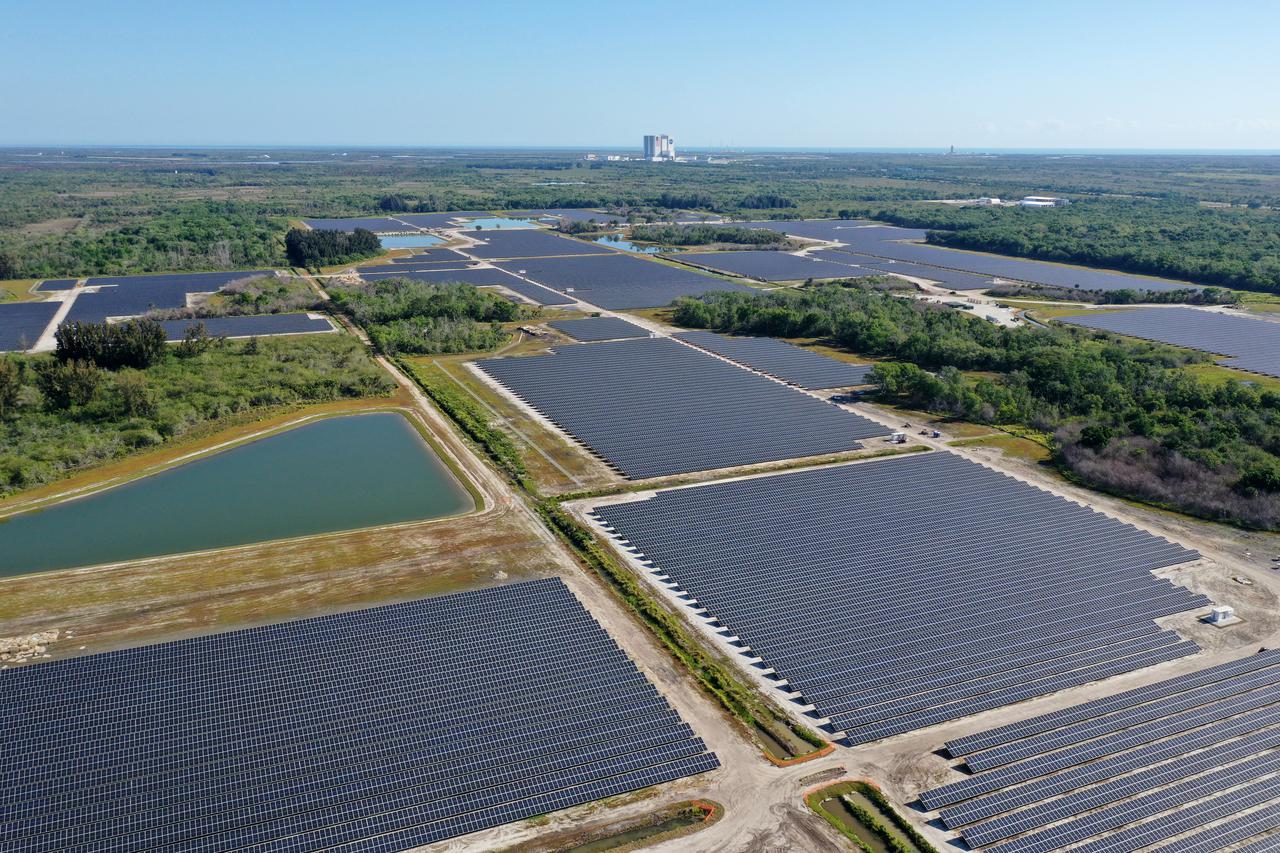

Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center is a 74.5 megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels, and once it’s operational, will produce enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Construction began in spring 2020, and teams expect to have the solar site finished by May 2021. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels will not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, will send energy directly to FPL’s electricity grid for distribution to existing customers.
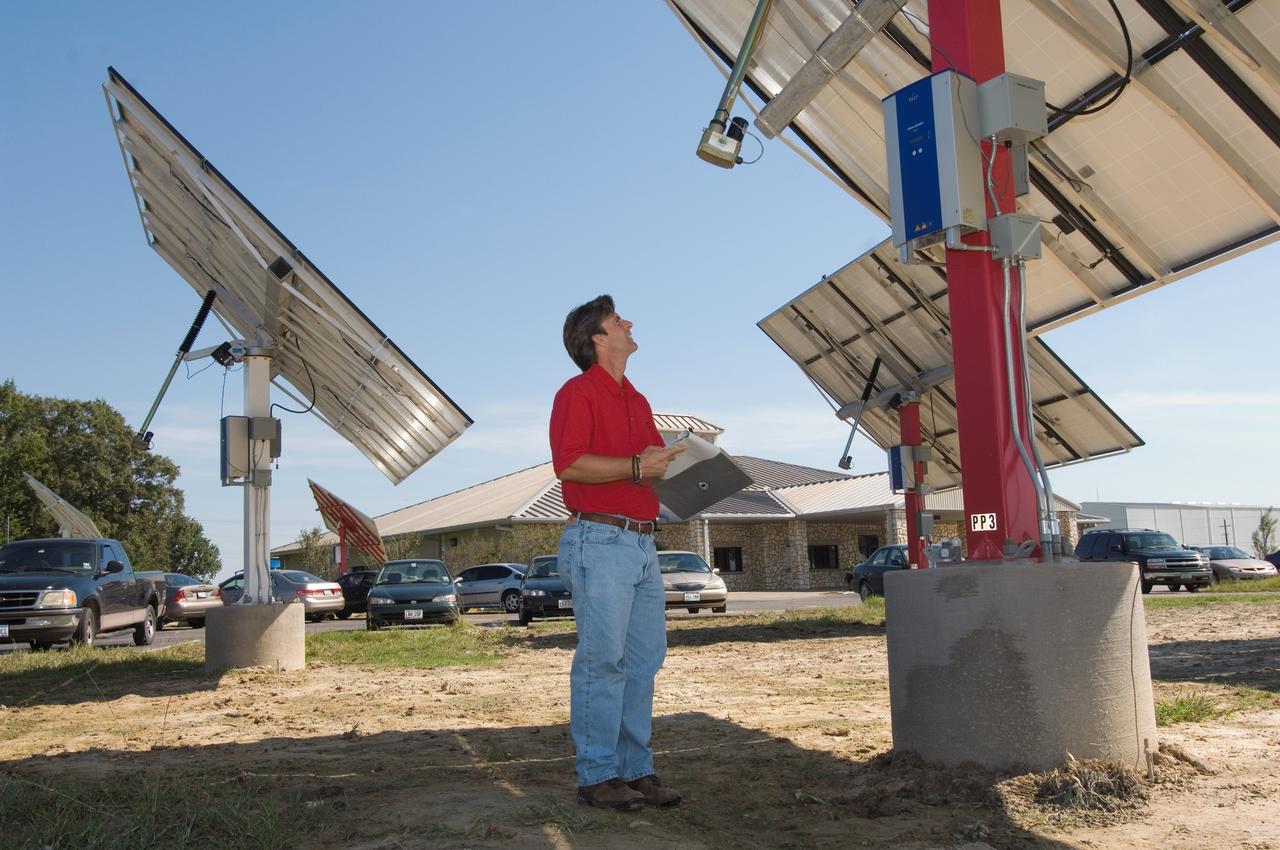

Solar panel and wind farm at the JSC Child Care Center. View of Jerry Rowlands, Energy Management and Control System manager for CSC.

On February 15, 2015 the Desert Sunlight solar project in California’s Mojave Desert became operational. This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the 550-megawatt plant generates enough electricity to power 160,000 average homes. Covering an area of 16 km2, the 8.8 million cadmium telluride photovoltaic modules take advantage of the more than 300 days of sunshine. Desert Sunlight joins the similar-sized Topaz Solar Farm in San Luis Obispo County, CA, that became operational in June, 2014. The Desert Sunlight image (left) was acquired March 12, 2015 and is located at 33.8 degrees north, 115.4 degrees west; the Topaz image (right) was acquired September 11, 2014 and is located at 35.4 degrees north, 120.1 degrees west. Each image covers an area of 10.5 x 12 km. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19268

NASA photographer Jim Ross captured this shot while pilot Troy Asher flew inverted in an F-15D. The F-15B is seen here flying over the mirror farm, AKA the Abengoa Mojave Solar Project, east of Four Corners off of Highway 58 in Southern California.

Space Farm 7 Program; NASA Day at the Dell'osso Family Farm, Lathrop,CA for the opening of the Kepler Solar System (Corn) Maze. Lots of fun activities were available and Kepler scientists gave talks and hands on demos to the audience of kids and adults alike to better understand Kepler and it's mission.
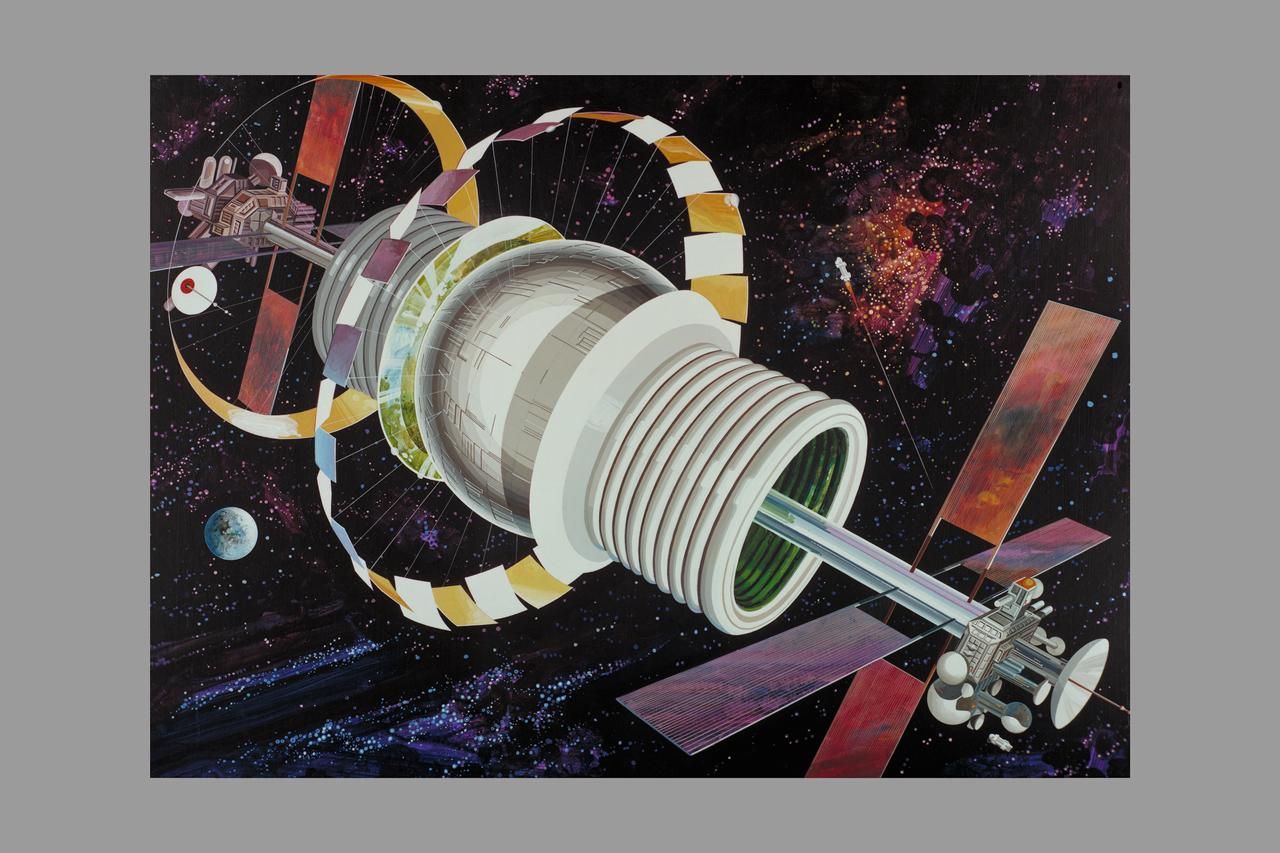
Artist: Rick Guidice Space Colonization - Bernal Sphere - The residential area is in the central sphere. Farming regions are in the 'tires.' Mirrors reflect sunlight into the habitat and farms. The large flat panels radiate away extra heat into space, and panels of solar cells provide electricity. Factories and docks for spaceships are at either end of the long central tube. (NOTE: art printed in Book 'Space Colony - Frontier of the 21st Century by Franklyn M. Branley)
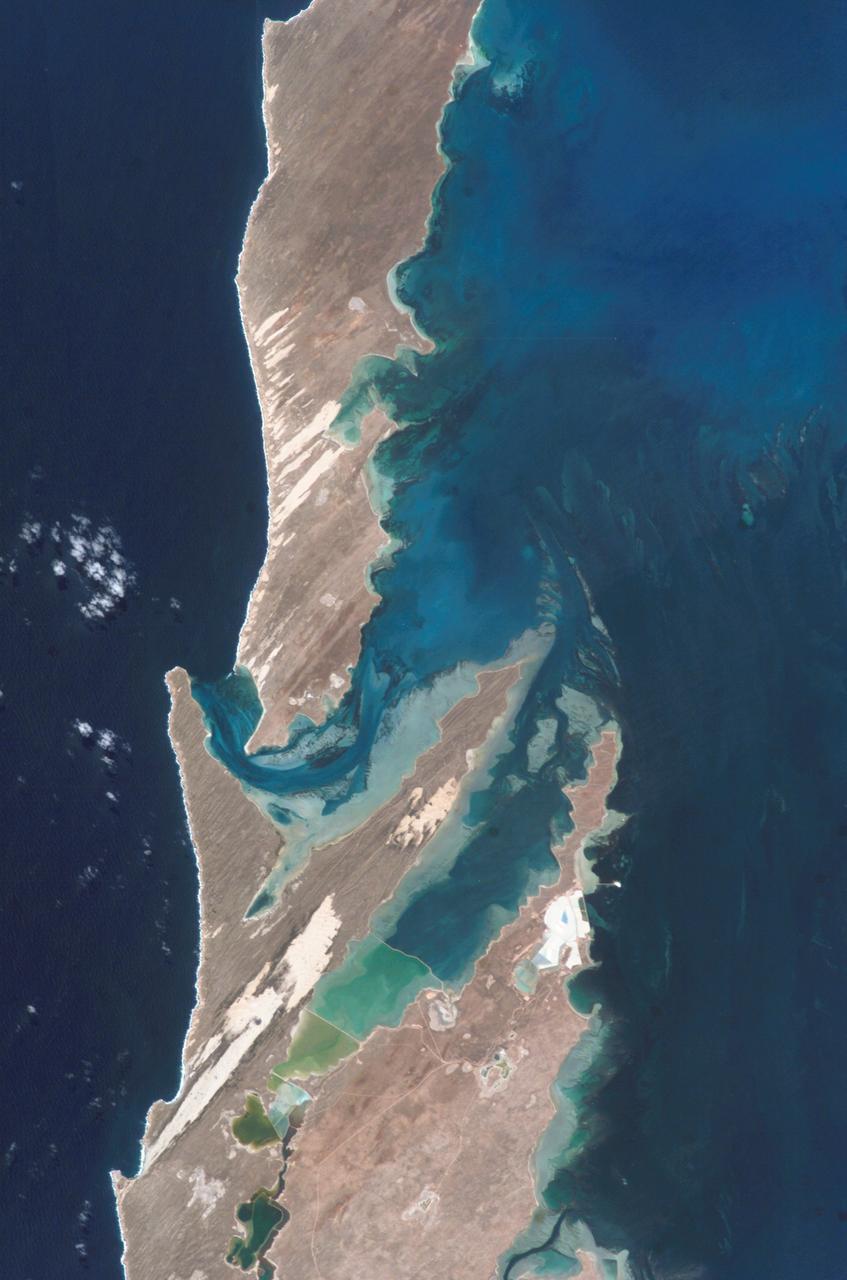

ISS010-E-06681 (12 November 2004) --- Shark Bay, Australia is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 10 crewmember on the International Space Station (ISS). This image shows large solar salt works developed in Useless Loop and Useless Inlet, Shark Bay, Western Australia. The salt (sodium chloride) is produced when ponds are repeatedly flooded with seawater, which is progressively concentrated by evaporation. This particular salt farm opened in 1967 and expanded operations in the 1990s. Today, this salt farm comprises over 50 ponds, the newest pond in the outermost pond in Useless Inlet, which provides the first evaporation cycle to increase the salinity of the water prior to entering the next pond. Complex chemical and biological adjustments occur in the system each time the configuration of ponds is changed.
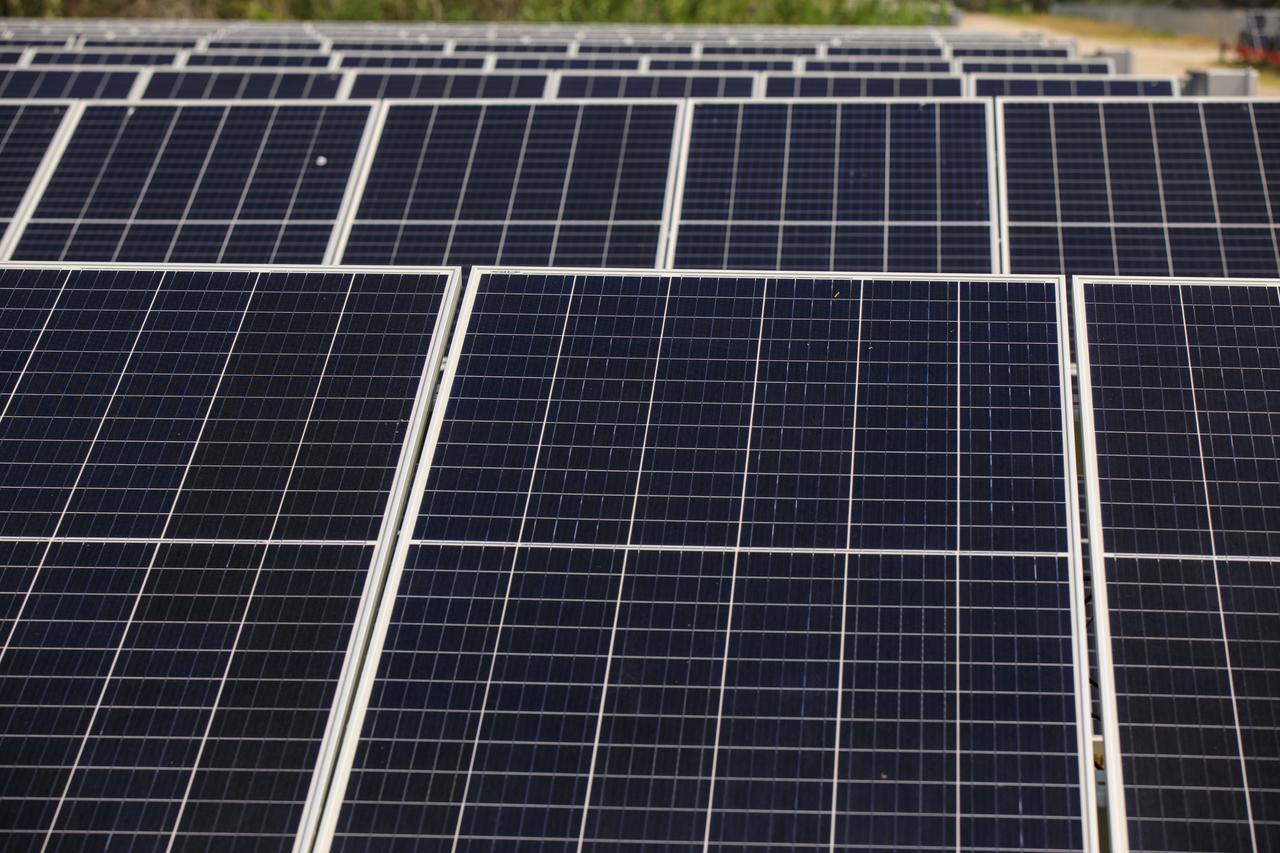

Seen here is an up-close view of solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center – a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.

Seen here is an up-close view of solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center – a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
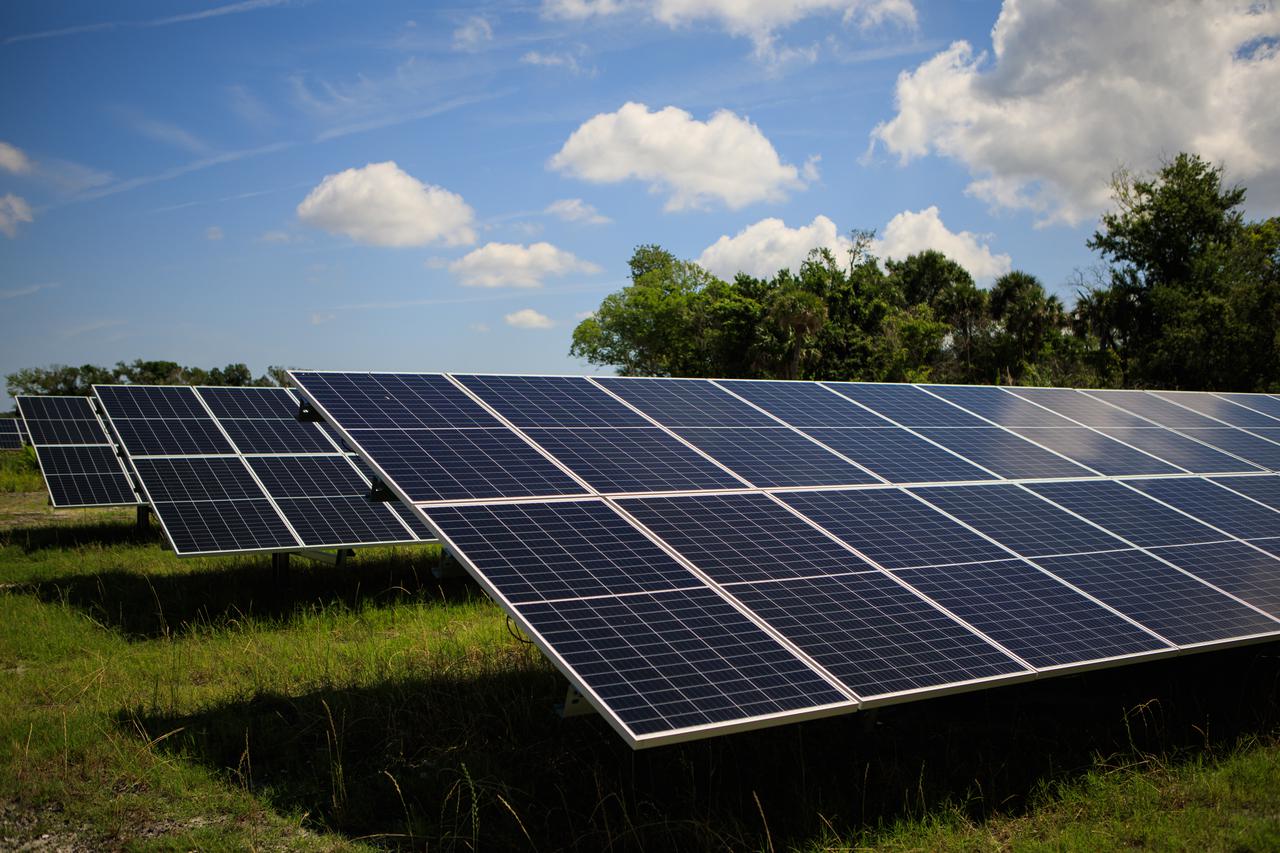

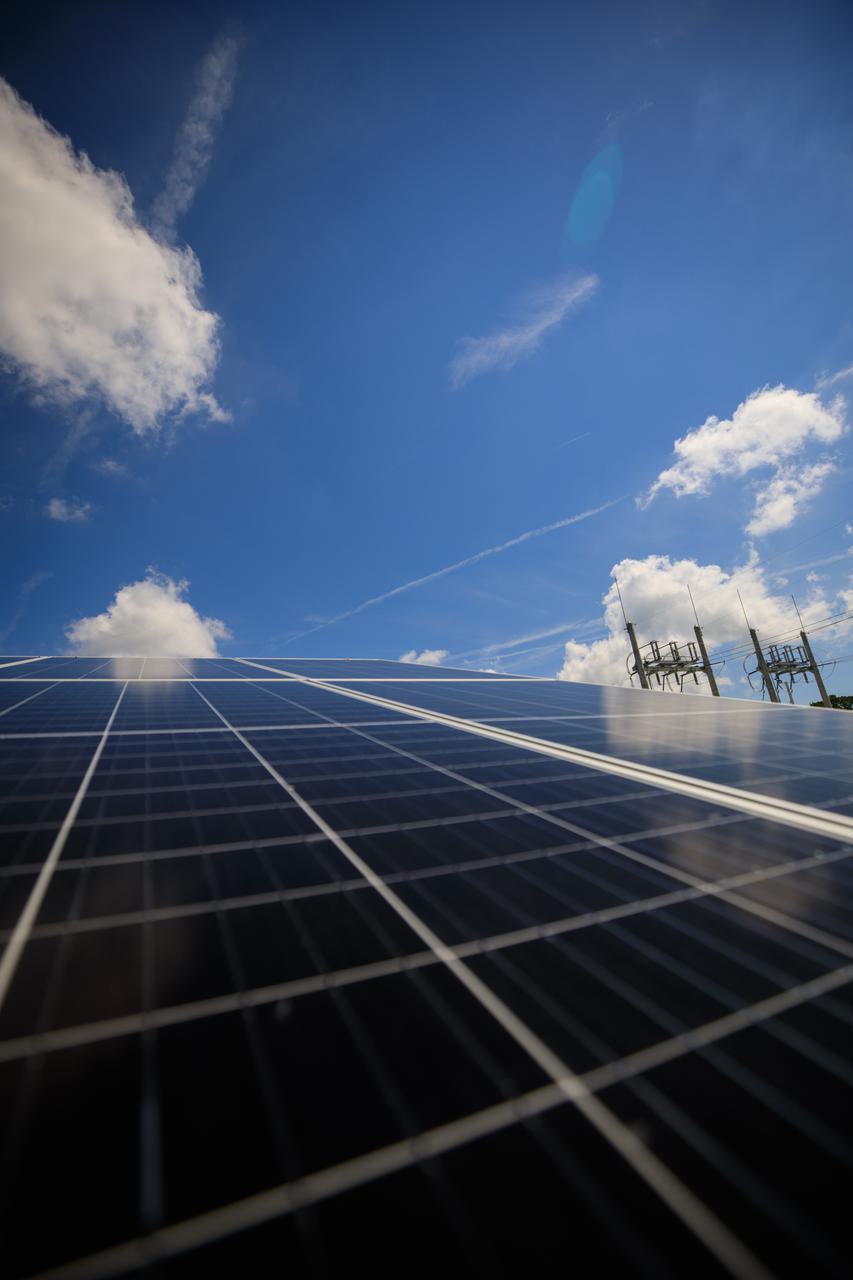
In this view are solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center – a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
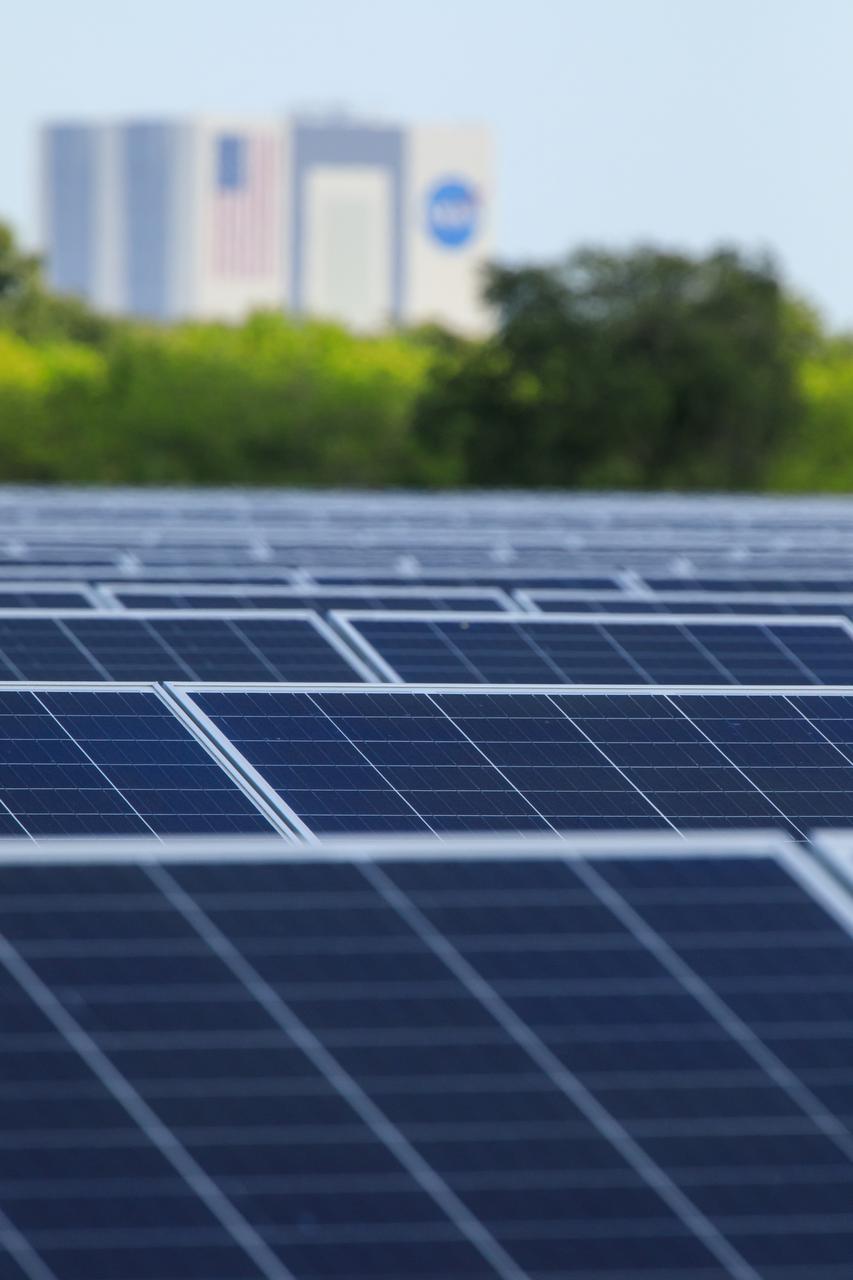

Seen here, with the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building in the background, is an up-close view of solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 74.5-megawatt solar site spans 491 acres at Kennedy and contains about 250,000 solar panels. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels produce enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. The panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, and instead, send energy directly to FPL’s electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
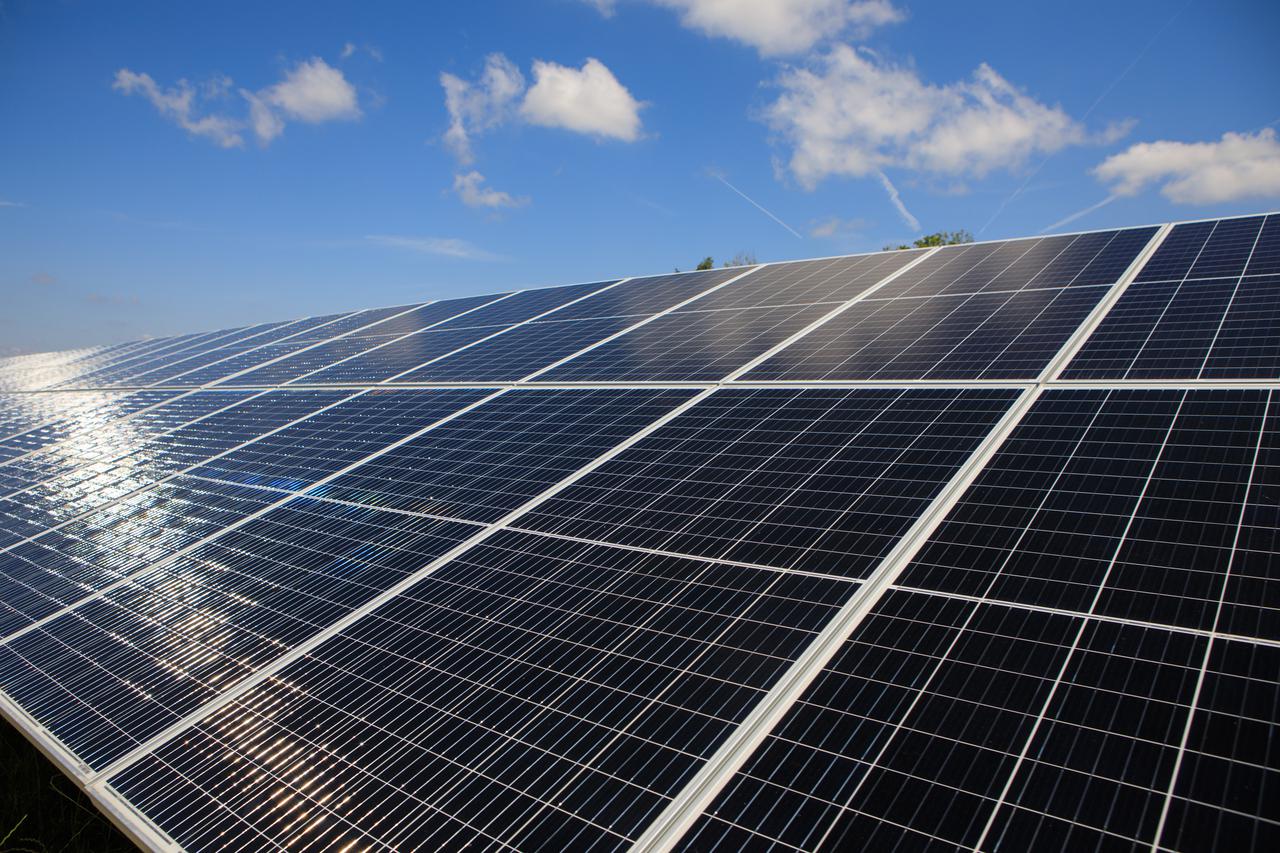

Seen here is an up-close view of solar panels that are part of Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center – a 74.5-megawatt solar site, spanning 491 acres at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The site contains about 250,000 solar panels in total, producing enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, but rather, send energy directly to FPL's electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
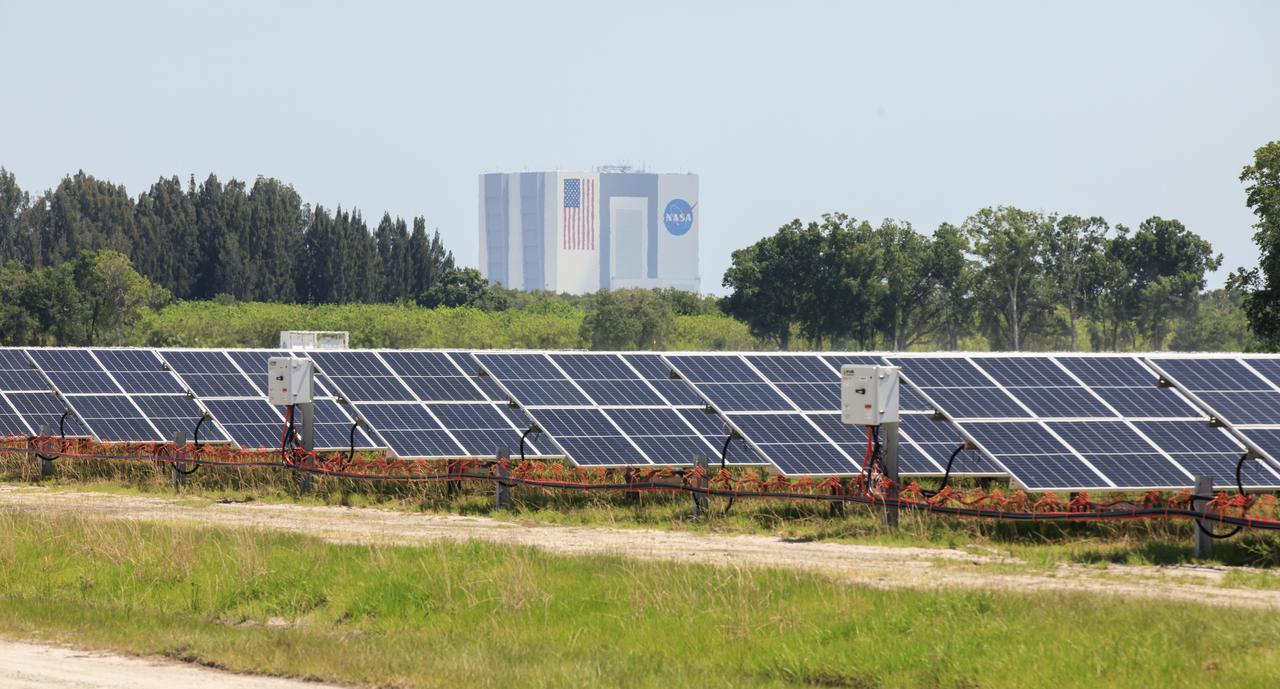

With the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building serving as the backdrop, a portion of the solar panels that make up Florida Power and Light’s (FPL) new Discovery Solar Energy Center is seen at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 74.5-megawatt solar site spans 491 acres at Kennedy and contains about 250,000 solar panels. Harnessing energy from the Sun, the panels produce enough energy to power approximately 15,000 homes. The panels do not directly power anything at Kennedy, and instead, send energy directly to FPL’s electricity grid for distribution to existing customers. Construction began in spring 2020, and the energy center became fully operational on May 30, 2021.
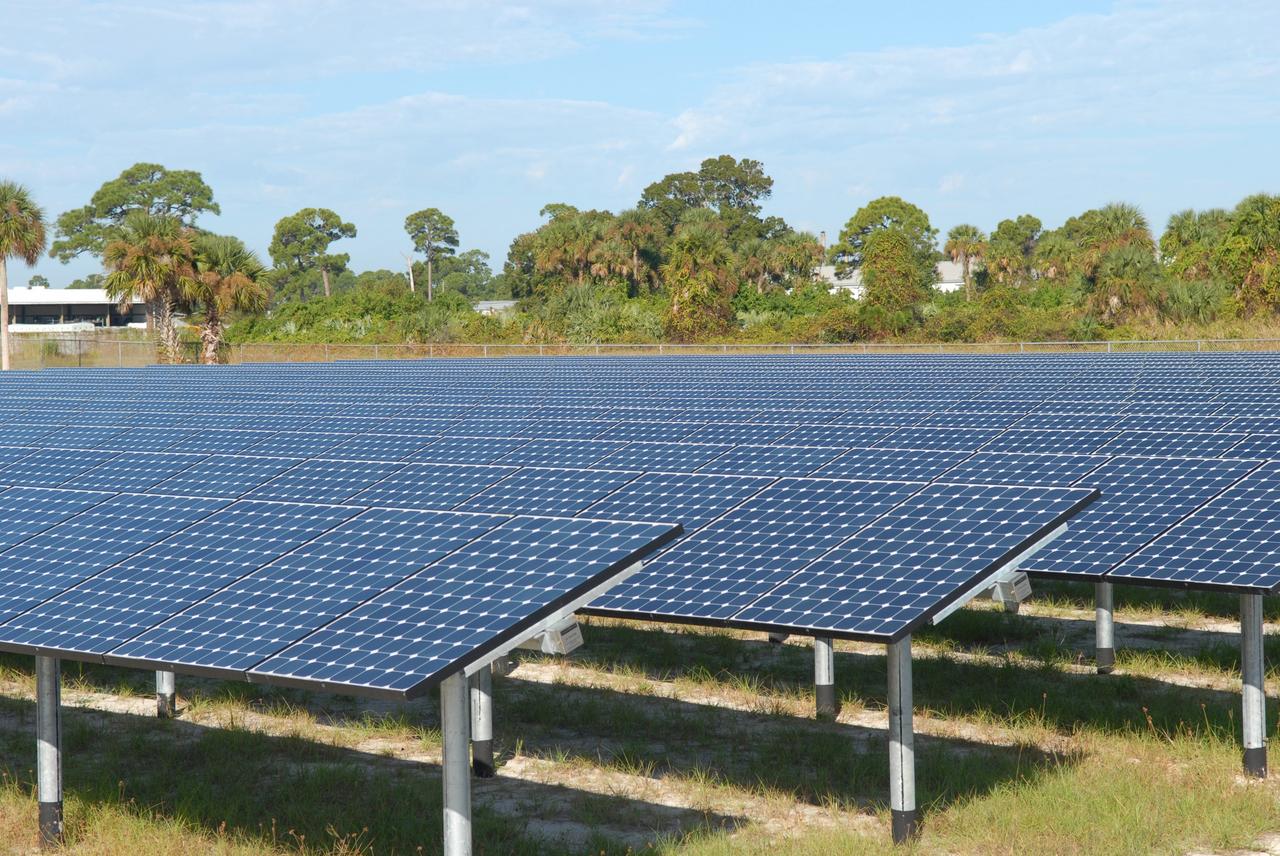

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility opens at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
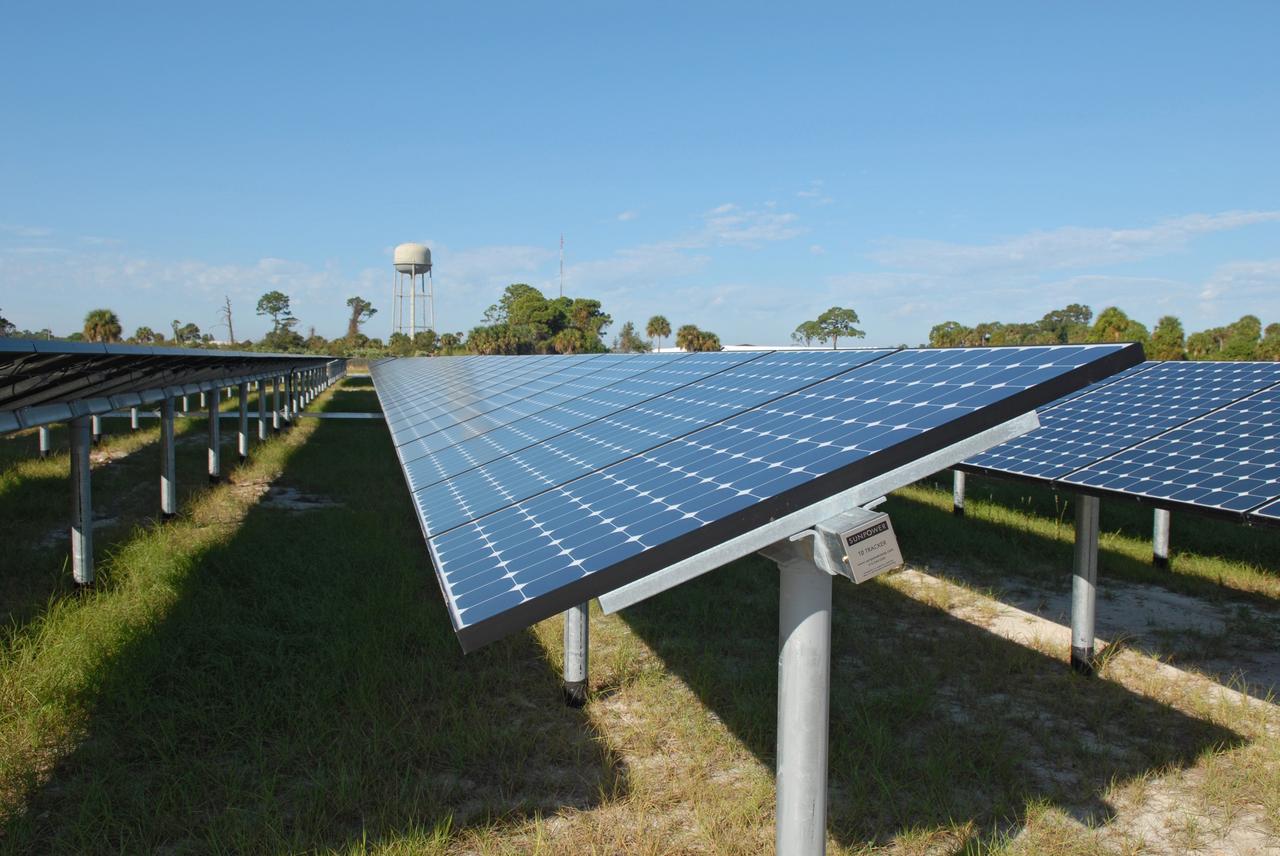

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility is unveiled at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
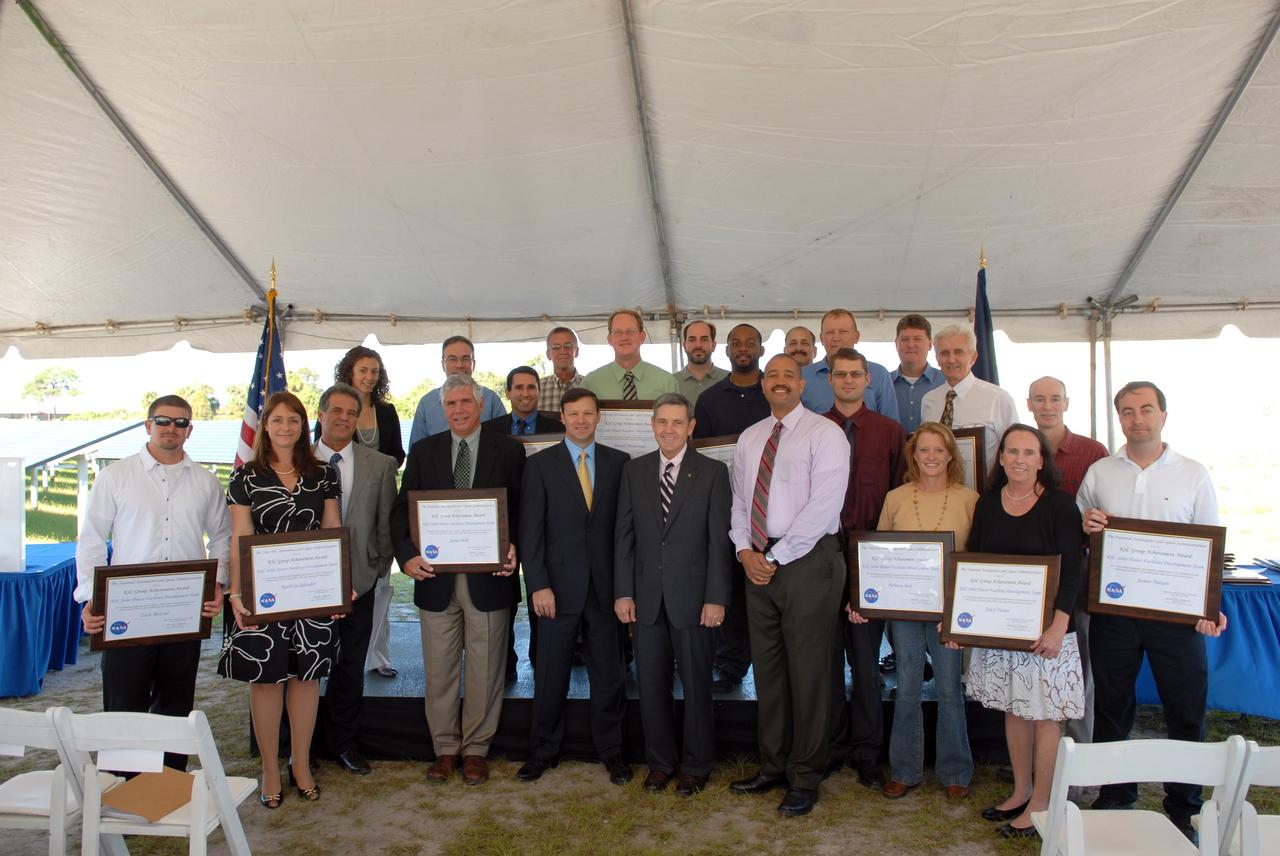

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, recipients of a NASA Team Award for their parts in the successful construction of NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility pose for a group portrait. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
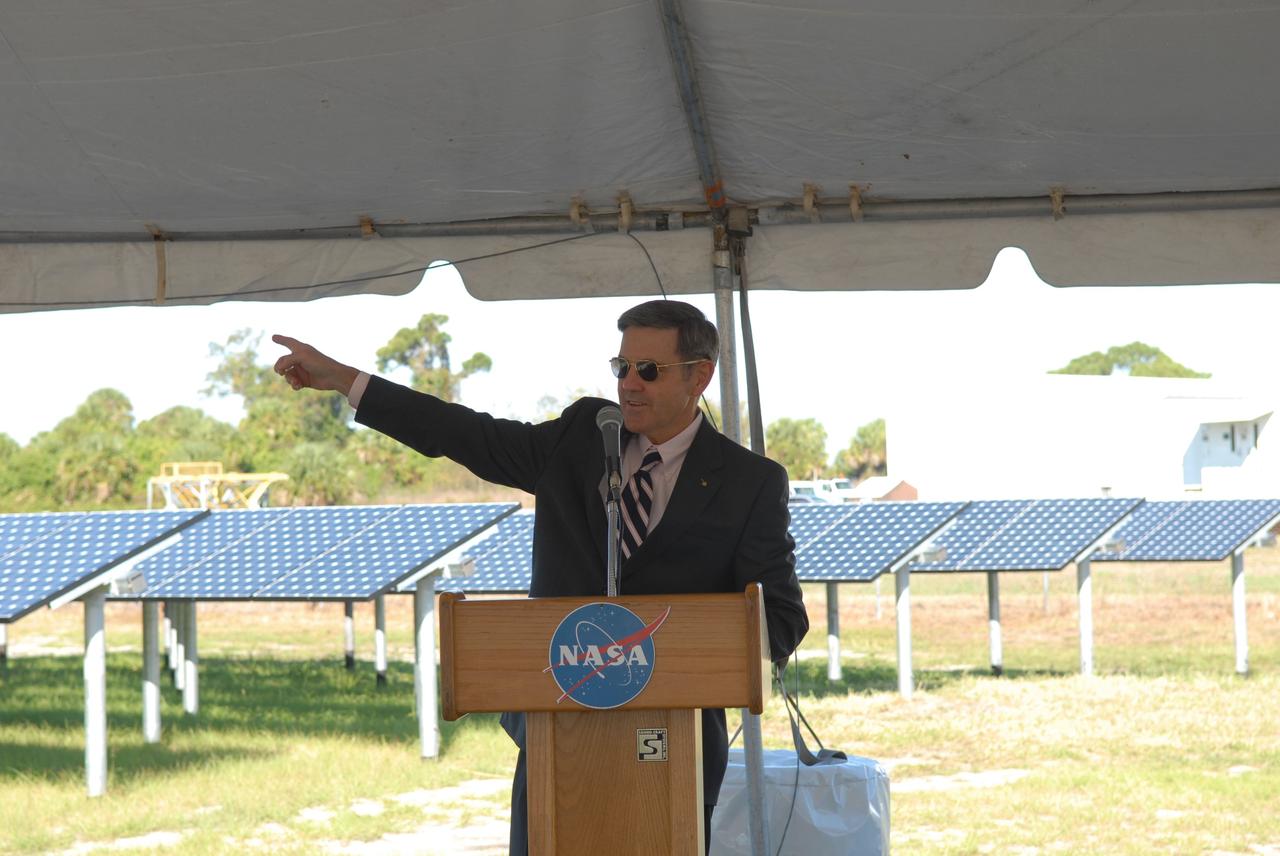

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana addresses the audience on hand for the unveiling of NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility at Kennedy in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
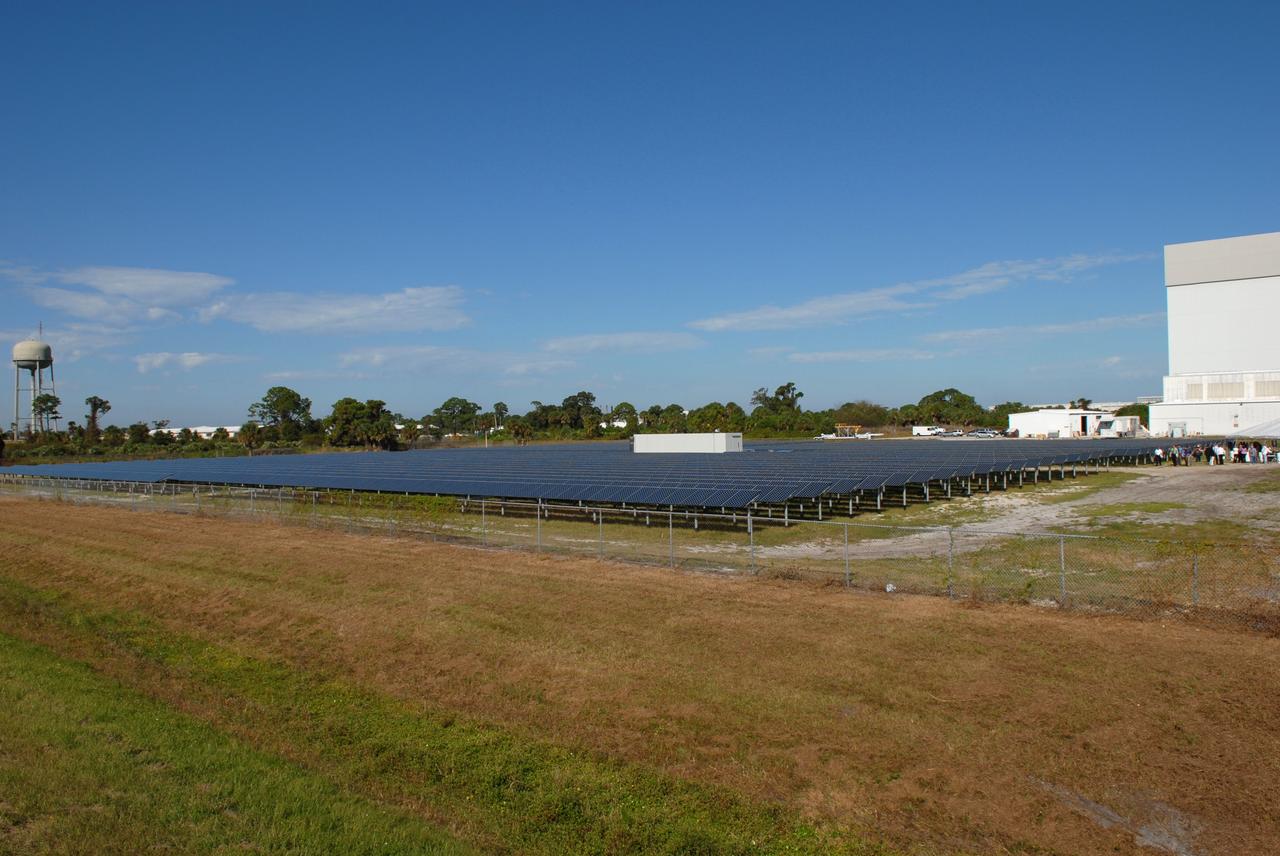

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility is ready for operation at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
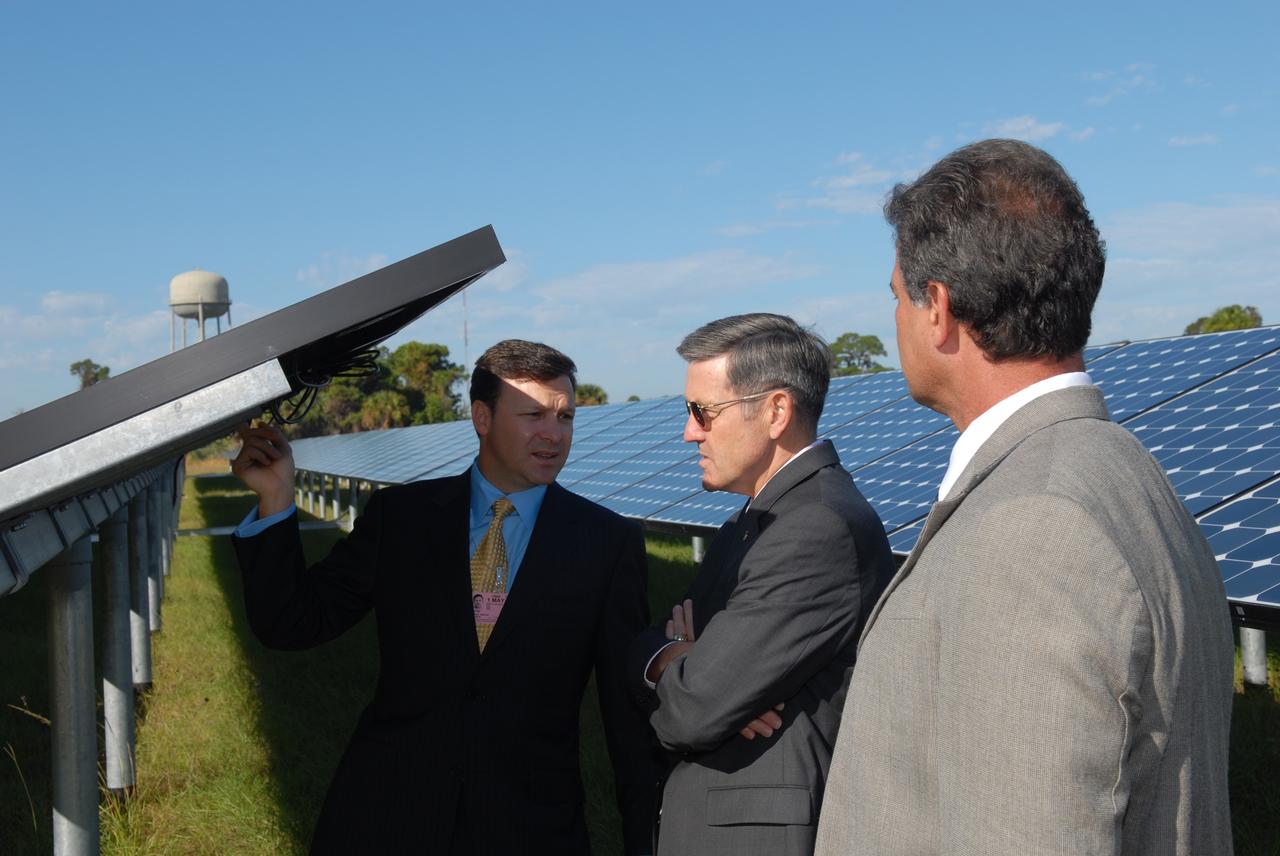

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Florida Power & Light Company Vice President and Chief Development Officer Eric Silagy, left, and NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, center, examine one of the solar panels at the unveiling of NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility at Kennedy in Florida. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
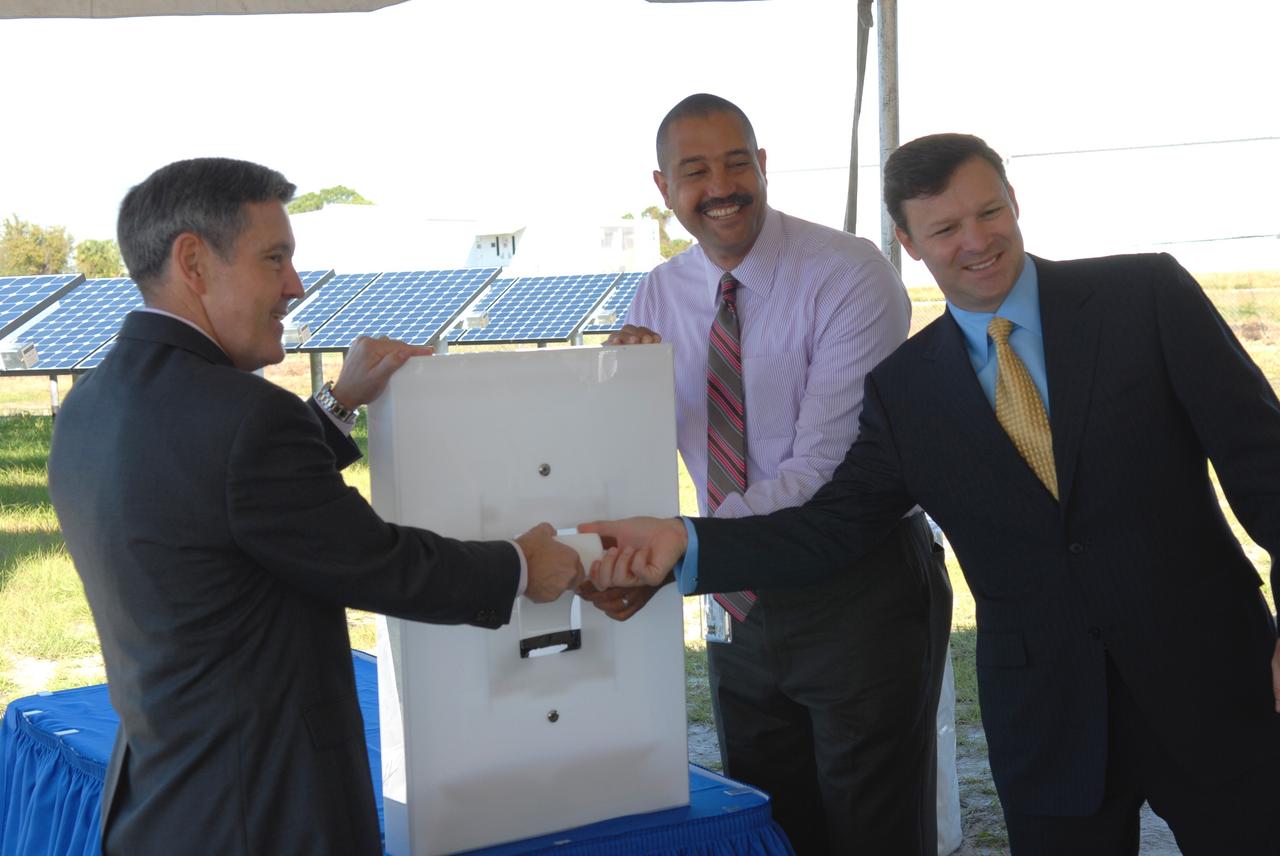

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A ceremonial "flipping of the switch" officially begins operation of NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Flipping the four-foot-tall light switch in unison are, from left, Bob Cabana, Kennedy center director; Roderick Roche, senior manager, Project Management Office of North America, SunPower Corporation; and Eric Silagy, Florida Power & Light Company vice president and chief development officer. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
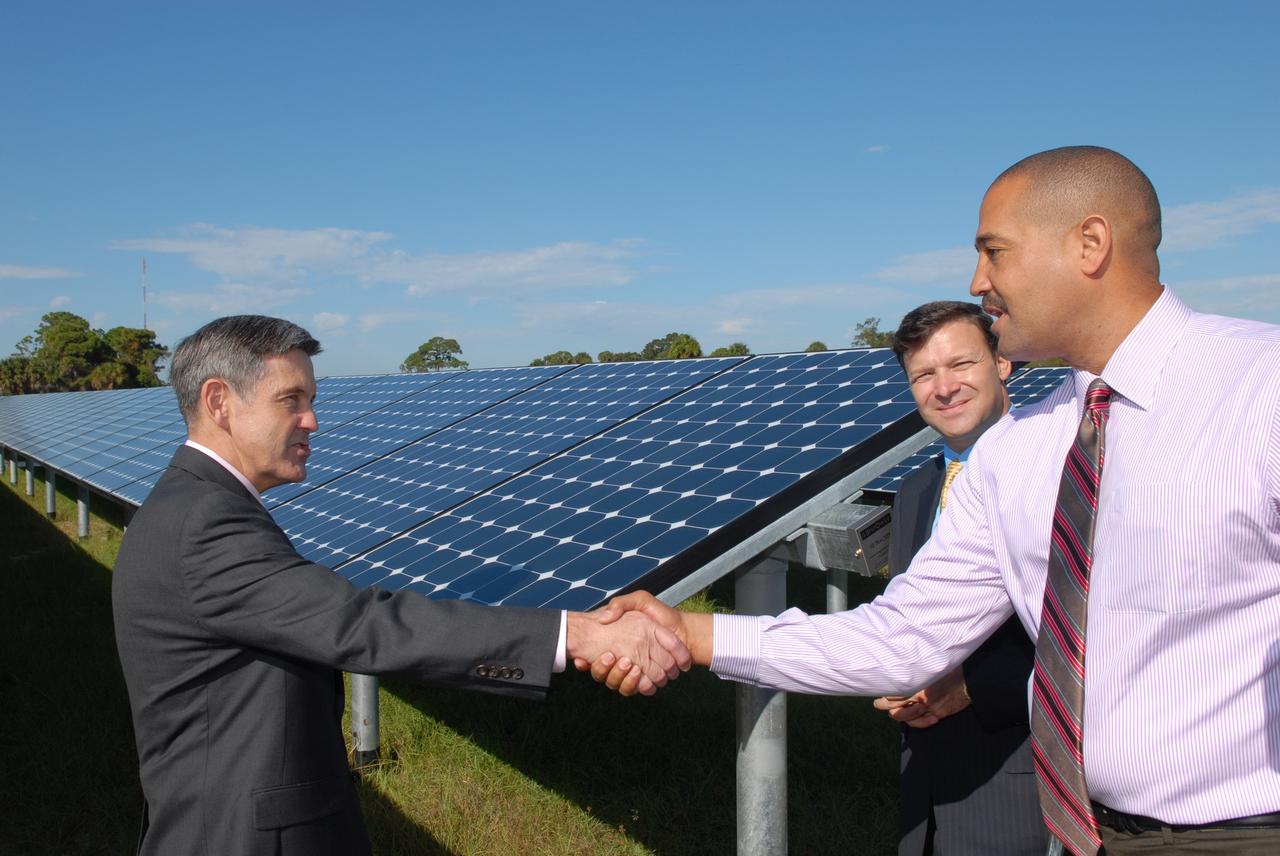

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, left, congratulates Roderick Roche, senior manager, Project Management Office of North America, SunPower Corporation, for his part in the construction of NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility as Eric Silagy, Florida Power & Light Company vice president and chief development officer, looks on. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
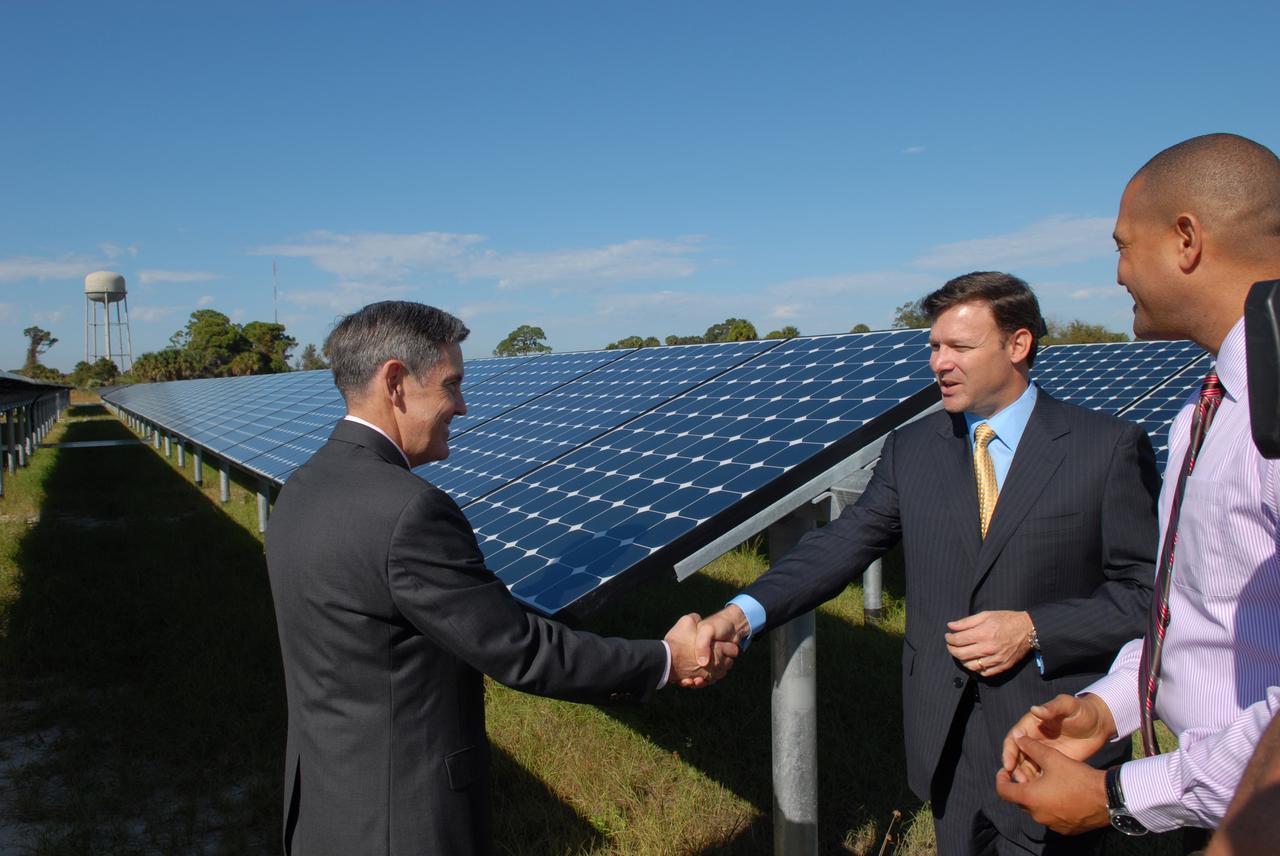

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, left, congratulates, Eric Silagy, Florida Power & Light Company vice president and chief development officer, for his part in the construction of NASA's first large-scale solar power generation facility as Roderick Roche, senior manager, Project Management Office of North America, SunPower Corporation, looks on. Representatives from NASA, Florida Power & Light Company, or FPL, and SunPower Corporation formally commissioned the one-megawatt facility and announced plans to pursue a new research, development and demonstration project at Kennedy to advance America's use of renewable energy. The facility is the first element of a major renewable energy project currently under construction at Kennedy. The completed system features a fixed-tilt, ground-mounted solar power system designed and built by SunPower, along with SunPower solar panels. A 10-megawatt solar farm, which SunPower is building on nearby Kennedy property, will supply power to FPL's customers when it is completed in April 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
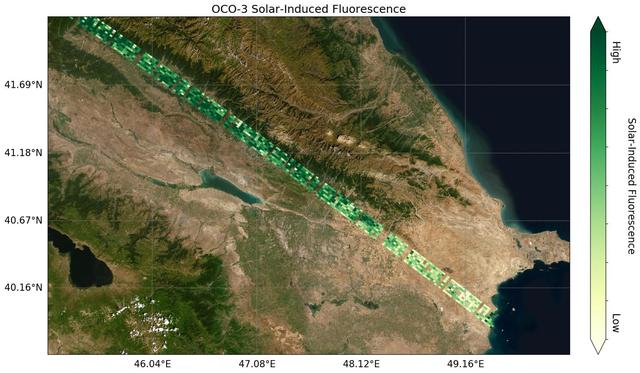
Image shows OCO-3's first preliminary solar-induced fluorescence (SIF) measurements over western Asia. Solar-induced fluorescence is the glow plants emit from photosynthesis — the process of plant growth that includes the capture of carbon from the atmosphere. Areas with lower photosynthesis activity are in shown in light green; areas with higher photosynthesis activity are shown in dark green. As expected, there is significant contrast in plant activity from areas of low vegetation near the Caspian Sea to areas of more dense vegetation like the forests and farms north and east of the Mingachevir Reservoir (near the center of the image). The mission team expects to complete OCO-3's In-orbit checkout phase — the period where they ensure all instruments and components are working and calibrated correctly — in August 2019. They are scheduled to release official CO2 and solar-induced fluorescence data to the science community a year later; however, the data will likely be available sooner given the quality of the measurements that OCO-3 is already making. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23353
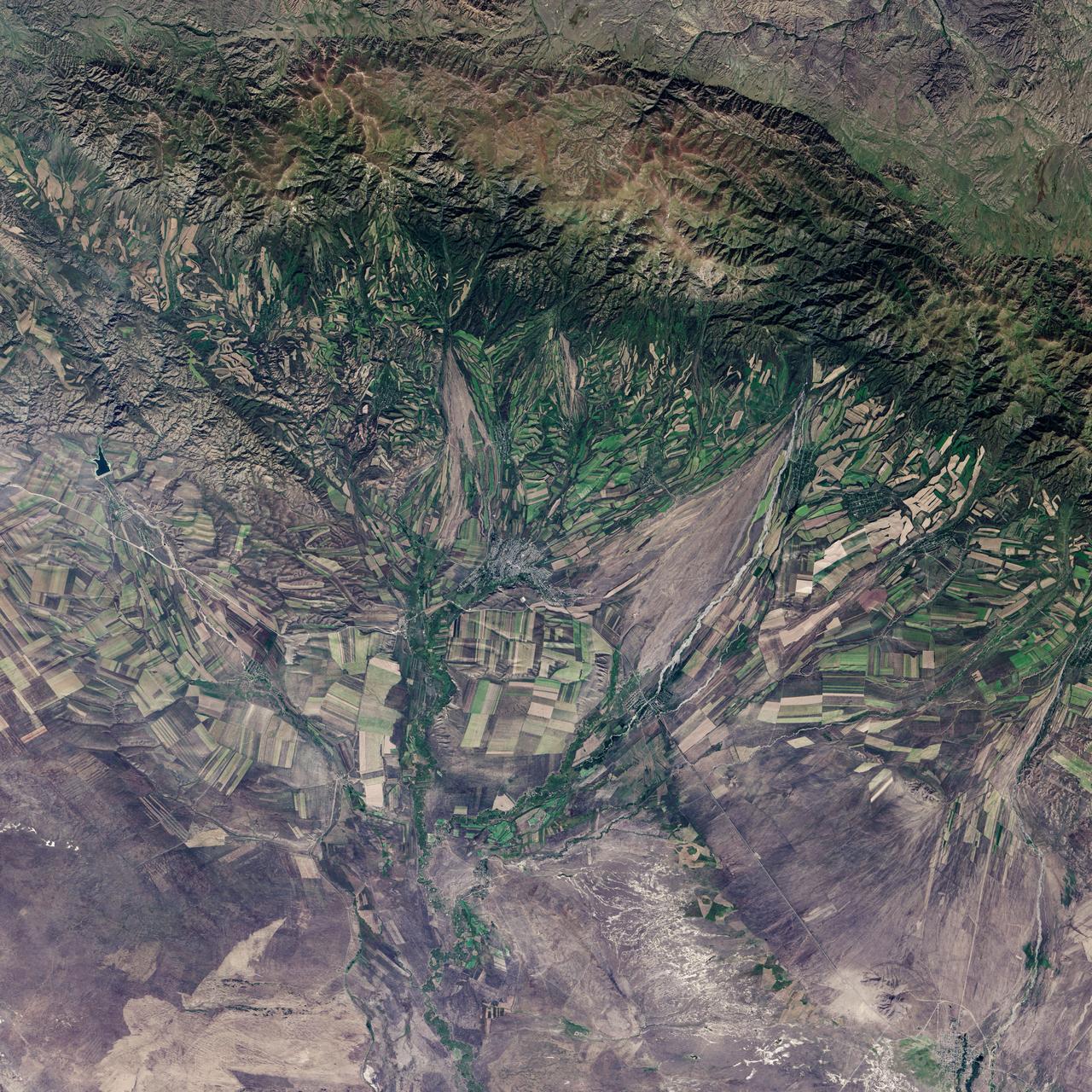

September 22, the autumnal equinox, marks the beginning of fall in the Northern Hemisphere, but the fall harvest begins early in the harsh continental climate of eastern Kazakhstan. By September 9, 2013, when the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on the Landsat 8 satellite acquired this image, several fields were already harvested and bare. Others were dark green with pasture grasses or ripening crops. The fields fill the contours of the land, running long and narrow down mountain valleys and spreading in large squares over the plains. Agriculture is an important segment of the economy in Kazakhstan: the country’s dry climate is ideal for producing high quality wheat for export. However, 61 percent of the country’s agricultural land is pasture for livestock. The area shown in this image, far eastern Kazakhstan near the Chinese border, is a minor wheat-growing region and may also produce sunflowers, barley, and other food crops. An artifact of Soviet-era collective farms, most of the farms in Kazakhstan are large, covering more than 5,000 hectares (12,500 acres). Some of the larger fields in the image reflect the big business side of agriculture. However, family farms and small agriculture businesses account for 35 percent of the country’s agricultural production, and some of these are visible as well, particularly in the uneven hills and mountains. Nearly all agriculture in Kazakhstan is rain fed. Farmers in this region have designed their fields to take advantage of rain flowing down hills, allowing the natural shape of the land to channel water to crops. The effect is a mosaic of green and tan with tones matching the natural vegetation in the mountains to the north. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Caption by Holli Riebeek. Instrument: Landsat 8 - OLI More info: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/16IZ047" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/16IZ047</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
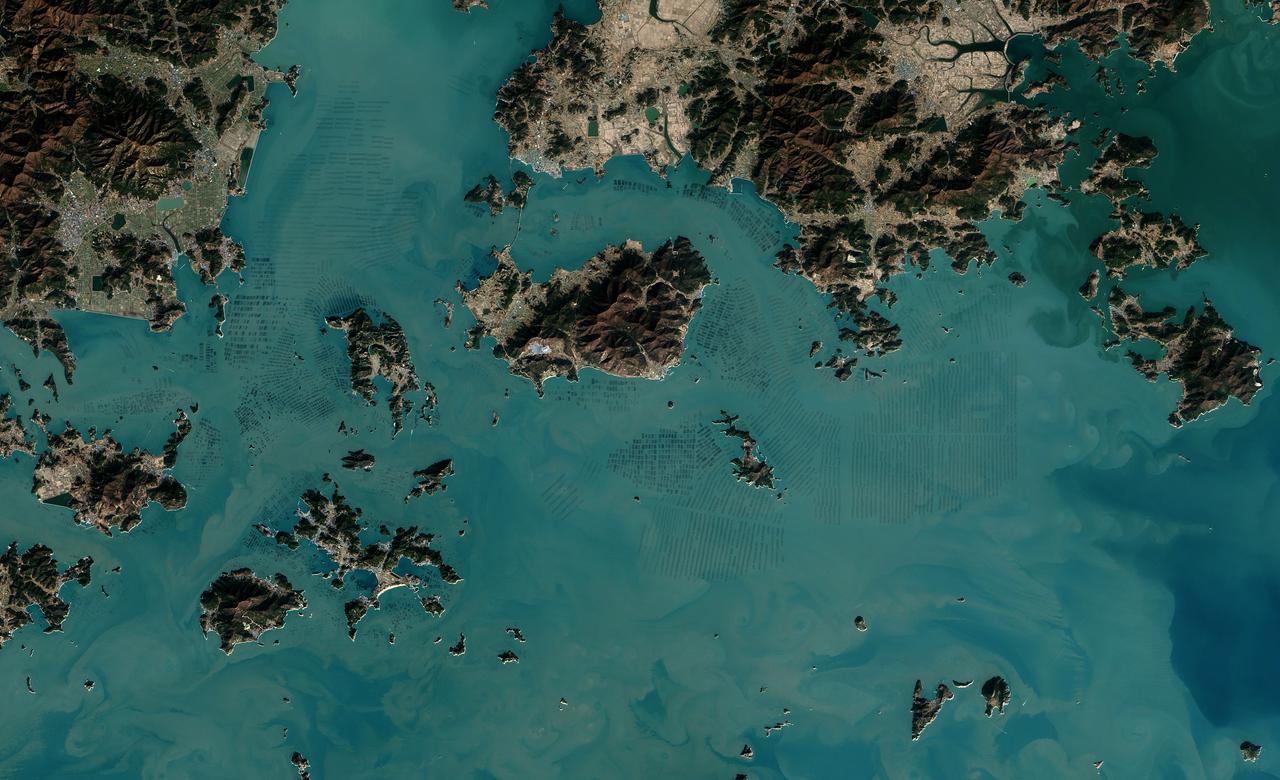

The dark squares that make up the checkerboard pattern in this image are fields of a sort—fields of seaweed. Along the south coast of South Korea, seaweed is often grown on ropes, which are held near the surface with buoys. This technique ensures that the seaweed stays close enough to the surface to get enough light during high tide but doesn’t scrape against the bottom during low tide. The Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 acquired this image of seaweed cultivation in the shallow waters around Sisan Island on January 31, 2014. Home to a thriving aquaculture industry, the south coast of South Korea produces about 90 percent of the country’s seaweed crop. The waters around Sisan are not the only place where aquaculture is common. View the large image to see how ubiquitous seaweed aquaculture is along the coast in Jeollanam-do, the southernmost province on the Korean peninsula. Two main types of seaweed are cultivated in South Korea: Undaria (known as miyeok in Korean, wakame in Japanese) and Pyropia (gim in Korean, nori in Japanese). Both types are used generously in traditional Korean, Japanese, and Chinese food. Since 1970, farmed seaweed production has increased by approximately 8 percent per year. Today, about 90 percent of all the seaweed that humans consume globally is farmed. That may be good for the environment. In comparison to other types of food production, seaweed farming has a light environmental footprint because it does not require fresh water or fertilizer. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Caption by Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
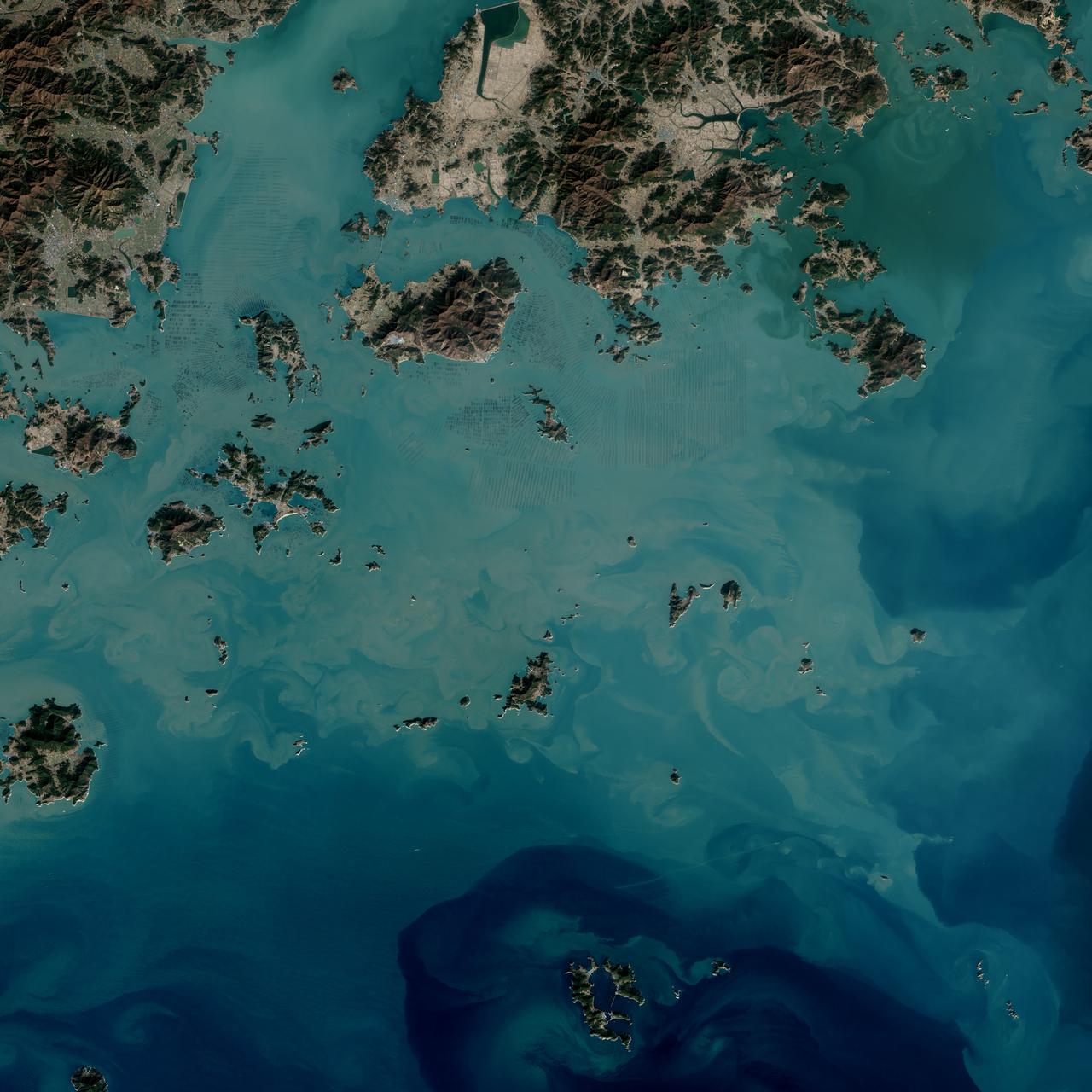

The dark squares that make up the checkerboard pattern in this image are fields of a sort—fields of seaweed. Along the south coast of South Korea, seaweed is often grown on ropes, which are held near the surface with buoys. This technique ensures that the seaweed stays close enough to the surface to get enough light during high tide but doesn’t scrape against the bottom during low tide. The Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 acquired this image of seaweed cultivation in the shallow waters around Sisan Island on January 31, 2014. Home to a thriving aquaculture industry, the south coast of South Korea produces about 90 percent of the country’s seaweed crop. The waters around Sisan are not the only place where aquaculture is common. View the large image to see how ubiquitous seaweed aquaculture is along the coast in Jeollanam-do, the southernmost province on the Korean peninsula. Two main types of seaweed are cultivated in South Korea: Undaria (known as miyeok in Korean, wakame in Japanese) and Pyropia (gim in Korean, nori in Japanese). Both types are used generously in traditional Korean, Japanese, and Chinese food. Since 1970, farmed seaweed production has increased by approximately 8 percent per year. Today, about 90 percent of all the seaweed that humans consume globally is farmed. That may be good for the environment. In comparison to other types of food production, seaweed farming has a light environmental footprint because it does not require fresh water or fertilizer. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Caption by Adam Voiland. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
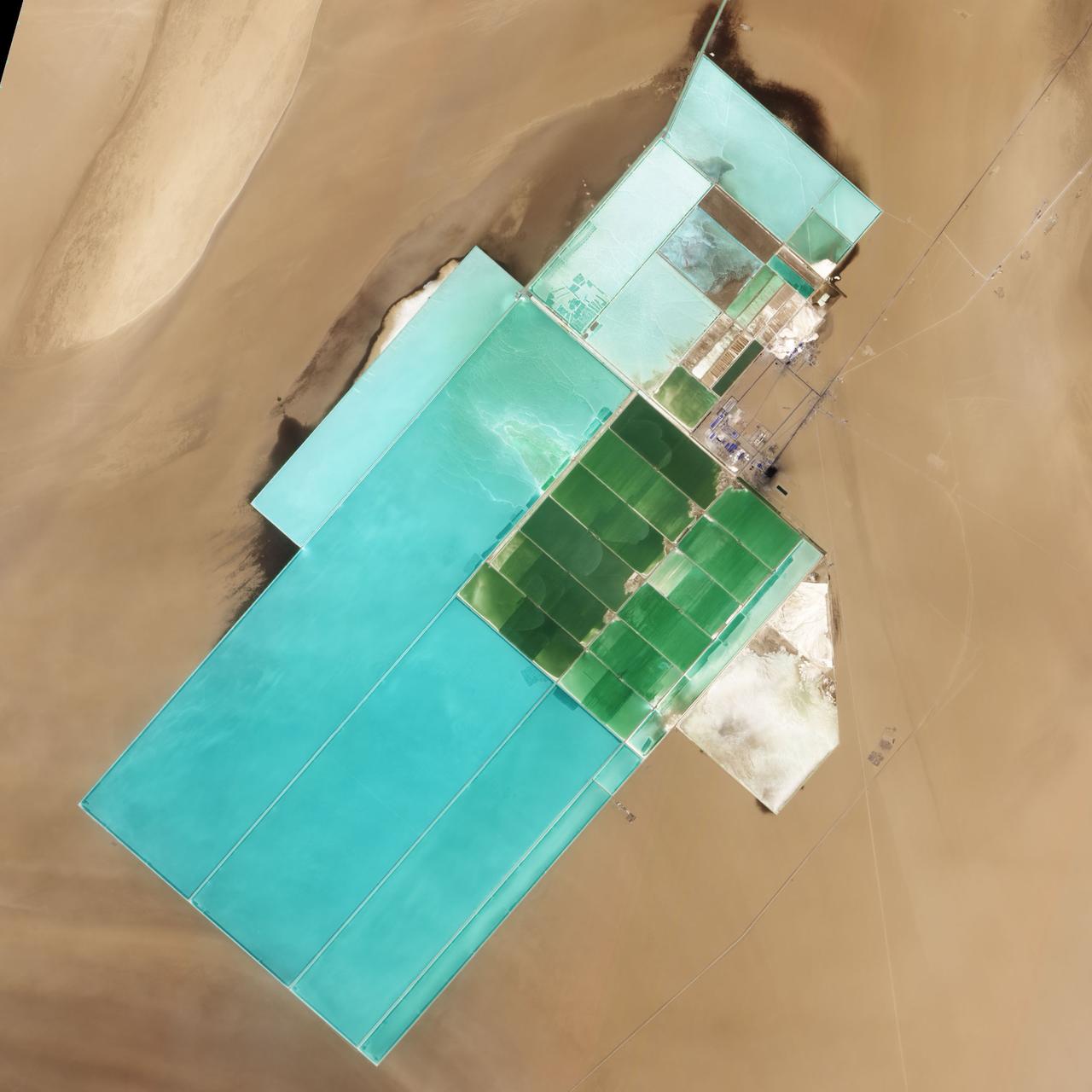

NASA image acquired May 17, 2011 Located in China’s resource-rich but moisture-poor Xinjiang autonomous region, Lop Nur is an uninviting location for any kind of agriculture. It sits at the eastern end of the Taklimakan Desert, where marching sand dunes can reach heights of 200 meters (650 feet), and dust storms rage across the landscape. Yet for all it lacks in agricultural appeal, Lop Nur offers something valuable to farmers the world over: potash. This potassium salt provides a major nutrient required for plant growth, making it a key ingredient in fertilizer. The discovery of potash at Lop Nur in the mid-1990s turned the area into a large-scale mining operation. The Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite captured this natural-color image of Lop Nur on May 17, 2011. The rectangular shapes in this image show the bright colors characteristic of solar evaporation ponds. Around the evaporation ponds are the earth tones typical of sandy desert. During the early and middle Pleistocene epoch, this area held a large brackish lake. Uplift of the northern part of the lake in the late Pleistocene created hollows that became receptacles for potash deposition. The main potash deposits found at Lop Nur today are brine potash, and this site is the second-largest source of potash in China. Lop Nur slowly dried up in the Holocene. The area now receives average annual precipitation of just 31.2 millimeters (1.2 inches), and experiences annual evaporation of 2,901 millimeters (114 inches), according to a study published in 2008. The study found, however, that this area has experienced seven major climate changes since the end of the Pleistocene, including climatic conditions far more favorable to farming and settlement than today. Examination of plant and mollusk remains at the lake, as well as studies of sediments, indicate that the Lop Nur region experienced a severe drought about 3,000 years ago, followed by wetter conditions. Between 1,250 and 400 years ago, Lop Nur likely experienced the conditions most favorable to farming and settlement, and red willow trees grew in the area. Pottery dating from the Tang and Song dynasties further testifies to welcoming conditions at the lake centuries ago. Starting around 400 years ago, however, a more arid climate took hold, completely drying out Lop Nur. Today, by providing potash, the desiccated lake still supports agriculture, but it does so for farming efforts further afield. NASA Earth Observatory image created by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: EO-1 - ALI Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://web.stagram.com/n/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
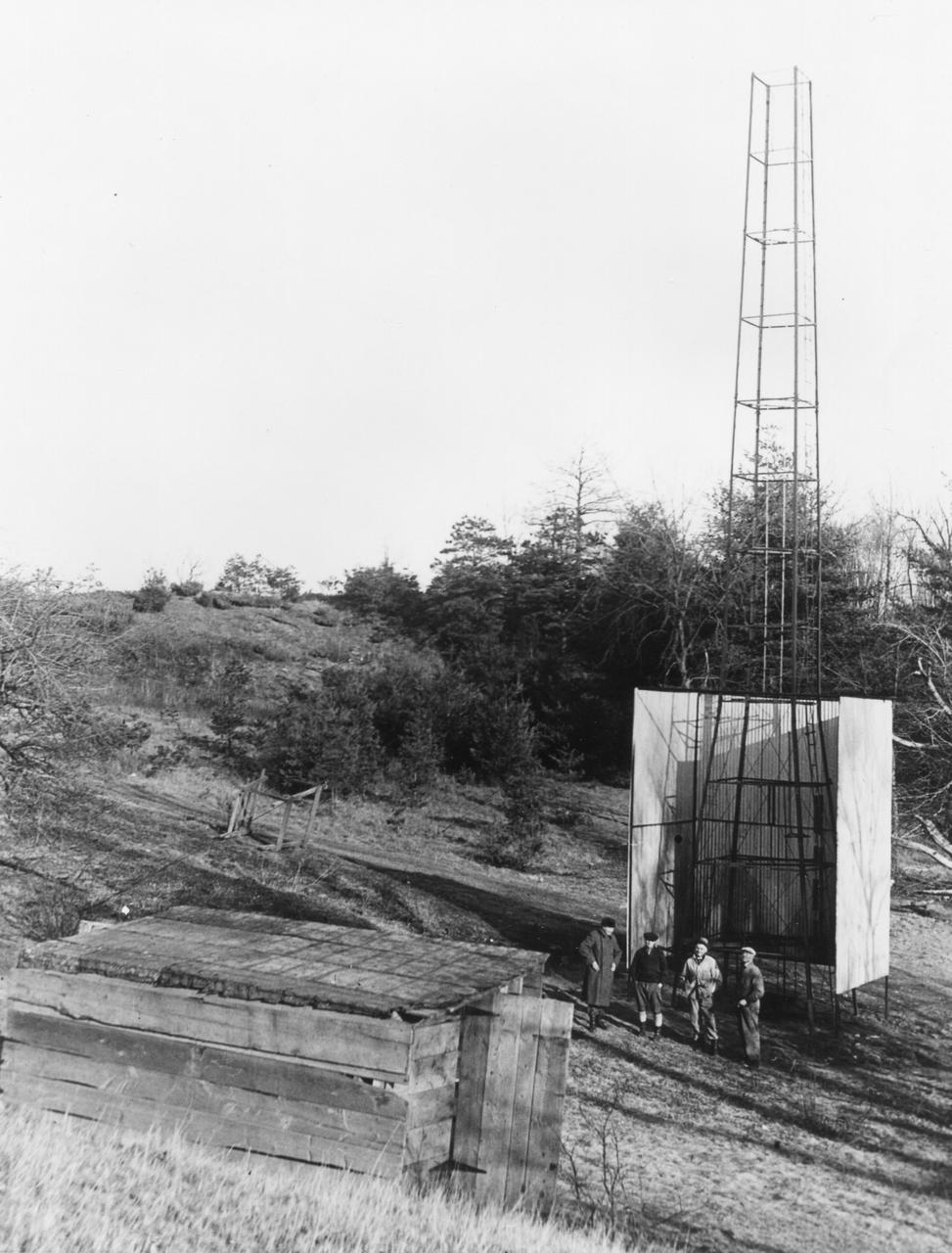

Dr. Robert H. Goddard's tower and shelter at the Army artillery range at Camp Devens, in Ayer, Massachusetts in the winter of 1929-1930. Goddard originally began testing rockets on his aunt's farm in Auburn, Massachusetts until the local police, fire department and townspeople became concerned about the noise and menace to the public the rockets created. Although Goddard maintained that the rockets were not a danger, he soon moved to Camp Devens, Massachusetts. There he was able to launch the rockets without attracting attention. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
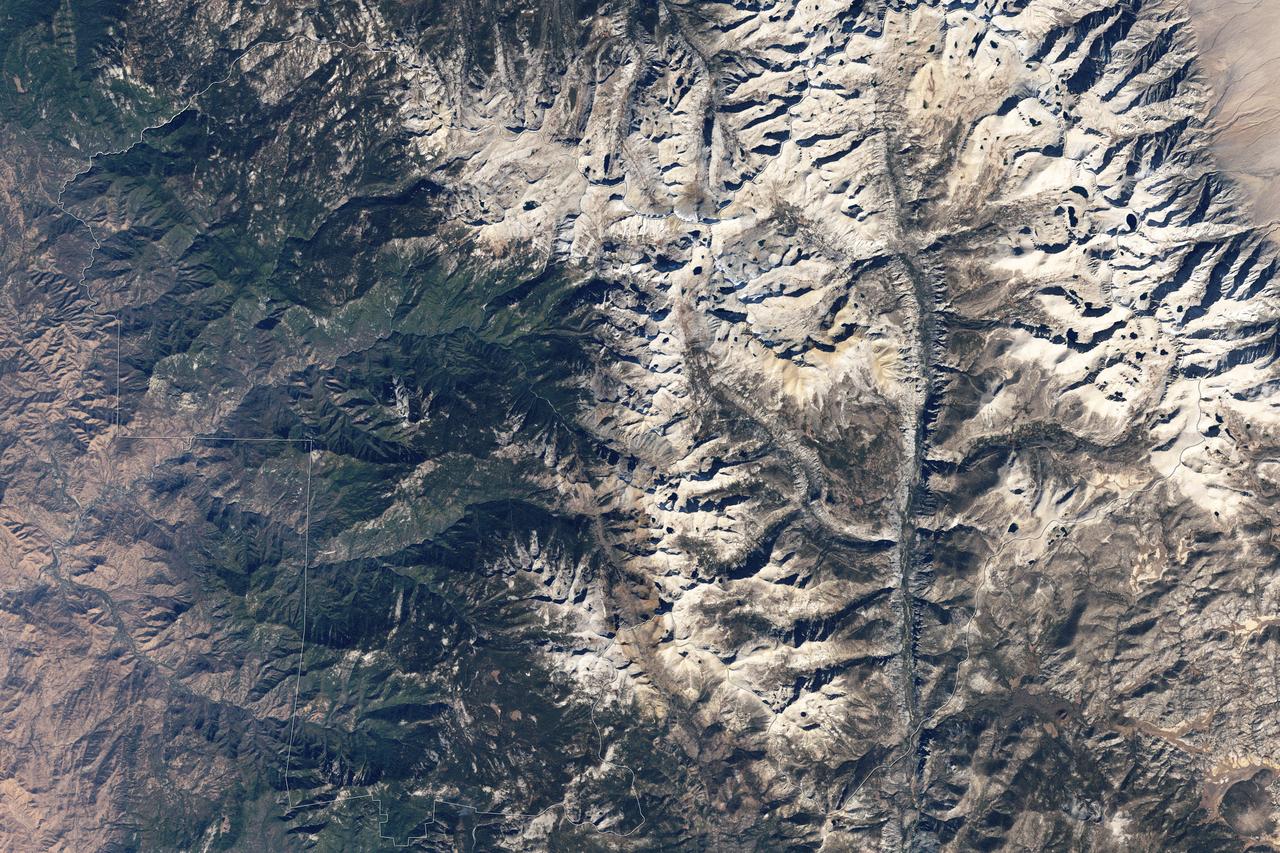

Naked peaks, sheltered valleys, snowfields, towering trees, and alpine meadows make up the varied landscape of Sequoia National Park in California. Established as a National Park by Congress on September 25, 1890, Sequoia National Park is the second-oldest U.S. National Park, after Yellowstone. This national park borders Kings Canyon National Park. The Thematic Mapper sensor on NASA’s Landsat 5 satellite captured this true-color image of Sequoia National Park, outlined in white, on October 22, 2008. Sunlight illuminates southern slopes, leaving northern faces in shadow in this autumn image. In the west, deep green conifers carpet most of the land. These forested mountains are home to the park’s most famous giant sequoia trees. Sequoia National Park sits at the southern end of the Sierra Nevada mountains. Terrain alternates between extremes, from peaks such as Mt. Whitney—the highest peak in the contiguous United States—to deep caverns. The rivers and lakes in this region are part of a watershed valuable not only to the plants and animals of the park, but also to farms and cities in California’s Central Valley. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2bzGOXr" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2bzGOXr</a> Credit: NASA/Landsat5 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Over the last 25 years, Chandler, Arizona has traded its grid of fields for a grid of streets. Founded in 1912 on cotton, grains, alfalfa, and ostrich farms, brown and green irrigated fields still dominate the region southeast of Phoenix in this 1985 natural color image taken by Landsat 5. By 2011, the blue gray city streets in this Landsat 5 image have taken over. Chandler's economy has shifted from agriculture to manufacturing and electronics, and its population boomed from 30,000 people in 1980 to 236,000 in 2010. ---- Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
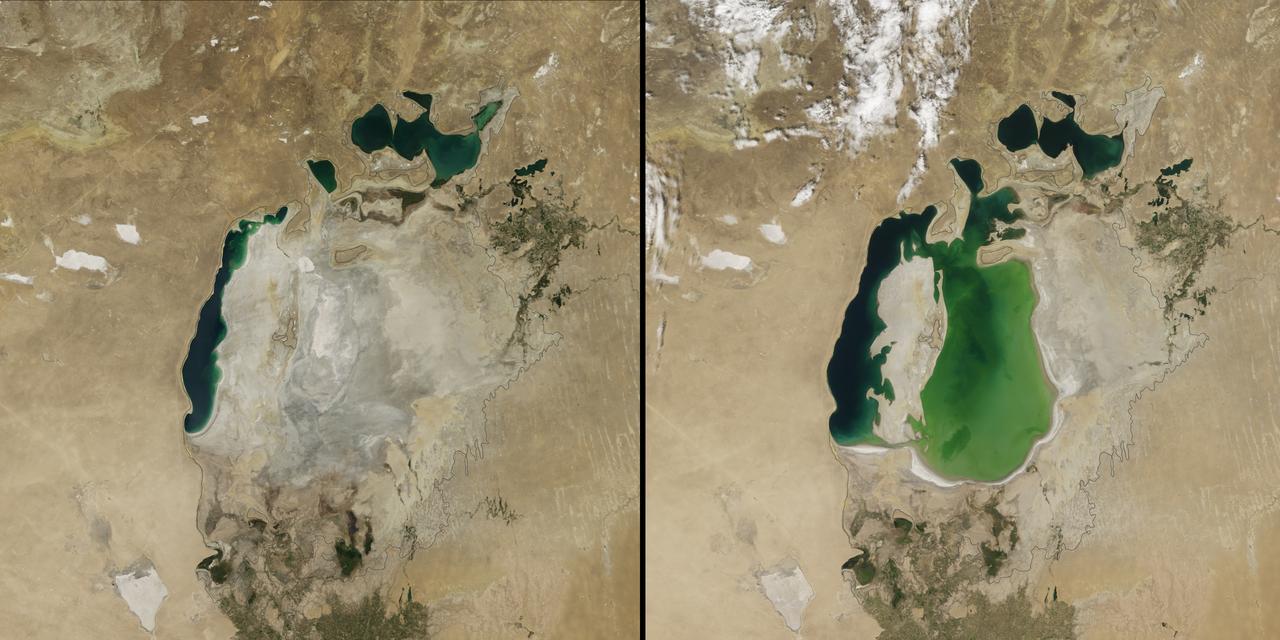

(Aral Sea: left 2014 and right 2000, 1960 extent black line) In the 1960s, the Soviet Union undertook a major water diversion project on the arid plains of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. The region’s two major rivers, fed by snowmelt and precipitation in faraway mountains, were used to transform the desert into farms for cotton and other crops. Before the project, the Syr Darya and the Amu Darya rivers flowed down from the mountains, cut northwest through the Kyzylkum Desert, and finally pooled together in the lowest part of the basin. The lake they made, the Aral Sea, was once the fourth largest in the world. Although irrigation made the desert bloom, it devastated the Aral Sea. This series of images from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite documents the changes. At the start of the series in 2000, the lake was already a fraction of its 1960 extent (black line). The Northern Aral Sea (sometimes called the Small Aral Sea) had separated from the Southern (Large) Aral Sea. The Southern Aral Sea had split into eastern and western lobes that remained tenuously connected at both ends. By 2001, the southern connection had been severed, and the shallower eastern part retreated rapidly over the next several years. Especially large retreats in the eastern lobe of the Southern Sea appear to have occurred between 2005 and 2009, when drought limited and then cut off the flow of the Amu Darya. Water levels then fluctuated annually between 2009 and 2014 in alternately dry and wet years. Dry conditions in 2014 caused the Southern Sea’s eastern lobe to completely dry up for the first time in modern times. Continue reading: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1nLX9Ku" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1nLX9Ku</a> Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1pqEnDj" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1pqEnDj</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
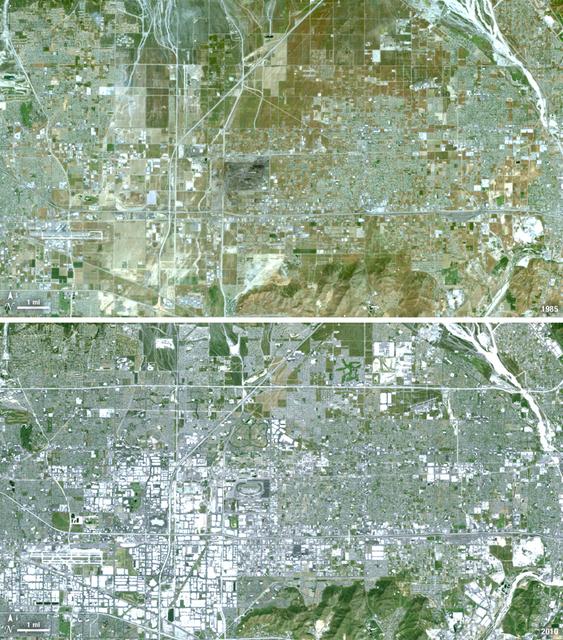
Thirty-five miles due east of downtown Los Angeles lies the city of Ontario, California. In 1881 two Canadian brothers established the town, naming it after their native city. By 1891 Ontario, Calif., was incorporated as a city. The farming-based economy (olives, citrus, dairy) of the city helped it grow to 20,000 by the 1960s. Subsequently, warehousing and freight trafficking took over as the major industry and the city’s population was over 160,000 by 2010. The L.A./Ontario International Airport is now America’s 15th busiest cargo airport. In these natural color Landsat 5 images, the massive growth of the city between 1985 and 2010 can be seen. The airport, found in the southwest portion of the images, added a number of runways and large warehousing structures now dominate the once rural areas surrounding the airport. In these images vegetation is green and brown and urban structures are bright white and gray. (Note there is a large dry riverbed in the northeast corner that is also bright white, but its nonlinear appearance sets it apart visually). ---- NASA and the U.S. Department of the Interior through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) jointly manage Landsat, and the USGS preserves a 40-year archive of Landsat images that is freely available over the Internet. The next Landsat satellite, now known as the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) and later to be called Landsat 8, is scheduled for launch in 2013. In honor of Landsat’s 40th anniversary in July 2012, the USGS released the LandsatLook viewer – a quick, simple way to go forward and backward in time, pulling images of anywhere in the world out of the Landsat archive. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
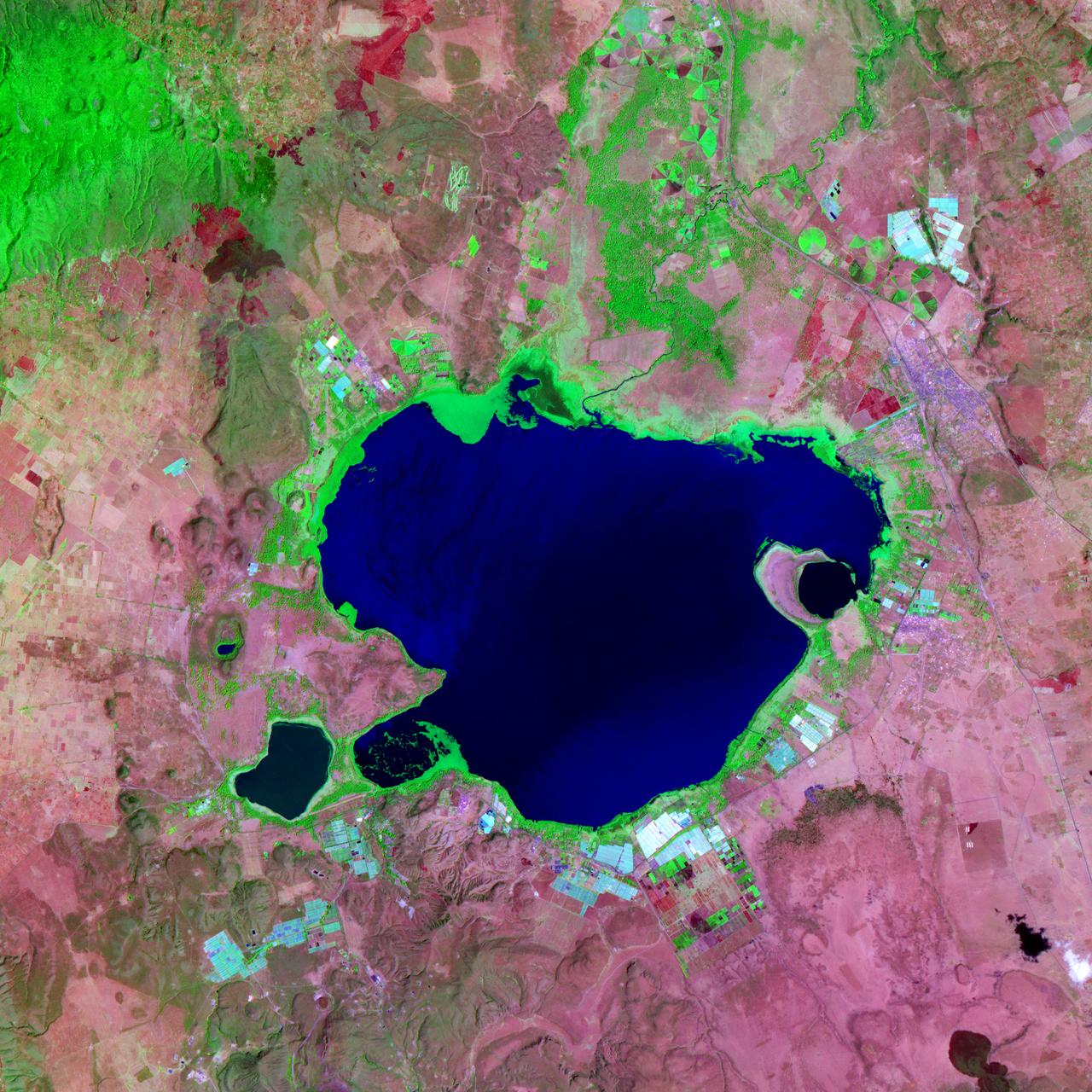

NASA satellite image acquired February 2, 2008. Outside the ground is frozen, quite possibly covered in snow and ice, and yet, stroll through a supermarket in North America or Europe in February, and you’ll be confronted with large displays of roses. We expect flowers in winter, and equatorial countries meet those expectations. A quarter of the cut flowers sold in Europe are grown in Kenya. Straddling the equator, Kenya gets steady sunlight dealt out in days that vary little in length. It’s the perfect climate for flowers year-round. The center of Kenya’s flower industry is Lake Naivasha, shown here. The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) flying on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this image of Lake Naivasha on February 2, 2008. Bright white squares mix with fields of green, tan, and purple along the shores of the lake. Sunlight glints off the long rows of glass greenhouses, turning them silvery blue and white in this view from space. Fallow fields are tan and pink, while growing plants turn the ground bright green. Roses, lilies, and carnations are the most common flowers grown in the greenhouses and fields scattered around the lake. The large-scale industry shown here extends into small-scale rural farms elsewhere in Kenya, where smaller filler flowers are grown. The flowers provide an important source of income to Kenya, but the industry comes with a price. Flowers are not held to the same standards for chemical residues as food products, which are tightly regulated. Strong chemical pesticides can be used on the flowers to produce the perfect, pest-free bloom, and this could pose a health risk to workers and local wildlife, including hippos, environmental groups told the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations in 2002. The chemicals may also have threatened the water quality of Lake Naivasha, one of Kenya’s few freshwater lakes. The Kenya Flower Council instituted a code of conduct establishing guidelines for pesticide that phases out the use of one of the most toxic pesticides. NASA image created by Jesse Allen, using data provided courtesy of NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team. Caption by Holli Riebeek. Instrument: Terra - ASTER <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
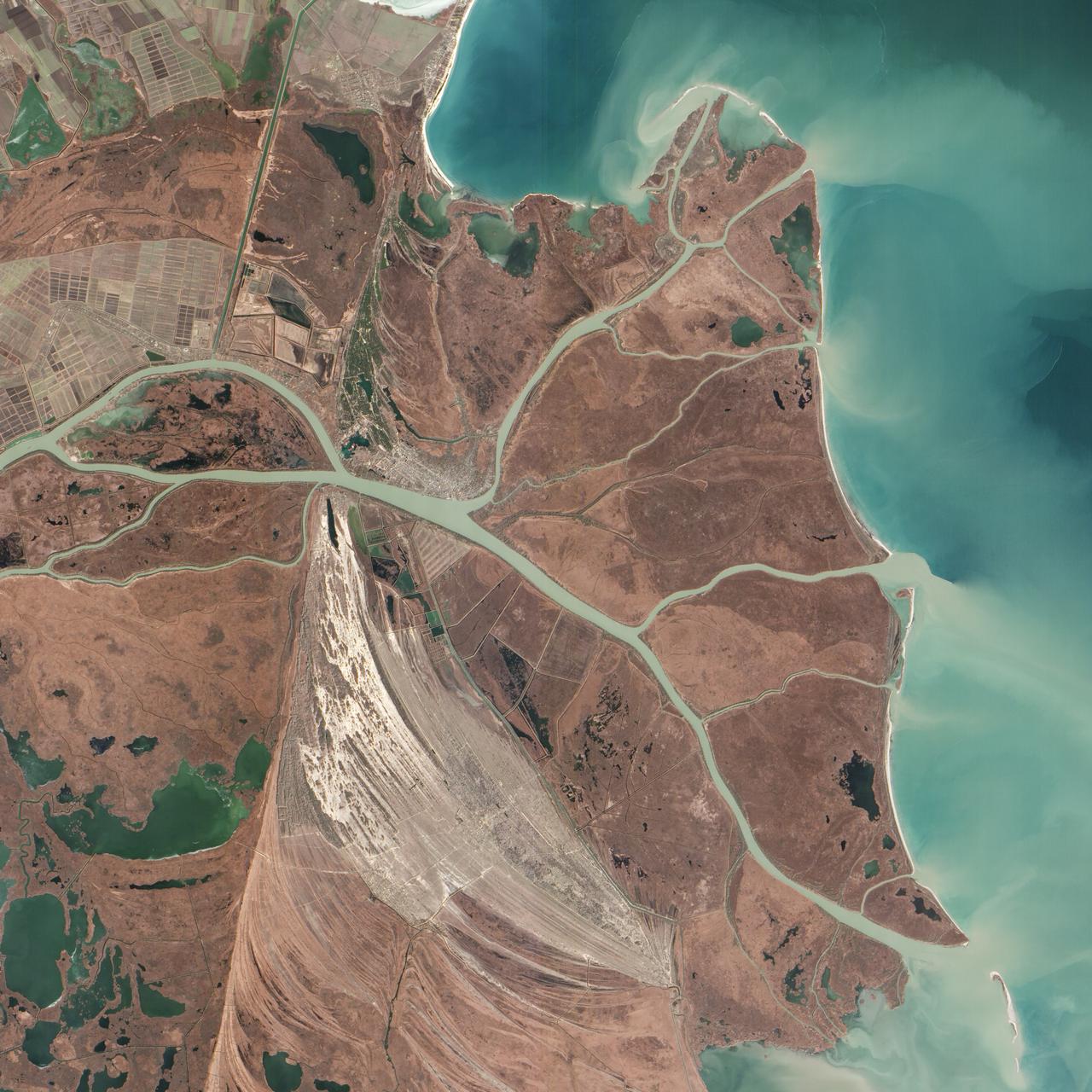

Acquired February 5, 2013 The Danube River is the largest in the European Union, its watershed draining 801,463 square kilometers (309,447 square miles) of land across 19 countries. Where that great river reaches the Black Sea, a remarkable delta has formed—the “Everglades” of Europe. The Danube Delta is home to more than 300 species of bird and 45 species of freshwater fish. The Danube Delta has been home to human settlements since the end of the Stone Age (the Neolithic Period), and the ancient Greeks, Romans, and Byzantines all built trading ports and military outposts along this coast. Today, the border between Romania and Ukraine cuts through the northern part of the delta. The area is a United Nations World Heritage Site, both for its natural and human history, and for the traditional maritime culture that persists in its marshes. All the while, the landscape has been shaped and re-shaped by nature and man. The image above was acquired on February 5, 2013, by the Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite. The Danube Delta has a number of lobes formed over the past several thousand years, and this image is focused largely on the northernmost Chilia (or Kilia) lobe. It is the youngest section of the delta—somewhere between 300 to 400 years old—and lies mostly within Ukraine. Much of the land in the image above is officially considered part of the Danube Biosphere Reserve. Near the center of the image, the small city of Vylkove is known as the “Ukranian Venice,” due to its canals. To the lower left, the older Sulina lobe of the delta stretches to the south and further inland into Romania. White and brown curved lines reveal beach ridges and former shorelines, with the whiter ridges composed almost entirely of pure quartz sand in high dunes. To the east of the ridges, most of the landscape is flat marshland that is mostly brown in the barren days of winter. The Bystroye Canal through the center of the Chilia lobe has been the subject of heated debate over the past two decades. Over the centuries, damming and channeling of the Danube throughout Europe has reduced its water flow and sediment load to roughly 30 percent of what it once was, according to coastal geologist Liviu Giosan of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. In recent years, the Ukrainian government has dredged some delta channels (including Bystroye) and proposed extensive dredging of others in order to provide navigational channels for large ships. Proponents argue for the economic needs of water transportation routes. Opponents note that deeper, faster channels mean less mud and sand is deposited in the delta; in some places, more is carried away by swifter currents. Both affect the sensitive ecosystems and the ability of the delta to restore itself and grow. In a 2012 report led by Giosan, scientists noted that the shape, water chemistry, and biology of Danube Delta was being altered long before the modern Industrial Era. Land use practices—particularly farming and forest clearing—added significant amounts of nutrients into the water and reduced salinity in the Black Sea, changing the dominant species of phytoplankton and sending a ripple of effects through the entire food web. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team and the U.S. Geological Survey. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Instrument: EO-1 - ALI More info: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=80459" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=80459</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>