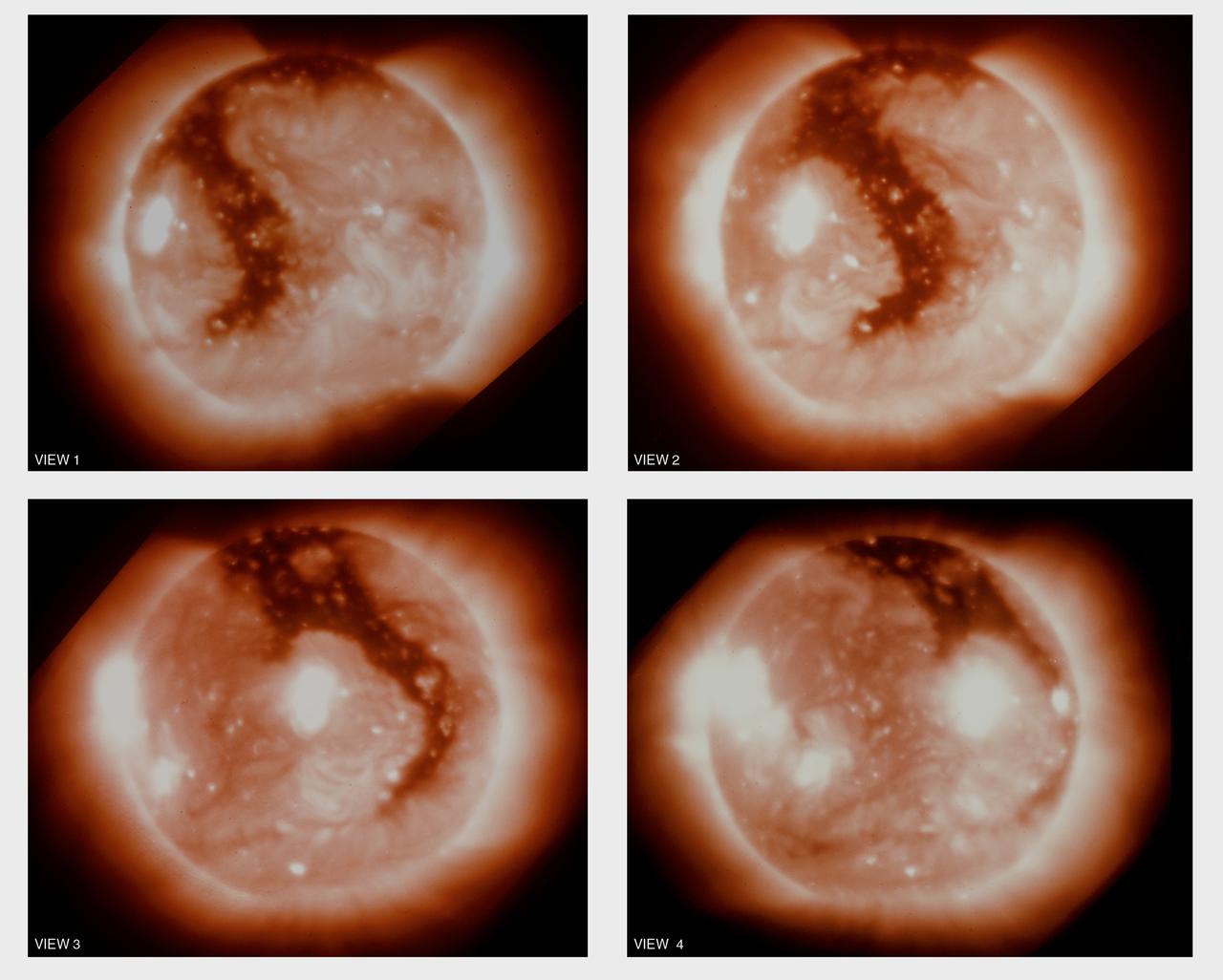
This montage is a sequence of soft x-ray photographs of the boot-shaped coronal hole rotating with the sun. The individual pictures were taken about 2 days apart by the Skylab telescope. Most of the apparent changes in this 6-day period resulted from a changing perspective. Skylab data helped demonstrate that coronal holes are sources of high-velocity streams in the solar wind. These high-velocity streams can be electrons, protons, and atomic nuclei that spray out from the Sun into interplanetary space. When the coronal hole is near the center of the Sun, as in view 2, the sprinkler is directed at Earth. These high-speed streams of solar wind distort Earth's magnetic field and disturb it's upper atmosphere.
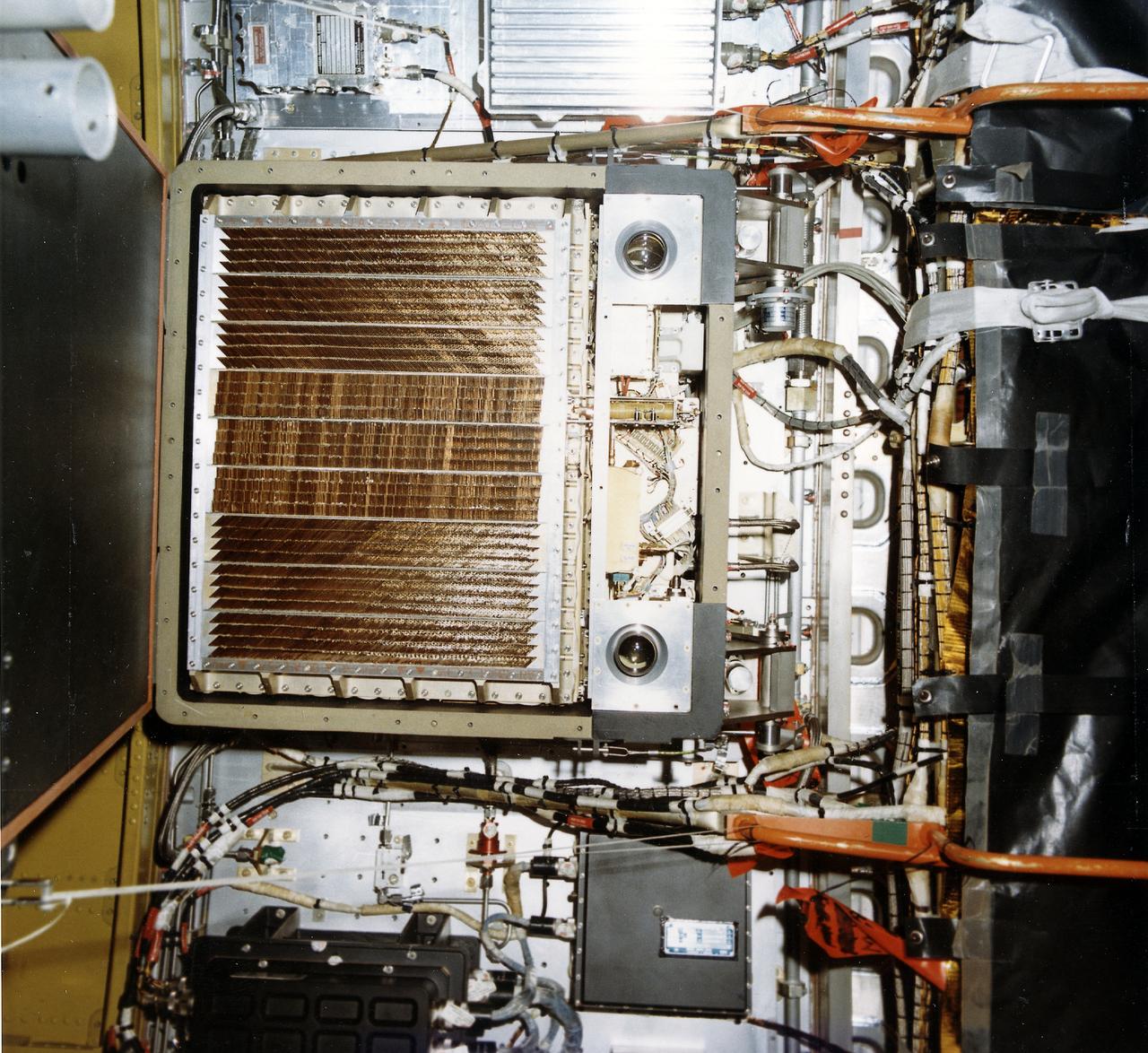
This photograph shows Skylab's Galactic X-Ray Mapping facility (S150), an astrophysics and space sciences investigation. An objective of this experiment was to extend the search for the origin of galactic x-rays beyond the sensitivity possible with short flights of small research rockets. This was accomplished by placing a large-area, soft x-ray detector in orbit to collect data for a much longer time. The S150 instrument was not in Skylab but in the instrument unit of the second stage of the Skylab-3 Saturn IB rocket.