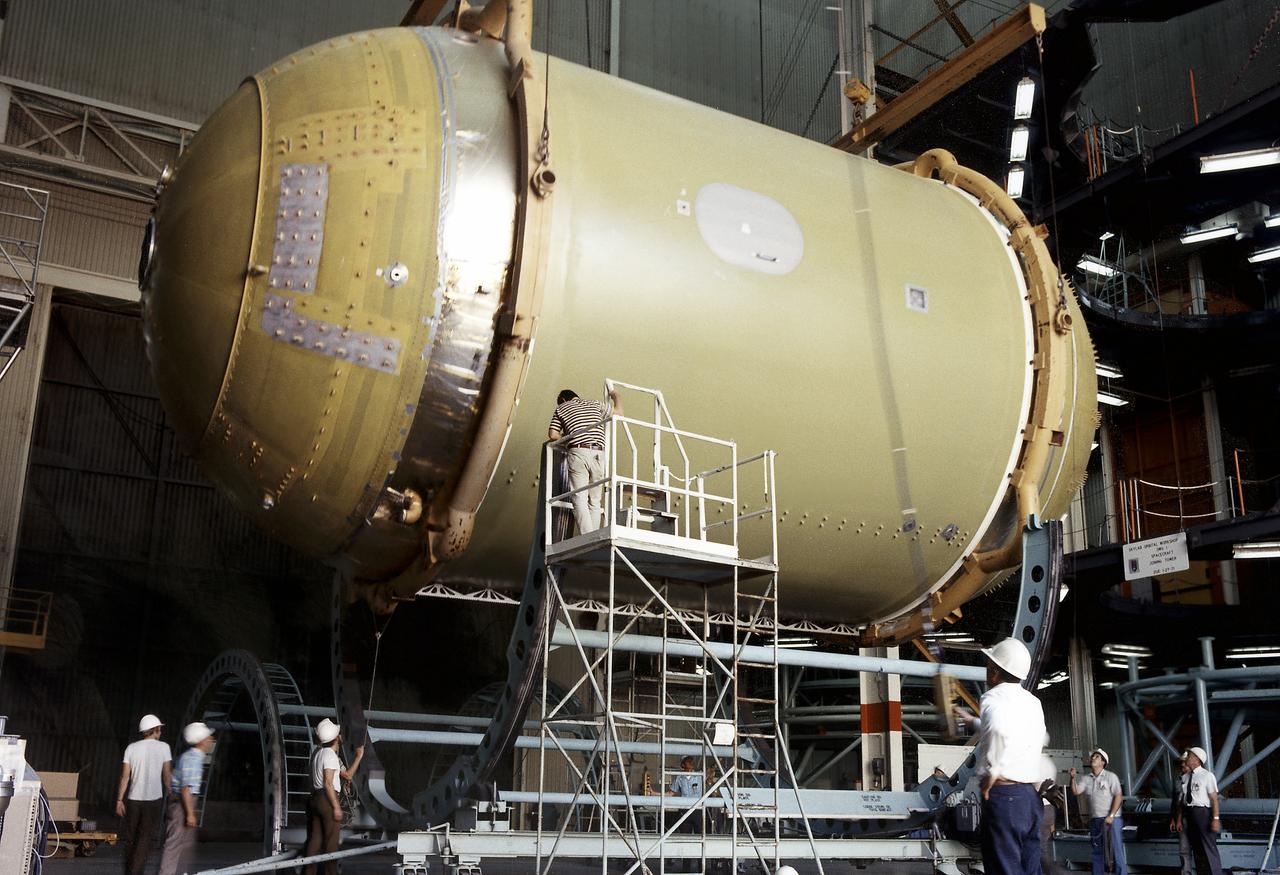

This photographs shows technicians positioning the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) on a rotating work dolly during the assembly phase of the OWS at the McDornell Douglas facility in California. The OWS was the living and working quarters for the astronauts. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments.
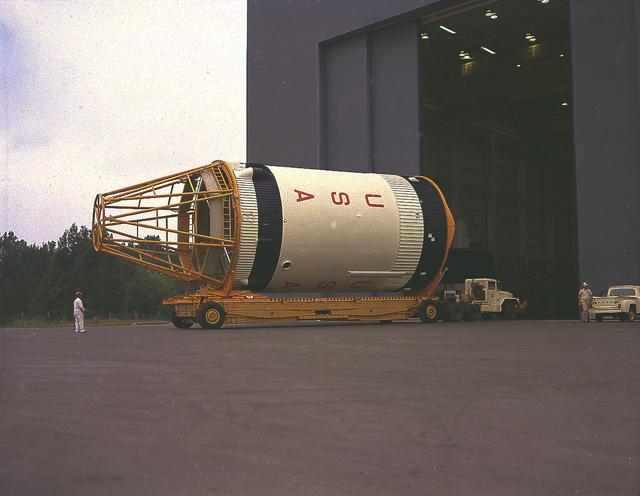

This September 1967 photograph shows workmen removing a mockup of the Saturn V S-IVB stage that housed the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) from the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), building 4755. The mockup was shipped to McDornell Douglas in Huntington, California for design modifications. NASA used the mockup as an engineering design tool to plan structures, equipment, and experiments for Skylab, an orbiting space laboratory. The MSFC had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments, including the OWS.

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image shows the sun-ravaged skin of the Orbital Workshop, bared by the missing heat shield, with blister scars and tarnish from temperatures that reached 300 degrees F. The rectangular opening at the upper center is the scientific airlock through which the parasol to protect the workshop from sun's rays was later deployed. This view was taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew. The Marshall Space Flight Center had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.
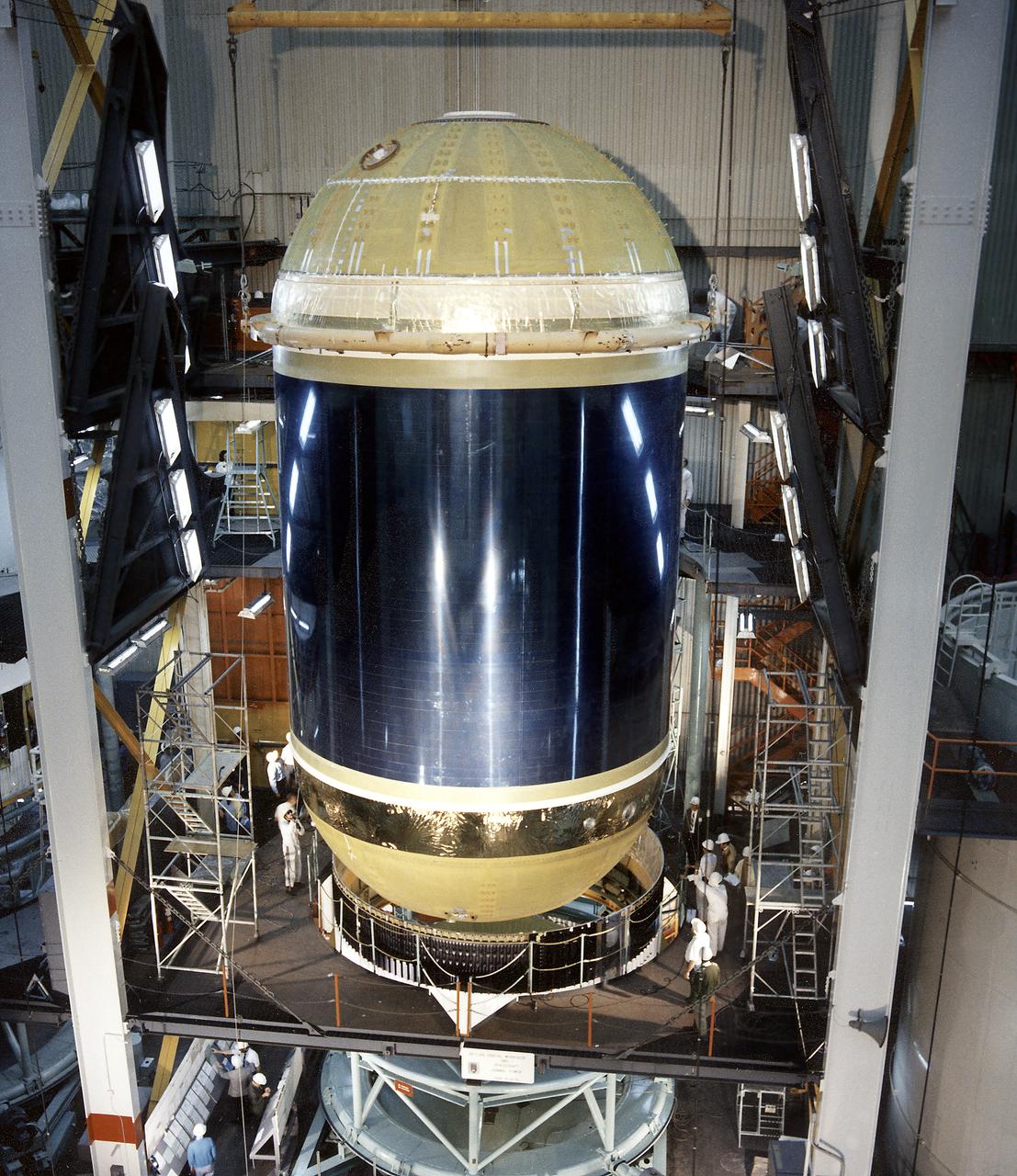
Assembling activities of the Skylab cluster are shown in this photograph. The Orbital Workshop (OWS) was lowered for joining to aft skirt and placed over the thrust structure inside the assembly tower. The OWS provided living and working quarters for the Skylab crew and the thruster provided short-term attitude control of the Skylab. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibilities for the design and development of the Skylab hardware, and management of experiments.
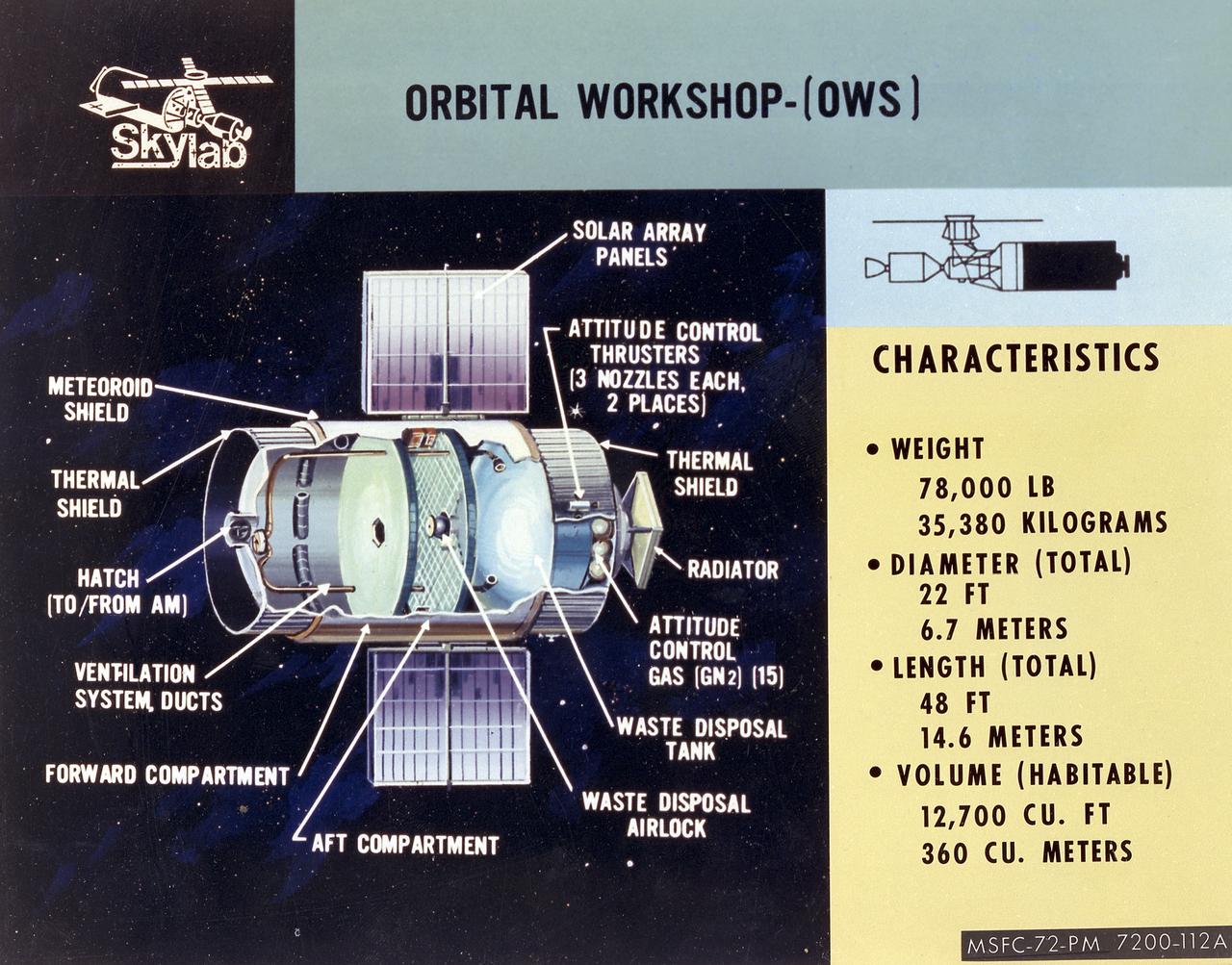
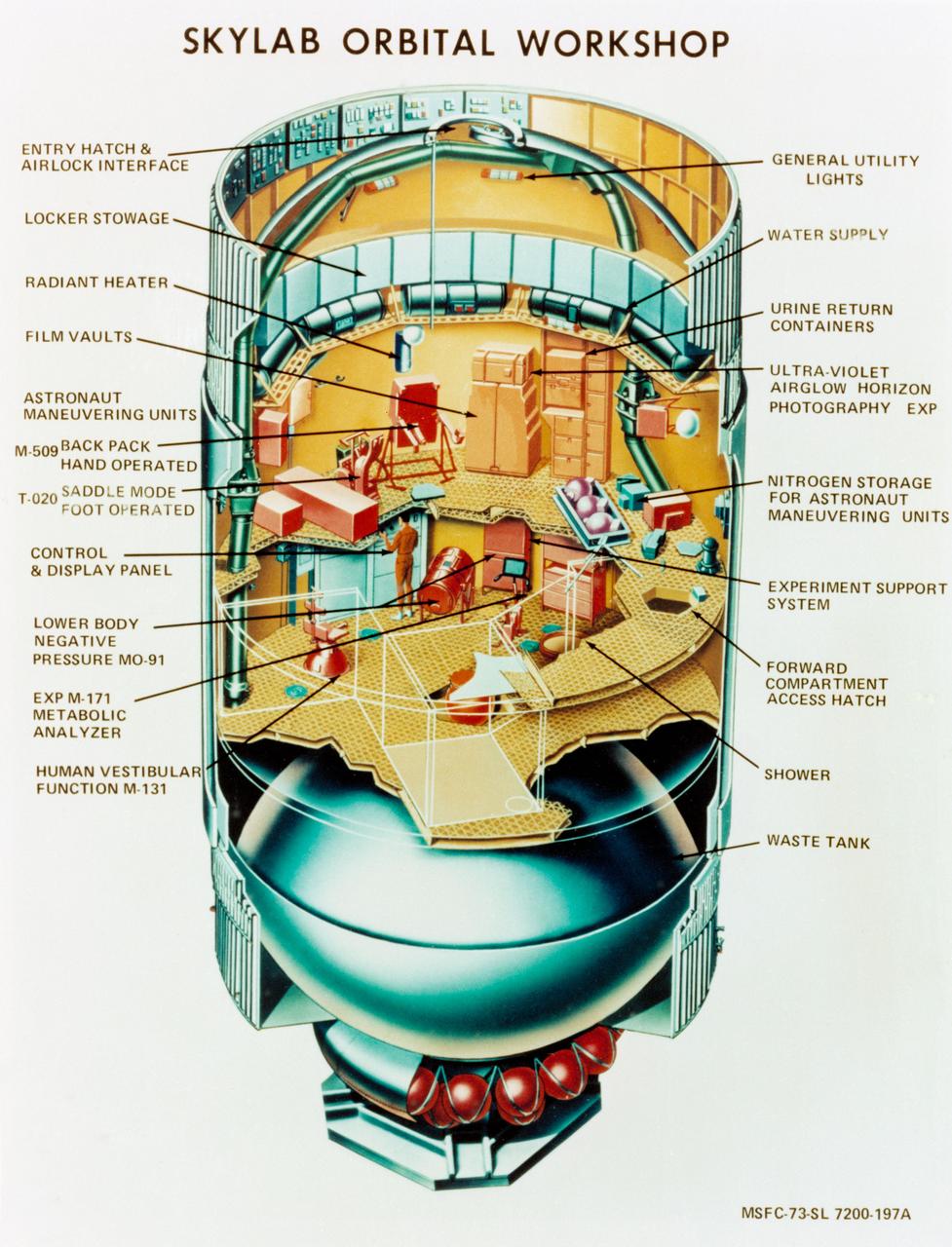
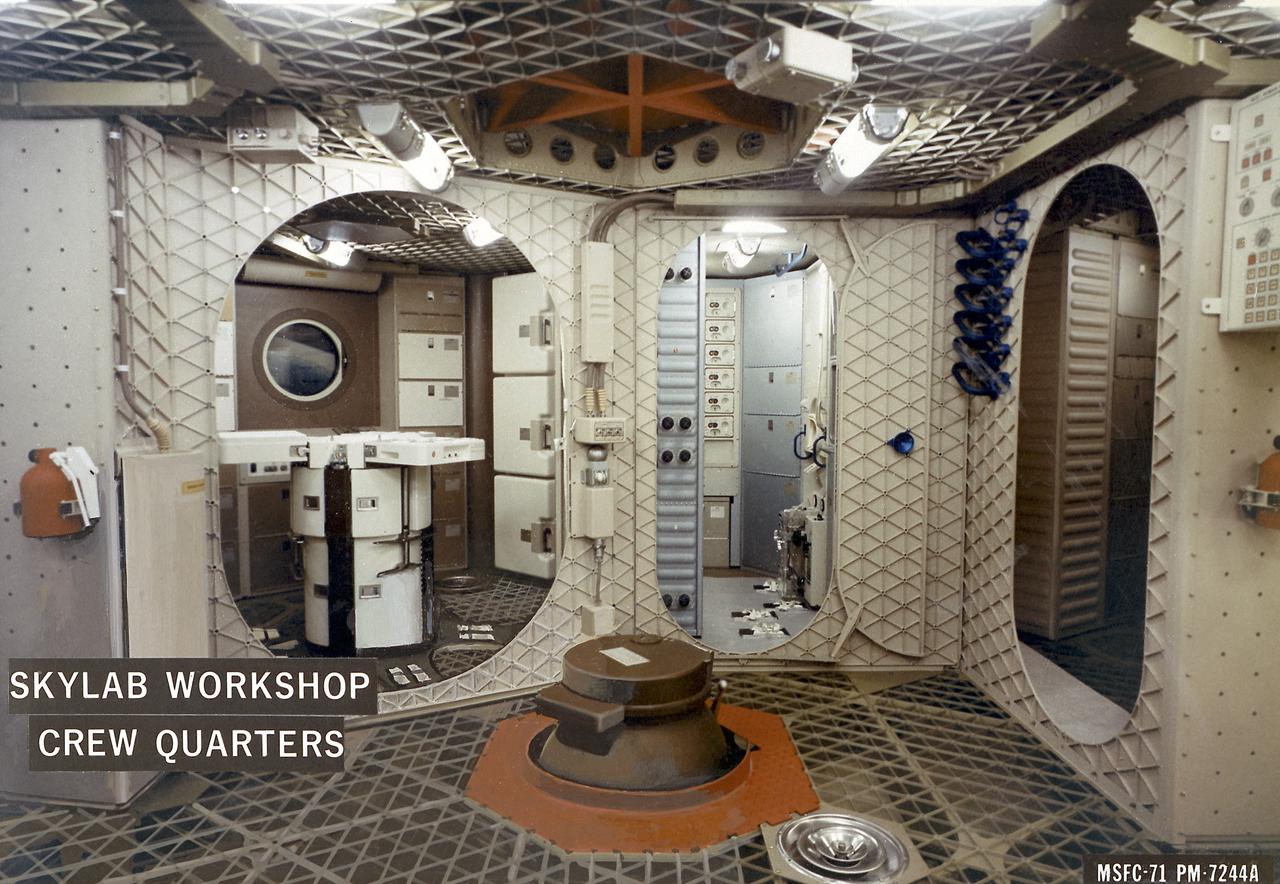
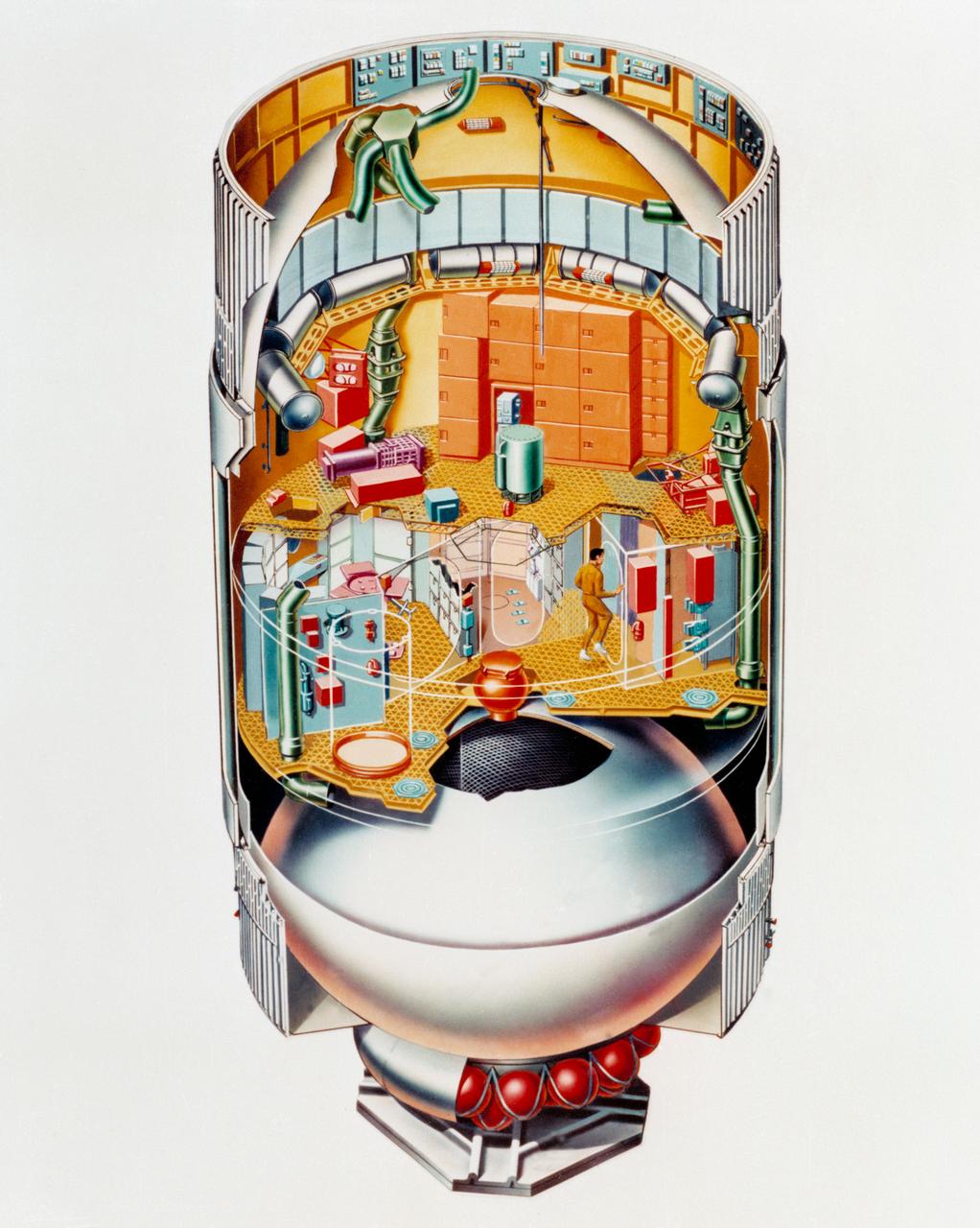
This cutaway illustration shows the characteristics and basic elements of the Skylab Orbiter Workshop (OWS). The OWS was divided into two major compartments. The lower level provided crew accommodations for sleeping, food preparation and consumption, hygiene, waste processing and disposal, and performance of certain experiments. The upper level consisted of a large work area and housed water storage tanks, a food freezer, storage vaults for film, scientific airlocks, mobility and stability experiment equipment, and other experimental equipment. The compartment below the crew quarters was a container for liquid and solid waste and trash accumulated throughout the mission. A solar array, consisting of two wings covered on one side with solar cells, was mounted outside the workshop to generate electrical power to augment the power generated by another solar array mounted on the solar observatory. Thrusters were provided at one end of the workshop for short-term control of the attitude of the space station.
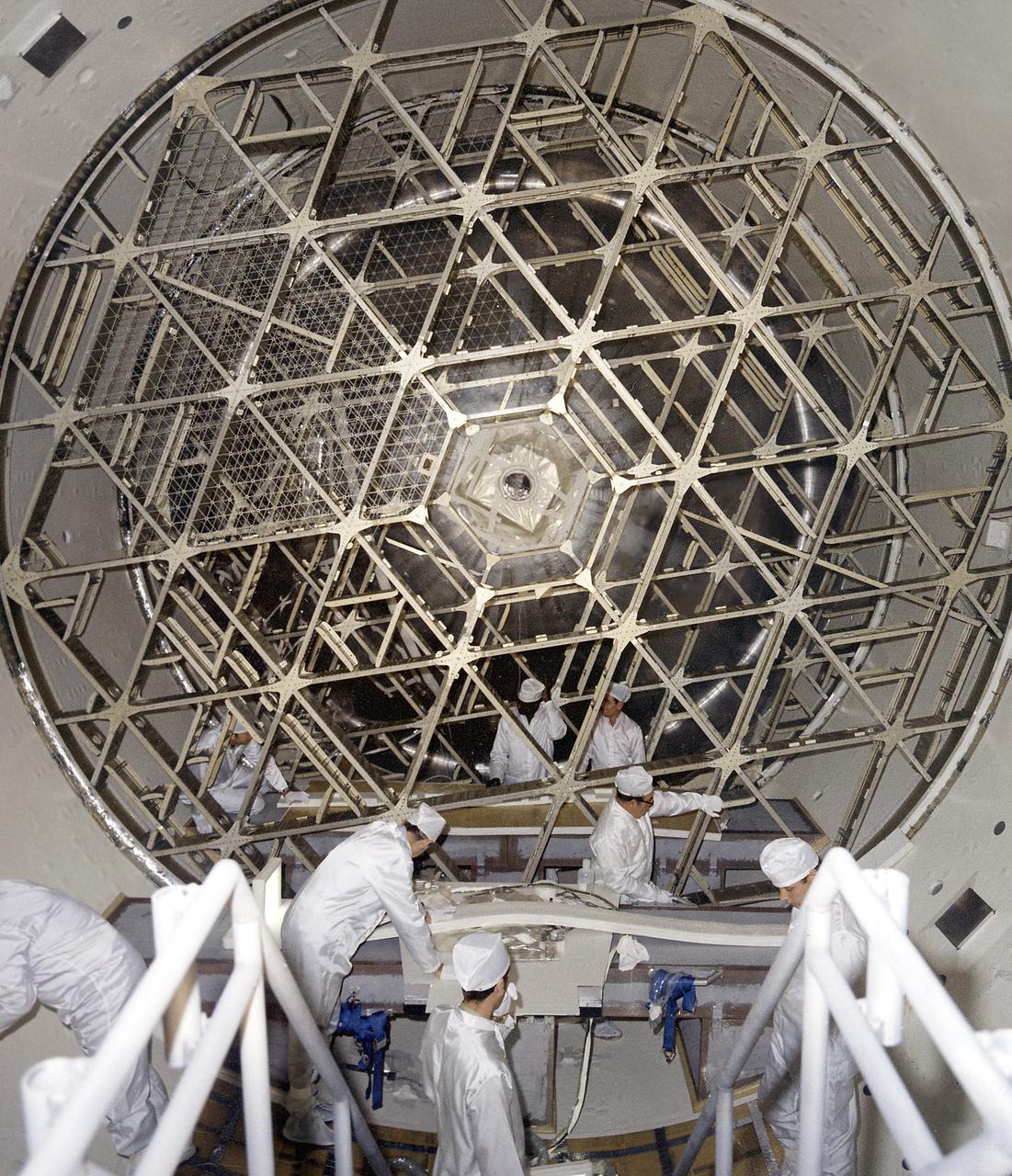

This photograph was taken during installation of floor grids on the upper and lower floors inside the Skylab Orbital Workshop at the McDornell Douglas plant at Huntington Beach, California. The OWS was divided into two major compartments. The lower level provided crew accommodations for sleeping, food preparation and consumption, hygiene, waste processing and disposal, and performance of certain experiments. The upper level consisted of a large work area and housed water storage tanks, a food freezer, storage vaults for film, scientific airlocks, mobility and stability experiment equipment, and other experimental equipment.
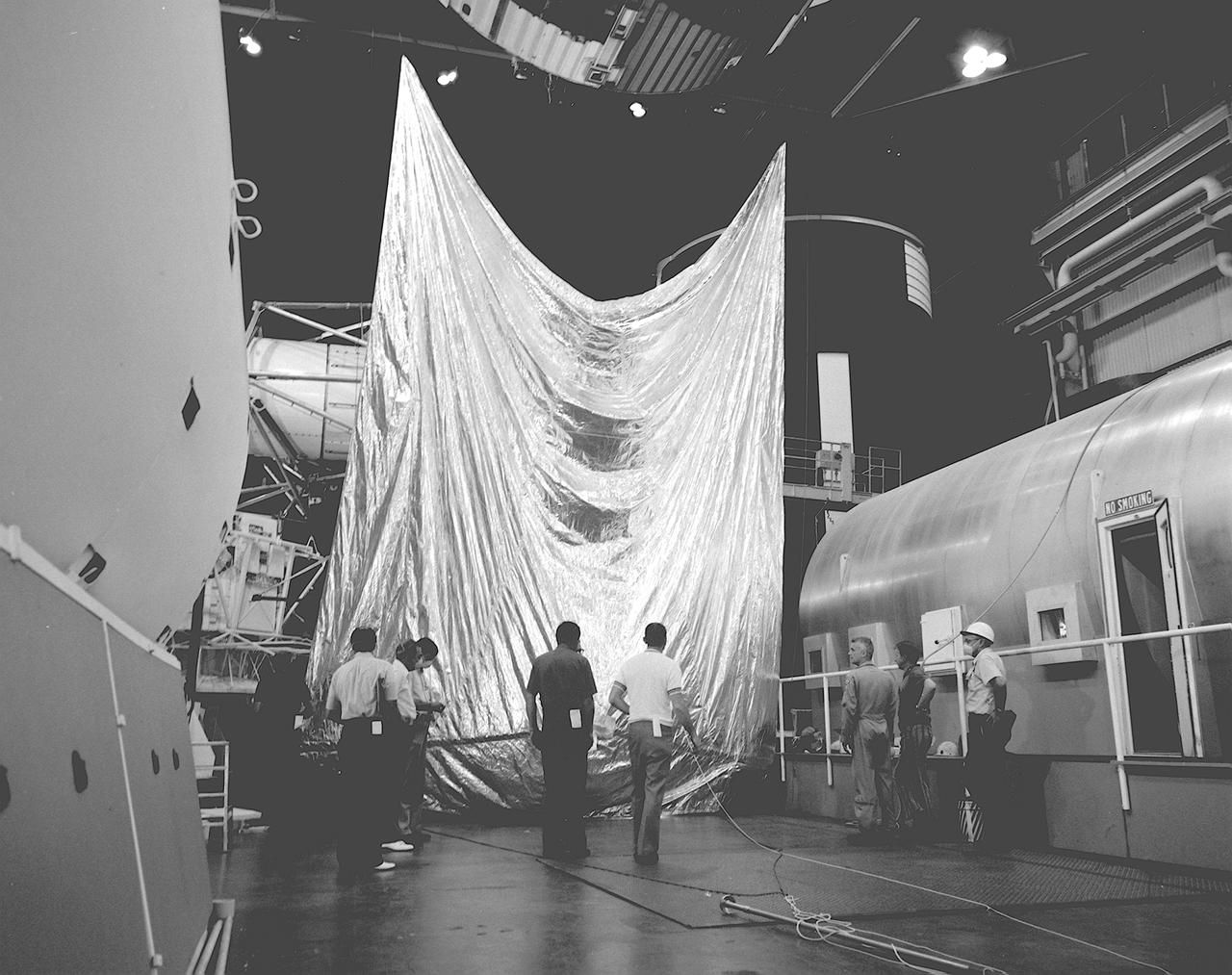

Engineers from the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and its contractors were testing the twin-pole sunshade at the Skylab mockup in the MSFC Building 4619. The Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) lost its thermal protection shield during launch on May 14, 1963. Without the heat shield, the temperature inside the OWS became dangerously high, rendering the workshop uninhabitable and threatened deterioration of the interior insulation and adhesive. Engineers from the MSFC, its contractors, and NASA persornel at other centers worked day and night for several days to develop the way to save the Skylab OWS. Eventually, they developed, tested, rehearsed, and approved three repair options. These options included a parasol sunshade and a twin-pole sunshade to restore the temperature inside the workshop, and a set of metal cutting tools to free the jammed solar panel.
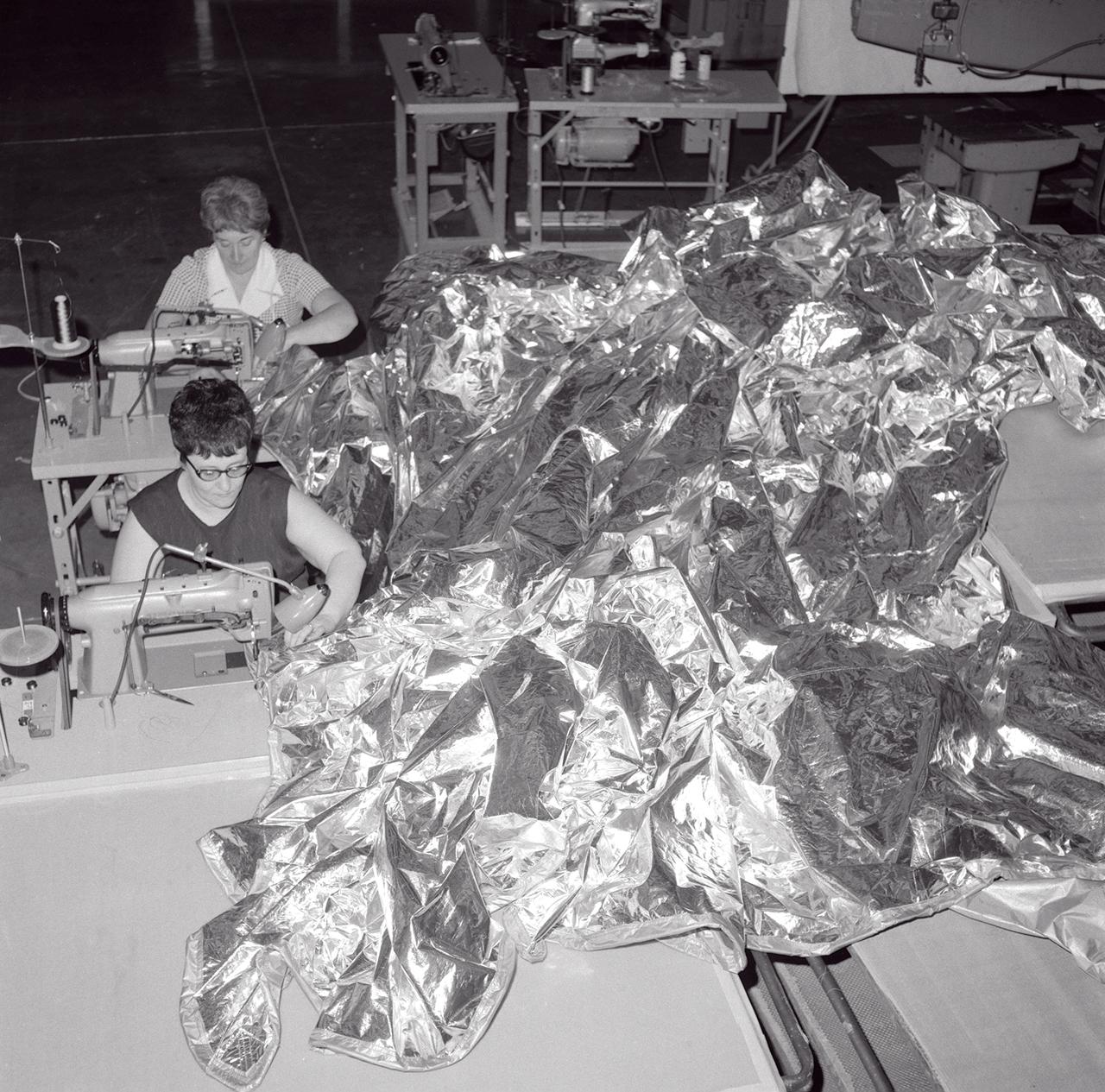

Two seamstresses stitch together a sun-shade for Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS), the first U.S. experimental space station in orbit, which lost its thermal protection shield during the launch on May 14, 1973. Without the heat shield, the temperature inside the Orbital Workshop became dangerously high, rendering the workshop uninhabitable and threatened deterioration of the interior insulation and adhesive. Engineers and scientists at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) worked tirelessly around the clock on the emergency repair procedure. The Skylab crew and the repair kits were launched just 11 days after the incident. The crew successfully deployed the twin-pole sail parasol sun-shade during their EVA (Extravehicular Activity) the next day.
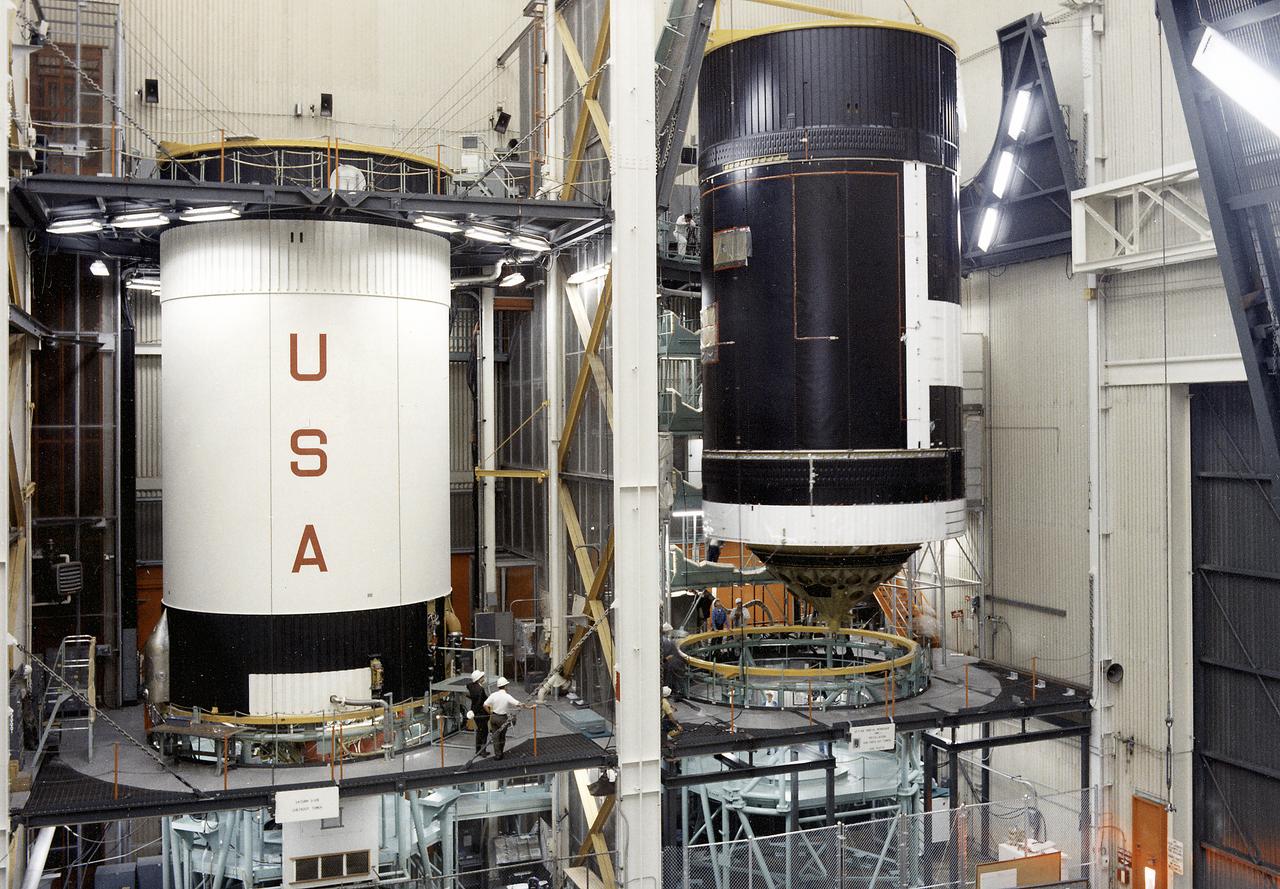
This photograph shows activities during assembly of the Skylab cluster at the Vehicle Assembly/Checkout building. The Saturn V S-IVB stage is shown at left, and right is the Orbital Workshop (OWS) being readied for mating to the thruster. The S-IVB stage was modified to house the OWS, which provided living and working quarters for the Skylab crews. The Marshall Space Flight Center had responsibilities for the design and development of the Skylab hardware, and management of experiments.
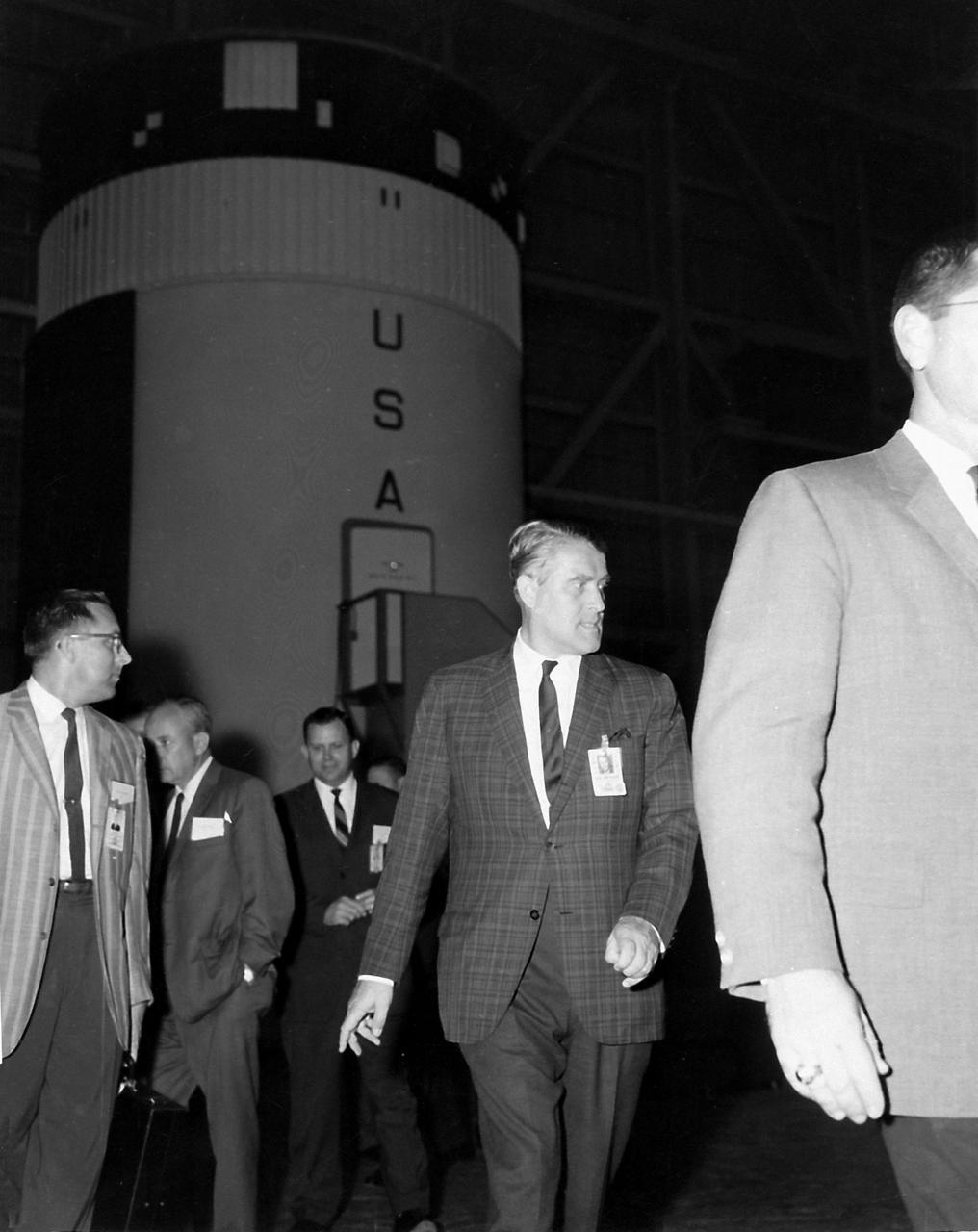

MSFC Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun is photographed inspecting a mockup of the Skylab Orbital Workshop, a major project at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in 1967. The mockup would be used as an engineering tool to design structures, equipment and experiments for an initial mission expected to last twenty-eight days. The workshop was intended to serve as America's first Space Station.
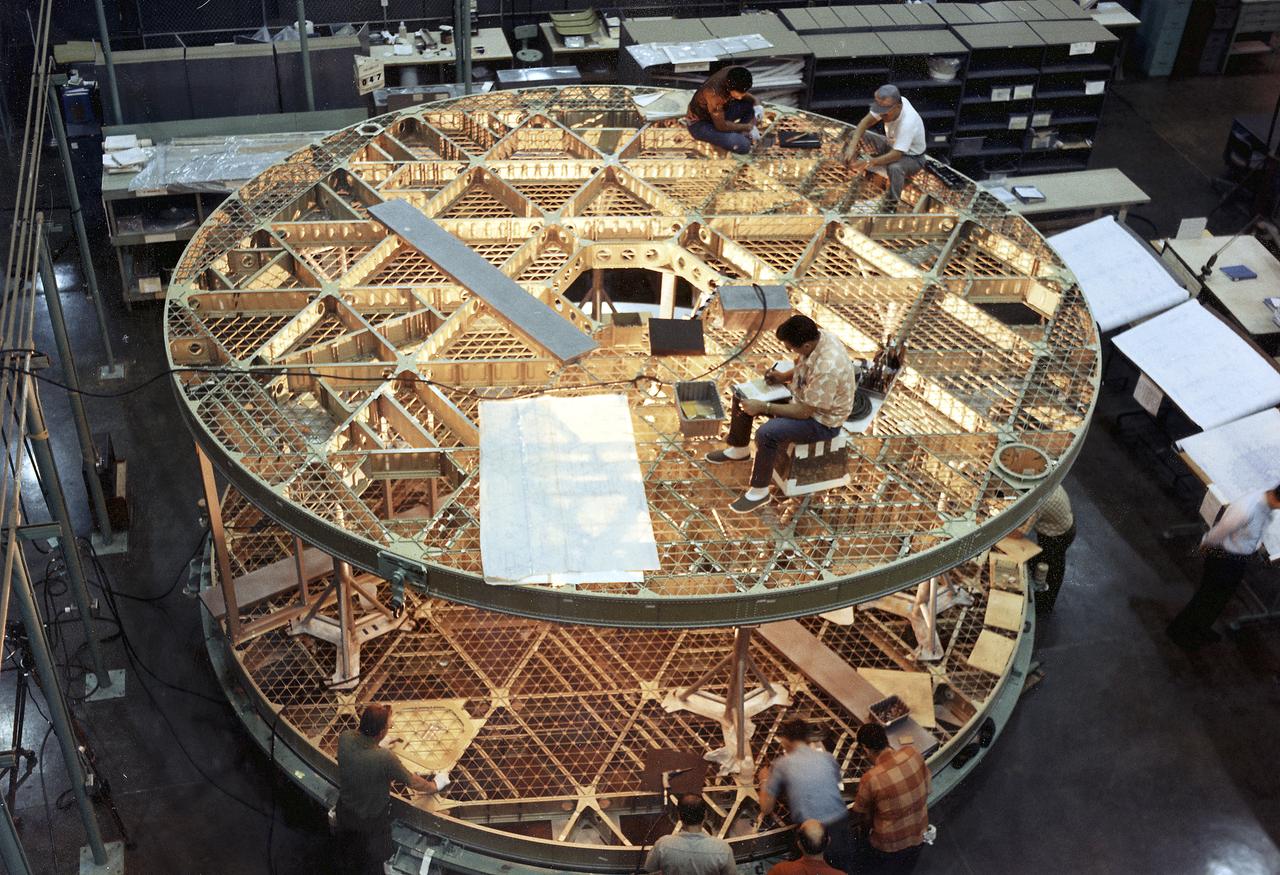
This photograph was taken during assembly of the bottom and upper floors of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS). The OWS was divided into two major compartments. The lower level provided crew accommodations for sleeping, food preparation and consumption, hygiene, waste processing and disposal, and performance of certain experiments. The upper level consisted of a large work area and housed water storage tanks, a food freezer, storage vaults for film, scientific airlocks, mobility and stability experiment equipment, and other experimental equipment.
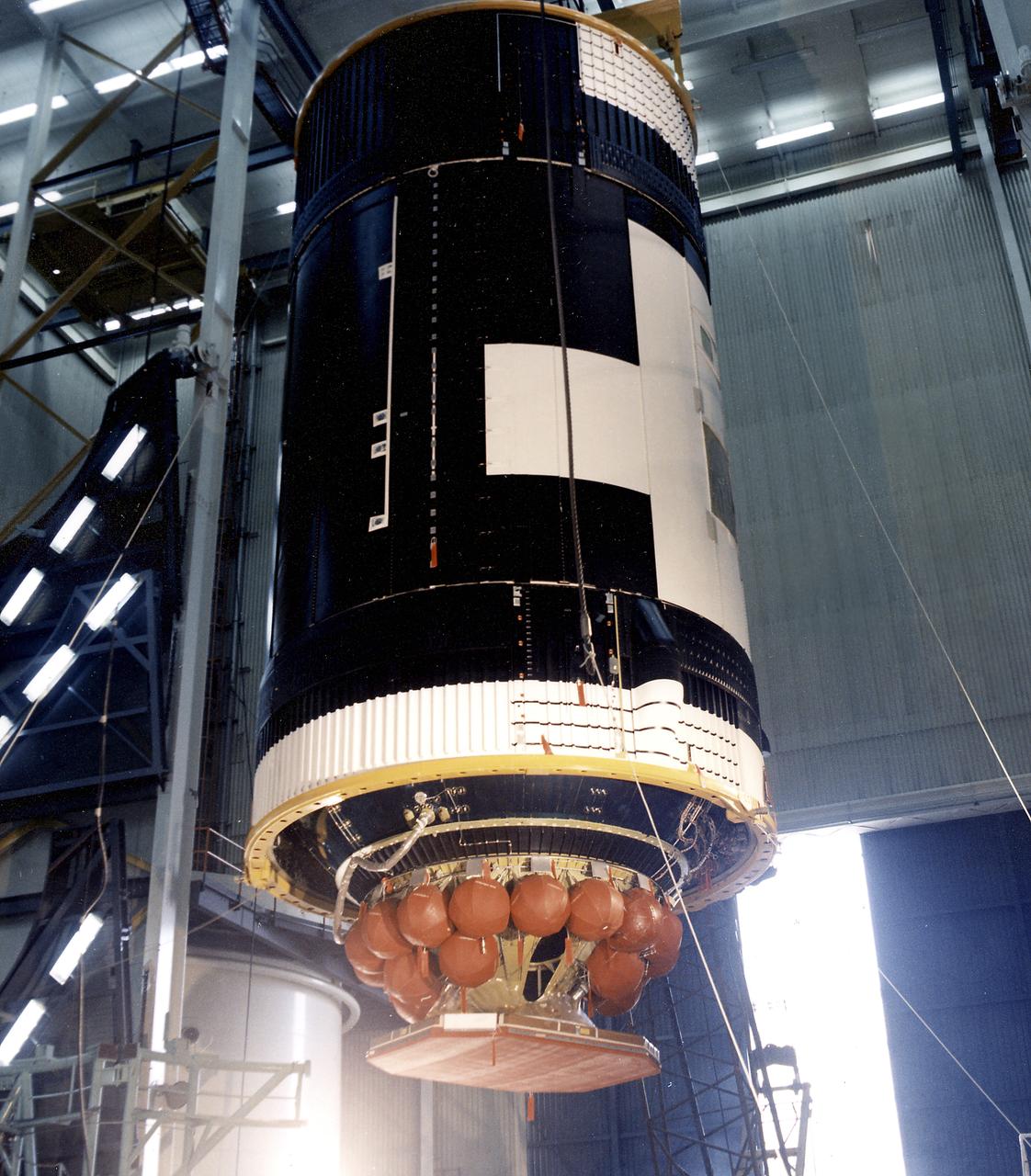
This photograph shows the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) assembled, with its Thruster Attitude Control System (TACS) and radiator, ready for placing on the transporter. Twenty-two titanium spheres above the radiator housed the nitrogen required for operation of the TACS. At one end of the OWS, the TACS provided short-term control of the attitude of the Skylab.
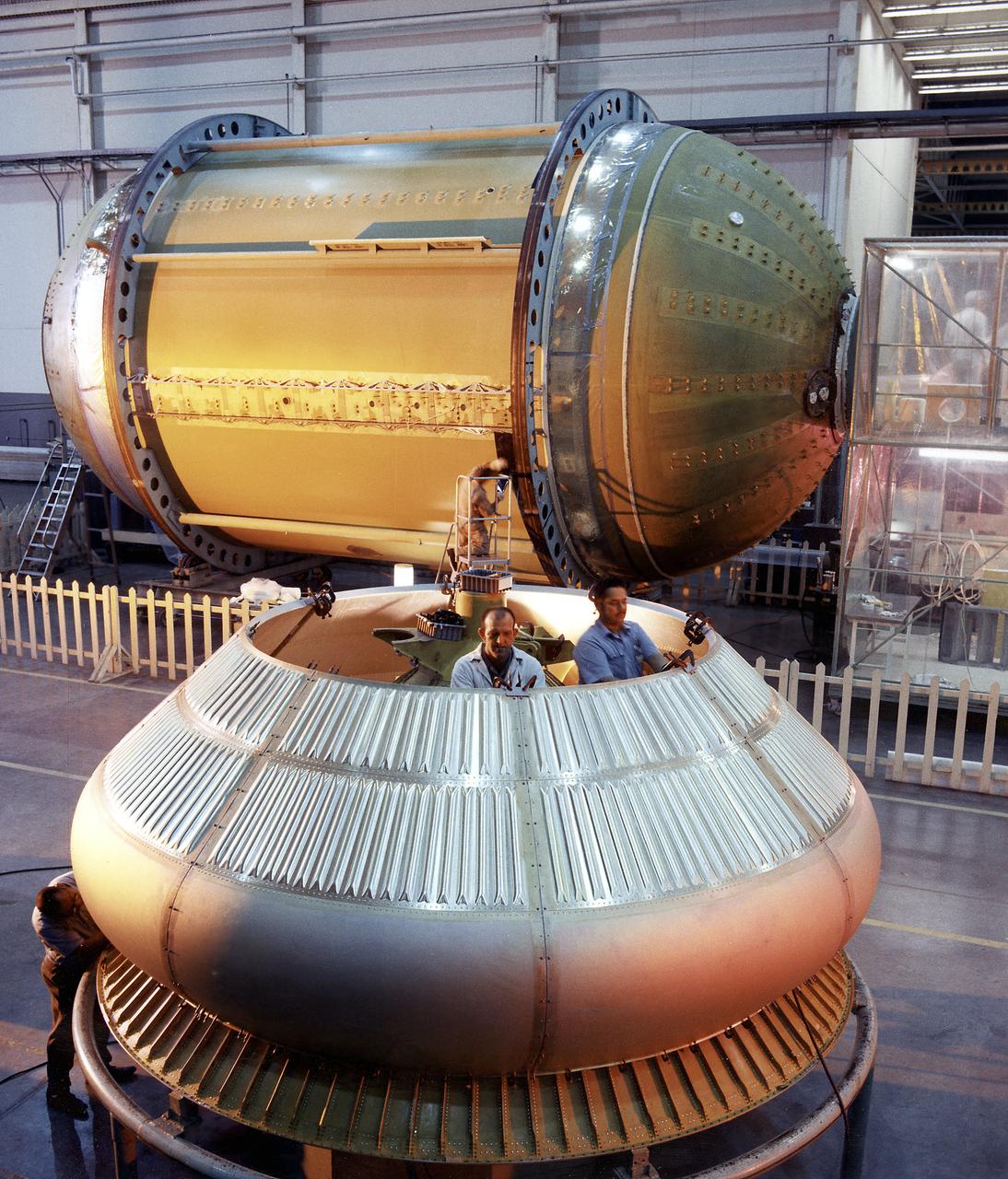
This photograph shows technicians installing the meteoroid shield on the Thruster Attitude Control Subsystem (TACS). At one end of the Orbital Workshop (OWS), the TACS provided short-term control of the attitude of the Skylab.
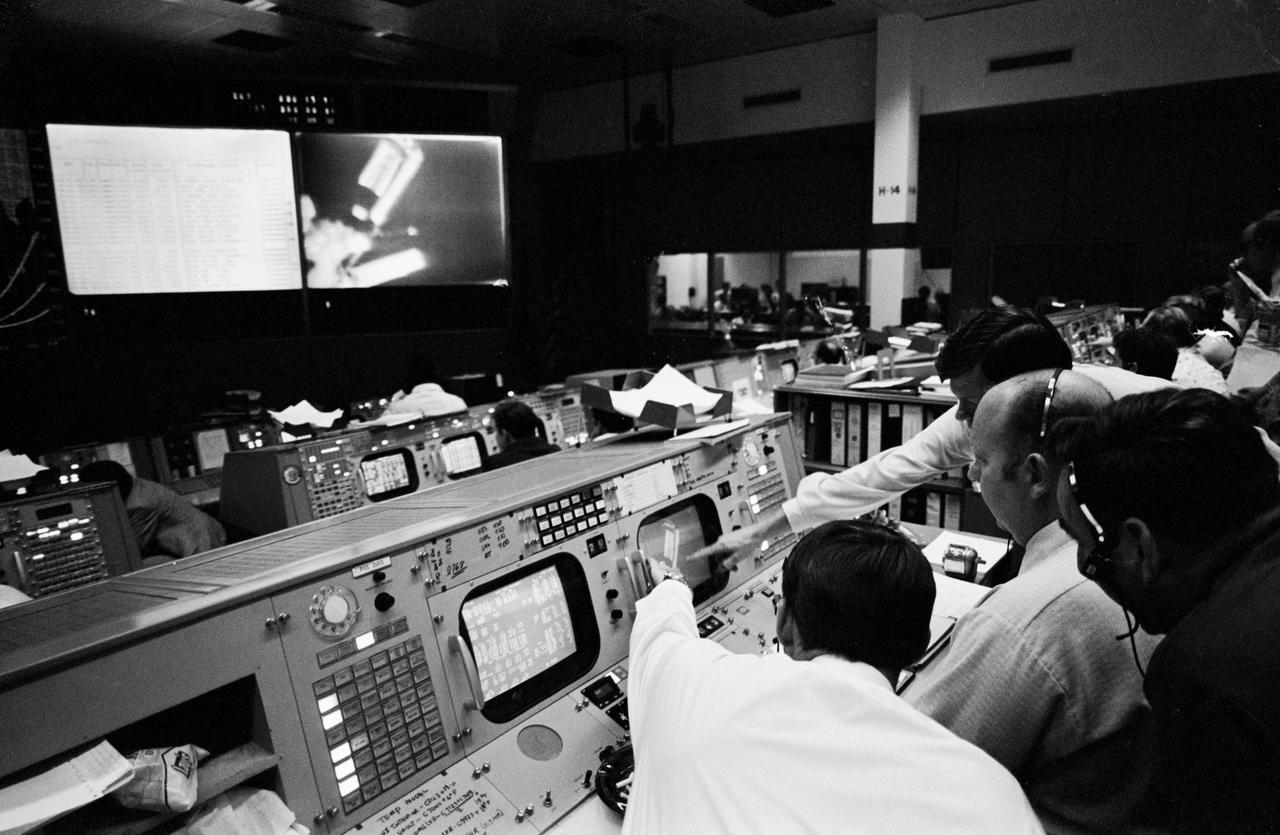

S73-26849 (25 May 1973) --- Four flight directors for the Skylab 1 and 2 mission are grouped around the flight director's console in the Mission Operations Control Room in the Mission Control Center at Johnson Space Center during the Skylab 2 Command/Service Module (CSM) "fly around" inspection of the Skylab 1 space station cluster. They are, going counterclockwise from center foreground, Donald R. Puddy (white shirt), Milton Windler, Philip C. Shaffer and M.P. Frank. A view of the Skylab 1 Orbital Workshop seen from the Skylab 2 CSM is visible on the television monitor in the background. Photo credit: NASA

This wide-angle view depicts the Orbital Workshop (OWS) wardroom/galley located in the lower level of the OWS. The galley in the wardroom provided the daily supply of food; galley-located equipment was used for preparation and disposal of food. The Skylab astronauts used the wardroom as kitchen and dining room. The hexagonal food table, shown in the middle of this image, allowed three crewmen to simultaneously heat their food and eat their meals in an efficient and comfortable marner. Chairs were pointless in the zero-gravity environment. The table also supported components of the water system, including the water chiller and the wardroom water heater.
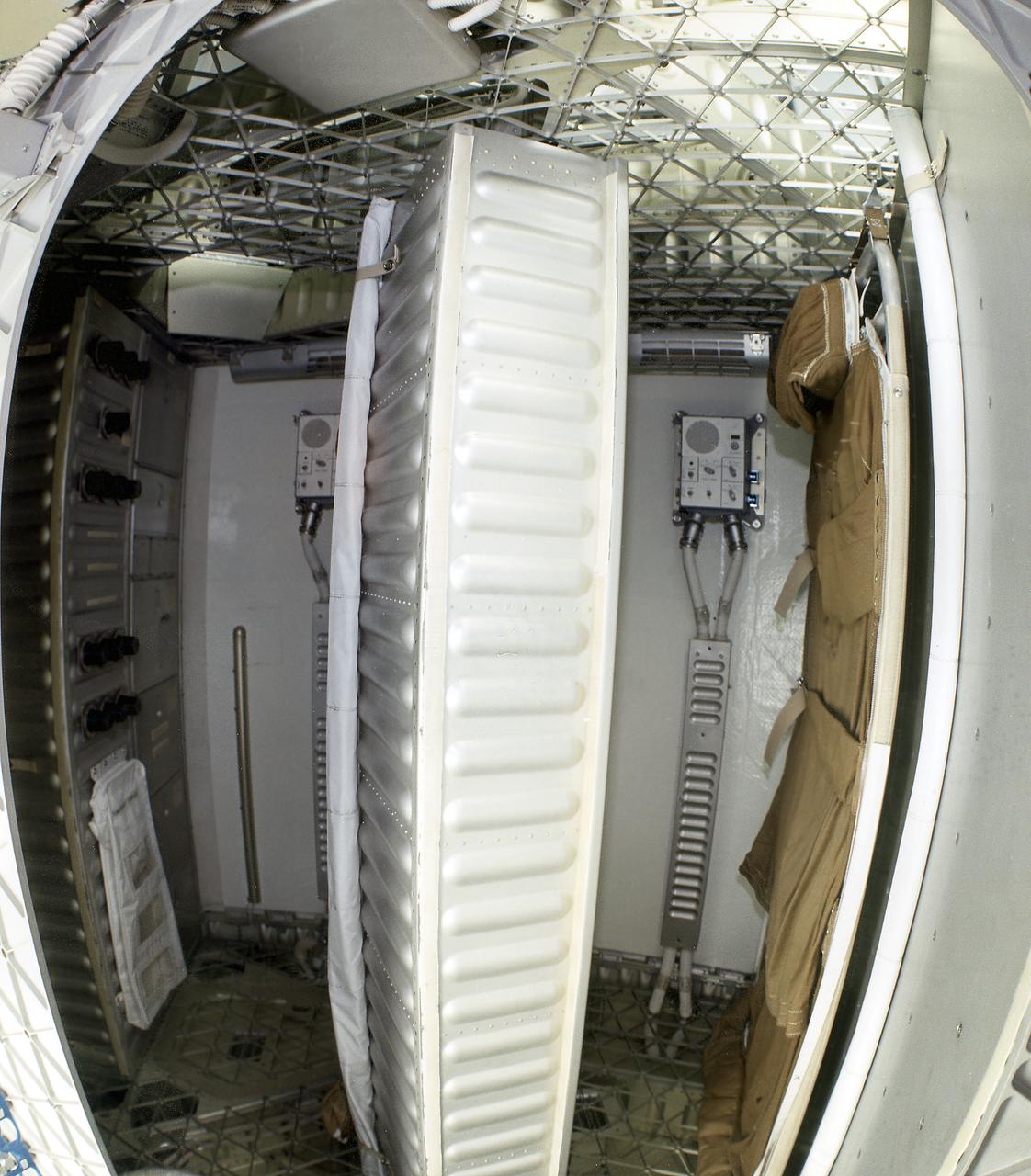

This wide-angle view is of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) sleep compartment, located in the lower level of the OWS. Each crewman was assigned a small space for sleeping and zipped themselves into sleeping bags stretched against the wall. Because of the absence of gravity, sleeping comfort was achieved in any position relative to the spacecraft; body support was not necessary. Sleeping could be accommodated quite comfortably in a bag that held the body at a given place in Skylab.
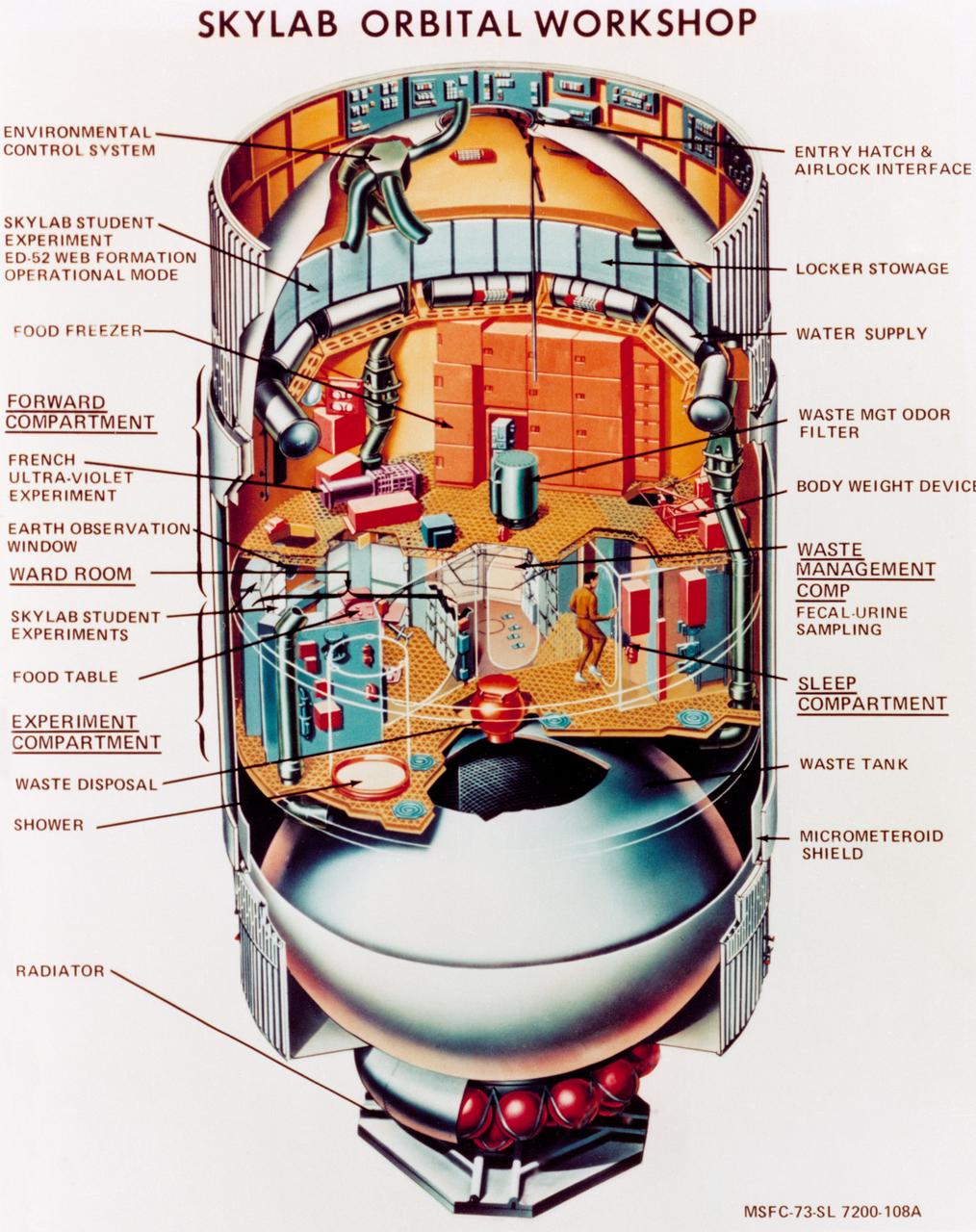
S73-23919 (May 1973) --- An artist's concept illustrating a cutaway view of the Skylab 1 Orbital Workshop (OWS). The OWS is one of the five major components of the Skylab 1 space station cluster which was launched by a Saturn V on May 14, 1973 into Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
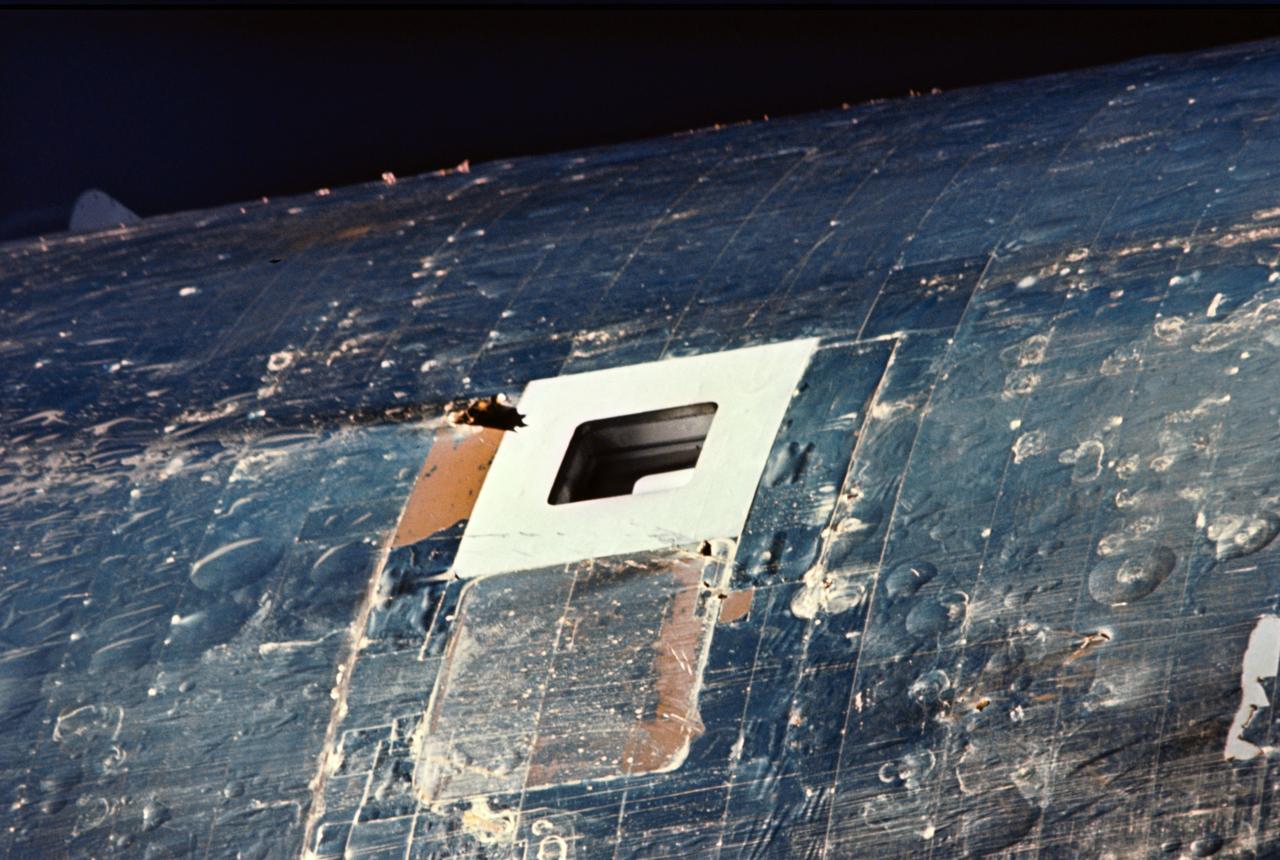

This close up view of one of the two scientific airlocks on the Skylab Orbital Workshop Section was taken from the Skylab 2 Command/Service Module during its initial fly around inspection. The micrometeoroid shield can be seen to be missing from this section of the orbital workshop. A parasol solar shield was later devised and put in place over this damaged area through this very same airlock opening.
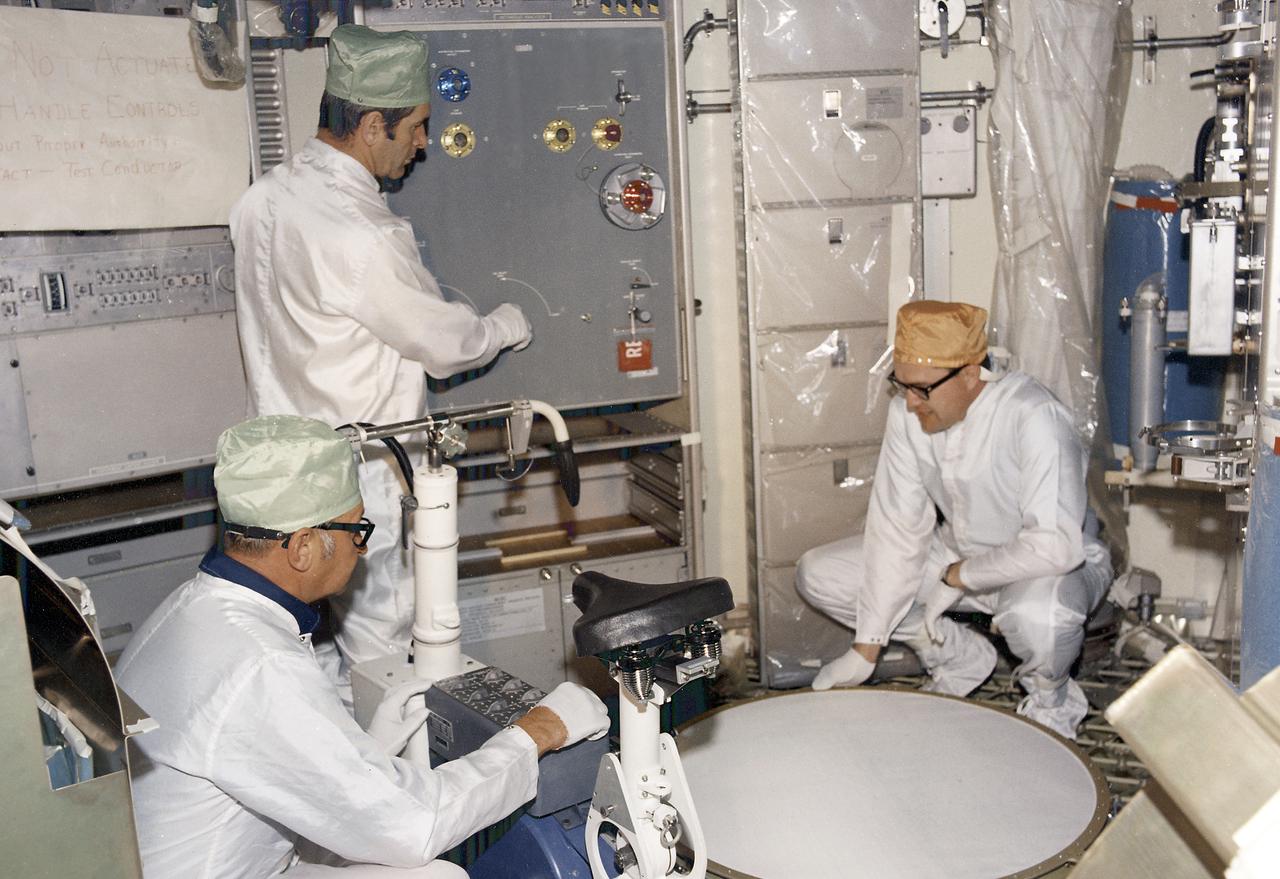

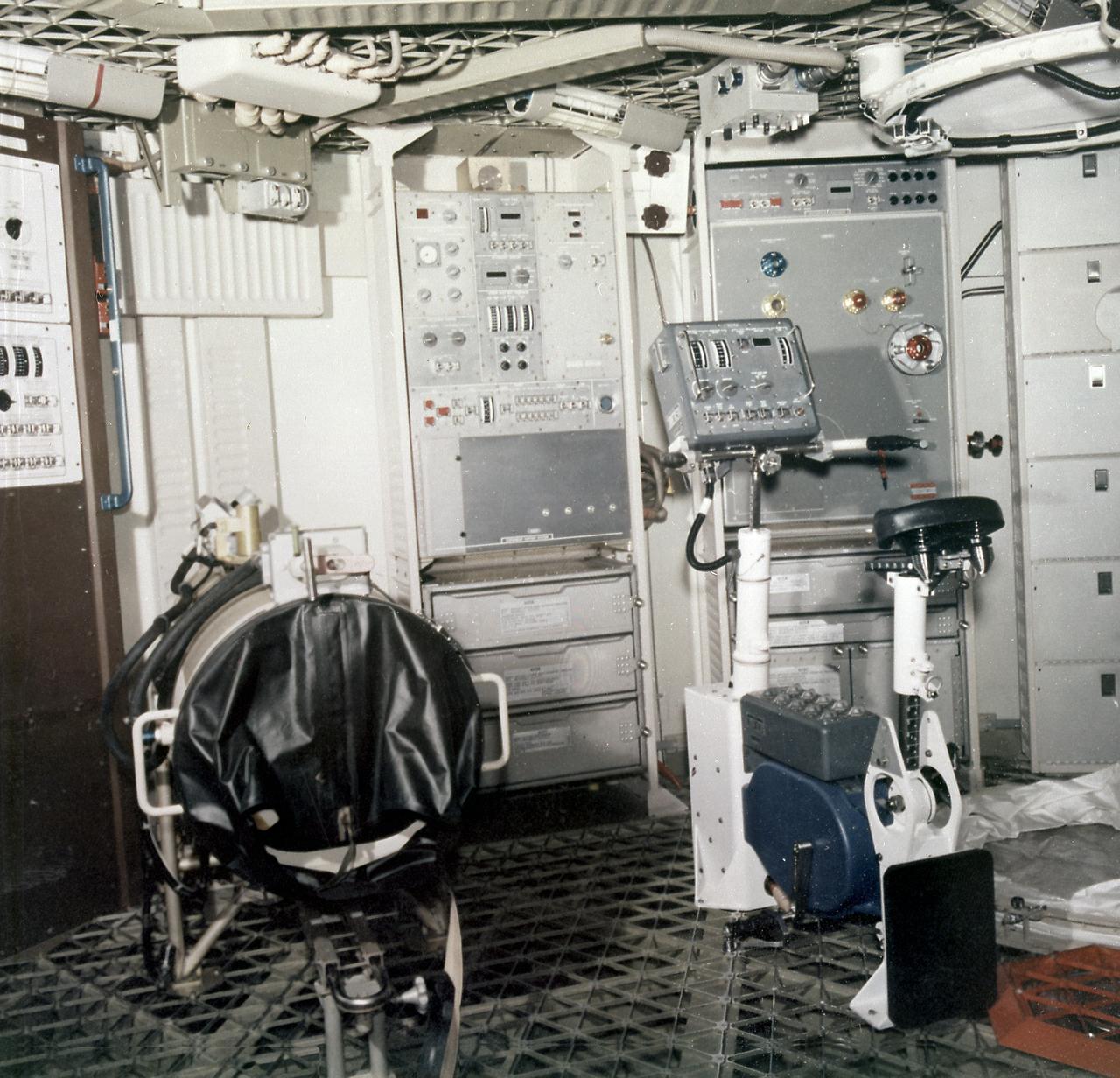
This photograph shows technicians performing a checkout of the Metabolic Analyzer (center background) and the Ergometer (foreground) in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The shower compartment is at right. The Ergometer (Skylab Experiment M171) evaluated man's metabolic effectiveness and cost of work in space environment. Located in the experiment and work area of the OWS, the shower compartment was a cylindrical cloth enclosure that was folded flat when not in use. The bottom ring of the shower was fastened to the floor and contained foot restraints. The upper ring contained the shower head and hose. To use the shower, the astronaut filled a pressurized portable bottle with heated water and attached the bottle to the ceiling. A flexible hose cornected the water bottle to a handheld shower head. The astronaut pulled the cylindrical shower wall up into position and bathed, using liquid soap. Both soap and water were carefully rationed, having been premeasured for economical use.
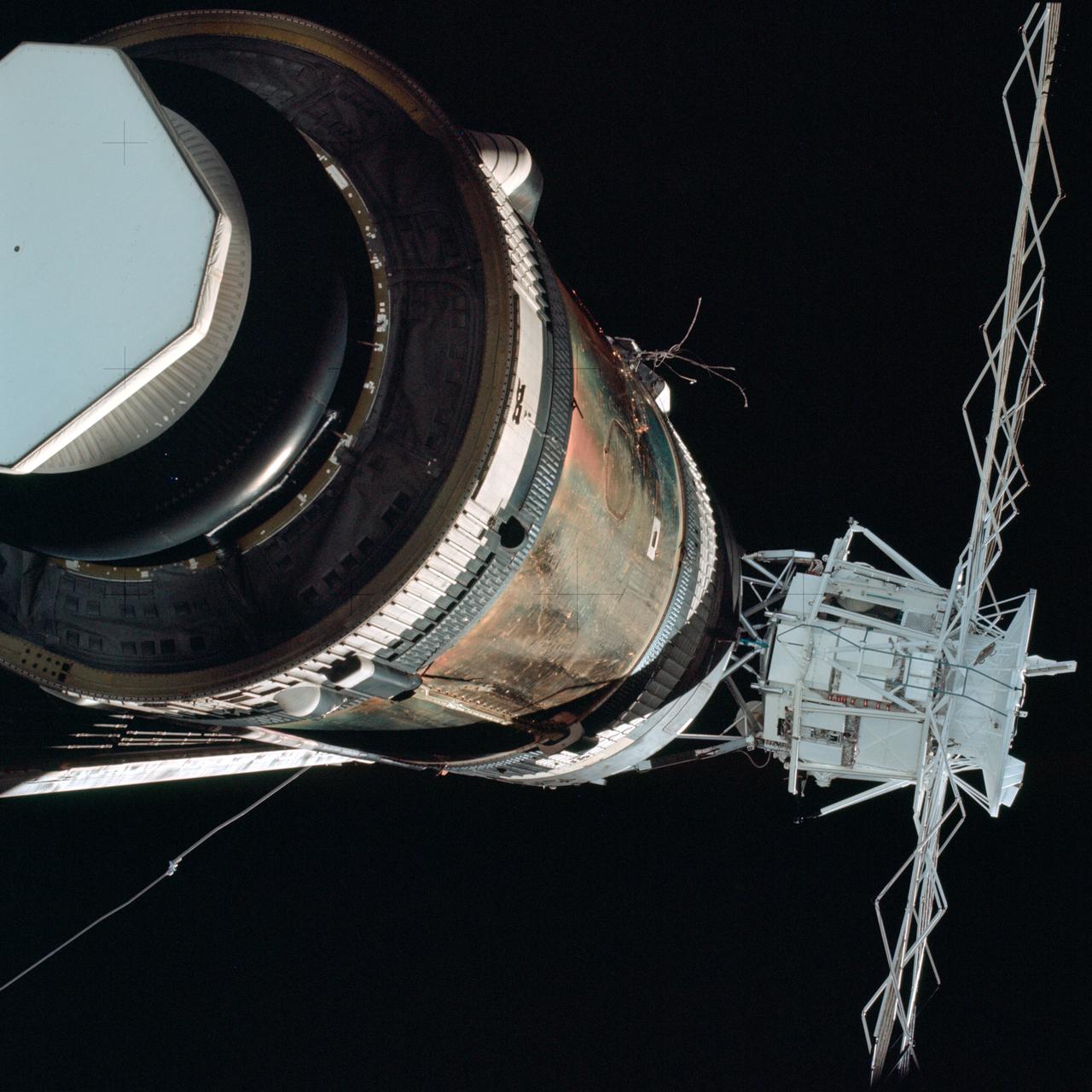

SL2-4-265 (25 May 1973) --- Skylab 2, approach to Skylab at long range, fly-around inspection. Orbital Workshop with area of missing micrometeoroid shield visible and partially deployed solar array visible. Photo credit: NASA
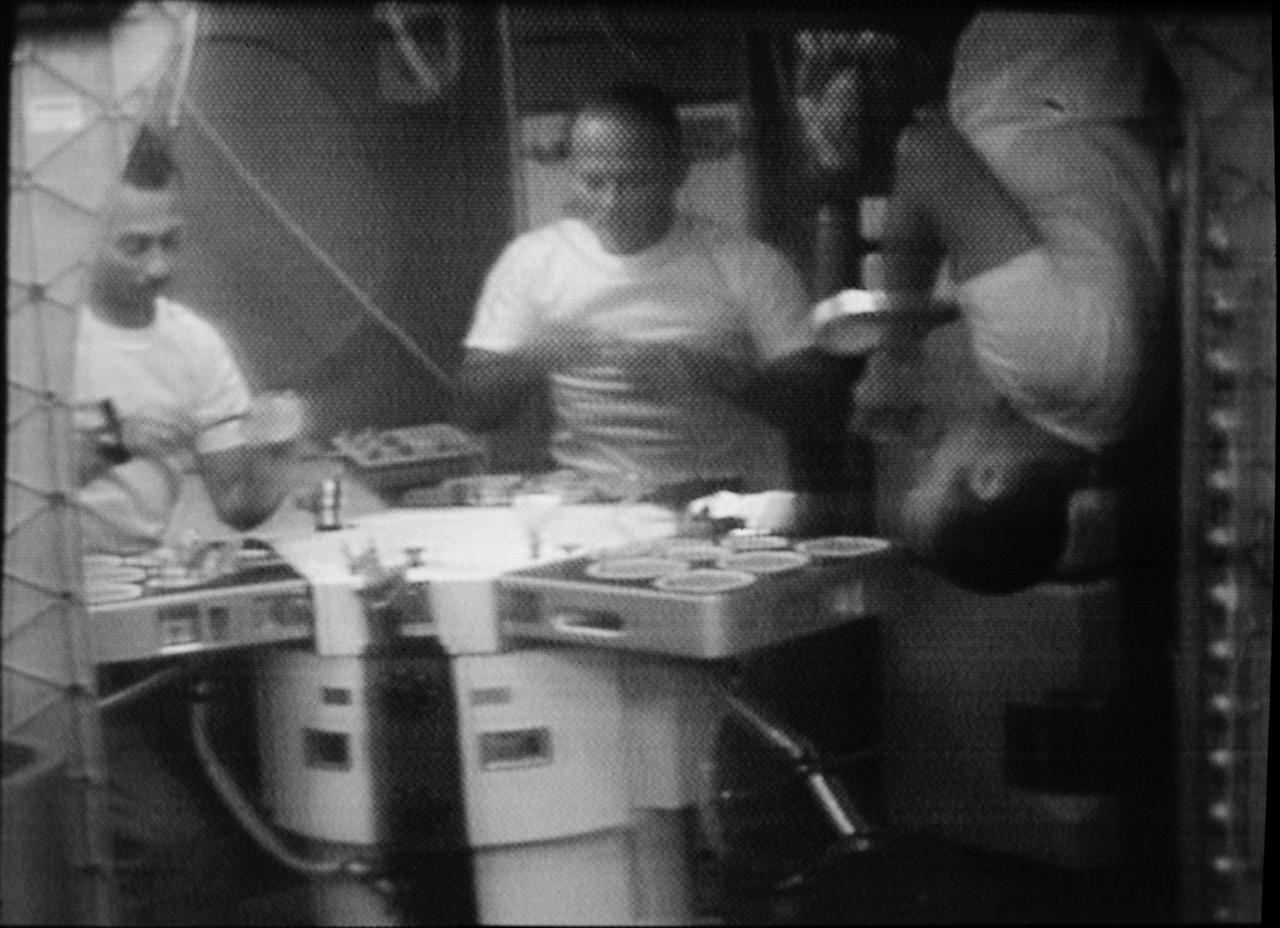
S73-31705 (1 Aug. 1973) --- The three Skylab 3 crewmen are shown eating in the Orbital Workshop (OWS) wardroom of the Skylab space station in Earth orbit, in this photographic reproduction taken from a television transmission made by a color TV camera aboard the OWS. Astronaut Alan L. Bean (right), commander, illustrates eating under zero-gravity conditions upsidedown. The two other crewmen are scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott (left), science pilot; and astronaut Jack R. Lousma, pilot. Photo credit: NASA
S73-23918 (May 1973) --- An artist's concept illustrating a cutaway view of the Skylab 1 Orbital Workshop (OWS). The OWS is one of the five major components of the Skylab 1 space station cluster which was launched by a Saturn V on May 14, 1973 into Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
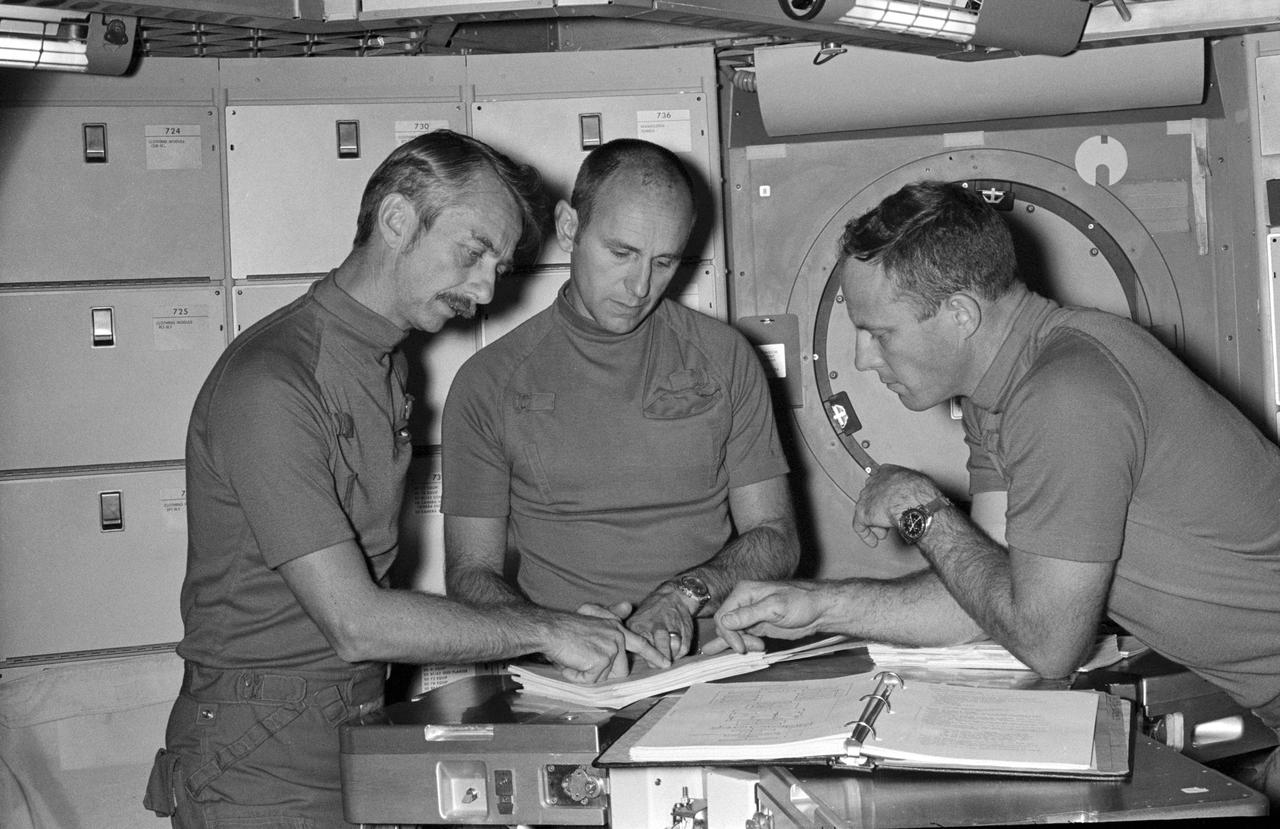

S73-28419 (16 June 1973) --- The three prime crewmen of the Skylab 3 mission check over flight data during a training session in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). They are, from left to right, scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot; and astronauts Alan L. Bean, commander, and Jack R. Lousma, pilot. The 56-day, second manned Skylab Earth-orbital mission is scheduled for liftoff in the latter part of July 1973. Photo credit: NASA
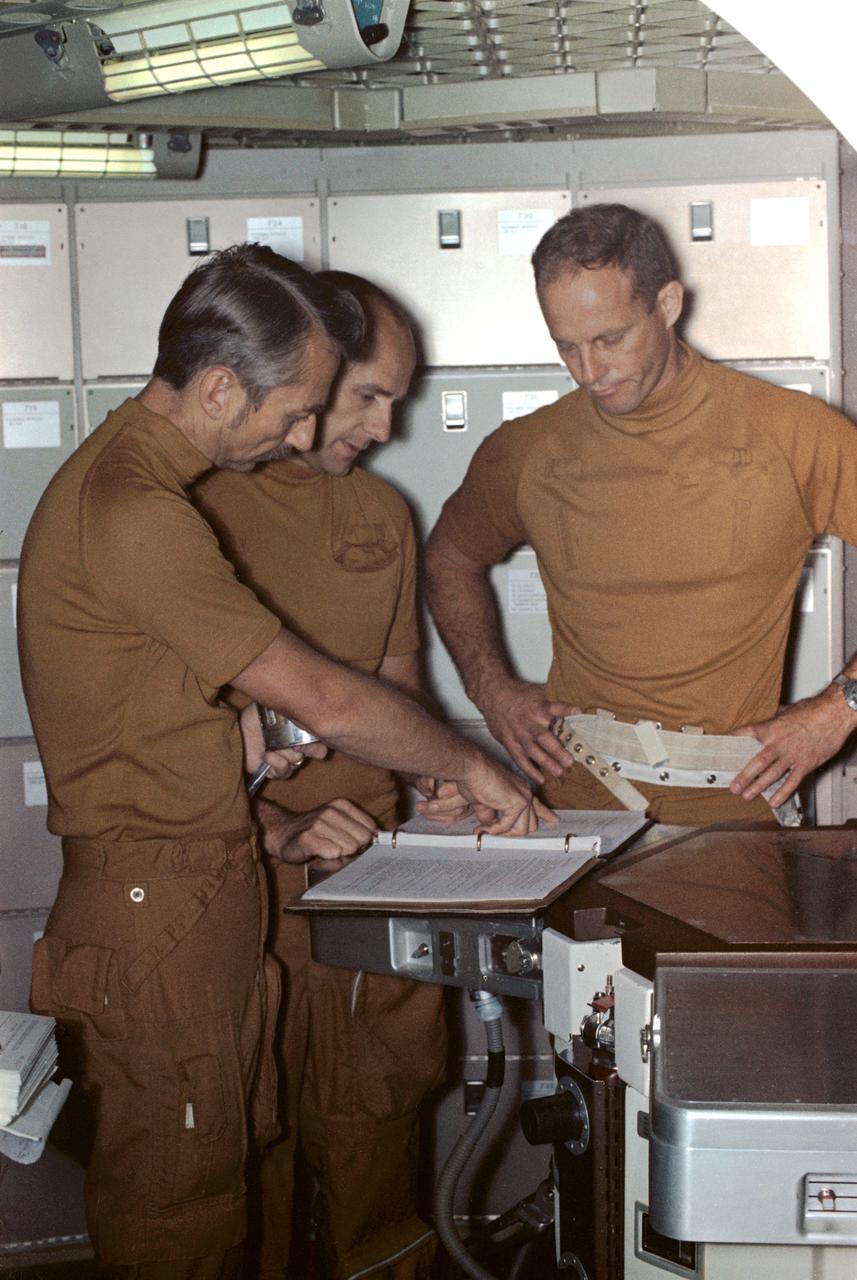

S73-28793 (16 July 1973) --- The three crewmen of the second manned Skylab mission (Skylab 3) go over a checklist during preflight training at the Johnson Space Center. They are, left to right, scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot; astronaut Alan L. Bean, commander; and astronaut Jack R. Lousma, pilot. They are in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop trainer in the Mission Training and Simulation Facility, Building 5, at JSC. Skylab 3 is scheduled as a 59-day mission in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
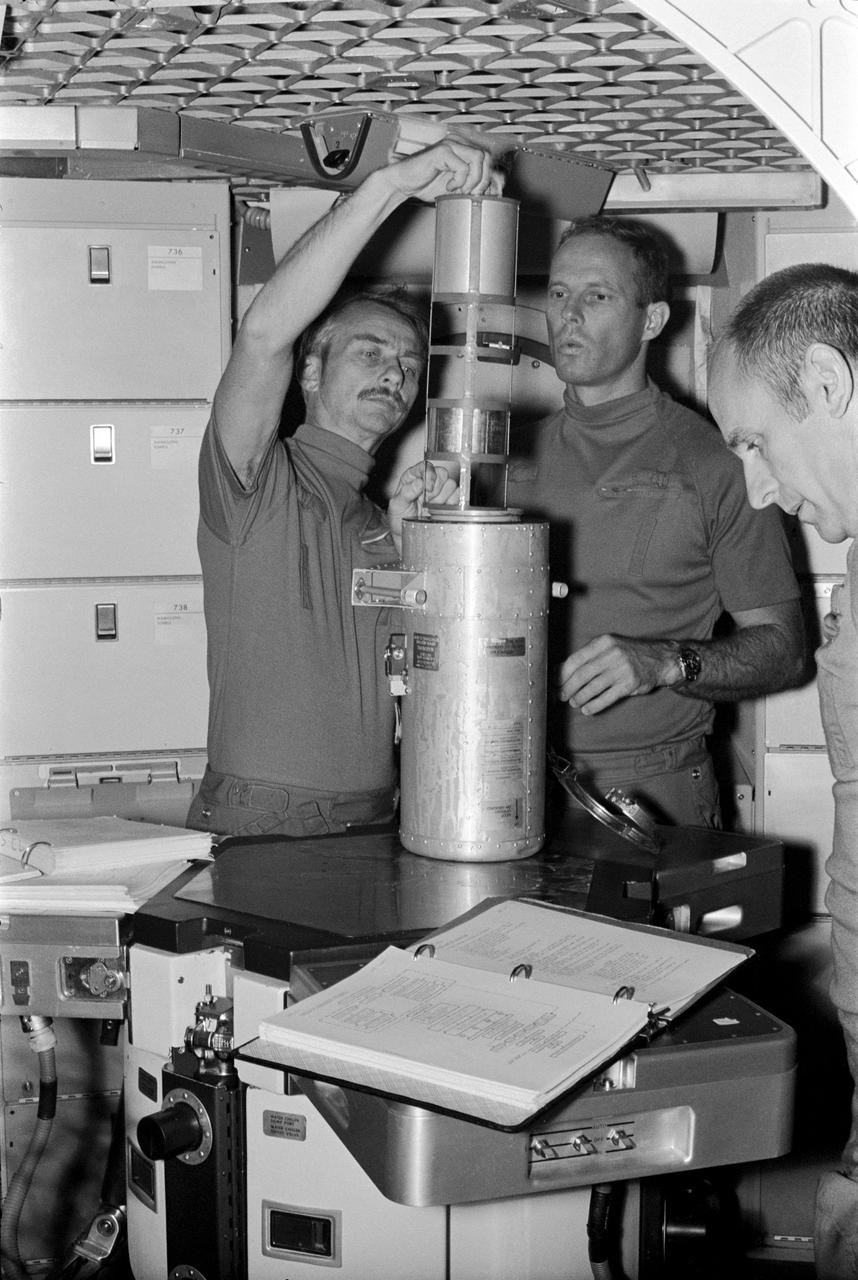

S73-28420 (16 June 1973) --- The three prime crewmen of the Skylab 3 mission check over flight data during a training session in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer in the Mission Simulation and Training Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Skylab 3 crew work with Inflight Medical Support System (IMSS) resupply container atop the food table in the OWS. They are from left to right, scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, science pilot; and astronauts Jack R. Lousma, pilot; and Alan L. Bean, commander. Photo credit: NASA
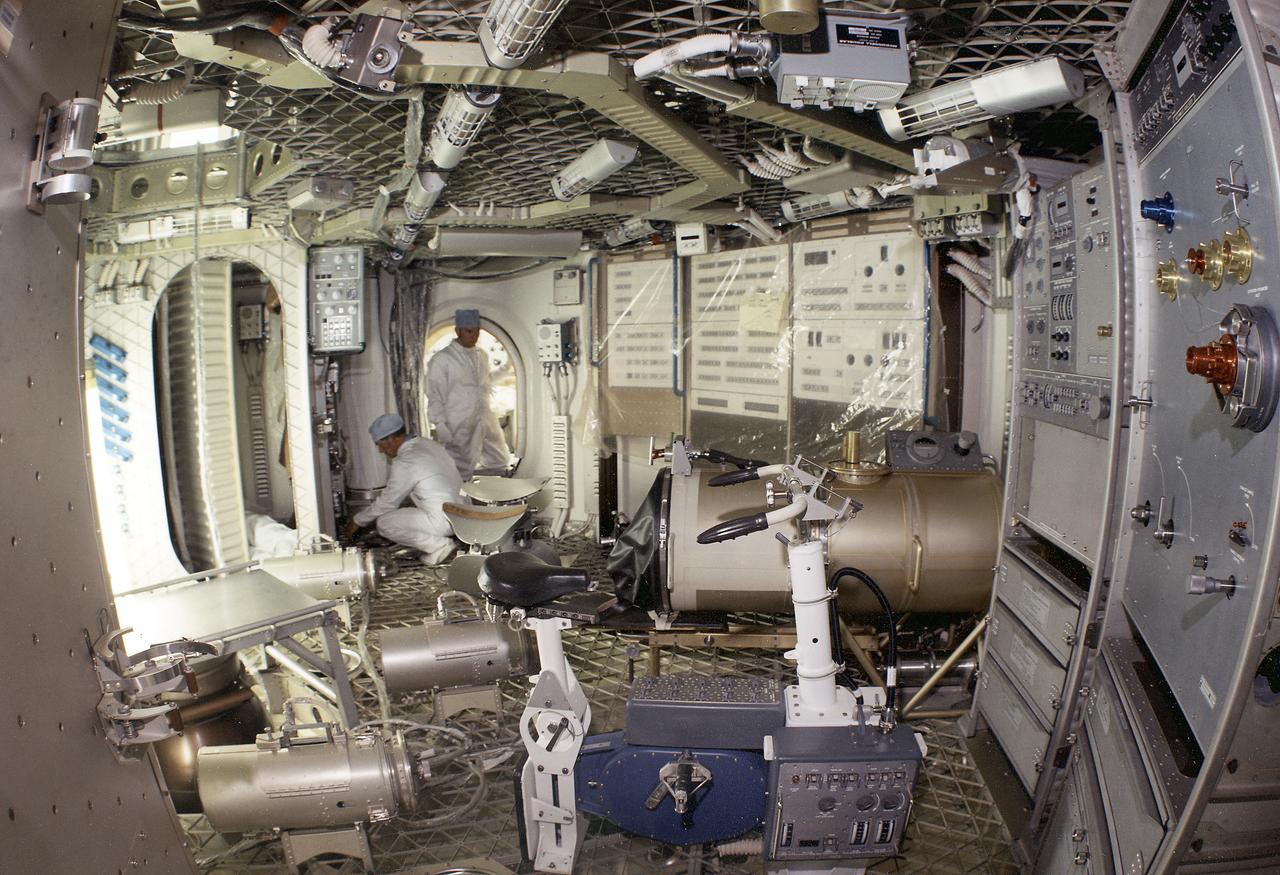
This is a wide-angle view of the Orbital Workshop lower level experiment area. In center foreground is the ergometer bicycle. In center background is a litter chair for the Human Vestibular Function experiment (Skylab Experiment M131) and in right background is the Lower Body Negative Pressure System experiment (Skylab Experiment M092). The ergometer bicycle was used for metabolic activity experiments and exercise. The purpose of the Human Vestibular (irner ear) Function experiment was to examine the effect of weightlessness on man's sensitivity and susceptibility to motion rotation, and his perception of orientation. The Lower Body Negative Pressure experiment investigated the relationship between the zero gravity environment and cardiovascular deconditioning. A characteristic of cardiovascular deconditoning is the partial failure of the blood vessels resulting in the excessive pooling of the blood in the legs when a person assumes an erect posture in a gravity field. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.

S73-32840 (10 Sept. 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, Skylab 4 science pilot, turns on a switch on the control box of the S190B camera, one of the components of the Earth Resources Experiments Package (EREP). The single lens Earth Terrain Camera takes five-inch photographs. Behind Gibson is the stowed suit of astronaut Gerald P. Carr, commander for the third manned mission. The crew's other member is astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot. The training exercise took place in the Orbital Workshop one-G trainer at Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
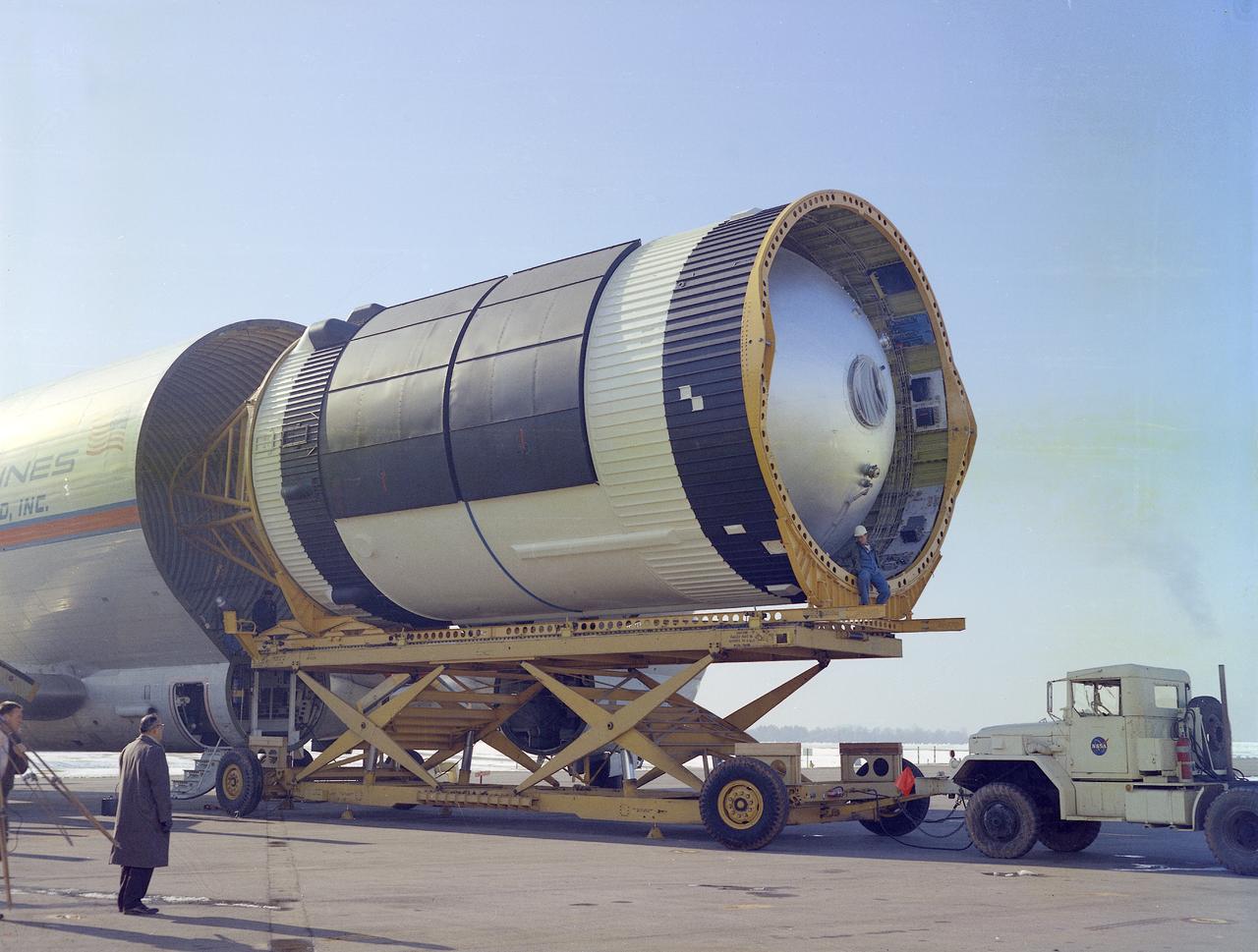

This photograph was taken at the Redstone airfield, Huntsville, Alabama, during the unloading of the Saturn V S-IVB stage that housed the Orbital Workshop (OWS) from the Super Guppy, the NASA plane that was specially built to carry oversized cargo. The OWS measured 22 feet (6.7 m) in diameter, and 48 feet (14.6 m) in length. The Saturn V S-IVB stage was modified at the McDornell Douglas facility at Huntington Beach, California, for a new role, which was to house the OWS. In addition to the test articles, engineering mockups, and flight equipment, both McDonnell Douglas and Martin Marietta built 0-G trainers, neutral buoyancy trainers, and high-fidelity mockups for the 1-G trainer to be used in the KC-135 aircraft. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.

The Orbital Workshop internal arrangement shown here is the medical experimental equipment. In this view, looking from the wardroom area, are the lower-body Negative Pressure (Experiment M092) unit, left, and the ergometer for the vectorcardiograph (Experiment - M093). Both are used in several ways to keep check on the astronauts' condition and tolerance in extended weightlessness. The 1-G trainer permits the astronauts to get experience with all of the equipment and operations except the absence of gravity.

The wardroom deck of the Orbital Workshop, showing the living quarters arrangement, is seen here in good detail. From left to right is the dining area, waste management, and sleeping quarters. Portable restraints are on the wall beside the sleeping quarters. The ergometer for the vectorcardiograph (Experiment - M093) and lower-body Negative Pressure (Experiment M092) unit, used in some of the medical experiments, are in the foreground. The round brown object in the center of the room is the trash disposal airlock.
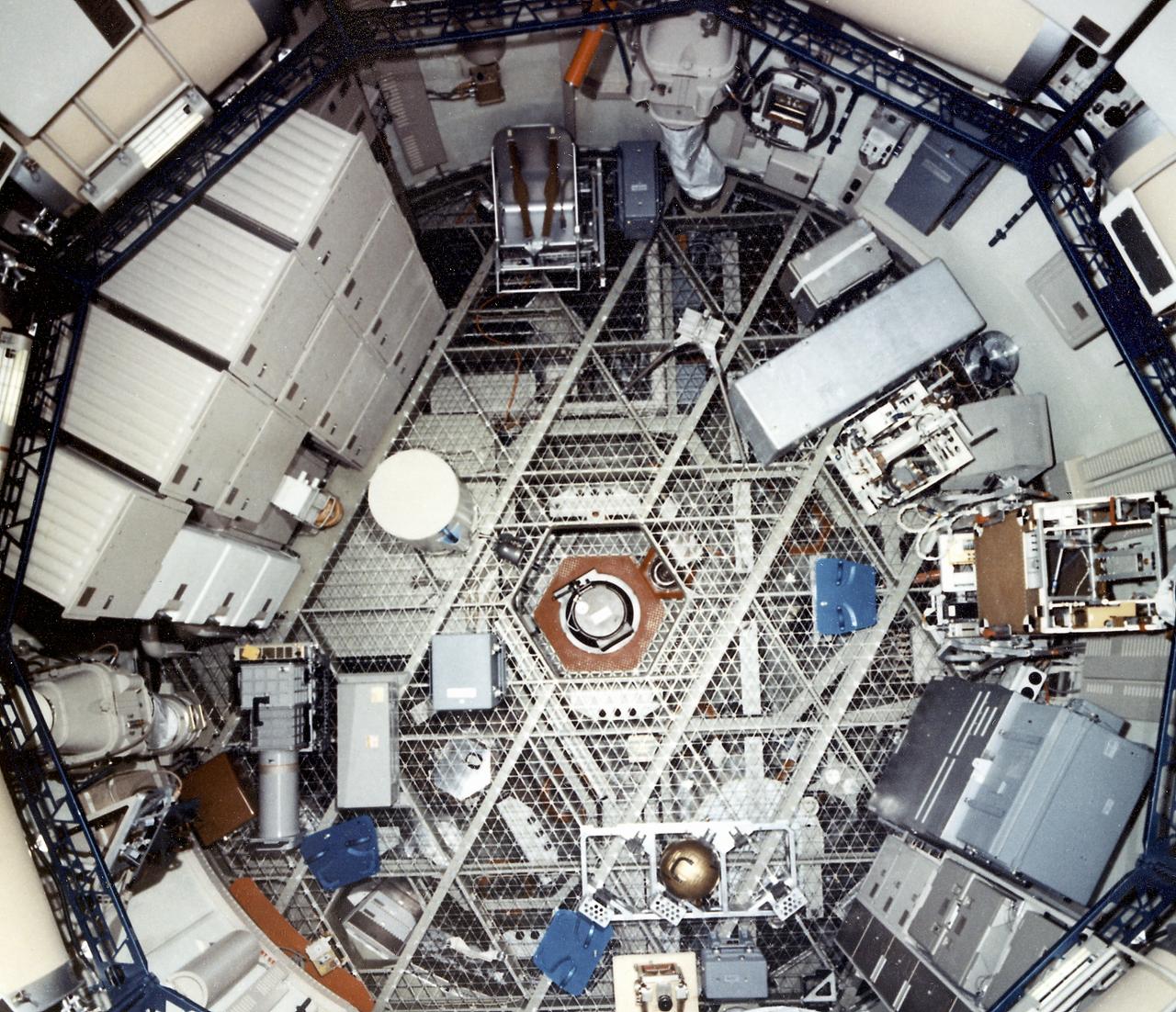
This photograph is an interior view of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) upper level looking from the airlock hatch, showing the octagonal opening that separated the workshop's two levels. The trash airlock can be seen at center. The lower level of the OWS provided crew accommodations for sleeping, food preparation and consumption, hygiene, waste processing and disposal, and performance of certain experiments. The upper level consisted of a large work area and housed water storage tanks, a food freezer, storage vaults for film, scientific airlocks, mobility and stability experiment equipment, and other experimental equipment.
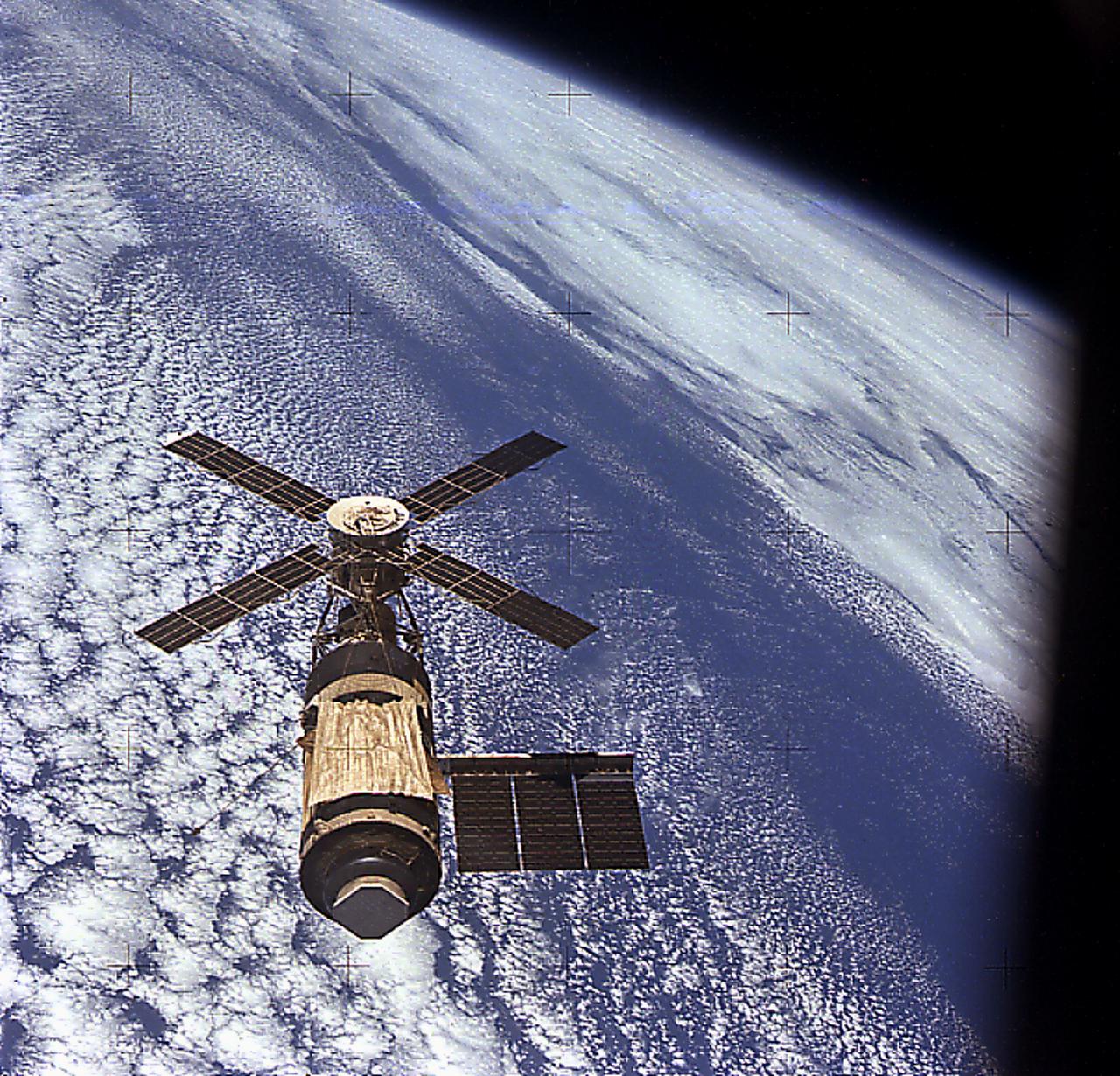

The idea that ultimately became Skylab first surfaced in 1962 as a proposal to convert a spent Saturn upper stage (Saturn V S-II stage) into an orbital workshop. In 1968, the Marshall Space Flight Center proposed an alternative to the wet workshop concept of refurbishing a space station in orbit. Instead, a fully equipped dry workshop could be launched as a complete unit ready for occupancy. Skylab became the free world's first space station. Launched in May 1973, the Skylab space station was occupied in succession by three teams of three crewmembers. These crews spent 28, 59, and 84 days respectively, orbiting the Earth and performing nearly 300 experiments. This view of Skylab in orbit was taken by the Skylab 4 (the last Skylab mission) crew.

Astronaut Gerald P. Carr, commander for the Skylab 4 mission, demonstrates the effects of zero-gravity as he floats in the forward dome area of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab space station while in Earth orbit.

S73-16765 (1 Feb. 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr. is seen working with the control panels of the Skylab Orbital Workshop trainer during Skylab training at the Johnson Space Center. Photo credit: NASA
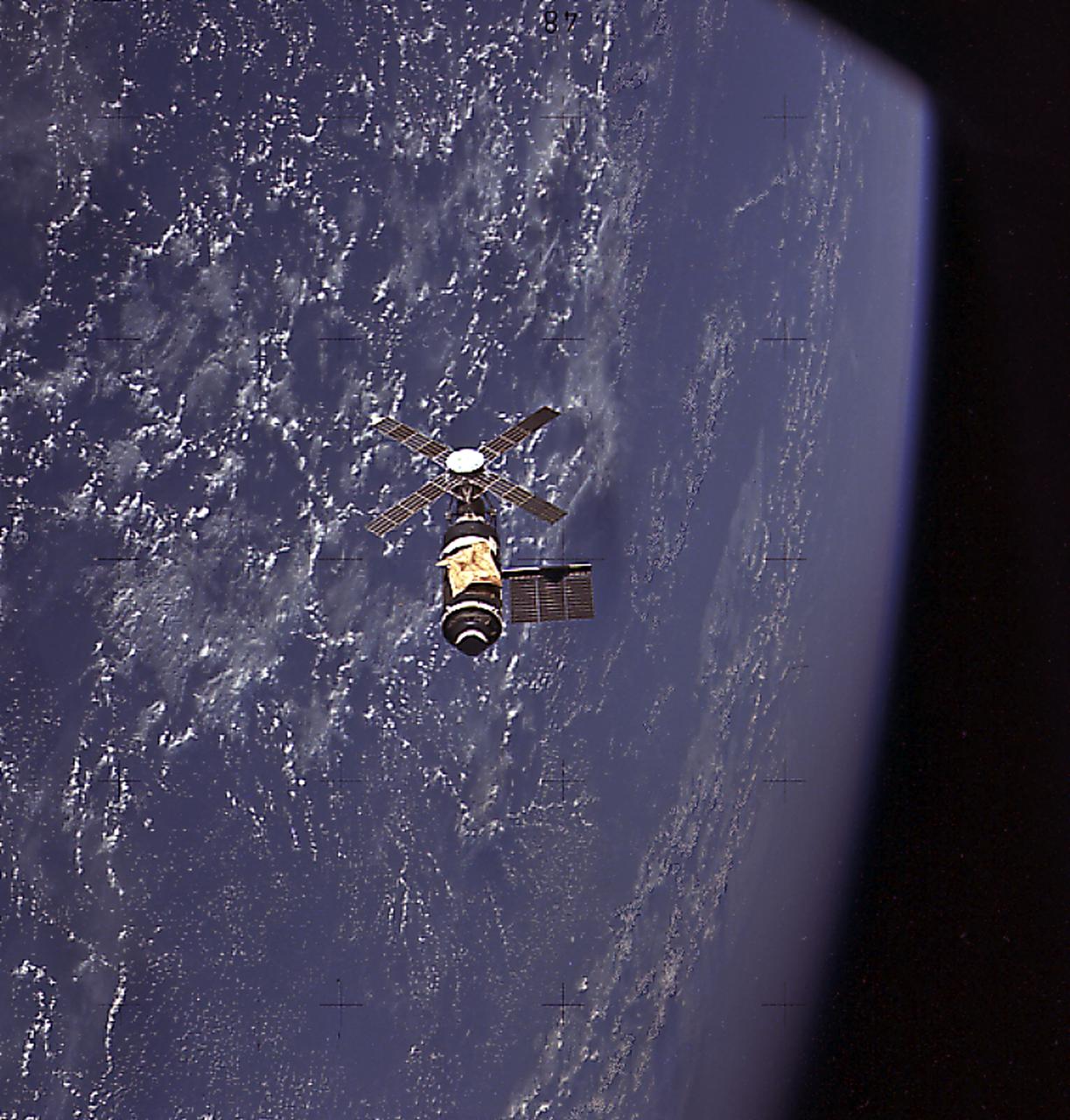

This image of Skylab in orbit was taken by the Skylab-2 crew before departing for Earth. The crew made a careful visual and photographic inspection of the orbiting laboratory. It shows the parasol sunshade, deployed by the crew, protecting the workshop. While unmarned, it operated at reduced power with many of its systems either inoperative or operating at reduced capacity.

S73-34172 (August 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, watches a drink container spinning and tumbling in zero-gravity during a science demonstration television transmission from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Garriott is in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). Photo credit: NASA

S73-24316 (May 1973) --- An artist's concept illustrating a cutaway view of the Skylab 1 Orbital Workshop (OWS). The OWS is one of the five major components of the Skylab 1 space station cluster which was launched by a Saturn V on May 14, 1973 into Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

This image is a wide-angle view of the Orbital Workshop waste management compartment. The waste management facilities presented a unique challenge to spacecraft designers. In addition to collection of liquid and solid human wastes, there was a medical requirement to dry all solid human waste products and to return the residue to Earth for examination. Liquid human waste (urine) was frozen for return to Earth. Total quantities of each astronaut's liquid and solid wastes were precisely measured. Cabin air was drawn into the toilet, shown on the wall at right in this photograph, and over the waste products to generate a flow of the waste in the desired direction. The air was then filtered for odor control and antiseptic purposes prior to being discharged back into the cabin.

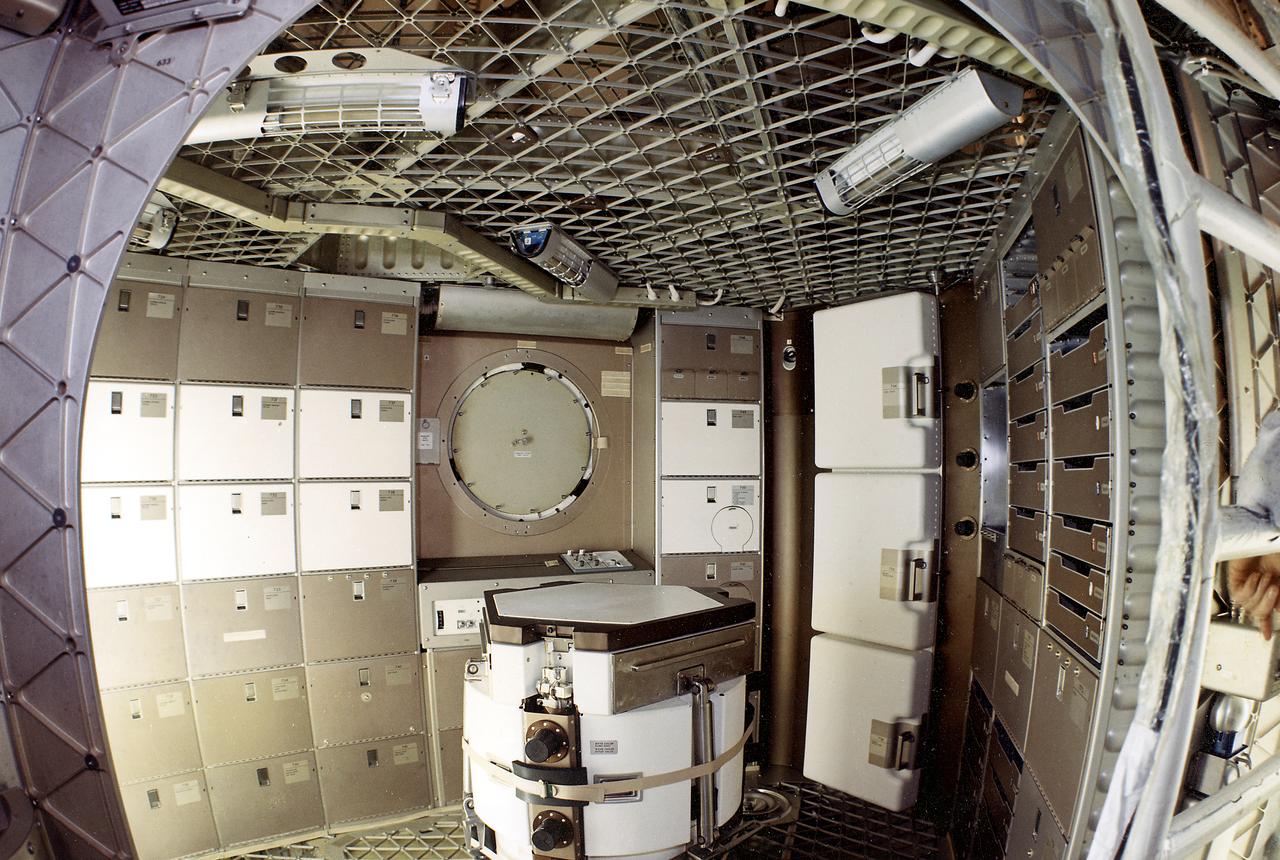
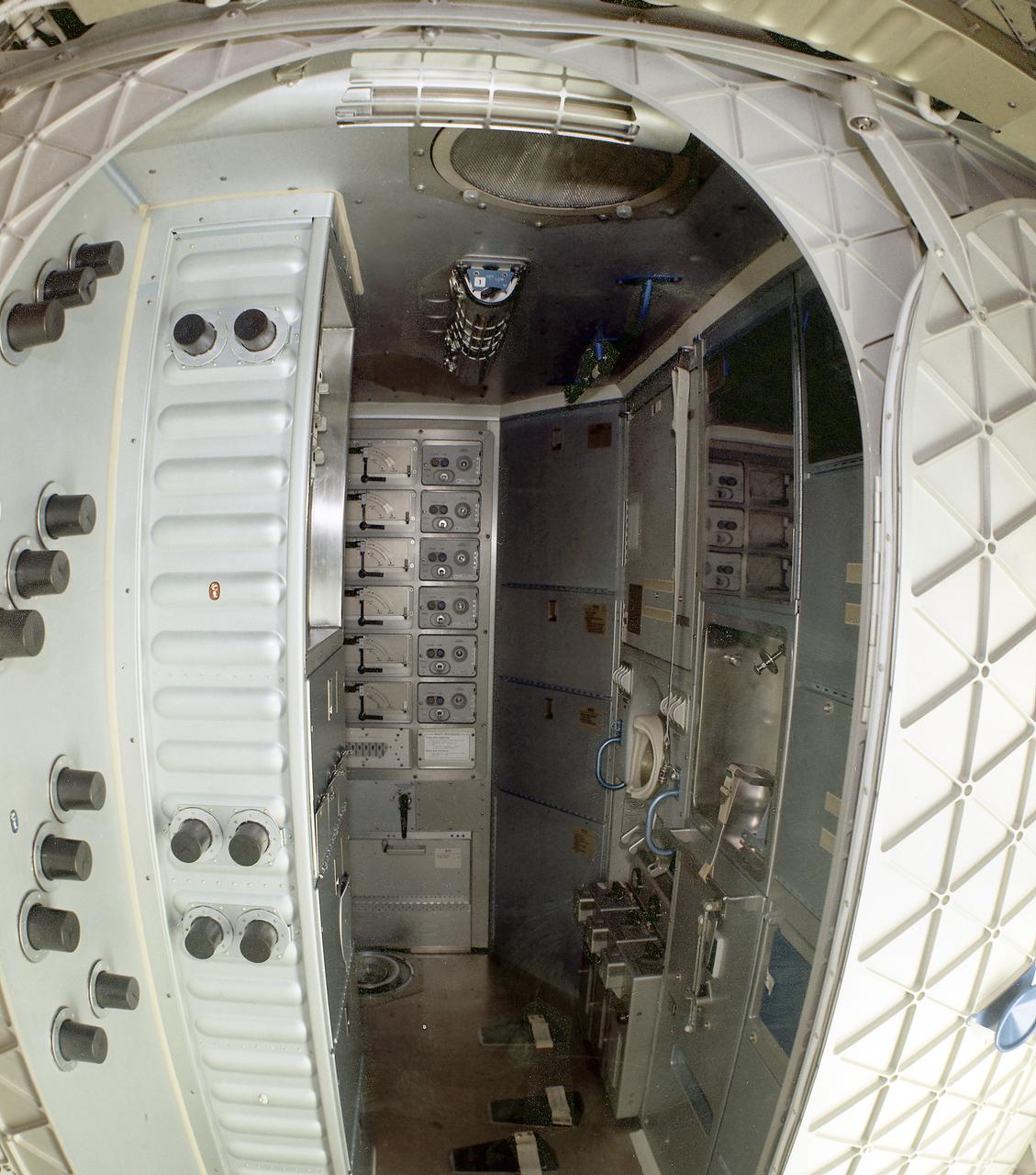
This image, with callouts, depicts the storage area of the forward compartment at the upper level of the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The upper level consisted of a large work area and housed water storage tanks, a food freezer, storage vaults for film, scientific airlocks, mobility and stability experiment equipment, and other experimental equipment.
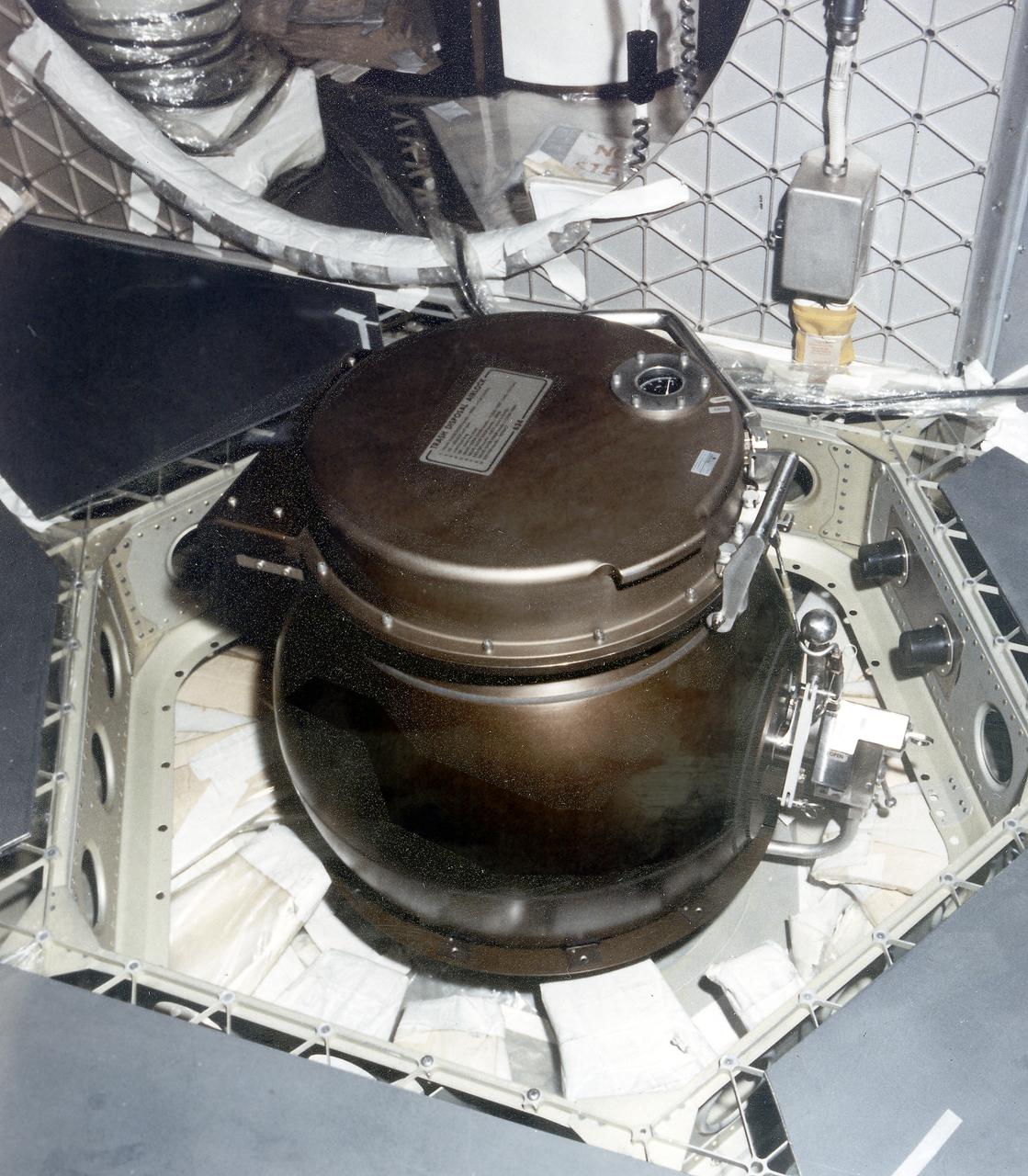
This is a close-up photograph of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) trash disposal airlock located on the floor of the lower level of the OWS. It provided a means of passing trash from the pressurized habitable area into the unpressurized waste tank. The crewman opened a valve which brought the airlock to the same pressure as that within the workshop. He then opened the lid, placed the bagged trash inside, closed the lid and locked it. By turning the valve handle, he reduced the pressure within the airlock until it reached the vacuum of the waste tank. The crewman then operated an ejector handle that caused a scissors-type mechanism to push the bagged trash from the airlock into the tank.
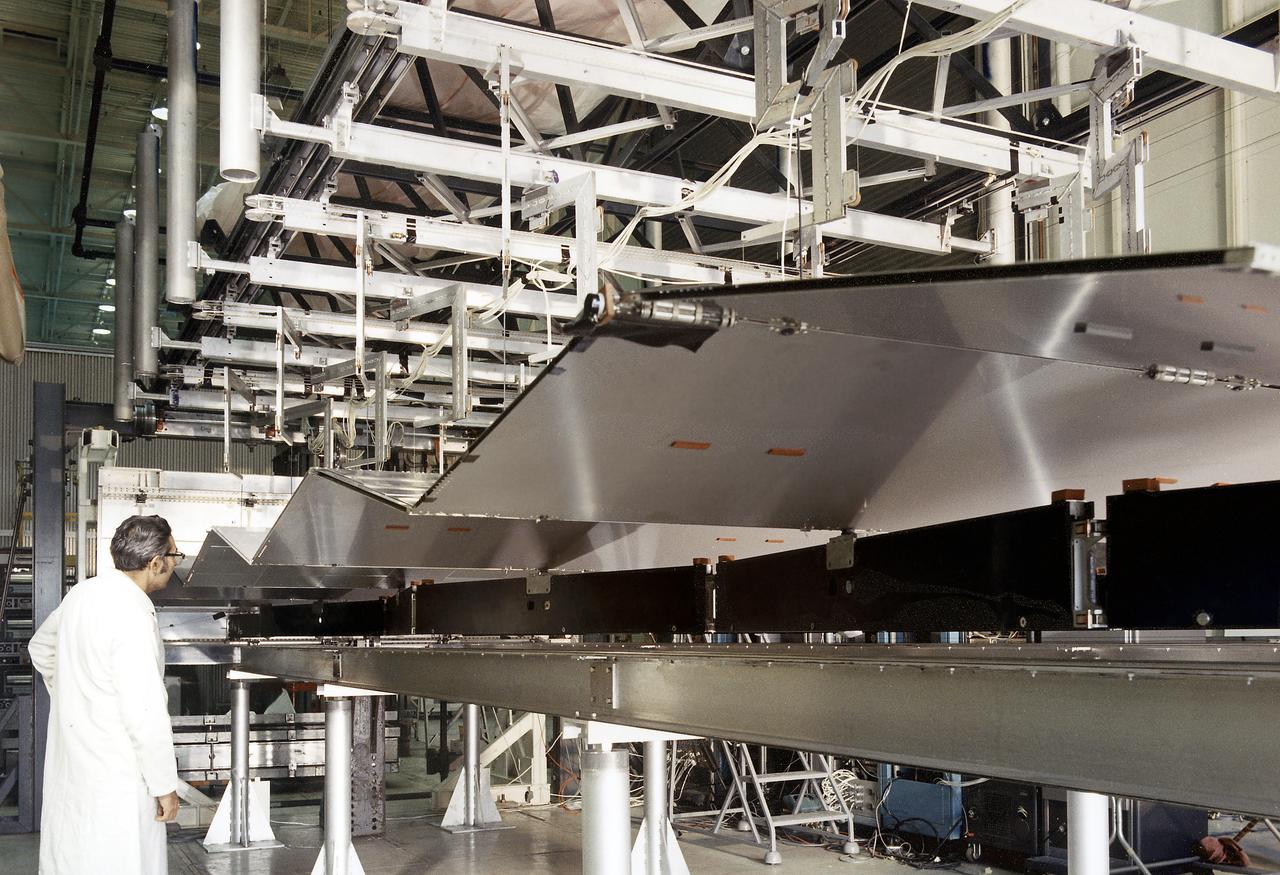

This is a photograph of a technician checking on a solar array wing for the Orbital Workshop as it is deployed. A solar array, consisting of two wings covered on one side with solar cells, was mounted outside the workshop to generate electrical power to augment the power generated by another solar array mounted on the solar observatory.

In this photograph, the Orbital Workshop shower compartment was unfolded by technicians for inspection. The shower compartment was a cylindrical cloth enclosure that was folded flat when not in use. The bottom ring of the shower was fastened to the floor and contained foot restraints. The upper ring contained the shower head and hose. To use the shower, the astronaut filled a pressurized portable bottle with heated water and attached the bottle to the ceiling. A flexible hose cornected the water bottle to a handheld shower head. The astronaut pulled the cylindrical shower wall up into position and bathed, using liquid soap. Both soap and water were carefully rationed, having been premeasured for economical use.
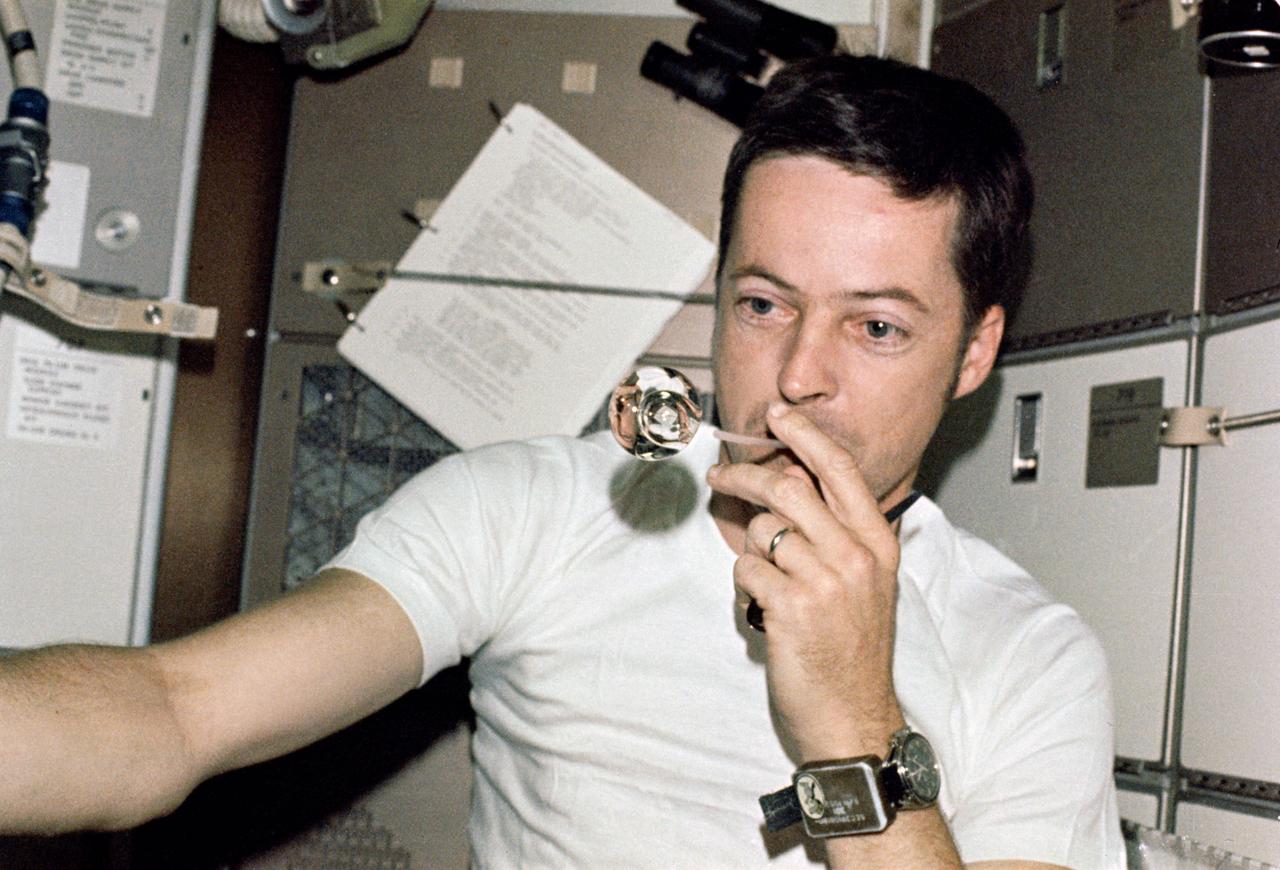

SL2-X9-730 (1 June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, forms a perfect sphere by blowing water droplets from a straw in zero-gravity. He is in the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA
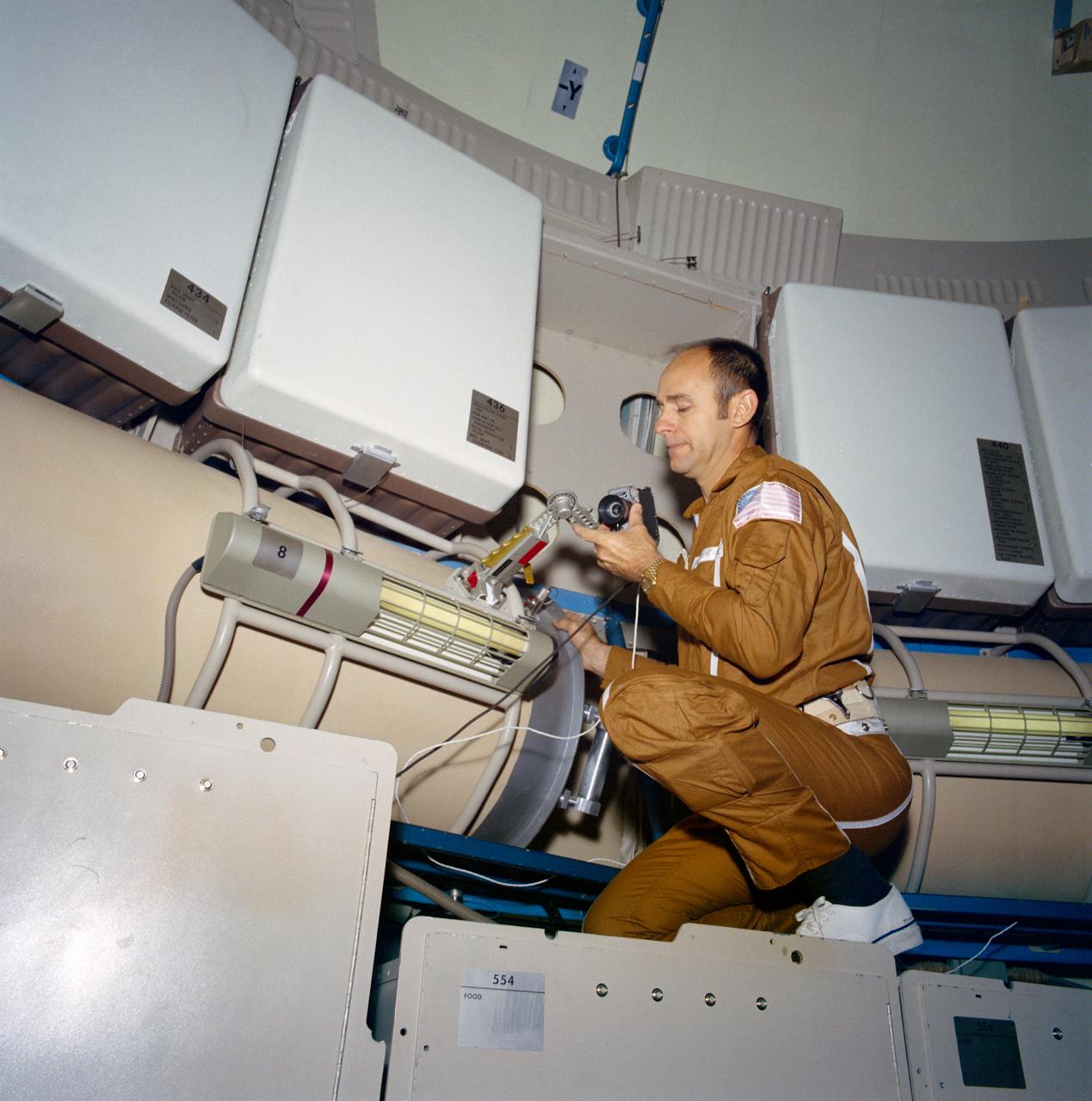

S72-39256 (1972) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, commander for Skylab 3, the second manned Skylab mission, looks over the data acquisition camera mounted on the water tank in the upper level of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) one-G trainer at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Photo credit: NASA
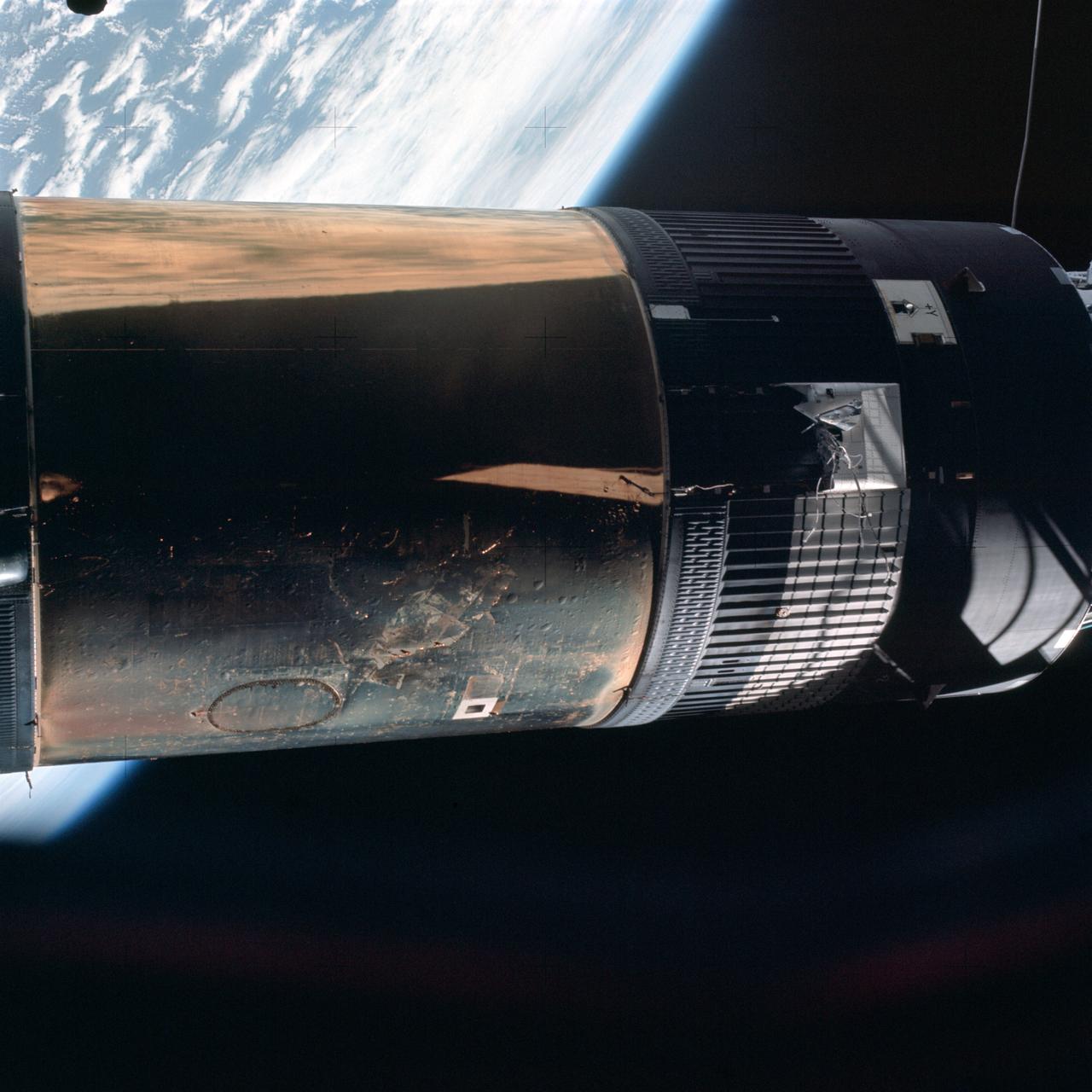
SL2-X4-256 (25 May 1973) --- This photo, made at long range from the command module during Skylab 2's approach to the Skylab complex during fly-around inspection, features the orbital workshop with the area of the missing micrometeoroid shield visible. Photo credit: NASA

This artist's concept depicts the separation of the Skylab payload shroud. The payload shroud was both an environmental shield and an aerodynamic fairing. Attached to the forward end of the fixed airlock shroud, it protected the airlock, the docking adapter, and the solar observatory before and during launch. It also provided structural support for the solar observatory in the launch configuration. The payload shroud was jettisoned once Skylab reached orbit after separation of the S-II second stage of the Saturn V vehicle. Five major assemblies clustered together made up the orbiting space station called Skylab. The largest of these was the orbital workshop, that housed the crew quarters and a major experiment area. The airlock module, attached to the forward end of the workshop, enabled crewmembers to make excursions outside Skylab. The docking adapter, attached to the forward end of the airlock module, provided the docking port for the Apollo command and service module. The Apollo Telescope Mount was the first marned astronomical observatory designed for solar research from Earth orbit.
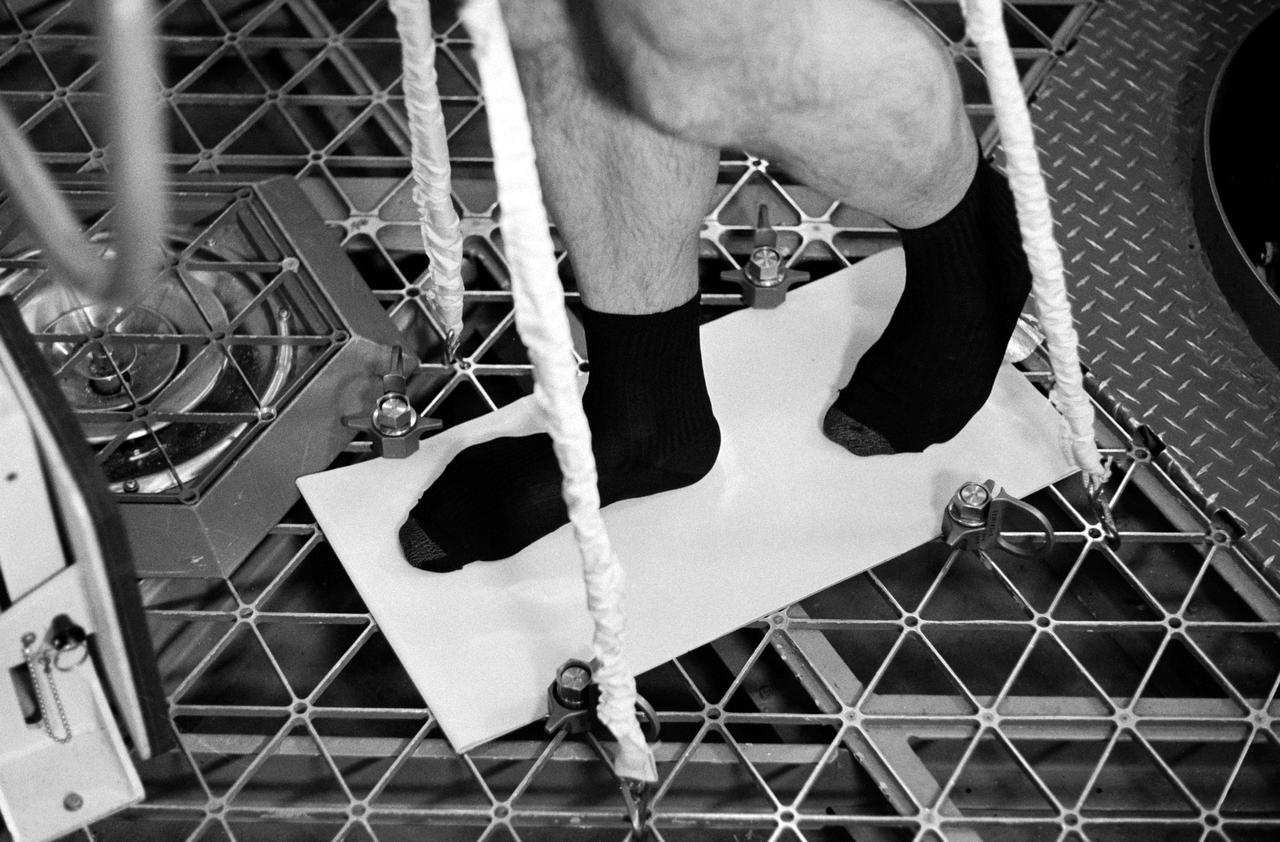

S73-33858 (November 1973) --- A close-up view of the feet of scientist-astronaut William E. Thornton as he demonstrates the use of a treadmill-like exercise device which was developed for maintaining the leg and back muscles of the Skylab 4 crewman. Thornton is in the Skylab Orbital Workshop simulator in Building 5 at the Johnson Space Center. The Skylab 2 and Skylab 3 astronauts had no exercise device onboard capable of adequately maintaining their leg and back muscles. The treadmill device consists of a Teflon-coated aluminum plate or sheet bolted to the floor of the Skylab Orbital Workshop. The crewmen will wear the bicycle ergometer harness while exercising. Bungee cords attached to the floor and to the harness will supply the downward pressure or force for the back and leg muscles. The astronaut's feet will slide over the Teflon-coated plate as he "marches in place." Photo credit: NASA
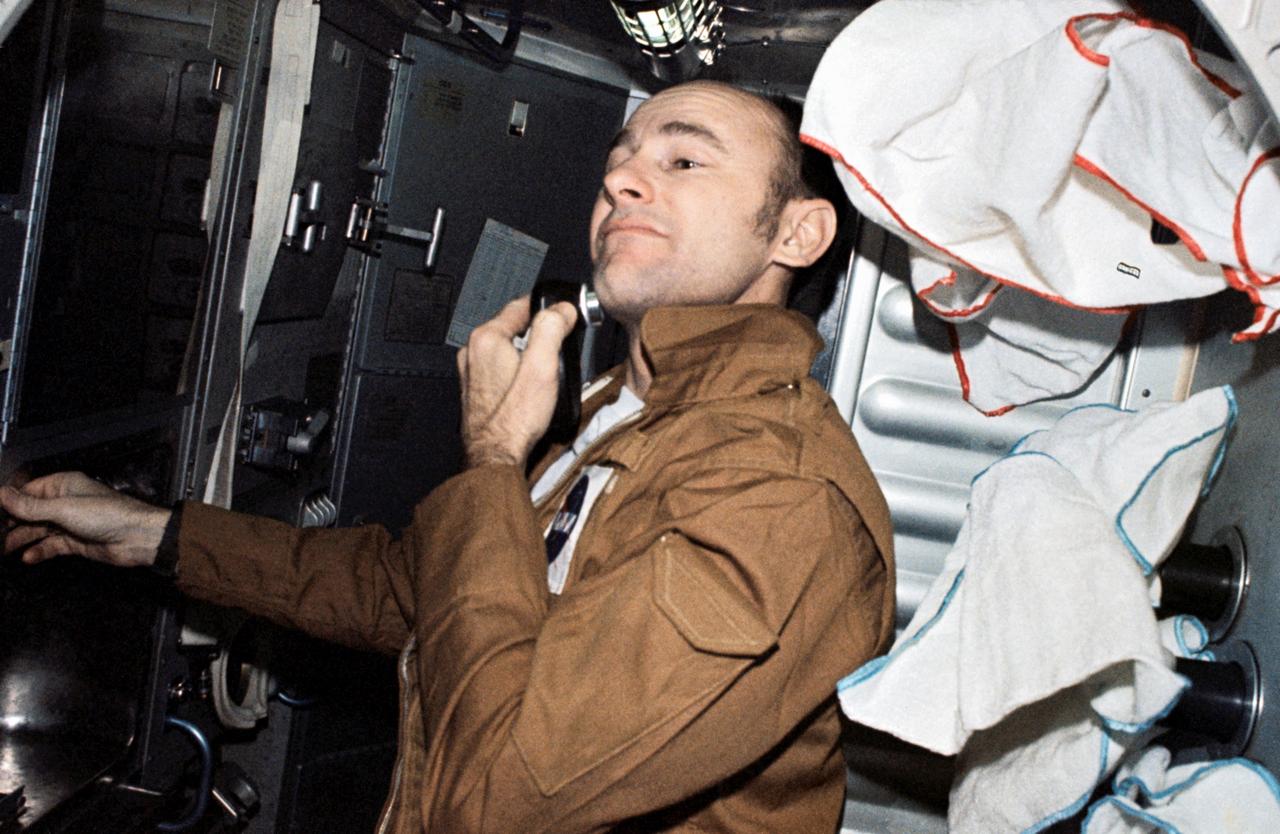

SL3-111-1516 (July-September 1973) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, Skylab 3 commander, uses a battery powered shaver in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) aboard the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. Astronaut Bean, Owen K. Garriott, science pilot, and Jack R. Lousma, pilot, went on to successfully complete 59 days aboard the Skylab cluster in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
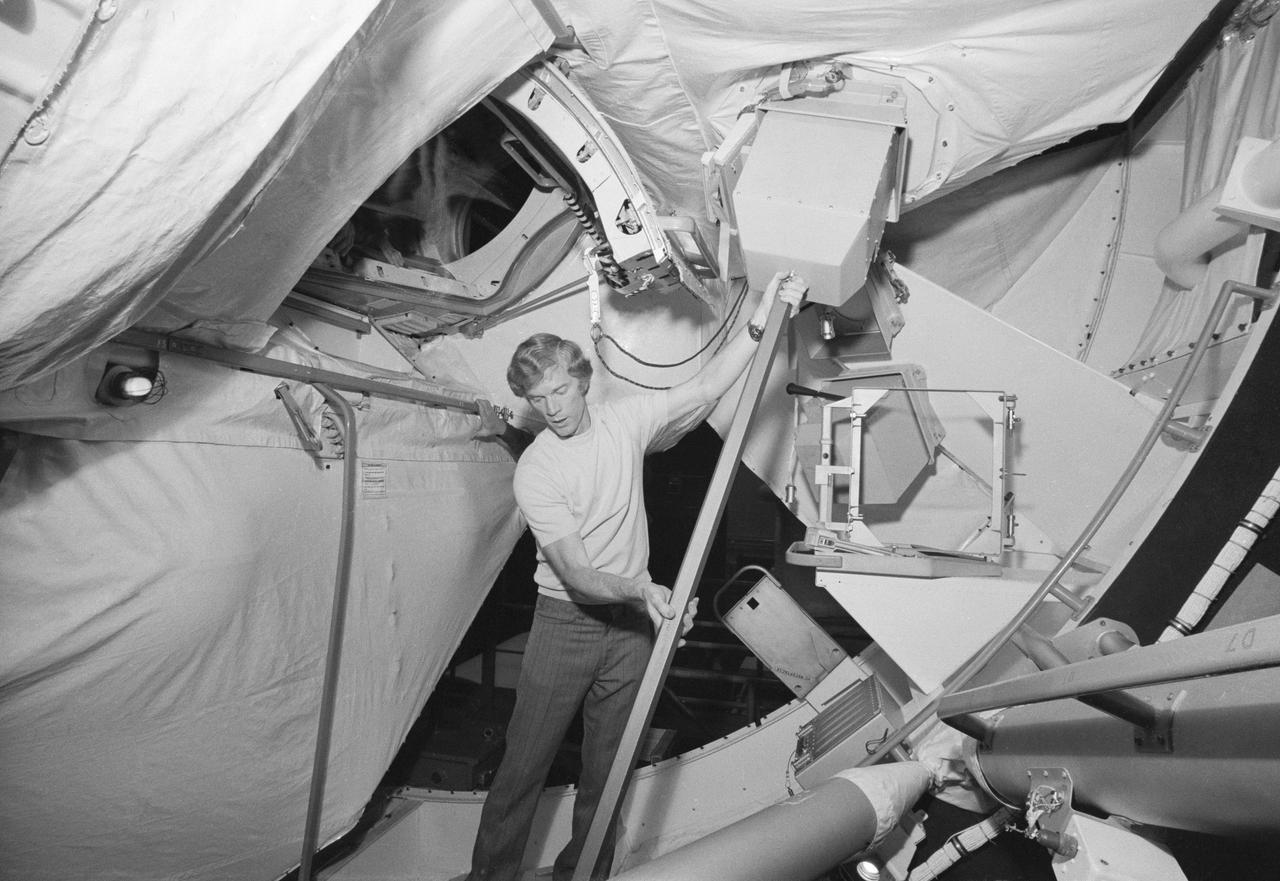

S73-25884 (1973) --- Astronaut Russell Schweickart in Orbital Workshop Simulator (OWS) working out procedure to be used for repair of damaged thermal protection cover on Skylab 2 spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA

SL3-111-1505 (July-September 1973) --- View of scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, in his sleep restraints in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop (OWS). Photo credit: NASA
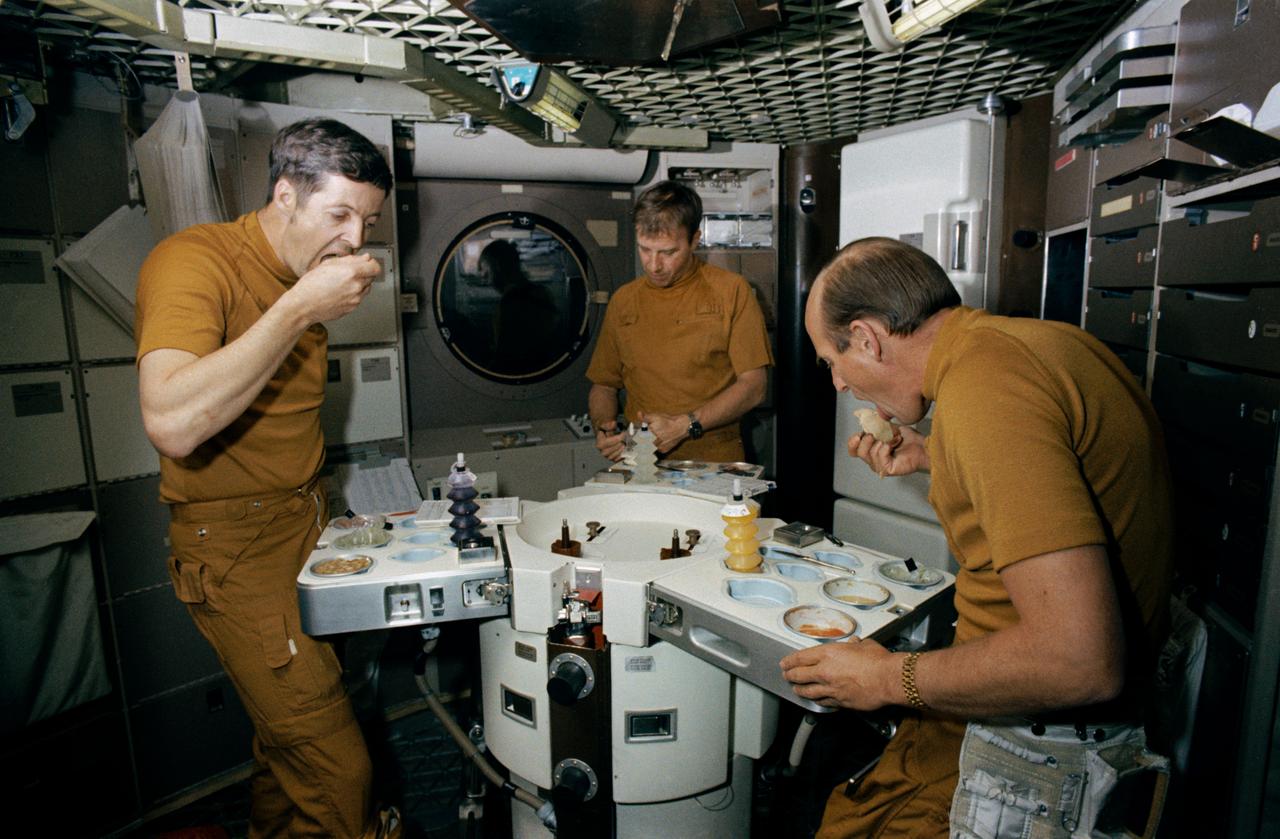

S73-20236 (1 March 1973) --- The three members of the prime crew of the first manned Skylab mission dine on specially prepared Skylab space food in the wardroom of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer during Skylab training at the Johnson Space Center. They are, left to right, scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot; astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot; and astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander. Photo credit: NASA
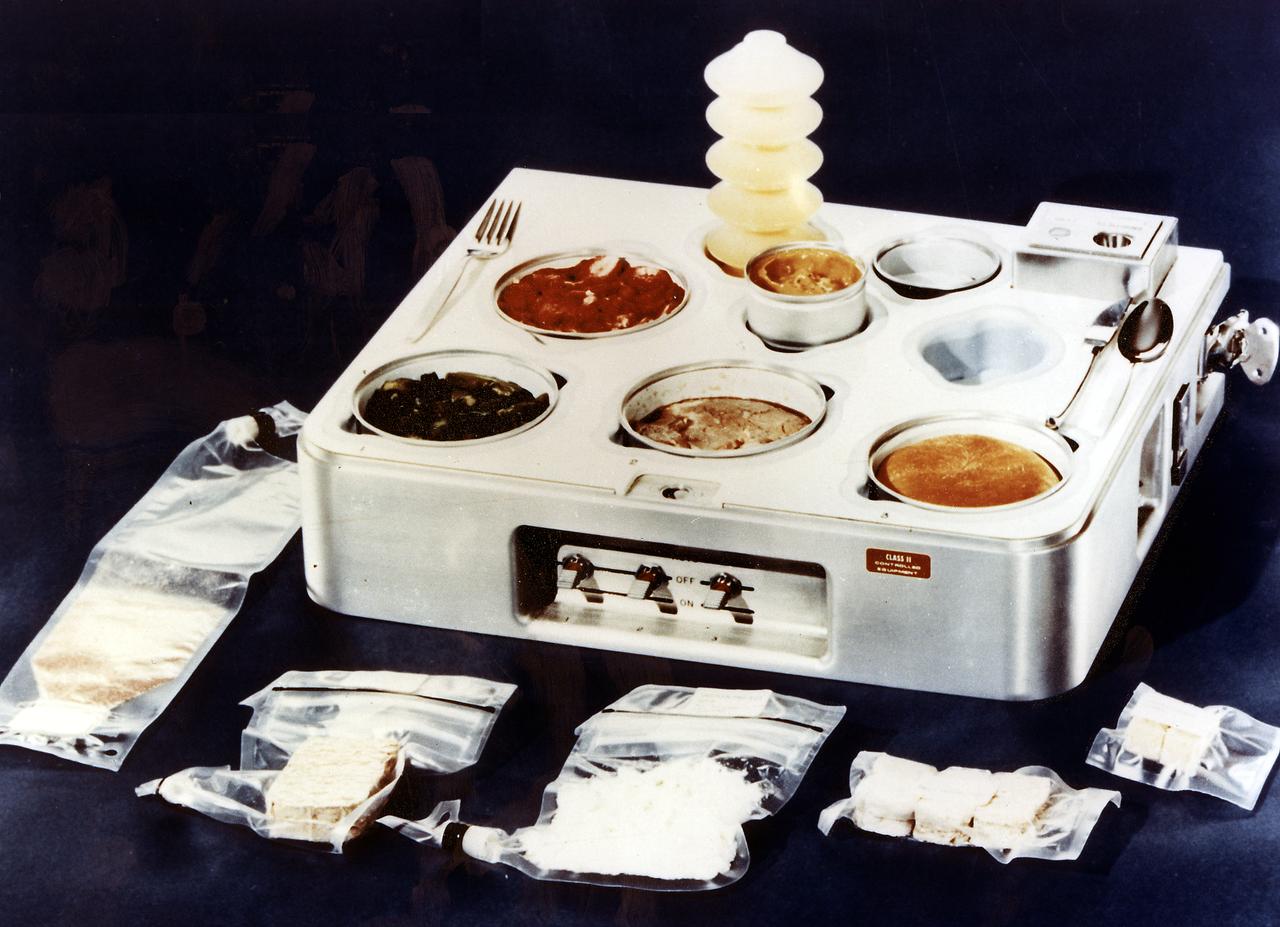

Shown here is the Skylab food heating and serving tray with food, drink, and utensils. The tray contained heating elements for preparing the individual food packets. The food on Skylab was a great improvement over that on earlier spaceflights. It was no longer necessary to squeeze liquified food from plastic tubes. Skylab's kitchen in the Orbital Workshop wardroom was so equipped that each crewman could select his own menu and prepare it to his own taste. The Marshall Space Flight Center had program management responsibility for the development of Skylab hardware and experiments.
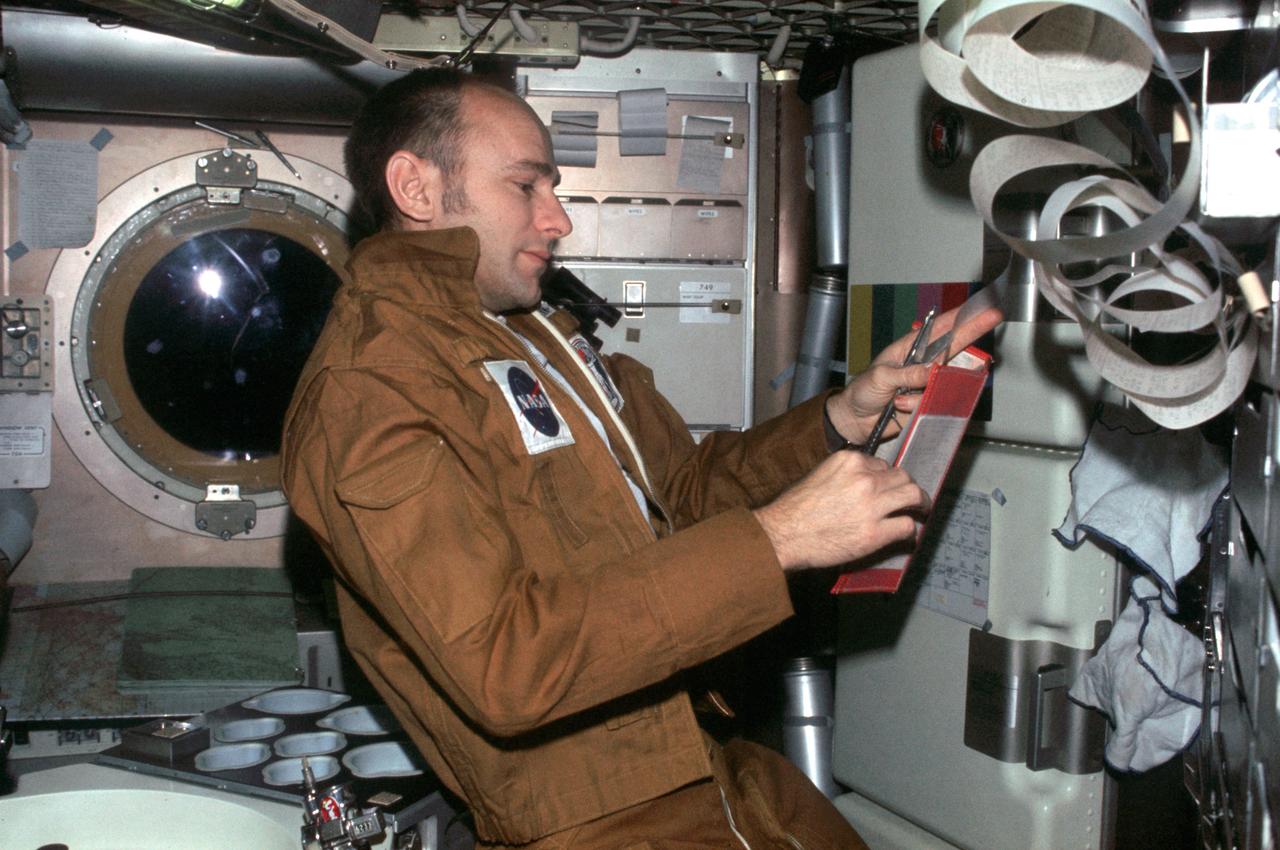

SL3-111-1514 (July-September 1973) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, Skylab 3 commander, reads data from book in his right hand while holding teleprinter tape in his left hand, in the ward room of the Skylab space station's Orbital Workshop (OWS) crew quarters. This photograph was taken with a 35mm Nikon camera held by one of Bean's fellow crewmen during the 56.5 day second manned Skylab mission in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

S73-26127 (1973) --- An artist's concept of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit illustrating the deployment of the twin pole thermal shield to shade the Orbital Workshop (OWS) from the sun. This is one of the sunshade possibilities considered to solve the problem of the overheated OWS. Here the two Skylab 2 astronauts have completely deployed the sunshade. Note the evidence of another Skylab problem - the solar panels on the OWS are not deployed as required. Photo credit: NASA
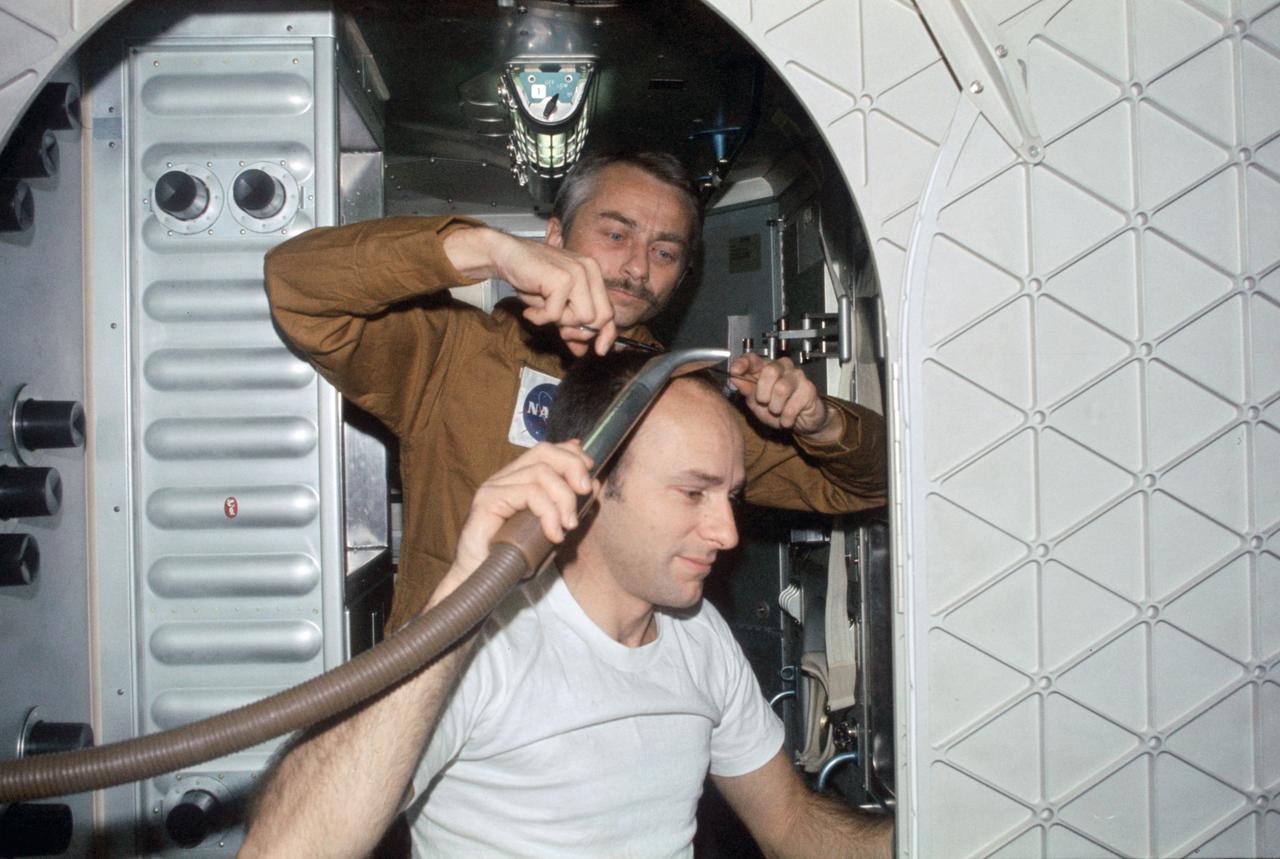
SL3-108-1292 (19 Aug. 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, trims the hair of astronaut Alan L. Bean, commander, in this onboard photograph from the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) in Earth orbit. Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, pilot, took this picture with a 35mm Nikon camera. Bean holds a vacuum hose to gather in loose hair. The crew of the second manned Skylab flight went on to successfully complete 59 days aboard the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA
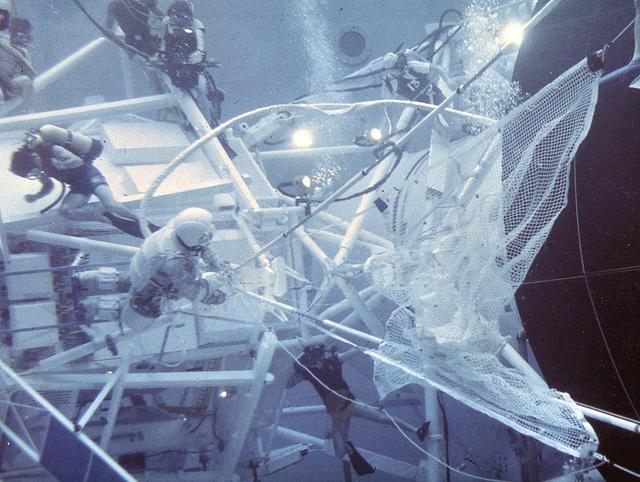

After its launch on May 14, 1973, it was immediately known that there were some major problems with Skylab. The large, delicate, meteoroid shield on the outside of the workshop was ripped off by the vibration of the launch. Its tearing off caused serious damage to the two wings of solar cells that were to supply most of the electric power to the workshop. Once in orbit, the news worsened. The loss of the big shade exposed the metal skin of the workshop to the sun. Internal temperatures soared to 126 degrees F. This heat not only threatened its habitation by astronauts, but if prolonged, would cause serious damage to instruments and film. After twice delaying the launch of the first astronaut crew, engineers worked frantically to develop solutions to these problems and salvage the Skylab. After designing a protective solar sail to cover the workshop, crews needed to practice using the specially designed tools and materials to facilitate the repair procedure. Marshall Space Flight Center's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS), was used to practice these maneuvers. Pictured here are the astronauts in the NBS deploying the protecticve solar sail. On may 25, 1973, an Apollo command and service module was launched and later docked with Skylab. The next day, astronauts Conrad and Kerwin were able to complete the needed repairs to Skylab, salvaging the entire program.
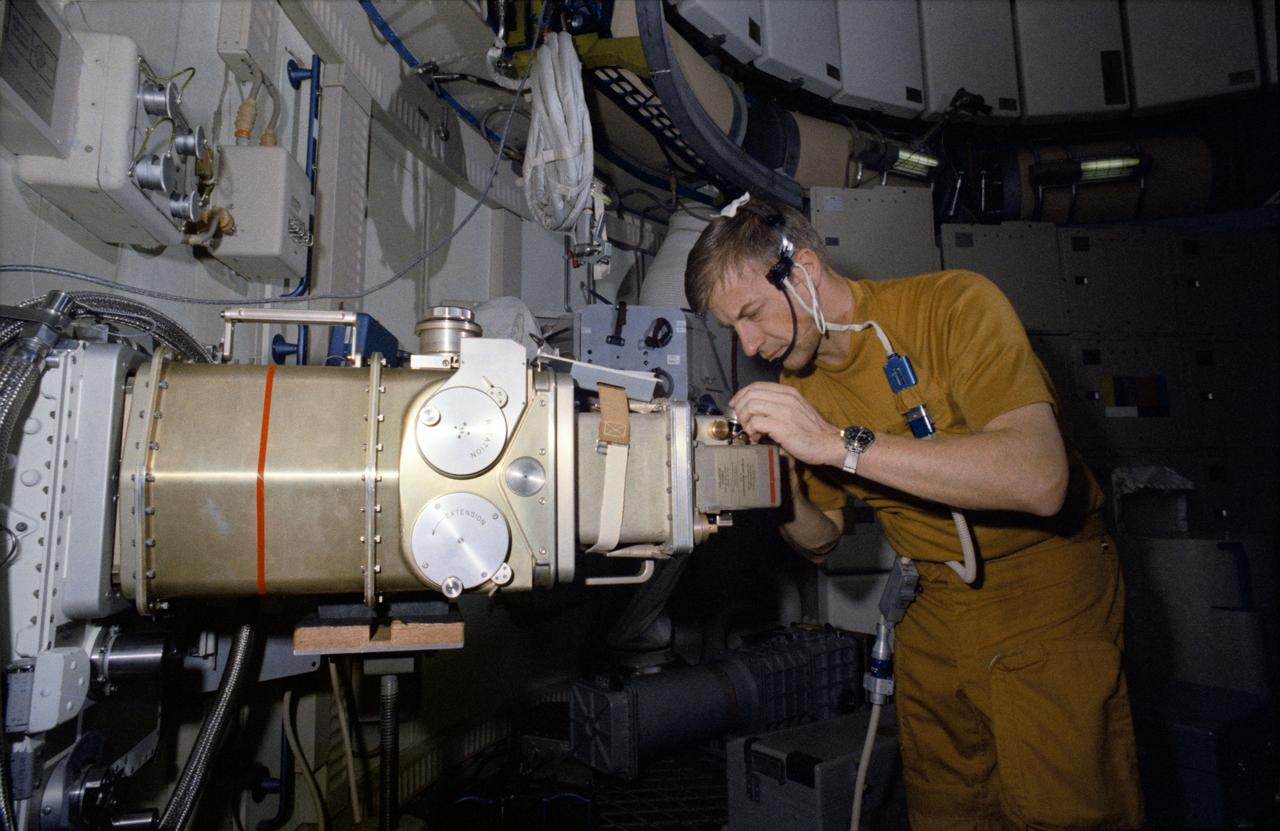

S73-20716 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot of the first manned Skylab mission, works with the UV Stellar Astronomy Experiment S019 in the forward compartment of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. The equipment consists of a reflecting telescope, a 35mm camera and an additional mirror. It is mounted in an anti-solar scientific airlock in the side of the OWS. Photo credit: NASA
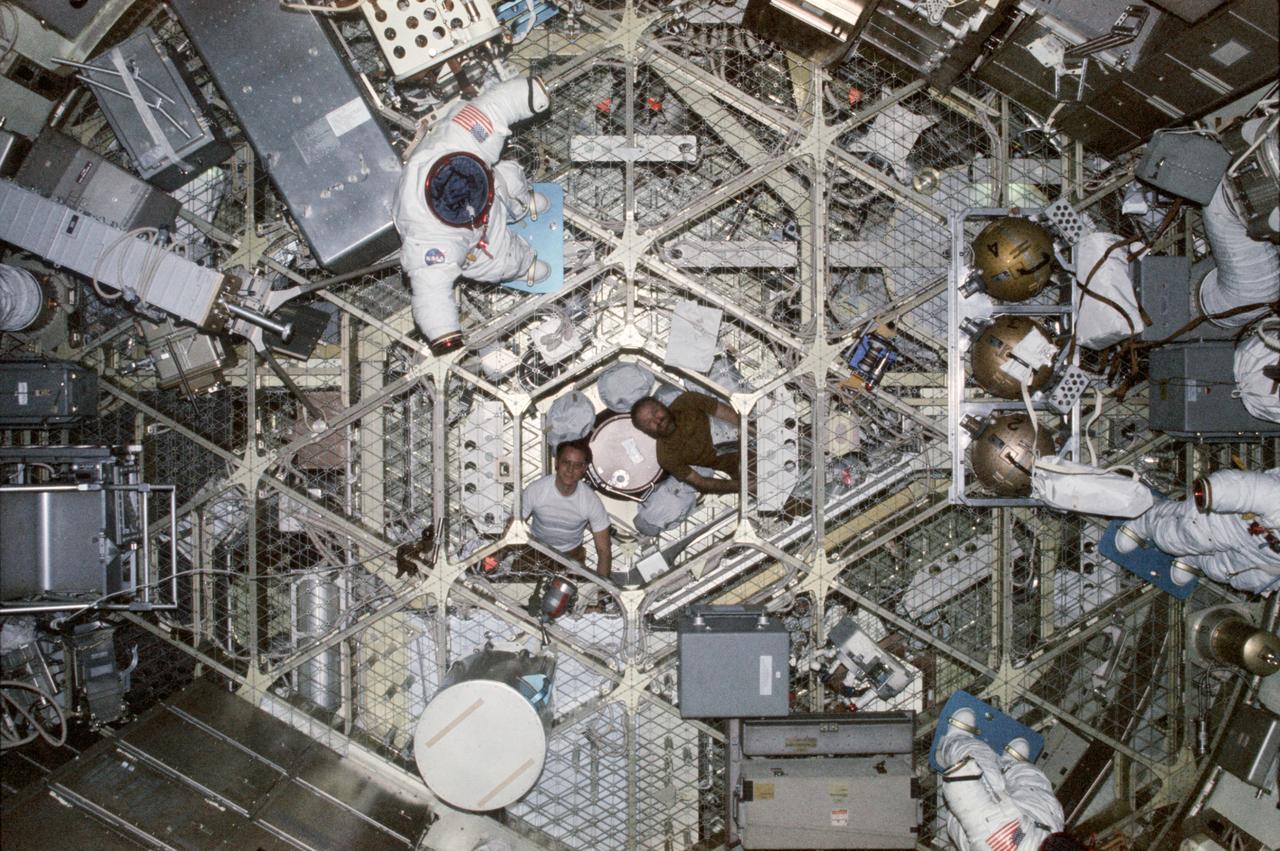
SL4-150-5062 (January 1974) --- A 35mm camera, operated by astronaut William R. Pogue, Skylab 4 pilot, recorded this wide scene of his Skylab 4 crewmates on the other end of the orbital workshop. Astronauts Jerry P. Carr (right), commander, and Edward G. Gibson, science pilot, pose for the snapshot. Also in the frame are parts of three Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuits, used on several EVA sessions during the third manning of the Skylab space station. Photo credit: NASA
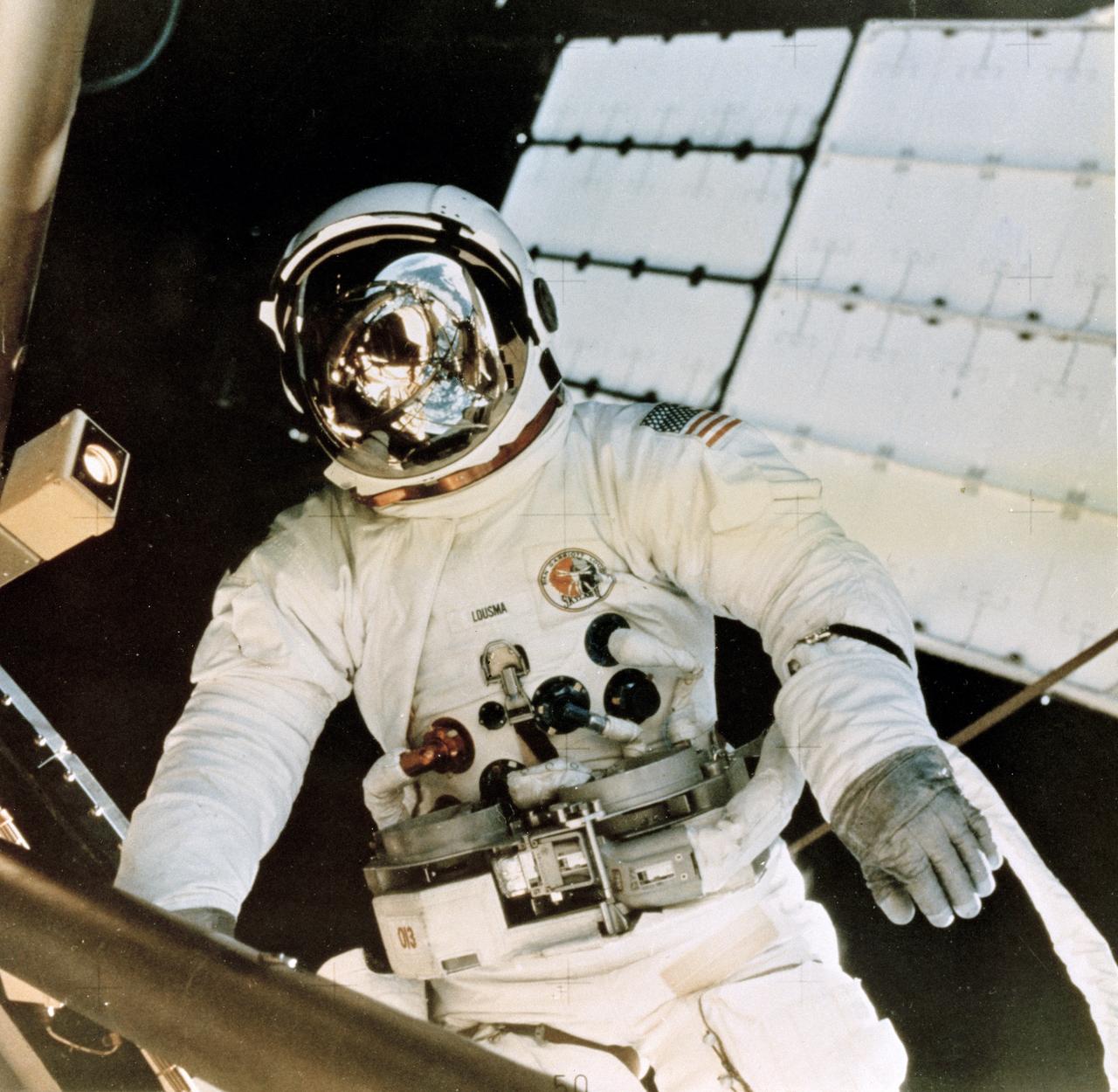

Skylab-3 was the second marned mission in the skylab project. The crew spent 59 days in orbit. In this photo, Astronaut Jack Lousma deploys the Twin Pole Sun Shield created by Marshall Space Flight Center team members to replace the micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat. The shield was damaged during the Skylab-2 mission.
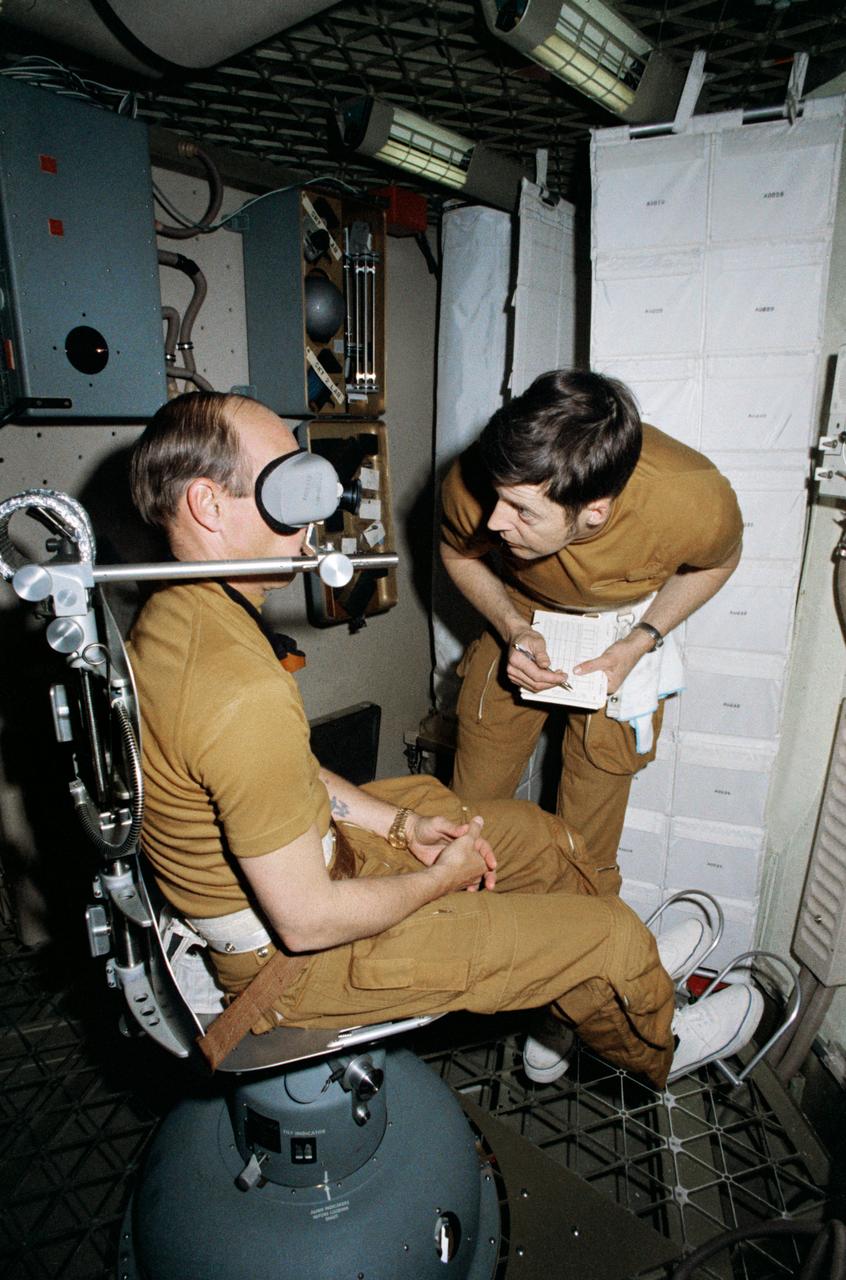
S73-20678 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander of the first manned Skylab mission, checks out the Human Vestibular Function, Experiment M131, during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot of the mission, goes over a checklist. The two men are in the work and experiments compartment of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer at JSC. Photo credit: NASA
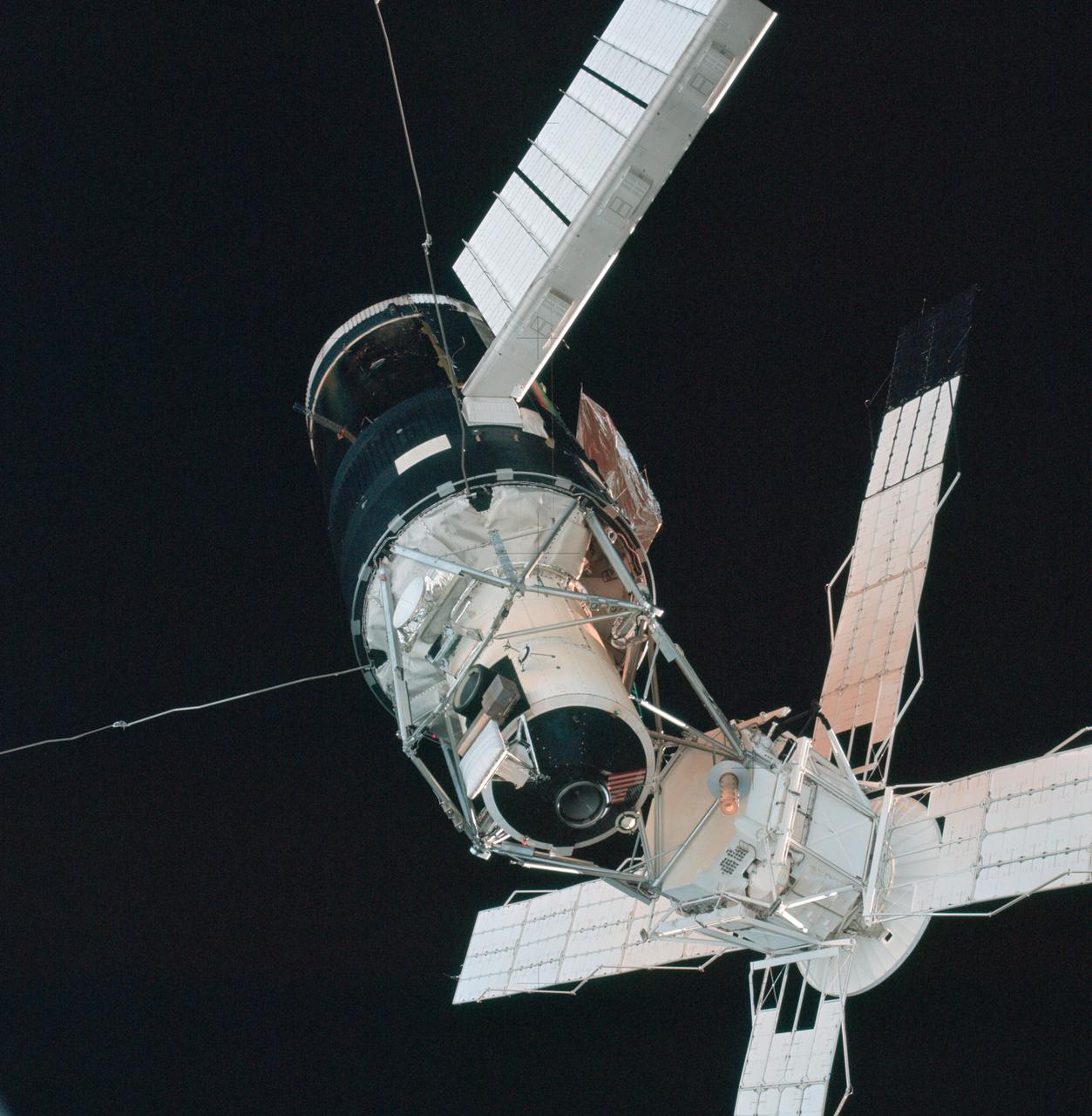
A close-up view of the Skylab space station cluster photographed against a black sky background from the Skylab 3 command module during the "fly around" inspection prior to docking. Note the one solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop (OWS) which was successfully deployed during EVA on the first manned Skylab mission. The primary docking part at the forward end of the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA) is visible below the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM).
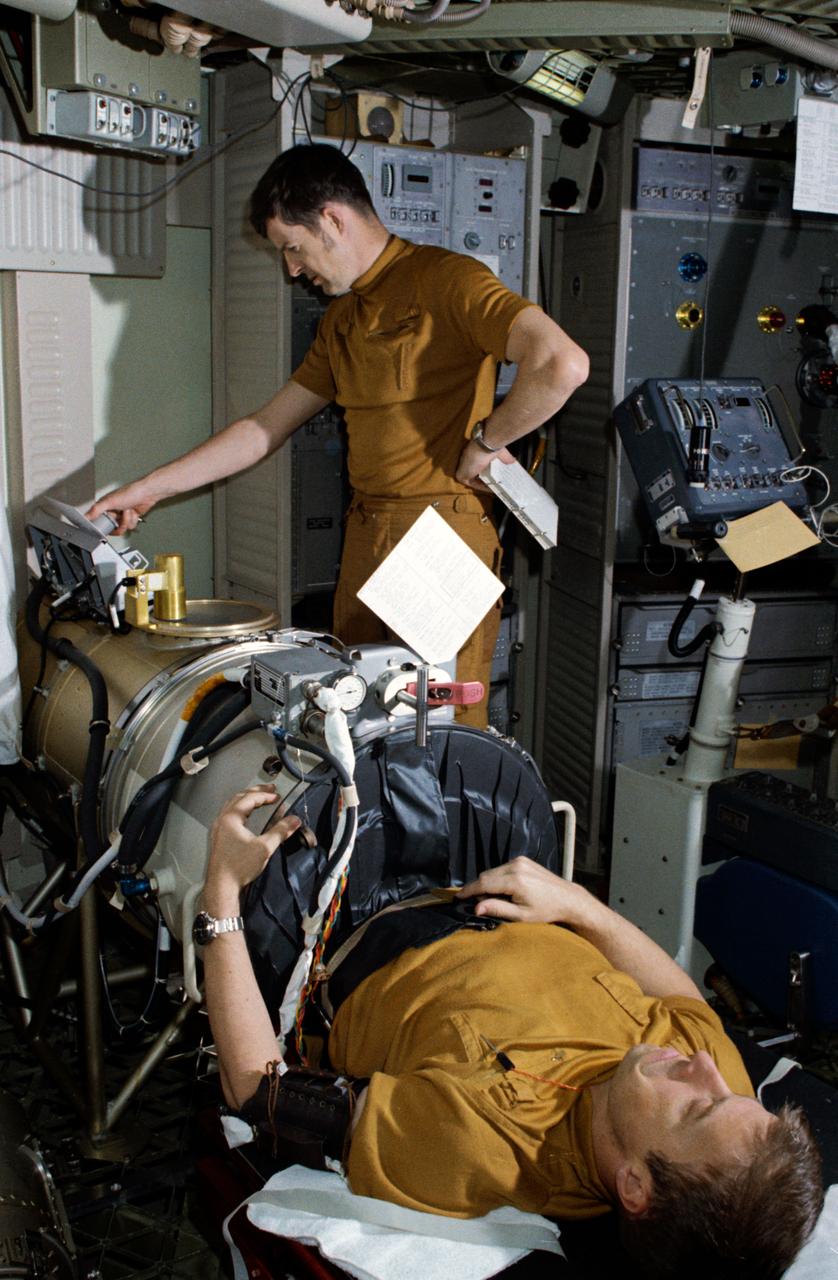

S73-20276 (1 March 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot of the first manned Skylab mission, lies in the lower body negative pressure device during Skylab training at Johnson Space Center. Operating the controls in the background is scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot of the mission. They are in the work and experiments area of the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer at JSC. Photo credit: NASA
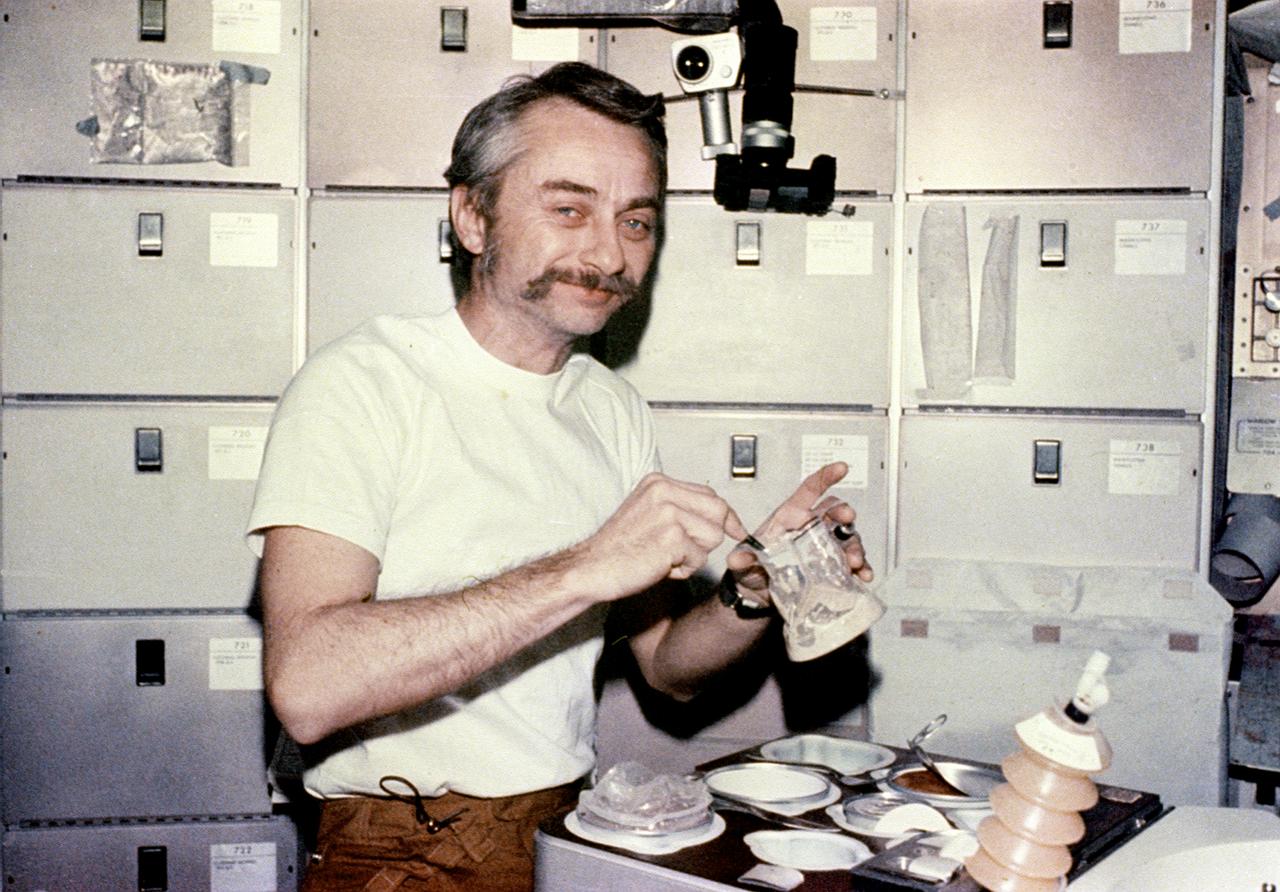

This photograph was taken during the Skylab-3 mission (2nd marned mission), showing Astronaut Owen Garriott enjoying his meal in the Orbital Workshop crew wardroom. The tray contained heating elements for preparing the individual food packets. The food on Skylab was a great improvement over that on earlier spaceflights. It was no longer necessary to squeeze liquified food from plastic tubes. Skylab's kitchen was so equipped that each crewman could select his own menu and prepare it to his own taste.

S73-27729 (1 June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, floats with his body outstretched as he demonstrates weightlessness in the forward compartment of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 & 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, is visible on Kerwin's right. The Skylab 2 crewmen performed exercises while floating. Photo credit: NASA
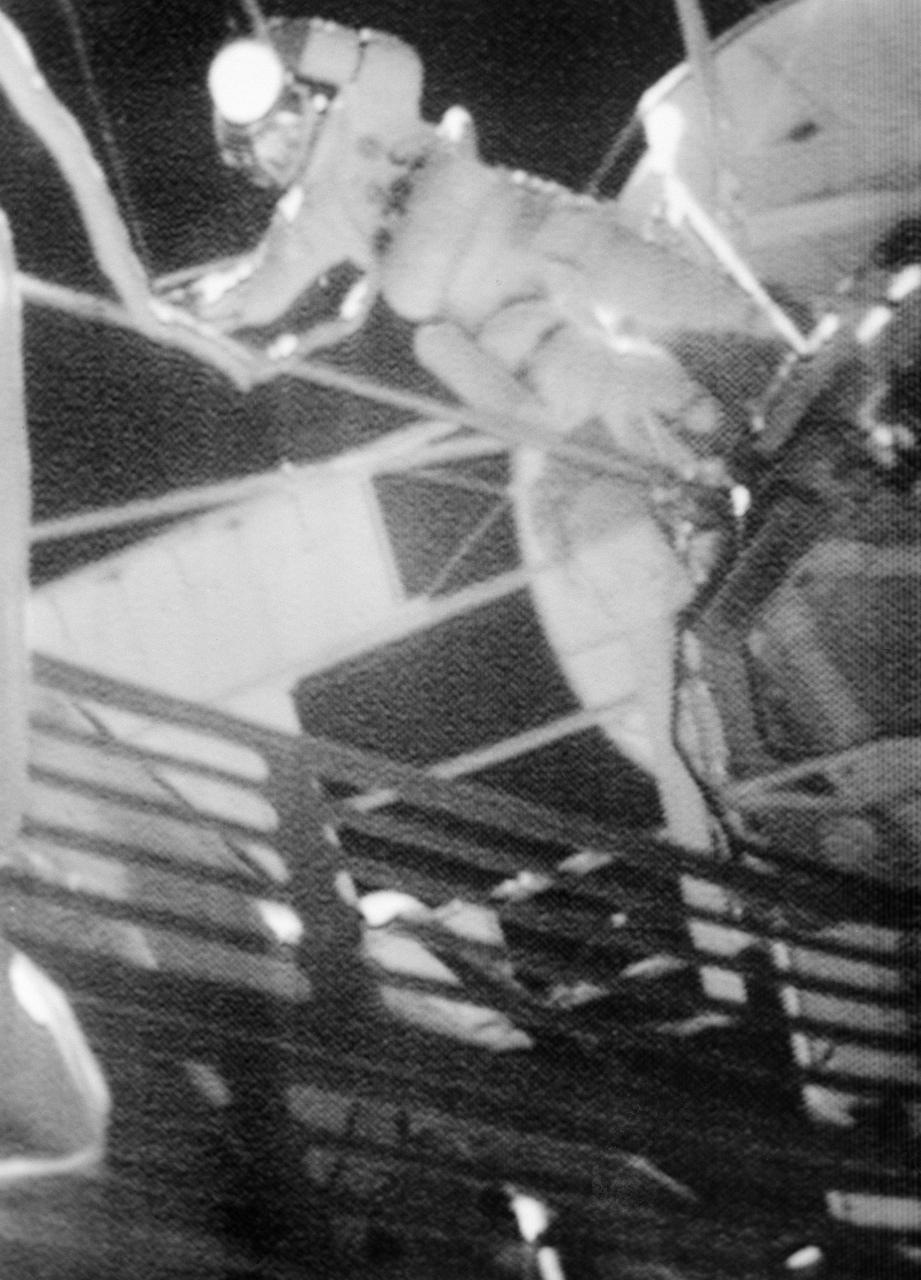

S73-31976 (5 Aug. 1973) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Skylab 3 pilot, is seen outside the Skylab space station in Earth orbit during the Aug. 5, 1973 Skylab 3 extravehicular activity (EVA) in this photographic reproduction taken from a television transmission made by a color TV camera aboard the space station. Scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, participated in the EVA with Lousma. During the EVA the two crewmen deployed the twin pole solar shield to help shade the Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA
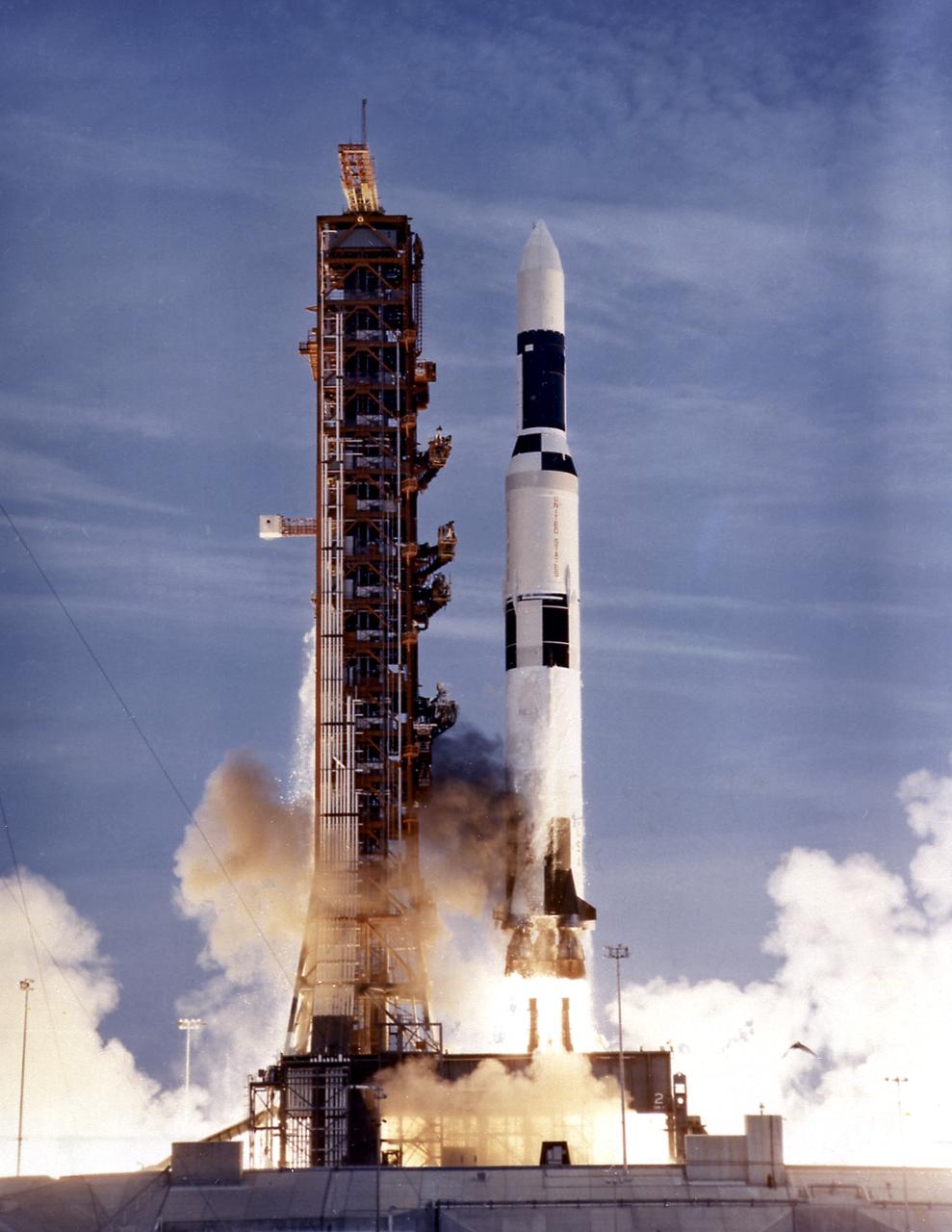
This photograph shows the launch of the SA-513, a modified unmarned two-stage Saturn V vehicle for the Skylab-1 mission, which placed the Skylab cluster into the Earth orbit on May 14, 1973. The initial step in the Skylab mission was the launch of a two-stage Saturn V booster, consisting of the S-IC first stage and the S-II second stage, from Launch Complex 39A at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Its payload was the unmanned Skylab, which consisted of the Orbital Workshop, the Airlock Module, the Multiple Docking Adapter, the Apollo Telescope Mount and an Instrument Unit.

S73-17859 (January 1973) --- Astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot for Skylab 2 (first Skylab manned) mission, looks over off-duty recreational equipment in the crew quarters of the Skylab Orbital Workshop (OWS) trainer during Skylab simulation activity at the Manned Spacecraft Center. The equipment includes such items as tape decks and stereo music equipment, playing cards, darts, etc. The OWS is a component of the Skylab space station cluster which will be launched unmanned aboard a Saturn V in summer of 1973, and will be visited three times by three-man crews over an eight month period. Photo credit: NASA
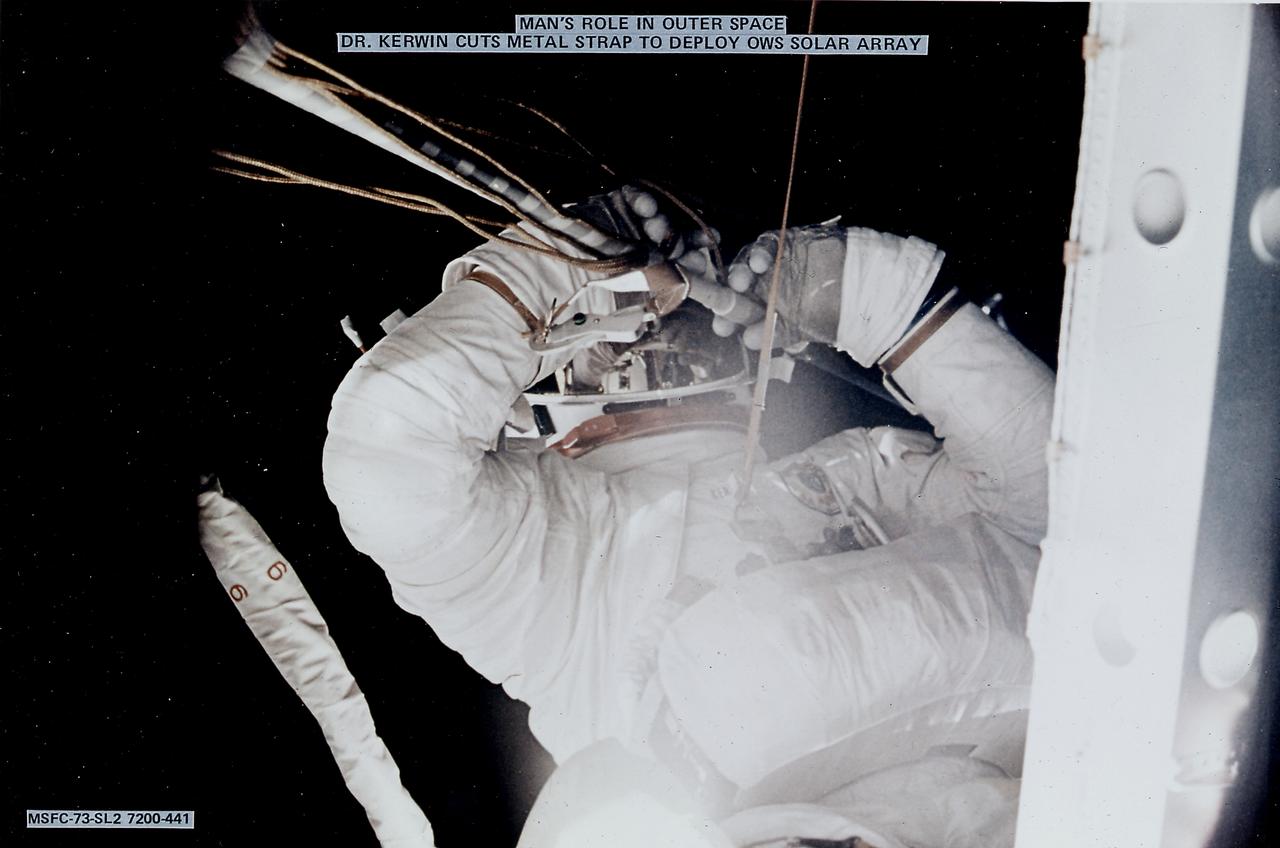

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into the flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Intrnal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image shows astronaut Kerwin cutting the metal strap to free and deploy the Orbital Workshop solar array. Kerwin used special cutting tools developed by engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The MSFC had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.
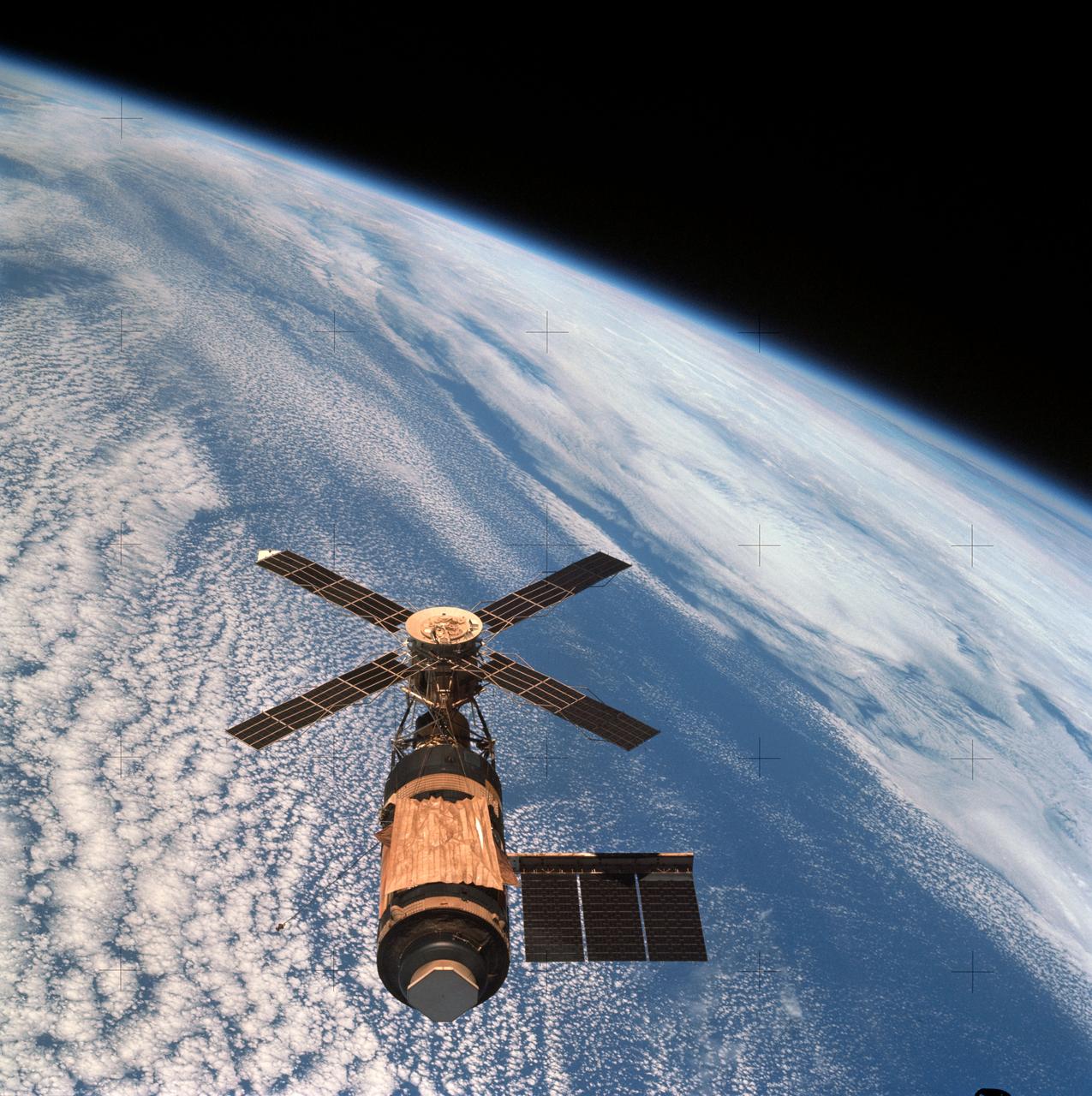

SL4-143-4706 (8 Feb. 1974) --- An overhead view of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit as photographed from the Skylab 4 Command and Service Modules (CSM) during the final fly-around by the CSM before returning home. The space station is contrasted against a cloud-covered Earth. Note the solar shield which was deployed by the second crew of Skylab and from which a micro meteoroid shield has been missing since the cluster was launched on May 14, 1973. The Orbital Workshop (OWS) solar panel on the left side was also lost on workshop launch day. Inside the Command Module (CM) when this picture was made were astronaut Gerald P. Carr, commander; scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot; and astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot. The crew used a 70mm hand-held Hasselblad camera to take this photograph. Photo credit: NASA
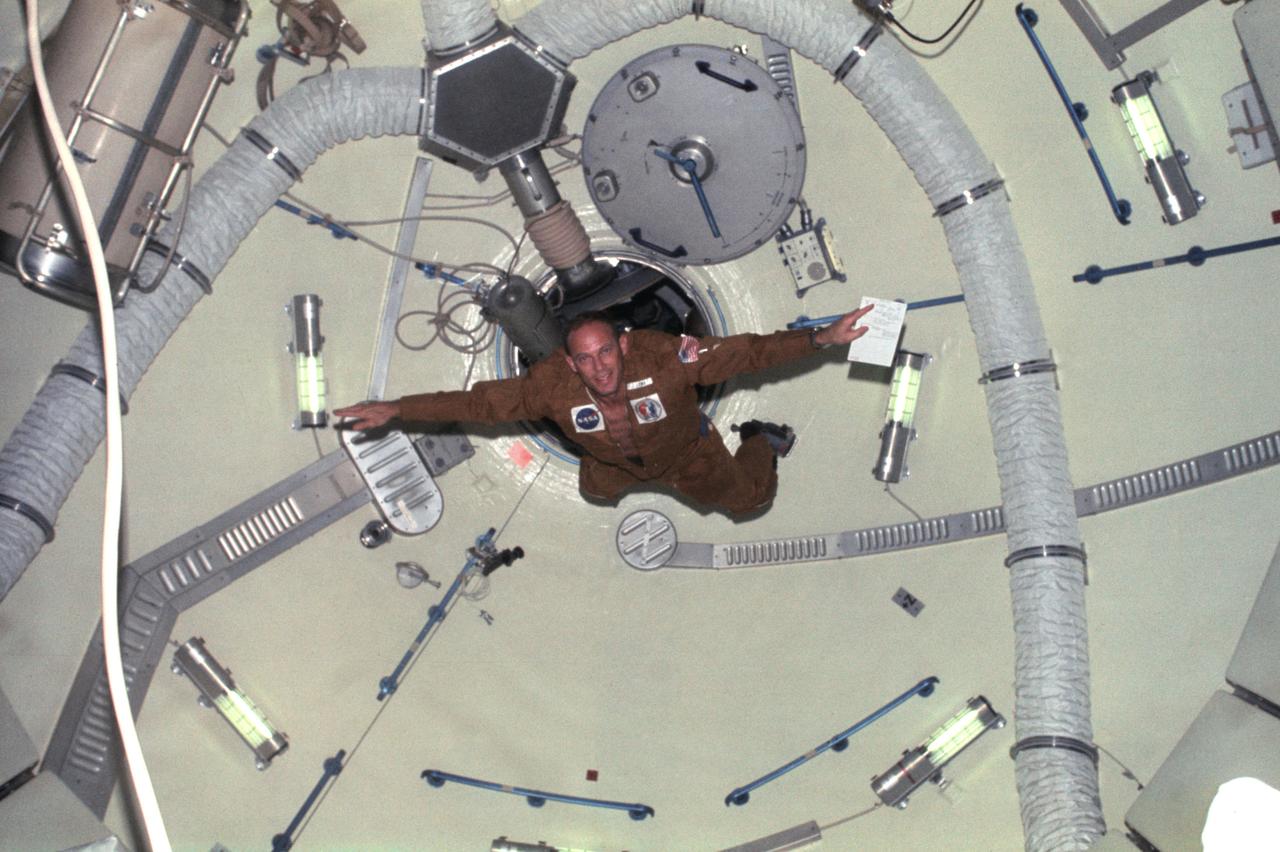

Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Skylab 3 pilot, doing acrobatics in the dome area of the Orbital Workshop (OWS) on the space station cluster in Earth orbit. The dome area is about 22 feet in diameter and 19 feet from top to bottom.
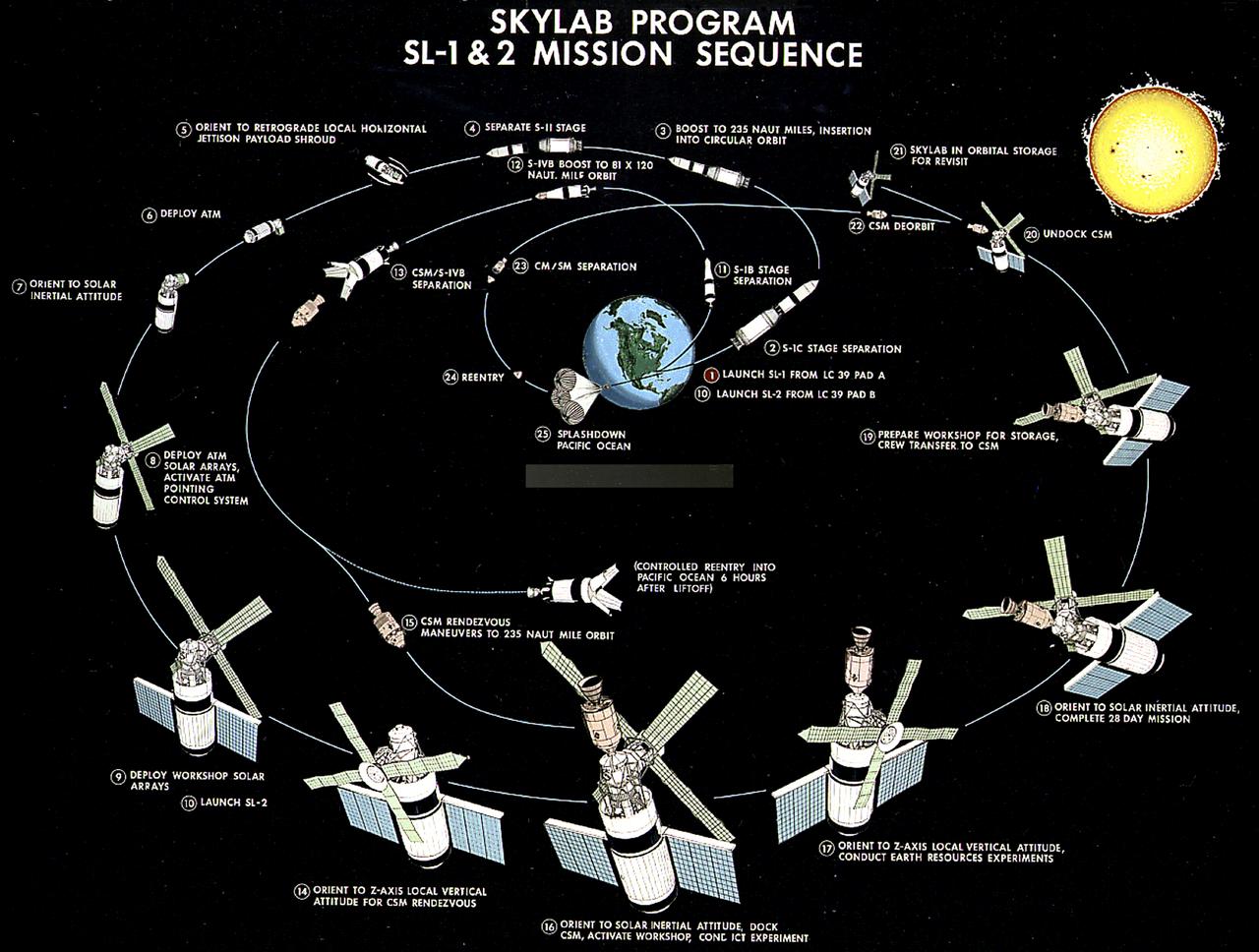
This illustration depicts the Skylab-1 and Skylab-2 mission sequence. The goals of the Skylab were to enrich our scientific knowledge of the Earth, the Sun, the stars, and cosmic space; to study the effects of weightlessness on living organisms, including man; to study the effects of the processing and manufacturing of materials utilizing the absence of gravity; and to conduct Earth resource observations. The Skylab also conducted 19 selected experiments submitted by high school students. Skylab's 3 different 3-man crews spent up to 84 days in Earth orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) had responsibility for developing and integrating most of the major components of the Skylab: the Orbital Workshop (OWS), Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), Payload Shroud (PS), and most of the experiments. MSFC was also responsible for providing the Saturn IB launch vehicles for three Apollo spacecraft and crews and a Saturn V launch vehicle for the Skylab.

S73-26776 (26 May 1973) --- An interior view of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 space station cluster in Earth orbit can be seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, is floating up through the hatch. Food lockers are in the foreground. Photo credit: NASA

S73-34193 (1 Aug. 1973) --- Astronaut Jack R. Lousma, Skylab 3 pilot, looks at a map of Earth at the food table in the ward room of the Orbital Workshop (OWS). In this photographic reproduction taken from a television transmission made by a color TV camera aboard the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27260 (1 June 1973) --- Two of the three Skylab 2 crewmen demonstrate weightlessness in the forward compartment of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 & 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot, floats with his body extended. Kerwin is steadied by astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander. The crewmen performed exercises while floating. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27081 (30 May 1973) --- Two of the three Skylab 2 astronauts are seen in the wardroom of the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 space station cluster in Earth orbit in this reproduction taken from a television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. They are preparing to eat a meal. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, is in the right foreground. In the background is astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. Photo credit: NASA
S73-32632 (19 Aug. 1973) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, Skylab 3 commander, performs acrobatics and simulated gymnastics in the dome area of the Orbital Workshop in this photographic reproduction taken from a television transmission made by a color TV camera aboard the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Bean appears to be floating in a diving position. Photo credit: NASA

SL2-X3-205 (June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, is photographed strapped into the sleep restraint in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 & 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. Kerwin is wearing the special cap which contains biomedical instrumentation for the M133 Sleep Monitoring Experiment. The purpose of the M133 experiment is to evaluate quantity and quality of sleep during prolonged space flight by the analysis of electroencephalographic (EEG) and electrooculographic (EOG) activity. Photo credit: NASA

S73-37274 (1973) --- An artist's concept illustrating how the Skylab 4 astronauts will observe, through the scientific airlock of the Orbital Workshop, the passing of the newly-discovered Comet Kohoutek. The favorable location of the Skylab space station in Earth orbit will help provide a comprehensive investigation of the nature and evolution of the coma and tails as the comet approaches, passes, and recedes from the sun. Photo credit: NASA

Scientist-Astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, is photographed strapped into the sleep restraint in the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. Kerwin is wearing the special cap which contains biomedical instrumentation for the M133 Sleep Monitoring Experiment. The purpose of the M133 experiment is to evaluate quantity and quality of sleep during prolonged space flight by the analysis of electroencephalographic (EEG) and electrooculographic (EOG) activity.
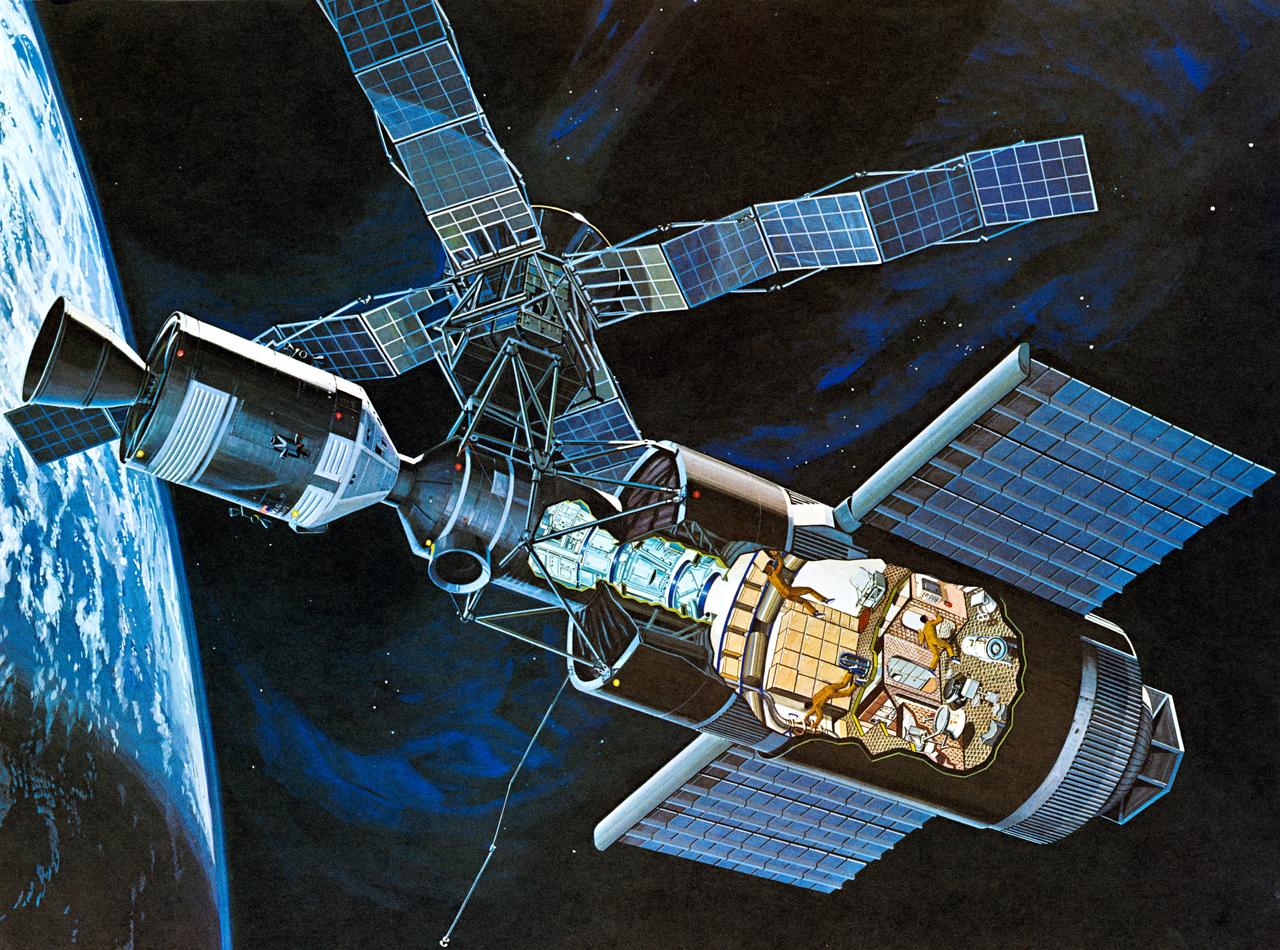

S71-52192 (1971) --- An artist's concept of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth's orbit. The cutaway view shows astronaut activity in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). The Skylab cluster is composed of the OWS, Airlock Module (AM), Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), and the Command and Service Module (CSM). Photo credit: NASA

S73-31973 (August 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, looks at a map of Earth at the food table in the ward room of the Orbital Workshop (OWS). In this photographic reproduction taken from a television transmission made by a color TV camera aboard the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA

S73-26128 (1973) --- An artist's concept of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit illustrating the deployment of the twin pole thermal shield to shade the Orbital Workshop (OWS) from the sun. This is one of the sunshade possibilities considered to solve the problem of the overheated OWS. In this view the Skylab astronauts have partially deployed the sunshade. Photo credit: NASA

S73-27467 (5 June 1973) --- An overhead view of astronaut Paul J. Weitz, Skylab 2 pilot, at the video tape recorder in the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit. Weitz is changing the tape in the recorder and storing the used data tape. This photograph was reproduced from a color television transmission made on June 5, 1973. Photo credit: NASA

This montage illustrates the various configurations and missions of the three classes of the Saturn vehicles developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The missions for the Saturn I included atmospheric science investigations and the deployment of the Pegasus meteroid-detection satellite as well as launch vehicle development. The Saturn IB vehicle tested the Apollo spacecraft and launched the three marned Skylab missions as well as the Apollo Soyuz test project. The Saturn V vehicle launched the manned lunar orbital/landing missions, and the Skylab Orbital Workshop in 1973.

S73-26794 (26 May 1973) --- Two of the three Skylab 2 astronauts are seen in the wardroom of the crew quarters of the Orbital Workshop of the Skylab 1 space station cluster in Earth orbit in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the space station. They are preparing a meal. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, is in the right foreground. In the background is scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot. Photo credit: NASA

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A wreath is placed next to a photo of former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue during a ceremony to honor Pogue held at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Gerald P. Carr and science-pilot Dr. Edward G. Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former NASA astronaut Edward G. Gibson, Ph.D., remarks on his friendship with former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue during a wreath laying ceremony at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Gerald P. Carr and science-pilot Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former NASA astronaut Gerald P. Carr remarks on his friendship with former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue during a wreath laying ceremony at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Carr and science-pilot Dr. Edward G. Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former NASA astronauts Gerald P. Carr, left, and Edward G. Gibson place a wreath on an easel during a ceremony to honor former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. In the background is a painting by former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Carr and science-pilot Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – From left, former NASA astronauts Robert Cabana, Gerald P. Carr and Edward G. Gibson pay their respects to former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue during a wreath laying ceremony at the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Cabana now is the director of Kennedy Space Center. In the background is a painting by former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Carr and science-pilot Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Robert Cabana welcomes guests to the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex for a wreath laying ceremony to honor former NASA astronaut William R. Pogue. Col. Pogue, pilot on NASA's Skylab 4 mission in 1973-74, died March 3. He was 84 years old. Skylab 4 was the third and final manned visit to the Skylab orbital workshop, launched Nov. 16, 1973, and concluded Feb. 8, 1974. At 84 days, 1 hour and 15 minutes, Skylab 4 was the longest manned space flight to that date. Pogue was accompanied on the record-setting 34.5-million-mile flight by Commander Gerald P. Carr and science-pilot Dr. Edward G. Gibson. They conducted dozens of experiments and science demonstrations during their 1,214 orbits of Earth. Pogue logged 13 hours and 31 minutes in two spacewalks outside the orbital workshop. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/content/skylab-4-pilot-william-pogue-dies. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image, taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew, shows the damaged meteoroid shield being held by a thin aluminum strap entangled with green-hued remnants of the lost heat shield. The Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed, tested, rehearsed, and approved three repair options. These options included a parasol sunshade and a twin-pole sunshade to restore the temperature inside the workshop, and a set of metal cutting tools to free the jammed solar panel.

S73-27562 (June 1973) --- Scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, Skylab 2 science pilot, performs extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Skylab 1 and 2 space station cluster in Earth orbit, as seen in this reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by a TV camera aboard the station. Kerwin is just outside the Airlock Module. Kerwin assisted astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., Skylab 2 commander, during the successful EVA attempt to free the stuck solar array system wing on the Orbital Workshop. Photo credit: NASA
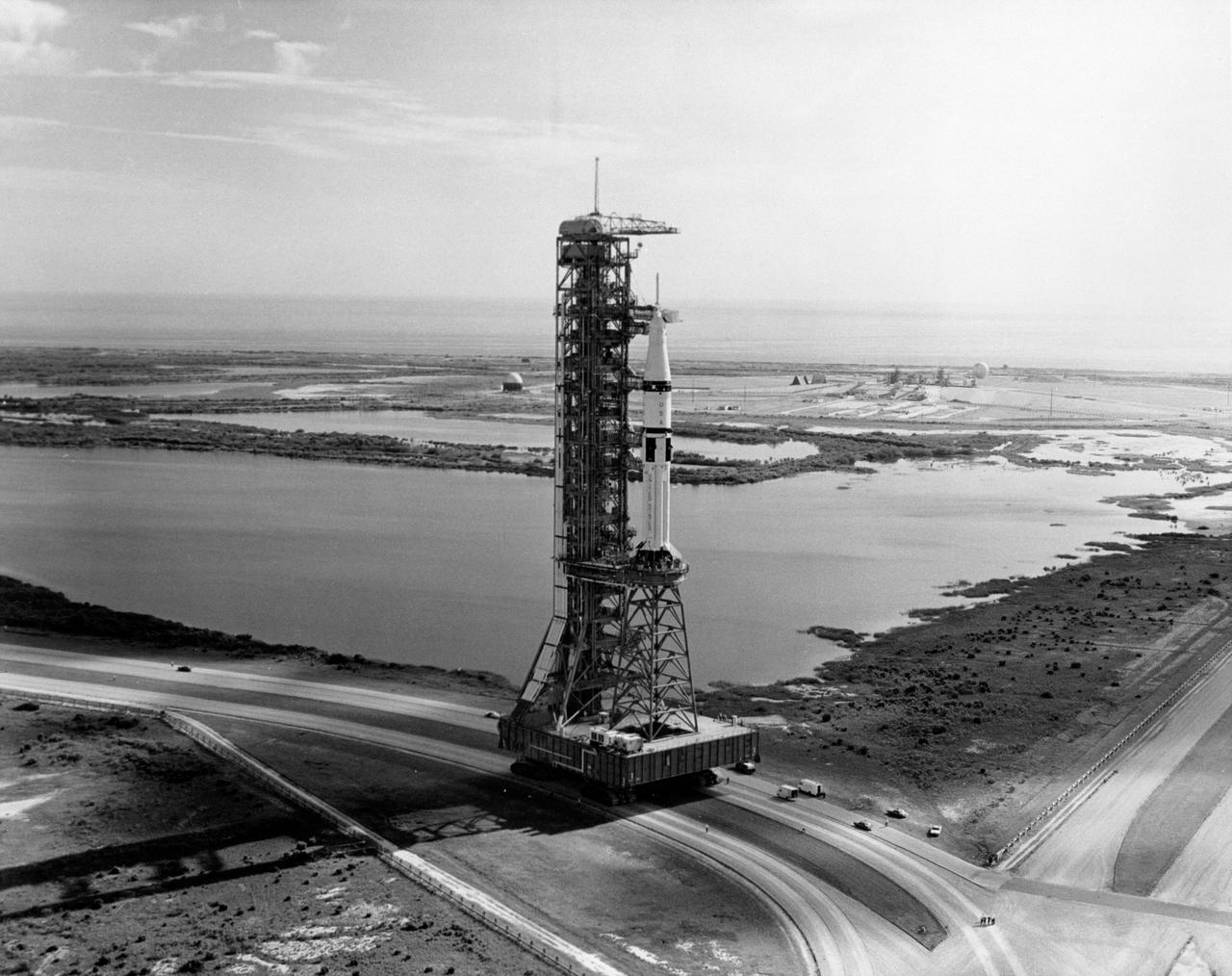

S73-34369 (14 Aug. 1973) --- A Saturn 1B launch vehicle is rolled to Launch Complex 39, Pad B. The space vehicle, to be launched by the Saturn 1B, will carry the third Skylab crew (Skylab 4) to the now-orbiting Orbital Workshop (OWS) and the other four components making up the cluster. The Skylab crewmen, astronaut Gerald P. Carr, commander; scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot; and astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot, are scheduled to be launched from here in November 1973. Photo credit: NASA

S73-37650 (28 Nov. 1973) --- Astronaut Gerald P. Carr, right, Skylab 4 commander, enjoys a meal aboard the orbiting Skylab space station in this photographic reproduction from a television of Nov. 28, 1973. Scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot for the third manned Skylab flight, demonstrates the zero-gravity environment by turning upside. The two crewmen were joined by astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot, for the evening meal. The food station is in the wardroom of the Crew Quarters in the Orbital Workshop (OWS). Photo credit: NASA

The Saturn V vehicle, carrying the unmarned orbital workshop for the Skylab-1 mission, lifted off successfully and all systems performed normally. Sixty-three seconds into the flight, engineers in the operation support and control center saw an unexpected telemetry indication that signalled that damages occurred on one solar array and the micrometeoroid shield during the launch. The micrometeoroid shield, a thin protective cylinder surrounding the workshop protecting it from tiny space particles and the sun's scorching heat, ripped loose from its position around the workshop. This caused the loss of one solar wing and jammed the other. Still unoccupied, the Skylab was stricken with the loss of the heat shield and sunlight beat mercilessly on the lab's sensitive skin. Internal temperatures soared, rendering the station uninhabitable, threatening foods, medicines, films, and experiments. This image, taken during a fly-around inspection by the Skylab-2 crew, shows the station's remaining solar panel jammed against its side. The Marshall Space Flight Center had a major role in developing the procedures to repair the damaged Skylab.
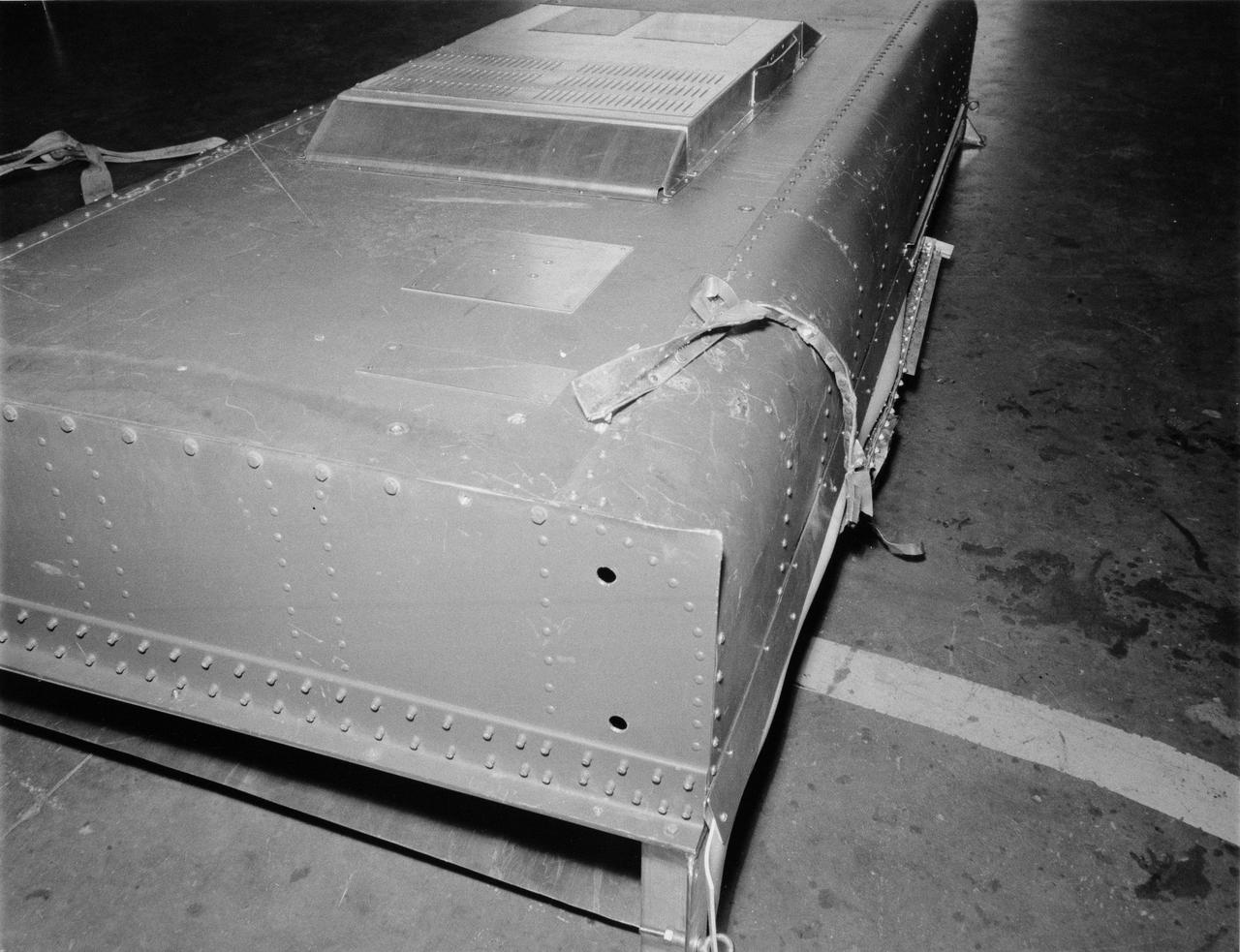

S73-27406 (5 June 1973) --- This structure duplicates the current problem with solar array wing number one on Skylab. The wing is being held against the side of the Orbital Workshop by what appears to be a strip of metal from the Meteoroid shield. Photo credit: NASA
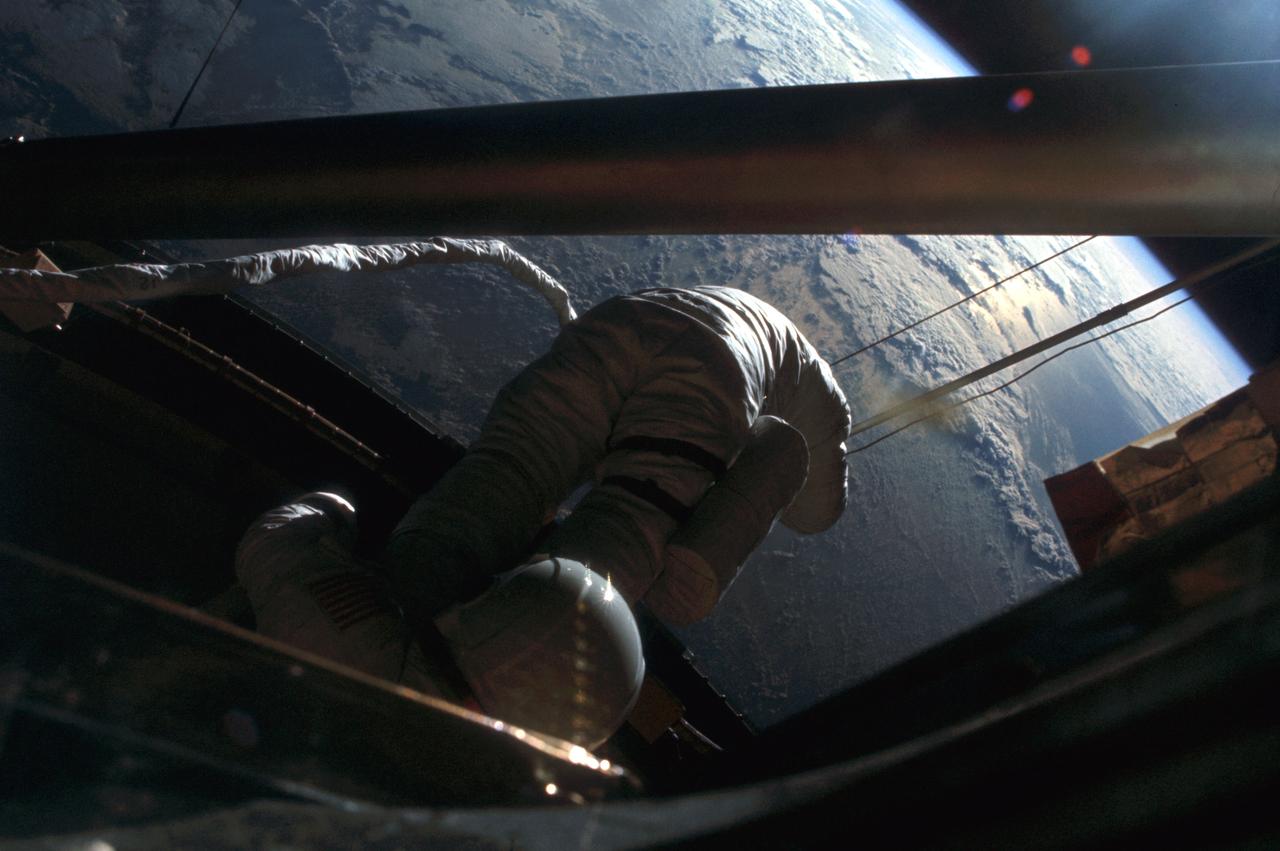

SL3-118-2182 (6 Aug. 1973) --- Skylab 3 astronaut participates in the Aug. 6, 1973 extravehicular activity (EVA) during which the twin pole solar shield was deployed to help shade the Orbital Workshop (OWS). Photo credit: NASA
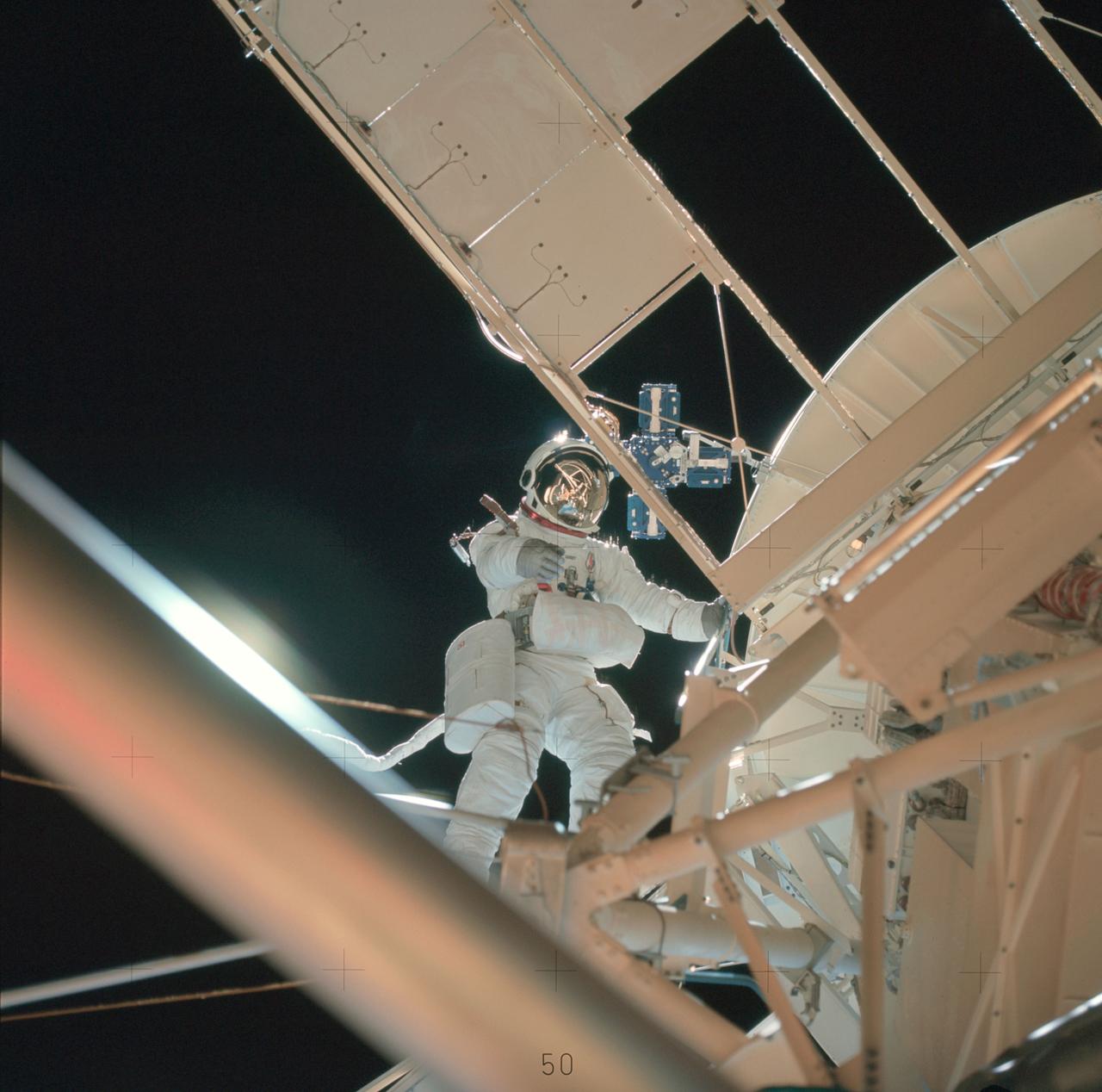

Scientist-Astronaut Owen K. Garriott, Skylab 3 science pilot, participates in the August 6, 1973 extravehicular activity (EVA) during which he and Astronaut Jack Lousma, Skylab pilot, deployed the twin pole solar shield to help shade the Orbital Workshop (OWS). Note the reflection of the solar shield in Garriett's helmet visor.
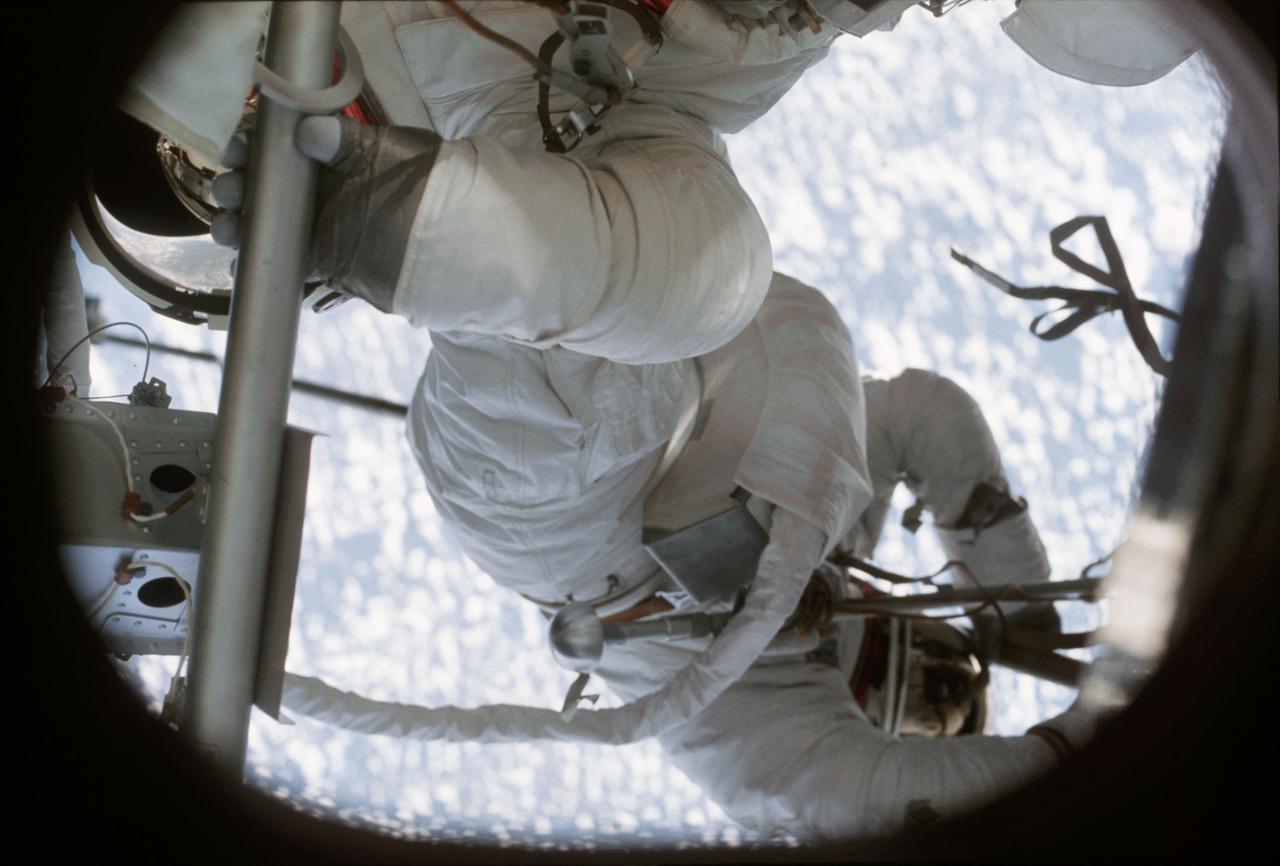

SL2-100-799 (7 June 1973) --- This medium close-up view shows astronauts Charles Conrad, commander for Skylab 2, and Science Pilot Joseph P. Kerwin performing an extravehicular activity (EVA) to repair the damaged and partially deployed solar array system on the Skylab complex. The photo was taken from inside the Orbital Workshop (OWS) by astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot. Photo credit: NASA