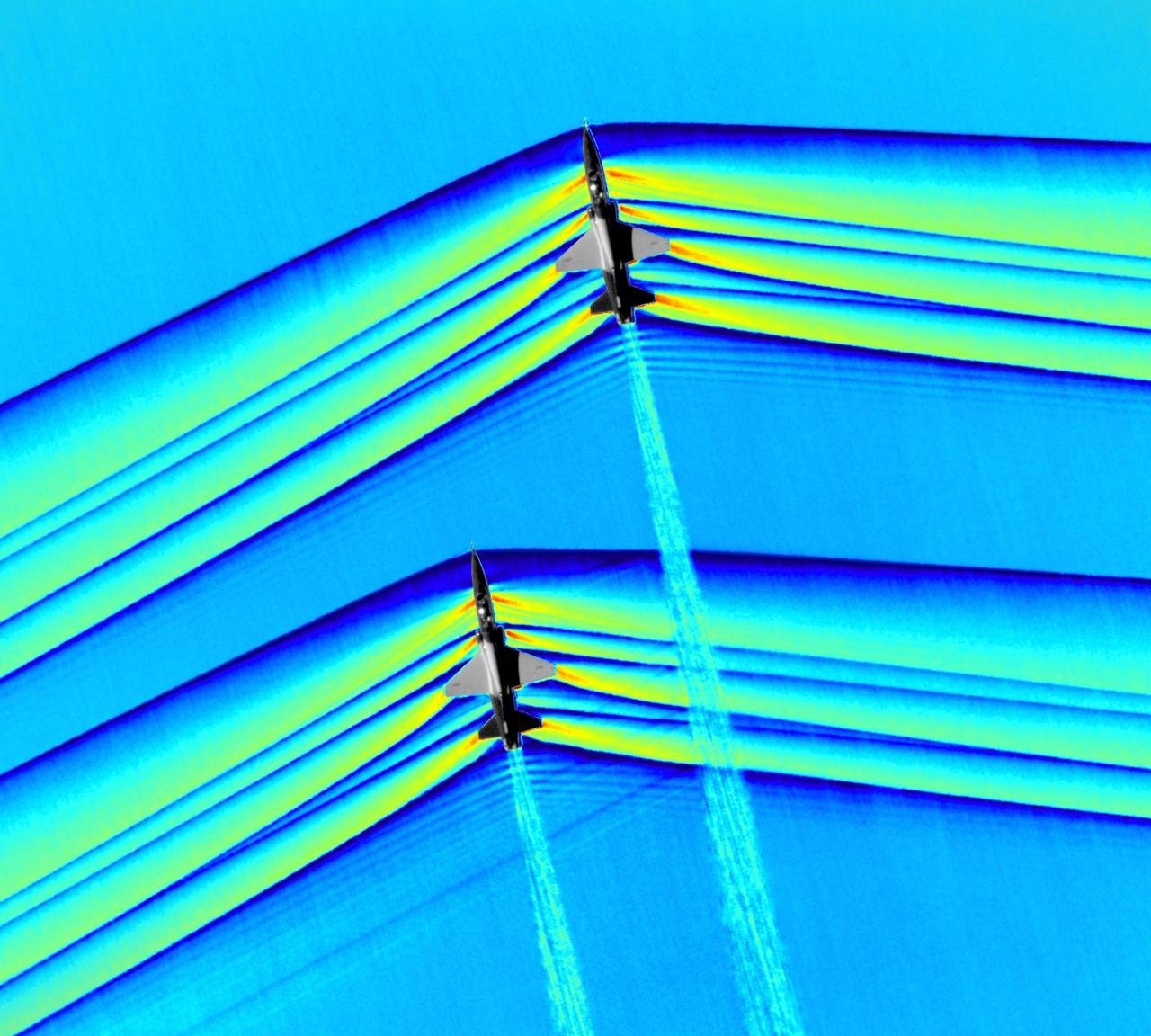
Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.02 pass. The interaction of the shockwave of the trailing aircraft with the exhaust plume of the lead aircraft shows a shockwave reflection. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith.

Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.02 pass. The interaction of the shockwave of the trailing aircraft with the exhaust plume of the lead aircraft shows a shockwave reflection. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith.
Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.02 pass. The interaction of the shockwave of the trailing aircraft with the exhaust plume of the lead aircraft shows a shockwave reflection. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith.
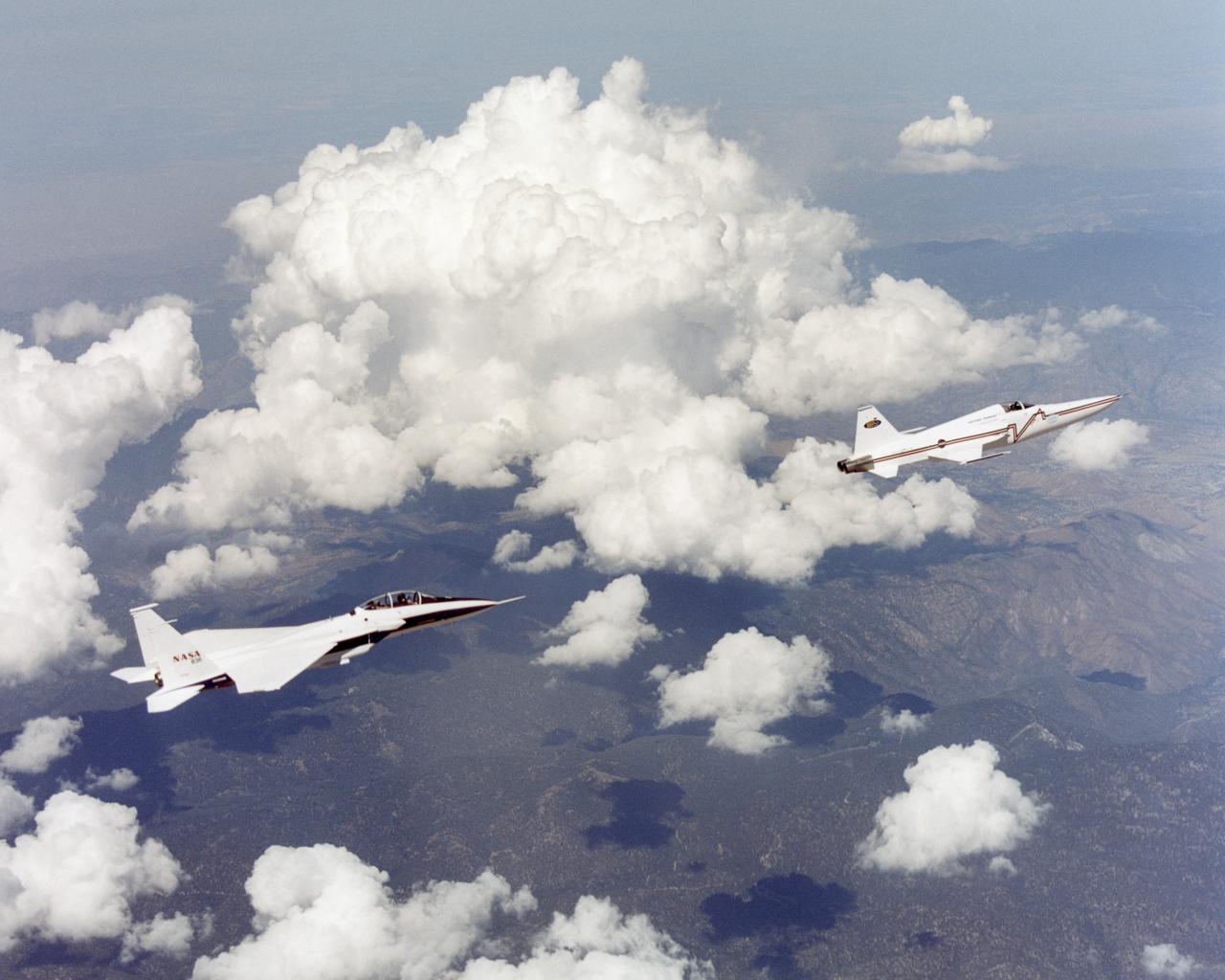

NASA's F-15B research testbed jet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center flew in the supersonic shockwave of a Northrop Grumman Corp. modified U.S. Navy F-5E jet in support of the Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, which is part of the DARPA's Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. On Aug. 27, 2003, the F-5 SSBD aircraft demonstrated a method to reduce the intensity of sonic booms.
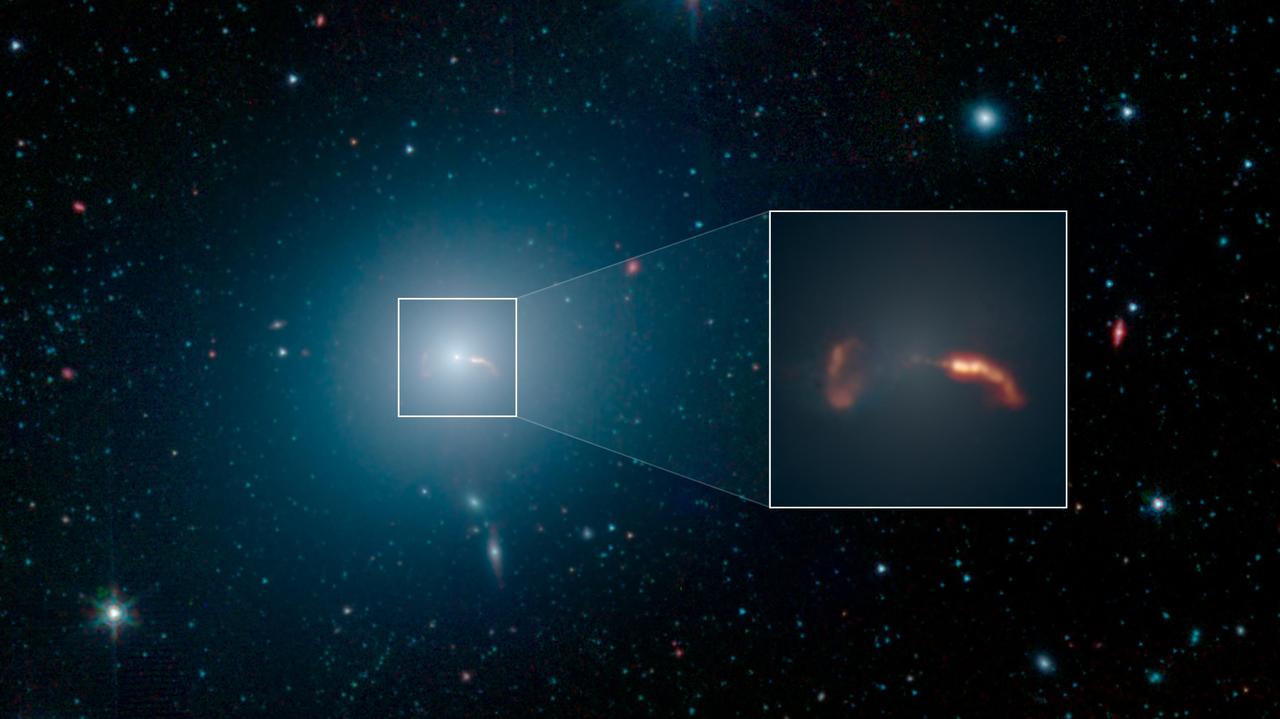

This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows the elliptical galaxy Messier 87 (M87), the home galaxy of the supermassive black hole recently imaged by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). Spitzer's infrared view shows a faint trace of a jet of material spewing to the right of the galaxy - a feature that was previously one key indicator that a supermassive black hole lived at the galaxy's center. More prominent in the image is the shockwave created by that jet. The inset in the image below shows a close-up view of the shockwave on the right side of the galaxy, as well as the shockwave from a second jet traveling to the left of the galaxy. Located about 55 million light-years from Earth, M87 has been a subject of astronomical study for more than 100 years and has been imaged by many NASA observatories, including the Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-ray Observatory and NuSTAR. In 1918, astronomer Heber Curtis first noticed "a curious straight ray" extending from the galaxy's center. This bright jet (which appears to extend to the right of the galaxy) is visible in multiple wavelengths of light, from radio waves through X-rays. The jet is produced by a disk of material spinning rapidly around the black hole, and spewing in opposite directions away from the galaxy. When the particles in the jet impact the interstellar medium (the sparse material filling the space between stars in M87), they create a shockwave that radiates in infrared and radio wavelengths of light, but not visible light. The jet on the right is traveling almost directly toward Earth, and its brightness is amplified due to its high speed in our direction. But the jet's trajectory is just slightly offset from our line of sight with the galaxy, so we can still see some of the length of the jet. The shockwave begins around the point where the jet appears to curve down, highlighting the regions where the fast-moving particles are colliding with gas in the galaxy and slowing down. There is also a second jet on the left that is moving so rapidly away from us it is rendered invisible at all wavelengths. But the shockwave it creates in the interstellar medium can still be seen here. In the Spitzer image, the shockwave is on the left side of the galaxy and looks like an inverted letter "C." Scientists are still striving for a solid theoretical understanding of how inflowing gas around black holes creates outflowing jets. Infrared light at wavelengths of 3.6 and 4.5 microns are rendered in blue and green, showing the distribution of stars, while dust features that glow brightly at 8.0 microns are shown in red. The image was taken during Spitzer's initial "cold" mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23122
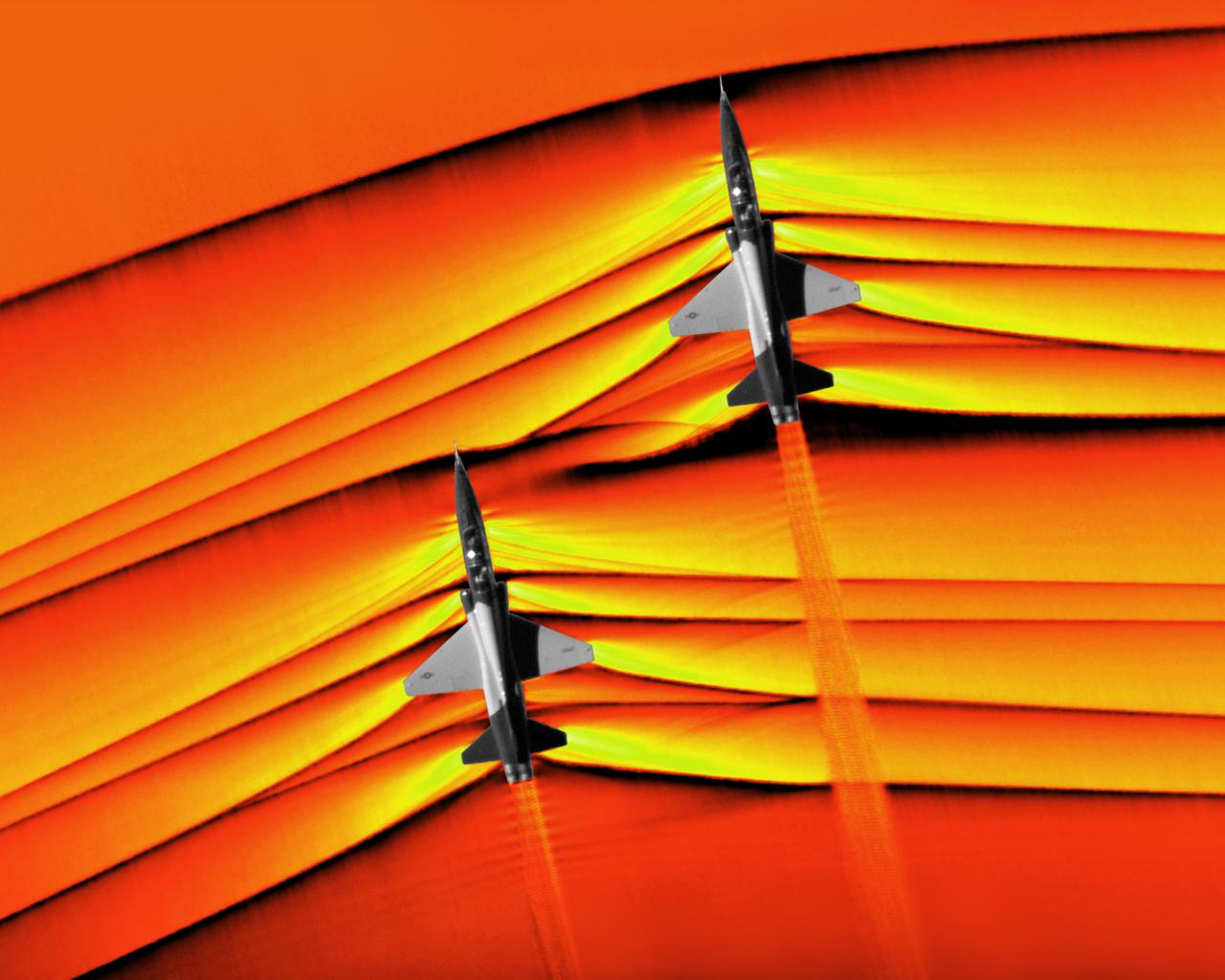
Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.01 pass. This data is the first time shockwave interactions between two full scale aircraft traveling faster than the speed of sound have been imaged and shown with schlieren visualization. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith
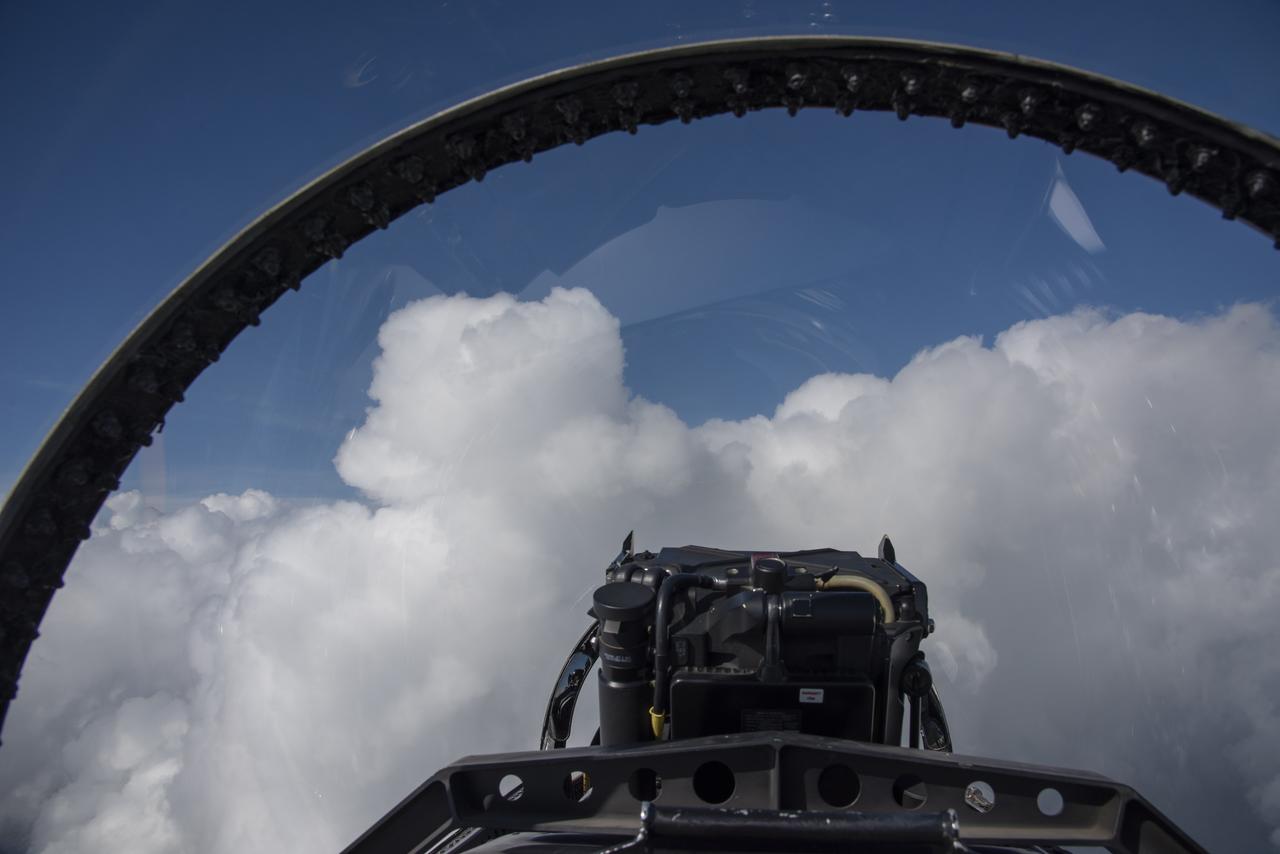

The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.

The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.

The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.

The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.

Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.01 pass. This data is the first time shockwave interactions between two full scale aircraft traveling faster than the speed of sound have been imaged and shown with schlieren visualization. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith
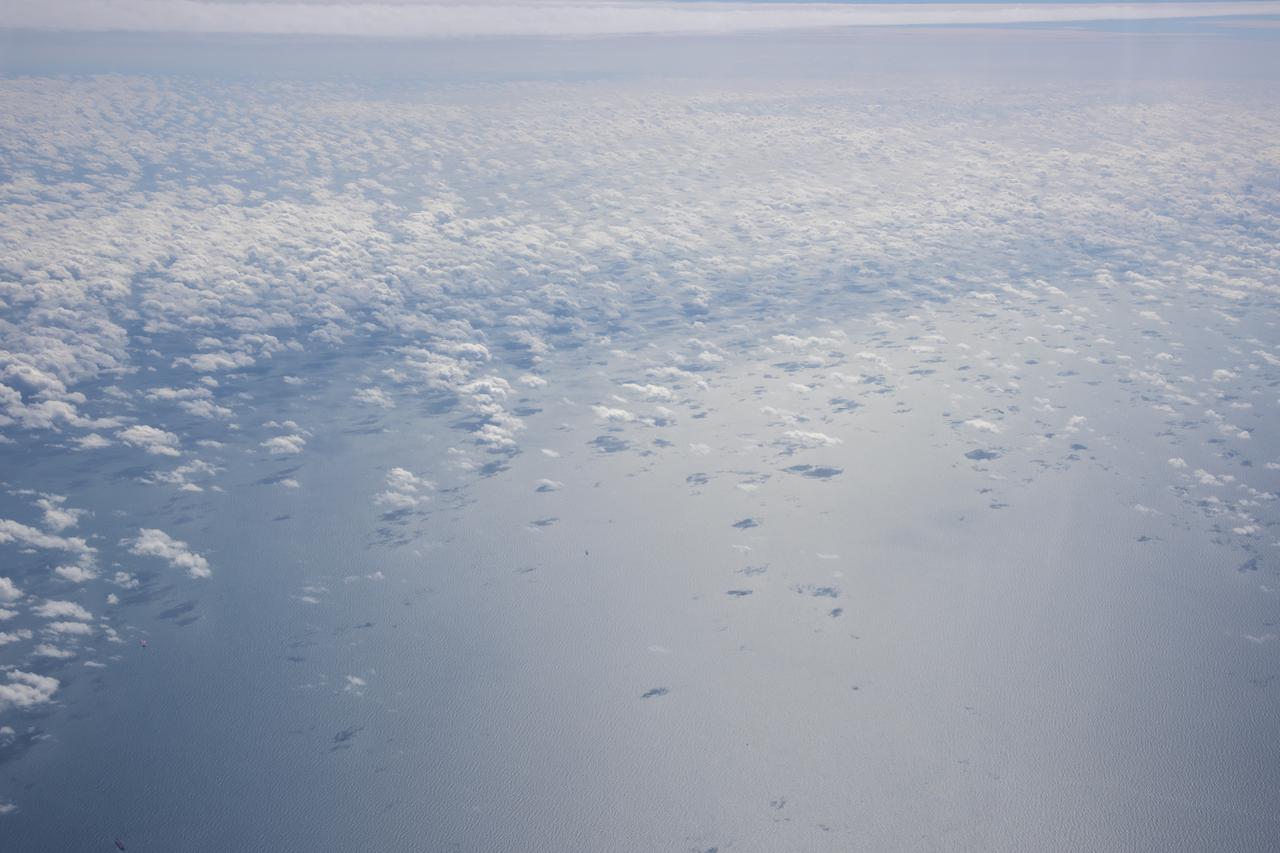

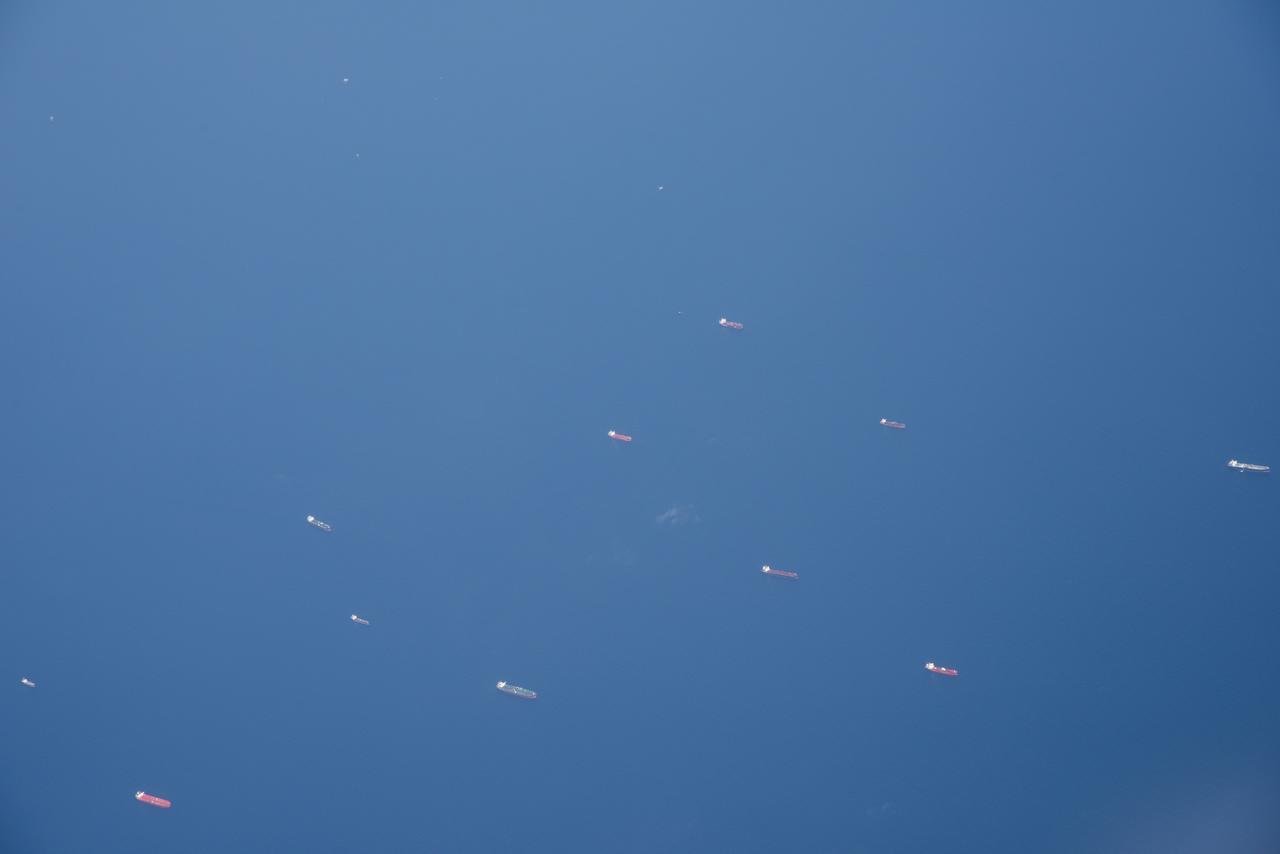
The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.
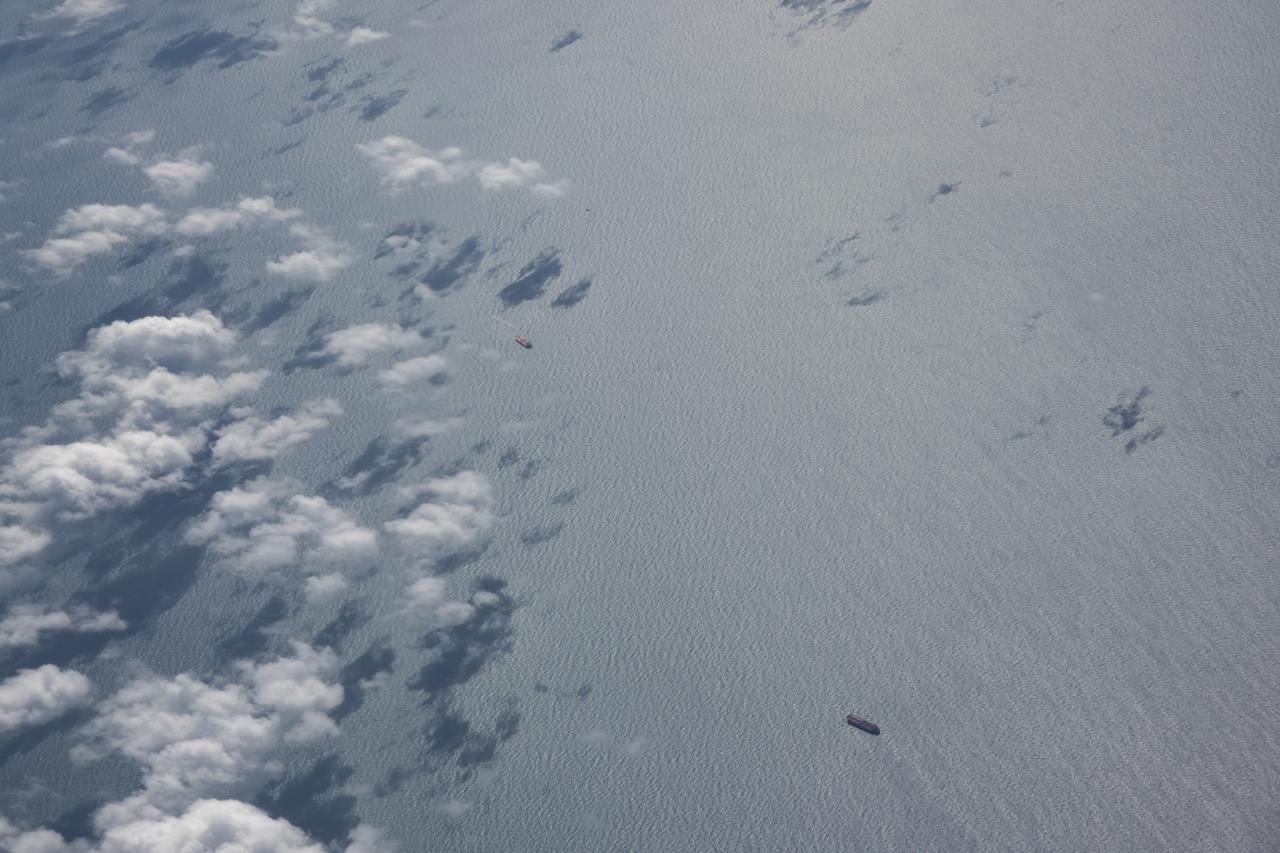

The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.
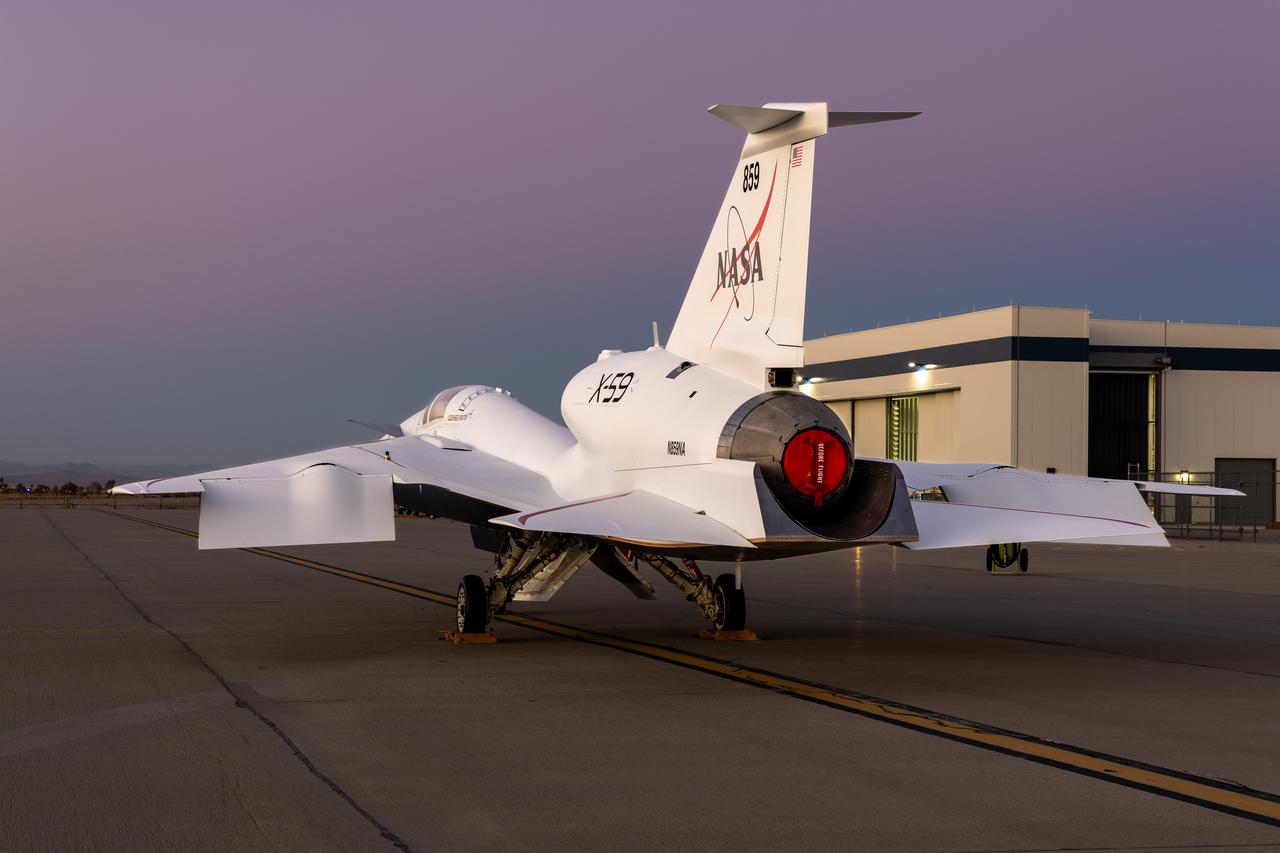

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on a ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, during sunset. The one-of-a-kind aircraft is powered by a General Electric F414 engine, a variant of the engines used on F/A-18 fighter jets. The engine is mounted above the fuselage to reduce the number of shockwaves that reach the ground. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA's Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and enable future commercial travel over land – faster than the speed of sound.
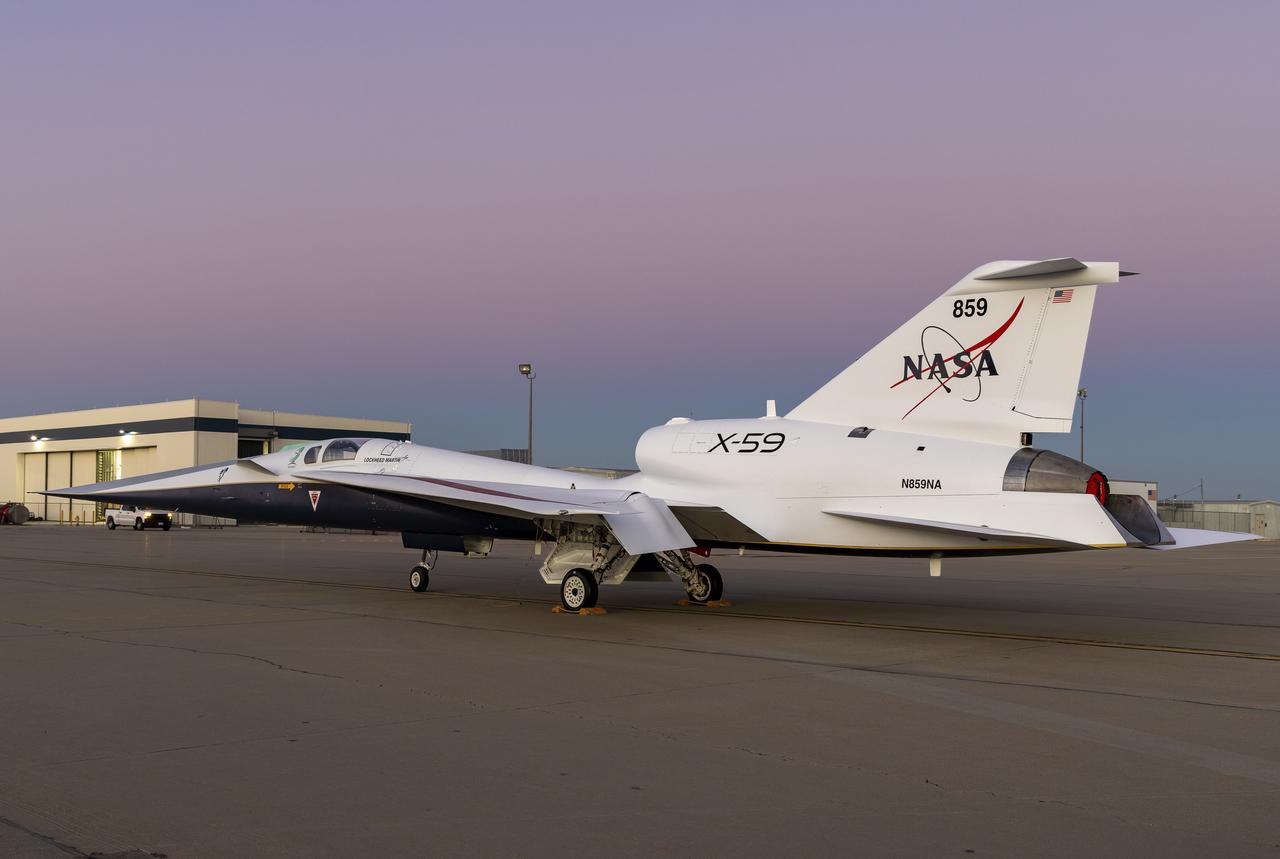

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on a ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, during sunset. The one-of-a-kind aircraft is powered by a General Electric F414 engine, a variant of the engines used on F/A-18 fighter jets. The engine is mounted above the fuselage to reduce the number of shockwaves that reach the ground. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA's Quesst mission, which aims to demonstrate quiet supersonic flight and enable future commercial travel over land – faster than the speed of sound.
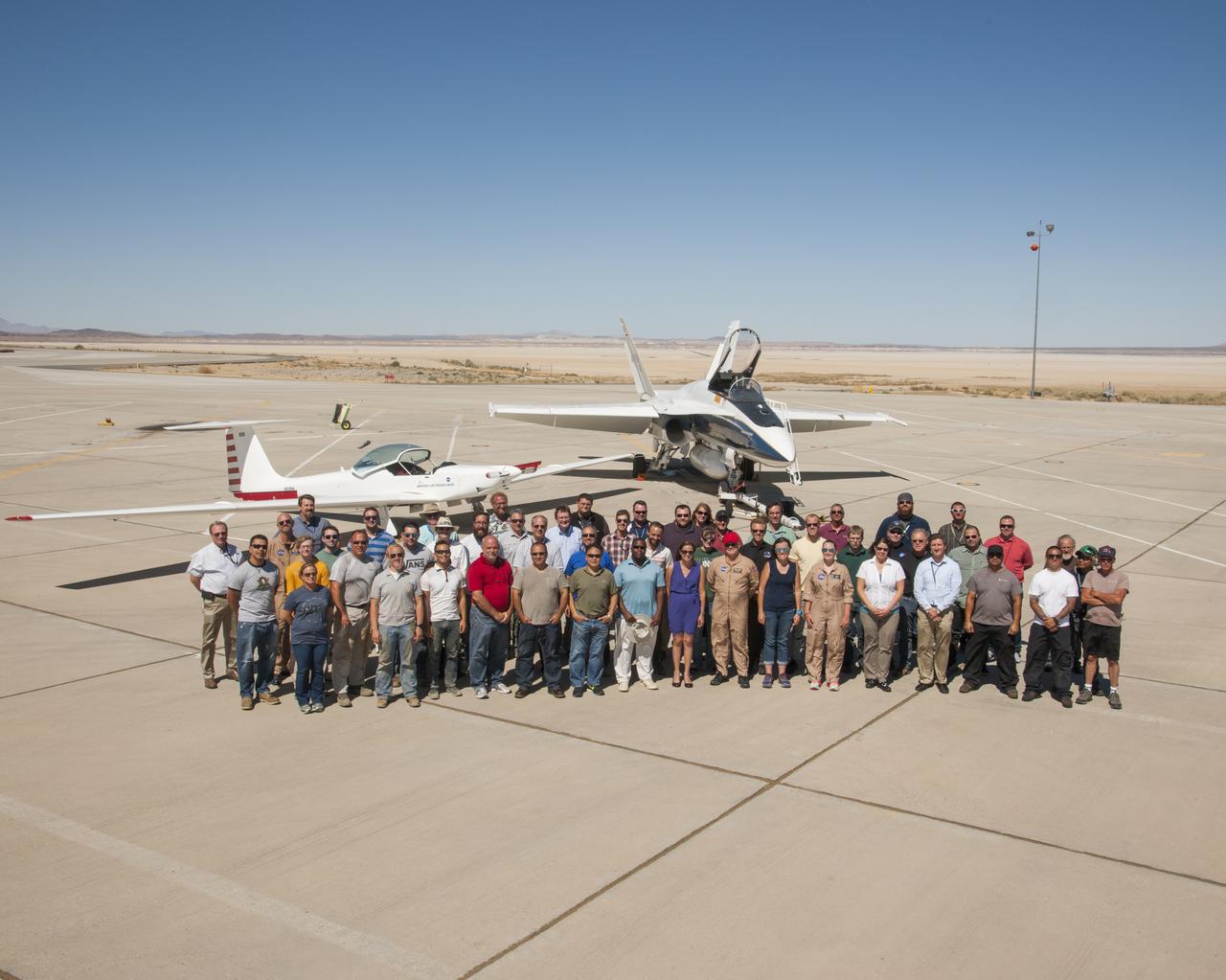

NASA’s SonicBAT team poses in front of the TG-14 motor glider and F/A-18 research aircraft, sitting side-by-side in front of Rogers Dry Lake prior to a SonicBAT flight at Armstrong Flight Research Center on Edwards Air Force Base, California. The TG-14 collected sound signatures of shockwaves created by the F/A-18, to compare with signatures collected on the ground.
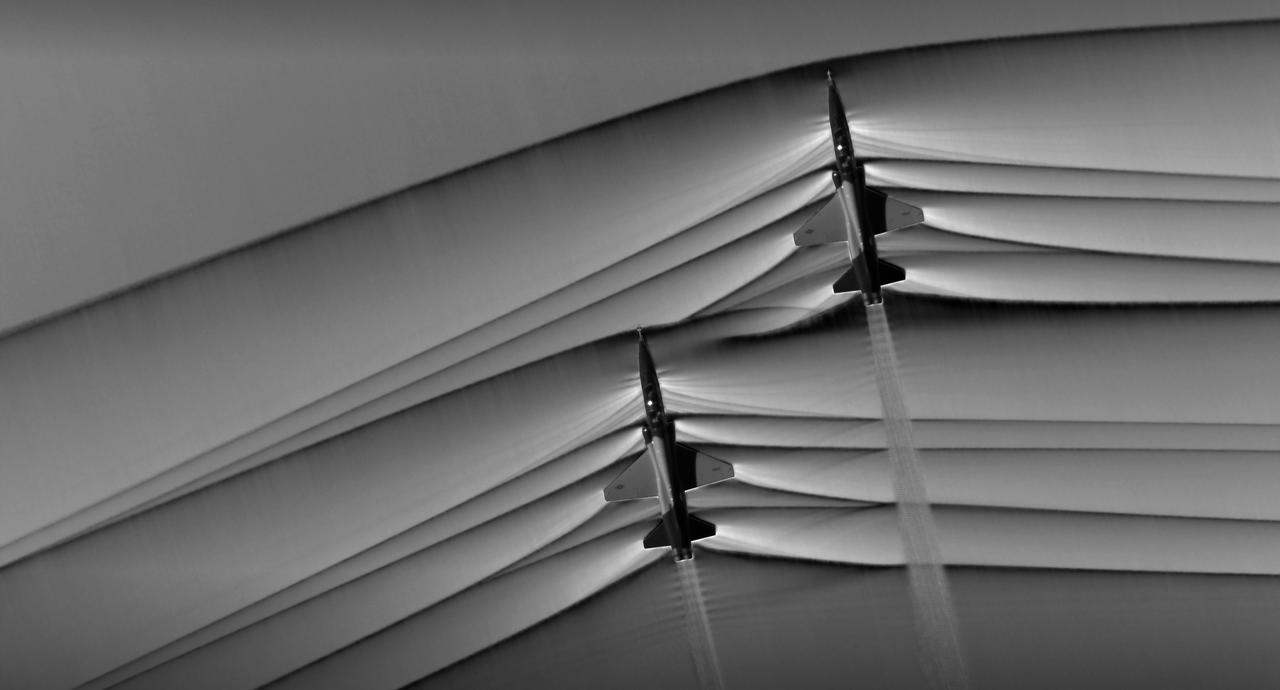
Composite image of Background Oriented Schlieren (BOS) data (contour) with a cut-out images of the T-38’s during a Mach Number 1.01 pass. This data is the first time shockwave interactions between two full scale aircraft traveling faster than the speed of sound have been imaged and shown with schlieren visualization. Original recording of the pass taken in the Black Mountain Supersonic Corridor at near Edwards AFB in December of 2018. Image acquired by JT Heineck, schlieren data processed by Neal Smith.
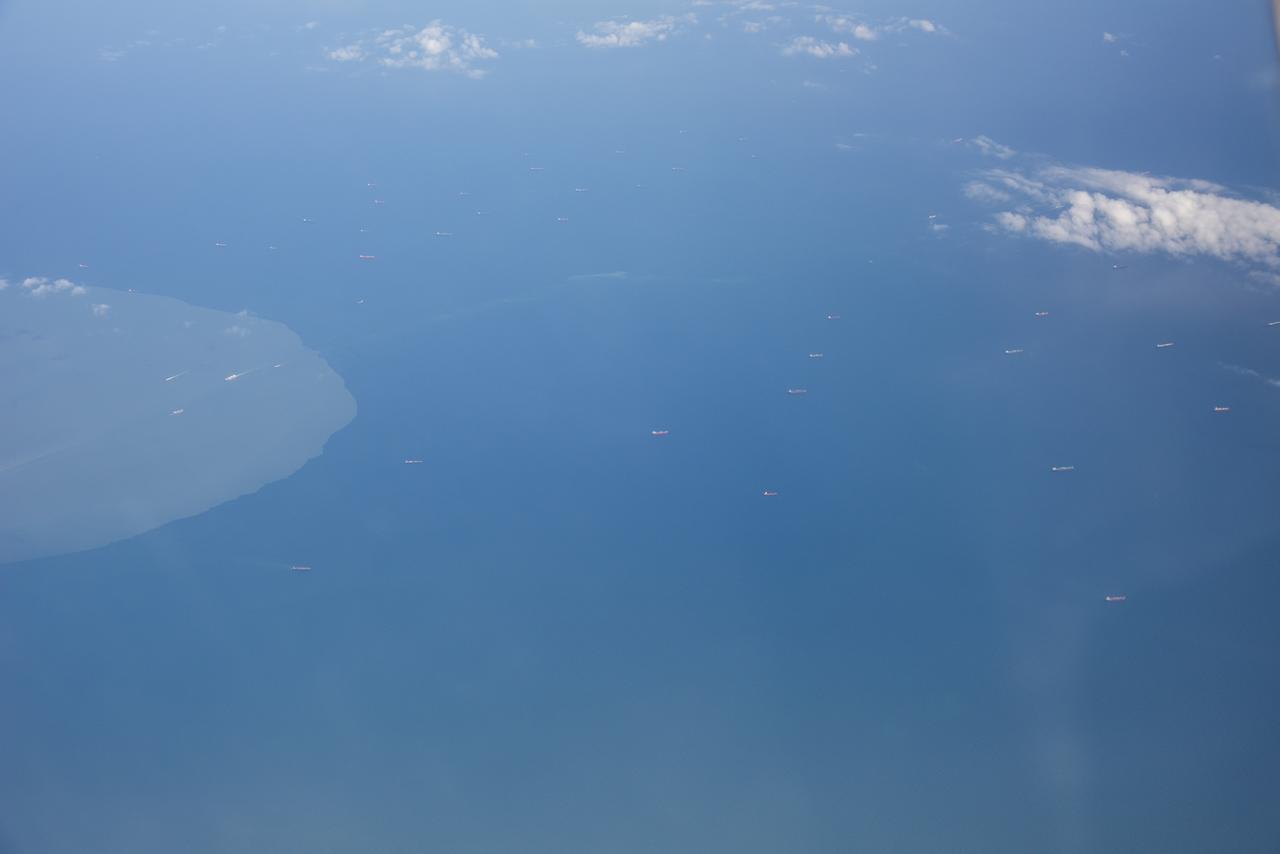

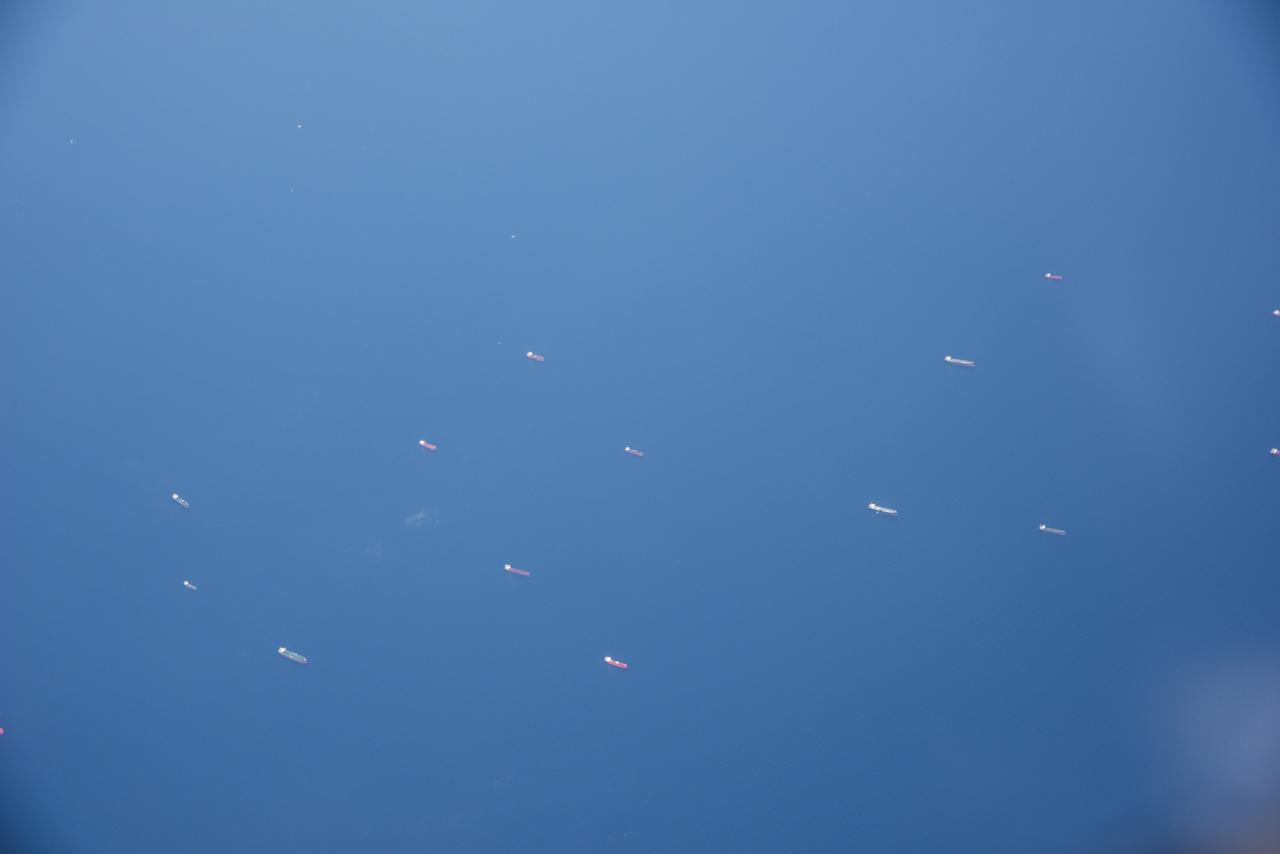
The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.
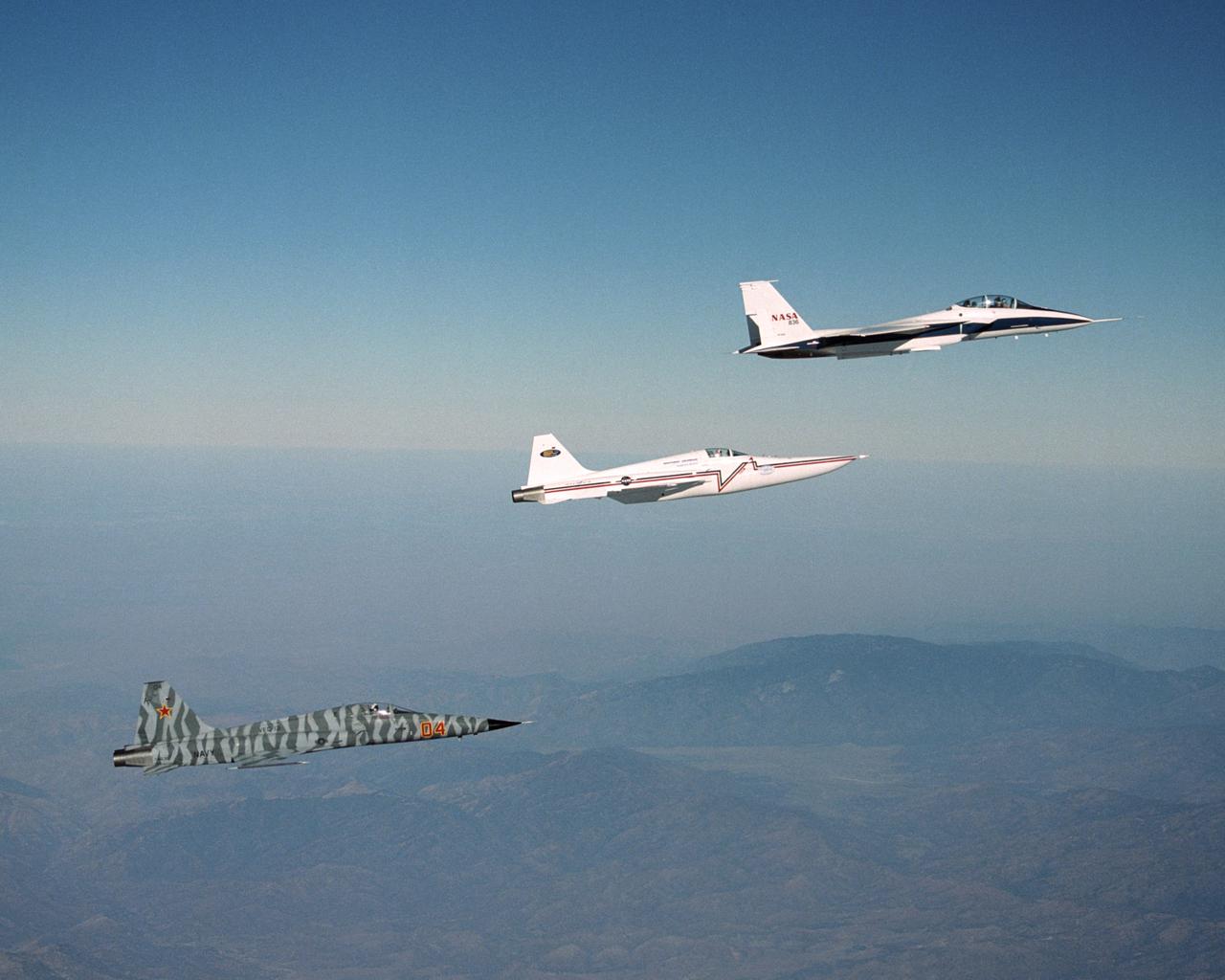

In a role-reversal, Northrop Grumman Corp.'s modified F-5E Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) aircraft flies off the wing of NASA's F-15B Research testbed aircraft. The F-15B, from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, flew in the supersonic shockwave of the F-5E as part of the SSBD project. Following the two aircraft is an unmodified U.S. Navy F-5E used for baseline sonic boom measurements.
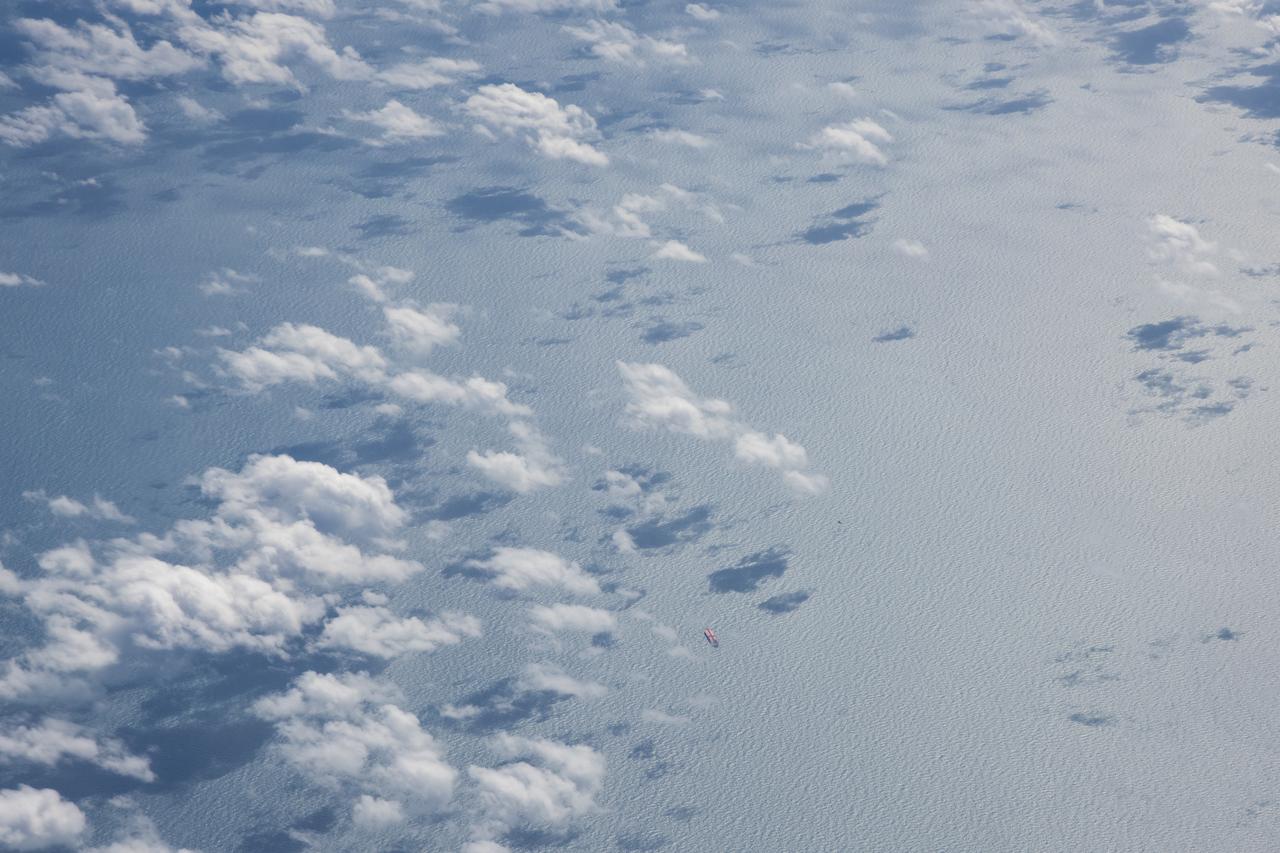

The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.

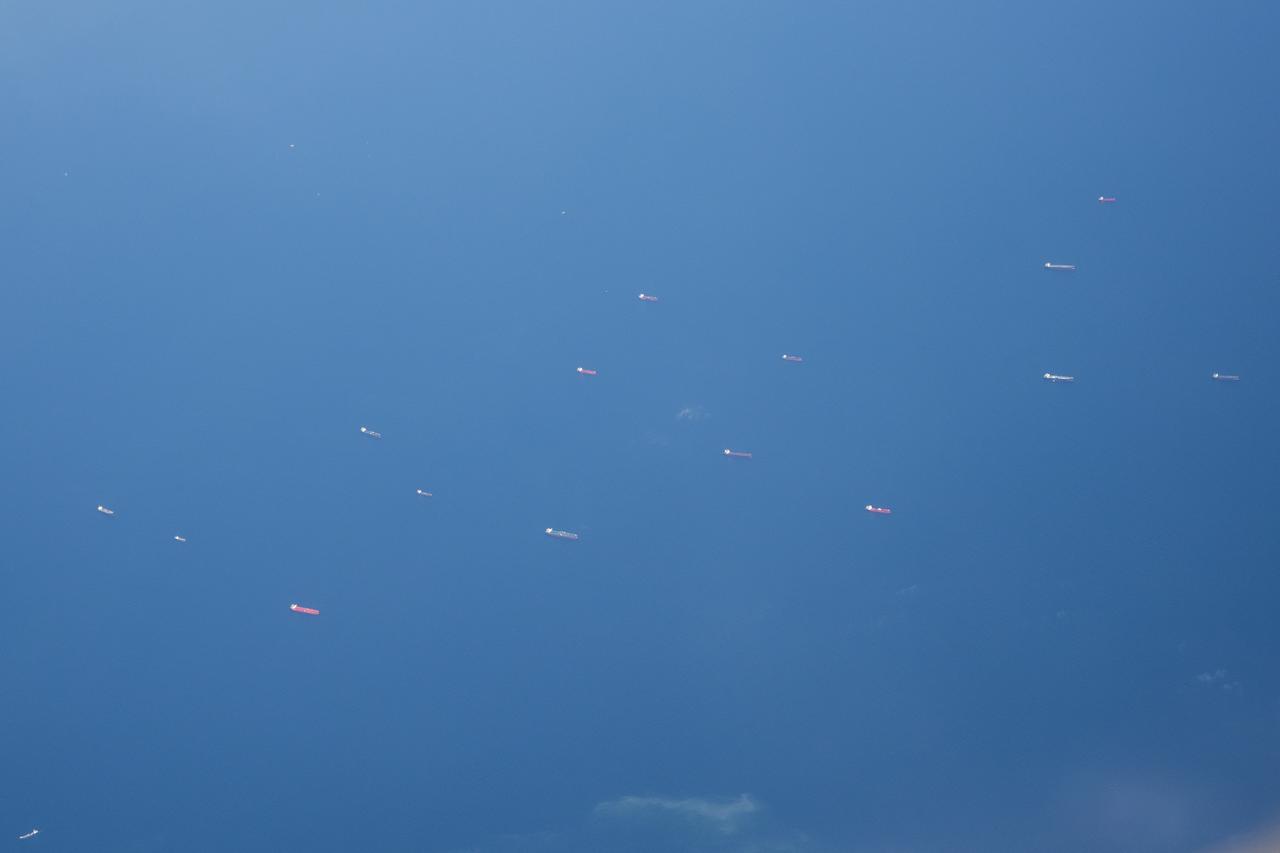
The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.

The Gulf of Mexico as seen from NASA photographer Carla Thomas at high altitude in the F/A-18 research aircraft during a flight in support of the Quiet Supersonic Flights 2018 series, or QSF18. The high altitude is necessary as part of the quiet supersonic dive maneuver, climbing to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area.
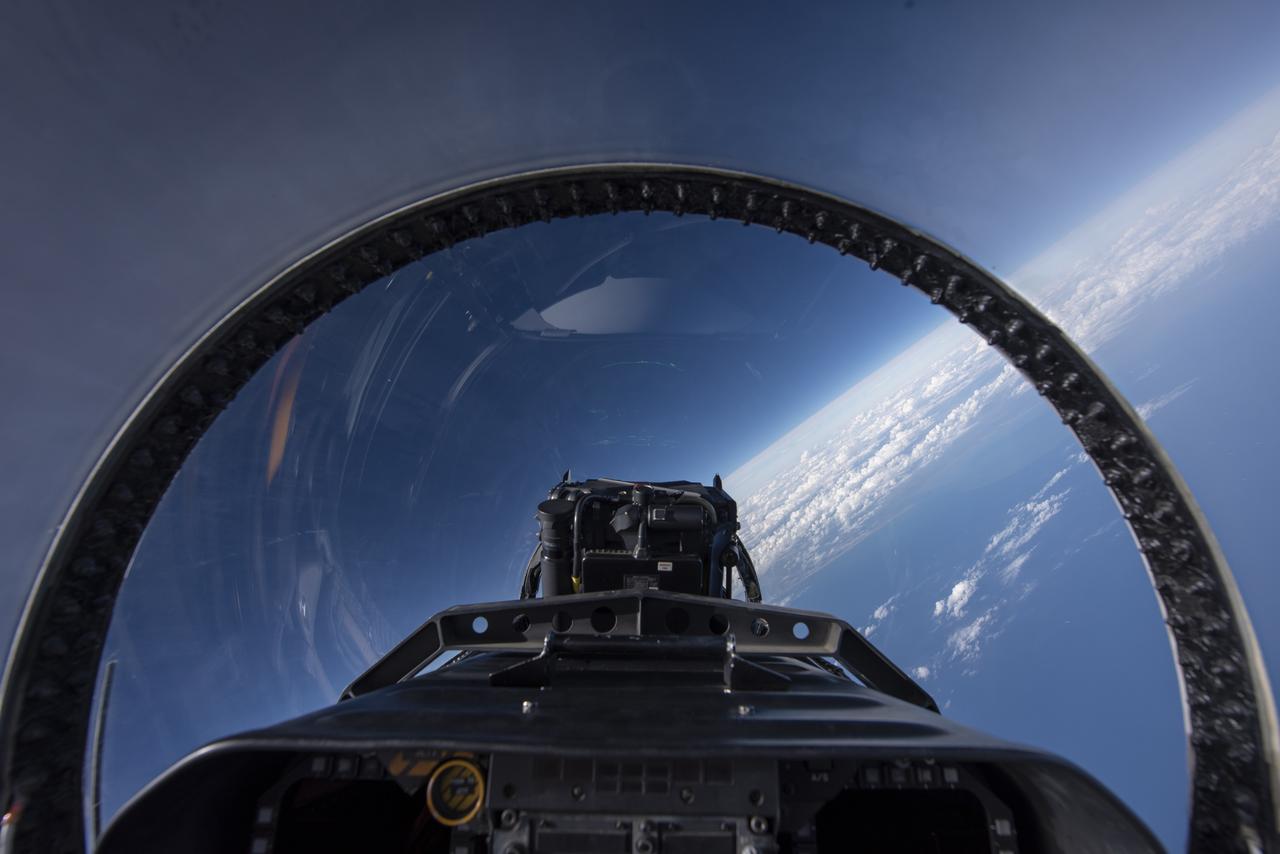

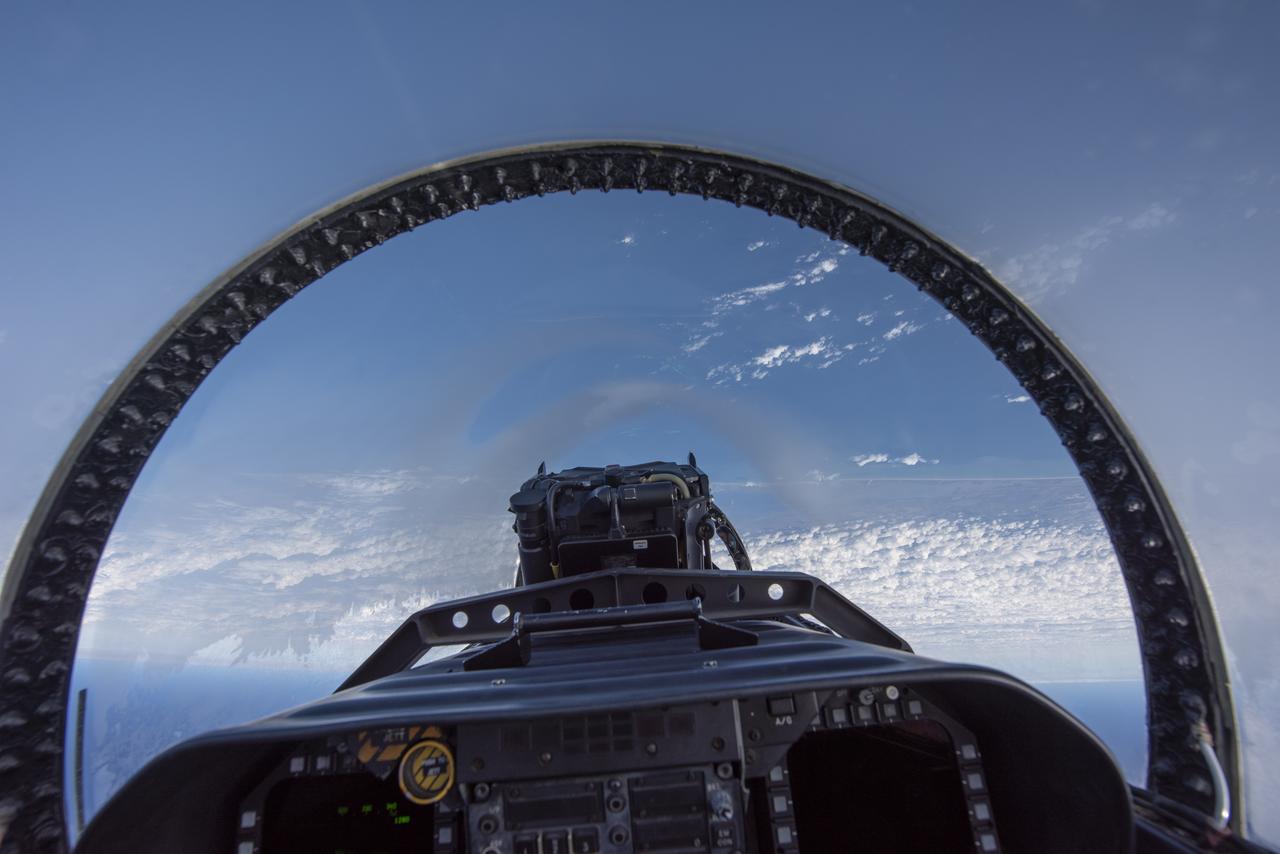
NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
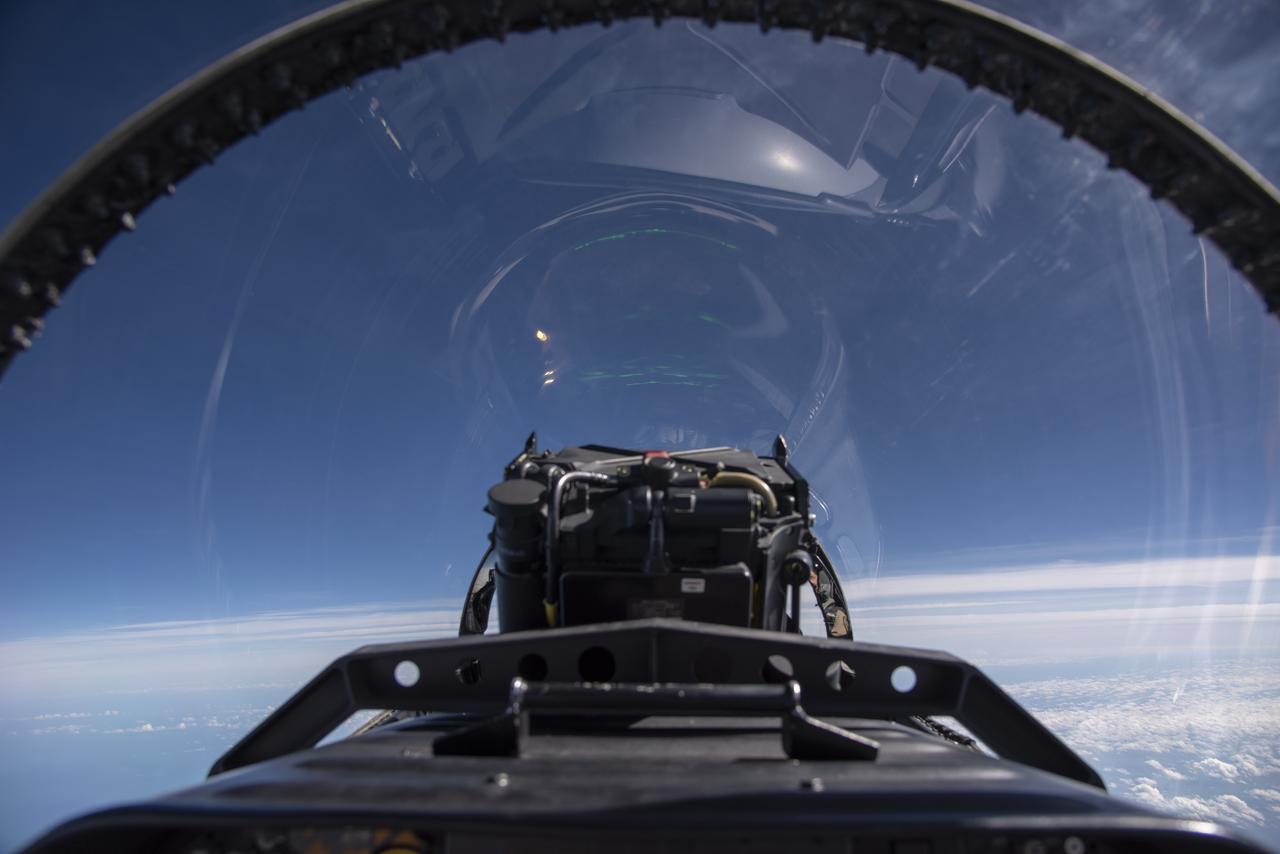

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
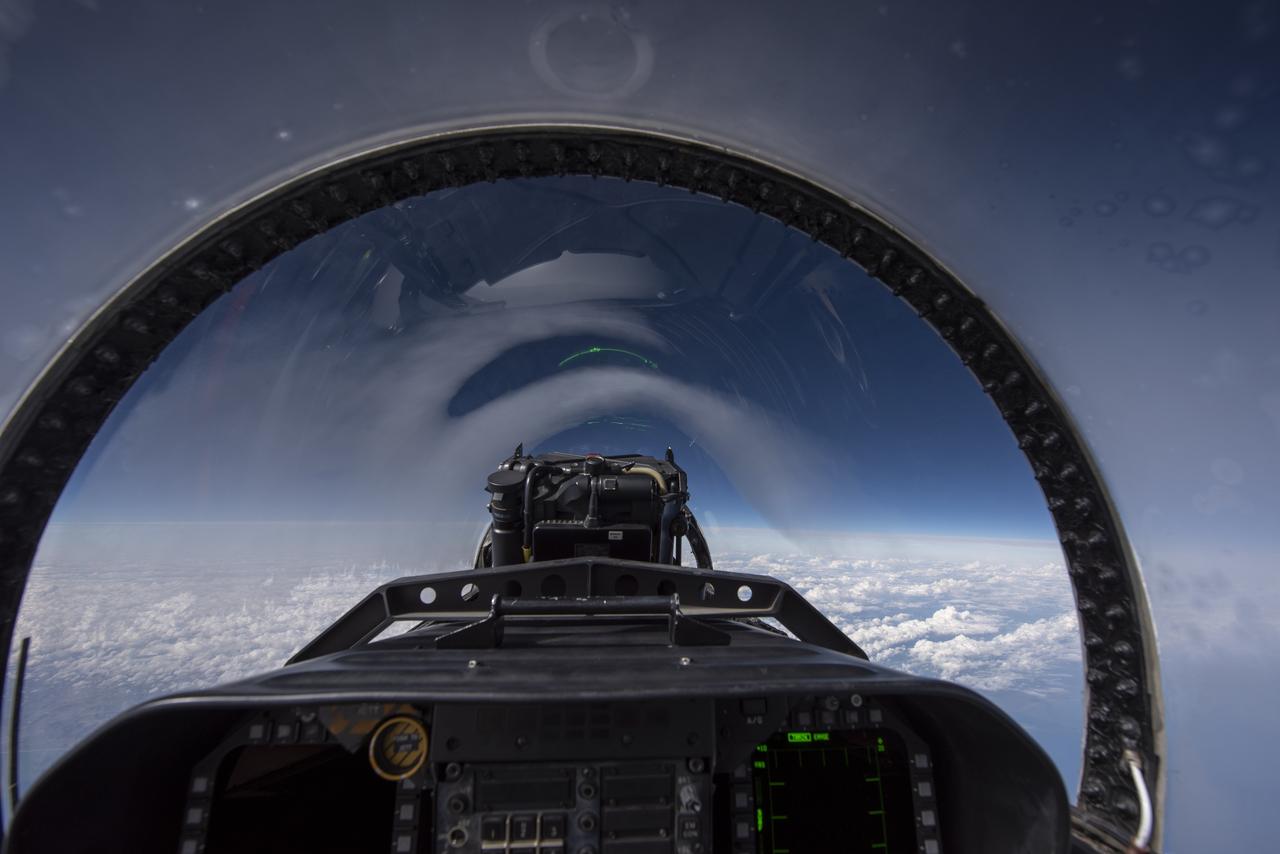

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
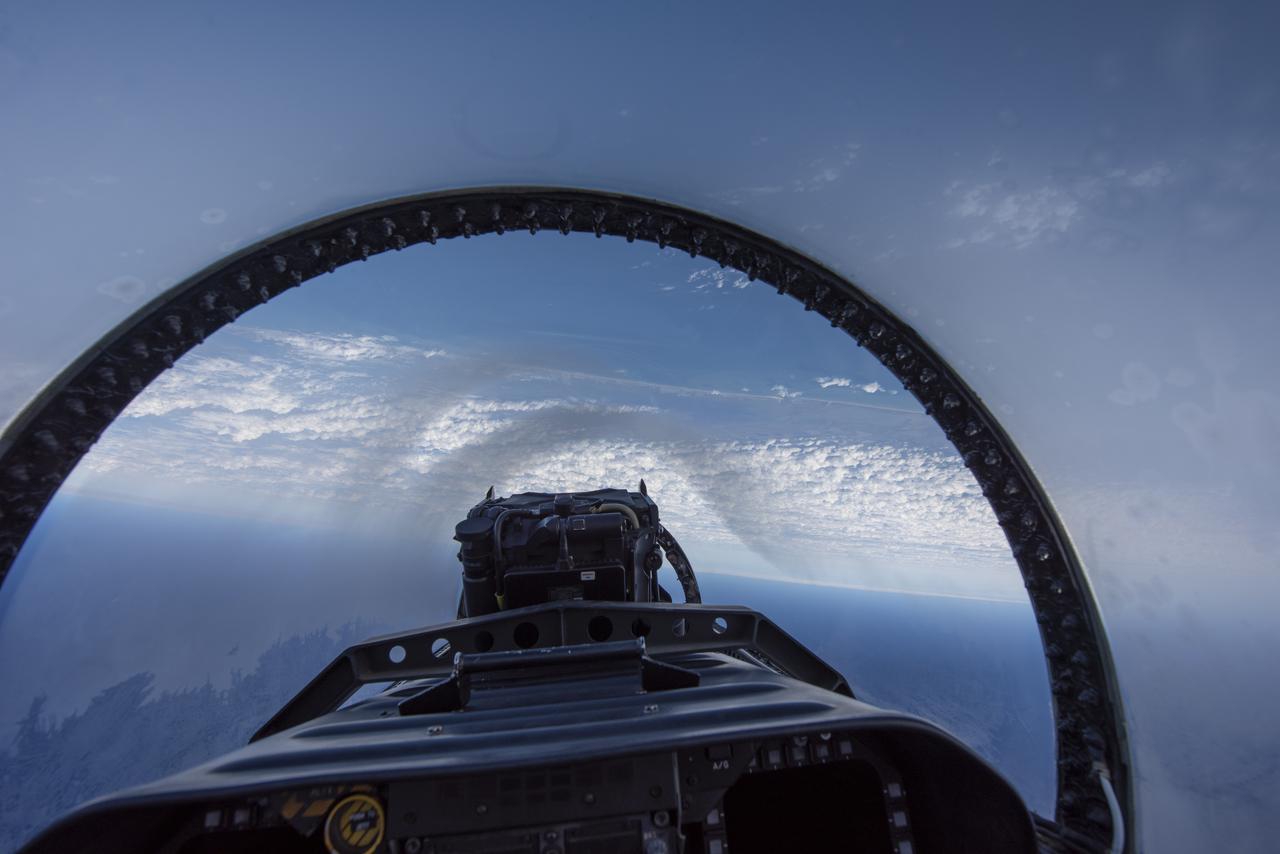

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
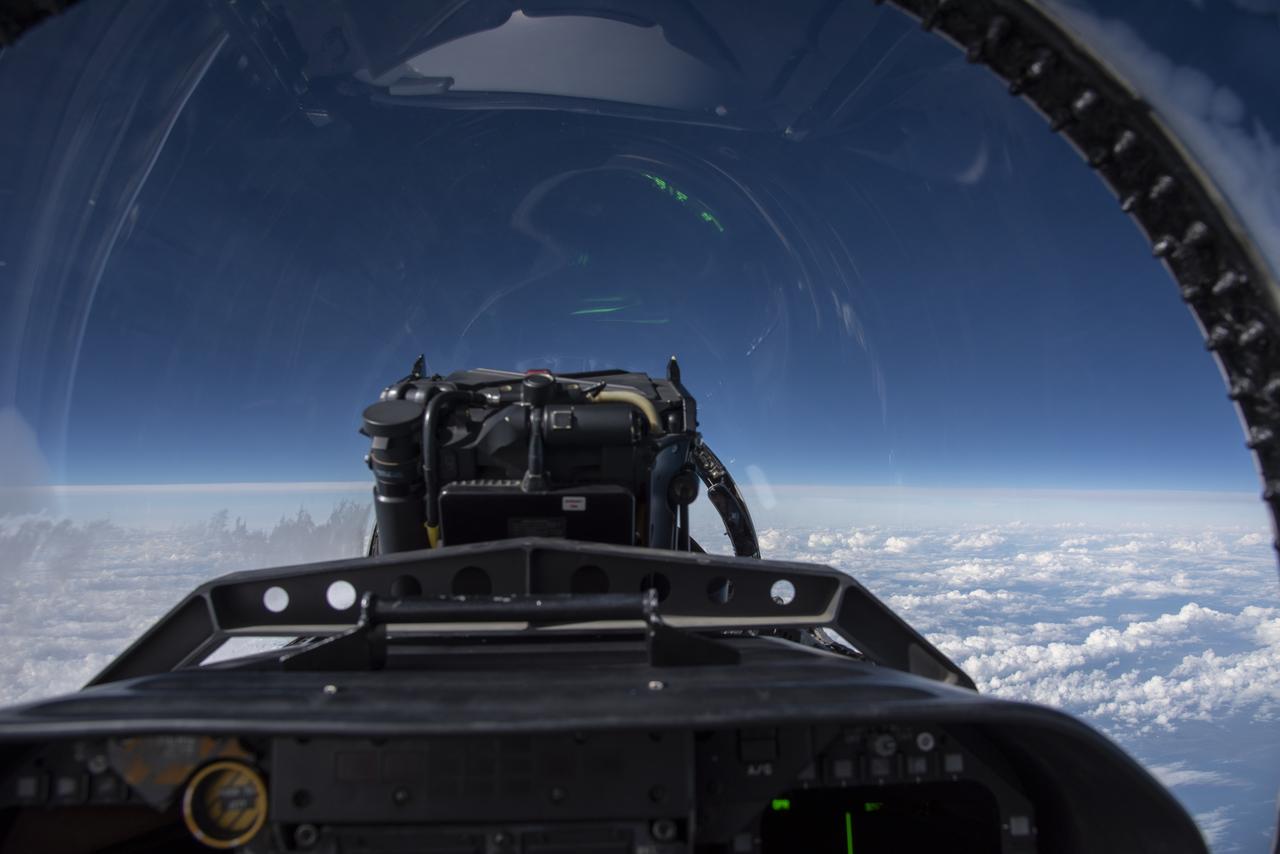

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
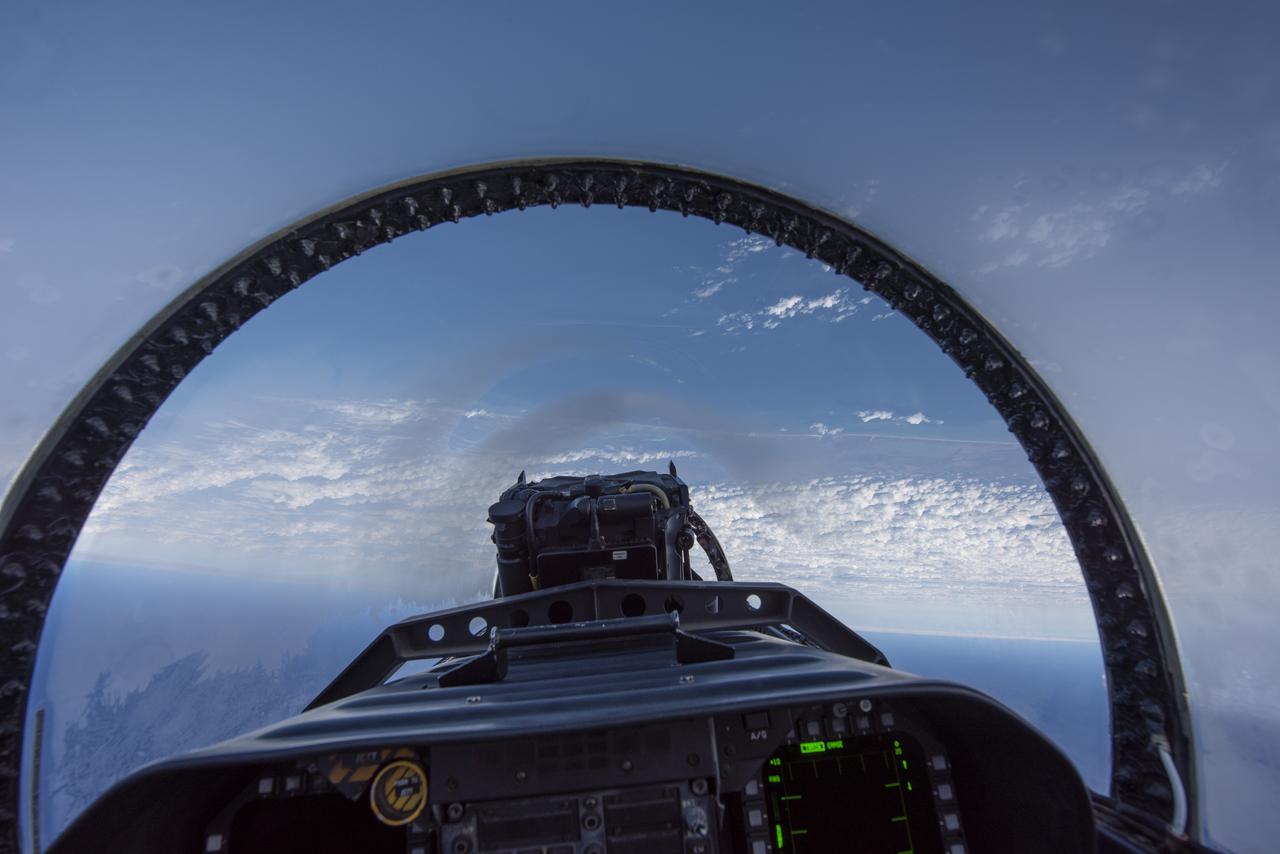

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
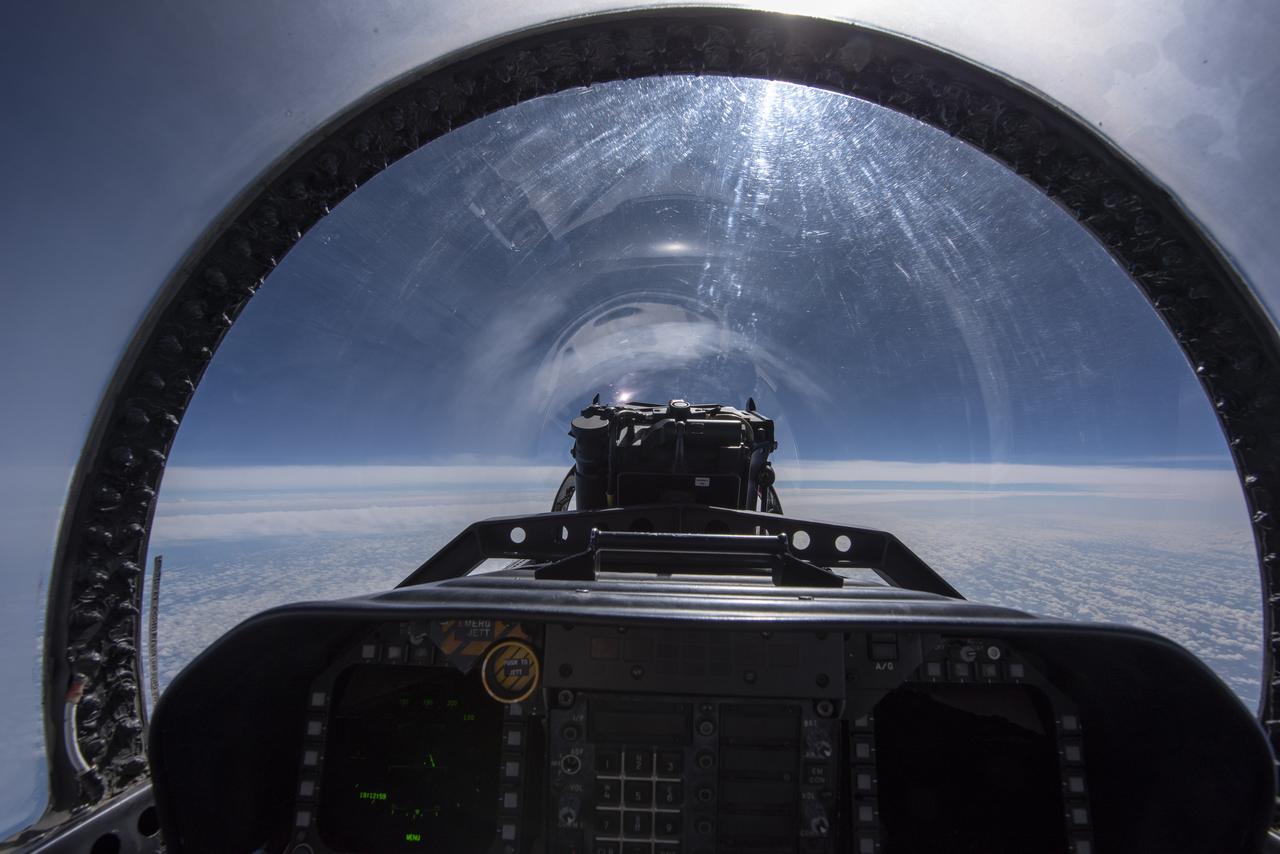

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
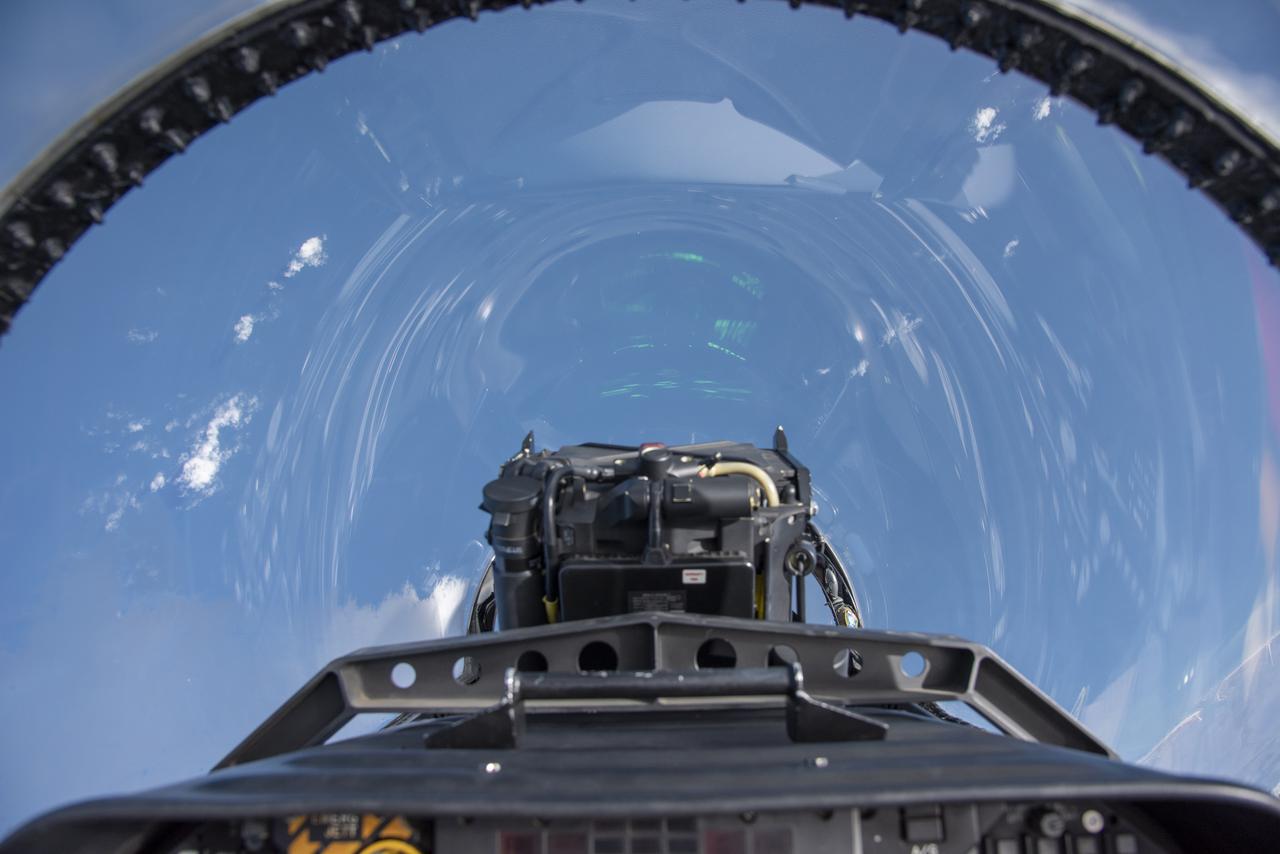

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
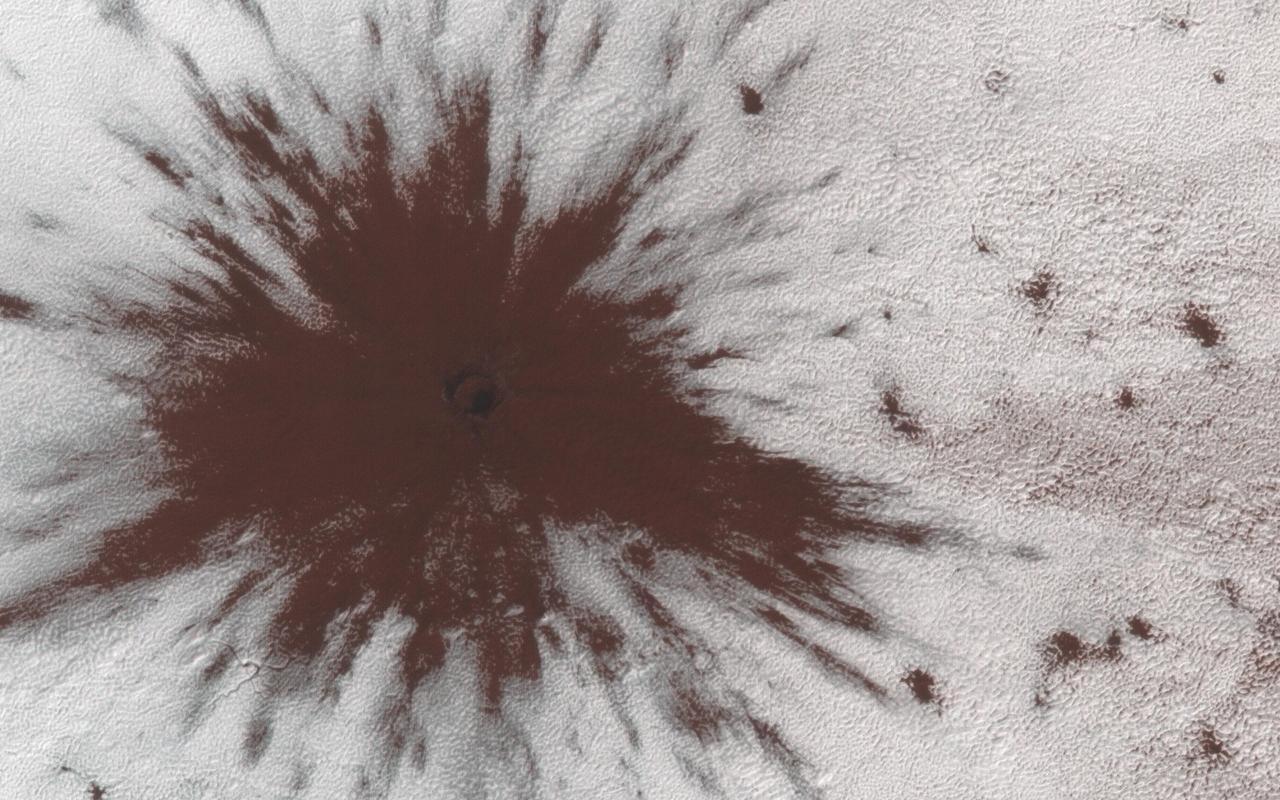

This image shows a new impact crater that formed between July and September 2018. It's notable because it occurred in the seasonal southern ice cap, and has apparently punched through it, creating a two-toned blast pattern. The impact hit on the ice layer, and the tones of the blast pattern tell us the sequence. When an impactor hits the ground, there is a tremendous amount of force like an explosion. The larger, lighter-colored blast pattern could be the result of scouring by winds from the impact shockwave. The darker-colored inner blast pattern is because the impactor penetrated the thin ice layer, excavated the dark sand underneath, and threw it out in all directions on top of the layer. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23019
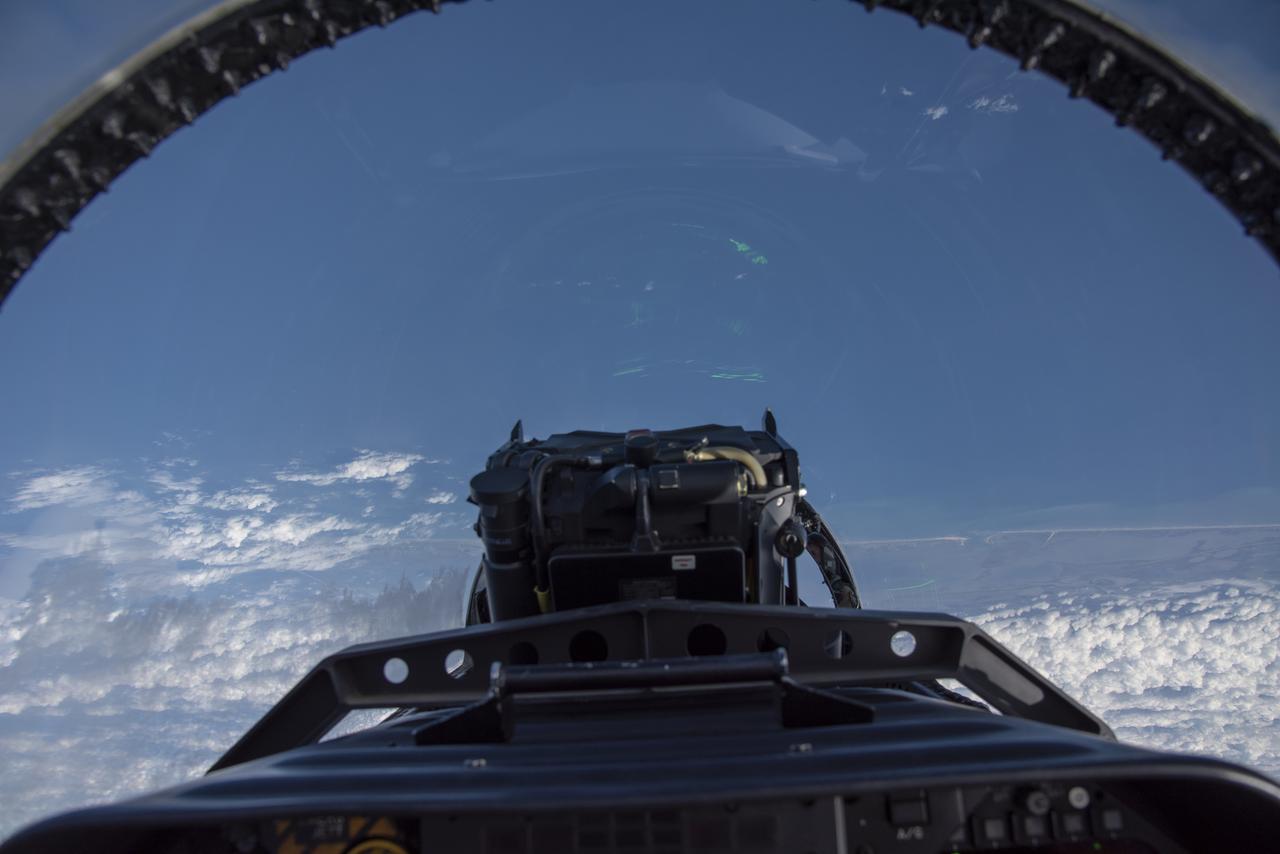

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
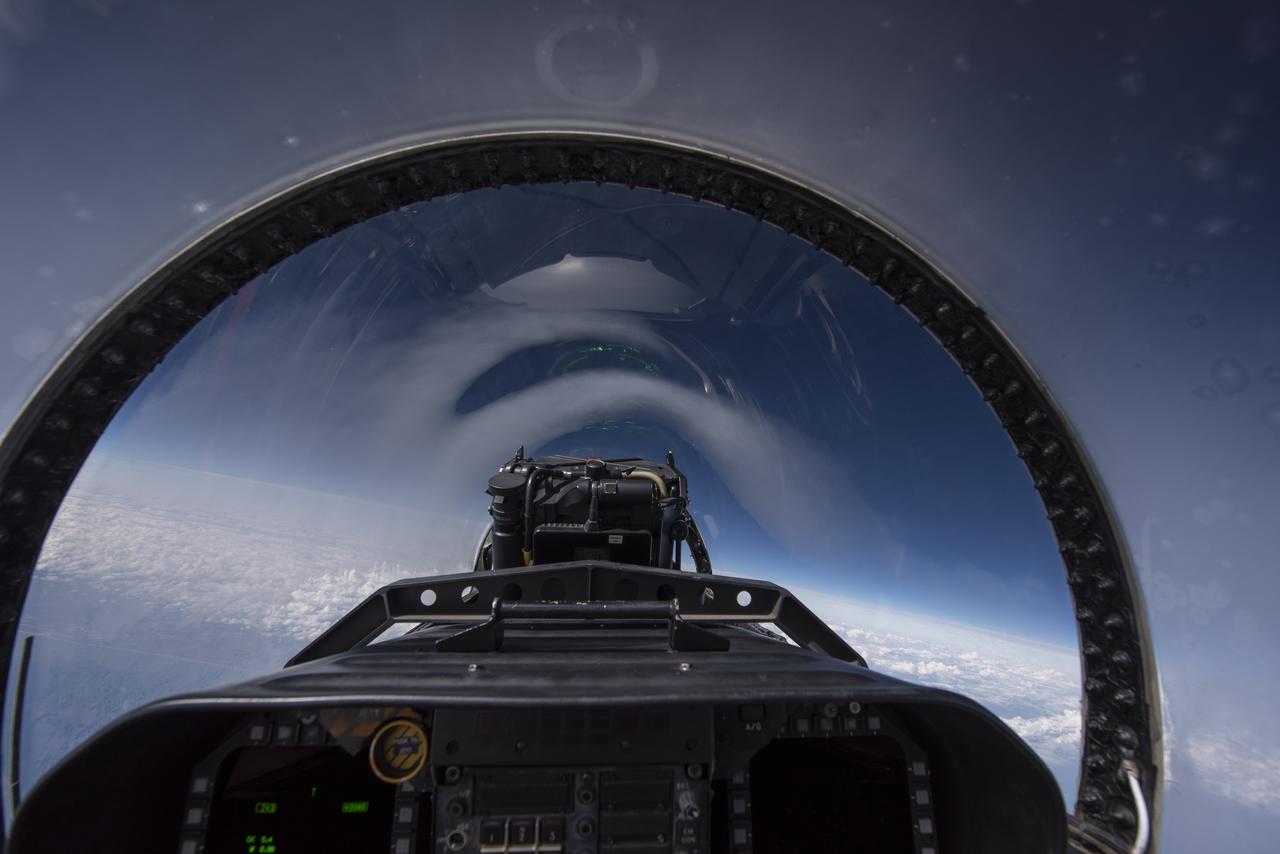

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
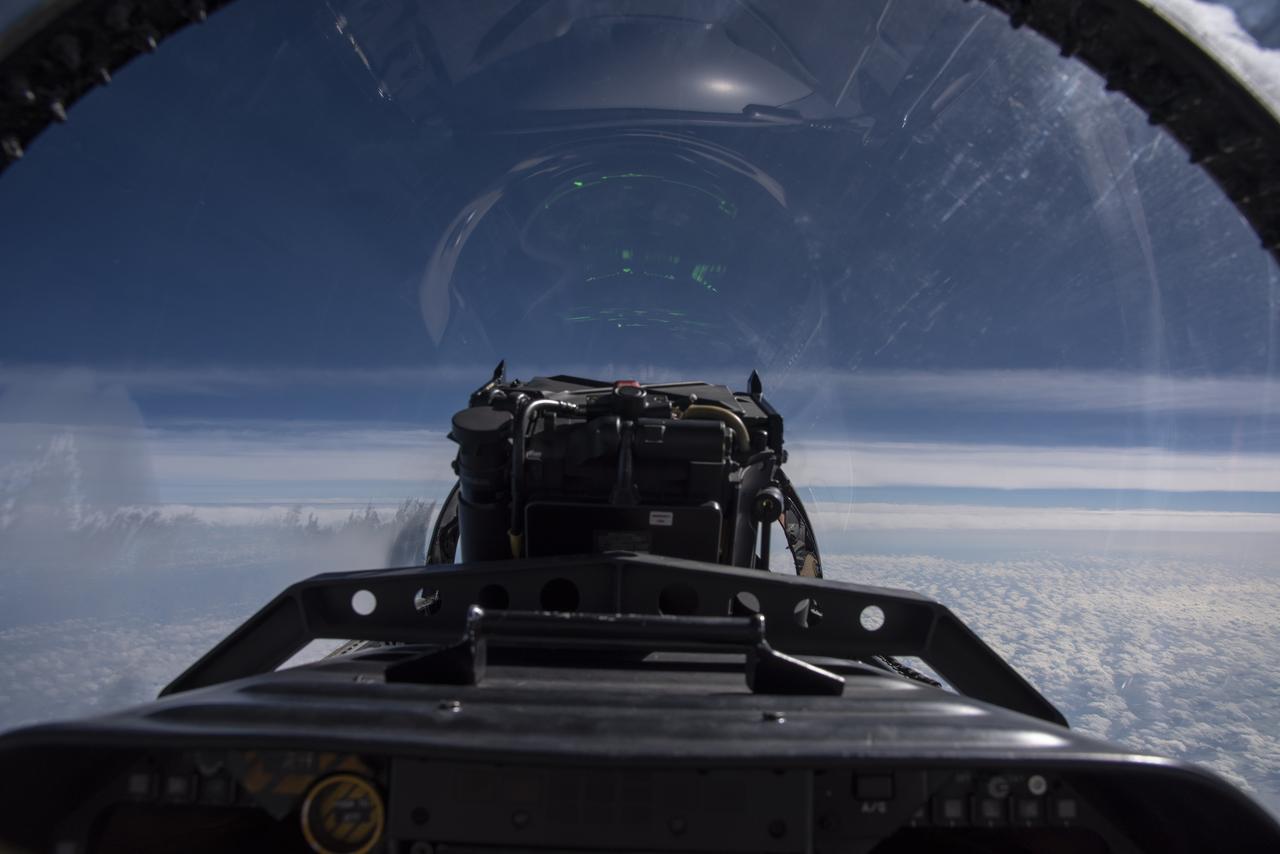

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
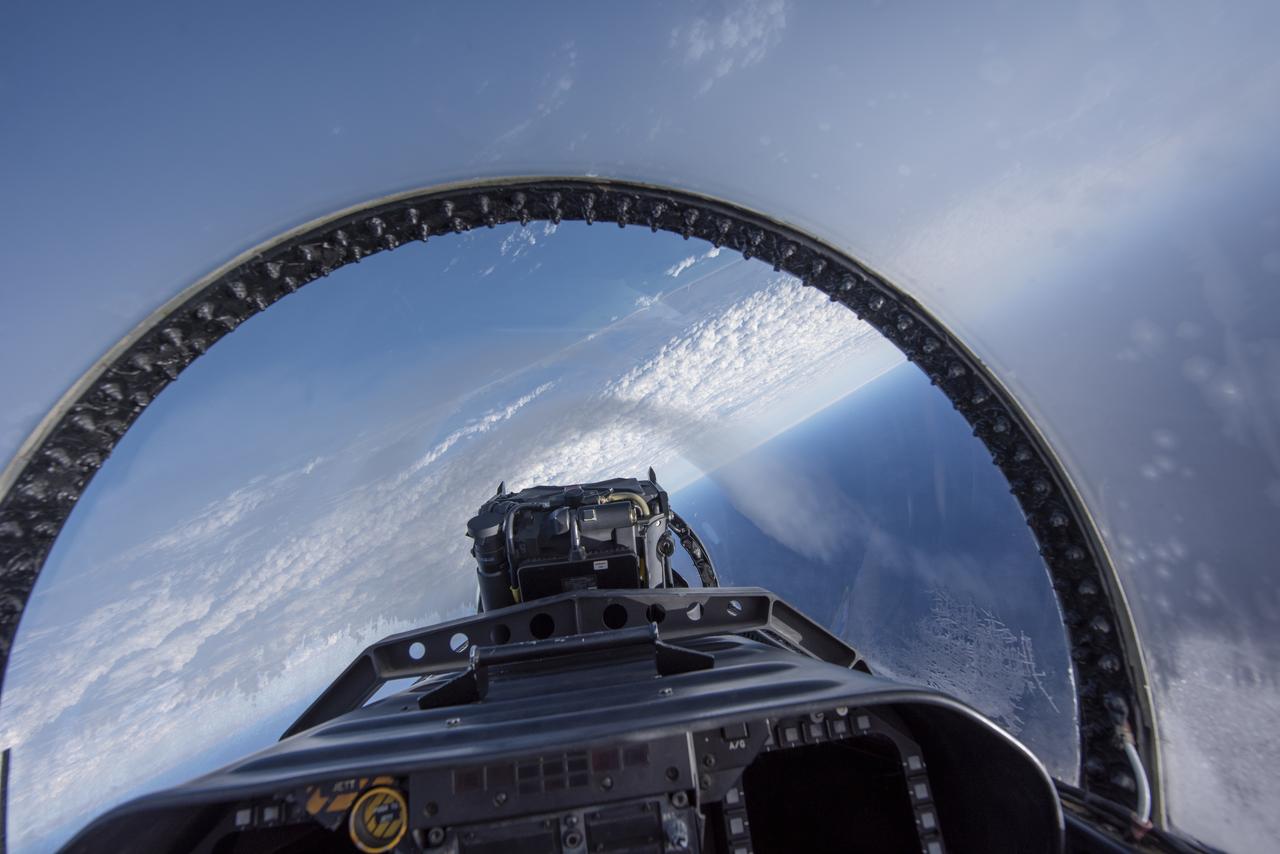

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
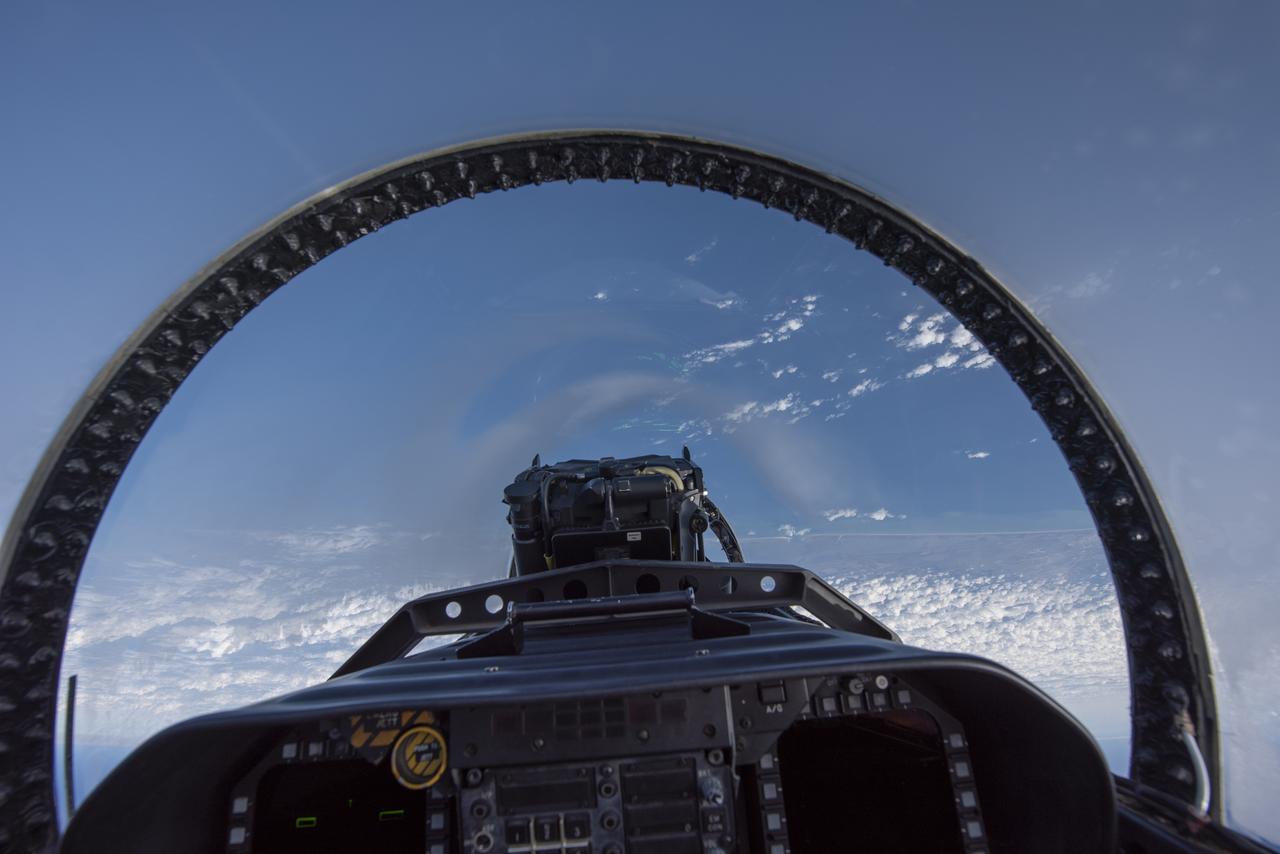

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
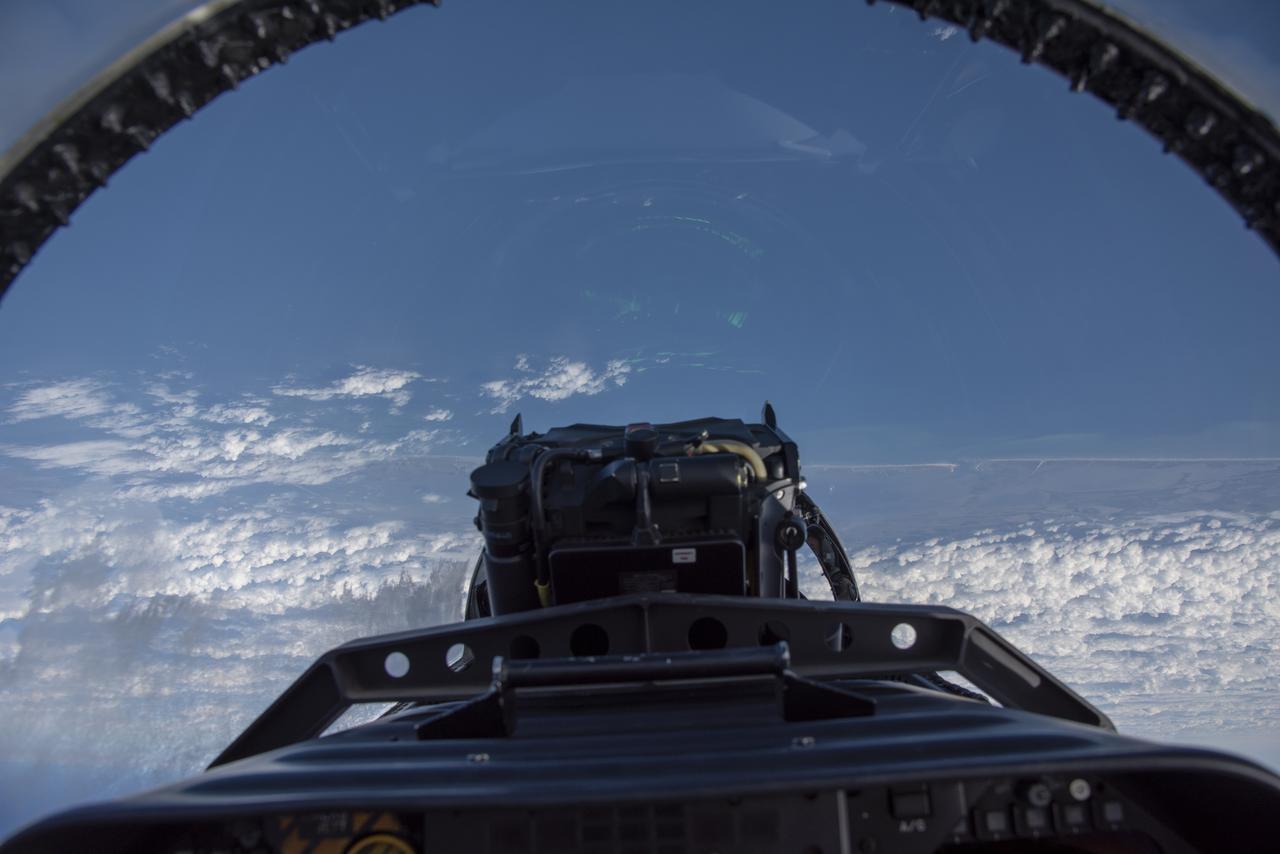

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
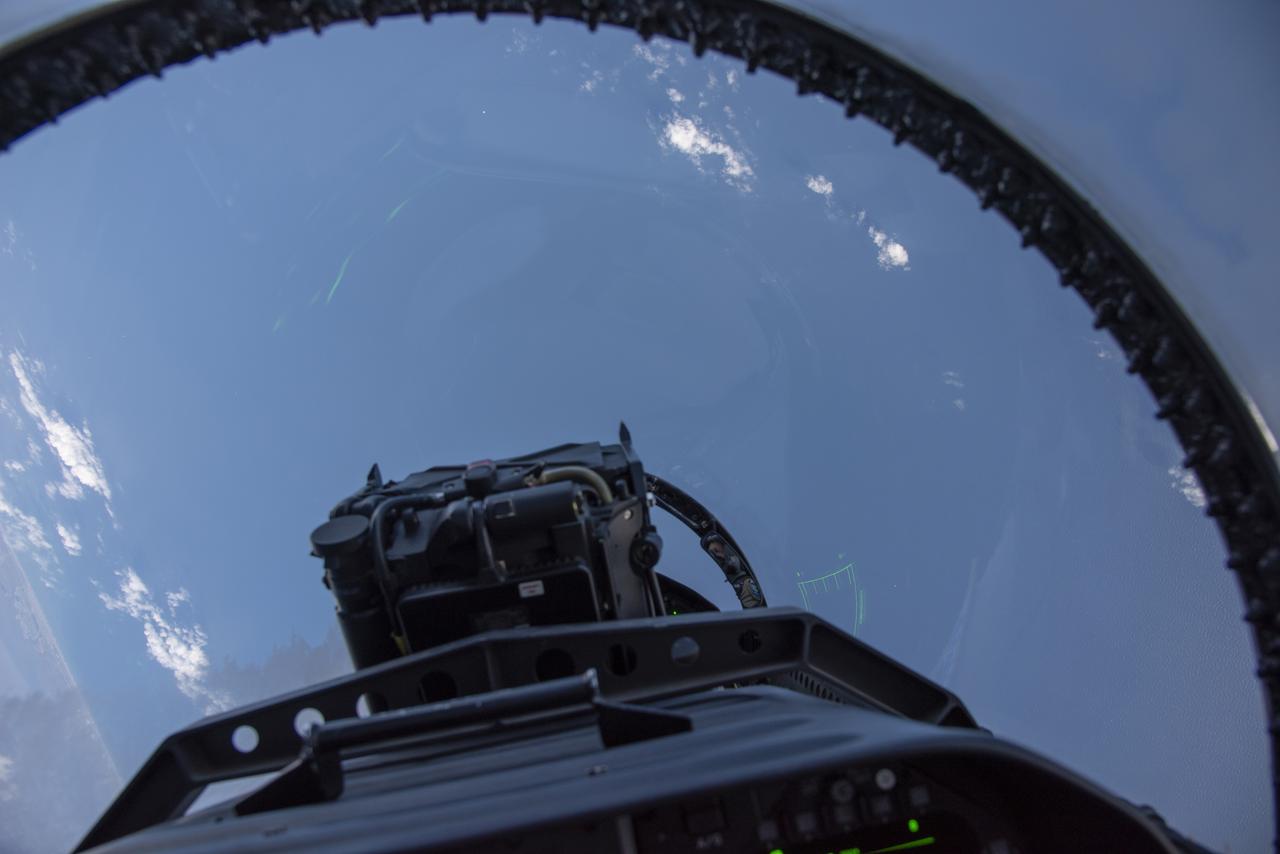

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
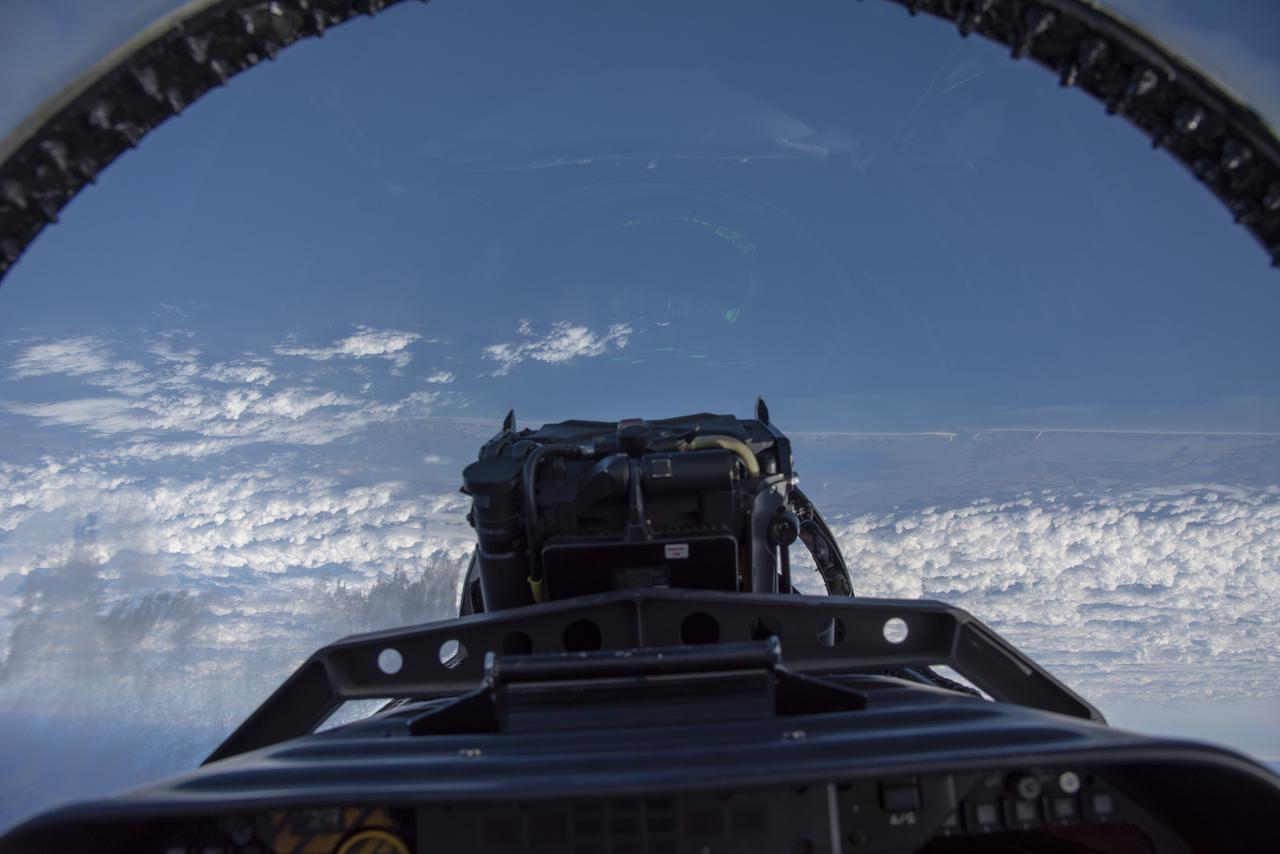

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
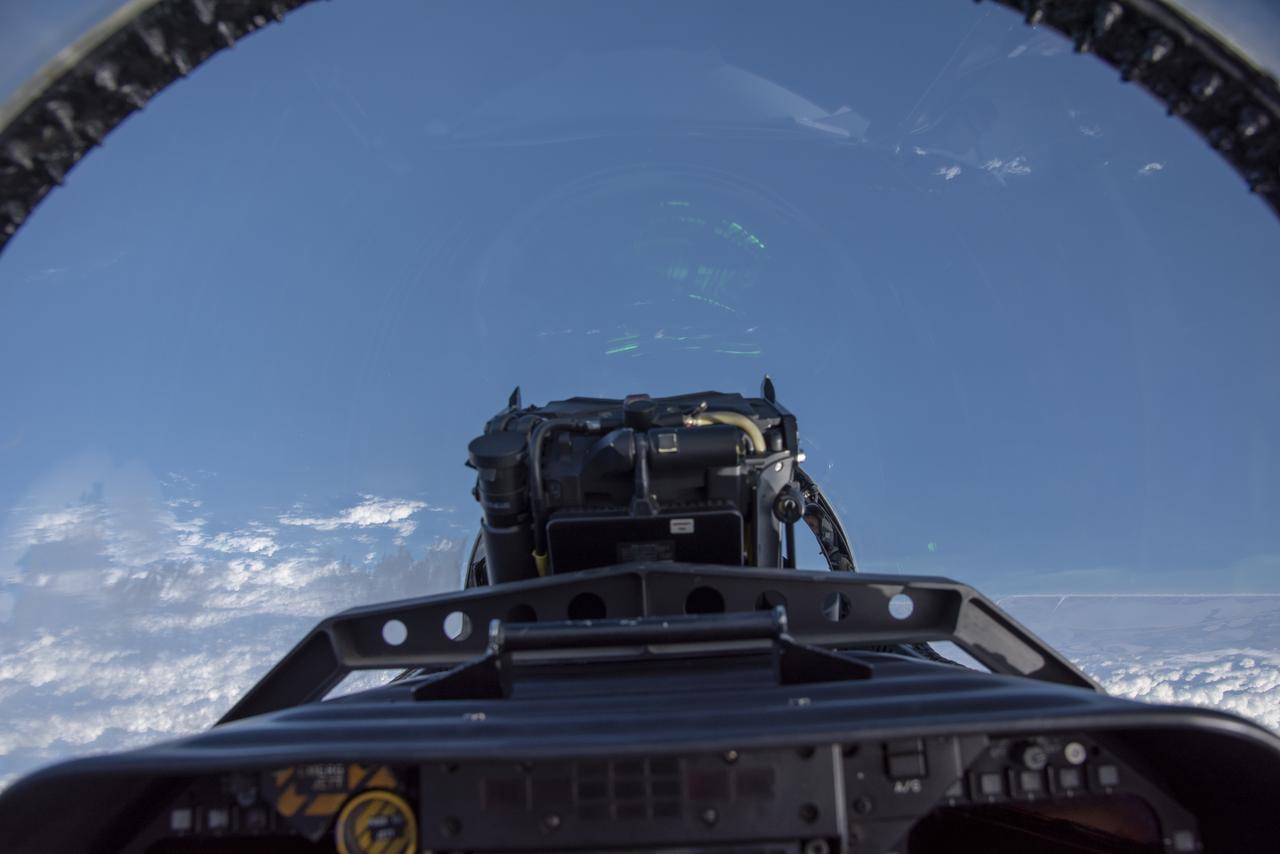

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
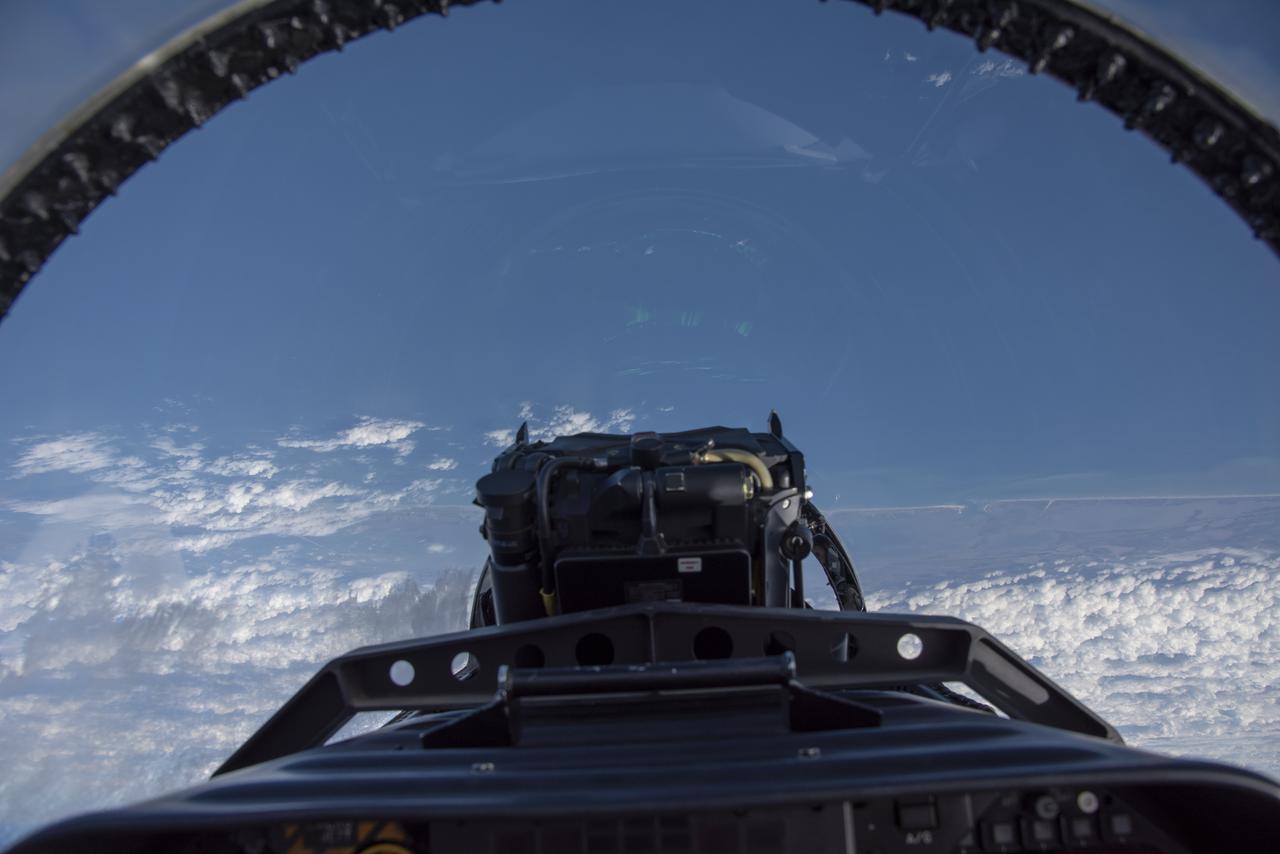

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
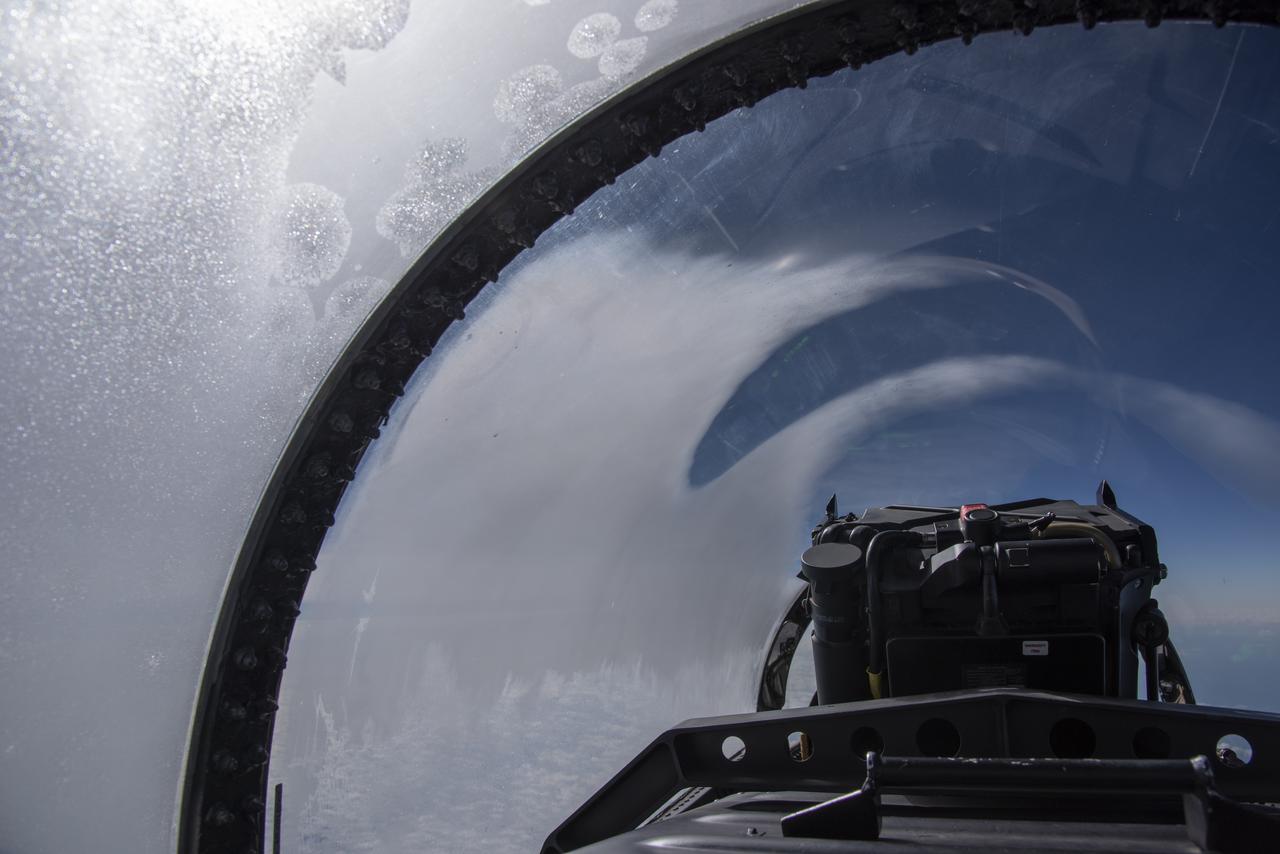

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
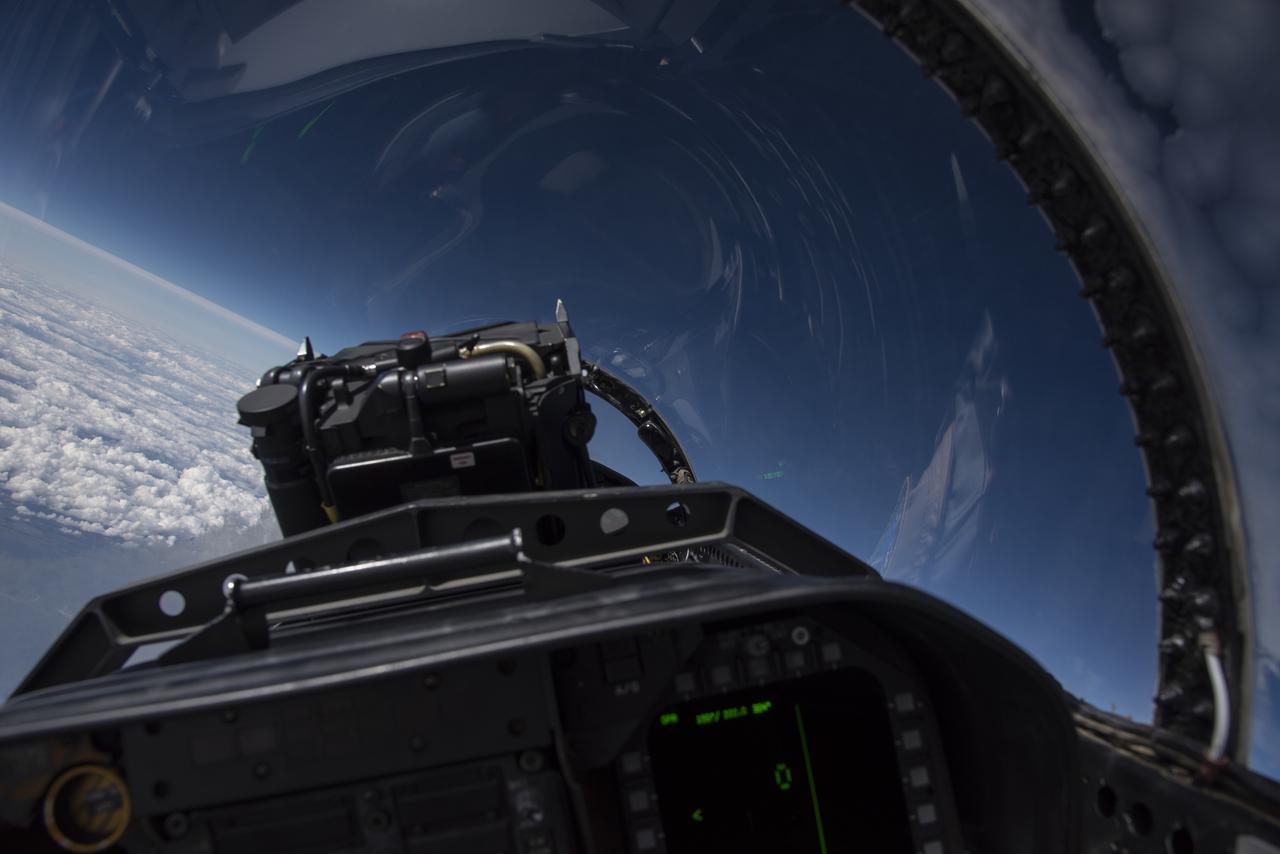

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
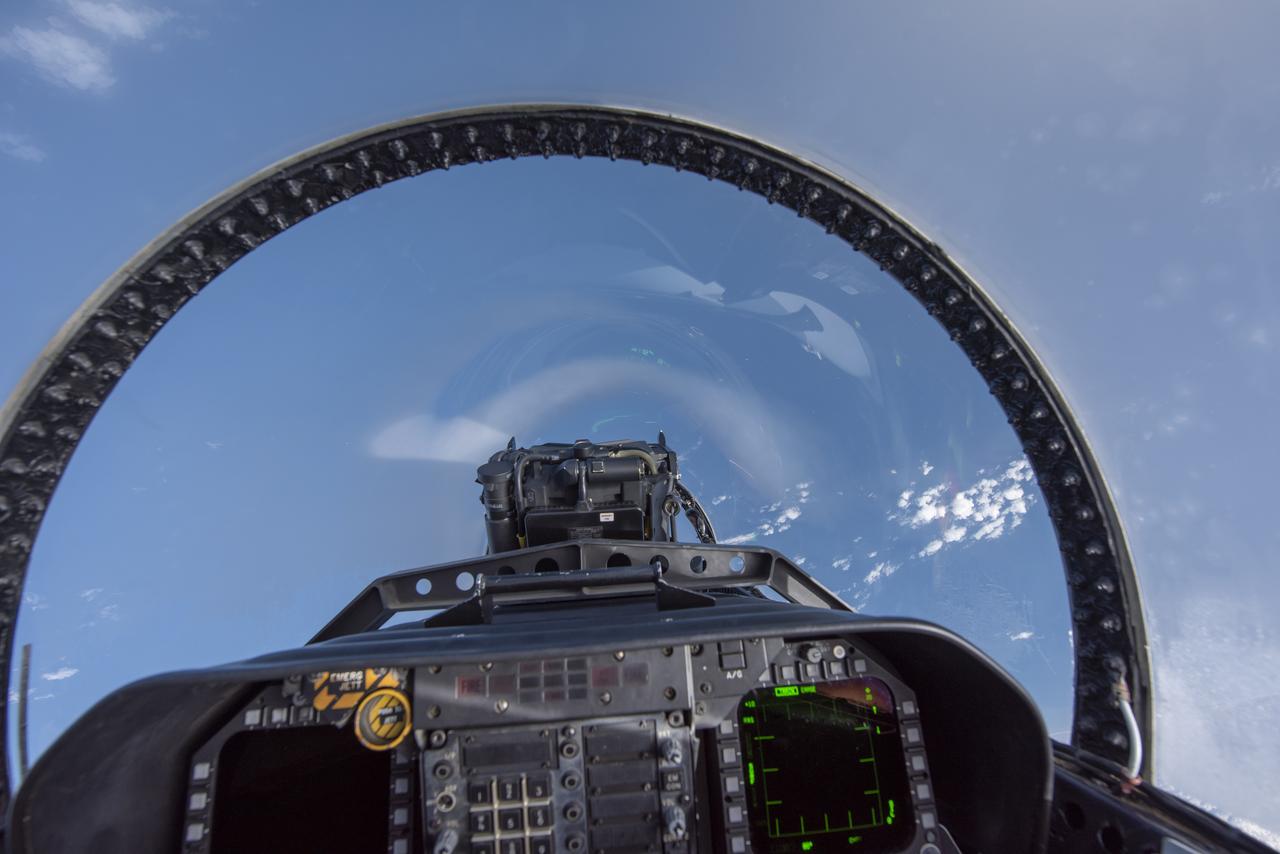

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
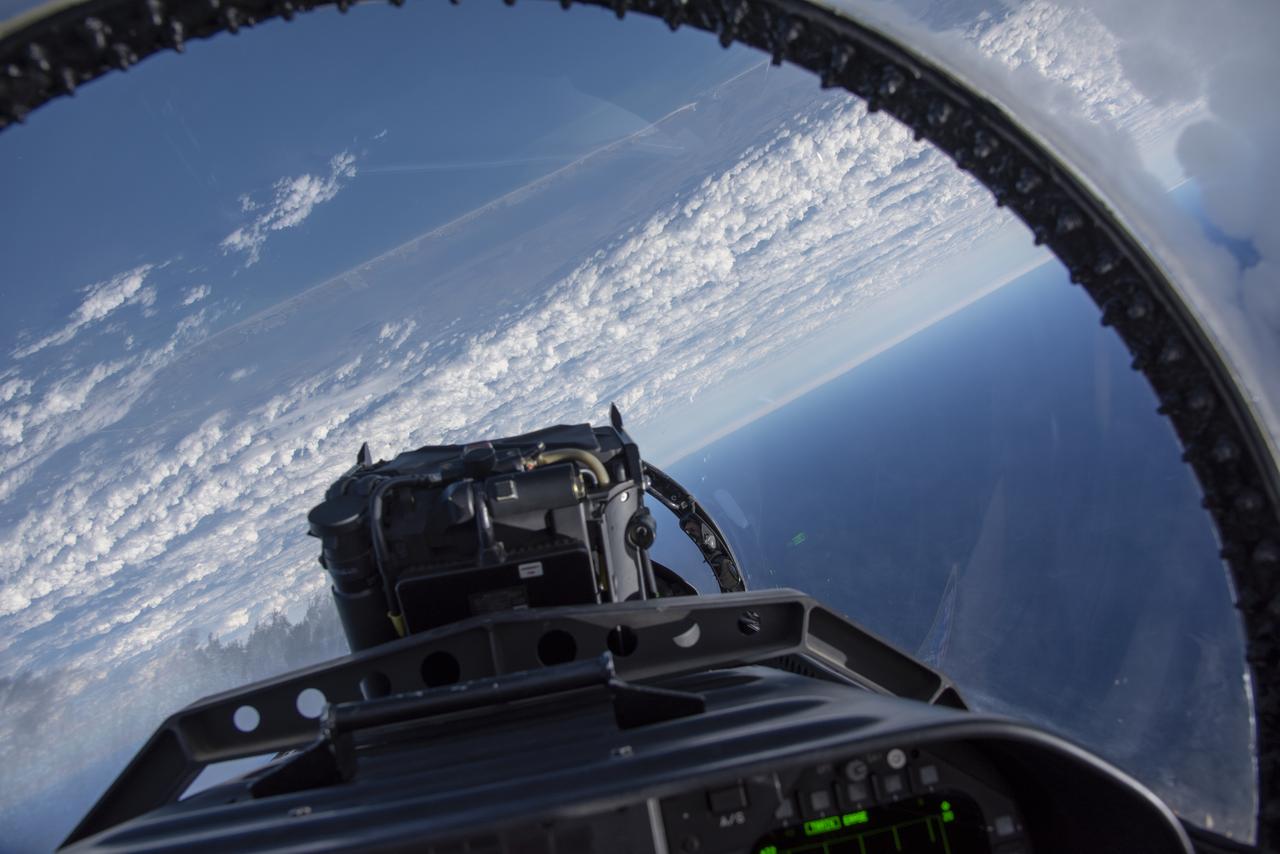

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
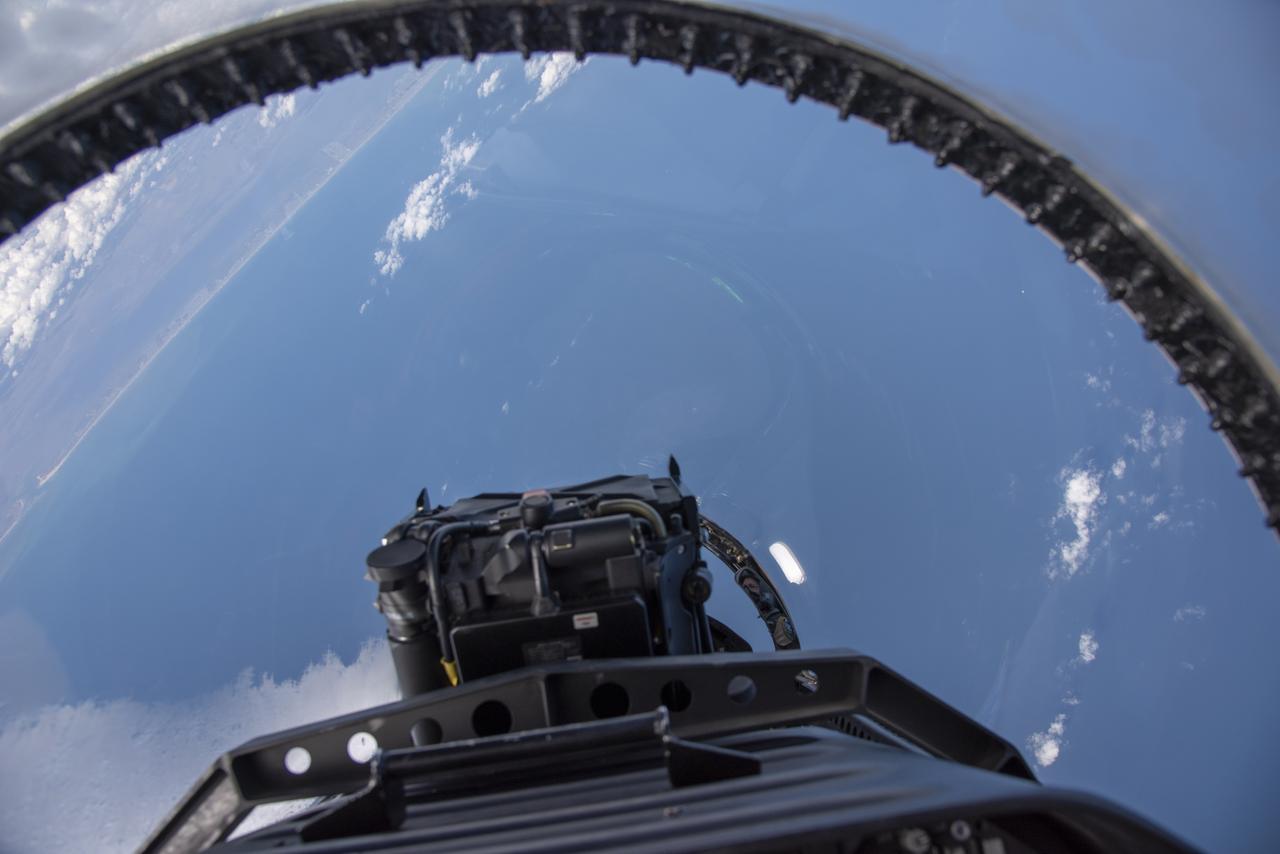

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
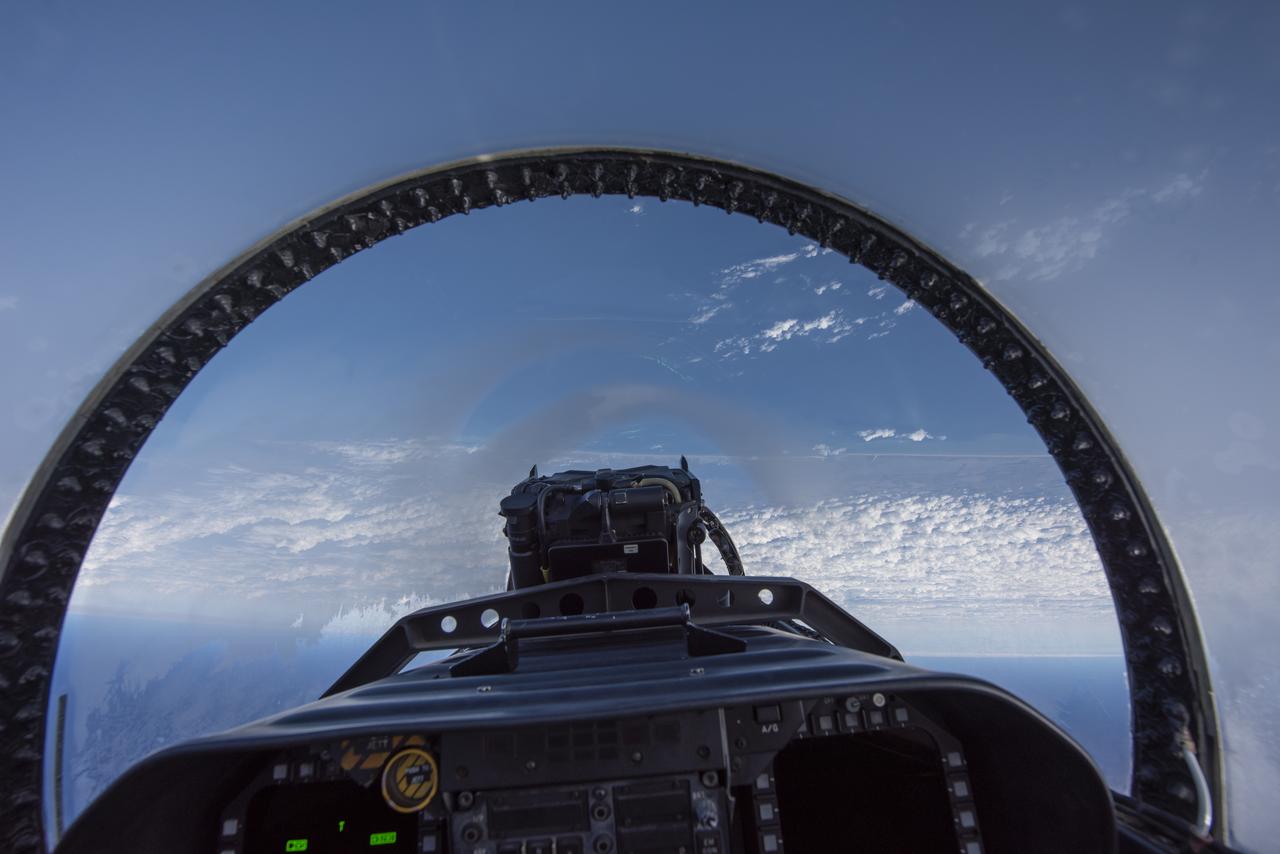

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
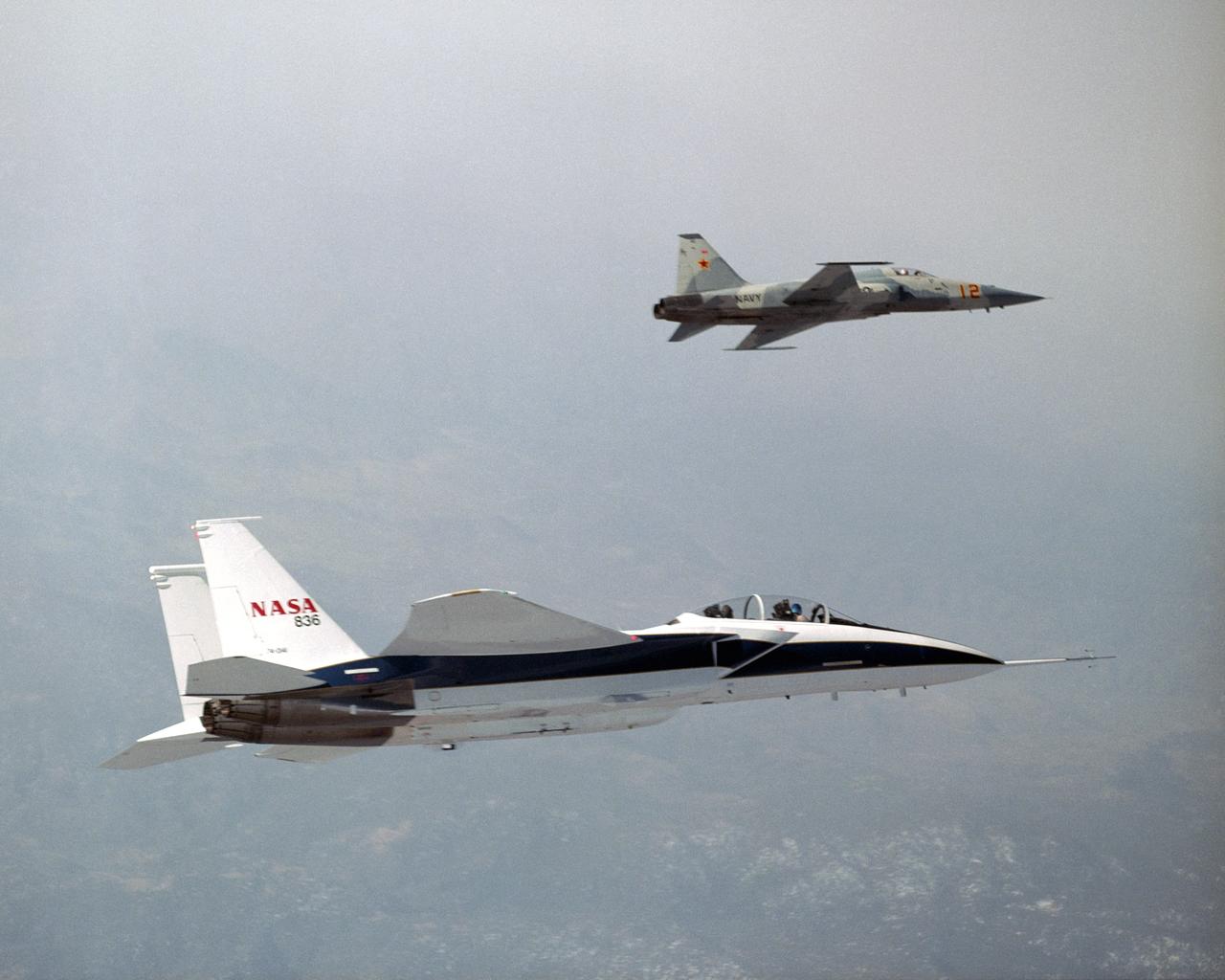

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
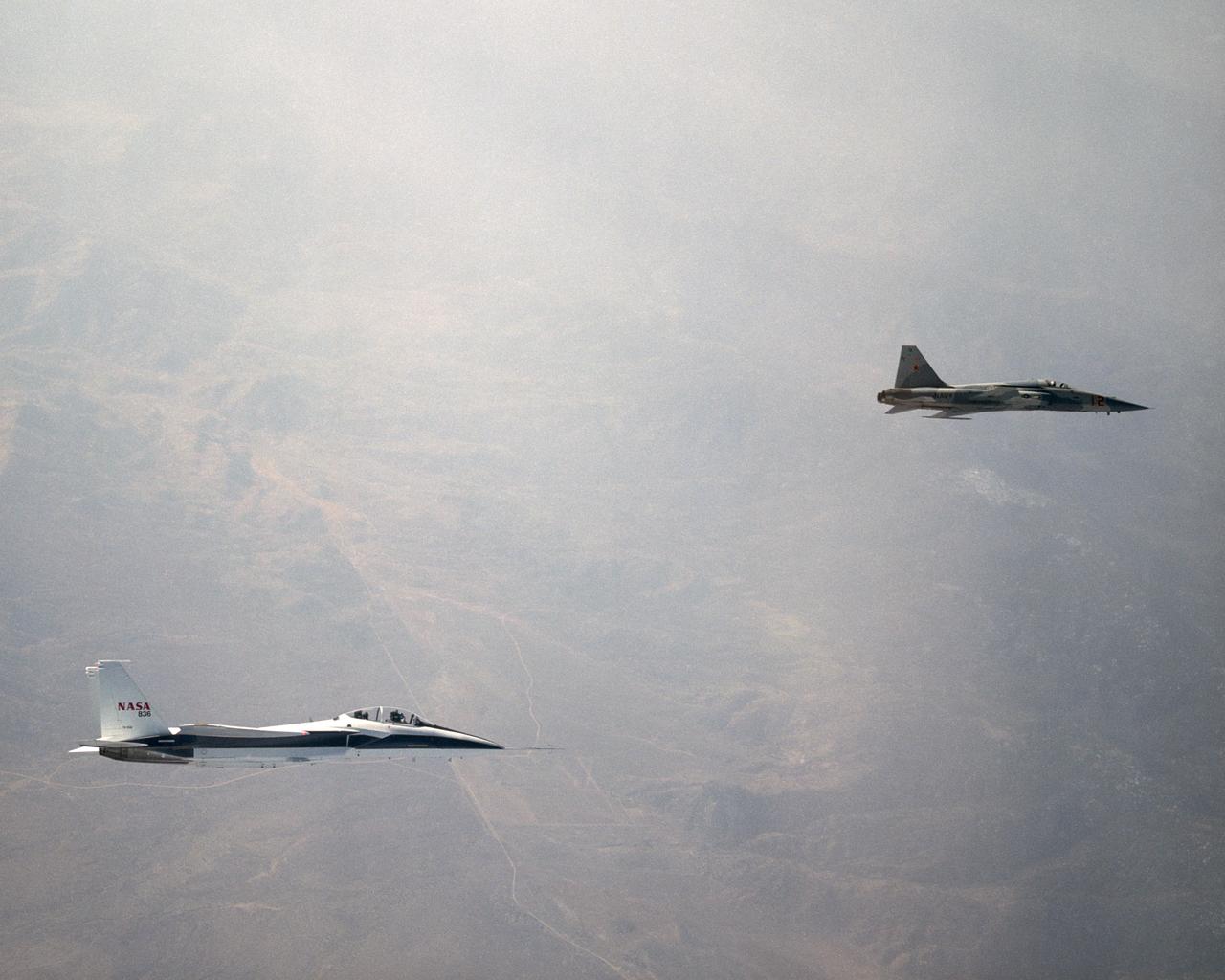

NASA's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft recently flew in the supersonic shock wave of a U.S. Navy F-5E in support of the F-5 Shaped Sonic Boom Demonstration (SSBD) project, part of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency's (DARPA) Quiet Supersonic Platform (QSP) program. The flights originated from the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, California. Four flights were flown in order to measure the F-5E's near-field (close-up) sonic boom signature at Mach 1.4, during which more than 50 shockwave patterns were measured at distances as close as 100 feet below the F-5E.
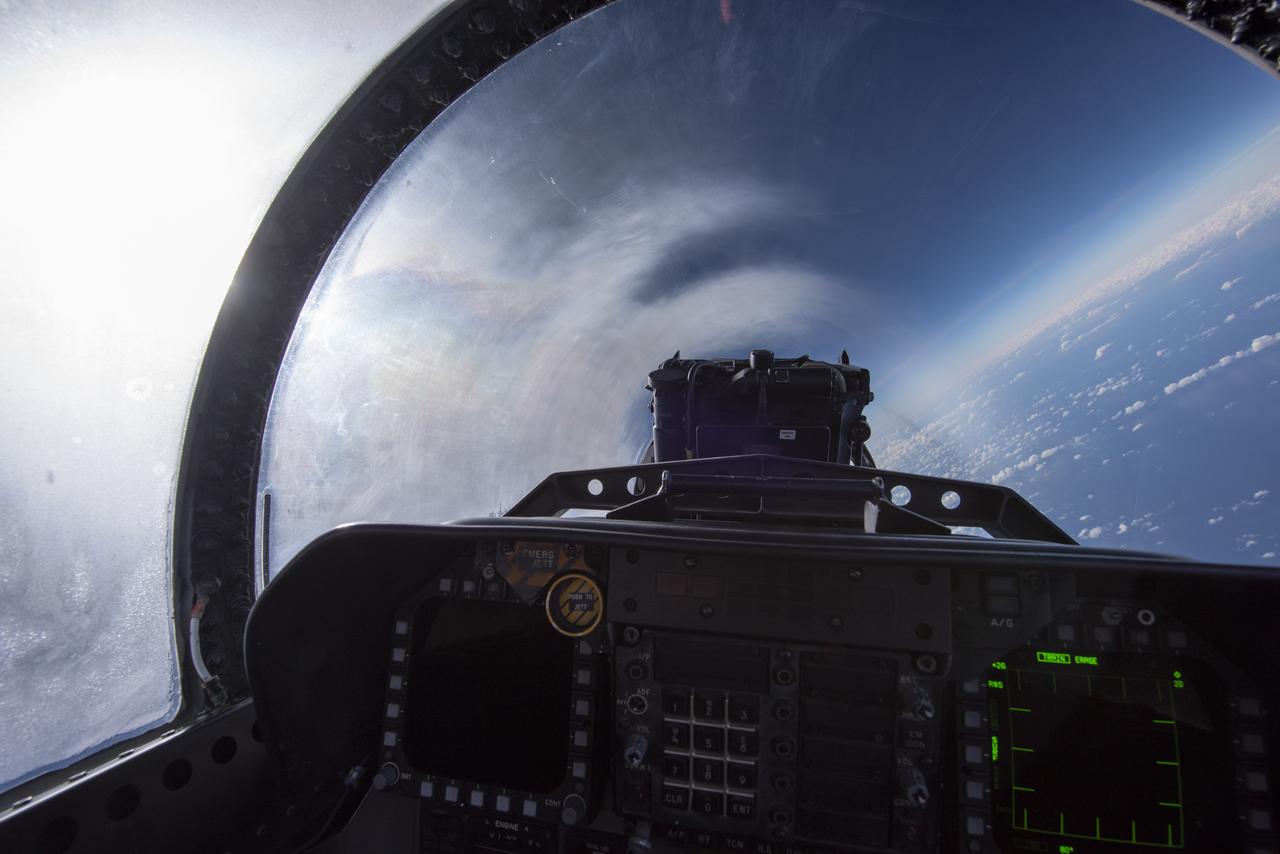

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
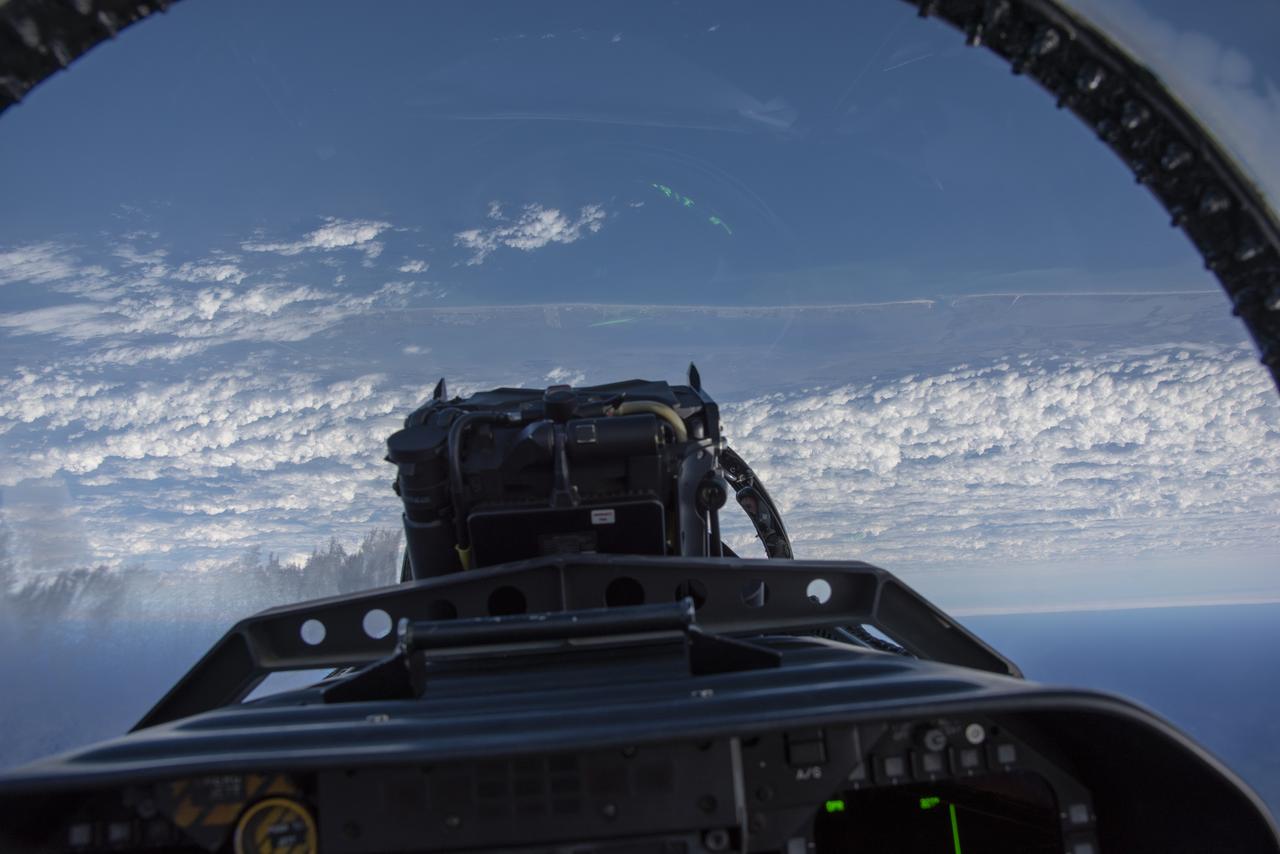

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
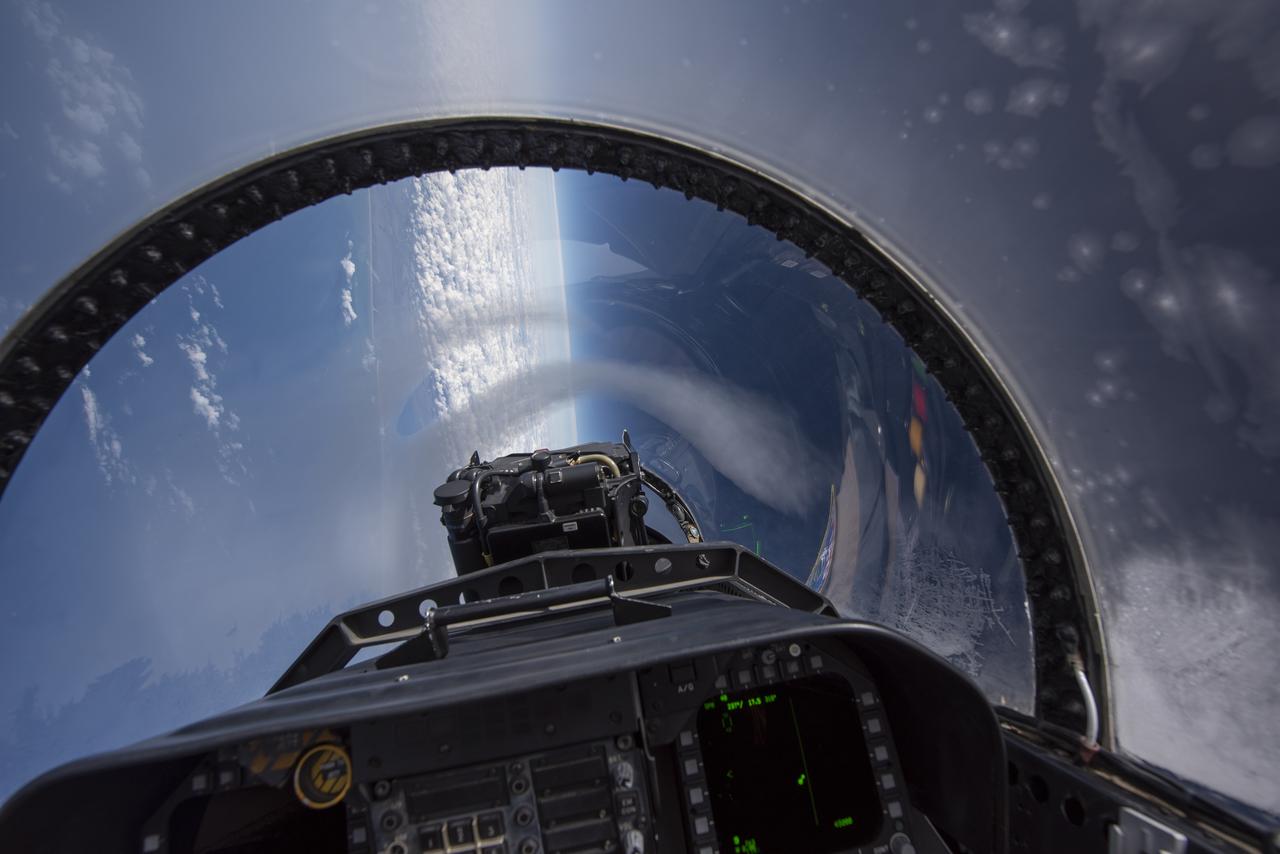

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
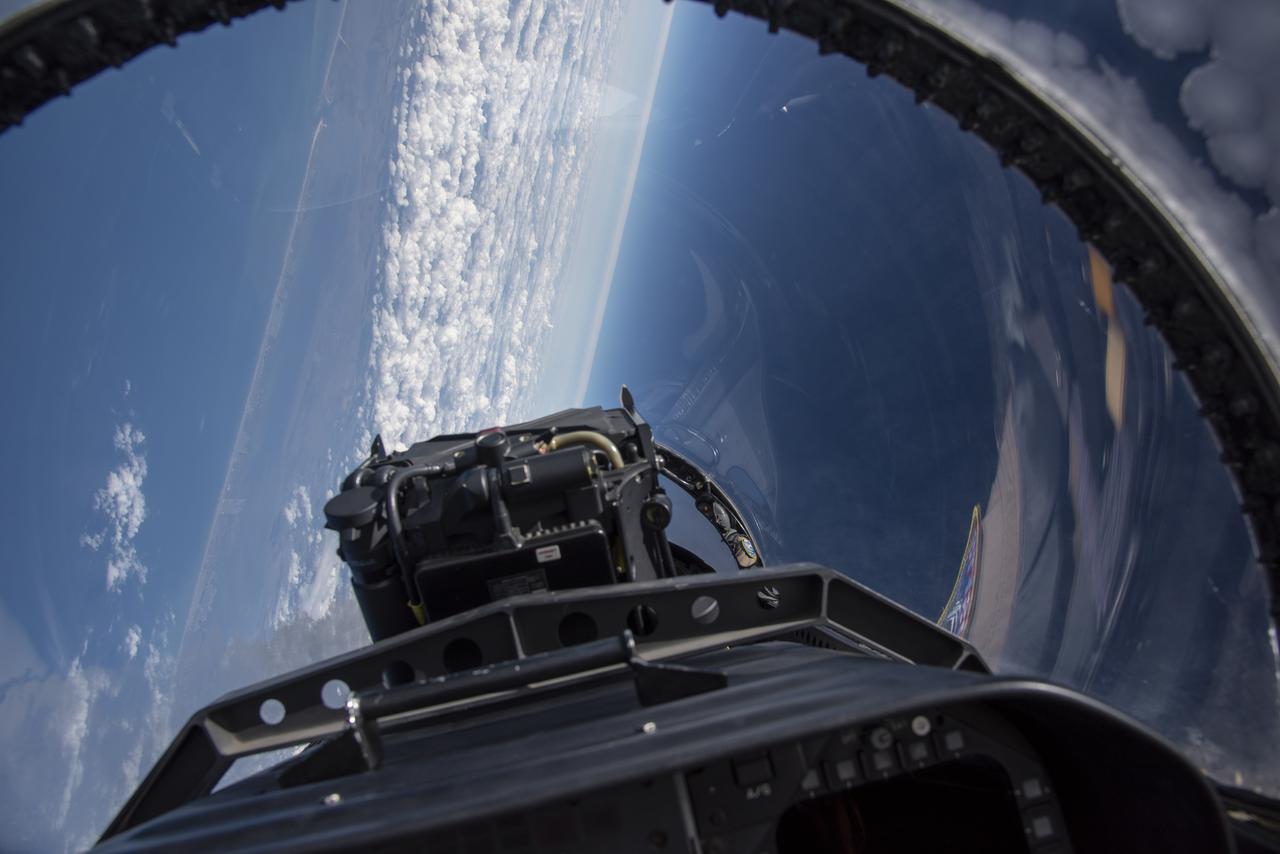

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
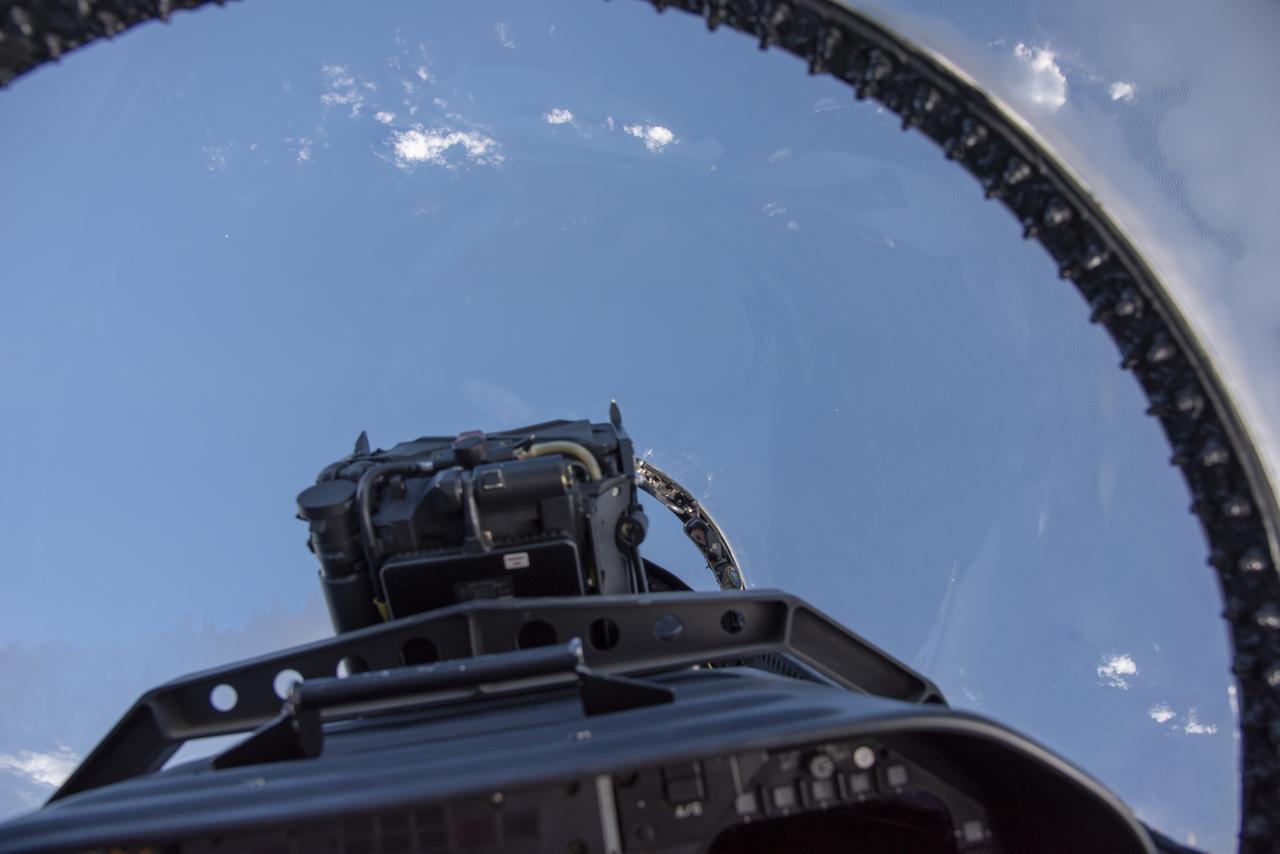

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
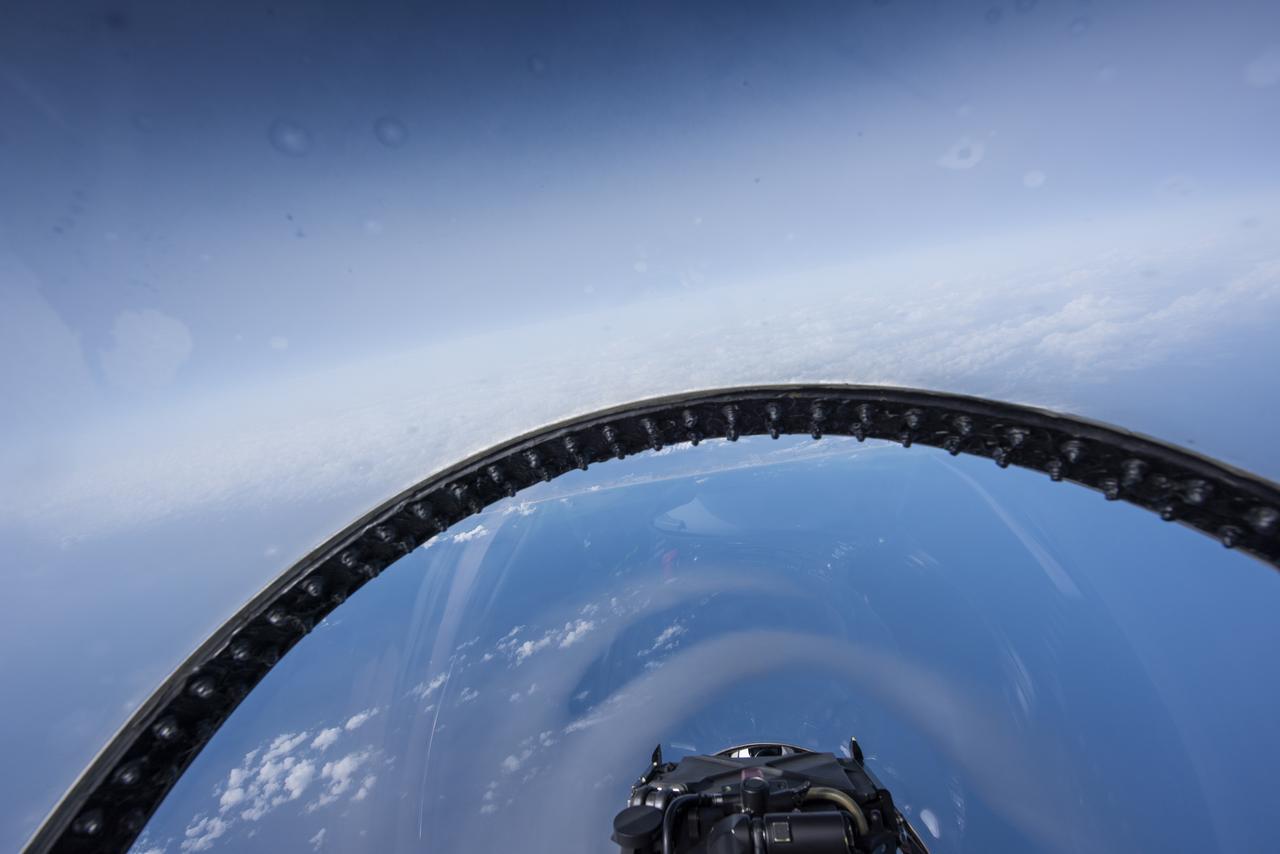

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
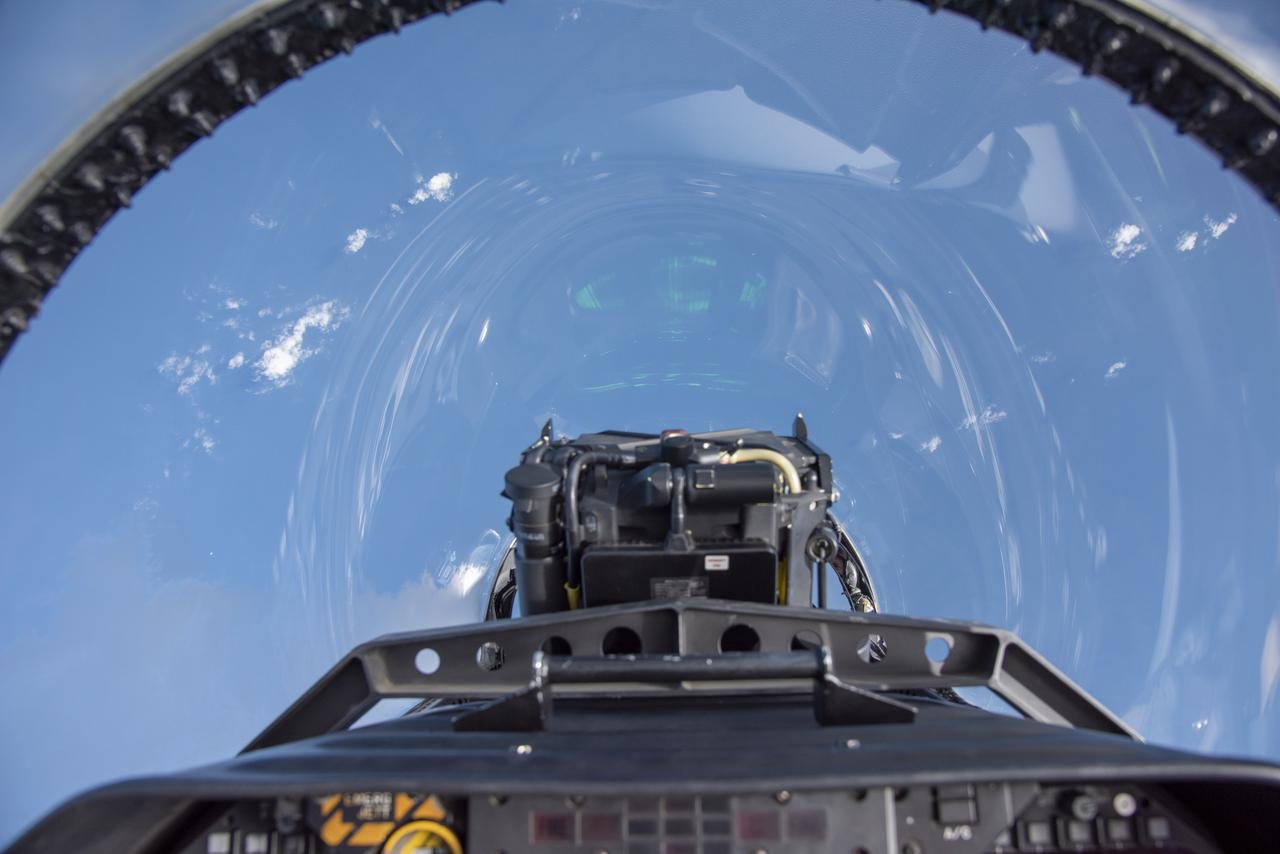

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
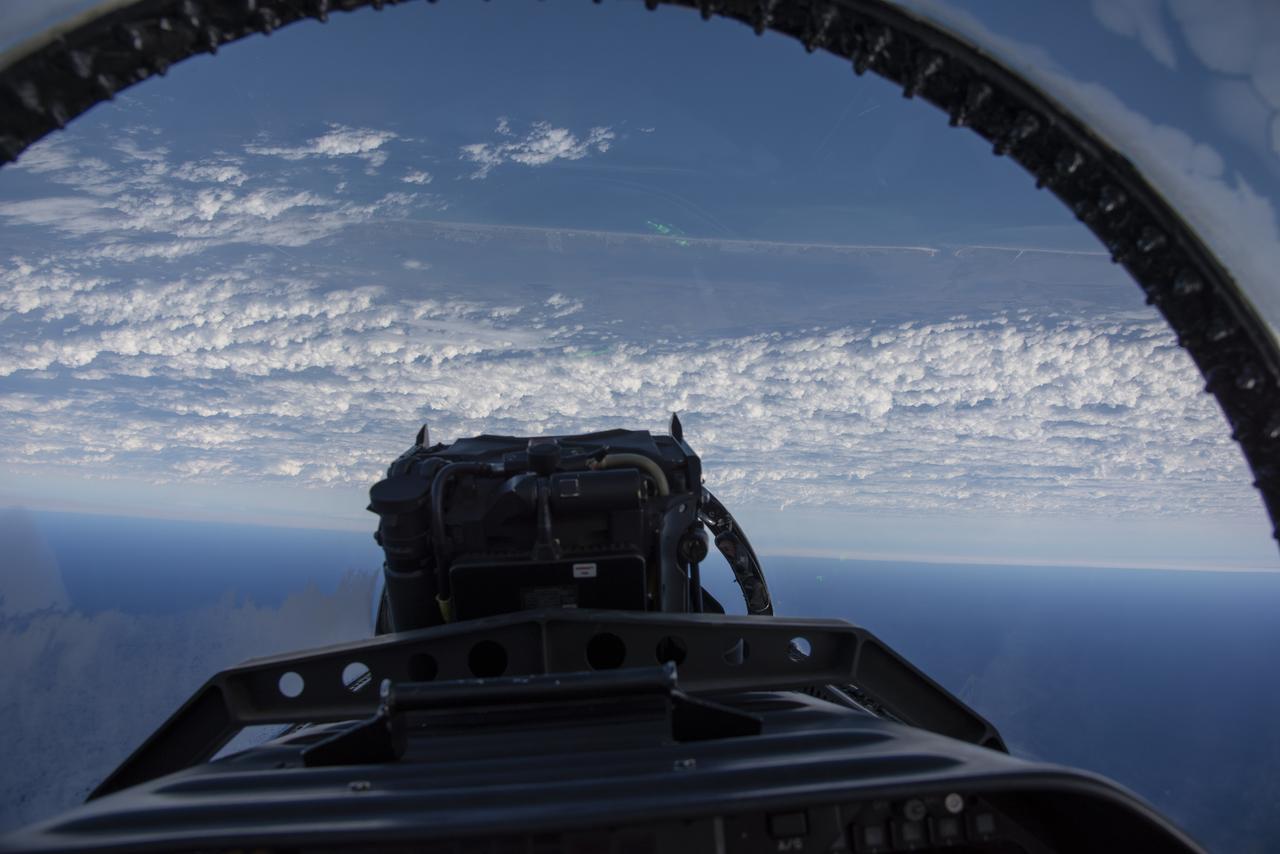

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
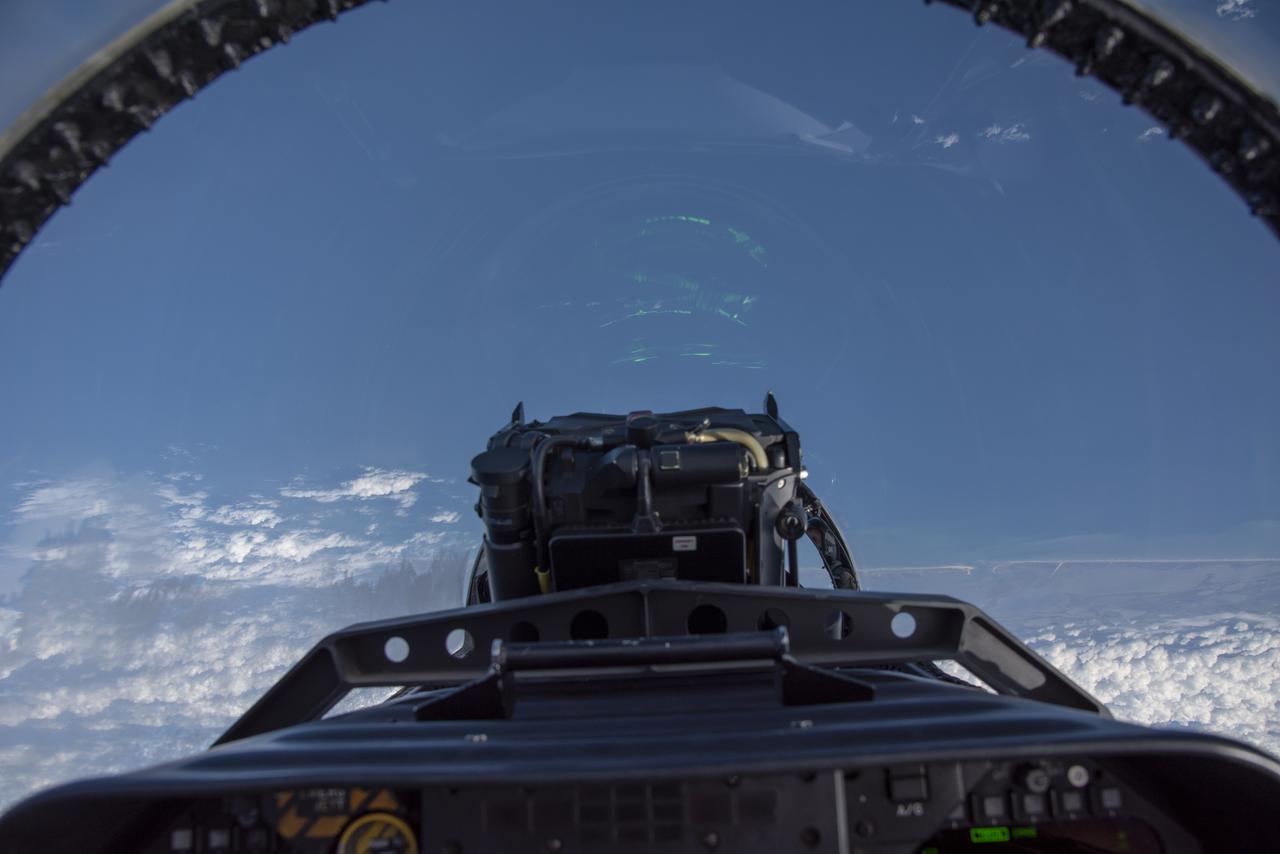

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
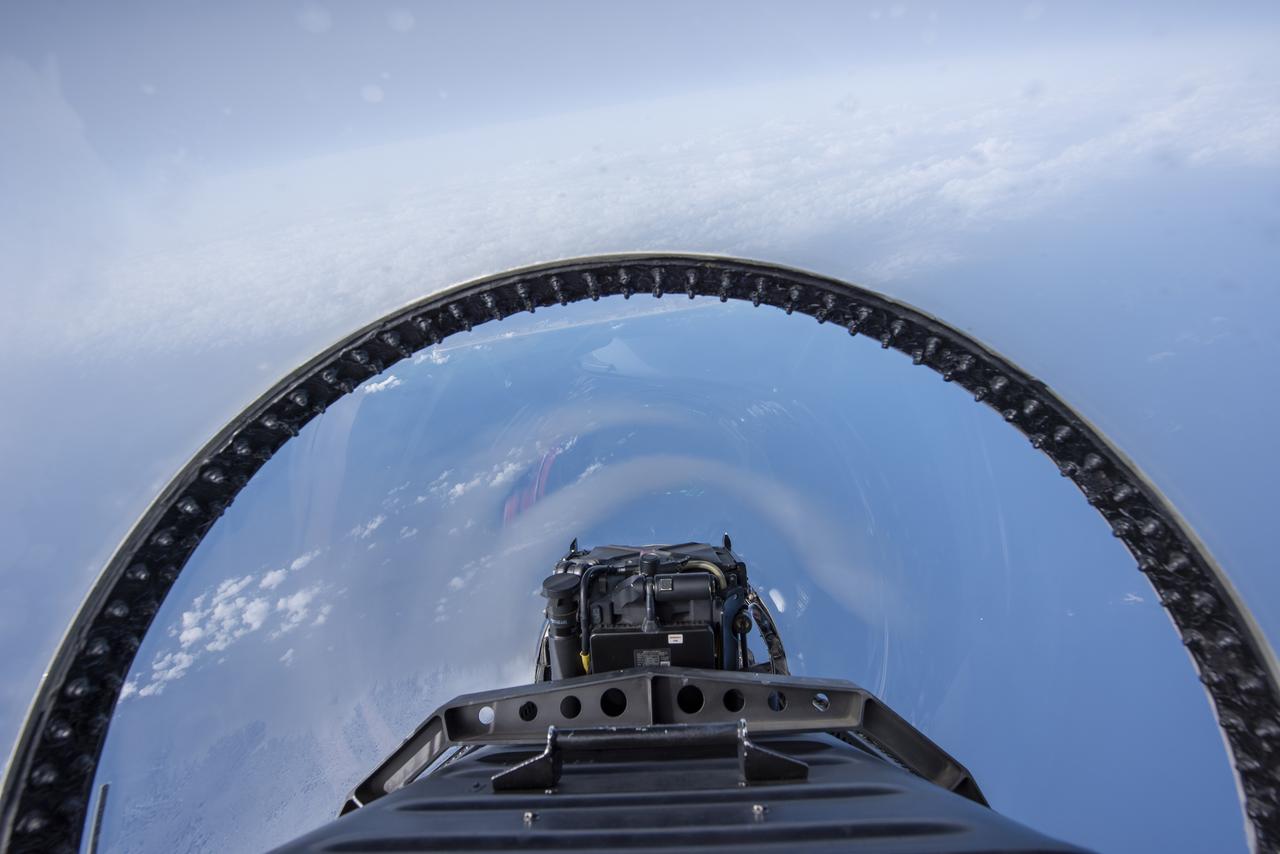

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
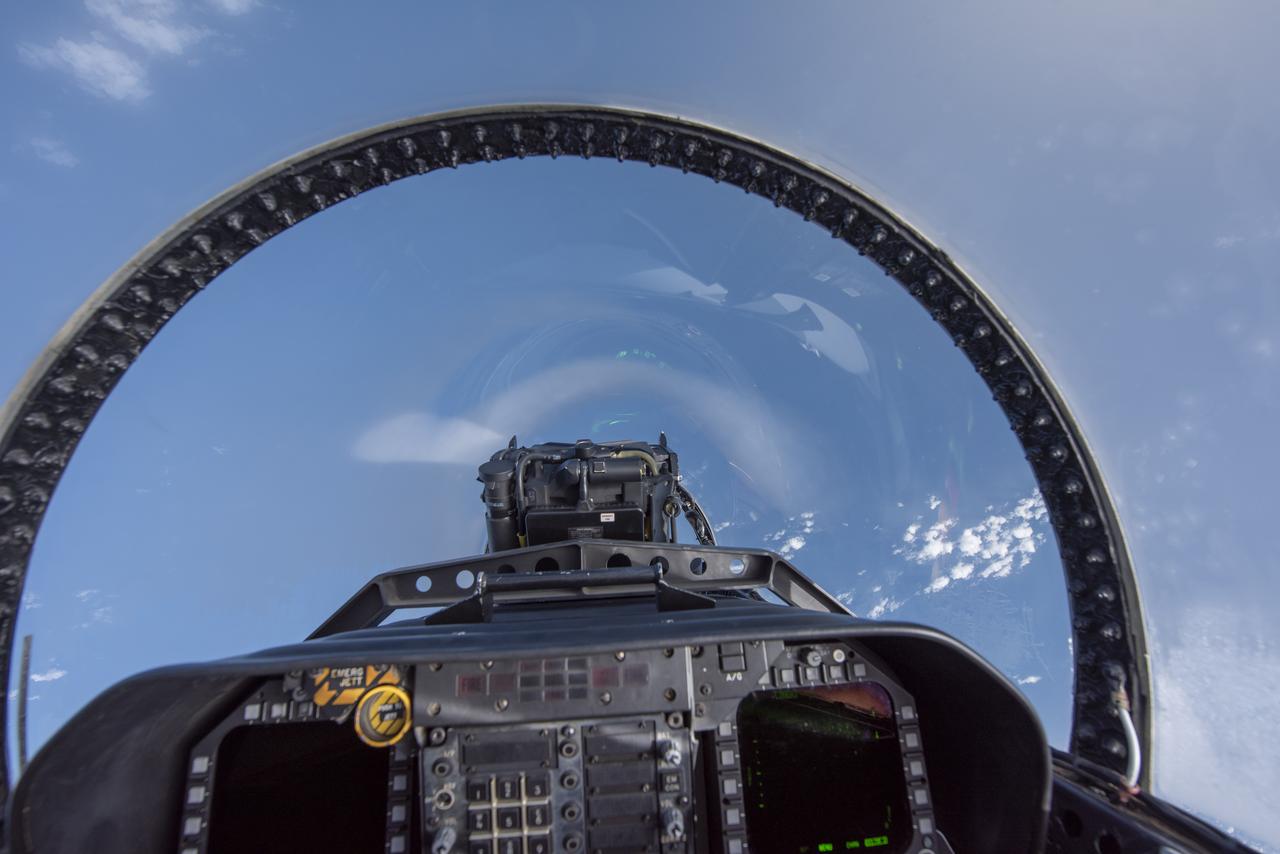

NASA test pilots perform the quiet supersonic dive maneuver off the coast of Galveston, Texas to create a quieter version of the sonic boom, in order to obtain recruited community survey feedback data. The test pilot climbs to around 50,000 feet, followed by a supersonic, inverted dive. This creates sonic boom shockwaves in a way that they are quieter in a specific area. Meanwhile, NASA researchers match community feedback to the sound levels of the flights, using an electronic survey and microphone monitor stations on the ground. This is preparing NASA for community response models for the future X-59 QueSST.
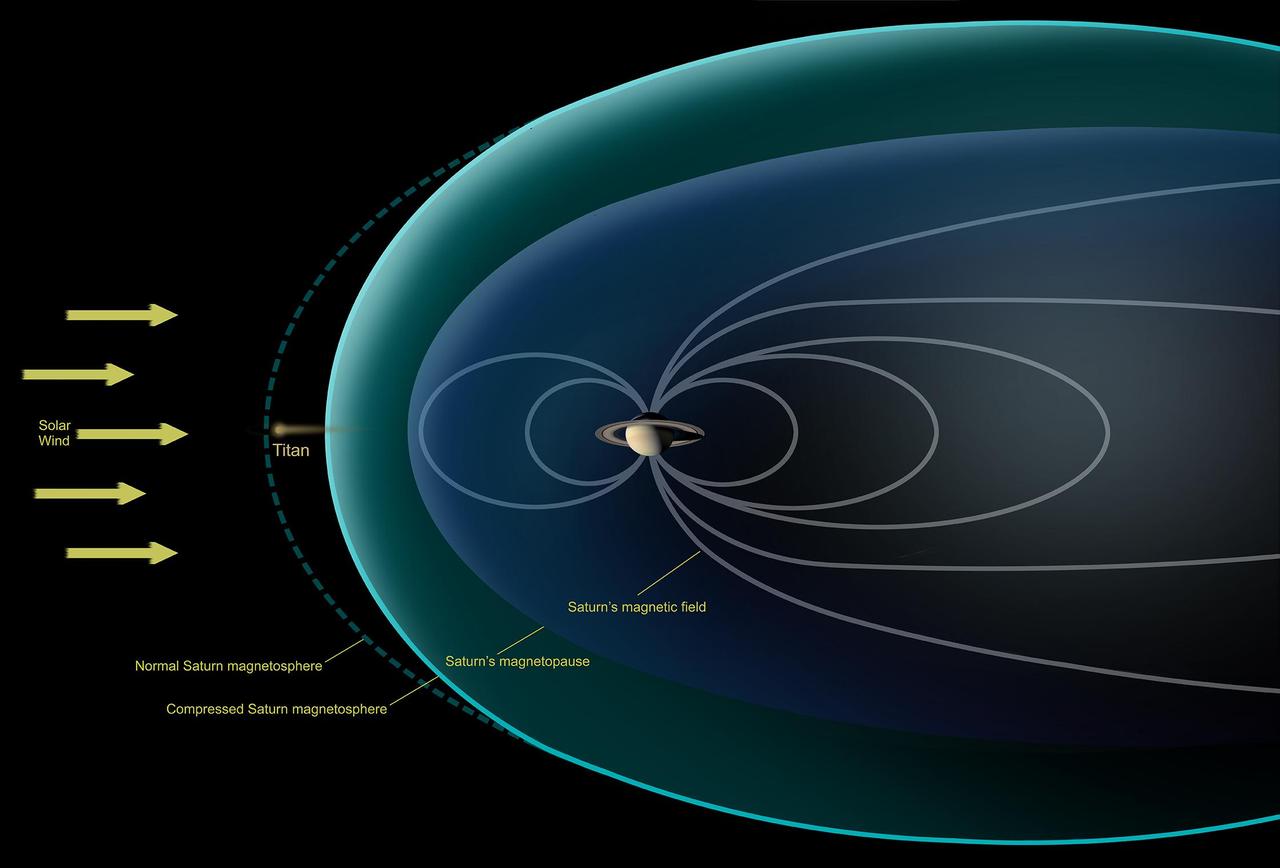
This diagram depicts conditions observed by NASA's Cassini spacecraft during a flyby in Dec. 2013, when Saturn's magnetosphere was highly compressed, exposing Titan to the full force of the solar wind. In analyzing data from the encounter, scientists with Cassini's magnetometer team observed that the giant moon interacted with the solar wind much like the planets Mars and Venus, or a comet -- none of which possess their own internal magnetic field. Specifically, they saw that the solar wind draped itself around Titan, creating a shockwave that formed around Titan where the full-force solar wind rammed into the moon's atmosphere. Previously, researchers had thought Titan would have a different sort of interaction with the solar wind because of the moon's complex atmospheric chemistry. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19055
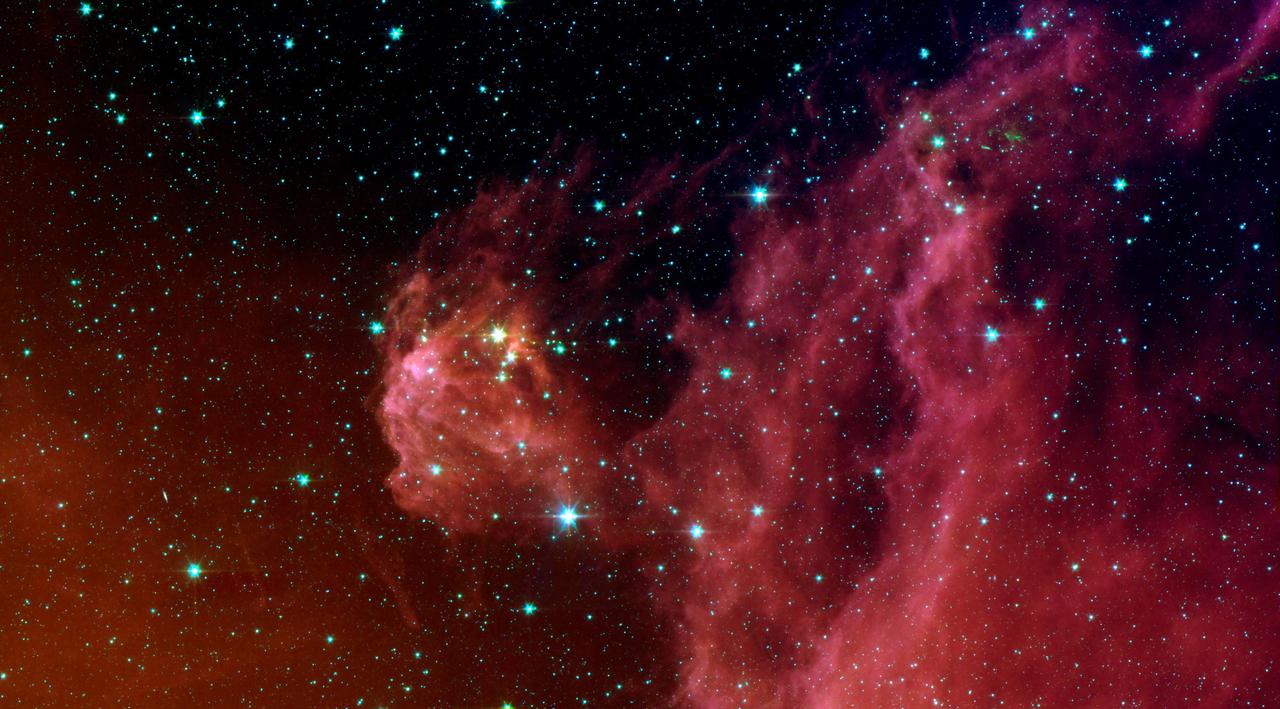

This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows infant stars "hatching" in the head of the hunter constellation, Orion. Astronomers suspect that shockwaves from a supernova explosion in Orion's head, nearly three million years ago, may have initiated this newfound birth . The region featured in this Spitzer image is called Barnard 30. It is located approximately 1,300 light-years away and sits on the right side of Orion's "head," just north of the massive star Lambda Orionis. Wisps of red in the cloud are organic molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. These molecules are formed anytime carbon-based materials are burned incompletely. On Earth, they can be found in the sooty exhaust from automobile and airplane engines. They also coat the grills where charcoal-broiled meats are cooked. This image shows infrared light captured by Spitzer's infrared array camera. Light with wavelengths of 8 and 5.8 microns (red and orange) comes mainly from dust that has been heated by starlight. Light of 4.5 microns (green) shows hot gas and dust; and light of 3.6 microns (blue) is from starlight. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09412
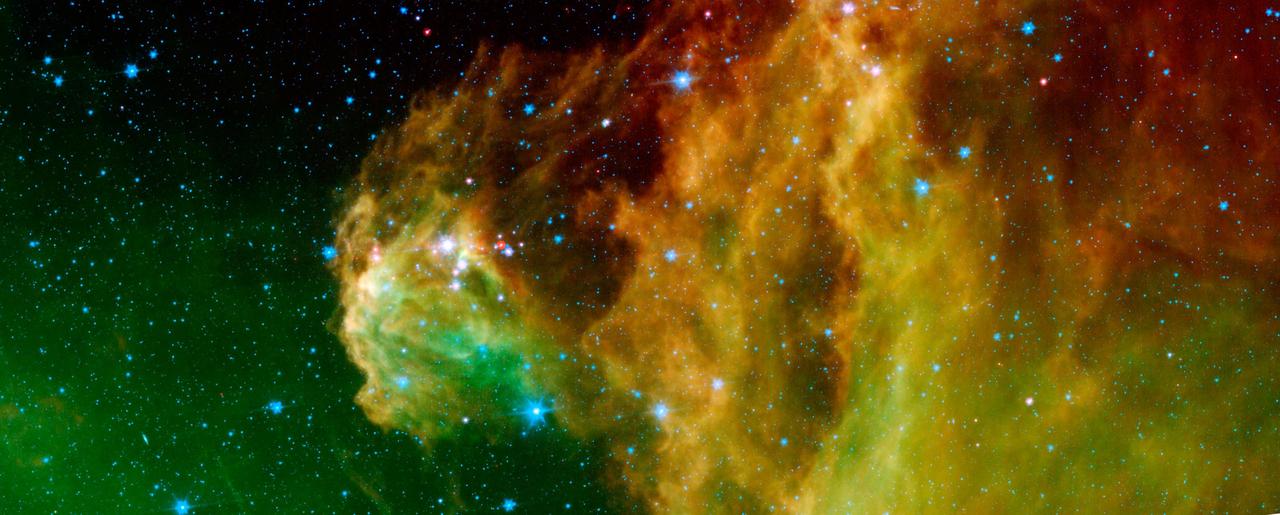

This image from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope shows infant stars "hatching" in the head of the hunter constellation, Orion. Astronomers suspect that shockwaves from a supernova explosion in Orion's head, nearly three million years ago, may have initiated this newfound birth. The region featured in this Spitzer image is called Barnard 30. It is located approximately 1,300 light-years away and sits on the right side of Orion's "head," just north of the massive star Lambda Orionis. Wisps of green in the cloud are organic molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. These molecules are formed anytime carbon-based materials are burned incompletely. On Earth, they can be found in the sooty exhaust from automobile and airplane engines. They also coat the grills where charcoal-broiled meats are cooked. Tints of orange-red in the cloud are dust particles warmed by the newly forming stars. The reddish-pink dots at the top of the cloud are very young stars embedded in a cocoon of cosmic gas and dust. Blue spots throughout the image are background Milky Way along this line of sight. This composite includes data from Spitzer's infrared array camera instrument, and multiband imaging photometer instrument. Light at 4.5 microns is shown as blue, 8.0 microns is green, and 24 microns is red. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09411

The Blue Ring Nebula was discovered in 2004 by NASA's Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) mission. Astronomers think the nebula was created by the merger of two stars, and that we are seeing the system a few thousand years after the merger, when evidence of the collision is still apparent. The blue light in the image shows the debris cloud created by the merger. As the hot cloud of material expanded into space and cooled down, it formed hydrogen molecules that collided with the interstellar medium (the particles occupying the space between stars). These collisions caused the hydrogen molecules to radiate far-ultraviolet light, which was detected by GALEX. Yellow indicates near-ultraviolet light, also detected by GALEX, which is emitted by the star at the center of the nebula and many surrounding stars. Infrared light observed by NASA's Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) is also shown in red, and is primarily emitted by the central star. Detailed analysis of the WISE data revealed a ring of debris around the star – further evidence of a merger. Magenta indicates optical light — light visible to the human eye — collected using the Hale Telescope. This light comes from the shockwave at the front of the expanding debris cones. The optical light helped astronomers discover that the nebula actually consists of two cones moving away from the central star. The base of one cone is moving almost directly toward Earth, while the other is moving almost directly away, and the magenta light outlines the two bases. The blue region in the image shows where the cones overlap; the non-overlapping regions are too faint for GALEX to see. Figure A shows the orientation of the cones to Earth and the way they appear to overlap. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23867
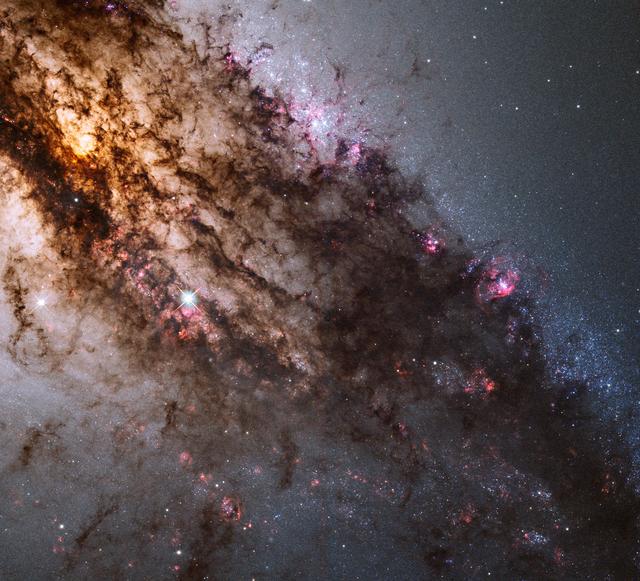

NASA image release June 16, 2011 Resembling looming rain clouds on a stormy day, dark lanes of dust crisscross the giant elliptical galaxy Centaurus A. Hubble's panchromatic vision, stretching from ultraviolet through near-infrared wavelengths, reveals the vibrant glow of young, blue star clusters and a glimpse into regions normally obscured by the dust. The warped shape of Centaurus A's disk of gas and dust is evidence for a past collision and merger with another galaxy. The resulting shockwaves cause hydrogen gas clouds to compress, triggering a firestorm of new star formation. These are visible in the red patches in this Hubble close-up. At a distance of just over 11 million light-years, Centaurus A contains the closest active galactic nucleus to Earth. The center is home for a supermassive black hole that ejects jets of high-speed gas into space, but neither the supermassive or the jets are visible in this image. This image was taken in July 2010 with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., in Washington, D.C. For images and more information about the findings, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/hubble" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/hubble</a> and <a href="http://www.hubblesite.org/news/2011/18" rel="nofollow">www.hubblesite.org/news/2011/18</a> Cheryl Gundy, STSCI <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
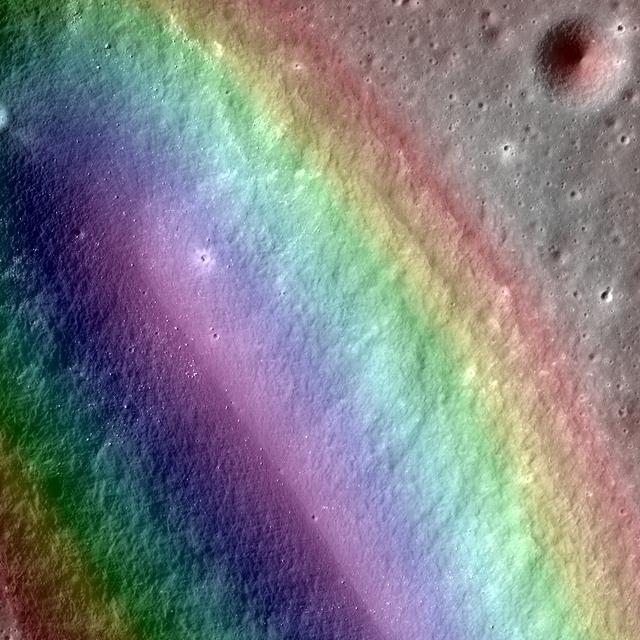

This false color image of Birt E crater shows the topography of the moon and it is thought to be the source region for lava that carved out Rima Birt, a rille in Mare Nubium. This mare is older than 3.4 billion years, and so is this vent! LROC NAC M1144849711L/R with the a color DTM overlaid; North is up. Download high res: <a href="http://lroc.sese.asu.edu/posts/794" rel="nofollow">lroc.sese.asu.edu/posts/794</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Arizona State University More info: Birt E crater was not created like most craters on the Moon; there was no meteorite impact. Lava sputtered out of this pyroclastic vent in Mare Nubium over 3.4 billion years ago, dispersing lava onto the surface and leaving the crater we see today. How can we tell it is a volcanic vent and not an impact crater? Impact craters and volcanic vents can be differentiated because vents often have an irregular or elongated shape (as with Birt E). Impact craters are usually circular in shape, created by the shockwave during an impact event. Also, the vee-shape of this crater is likely a product of the formation mechanism. Vee-shaped vents are thought to be formed from a pyroclastic eruption. Gasses fractionating out of the liquid rock create violent events during eruptions. Explosive eruptions created the shape that we see today, but Birt E could have had a complex history with effusive eruptions forming Rima Birt, a rille flowing from Birt E to the SE. Over long enough time scales Birt E will be filled in with ejecta from newly formed craters around Mare Nubium or by mass wasting of the walls into the crater. Let’s enjoy this ancient crater today while we still can! <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
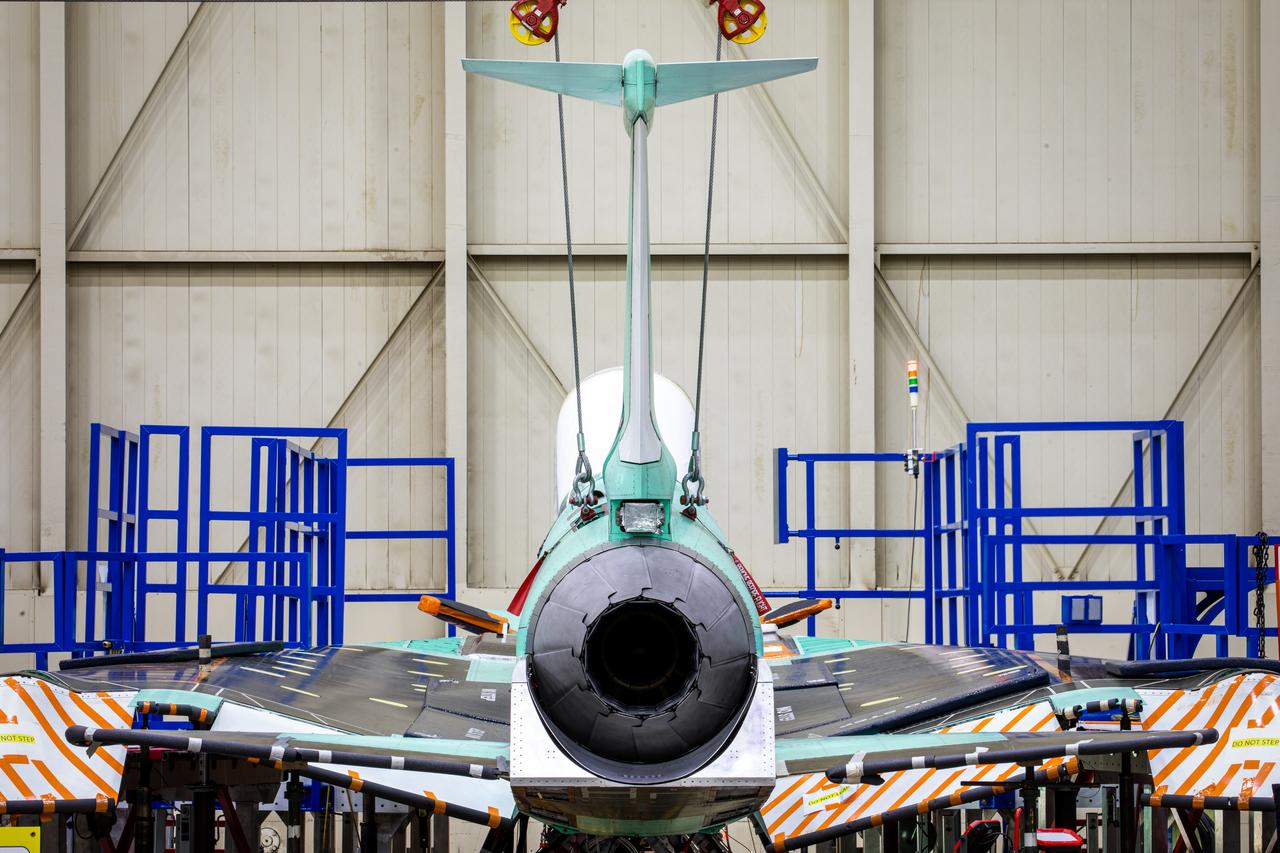

A perfectly framed up rearview shot of NASA’s X-59 tail after its recent installation of the lower empennage, or tail section, in late March at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California.
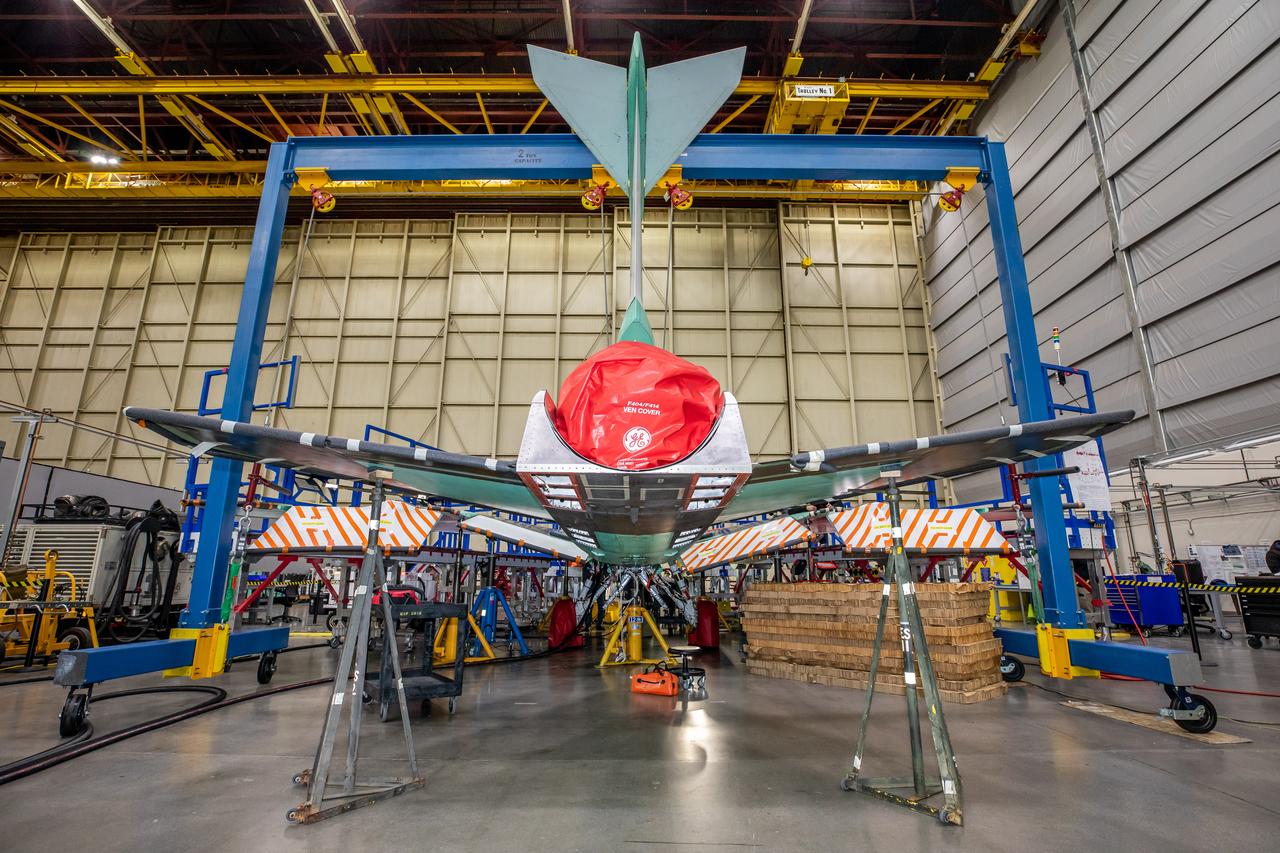

NASA’s X-59 sits in support framing while undergoing the installation of its lower empennage, or tail section, at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California in late March.
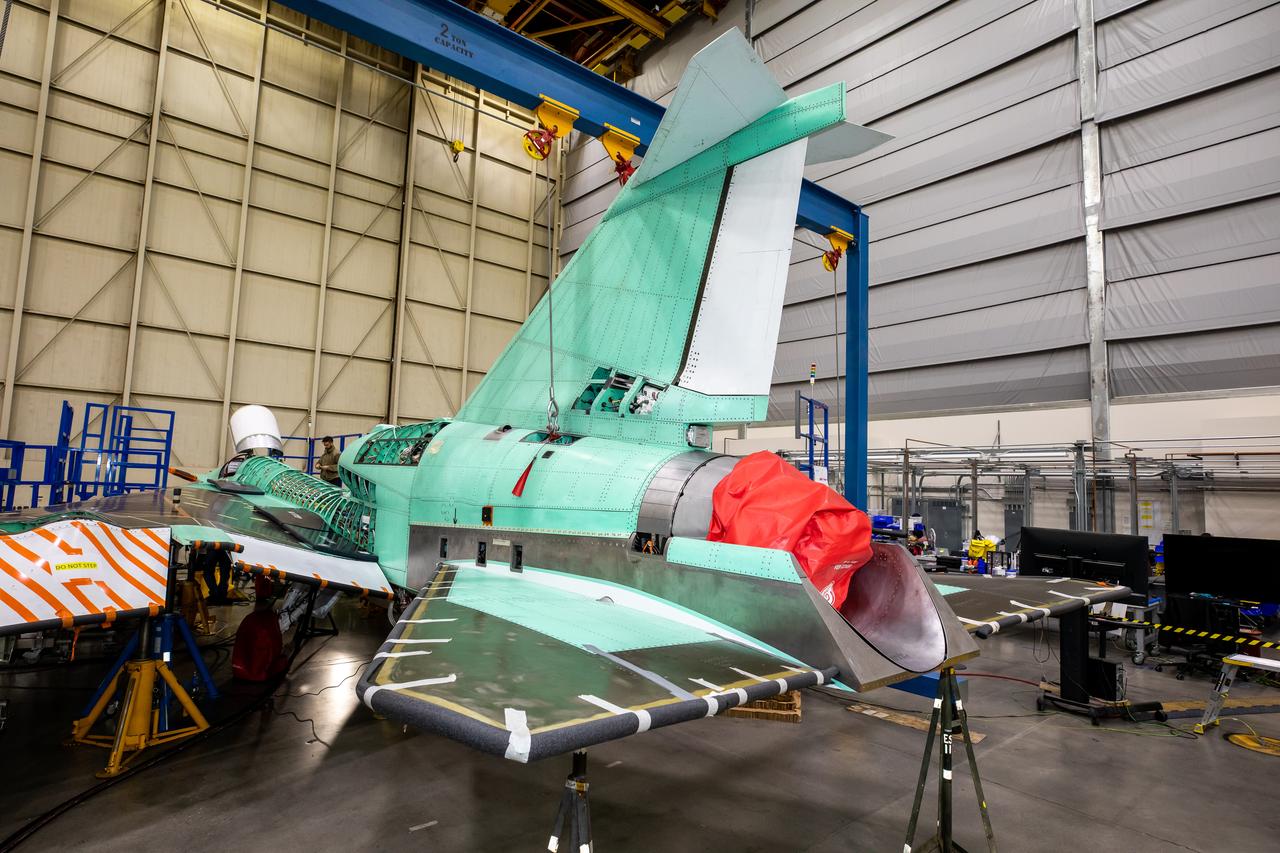

The tail of NASA’s X-59 aircraft is shown here in late March at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California where the plane recently underwent a final install of the lower empennage or better known as tail section of the plane.