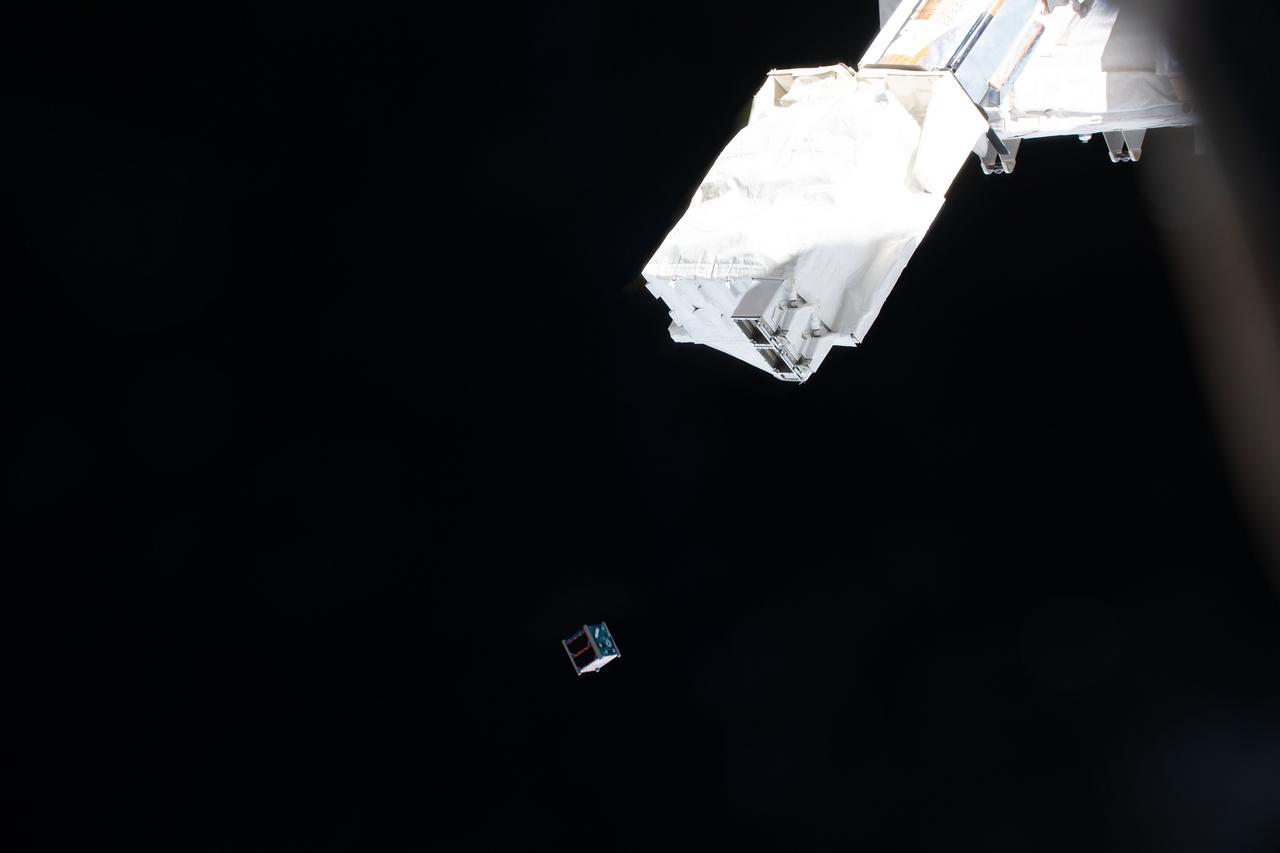

iss070e041245 (Dec. 18, 2023) --- The Clark sat-1 CubeSat is deployed from a small satellie deployer in the grips of the Japanese robotic arm attached to the Kibo laboratory module. Clark sat-1, launched to the Interational Space Station aboard the SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft, was developed by students at Clark Next High School in Tokyo, Japan, and its primary mission is to transmit voice and imagery data to ground control stations on Earth.
![iss056e200730 (10/3/2018) --- Photo documentation of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (SSOD) on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP) installation in preparation of the [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) mission. J-SSOD-10 deploys the cubesats SPATIUM-I from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, and the Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan, RSP-00 from Ryman Sat Spaces General Incorporated Association, Japan, and STARS-Me from Shizuoka University, Japan.](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss056e200730/iss056e200730~medium.jpg)
iss056e200730 (10/3/2018) --- Photo documentation of the JEM Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (SSOD) on the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform (MPEP) installation in preparation of the [Japanese Experiment Module]-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer 10 (J-SSOD 10) mission. J-SSOD-10 deploys the cubesats SPATIUM-I from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, and the Kyushu Institute of Technology, Japan, RSP-00 from Ryman Sat Spaces General Incorporated Association, Japan, and STARS-Me from Shizuoka University, Japan.

TechEdSat 5 PhoneSat 5 Team photo on July 26, 2016. Taken in fron of the 1/3 scale Shuttle Orbiter Model, in front of the Parade Ground on Clark Road at NASA Research Park. Mark Murbach Sarosh Hussain Ali Guarneros Luna David Handy Jonathan Hanson Jakqueline Granillo Sarah Chu Alejandro Sales
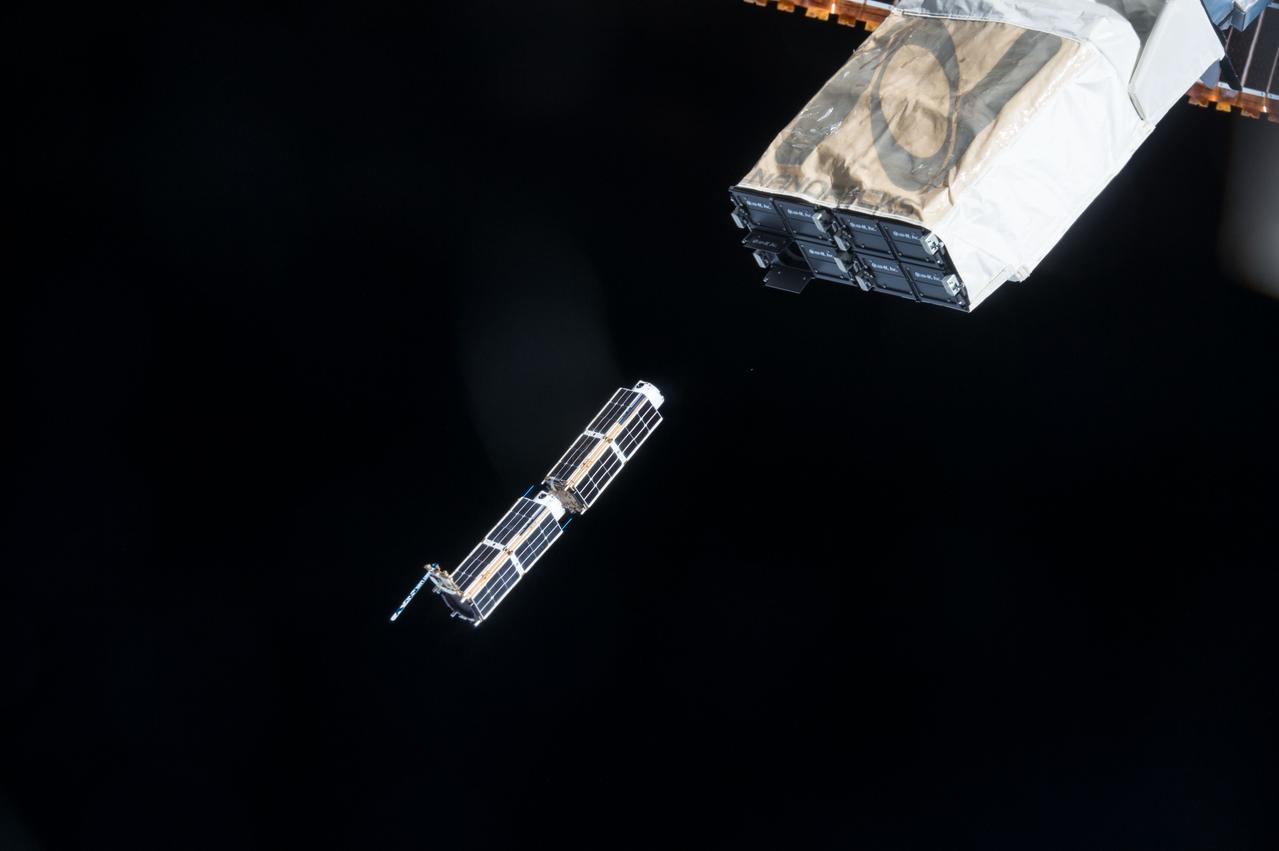

ISS042E290579 (02/27/2015) --- On Feb. 27 2015, a series of CubeSats, small experimental satellites, were deployed via a special device mounted on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Remote Manipulator System (JEMRMS). Deployed satellites included twelve Dove sats, one TechEdSat-4, one GEARRSat, one LambdaSat, one MicroMas. These satellites perform a variety of functions from capturing new Earth imagery, to using microwave scanners to create 3D images of hurricanes, to even developing new methods for returning science samples back to Earth from space. The small satellites were deployed through the first week in March.
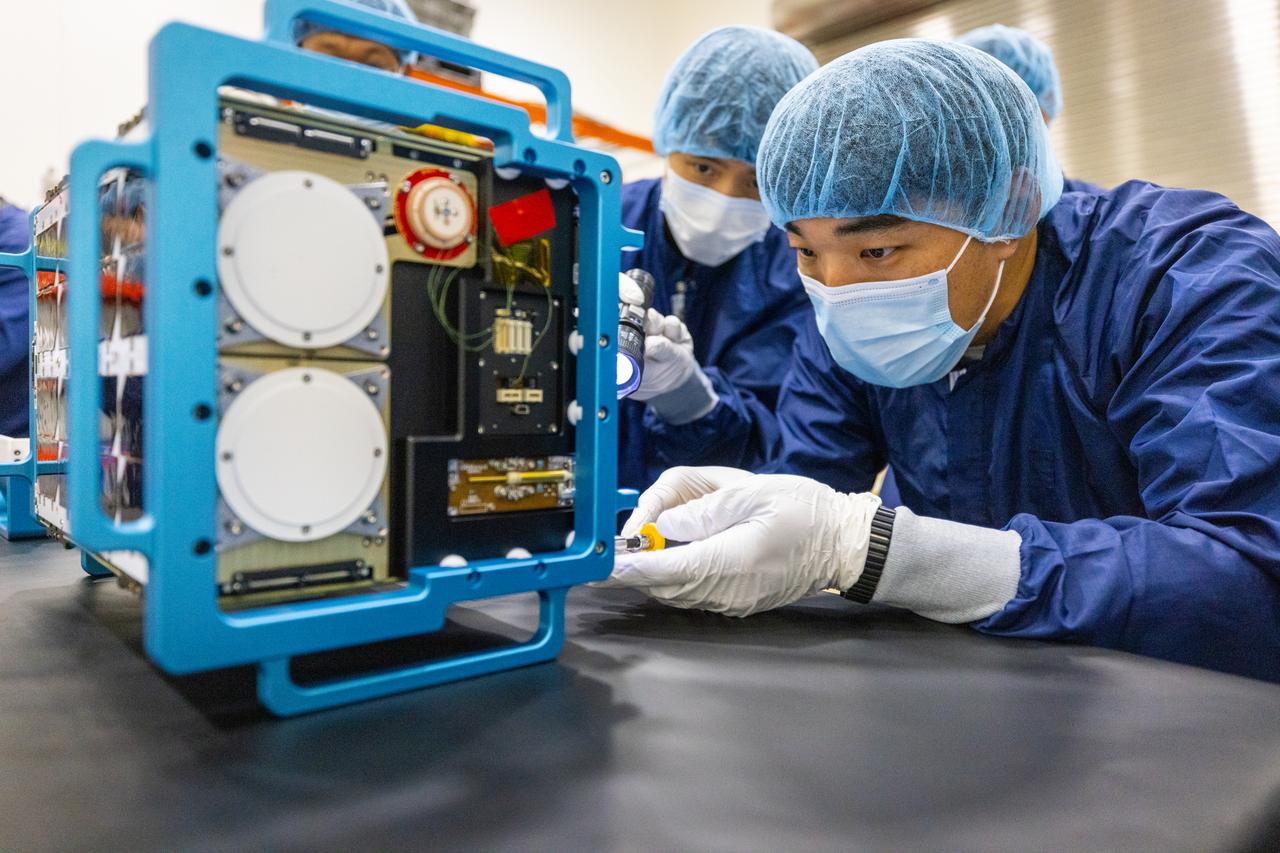

Inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Tuesday, Aug. 26, 2025, technicians with the Korea AeroSpace Administration (KASA) inspect the K-Rad Cube, one of several international CubeSats slated to fly on NASA’s Artemis II test flight in 2026. Deploying in high Earth orbit from a spacecraft adapter on NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket after Orion is safely flying on its own with its crew of four astronauts, K-Rad Cube will use a dosimeter made of material designed to mimic human tissue to measure space radiation and assess biological effects at various altitudes across the Van Allen radiation belts, a critical area of research for human presence at the Moon and Mars.
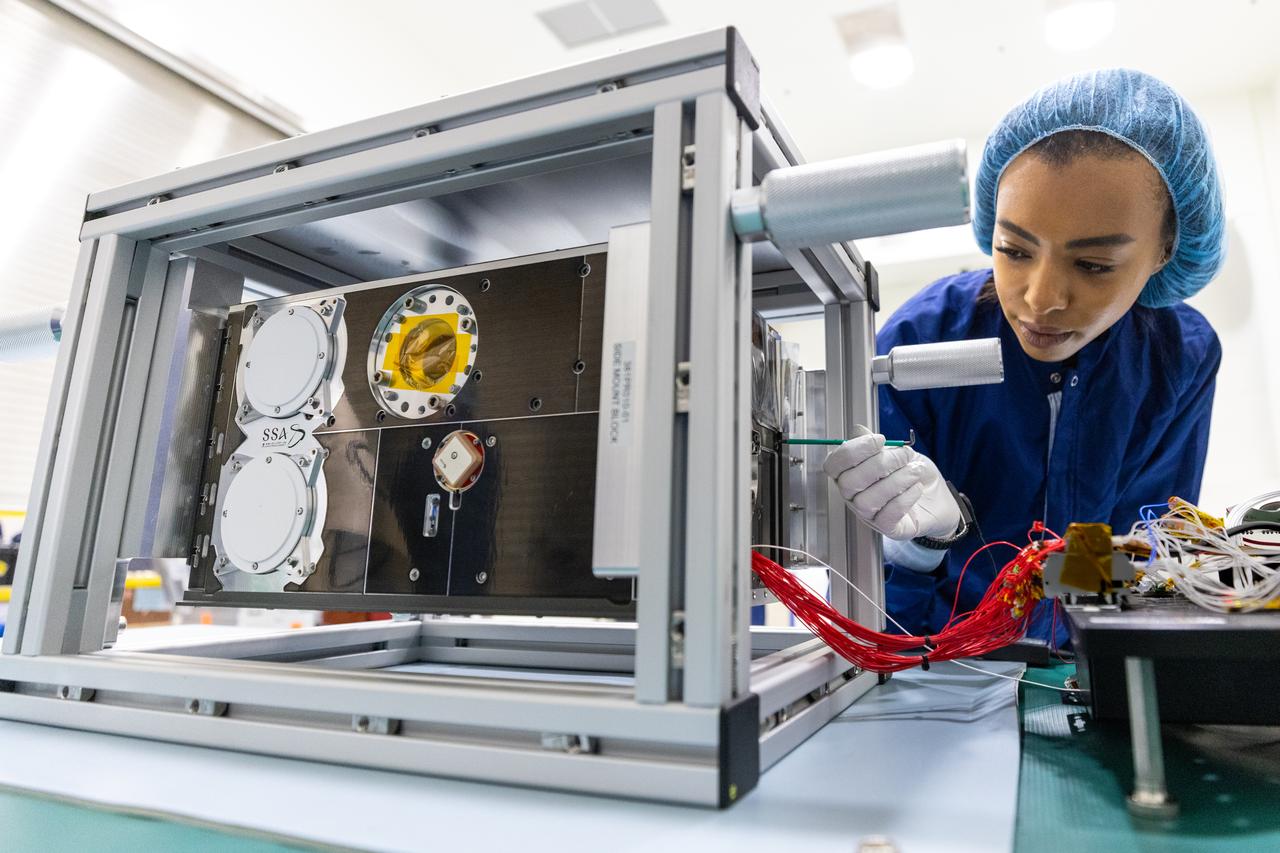

Inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Tuesday, Aug. 26, 2025, a technician inspects the Saudi Space Agency’s Space Weather CubeSat, one of several international CubeSats slated to fly on NASA’s Artemis II test flight in 2026. Deploying in high Earth orbit from a spacecraft adapter on NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket after Orion is safely flying on its own with its crew of four astronauts, the CubeSat will measure aspects of space weather – space radiation, solar X-rays, solar energetic particles, and magnetic fields – at a range of distances from Earth.
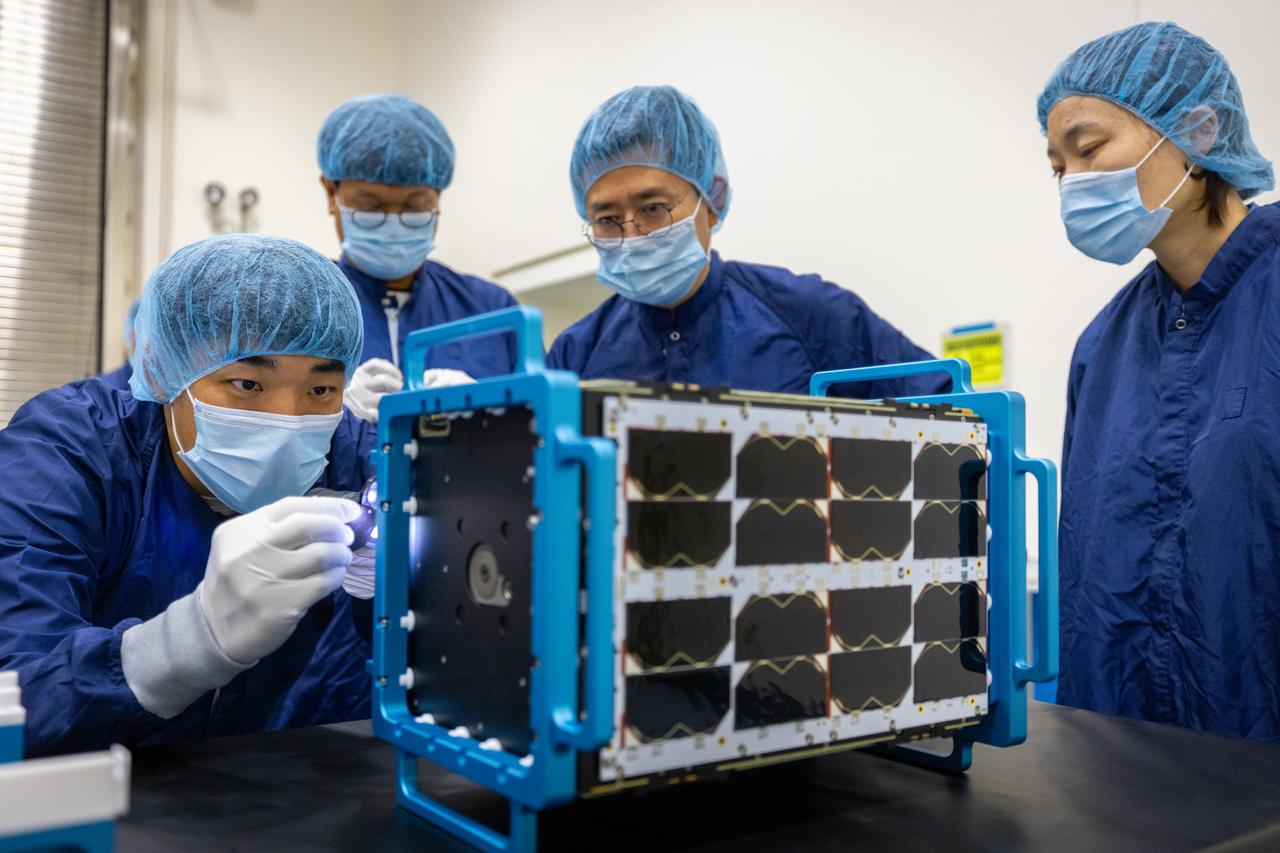

Inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Tuesday, Aug. 26, 2025, technicians with the Korea AeroSpace Administration (KASA) inspect the K-Rad Cube, one of several international CubeSats slated to fly on NASA’s Artemis II test flight in 2026. Deploying in high Earth orbit from a spacecraft adapter on NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket after Orion is safely flying on its own with its crew of four astronauts, K-Rad Cube will use a dosimeter made of material designed to mimic human tissue to measure space radiation and assess biological effects at various altitudes across the Van Allen radiation belts, a critical area of research for human presence at the Moon and Mars.
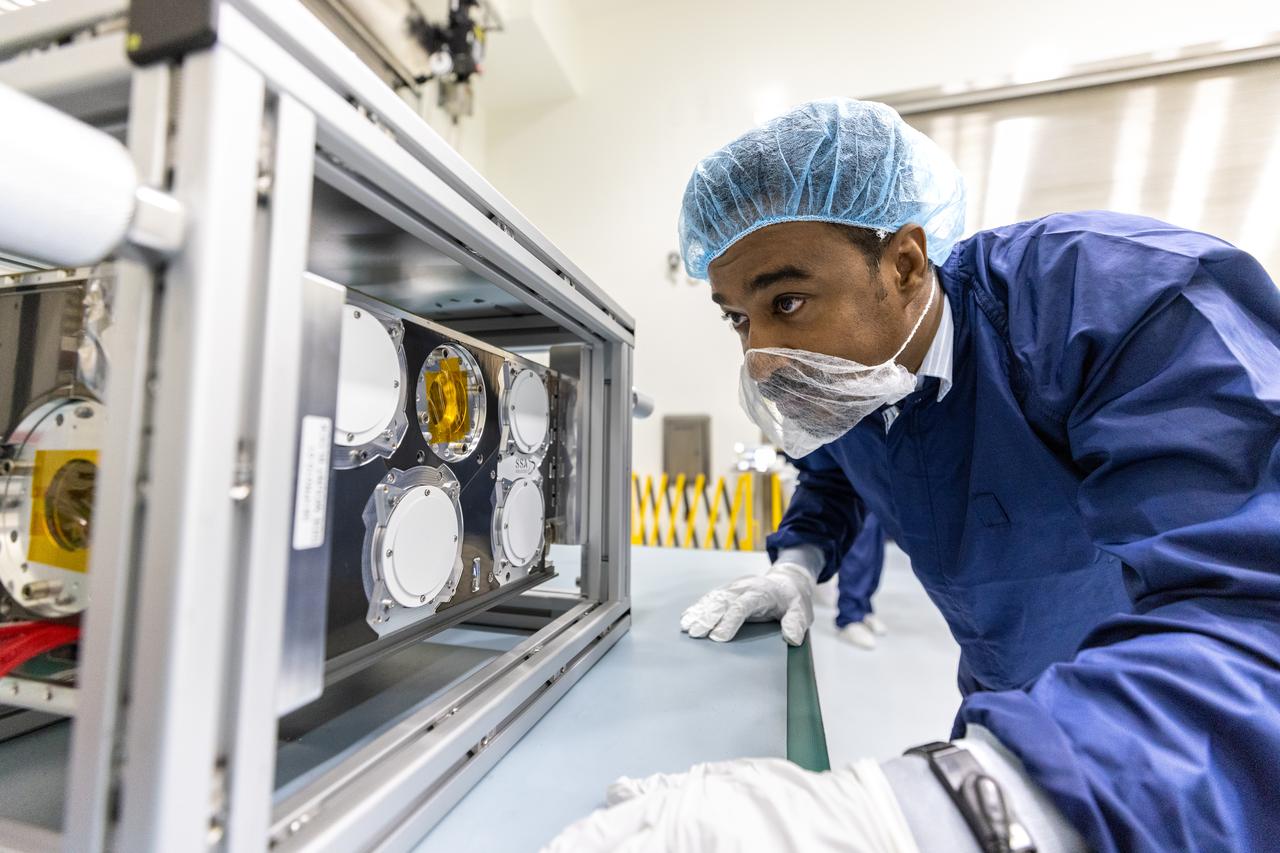
Inside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Tuesday, Aug. 26, 2025, a technician inspects the Saudi Space Agency’s Space Weather CubeSat, one of several international CubeSats slated to fly on NASA’s Artemis II test flight in 2026. Deploying in high Earth orbit from a spacecraft adapter on NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket after Orion is safely flying on its own with its crew of four astronauts, the CubeSat will measure aspects of space weather – space radiation, solar X-rays, solar energetic particles, and magnetic fields – at a range of distances from Earth.
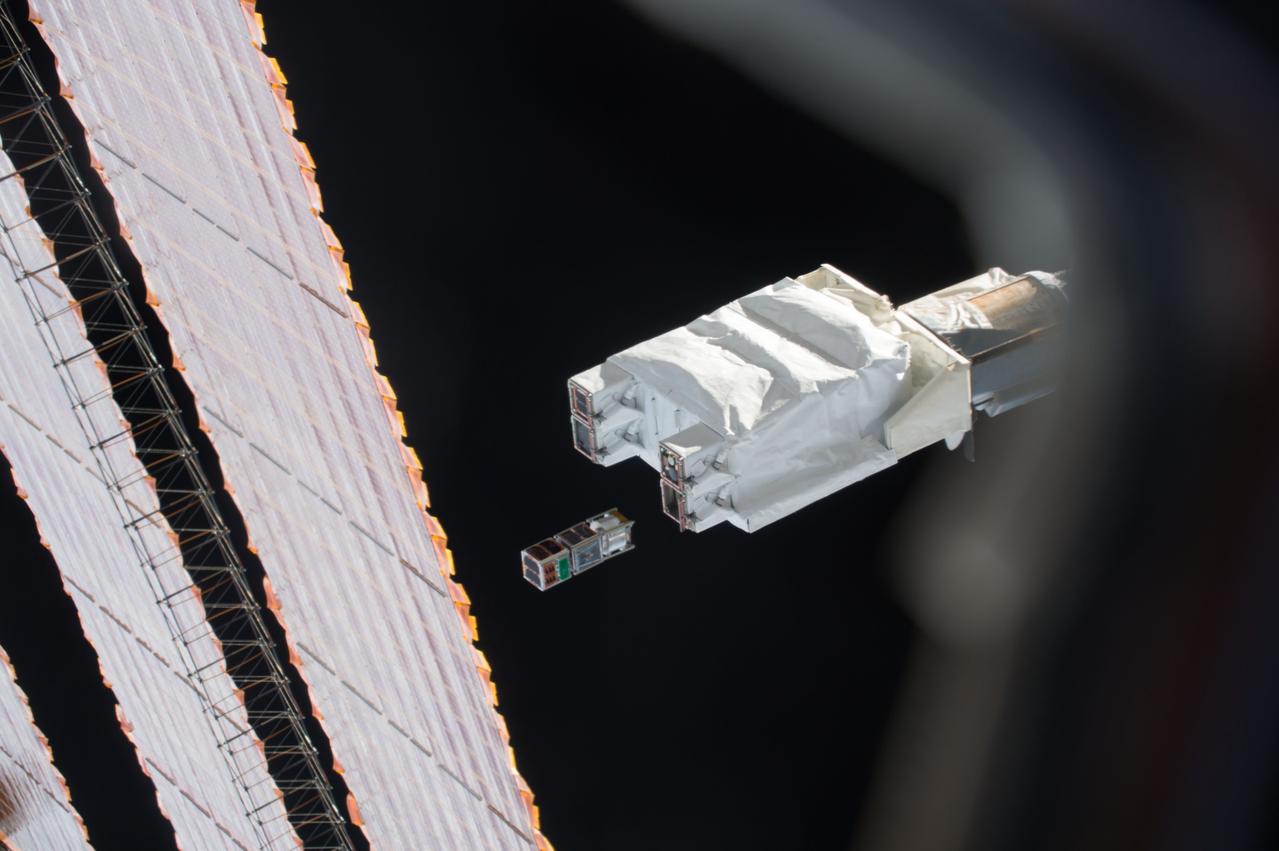
iss050e031198 (1/17/2017) --- Photo documentation of the Japanese-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-6 (J-SSOD-6) deployment of the ITF-2, Waseda-SAT3 and Freedom CubeSats. The Imagine The Future-2 (ITF-2) CubeSat mission supports amateur radio networking by testing a micro engineered 1/20 wavelength small antenna. The WASEDA SAT-3 is a CubeSat developed by Waseda University aiming to test an ultra-light drag chute for accelerated deorbit. An LCD projector shows images on the chute with imagery sent back to Earth via an onboard camera. FREEDOM is a 1 Unit (1U) CubeSat developed by the Nakashimada Engineering Works and the Tohoku University to demonstrate a deployable deorbit device “DOM” for application in future missions for space debris mitigation.
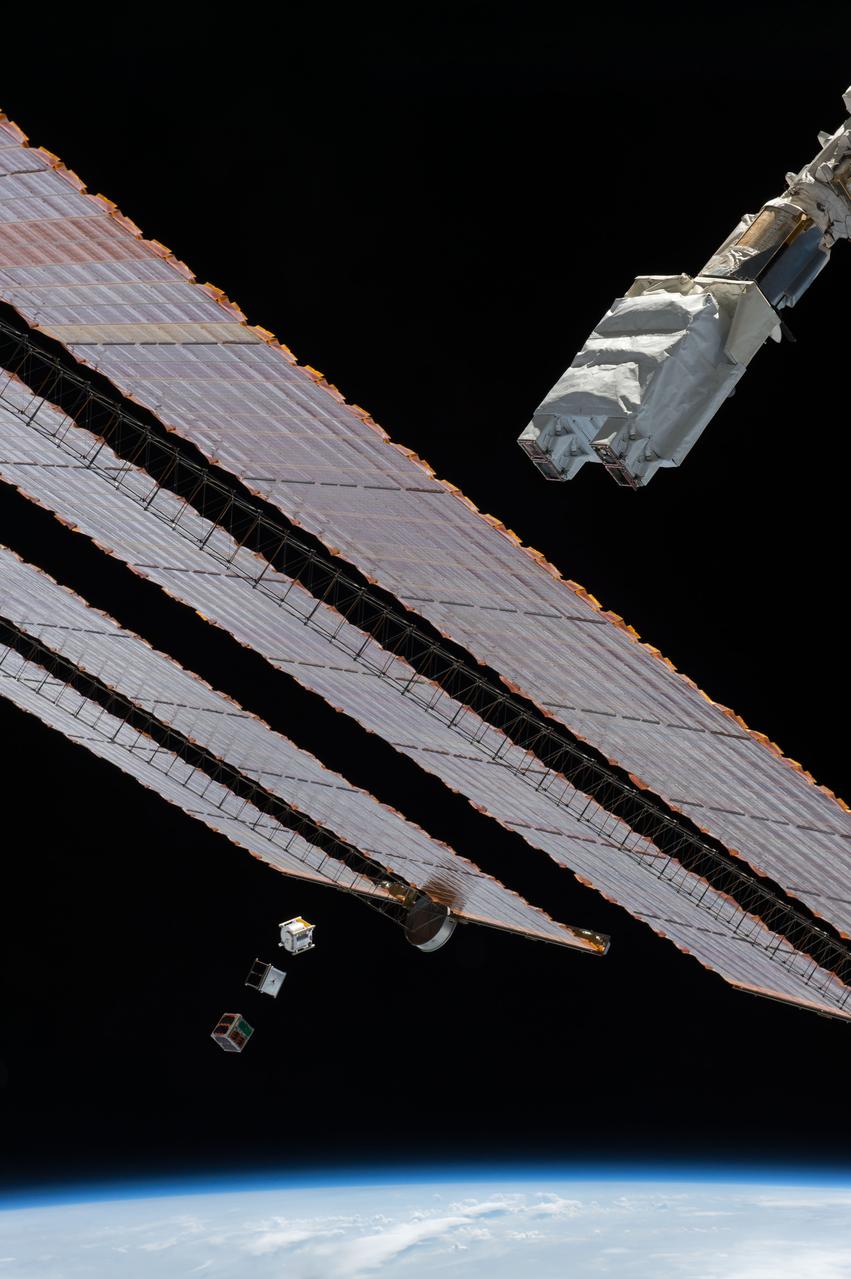

iss050e032565 (1/17/2017) --- Photo documentation of the Japanese-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer-6 (J-SSOD-6) deployment of the ITF-2, Waseda-SAT3 and Freedom CubeSats. The Imagine The Future-2 (ITF-2) CubeSat mission supports amateur radio networking by testing a micro engineered 1/20 wavelength small antenna. The WASEDA SAT-3 is a CubeSat developed by Waseda University aiming to test an ultra-light drag chute for accelerated deorbit. An LCD projector shows images on the chute with imagery sent back to Earth via an onboard camera. FREEDOM is a 1 Unit (1U) CubeSat developed by the Nakashimada Engineering Works and the Tohoku University to demonstrate a deployable deorbit device “DOM” for application in future missions for space debris mitigation.
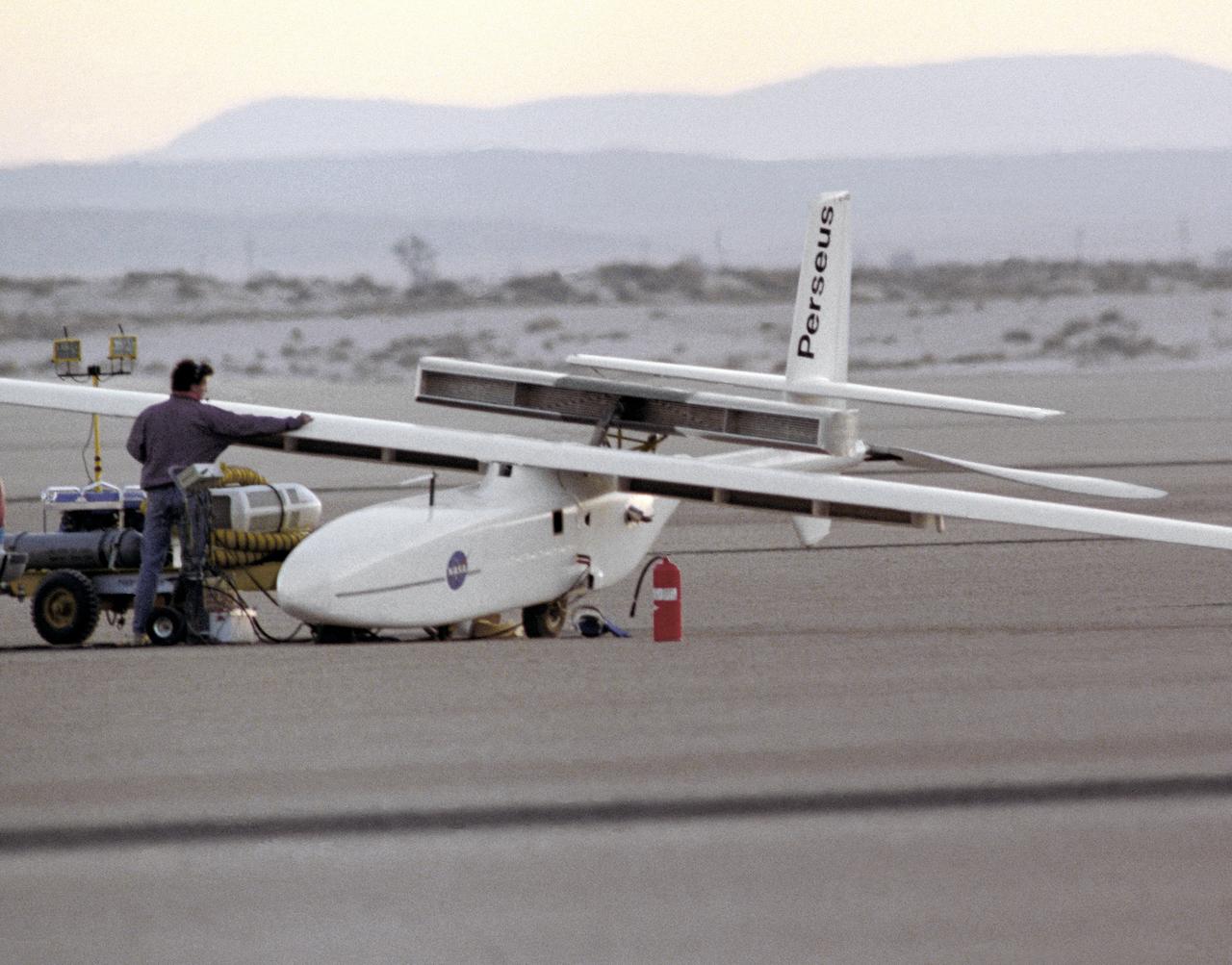

The Perseus A, a remotely-piloted, high-altitude research vehicle, is seen just after landing on Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The Perseus A had a unique method of takeoff and landing. To make the aircraft as aerodynamic and lightweight as possible, designers gave it only two very small centerline wheels for landing. These wheels were very close to the fuselage, and therefore produced very little drag. However, since the fuselage sat so close to the ground, it was necessary to keep the large propeller at the rear of the aircraft locked in a horizontal position during takeoff. The aircraft was towed to about 700 feet in the air, where the engine was started and the aircraft began flying under its own power.
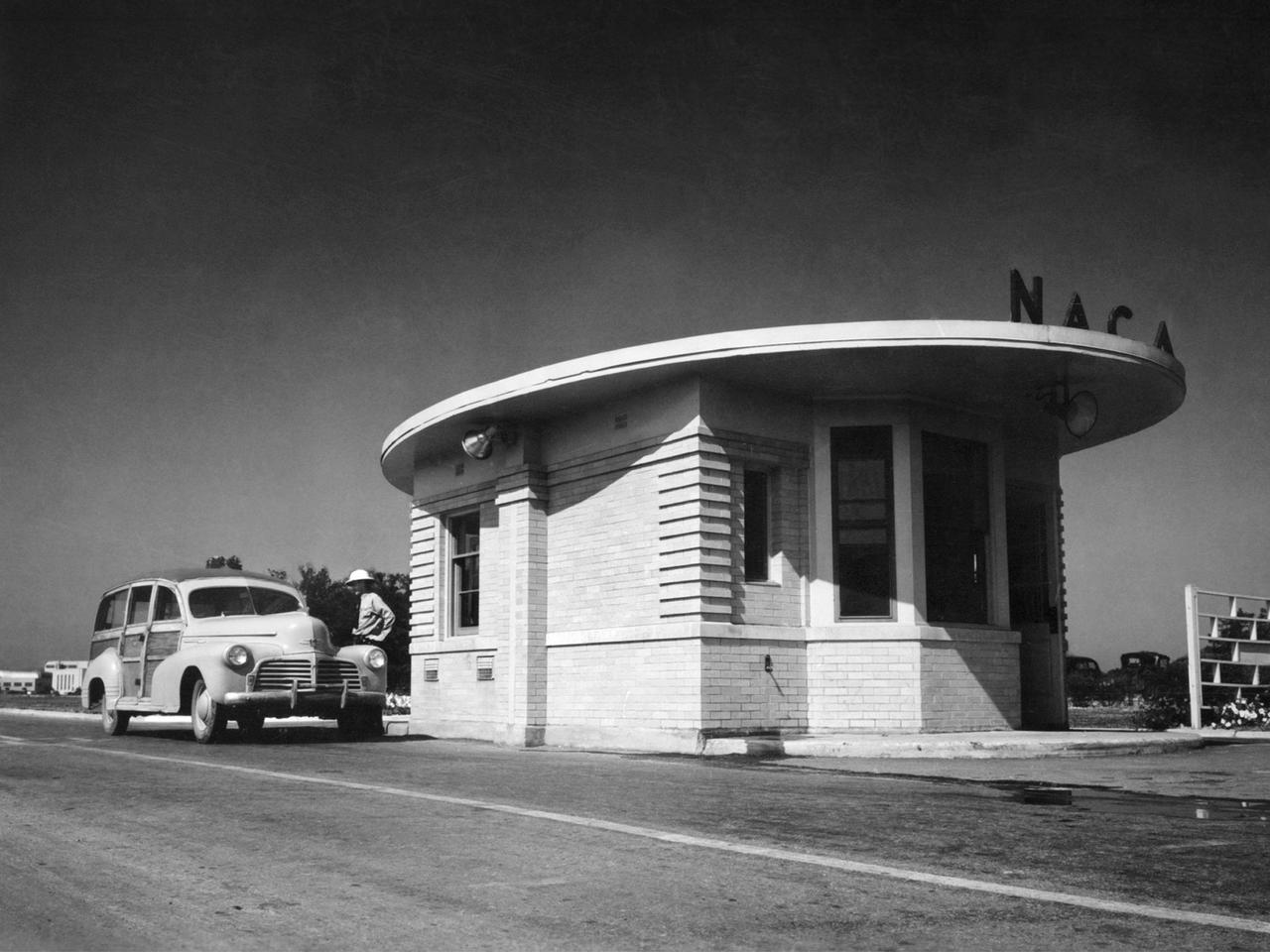

A vehicle leaves the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory on August 14, 1945. At 7 p.m. that evening President Truman announced that Japan had accepted terms for surrender and World War II was over. The end of the war brought significant changes for the laboratory. The NACA would cease its troubleshooting of military aircraft and return to research. Researchers would increase their efforts to address the new technologies that emerged during the war. The entire laboratory was reorganized in October to better investigate turbojets, ramjets, and rockets. The guard house sat on the main entrance to the laboratory off of Brookpark Road. The building was fairly small and easily crowded. In the early 1960s a new security facility was built several hundred feet beyond the original guard house. The original structure remained in place for several years but was not utilized. The subsequent structure was replaced in 2011 by a new building and entrance configuration.