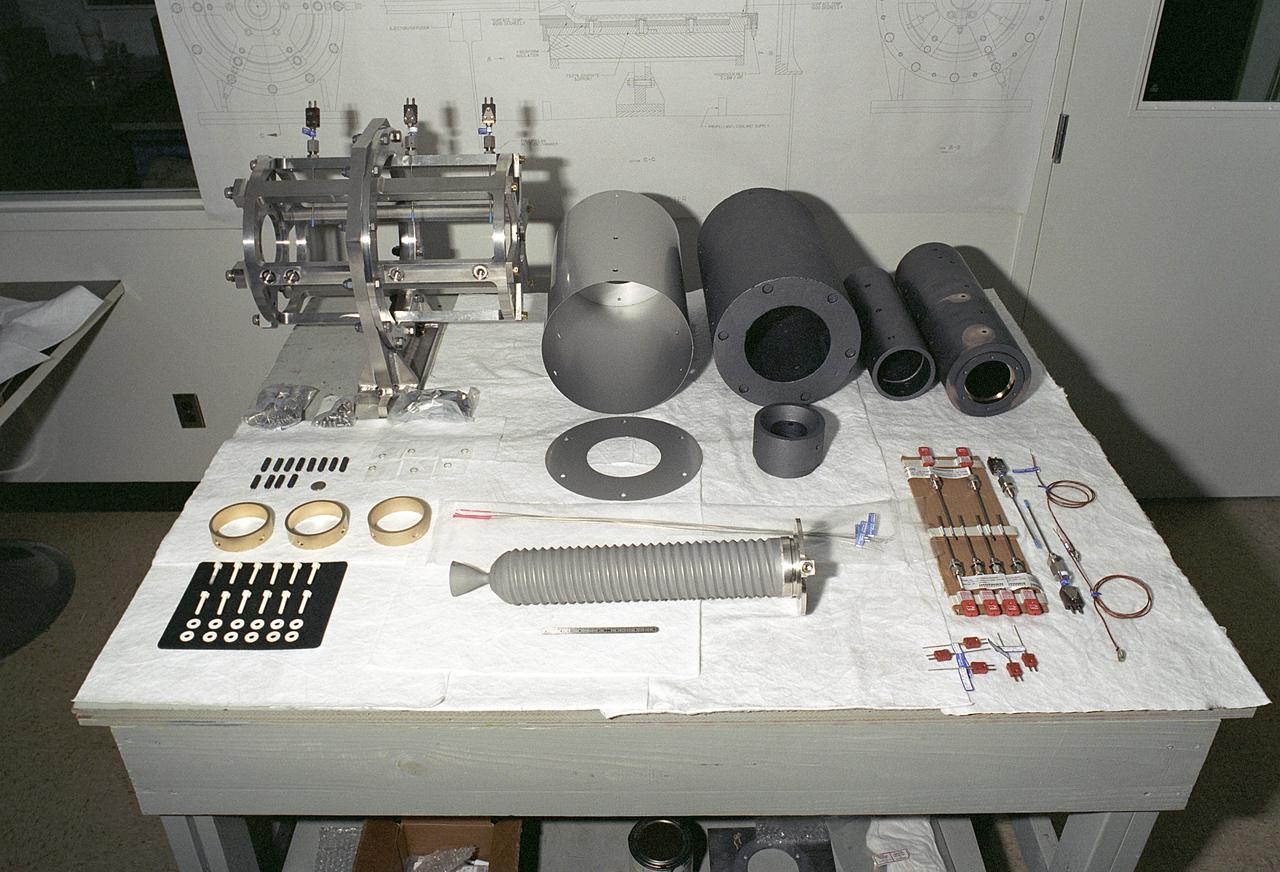

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. This photograph shows components for the thermal propulsion engine being laid out prior to assembly. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth-orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
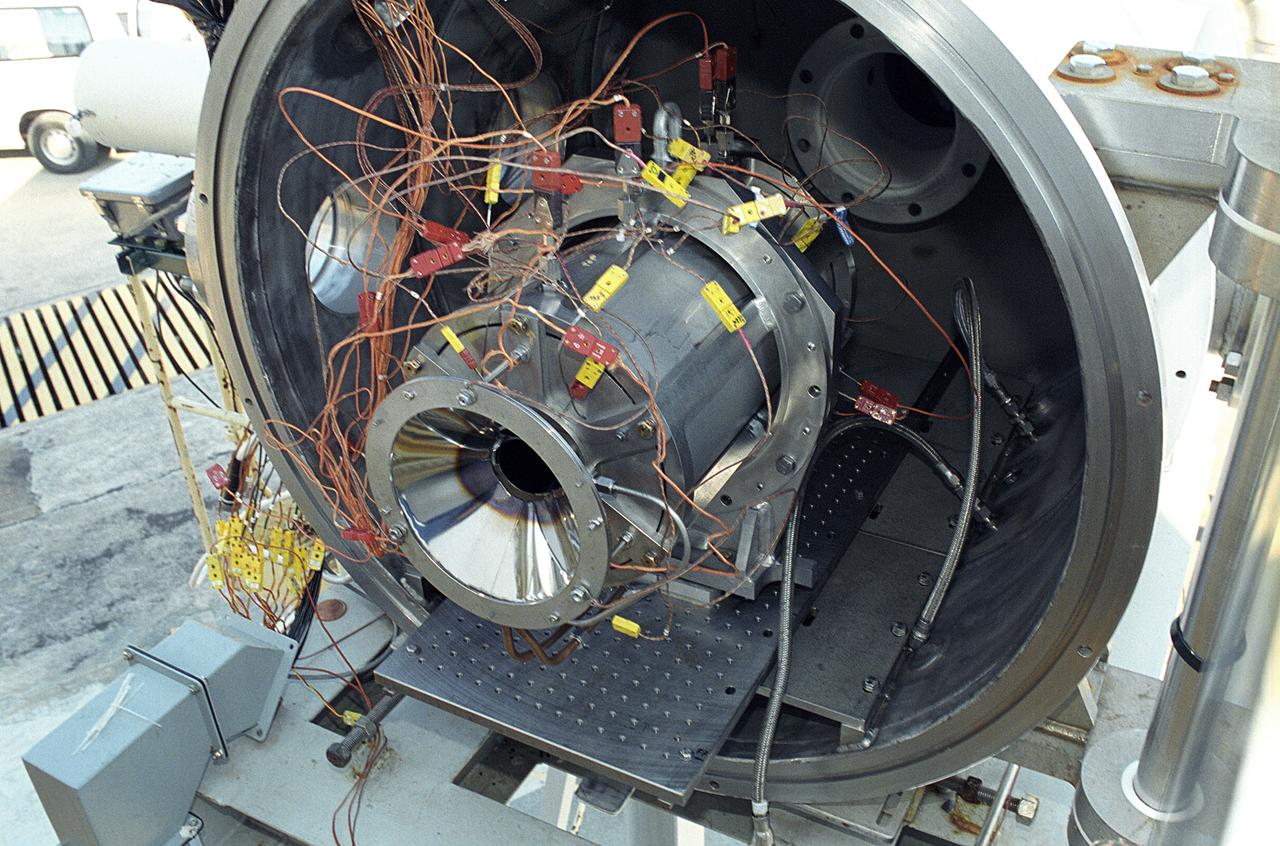

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. This photograph shows a fully assembled solar thermal engine placed inside the vacuum chamber at the test facility prior to testing. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has a dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on the 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move theNation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.

The Direct Gain Solar Thermal Engine was designed with no moving parts. The concept of Solar Thermal Propulsion Research uses focused solar energy from an inflatable concentrator (a giant magnifying glass) to heat a propellant (hydrogen) and allows thermal expansion through the nozzle for low thrust without chemical combustion. Energy limitations and propellant weight associated with traditional combustion engines are non-existant with this concept. The Direct Gain Solar Thermal Engine would be used for moving from a lower orbit to an upper synchronous orbit.

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on an 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. This photograph is a close-up view of a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber at the MSFC Solar Thermal Propulsion Test facility. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. This photograph, taken at MSFC's Solar Thermal Propulsion Test Facility, shows a concentrator mirror, a combination of 144 mirrors forming this 18-ft diameter concentrator, and a vacuum chamber that houses the focal point. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has a dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on the 18-foot diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth-orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
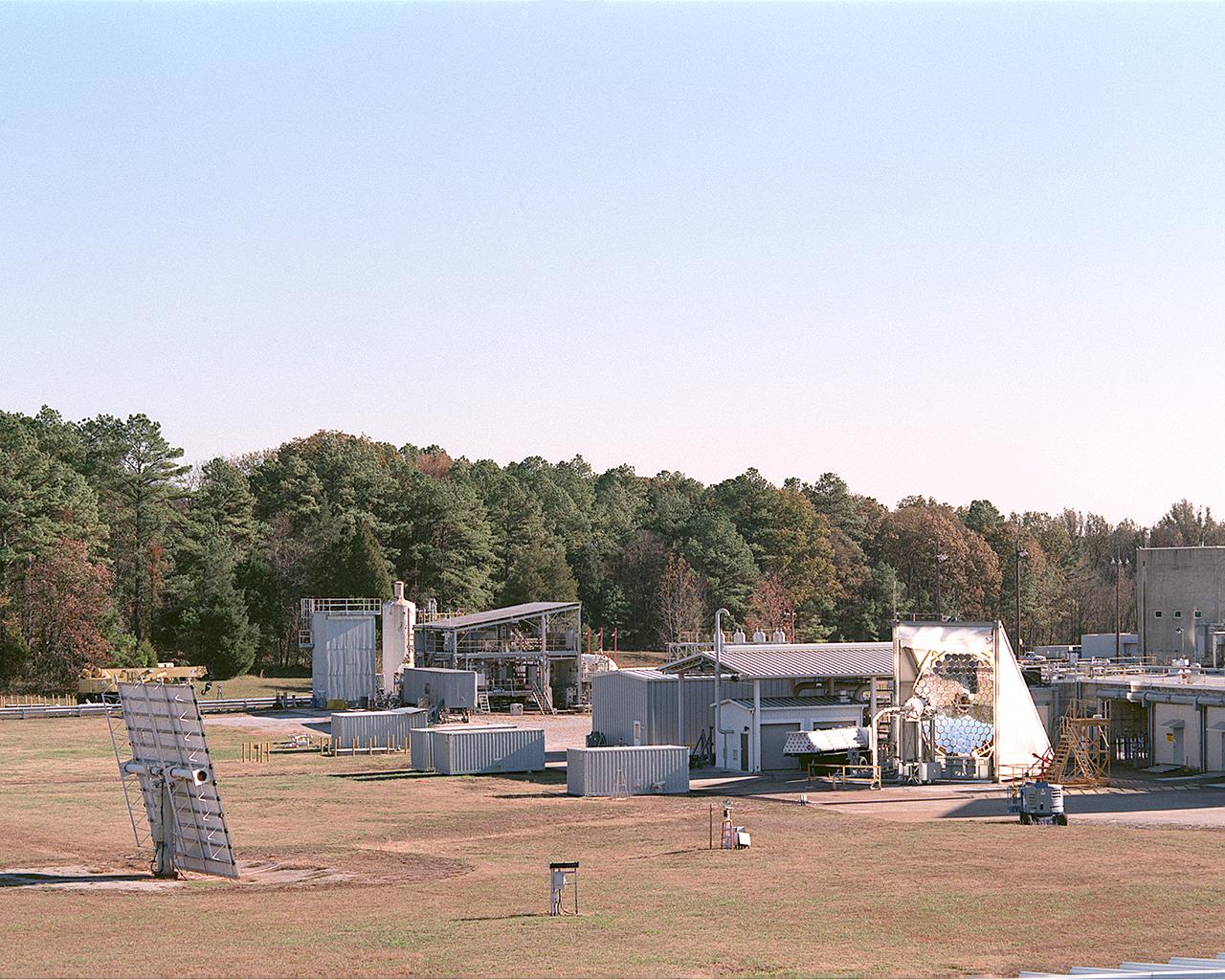

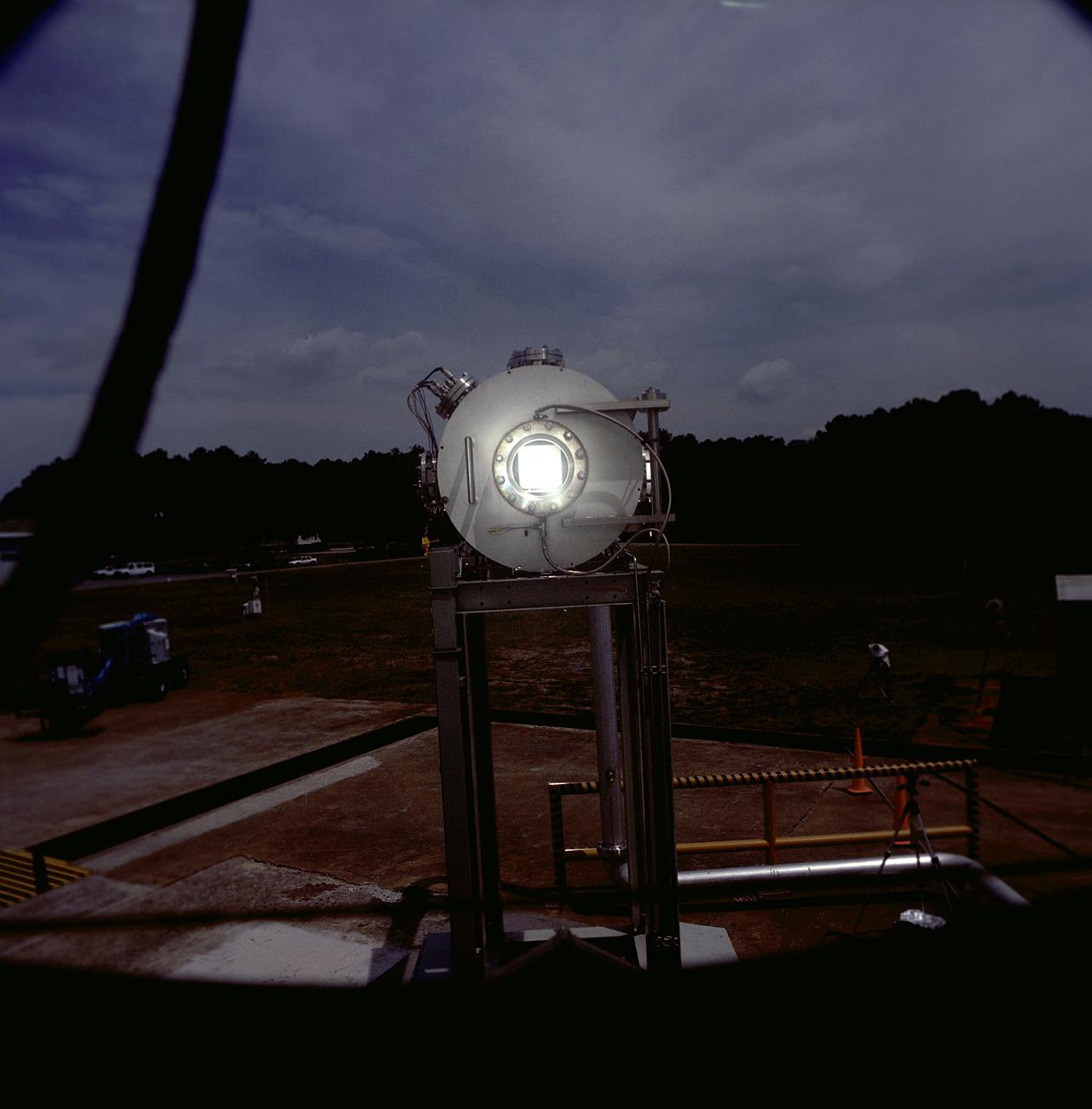
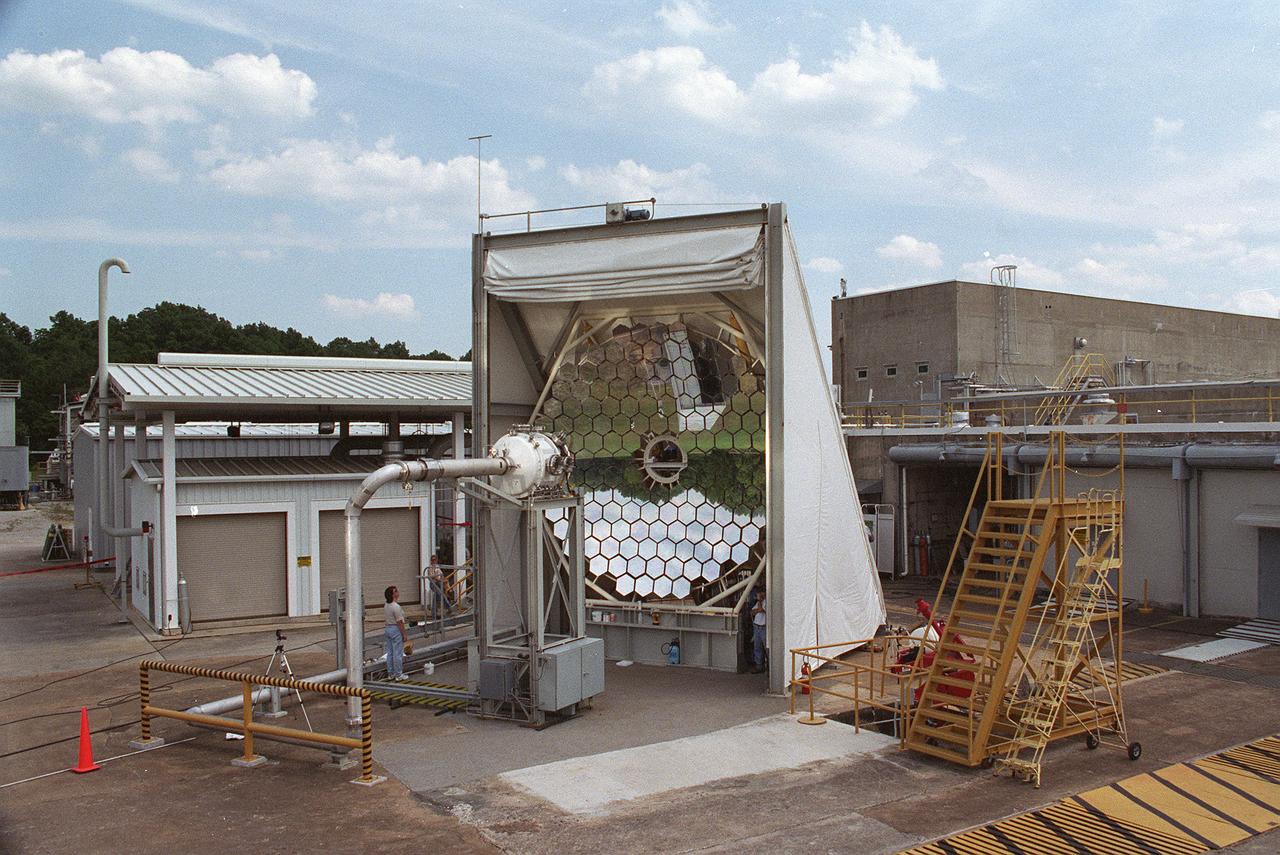
This photograph shows an overall view of the Solar Thermal Propulsion Test Facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The 20-by 24-ft heliostat mirror, shown at the left, has dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on an 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror (right). The concentrator mirror then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber, shown at the front of concentrator mirror. Researchers at MSFC have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than chemical a combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propell nt. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth-orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.
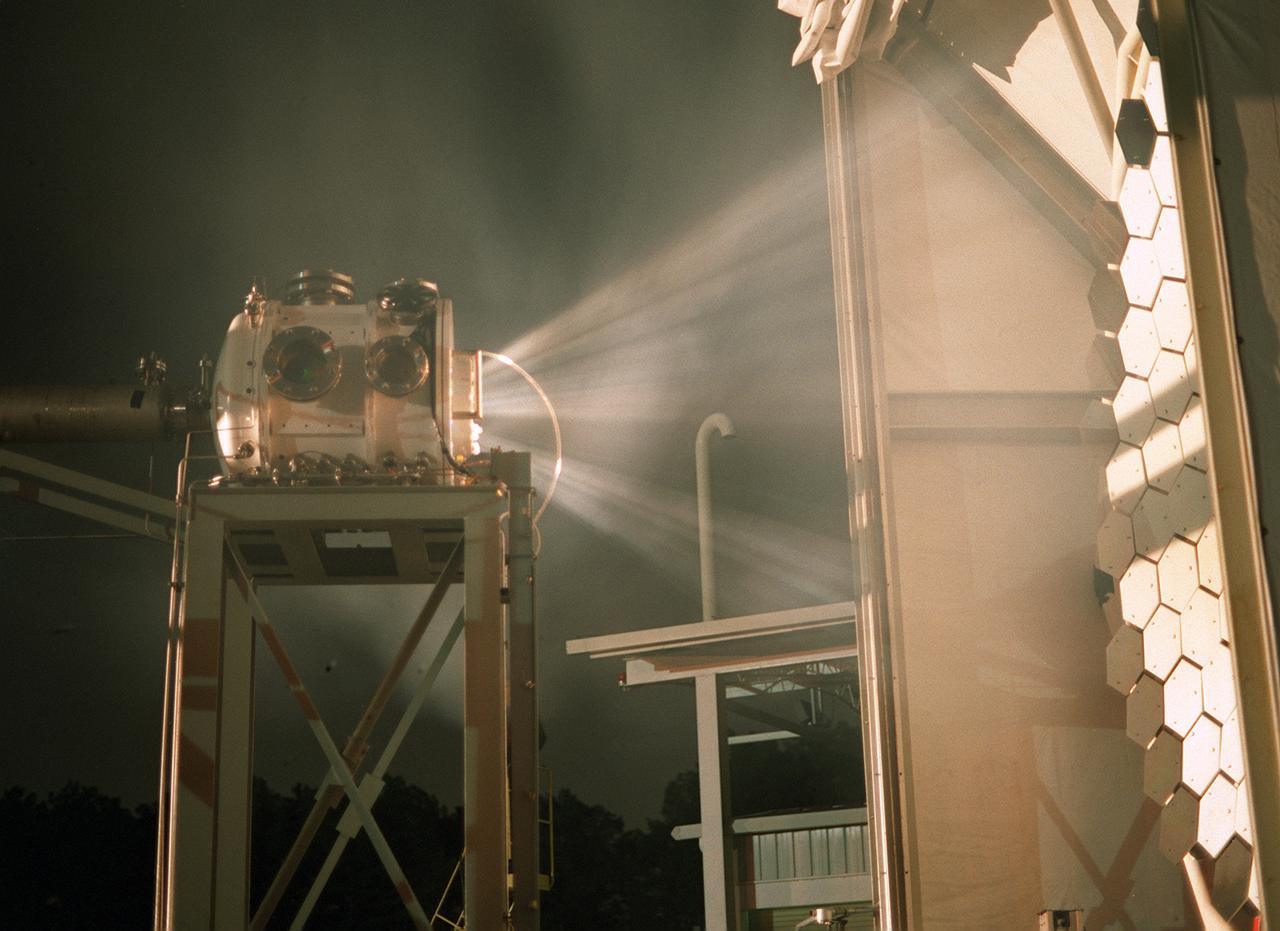

Researchers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket engine that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than a chemical combustion engine. MSFC turned to solar thermal propulsion in the early 1990s due to its simplicity, safety, low cost, and commonality with other propulsion systems. Solar thermal propulsion works by acquiring and redirecting solar energy to heat a propellant. The 20- by 24-ft heliostat mirror (not shown in this photograph) has a dual-axis control that keeps a reflection of the sunlight on the 18-ft diameter concentrator mirror, which then focuses the sunlight to a 4-in focal point inside the vacuum chamber. The focal point has 10 kilowatts of intense solar power. This image, taken during the test, depicts the light being concentrated into the focal point inside the vacuum chamber. As part of MSFC's Space Transportation Directorate, the Propulsion Research Center serves as a national resource for research of advanced, revolutionary propulsion technologies. The mission is to move the Nation's capabilities beyond the confines of conventional chemical propulsion into an era of aircraft-like access to Earth orbit, rapid travel throughout the solar system, and exploration of interstellar space.

A team of engineers at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) has designed, fabricated, and tested the first solar thermal engine, a non-chemical rocket that produces lower thrust but has better thrust efficiency than the chemical combustion engines. This segmented array of mirrors is the solar concentrator test stand at MSFC for firing the thermal propulsion engines. The 144 mirrors are combined to form an 18-foot diameter array concentrator. The mirror segments are aluminum hexagons that have the reflective surface cut into it by a diamond turning machine, which is developed by MSFC Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center.
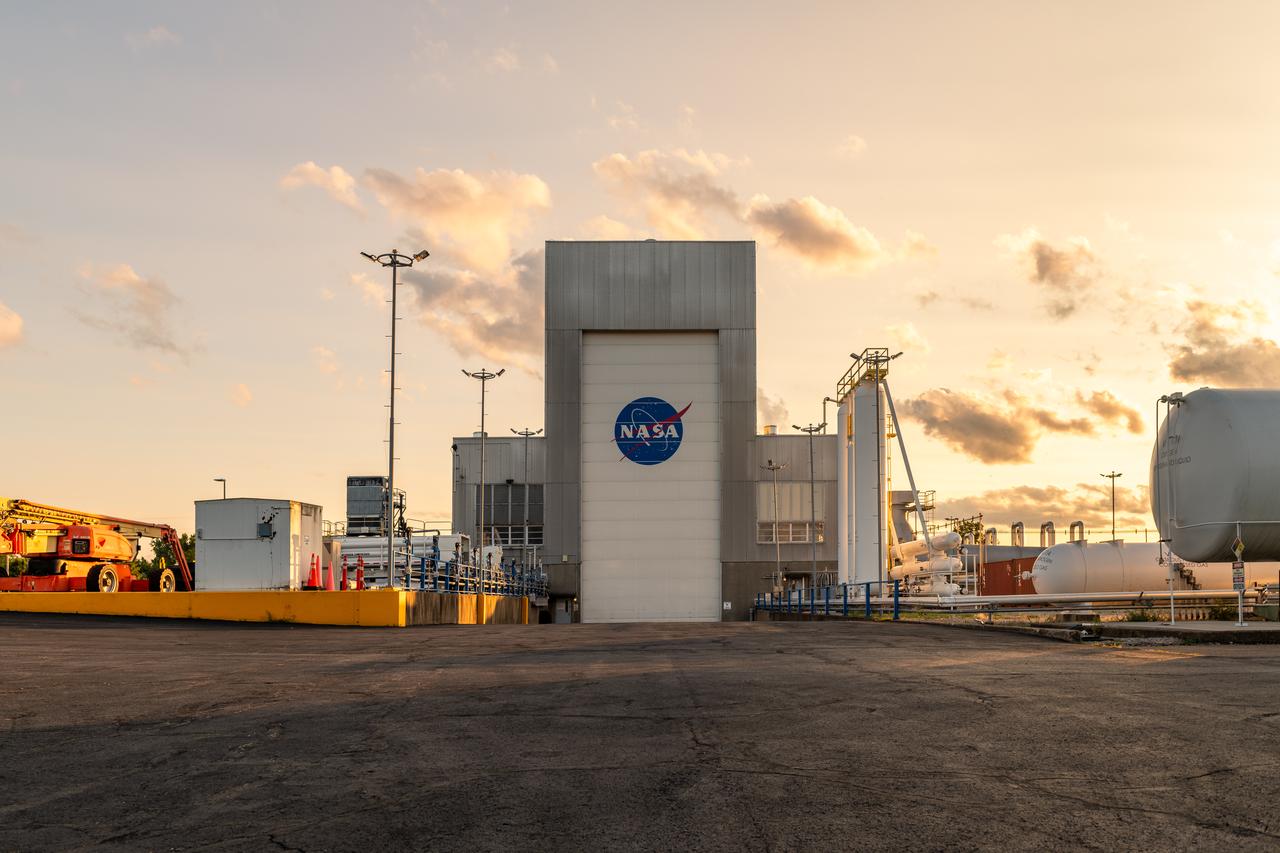

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
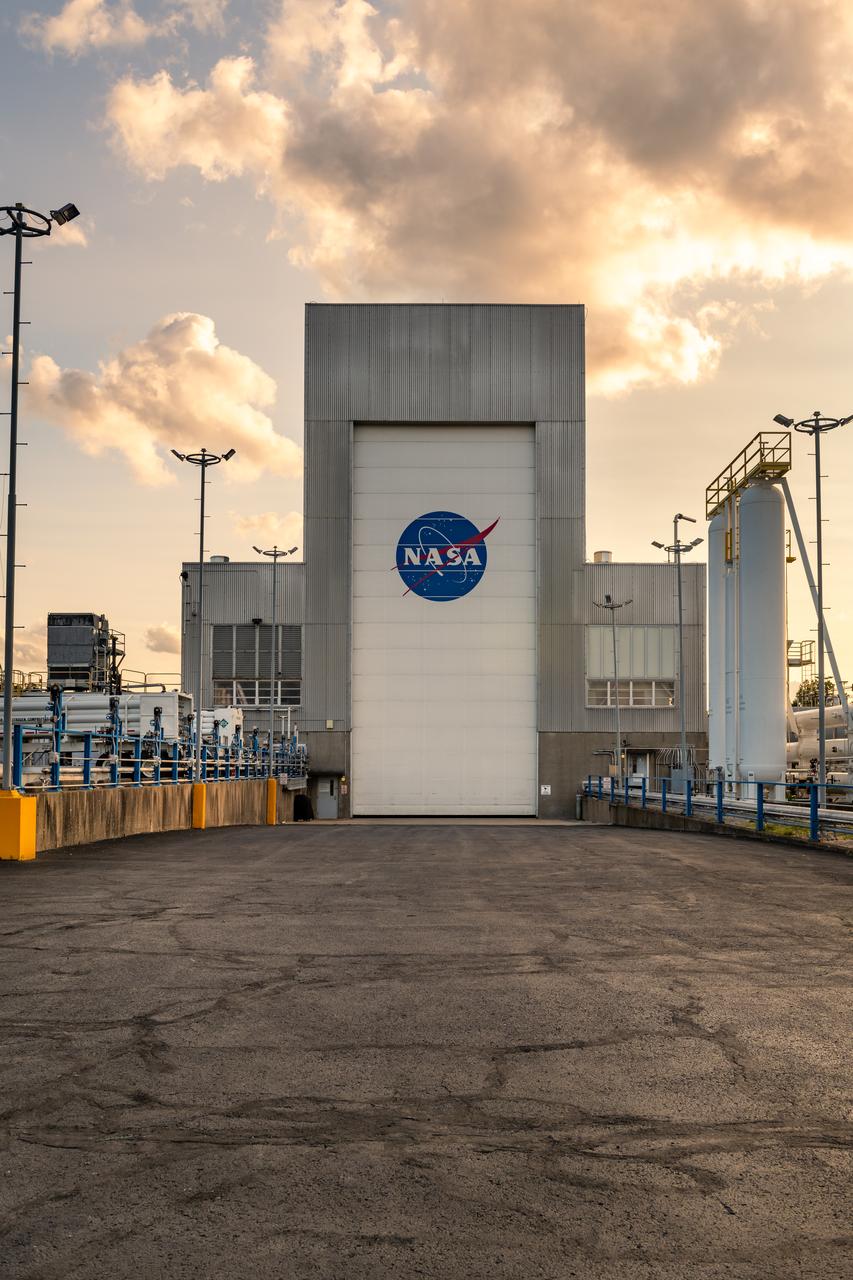

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
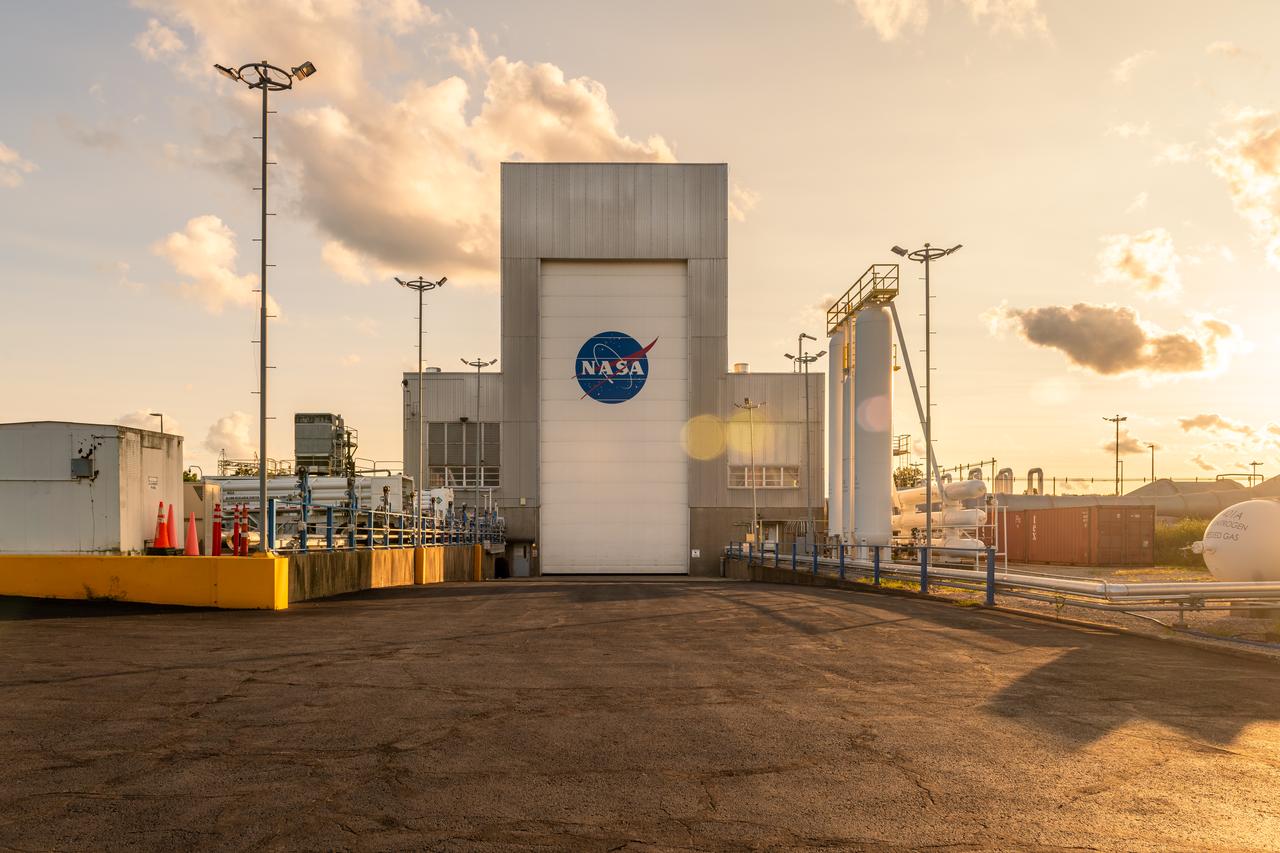

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
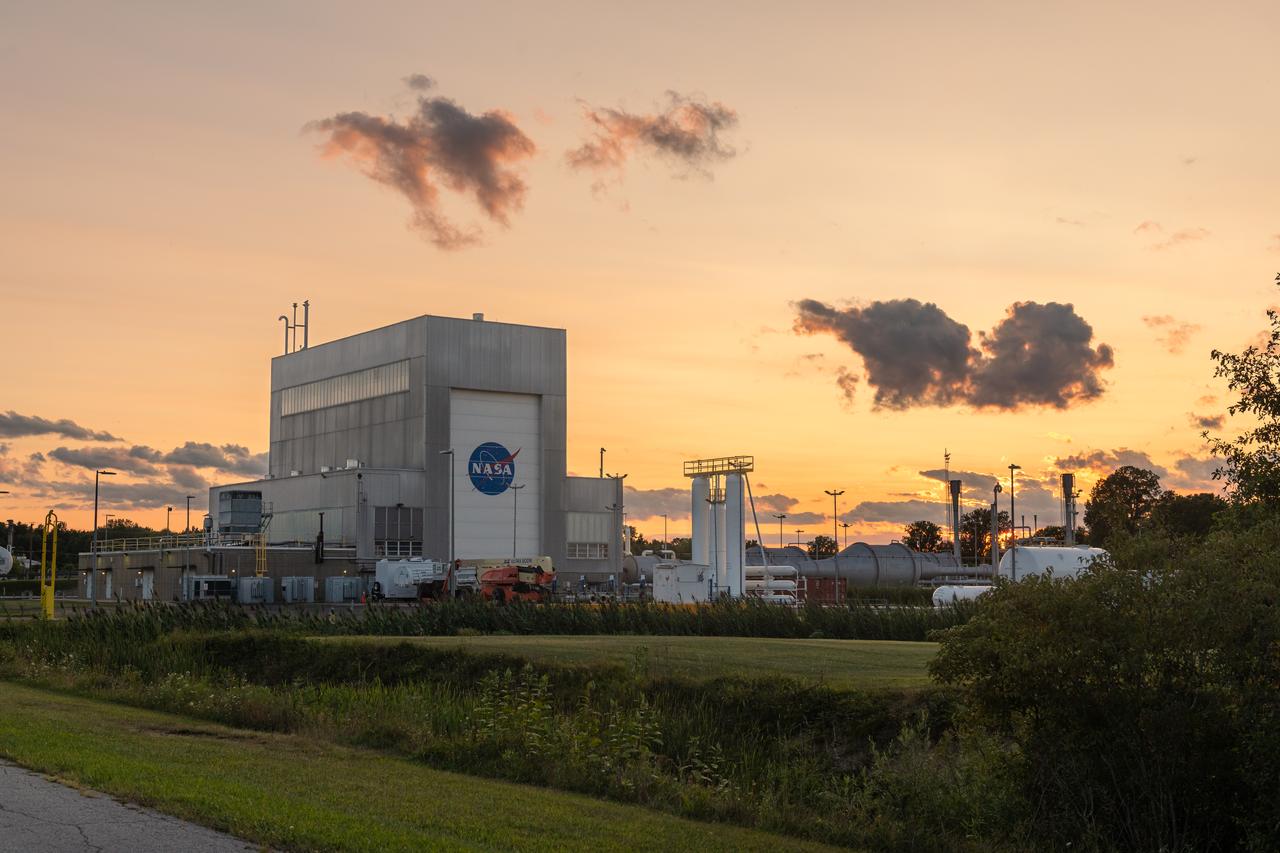

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
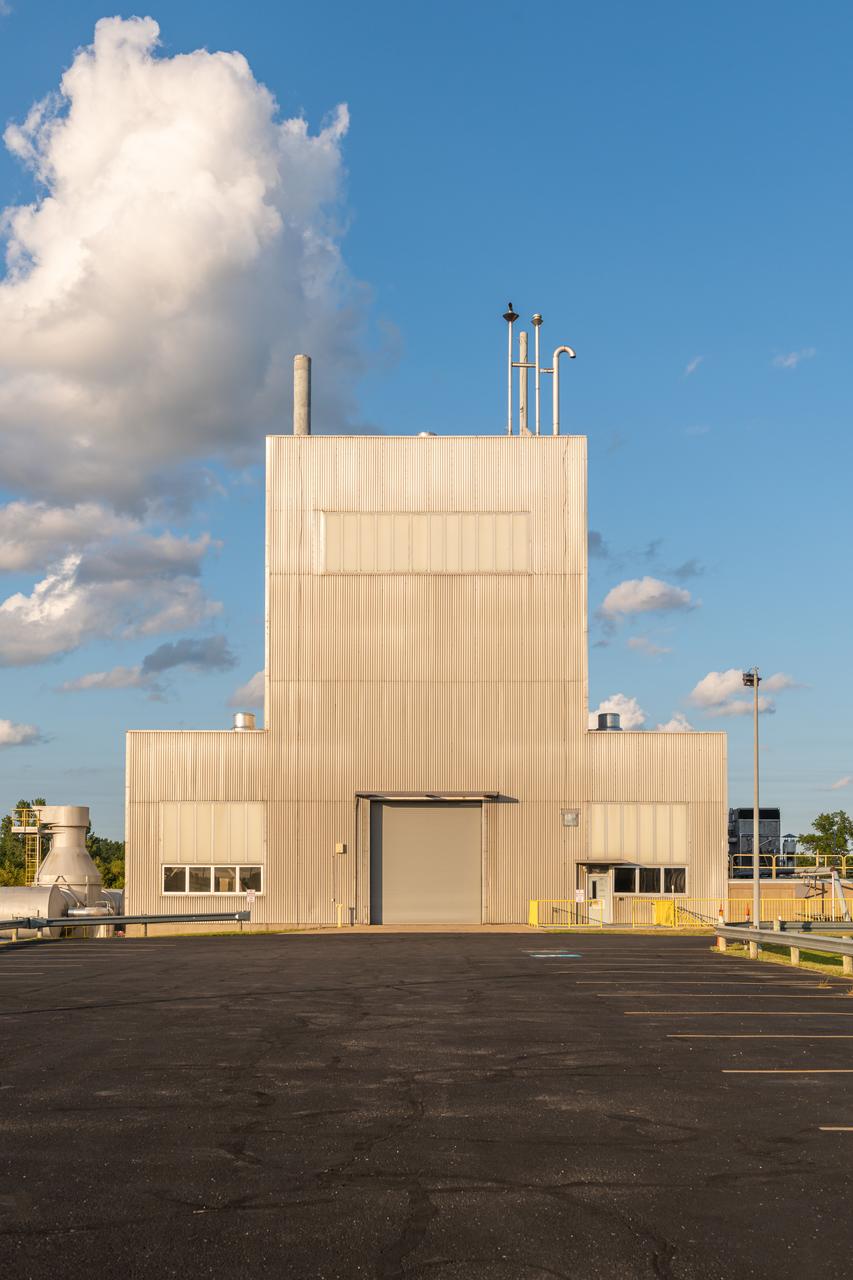

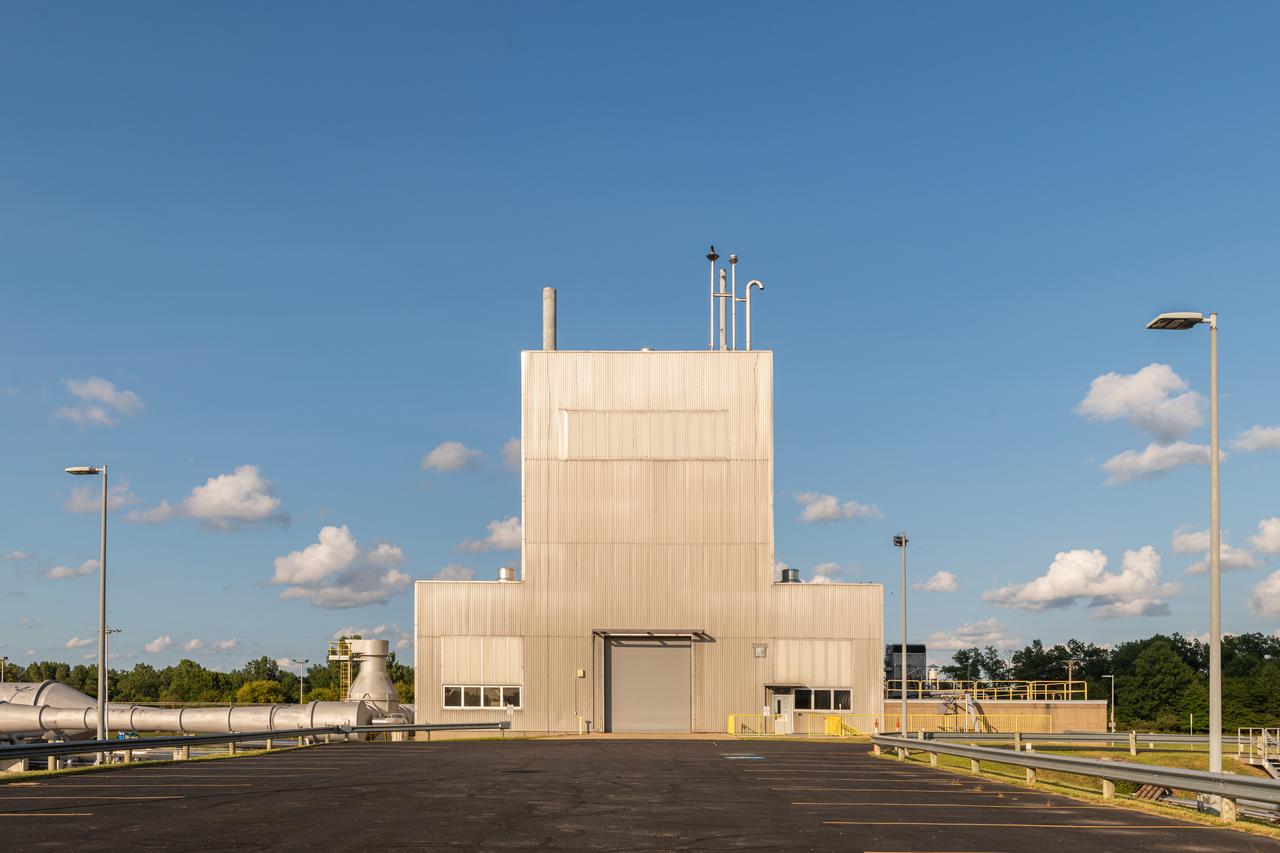
NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
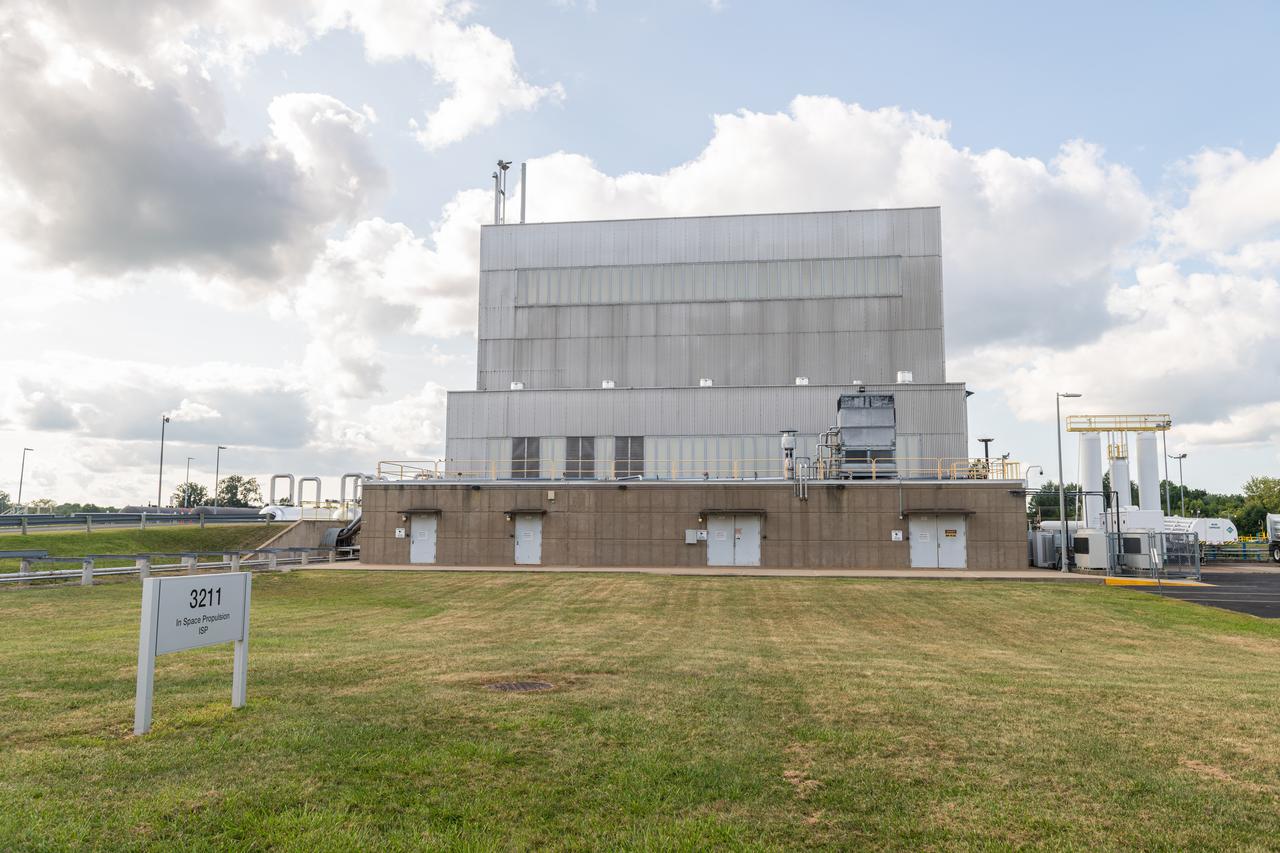

NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
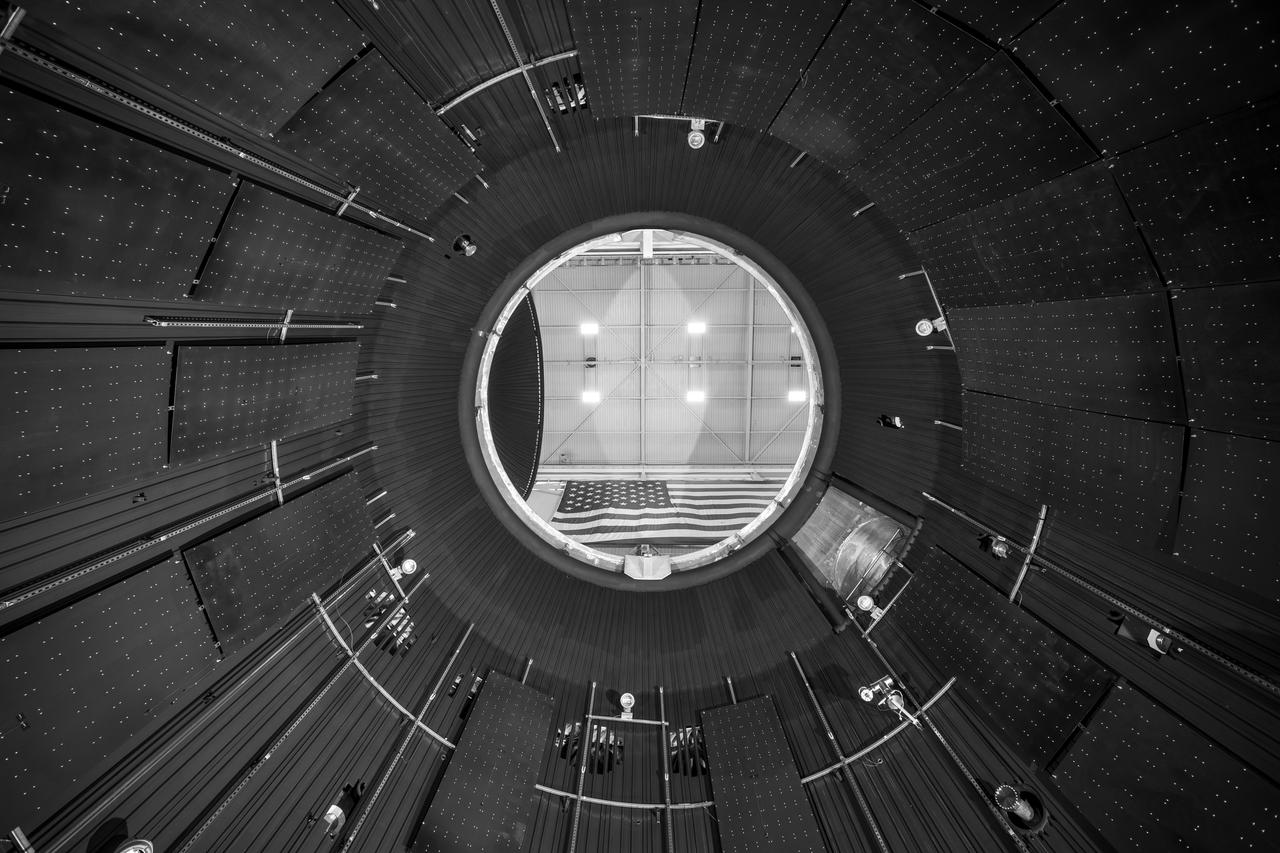

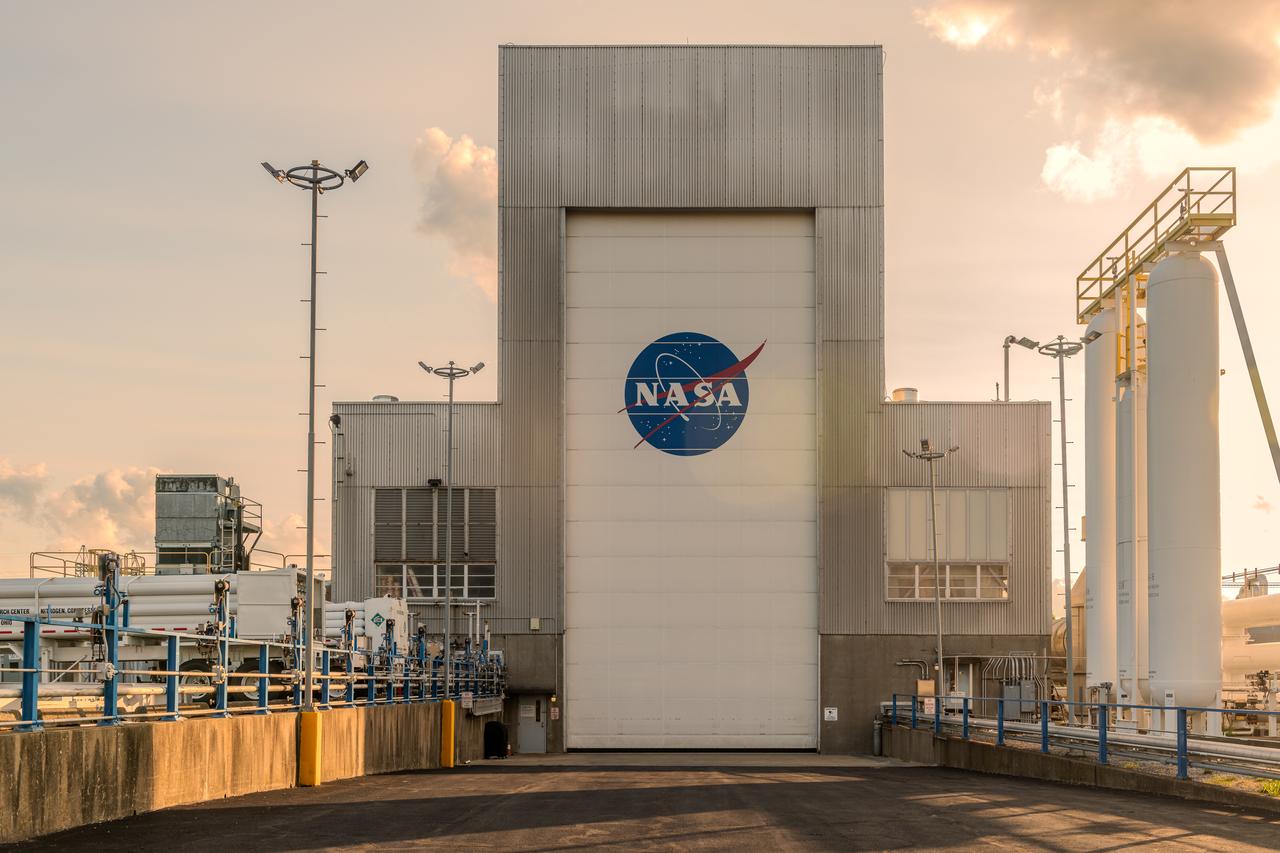
NASA’s In-Space Propulsion Facility located at Neil Armstrong Test Facility in Sandusky Ohio is the world’s only high altitude test facility capable of full-scale rocket engine and launch vehicle system level tests. The facility supports mission profile thermal vacuum simulation and engine firing. The engine or vehicle can be exposed for indefinite periods to low ambient pressures, low-background temperatures, and dynamic solar heating, simulating the environment the hardware will encounter during orbital or interplanetary travel. This is a view from inside the chamber looking up toward the American flag. Photo Credit: (NASA/Jordan Salkin)
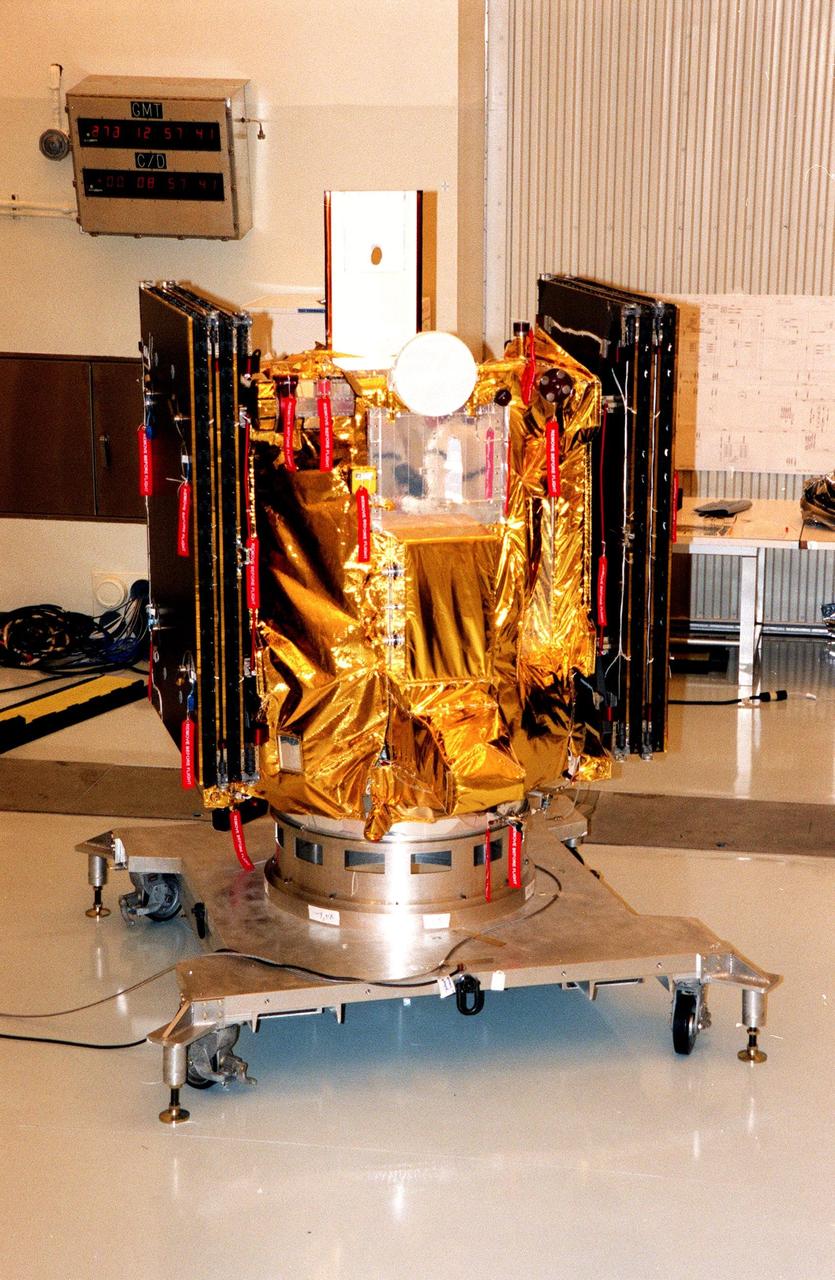
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Deep Space 1 rests on its work platform after being fitted with thermal insulation. The reflective insulation is designed to protect the spacecraft as this side faces the sun. At either side of the spacecraft are its solar wings, folded for launch. When fully extended, the wings measure 38.6 feet from tip to tip. The first flight in NASA's New Millennium Program, Deep Space 1 is designed to validate 12 new technologies for scientific space missions of the next century. Onboard experiments include a solar-powered ion propulsion engine and software that tracks celestial bodies so the spacecraft can make its own navigation decisions without the intervention of ground controllers. The ion propulsion engine is the first non-chemical propulsion to be used as the primary means of propelling a spacecraft. Deep Space 1 will complete most of its mission objectives within the first two months, but may also do a flyby of a near-Earth asteroid, 1992 KD, in July 1999. Deep Space 1 will be launched aboard a Boeing Delta 7326 rocket from Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, in October. Delta II rockets are medium capacity expendable launch vehicles derived from the Delta family of rockets built and launched since 1960. Since then there have been more than 245 Delta launches
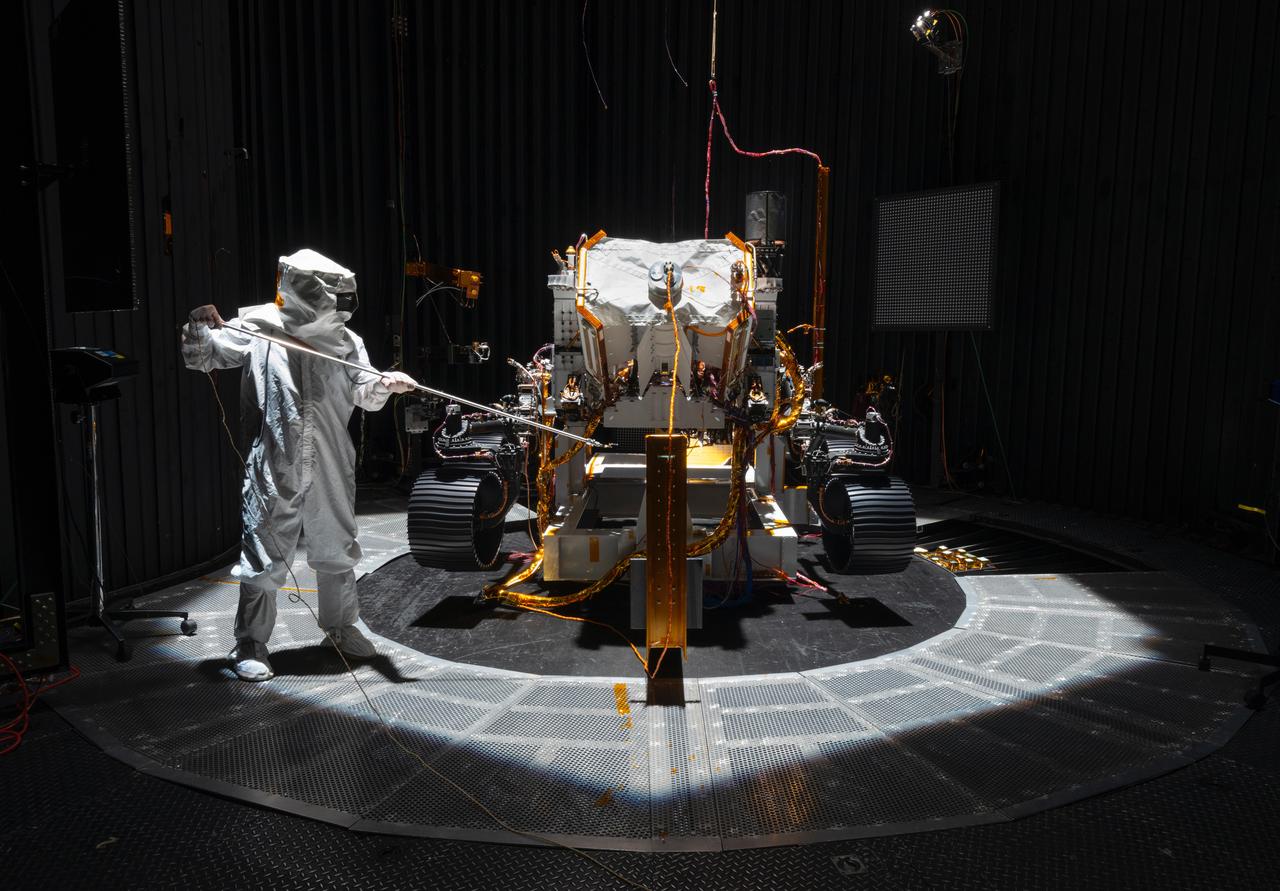

An engineer working on NASA's Mars 2020 mission uses a solar intensity probe to measure and compare the amount of artificial sunlight that reaches different portions of the rover. To simulate the Sun's rays for the test, powerful xenon lamps several floors below the chamber were illuminated, their light directed onto a mirror at the top of the chamber and reflected down on the spacecraft. The data collected during this test will be used to confirm thermal models the team has generated regarding how the Sun's rays will interact with the 2020 rover while on the surface of Mars. The image was taken on Oct. 14, 2019, in the Space Simulator Facility at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23469
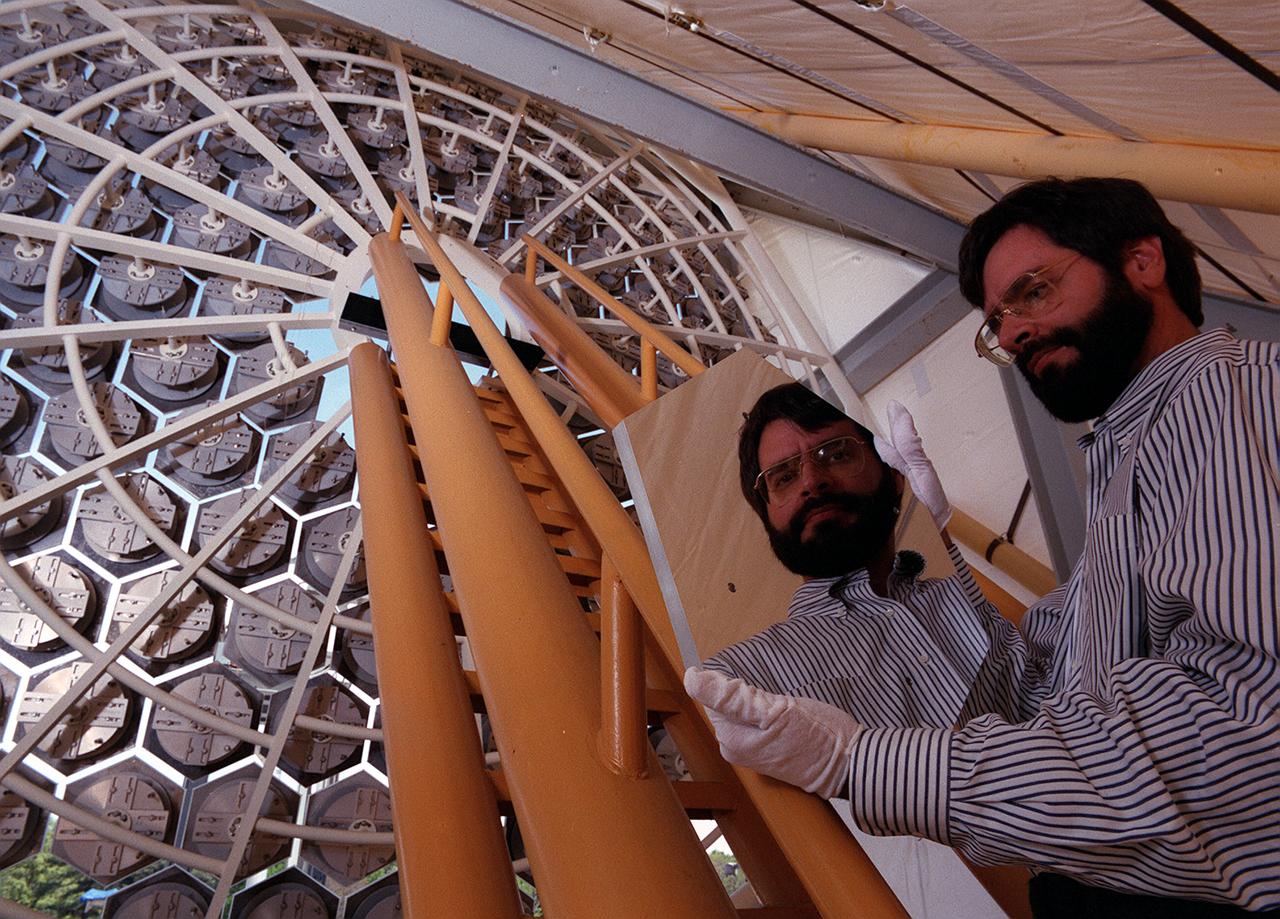

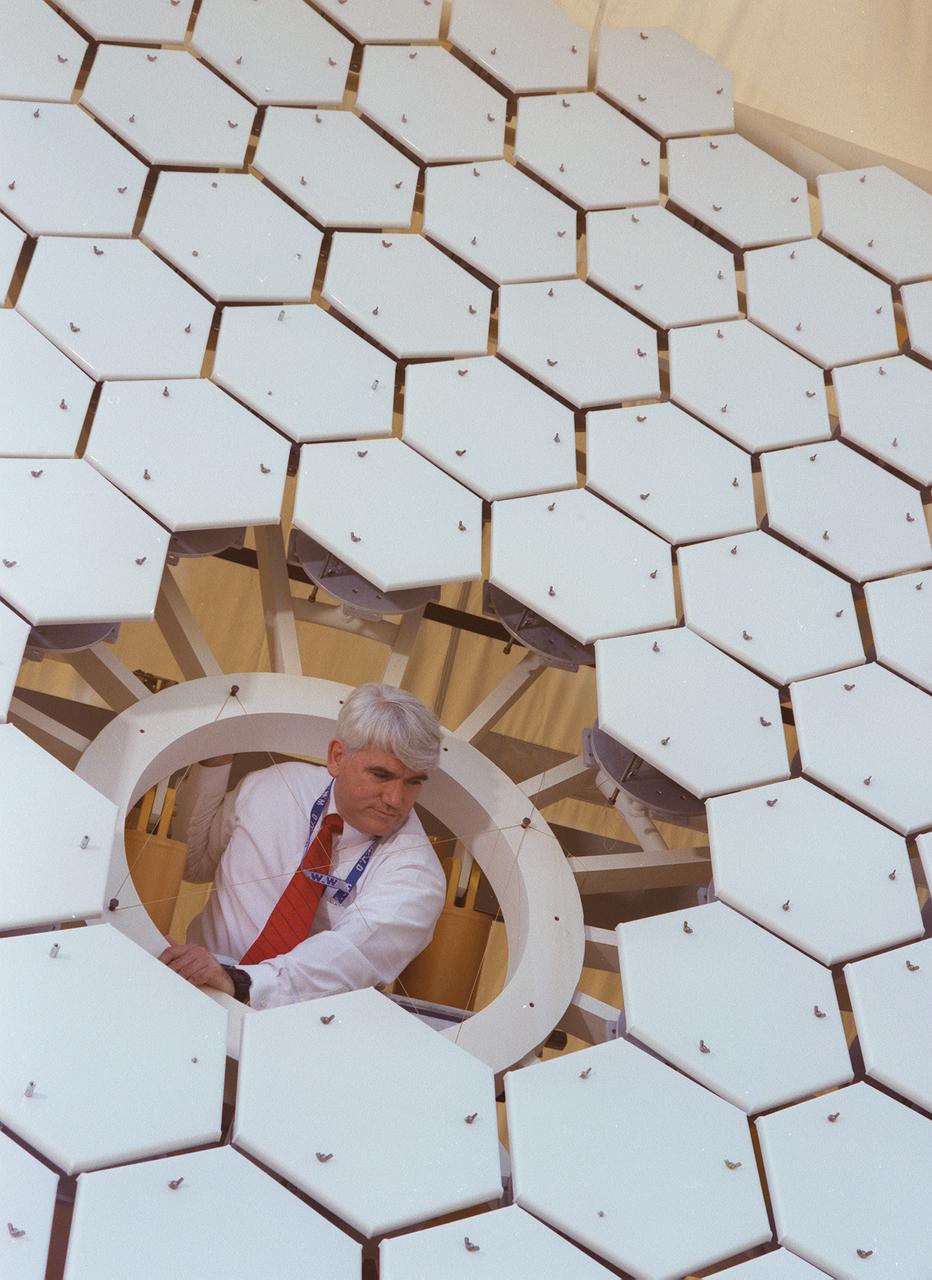
NASA's Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center has been working to expand our view of the universe via sophisticated new telescopes. The Optics Center's goal is to develop low-cost, advanced space optics technologies for the NASA program in the 21st century, including the long-term goal of imaging Earth-like planets in distant solar systems. A segmented array of mirrors was designed by the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center for solar the concentrator test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) for powering solar thermal propulsion engines. Each hexagon mirror has a spherical surface to approximate a parabolic concentrator when combined into the entire 18-foot diameter array. The aluminum mirrors were polished with a diamond turning machine, that creates a glass-like reflective finish on metal. The precision fabrication machinery at the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center at MSFC can polish specialized optical elements to a world class quality of smoothness. This image shows optics physicist, Vince Huegele, examining one of the 144-segment hexagonal mirrors of the 18-foot diameter array at the MSFC solar concentrator test stand.
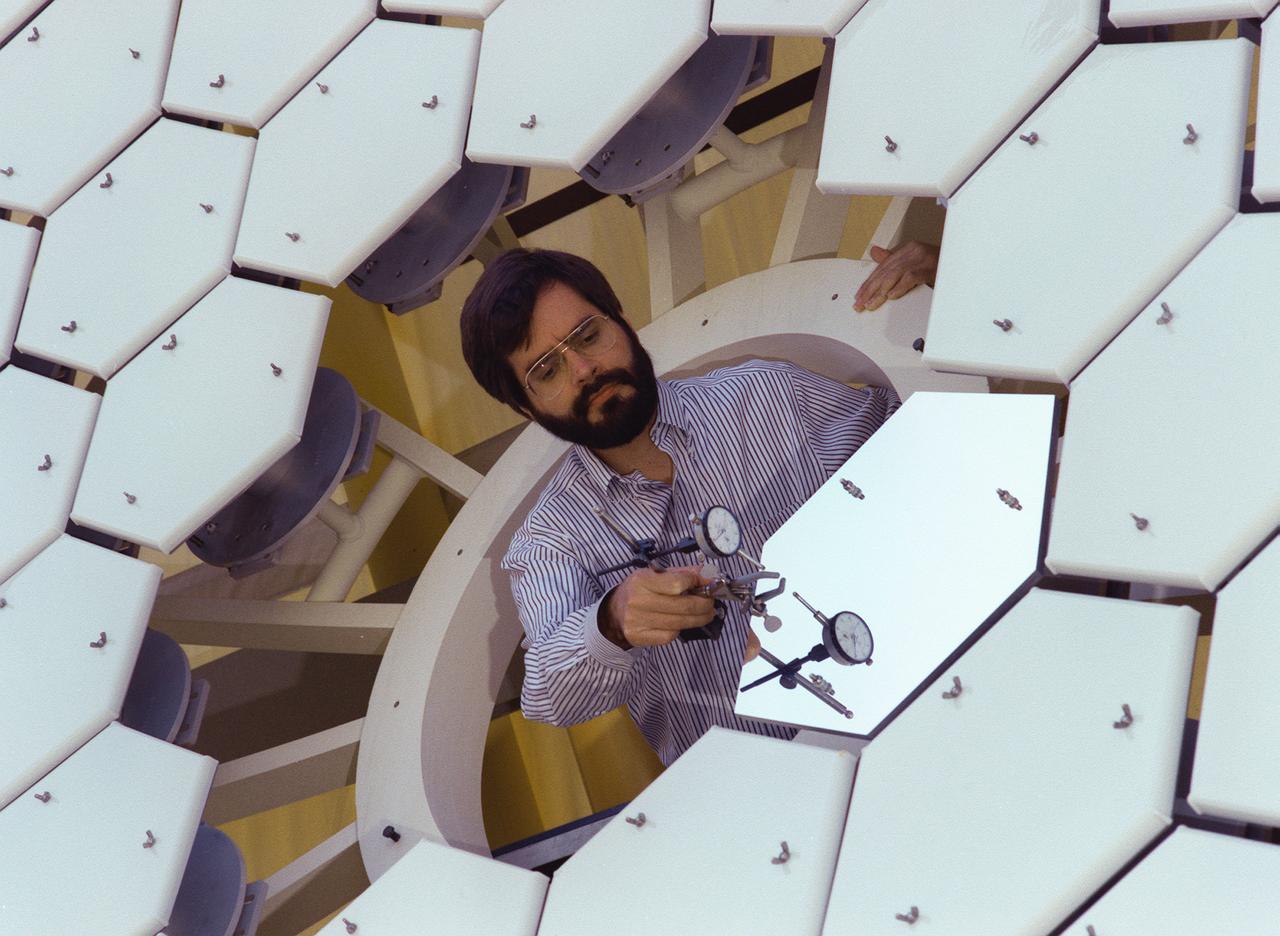

NASA's Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center has been working to expand our view of the universe via sophisticated new telescopes. The Optics Center's goal is to develop low-cost, advanced space optics technologies for the NASA program in the 21st century, including the long-term goal of imaging Earth-like planets in distant solar systems. A segmented array of mirrors was designed by the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center for the solar concentrator test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) for powering solar thermal propulsion engines. Each hexagon mirror has a spherical surface to approximate a parabolic concentrator when combined into the entire 18-foot diameter array. The aluminum mirrors were polished with a diamond turning machine that creates a glass-like reflective finish on metal. The precision fabrication machinery at the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center at MSFC can polish specialized optical elements to a world class quality of smoothness. This image shows optics physicist, Vince Huegele, examining one of the 144-segment hexagonal mirrors of the 18-foot diameter array at the MSFC solar concentrator test stand.
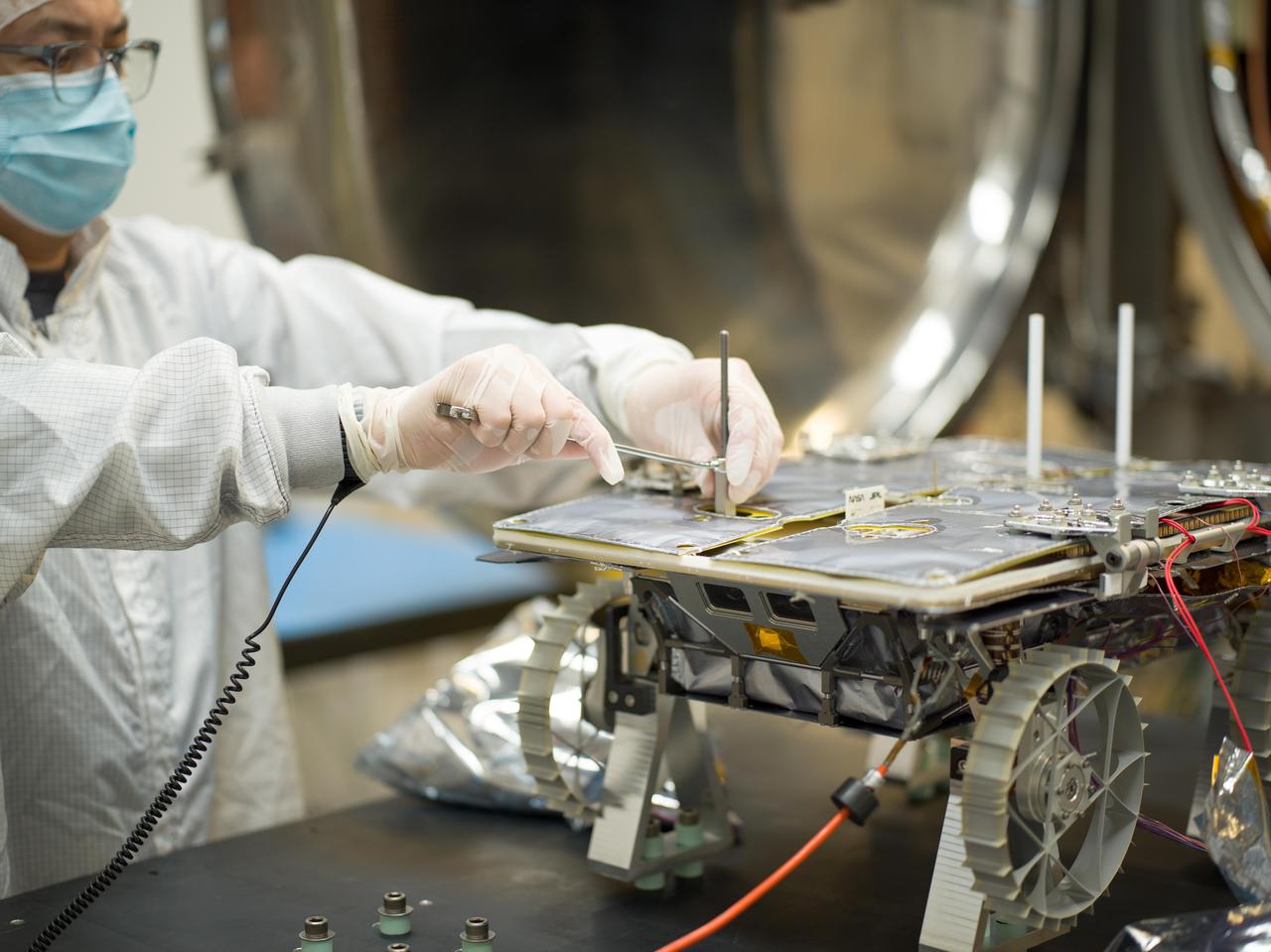
An engineer prepares a small rover – part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration that's headed to the Moon – for testing in a thermal vacuum chamber at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in October 2023. Slated to arrive at the Moon in 2024 as part of NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, CADRE is designed to demonstrate that multiple robots can cooperate and explore together autonomously – without direct input from human mission controllers. A trio of the miniature solar-powered rovers, each about the size of a carry-on suitcase, will explore the Moon as a team, communicating via radio with each other and a base station aboard a lunar lander. By taking simultaneous measurements from multiple locations, CADRE will also demonstrate how multirobot missions can record data impossible for a single robot to achieve – a tantalizing prospect for future missions. The rover being tested is the first flight model to be completed. Thermal vacuum testing simulates the harsh environment the rovers will face on the journey to the Moon and on the lunar surface: All the air is pumped out of the chamber and the temperature is cycled to high and low extremes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25669
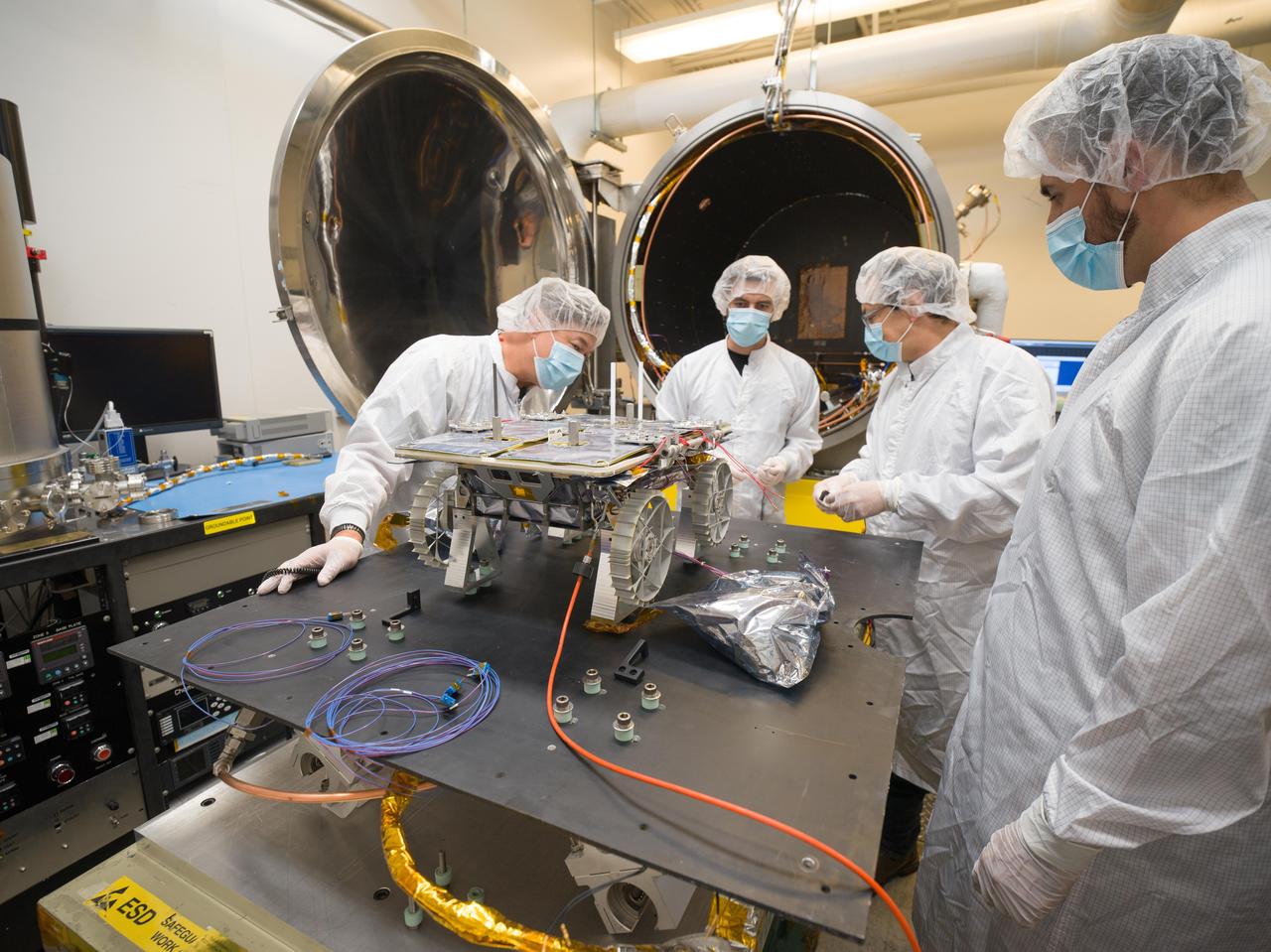

Engineers prepare a small rover – part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration that's headed to the Moon – for testing in the thermal vacuum chamber behind them at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in October 2023. Slated to arrive at the Moon in 2024 as part of NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, CADRE is designed to demonstrate that multiple robots can cooperate and explore together autonomously – without direct input from human mission controllers. A trio of the miniature solar-powered rovers, each about the size of a carry-on suitcase, will explore the Moon as a team, communicating via radio with each other and a base station aboard a lunar lander. By taking simultaneous measurements from multiple locations, CADRE will also demonstrate how multirobot missions can record data impossible for a single robot to achieve – a tantalizing prospect for future missions. The rover being tested is the first flight model to be completed. Thermal vacuum testing simulates the harsh environment the rovers will face on the journey to the Moon and on the lunar surface: All the air is pumped out of the chamber and the temperature is cycled to high and low extremes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25670

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After covering the bulk of Deep Space 1 in thermal insulating blankets, workers in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility lift it from its work platform before moving it onto its transporter (behind workers at left). Deep Space 1 is being moved to the Defense Satellite Communications System Processing Facility (DPF), Cape Canaveral Air Station, for testing. At either side of the spacecraft are its solar wings, folded for launch. When fully extended, the wings measure 38.6 feet from tip to tip. The first flight in NASA's New Millennium Program, Deep Space 1 is designed to validate 12 new technologies for scientific space missions of the next century. Onboard experiments include a solar-powered ion propulsion engine and software that tracks celestial bodies so the spacecraft can make its own navigation decisions without the intervention of ground controllers. The ion propulsion engine is the first non-chemical propulsion to be used as the primary means of propelling a spacecraft. Deep Space 1 will complete most of its mission objectives within the first two months, but may also do a flyby of a near-Earth asteroid, 1992 KD, in July 1999. Deep Space 1 will be launched aboard a Boeing Delta 7326 rocket from Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, in October. Delta II rockets are medium capacity expendable launch vehicles derived from the Delta family of rockets built and launched since 1960. Since then there have been more than 245 Delta launches
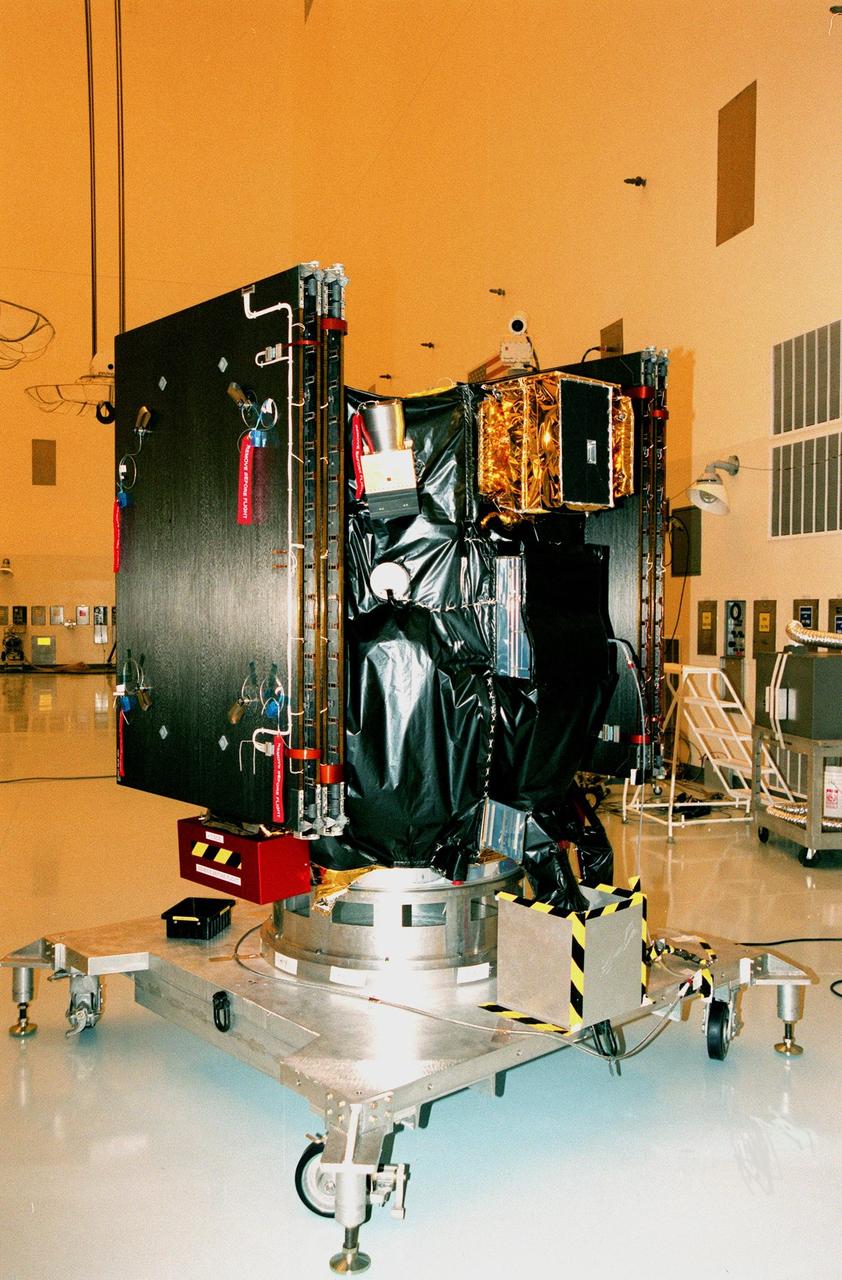

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Deep Space 1 rests on its work platform after being fitted with thermal insulation. The dark insulation is designed to protect the side of the spacecraft that faces away from the sun. At either side of the spacecraft are its solar wings, folded for launch. When fully extended, the wings measure 38.6 feet from tip to tip. The first flight in NASA's New Millennium Program, Deep Space 1 is designed to validate 12 new technologies for scientific space missions of the next century. Onboard experiments include a solar-powered ion propulsion engine and software that tracks celestial bodies so the spacecraft can make its own navigation decisions without the intervention of ground controllers. The ion propulsion engine is the first non-chemical propulsion to be used as the primary means of propelling a spacecraft. Deep Space 1 will complete most of its mission objectives within the first two months, but may also do a flyby of a near-Earth asteroid, 1992 KD, in July 1999. Deep Space 1 will be launched aboard a Boeing Delta 7326 rocket from Launch Pad 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, in October. Delta II rockets are medium capacity expendable launch vehicles derived from the Delta family of rockets built and launched since 1960. Since then there have been more than 245 Delta launches
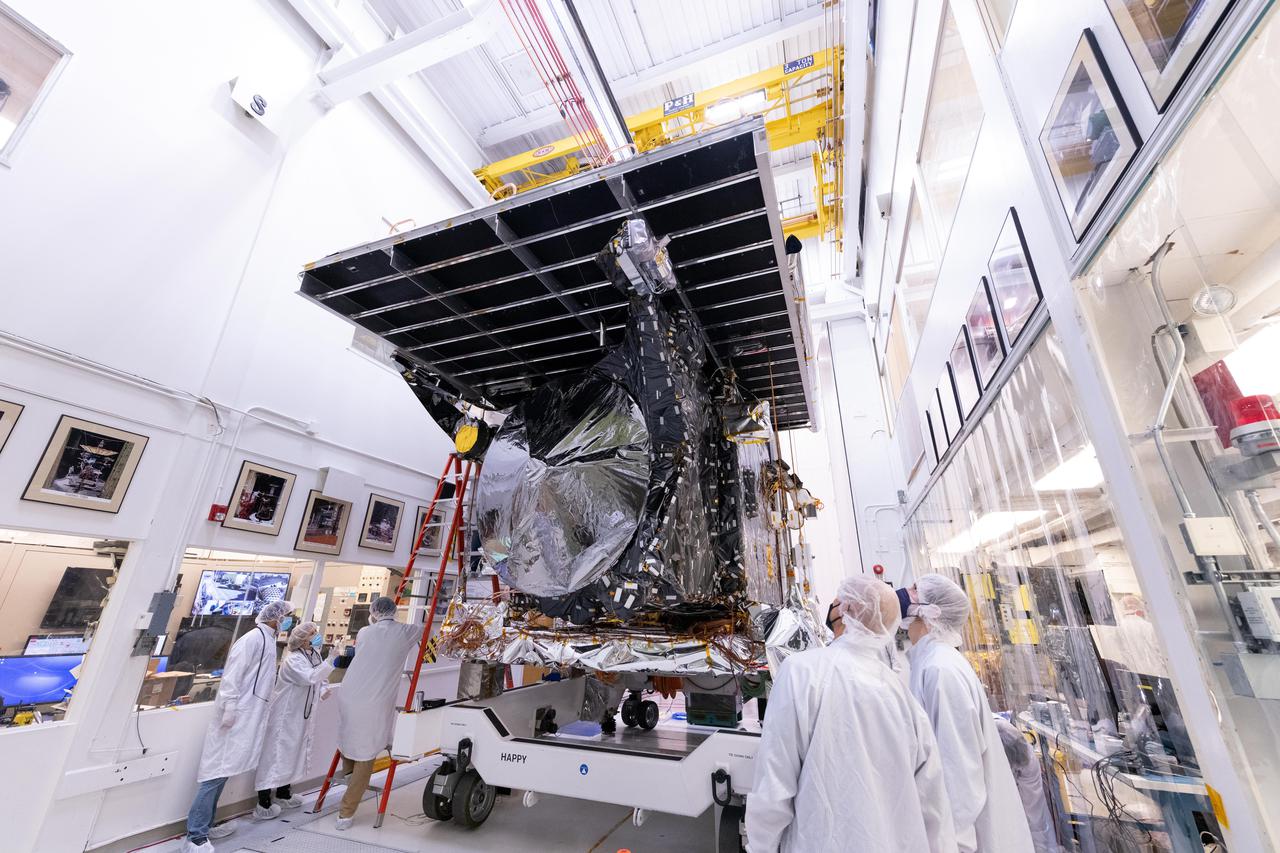

NASA's Psyche spacecraft is seen in early 2022 on its way to the vacuum chamber at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Thermal-vacuum (TVAC) testing is part of a regimen of environmental tests that are crucial for ensuring the spacecraft can survive the extreme conditions of launch and outer space. The orbiter will travel 1.5 billion miles (2.4 billion kilometers) to its target in the main asteroid belt, a metal-rich asteroid also called Psyche. Scientists believe the asteroid could be part or all of the iron-rich interior of an early planetary building block that was stripped of its outer rocky shell in the early days of the solar system. Over 18 days of TVAC testing, engineers exposed the spacecraft to the coldest and warmest conditions it will experience in flight, to prove that it is capable of regulating its own temperature. All of the air was sucked out of the chamber to replicate the airless vacuum of space. This test ensures that the spacecraft can survive the vacuum of space, and it helps engineers see how the spacecraft heats and cools itself without the movement of air to help it regulate temperature. Psyche is set to launch in August 2022. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25231
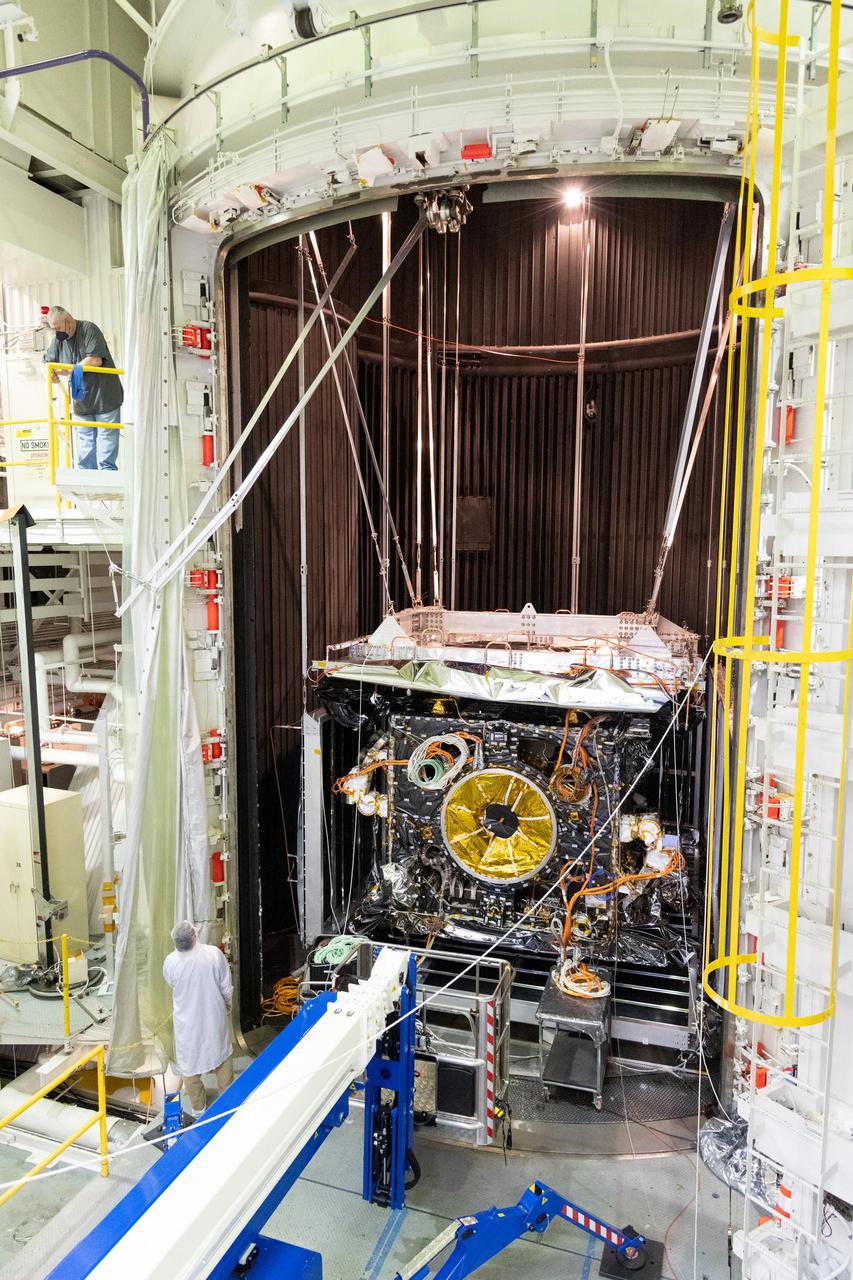

NASA's Psyche spacecraft is seen in early 2022 as it is placed in the 85-foot-tall, 25-foot-wide (26-meter-by-8-meter) ultra-sturdy vacuum chamber at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Thermal-vacuum (TVAC) testing is part of a regimen of environmental tests that are crucial for ensuring the spacecraft can survive the extreme conditions of launch and outer space. The orbiter will travel 1.5 billion miles (2.4 billion kilometers) to its target in the main asteroid belt, a metal-rich asteroid also called Psyche. Scientists believe the asteroid could be part or all of the iron-rich interior of an early planetary building block that was stripped of its outer rocky shell in the early days of the solar system. Over 18 days of TVAC testing, engineers exposed the spacecraft to the coldest and warmest conditions it will experience in flight, to prove that it is capable of regulating its own temperature. All of the air was sucked out of the chamber to replicate the airless vacuum of space. This test ensures that the spacecraft can survive the vacuum of space, and it helps engineers see how the spacecraft heats and cools itself without the movement of air to help it regulate temperature. Psyche is set to launch in August 2022. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25232
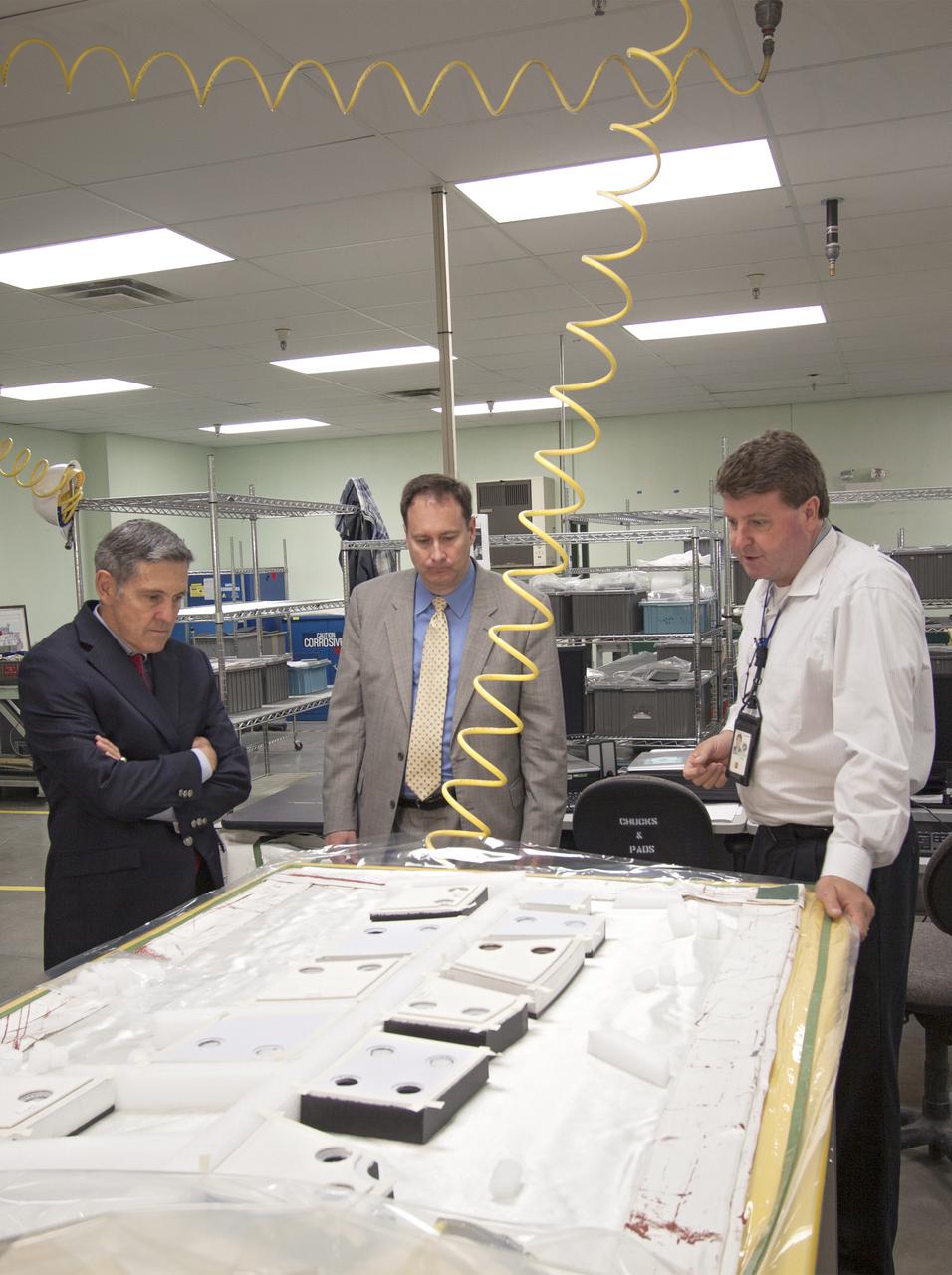

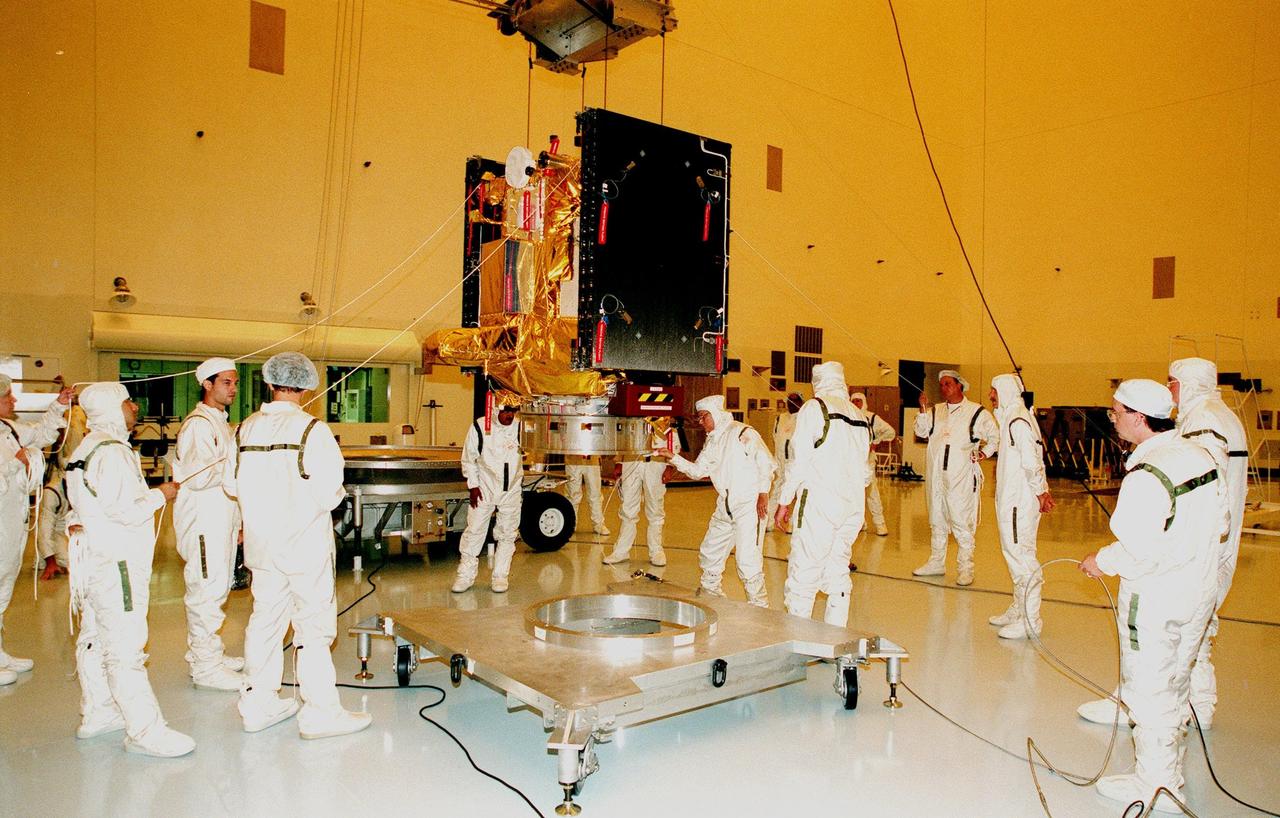
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot, center, tours the Thermal Protection System Facility, or TPSF, during a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, Lightfoot, and Martin Boyd, TPSF manager with Jacobs Technologies, briefing his guests on the production of TPS tile for NASA's new Orion spacecraft. NASA's FY2014 budget proposal includes a plan to robotically capture a small near-Earth asteroid and redirect it safely to a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system where astronauts can visit and explore it. Performing these elements for the proposed asteroid initiative integrates the best of NASA's science, technology and human exploration capabilities and draws on the innovation of America's brightest scientists and engineers. It uses current and developing capabilities to find both large asteroids that pose a hazard to Earth and small asteroids that could be candidates for the initiative, accelerates our technology development activities in high-powered solar electric propulsion and takes advantage of our hard work on the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, helping to keep NASA on target to reach the President's goal of sending humans to Mars in the 2030s. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

A major component of NASA's Psyche spacecraft has been delivered to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, where the phase known as assembly, test, and launch operations (ATLO) is now underway. This photo, shot March 28, 2021 shows engineers and technicians preparing to move the Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) Chassis from its shipping container to a dolly in High Bay 1 of JPL's Spacecraft Assembly Facility. The photo was captured just after the chassis was delivered to JPL by Maxar Technologies. Maxar's team in Palo Alto, California, designed and built the SEP Chassis, which includes all the primary and secondary structure and the hardware components needed for the high-power electrical system, the propulsion system, the thermal system, guidance and navigation sensors and actuators, and the high-gain antenna. Over the next year, additional hardware will be added to the spacecraft including the command and data handling system, a power distribution assembly, the X-band telecommunications hardware suite, three science instruments (two imagers, two magnetometers, and a gamma ray neutron Spectrometer), and a deep space optical communications technology demonstrator. The spacecraft will finish assembly and then undergo rigorous checkout and testing before being shipped to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, for an August 2022 launch to the main asteroid belt. Psyche will arrive at the metal-rich asteroid of the same name in 2026, orbiting for 21 months to investigate its composition. Scientists think that Psyche is made up of mostly iron and nickel — similar to Earth's core. Exploring the asteroid could give valuable insight into how our own planet and others formed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24475

This view of Mars was captured by NASA's Odyssey orbiter using its Thermal Emission Imaging System, or THEMIS, camera. This image is a false color composite, made by combining three channels of infrared data that highlight water-ice clouds and dust in the atmosphere. This panorama was one of 10 captured on May 9, 2023, from an altitude of roughly 250 miles (400 kilometers) above the Martian surface – about the same altitude at which the International Space Station flies over Earth. The 10 panoramas of the Martian horizon were taken to capture a one-of-a-kind view of the Martian atmosphere as Odyssey circled the planet during its two-hour orbit. The reason why the view is so uncommon is because of the challenges involved in creating it. Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California (which leads the Odyssey mission) and Lockheed Martin Space (which built Odyssey and co-leads day-to-day operations) spent three months planning the observations. THEMIS' sensitivity to warmth enables it to map ice, rock, sand, and dust, along with temperature changes, on the planet's surface. It can also measure how much water ice or dust is in the atmosphere, but only in a narrow column directly below the spacecraft. That's because THEMIS is fixed in place on the orbiter; it usually points straight down. Mission scientists wanted a more expansive view of the atmosphere. Seeing where those layers of water-ice clouds and dust are in relation to each other – whether there's one layer or several stacked on top of each other – helps them improve models of Mars' atmosphere. Because THEMIS can't pivot, adjusting the angle of the camera requires adjusting the position of the whole spacecraft. In this case, the team needed to rotate the orbiter almost 90 degrees while making sure the Sun would still shine on the spacecraft's solar panels but not on sensitive equipment that could overheat. The easiest orientation turned out to be one where the orbiter's antenna pointed away from Earth. That meant the team was out of communication with Odyssey for several hours until the operation was completed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26203