
iss071e014284 (April 20, 2024) -- Lake Tahoe, situated in the Sierra Nevada Mountains and straddling the border of California and Nevada, was photographed as the International Space Station orbited 258 miles above.
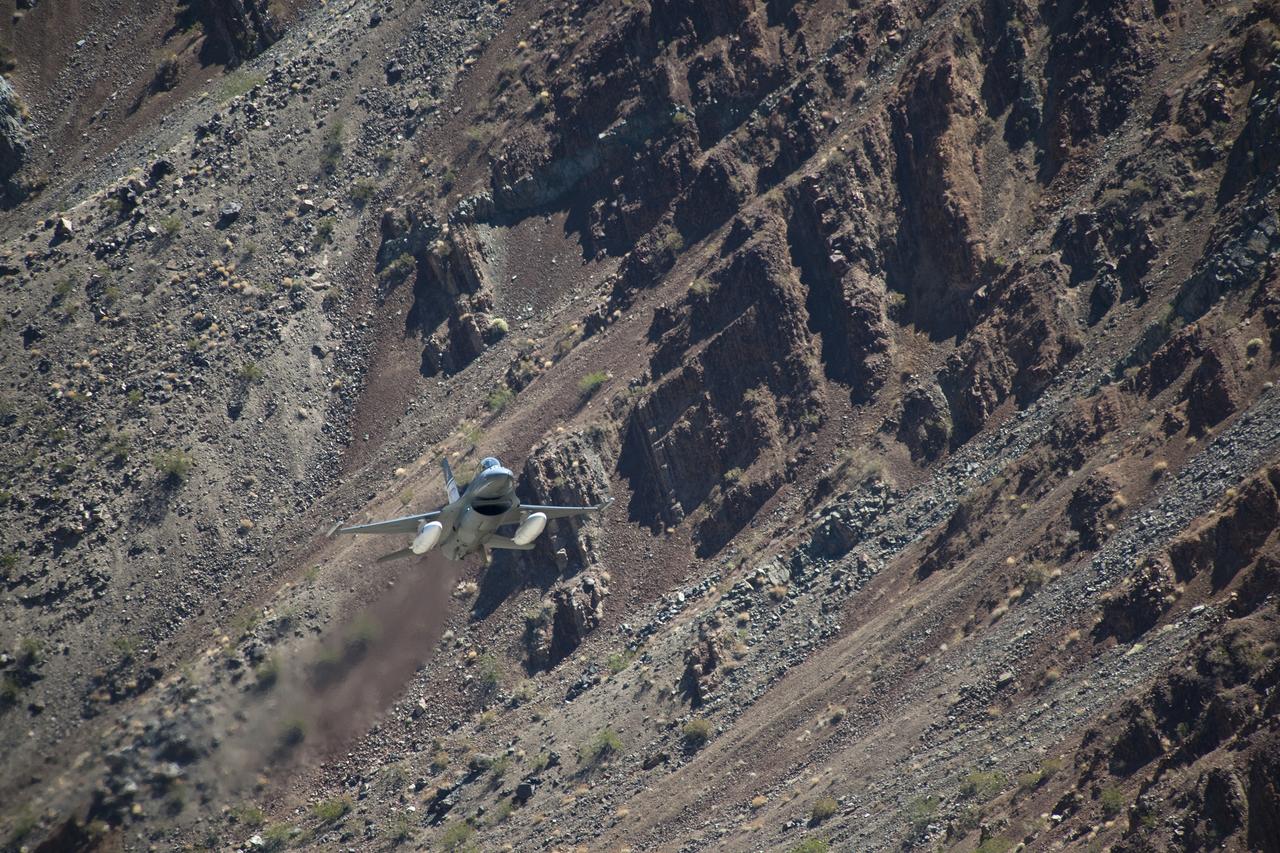

The Air Force F-16D Automatic Collision Avoidance Technology aircraft flew at low levels above the Sierra Nevada Mountains to test the ACAT Fighter Risk Reduction Project to develop collision avoidance technologies for aircraft, to reduce the risk of ground collisions.
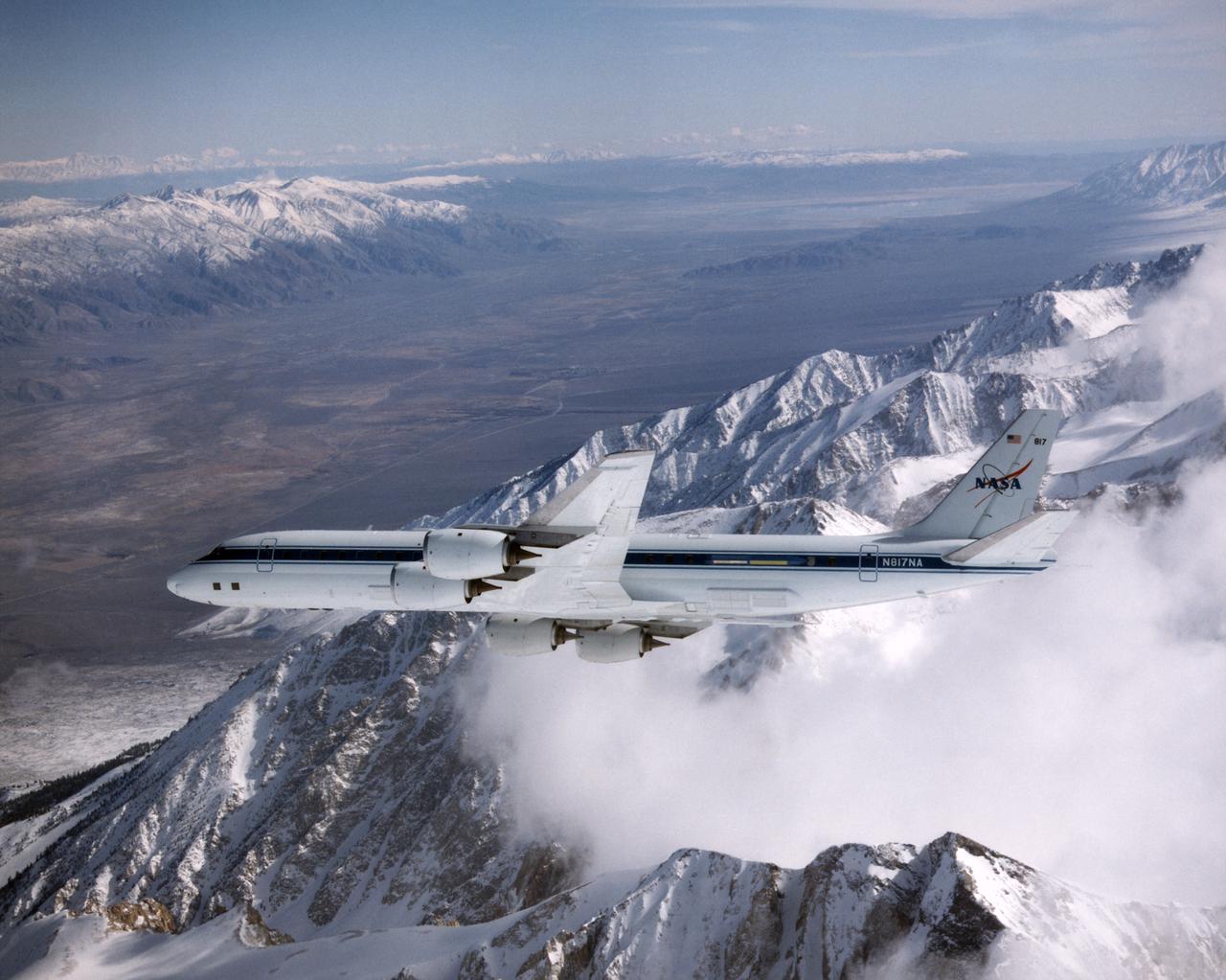

DC-8 Airborne Laboratory in banked flight over snow-capped Sierra Nevada mountain range

STS058-72-004 (18 Oct-1 Nov 1993) --- The Sierra Nevada Mountain Range can be seen in this north-looking high oblique view taken in October, 1993, by the STS-58 crew. Visible in the view to the west of the Sierra Nevada are the San Joaquin and Sacramento Valleys of central California. The San Francisco/Oakland Bay Area can be seen to the west of the valley at the extreme left of the photograph. To the east or right of the Sierra Nevada, the basin and Range Region of central and northern Nevada is visible. Mono Lake, Lake Tahoe and Pyramid Lake are also visible in this scene. The long northwest/southeast trending Walker Lane Shear Zone, which lies just to the east (right) of the Sierra Nevada is also visible. Near the top of the view (near the horizon), the snow covered volcanic peak Mount Shasta can be seen. Over 645 kilometers (400 miles) long and from 65 to 130 kilometers (40 to 80 miles) wide, the Sierra Nevada have many peaks in excess of 3,300 meters (11,000 feet) above sea level. A titled fault block in structure (the largest in the United States) and shaped by glaciers during the last ice age over 12,000 years ago, the Sierra Nevada eastern front rises sharply from the Great Basin of Nevada, while its western slope descends gradually to the hills bordering the Central Valley of California. Snow-fed streams supply much of the irrigation water to the Central Valley and to western Nevada and also generate hydroelectricity. Recent above normal precipitation (snowfall) of the last two years has helped in alleviating the drought conditions that had prevailed throughout most of California in the mid and late 1980's and early 1990's.
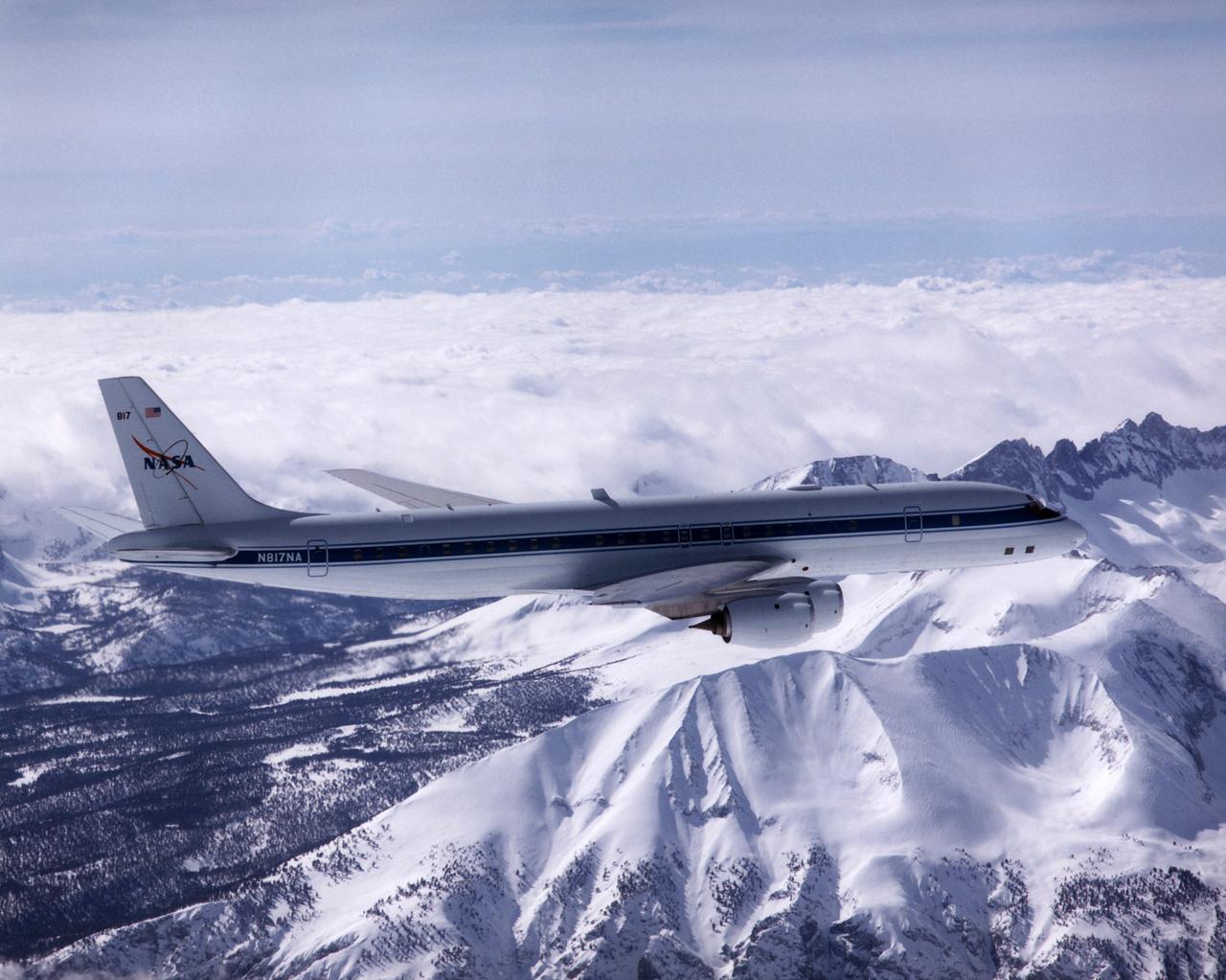

NASA's DC-8 Airborne Laboratory during a flight over the snow-covered Sierra Nevada Mountains. Over the past several years the DC-8 has conducted research missions in such diverse places as the Pacific in spring and Sweden in winter.
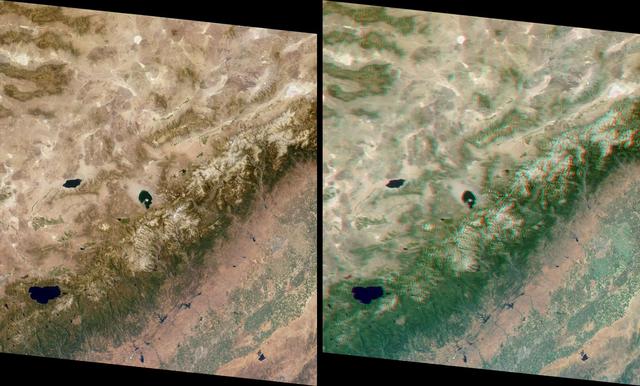
This stereo view of the Sierra Nevada mountains near the California-Nevada border was acquired on August 12, 2000 by NASA Terra satellite. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
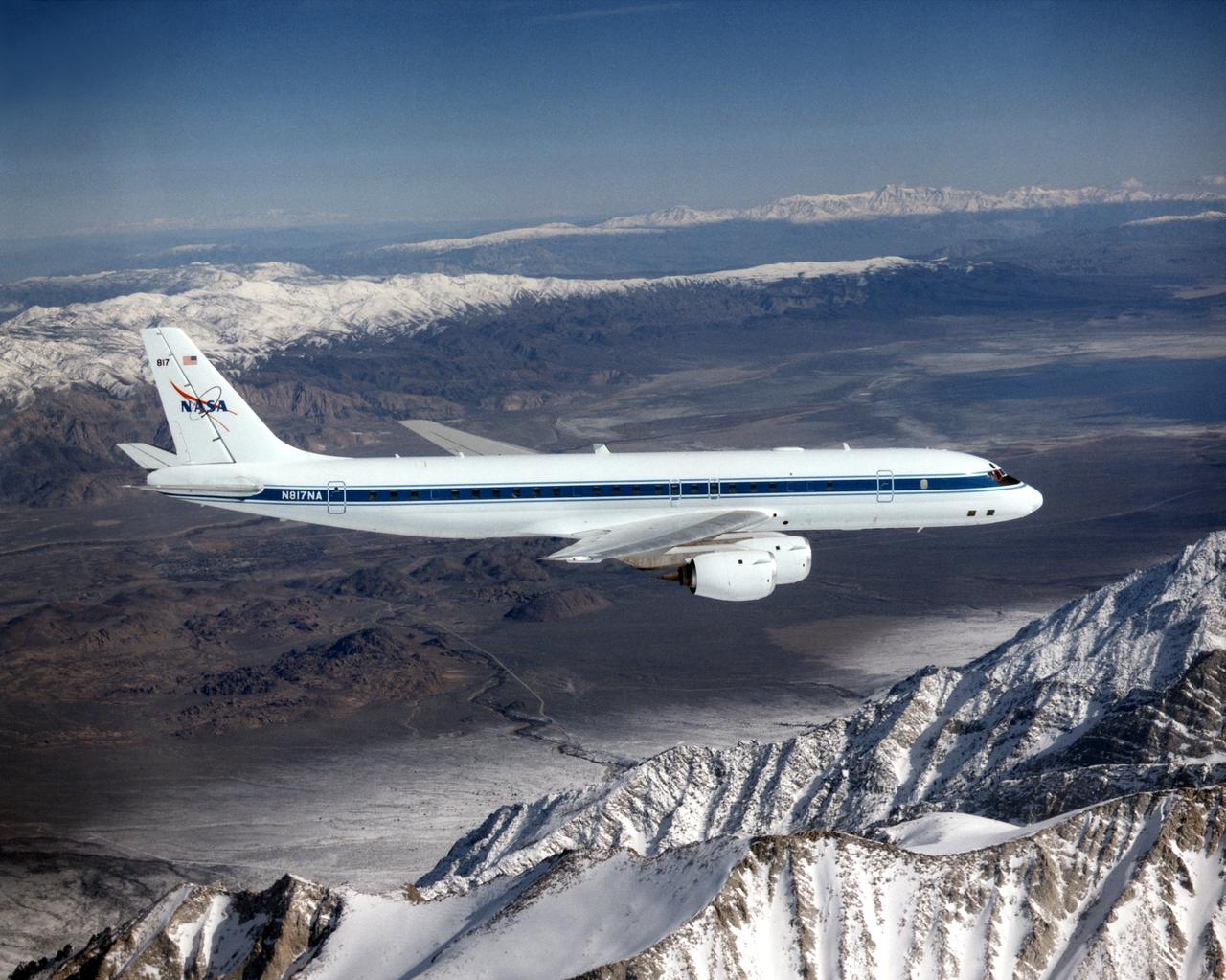

The DC-8 in flight near Lone Pine, Calif. In the foreground are the Sierra Nevada Mountains, covered with winter snow. In the distance are the White Mountains. The DC-8's fuselage is painted white with a dark blue stripe down the side. The wings are silver, while the engine pods are white. In this view of the airplane's right-hand side, only a few of its antennas are visible. The experimental payload can be as great as 30,000 pounds of equipment for gathering data of various sorts.

This image is a false-color composite of the Mammoth Mountain area in the Sierra Nevada Mountains, California. The image is centered at 37.6 degrees north latitude and 119.0 degrees west longitude.

At 14,505 feet high, Mt. Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous U.S., is located in California Sierra Nevada Mountains, on the west side of Owens Valley. The Alabama Hills appear in the foreground of this image from NASA Terra spacecraft.
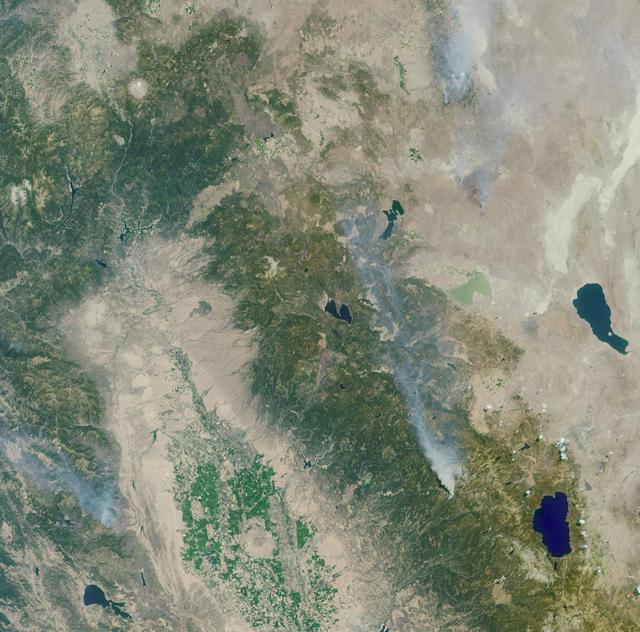

These images from NASA Terra satellite are of the Central Valley and the Sierra Nevada Mountains showing several smoke plumes from wildfires burning throughout Northern California on August 13, 2001.
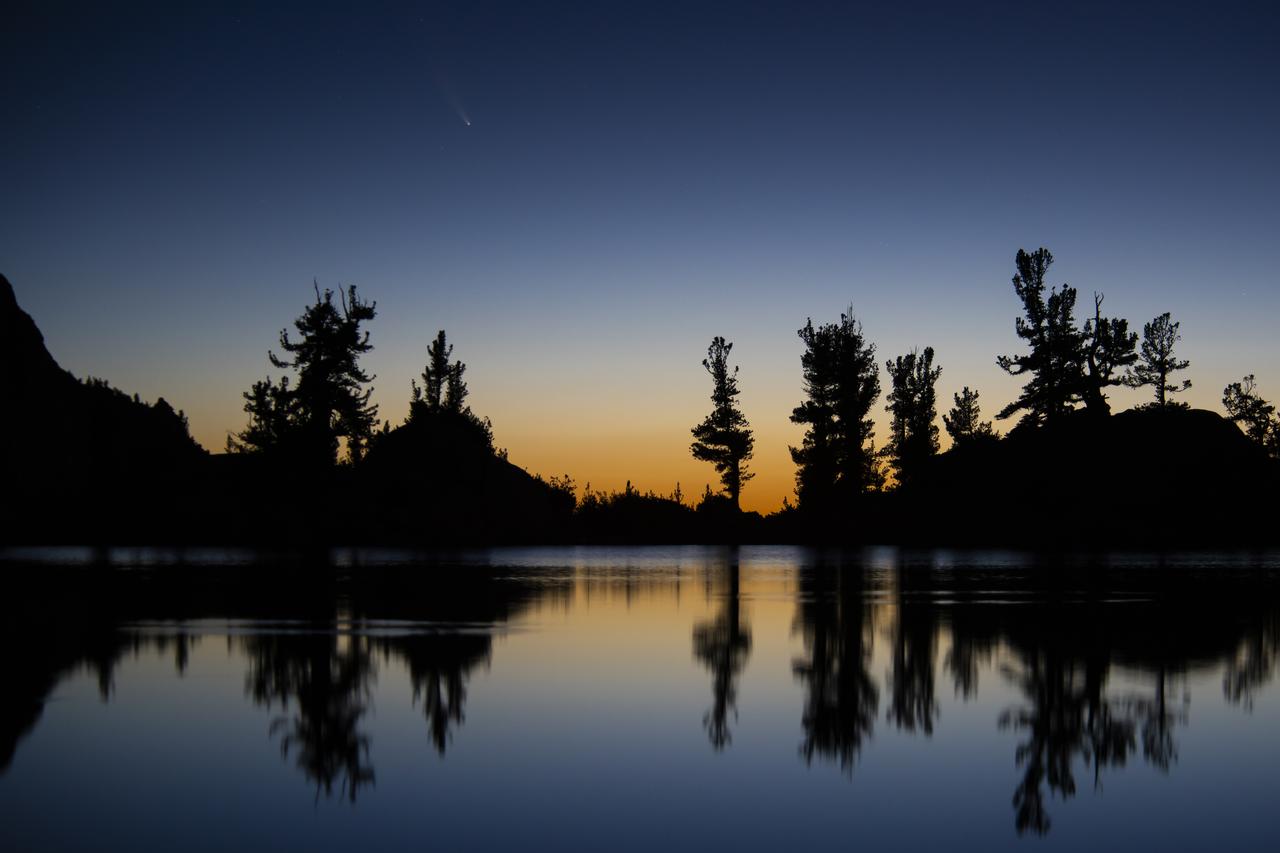

An image of the Comet C/2020 F3 NEOWISE (Comet NEOWISE) captured above the tree line of Lone Pine Lake, located on the Mount Whitney Trail in the Eastern Sierra Nevada Mountains in California. The photo was taken at 4:59 am on July 14, 2020. Visiting from the distant parts of the solar system, it’s characterized by a glowing tail and is visible during the month of July. The comet returns in 6,800 years.

ISS012-E-11144 (11 Dec. 2005) --- Sierra Nevada, Spain is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 12 crew member on the International Space Station. According to scientists, the Sierra Nevada, part of the Betic Cordillera of southern Spain, was formed during the Alpine Orogeny (or mountain-building event) that also formed the European Alps to the east and the Atlas Mountains of northern Africa across the Mediterranean Sea to the south. The Sierra as observed today formed during the Tertiary Period (65 to 1.8 million years ago) during collision of the African and Eurasian continental plates. The former Tethys Sea also closed during this time period, the scientists say, and the Mediterranean Sea is the largest surviving remnant basin of the ancient Tethys. The Sierra Nevada in the Granada province of Spain is perhaps the southernmost skiing location in all of Europe. Veleta Peak, at an elevation of 3,398 meters above sea level, is a popular destination for skiers and snowboarders. The rapid transition from lofty ski runs to Mediterranean beaches within a few hours’ drive has made the Sierra Nevada region popular for both outdoor and urban tourism. This photograph depicts the Veleta Peak region of the range and illustrates the sharp contrast between the snow capped mountains, adjacent dry lowlands to the west and north, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south.

iss064e015104 (Dec. 23, 2020) --- Pyramid Lake (upper right) in Nevada; Lake Tahoe (lower left) in California; and the snow-capped Sierra Nevada mountains are pictured from the International Space Station as it was orbiting 262 miles above the southwestern United States.
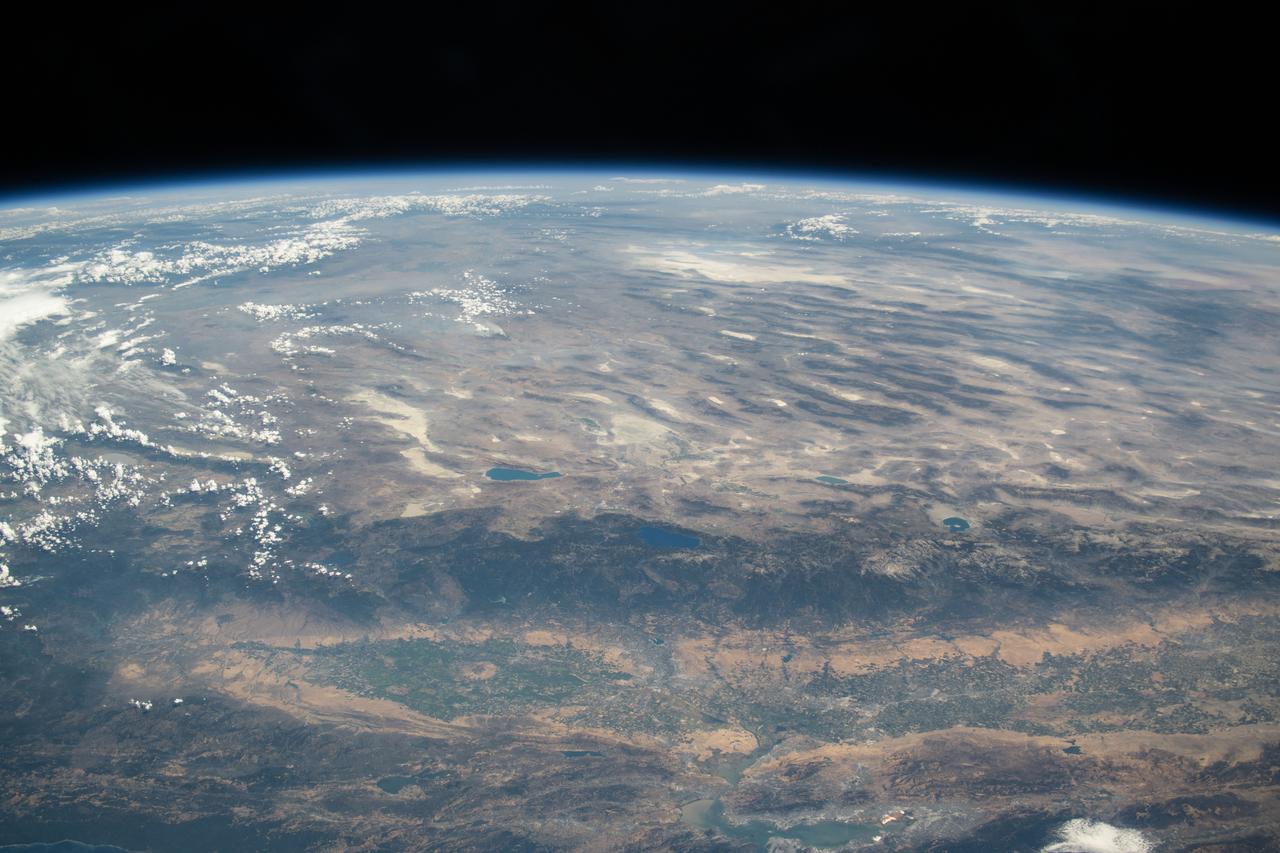

iss073e0420556 (Aug. 3, 2025) --- From bottom to top, or from west to east in this orientation, California's Central Valley extends across the bottom of this photograph and just above the San Francisco Bay Area. Past the Central Valley is the Sierra Nevada mountain range that leads into Nevada's Great Basin region and eastward toward the Rocky Mountains. The International Space Station was soaring 260 miles above the Pacific Ocean at the time of this photograph.
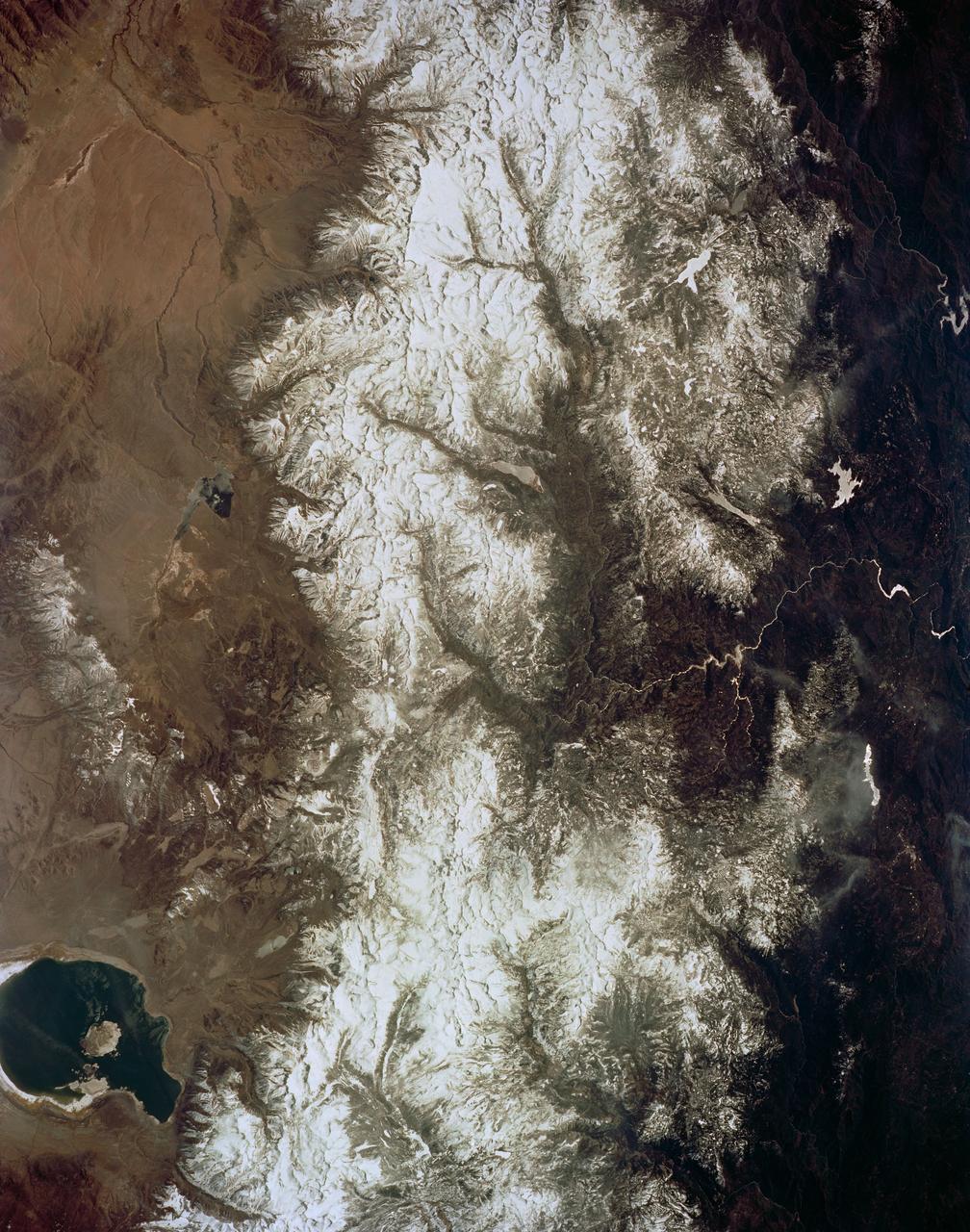

STS059-154-160 (9-20 April 1994) --- Orient with Mono Lake, California at the lower right; then the view is westward across the Sierra Nevada into the San Joaquin River drainage. A tiny network of ski trails can be seen on the Mono Lake side of the Sierras, on a line between Mono Lake and the snow-free San Joaquin headwaters. The ski trails mark Mammoth Mountain, where SRL investigators are studying microwave measurements of the water content of snowpacks. Linhof camera.

An ER-2 high-altitude Earth science aircraft banks away during a flight over the southern Sierra Nevada. NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center operates two of the Lockheed-built aircraft on a wide variety of environmental science, atmospheric sampling, and satellite data verification missions.
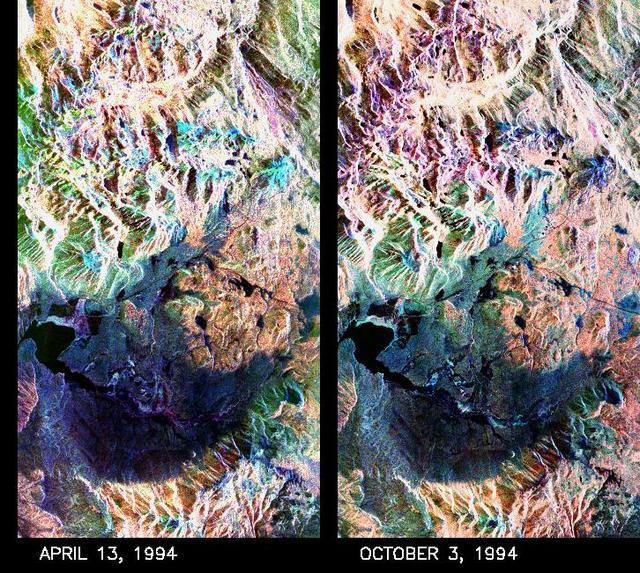

These two false-color composite images of the Mammoth Mountain area in the Sierra Nevada Mountains, Calif., show significant seasonal changes in snow cover. The image at left was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on its 67th orbit on April 13, 1994. The image is centered at 37.6 degrees north latitude and 119 degrees west longitude. The area is about 36 kilometers by 48 kilometers (22 miles by 29 miles). In this image, red is L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received) polarization data; green is C-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received) polarization data; and blue is C-band (horizontally transmitted and received) polarization data. The image at right was acquired on October 3, 1994, on the space shuttle Endeavour's 67th orbit of the second radar mission. Crowley Lake appears dark at the center left of the image, just above or south of Long Valley. The Mammoth Mountain ski area is visible at the top right of the scene. The red areas correspond to forests, the dark blue areas are bare surfaces and the green areas are short vegetation, mainly brush. The changes in color tone at the higher elevations (e.g. the Mammoth Mountain ski area) from green-blue in April to purple in September reflect changes in snow cover between the two missions. The April mission occurred immediately following a moderate snow storm. During the mission the snow evolved from a dry, fine-grained snowpack with few distinct layers to a wet, coarse-grained pack with multiple ice inclusions. Since that mission, all snow in the area has melted except for small glaciers and permanent snowfields on the Silver Divide and near the headwaters of Rock Creek. On October 3, 1994, only discontinuous patches of snow cover were present at very high elevations following the first snow storm of the season on September 28, 1994. For investigations in hydrology and land-surface climatology, seasonal snow cover and alpine glaciers are critical to the radiation and water balances. SIR-C/X-SAR is a powerful tool because it is sensitive to most snowpack conditions and is less influenced by weather conditions than other remote sensing instruments, such as Landsat. In parallel with the operational SIR-C data processing, an experimental effort is being conducted to test SAR data processing using the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's massively parallel supercomputing facility, centered around the Cray Research T3D. These experiments will assess the abilities of large supercomputers to produce high throughput SAR processing in preparation for upcoming data-intensive SAR missions. The images released here were produced as part of this experimental effort. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01753
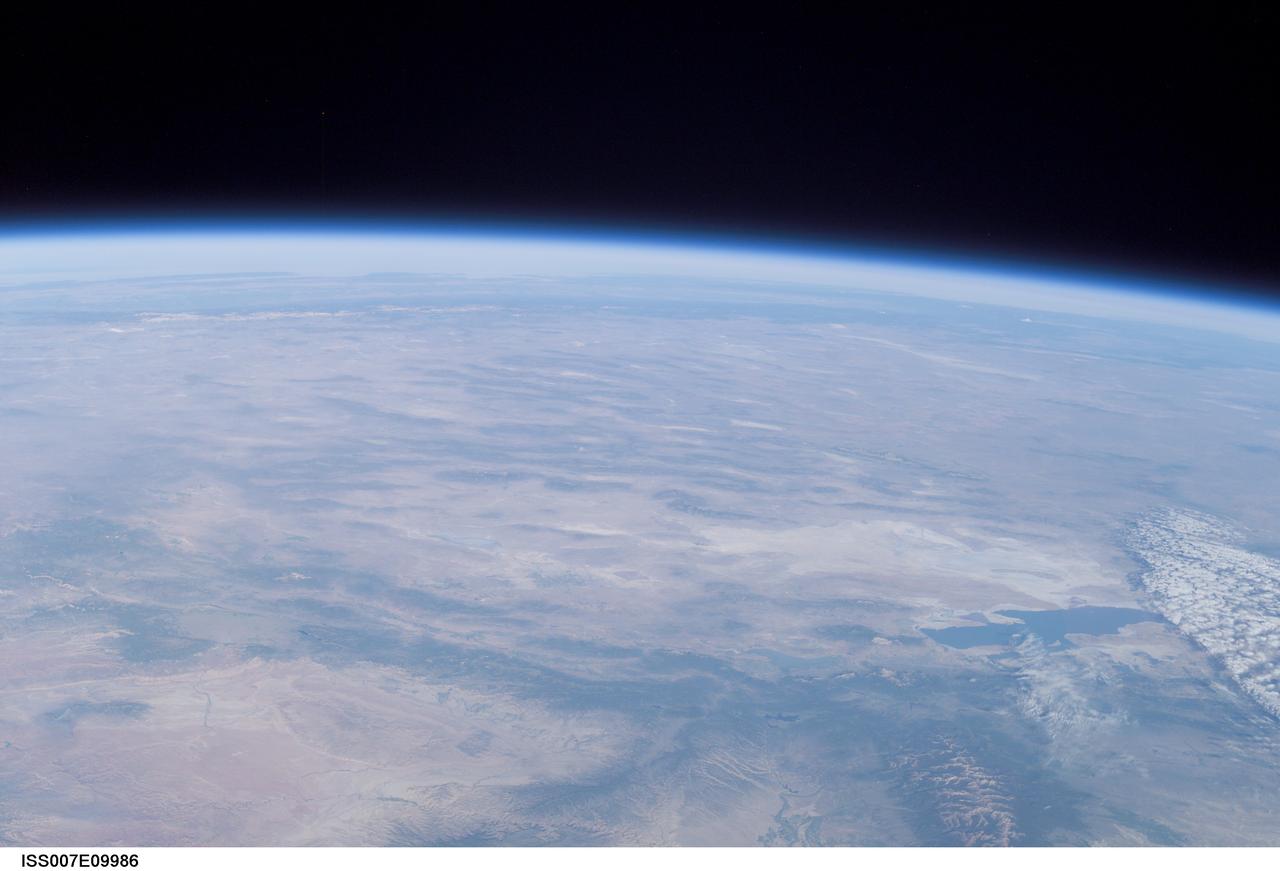

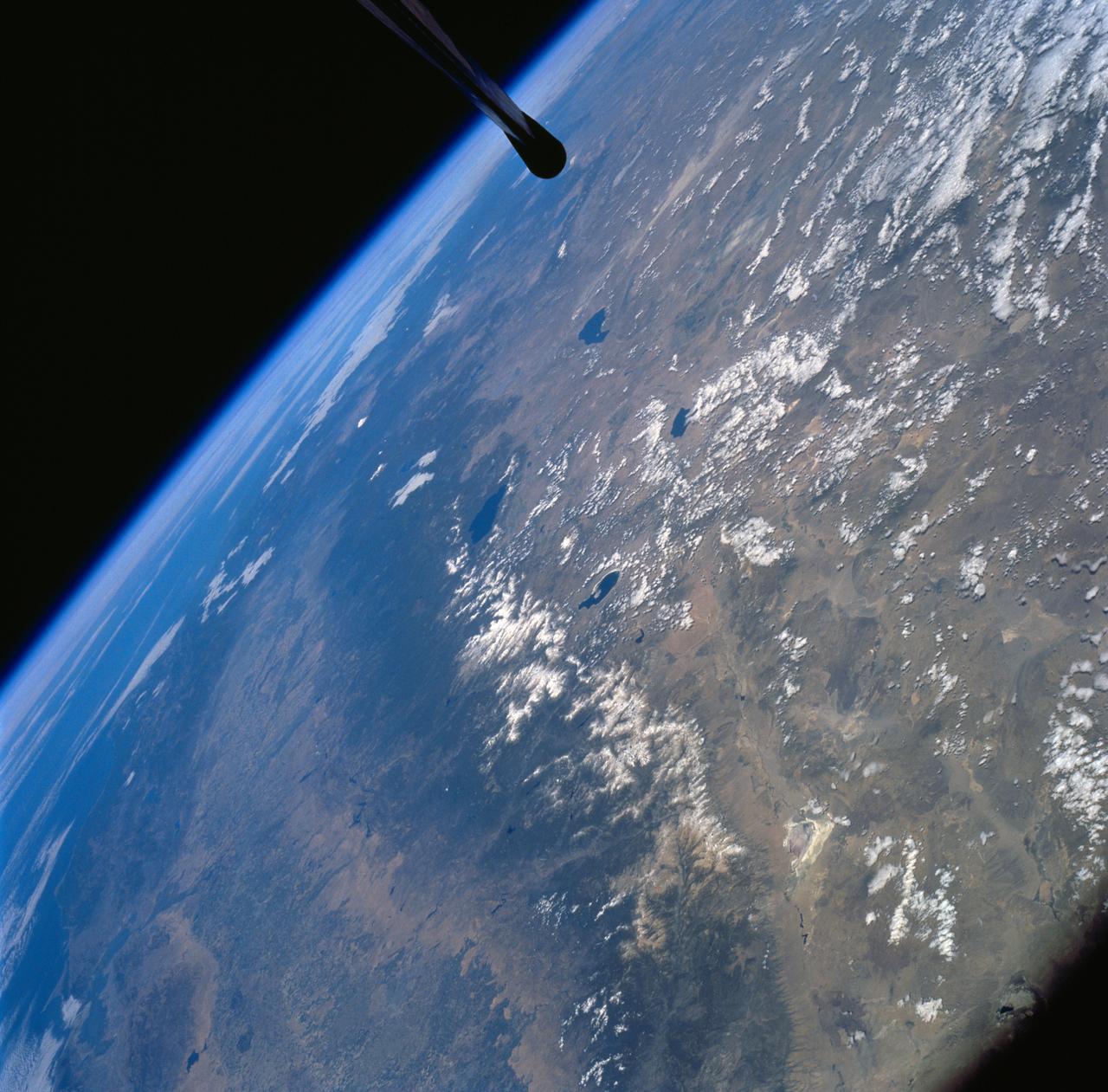
ISS007-E-09986 (11 July 2003) --- This view of Earth’s horizon was taken by an Expedition 7 crewmember onboard the International Space Station (ISS) while the Station was in orbit over Dodge City, Kansas. In the lower right is the Great Salt Lake. At the left side in the distance are the Sierra Nevada Mountains with elevations between 12,000 and 15,000 feet, and coastal California.
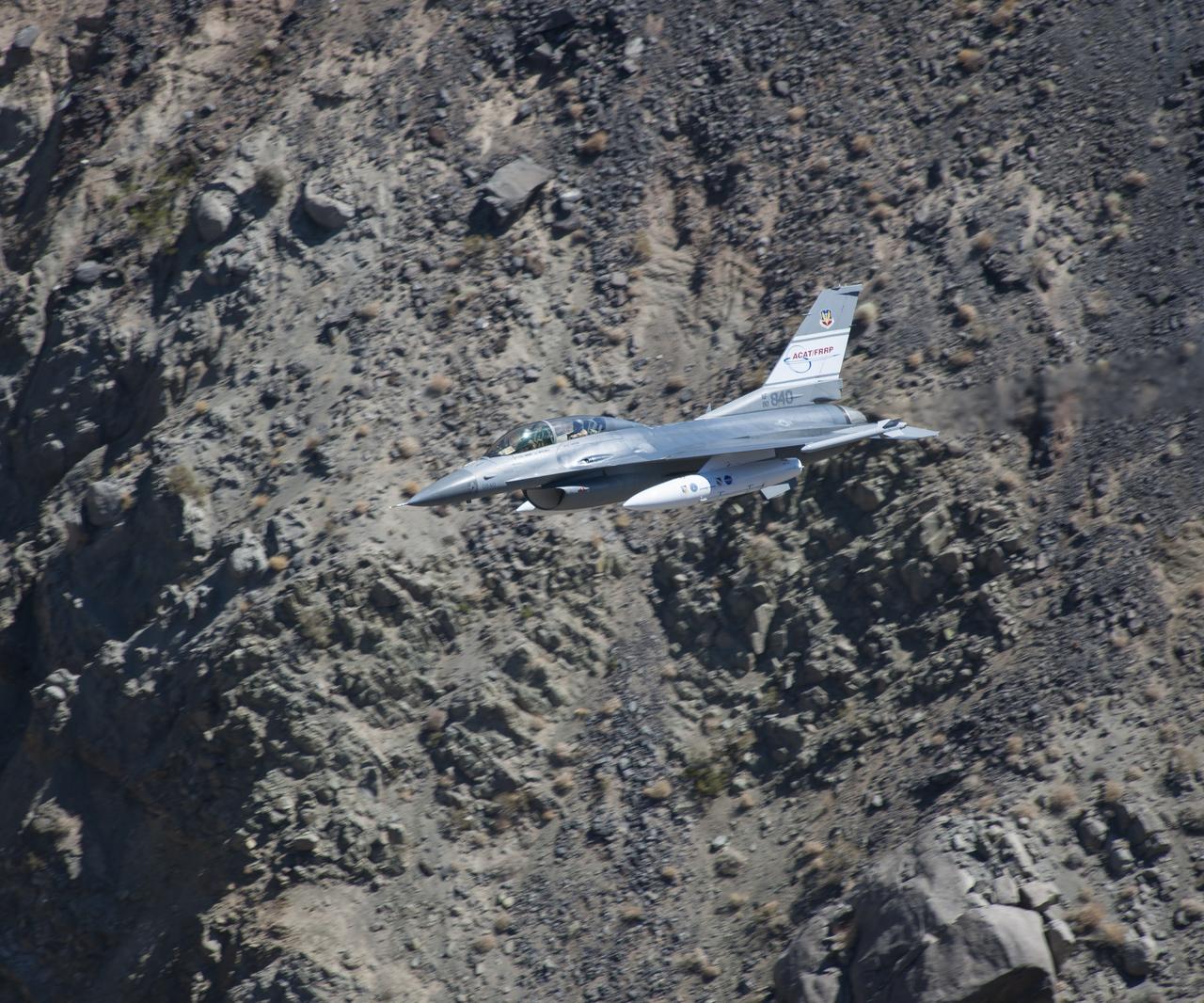

The U.S. Air Force F-16D Automatic Collision Avoidance Technology aircraft flew at low levels above the Sierra Nevada Mountains to test the ACAT Fighter Risk Reduction project. The goal was to develop collision avoidance technologies for aircraft to reduce the risk of ground collisions. Such systems on U.S. Air Force aircraft have resulted in saving eight lives and seven aircraft.
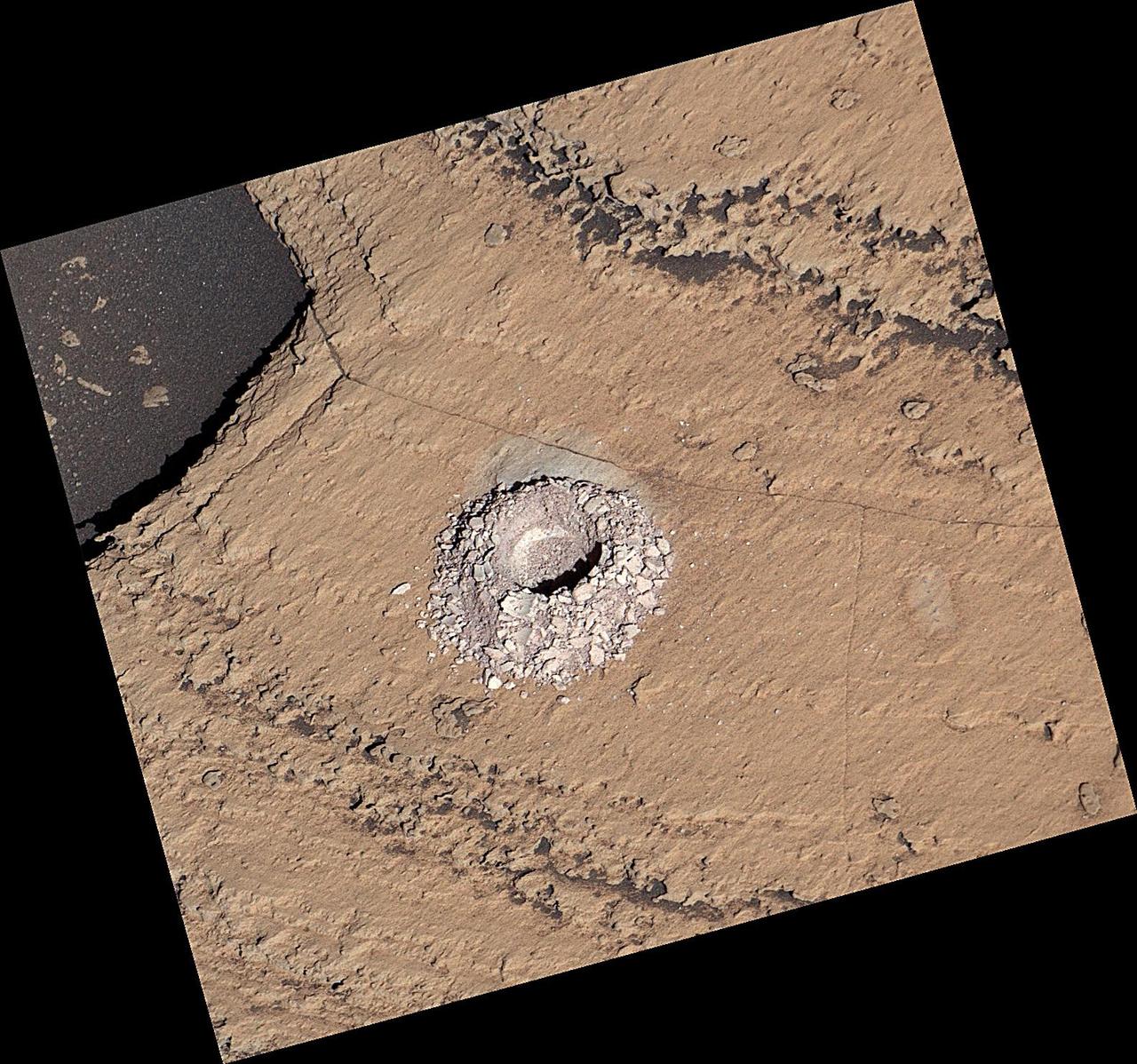

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover used the drill on the end of its robotic arm to collect a sample from a rock nicknamed "Sequoia" on Oct. 17, 2023, the 3,980th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The mission was naming science targets after locations in California's Sierra Nevada mountain range at the time this sample was collected. This image was captured by the rover's Mast Camera, or Mastcam. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26048
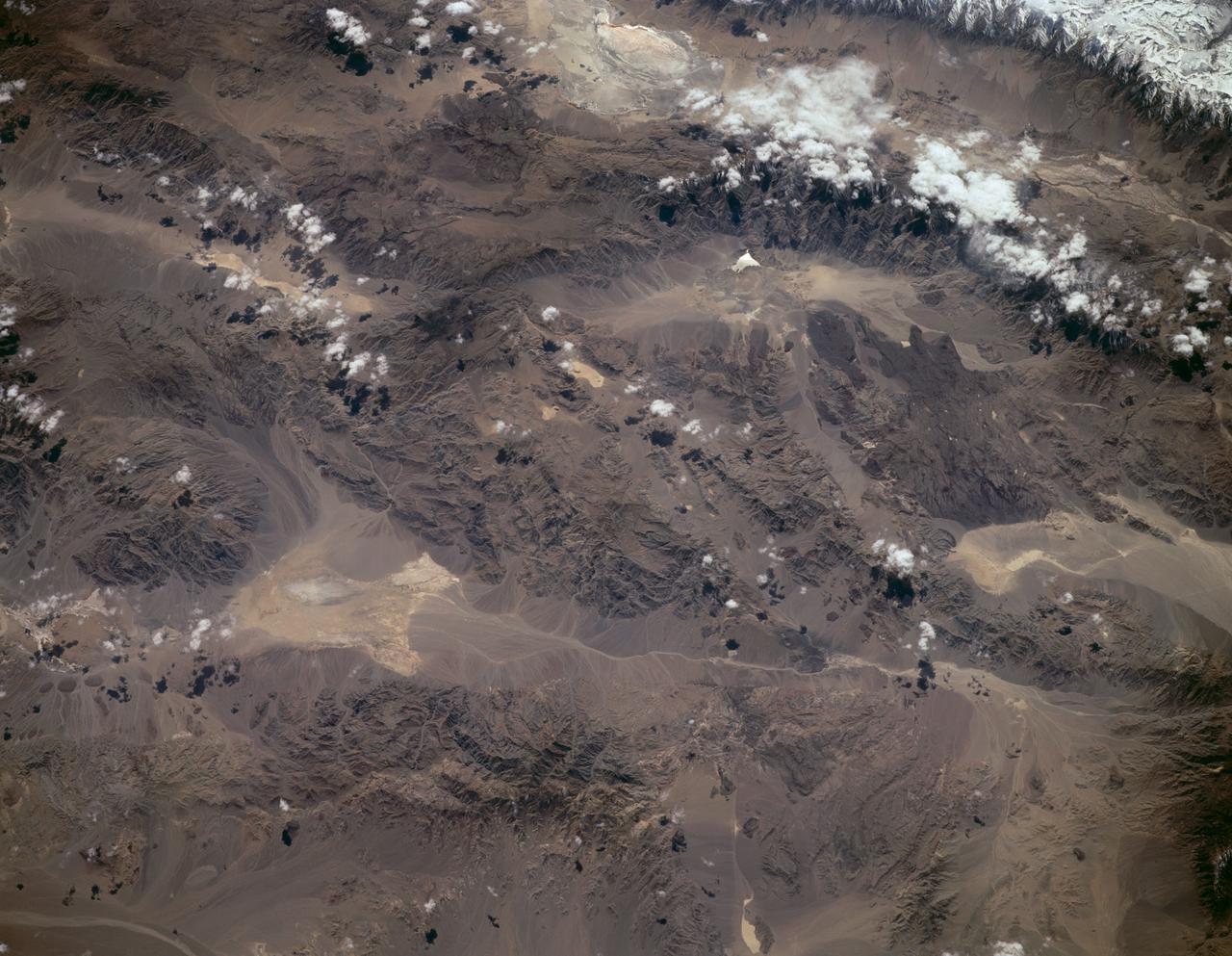

STS059-L09-162 (9-20 April 1994) --- Orient with the snow-covered mountains (Sierra Nevada of California) in the upper right corner. Then Owens Valley runs along the top of the photograph to Owens Lake playa at top center. The upper end of Death Valley extends from right to left in the foreground, with the drainage running down to a playa at Stovepipe Wells in the left foreground. Geologists are studying microwave signatures of the different playa surfaces, and the coatings on alluvial fans that extend from mountain masses, to try to sort out the history of different climates in this formerly wet but now hyperarid region.
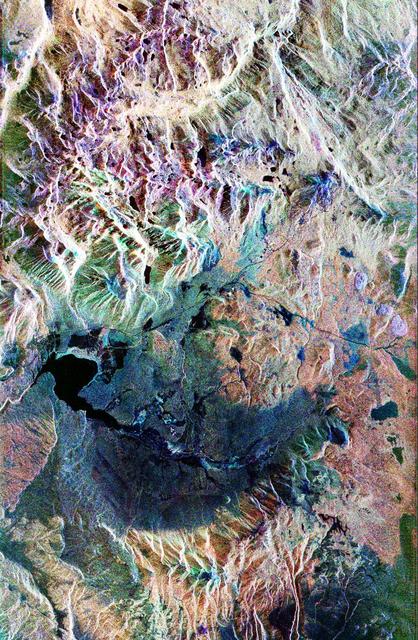

This false-color composite radar image of the Mammoth Mountain area in the Sierra Nevada Mountains, California, was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on its 67th orbit on October 3, 1994. The image is centered at 37.6 degrees north latitude and 119.0 degrees west longitude. The area is about 39 kilometers by 51 kilometers (24 miles by 31 miles). North is toward the bottom, about 45 degrees to the right. In this image, red was created using L-band (horizontally transmitted/vertically received) polarization data; green was created using C-band (horizontally transmitted/vertically received) polarization data; and blue was created using C-band (horizontally transmitted and received) polarization data. Crawley Lake appears dark at the center left of the image, just above or south of Long Valley. The Mammoth Mountain ski area is visible at the top right of the scene. The red areas correspond to forests, the dark blue areas are bare surfaces and the green areas are short vegetation, mainly brush. The purple areas at the higher elevations in the upper part of the scene are discontinuous patches of snow cover from a September 28 storm. New, very thin snow was falling before and during the second space shuttle pass. In parallel with the operational SIR-C data processing, an experimental effort is being conducted to test SAR data processing using the Jet Propulsion Laboratory's massively parallel supercomputing facility, centered around the Cray Research T3D. These experiments will assess the abilities of large supercomputers to produce high throughput Synthetic Aperture Radar processing in preparation for upcoming data-intensive SAR missions. The image released here was produced as part of this experimental effort. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01746
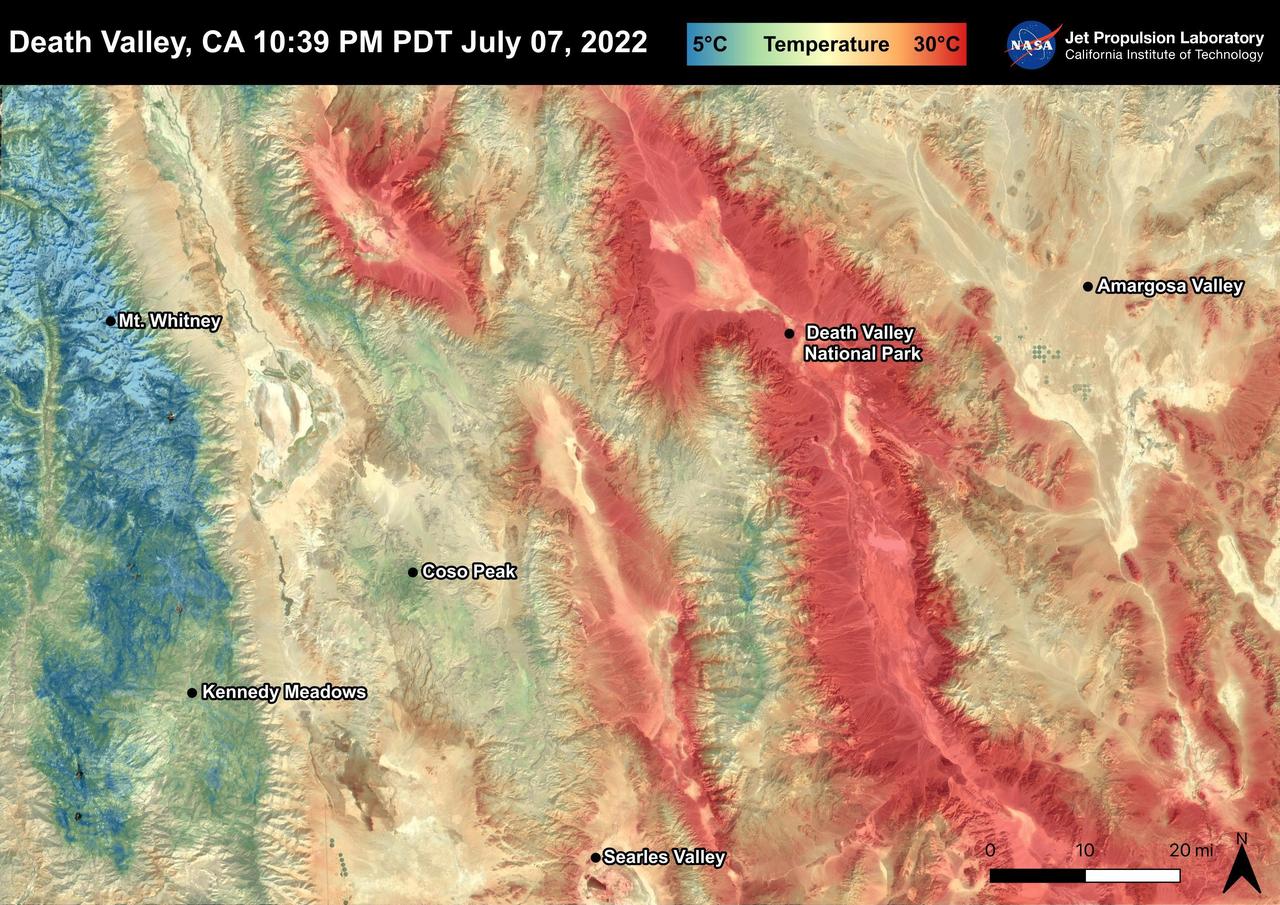
Death Valley, California is a desert valley in the Northern Mojave Desert. During the summer months, Death Valley can become one of the hottest places on Earth. Death Valley is about 85 miles from Mt. Whitney, the highest point in the contiguous United States with an elevation of 14,505 ft. This Land Surface Temperature image captured by ECOSTRESS on July 07, 2022 shows temperatures exceeding 90 degrees Fahrenheit in Death Valley and temperatures below 40 degrees Fahrenheit in the Sierra Nevada Mountain Range. ECOSTRESS is a thermal instrument on the International Space Station that measures the temperature of the ground, which is hotter than the air temperature during the day. It was launched to the space station in 2018. Its primary mission is to identify critical thresholds of water use and water stress in plants and to detect the timing, location, and predictive factors leading to plant water uptake decline and/or cessation. The nature of the high-resolution data provided by ECOSTRESS allows it to record heat related phenomena such as heat waves and wildfires. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25482
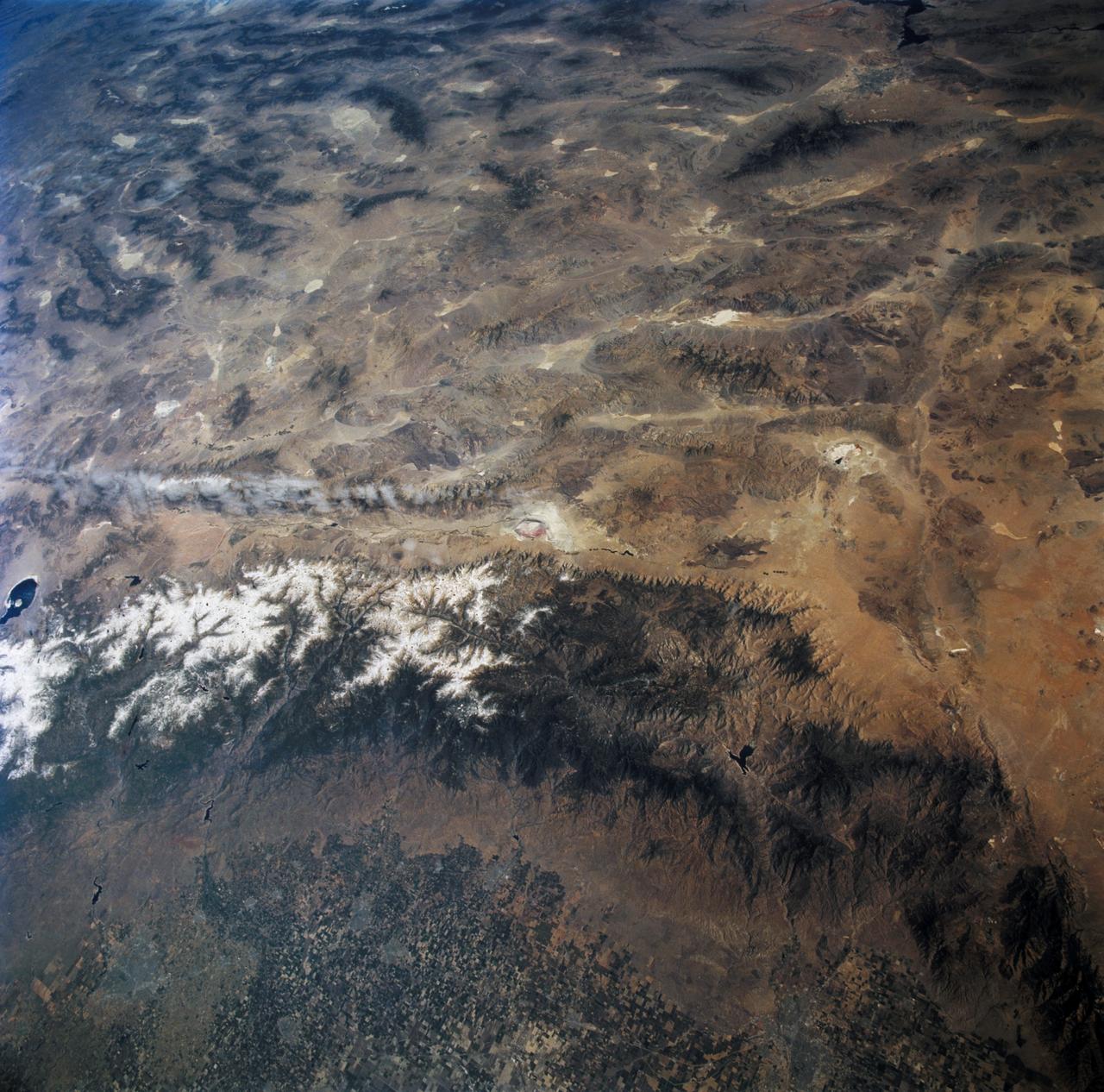

STS068-267-097 (30 September-11 October 1994) --- An extensive view eastward from the irrigated San Joaquin Valley in the foreground, across the Sierra Nevada (living up to its name in early October), into the desert of eastern California and Nevada (which has no snow, despite the name). Mono Lake is just visible at the left edge of the frame; Owens Valley extends southward to Owens Lake, the next valley is Panamint Valley, and then Death Valley. Las Vegas and Lake Mead are visible at the upper right of the frame. The Space Radar Laboratory 2 (SRL-2) obtained extensive, multiple-pass data from many test sites within the region displayed, including Mammoth Mountain ski area south of Mono Lake, and in Death Valley.
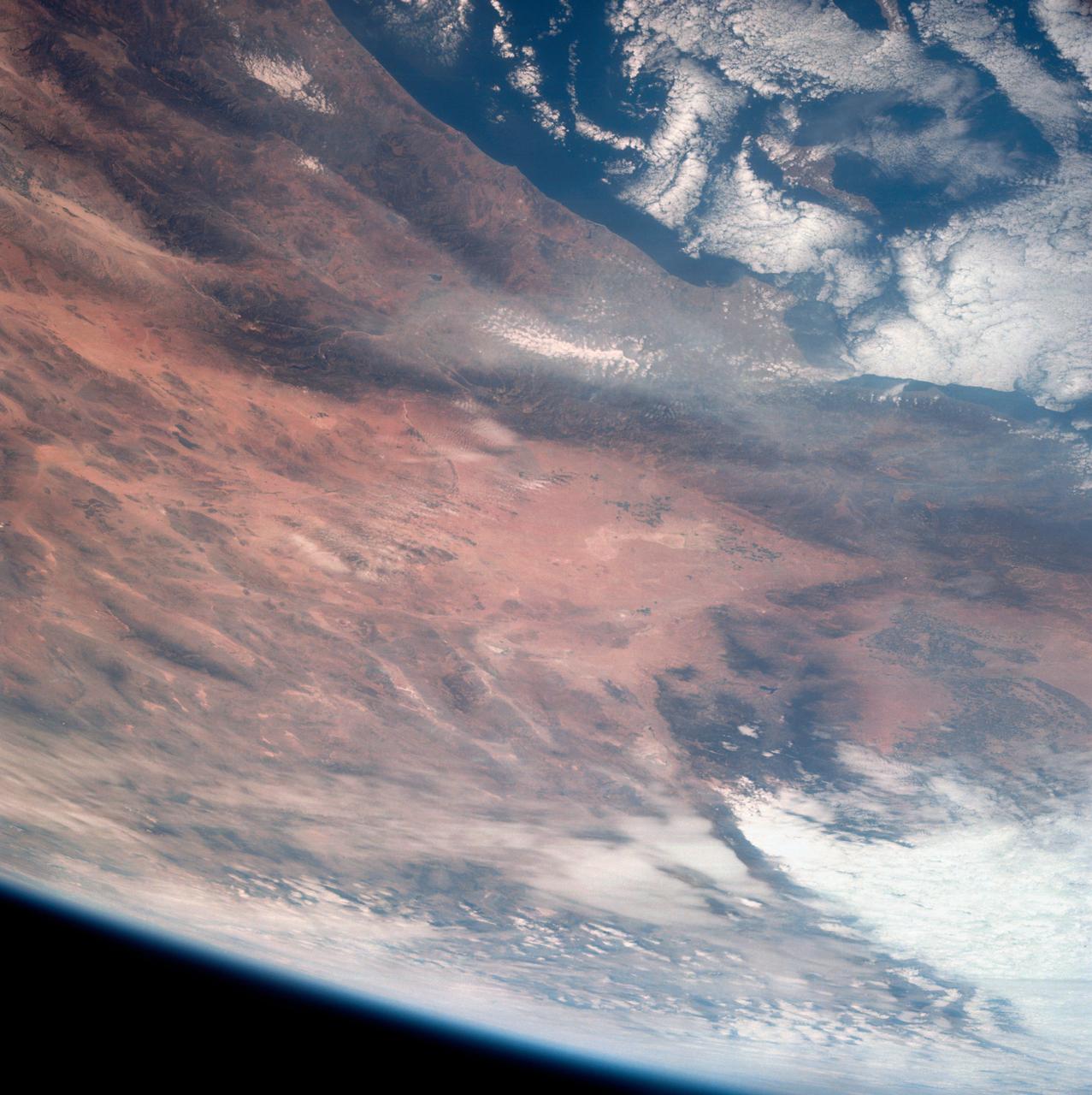

This view of southern California as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 18th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 124 nautical miles. The coast of California can be seen from Point Mugu southward to Oceanside. Santa Catalina can be seen below the off shore clouds. Details of the Los Angeles area are obscured by pollution which extends from Banning westard for 100 miles to beyond Malibu. In the upper portion of the photograph can be seen (left to right) the San Joaquin Valley beyond Bakersfield, the Techachapi Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, Owens Valley, Death Valley and the Mojave Desert.
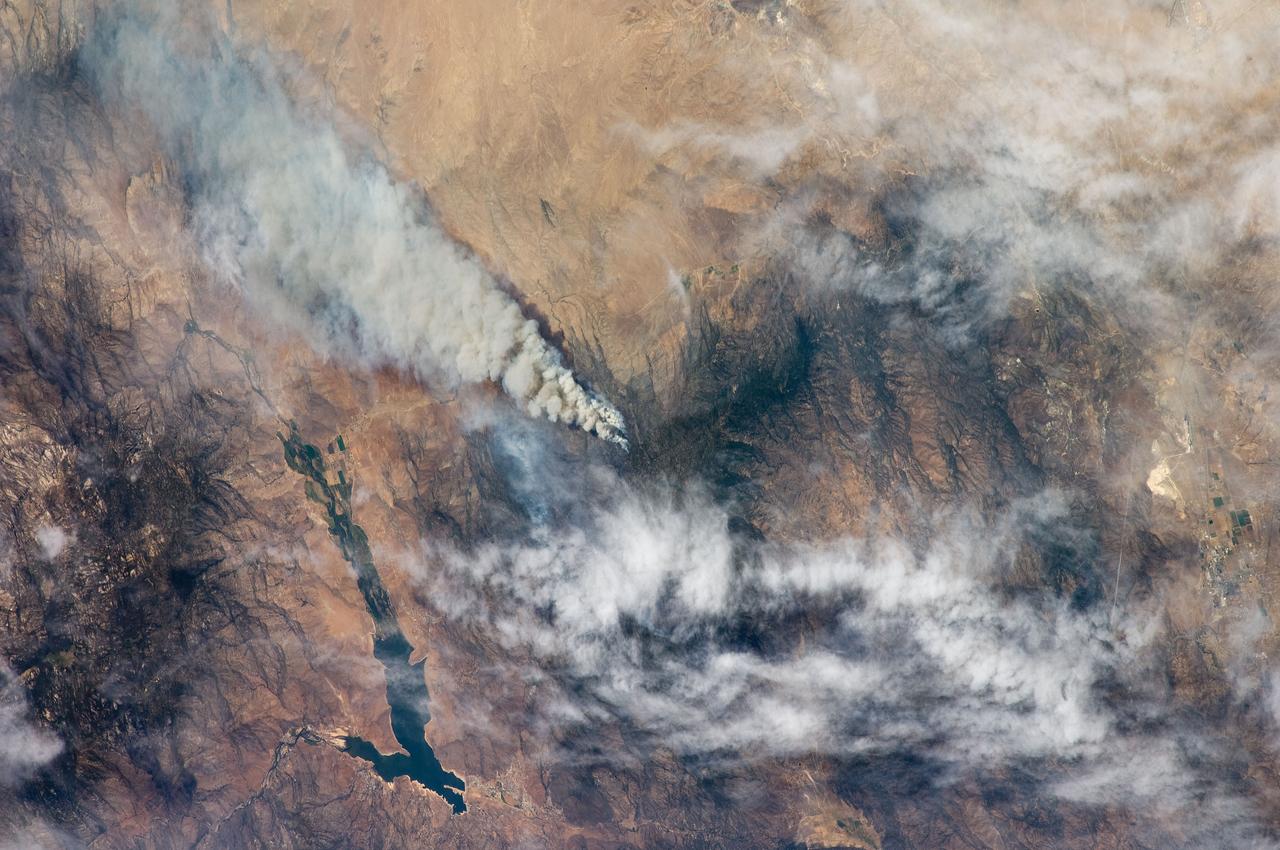

ISS017-E-010310 (4 July 2008) --- The Piute fire in California is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 17 crewmember on the International Space Station. The Piute fire, burning south of Lake Isabella in the Sequoia National Forest in the southern Sierra Nevada Mountains, is one of the more than 300 wildfires burning across the state of California. The fire started June 28 just north of Twin Oaks, California, and has burned nearly 14,000 acres so far. Current estimates by fire officials suggest the fire may not be brought under control for another two weeks.

The NASA DC-8 in a right bank over the rugged Sierra Nevada Mountains. The former airliner is a "dash-72" model and has a range of 5,500 miles. The craft can stay airborne for 12 hours and has an operational speed range between 300 and 500 knots. The research flights are made at between 500 and 41,000 feet. The aircraft can carry up to 30,000 lbs of research/science payload equipment installed in 15 mission-definable spaces. In this photo, the aircraft is shown in flight from below, with the DC-8 silhouetted against a blue sky.
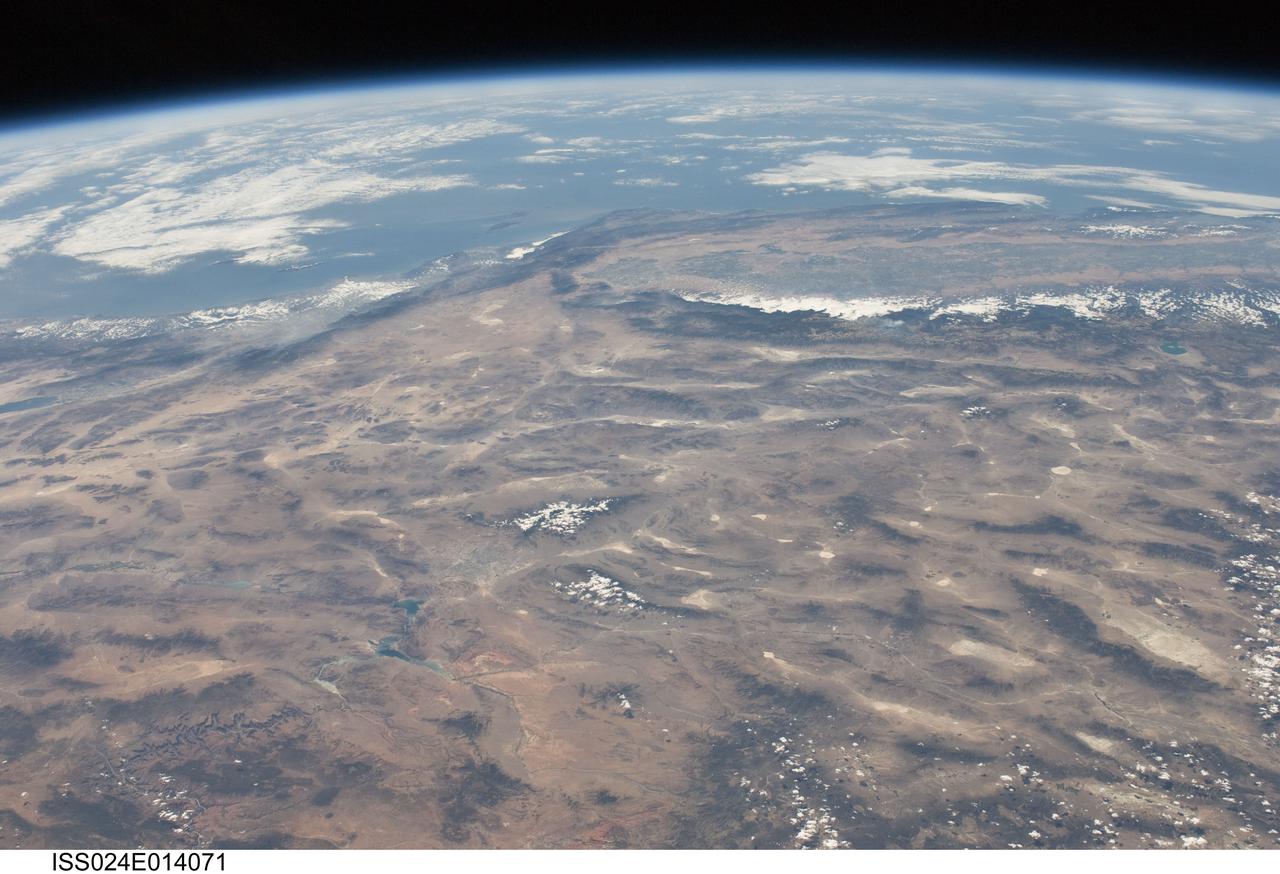

ISS024-E-014071 (9 Sept. 2010) --- This striking panoramic view of the southwestern USA and Pacific Ocean is an oblique image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member looking outwards at an angle from the International Space Station (ISS). While most unmanned orbital satellites view Earth from a nadir perspective?in other words, collecting data with a ?straight down? viewing geometry?crew members onboard the space station can acquire imagery at a wide range of viewing angles using handheld digital cameras. The ISS nadir point (the point on Earth?s surface directly below the spacecraft) was located in northwestern Arizona, approximately 260 kilometers to the east-southeast, when this image was taken. The image includes parts of the States of Arizona, Nevada, Utah, and California together with a small segment of the Baja California, Mexico coastline at center left. Several landmarks and physiographic features are readily visible. The Las Vegas, NV metropolitan area appears as a gray region adjacent to the Spring Mountains and Sheep Range (both covered by white clouds). The Grand Canyon, located on the Colorado Plateau in Arizona, is visible (lower left) to the east of Las Vegas with the blue waters of Lake Mead in between. The image also includes the Mojave Desert, stretching north from the Salton Sea (left) to the Sierra Nevada mountain range. The Sierra Nevada range is roughly 640 kilometers long (north-south) and forms the boundary between the Central Valley of California and the adjacent Basin and Range. The Basin and Range is so called due to the pattern of long linear valleys separated by parallel linear mountain ranges ? this landscape, formed by extension and thinning of Earth?s crust, is particularly visible at right.
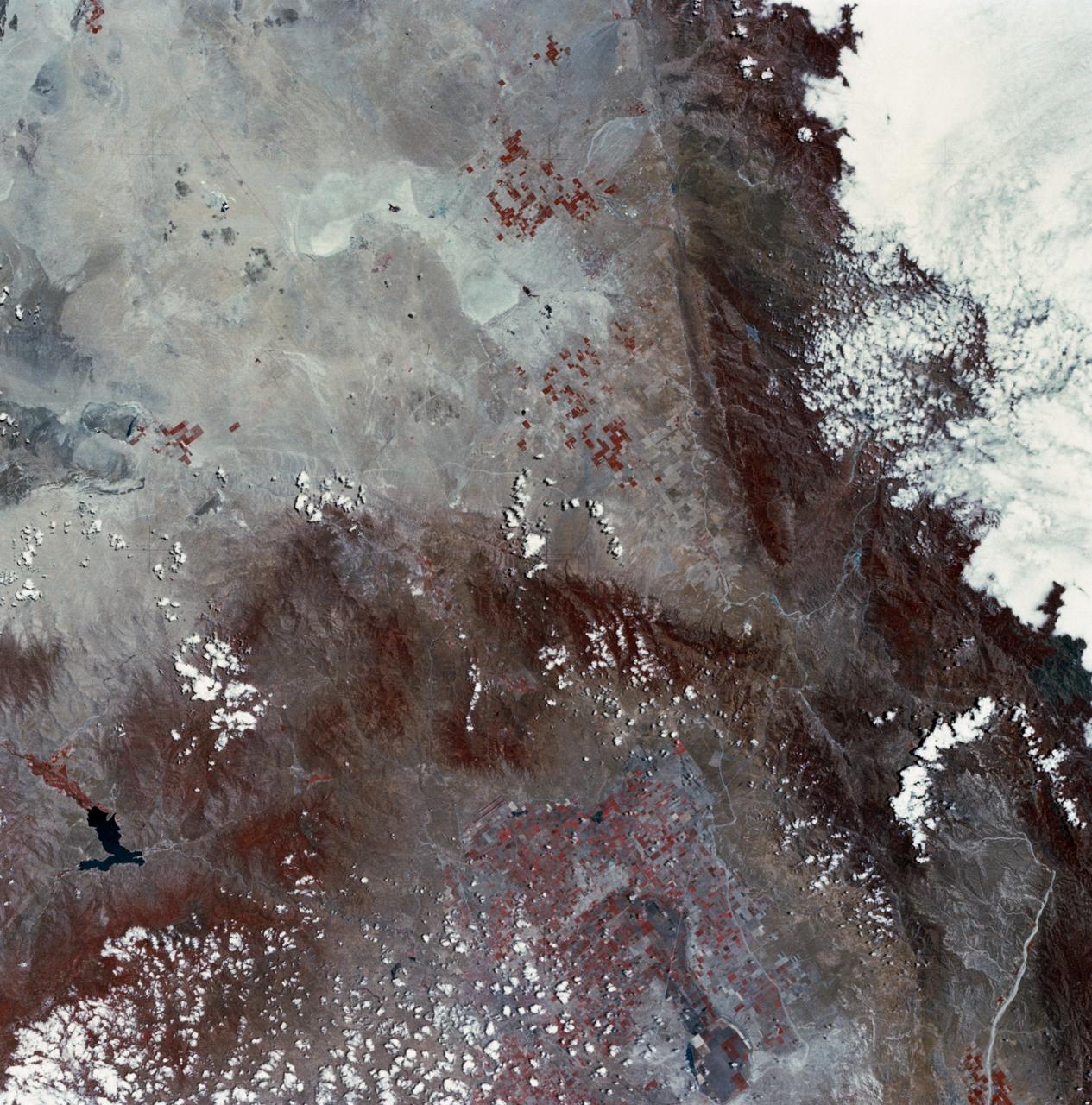

SL2-03-126 (June 1973) --- A color infrared photograph of the Los Angeles County and Kern County area, taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit during its first manned Skylab mission. The Mojave Desert occupies the northeast one-fourth of the photograph. Lake Isabella in the Sierra Nevada Mountains is the v-shaped body of water. The San Gabriel Mountains extend across the southern part of the picture. At lower center is the intersection of the San Andreas and Garlock faults. The San Joaquin Valley is in the center at the left edge. (The picture should be held with the heavy cloud cover at lower right corner so that north will be at top.) This picture was exposed by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility experiment in the Multiple Docking Adapter of the Skylab space station. Type 2443 film was used. Photo credit: NASA
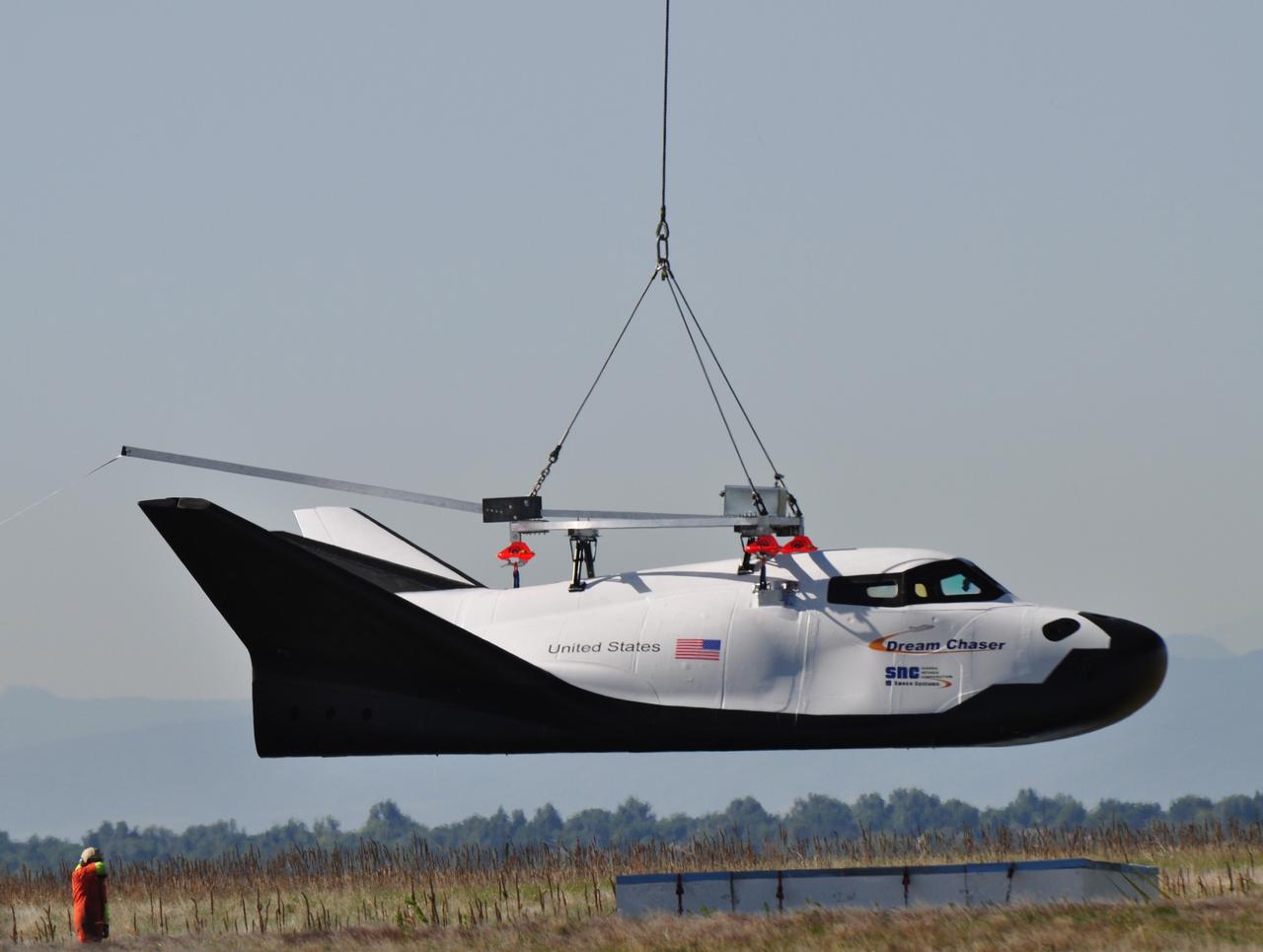

LOUISVILLE, Colo. – Sierra Nevada Corporation Space Systems’ Dream Chaser full-scale test vehicle is lifted by an Erickson Air-Crane helicopter to verify proper aerodynamic flight performance near the Rocky Mountain Metropolitan Airport in Jefferson County, Colo. This captive-carry test is one of several milestones the company is meeting during its partnership with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program CCP. Data from this test will provide SNC an early opportunity to evaluate and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations in preparation for approach and landing tests scheduled for later this year. In 2011, NASA selected Sierra Nevada during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Sierra Nevada Corp.
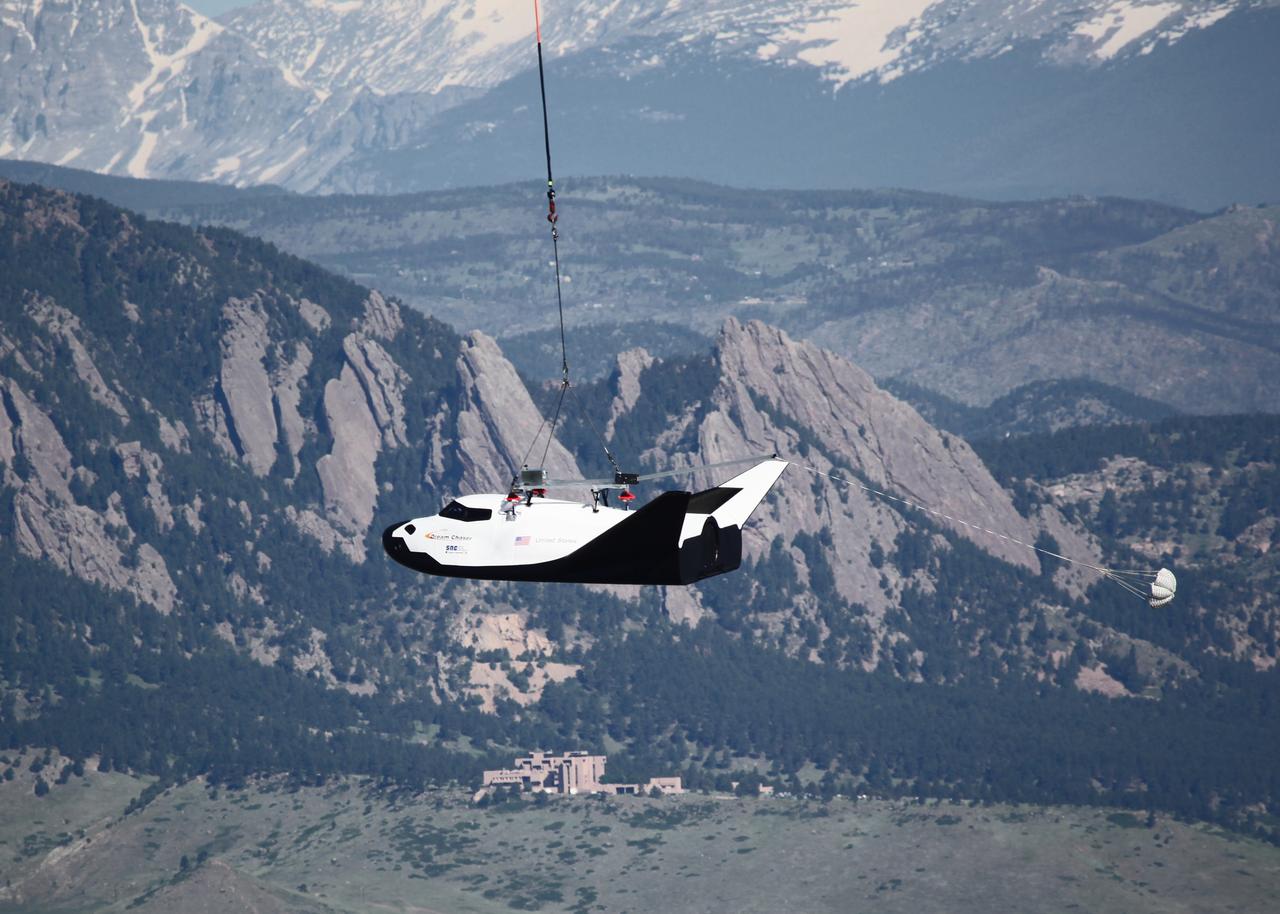

LOUISVILLE, Colo. – Sierra Nevada Corporation Space Systems’ Dream Chaser full-scale test vehicle is lifted by an Erickson Air-Crane helicopter to verify proper aerodynamic flight performance near the Rocky Mountain Metropolitan Airport in Jefferson County, Colo. This captive-carry test is one of several milestones the company is meeting during its partnership with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program CCP. Data from this test will provide SNC an early opportunity to evaluate and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations in preparation for approach and landing tests scheduled for later this year. In 2011, NASA selected Sierra Nevada during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Sierra Nevada Corp.
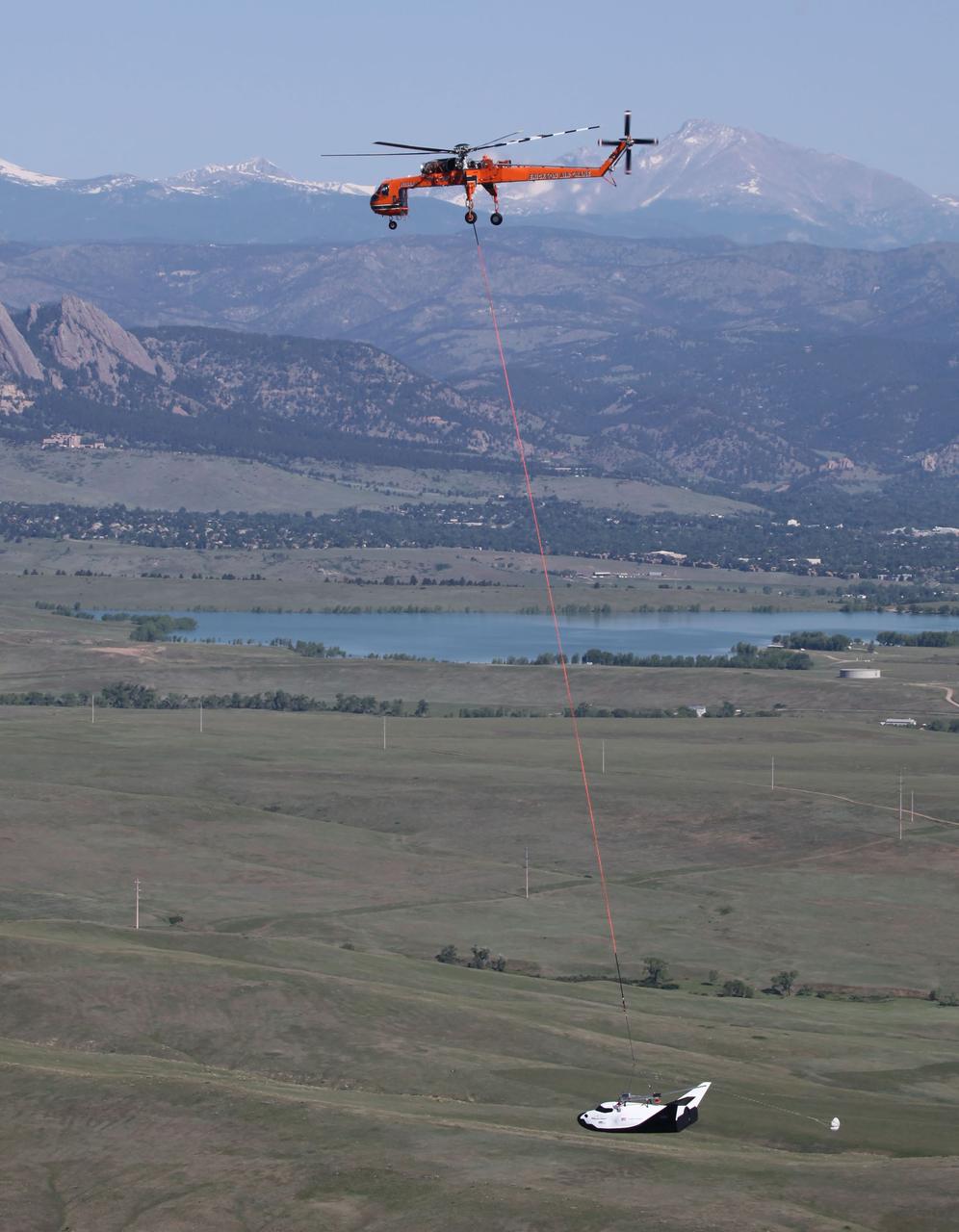

LOUISVILLE, Colo. – An Erickson Air-Crane helicopter lifts Sierra Nevada Corporation Space Systems’ Dream Chaser full-scale test vehicle to verify proper aerodynamic flight performance near the Rocky Mountain Metropolitan Airport in Jefferson County, Colo. This captive-carry test is one of several milestones the company is meeting during its partnership with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program CCP. Data from this test will provide SNC an early opportunity to evaluate and prove hardware, facilities and ground operations in preparation for approach and landing tests scheduled for later this year. In 2011, NASA selected Sierra Nevada during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, The Boeing Co., Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Sierra Nevada Corp.
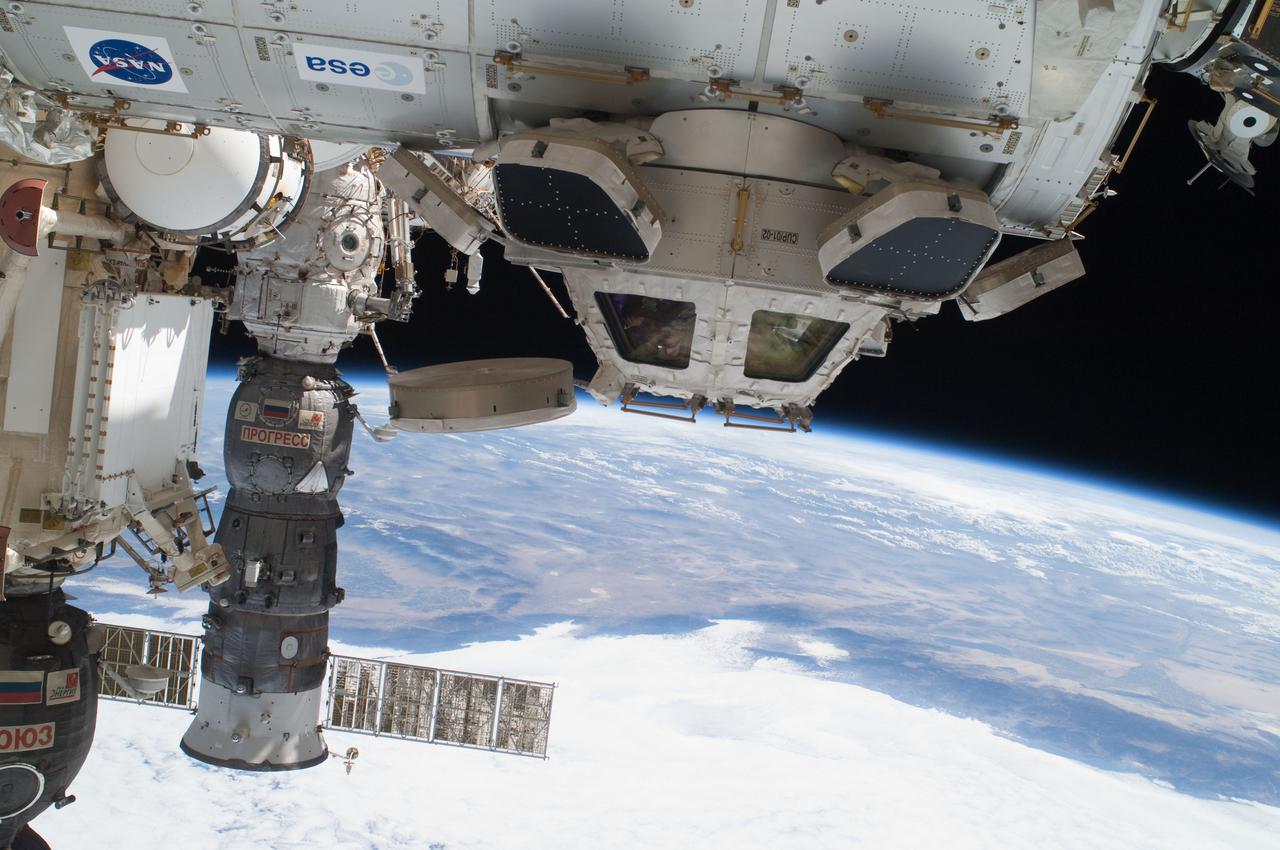

ISS028-E-016225 (12 July 2011) --- Components of the International Space Station, though moving along at 17,500 miles per hour, appear to hover above the Pacific Ocean just off the California coast. Ten cosmonauts and astronauts were working together when this photo was taken -- four of them as STS-135 visitors from the docked space shuttle Atlantis and six as members of the Expedition 28 crew. The Cupola, near center of frame, is attached to Node 3 or Tranquility. A Russian Soyuz and a Russian Progress spacecraft are parked at the station, left side of frame. While much of the coast is obscured by clouds, just inland from left to right, one can see the agriculture of the San Joaquin Valley, the southern Sierra Nevada, the Los Angeles Basin (center), the Mojave Desert, coastal mountains of southern California, the Salton Sea, the Imperial Valley, and the mouth of the Colorado River on the extreme right edge.
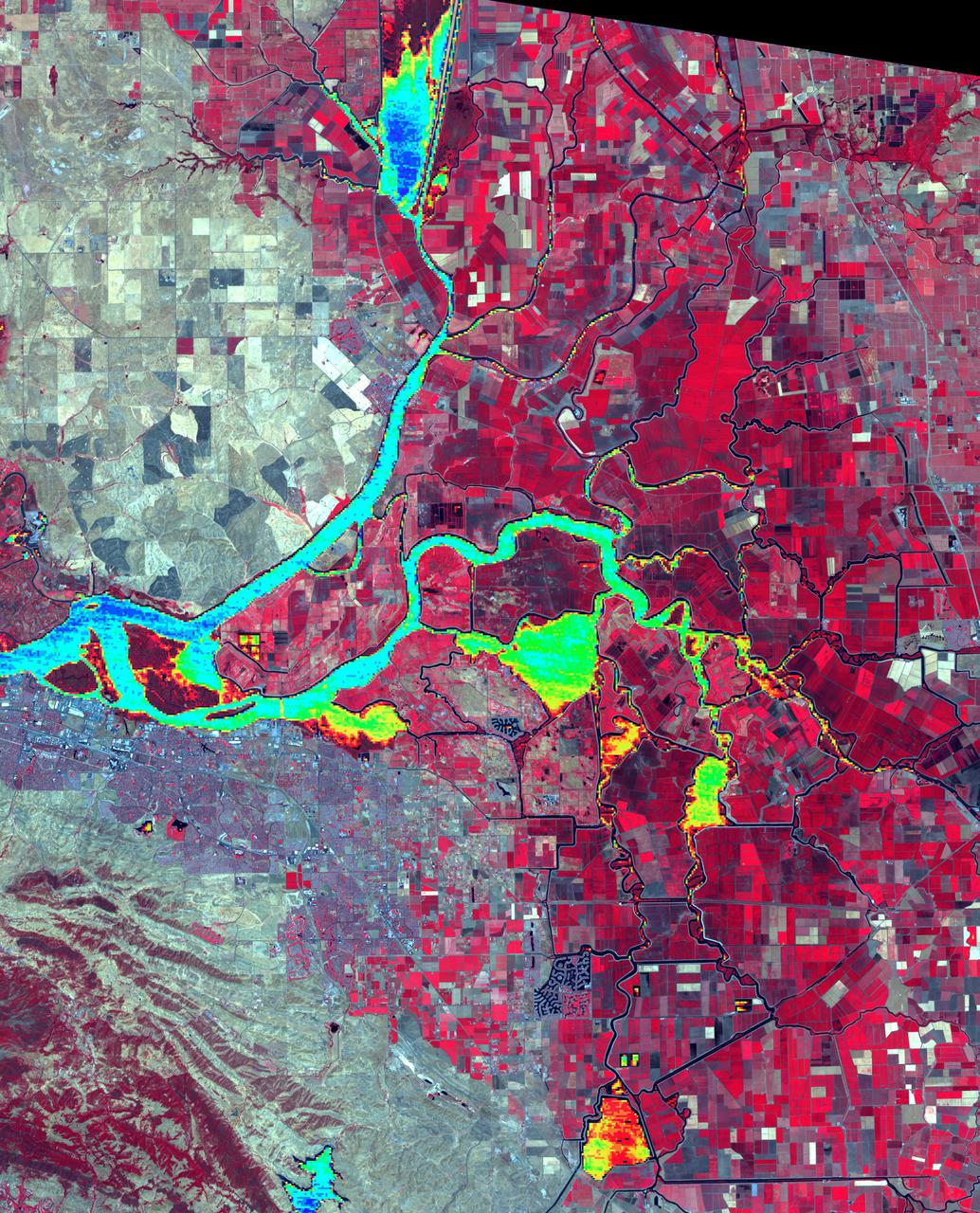
The Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta, CA (or California Delta) has an area of about 3000 km2, and provides a large fraction of all the water used in California. The Delta drains about 50% of the water coming from the Sierra Nevada Mountains, and channels it through San Francisco's Golden Gate to the Pacific Ocean. Thousands of miles of levees now carefully control the Delta's flow, to maximize water use. The image combines a false color infrared composite (with vegetation depicted in red) with a colorized thermal infrared band to show the water temperature for the larger water bodies. Warmer temperatures are red and yellow, cooler water temperatures are blue and green. The image was acquired July 3, 2012, covers an area of 46.5 by 57.5 km, and is located at 38.1 degrees north, 121.3 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24691
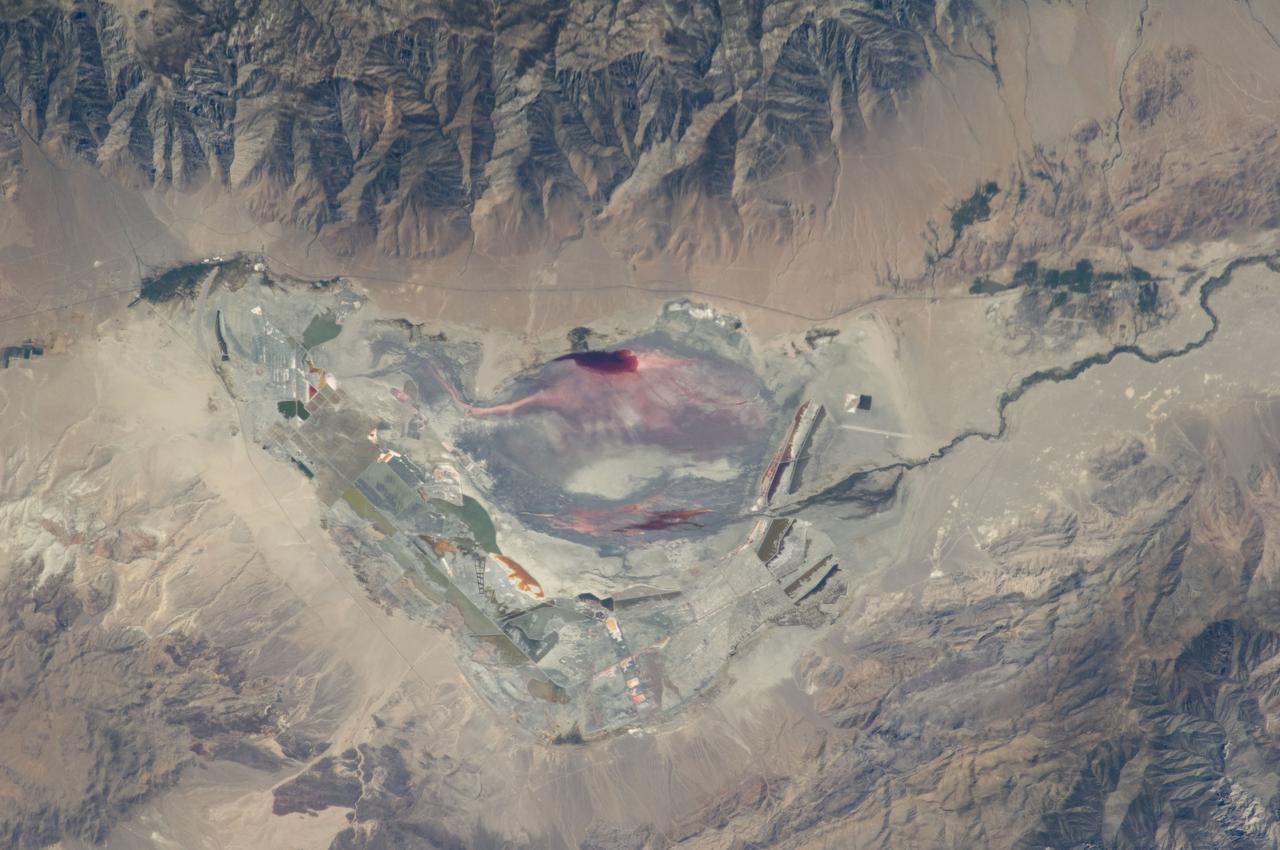

ISS028-E-035137 (30 Aug. 2011) --- Owens Lake in California is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 28 crew member on the International Space Station. This photograph highlights the mostly dry bed of Owens Lake, located in the Owens River Valley between the Inyo Mountains and the Sierra Nevada. Shallow groundwater, springs, and seeps support minor wetlands and a central brine pool. Two bright red areas along the margins of the brine pool indicate the presence of halophilic, or salt-loving organisms known as Achaeans. Grey and white materials within the lake bed are exposed lakebed sediments and salt crusts. The towns of Olancha and Lone Pine are delineated by the presence of green vegetation indicating a more constant availability of water. According to scientists, the present-day Owens Lake was part of a much larger lake and river system that existed during the Pleistocene Epoch (approximately 3 million to approximately 12,000 years ago) along the current northeastern border of California with Nevada. Meltwater from alpine glaciers in the Sierra Nevada filled the regional valleys of the Basin and Range to form several glacial lakes that were ancestral to the now-dry lakebeds (or playas) of Owens, Searles Lake, and China Lake. While Searles and China Lakes dried out due to regional changes to a hotter and drier climate over thousands of years, Owens Lake became desiccated largely due to the diversion of Owens River water in the early 20th century to serve the needs of the City of Los Angeles, CA located 266 kilometers to the south. Following complete desiccation of the lakebed in 1926, significant amounts of windblown dust were produced ? indeed, the term ?Keeler fog? was coined by residents of the now largely abandoned town on the eastern side of Owens Lake due to the dust. In addition to adverse health effects on local residents, dust from Owens Lake has been linked to visibility reduction in nearby national parks, forests, and wilderness areas. Recently, efforts to control dust evolution from the lakebed have been undertaken by the City of Los Angeles.
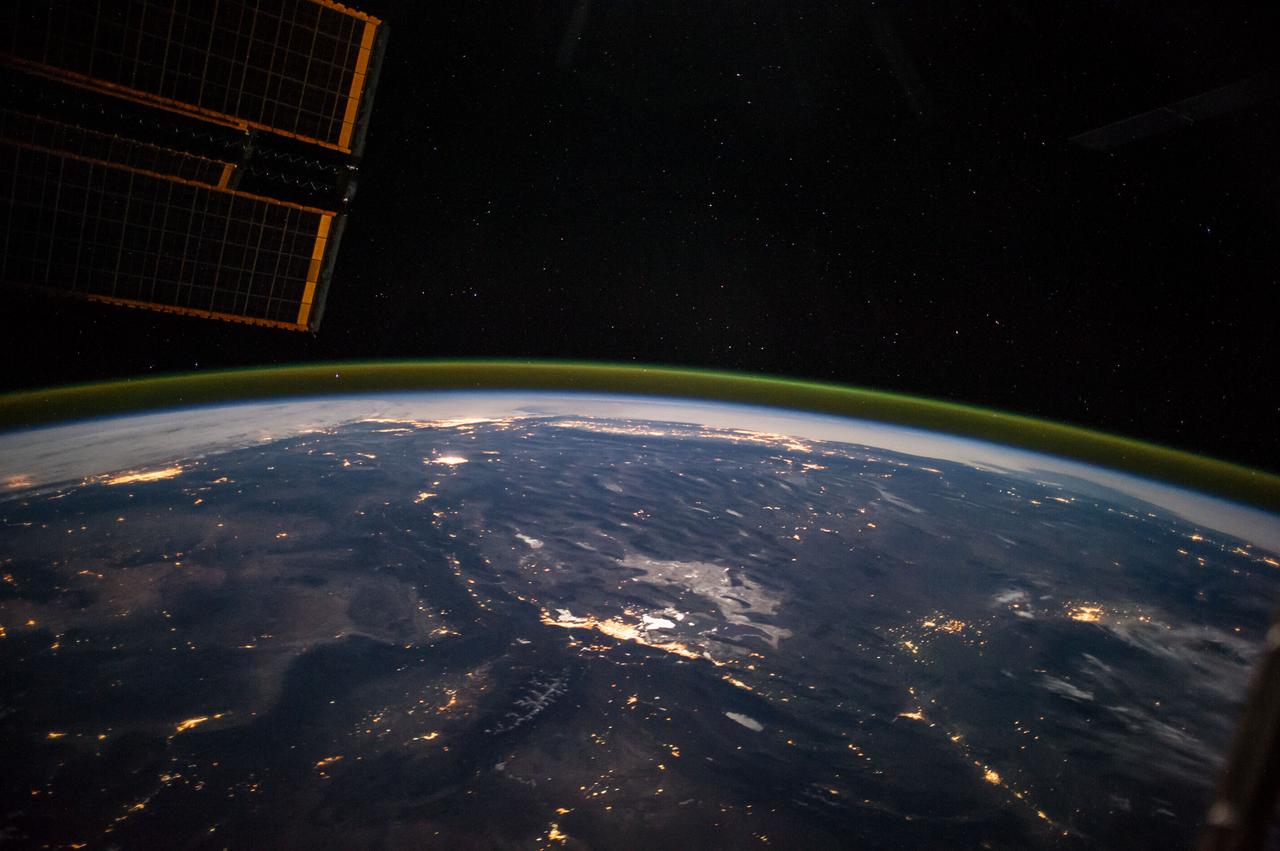

ISS041-E-067595 (6 Oct. 2014) --- This moonlit panorama was shot recently with a wide-angle lens by an Expedition 41 crew member aboard the International Space Station, as they looked southwest from a point over Nebraska. The wide-angle lens shows a huge swath of country that stretches from Portland, Oregon (right) to Phoenix, Arizona (left). The largest string of lights is the Ogden-Salt Lake City-Provo area (lower center) in Utah. The Los Angeles and San Francisco metropolitan regions, and the cities of the central valley of California (Bakersfield to Redding) stretch across the horizon. The green airglow layer always appears in night images. Moonlight shows the red tinge of the space station?s solar arrays top left. Moonlight emphasizes the broader-scale geological zones. Nevada?s short, dark, parallel mountain ranges of the basin and range geological province (center) contrast with the expanses of flat terrain of the Colorado Plateau (left) in Colorado, Arizona, Utah and New Mexico. The near-full moon even reveals the vast dry lake bed known as the Bonneville Salt Flats. The black line of the Sierra Nevada marks the edge of California?s well-lit central valley (directly below the San Francisco Bay area).

ISS013-E-81687 (17 Sept. 2006) --- A forest fire in southern California is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 13 crewmember on the International Space Station. The day fire started in Los Padres National Forest north of Los Angeles on Sept. 4, 2006. Easterly winds on Sept. 17 blew the smoke west out to sea, and this wind shift was observed by station crewmembers. The forested mountains north of Los Angeles appear dark green, the smoke a dusky gray. Dense farmland at the south end of California's central valley is framed by the forested Sierra Nevada mountain range. White patches near the center of the view are dry lakes of the Mojave Desert, one of which acts as a landing site for the space shuttle. The dark irregular shape at image right is part of the space station. Death Valley and Las Vegas are visible at image right. The extent of the day fire smoke plume can be gauged from the gray urban region of greater Los Angeles (center) which stretches along 50 miles of coastline. The plume obscures the northern Channel Islands, but the southern Channel Islands are silhouetted against the ocean.
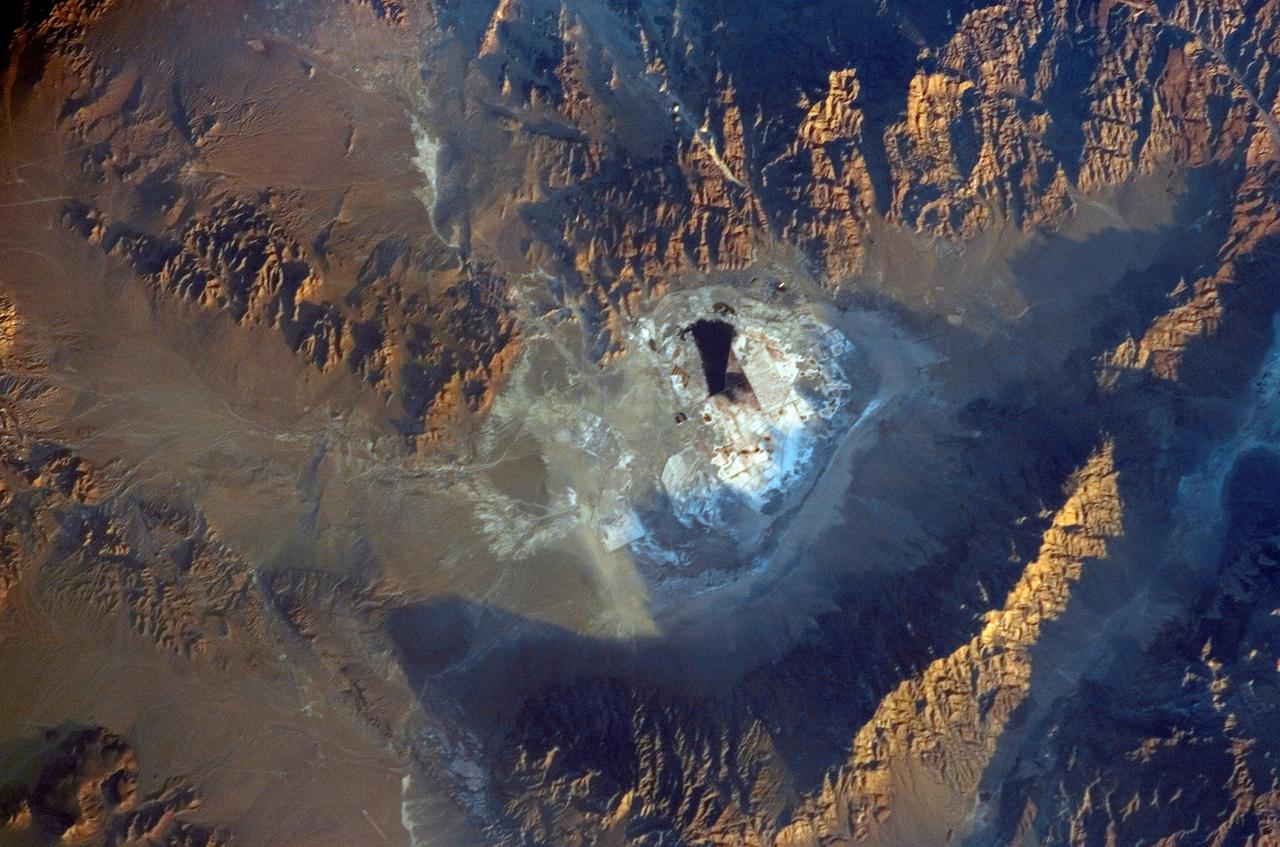

ISS011-E-09680 (27 June 2005) --- Searles Lake, California is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 11 crewmember on the International Space Station. Searles Lake is known for the abundance of rare elements and evaporite minerals, such as trona, hanksite, and halite formed within its sediments. These minerals dissolve in water or very humid environments. According to NASA scientists who are studying the Space Station photography, during the Pleistocene Epoch (beginning approximately two million years ago), Searles Lake was one of a chain of lakes fed by streamflow from the Sierra Nevada to the west. Lake levels rose and fell dependant on glacial outwash from the Sierra Nevada as climates shifted. Successive layers of sediment were deposited as lake levels fluctuated, preserving an important record of regional climate change. The lakes gradually dried up completely as climatic conditions became hotter and drier (as today), forming a string of enclosed basins with no outlets (playas). This photograph depicts the Searles Lake playa (characterized by white surface mineral deposits) bounded by the Argus and Slate Mountains. The width of the playa is approximately 10 kilometers. The center of the image is dominated by mining operations that extract sodium- and potassium-rich minerals (primarily borax and salt) for industrial use. Minerals are primarily in naturally-occurring brines that are pumped to the surface and evaporated to crystallize the minerals. A large evaporation pond (black) is visible in the center of the image. Further processing concentrates the minerals and removes excess water.

Naked peaks, sheltered valleys, snowfields, towering trees, and alpine meadows make up the varied landscape of Sequoia National Park in California. Established as a National Park by Congress on September 25, 1890, Sequoia National Park is the second-oldest U.S. National Park, after Yellowstone. This national park borders Kings Canyon National Park. The Thematic Mapper sensor on NASA’s Landsat 5 satellite captured this true-color image of Sequoia National Park, outlined in white, on October 22, 2008. Sunlight illuminates southern slopes, leaving northern faces in shadow in this autumn image. In the west, deep green conifers carpet most of the land. These forested mountains are home to the park’s most famous giant sequoia trees. Sequoia National Park sits at the southern end of the Sierra Nevada mountains. Terrain alternates between extremes, from peaks such as Mt. Whitney—the highest peak in the contiguous United States—to deep caverns. The rivers and lakes in this region are part of a watershed valuable not only to the plants and animals of the park, but also to farms and cities in California’s Central Valley. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2bzGOXr" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2bzGOXr</a> Credit: NASA/Landsat5 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
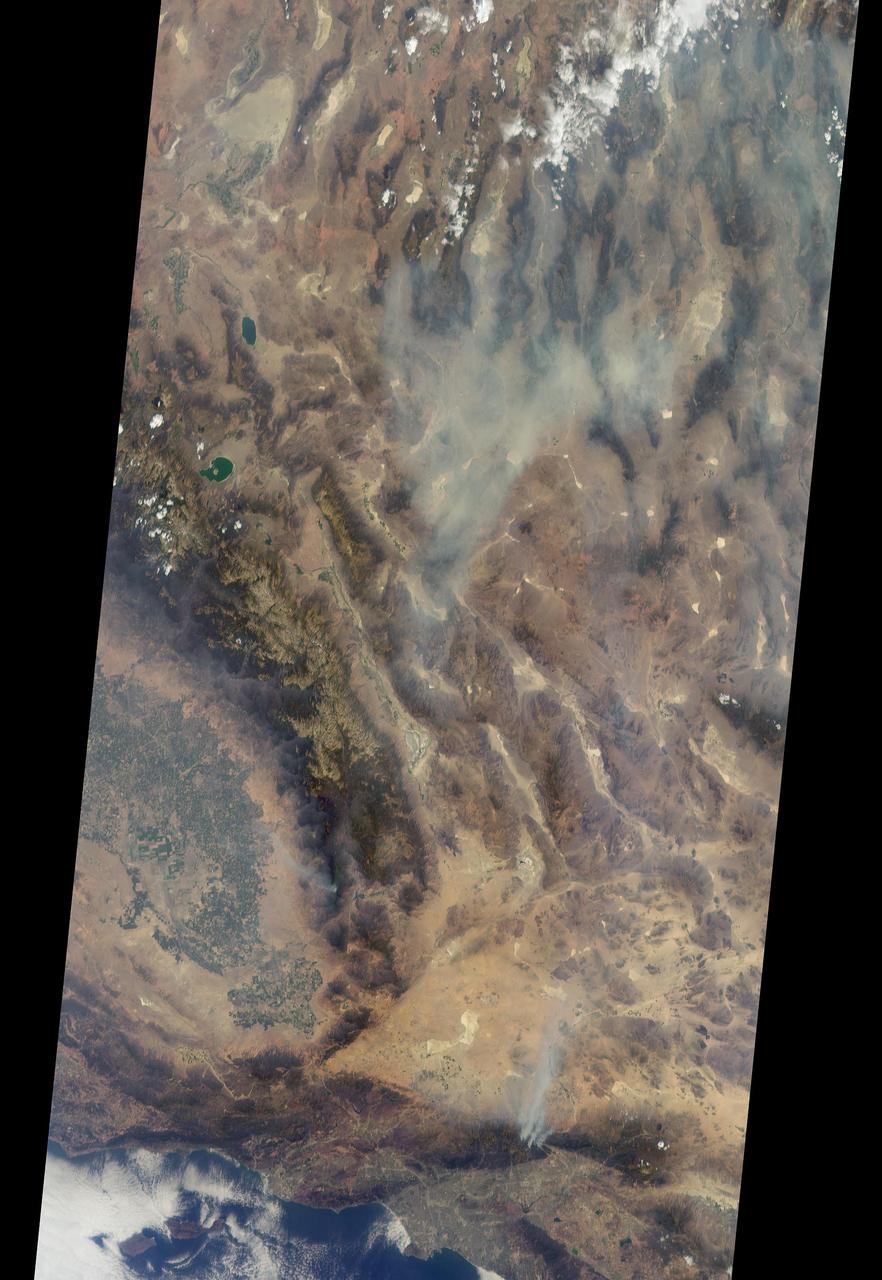

On Aug. 16, 2016, at around 10:30 a.m., a brush fire ignited in the Cajon Pass east of Los Angeles, just to the west of Interstate 15. Within a matter of hours, extreme temperatures, high winds and low humidity allowed the fire to spread rapidly, burning through brush left tinder-dry by years of drought. Firefighters quickly responded, ordering the evacuation of about 83,000 people in and around the Cajon Pass, Wrightwood, Lytle Creek, Oak Hills and surrounding areas. An as-yet uncounted number of homes and structures have burned, and Interstate 15 remains closed to downed power lines and barrier damage. By Aug. 17, the fire had expanded to more than 30,000 acres and remains zero percent contained as some 1,300 firefighters continue to battle to save homes and evacuate residents. The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite passed over the region on Aug. 17 around 11:50 a.m. PDT and captured this natural-color image from MISR's 70-degree forward-viewing camera, which covers an areas about 257 miles (414 kilometers) wide. The oblique view angle makes the smoke more apparent than it would be in a more conventional vertical view. The Los Angeles metropolitan area is the large gray area on the coast in the center of the image. Three plumes from the Blue Cut Fire are clearly visible in the mountains to the north. This oblique view also shows an enormous cloud of smoke spreading northeastward over a significant portion of eastern California and Nevada. This smoke probably originated from the fire as it consumed almost 20,000 acres on the evening of the 16th and traveled north overnight. Also visible from this oblique view is considerable haziness filling California's Central Valley, to the northwest of the Blue Cut Fire. This haziness is most likely due to smoke from several other fires burning in California, including the Soberanes Fire near Monterey, the Clayton Fire that has destroyed 175 structures north of San Francisco, the Chimney Fire and the Cedar Fire, which is visible in the image in the southern Sierra Nevada. The total number of acres burned in California this year has tripled in just the past week. The 3D stereo anaglyph is made by combining data from MISR's 60-degree and 70-degree forward-viewing cameras. You will need red-blue glasses to view the 3D effect (ensure the red lens is over your left eye). In order to enable stereo viewing, the image has been rotated so north is to the left. These data were acquired during Terra orbit 88648. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20888
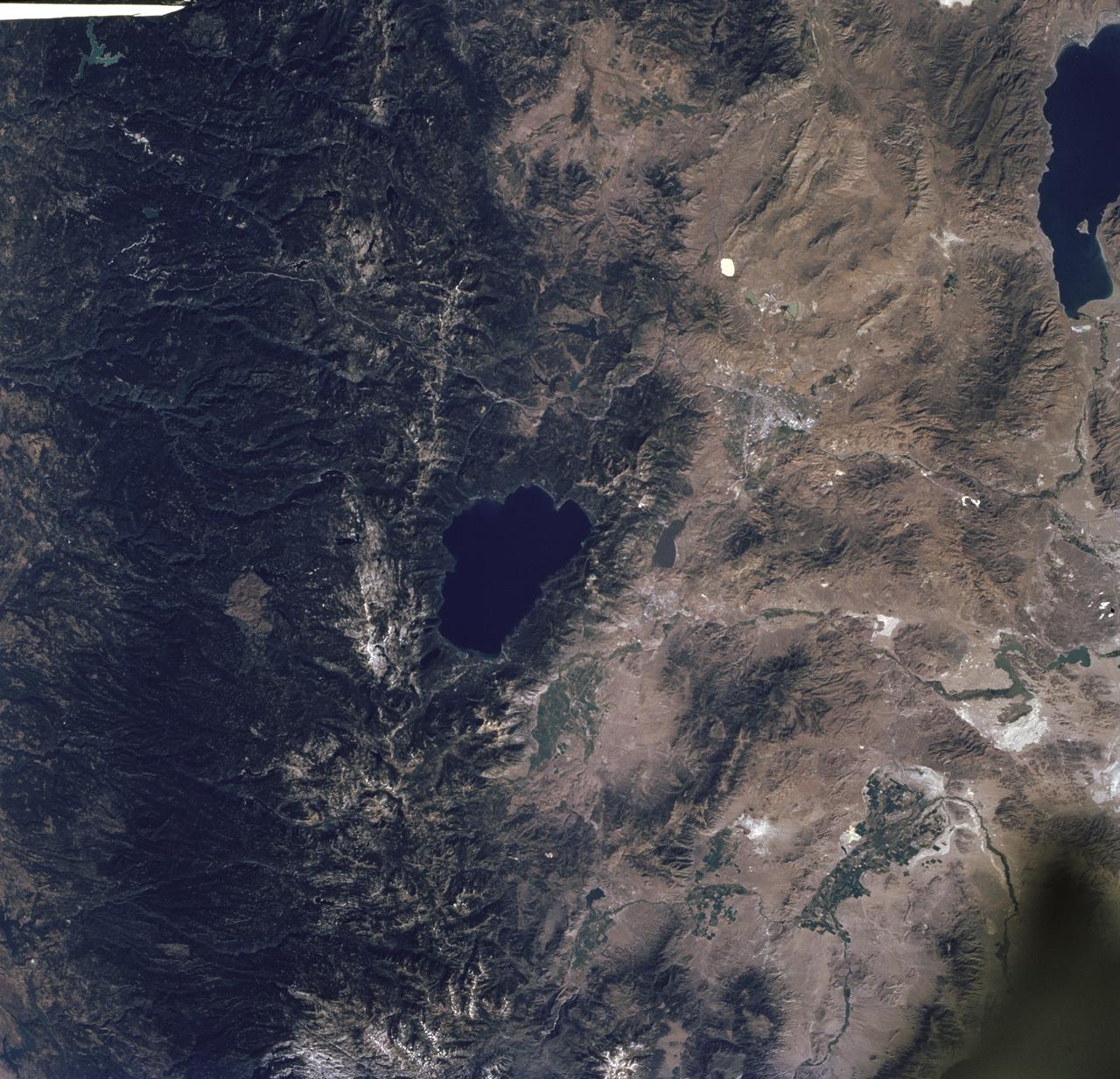

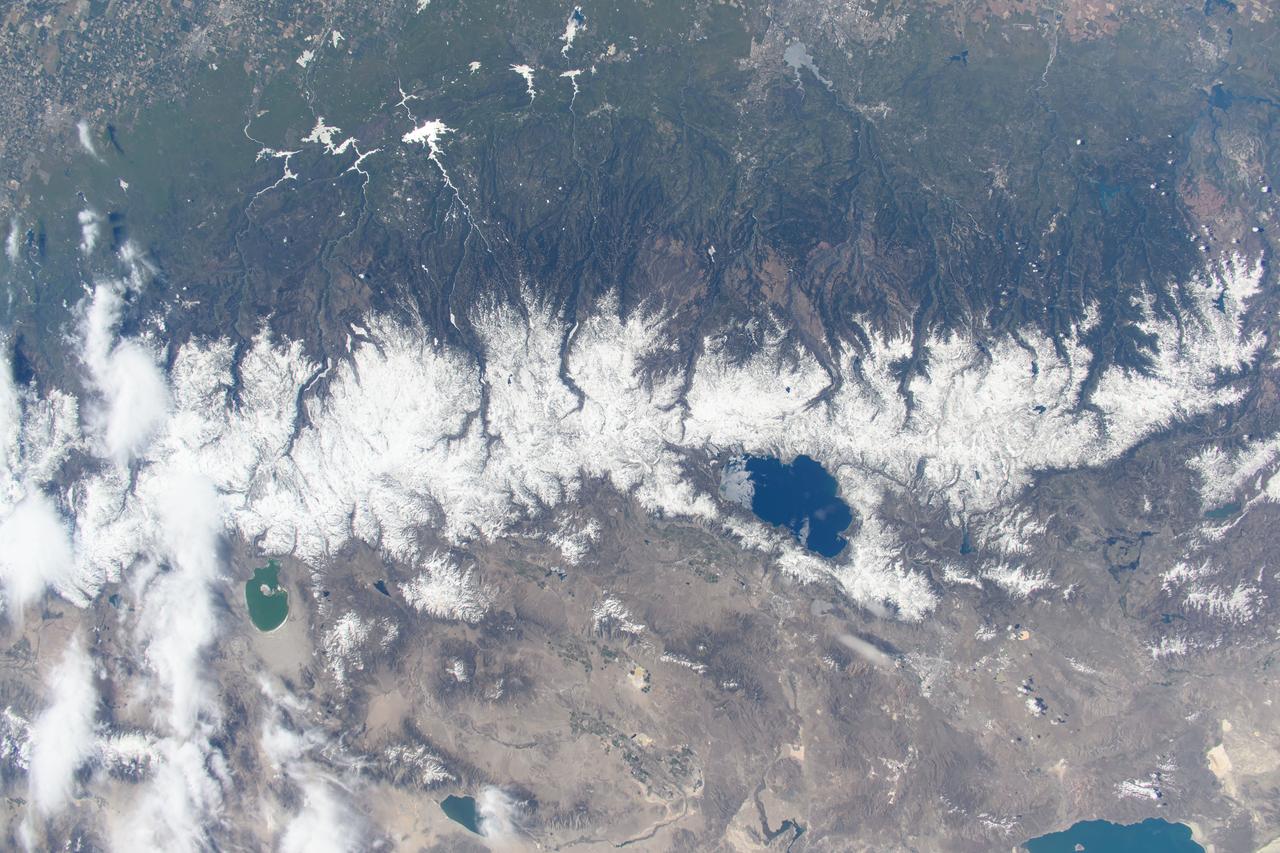
STS085-716-061 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- The dark green forests of the Sierra Nevada Mts. occupy the left side of the picture. Reno lies between Lake Tahoe (center) and Pyramid Lake (top right). Lake Tahoe, is a clear, deep alpine lake (over 505 meters deep), surrounded by Montane forest, ski resorts and casinos. Although Tahoe is known as one of the clearest lakes in the world, water quality in the lake has been declining due to soil erosion from development. Since 1968, it has lost about 30 feet of clarity. A partnership was recently formed between environmentalists and resort owners to protect their common interest in keeping the lake as clear as possible. Over the last five years they have slowed the erosion and the growth of algae that it causes so that clarity is now "only" lost at a rate of roughly one foot per year. Pyramid Lake (on the upper right of the photo) is as different from Tahoe as a lake could be. The sagebrush desert around the lake and is owned by the Pyramid Lake Paiute tribe who manage it as a fishery for an endangered sucker (fish), the cui-cui. The tribe has added modern fisheries' biology methods to their traditional management and chooses not to develop the lake as a recreation destination. Anaho Island, in the lower half of the lake, is a wildlife refuge managed for American White Pelicans which fly hundreds of miles each day to get from this safe breeding area to the shallow marshes where they feed. Directly above Lake Tahoe is Donner pass, near the site where the beleaguered Donner Party spent the winter of 1846 - 1847 trapped in the mountains. Several shallow ephemeral lakes can be seen in Lemmon Valley north of Reno's core urban area. These lakes would normally have dried up by August when this photo was taken, but are still wet because of the extremely wet winter and floods of January 1997.