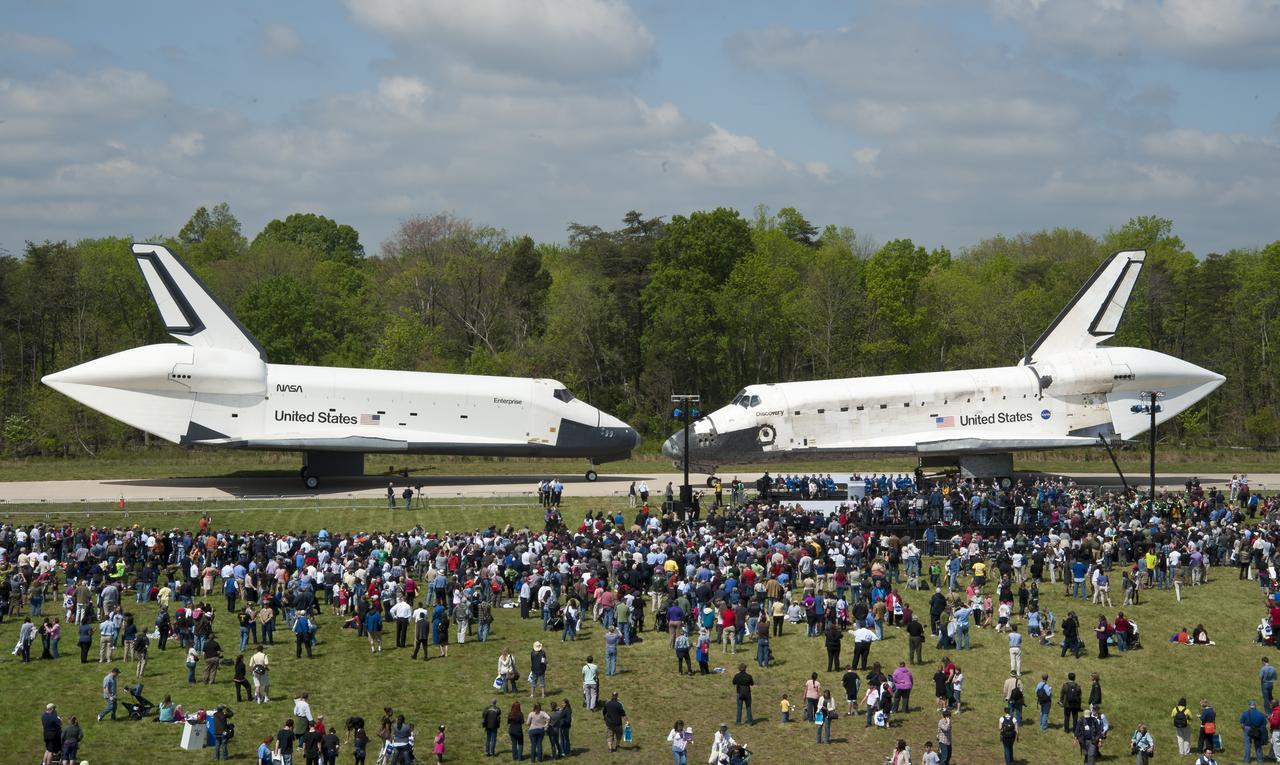

Space Shuttles Enterprise, left, and Discovery meet nose-to-nose at the beginning of a transfer ceremony at the Smithsonian's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Thursday, April 19, 2012, in Chantilly, Va. Space shuttle Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles will take the place of Enterprise at the center to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers at the center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Carolyn Russo)
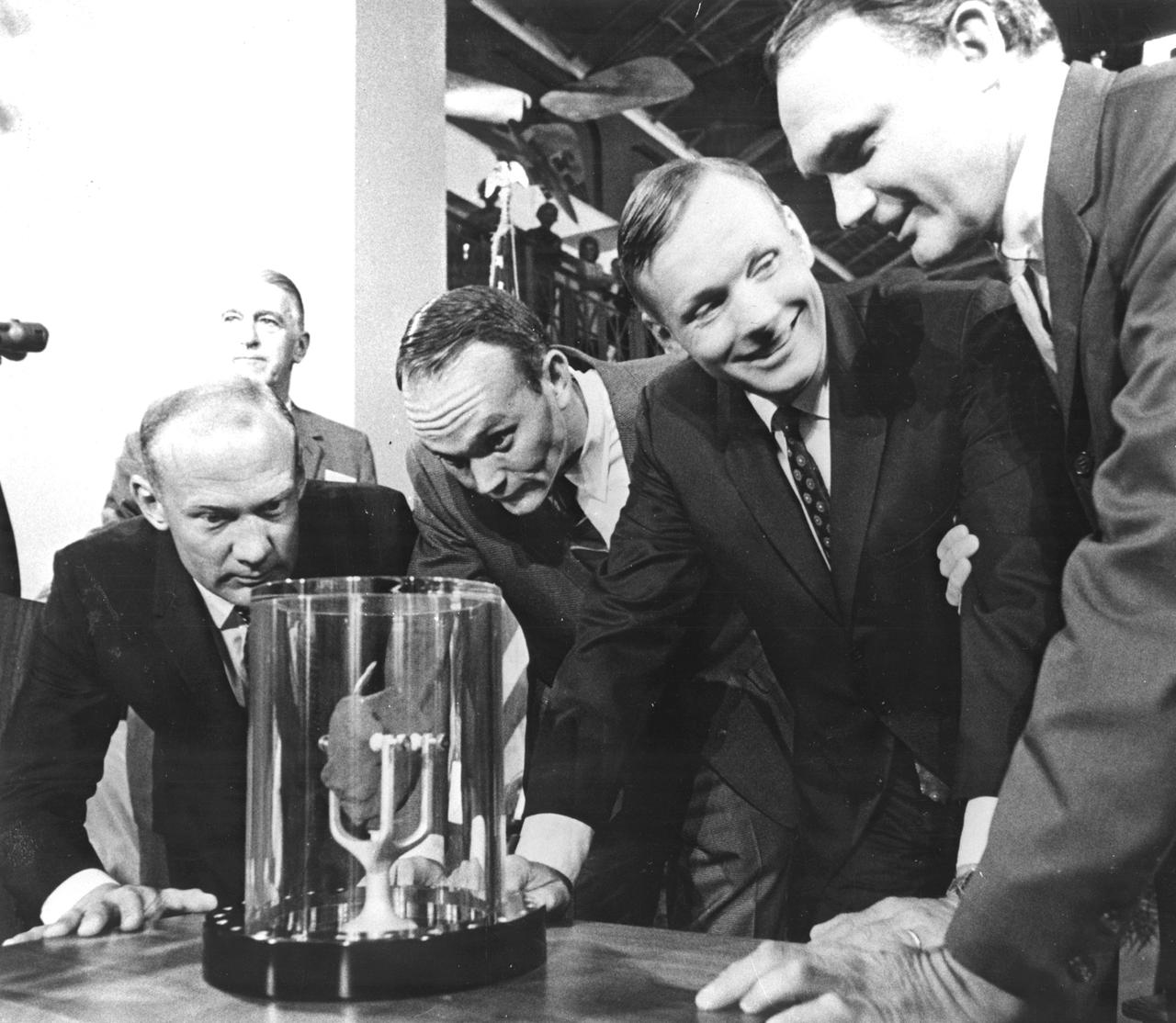

Apollo 11 astronauts, (left to right) Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module pilot; Michael Collins, Command Module pilot; and Neil A. Armstrong, commander, are showing a two-pound Moon rock to Frank Taylor, director of the Smithsonian Institute in Washington D.C. The rock was picked up from the Moon’s surface during the Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) of Aldrin and Armstrong following man’s first Moon landing and was was presented to the Institute for display in the Art and Industries Building. The Apollo 11 mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
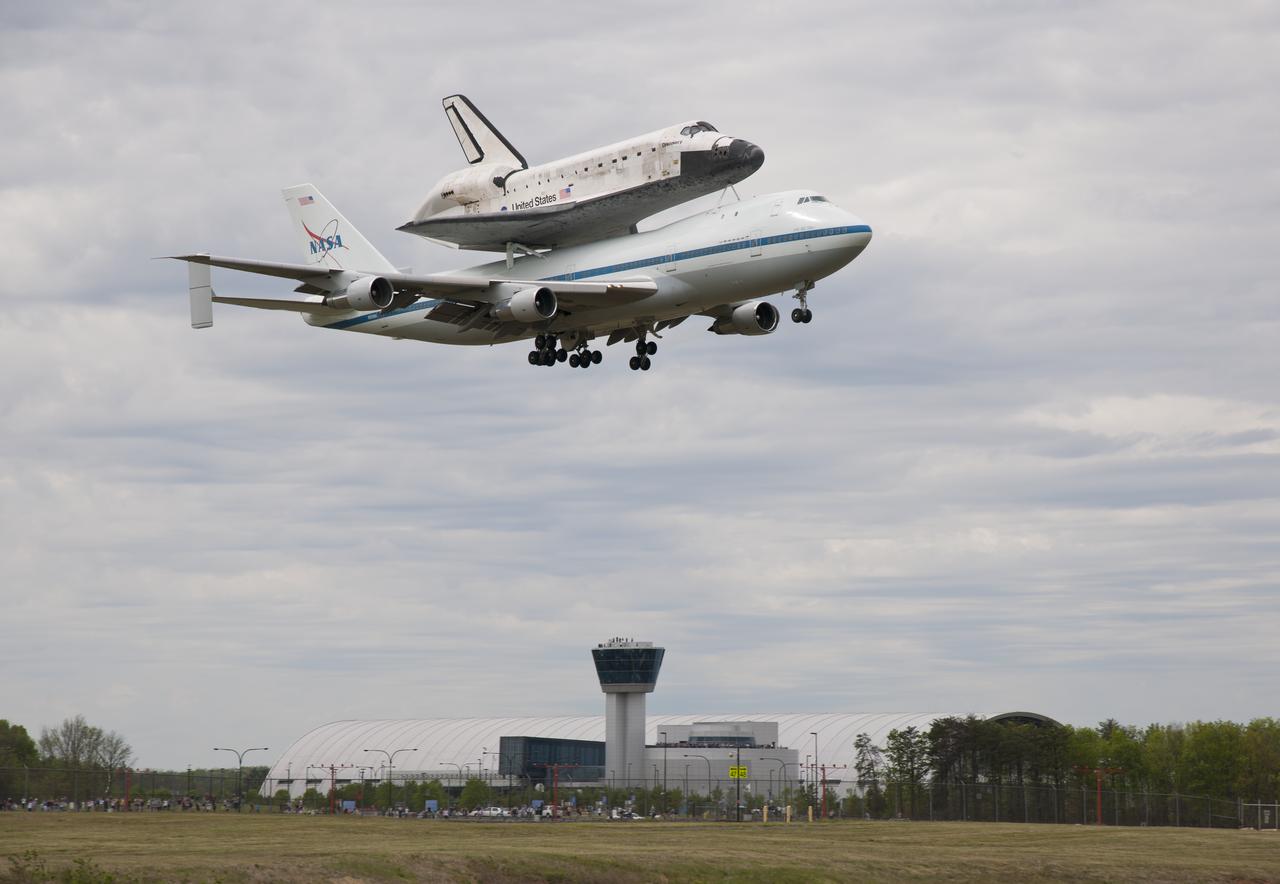

Space shuttle Discovery, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) flies over the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Tuesday, April 17, 2012, in Washington. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Dane Penland)
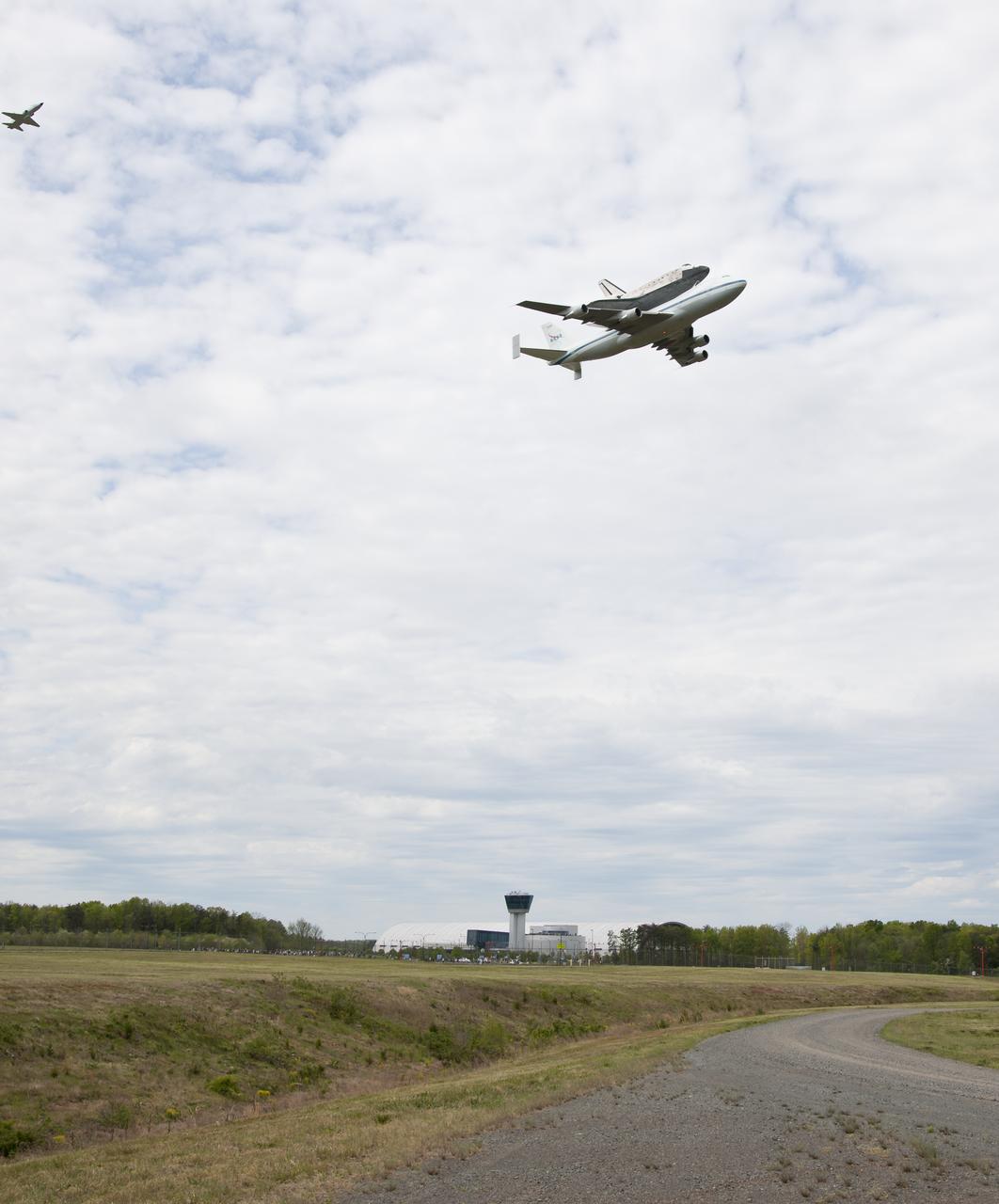

Space shuttle Discovery, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) flies over the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Tuesday, April 17, 2012, in Washington. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Dane Penland)

Space shuttle Discovery, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) taxis in front of the main terminal at Washington Dulles International Airport, Tuesday, April 17, 2012, in Sterling, Va. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Eric Long)

Space shuttle Discovery, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) lands at Washington Dulles International Airport, Tuesday, April 17, 2012, in Sterling, Va. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Eric Long)

Space shuttle Discovery, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) flies over the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Tuesday, April 17, 2012, in Washington. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Eric Long)

Space shuttle Discovery, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) lands at Washington Dulles International Airport, Tuesday, April 17, 2012, in Sterling, Va. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Eric Long)

Space shuttle Discovery, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) lands at Washington Dulles International Airport, Tuesday, April 17, 2012, in Sterling, Va. The Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center is seen in the background. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Eric Long)

NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver, at podium, speaks to those in attendance at Apron W after the 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) with space shuttle Discovery mounted on top rolled to a halt at Washington Dulles International Airport, Tuesday, April 17, 2012 in Sterling, Va. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Dane Penland)
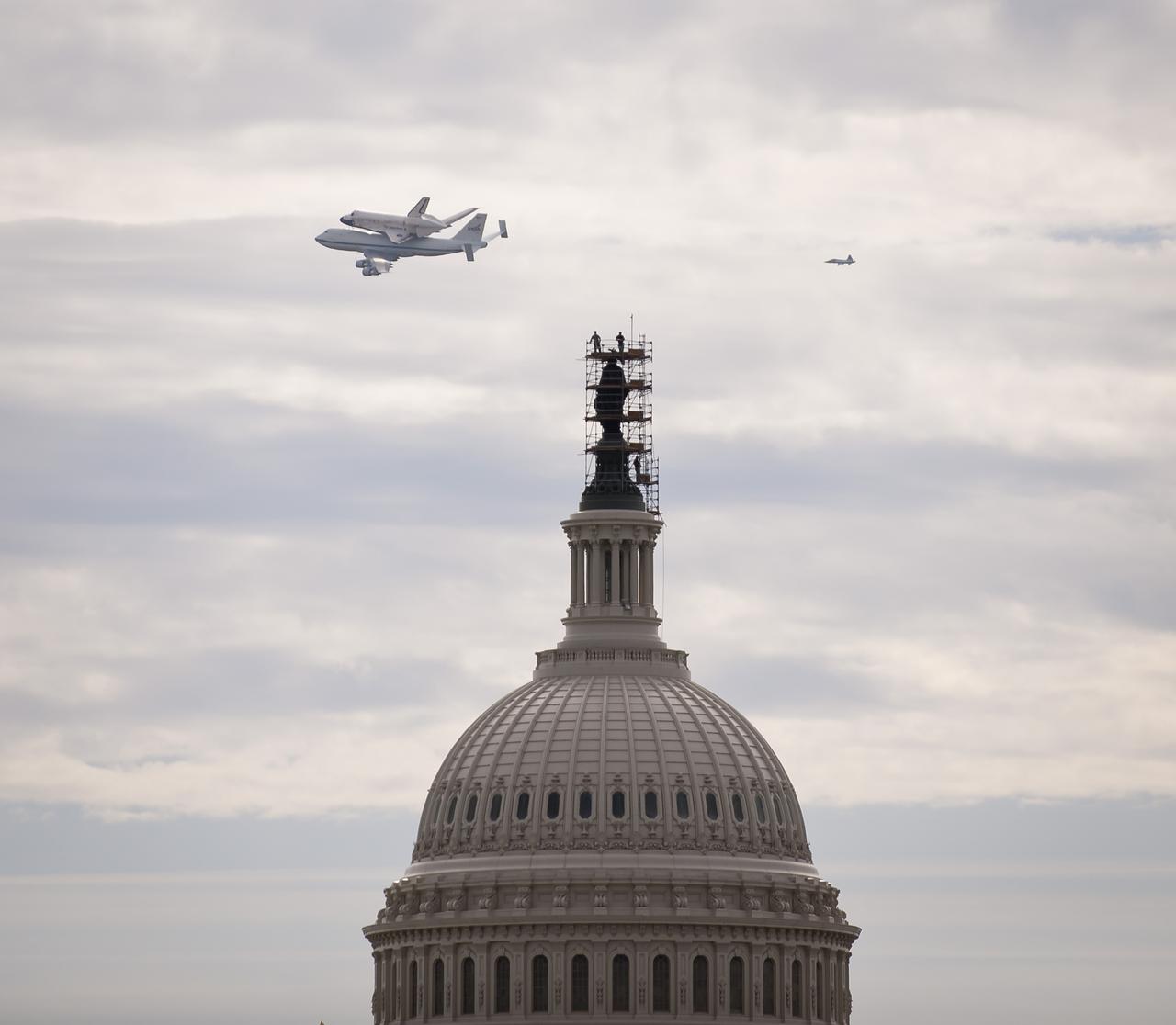

Space shuttle Discovery, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) is seen as it flies near the U.S. Capitol, Tuesday, April 17, 2012, in Washington. Discovery, the first orbiter retired from NASA’s shuttle fleet, completed 39 missions, spent 365 days in space, orbited the Earth 5,830 times, and traveled 148,221,675 miles. NASA will transfer Discovery to the National Air and Space Museum to begin its new mission to commemorate past achievements in space and to educate and inspire future generations of explorers. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Harold Dorwin)

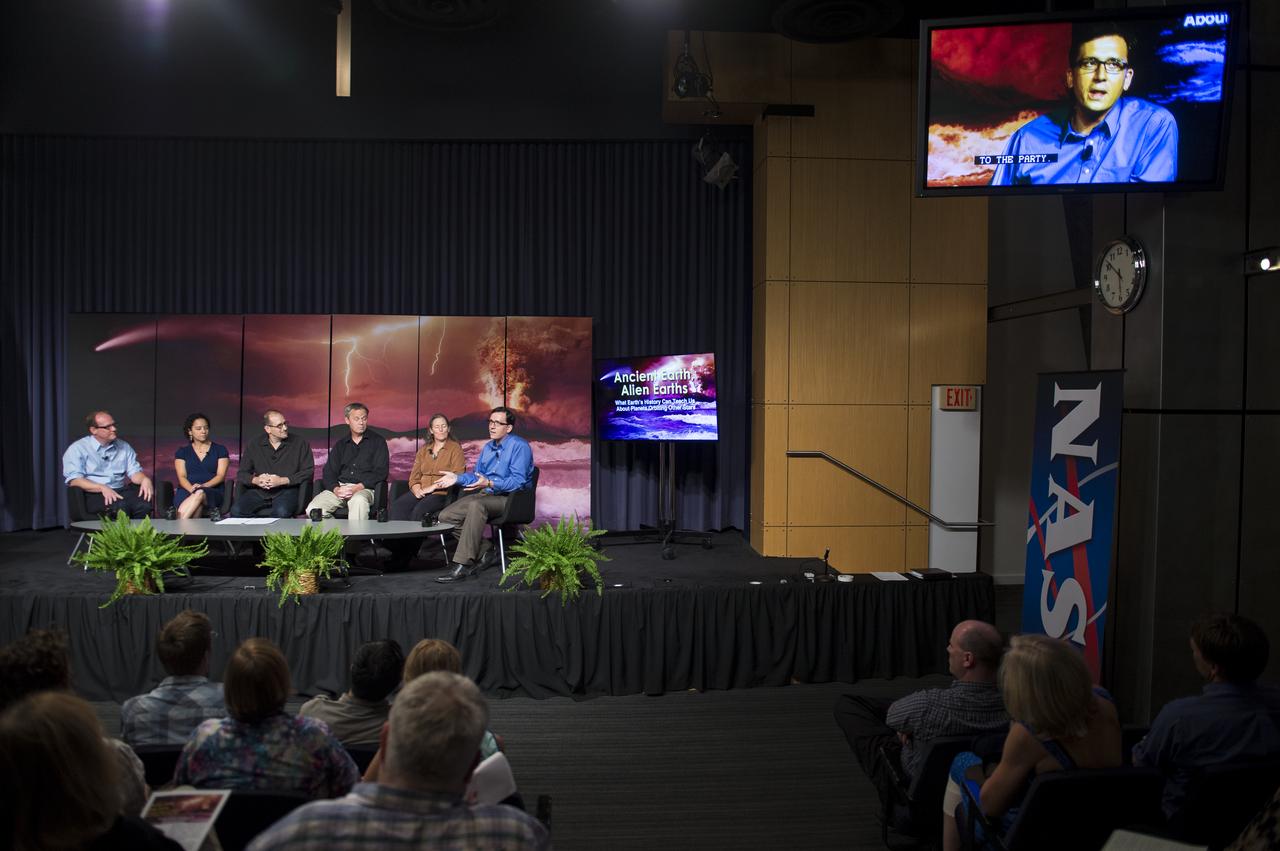
Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist, Planetary Science Institute, moderates a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and highlighted how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Christopher House, Professor of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Timothy Lyons, Professor of Biogeochemistry, UC Riverside, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

An audience member asks the panelists a question at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Dawn Sumner, Professor of Geology, UC Davis, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Phoebe Cohen, Professor of Geosciences, Williams College, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
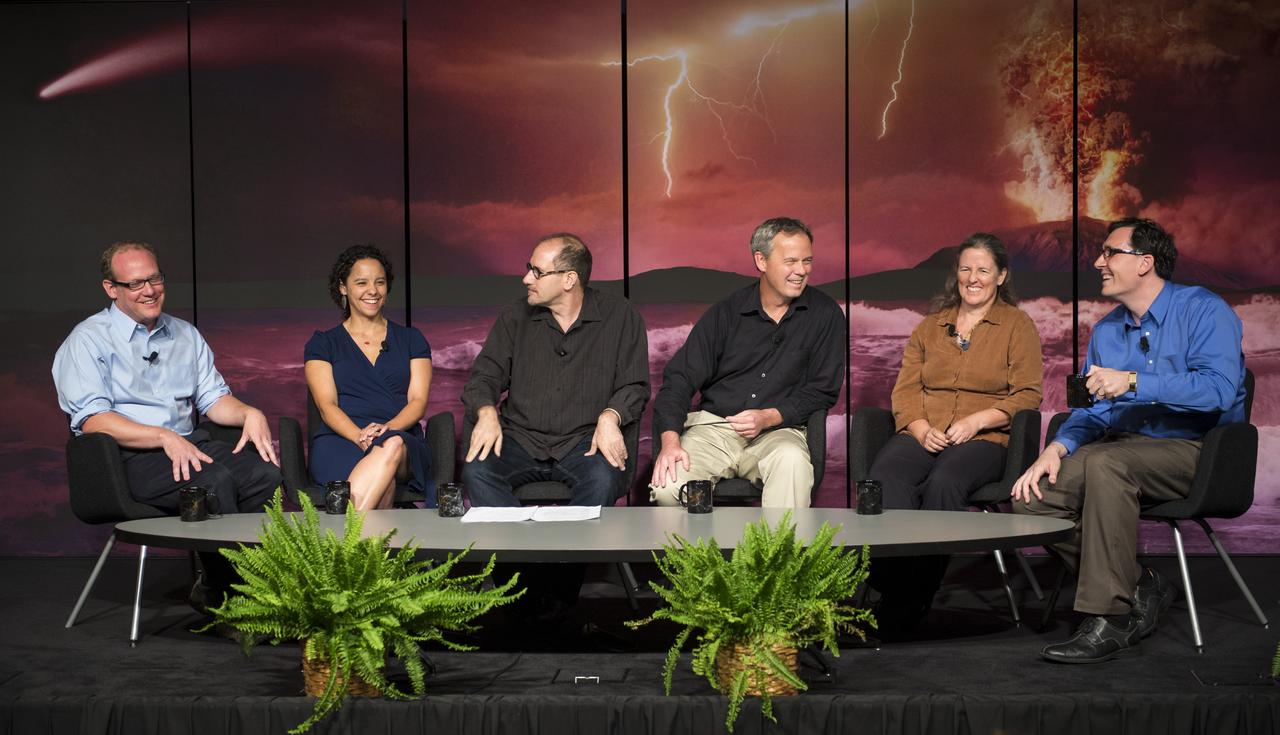

Panelists discuss how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
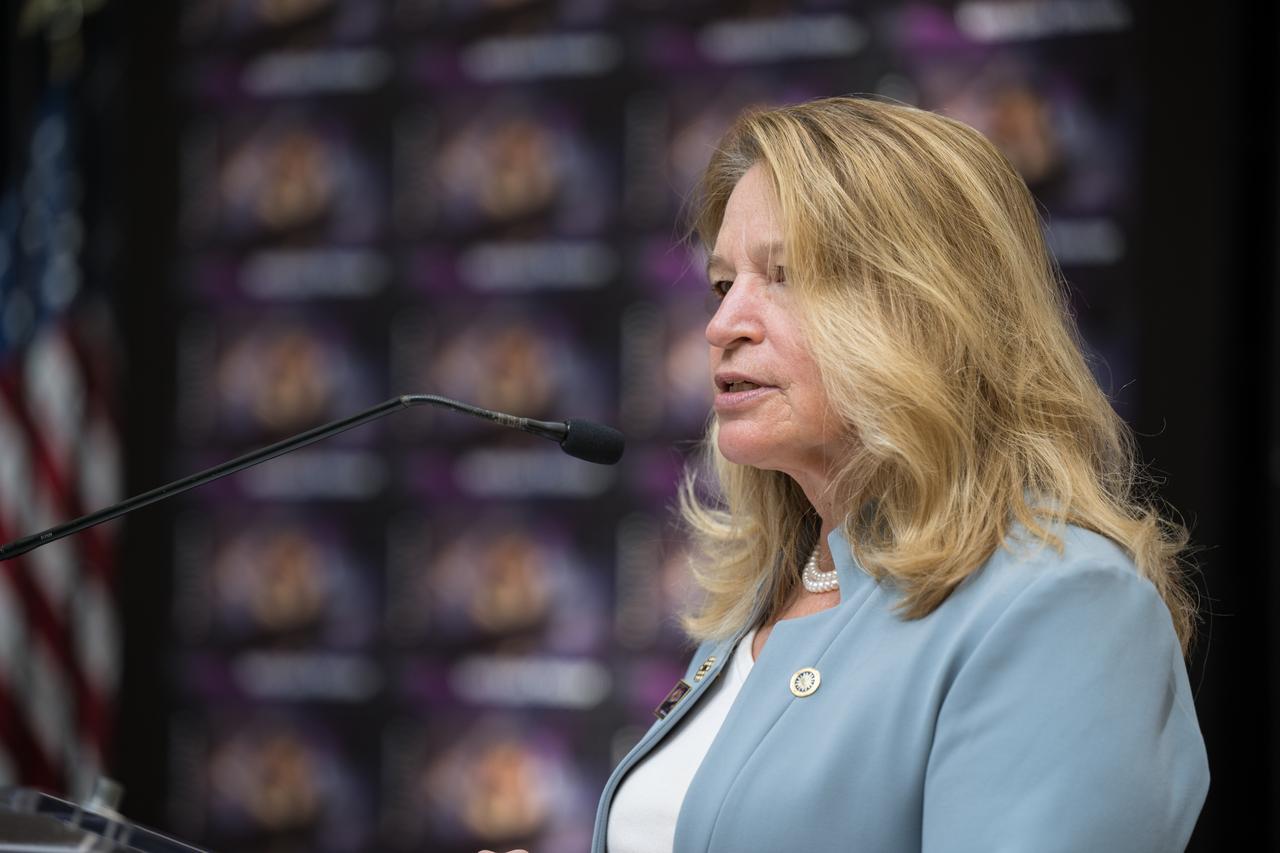

Smithsonian Institution Under Secretary for Service and Research, Ellen Stofan, provides remarks at the first-day-of-issue event for the United States Postal Service’s new stamp celebrating NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) on Thursday, Sept. 8, 2022, at the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum in Washington. The stamp, which features an illustration of the observatory, honors Webb’s mission to explore the unknown in our universe – solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
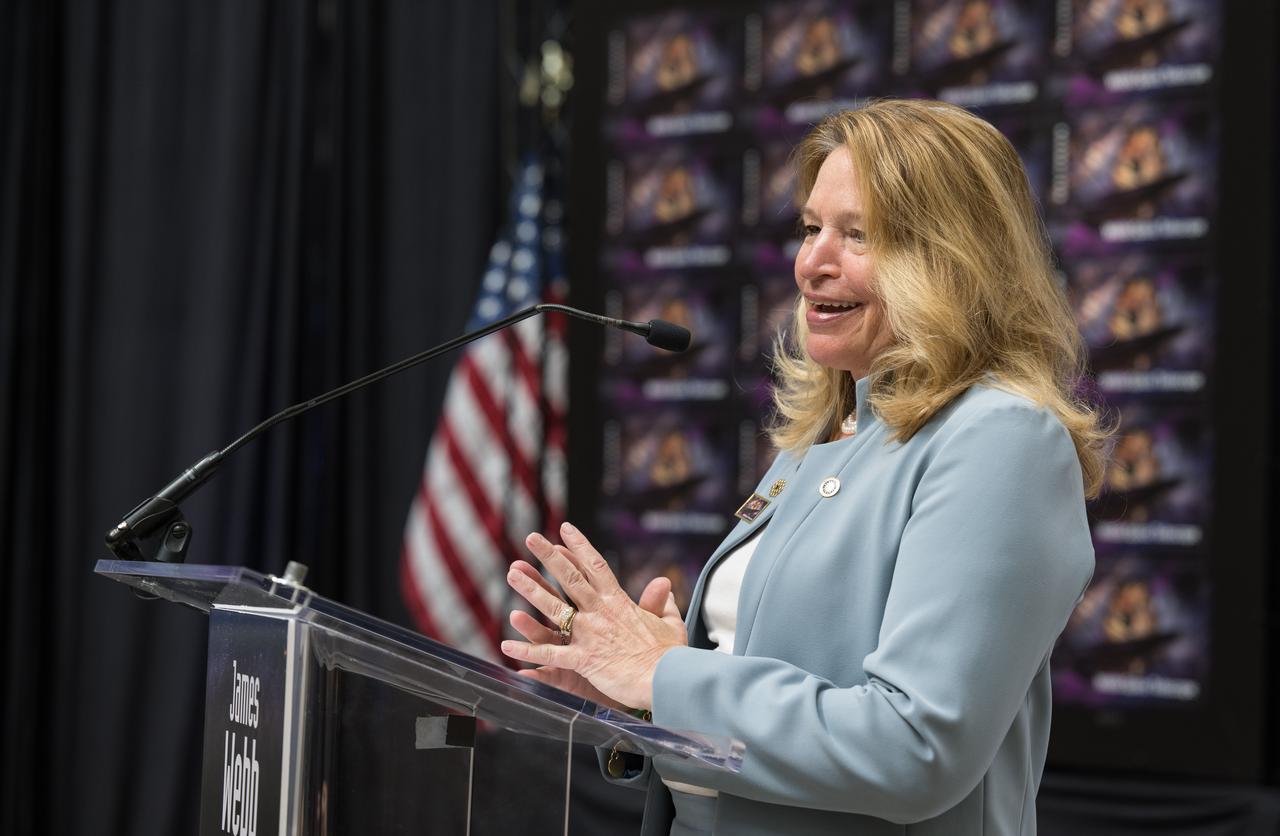

Smithsonian Institution Under Secretary for Service and Research, Ellen Stofan, provides remarks at the first-day-of-issue event for the United States Postal Service’s new stamp celebrating NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) on Thursday, Sept. 8, 2022, at the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum in Washington. The stamp, which features an illustration of the observatory, honors Webb’s mission to explore the unknown in our universe – solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
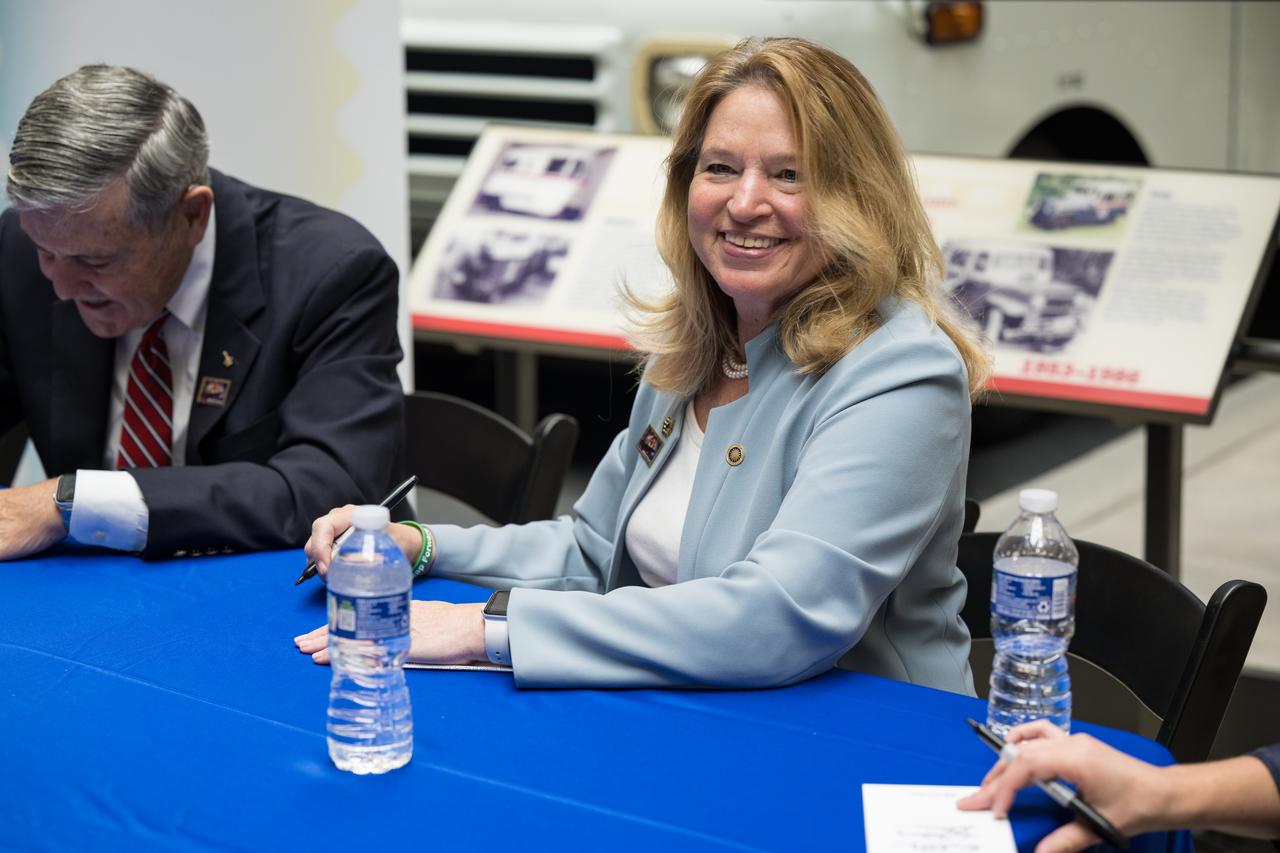

Smithsonian Institution Under Secretary for Service and Research, Ellen Stofan, autographs a piece of mail with the United States Postal Service’s new stamp celebrating NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) on it, at the first-day-of-issue event, Thursday, Sept. 8, 2022, at the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum in Washington. The stamp, which features an illustration of the observatory, honors Webb’s mission to explore the unknown in our universe – solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Shawn Domagal-Goldman, Research Space Scientist, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Shawn Domagal-Goldman, Research Space Scientist, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Panelists pose for a group photo at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and highlighted how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
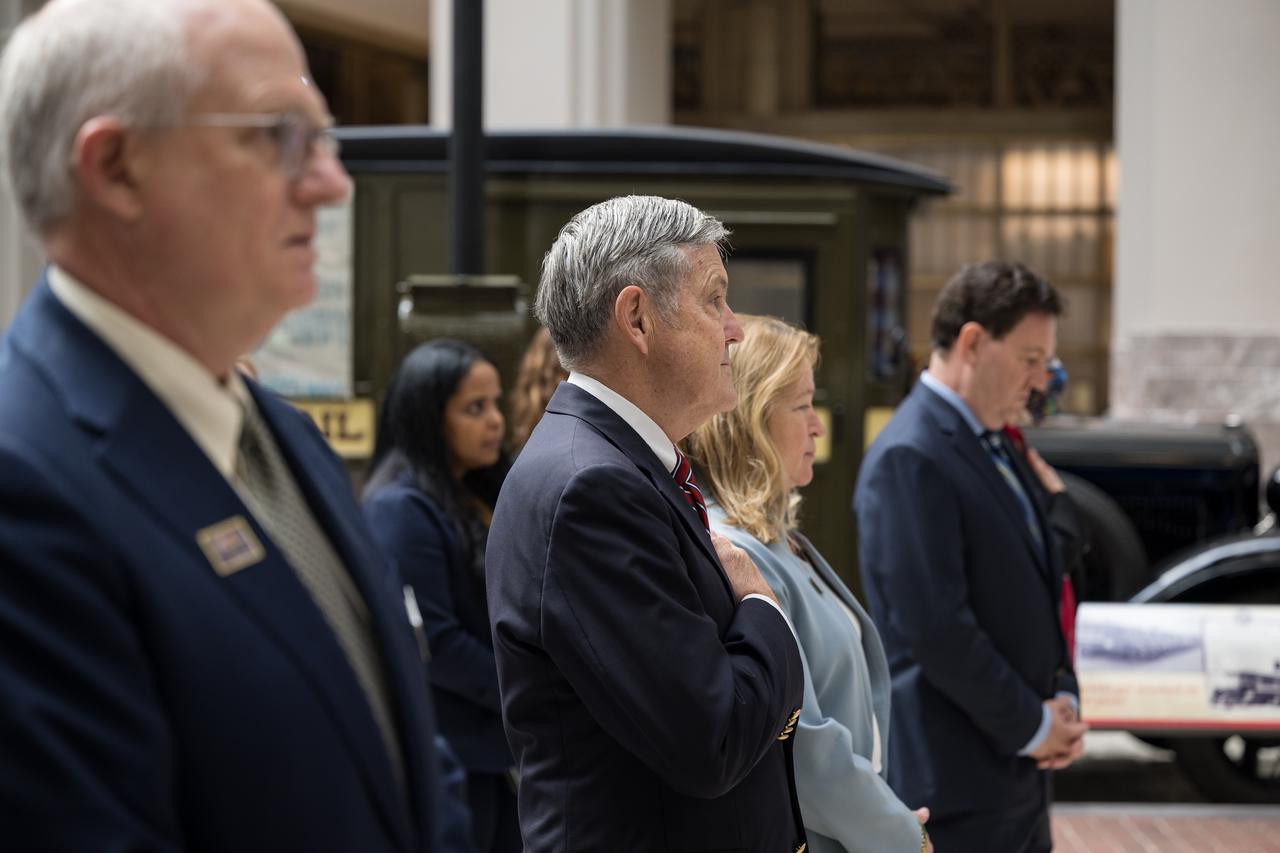

NASA Associate Administrator and former astronaut, Bob Cabana, second from left, and Smithsonian Institution Under Secretary for Service and Research, Ellen Stofan, third from left, are seen during the singing of the national anthem at the first-day-of-issue event for the United States Postal Service’s new stamp celebrating NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) on Thursday, Sept. 8, 2022, at the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum in Washington. The stamp, which features an illustration of the observatory, honors Webb’s mission to explore the unknown in our universe – solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Kepler conference at SETI Institute - interview with Kepler scientist Dave Latham discussing classifying 20 million stars to generate target catalog, Smithsonian Astrophysics Observatory
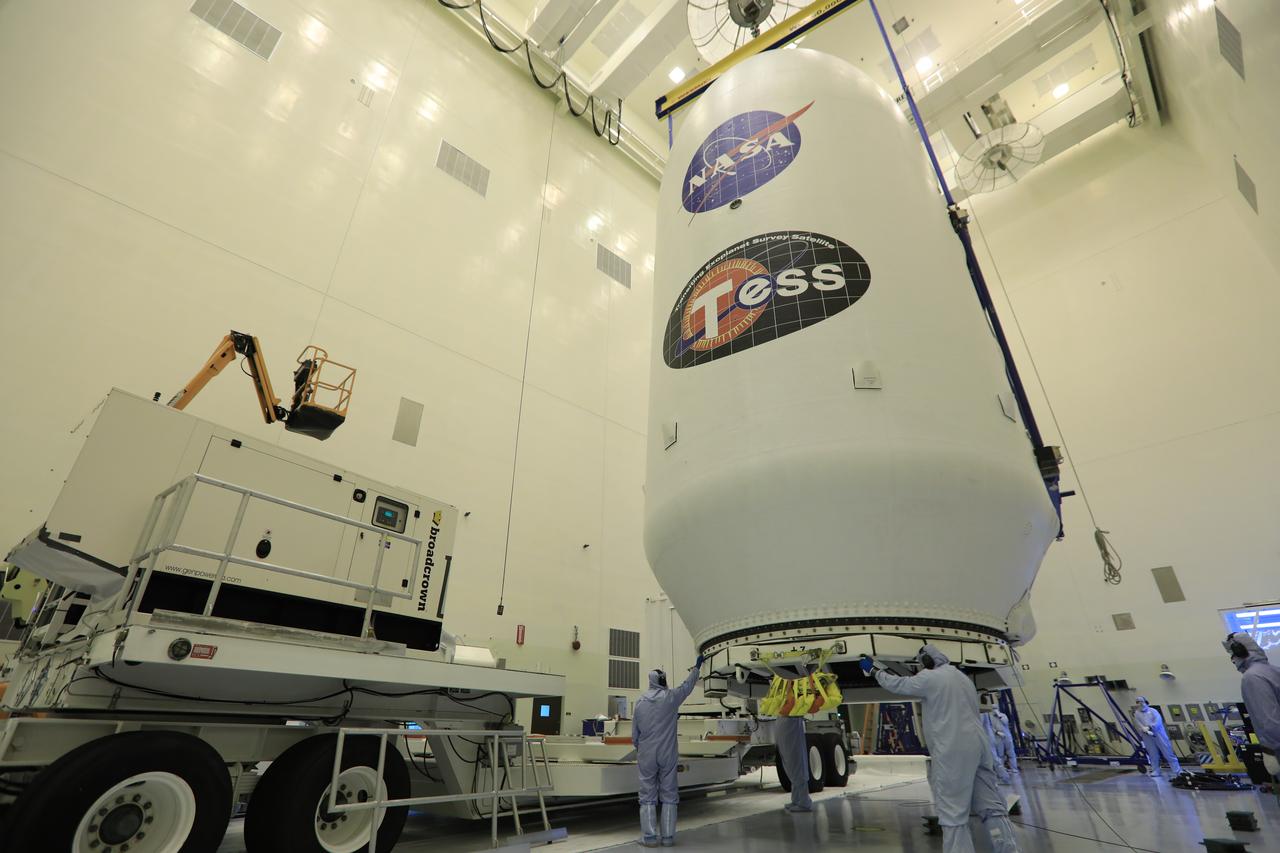

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is moved by crane to a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is scheduled to launch on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
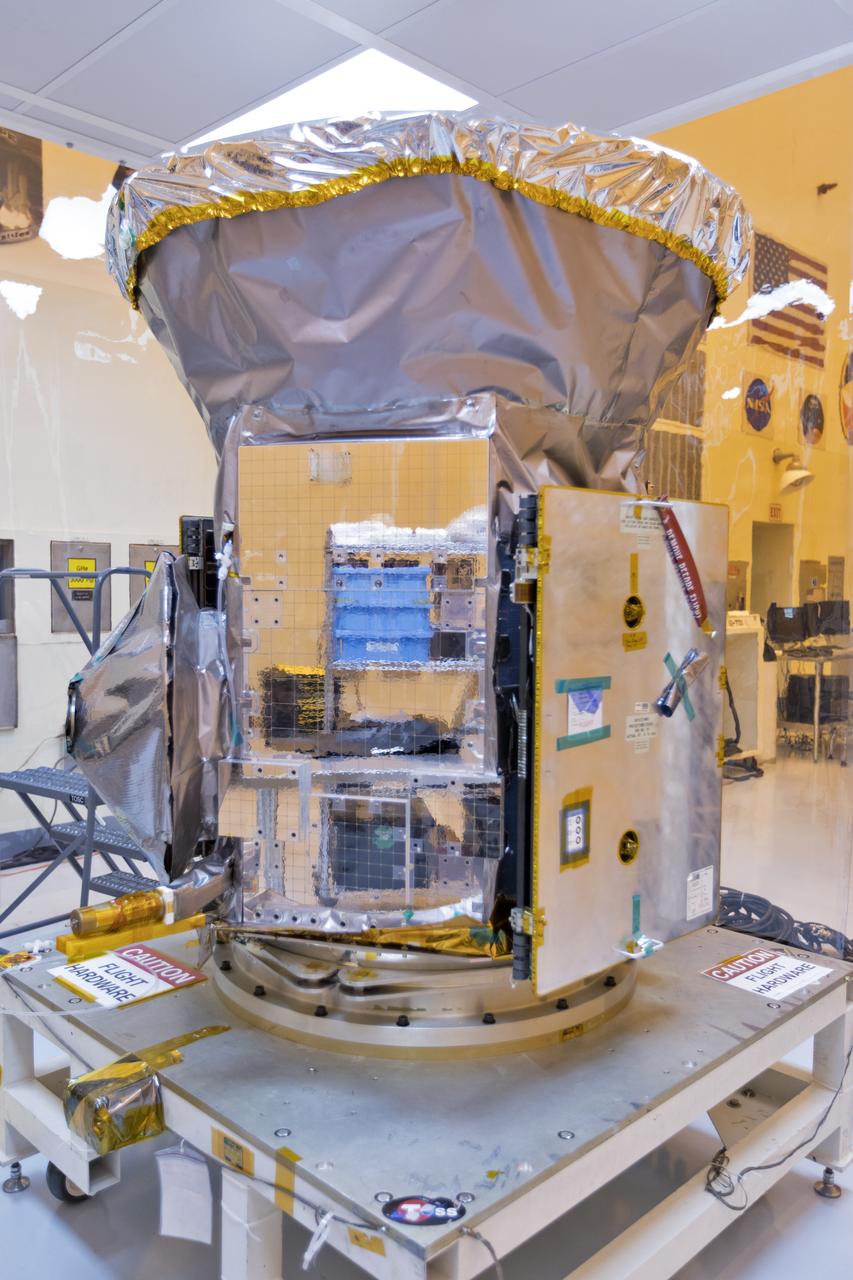

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, or TESS, has been uncreated from its shipping container for inspections and preflight processing. The satellite is NASA's next step in the search for planets outside of the solar system also known as "exoplanets." TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management. SpaceX of Hawthorne, California, is the provider of the Falcon 9 launch service. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket no earlier than April 16, 2018 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

The SpaceX payload fairing containing NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is prepared for the move from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
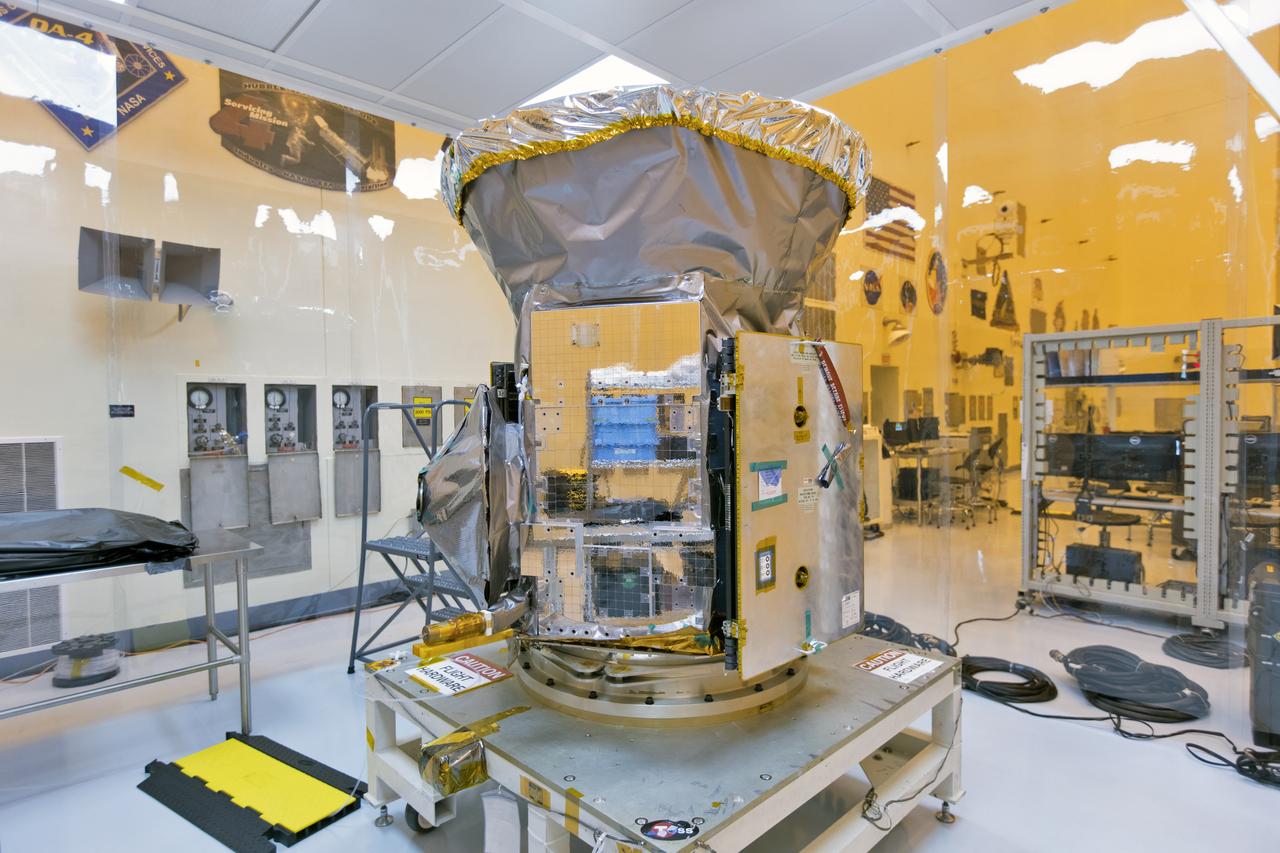

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, or TESS, has been uncreated from its shipping container for inspections and preflight processing. The satellite is NASA's next step in the search for planets outside of the solar system also known as "exoplanets." TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management. SpaceX of Hawthorne, California, is the provider of the Falcon 9 launch service. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket no earlier than April 16, 2018 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
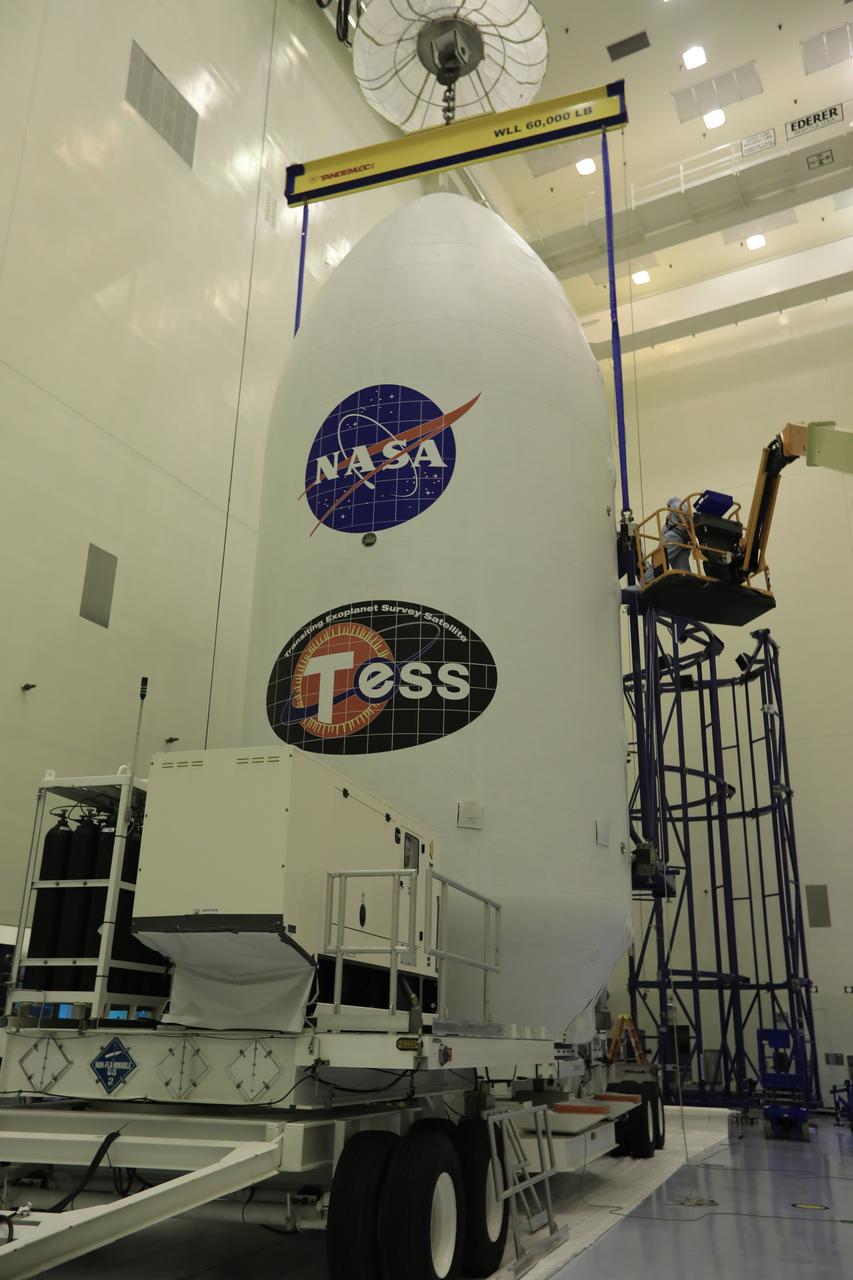

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is secured onto a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is scheduled to launch on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
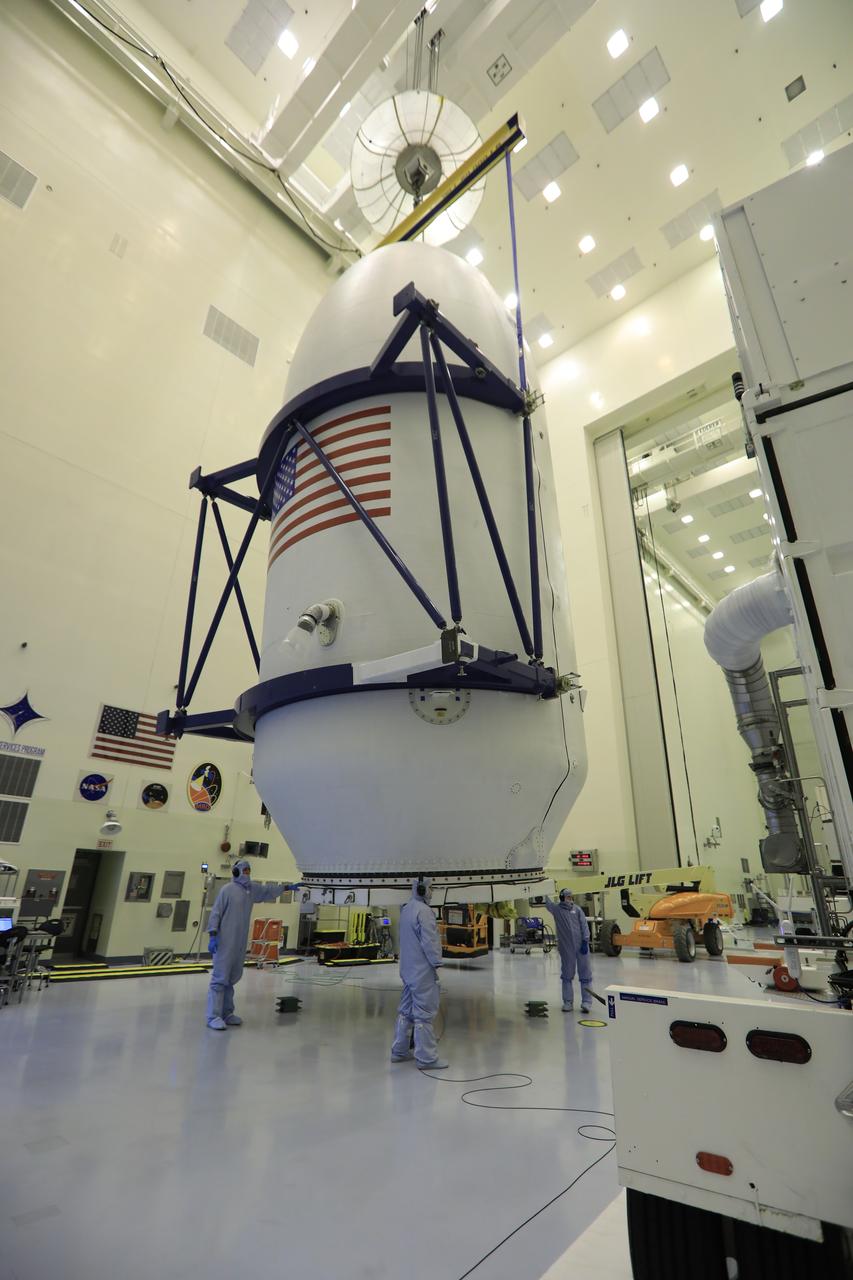

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is lifted for the move to a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.

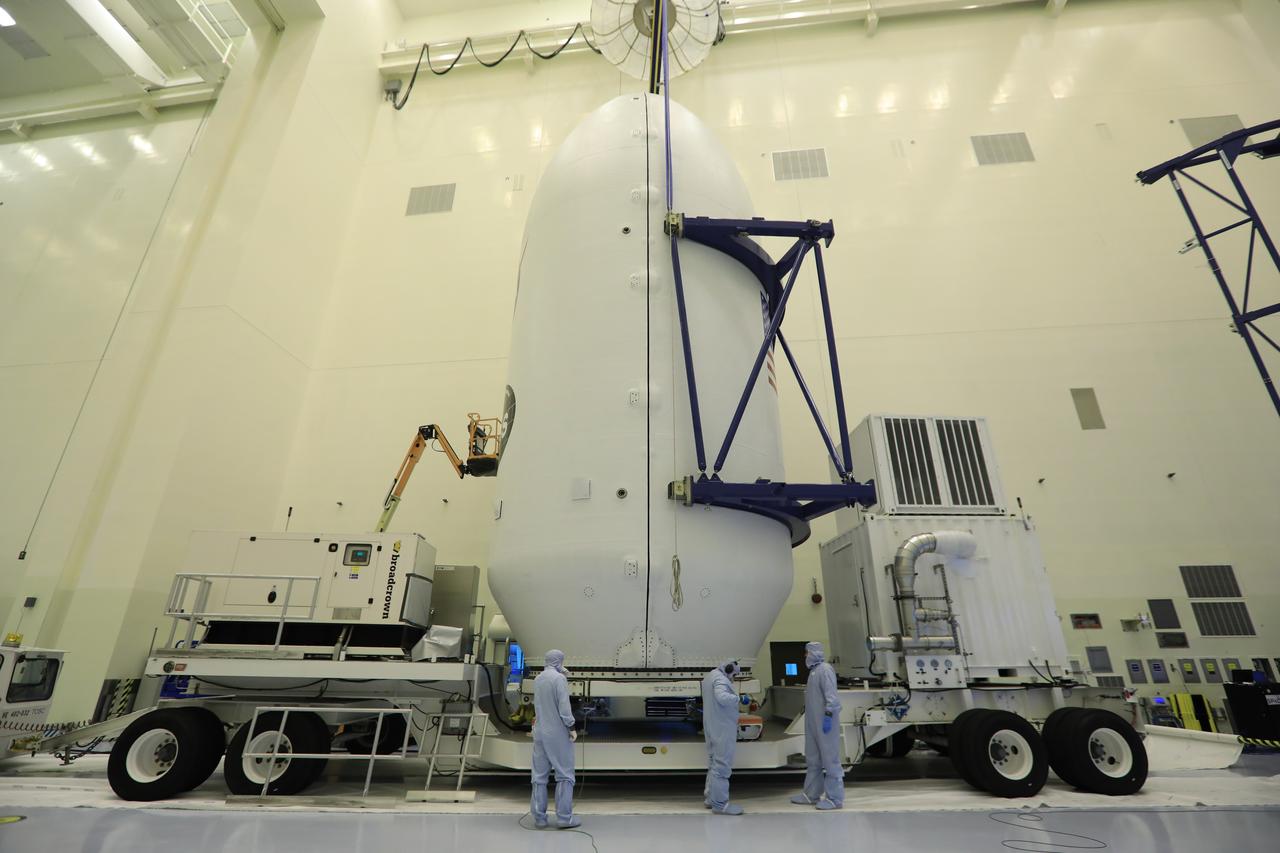
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is lowered by crane onto a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is scheduled to launch on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
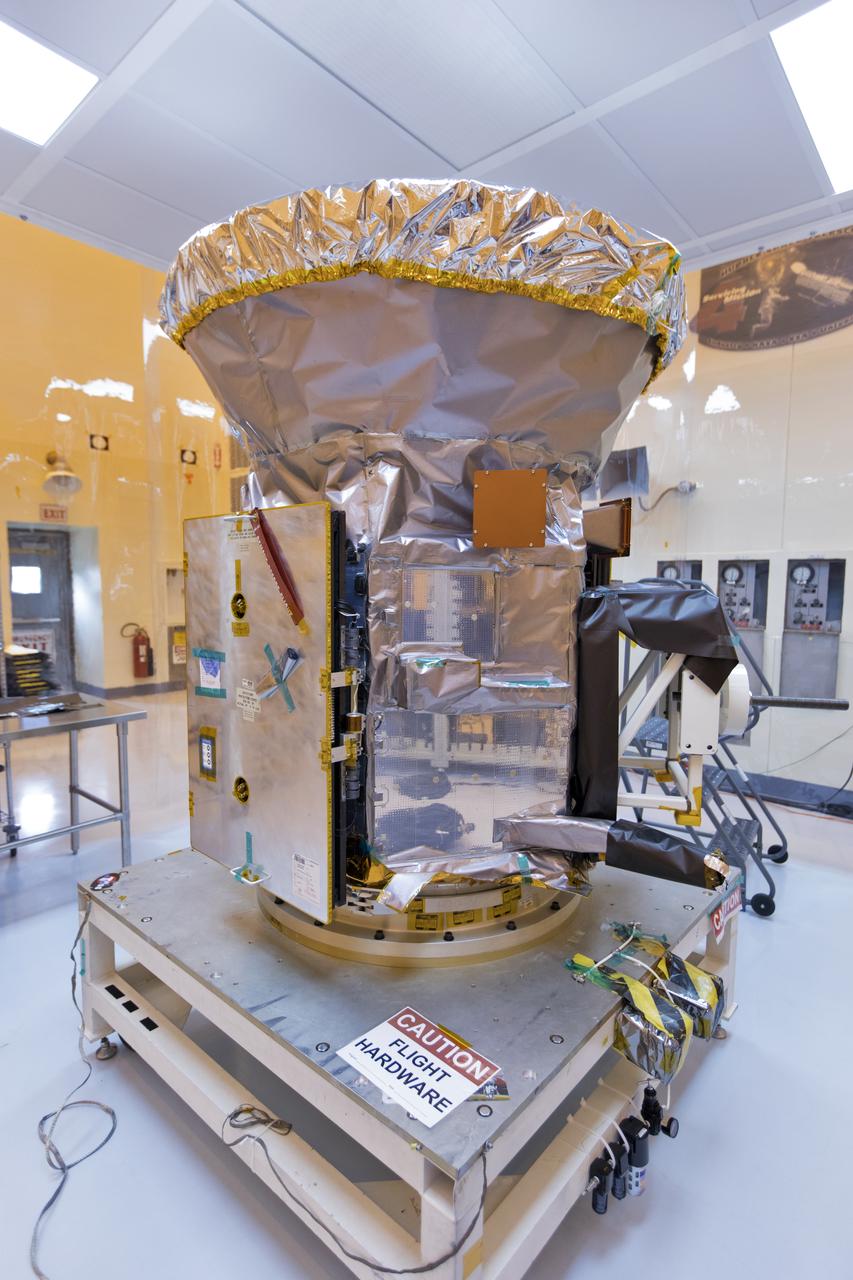

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, or TESS, has been uncreated from its shipping container for inspections and preflight processing. The satellite is NASA's next step in the search for planets outside of the solar system also known as "exoplanets." TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, and the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management. SpaceX of Hawthorne, California, is the provider of the Falcon 9 launch service. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a Falcon 9 rocket no earlier than April 16, 2018 from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.

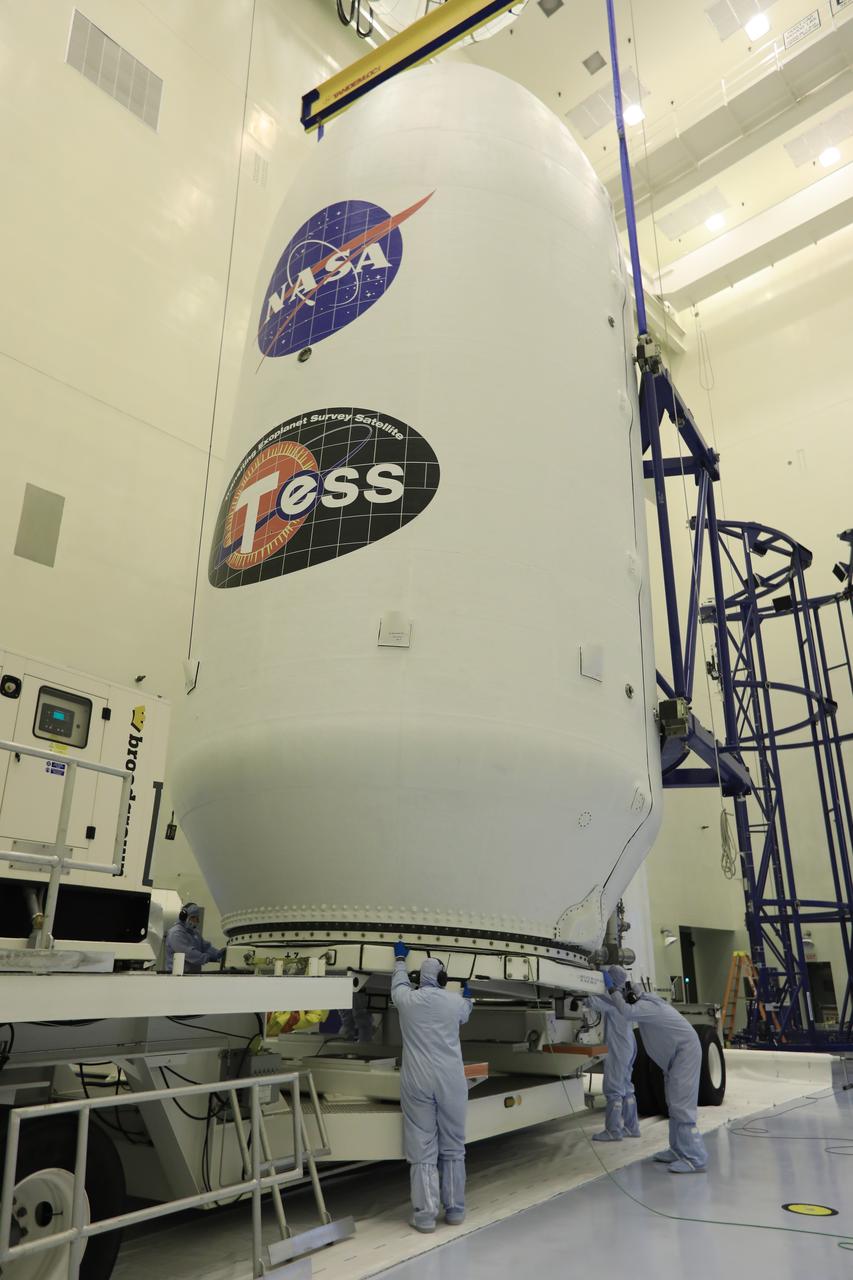
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the SpaceX payload fairing containing the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is secured onto a transporter. The fairing will be moved to Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is scheduled to launch on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 6:32 p.m. EDT on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.

Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution Wayne Clough speaks at the Apollo 40th anniversary celebration held at the National Air and Space Museum, Monday, July 20, 2009 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
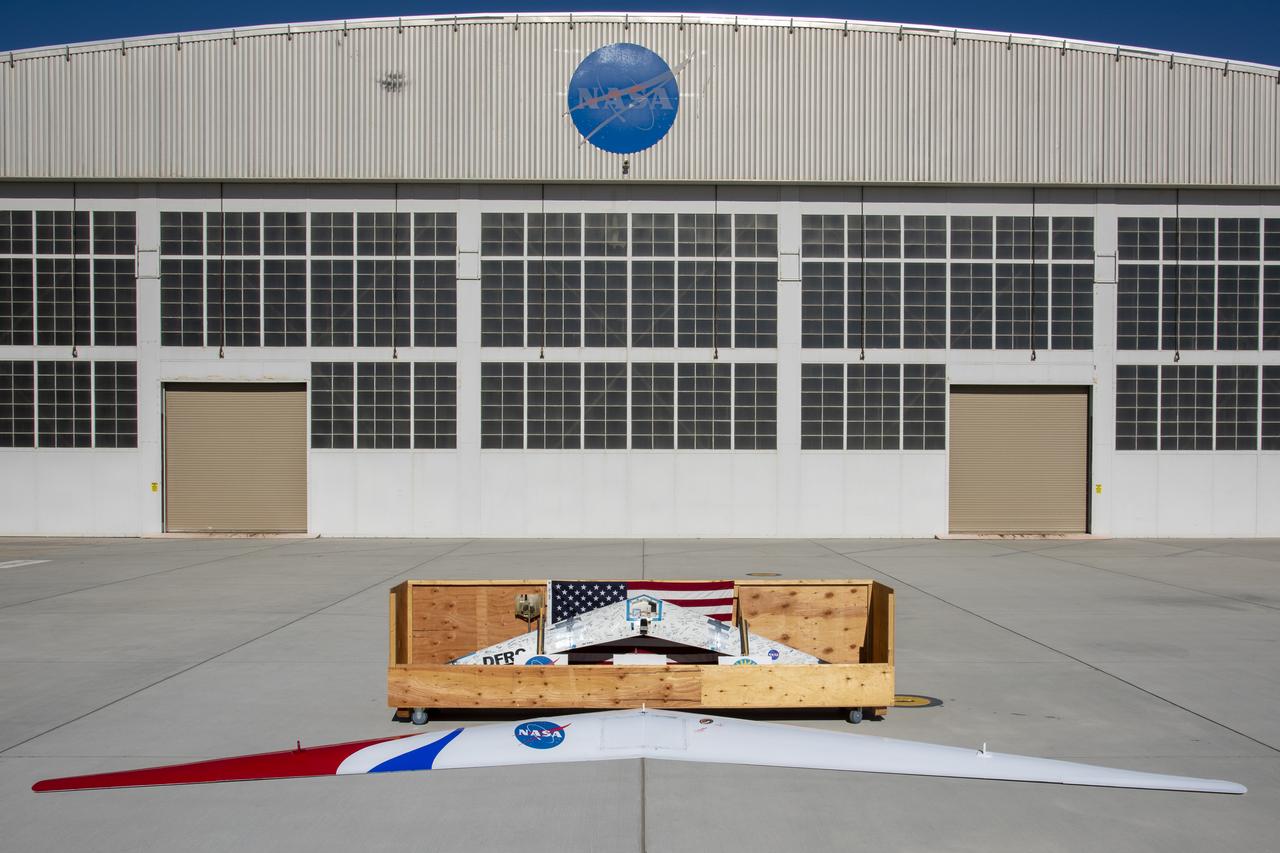

NASA Armstrong says goodbye to its Prandtl-D1 that is being shipped to the National Air and Space Museum, Smithsonian Institution and Prandl-D3 that will be going to the California Science Center.
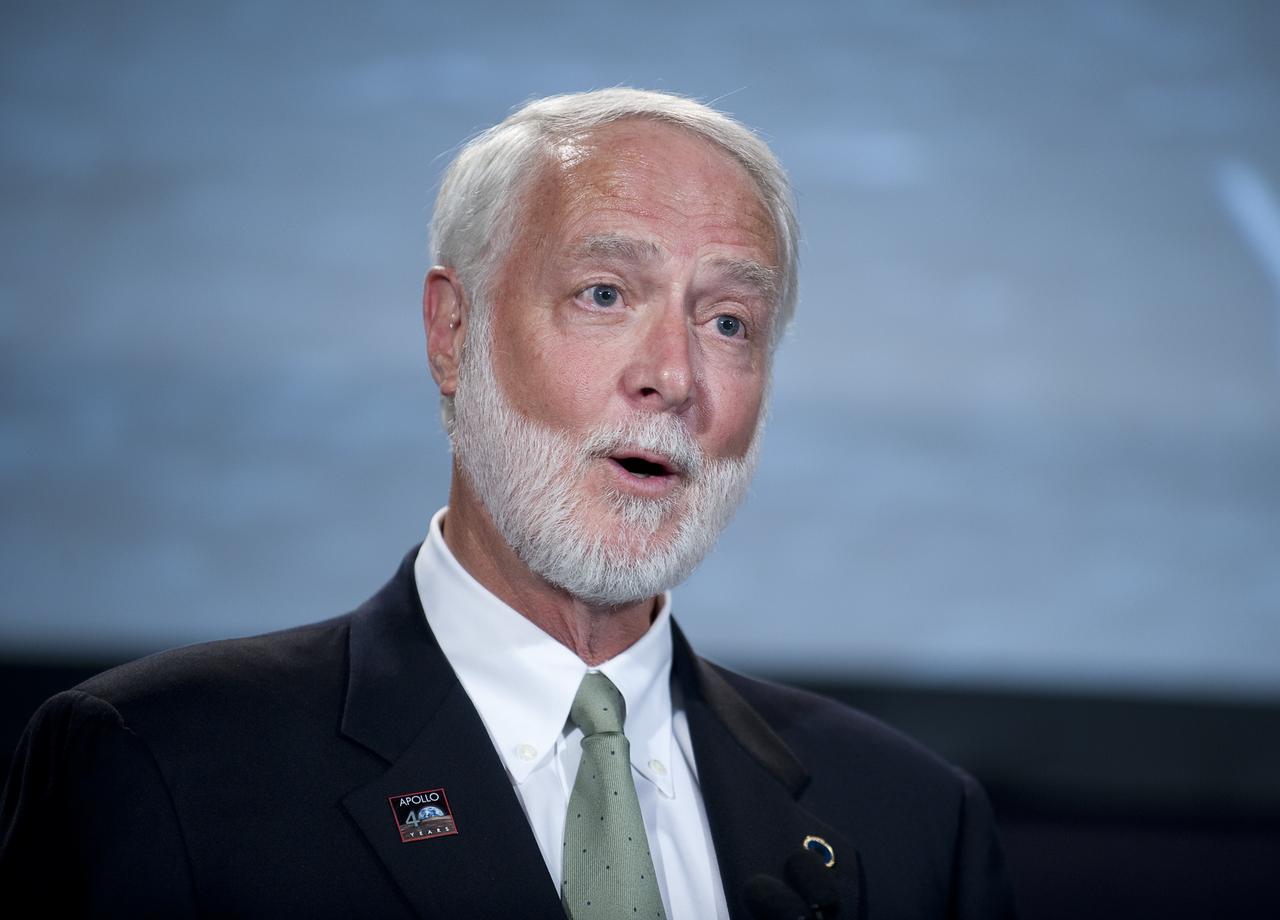

Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution Wayne Clough speaks at the Apollo 40th anniversary celebration held at the National Air and Space Museum, Monday, July 20, 2009 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
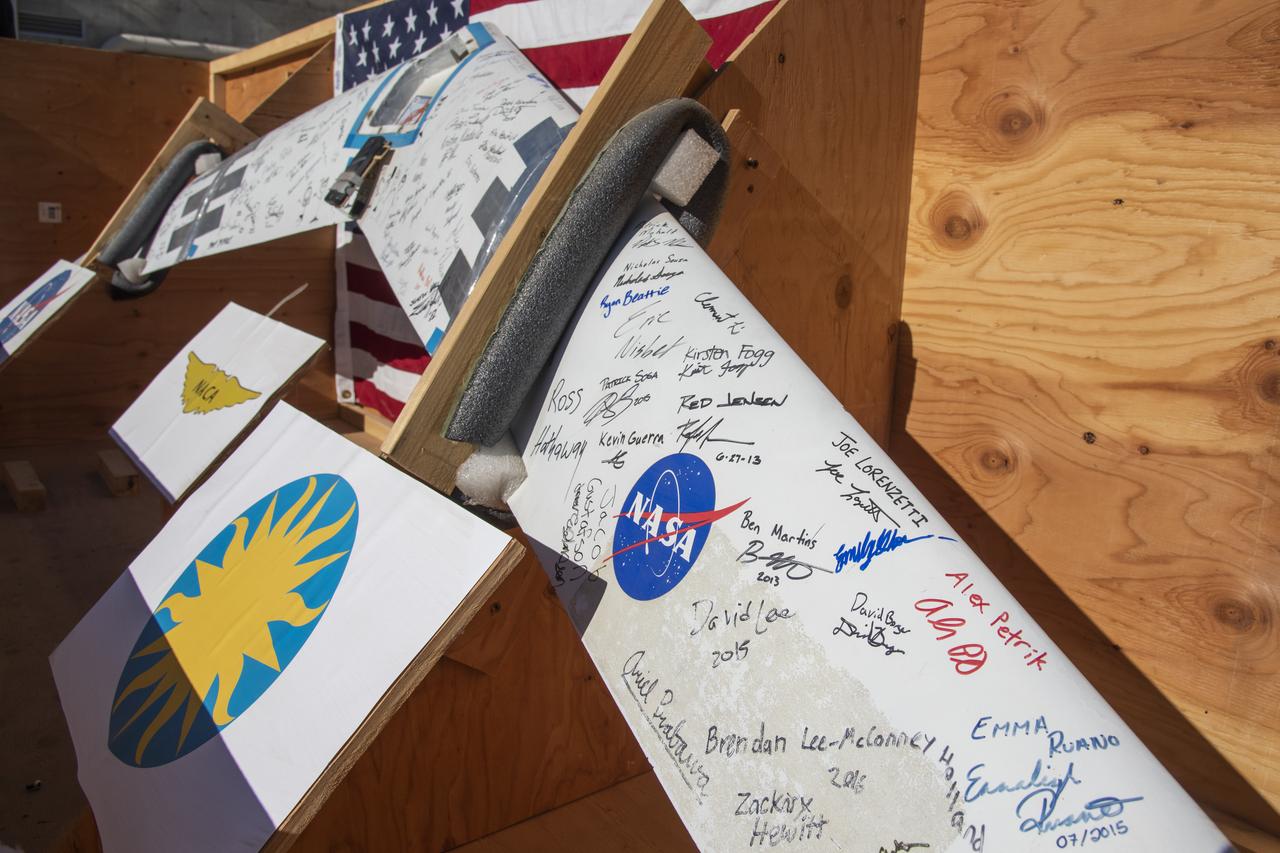

NASA Armstrong's Prandtl-D1, is autographed by all the interns that have worked on the project. Prandtl-D1 is being shipped to the National Air and Space Museum, Smithsonian Institution to be featured in its Innovations Gallery.

Technicians prepare NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) for encapsulation in the SpaceX payload fairing inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
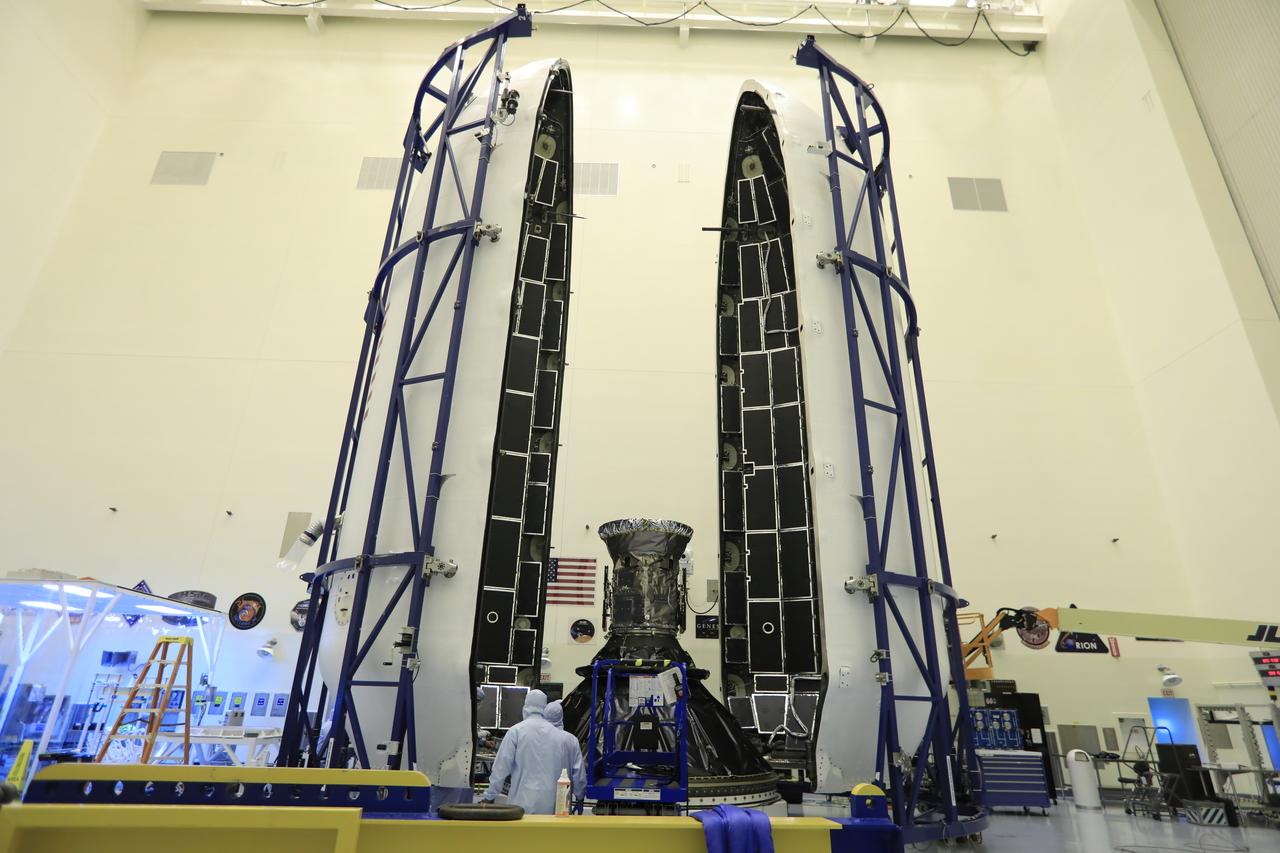

Technicians prepare NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) for encapsulation in the SpaceX payload fairing inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
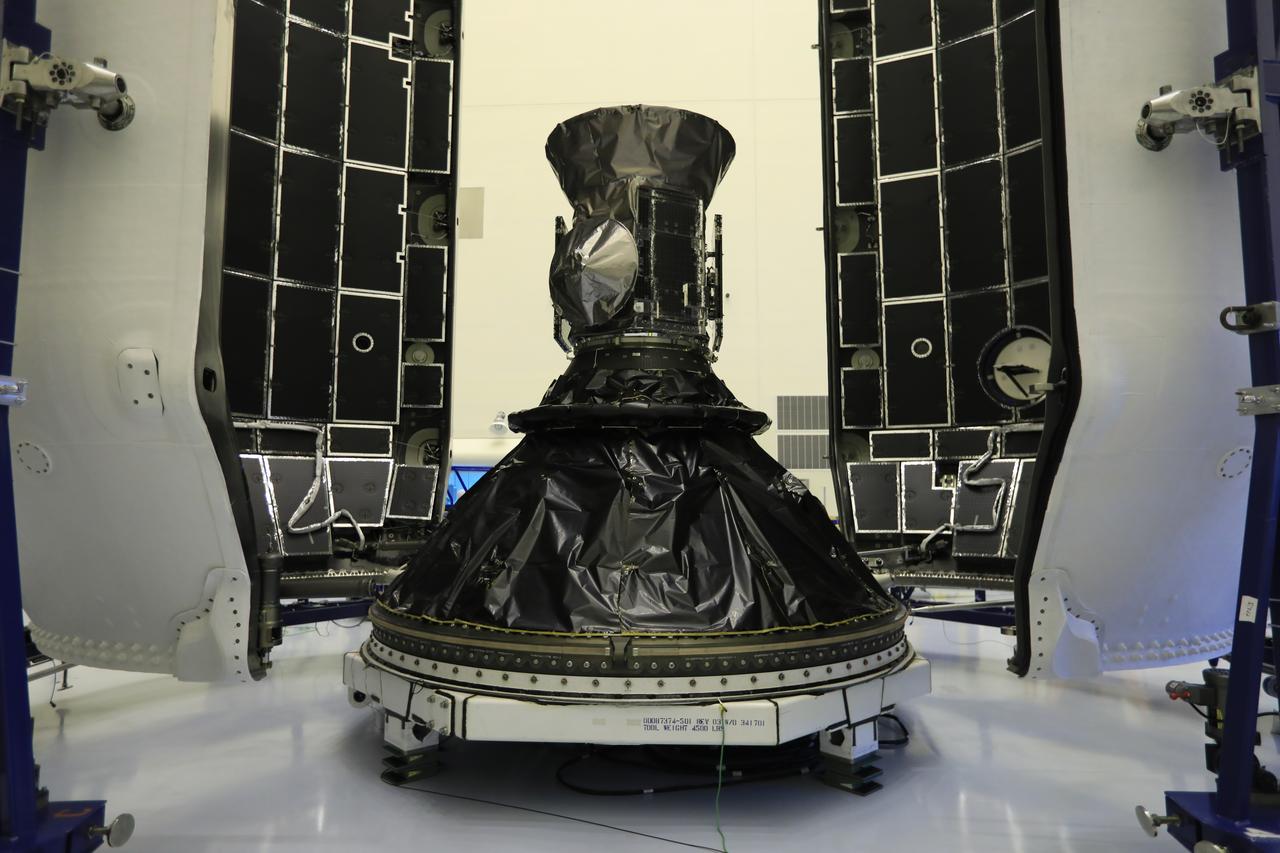
Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is being prepared for encapsulation in the SpaceX payload fairing. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on April 16. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
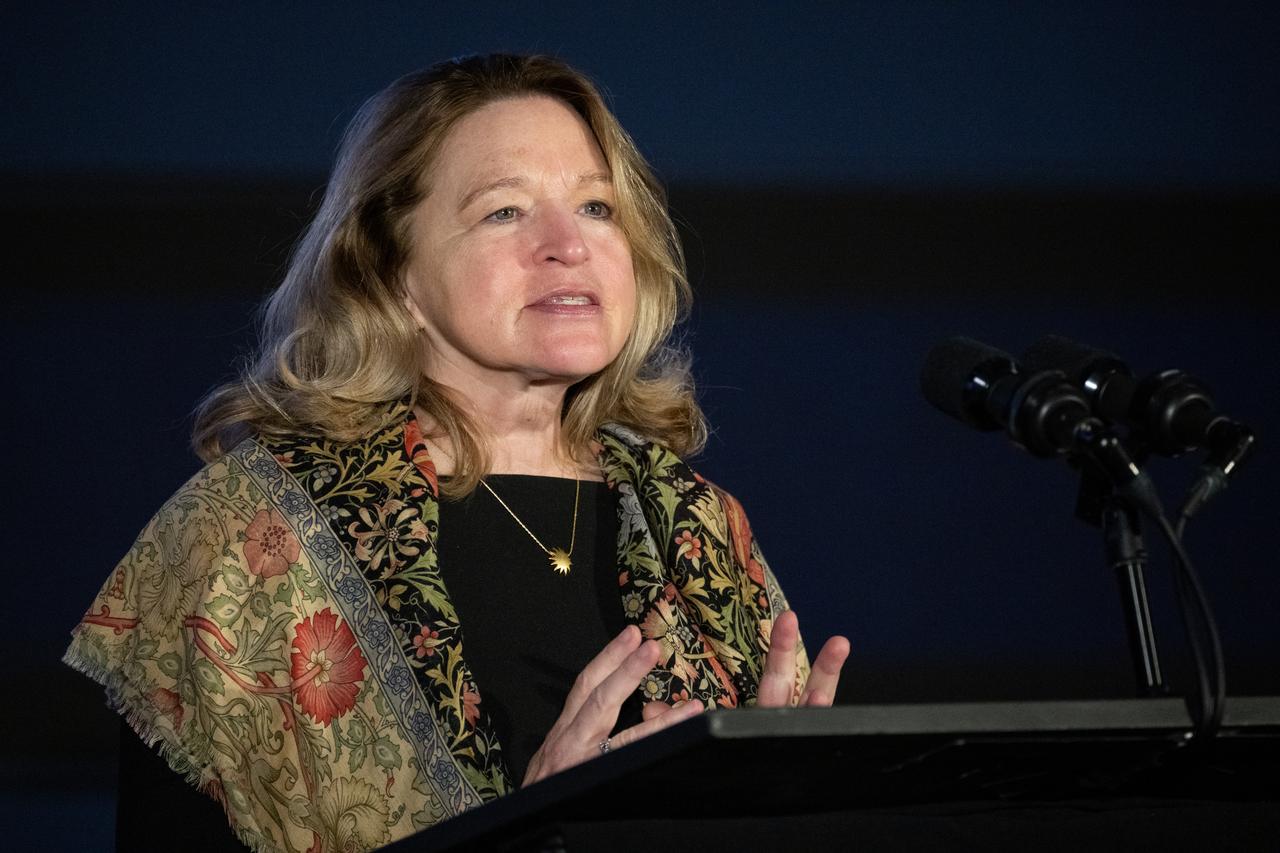

Ellen Stofan, under secretary for Science and Research at the Smithsonian Institution, speaks during a briefing on NASA’s TEMPO (Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution) instrument, Tuesday, March 14, 2023 at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA’s TEMPO instrument, the first Earth Venture Instrument mission, will measure air pollution across North America from Mexico City to the Canadian oil sands and from the Atlantic to the Pacific hourly and at a high spatial resolution. A partnership between NASA and the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, TEMPO will launch on a commercial satellite to geostationary orbit as early as April. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
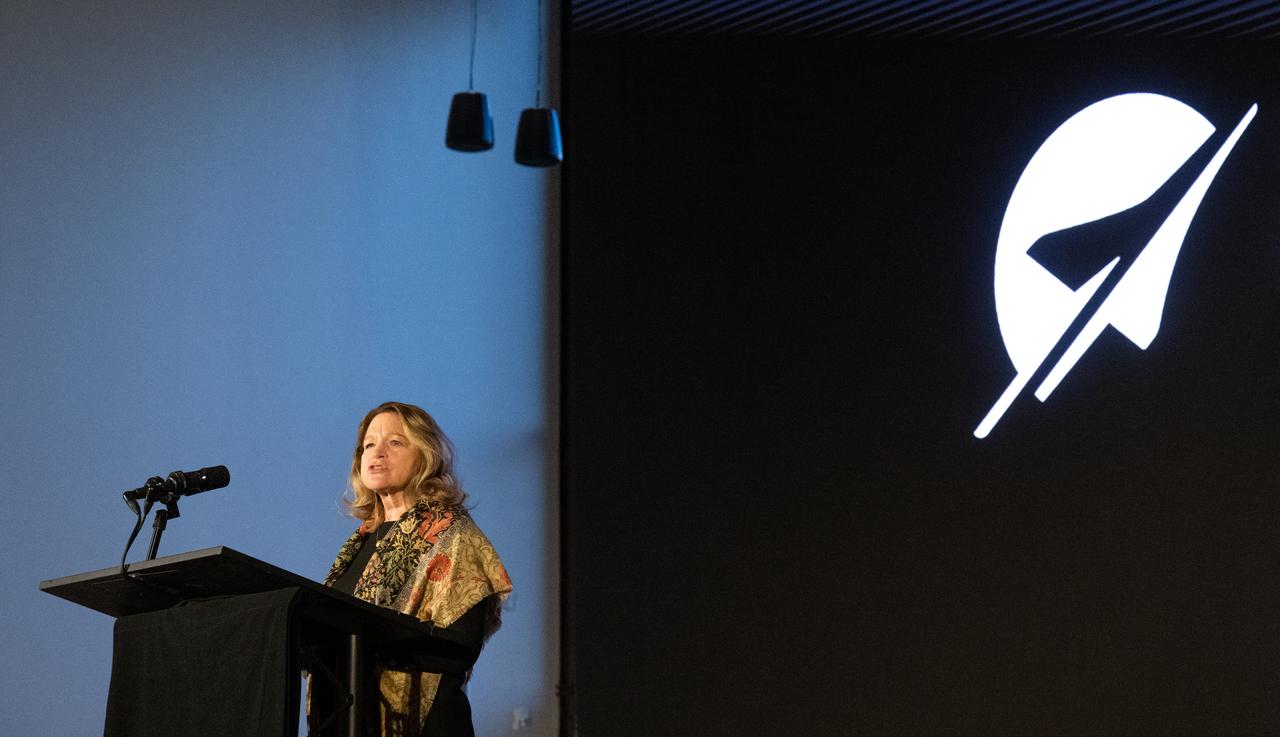

Ellen Stofan, under secretary for Science and Research at the Smithsonian Institution, speaks during a briefing on NASA’s TEMPO (Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution) instrument, Tuesday, March 14, 2023 at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA’s TEMPO instrument, the first Earth Venture Instrument mission, will measure air pollution across North America from Mexico City to the Canadian oil sands and from the Atlantic to the Pacific hourly and at a high spatial resolution. A partnership between NASA and the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, TEMPO will launch on a commercial satellite to geostationary orbit as early as April. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
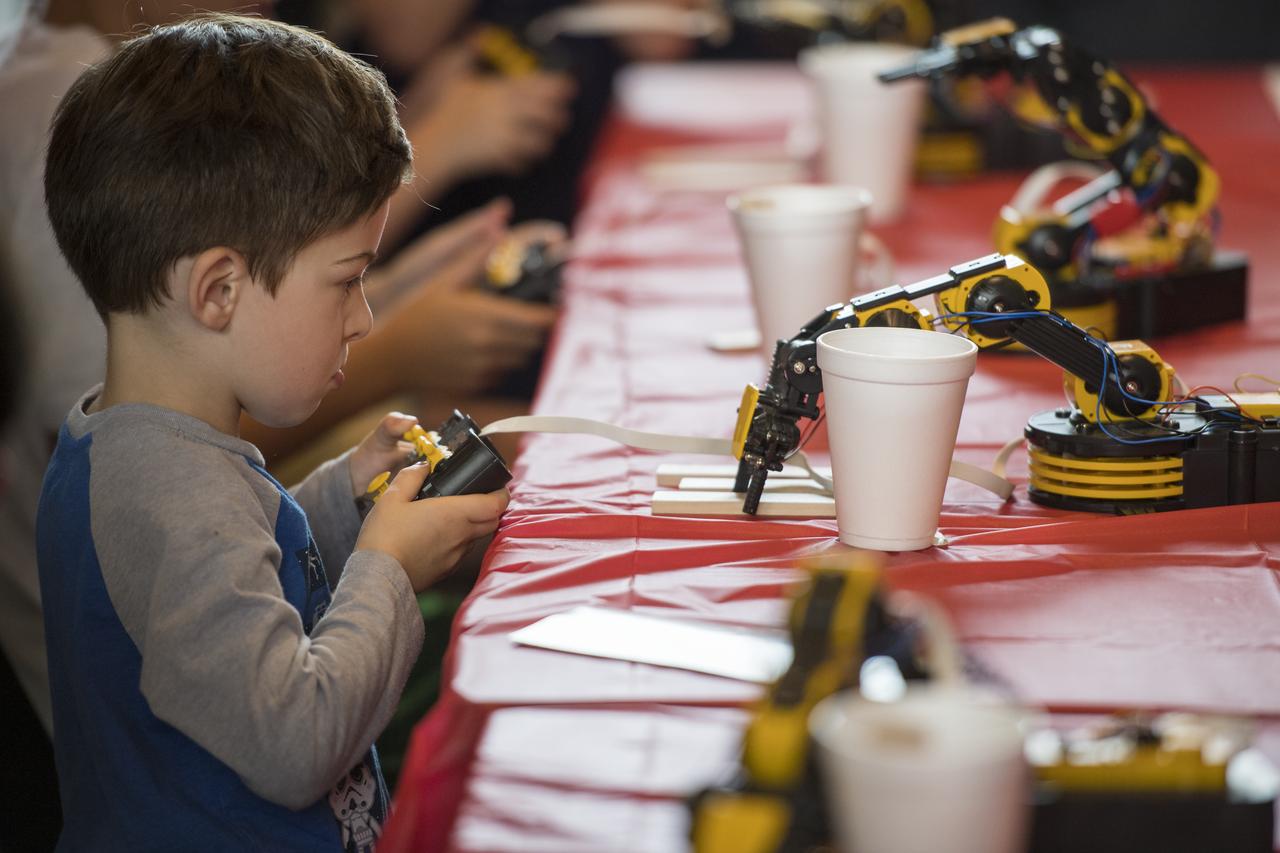

Visitors operate robotic arms at the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, an annual event celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
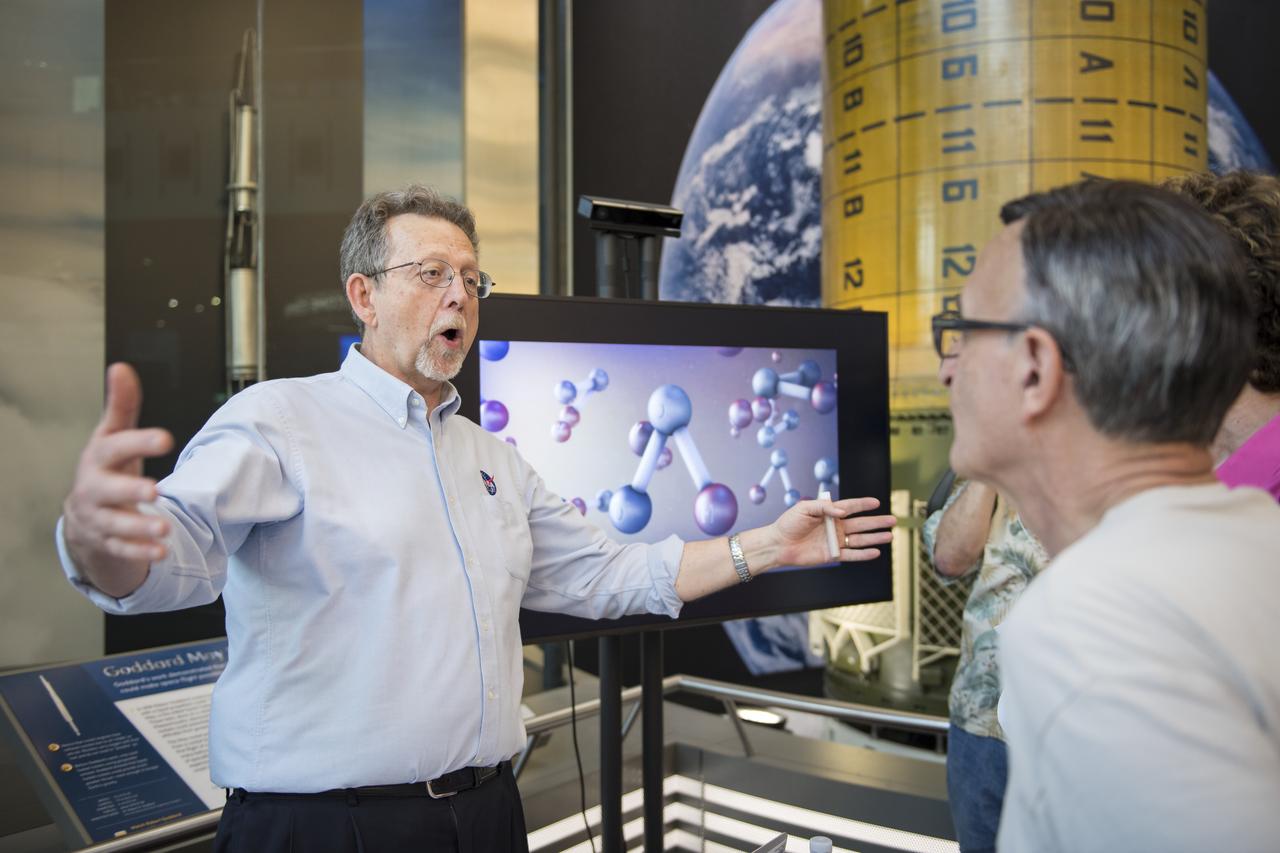

Jim Green, director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division, discusses NASA’s Mars missions with visitors during the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
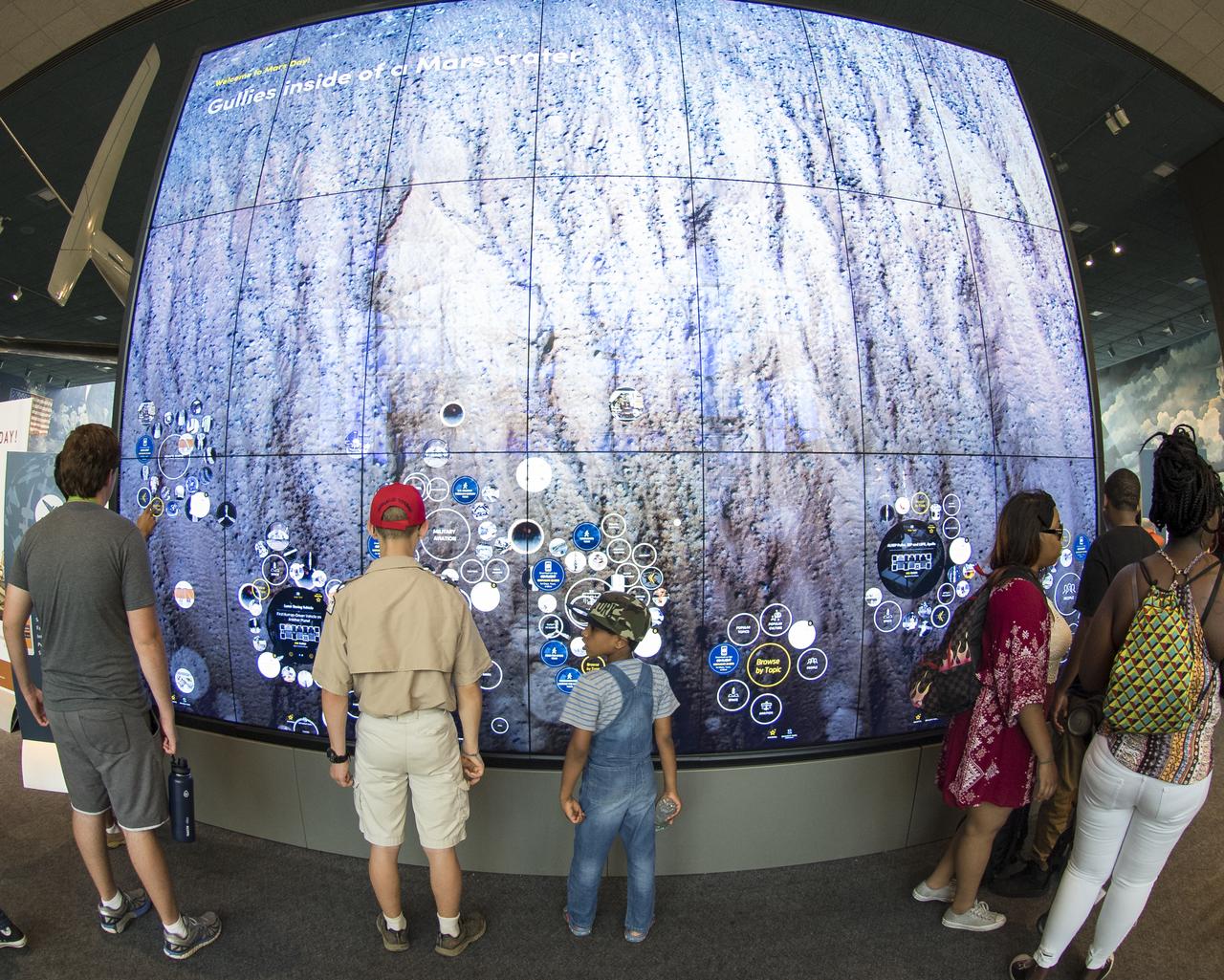

Visitors explore an interactive map of the surface of Mars at the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, an annual event celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
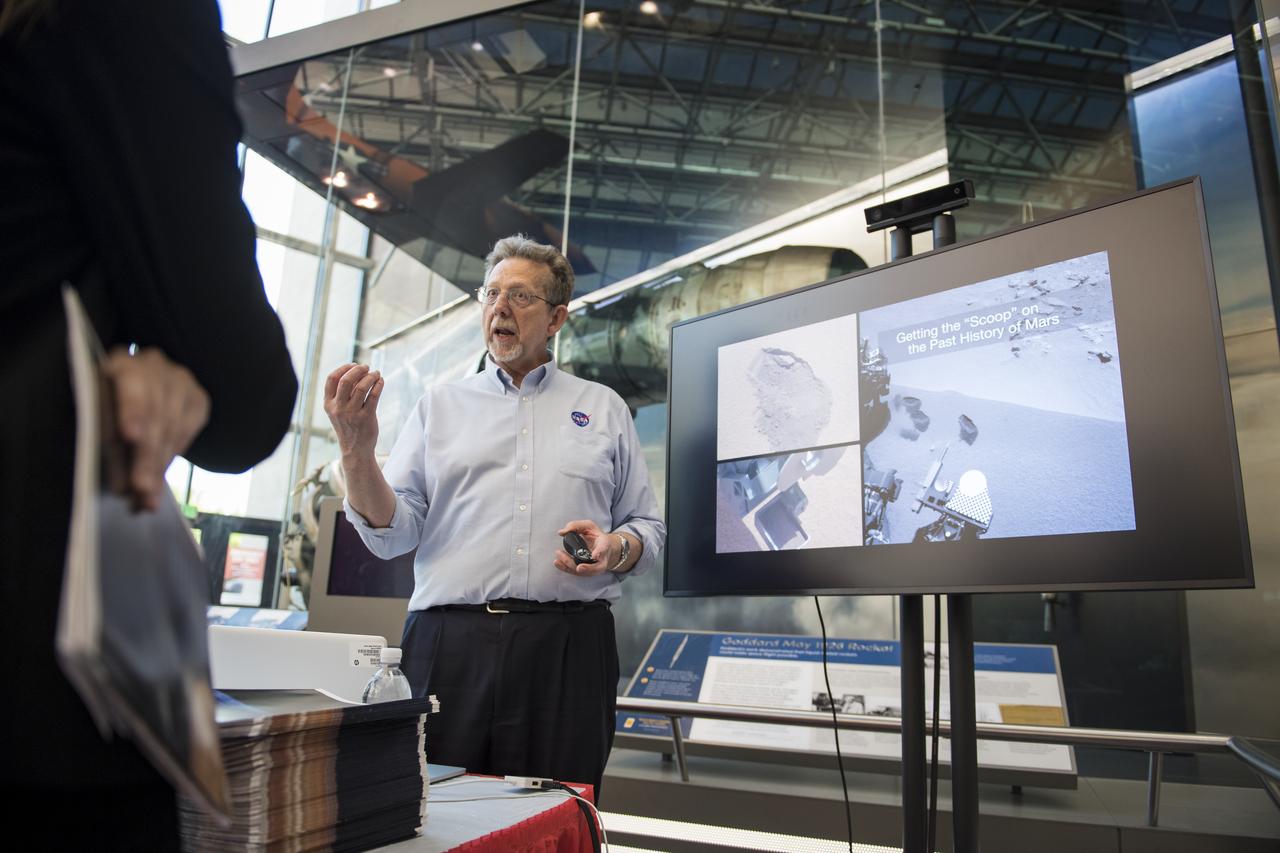

Jim Green, director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division, discusses NASA’s Mars missions with visitors during the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
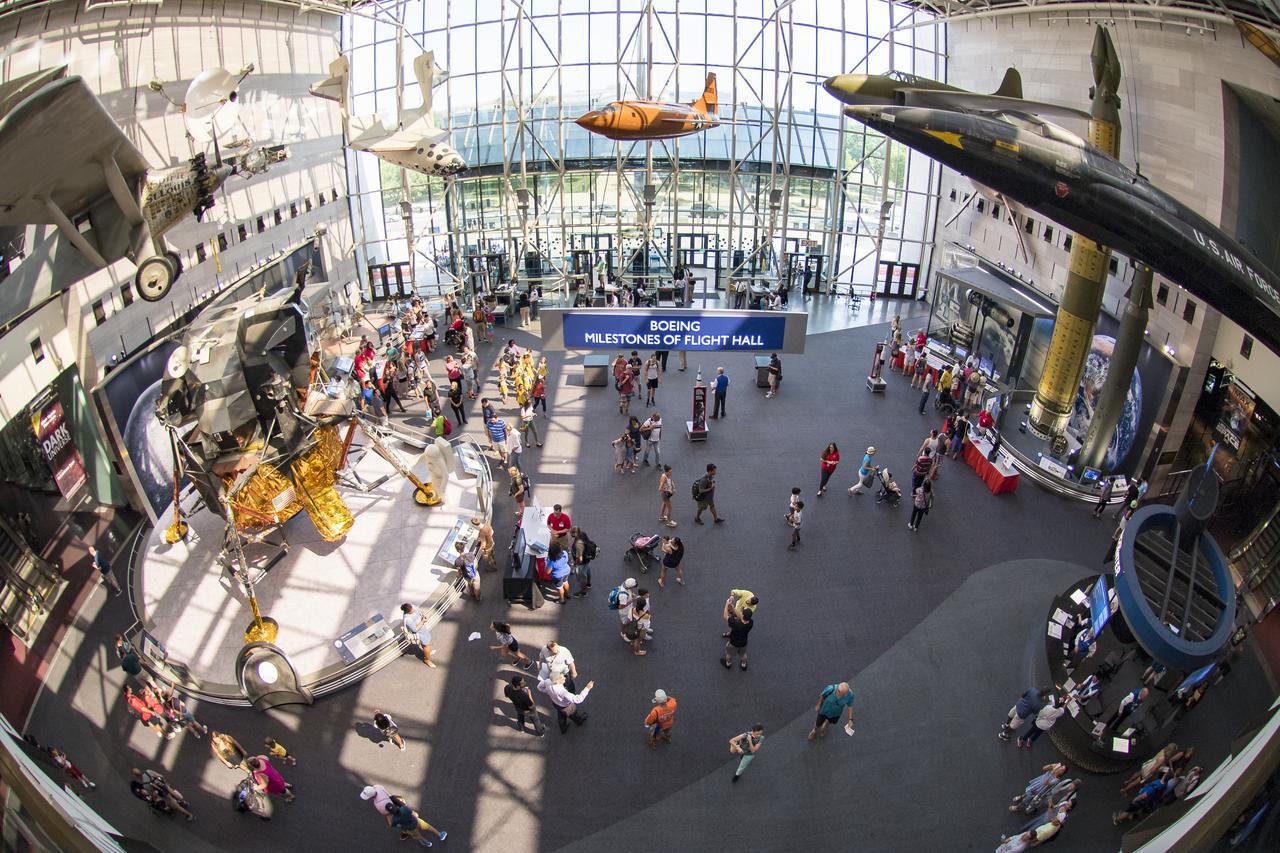

Visitors explore Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum’s Mars Day, an annual event celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
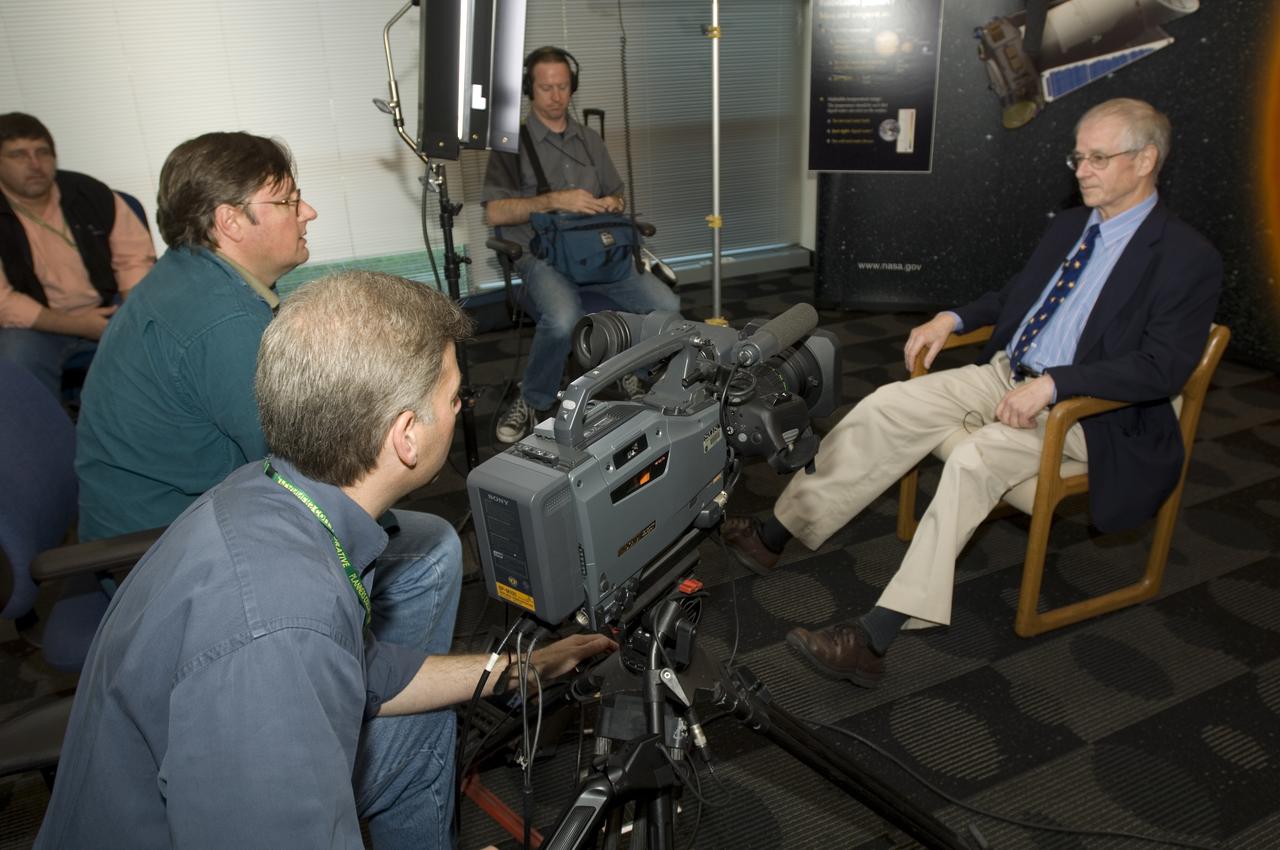

Ames Video group during interviewing Dave Lathem, Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, MR at the SETI Institute during a NASA Ames Kepler Mission conference. Dave Maurantonio, Ed Schilling, Bill Moede, and Eric Land, Ames/Planners Video crew (Kepler a search for habitable planets was selected for Discovery Program)
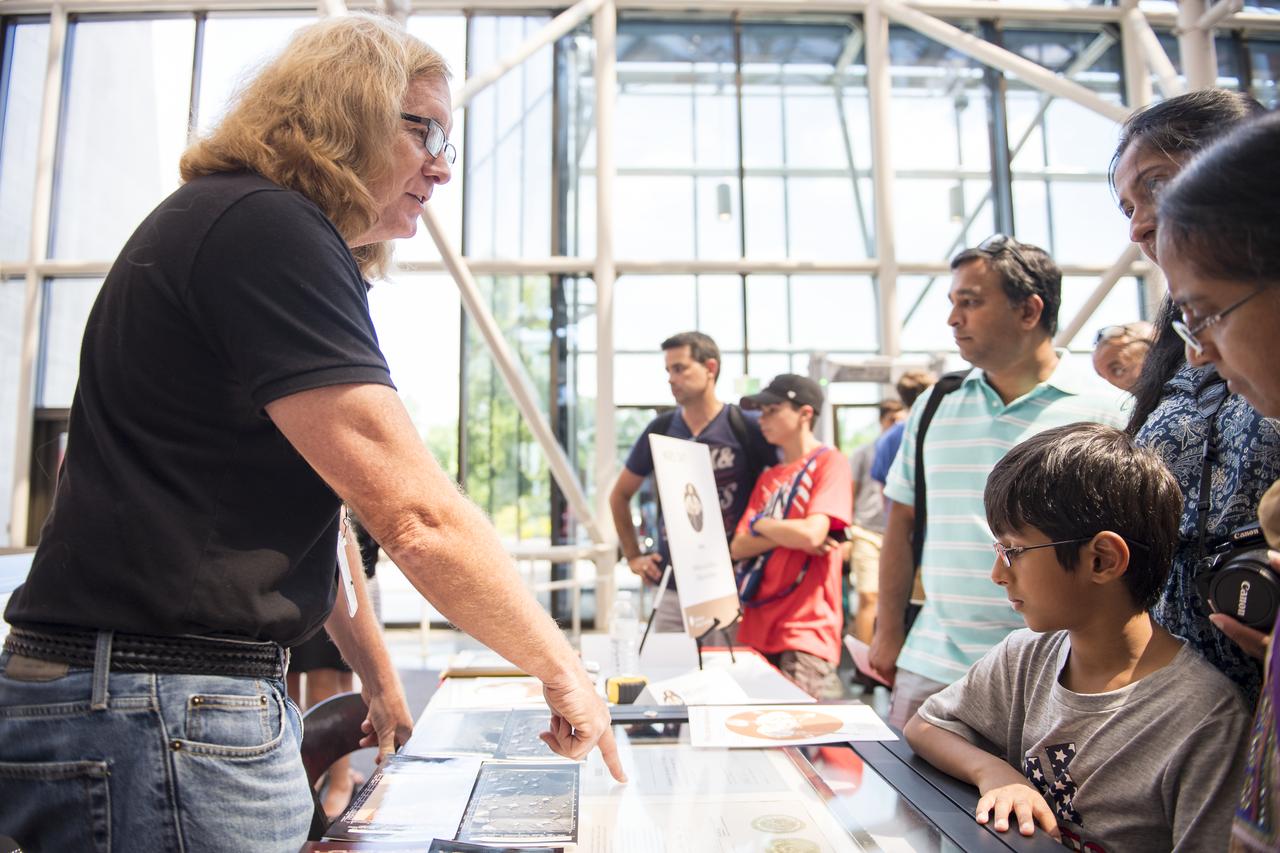

Visitors learn about the Viking landers at the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, an annual event celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
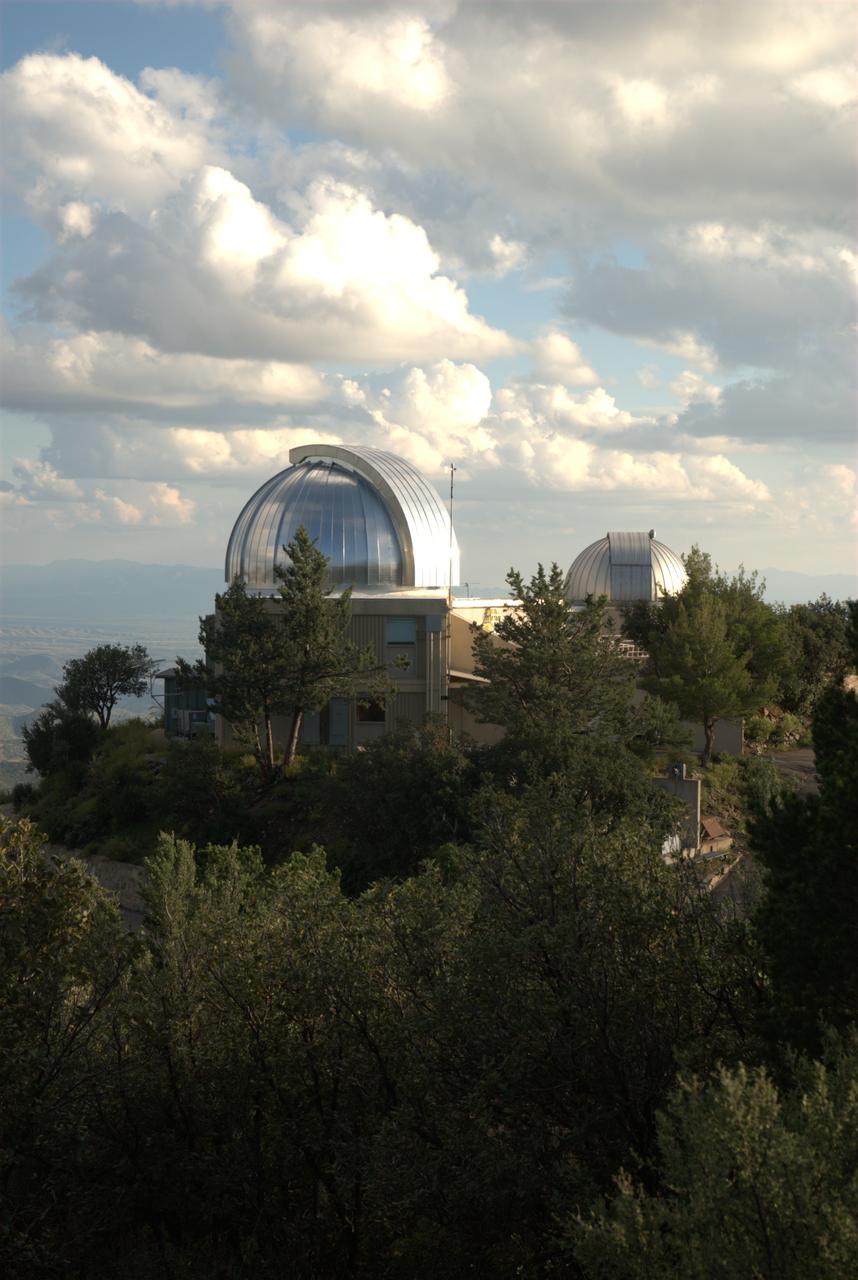

Kepler activities at Smithsonian Institution; Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory, Mt Hopkins AZ for Kepler input catalog (nearing completion). Protective domes cover the 1.5-meter (60-inch, left) and 1.2-meter (48-inch, right) telescopes.
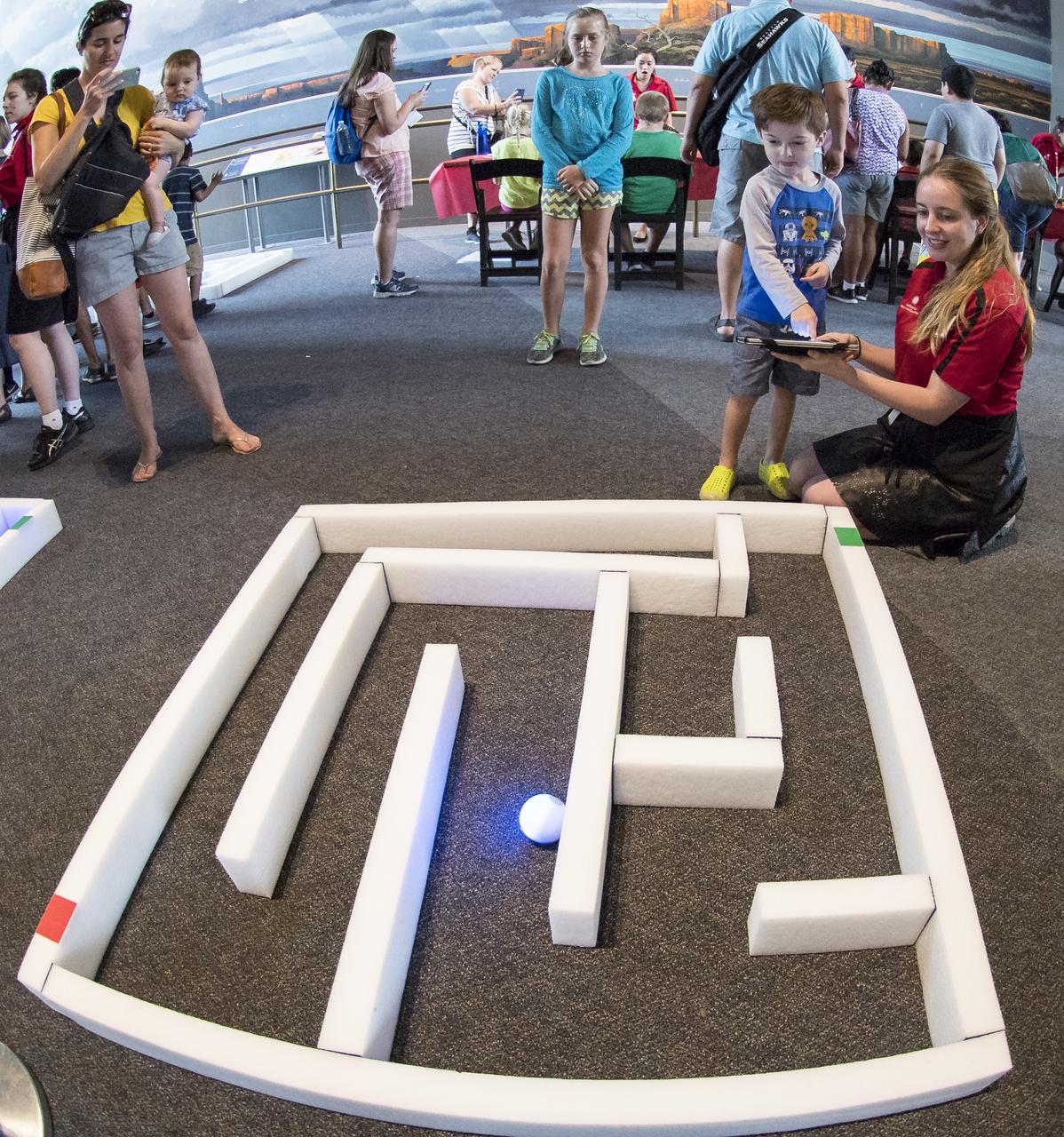

Visitors direct a robotic ball through a maze at the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, an annual event celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
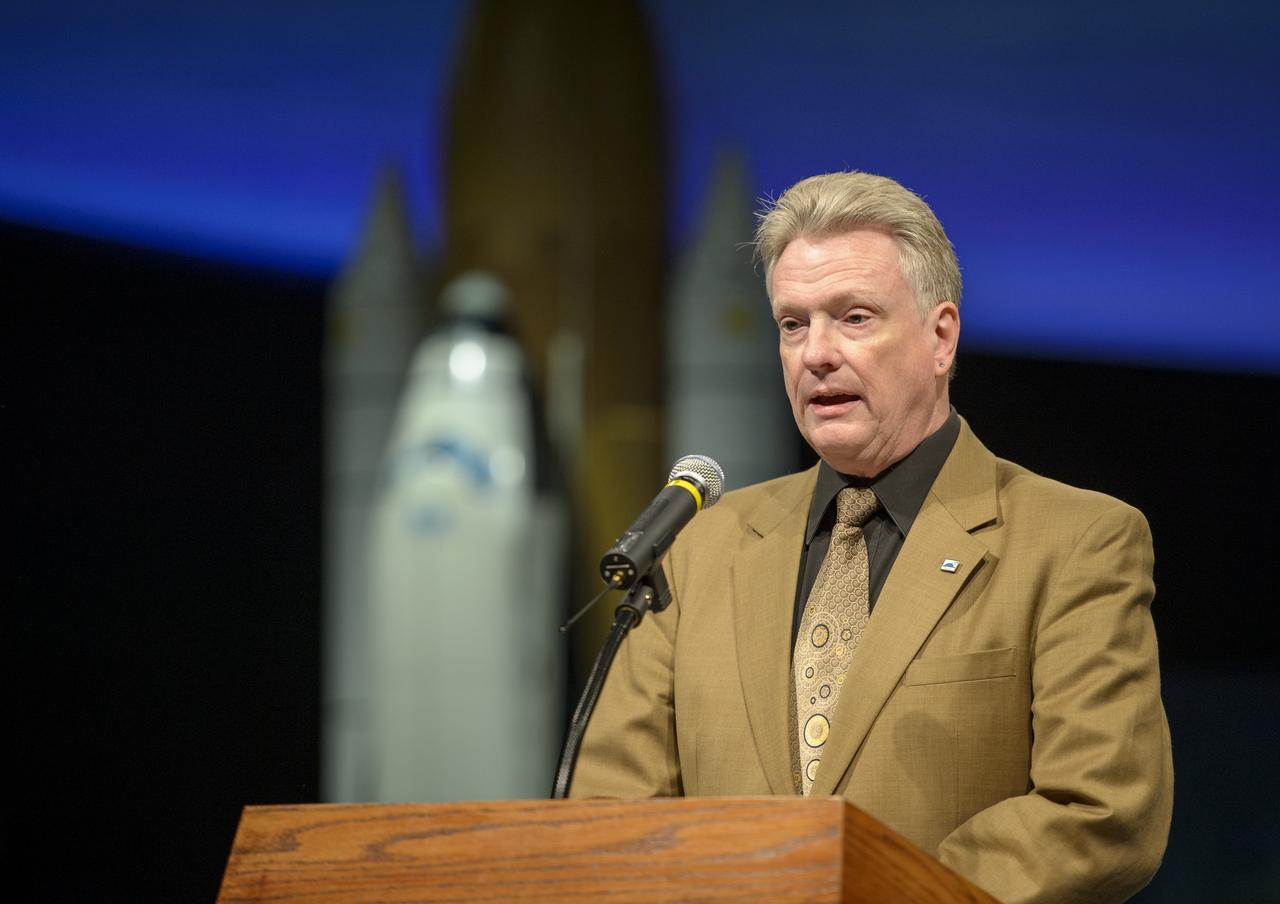

Smithsonian Institution's National Air and Space Museum Senior Curator in the Division of Space History Dr. Roger Launious begins a program titled "Sally Ride: How Her Historic Space Mission Opened Doors for Women in Science" held on Friday, May 17, 2013 at the Museum in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
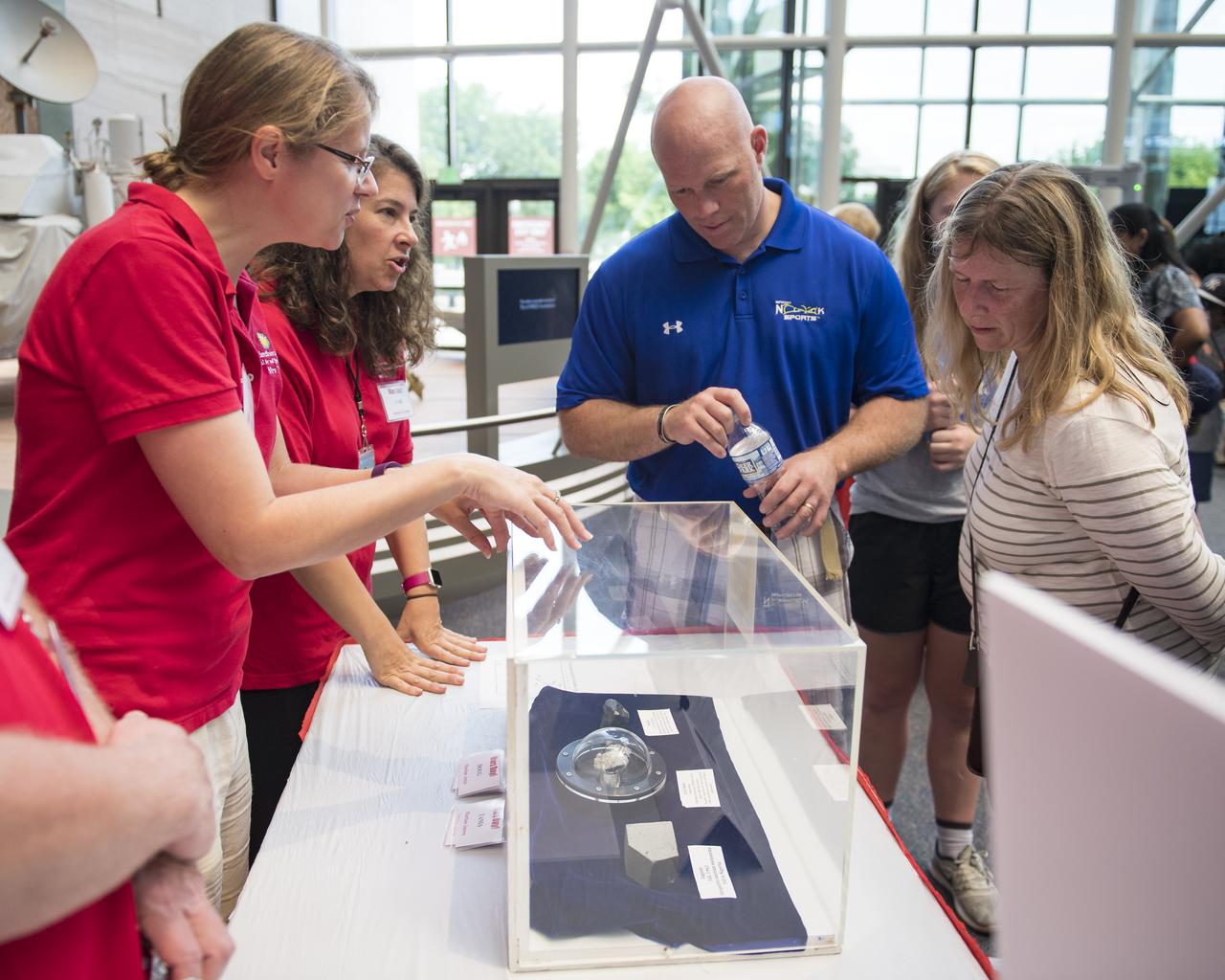

Visitors view a piece of Mars at the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, an annual event celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
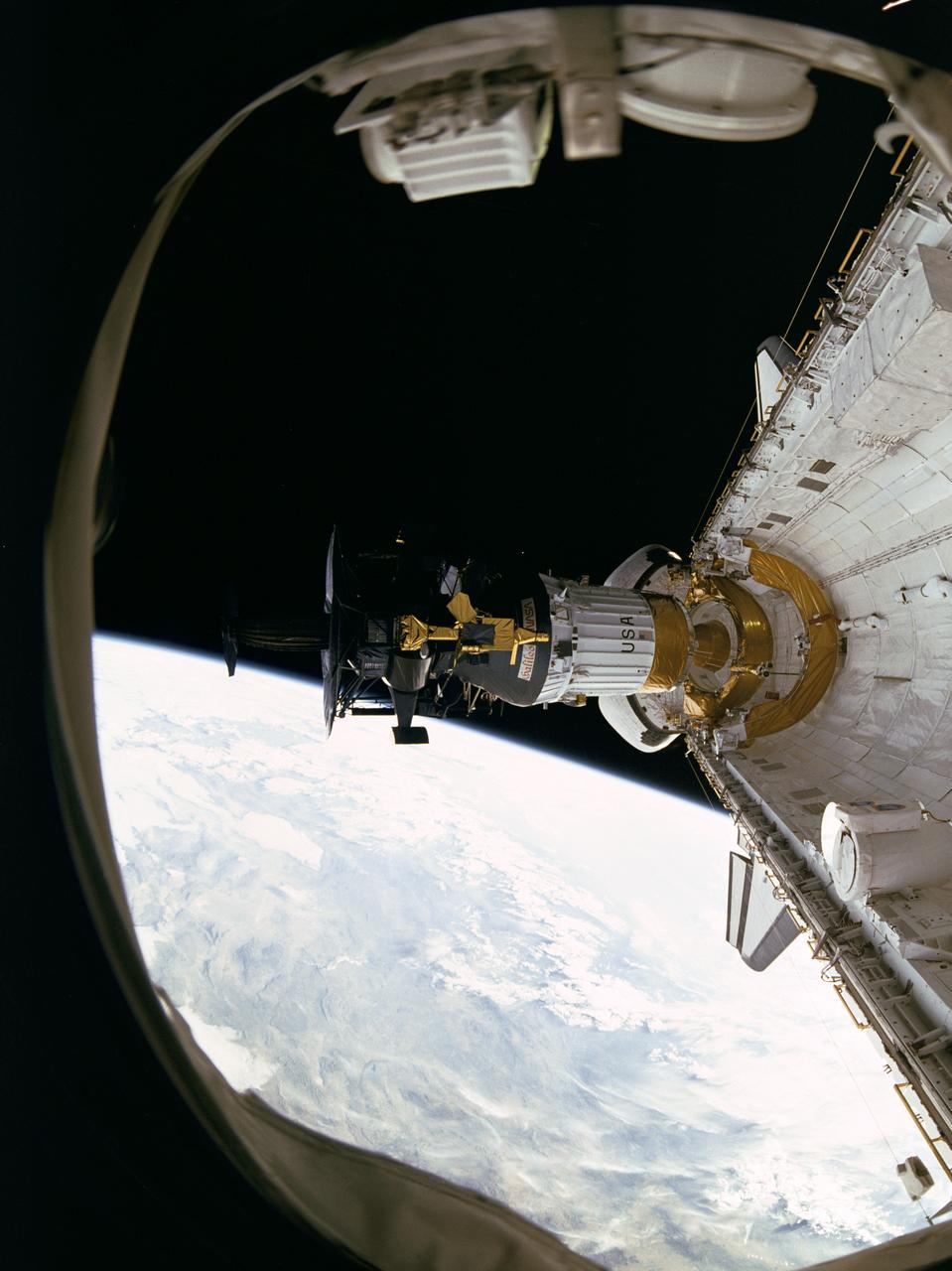

S89-48714 (18 Oct 1989) --- This photograph was taken by the STS-34 crew aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis and shows the Galileo spacecraft being deployed on Oct. 18, 1989 from the payload bay. Galileo is a scientific craft that will go into orbit around the planet Jupiter and drop a probe into its atmosphere in search of primordial solar system material believed to be present there. The 70mm motion picture film will be used in the forthcoming "Blue Planet," which will address Earth's environmental problems from the perspective of space-based observation and solar system exploration. The film is being produced by IMAX Space Technology Inc. for the sponsor, the Smithsonian Institution, with funding provided by the Lockheed Corporation. PHOTO CREDIT: NASA/Smithsonian Institution
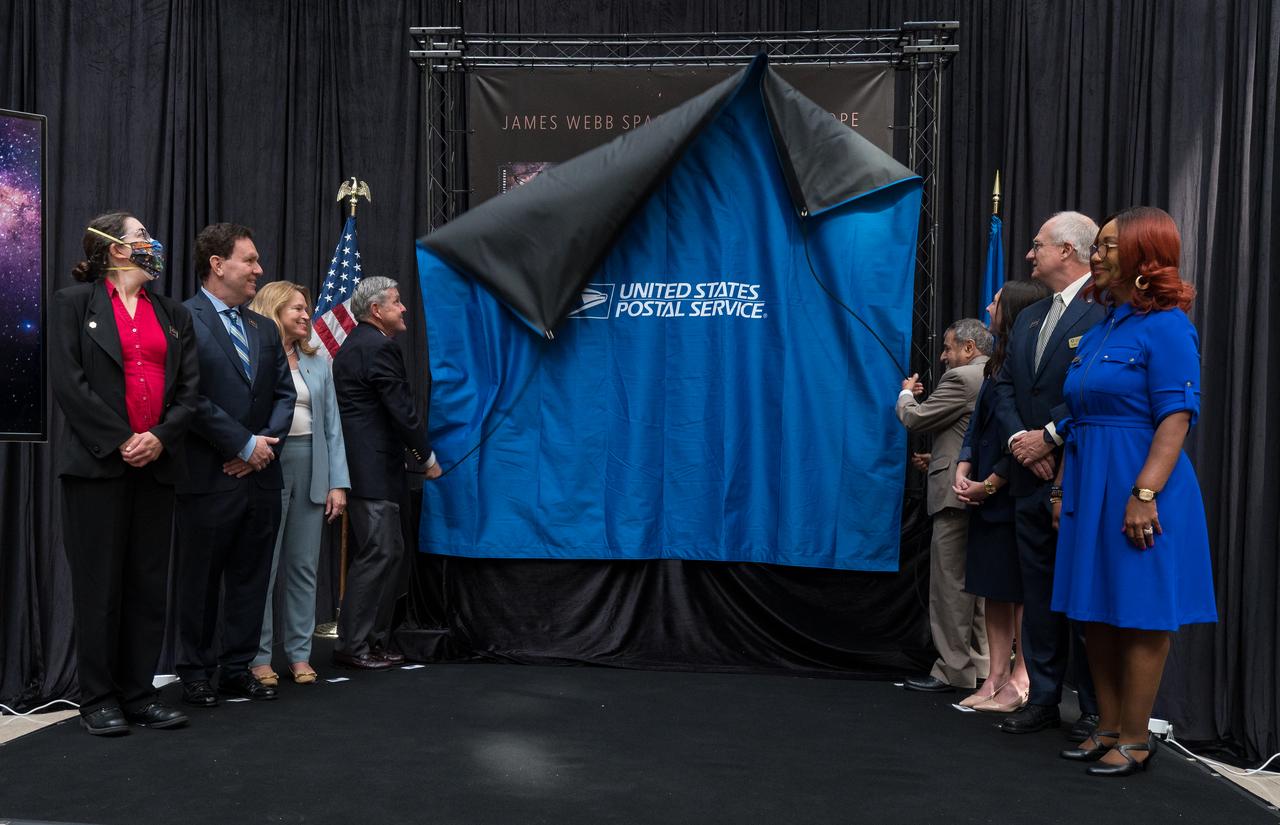

From left to right, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Webb Deputy Observatory Project Scientist, Erin Smith, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Webb Optical Telescope Element Manager, Lee Feinberg, Smithsonian Institution Under Secretary for Service and Research, Ellen Stofan, NASA Associate Administrator and former astronaut Bob Cabana, United States Postal Service Vice Chairman, Board of Governors, Anton Hajjar, NASA public affairs specialist Alice Fisher, National Postal Museum Deputy Director, Toby Mensforth, and Lisa Whitehead, USPS, unveil the United States Postal Service’s new stamp celebrating NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) at the first-day-of-issue event on Thursday, Sept. 8, 2022, at the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum in Washington. The stamp, which features an illustration of the observatory, honors Webb’s mission to explore the unknown in our universe – solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
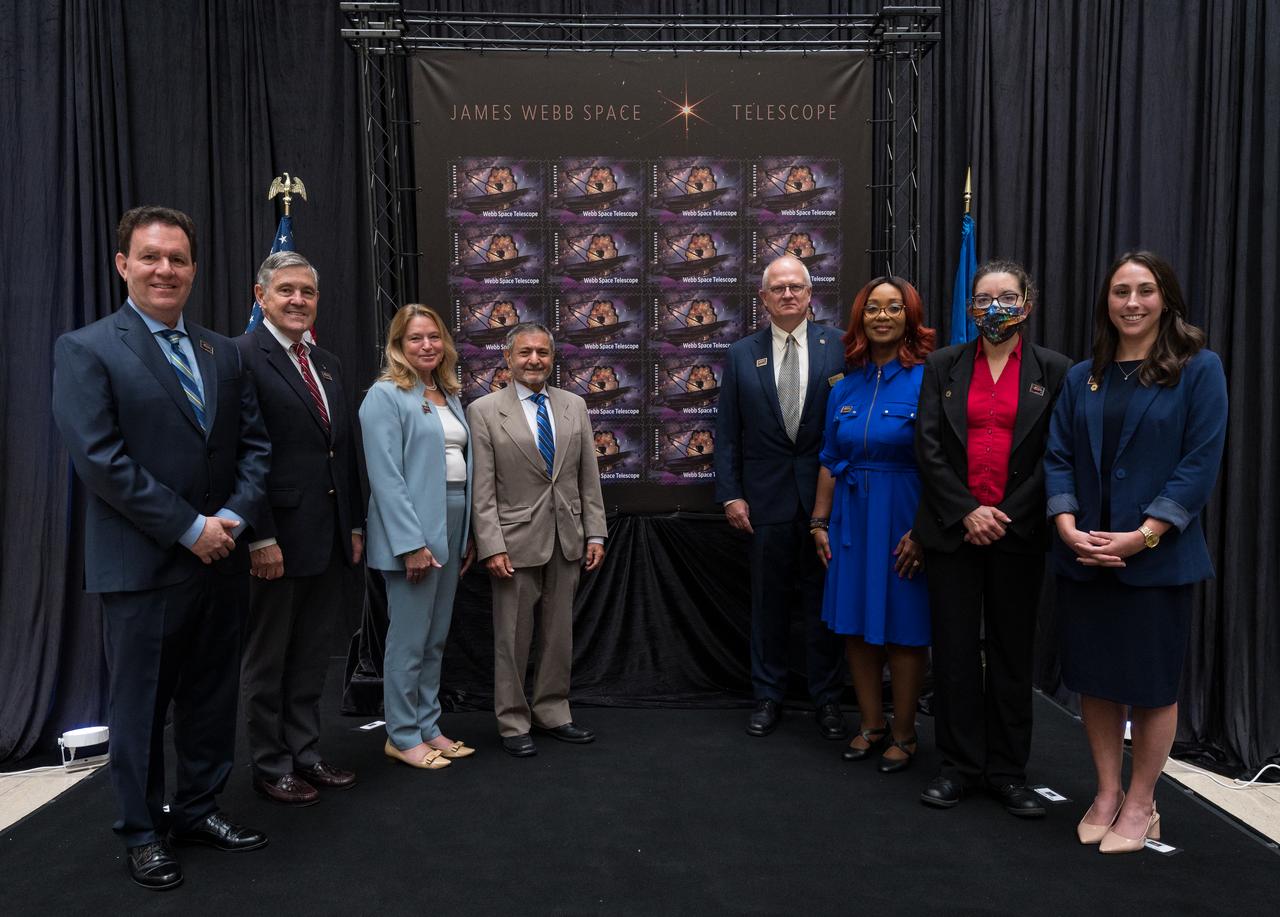

From left to right, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Webb Optical Telescope Element Manager, Lee Feinberg, NASA Associate Administrator and former astronaut Bob Cabana, Smithsonian Institution Under Secretary for Service and Research, Ellen Stofan, United States Postal Service Vice Chairman, Board of Governors, Anton Hajjar, National Postal Museum Deputy Director Toby Mensforth, Lisa Whitehead, USPS, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Webb Deputy Observatory Project Scientist, Erin Smith, and NASA public affairs specialist, Alice Fisher, pose for a photo at the conclusion of the first-day-of-issue event for the United States Postal Service’s new stamp celebrating NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) on Thursday, Sept. 8, 2022, at the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum in Washington. The stamp, which features an illustration of the observatory, honors Webb’s mission to explore the unknown in our universe – solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
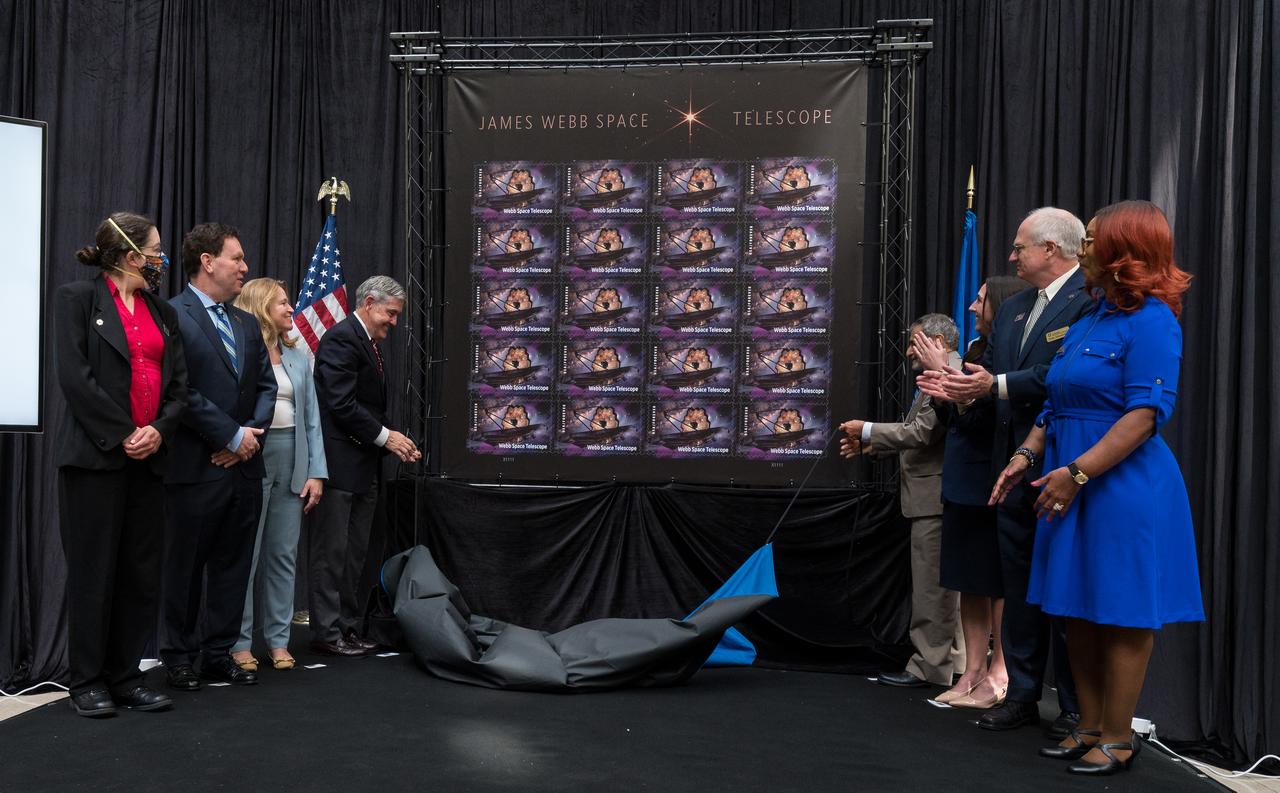

From left to right, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Webb Deputy Observatory Project Scientist, Erin Smith, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Webb Optical Telescope Element Manager, Lee Feinberg, Smithsonian Institution Under Secretary for Service and Research, Ellen Stofan, NASA Associate Administrator and former astronaut Bob Cabana, United States Postal Service Vice Chairman, Board of Governors, Anton Hajjar, NASA public affairs specialist Alice Fisher, National Postal Museum Deputy Director, Toby Mensforth, and Lisa Whitehead, USPS, unveil the United States Postal Service’s new stamp celebrating NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) at the first-day-of-issue event on Thursday, Sept. 8, 2022, at the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum in Washington. The stamp, which features an illustration of the observatory, honors Webb’s mission to explore the unknown in our universe – solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
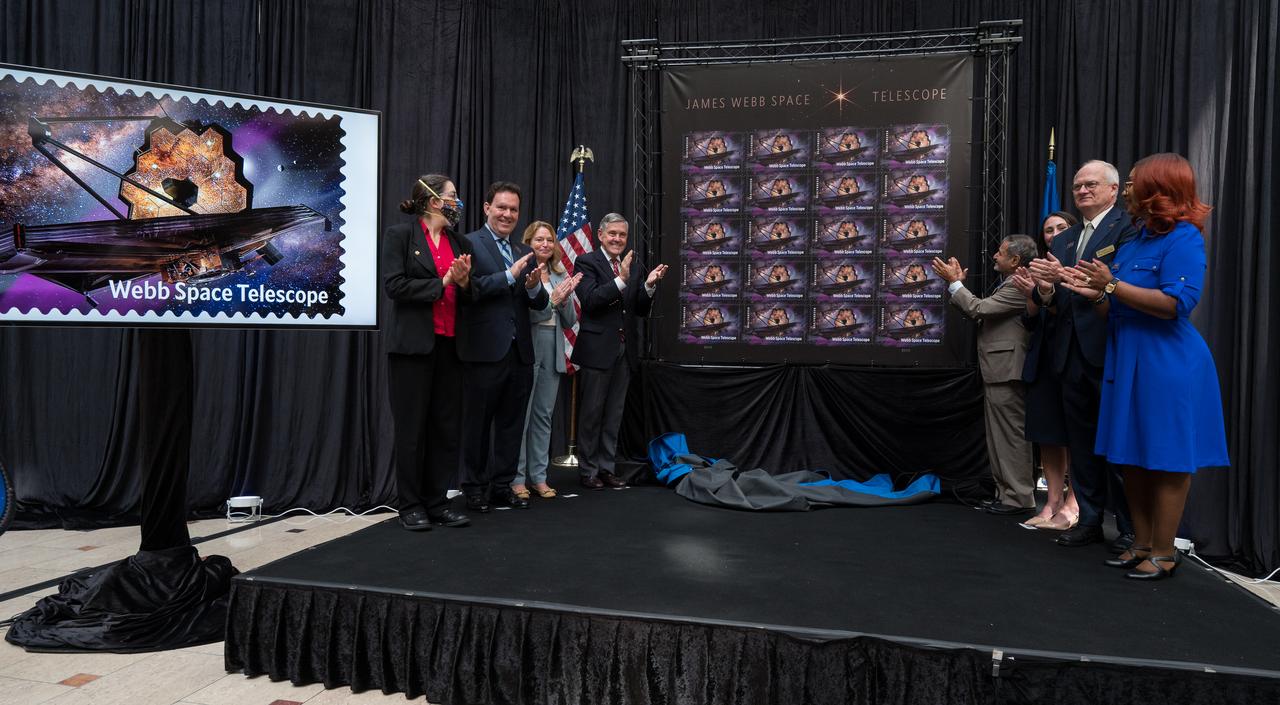

From left to right, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Webb Deputy Observatory Project Scientist, Erin Smith, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Webb Optical Telescope Element Manager, Lee Feinberg, Smithsonian Institution Under Secretary for Service and Research, Ellen Stofan, NASA Associate Administrator and former astronaut Bob Cabana, United States Postal Service Vice Chairman, Board of Governors, Anton Hajjar, NASA public affairs specialist Alice Fisher, National Postal Museum Deputy Director, Toby Mensforth, and Lisa Whitehead, USPS, applaud after unveiling the United States Postal Service’s new stamp celebrating NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) at the first-day-of-issue event on Thursday, Sept. 8, 2022, at the Smithsonian’s National Postal Museum in Washington. The stamp, which features an illustration of the observatory, honors Webb’s mission to explore the unknown in our universe – solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Space shuttle Enterprise, mounted atop a NASA 747 Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), is seen as it takes off for New York from Washington Dulles International Airport, Friday, April 27, 2012, in Sterling, VA. Enterprise was the first shuttle orbiter built for NASA performing test flights in the atmosphere and was incapable of spaceflight. Originally housed at the Smithsonian's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, Enterprise will be demated from the SCA and placed on a barge that will eventually be moved by tugboat up the Hudson River to the Intrepid Sea, Air & Space Museum in June. Photo Credit: (NASA/Smithsonian Institution/Mark Avino)
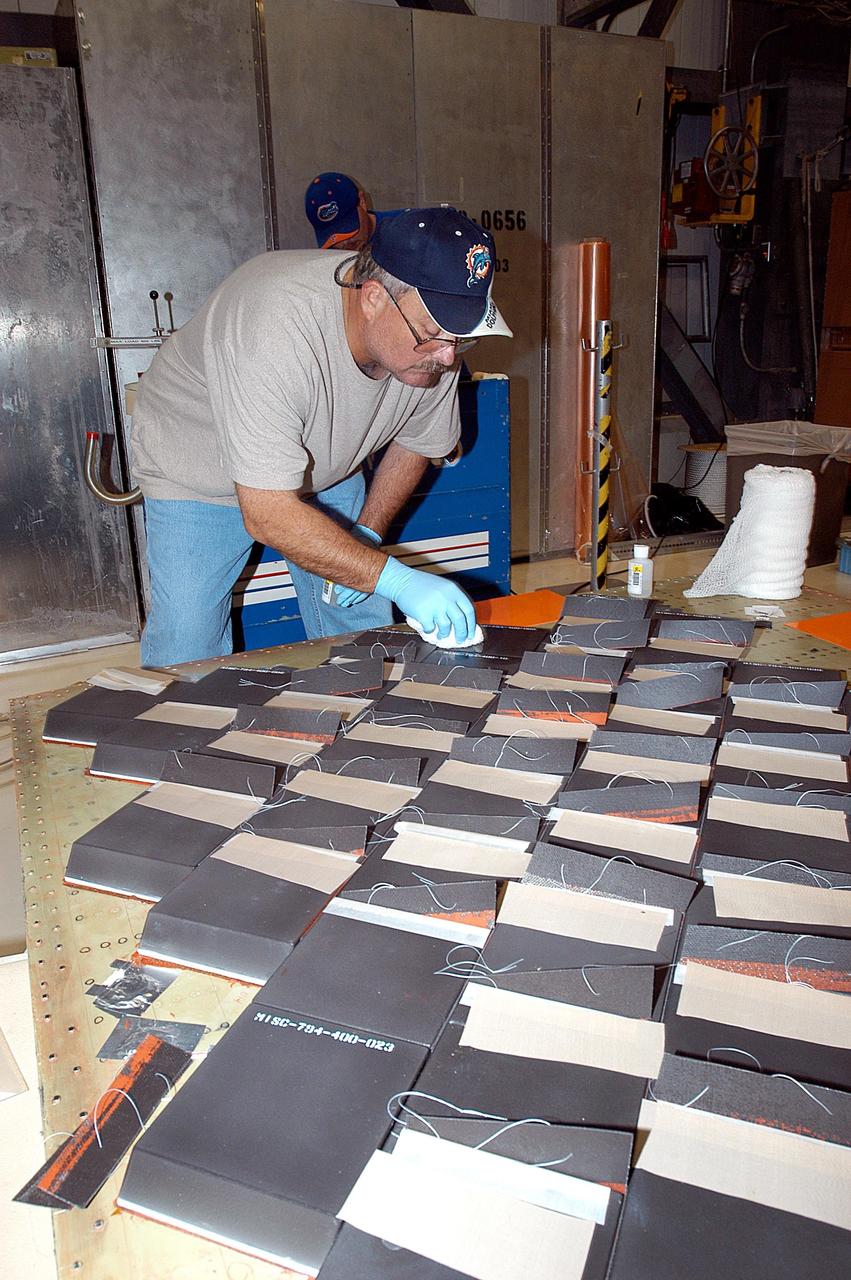

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Dave Sanborn installs Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
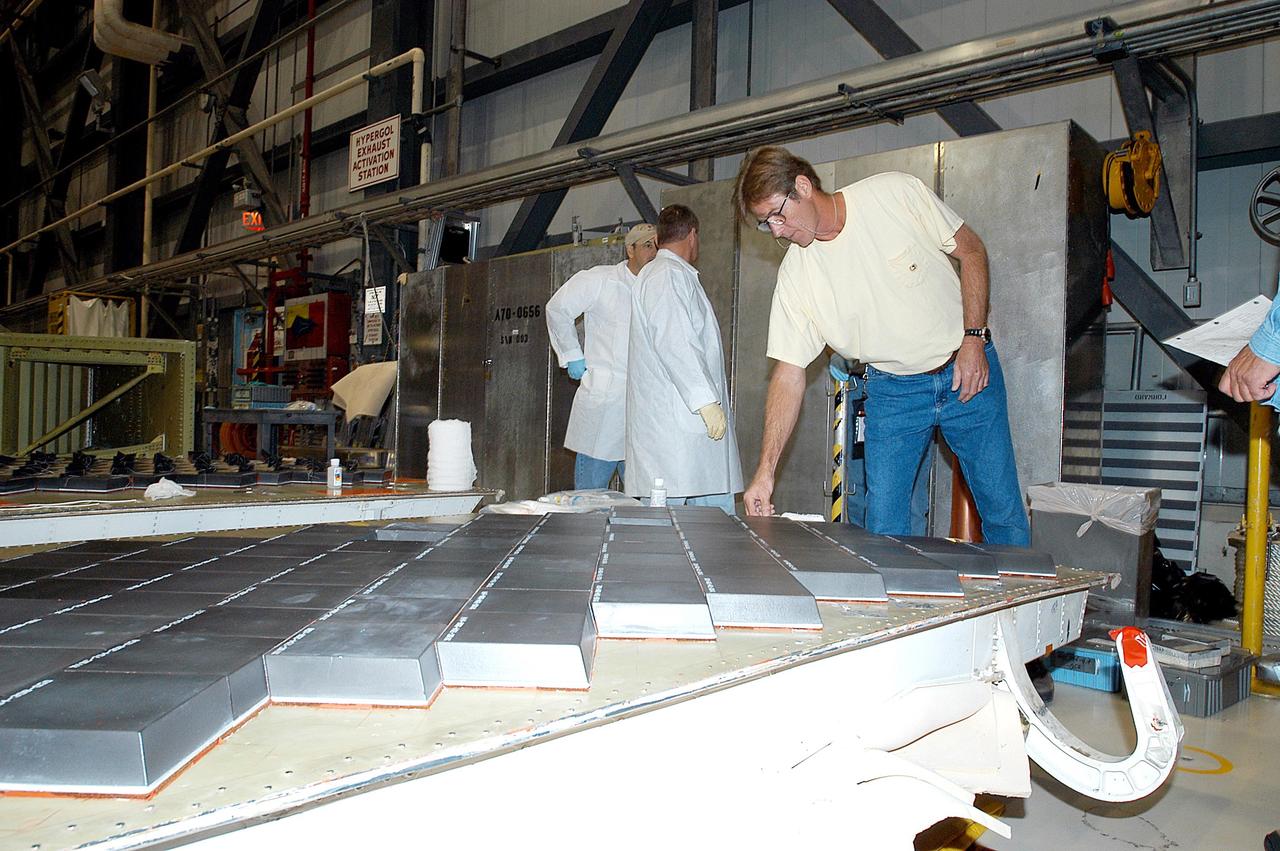

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Harrell Watts (right) installs Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
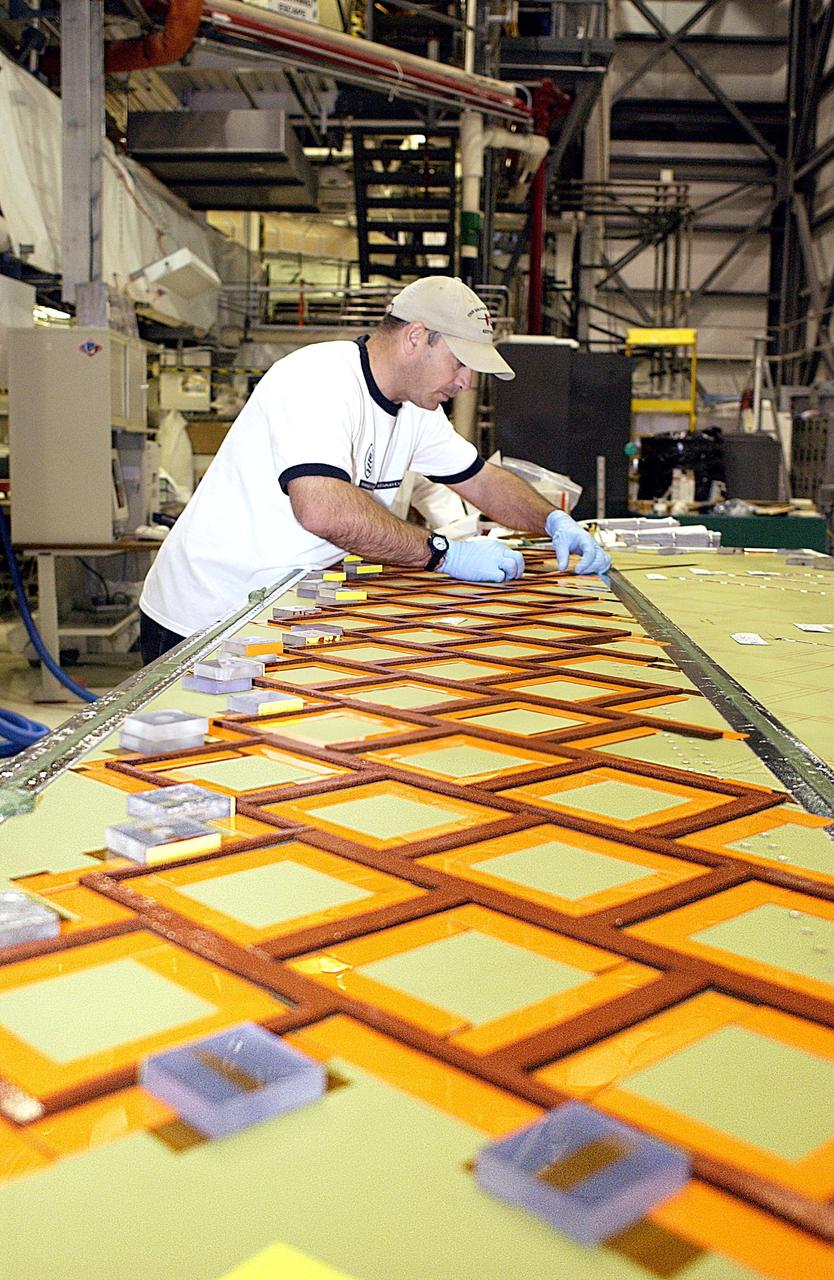

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Mike Cote installs Thermal Protection System tiles on a test panel. The test panel and sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Harrell Watts installs Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
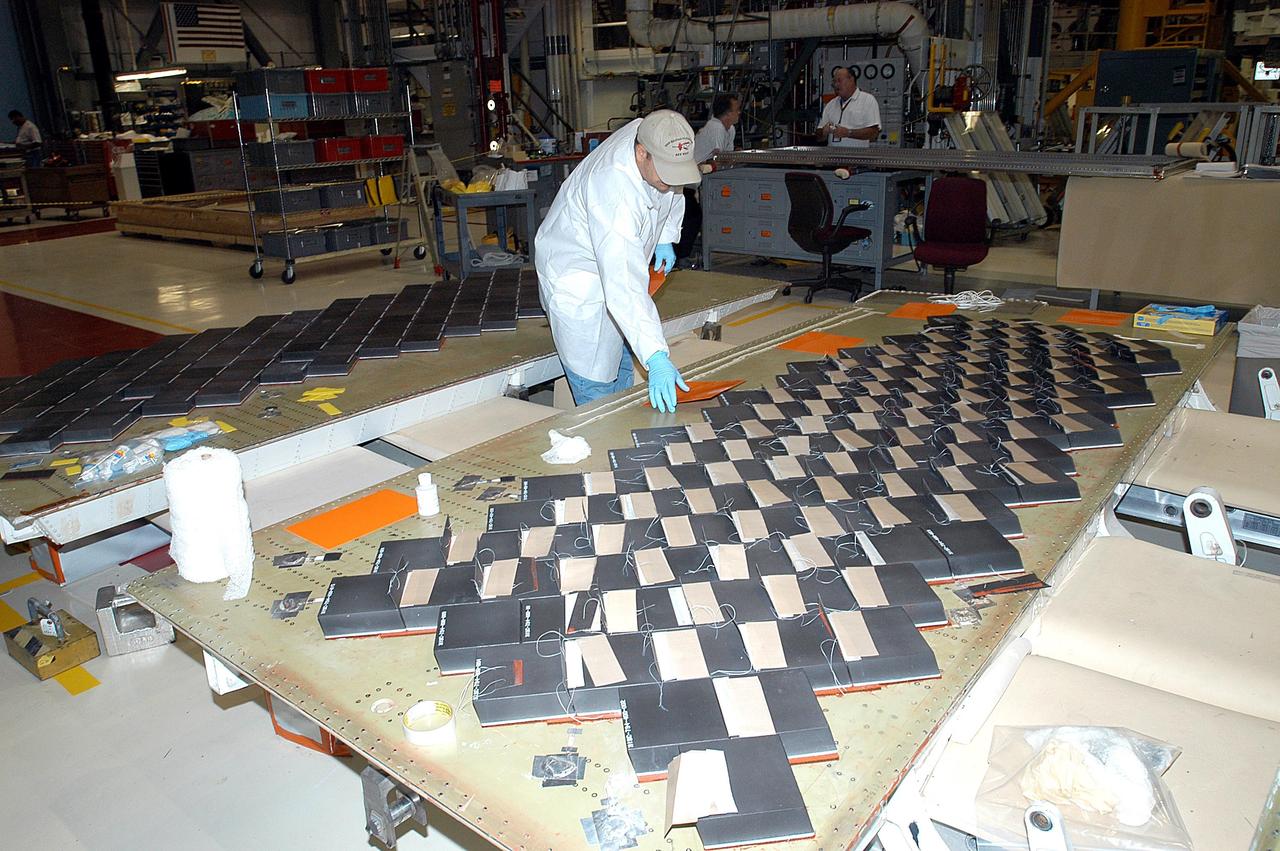

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Mike Cote works on installing Thermal Protection System tiles on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
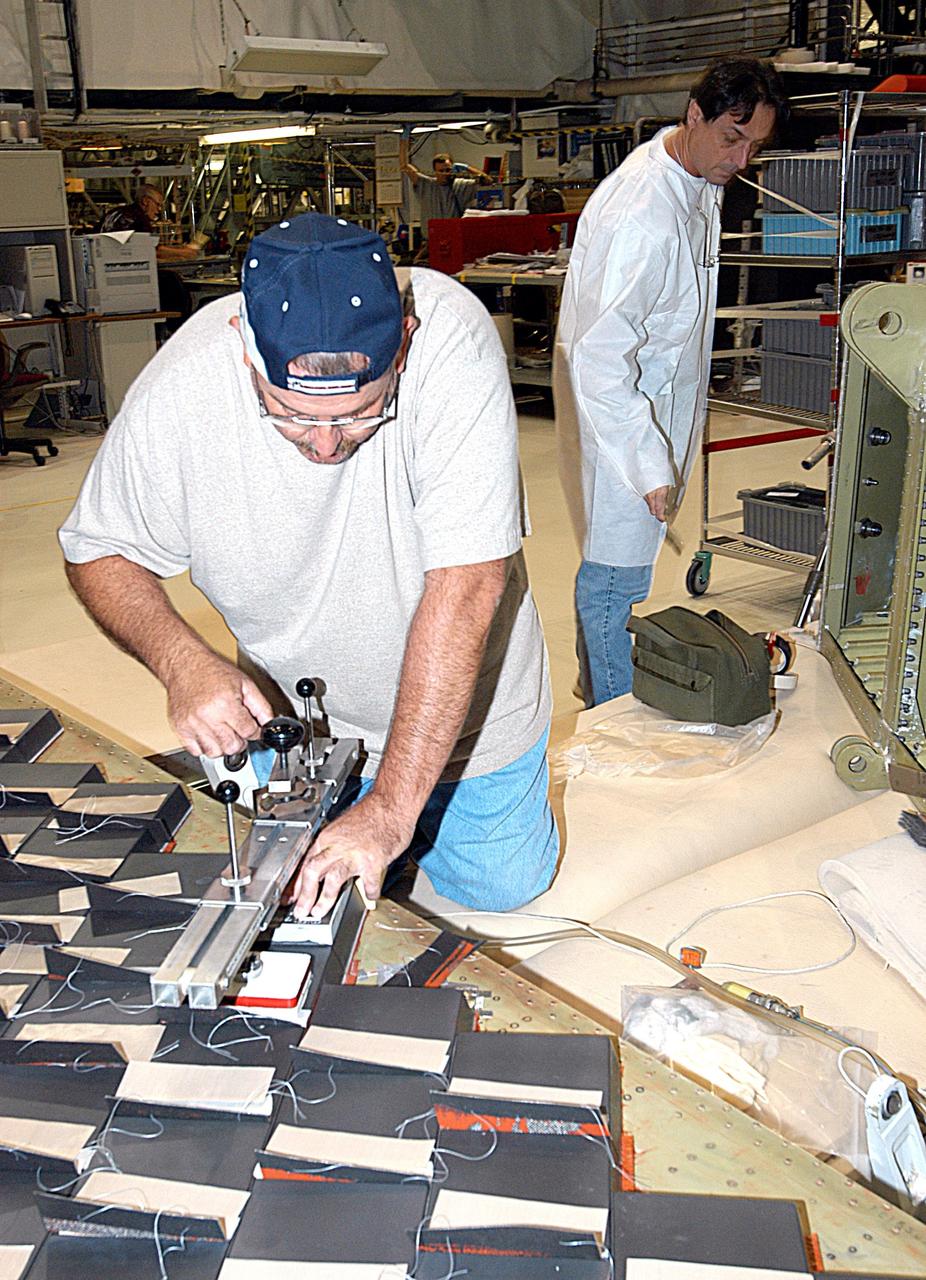

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Dave Sanborn (left) conducts a bond verification test on Thermal Protection System tiles installed on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
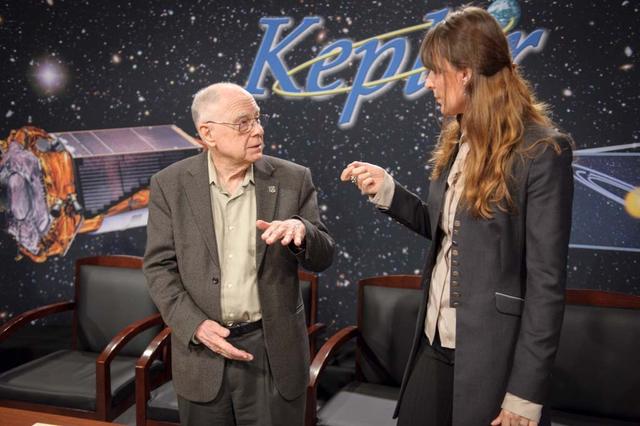

Kepler News Briefing, held in the Syvertson auditorium at the NASA Ames Research Center. The briefing presented discoveries from the continuing Kepler mission (K2). The team discovered some of the smallest planets found in the habitable zone of two newly discovered planetary systems. Bill Borucki (left), Kepler Scientist, Principal Investigator, NASA Ames Lisa Kaltengger (right), Research Group Leader, Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Germany and Research Associate, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge Massachusetts.
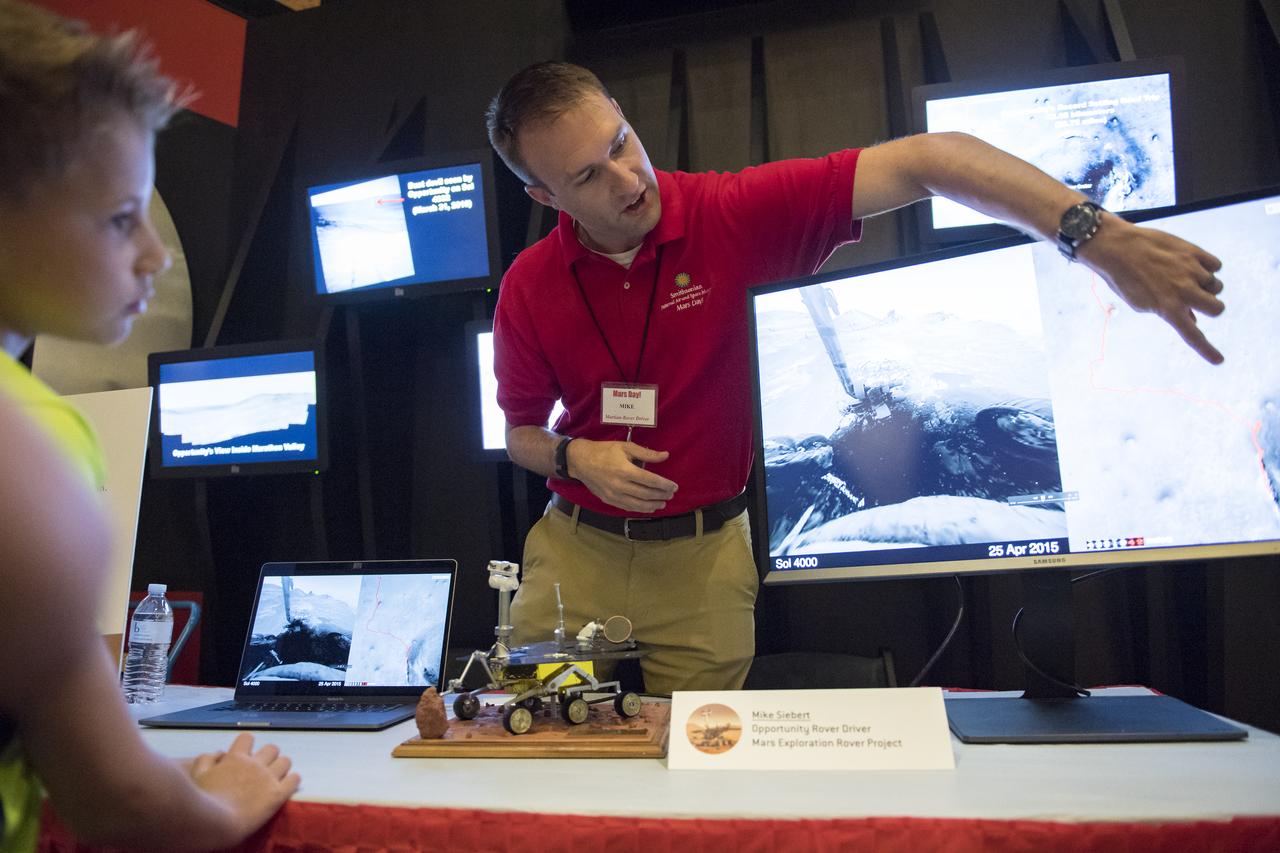

Mike Seibert, rover driver for NASA’s Opportunity rover on Mars talks with visitors about navigating the surface of Mars at the Smithsonian Institution’s National Air and Space Museum Mars Day, an annual event celebrating the Red Planet with exhibits, speakers, and educational activities, Friday, July 21, 2017 in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
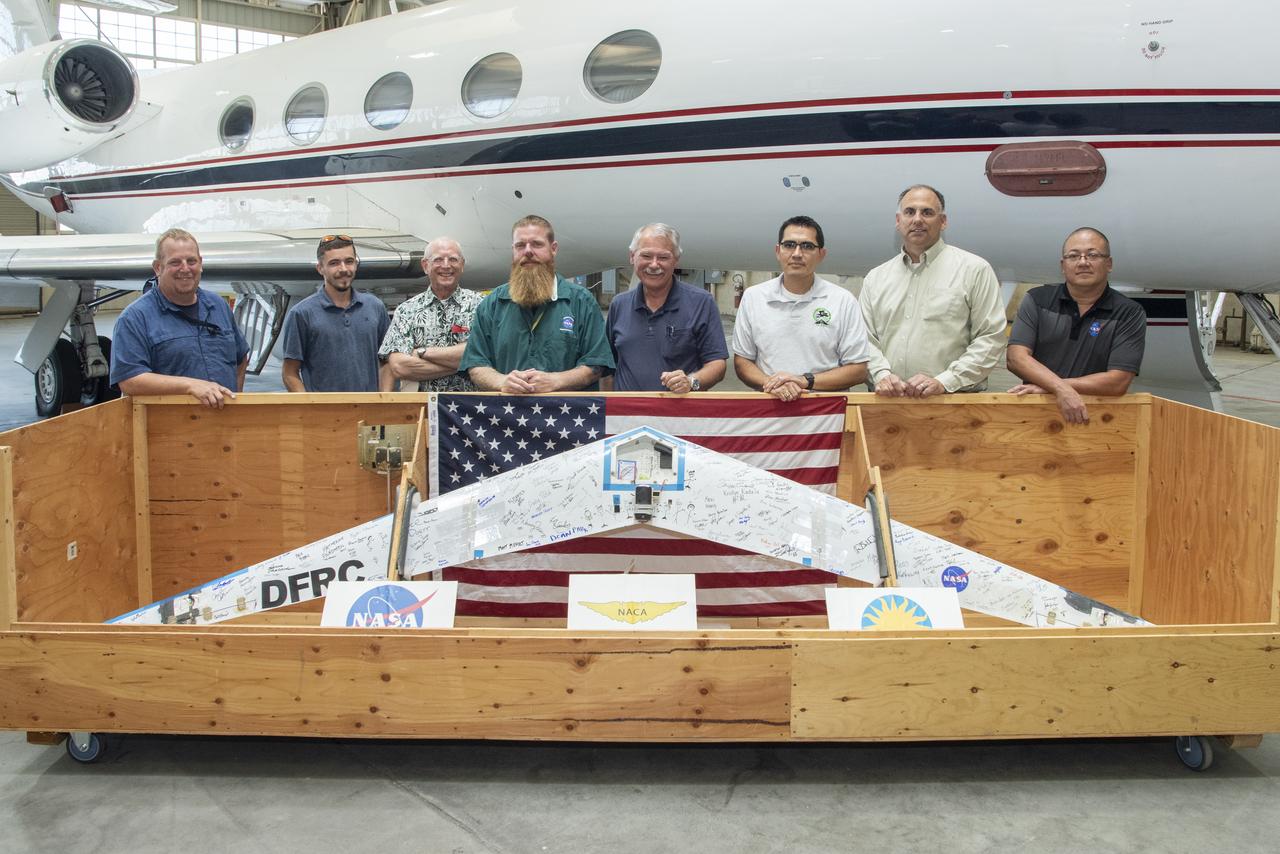

Preliminary Research Aerodynamic Design to Lower Drag, or Prandtl-D1, will be displayed in an upcoming Innovations Gallery at the National Air and Space Museum, the Smithsonian Institute. The aircraft, which flew from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, uses a method of aircraft design that introduces a twist that results in a more efficient wing. From left are Robert "Red" Jensen, Logan Shaw, Christian Gelzer, Justin Hall, Al Bowers, Oscar Murillo, Brian Eslinger and Derek Abramson
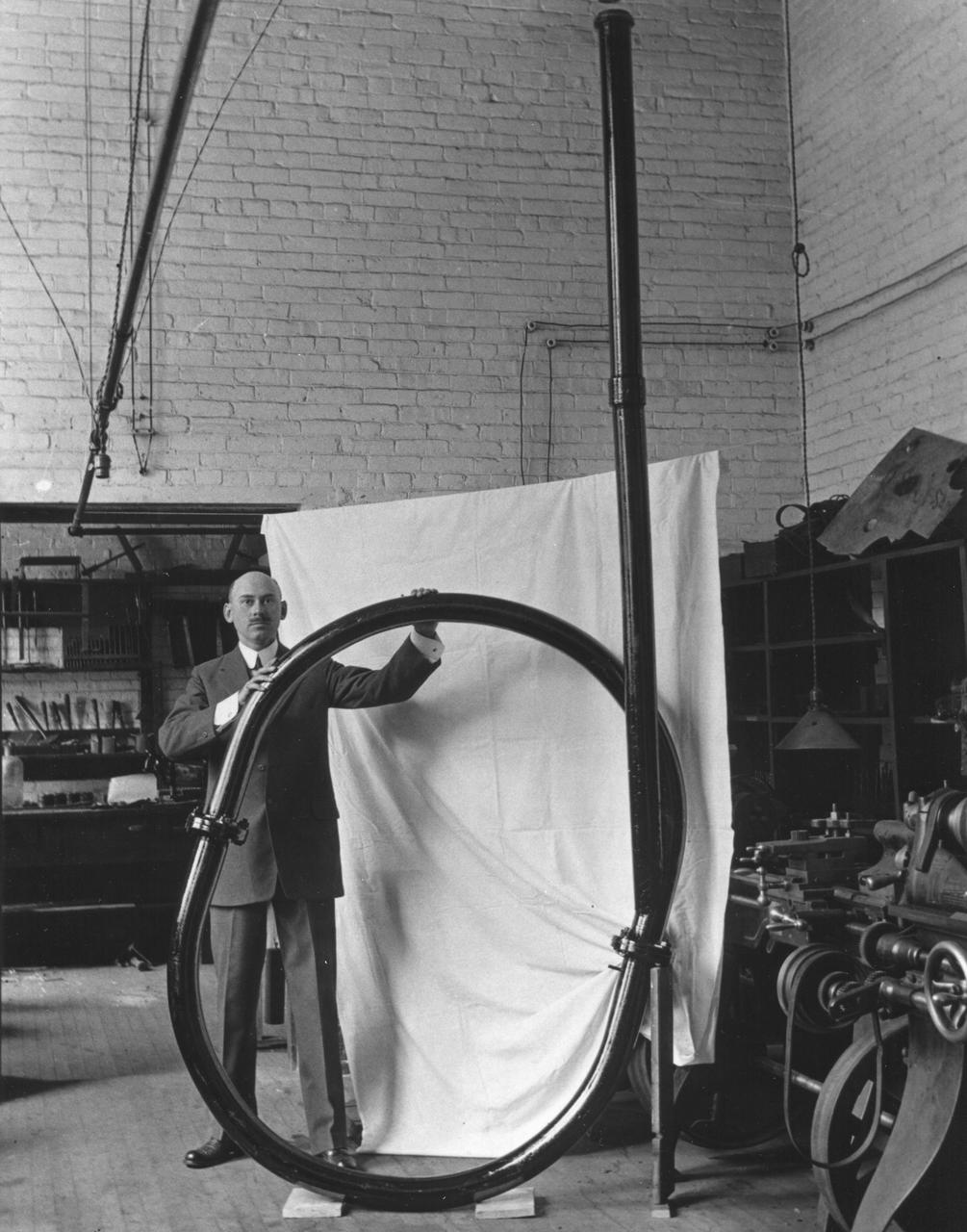

Robert H. Goddard with vacuum tube apparatus he built in 1916 to research rocket efficiency. Dr. Robert Hutchings Goddard is commonly referred to as the father of American rocketry. The same year he built the apparatus, Goddard wrote a study requesting funding from the Smithsonian Institution so that he could continue his rocket research, which he had begun in 1907 while still a student at Worcester Polytechnic Institute. A brilliant physicist, with a unique genius for invention, Goddard may not have succeeded had it not been for the Smithsonian Institution and later the Daniel Guggenheim Foundation and his employer the Worcester Polytechnic Institute of Clark University. The former gave him research monies while the Institute provided leaves of absence so that he could continue his life's work. He was the first scientist who not only realized the potential of missiles and space flight, but also contributed directly to making them a reality. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, raise a cage over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett

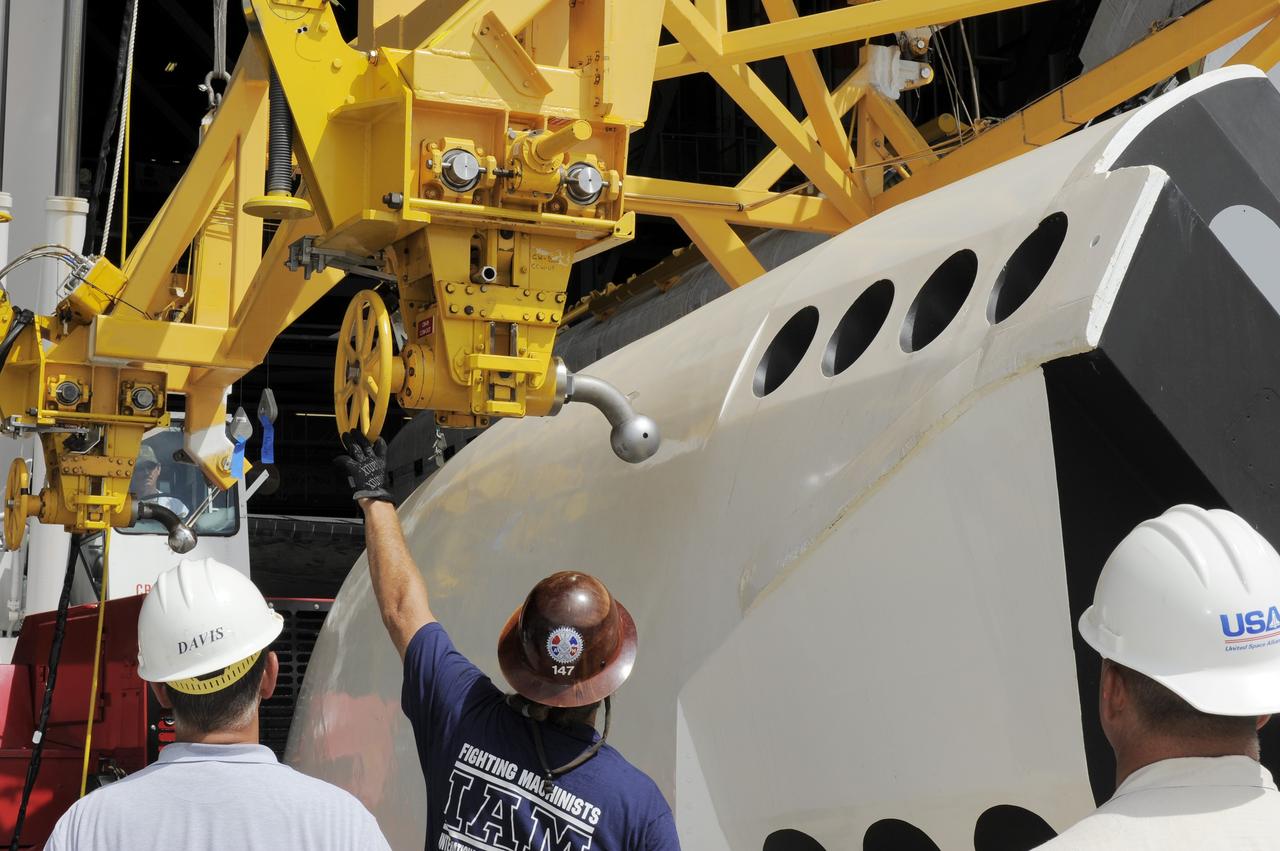
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers lower the cage containing an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod over the rear of space shuttle Endeavour. The ALTA pod is being attached to the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va. to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_shuttle. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
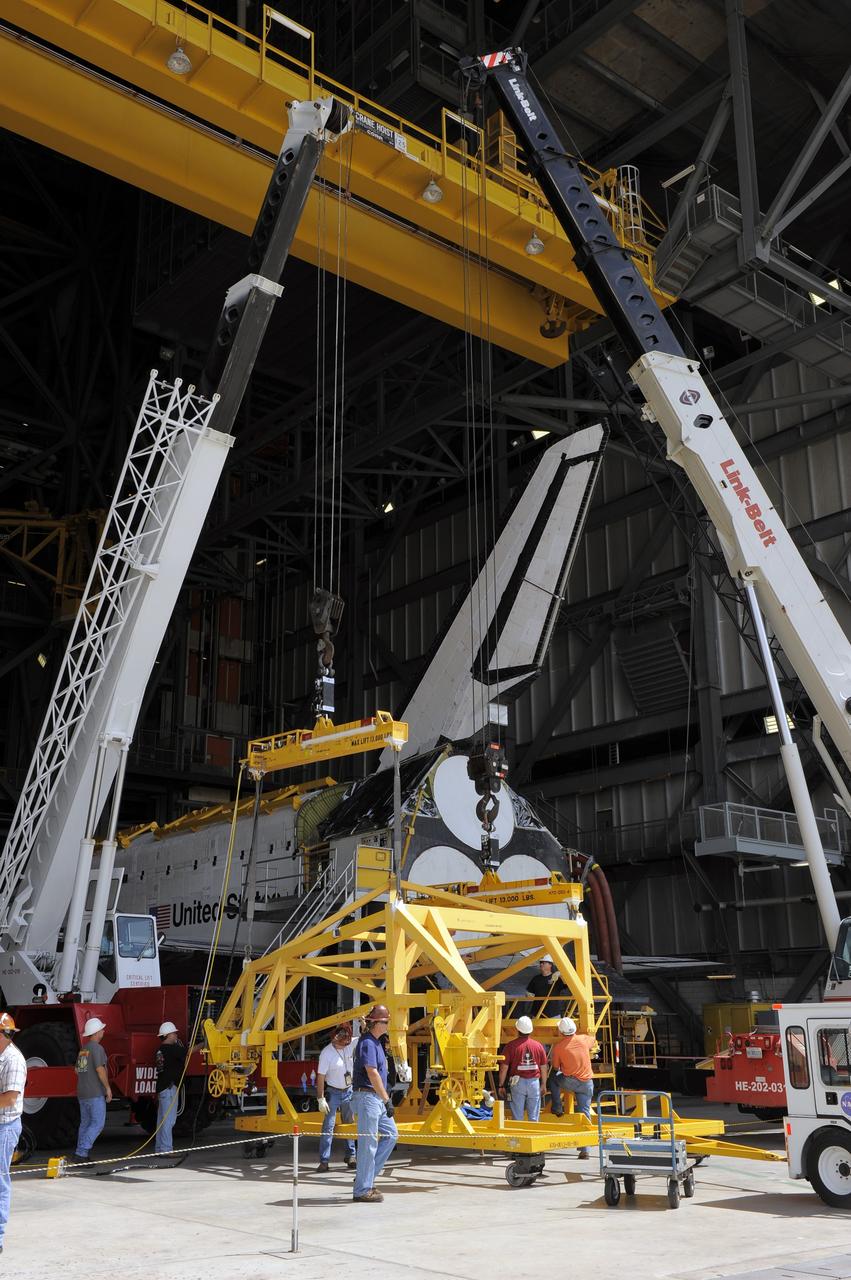

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, begin to raise a cage which will be placed over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
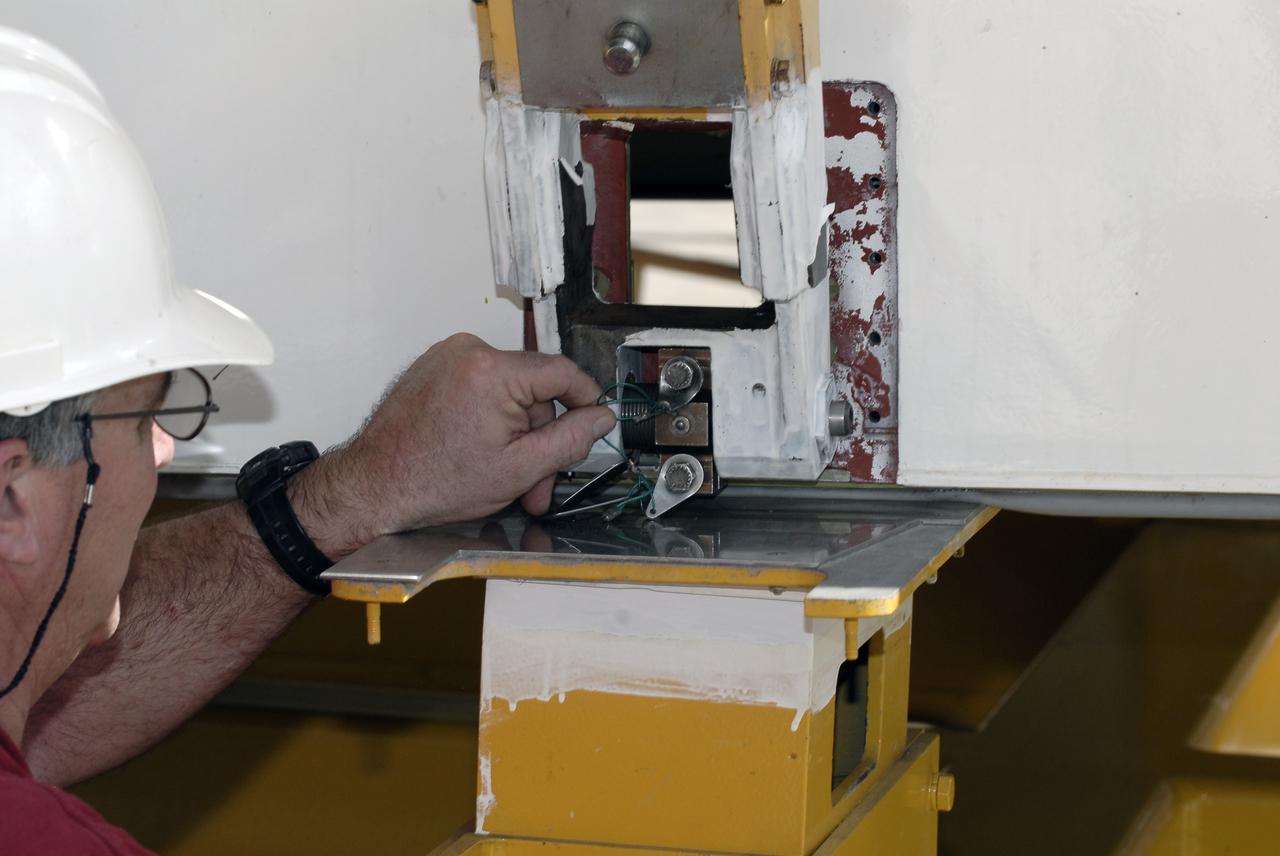

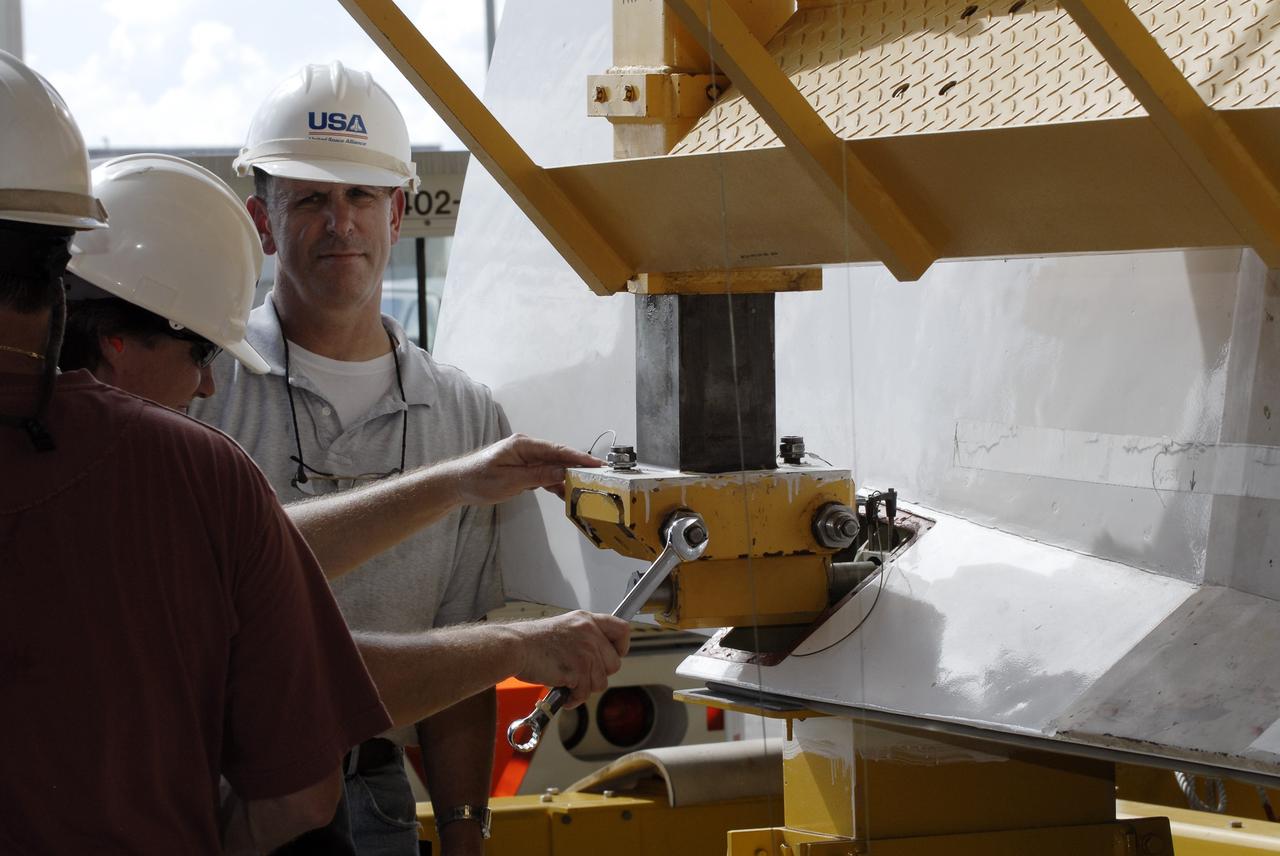
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker connects an aerial lift to the Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The lift will be used to raise the ALTA pod onto space shuttle Endeavour. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
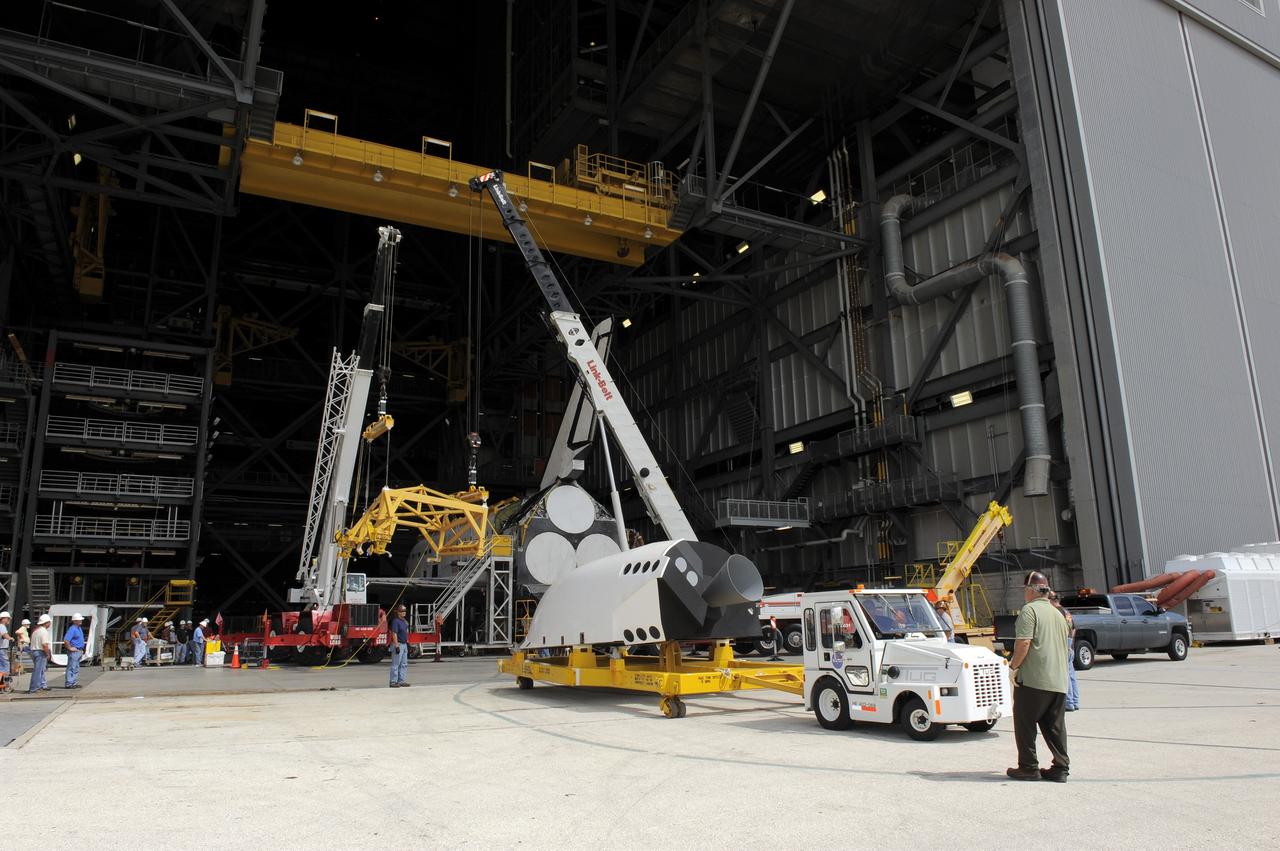

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, raise a cage which will be placed over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod (in the foreground). The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
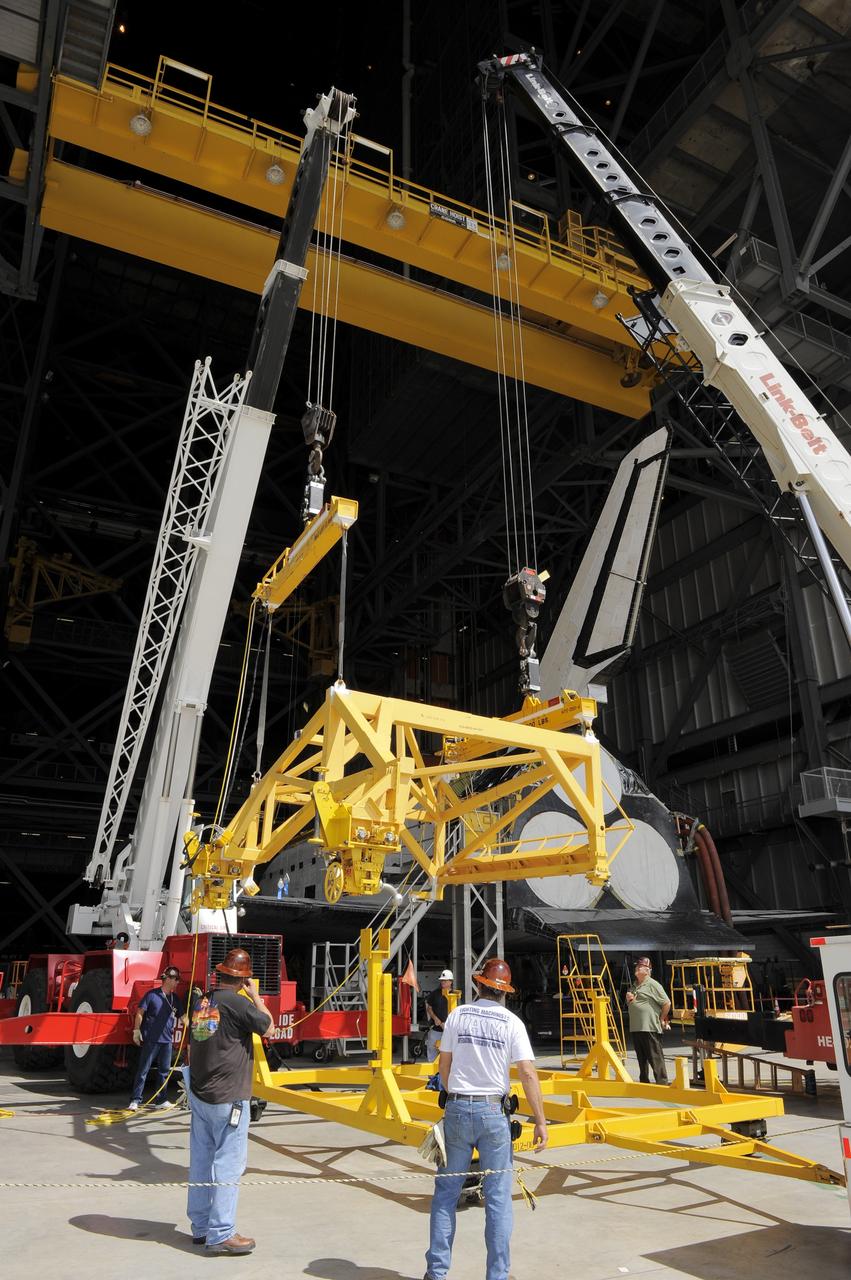

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, raise a cage which will be placed over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
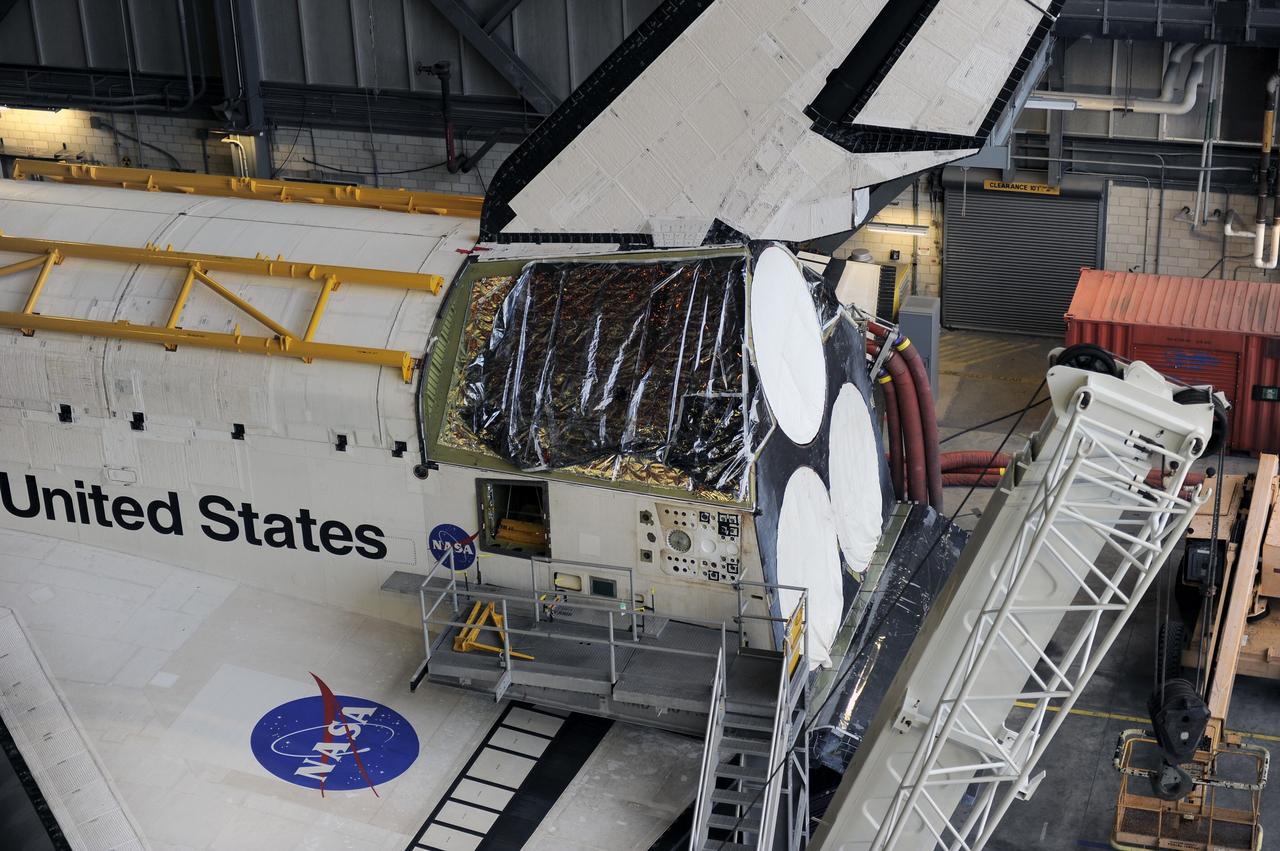

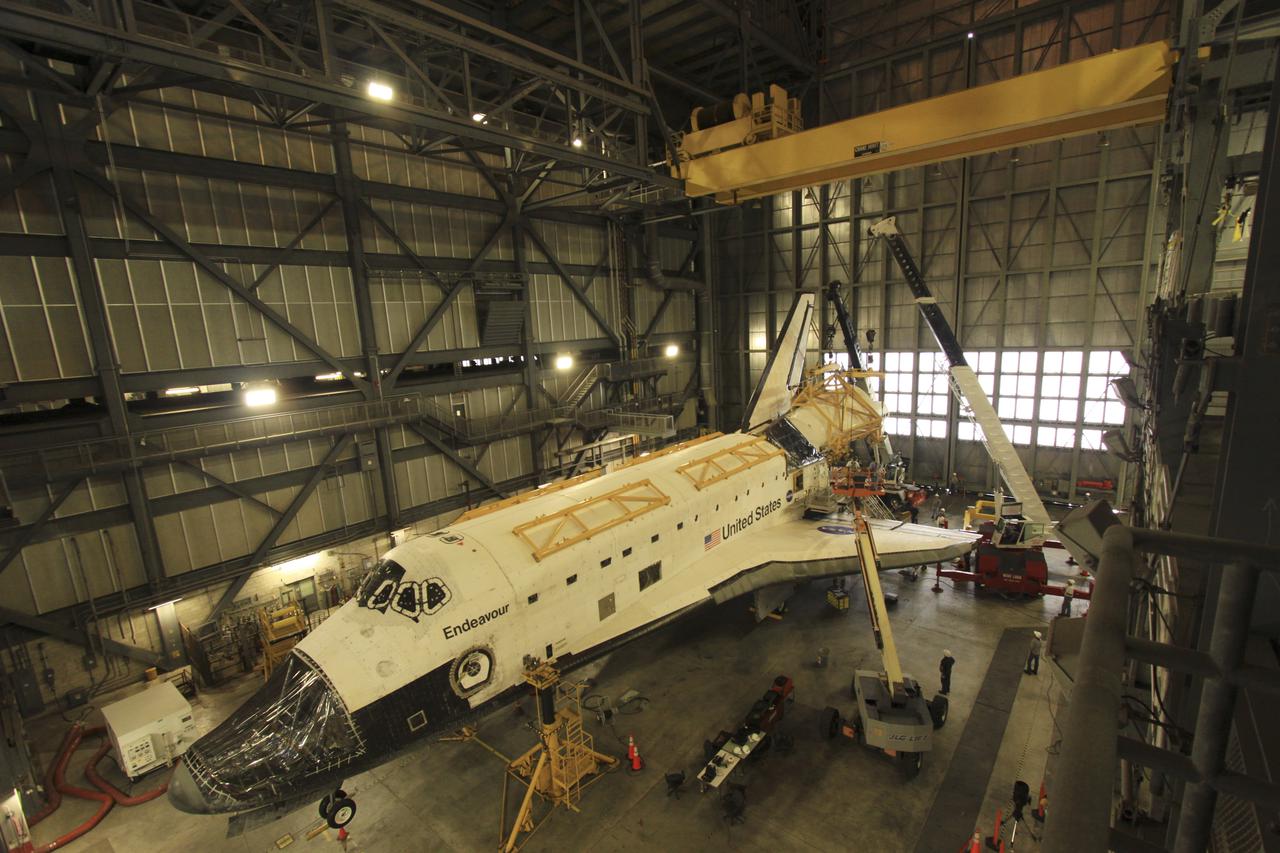
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a rear view of space shuttle Endeavour shows a protective plastic covering the area once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. An aerial lift will raise an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod to fit over the OMS site. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use an aerial lift to raise the Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod onto space shuttle Endeavour. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
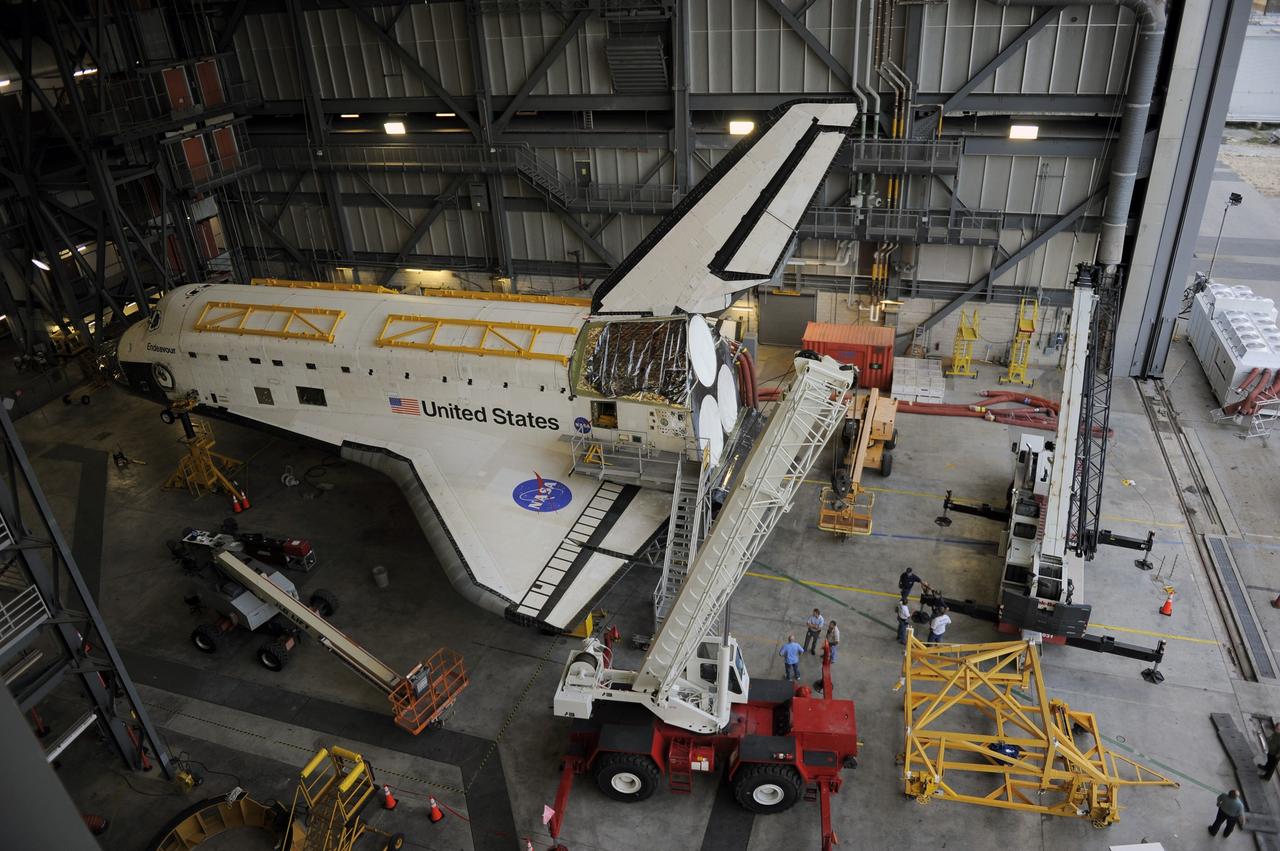

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour sits surrounded by cranes and lifts. Workers are preparing to raise an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod for attachment to the shuttle at the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
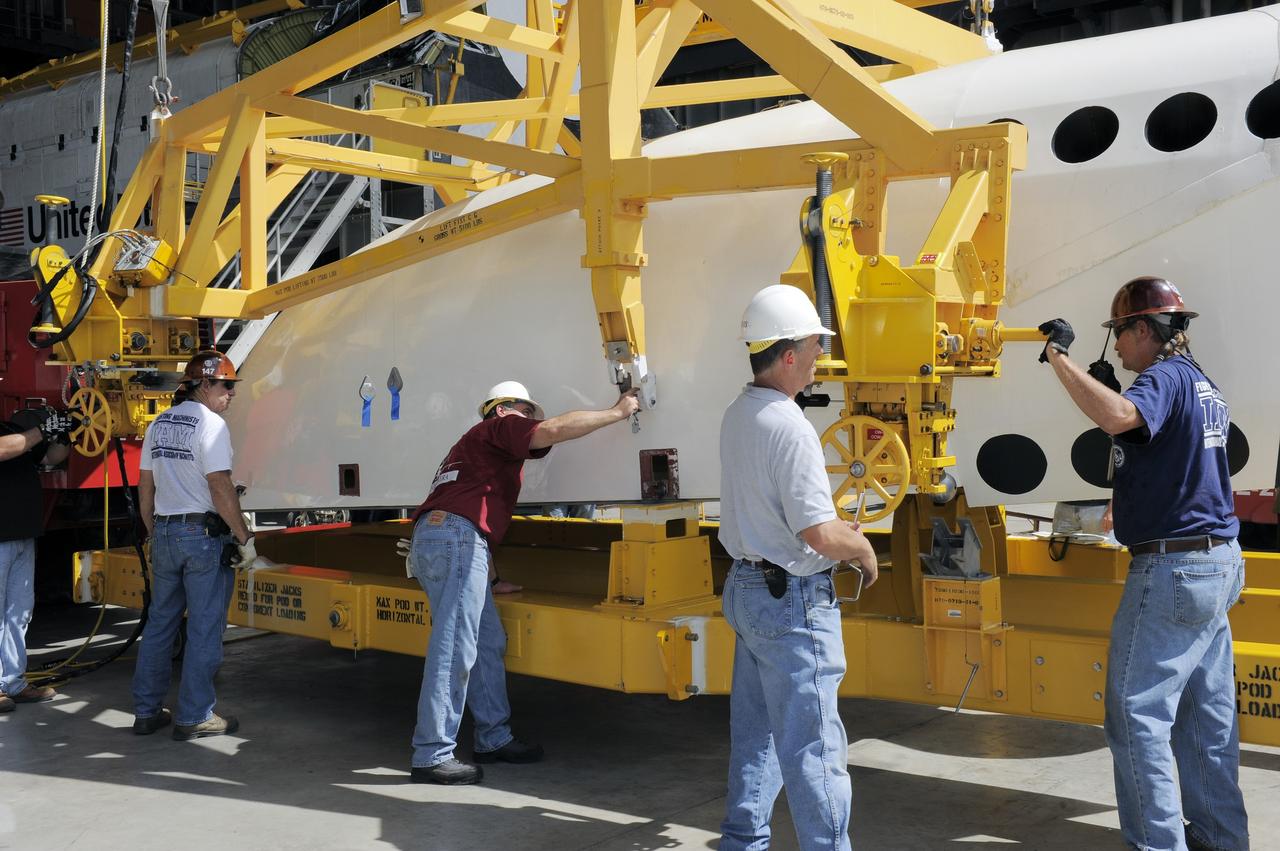

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, lower a cage over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
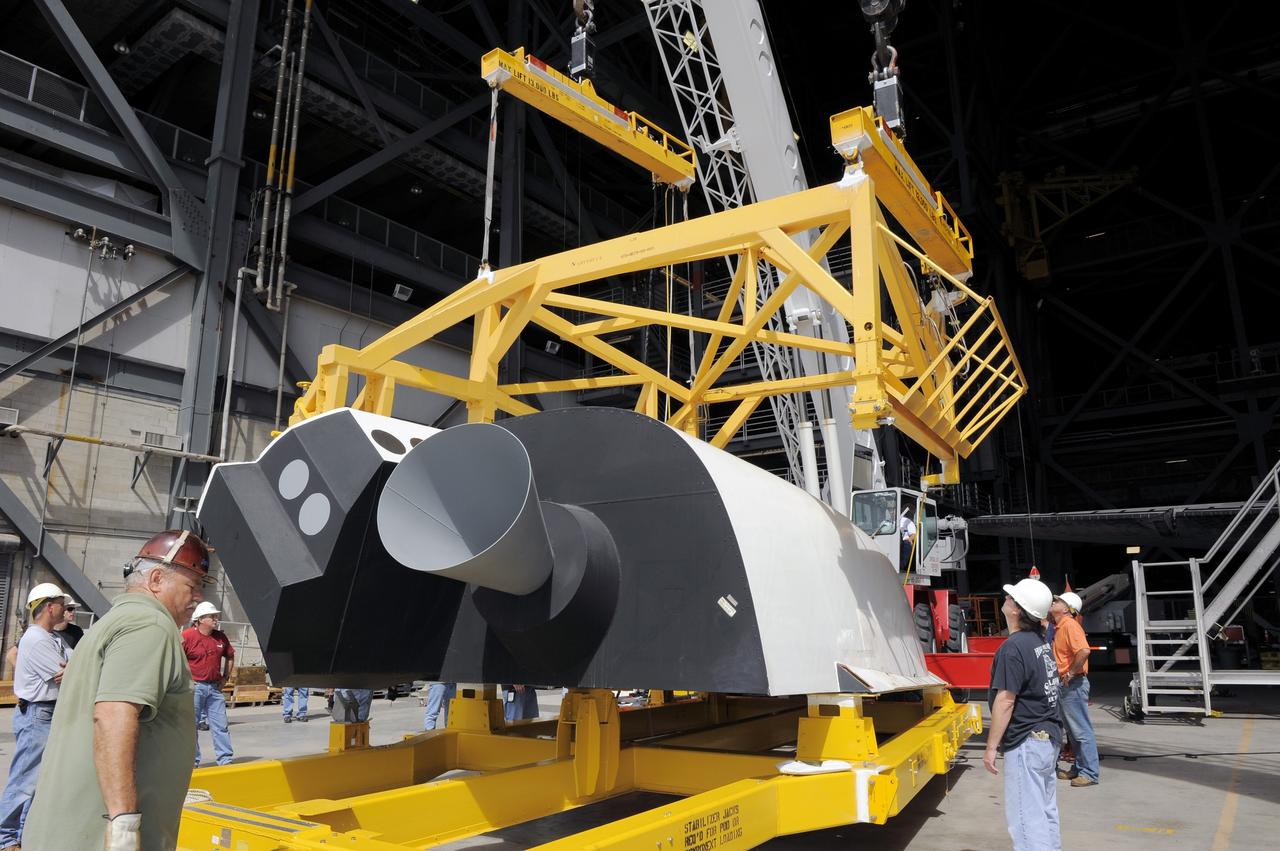

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, raise a cage over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
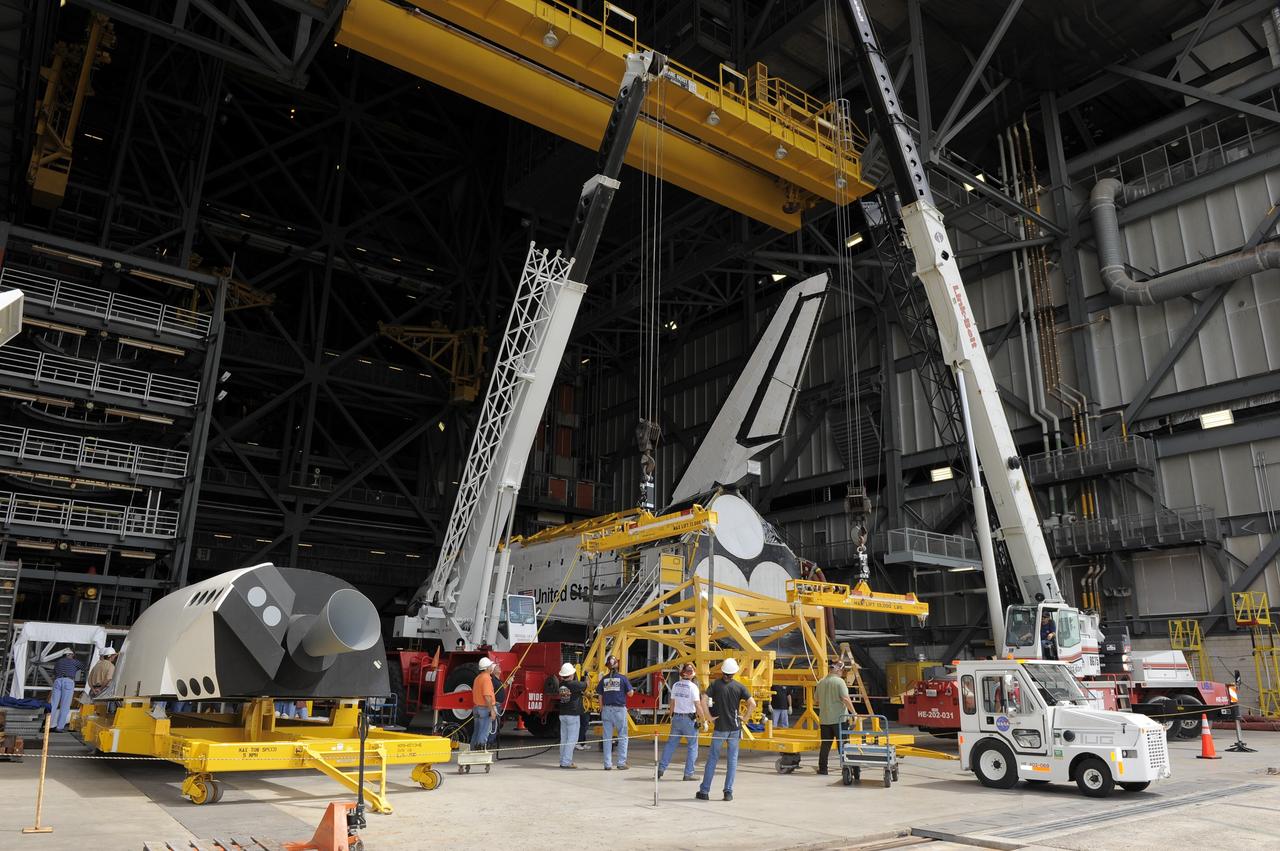

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers, using overhead cranes, prepare to raise a cage over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod (to the left of the photo). The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
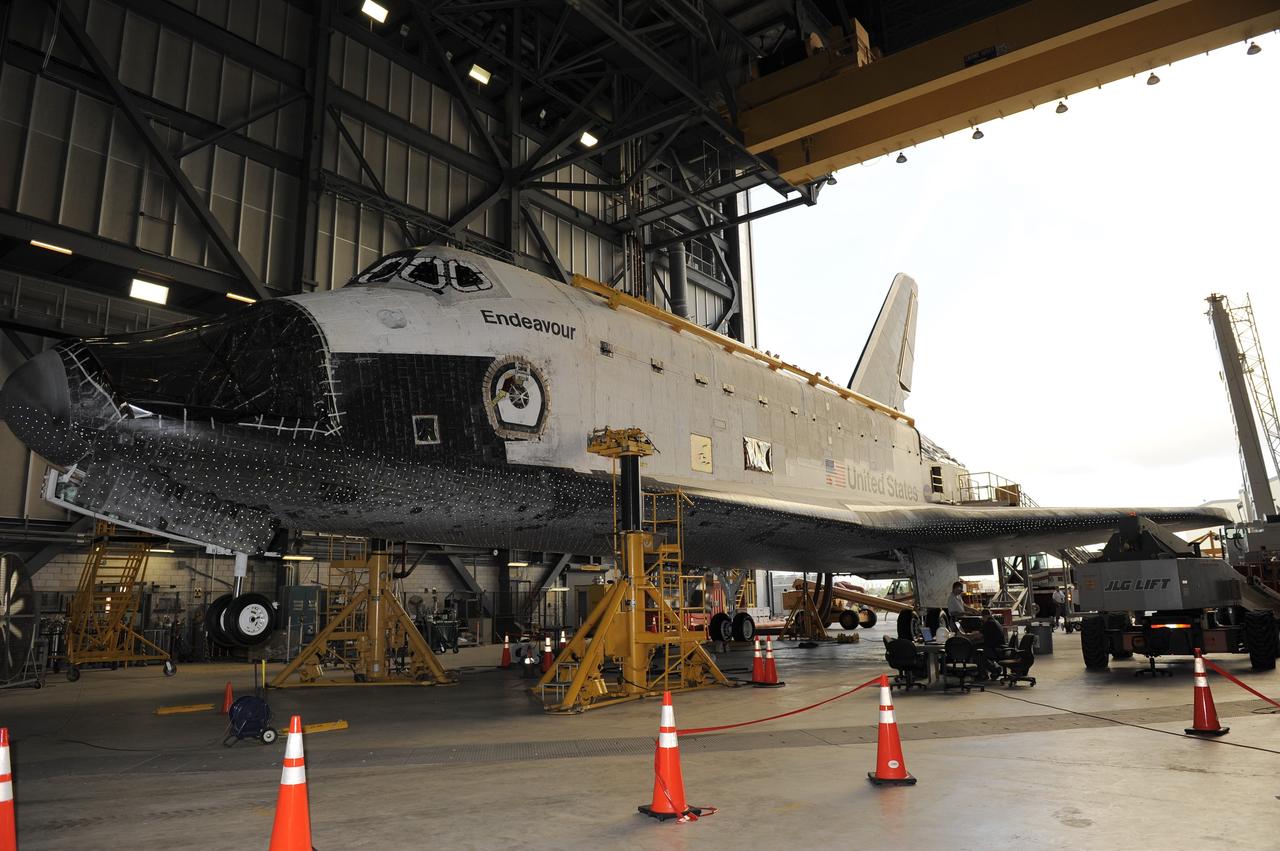

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the front end of space shuttle Endeavour is raised off the floor of the VAB by lifts, as workers prepare to attach an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod to the back of the shuttle. The ALTA pod will be fitted over the area once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also will test procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
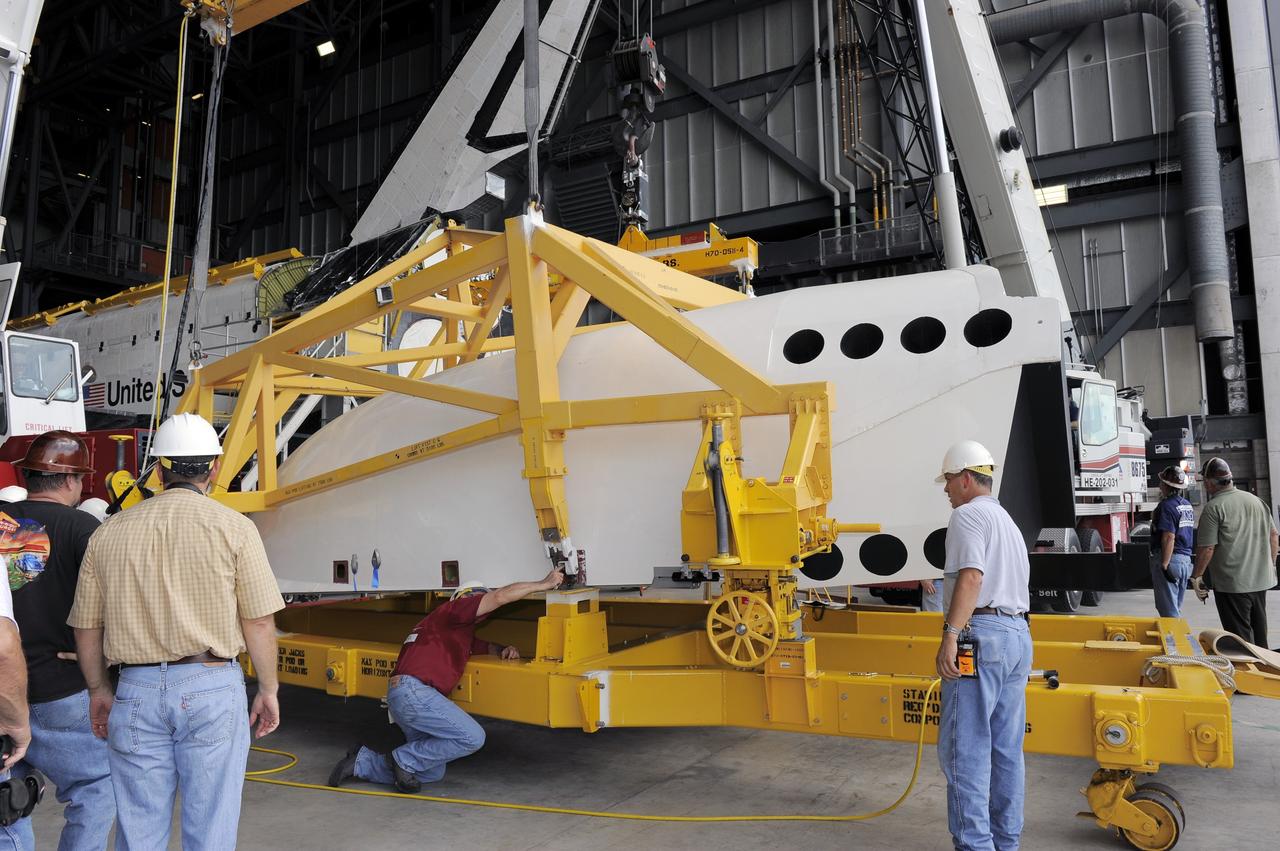

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers affix a cage over an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod. The ALTA pod will be lifted for attachment to space shuttle Endeavour on the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
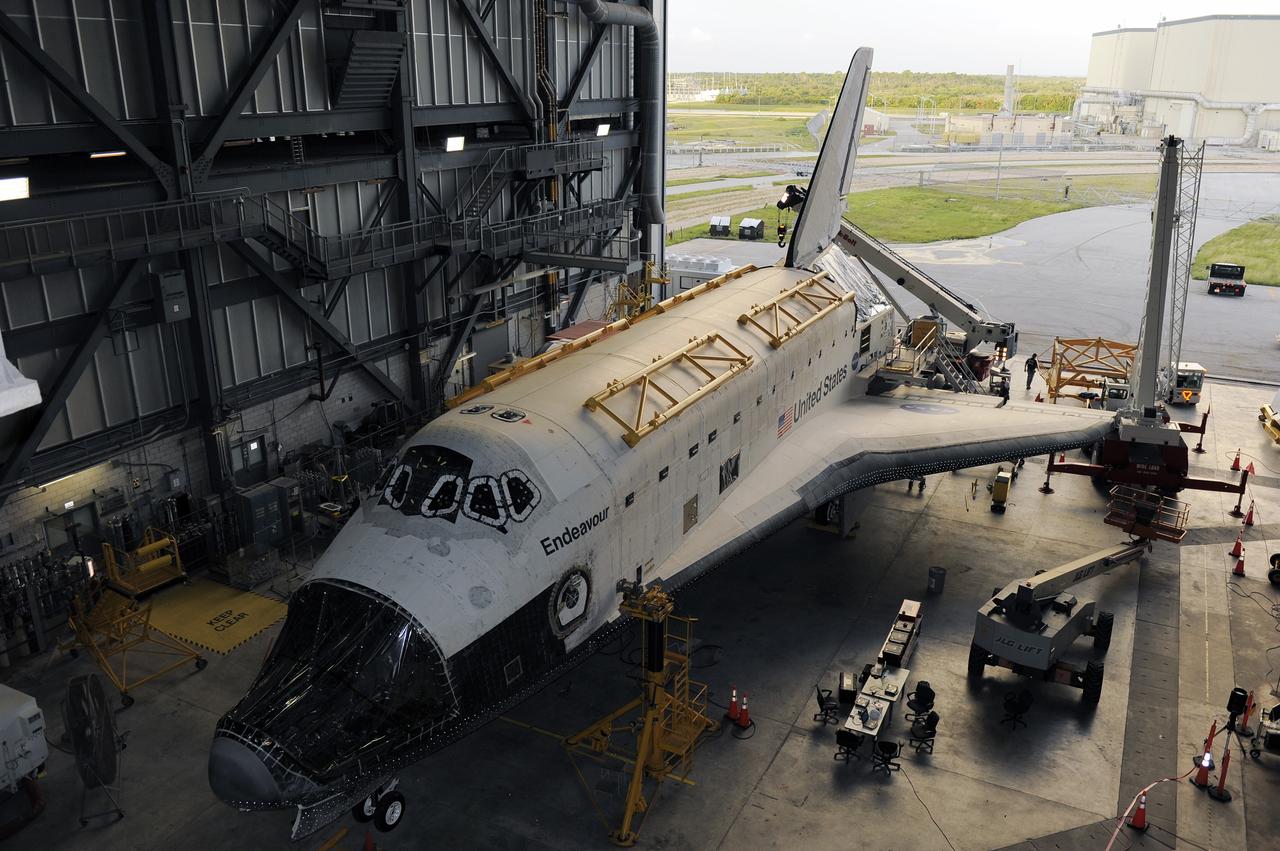

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour sits surrounded by cranes and lifts. Workers are preparing to raise an Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod to the rear of the shuttle for attachment over the site once housing the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
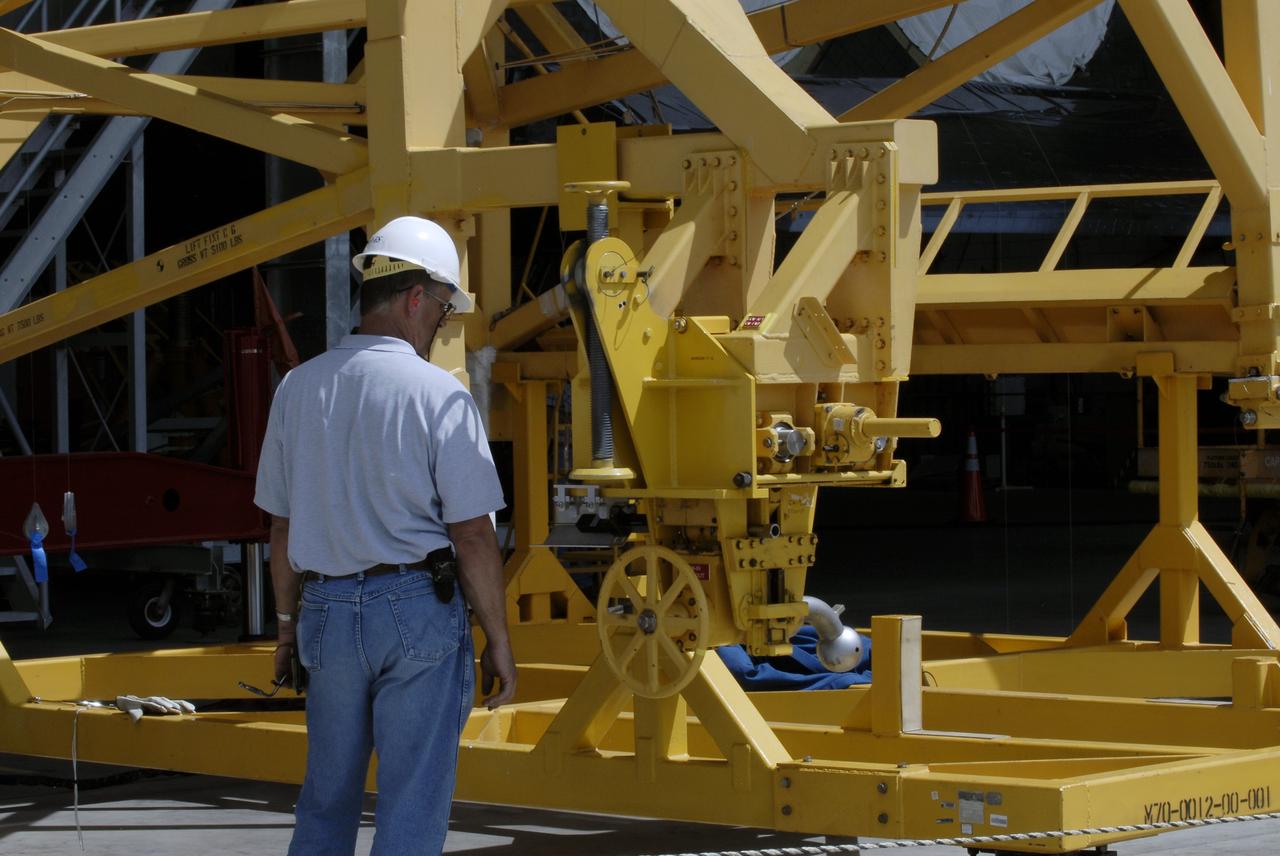

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker prepares an aerial lift which will be used to raise the Approach and Landing Test Assembly (ALTA) pod onto space shuttle Endeavour. The demonstration test is being conducted to ensure the center’s equipment will fit into the hangar at the National Air and Space Museum when installing an ALTA pod on shuttle Enterprise. The pod must be reinstalled on a shuttle for transport on a 747 carrier aircraft. The simulation also tests procedures and timelines necessary to carry out the process. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing. Enterprise, which was not equipped for space flight, was built as a test vehicle to demonstrate that the orbiter could fly in the atmosphere and land like an airplane. In 1985, Enterprise was ferried from the Kennedy Space Center to Dulles Airport, Washington, D.C., and became the property of the Smithsonian Institute. Enterprise will be moved from the Smithsonian Institution National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., to the Intrepid Sea, Air and Space Museum in New York. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Shiflett
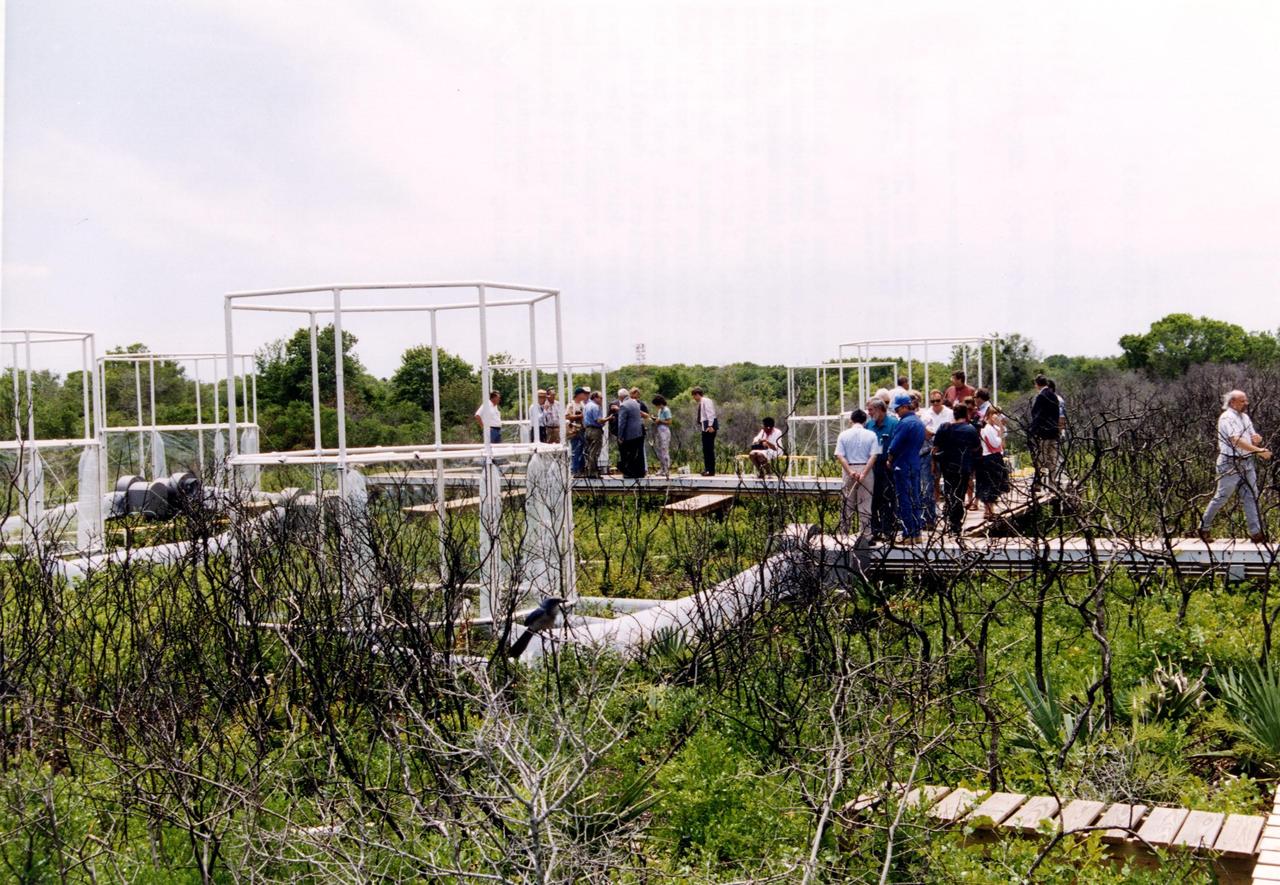

Researchers from the Smithsonian Institution hope their experiment in a local scrub oak community at KSC will yield new insights into the effects of increased carbon dioxide on natural vegetation. The experiment features a four-acre site just north of the Launch Complex 39 area. Increased amoounts of carbon dioxide are piped into 16 open-top chambers that house pristine Florida scrub vegetation, chosen because it is small and woody and fits in the chambers and can be controlled, yet has the attributes of much larger forests. Experts predict a doubling of the carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere during the next century, and the three-year KSC project being conducted by the Smithsonian-led team hopes that by simulating the increase, they can determine how natural ecosystems and vegetation will respond. Also participating in the effort are KSC, academic and international organizations. The study is being funded by a Department of energy grant
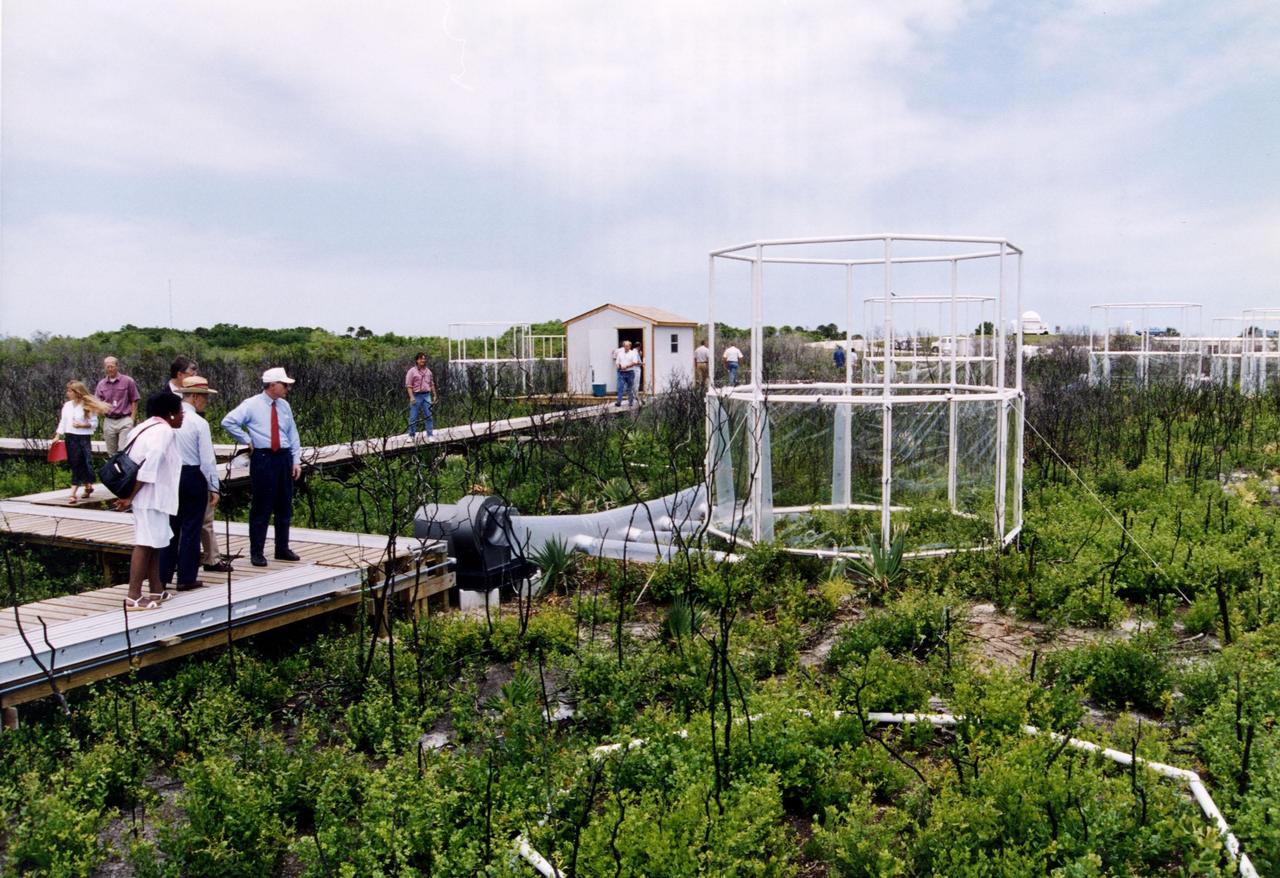

Researchers from the Smithsonian Institution hope their experiment in a local scrub oak community at KSC will yield new insights into the effects of increased carbon dioxide on natural vegetation. The experiment features a four-acre site just north of the Launch Complex 39 area. Increased amoounts of carbon dioxide are piped into 16 open-top chambers that house pristine Florida scrub vegetation, chosen because it is small and woody and fits in the chambers and can be controlled, yet has the attributes of much larger forests. Experts predict a doubling of the carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere during the next century, and the three-year KSC project being conducted by the Smithsonian-led team hopes that by simulating the increase, they can determine how natural ecosystems and vegetation will respond. Also participating in the effort are KSC, academic and international organizations. The study is being funded by a Department of energy grant
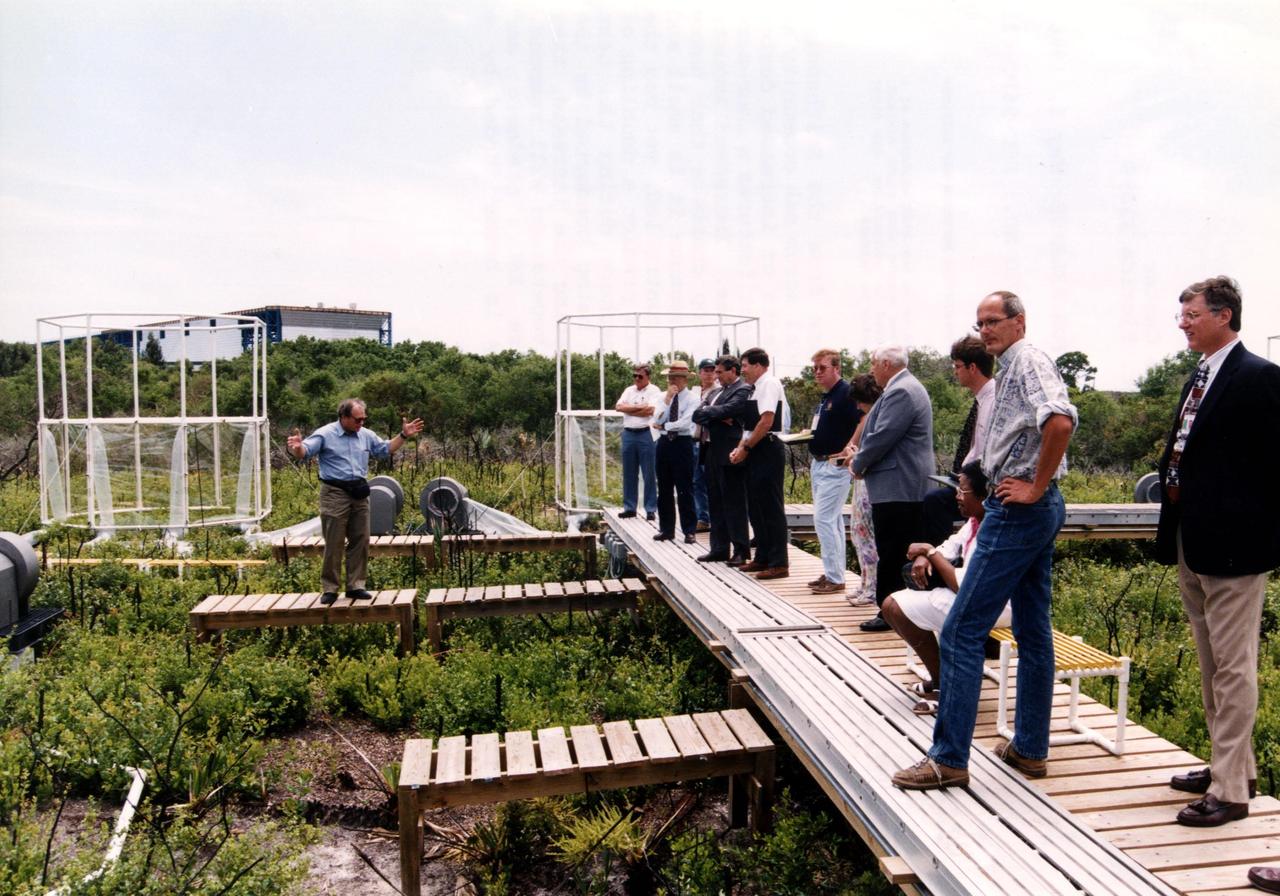

Researchers from the Smithsonian Institution hope their experiment in a local scrub oak community at KSC will yield new insights into the effects of increased carbon dioxide on natural vegetation. The experiment features a four-acre site just north of the Launch Complex 39 area. Increased amoounts of carbon dioxide are piped into 16 open-top chambers that house pristine Florida scrub vegetation, chosen because it is small and woody and fits in the chambers and can be controlled, yet has the attributes of much larger forests. Experts predict a doubling of the carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere during the next century, and the three-year KSC project being conducted by the Smithsonian-led team hopes that by simulating the increase, they can determine how natural ecosystems and vegetation will respond. Also participating in the effort are KSC, academic and international organizations. The study is being funded by a Department of energy grant
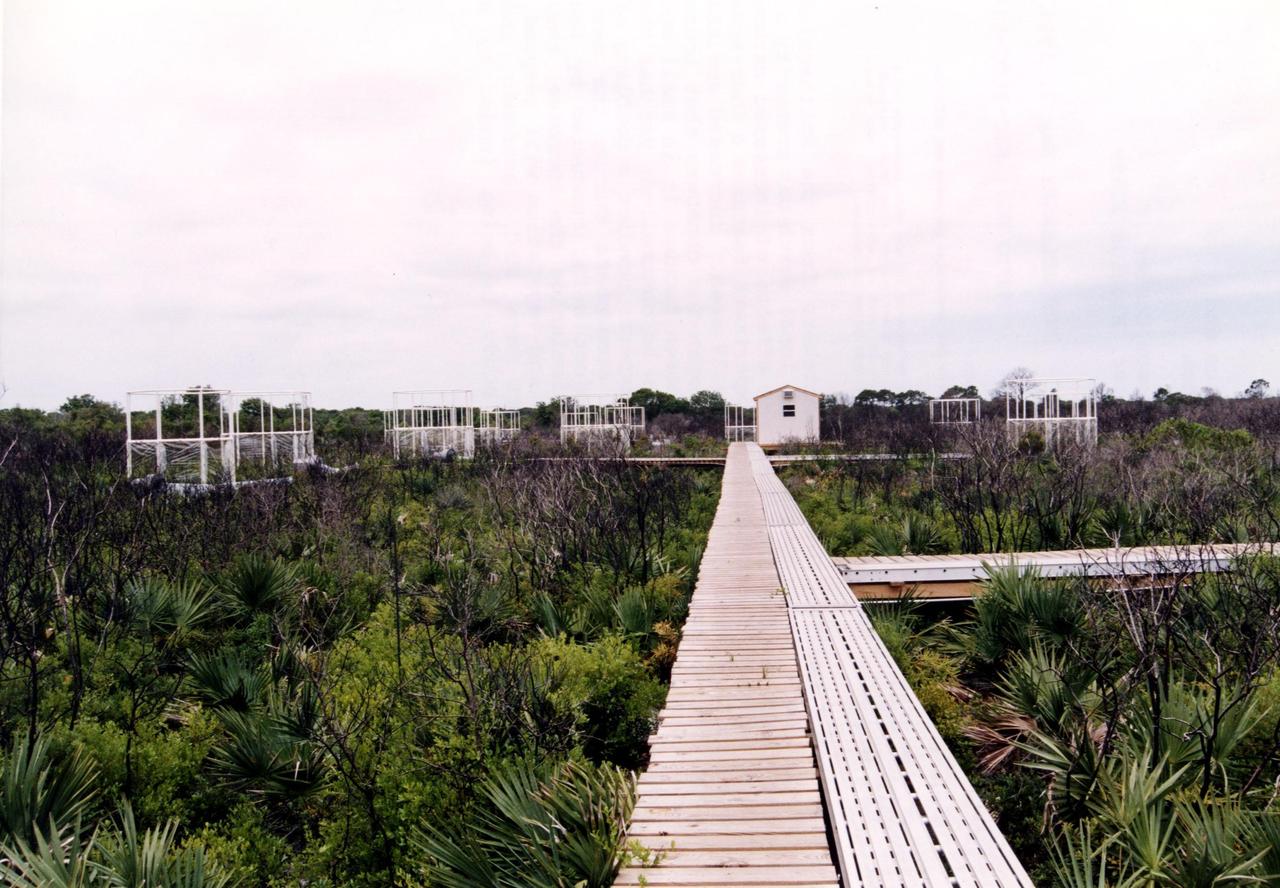

Researchers from the Smithsonian Institution hope their experiment in a local scrub oak community at KSC will yield new insights into the effects of increased carbon dioxide on natural vegetation. The experiment features a four-acre site just north of the Launch Complex 39 area. Increased amoounts of carbon dioxide are piped into 16 open-top chambers that house pristine Florida scrub vegetation, chosen because it is small and woody and fits in the chambers and can be controlled, yet has the attributes of much larger forests. Experts predict a doubling of the carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere during the next century, and the three-year KSC project being conducted by the Smithsonian-led team hopes that by simulating the increase, they can determine how natural ecosystems and vegetation will respond. Also participating in the effort are KSC, academic and international organizations. The study is being funded by a Department of energy grant
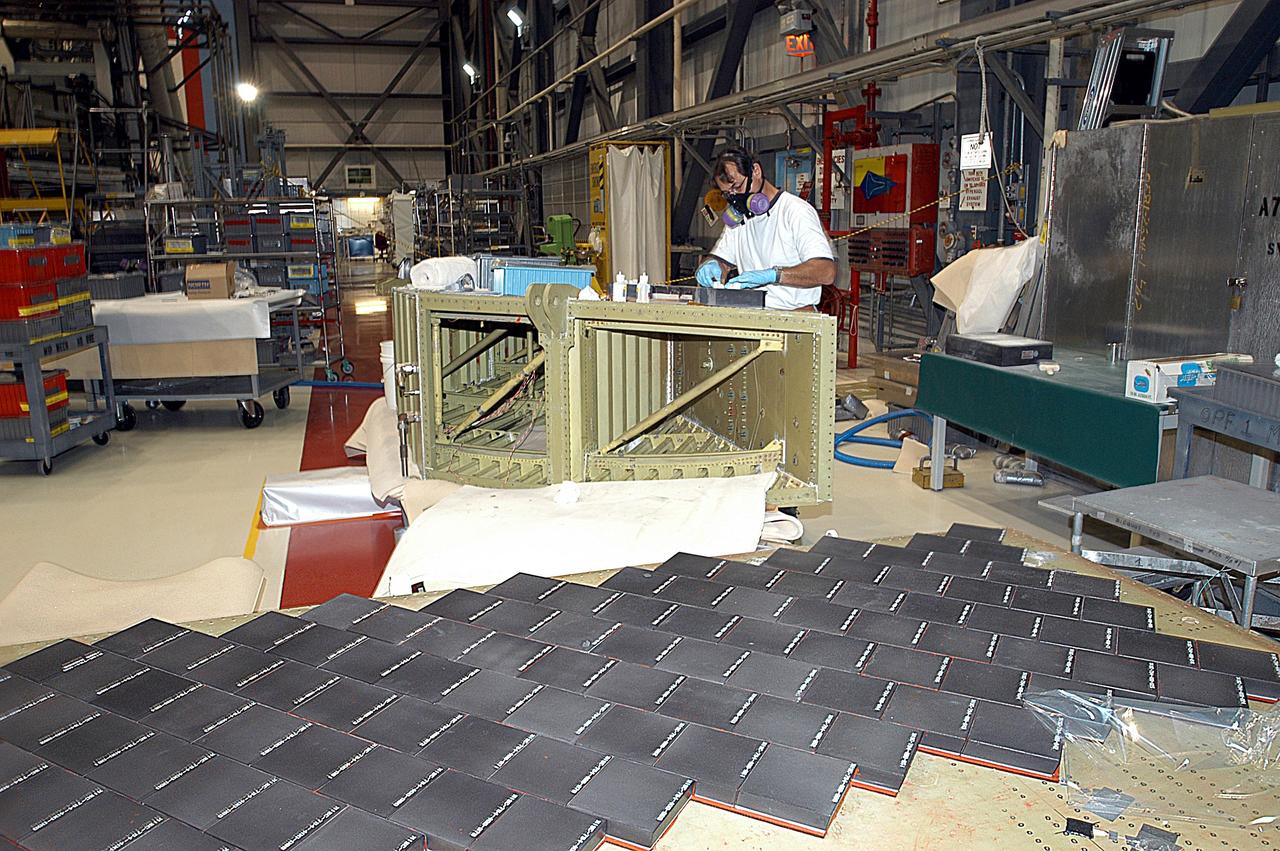

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), United Space Alliance (USA) technician Mark Jetton installs Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile on a simulated orbiter wing. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, employees from The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., install a strain gauge on a test panel prior to installation of Thermal Protection System tile on the panel. The test panel and sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
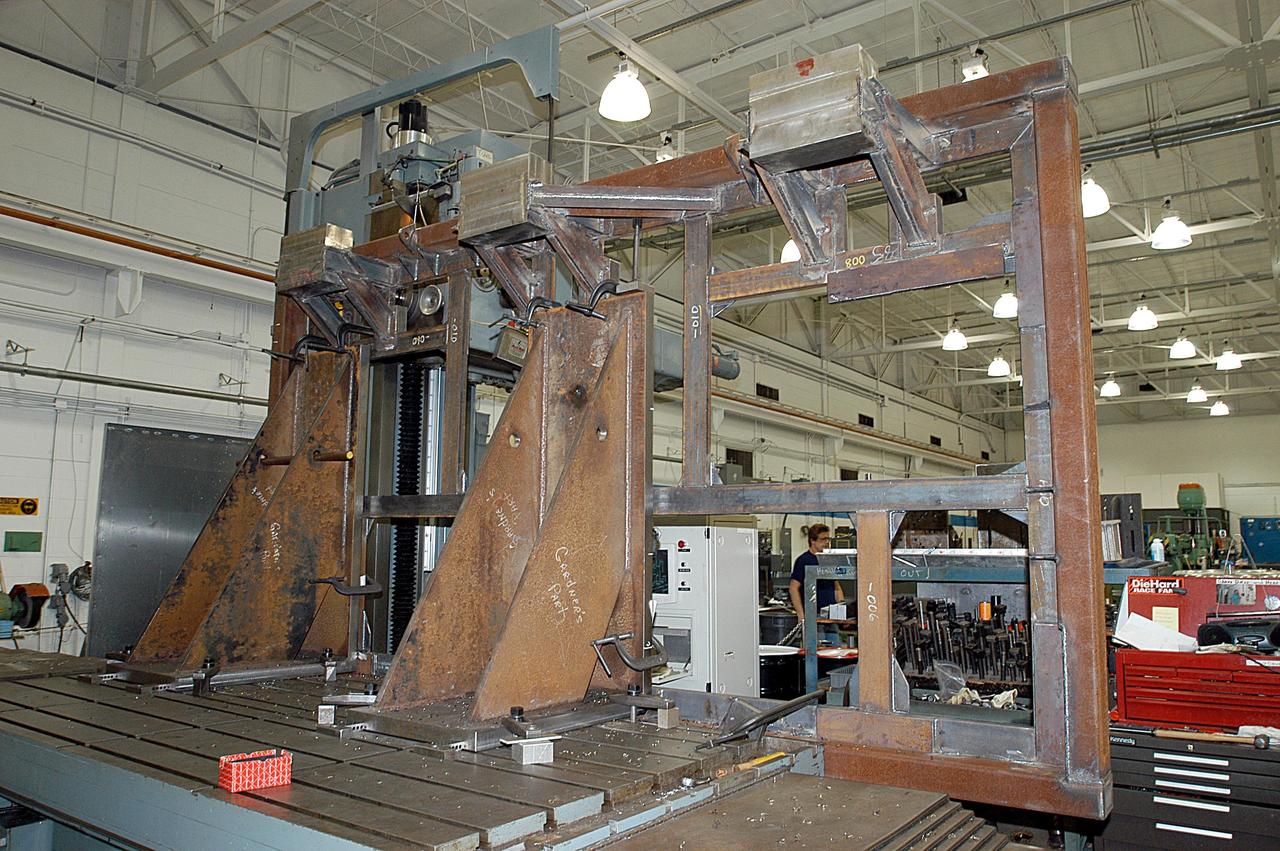

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A main landing gear door mounting fixture in the Launch Equipment Shop is being used to support the Columbia mishap investigation. A simulated orbiter wing and several test panels, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
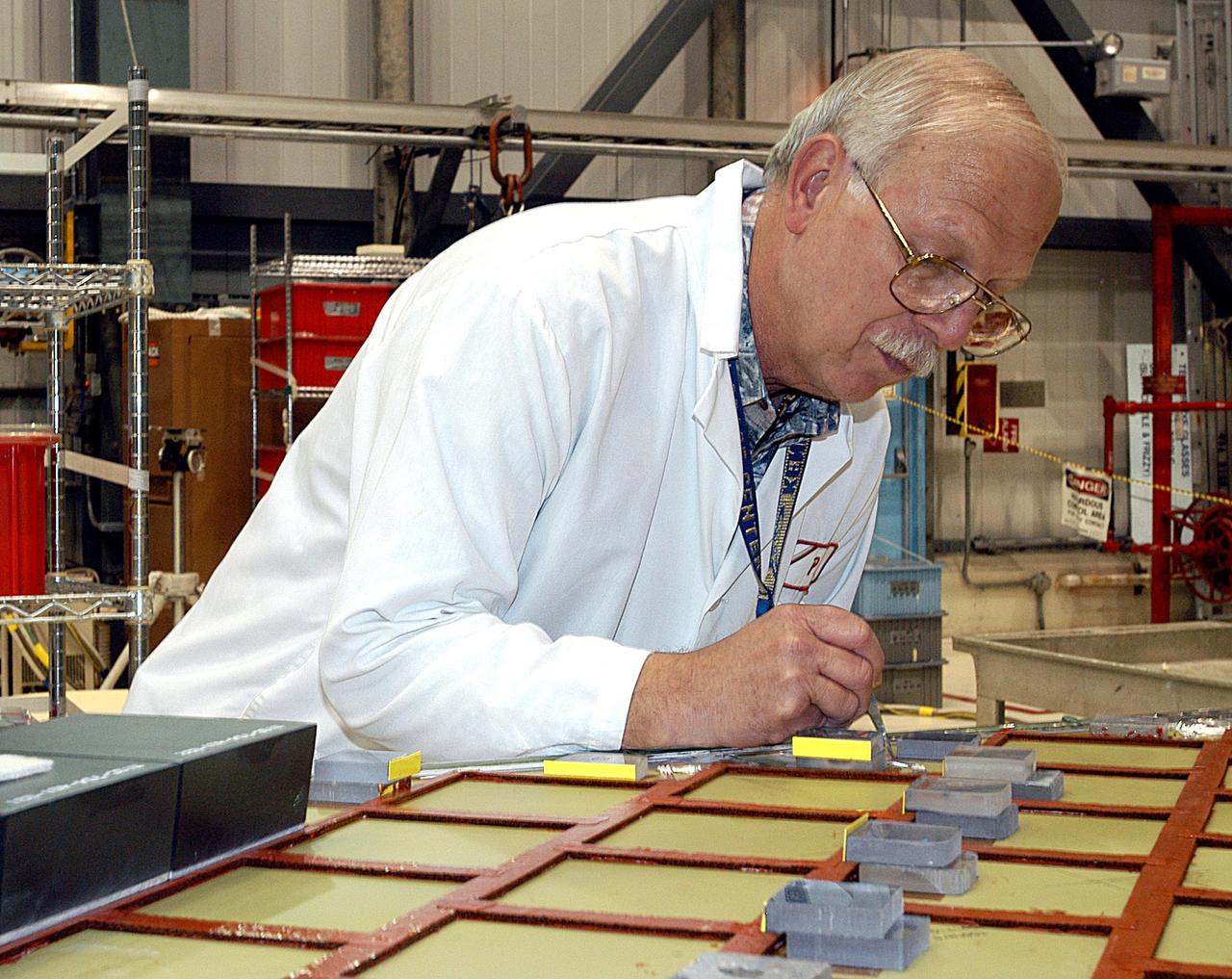

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), Paul King, an employee of The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., installs a strain gauge on a simulated orbiter wing in preparation for Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile installation. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
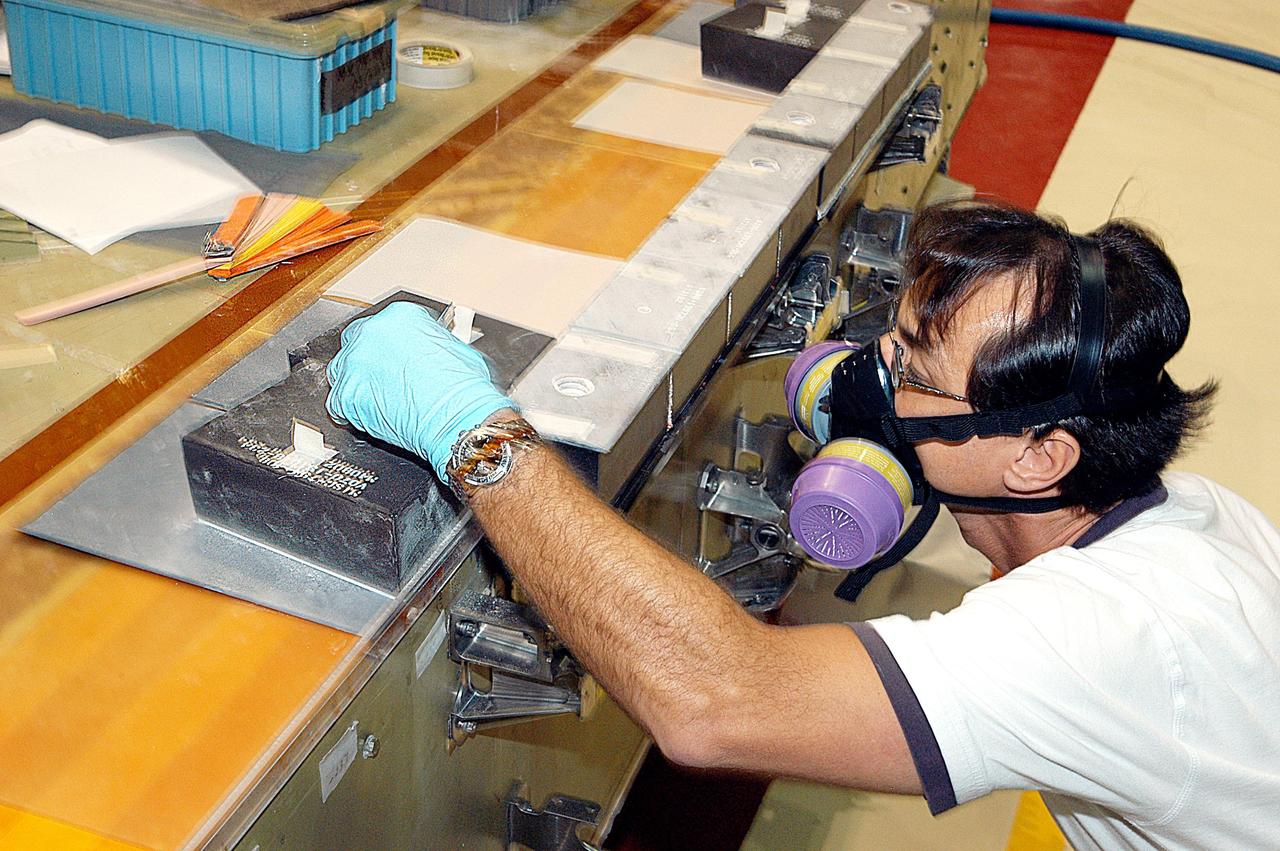

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), United Space Alliance (USA) technician Mark Jetton installs Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile on a simulated orbiter wing. The wing, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
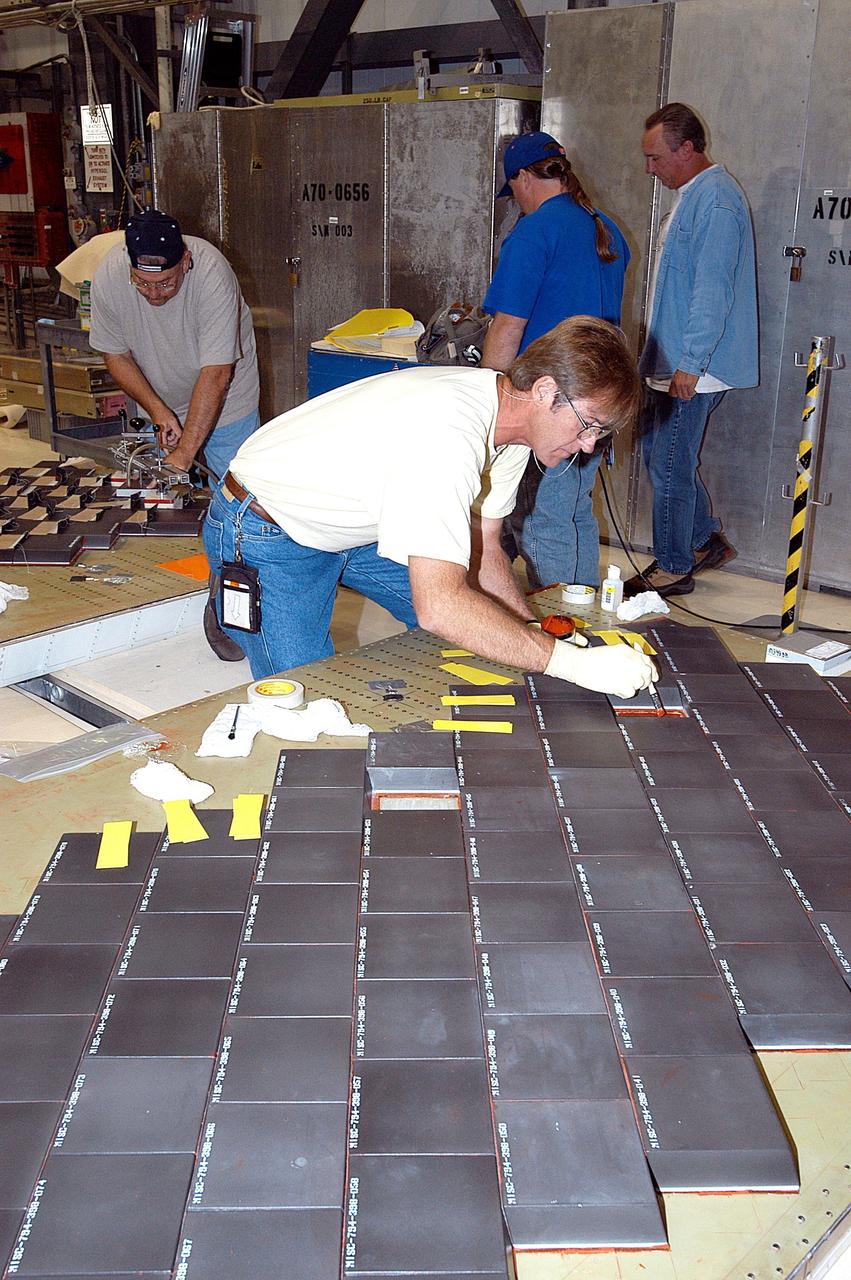

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employee Harrell Watts applies RTV, a room-temperature vulcanizing silicone adhesive, to a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) on which Thermal Protection System tiles are being installed. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.
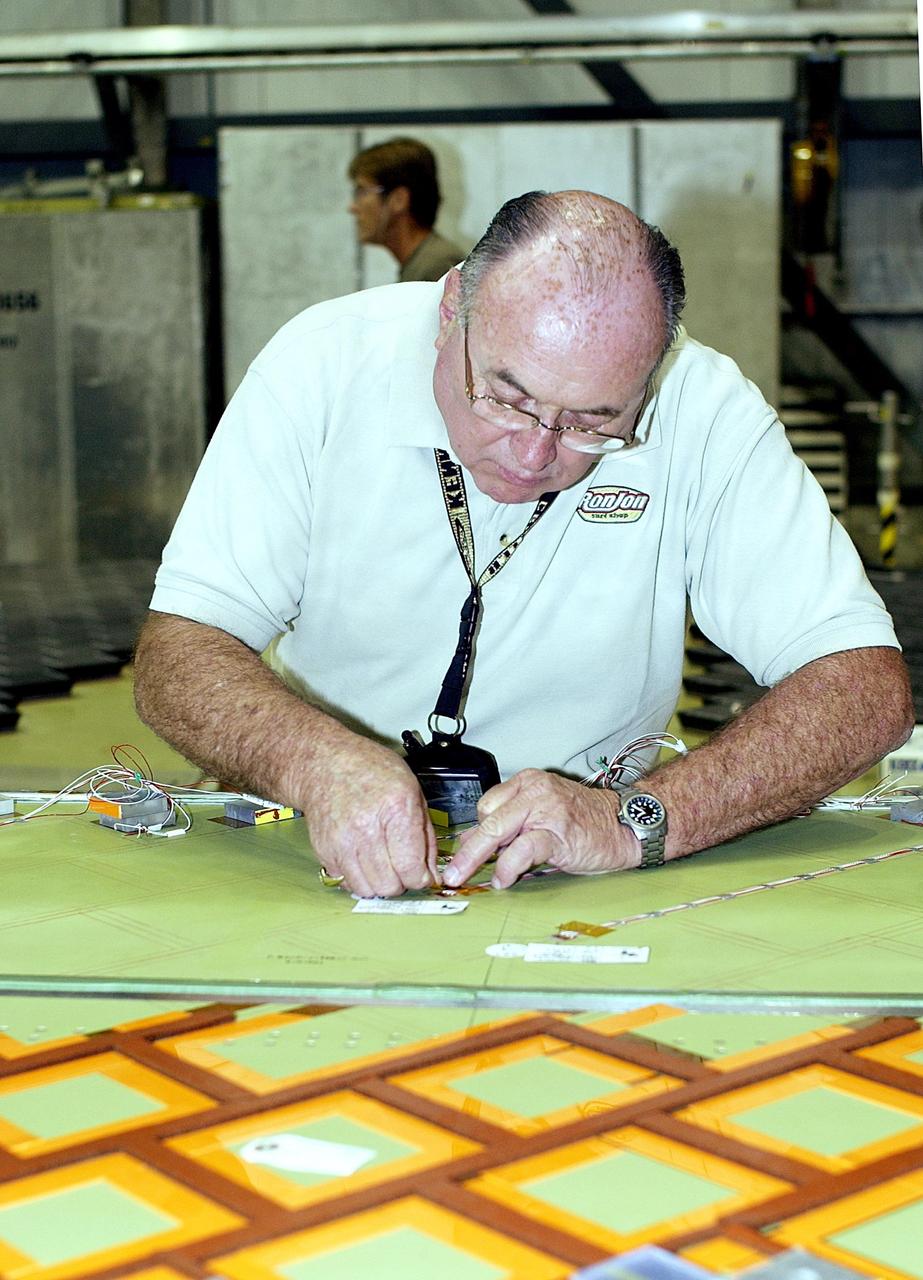

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, an employee from The Boeing Co., Huntington Beach, Calif., installs a strain gauge on a test panel prior to installation of Thermal Protection System tile on the panel. The test panel and sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101) will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after the tile installation is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
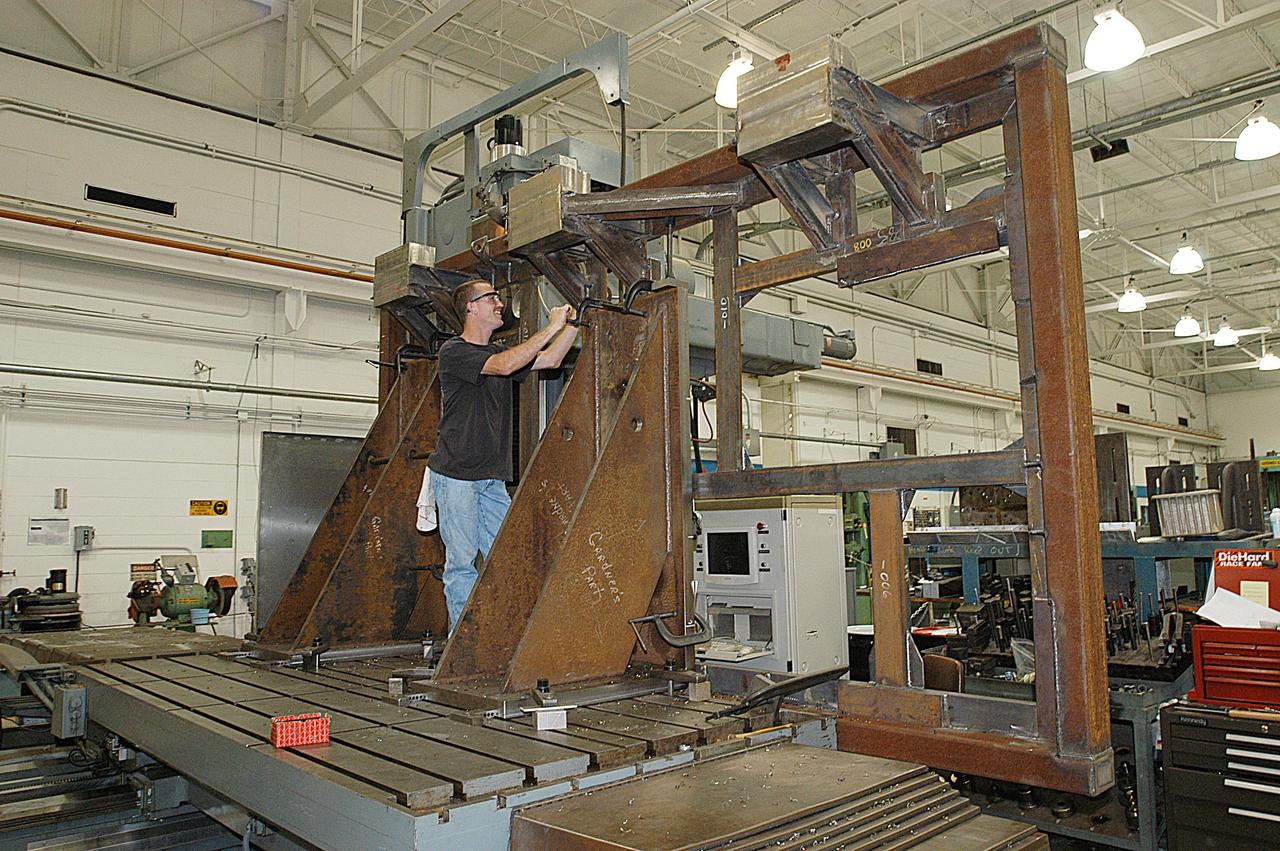

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- United Space Alliance technician Matt Boonstra works on a main landing gear door mounting fixture in the Launch Equipment Shop. The fixture is being used to support the Columbia mishap investigation. A simulated orbiter wing and several test panels, along with sections of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101), will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing after Thermal Protection System (TPS) tile installation on them is complete. The testing has been requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board. For this initiative, sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight.
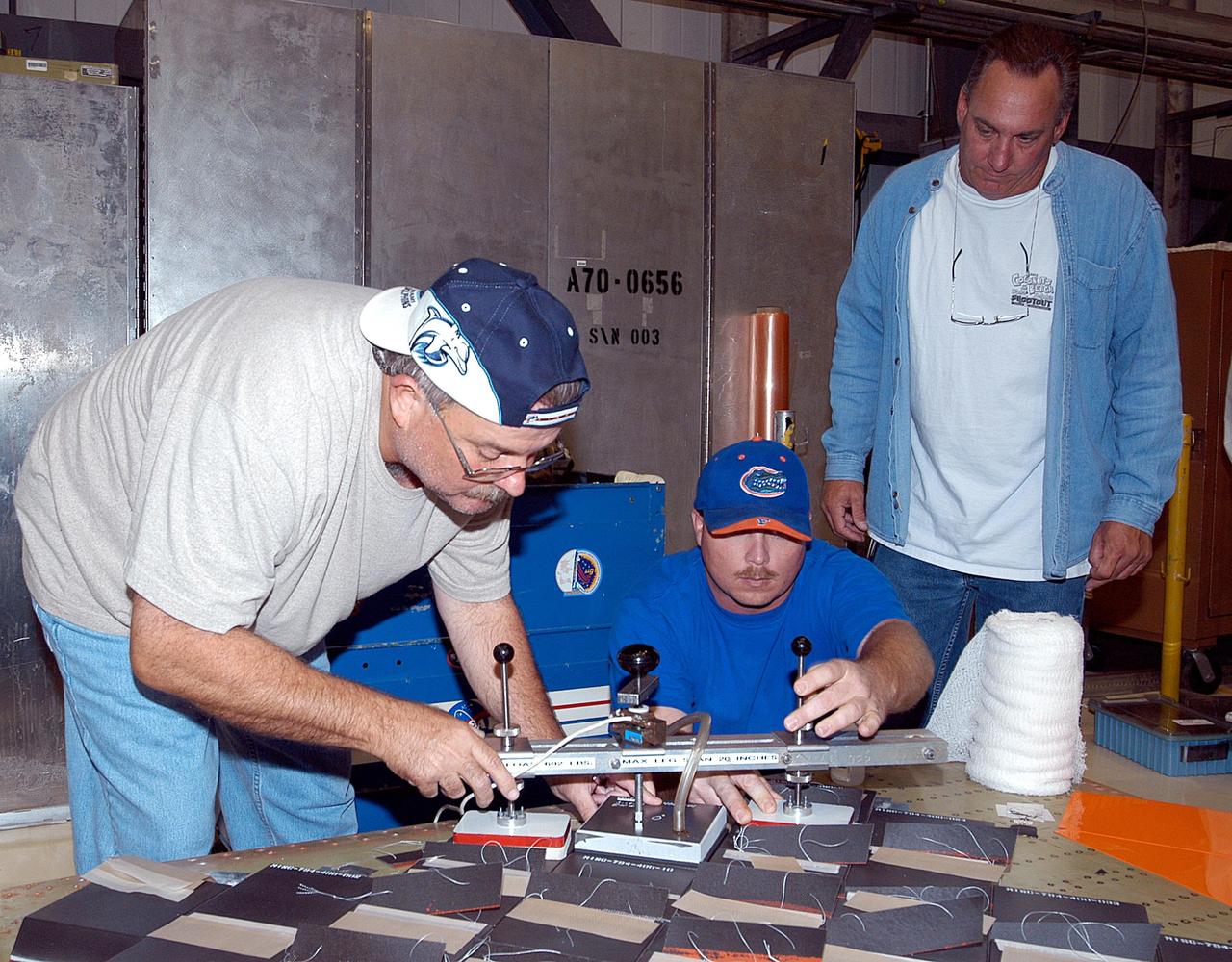

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance employees (from left) Dave Sanborn, Butch Lato, and Bill Brooks conduct a bond verification test on Thermal Protection System tiles newly installed on a main landing gear door of Space Shuttle orbiter Enterprise (OV-101). Sections of Enterprise were borrowed from the Smithsonian Institution's Air and Space Museum where the orbiter is being stored at the Washington Dulles International Airport. Enterprise was the first orbiter built in the Shuttle fleet and was used to conduct the Approach and Landing Test Program before the first powered Shuttle flight. After the tile installation is complete, the sections will be transferred to the Southwest Research Institute for testing requested by the Columbia Accident Investigation Board.